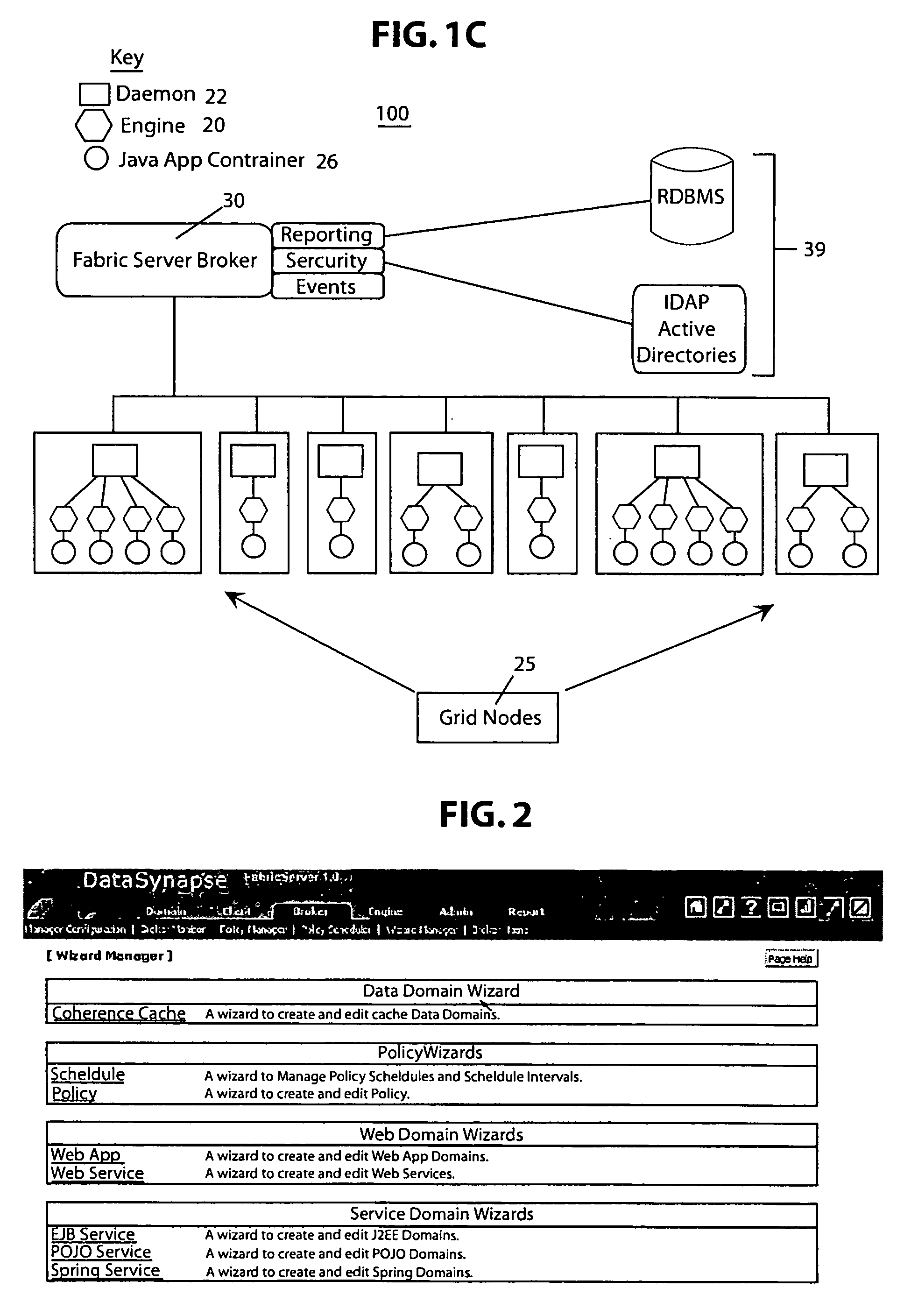
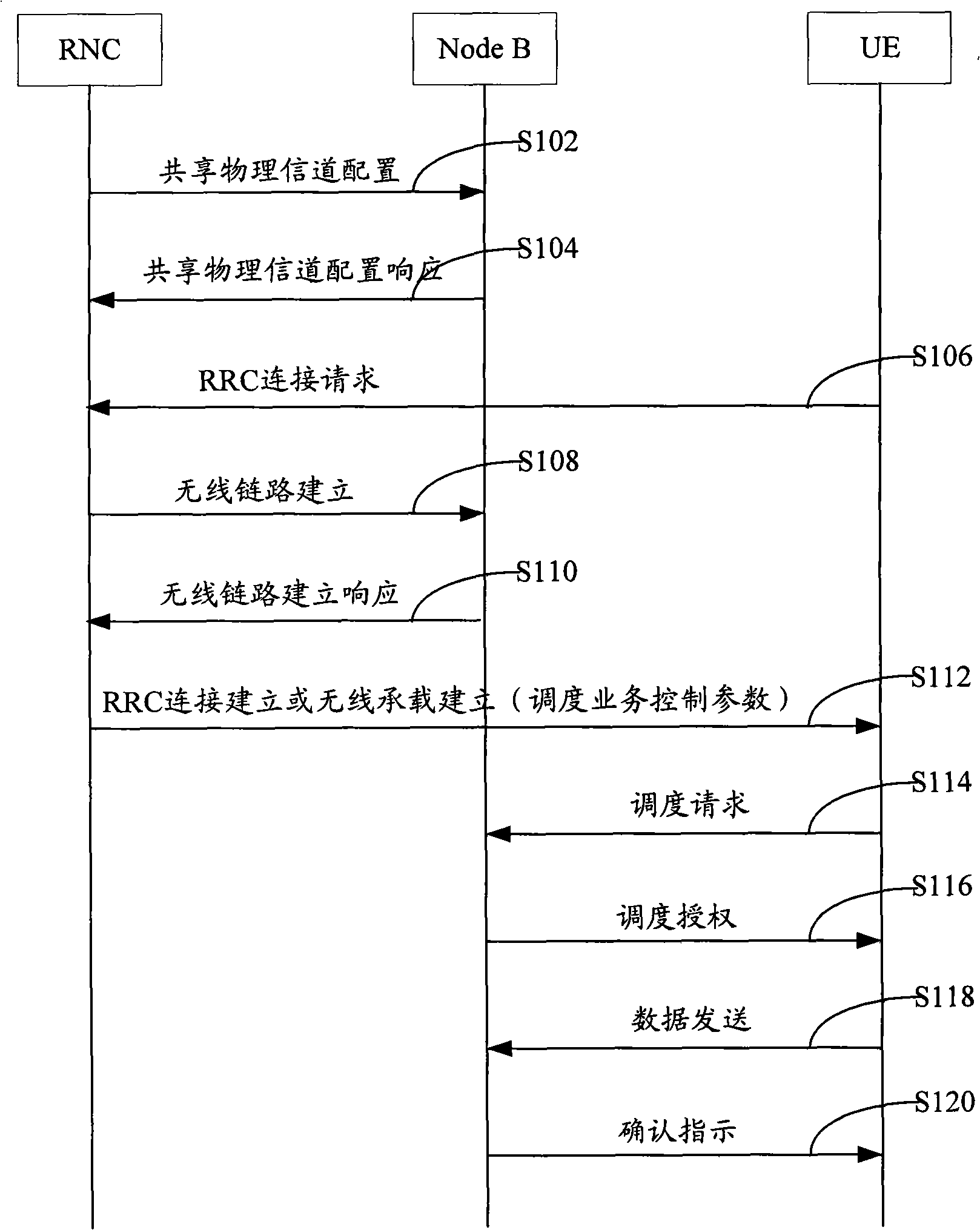
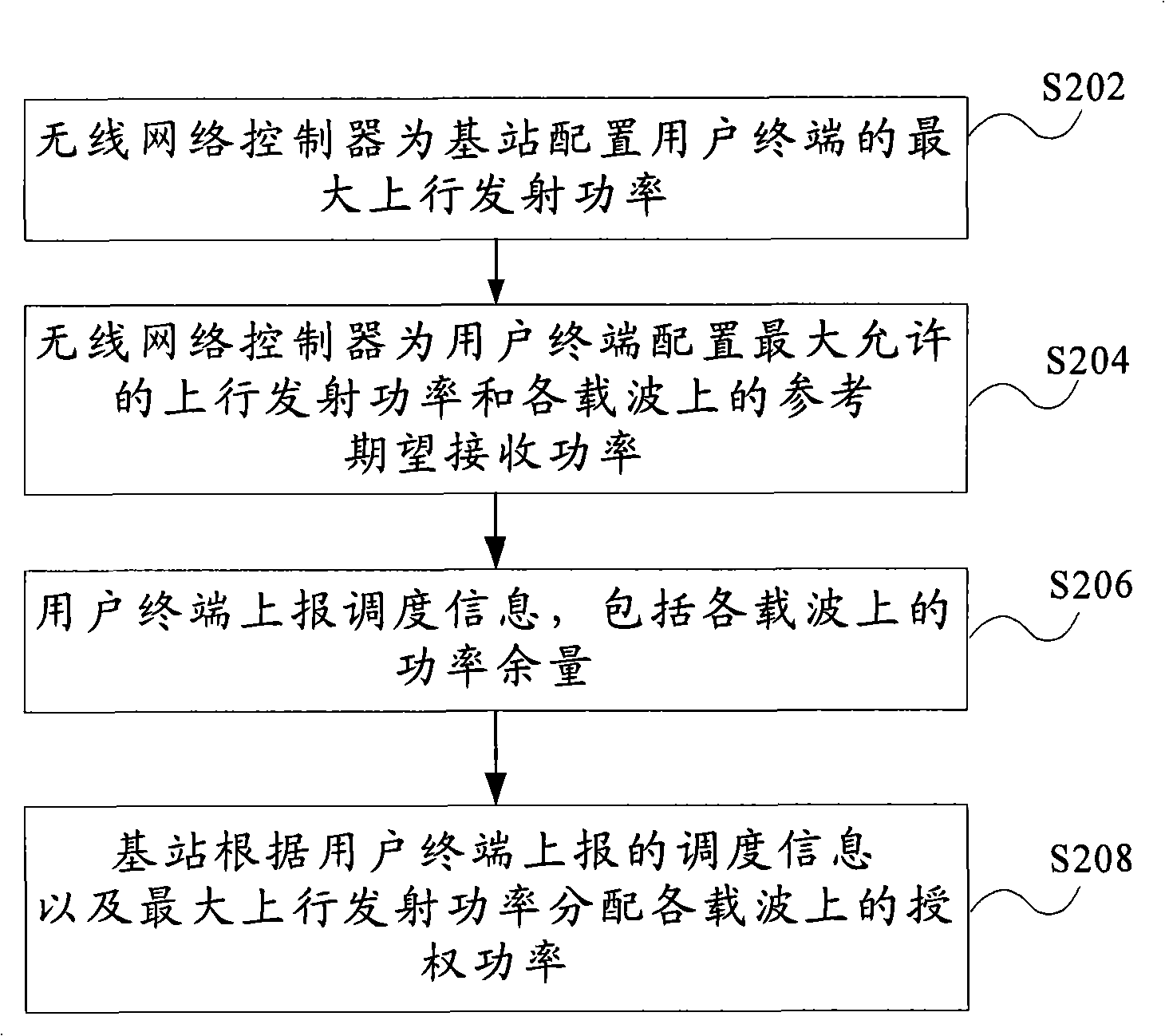
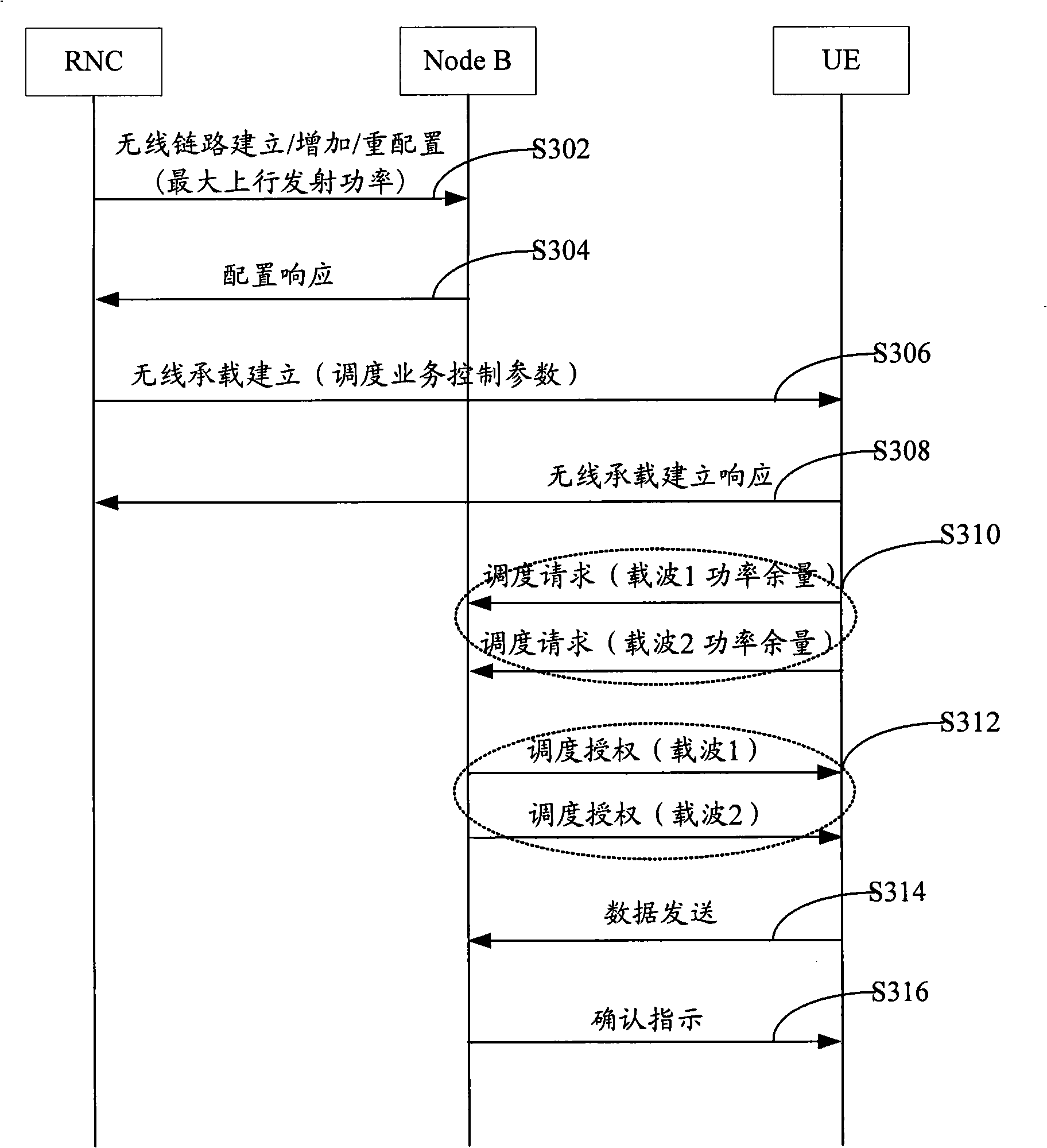
Patents
Literature
7967 results about "Allocation method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
This method provides a better picture of how costs are incurred, but requires more accounting effort. It also tends to delay the recognition of expenses until a later period, when some portion of the produced goods are sold. Indirect (or interdepartmental) allocation method.
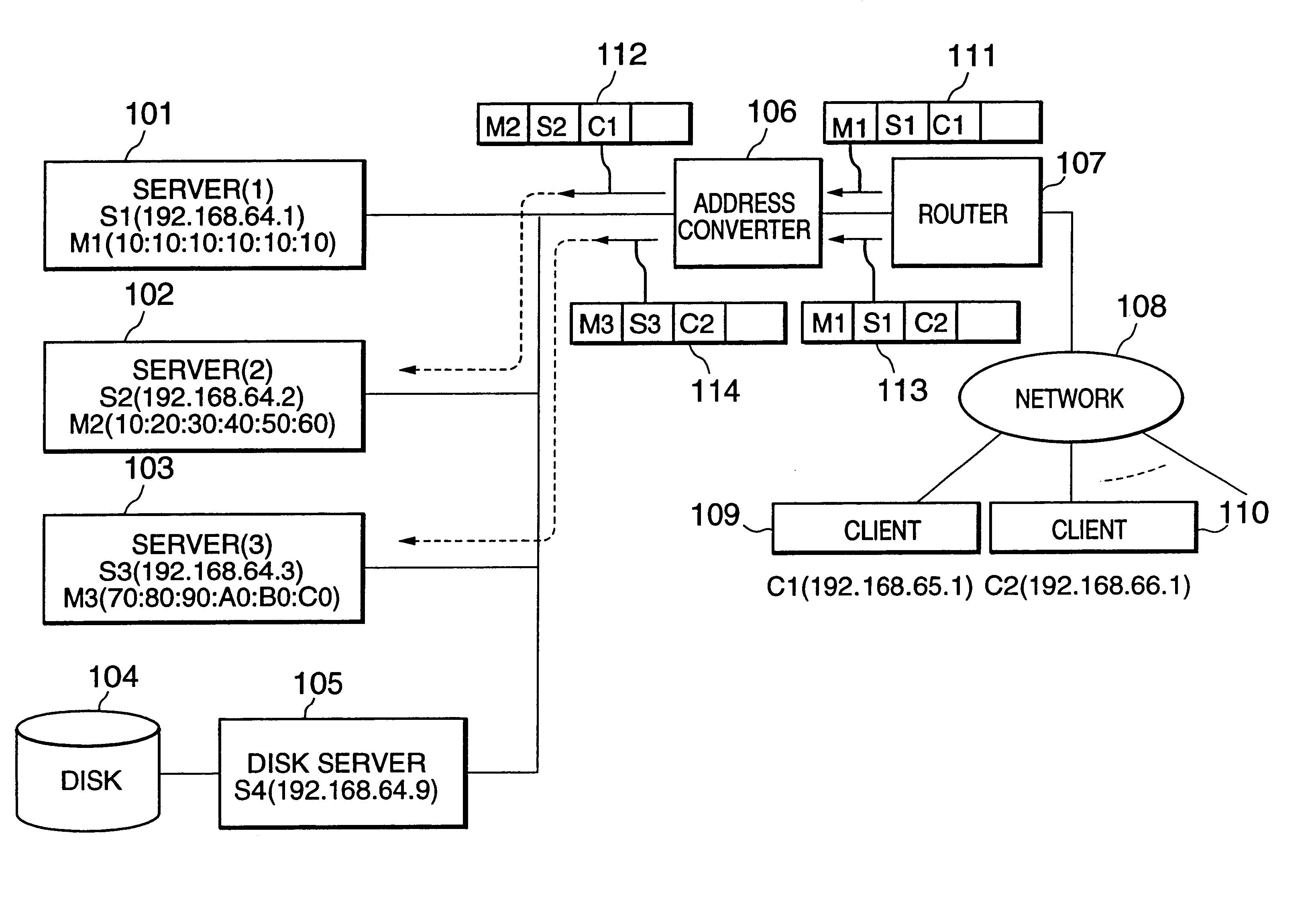
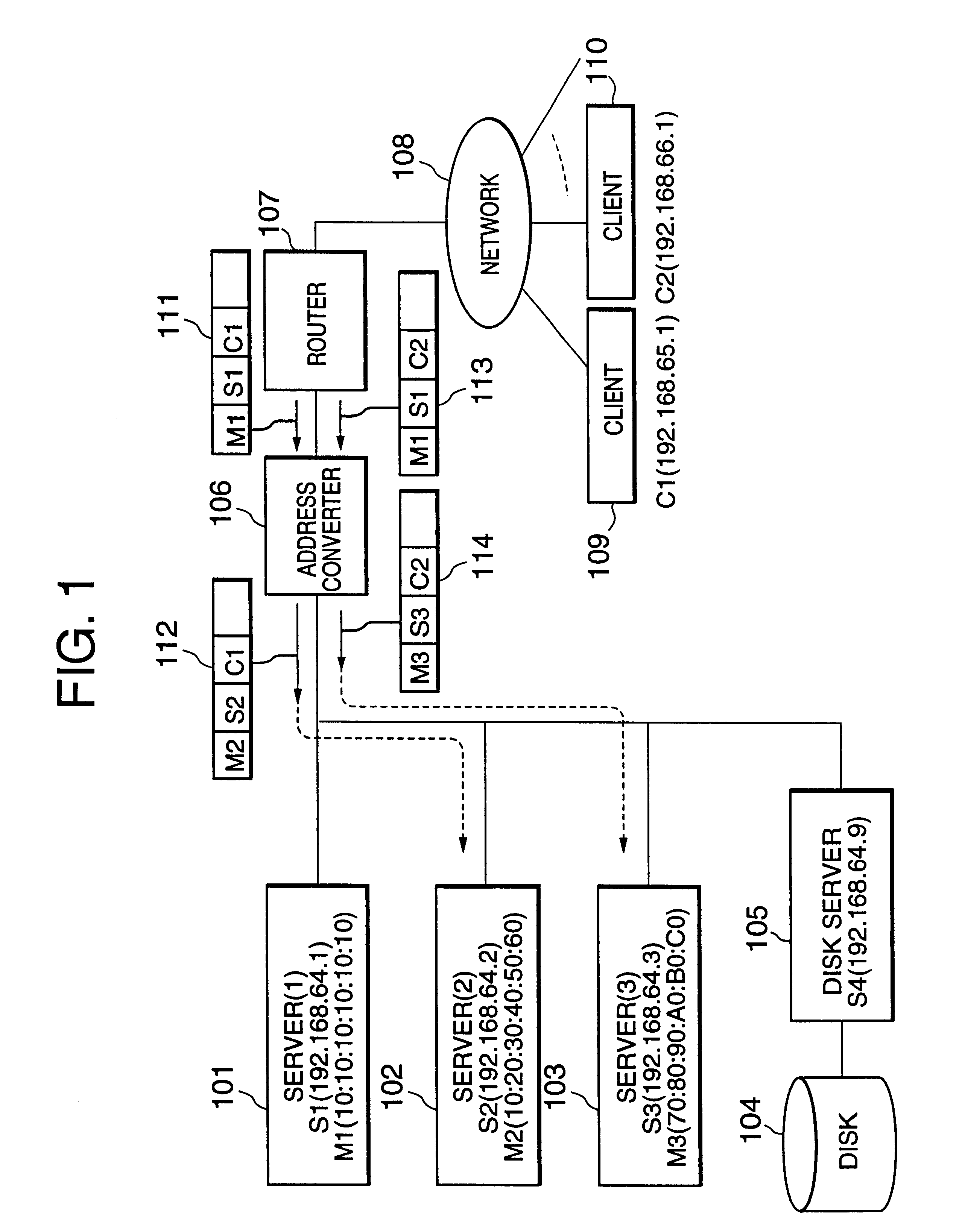
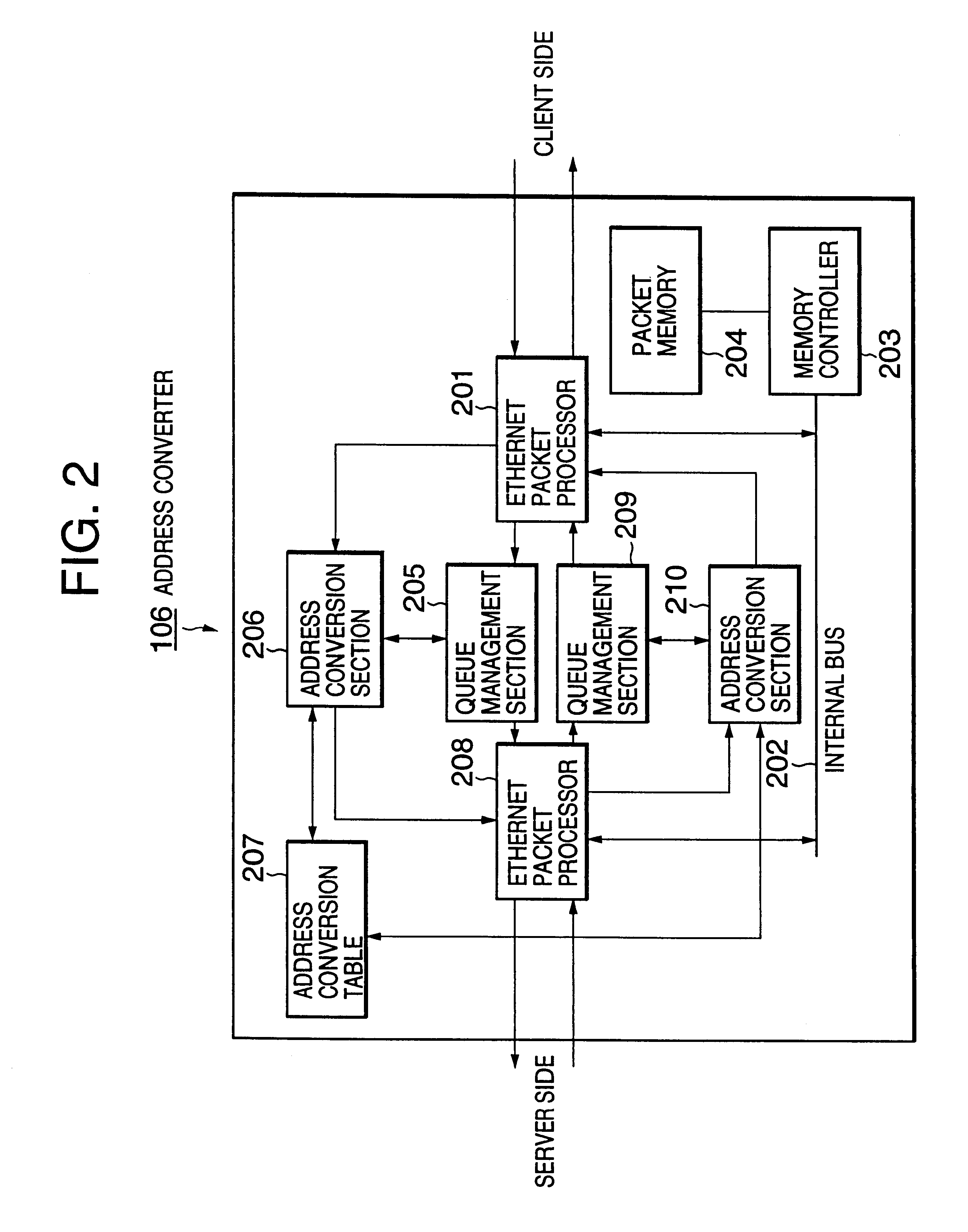
Address-based service request distributing method and address converter
InactiveUS6611873B1Disperse the load of each serverEasy to implementData processing applicationsMultiprogramming arrangementsSession managementDistributed services
A method for distributing service requests to a plurality of servers without any need for preparing a special measure in the clients or performing session management is disclosed. Addresses of a plurality of clients are classified in advance into a plurality of address groups. Each of the plurality of address groups is correlated with one of a plurality of servers. A service request of a client is distributed to a corresponding server depending on which address group the client belongs to.
Owner:NEC CORP
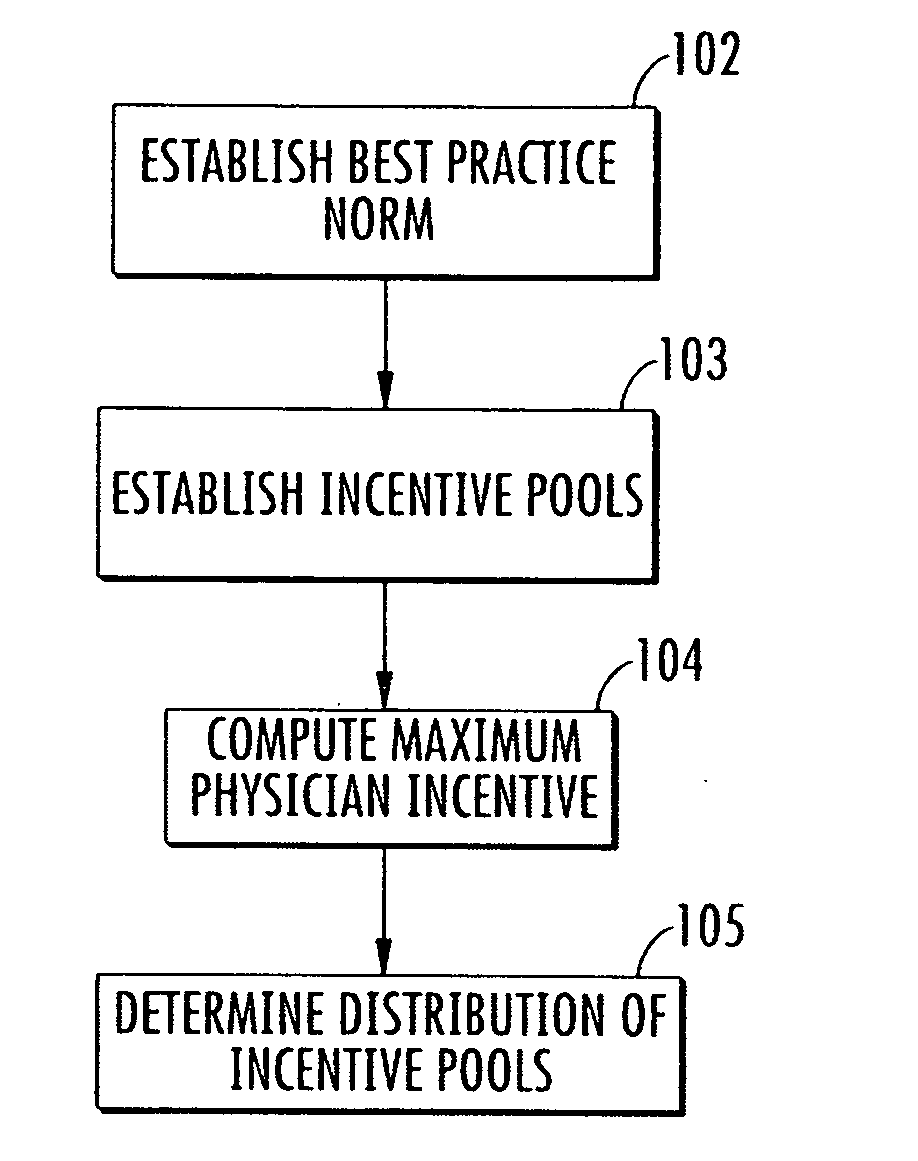
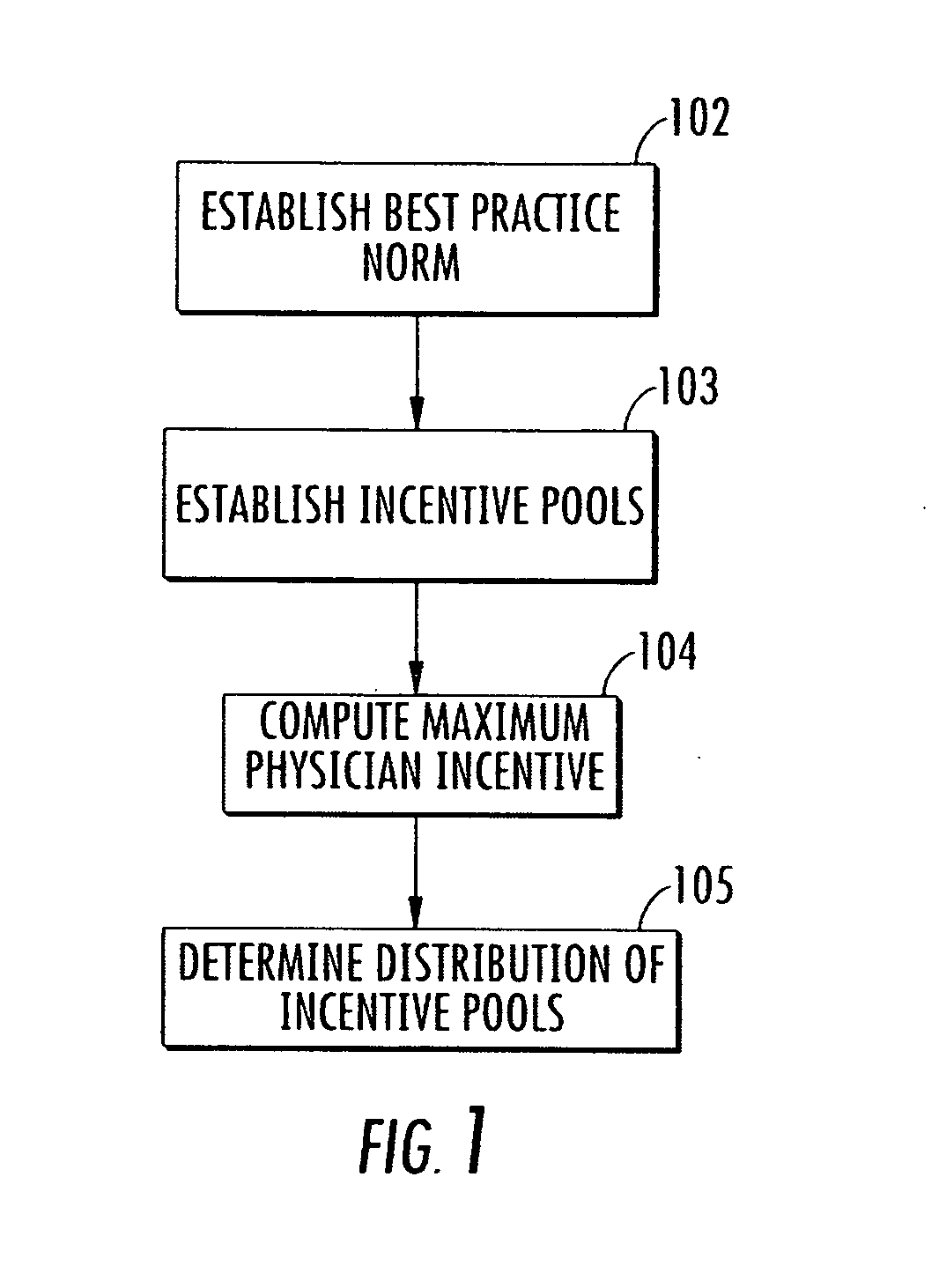
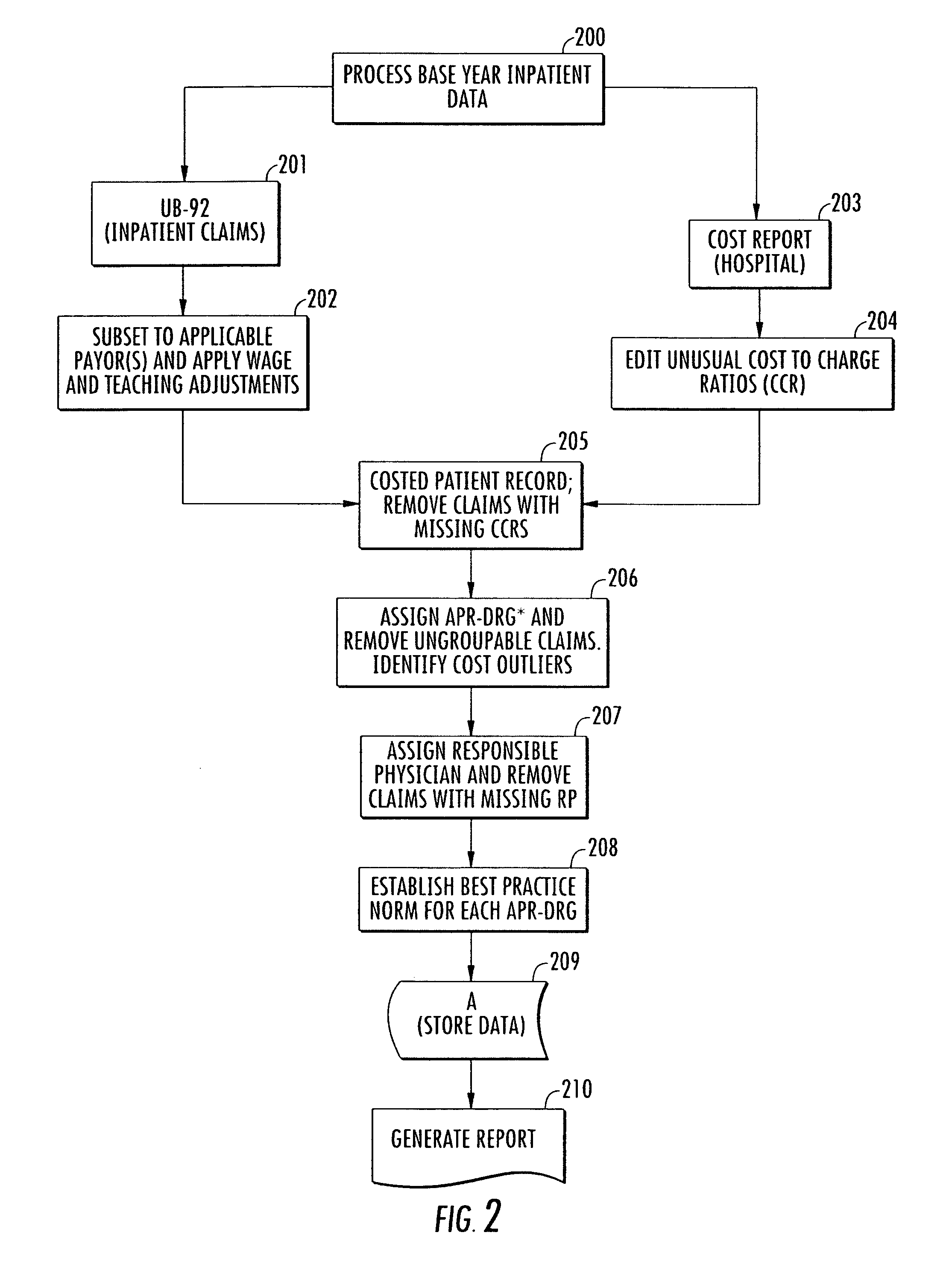
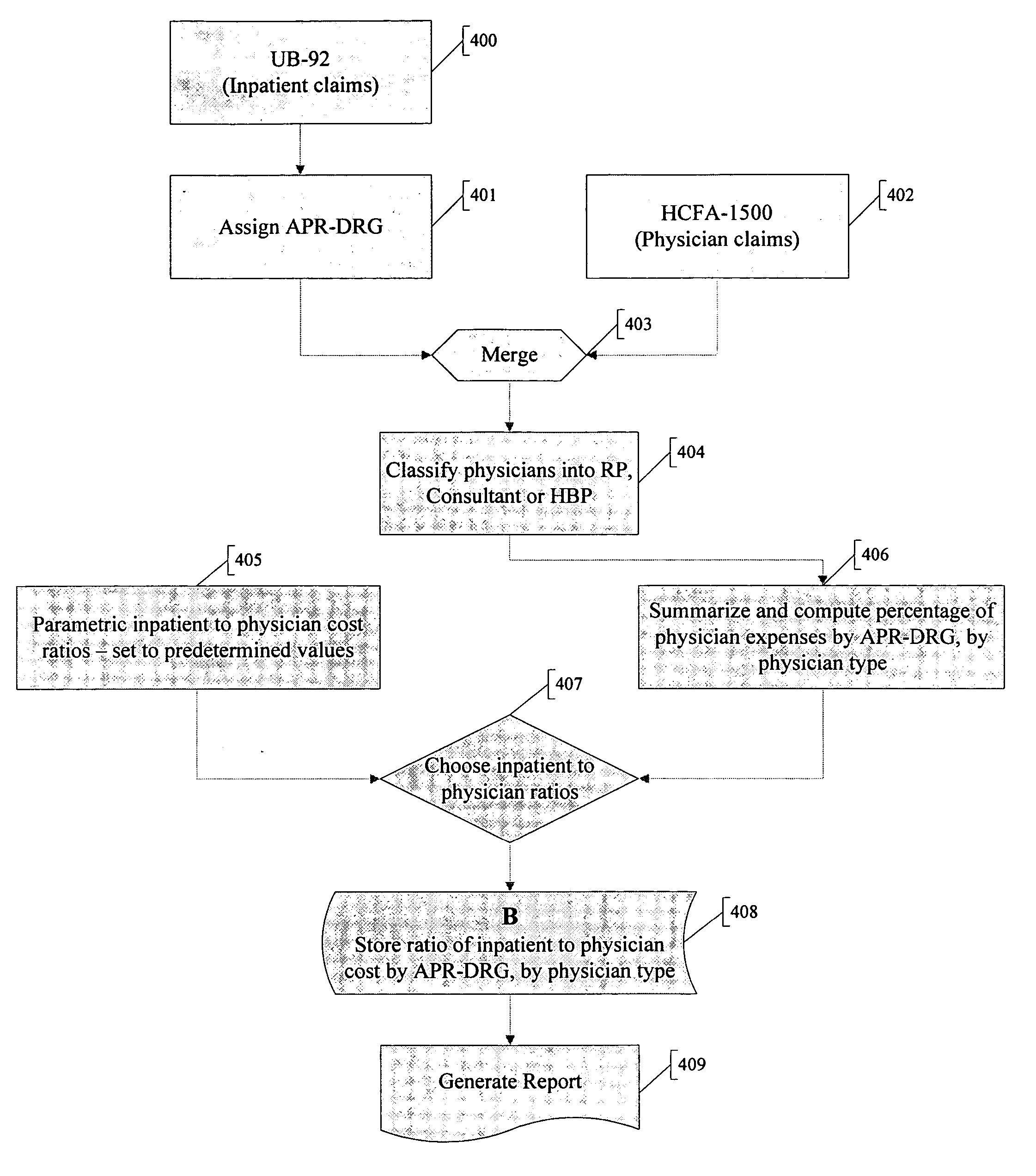
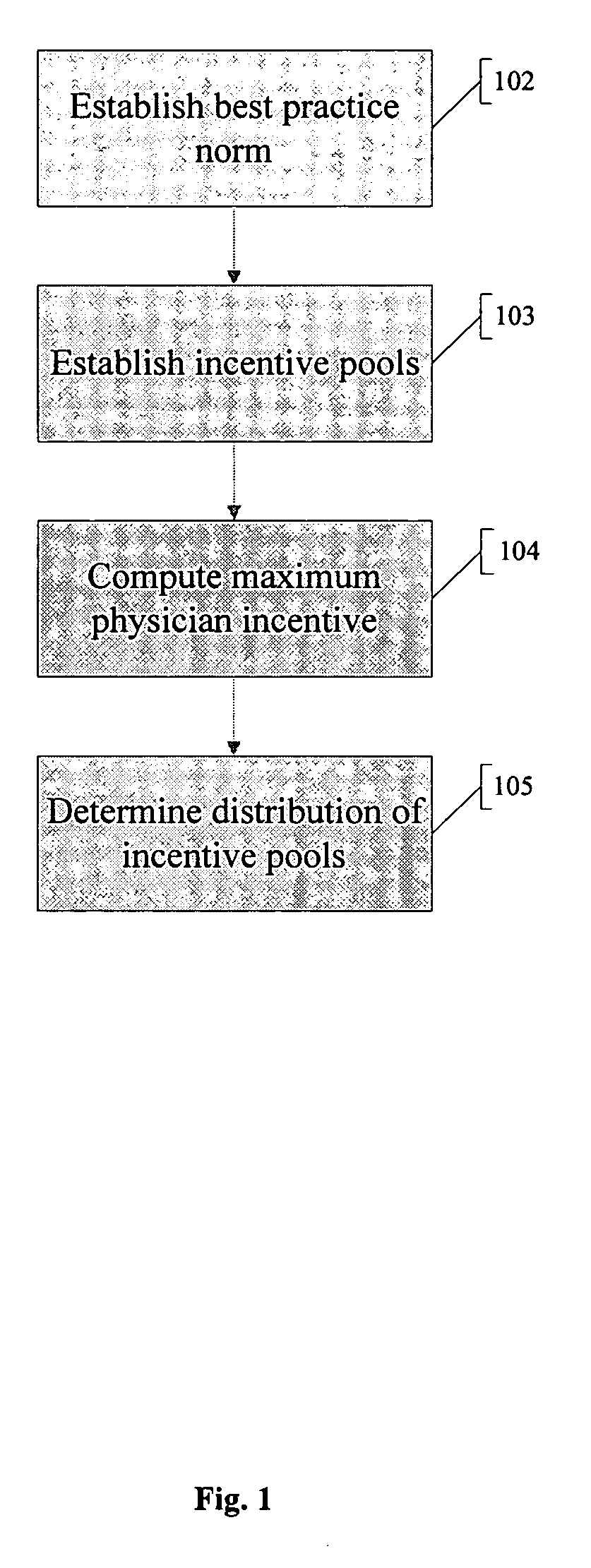
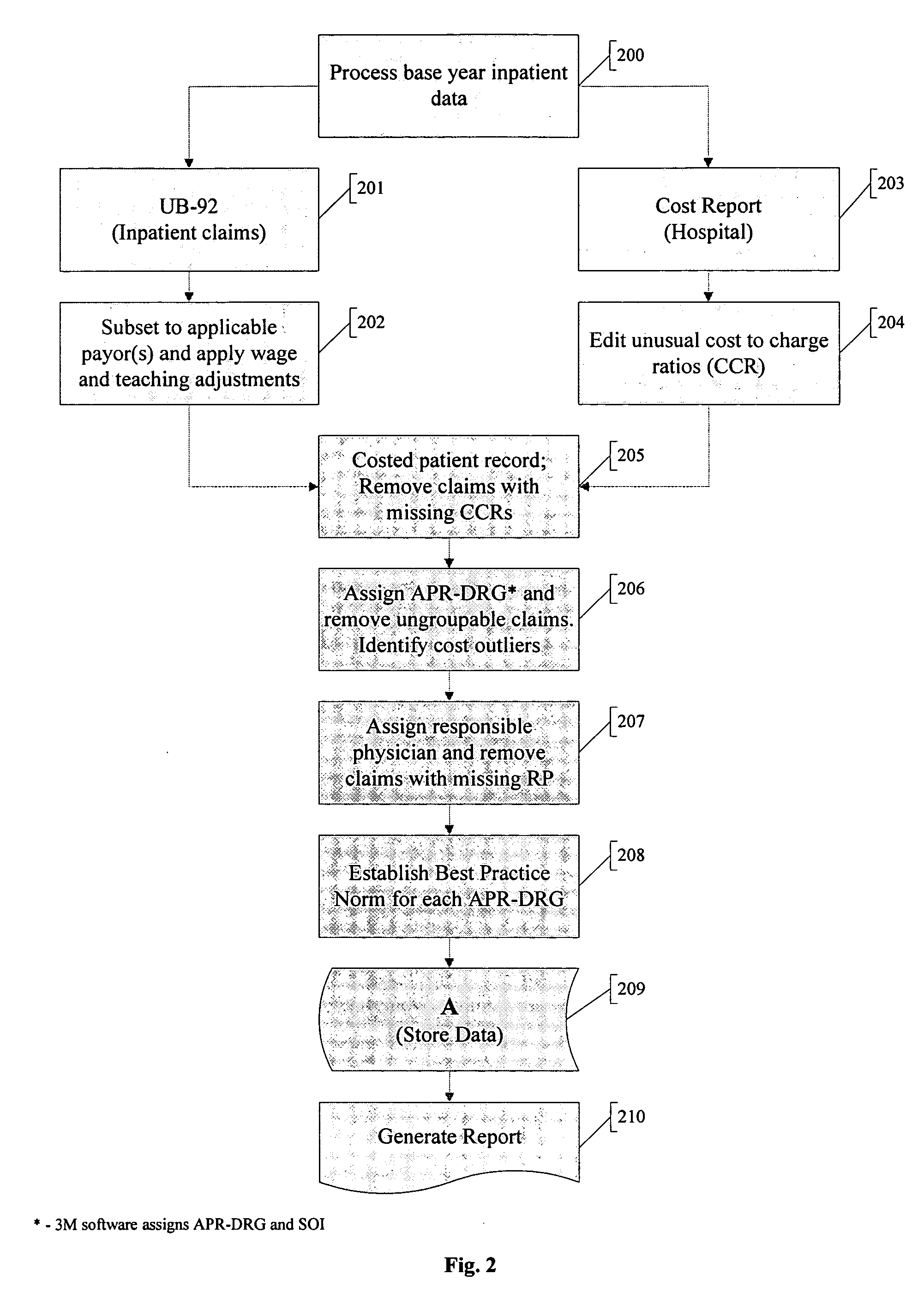
Method and system for evaluating a physician's economic performance and gainsharing of physician services
InactiveUS20080195417A1Impose significant, additional data collection burdens on providersEfficient and inexpensiveFinanceOffice automationPaymentDisease
The invention relates to a method and system of physician economic performance evaluation in which the relative medical difficulty associated with patients admitted by a particular physician is determined and, given that measurement, judgments made concerning the relative amount of inpatient resources that the physician required. Also, one application of the present invention relates to a method for gainsharing of physician services using a surplus allocation methodology for rewarding physicians in relation to their performance. An incentive pool is determined from previous patient claims and payments made to physicians in advance, such as in a base year. Best practice norms are established for a plurality of classified diagnosis groups. In one embodiment of the present invention, the classified diagnosis related groups are adjusted for severity of illness to compensate for actual clinical challenges faced by individual physicians. The best practice norms can be used in the surplus allocation method for determining physician performance. The incentive is established proportional to the relationship between a physician's individual performance and the best practice norm.
Owner:AMS APPLIED MEDICAL SOFTWARE
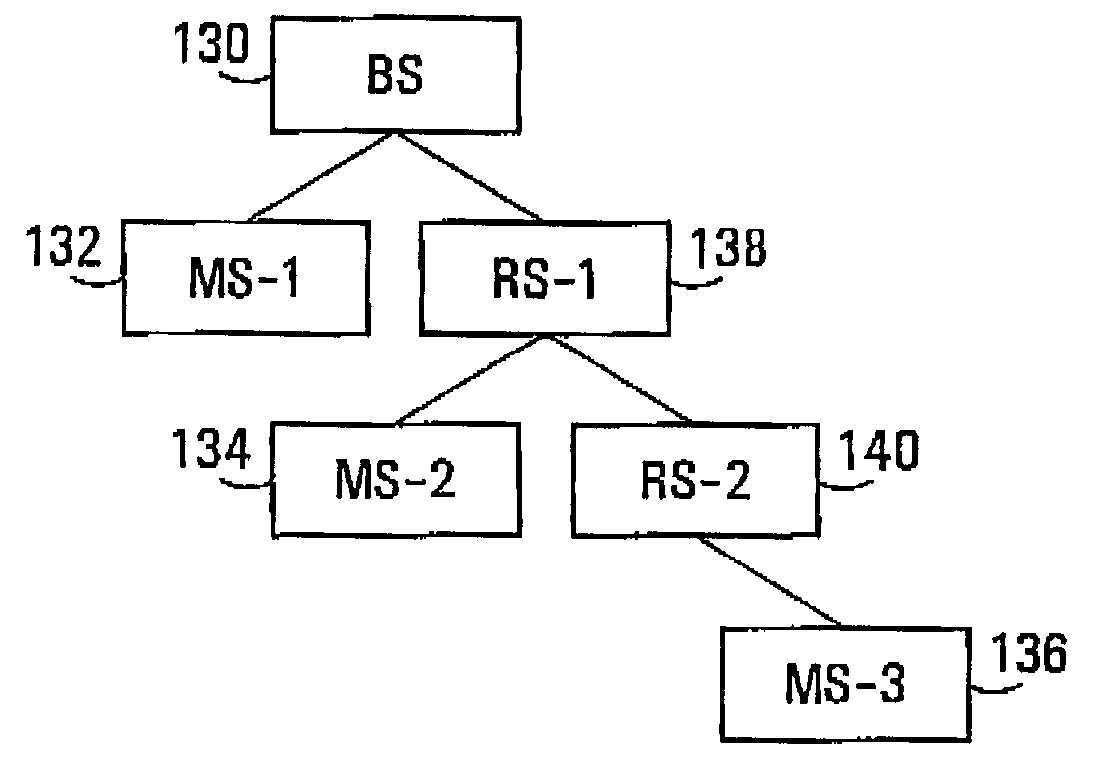
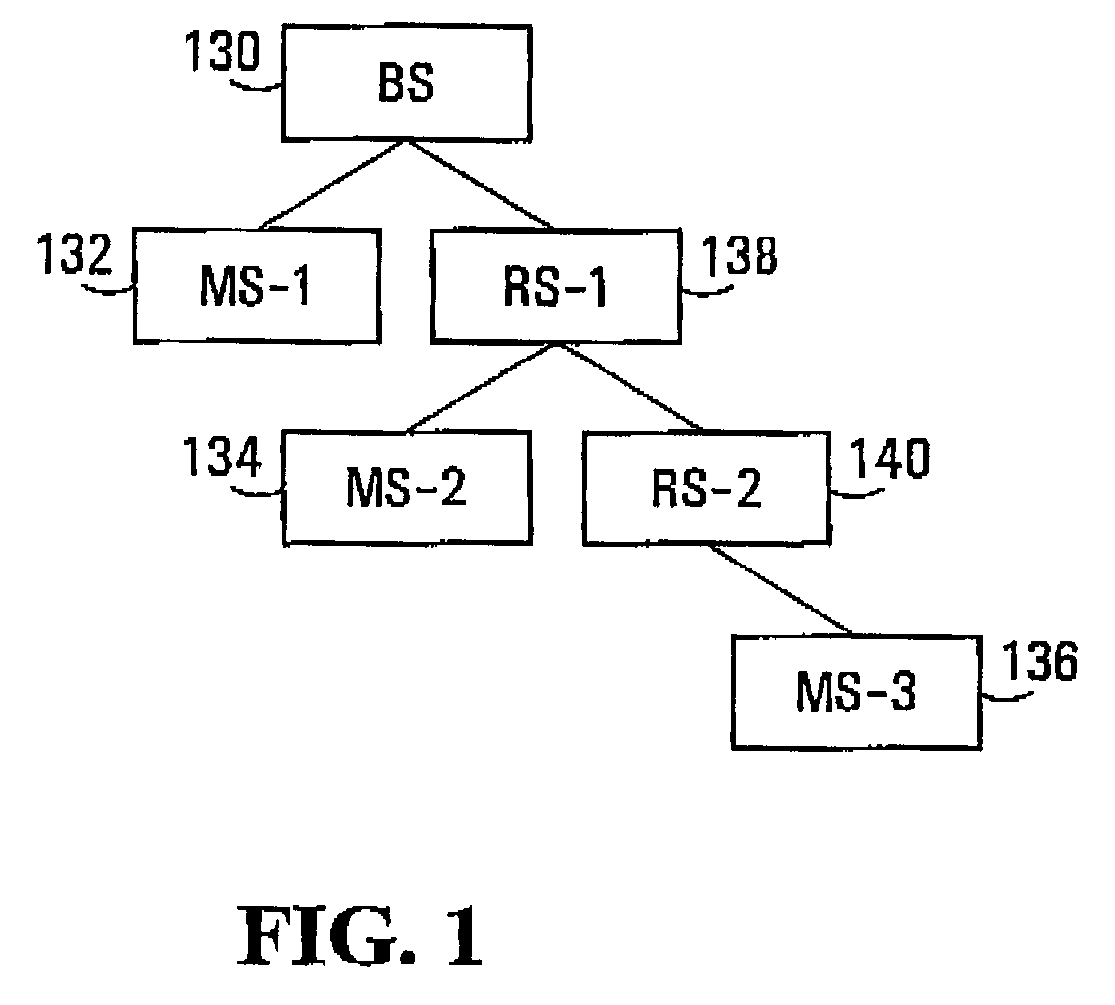
Zones for wireless networks with relays
ActiveUS20090303918A1Easy to detectAvoid collisionFrequency-division multiplex detailsModulated-carrier systemsDistribution methodMobile station
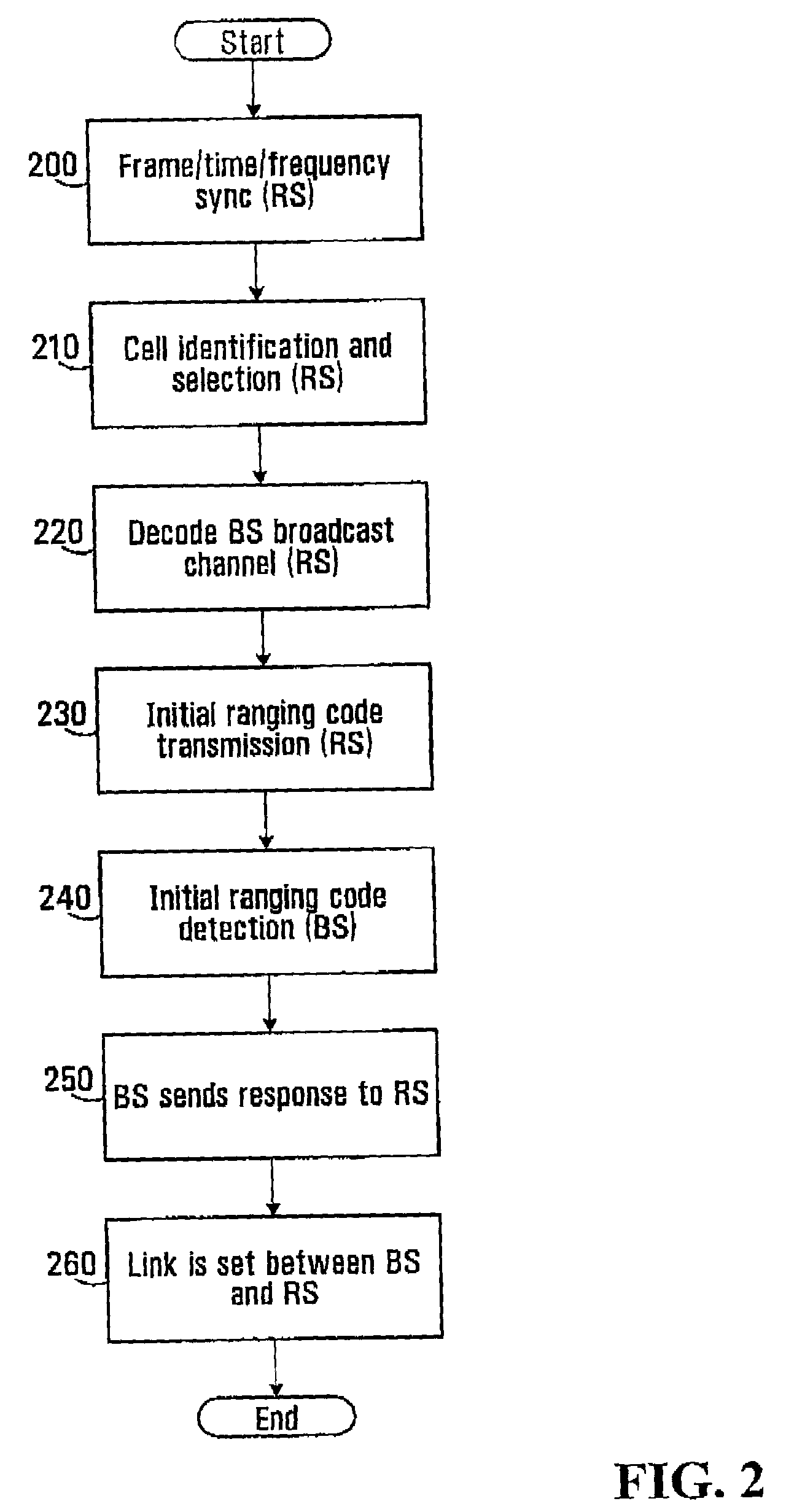
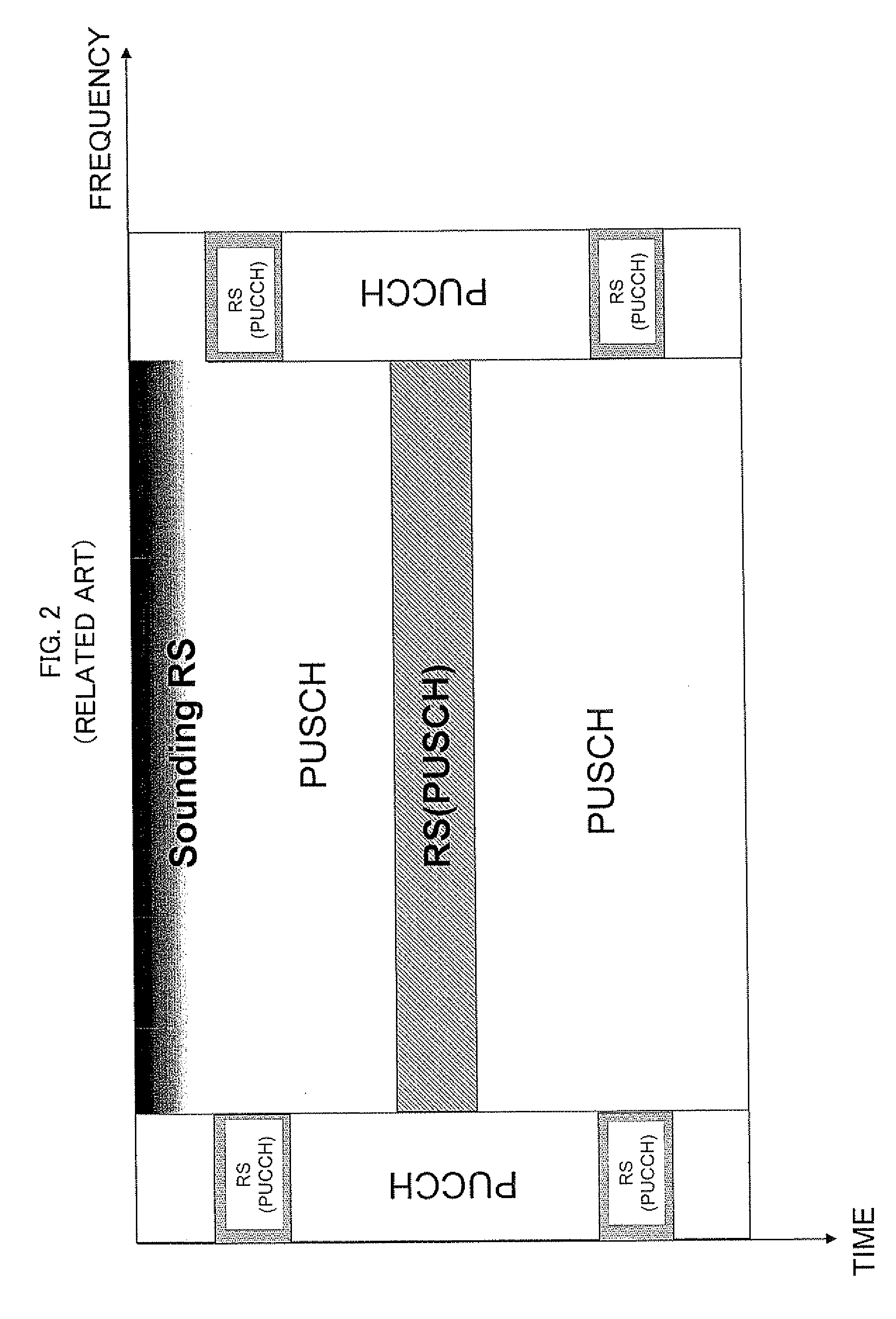
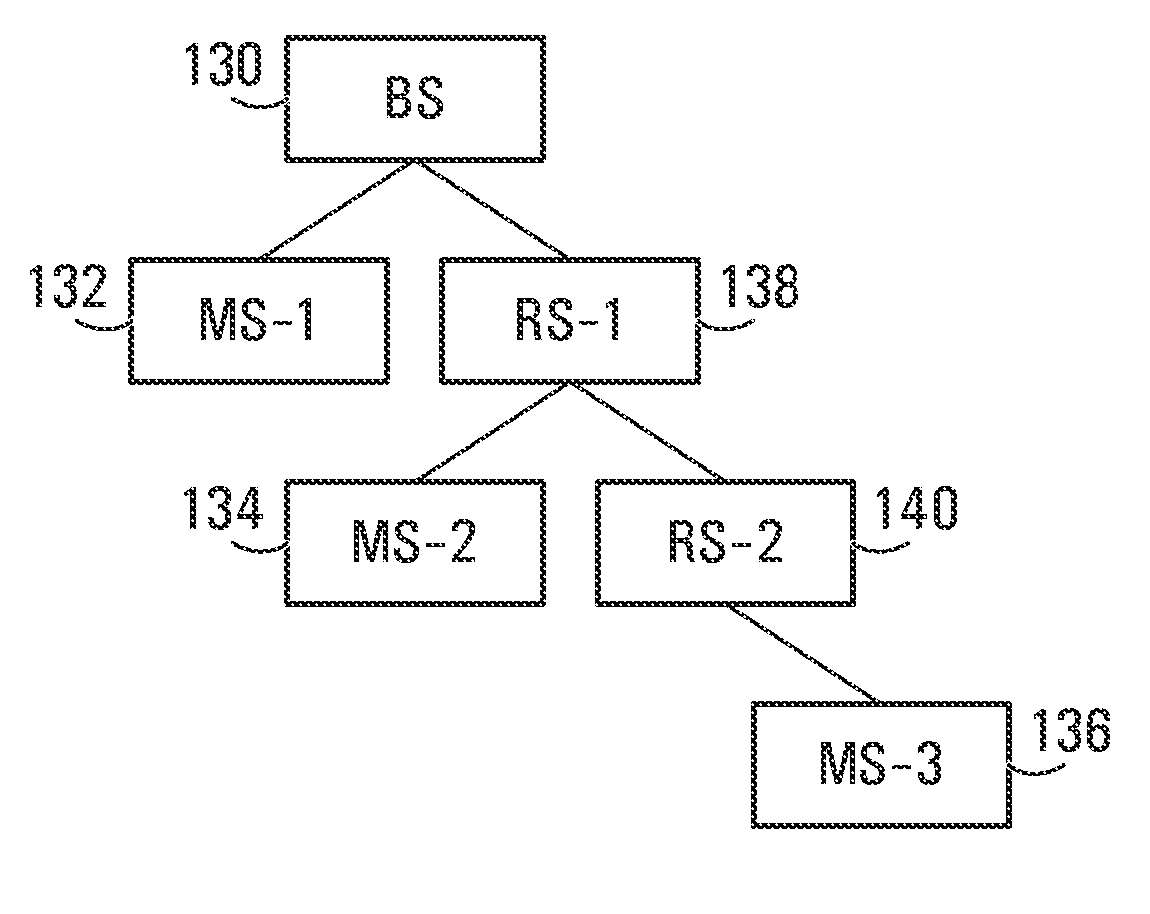
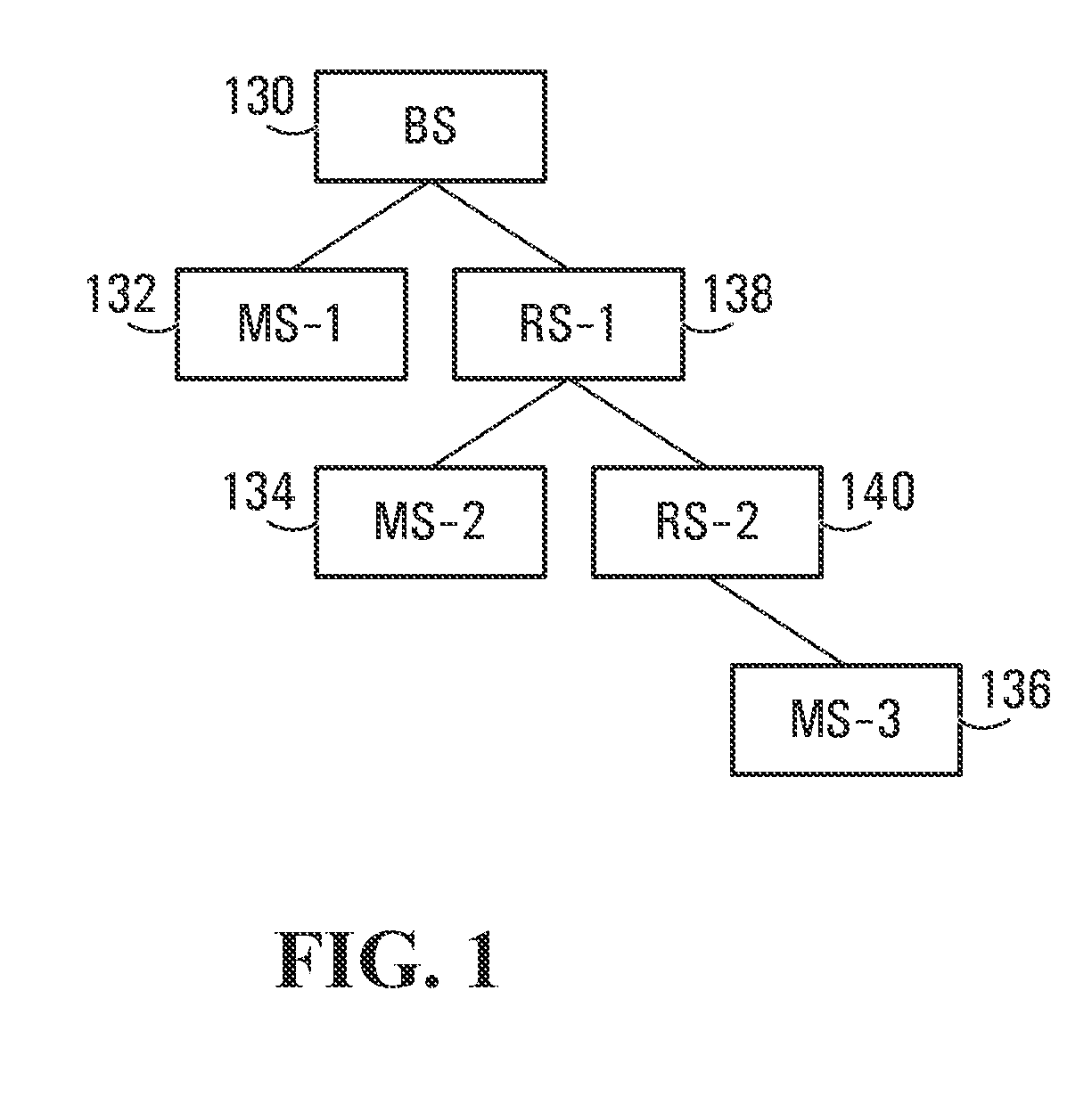
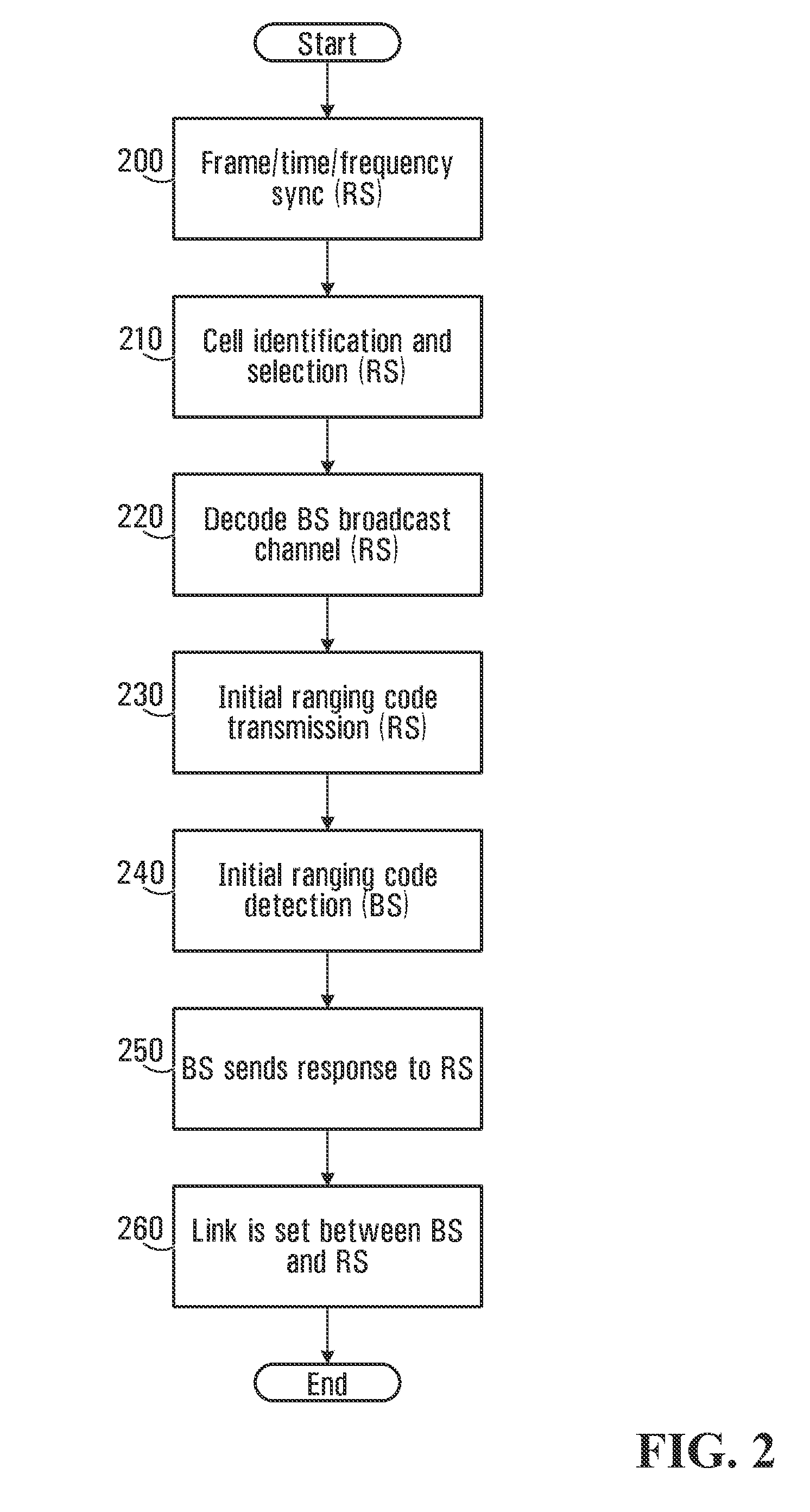
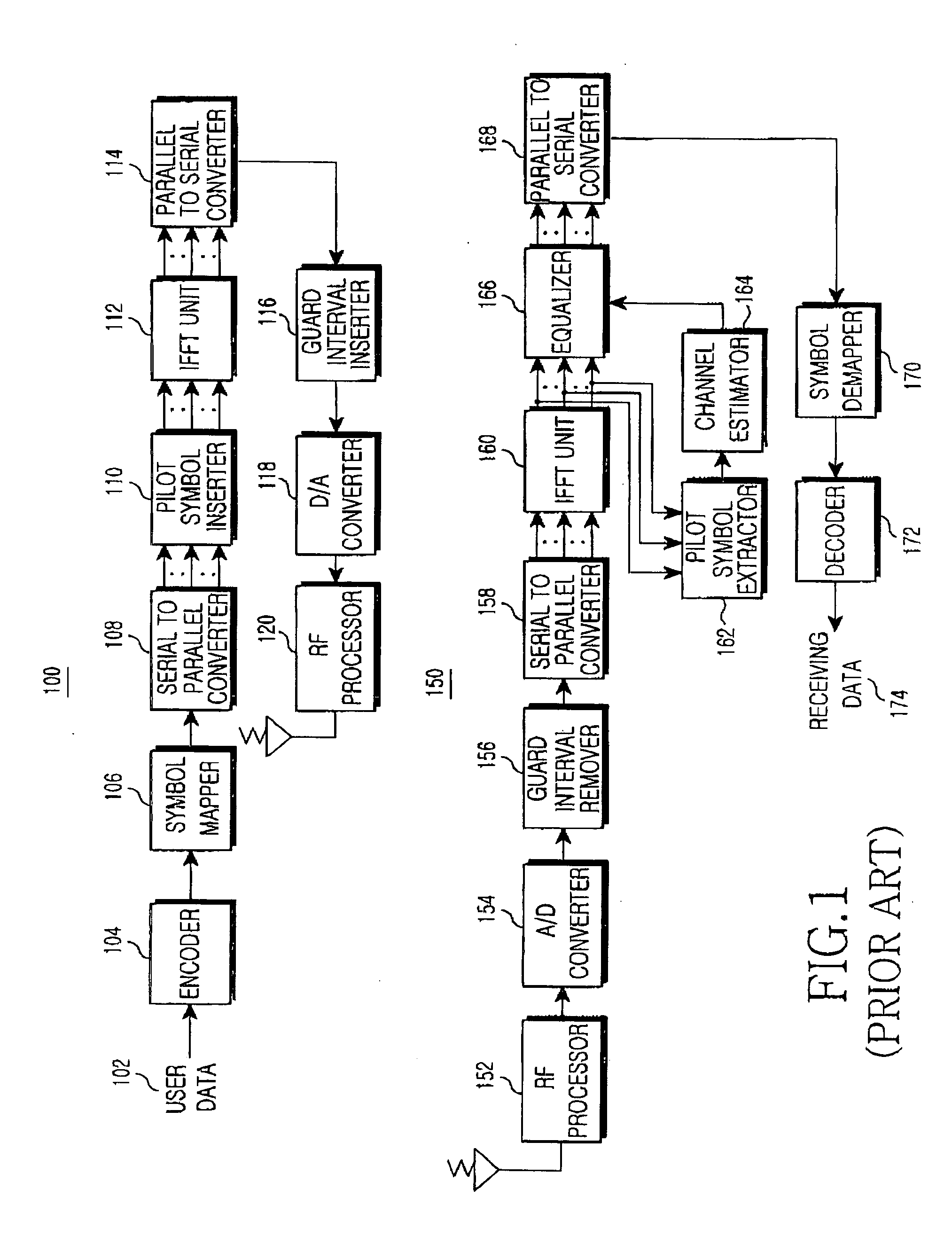
Methods and systems are provided for use with wireless networks having once or more cell in which each cell includes a base station (BS), at least one relay station (RS) and at least one mobile station (MS). The at least one relay station can be used as an intermediate station for providing communication between the BS and MS. Methods are provided for an RS to initially access the network, access of the RS by MSs initially accessing the network, methods of allocating OFDM resources for communicating between the BS, RS and / or MS for example dividing transmission resources into uplink and downlink transmissions, and methods of inserting pilot symbols into transmission resources used by the RS. In some embodiments on the invention, the methods are consistent and / or can be used in conjunction with existing standards such as 802.16e.
Owner:APPLE INC
Adaptive bandwidth allocation method for non-reserved traffic in a high-speed data transmission network, and system for implementing said method
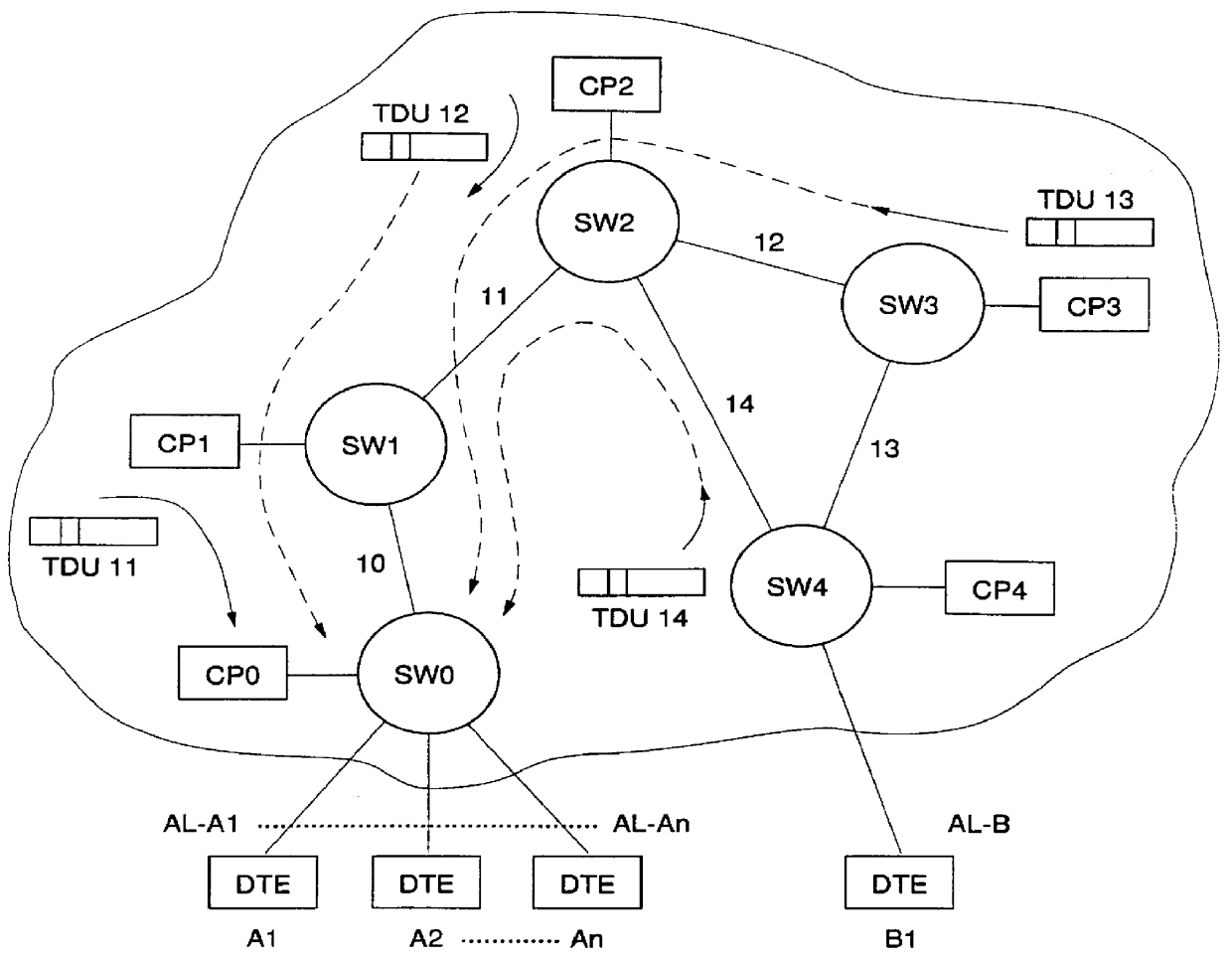
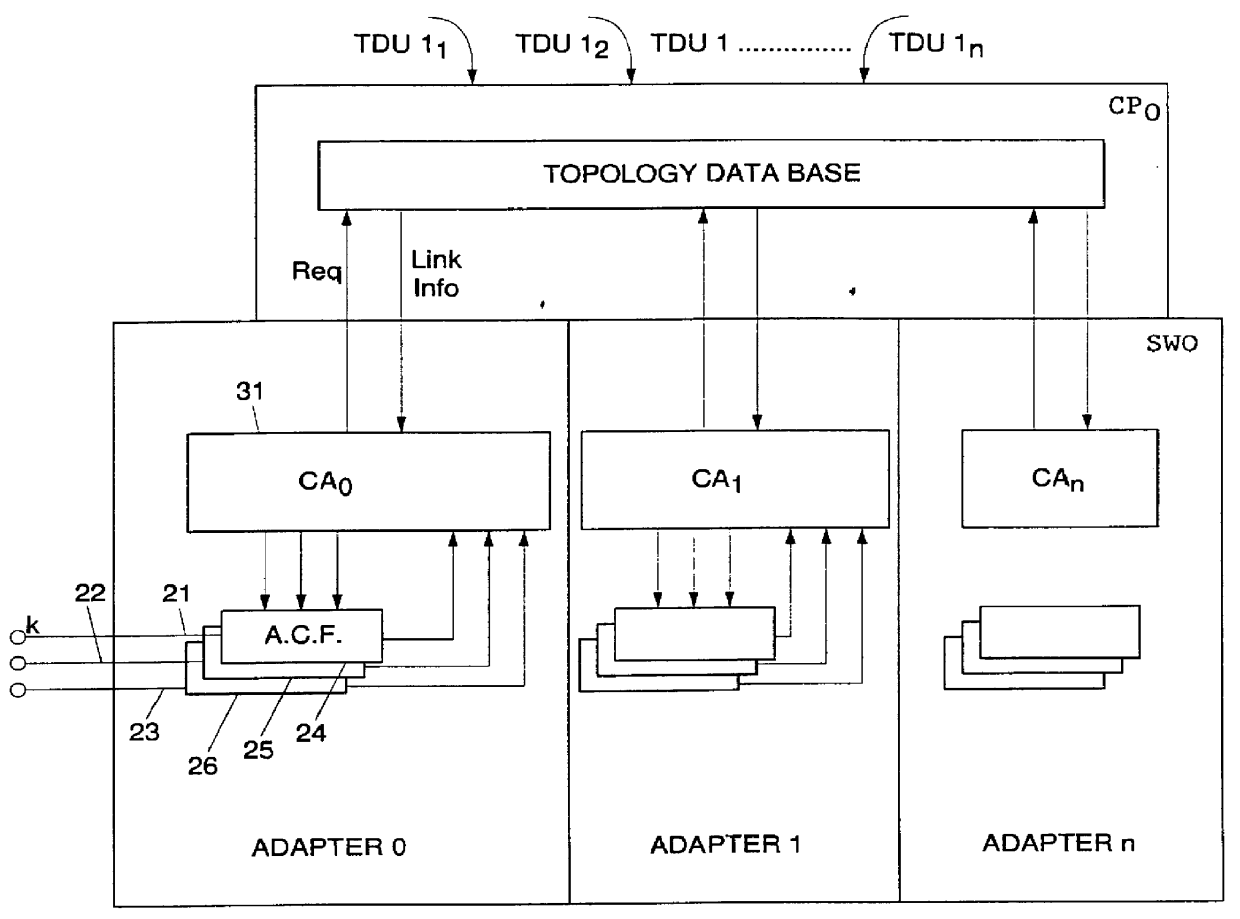
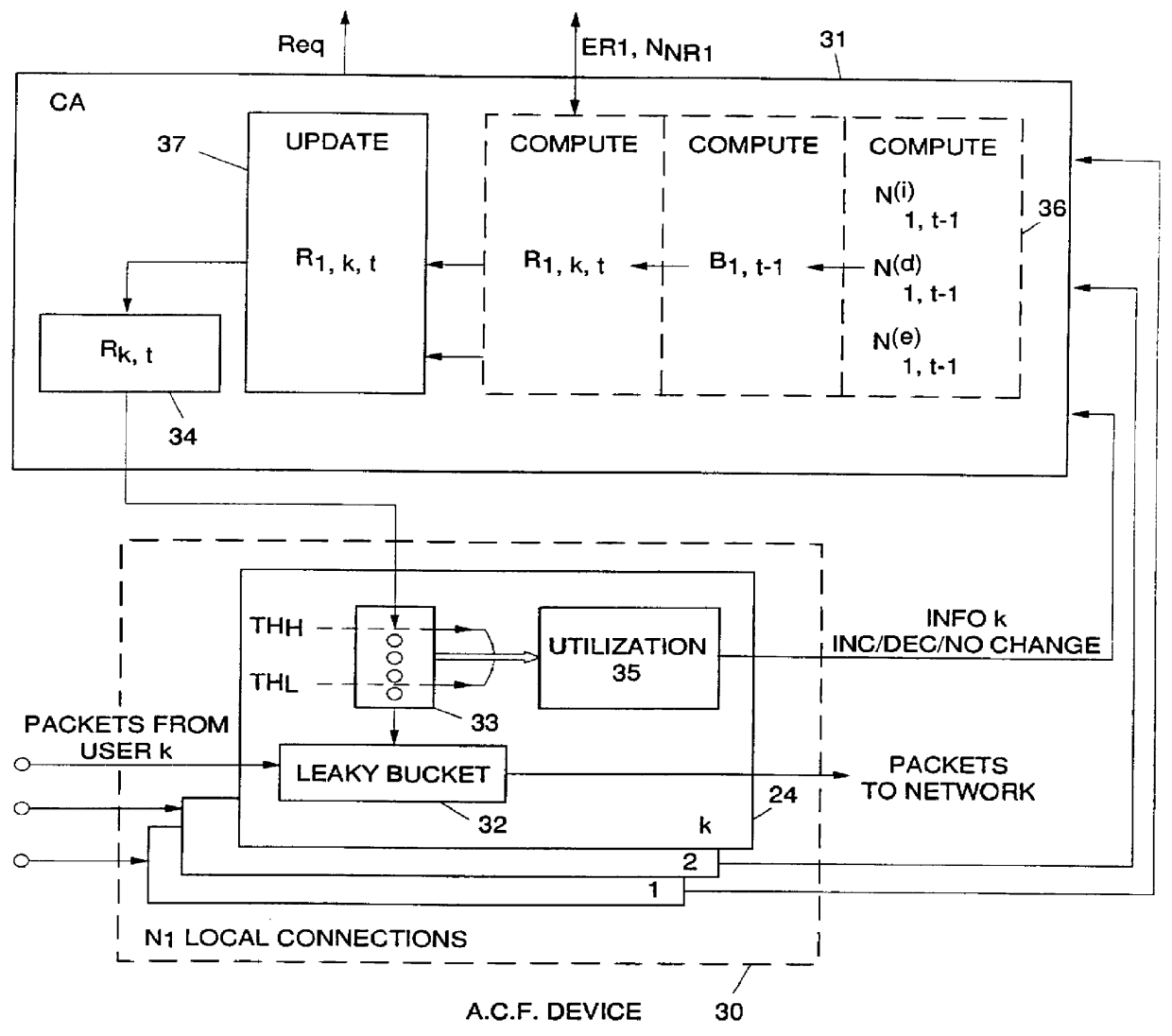
Adaptive bandwidth allocation for Non-Reserved traffic over high speed transmission links of a digital network is operated through regulation of data packet transfers over network nodes / ports including input / output adapters connected through a switching device. A network node is assigned with a Control Point computing devise (CP) storing a Topology Data Base containing an image of the network. This Data Base is periodically and at call set up updated by Topology Data Base Update messages (TDUs) including an Explicit Rate parameter for link l indicating the current available bandwidth on link l, and a parameter NNRl indicating the number of Non-Reserved connections on link l. This information are used within each Adapter to periodically regulate the transmission bandwidth assigned to each Non-Reserved traffic connection within the network. To that end, each adapter is provided with an Access Control Function device for each attached connection (data source) and a Connection Agent (CA) getting, on request, required current link informations from the attached Topology Data Base.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for evaluating a physician's economic performance and gainsharing of physician services
The invention relates to a method and system of physician economic performance evaluation in which the relative medical difficulty associated with patients admitted by a particular physician is determined and, given that measurement, judgments made concerning the relative amount of inpatient resources that the physician required. Also, one application of the present invention relates to a method for gainsharing of physician services using a surplus allocation methodology for rewarding physicians in relation to their performance. An incentive pool is determined from previous patient claims and payments made to physicians in advance, such as in a base year. Best practice norms are established for a plurality of classified diagnosis groups. In one embodiment of the present invention, the classified diagnosis related groups are adjusted for severity of illness to compensate for actual clinical challenges faced by individual physicians. The best practice norms can be used in the surplus allocation method for determining physician performance. The incentive is established proportional to the relationship between a physician's individual performance and the best practice norm.
Owner:AMS APPLIED MEDICAL SOFTWARE
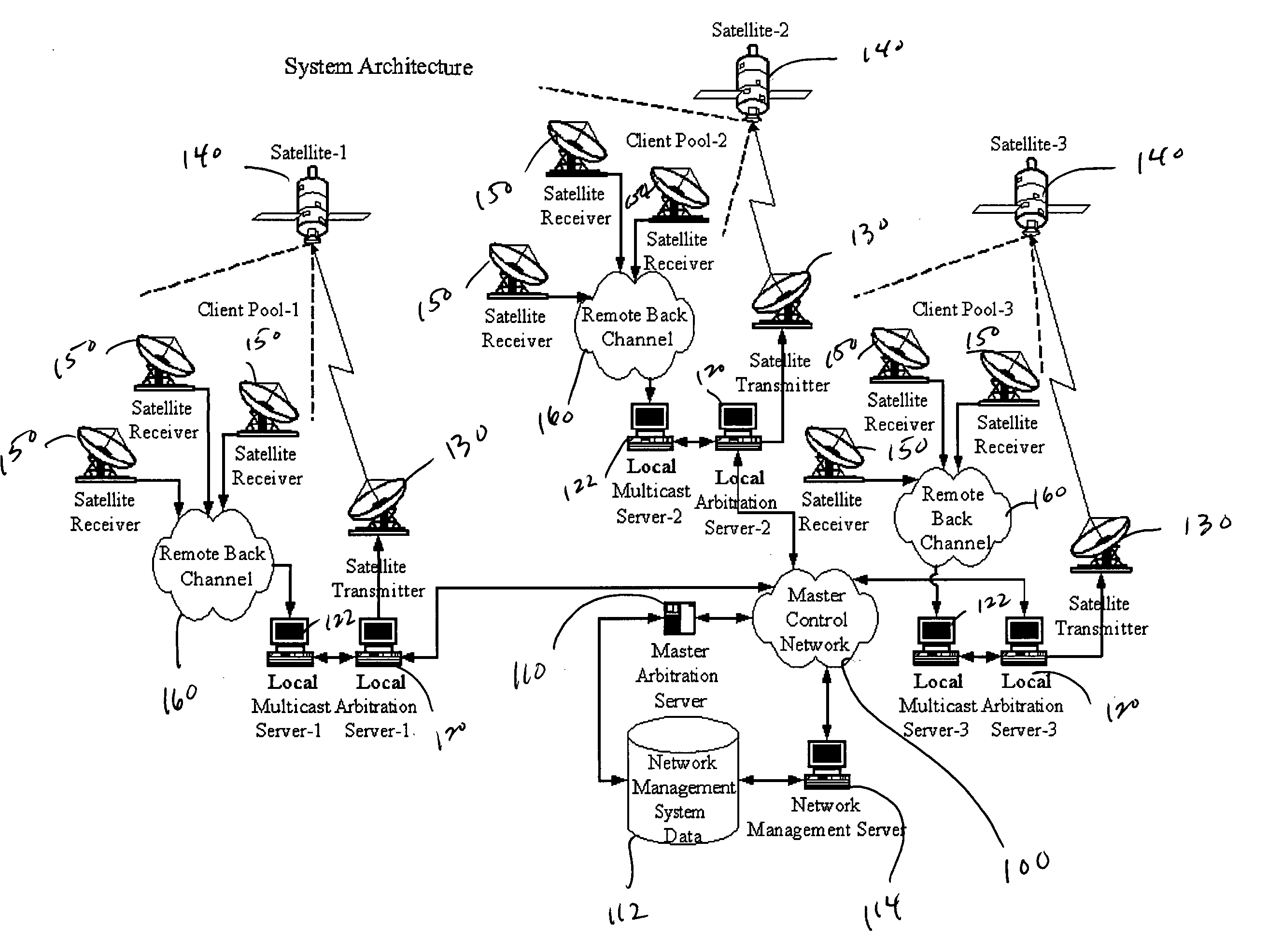
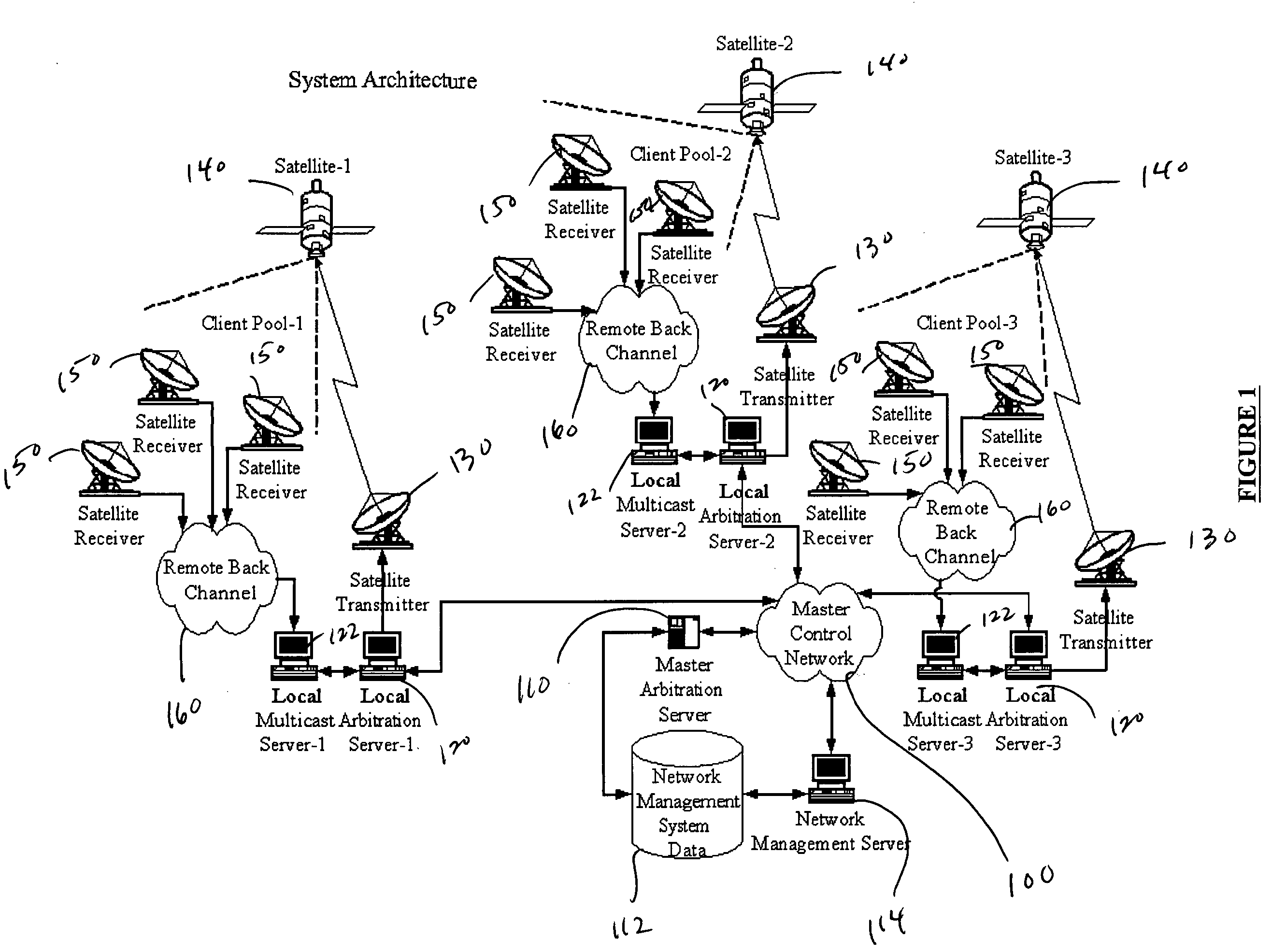
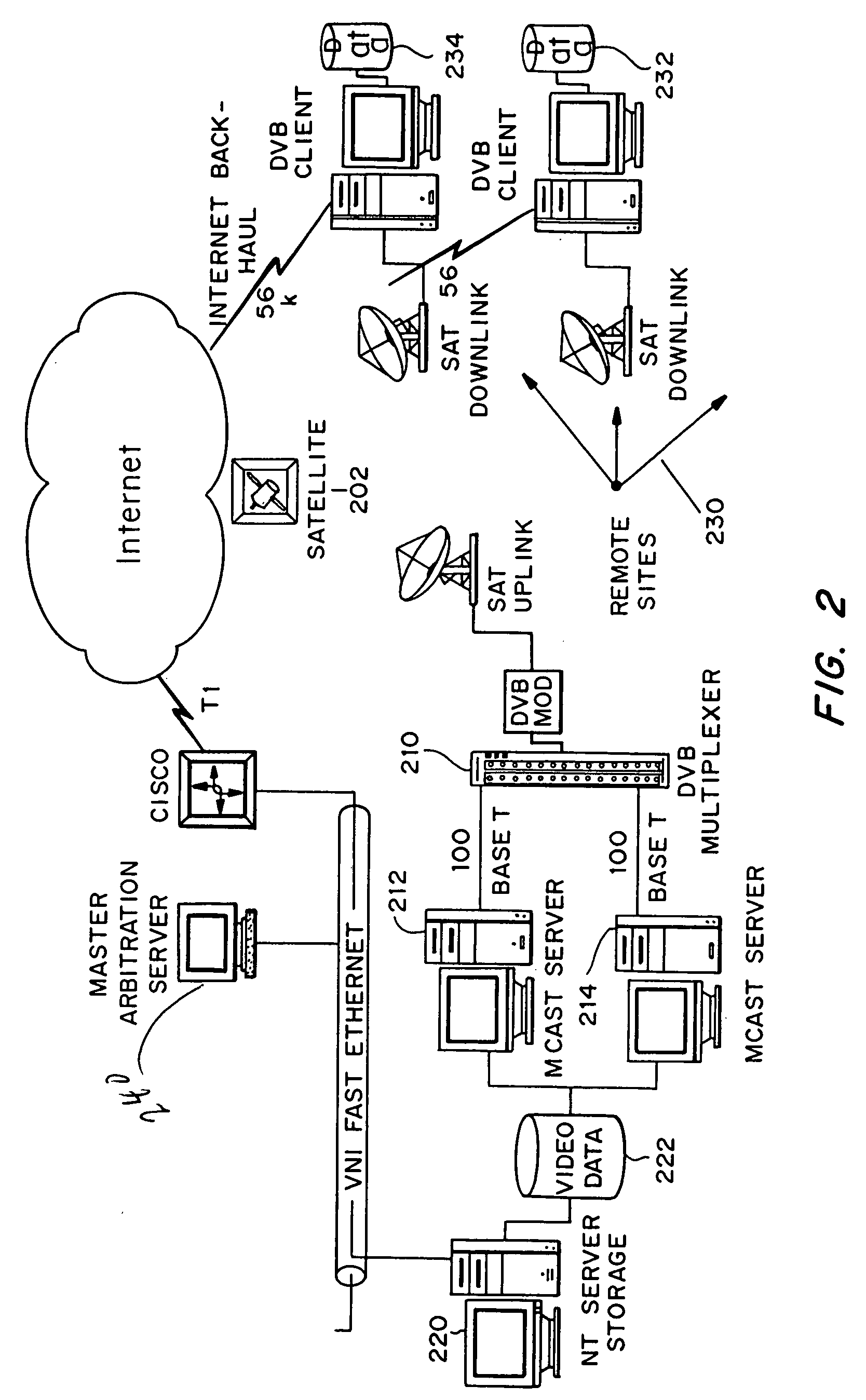
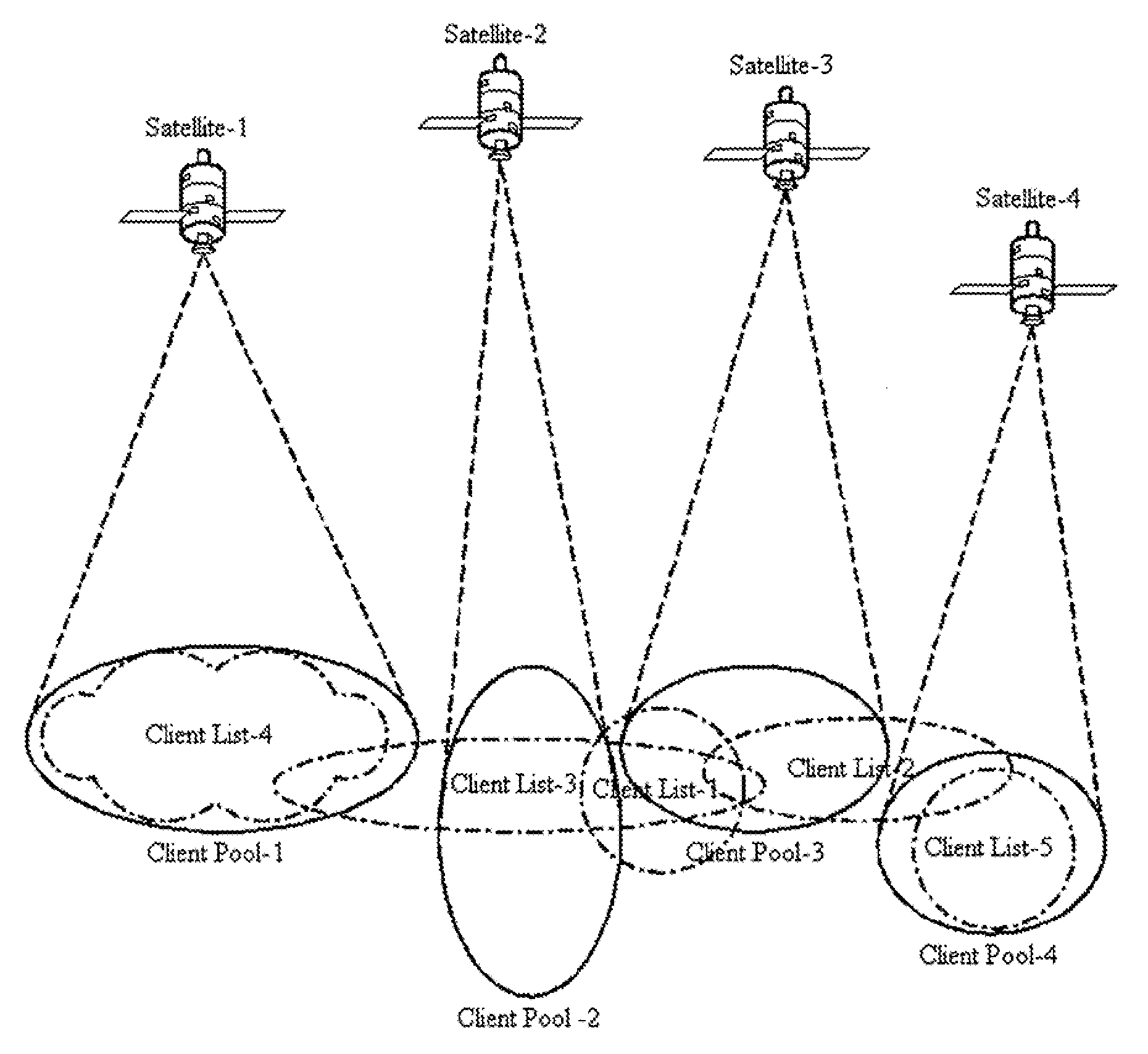
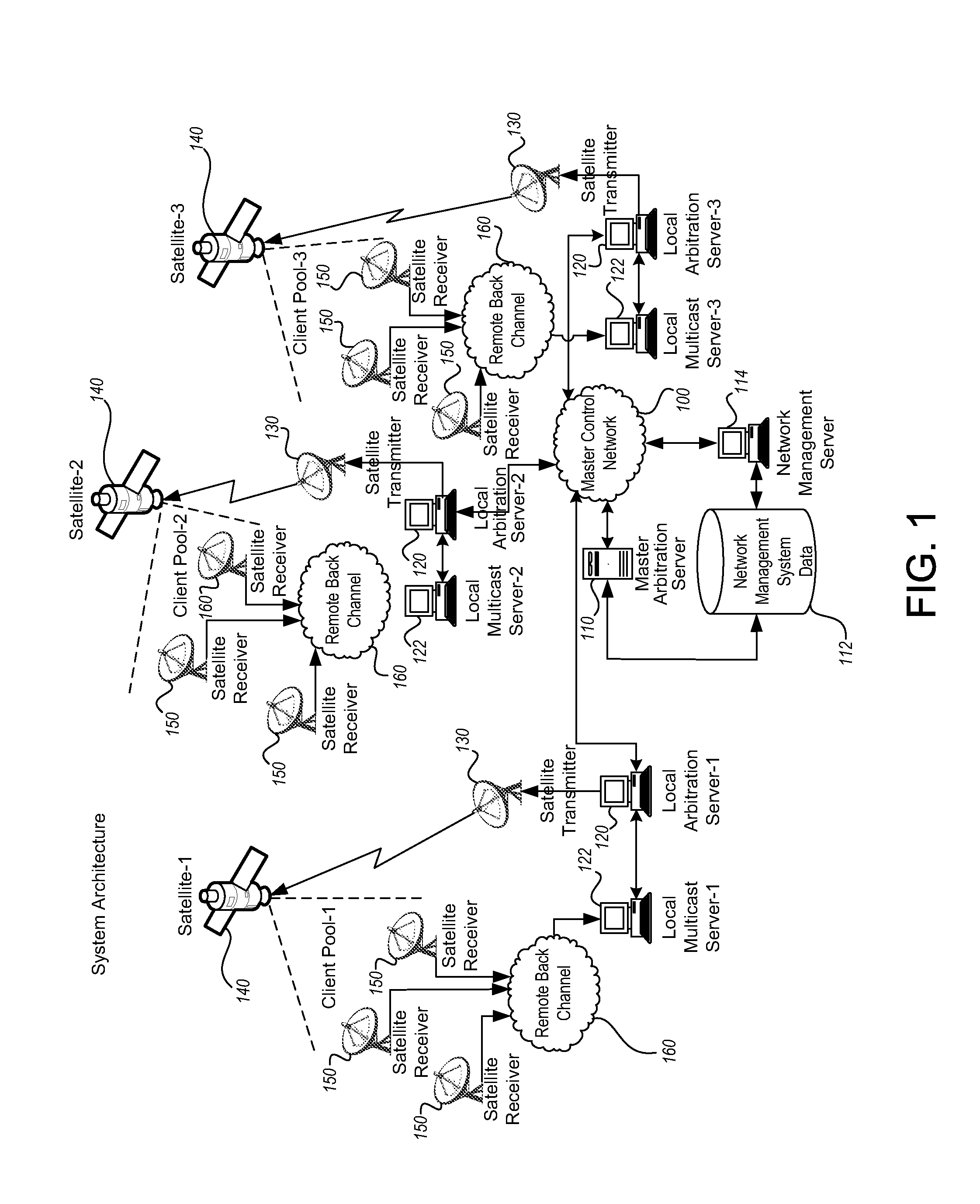
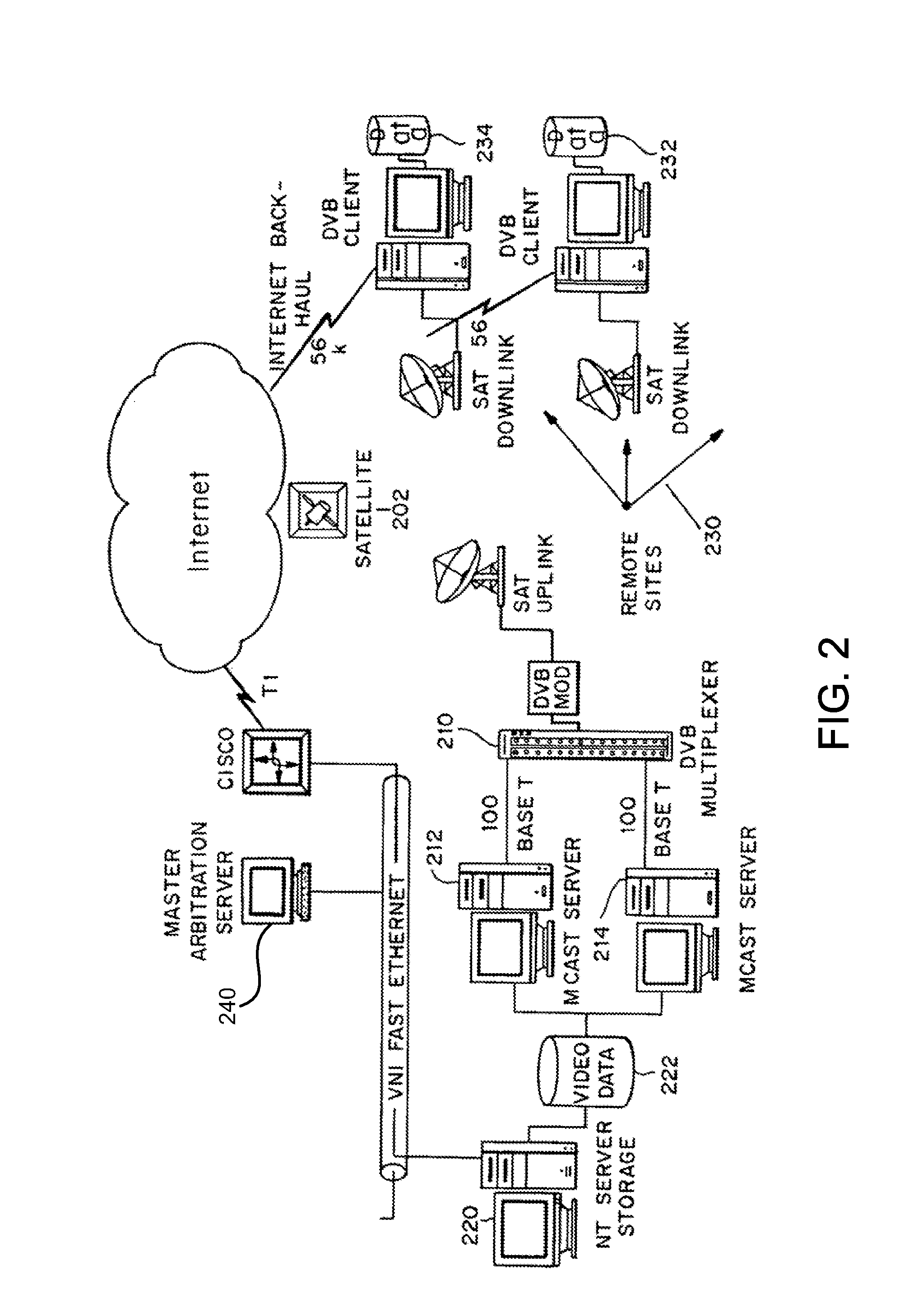
Multicast control systems and methods for dynamic, adaptive time, bandwidth,frequency, and satellite allocations
InactiveUS20050037706A1Improve transmission performanceMaximizing numberBroadcast with distributionNetwork traffic/resource managementControl systemThe Internet
Methods and systems to efficiently share multiple satellites and associated transponders or links among a network of uplinking earth stations are disclosed. An embodiment of this invention uses a terrestrial communications link, such as the Internet, to control access to the transponder or satellite links. Communications over this link may employ a TCP / IP protocol to connect the requesting uplinking earth stations with a centralized controller. This control system creates more efficient use of satellite resources and reduces the overall amount of time needed for transmitting data through the satellite. By reducing the overall amount of time needed for transmitting data, the control system may reduce the cost of using the satellite transponder capacity.
Owner:EXTREME REACH INC +1
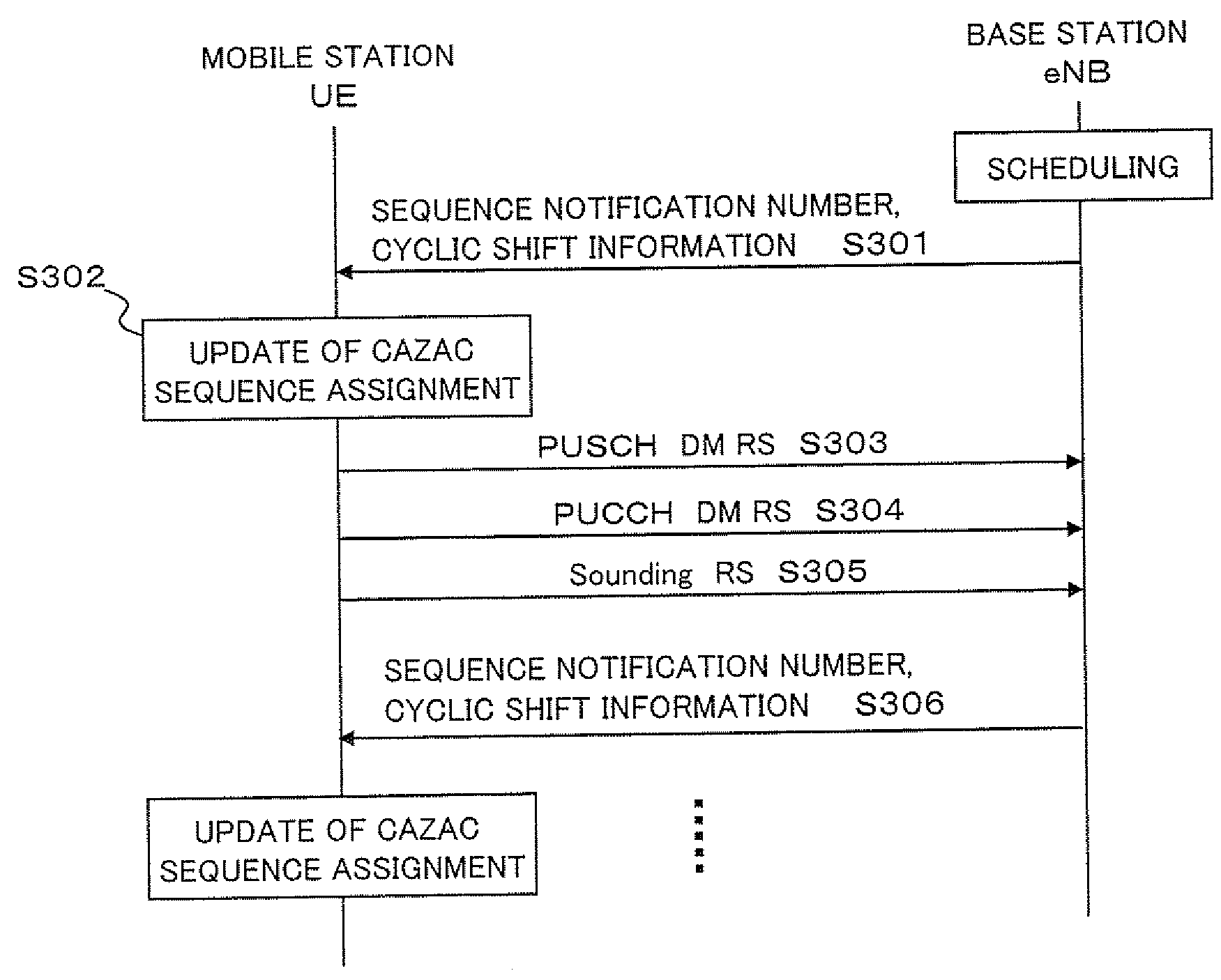
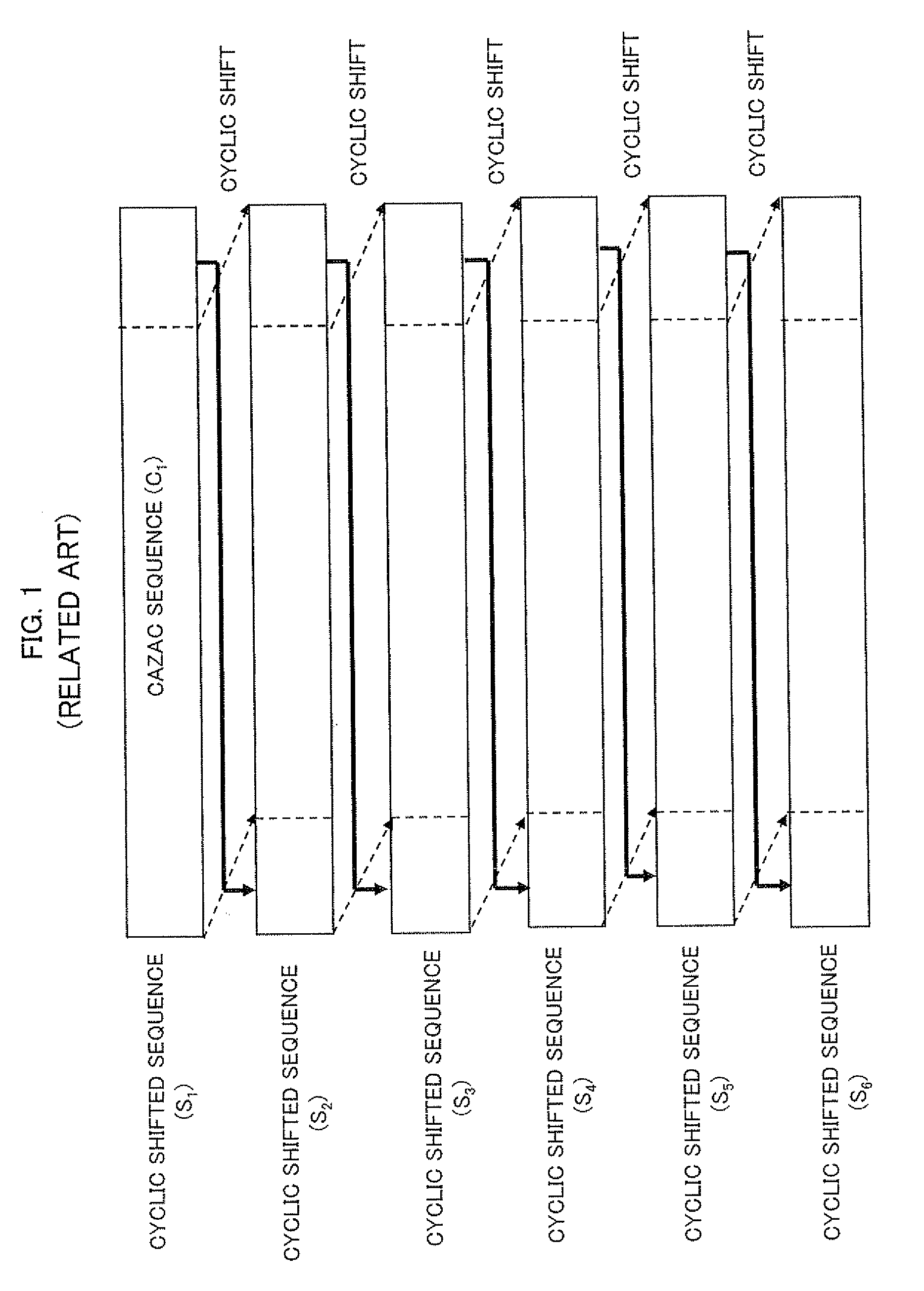
Method and device for assigning reference signal sequences in mobile communications system
ActiveUS20080318608A1Reduce impactIncrease the number ofModulated-carrier systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemOrthogonal sequence
A reference signal sequence assignment method and device are provided by which the influence of inter-cell interference can be reduced and the number of usable cyclic shifted sequences per sector can be increased. In a mobile communications system with a structure including multiple cells each including multiple sectors, a sequence assignment method is employed by which pseudo-orthogonal sequences used for reference signals are assigned to cells or sectors. According to this method, the multiple pseudo-orthogonal sequences are assigned to cells or sectors by using multiple repetition patterns.
Owner:NEC CORP
Methods and systems for wireless networks with relays
ActiveUS20130010679A1Avoid collisionPower managementModulated-carrier systemsMobile stationDownlink transmission
Methods and systems are provided for use with wireless networks having one or more cell in which each cell includes a base station (BS), at least one relay station (RS) and at least one mobile station (MS). The at least one relay station can be used as an intermediate station for providing communication between the BS and MS. Methods are provided for an RS to initially access the network, access of the RS by MSs initially accessing the network, methods of allocating OFDM resources for communicating between the BS, RS and / or MS for example dividing transmission resources into uplink and downlink transmissions, and methods of inserting pilot symbols into transmission resources used by the RS. In some embodiments on the invention, the methods are consistent and / or can be used in conjunction with existing standards such as 802.16e.
Owner:APPLE INC
Dynamic resource allocating method and apparatus, base station, terminal
ActiveCN105099634ASolve problems such as high costReduce overheadTransmission path divisionSignal allocationTime domainDynamic resource
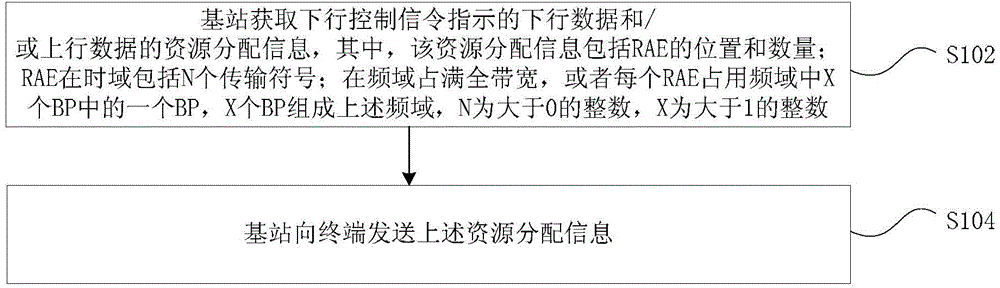
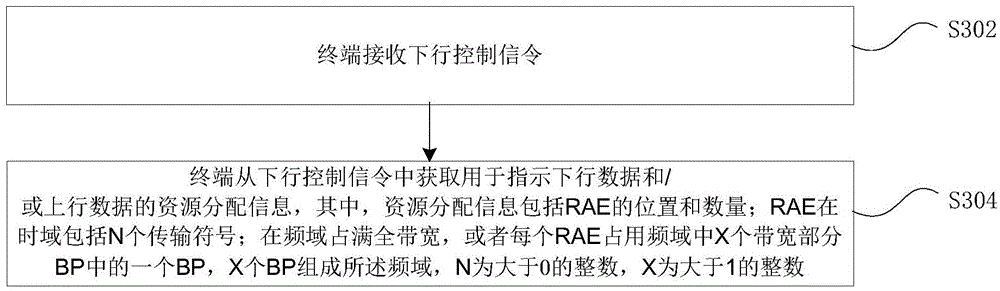
Provided are a dynamic resource allocation method and device, a base station and a terminal. The method comprises: a base station acquiring resource allocation information about downlink data and / or uplink data indicated by downlink control signalling, wherein the resource allocation information comprises the location and number of resource allocation elements (RAEs); the RAEs comprise N transmission symbols in a time domain; and the RAEs completely occupy the full bandwidth in a frequency domain, or each RAE occupies one BP among X bandwidth parts (BPs) in the frequency domain, the X BPs forming the frequency domain, where N is an integer greater than 0, and X is an integer greater than 1; and the base station sending the resource allocation information to a terminal. By means of the technical solution provided in the present invention, the problems in the related art that it is not possible to use an LTE control channel to schedule uplink and downlink services of a plurality of transmission symbols on a high-frequency carrier and the transmission of uplink services, and that the overhead of control signalling is relatively high in a network independently networked by an LTE carrier and the high-frequency carrier and the like are solved, thus achieving that the LTE carrier schedules the high-frequency carrier across carriers.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Channel assignment apparatus and method for a common packet channel in a WCDMA mobile communication system
InactiveUS6859445B1Improve reliabilityReduce complexityPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemCollision detection
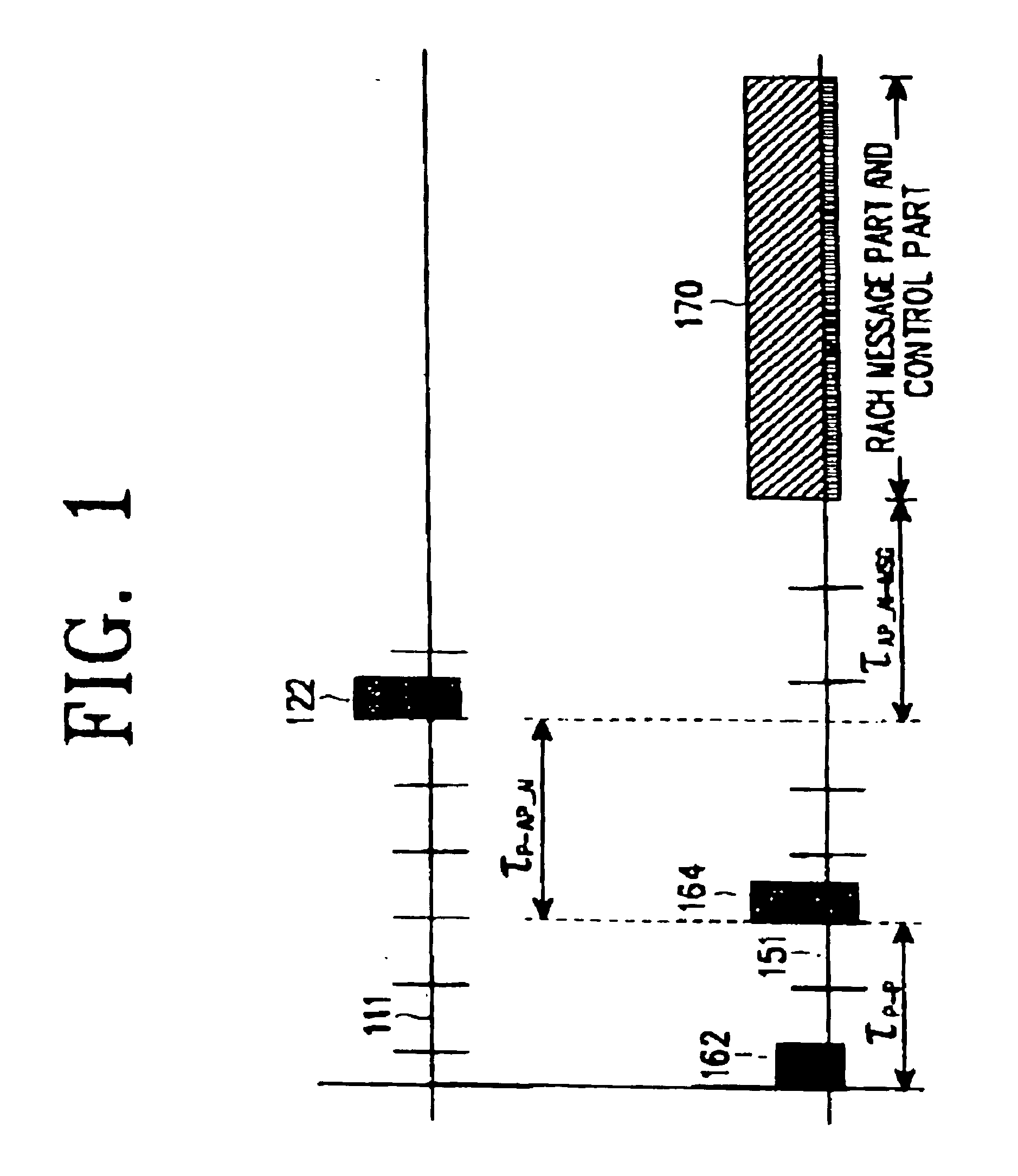
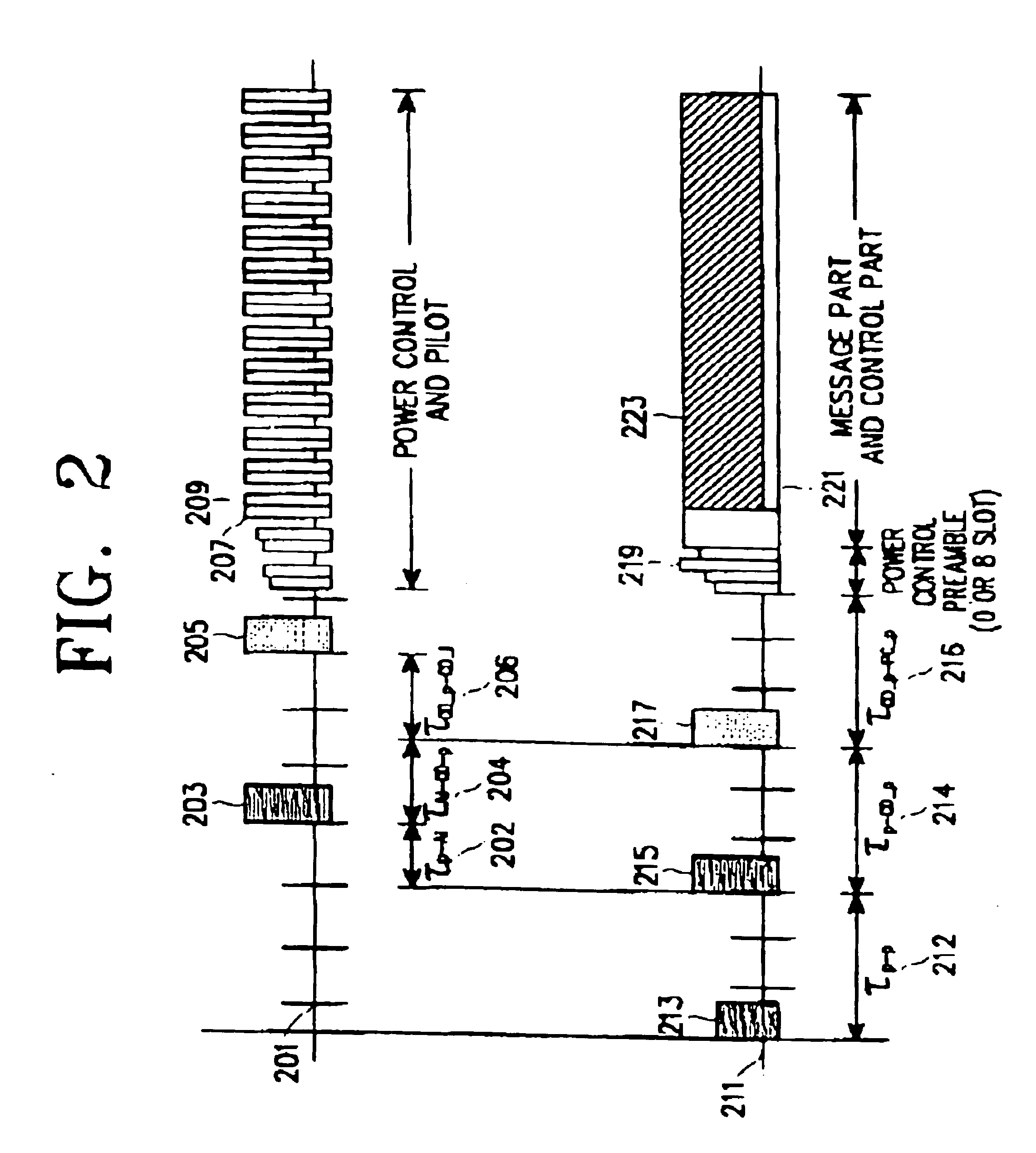
A common packet channel assignment method and device in a CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) communication system is disclosed. The method comprises transmitting an access preamble signal having channel information which is used to access a base station, and then receiving an; access preamble acquisition indicator signal from the base station in response to the access preamble signal. A collision detection preamble for detecting a collision is transmitted in response to the received access preamble acquisition indicator signal. A first signal indicating acquisition of the collision detection preamble and a second signal indicating channel assignment are received, both of which the base station has transmitted in response to the collision acquisition signal. Upon receipt of the first signal, a common packet channel is assigned according to information designated by the second signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
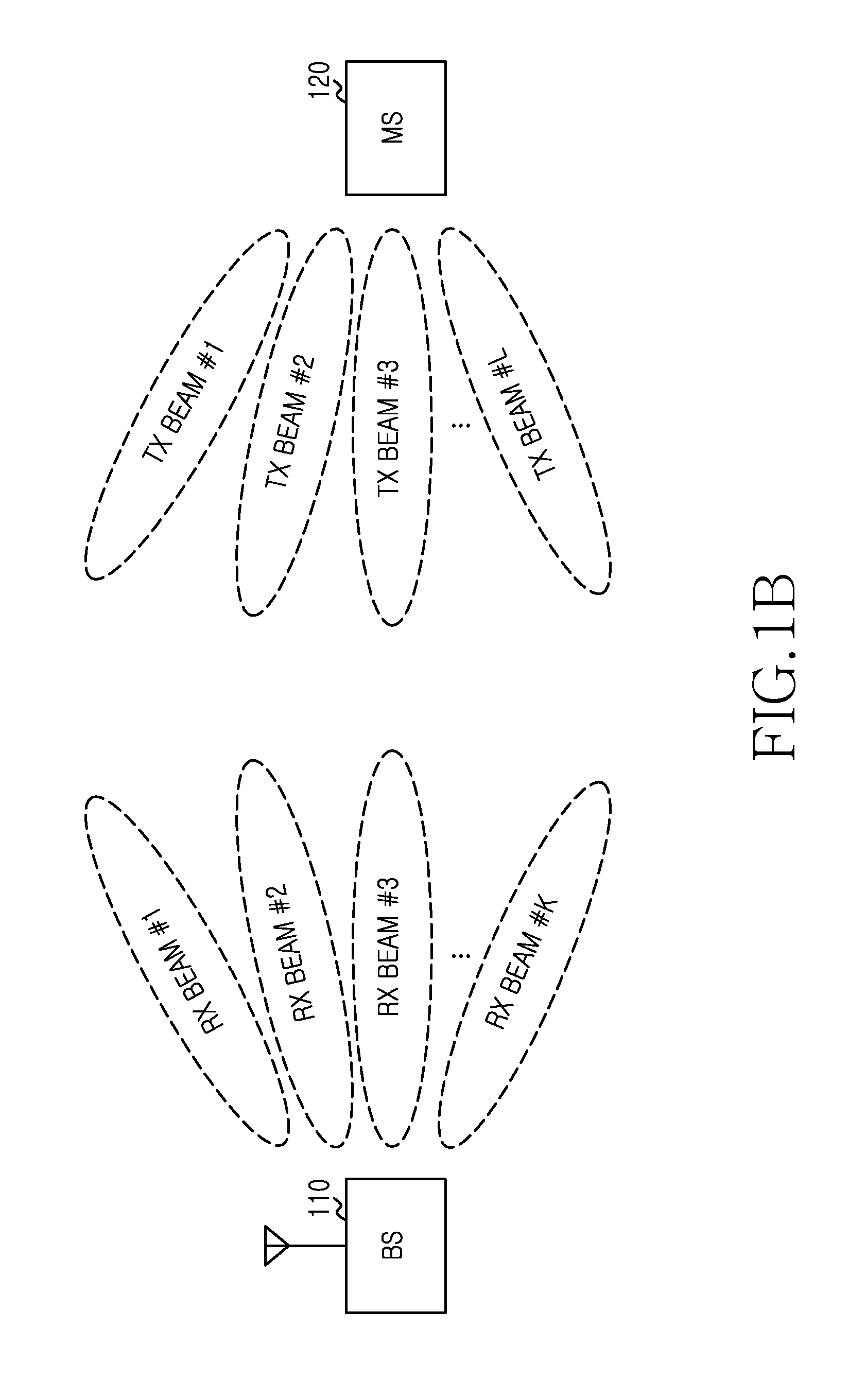
Method and apparatus for beam allocation in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20130072243A1Effective distributionRadio transmissionWireless communicationCommunications systemBurst transmission
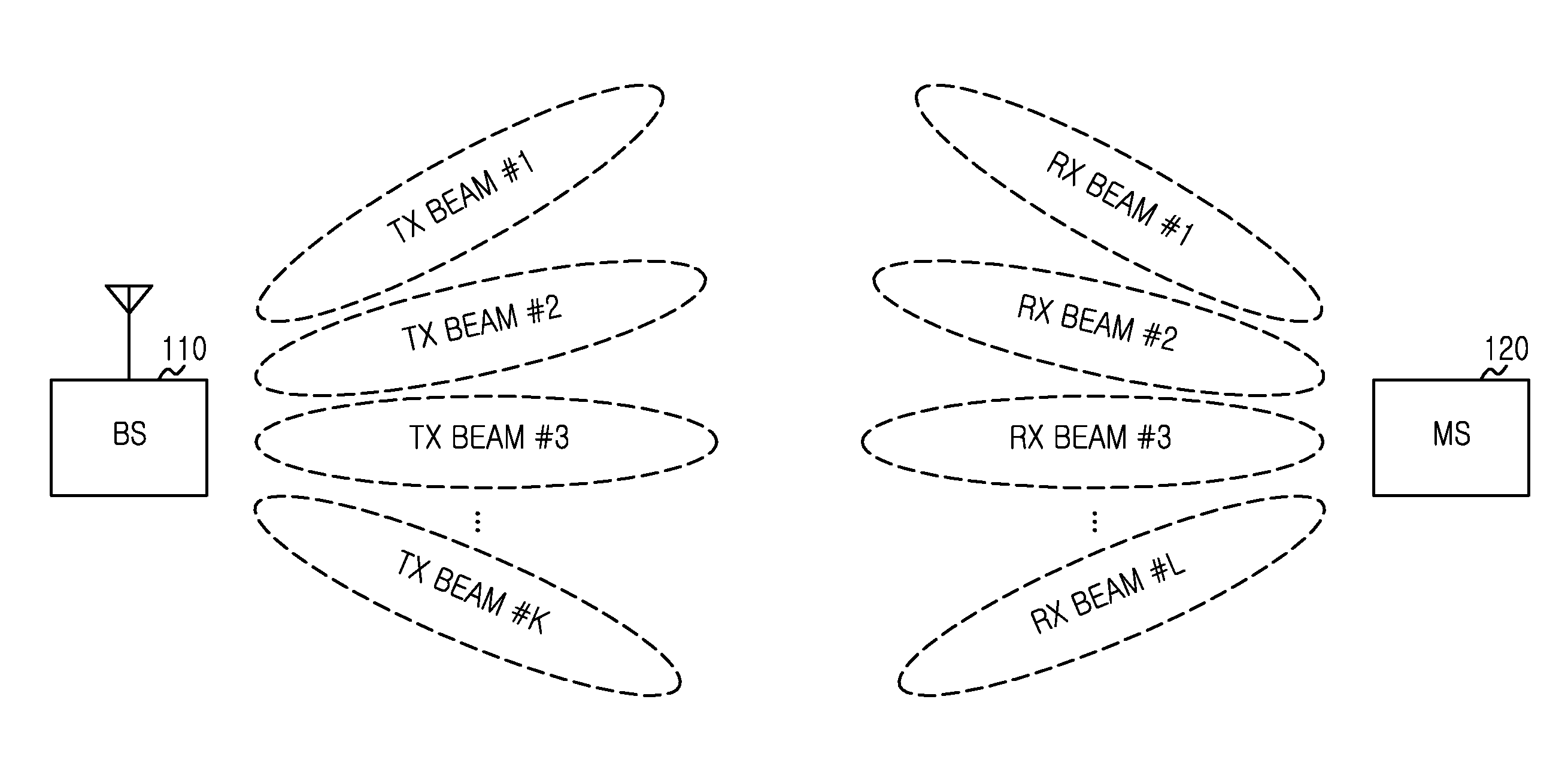
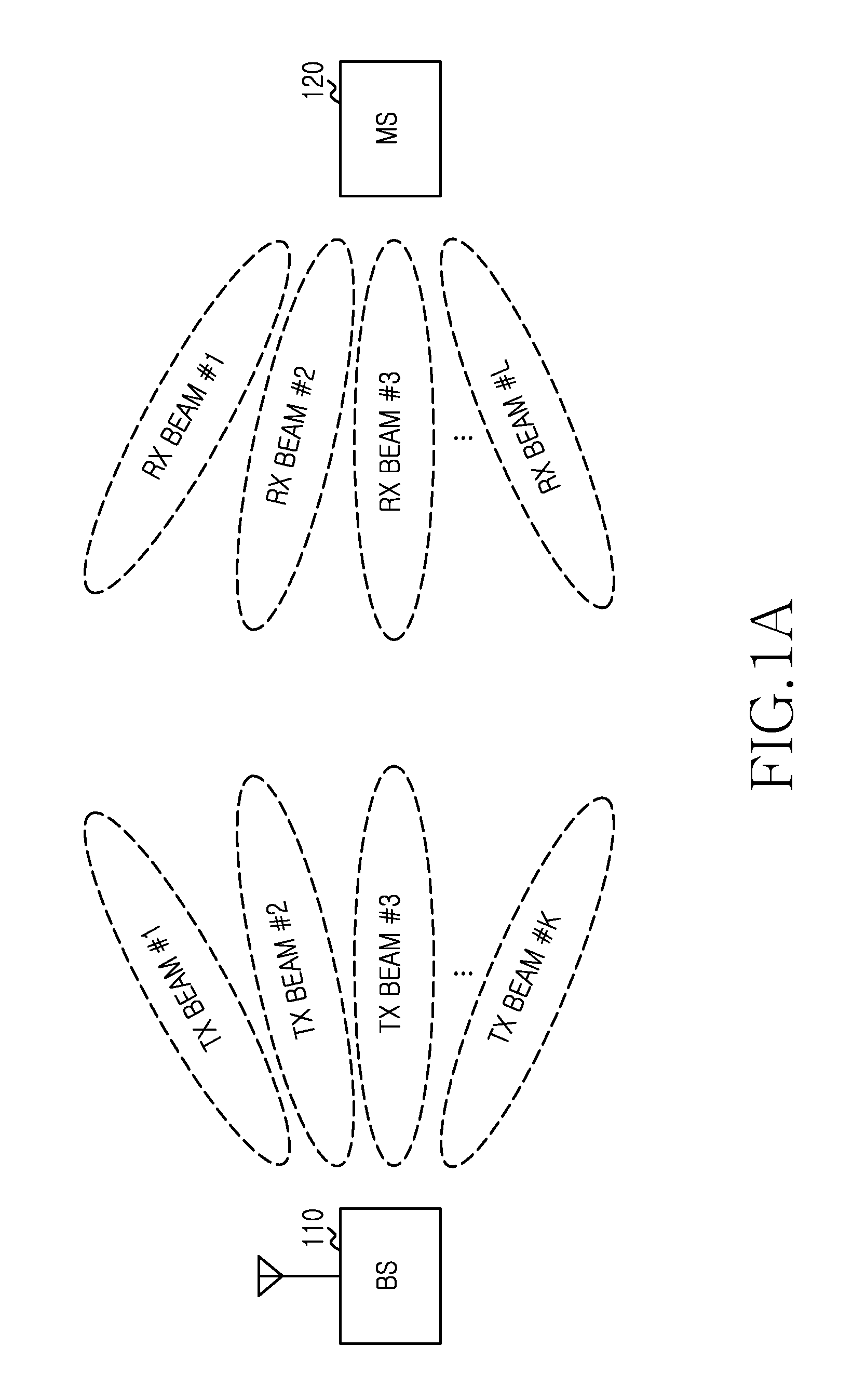
A beam allocation method of a Base Station (BS) in a wireless communication system is provided. The method includes transmitting a reference signal to a Mobile Station (MS) using a plurality of downlink transmit (Tx) beams, receiving information of a plurality of candidate downlink Tx beams determined by the MS in response to the received reference signal, selecting at least one downlink Tx beam from the plurality of candidate downlink Tx beams according to a predefined rule, generating control information for burst transmission, comprising the selected at least one downlink Tx beam information, transmitting the control information to the MS using the selected at least one downlink Tx beam, and transmitting a data burst based on Tx beam information included in the control information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multicast control systems and methods for dynamic, adaptive time, bandwidth,frequency, and satellite allocations
InactiveUS7236738B2Additional satellite capacityOptimize resource allocationNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesControl systemThe Internet
Methods and systems to efficiently share multiple satellites and associated transponders or links among a network of uplinking earth stations are disclosed. An embodiment of this invention uses a terrestrial communications link, such as the Internet, to control access to the transponder or satellite links. Communications over this link may employ a TCP / IP protocol to connect the requesting uplinking earth stations with a centralized controller. This control system creates more efficient use of satellite resources and reduces the overall amount of time needed for transmitting data through the satellite. By reducing the overall amount of time needed for transmitting data, the control system may reduce the cost of using the satellite transponder capacity.
Owner:EXTREME REACH INC +1
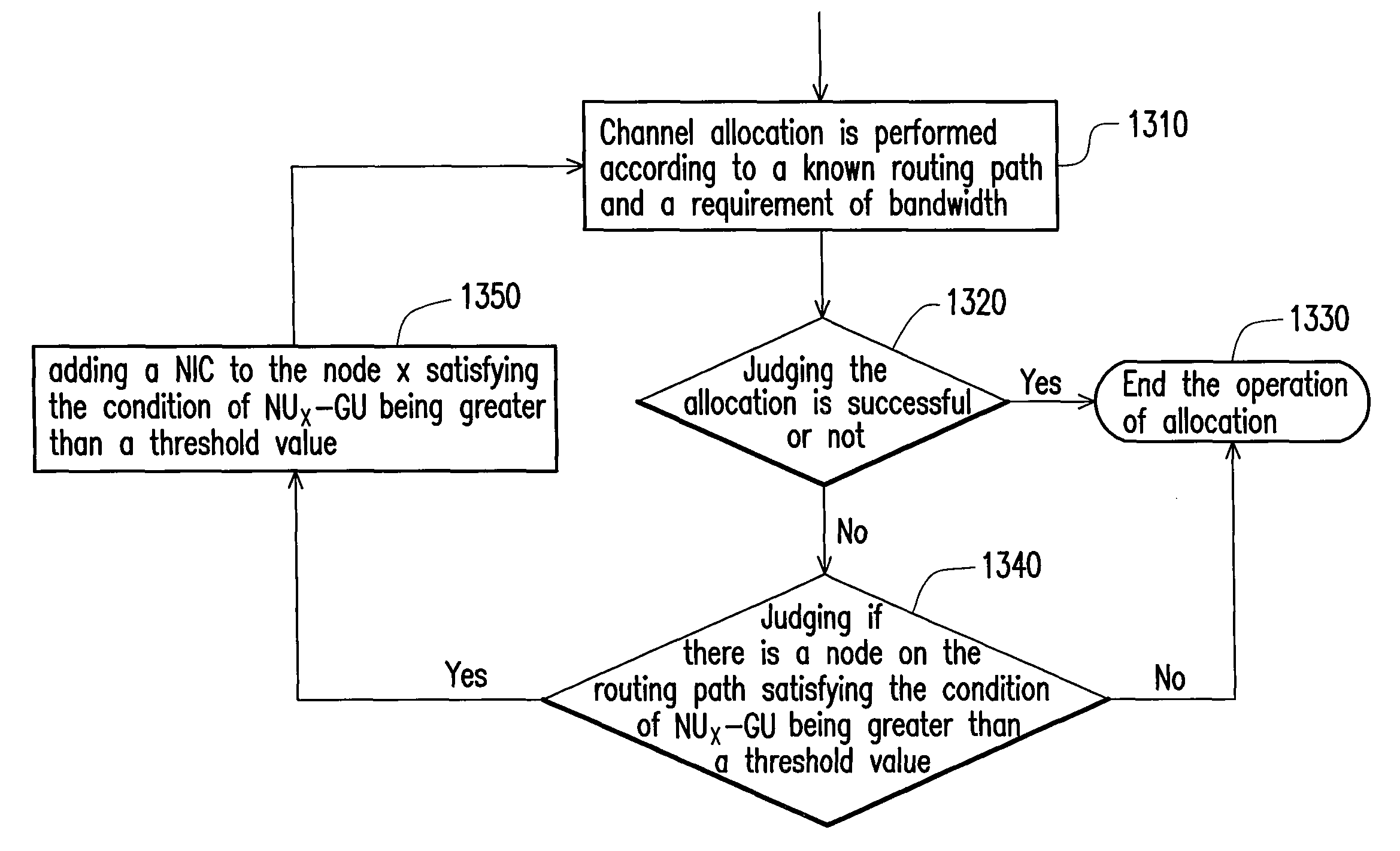
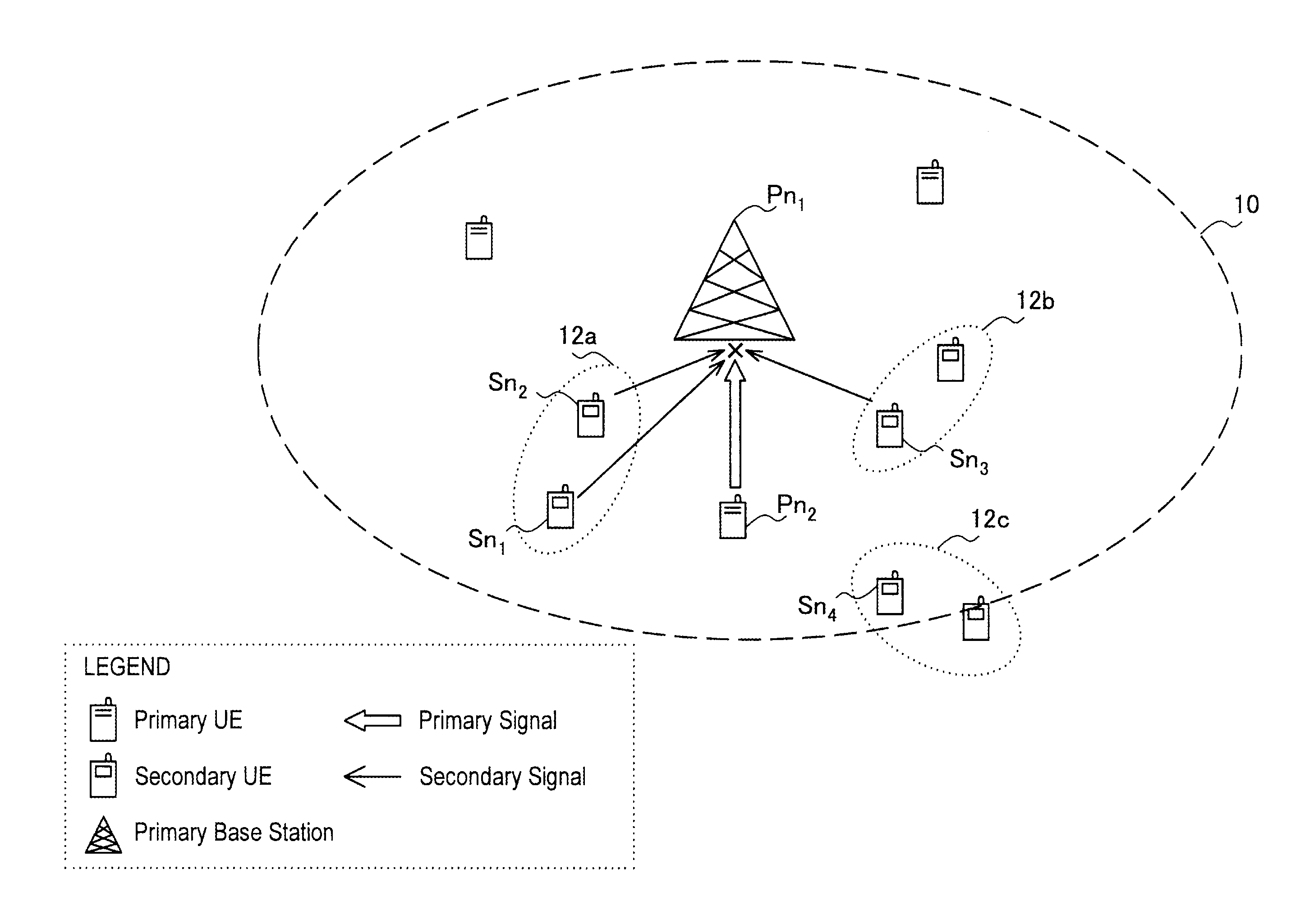
Distributed channel allocation method and wireless mesh network therewith
InactiveUS8059593B2Avoid interferenceGuaranteed bandwidthRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesWireless mesh networkDistributed computing
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
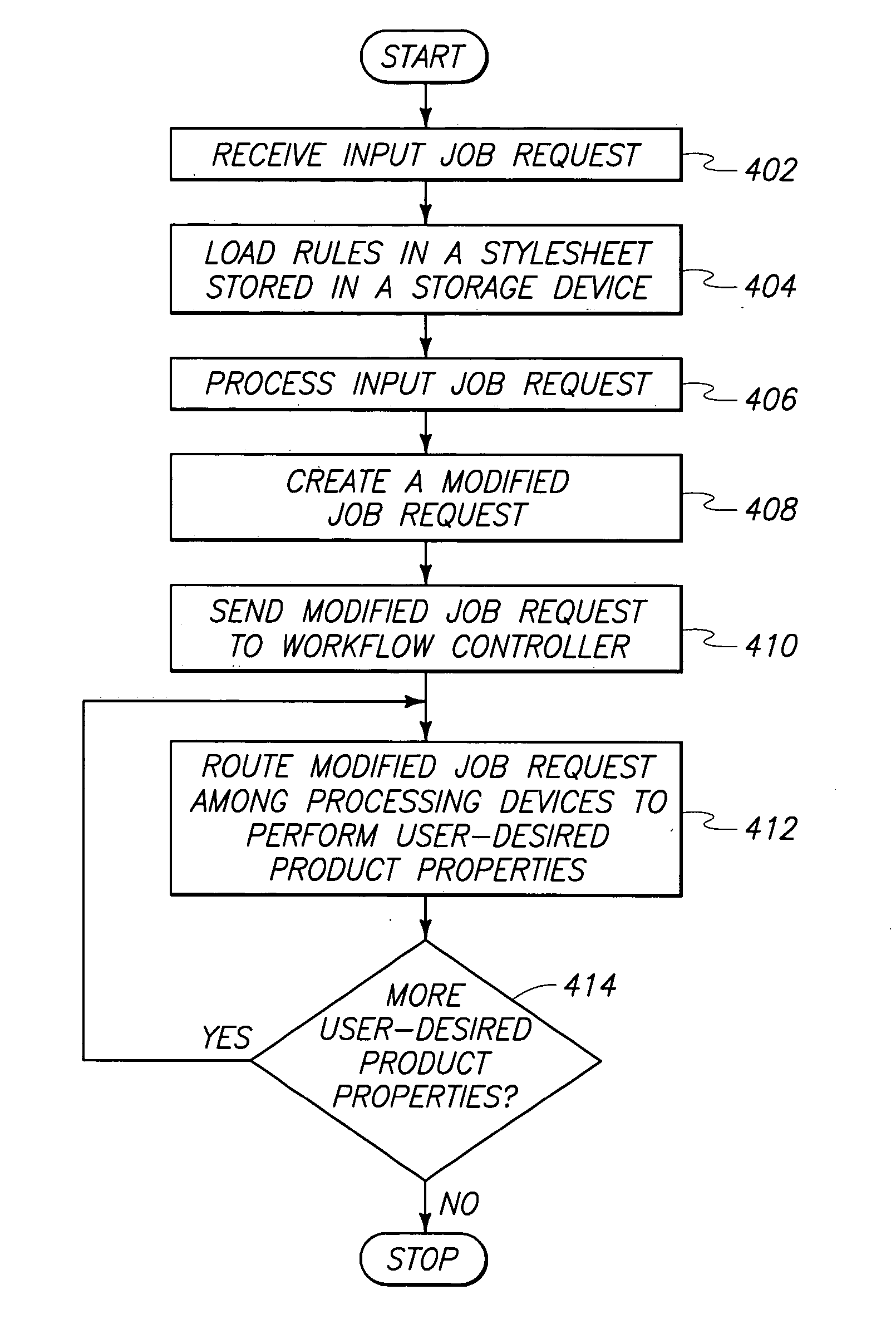
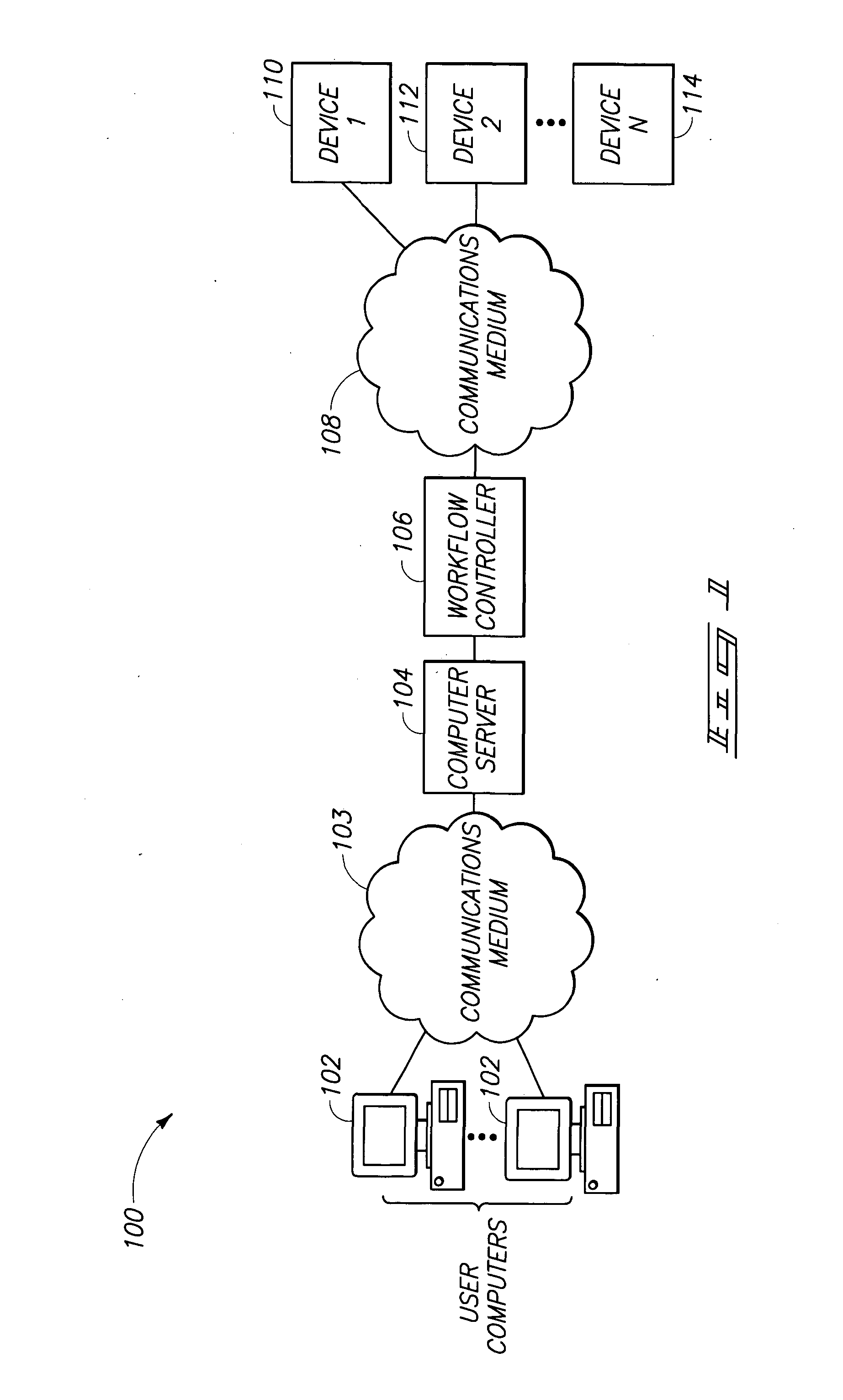
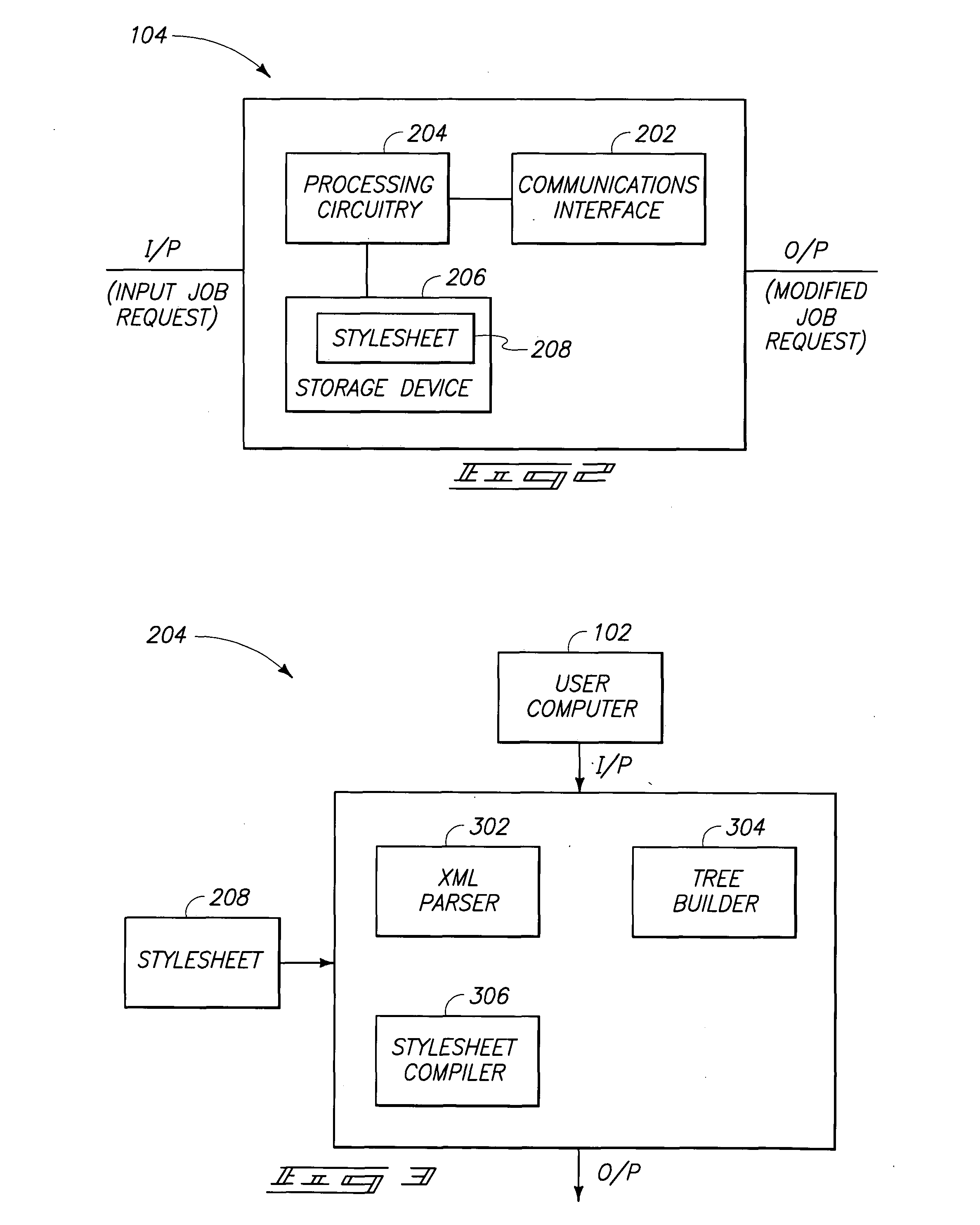
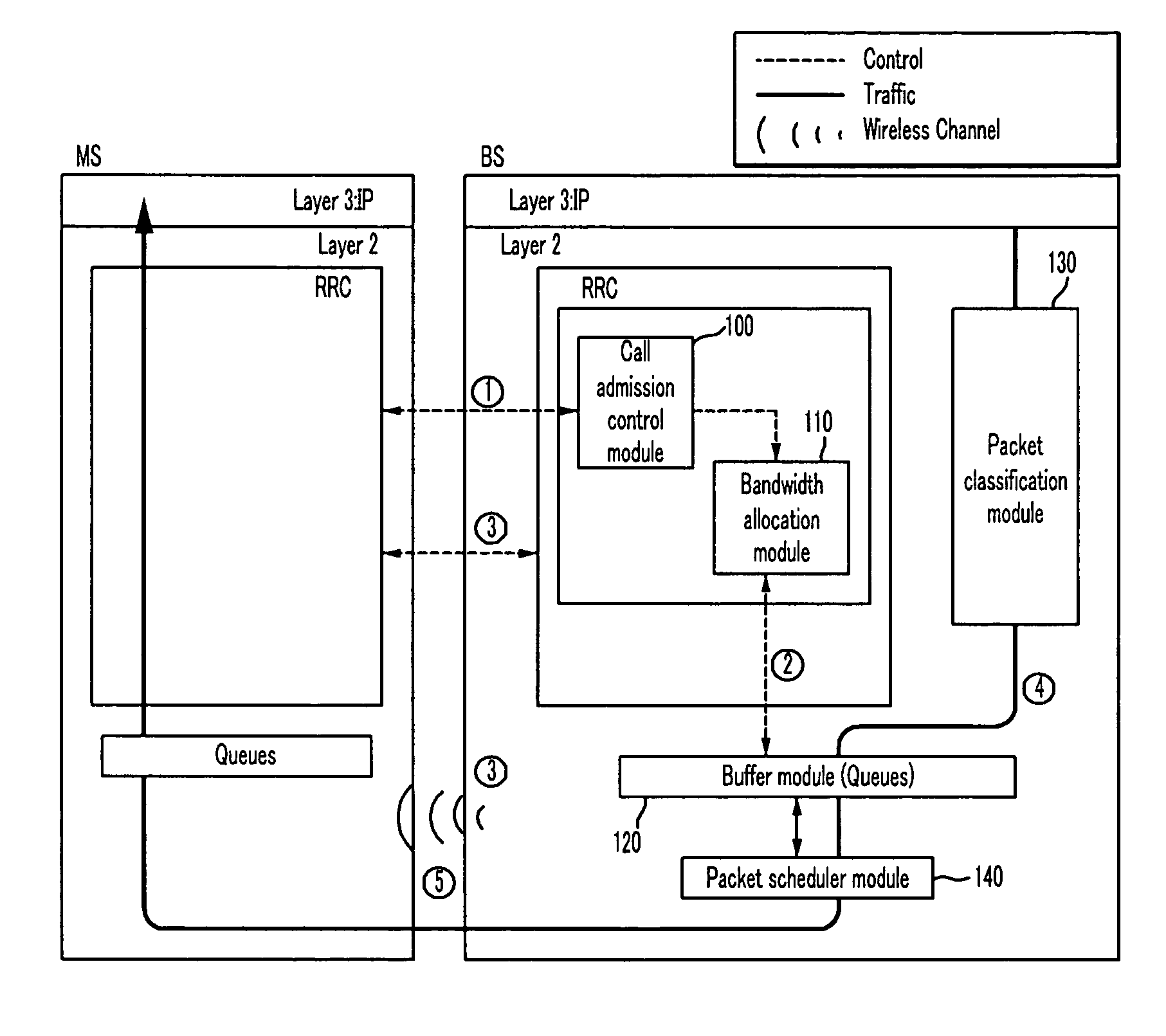
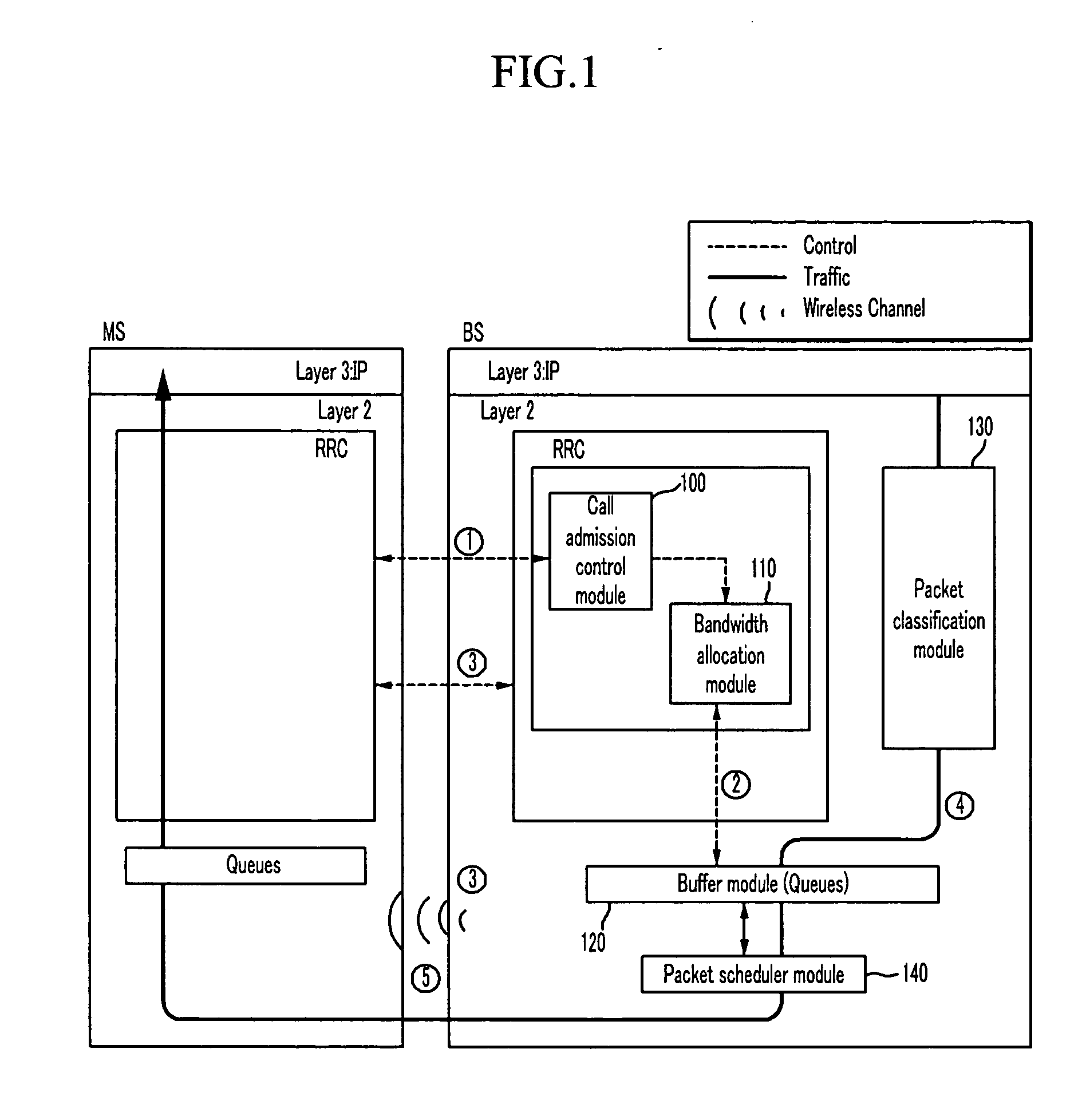
Workflow management devices and systems, and workflow assignment and management methods
InactiveUS20050004893A1Digital data processing detailsOffice automationCommunication interfaceWorkflow management system
Aspects of the invention relate to workflow management devices, workflow management systems, workflow management methods, workflow assignment methods, and data processing methods. In one aspect, a workflow management device includes a communications interface configured to receive a user request having one or more user-desired product properties to achieve a user-desired product. The communications interface is further configured to communicate with one or more devices located external of the workflow management device. The management device also includes a storage device configured to store data for processing the user request, and processing circuitry configured to process the user request using the data to produce a transformed user request. The transformed user request includes information for automatically organizing workflow to process the one or more user-desired product properties to achieve the user-desired product.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
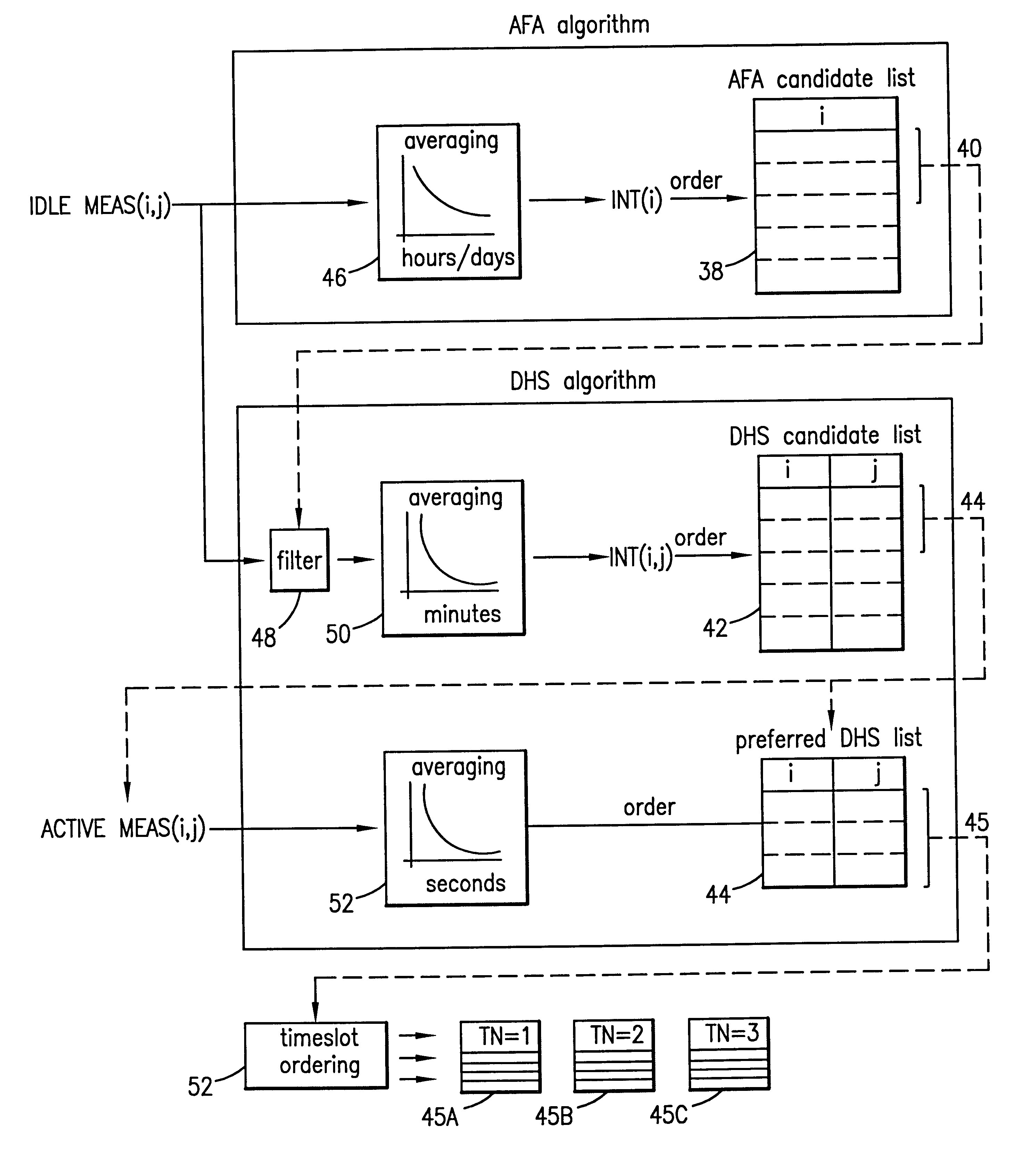
Method and system for autonomously allocating a frequency hopping traffic channel in a private radio system
InactiveUS6351643B1Avoid interferencePreventing situationNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSkip listTelecommunications link
An allocation method and system for allocating a least-interfered communications link between a cellular mobile station and a private radio base station within a cellular system is disclosed. A set of candidate carrier frequencies are first selected and ordered by the amount of interference present within the cellular system, and a subset thereof selected. A second set of candidate frequencies and associated timeslots are then selected from the subset and ordered by the amount of interference present in the private radio system environment, and a second subset thereof selected. A plurality of discrete hop lists for each timeslot are then formed, and one of the hop lists exhibiting the least amount of interference is then selected to be applied in the communications link.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Beam and power allocation method for MIMO communication system
InactiveUS20060209980A1Improve performanceDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSubstation equipmentCommunications systemEngineering
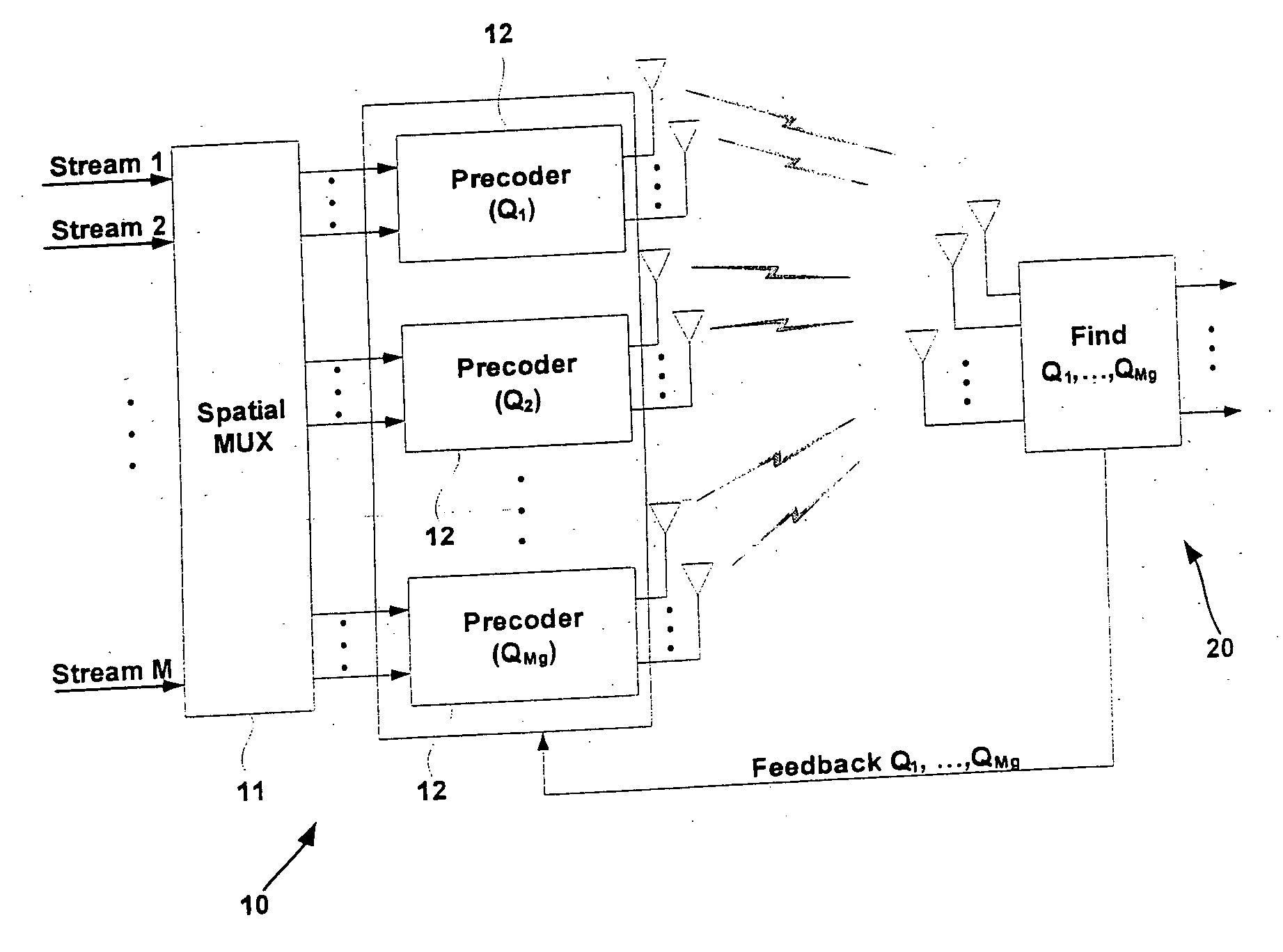
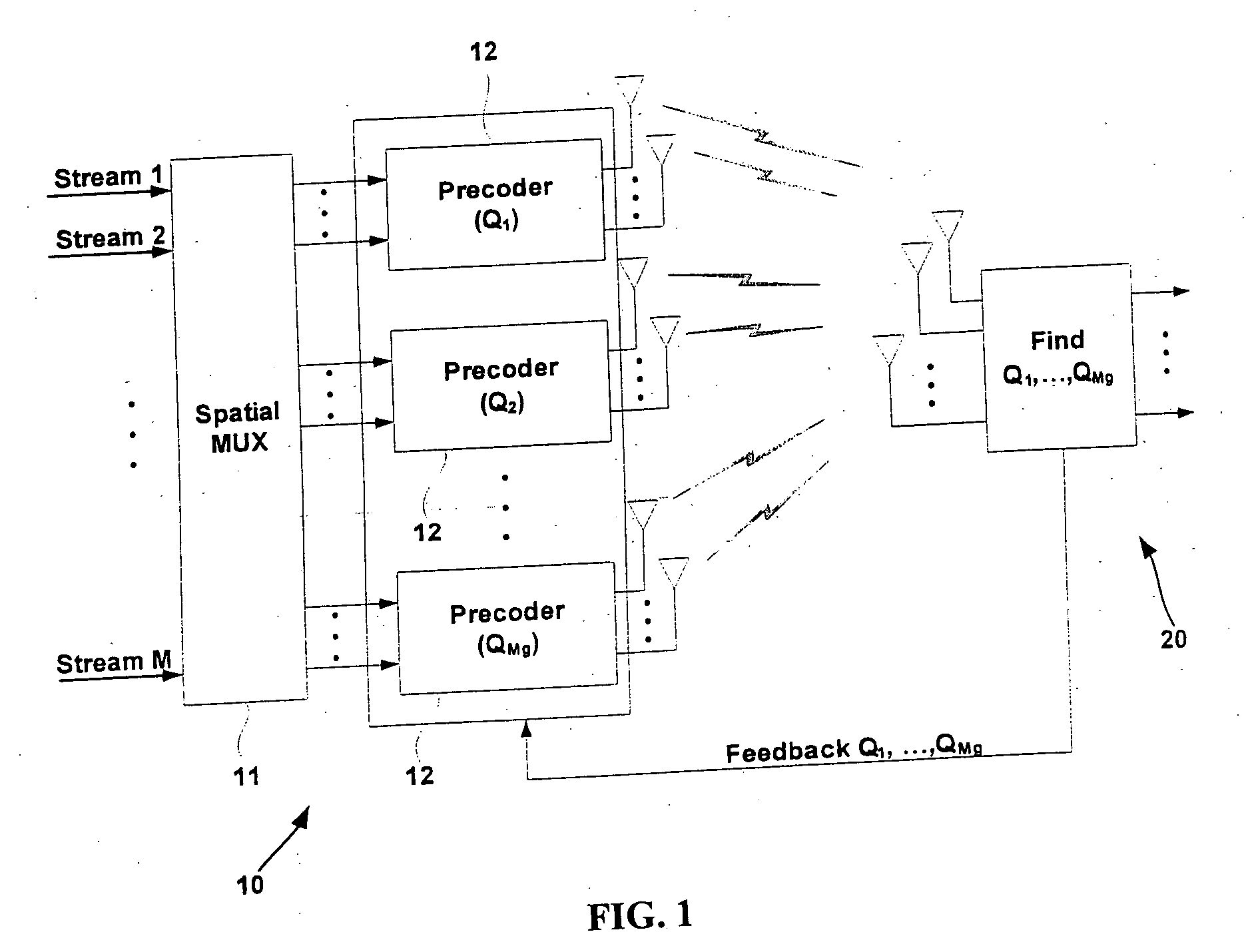
The present invention provides the multiuser Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) systems with a feedback method which includes measuring, at the terminal, received Signal to Noise Ratios (SNRs) for all transmit antennas, selecting one of precoding matrixes, which has best SNRs, retrieving an index mapped to the selected preceding matrix from a predetermined mapping table, and transmitting the index with the SNRs of the selected precoding matrix. In the present invention, it is possible to reduce feedback information amount without degradation of the sum rate performance of the system since the feedback information is transmitted in a form of index implying appropriate precoding matrix and corresponding SNRs.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
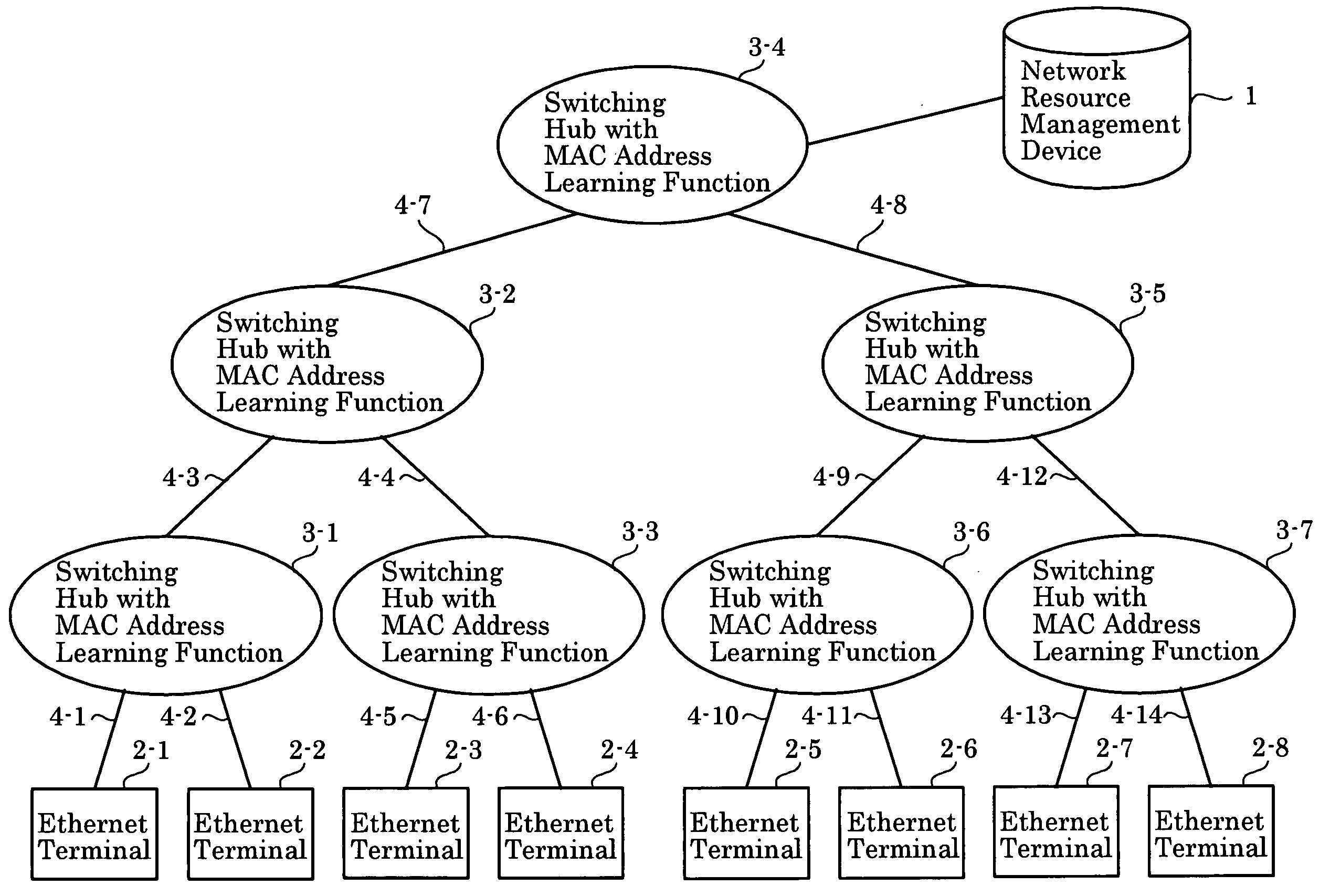
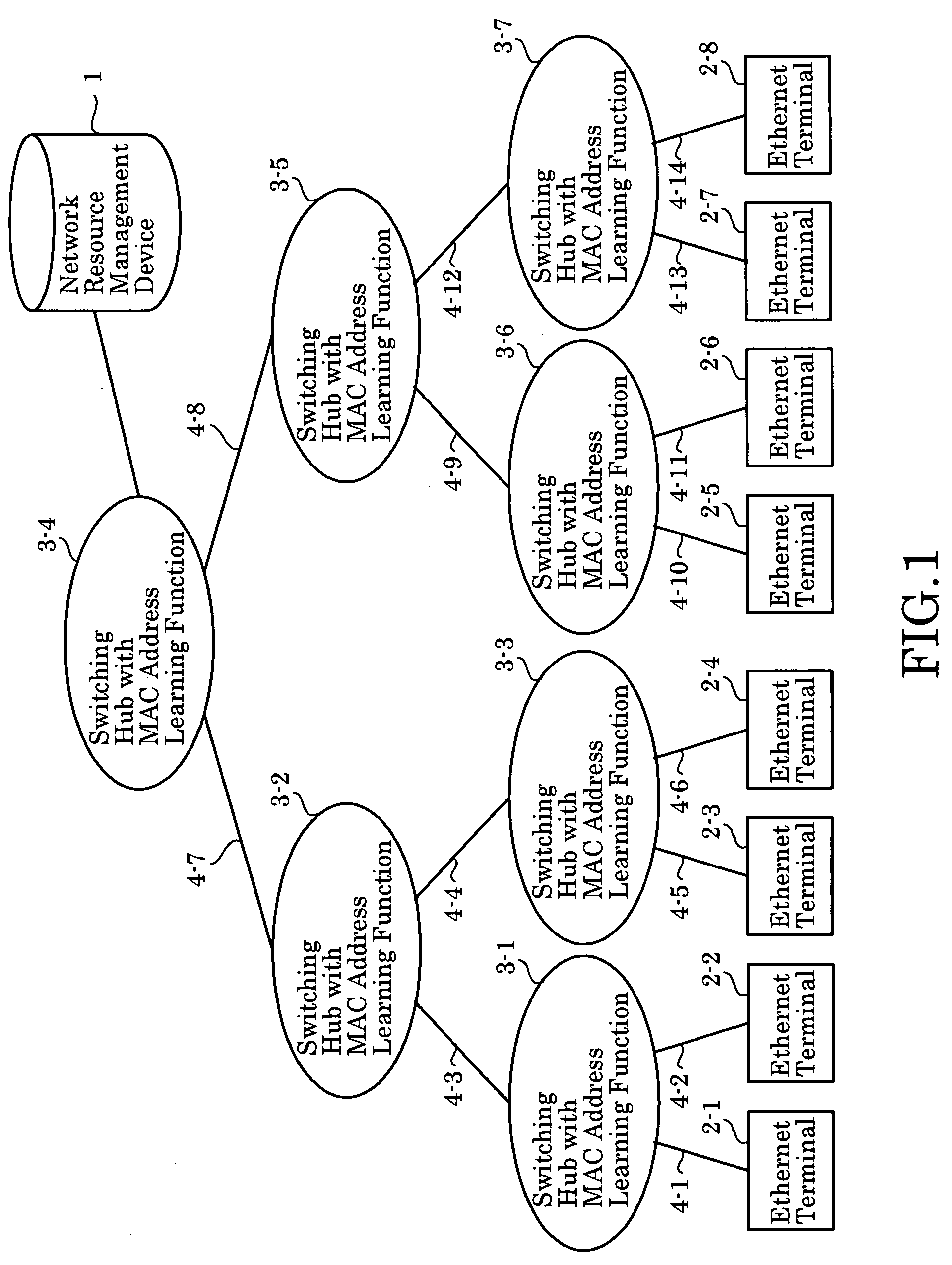
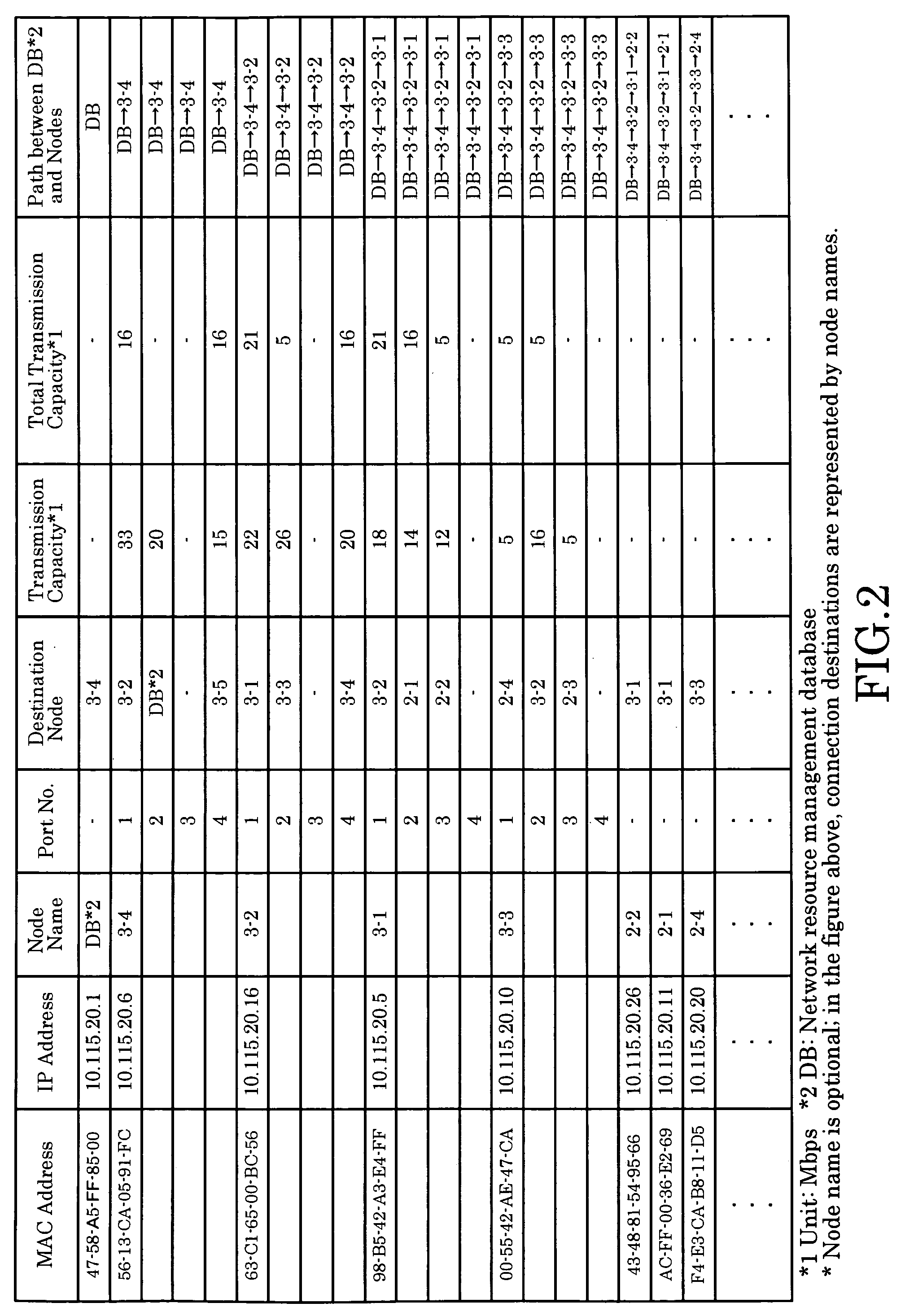
Ransmission Capacity Allocation Method, Communications Network, and Network Resource Management Device
InactiveUS20080239957A1Wasting network resourceError preventionTransmission systemsNetwork resource managementComputer terminal
The invention implements inter-terminal transmission with guaranteed capacity based on the single-path configuration function of networks composed of switching hubs with an MAC address learning function and centralized management of transmission capacity, without control over hubs. The capacity to be used by transmission links on a network is stored in advance and transmission capacity along the path to be used is allocated based on requests from terminals, with the allocation removed using a Terminate Request. At such time, by using transmission links and switching hubs with an MAC address learning function, transmission is limited to single-path transmission.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
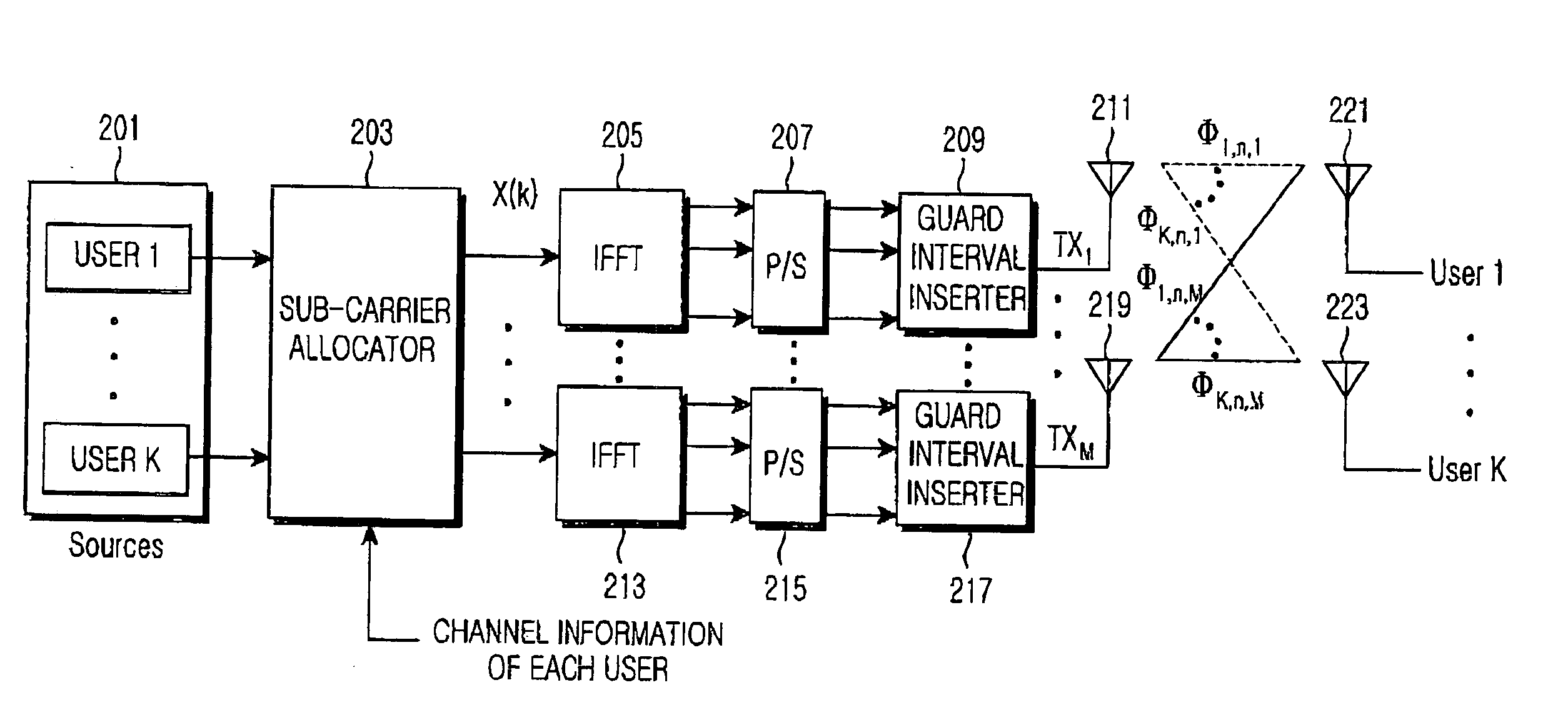
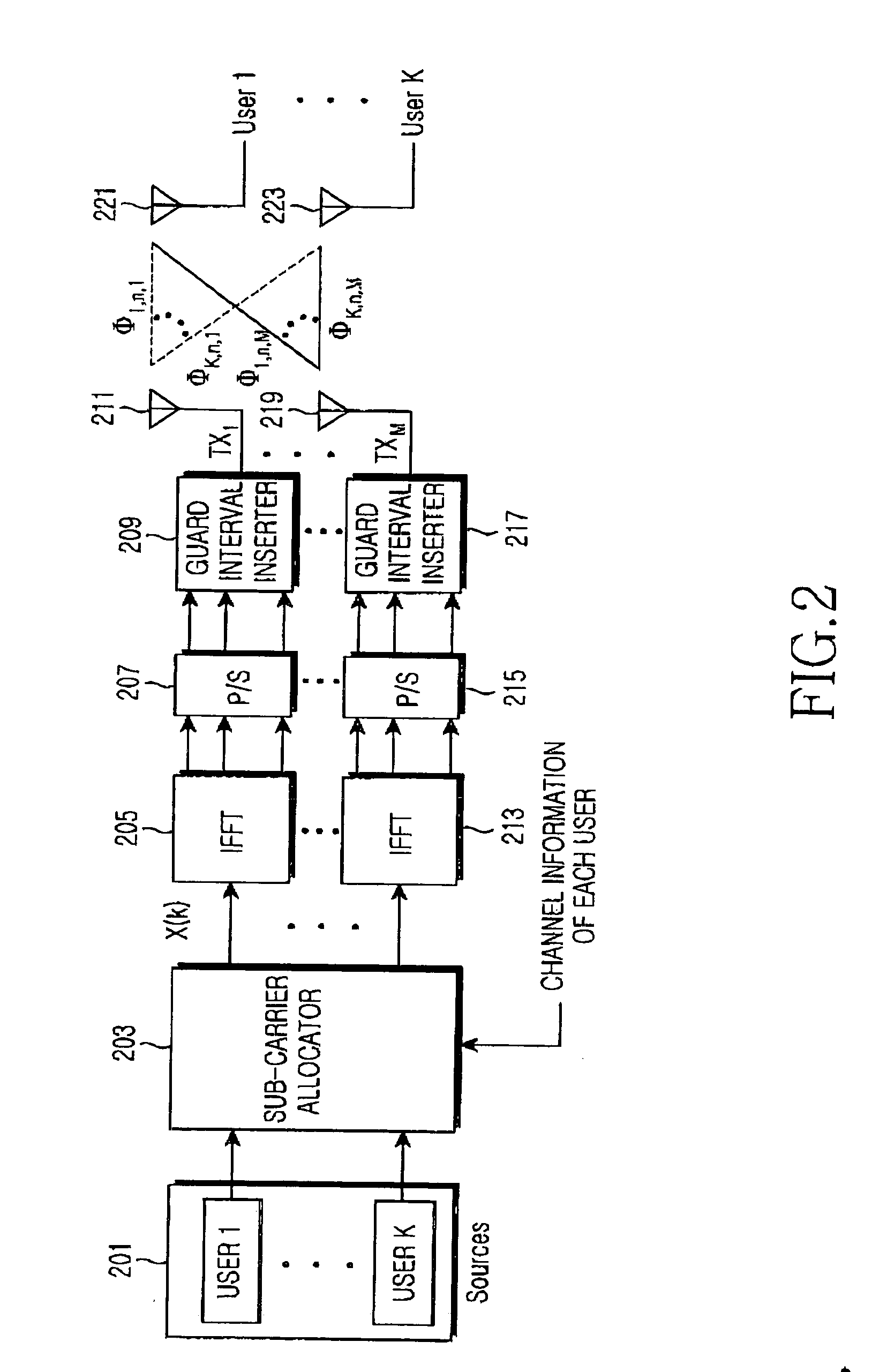
Apparatus and method for sub-carrier allocation in a multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) communication system
ActiveUS20050099937A1Effective distributionEnergy efficient ICTCriteria allocationQuality of serviceCarrier signal
An apparatus and a method capable of effectively allocating sub-carriers for a plurality of users and transmitting the sub-carriers to users through multiple antennas in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDMA) mobile communication system are provided. A sub-carrier allocation method reduces transmission power by taking a desired bit rate and power budget into consideration. The sub-carriers are optimally allocated to each antenna, so that peak to average power ratio (PARR) is reduced and Quality of Service (QoS) is improved. The apparatus and the method are adaptable for multi-users and obtain space diversity gain through multiple antennas.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
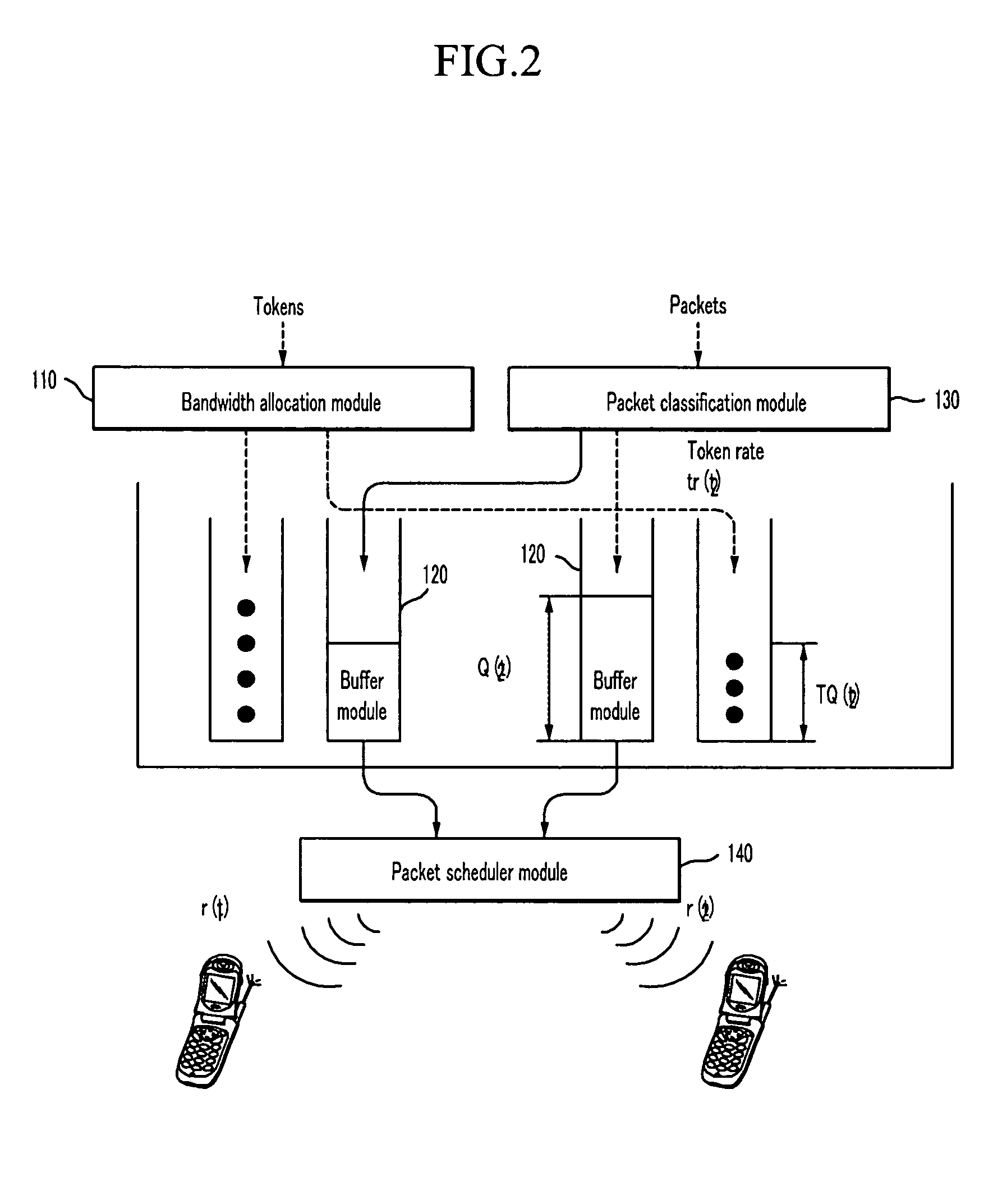
Dynamic bandwidth allocation apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070133407A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDynamic bandwidth allocationDistribution method
The present invention relates to a bandwidth allocation apparatus and a method thereof. The present invention provides a method for adaptively allocating and controlling radio channels to multimedia traffic having various characteristics. Particularly, the present invention proposes a method for maximizing a system resource use rate while satisfying a communication QoS requirement for individual video traffic. Therefore, the adaptive bandwidth allocation method according to the present invention guarantees system performance and user-required communication QoS.
Owner:KT CORP +2
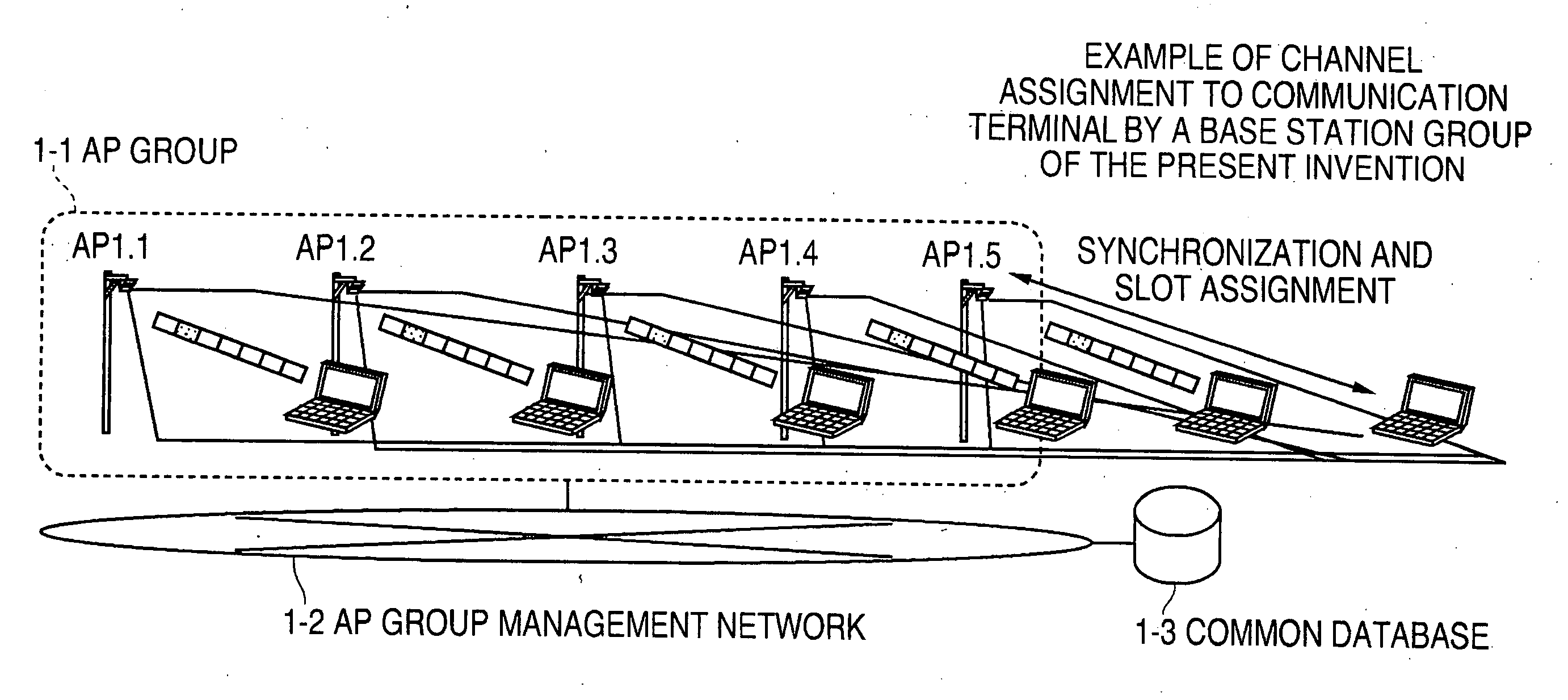
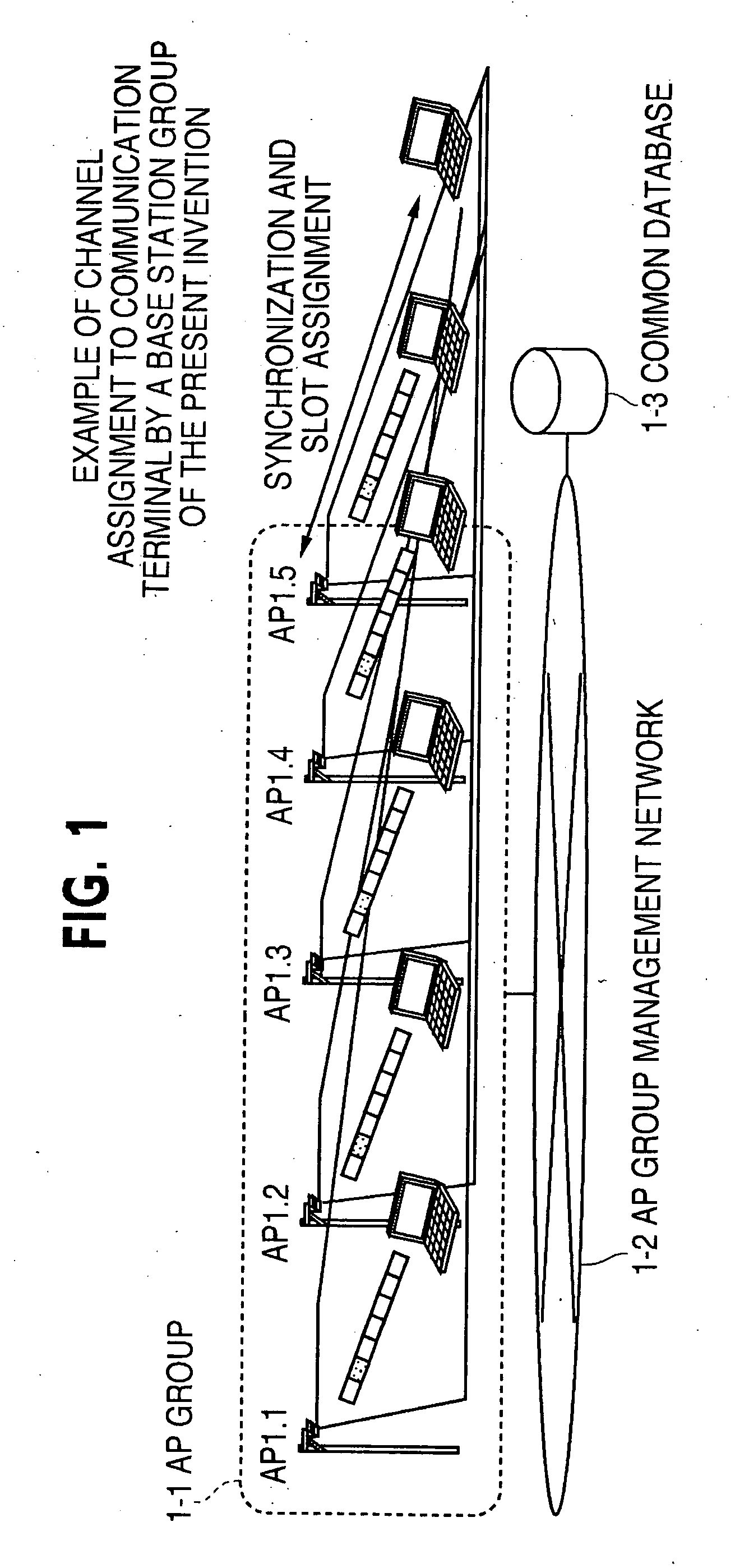
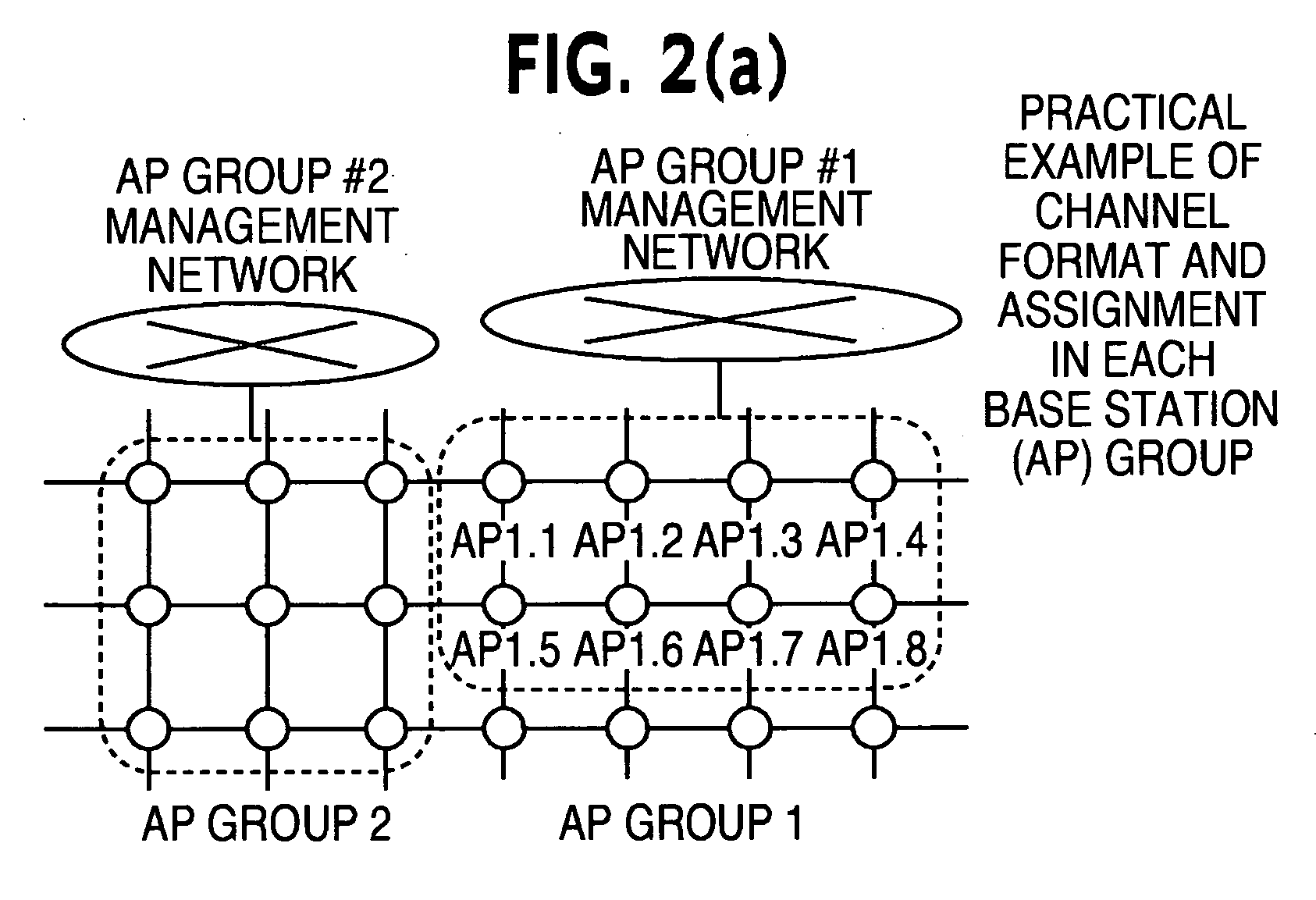
Channel assigning method and system for radio base station group
InactiveUS20070135150A1Quality improvementReduce processing loadNetwork topologiesConnection managementRadio Base StationAuthentication
To reduce the processing load such as channel assignment and an authentication process in a plurality of radio base stations and communication terminals, and quickly and efficiently assign channels to the communication channels. The channel assigning method by a radio base station group, includes determining assignment of a communication channel between a communication terminal entering a radio area of the radio station group and all radio base stations within the radio station group by a base station in the radio base station group. Channel assigning information common to the radio base station group is updated as to the determined communication channel and a communication channel is assigned to the communication terminal with reference to the channel assigning information by each radio base station in the radio base station group other than the radio base station.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
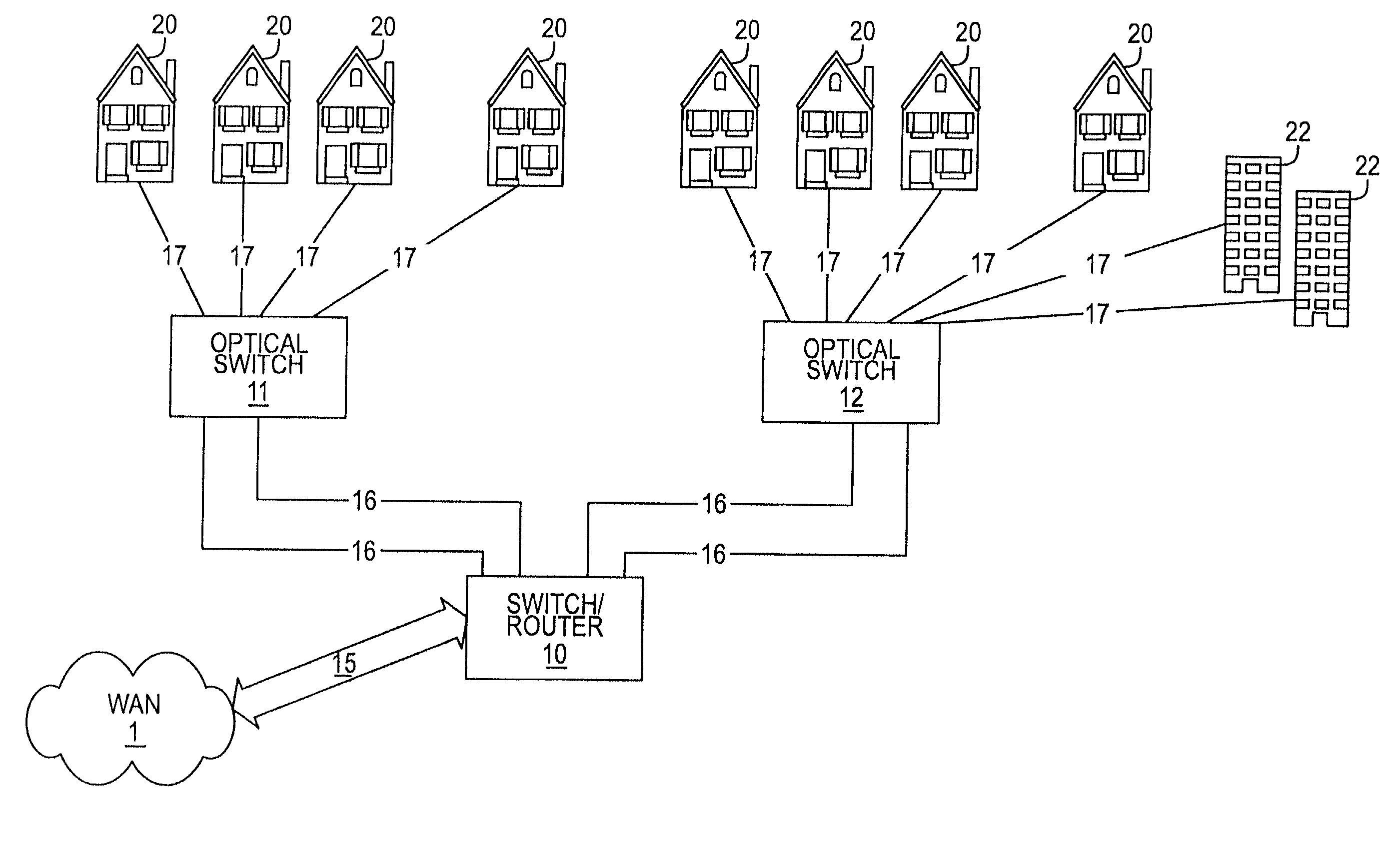
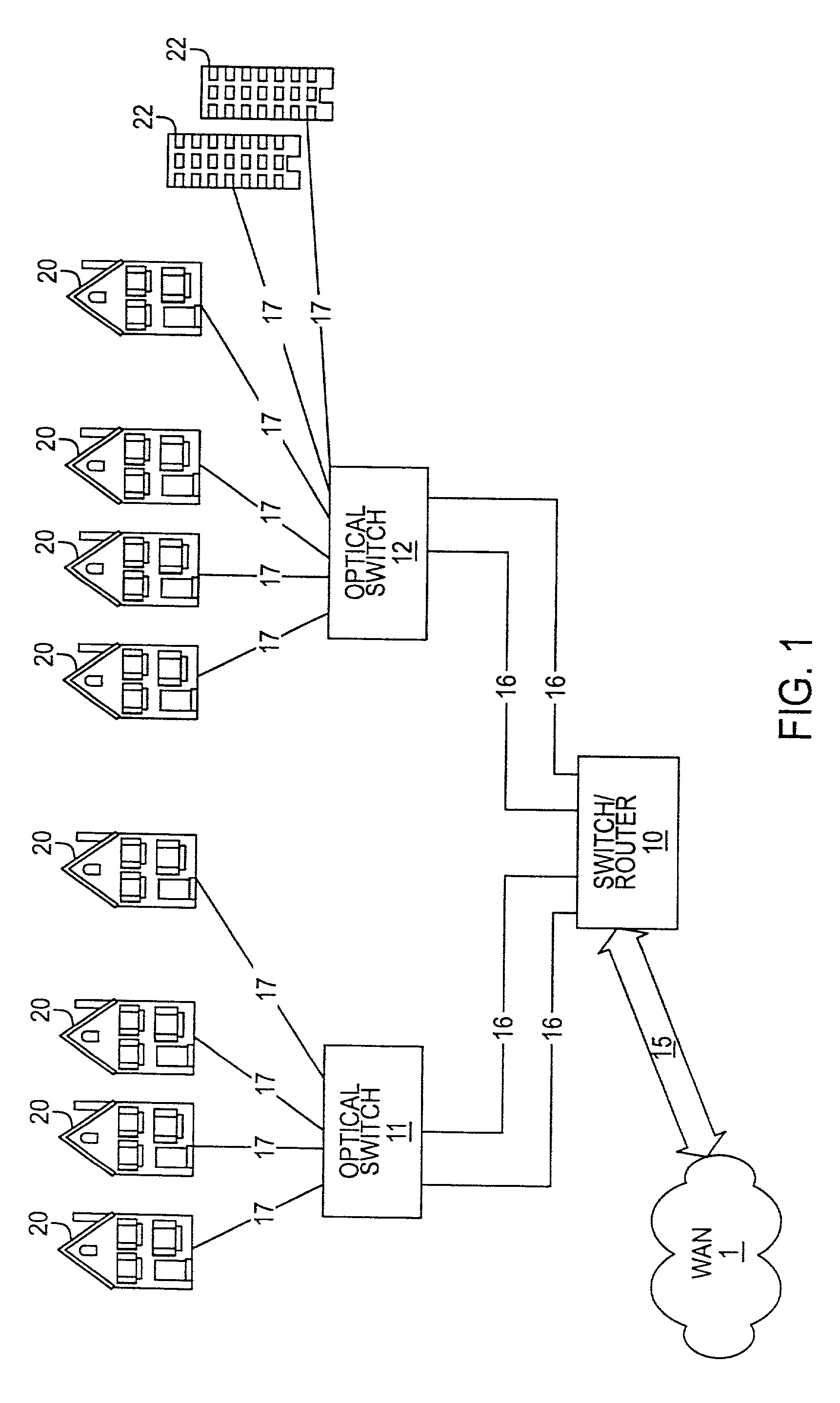
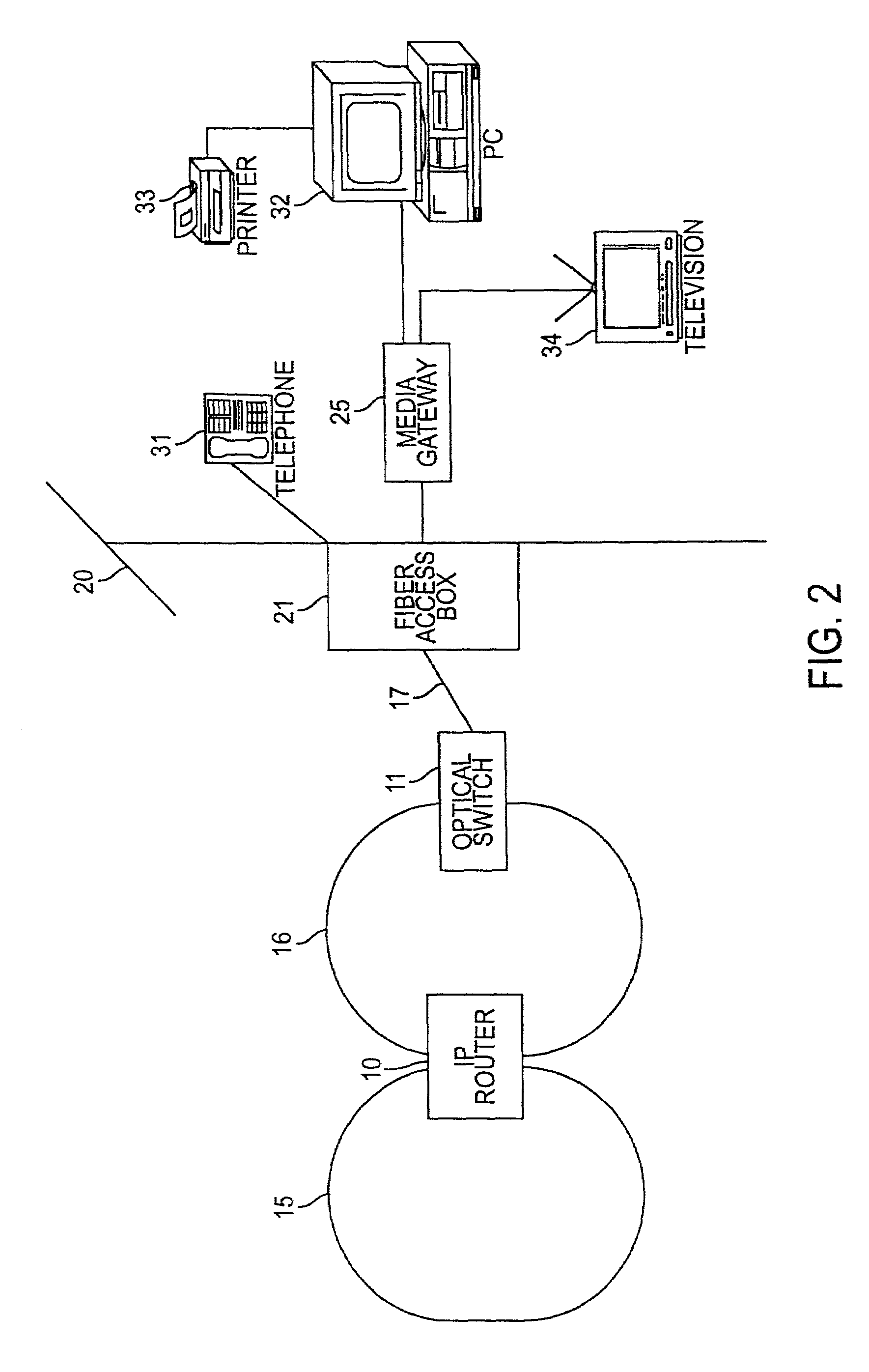
Optical network subscriber access architecture
InactiveUS7171121B1Provides redundancyMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexConnection typeFiber
A technique for providing an optical signal to a destination. In one embodiment, the technique is realized through the use of an environmentally hardened, modular switch and a fiber distribution methodology. The modular switch may include fiber access ports, power access ports, dual power supply modules, dual switch fabric modules, dual optical trunking modules, and multiple subscriber service modules that house subscriber service ports and serve a total of up to 96 end points. The dual optical trunking modules may act as an interface between an optical network and the dual switch fabrics, and provide redundancy and variable optical transmission distance between the modular switch and the optical network to which the modular switch is connected. The dual switch fabrics are used for switching and aggregating signals and providing redundancy. Each subscriber service module acts as an interface between one or more subscriber end points and the dual switch fabrics of the modular switch. The subscriber service modules may be coupled to one or both of the dual switch fabrics and a total of up to 96 subscriber end points. Subscriber end point connectivity may be achieved via subscriber service ports (housed within a subscriber service module), one or more of the fiber access ports, external fiber optic splice cabinet, fiber optic trunk cable, and one or more fiber breakout points (housed by pedestals). The subscriber end points may consist of one or more optical or electrical subscriber connection types.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Transmission power allocation method, communication device and program
ActiveUS8249631B2Reduce distractionsPower managementTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumDistributed computing
Owner:SONY CORP
Methods And Systems For Dynamic Bandwidth Management For Quality Of Service In IP Core And Access Networks
InactiveUS20080130495A1Easy to useStringent qualityError preventionTransmission systemsPresent methodKey issues
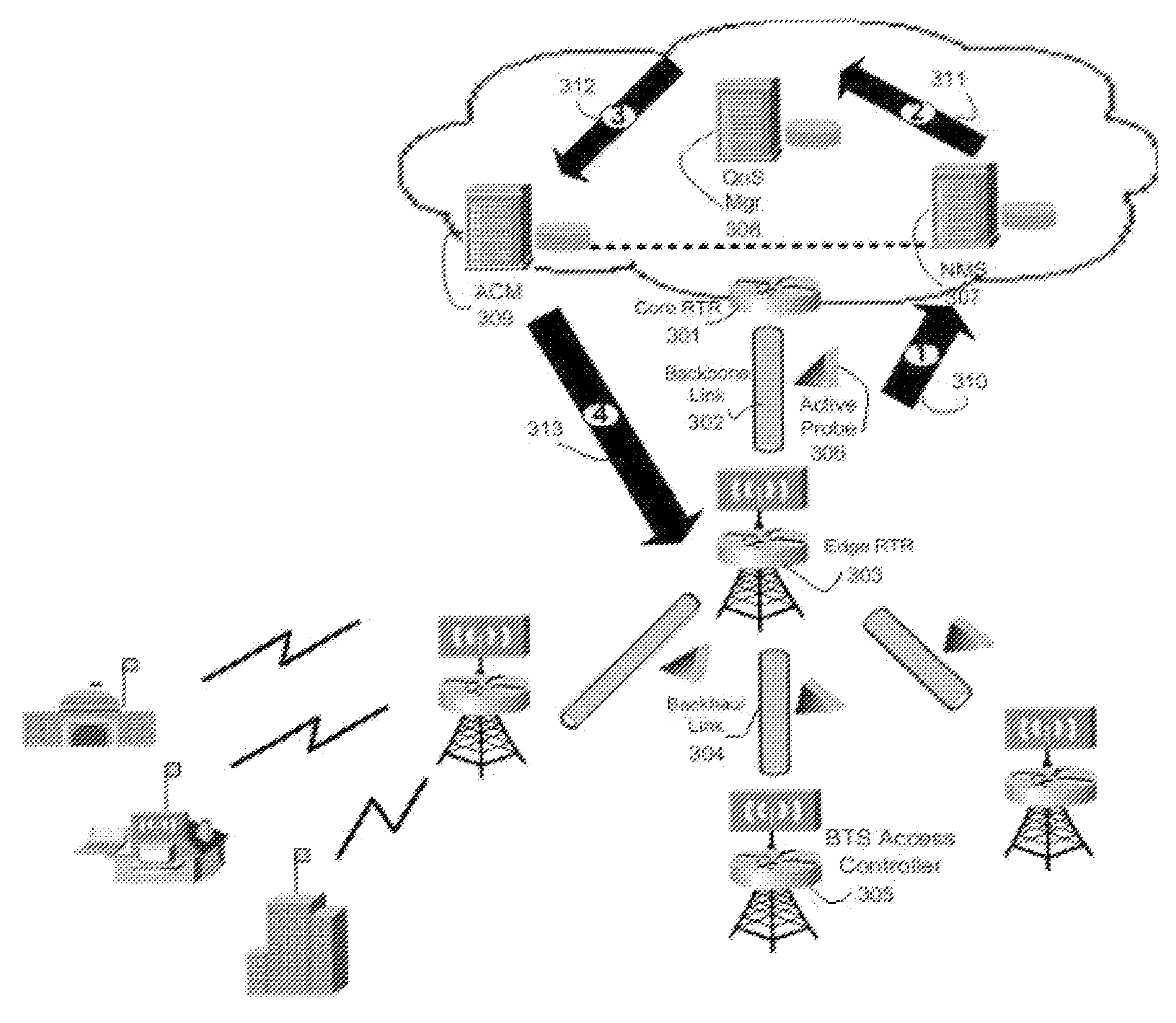
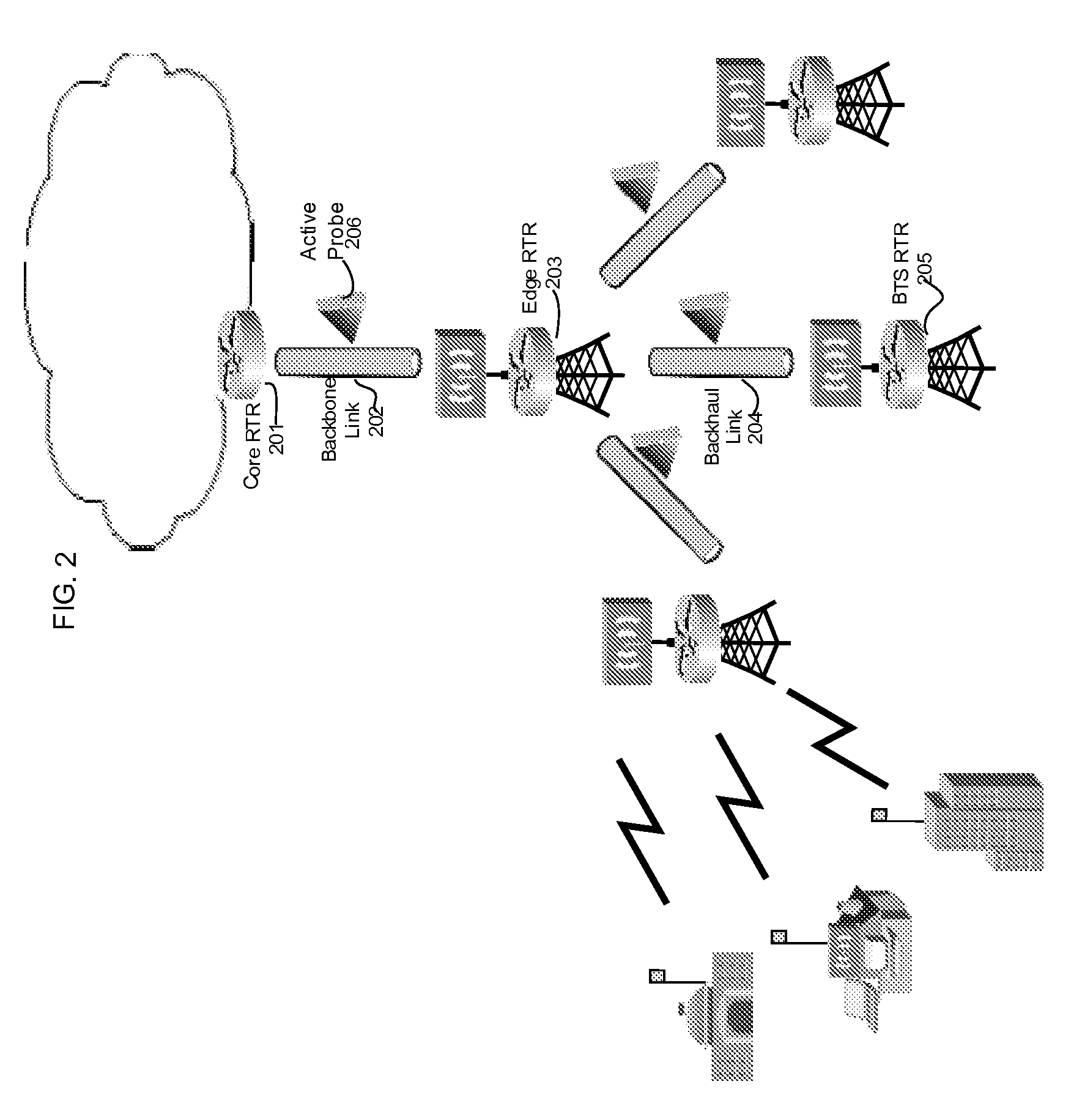
Proper allocation of network bandwidth is a crucial issue in rendering certain performance guarantees to meet the growing customer demands. Hence, allocation methodologies must explicitly be carried out for these guarantees to be given as efficiently as possible since the shared resources are limited. This invention presents methods and systems for Dynamic Bandwidth Management (DBM) and Quality of Service (QoS) in packet-based networks. DBM is an algorithm that dynamically adjusts the resource allocation in the IP Access Networks based upon measured QoS at the IP Core Network through an implementation of a Feedback Control Mechanism to manage available core transport bandwidth. Such a Feedback Control Mechanism is capable of maintaining a condition of non-congestion, a sufficient and necessary condition to meet end-to-end QoS requirements in a Next Generation Network (NGN). The emphasis is given on the system implementation of QoS policies for the fair distribution of network resources through a scalable architecture comprising key Resource and Admission Control Functional (RACF) entities, namely: a Network Management System (NMS), a QoS Manager, an Access Controller Manager (ACM), the Access Controllers, and the active probes.
Owner:LATITUDE BROADBAND
Beam and power allocation method for MIMO communication system
InactiveUS20060098754A1Maximizing rate capabilityReduce the amount requiredPower managementDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCommunications systemData stream
A beam and power allocation method for a MIMO system transmitting multiple data streams from a transmitter having a plurality of transmit antennas to a receiver having at least two receive antennas, the transmit antennas being grouped based on feedback information from the receiver, includes obtaining covariance matrices for respective transmit antenna group, and allocating beam and power to the transmit antenna groups according to the covariance matrices of the respective antenna groups. The power allocation method can be adapted to various partial beamforming techniques by generalizing the optimization problem as a function of transmit covariance matrices.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
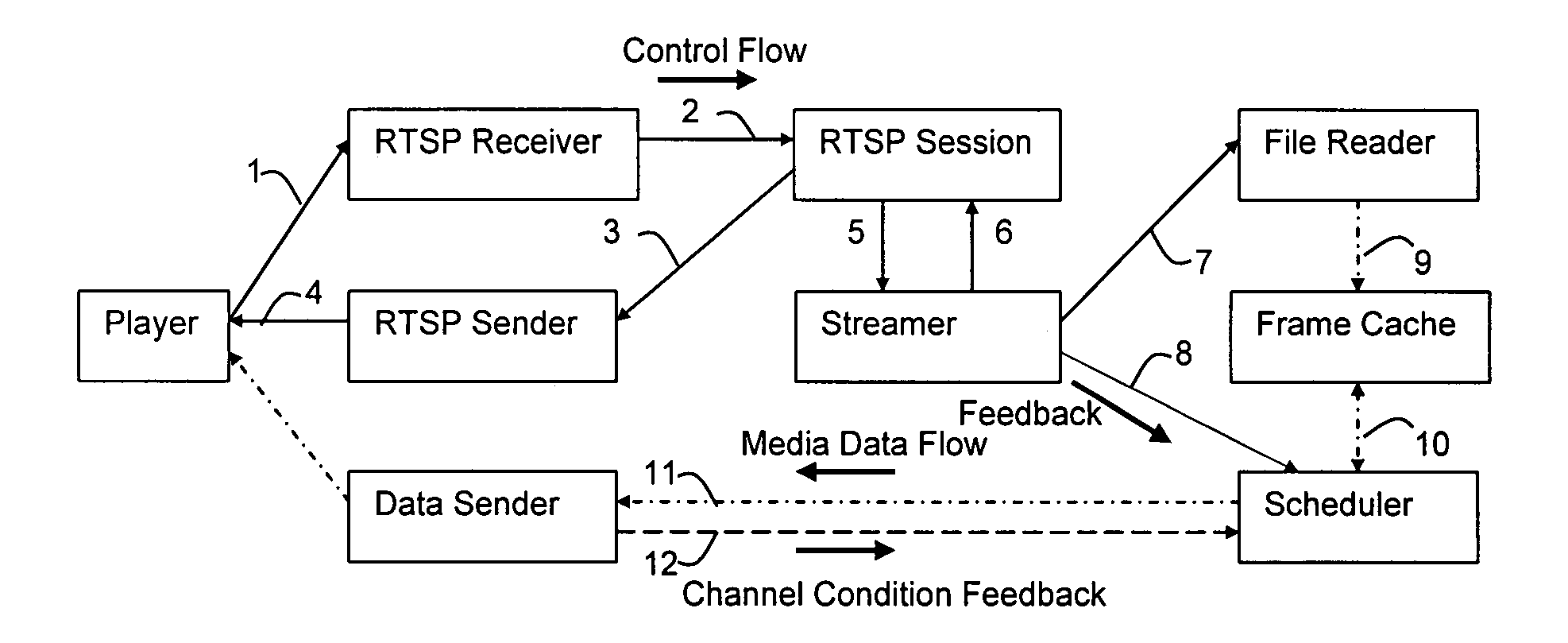
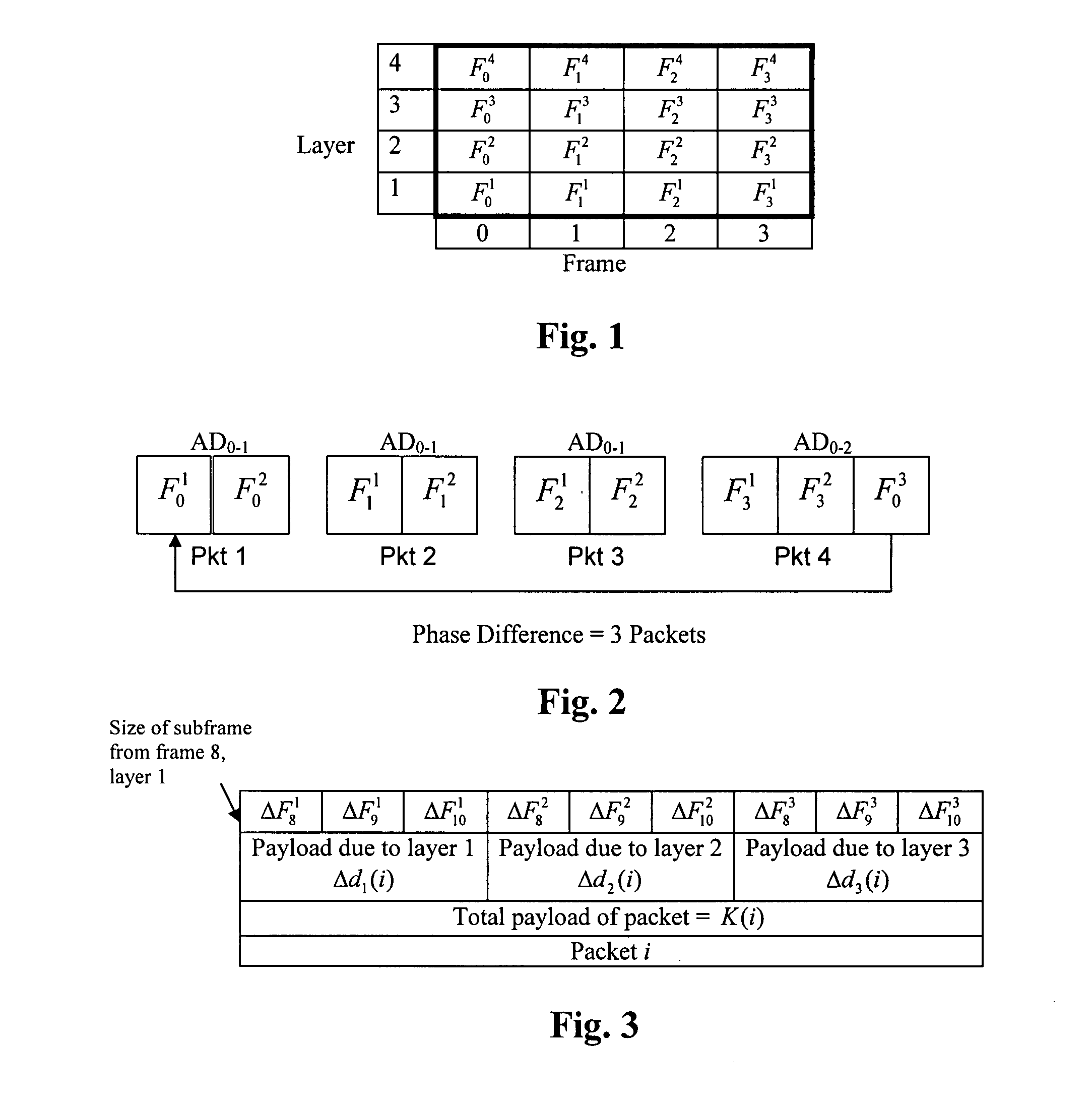
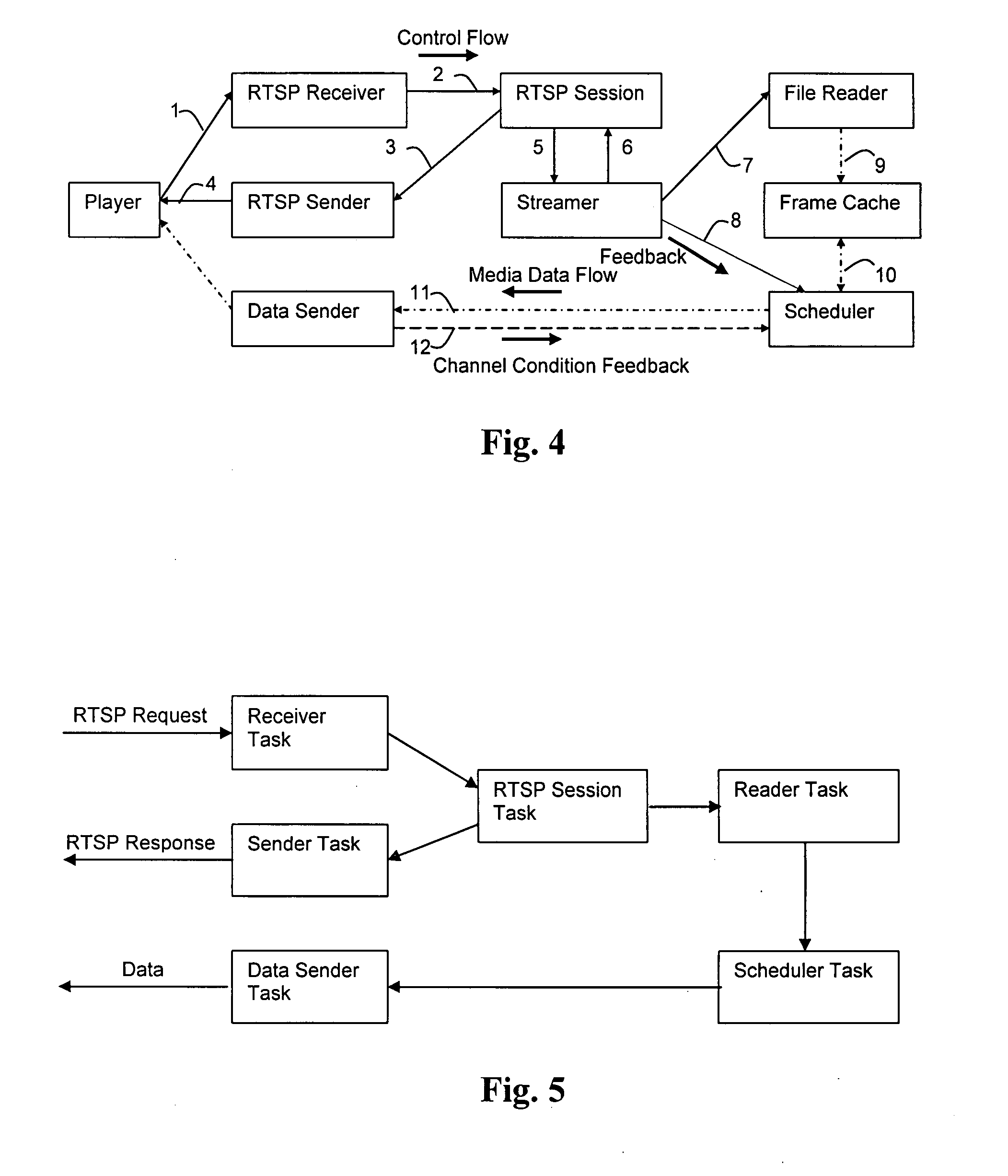
Payload allocation methods for scalable multimedia servers
InactiveUS20090125636A1Rapid and accurate characterizationRapid and intelligent responseMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionMultimedia serversNetwork conditions
The dynamic streaming of multimedia data between a data server and one or more clients is disclosed. Dynamic streaming enables the rapid and accurate characterization of the end-to-end path conditions in a server-client streaming session, as well as the rapid and intelligent response to those conditions in terms of source compression prior to data packetization. The most significant bits of an original bit stream can be adaptively and immediately selected in response to network conditions. The adaptive selection process is informed by feedback from the client receiver indicative of a time-to-transit the network from server to client. A control protocol and server architecture, including file format, data structure, data processing procedures, cache control mechanisms, and adaptation algorithms useful in implementing dynamic streaming are also disclosed.
Owner:BRAINMEDIA
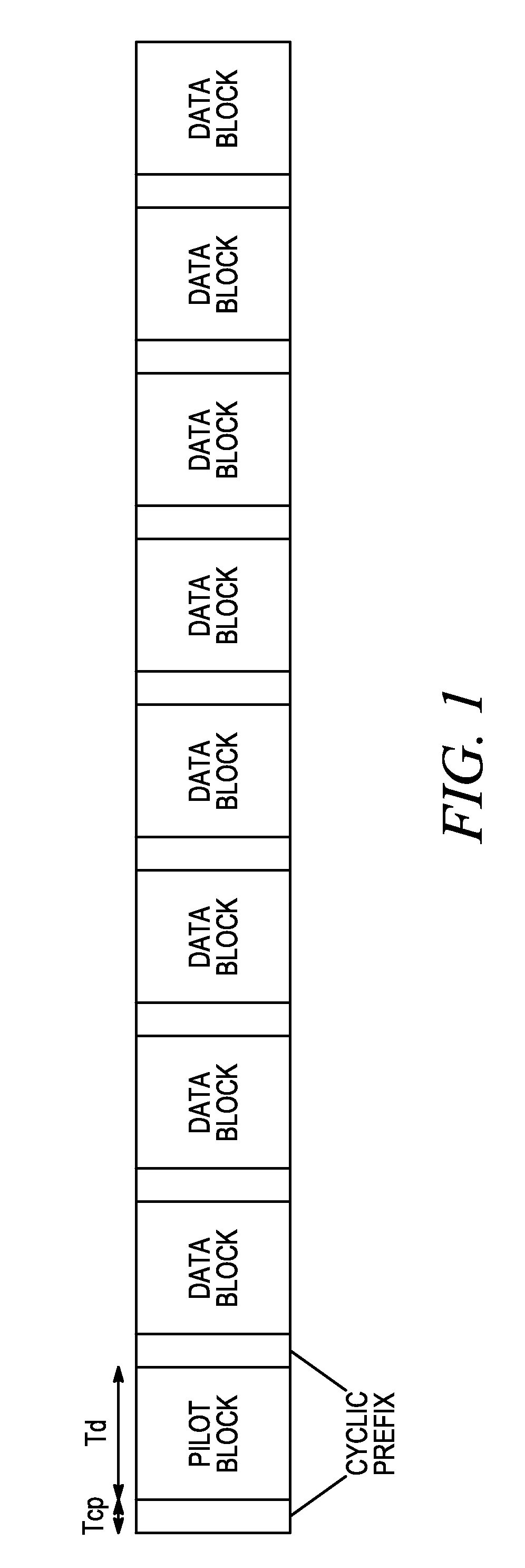
Pilot Signal Allocation Method and Apparatus
A pilot (or reference) transmission scheme is utilized where different transmitters are assigned pilot sequences with possibly different cyclic time shifts and different base pilot sequences. A pilot signal is transmitted concurrently by the transmitters in a plurality of pilot blocks, and a receiver processes the plurality of received pilot blocks to recover a channel estimate for at least one of the transmitters while suppressing the interference due to the pilot signals from the other transmitters.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
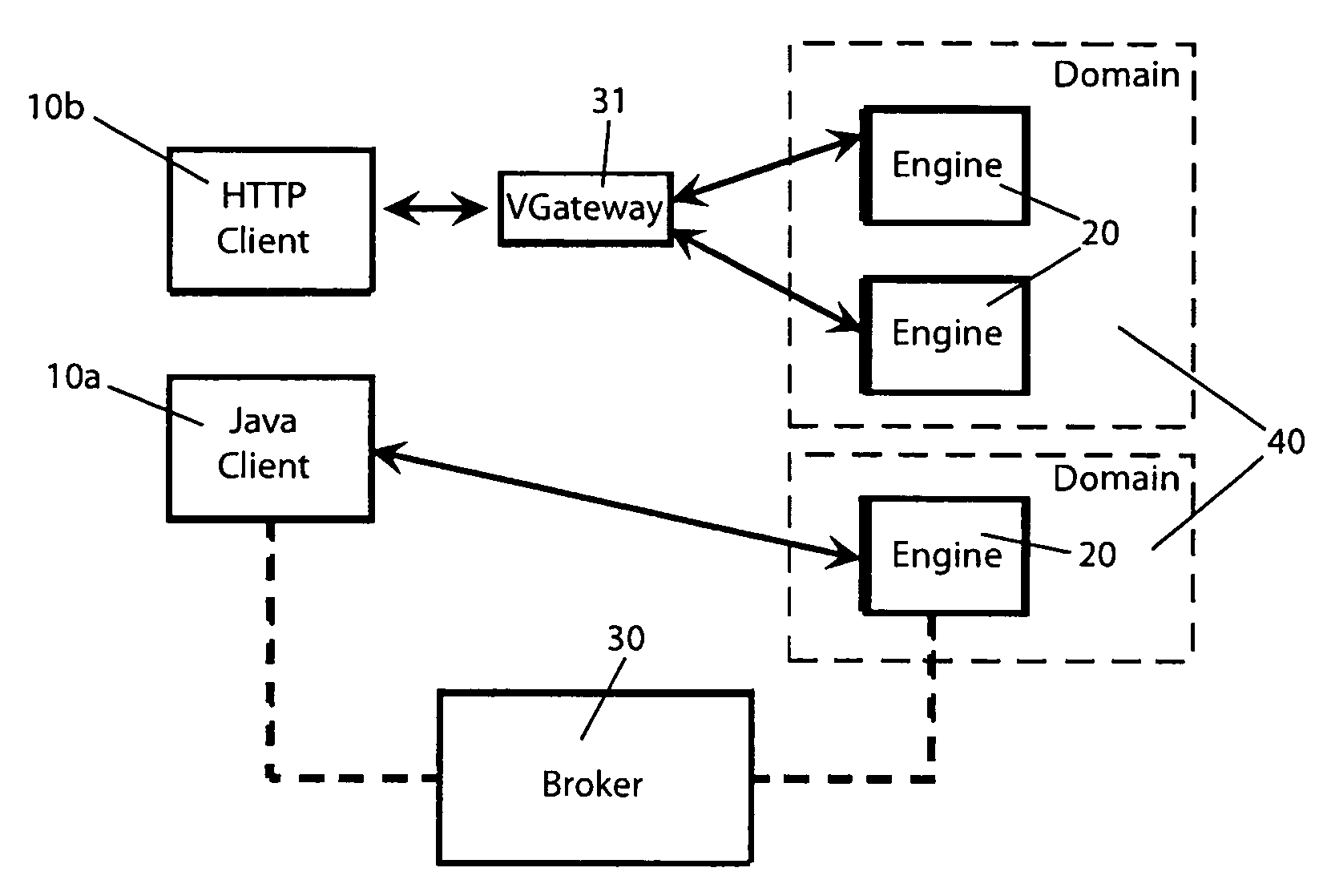
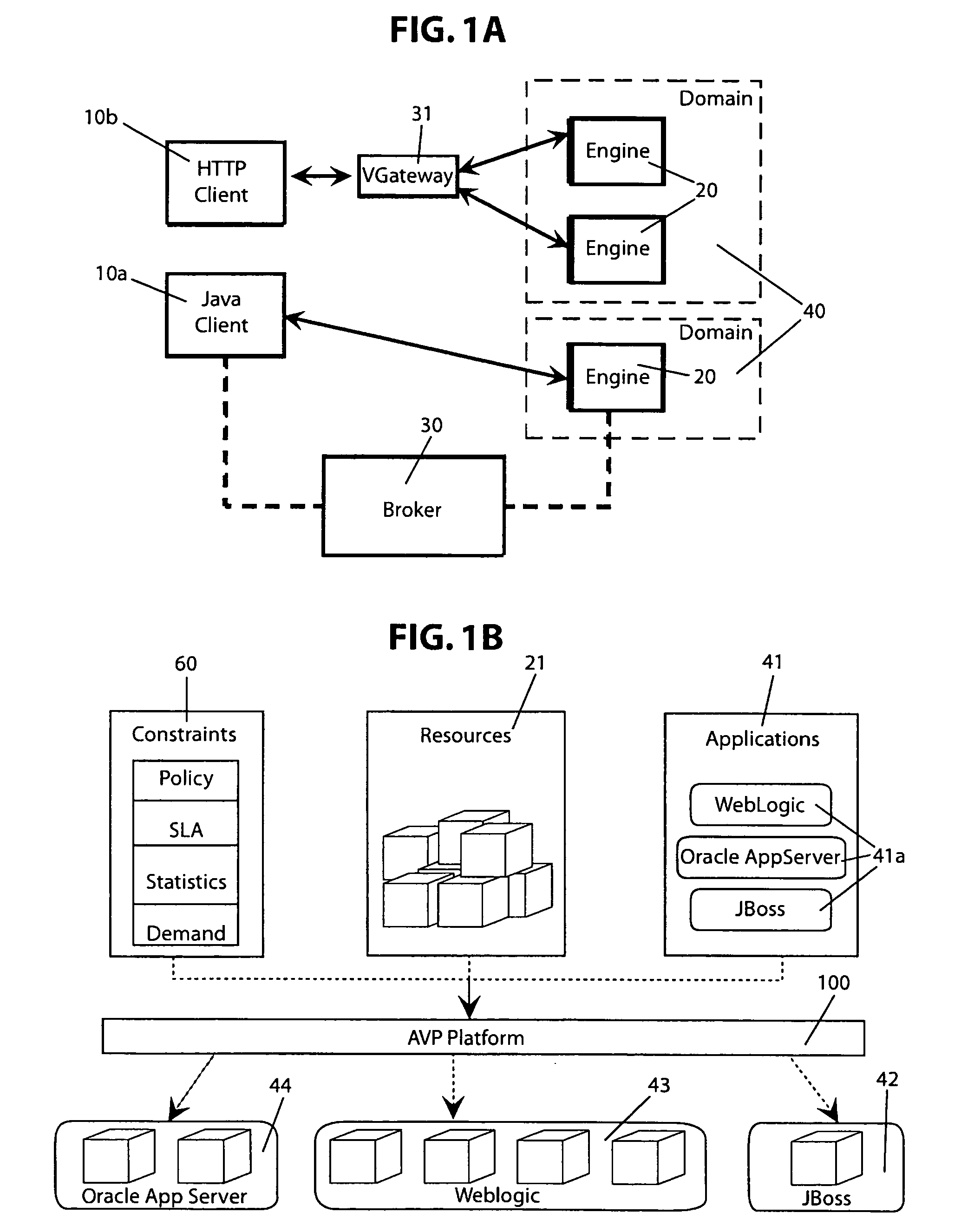
Method for allocating shared computing infrastructure for application server-based deployments
A shared computing infrastructure includes a plurality of computing engines, applications servers, and computing domains. A broker component executes a method for dynamically allocating the computing engines among the computing domains. The allocation method begins with the step of determining an expected number of computing engines to be allocated to each of the computing domains as a function of a predetermined service policy and a predicted demand for the domain While fewer than the expected number of computing engines has been allocated to each domain, the computing domains are sequentially selecting as a function of predetermined domain priorities. Unallocated computing engines are identified, and the unallocated computing engines are allocated to each selected computing domain according to predetermined selection rules for the domain. During an allocation improvement step, allocations among the computing domains are further adjusted to maximize a fitness statistic computed for the allocations.
Owner:CLOUD SOFTWARE GRP INC
Distribution method of multi-carrier reinforced uplink power resource
InactiveCN101340622ATransmission control/equalisingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTD-SCDMATransmitted power
The invention provides a method for distributing power resource of a multi-carrier enhanced uplink, which includes the steps that: a wireless network controller configures maximum uplink transmitted power of a user terminal for a base station; the wireless network controller configures allowable maximum uplink transmitted power for the user terminal and expected reference received power of each carrier; the user terminal reports dispatching information including remained power of each carrier; the base station, after receiving the reported dispatching information from the user terminal, distributes power for each carrier according to the reported dispatching information and the maximum uplink transmitted power. Therefore, by adopting the method of the invention, the remained power of each carrier of UE can be concerned without transcending the capacity of the UE; furthermore, the method of the invention can be applied to a TD-SCDMA system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
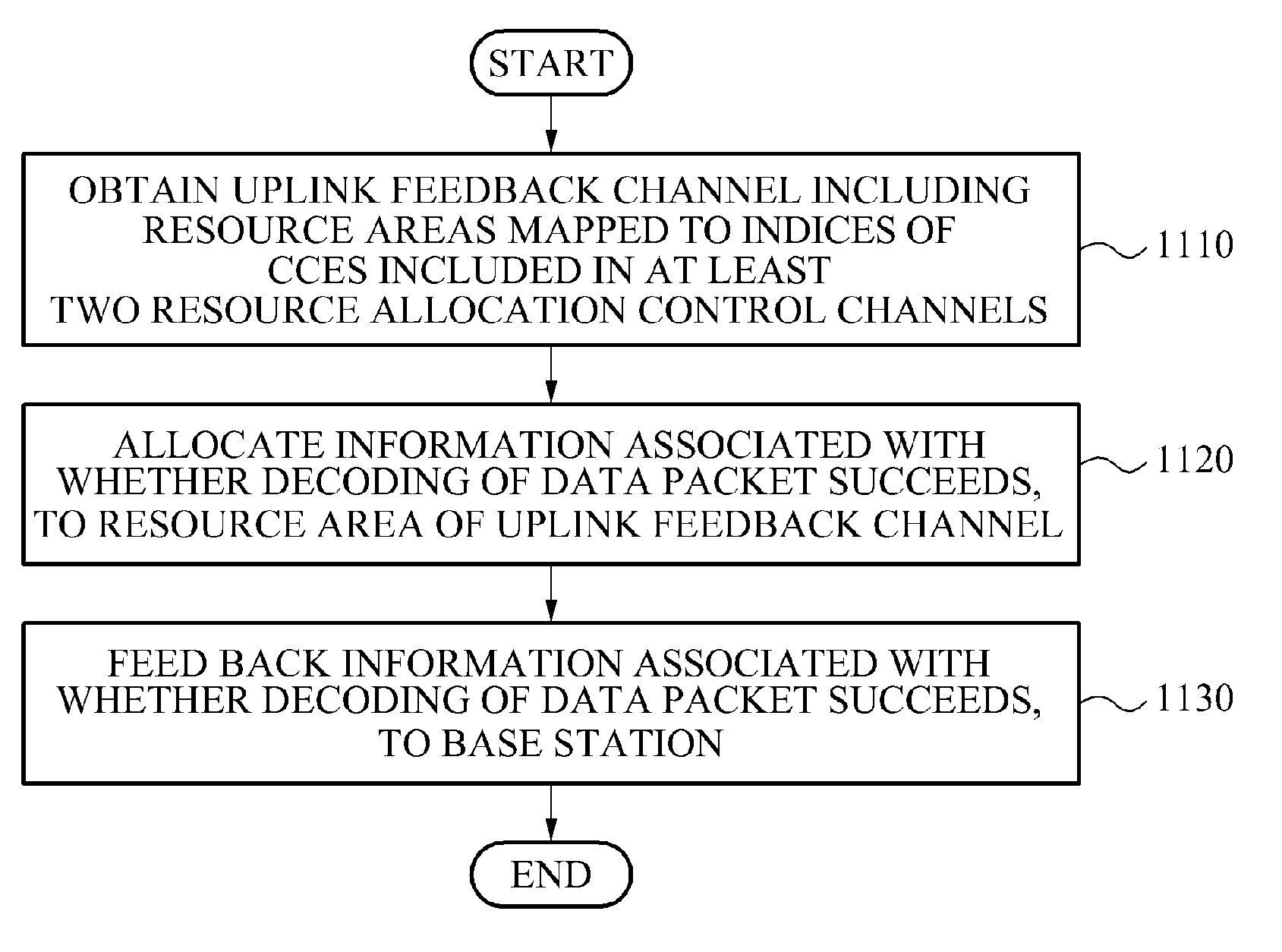
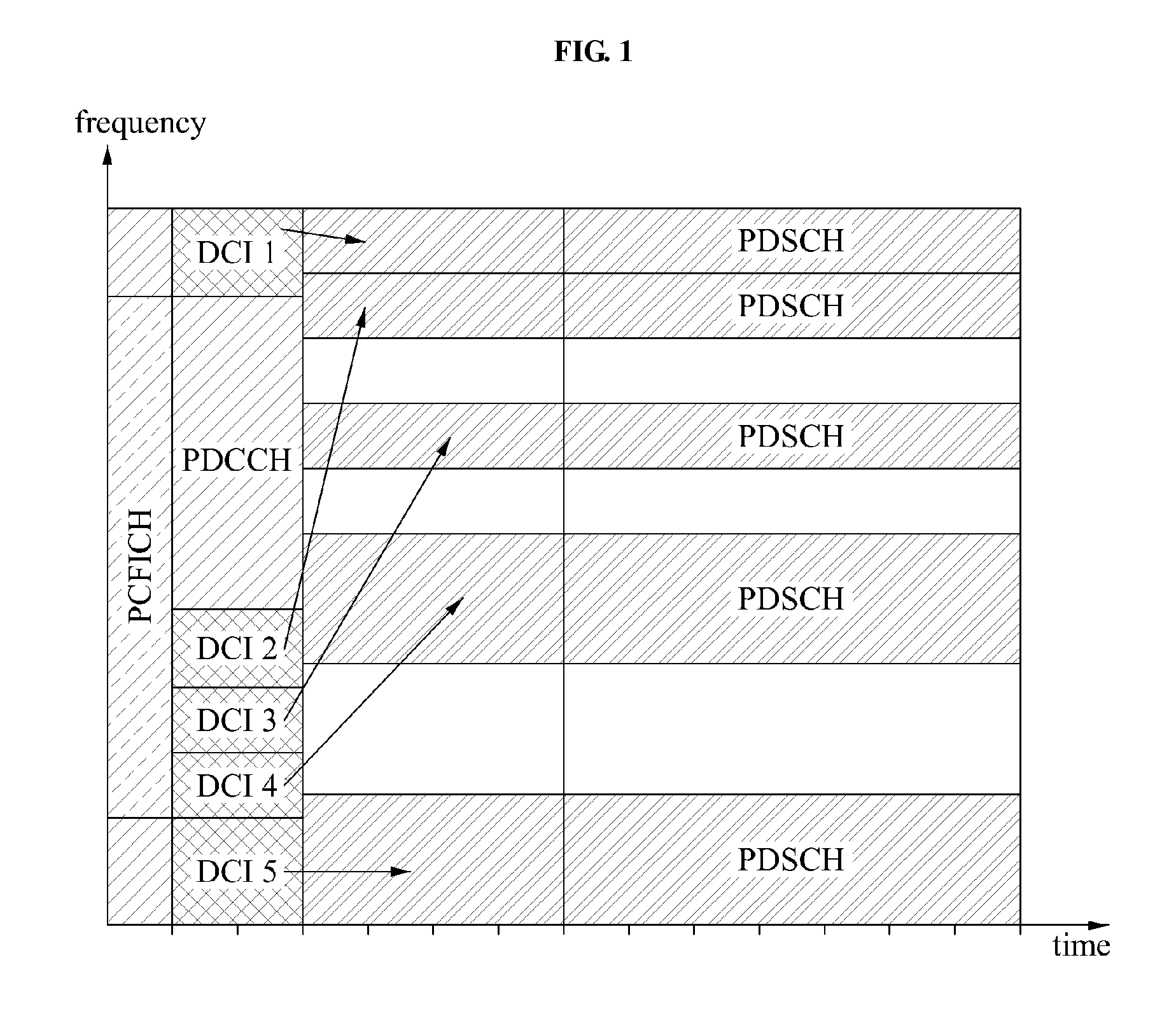
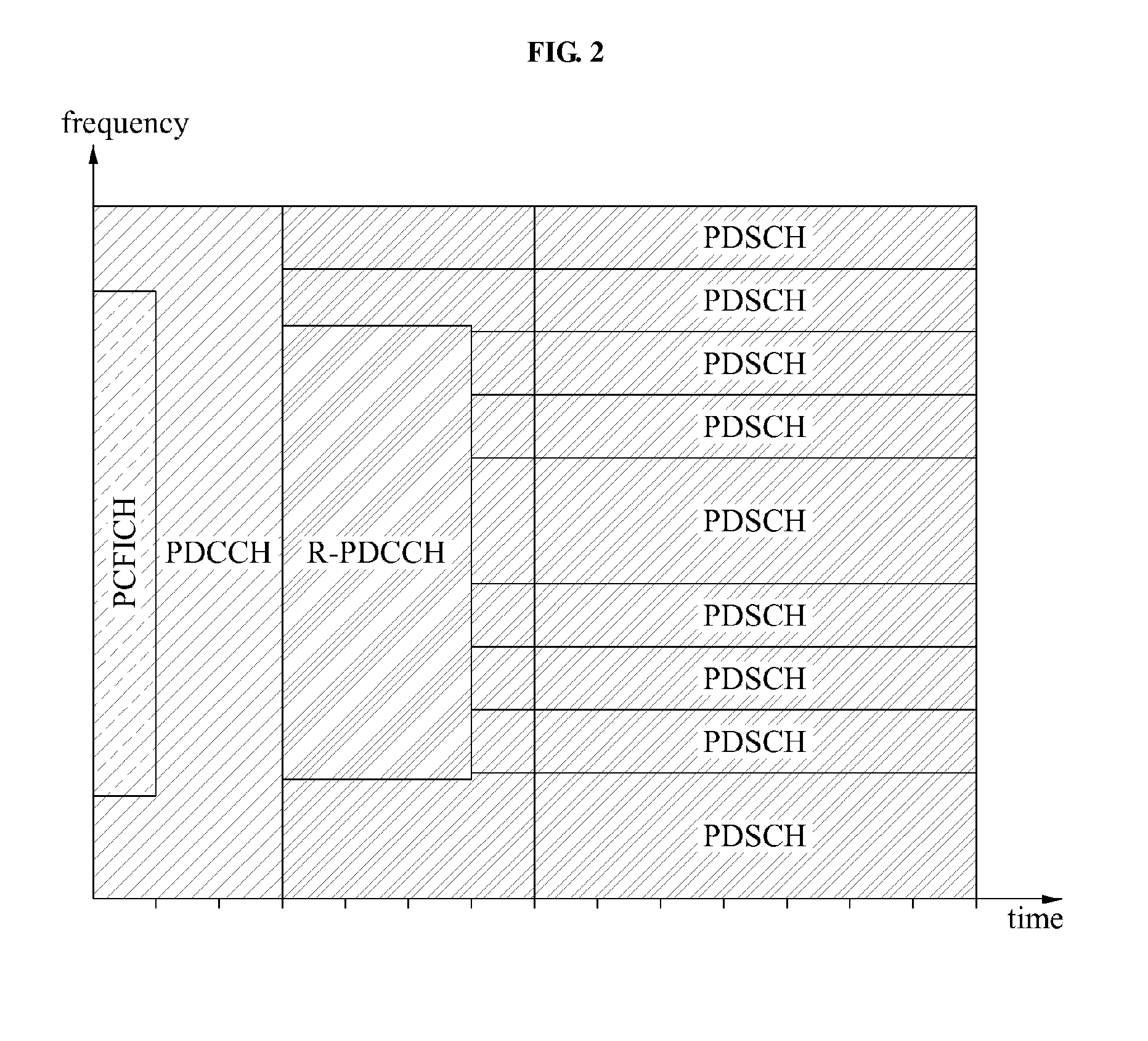
Method and apparatus of allocating uplink feedback channel for feeding back data corresponding to an enhanced-physical downlink control channel (e-pdcch)
Provided is an uplink feedback channel allocation method and apparatus used to feedback data to indicate whether data packets corresponding an enhanced physical downlink control channel (E-PDCCH) were successfully decoded. A terminal may use an additional resource area of an uplink feedback channel or may use an empty resource area of the uplink feedback channel to which feedback information of a data packet corresponding to a physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) is not allocated, to perform feedback.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
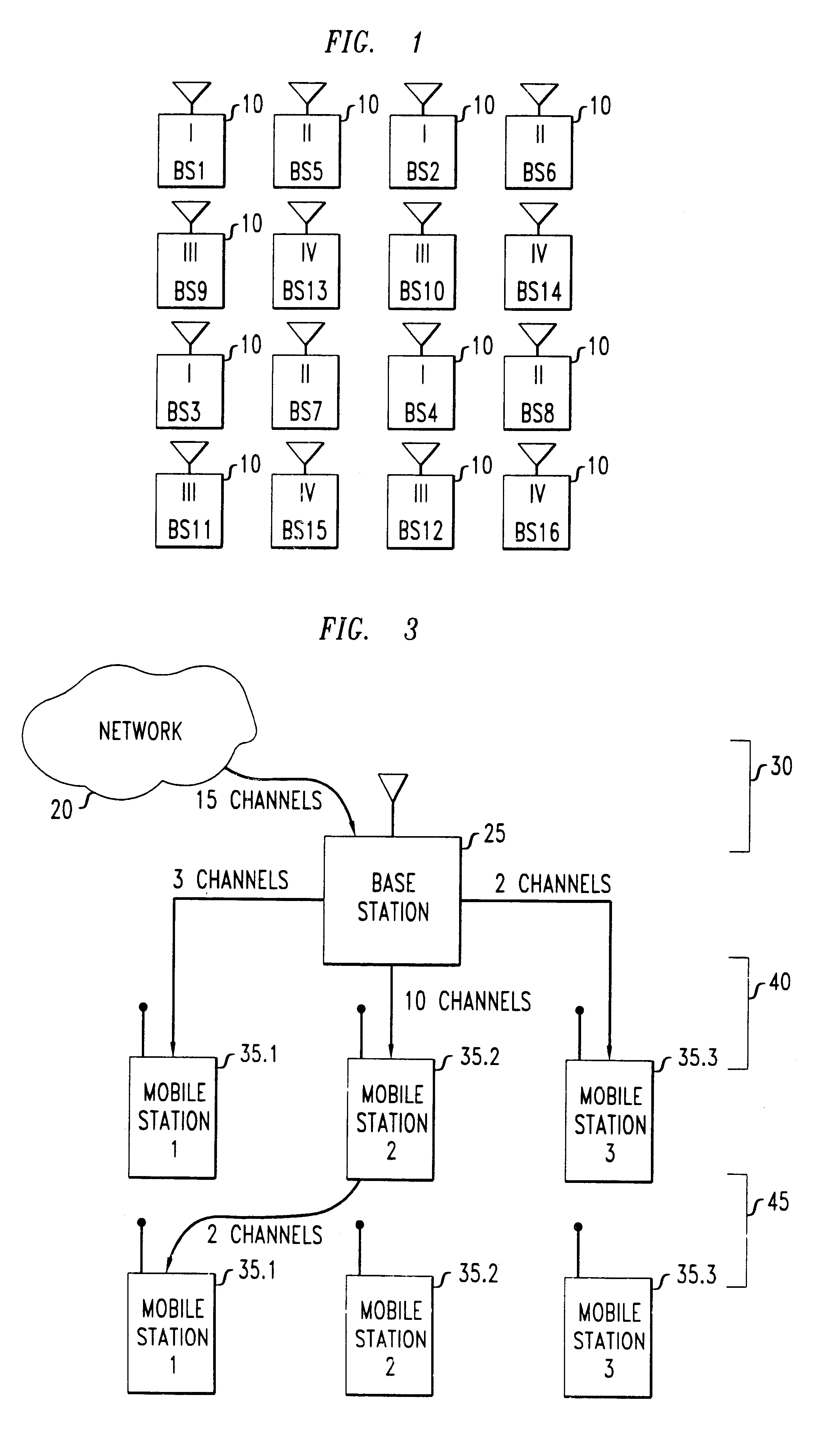
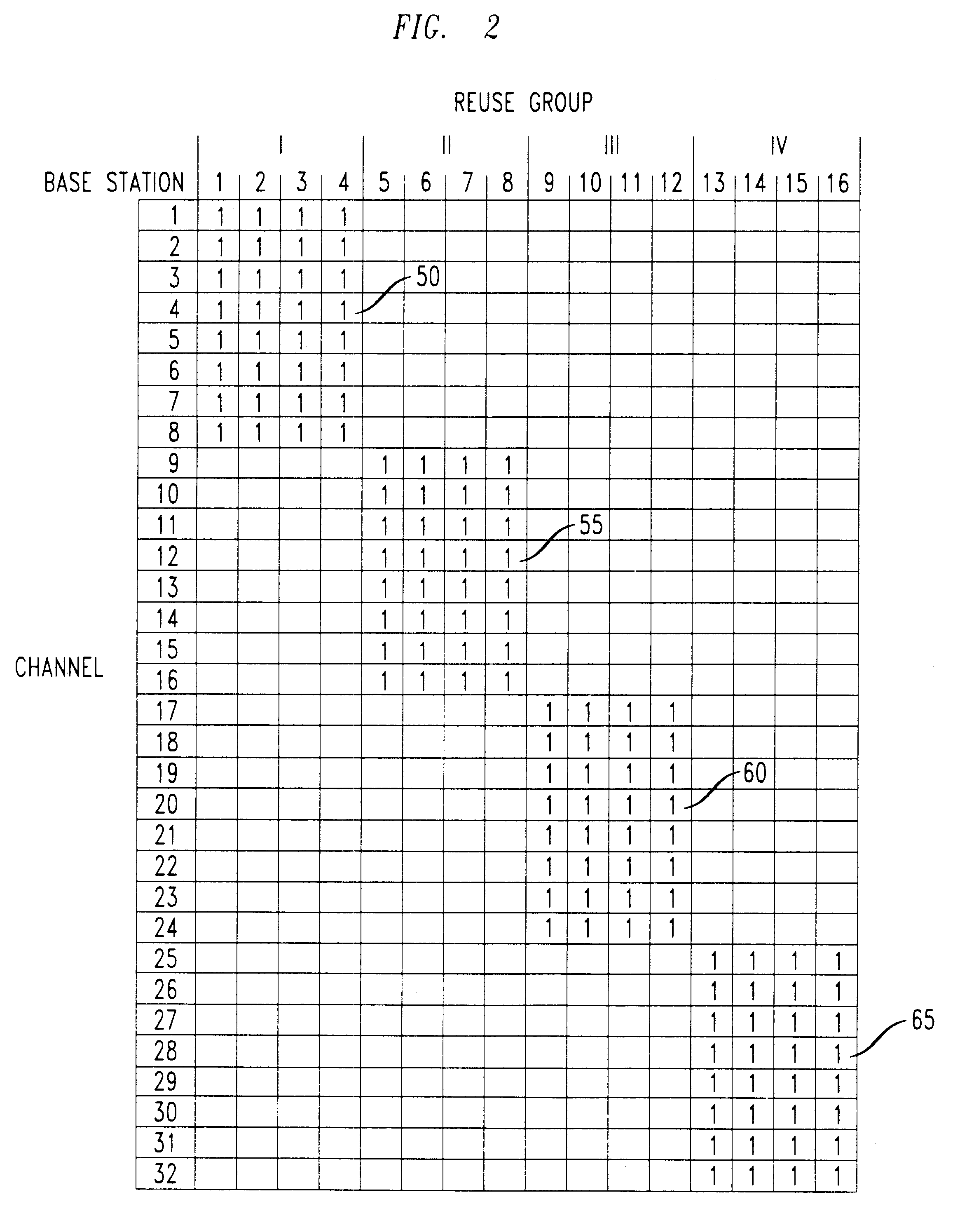
Method for dynamically allocating carriers in a wireless packet network, with reuse of carriers
InactiveUS6496490B1Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexMultiplexingDynamic channel
We disclose a method of dynamic channel assignment for wireless transmission systems that employ time or frequency multiplexing, or both time and frequency multiplexing. The invention is specifically addressed to the problem of avoiding interference in the channels of such systems. In a broad aspect, the invention involves partitioning base stations of a network into non-interfering sets. Channels are allocated to the non-interfering sets according to need. Stages of channel reallocation take place periodically. The reallocation takes place through coordinated activity by the base stations. That is, the channel reallocation is carried out in response to information that is exchanged between base stations, or it is centrally directed by the network in response to information passed to the network by the base stations.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com