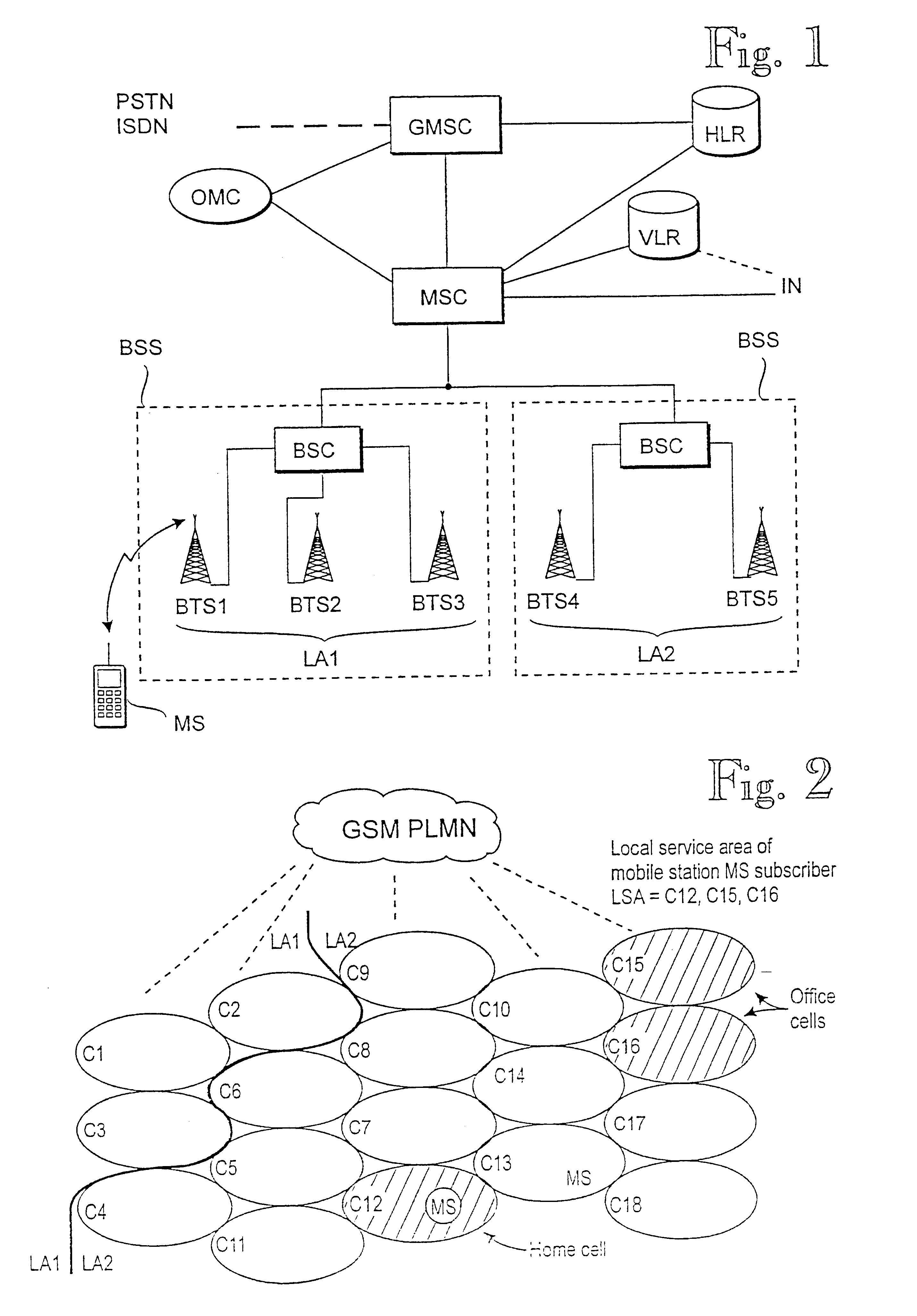
Patents
Literature
1038 results about "Cell selection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
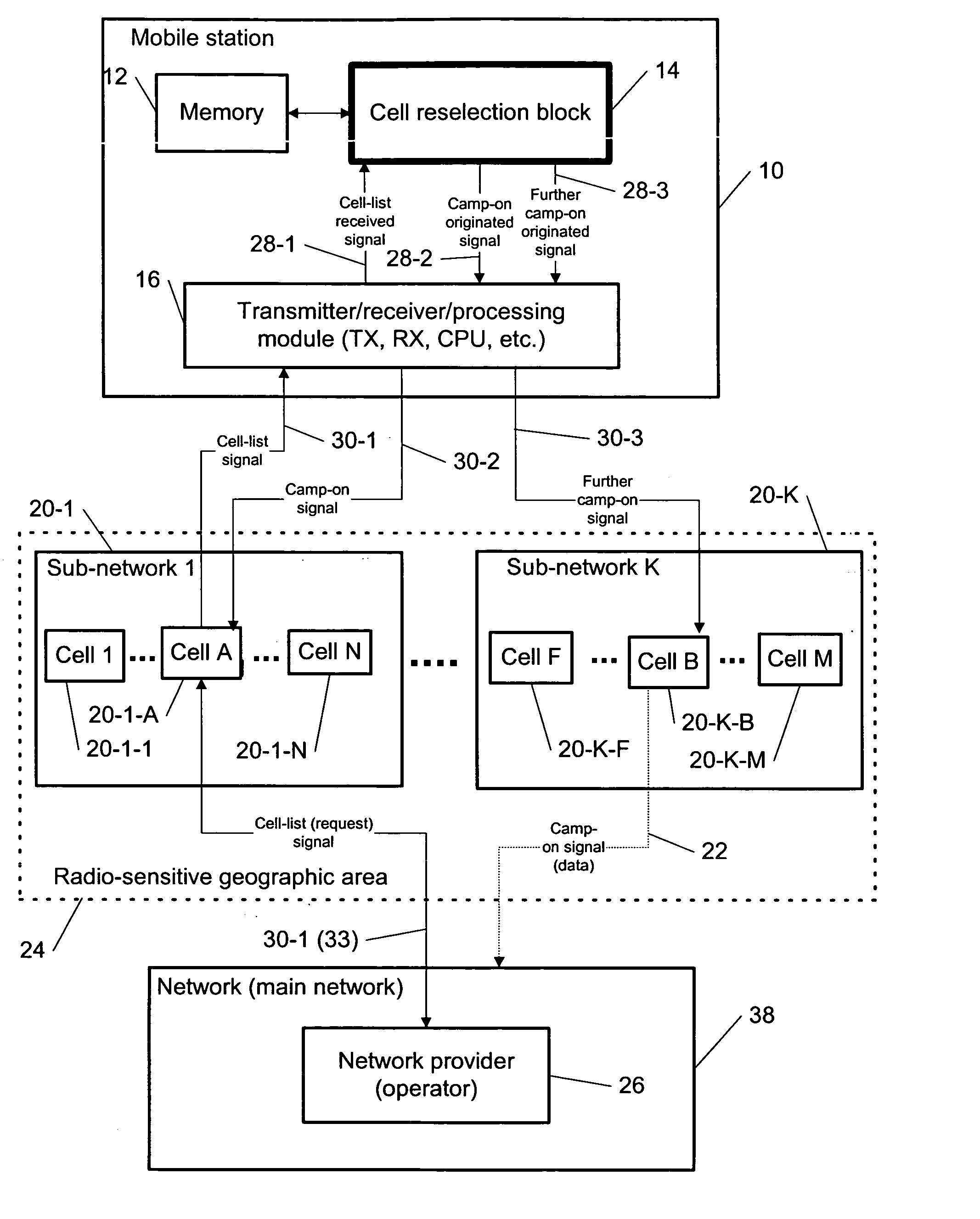
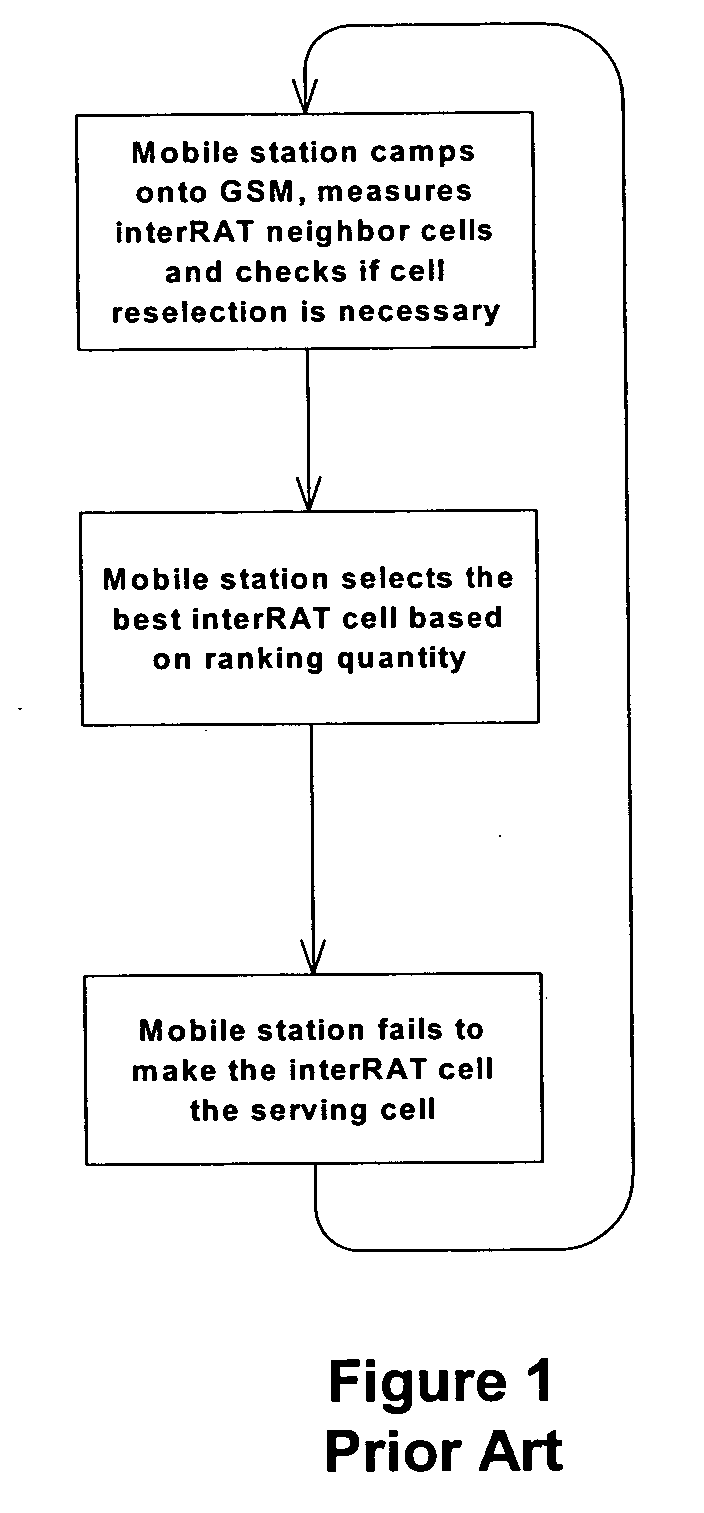
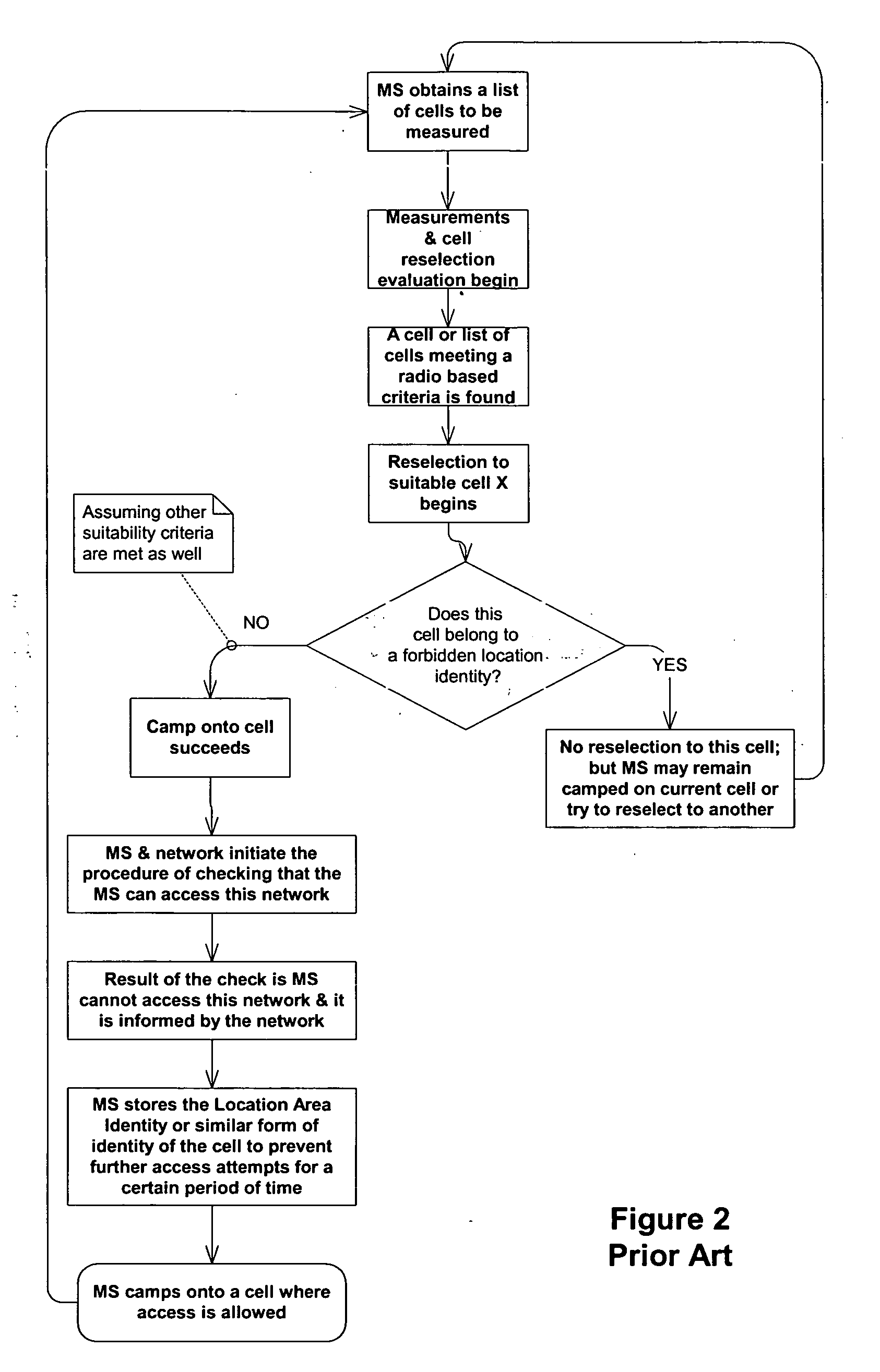
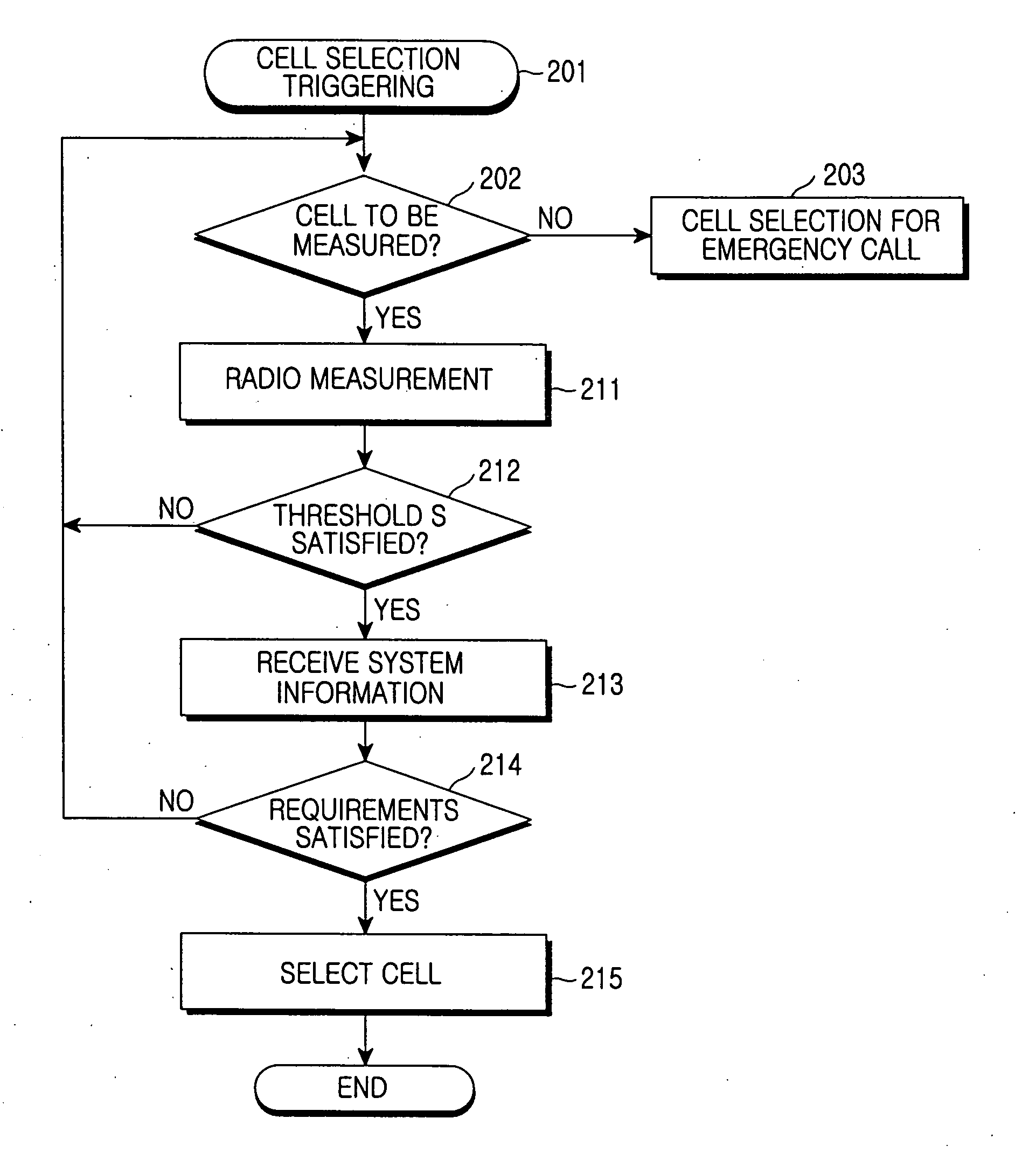
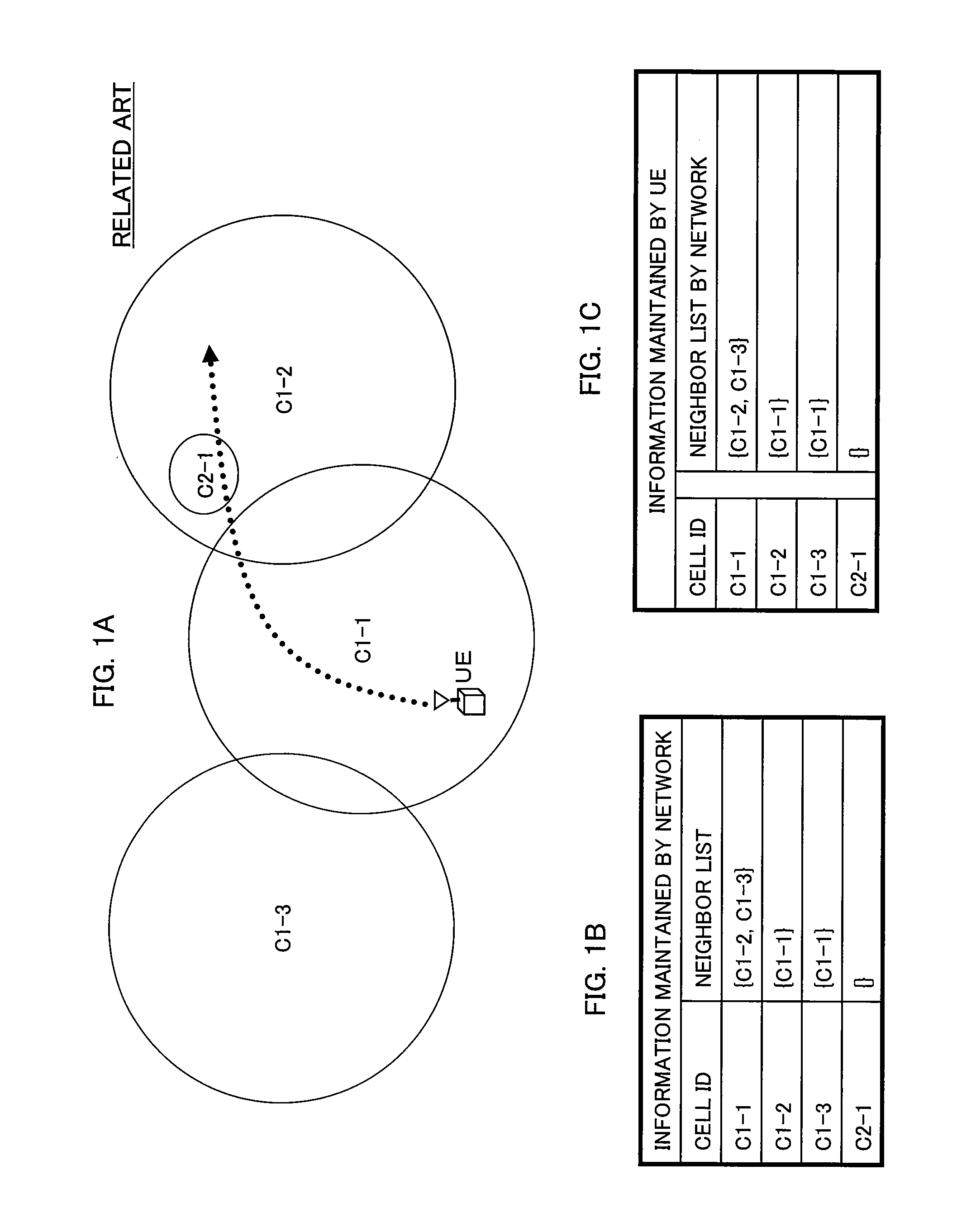
Cell reselection for improving network interconnection
InactiveUS20060084443A1Improving network interconnectionImprove interoperabilityAssess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCell selectionInterconnection
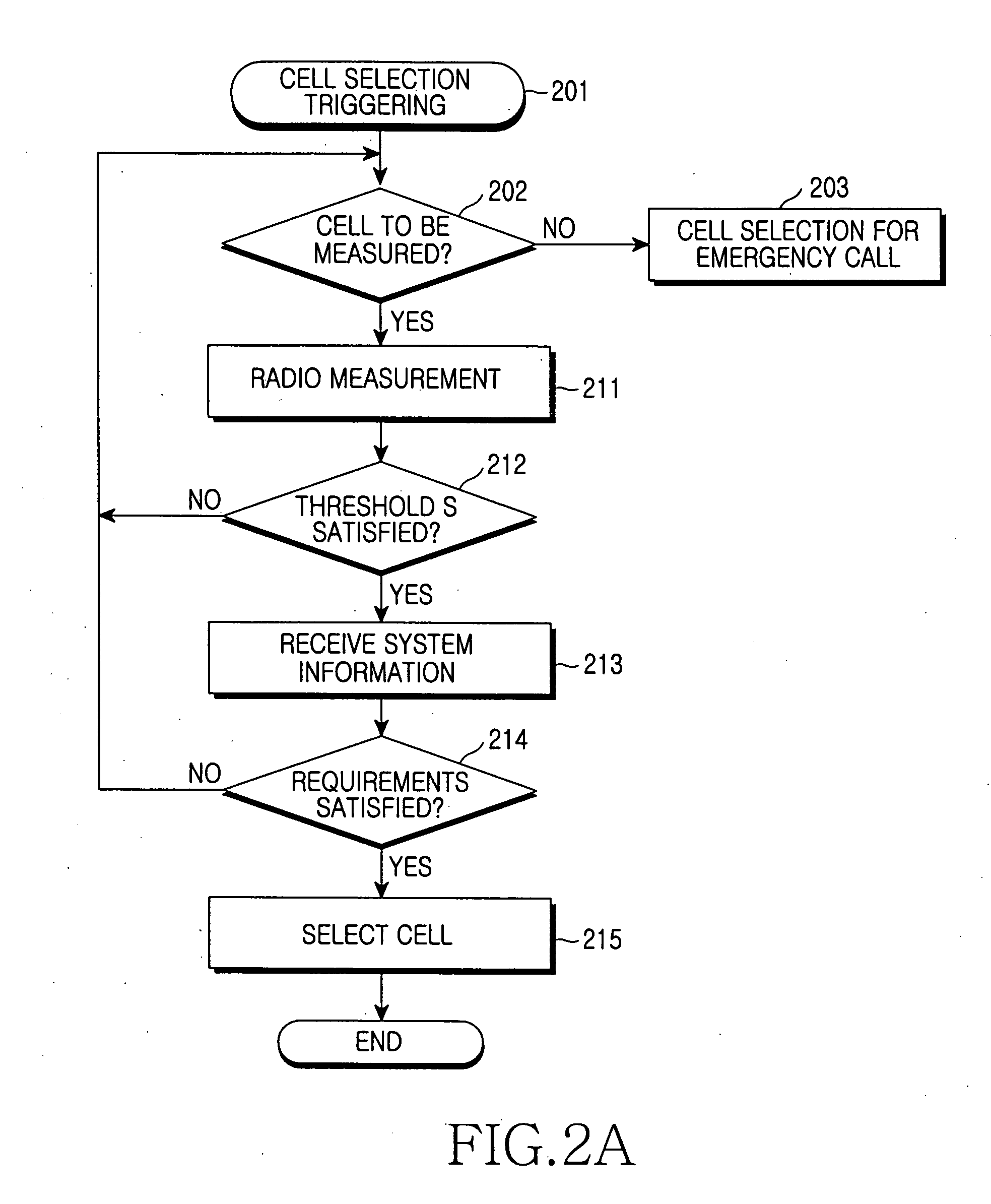
This invention describes a new methodology for a cell reselection by a mobile station (MS) for improving network interconnection and interoperability in a limited mobile access environment. The invention is applicable to any kind of networks and their interconnections. The invention describes how the MS can better recover from failed intersystem cell reselection attempts so that there are fewer subsequent failed attempts using two major improvements. First, the MS takes into consideration during cell reselection evaluation and candidate-cell selection, whether the MS had previously been unsuccessful in reselecting the considered cell. This means treating neighbor cells to which the MS had failed reselection before with a lower priority in subsequent cell reselection evaluations. Second, the MS is allowed to stop monitoring and thus, to stop evaluating cells if it was earlier found that the access to those cells is forbidden.
Owner:RPX CORP
Method and system for cell selection/reselection taking into account congestion status of target cell in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS20060035662A1Assess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsCell selection
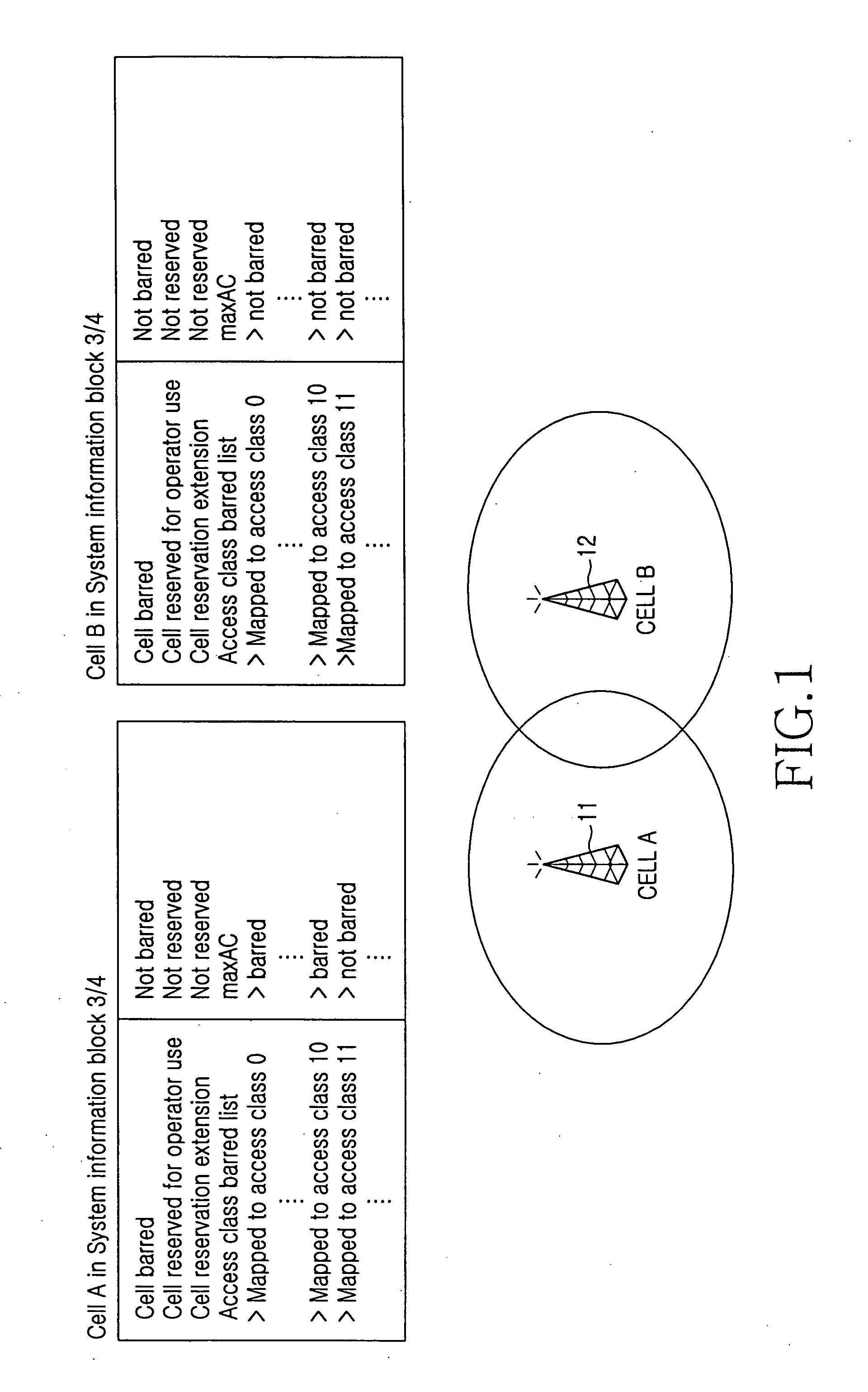
A method and system for ensuring continuous service reception at a UE for each access class by carrying out cell selection / reselection taking into account the congestion status of a target cell in a mobile communication system. The method and system takes into account the congestion status of a target cell, and the UE selects / reselects the target cell of which the access class barred list indicates the access class of the UE as not barred. For cell selection / reselection, the UE can refer to the access class barred list of the target cell all the time, or only when it is necessary to access the network for a specific service indicated by an upper layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DYNAMIC CELL SELECTION AND RESOURCE MAPPING FOR CoMP JOINT TRANSMISSION
A wireless communication system includes a number of base stations capable of communicating with a plurality of subscriber stations. The base station coordinates transmission of resource blocks with a transmission of resource blocks from a second base station. The resource blocks include at least one reference signal (RS) patterns. In addition, base station punctures a plurality of resource elements in the resource blocks that might overlap with one of the CRS patterns in another resource block transmitted by the second base station such that no data is transmitted in the plurality of punctured resource elements. The subscriber station receives the resource blocks from at least two base stations and can avoid reading data from the resource elements that might overlap.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Cell selection
InactiveUS7277709B2Avoid the needAccurate measurementError preventionTransmission systemsCell selectionCell site
Cell selection techniques for use in cellular communications systems are disclosed. A decision as to whether to use a cell for data transmission is made in dependence on a measure of a congestion level in the cell. The decision may either be part of a cell selection decision, or used to override a cell selection decision. The techniques may be used in fast cell site selection.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
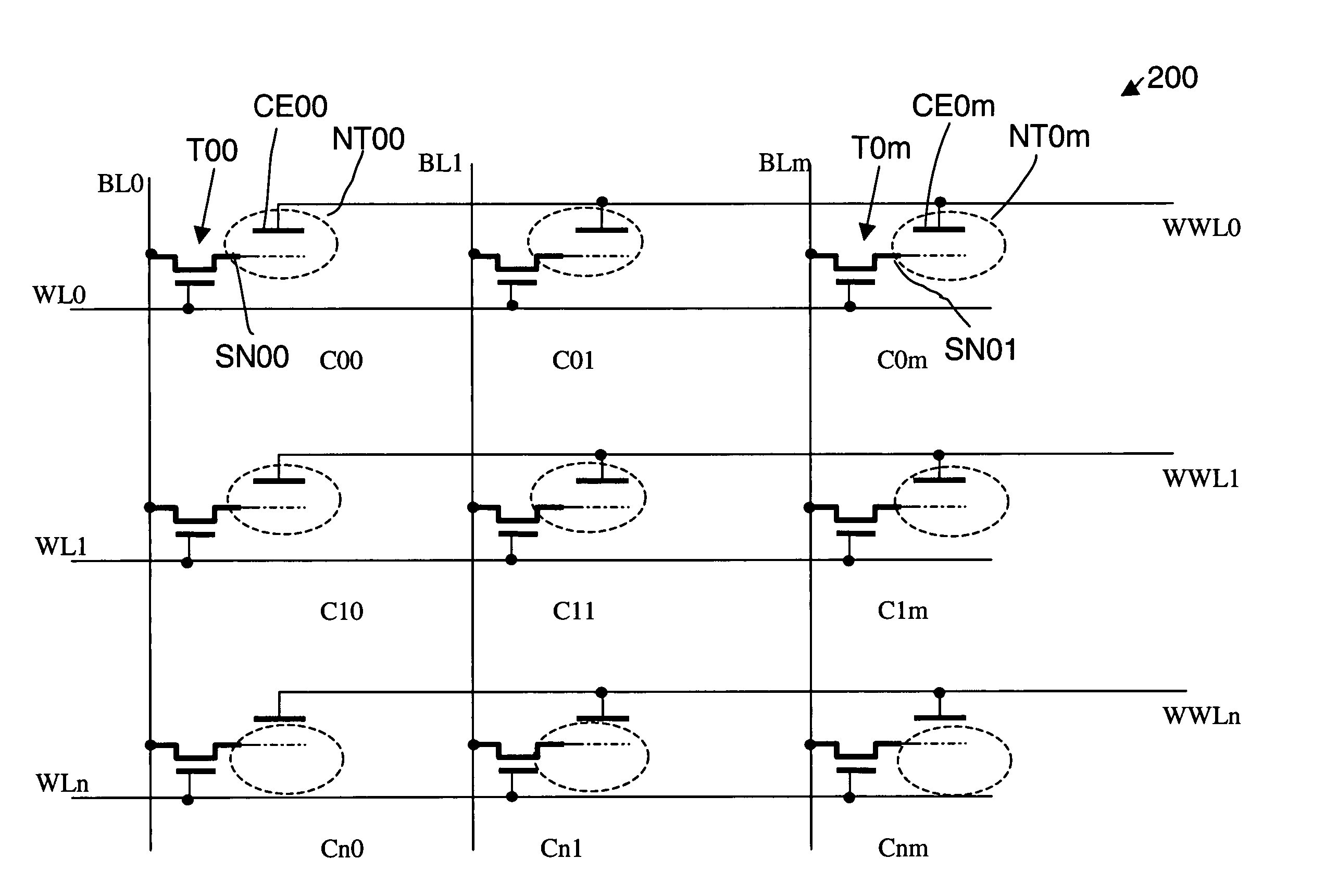
Memory arrays using nanotube articles with reprogrammable resistance
A memory array includes a plurality of memory cells, each of which receives a bit line, a first word line, and a second word line. Each memory cell includes a cell selection circuit, which allows the memory cell to be selected. Each memory cell also includes a two-terminal switching device, which includes first and second conductive terminals in electrical communication with a nanotube article. The memory array also includes a memory operation circuit, which is operably coupled to the bit line, the first word line, and the second word line of each cell. The circuit can select the cell by activating an appropriate line, and can apply appropriate electrical stimuli to an appropriate line to reprogrammably change the relative resistance of the nanotube article between the first and second terminals. The relative resistance corresponds to an informational state of the memory cell.
Owner:NANTERO
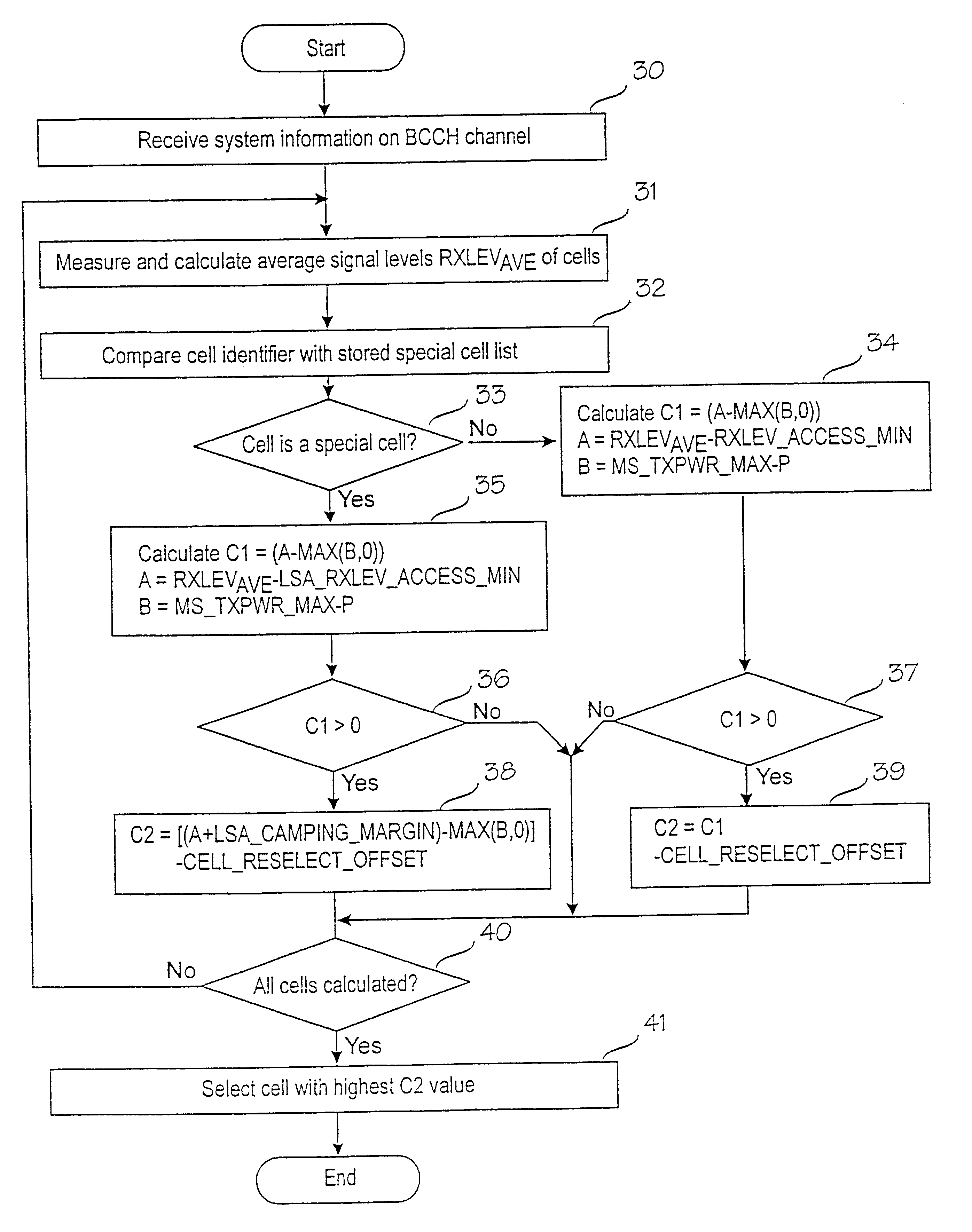
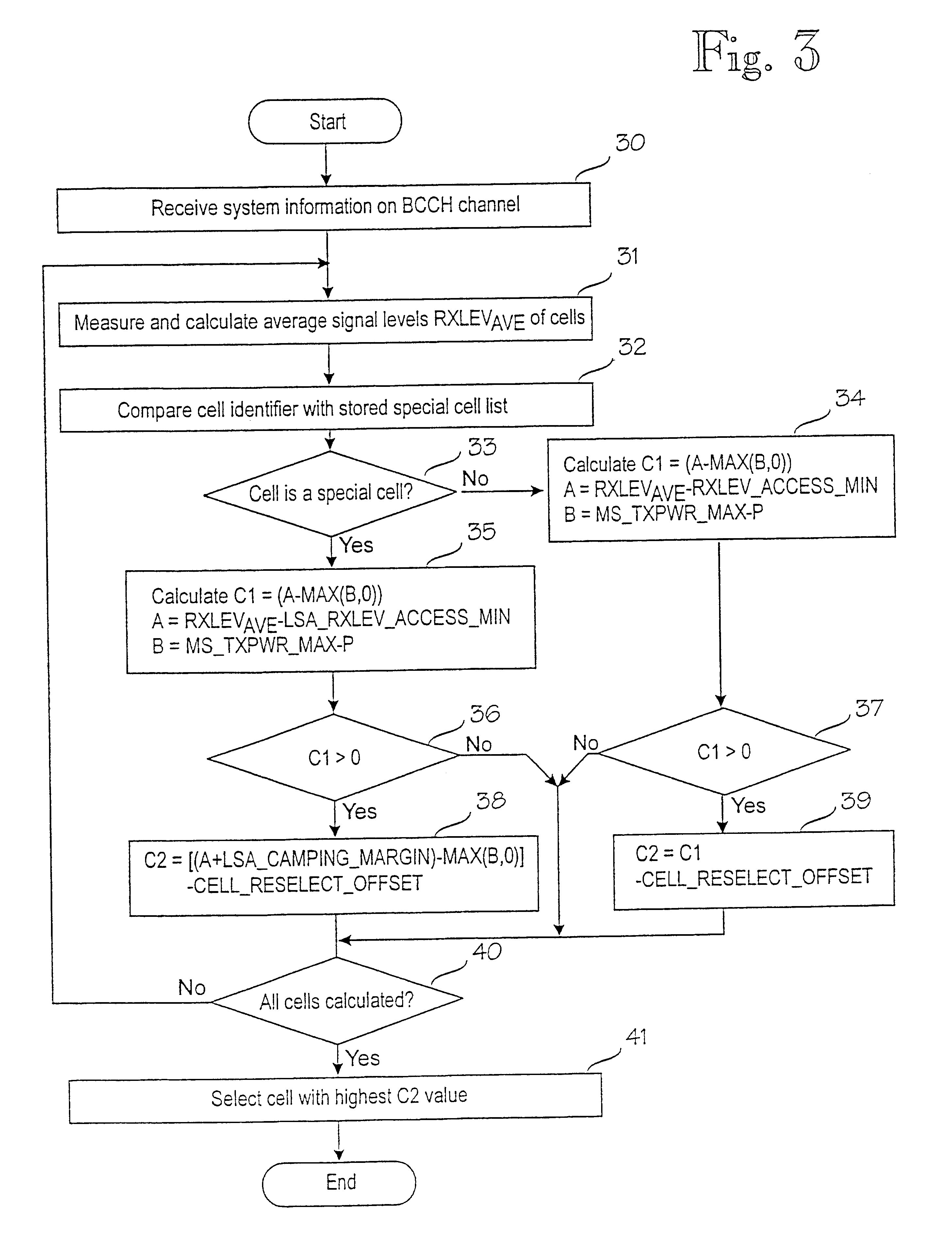
Method for selecting cell in cellular network
InactiveUS6434389B1Enhance cell selectionExpand selectionAssess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCellular radioRadio networks
The present invention relates to prioritizing special cells in cell selection in a cellular radio network. In a cellular radio network one or more cells provide a subscriber with special services or tariffs not offered to all subscribers. These cells are called subscriber's special cells. The mobile station measures an average reception level and calculates by means of them cell selection parameters on the basis of which the best cell is selected. In accordance with the invention, when the mobile station detects that the cell is one of cells of a special cell list stored in a memory, it checks first if the cell fulfils a minimum requirement of cell selection on the basis of the measured signal level. If the minimum requirement is fulfilled, the mobile station manipulates the calculation of the cell selection parameter of a special cell to the effect that the selection probability of a special cell is improved with respect to a normal cell. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the manipulation of the calculation comprises a step of adding a predetermined margin to the measured signal level of a special cell before the cell selection parameter is calculated. This will minimize the possibility that the mobile station would accidentally be camped on a normal cell when it is within the area of a special cell.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
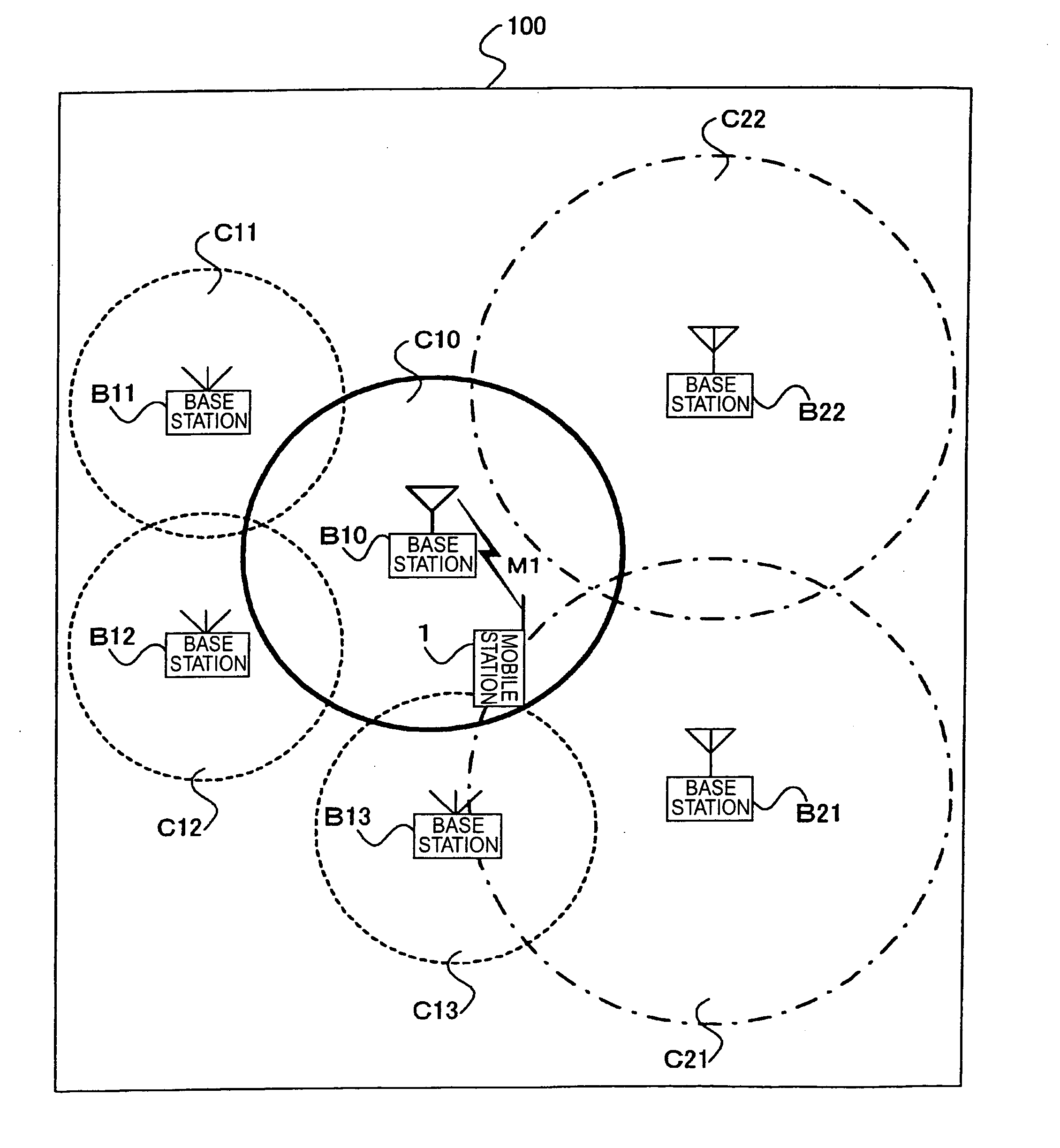
Mobile station, mobile communication system, and cell selection method
InactiveUS20050037798A1Stabilize good communication qualityCommunication quality is not deterioratedRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionCell selectionMobile station
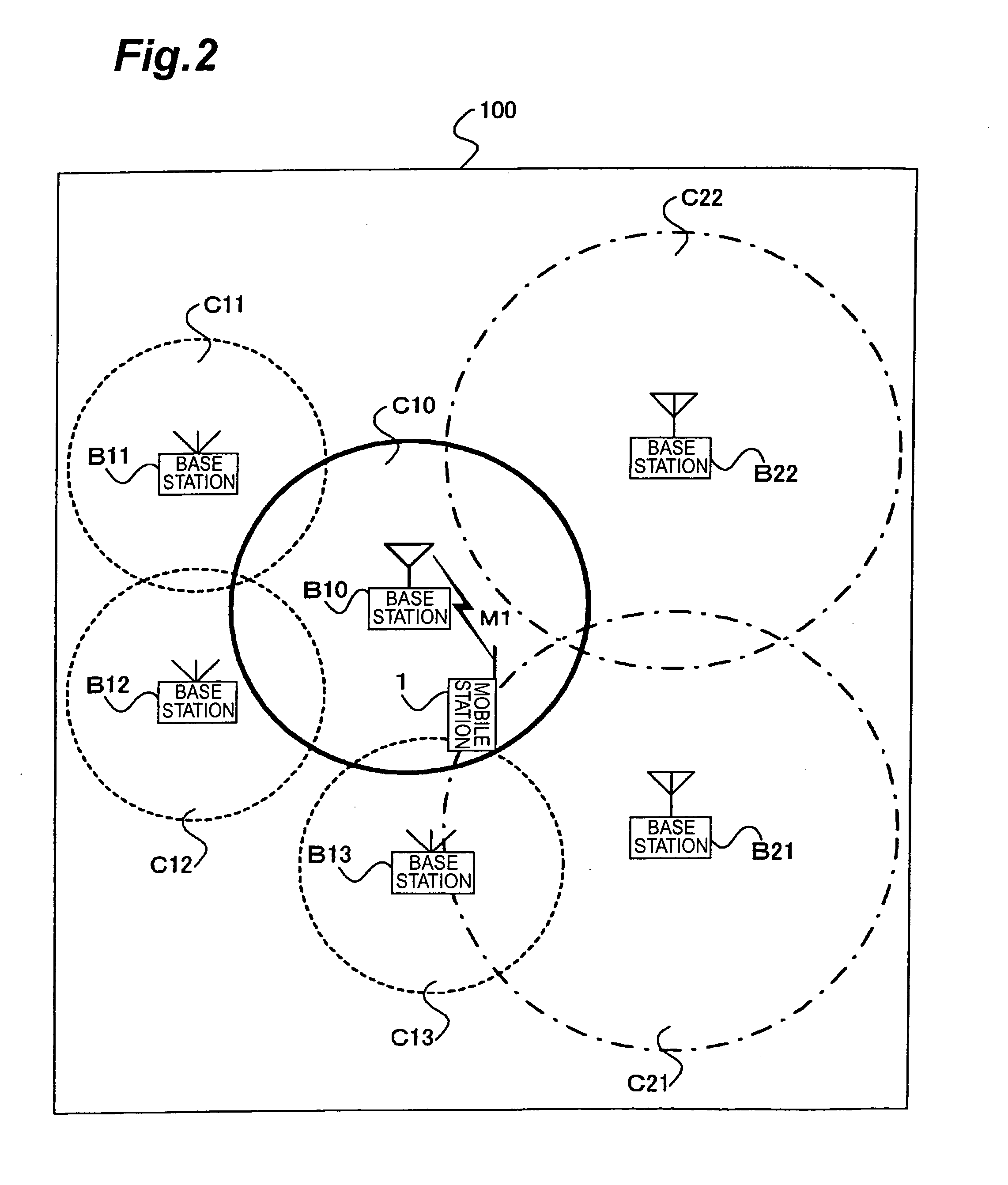
In mobile communication system 100 according to the present invention, mobile station 1 is camped on cell C10 established by base station B10. In the cell C10, there exist indoor cells C11-C13 and outdoor cells C21, C22 as neighboring cells. Mobile station 1 measures received levels of cells C10-C13, C21, C22 and determines cell types of the respective cells, i.e., whether each cell is an indoor cell or not, based on broadcast information M1. Mobile station 1 selects a cell as a reselection target on the basis of the received levels and cell types.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
System and method for providing closed subscriber groups in a packet-based wireless communication system
ActiveUS20100110945A1Save battery powerTimely controlAssess restrictionSubstation equipmentTransceiverCommunications system
Systems and methods for providing radio frequency transceiver user equipment in a packet based radio frequency signaling communication system are disclosed. User equipment is provided with closed subscriber group “CSG” capability including permanent storage for a CSG whitelist, the whitelist including identifiers of CSGs the user equipment is a member of. Base stations transmit signals including identifiers corresponding to CSGs the base station supports. The base station or cell selection process performed by the user equipment includes selecting cells that are part of the CSG whitelist. In additional embodiments, the user equipment includes user alterable storage for a user controlled CSG whitelist. The user alterable storage may further be partitioned into permanent and temporary portions. In an exemplary method, the user controls the cell selection process using the CSG whitelist information stored in the user equipment. Methods for managing the CSG whitelist are described.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
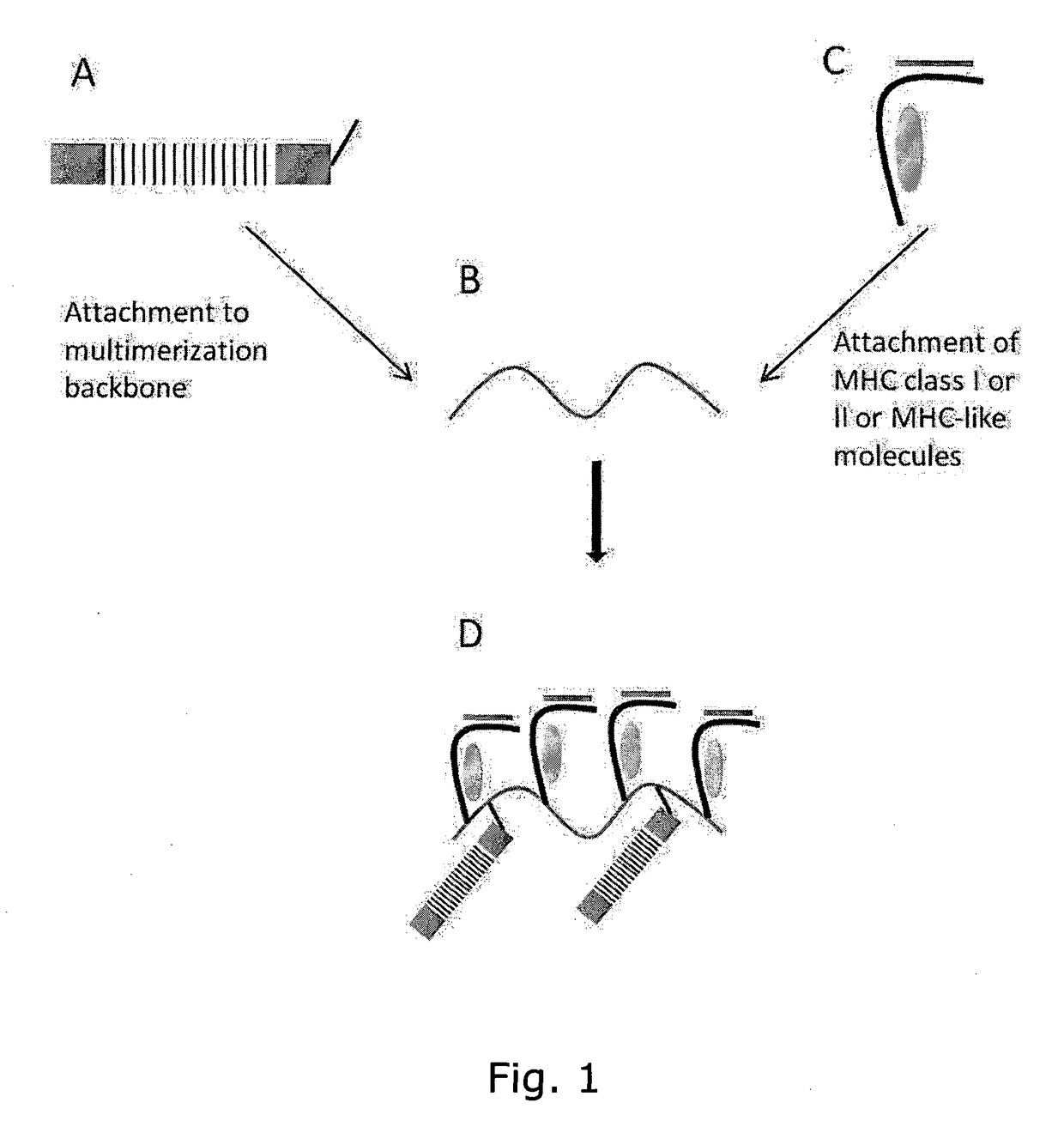
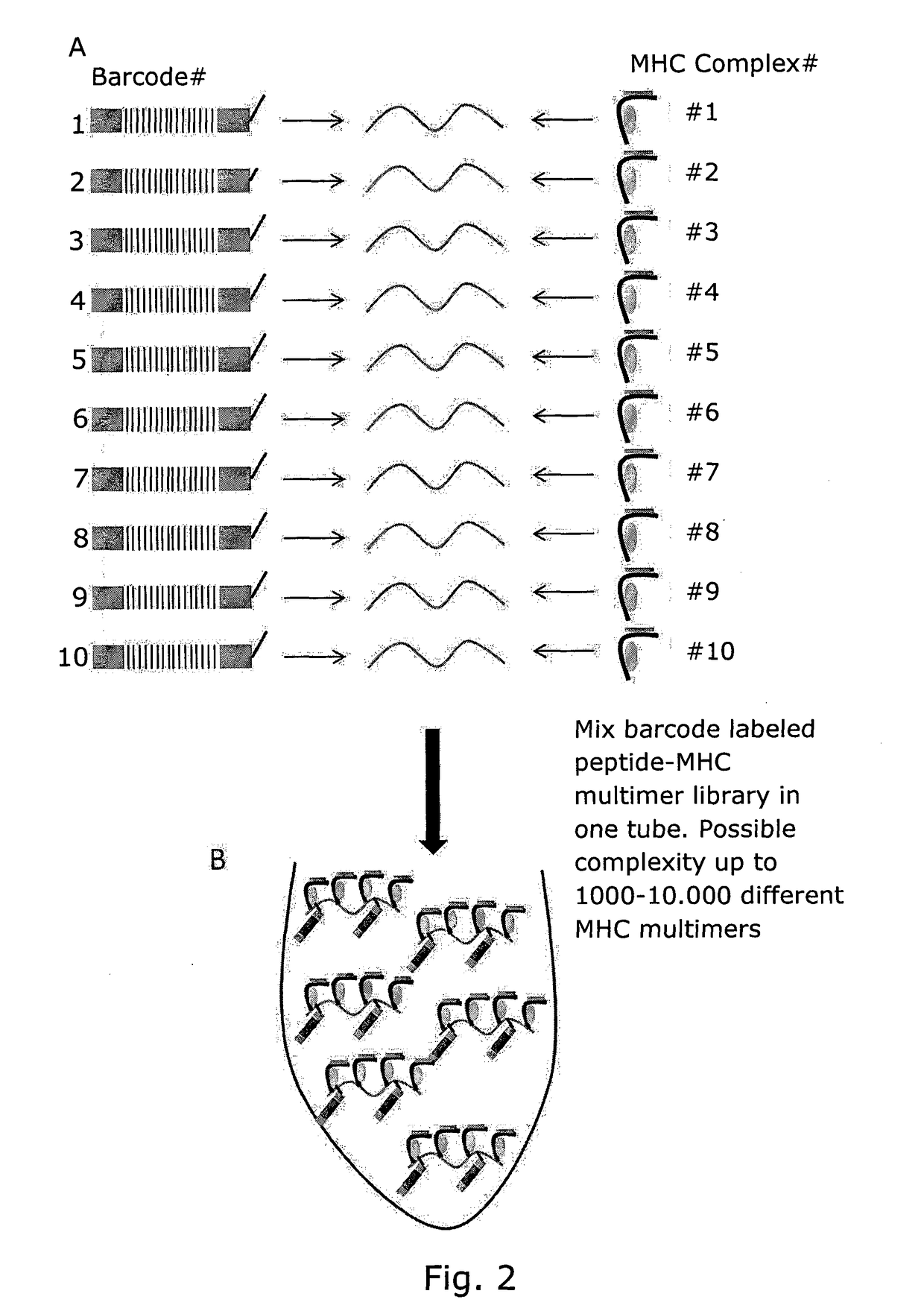
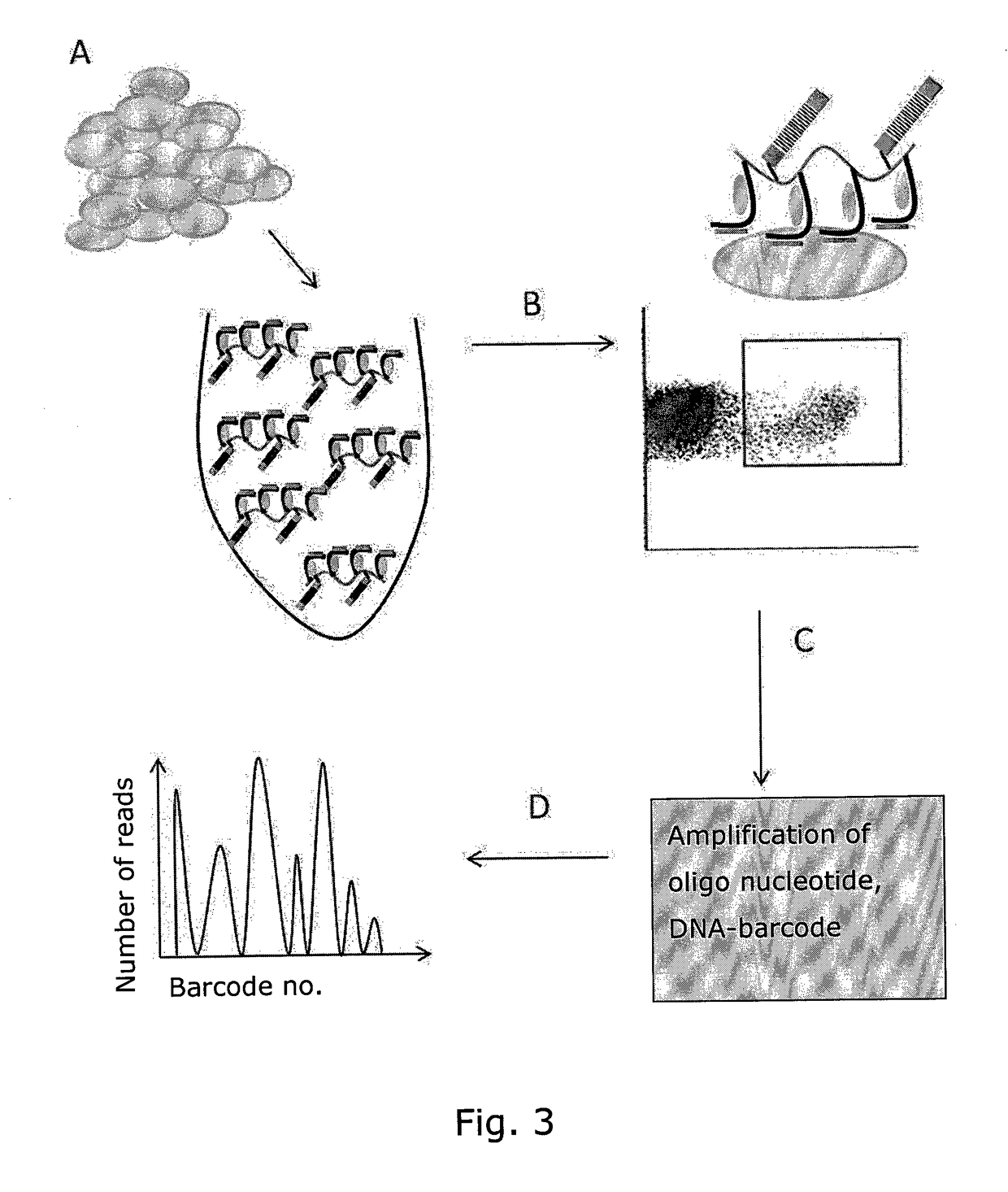
Determining Antigen Recognition through Barcoding of MHC Multimers
PendingUS20170343545A1Improve understandingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSingle sampleVaccination
The present invention describes the use of nucleic acid barcodes as specific labels for MHC multimers to determine the antigen responsiveness in biological samples. After cellular selection the barcode sequence will be revealed by sequencing. This technology allows for detection of multiple (potentially >1000) different antigen-specific cells in a single sample. The technology can be used for T-cell epitope mapping, immune-recognition discovery, diagnostics tests and measuring immune reactivity after vaccination or immune-related therapies.
Owner:IMMUDEX APS +1
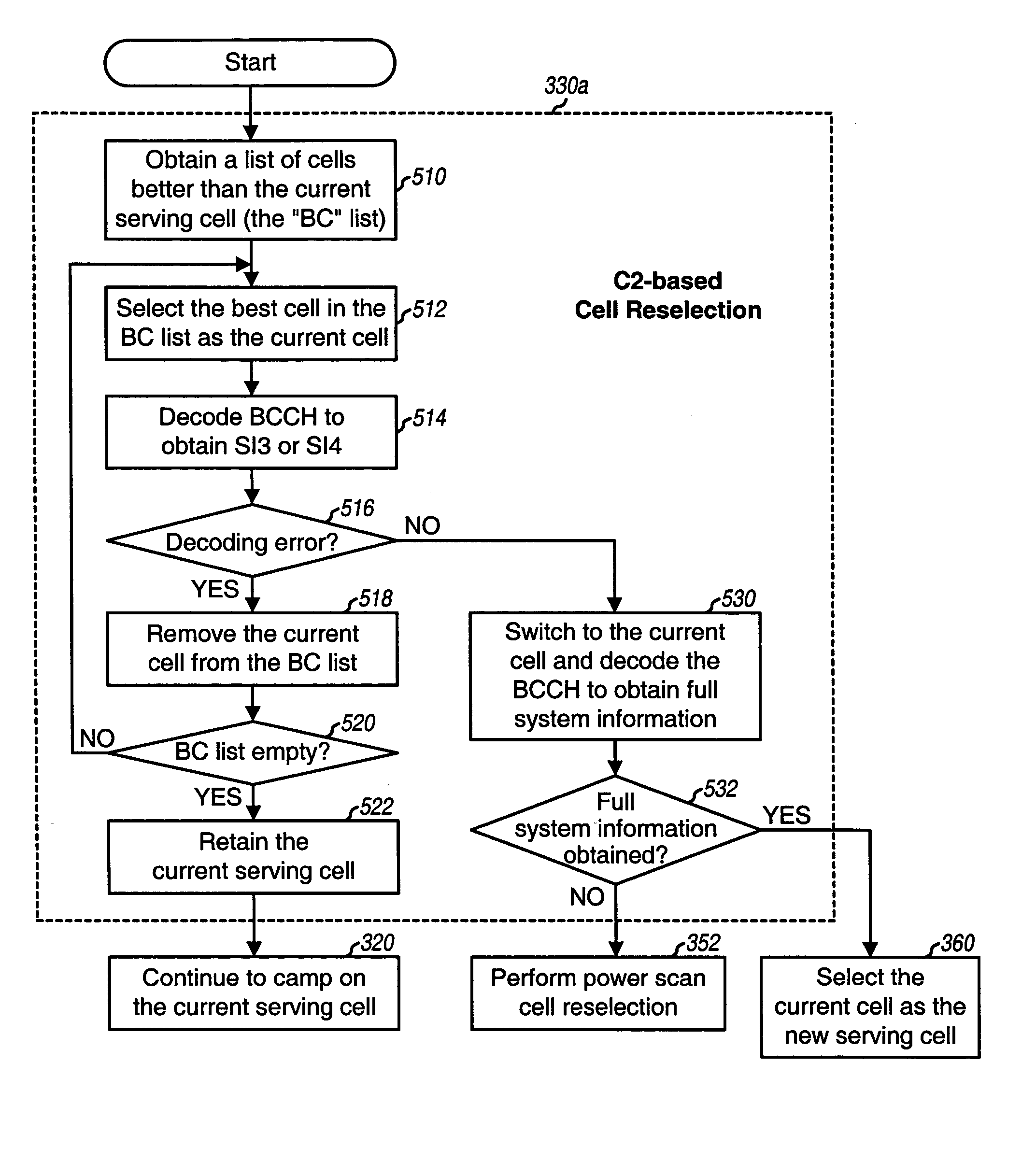
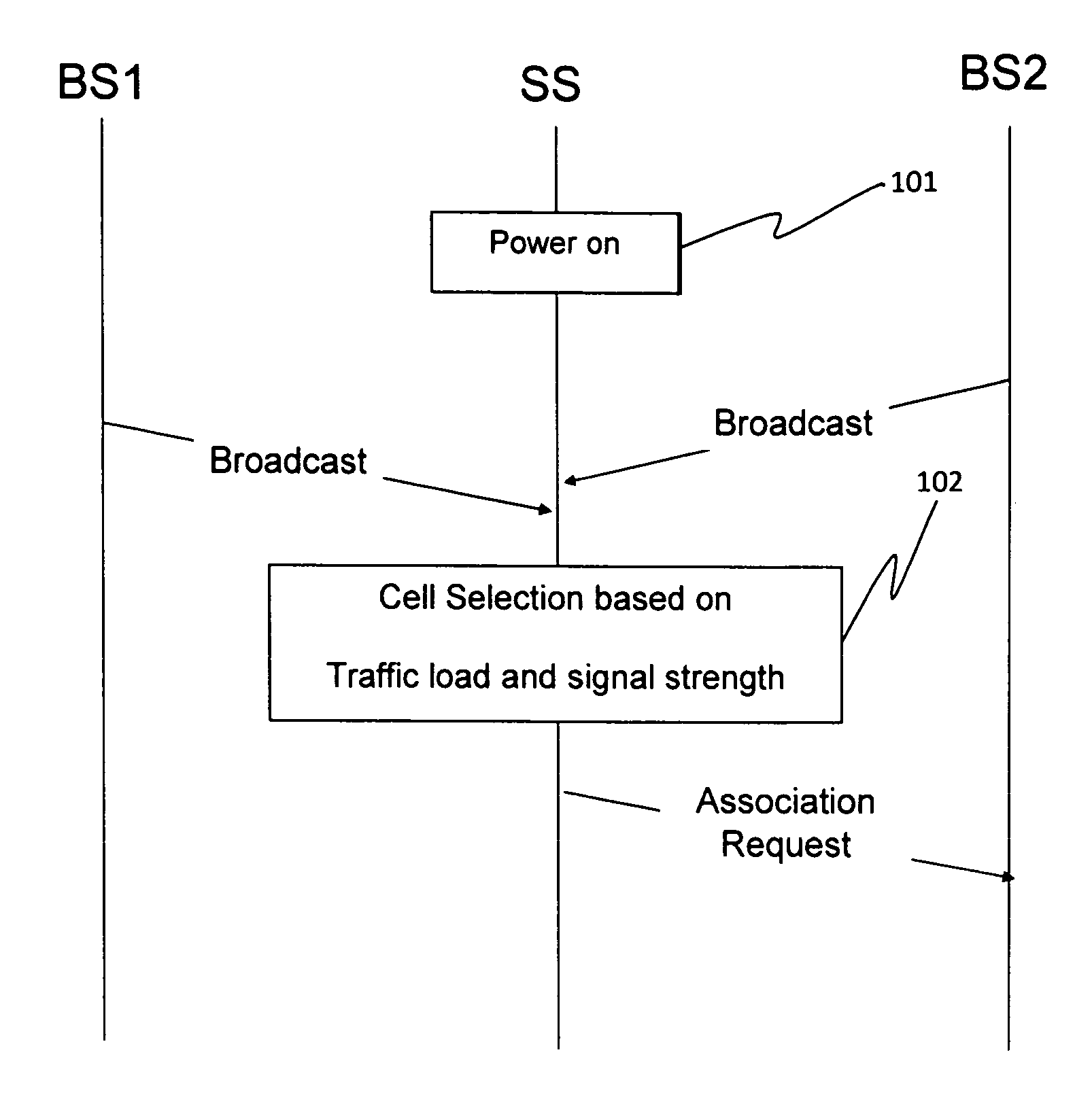
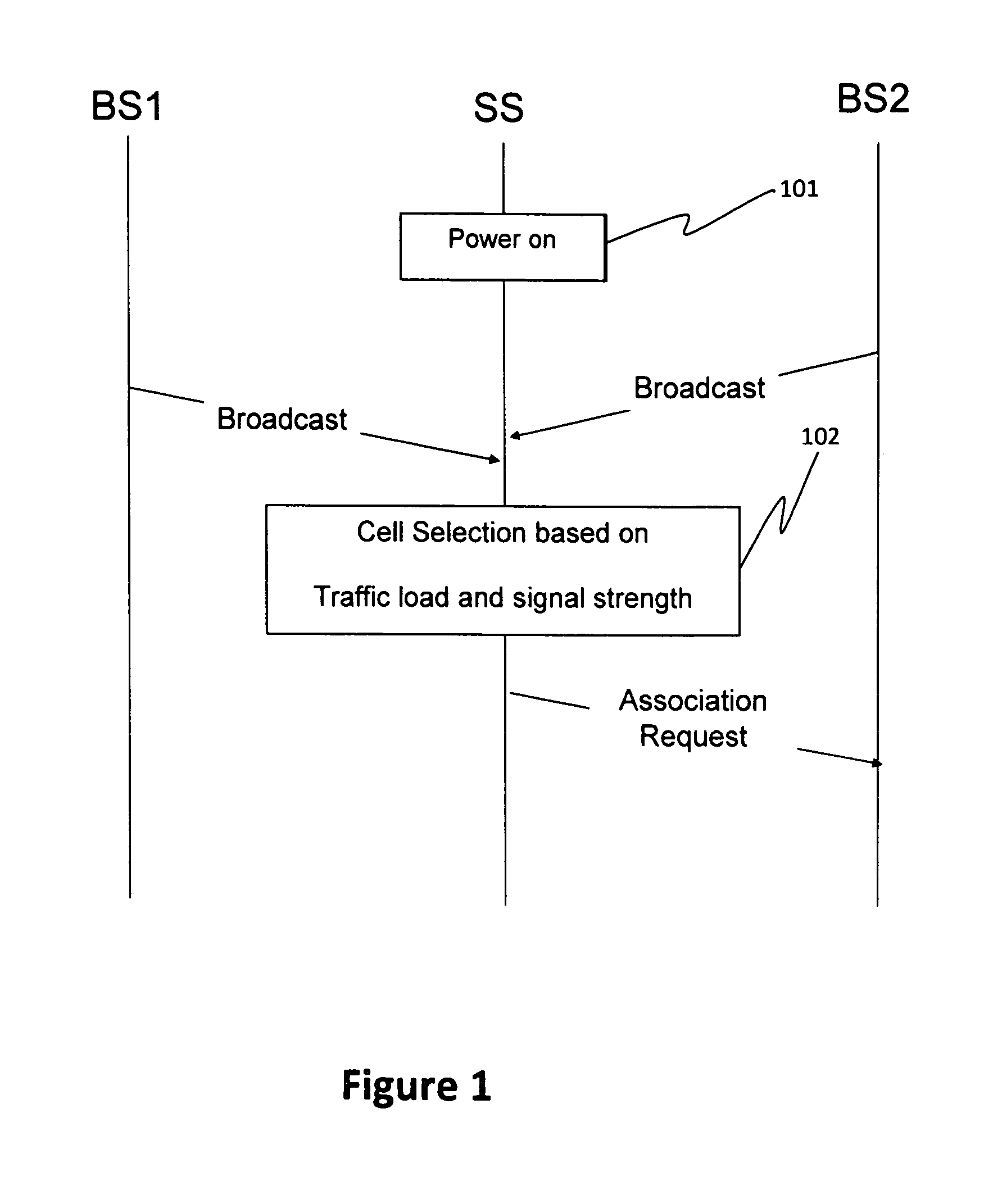
Cell reselection with power scan and parallel decoding
ActiveUS20050079870A1Reduce downtimeImprove performanceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionCell selectionComputer science
Upon power on, a terminal performs cell selection, finds the most suitable cell to receive communication service, and camps on this cell (the serving cell). The terminal thereafter performs “C2-based” cell reselection if a better cell is found, “non-C2 based” cell reselection if the current serving cell cannot be camped on, “power scan” cell reselection if the C2-based or non-C2 based cell reselection fails, and cell selection if the power scan cell reselection fails. For the power scan cell reselection, the terminal initially performs a power scan and obtains received signal strength measurements for a list of RF channels. This list includes fewer than all RF channels evaluated by the cell selection. The terminal then acquires and decodes the N strongest RF channels, preferably in parallel, to find a suitable cell. The terminal selects a suitable cell, if found, with the highest C2 value as the new serving cell from which to receive service.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
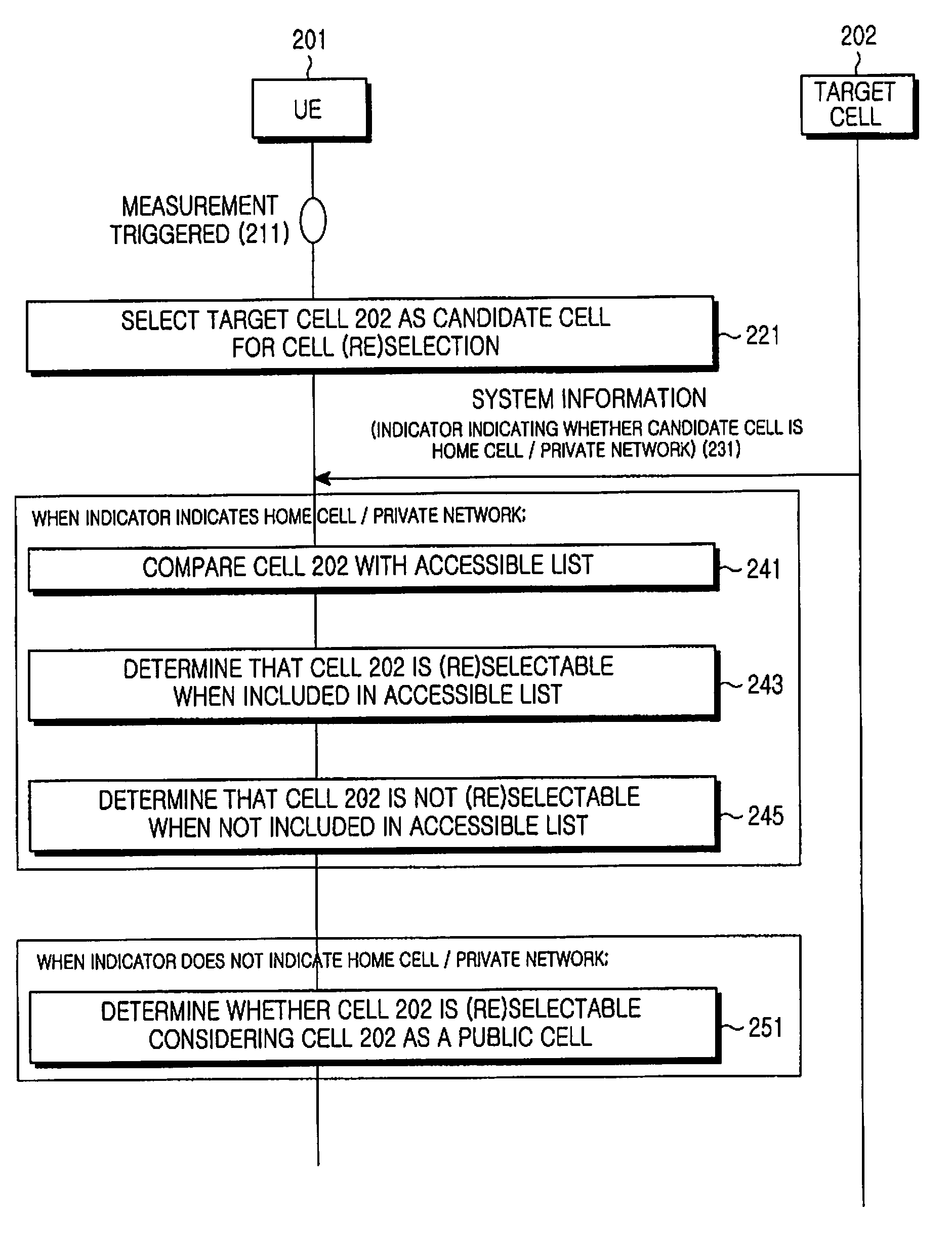
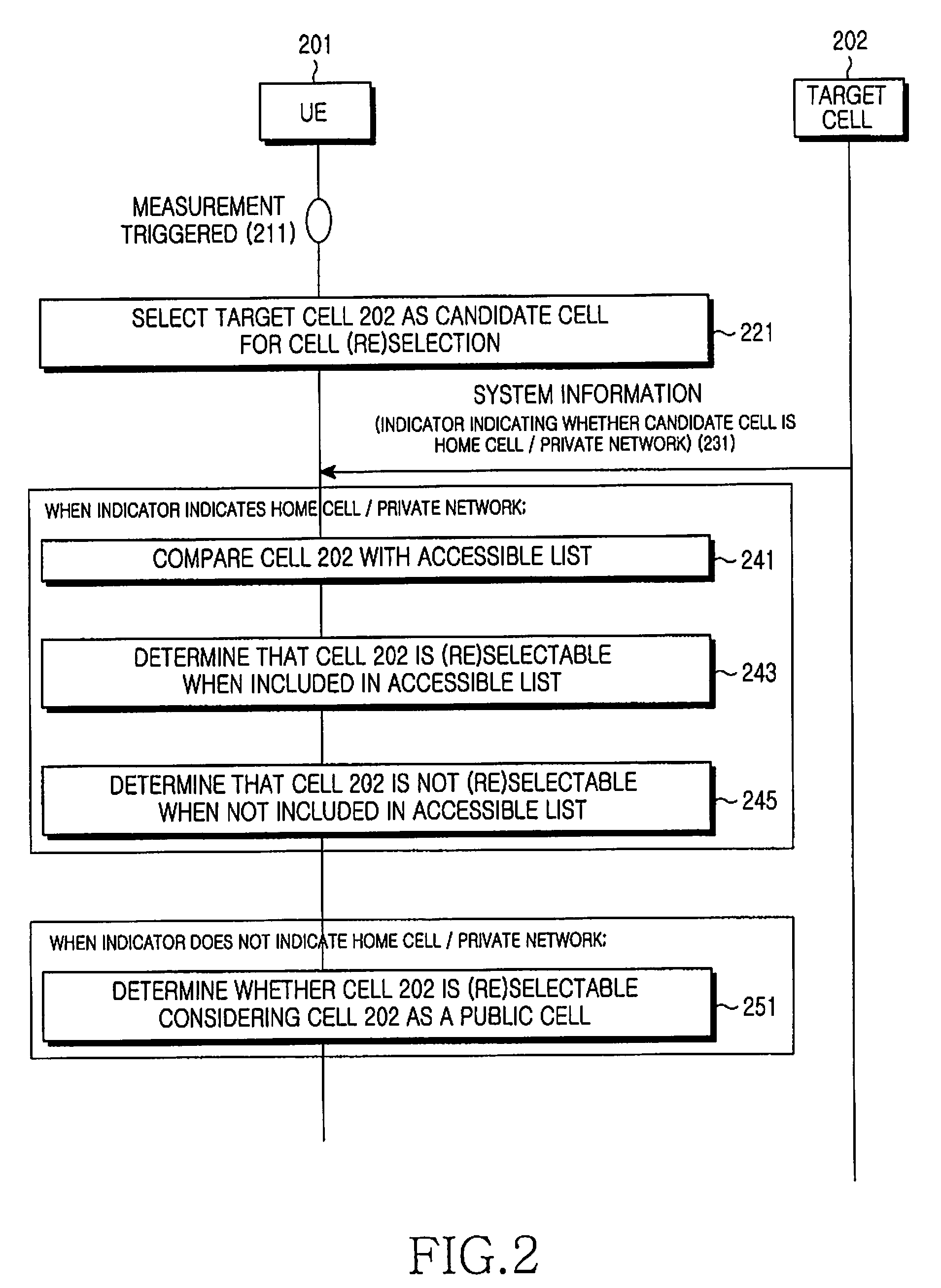
Apparatus and method for performing cell selection to home cell or private network in a mobile communication system
An apparatus and method for performing cell selection to a Home cell or a Private network in a mobile communication system are provided, in which a User Equipment (UE) determines a candidate cell by measuring a serving cell and neighbor cells, receives an indicator indicating a Home cell or a Private network in system information from the candidate cell, determines whether the candidate cell is included in a Home cell or Private network list set in the UE, and selects the candidate cell if the candidate cell is included in the Home cell or Private network list.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Nram bit selectable two-device nanotube array
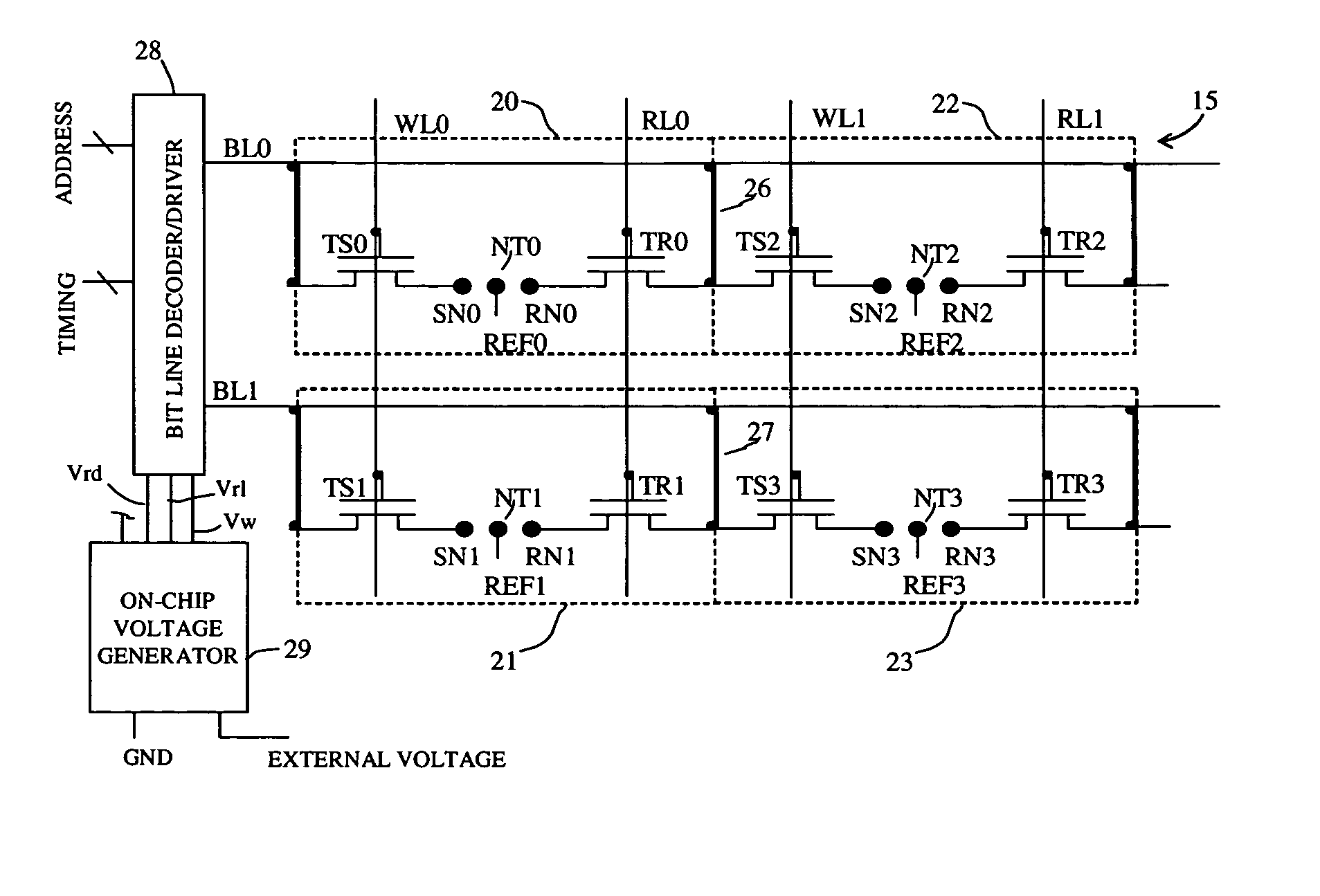
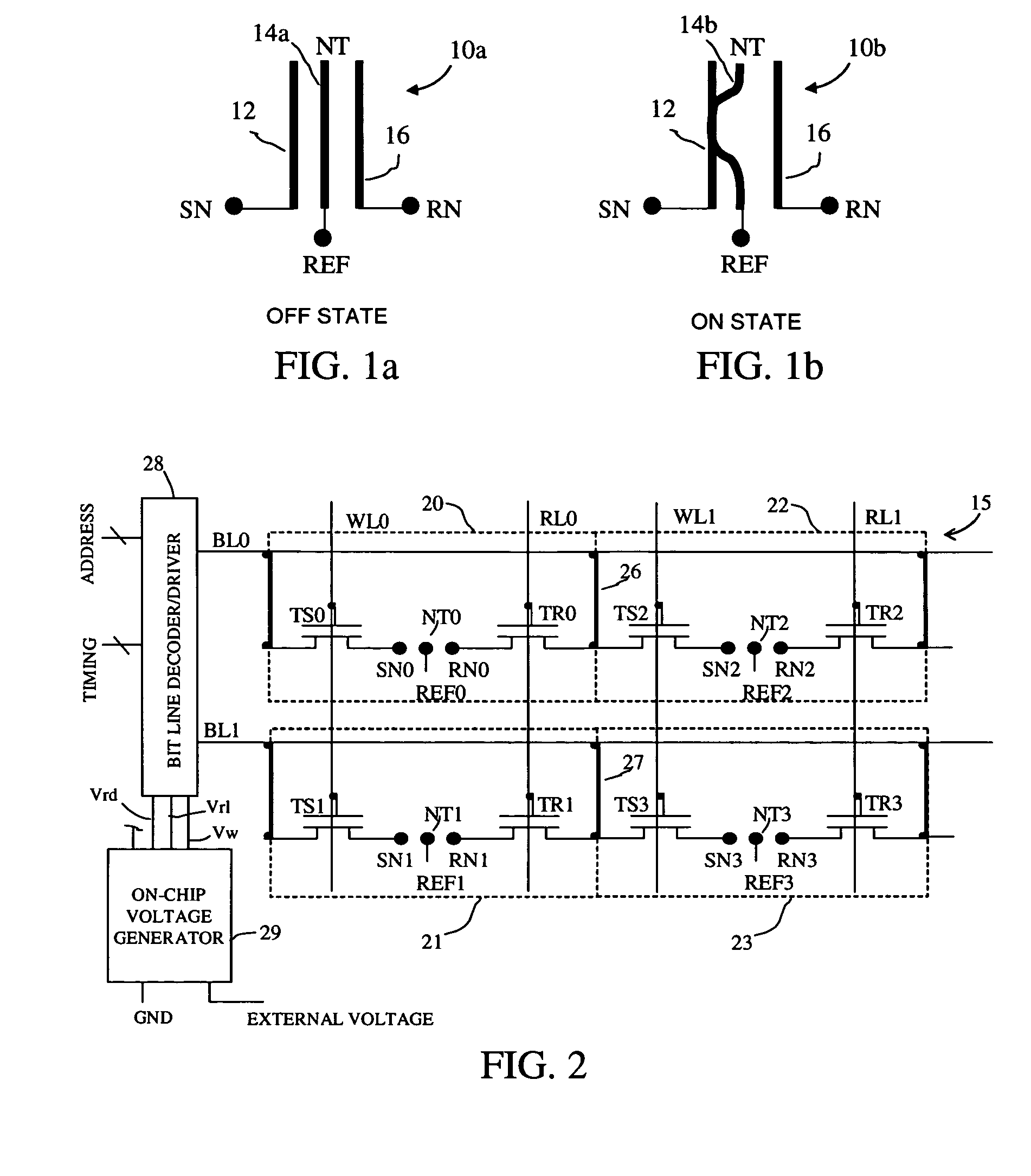
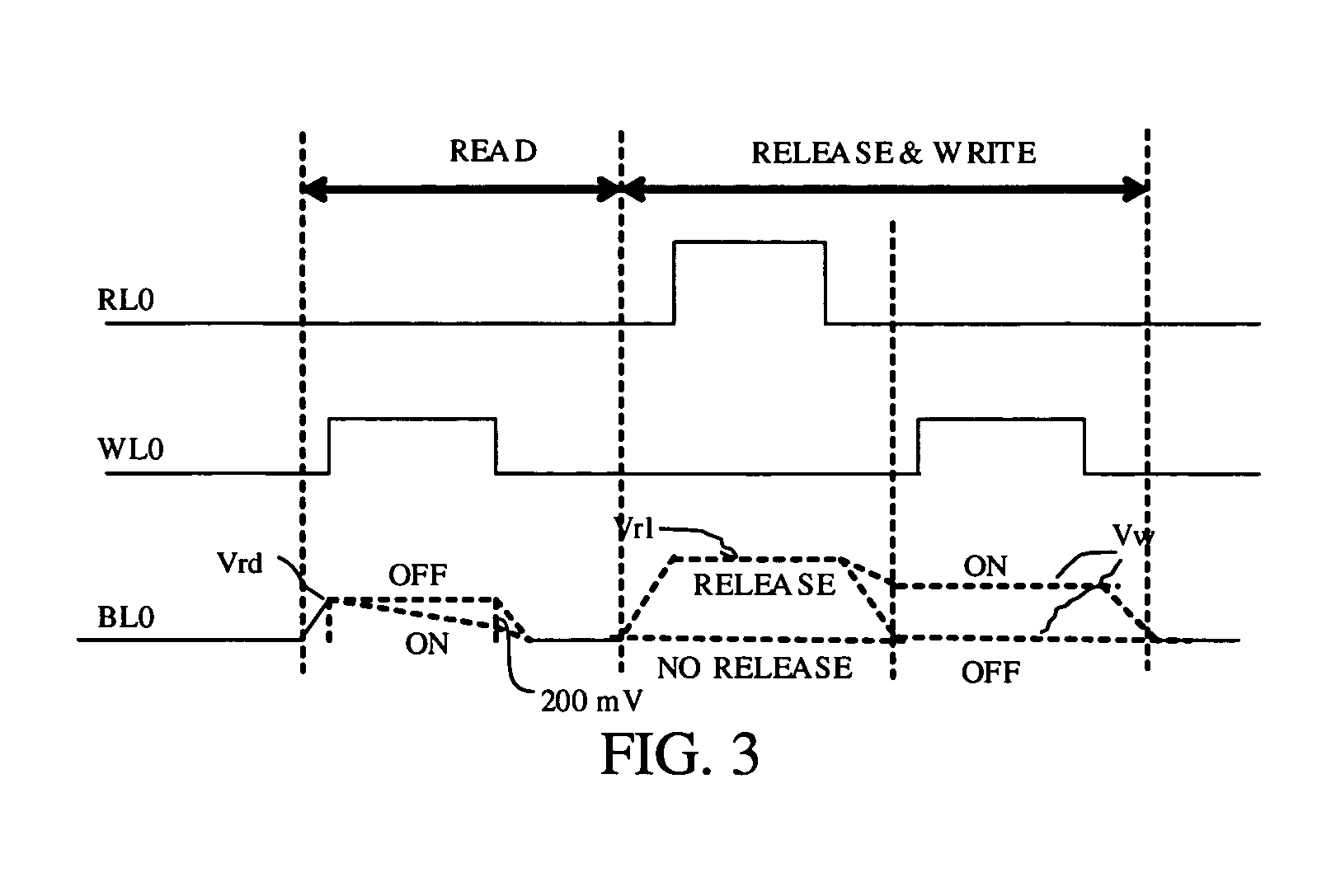
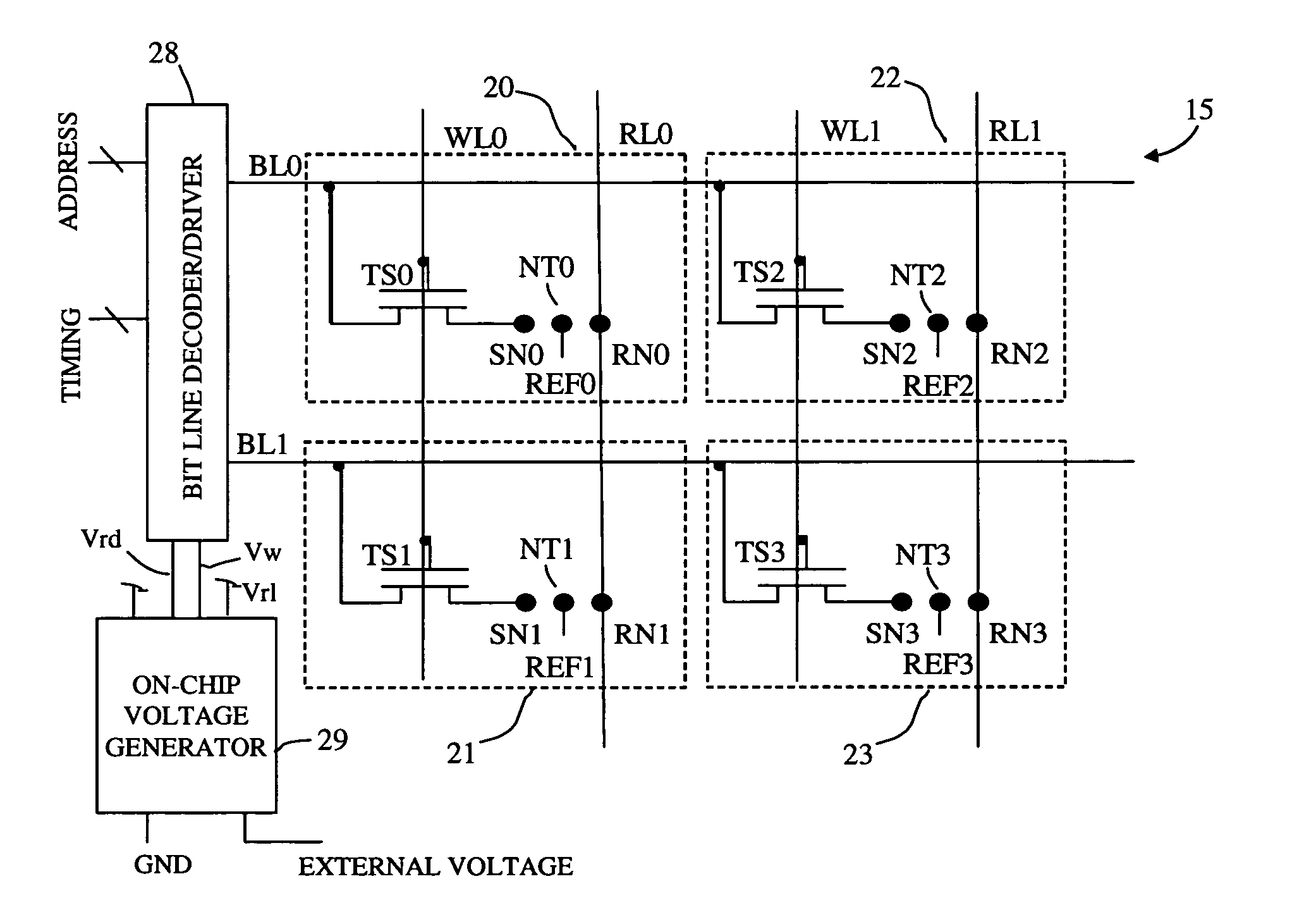
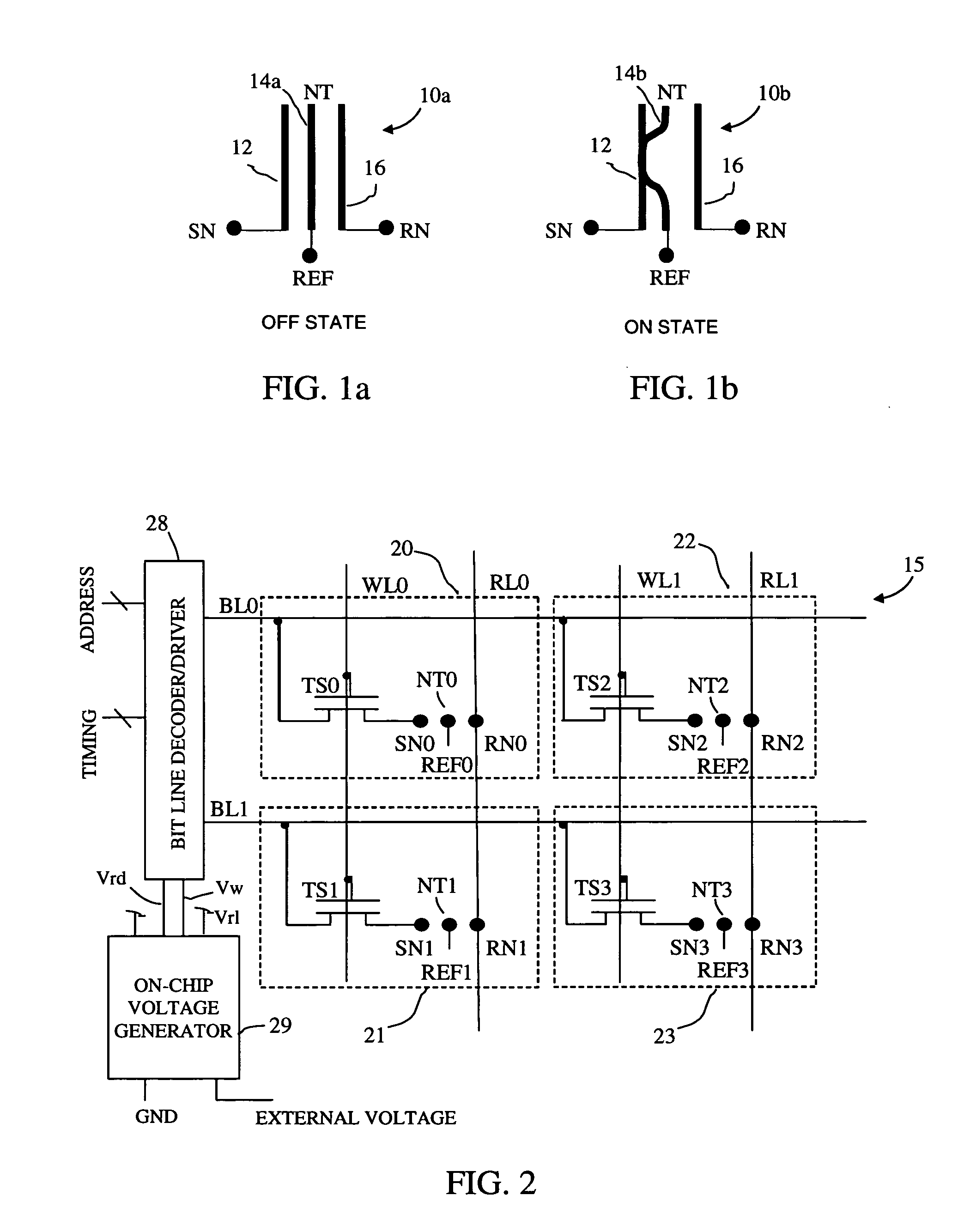
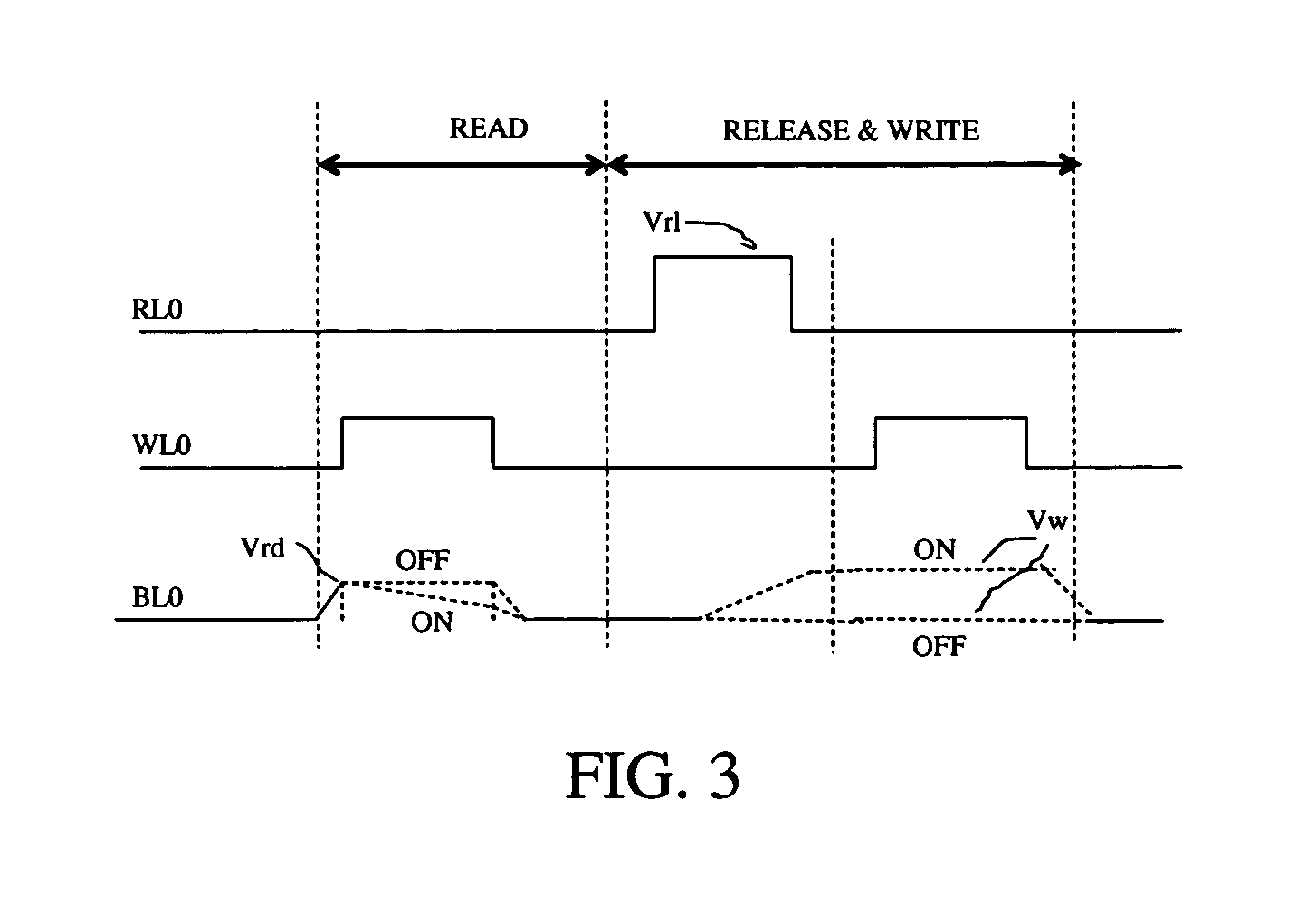
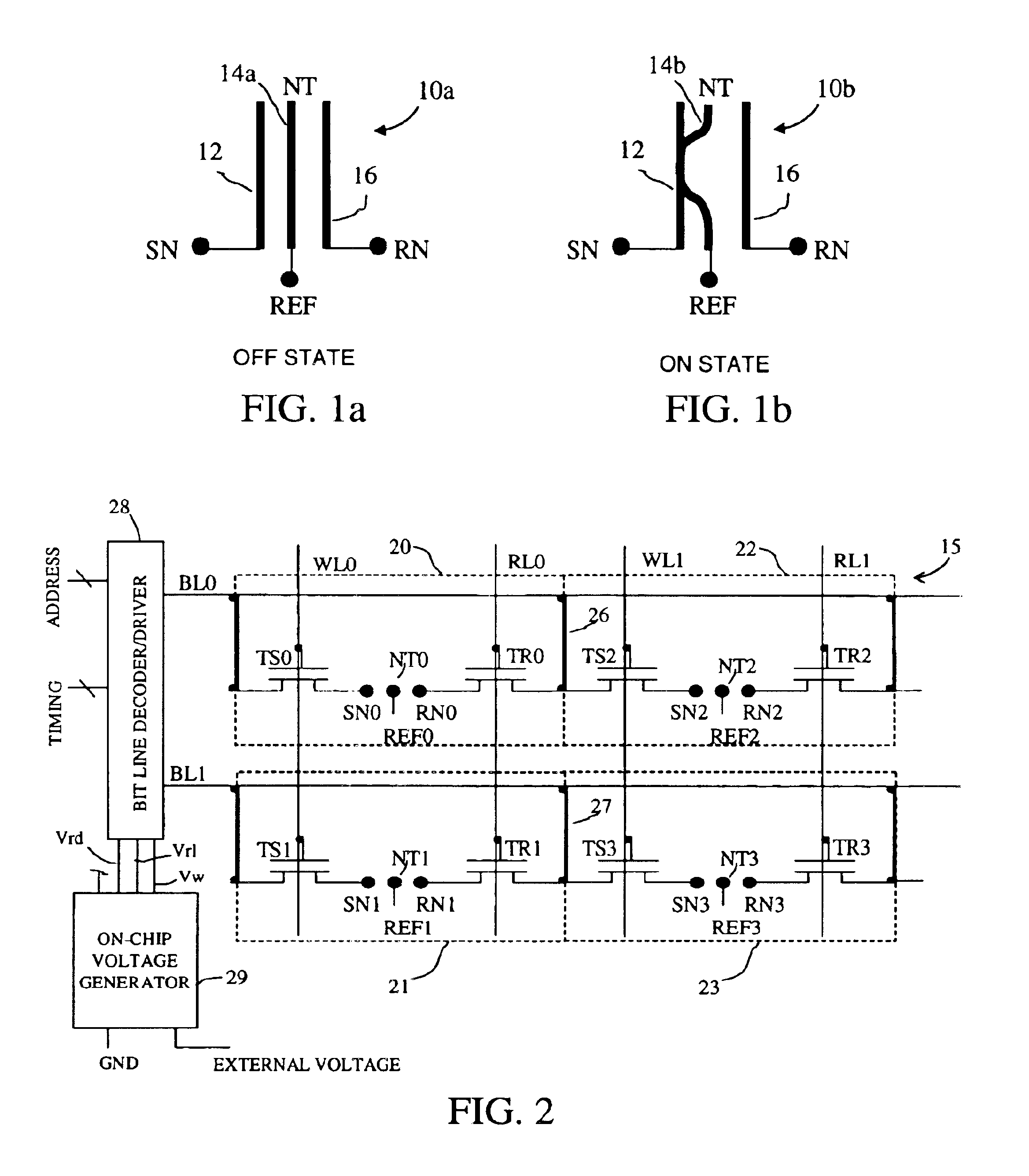
A non-volatile memory array includes a plurality of memory cells, each cell receiving a bit line, word line, and release line. Each memory cell includes a cell selection transistor and a restore transistor with first, second and third nodes. Each cell further includes an electromechanically deflectable switch, the position of which manifests the logical state of the cell. Each cell is bit selectable for read and write operations.
Owner:NANTERO
Non-volatile RAM cell and array using nanotube switch position for information state
Non-Volatile RAM Cell and Array using Nanotube Switch Position for Information State. A non-volatile memory array includes a plurality of memory cells, each cell receiving a bit line, word line, and release line. Each memory cell includes a cell selection transistor with first, second and third nodes. The first and second nodes are in respective electrical communication with the bit line and the word line. Each cell further includes an electromechanically deflectable switch, having a first, second and third node. The first node is in electrical communication with the release line, and a third node is in electrical communication with the third node of the cell selection transistor. The electromechanically deflectable switch includes a nanotube switching element physically positioned between the first and third nodes of the switch and in electrical communication with the second node of the switch. The second node of the switch is in communication with a reference signal. Each nanotube switching element is deflectable into contact with the third node of the switch in response to signals at the first and second node of the cell selection transistor and is releasable from such contact in response to a signal at the release line. In preferred embodiments, the cell selection transistor is a FET and the second node of the transistor is a gate of the FET.
Owner:NANTERO
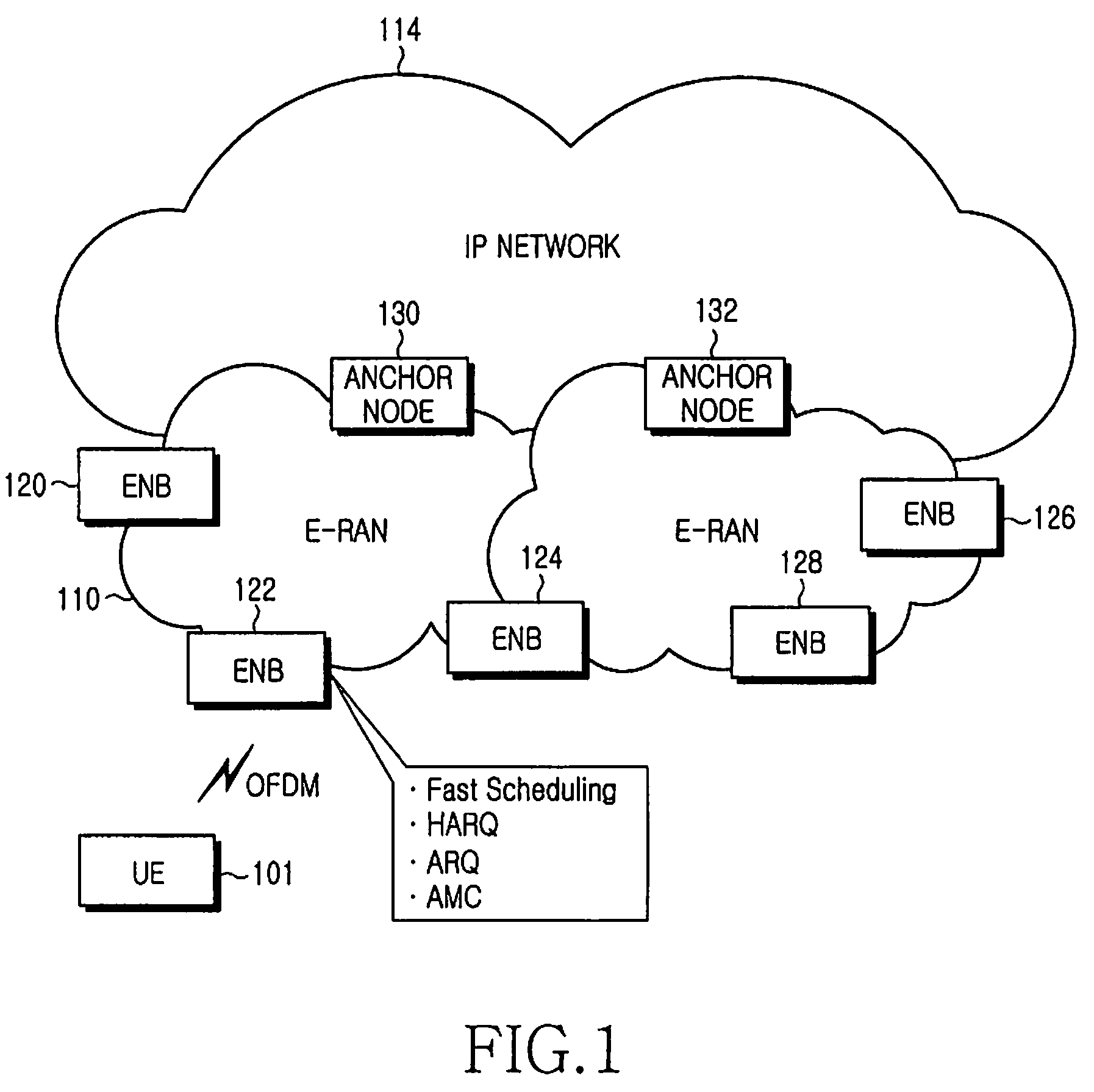
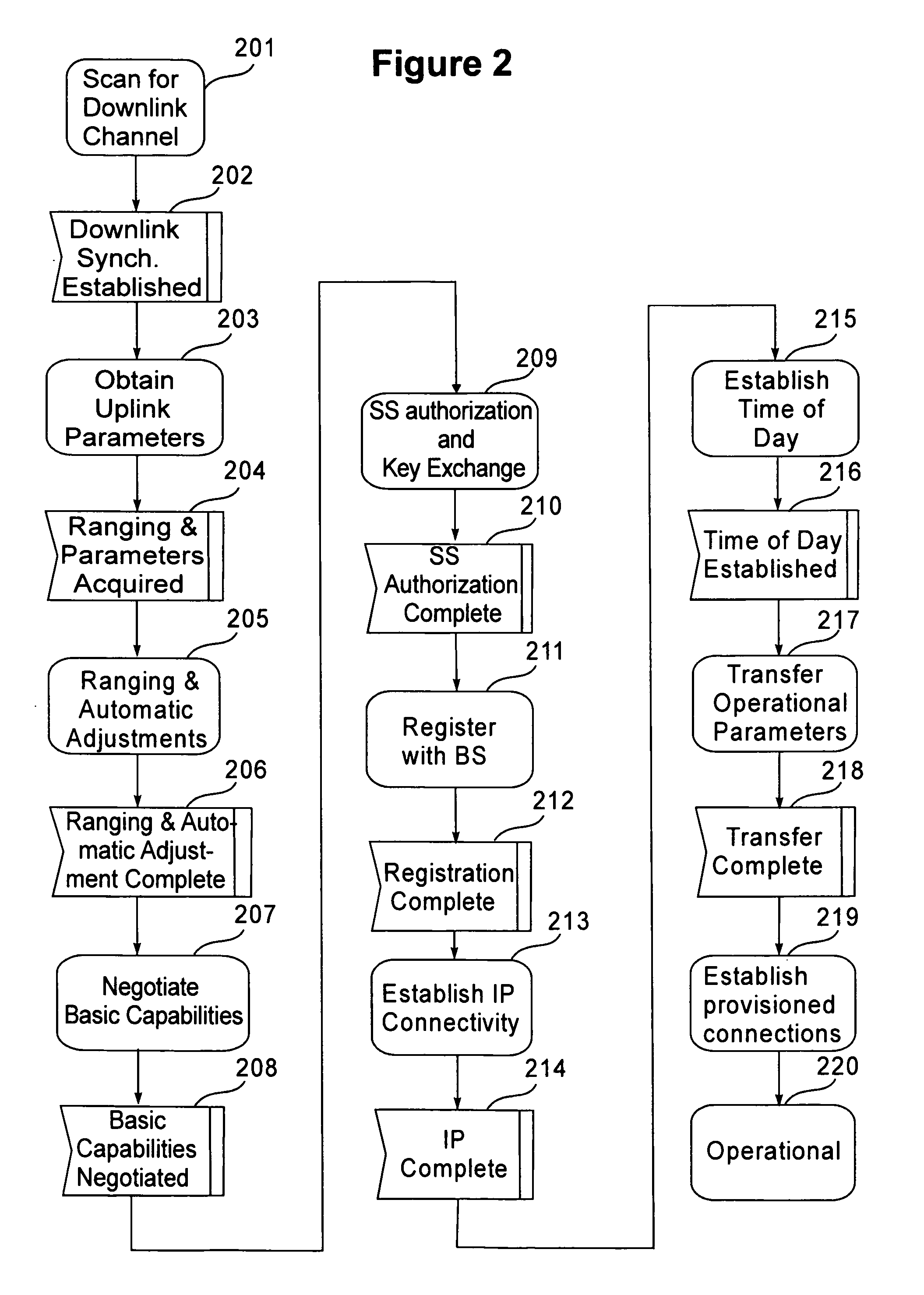
Method and apparatus for cell reselection enhancement for e-utran
InactiveUS20090067386A1Easy to determineFacilitate selection of cellAssess restrictionOrthogonal multiplexRelevant informationTelecommunications
A framework for the cell reselection and associated measurement behavior is proposed based on a state in which a UE is camped on the cell. If the UE is ‘camped in any cell state’, inter-frequency and / or inter-RAT measurements are prioritized over intra-frequency measurements. The proposed scheme helps the UE to find a suitable cell while in the camped on any cell state. If the UE subscribes to specific frequencies, separate measurement rules are implemented to aid the UE to find and camp on the preferred frequencies. The proposed scheme also considers access related information in addition to radio quality to help the UE in making cell selections thereby mitigating the UE from camping on restricted cells. Such aspects minimize situations wherein users are limited due to the service provided by an operator.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
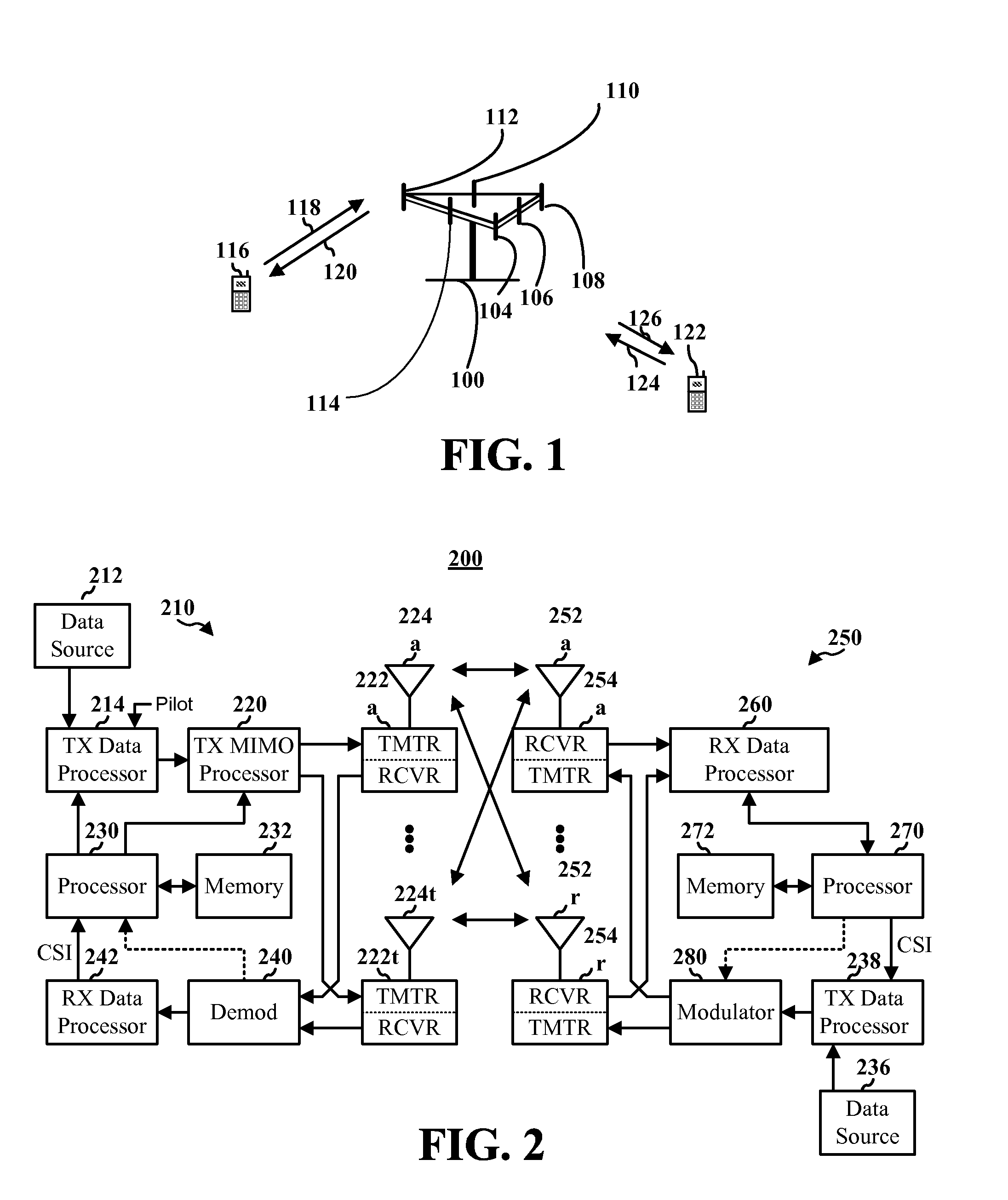
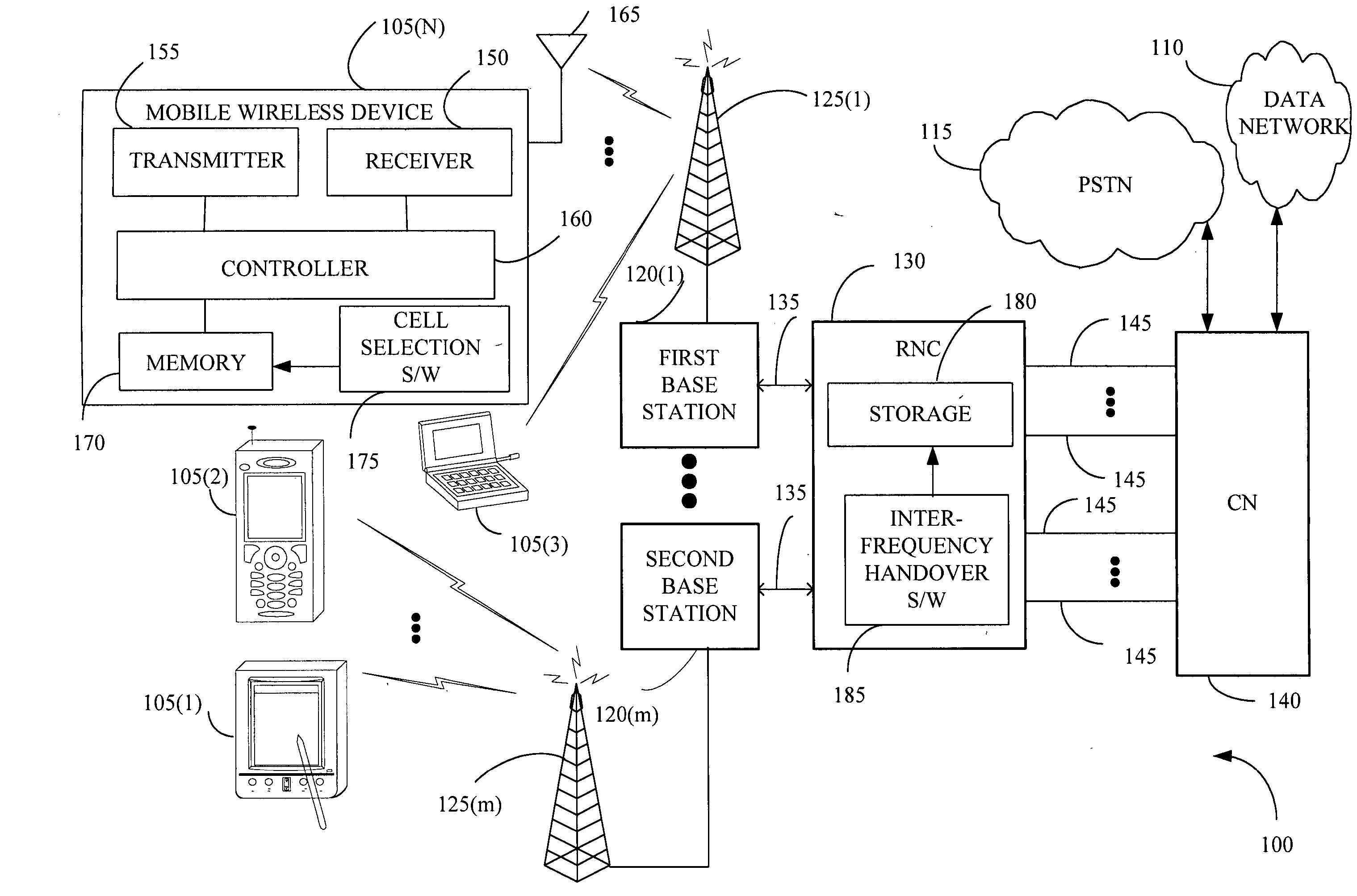
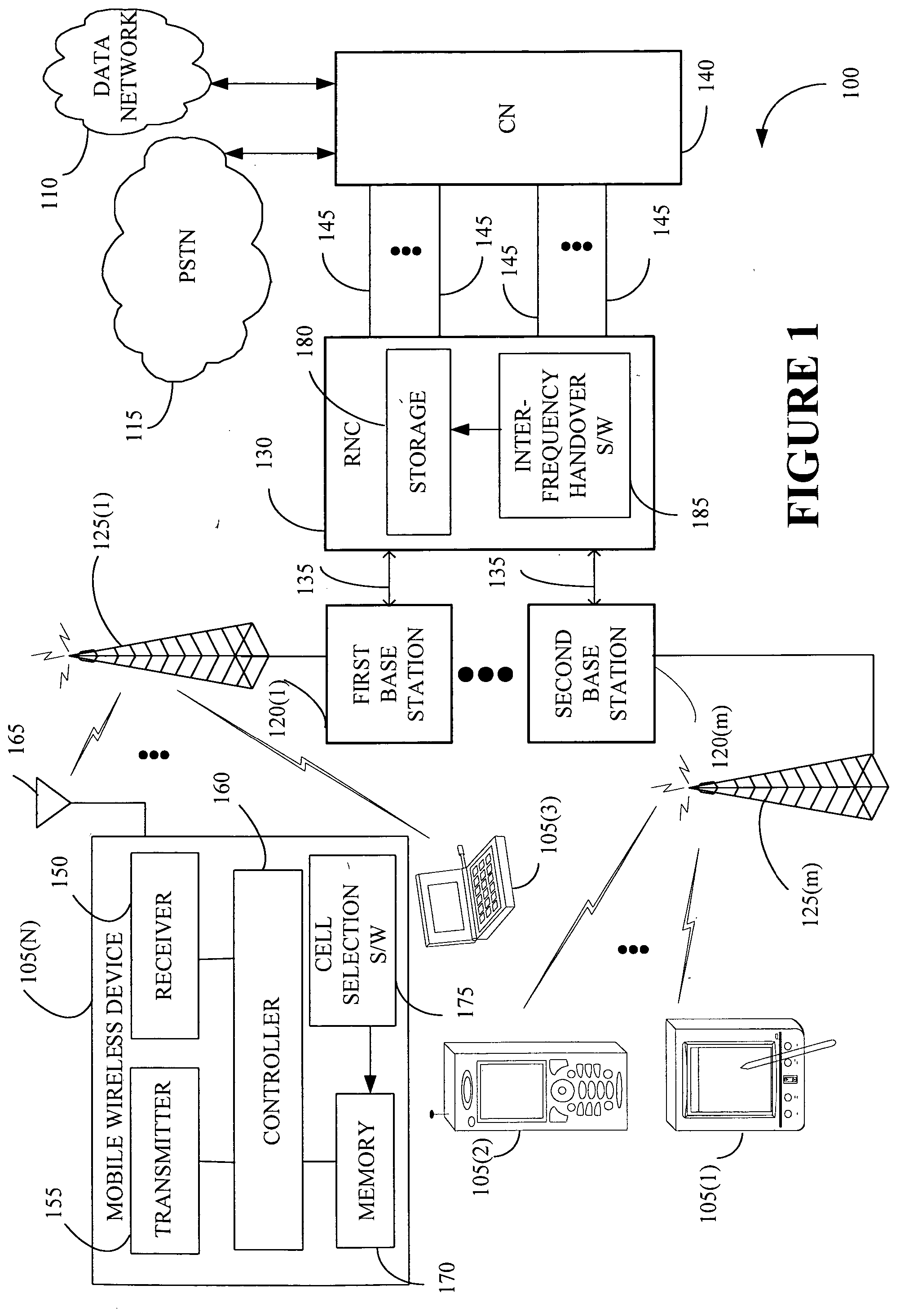
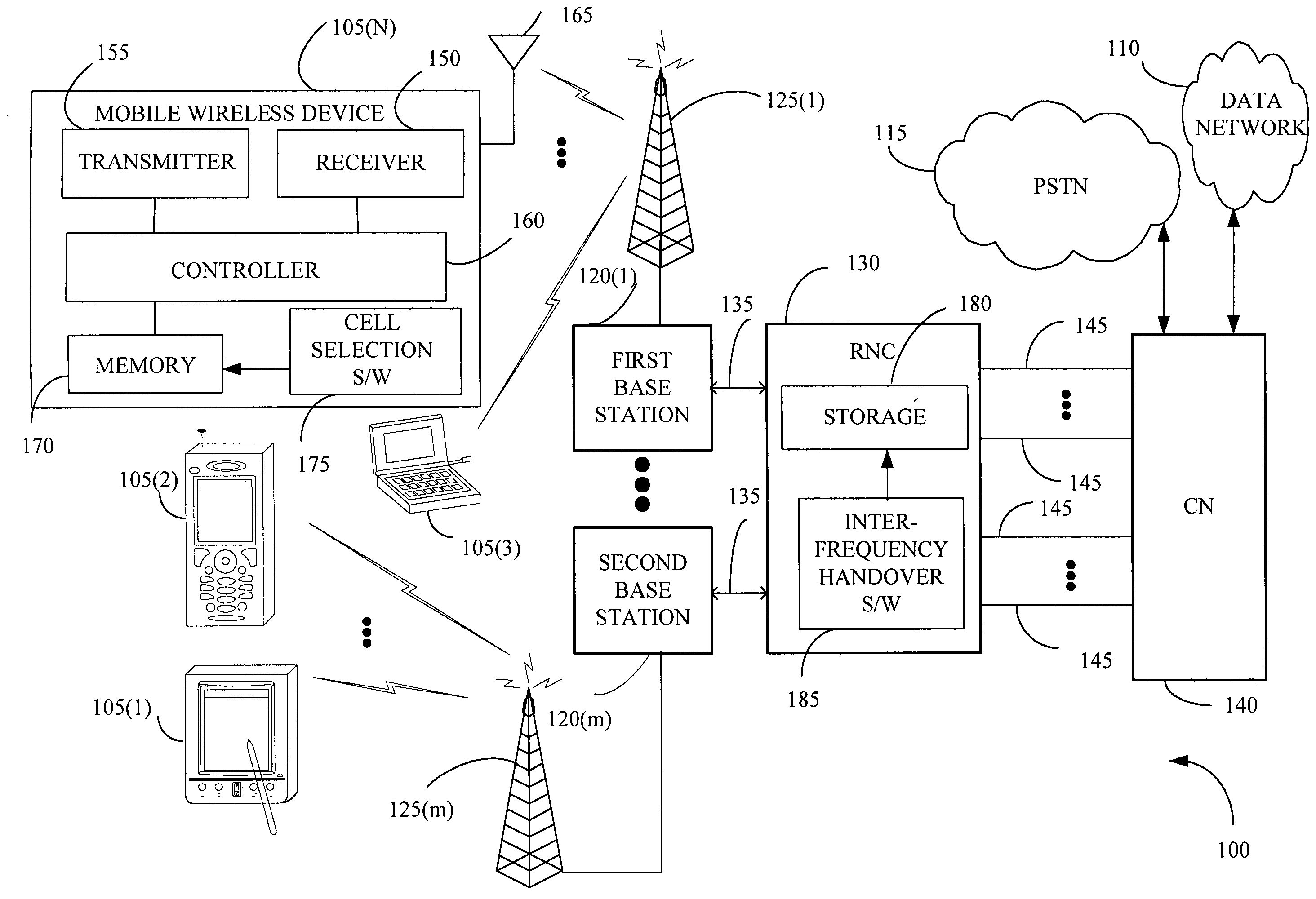
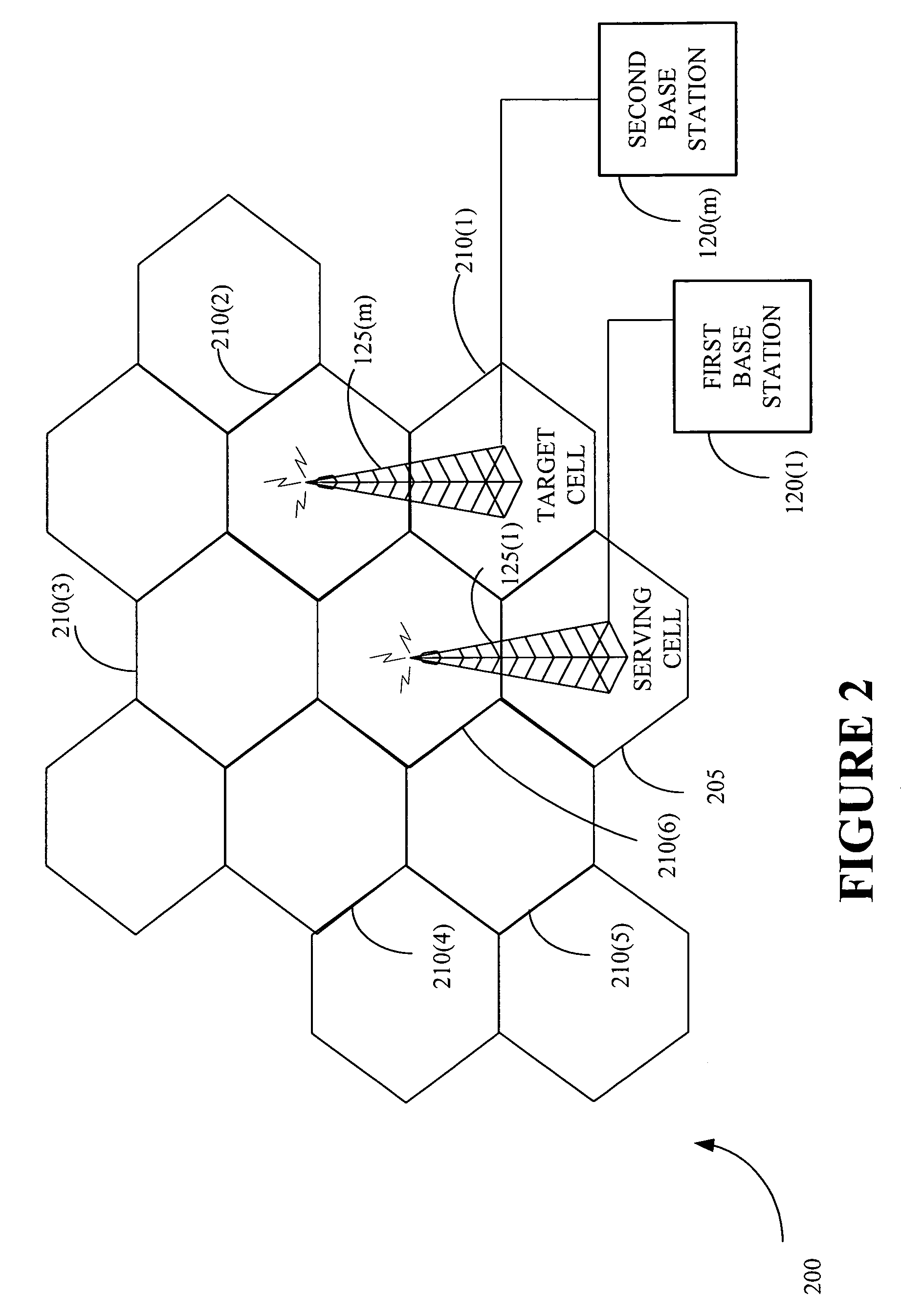
Cell selection and inter-frequency handover
InactiveUS20060142032A1Emission reductionEnergy efficient ICTTime-division multiplexElectromagnetic exposureControl communications
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for controlling a communications system that includes a mobile wireless device, a first and a second base station and a radio network controller. The communications system may allocate frequency bands to users on a multiplicity of channels associated with a multi-layer access network across at least two cells communicatively coupled to a first and a second base station, respectively. The method comprises monitoring a radio emission parameter associated with the first and second base stations that communicate with the mobile wireless device. A radio emission parameter associated with the first and second base stations, such as signal strength or quality, is monitored, to select a target cell among a set of candidate cells for the mobile wireless device and to transfer the mobile wireless device from a first frequency band to a second frequency band. For example, radio resource management algorithms may cause emission-controlled cell selection and inter-frequency handover from a first frequency band to a second frequency band with a transmit power level lower than that of the first frequency band. In accordance with one aspect of the instant application, electromagnetic exposure to a user of the mobile wireless device is substantially decreased, resulting in lower energy costs and reduced environmental impacts.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Method for data rate selection in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS20020110101A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsOrthogonal multiplexCommunications systemCell selection
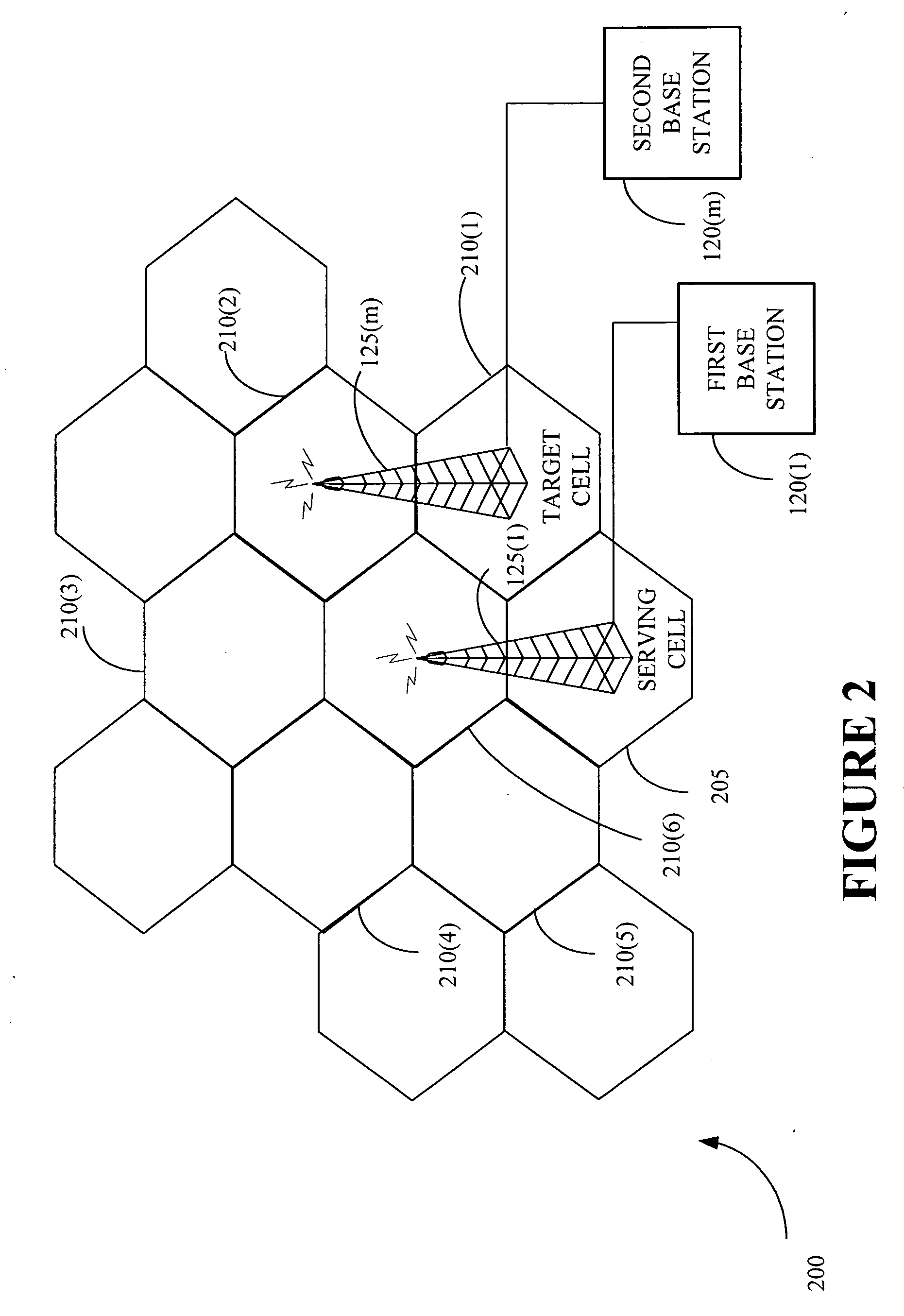
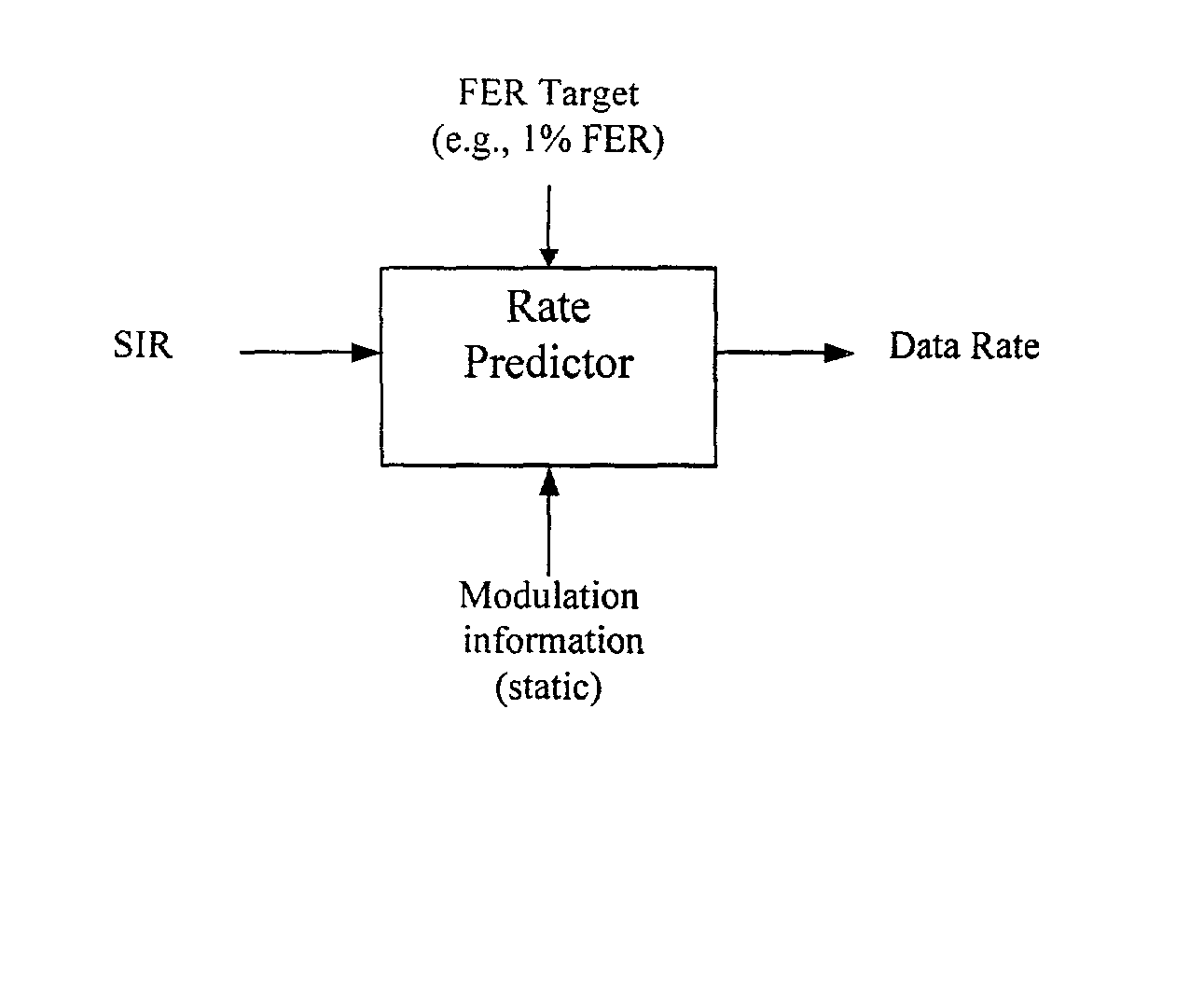
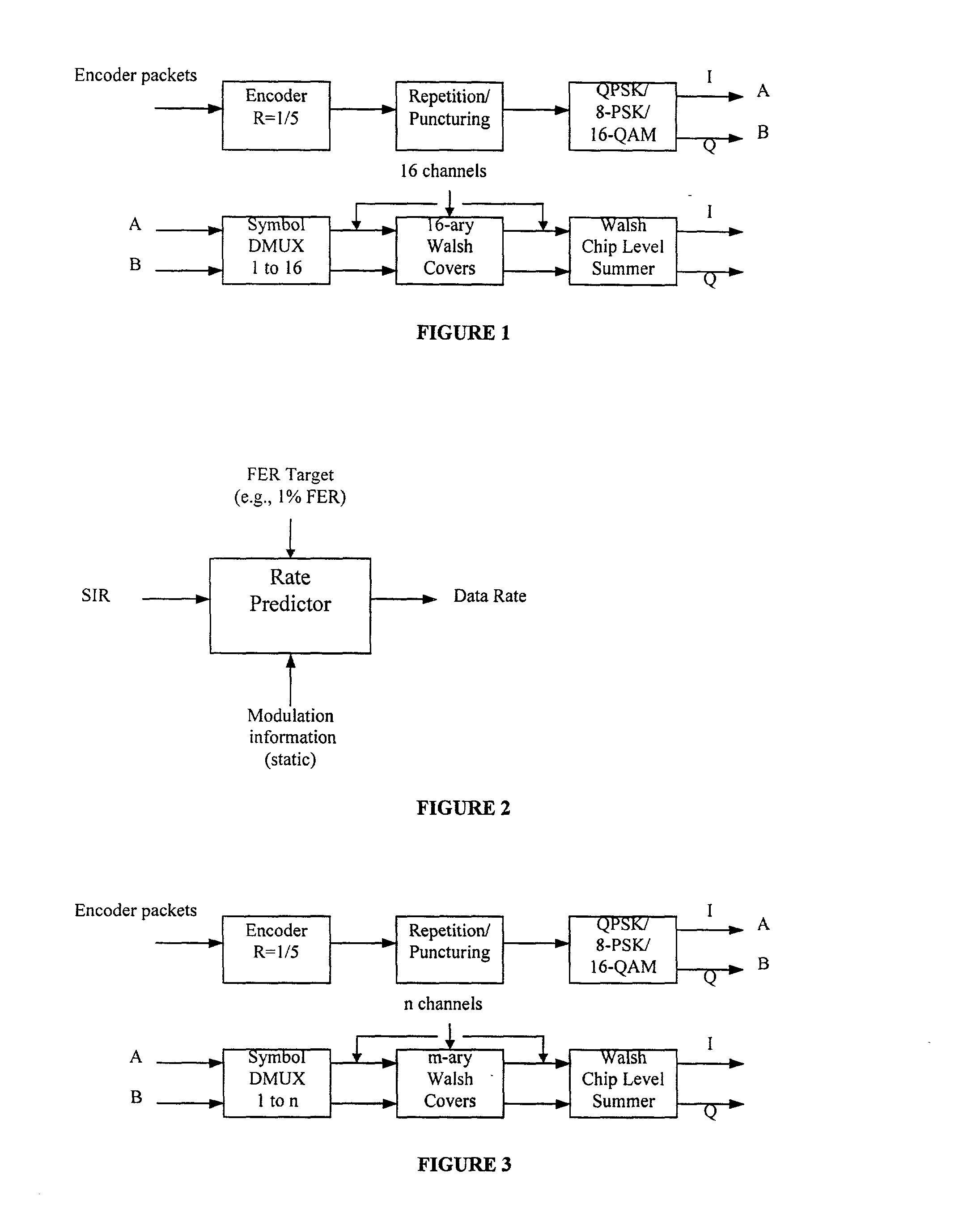
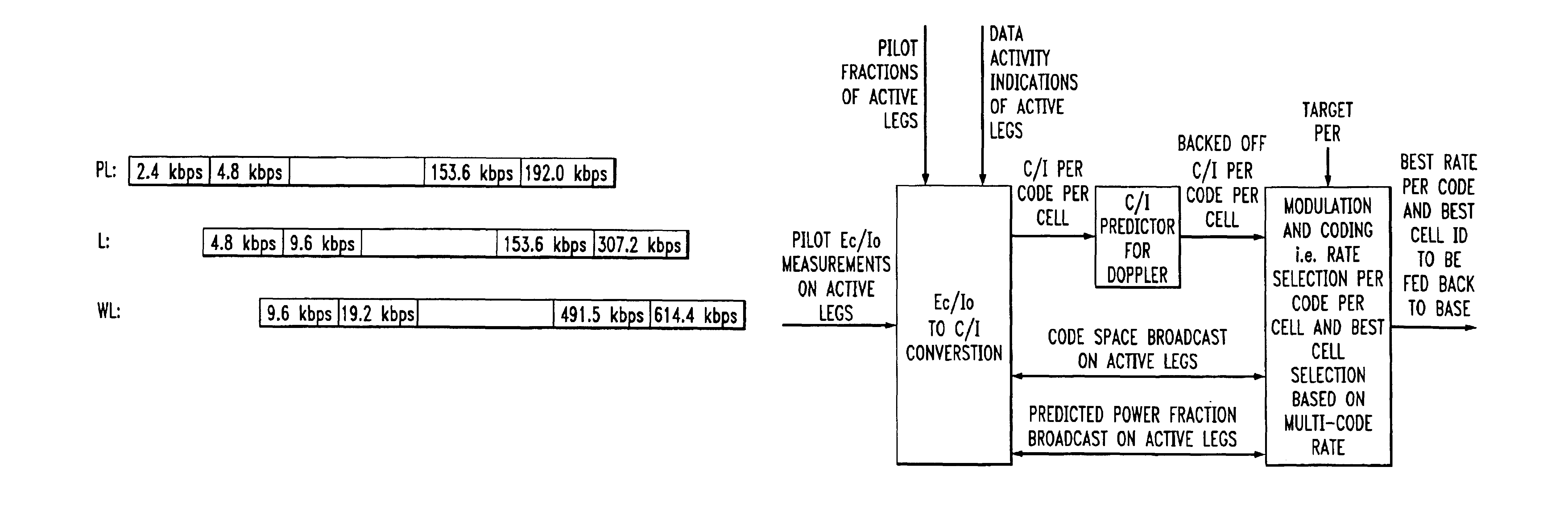
Data rate determination is provided in a system where the available power fraction and available Walsh codes in each active leg are dynamically changing over time. This method adapts the rate (modulation and coding) based on the combined resource (power & code space) levels seen at each cell. The method results in maximization of the rate supportable by each cell given their resource constrained situation while meeting the constraints of target packet or frame error rate and orthogonality. Furthermore, improved fast cell selection by the mobile results due to this approach that is based on knowledge of combined resource (power & code space) levels across the cells in the active set.
Owner:GEMPLU
Method of controlling cell selection for a wireless communication system and related device
ActiveUS20100075670A1Assess restrictionBroadcast service distributionCommunications systemCell selection
A method of controlling CSG, known as closed subscriber group, cell selection for a wireless communication system is provided. The wireless communication system includes a network and a user equipment including a whitelist capable of providing a list of accessible CSG cells. The method includes updating the whitelist when the user equipment subscribes to a CSG cell that is not included in the whitelist or does not subscribe to a CSG cell in the whitelist.
Owner:HTC CORP
NRAM bit selectable two-device nanotube array
Owner:NANTERO
Rrm measurement and reporting for license assisted access
Methods, systems, and devices for radio resource management (RRM) measurement and reporting for license assisted access (LAA) cells operating in unlicensed or shared frequency spectrum are described. A user equipment (UE) may receive an RRM measurement configuration including a channel occupancy parameter for measuring neighbor cells of a shared frequency band. The channel occupancy parameter may be used to determine a channel occupancy metric that may be sent to a base station for cell selection. The channel occupancy metric may include an averaged or filtered received signal strength and may be reported for serving cells and / or intra-frequency neighbor cells. A base station may further configure a UE with a discovery reference signals (DRS) measurement timing configuration (DMTC), which may include an extended DMTC search window. The UE may search for DRS transmissions from neighbor cells according to the DMTC.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Frequency layer convergence method for MBMS
ActiveUS20050245260A1Minimize migrationInhibit migrationAssess restrictionTime-division multiplexCommunications systemCell selection
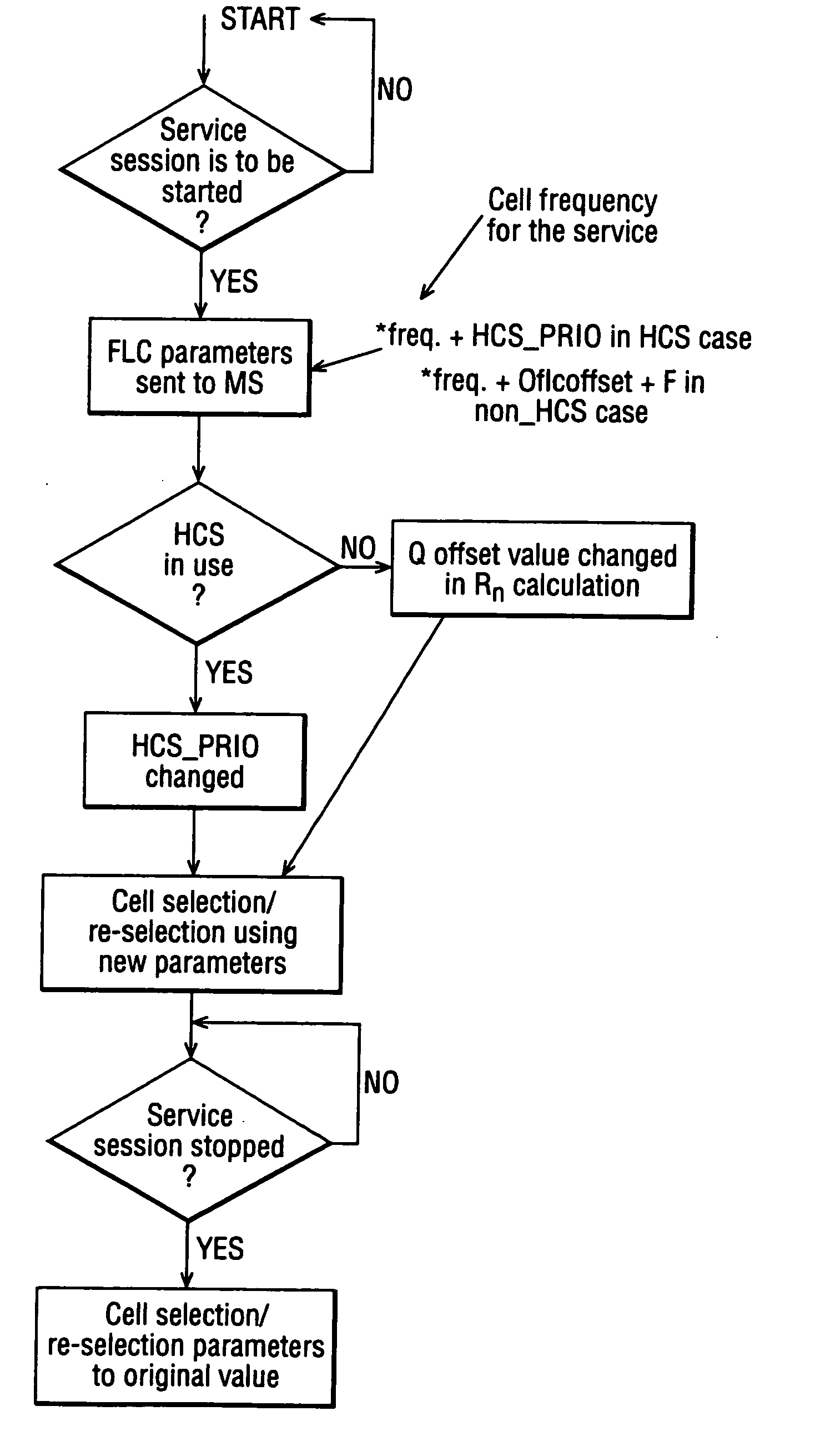
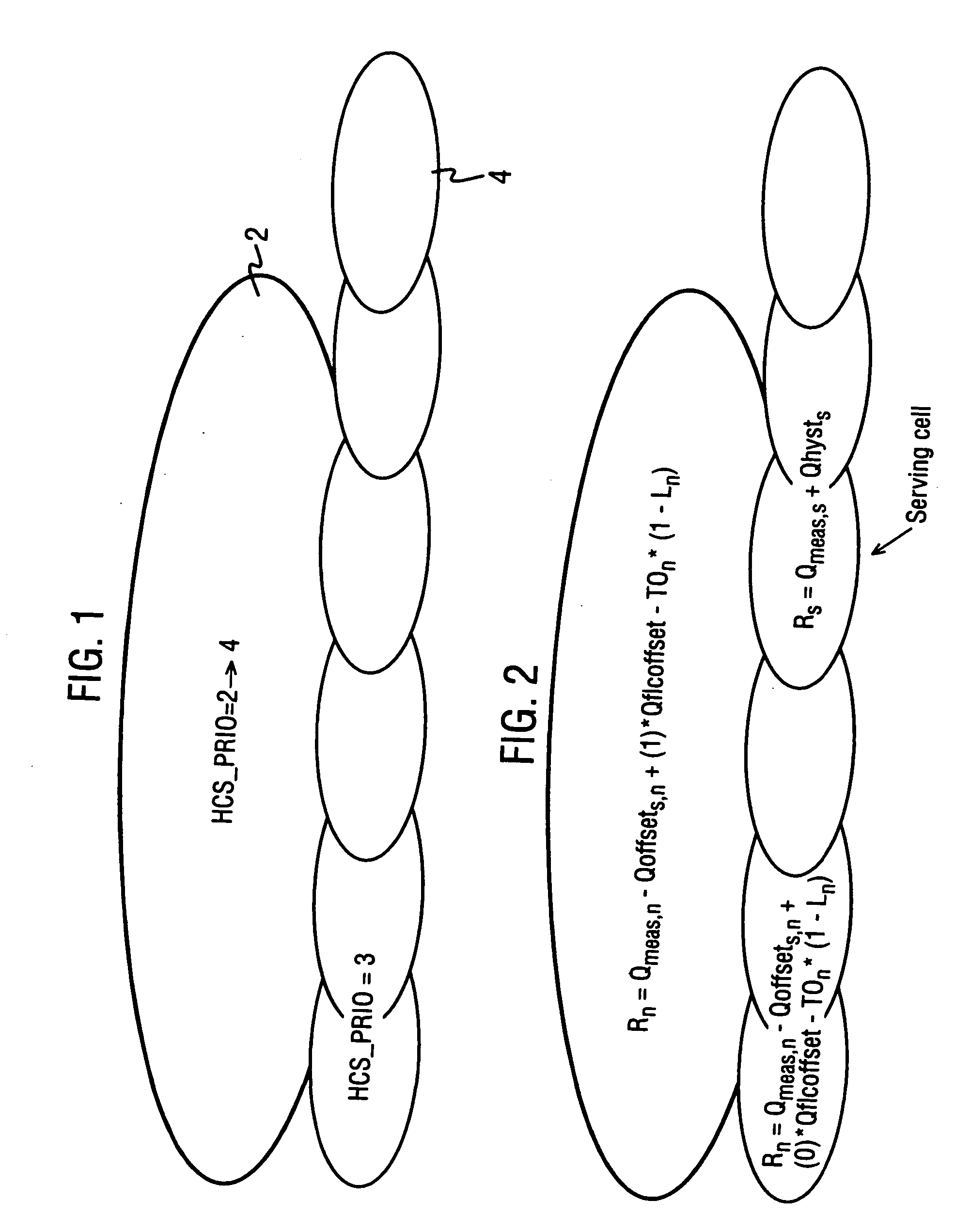
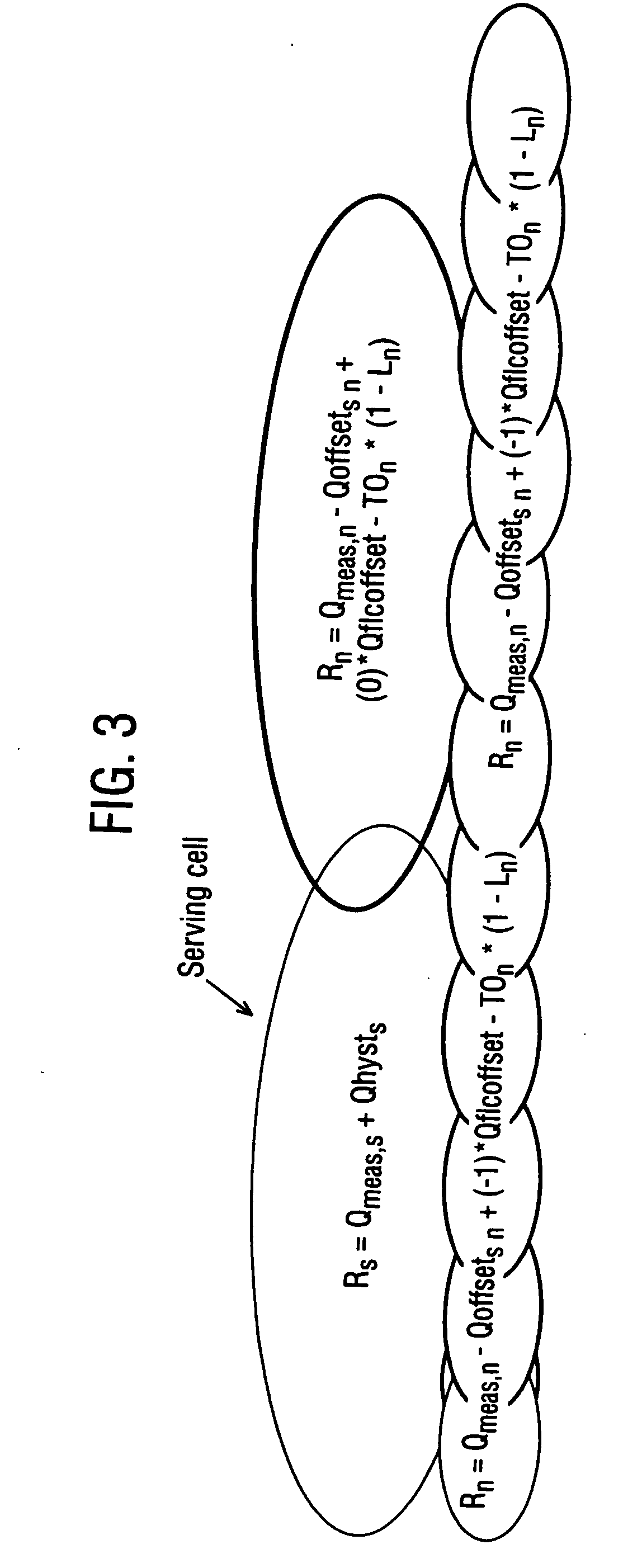
A method to control cell selection and / or re-selection in a communication system comprising a plurality of cells with which terminal devices may communicate, the method including the steps of: determining that a terminal device is to start a session for a certain service, the service using a reception frequency; based on that determination, changing at least one cell selection and / or re-selection parameter in respect of the terminal device with the effect that a subsequent cell selection and / or re-selection performed by the device would favor cells that use the reception frequency used in the service session over other cells.
Owner:CONVERSANT WIRELESS LICENSING LTD
Method for data rate selection in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS6930981B2Easy to useEfficiently using bandwidthFrequency-division multiplex detailsOrthogonal multiplexCommunications systemCell selection
Data rate determination is provided in a system where the available power fraction and available Walsh codes in each active leg are dynamically changing over time. This method adapts the rate (modulation and coding) based on the combined resource (power & code space) levels seen at each cell. The method results in maximization of the rate supportable by each cell given their resource constrained situation while meeting the constraints of target packet or frame error rate and orthogonality. Furthermore, improved fast cell selection by the mobile results due to this approach that is based on knowledge of combined resource (power & code space) levels across the cells in the active set.
Owner:GEMPLU
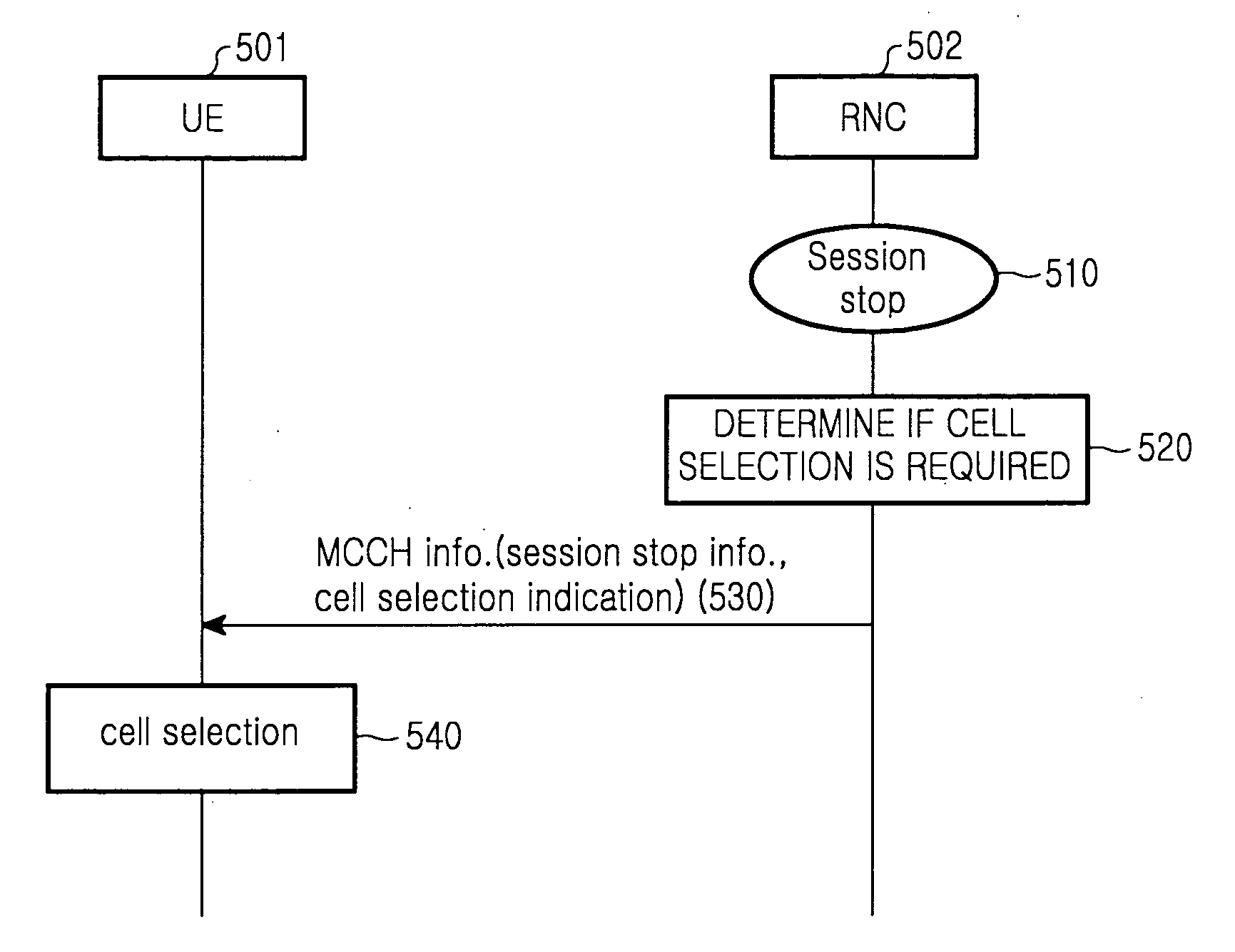
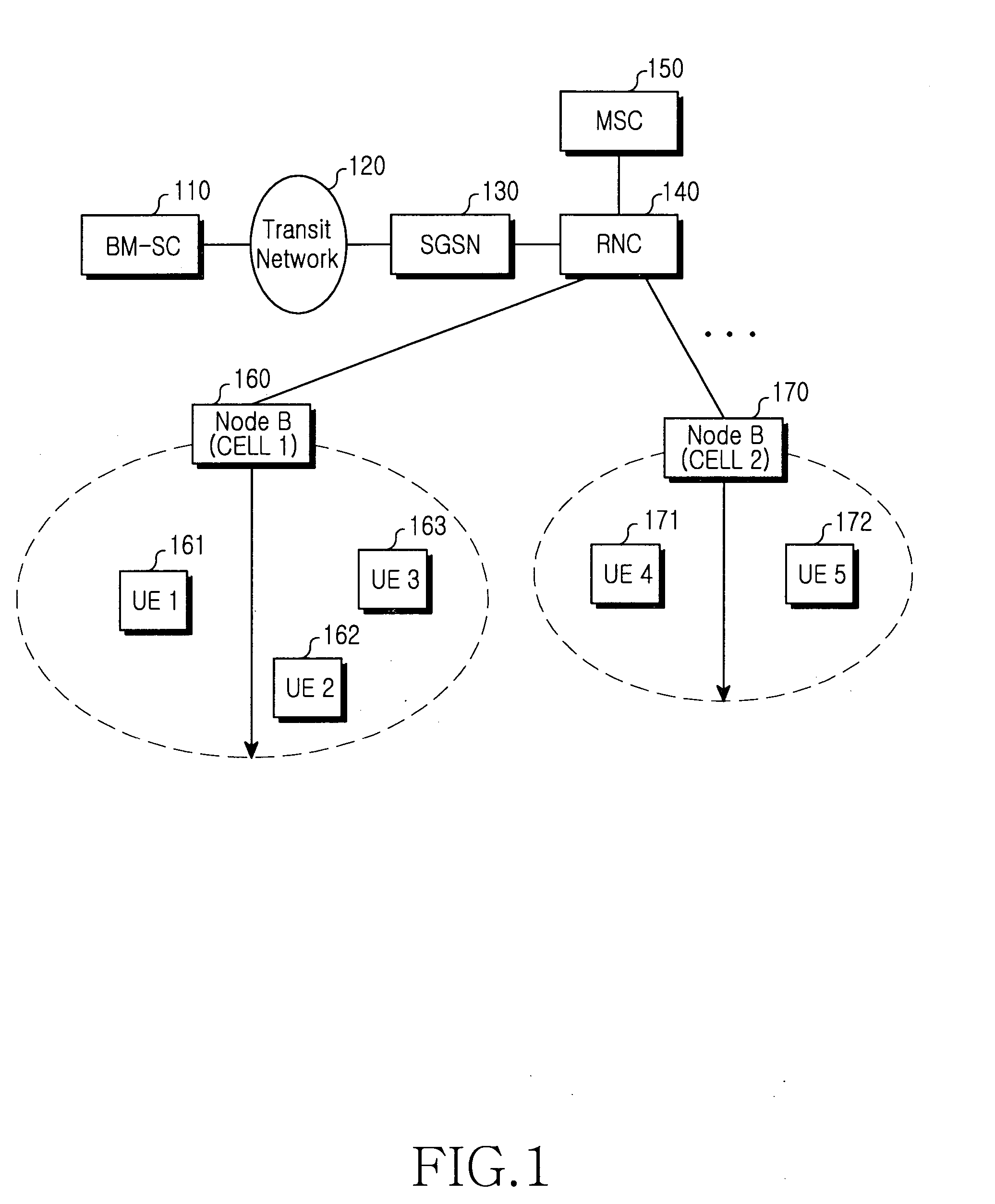
Method and apparatus for indicating cell selection when a session is stopped in a multimedia broadcast/multicast service system
ActiveUS20060056347A1Assess restrictionBroadcast service distributionMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceCurrent cell
A multimedia broadcast / multicast service (MBMS) service and a method and apparatus for maintaining congestion and a signal transfer load of a cell at a suitable level when a session of the MBMS service is terminated in a frequency layer convergence (FLC) situation in which the MBMS service is provided in a preferred frequency layer (PL). When a session of the MBMS service is terminated, a radio network controller (RNC) determines if a cell selection is required in UEs, desiring to receive the MBMS service located in the PL cell, by using a start time of a new session and load levels of a current cell and other cells, and sends, to the UEs, explicit cell selection indication information along with session stop information according to a determination result. Therefore, the congestion and signal transfer load of the cell can be maintained in the suitable level.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
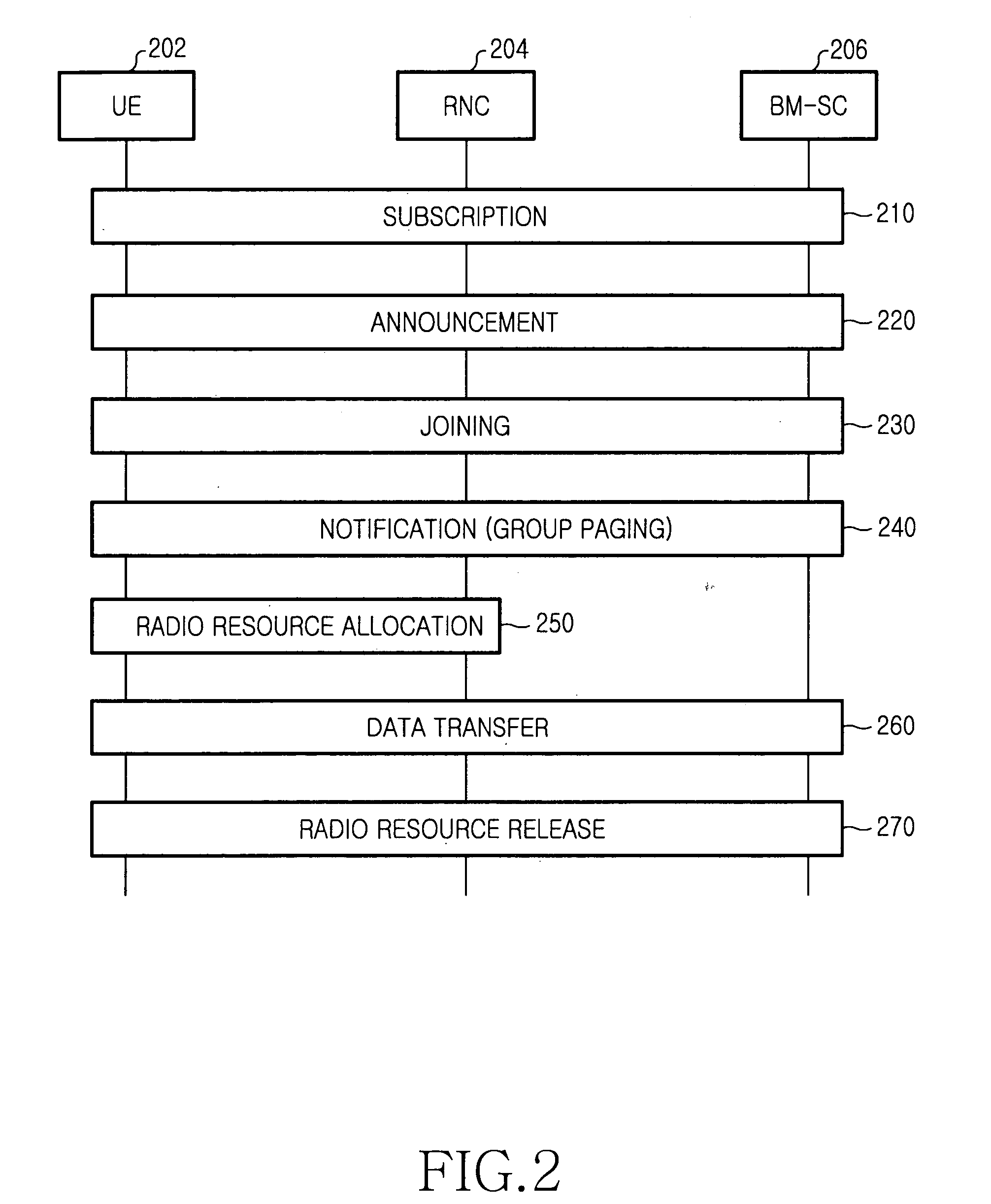
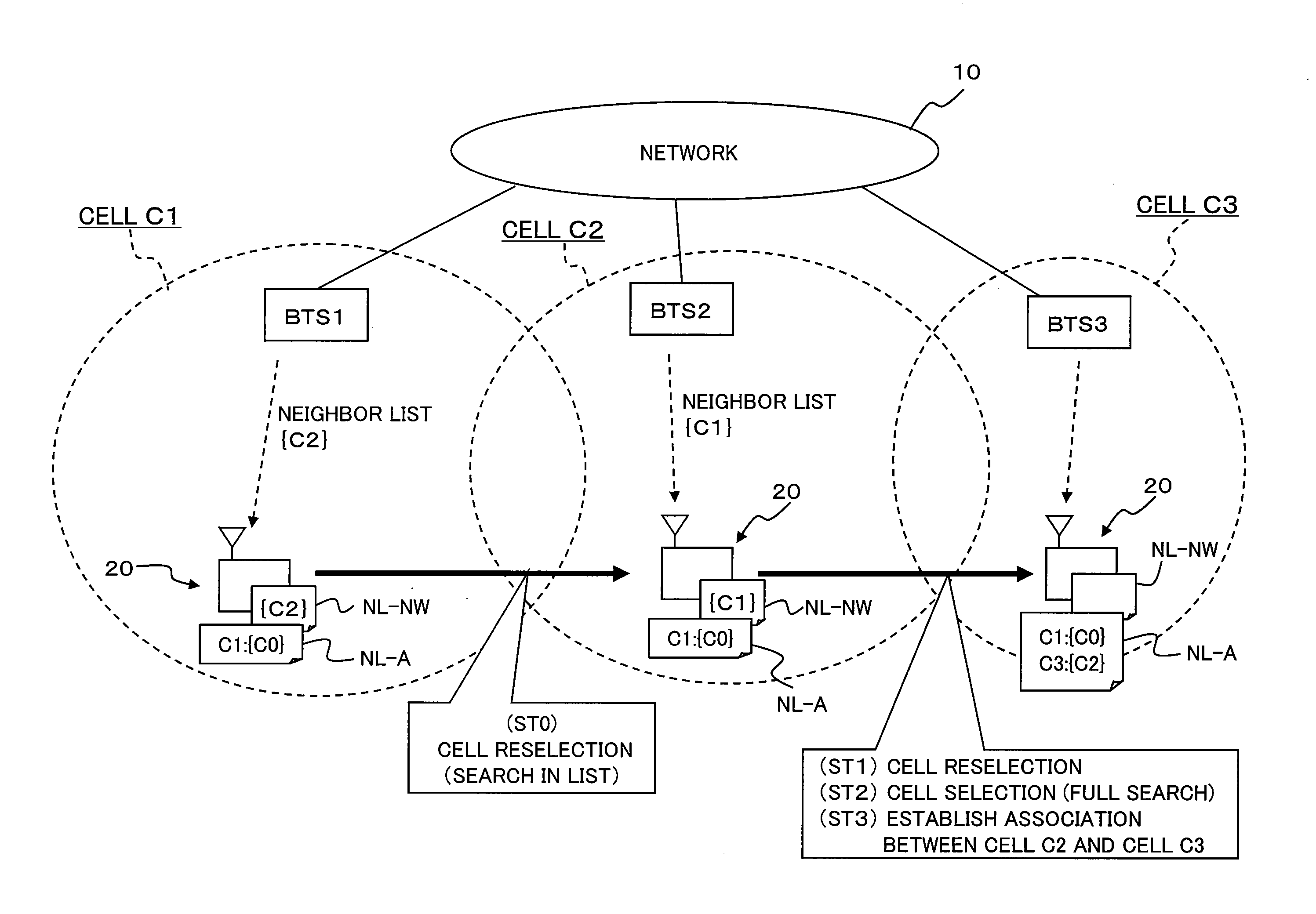
Method and device for mobility management of mobile station in mobile communications system
ActiveUS20080108353A1Increase in interruption can be avoidedAssess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemCell selection
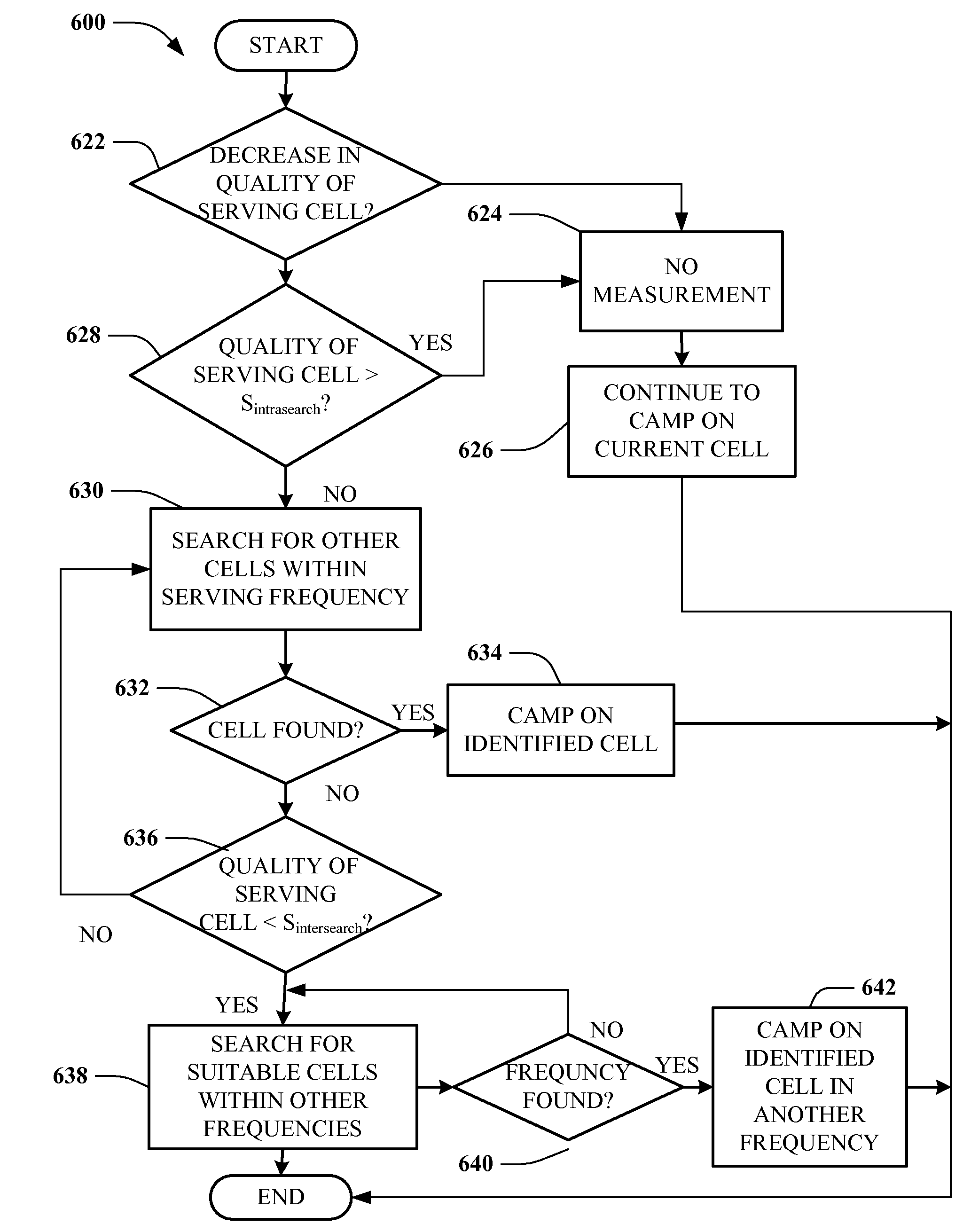
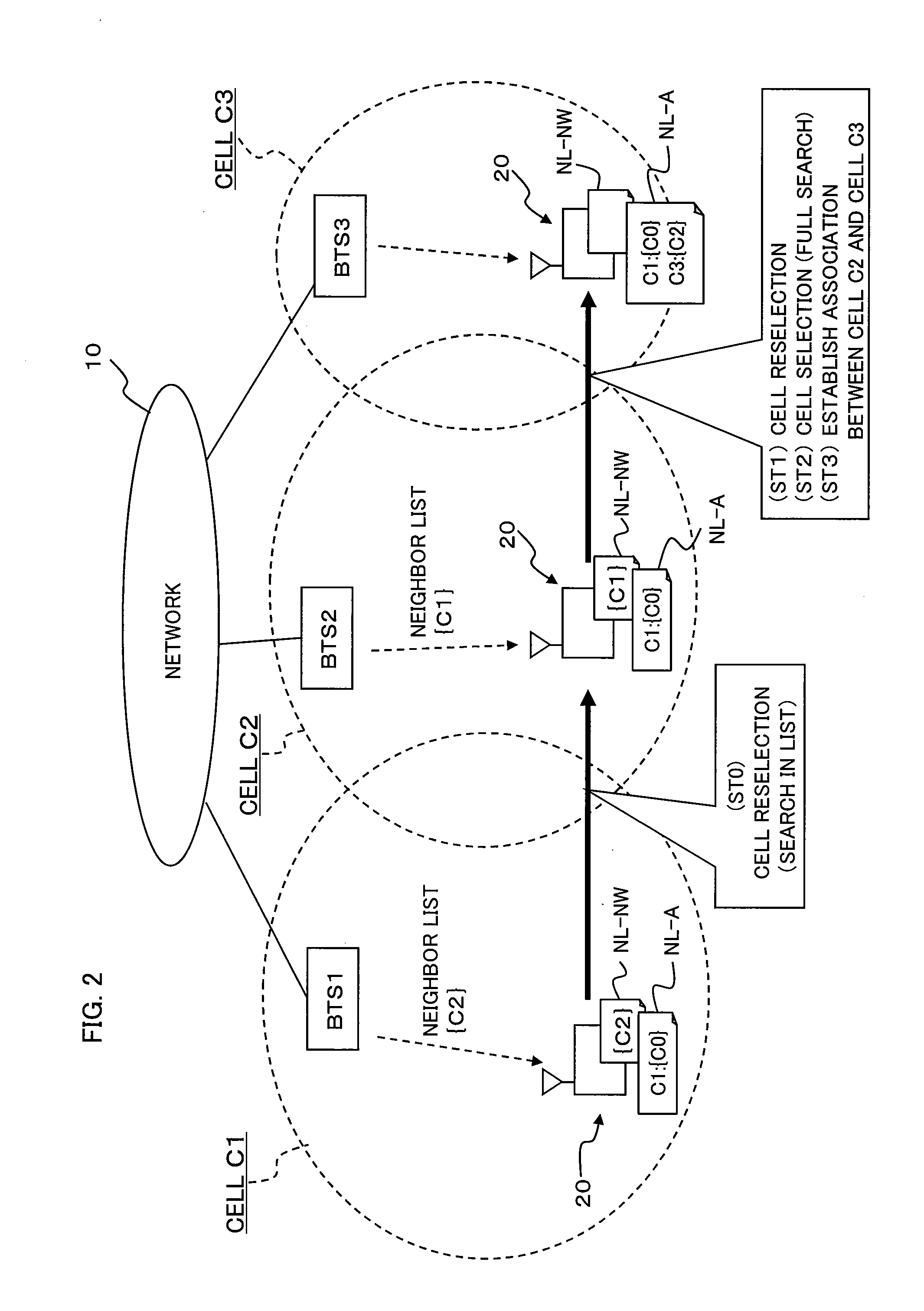
A method and an apparatus for mobility management of a mobile station that can efficiently avoid interruption of services to the mobile station, without imposing loads on a network and the mobile station, are provided. Upon change of serving cell, a mobile station receives a neighbor list from a new serving cell and stores it in a neighbor list (NL-NW). Upon cell selection, the mobile station associates the new serving cell with the previous serving cell and stores information about this association in a neighbor list (NL-A). Upon detection of deterioration in the quality of the current serving cell, the mobile station measures the quality of each cell on the neighbor list (NL-NW) and the neighbor list (NL-A). Upon detection of a cell that is better than the current serving cell, the mobile station reselects this detected better cell as its new serving cell.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method for reselecting a cell and detecting whether a terminal is stationay in mobile telecommunications system
ActiveUS20100240356A1Assess restrictionWireless commuication servicesTelecommunicationsCell selection
Disclosed is a method for determining, by a terminal, its mobility and deciding a time to select another cell in a mobile communication system, in which the terminal determines the mobility by using variation information in signal characteristic values of measurable specific cells, thereby appropriately controlling a size of a time restriction (e.g., Treselection) for a cell re-selection and preventing frequent occurrence of cell selection such as a ping-pong situation, thus to reduce an unnecessary service delay due to the cell re-selection and maximize a service quality for a user.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Cell selection and inter-frequency handover
InactiveUS7430420B2Emission reductionEnergy efficient ICTTime-division multiplexElectromagnetic exposureRadio networks
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for controlling a communications system that includes a mobile wireless device, a first and a second base station and a radio network controller. The communications system may allocate frequency bands to users on a multiplicity of channels associated with a multi-layer access network across at least two cells communicatively coupled to a first and a second base station, respectively. The method comprises monitoring a radio emission parameter associated with the first and second base stations that communicate with the mobile wireless device. A radio emission parameter associated with the first and second base stations, such as signal strength or quality, is monitored, to select a target cell among a set of candidate cells for the mobile wireless device and to transfer the mobile wireless device from a first frequency band to a second frequency band. For example, radio resource management algorithms may cause emission-controlled cell selection and inter-frequency handover from a first frequency band to a second frequency band with a transmit power level lower than that of the first frequency band. In accordance with one aspect of the instant application, electromagnetic exposure to a user of the mobile wireless device is substantially decreased, resulting in lower energy costs and reduced environmental impacts.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Calculation and broadcast of cell-load ratio and intelligent cell selection for IEEE802.16M
ActiveUS20090137251A1Quality improvementImprove service qualityAssess restrictionSubstation equipmentCell selectionForgetting factor
A method for data transmission, contemplates calculating a cell-load ratio by:rcl,n=(1-α)·rcl,n-1+dnSn,where rcl,n-1 is a cell-load ratio calculated in a previous stage, rcl,n is an instant cell-load ratio, α is a forgetting factor, dn is an instantaneous cell load, and Sn is a frame capacity; and broadcasting the calculated cell-load ratio by carrying the cell-load ratio in a designated message.Methods of a cell selection and a handover for a subscriber which are initiated by a subscriber are in dependence upon both of the cell-load ratio and the signal strength provided by the base stations.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for performing cell selection in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20100197310A1Better-quality serviceQuality assuranceNetwork topologiesWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemCell selection
A method and apparatus for performing cell selection is provided. The apparatus includes a memory configured to store basic priorities of a plurality of frequencies, and a processor configured to measure the signal strength of at least one cell in at least one of the plurality of frequencies, and perform cell selection based on an overrided priority if a cell with a highest measured signal strength is a closed subscriber group (CSG) cell and the highest measured signal strength is greater than a CSG threshold. When the quality of a serving CSG cell deteriorates, another cell from a different frequency may be selected.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
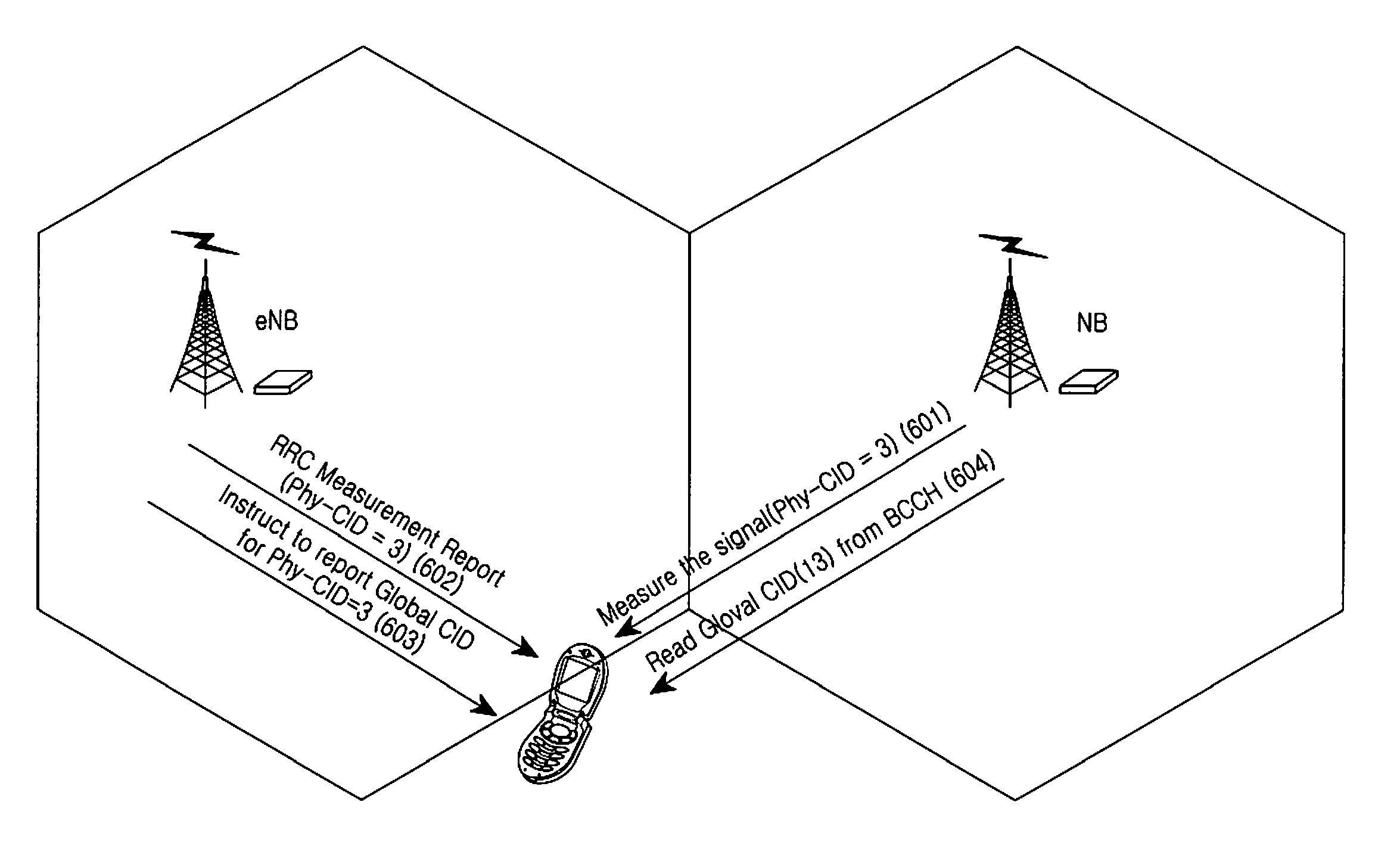
Methods and apparatus for cell selection/reselection of a mobile teriminal from a legacy network to an advanced network
ActiveUS20110098046A1Reduce power consumptionAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesCell selectionNetworked system
Methods and apparatus are provided for performing a cell selection by a multi-mode terminal from a legacy network (2G, 3G) to a advanced network (4G). The terminal performs the cell selection upon the existence of a Base Station (BS) on the advanced network system. The terminal does not attempt to perform the cell selection when the LTE BS does not exist.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
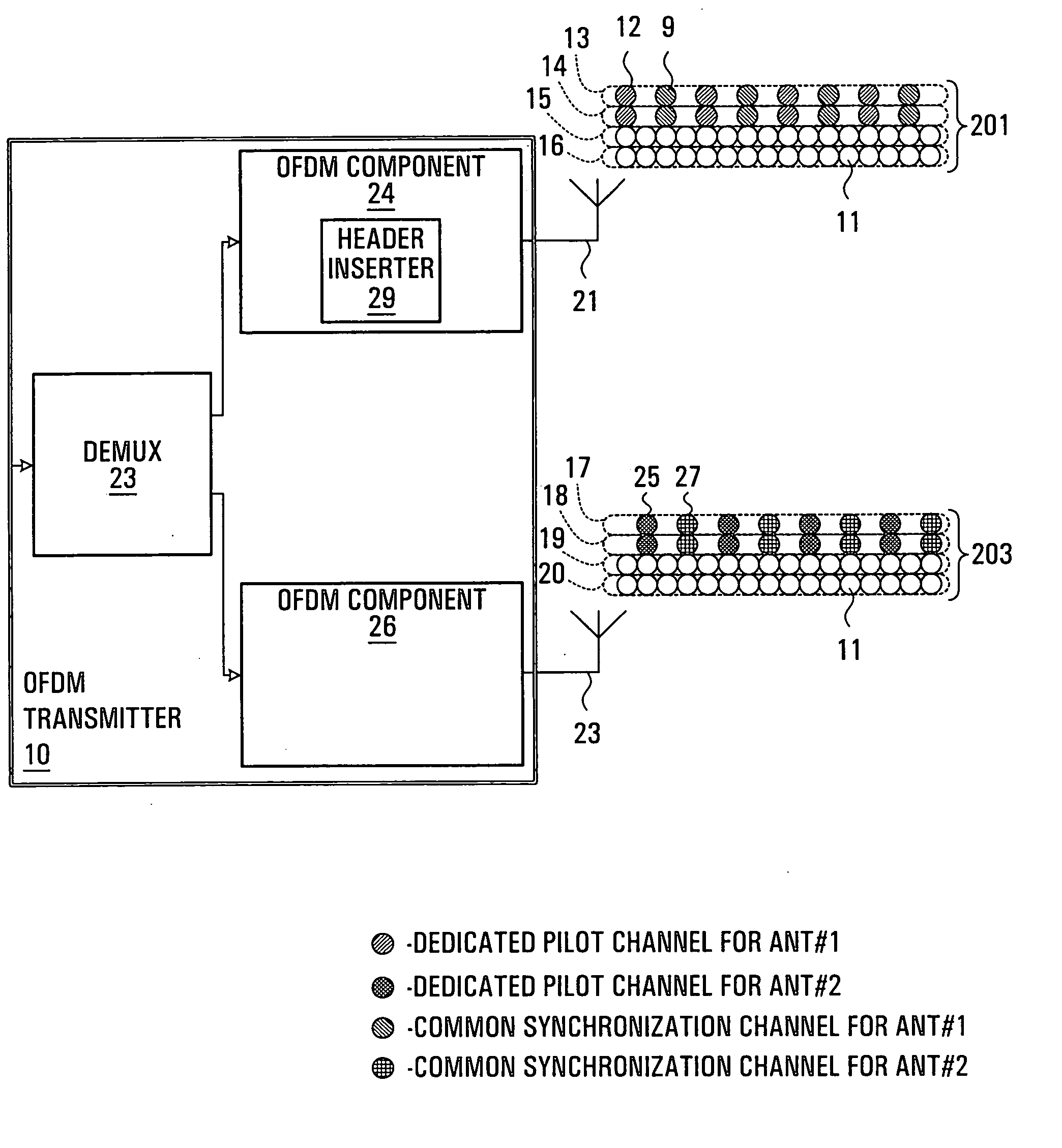
Frame structure, system and method for OFDM communications
ActiveUS20070066362A1Efficient identificationFast and accurate initial acquisitionSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemCell selection
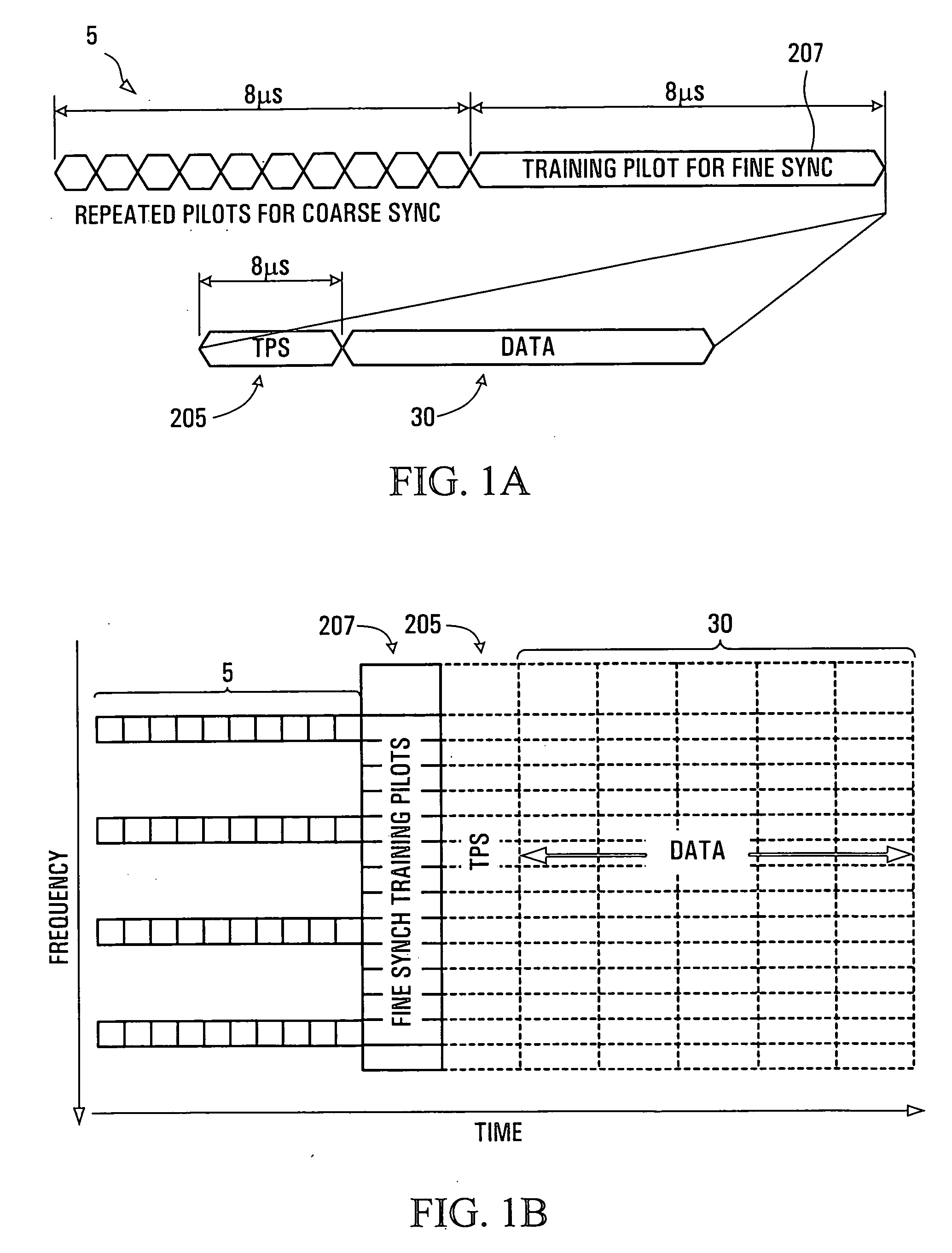
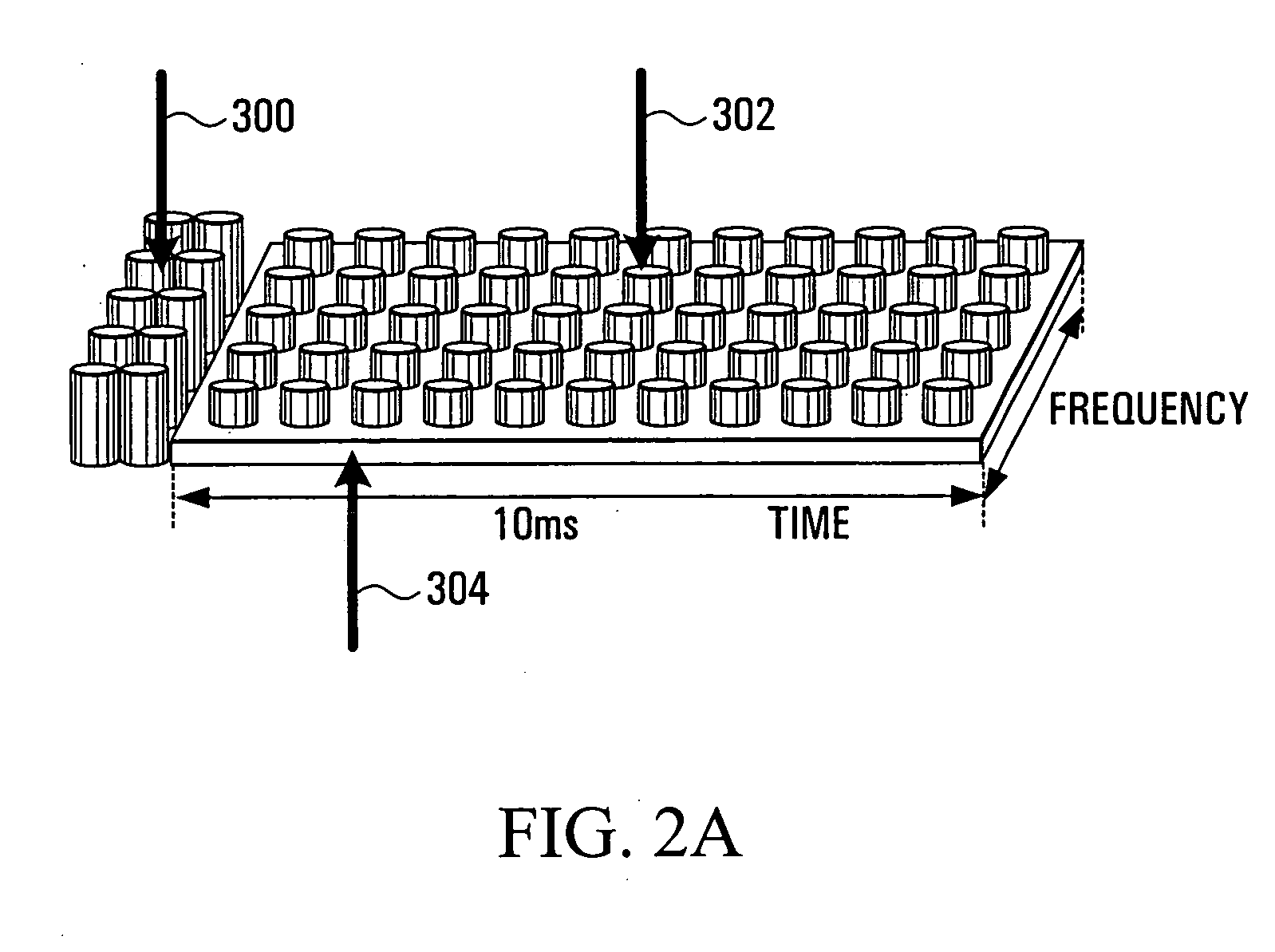
A method and apparatus are provided for performing acquisition, synchronization and cell selection within an MIMO-OFDM communication system. A coarse synchronization is performed to determine a searching window. A fine synchronization is then performed by measuring correlations between subsets of signal samples, whose first signal sample lies within the searching window, and known values. The correlations are performed in the frequency domain of the received signal. In a multiple-output OFDM system, each antenna of the OFDM transmitter has a unique known value. The known value is transmitted as pairs of consecutive pilot symbols, each pair of pilot symbols being transmitted at the same subset of sub-carrier frequencies within the OFDM frame.
Owner:APPLE INC
Methods and Apparatus for Communications Terminal Enabling Self Optimizing Networks in Air Interface Communications Systems
InactiveUS20100311421A1Enhance SON algorithmImprove efficiencyAssess restrictionCell selectionOn board
Systems and methods for providing a framework for supporting a self organizing / optimization network (SON) feature in an over the air communications system. An enhanced mobile communications device is provided that performs functions to creating a framework for enhancing SON algorithms. The communications device stores event analysis data in an on board memory and, on certain conditions, signals the analysis to the network. The analysis includes information useful in performing SON algorithms at the network level, such as cell coverage and neighboring cell signal level information, cell selection and reselection information at different locations, relative signal strength between cell base stations at different locations, and coverage hole information. Utilizing the stored information, the network can automatically perform SON algorithms to improve network efficiency without the need for manual intervention by an operator. Embodiments include event filtering by the communications device to efficiently utilize the on board storage.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com