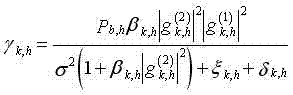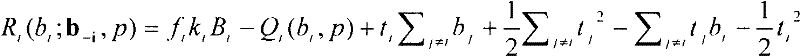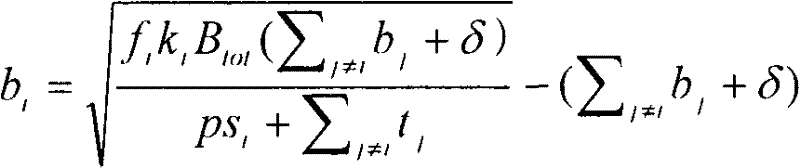Patents
Literature
576 results about "Spectrum sharing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
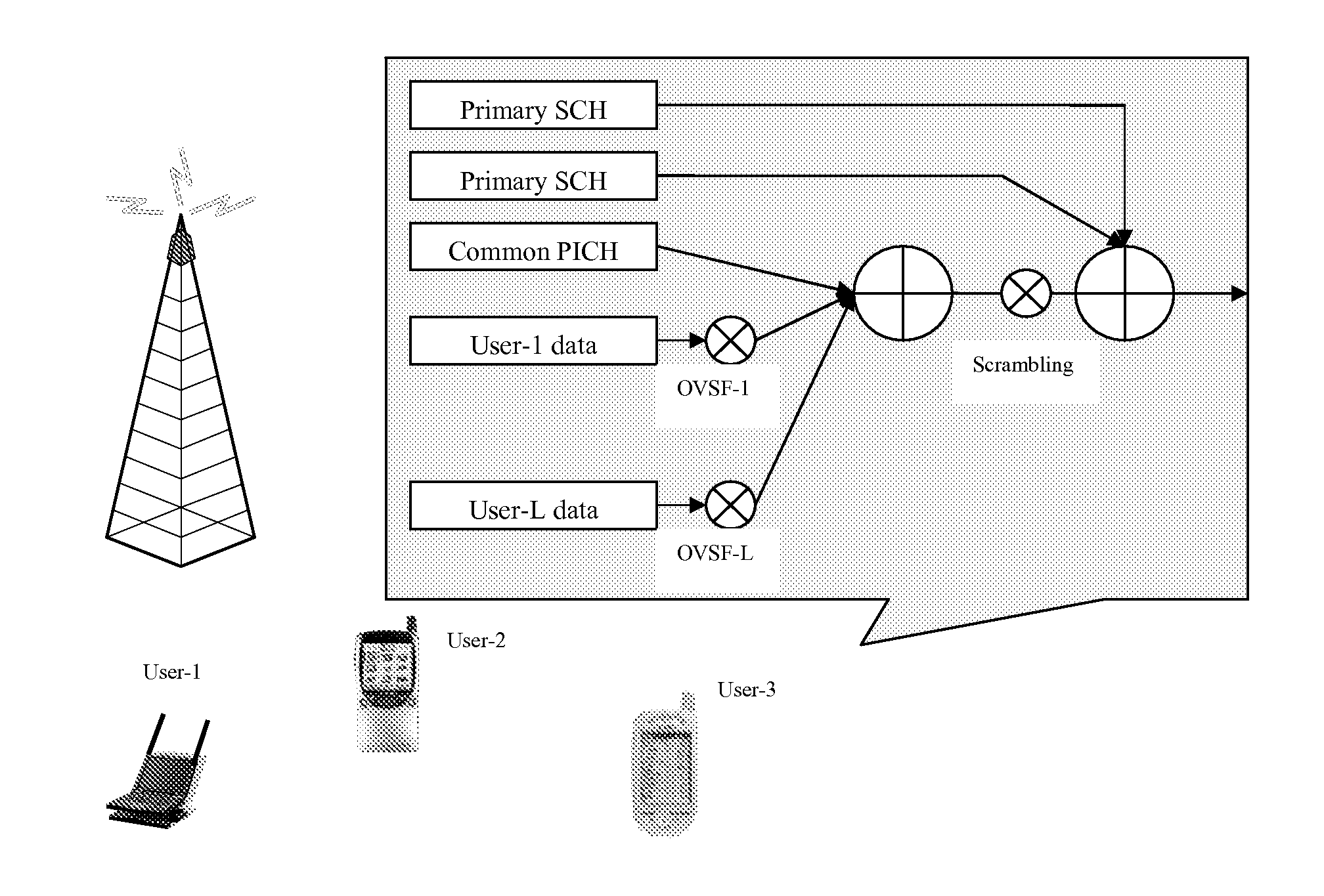
Spectrum sharing is a way to optimize the use of the airwaves, or wireless communications channels, by enabling multiple categories of users to safely share the same frequency bands. Spectrum sharing is necessary because growing demand is crowding the airwaves.
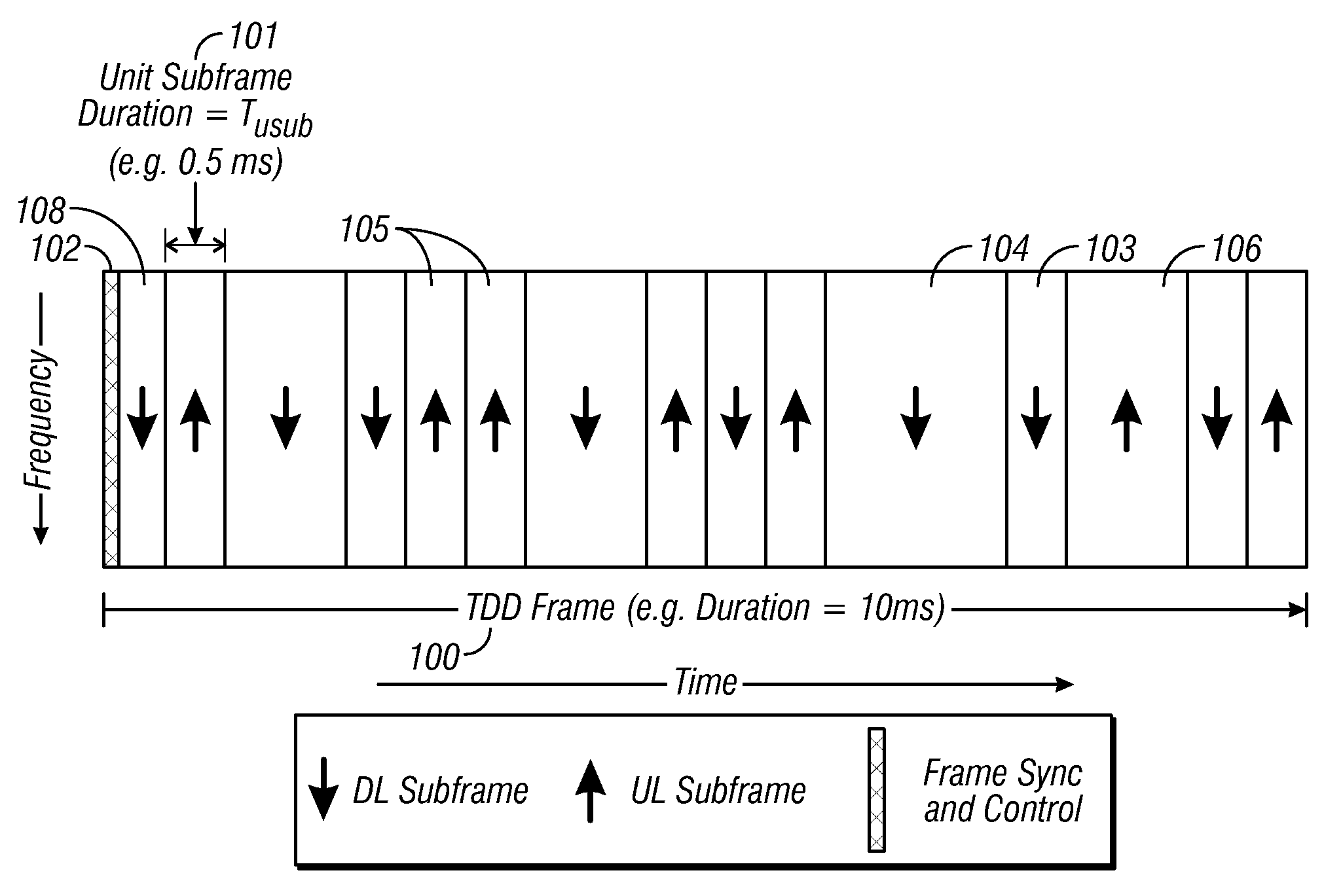
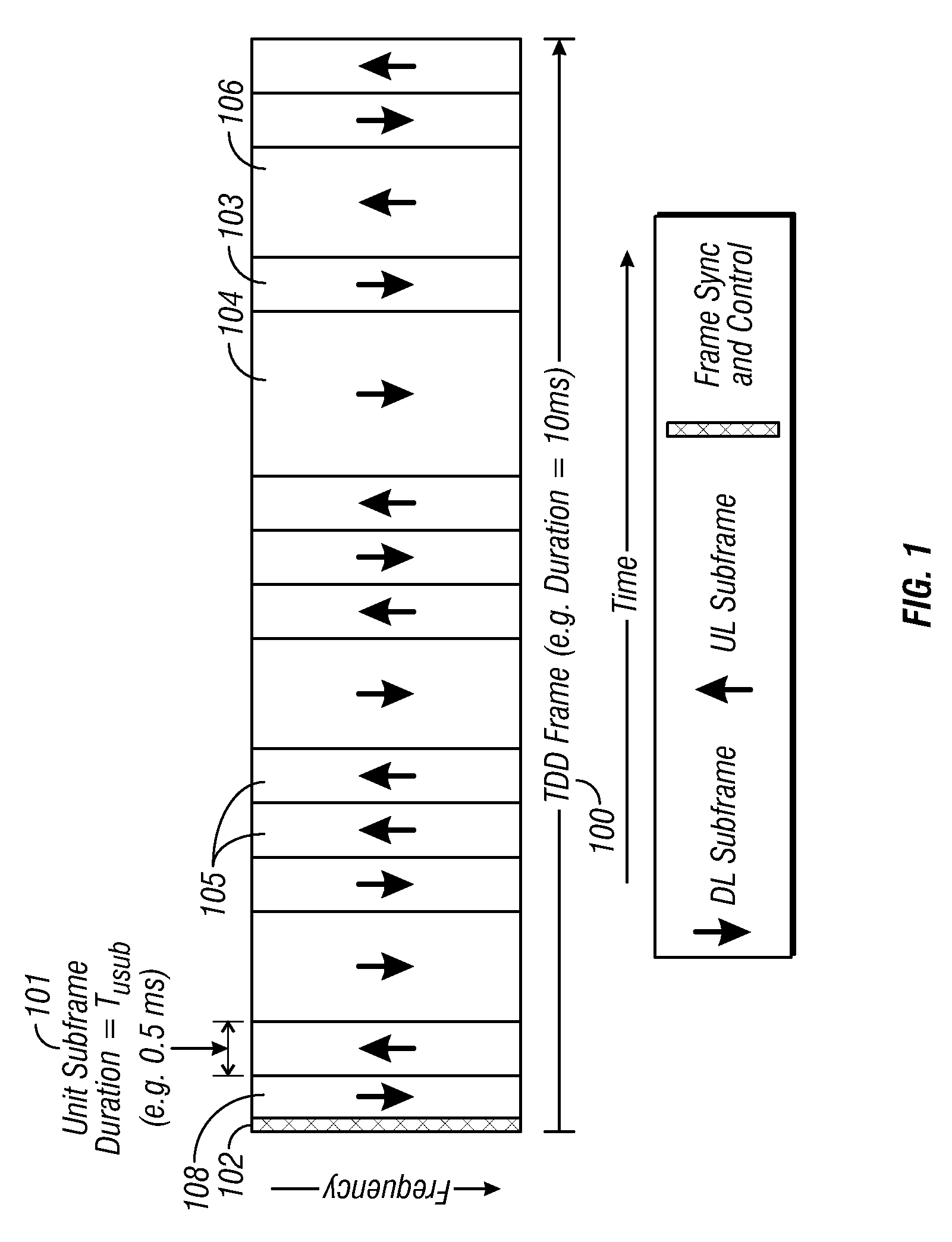
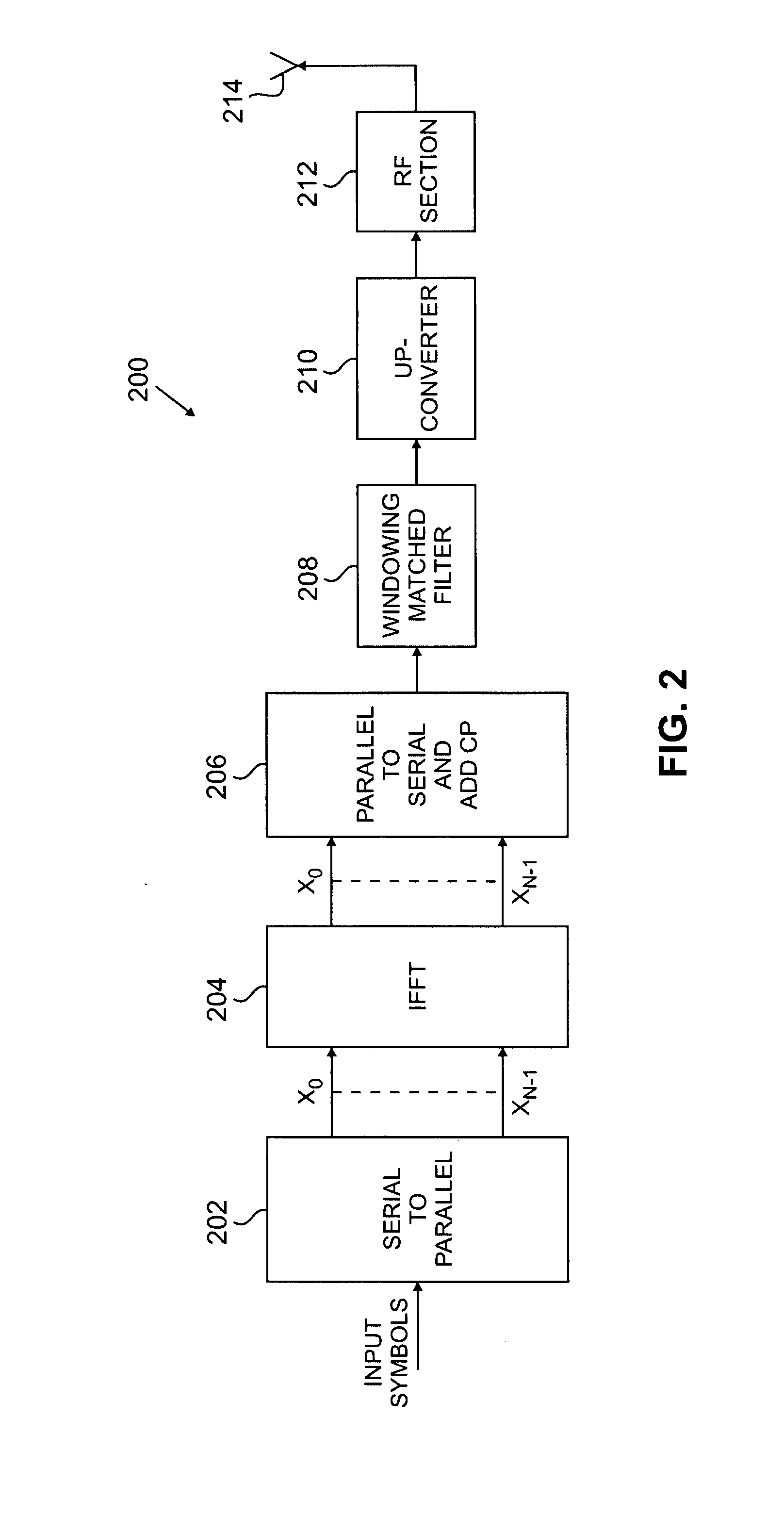
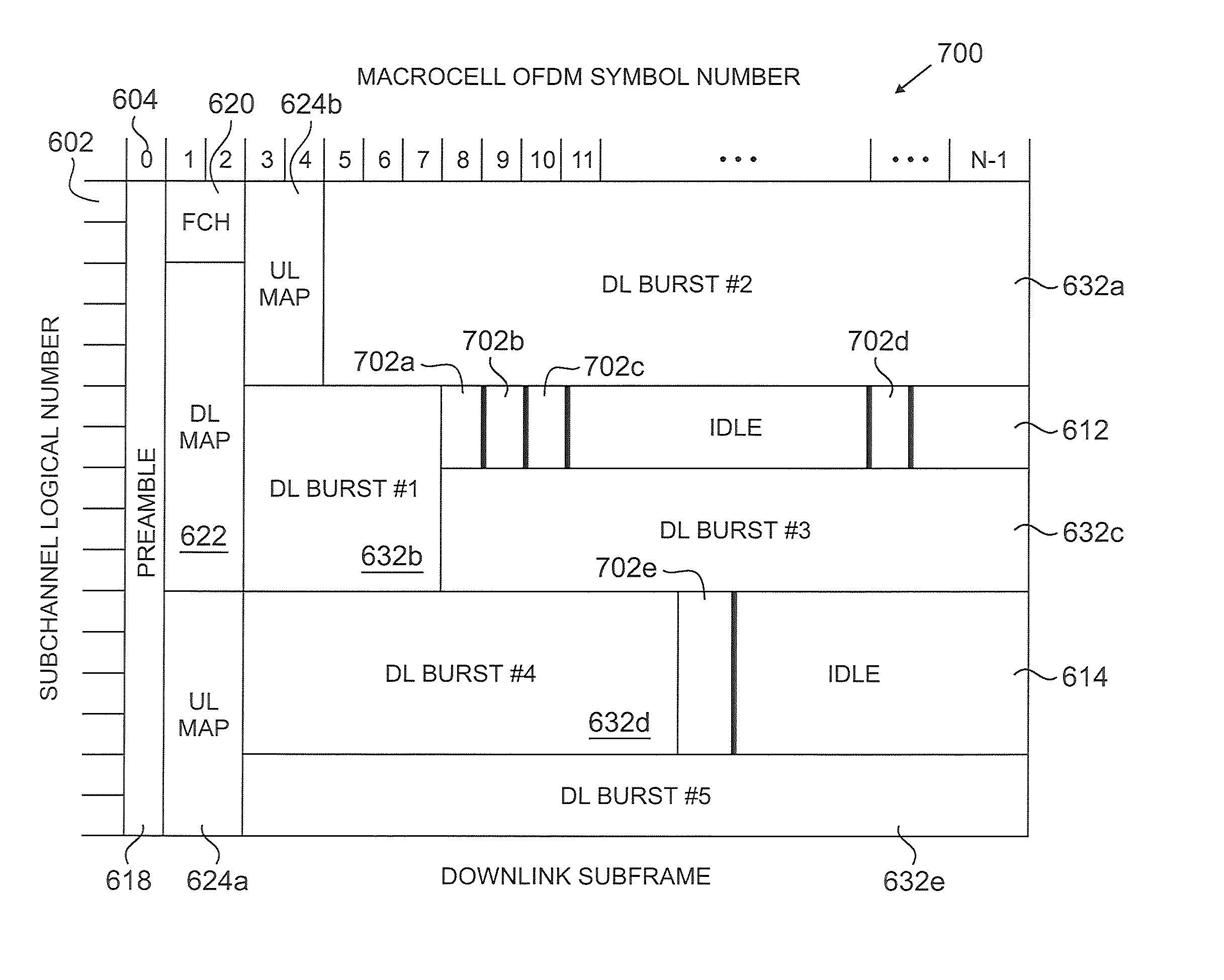
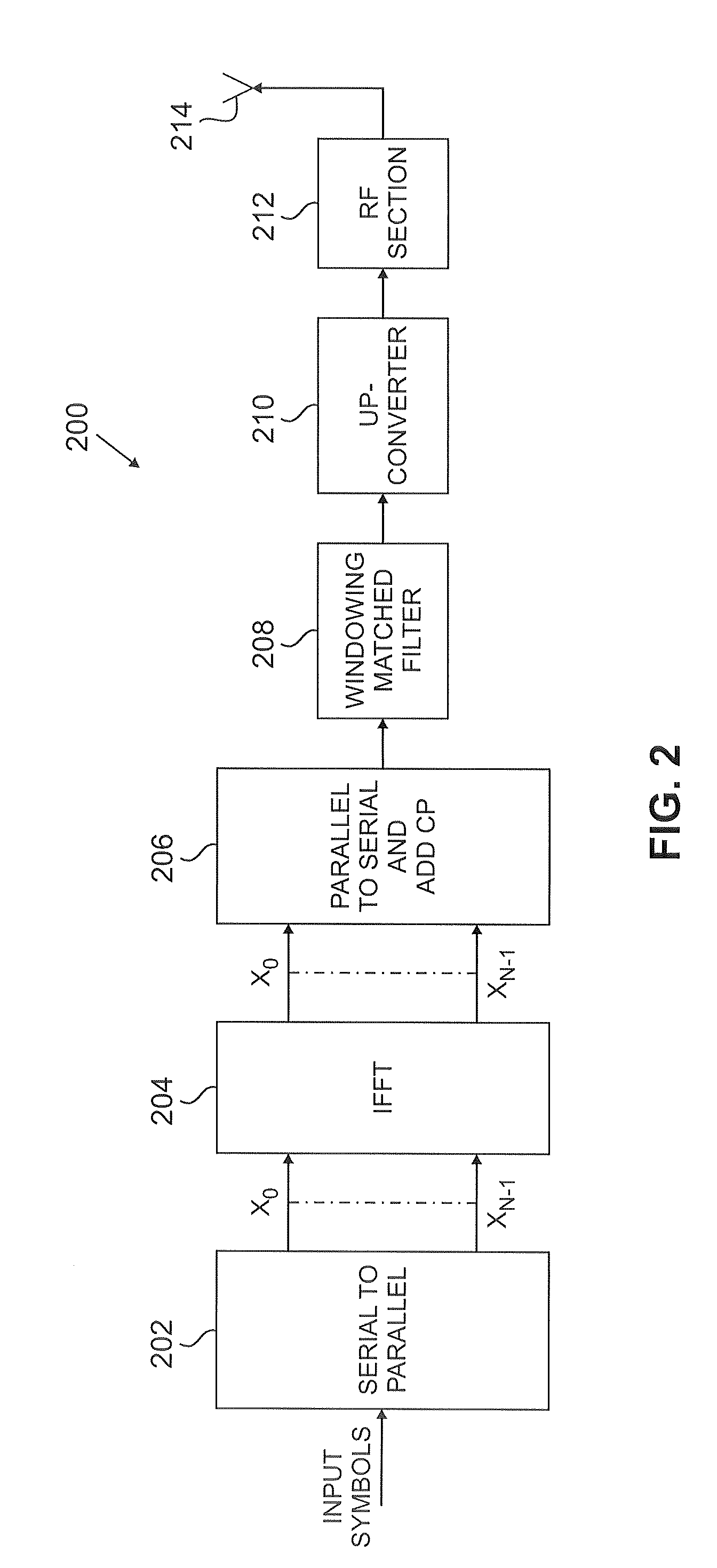
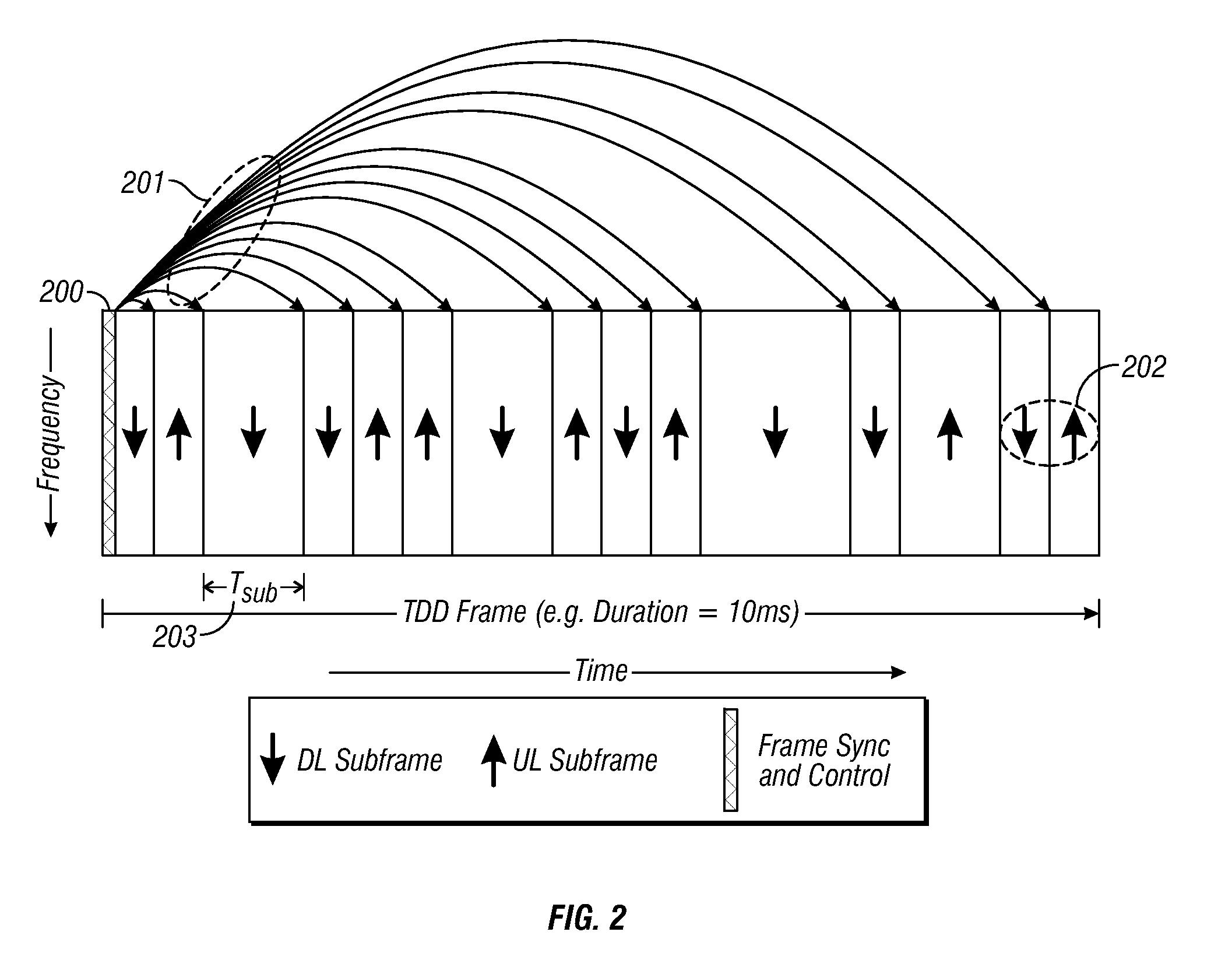
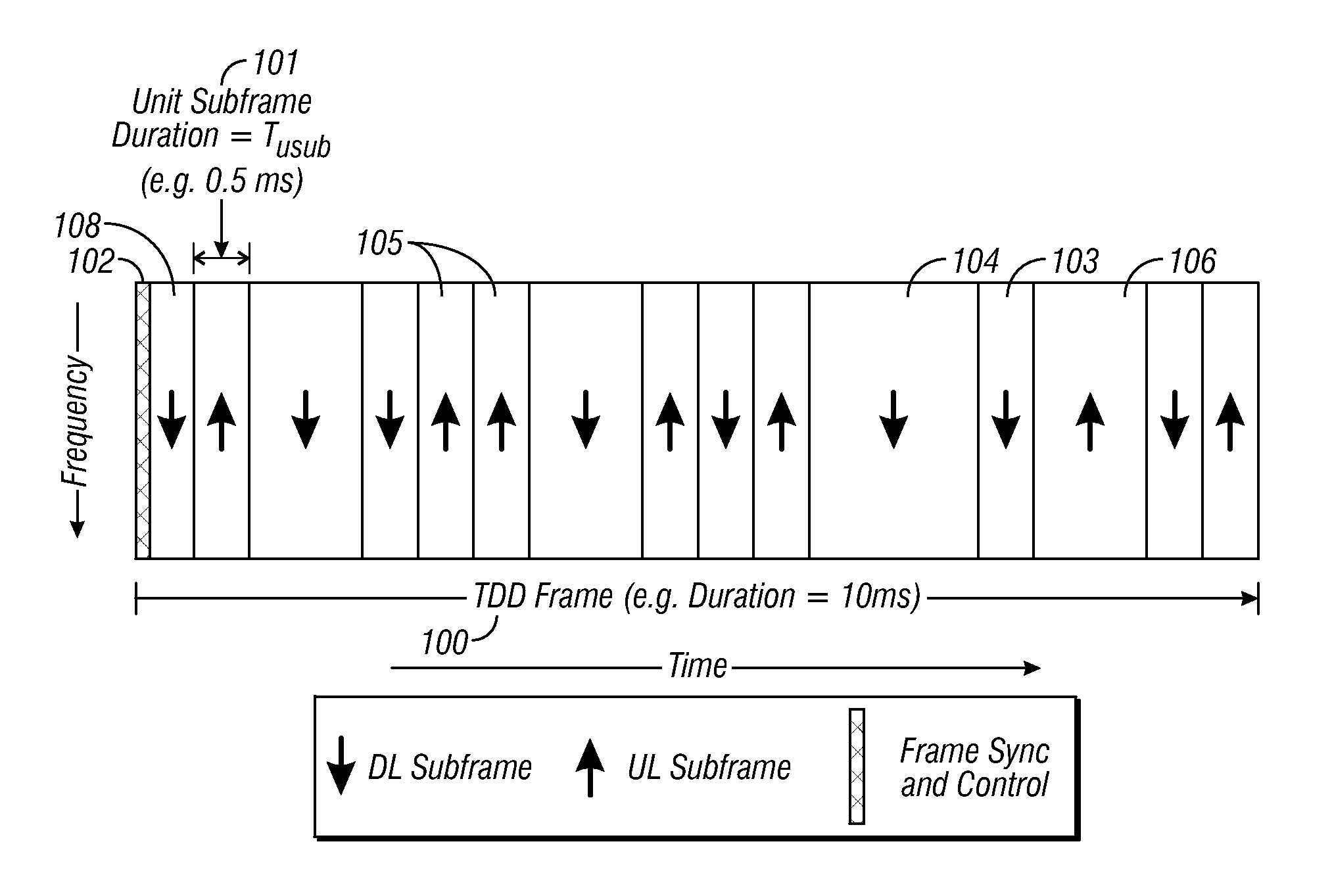
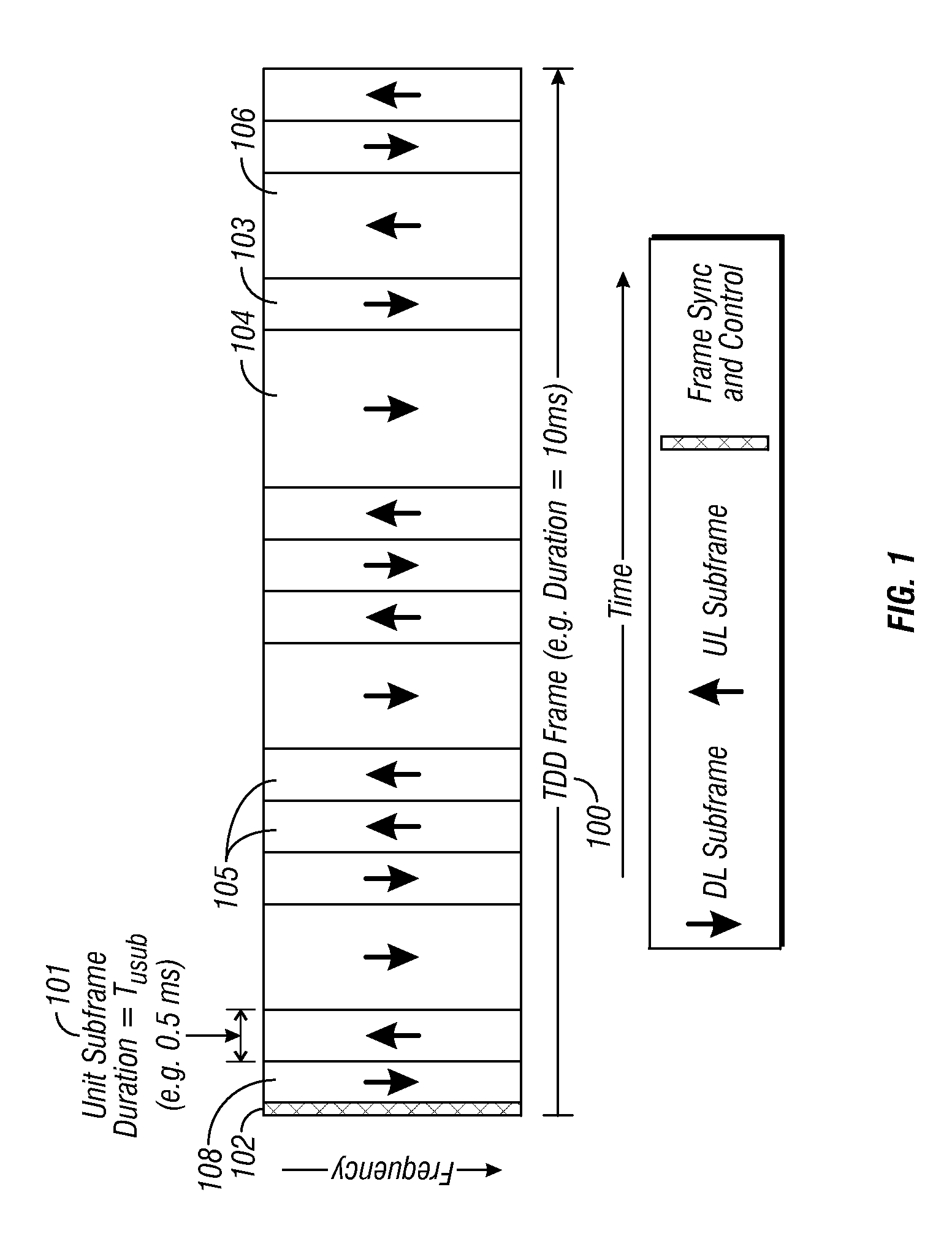
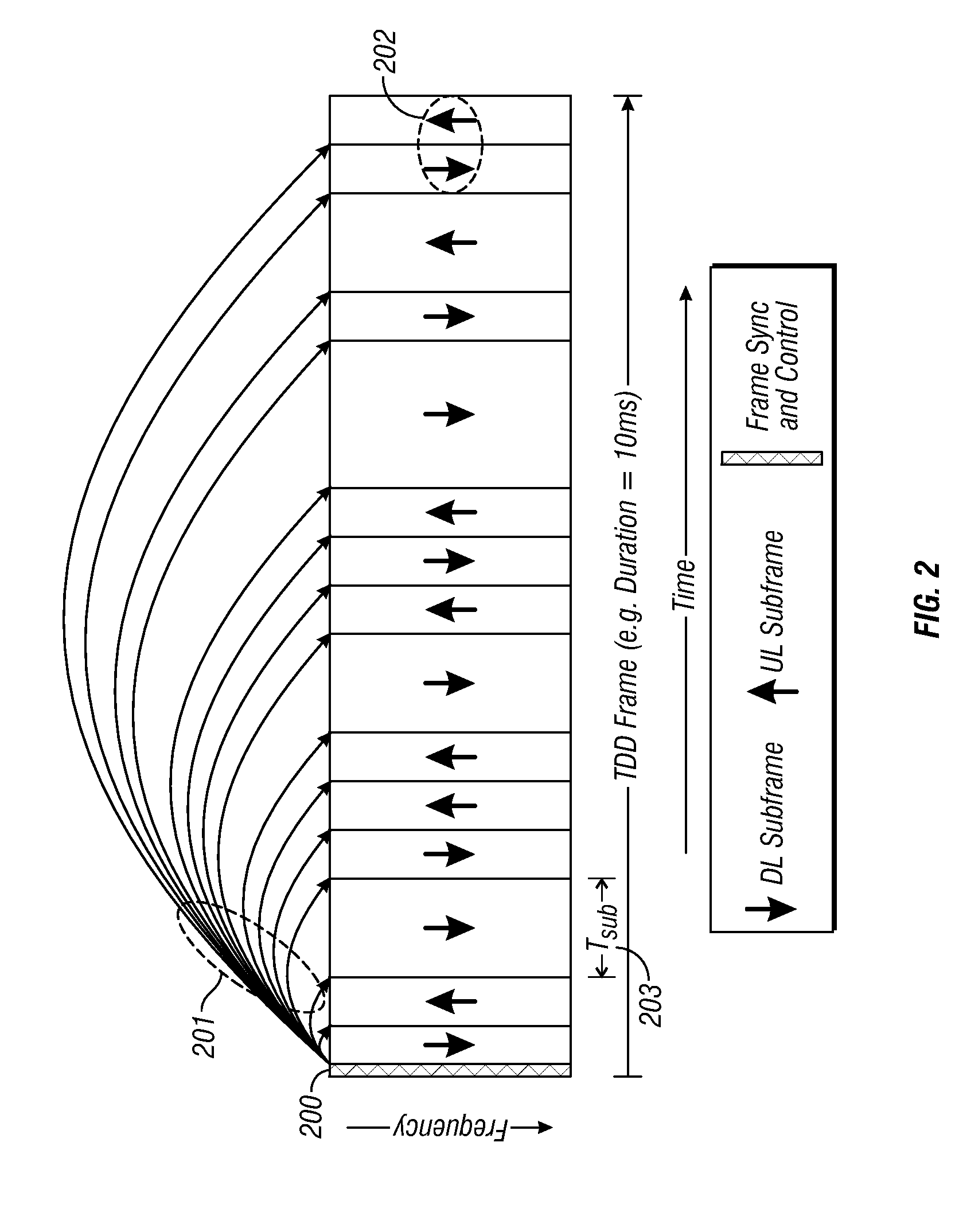
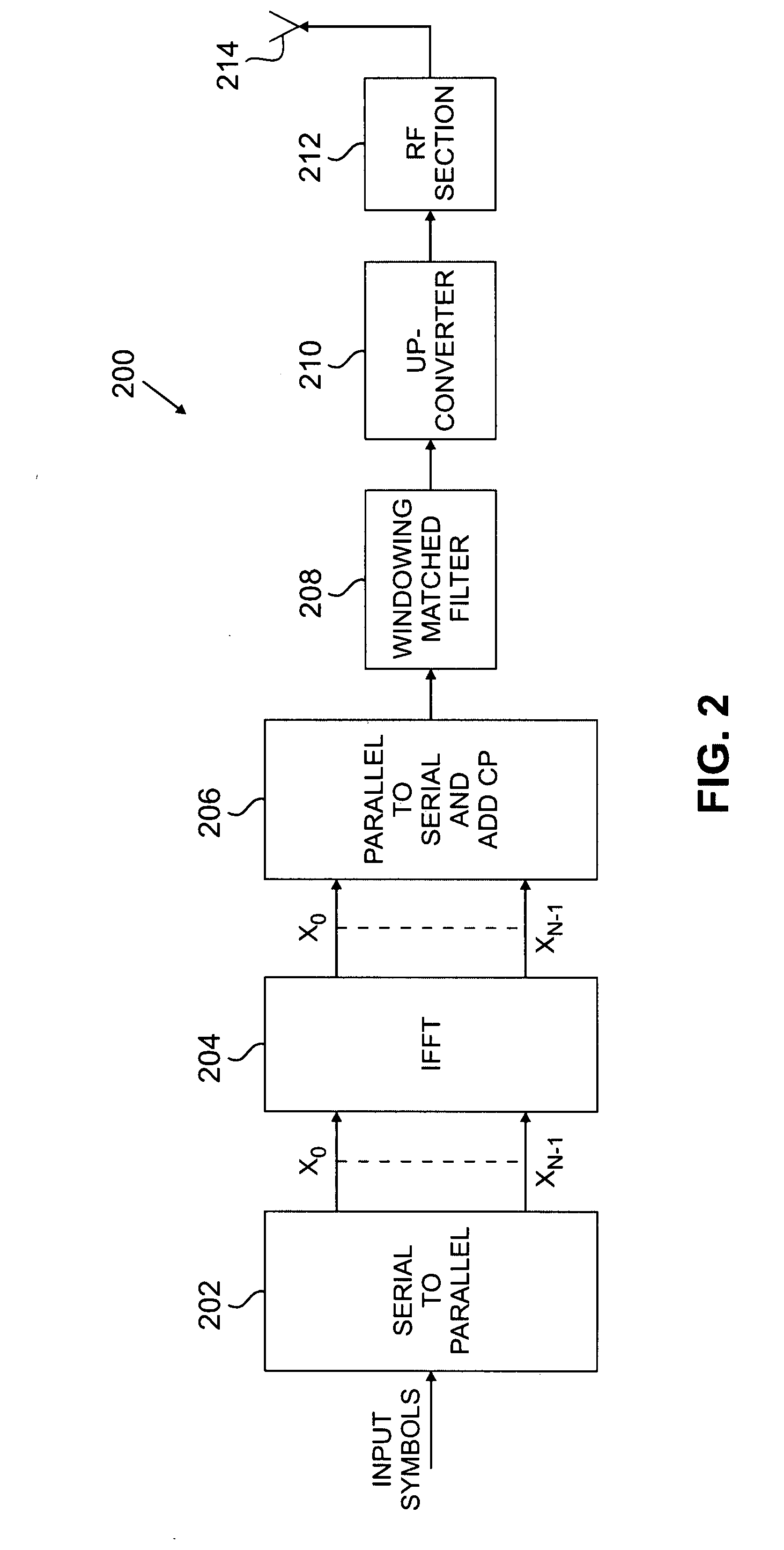
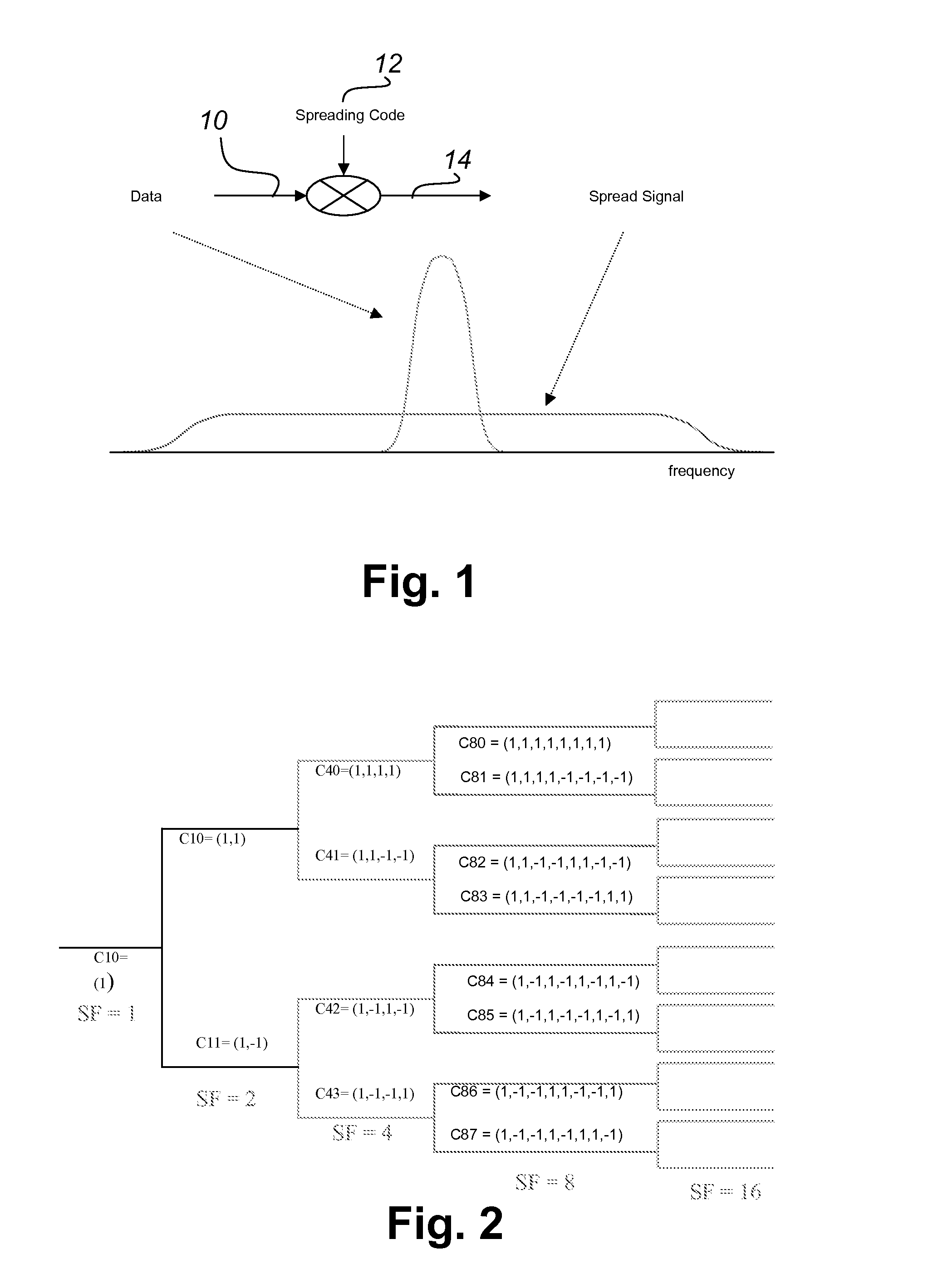
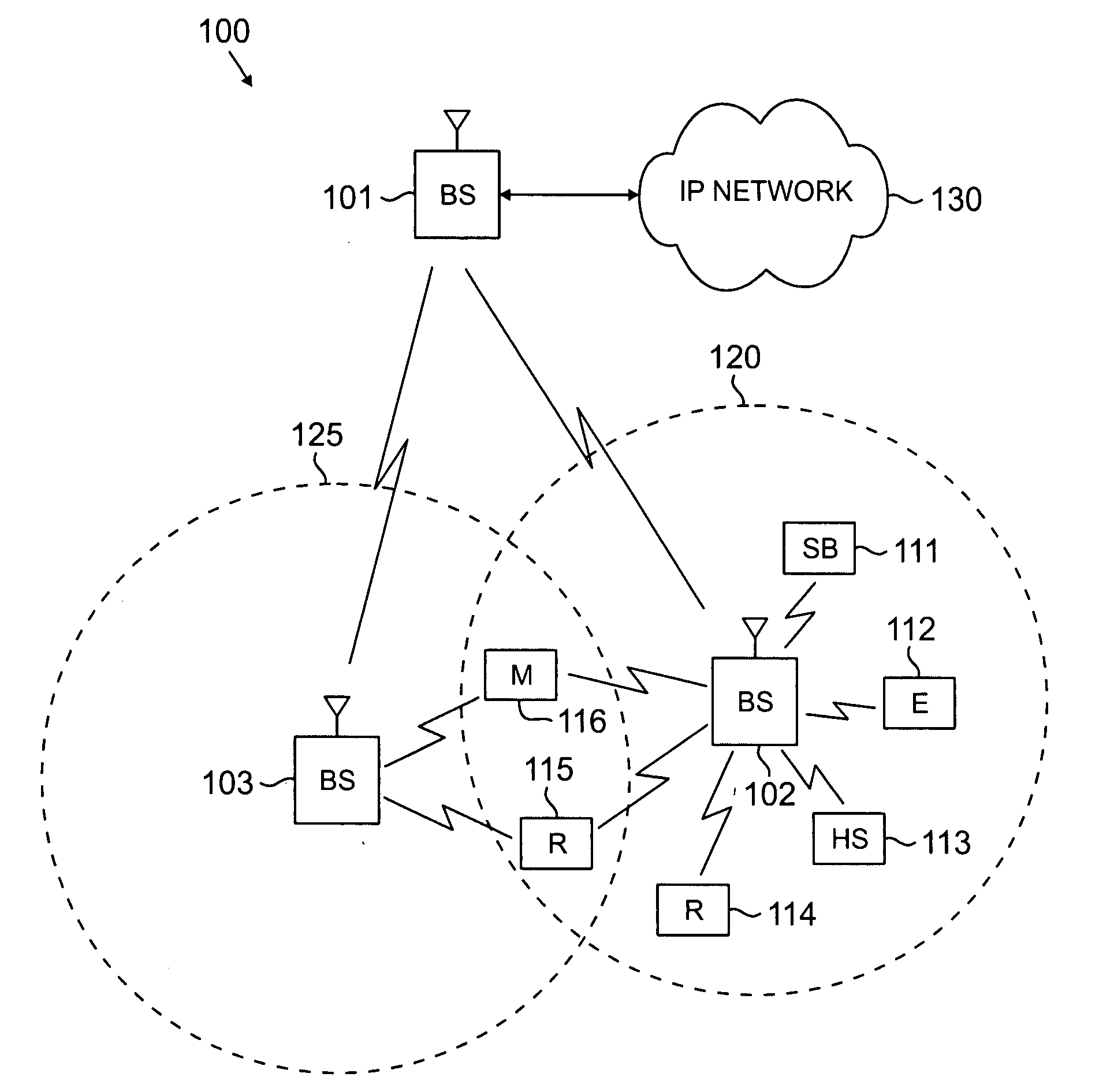
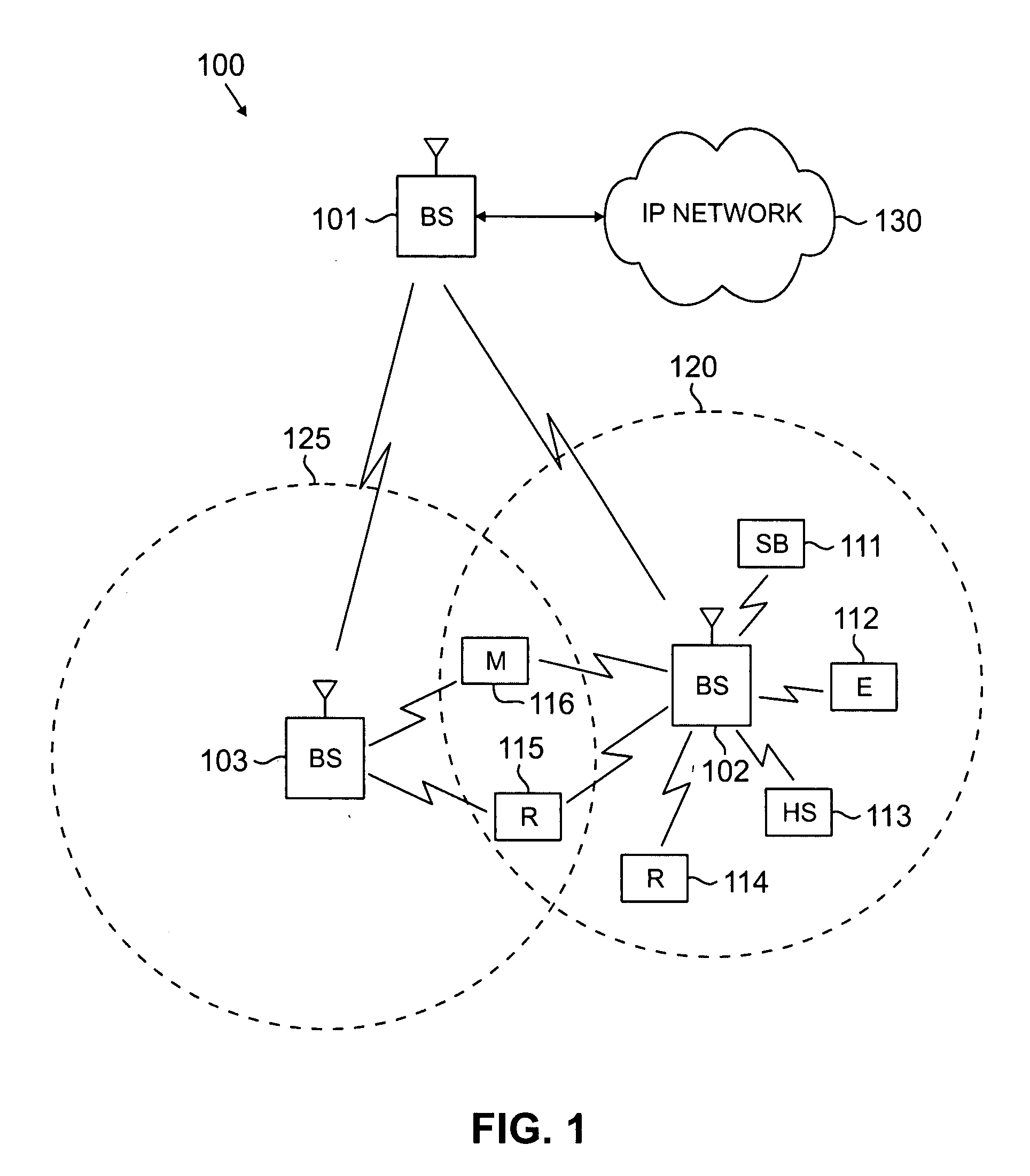
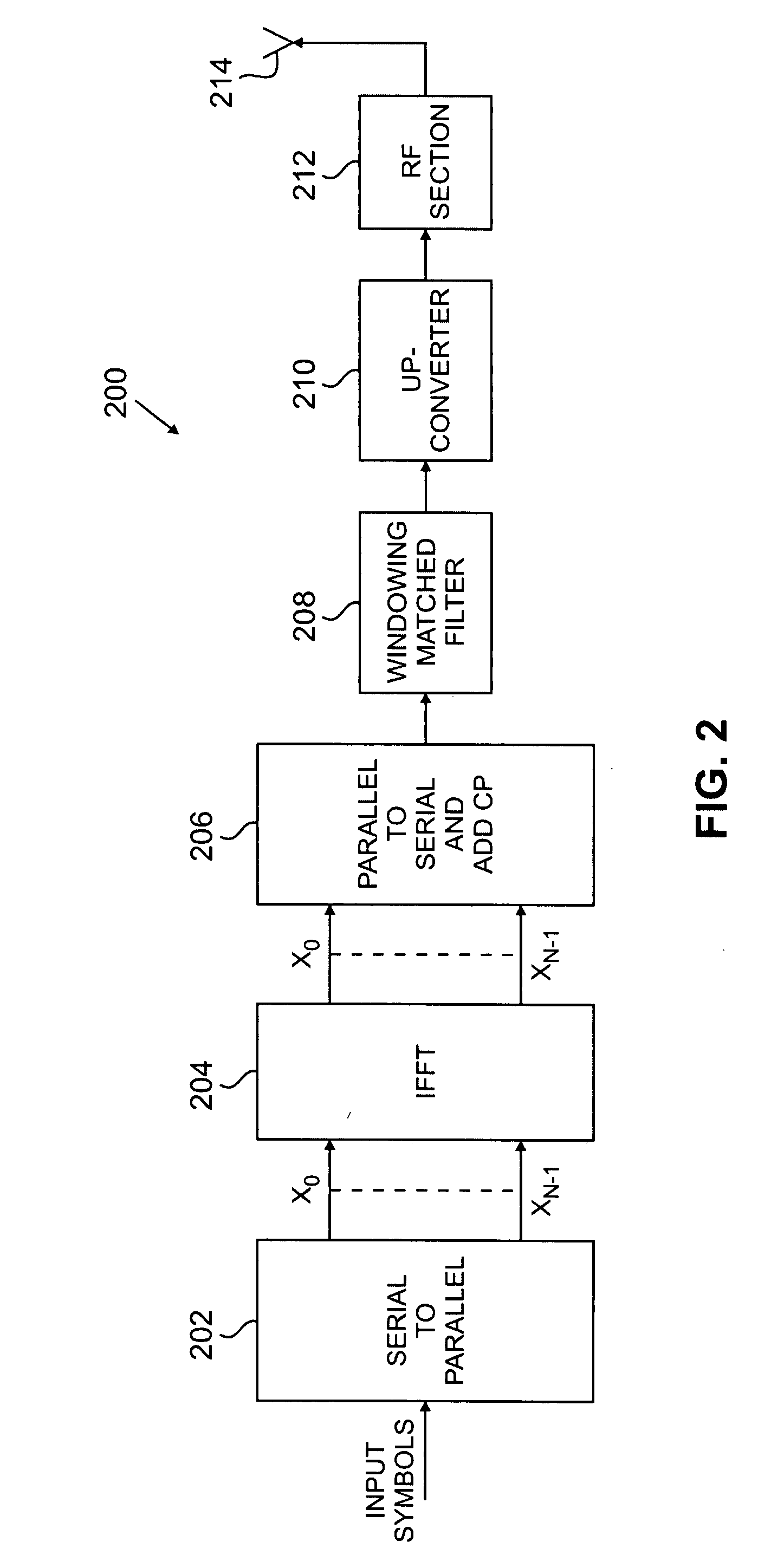
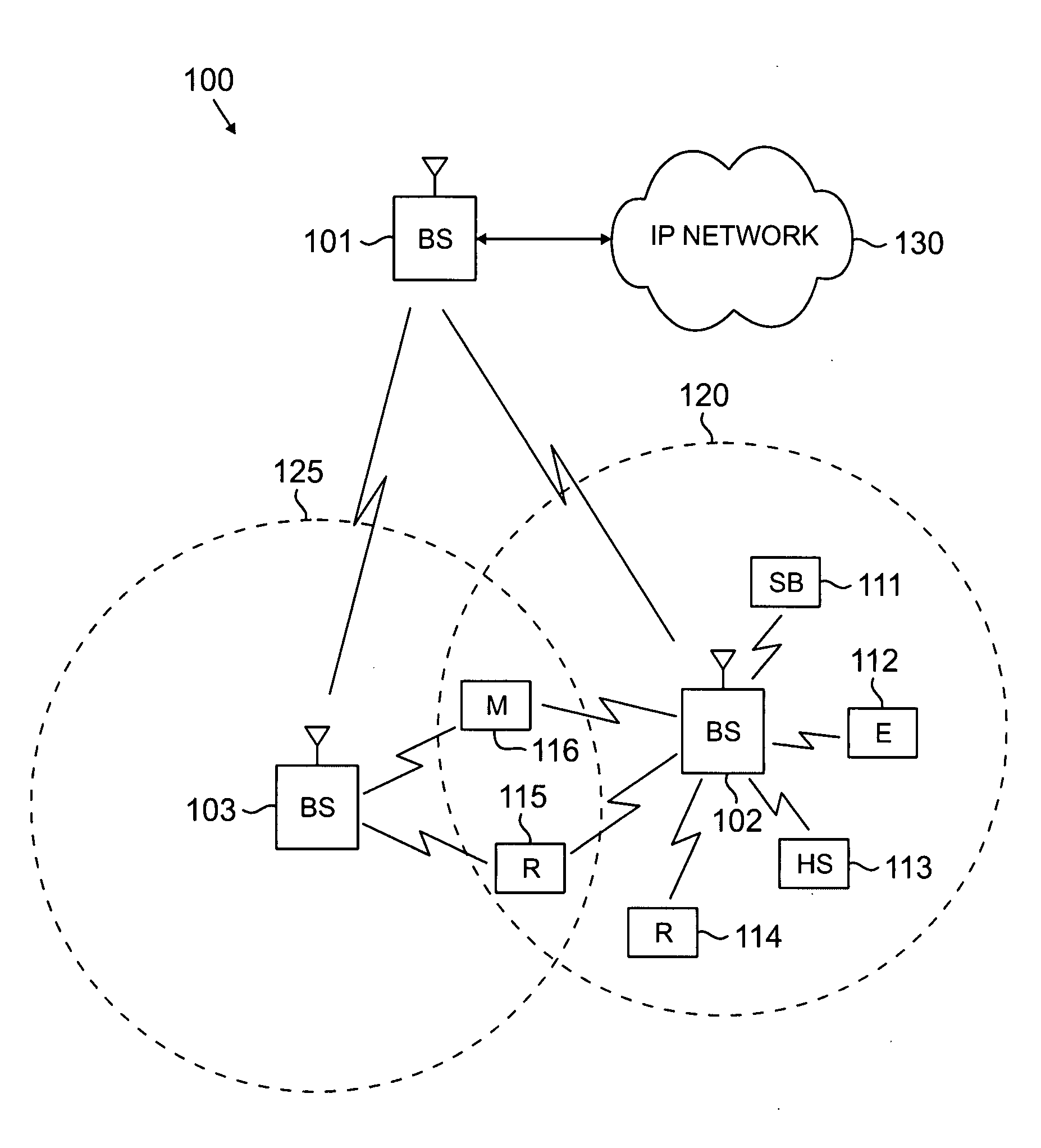
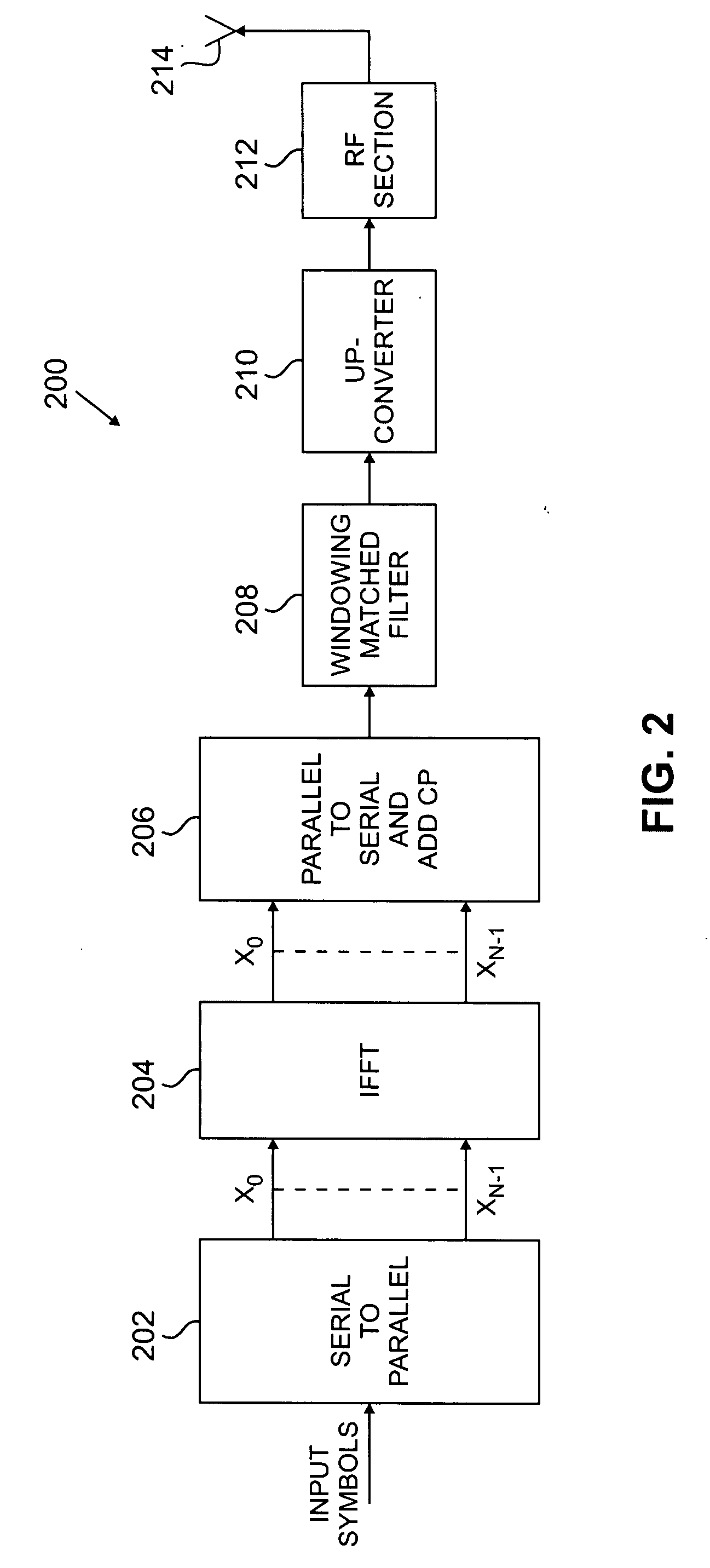
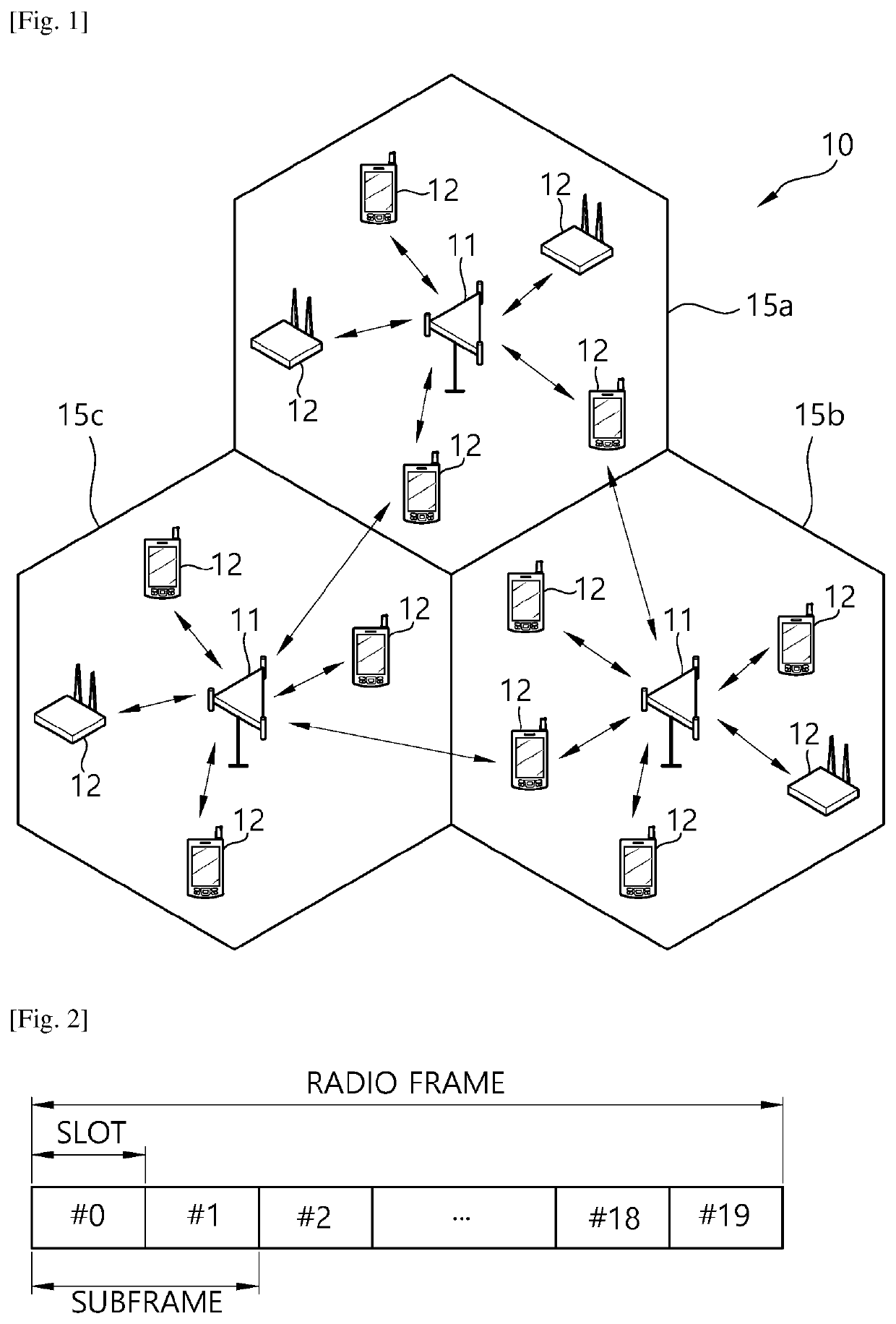
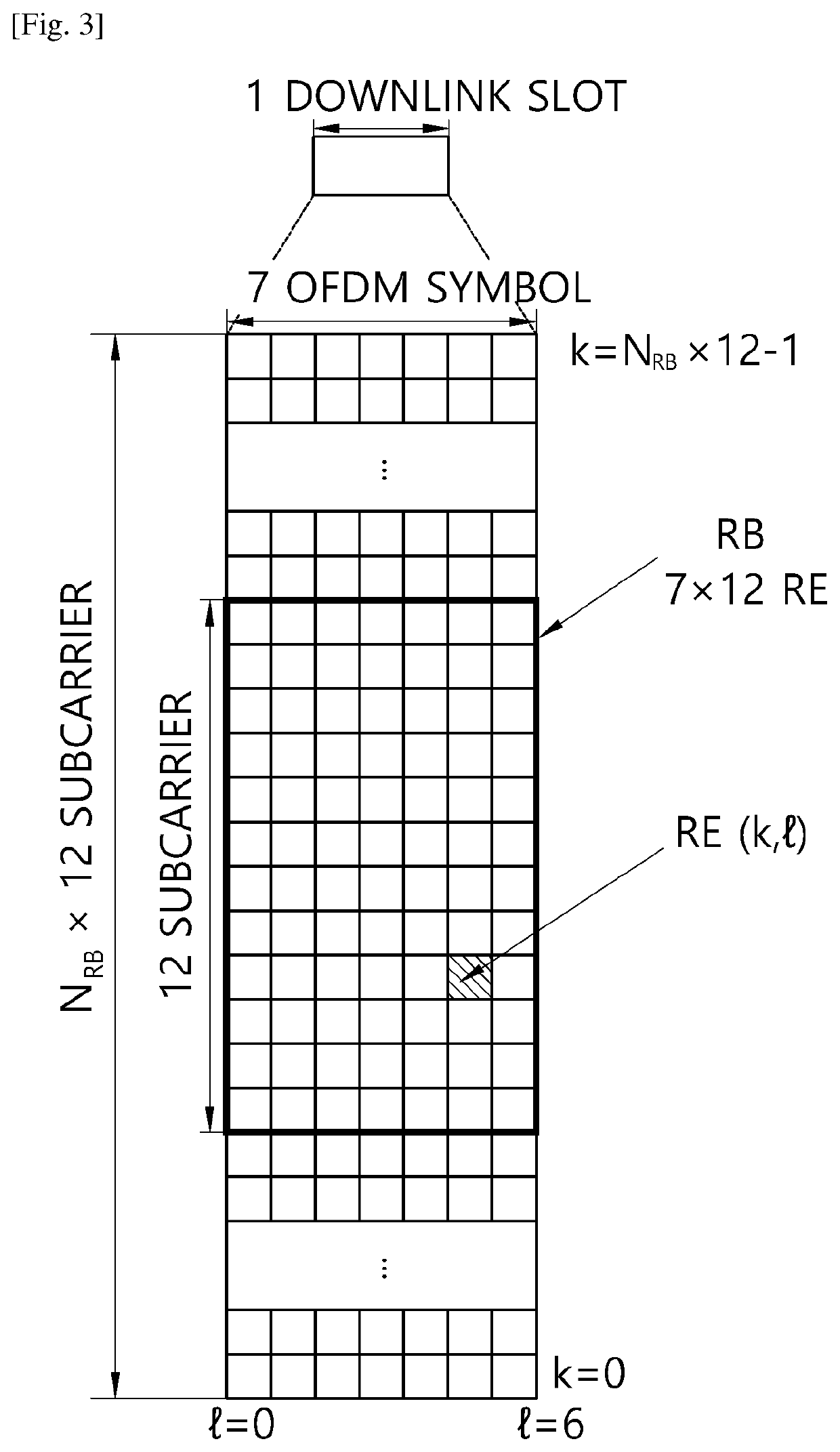
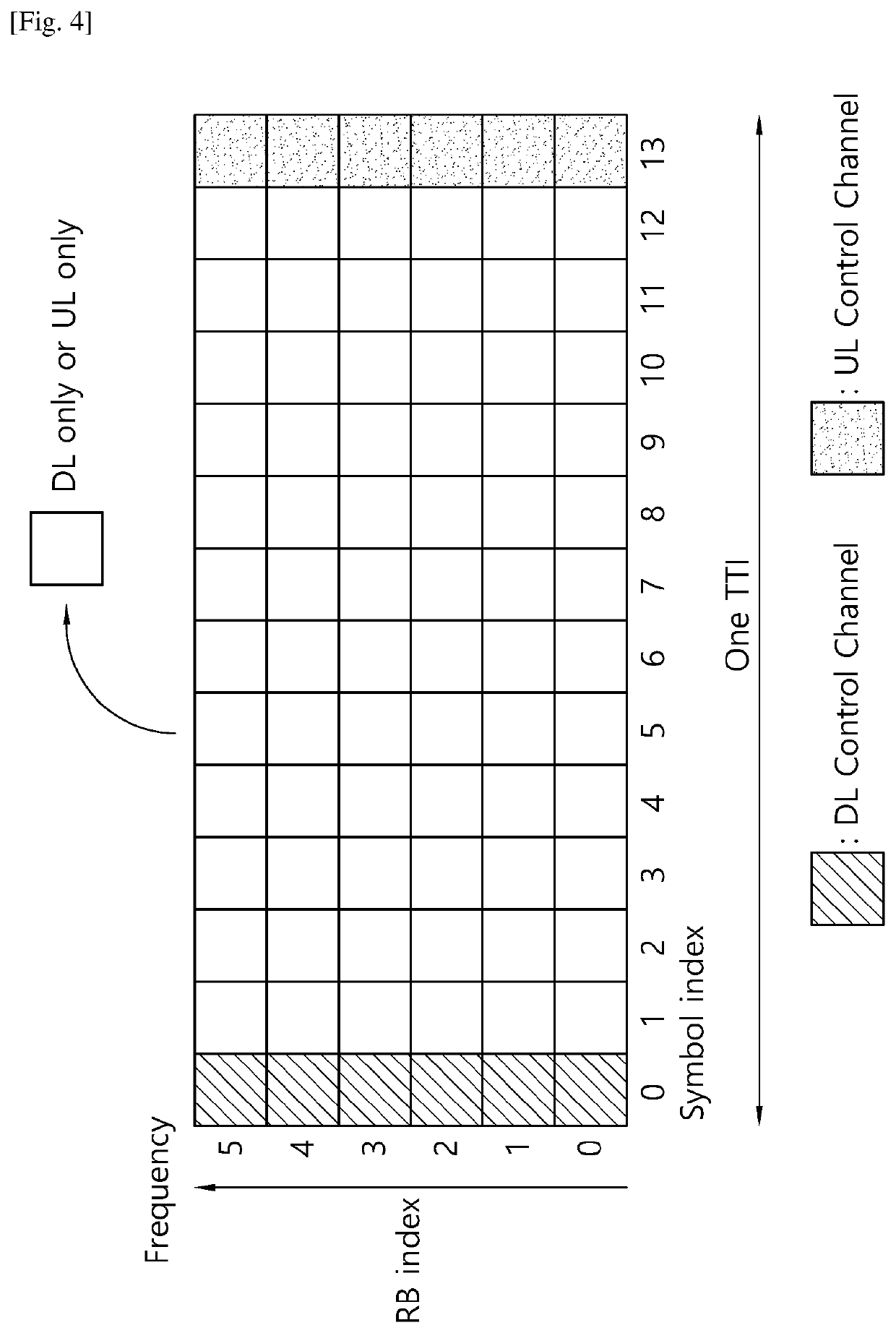
Flexible ofdm/ofdma frame structure for communication systems
ActiveUS20090185632A1Efficient use ofFacilitates spectrum sharingTransmission path divisionSignal allocationCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
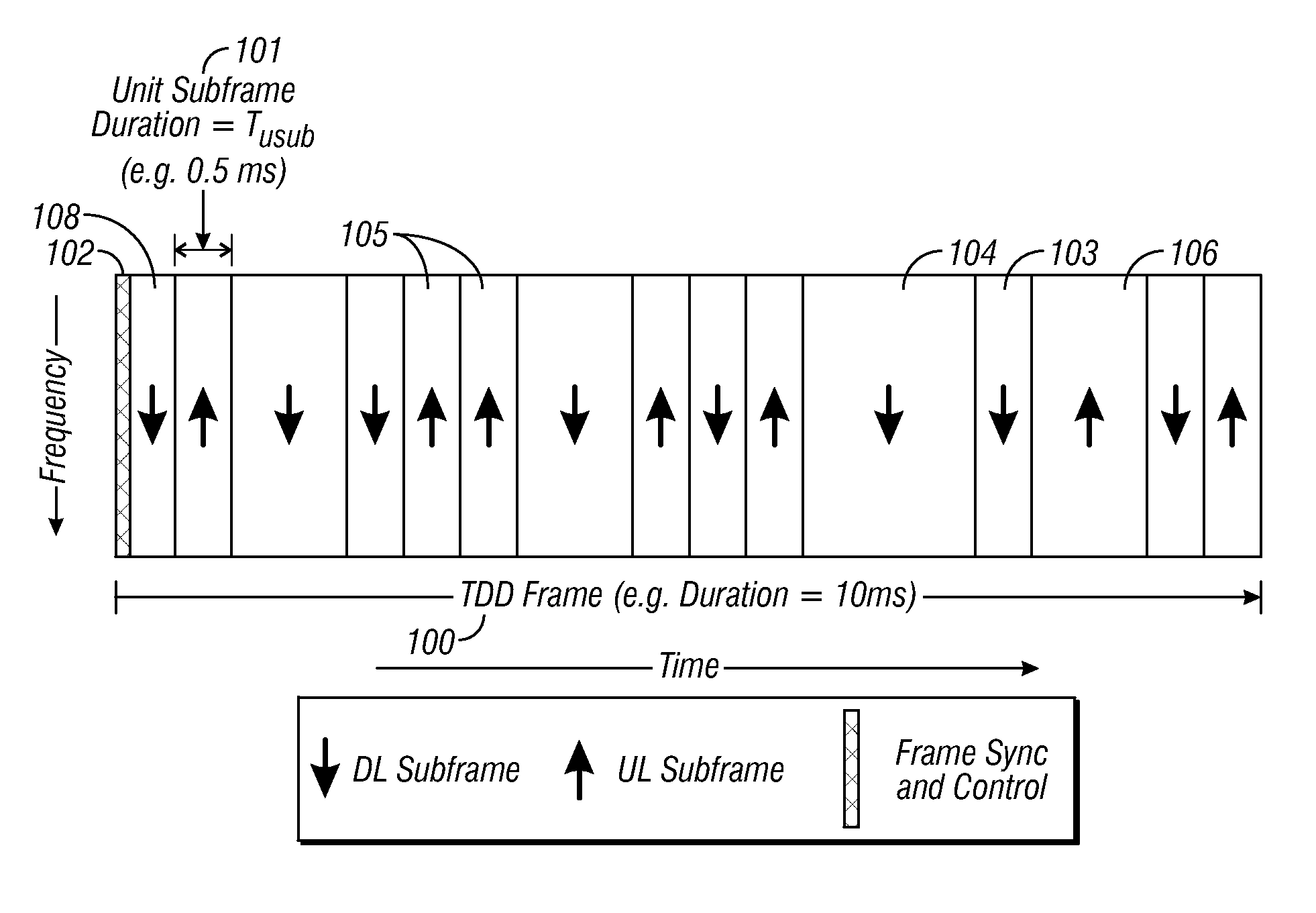
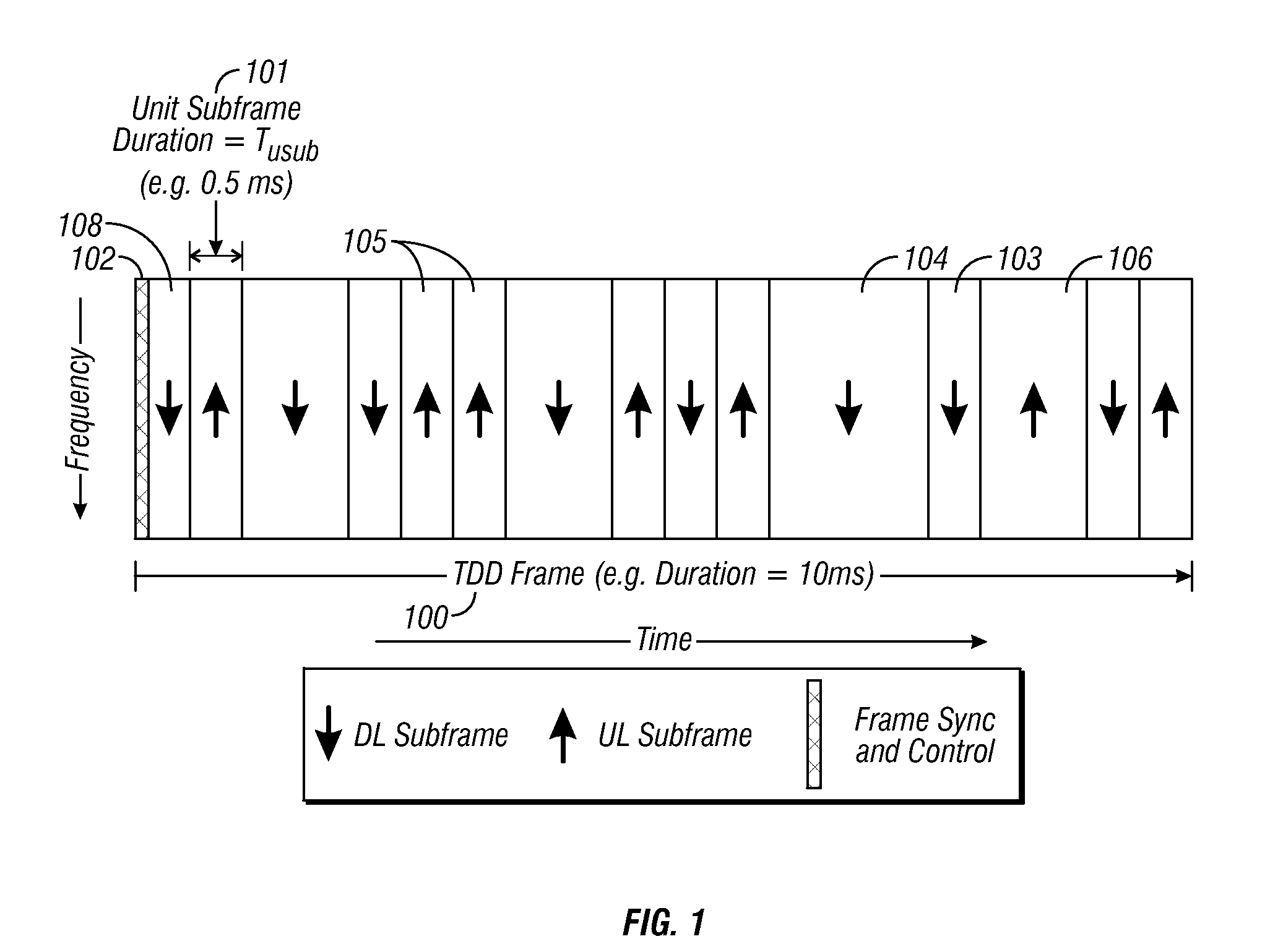
A flexible OFDM / OFDMA frame structure technology for communication systems is disclosed. The OFDM frame structure technology comprises a configurable-length frame which contains a variable length subframe structure to effectively utilize OFDM bandwidth. Furthermore, the frame structure facilitates spectrum sharing between multiple communication systems.
Owner:ZTE (USA) INC
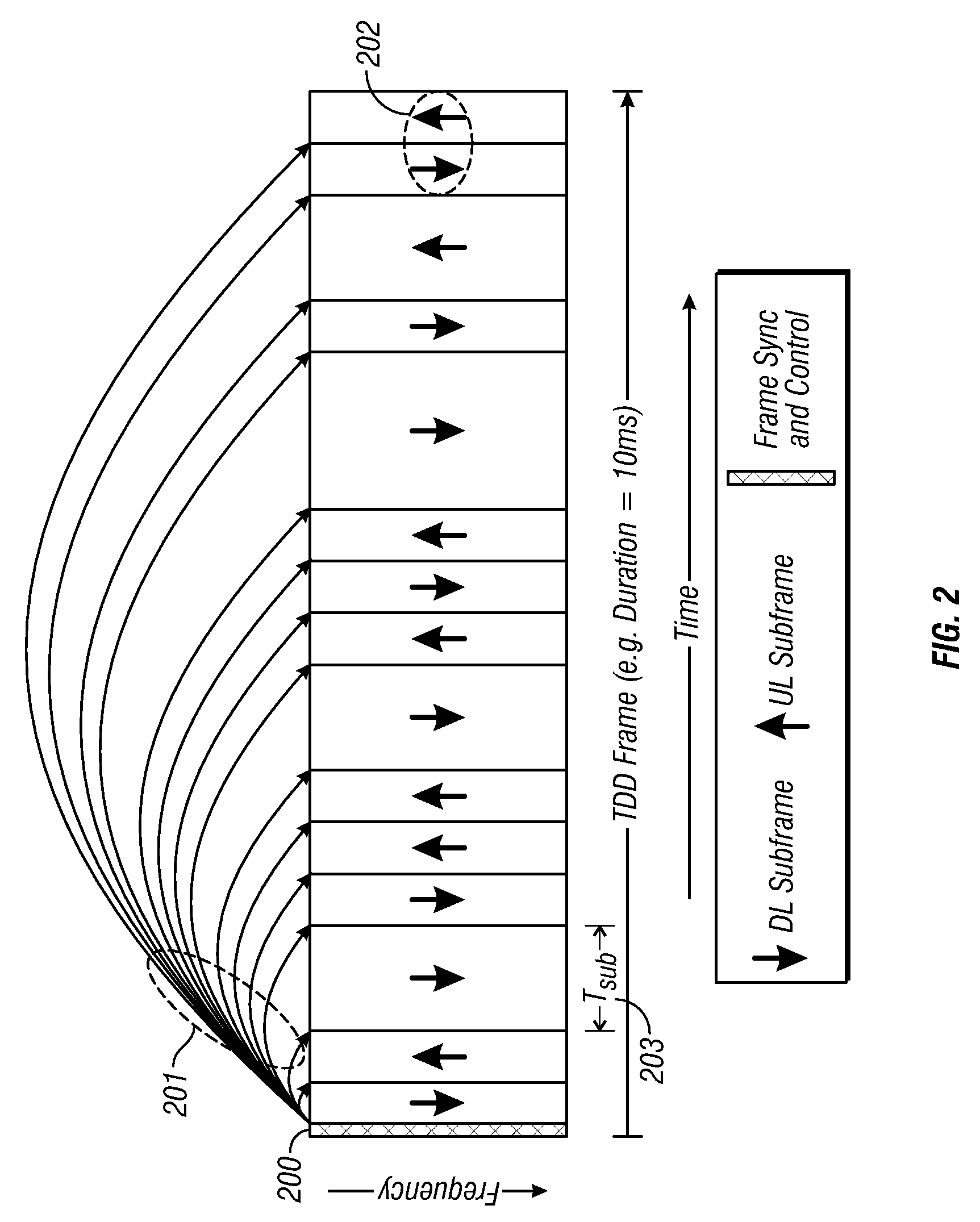
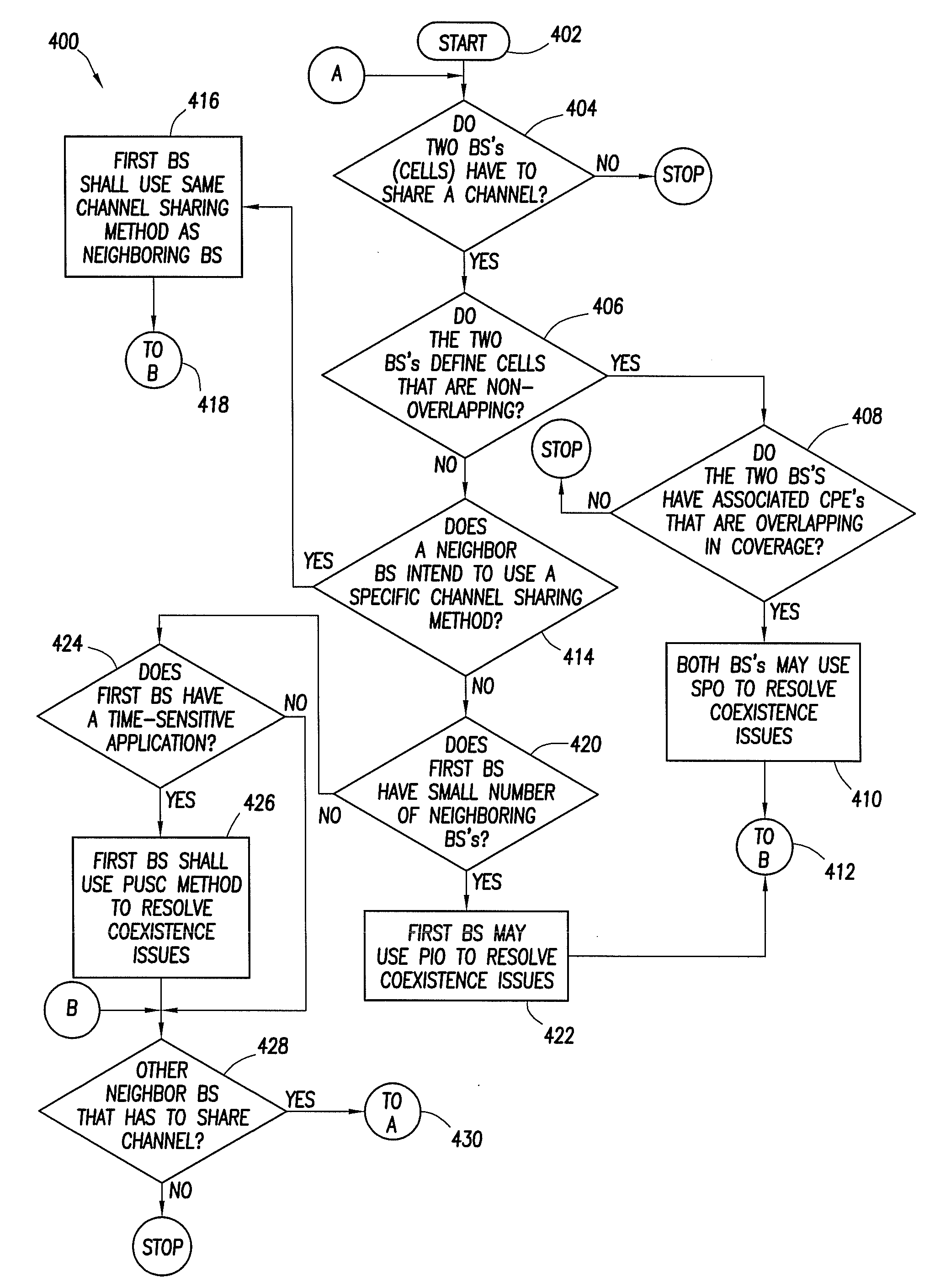
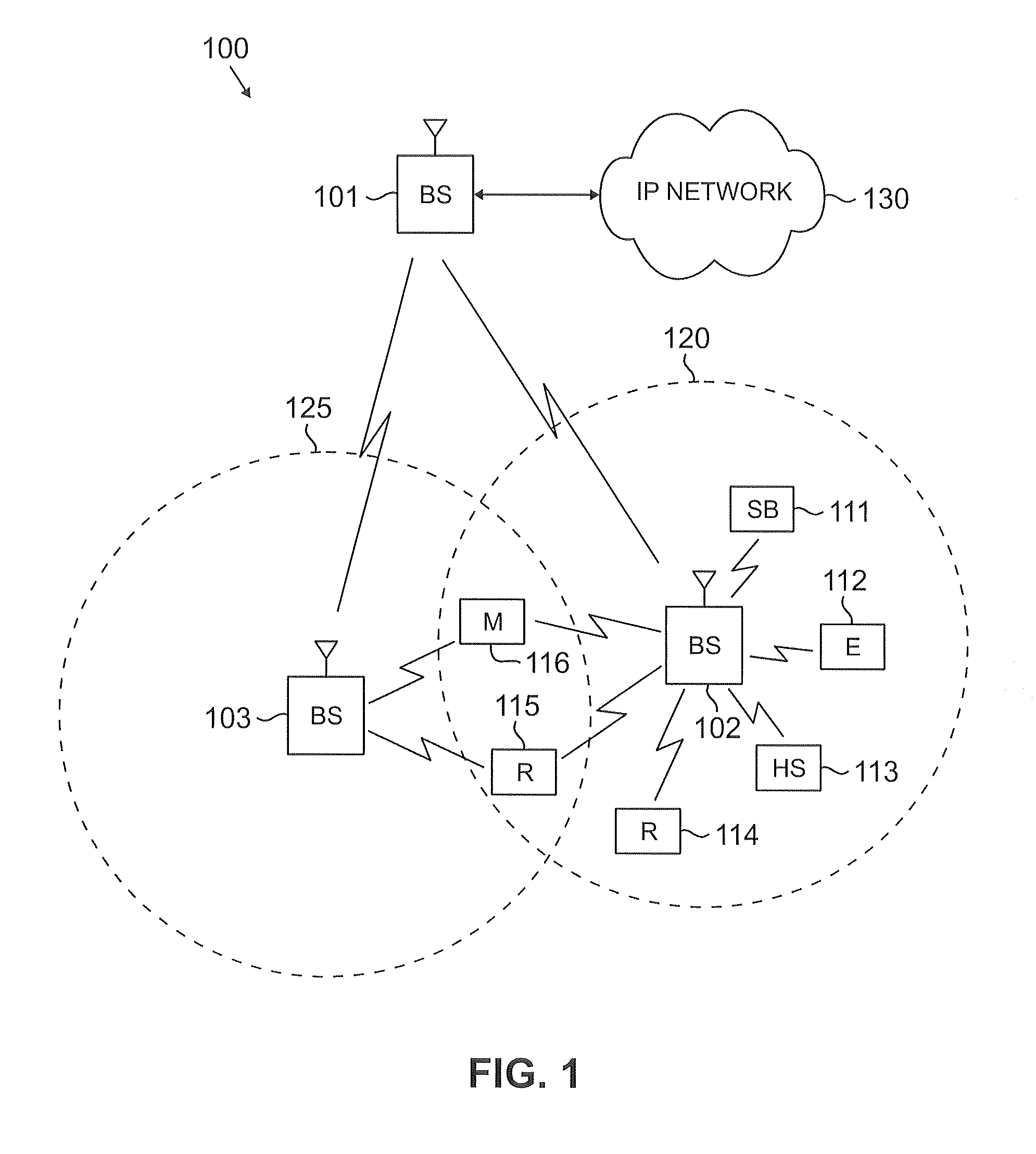
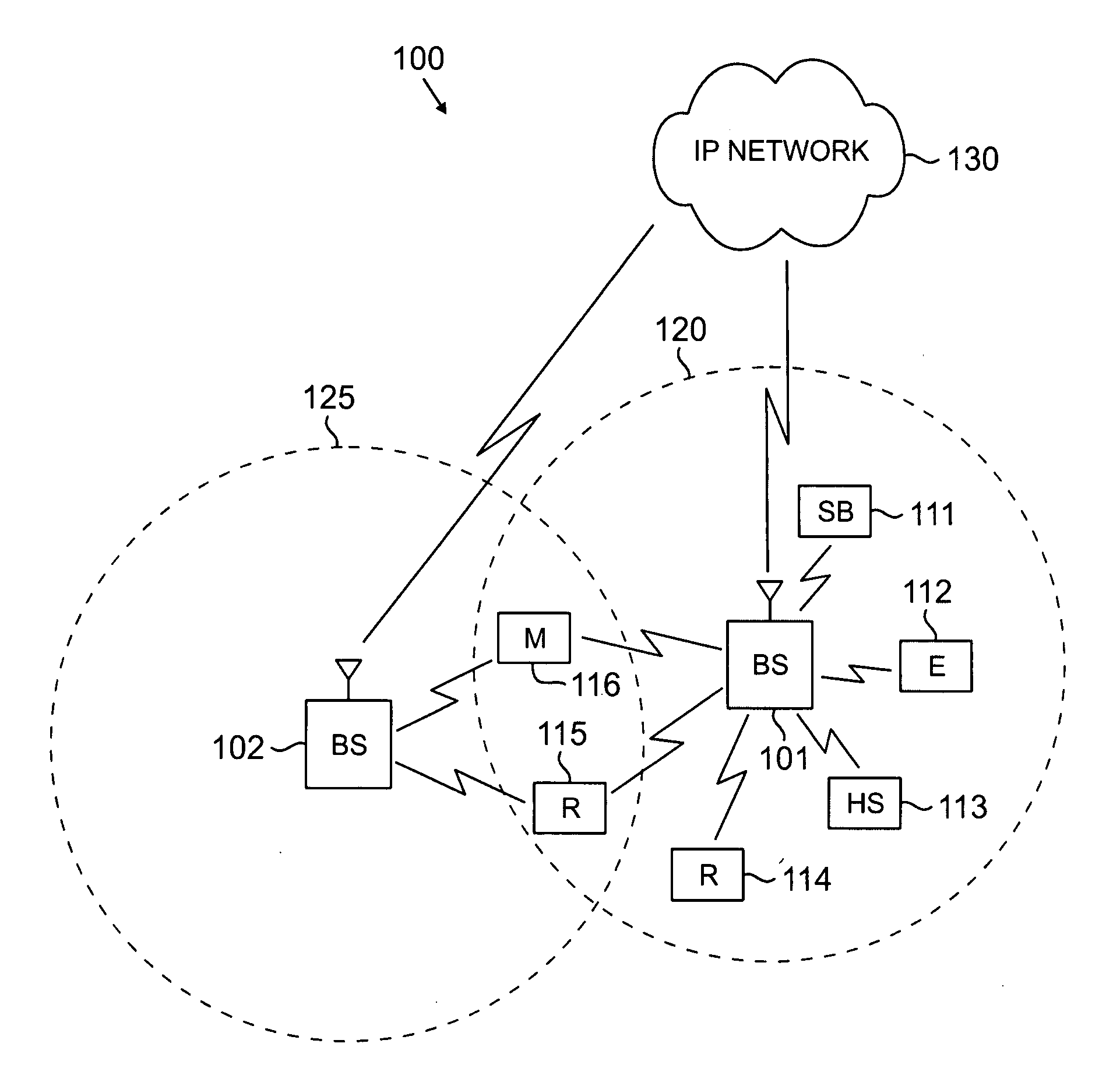
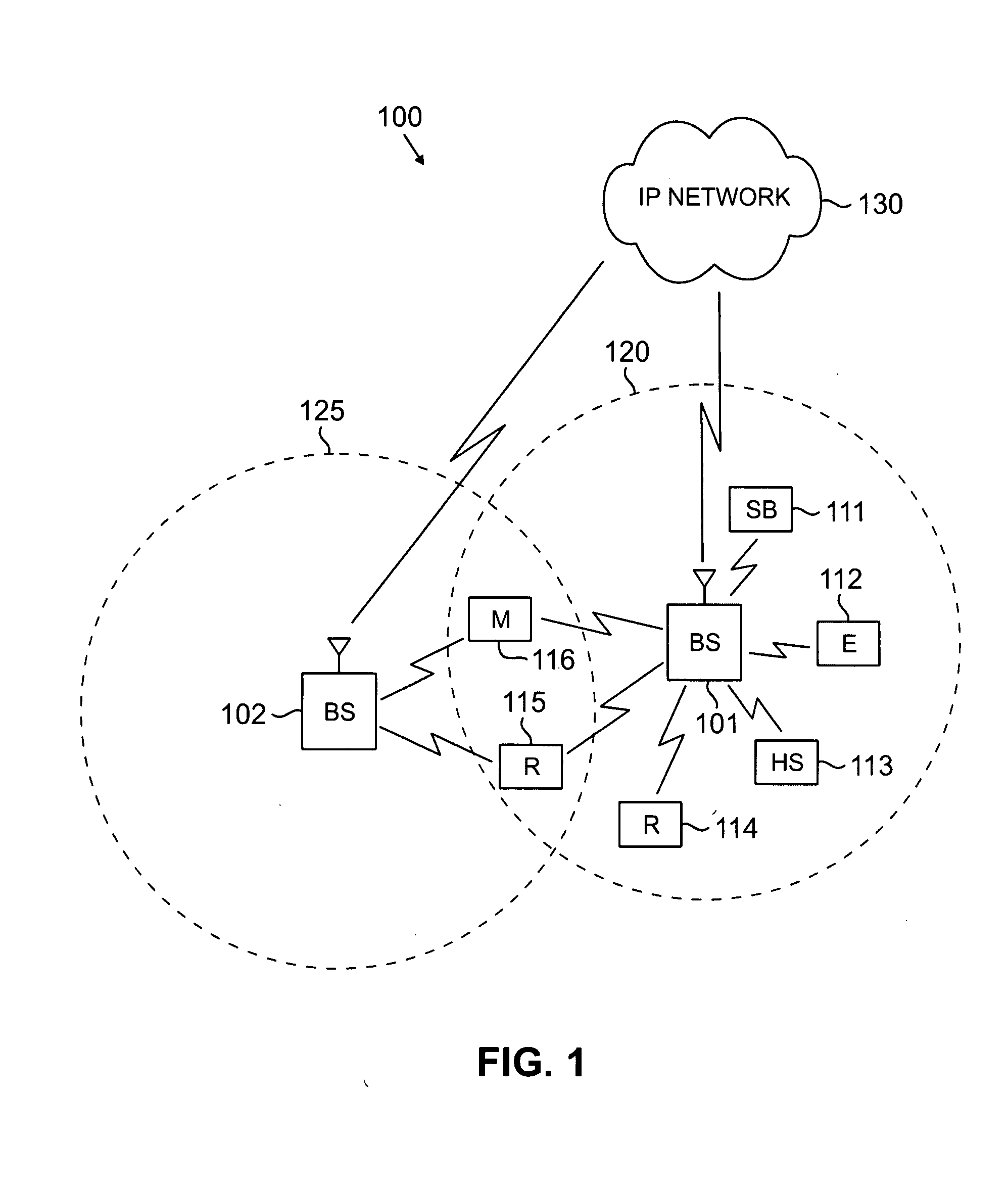
Method and system for sharing spectrum in a wireless communications network
InactiveUS20070223419A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesFrequency spectrumCommunication unit
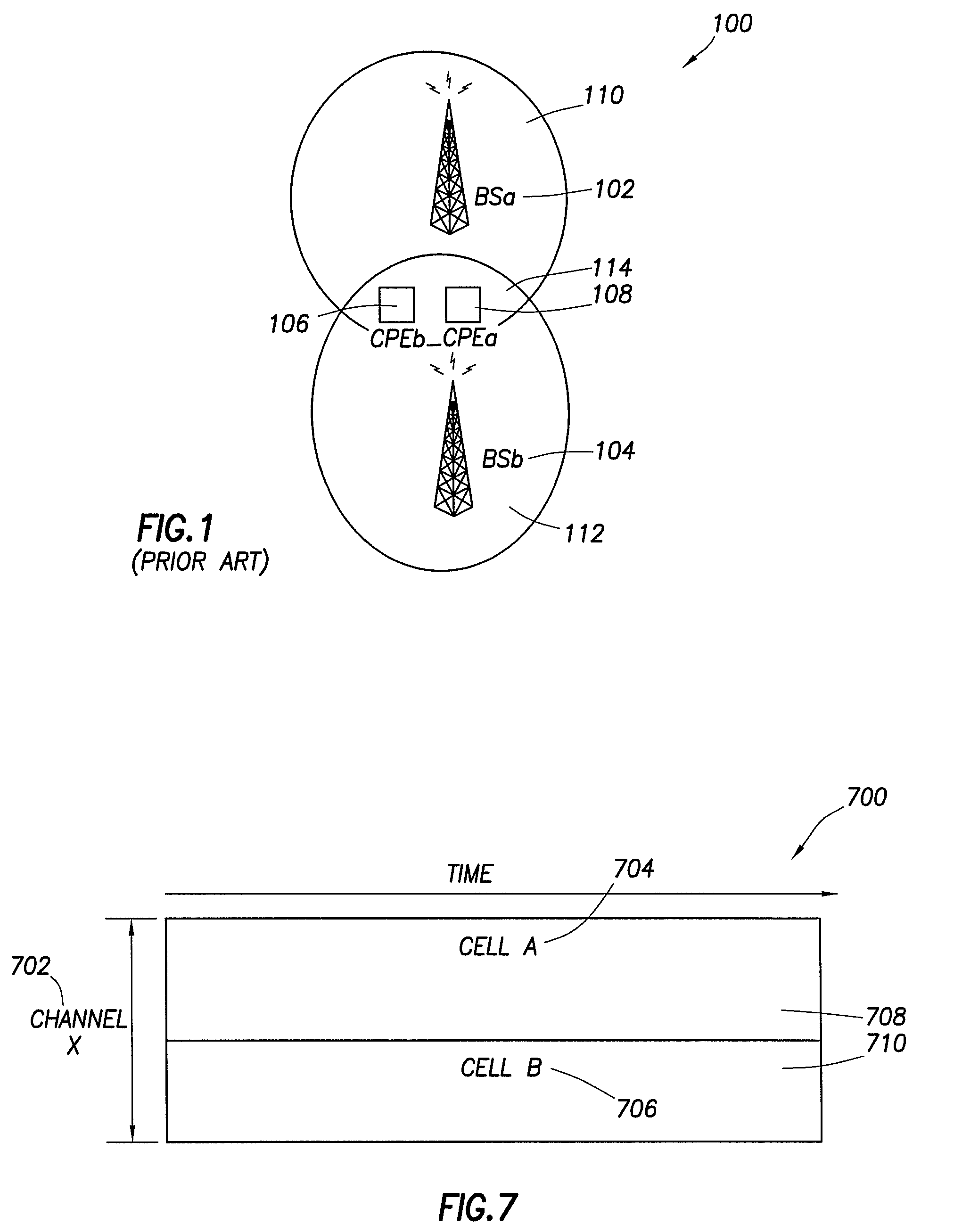
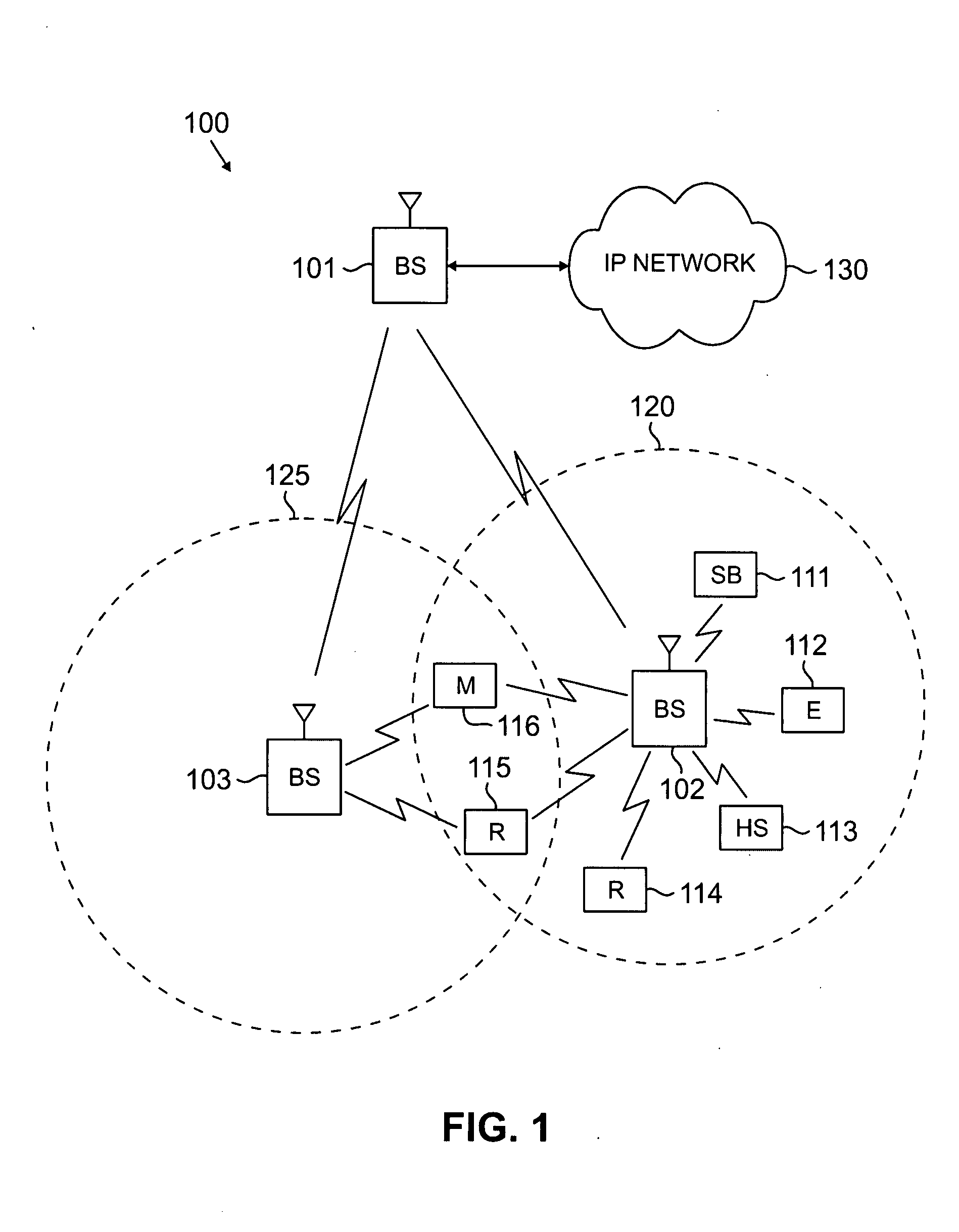
A method and system for sharing spectrum in a wireless communications network are disclosed. As one example, a method for sharing spectrum is disclosed, which includes the steps of determining if two base stations in the wireless communications network are to share a frequency spectrum, and if two base stations in the wireless communications network are to share a frequency spectrum, determining if the two base stations in the wireless communications network have non-overlapping wireless communications coverage. Also, if the two base stations in the wireless communications network have non-overlapping wireless communications coverage, determining if a first mobile communications unit associated with a first base station of the two base stations has wireless communications coverage that overlaps with wireless communications coverage of a second mobile communications unit associated with a second base station of the two base stations, and if the first mobile communications unit has wireless communications coverage that overlaps with wireless communications coverage of the second mobile communications unit, enabling the two base stations to use a synchronized parallel operation spectrum sharing mode for communications. Also, a Contention-for-being-Master approach is disclosed as one primary method for sharing spectrum, which can be treated separately from all other contention methods, or combined with the exemplary contention method disclosed herein.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transmit co-channel spectrum sharing
ActiveUS8502733B1Reduce the possibilityOvercome limitationsPolarisation/directional diversityPosition fixationAccess networkFrequency spectrum
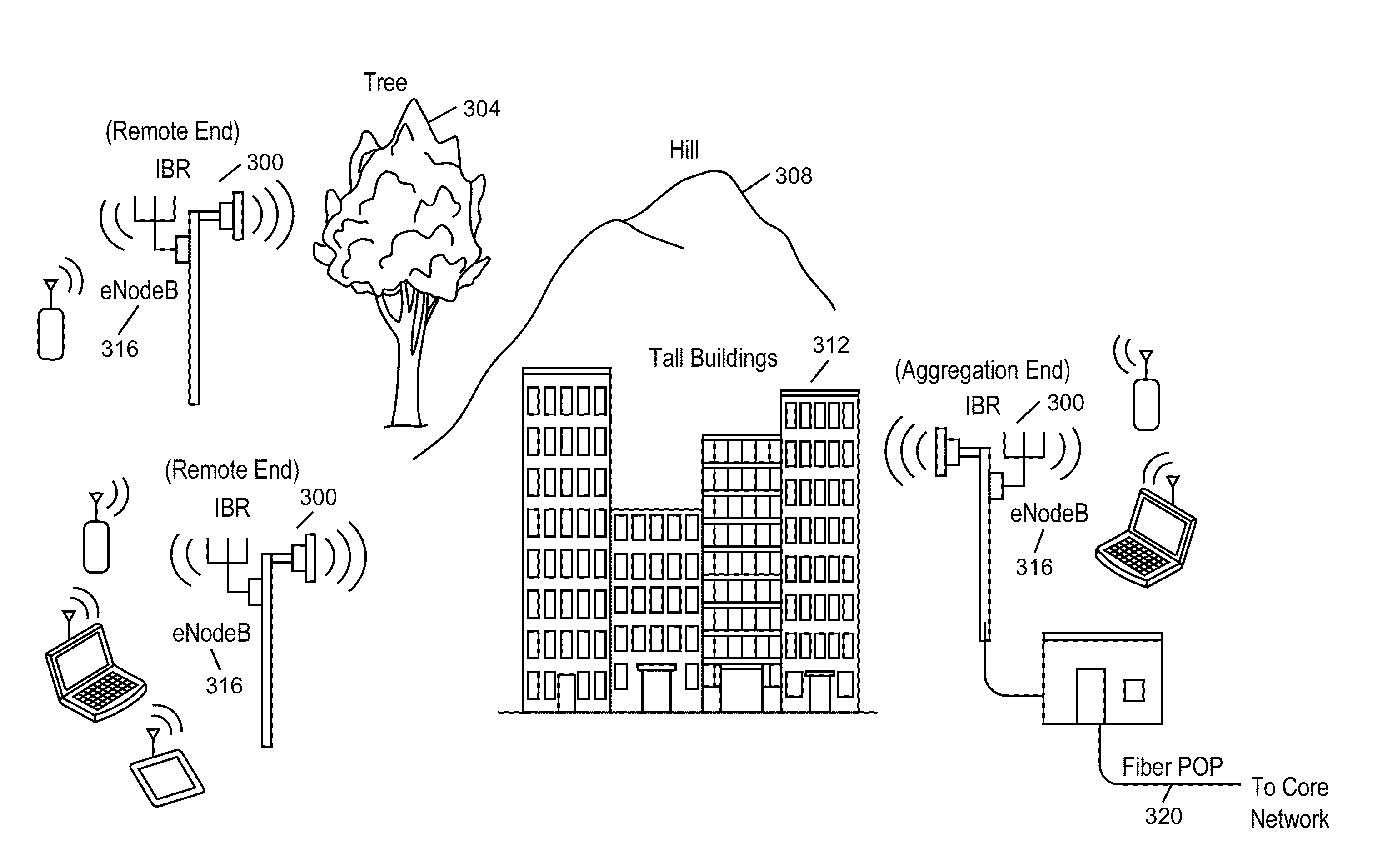
An intelligent backhaul system is disclosed for deployment in the presence of existing radio systems. A backhaul system for co-channel deployment with existing licensed and unlicensed wireless networks, including conventional cellular backhaul radios, Common Carrier Fixed Point-to-Point Microwave Service, Private Operational Fixed Point-to-Point Microwave Service and other FCC 47 C.F.R. §101 licensed microwave networks is disclosed. Processing and network elements to manage and control the deployment and management of backhaul of radios that connect remote edge access networks to core networks in a geographic zone which co-exist with such existing systems or other sources of interference within a radio environment are also disclosed.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
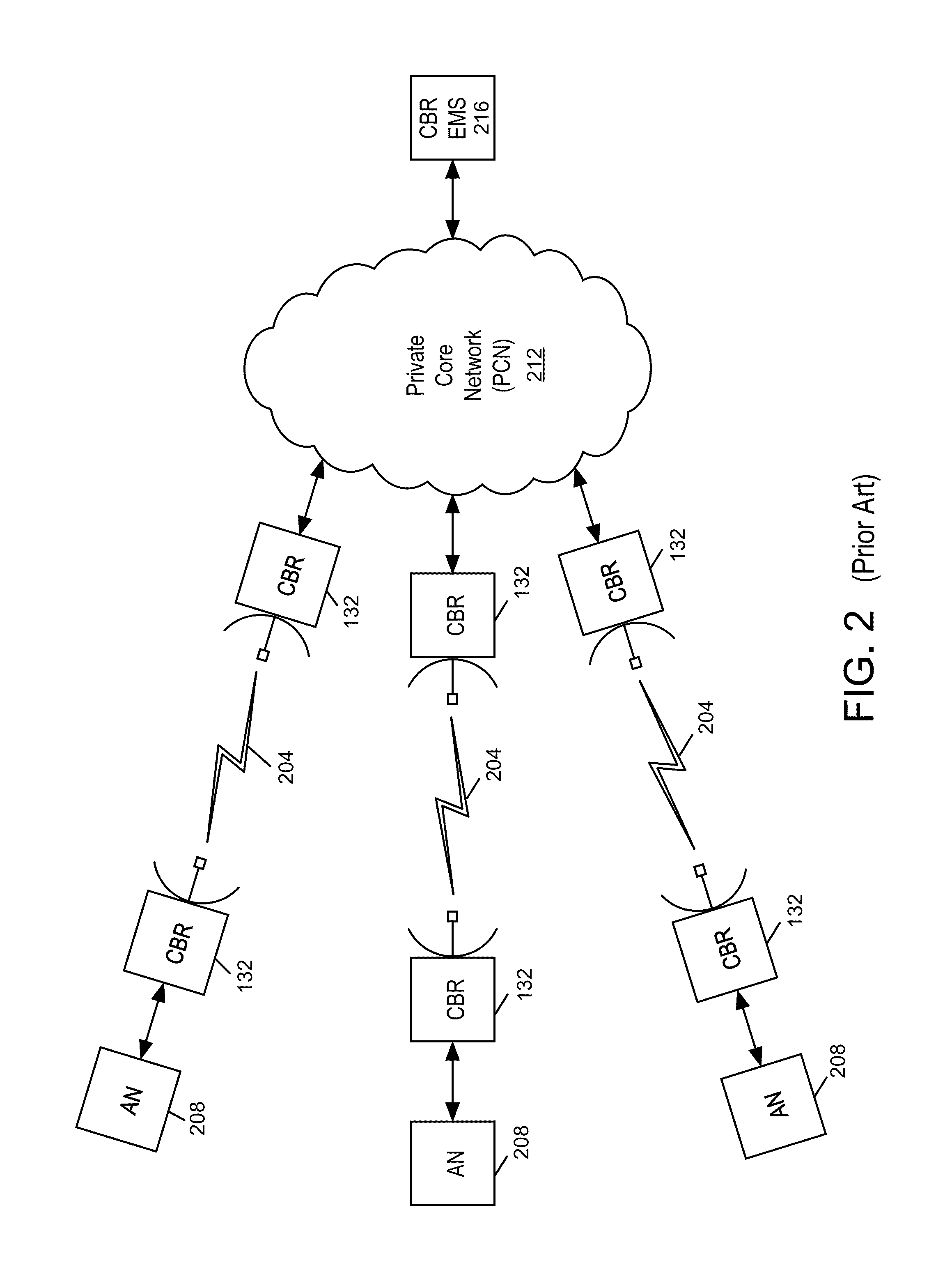
Synchronous spectrum sharing by dedicated networks using OFDM/OFDMA signaling
ActiveUS20080095100A1Transmission path divisionSignal allocationCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
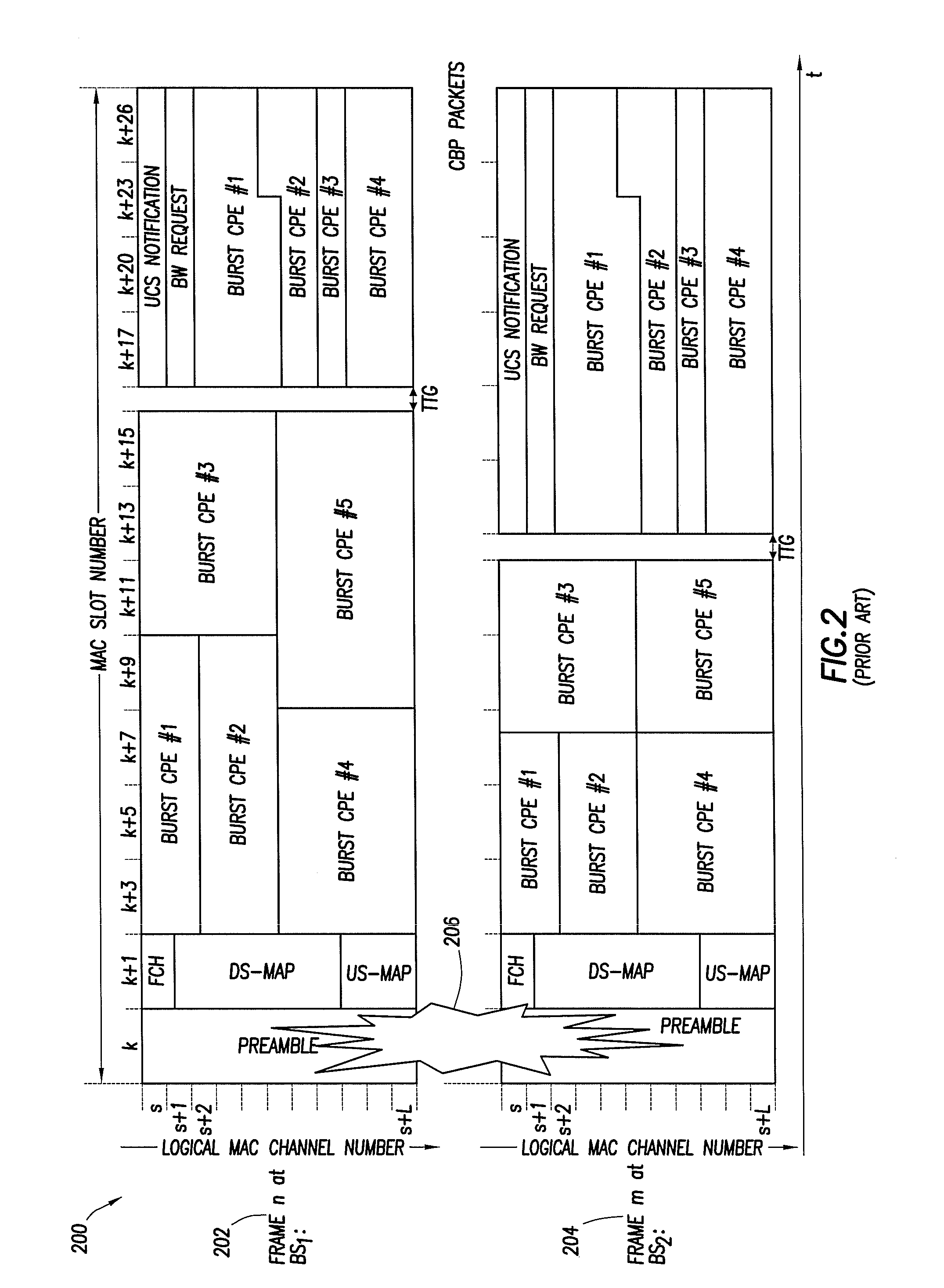
A system and method for synchronous spectrum sharing for a dedicated network in a wireless communication system based on orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) or orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) signaling is disclosed. The system and method includes detecting a frame of a broadcast waveform and extracting idle spectrum information associated with the dedicated subchannel to the secondary user node. The system allows transmitting data from the secondary user node in unused symbol slots identified in the idle spectrum information thereby making efficient use of unused or idle spectrum. Accordingly, secondary users of the wireless communication system can dynamically form ad-hoc mesh network communications in fixed or mobile scenarios.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Synchronous spectrum sharing based on OFDM/OFDMA signaling
InactiveUS8520606B2Spectral gaps assessmentTransmission path divisionFrequency spectrumCommunications system
A system and method for synchronous spectrum sharing for use in a wireless communication system based on orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) or orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) signaling is disclosed. The system includes a frame detector configured to detect a frame of a broadcast waveform and extract idle spectrum information for the frame to the secondary user node. The system allows transmitting data from the secondary user node in unused symbol slots identified in the idle spectrum information thereby making efficient use of unused or idle spectrum. Accordingly, secondary users of the wireless communication system can dynamically form ad-hoc mesh network communications in fixed or mobile scenarios.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
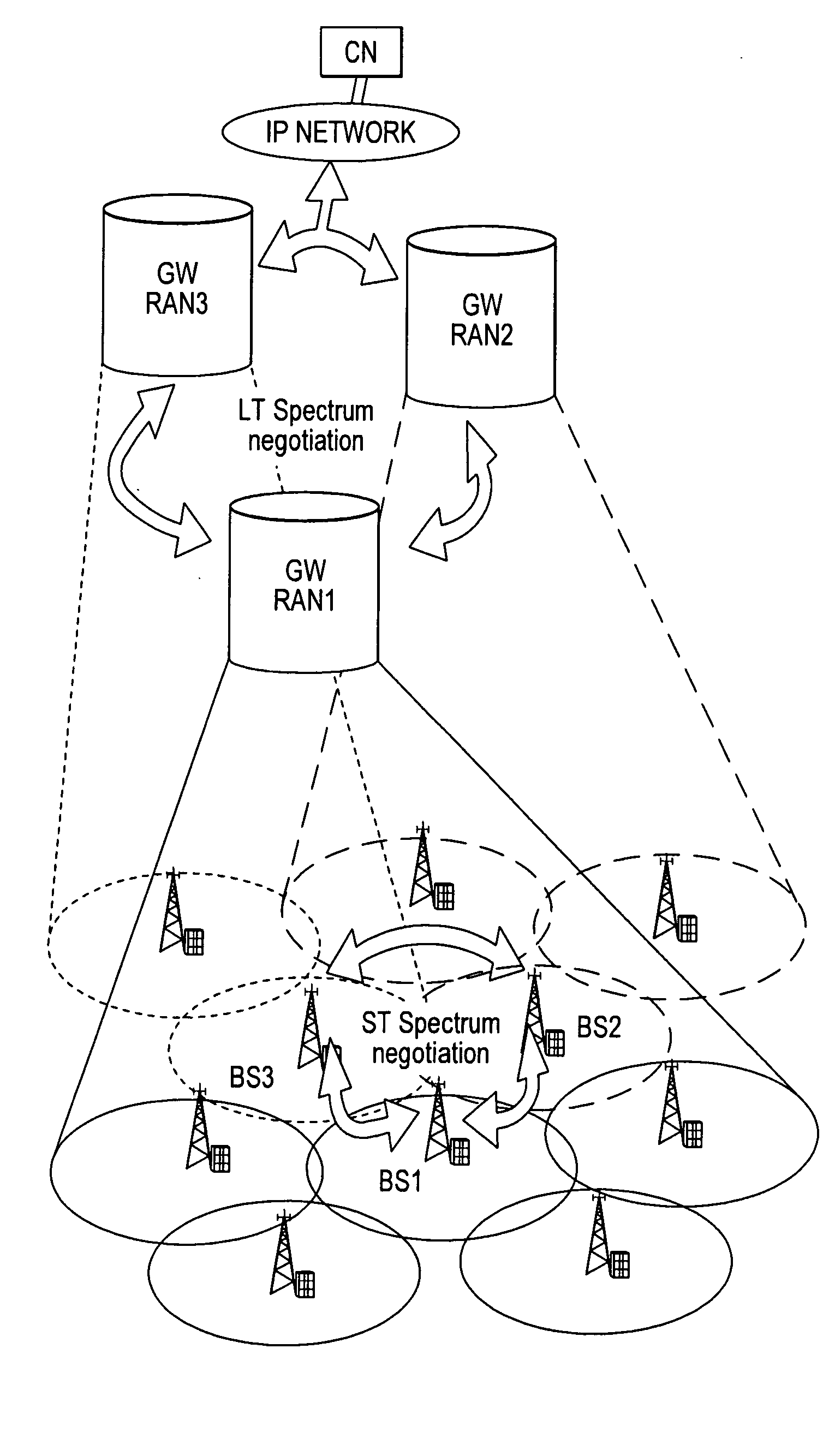
Communication systems
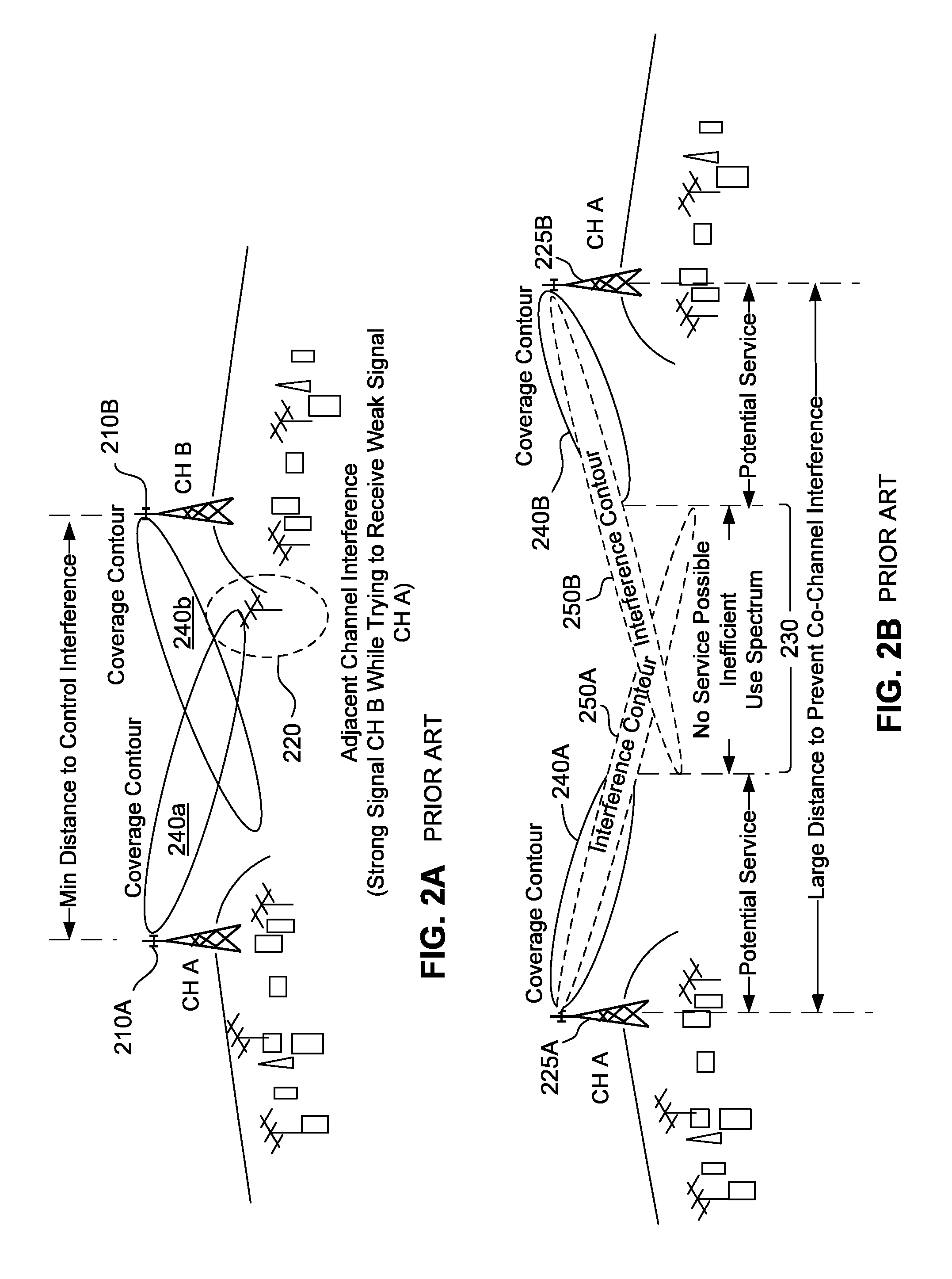
ActiveUS20090191906A1Lower Level RequirementsReduce noise levelNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumDynamic channel
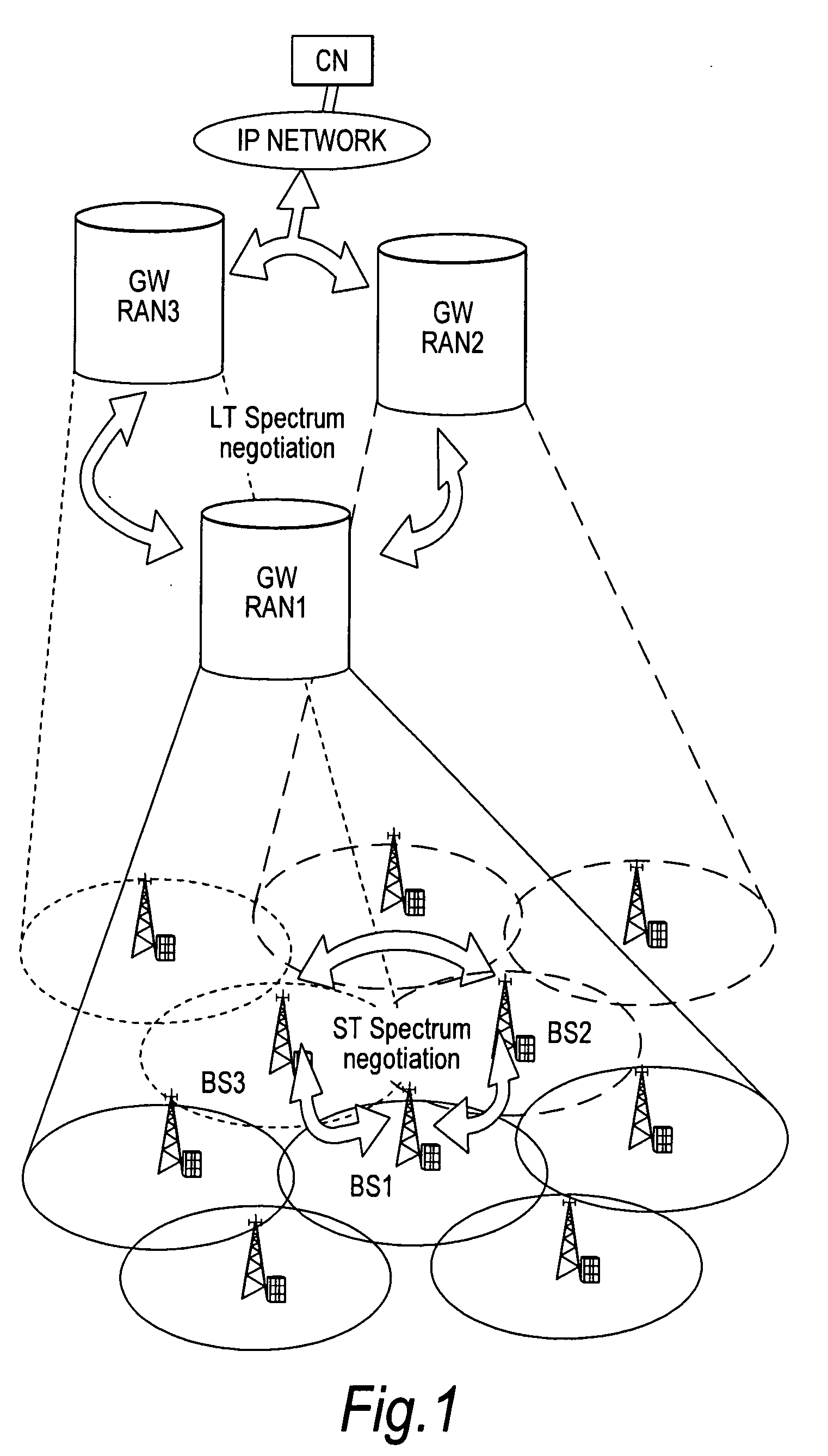
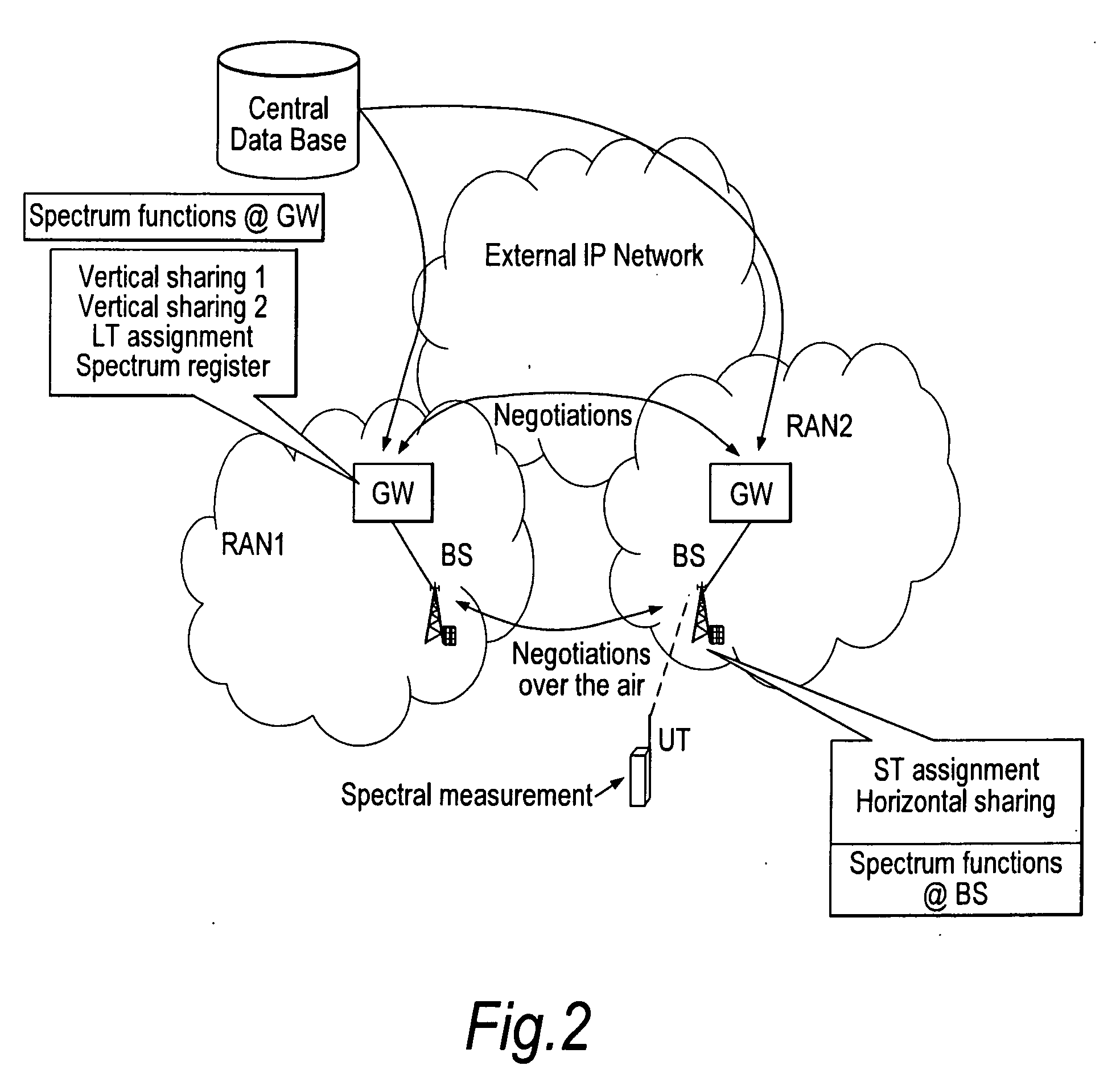
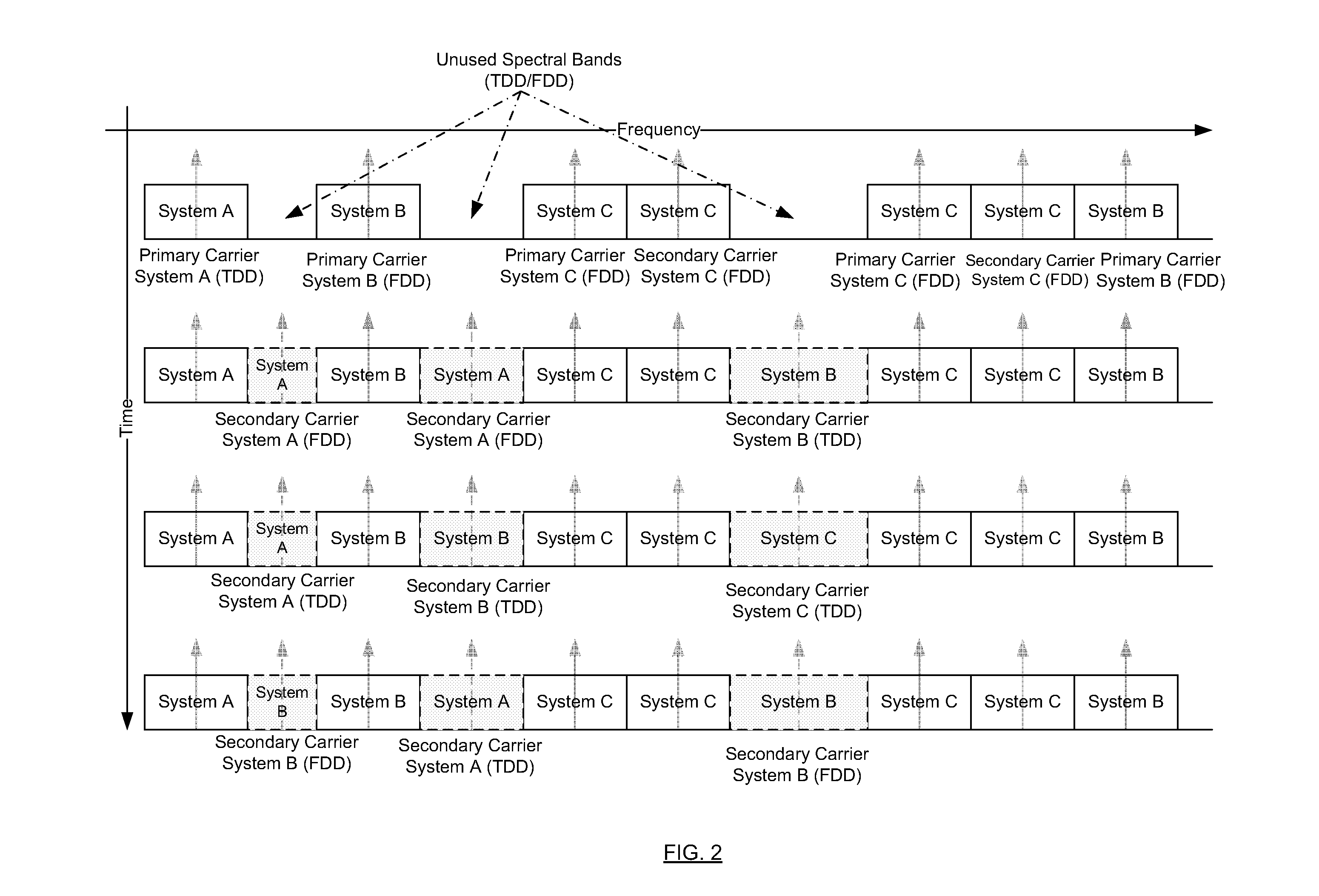
A wireless communication system is comprised of multiple radio access networks—RANs—which at least partly share the same frequency spectrum. Each RAN is provided with a gateway—GW—(GW1, GW2, GW3) for managing the network. Spectrum sharing in the system is achieved through a hierarchy of processes including long-term—LT—spectrum assignment, short-term—ST—spectrum assignment, and dynamic channel allocation, the latter process assigning sub-channels to base stations (BS1, . . . BS5; BS6, . . . BS10; BS11, . . . BS16) in each RAN. However, so-called “red” sub-channels (subject to interference) are liable to arise.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Flexible ofdm/ofdma frame structure for communication systems
ActiveUS20110096783A1Efficient use ofFacilitates spectrum sharingModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
A flexible OFDM / OFDMA frame structure technology for communication systems is disclosed. The OFDM frame structure technology comprises a configurable-length frame which contains a variable length subframe structure to effectively utilize OFDM bandwidth. Furthermore, the frame structure facilitates spectrum sharing between multiple communication systems.
Owner:ZTE (USA) INC
Flexible ofdm/ofdma frame structure for communication systems
InactiveUS20110103406A1Efficient use ofFacilitates spectrum sharingModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
A flexible OFDM / OFDMA frame structure technology for communication systems is disclosed. The OFDM frame structure technology comprises a configurable-length frame which contains a variable length subframe structure to effectively utilize OFDM bandwidth. Furthermore, the frame structure facilitates spectrum sharing between multiple communication systems.
Owner:ZTE (USA) INC
Spectrum sharing in a wireless communication network
InactiveUS20080112308A1Electric signal transmission systemsTransmission path divisionCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
A system and method for synchronous spectrum sharing for use in a wireless communication system based on orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) or orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) signaling is disclosed. The system includes a frame detector configured to detect a frame of a broadcast waveform and extract sub-carrier information from the frame. Sub-carrier information may include information on usable sub-carrier and pilot sub-carriers for secondary users. The system allows transmitting data from the secondary user node in unused sub-carriers thereby making efficient use of unused or idle spectrum. Accordingly, secondary users of wireless communication systems can dynamically form ad-hoc mesh network communications in fixed or mobile scenarios.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
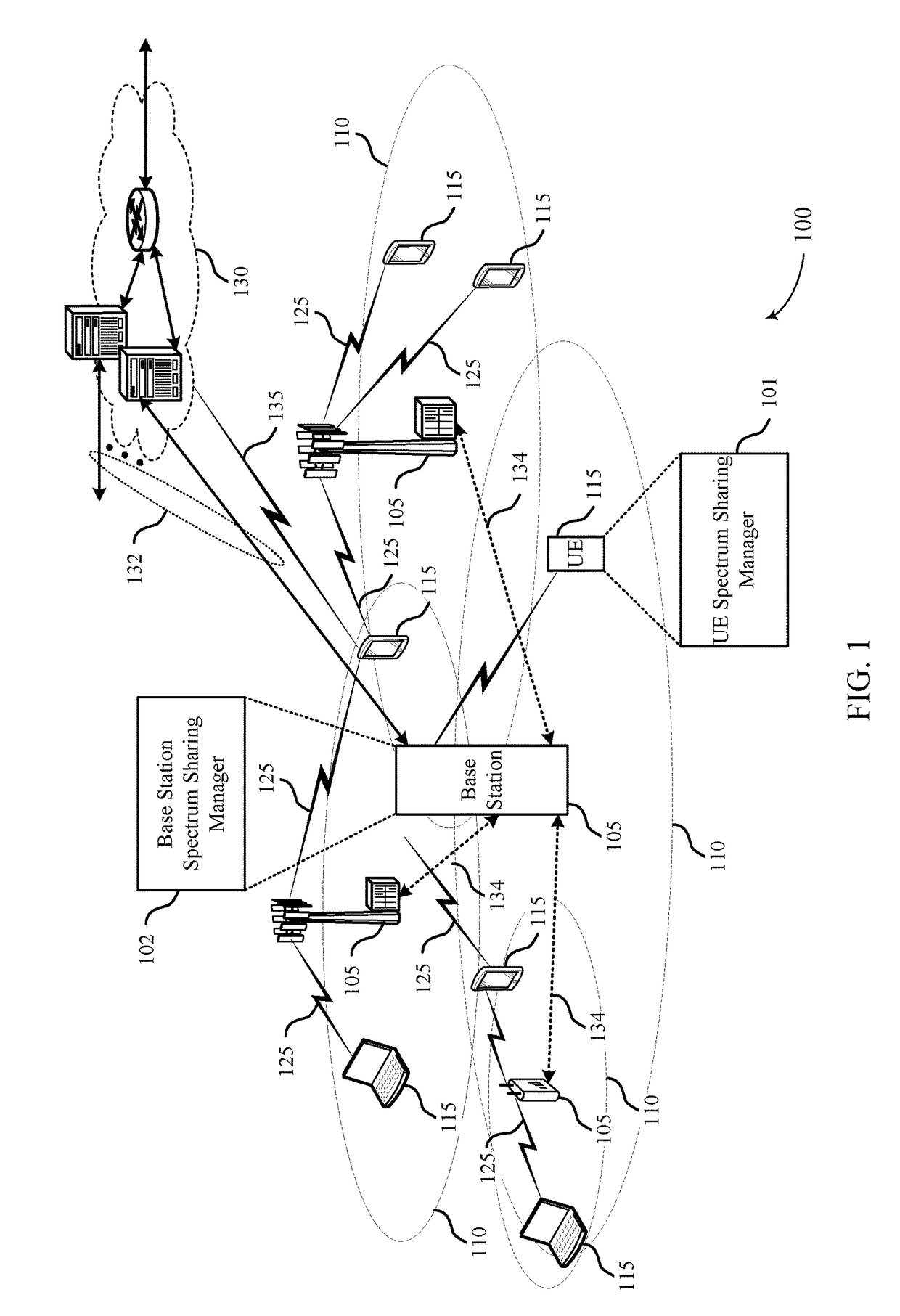
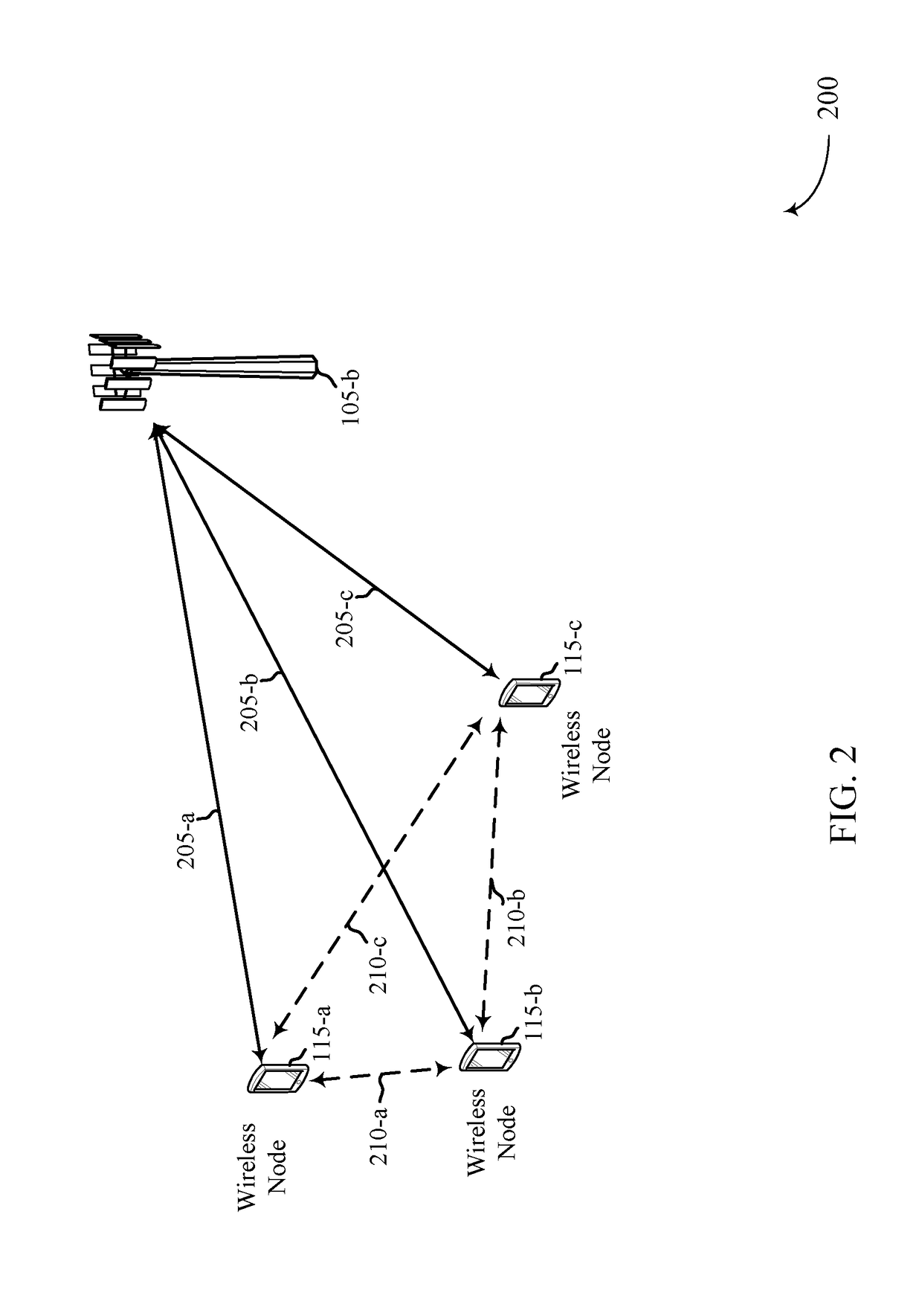
Listen before talk design for spectrum sharing in new radio (NR)
ActiveUS20180063799A1Minimize control interferingImprove interferencePower managementFrequency spectrumComputer science
Methods, systems, and devices for wireless communication are described. A wireless node may receive stress beacons on a channel. Each stress beacon may include an indication of an allowable interference level for a corresponding wireless node that transmitted the stress beacon on the channel. The wireless node may update a backoff window for the channel based on the allowable interference levels indicated in the stress beacons.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Transmit co-channel spectrum sharing
ActiveUS20130207841A1Overcome limitationsReduce the possibilityPolarisation/directional diversityIndividually energised antenna arraysAccess networkFrequency spectrum
An intelligent backhaul system is disclosed for deployment in the presence of existing radio systems. A backhaul system for co-channel deployment with existing licensed and unlicensed wireless networks, including conventional cellular backhaul radios, Common Carrier Fixed Point-to-Point Microwave Service, Private Operational Fixed Point-to-Point Microwave Service and other FCC 47 C.F.R. §101 licensed microwave networks is disclosed. Processing and network elements to manage and control the deployment and management of backhaul of radios that connect remote edge access networks to core networks in a geographic zone which co-exist with such existing systems or other sources of interference within a radio environment are also disclosed.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
Method And Apparatus Of Dynamic Spectrum Sharing In Cellular Networks
InactiveUS20130295946A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork planningApplying knowledgeFrequency spectrum
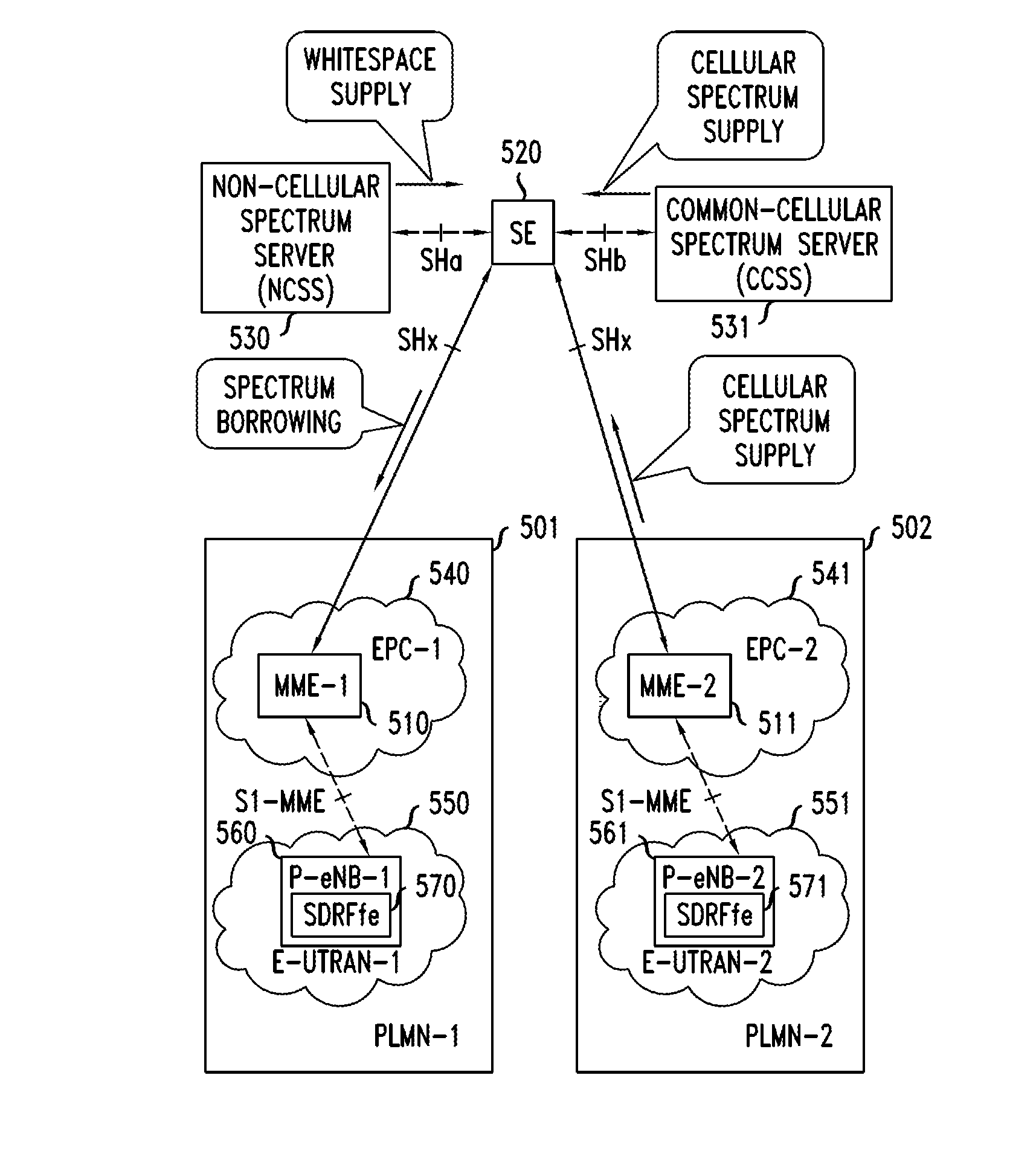
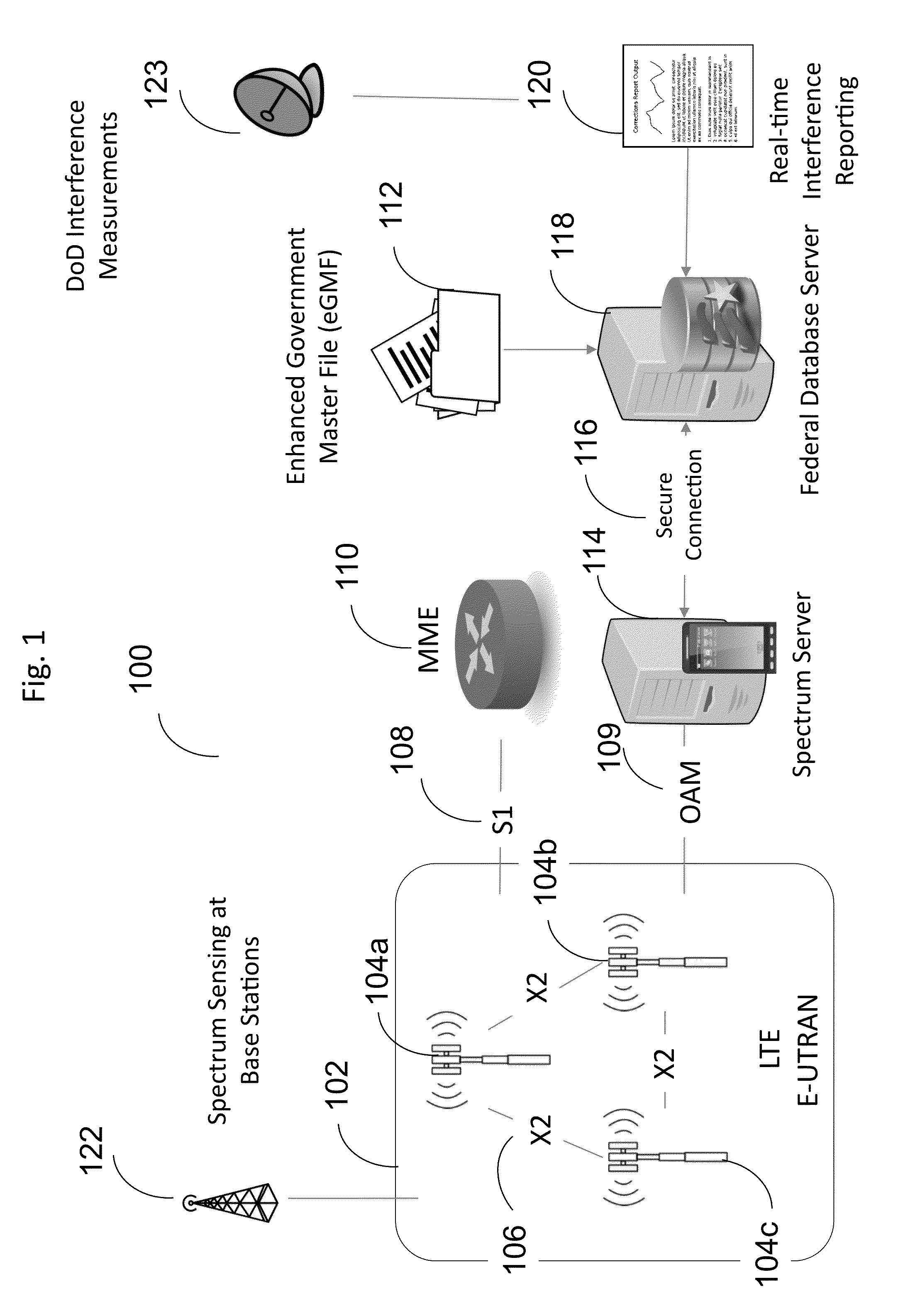
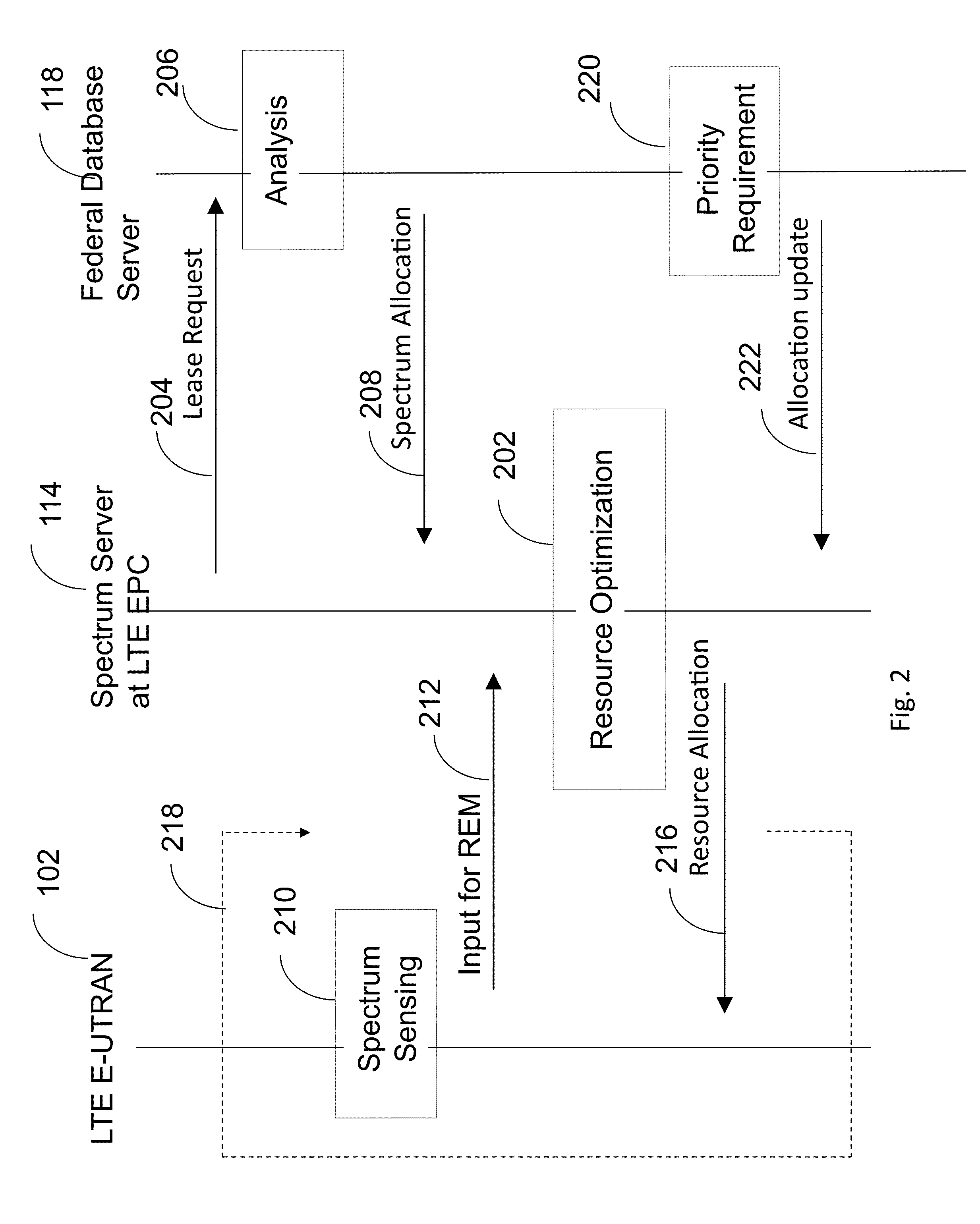
According to a disclosed method, an MME in a network analyzes KPIs from the cells it serves and based on the KPIs, it decides to engage in sharing. The MME then contacts a sharing entity (SE) to announce that it wants to supply spectrum for sharing. The MME obtains terms of a sharing agreement from the SE and the MME obtains the identity of the other network. In response to this information, the MME configures its base stations to support the supplying of spectrum to the other network. The SE applies knowledge of network topology and of services offered. This knowledge is obtained from a sharing database. At the expiration of the sharing agreement, the SE tells the MMEs to deactivate the sharing agreement.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
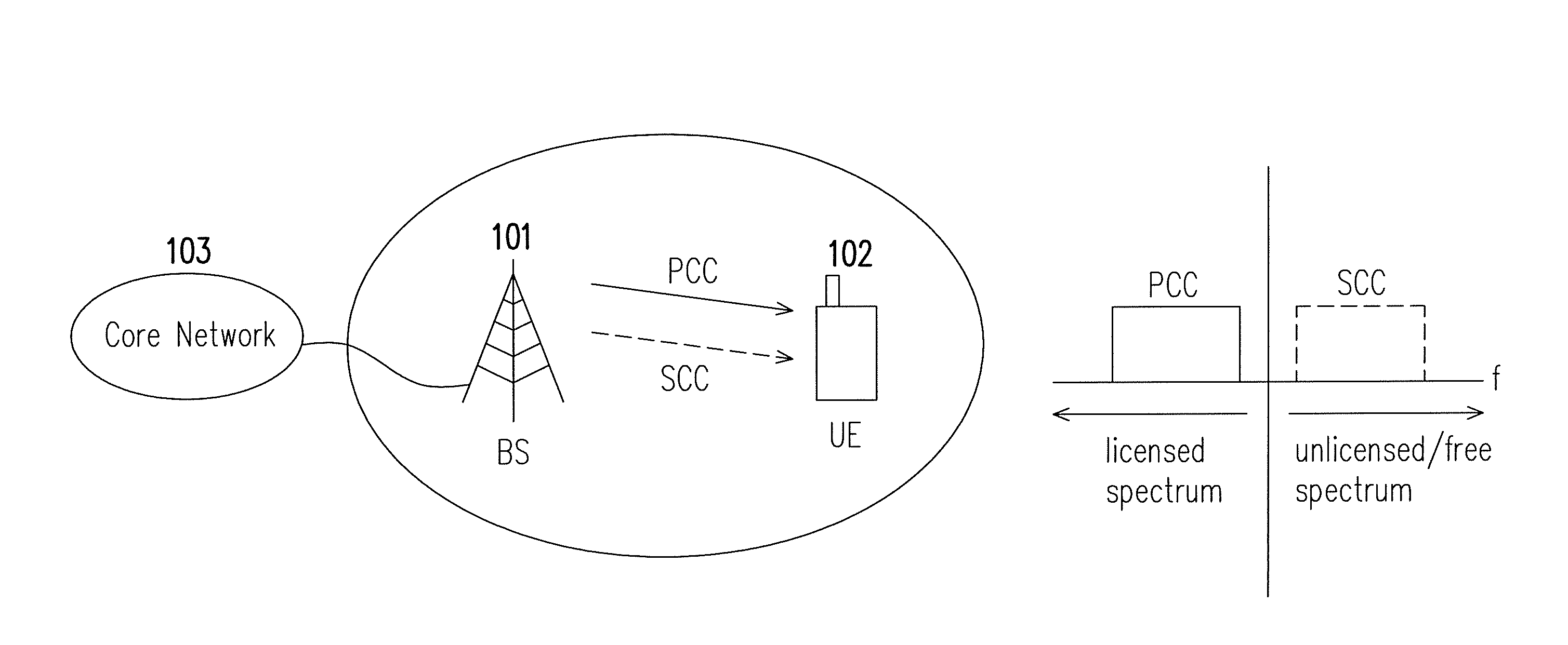
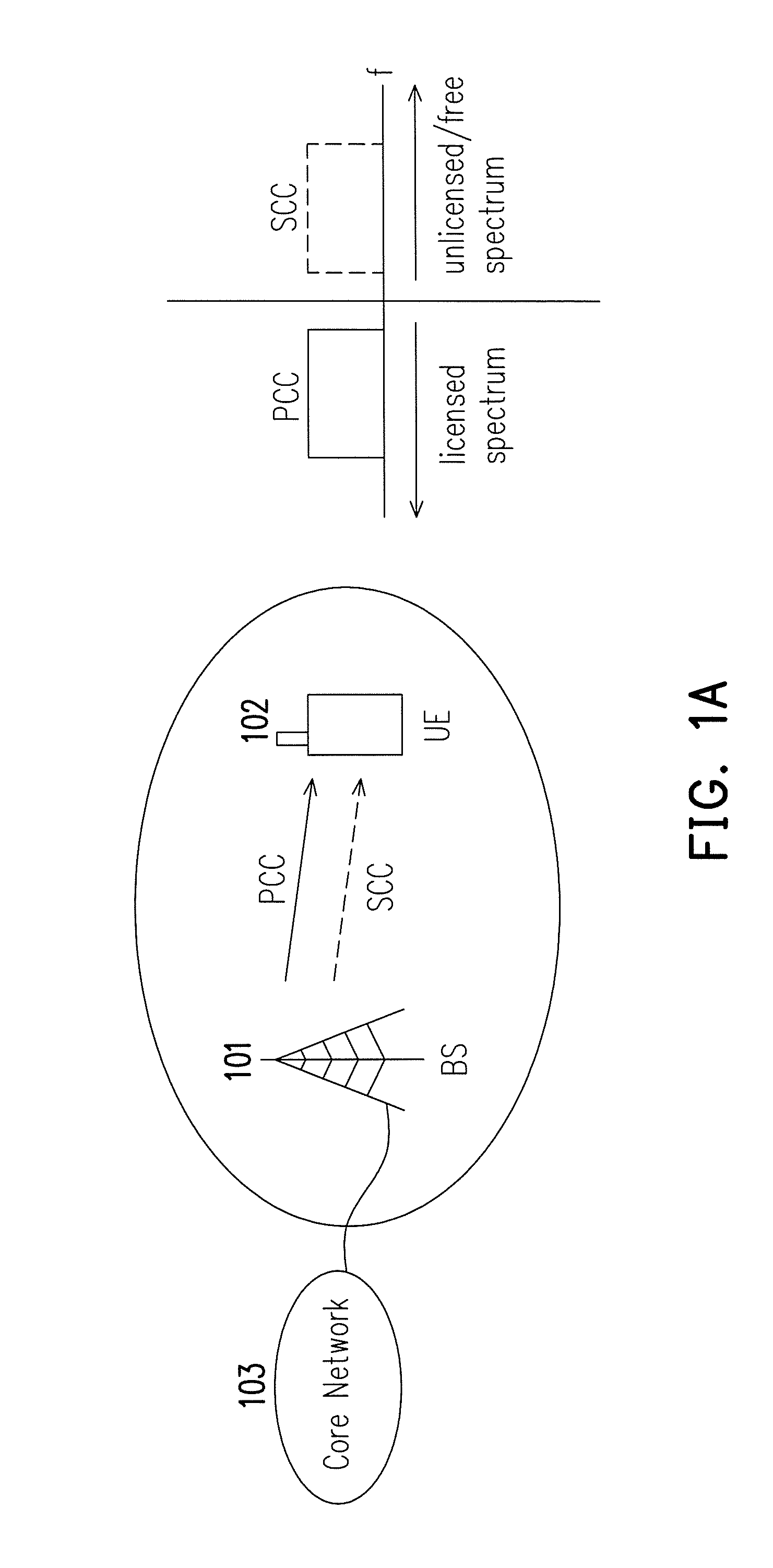
Unlicensed spectrum sharing method, base station using the same, and user equipment using the same
ActiveUS20150245219A1Network traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
The disclosure is directed to an unlicensed spectrum sharing method that is applicable to a user equipment and a base station, a user equipment using the same method, and a base station using the same method. In one of the exemplary embodiments, the disclosure is directed to an unlicensed spectrum sharing method applicable to a user equipment. The method would include receiving a configuration message over a first component carrier in a licensed spectrum to operate in an unlicensed spectrum, receiving a user message of the UE over a second component carrier in the unlicensed spectrum in response to receiving the configuration message, wherein the first component carrier and the second component carrier are aggregated carriers, and receiving a re-configuration message over the first component carrier in the licensed spectrum to operate in the unlicensed spectrum.
Owner:ACER INC
Network oriented spectrum sharing system
ActiveUS20080112361A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumTransceiver
There is provided a system and method for sharing a wireless spectrum compromising a first transceiver for establishing the communication channels within the allocated bandwidth using a first protocol, a broker for determining the unused bandwidth within the allocated bandwidth, and a second transceiver for establishing the further communication channels within the unused allocated bandwidth using a second protocol. The first protocol is UMTS and the second protocol is WiMax. The broker may monitor UMTS traffic and allocate bandwidth to WiMax traffic whenever resources are idle or traffic are low or allocate bandwidth in dependence upon time division multiplexing, or frequency division multiplexing or may overlap a WiMax signal with a UMTS signal.
Owner:WU SHIQUAN
Universal broadband broadcasting
A universal broadband broadcasting service is provided. A spectrum-sharing database stores attributes associated with a shared spectrum, a policy controller controls access to the shared spectrum by broadcast service entities, and a gateway receives IP multicast traffic from the broadcast service entities and communicates the IP multicast traffic to a broadcast single frequency network.
Owner:ROHDE & SCHWARZ GMBH & CO KG
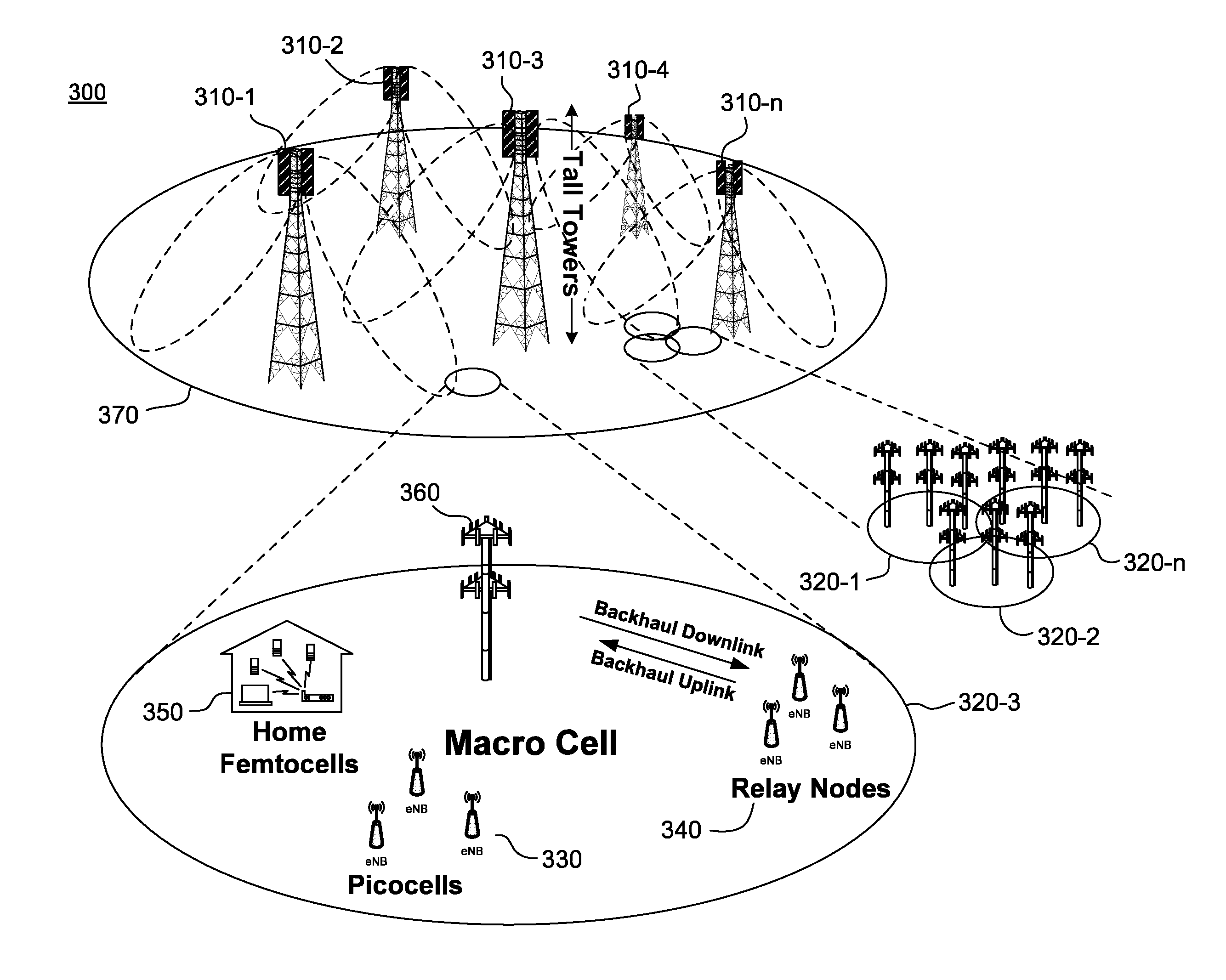
Wireless resource management system and method of implementing frequency spectrum sharing
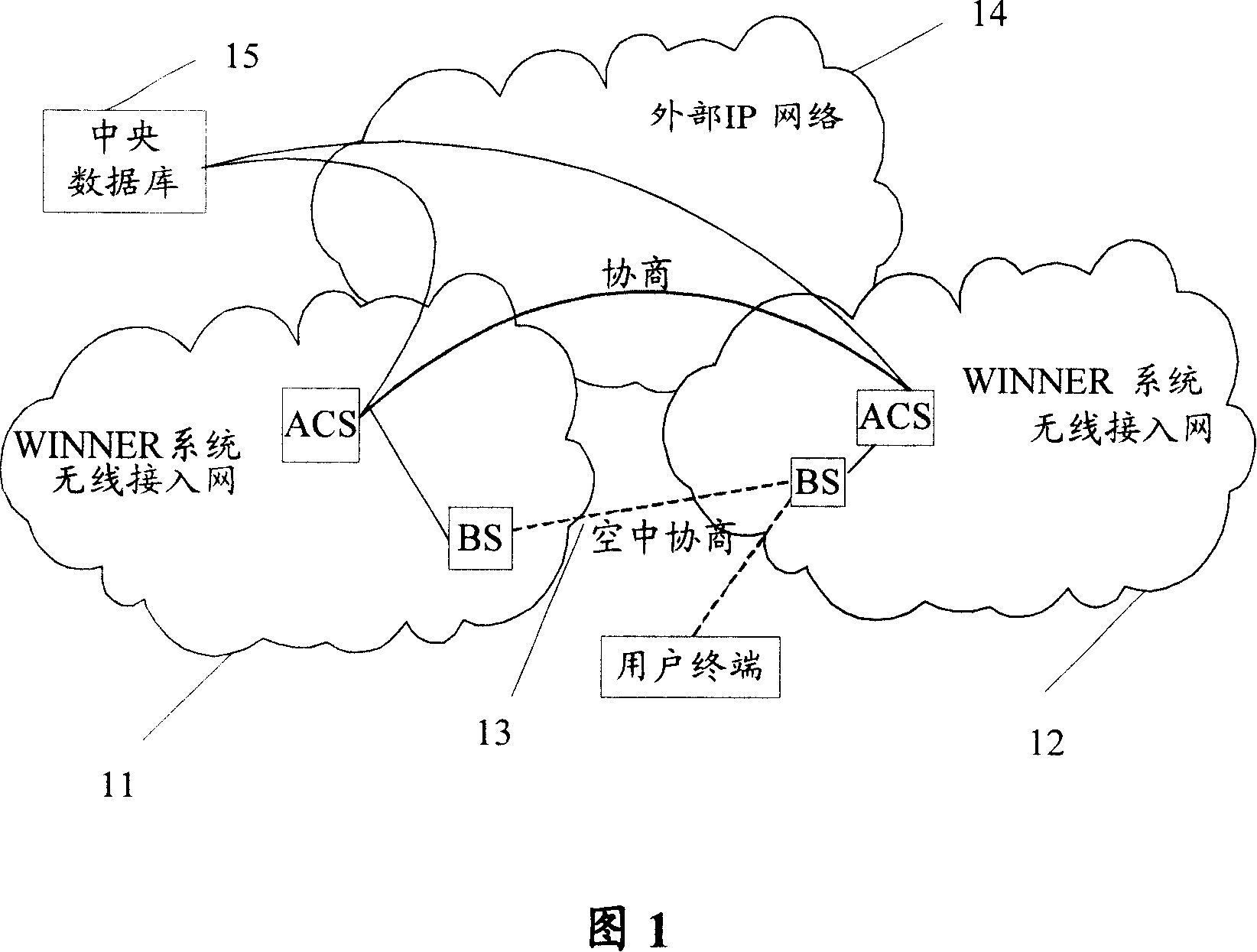
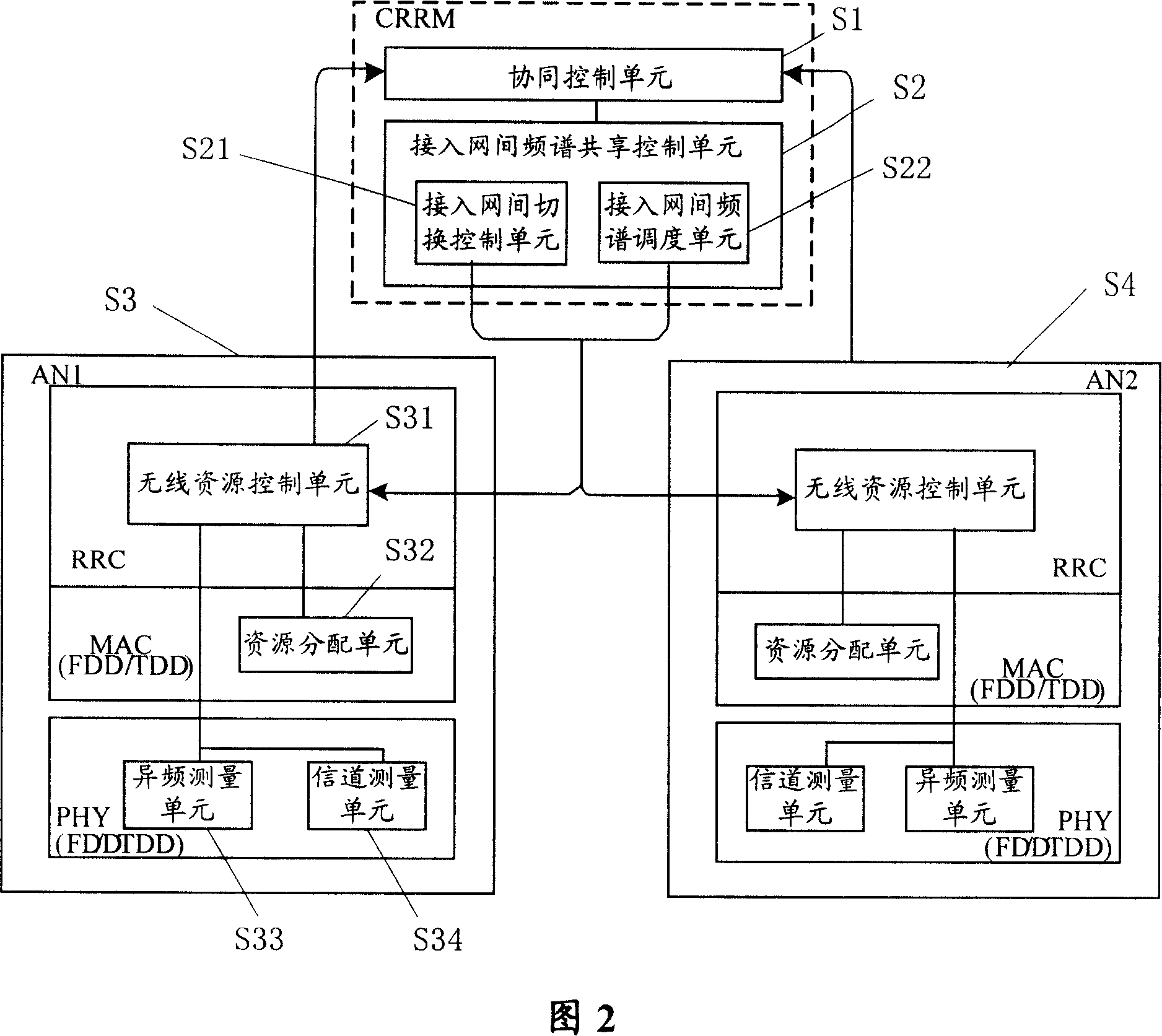
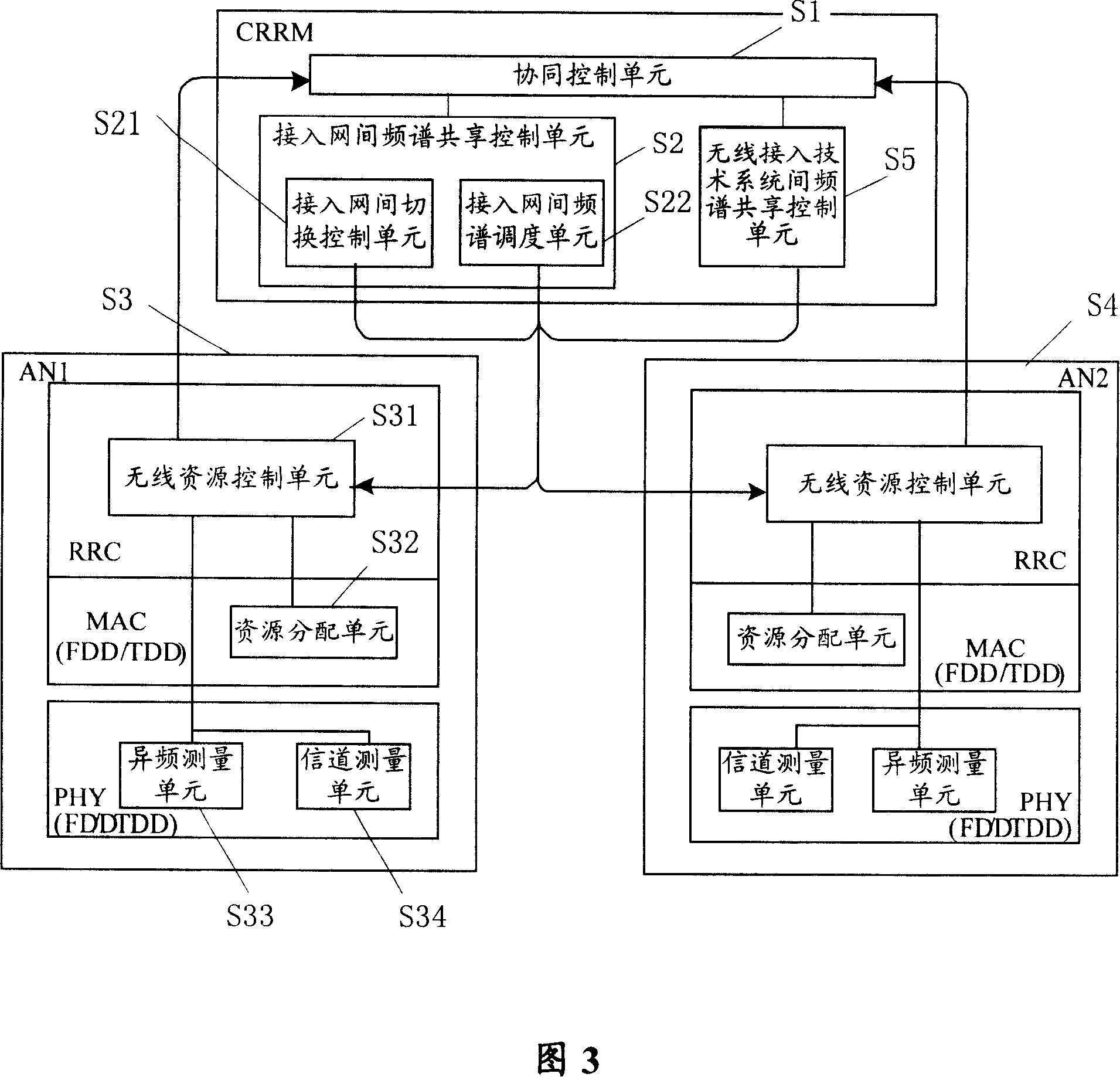
ActiveCN101141771AReduce the amount of information transmittedImprove acceleration performanceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork planningAccess networkWireless resource management
The present invention discloses a wireless resource management system for realizing the frequency spectrum sharing. The system comprises a cooperation control unit for determining frequency spectrum sharing strategy according to the frequency spectrum sharing request which is accessed in a network and / or each running statistical information which is accessed in a network and the frequency spectrum using condition; an accessing network frequency spectrum sharing control unit communicated with the cooperation control unit is used for matching the different local wireless resource management accessed in the network to make the accessing network share the frequency spectrum resource according to the frequency spectrum sharing strategy determined by the cooperation control unit. The present invention also discloses a wireless resource management method for realizing the frequency spectrum sharing. With the present invention, the frequency spectrum sharing between different wireless accessing technologies and wireless accessing networks can be simply and effectively realized, and the utilization ratio of the frequency spectrum resource can be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Synchronous spectrum sharing by dedicated networks using OFDM/OFDMA signaling
InactiveUS20080232487A1Transmission path divisionBroadcast transmission systemsCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
A system and method for synchronous spectrum sharing for a dedicated network in a wireless communication system based on orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) or orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) signaling is disclosed. The system and method includes detecting a frame of a broadcast waveform and extracting idle spectrum information from a subframe associated with the dedicated subchannel to the secondary user node. The system allows transmitting data from the secondary user node in unused symbol slots identified in the idle spectrum information thereby making efficient use of unused or idle spectrum. Accordingly, secondary users of the wireless communication system can dynamically form ad-hoc mesh network communications in fixed or mobile scenarios.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Spectrum sharing in a wireless communication network
ActiveUS20080112359A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmission path multiple useFrequency spectrumCommunications system
A system and method for synchronous spectrum sharing for use in a wireless communication system based on orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) or orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) signaling is disclosed. The system includes a frame detector configured to detect a frame of a broadcast waveform and extract sub-carrier information from a subframe or Secondary User Map (SU MAP). SU MAP includes information on usable sub-carrier and pilot sub-carriers for secondary users. The system allows transmitting data from the secondary user node in unused sub-carriers thereby making efficient use of unused or idle spectrum. Accordingly, secondary users of wireless communication systems can dynamically form ad-hoc mesh network communications in fixed or mobile scenarios.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of inter-system communications dynamic spectrum access network systems-logical control connections
ActiveUS20080089306A1Low incurred communication overheadReduce overheadTime-division multiplexConnection managementAccess networkFrequency spectrum
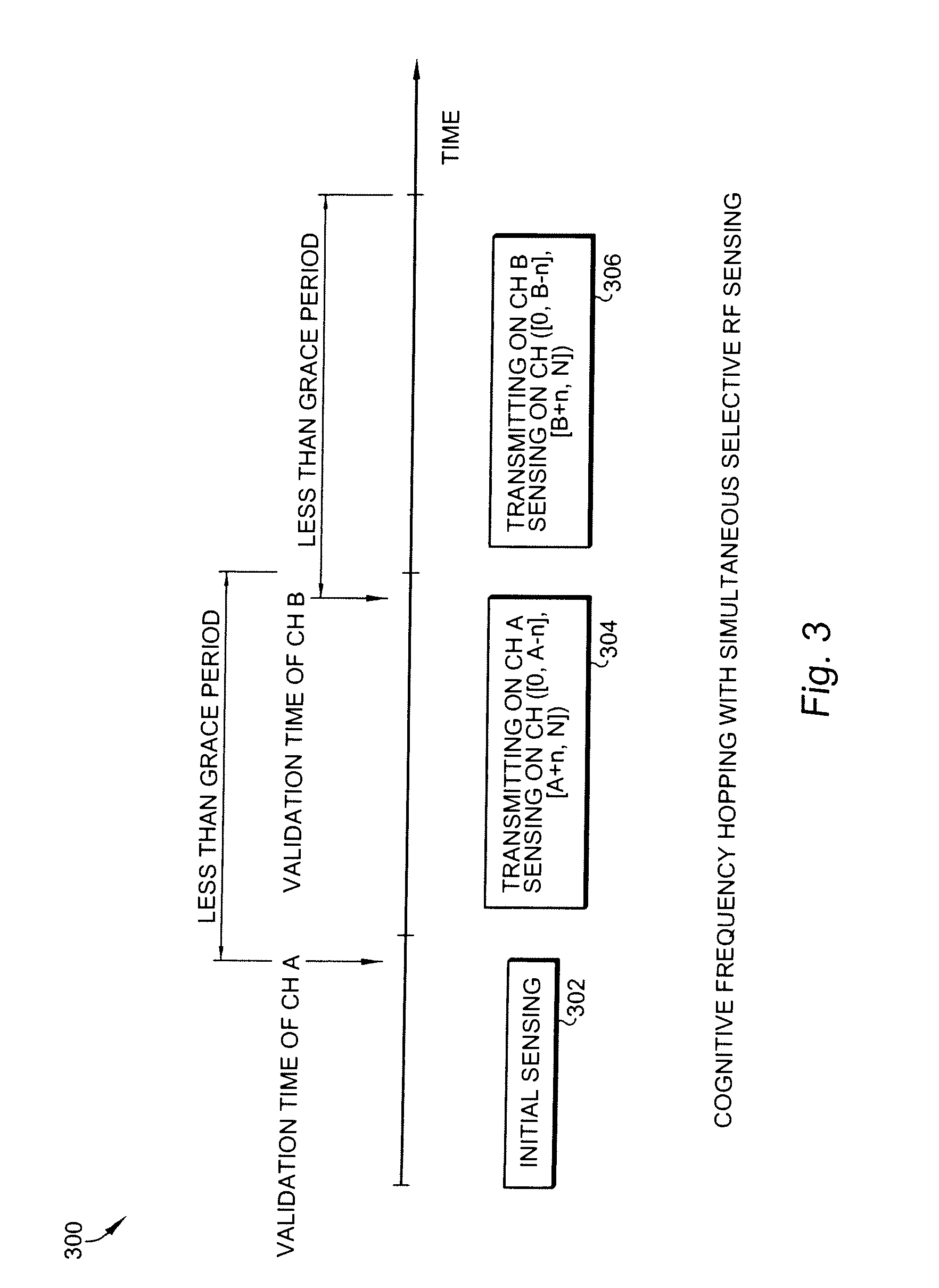
This invention relates to cognitive radio based wireless communications of dynamic spectrum access networks, and more particularly to a method of addressing inter-systems (cells) communications for coexistence and spectrum sharing. A method, called Logical Control Connections, is described for reliable connection-based inter-system coordination and communications, which can be established and maintained either over the air or over the backhaul with very low incurred communications overhead in terms of spectrum bandwidth, messaging latency, and hardware / software complexities.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
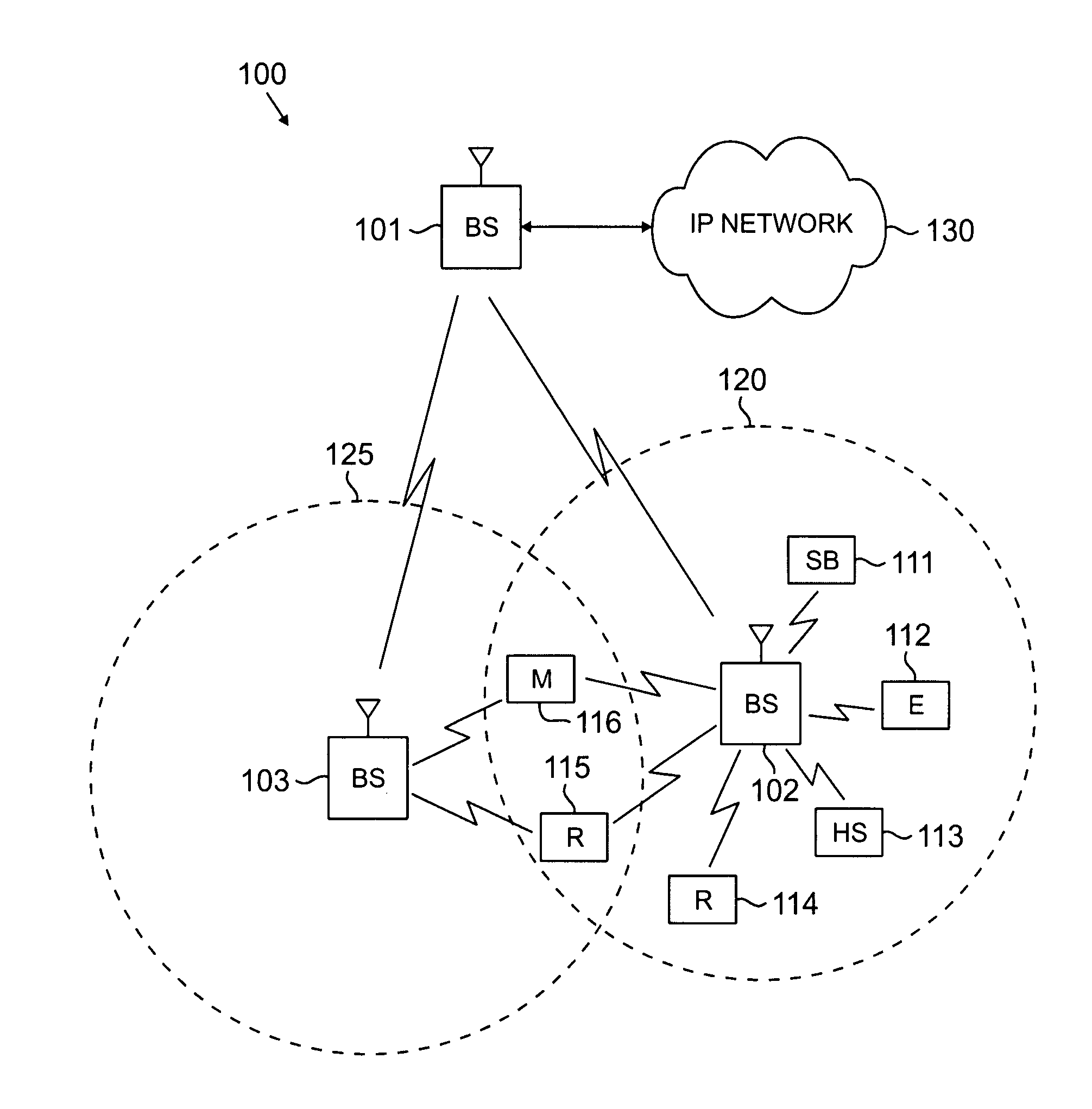
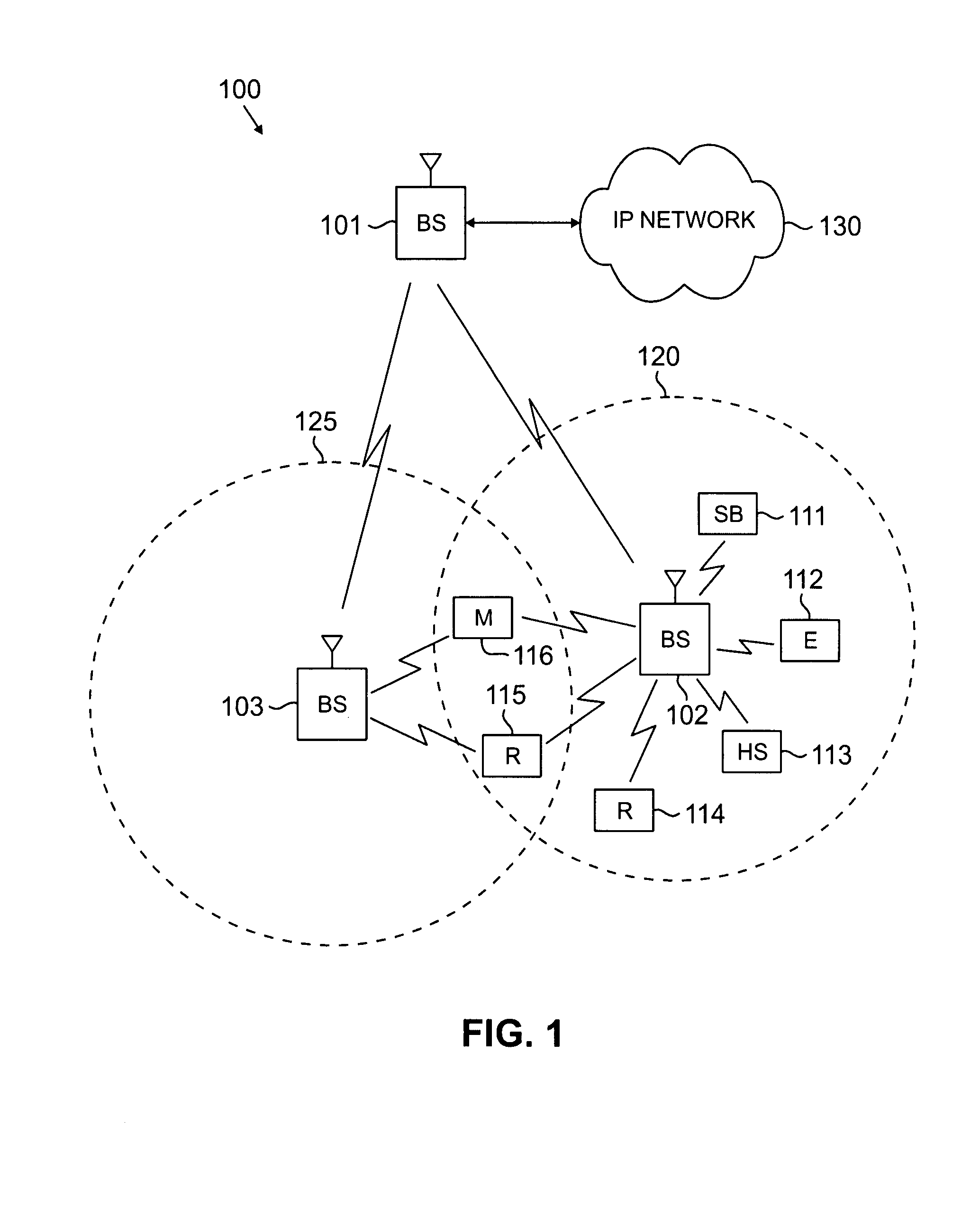
Shared Spectrum Access for Broadcast and Bi-Directional, Packet-Switched Communications
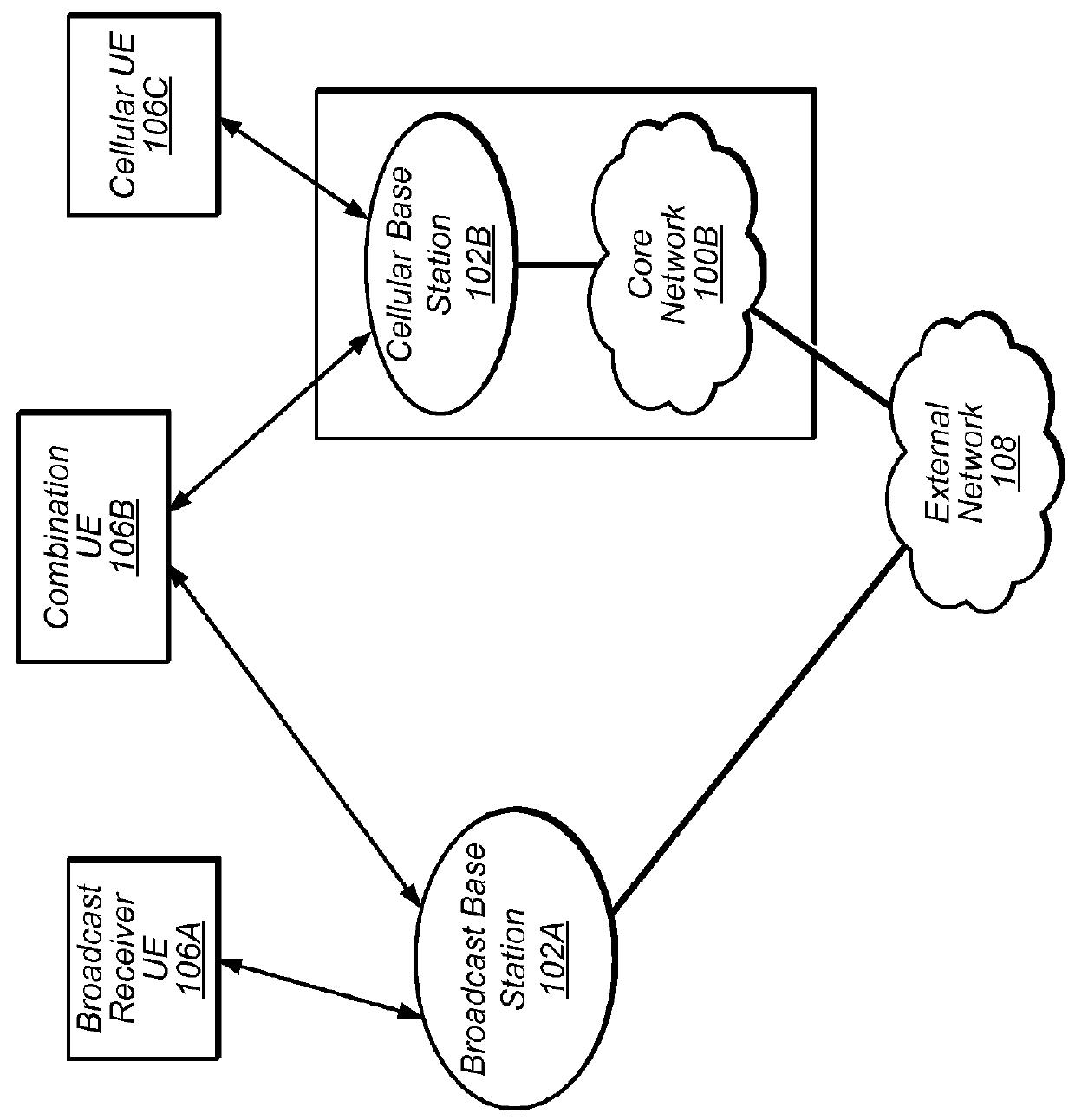
ActiveUS20160057504A1Stay connectedAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsBroadcast service distributionRadio access technologyFrequency spectrum
Techniques are disclosed relating to spectrum sharing between different radio access technologies. In some embodiments, a broadcast base station is configured to wirelessly broadcast audio and video data to a plurality of broadcast receiver devices using a particular frequency band. In these embodiments, the broadcast base station is configured to discontinue broadcasting in the particular frequency band during a scheduled time interval, to enable one or more cellular base stations to perform bi-directional packet-switched wireless data communications using the particular frequency band.
Owner:COHERENT LOGIX
Method and apparatus for sharing spectrum between 3gpp LTE and nr in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20190357264A1Power managementError prevention/detection by using return channelRadio access technologyCommunications system
A method and apparatus for transmitting a physical random access channel (PRACH) in a wireless communication system is provided. A user equipment (UE) receives multiple PRACH configurations which include a first PRACH configuration for new radio access technology (NR) downlink / uplink (DL / UL) carrier in a NR band and a second PRACH configuration for a supplemental UL carrier in a long-term evolution (LTE) band, and transmits at least one of a first PRACH for accessing the NR DL / UL carrier in the NL band by using a first PRACH power based on the first PRACH configuration, or a second PRACH for accessing the supplemental UL carrier in the LTE band by using a second PRACH power based on the second PRACH configuration. The first PRACH configuration and the second PRACH configuration include different PRACH power configuration.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
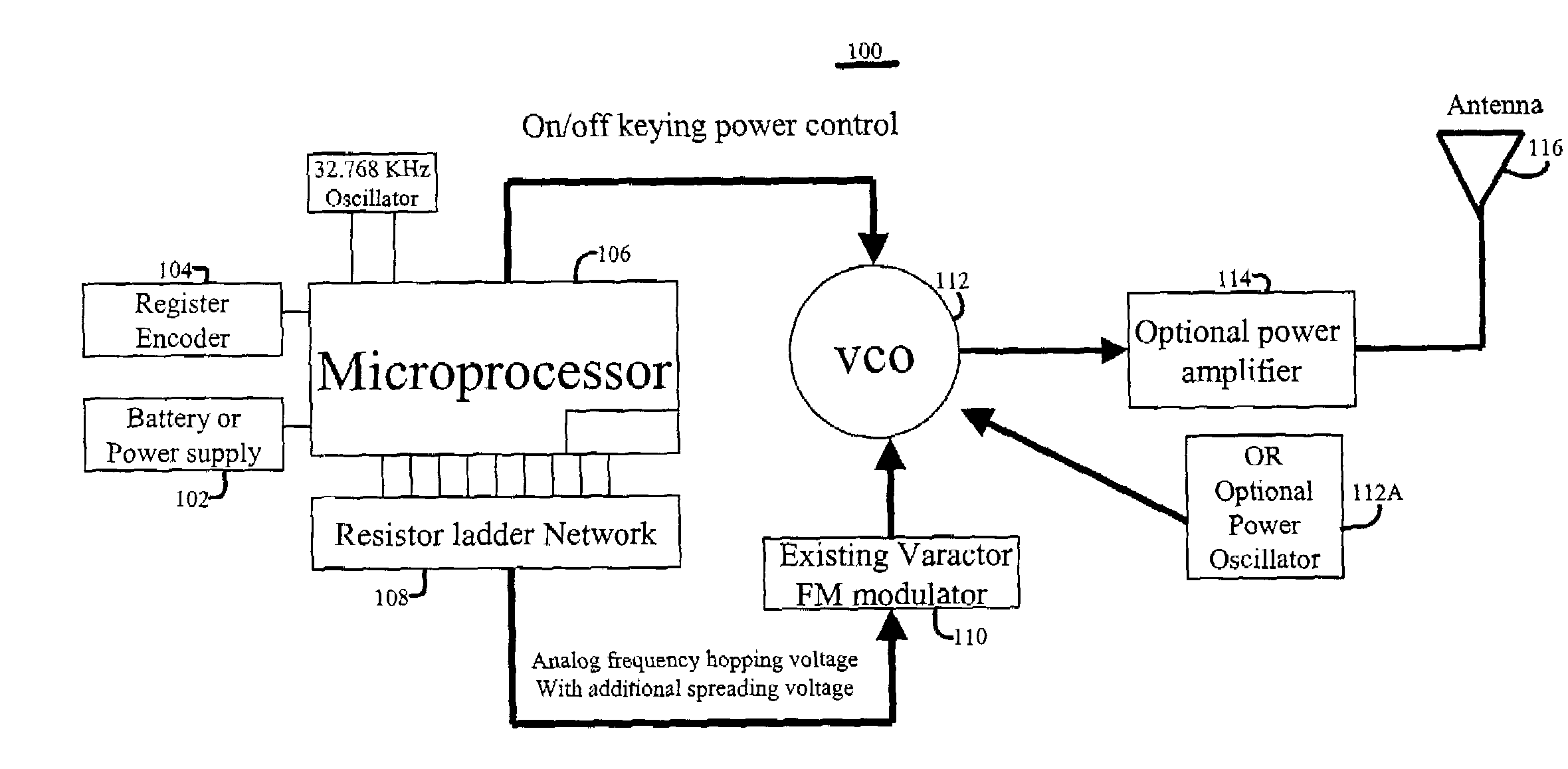
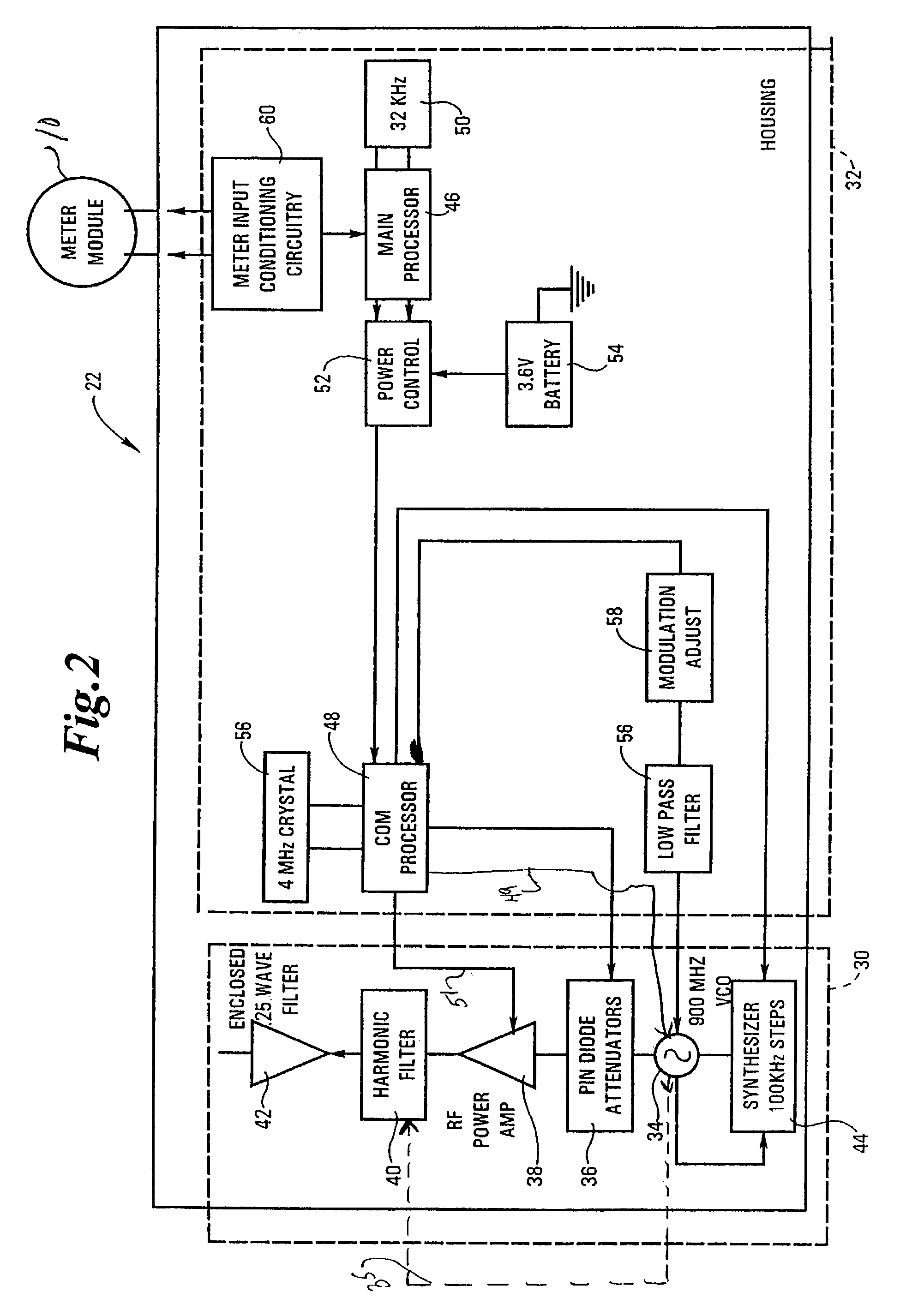
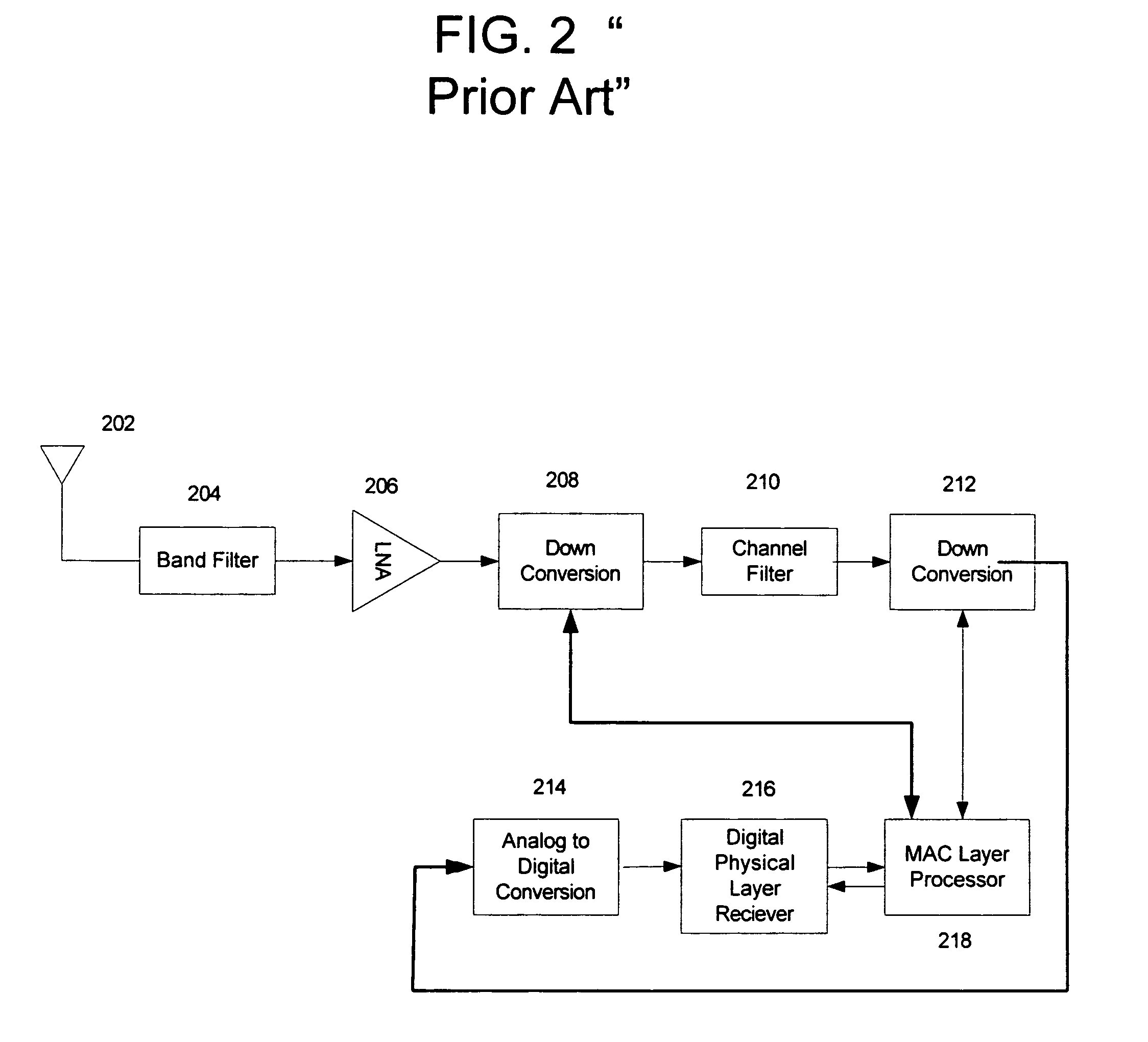
RF communications system utilizing digital modulation to transmit and receive data
InactiveUS7154938B2Reduce the impact of interferenceFacilitating spectrum sharingElectric signal transmission systemsAngle modulationOn-off keyingFrequency spectrum
The RF communications system of the present invention wirelessly communicates data without encountering undue interference problems with other devices and complies with rules governing unlicensed, spectrum-sharing devices. In an example embodiment, a transmitter device includes a digital subsystem powered by a power supply that processes data from another device and a radio frequency (RF) sub-system that transmits the processed data using a frequency hopping scheme. The RF sub-system includes a microprocessor arrangement that ON-OFF keys a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) and provides a frequency-hopping scheme. The VCO is coupled to a signal frequency spreading arrangement that spreads the signal to a predetermined transmission bandwidth, wherein the frequency spreading occurs during an ON state of the ON-OFF keying and the transmission bandwidth exceeds a reception bandwidth at which the signal will be decoded.
Owner:ITRON
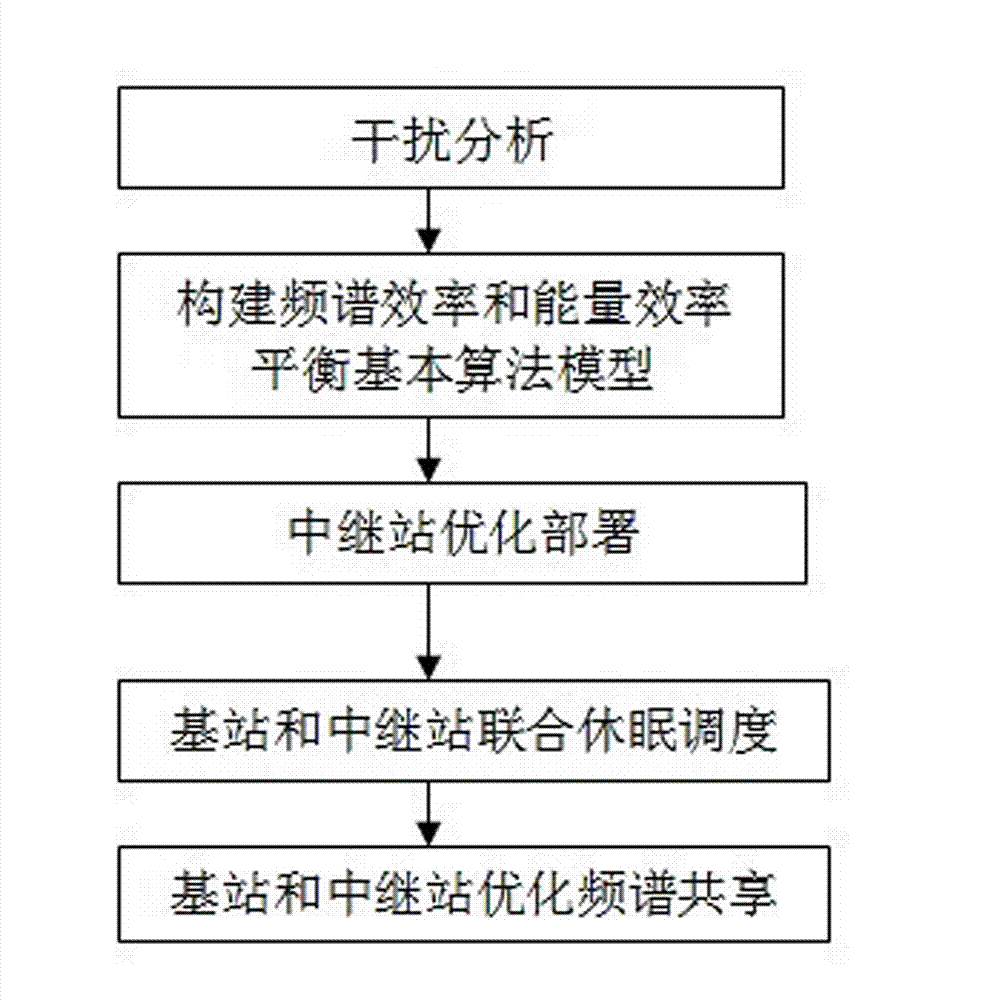
Optimization method of spectrum efficiency and energy efficiency of wireless communication system
InactiveCN103096335AReduce energy consumptionImprove throughputEnergy efficient ICTNetwork planningFrequency spectrumCommunications system
The invention discloses an optimization method of spectrum efficiency and energy efficiency of a wireless communication system. The optimization method of the spectrum efficiency and the energy efficiency of the wireless communication system aims at the defects that an existing wireless communication system particularly emphasizes on improvement of the spectrum efficiency and pays less attention to decrease of the corresponding energy efficiency. Firstly, through analysis of intra-cell interference and inter-cell interference of the wireless communication system, spectrum efficiency and energy efficiency expressions about the number and location of relay stations are obtained, a spectrum efficiency and energy efficiency balance primary algorithm model is built, and optimized deployment is carried out according to the relay stations. Secondary, united dormancy dispatch of a base station and the relay station is carried out according to business flow. Finally, optimized spectrum sharing of the base station and the relay station is carried out. The optimization method of the spectrum efficiency and the energy efficiency of the wireless communication system can be applied to a cellular relay network, enables the communication system to reduce energy consumption and improve system throughput through balancing the spectrum efficiency and the energy efficiency of the wireless communication system, and satisfies requirements of energy conservation and emission reduction and requirements of reducing communication operating cost.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
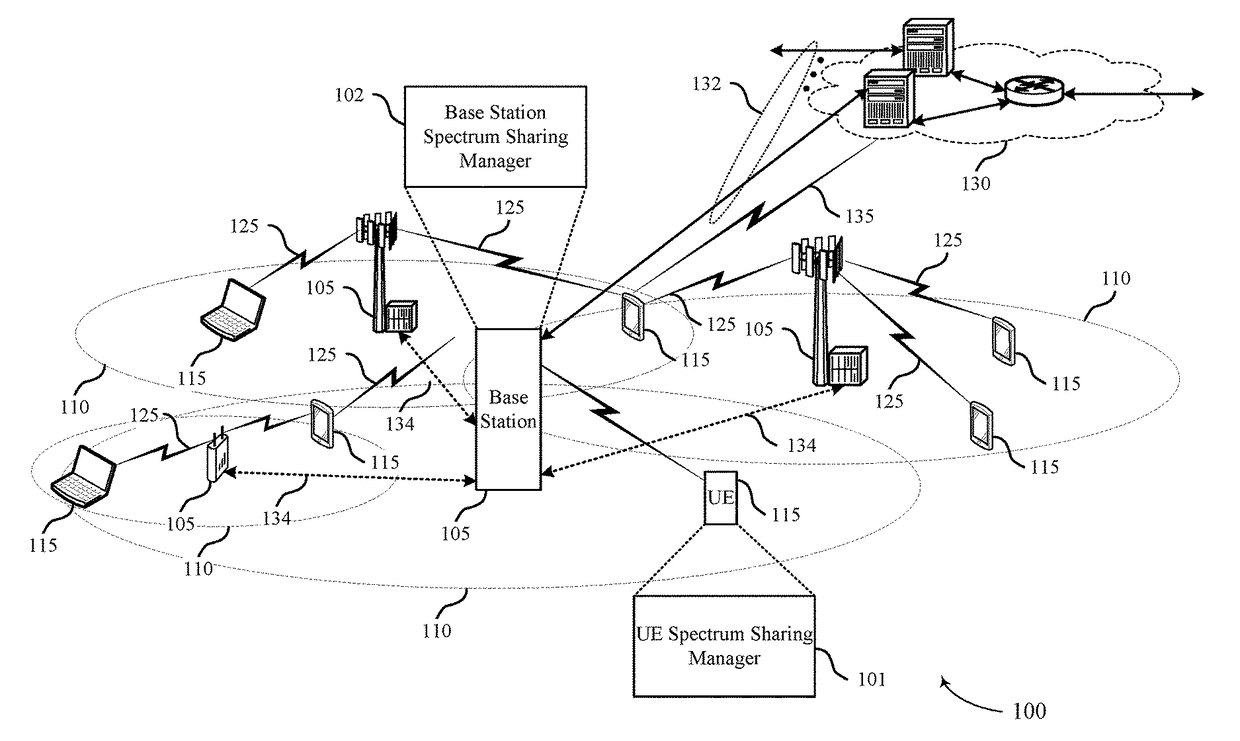
Techniques for dynamic spectrum management, allocation, and sharing
ActiveUS20120082100A1Error preventionTime-division multiplexFrequency spectrumDynamic spectrum management
Techniques for managing detection, dynamic allocation, and sharing of available spectrum via cognitive radio systems and dynamic spectrum sharing. In some cases, RF carriers (e.g., secondary carriers or secondary cells) are not permanently assigned to base stations, user terminals, or the network. A base station can request allocation of secondary carriers using a reservation request. The assigned secondary carriers can be released and made available for assignment to another base station or radio access network.
Owner:APPLE INC
System, Network, Device and Stacked Spectrum Method for Implementing Spectrum Sharing of Multiple Contiguous and Non-Contiguous Spectrum Bands Utilizing Universal Wireless Access Gateways to Enable Dynamic Security and Bandwidth Policy Management
InactiveUS20180376006A1Improve rendering capabilitiesQuality improvementService provisioningInterconnection arrangementsFrequency spectrumAir interface
A system and method in various embodiments implements a virtual spectrum band stacking technique facilitating spectrum sharing by converting and combining spectrum bands consisting of several different RF channels, common air interfaces, and radio channel protocols in the radio frequency channel domain to form IP Virtual Radio Channels (IP-VRCs) in the packet data domain. This virtual spectrum stacking technique combines the transmissions of contiguous and non-contiguous RF channels with differing physical layers into IP-VRCs. This technique enables simultaneous parallel high-speed wireless transmission; virtual radio channel hopping for enhanced security; and customized security schemes for different IP-VRC Groups. The deployment of the combination of IP-VRC Groups; Universal “Small Cell” Base Stations; and Universal Wireless End-Point Devices allows the aggregation of all available spectrum bands for use within a building environment. Some benefits of this deployment include expansion of spectrum utilization, service quality, security, applications and transmission throughput for wireless end-point devices.
Owner:INCNETWORKS
System and method for heterogenous spectrum sharing between commercial cellular operators and legacy incumbent users in wireless networks
ActiveUS20140274104A1Minimize potentialMaximize fallow spectrumNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesFrequency spectrumReference database
Described herein are systems and methods for telecommunications spectrum sharing between multiple heterogeneous users, which leverage a hybrid approach that includes both distributed spectrum sharing, spectrum-sensing, and use of geo-reference databases.
Owner:FEDERATED WIRELESS +1
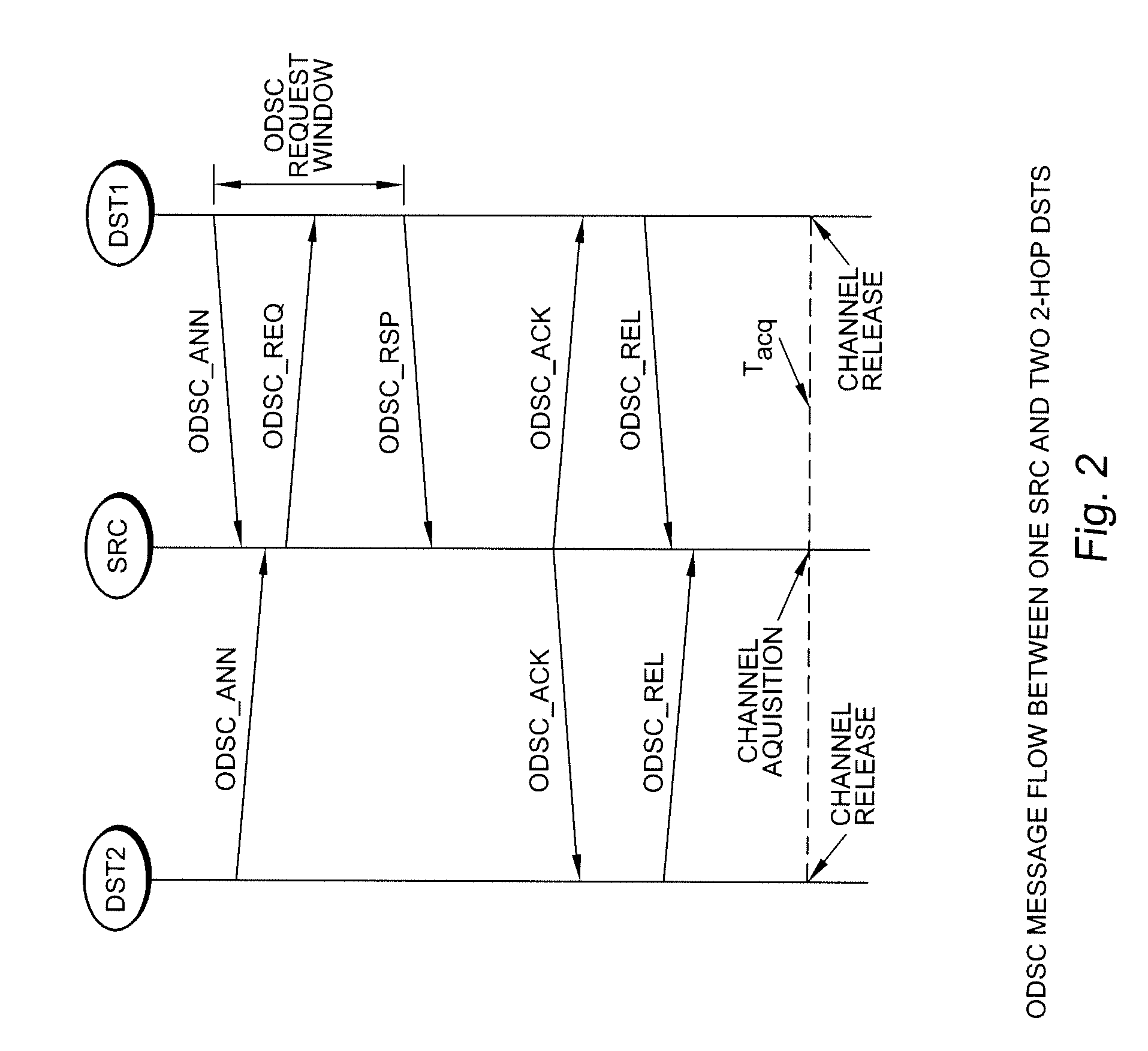
Frame-based on-demand spectrum contention protocol-messaging method
InactiveUS20100142463A1Efficient and scalable and fair sharingPower managementTransmission path divisionTelecommunicationsFrequency spectrum
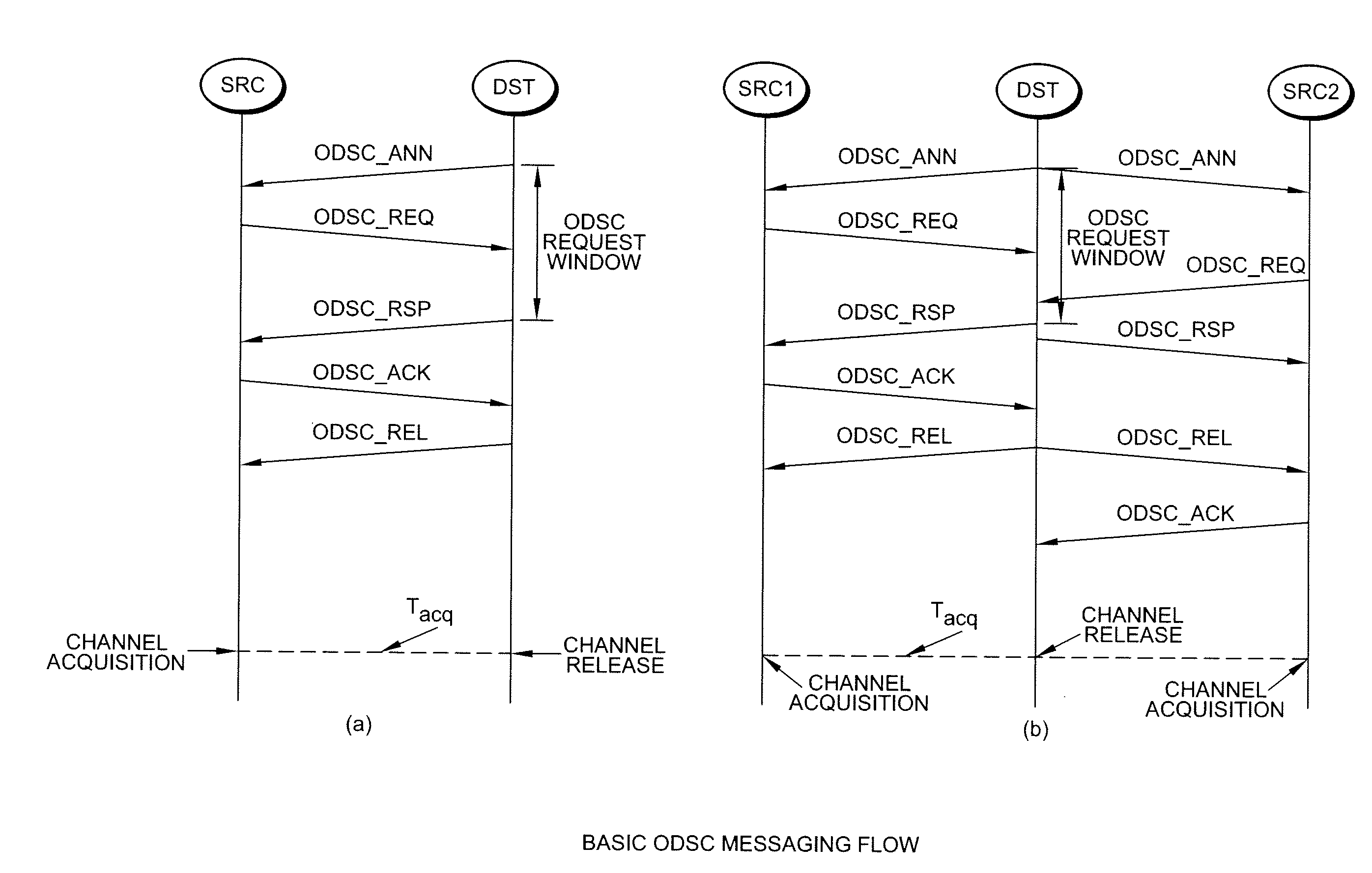
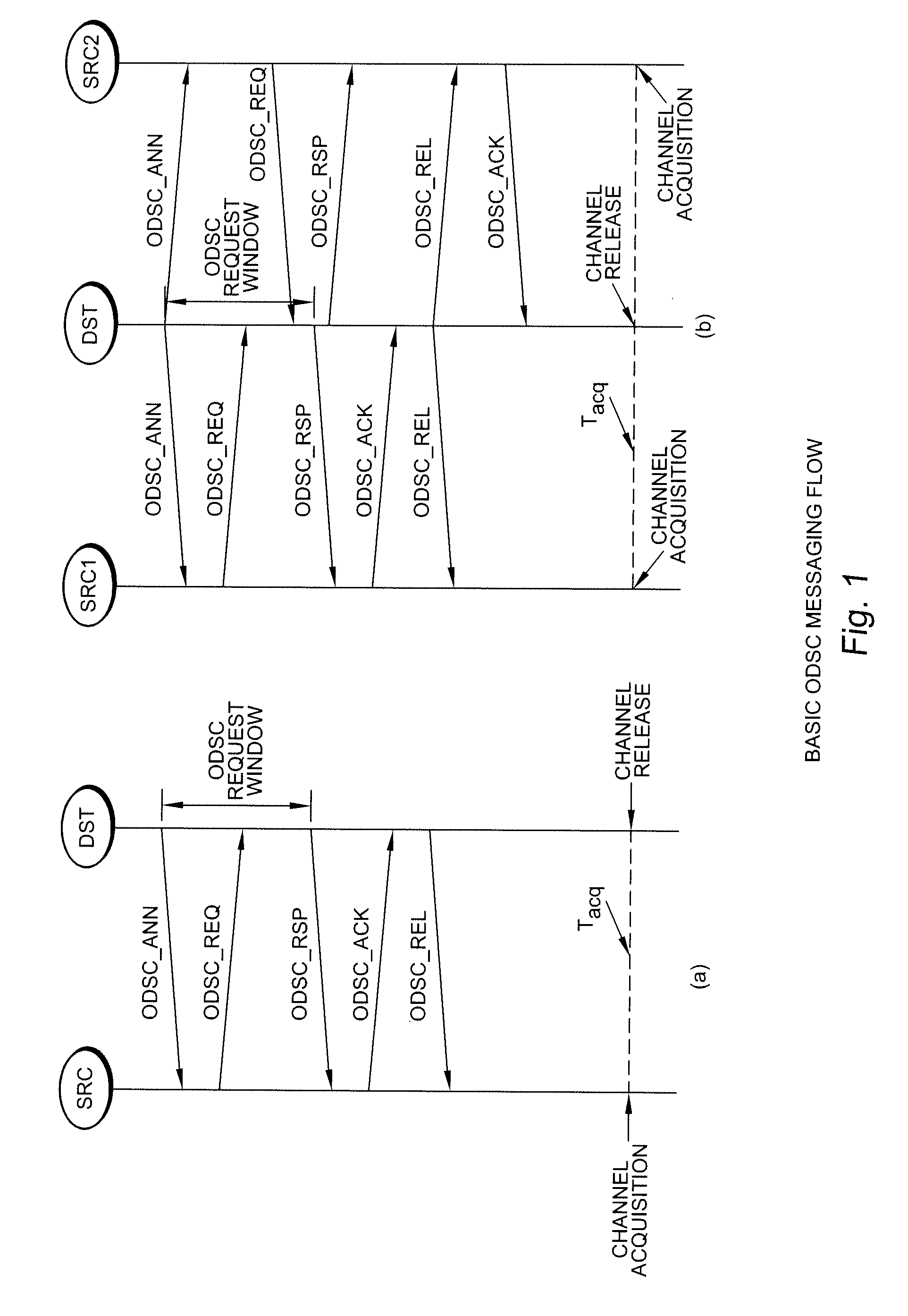
The message flows of a distributed, cooperative, and real-time protocol for frame-based spectrum sharing called Frame-based On-Demand Spectrum Contention (FODSC) employs interactive MAC messaging on an inter-network communication channel to provide efficient, scalable, and fair inter-network spectrum sharing among the coexisting cognitive radio cells.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
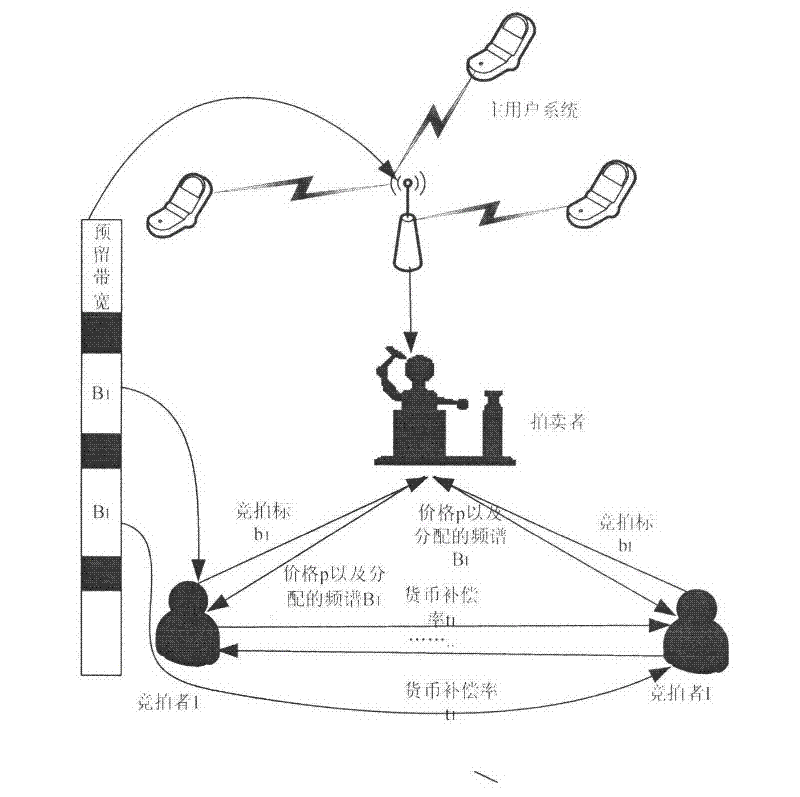
Spectrum Sharing Method Based on Auction Theory and Compensation Incentives
ActiveCN102291722ASelf-enforcingFairNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork planningCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
The invention aims at providing a spectrum sharing method based on auction theory and compensation stimulation in a cognitive radio system. The method aims at primary and secondary user spectrum sharing problems, the cooperative relationship between secondary users is introduced on the basis of a simplified video channel generator (VCG) auction model, in addition, a currency compensation stimulation principle is utilized for building an expansive non-cooperative game model including negotiation and consulting links. The cooperative relationship between the secondary users is discussed in a non-cooperative game framework by the game model, the game is carried out through the specific cooperative strategy, the decision mode characteristic of automatic implementation of the non-cooperative game model is realized, and the fairness characteristic of an oligarch combination model is also realized. In addition, because the adopted communication system model is the auction model, the primary users can adopts preserved bandwidth measures for ensuring that the self performance is protected from being influenced by secondary user spectrum sharing, and the spectrum shearing environment between the primary users and the secondary users is better ensured.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Spectrum sharing in the unlicensed band
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
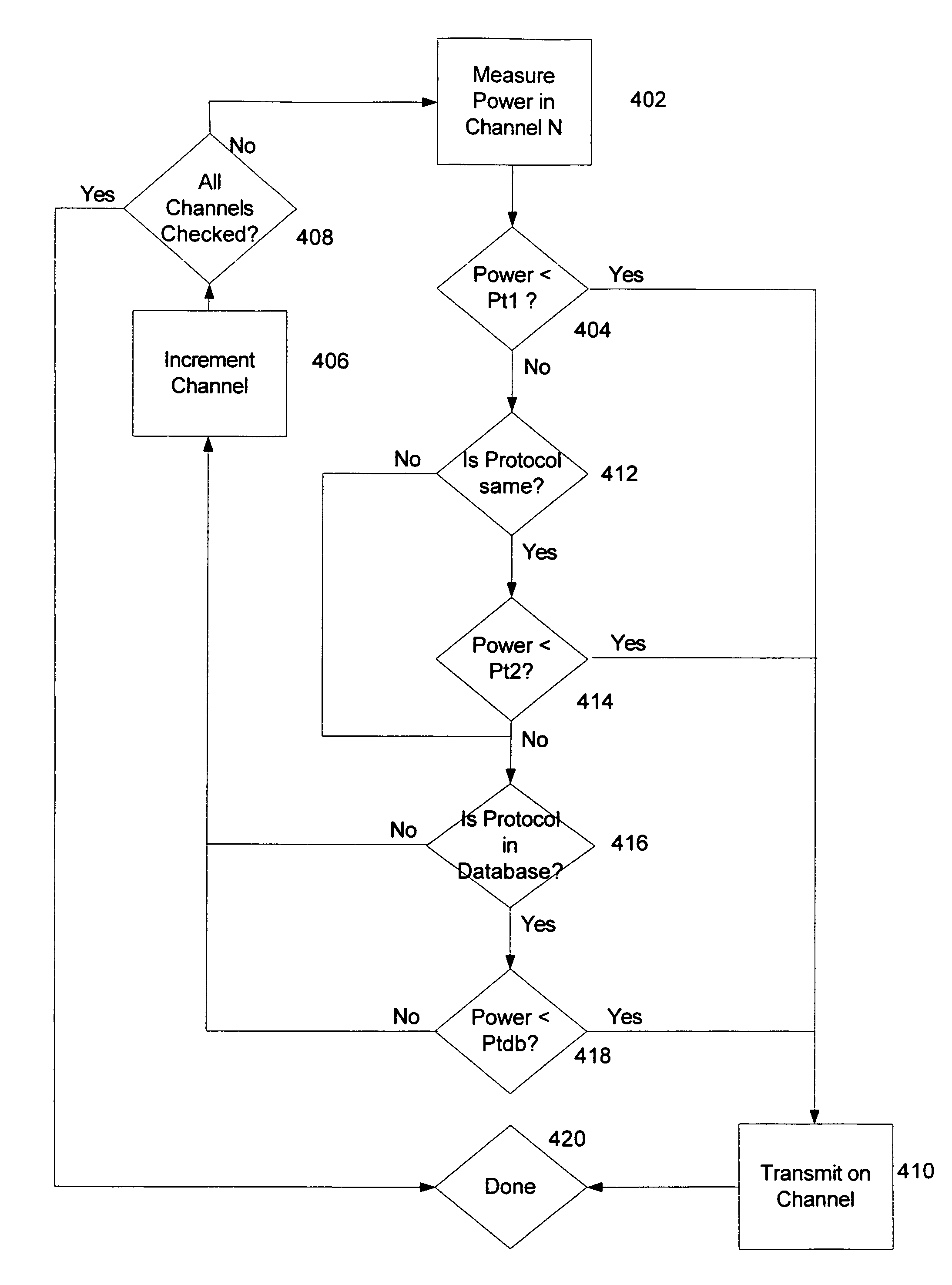
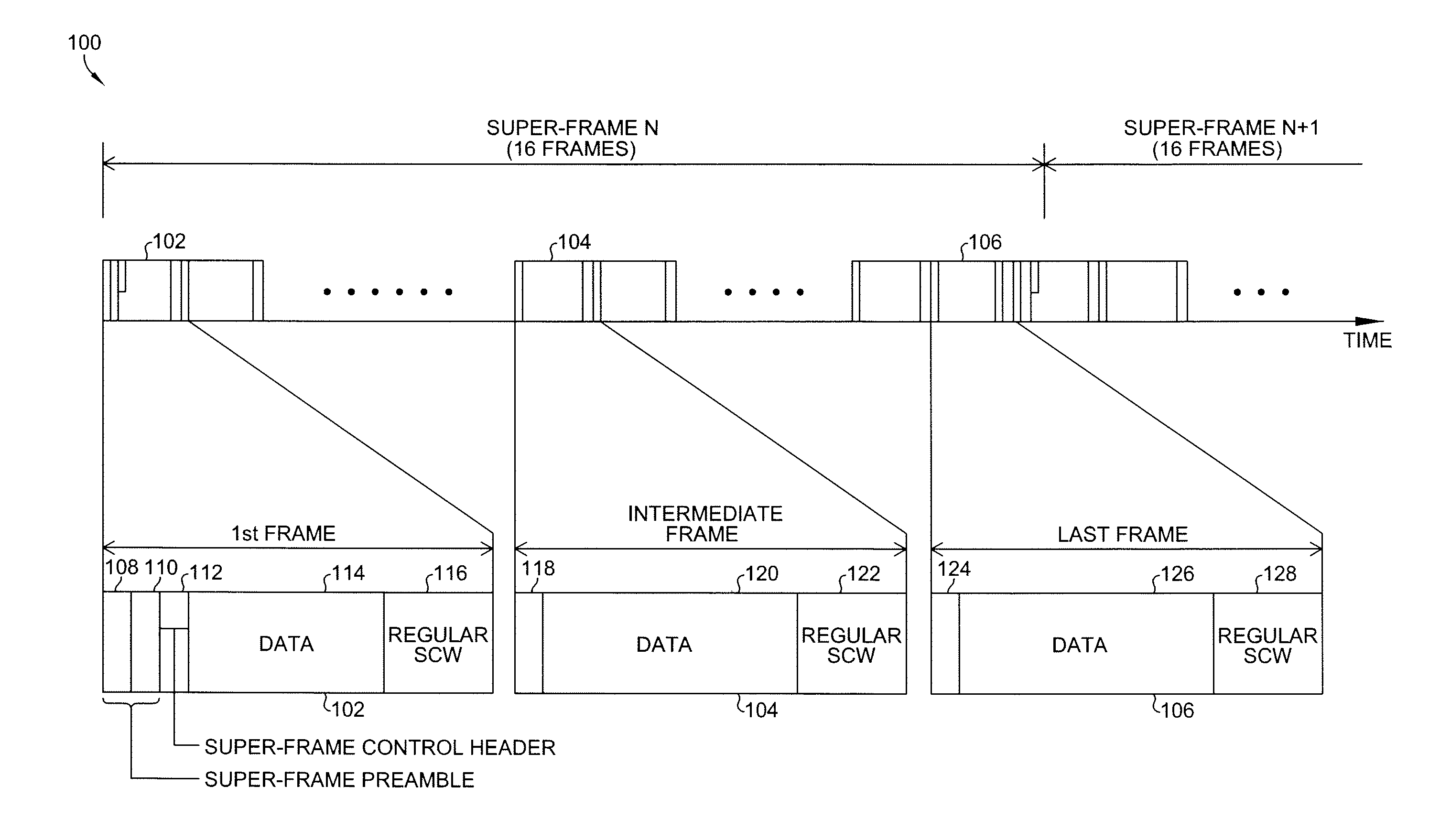
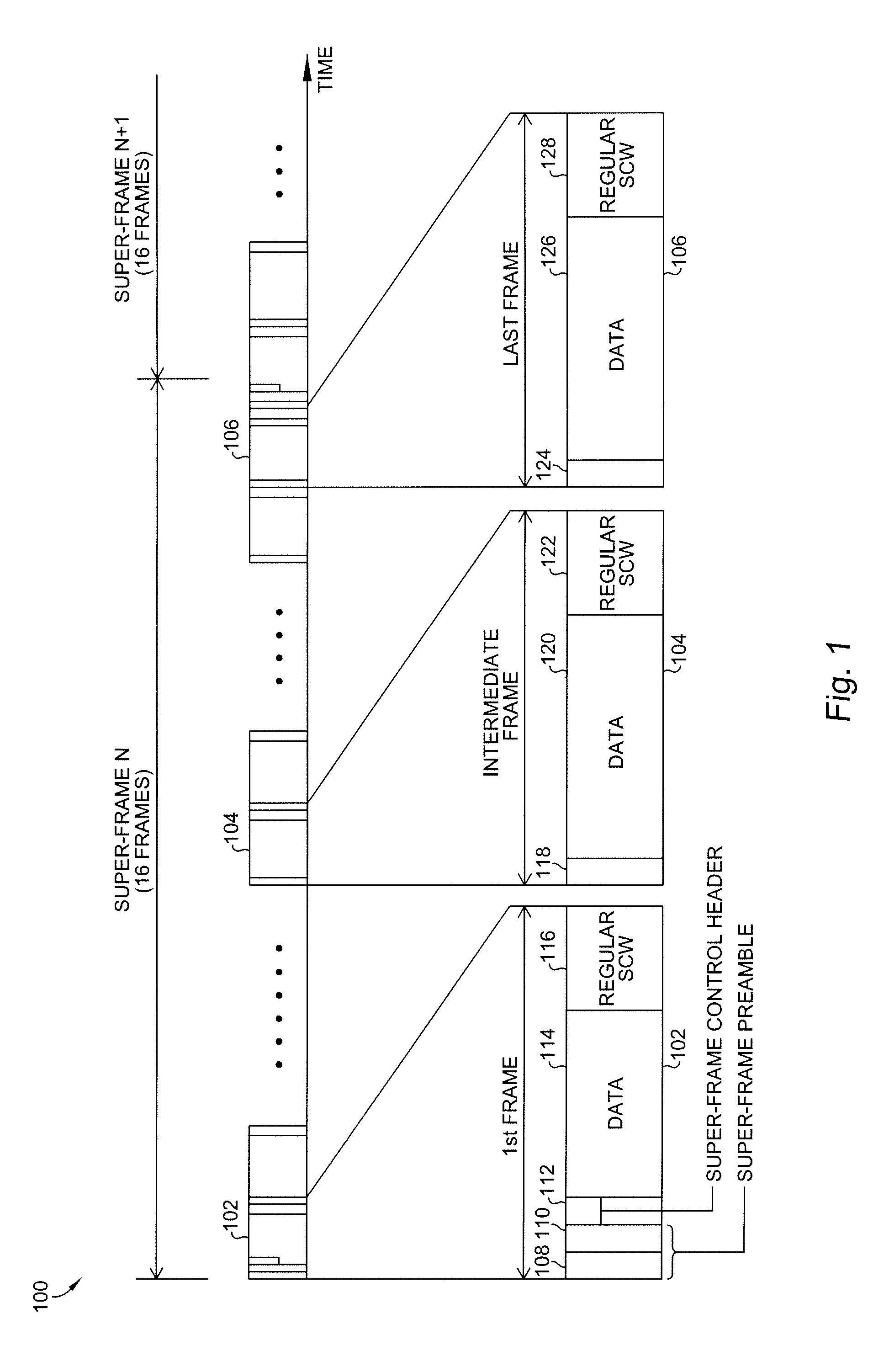
Super-frame structure for dynamic spectrum sharing in wireless networks
ActiveUS20100142559A1Modulated-carrier systemsAssess restrictionWireless mesh networkFrequency spectrum
A coexistence communications method for use between wireless networks includes adopting a super-frame structure for use in a wireless network having a plurality of frames, wherein a first frame includes a super-frame preamble, a super-frame control header, a data portion, and a regular self-coexistence window, an intermediate frame includes an OFDM symbol, a data portion, and a regular self-coexistence window, and a last frame includes an OFDM symbol, a data portion, and a joining self-coexistence window, using the self-coexistence windows to exchange inter-wireless network co-existence messages, and using a last reserved self-coexistence window to announce intra-wireless network negotiation decisions.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com