Patents
Literature
350 results about "Dynamic channel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
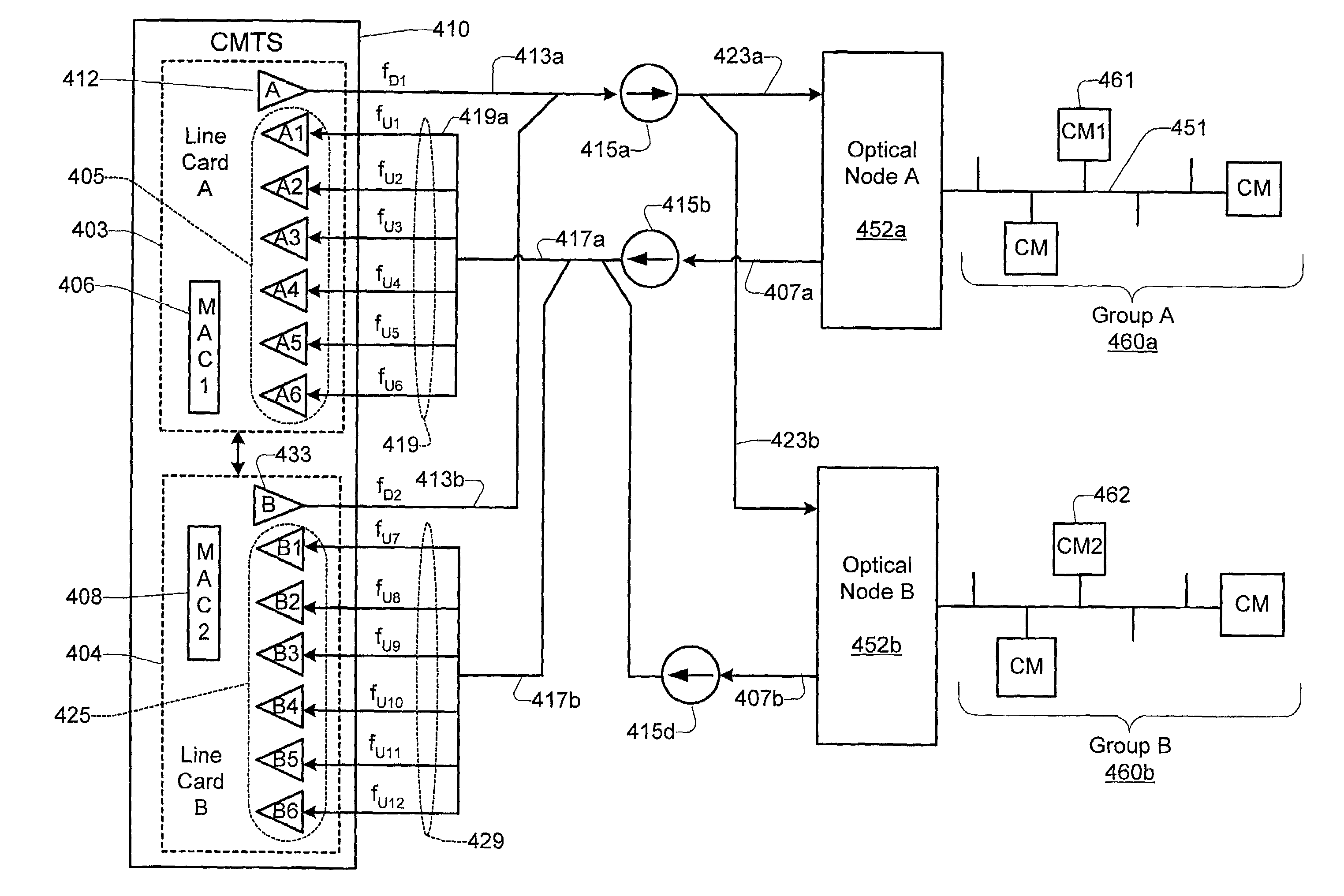
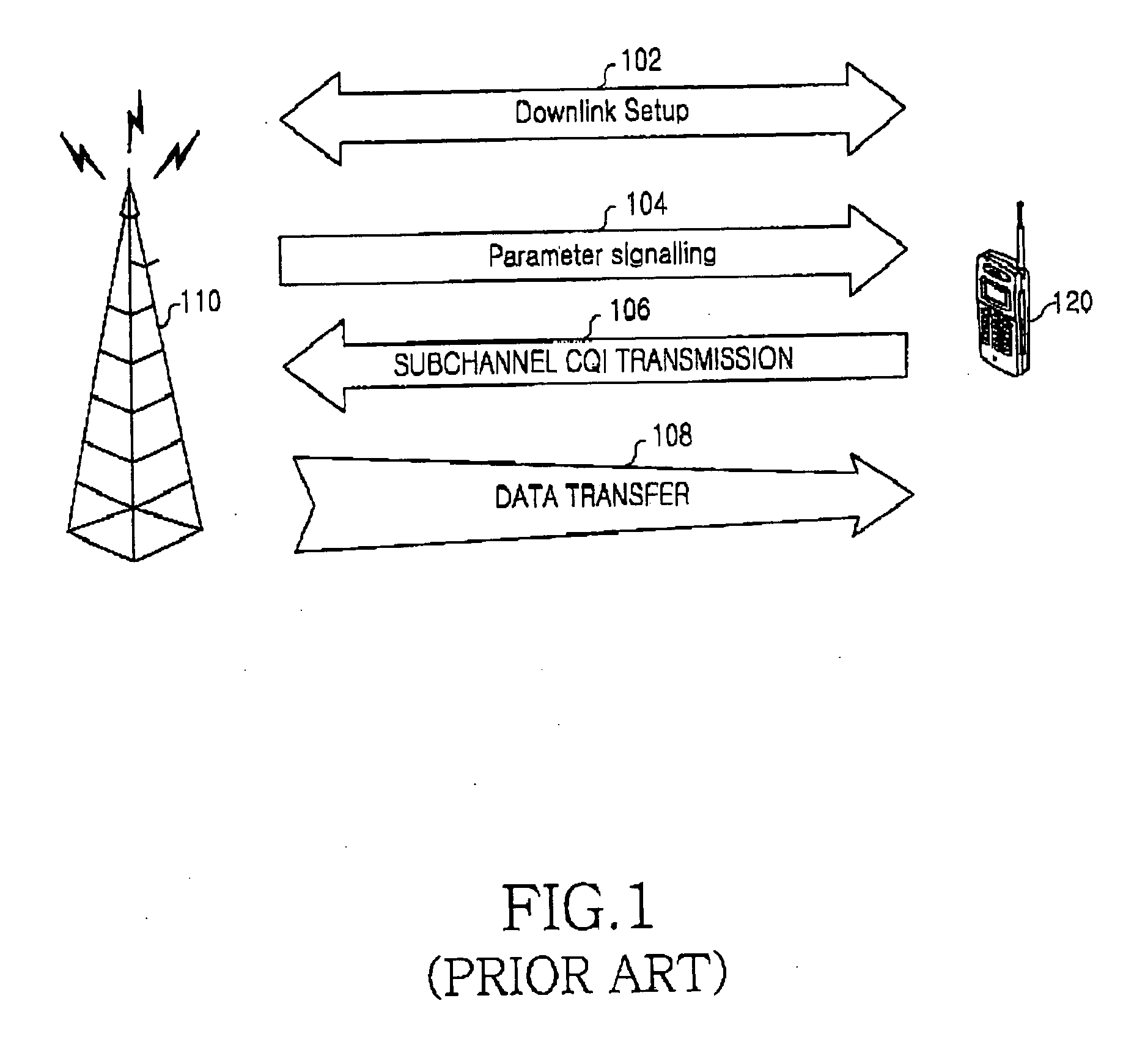
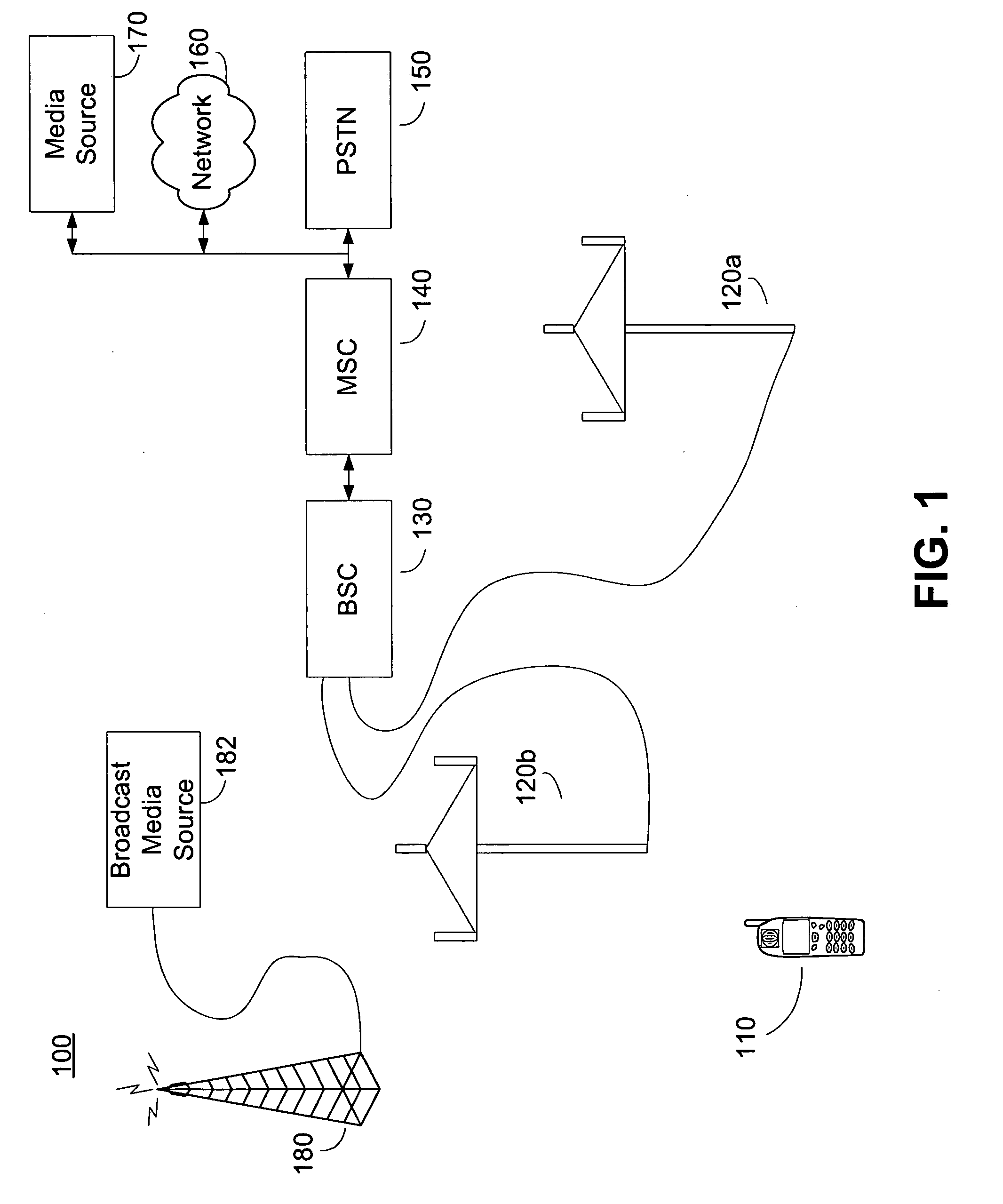
Downstream channel change technique implemented in an access network
A dynamic channel change technique is disclosed which may be implemented between nodes and a Head End of an access network. Initially a network device may communicate with the Head End via a first downstream channel and a first upstream channel. When the network device receives a dynamic channel change request which includes instructions for the network device to switch to a second downstream channel, the network device may respond by switching from the first downstream channel to the second downstream channel. Thereafter, the network device may communicate with the Head End via the second downstream channel and first upstream channel. Further, according to a specific embodiment, the dynamic channel change request may also include an upstream channel change request for causing the network device to switch from a first upstream channel to a second upstream channel.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
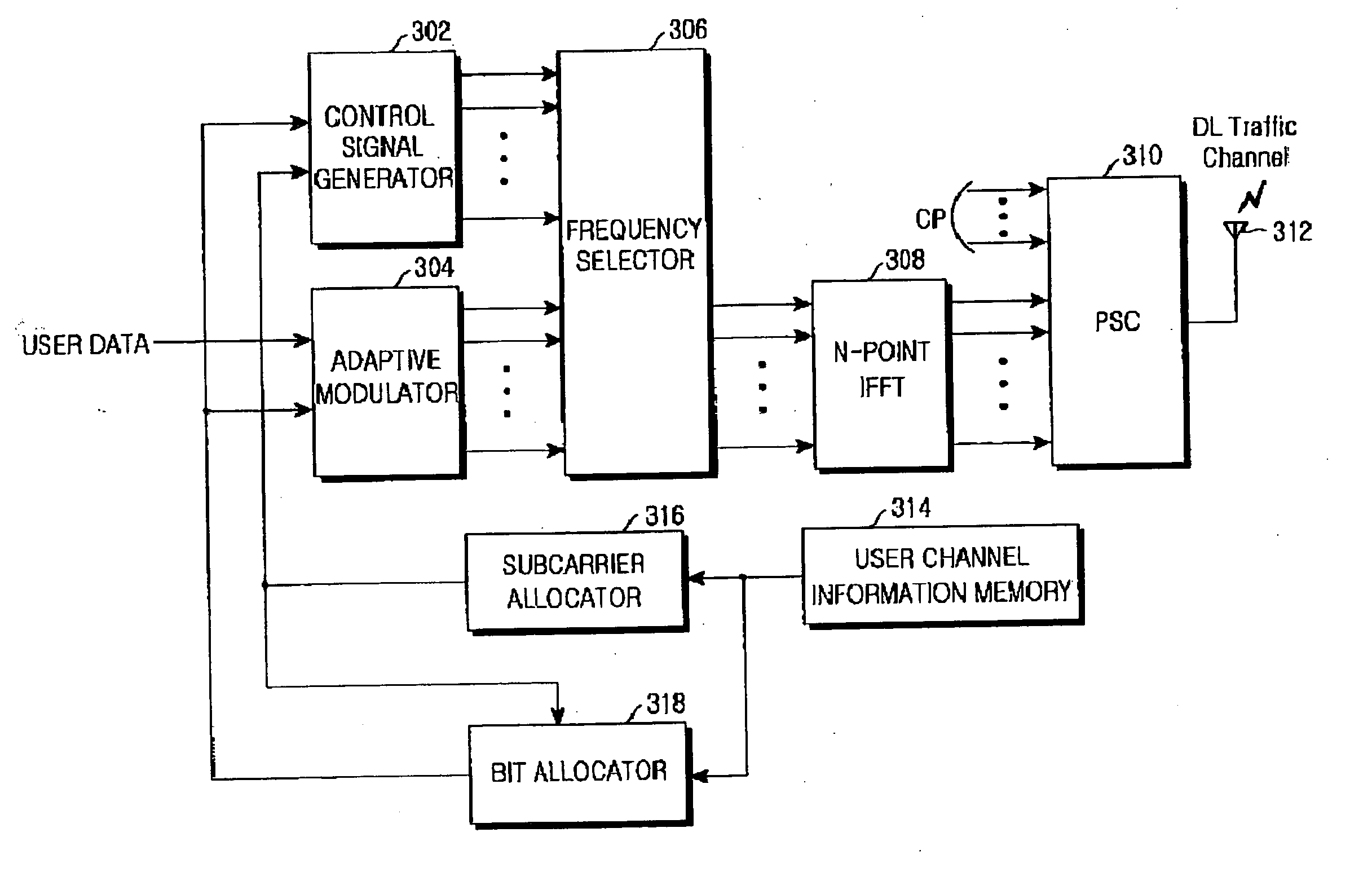
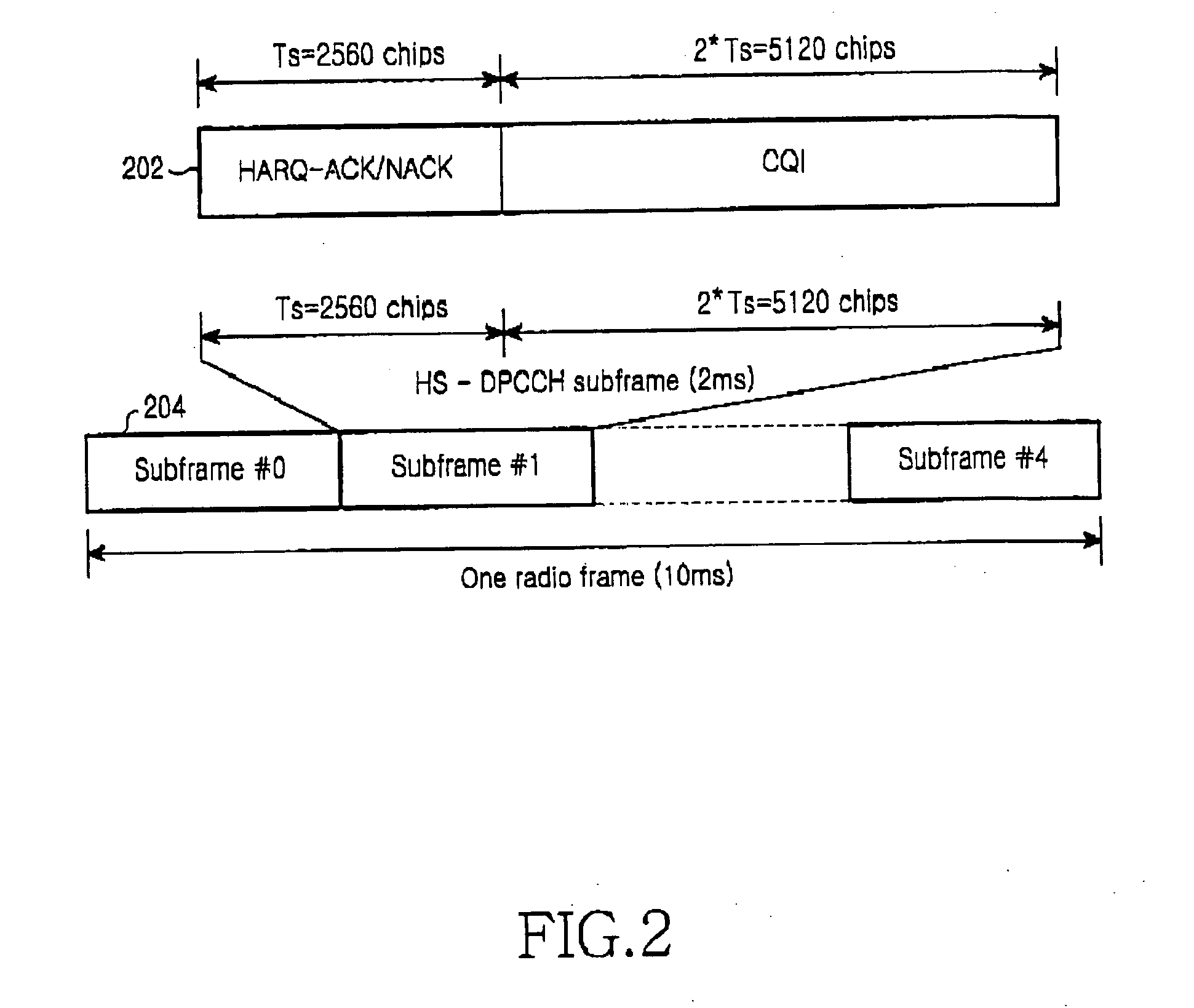
Method and apparatus for transmitting channel quality information in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication system
InactiveUS20050201474A1Guaranteed normal transmissionReduce overheadError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission path divisionAsynchronous cdmaAsynchronous communication
A method and apparatus for efficiently transmitting channel quality information in an OFDM communication system using dynamic channel allocation and adaptive modulation, and determining parameters required for time-division channel quality information transmission in an asynchronous CDMA communication system are provided. In the OFDM communication system in which a plurality of subcarriers are allocated to a plurality of UEs, the subcarriers are divided into a plurality of subcarrier groups each having at least one subcarrier. Each of the UEs determines and transmits the channel quality information of each of the subcarrier groups according to predetermined transmission parameters at transmission time points that do not overlap with those of other UEs. A Node B dynamically allocates the subcarriers to the UEs and their corresponding modulation schemes according to the channel quality information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
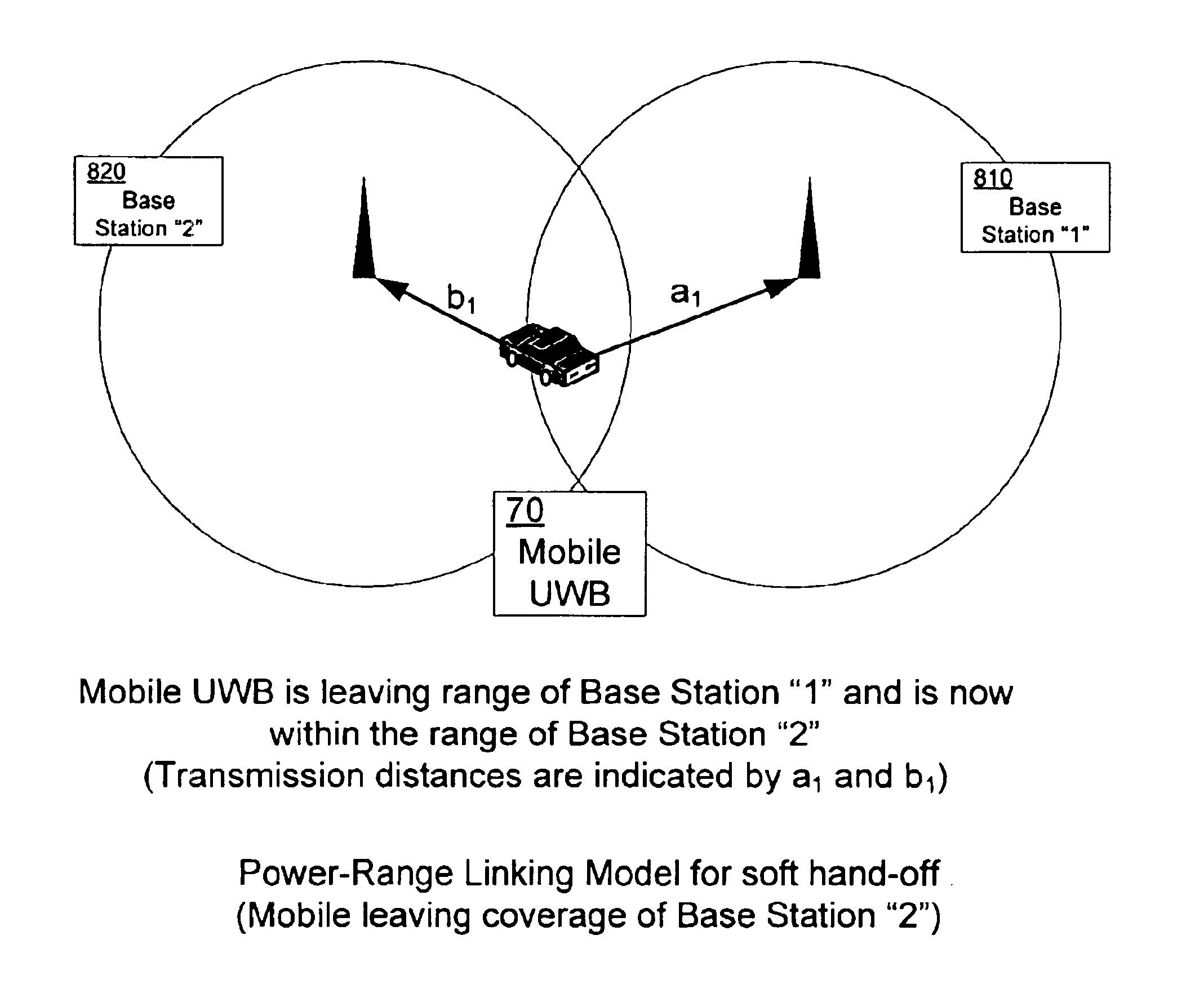
Hand-off between ultra-wideband cell sites
InactiveUS6907244B2Effectively linkedAcceptable levelError prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorDynamic channelCell site
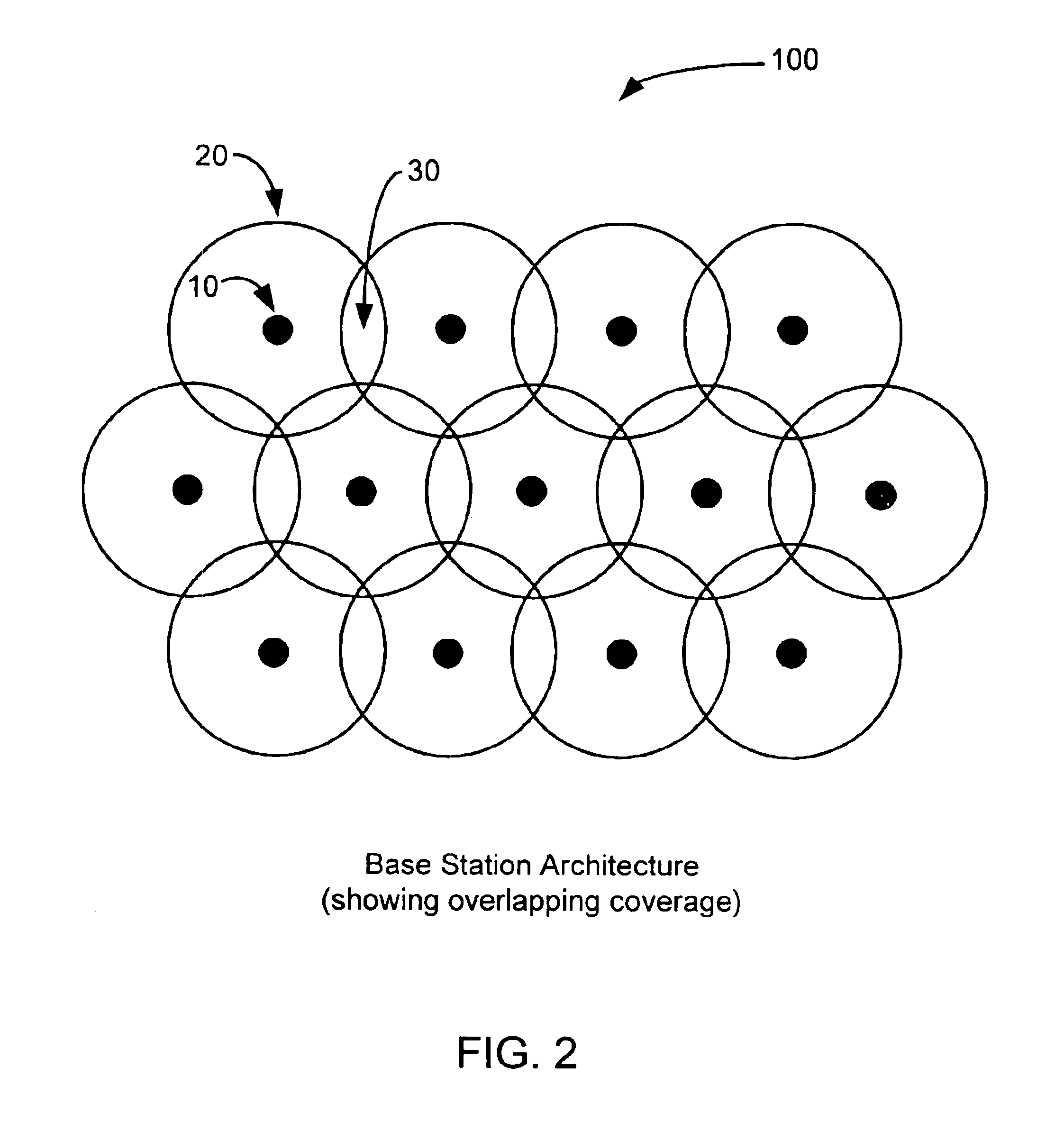
Briefly, the present invention provides a dynamic channel re-assignment capability between mobile units, base stations and sectors within base station coverage areas. The wireless devices used in the present invention may include impulse radio communication devices such as, for example ultra-wideband radio (also known as digital pulse wireless) communication devices. Ultra-wideband bandwidth and channel allocation can be effectively managed, even though link quality generally deteriorates near the outer boundary of the base station. By maintaining dual communications with an adjoining base station, the present invention reduces the bit error rate and maintains signal strength (e.g., RF signal strength). This procedure is termed a “soft-handoff”.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
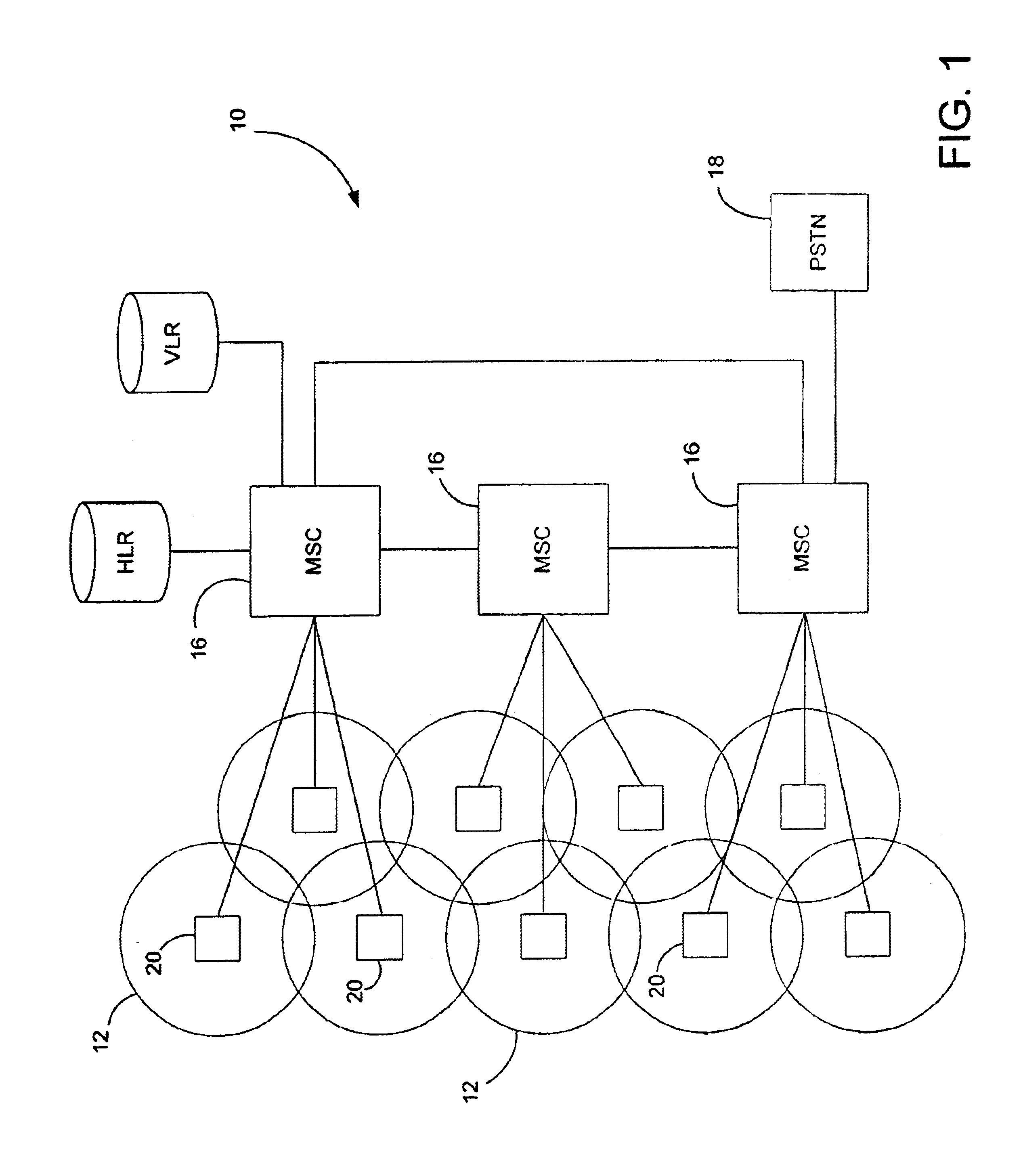
Wireless communication system with dynamic channel allocation
InactiveUS6023622AFacilitate communicationReduce distractionsNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDynamic channelTransceiver
A plurality of base stations communicate with a plurality of mobile units. Each base station includes a base station transceiver that receives inbound information from the mobile units and transmits outbound information to the mobile units. A mobile switching center (MSC) is coupled to the base stations and communicates the inbound information and outbound information with the base stations. The base stations each include signal detectors that detect signal strength of the inbound information, co-channel information and adjacent channel information. The MSC maintains a table of signal strength per communication channel and allocates communication channels to the base stations based on the signal strength information. The inventive dynamic channel allocation includes several channel allocation algorithms that can be active at the same time. Only one of the algorithms is active at a time. The choice of the algorithm is based on current interference conditions and traffic load. The invention is implemented in the MSC and base stations of a digital cellular network using wideband technology for its air interface. While the decision-making mechanism and the channel allocation algorithms are implemented in the MSC, the protocol between the MSC and base stations is extended to support the proposed concept for dynamic channel allocation. Advantages of the invention includes improved communication and reduced interference.
Owner:WJ COMM
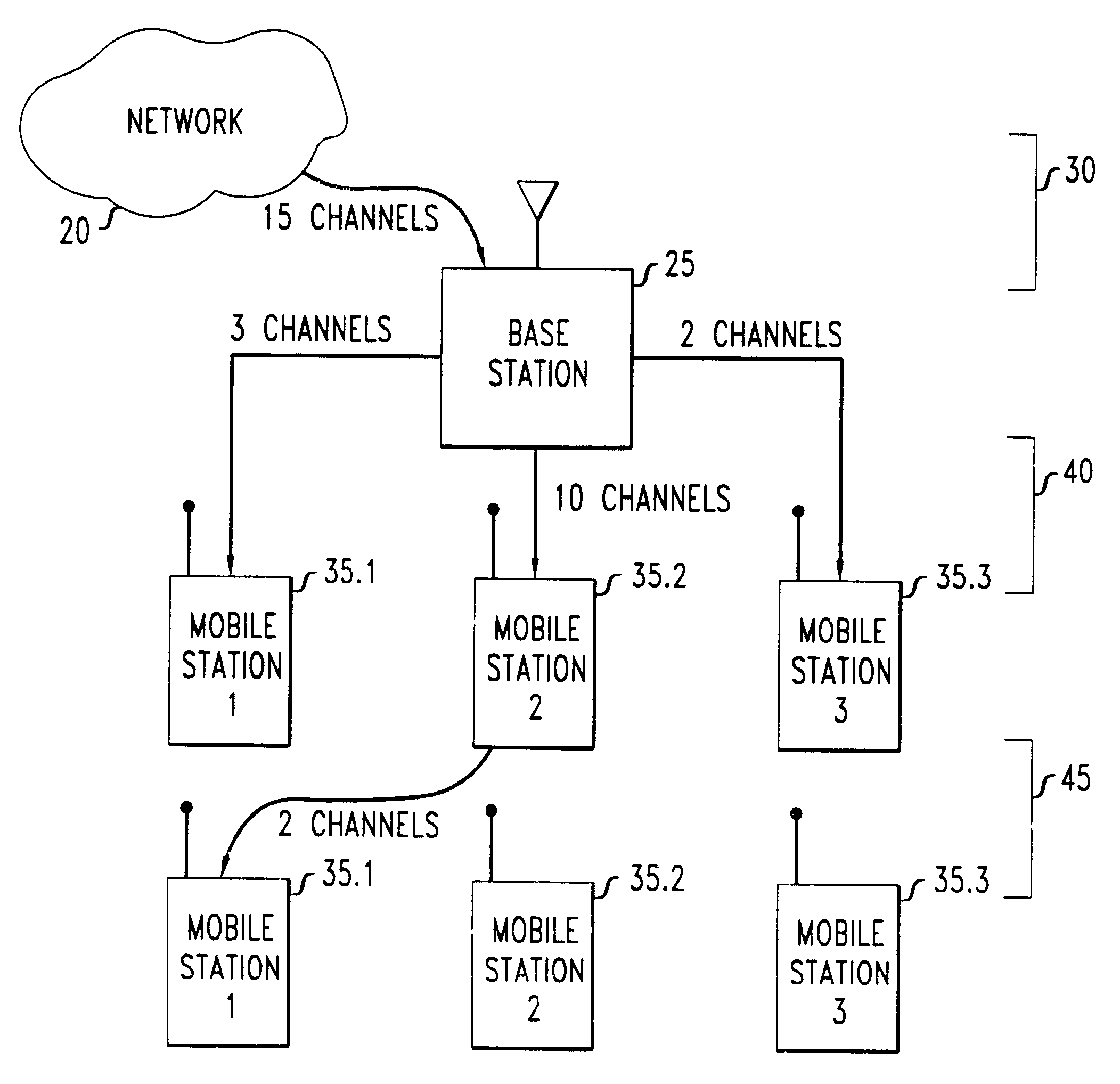
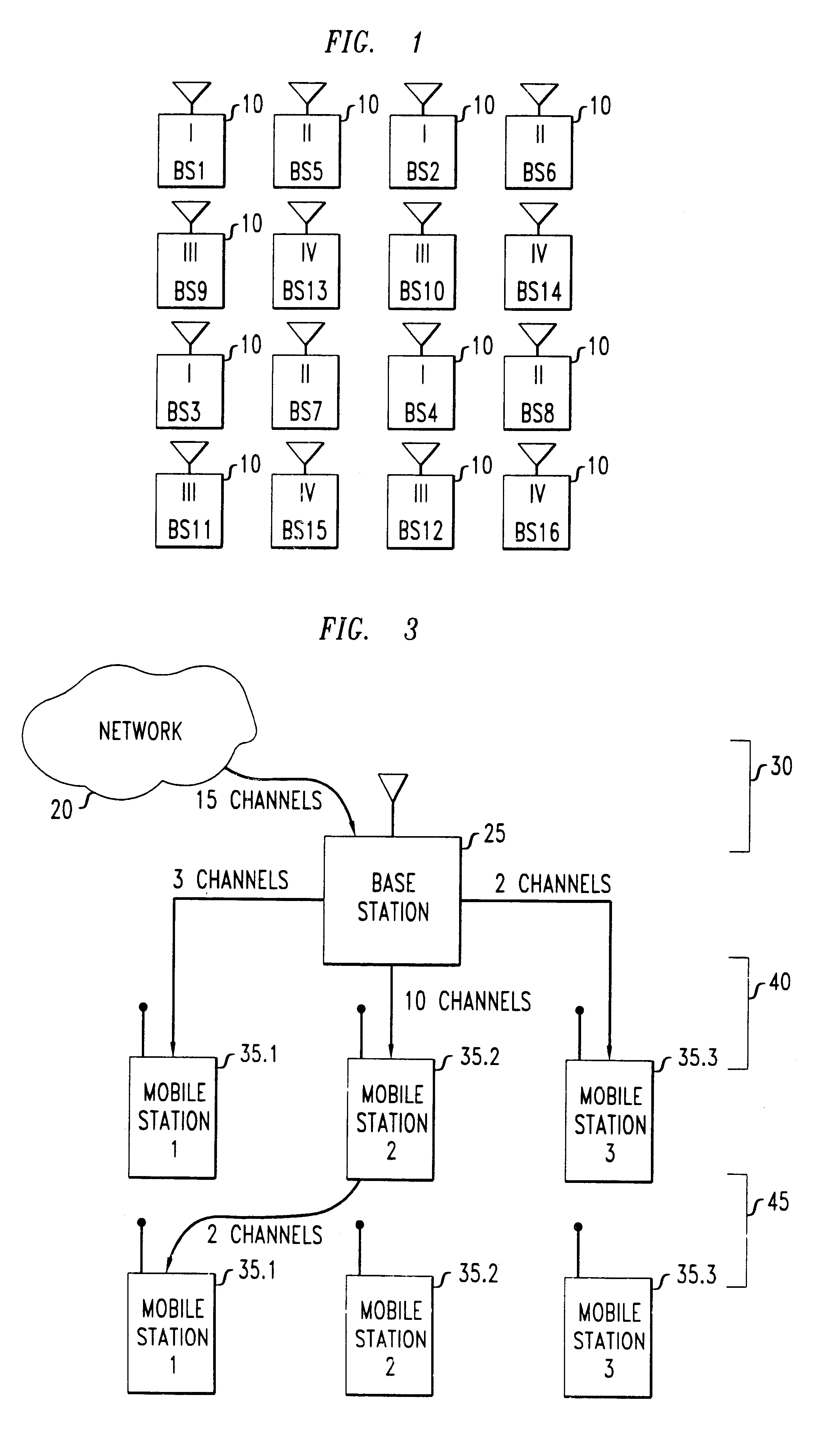
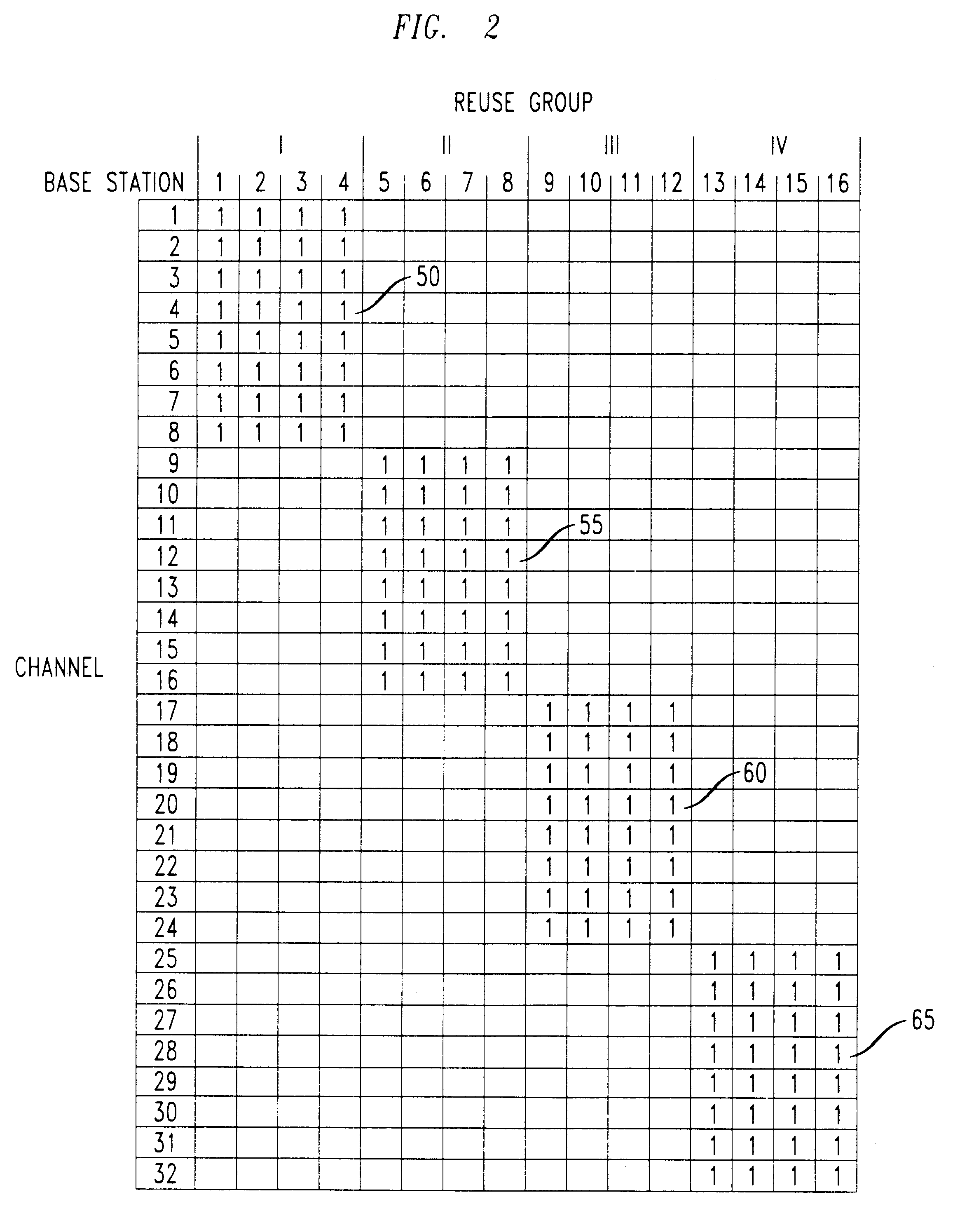
Method for dynamically allocating carriers in a wireless packet network, with reuse of carriers
InactiveUS6496490B1Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexMultiplexingDynamic channel
We disclose a method of dynamic channel assignment for wireless transmission systems that employ time or frequency multiplexing, or both time and frequency multiplexing. The invention is specifically addressed to the problem of avoiding interference in the channels of such systems. In a broad aspect, the invention involves partitioning base stations of a network into non-interfering sets. Channels are allocated to the non-interfering sets according to need. Stages of channel reallocation take place periodically. The reallocation takes place through coordinated activity by the base stations. That is, the channel reallocation is carried out in response to information that is exchanged between base stations, or it is centrally directed by the network in response to information passed to the network by the base stations.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
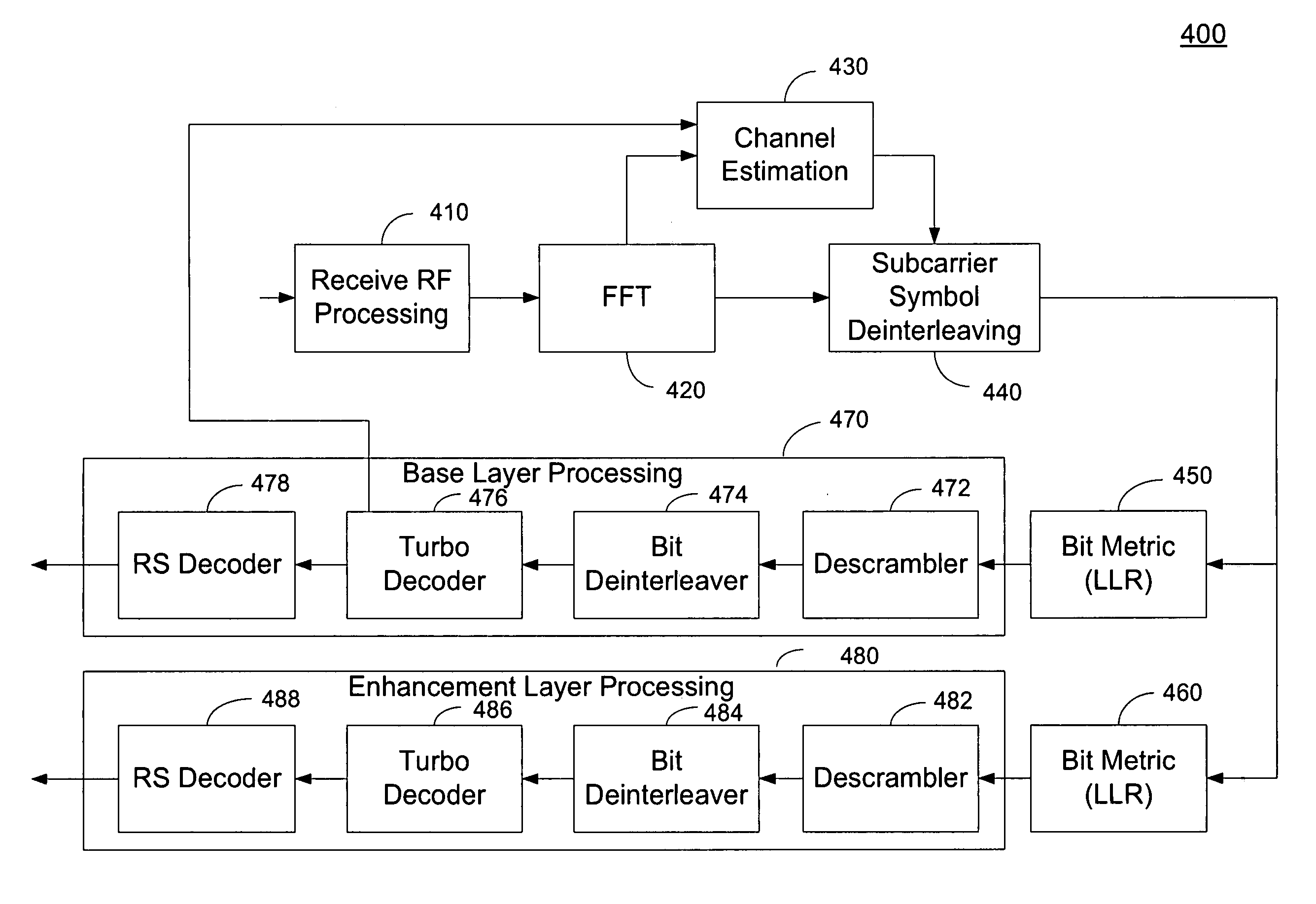
Adaptive channel estimation thresholds in a layered modulation system
Dynamic channel estimation thresholds allow for determining optimal threshold values for channel estimation in a layered-modulation wireless communication system. A channel estimation threshold can be used to remove or otherwise filter out channel estimate components that may be significantly influenced by noise. The channel estimation threshold value can be used to generate a refined channel estimate that is used in decoding multiple layers of a layered modulation signal. The channel estimation threshold value can be varied based on the performance of the various signal layer decoders. The adaptive channel estimation threshold provides for decoding a base layer based on an optimal threshold value for the base layer; determining an error rate associated with decoding the base layer; and using an optimal threshold value for an enhancement layer in a channel estimation algorithm if the error rate is lower than a predetermined level.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
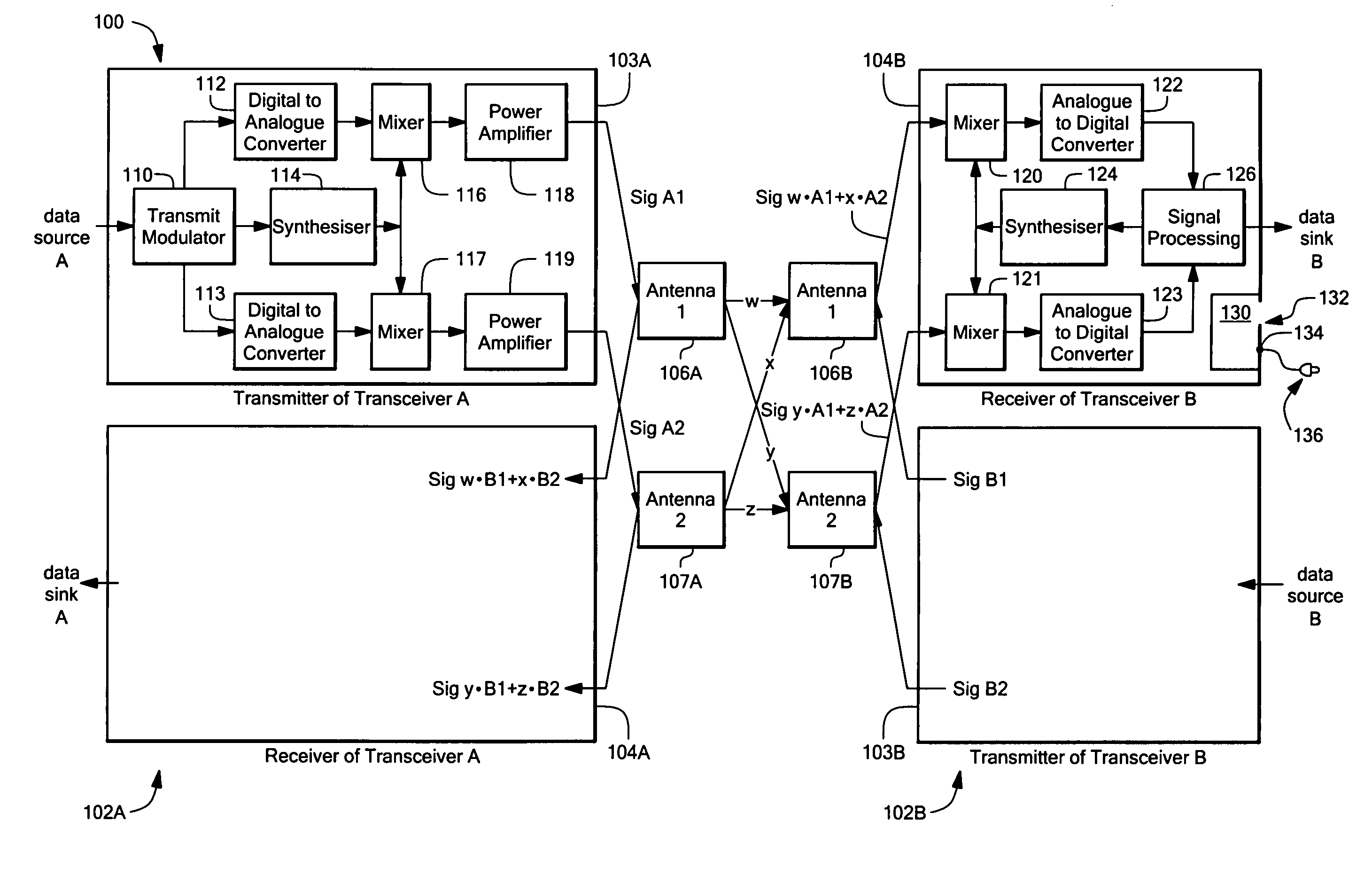
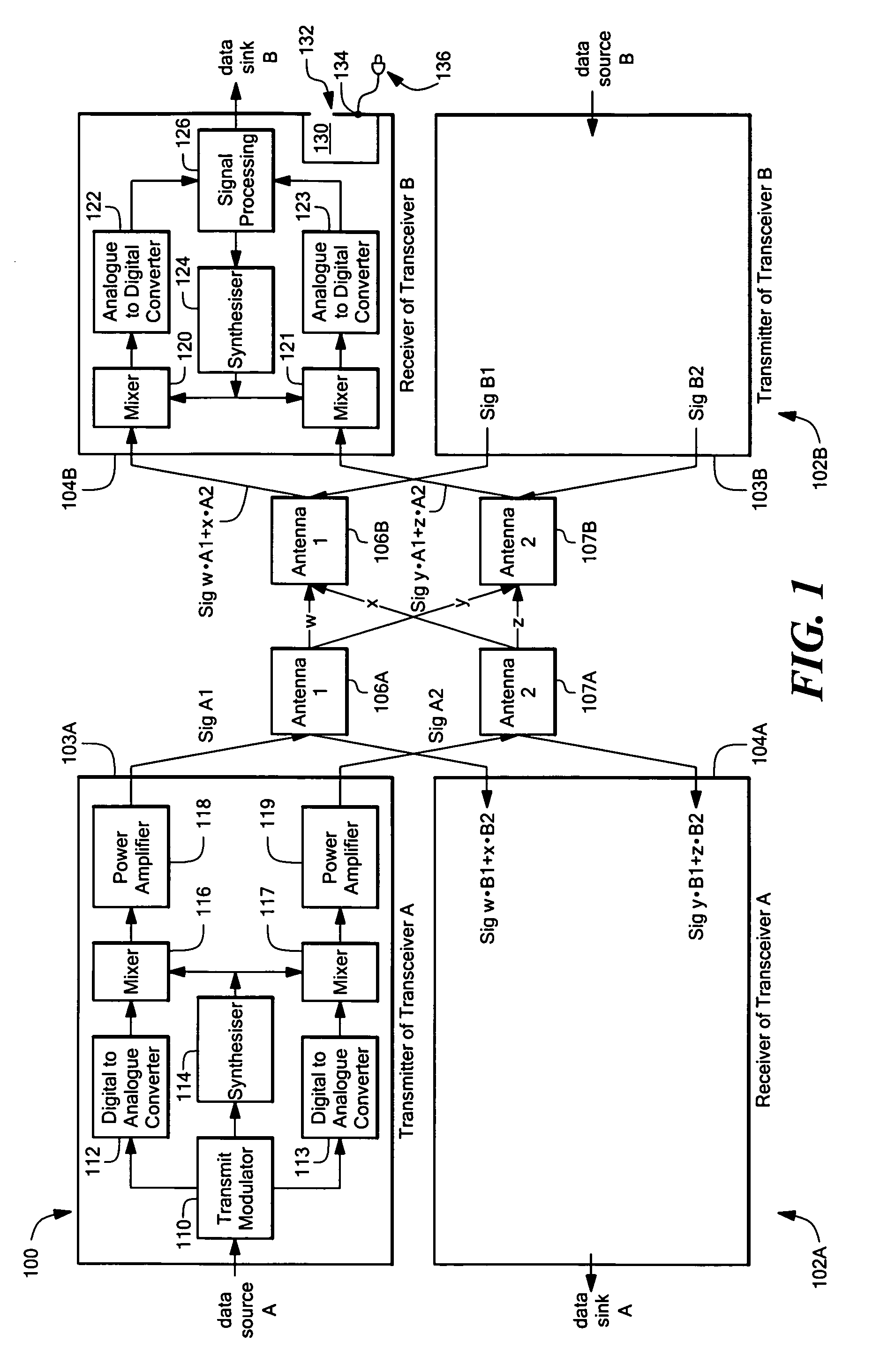
Intelligent adaptive modulation in a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) wireless communications system
ActiveUS7469013B1Reduce power levelIncreased de-correlationSpatial transmit diversityError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorOperational systemDynamic channel
A wireless broadband communications system that can maintain high data rates while taking into account channel interference resulting from operating in shared frequency bands, signal fading resulting from dynamic channel degradation, and signal distortion resulting from compliance with maximum power output regulations. In one mode of operation, the system performs adaptive modulation by transmitting a first signal over a selected channel using a first modulation mode having a level of distortion associated therewith resulting from operating the system at a predetermined maximum power output level. Next, a SINAD level is measured on the first channel. The level of distortion associated with the first modulation mode is then subtracted from the measured SINAD level to obtain a first noise level. In the event the first noise level is less than a noise level required to achieve an acceptable error rate in a next modulation mode, a second signal is transmitted over the selected channel using the next modulation mode.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Communication systems
ActiveUS20090191906A1Lower Level RequirementsReduce noise levelNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumDynamic channel
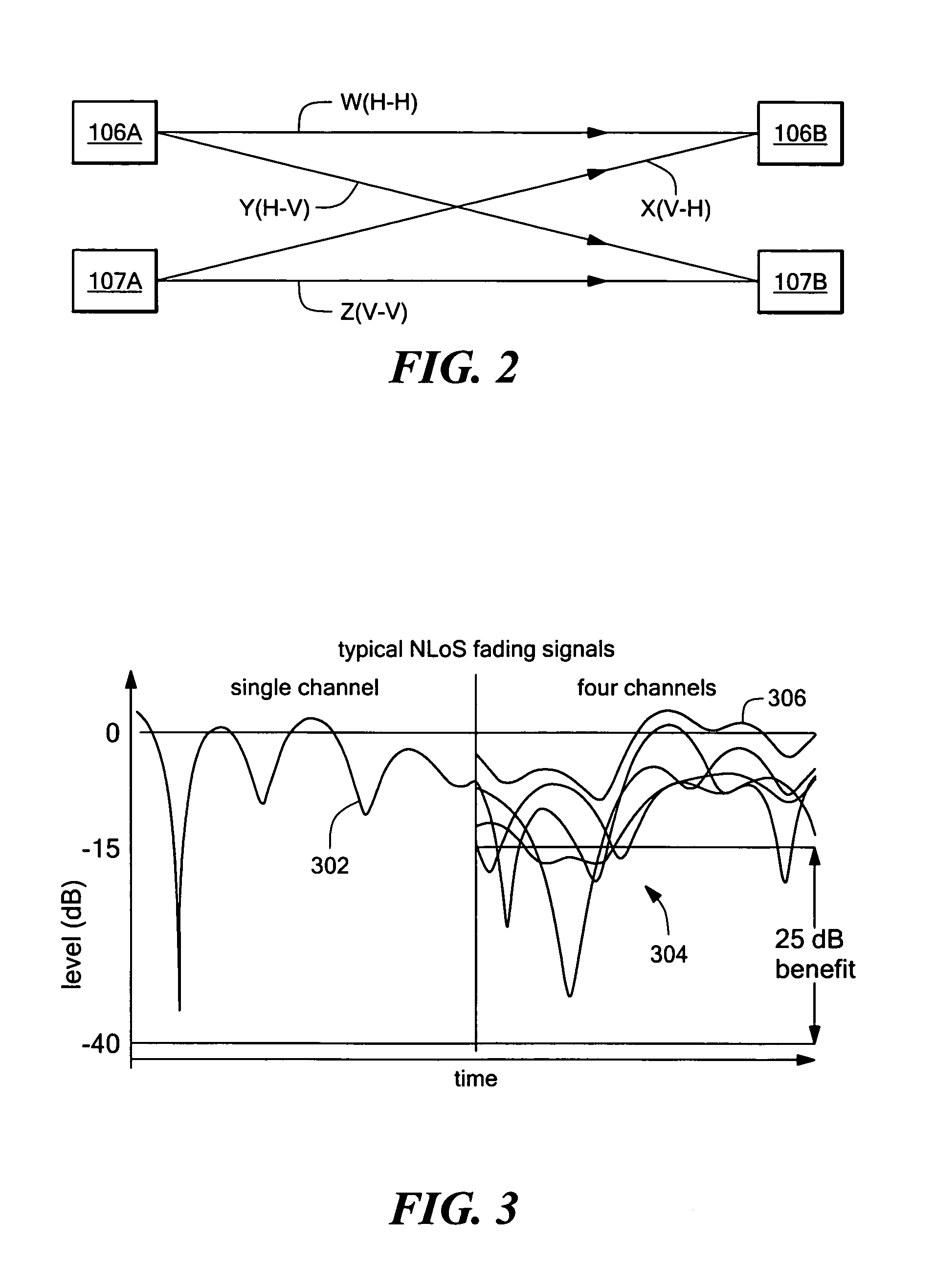
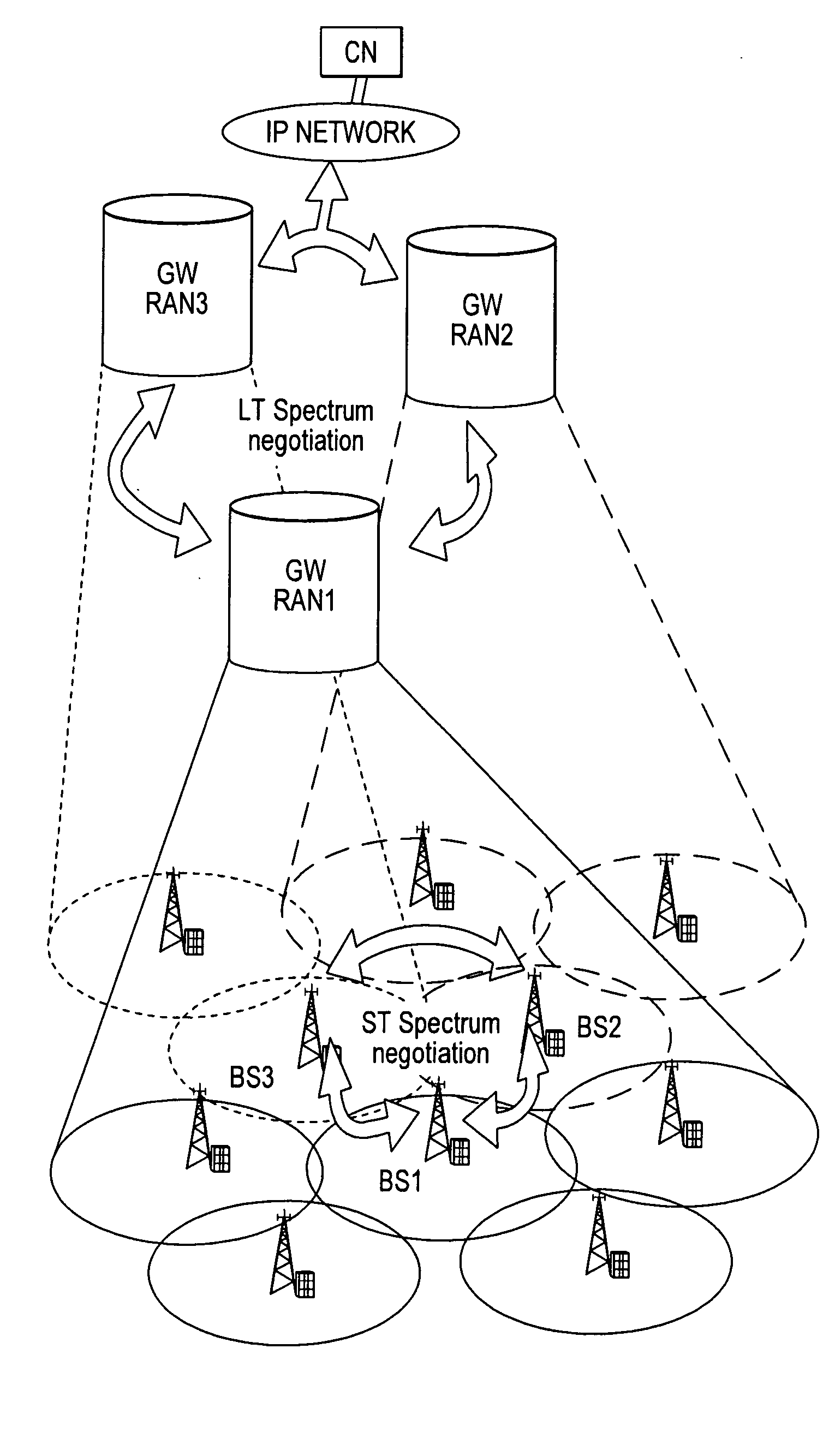
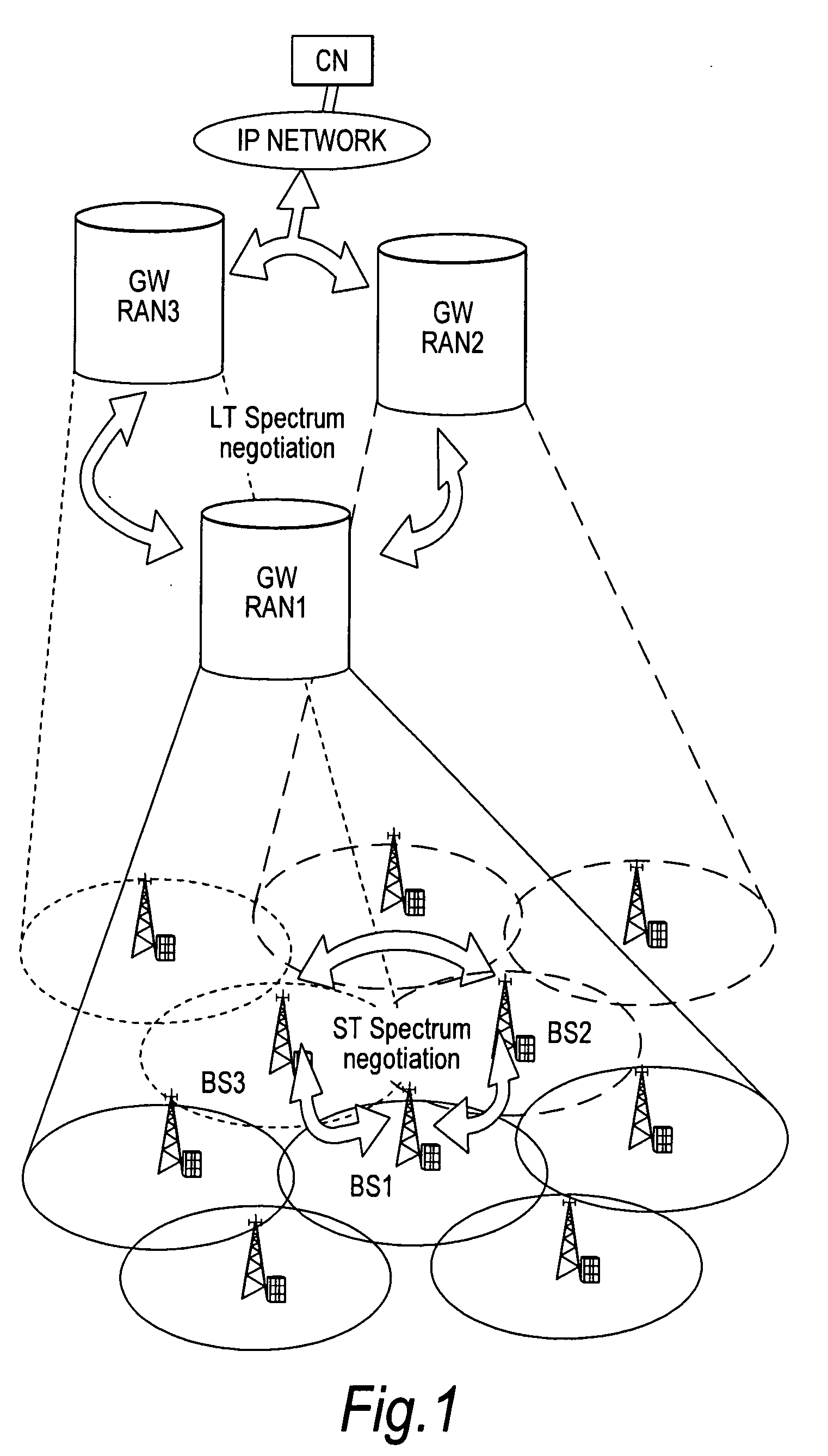
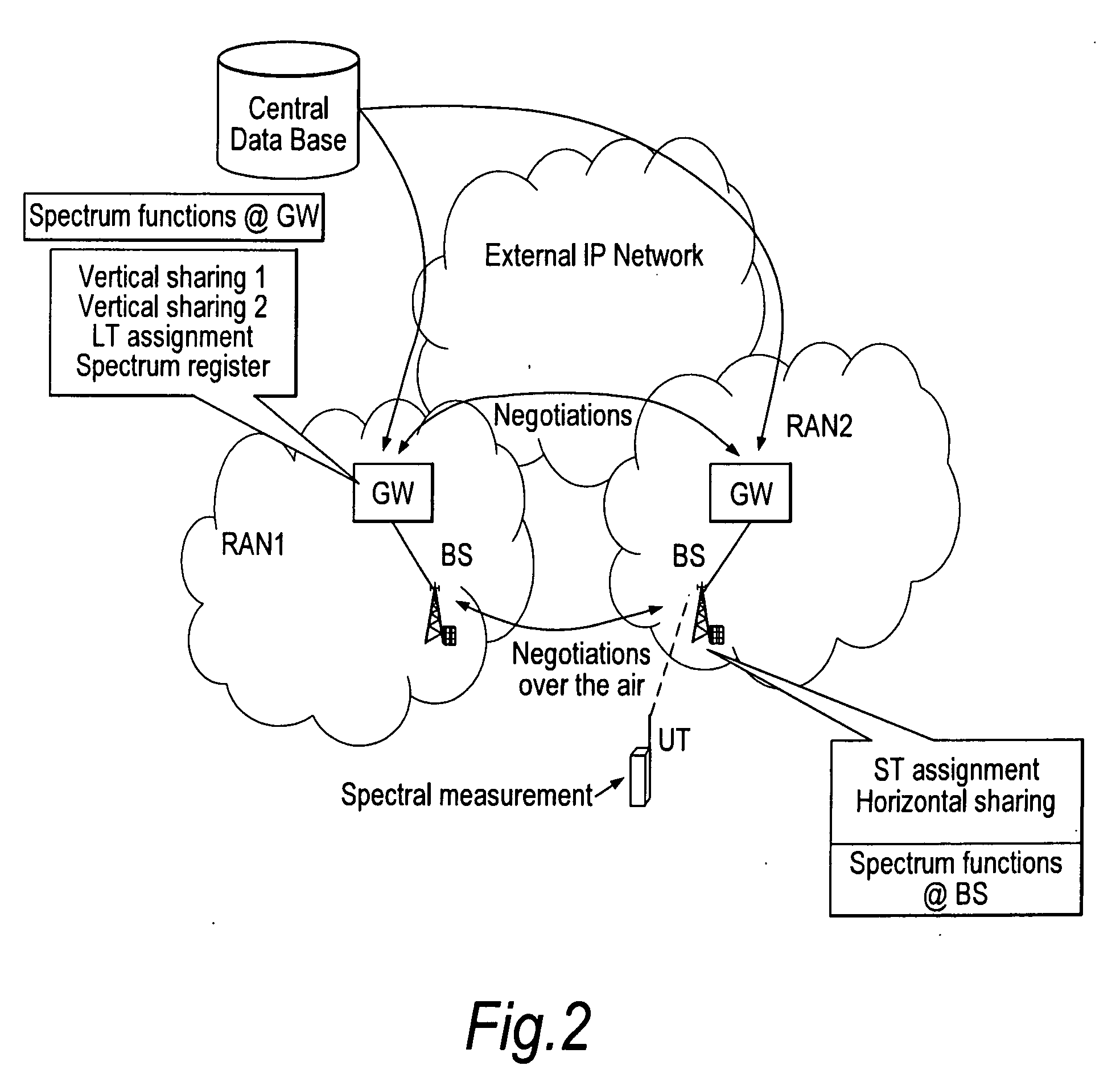
A wireless communication system is comprised of multiple radio access networks—RANs—which at least partly share the same frequency spectrum. Each RAN is provided with a gateway—GW—(GW1, GW2, GW3) for managing the network. Spectrum sharing in the system is achieved through a hierarchy of processes including long-term—LT—spectrum assignment, short-term—ST—spectrum assignment, and dynamic channel allocation, the latter process assigning sub-channels to base stations (BS1, . . . BS5; BS6, . . . BS10; BS11, . . . BS16) in each RAN. However, so-called “red” sub-channels (subject to interference) are liable to arise.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
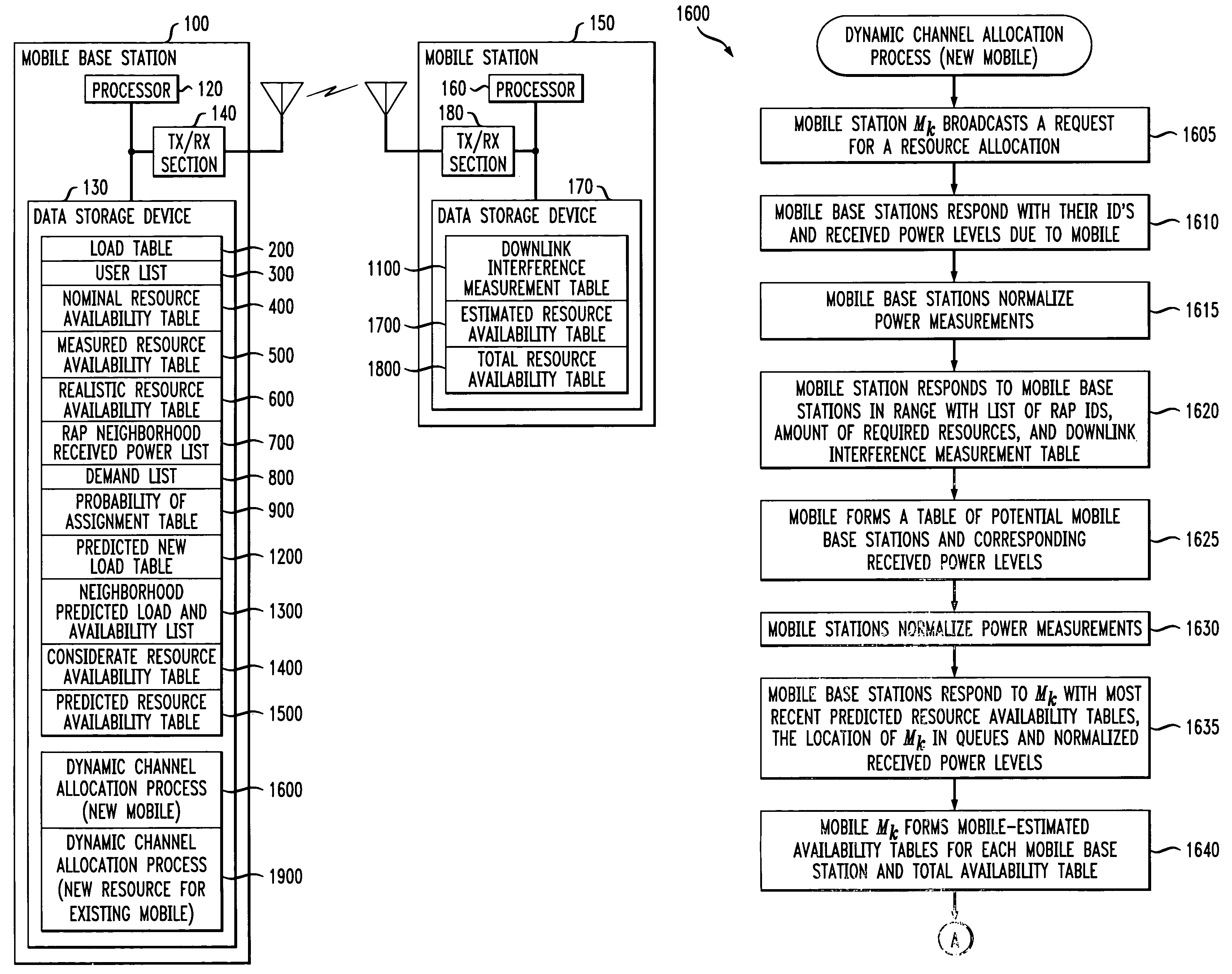
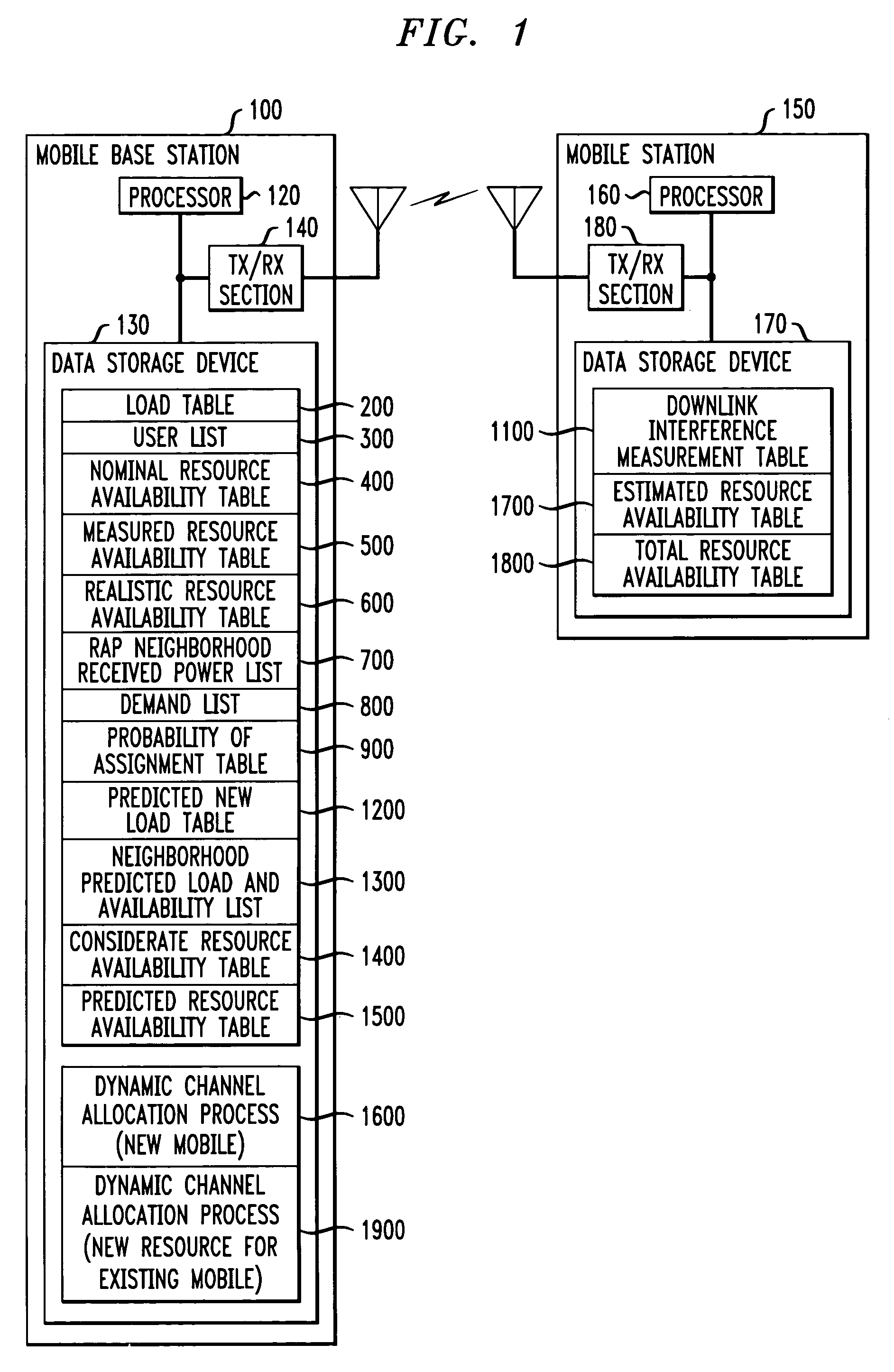
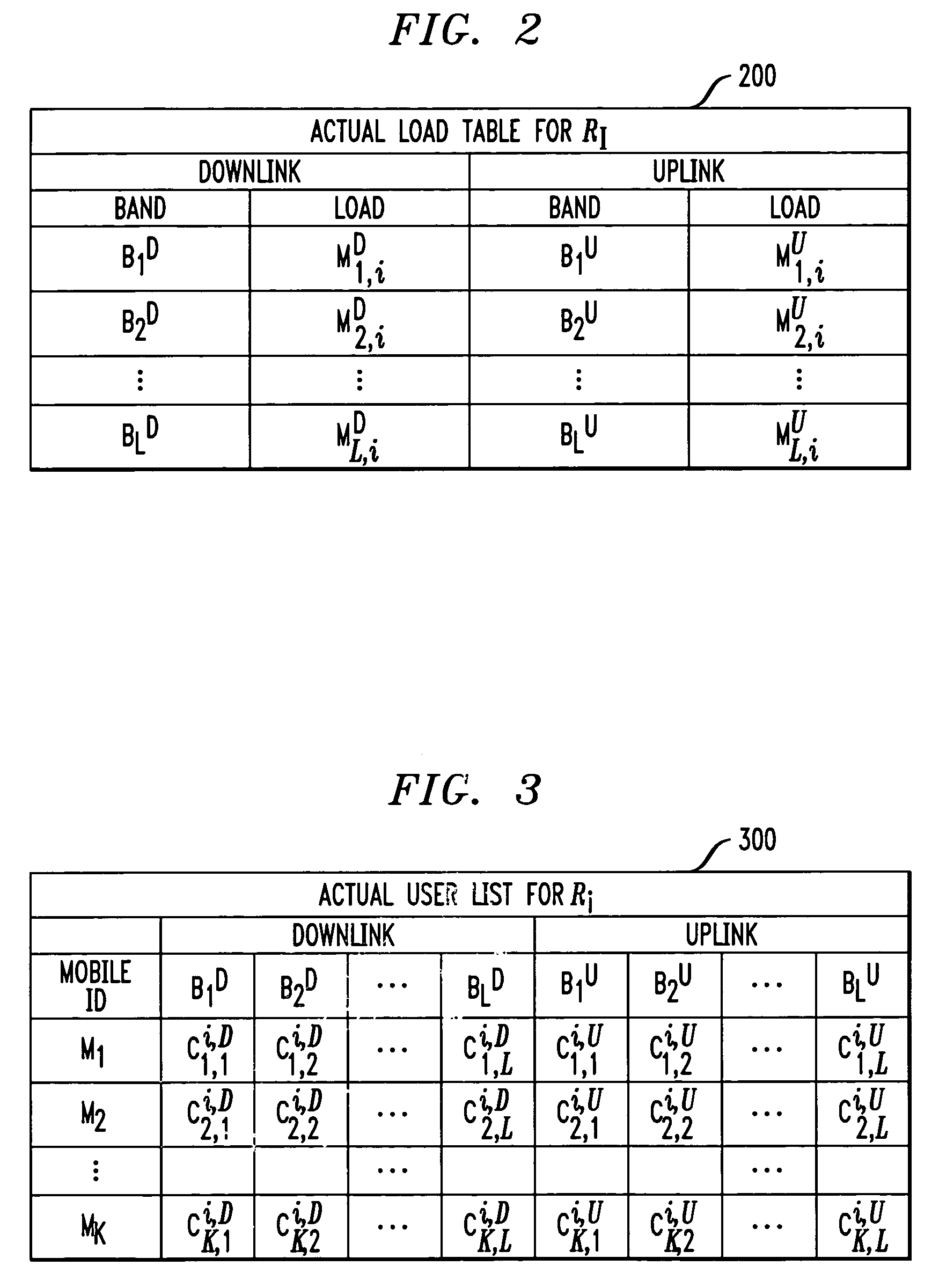
Distributed dynamic channel allocation technique for multi-carrier CDMA cellular systems with mobile base stations
InactiveUS7373151B1Light loadNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsChannel powerDynamic channel
A distributed dynamic channel allocation algorithm for a multi-carrier CDMA cellular system having at least one mobile base station. The distributed dynamic channel allocation algorithm uses channel power measurements from both the requesting mobile station and the mobile base station attempting to allocate an available resource to the mobile station. The distributed dynamic channel allocation algorithm attempts to allocate the best available resource for the requesting mobile station, in terms of interference, while minimizing the amount of interruption that the allocated resource may cause to existing connections in neighboring cells. Thus, the distributed dynamic channel allocation algorithm follows a “least-interference, least-interruption” strategy. The distributed dynamic channel allocation algorithm is load balancing, since it tends to assign new resources to mobile base station with lighter loads.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
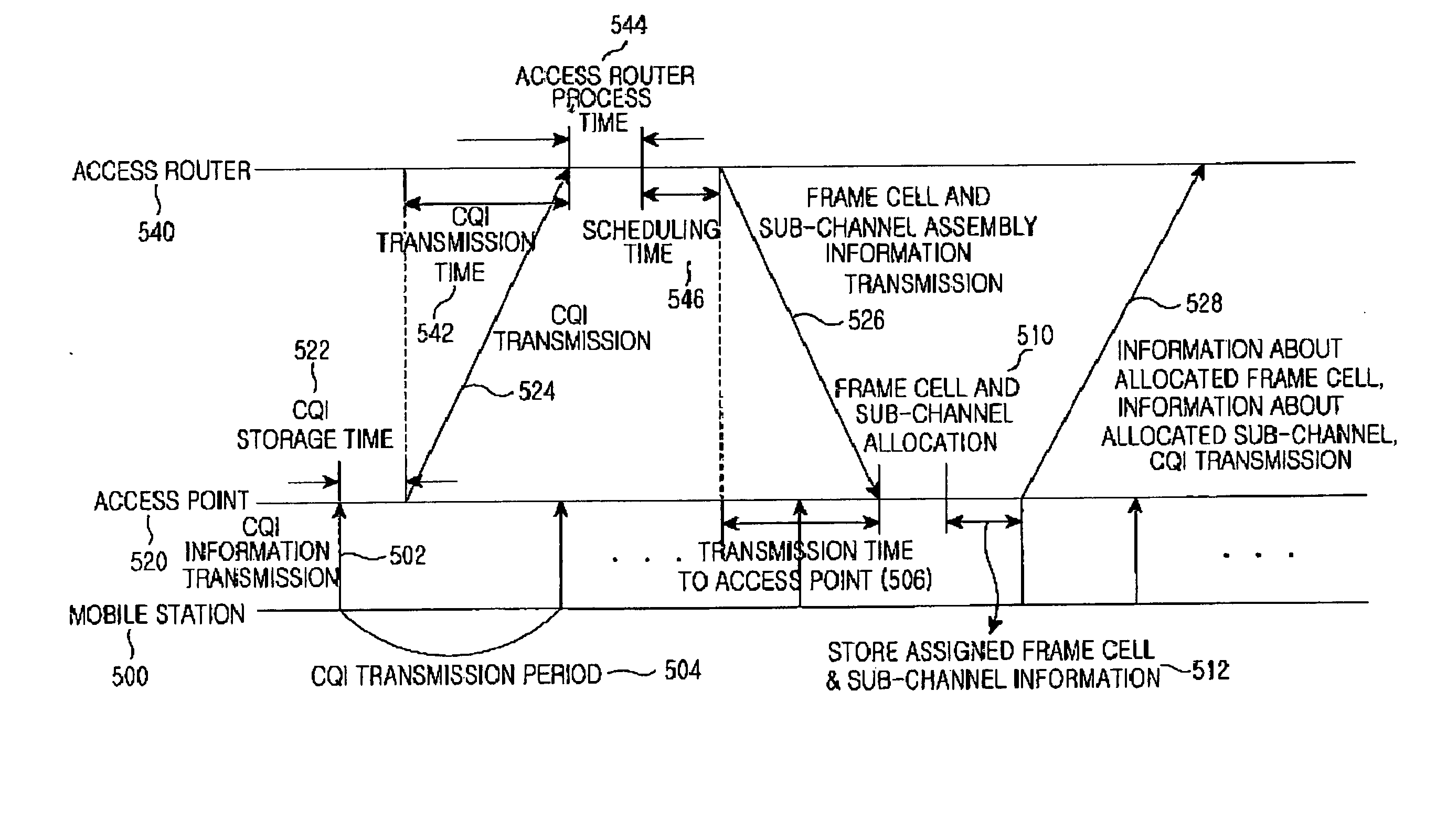
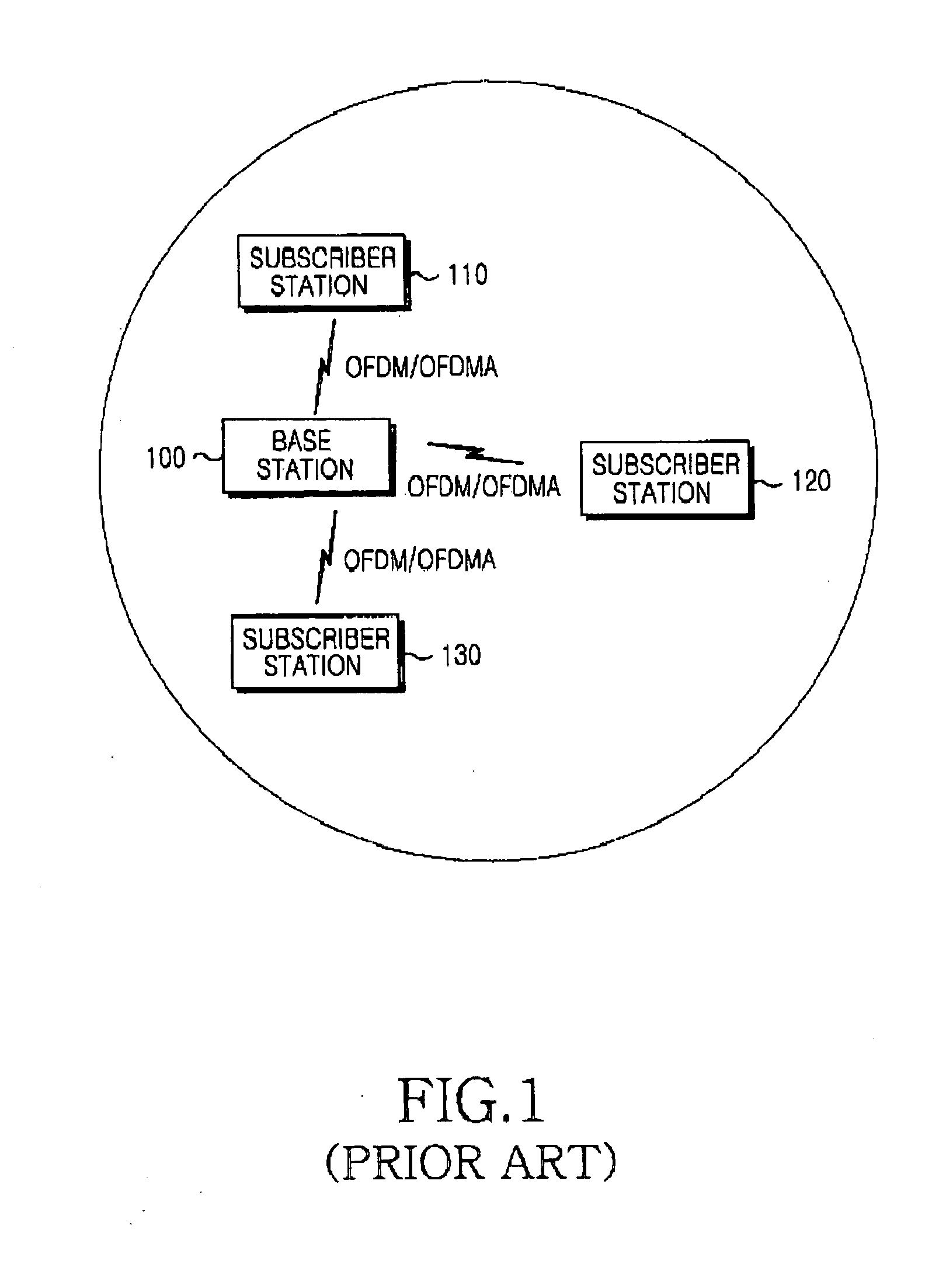
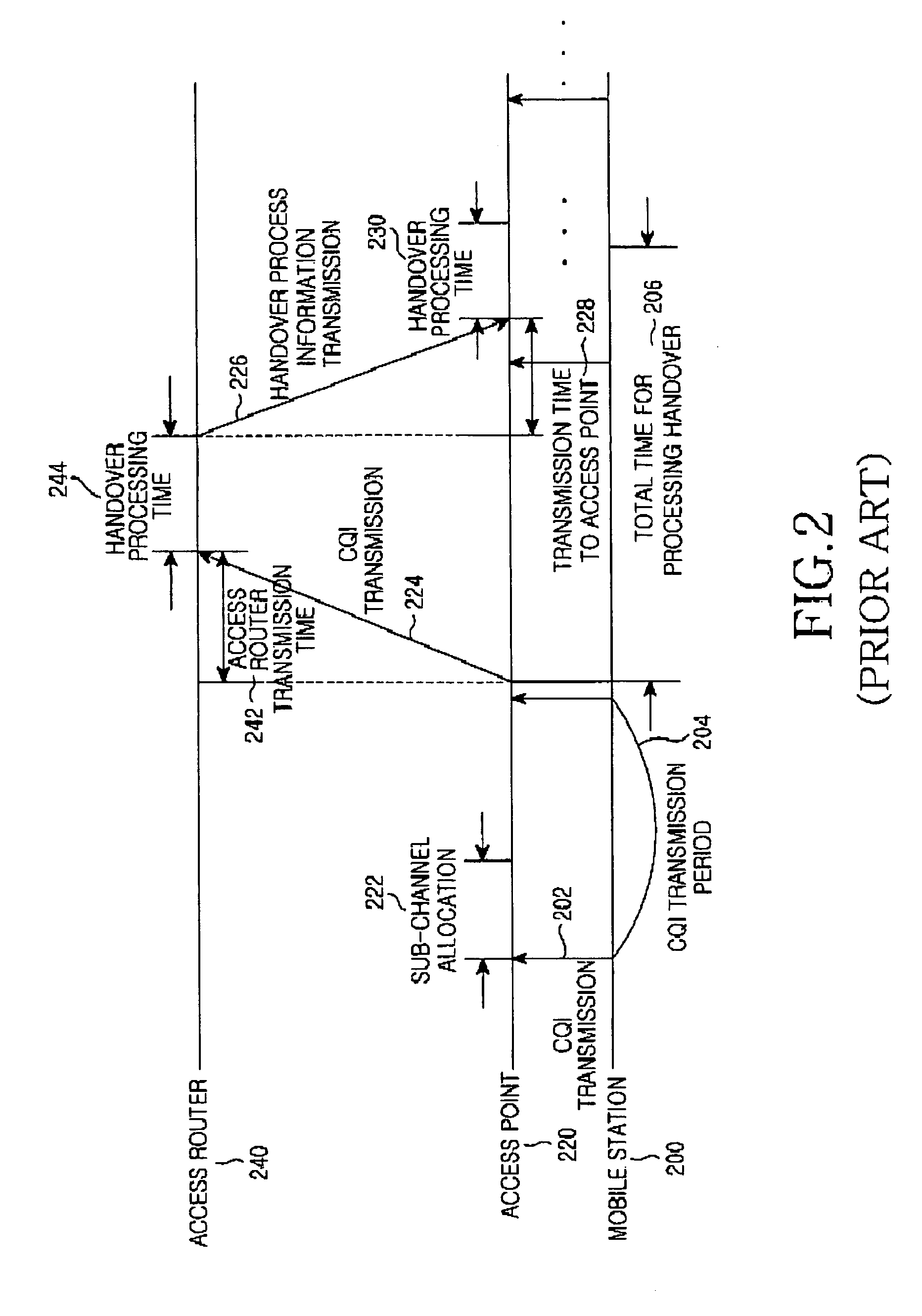
System and method for dynamic channel allocation in a communication system using an orthogonal frequency division multiple access network
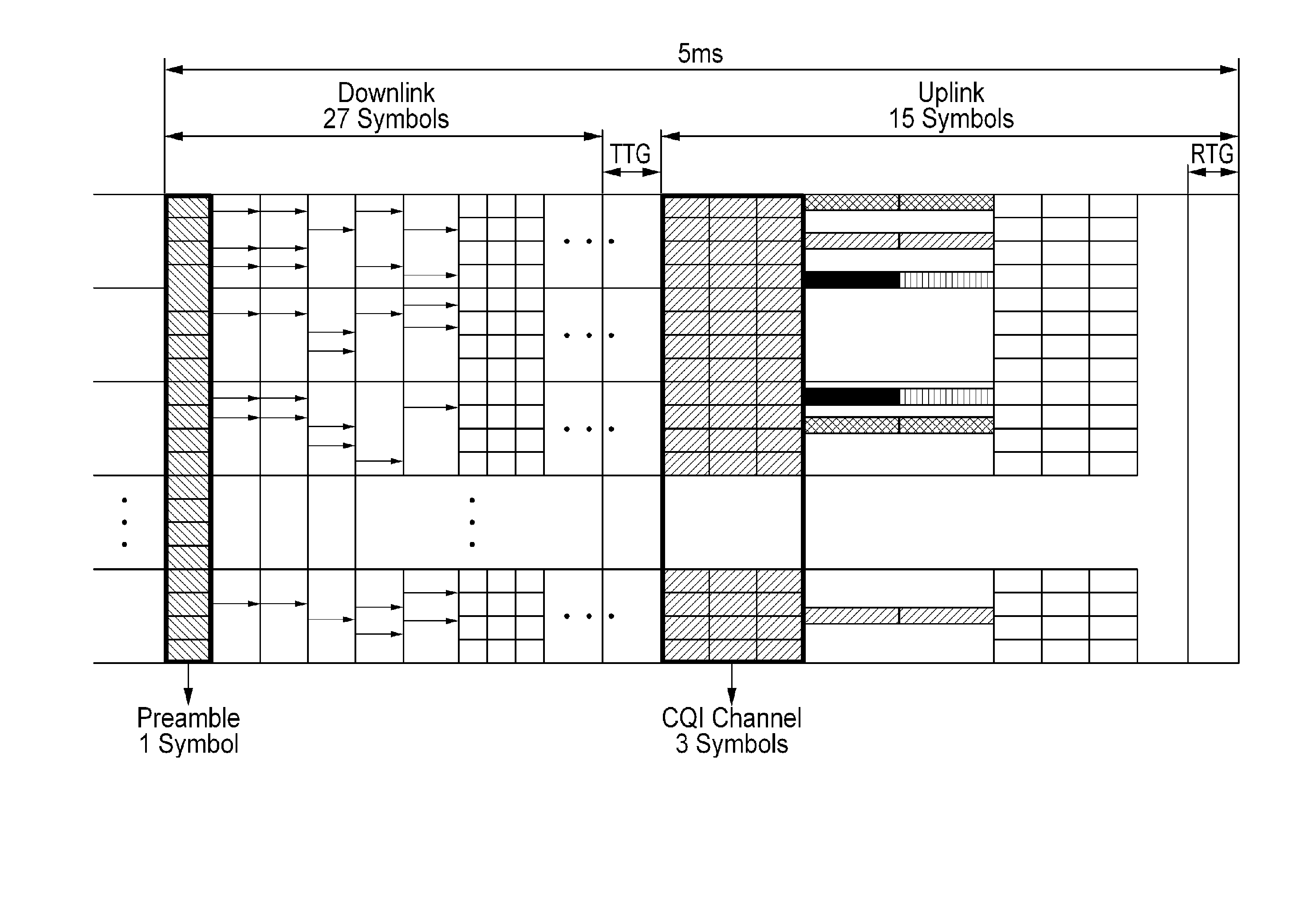
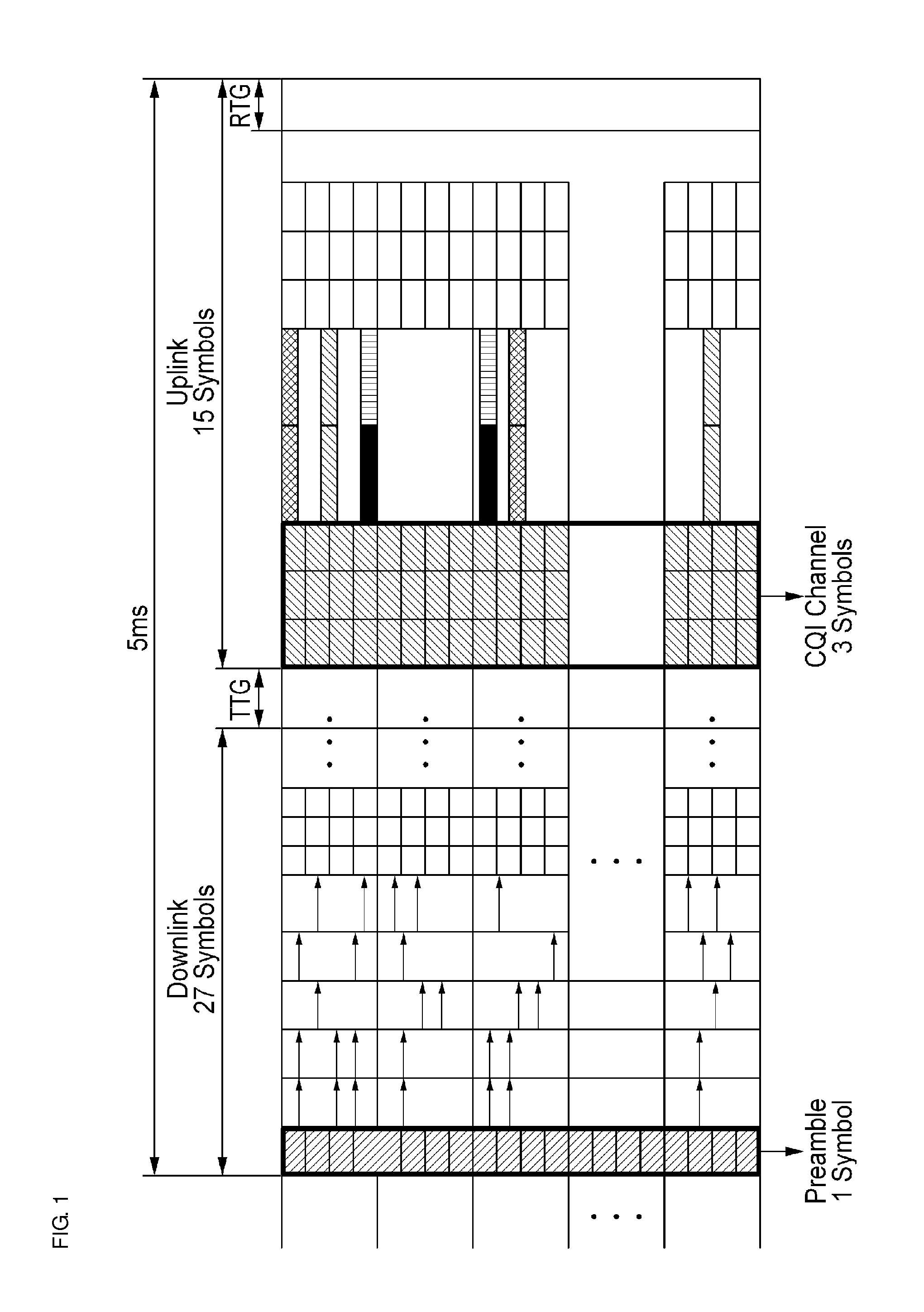
InactiveUS20050058097A1Good channel conditionNetwork traffic/resource managementFrequency-division multiplexTime domainCommunications system
A system and method for dynamically allocating channels in a wireless communication system including multiple sub-channels and multiple frame cells, each of the sub-channels being an assembly including a preset number of sub-frequency bands divided from an overall frequency band, the frame cells using each of the sub-channels as a basic transmission unit and having a frequency domain and a time domain occupied by the sub-channels. A mobile station transmits channel quality information of frame cells to an access point. An access router transmits channel allocation information about the multiple frame cells and sub-channels determined according to the received channel quality information to the access point, and the access point receives the channel allocation information about the multiple frame cells and sub-channels, compares the channel allocation information with newest channel quality information, and allocates a sub-channel of a frame cell selected according to the comparison to the mobile station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
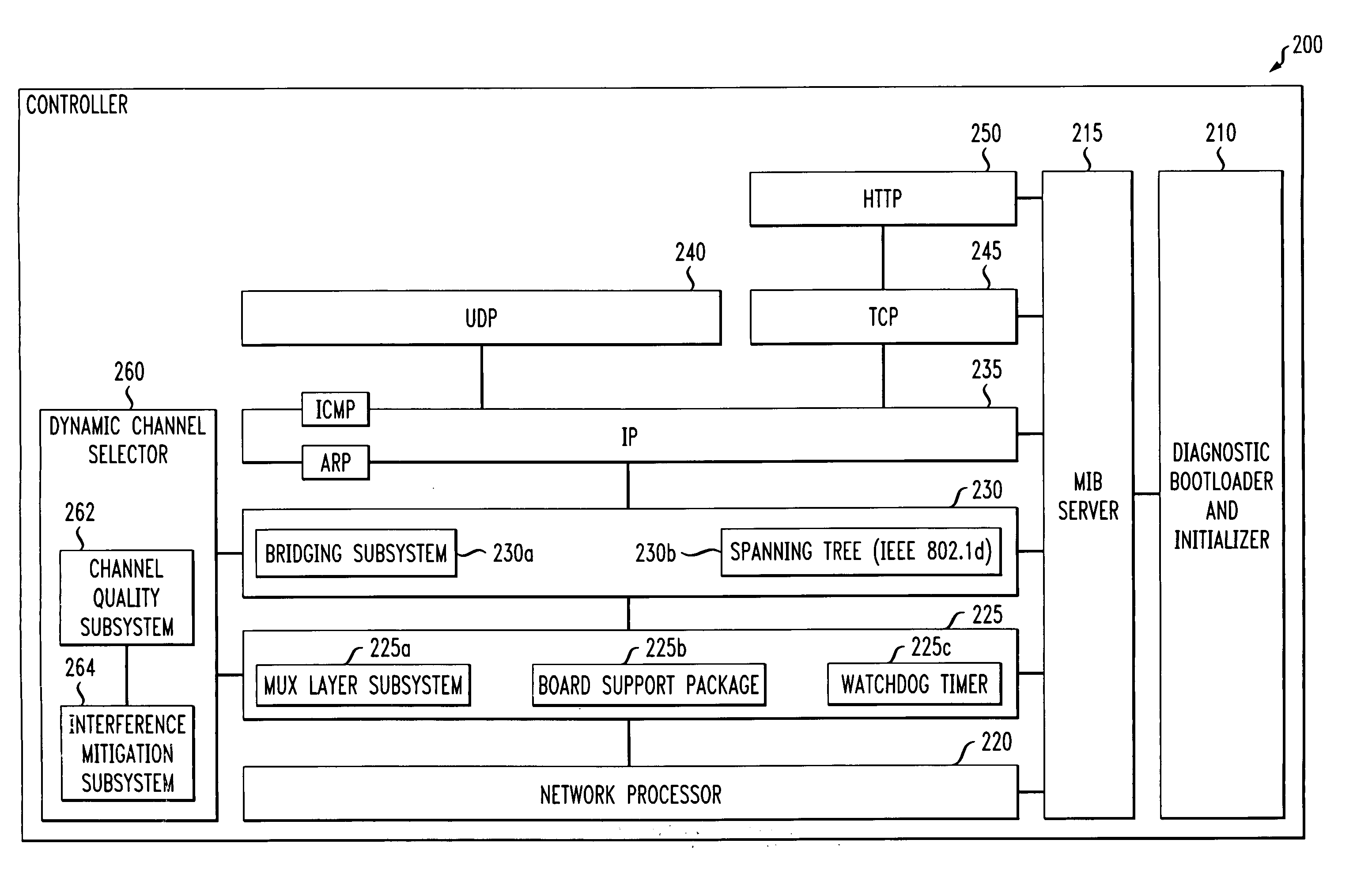
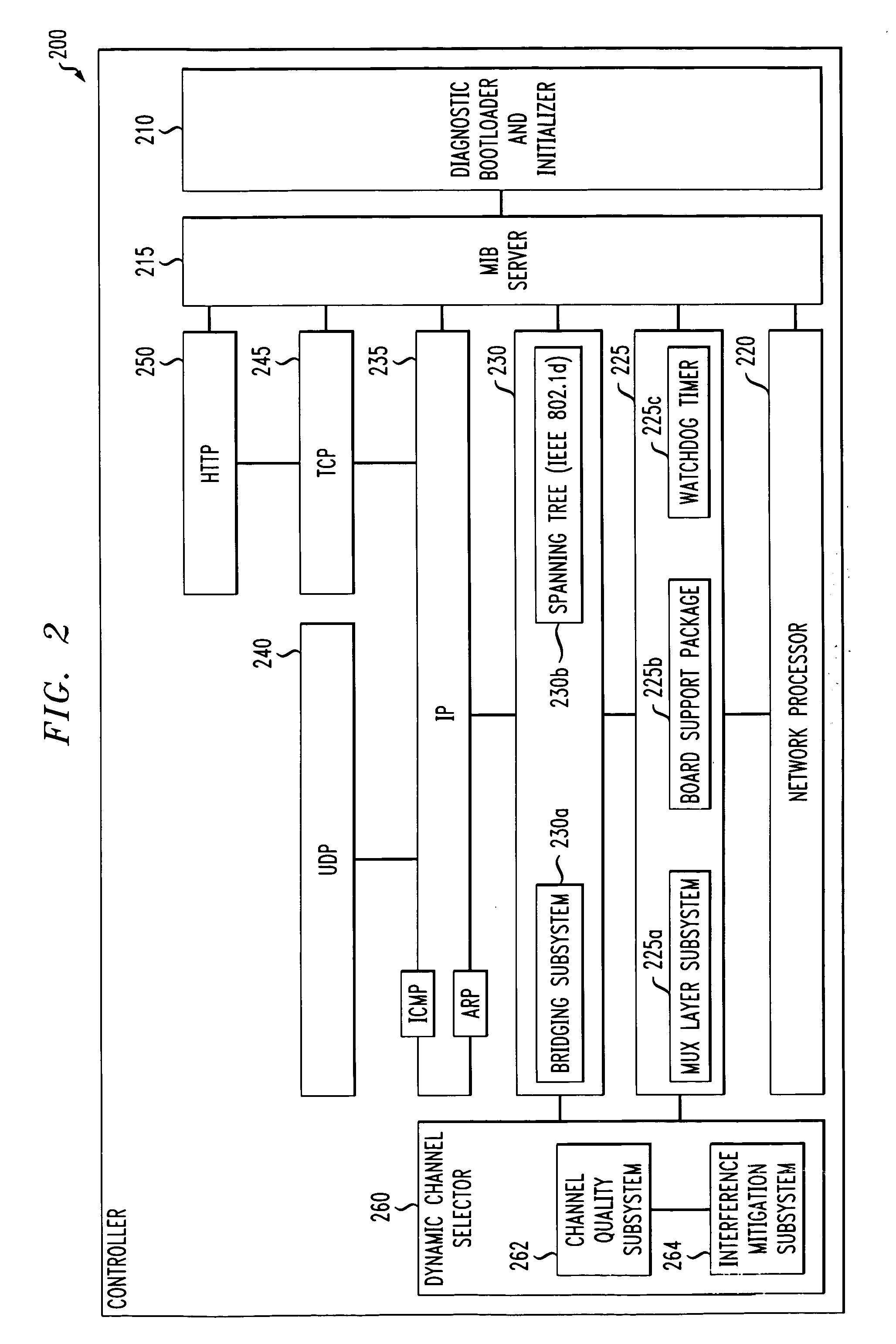
Dynamic channel selector and method of selecting a channel in a wireless local area network
ActiveUS7224697B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsDynamic channelTelecommunications
The present invention is directed to a dynamic channel selector for use with a wireless local area network and a method of selecting a channel therein. In one embodiment, the dynamic channel selector includes a channel quality subsystem that monitors a signal quality of a signal traversing a first channel of the wireless local area network and a noise level of the first channel. The dynamic channel selector also includes an interference mitigation subsystem, coupled to the channel quality subsystem, that selects a second channel of the wireless local area network as a function of the signal quality of the signal traversing the first channel and the noise level of the first channel.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
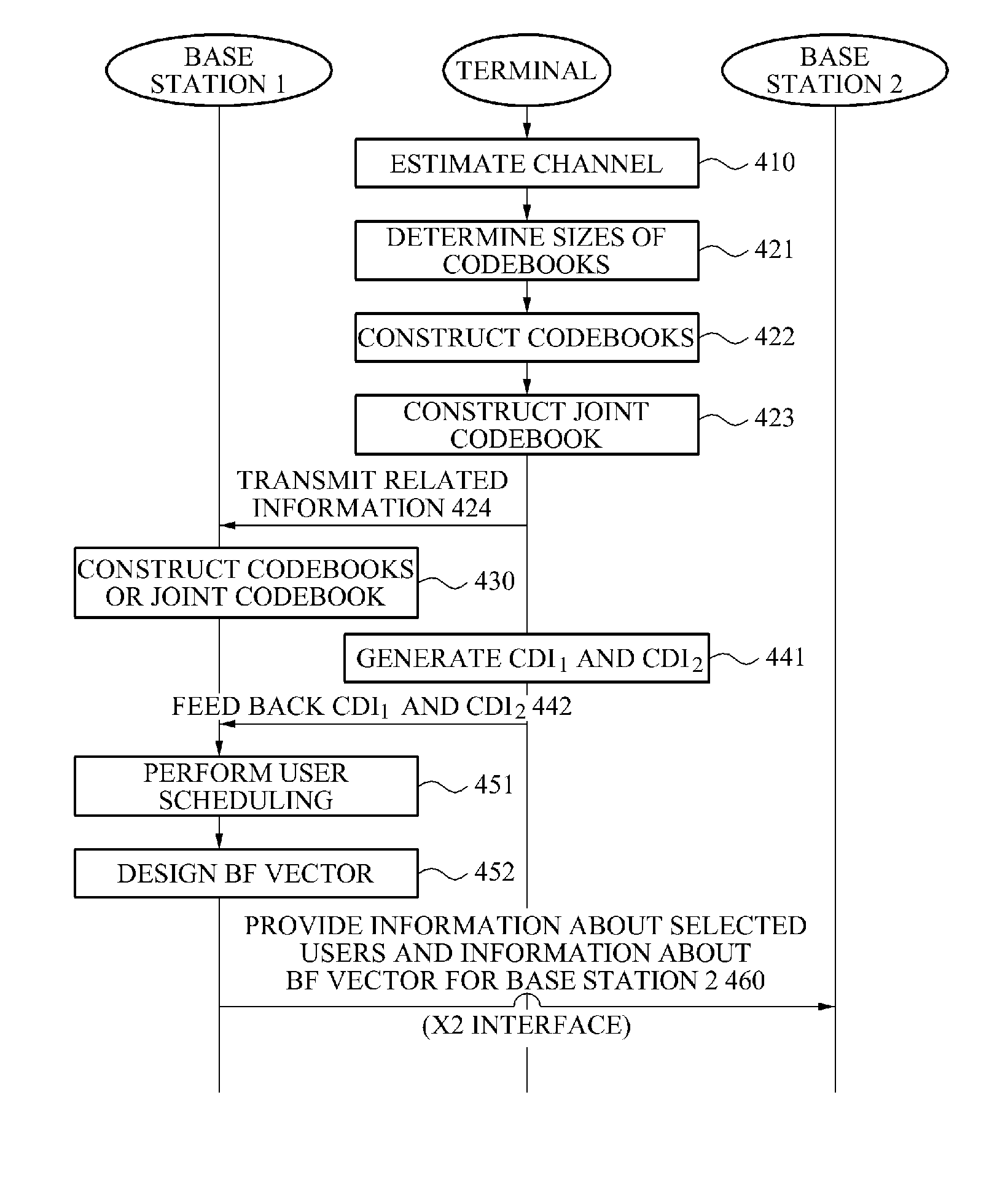
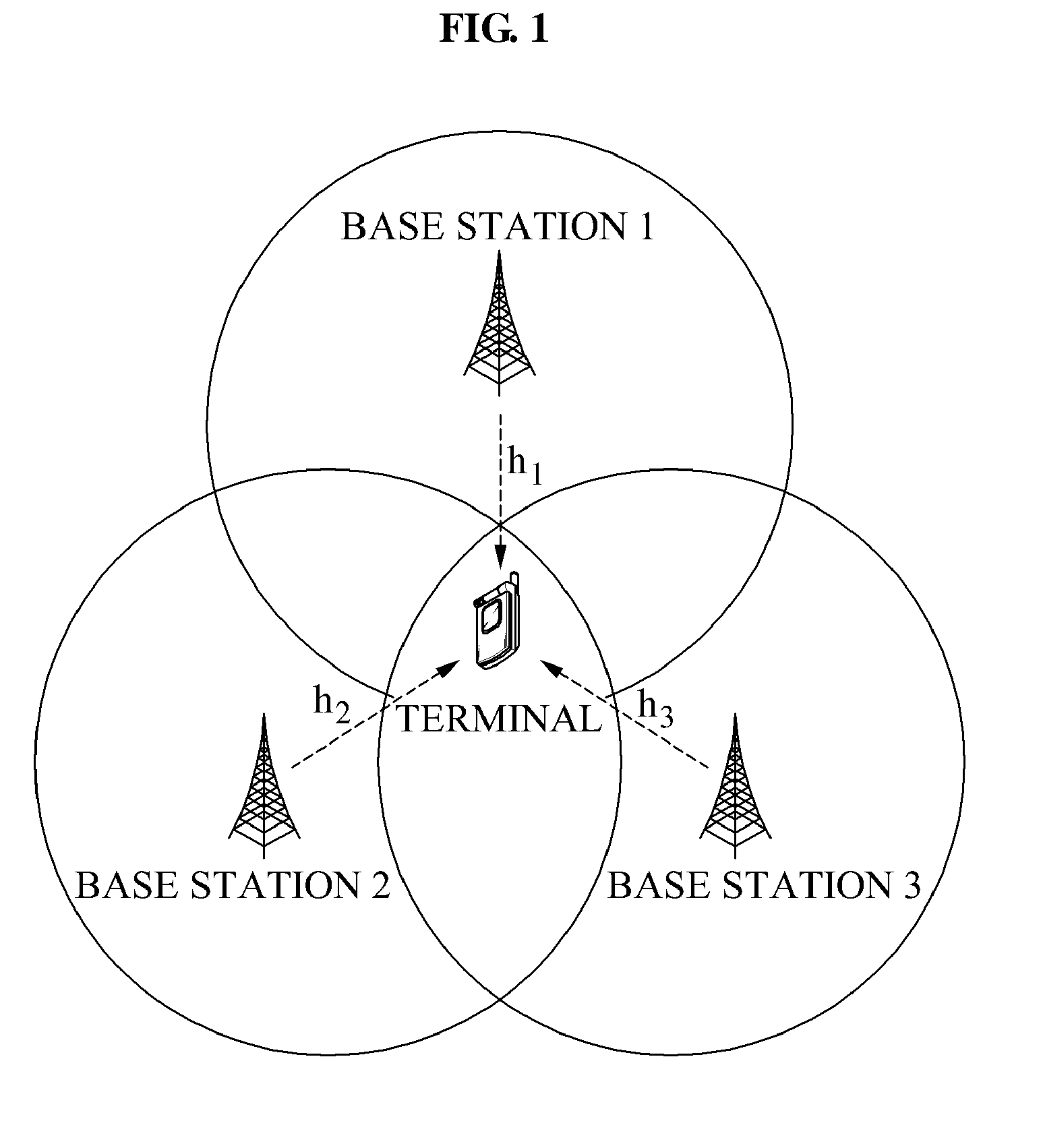
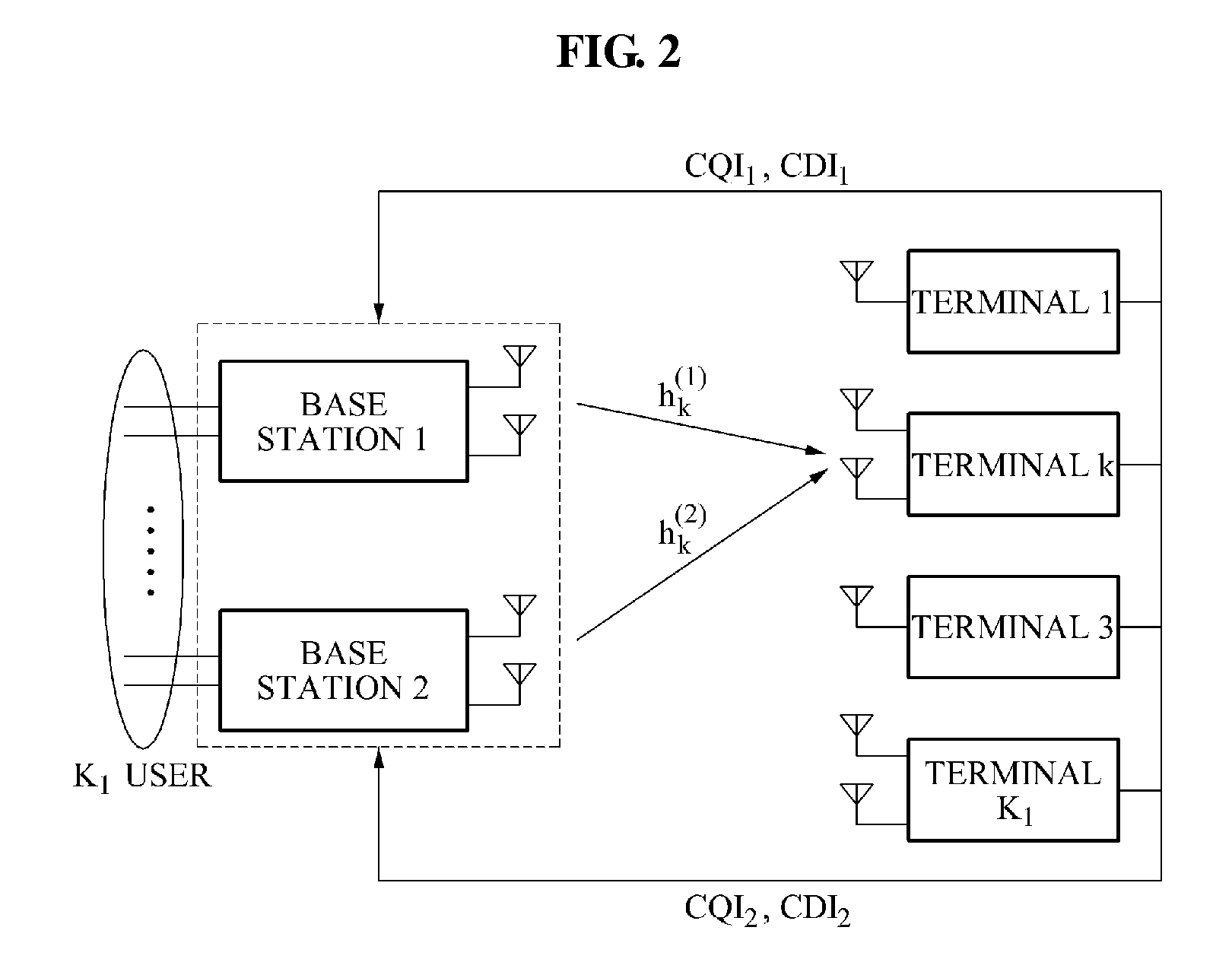
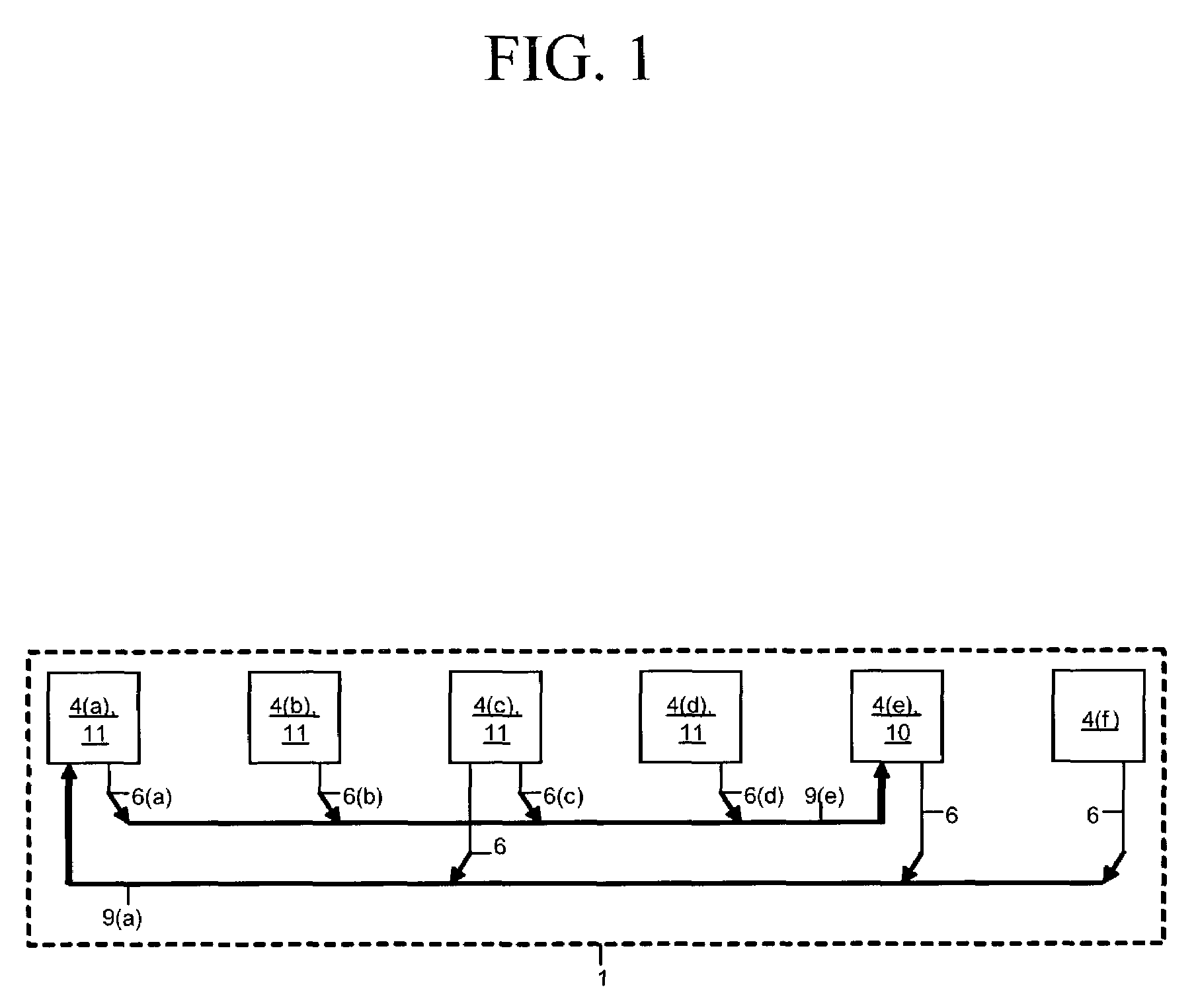
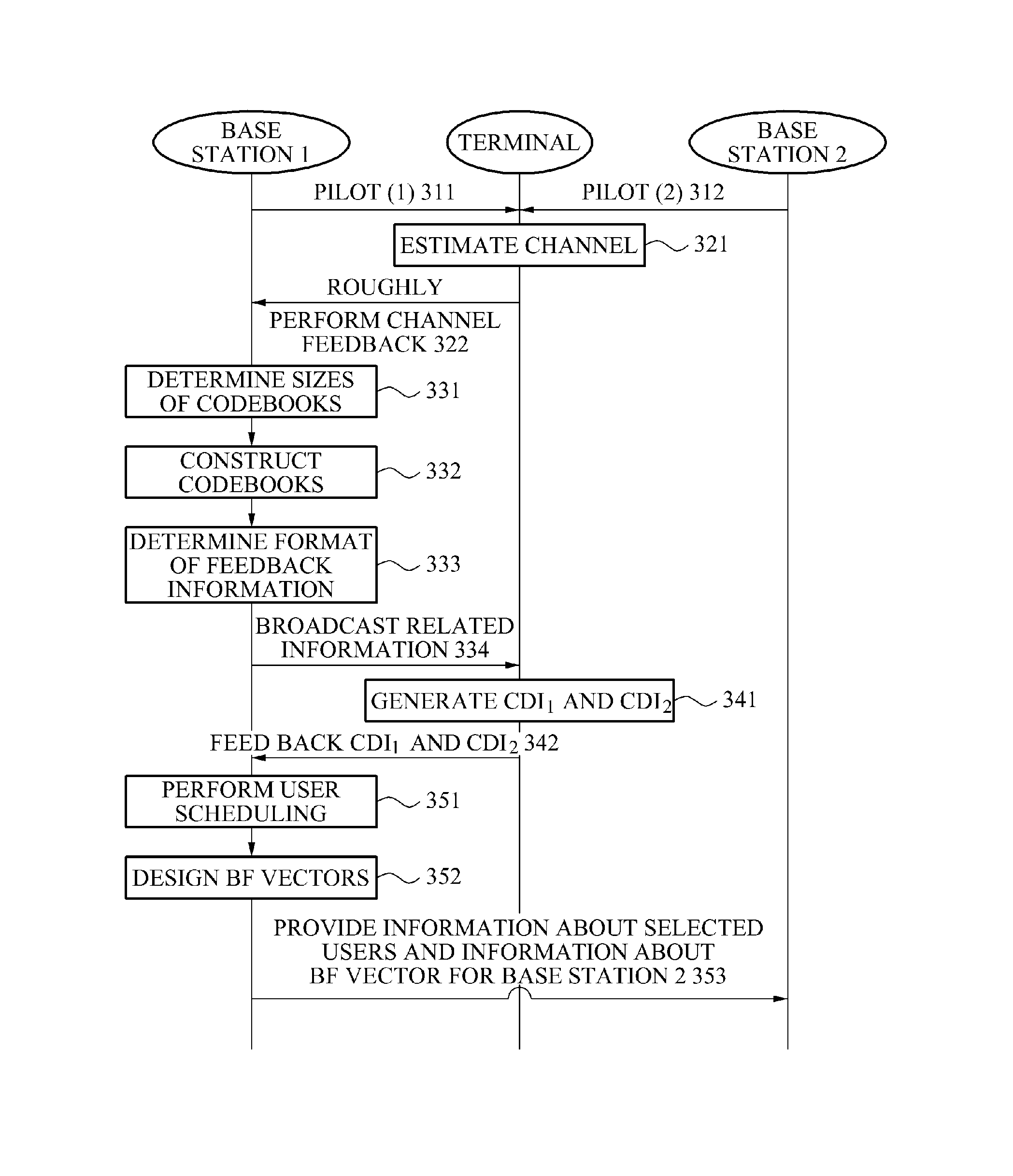
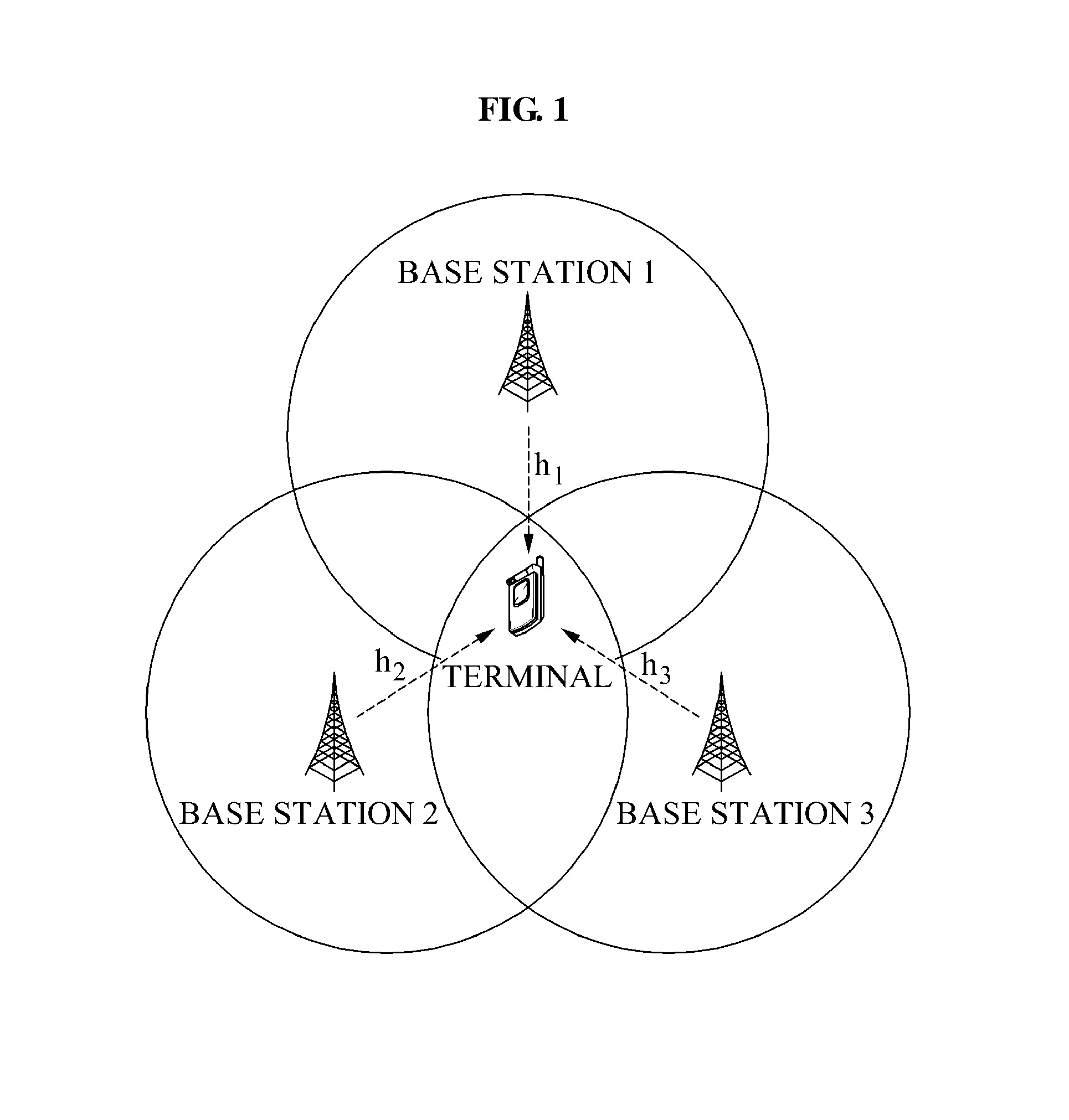
Method and apparatus for controlling dynamic channel feedback in a MIMO network
ActiveUS20110103503A1Increase in sizeSmall sizeSite diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionDynamic channelDirection information
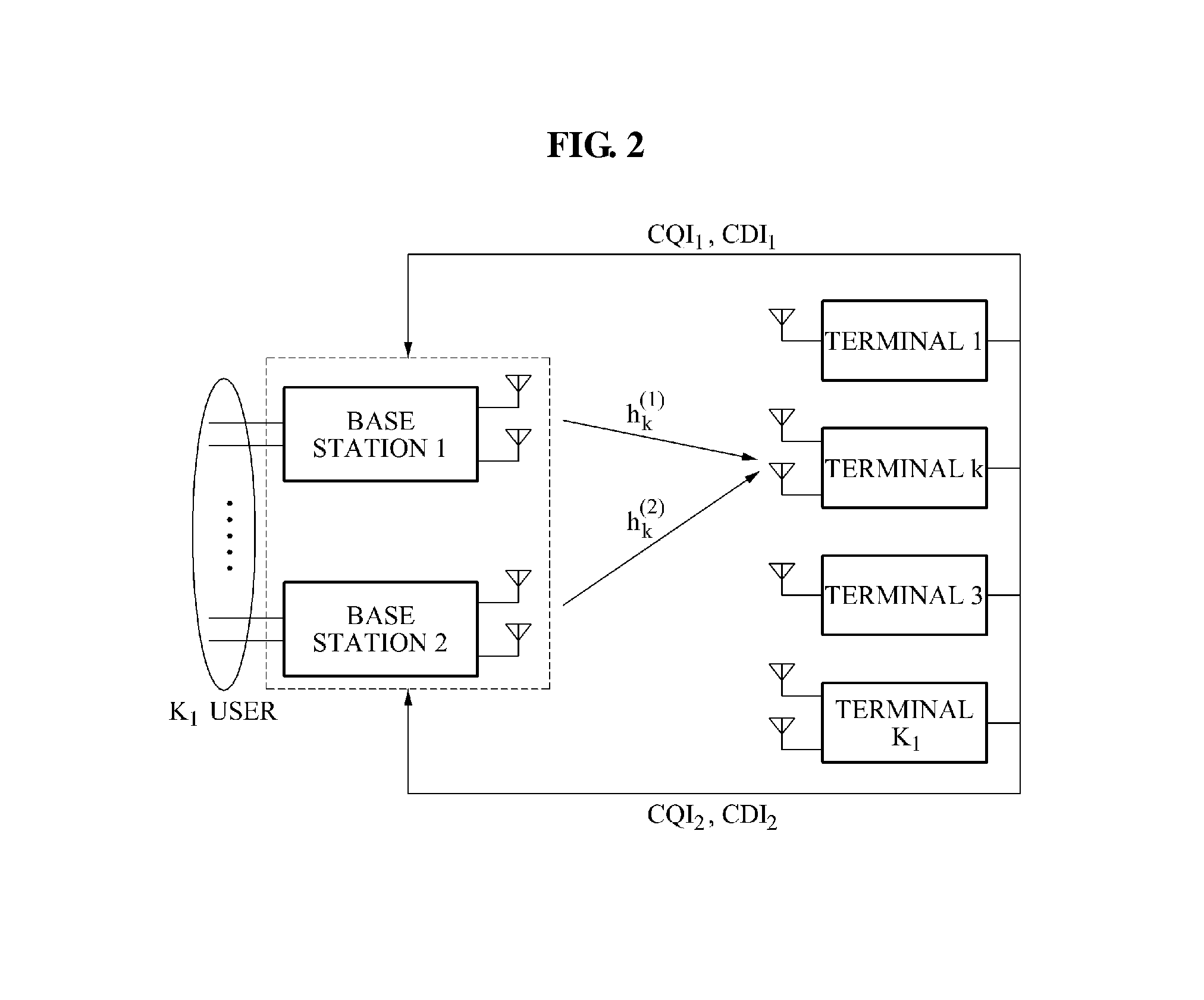
A communication method and apparatus for coordinated multi-point (CoMP) transmission, is provided. Sizes of codebooks for a plurality of base stations may be adjusted based on a status of channels between a target terminal and a plurality of base stations. The terminal feeds back, to at least one of the plurality of base stations, channel direction information (CDI) including a number of bits of feedback.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for implementing fast-dynamic channel allocation call admission control for radio link reconfiguration in radio resource management
InactiveUS20050026623A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsLoop networksWireless resource managementCommunications system
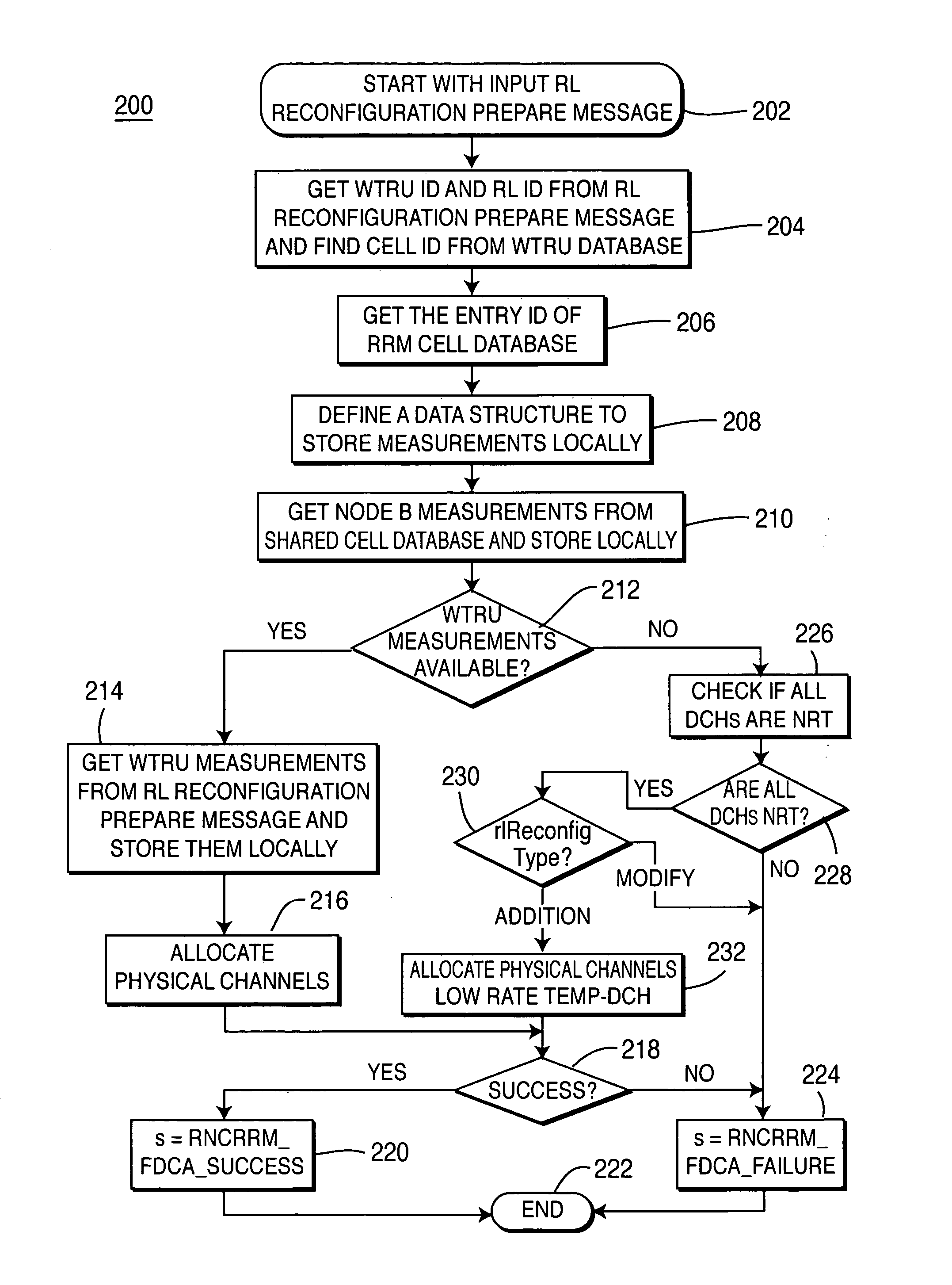
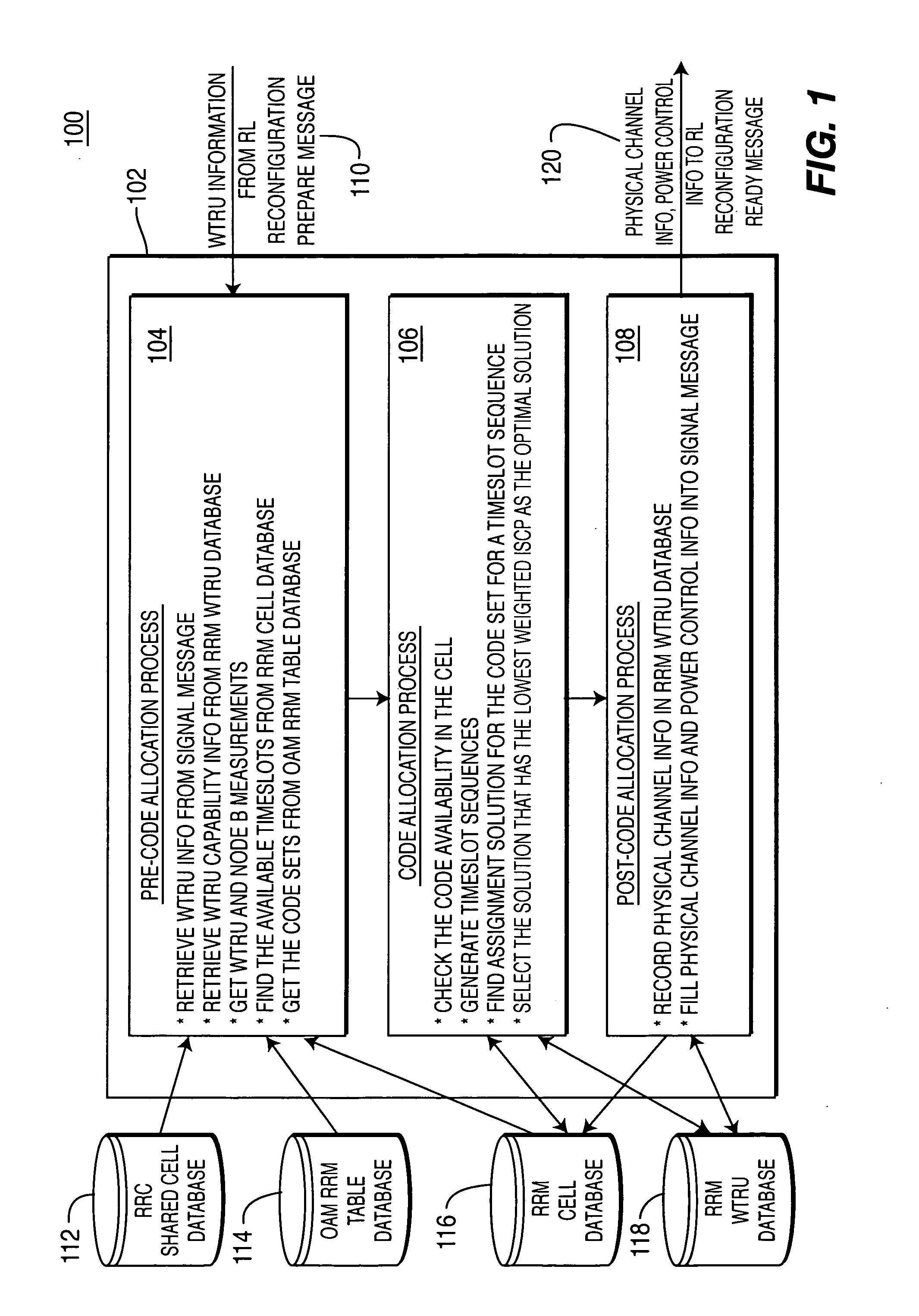
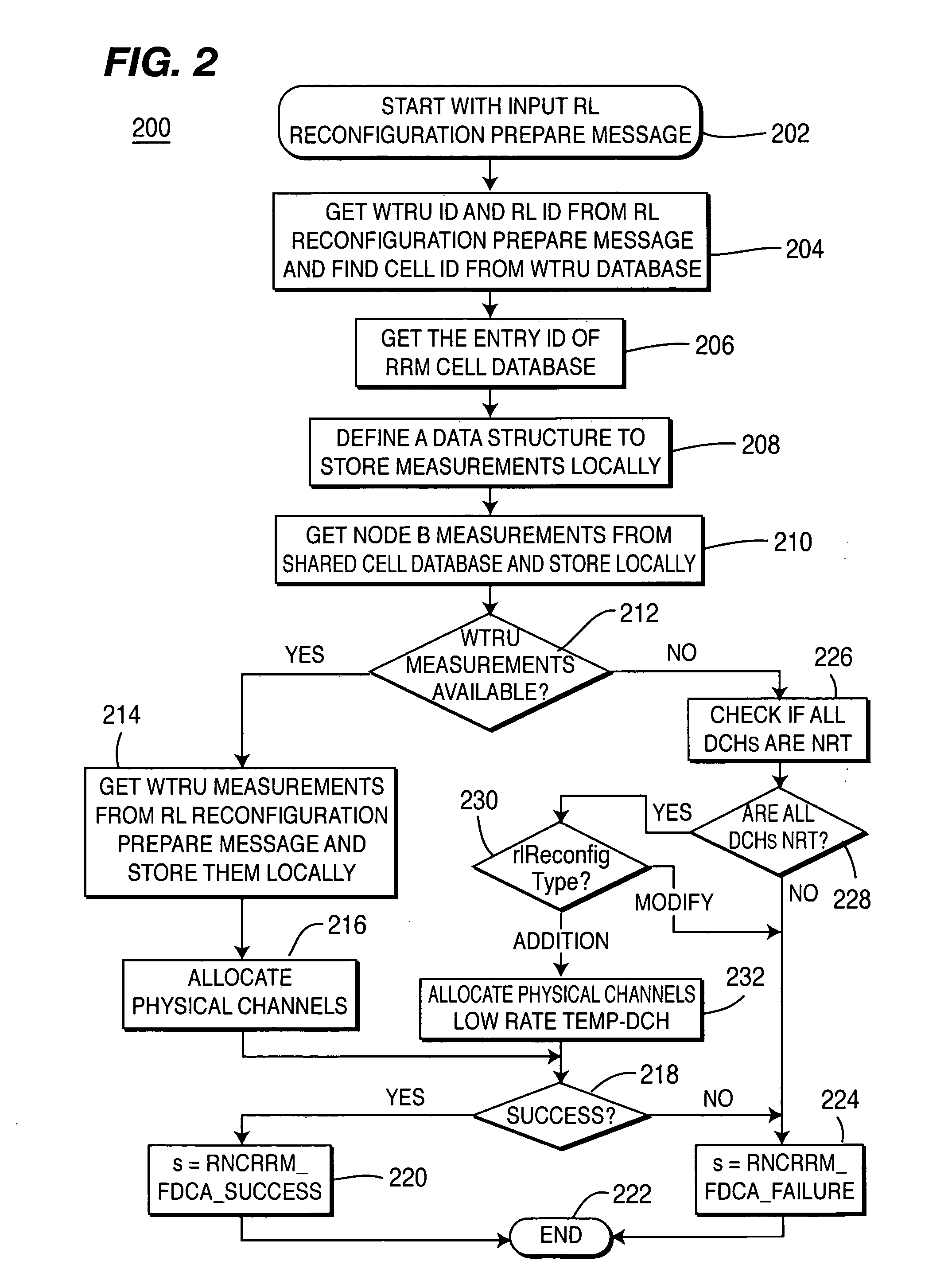
A method of implementing fast dynamic channel allocation call admission control for radio link reconfiguration in a wireless communication system includes a precode allocation procedure, a signal-independent code allocation procedure, and a post-code allocation procedure. The pre-code allocation procedure receives and processes a request message and retrieves system measurements and wireless transmit / receive unit (WTRU) capability information from a centralized database. A list of available timeslots and a list of code sets is retrieved from the centralized database. The code sets are allocated to the available timeslots, wherein a successful assignment is a solution. The solution having the lowest weighted interference signal code power is an optimal solution. The WTRU information with new allocation information is updated in the centralized database. A radio link reconfiguration ready message with the results of the code allocation process is then sent.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Control signalling and dynamic channel allocation in a wireless network
InactiveUS6977912B1Efficient reuseComplete informationNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationDynamic channelSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Owner:ADAPTIVE BROADBAND CORP
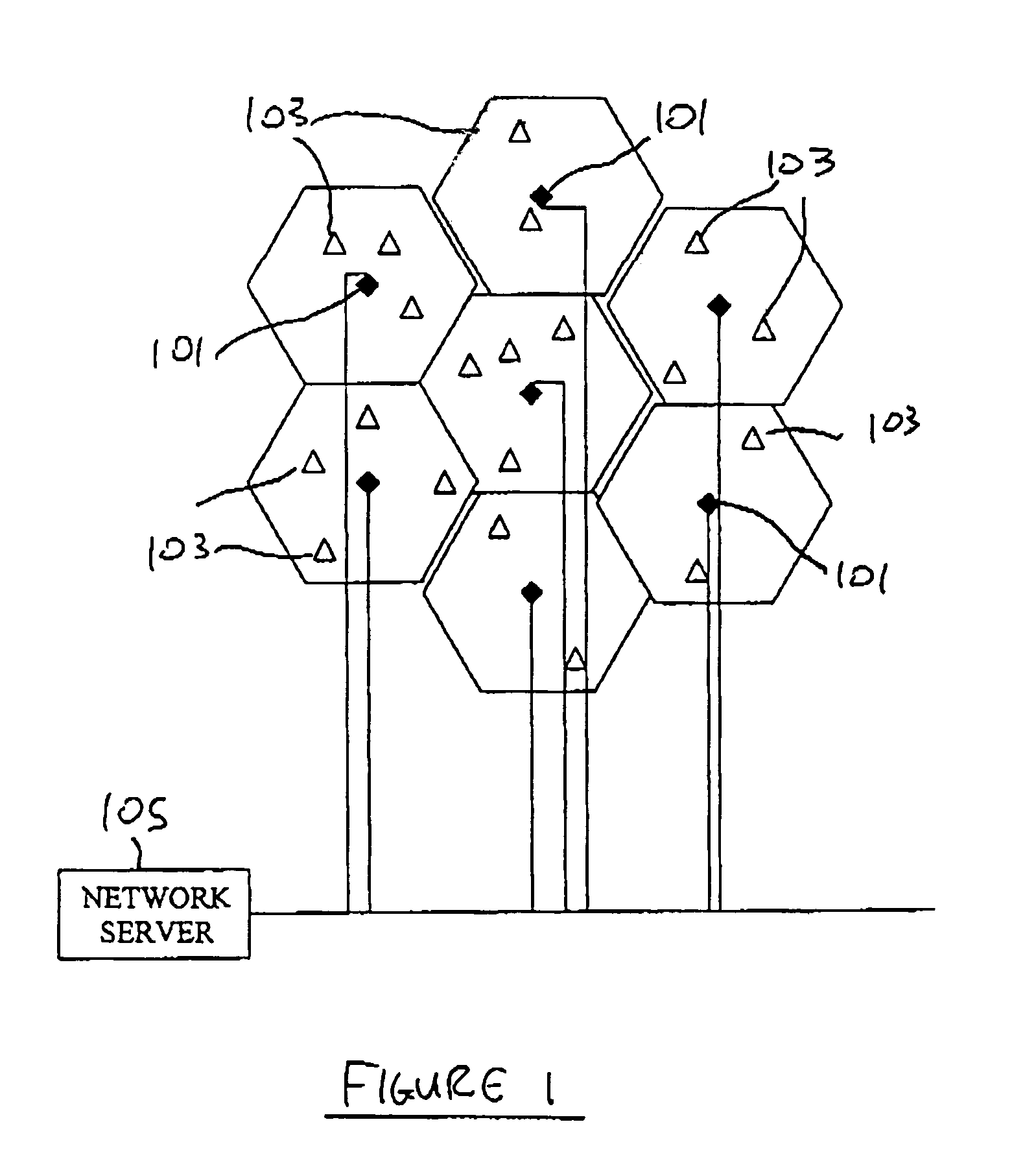
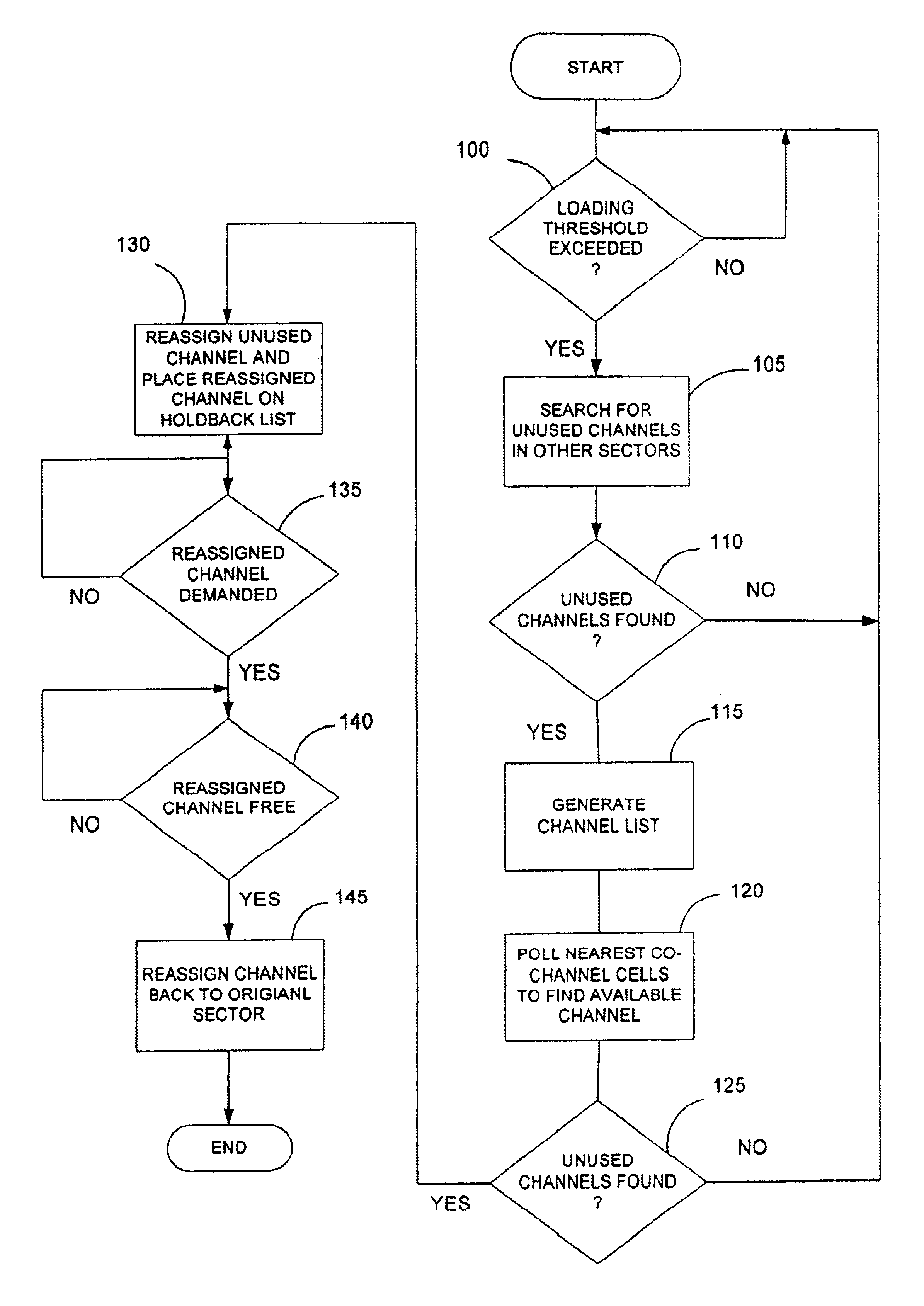
Dynamic channel allocation in a sectored cell of a cellular communication system
InactiveUS6898431B1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionDynamic channelCellular communication systems
In a sectored cell of a cellular communication network, channels are dynamically reassigned from a first sector in the cell to a second sector in the same cell when the loading in the first sector reaches a predetermined threshold. The channels allocated to the cell are further subdivided into subgroups and assigned initially to respective sectors in the cell. During normal operation, the channels in each sector are allocated to users in that sector in the usual manner. When the number of channels allocated in a first sector of the cell reaches a predetermined threshold, the base station controller polls the remaining sectors for unused channels. If an unused channel is found, that channel may be reassigned to the first sector. In one embodiment, the base station controller polls the controller in the nearest co-channel cells before reassigning the channel to prevent co-channel interference.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
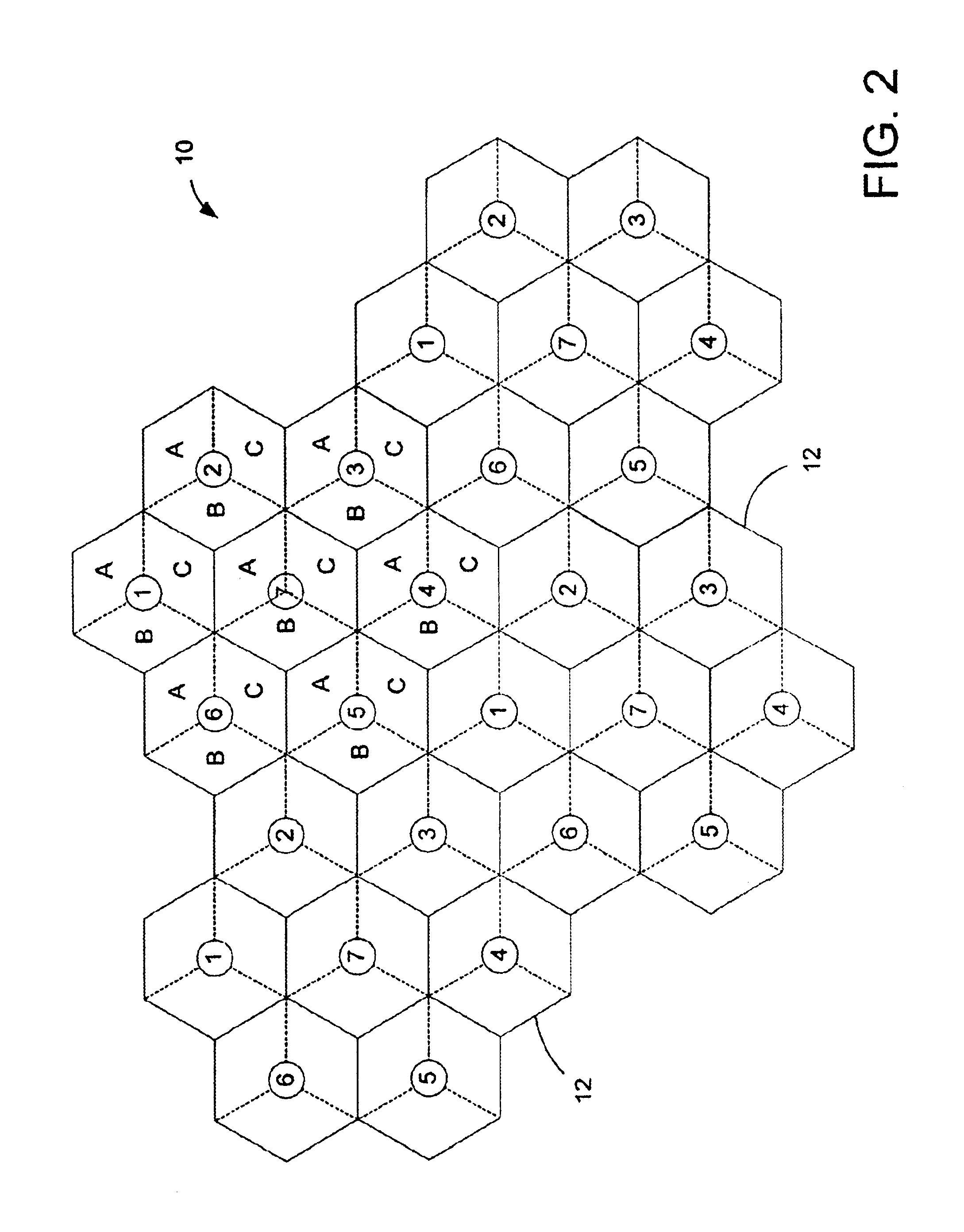
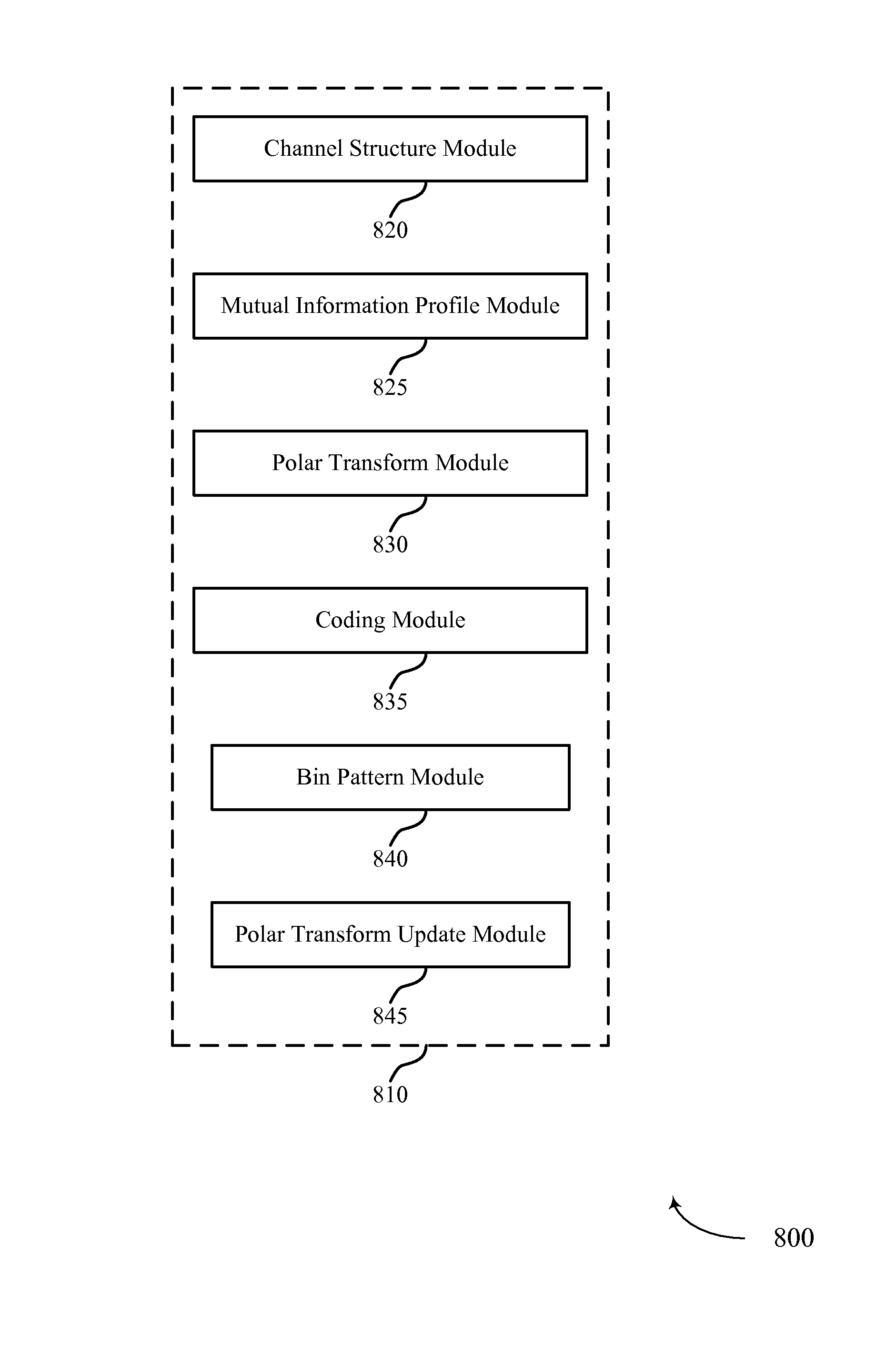
Adaptive channel coding using polarization
Methods, systems, and devices are described for wireless communications at a wireless device. A wireless device may adaptively select a parity check matrix to increase the reliability of signal transmission by adapting to different channel statistics and channel types (e.g., erasure channels, channels with additive white Gaussian noise, and channels with discrete or continuous alphabets). For example, polarization codes (i.e., codes based on rows of a polarization matrix) may be used to construct parity check matrices “on-the-fly” given an estimation of dynamic channel conditions or diverse channel structures. The channel may be decomposed into polarized sub-channels corresponding to the polarization codes, and mutual information profiles may be determined for each of the polarized sub-channels. The parity check matrix corresponding to the polarization codes may be constructed based on the mutual information profile of all polarized sub-channels. The wireless device may encode or decode data based on the constructed parity check matrix.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Dynamic channel allocation in multiple-access communication systems
InactiveUS7177298B2Maximizing network spectrum efficiencyMaximize Spectral EfficiencyNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionCommunication unitDynamic channel
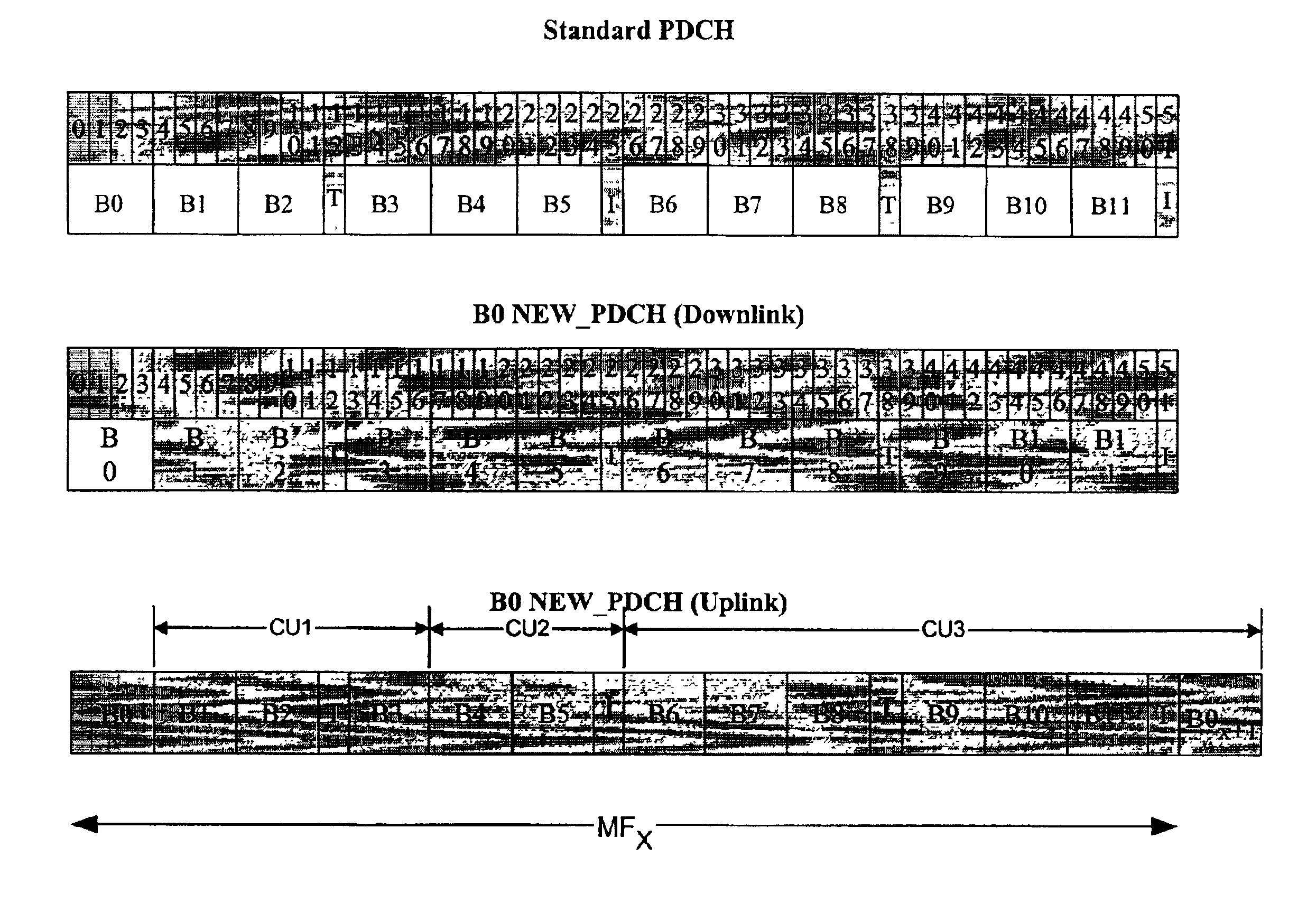
Dynamic allocation of communication channels among communication units (CU) in a communications system. Dynamic channel allocation employs a reservation set for reserving channels and an allocation set corresponding to the reservation set for receiving allocated channels. The reservation set and the allocation set are changed dynamically as a function of network parameters to control the dynamic channel operation. Reservation set information is broadcast downlink to multiple users to reserve an allocation set of uplink radio resources for specific ones of the users. The system uses a modification of the packet data channel (PDCH) of a GPRS / EGPRS or EDGE system which employs an Uplink Status Flag (USF) on each PDCH downlink radio block. The downlink reservation set information is commonly received by all users in the group of users. Allocation delay, bandwidth efficiency and other system parameters are optimized.
Owner:IOT INNOVATIONS LLC
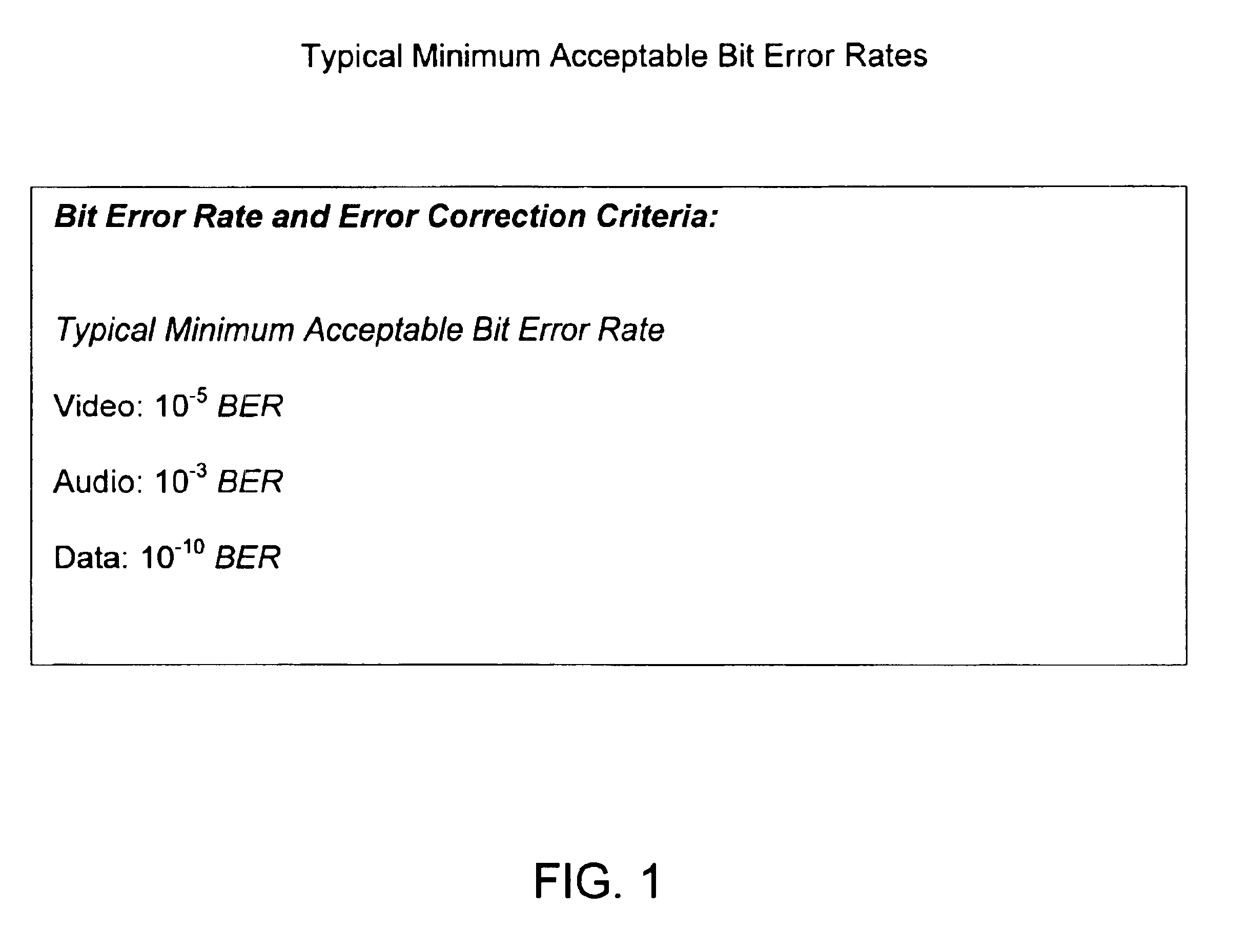
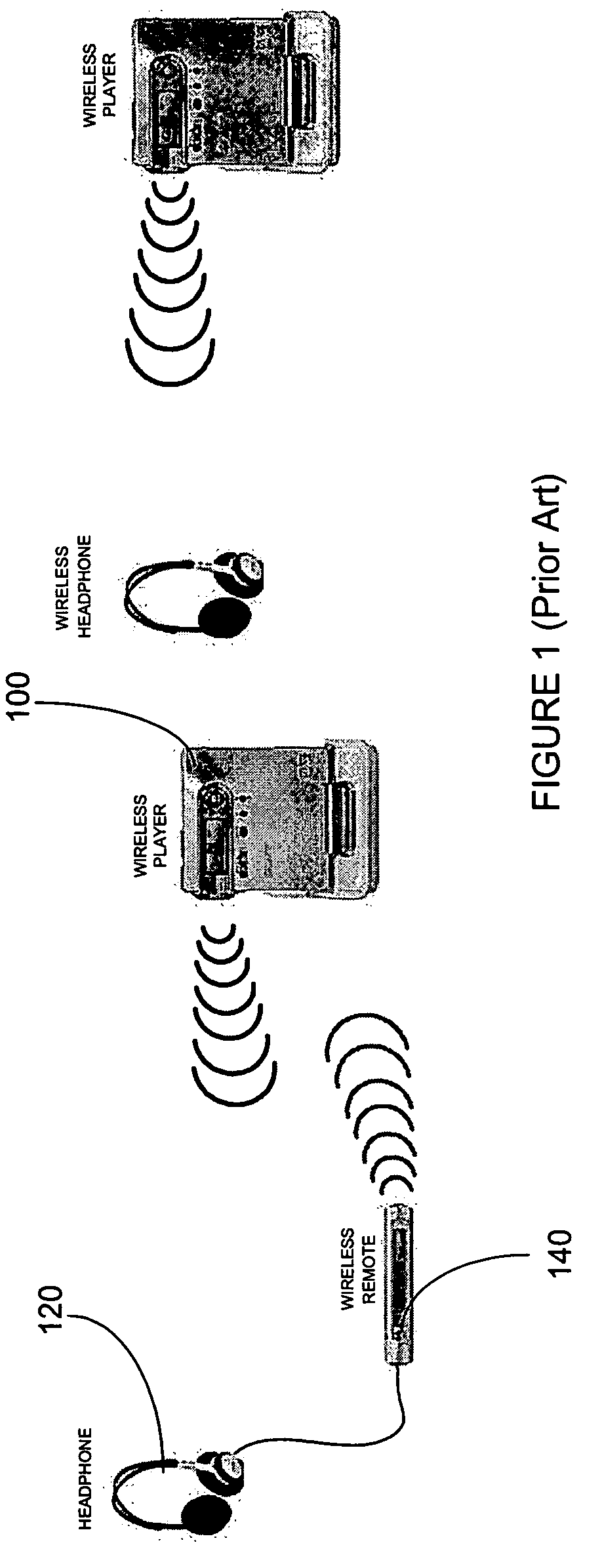
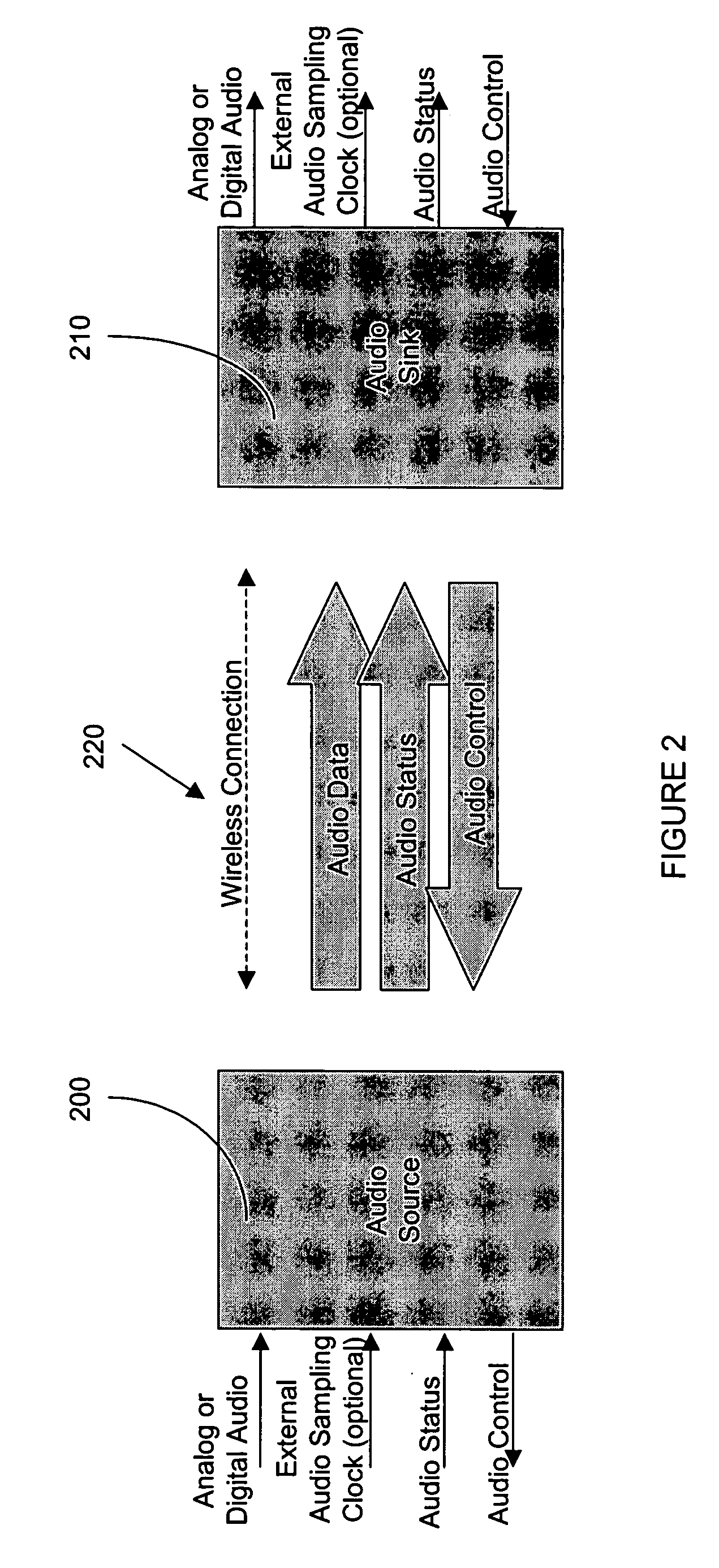
High quality, low power, wireless audio system
ActiveUS20060193273A1Improved audio synchronizationQuality improvementEnergy efficient ICTNon-electrical signal transmission systemsDynamic channelWireless transmission
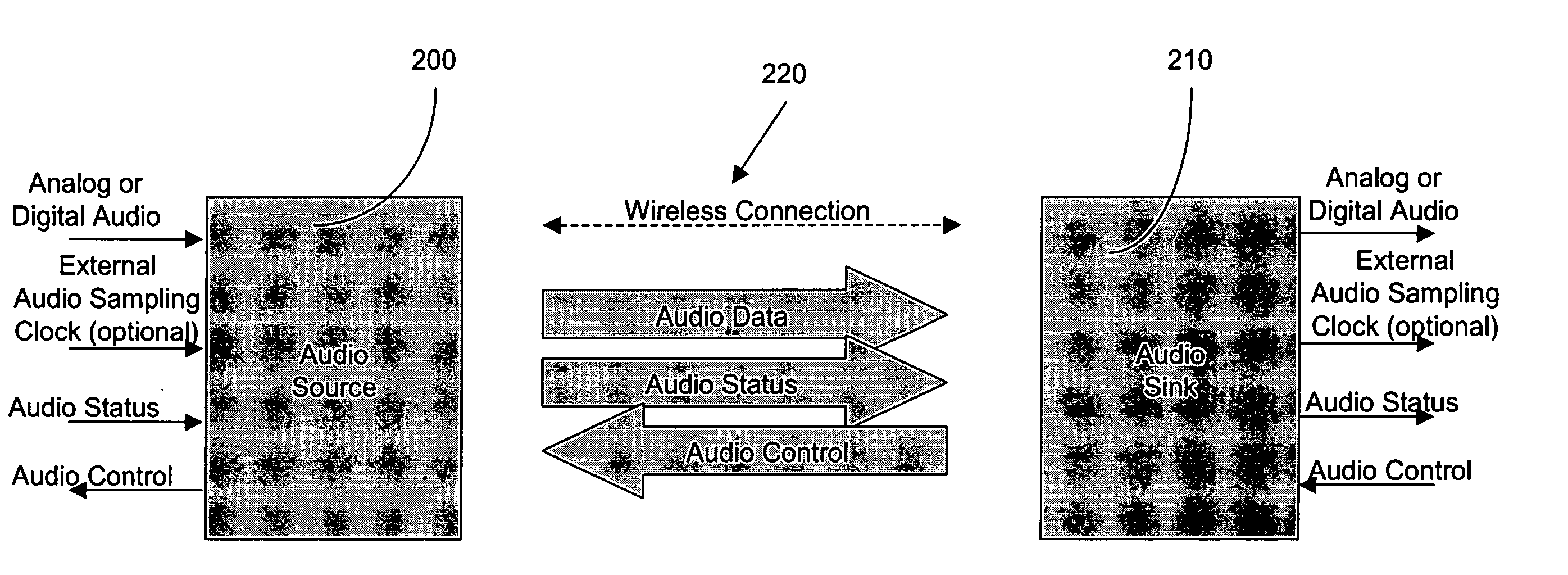
The invention relates to the field of wireless communications and more specifically to an high quality, low power wireless audio system. More specifically, the invention comprises an audio source for receiving audio signals (e.g. music) and audio status information (e.g. song title) from a first external device (e.g. an MP3 player) and transmitting the audio signals and the audio status information over a wireless connection; and at least one audio sink for receiving the audio signals and said audio status information from the audio source and communicating the audio signals and the audio status information to a second external device (e.g. headphones), wherein a specified one of the at least one audio sink receives audio control information (e.g. pause) from the second external device and transmits said audio control information to said audio source via said wireless connection. Among other features, the wireless audio system of the present invention incorporates dynamic channel selection as well as dynamic adjustment of the transmission interval to ensure enhanced audio quality using the lowest possible power.
Owner:SMSC HLDG
Dynamic channel assignment
InactiveUS20050286467A1Easy to measureRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionDynamic channelEngineering
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method and apparatus for adapting to dynamic channel conditions in a multi-channel communication system
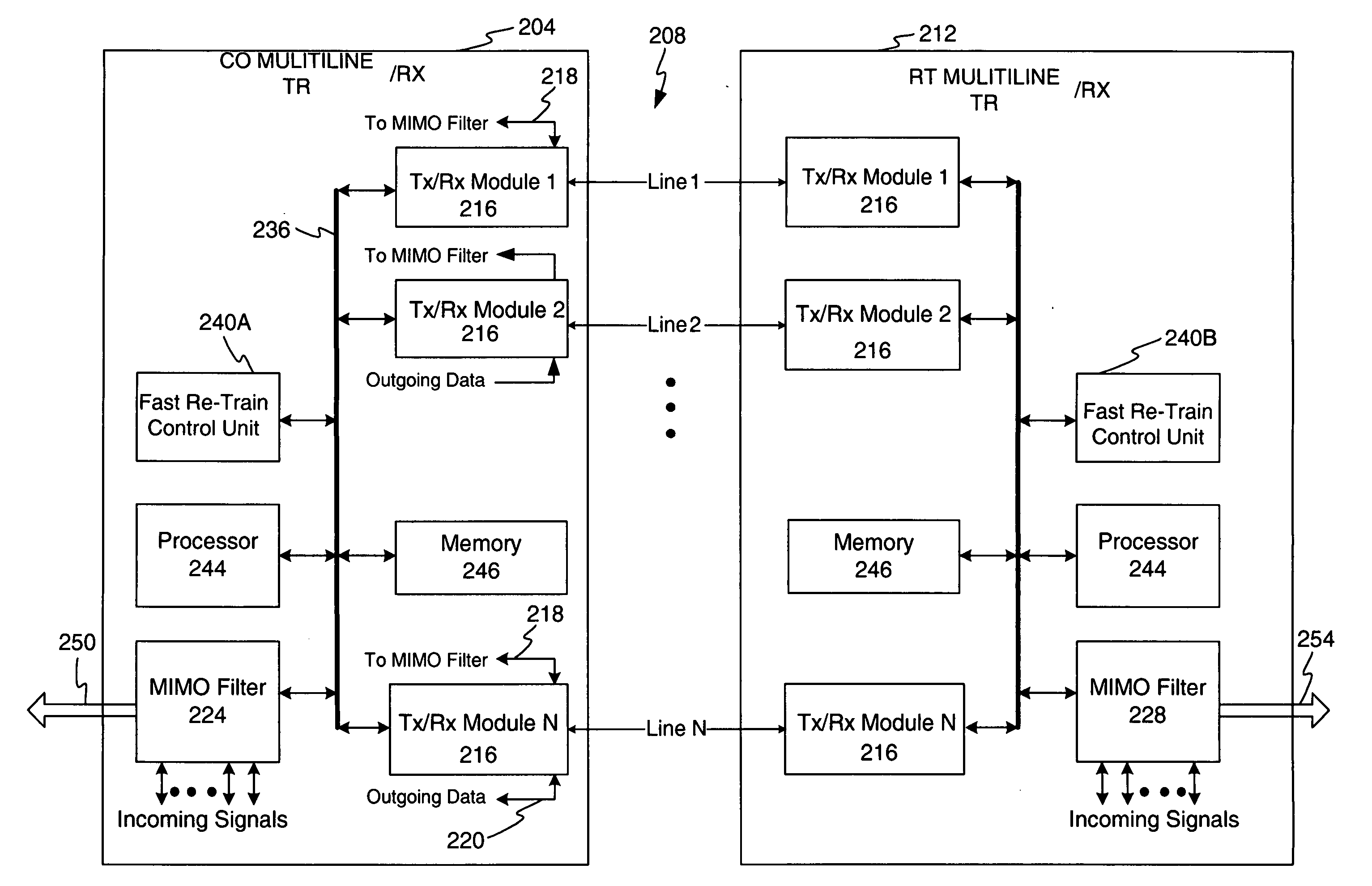
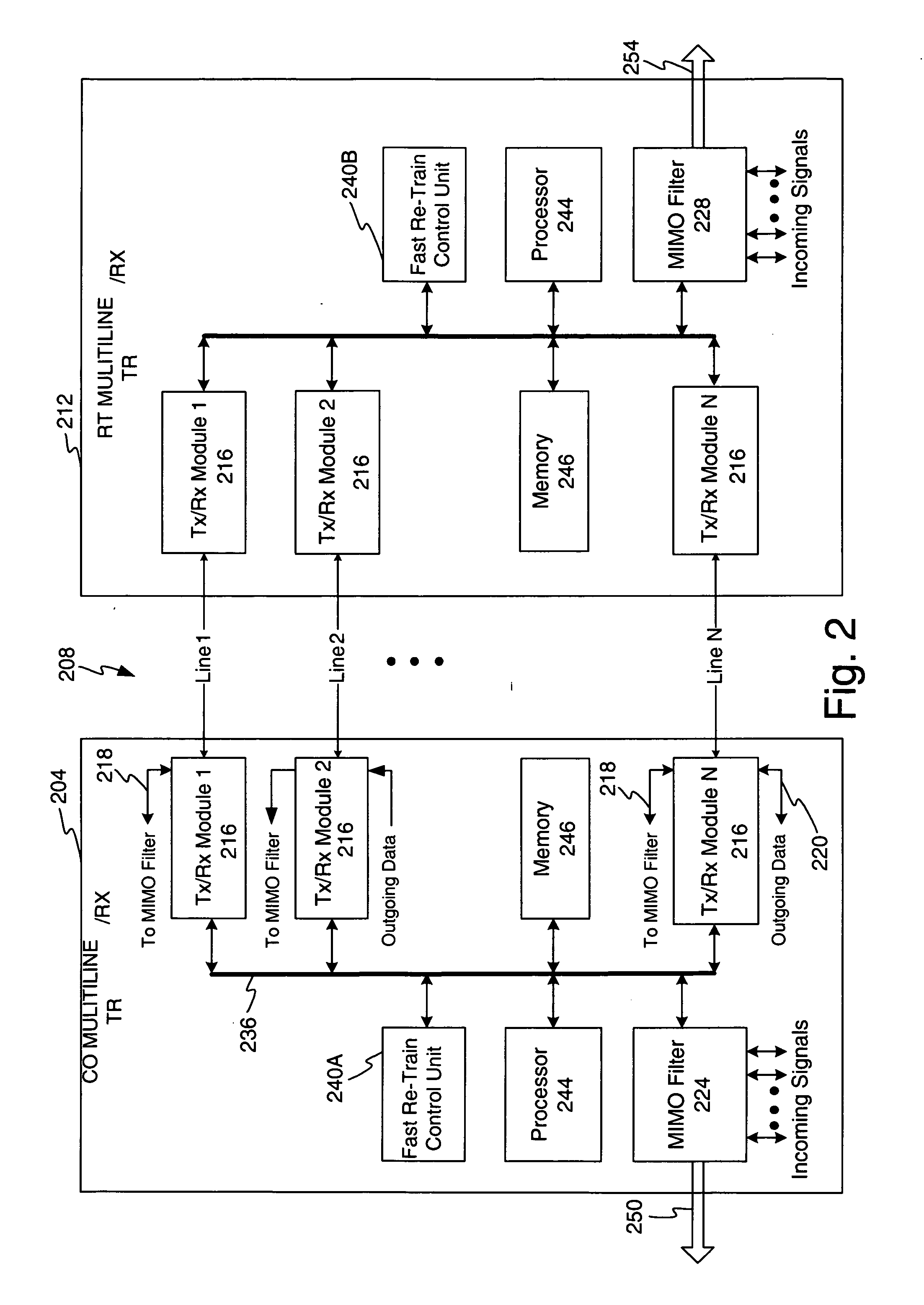
InactiveUS20080089433A1Fast retrain operationReceivers monitoringCorrect operation testingCommunications systemDynamic channel
A disturbance detection and fast re-train method and apparatus configured for use in a multi-channel communication is disclosed. During data communication disturbance detection occurs by monitoring error rates or other factors, such as crosstalk profiles. Upon detection of a disturbance, the system generates and transmits a line upset condition signal to an opposing terminal and monitors for a similar response from the opposing terminal. Channels which fail to convey such signals may be switch out of service. The signals received via the channels may be utilized as training signals to thereby yield a new crosstalk profile. The new crosstalk profile is processed to establish one or more new multiple input, multiple output filter coefficients, bit loading settings, and gain level settings. These new settings may exchanged with the opposing terminal. In addition, channels which, although transporting signals, yield CRC error rates over a pre-determined threshold, are removed from service.
Owner:POSITRON ACCESS SOLUTIONS
Method for dynamic resource allocation of uplink and downlink in ofdma/TDD cellular system
InactiveUS20080076438A1Improve fairnessEnhancing sector throughputPower managementCriteria allocationDynamic channelDynamic resource
Provided is a method for dynamic resource allocation of uplink and downlink in an OFDMA / TDD cellular system. The method for dynamic resource allocation of uplink in an OFDMA / TDD cellular system includes the steps of determining the number of sub-channels which can be allocated to each user through an FLR algorithm; performing channel allocation for a first frame through a round-robin algorithm in which channel information is not needed; performing dynamic channel allocation for a next frame through uplink channel information measured by uplink channel sounding; and performing power control. The method for dynamic resource allocation of downlink in an OFDMA / TDD cellular system includes the steps of selecting a user through a GPF algorithm; performing dynamic channel allocation through an ASA algorithm so as to perform a FASA algorithm for obtaining a multiuser diversity gain; and performing dynamic power allocation through an improved CHC algorithm, in consideration of a data rate provided to each user and a channel state.
Owner:INHA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUNDATION
Method and apparatus for dynamic channel access within wireless networks
ActiveUS7639663B1High strengthExtend signal rangeNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesQuality of serviceDynamic channel
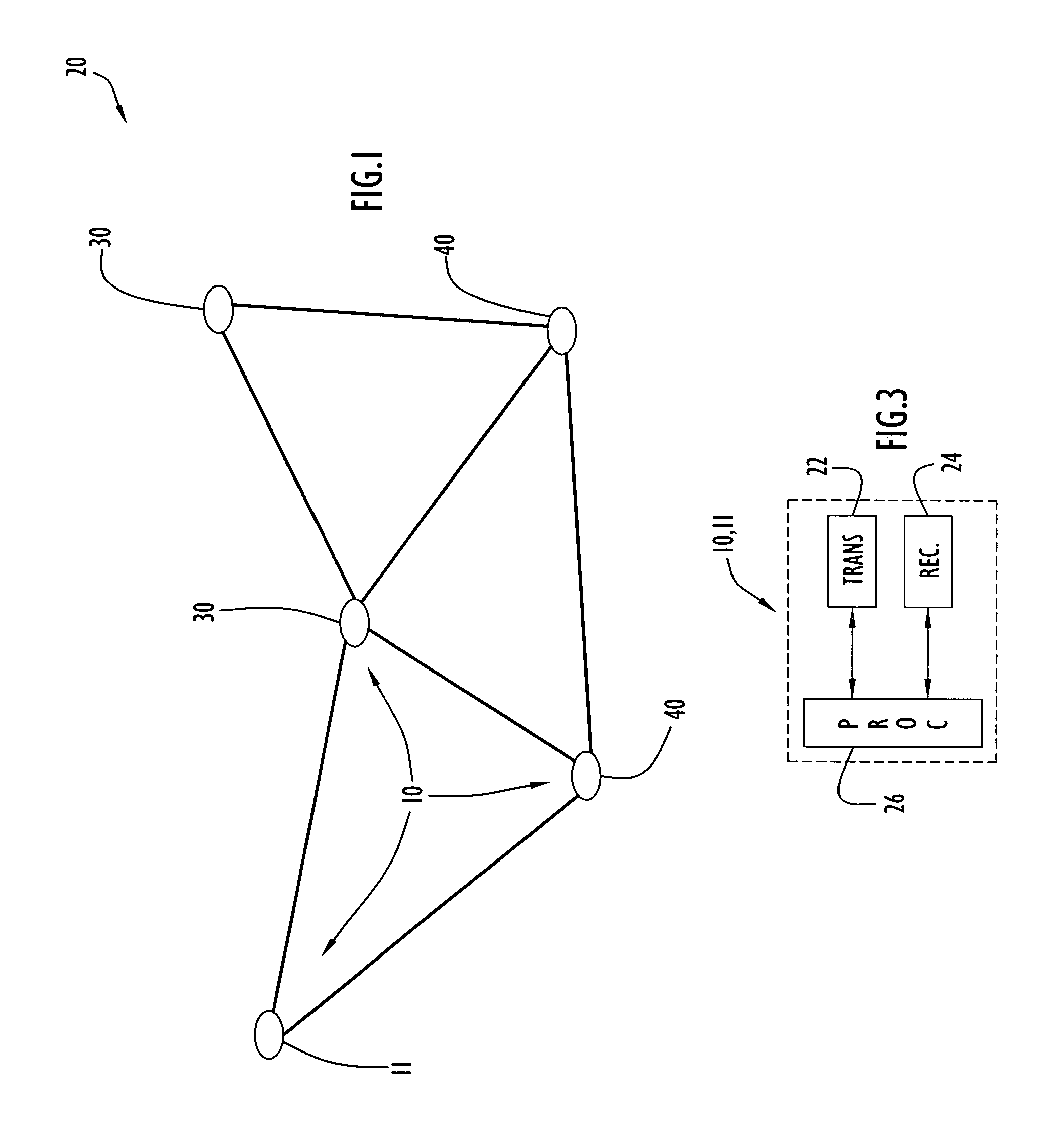
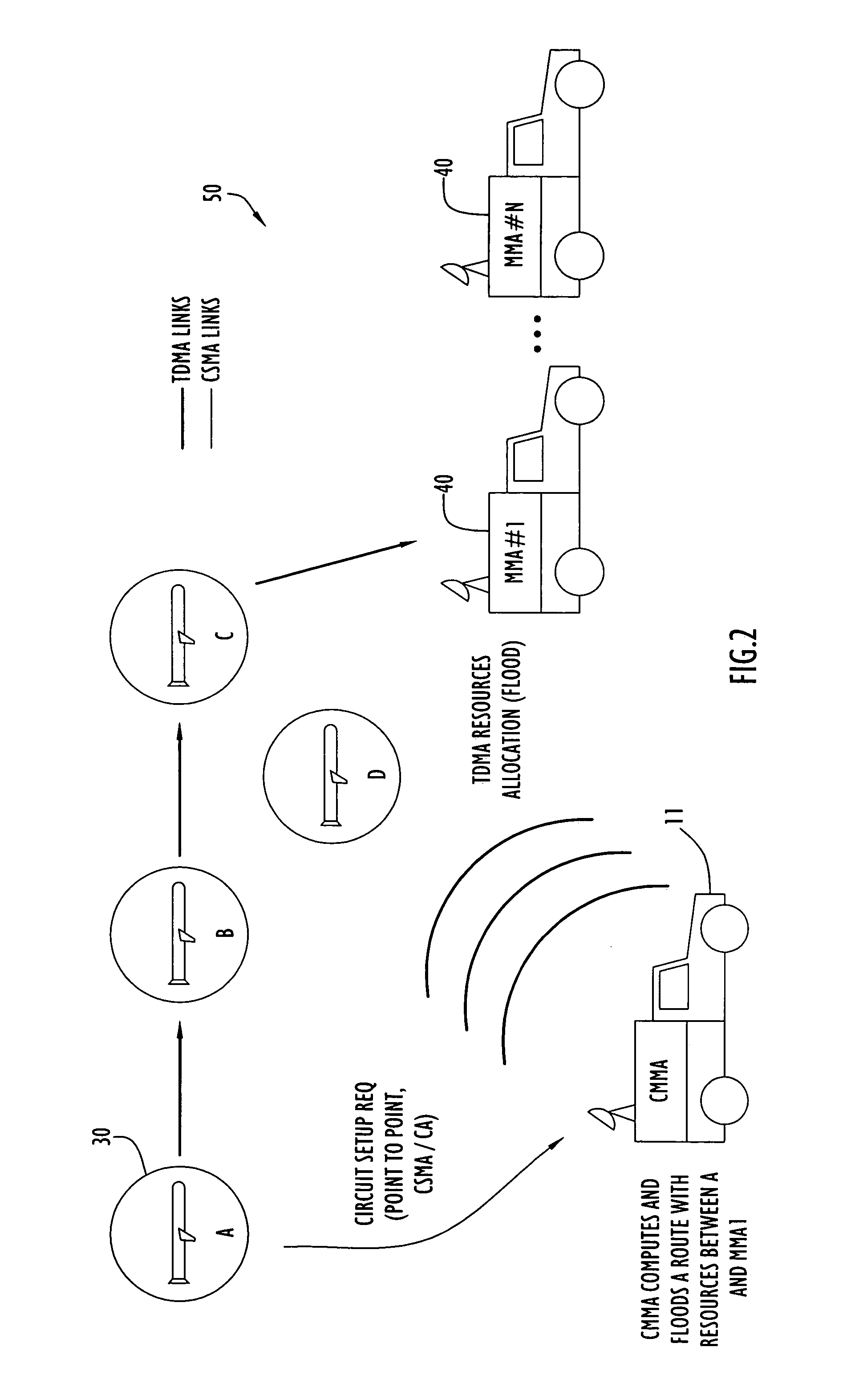
The present invention protocol offers guaranteed Quality of Service (QoS) for a predetermined number of circuits in a highly dynamic, scalable network. The present invention protocol employs a Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) reservation scheme to transmit deterministic data (e.g., image data) to a destination, while utilizing a Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Avoidance (CSMA / CA) contention scheme to support non-deterministic data traffic. The protocol operates over a link-state based routing protocol that reliably floods routing and resource reservation information to the nodes in the network. Moreover, the present invention capitalizes on certain properties of a radio, such as a RAKE type receiver, to enable simultaneous re-transmissions of resource and route reservation information to constructively interfere and enhance the strength and range of the signal.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMMUNICATIONS INC
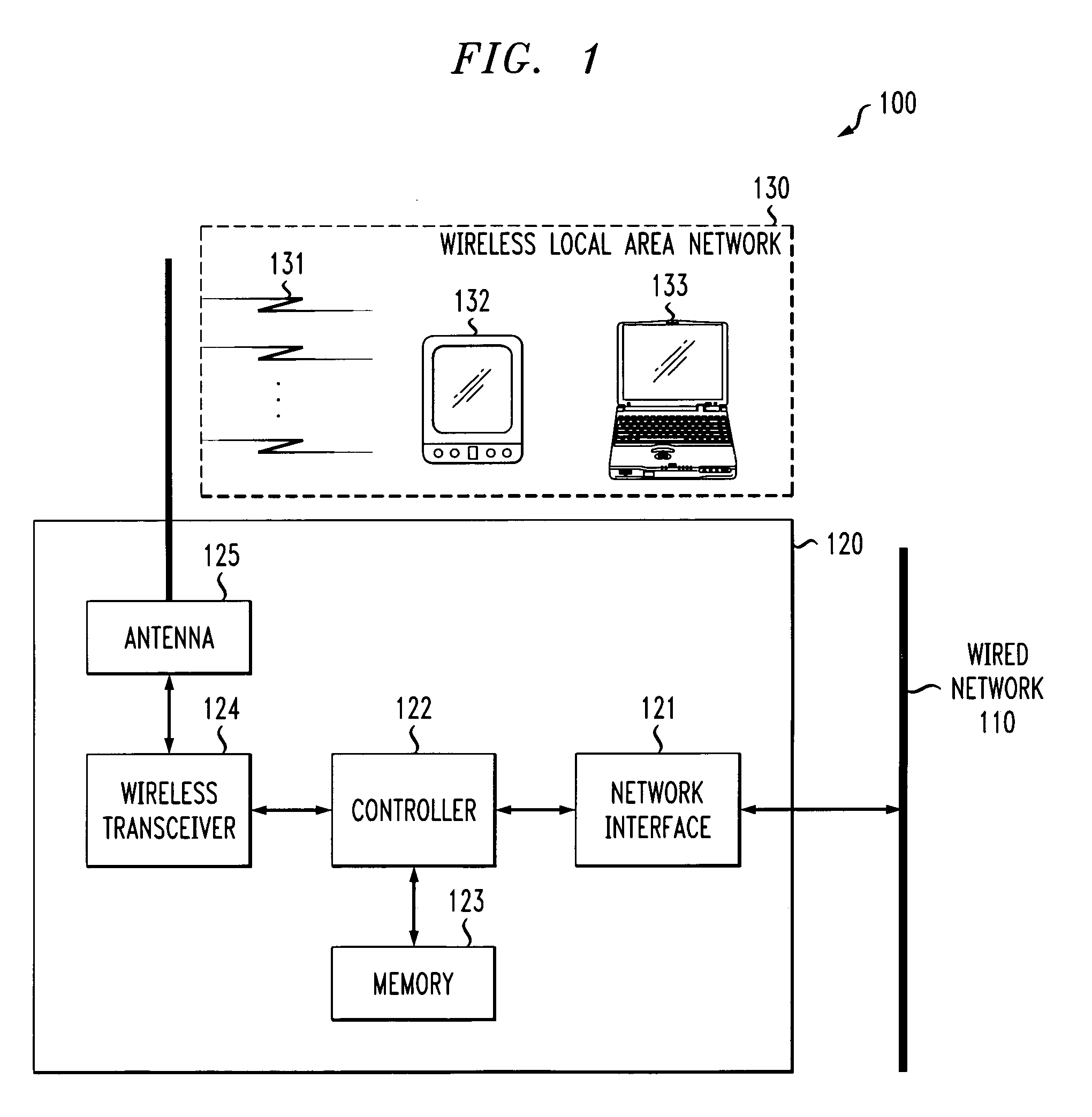
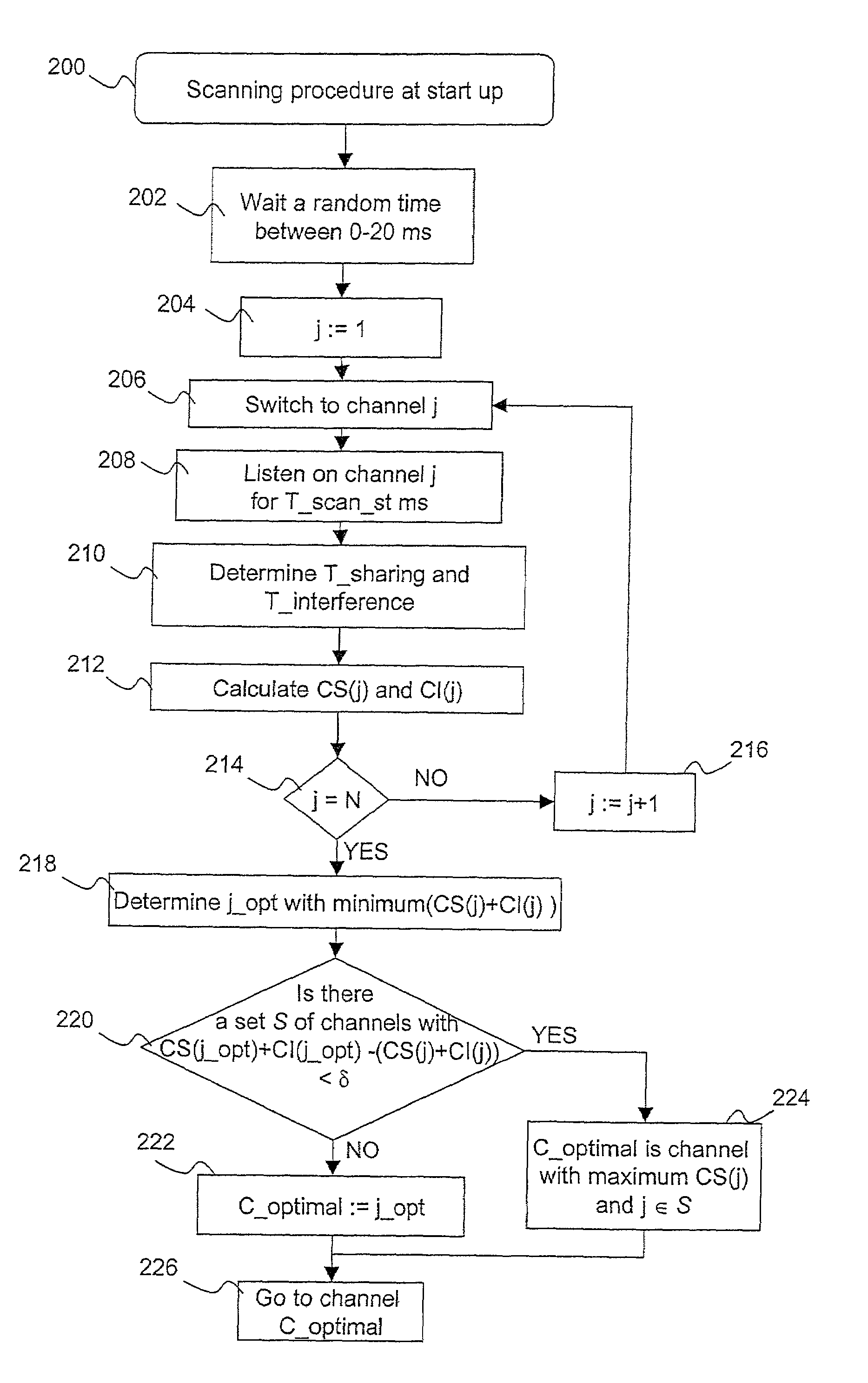
Wireless LAN with dynamic channel selection
The present invention describes an algorithm for the assignment of channels used by access points (APs) in wireless LANs in a dynamic way in order to achieve the best performance. The assignment of channels is based on a procedure in which an AP is passively listening on the other channels during idle time. The AP is calculating the optimal channel with the least interference and sharing. If the AP experiences too much disturbance, it will decide to switch to the calculated optimal channel.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Method and frame structure for supporting dynamic channel allocation and dynamic power allocation in frequency reuse partitioning based OFDMA system
InactiveUS20080089278A1OptimizationRatio is smallPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunicationsDynamic channel
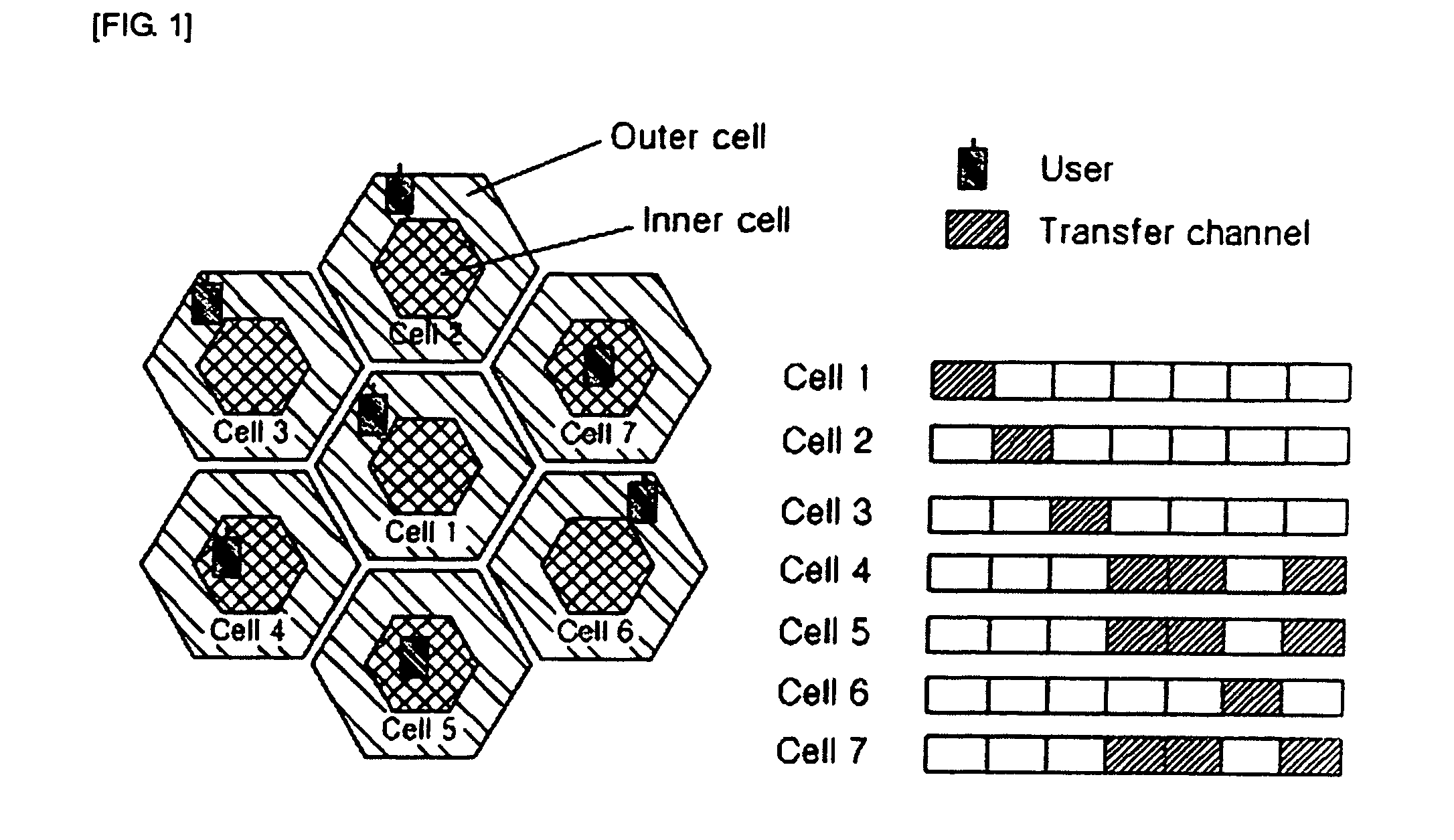
Provided are a dynamic channel / power allocation method for an FRP-based OFDMA system and a frame / slot structure capable of supporting the dynamic channel / power allocation method. In the FRP-based OFDMA system, each of cells has an inner cell, an outer cell and a plurality of sectors and performs data communication with a plurality of MSs therein through one or more orthogonal subchannel groups. In the dynamic channel / power allocation method, a BS receives a feedback channel condition from an MS provided with a service of the BS and allocates a subchannel group with a high SINR to each MS in consideration of the fairness and the distance information of each MS. Power is allocated to each MS on the basis of the conditions of a channel allocated to each MS, thereby obtaining a multi-user diversity gain.
Owner:INHA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUNDATION
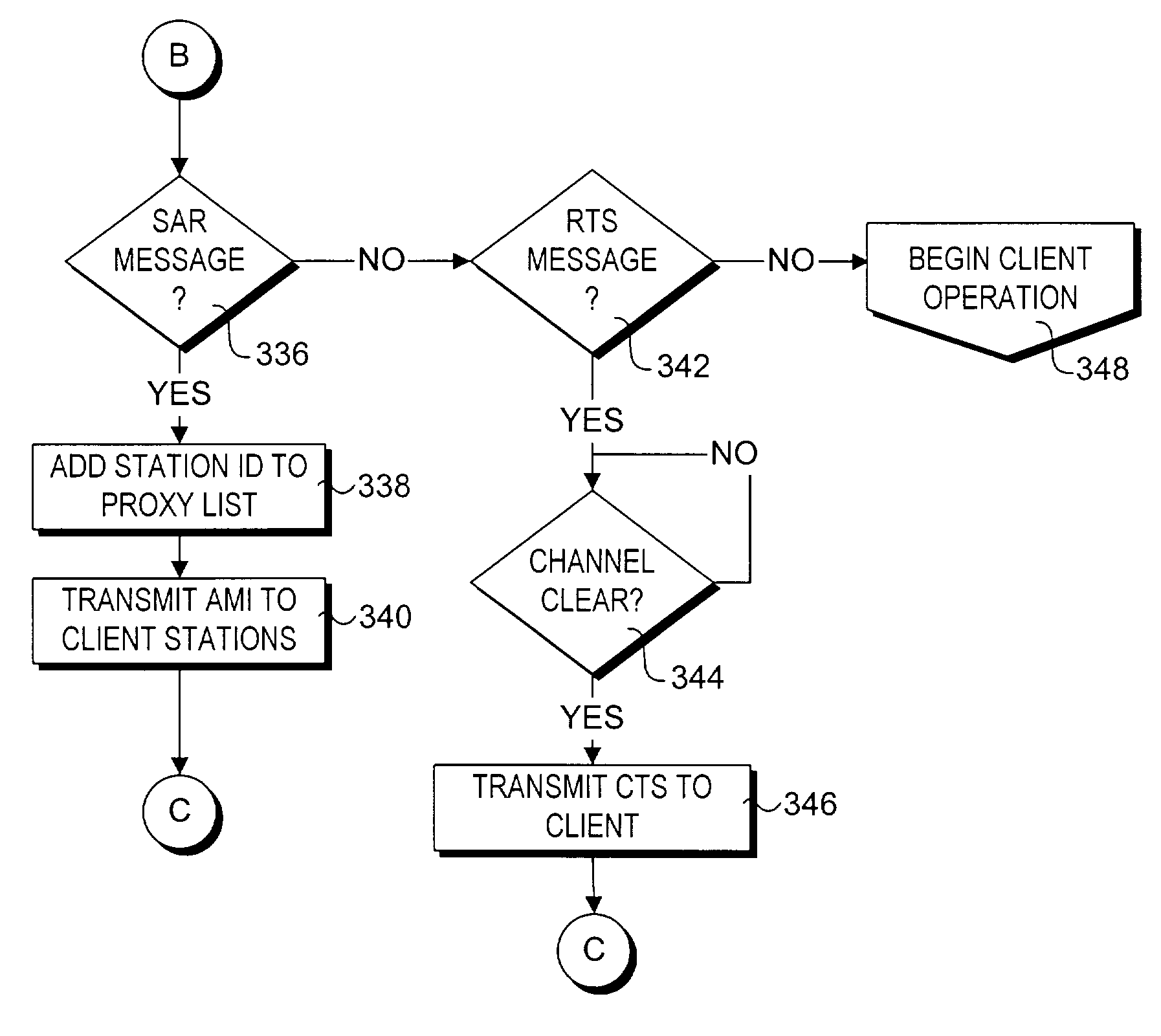
Wireless LAN with dynamic channel access management
A system and method for implementing a peer-to-peer wireless local area network (WLAN) that does not require a conventional wireless access point, yet facilitates many of the features provided by an access point, such as channel access management and Quality of Service functions. A method for dynamically selecting a Channel Access Manager (CAM) that (preferably) has the ability to communicate with the greatest number of wireless stations in a given WLAN is provided. The CAM is then used to manage channel access for the WLAN. A method for selecting one or more proxy CAMs that establish communication paths between the CAM and wireless stations with which the CAM traditionally would not be able to communicate is also provided. The invention also provides a method for resolving the issues that occur when a new station is added to the WLAN, and provides optimize routing of messages to maximize transmission bandwidths.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Dynamically channelizable packet transport network
ActiveUS7333511B2Minimized network capacityEfficient implementationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDynamic channelInternet traffic
A communications network for transporting data packets among L2 / L3 nodes based on dynamically L1-channelizable multi-source buses. The dynamic channelization of a packet transport bus among source-node-specific L1 connections is managed by a bus control process, which periodically optimizes the allocation of bus capacity pool among the source nodes based on real-time bus capacity demand figures by the source nodes of the bus. The invention provides means for real-time dynamic, traffic load adaptive allocation of transport network capacity to continuously maximize the data throughput of the transport network for dynamic packet traffic, such as Internet traffic.
Owner:OPTIMUM COMM SERVICES +1
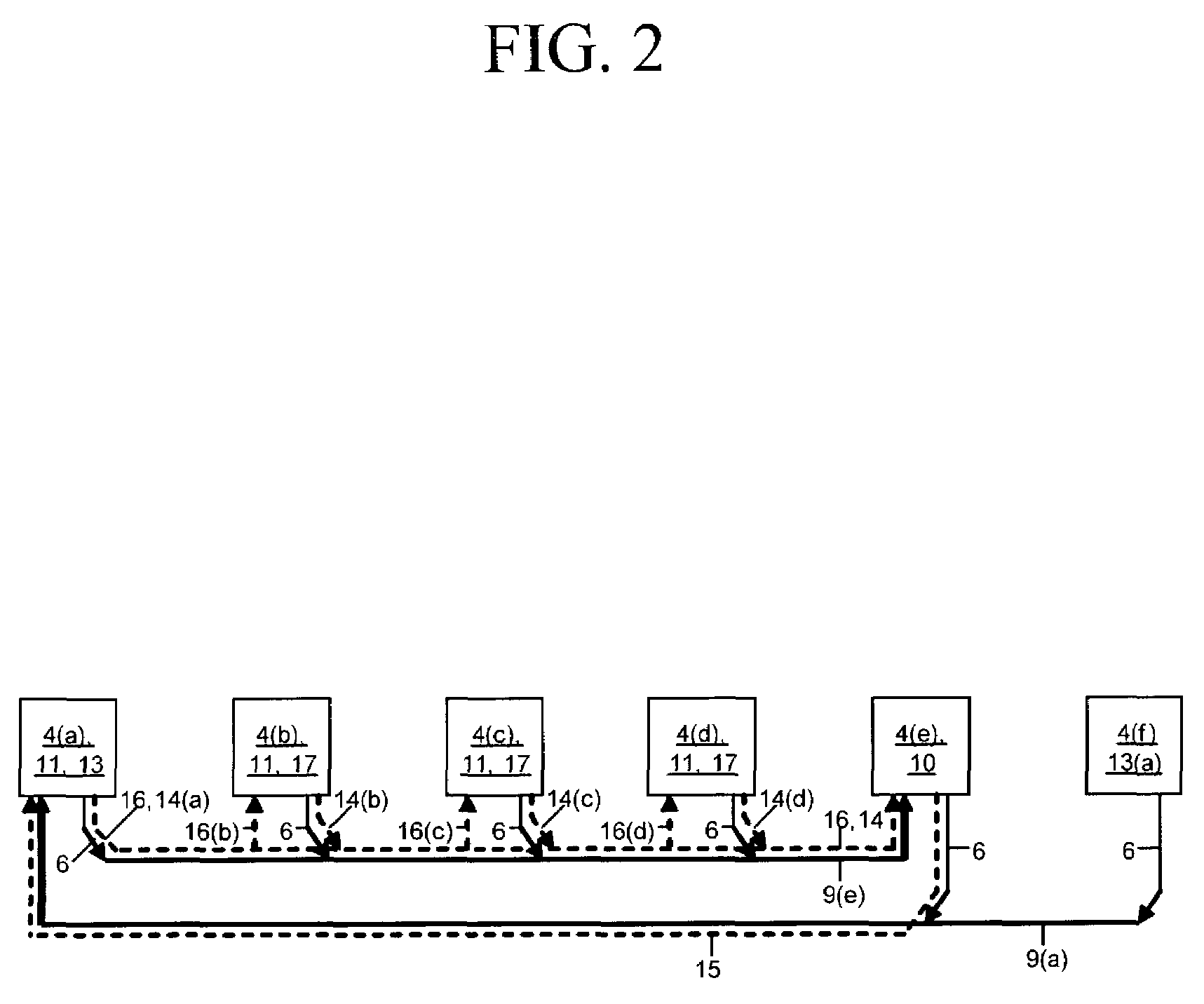
Method and apparatus for controlling dynamic channel feedback in a MIMO network
ActiveUS8837619B2Increase in sizeSmall sizeError preventionModulated-carrier systemsDynamic channelDirection information
A communication method and apparatus for coordinated multi-point (CoMP) transmission, is provided. Sizes of codebooks for a plurality of base stations may be adjusted based on a status of channels between a target terminal and a plurality of base stations. The terminal feeds back, to at least one of the plurality of base stations, channel direction information (CDI) including a number of bits of feedback.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for dynamic channel sensing for direct link in a high efficiency wireless LAN
Methods and apparatus for dynamic channel sensing for direct link in a High Efficiency WLAN (HEW) are provided. The methods include a method for dynamic channel sensing for a direct link by a first station (STA) in a wireless local area network. The method may include determining a first COLOR parameter of an access point to which the first STA is associated, exchanging with a second STA a COLOR parameter related to the direct link, the second STA being a peer STA of the first STA in the direct link, and determining a channel state based on a value of a COLOR field included in a received physical layer protocol data unit (PPDU) having a valid SIGNAL (SIG) field, the first COLOR parameter, and the COLOR parameter related to the direct link.
Owner:ATLAS GLOBAL TECH LLC
Dynamic channel distributing method of TD-SCDMA
InactiveCN1564483AReduce distractionsEasy to implementRadio transmission for post communicationTD-SCDMACommunications system
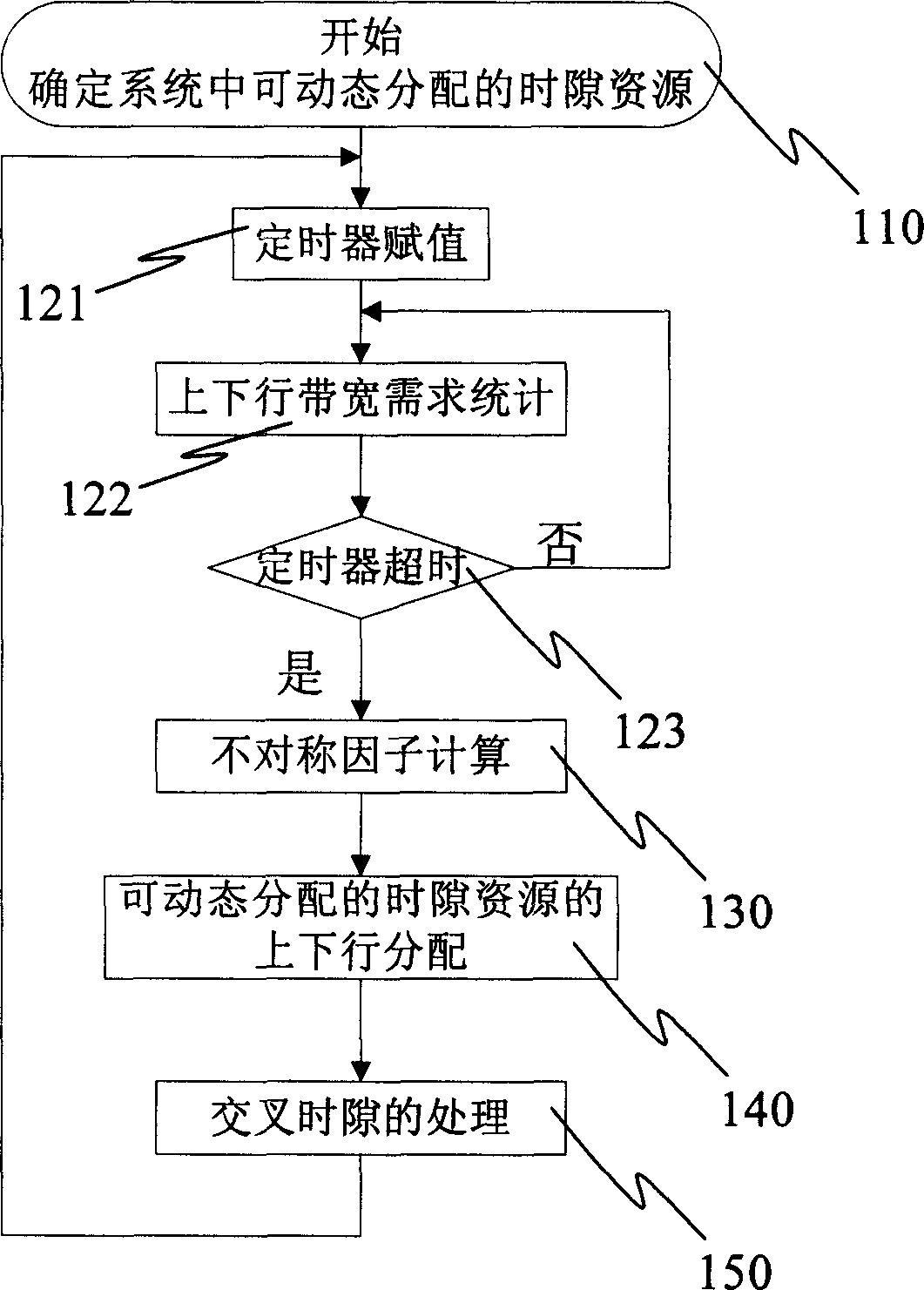
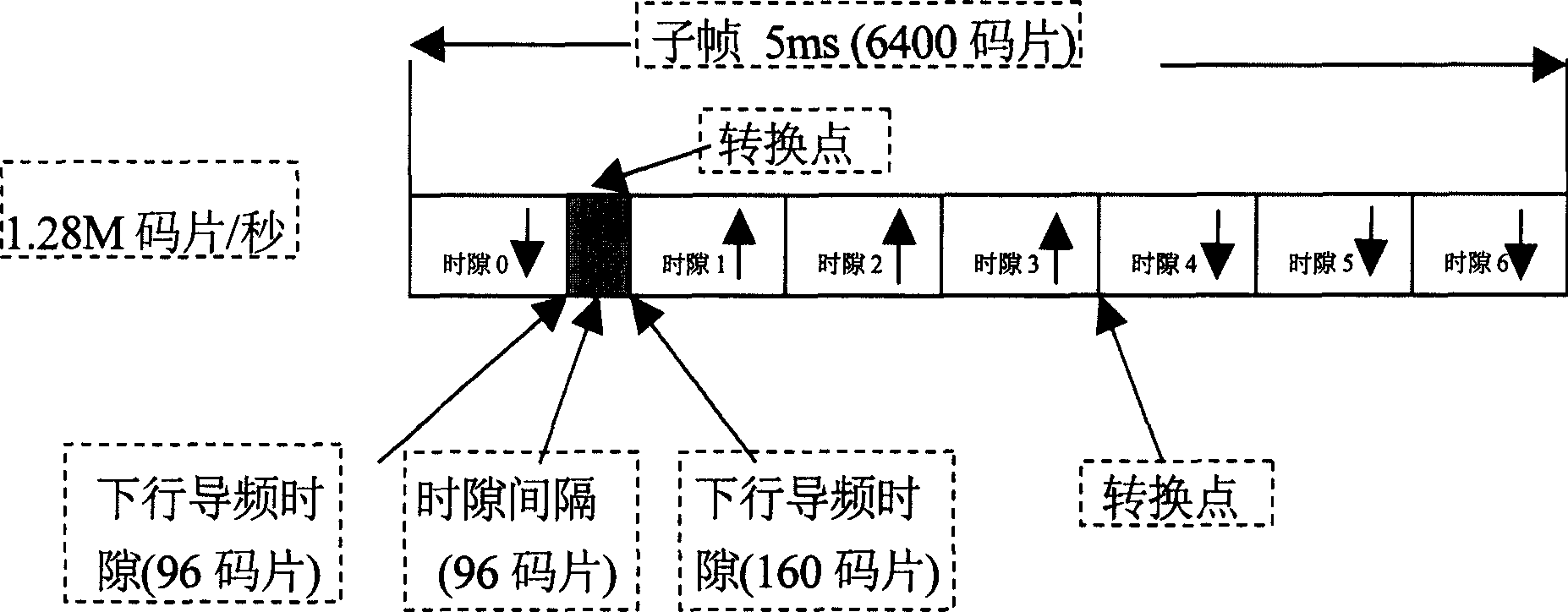
The method includes steps: determining assignable dynamic time slot resources and fixed time slot resources in frame structure of communication system; carrying out statistics for demanding of up going and down going bandwidths on small zone or cluster of small zone in a period of time preset; based on result of statistics, calculating parameters of reflecting demand relation between up going and down going bandwidths; based on the said parameters, allotting assignable dynamic time slot resources for up going and down going bandwidths. The invention realizes dynamic channel allocation at slow speed in TD_SCDMA.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Dynamic channel estimation apparatus, systems and methods
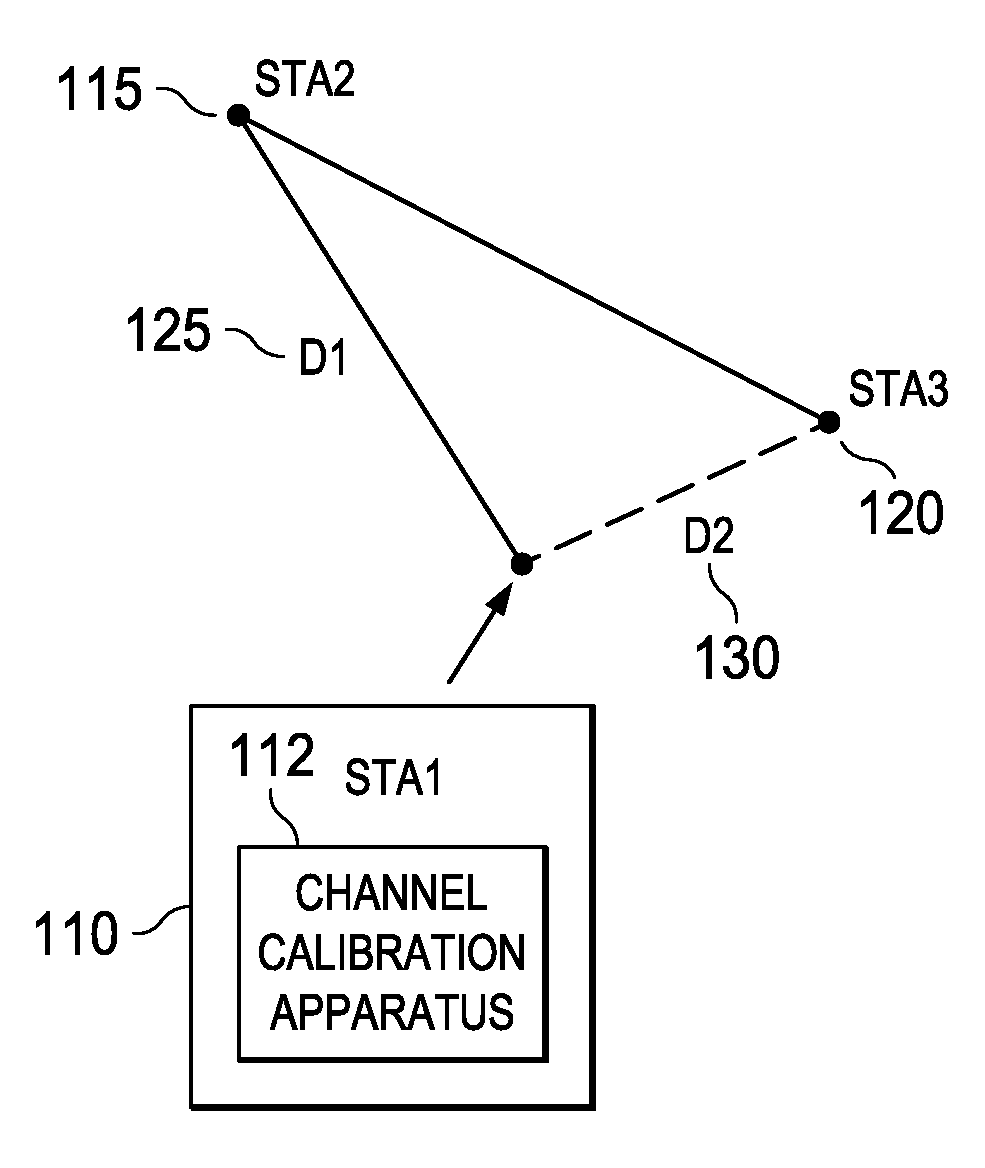
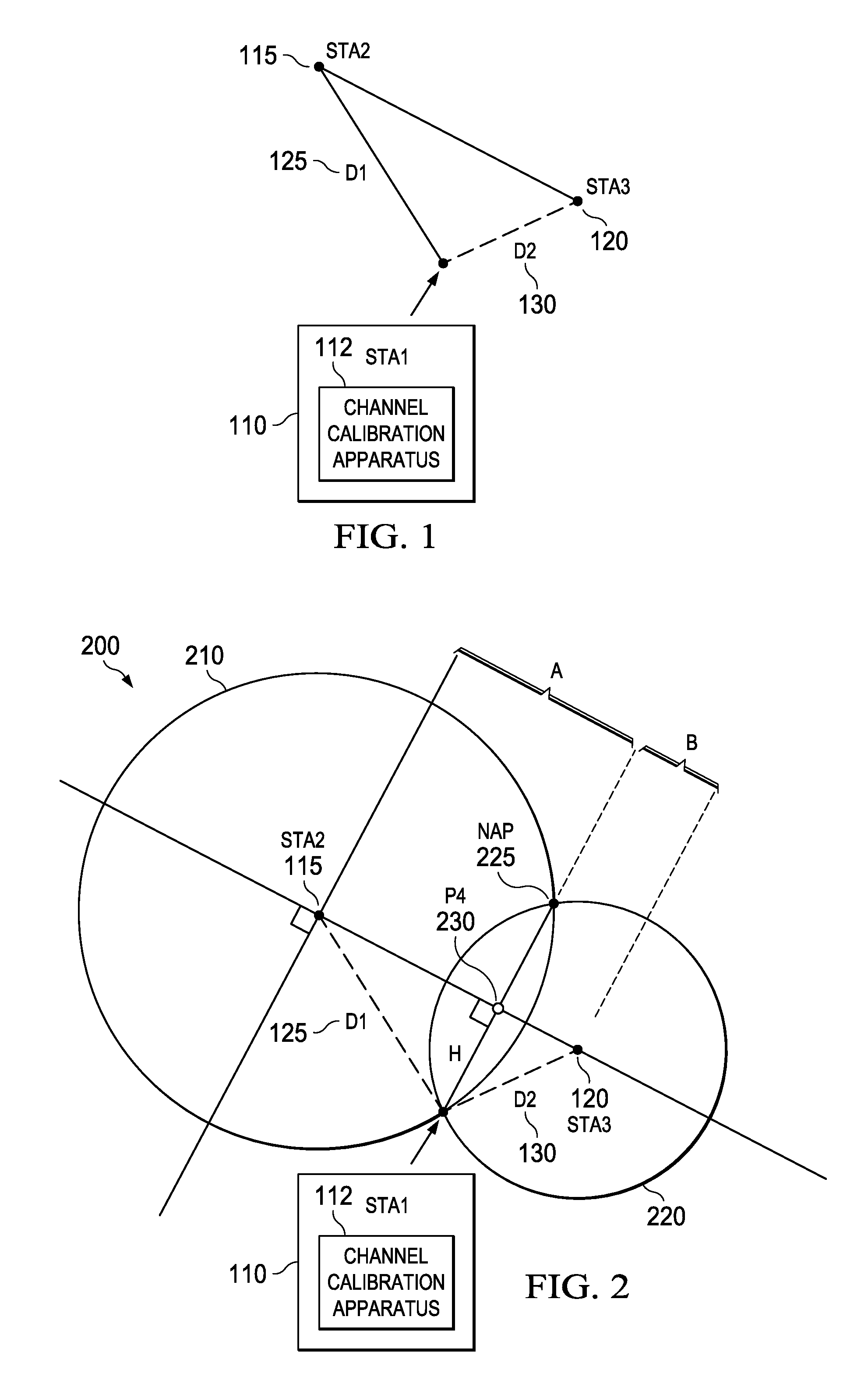
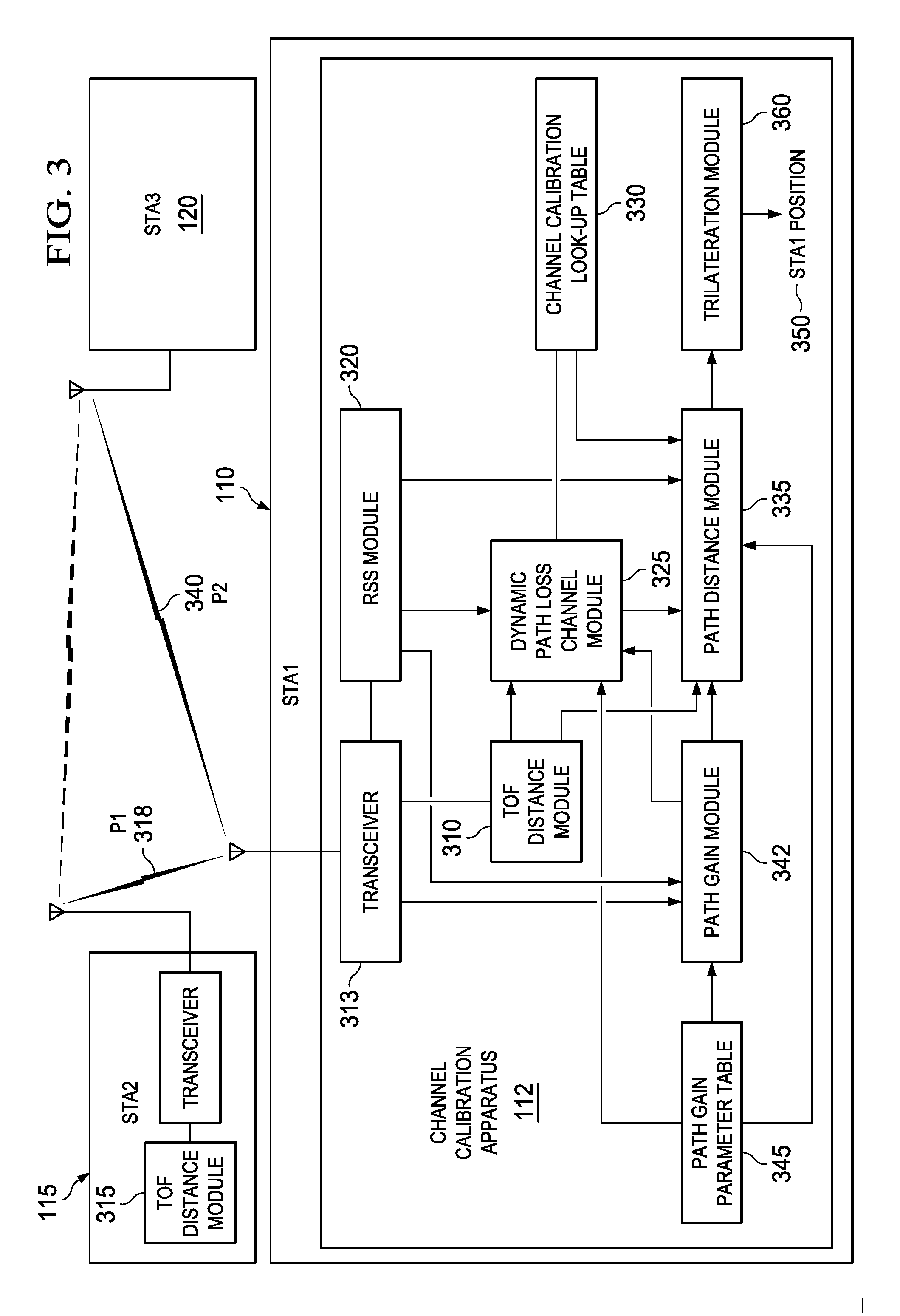
Apparatus, systems, and methods disclosed herein operate to calibrate path loss parameters corresponding to a communication channel between wireless stations, including a path loss exponent. A time-of-flight (TOF) associated with packet transmissions traversing a path between a first wireless station and a second wireless station is measured. A path length D1 corresponding to the path is calculated from the TOF measurements. One or more received signal strength (RSS) measurements corresponding to the packet transmissions are then made at the first wireless station. The path loss exponent associated with the path is calculated from D1 and the RSS measurements. Some embodiments may also measure RSS values associated with transmissions from a third wireless station. The latter measurements may be used in conjunction with the previously-determined path loss exponent to derive an unknown transmission path length between the first and third wireless stations. The latter path length may be used together with other known station geometry to determine the coordinate position of the first wireless station.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com