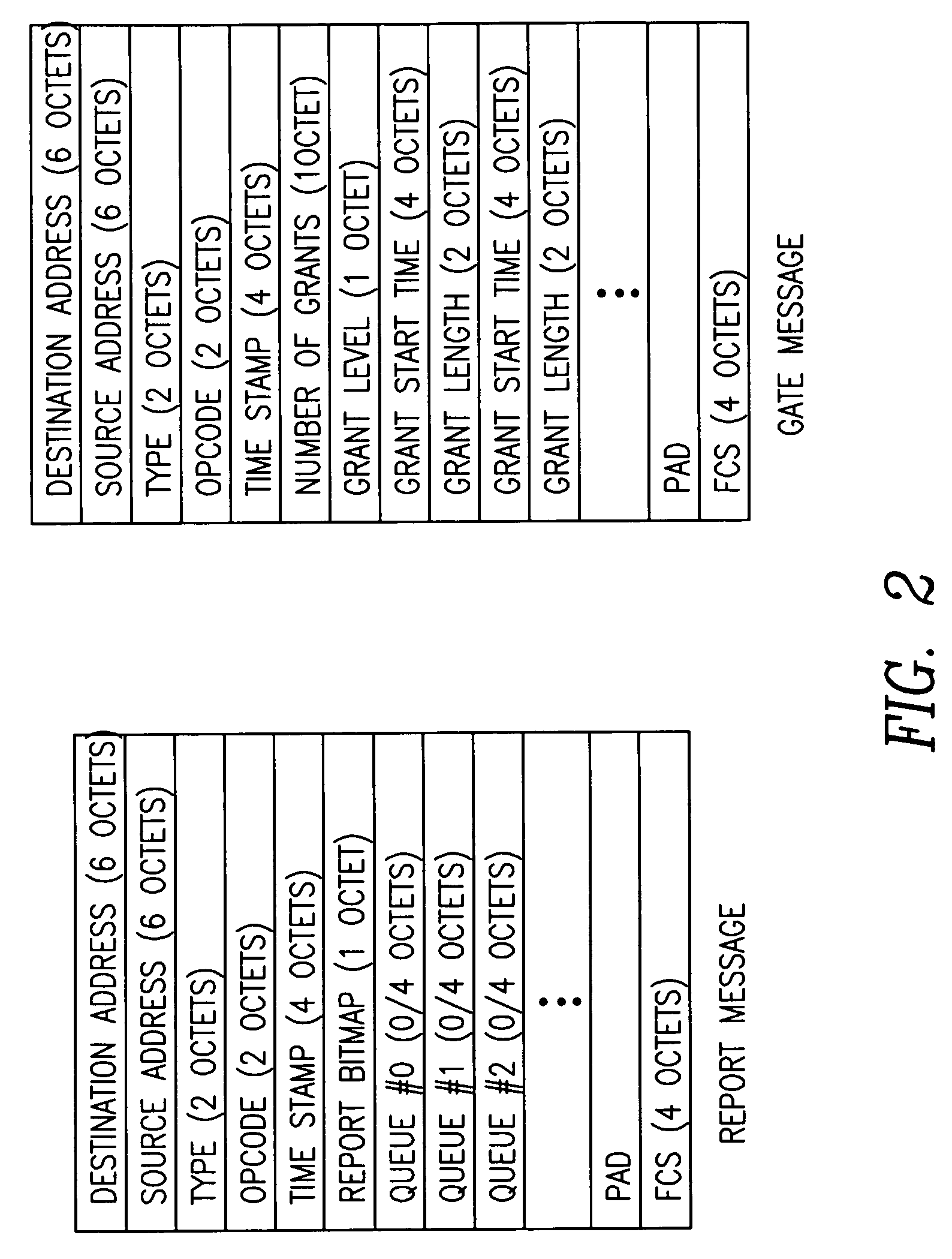
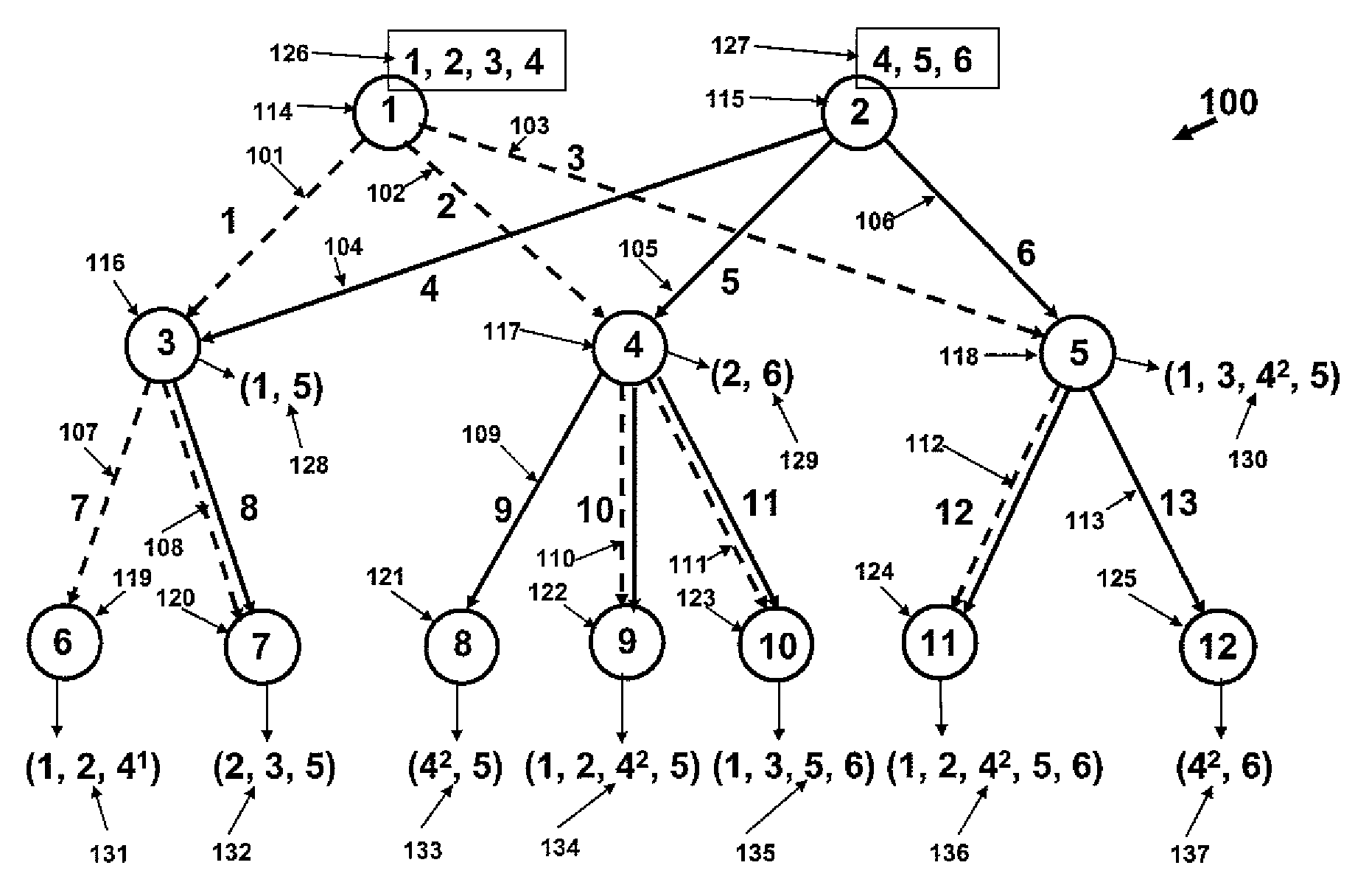
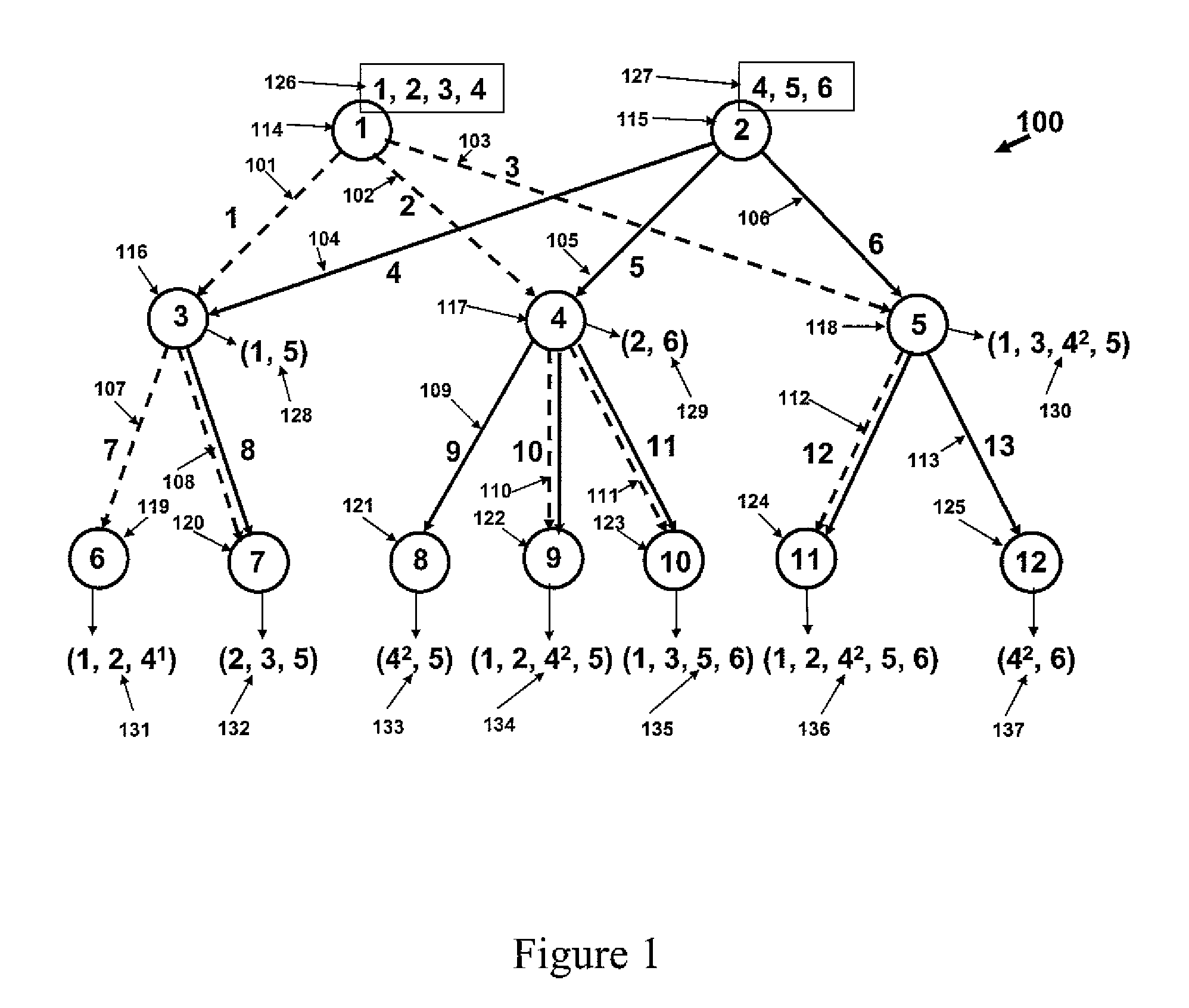
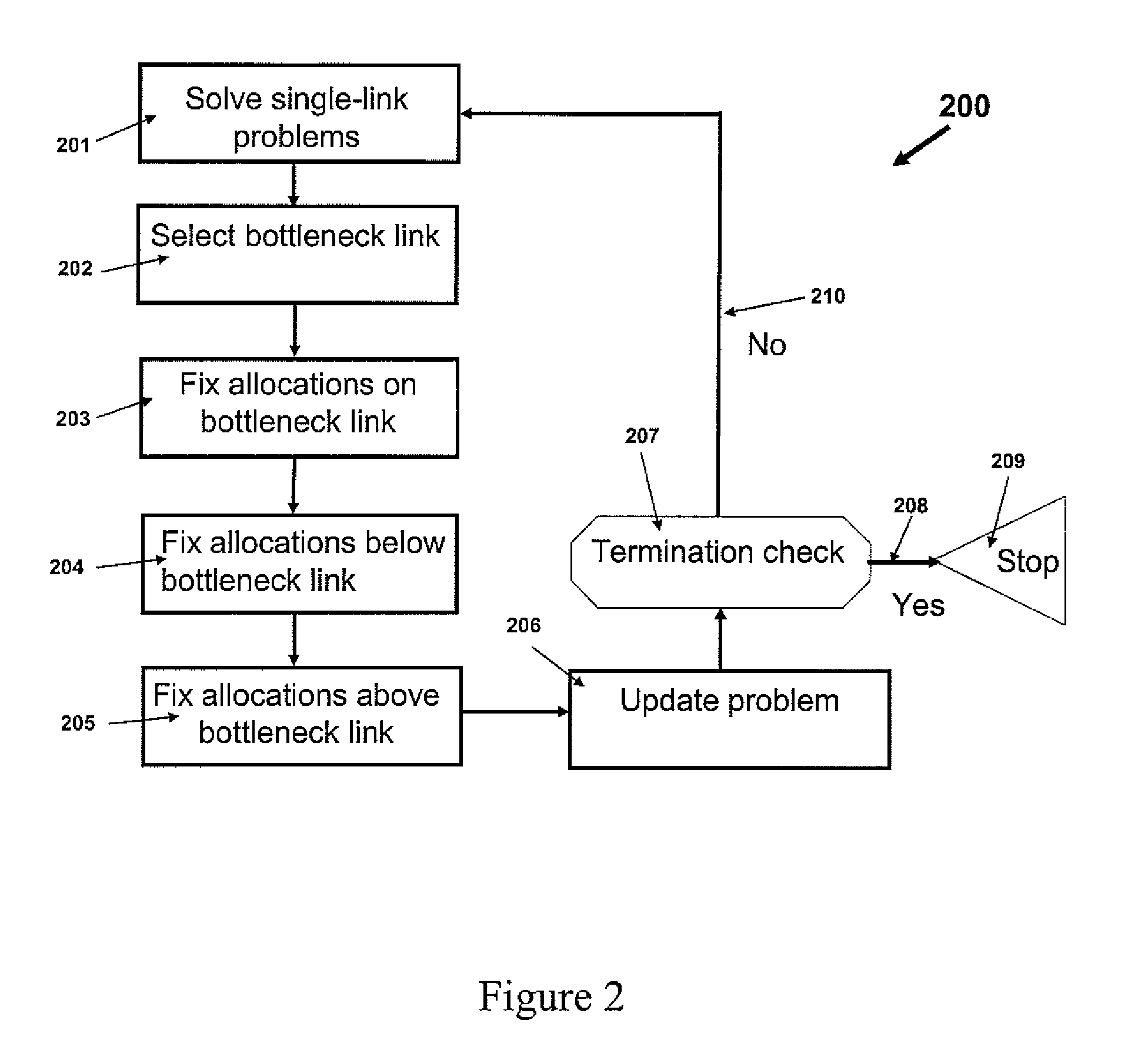
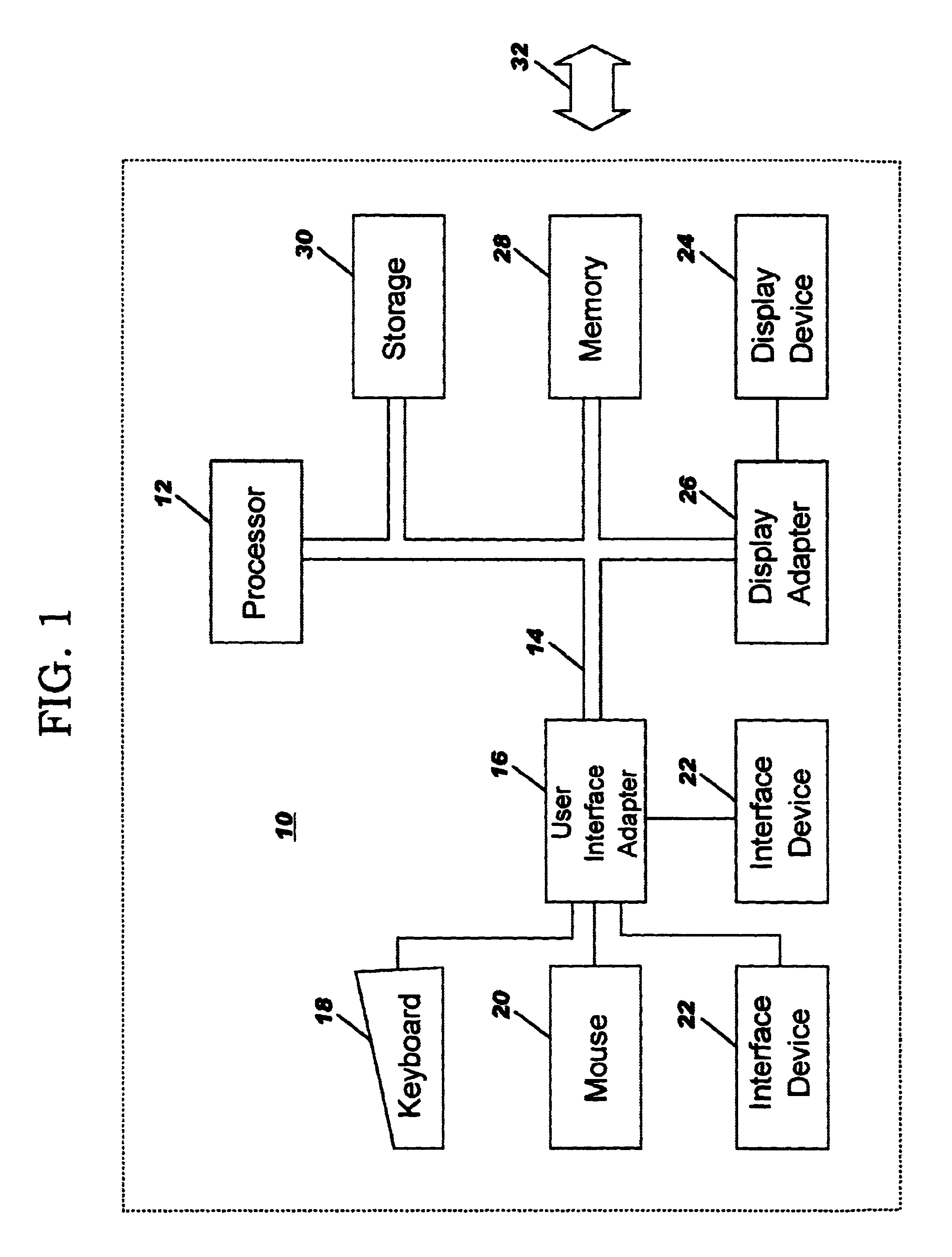
Patents
Literature
2054 results about "Bandwidth allocation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
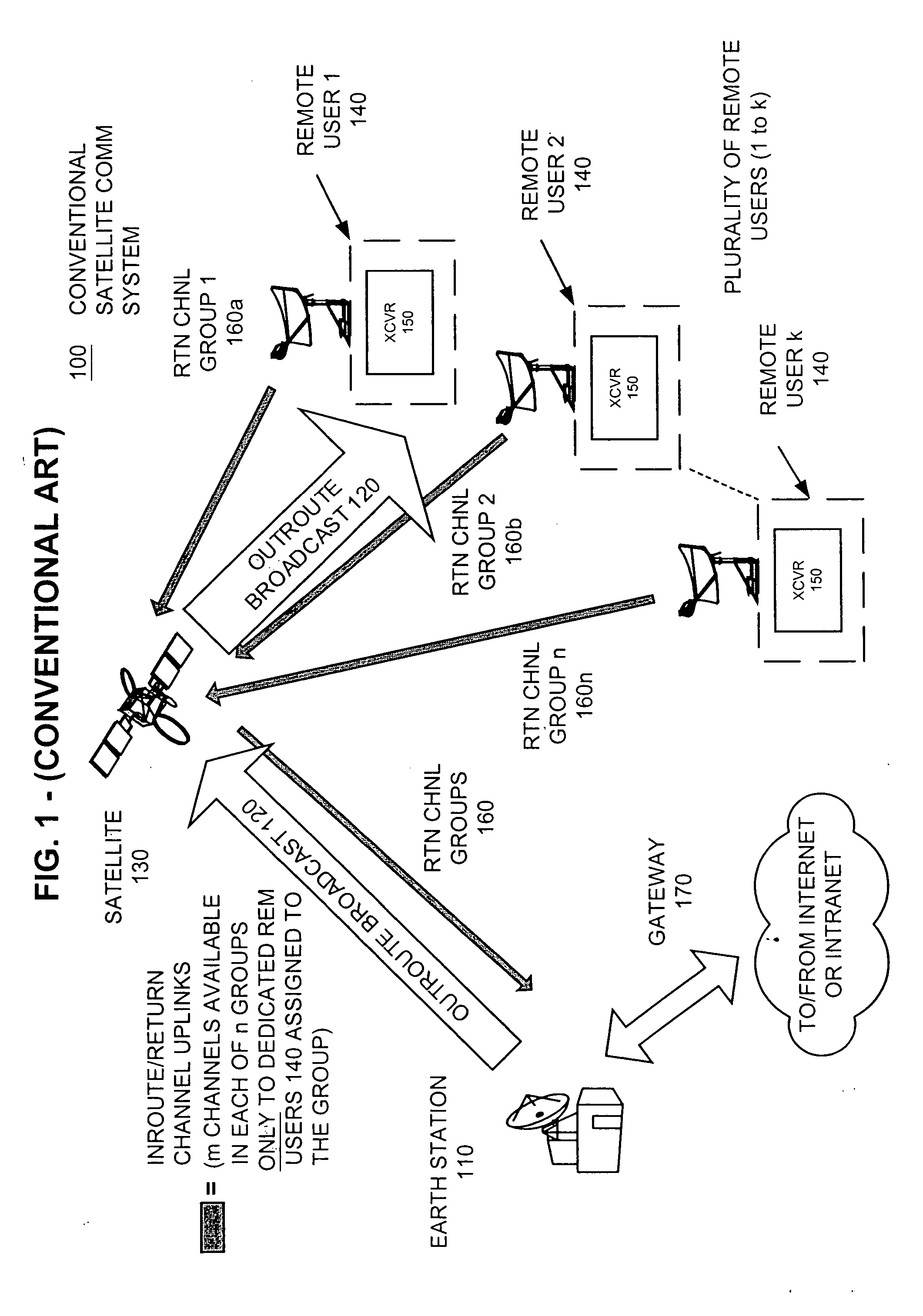
Bandwidth allocation is the process of assigning radio frequencies to different applications. The radio spectrum is a finite resource, which means there is great need for an effective allocation process. In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission or FCC has the responsibility of allocating discrete portions of the spectrum, or bands, to various industries. The FCC did this recently, when it shifted the location of television broadcasting on the spectrum in order to open up more space for mobile data. Different bands of spectrum are able to transmit more data than others, and some bands of the spectrum transmit a clearer signal than others. Bands that are particularly fast or that have long range are of critical importance for companies that intend to operate a business involving wireless communications.
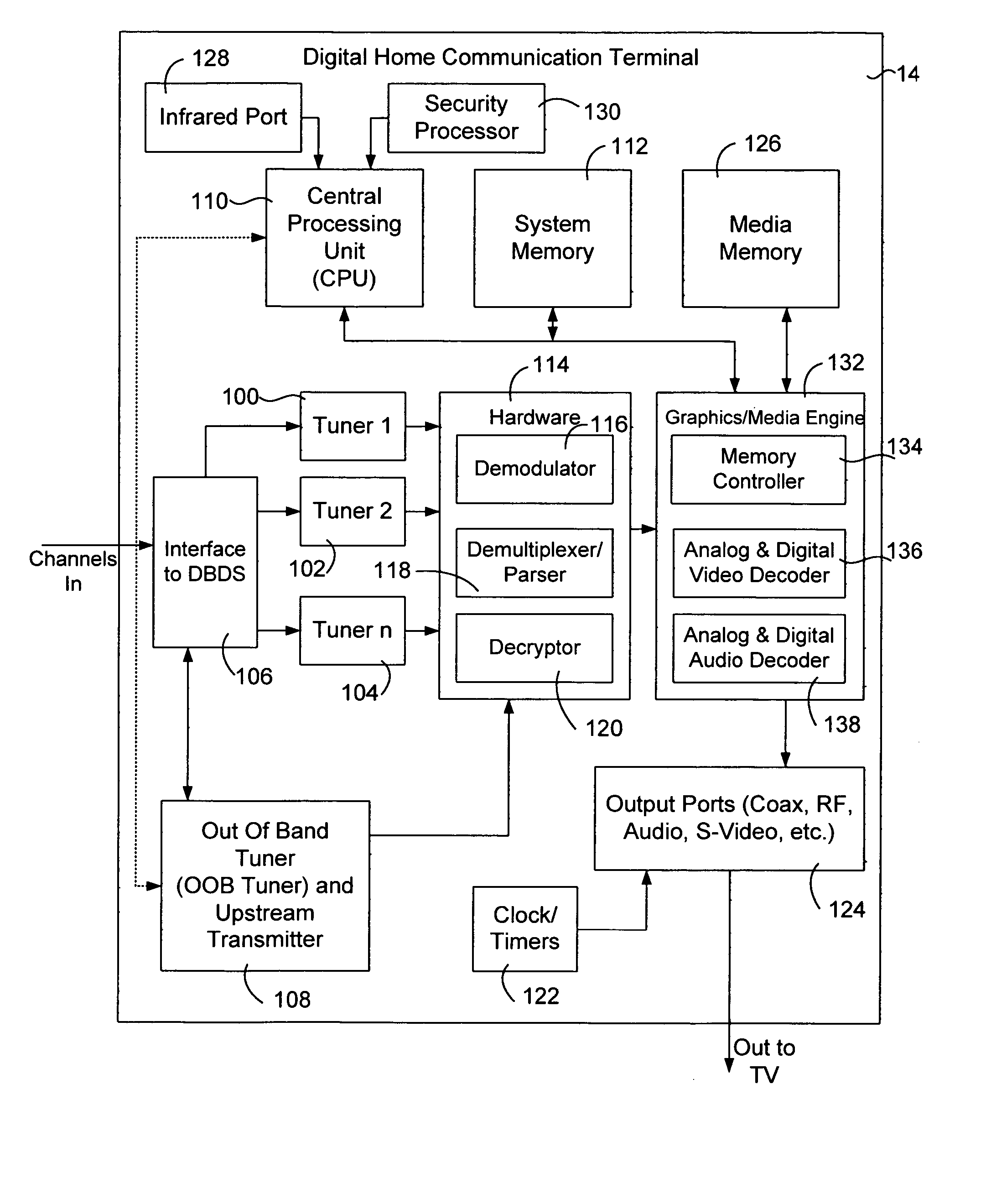
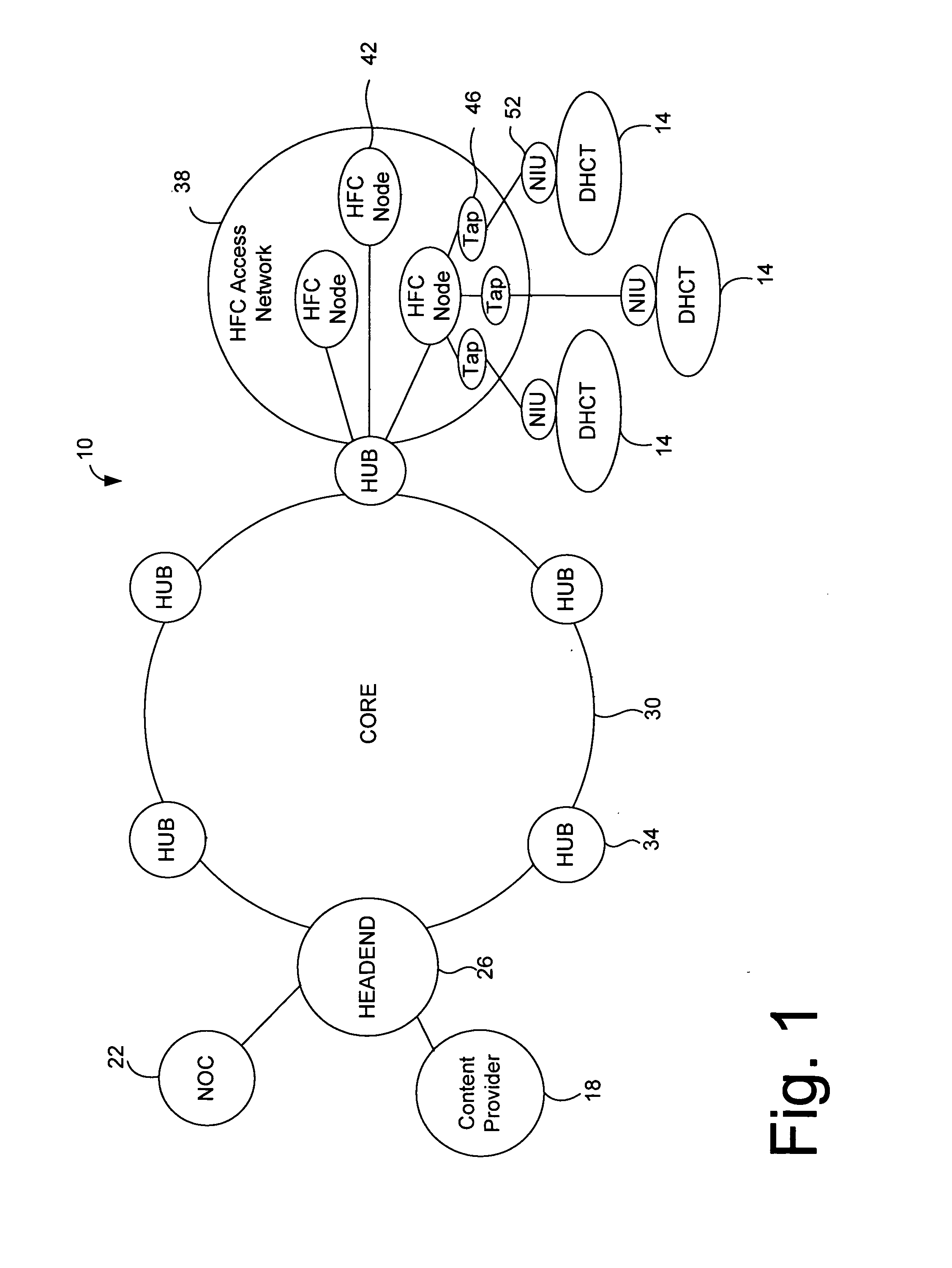
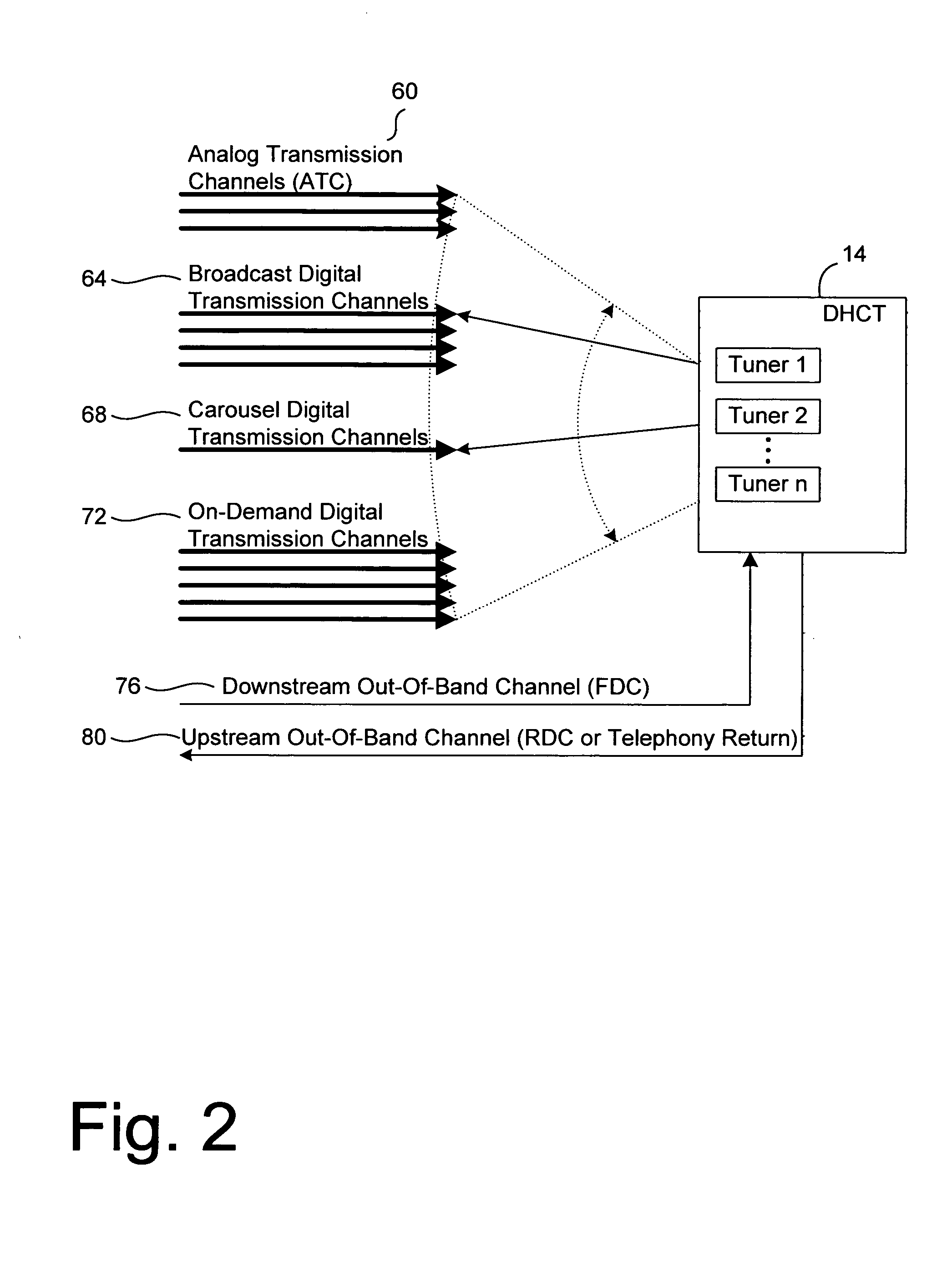
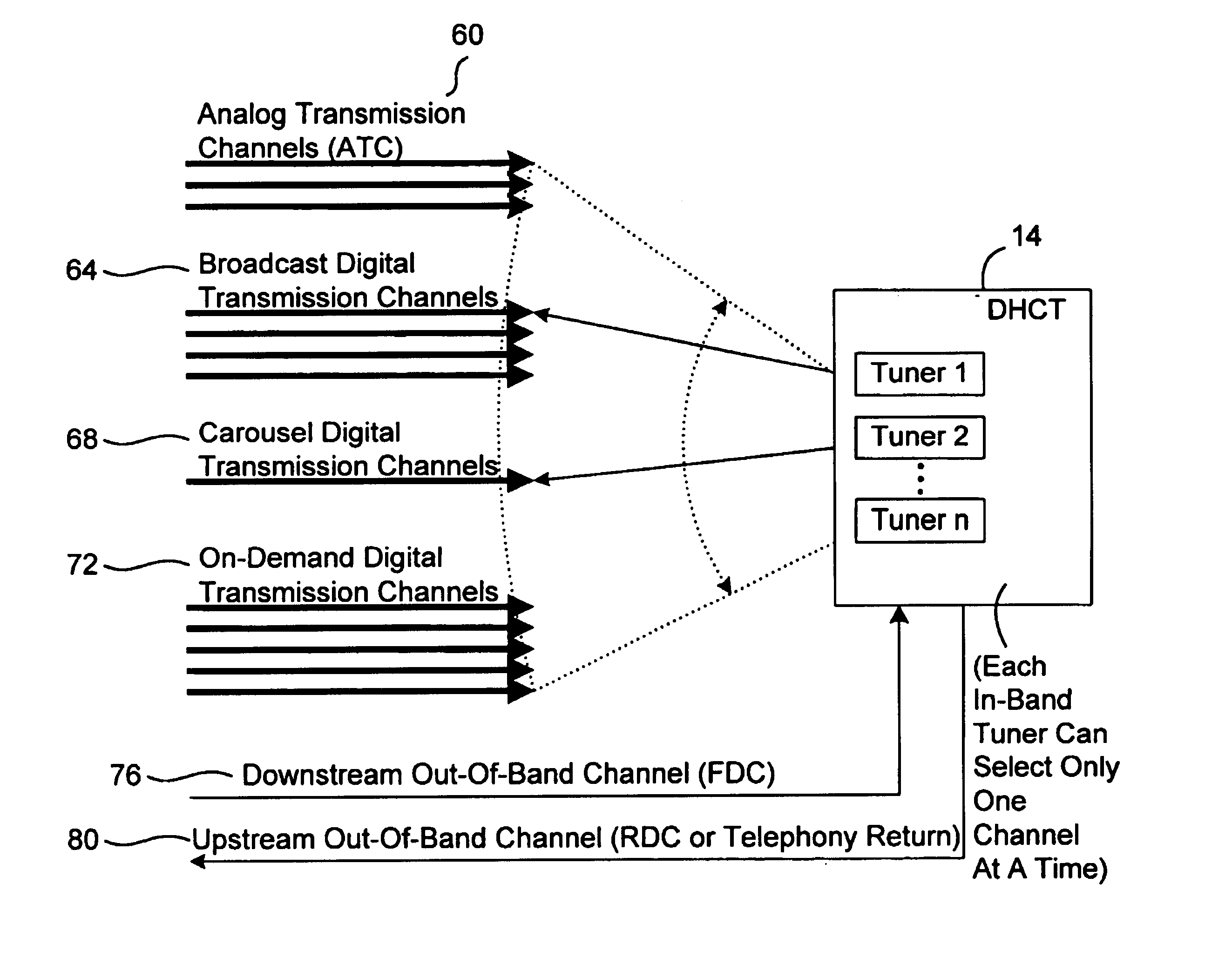
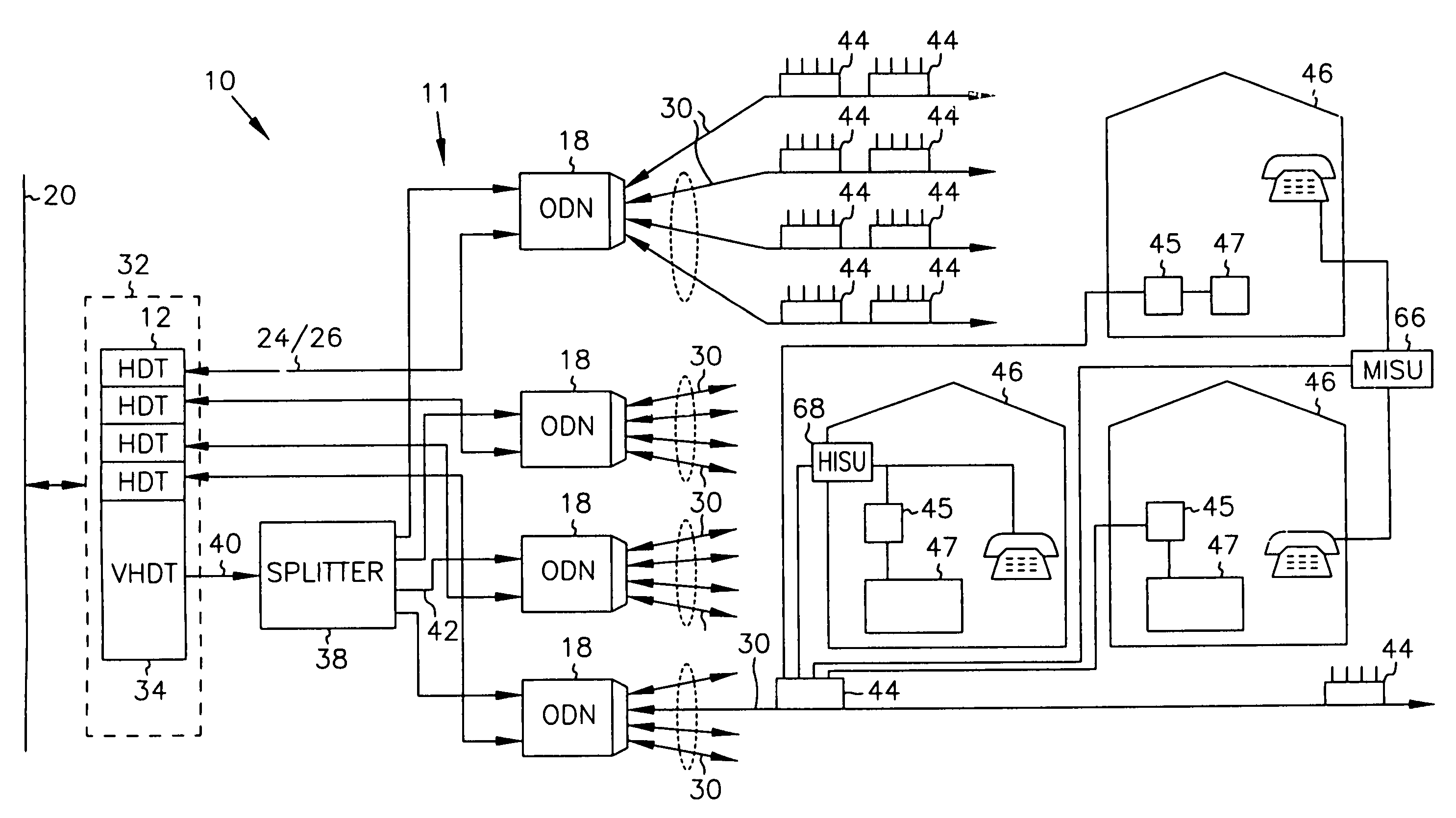
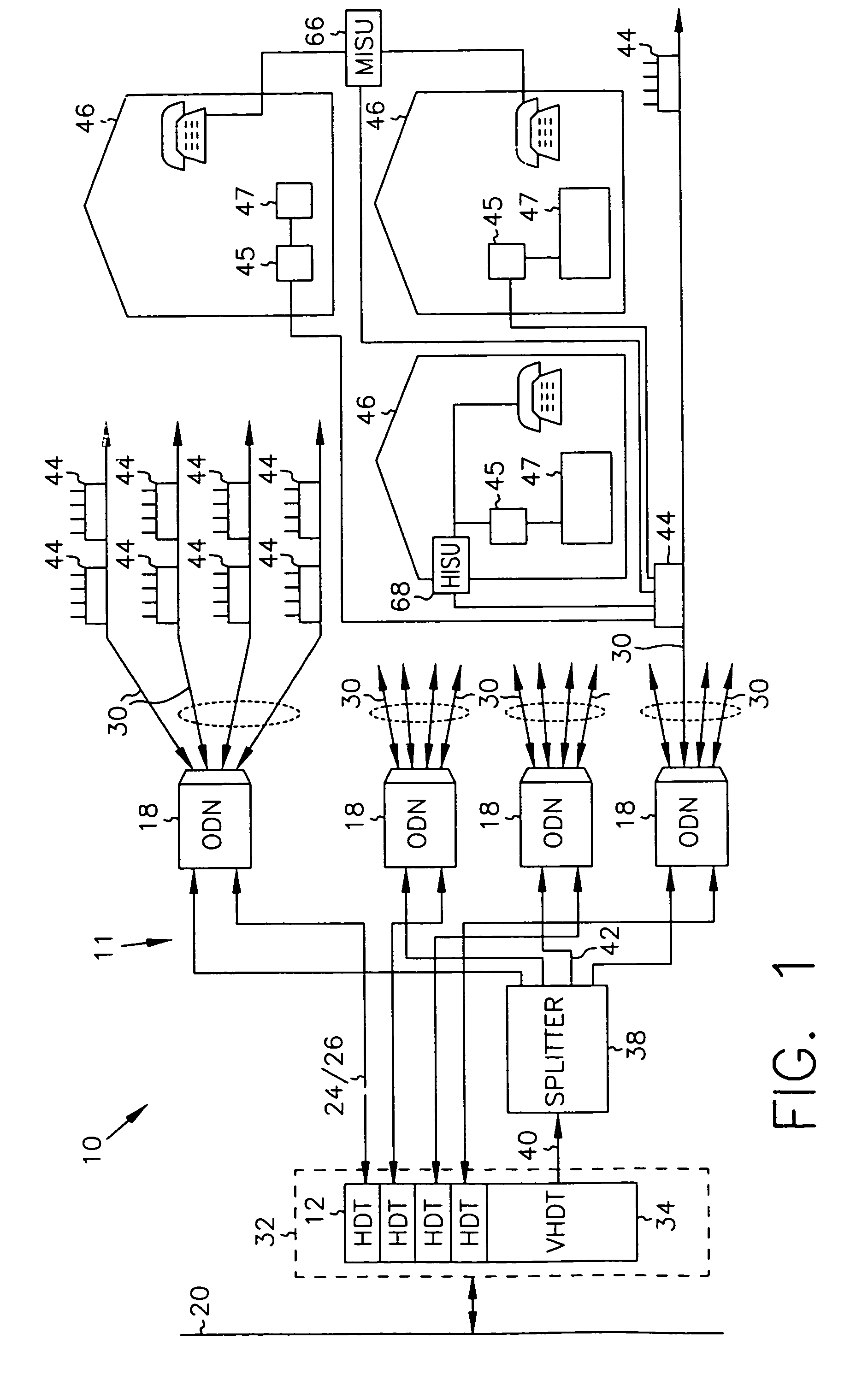
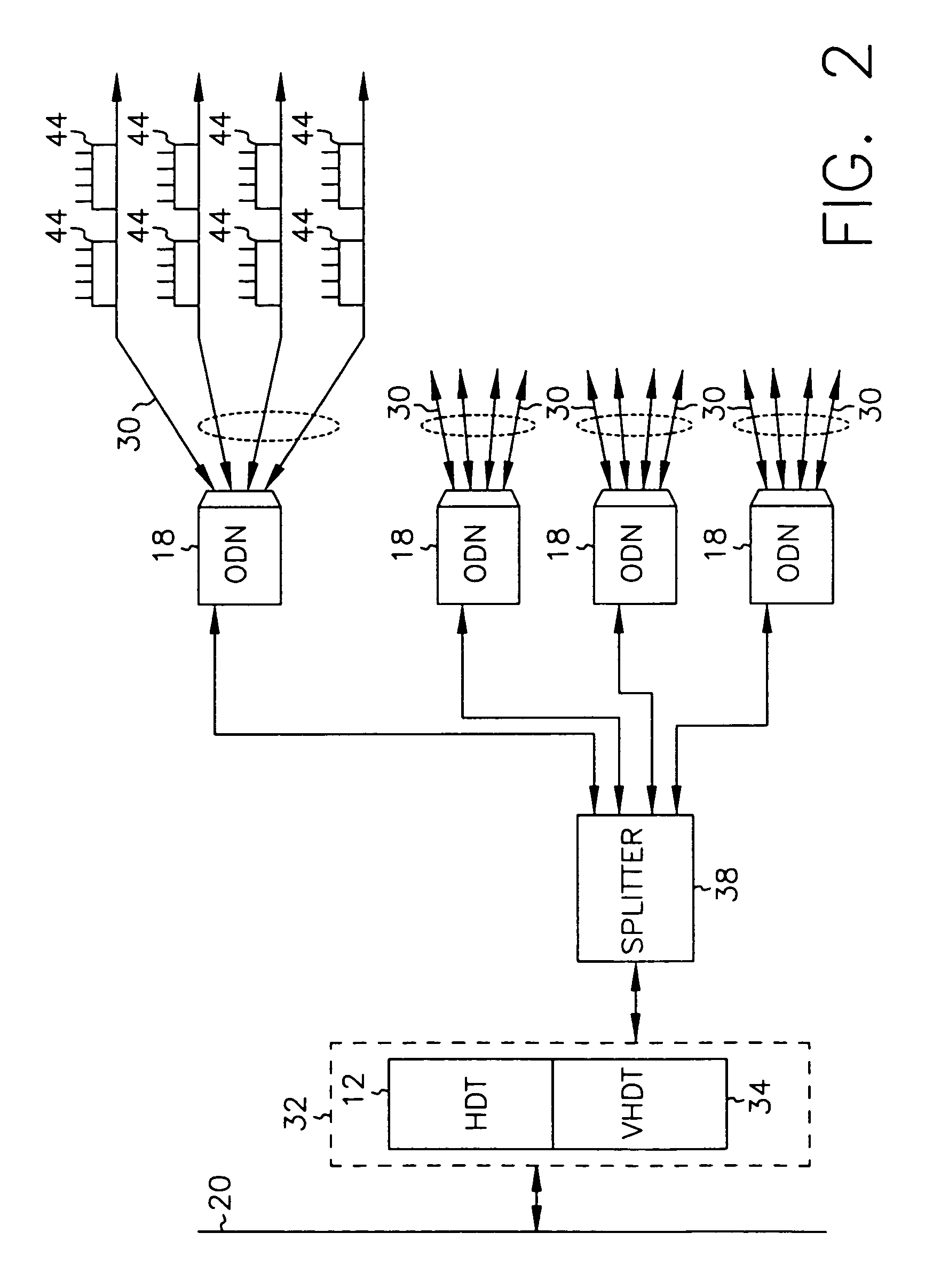
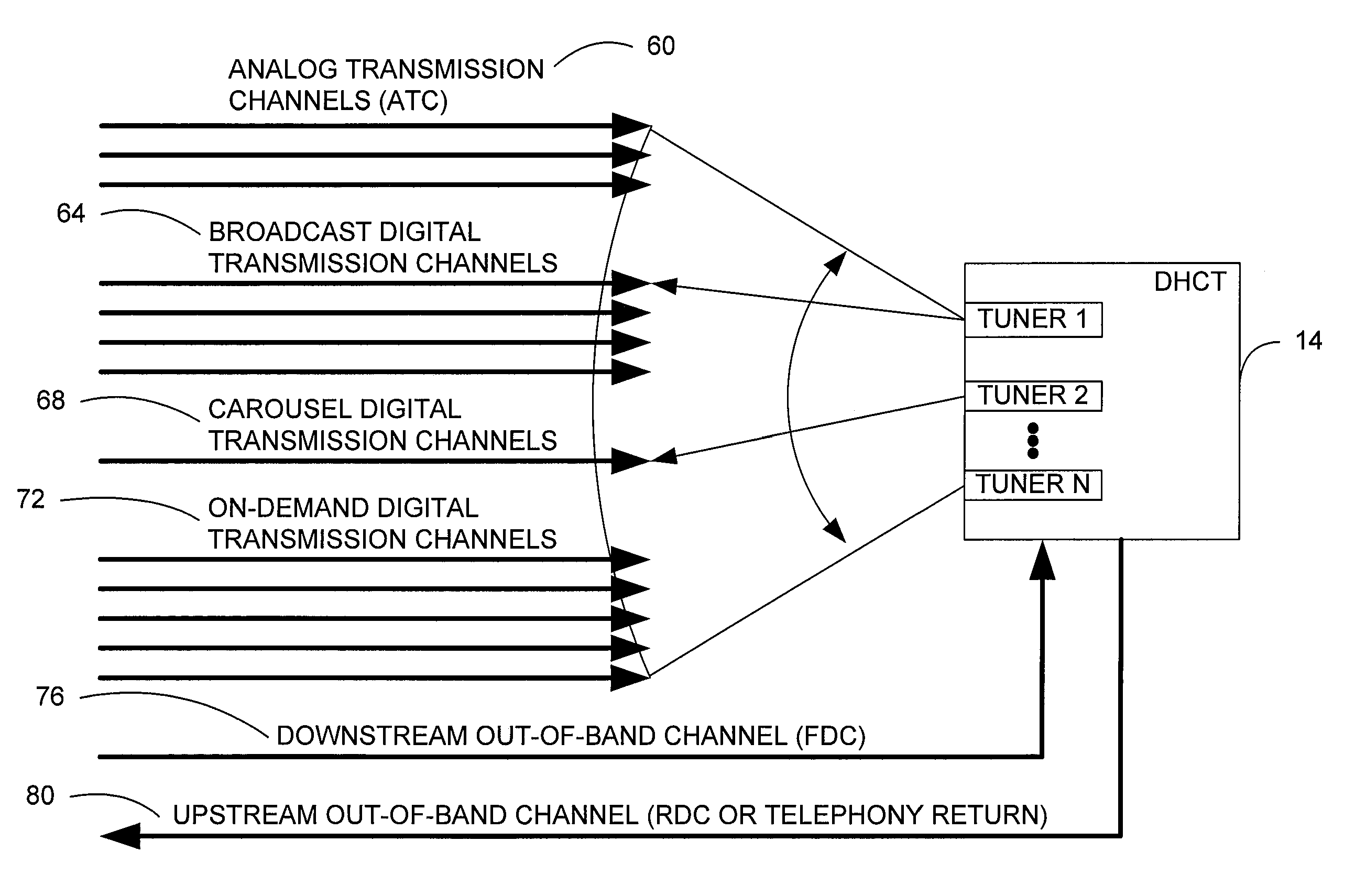
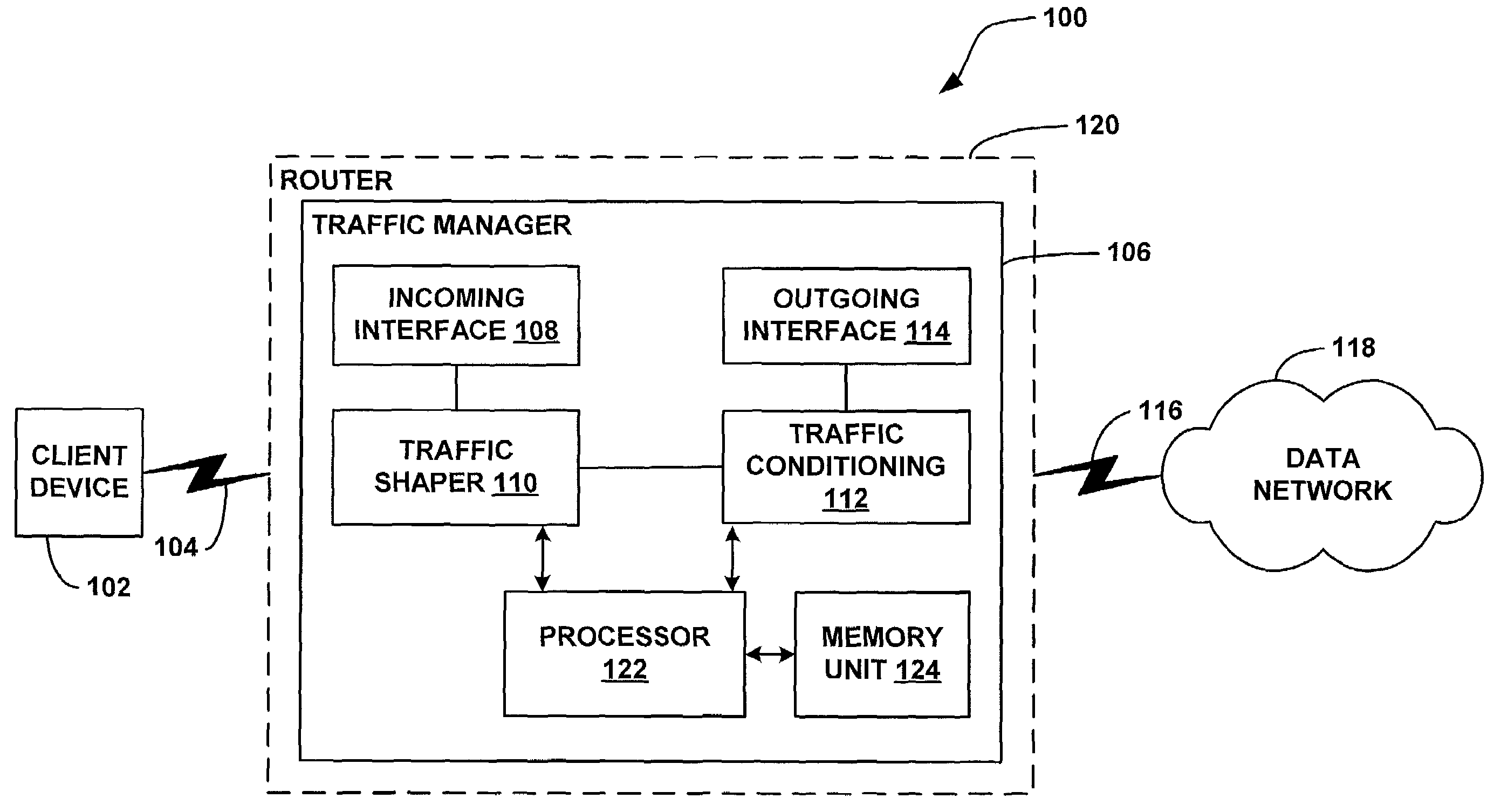
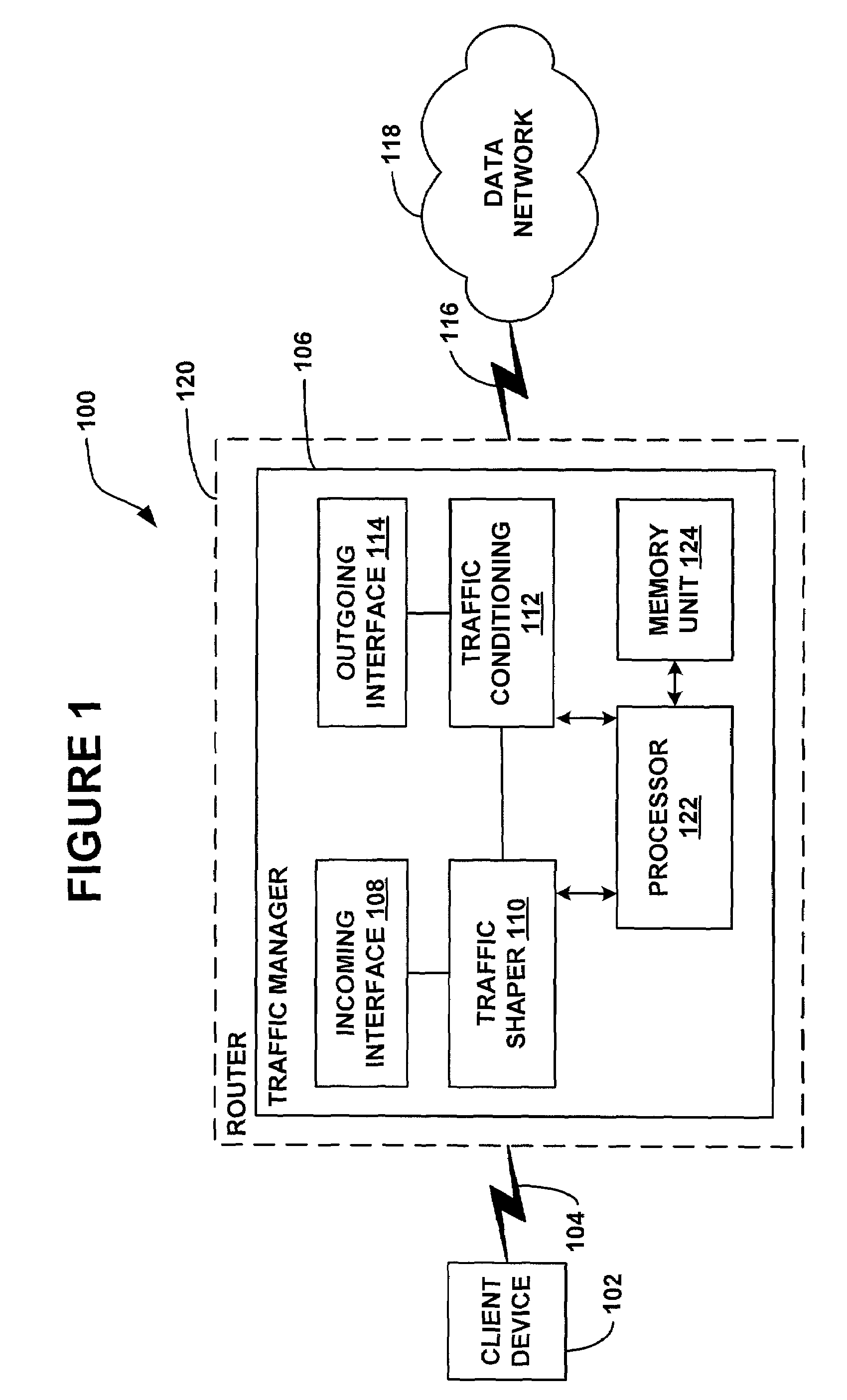
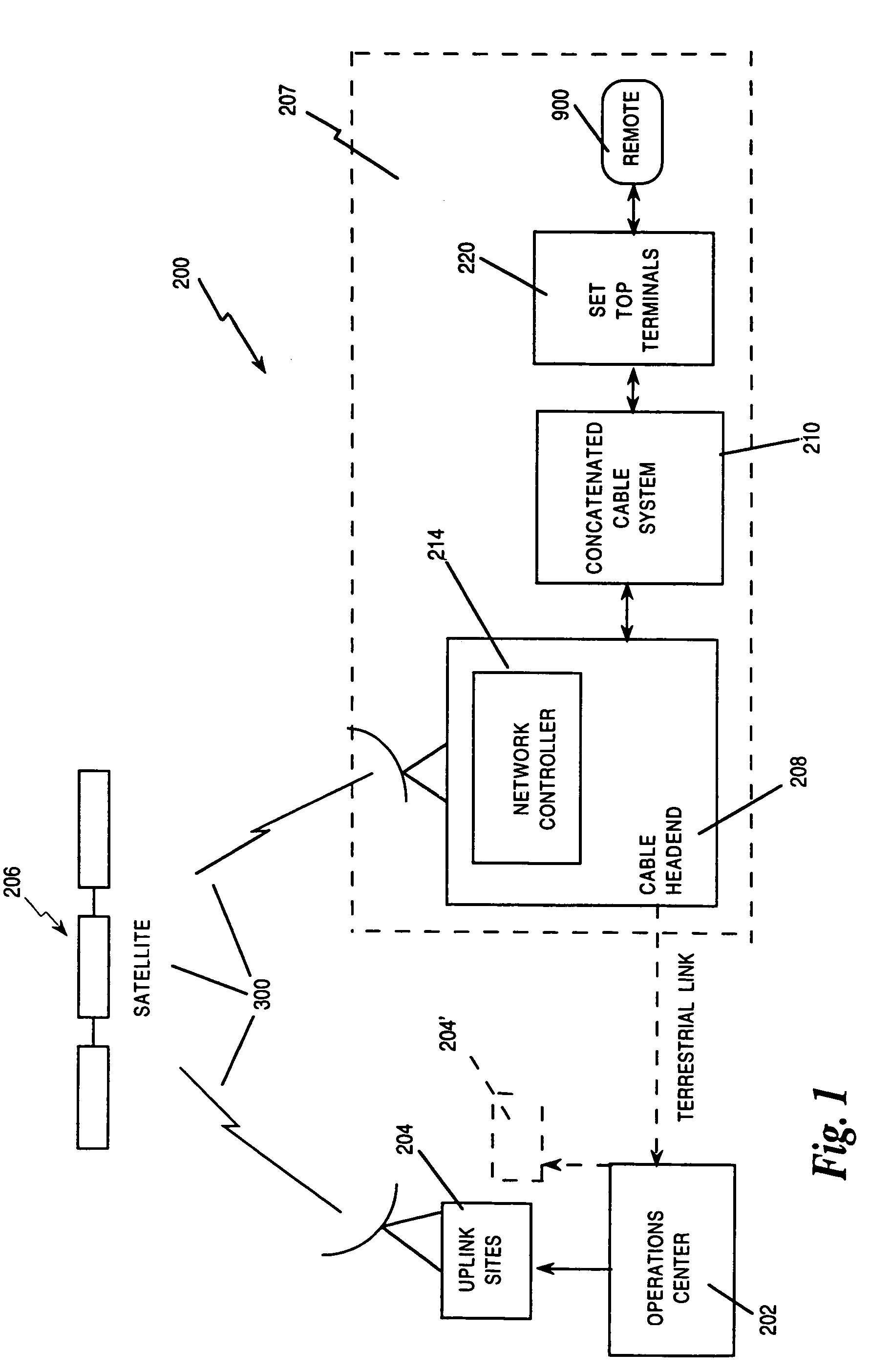
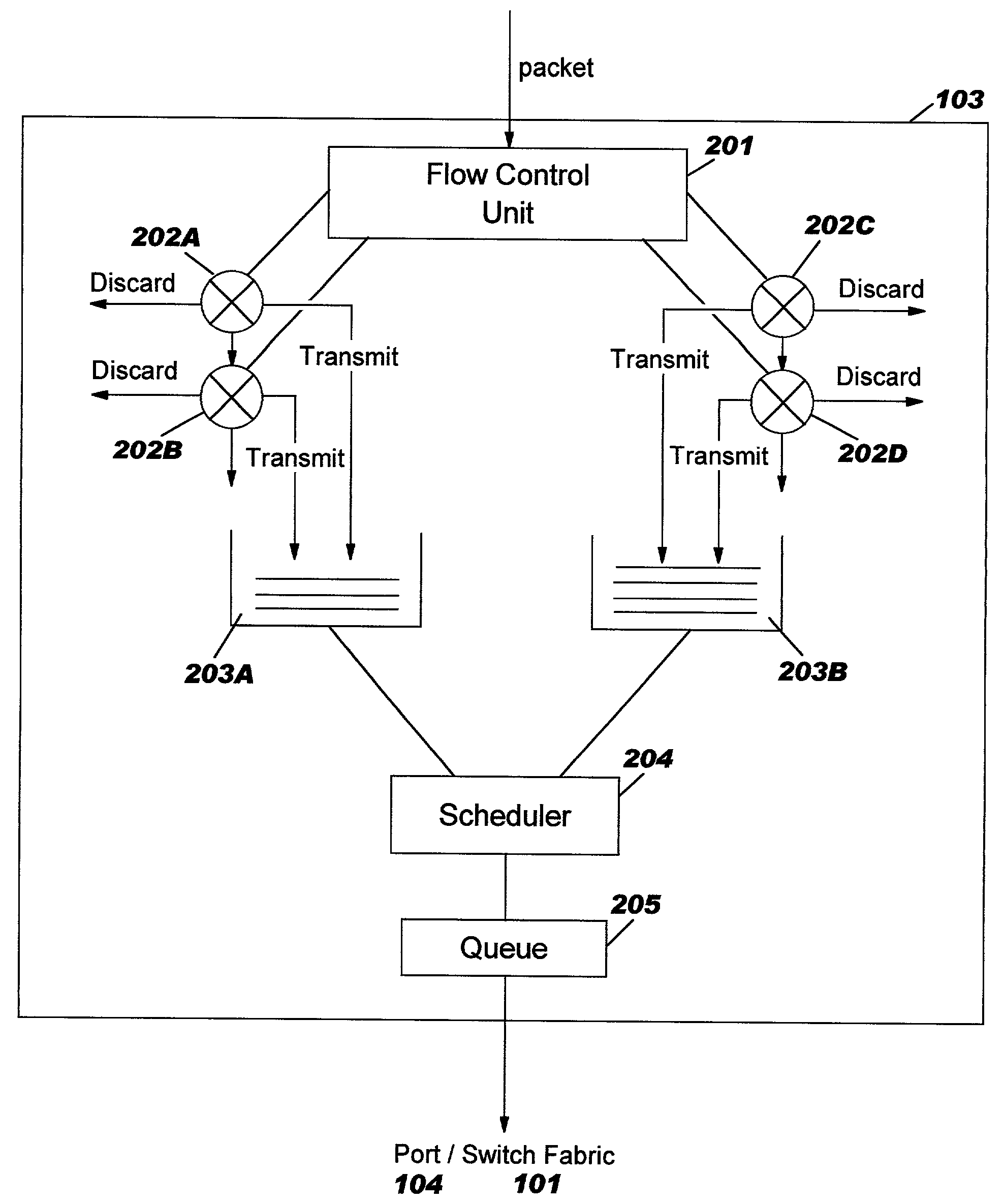
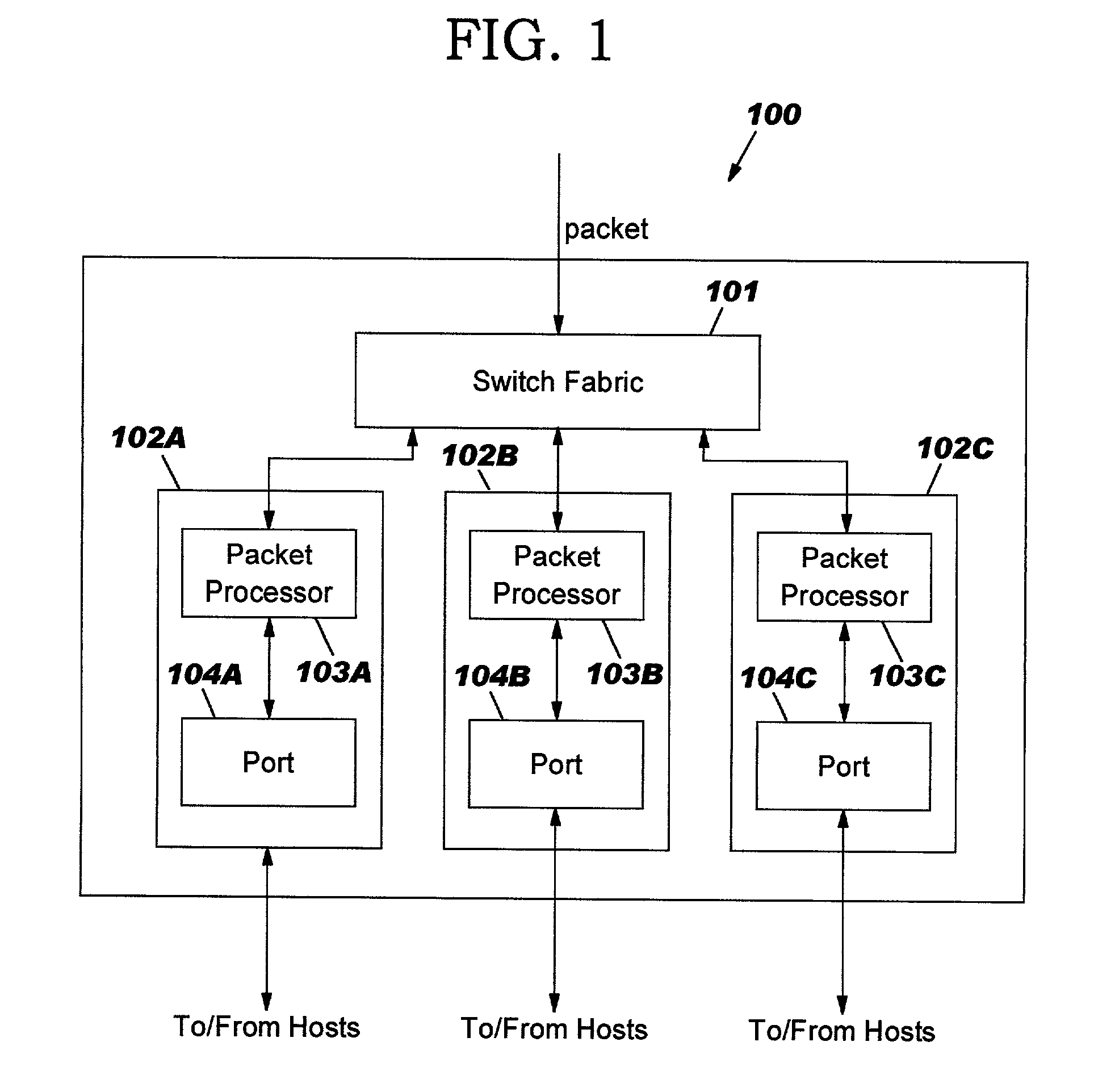
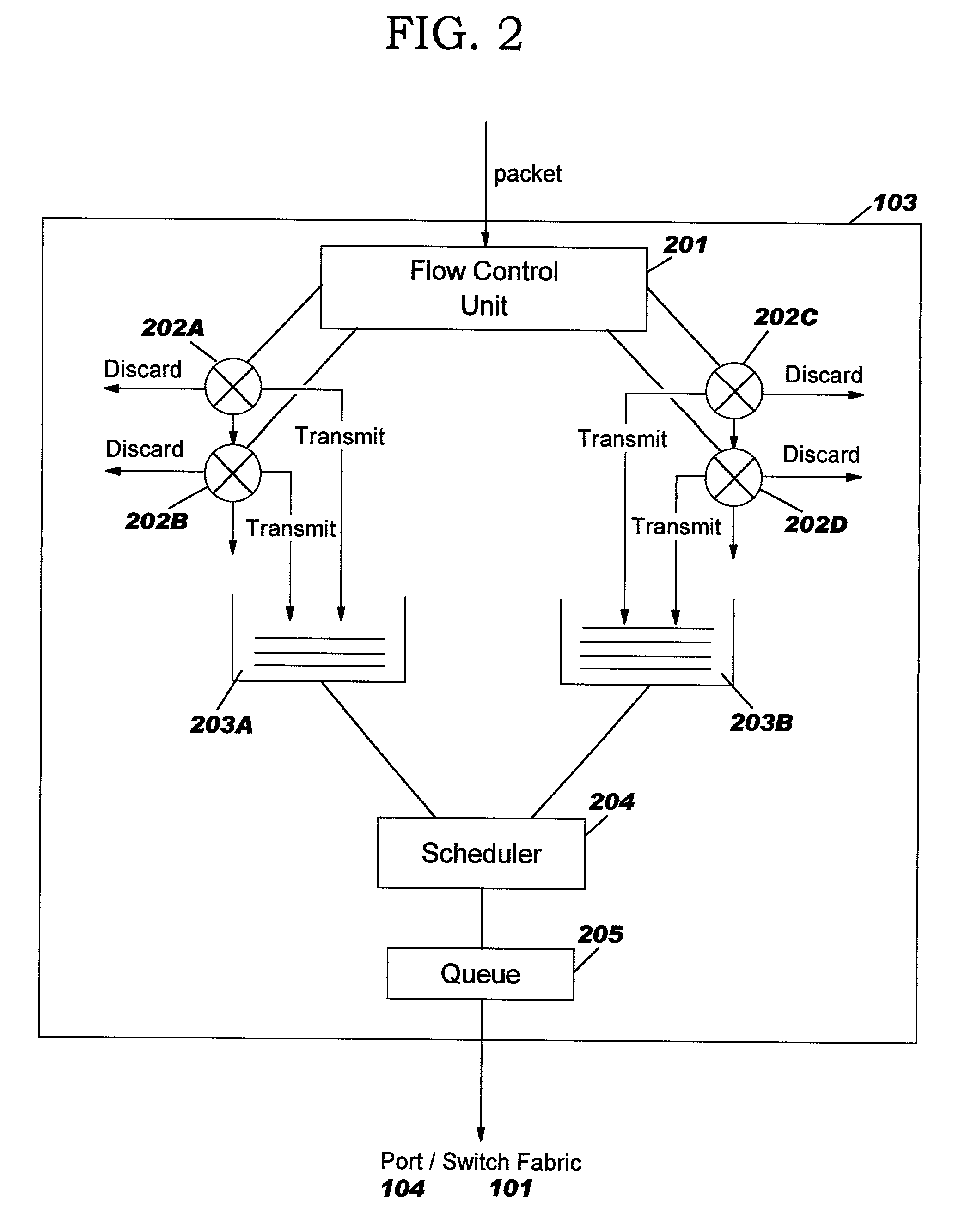
Systems and method for adaptive scheduling and dynamic bandwidth resource allocation management in a digital broadband delivery system
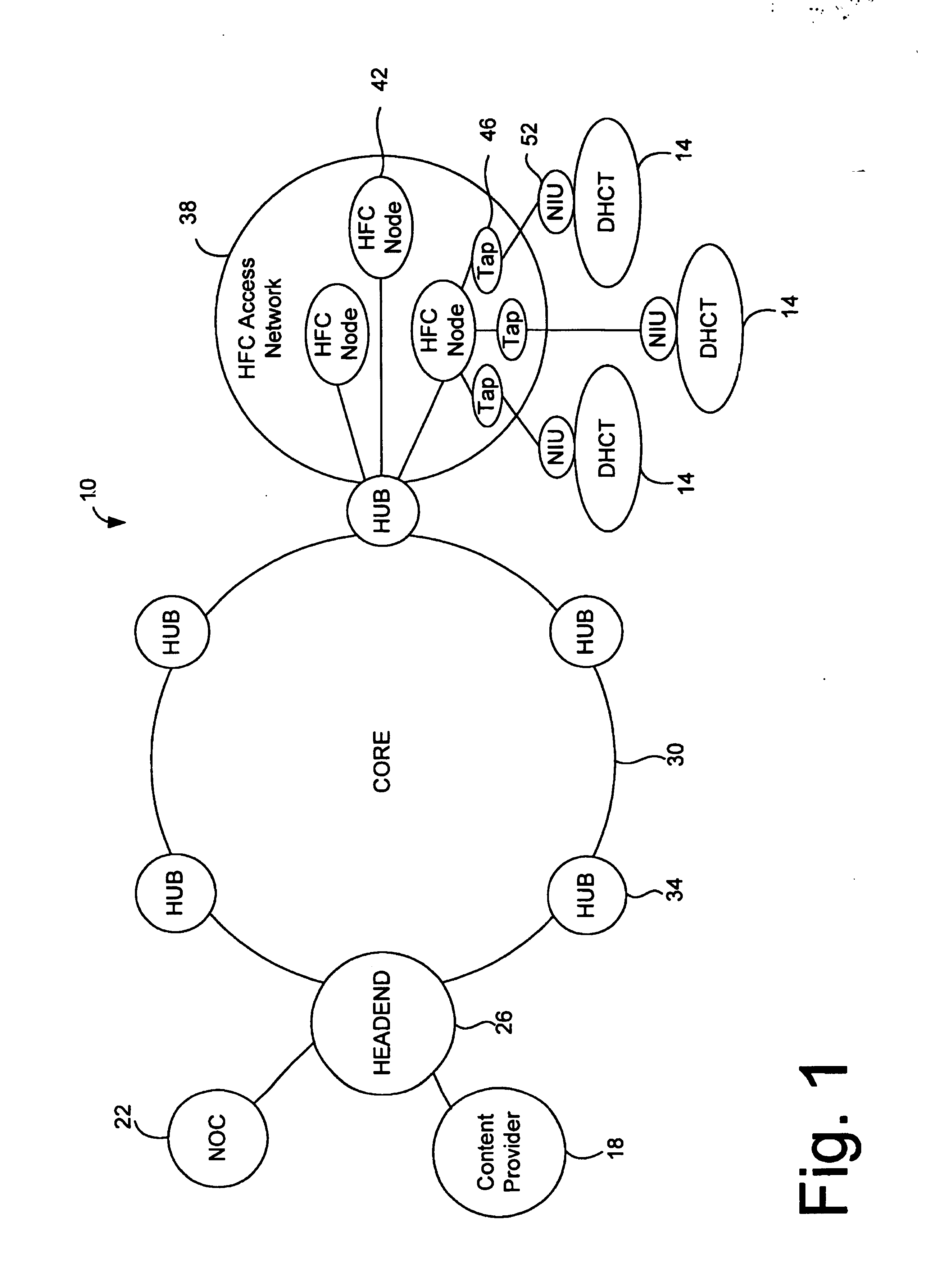
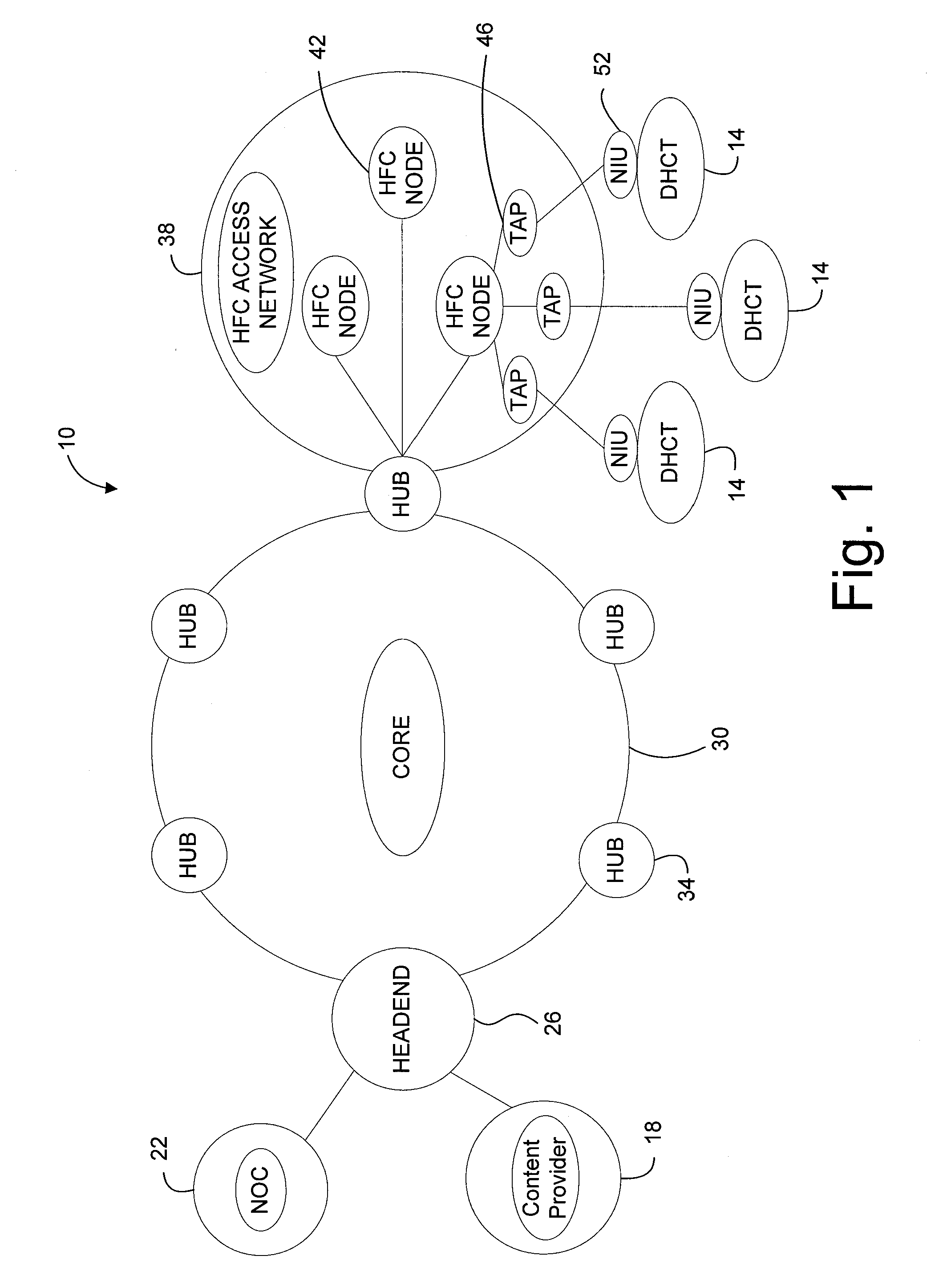
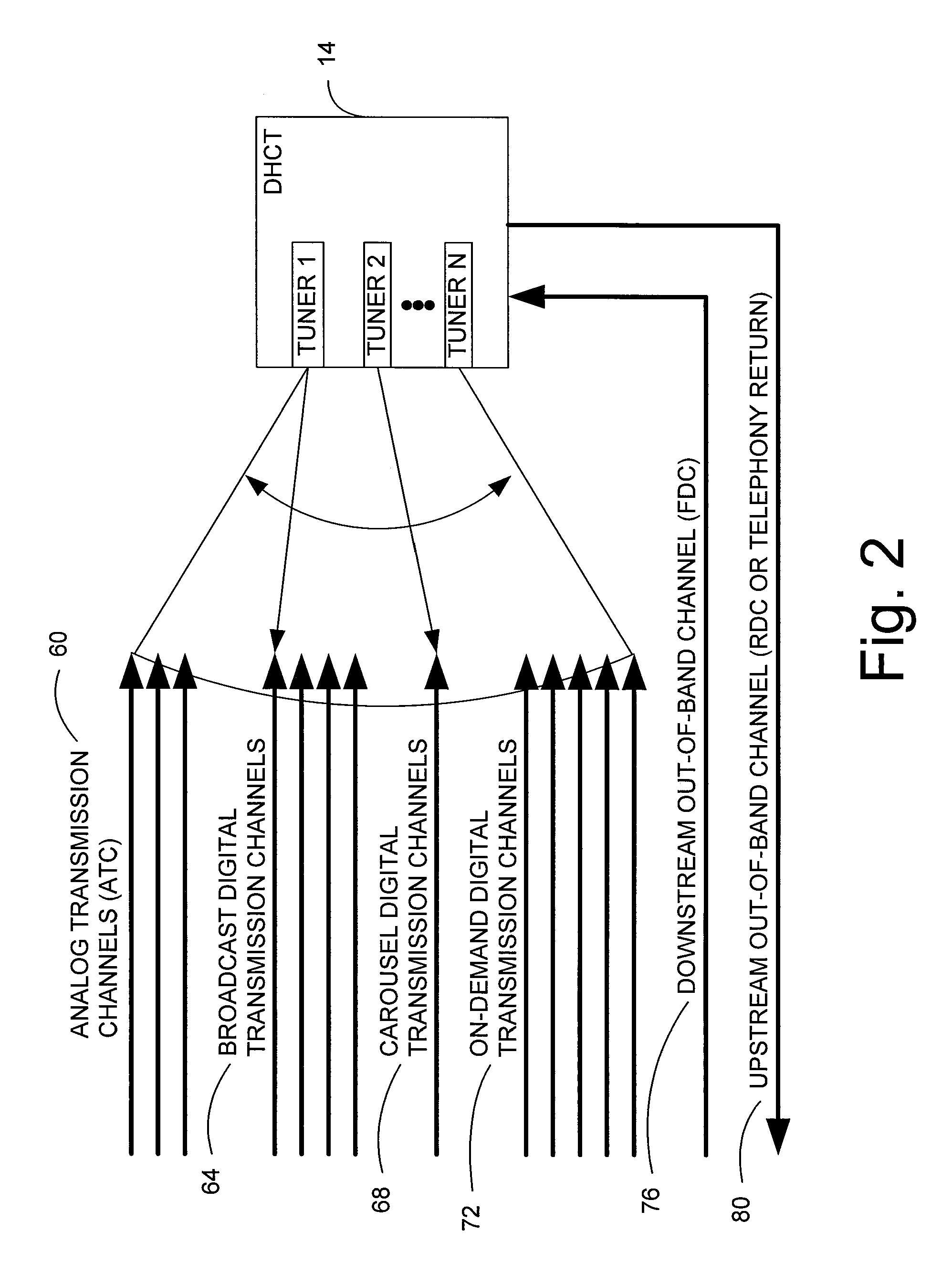
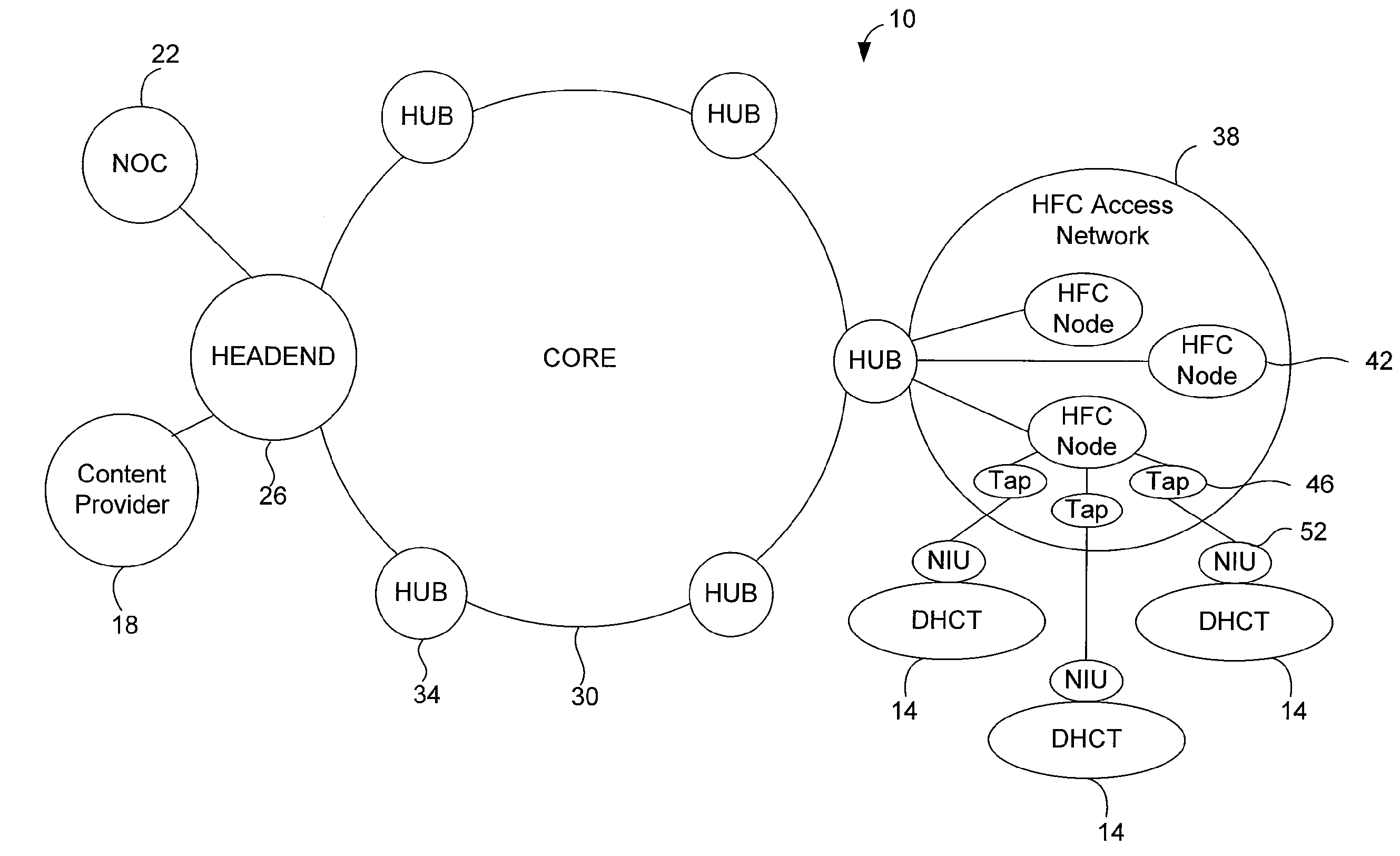
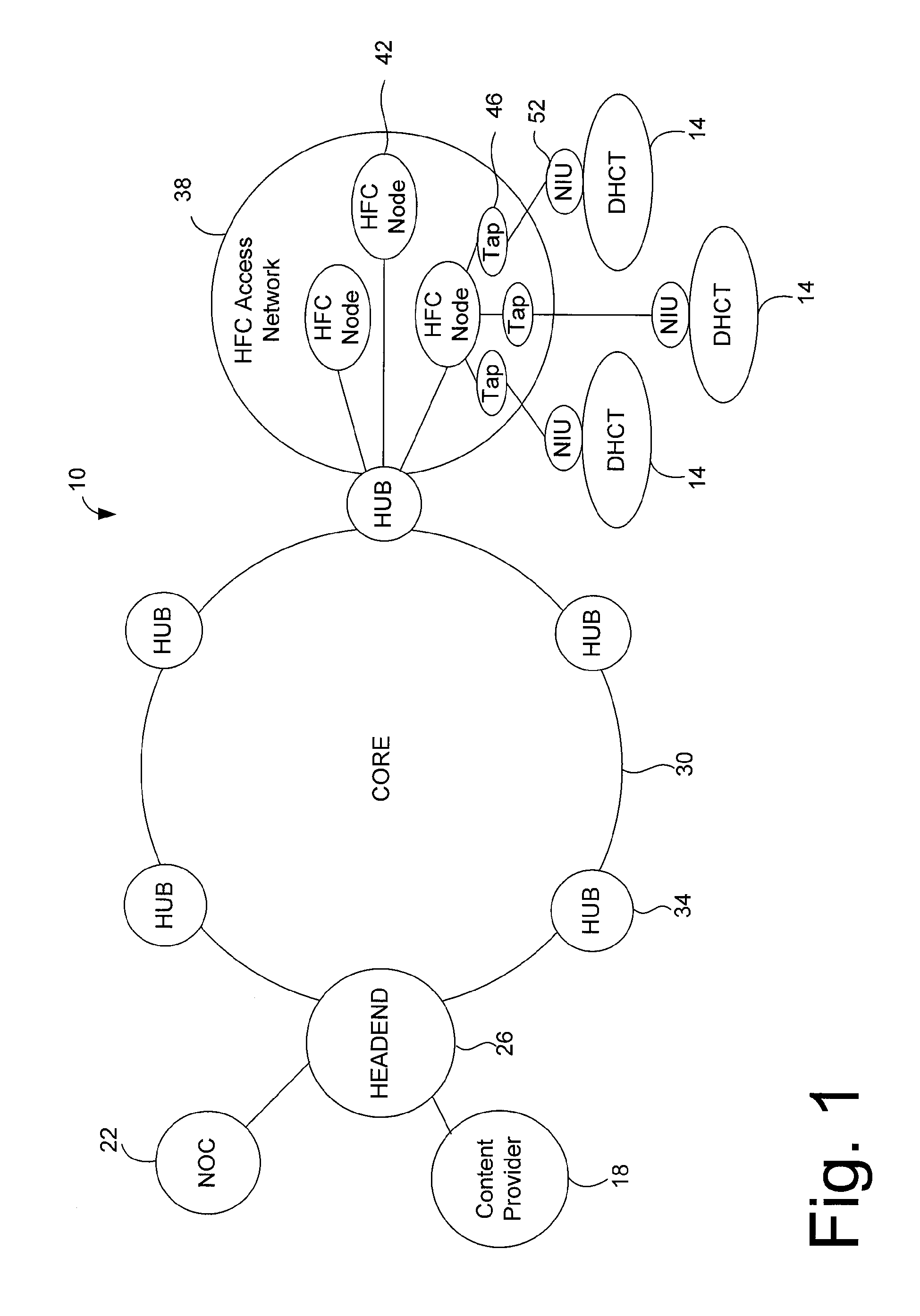
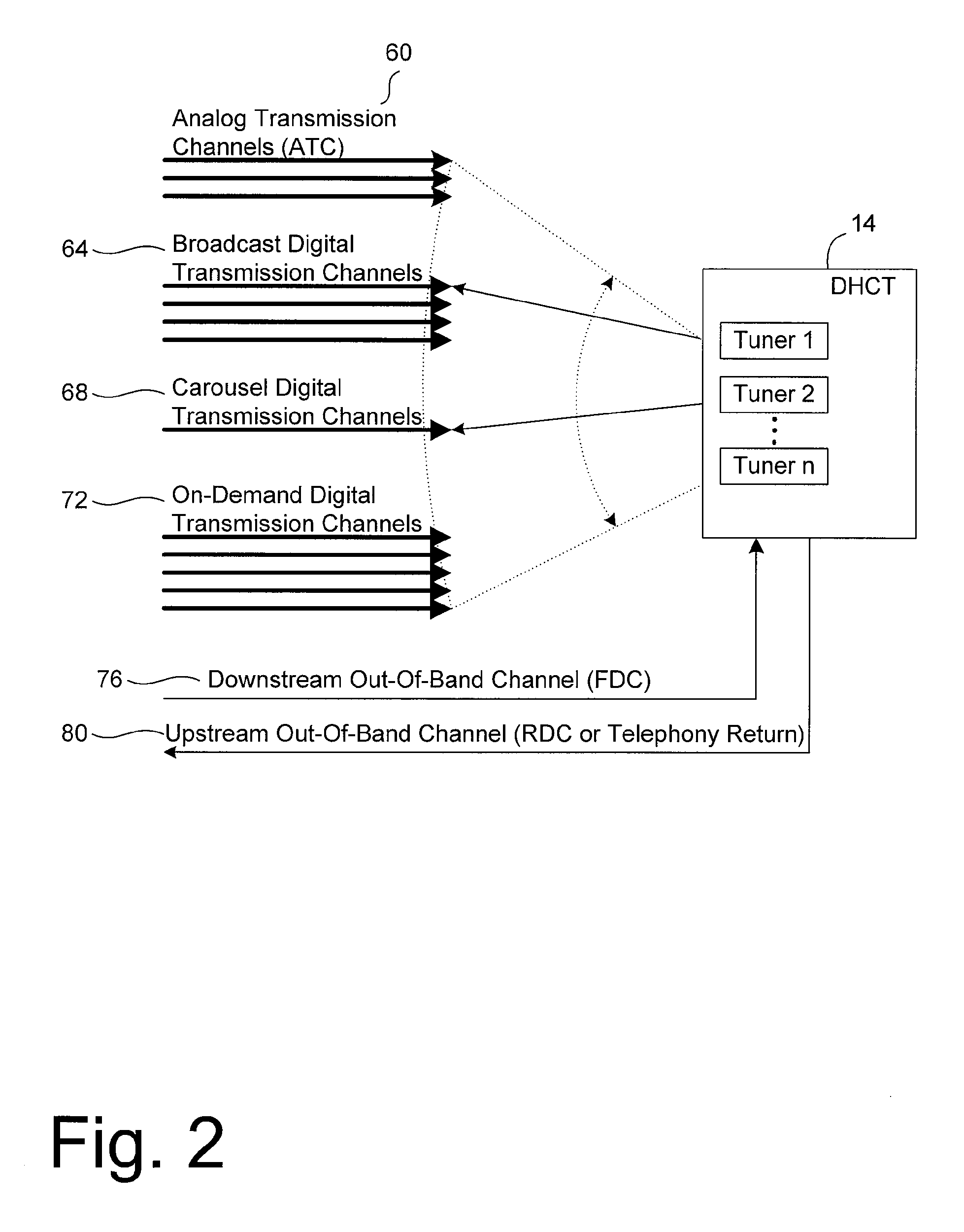
InactiveUS20050071882A1Bandwidth to be flexibly and efficiently-allocatedTelevision system detailsResource management arrangementsTransmission channelBroadband
A technique for allocating bandwidth in a digital broadband delivery system (DBDS) using a bandwidth allocation manager to dynamically assign a content delivery mode to a plurality of digital transmission channels based on an allocation criteria received from a subscriber is disclosed herein. The bandwidth allocation manager determines a bandwidth allocation schedule for a predetermined bandwidth based on allocation criteria comprising a criteria received from a subscriber. The allocation criteria received from the subscriber may comprise a subscriber reservation request which is processed by the bandwidth allocation manager to determine the bandwidth allocation schedule.
Owner:TRITON US VP ACQUISITION CO
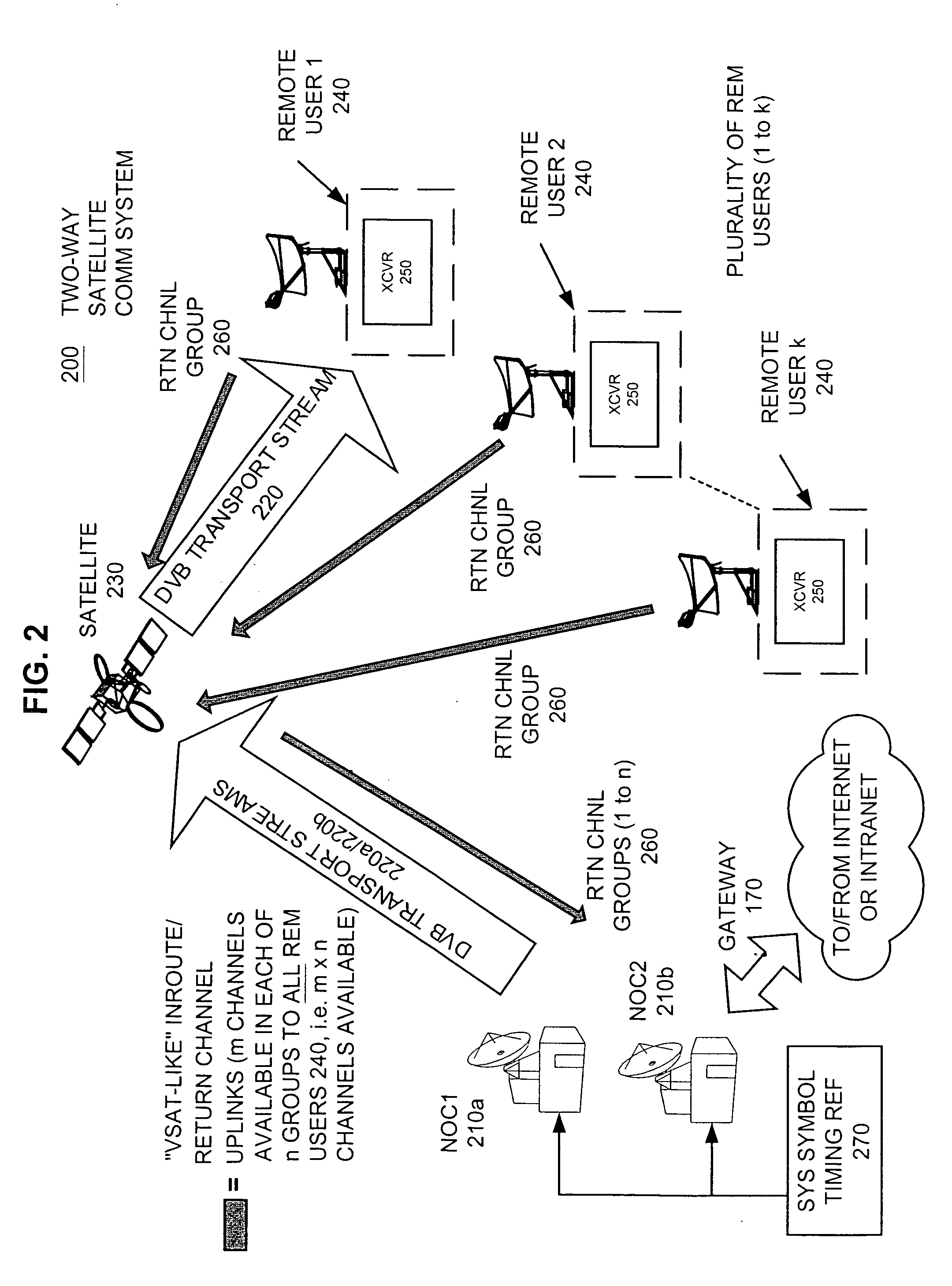
Systems and methods for adaptive scheduling and dynamic bandwidth resource allocation management in a digital broadband delivery system
InactiveUS6986156B1Flexibly efficiently allocatedTelevision system detailsResource management arrangementsTransmission channelBroadband
Owner:TRITON US VP ACQUISITION CO
Methods and systems for providing video on demand over a communication network using managed quality of service, bandwidth allocation and/or user profiles
ActiveUS7617516B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsTelevision conference systemsAccess networkDynamic bandwidth allocation
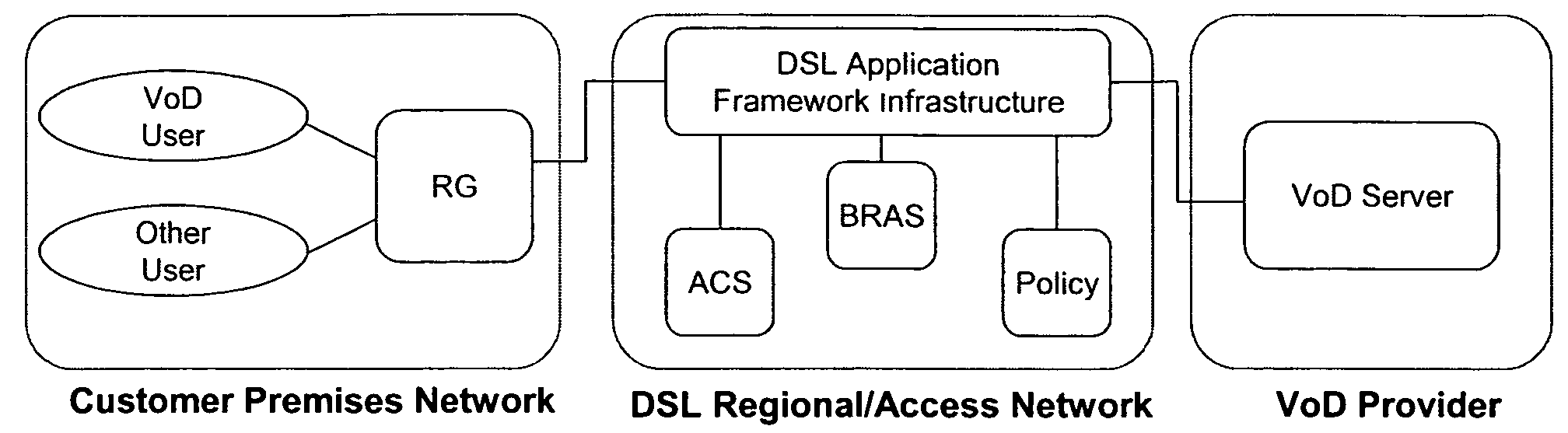
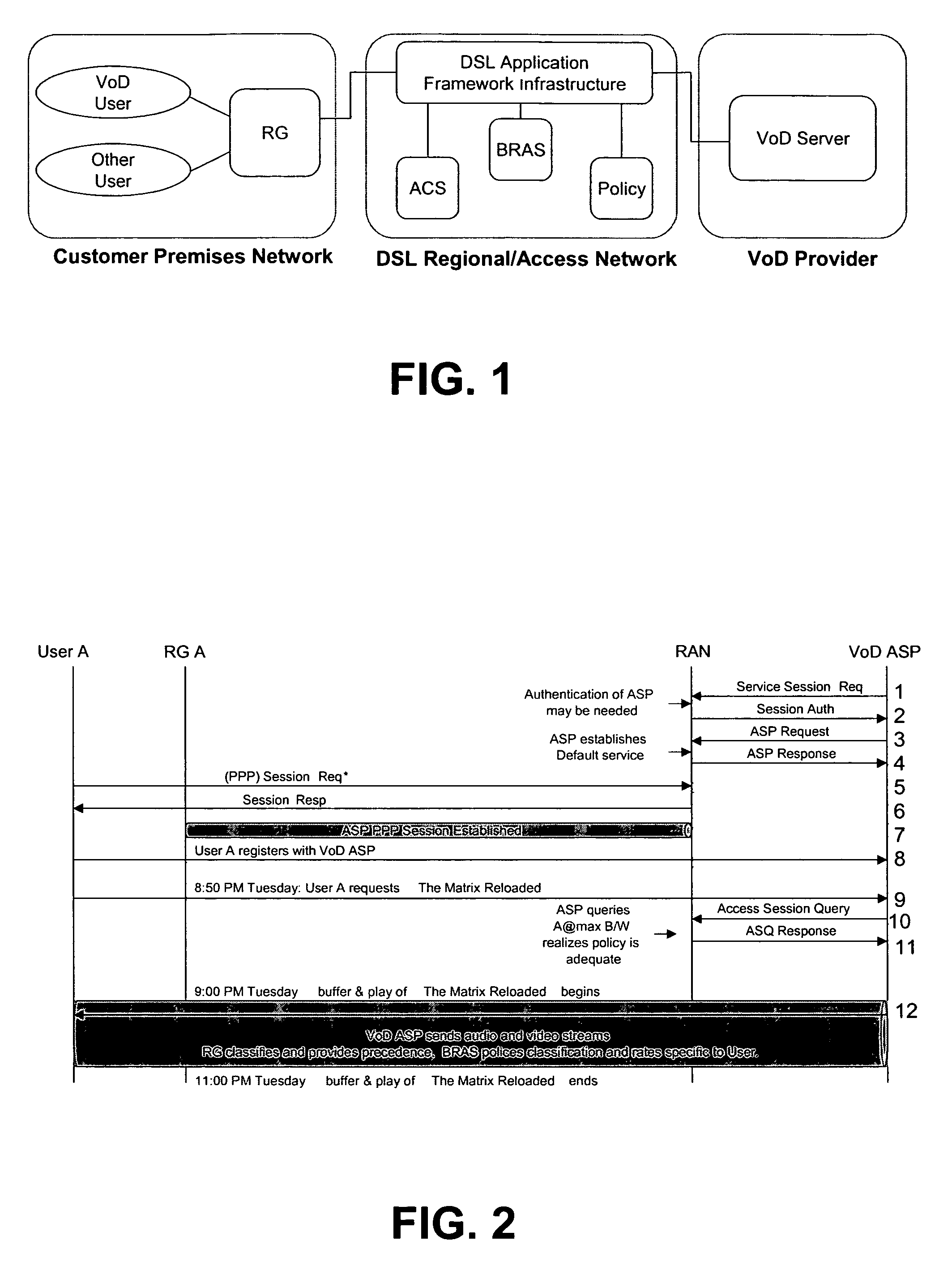
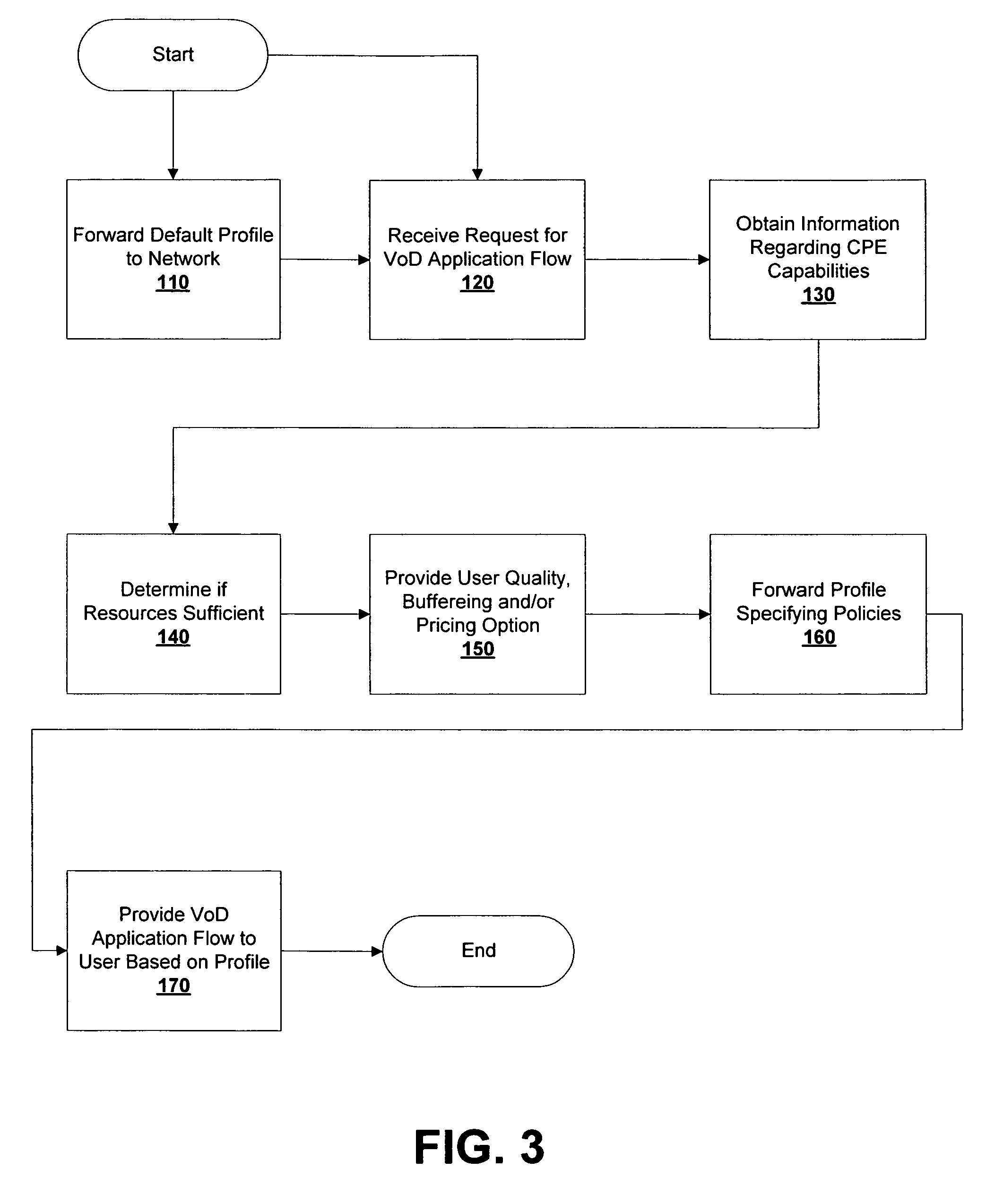
Methods for providing video on demand service from an Application Service Provider (“ASP”) to a user over a Regional / Access Network (“RAN”) are provided. A request for a video on demand application flow may be received from the user. In response to the request, information may be obtained from the RAN regarding the capabilities of the user's Customer Premises Equipment (“CPE”). A profile may then be forwarded from the ASP to the RAN that specifies at least one policy regarding the transmission of data associated with the video on demand application flow across the RAN. The data associated with the video on demand application flow may then be forwarded across the RAN in accordance with the profile. The RAN may also be provided a default profile that specifies default policies that apply with respect to video on demand application flows that are transmitted across the RAN prior to obtaining information from the RAN regarding the capabilities of the CPE of any specific user. The user specific profiles may then be used to alter one or more policies specified in the default profile.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
Apparatus and methods for dynamic bandwidth allocation
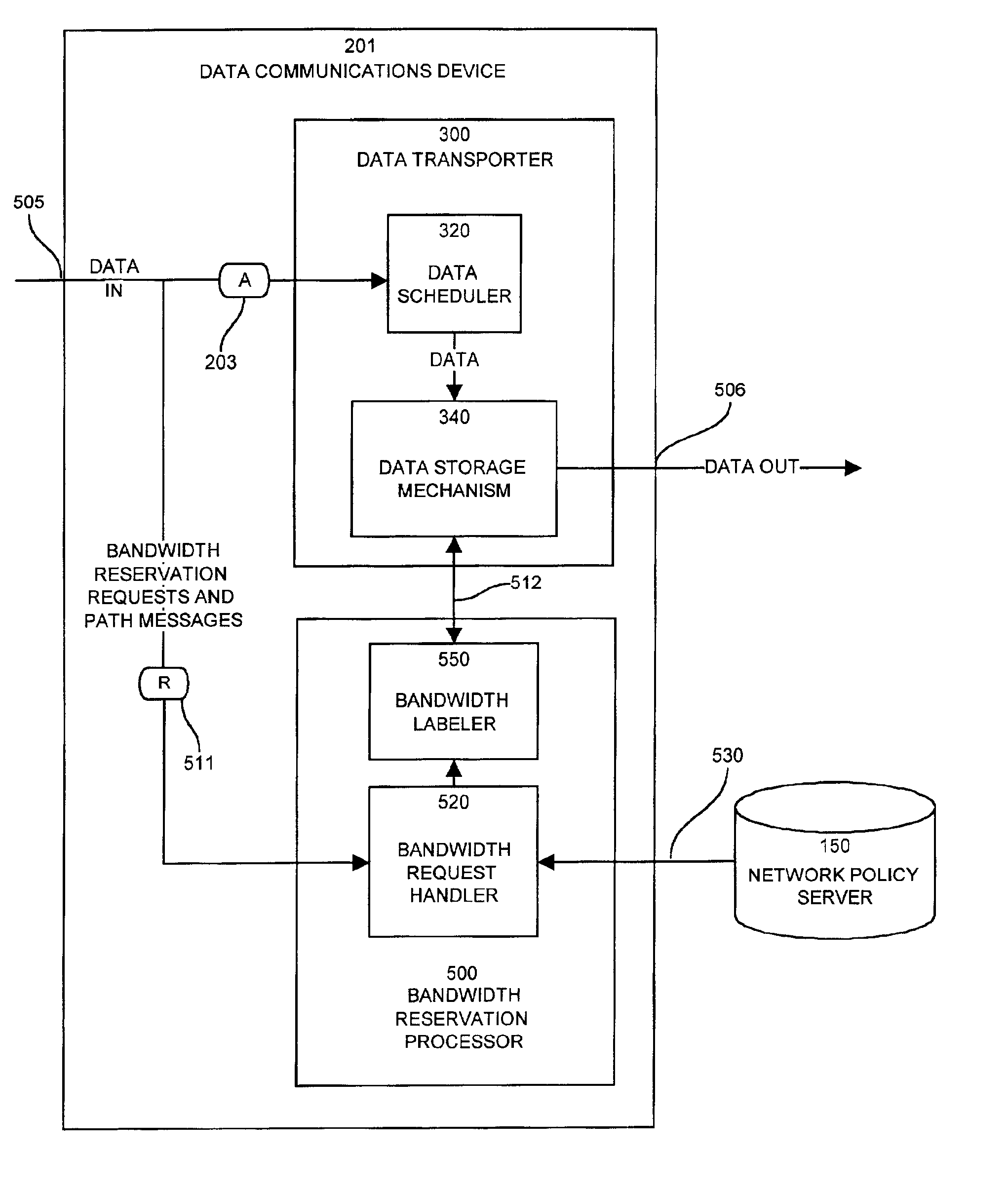
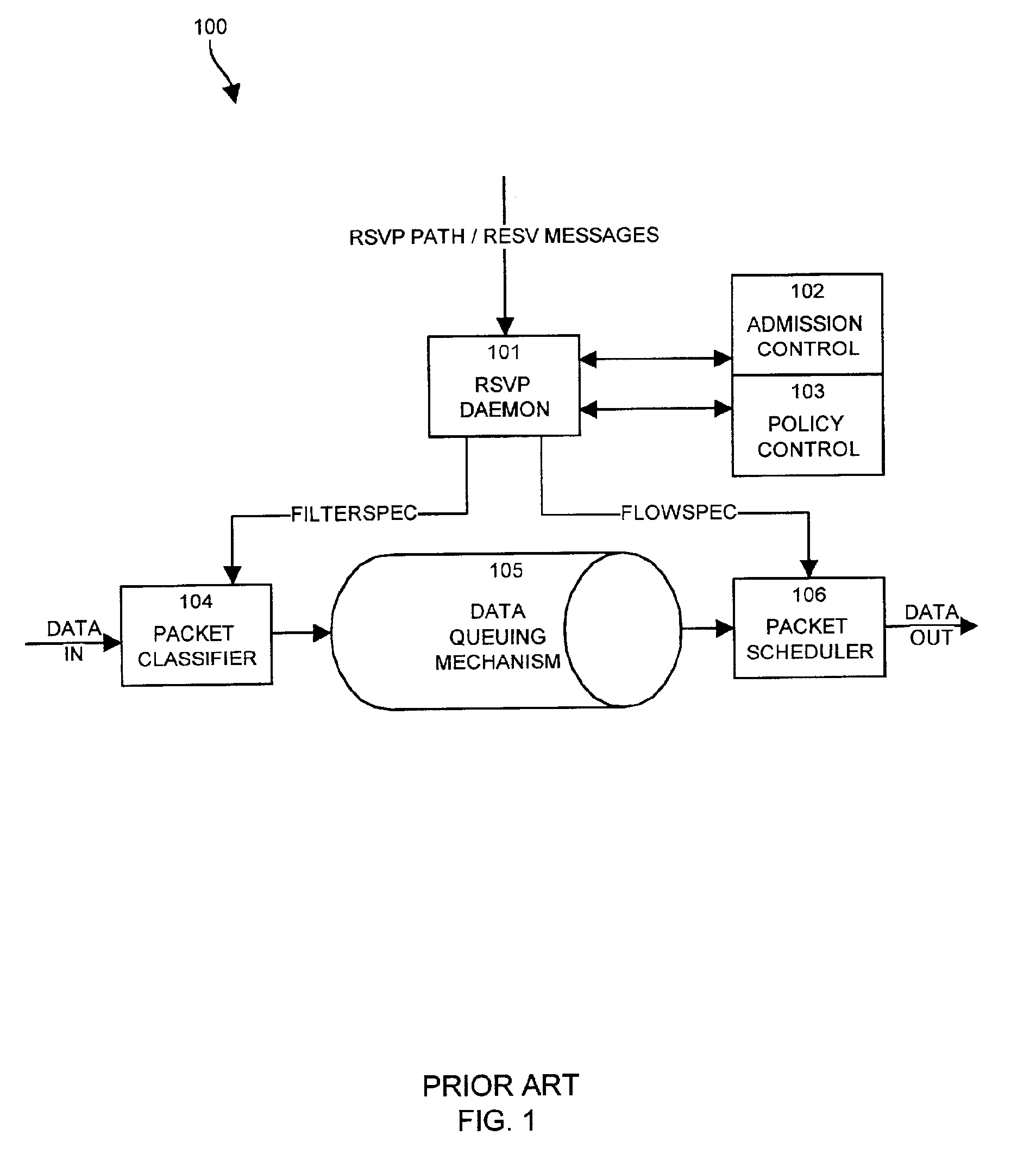
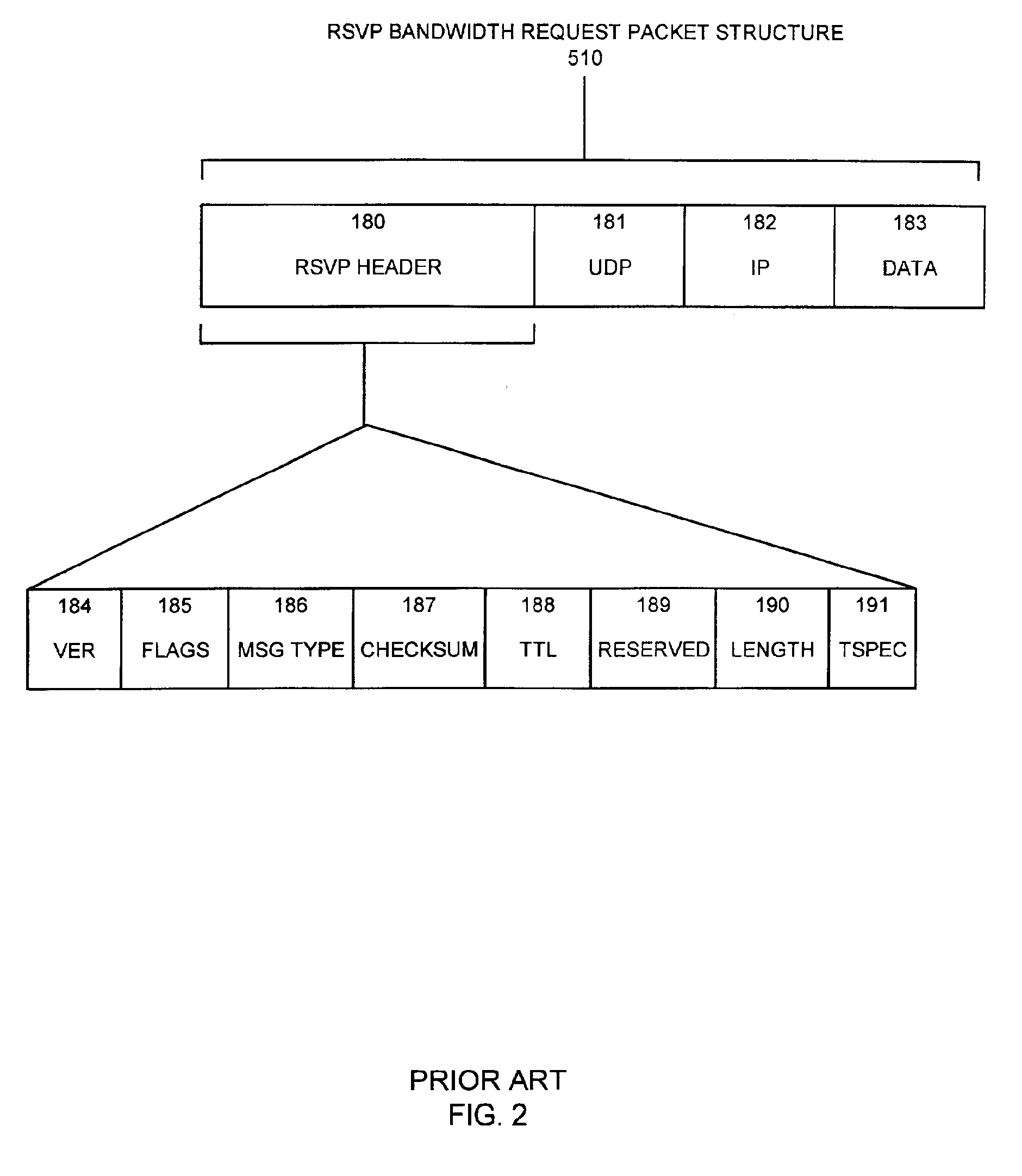
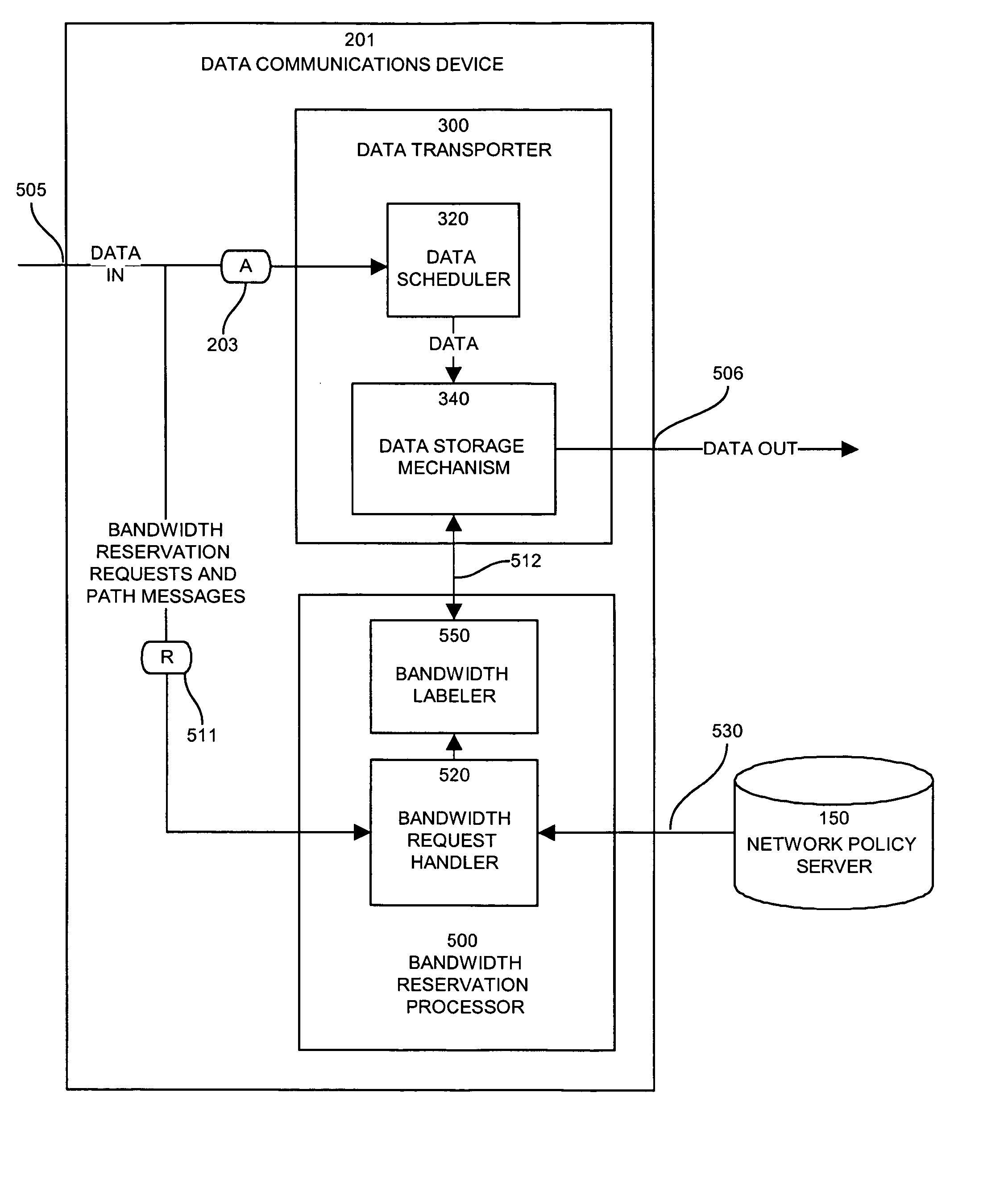
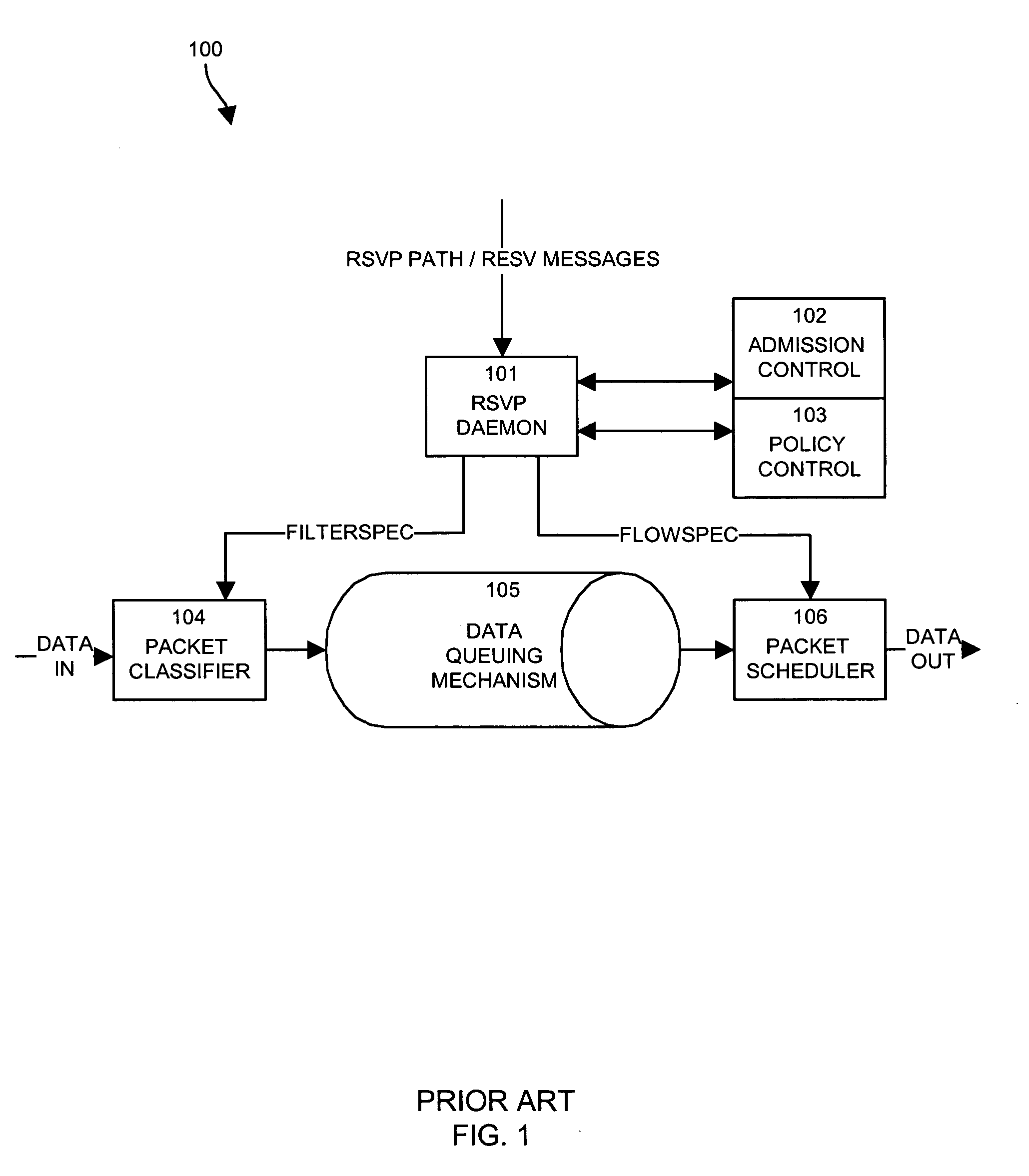
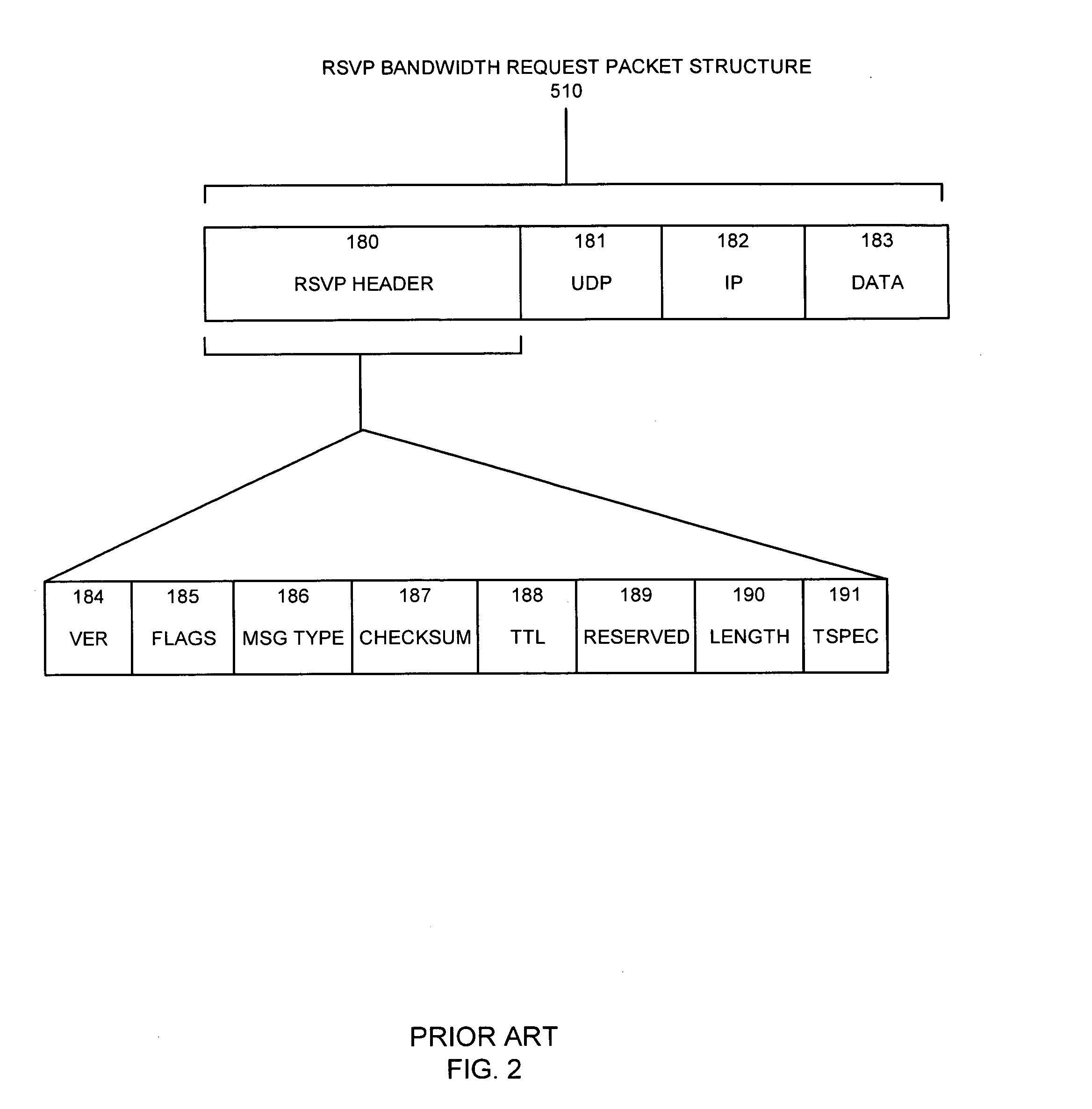
A system capable of dynamically reserving bandwidth and adjusting bandwidth reservations for active sessions of data communication in a data communications device is provided. The system generally separates the operation of bandwidth allocation and adjustment from the operation of data transport through the device, thereby allowing bandwidth reservations and adjustments to be made without disturbing sessions of data communication that are actively being transported through the device. The system can accept requests to allocate or reserve bandwidth in a data communications device using bandwidth reservation protocols such as RSVP. The reservation requests create sender state data that can be used to compute resource allocation data. The resource allocation data can be used to label data storage locations in a data storage mechanism according to the required bandwidth reservations. A data scheduling apparatus, which is ignorant of particular sessions and specific amounts of reserved bandwidth, examines data and deposits data into data storage locations having a label corresponding to a session identification specified in the data, if any. If an unknown or no session identification is specified in the data, the data scheduler deposits data into a data storage location that is unlabeled or that has an unreserved label. Thus session bandwidth is determined by the percentage of labeled data storage locations for the session. Changes in bandwidth reservations are reflected in the separate operation of alterations made in the data storage labeling scheme, and do not affect the data scheduler, or data dequeuing mechanisms, thus allowing data sessions to continue without interruption during bandwidth adjustments.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Dynamic bandwidth allocation
InactiveUS7069577B2Prevents untoward spectral effectMore balancedError preventionModulated-carrier systemsFiberModem device
The communication system includes a hybride fiber / coax distribution network. A head end provides for downstream transmission of telephony and control data in a first frequency bandwidth over the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network and reception of upstream telephony and control data in a second frequency bandwidth over the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network. The head end includes head end multicarrier modem for modulating at least downstream telephony information on a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the first frequency bandwidth and demodulating at least upstream telephony information modulated on a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the second frequency bandwidth. The head end further includes a controller operatively connected to the head end multicarrier modem for controlling transmission of the downstream telephony information and downstream control data and for controlling receipt of the upstream control data and upstream telephony information. The system further includes service units, each service unit operatively connected to the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network for upstream transmission of telephony and control data in the second frequency bandwidth and for receipt of the downstream control data and telephony in the first frequency bandwidth. Each service unit includes a service unit multicarrier modem for modulating at least the upstream telephony information on at least one carrier orthogonal at the head end terminal to another carrier in the second frequency bandwidth and for demodulating at least downstream telephony information modulated on at least a band of a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the first frequency bandwidth. Each service unit also includes a controller operatively connected to the service unit multicarrier modem for controlling the modulation of and demodulation performed by the service unit multicarrier modem. A method of monitoring communication channels, a distributed loop method for adjusting transmission characteristics to allow for transmission of data in a multi-point to point communication system, a polyphase filter technique for providing ingress protection and a scanning method for identifying frequency bands to be used for transmission by service units are also included. Also provided is a method and apparatus for performing a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). In one embodiment, a scalable FFT system is built using a novel dual-radix butterfly core.
Owner:HTC CORP
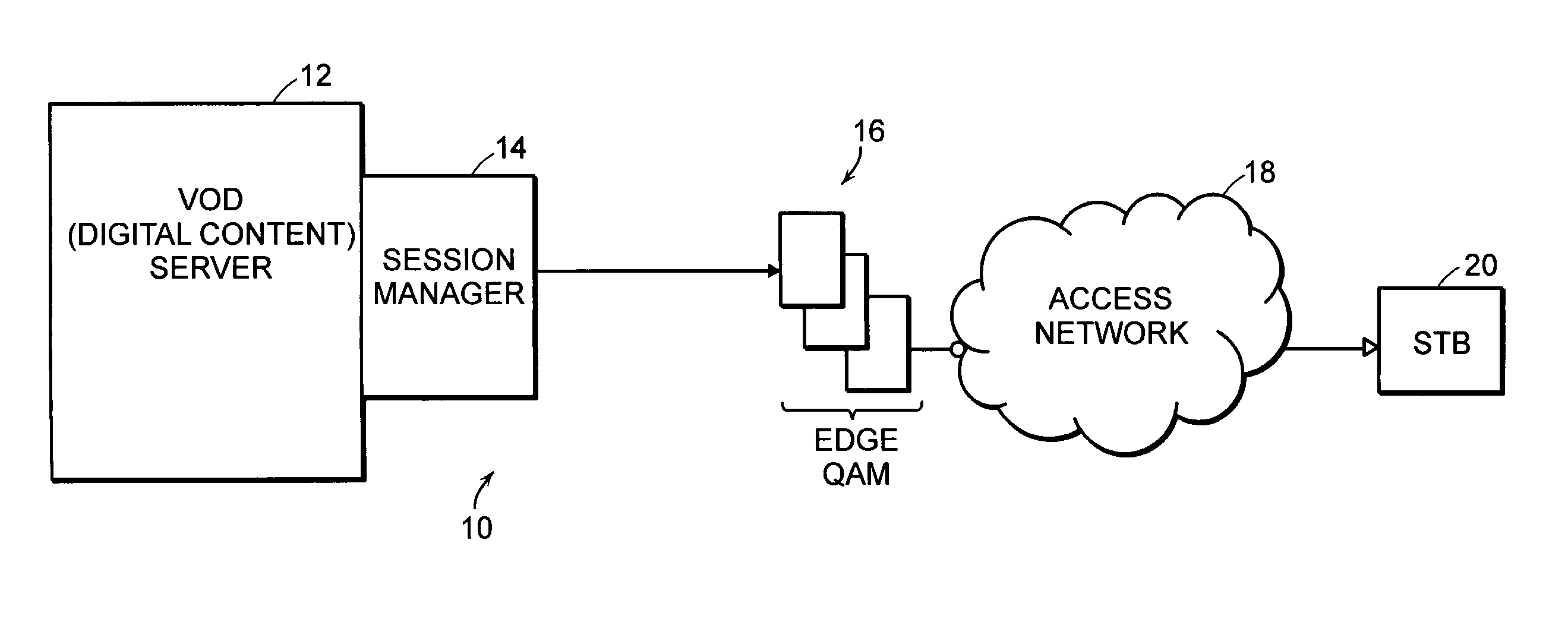
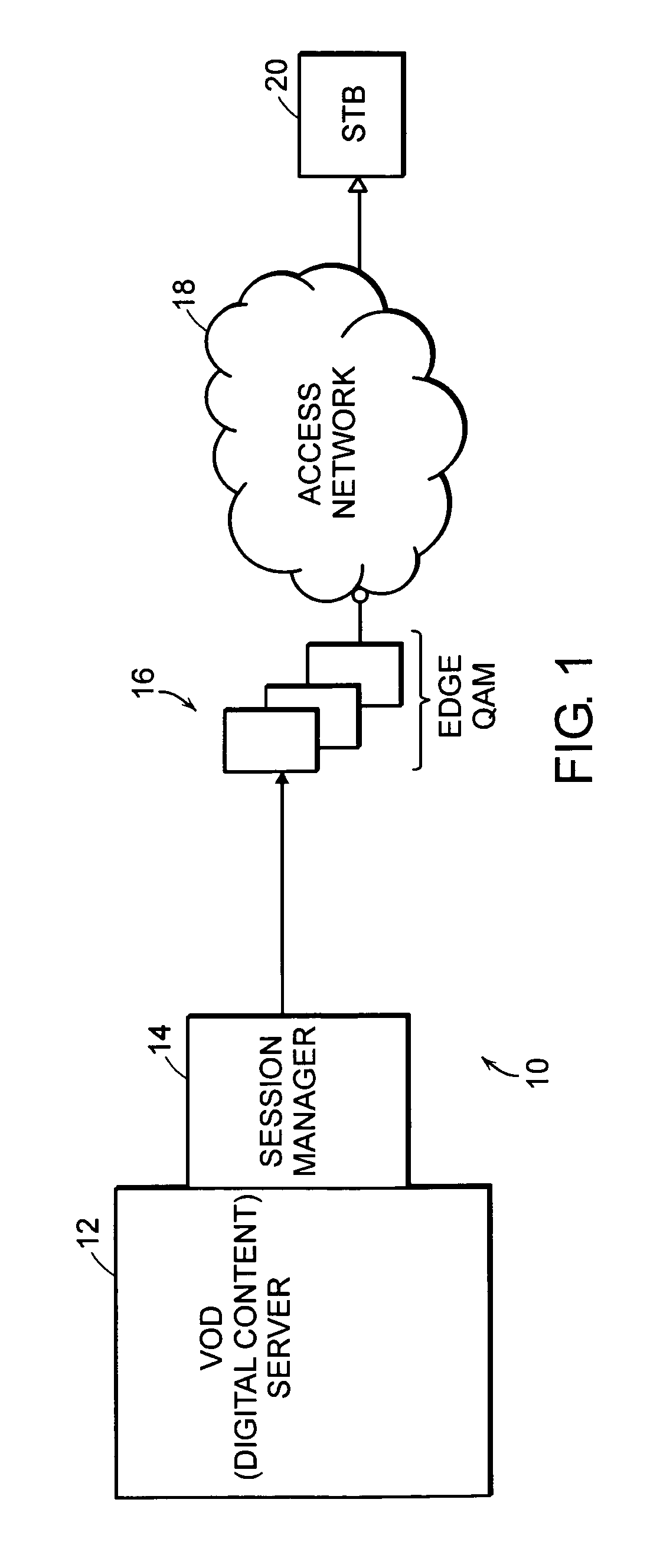
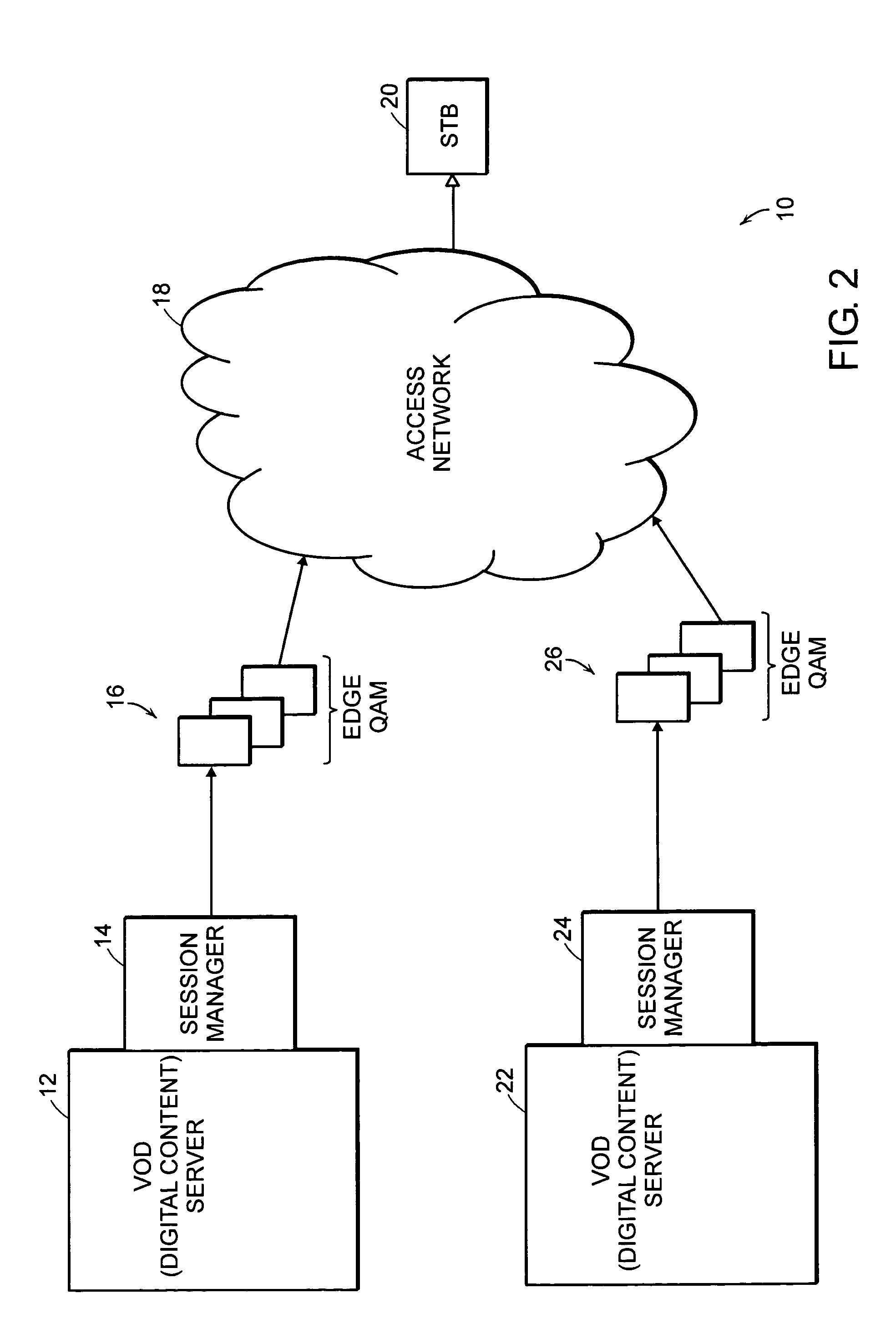
Video policy server
InactiveUS20050188415A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsTwo-way working systemsAccess networkSession management
A system for distributing digital content includes two or more digital content sources. Each source has a separate session manager that is distinct from other session managers associated with other digital content sources. The system further includes at least one set of network resources that receive digital content from the two or more digital content sources, modulate the digital content onto a carrier signal suitable for transmission over an access network, and transmit the carrier signal over the access network. The system also includes a receiving device for terminating the carrier signal. The receiving device generates a digital content stream corresponding to the digital content from the two or more digital content sources. The system further includes a policy server for allocating bandwidth of the network resources to the digital content sources, and for monitoring a utilization state of the network resources.
Owner:CAMIANT INC
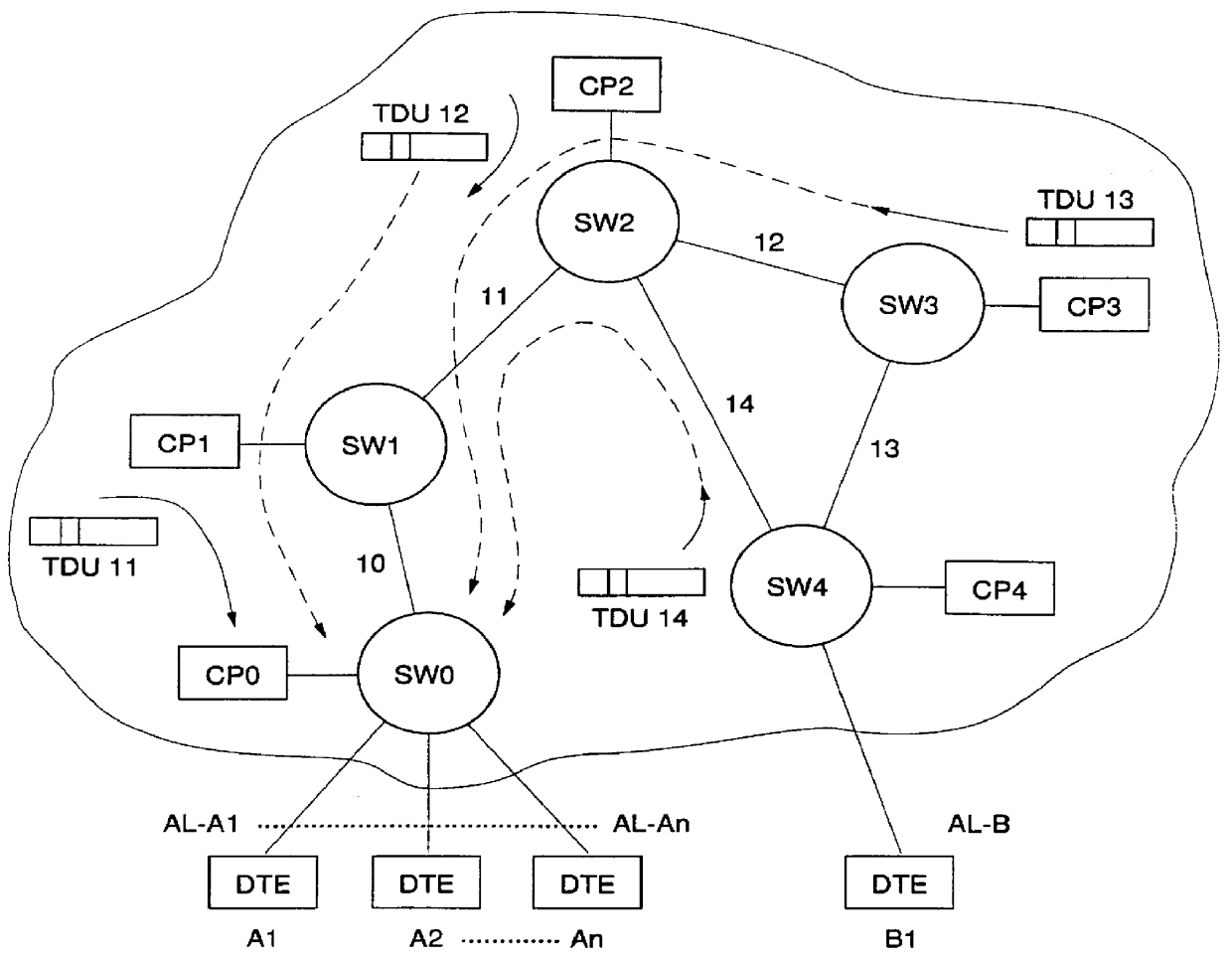
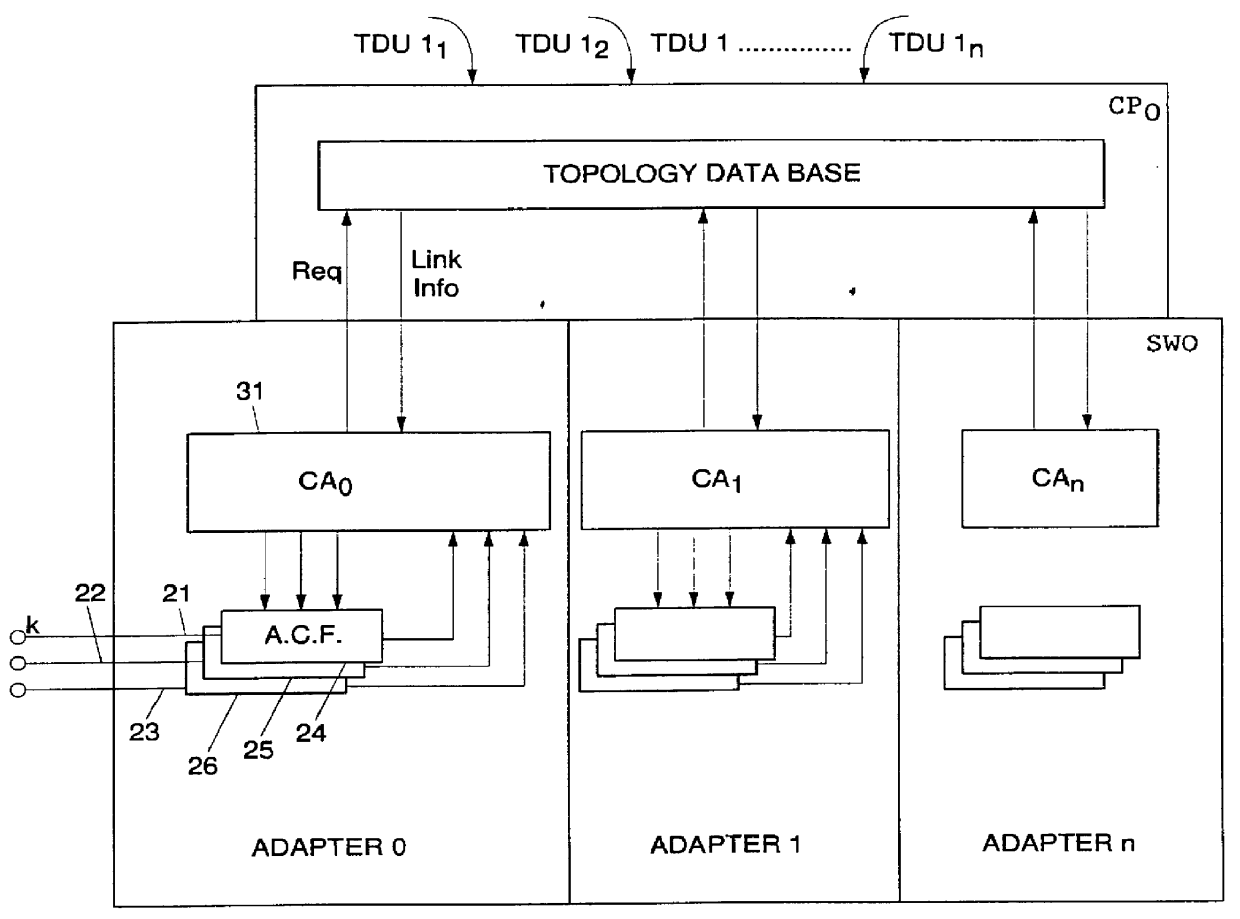
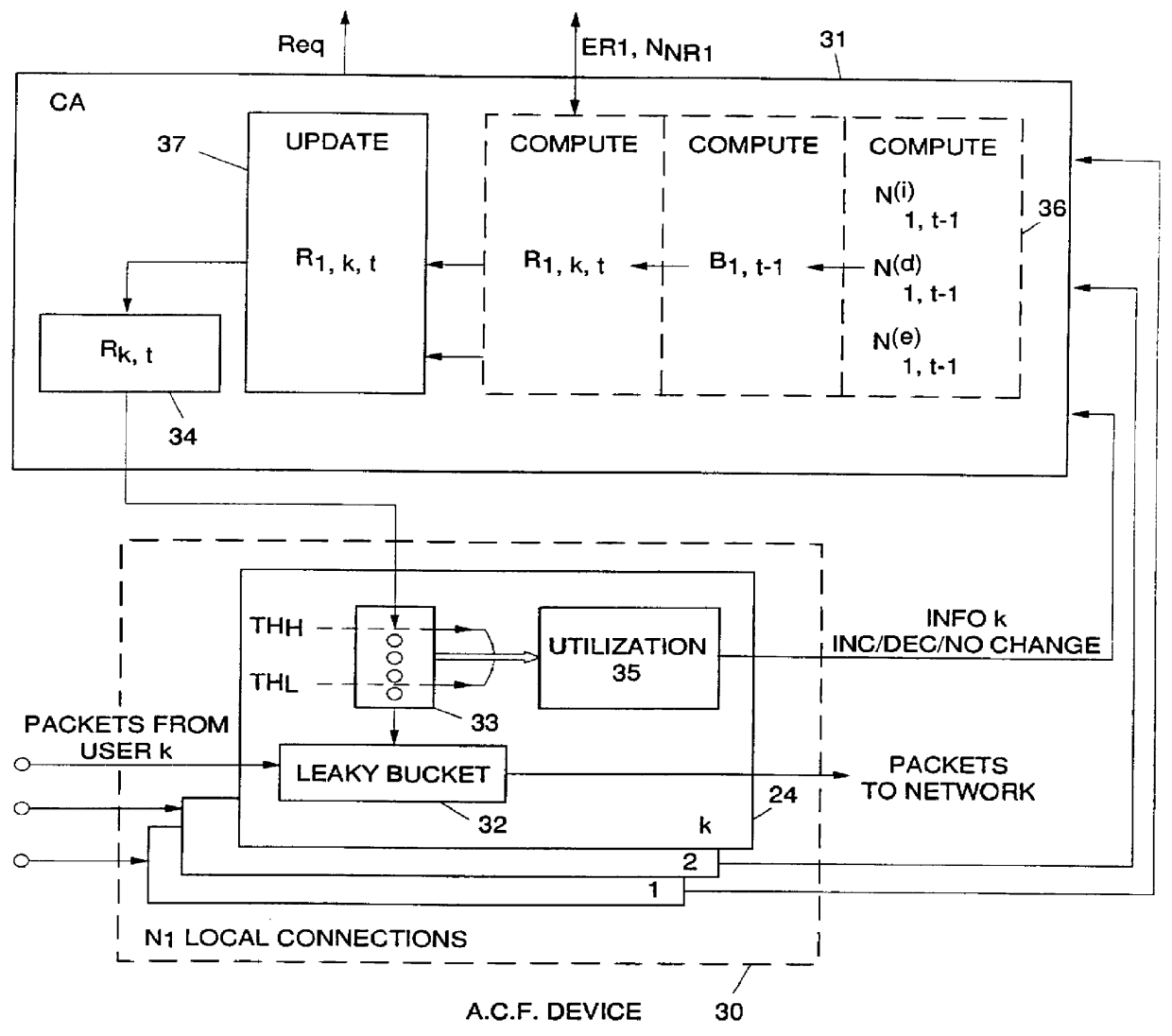
Adaptive bandwidth allocation method for non-reserved traffic in a high-speed data transmission network, and system for implementing said method
Adaptive bandwidth allocation for Non-Reserved traffic over high speed transmission links of a digital network is operated through regulation of data packet transfers over network nodes / ports including input / output adapters connected through a switching device. A network node is assigned with a Control Point computing devise (CP) storing a Topology Data Base containing an image of the network. This Data Base is periodically and at call set up updated by Topology Data Base Update messages (TDUs) including an Explicit Rate parameter for link l indicating the current available bandwidth on link l, and a parameter NNRl indicating the number of Non-Reserved connections on link l. This information are used within each Adapter to periodically regulate the transmission bandwidth assigned to each Non-Reserved traffic connection within the network. To that end, each adapter is provided with an Access Control Function device for each attached connection (data source) and a Connection Agent (CA) getting, on request, required current link informations from the attached Topology Data Base.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Cost-aware, bandwidth management systems adaptive to network conditions
ActiveUS8489720B1Improve load conditionsLow costMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksNetwork conditionsApplication software
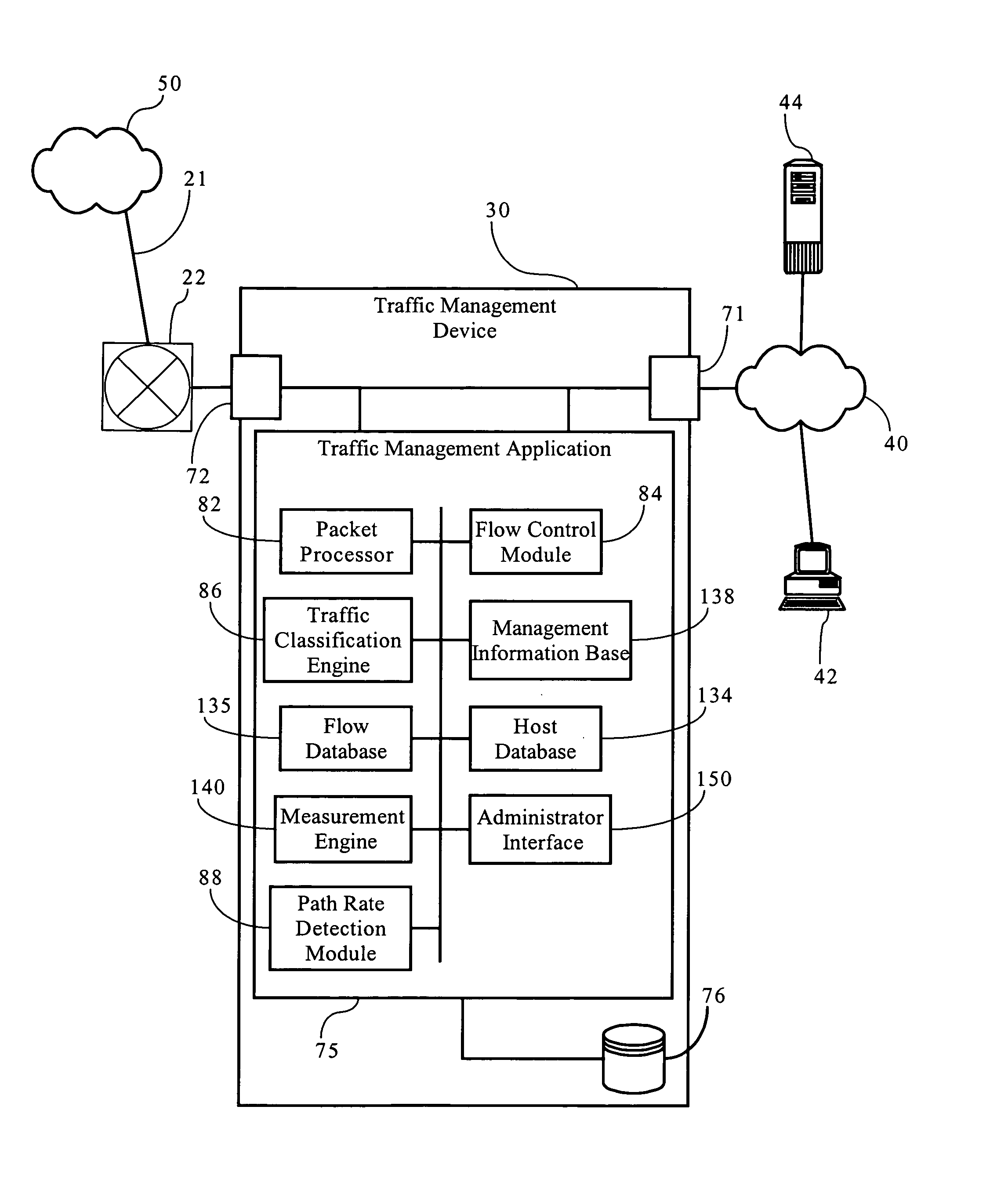
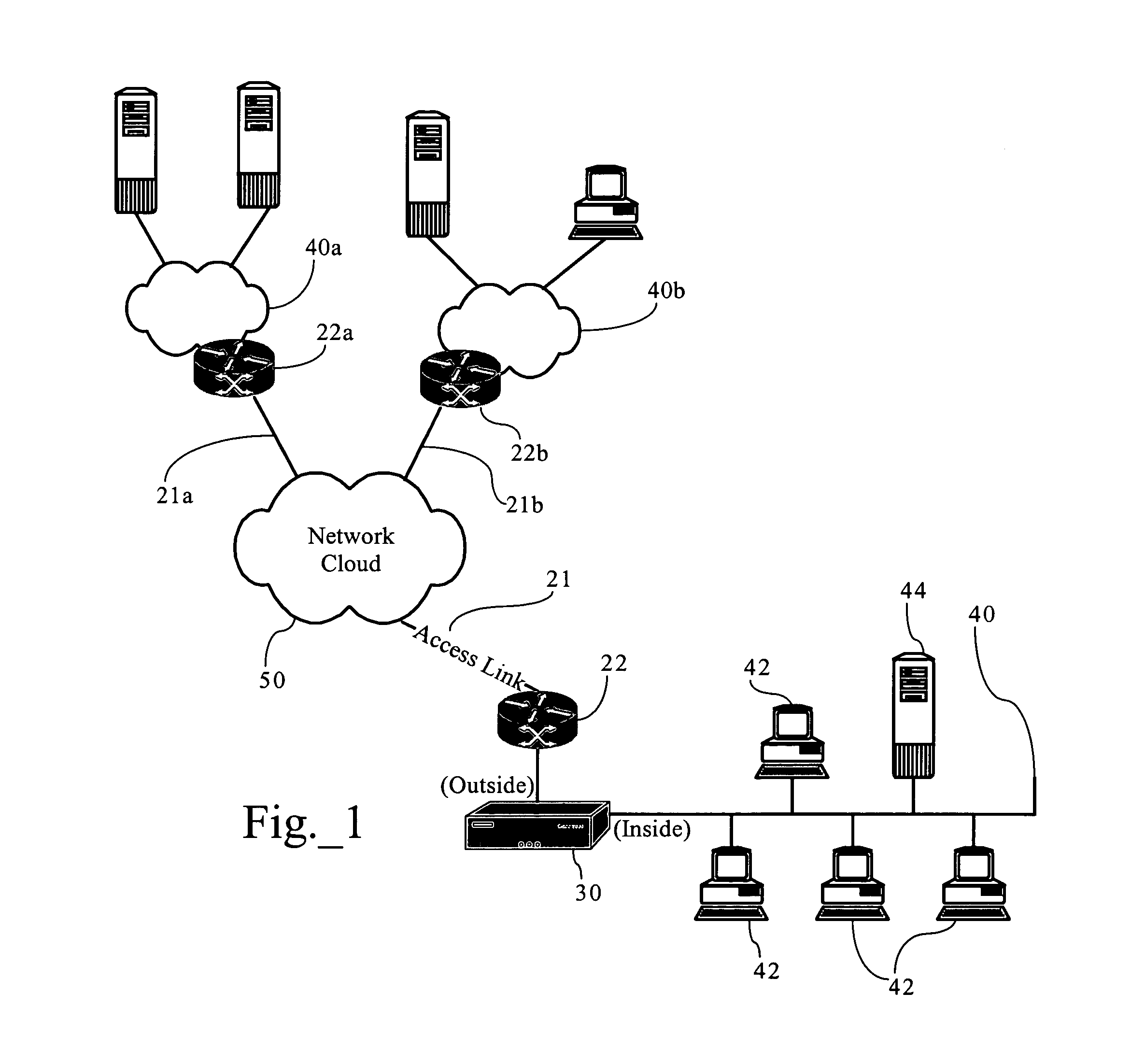
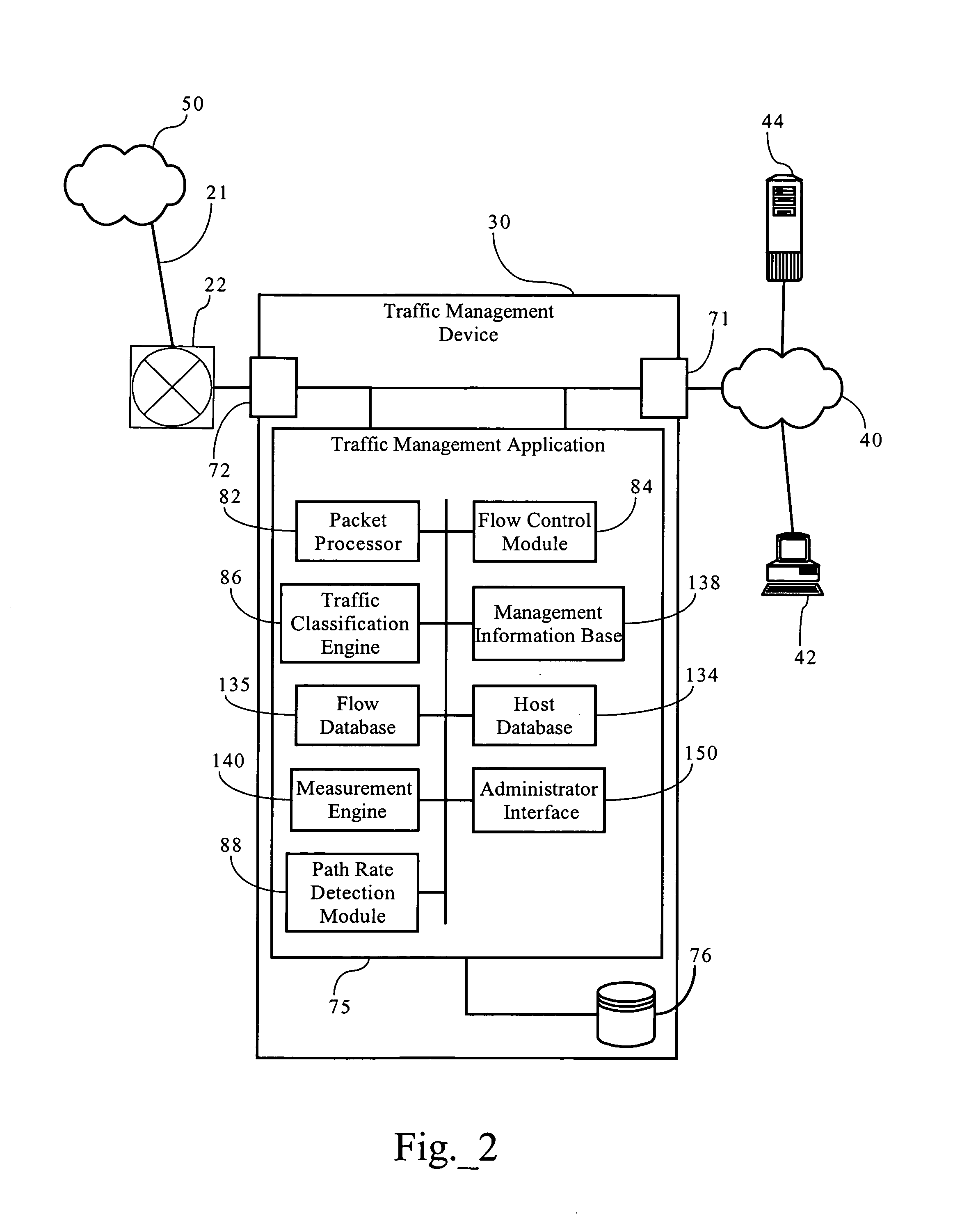
Methods, apparatuses, and systems directed to cost-aware bandwidth management schemes that are adaptive to monitored network or application performance attributes. In one embodiment, the present invention supports bandwidth management systems that adapt to network conditions, while managing tradeoffs between bandwidth costs and application performance. One implementation of the present invention tracks bandwidth usage over an applicable billing period and applies a statistical model to allow for bursting to address increased network loading conditions that degrade network or application performance. One implementation allows for bursting at selected time periods based on computations minimizing cost relative to an applicable billing model. One implementation of the present invention is also application-aware, monitoring network application performance and increasing bandwidth allocations in response to degradations in the performance of selected applications.
Owner:CA TECH INC
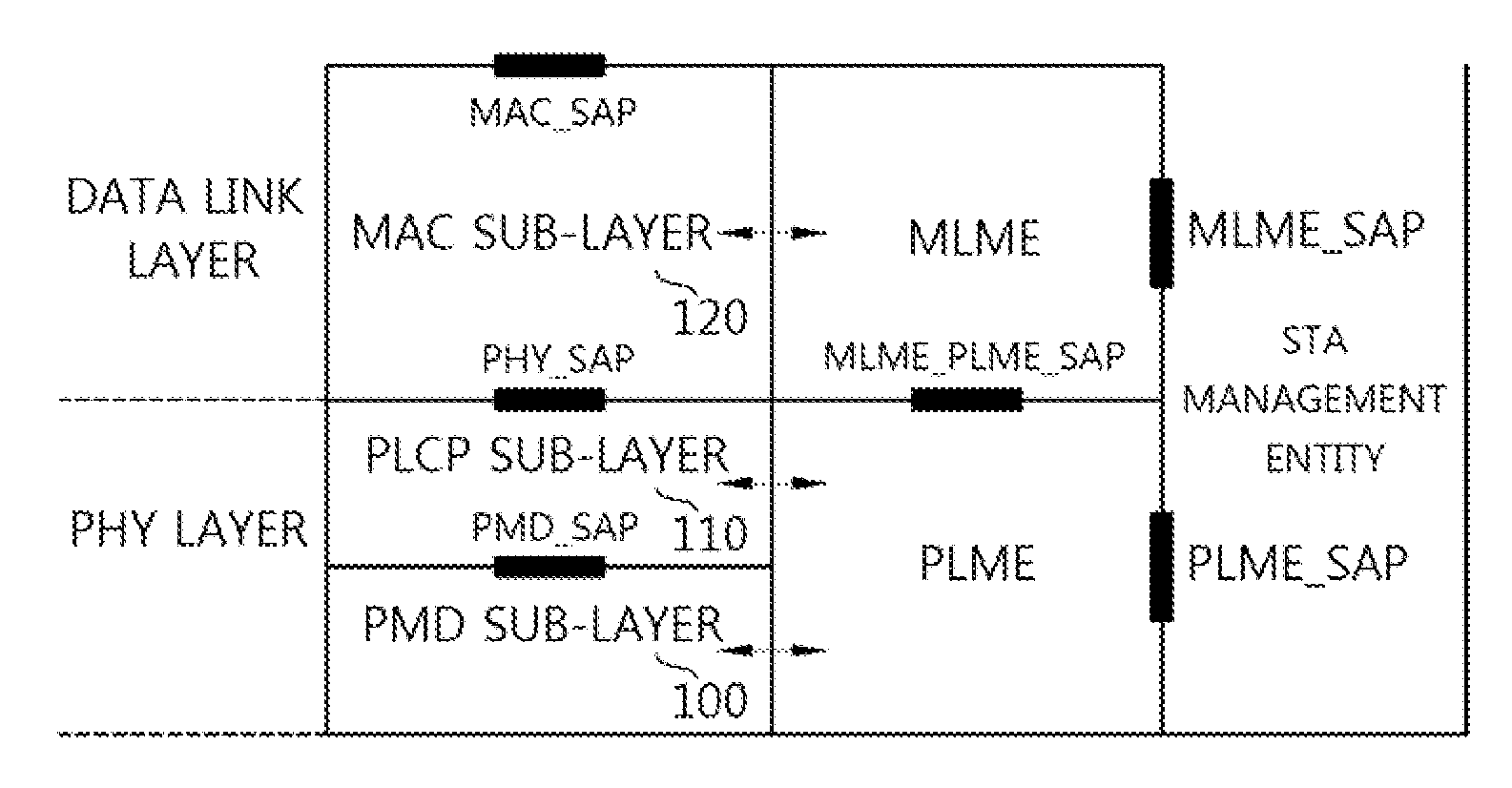
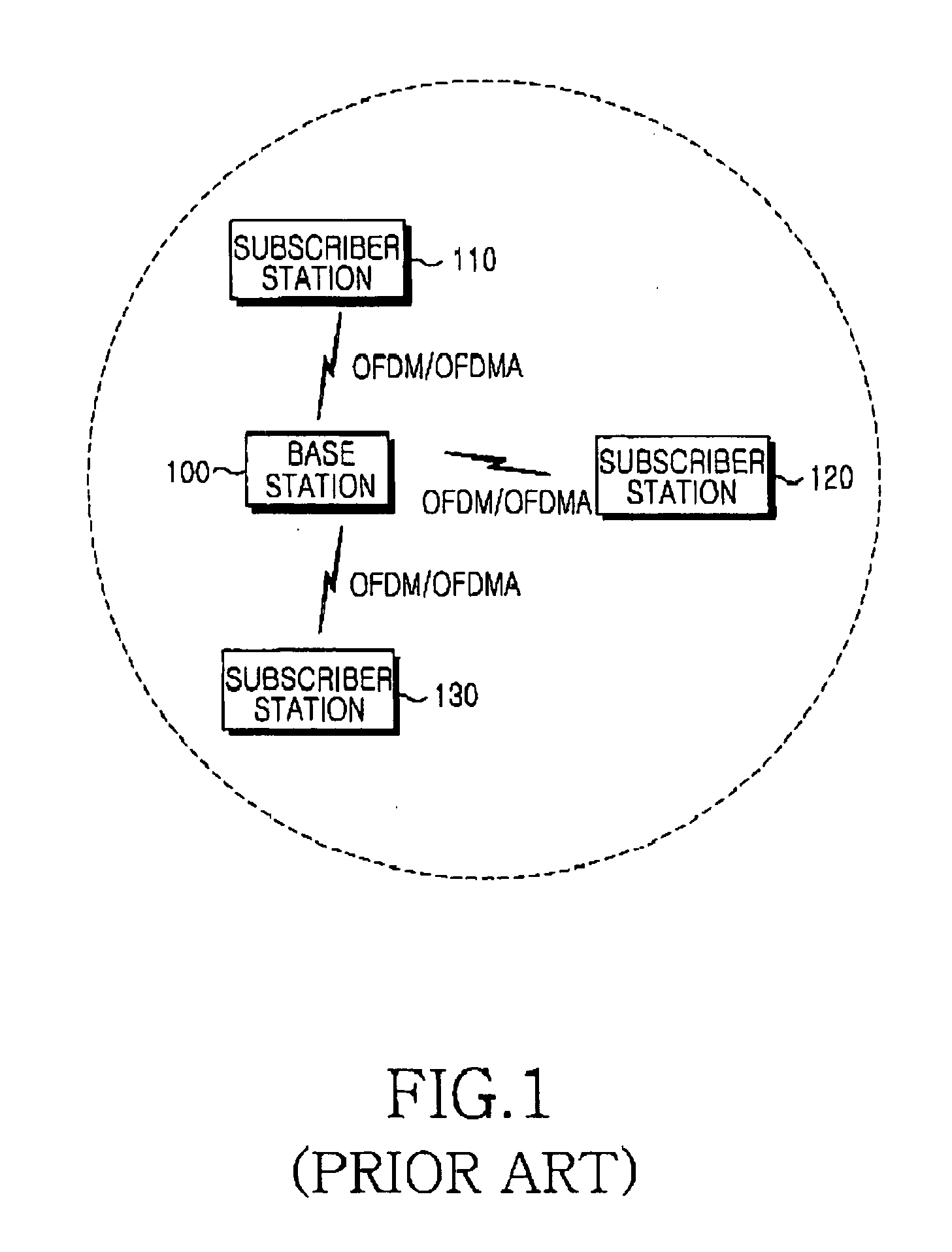
Ppdu receiving method and apparatus based on the MIMO technique in a WLAN system
ActiveUS20120327915A1Improve throughputBottleneck phenomenon can be decreasedError preventionTransmission path divisionMulti inputTelecommunications
Provided is a method of receiving a physical layer convergence procedure (PLCP) protocol data unit (PPDU) by an access point (AP) in a wireless local area (LAN) system. The method includes: allocating a first transmission channel bandwidth to a first station (STA) which is multiple input multiple output (MIMO)-paired with the AP; allocating a second transmission channel bandwidth to a second STA which is MIMO-paired with the AP; transmitting to the first STA and the second STA a sync trigger for determining a time point at which the first STA transmits a first PPDU and a time point at which the second STA transmits a second PPDU; and receiving simultaneously the first PPDU and the second PPDU from the first STA and the second STA.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Systems and methods for adaptive pricing in a digital broadband delivery system
InactiveUS7340759B1Influence viewing patternEasy to useAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSelective content distributionSelf adaptiveComputer science
Methods and systems are provided for dynamically pricing viewing options in a digital broadband communication network by receiving bandwidth allocation information from a bandwidth allocation manager and dynamically assigning a price criterion to each of a group of viewing options based at least in part on the bandwidth allocation information. The group of viewing options may, for example, comprise a reservation option, a normal-play option, a random access option, an on-demand random access option, and an adjust preference option. In addition, the method may optionally comprise receiving a subscriber request related to at least one viewing option selected from the group of viewing options and transmitting a price criterion for the viewing option to the subscriber in response to the subscriber request. The subscriber request may comprise, for example, a request for a price criterion for a viewing option, a request for viewing a program according to a viewing option, and / or a request for a list of available viewing options. In addition, the price criterion may be based, in part, on subscriber profile data.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
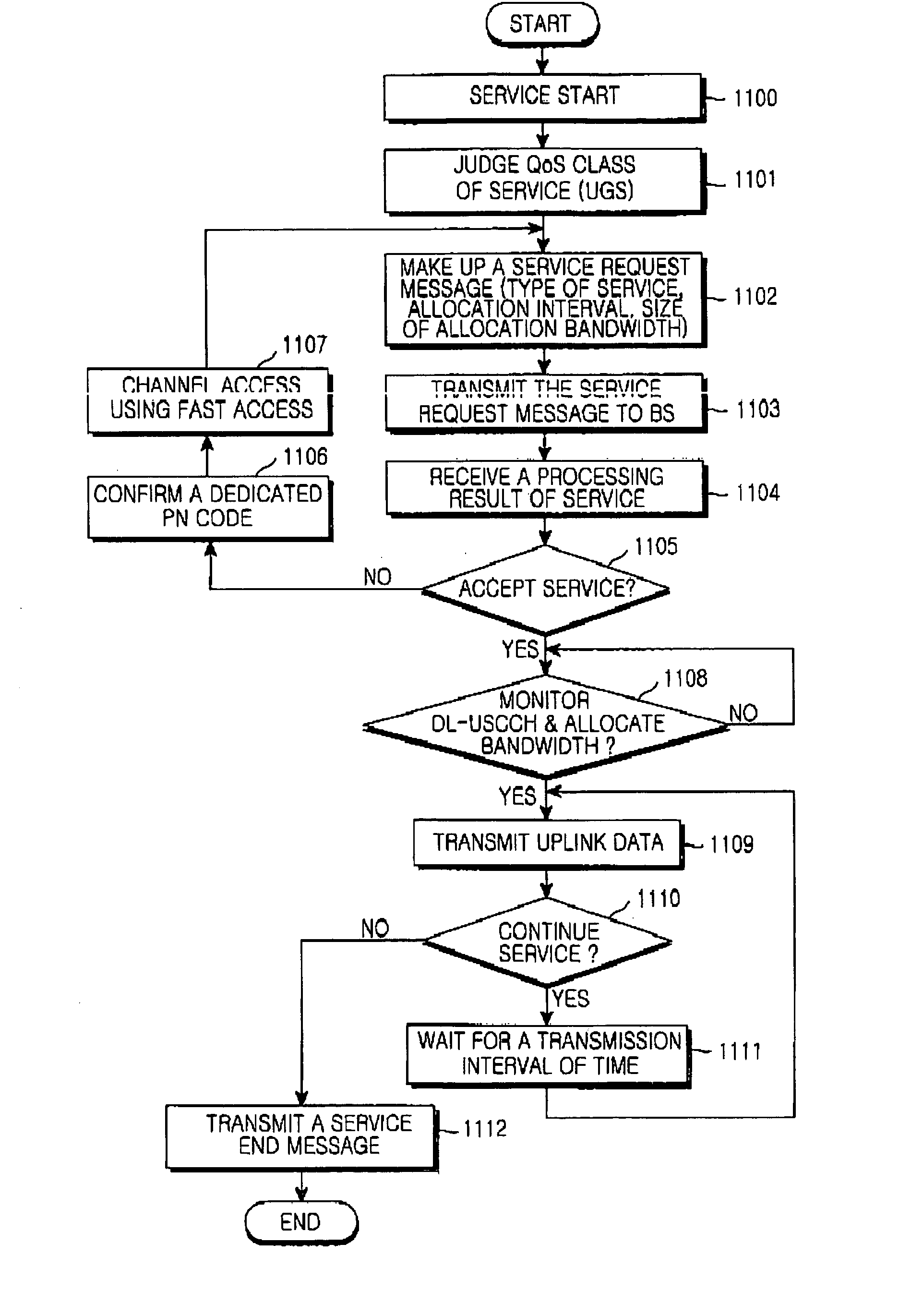
Method for uplink bandwidth request and allocation based on a quality of service class in a broadband wireless access communication system
InactiveUS20050063330A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemUplink scheduling
A bandwidth allocation method for an uplink data transmission between a mobile subscriber station and a base station in a broadband wireless access communication system. The method includes inserting type information of a service requested by the mobile subscriber station into the access channel signal and transmitting the access channel signal to the base station, receiving uplink scheduling information according to the type of the service requested by the mobile subscriber station from the base station, and transmitting data using a transmission bandwidth allocated according to the uplink scheduling information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
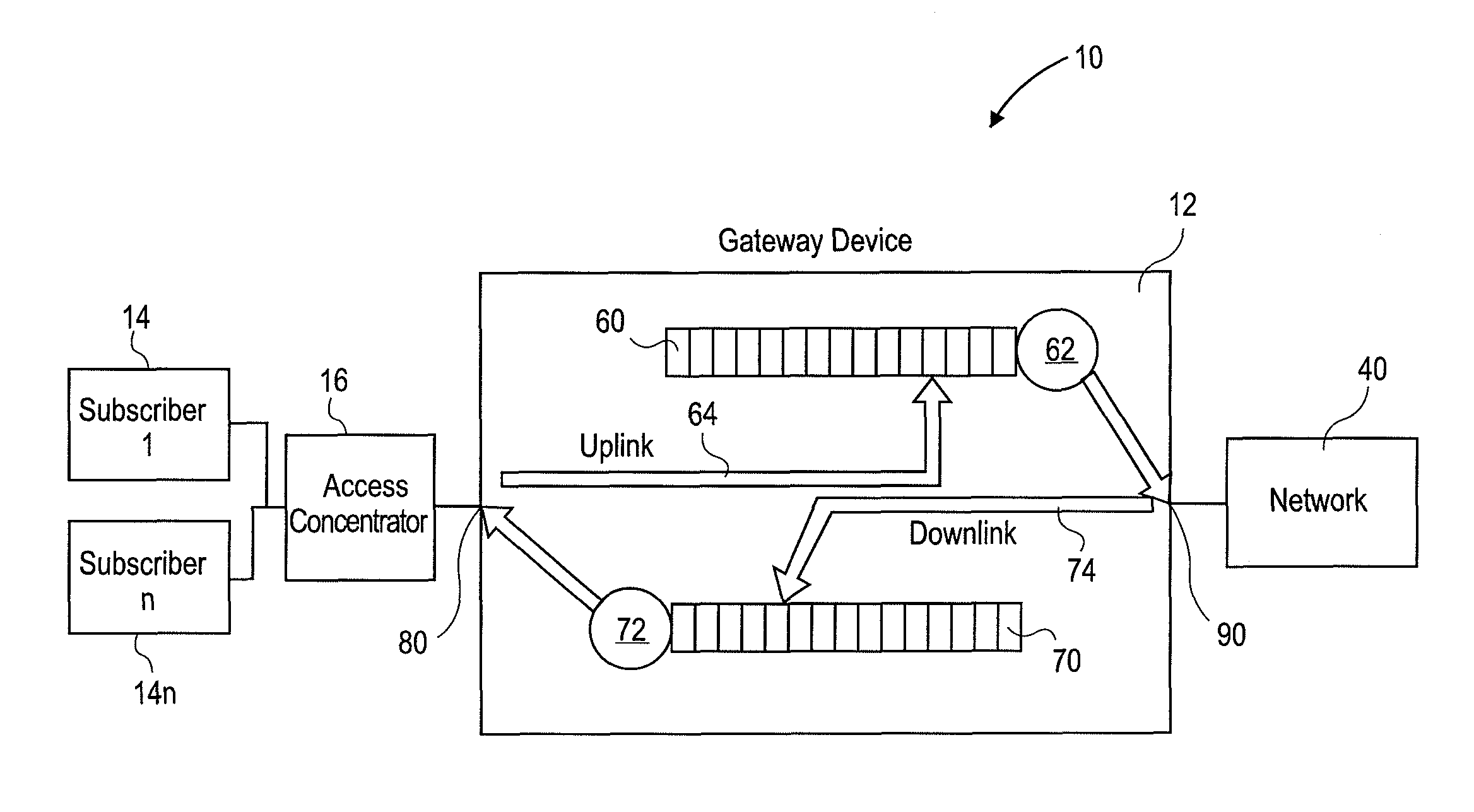
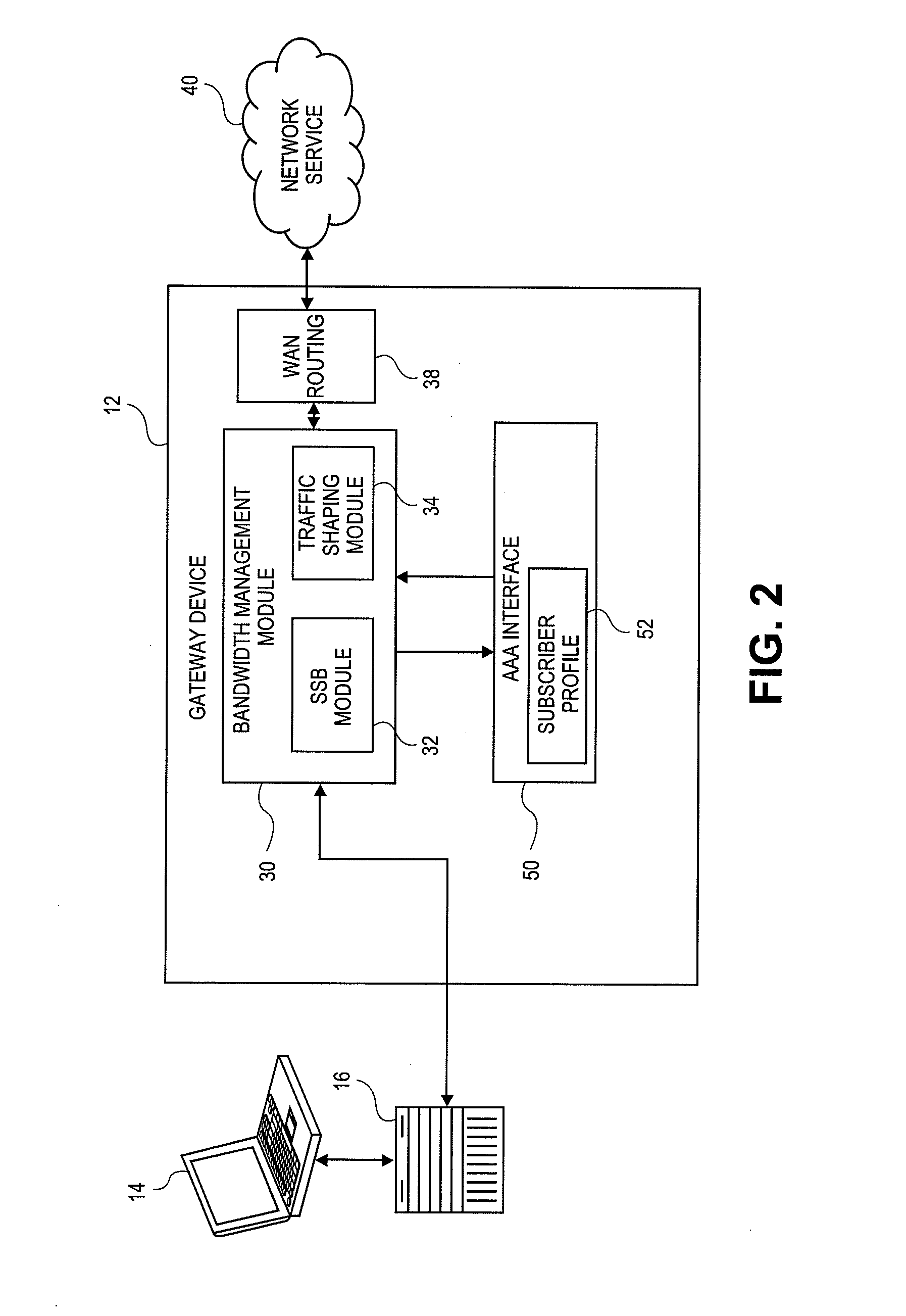
Systems and methods for dynamic bandwidth management on a per subscriber basis in a communications network
InactiveUS7739383B1Efficient managementImprove throughputMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsUplink transmissionNetwork management
A subscriber bandwidth management process and device that allows users / subscribers in a communications network to dynamically alter bandwidth limits independently in both the uplink and downlink data transmission paths. This is accomplished by providing for a single queue in the uplink transmission path and a single queue in the downlink transmission path. Thus, the user / subscriber can efficiently manage their network access according to the specific activity on the network. The network manager benefits from being able structure bandwidth allocation on a per subscriber basis so that overall data transmission is made more efficient. In addition, the bandwidth manager provides active management of the delivery of data (also known as and referred to herein as traffic shaping) to increase throughput from a gateway device onto the network.
Owner:NOMADIX INC
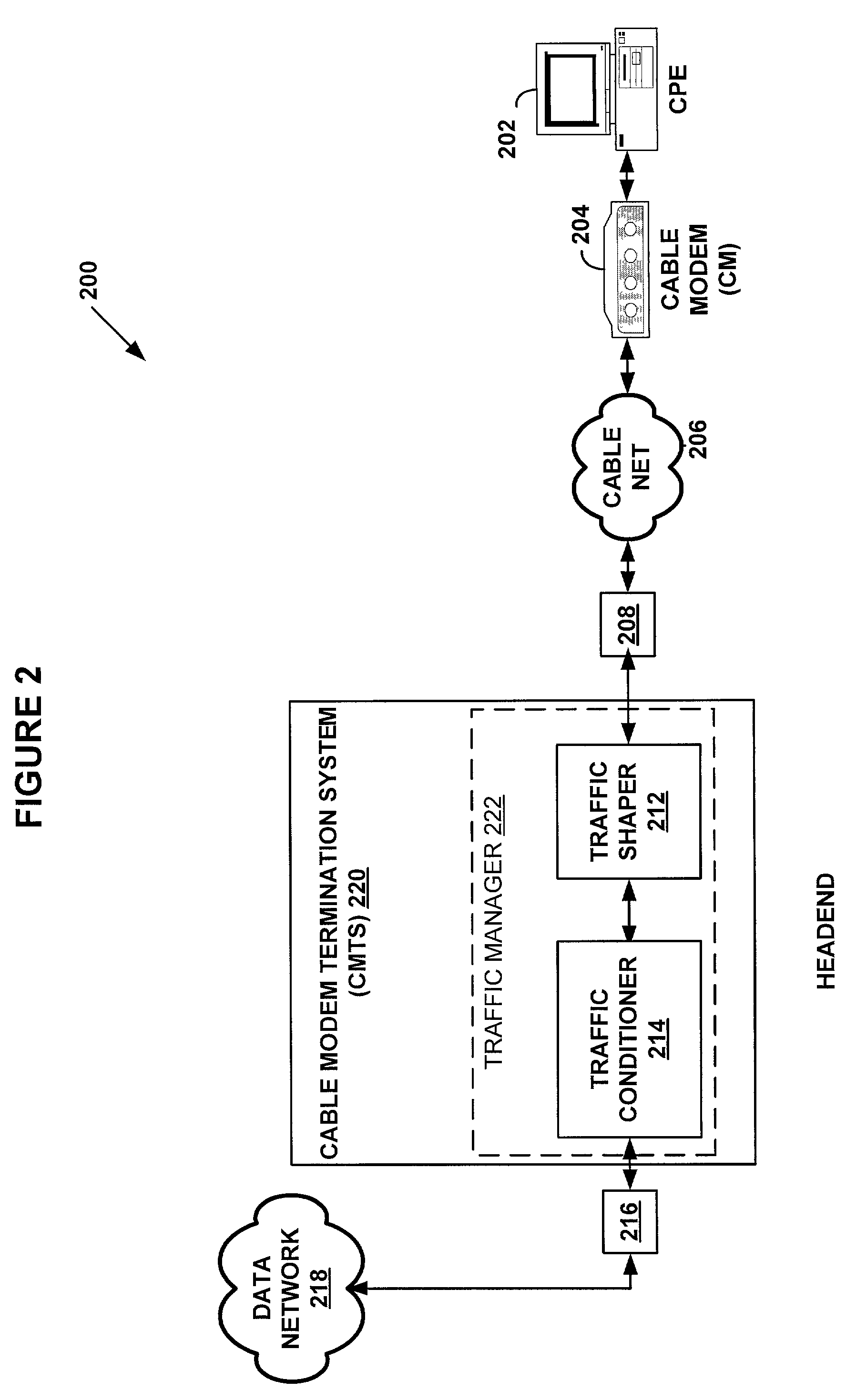
System and method for traffic shaping based on generalized congestion and flow control
ActiveUS7088678B1Overcome problemsError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket arrivalModem device
A system and methods are shown for traffic shaping and congestion avoidance in a computer network such as a data-over-cable network. A headend of the data-over-cable system includes a traffic shaper configured to calculate a packet arrival rate from a cable modem and a traffic conditioner configured to calculate an average queue size on an output interface to an external network. For example, the traffic shaper compares the packet arrival rate to three packet arrival thresholds including a committed rate threshold, a control rate threshold and a peak rate threshold. If the calculated packet arrival rate falls between the committed threshold and control rate threshold, the traffic shaper applies a link layer mechanism, such as a MAP bandwidth allocation mechanism, to lower the transmission rate from the cable modem.
Owner:VL COLLECTIVE IP LLC
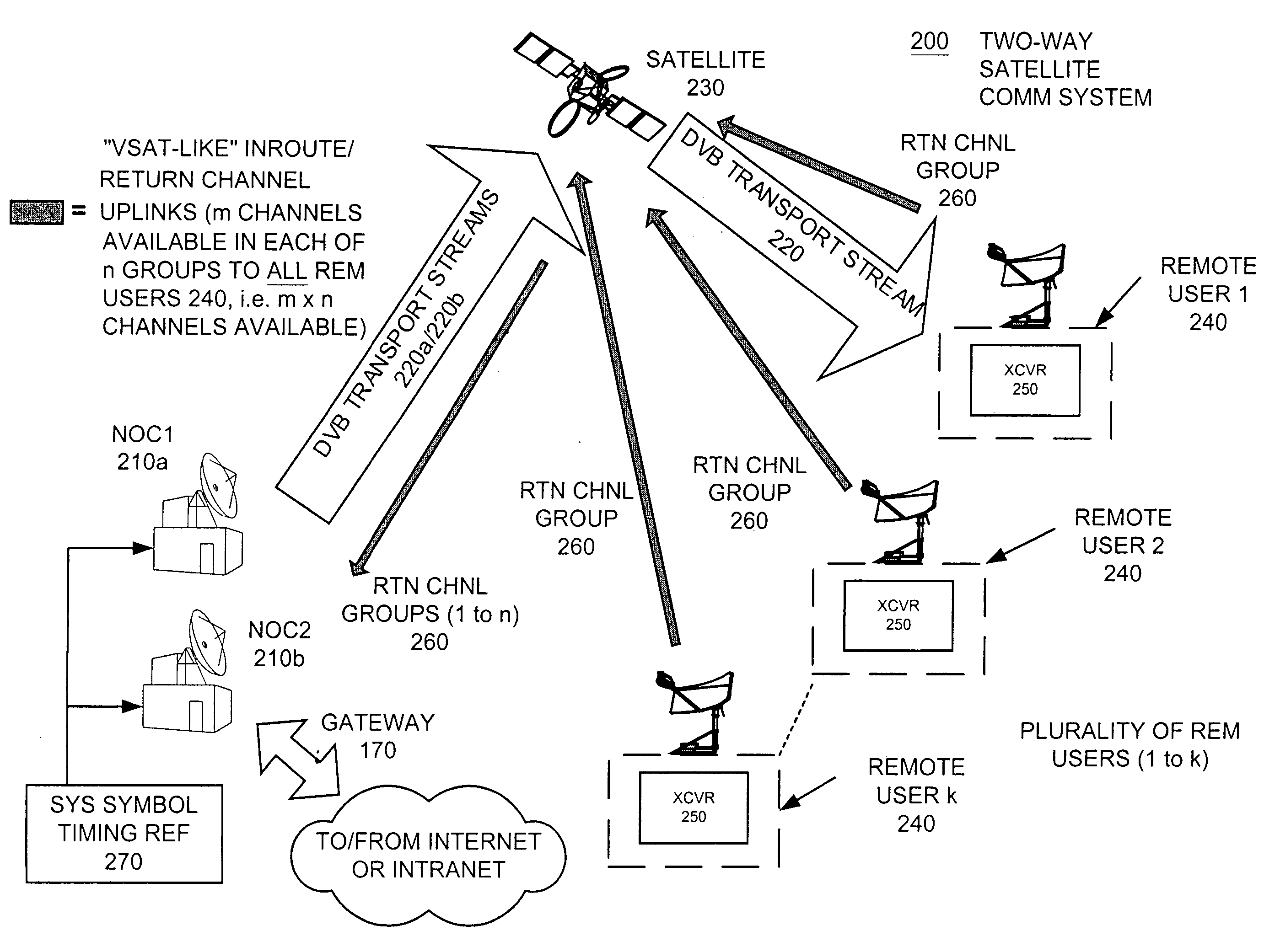
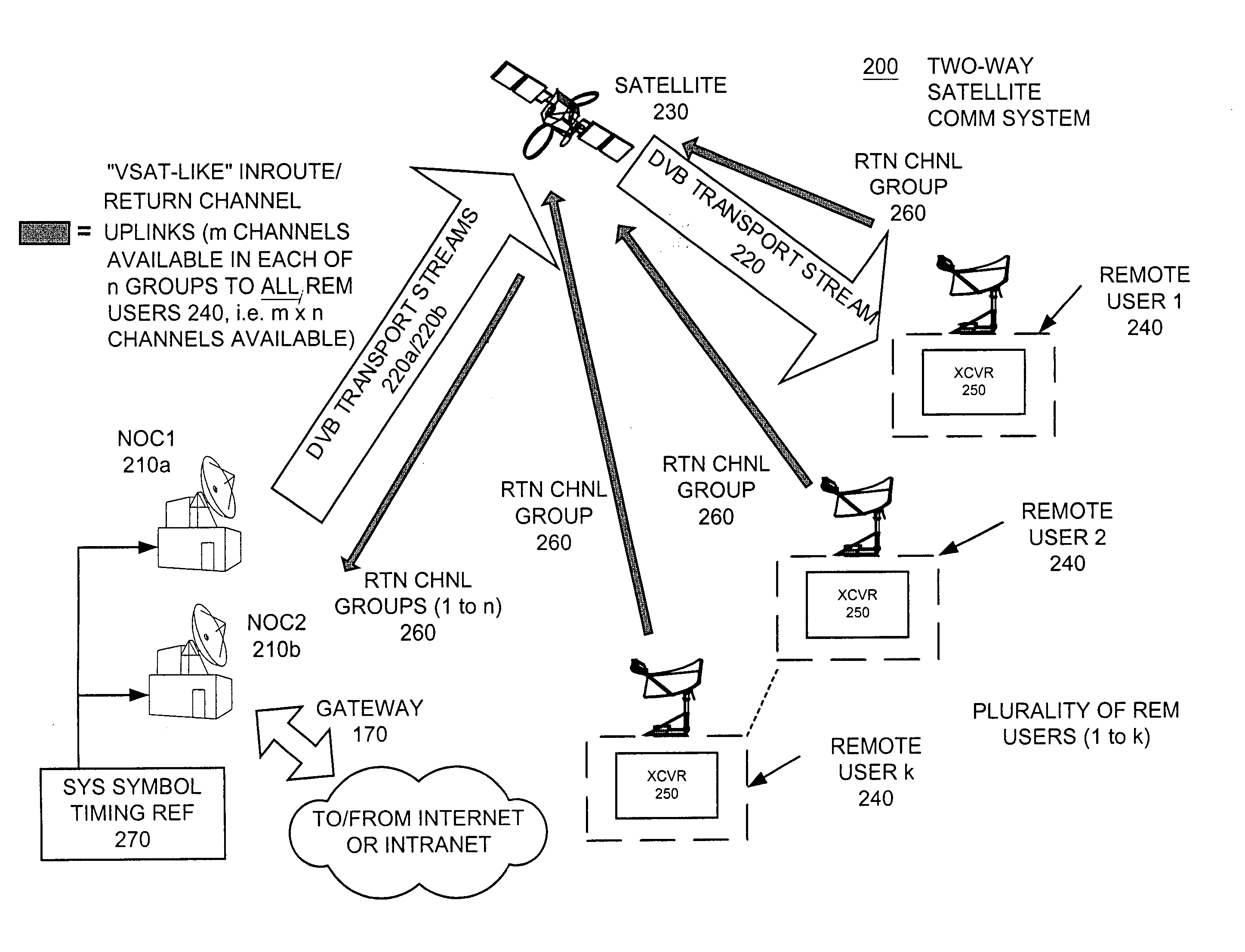
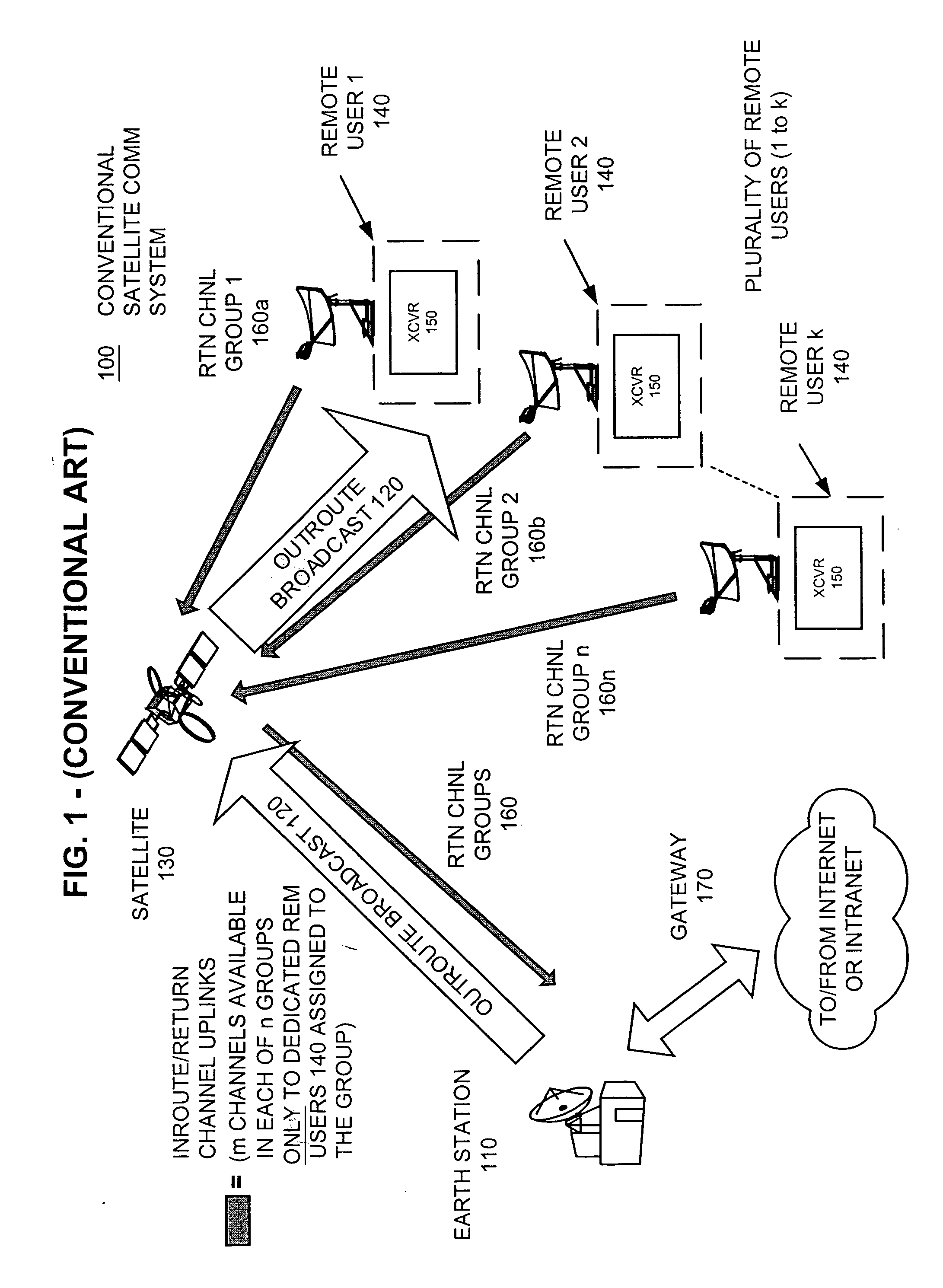
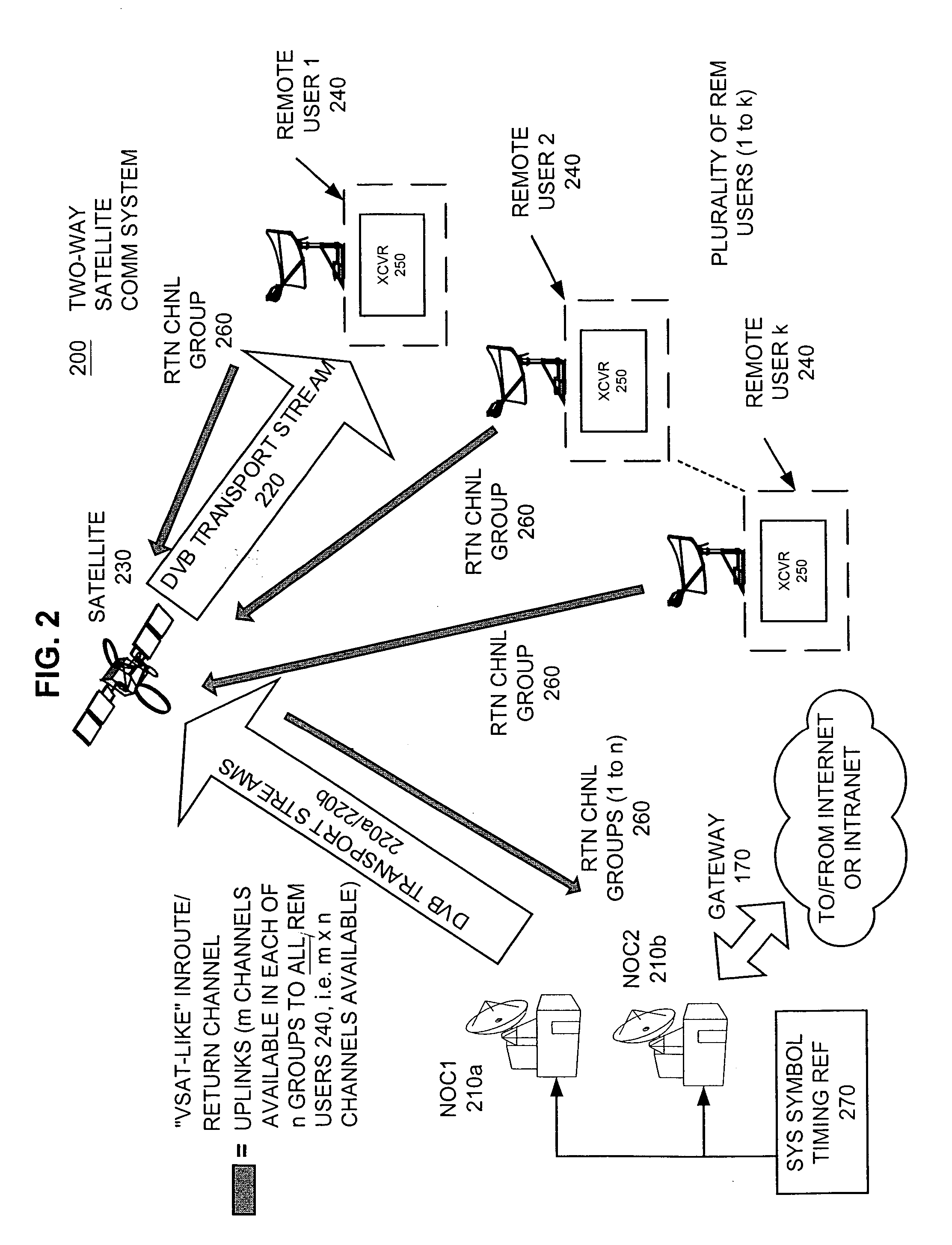
Apparatus and method for efficient TDMA bandwidth allocation for TCP/IP satellite-based networks
InactiveUS20050053033A1Balance traffic loadOptimize bandwidth allocationFrequency-division multiplex detailsAntenna supports/mountingsCommunications systemAloha
A communication system balances message traffic between return channel groups and within the groups, so that the user does not control the specific transmission frequency used. Uplink frequencies and bandwidths for the return channels are set by the system in a return channel control message in the broadcast signal so as to account for system and return channel group loading, and to account for user message backlogs. An initial transmission from a remote user may be made using an ALOHA-type burst signal that provides a message backlog to the control station, and is made on a frequency determined from a randomly weighted, load-based frequency selection process. The system, and not the individual users determine the frequency and channel allocations. For large backlogs or priority users, periodic bandwidth is provided. A method for balancing loads among and between groups of return channels in the communication system includes requesting return channel bandwidth in an uplink message from a remote user to a control station. The uplink message may include a both a backlog indicator and a bandwidth allocation request provided to a Network Operations Center (NOC) which can be used to set the return channel bandwidth and frequency for the remote uplink. A user message is transmitted on the designated return channel frequency using bandwidth allocated in accordance with the backlog indicator and a bandwidth allocation request so that traffic loads are maintained in balance between established return channel frequency groups, and within each return channel frequency group.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
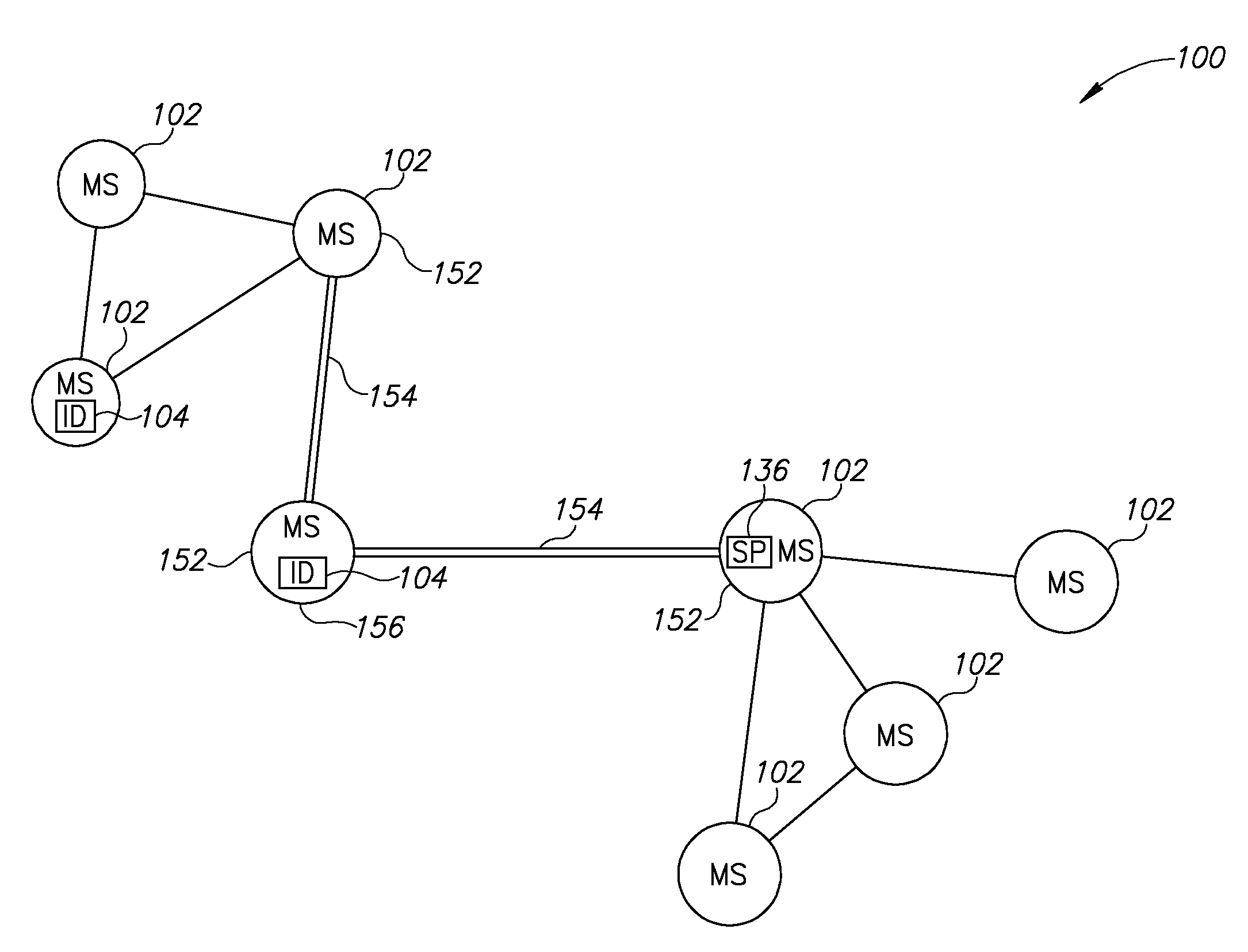
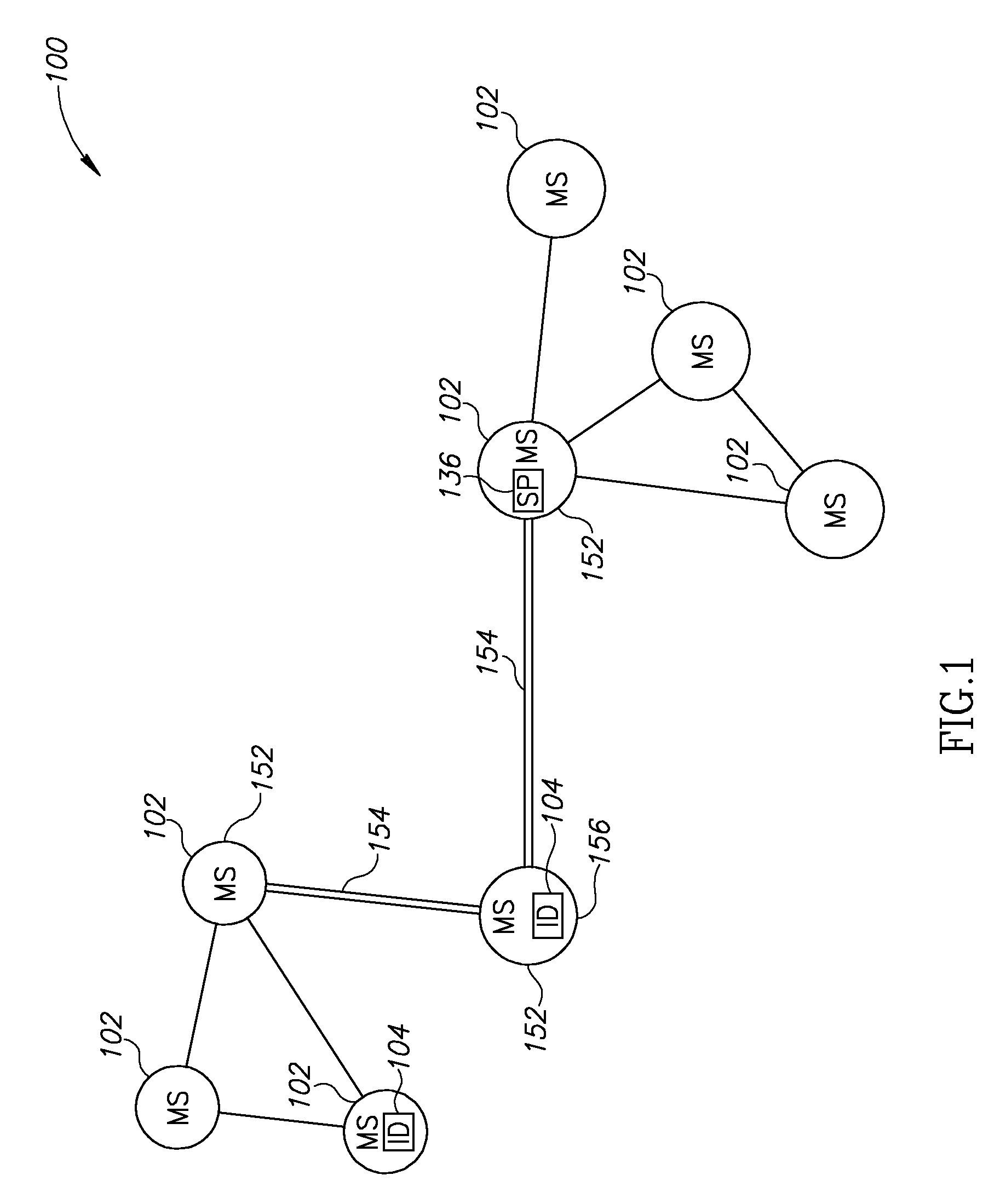
Real Time Peer to Peer Network
ActiveUS20080268855A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesMobile stationData transmission
A method of managing data transmission in a mesh-topology ad-hoc network. The method includes transmitting management information by a plurality of mobile stations of the network, selecting a mobile station to serve as a master, responsive to the transmitted management information, transmitting to the master requests for bandwidth, allocating bandwidth by the master, responsive to the requests and forwarding the bandwidth allocation to the mobile stations of the network.
Owner:MAXTECH COMM NETWORKS
Slow-start adaptive mechanisms to improve efficiency of bandwidth allocation
ActiveUS7426181B1Improve efficiencyReducing over-allocationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDynamic bandwidth allocationSlow-start
Methods, apparatuses and systems directed to improving the efficiency of bandwidth allocation schemes by adapting to slow-start mechanisms associated with network communications protocols, such as the TCP / IP protocol suite. In one implementation, the present invention scales down the initial target rate assigned to a data flow to a fraction of an initial estimate of the effective rate capacity of the communications path between two hosts. As packets are received, the target rate is gradually increased, eventually up to the detected rate capacity of the communications path. Implementations of the present invention improve the efficiency of bandwidth allocation by reducing the over-allocation of bandwidth to data flows during the slow-start phase, leaving more bandwidth available to other data flows.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Dynamic network bandwidth allocation for multimedia applications with soft quality-of-service requirements
InactiveUS6404738B1Lower connection costsLow costError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDynamic bandwidth allocationService level requirement
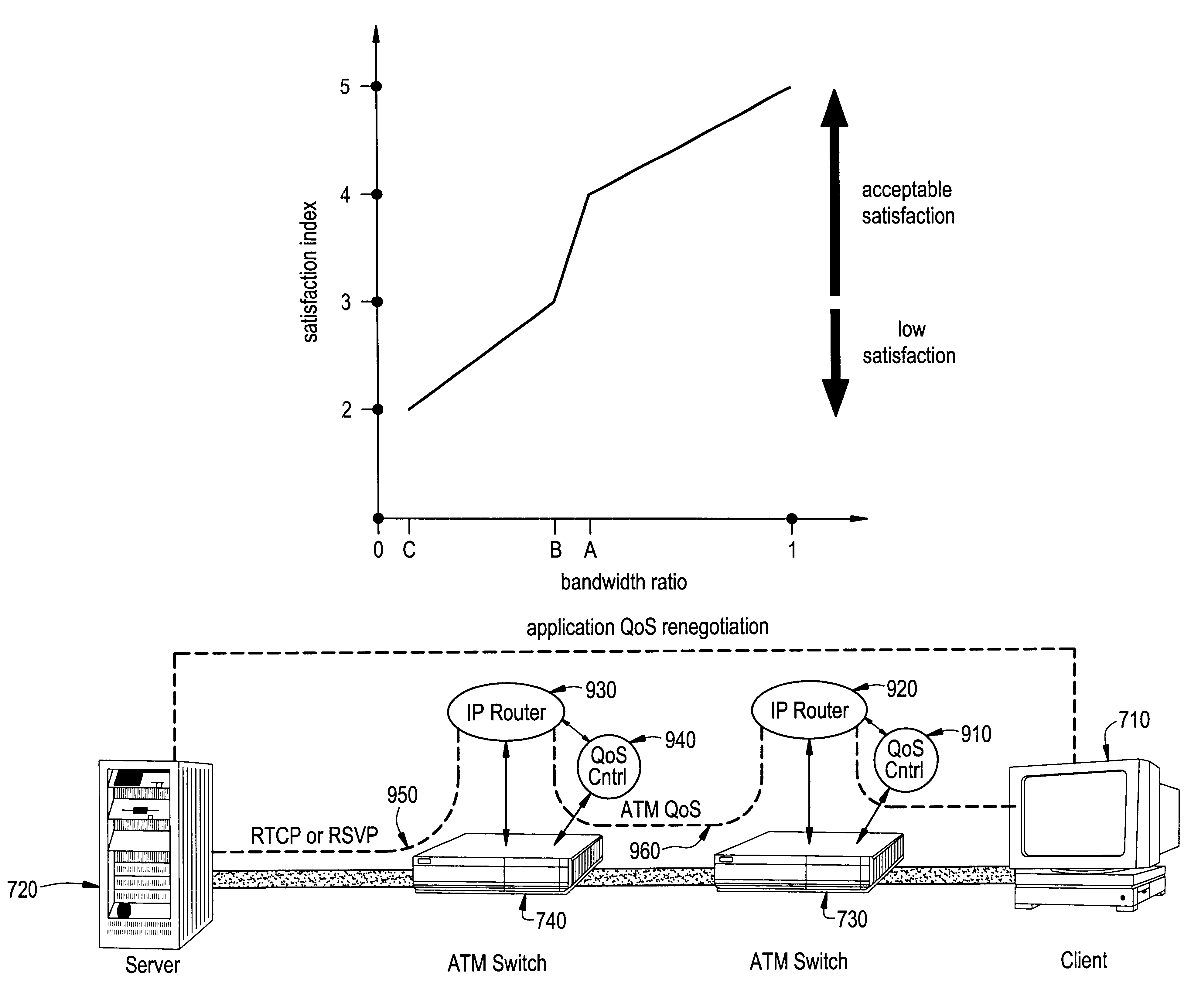
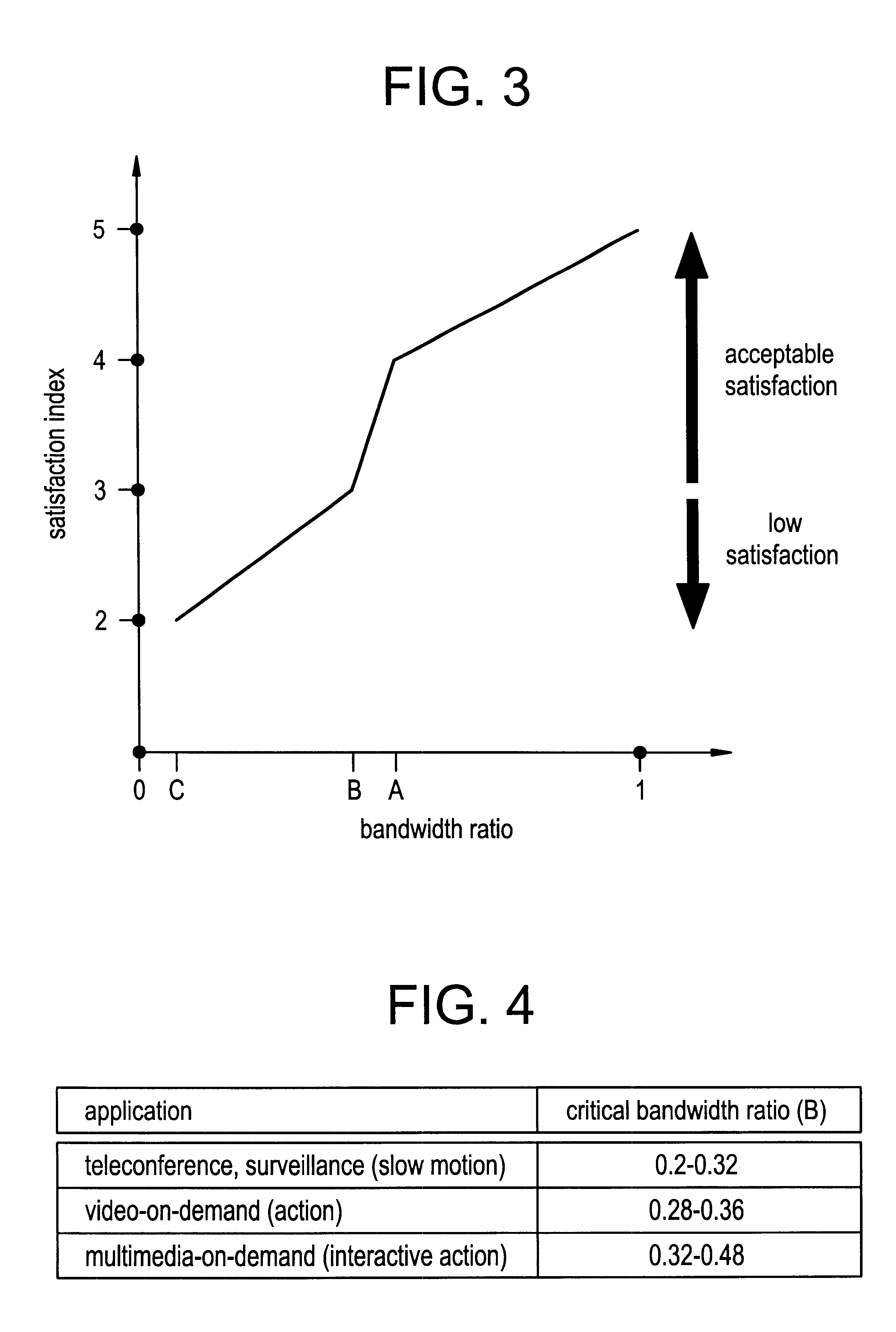
A new concept of soft quality-of-service (soft-QoS) is developed that bridges the gap between the efficient provision of network-level QoS and the requirements of multimedia applications. Soft-QoS is defined by a satisfaction index (a number that rates users' perceptual quality) and a softness profile (a function that captures the robustness of multimedia applications to network congestion). Another aspect of this invention is a bandwidth allocation scheme for multimedia applications with soft-QoS requirements is presented. The implementation of the bandwidth allocation scheme on a network element realizes a soft-QoS controller. The controller uses the connections' softness profiles to compute a bandwidth allocation that maximizes the minimum satisfaction index of active connections.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Path rerouting mechanism utilizing multiple link bandwidth allocations
InactiveUS6895441B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityDistributed computing
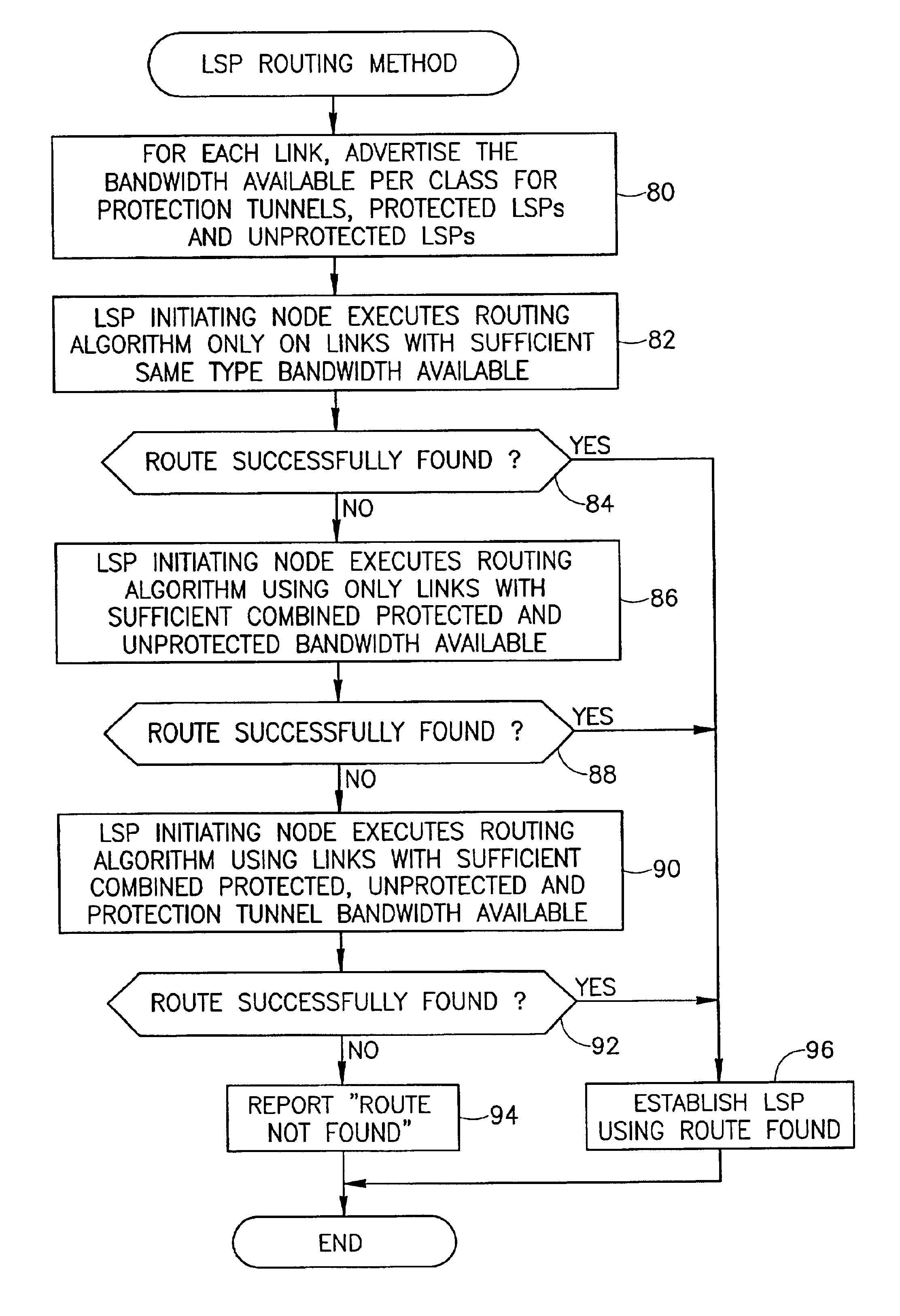
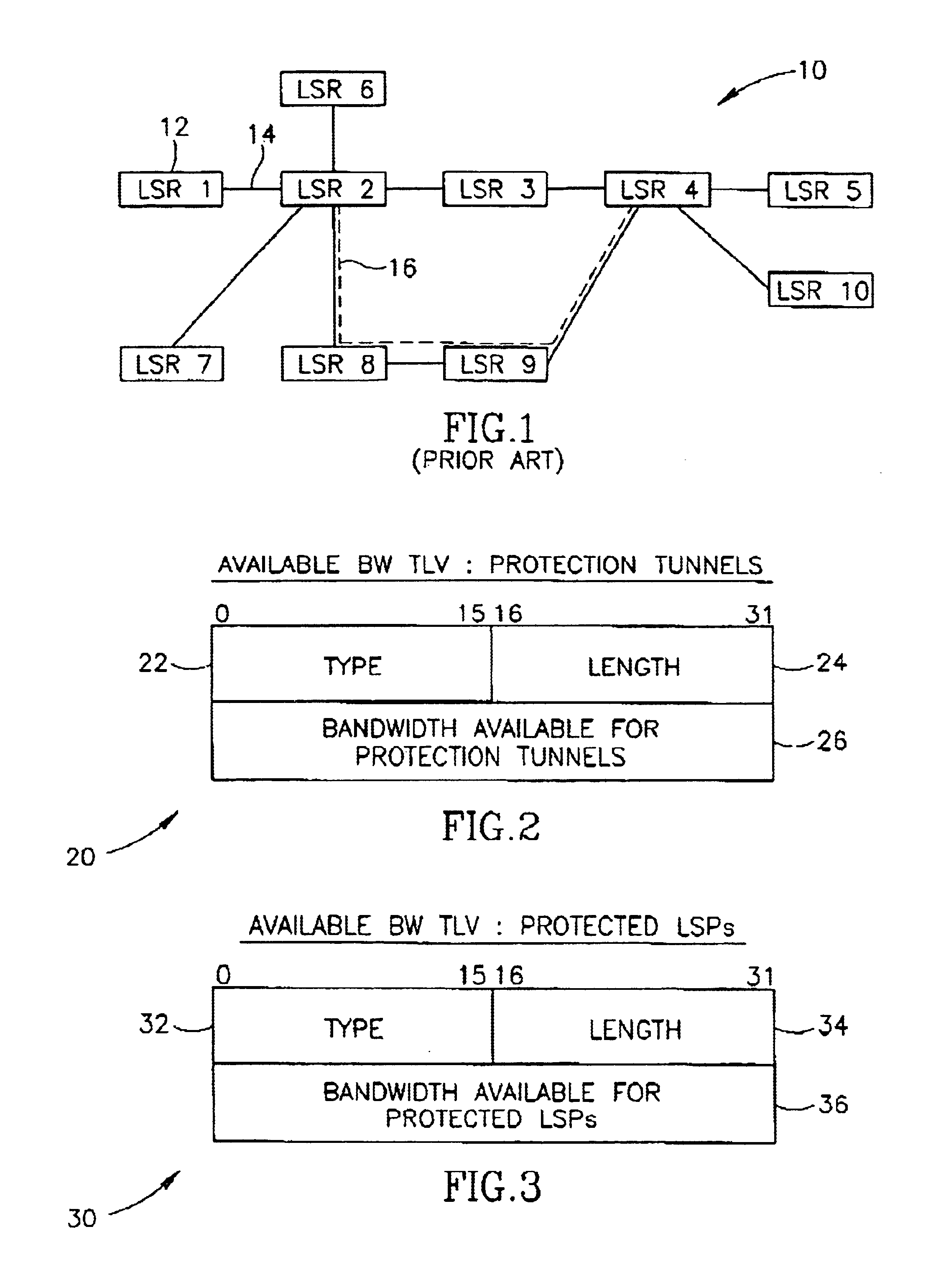
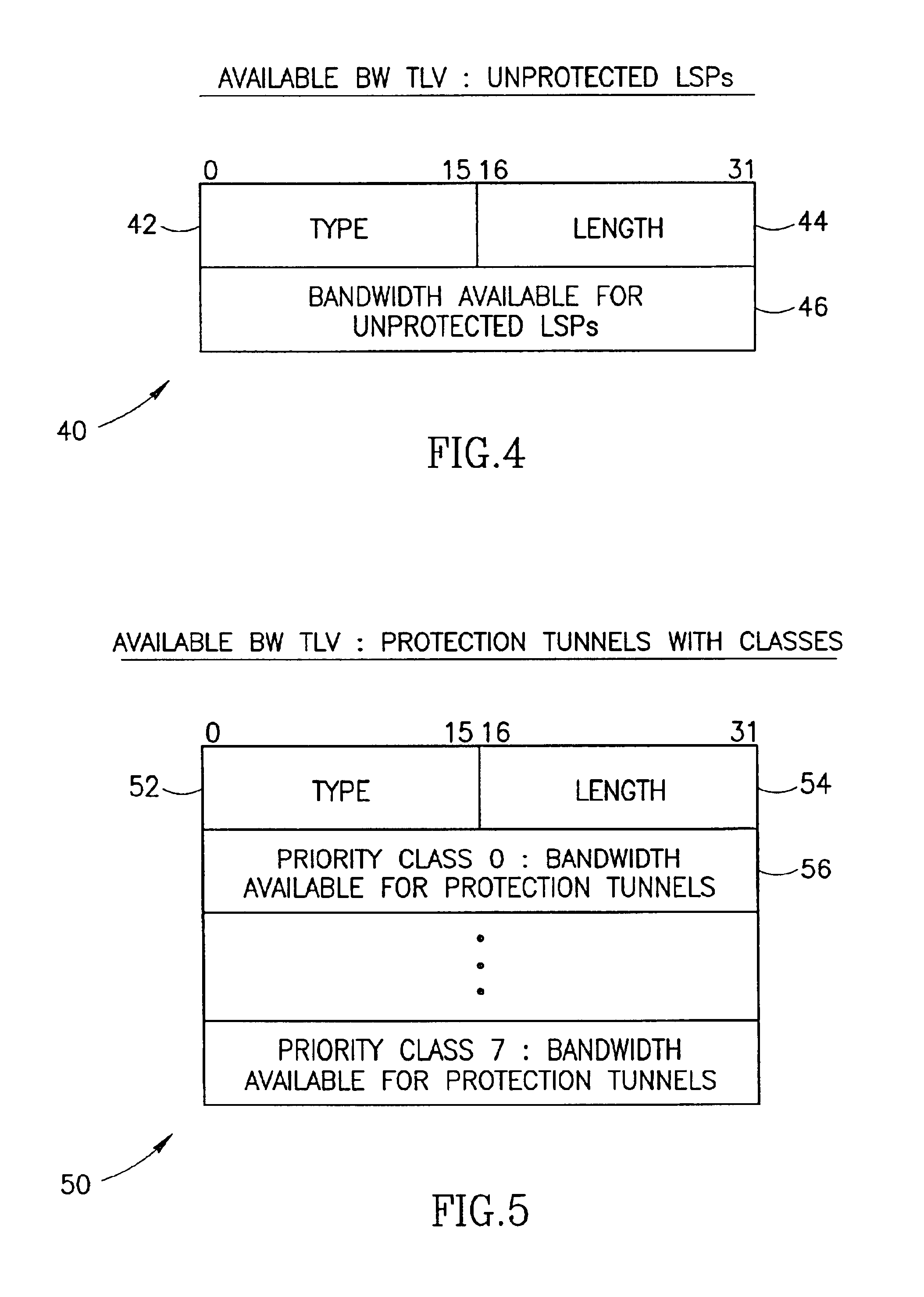
A path reroute mechanism for use in communication networks comprising multiple searches for a routing path to restore traffic following a failure that could not be protected by a previously established protection route (i.e. protection tunnel, bypass, etc.) or for routing or rerouting of traffic paths for optimization or any other purpose. Each node advertises TLVs that include bandwidth allocation information used to derive the actual amount of bandwidth available for protection purposes, protected paths and unprotected paths or a portion of this information such as in the case where unprotected paths are not supported. Searches are performed on larger and larger portions of the available bandwidth until a route for the path is found.
Owner:ATRICA INC
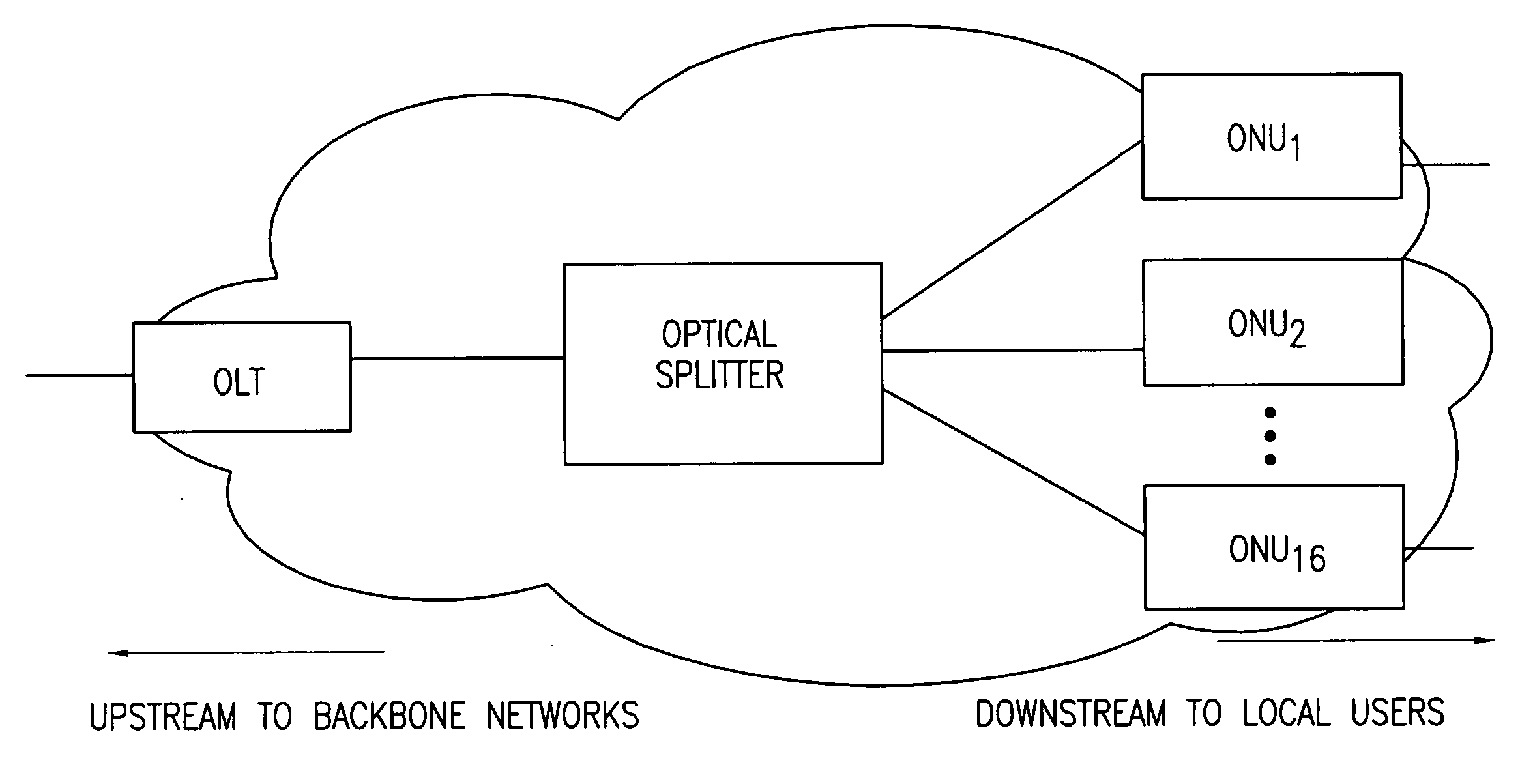
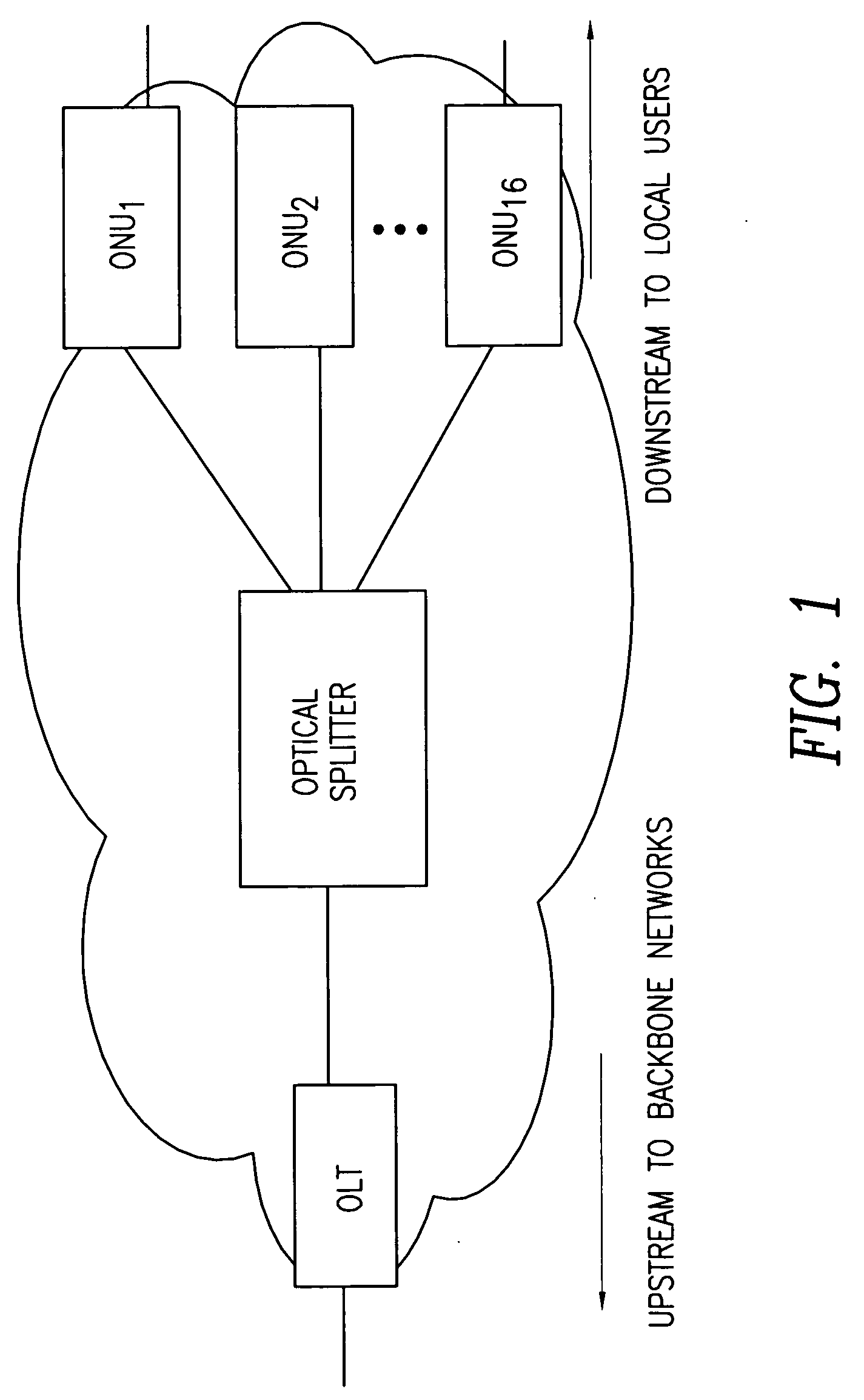
Dynamic bandwidth allocation and service differentiation for broadband passive optical networks
InactiveUS20060268704A1Effective bandwidthSpace complexityMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionService-level agreementTraffic prediction
A dynamic upstream bandwidth allocation scheme is disclosed, i.e., limited sharing with traffic prediction (LSTP), to improve the bandwidth efficiency of upstream transmission over PONs. LSTP adopts the PON MAC control messages, and dynamically allocates bandwidth according to the on-line traffic load. The ONU bandwidth requirement includes the already buffered data and a prediction of the incoming data, thus reducing the frame delay and alleviating the data loss. ONUs are served by the OLT in a fixed order in LSTP to facilitate the traffic prediction. Each optical network unit (ONU) classifies its local traffic into three classes with descending priorities: expedited forwarding (EF), assured forwarding (AF), and best effort (BE). Data with higher priority replace data with lower priority when the buffer is full. In order to alleviate uncontrolled delay and unfair drop of the lower priority data, the priority-based scheduling is employed to deliver the buffered data in a particular transmission timeslot. The bandwidth allocation incorporates the service level agreements (SLAs) and the on-line traffic dynamics. The basic limited sharing with traffic prediction (LSTP) scheme is extended to serve the classified network traffic.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for equitable bandwidth allocation for content distribution networks
ActiveUS7801177B2Optimize allocationReduce capacityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPerformance functionContent distribution
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Systems and Methods for Dynamically Allocating Bandwidth in a Digital Broadband Delivery System
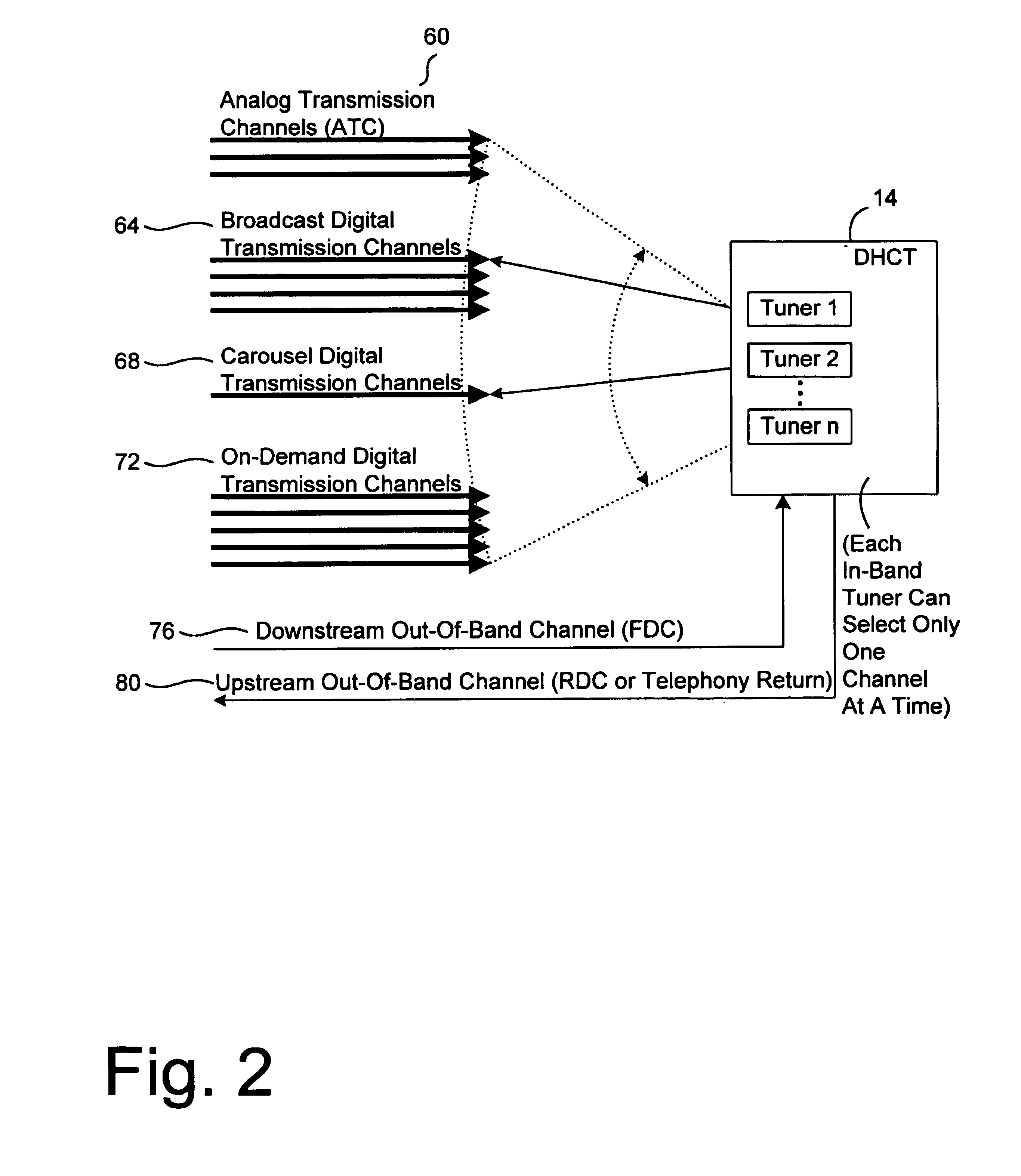
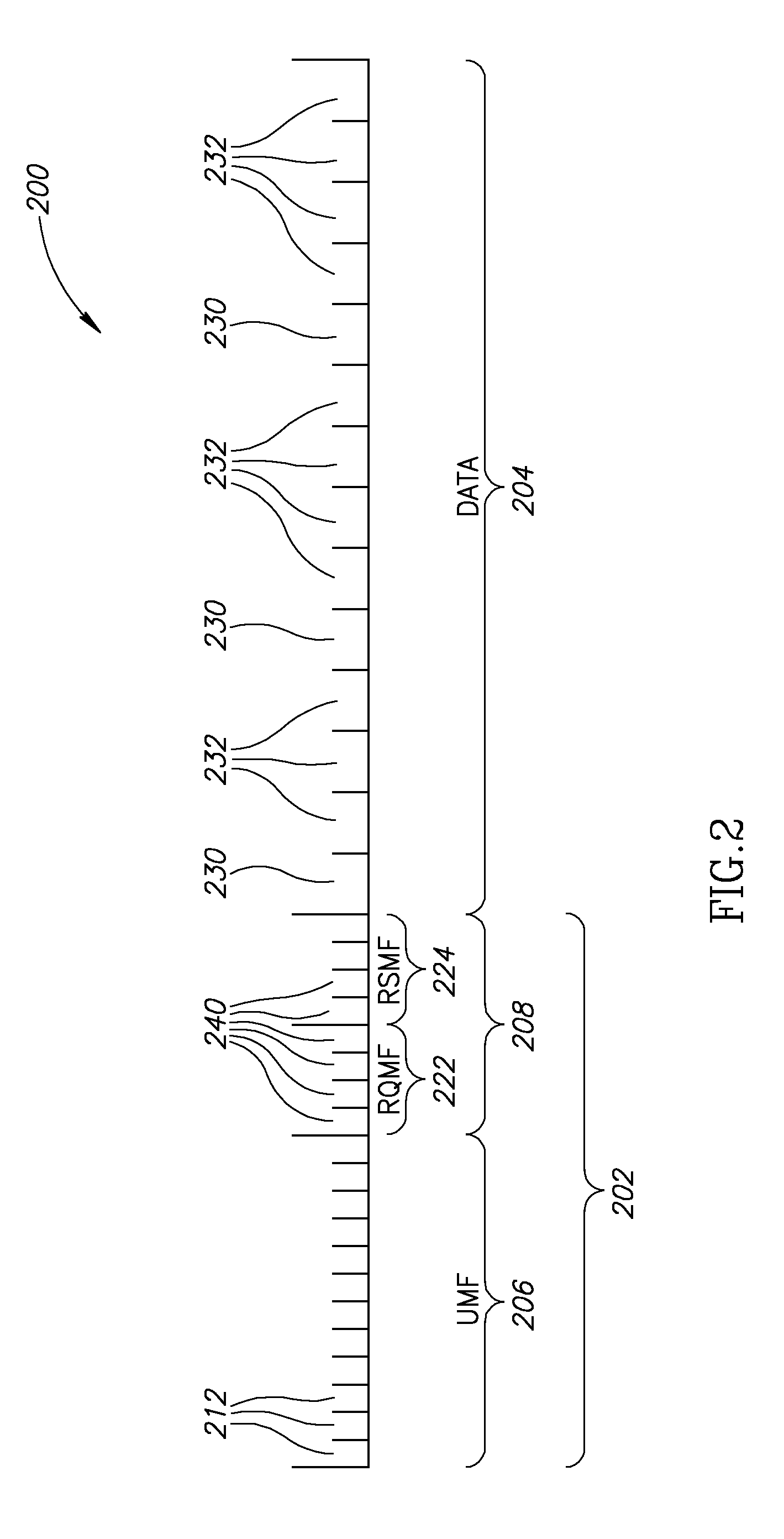
InactiveUS20080101460A1Increase flexibilityEasy to usePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningTime segmentTransmission channel
Systems and methods for dynamically allocating bandwidth in a digital broadband delivery system are disclosed. One example method includes receiving information describing subscriber requests for content delivery, receiving bandwidth allocation criteria, and processing the information describing subscriber requests and the bandwidth allocation criteria according to a statistical model. The bandwidth allocation criteria comprise at least one of subscriber pricing information, content delivery mode information, and program content information. The processing produces a bandwidth allocation schedule in which one of a plurality of content delivery modes is assigned to each of a plurality of digital transmission channels for each of a plurality of time periods.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
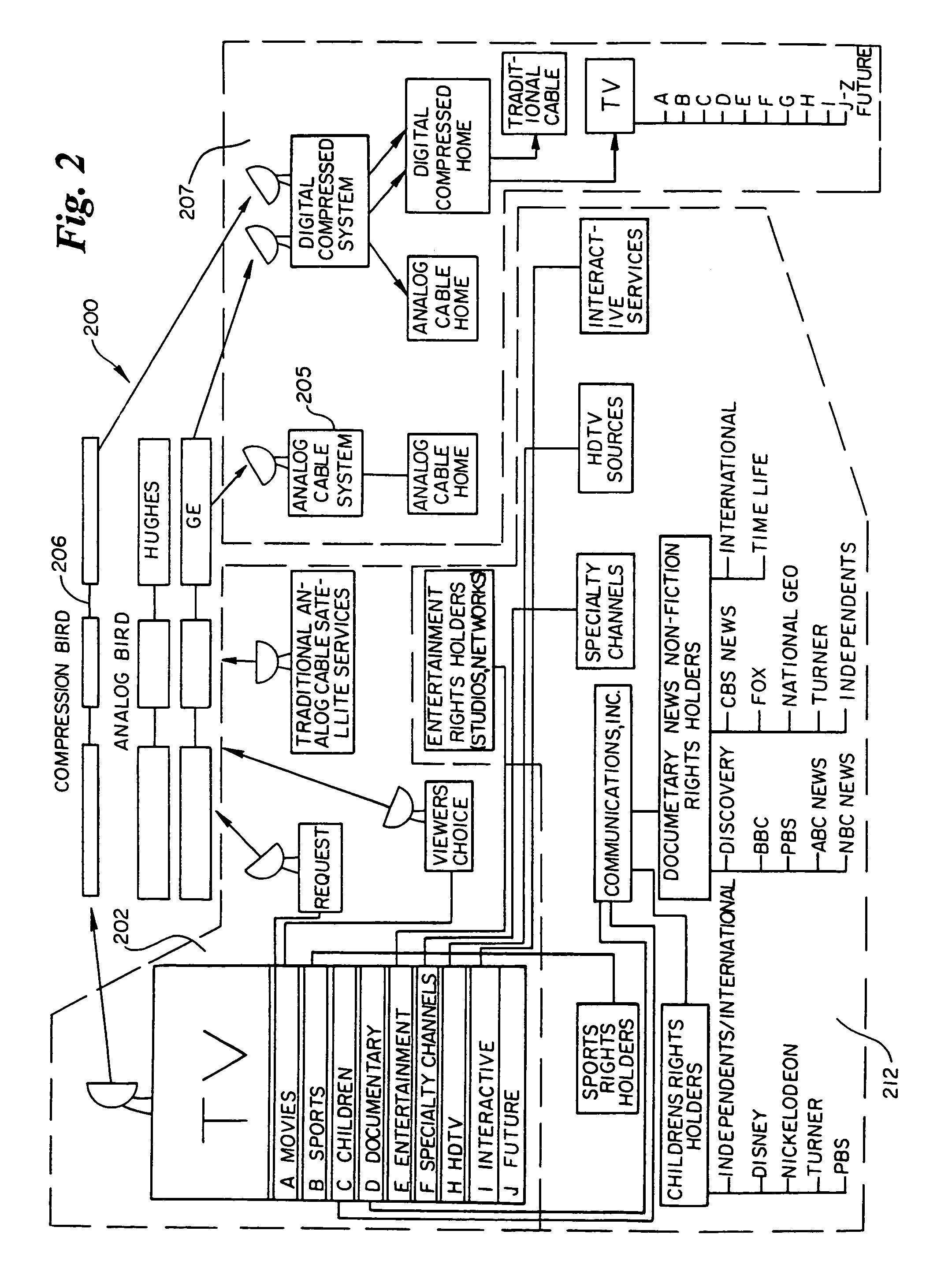
Bandwidth allocation for a television program delivery system
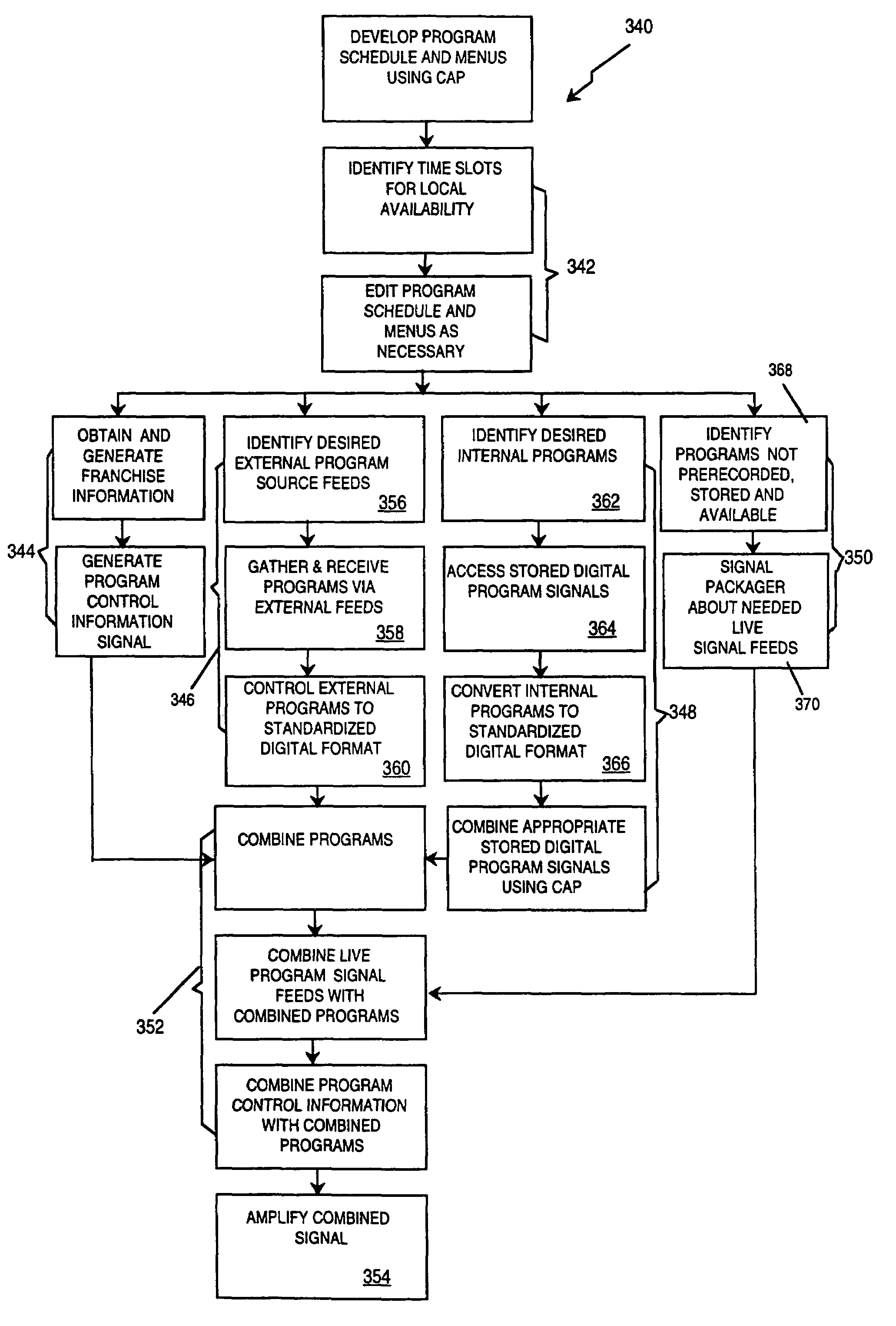
InactiveUS7207055B1Avoid difficult choicesOrganize effectivelyTelevision system detailsResource management arrangementsConsumer demandDistributed computing
This invention is a method of allocating bandwidth for a television program delivery system. This method selects specific programs from a plurality of programs, allocates the selected programs to a segment of bandwidth, and continues to allocate the programs until all the programs are allocated or all of the available bandwidth is allocated. The programs may be selected based on a variety of different factors or combination of factors. The selected programs may also be prioritized so that higher priority programs are distributed before lower priority programs in case there is not enough bandwidth to transmit all of the programs. This invention allows a television program delivery system to prioritize a large number of television programs and distribute these programs based on their priority levels. The invention also permits a television program delivery system to dynamically allocate bandwidth over time or based on marketing information, such as consumer demand.
Owner:COMCAST IP HLDG I
Apparatus and method for efficient TDMA bandwidth allocation for TCP/IP satellite-based networks
InactiveUS20050030932A1Optimized bandwidth allocation schemeBalance traffic loadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemAloha
A communication system balances message traffic between return channel groups and within the groups, so that the user does not control the specific transmission frequency used. Uplink frequencies and bandwidths for the return channels are set by the system in a return channel control message in the broadcast signal so as to account for system and return channel group loading, and to account for user message backlogs. An initial transmission from a remote user may be made using an ALOHA-type burst signal that provides a message backlog to the control station, and is made on a frequency determined from a randomly weighted, load-based frequency selection process. The system, and not the individual users determine the frequency and channel allocations. For large backlogs or priority users, periodic bandwidth is provided. A method for balancing loads among and between groups of return channels in the communication system includes requesting return channel bandwidth in an uplink message from a remote user to a control station. The uplink message may include a both a backlog indicator and a bandwidth allocation request provided to a Network Operations Center (NOC) which can be used to set the return channel bandwidth and frequency for the remote uplink. A user message is transmitted on the designated return channel frequency using bandwidth allocated in accordance with the backlog indicator and a bandwidth allocation request so that traffic loads are maintained in balance between established return channel frequency groups, and within each return channel frequency group.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
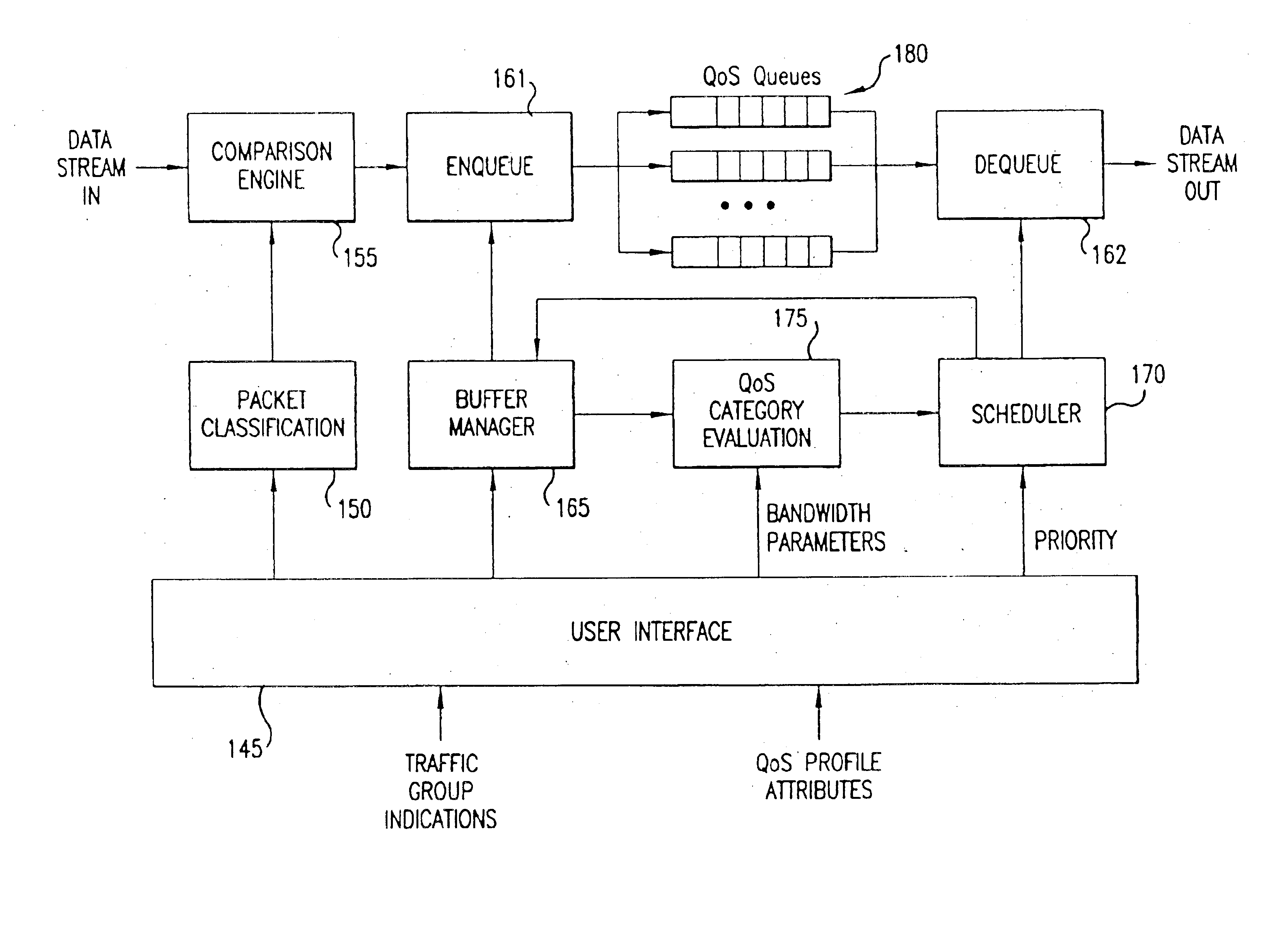
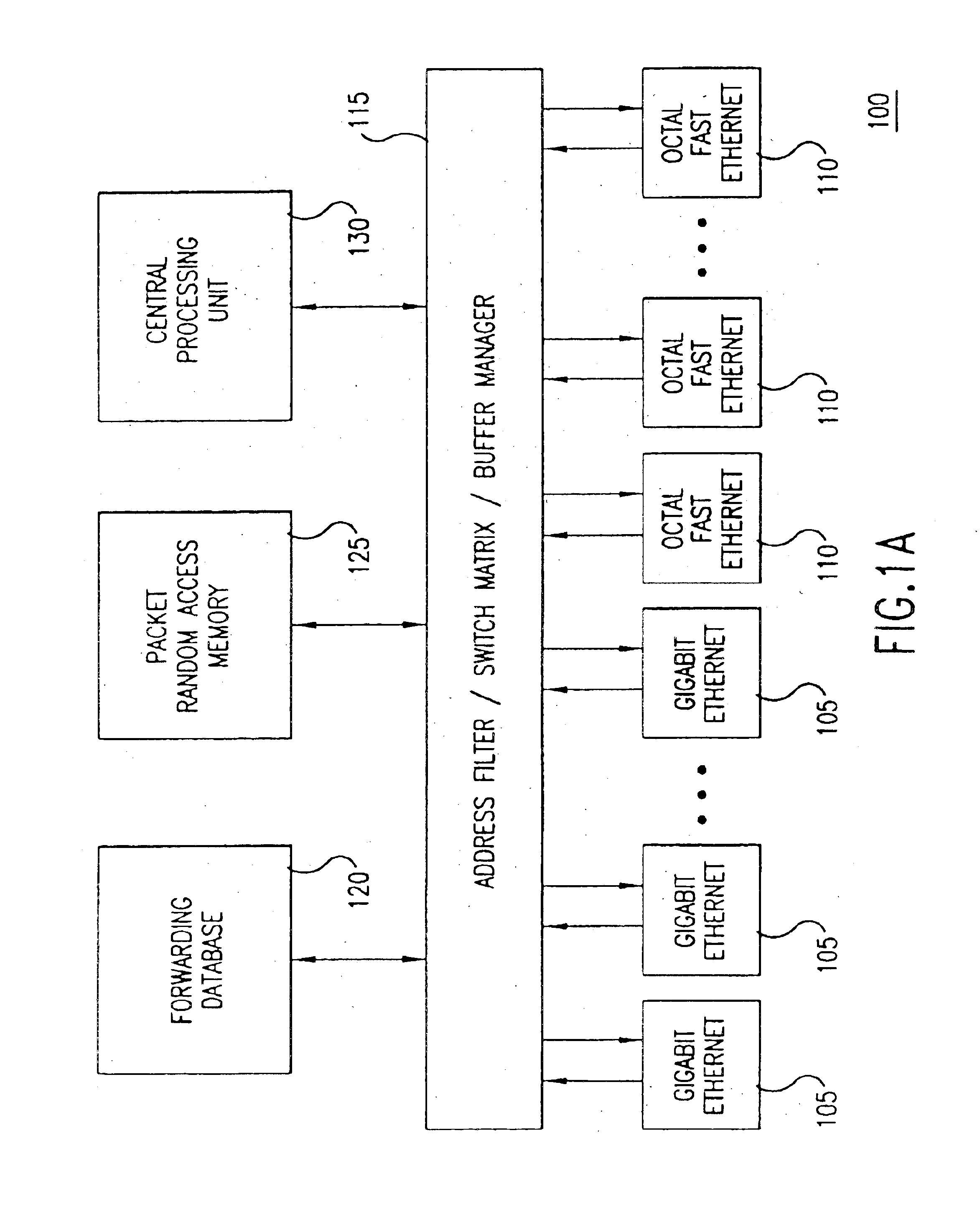
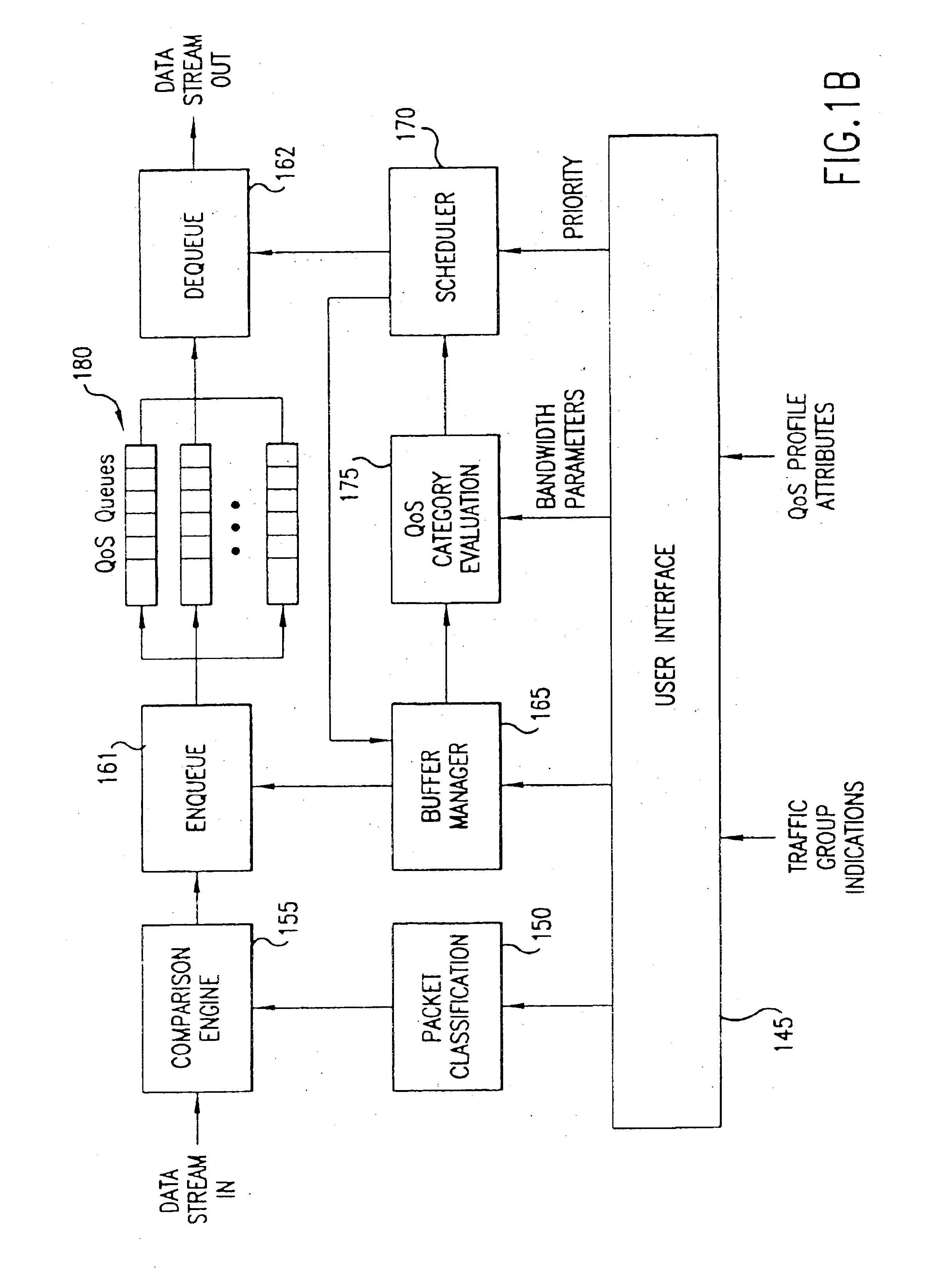
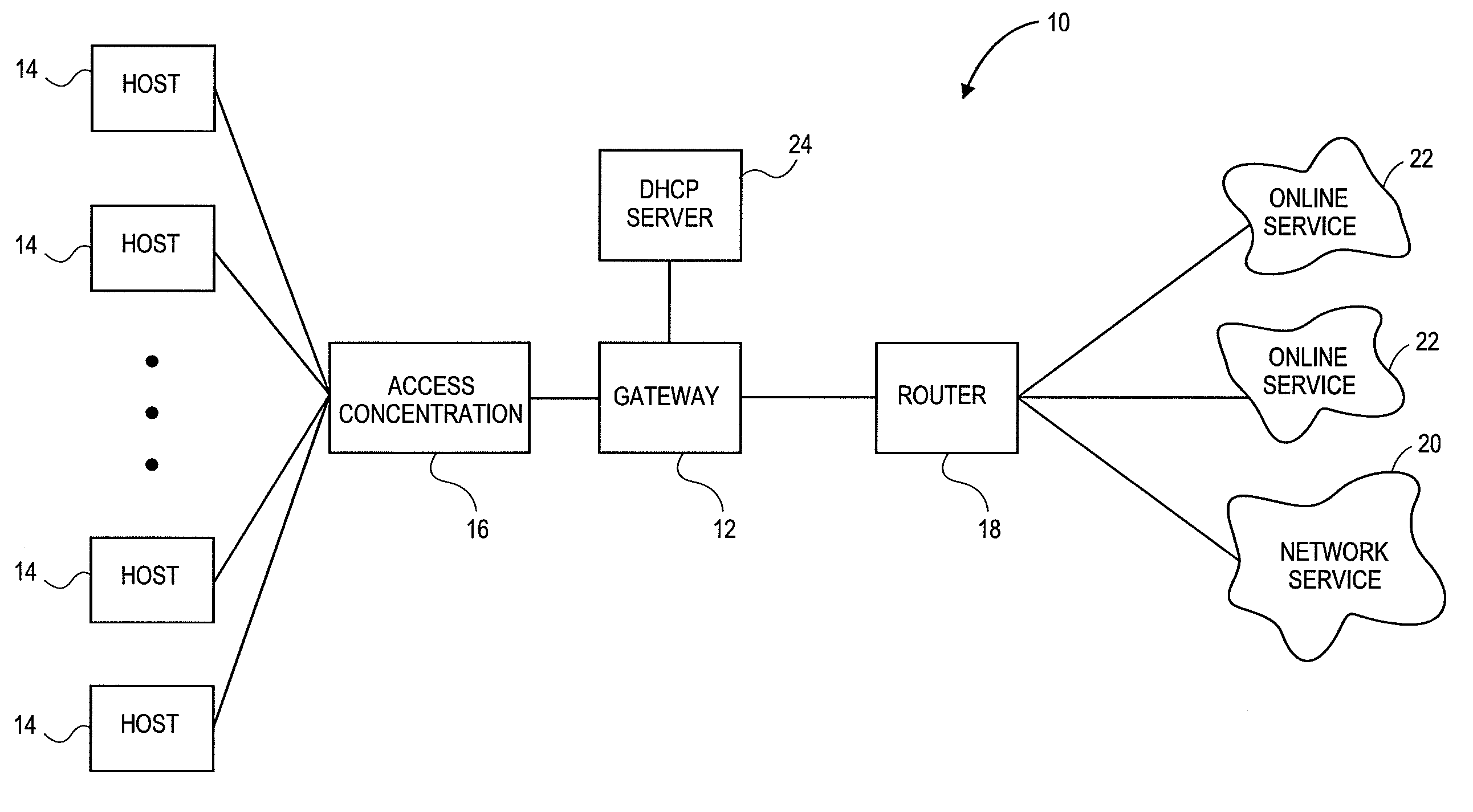
Policy based quality of service
A flexible, policy-based, mechanism for managing, monitoring, and prioritizing traffic within a network and allocating bandwidth to achieve true quality of service (QoS) is provided. According to one aspect of the present invention, a method is provided for managing bandwidth allocation in a network that employs a non-deterministic access protocol, such as an Ethernet network. A packet forwarding device receives information indicative of a set of traffic groups, such as: a MAC address, or IEEE 802.1p priority indicator or 802.1Q frame tag, if the QoS policy is based upon individual station applications; or a physical port if the QoS policy is based purely upon topology. The packet forwarding device additionally receives bandwidth parameters corresponding to the traffic groups. After receiving a packet associated with one of the traffic groups on a first port, the packet forwarding device schedules the packet for transmission from a second port based upon bandwidth parameters corresponding to the traffic group with which the packet is associated. According to another aspect of the present invention, a method is provided for managing bandwidth allocation in a packet forwarding device. The packet forwarding device receives information indicative of a set of traffic groups. The packet forwarding device additionally receives information defining a QoS policy for the traffic groups. After a packet is received by the packet forwarding device, a traffic group with which the packet is associated is identified. Subsequently, rather than relying on an end-to-end signaling protocol for scheduling, the packet is scheduled for transmission based upon the QoS policy for the identified traffic group.
Owner:ARISTA NETWORKS
Priority based bandwidth allocation within real-time and non-real-time traffic streams
InactiveUS7385997B2Raise prioritySimple designData switching by path configurationNon real timeReal-time data
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Systems and methods for dynamic bandwidth management on a per subscriber basis in a communications network
InactiveUS7698432B2Efficient managementImprove throughputMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsUplink transmissionNetwork management
A subscriber bandwidth management process and device that allows users / subscribers in a communications network to dynamically alter bandwidth limits independently in both the uplink and downlink data transmission paths. This is accomplished by providing for a single queue in the uplink transmission path and a single queue in the downlink transmission path. Thus, the user / subscriber can efficiently manage their network access according to the specific activity on the network. The network manager benefits from being able structure bandwidth allocation on a per subscriber basis so that overall data transmission is made more efficient. In addition, the bandwidth manager provides active management of the delivery of data (also known as and referred to herein as traffic shaping) to increase throughput from a gateway device onto the network.
Owner:NOMADIX INC
Method and apparatus for simple IP-layer bandwidth allocation using ingress control of egress bandwidth
InactiveUS6628609B2Reduce the possibilityMinimum bandwidthError preventionTransmission systemsDynamic bandwidth allocationData transmission
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Dynamic bandwidth allocation apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070133407A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDynamic bandwidth allocationDistribution method
The present invention relates to a bandwidth allocation apparatus and a method thereof. The present invention provides a method for adaptively allocating and controlling radio channels to multimedia traffic having various characteristics. Particularly, the present invention proposes a method for maximizing a system resource use rate while satisfying a communication QoS requirement for individual video traffic. Therefore, the adaptive bandwidth allocation method according to the present invention guarantees system performance and user-required communication QoS.
Owner:KT CORP +2
Apparatus and methods for dynamic bandwidth allocation
InactiveUS20050128951A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDynamic bandwidth allocationData transport
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Adapting receiver thresholds to improve rate-based flow control
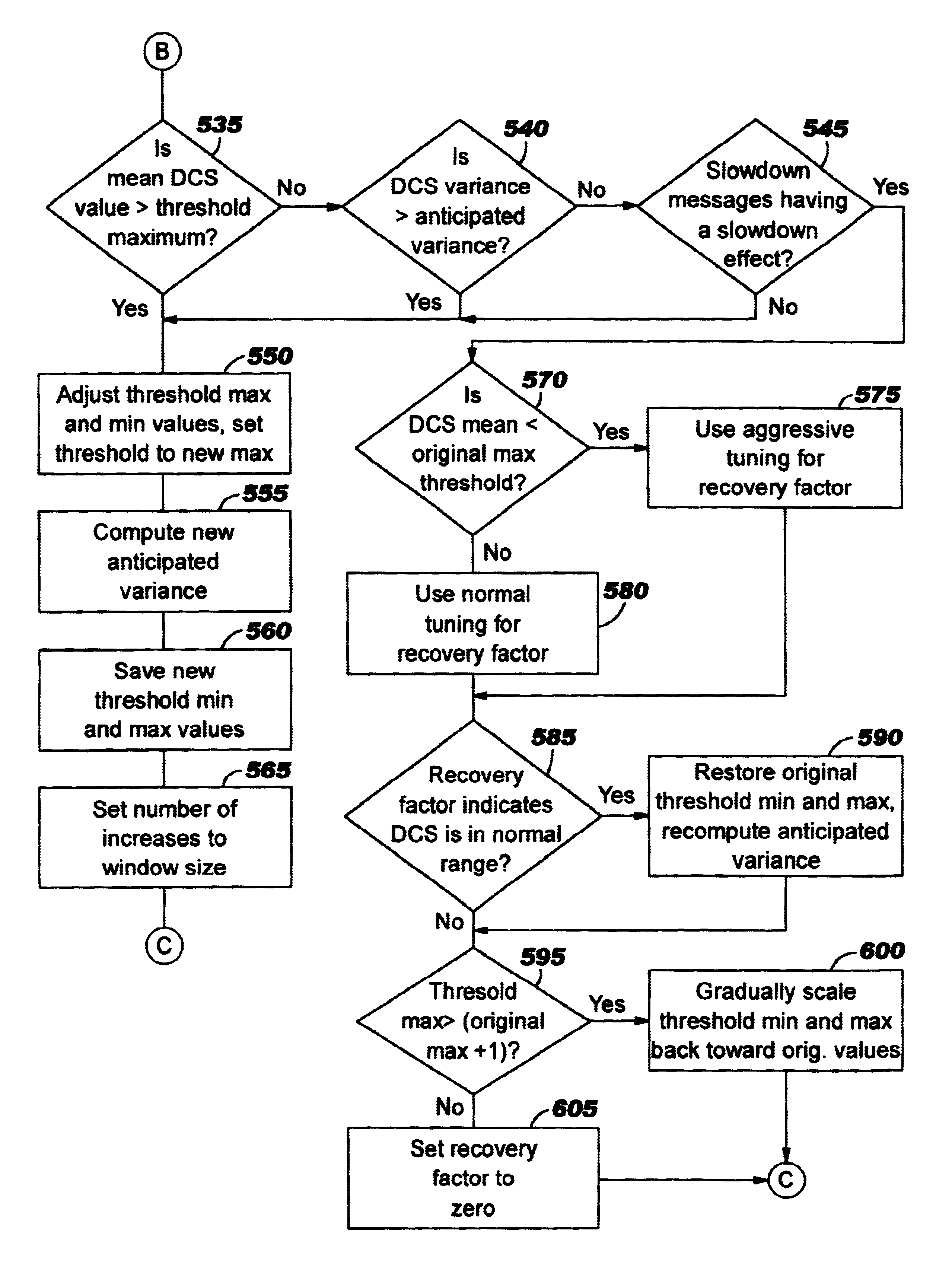
A technique for adapting receiver thresholds to improve rate-based flow control in a data communications network. With this invention, the flow control process becomes self-calibrating such that threshold values are dynamically adjusted to adapt to current network conditions, without requiring user intervention. Several different indicators of network conditions are monitored, and appropriate adjustments are made to the threshold(s) upon detecting these specific indicators. One monitor enables the threshold to increase when the network is uncongested, enabling the sender to increase its transmission rate. Conversely, the threshold is lowered if the network is congested, so that the transmission rate will be decreased. Another monitor balances bandwidth allocation among connections sharing a bottleneck resource, by lowering the threshold (and therefore decreasing the send rate) when a connection uses a high share of the resource. A third monitor detects the presence of traffic from protocols not using adaptive receiver thresholds, and adjusts the threshold (including an upper and lower threshold bound) in order to compete fairly for resources with these other protocols. The monitors may be implemented individually or in combination.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com