Patents
Literature
343 results about "Cell site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
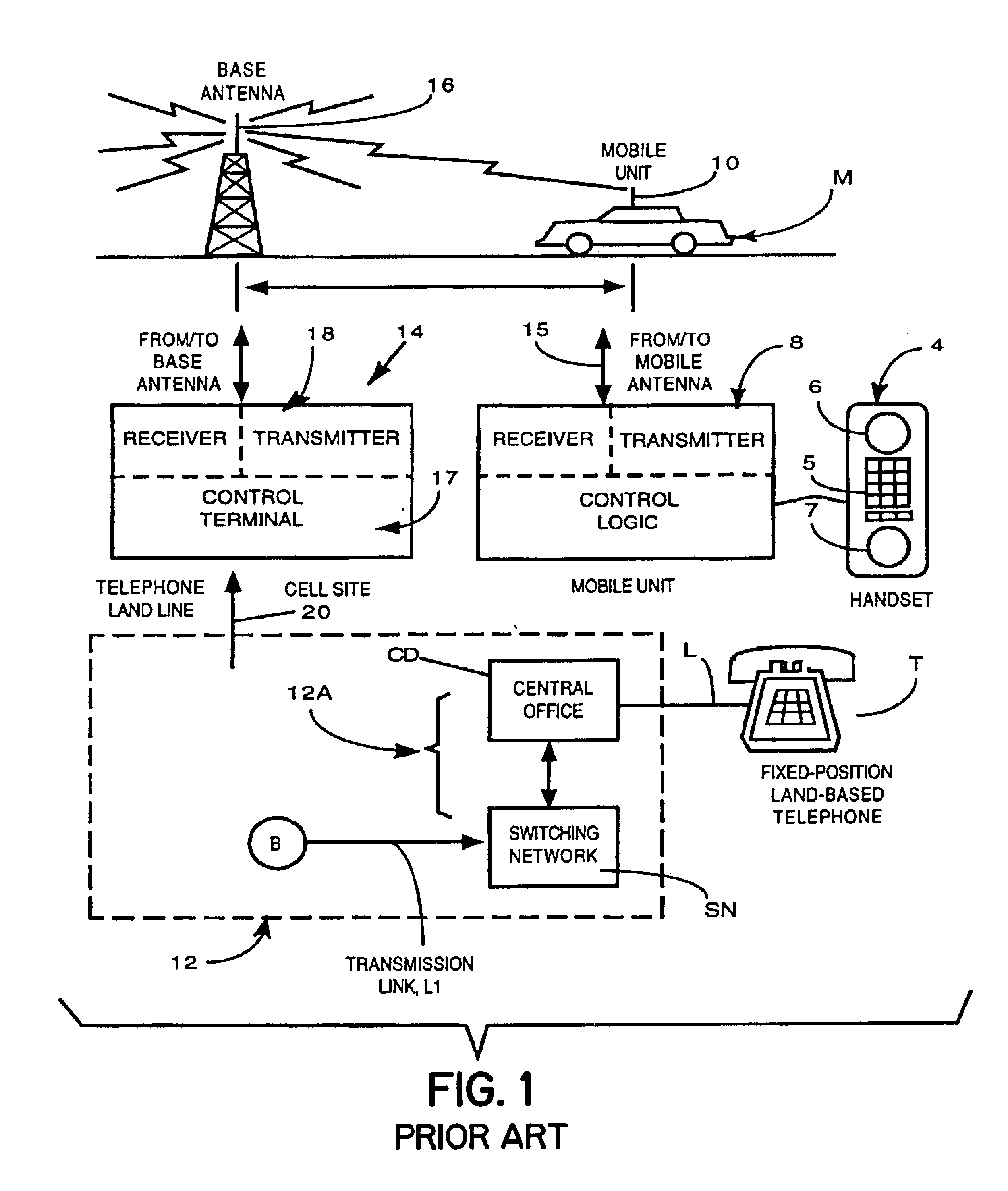
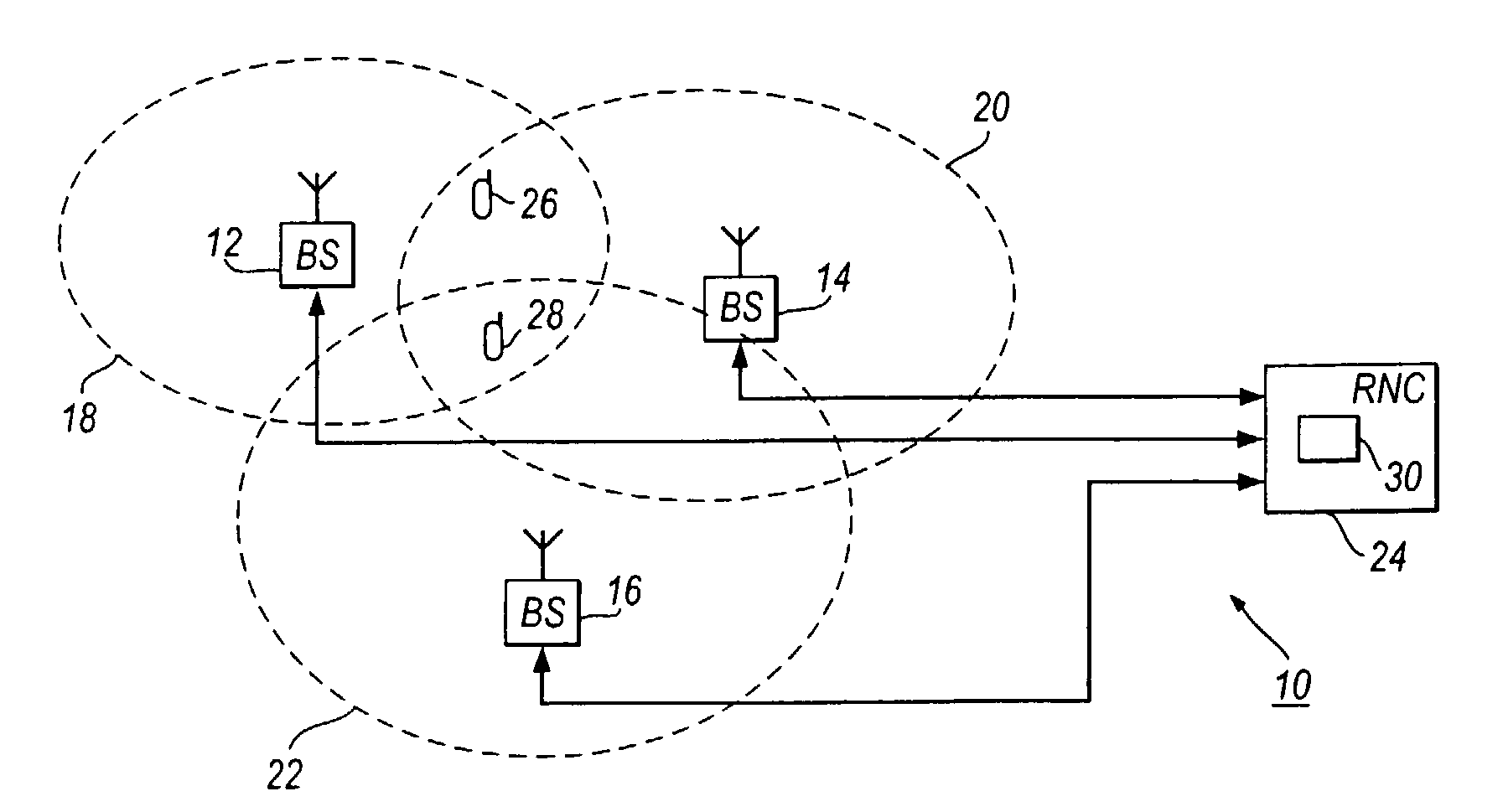
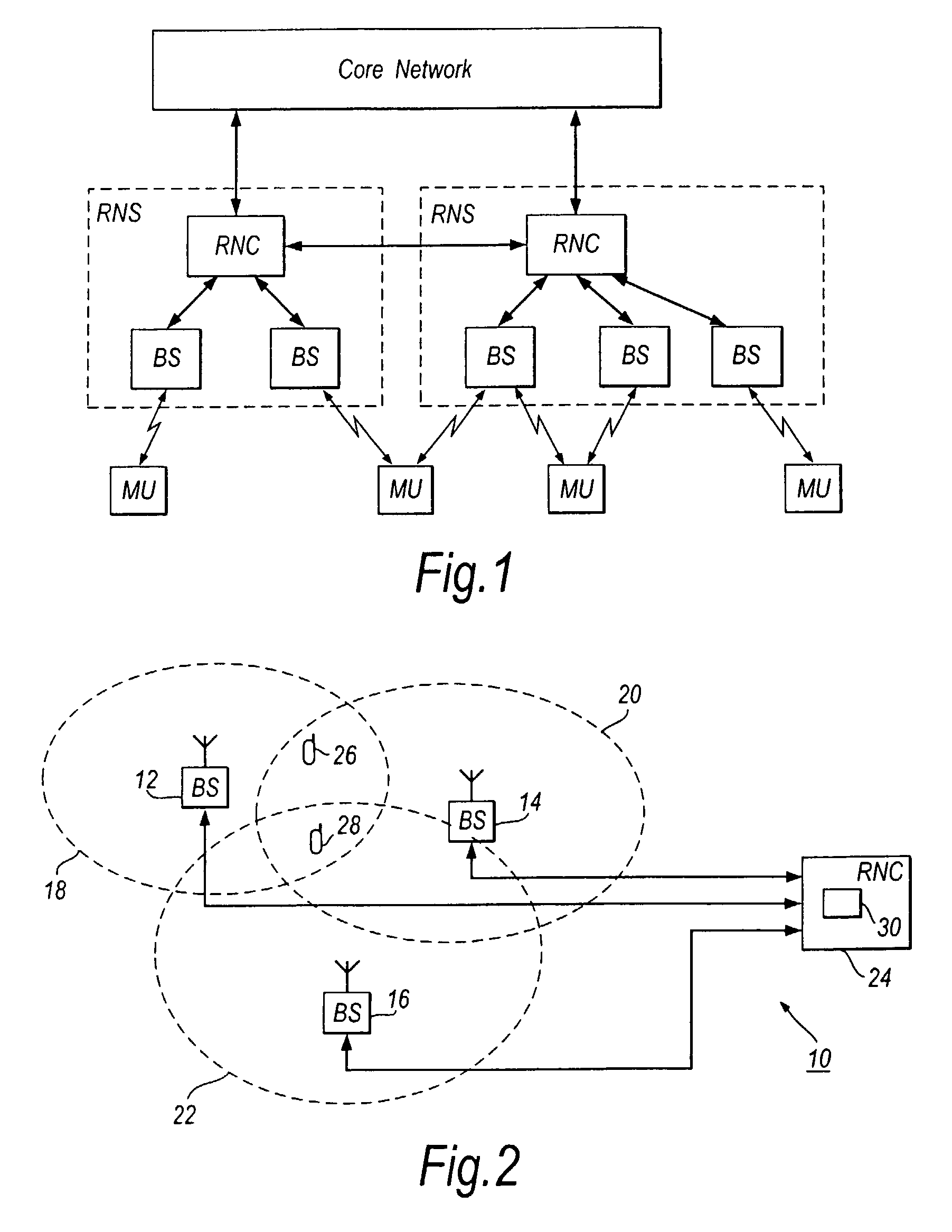
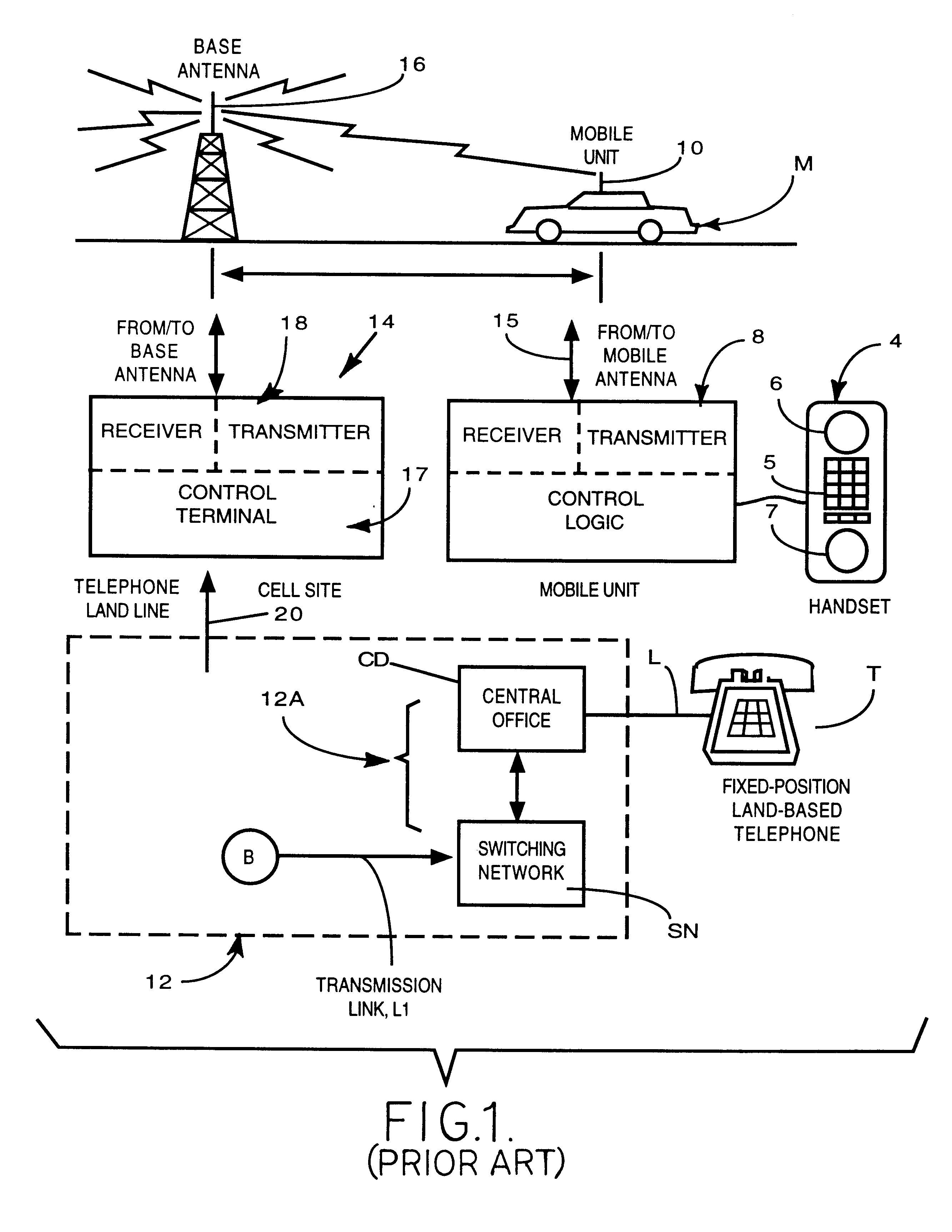
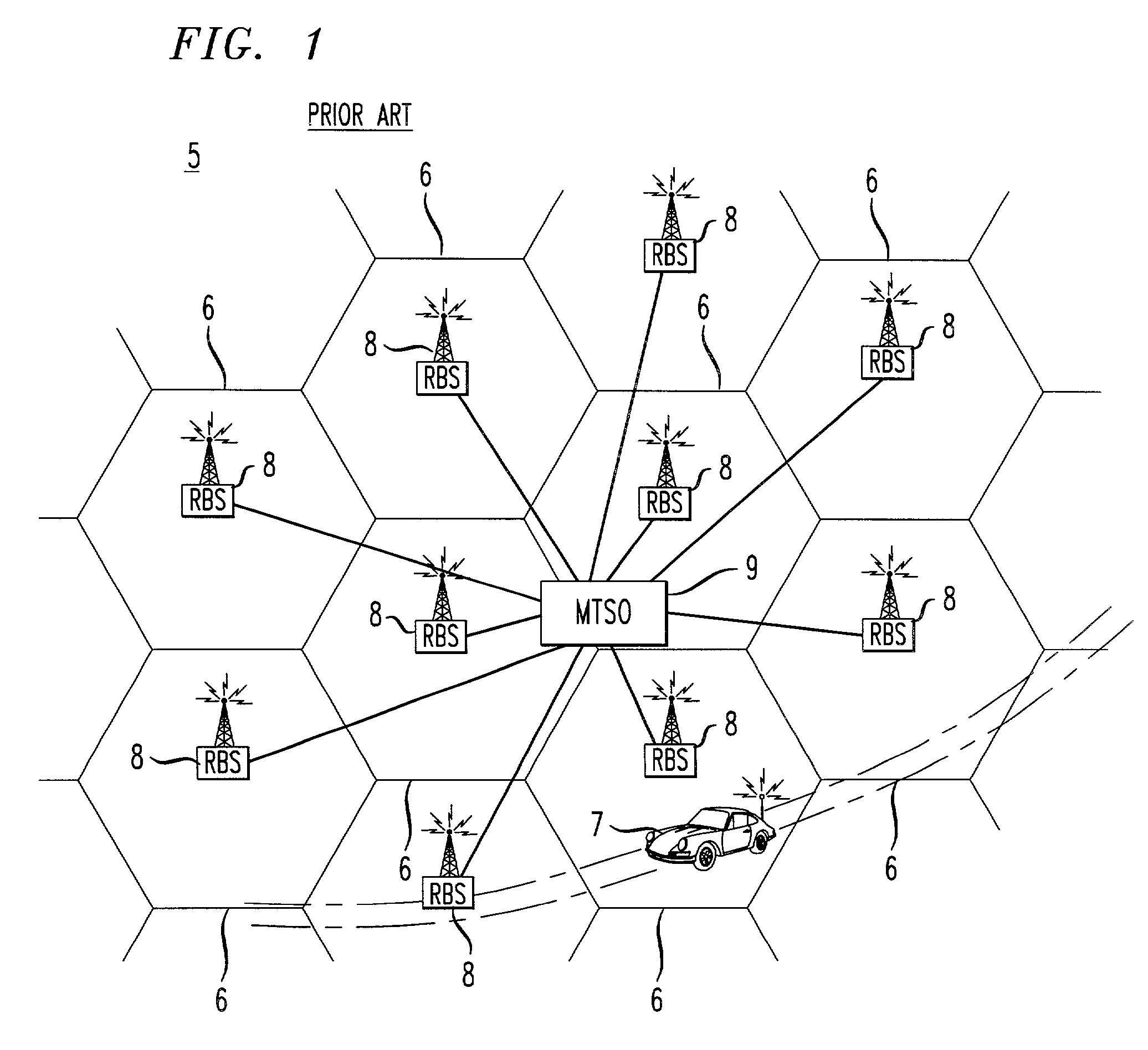
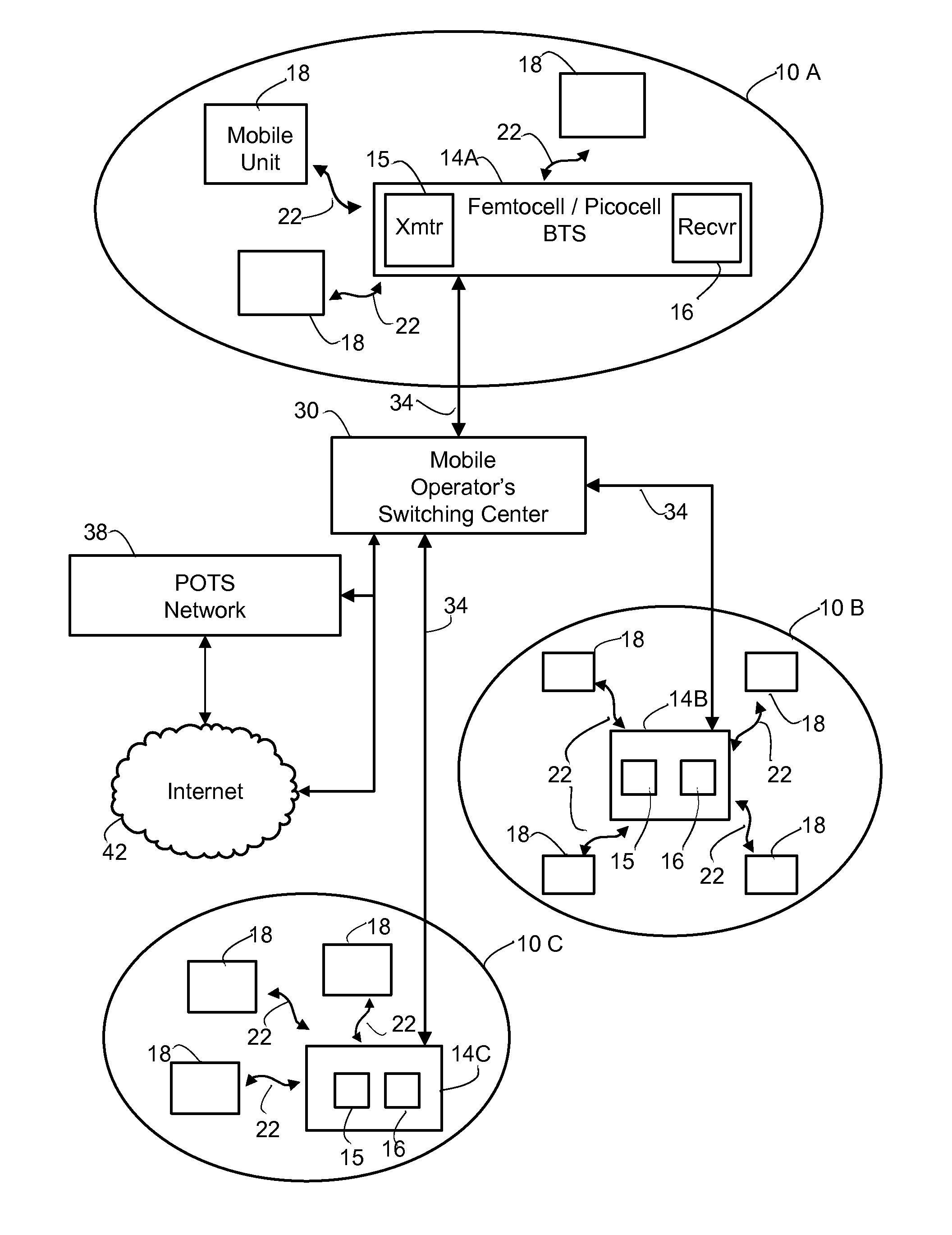
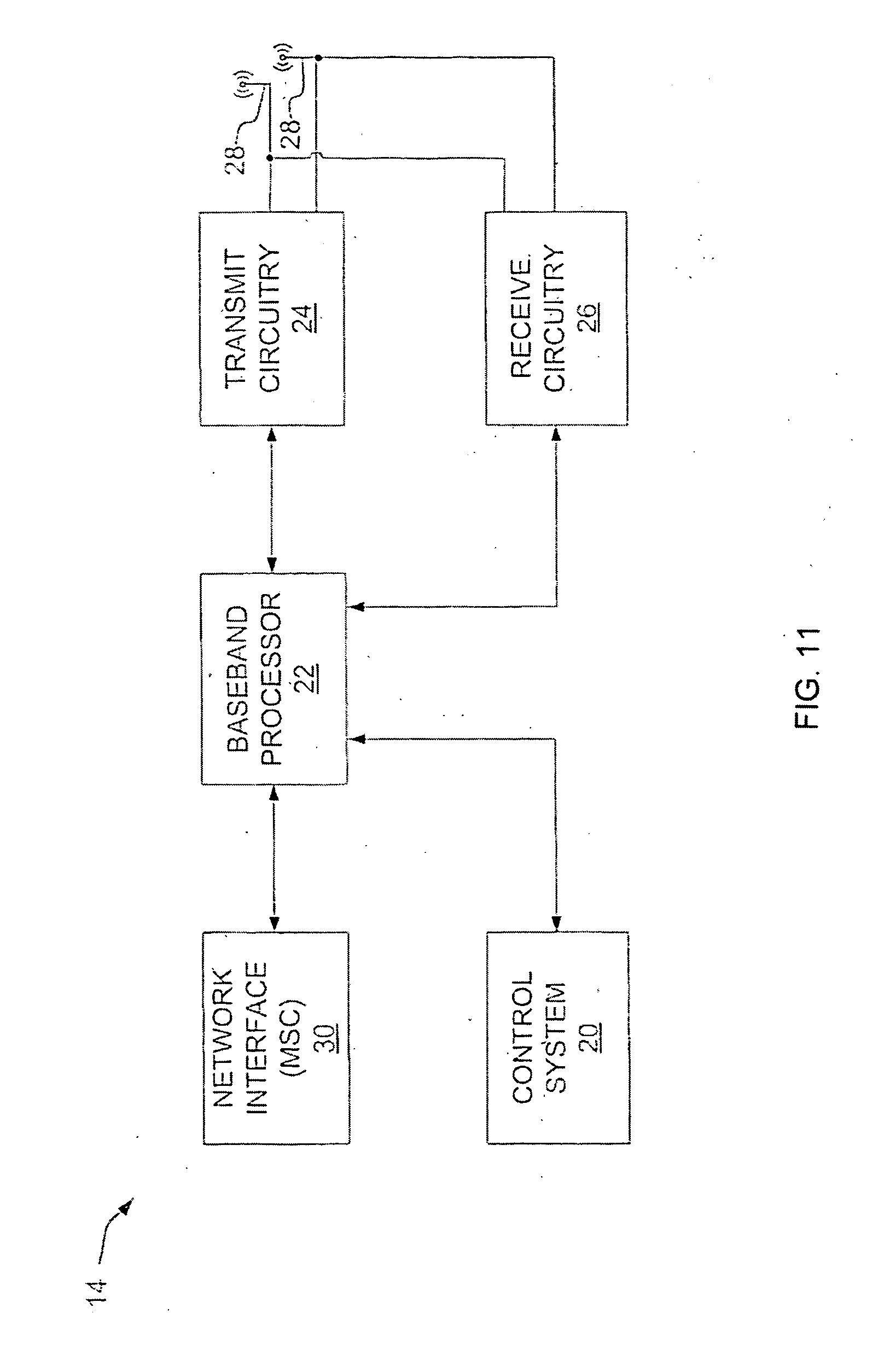
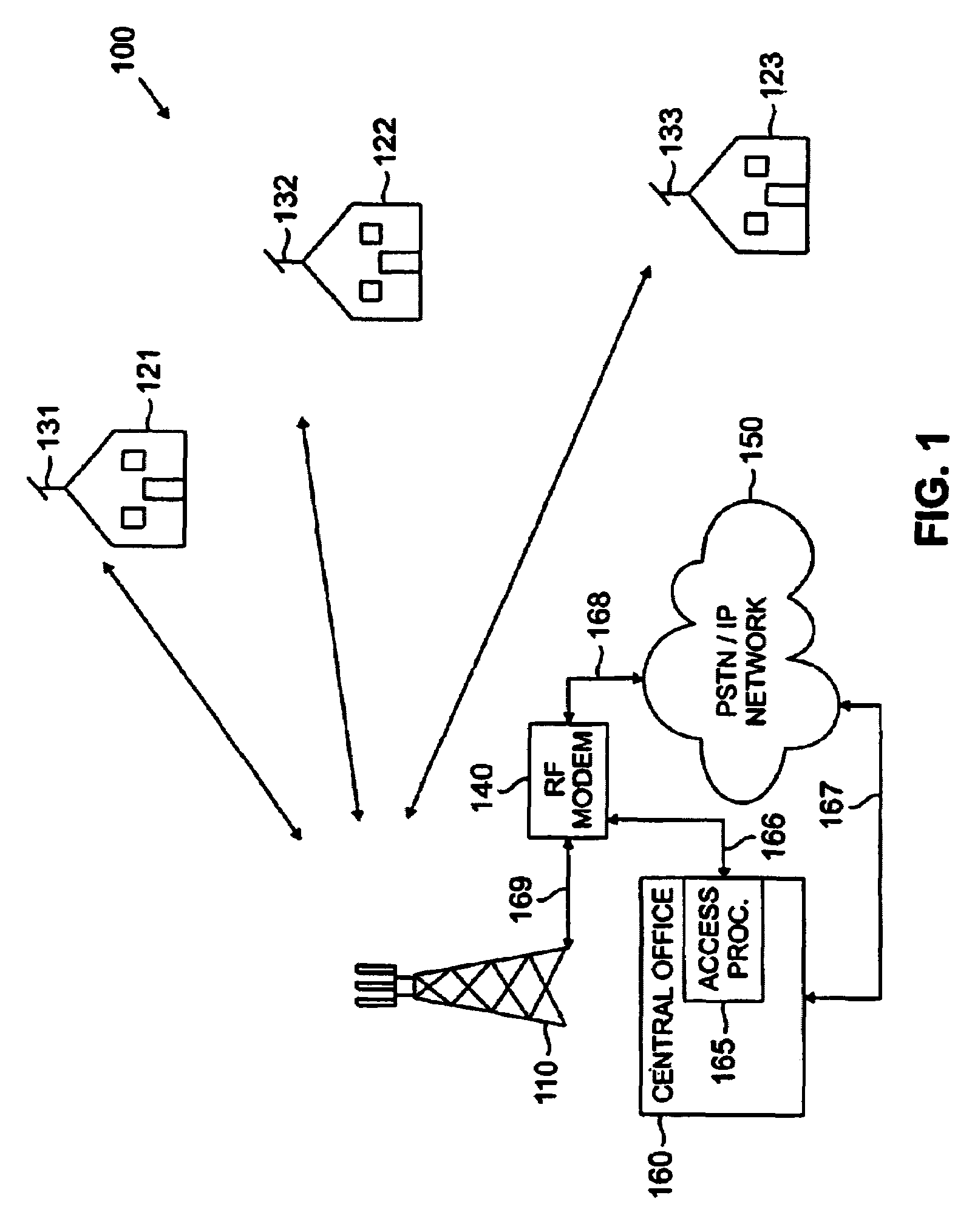
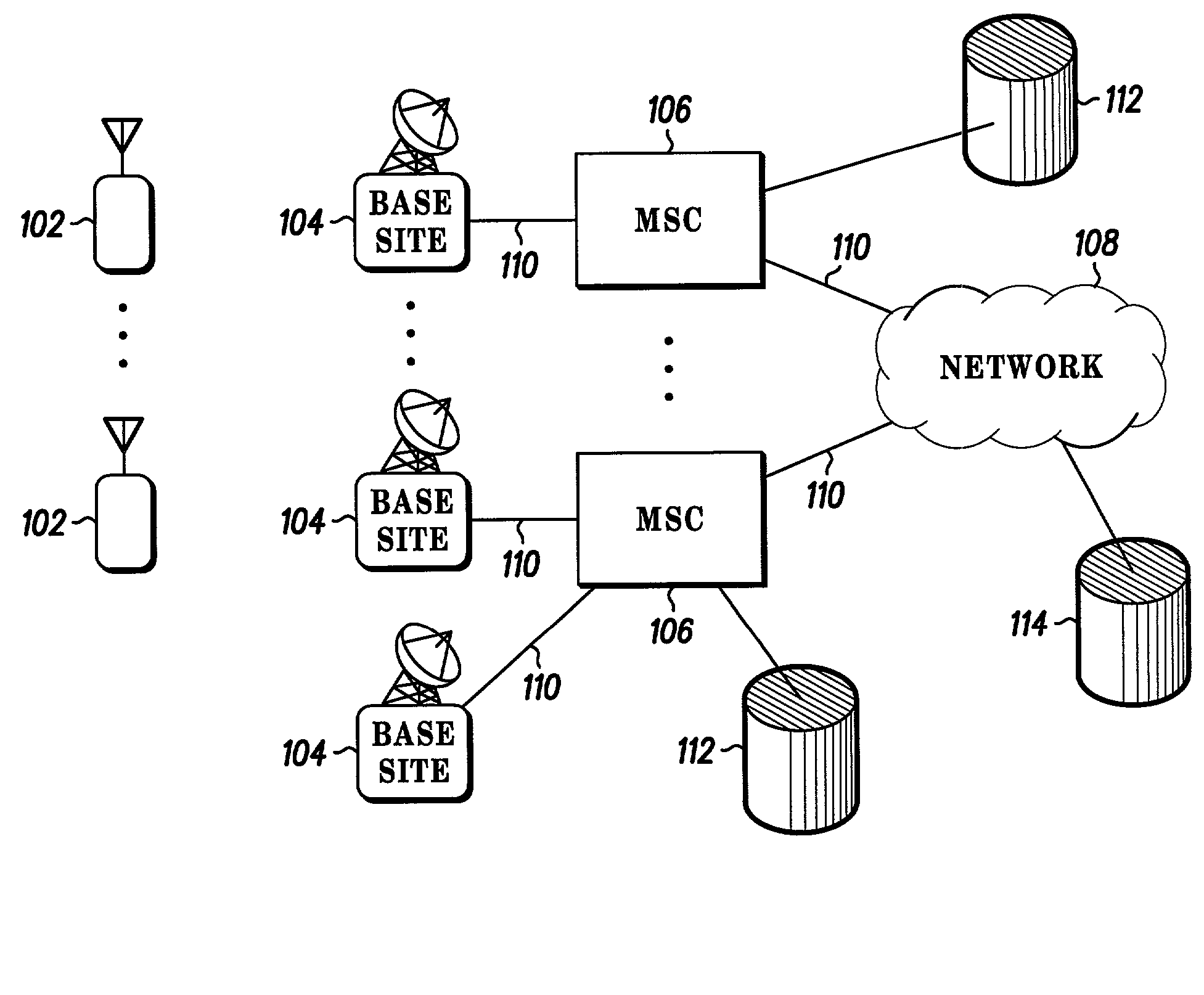
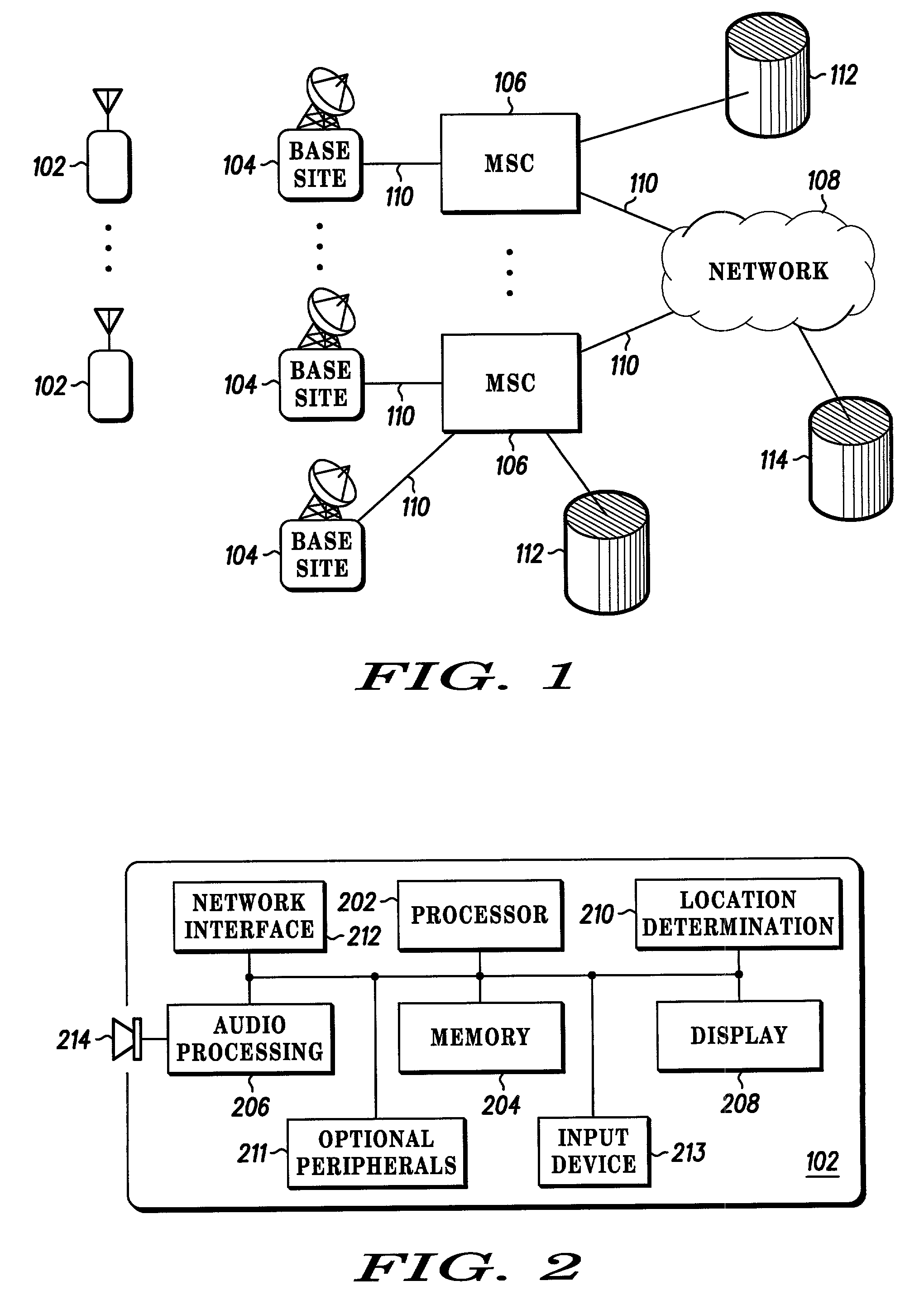
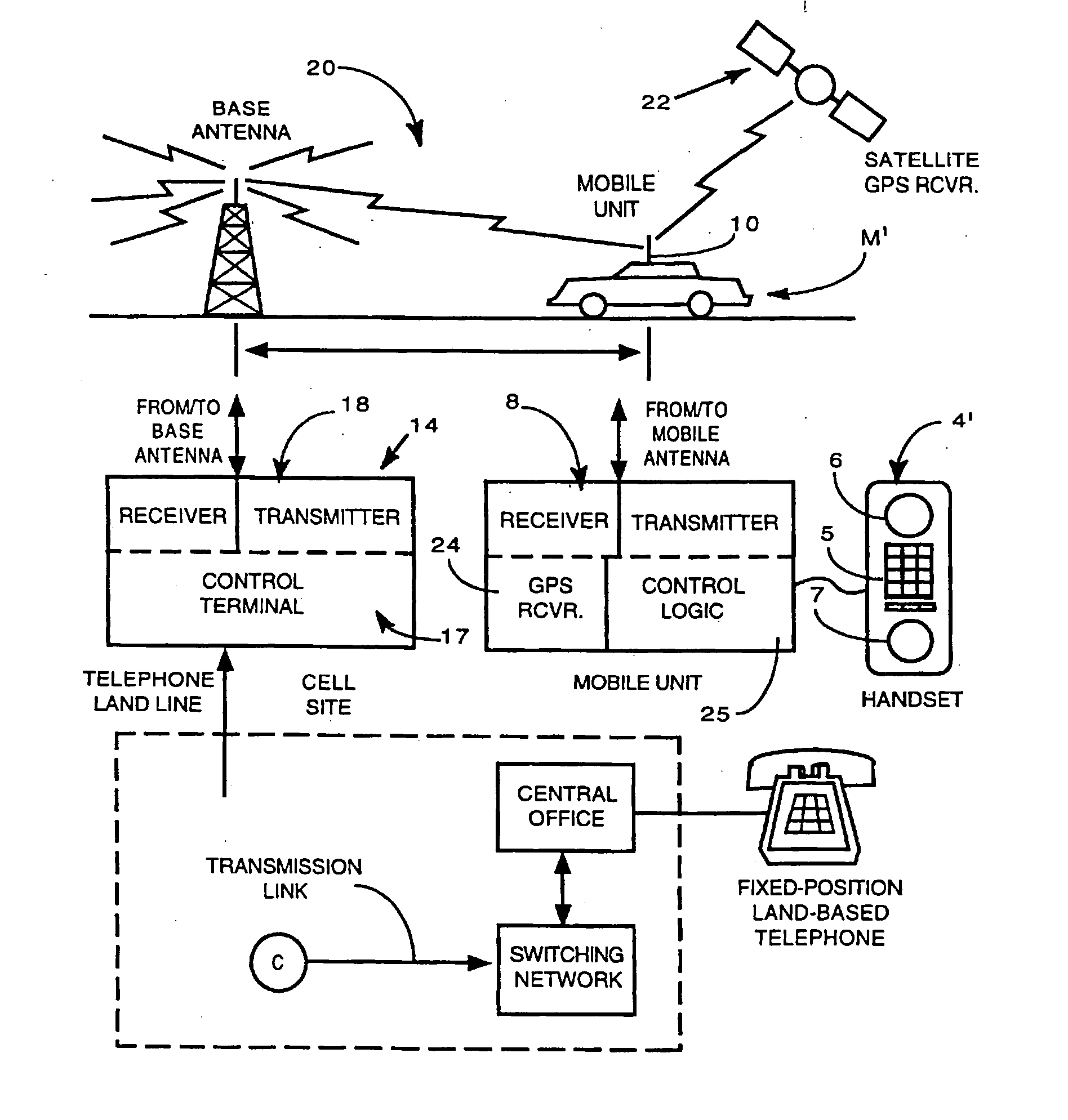
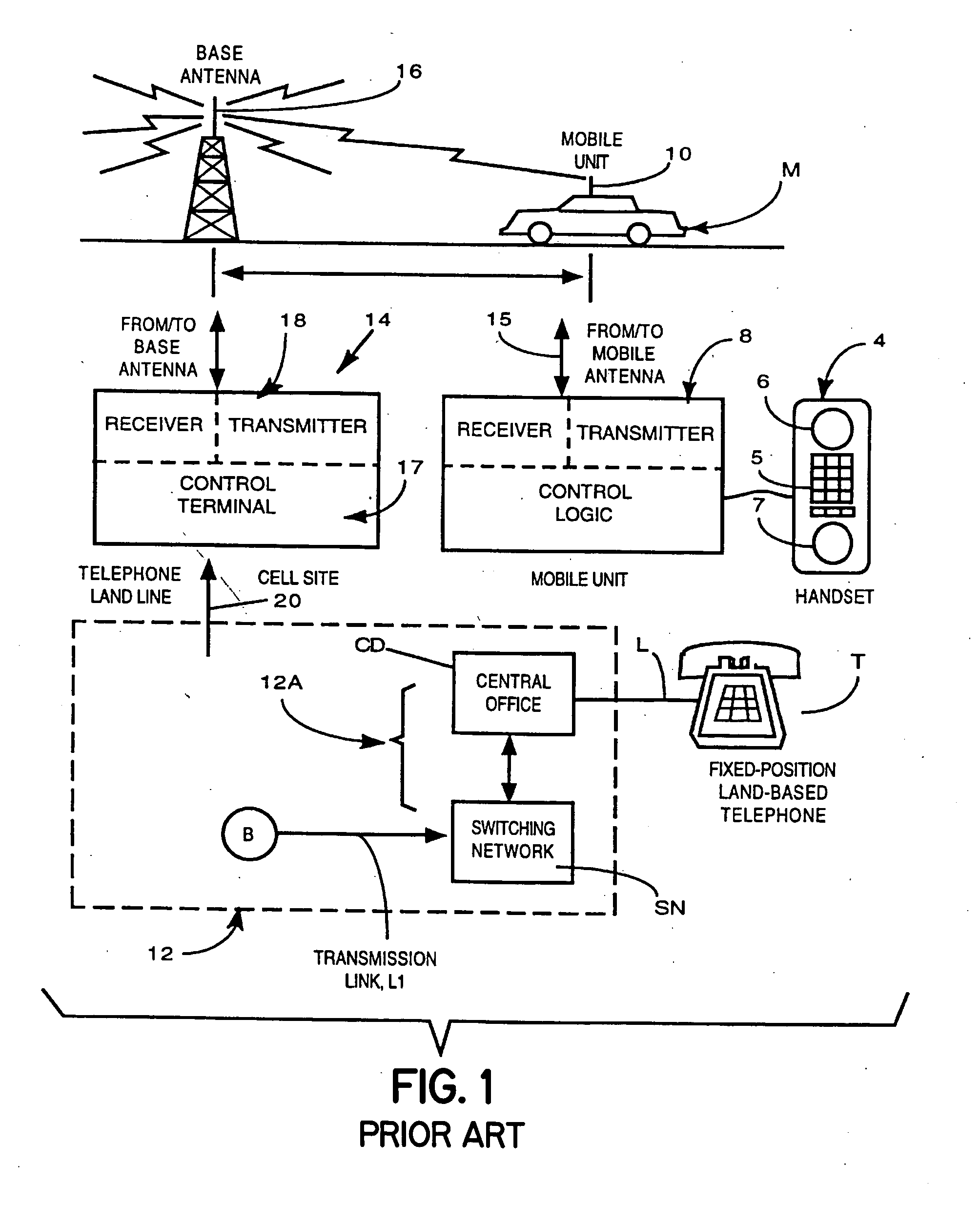
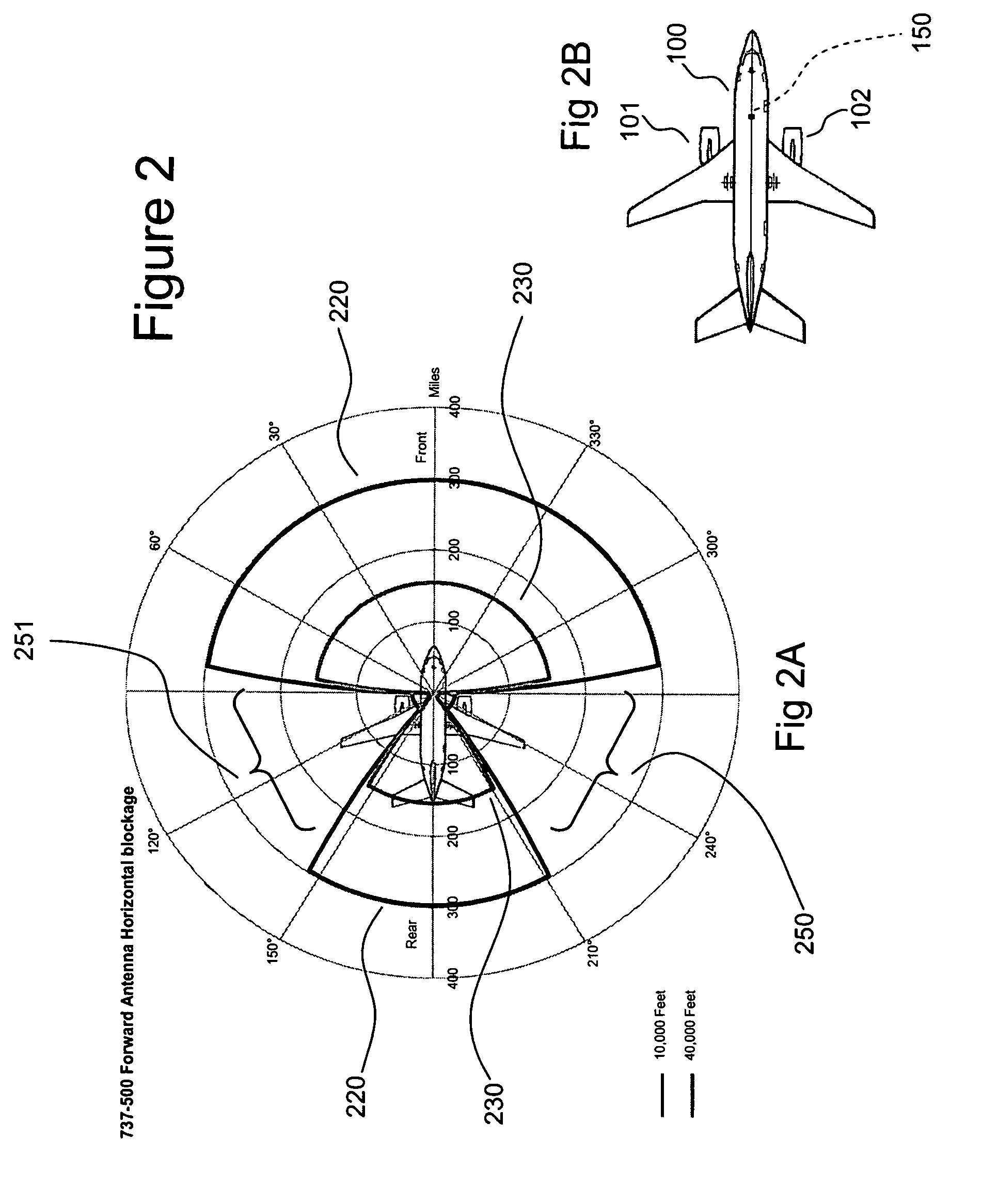
A cell site, cell tower, or cellular base station is a cellular-enabled mobile device site where antennae and electronic communications equipment are placed—typically on a radio mast, tower, or other raised structure—to create a cell (or adjacent cells) in a cellular network. The raised structure typically supports antenna and one or more sets of transmitter/receivers transceivers, digital signal processors, control electronics, a GPS receiver for timing (for CDMA2000/IS-95 or GSM systems), primary and backup electrical power sources, and sheltering.
System and method for optimizing network capacity in a cellular wireless network
InactiveUS20050007993A1Easy to adaptNetwork traffic/resource managementPower distribution line transmissionQuality of serviceFiber
Owner:CHAMBERS MAHDI +1
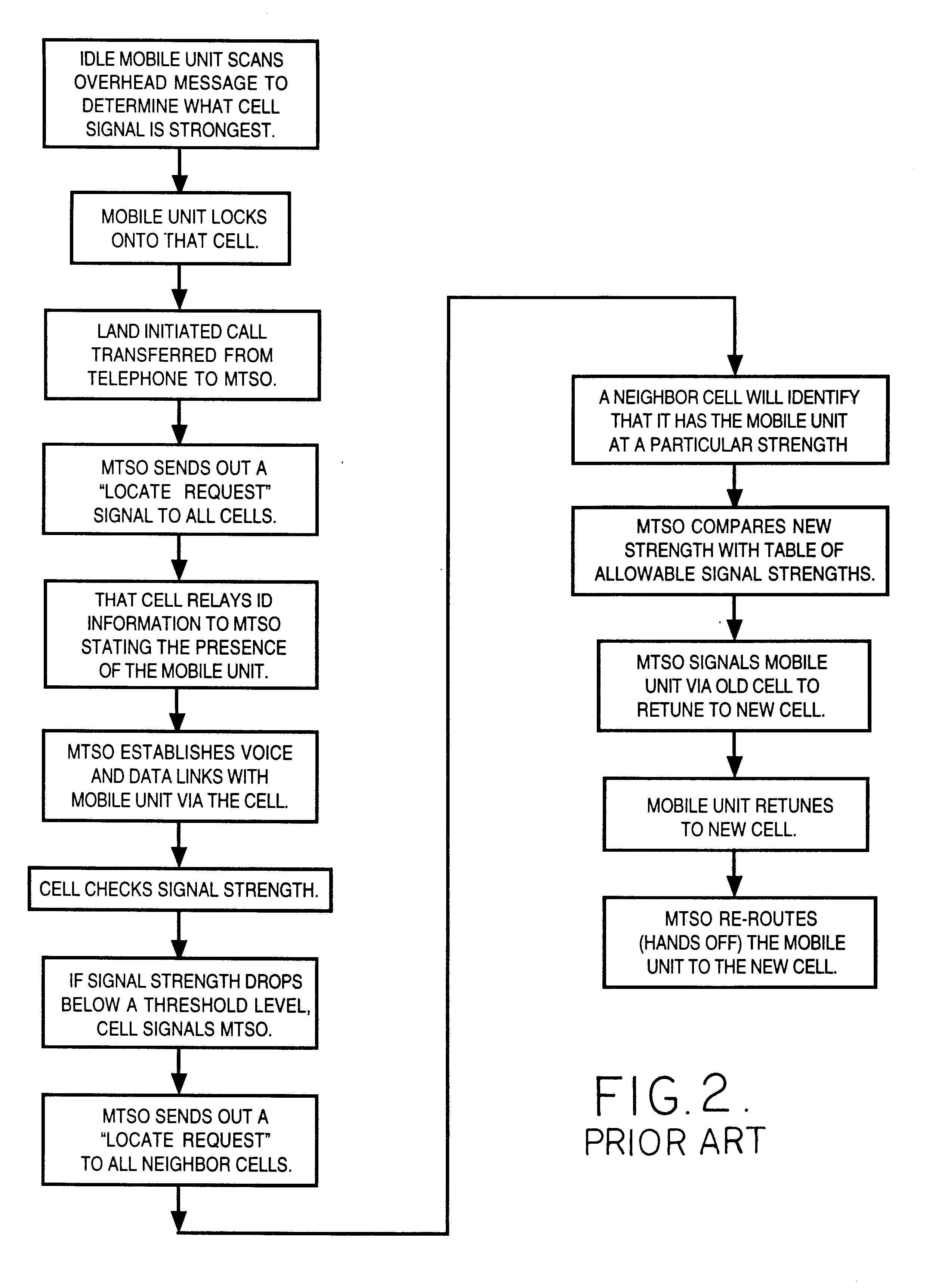
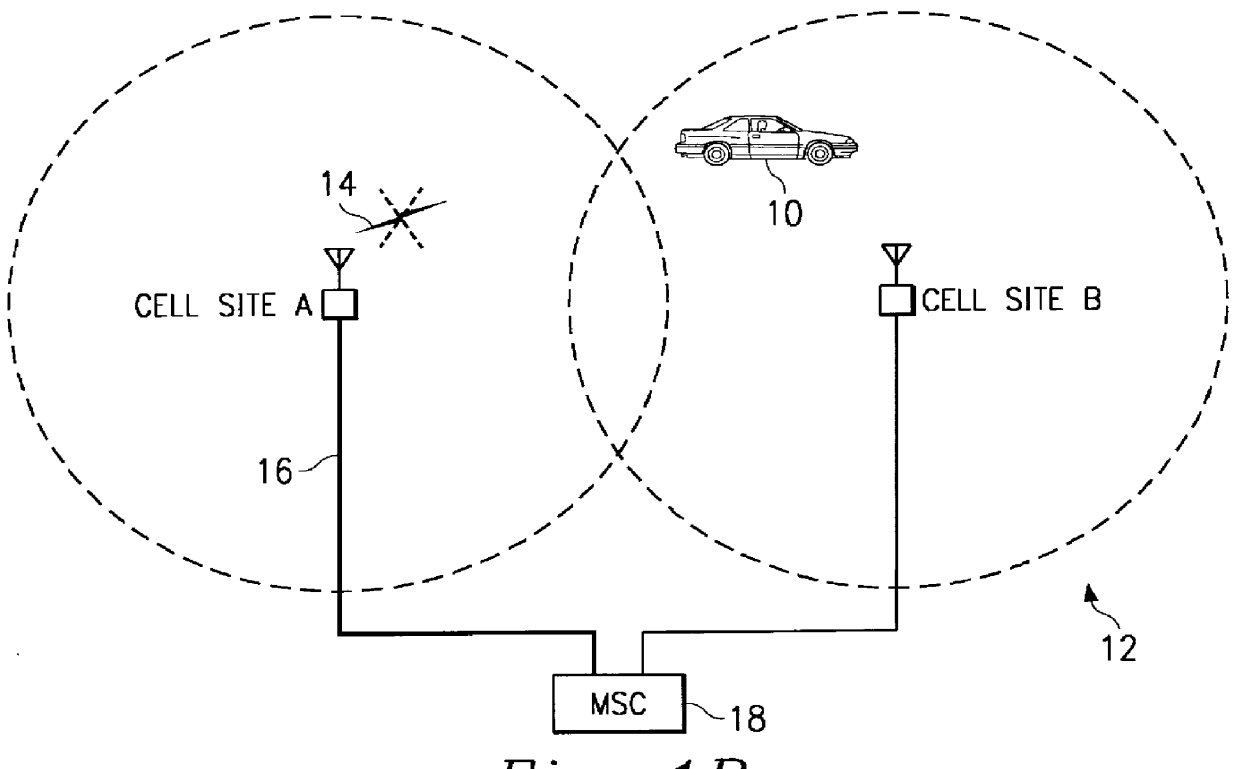
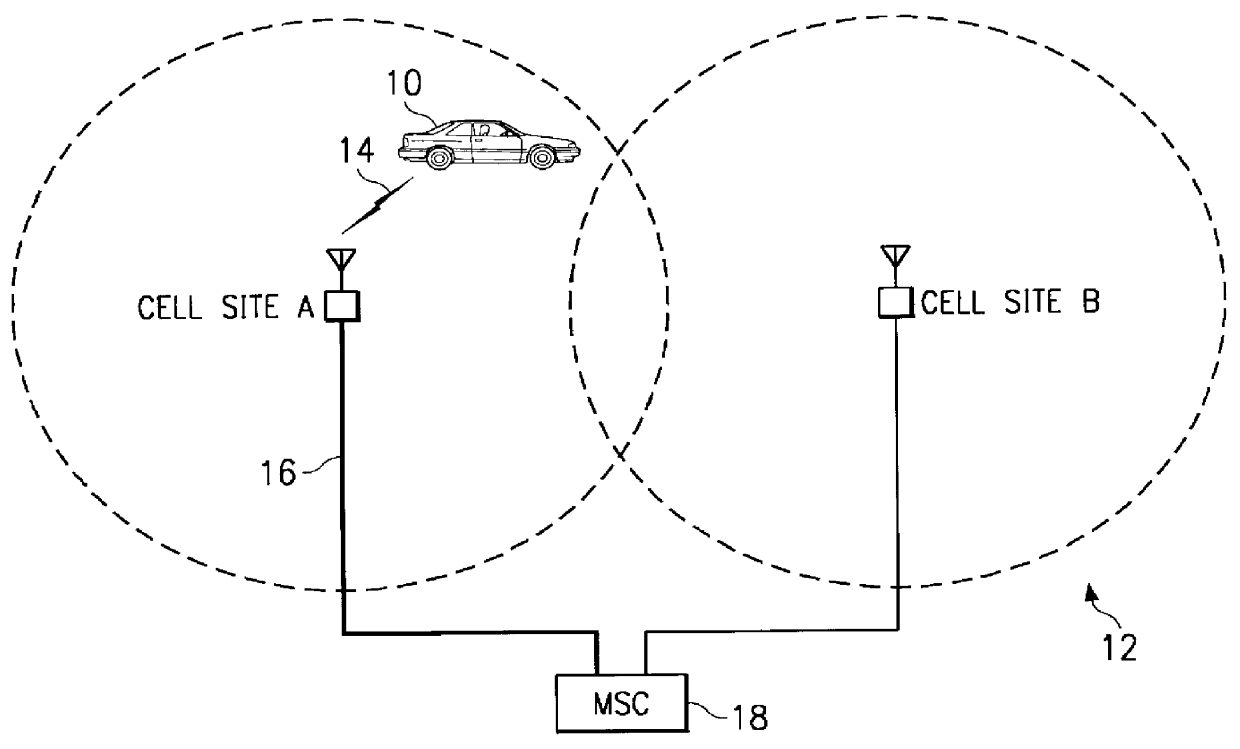
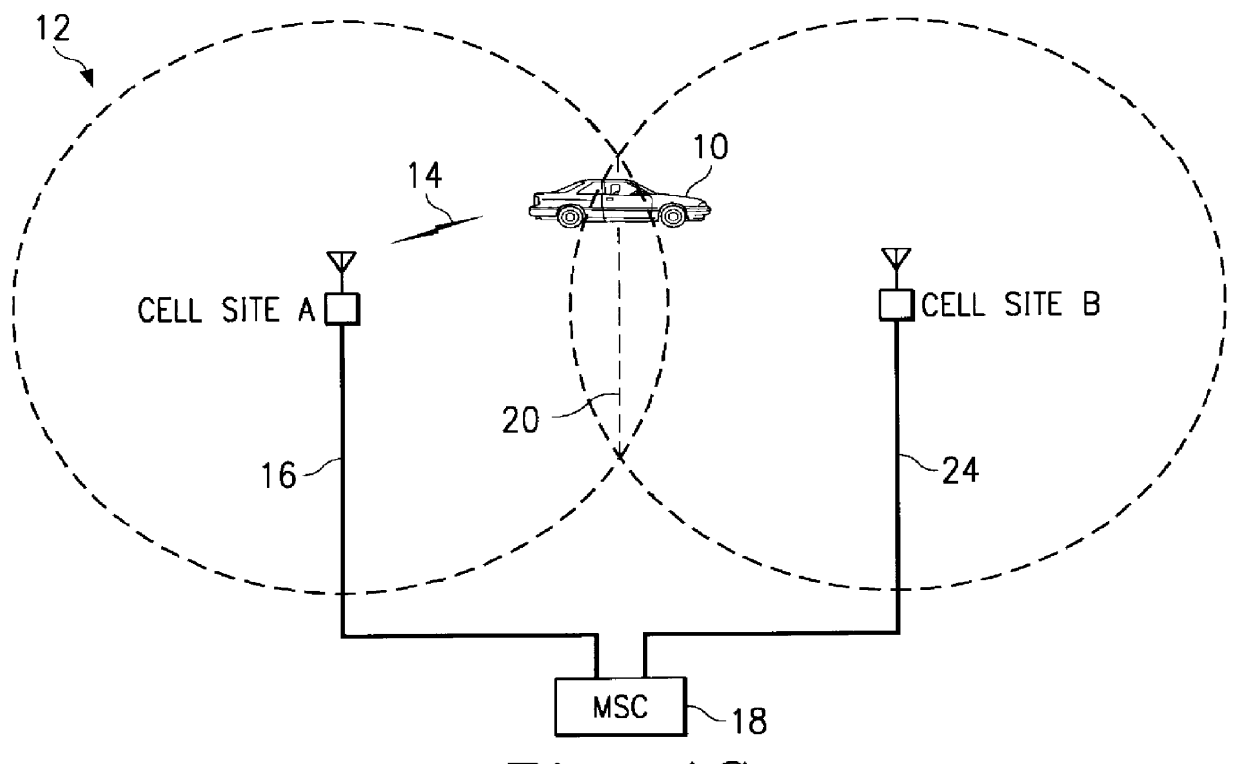
Cellular telephone system that uses position of a mobile unit to make call management decisions
InactiveUS6847822B1Efficient and accurate servicePrecise processingEmergency connection handlingTelephonic communicationCell siteGeolocation
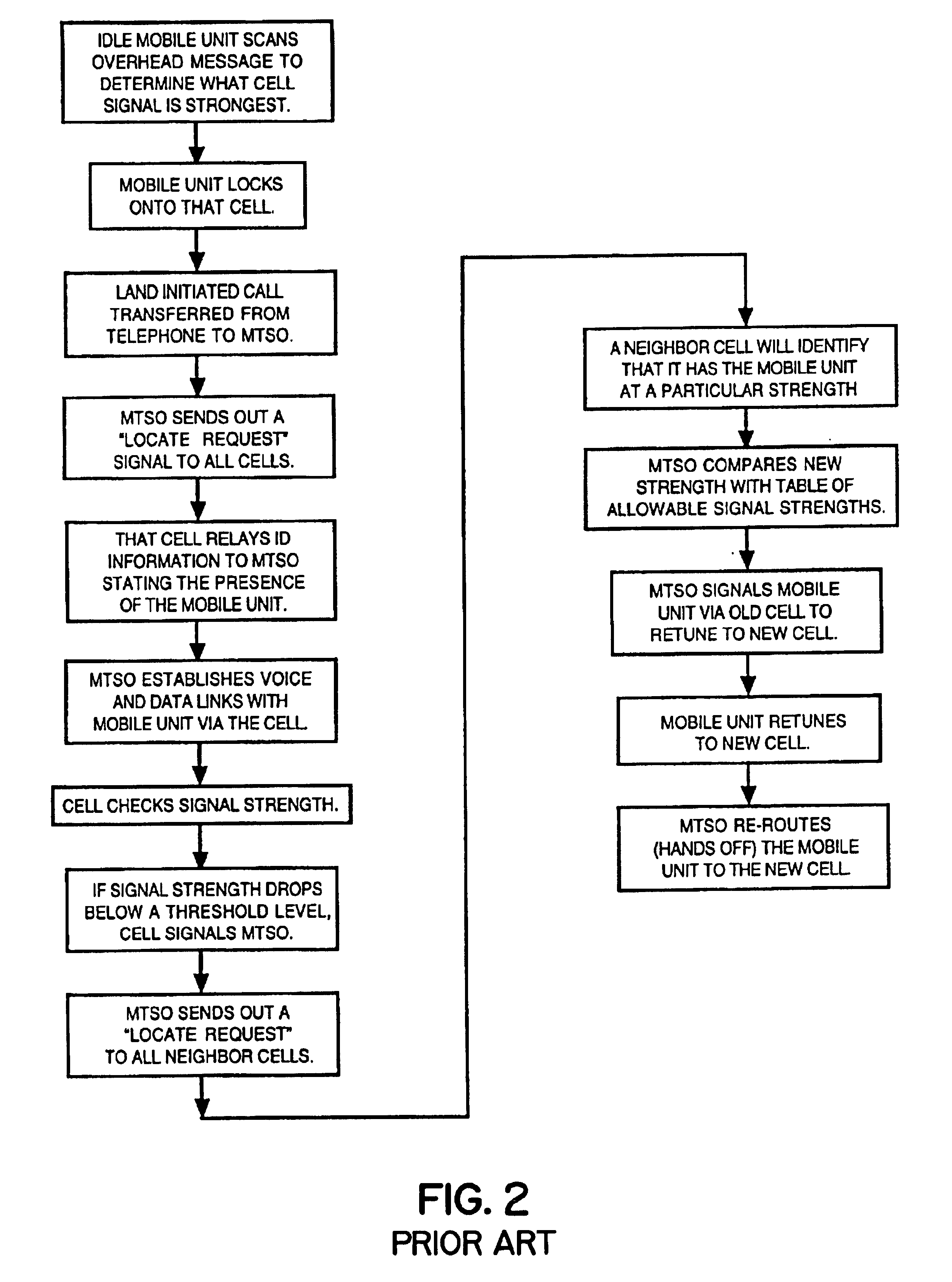
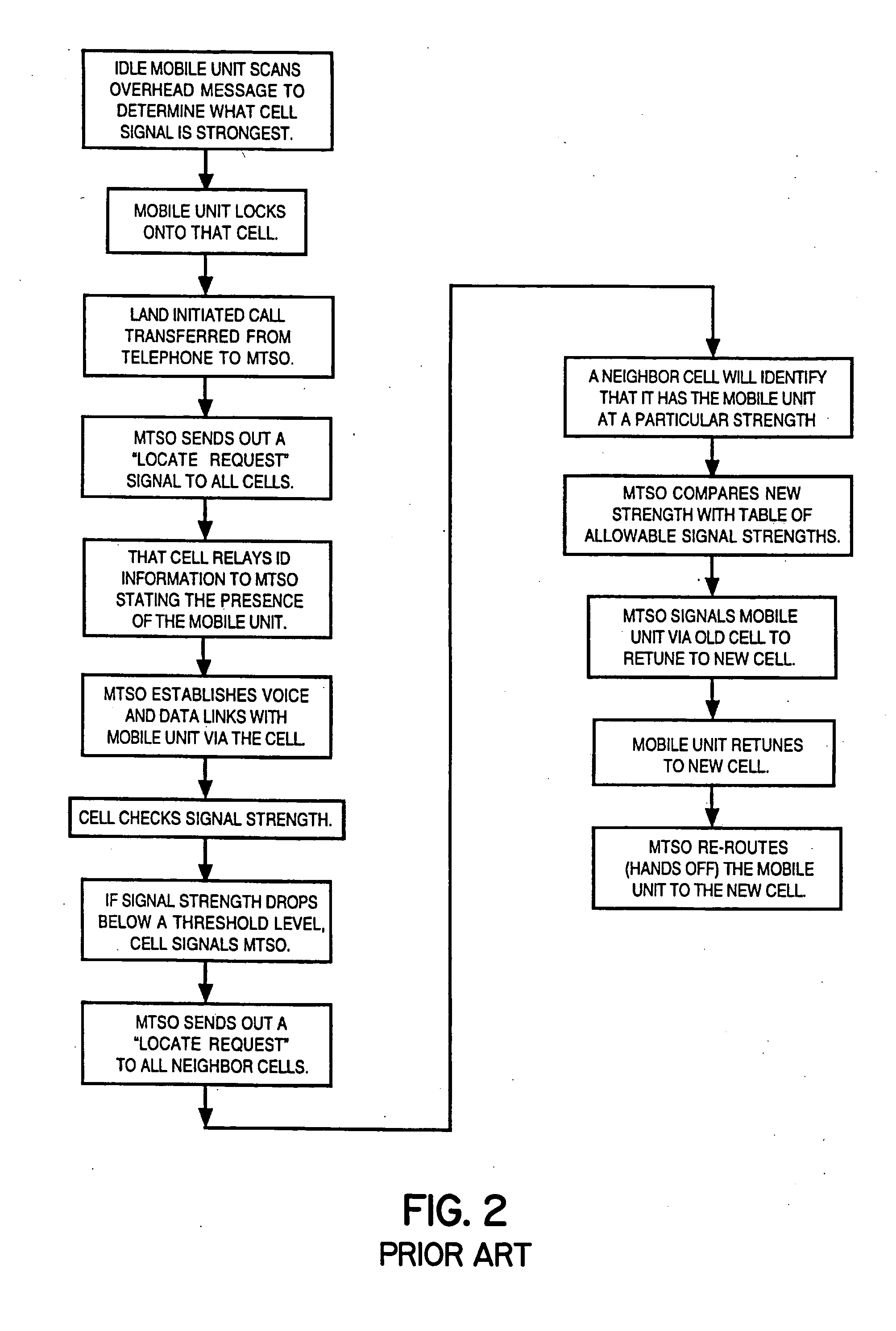
A cellular telephone system has call management decisions made based on the exact geographic location of the mobile unit. These call management decisions include billing and taxing decisions, cell site selection, frequency selection and even cellular system selection. The decisions are continuously updated during a call whereby decisions can be made and changed regardless of where a call originated. Cell site location, and even cellular system selection, can be made in a specific manner to best serve the needs of the mobile user, the cellular system as well as the public. It is even possible for a cellular system to locate one or more of its cell sites in the geographic area served by another cellular system. In some cases, cellular systems might even share cell sites.
Owner:EMSAT ADVANCED GEO LOCATION TECH
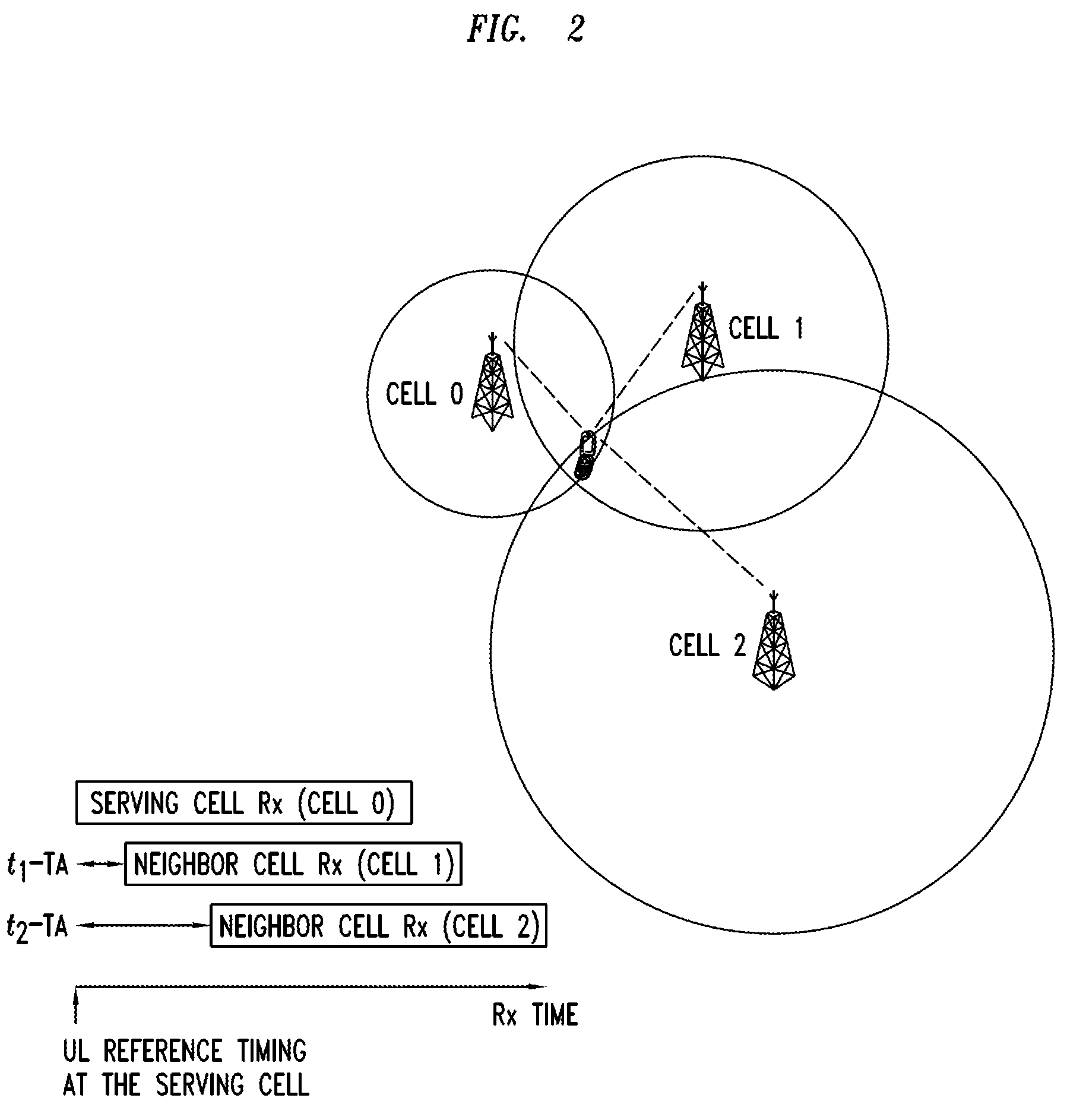
Method And Apparatus for UE Positioning in LTE Networks
Methods and apparatuses are provided for user equipment positioning in networks. An example method includes computing a location of a user equipment (UE). The computing includes joint scheduling of UL subframes and receiving a Up Link Positioning Reference Signal (UL-PRS). The computing is performed by a network equipment that serves at least one cell site. The UL-PRS is received in a known subframe. The computing may also include estimating an arrival time the UL-PRS from the UE for a plurality of cell sites. In another embodiment, the computing includes determining a one-way delay between
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
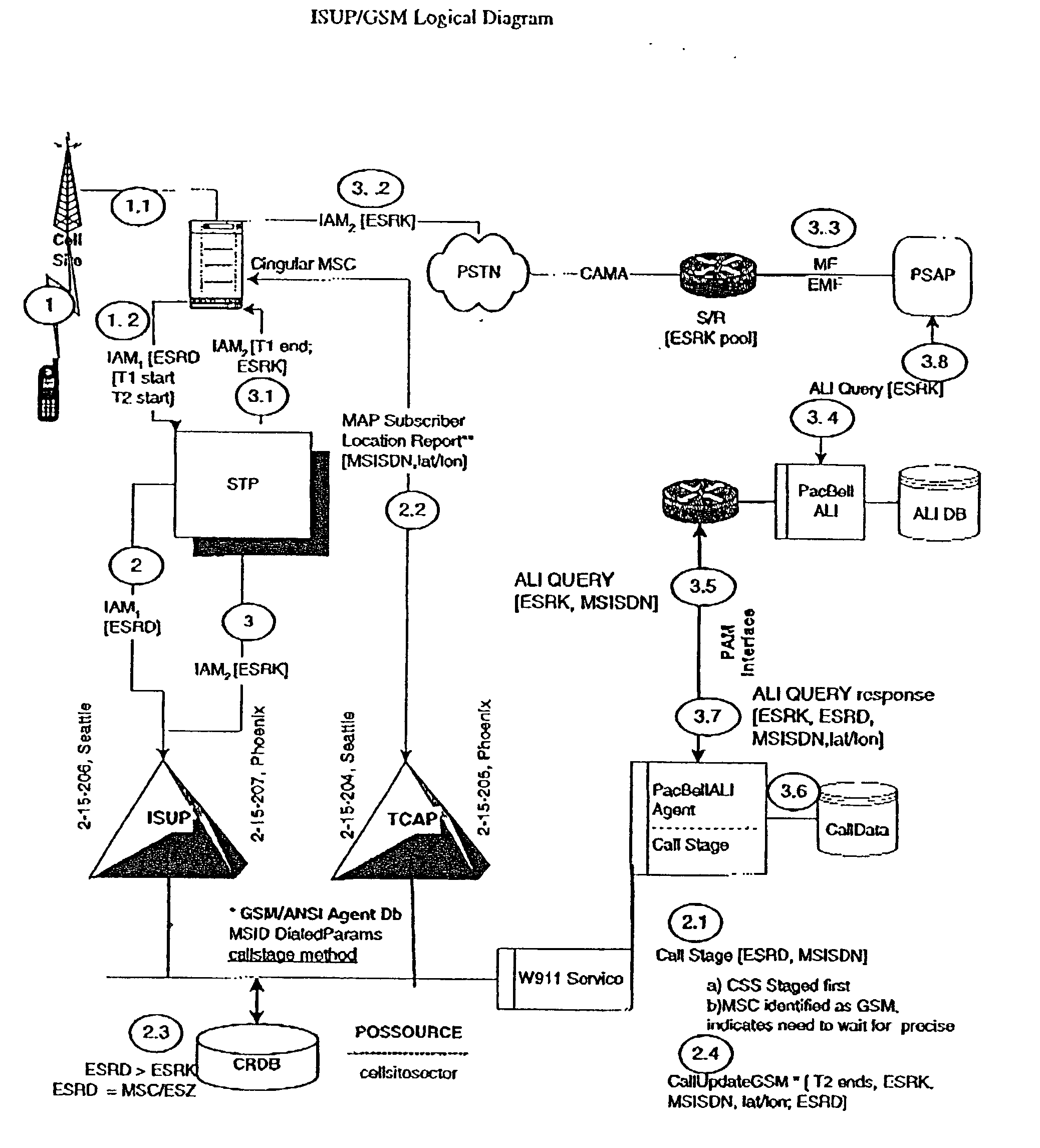
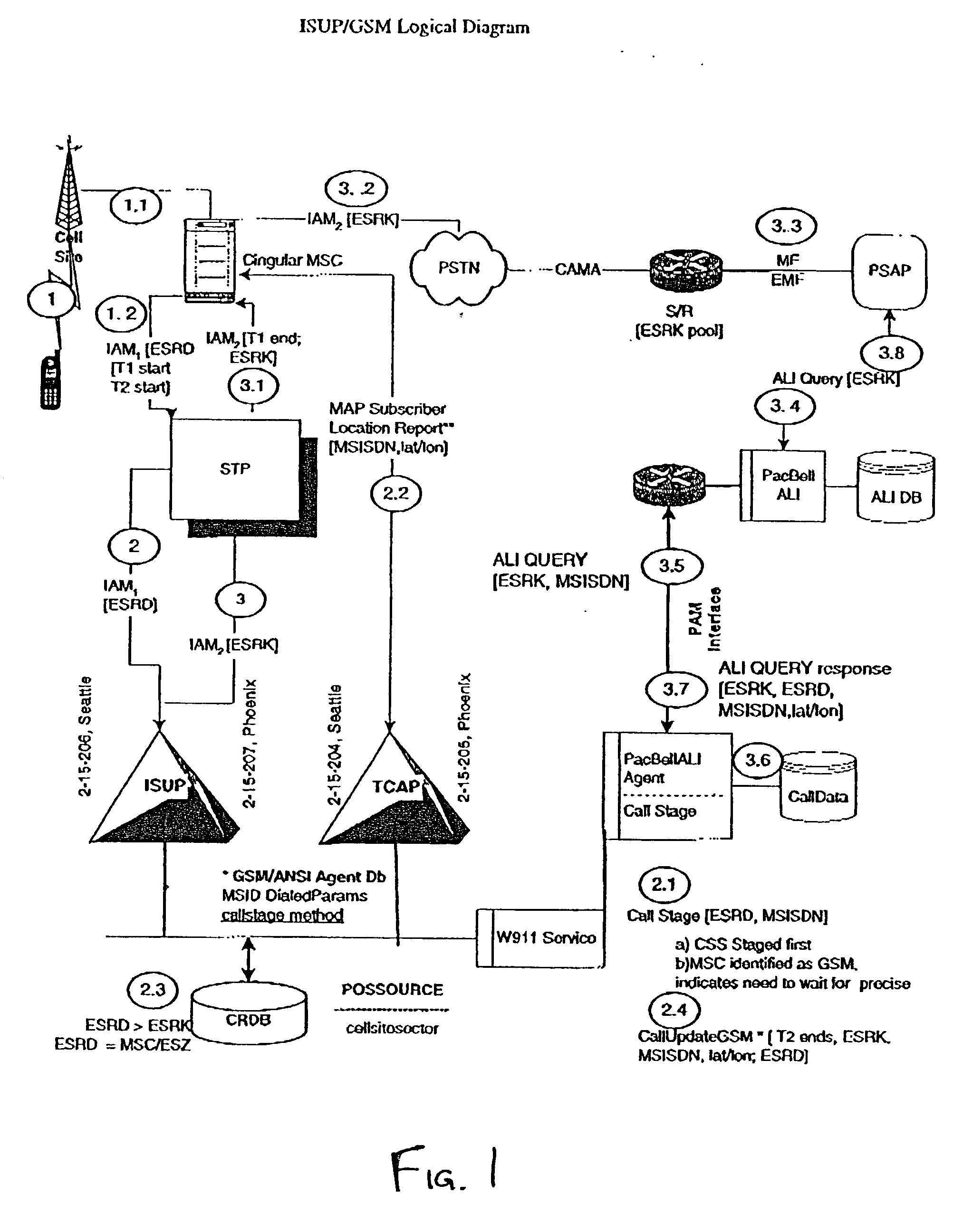
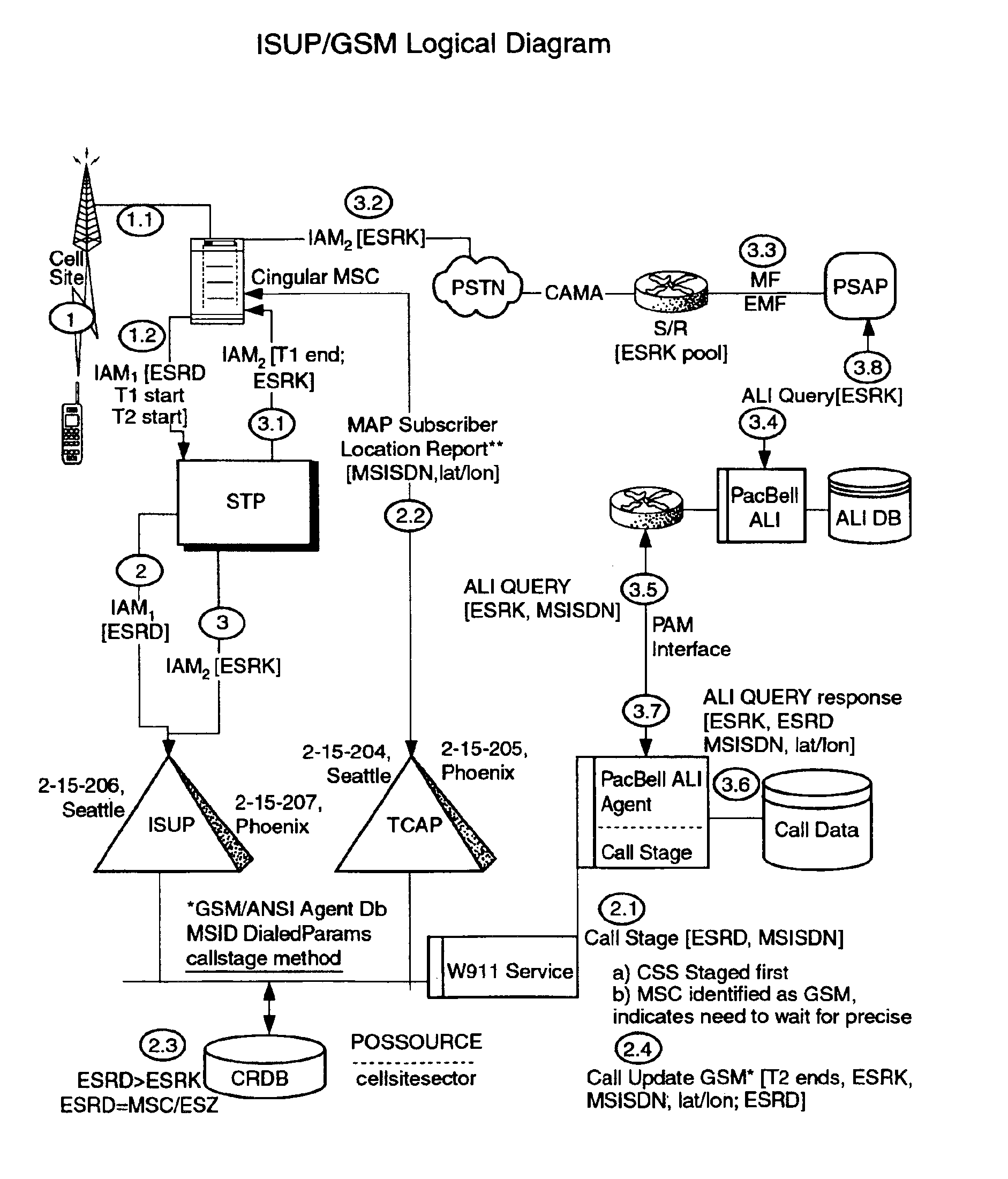
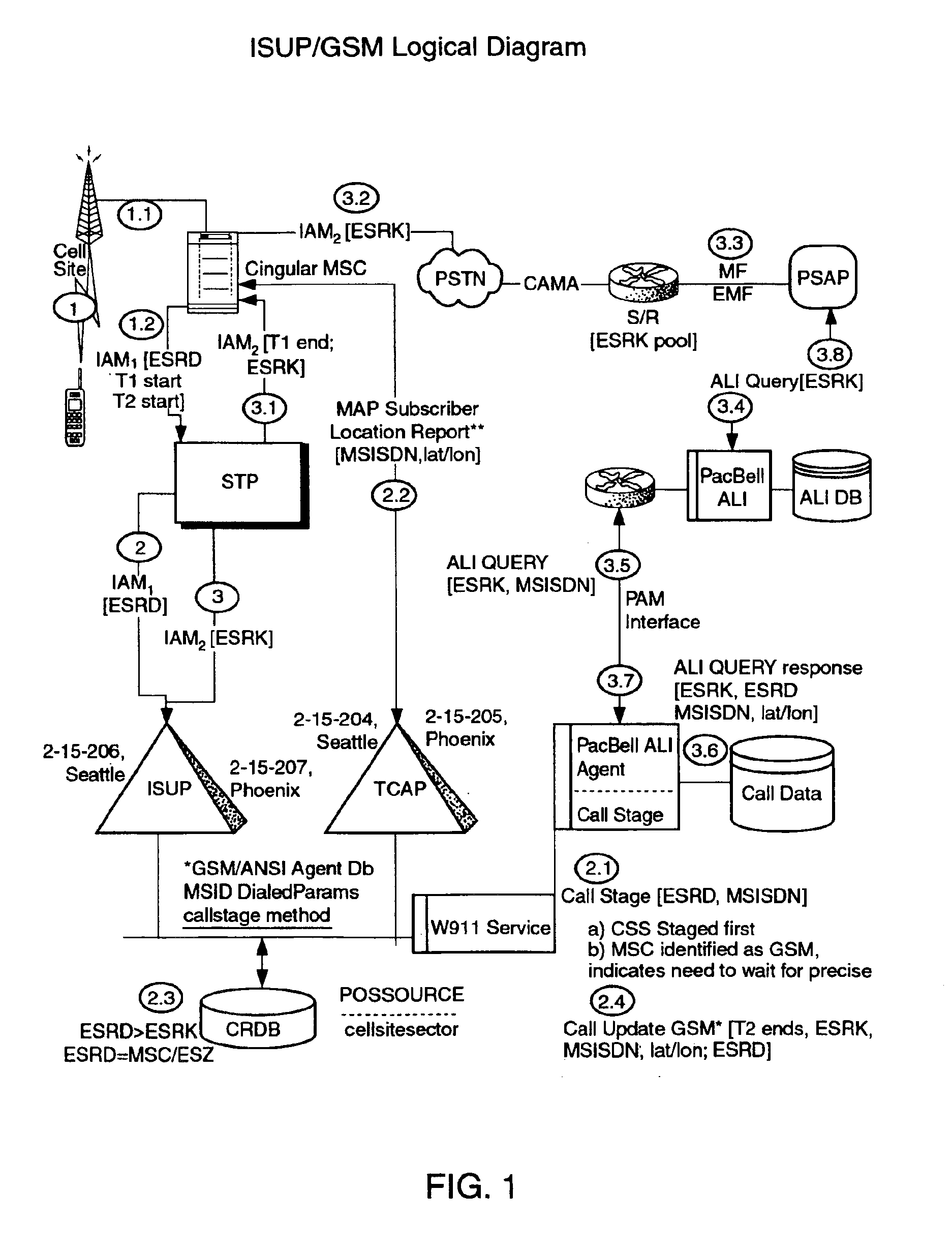
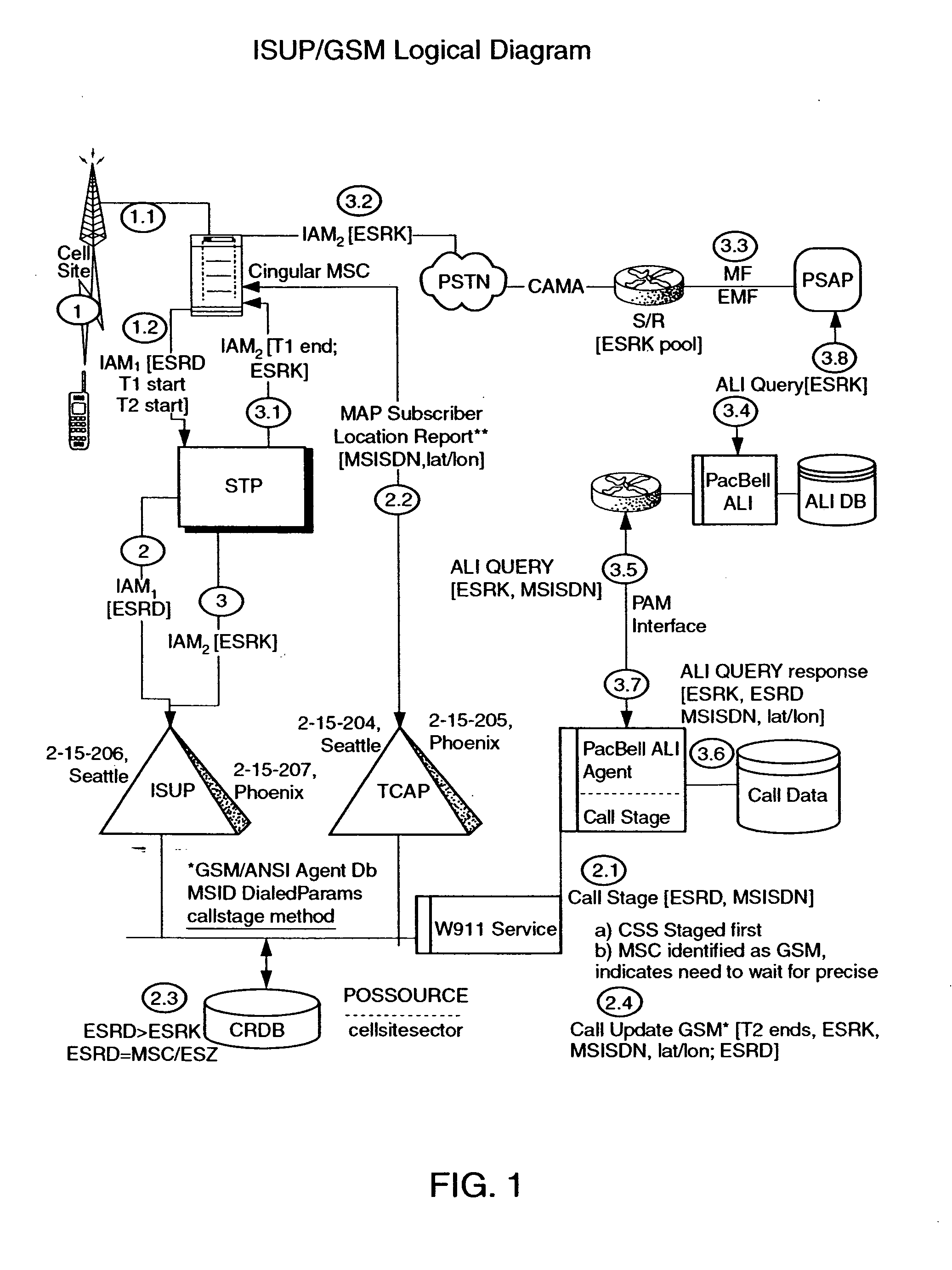
Public safety access point (PSAP) selection for E911 wireless callers in a GSM type system
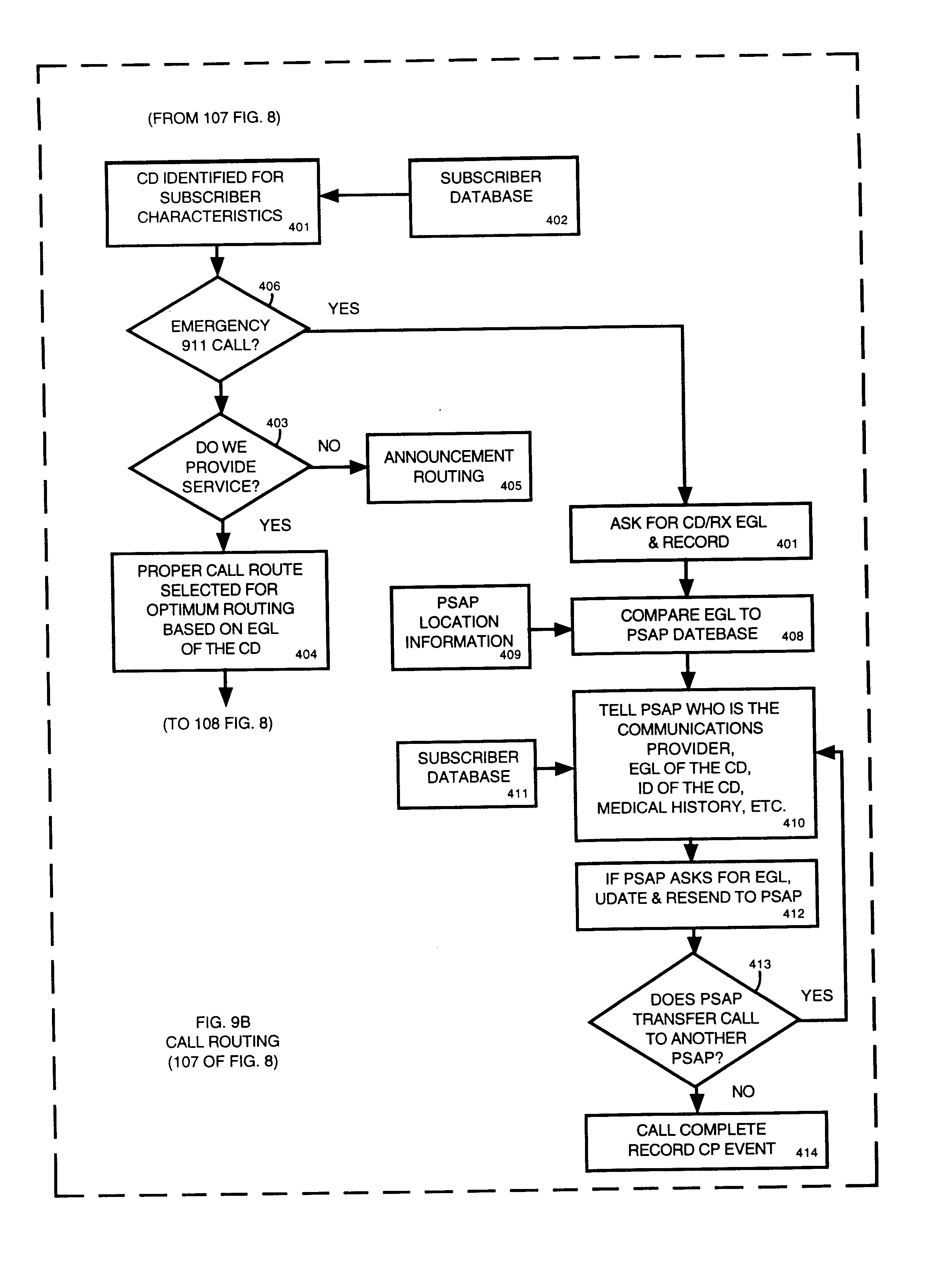
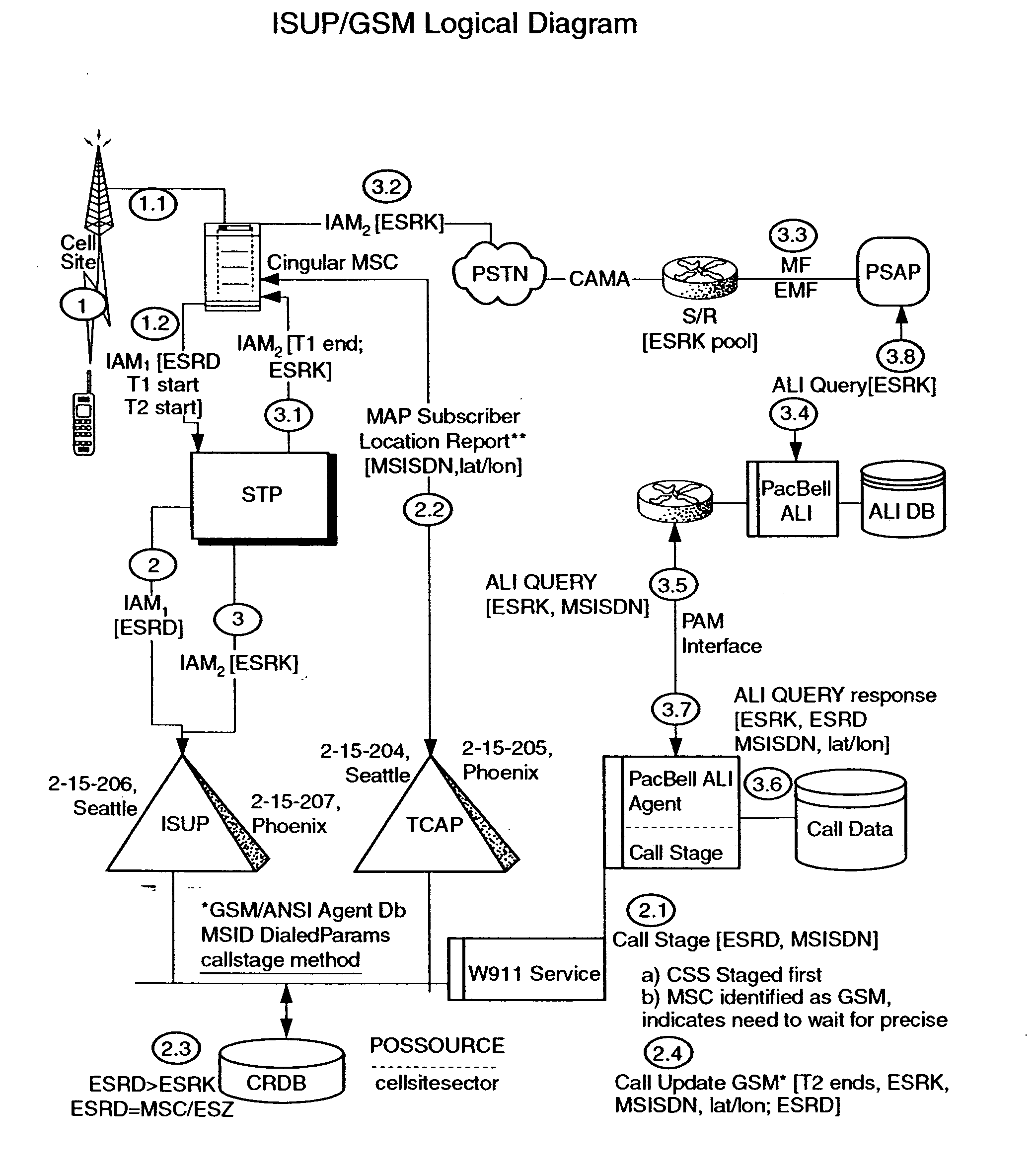
Public safety access points are selected in a wireless network for E911 calls based on ESRD substitution when ESRKs are not being used. The present invention was conceived as an ESRK workaround solution to implement Phase II of the E911 rules from the starting point of a Phase I implementation. ESRKs, ESRDs or ESRVs are initially obtained and managed for each PSAP in a particular carrier's area. Then, Phase I processes are modified to wait to see if Phase II GSM location information will be reported in a timely manner (e.g., within a second or two or so) before committing to a default selection of a particular PSAP based on information available (e.g., based on the location of a serving cell site).
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
Cell selection
InactiveUS7277709B2Avoid the needAccurate measurementError preventionTransmission systemsCell selectionCell site
Cell selection techniques for use in cellular communications systems are disclosed. A decision as to whether to use a cell for data transmission is made in dependence on a measure of a congestion level in the cell. The decision may either be part of a cell selection decision, or used to override a cell selection decision. The techniques may be used in fast cell site selection.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Cellular telephone system that uses position of a mobile unit to make call management decisions
InactiveUS6324404B1Efficient and accurate servicePrecise processingEmergency connection handlingTelephonic communicationCell siteGeolocation
A cellular telephone system has call management decisions made based on the exact geographic location of the mobile unit. These call management decisions include billing and taxing decisions, cell site selection, frequency selection and even cellular system selection. The decisions are continuously updated during a call whereby decisions can be made and changed regardless of where a call originated. Cell site location, and even cellular system selection, can be made in a specific manner to best serve the needs of the mobile user, the cellular system as well as the public. It is even possible for a cellular system to locate one or more of its cell sites in the geographic area served by another cellular system. In some cases, cellular systems might even share cell sites.
Owner:SYGNET COMM +1
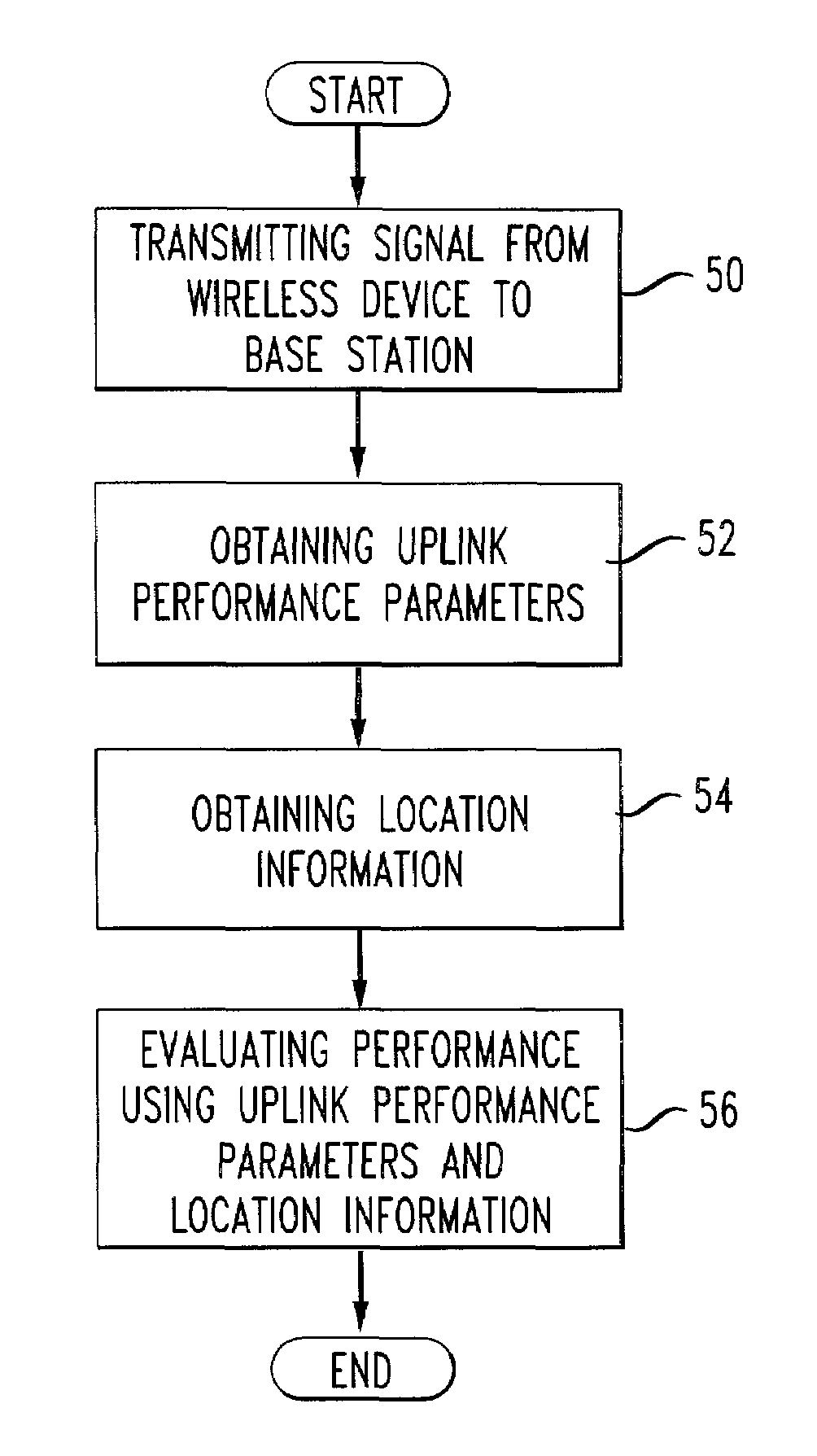
Monitoring network performance using individual cell phone location and performance information
A system and method of collecting call data from a Mobile Telephone Switching Office and combining this data with location information of a wireless device (or devices) to generate information reports concerning the electromagnetic coverage of a cell site. The collection of call data from a switch permits consideration of uplink information in the analysis of system performance. This information combined with location information obtained using a time difference of arrival (TDOA) technique allows the cell site to be evaluated and to remove transient effects associated with, for example, local terrain and other physical impairments.
Owner:AT&T WIRELESS SERVICES
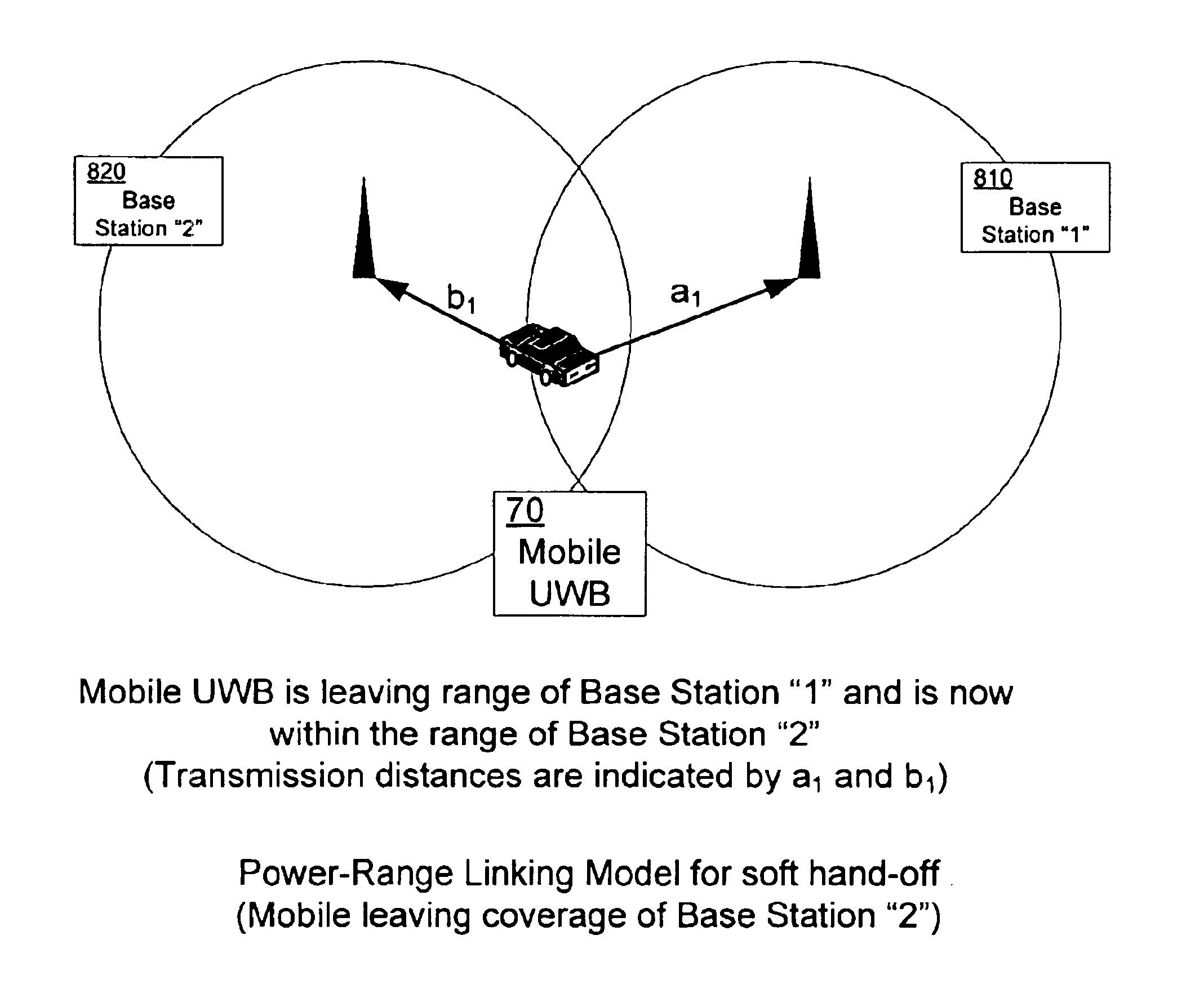
Hand-off between ultra-wideband cell sites
InactiveUS6907244B2Effectively linkedAcceptable levelError prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorDynamic channelCell site
Briefly, the present invention provides a dynamic channel re-assignment capability between mobile units, base stations and sectors within base station coverage areas. The wireless devices used in the present invention may include impulse radio communication devices such as, for example ultra-wideband radio (also known as digital pulse wireless) communication devices. Ultra-wideband bandwidth and channel allocation can be effectively managed, even though link quality generally deteriorates near the outer boundary of the base station. By maintaining dual communications with an adjoining base station, the present invention reduces the bit error rate and maintains signal strength (e.g., RF signal strength). This procedure is termed a “soft-handoff”.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
Method for hard handoff in a CDMA cellular environment
InactiveUS6026301AConserve costAvoid performanceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationCell siteCdma networks
A method for performing a hard handoff of a call from a first cell site of a CDMA cellular network to a target cell site of a second cellular network, such as an AMPS network or a second CDMA network. As a mobile unit operating in the first CDMA network moves toward the second cellular network, the first cell site uses two separate RTD thresholds for comparison with a measured RTD distance between the mobile unit and the first cell site. Handoff is initiated when the RTD distance exceeds the first RTD threshold and is completed when the RTD distance exceeds the second RTD threshold. If the first cell site is not co-located with a cell site of the second network, the first cell site utilizes receivers placed in the target cell site for handoff. If the first cell site is co-located with a second cell site of the second network, the second cell site of the second network is always the target cell site.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Self-organizing networks using directional beam antennas
A method for determining whether to reconfigure a self-organizing network (SON) comprising coverage areas each having a BTS and an antenna and mobile units operating in each coverage area. The method comprises: at each BTS, scanning an antenna beam, measuring performance data, and determining whether measured performance data indicates a network reconfiguration; if a result is negative, at a first BTS returning to the step of scanning the antenna beam; if the result is affirmative, selecting one or more of reconfiguring the SON by changing the RF output power of the first BTS, changing an antenna beam pattern of the antenna at the first BTS, changing an antenna tilt angle of the antenna at the first BTS, changing an operating frequency of the first BTS and updating a proximate cell site list of the first BTS.
Owner:LEE JUNGWOO +1
Method and System for User Equipment Location Determination on a Wireless Transmission System
ActiveUS20110286349A1Improve audibilityReduce signal to noise ratioError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrequency reuseResource block
Neighbor cell hearability can be improved by including an additional reference signal that can be detected at a low sensitivity and a low signal-to-noise ratio, by introducing non-unity frequency reuse for the signals used for a time difference of arrival (TDOA) measurement, e.g., orthogonality of signals transmitted from the serving cell sites and the various neighbor cell sites. The new reference signal, called the TDOA-RS, is proposed to improve the hearability of neighbor cells in a cellular network that deploys 3GPP EU-TRAN (LTE) system, and the TDOA-RS can be transmitted in any resource blocks (RB) for POSCH and / or MBSFN subframe, regardless of whether the latter is on a carrier supporting both PMCH and POSCH or not. Besides the additional TDOA-RS reference signal, an additional synchronization signal (TDOA-sync) may also be included to improve the hearability of neighbor cells.
Owner:APPLE INC
Wireless access system using selectively adaptable beam forming in TDD frames and method of operation
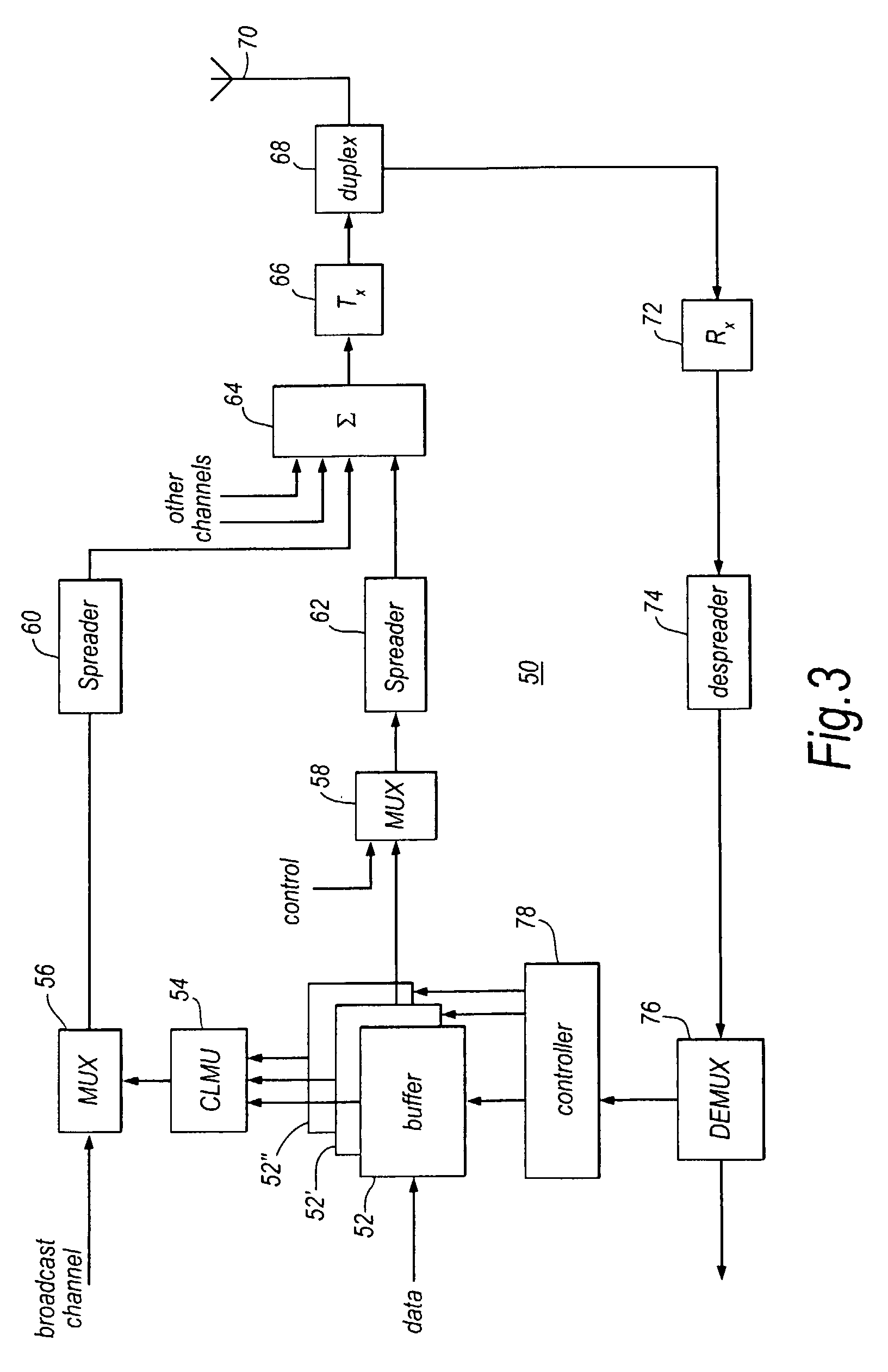
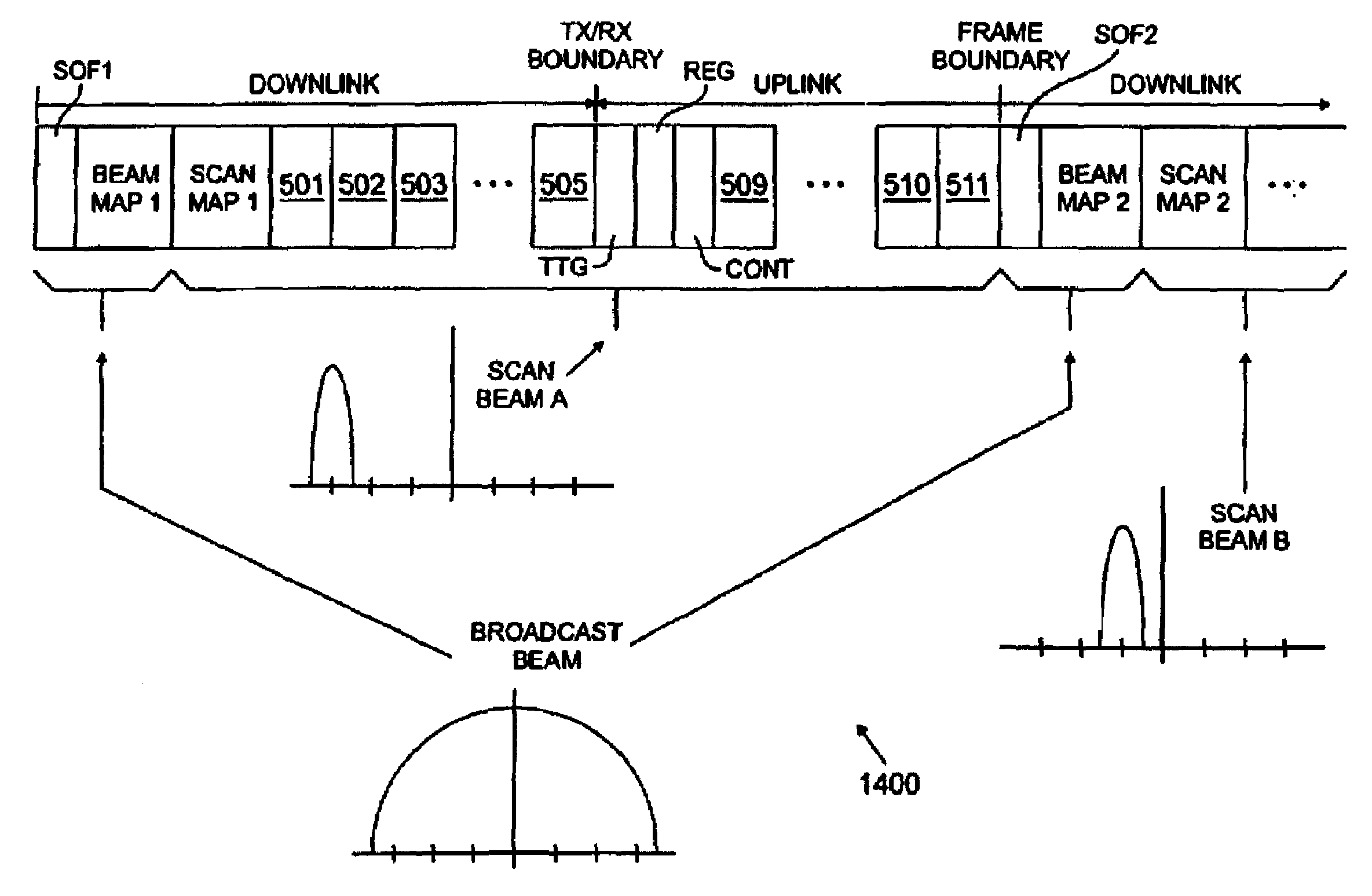
A transceiver for use in a wireless access network comprising a plurality of base stations, each of the plurality of base stations capable of bidirectional time division duplex (TDD) communication with wireless access devices disposed at a plurality of subscriber premises in a corresponding cell site of the wireless access network. The transceiver is associated with a first base station and comprises transmit path circuitry associated with a beam forming network for transmitting directed scanning beam signals in a sector of a cell site of the first base station. The transmit path circuitry transmits at a start of a TDD frame a broadcast beam signal comprising a start of frame field and subsequently transmits downlink data traffic in a downlink portion of the TDD frame to at least one of the wireless access devices using at least one directed scanning beam.
Owner:RAZE TECH
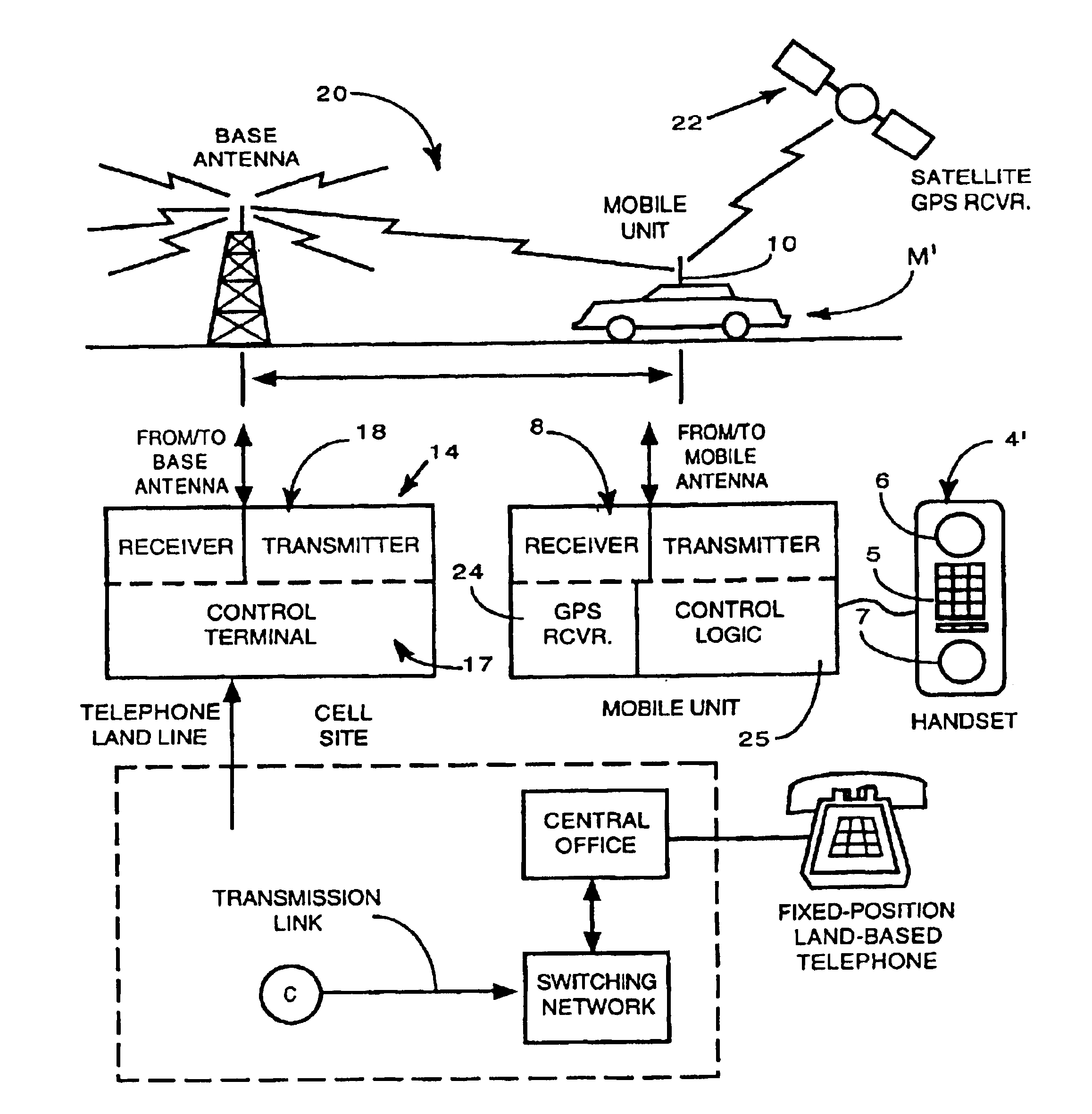
Position location method and apparatus for a mobile telecommunications system
InactiveUS6489923B1Limited bandwidthEasy CalibrationRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsBeacon systems using radio wavesRelative phaseDirectional antenna
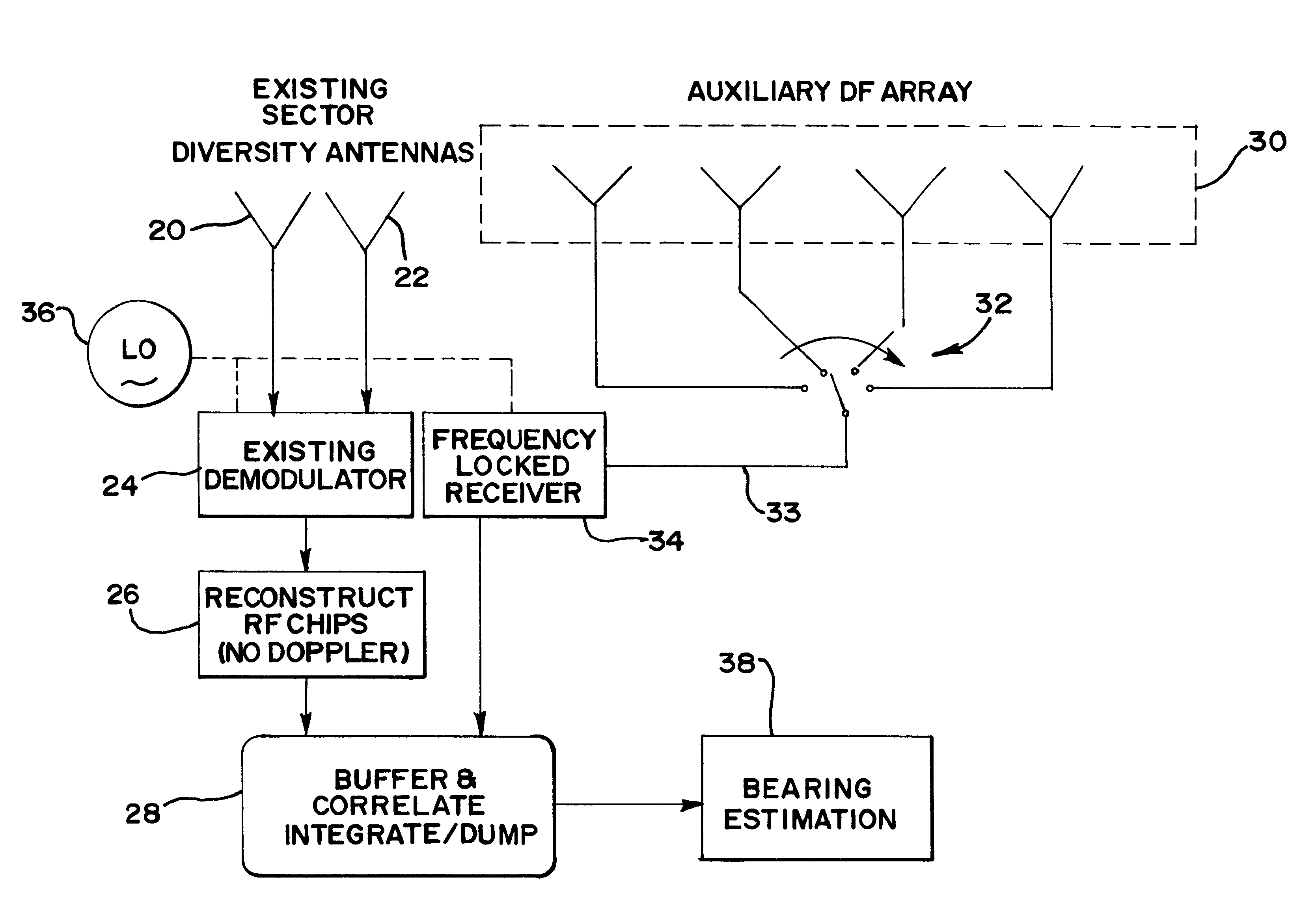
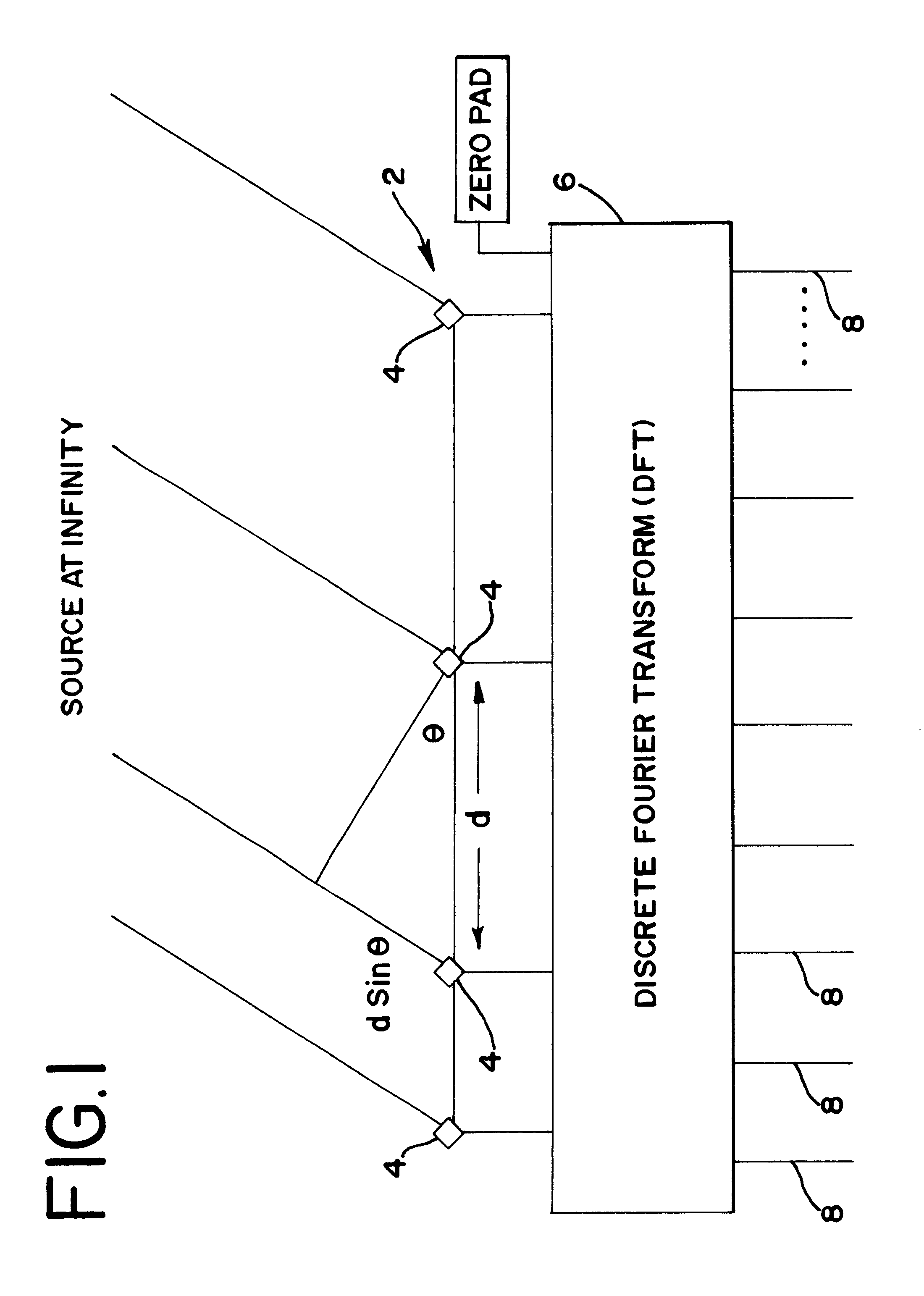
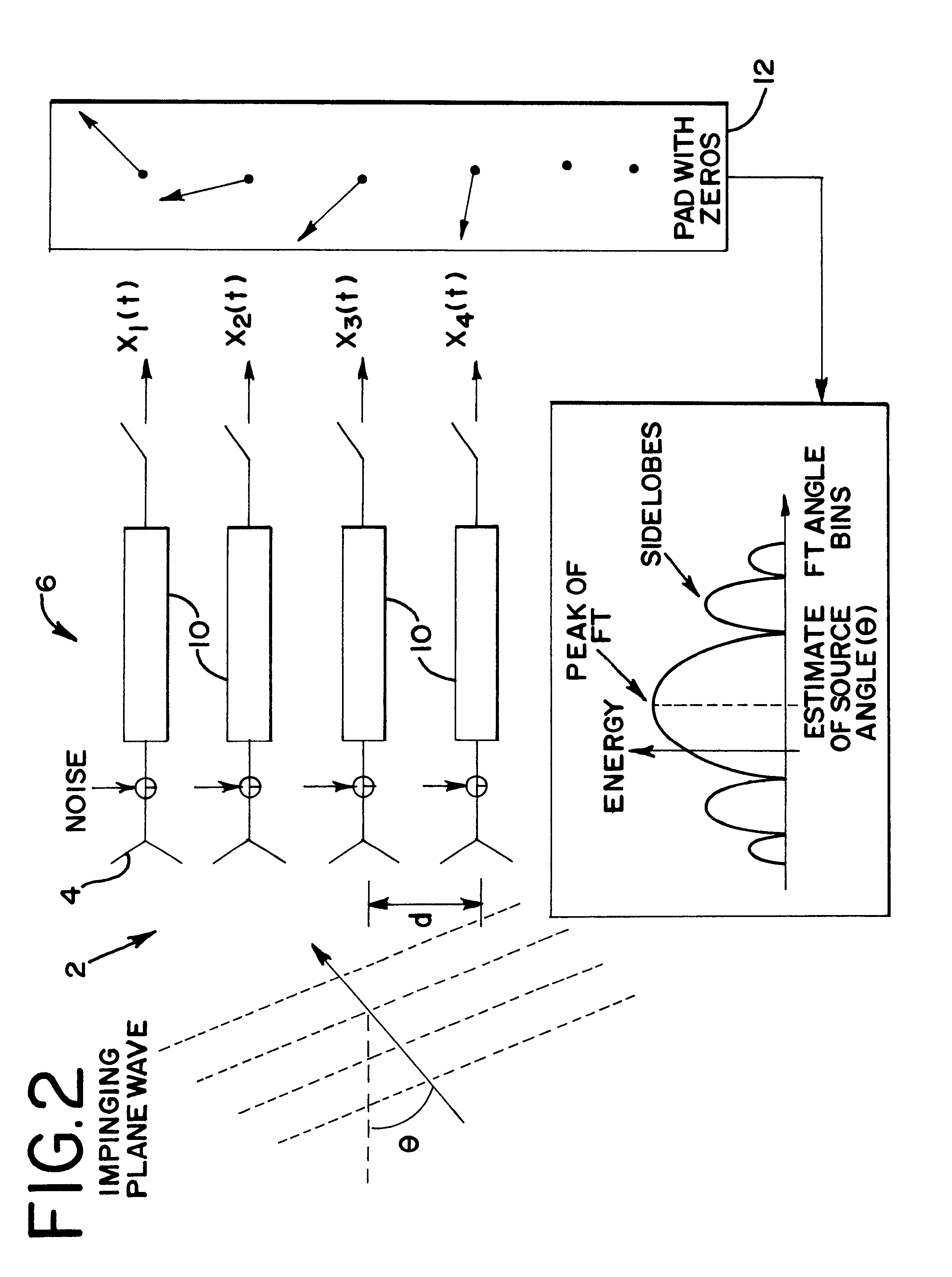
In a cellular mobile telecommunications system the position of a mobile station can be estimated in terms of its bearing and range from a cell site. A multi-element direction finding antenna at the cell site receives signals from the mobile station and a receiver circuit estimates the bearing using the relative phase of signals received at different antenna elements and estimates the range by measuring round trip delay of signals to and from the mobile station. Motion of the mobile station can introduce errors into the bearing estimate due to frequency offset and frequency spread when element sampling is non-simultaneous. Compensation for these errors is introduced by using signal samples successively received at the same antenna element to estimate Doppler frequency offset and spread. It is necessary to ensure accurate calibration of the direction finding antenna and the receiver circuit. This is done by injecting calibration signals into the circuit near the antenna or into the antenna itself from a near field probe. Other aspects of calibration, such as antenna position, are calibrated using a remote beacon. A beacon emulating a mobile station but at a fixed, known location, or a beacon at an adjacent cell site may be used.
Owner:APPLE INC
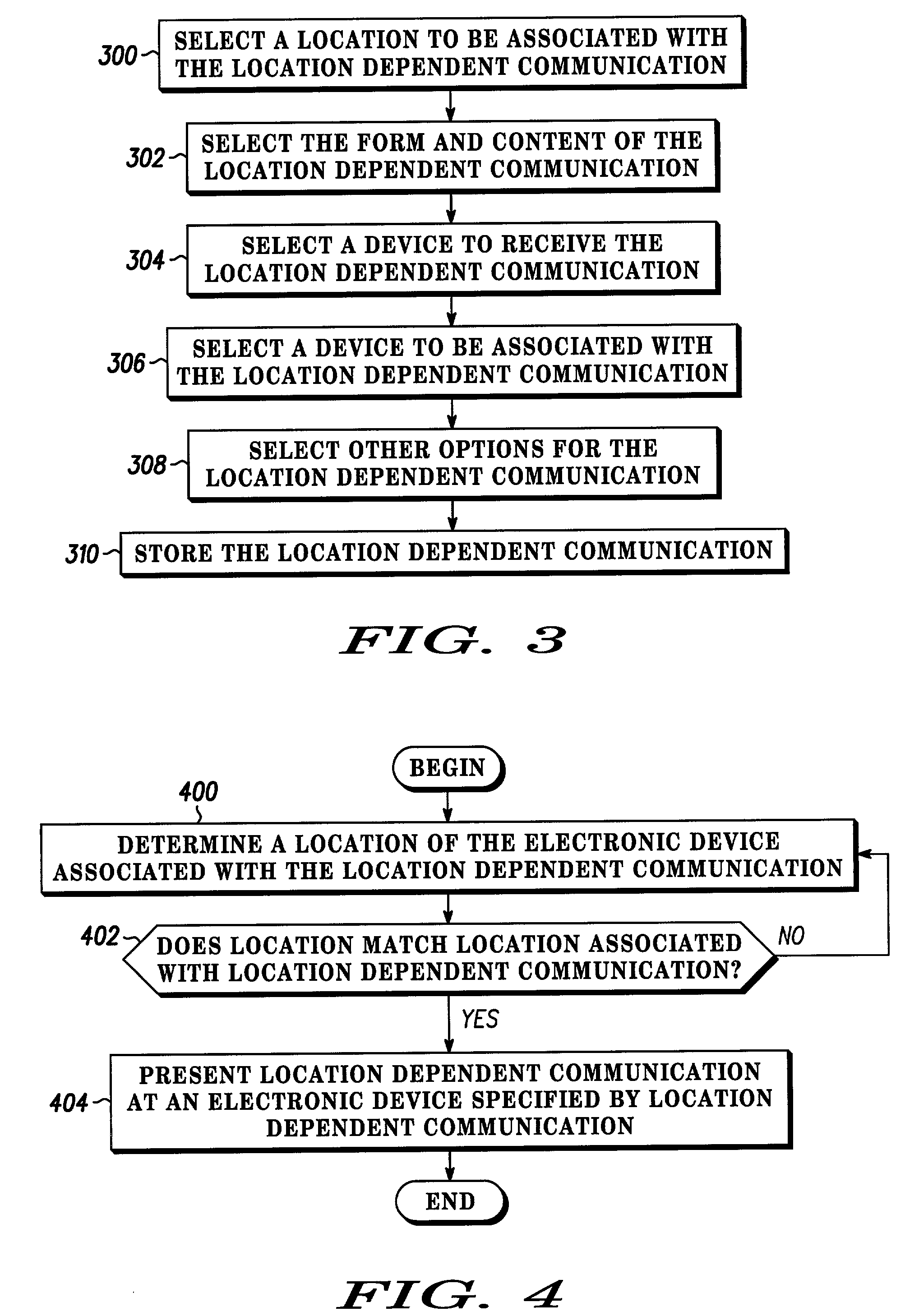
Method and apparatus for creating and presenting a location dependent communication with an electronic device
InactiveUS20020198003A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionCommunications systemCell site
Multimedia messages, including video, audio, text, and alarms, are presented on an electronic device (102) in response to an electronic device arriving at a particular location. These location dependent communications are created by a user of an electronic device and stored in the electronic device or a communication system (100) associated with the electronic device. The parameters associated with the location dependent communication include a location (300), the form and content of the location dependent communication (302), a device associated with the location (306), a device for receiving the location dependent communication (304), and other options (308), such as a time, a temperature, a speed, or a profile. The location dependent communication is presented on an electronic device when a device associated with the location dependent communication reaches the particular location (402. 404). Arrival at a location is determined by location determination technology, such as satellite based location determination, cell site location determination, inertial sensing, or the like.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
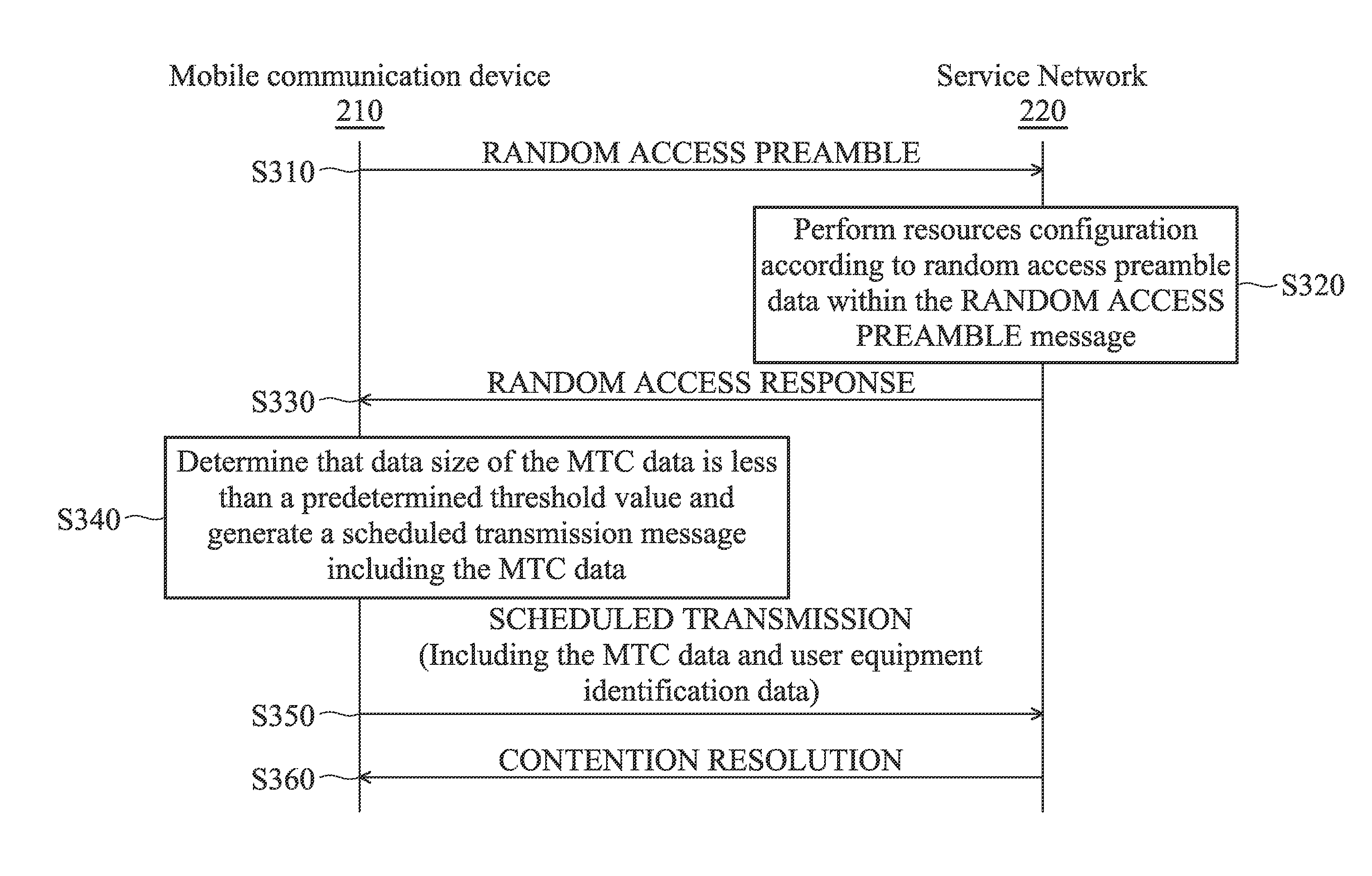
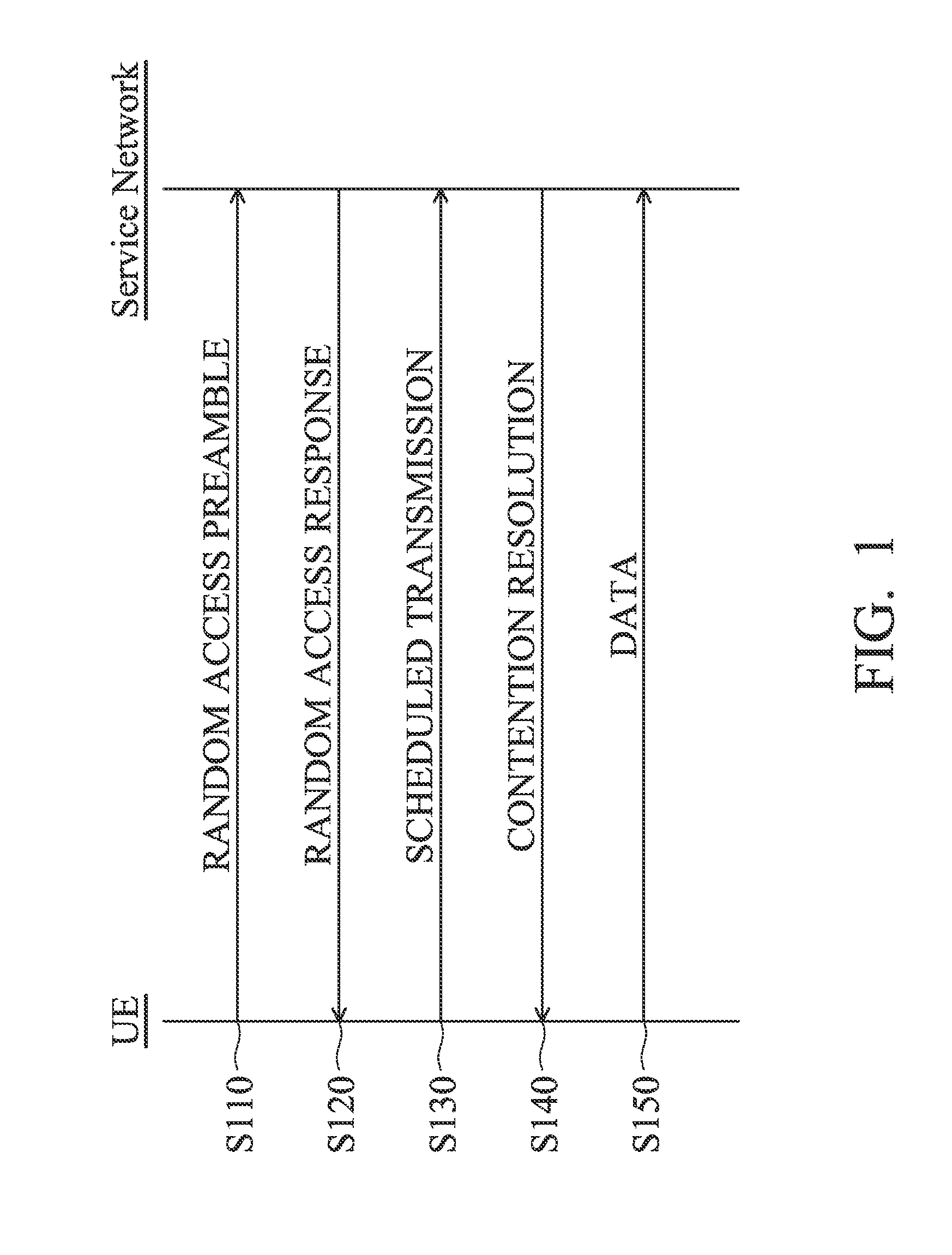
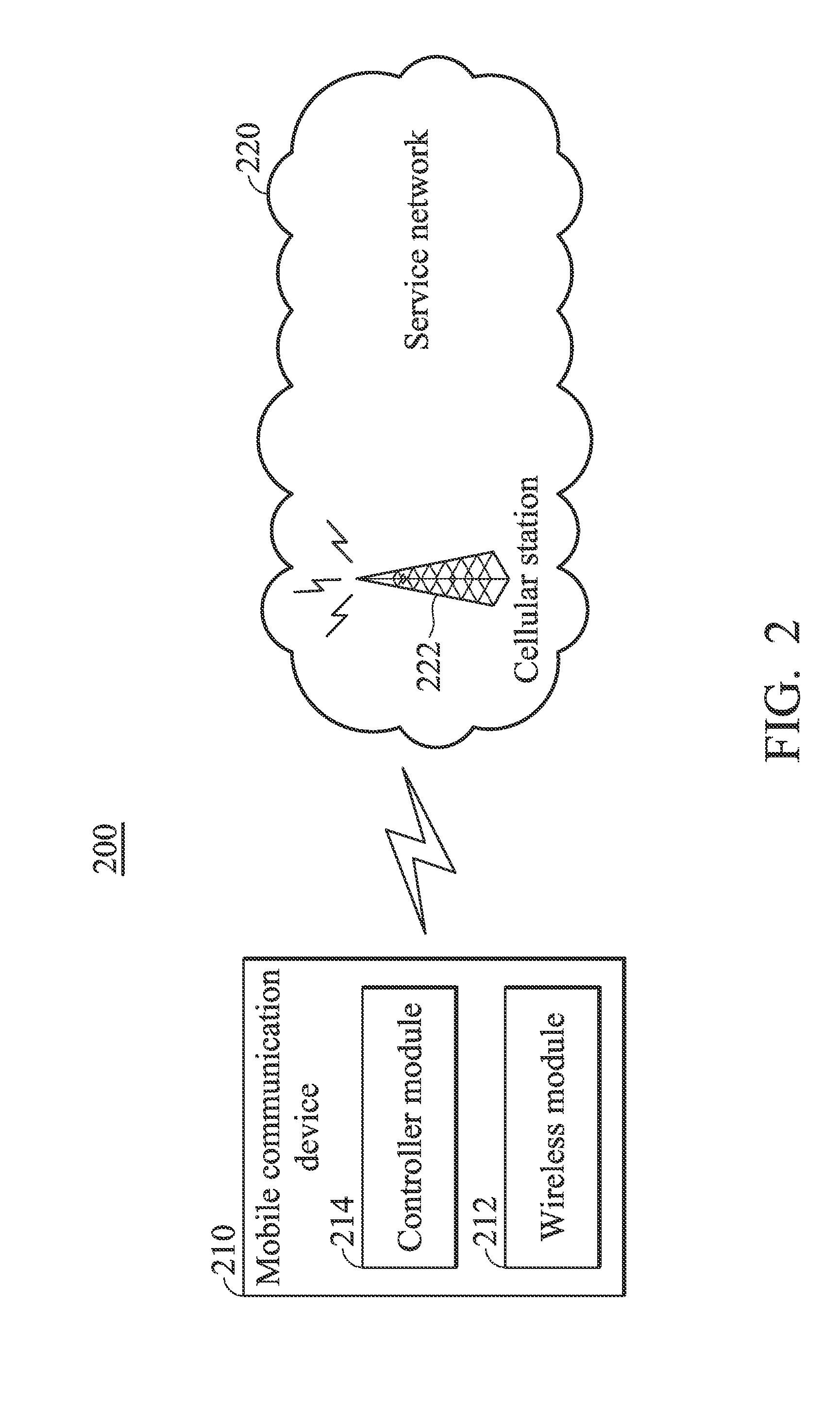
Mobile Communications Devices and Transmission Methods for Transmitting Machine Type Communication Data Thereof
ActiveUS20110299492A1Wireless commuication servicesMachine-to-machine/machine-type communication serviceTelecommunicationsWireless transmission
A mobile communications device with a wireless module and a controller module for performing an enhanced access procedure is provided. The wireless module performs wireless transmissions and receptions to and from a cellular station of a service network. The controller module transmits a random access preamble to the cellular station via the wireless module, receives a random access response message corresponding to the random access preamble from the cellular station via the wireless module, and transmits a scheduled transmission message including the MTC (machine type communication) data from the cellular station via the wireless module, in response to the random access response message. Then, the controller module completes the enhanced access procedure in response to receiving a contention resolution message from the cellular station via the wireless module.
Owner:APPLE INC
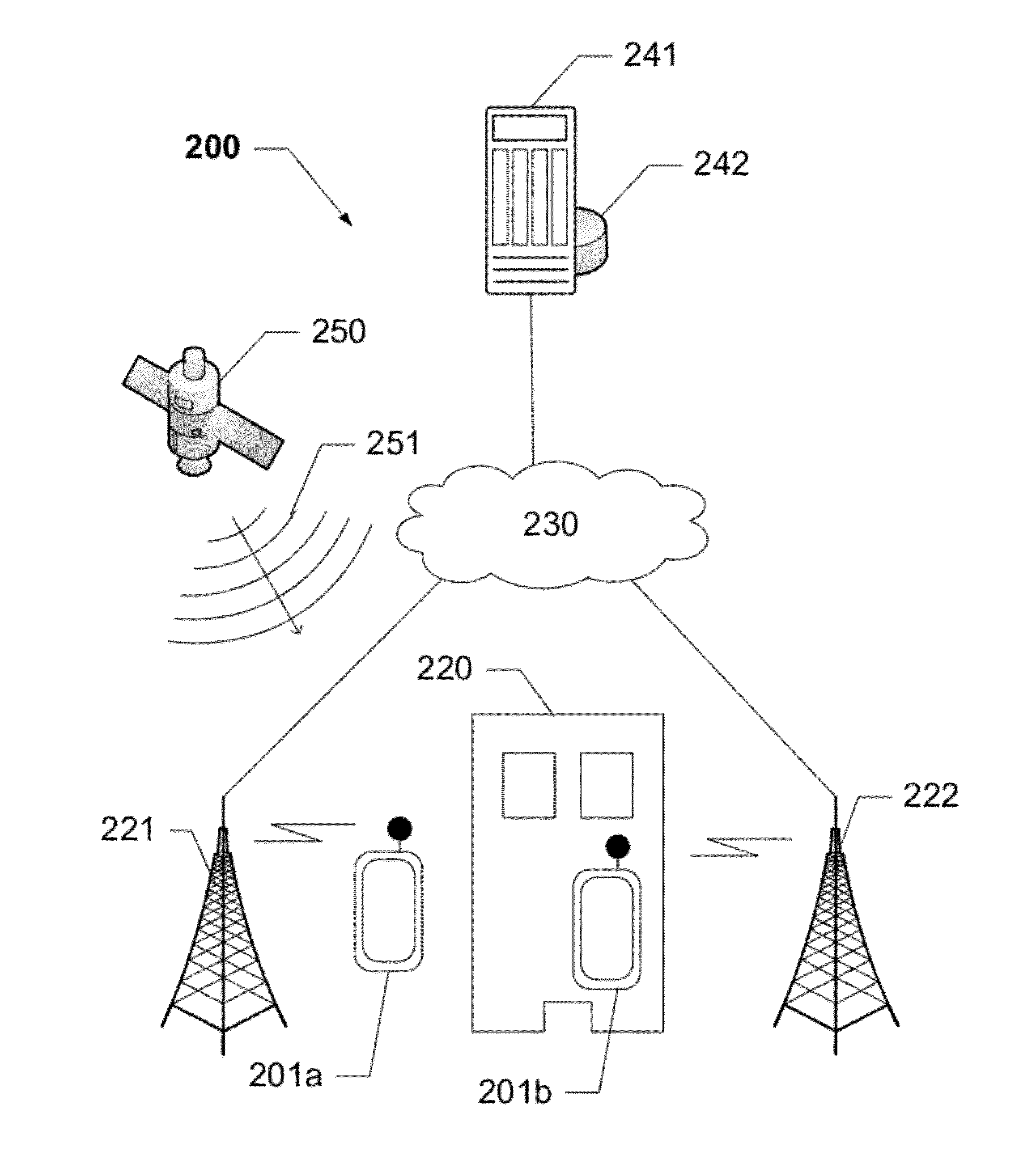
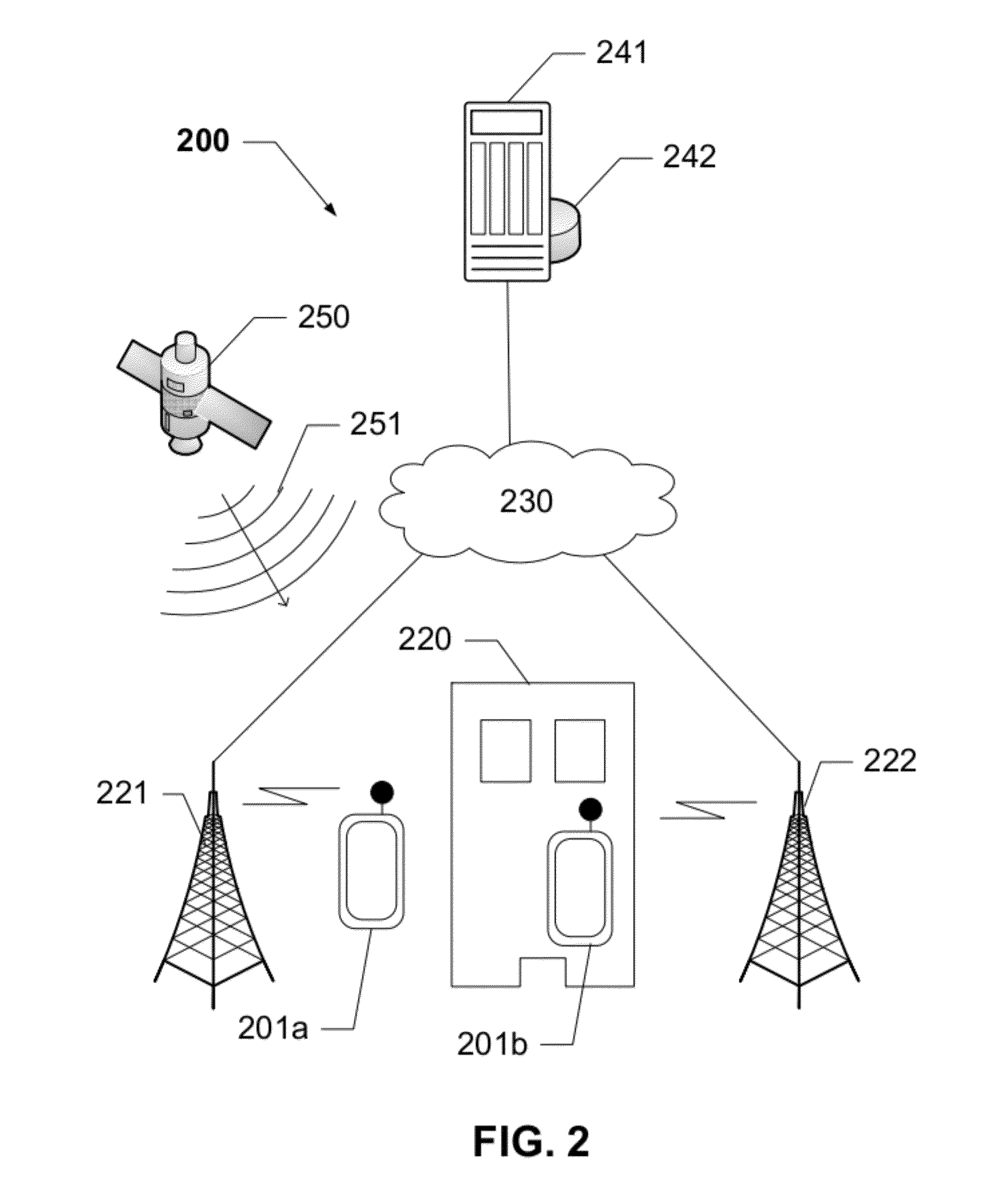
Location Estimation of a Mobile Device in a UMTS Network
ActiveUS20120052883A1Radio wave finder detailsSpecial service for subscribersPropagation delayCrowd sourcing
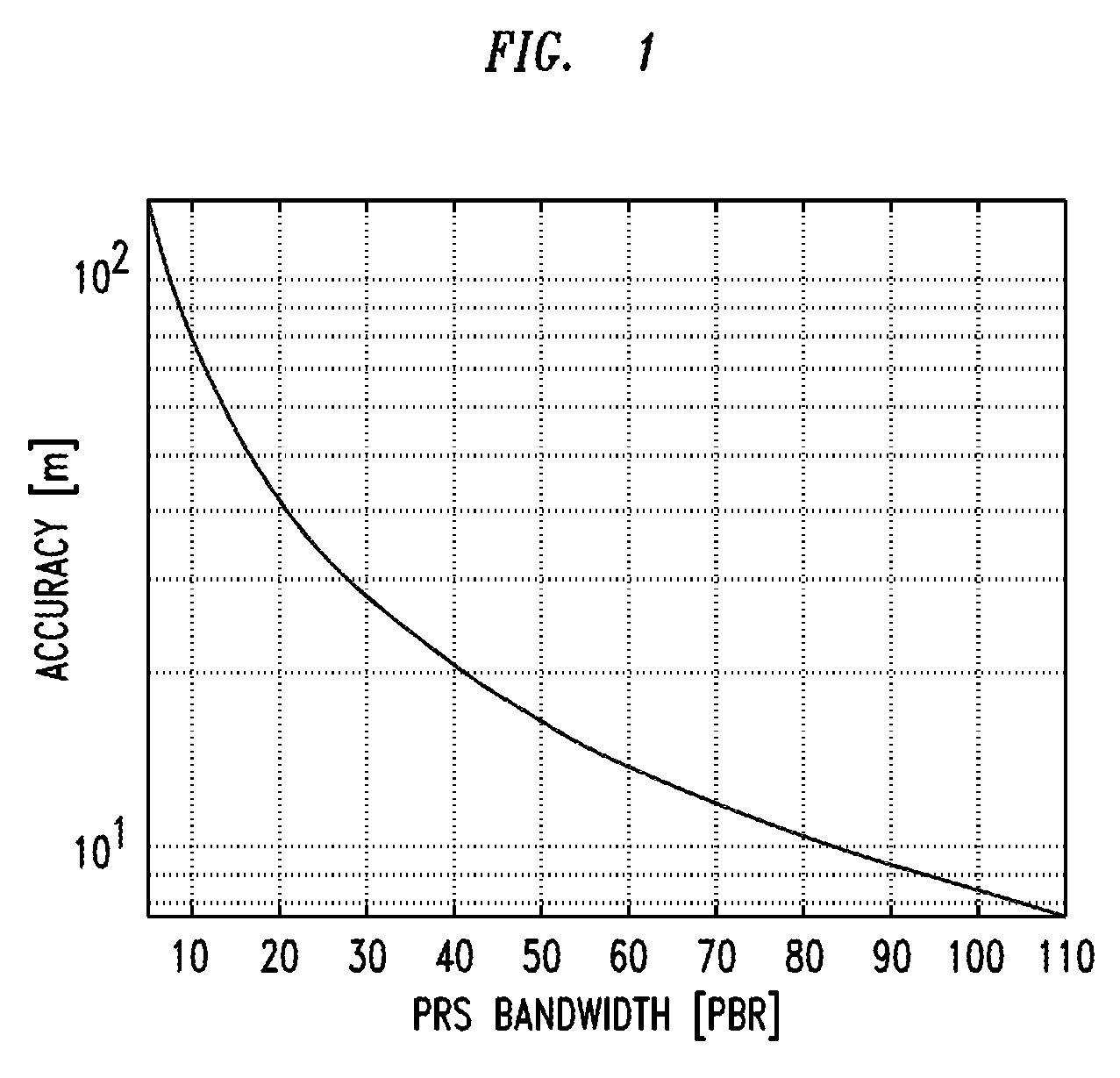
The present disclosure provides devices, systems, and methods to utilize relative timing offset information reported by one or more mobile devices. When coupled with AGPS information reported by one or more mobile devices, the offset information is be used to calibrate calculations and subsequently to locate all 3G mobiles with GPS-like accuracy, whether or not a GPS receiver is available on said mobile device being located. A determination of a propagation delay between one or more cell sites and a mobile device is reported to a network and used to calibrate unknown information such as a timing offset, to improve the accuracy of a detected location. The relative timing offset can be applied to determine a location for all other mobile devices within the area served by the known base station. The present disclosure utilizes this method in conjunction with information crowd-sourced from a plurality of mobile devices.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
Enhanced gain selected cell phone booster system
ActiveUS7221967B2Avoid distortionMinimal distortionPower managementResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierFixed gain
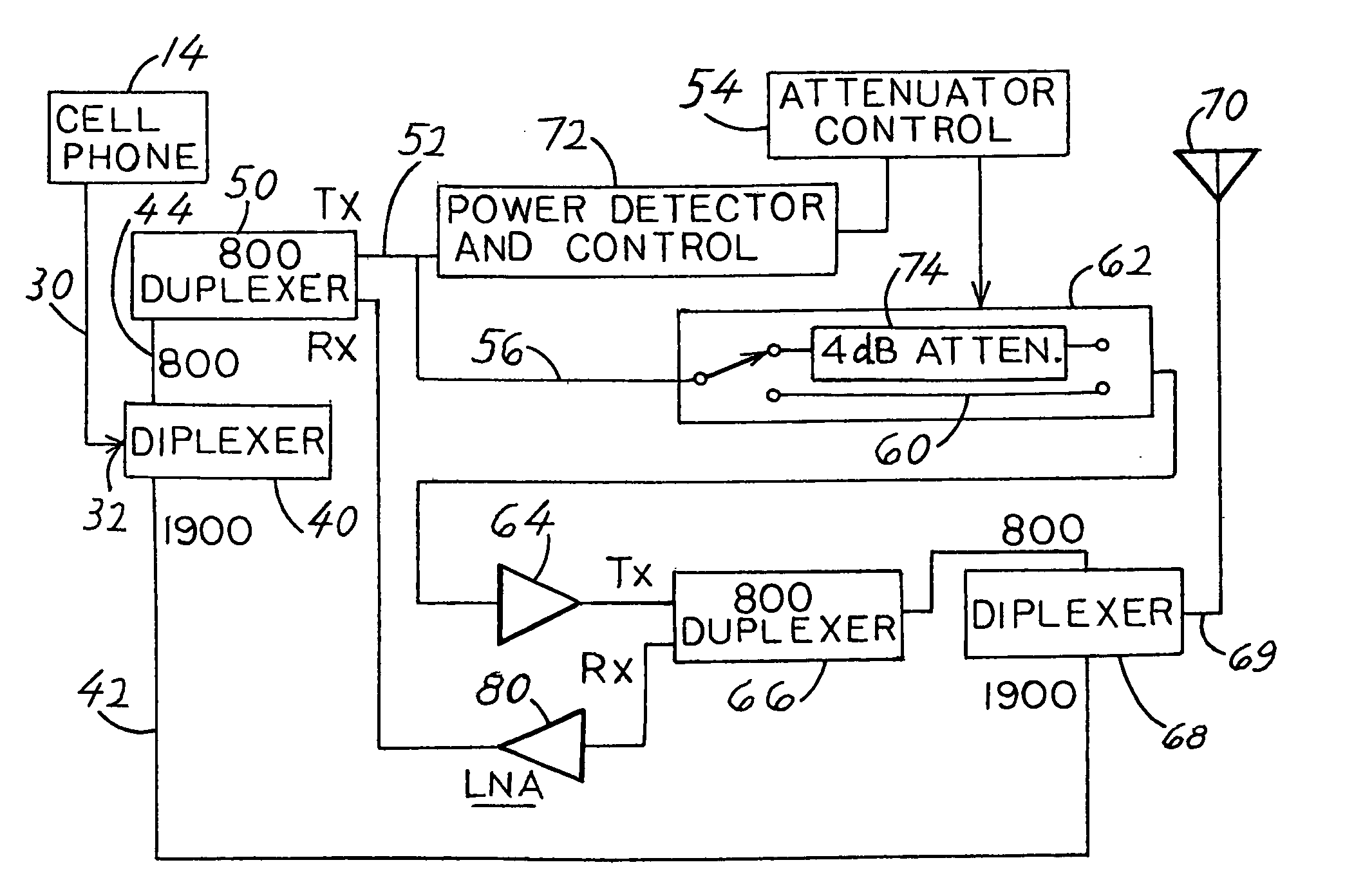
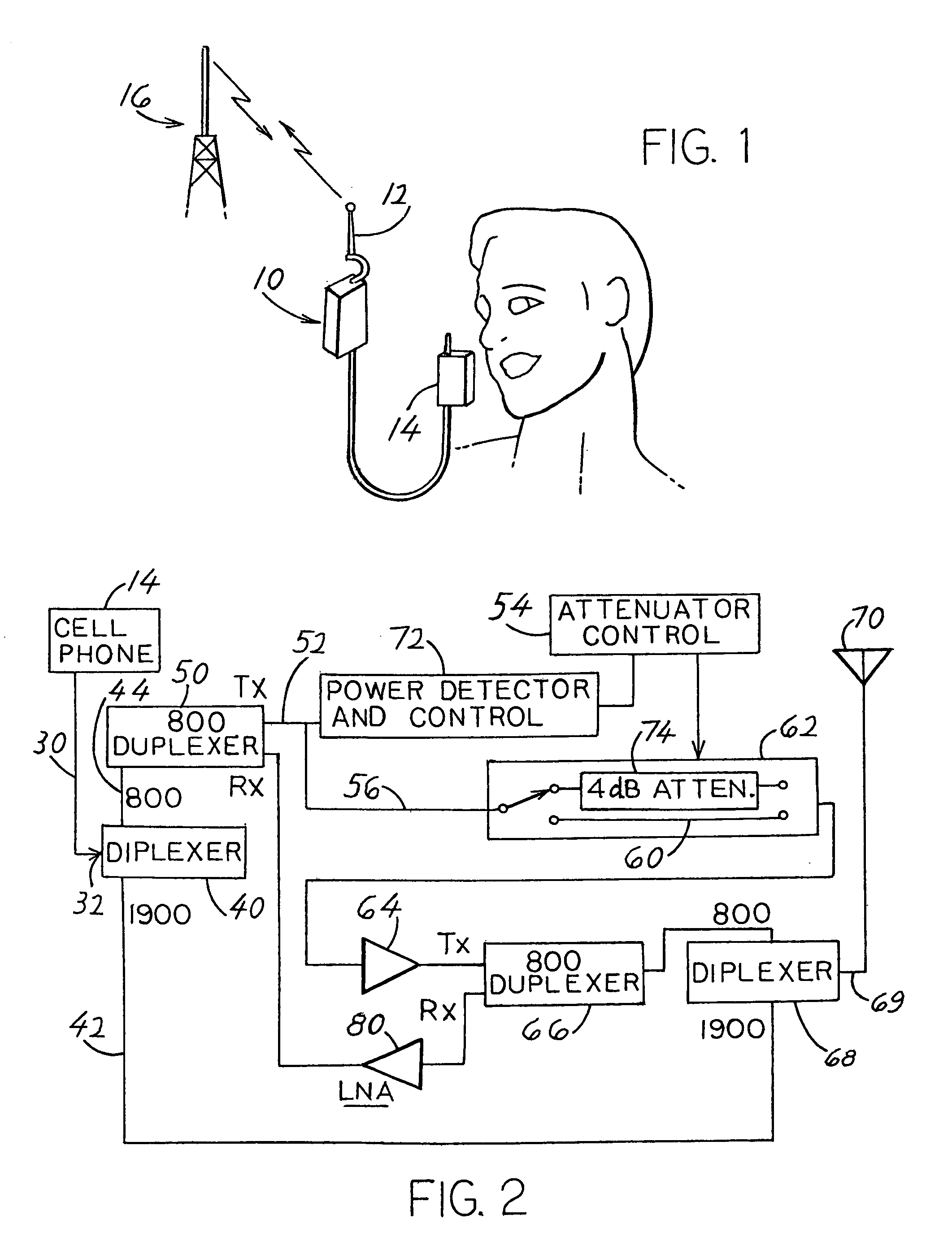
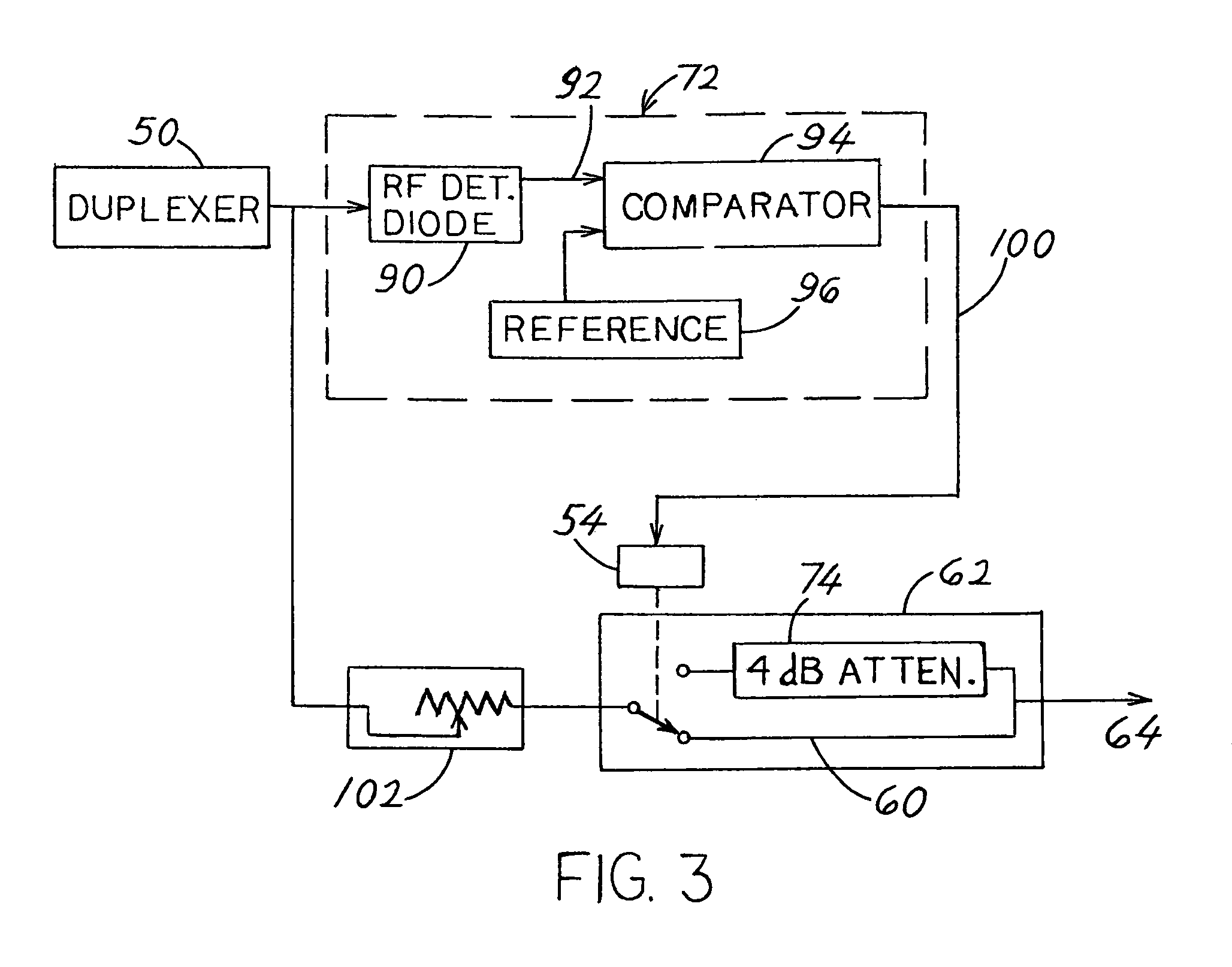
Apparatus for boosting the signal between a cell phone (14) and a cell site (16), which includes an amplifier (64) that continually operates at a fixed gain. A power detector (72) controls an attenuator (62) that can be switched to pass the amplified signal through an attenuator (74) of moderate resistance, or through an attenuator (60) of zero resistance so the power output is boosted within the limits allowed under cell phone system standards.
Owner:WILSON ELECTRONICS
Cellular telephone system that uses position of a mobile unit to make call management decisions
InactiveUS20050075114A1Efficient and accurate serviceAccurate billingEmergency connection handlingConnection managementCell siteCellular telephone
A cellular telephone system has call management decisions made based on the exact geographic location of the mobile unit. These call management decisions include billing and taxing decisions, cell site selection, frequency selection and even cellular system selection. The decisions are continuously updated during a call whereby decisions can be made and changed regardless of where a call originated. Cell site location, and even cellular system selection, can be made in a specific manner to best serve the needs of the mobile user, the cellular system as well as the public. It is even possible for a cellular system to locate one or more of its cell sites in the geographic area served by another cellular system. In some cases, cellular systems might even share cell sites.
Owner:EMSAT ADVANCED GEO LOCATION TECH
Method and apparatus for allocating a beacon signal in a wireless communications network
InactiveUS20060089141A1Improve spectral efficiencyReduce power consumptionAssess restrictionPosition fixationAdjacent-channel interferenceFrequency spectrum
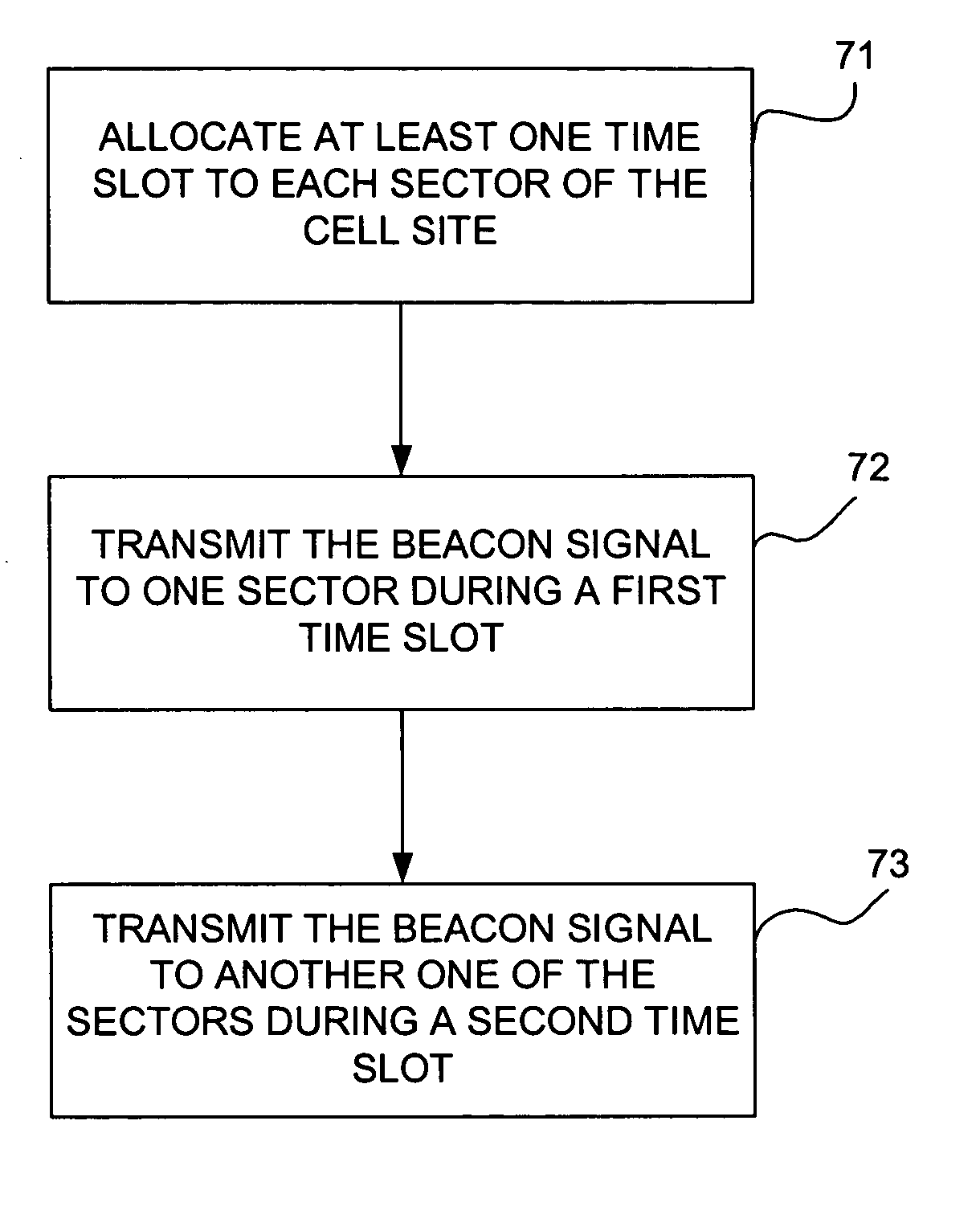
A method and apparatus for transmitting beacon signals in a wireless communications network. For a given cell site, a single frequency may be used for the beacon signal by assigning different beacon signal time slots to different sectors of the cell site. During one time slot, the beacon signal is transmitted to one of the sectors, and during another one of the time slots, the beacon signal is transmitted to a different one of the sectors. Because a single frequency can be used for all of the sectors of a cell site, more frequencies are available for other purposes, such as for user traffic, for example. The invention improves spectral efficiency, reduces adjacent channel interference and co-channel interference and allows power consumption to be controlled.
Owner:CINGULAR WIRELESS II LLC
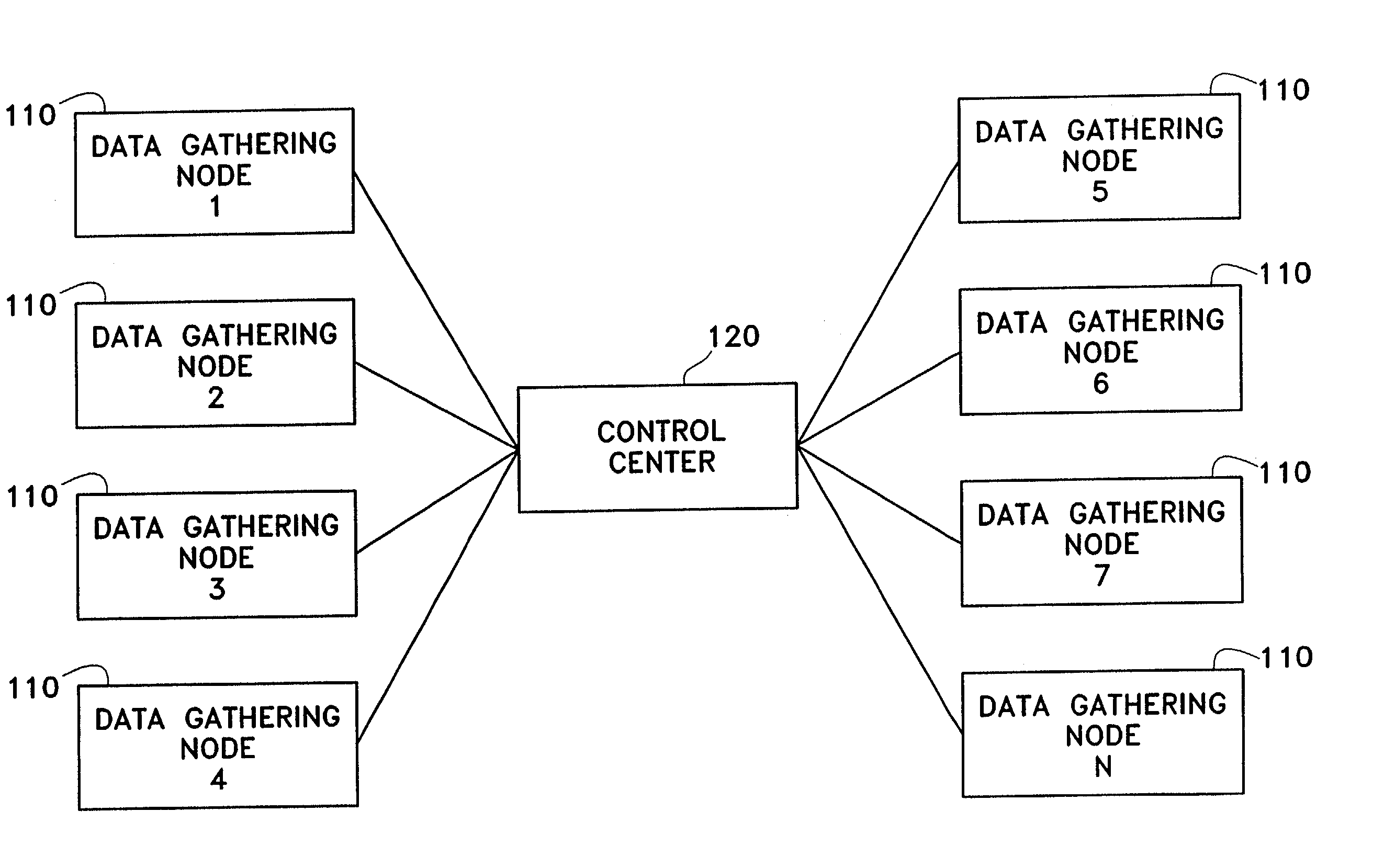
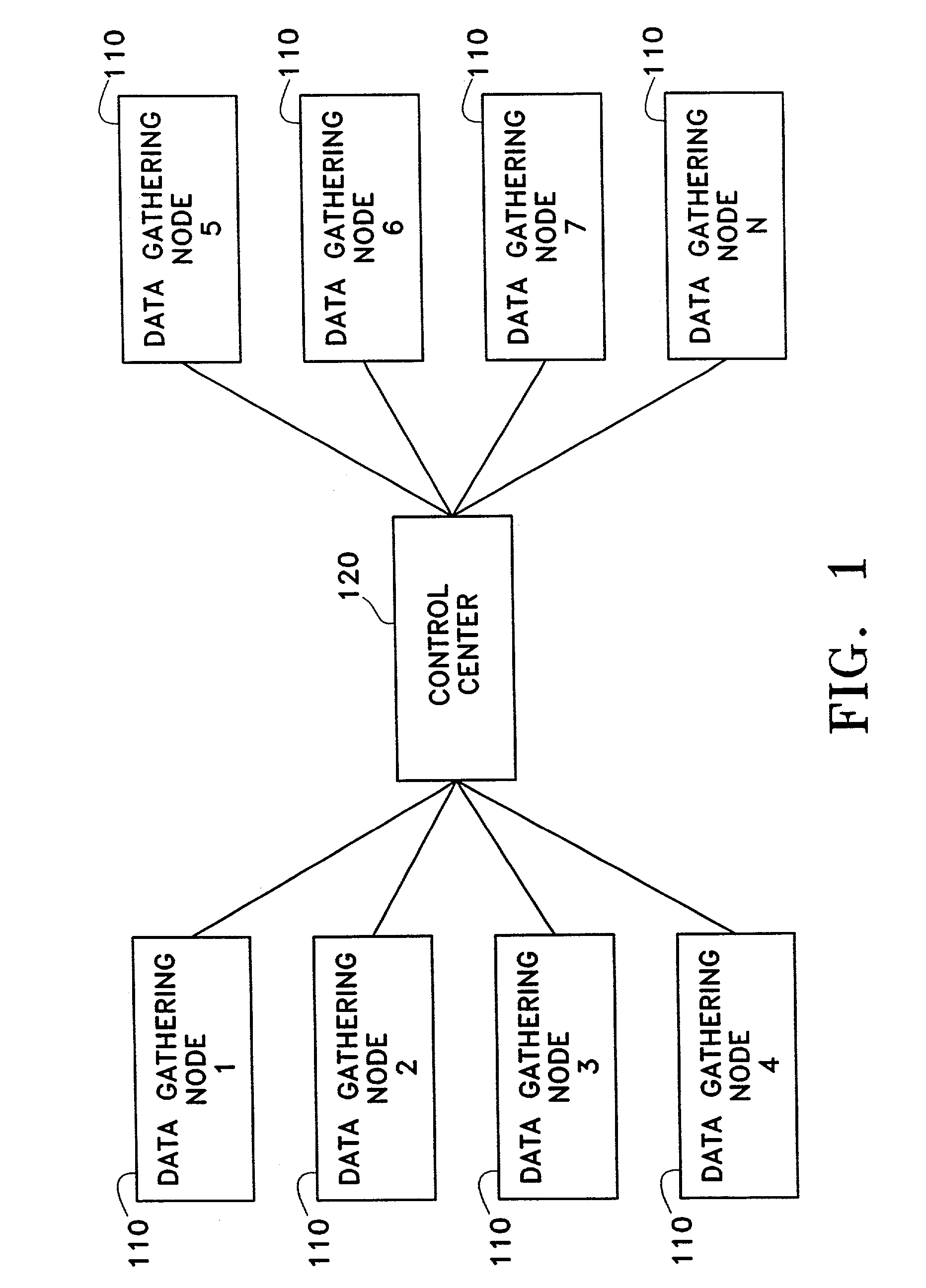
System and method for gathering data from wireless communications networks
A system and method for gathering data from wireless communication networks, the wireless communication network including a plurality of cell sites, mobile subscriber units, and a mobile telephone switching office. The data gathering system comprises a plurality of data gathering nodes and a control center. Each data gathering node comprises multiple receivers, with each receiver gathering data from a different wireless communication network. Stored data at the control center is processed to generate marketing information on each wireless communication network.
Owner:NIELSEN COMPANY US LLC THE A DELAWARE LIMITED LIABILITY
Public safety access point (PSAP) selection for E911 wireless callers in a GSM type system
Public safety access points are selected in a wireless network for E911 calls based on ESRD substitution when ESRKs are not being used. The present invention was conceived as an ESRK workaround solution to implement Phase II of the E911 rules from the starting point of a Phase I implementation. ESRKs, ESRDs or ESRVs are initially obtained and managed for each PSAP in a particular carrier's area. Then, Phase I processes are modified to wait to see if Phase II GSM location information will be reported in a timely manner (e.g., within a second or two or so) before committing to a default selection of a particular PSAP based on information available (e.g., based on the location of a serving cell site).
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
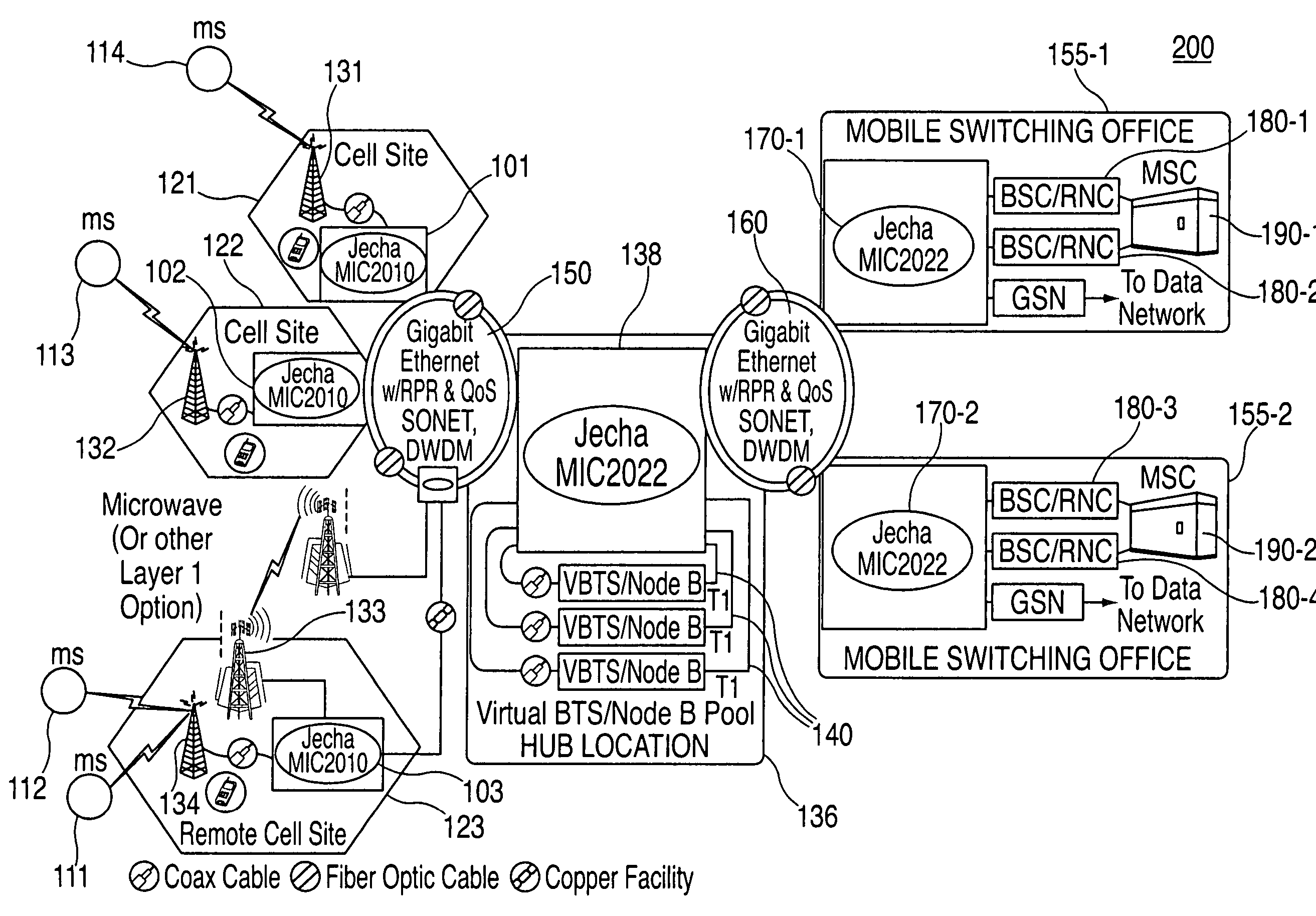
System and method for optimizing network capacity in a cellular wireless network
InactiveUS7573862B2Improve efficiencyReduce operating costsNetwork traffic/resource managementPower distribution line transmissionQuality of serviceFiber
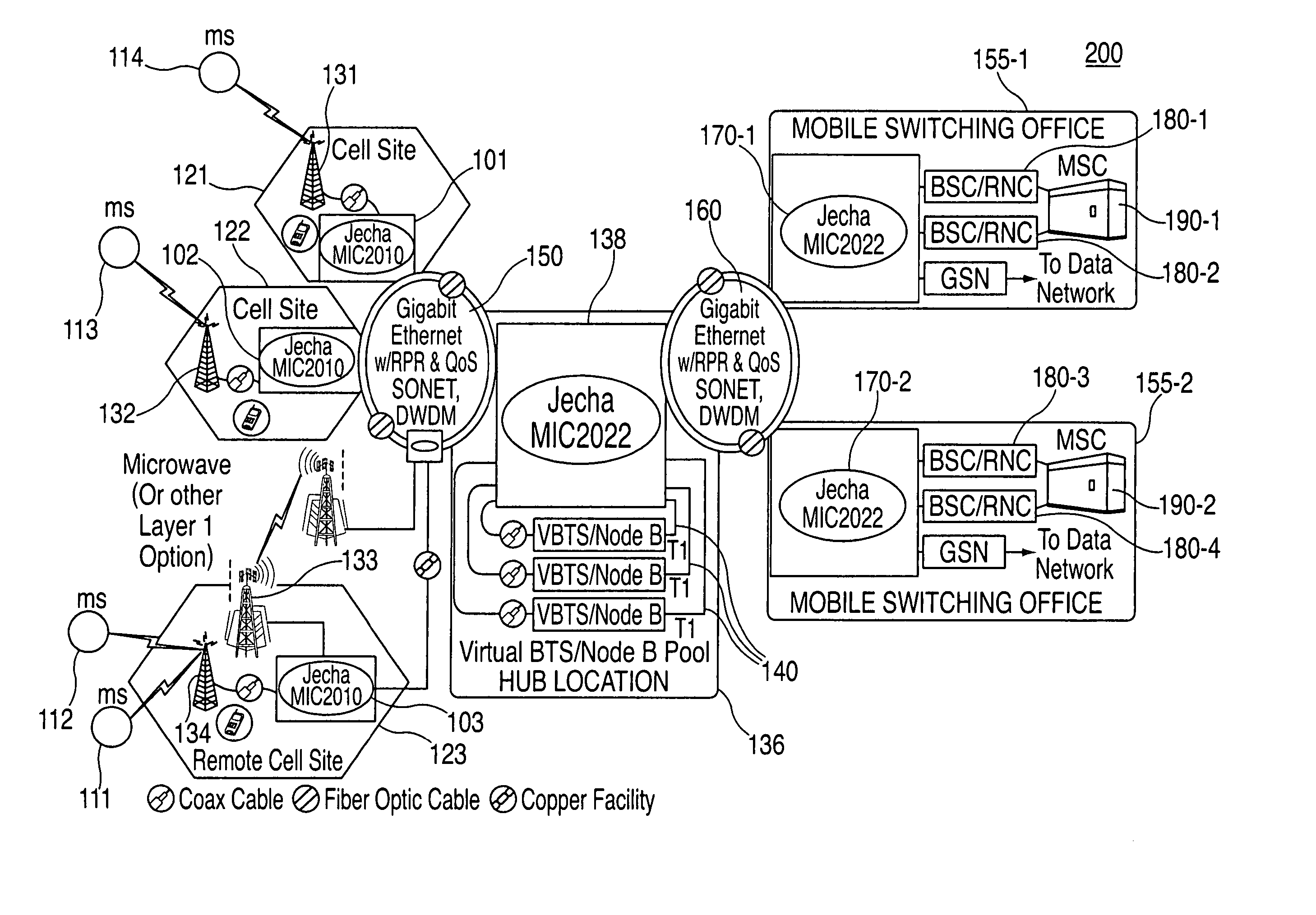
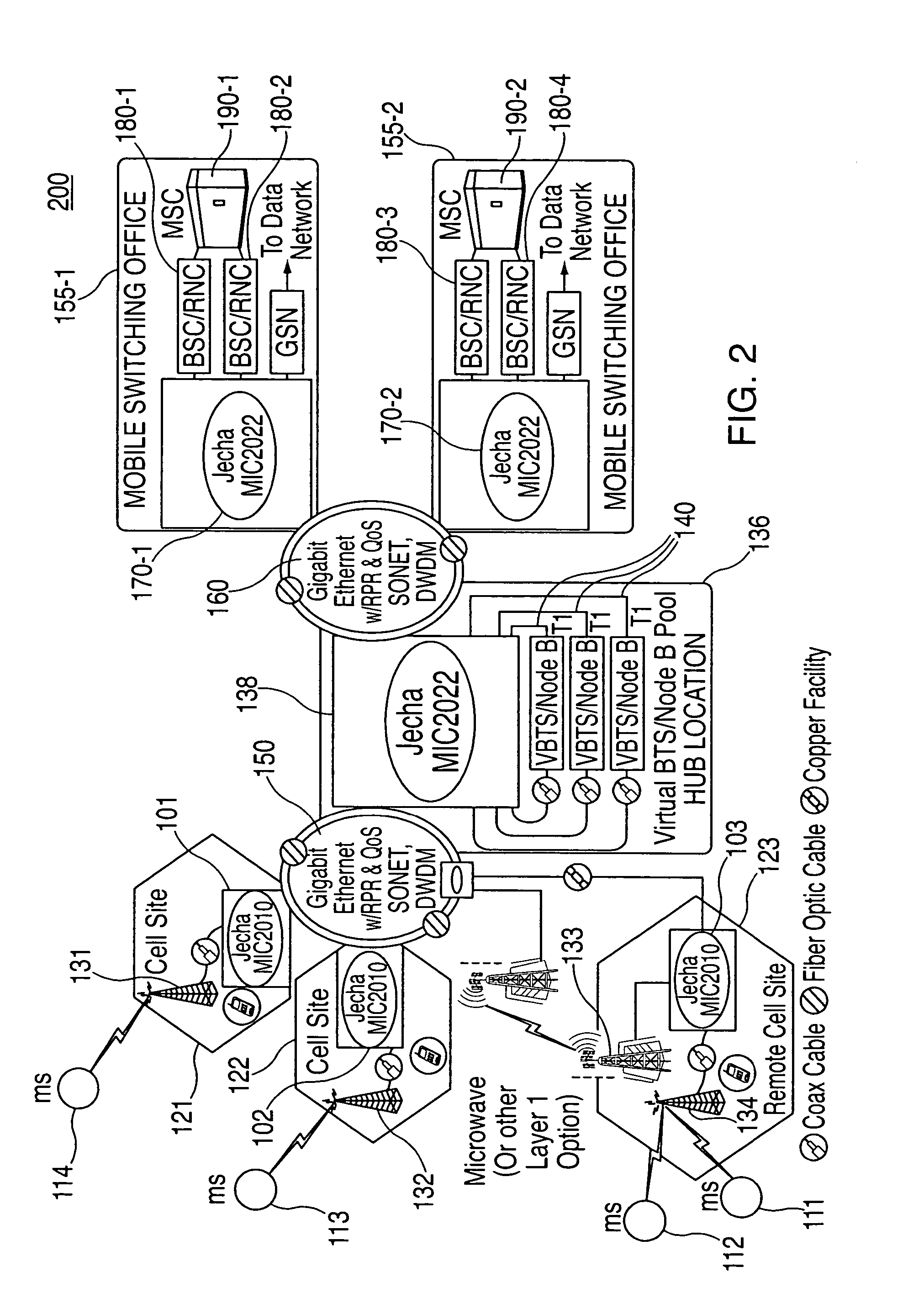
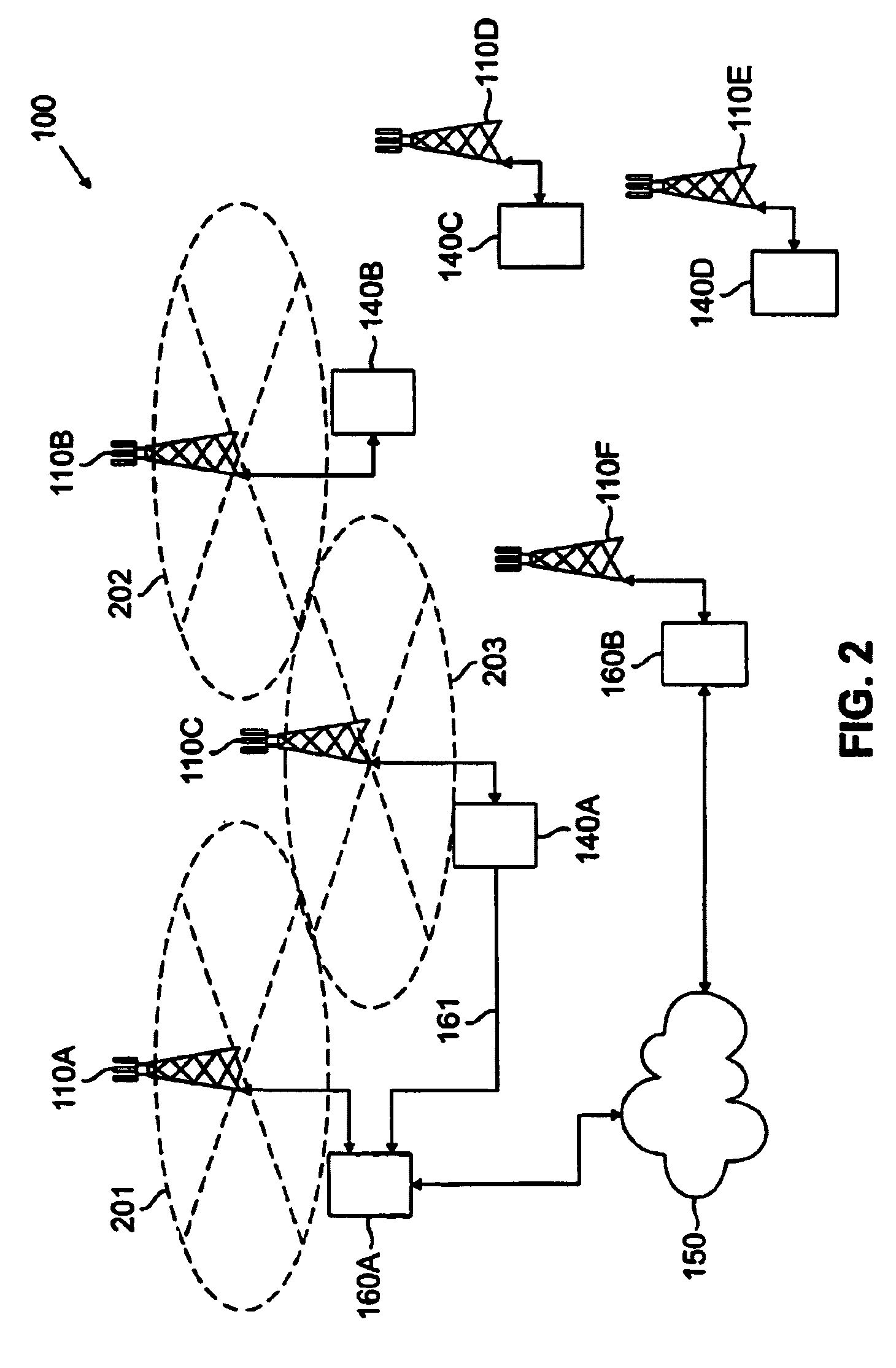
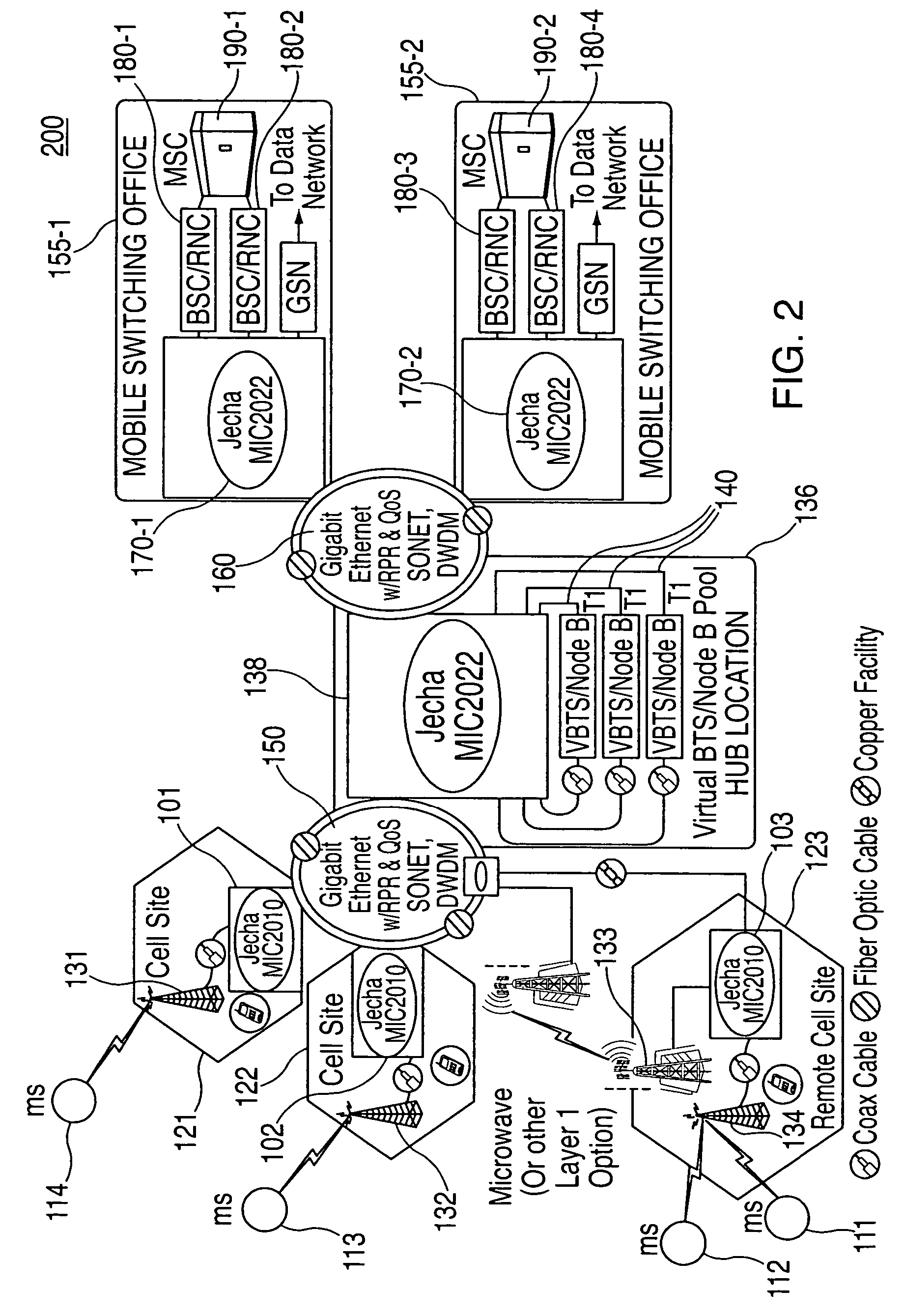
A system and method is disclosed for increasing the efficiency of a cellular communication network, reduce ongoing operating costs and increase revenue. According to one aspect, a method is disclosed for increasing the efficiency of a cellular communication network whereby network capacity in the radio access network (RAN) and baseband processing for wireless connections are dynamically adjusted to automatically provision sufficient bandwidth and baseband processing capacity in response to changes in the network. The method is further extended by implementing policy management which allows wireless carriers to develop and implement network based policies to automatically increase or decrease the amount of processing resources and network bandwidth required from any cell site, hub or mobile switching office. According to another aspect, network efficiency is enhanced by utilizing a novel cellular network infrastructure. RF signals from cell site antennas of various technology types are demodulated, digital bit information is extracted from the RF signals, processed, and groomed into Gigabit Ethernet / Resilient Packet Ring (GigE / RPR) or Ethernet over copper traffic flows using specific Quality of Service (QoS) priorities. The GigE / RPR traffic flows are routed to hub sites or mobile switching offices, at which point the packetized information is extracted and converted to RF signals that are equivalent to the signals that were received at the antenna. The RF signals are sent over coaxial cable to a network hub including a pool of Base Transceiver Stations (BTSs) (or Node Bs). The hub is coupled to one or more mobile switching offices via a second fiber optic ring.
Owner:CHAMBERS MAHDI +1
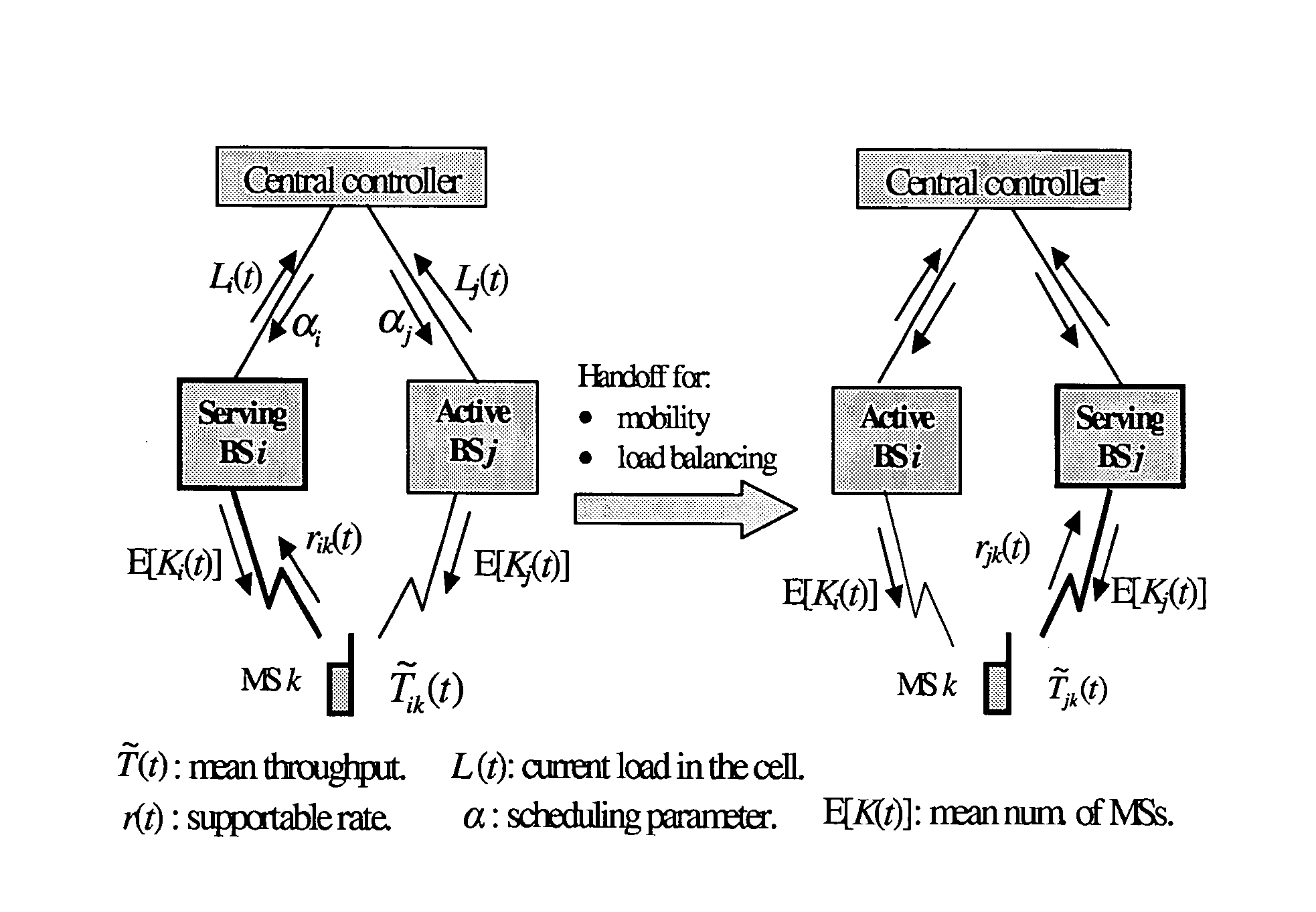
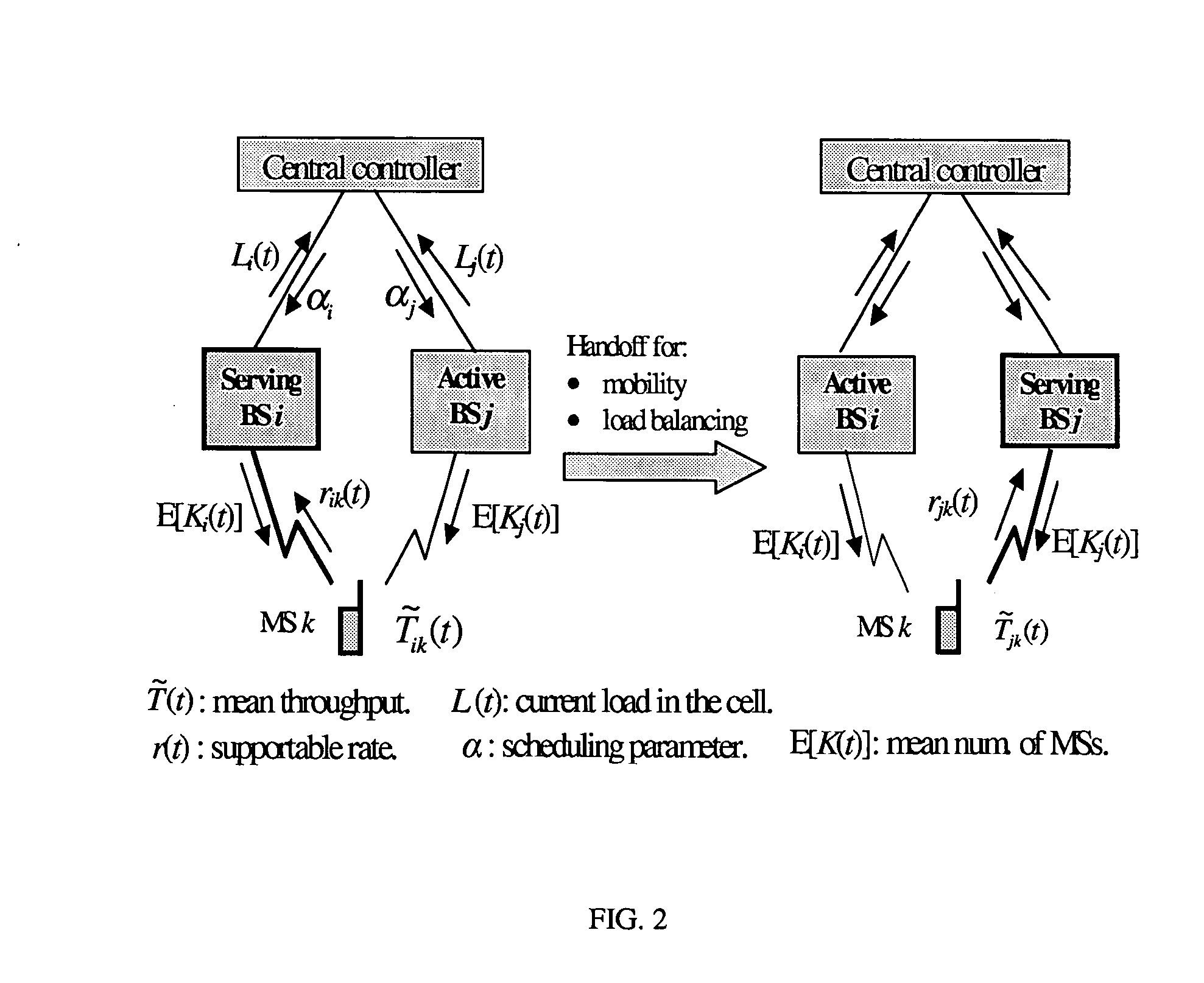
Load-aware handoff and site selection scheme
ActiveUS20050176440A1Robust to dynamicReduce regional congestionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationCell siteCell system
The present invention is directed to a distributed approach to handoff and cell site selection that takes into account the load dynamics in a multi-cell system.
Owner:NEC CORP
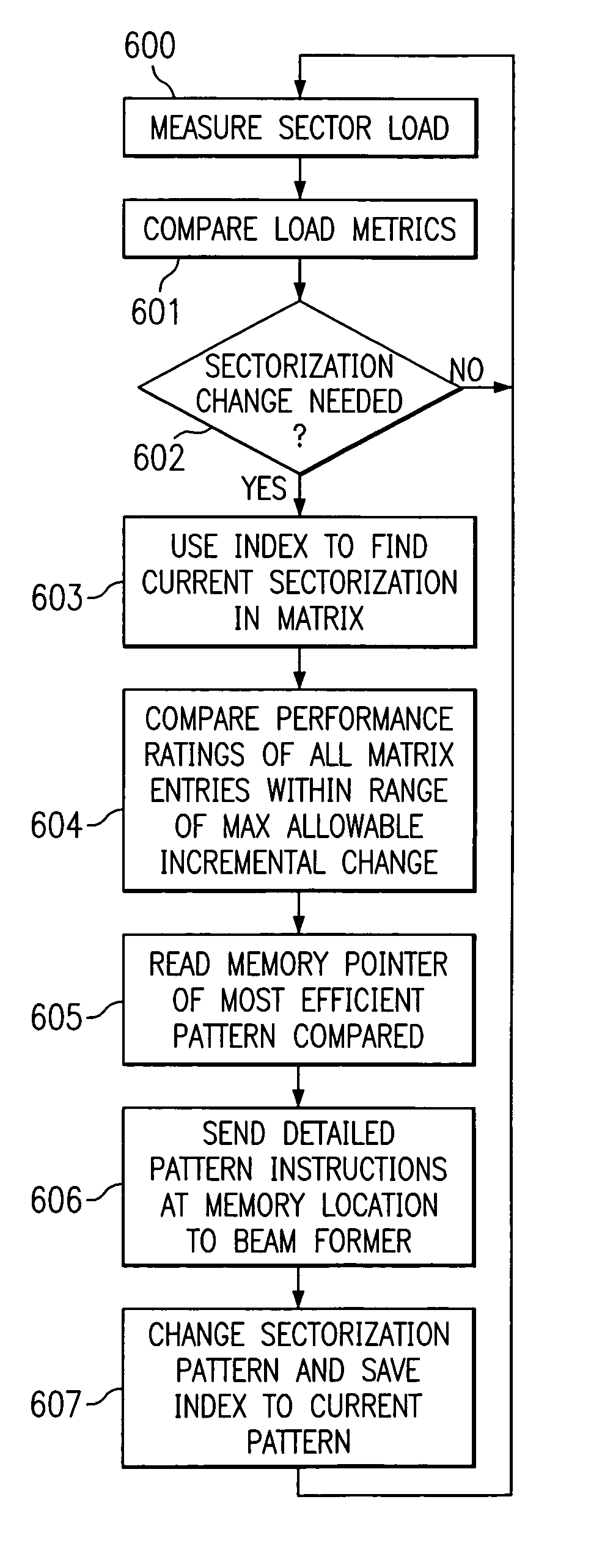
System and method for dynamically adjusting cell sectorization
ActiveUS6937863B1Improve representationThe result is accurateRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork planningCell siteTraffic conditions
The invention discloses a system and method which quantifies the traffic or load on a particular sector of a mobile communication cell site. The traffic quantification or load metric is preferably used to compare the load of each of the cell site's sectors. When the difference between load among the sectors reaches a certain level, the preferred embodiment of the present invention causes the sectorization of the site to change in order to alleviate or equalize the traffic load of the sectors. The system of the present invention continues to monitor the cell site for traffic conditions and for changes in the load responsive to the sectorization changes made in order to dynamically respond to the changing traffic conditions on the cell site.
Owner:F POSZAT HU
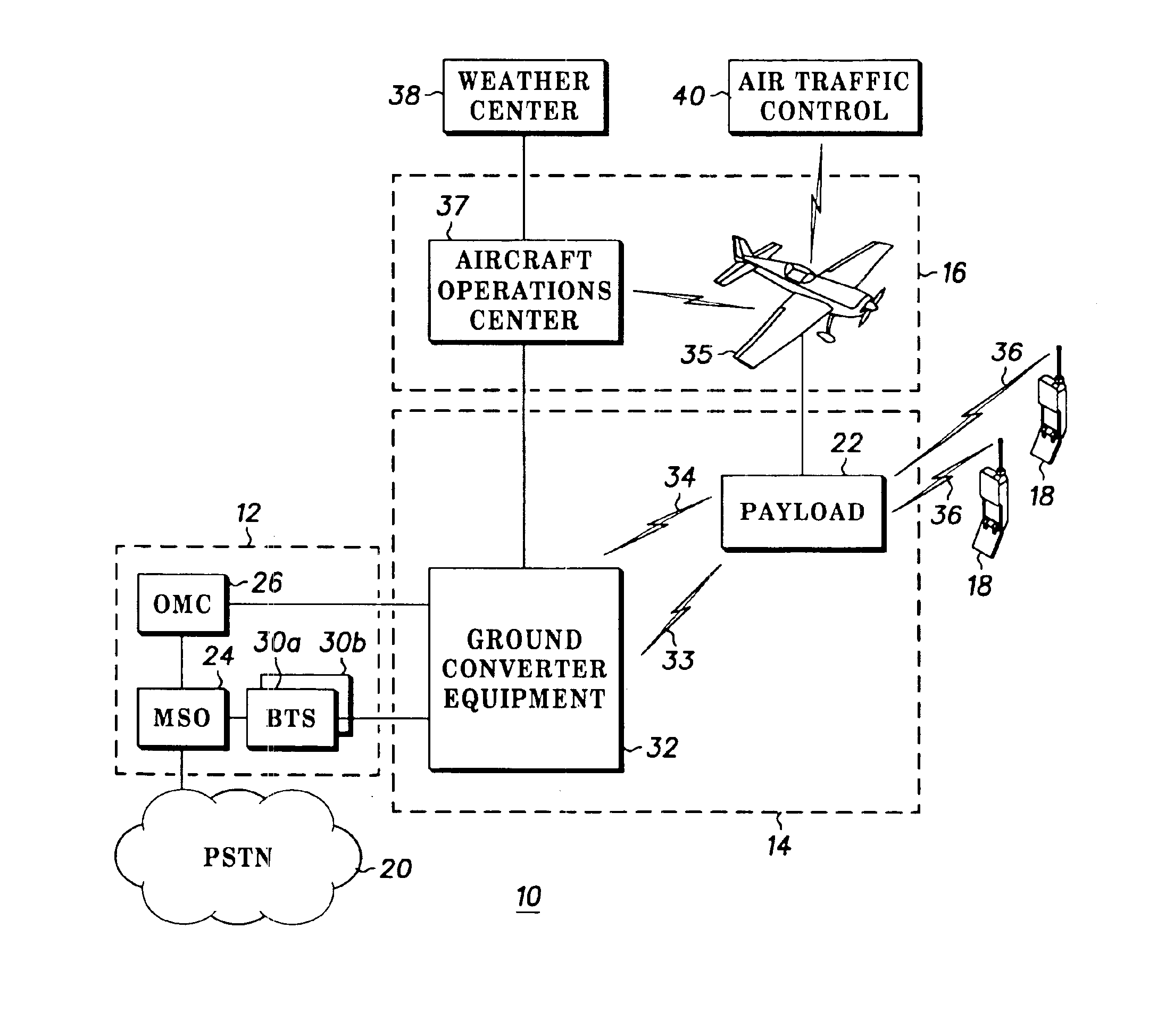
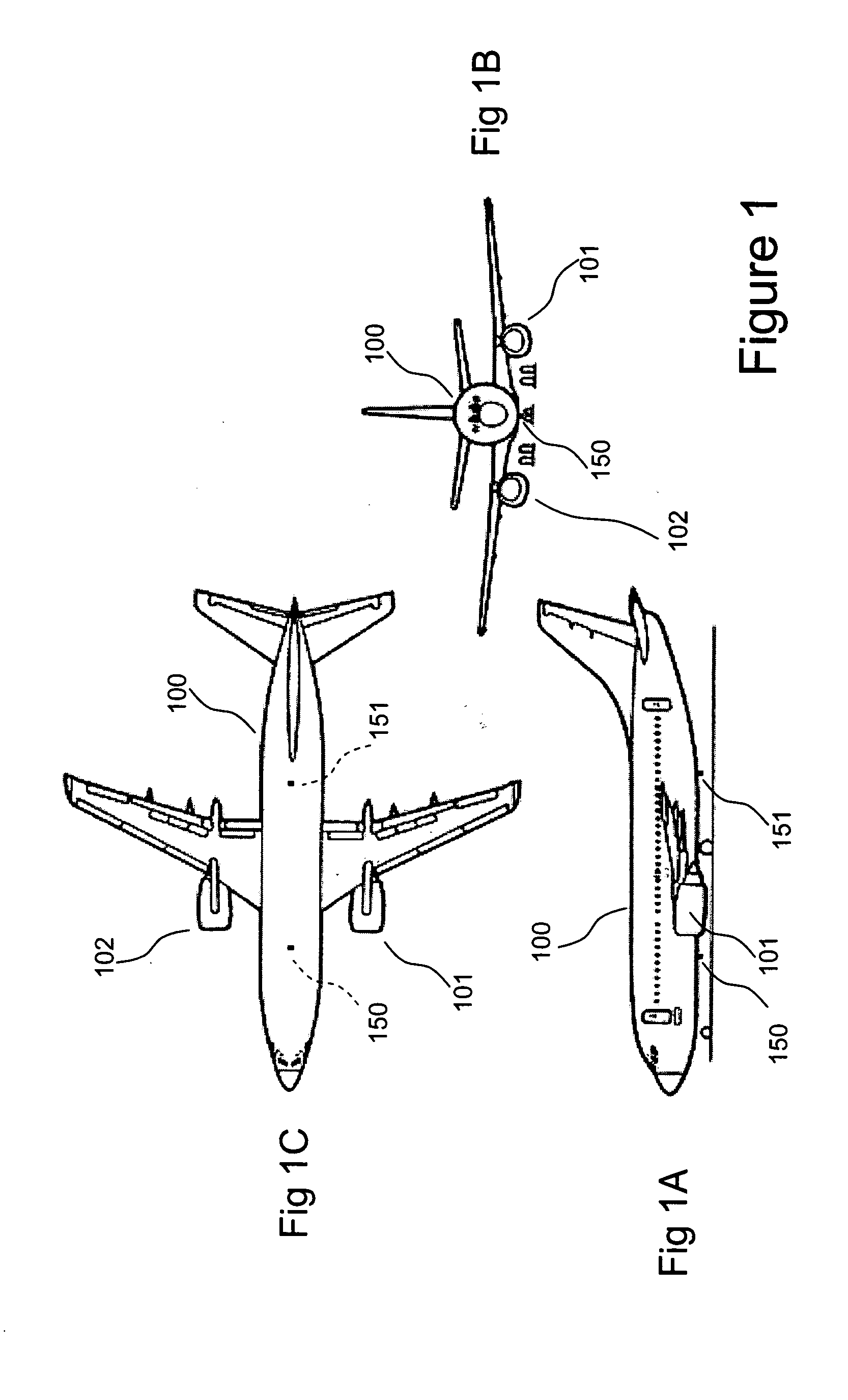
Method for maintaining candidate handoff list for airborne cellular system
InactiveUS6856803B1Network topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsJet aeroplaneBeam pattern
A terrestrial cell site handoff list is dynamically maintained for an airborne cellular system. A beam pattern is maintained relative to an airborne cellular system repeater, but rotates relative to the geographic area of coverage. A location and heading of the airplane, locations of respective beams transmitted from the airplane based on airplane flight pattern data, and locations of respective cell sites within a vicinity of footprints of the respective beams transmitted from the airplane are determined. A list of viable handoff terrestrial cell site candidates is then calculated based on the beam pattern, the location and heading of the airplane, the locations of respective beams transmitted from the airplane based on airplane flight pattern data, and the locations of respective cell sites.
Owner:CDC PROPRIETE INTELLECTUELLE
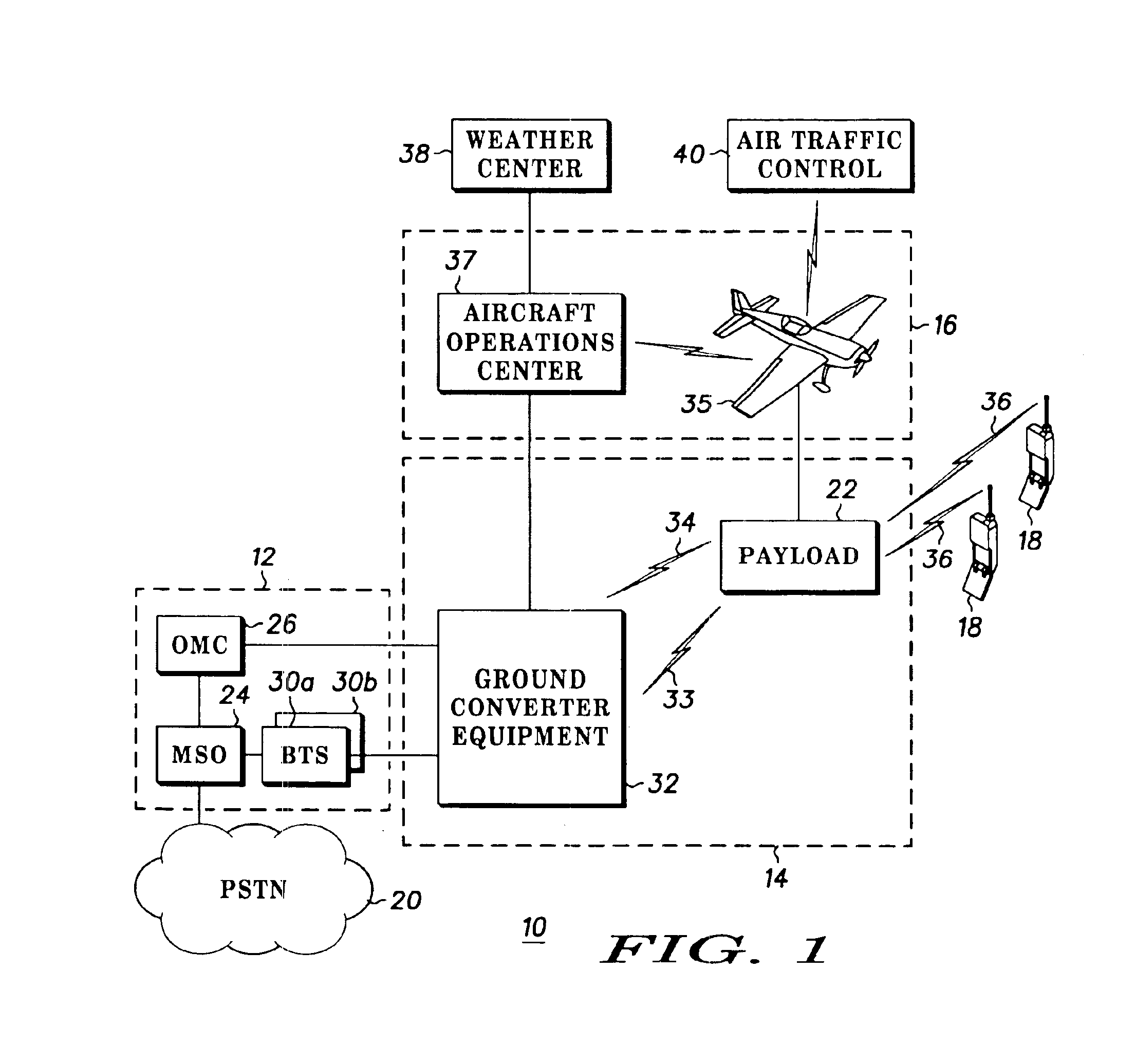
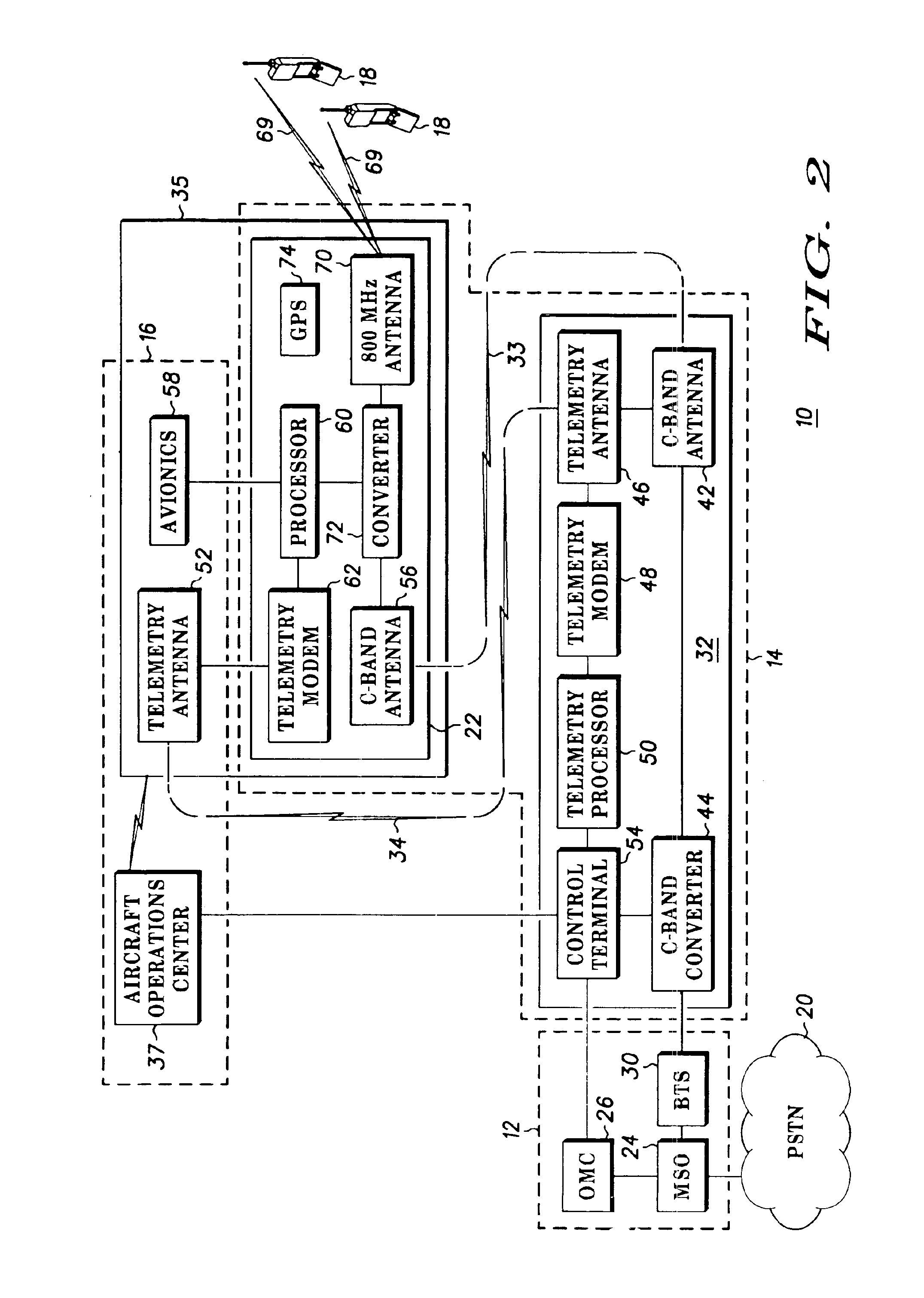
Multi-link aircraft cellular system for simultaneous communication with multiple terrestrial cell sites
ActiveUS20080102813A1Increase call handling capacityIncreases overall traffic throughputNetwork topologiesSubstation equipmentAviationCell site
The Multi-Link Aircraft Cellular System makes use of multiple physically separated antennas mounted on the aircraft, as well as the use of additional optional signal isolation and optimization techniques to improve the call handling capacity of the Air-To-Ground cellular communications network. These additional techniques can include polarization domain and ground antenna pattern shaping (in azimuth, in elevation, or in both planes). Further, if code domain separation is added, dramatic increases in capacity are realized. Thus, the Air-To-Ground cellular communications network can increase its capacity on a per aircraft basis by sharing its traffic load among more than one cell or sector and by making use of multiple physically separated antennas mounted on the aircraft, as well as the use of additional optional signal isolation and optimization techniques.
Owner:GOGO BUSINESS AVIATION LLC
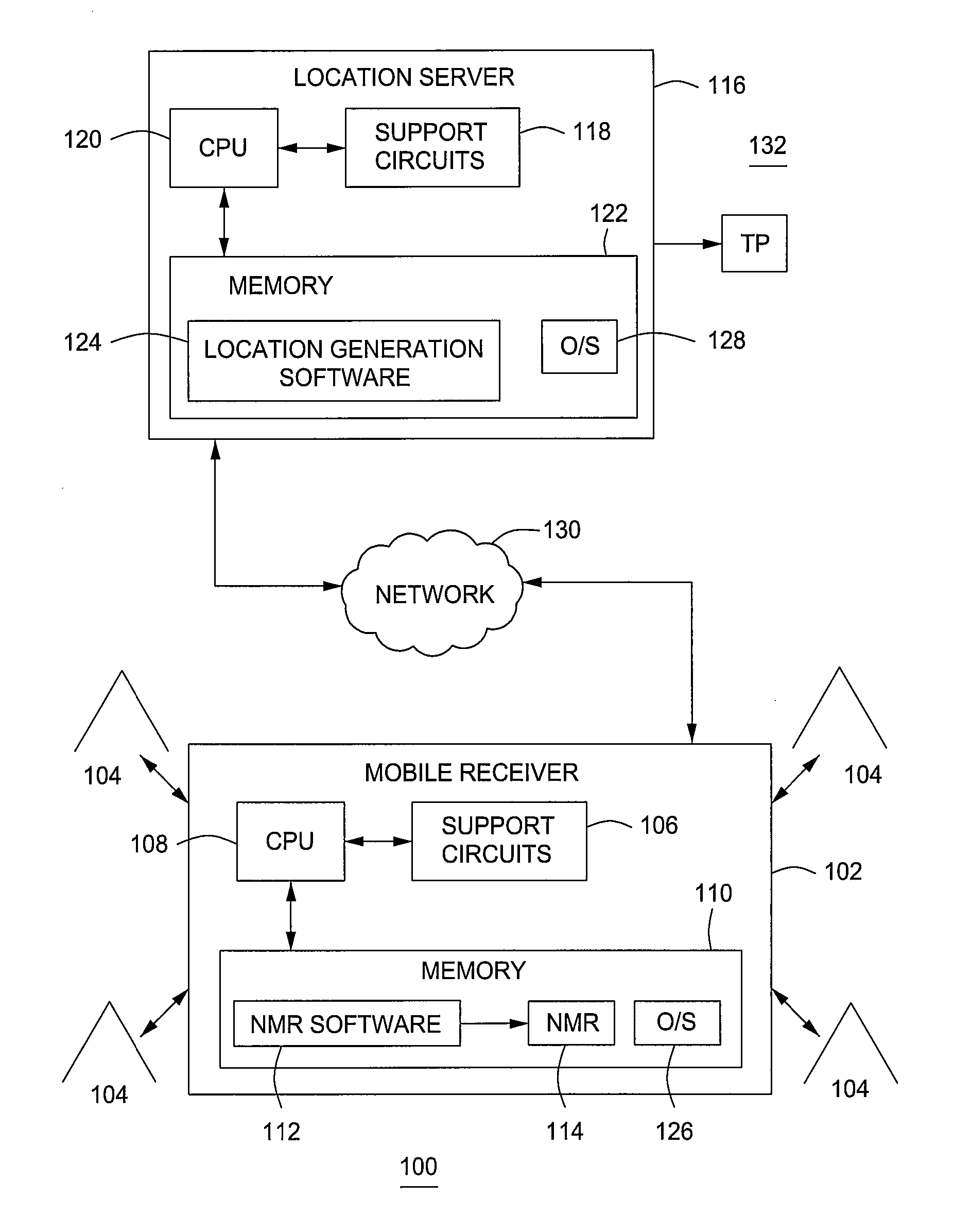
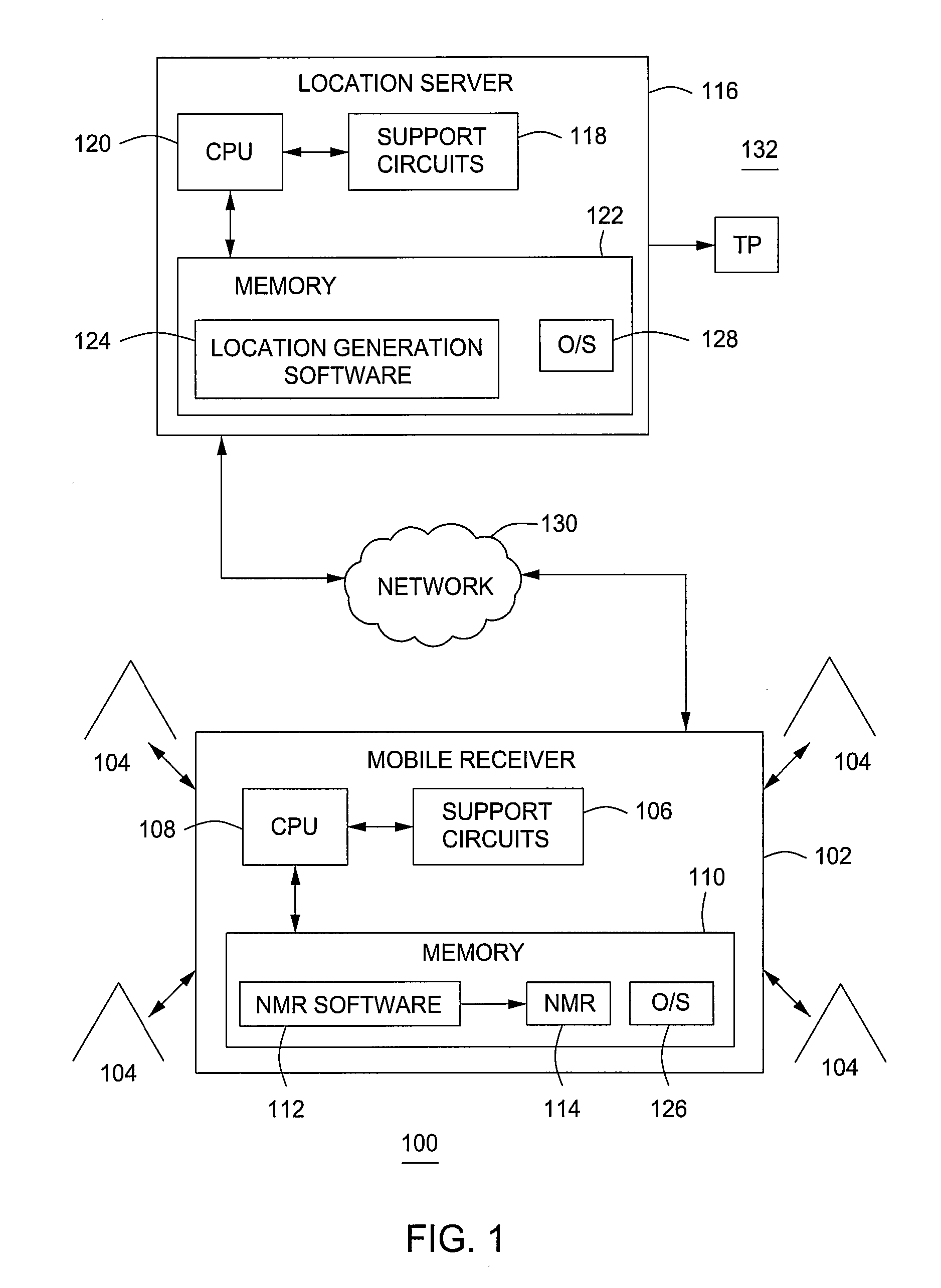
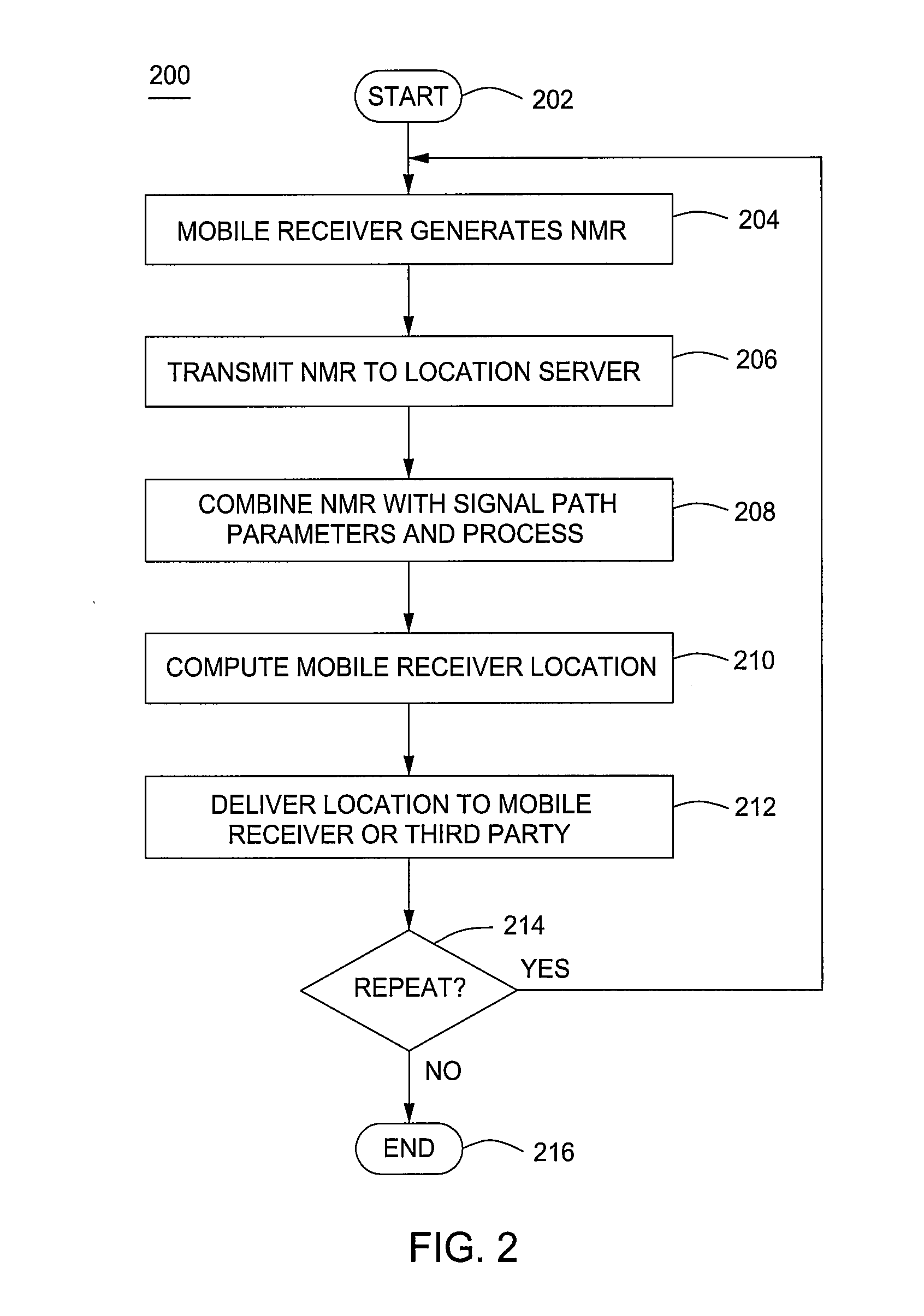
Computing geographical location of a mobile receiver using network measurement reports
InactiveUS20090088180A1Position fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork measurementGeolocation
A method and an apparatus for determining a location of a mobile receiver including the steps of measuring a plurality of signal strengths received by a mobile receiver, wherein the plurality of signal strengths are associated with a plurality of cellular stations, wherein the plurality of signal strengths is associated with a specific point in time, combining the plurality of signal strengths with a plurality of signal path modeling parameters to create a propagation path loss model of the path between the plurality of cellular stations and the mobile receiver, applying a non-linear estimation algorithm to the propagation path loss model, generating a plurality of distances, wherein each distance is associated with the mobile receiver and each of the plurality of cellular stations and computing the location of the mobile receiver by iterating the non-linear estimation algorithm and resulting mobile receiver position until converged.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Cellular handoff based on traffic load sharing
InactiveUS7299019B1Equally distributedImprove efficiencyRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmissionCell siteOrder set
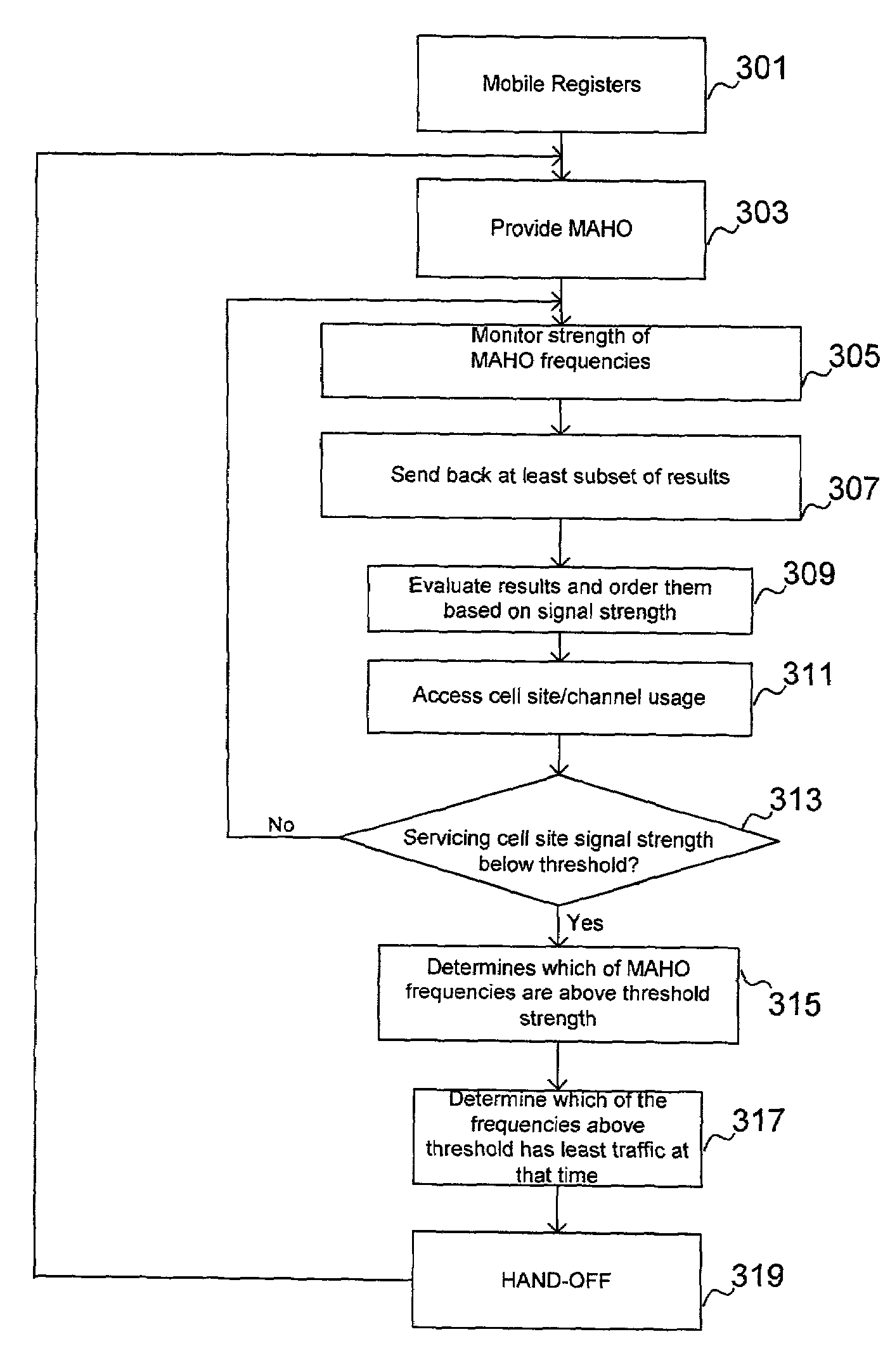
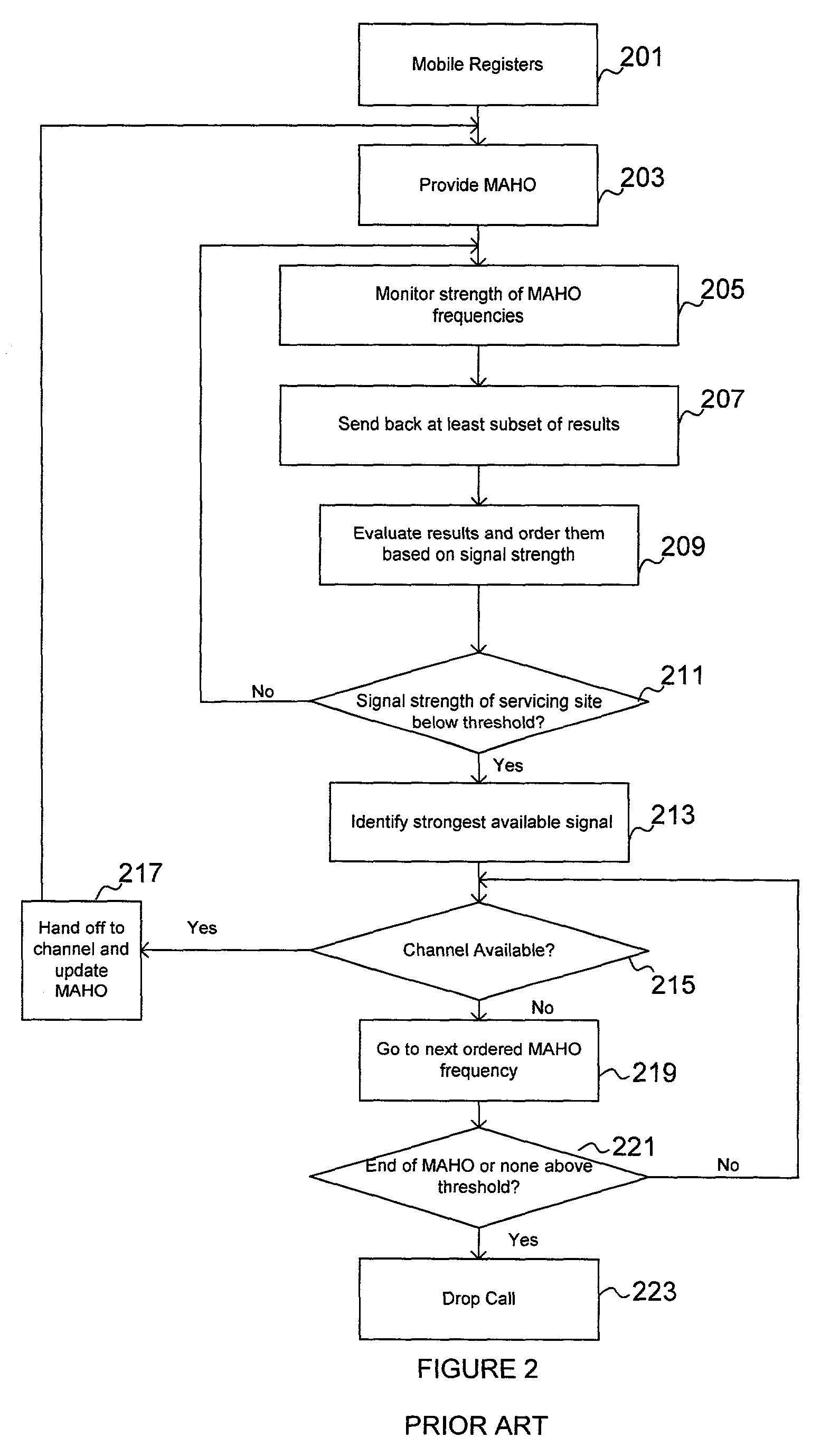
A method of effecting a handoff in a cellular network. The method includes monitoring a set of frequencies listed in a mobile assisted handoff (MAHO) list for their respective signal strengths, each of the frequencies being associated with neighbor cell site, logically ordering the frequencies based on their relative signal strengths, identifying in the logically ordered set of frequencies those frequencies having a signal strength higher than a predetermined threshold, determining a level of traffic at each frequency / cell site associated with the set of frequencies, and selecting a cell site for handoff based at least in part on signal strength and in part on the level of traffic at the neighbor cell site.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
Public safety access point (PSAP) selection for E911 wireless callers in a GSM type system
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
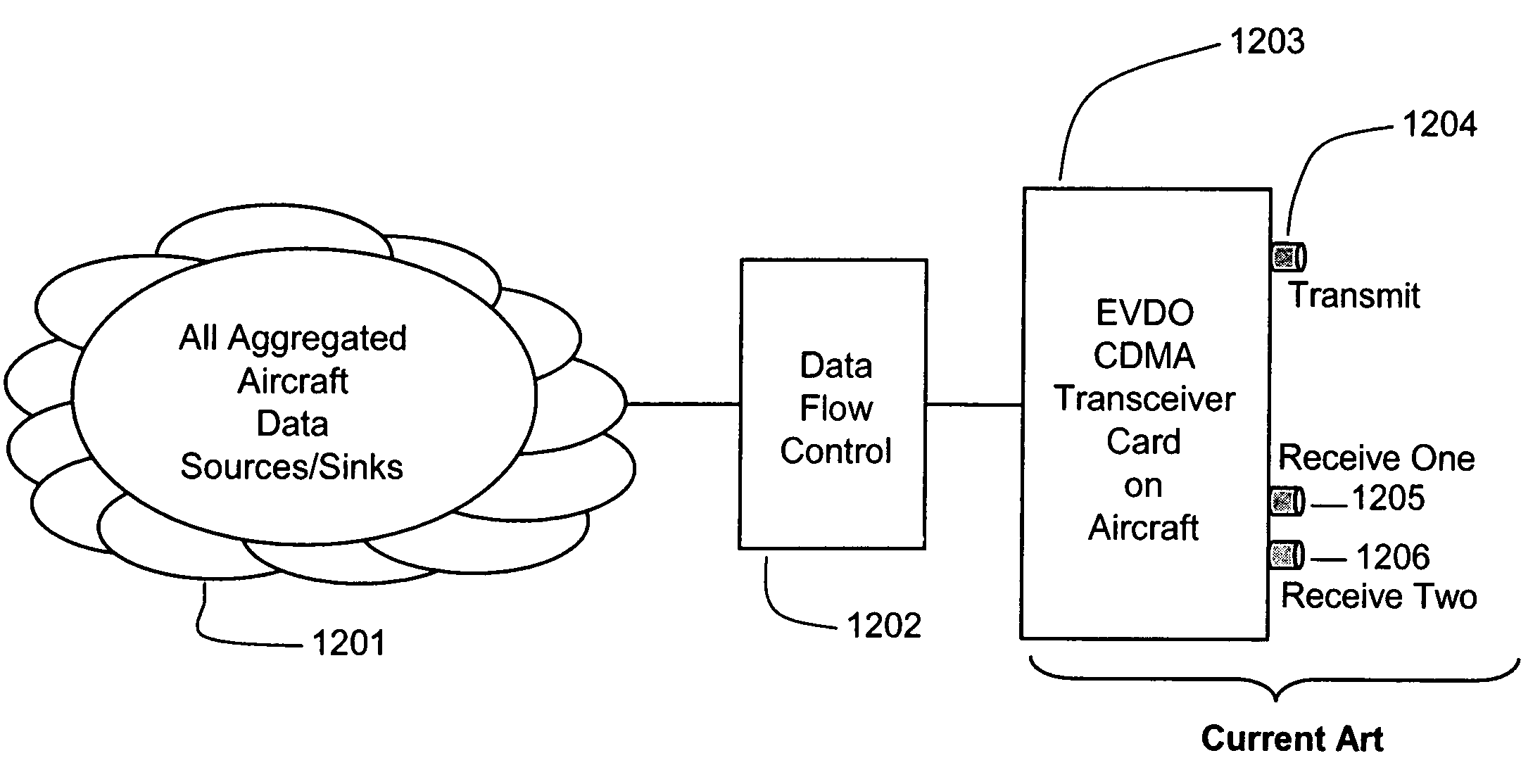
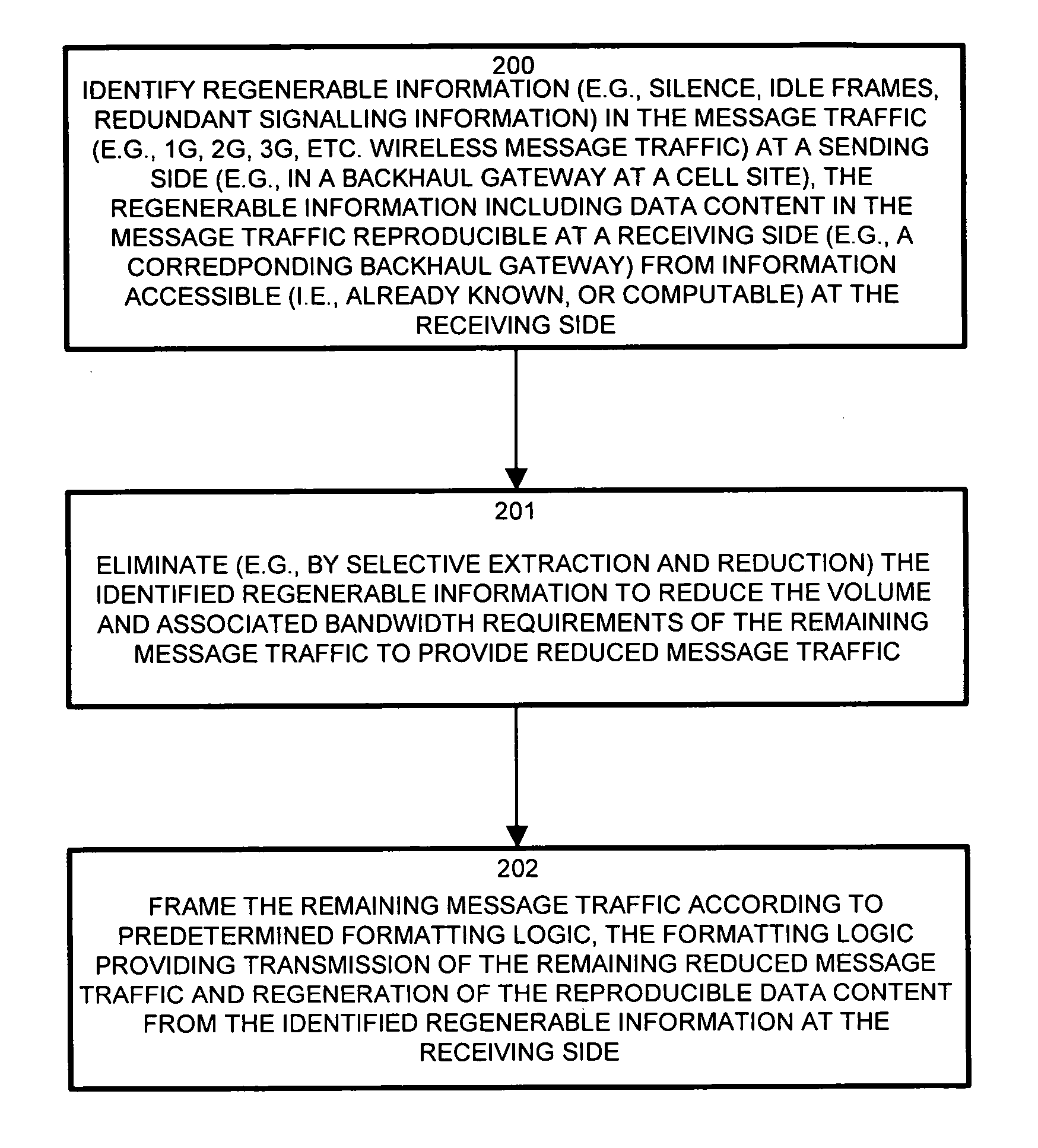
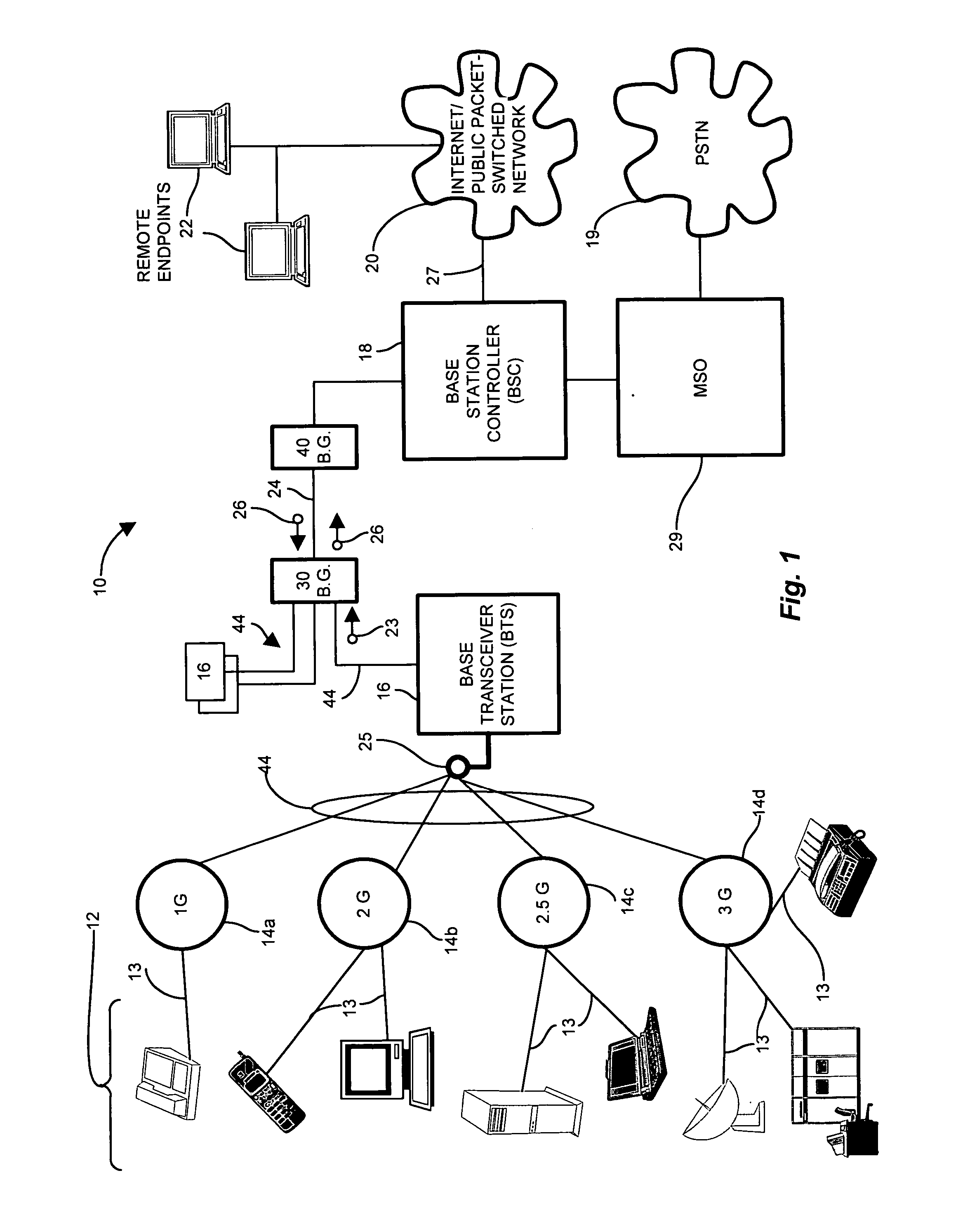
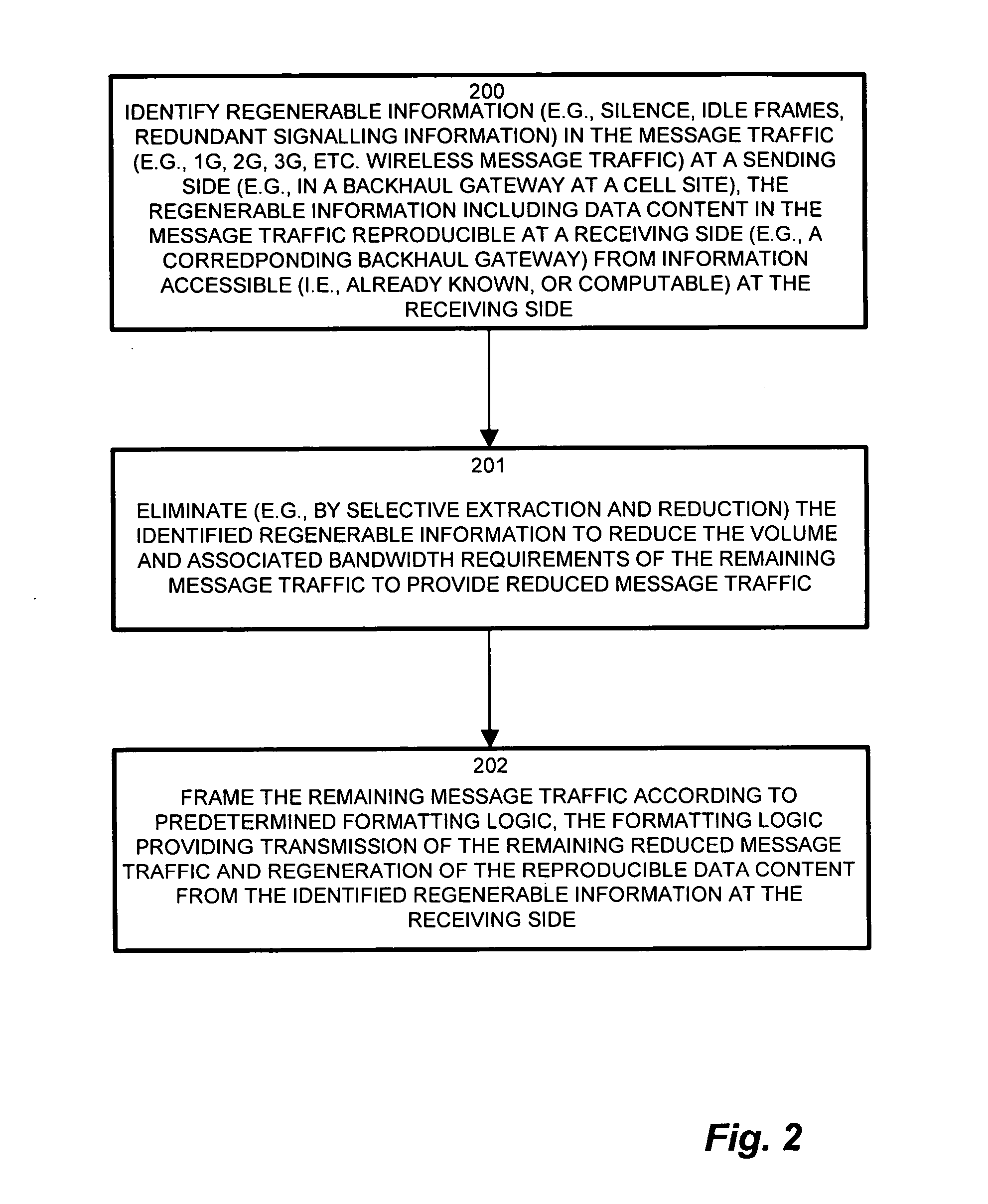
Methods and apparatus for low latency signal aggregation and bandwidth reduction
InactiveUS20070195815A1Minimize the numberFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork traffic/resource managementType specificService provision
Wireless network demands continually increase as wireless service providers pursue additional service capabilities. In a cellular communication system, leased lines between remote cell sites and the corresponding Mobile Switching Offices (MSOs) remain a major operating cost. Bandwidth reduction by identification and elimination of payload data and control information which need not be fully replicated because it can be deduced from information accessible or previously transmitted allows fewer lines to support the same bandwidth. A wireless access gateway is operable to aggregate such redundant and regenerable data on a backhaul link between a wireless cell site and the corresponding mobile switching office (MSO) to provide low-latency, type specific lossless bandwidth reduction. The wireless access gateway identifies regenerable information and eliminates portions of the data which the device need not transmit because the data is redundant, or accessible or recreatable, at the receiving side. In this manner, the access device allows fewer lines to carry the reduced message traffic by transmitting only the non-recreatable data and eliminating message traffic for regenerable information.
Owner:VERSO BACKHAUL SOLUTIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com