Patents
Literature
6330results about How to "Reduce quality problems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
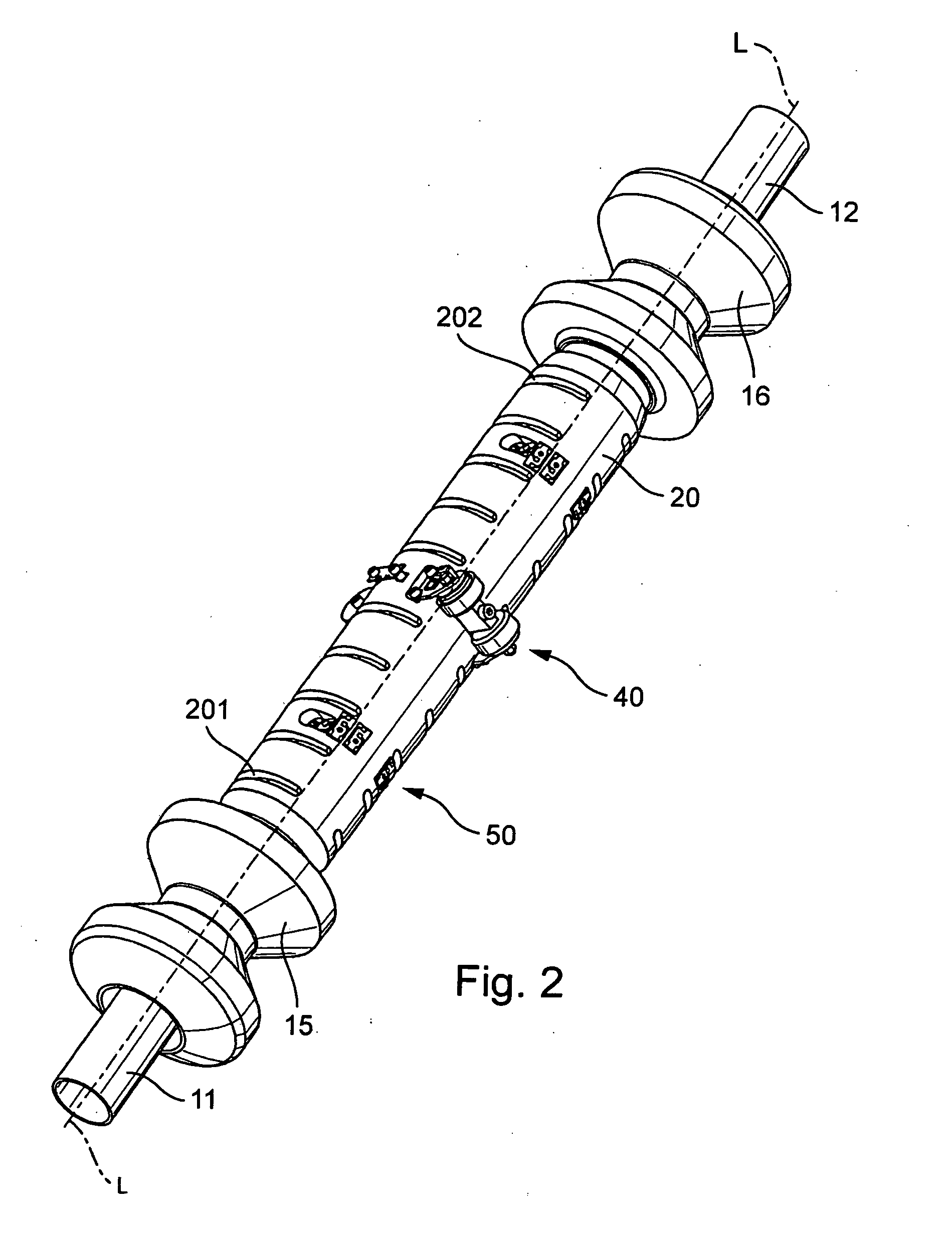
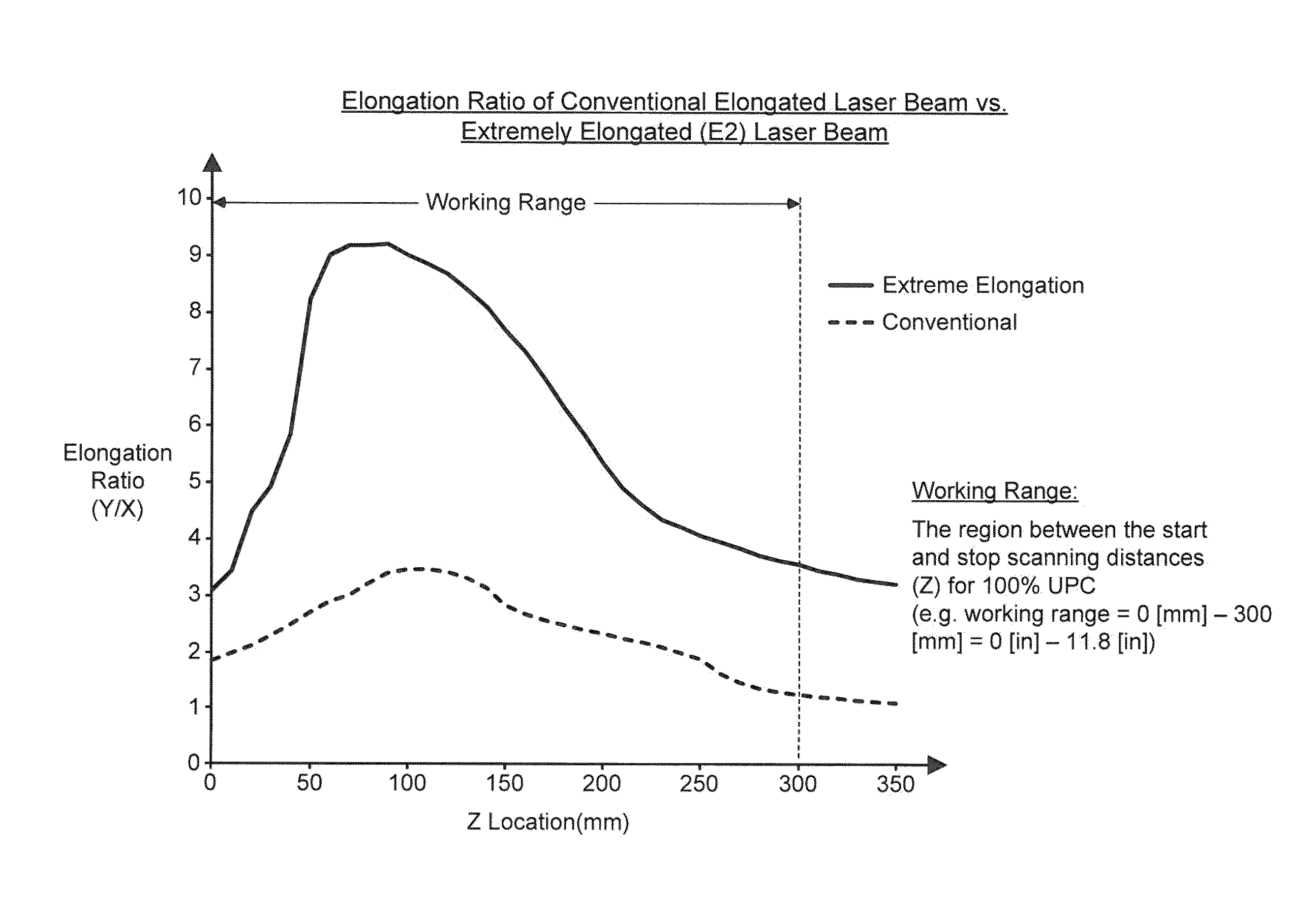
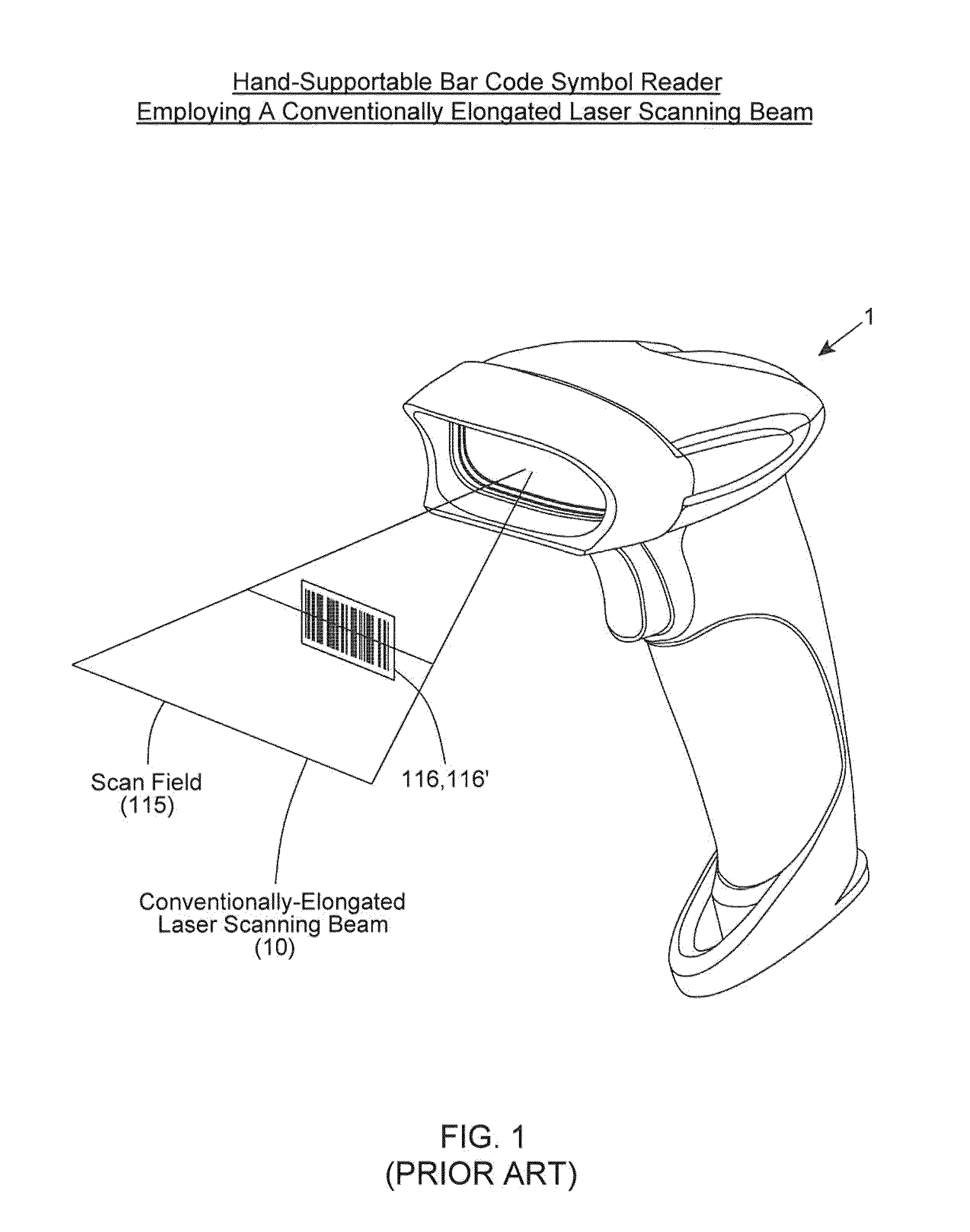
Bar code symbol reading system employing an extremely elongated laser scanning beam capable of reading poor and damaged quality bar code symbols with improved levels of performance
ActiveUS8376233B2Increase reflectionOptimized laser beam characteristicsTelevision system scanning detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionLaser scanningLight beam
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Low temperature electronic vaporization device and methods
ActiveUS20130042865A1Maintain efficiencyReduce the temperatureInput/output for user-computer interactionTobacco treatmentInhalationEnvironmental health
Low temperature electronic vaporization devices and method are described herein for emulating smoking wherein the devices generate an aerosol for inhalation by a subject by heating a viscous material that can have a tactile response in the mouth or respiratory tract.
Owner:JLI NAT SETTLEMENT TRUST
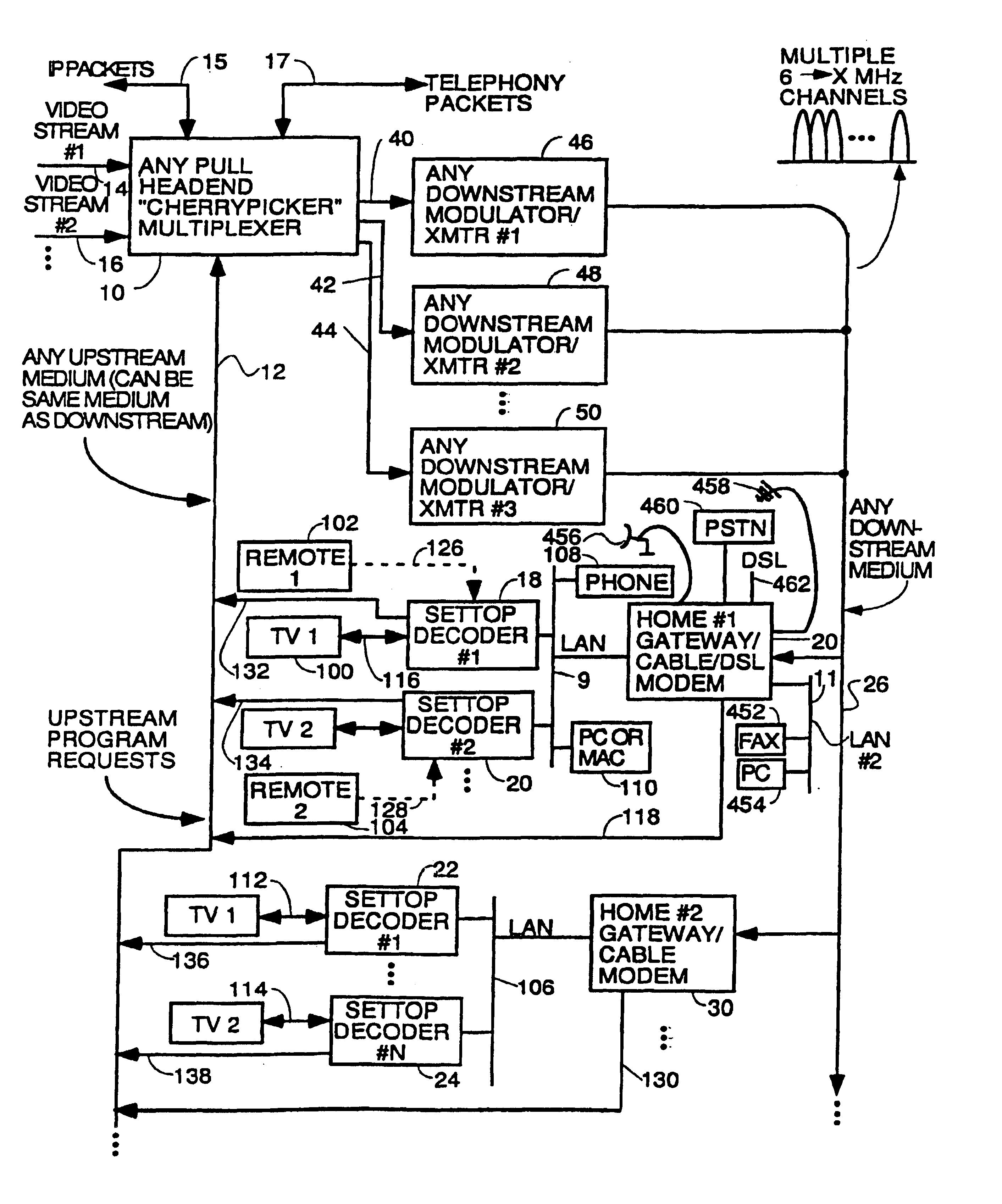
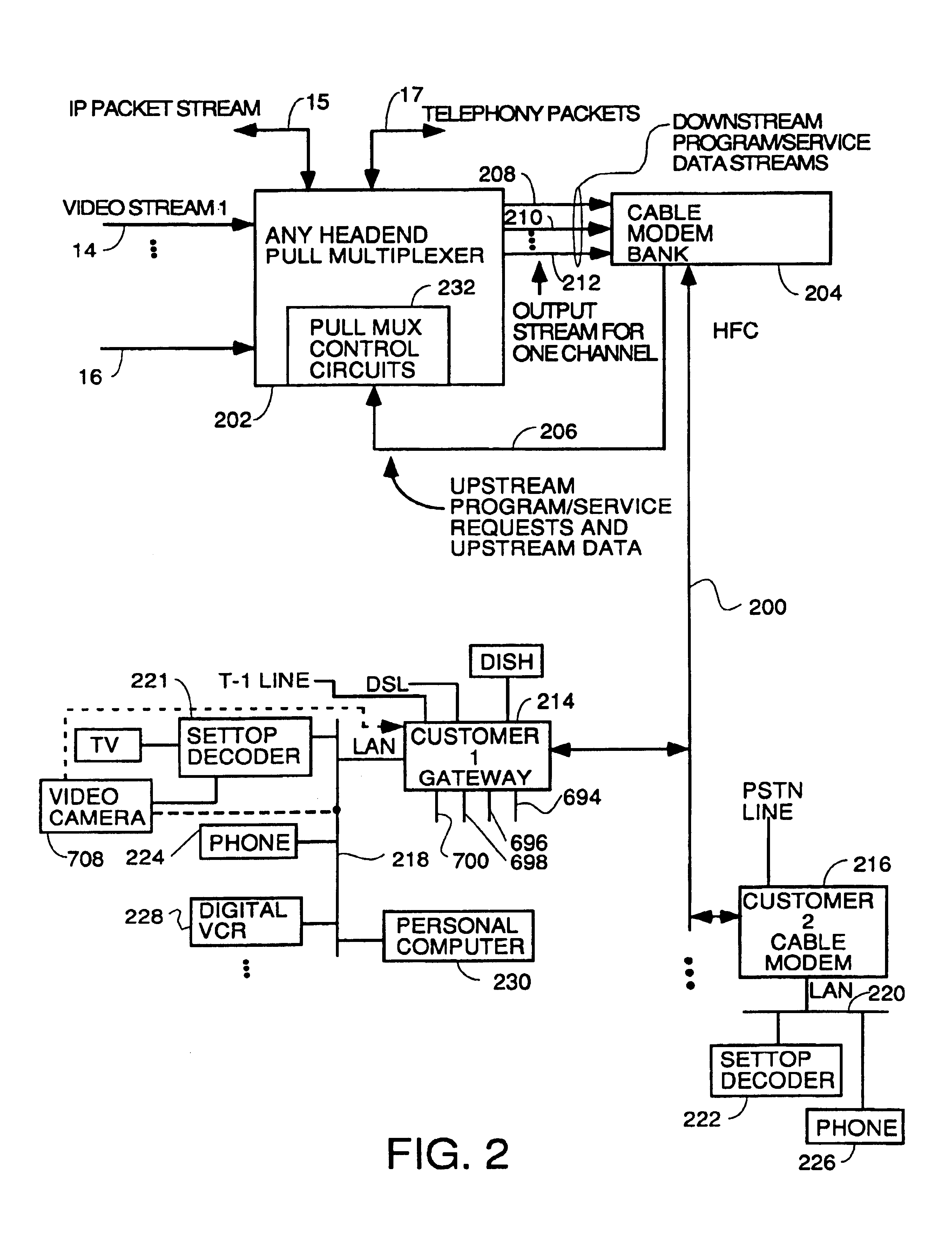
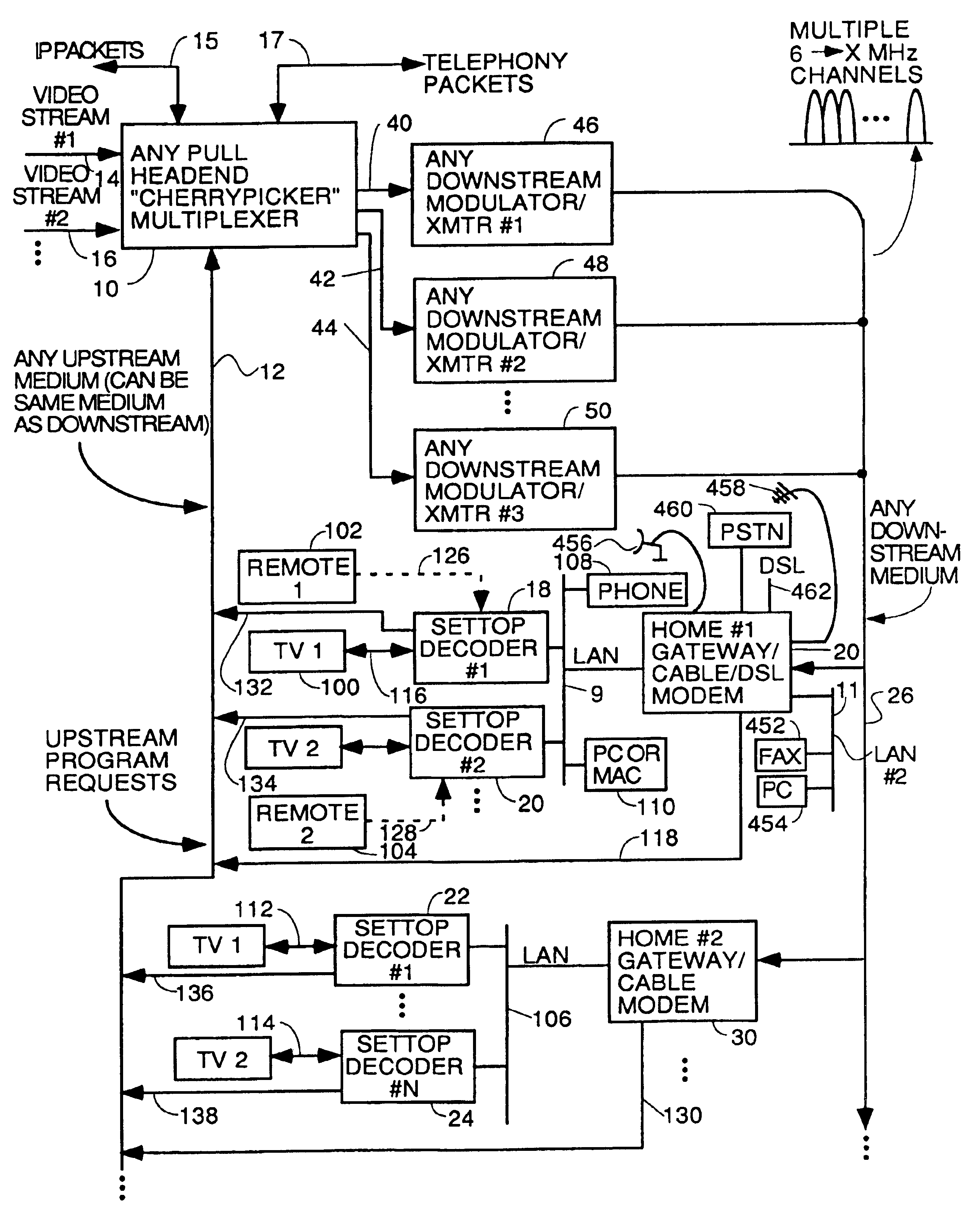
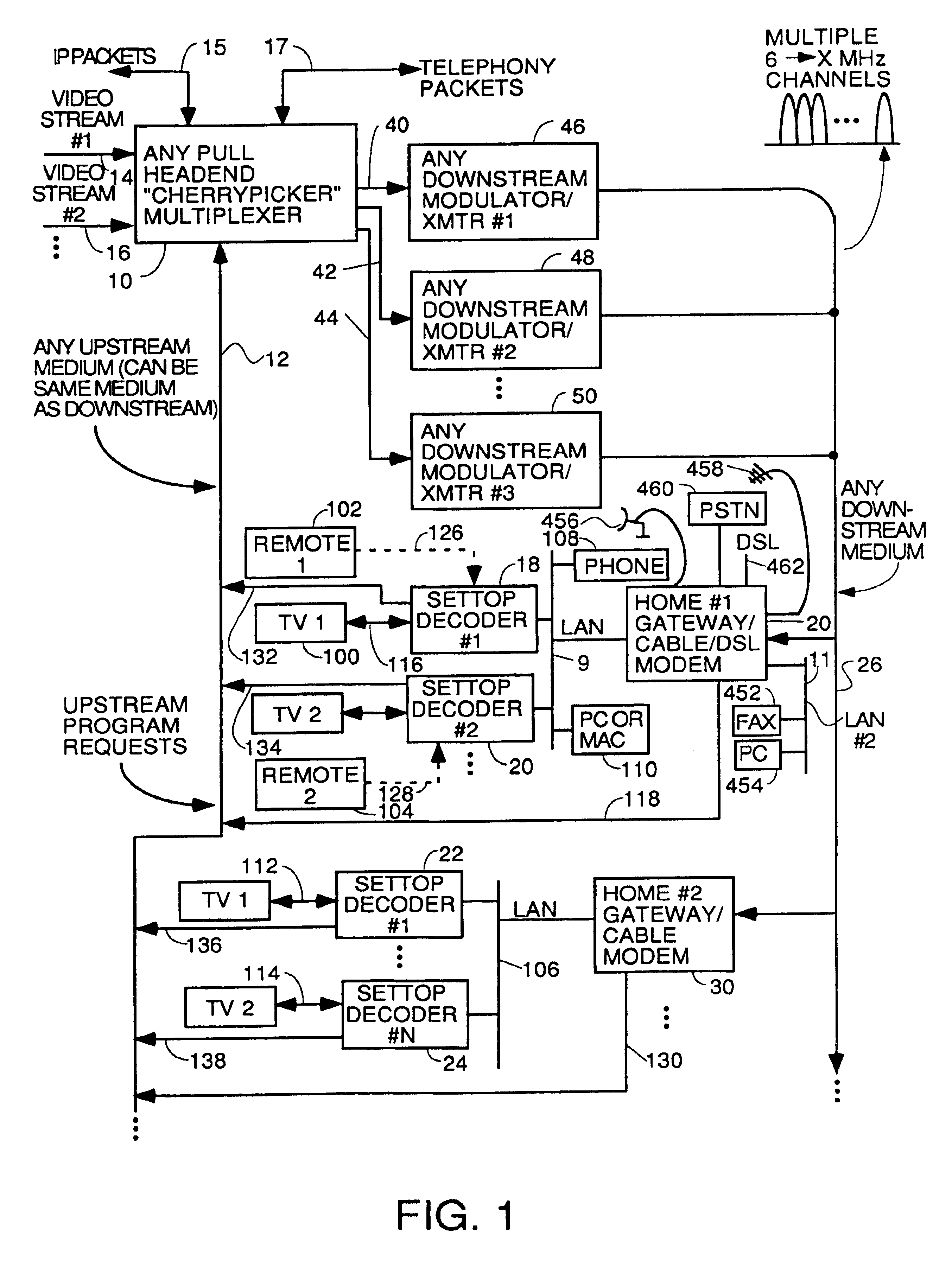
Home network for receiving video-on-demand and other requested programs and services
InactiveUS6889385B1Reduce quality problemsReduce bandwidth consumptionBroadband local area networksAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsVideocassette recorderTransceiver
A system for providing video-on-demand service, broadband internet access and other broadband services over T-carrier systems including a pull multiplexer cherrypicker at the head end is disclosed. The pull multiplexer receives upstream requests and cull out MPEG or other compressed video packets, IP packets and other data packet types to satisfy the requests or to send pushed programming downstream. The downstream can be DSL or HFC. Each customer has a cable modem, DSL modem or a gateway which interfaces multiple signal sources to a LAN to which settop decoders, digital phones, personal computers, digital FAX machines, video cameras, digital VCRs etc. can be attached. Each gateway can coupled the LAN to a DSL line or HFC through a cable modem or a satellite dish through a satellite transceiver. A PSTN and conventional TV antenna interface is also provided.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
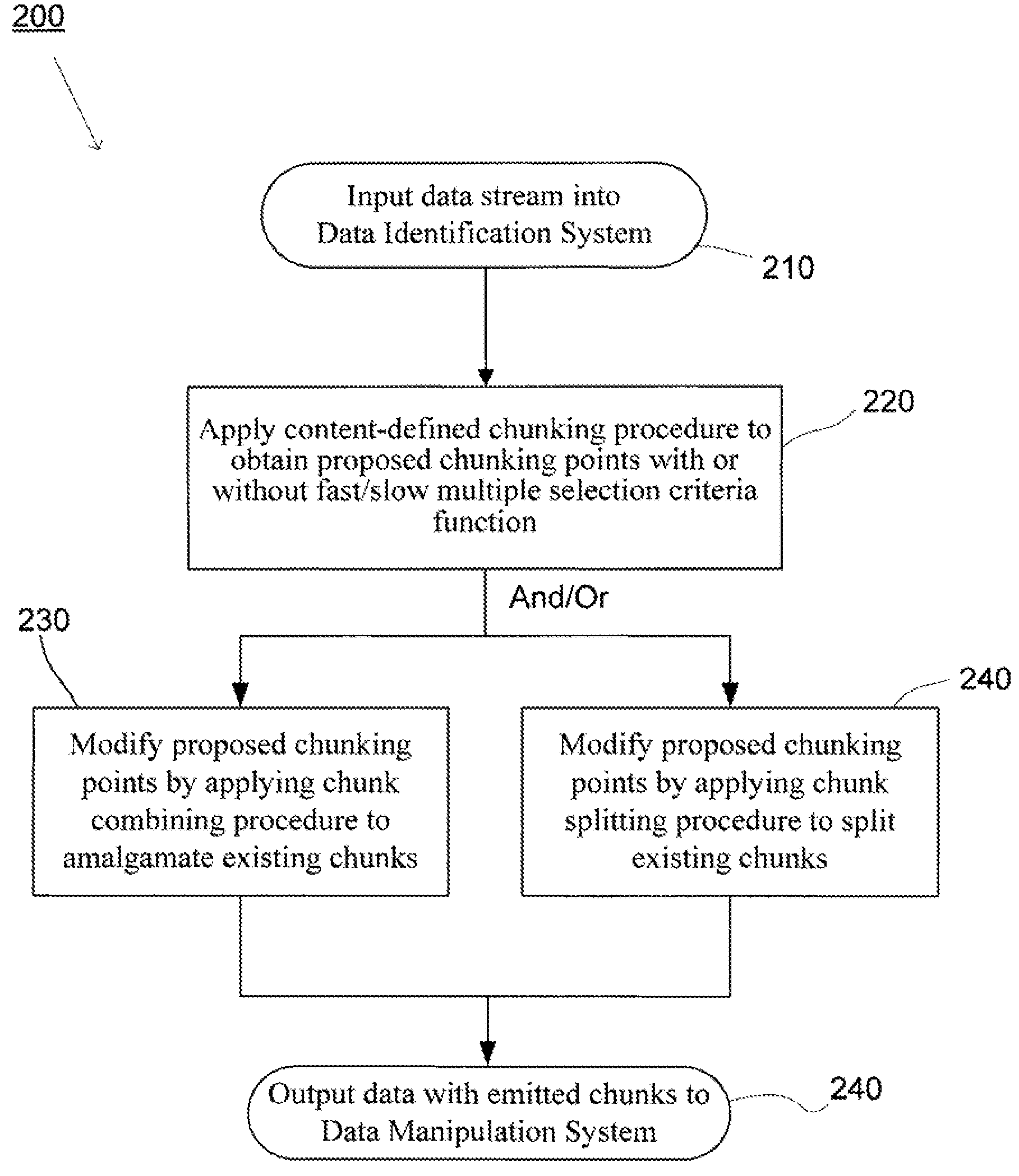
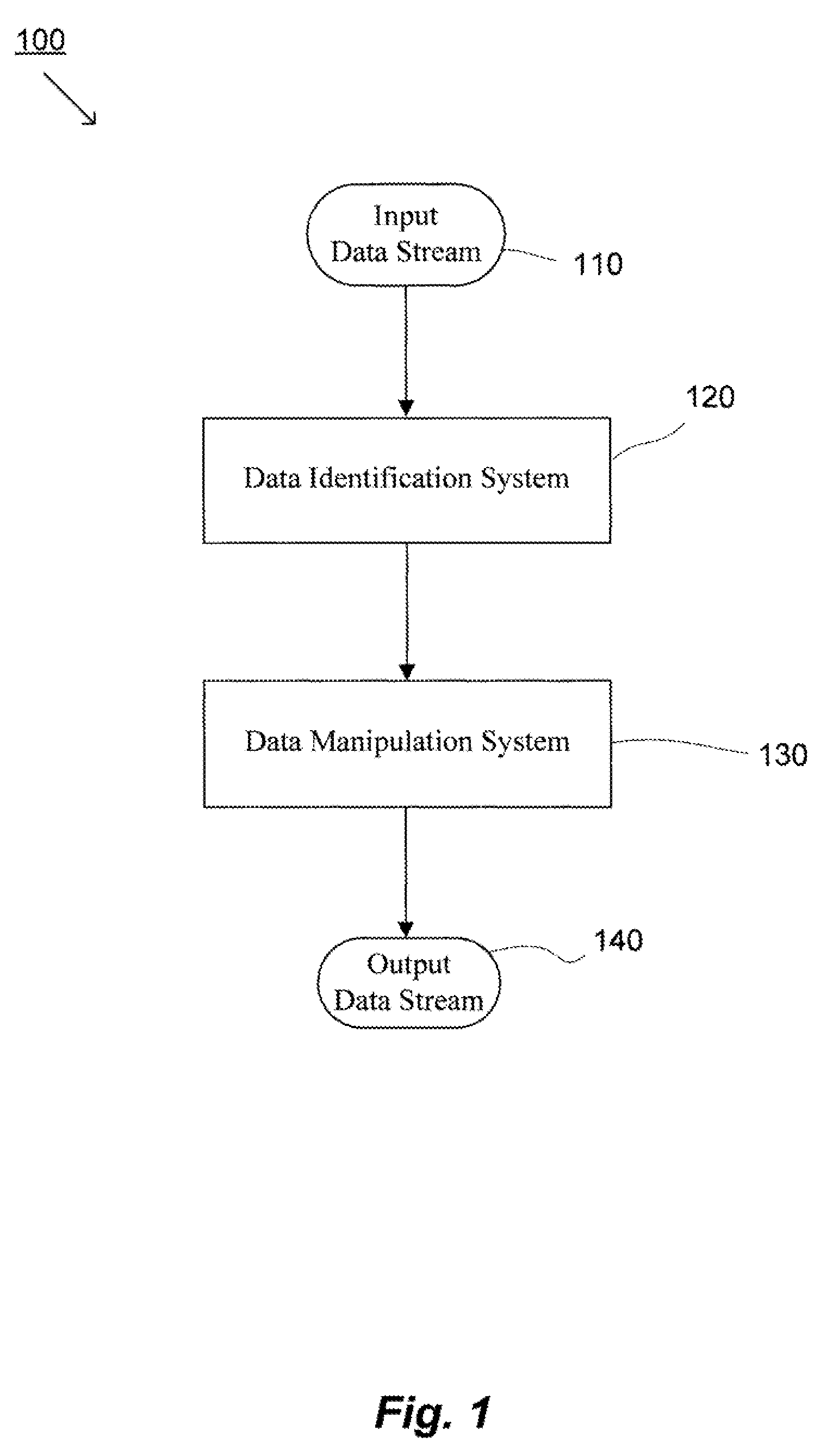
Methods and systems for quick and efficient data management and/or processing
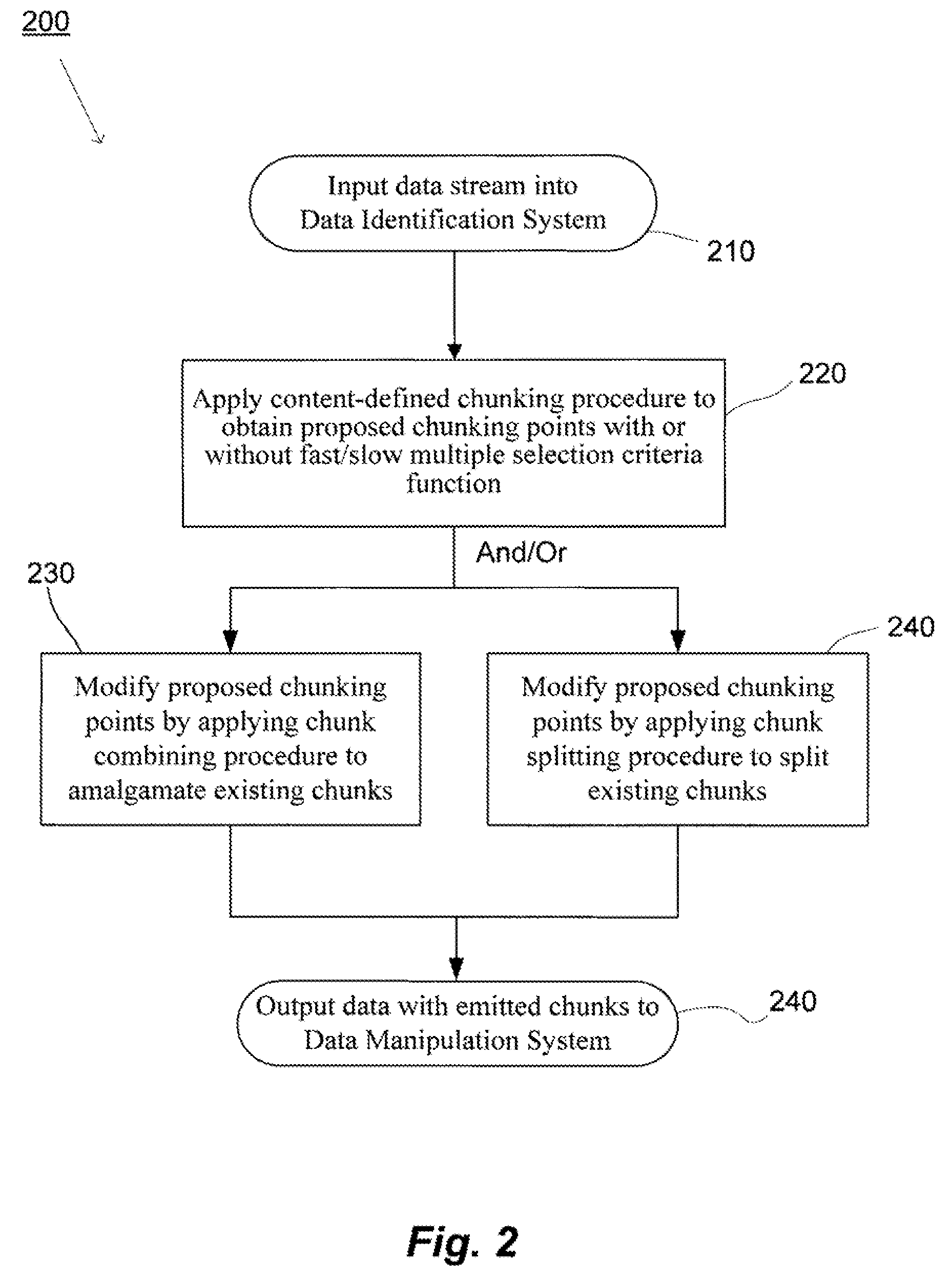
ActiveUS20080133561A1Improve data processing efficiencyReduce quality problemsDigital data information retrievalProgram control using stored programsData managementCombined technique
System(s) and method(s) are provided for data management and data processing. For example, various embodiments may include systems and methods relating to relatively larger groups of data being selected with comparable or better performing selection results (e.g., high data redundancy elimination and / or average chunk size). In various embodiments, the system(s) and method(s) may include, for example a data group, block, or chunk combining technique or / and a data group, block, or chunk splitting technique. Various embodiments may include a first standard or typical data grouping, blocking, or chunking technique and / or data group, block, or chunk combining technique or / and a data group, block, or chunk splitting technique. Exemplary system(s) and method(s) may relate to data hashing and / or data elimination. Embodiments may include a look-ahead buffer and determine whether to emit small chunks or large chunks based on characteristics of underlying data and / or particular application of the invention (e.g., for backup).
Owner:NEC CORP
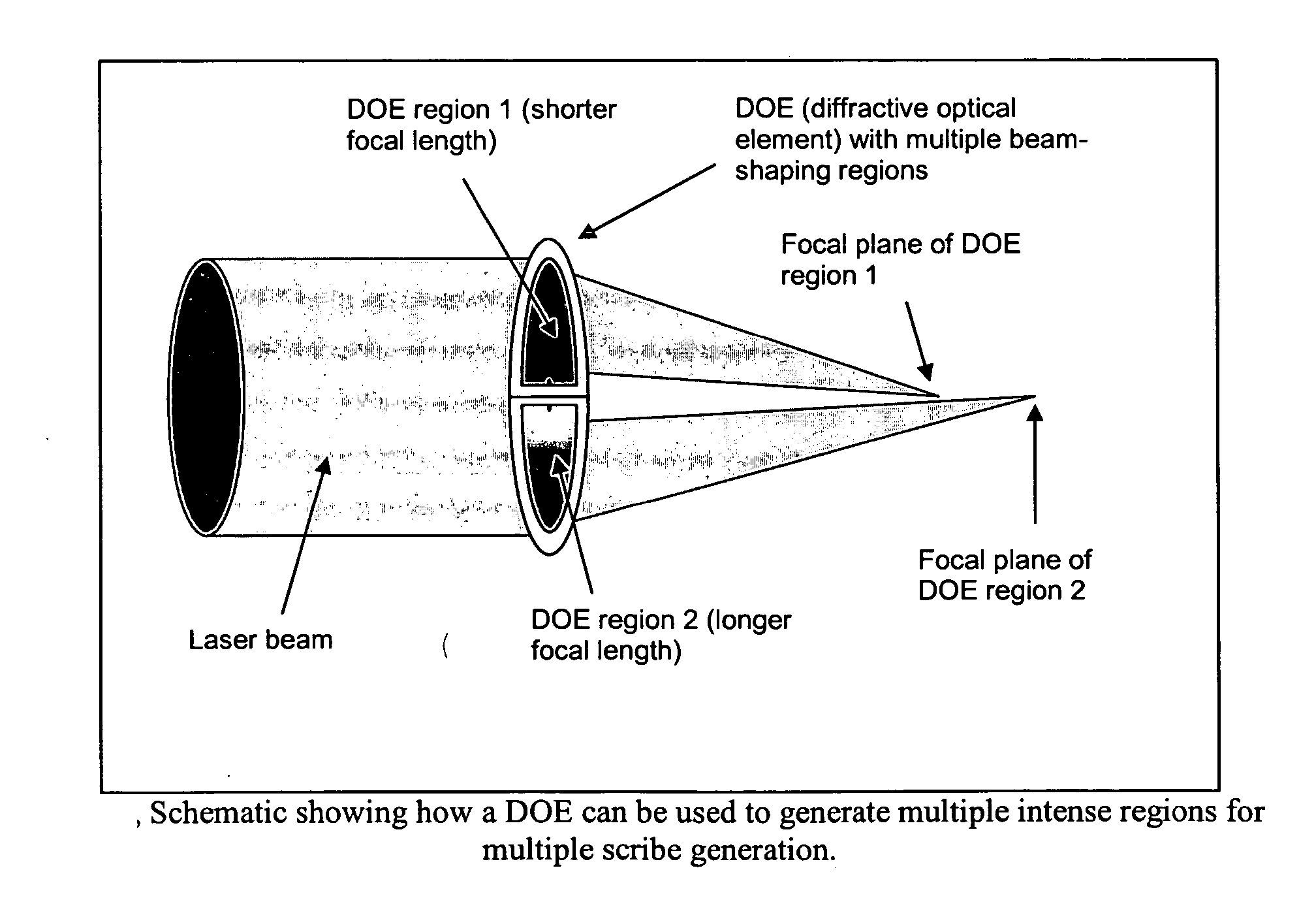
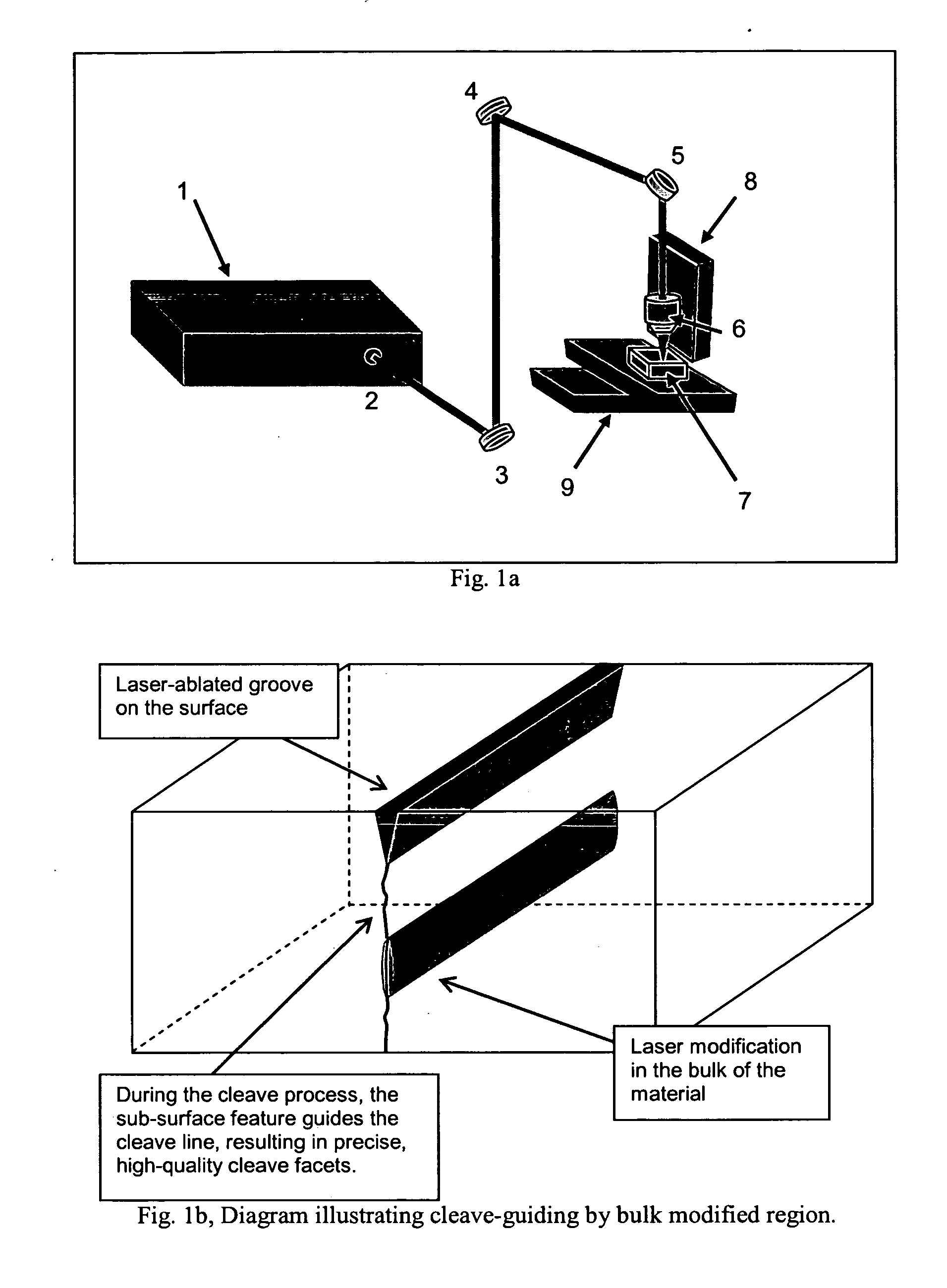
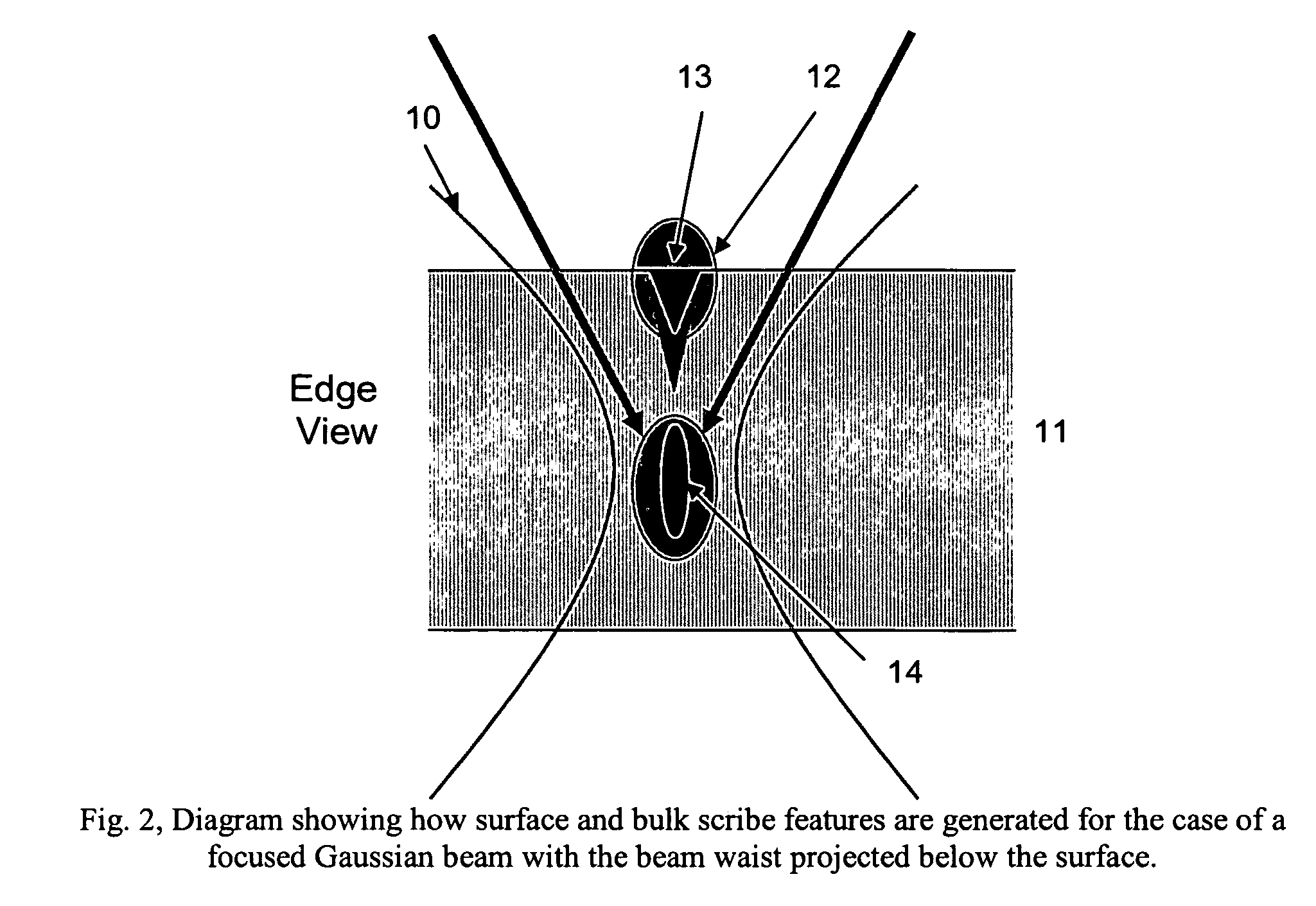
Transparent material processing with an ultrashort pulse laser
InactiveUS20100025387A1Reduce quality problemsPoor precisionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFine working devicesLight beamOptoelectronics
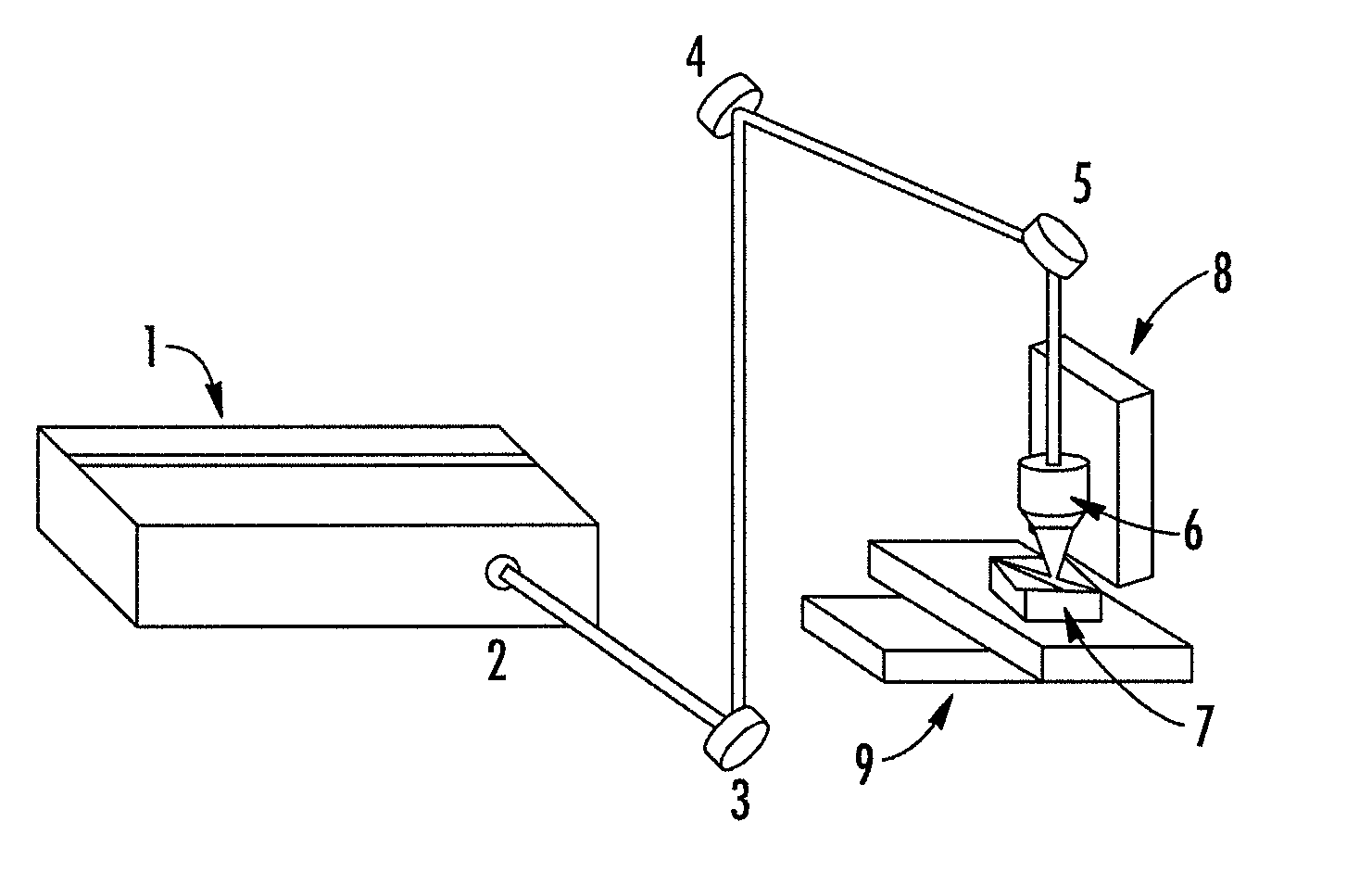
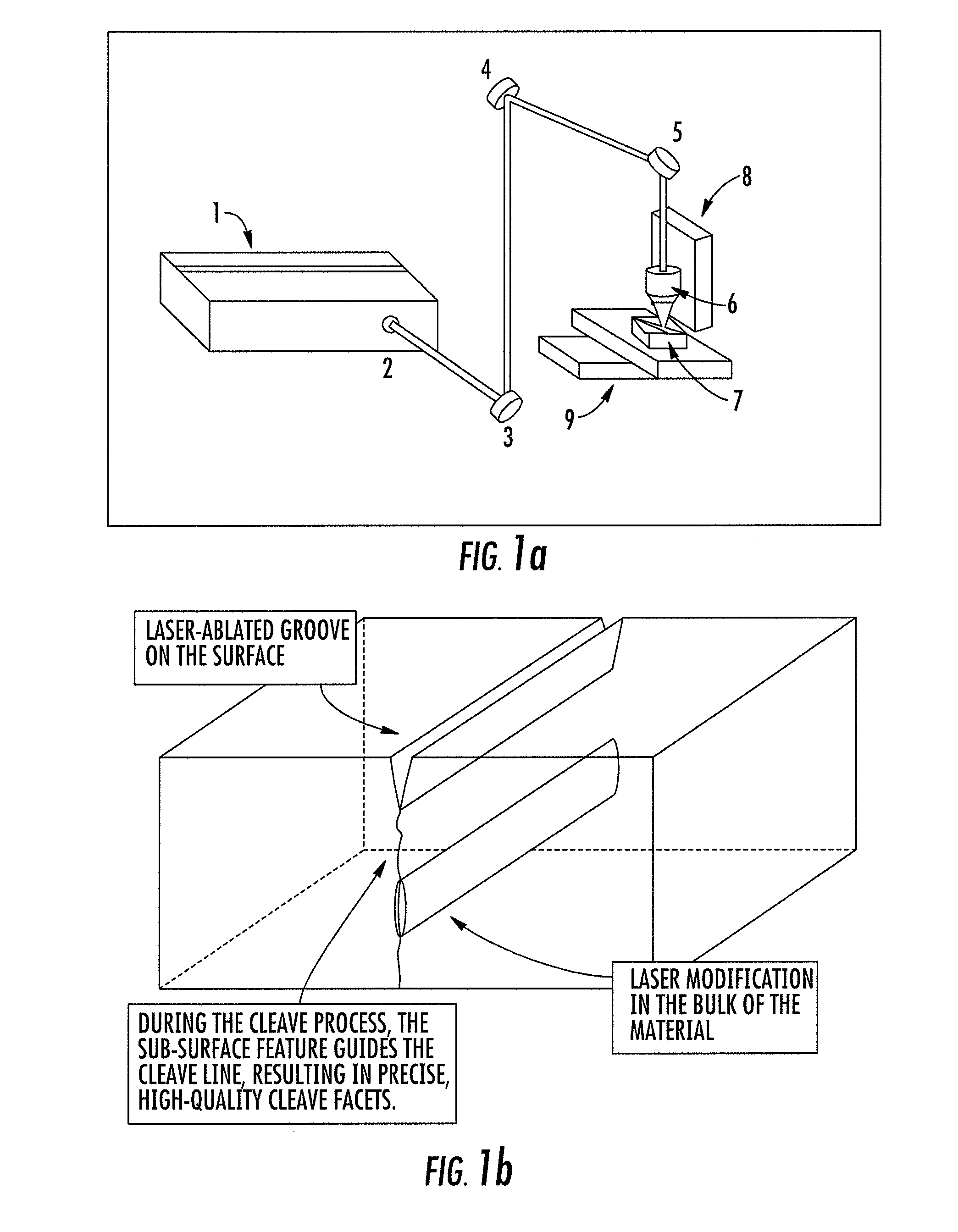
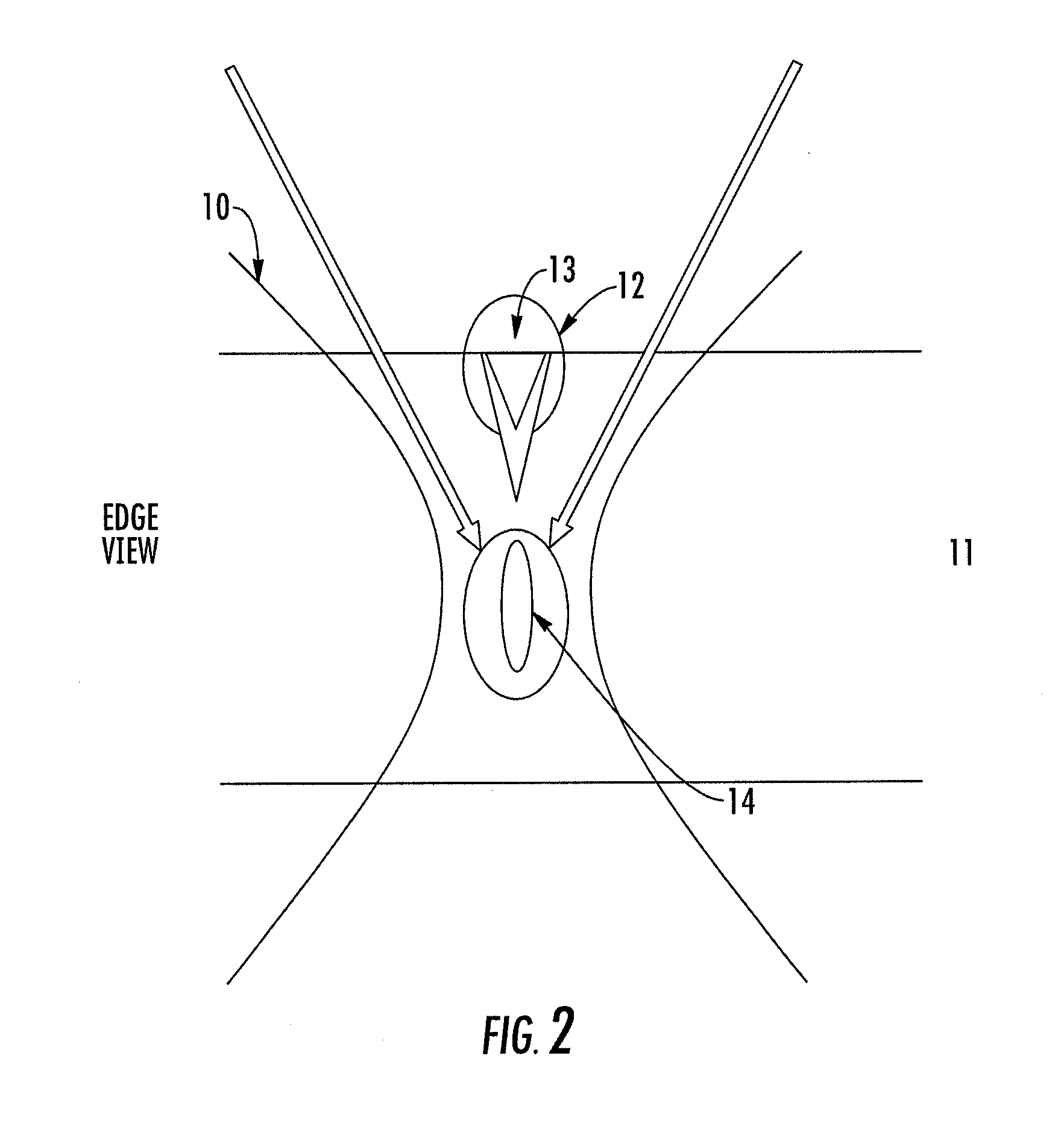
Methods, devices, and systems for ultrashort pulse laser processing of optically transparent materials are disclosed, with example applications in scribing, marking, welding, and joining. For example, ultrashort laser pulses create scribe features with one pass of the laser beam across the material, with at least one of the scribe features being formed below the surface of the material. Slightly modifying the ultrashort pulse laser processing conditions produces sub-surface marks. When properly arranged, these marks are clearly visible with correctly aligned illumination. Reflective marks may also be formed with control of laser parameters. A transparent material other than glass may be utilized. A method for welding transparent materials uses ultrashort laser pulses to create a bond through localized heating. In some embodiments of transparent material processing, a multifocus beam generator simultaneously forms multiple beam waists spaced depthwise relative to the transparent material, thereby increasing processing speed.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
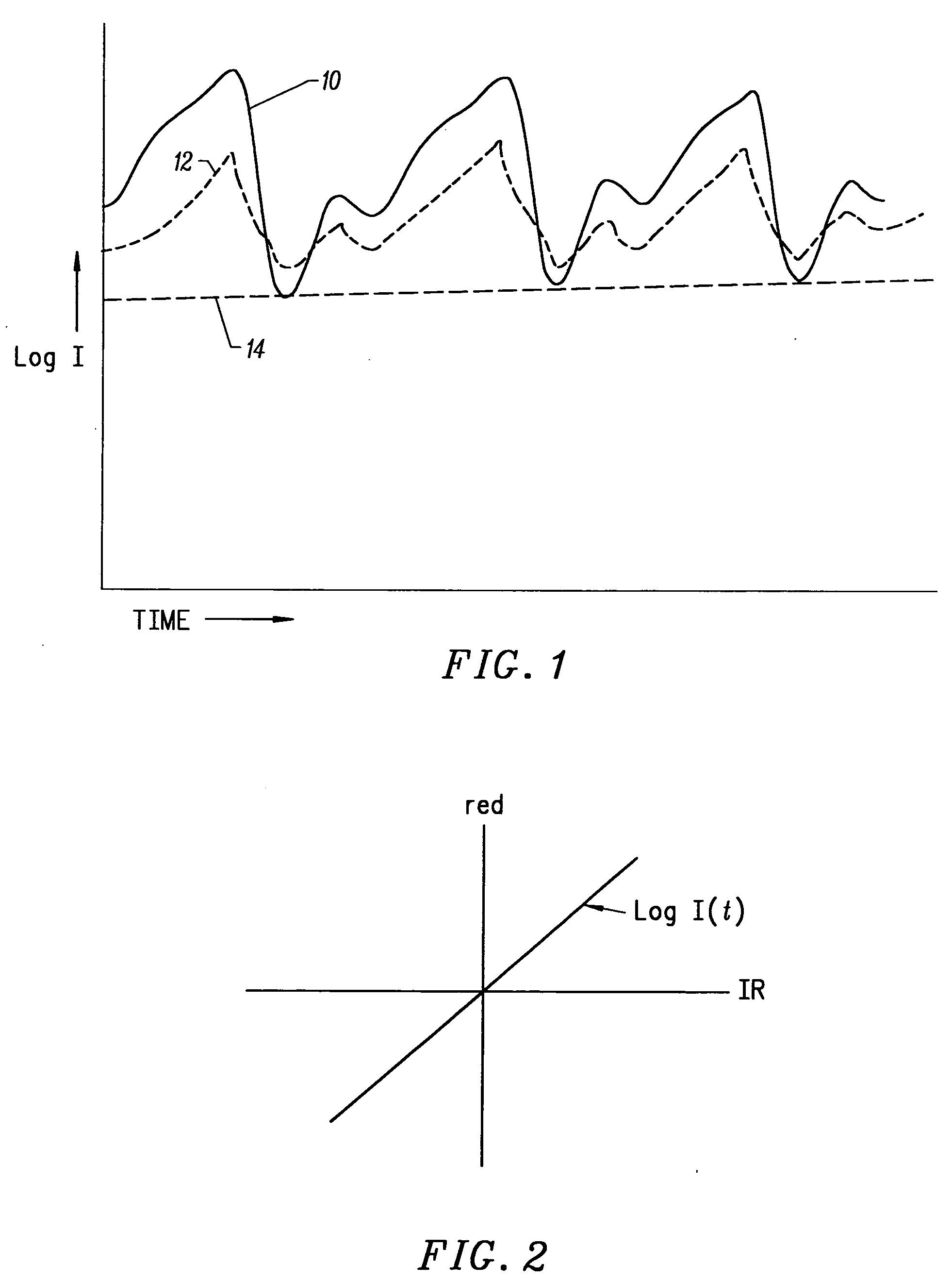
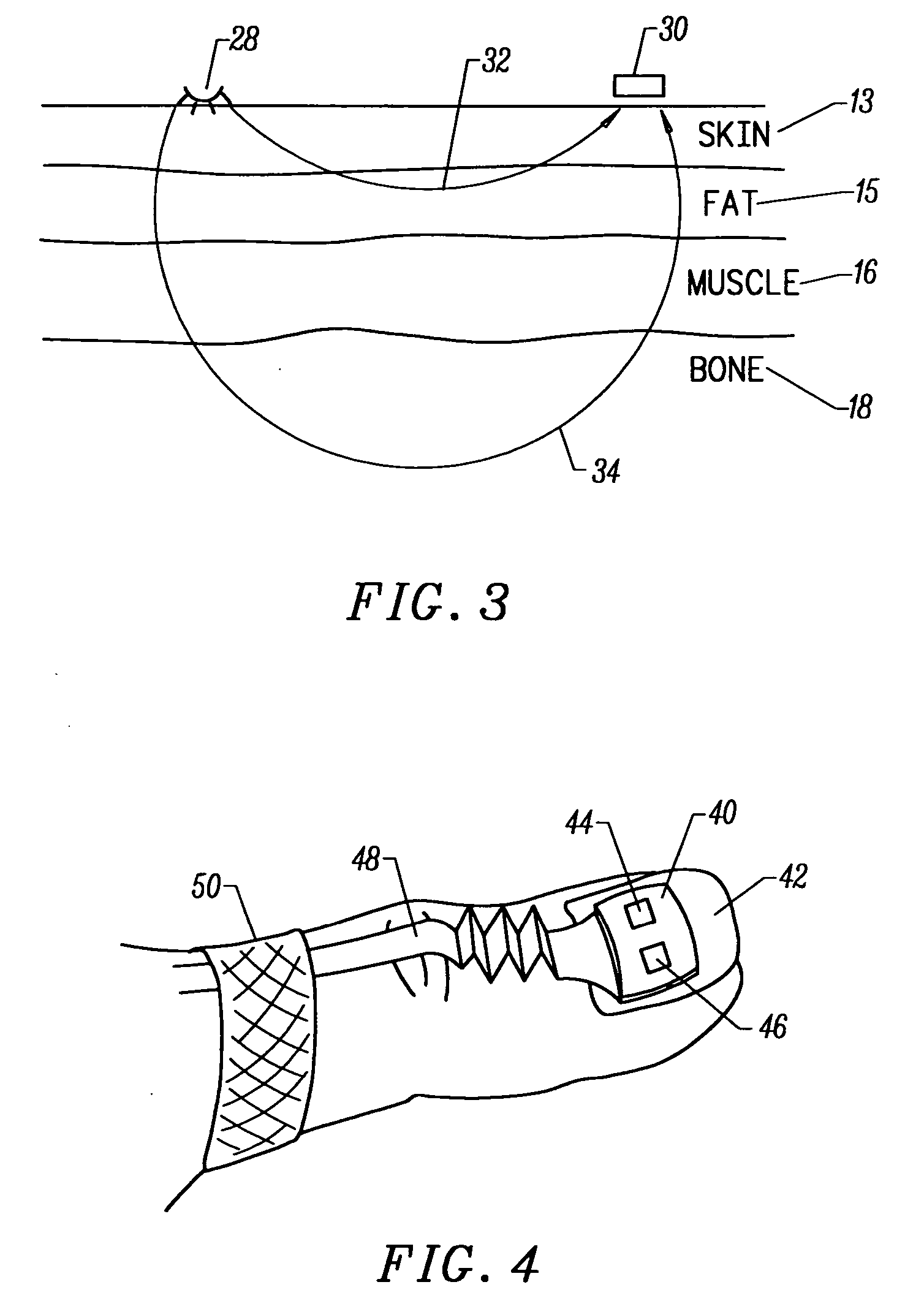
Motion compatible sensor for non-invasive optical blood analysis
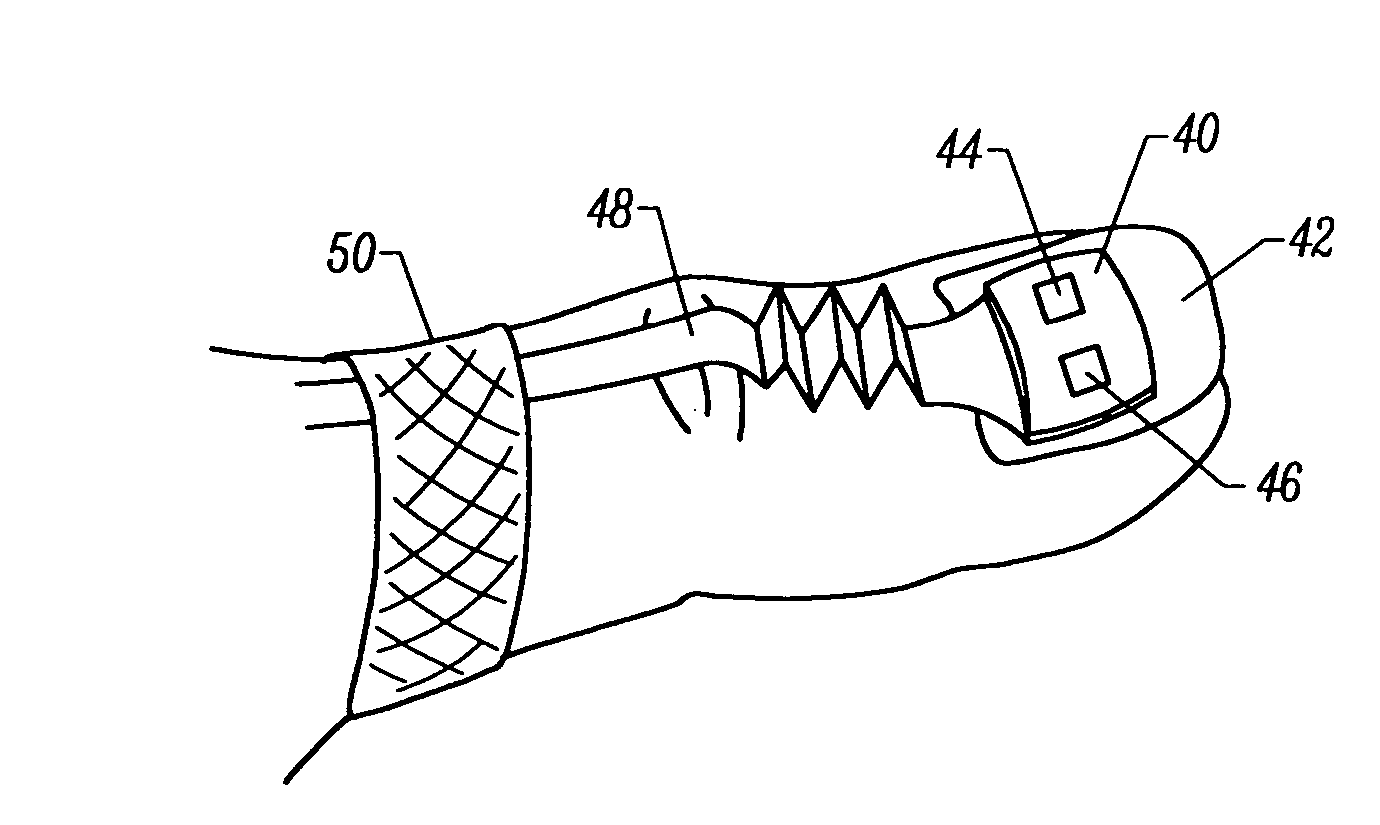
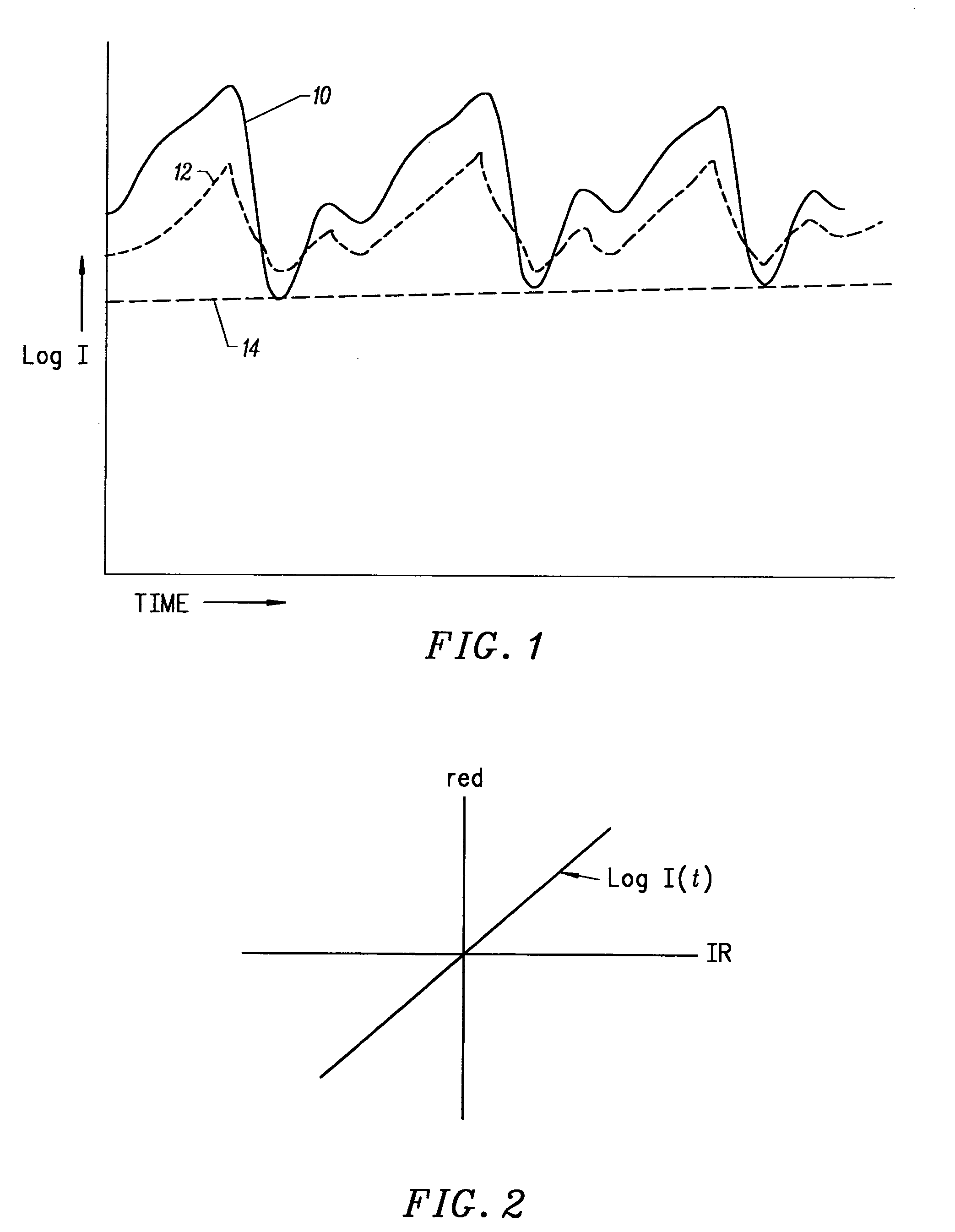
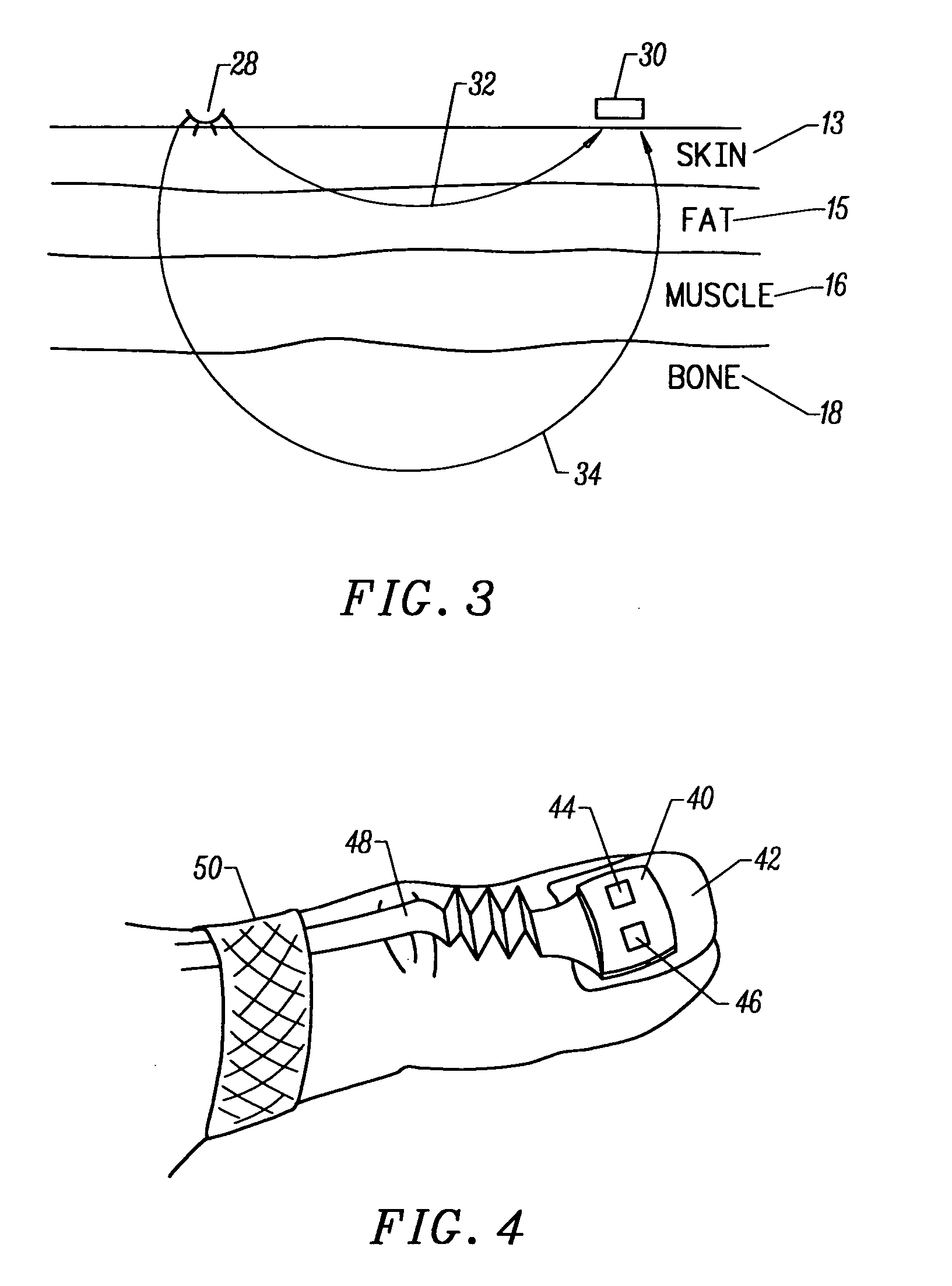
InactiveUS20050070773A1Low profileReduce quality problemsSensorsBlood characterising devicesClassical mechanicsPulse oximetry
A non-invasive optical sensor which uses the motion signal to calculate the physiological characteristic being measured. For pulse oximetry, a least squares or a ratio-of-ratios technique can be applied to the motion signal itself. This is made possible by selecting a site on the patient where variations in motion produce signals of two wavelengths which are sufficiently correlated. In particular, it has been determined that a sensor placed on a nail, in particular a thumbnail, exhibits the characteristics of having the red and infrared signals correlated when used for pulse oximetry, and the resulting signals correlate to arterial oxygen saturation.
Owner:NELLCOR PURITAN BENNETT LLC
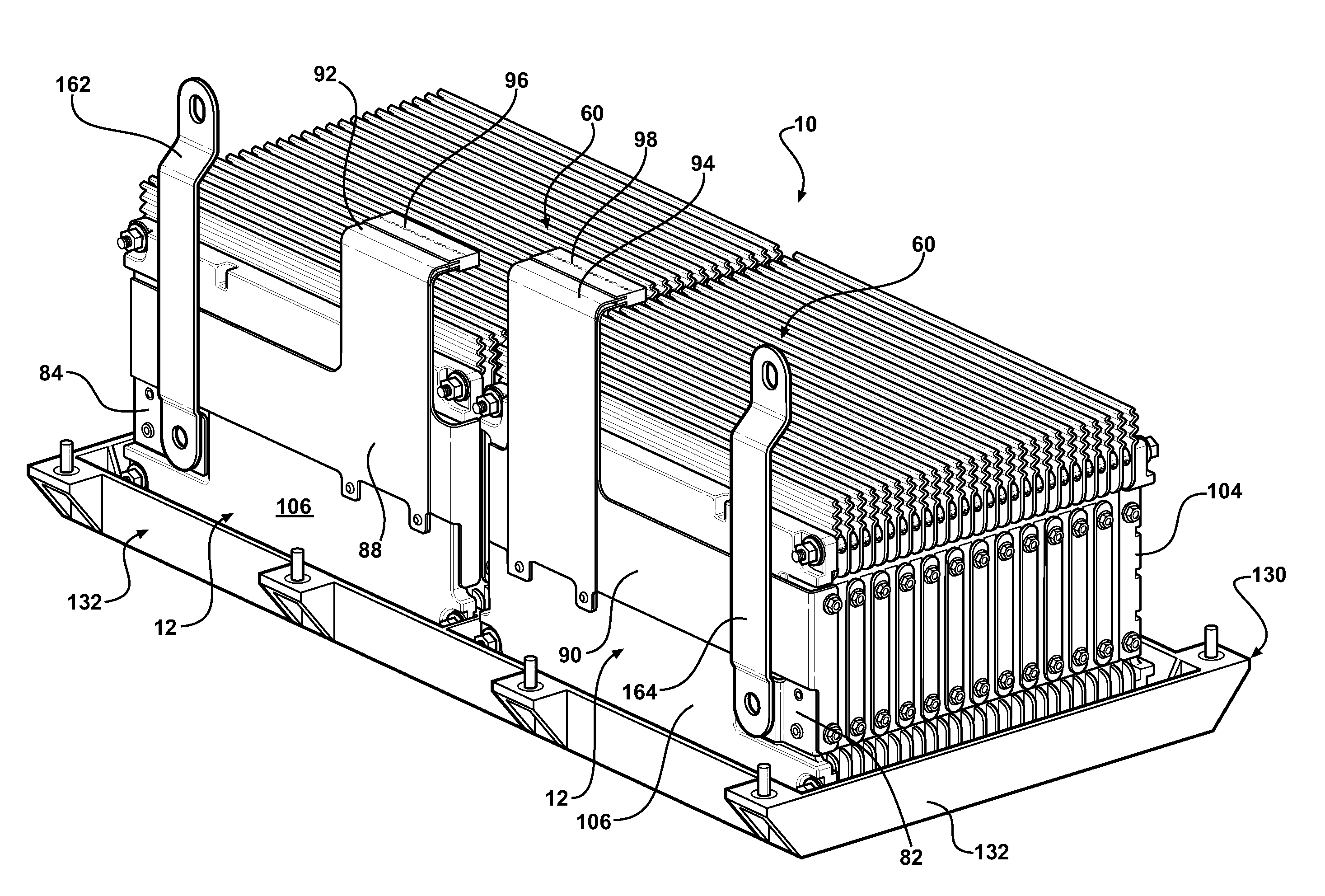
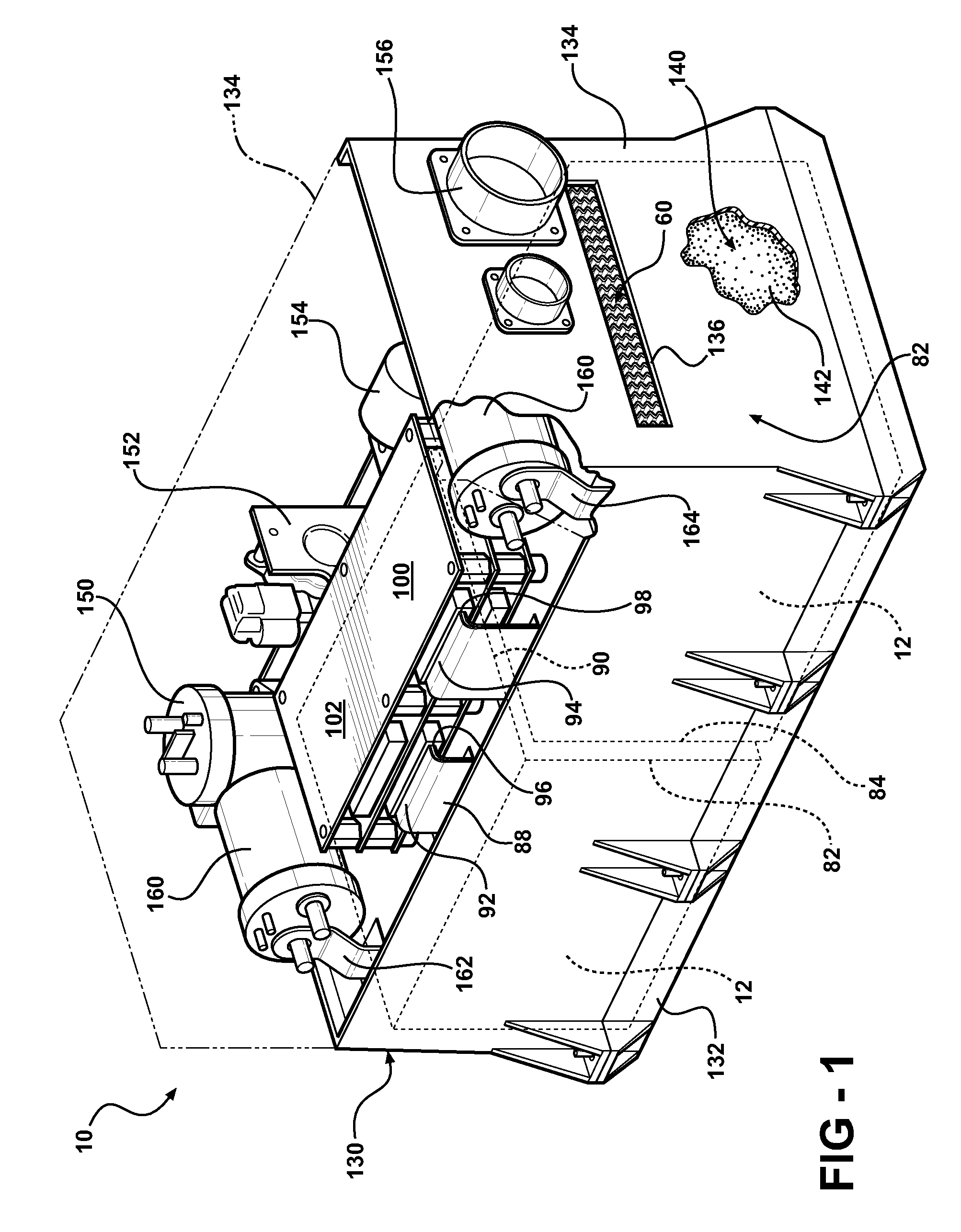
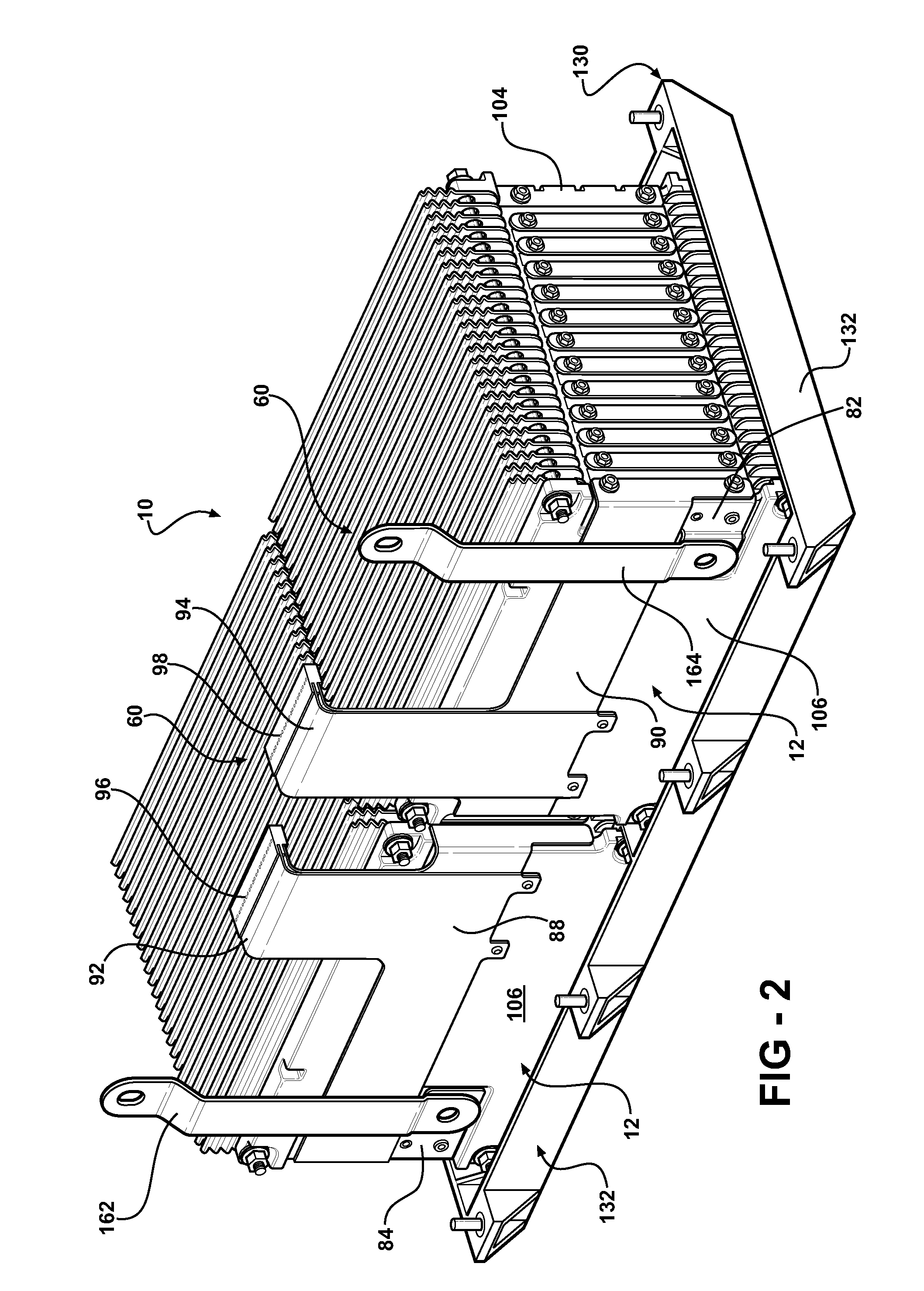
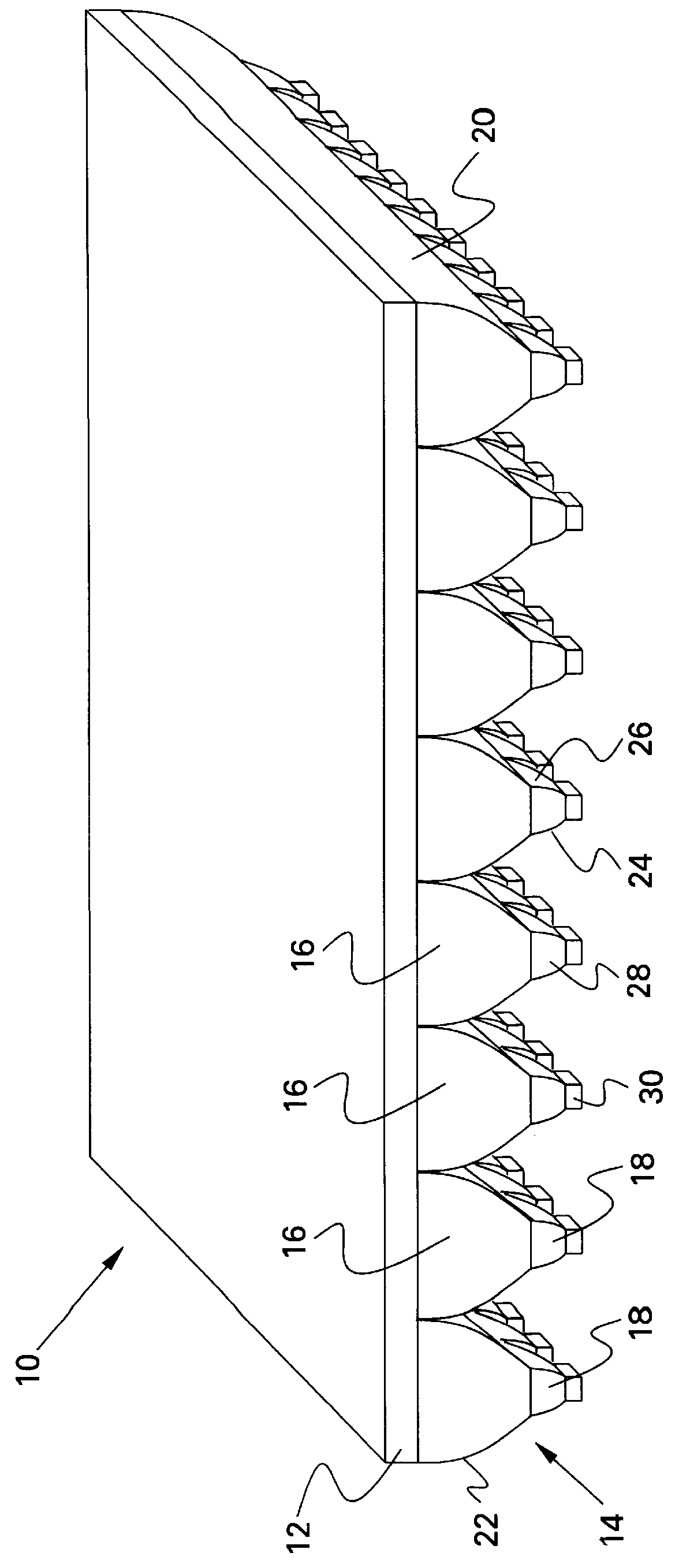
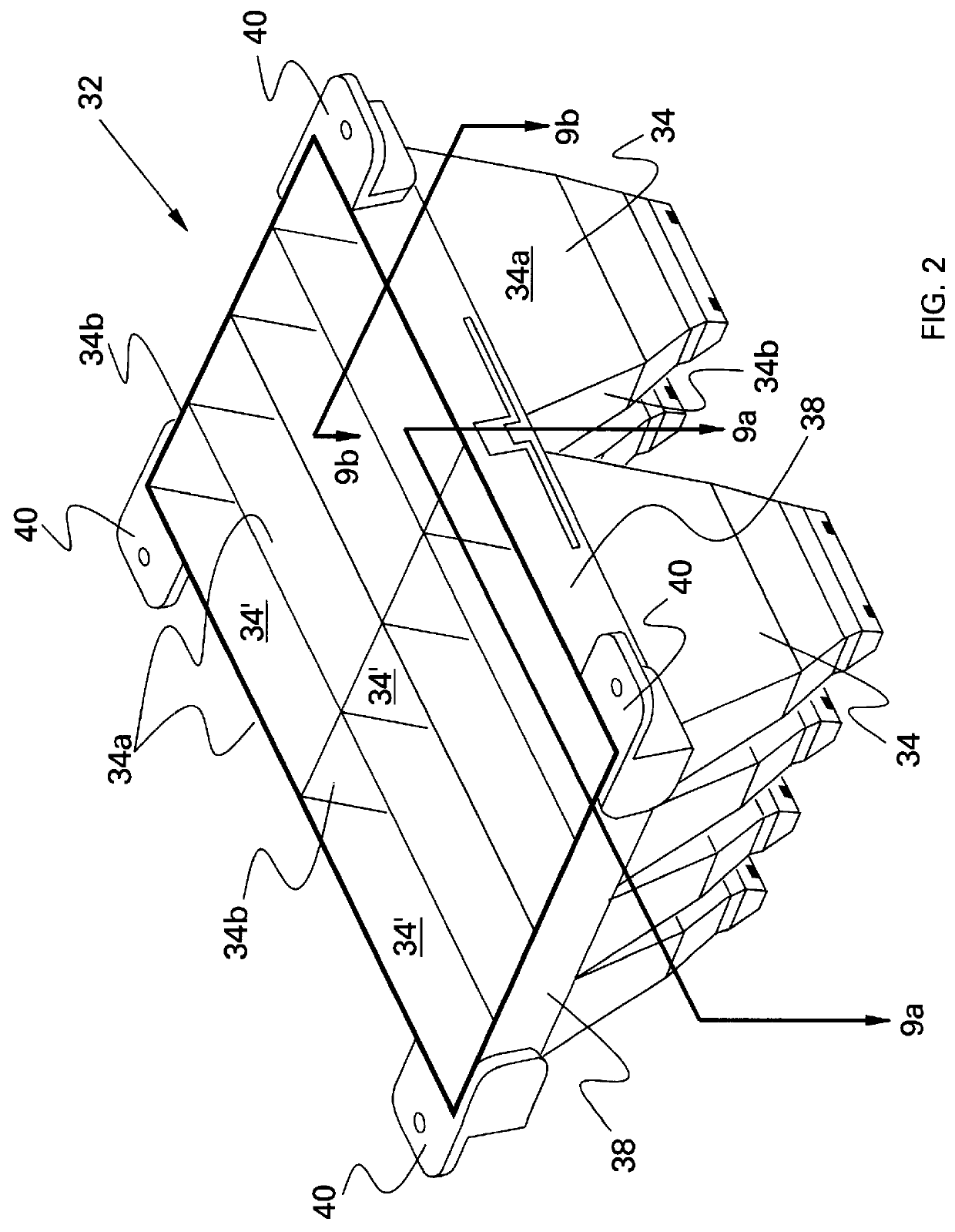
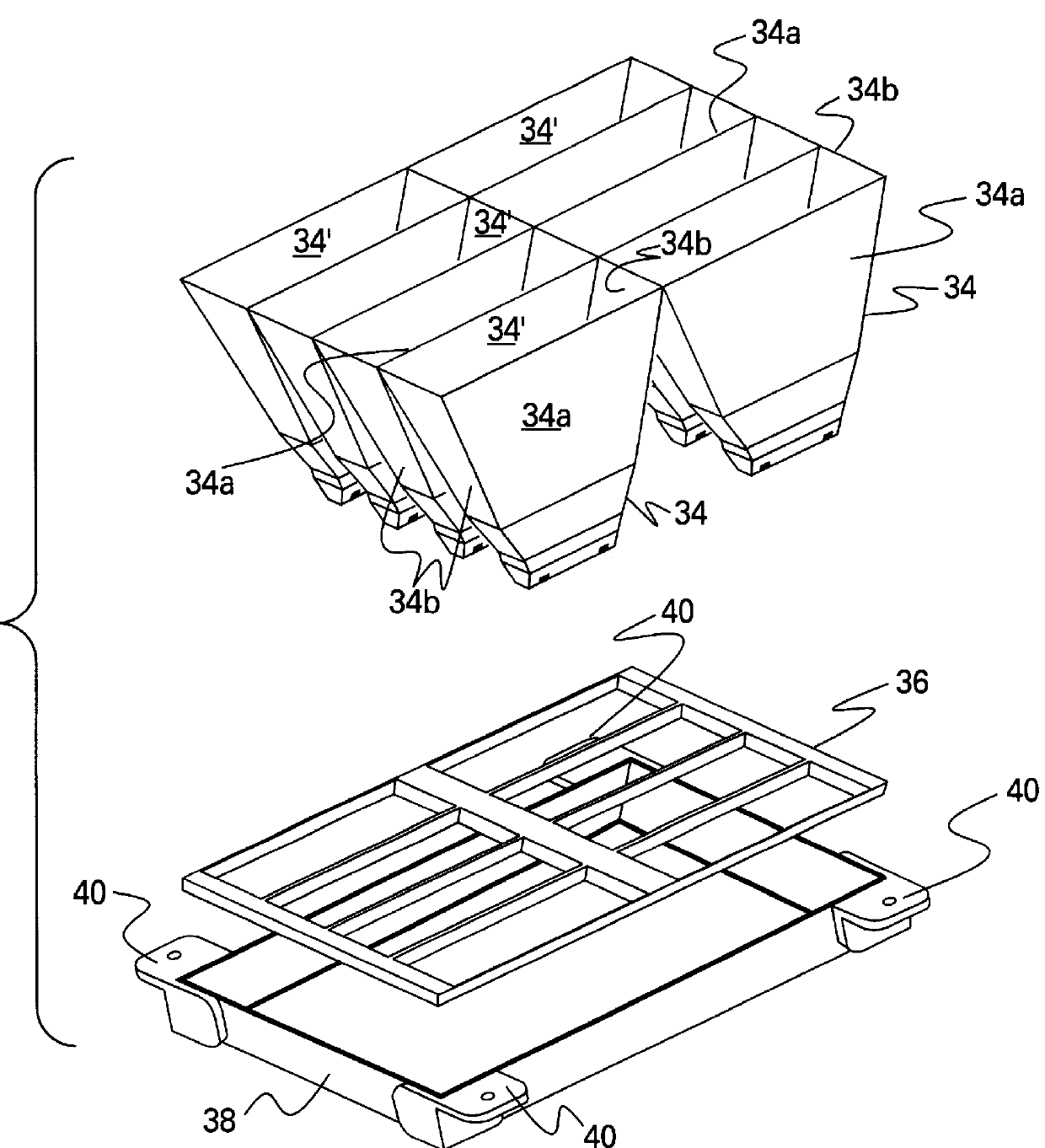
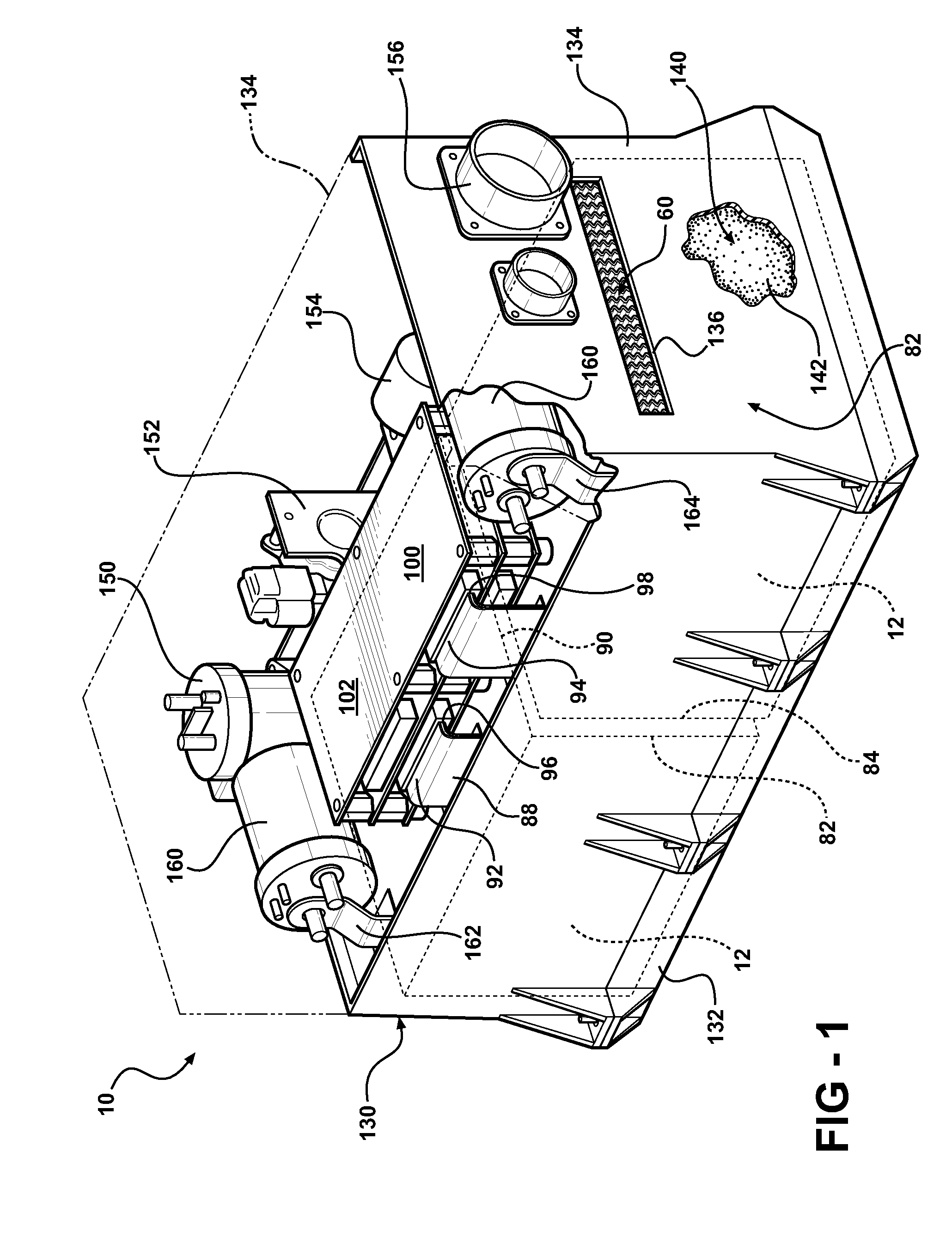
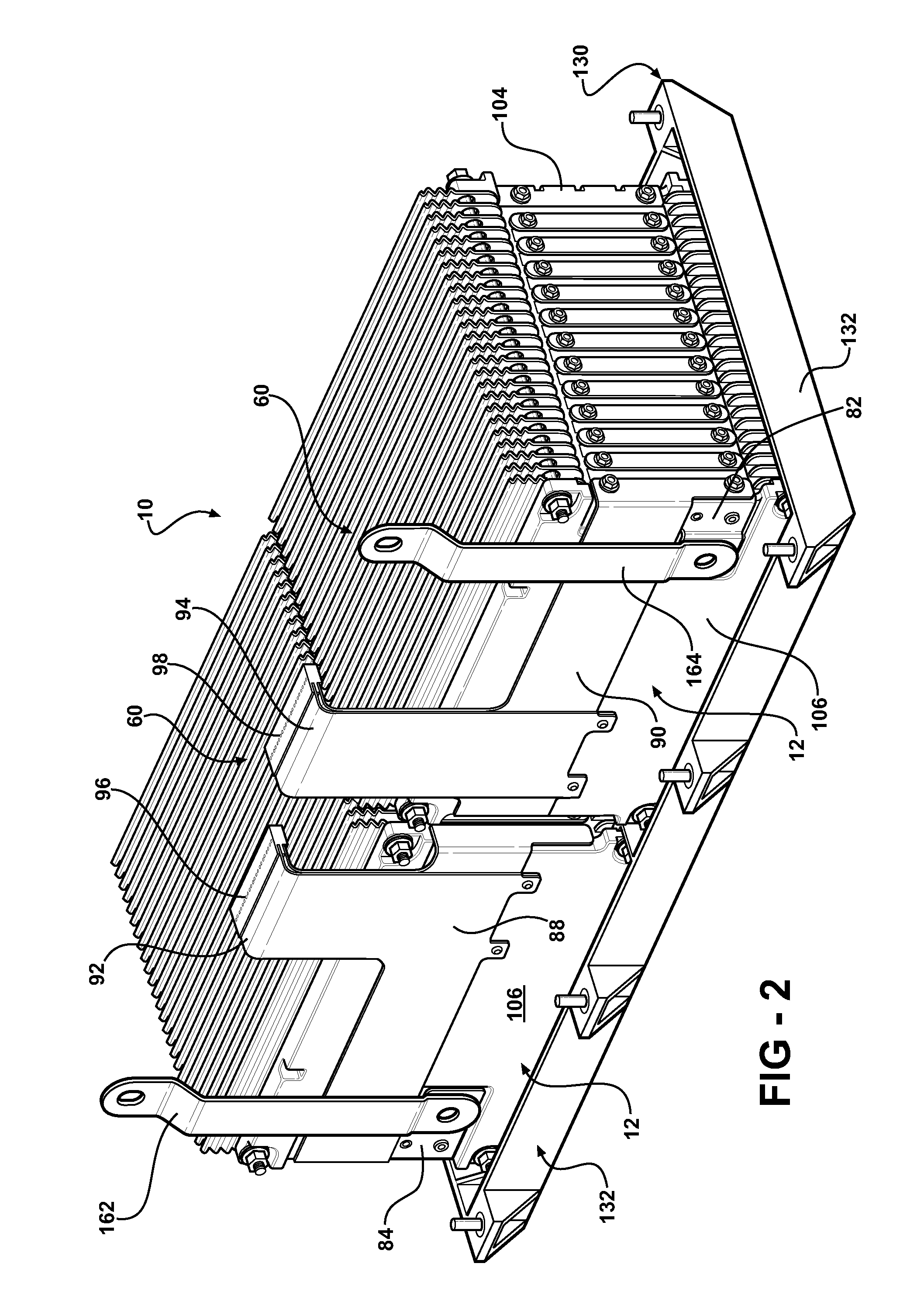
Battery pack with integral cooling and bussing devices
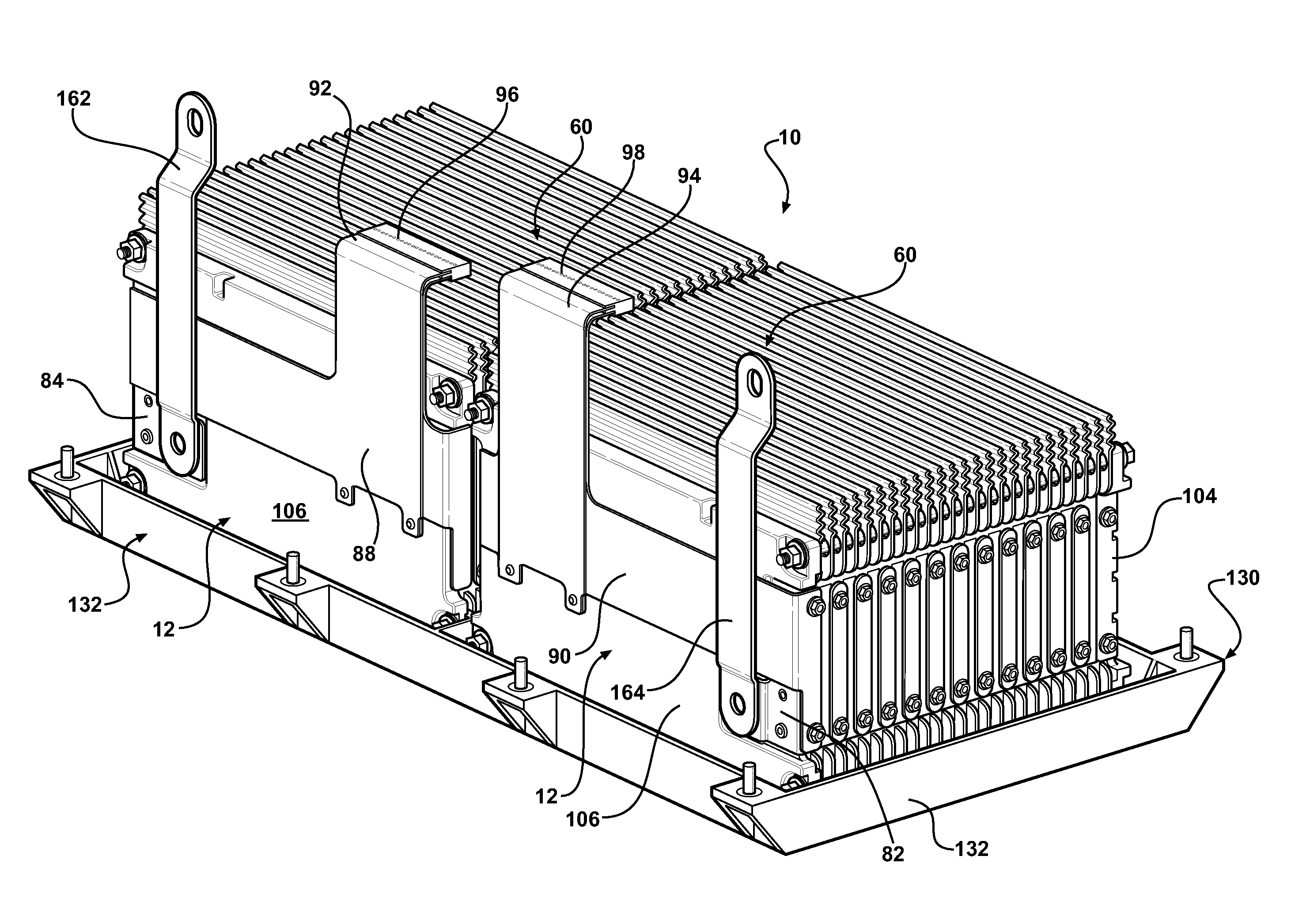
ActiveUS20080090137A1High energy density characteristicImproving packaging characteristicFinal product manufacturePrimary cellsMobile vehicleEngineering
A battery module of the present invention is adaptable to be utilized in various configurations including and not limited to an overlapping battery cell packaging configuration and a vertical stack battery cell packaging configuration used in an automotive vehicle. The battery module has a plurality of battery heatsink assemblies with the cells disposed therebetween. A plurality of rods extend through the each heatsink assemblies to secure the heatsink assemblies and the cell with one another to form the battery module.
Owner:ENERDEL
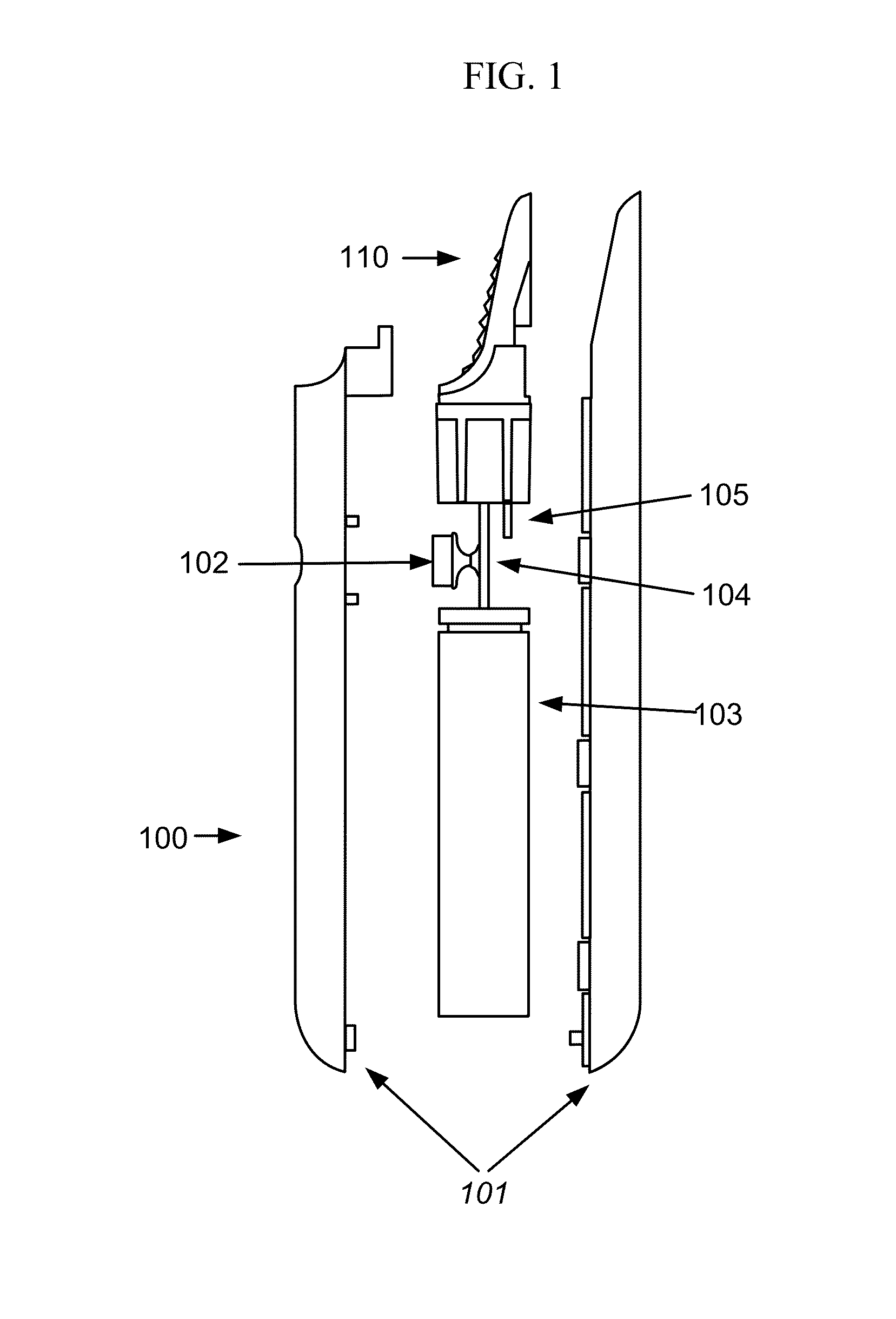
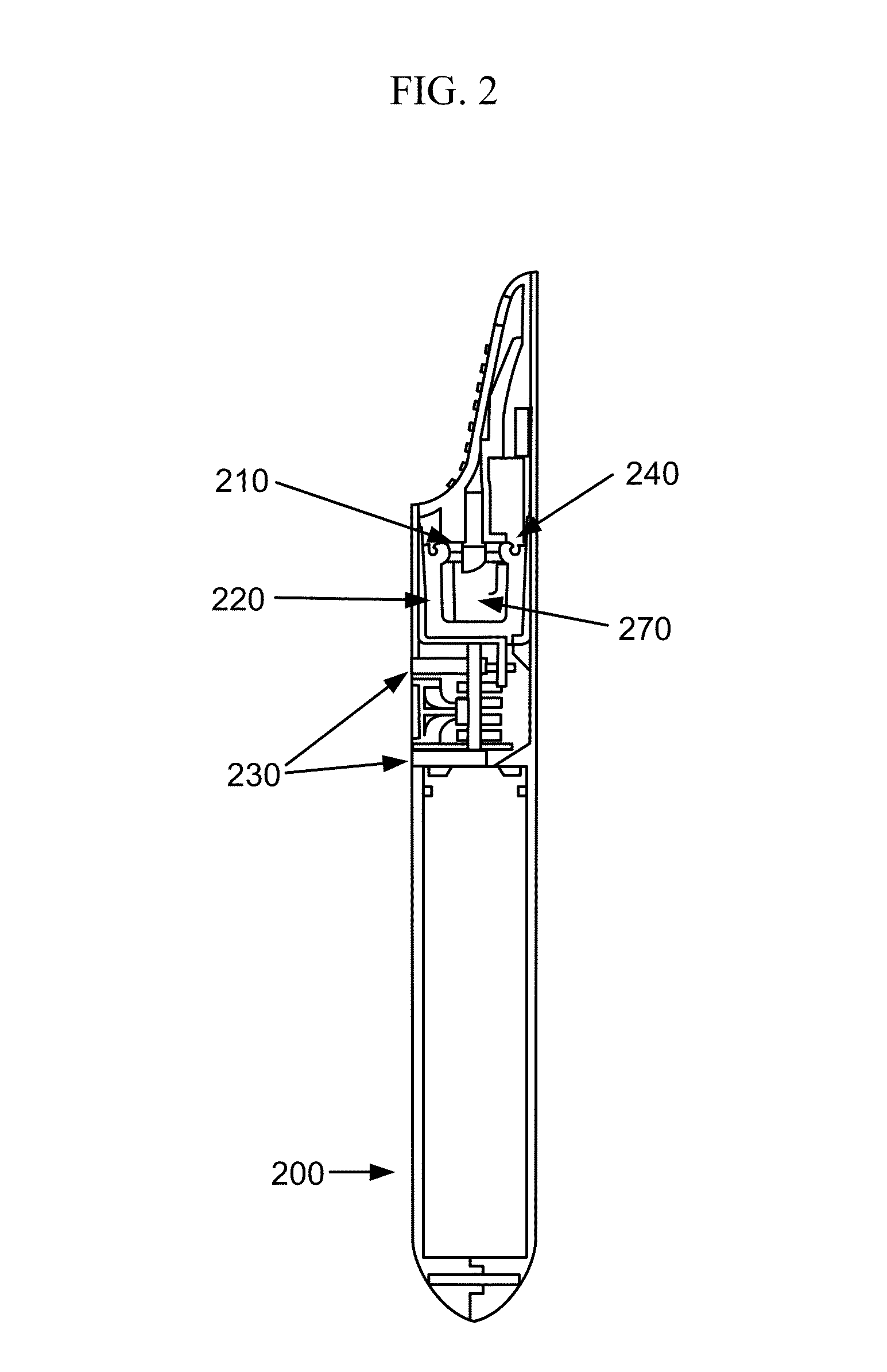
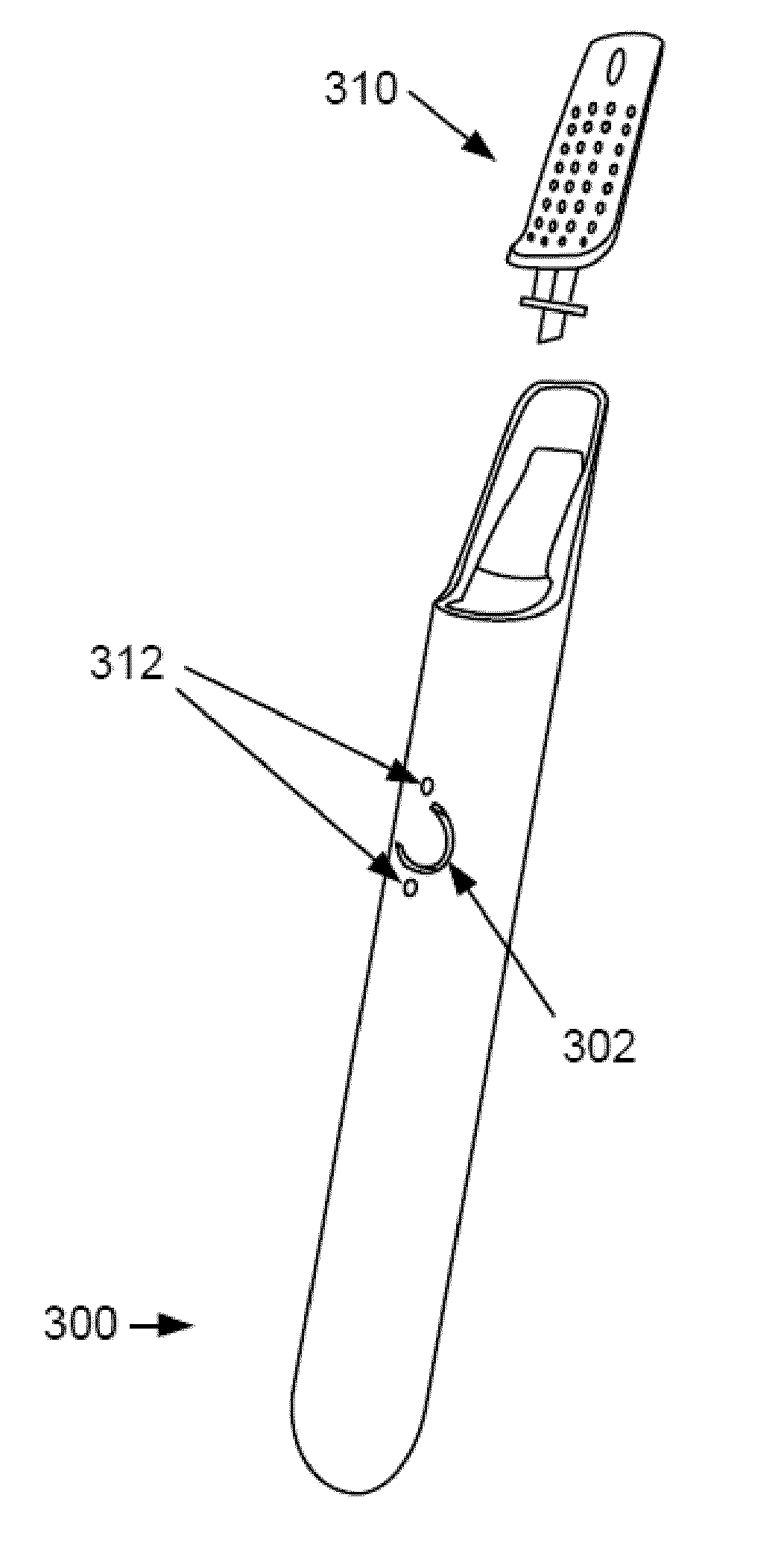
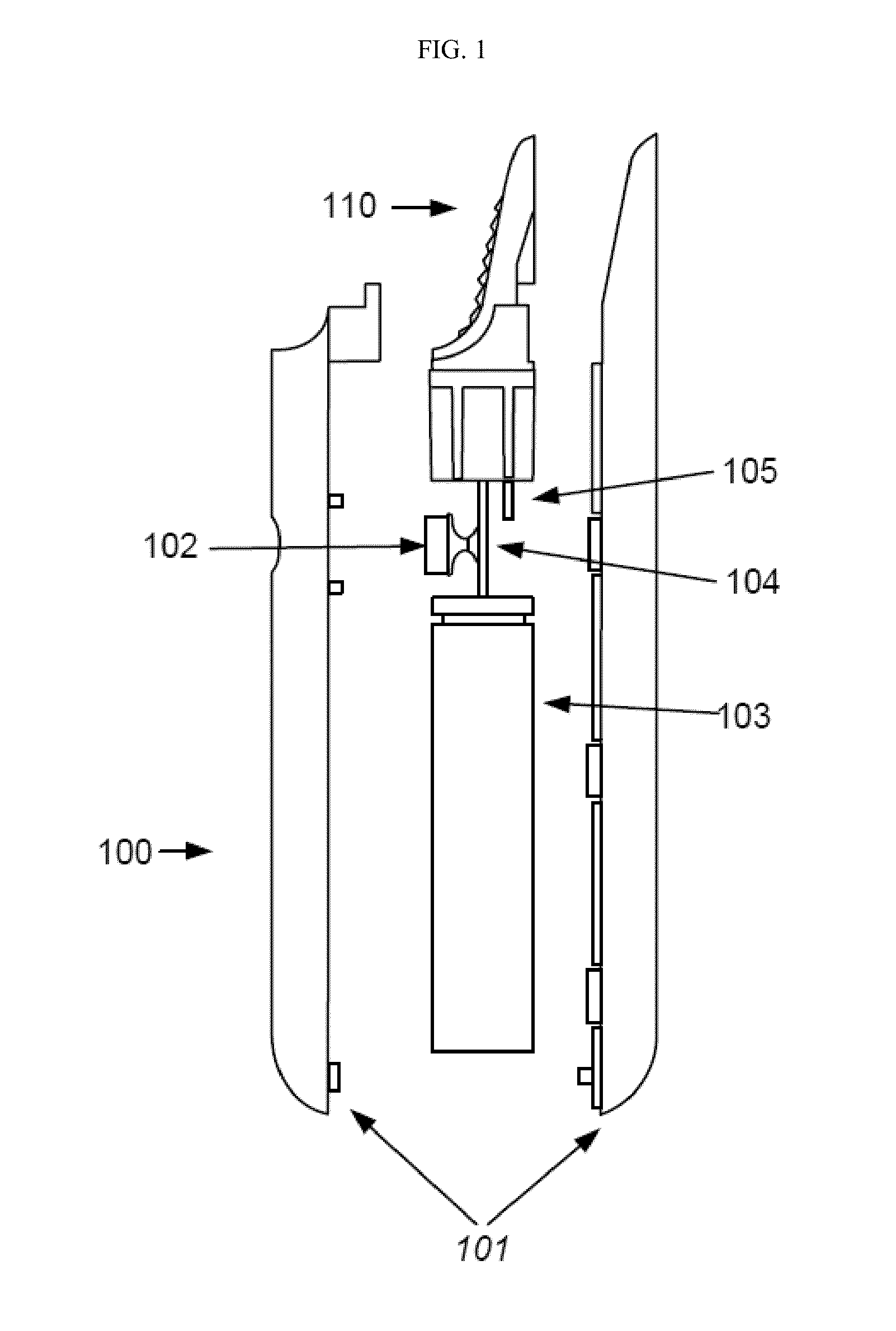
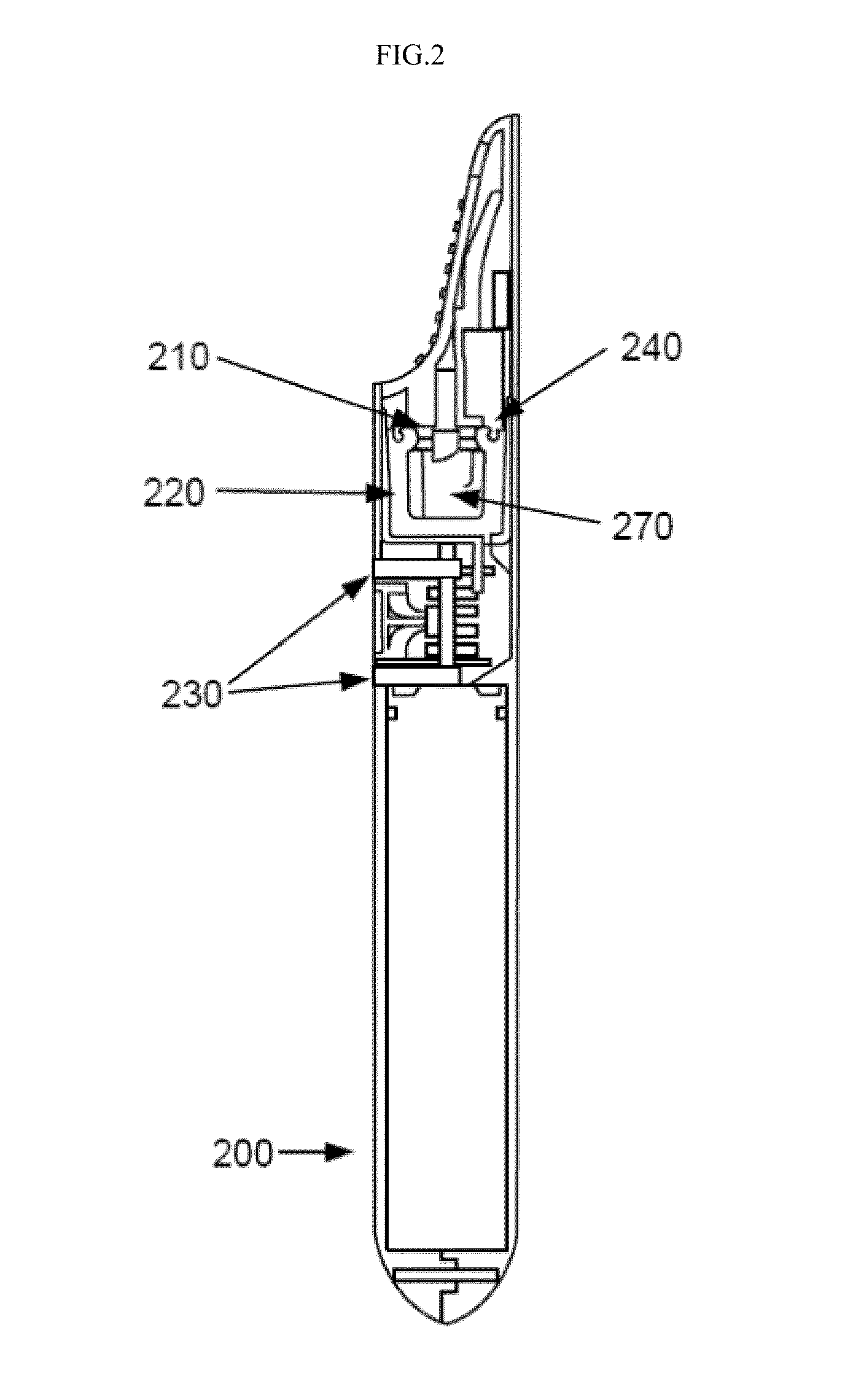
Picoprojector with Image Stabilization [Image-Stabilized Projector]
InactiveUS20120113514A1Unwanted motionReduce quality problemsOptical elementsUnintended MovementImage stabilization
A handheld projector is provided with an image stabilization system that acts to reduce (or even eliminate) unwanted motion of the projected image due to unintended movement of the projector. In certain preferred embodiments, a solid-state motion sensor provides input to an image stabilization system that computes a corrective signal. In embodiments having optical image stabilization, the corrective signal is supplied to a mechanical actuator that moves one or more optical elements within the projector. Other embodiments have electronic image stabilization. In these embodiments, the corrective signal from the image stabilization system is used by the image generator to shift the image so as to compensate for movement of the projector.
Owner:POLYCOM INC
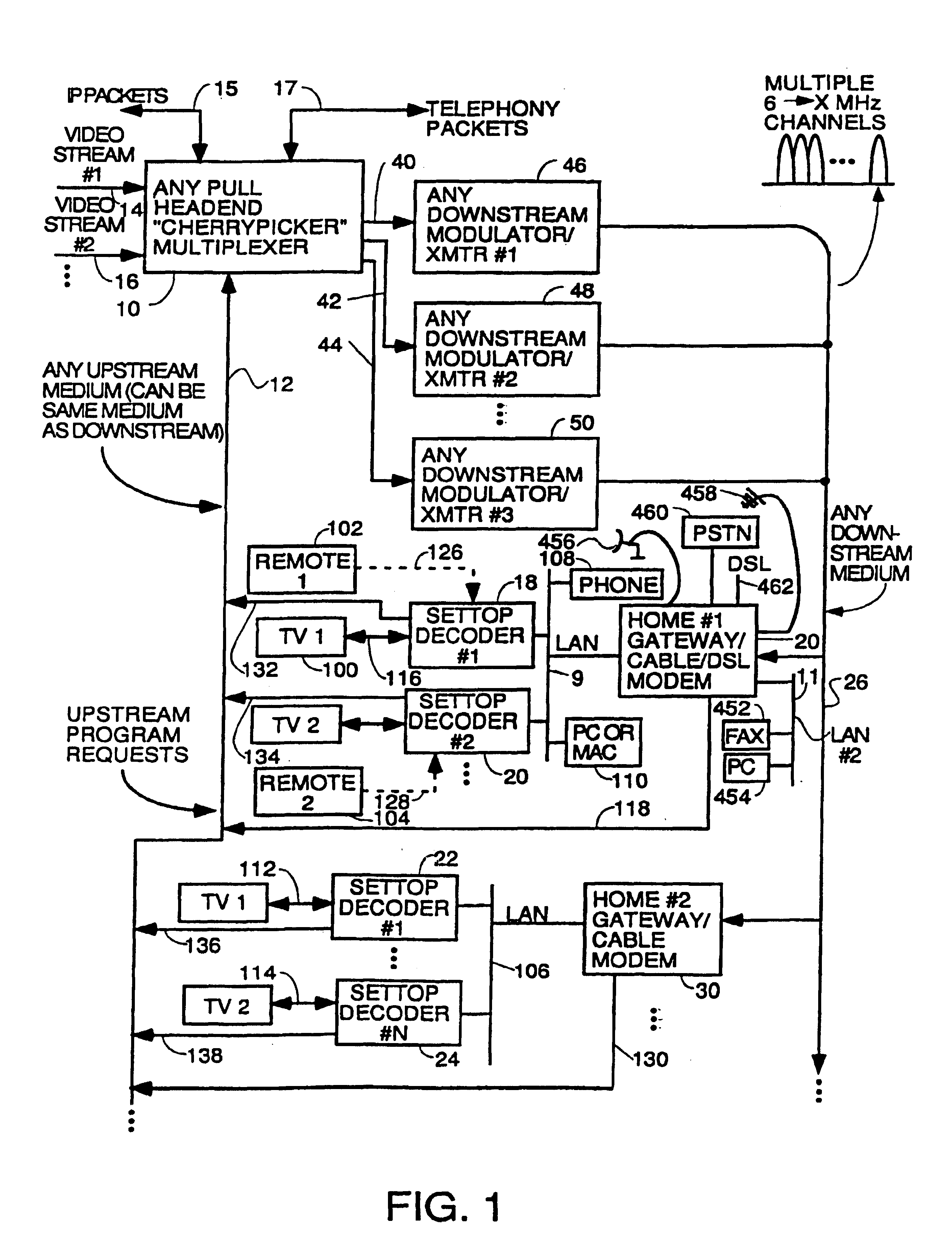
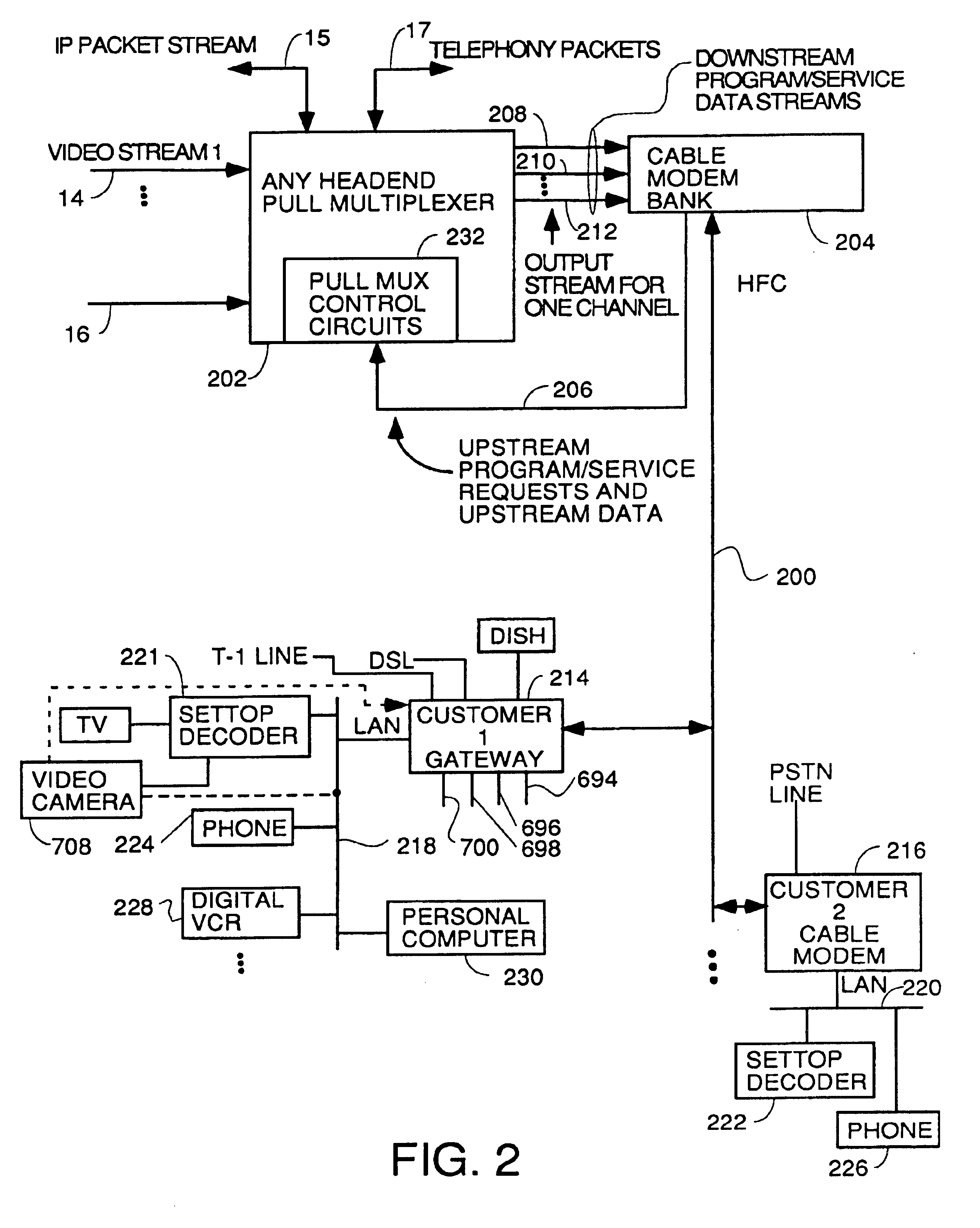
Process for supplying video-on-demand and other requested programs and services from a headend
InactiveUS7089577B1Reduce quality problemsReduce bandwidth consumptionTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionTransceiverT-carrier
A system for providing video-on-demand service, broadband internet access and other broadband services over T-carrier systems including a pull multiplexer cherrypicker at the head end is disclosed. The pull multiplexer receives upstream requests and cull out MPEG or other compressed video packets, IP packets and other data packet types to satisfy the requests or to send pushed programming downstream. The downstream can be DSL or HFC. Each customer has a cable modem, DSL modem or a gateway which interfaces multiple signal sources to a LAN to which settop decoders, digital phones, personal computers, digital FAX machines, video cameras, digital VCRs etc. can be attached. Each gateway can coupled the LAN to a DSL line or HFC through a cable modem or a satellite dish through a satellite transceiver. A PSTN and conventional TV antenna interface is also provided.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Low temperature electronic vaporization device and methods
InactiveUS20130312742A1Maintain efficiencyReduce the temperatureInput/output for user-computer interactionTobacco treatmentInhalationEnvironmental health
Low temperature electronic vaporization devices and method are described herein for emulating smoking wherein the devices generate an aerosol for inhalation by a subject by heating a viscous material that can have a tactile response in the mouth or respiratory tract.
Owner:JUUL LABS INC
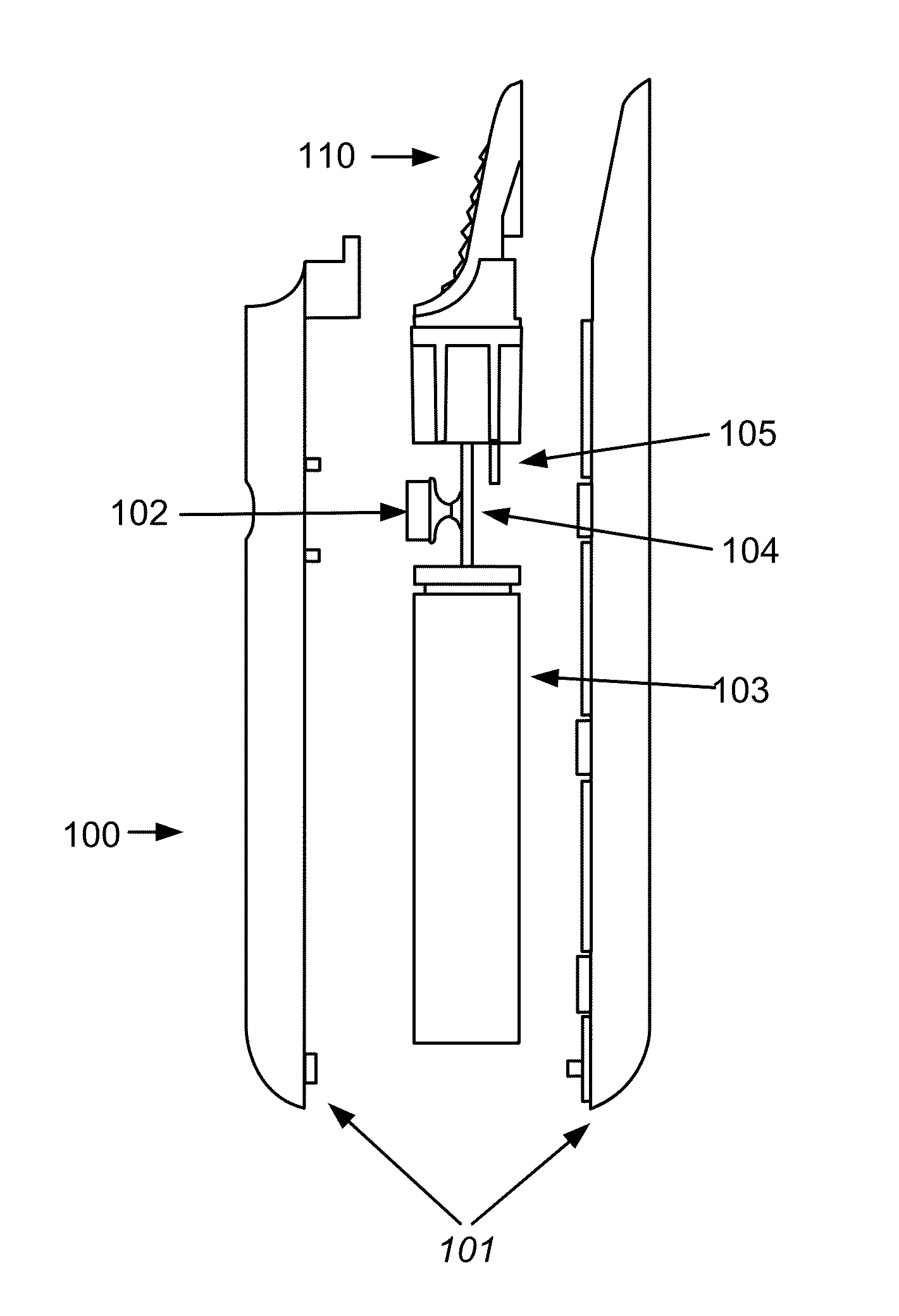
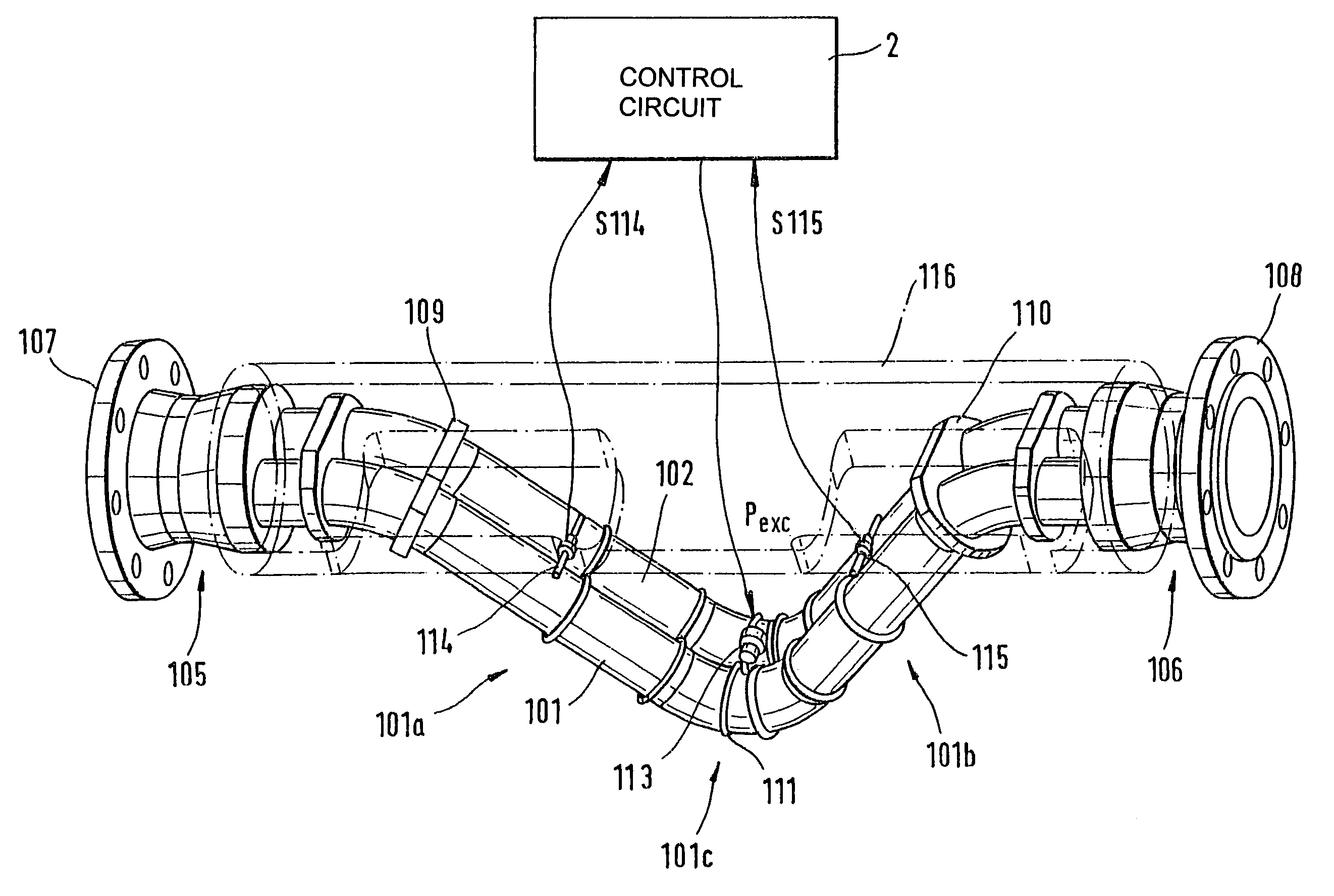
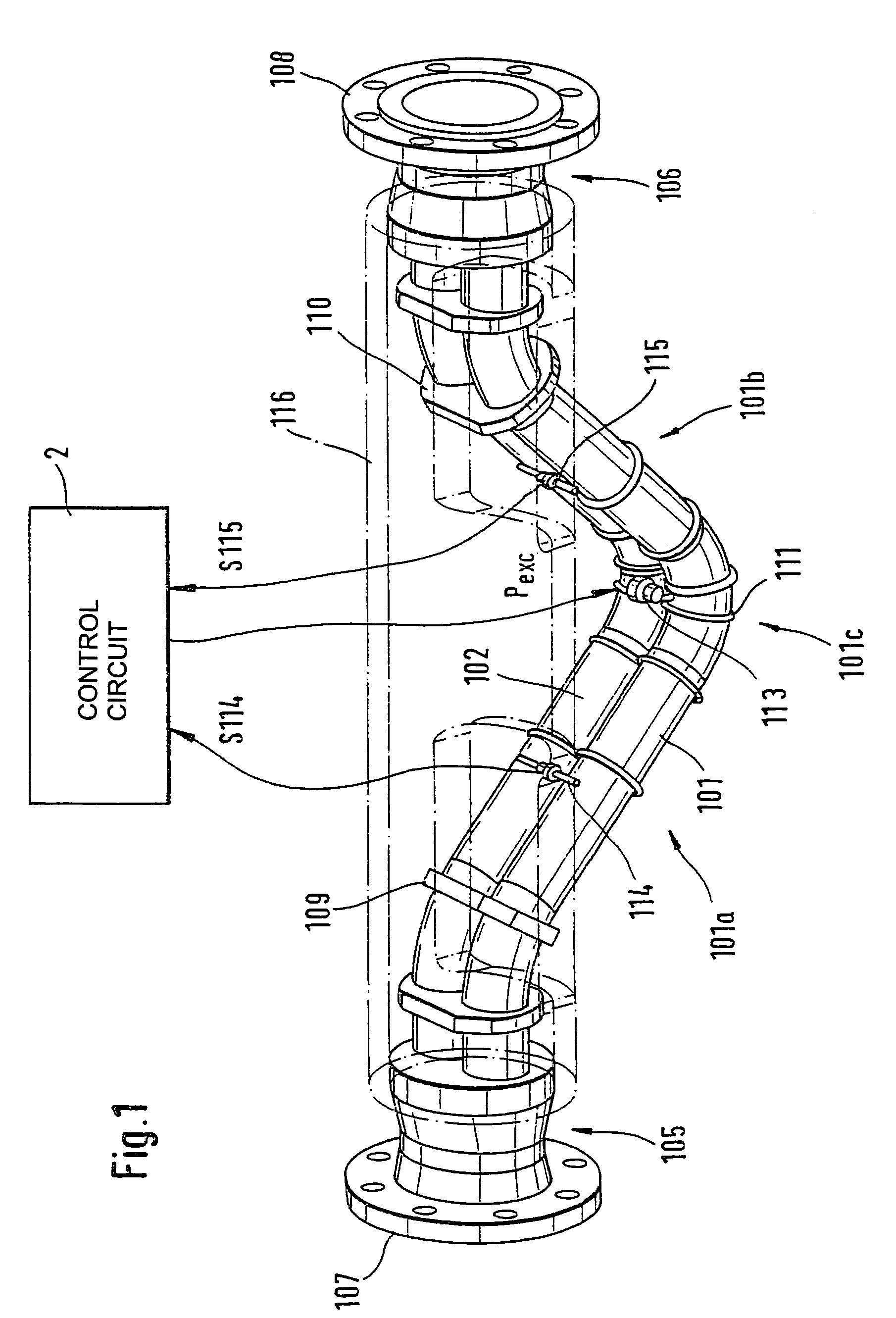
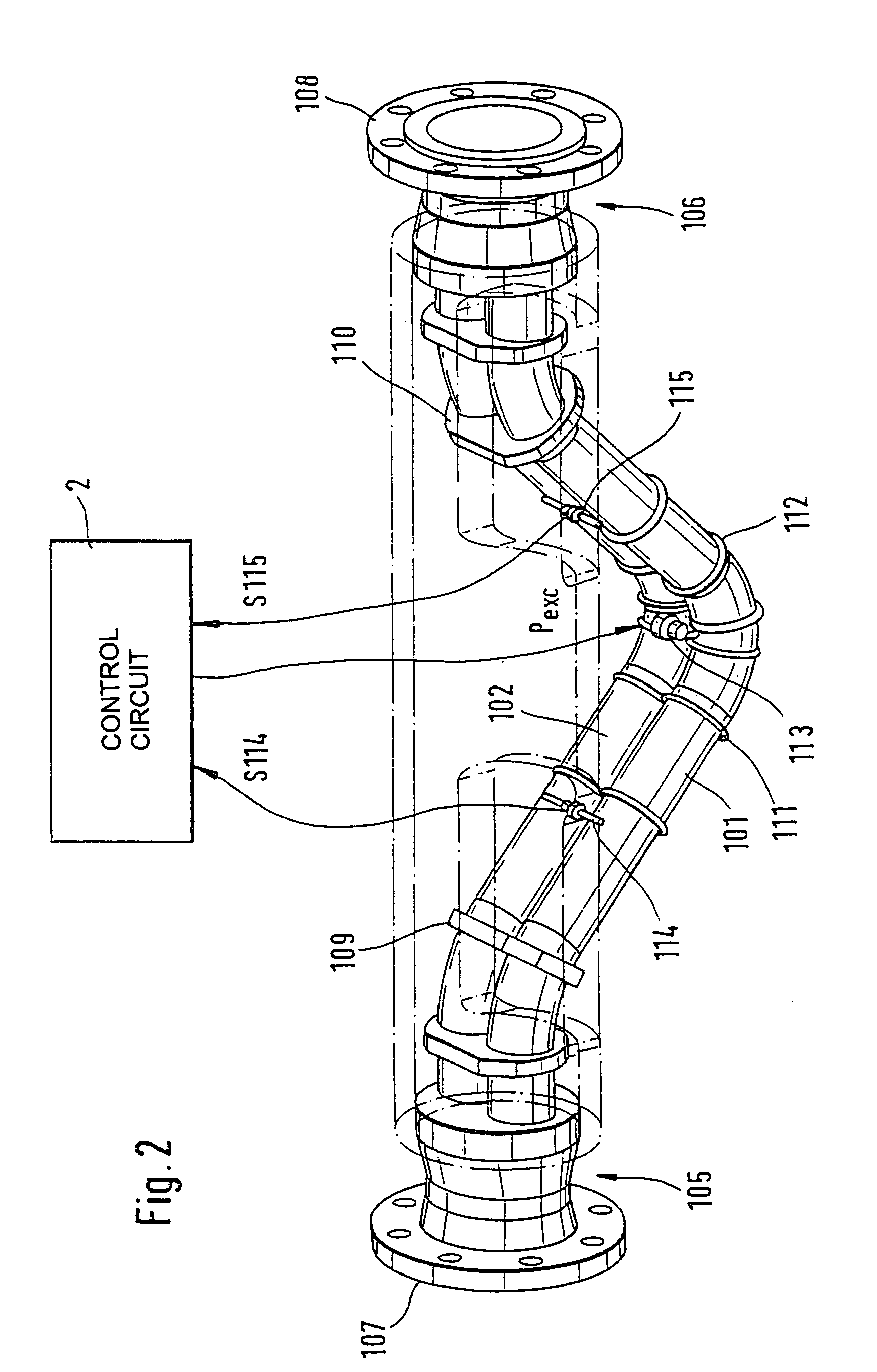
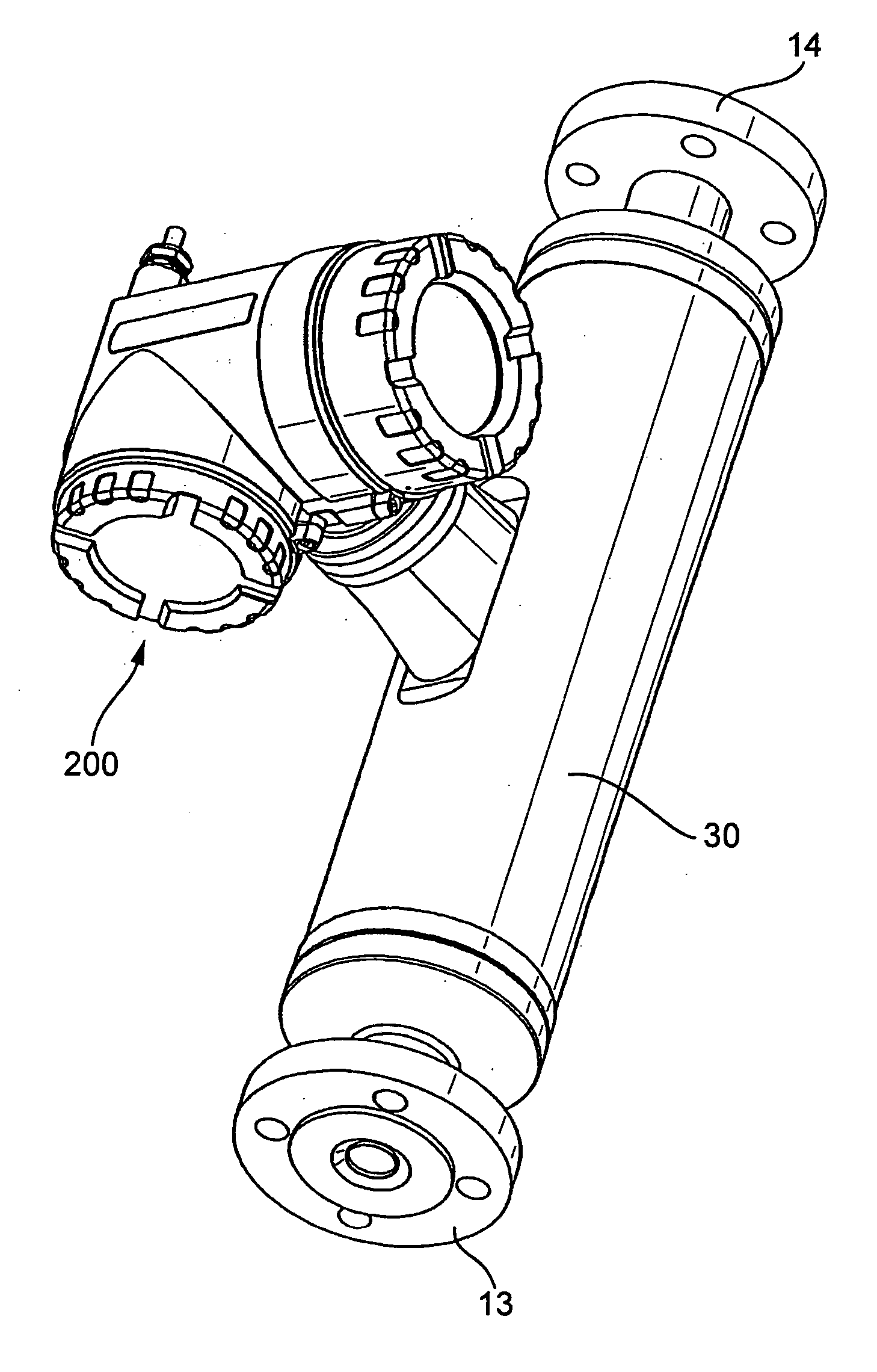
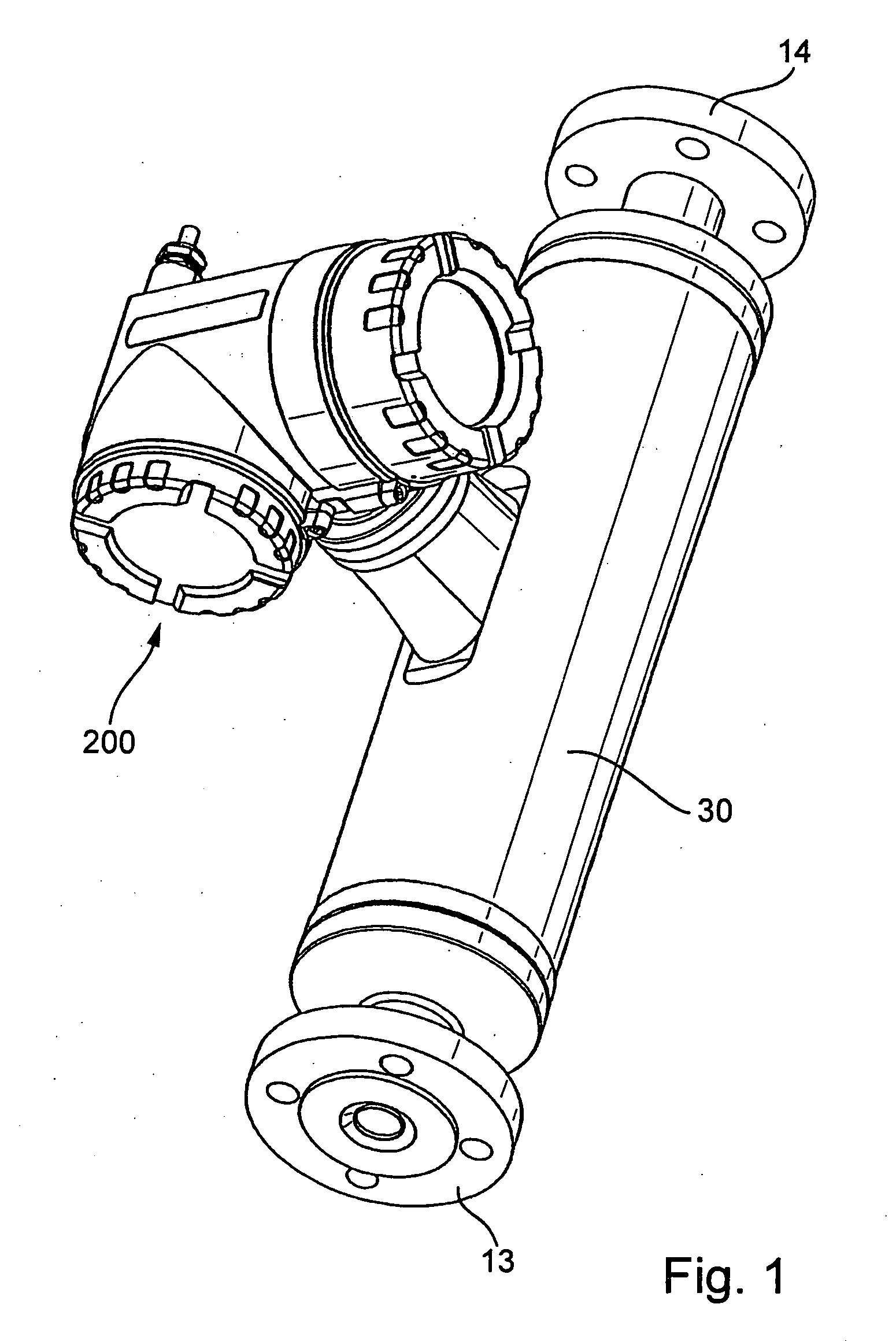
Vibratory transducer
InactiveUS6920798B2Easy to manufactureEasy to bendMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCross sensitivityStraight tube
The transducer (1) has at least one at least temporarily vibrating flow tube (101) of predeterminable lumen for conducting a fluid. The flow tube (101) communicates with a connected pipe via an inlet tube section (103), ending in an inlet end, and an outlet tube section (104), ending in an outlet end, and in operation performs flexural vibrations about an axis of vibration joining the inlet and outlet ends. The flow tube (101) has at least one arcuate tube section (101c) of predeterminable three-dimensional shape which adjoins a straight tube segment (101a) on the inlet side and a straight tube segment (101b) on the outlet side. At least one stiffening element (111, 112) is fixed directly on or in close proximity to the arcuate tube segment (101c) to stabilize the three-dimensional shape. By means of the at least one stiffening element (111, 112), the cross sensitivity of the transducer (1) is greatly reduced, so that cross talks from pressure to mass flow signals are minimized and the accuracy of the transducer is improved.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
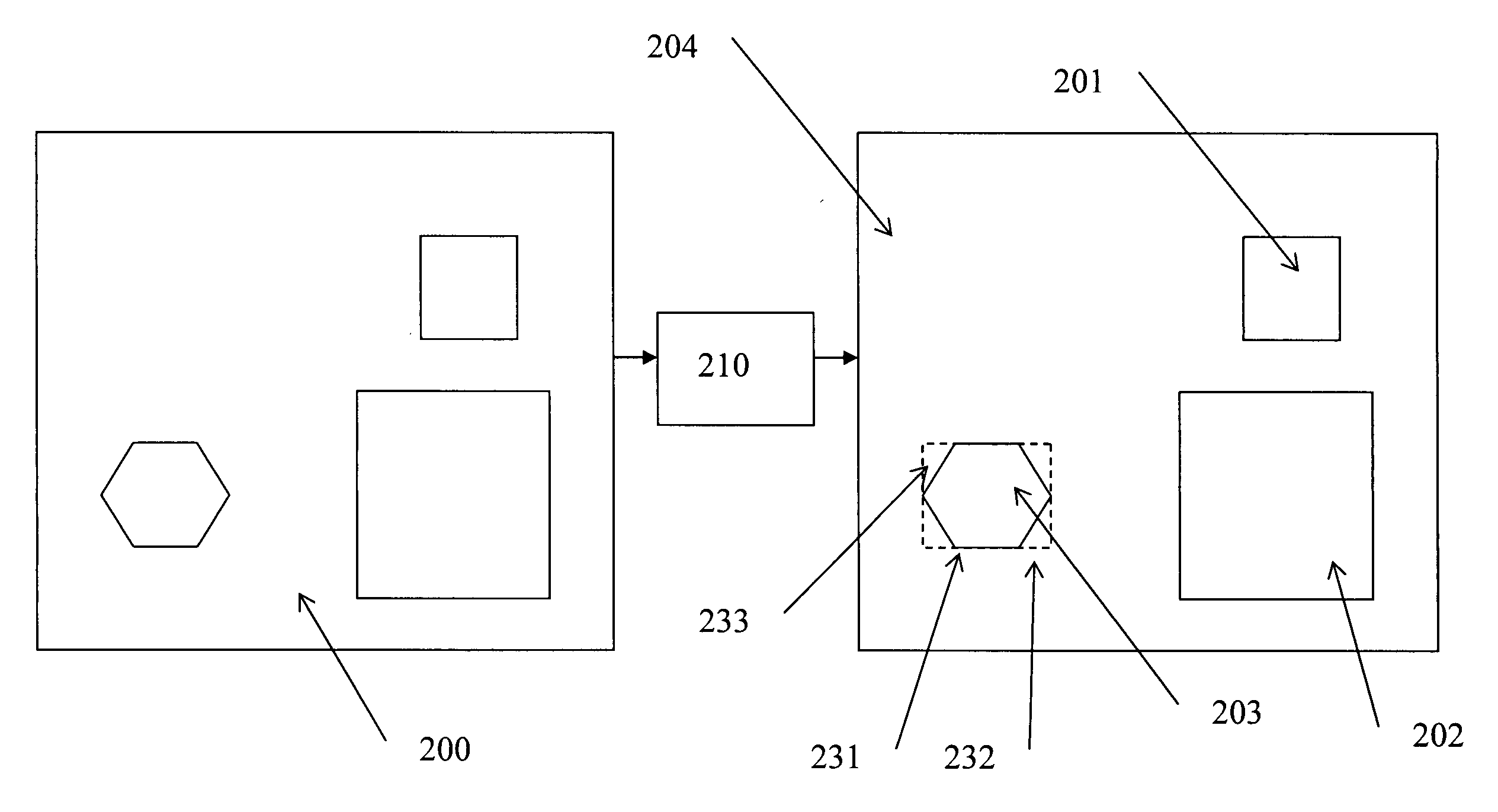
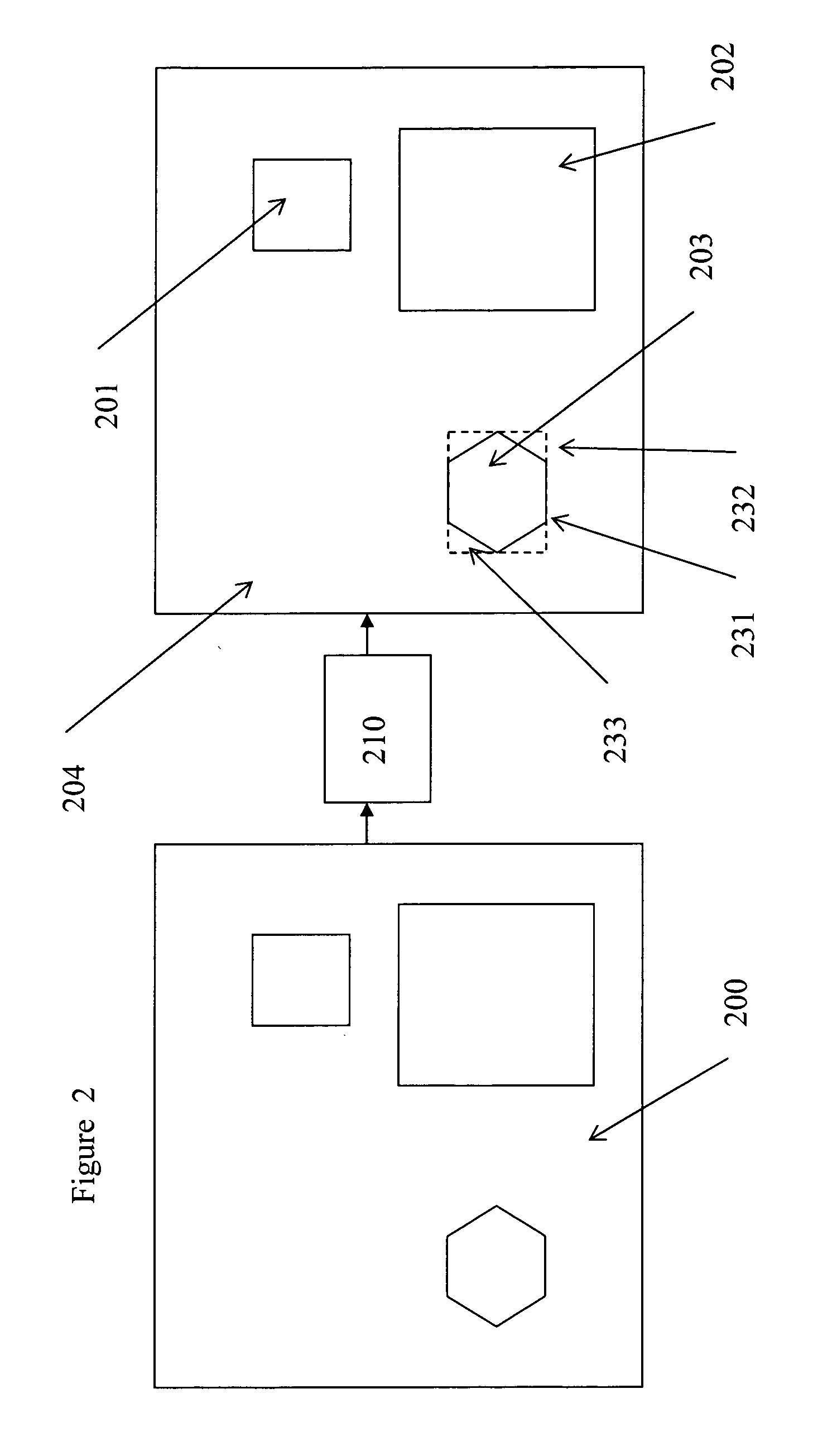
Method and device for image and video transmission over low-bandwidth and high-latency transmission channels
InactiveUS20070183493A1Increase the compression ratioLow priorityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningVideo transmissionEncoding algorithm
The present invention provides a method for transmission of a images and / or video over bandwidth limited transmission channels having varying available bandwidth, which method comprises the use of a classification algorithm for decomposing the images and / or video to be transmitted into multiple spatial areas, each area having a specific image type; detecting the image type of each of those areas separately selecting for each of those areas an image and / or video encoding algorithm having a compression ratio. The classification algorithm prioritizes each of the areas, the classification algorithm increasing the compression ratio of the image and / or video encoding algorithm dedicated to spatial areas having lower priority in case of decreasing bandwidth.
Owner:BARCO NV
Motion compatible sensor for non-invasive optical blood analysis
InactiveUS20050070775A1Low profileReduce quality problemsSensorsBlood characterising devicesClassical mechanicsPulse oximetry
A non-invasive optical sensor which uses the motion signal to calculate the physiological characteristic being measured. For pulse oximetry, a least squares or a ratio-of-ratios technique can be applied to the motion signal itself. This is made possible by selecting a site on the patient where variations in motion produce signals of two wavelengths which are sufficiently correlated. In particular, it has been determined that a sensor placed on a nail, in particular a thumbnail, exhibits the characteristics of having the red and infrared signals correlated when used for pulse oximetry, and the resulting signals correlate to arterial oxygen saturation.
Owner:NELL COR PURITAN BENNETT INC (US)
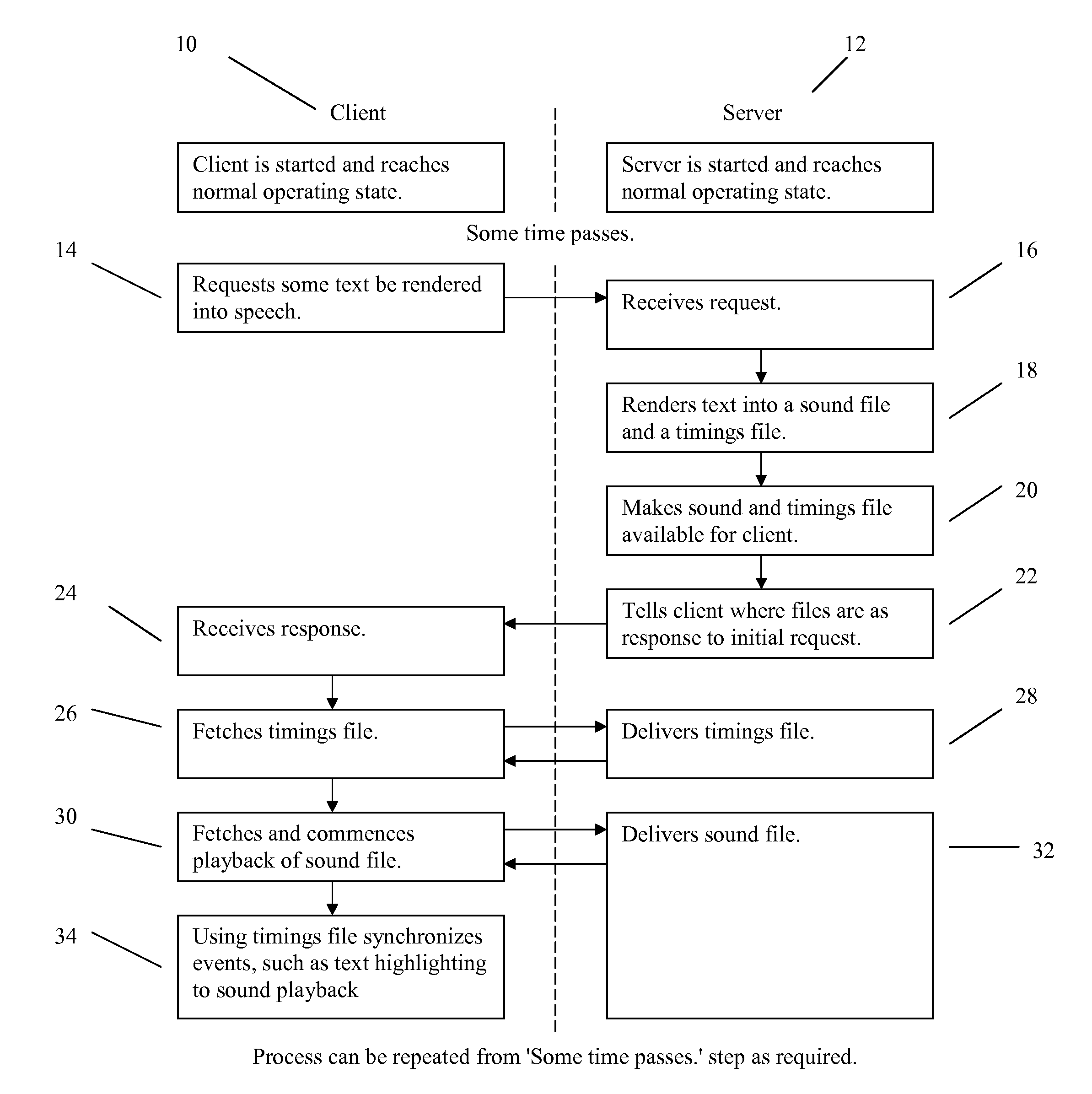
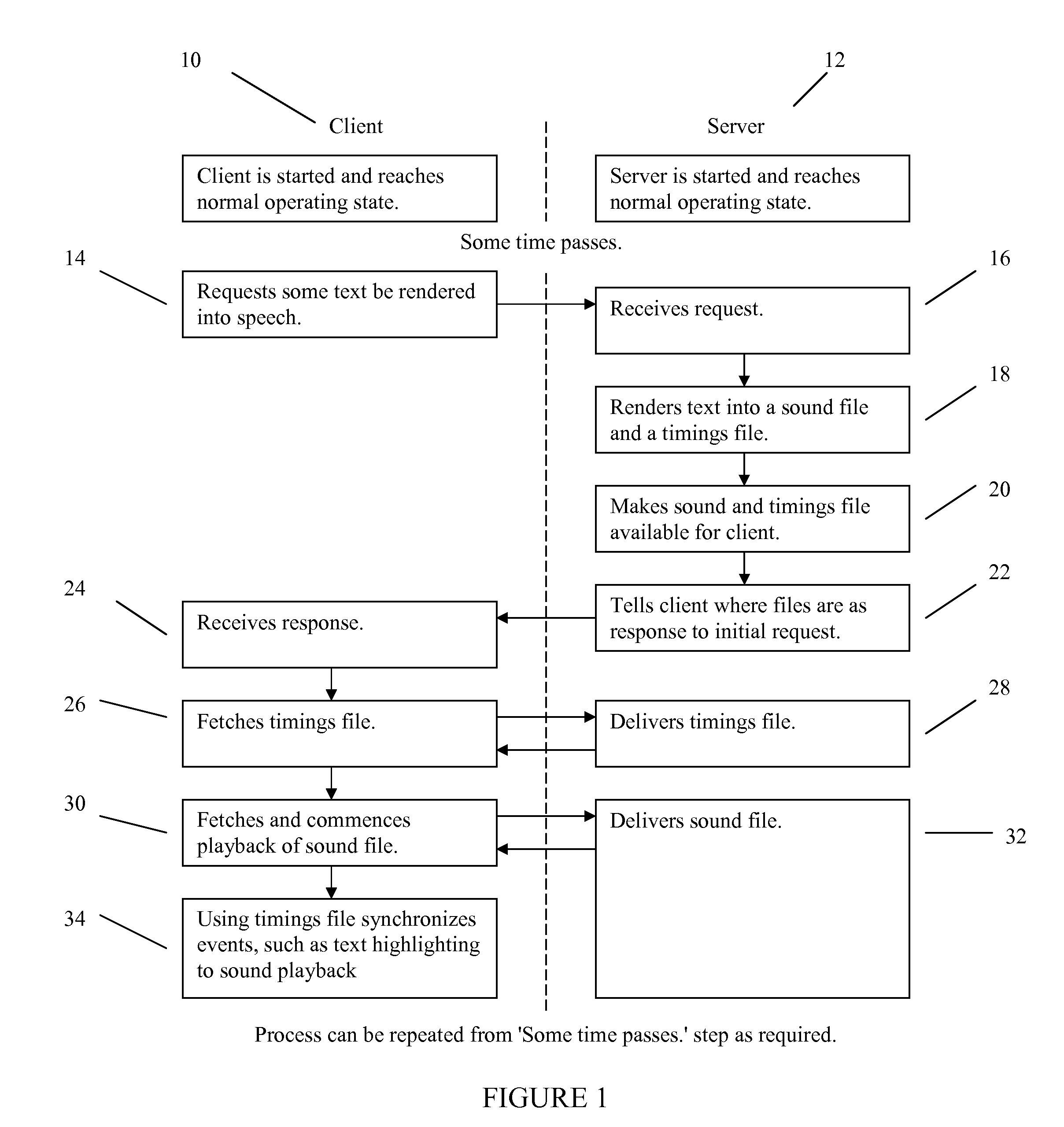
Streaming speech with synchronized highlighting generated by a server
InactiveUS20070271104A1Technically simpleReduce quality problemsSpeech synthesisThe InternetClient-side
A speech synthesis system and method including an application consisting of two networked parts, a client and a server, which uses the capabilities of the server to speech enable a client that does not have speech capabilities. The system has been designed to enable a client computer with audio capabilities to connect and request text to speech operations via a network or internet connection.
Owner:TEXTHELP SYST
Transparent material processing with an ultrashort pulse laser
InactiveUS20070051706A1Reduce quality problemsPoor precisionFixed microstructural devicesThin material handlingHigh energyNonlinear absorption
Methods for ultrashort pulse laser processing of optically transparent materials. A method for scribing transparent materials uses ultrashort laser pulses to create multiple scribe features with a single pass of the laser beam across the material, with at least one of the scribe features being formed below the surface of the material. This enables clean breaking of transparent materials at a higher speed than conventional techniques. Slightly modifying the ultrashort pulse laser processing conditions produces sub-surface marks. When properly arranged, these marks are clearly visible with side-illumination and not clearly visible without side-illumination. In addition, a method for welding transparent materials uses ultrashort laser pulses to create a bond through localized heating. The ultrashort pulse duration causes nonlinear absorption of the laser radiation, and the high repetition rate of the laser causes pulse-to-pulse accumulation of heat within the materials. The laser is focused near the interface of the materials, generating a high energy fluence at the region to be welded. This minimizes damage to the rest of the material and enables fine weld lines.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
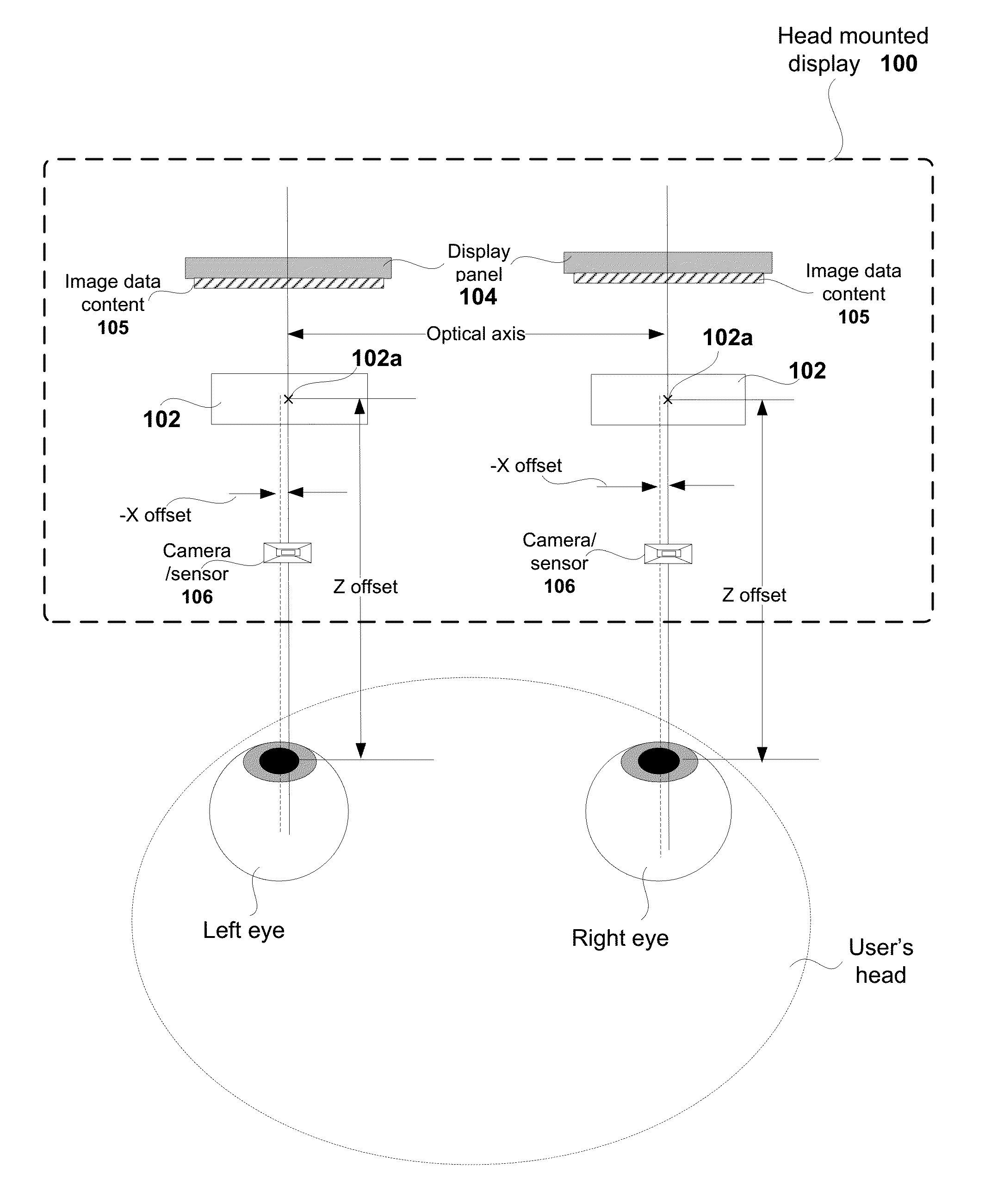
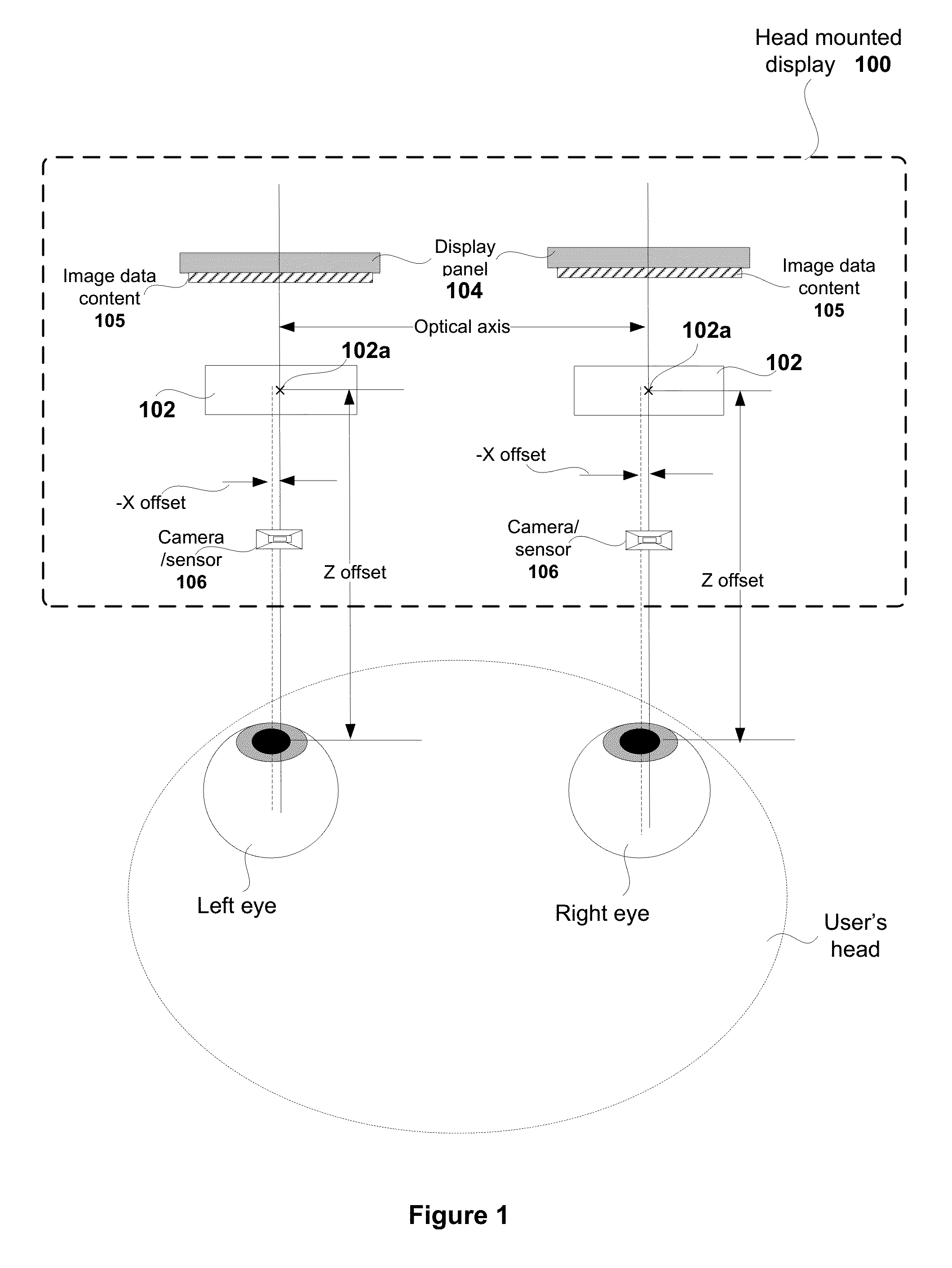
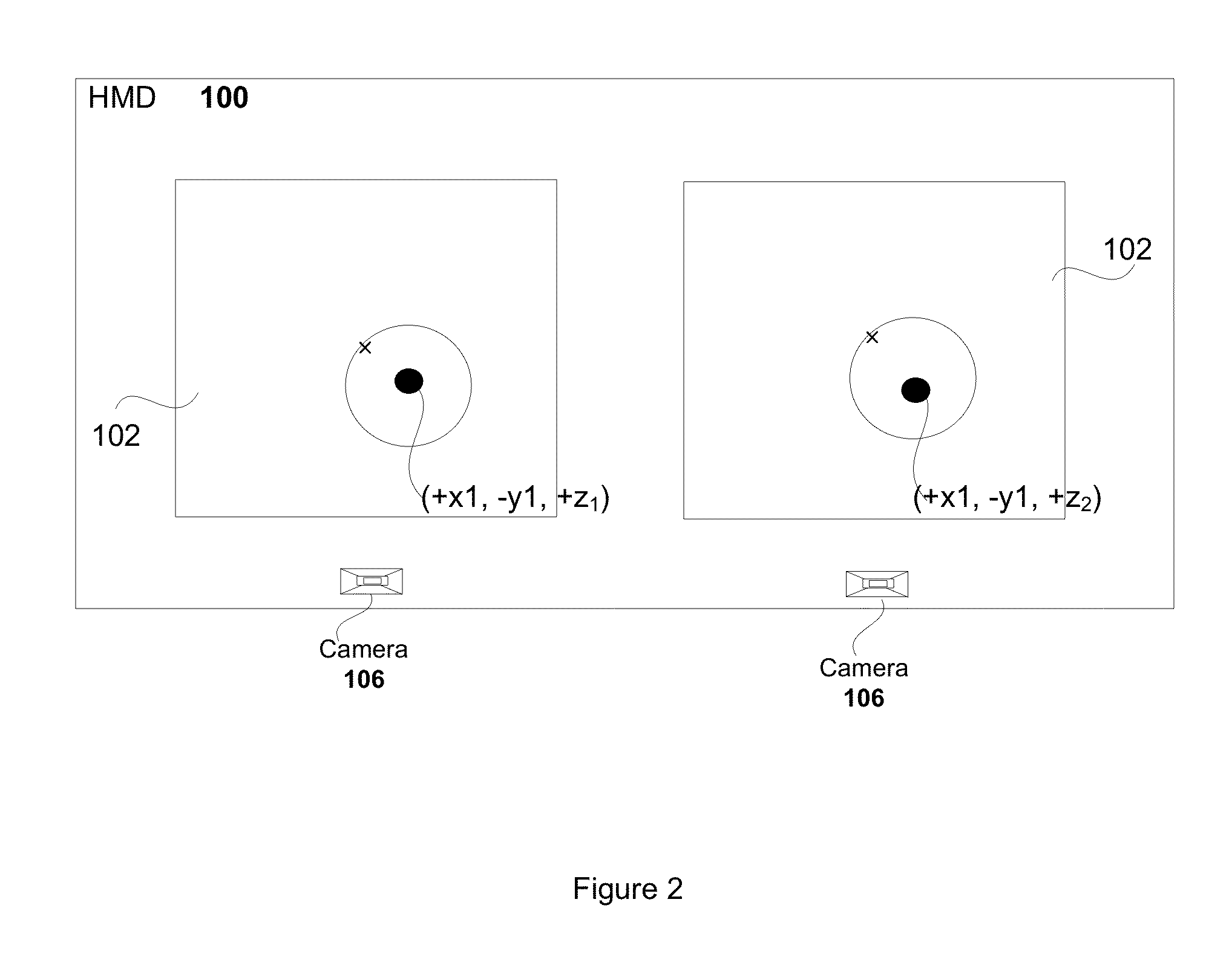
Realtime lens aberration correction from eye tracking
ActiveUS20160091720A1Eliminate aberrationsQuality improvementCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsCamera lensOptical axis
Systems and methods include receiving an image for presenting on a display screen of a head mounted display (HMD). The image is provided by an application. The received image is pre-distorted to enable optics provided in a HMD to render the image. An alignment offset is identified for an eye of a user wearing the HMD by determining a position of the eye relative to an optical axis of at least one lens of the optics of the HMD. The pre-distorted image provided by the application is adjusted to define a corrected pre-distorted image that accounts for the alignment offset. The corrected pre-distorted image is forwarded to the display screen of the HMD for rendering, such that the image presented through the optics of the HMD removes aberrations caused by the alignment offset.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
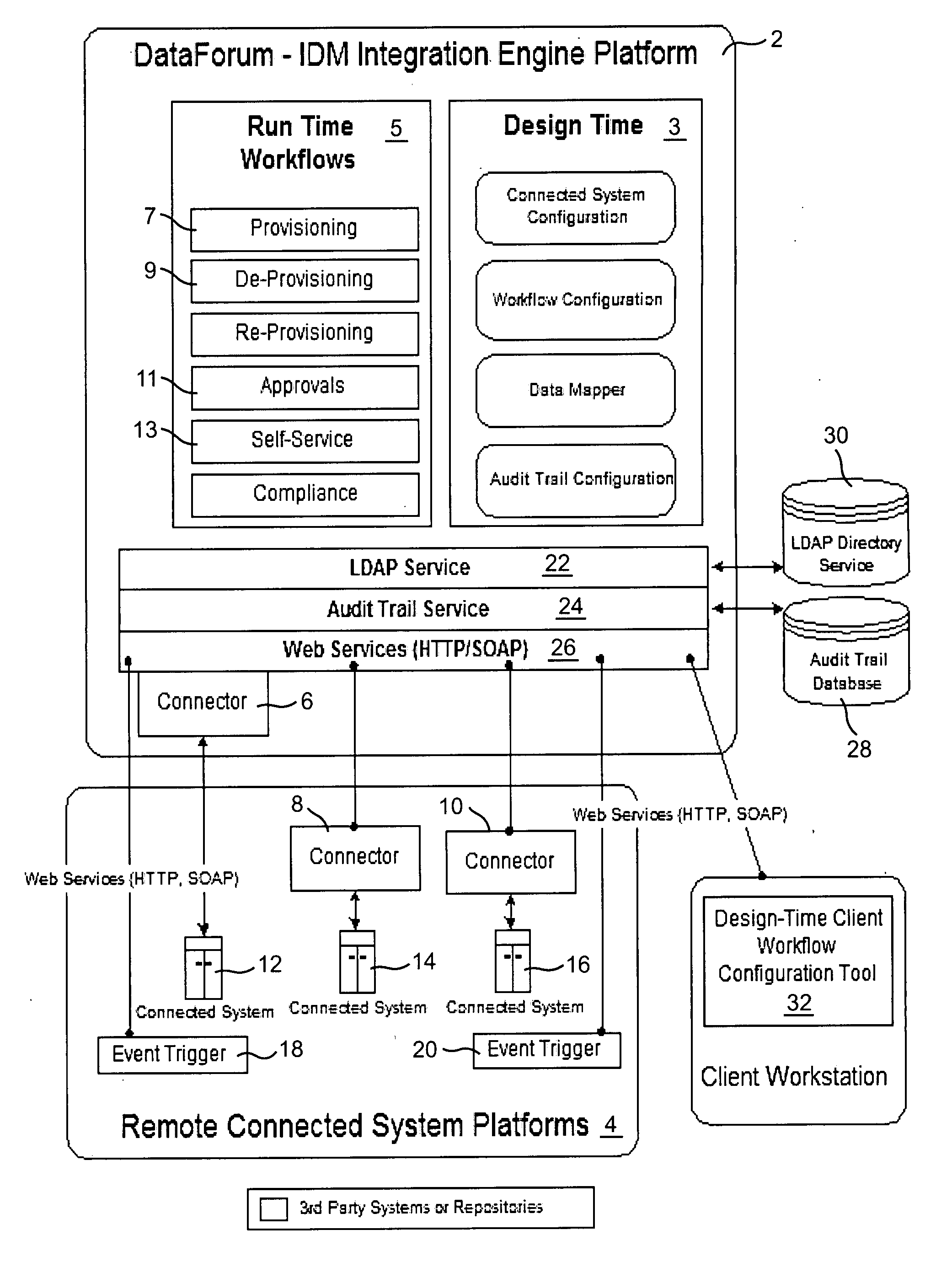
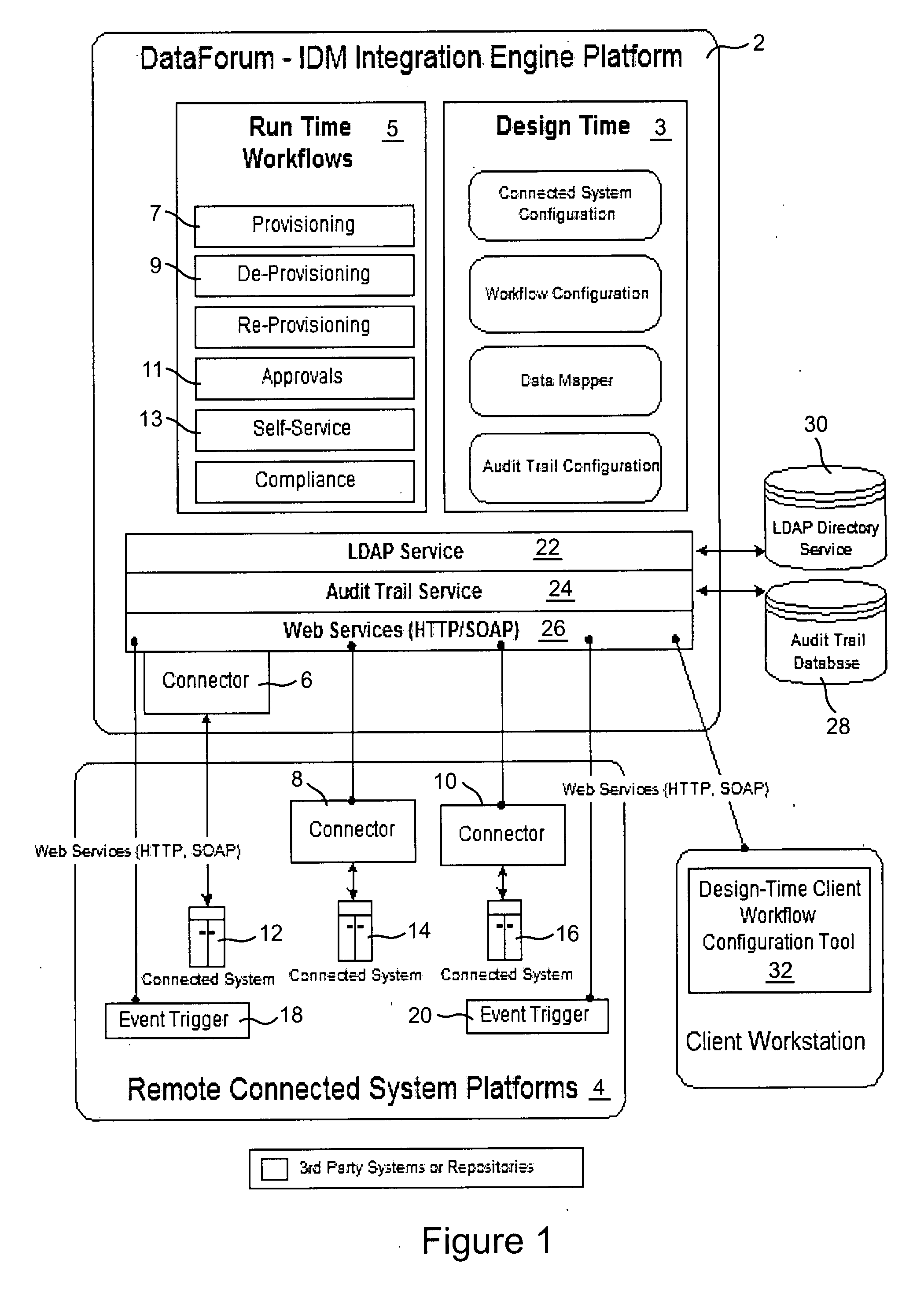
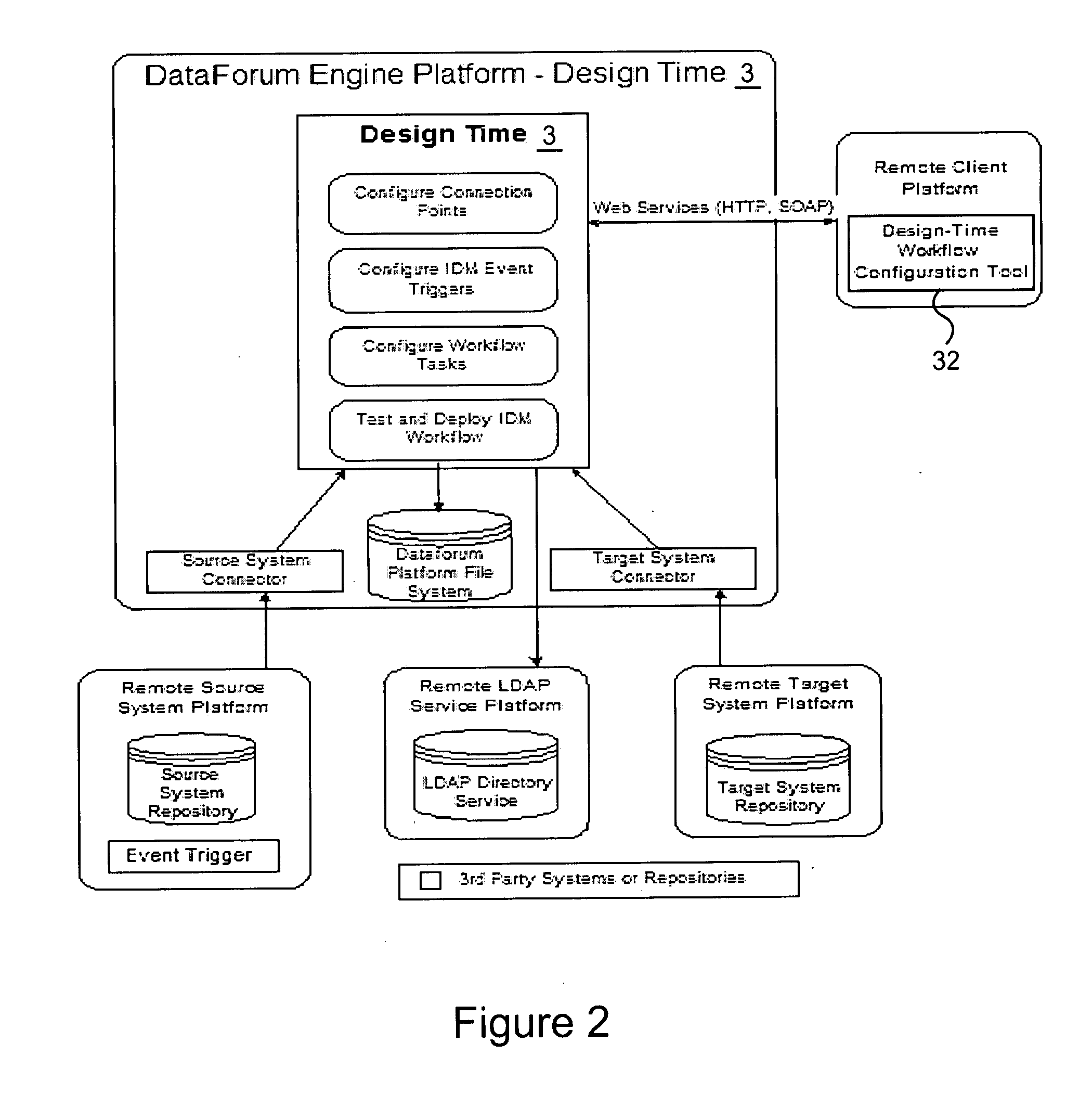
Cross domain provisioning methodology and apparatus
InactiveUS20070245013A1Increase valueKeep for a long timeDigital computer detailsComputer security arrangementsDigital identityCombined use
A cross domain provisioning method, system and architecture for securely managing digital identities across a wide variety of IT systems, providing unified administration, compliance and auditing, and simplified connectivity. The combined use of certain aspects of the illustrative IDM Provisioning Platform (DataForum™), Connectivity Component Architecture, Design-Time Client Workflow Tool, and the use of digital certificates to secure cross domain communication channels, collectively offer a unique approach to solving cross domain provisioning problems.
Owner:FISCHER INT IDENTITY
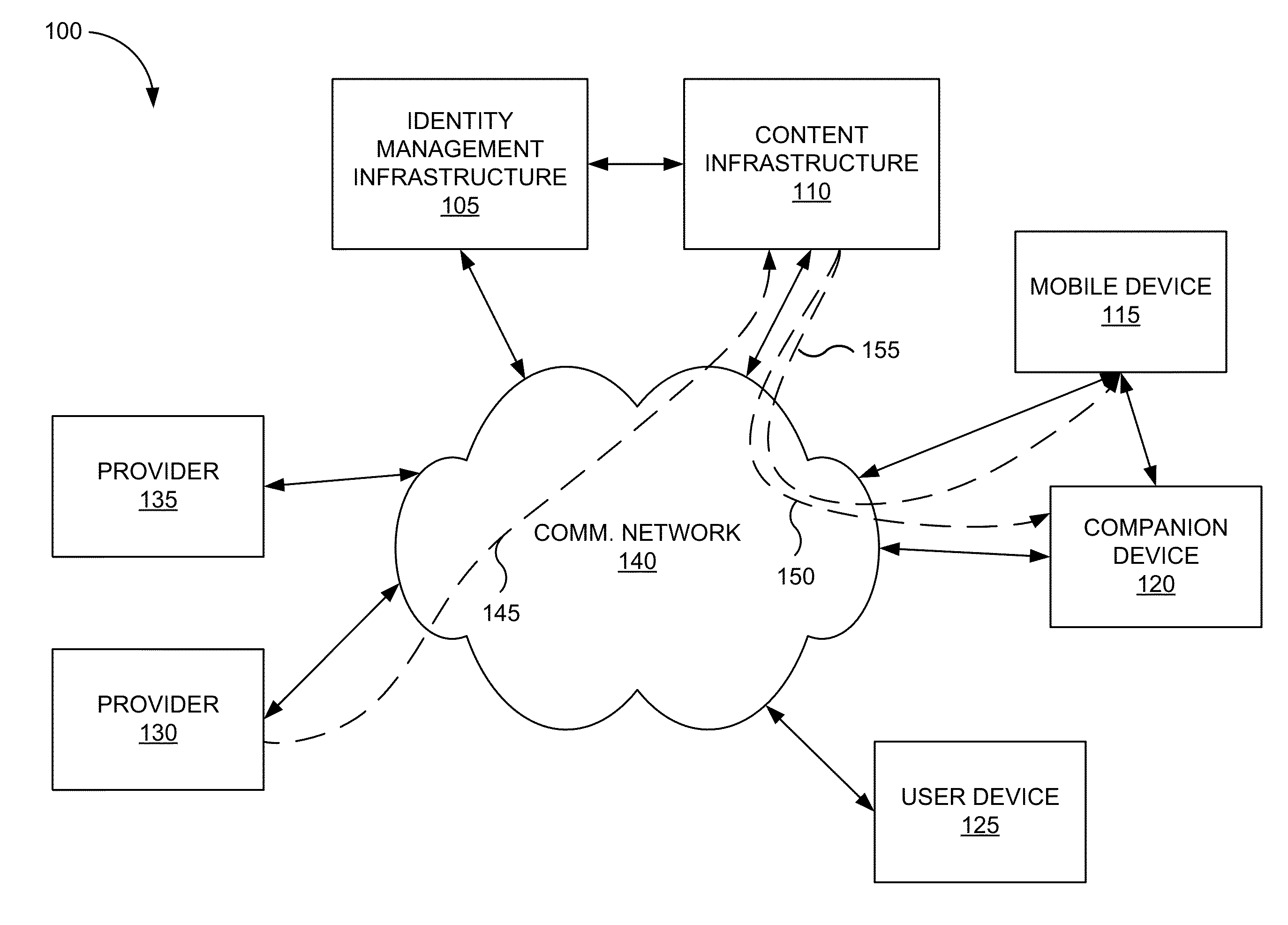
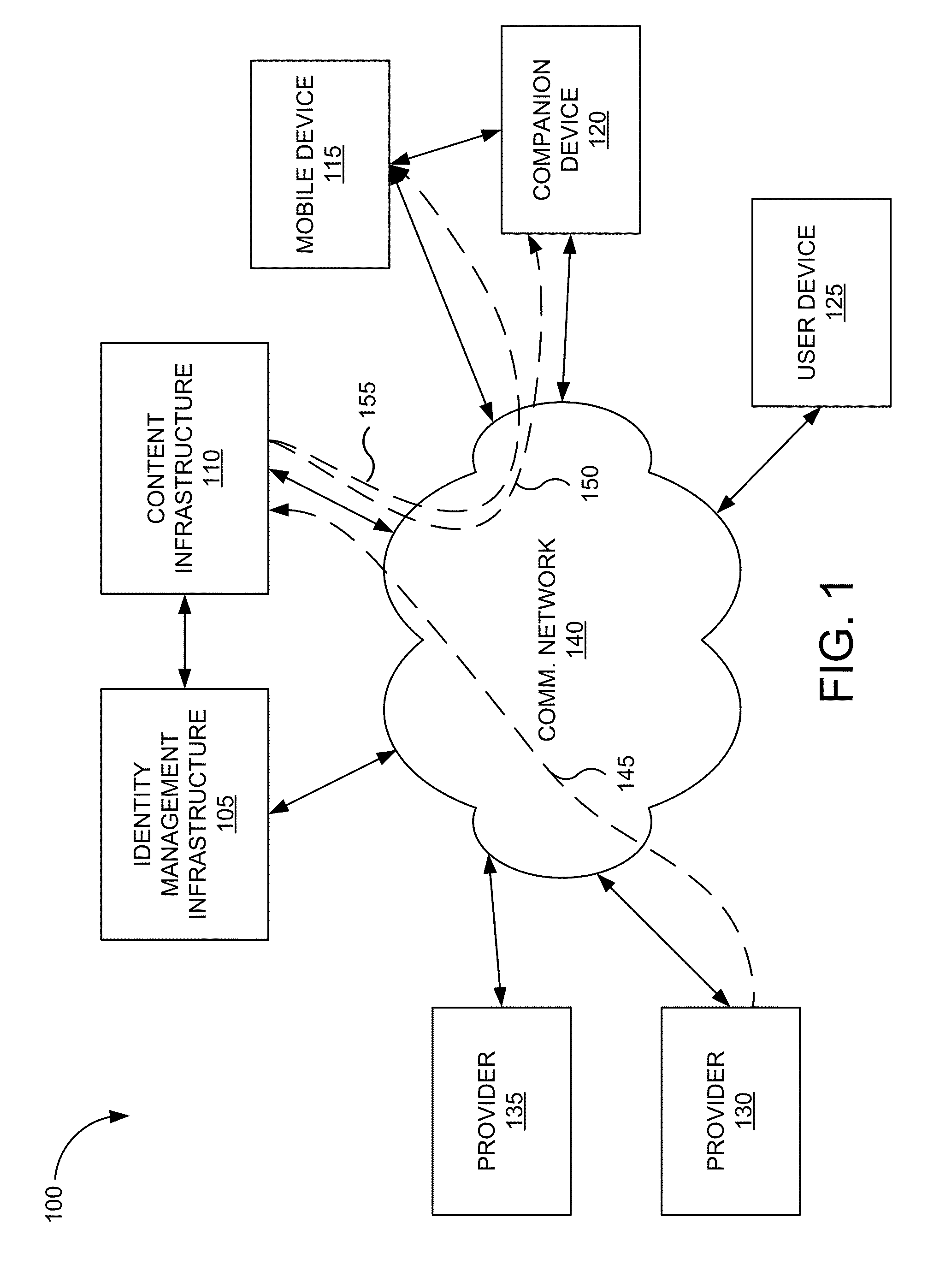
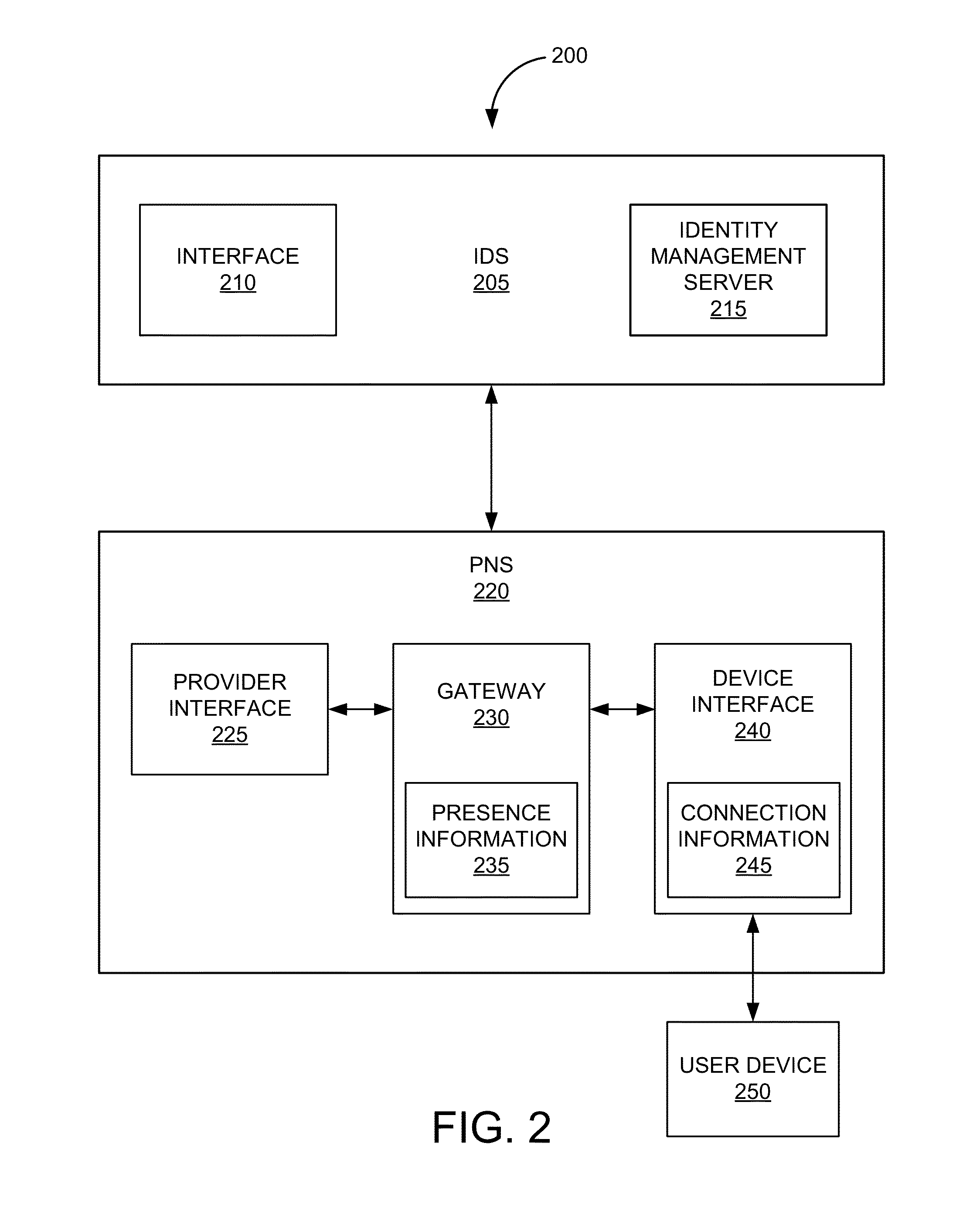
Proxied push
ActiveUS20150350362A1Maximize power consumptionReduce interfaceMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksNetwork connectionMobile device
A system and method are described for establishing two-way push communication between an intermediate or companion device and a mobile device. Mobile devices register to listen for push notifications delivered through a push notification service from a specified set of providers. The presence of the mobile devices is delivered to the push notification service that maps the mobile devices to connections made between their respective companion devices and the push notification service. If the push notification service determines that a mobile device is “online,” in response to receiving a push notification for the mobile device, a current network connection over which a companion device is listening for push notifications is identified and the push notification is forwarded to the companion device. The companion device then can deliver the push notification to the mobile device.
Owner:APPLE INC
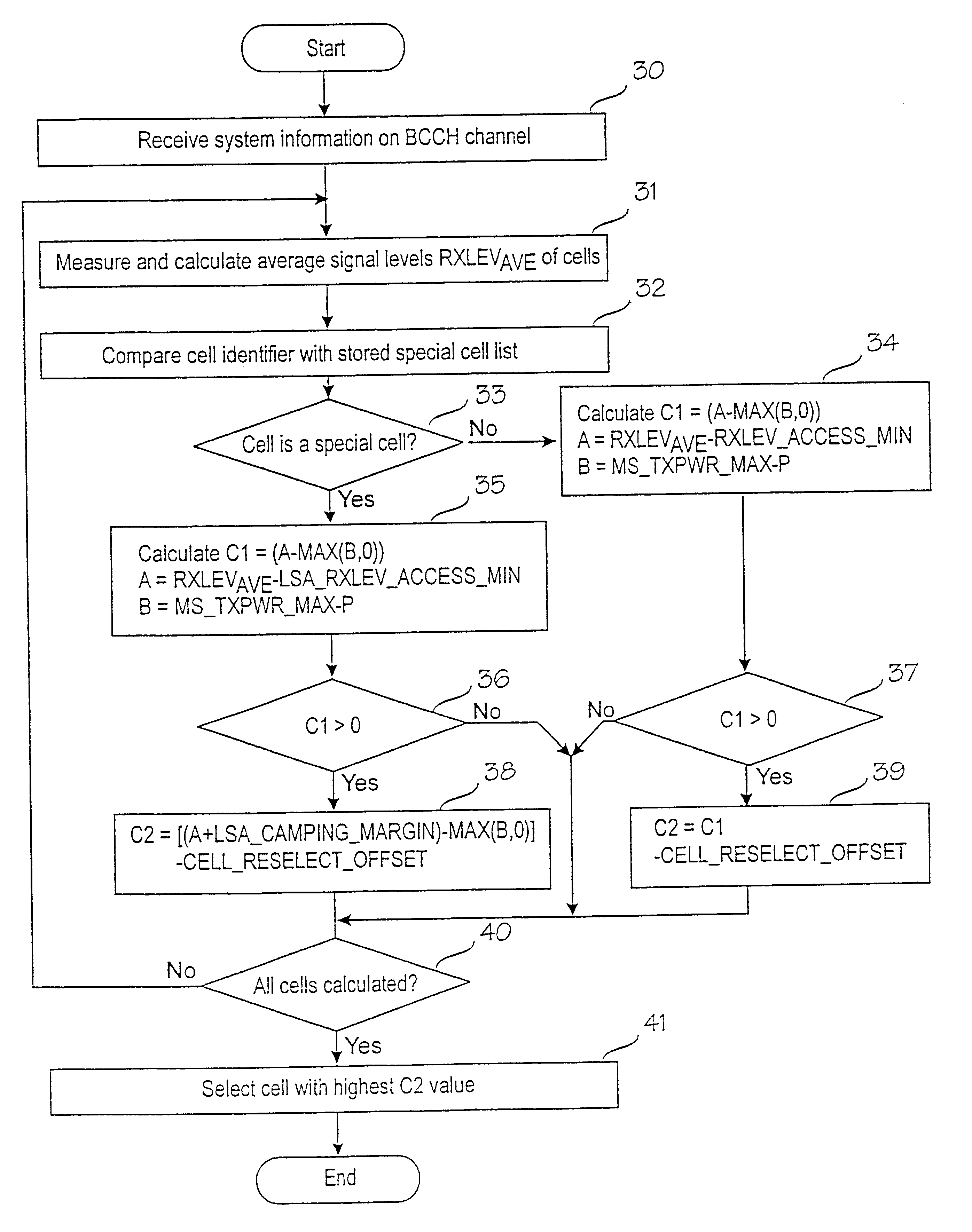
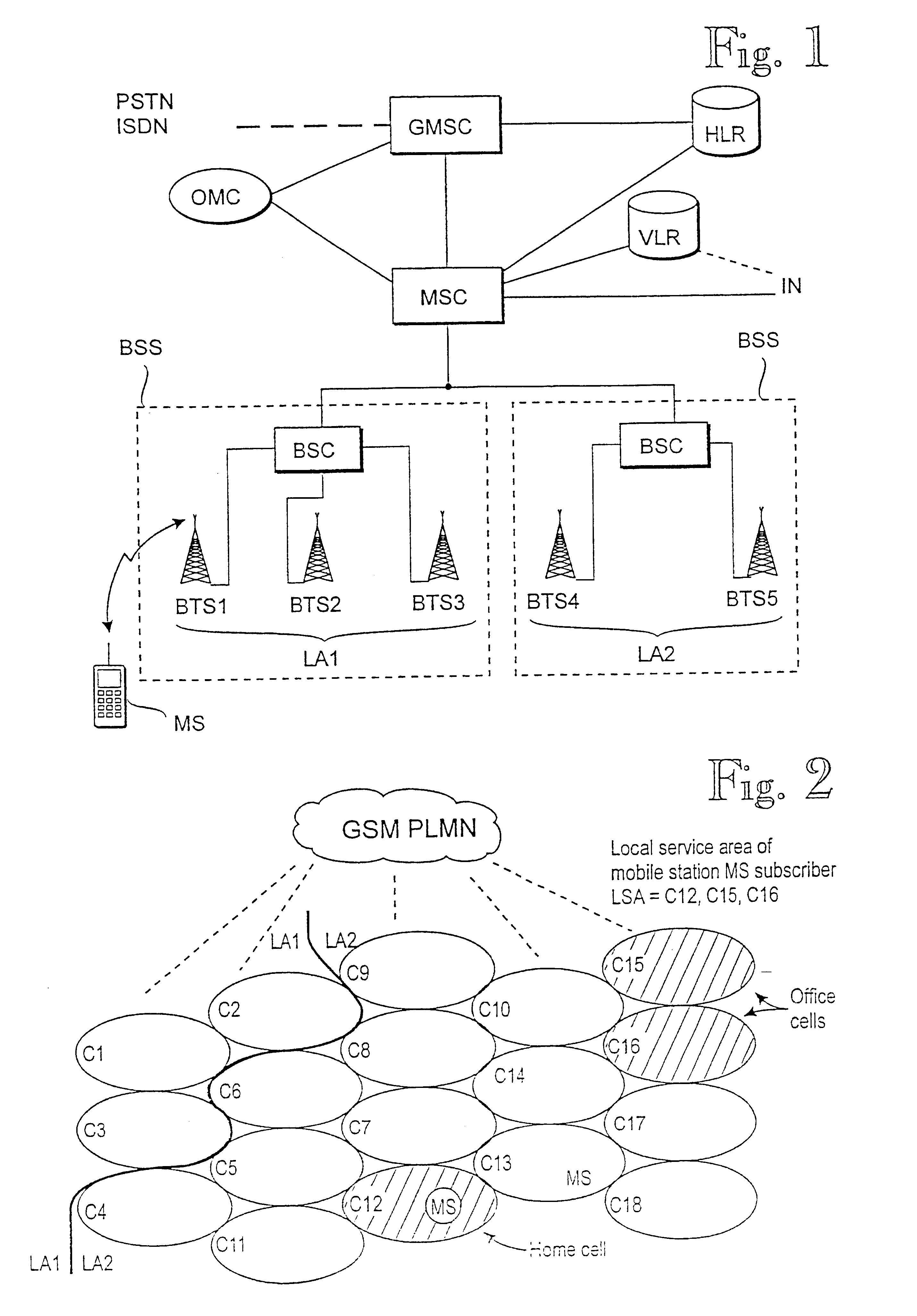
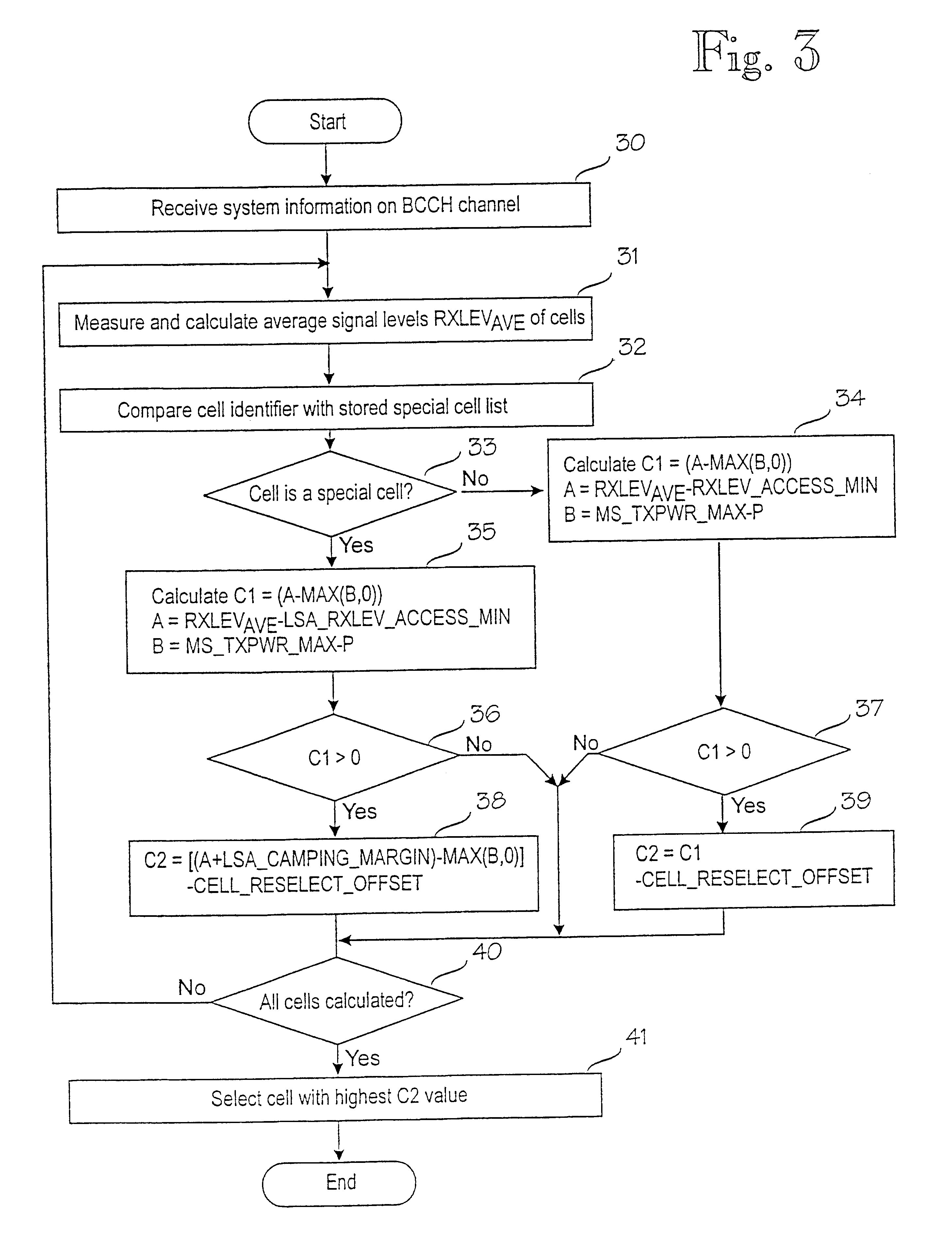
Method for selecting cell in cellular network
InactiveUS6434389B1Enhance cell selectionExpand selectionAssess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCellular radioRadio networks
The present invention relates to prioritizing special cells in cell selection in a cellular radio network. In a cellular radio network one or more cells provide a subscriber with special services or tariffs not offered to all subscribers. These cells are called subscriber's special cells. The mobile station measures an average reception level and calculates by means of them cell selection parameters on the basis of which the best cell is selected. In accordance with the invention, when the mobile station detects that the cell is one of cells of a special cell list stored in a memory, it checks first if the cell fulfils a minimum requirement of cell selection on the basis of the measured signal level. If the minimum requirement is fulfilled, the mobile station manipulates the calculation of the cell selection parameter of a special cell to the effect that the selection probability of a special cell is improved with respect to a normal cell. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the manipulation of the calculation comprises a step of adding a predetermined margin to the measured signal level of a special cell before the cell selection parameter is calculated. This will minimize the possibility that the mobile station would accidentally be camped on a normal cell when it is within the area of a special cell.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
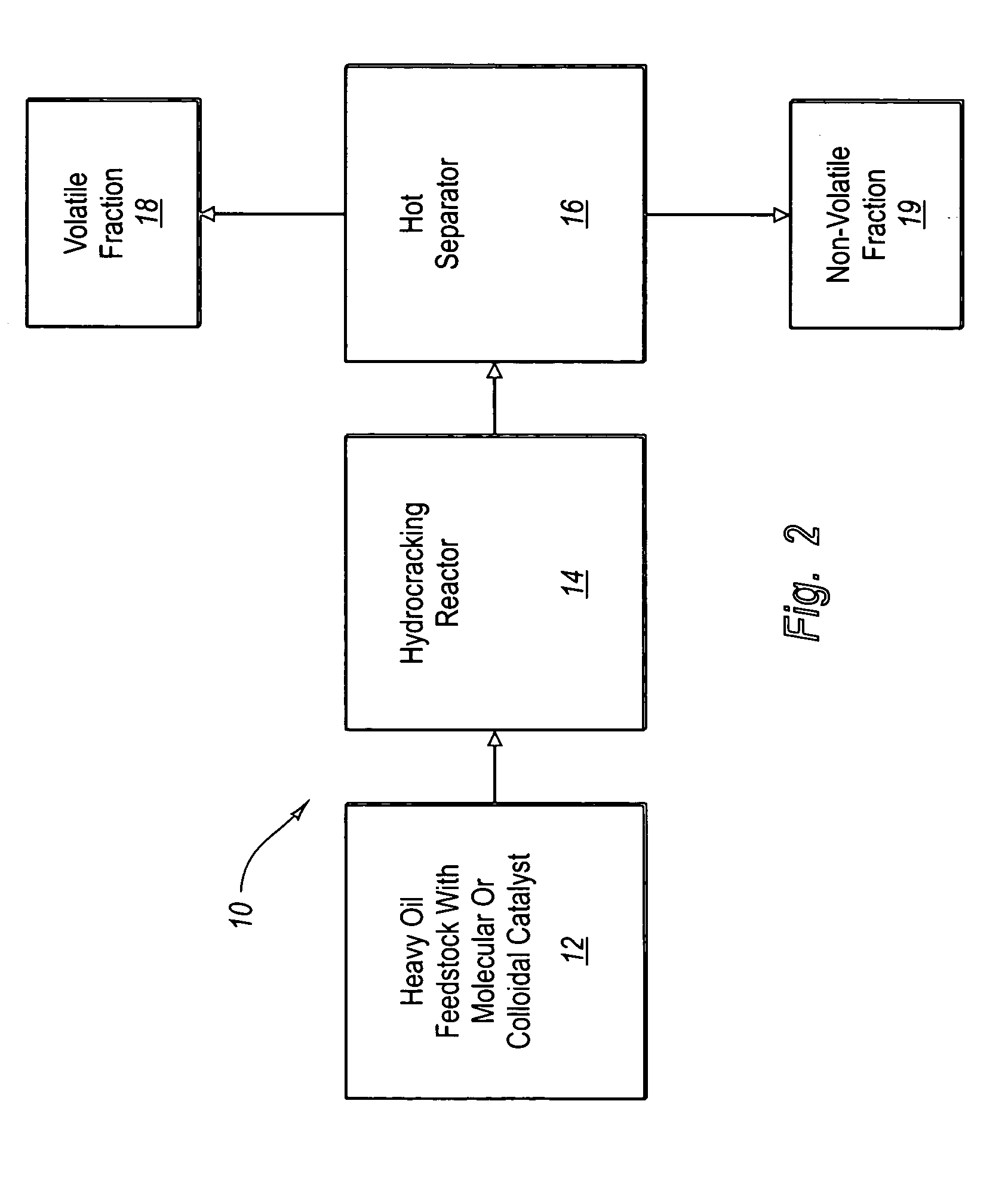
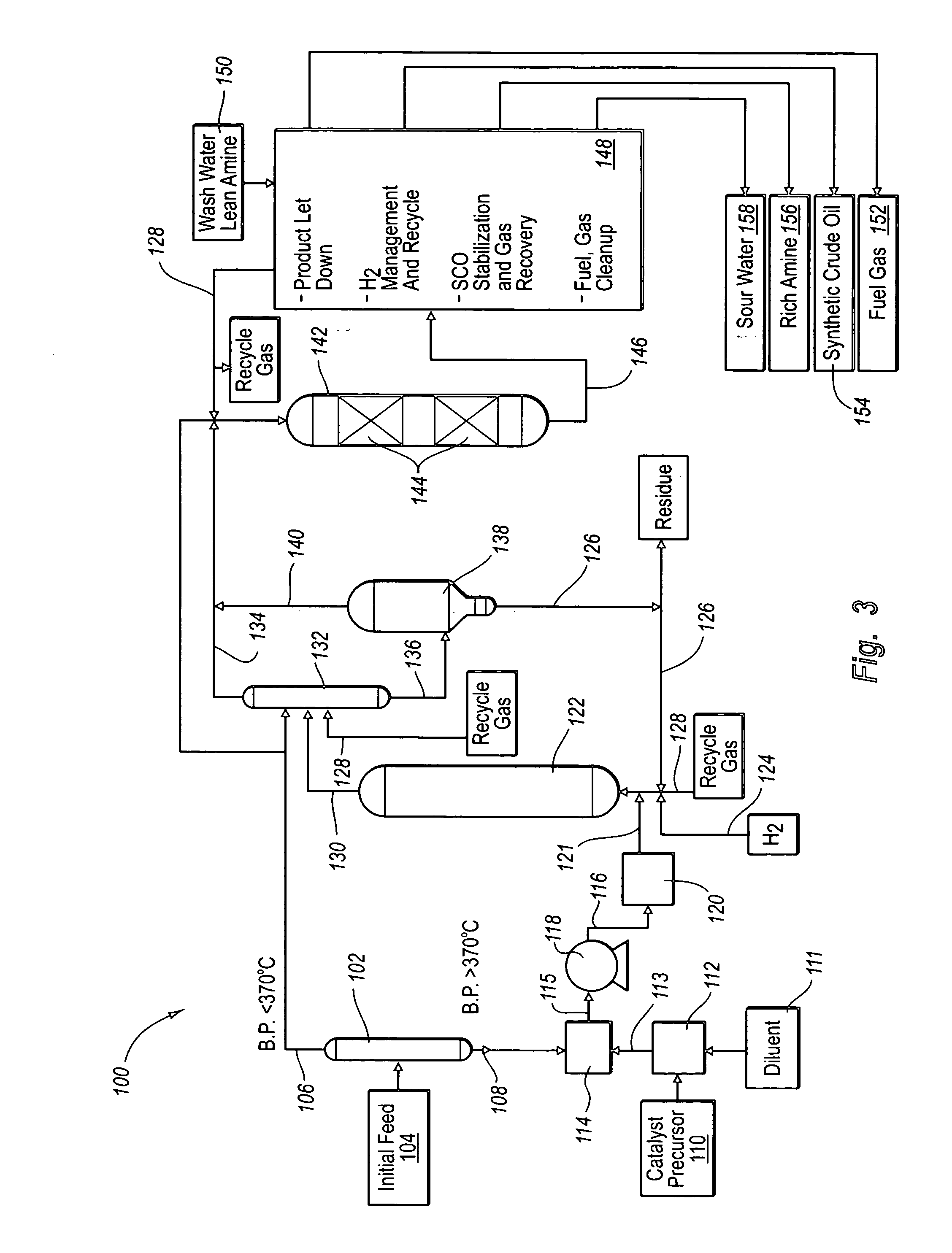
Hydroprocessing method and system for upgrading heavy oil using a colloidal or molecular catalyst
ActiveUS20050241993A1Inhibits eliminates formationEasy to useCatalyst regeneration/reactivationCatalyst activation/preparationColloidFuel oil
Methods and systems for hydroprocessing heavy oil feedstocks to form an upgraded material involve the use of a colloidal or molecular catalyst dispersed within a heavy oil feedstock, a hydrocracking reactor, and a hot separator. The colloidal or molecular catalyst promotes hydrocracking and other hydroprocessing reactions within the hydrocracking reactor. The catalyst is preferentially associated with asphaltenes within the heavy oil feedstock, which promotes upgrading reactions involving the asphaltenes rather than formation of coke precursors and sediment. The colloidal or molecular catalyst overcomes problems associated with porous supported catalysts in upgrading heavy oil feedstocks, particularly the inability of such catalysts to effectively process asphaltene molecules. The result is one or more of reduced equipment fouling, increased conversion level, and more efficient use of the supported catalyst if used in combination with the colloidal or molecular catalyst.
Owner:HEADWATERS TECH INNOVATION LLC
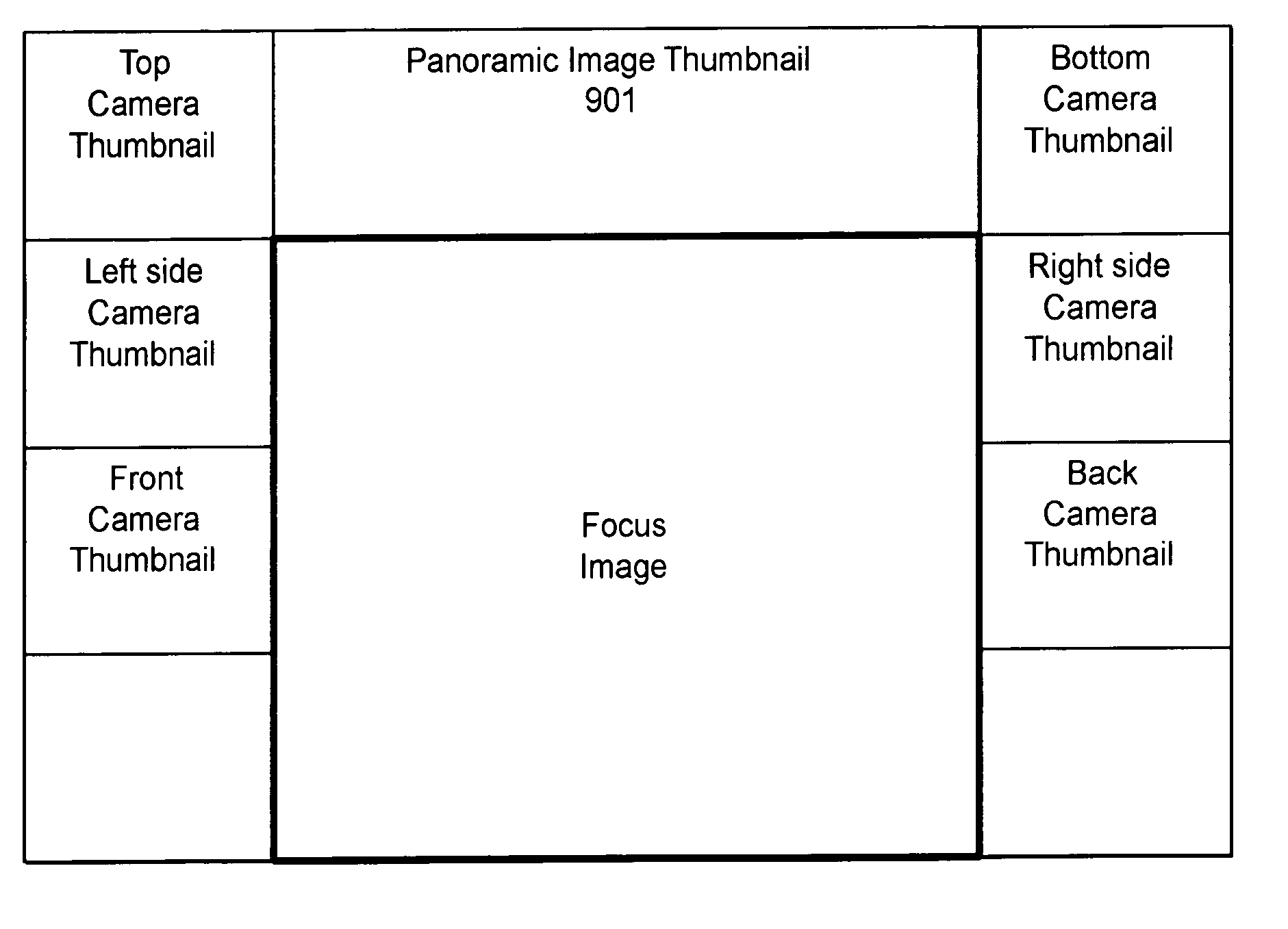
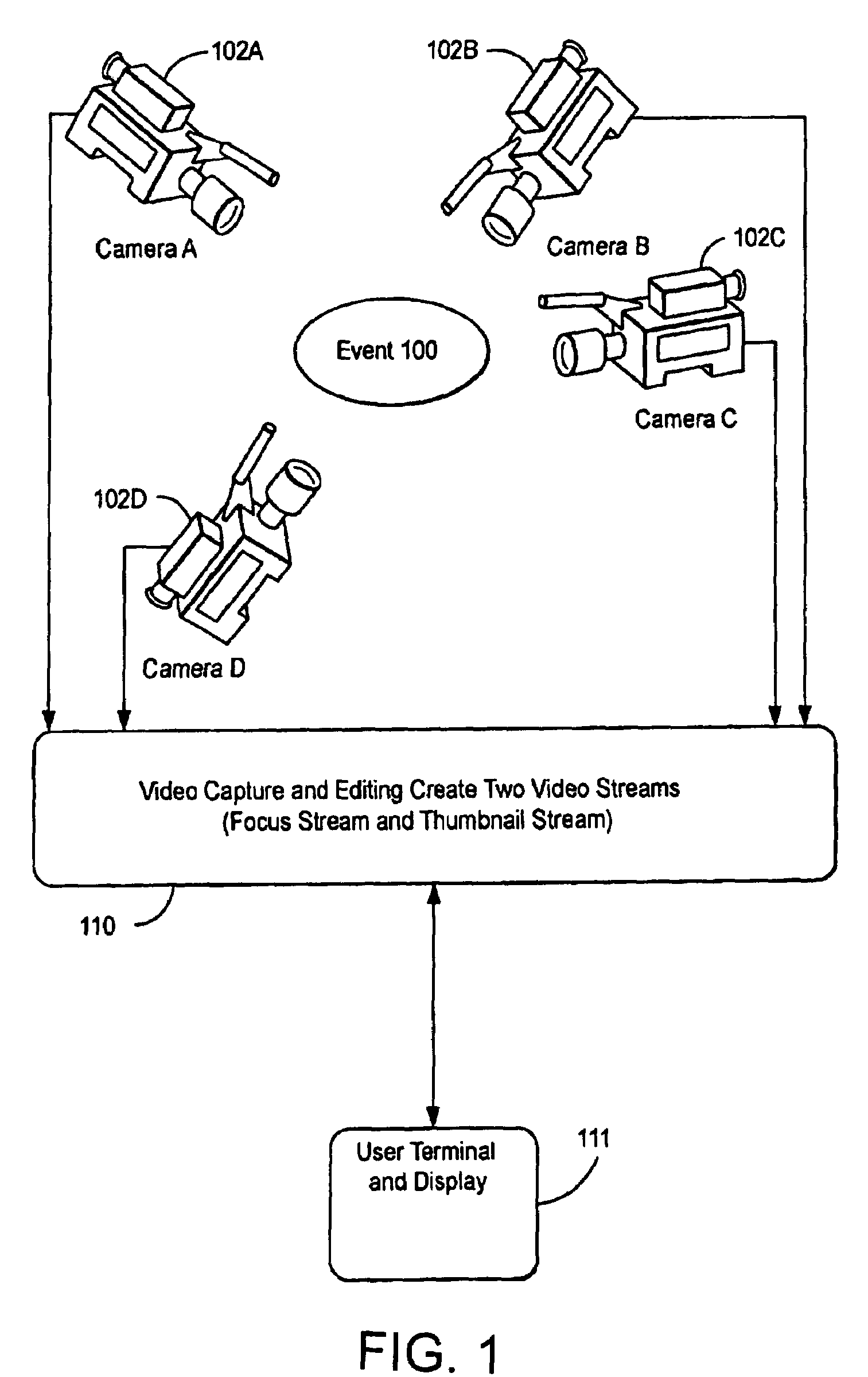
Multiple camera video system which displays selected images
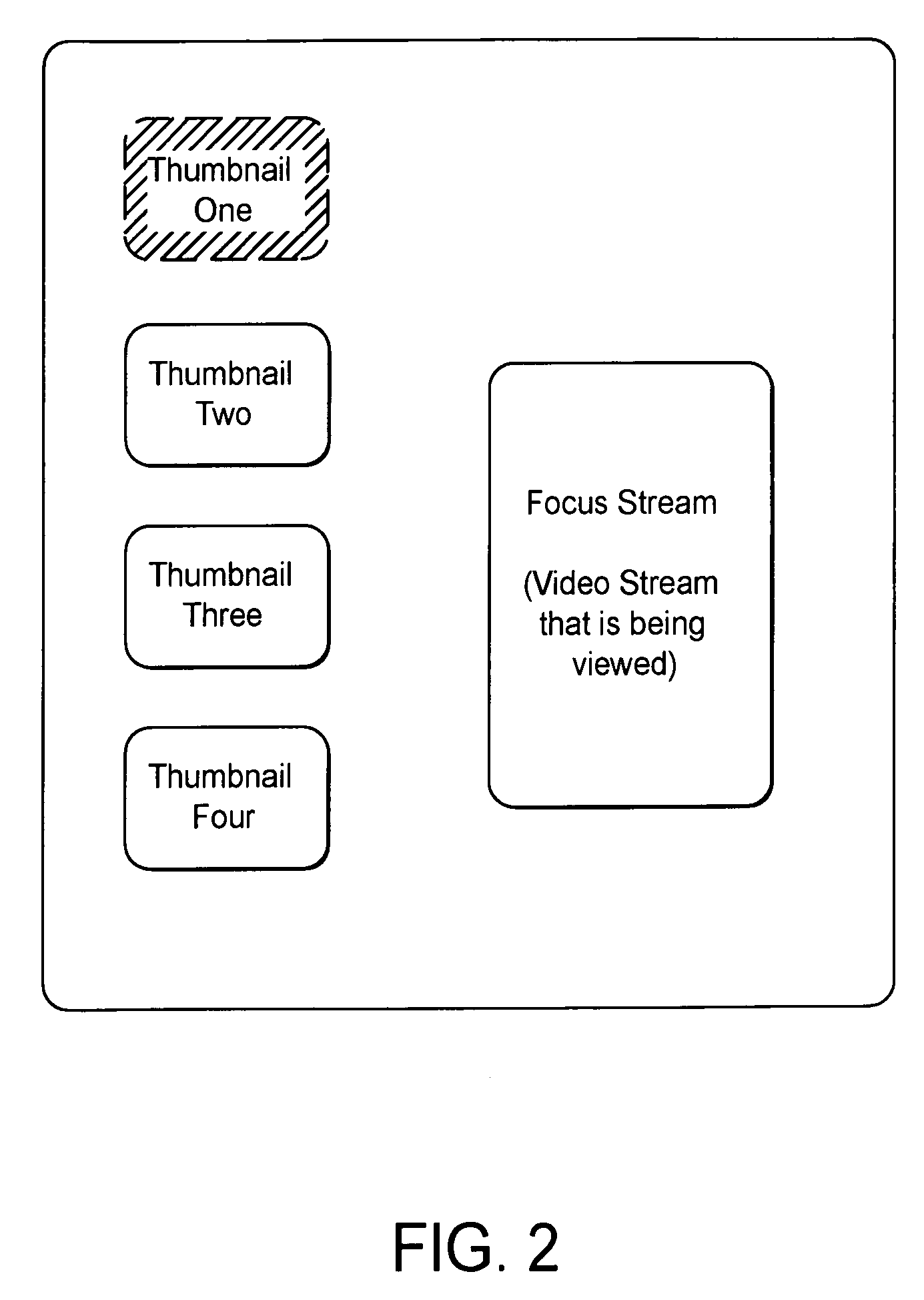
InactiveUS7196722B2Quality improvementSmall amount of bandwidthTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsData streamImage resolution
Multiple streams of data are streamed to a user's terminal with images from different cameras. Low resolution thumbnail images tell the user what image streams are available. A focus stream provides high resolution images from a selected camera. A user can switch the focus stream to another stream by clicking on the associated thumbnail. The users can also be provided with a thumbnail of panoramic image. Other data streams sent to the user can contain (a) audio data, (b) interactivity markup data which describes regions of the image which provide interactivity opportunities such as hotspots, (c) presentation markup data which defines how data is presented on the user's screen, (d) a telemetry data stream which can be used for various statistical data. One data stream contains a low quality base image for each data stream which can be enhanced to form a high resolution focus image.
Owner:IMMERSIVE LICENSING
Battery pack with integral cooling and bussing devices
ActiveUS7531270B2High densityIncrease energy densityFinal product manufactureCell temperature controlMobile vehicleBattery cell
A battery module of the present invention is adaptable to be utilized in various configurations including and not limited to an overlapping battery cell packaging configuration and a vertical stack battery cell packaging configuration used in an automotive vehicle. The battery module has a plurality of battery heatsink assemblies with the cells disposed therebetween. A plurality of rods extend through the each heatsink assemblies to secure the heatsink assemblies and the cell with one another to form the battery module.
Owner:ENERDEL
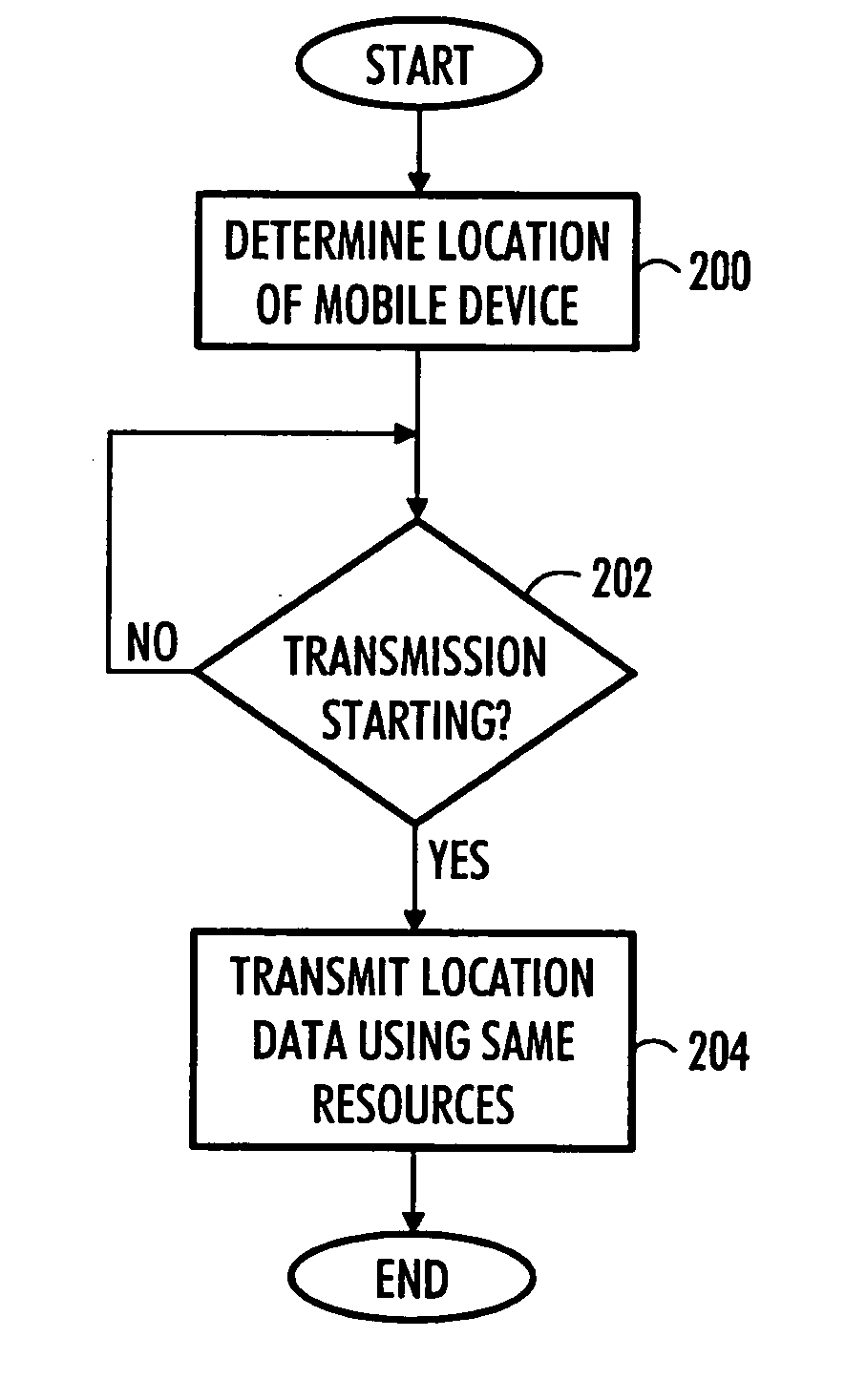
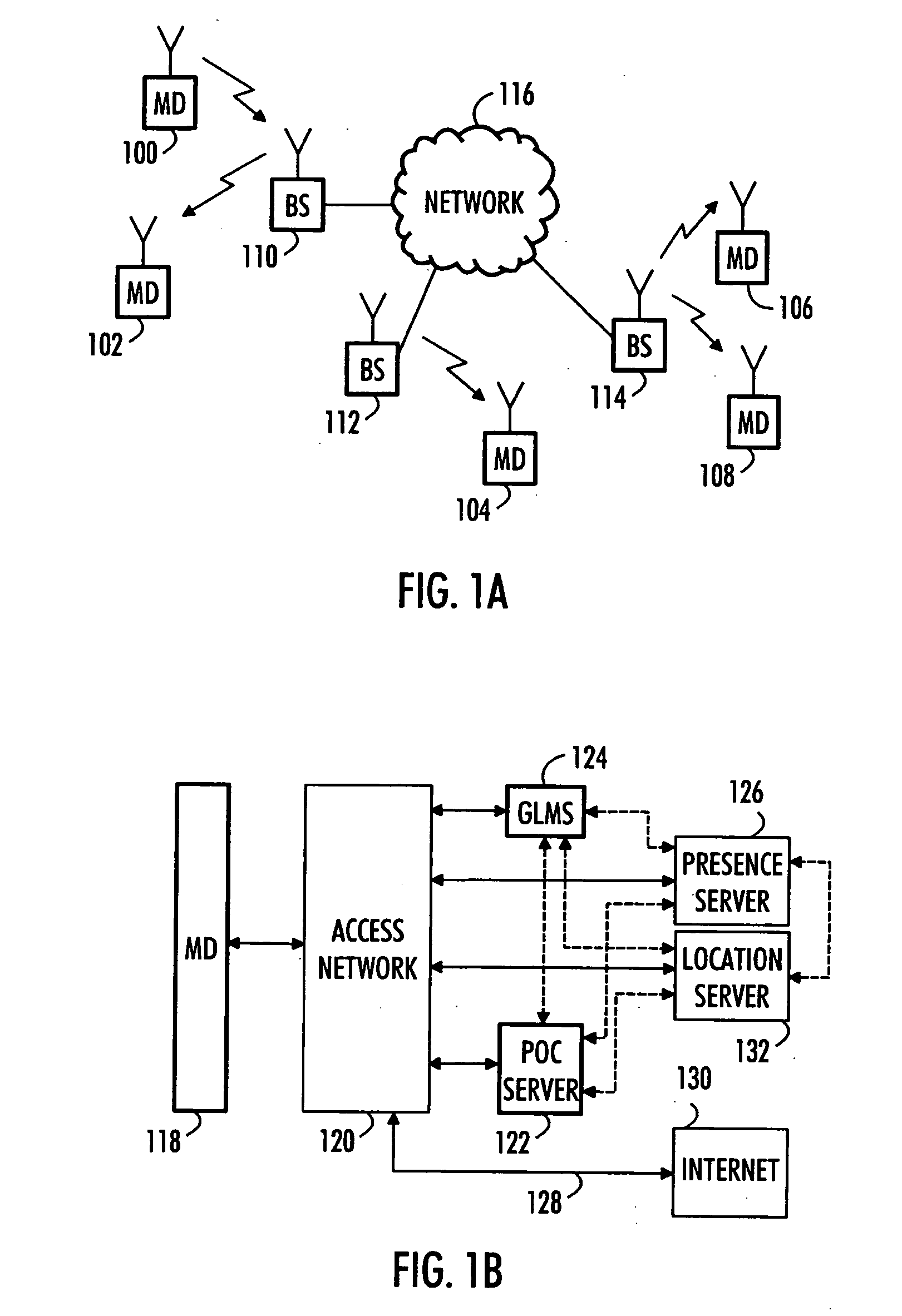
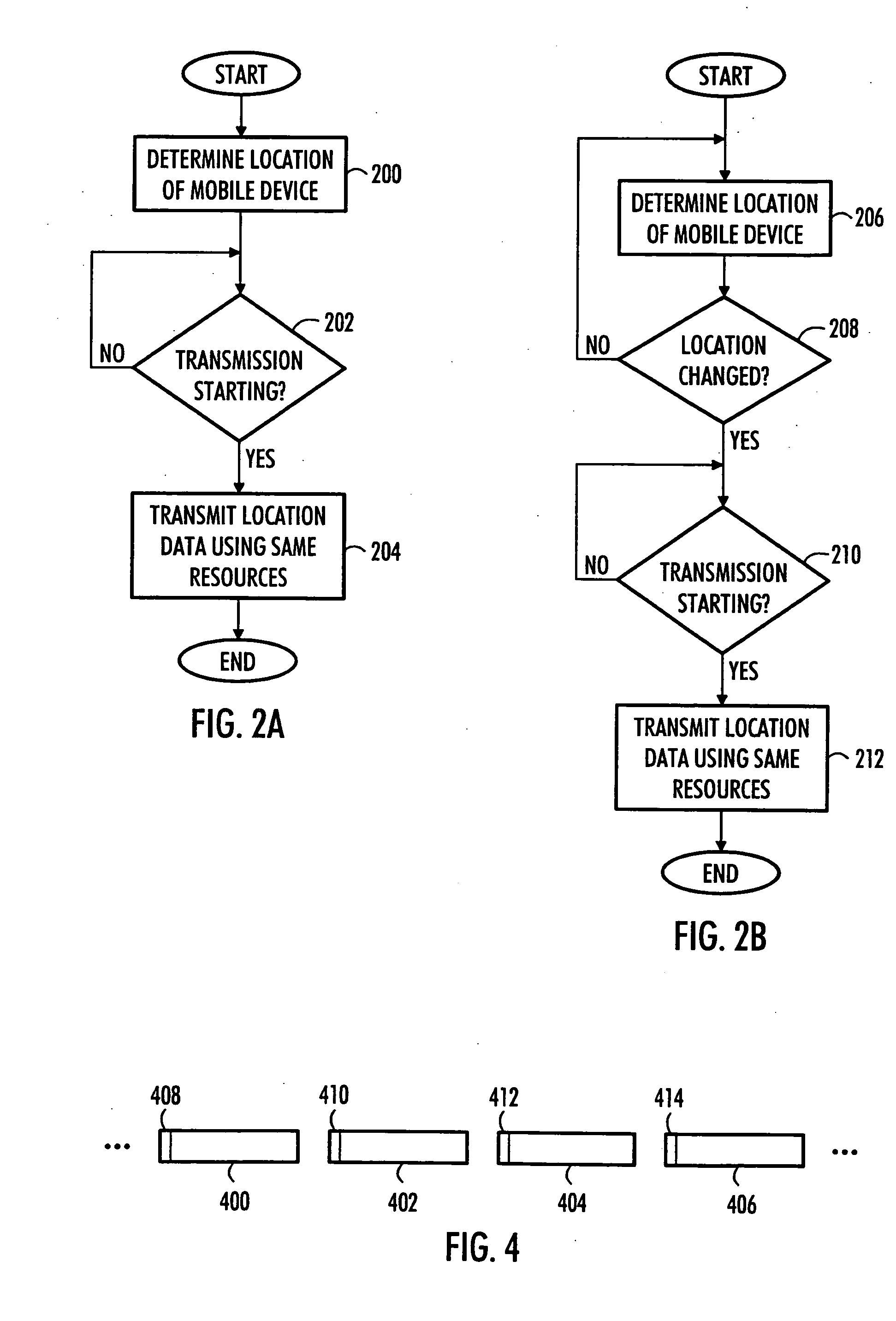
Data communication method, telecommunication system and mobile device
InactiveUS20050227705A1Increase connection related costSave resourcesConnection managementBroadcast service distributionCommunications systemMobile device
A data communication method in a communication system is provided. Speech and / or data is transmitted and received by a mobile device of the communication system using a predetermined transmission resource. The location of the mobile device of the communication system is determined. Information about the location of the mobile device is transmitted, with the speech or data, to a predetermined group of users by using the predetermined transmission resource.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Space concentrator for advanced solar cells
InactiveUS6252155B1Reduce quality problemsImprove efficiencySolar heating energyMirrorsConcentration ratioRefractive index
A solar concentrator is provided that comprises two stages. The first stage comprises either a trough-shaped concentrator cusp unit having two major opposed sides joined by two ends. The inner surfaces of the first stage concentrator are mirrored. Further, the ends have two flat, angled surfaces, while the two sides have a Bezier-generated cylindrical shape that approximate parabolic surfaces followed by a straight section. The second stage comprises a bi-axial gradient refractive index (GRIN) element, in which two gradient refractive index materials, each having a high index surface and a low index surface, are joined together along their high index surfaces. The two ends of the bi-axial element are flat, while the two sides also have a Bezier-generated cylindrical shape that approximate parabolic surfaces followed by a straight section. The top surface of the bi-axial element is provided with a cylindrical surface, while the bottom, or exit, surface is ground flat. The high index boundary is parallel to the side surfaces of the first stage unit. A solar cell is bonded to the flat exit surface of the second stage of the concentrator of the present invention. An array of such concentrators and solar cells, in which the solar cells are electrically interconnected, may then be deployed for converting solar energy into useful electrical energy. The 2-D / 3-D concentrator evidences much lower mass than prior art concentrators. Further, as the array, or panel, of solar cells wobbles in space, the concentrator will continue to operate, even at lower efficiencies, due to the larger acceptance angle. Concentration ratios on the order of 50x are realized with the present concentrator. However, design studies allow concentration ratios in excess of 300x when used with 3-D versions of the same concept. The second stage can comprise mirrored surfaces. Or, the first stage can comprise a conical section and the second stage a radial GRIN element.
Owner:ORTABASI UGUR
Composition for promoting healthy bone structure
InactiveUS6447809B1Increase bone densityPrevents radial bone lossBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsVitamin CRegimen
A dietary supplement for benefitting human bone health includes a calcium source, a source of vitamin D activity, and an osteoblast stimulant. A preferred calcium source is microcrystalline hydroxyapatite, which also contains protein (mostly collagen), phosphorus, fat, and other minerals. A preferred source of vitamin D activity is cholecalciferol, and a preferred osteoblast stimulant is ipriflavone. In addition to these basic ingredients, the composition can further include various other minerals known to occur in bone, vitamin C, and glucosamine sulfate, all of which exert beneficial effects on growth and maintenance of healthy bone. A method for benefitting human bone health involves administering a daily regimen of the dietary supplement.
Owner:PHOENIX DICHTUNGSTECHN +1
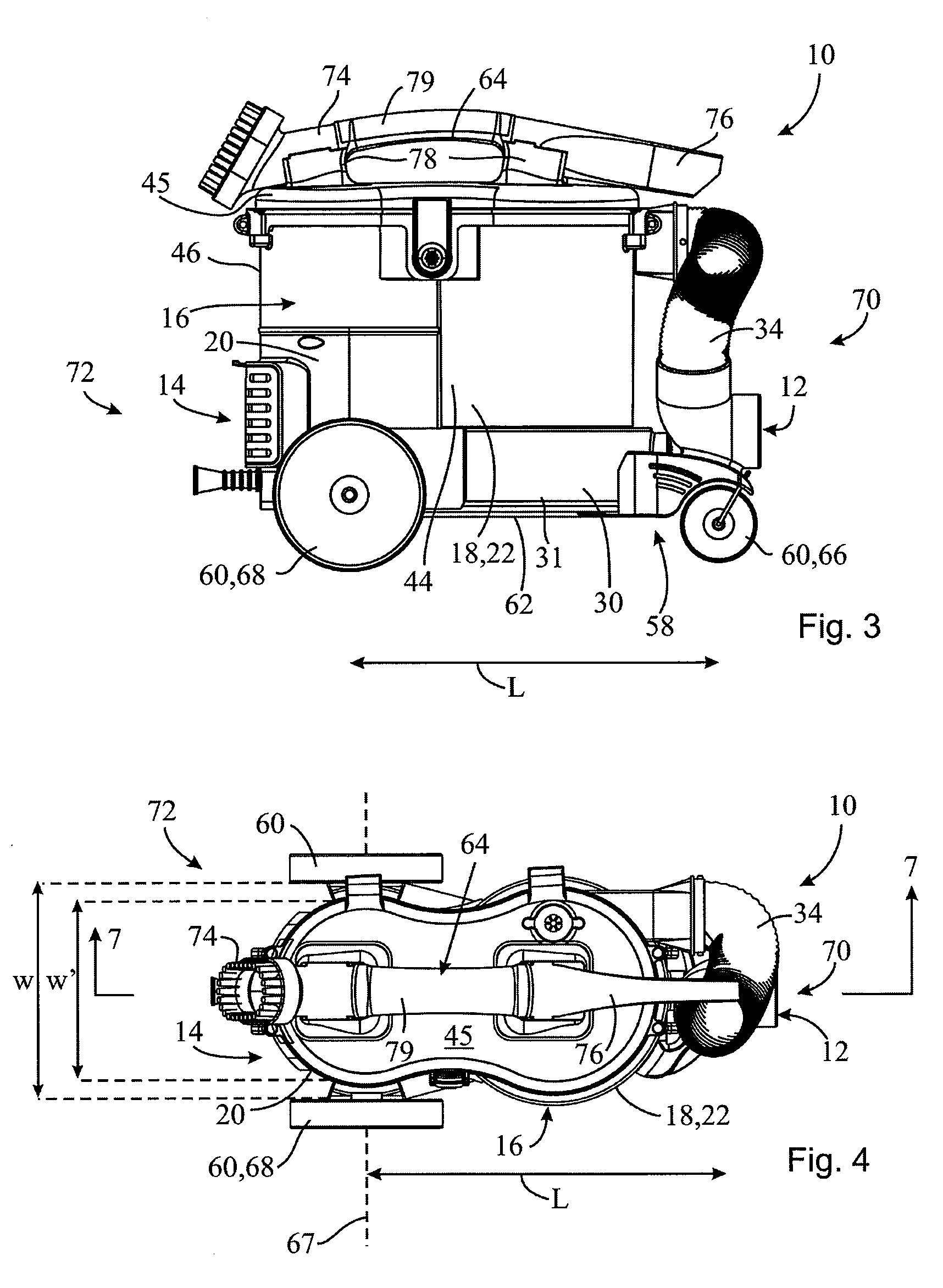
Vacuum cleaner with wheeled base
ActiveUS20080196196A1Improve mobilityImprove stabilityCleaning filter meansMechanical cleaningSurface cleaningEngineering
Owner:OMACHRON INTPROP
Space concentrator for advanced solar cells
InactiveUS6057505AReduce weightReduce quality problemsSolar heating energyMirrorsConcentration ratioRefractive index
A solar concentrator is provided that comprises two stages. The first stage comprises either a trough-shaped concentrator cusp unit having two major opposed sides joined by two ends. The inner surfaces of the first stage concentrator are mirrored. Further, the ends have two flat, angled surfaces, while the two sides have a Bezier-generated cylindrical shape that approximate parabolic surfaces followed by a straight section. The second stage comprises a bi-axial gradient refractive index (GRIN) element, in which two gradient refractive index materials, each having a high index surface and a low index surface, are joined together along their high index surfaces. The two ends of the bi-axial element are flat, while the two sides also have a Bezier-generated cylindrical shape that approximate parabolic surfaces followed by a straight section. The top surface of the bi-axial element is provided with a cylindrical surface, while the bottom, or exit, surface is ground flat. The high index boundary is parallel to the side surfaces of the first stage unit. A solar cell is bonded to the flat exit surface of the second stage of the concentrator of the present invention. An array of such concentrators and solar cells, in which the solar cells are electrically interconnected, may then be deployed for converting solar energy into useful electrical energy. The 2-D / 3-D concentrator evidences much lower mass than prior art concentrators. Further, as the array, or panel, of solar cells wobbles in space, the concentrator will continue to operate, even at lower efficiencies, due to the larger acceptance angle. Concentration ratios on the order of 50x are realized with the present concentrator. However, design studies allow concentration ratios in excess of 300x when used with 3-D versions of the same concept. The second stage can comprise mirrored surfaces. Or, the first stage can comprise a conical section and the second stage a radial GRIN element.
Owner:ORTABASI UGUR
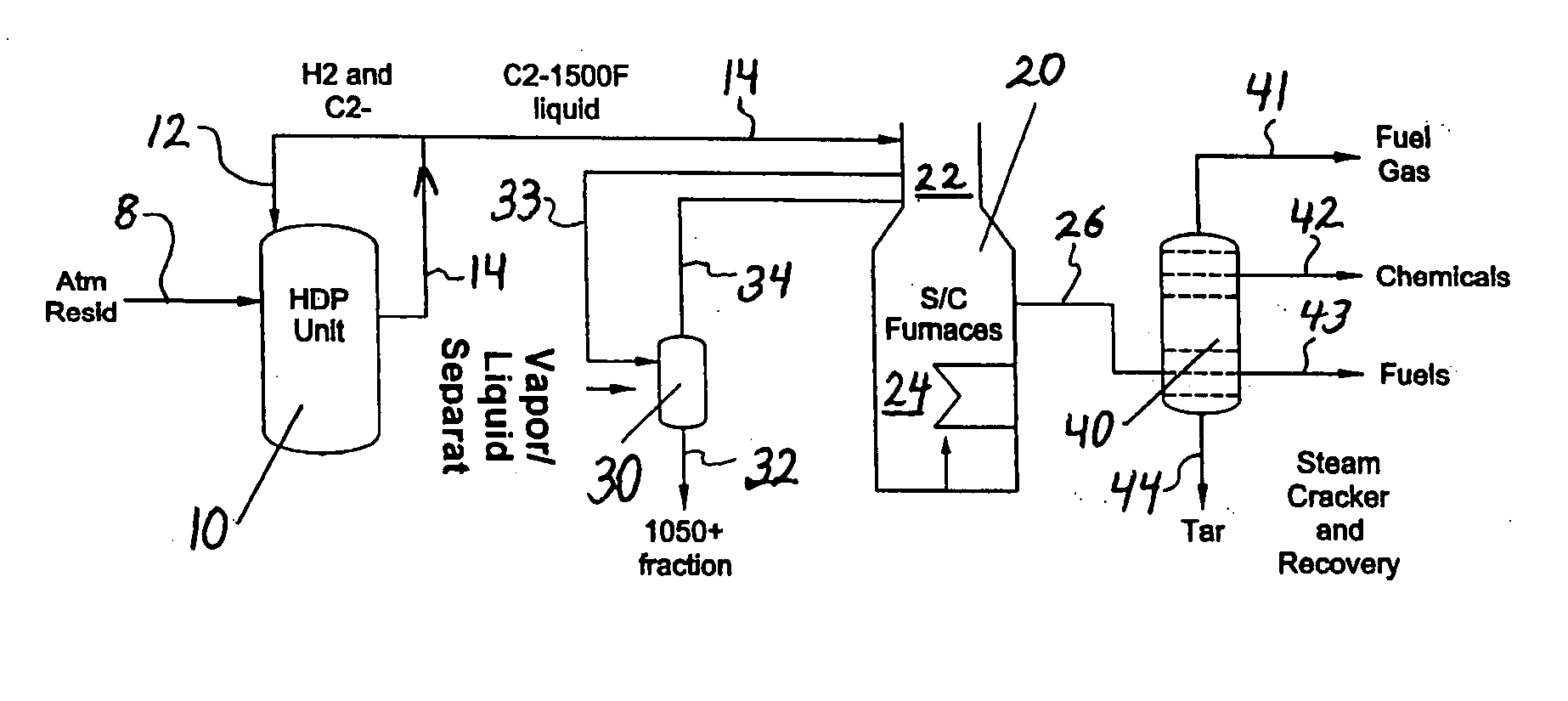
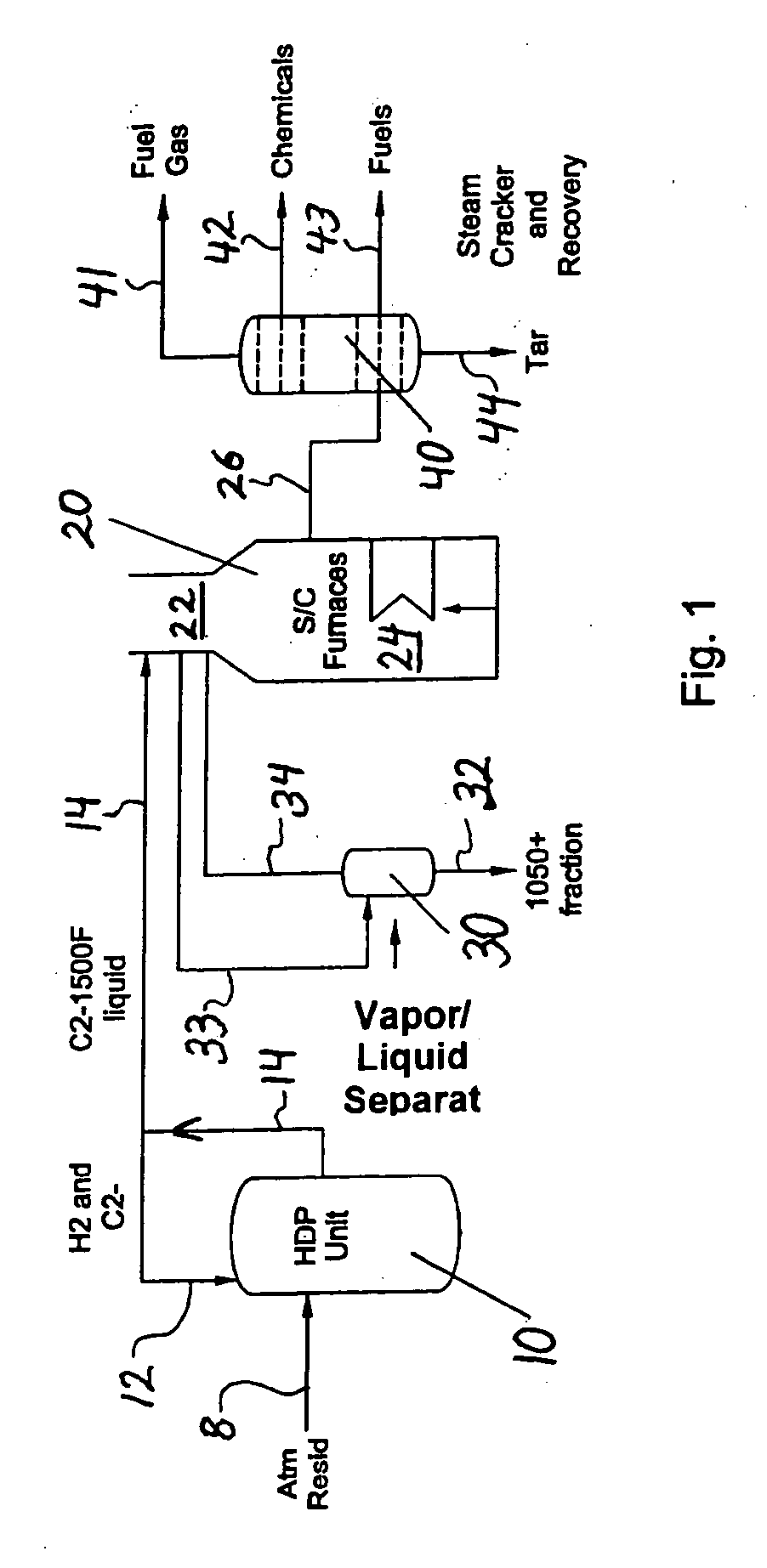
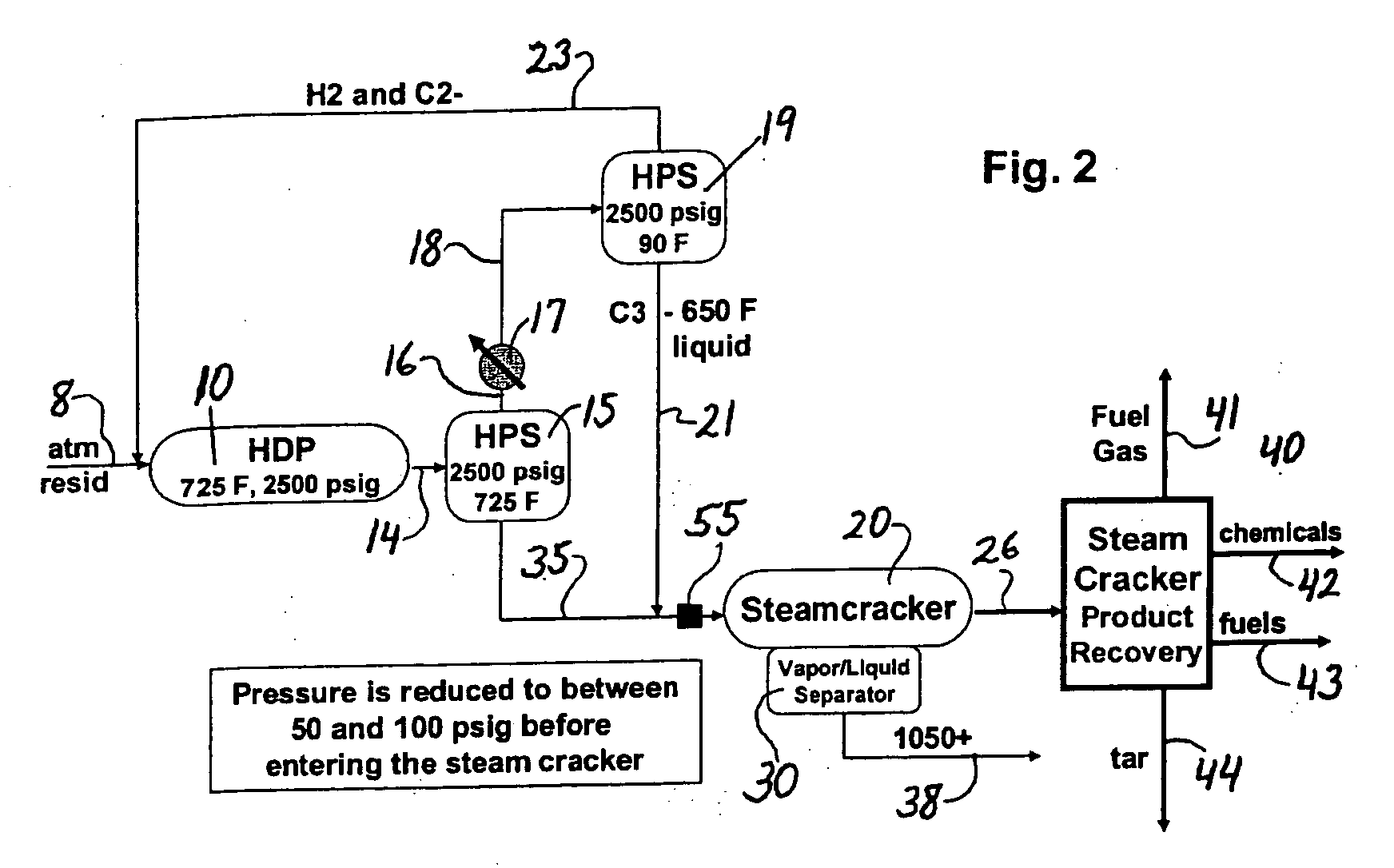
Resid processing for steam cracker feed and catalytic cracking
ActiveUS20070090020A1High hydrogen contentEliminate needThermal non-catalytic crackingHydrocarbon oil cracking processProcess engineeringAlkene
The invention concerns integration of hydroprocessing and steam cracking. A feed comprising crude or resid-containing fraction thereof is treated by hydroprocessing and visbreaking and then passed to a steam cracker to obtain a product comprising olefins.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
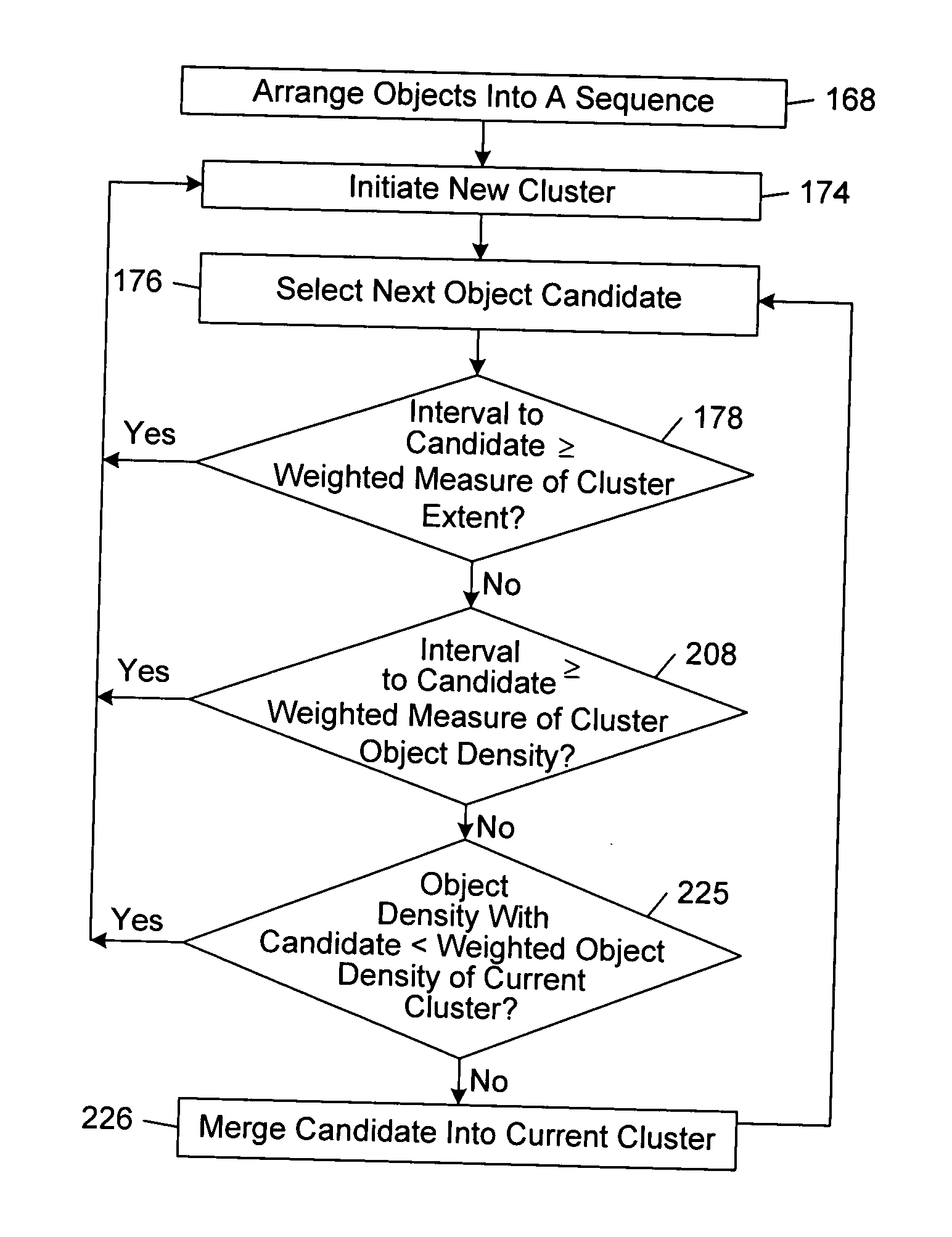
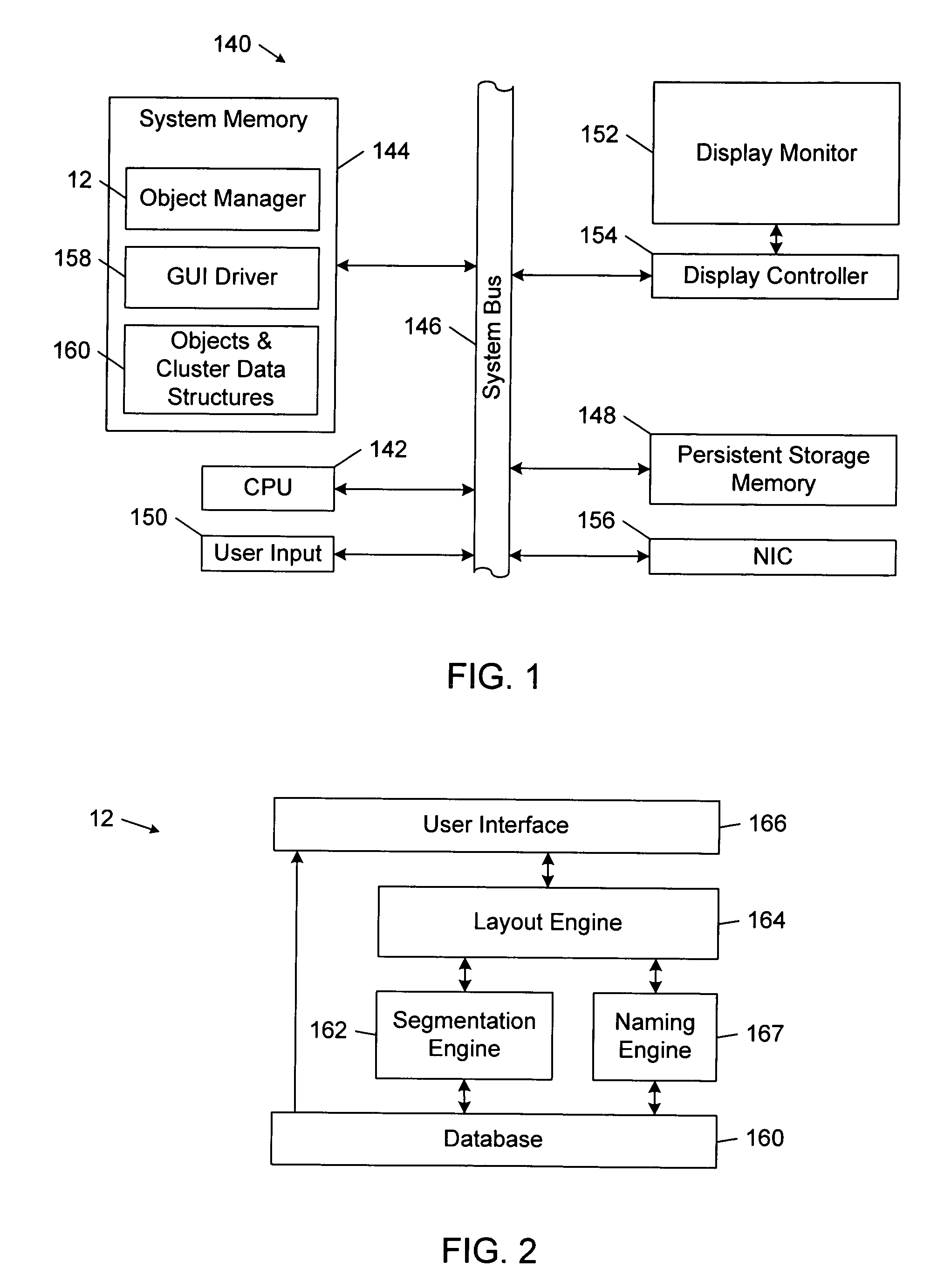
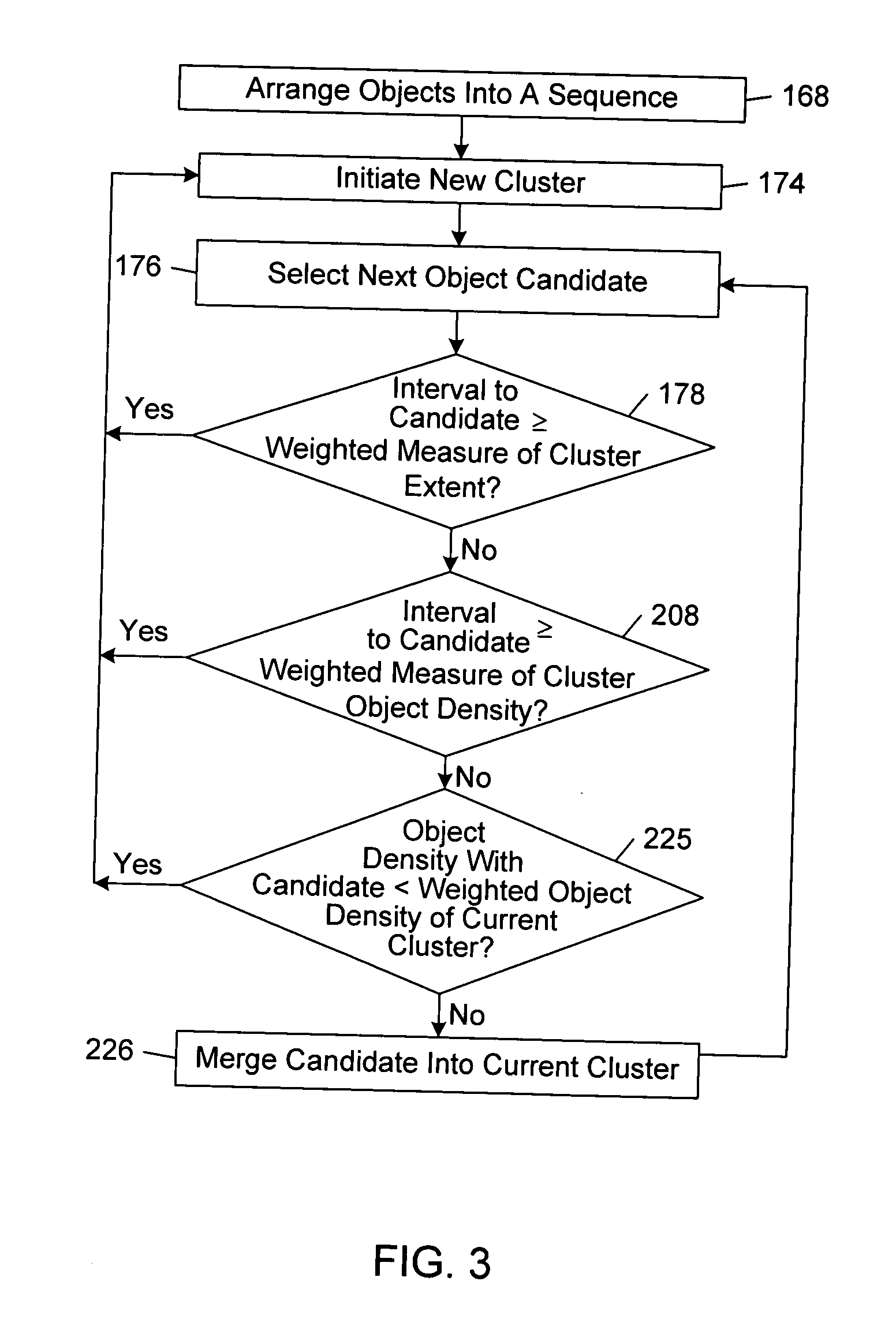
Organizing a collection of objects
InactiveUS20050027712A1Reduce quality problemsTransforming corporations, markets, and the global economyDigital data processing detailsStill image data browsing/visualisationGraphicsArtificial intelligence
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Measurement transducer of vibration-type
ActiveUS20070119264A1Improve balanceReduce quality problemsDirect mass flowmetersCantilevered beamCoupling
The measurement transducer includes: A measuring tube vibrating at least at times during operation and serving for the conveying of a medium, wherein the measuring tube communicates with a pipeline via an inlet tube piece at an inlet end and an outlet tube piece at an outlet end; a counteroscillator, which is affixed to the measuring tube on the inlet end to form a first coupling zone and affixed to the measuring tube on the outlet end to form a second coupling zone; and a first cantilever for producing bending moments in the inlet tube piece and coupled with the inlet tube piece and the measuring tube essentially rigidly in the area of the first coupling zone and having a center of mass lying in the region of the inlet tube piece, as well as a second cantilever for producing bending moments in the outlet tube piece and coupled essentially rigidly with the outlet tube piece and the measuring tube in the region of the second coupling zone and having a center of mass lying in the region of the outlet tube piece. The measurement transducer of the invention is especially suited also for measuring tubes having large nominal diameters of more than 50 mm.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Picoprojector with Image Stabilization [Image-Stabilized Projector] Picoprojector with Image Stabilization [Image-Stabilized Projector]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/69908f5d-c70f-43ec-b137-dbc7e98ba54d/US20120113514A1-20120510-D00000.png)
![Picoprojector with Image Stabilization [Image-Stabilized Projector] Picoprojector with Image Stabilization [Image-Stabilized Projector]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/69908f5d-c70f-43ec-b137-dbc7e98ba54d/US20120113514A1-20120510-D00001.png)
![Picoprojector with Image Stabilization [Image-Stabilized Projector] Picoprojector with Image Stabilization [Image-Stabilized Projector]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/69908f5d-c70f-43ec-b137-dbc7e98ba54d/US20120113514A1-20120510-D00002.png)