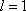Patents
Literature
207 results about "Aloha" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aloha (/ɑːˈloʊhɑː/; Hawaiian: [əˈloːˌha]) is the Hawaiian word for love, affection, peace, compassion and mercy, that is commonly used as a simple greeting but has a deeper cultural and spiritual significance to native Hawaiians.
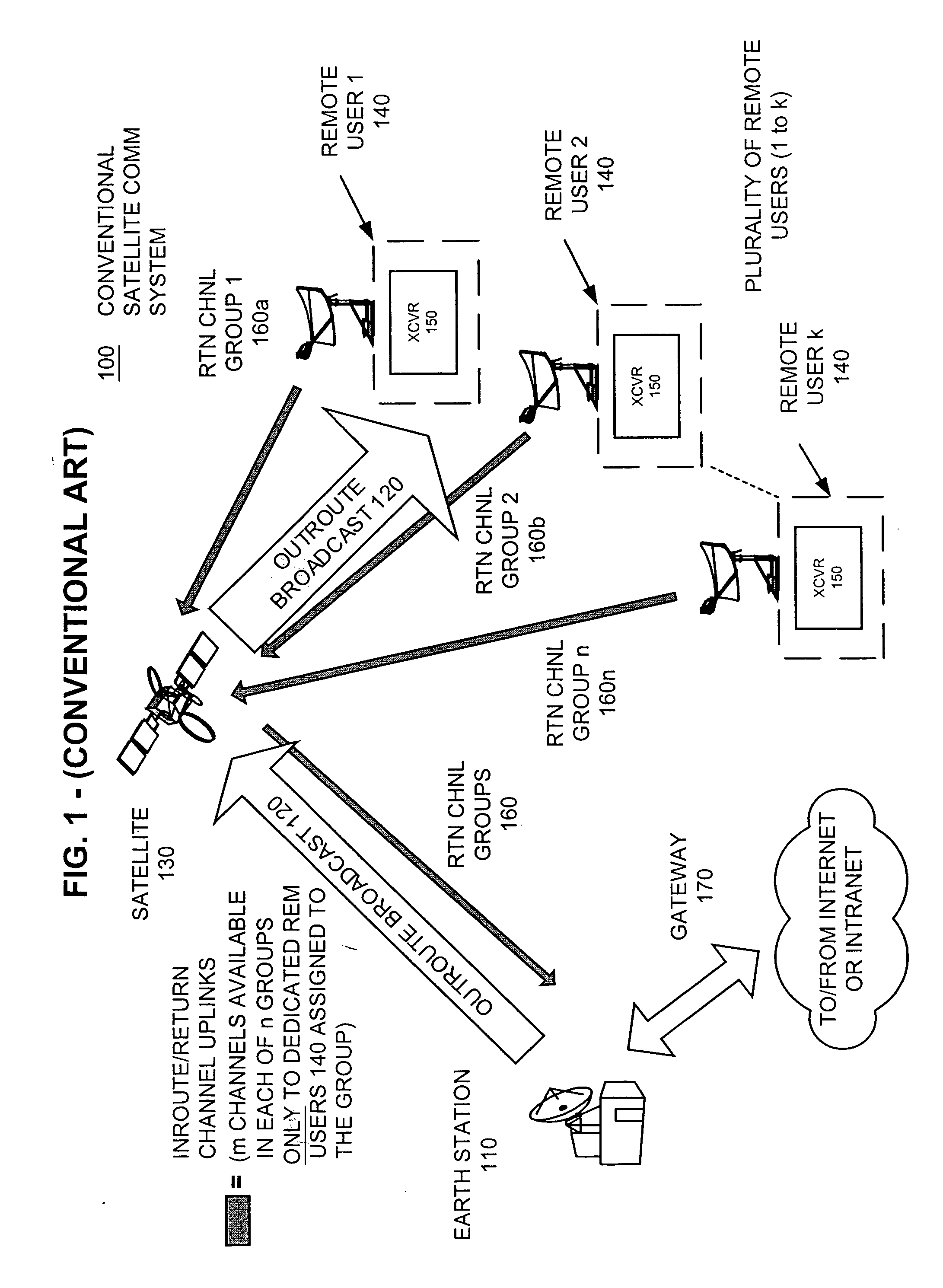
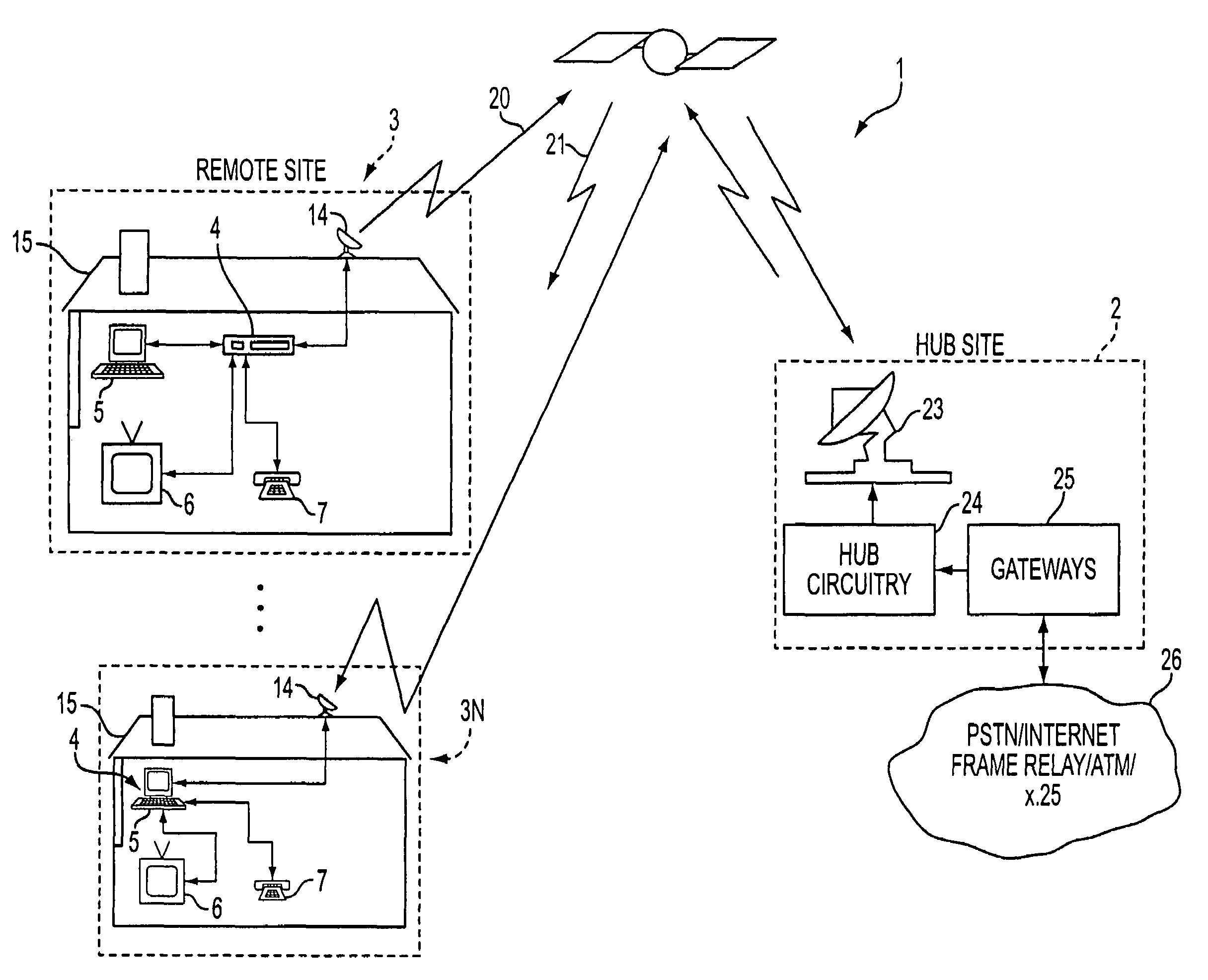
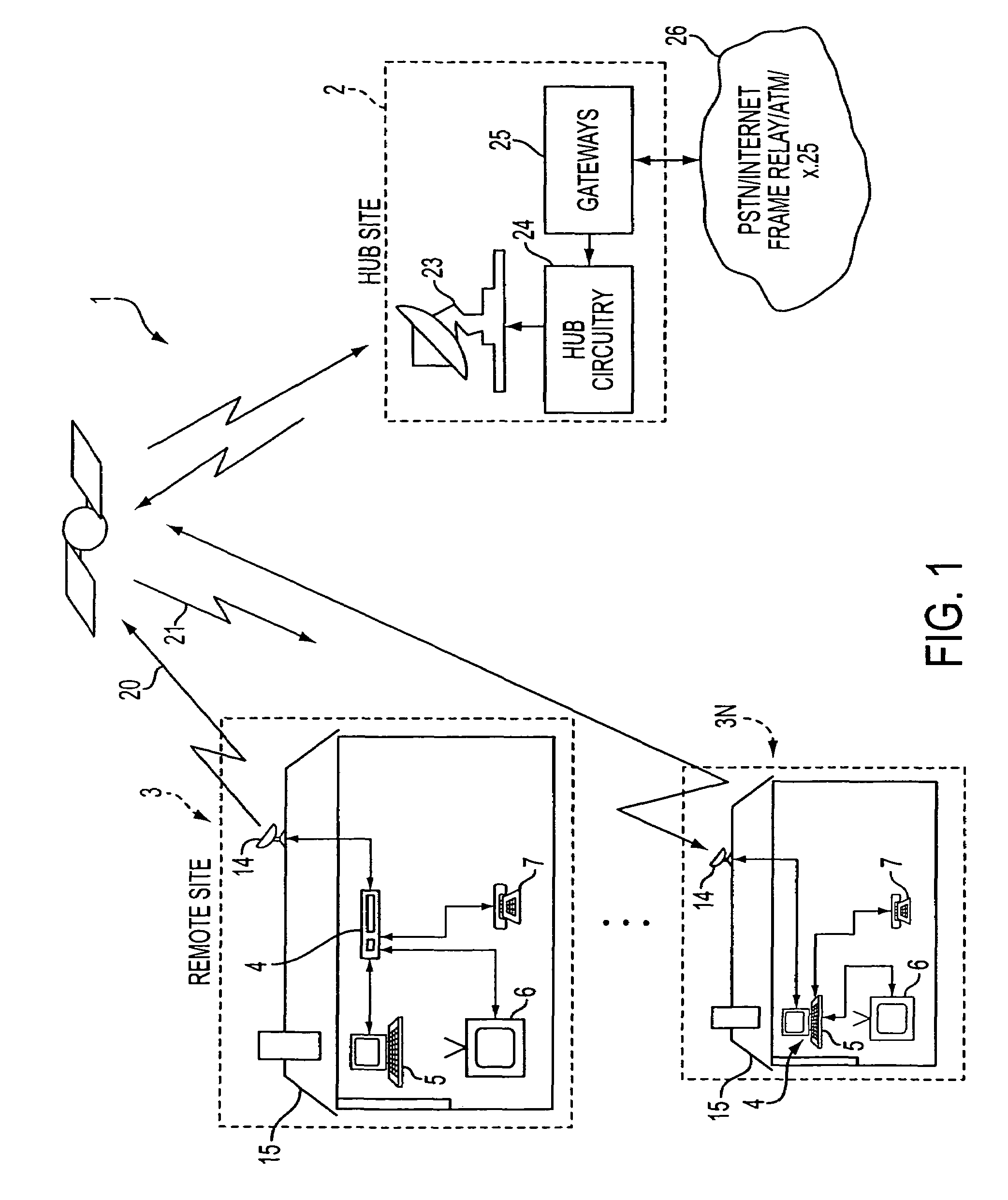
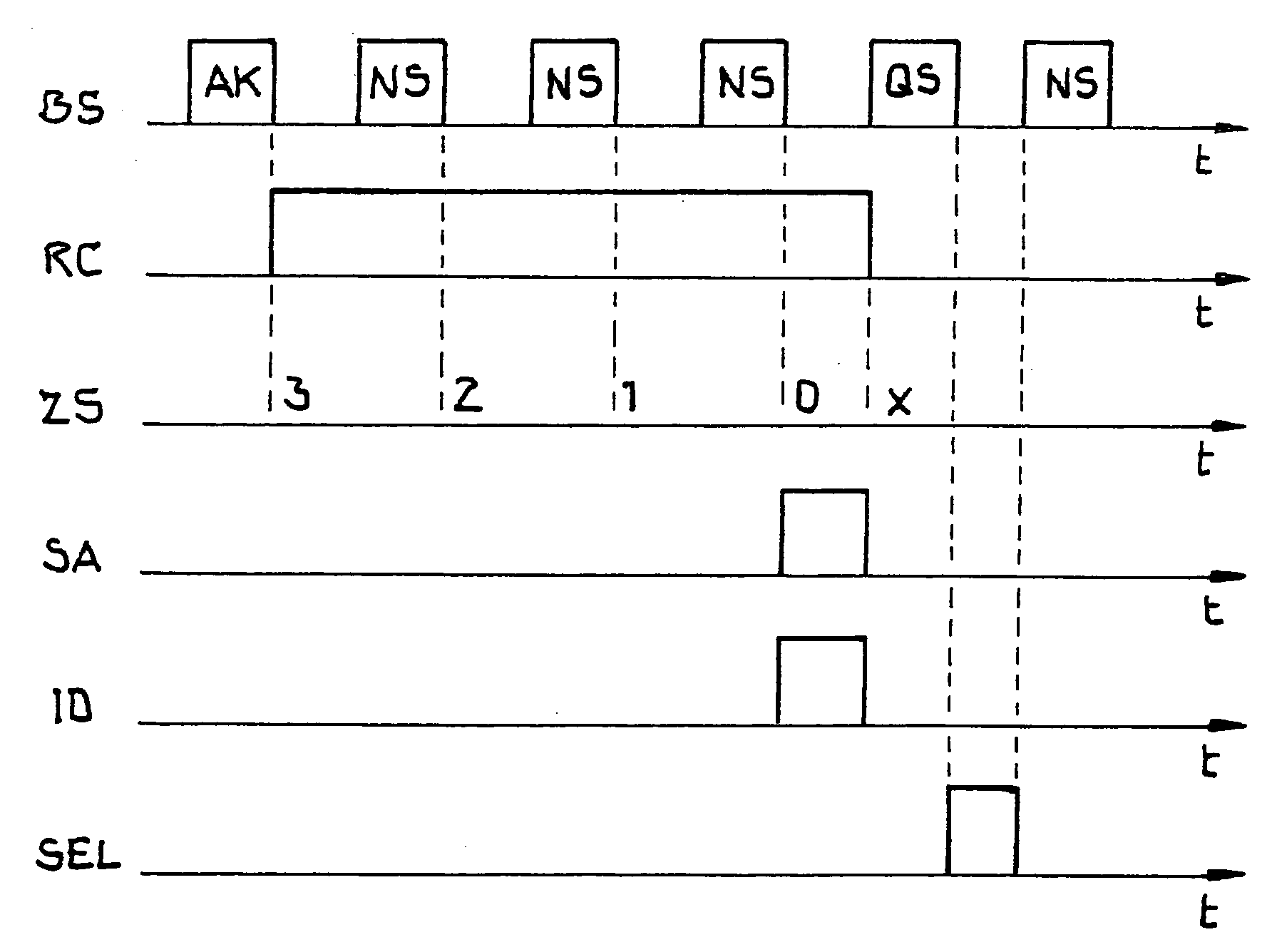
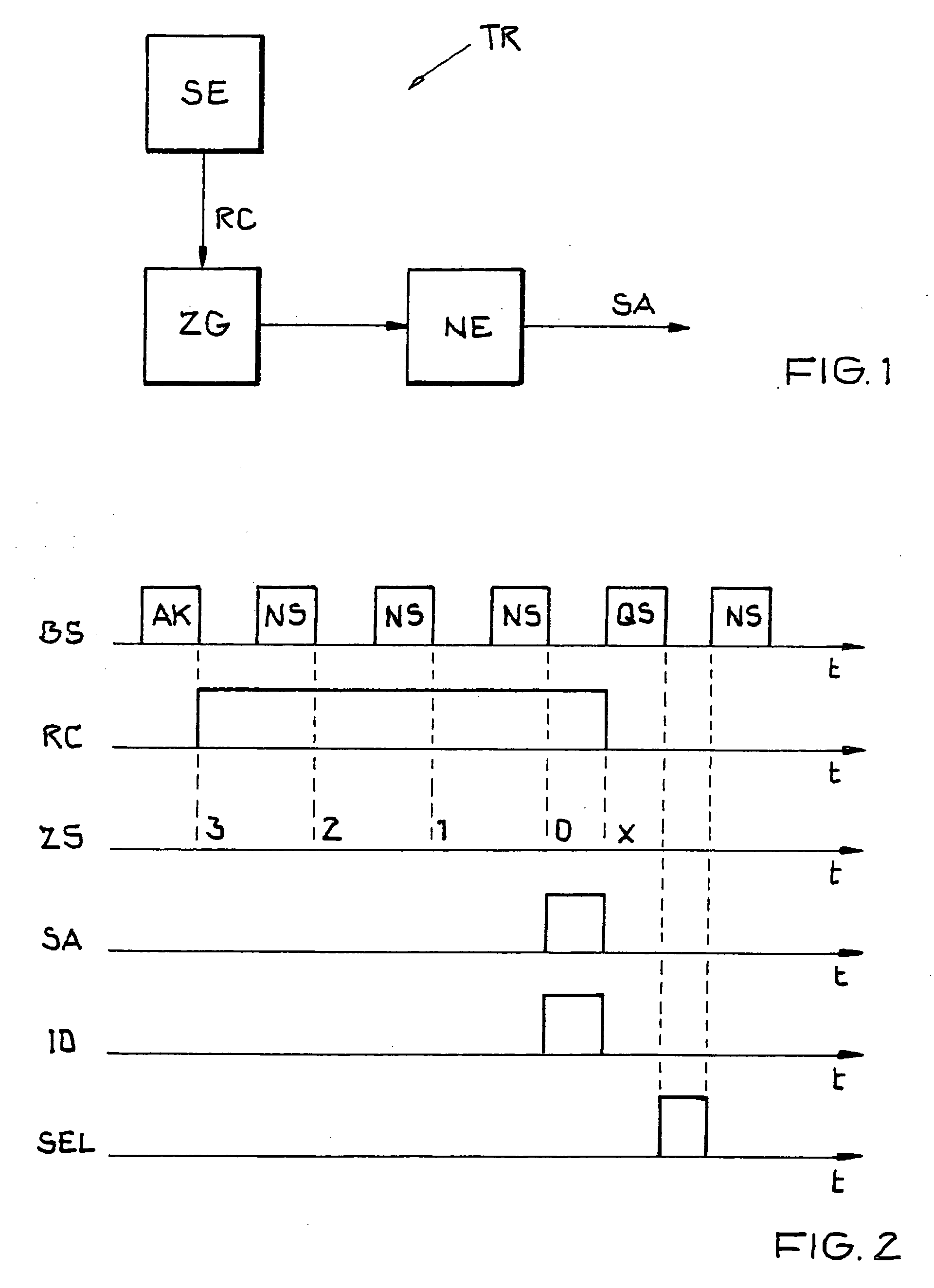
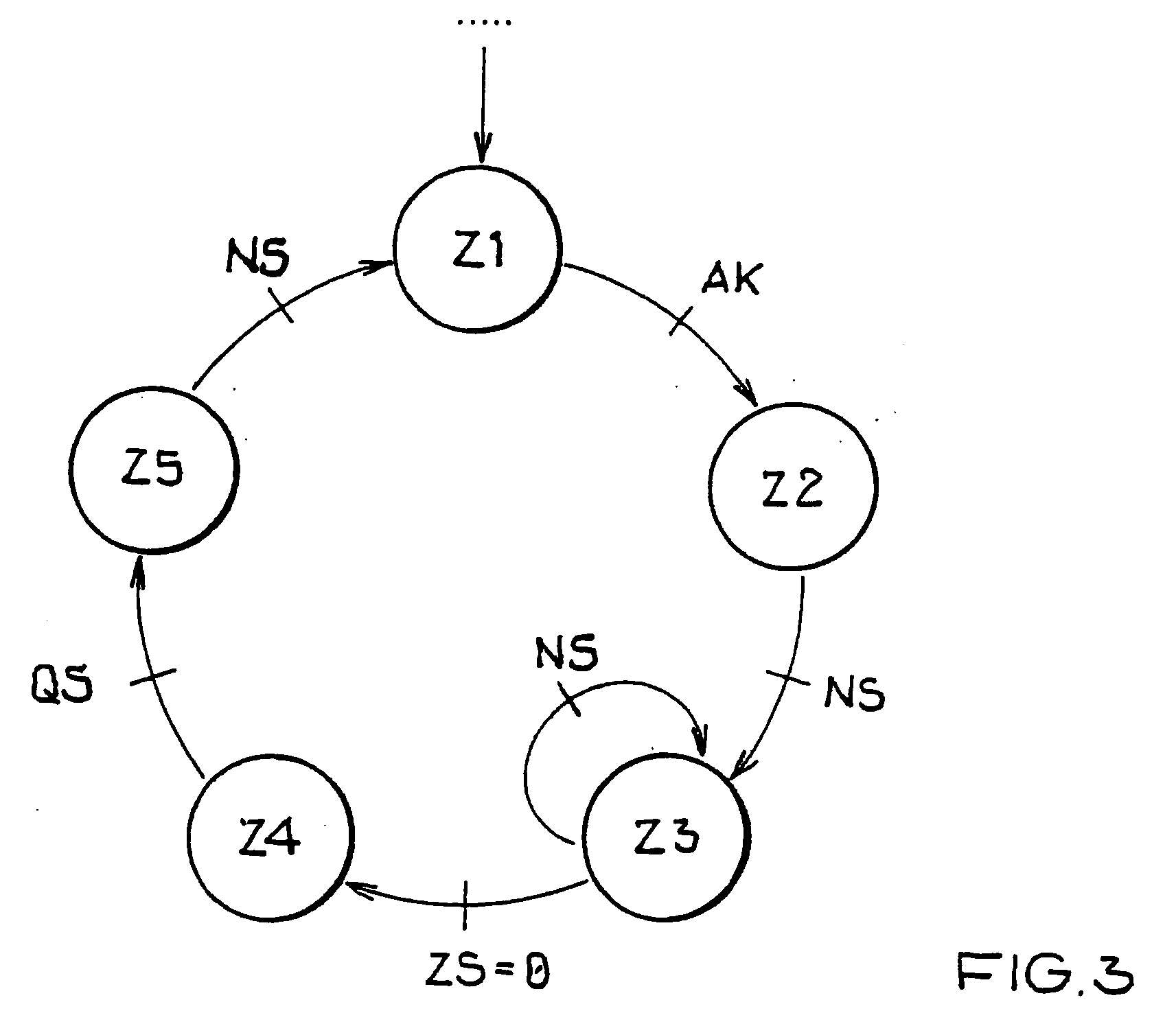
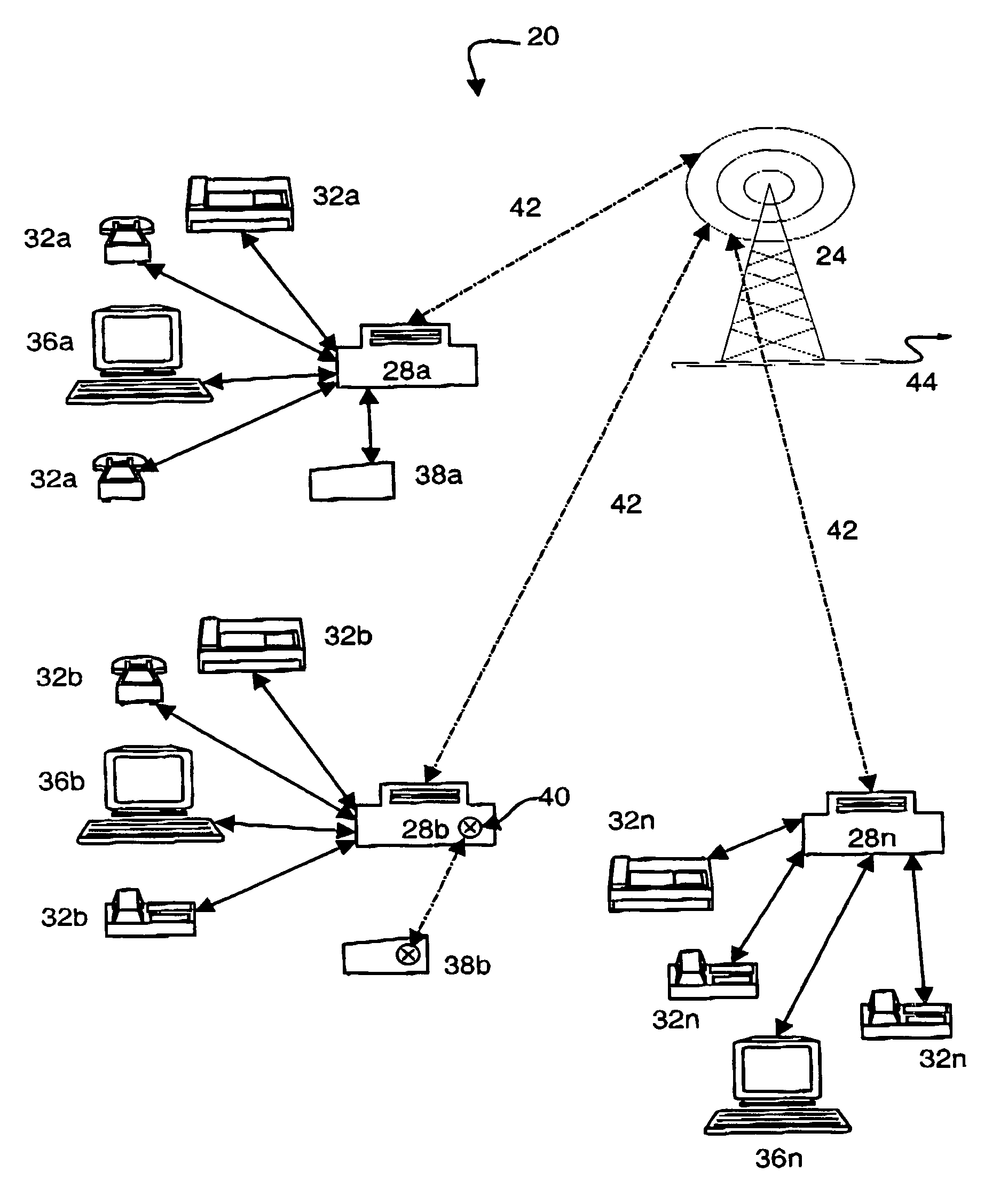
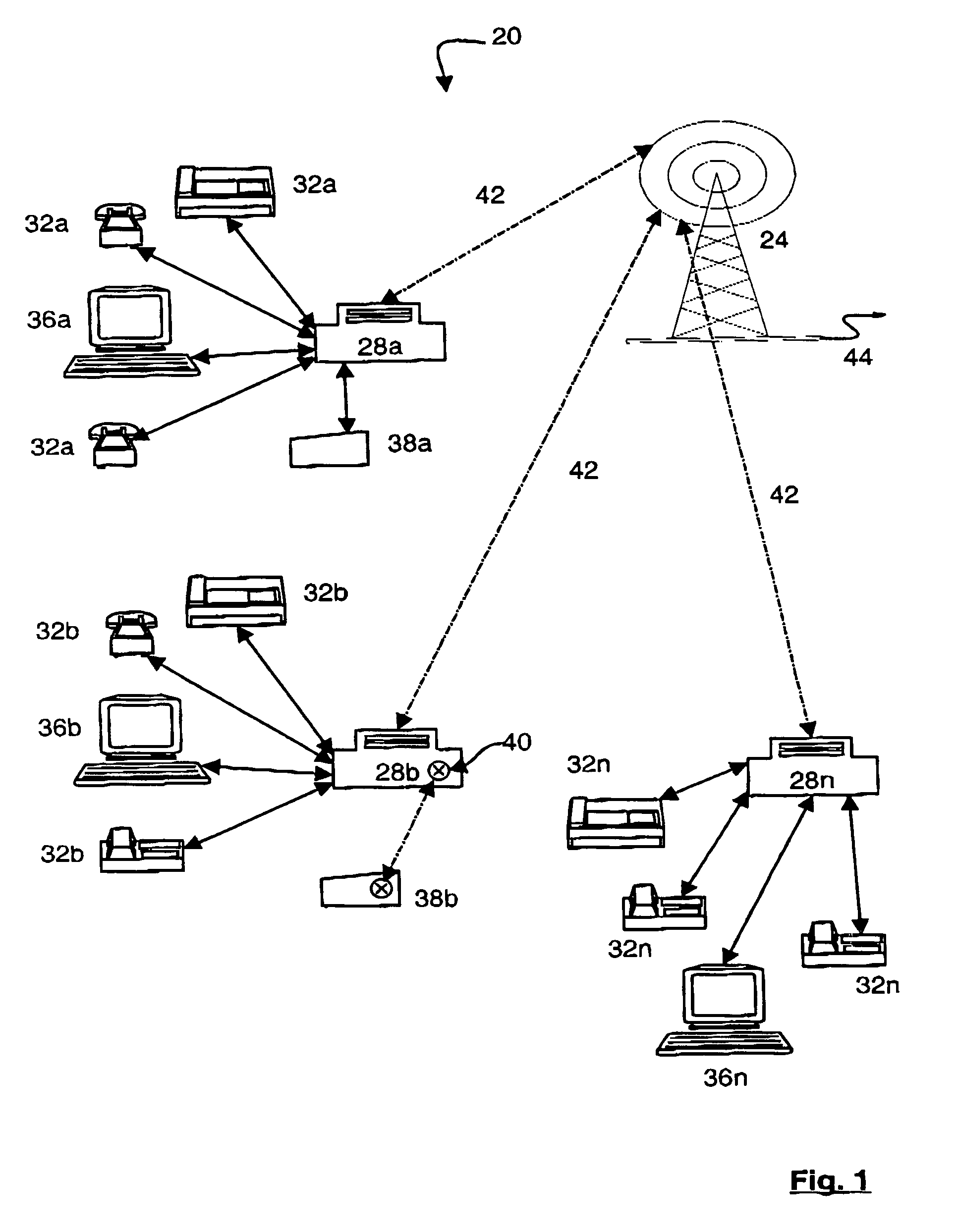
Apparatus and method for efficient TDMA bandwidth allocation for TCP/IP satellite-based networks
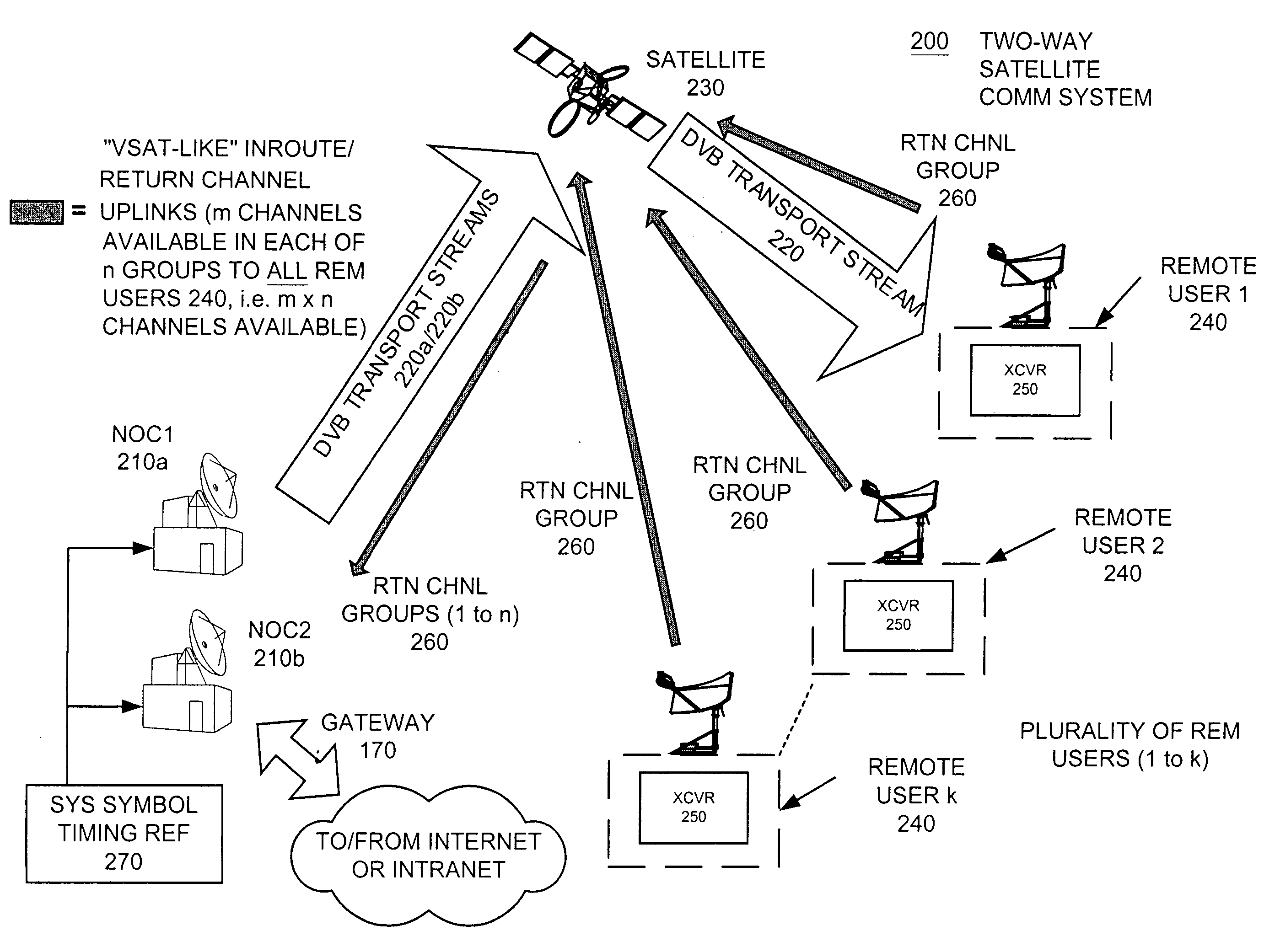
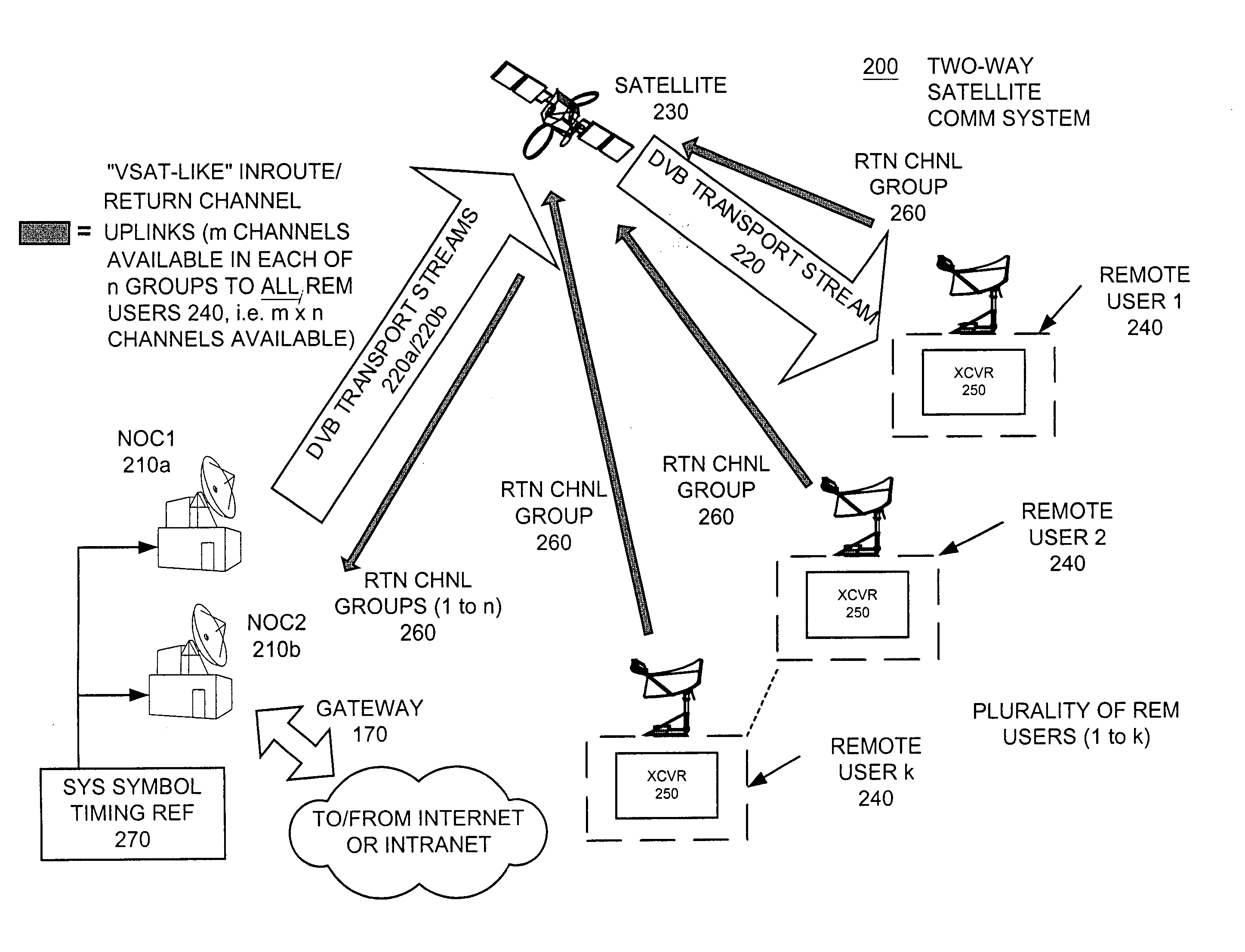
InactiveUS20050053033A1Balance traffic loadOptimize bandwidth allocationFrequency-division multiplex detailsAntenna supports/mountingsCommunications systemAloha
A communication system balances message traffic between return channel groups and within the groups, so that the user does not control the specific transmission frequency used. Uplink frequencies and bandwidths for the return channels are set by the system in a return channel control message in the broadcast signal so as to account for system and return channel group loading, and to account for user message backlogs. An initial transmission from a remote user may be made using an ALOHA-type burst signal that provides a message backlog to the control station, and is made on a frequency determined from a randomly weighted, load-based frequency selection process. The system, and not the individual users determine the frequency and channel allocations. For large backlogs or priority users, periodic bandwidth is provided. A method for balancing loads among and between groups of return channels in the communication system includes requesting return channel bandwidth in an uplink message from a remote user to a control station. The uplink message may include a both a backlog indicator and a bandwidth allocation request provided to a Network Operations Center (NOC) which can be used to set the return channel bandwidth and frequency for the remote uplink. A user message is transmitted on the designated return channel frequency using bandwidth allocated in accordance with the backlog indicator and a bandwidth allocation request so that traffic loads are maintained in balance between established return channel frequency groups, and within each return channel frequency group.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
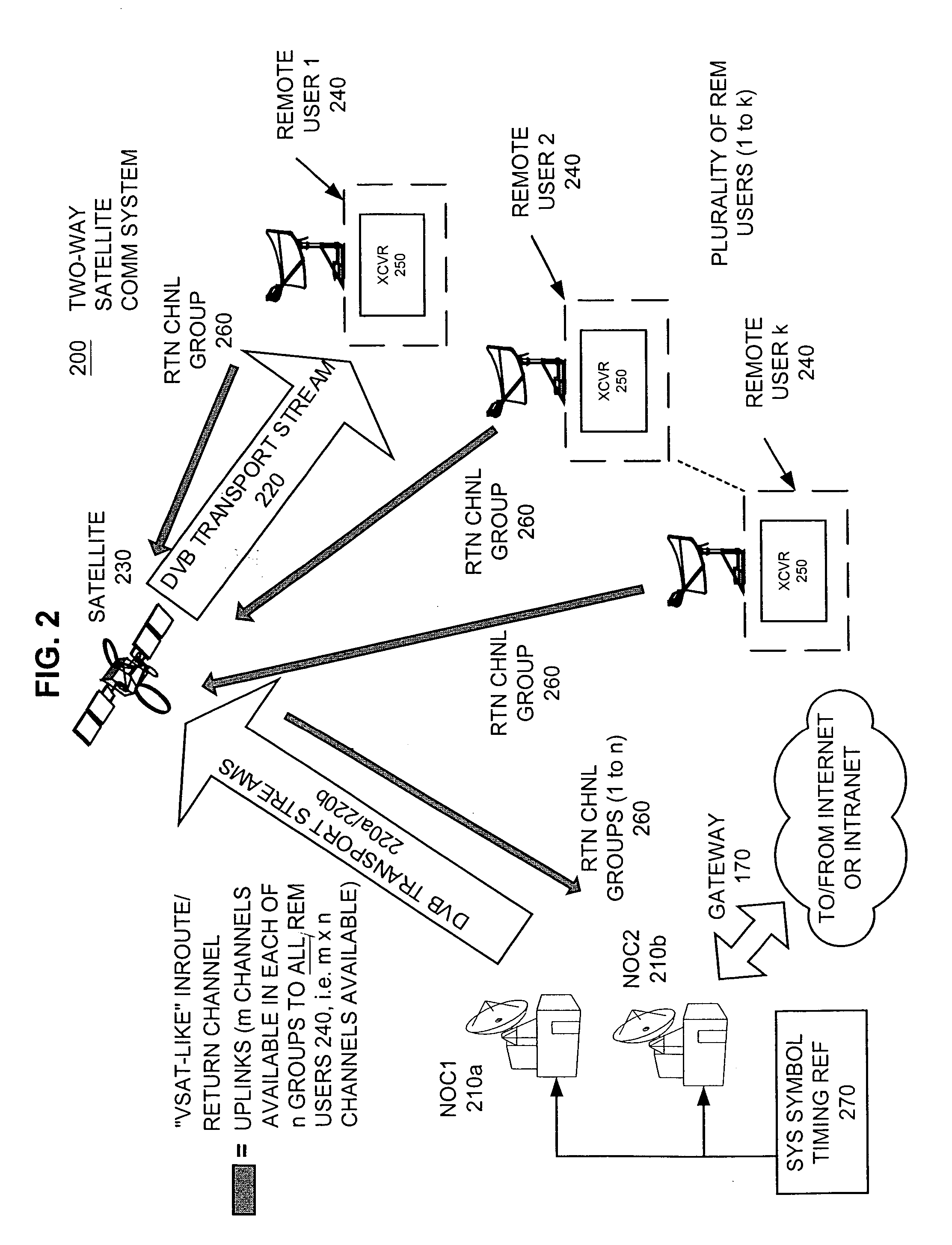
Apparatus and method for efficient TDMA bandwidth allocation for TCP/IP satellite-based networks
InactiveUS20050030932A1Optimized bandwidth allocation schemeBalance traffic loadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemAloha
A communication system balances message traffic between return channel groups and within the groups, so that the user does not control the specific transmission frequency used. Uplink frequencies and bandwidths for the return channels are set by the system in a return channel control message in the broadcast signal so as to account for system and return channel group loading, and to account for user message backlogs. An initial transmission from a remote user may be made using an ALOHA-type burst signal that provides a message backlog to the control station, and is made on a frequency determined from a randomly weighted, load-based frequency selection process. The system, and not the individual users determine the frequency and channel allocations. For large backlogs or priority users, periodic bandwidth is provided. A method for balancing loads among and between groups of return channels in the communication system includes requesting return channel bandwidth in an uplink message from a remote user to a control station. The uplink message may include a both a backlog indicator and a bandwidth allocation request provided to a Network Operations Center (NOC) which can be used to set the return channel bandwidth and frequency for the remote uplink. A user message is transmitted on the designated return channel frequency using bandwidth allocated in accordance with the backlog indicator and a bandwidth allocation request so that traffic loads are maintained in balance between established return channel frequency groups, and within each return channel frequency group.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
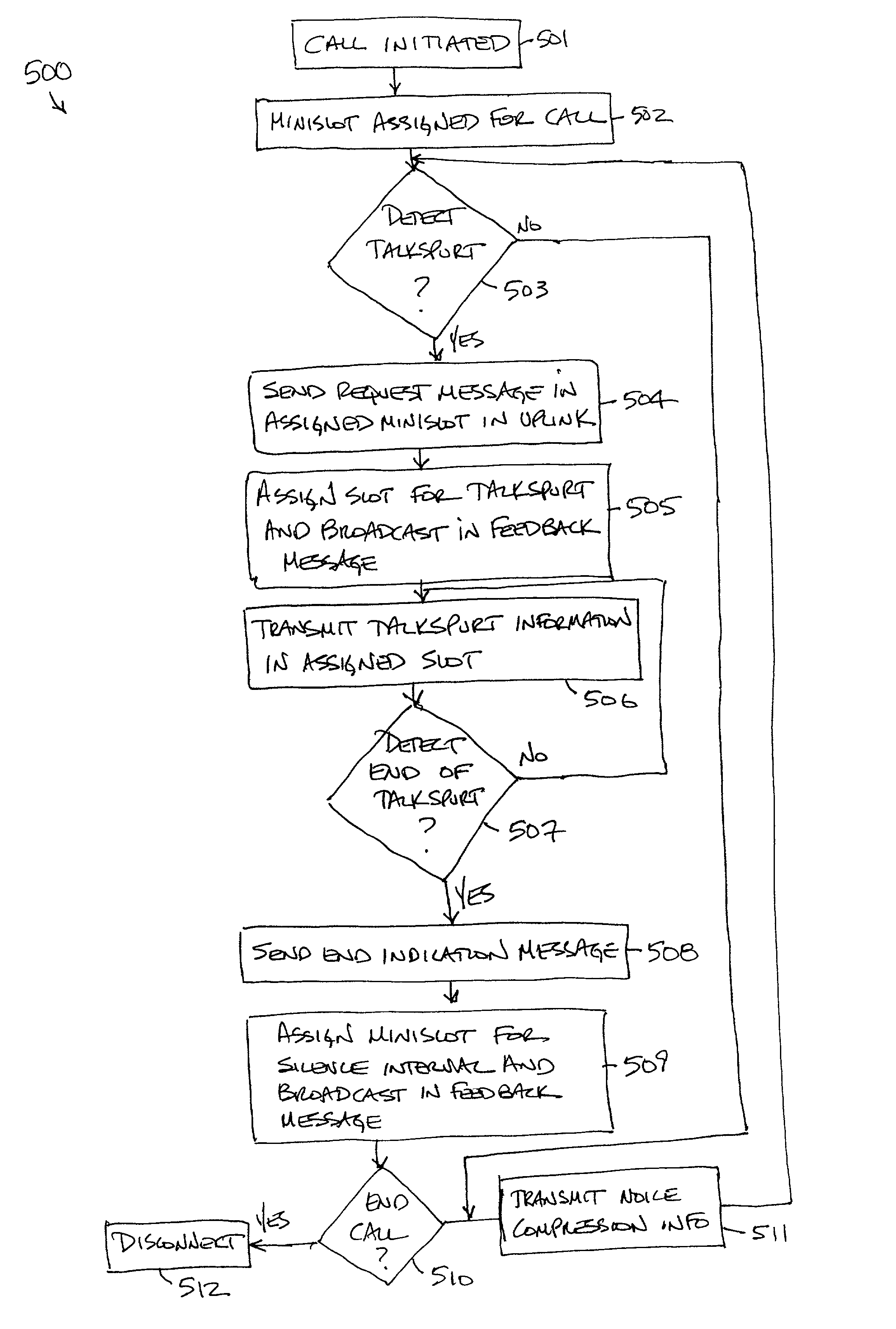
Voice-data integrated multiaccess by self-reservation and stabilized aloha contention
InactiveUS6963545B1Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexNetwork Communication ProtocolsAloha
A multiple access communication protocol that includes an uplink and a downlink channel is disclosed. The uplink channel has a plurality of frames, such that each frame has a first selectable number of minislots and a second selectable number of slots. A reservation request of a first type is sent into a first selected minislot of a selected frame of the uplink channel when information of a first type is to be sent. The reservation request of the first type requests an assignment for at least one slot for transmitting information of the first type in at least one frame that is subsequent to the selected frame. A reservation request of a second type is sent into a second selected minislot of the selected frame when the second selected minislot is available in the selected frame and when information of a second type is to be sent. The reservation request of the second type requests an assignment of at least one slot for transmitting information of the second type in at least one frame that is subsequent to the selected frame, and contends for the second selected minislot based on a pseudo-Bayesian Aloha algorithm. The downlink channel contains a feedback message that occurs prior to the end of the selected frame of the uplink channel. The feedback message includes minislot assignment information for sending reservation requests of the first and the second type and slot assignment information for transmitting information of the first and the second type, minislot contention information for the reservation requests of the second type sent in the selected frame, and reservation backlog information for an estimated number of reservation requests of the second type pending at a beginning of the selected frame.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
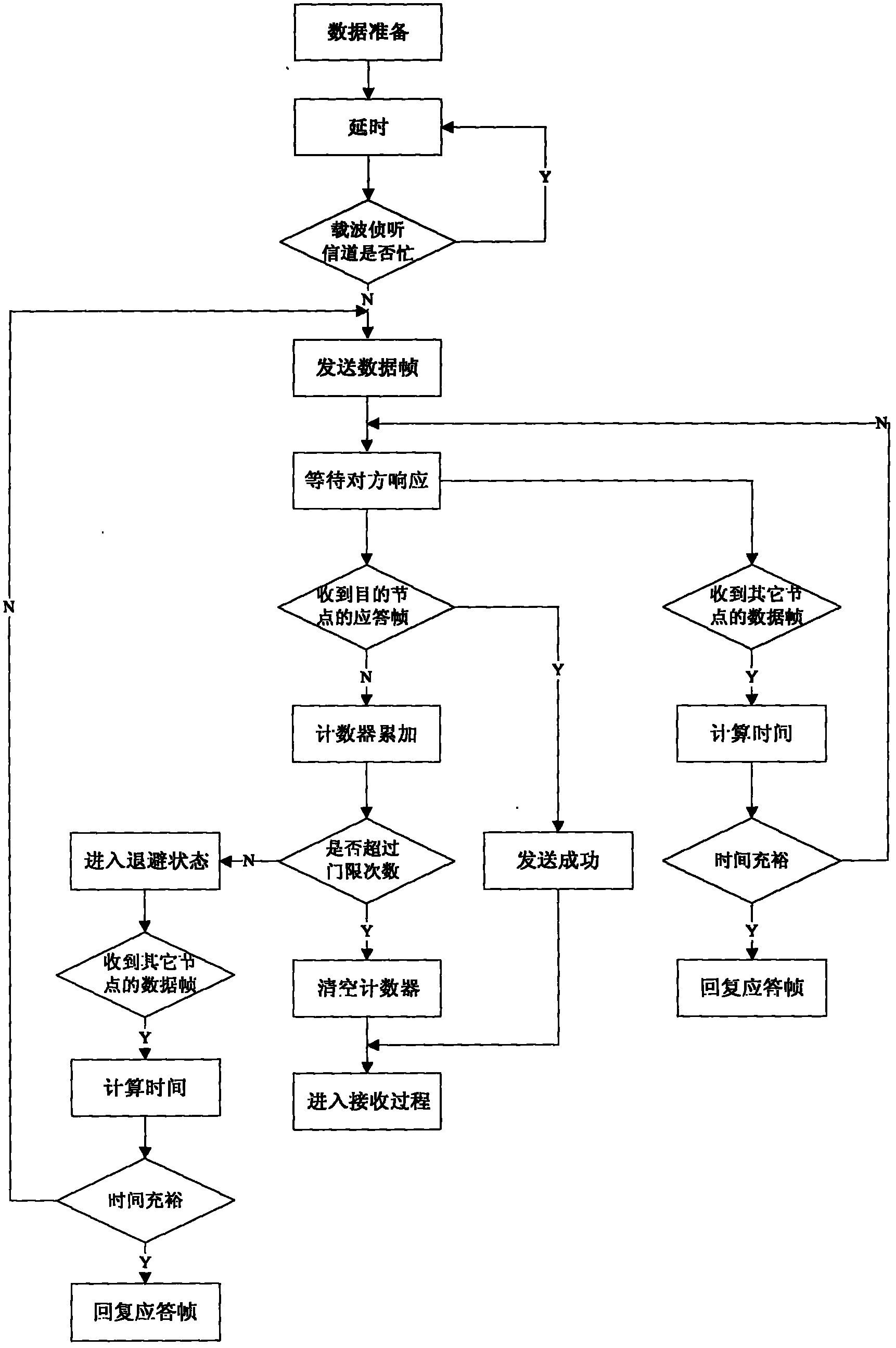
Method of packet mode digital communication over a transmission channel shared by a plurality of users
ActiveUS20060171418A1Improve performanceManage efficiently greatSpecial service provision for substationError preventionTime domainAloha
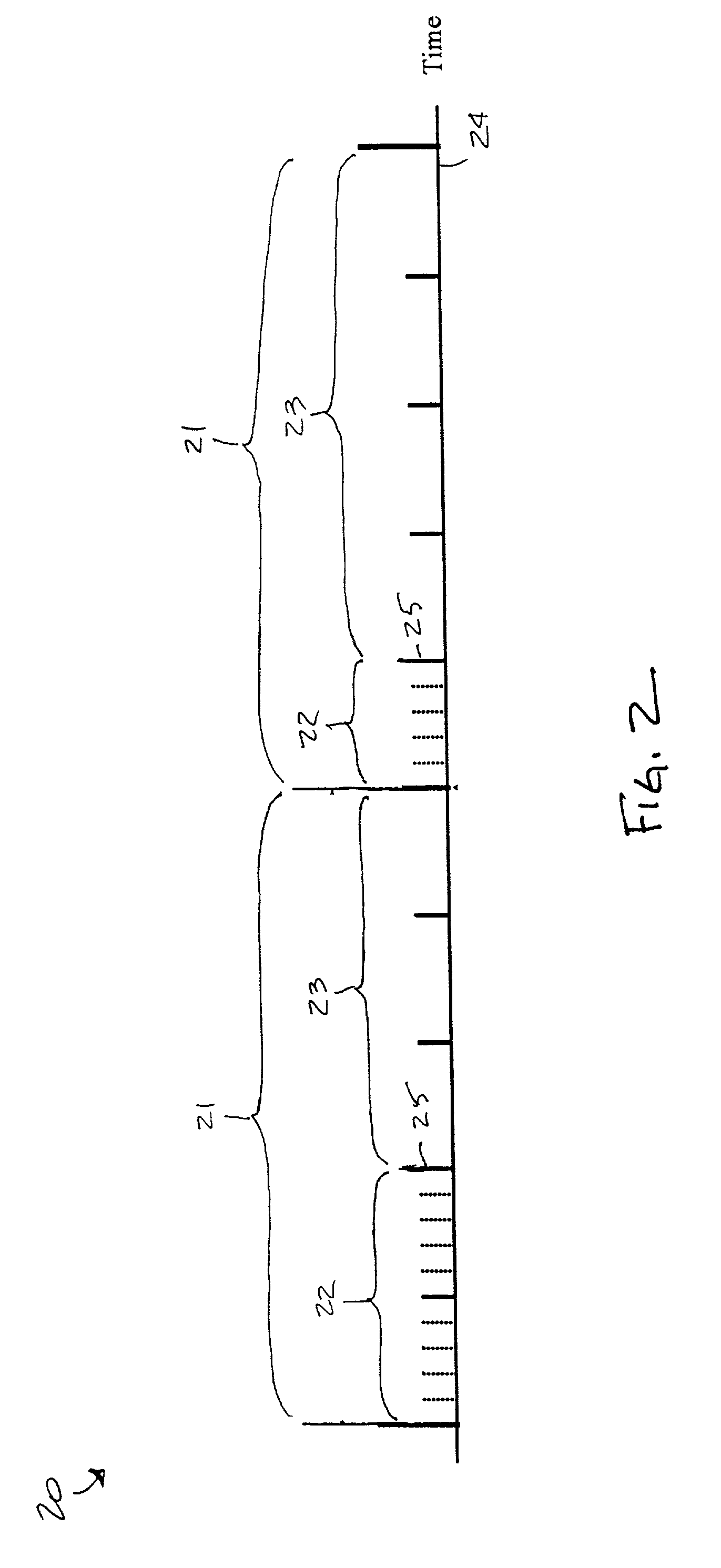
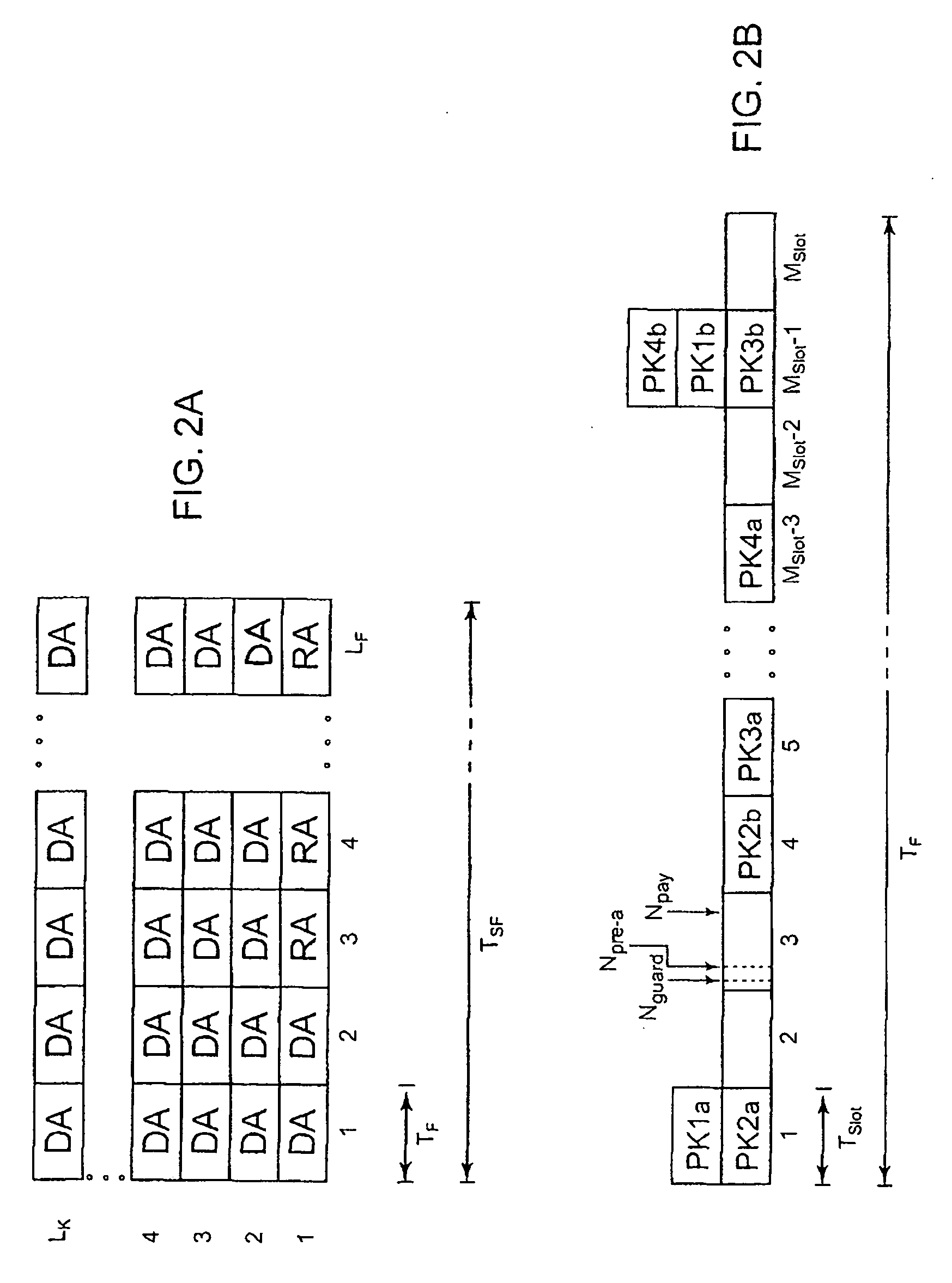
A first aspect of the invention is a method of transmitting data packets over a transmission channel shared by a plurality of users, based on the time and / or frequency diversity slotted Aloha technique, in which at least two replicas of each packet to be transmitted are sent over said transmission channel, wherein each replica transports signaling information enabling the other replica(s) of the same packet to be located in the time and / or frequency domain. A second aspect of the invention is a method of recovering packets in the receiver, the method exploiting said signaling information to execute an interference cancellation algorithm for recovering packets corrupted by collisions caused by access conflicts. Other aspects of the invention are a transmitter equipment and a receiver packet recovery equipment adapted to use said methods.
Owner:EUROPEAN SPACE AGENCY
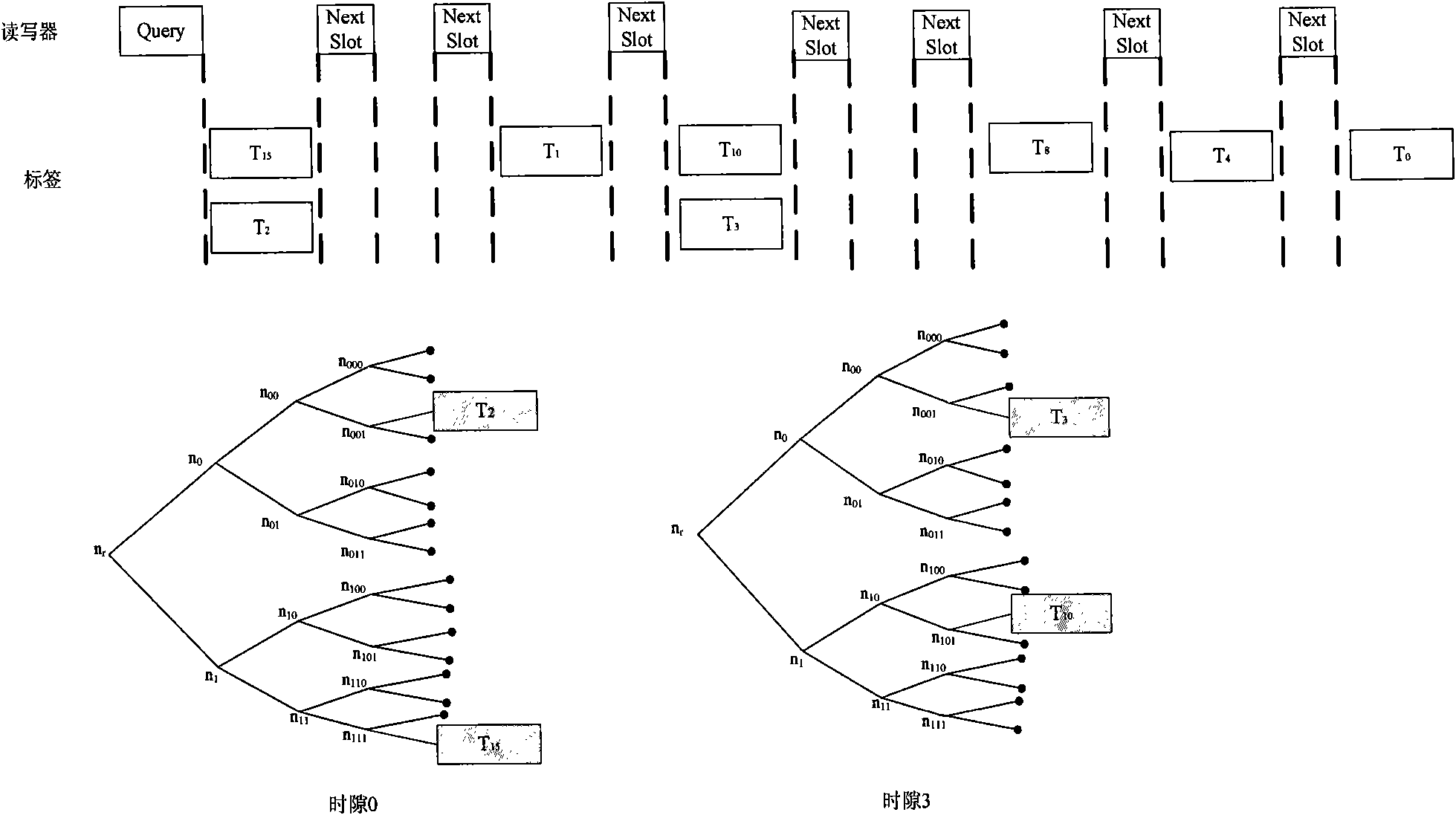
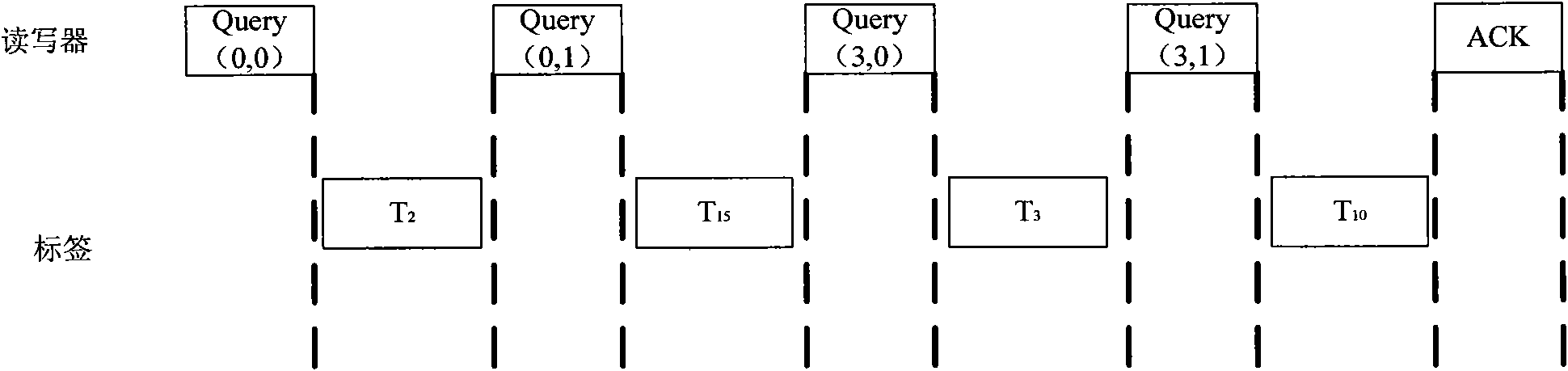
Time slot ALOHA anticollision algorithm suitable for dynamic environment
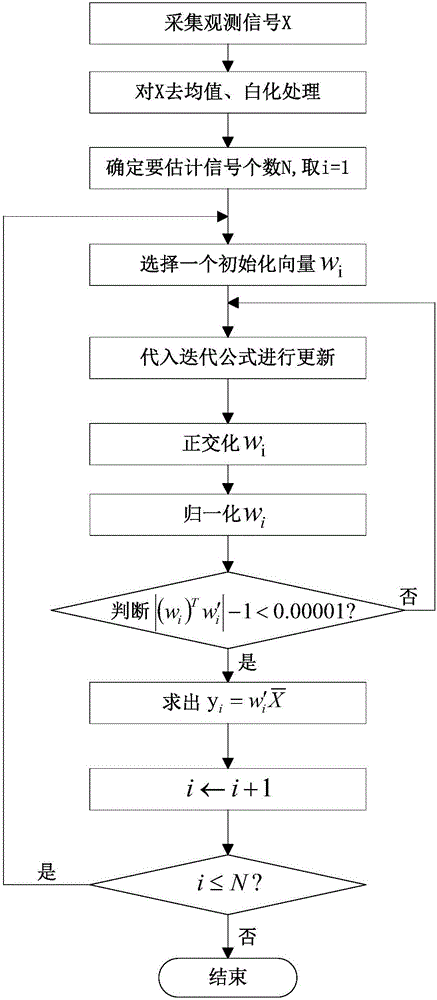
InactiveCN101286192AImprove computing efficiencyFast recognitionSensing record carriersAlohaComputer science
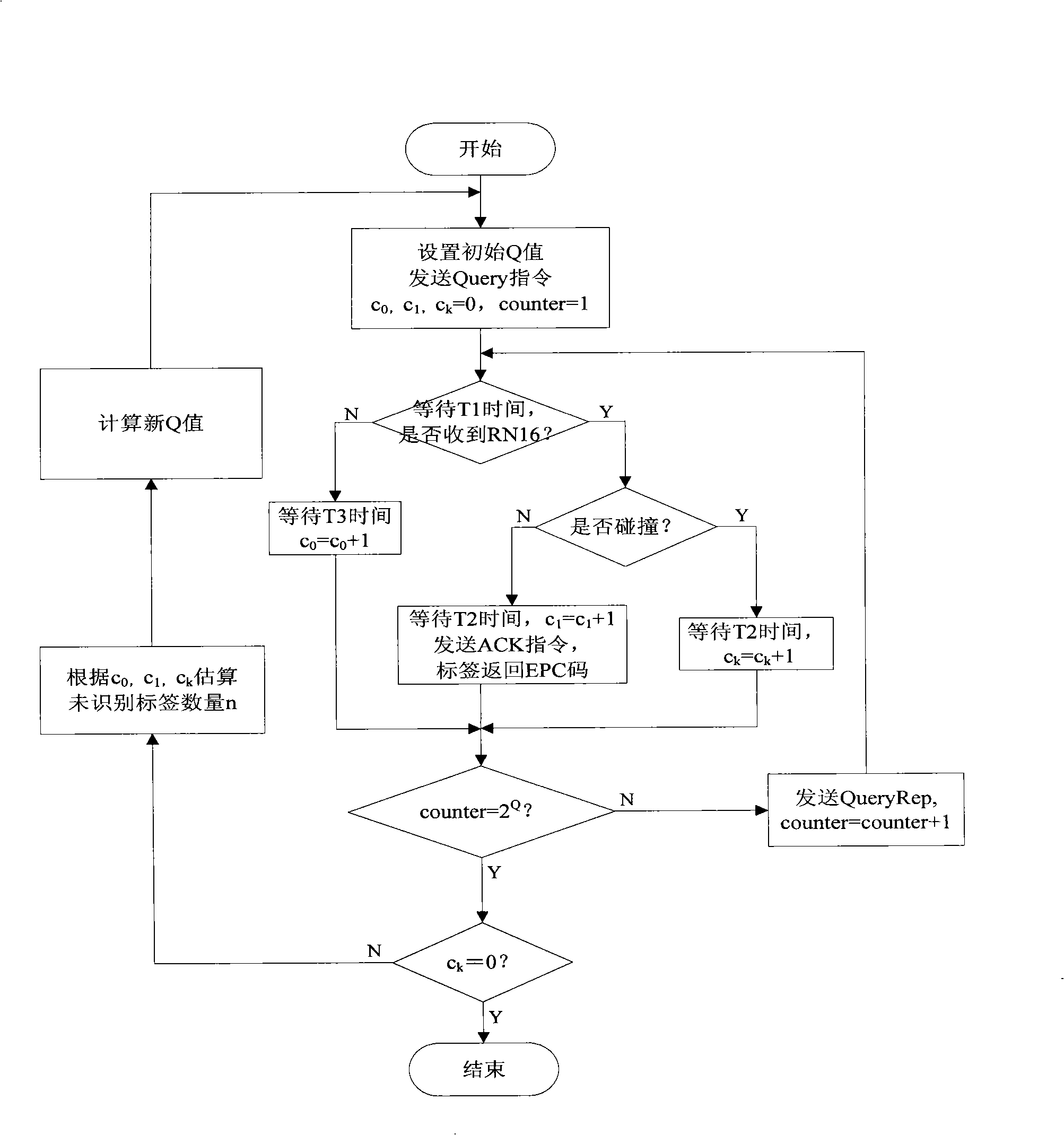
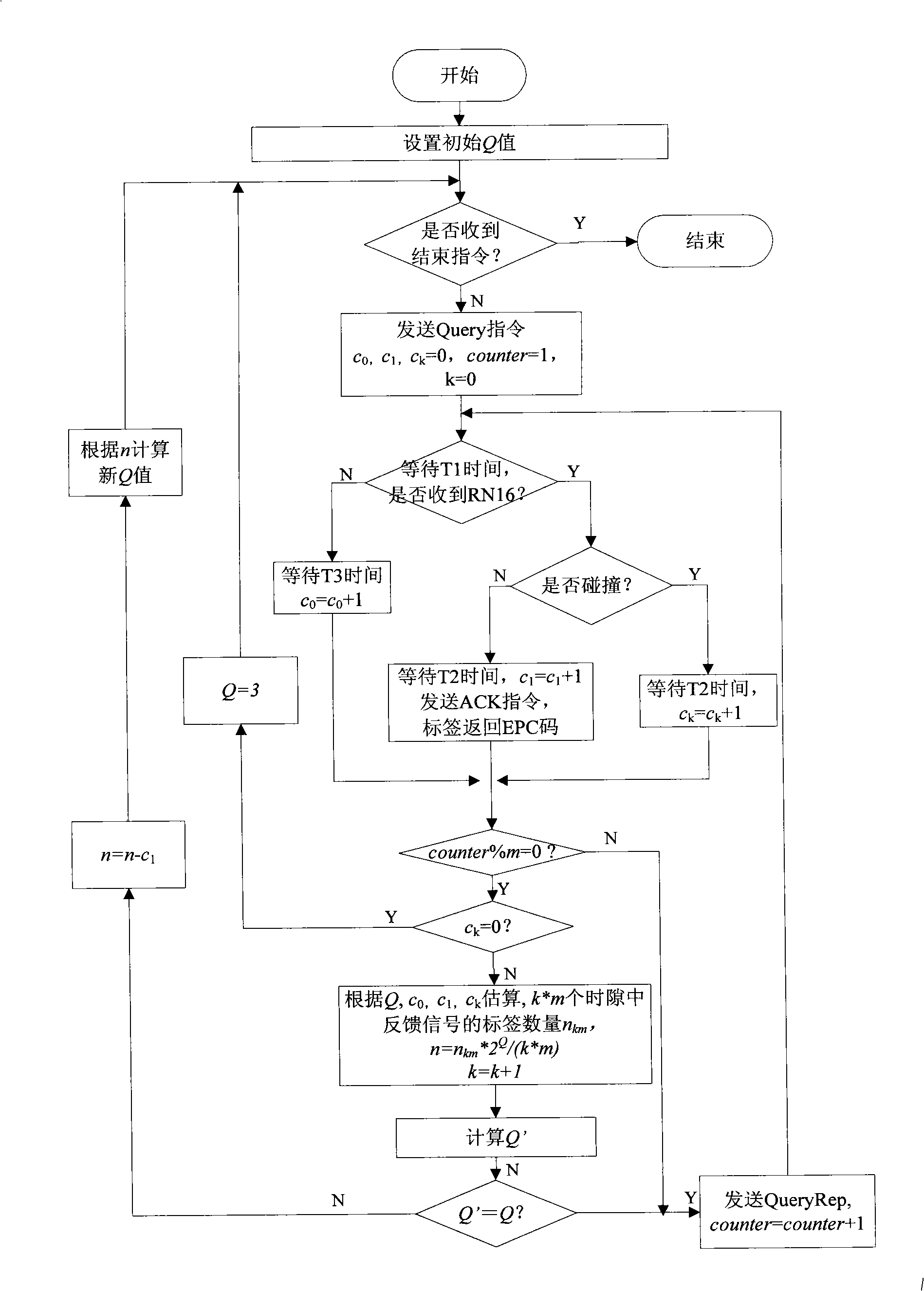
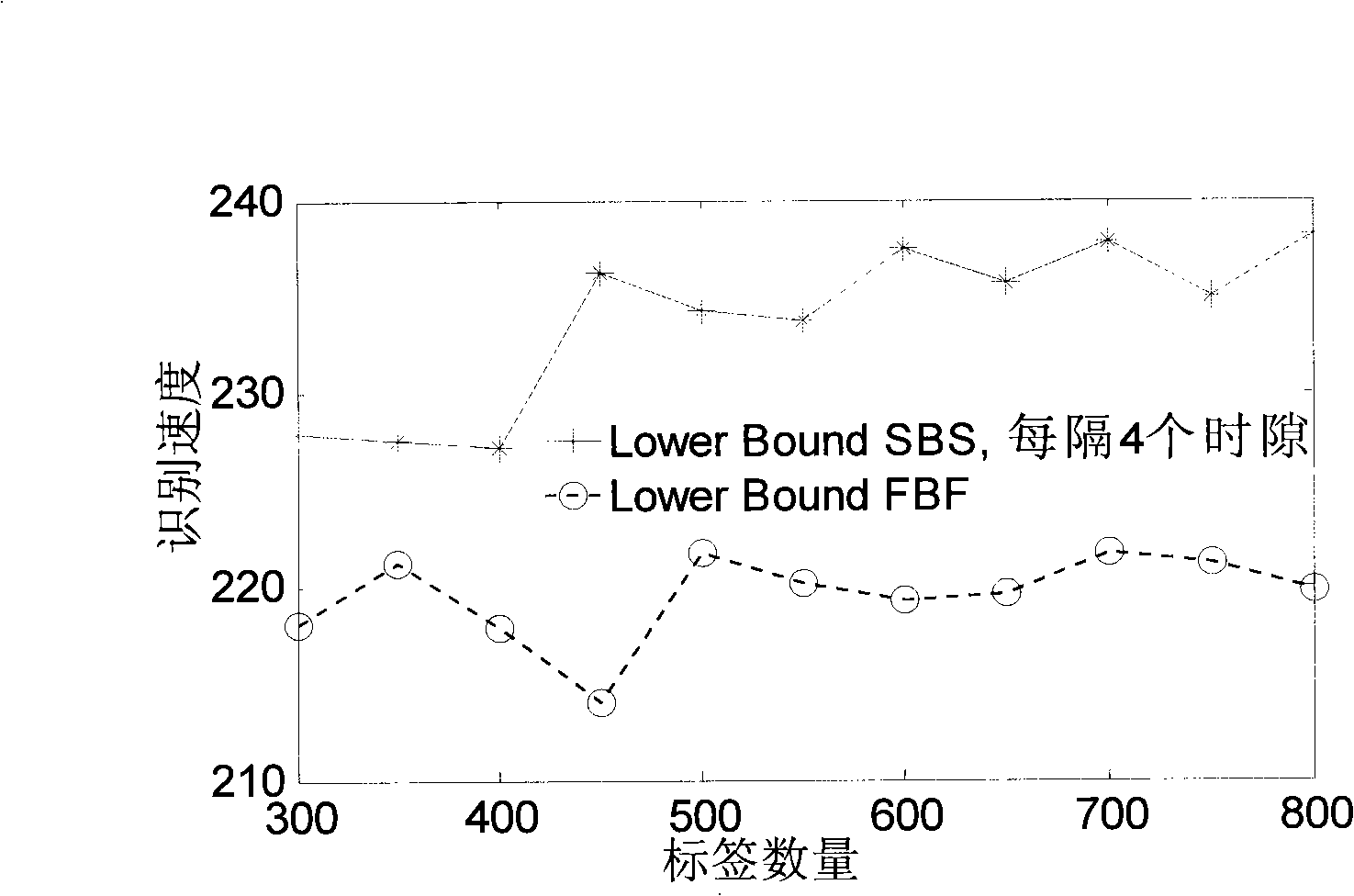
The invention pertains to the radio frequency identification technical field, in particular relates to a time slot ALOHA anti-collision algorithm which is applicable to the dynamic environment. The algorithm comprises the following steps that: the initialization is firstly carried out, and the detection of whether a termination command emitted by an upper computer is received or not; if the termination command is received, the algorithm is finished; otherwise, the data receiving is started, the number of the space slot, the time slot, the collision time slot and the success time slot are respectively carried out the statistics; whether a time slot counter and a 2<q> taking model are equal to 0 or not is judged, if equal to 0, the number n of labels is estimated, Q' is calculated, whether Q' is equal to Q or not is judged, if the two are equal, a new frame is started; if not, the new Q value is calculated, and then the algorithm returns to carry out the next round of identification process. The algorithm takes account of the factor of the change of the number of the labels, a reader can terminate the inappropriate frame as soon as possible and select the more reasonable frame length for the next from by calculating the number of the labels in a calculation field zone and judging whether the current frame length is appropriate or not during the identification process of the current frame, thus reducing the probability of occurrence of the collision of the labels and improving the identification speed of the reader under the dynamic environment.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
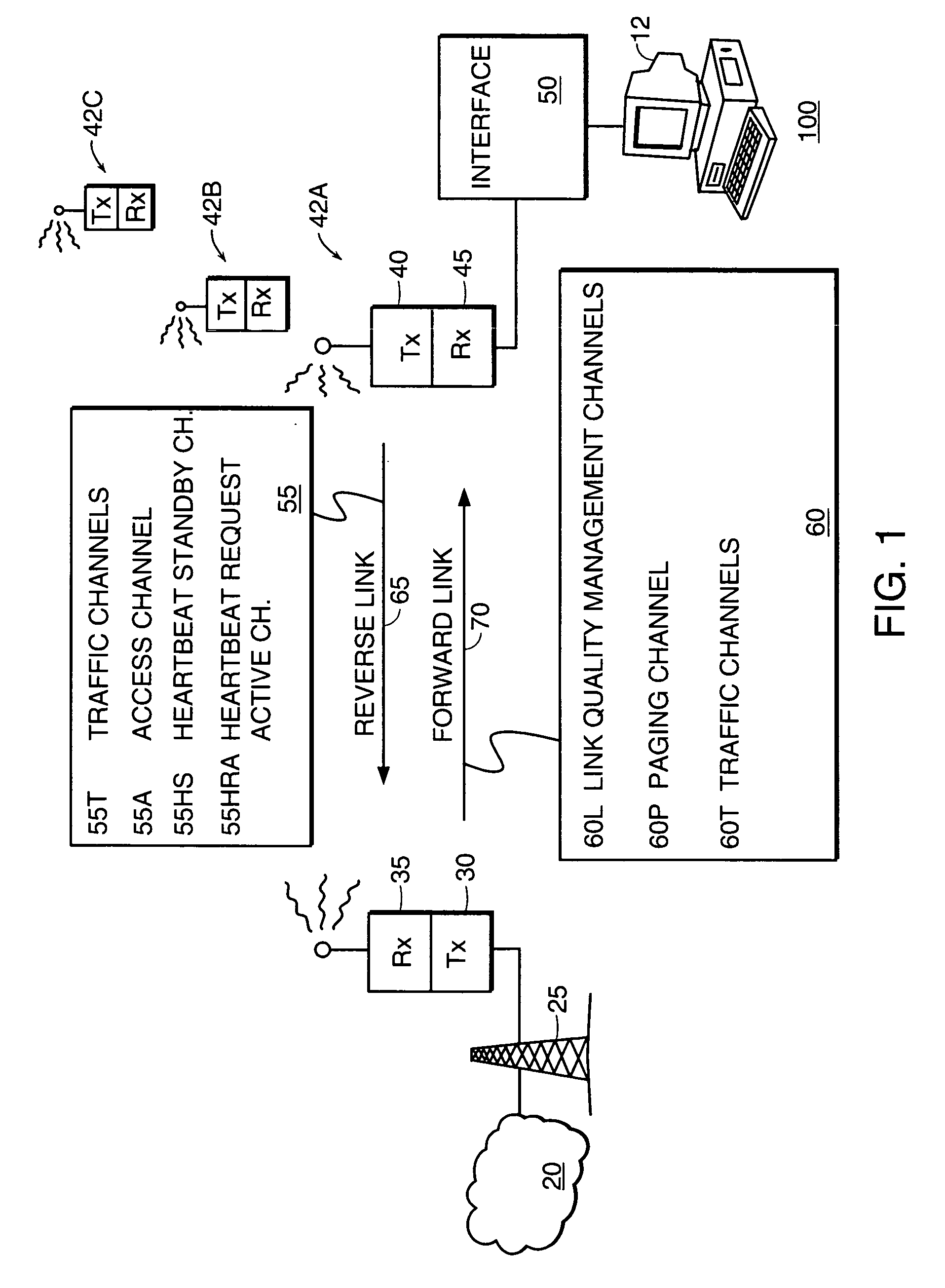
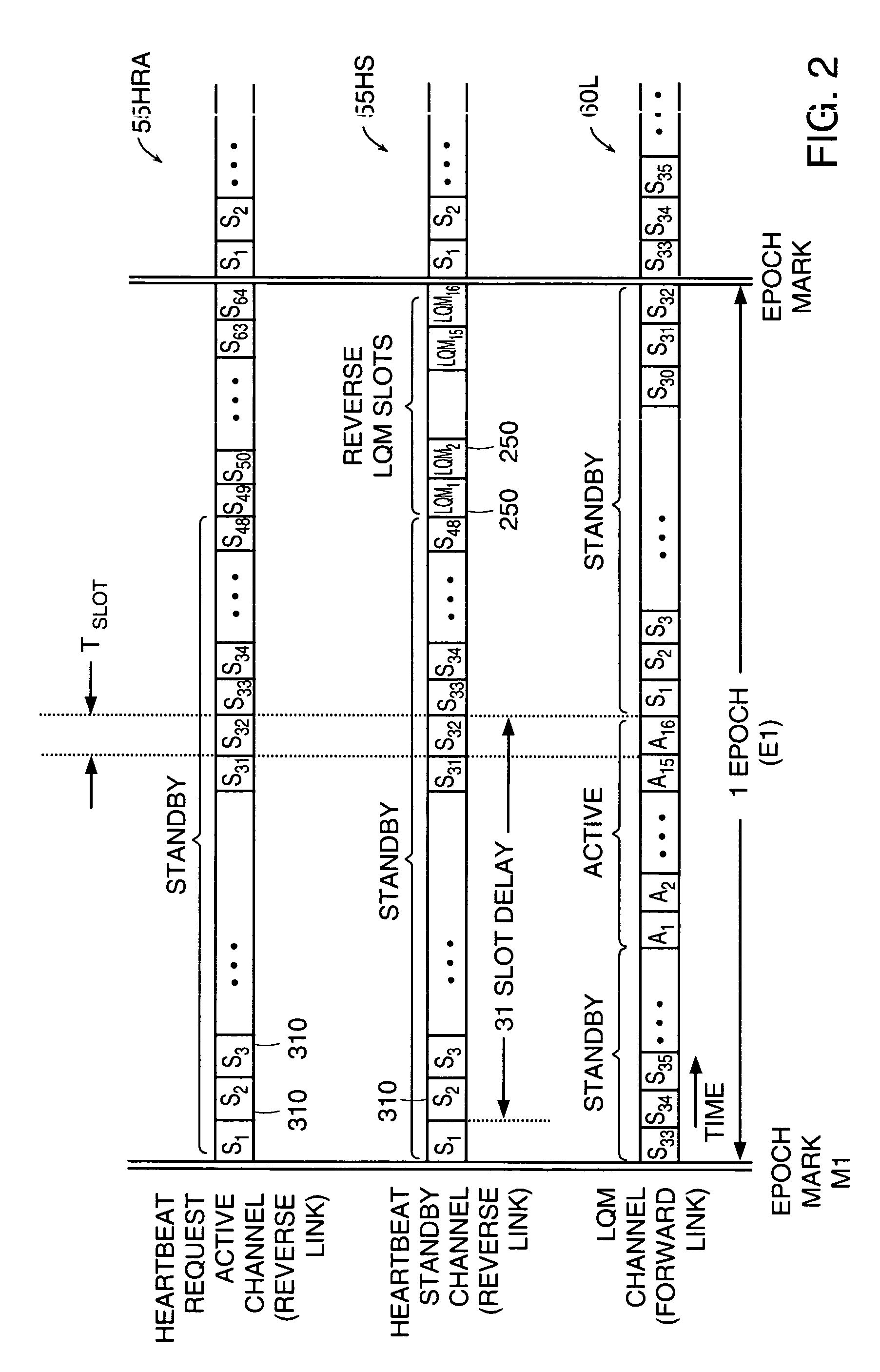
Maintenance link using active/standby request channels
Multiple field units in a CDMA system are synchronized for communication with a base station using shared forward and reverse link channels. In an illustrative embodiment, each field unit is assigned a time slot in a forward link channel to receive messages from the base station. Likewise, each field unit is assigned a time slot on a common reverse link channel for transmitting messages to the base station. Timing alignment and power level control among each of many field units and the base station is achieved by analyzing messages received at the base station in a corresponding time slot as transmitted by each field unit. Thereafter, a message is transmitted from the base station in a corresponding time slot to a particular field unit for adjusting its timing or power level so that future messages transmitted from the field unit are received in the appropriate time slot at the base station at a desired power level. In this way, minimal resources are deployed to maintain communication and precise synchronization between a base station and each of multiple users, minimizing collisions between field units transmitting in adjacent time slots on the reverse link. This method reduces the frequency a field unit must rely on the use of a slotted aloha random access channel according to IS-95.
Owner:NELSON G RODNEY JR +3
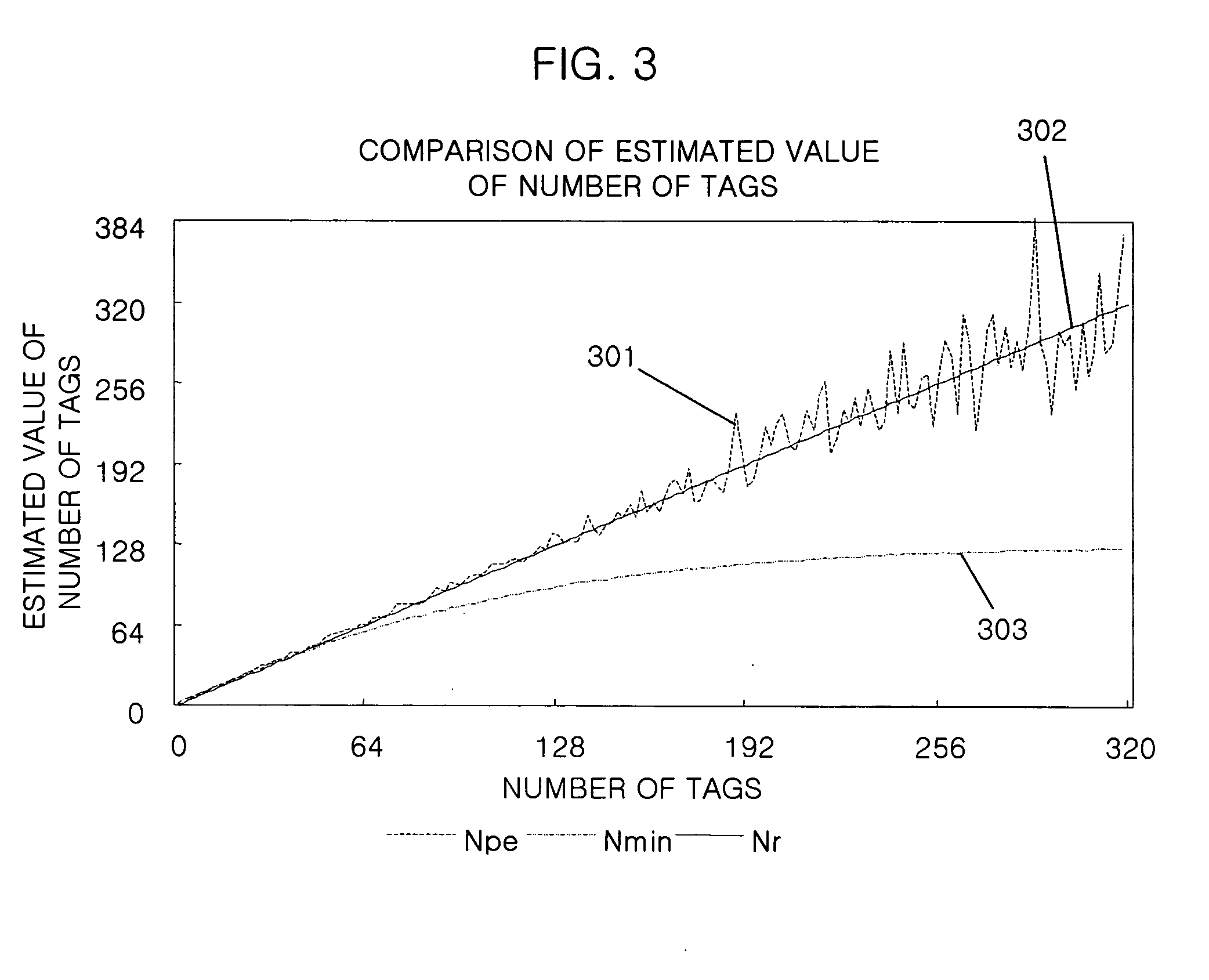
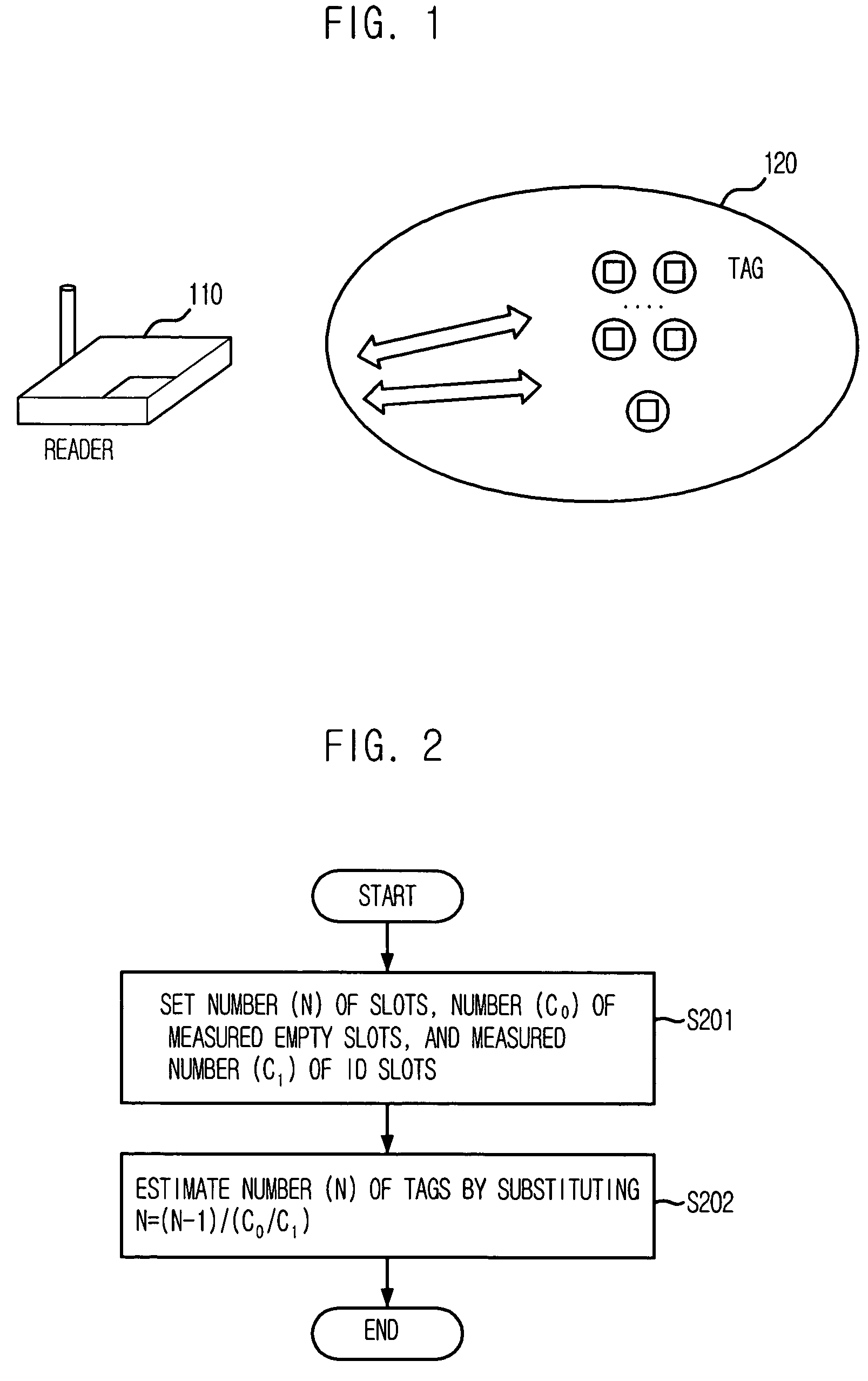
Method for estimating number of tags in slotted aloha-based RFID system
InactiveUS20070096877A1Memory record carrier reading problemsTime-division multiplexAlohaComputer science
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
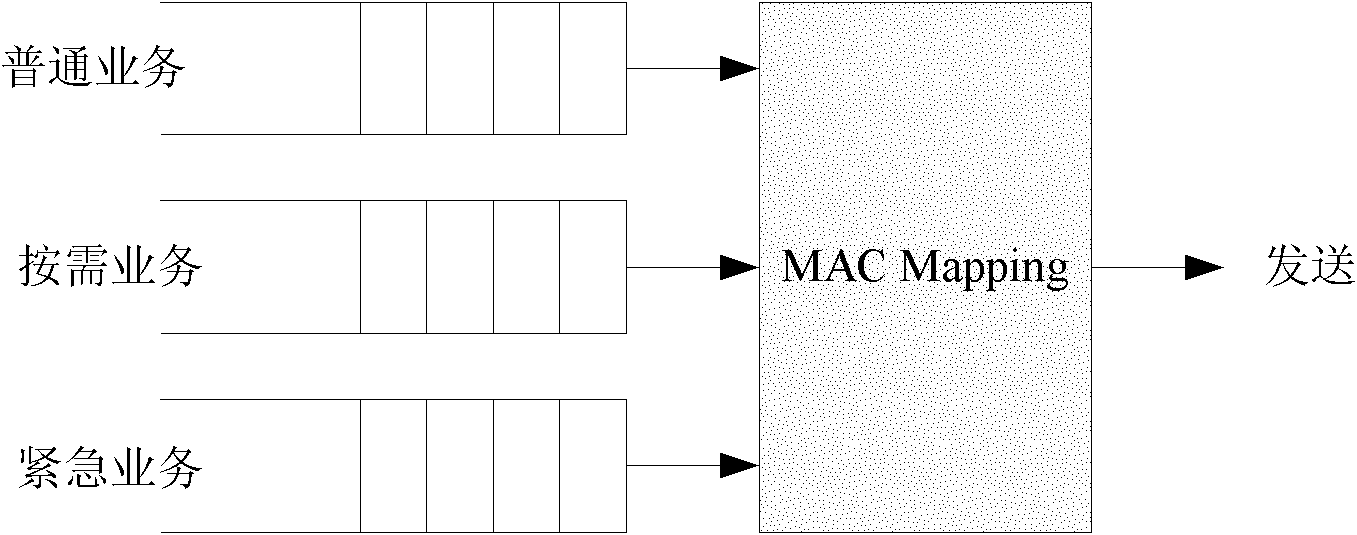
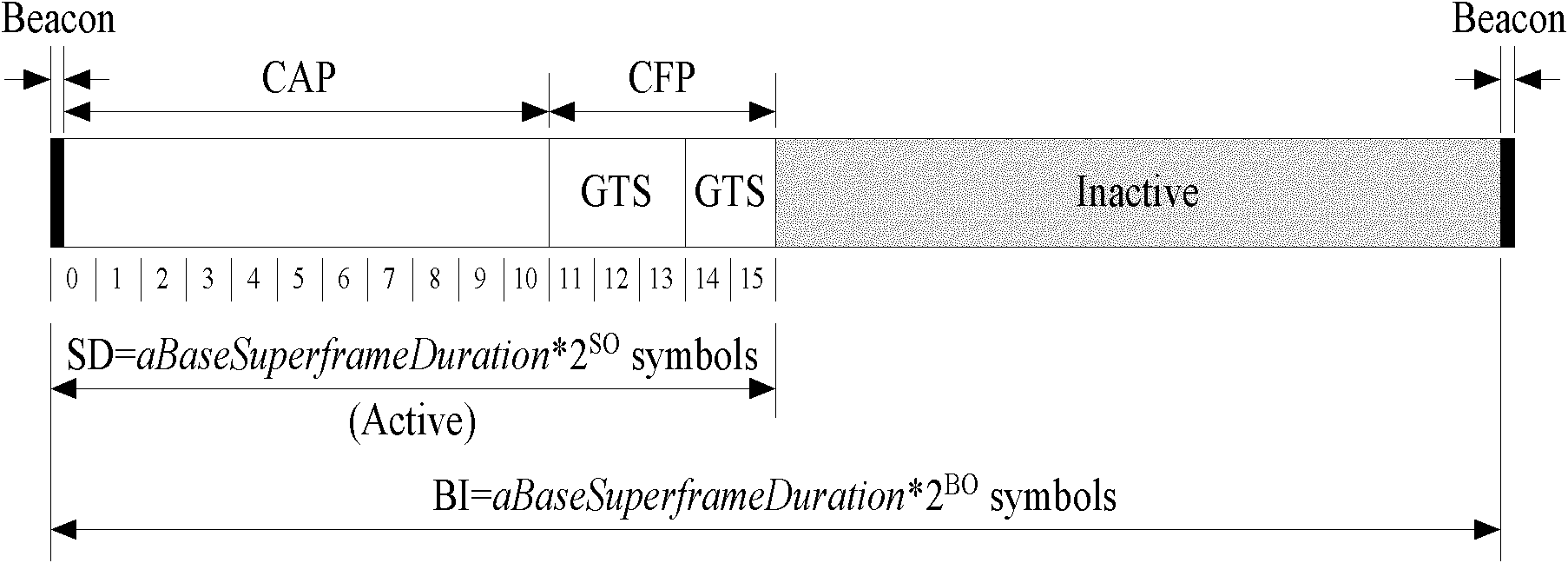
Superframe-based efficient media access control method in wireless body area network
ActiveCN102123515AIncrease success rateImprove performanceWireless communicationBody area networkAloha
The invention discloses a superframe-based efficient media access control method in a wireless body area network, mainly solving the problems that an IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers) 802.15.4 protocol is incapable of distinguishing service priorities and has time slot waste in a non-competitive period in a wireless body area network. The superframe-based efficient media access control method is realized by adopting the steps of: in a competitive period, setting the competitive period into a high priority service dedicated time slot H, a high priority service spare time slot h and a common time slot by adopting a time slot ALOHA competition mechanism based on the service priority, wherein a common node adopts the three different competition mechanisms according to the quantity of high priority services in the current superframe competitive period; and in a non-competitive period, ensuring that allocation and utilization of a GTS (Guarantee Time Slot) service are carried out by utilizing a micro time slot as a unit and adopting a micro time slot mechanism so as to realize the effective utilization of the time slot. Compared with the IEEE 802.15.4 protocol, thesuperframe-based efficient media access control method disclosed by the invention can not only ensure that the high priority service is transmitted with a higher success probability, but also effectively improve the time slot utilization ratio in the non-competitive period and is suitable for the wireless body area network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for estimating number of tags in slotted aloha-based RFID system
InactiveUS7675403B2Memory record carrier reading problemsTime-division multiplexAlohaComputer science
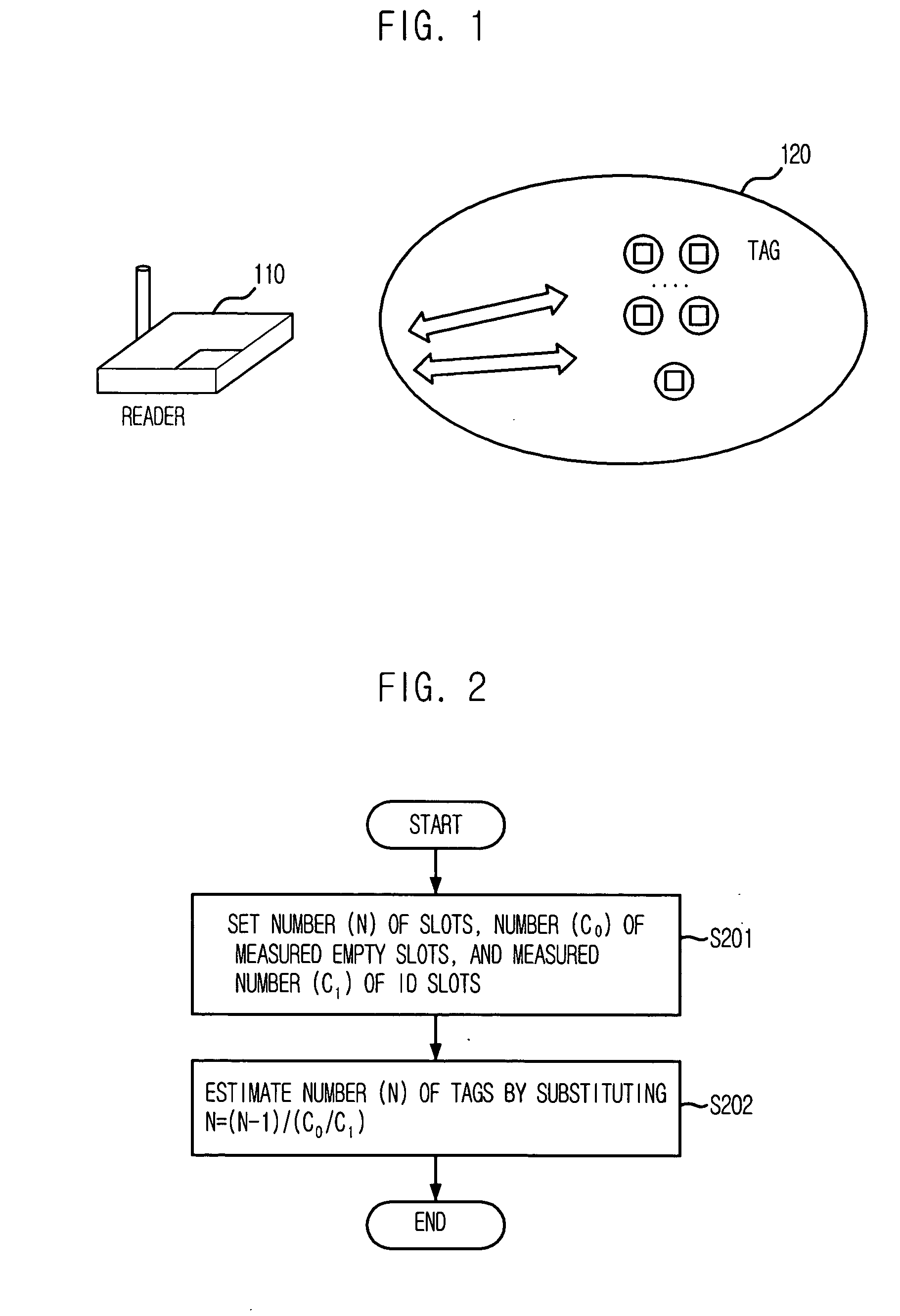
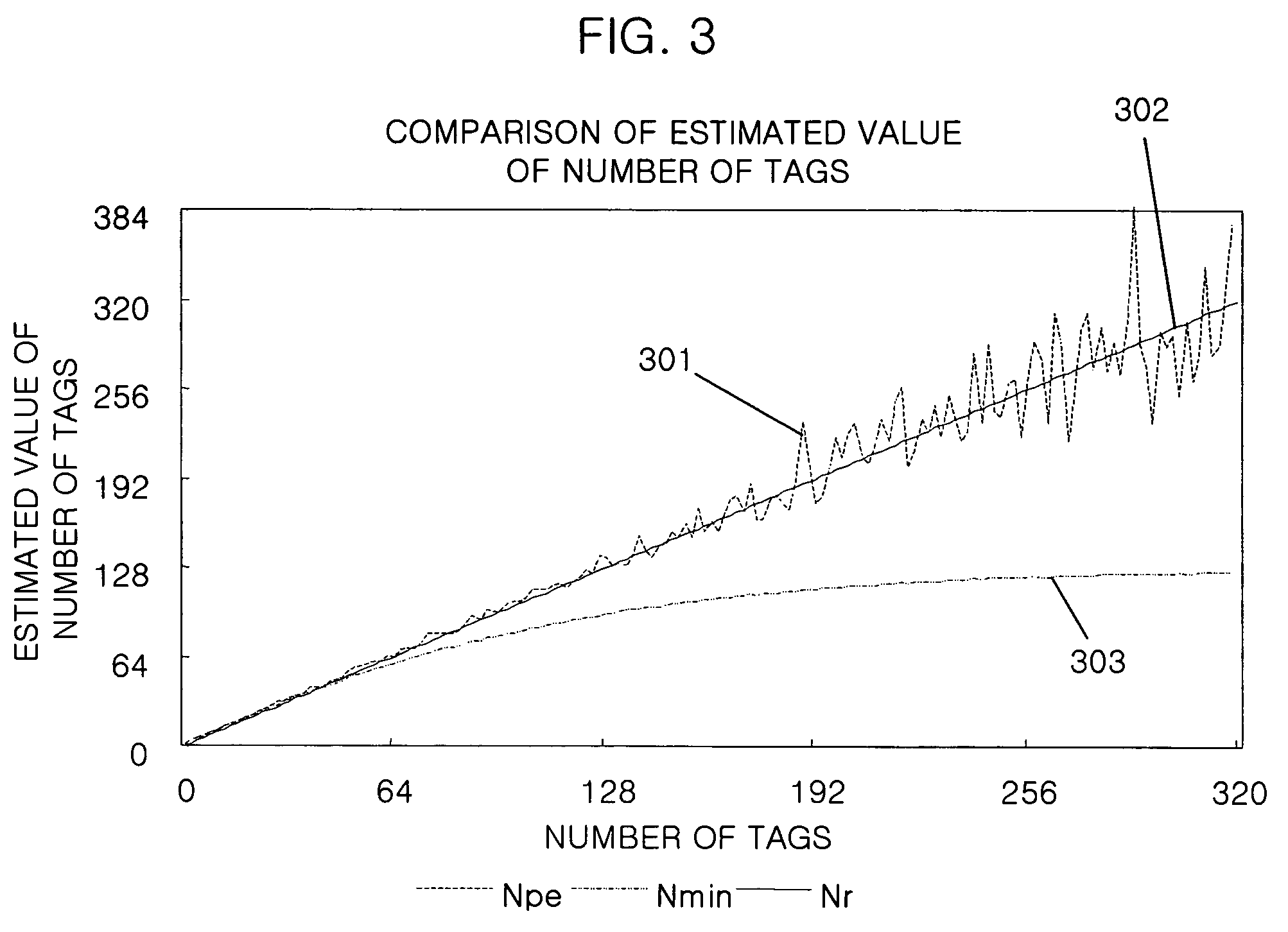
Provided is a method for estimating the number of tags in a slotted Aloha-based RFID system, which can estimate the number of tags through a new statistical average scheme using the number of slots, the measured number of empty slots, and the measured number of ID slots. The estimating method includes the steps of: a) setting the number (N) of slots, the measured number (c0) of empty slots, and the measured number (c1) of ID slots as parameters; and estimating the number (n) of the tags by substituting the set values into n=(N−1) / (c0 / c1).
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Self-adaptive media access control (MAC) protocol for vehicle-mounted wireless self-organized network
InactiveCN102724764AReal-time transmissionReliable transmissionWireless communicationReliable transmissionAloha
The invention discloses a self-adaptive media access control (MAC) protocol for a vehicle-mounted wireless self-organized network, comprising a DR-ALOHA protocol which is used by a control channel and a strategy for accessing a business channel through a node dynamic selection competition method or a pre-reservation method, wherein the DR-ALOHA protocol dynamically adjusts the number of fixed-length time slot in a time division multiplexing principle so that the secure information of all nodes in a network can be transmitted reliably in real time, and is applicable to networks with the node density and the topological structure being dynamically changed; in the strategy of accessing the business channel through the node dynamic selection competition method or the pre-reservation method, firstly the switching threshold of a business channel access method is determined by theoretical analysis and mathematical deduction and then the business channel is accessed through the node dynamic selection competition method or the pre-reservation method by integrating the real-time channel utilization rate of the business channel, so that the channel utilization rate of the business channel can be the highest in any node density.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Voice-data integrated multiaccess by self-reservation and stabilized aloha contention
InactiveUS20100220693A1Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexNetwork Communication ProtocolsAloha
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
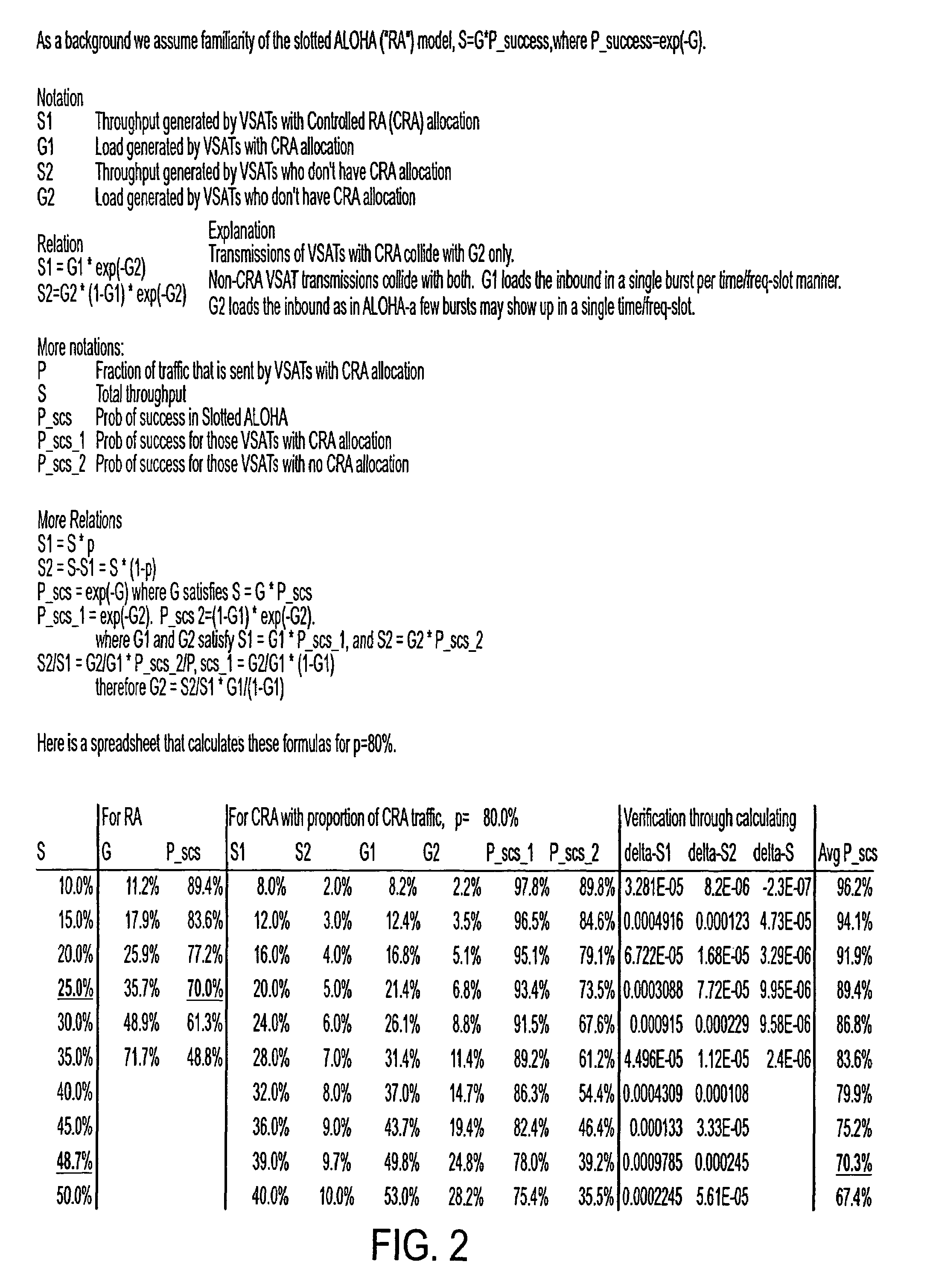
System and method for satellite based controlled ALOHA
A system and method for satellite based controlled ALOHA is provided. The system and method configure VSATs so that they accept guidance from a centralized and / or distributed system controller to determine when, where, and / or on what portion of a satellite resource to attempt to access a channel. The system and method take advantage of traffic patterns to maximize efficiency by utilizing a centralized and / or distributed control to determine which VSATs are and are not currently active, and to allocate to a portion of the inbound channel to the active VSATs and a portion of the inbound channel to the inactive VSATs. In a distributed approach, each VSAT decides for itself whether it captures a certain part of the inbound resource or not. This decision can be made based on previous transmissions that went through the part of the inbound intended to be captured.
Owner:GILAT SATELLITE NETWORKS
Multi-tag identification method of RFID reader
InactiveCN101944171AAvoid disadvantagesAvoid wastingCo-operative working arrangementsSensing record carriersAlohaBinary tree
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
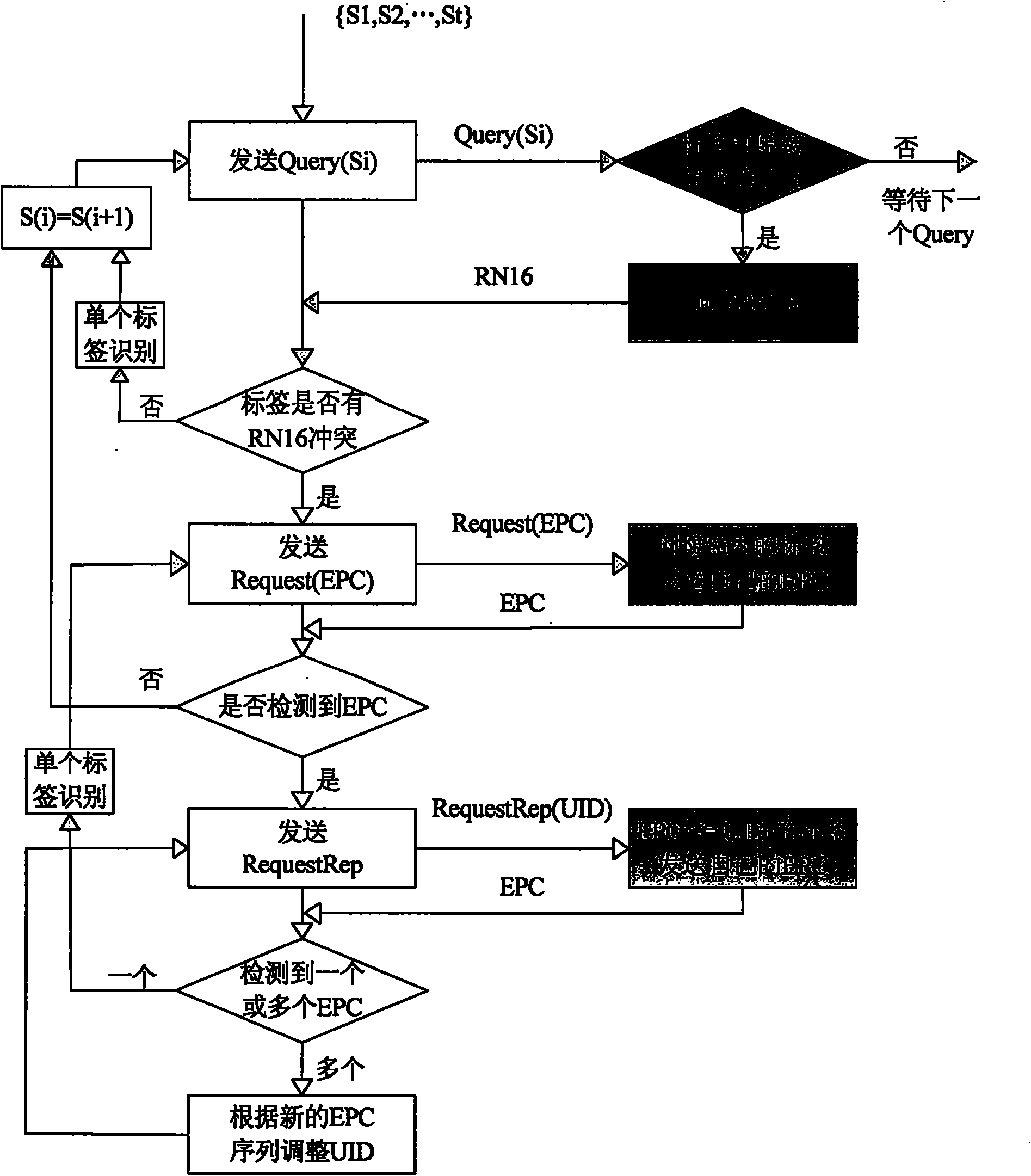
RFID (radio frequency identification) anti-collision method based on GASS (grouped adaptive allocating slots)
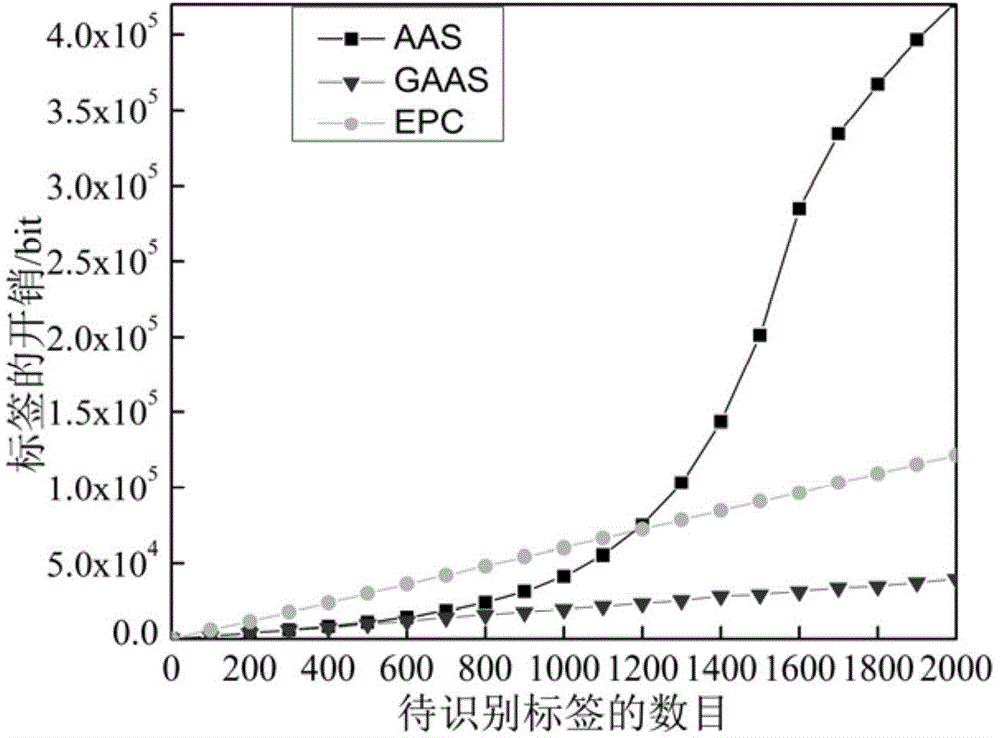
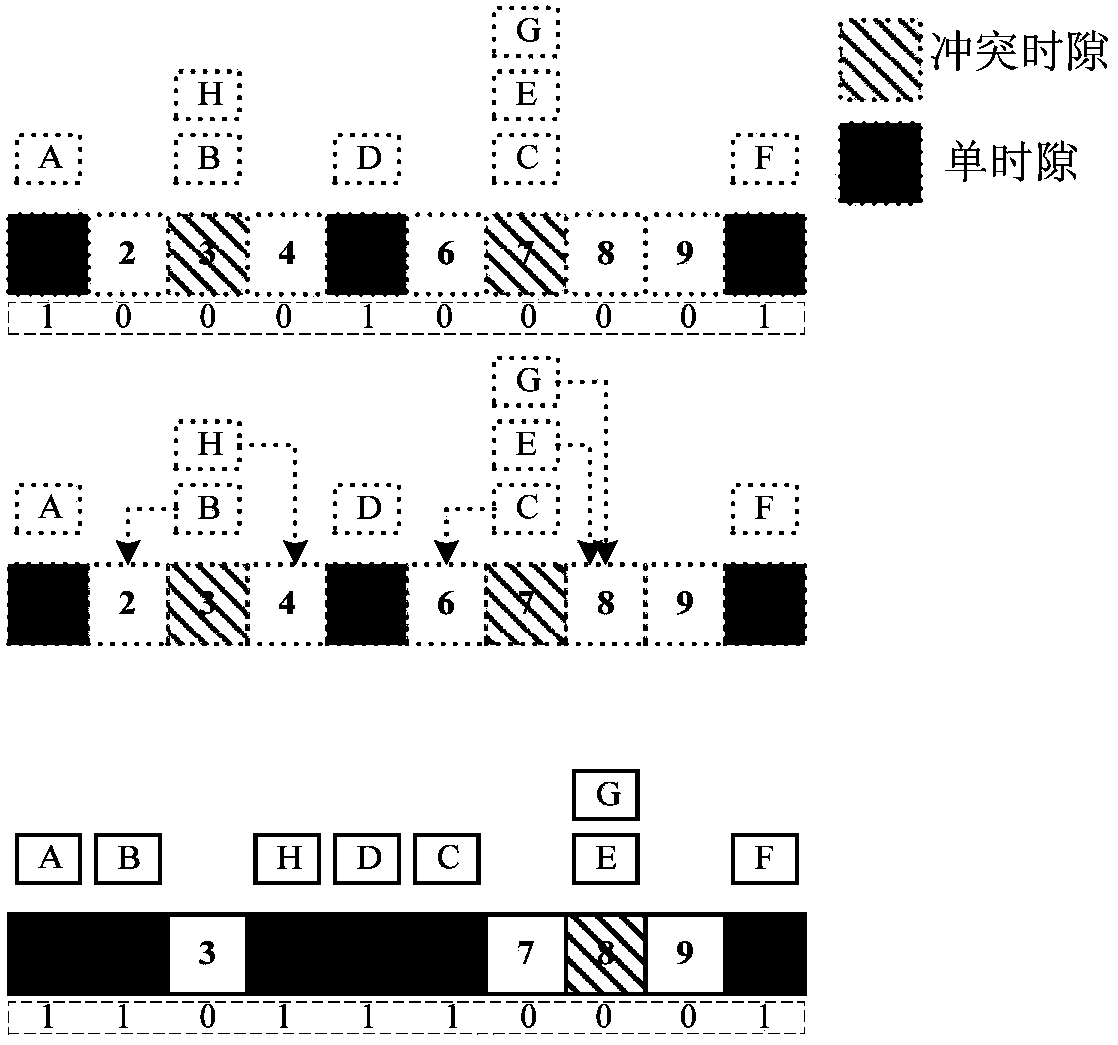
An RFID (radio frequency identification) anti-collision method based on GASS (grouped adaptive allocating slots) comprises steps as follows: firstly, a reader performs scanning statistics on slots randomly selected by tags and sends the slots to all the tags, then the tags perform corresponding slot adjustment, the reader skips free slots and collision slots and allocates effective slots adaptively, the tags are quickly identified, and when the number of unidentified tags is larger, the algorithm adopts strategies such as grouping, dynamic frame length adjustment and the like to shorten slot processing time. Simulation results indicate that with the adoption of the method, the identification efficiency and stability of a system are improved, the transmission cost is reduced, particularly when the number of the tags exceeds 1,000, the throughput of the algorithm is still kept higher than 71%, the efficiency of the system is 300% and 97.2% higher than that of a system adopting a traditional frame-slotted ALOHA-256 algorithm and that of a system adopting a grouped dynamic frame-slotted ALOHA algorithm respectively, and the method has practical application values for rapid identification of Internet-of-Things tags.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
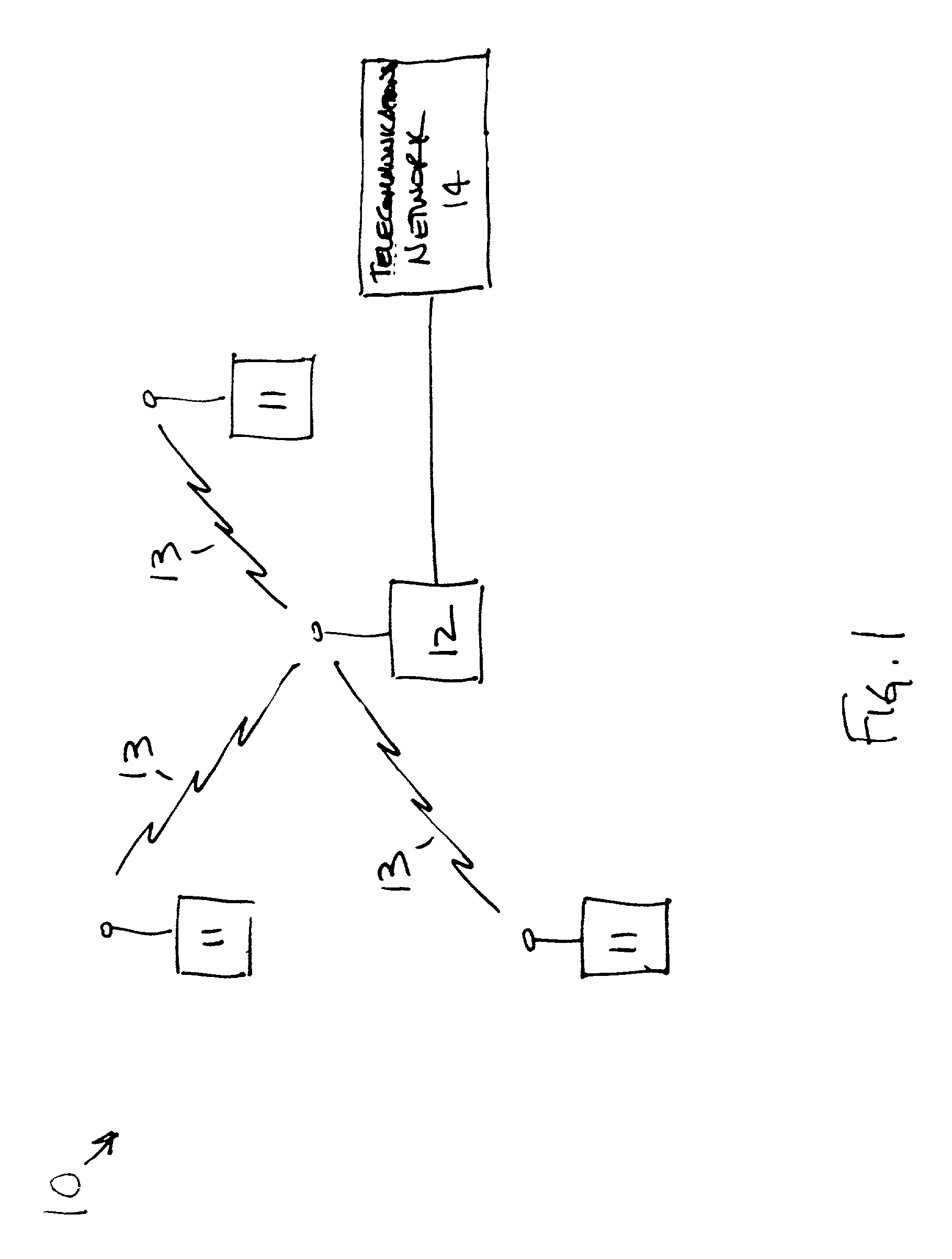
Method for dynamic load management of random access shared communications channels
InactiveUS20050054288A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesAlohaRandom-access channel
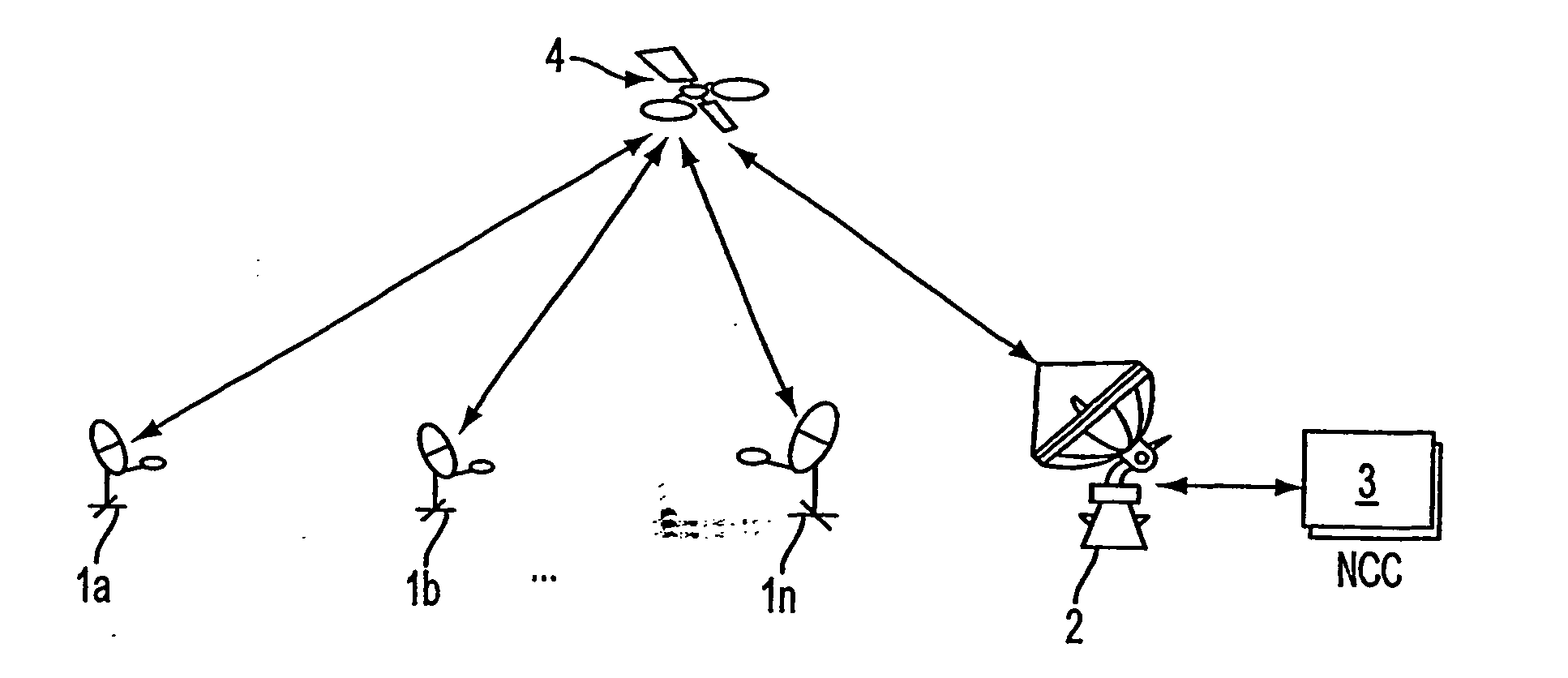
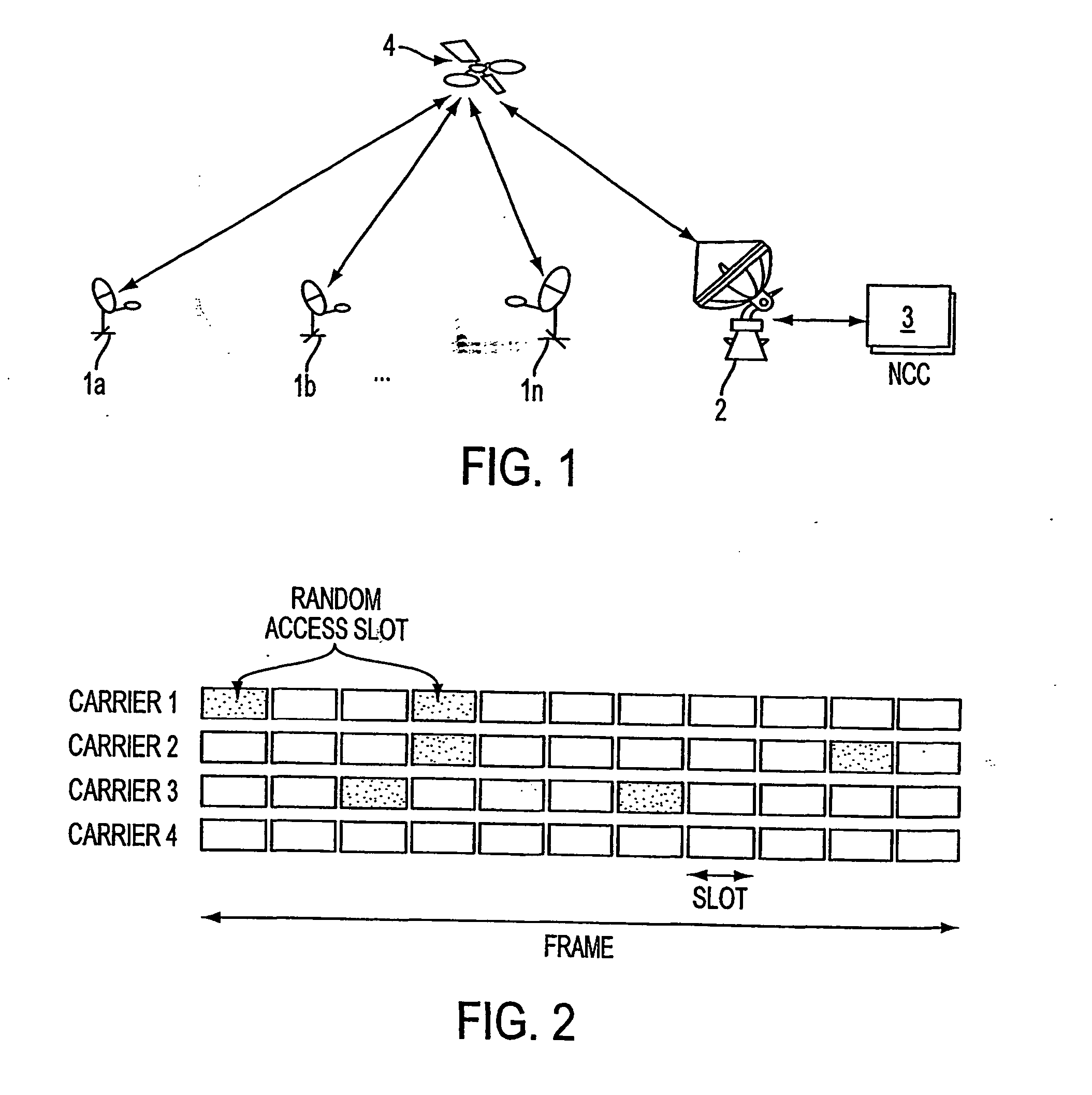
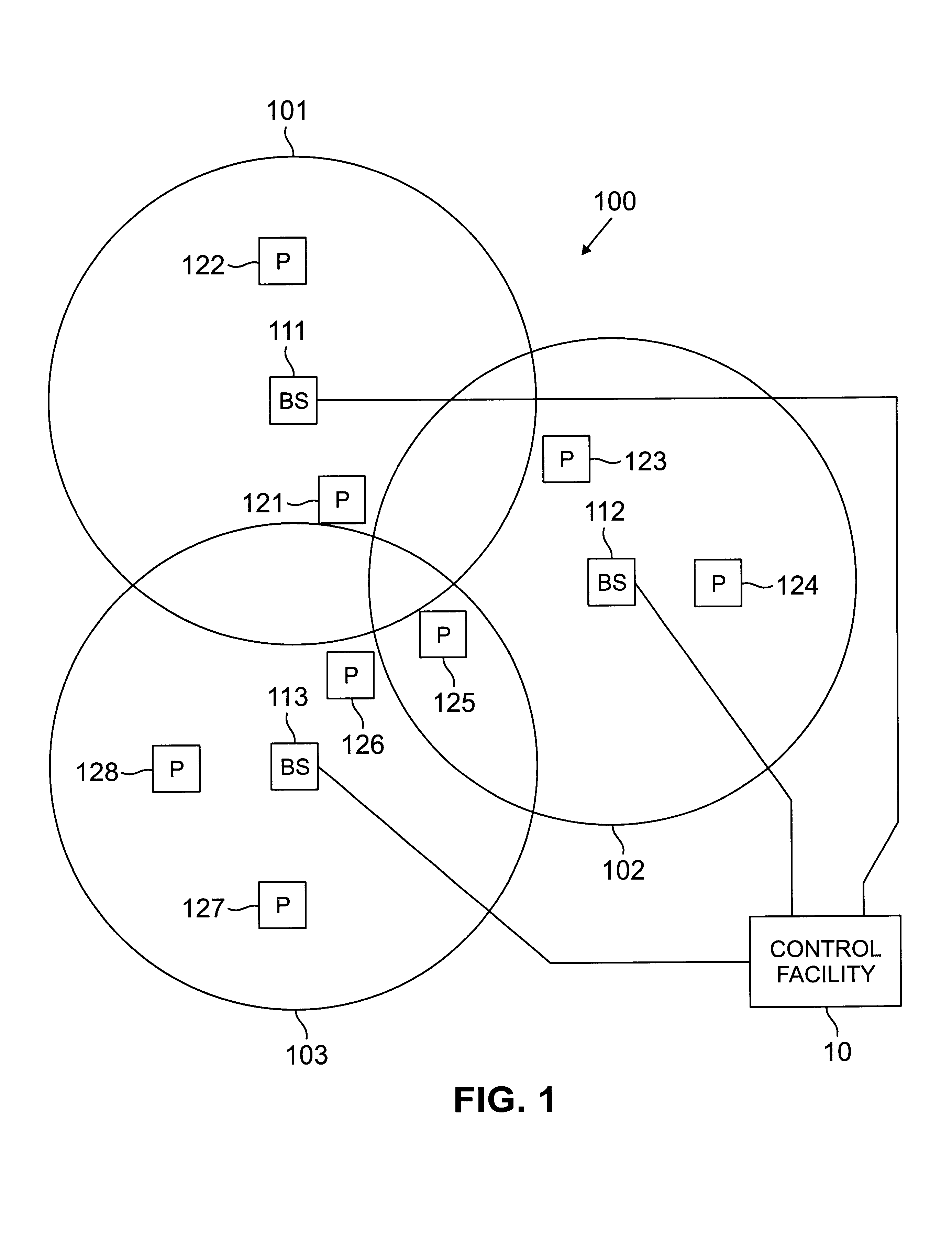
A novel method for dynamic load management of random access channels (also known as Aloha channels) in shared communications systems, such as satellite (4), cable, and wireless communications networks is provided. The method provides algorithms and procedures to accurately estimate traffic load offered by multiple distributed terminals (1a, 1b, . . . 1n) into the channel (2). And also provides for regulating traffic so that the channel (2) is not overloaded. The traffic load management algorithms can be done at a central site, such as a Network Control Center (3) or a cable head-end. Alternatively, traffic load management can be done in a distributed manner by all terminals. Traffic regulation is done in a fair manner across all terminals. The algorithms are designed for efficient implementation in software and / or hardware.
Owner:COMSAT
Method and system for identifying lost tag of RFID system
The invention provides a method for identifying a lost tag of an RFID system. The method for identifying the lost tag of the RFID system comprises the steps that a Bloom filter is used, the property whether an element exists in a set or not can be searched for, and tags in a set of an expected classification are activated to participate in the follow-up identification process; an empty time slot and a conflict time slot are made full use of on the basis of an ALOHA protocol, and identification of the lost tag in the classified RFID system is finally accomplished. According to the method for identifying the lost tag of the RFID system, the process of identifying the lost tag can be carried out by screening out the tags of the expected classification, the utilization rate of frames in the identification process is improved, and identification efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and apparatus for efficient and deterministic group alerting
ActiveUS7969959B2Efficient and deterministic alertingOvercome deficienciesFrequency-division multiplex detailsUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionAlohaConfusion
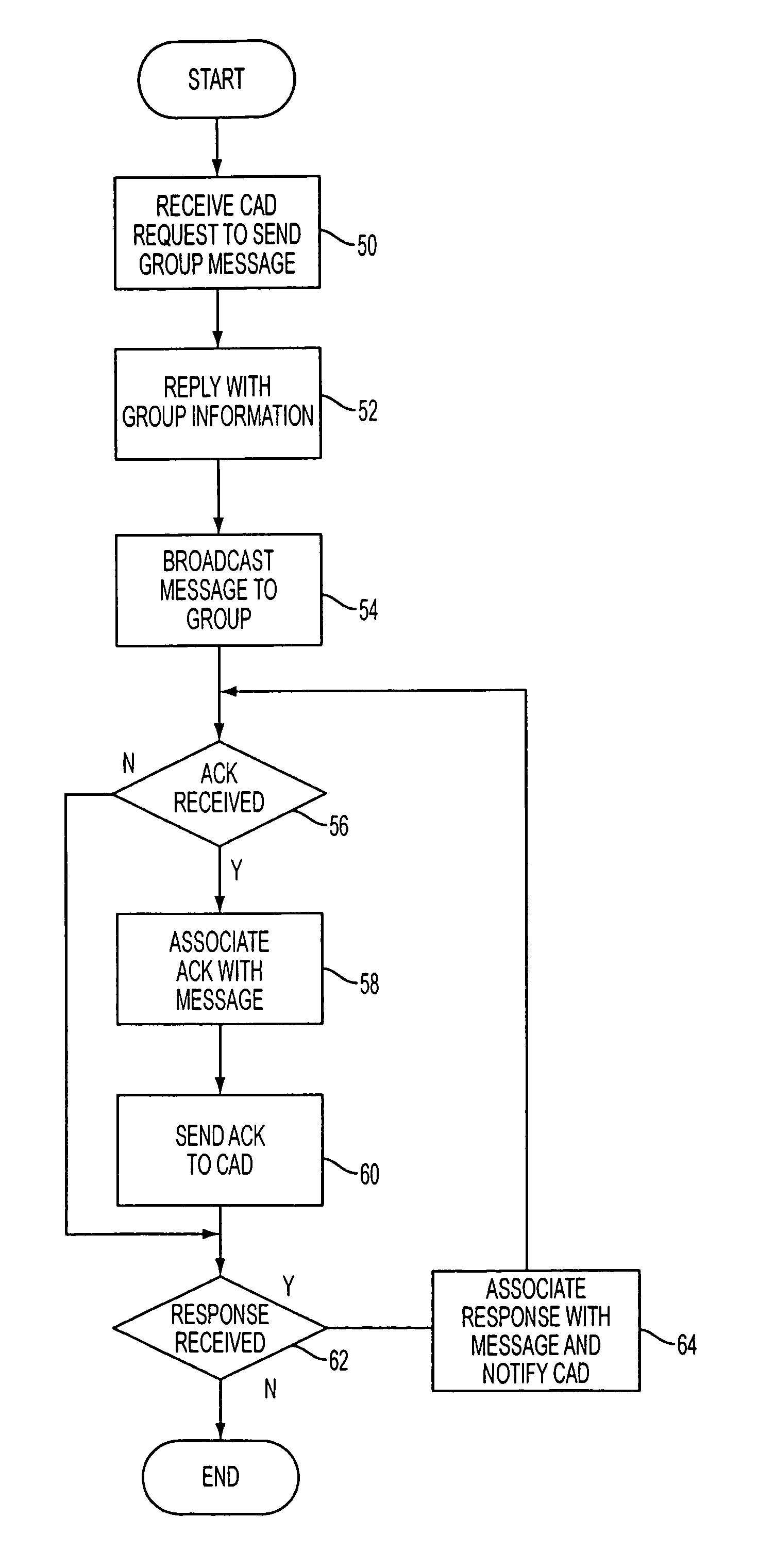
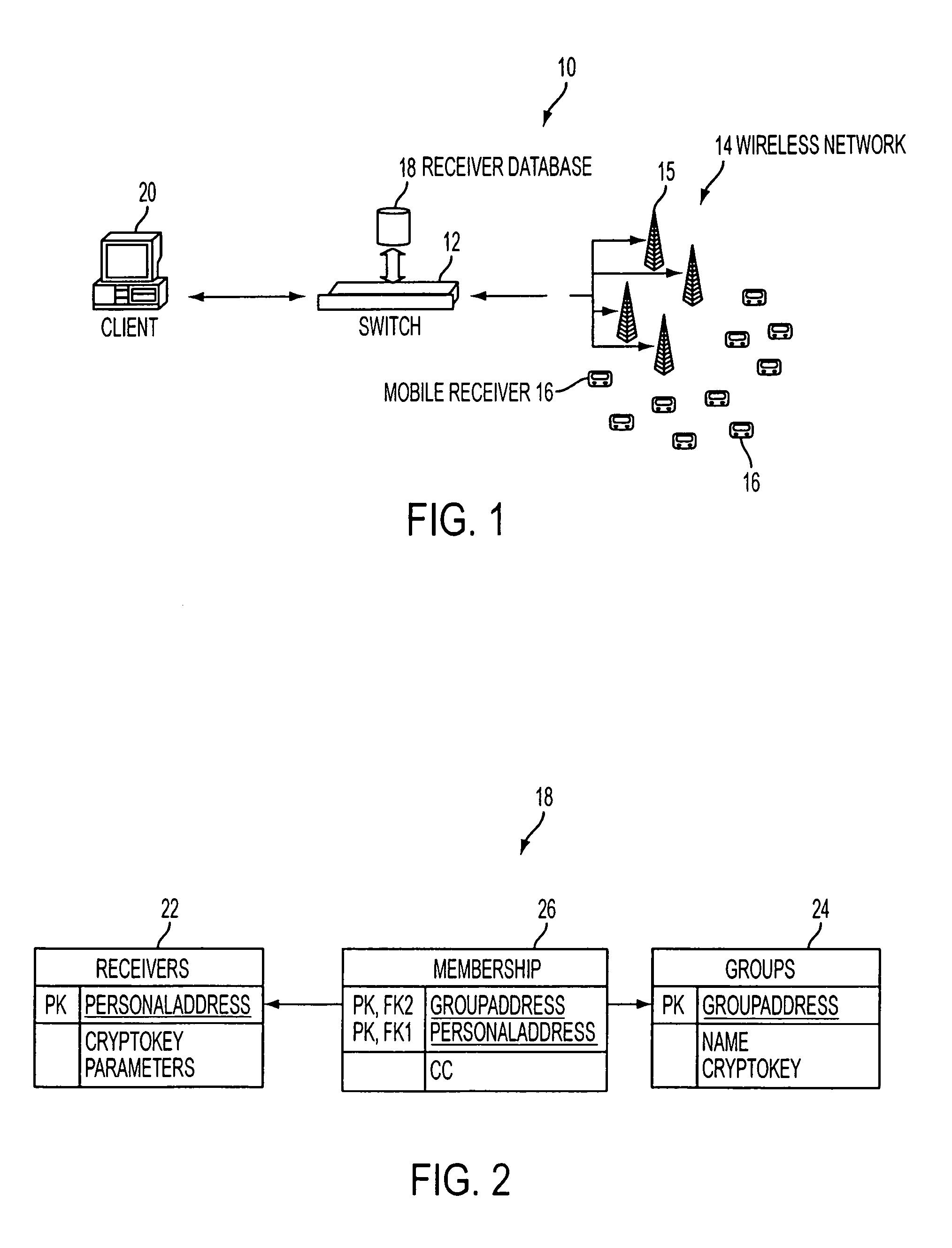
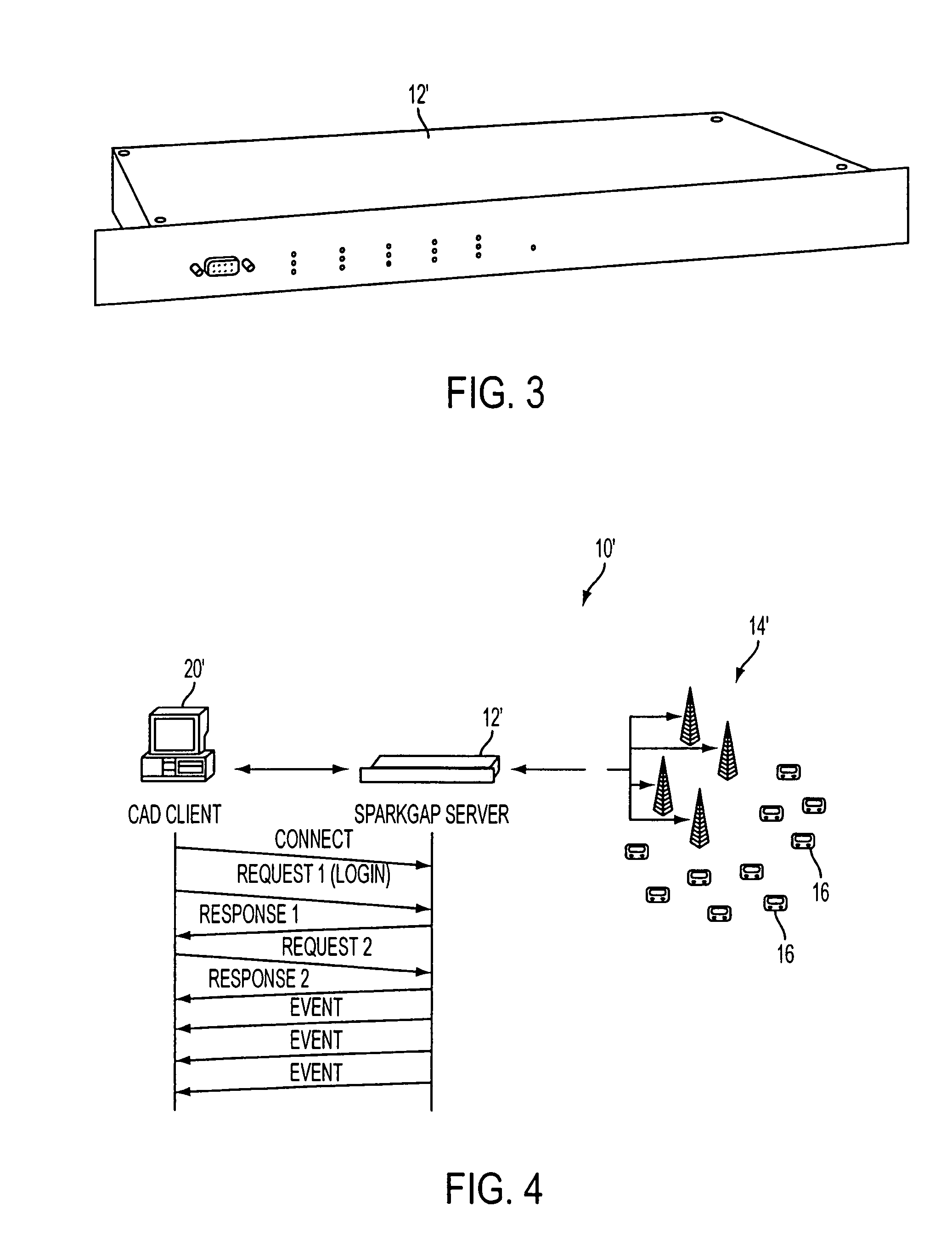
A system and method are provided for reliable, wireless group alerting in a system having a database, switch, wireless network, and a plurality of intelligent mobile receivers, and preferably employing a modified two-way paging based on ReFLEX™ protocol information service (IS) messages and a novel ALOHA command for multicast acknowledgement from mobile receivers. An encrypted message is broadcast to a group address and received by a selected number of the mobile receivers. The network replies to the sender with detailed information about the individual members in the alert group. Each of the mobile receivers in the group then acknowledges the common message back to the system, decrypts the message, displays it to the user, and allows the user to respond. The system employs centralized management to simplify the roles of the mobile users and administrators, minimizing configuration and operational human errors that would otherwise result in confusion or lost messages.
Owner:CRITICAL HLDG
High-efficiency multi-tag anti-collision radio frequency identification (RFID) method
InactiveCN102024134ANarrow searchQuick identificationCo-operative working arrangementsSensing record carriersTelecommunicationsMessage frame
The invention discloses a high-efficiency multi-tag anti-collision radio frequency identification (RFID) method, which mainly comprises a tag division process and a tag searching process. An ALOHA frame or other signal frames are established in the tag division process; and in the tag division process, time slots are randomly selected for tags to transmit IDs, and function in dividing a tag group consisting of all the tags in the range of a reader-writer into a plurality of independent small tag groups. In the tag searching process, a plurality of message frames are involved; and each frame corresponds to a specific collision time slot in the tag division process, and in the frame, the tags can be identified one by one by a backtracking binary-tree searching method and the like. The method can greatly reduce collision phenomena in a multi-tag identification process and reduce times of information interaction between the tags and the reader-writer, and ensures high efficiency and security.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
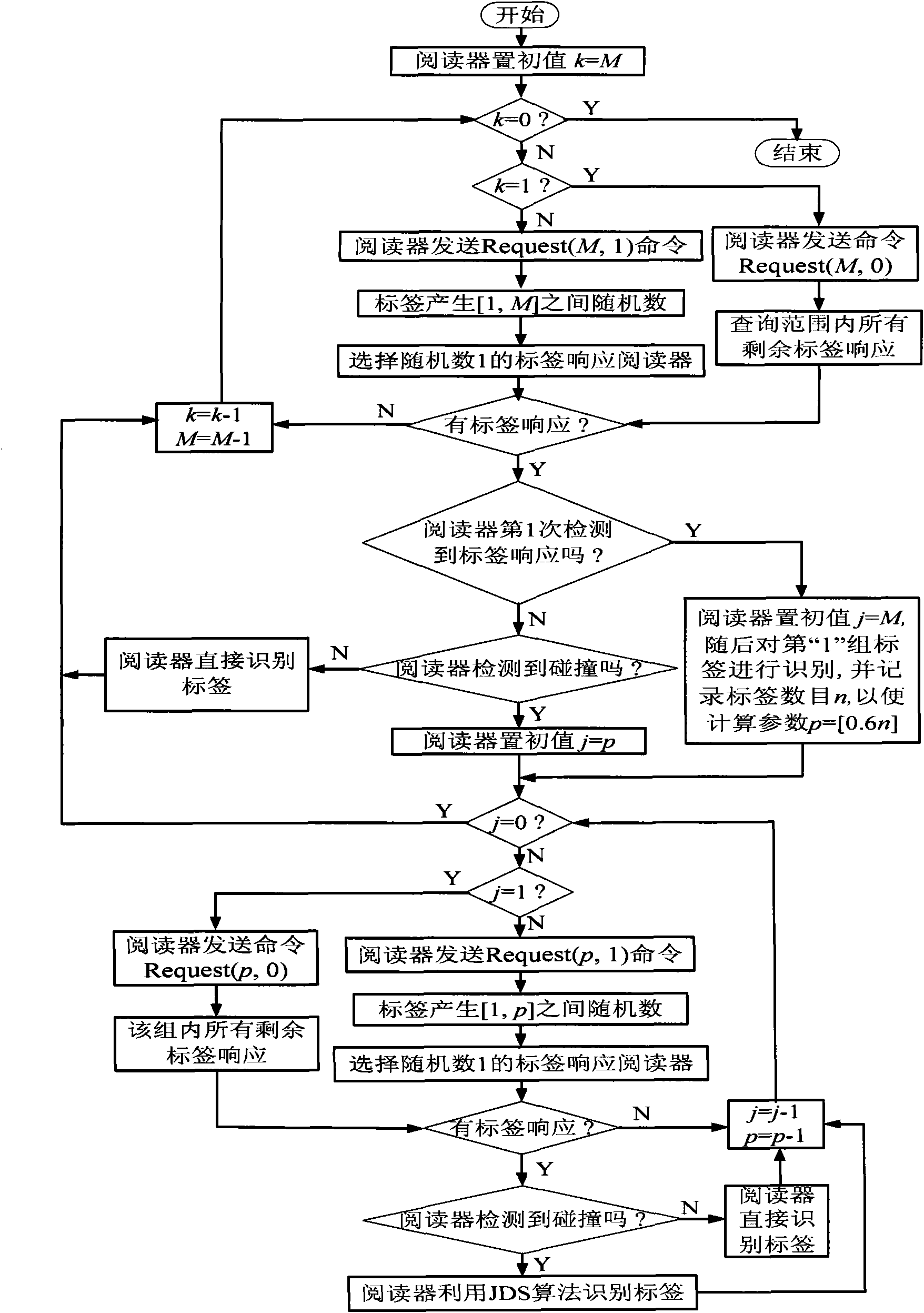
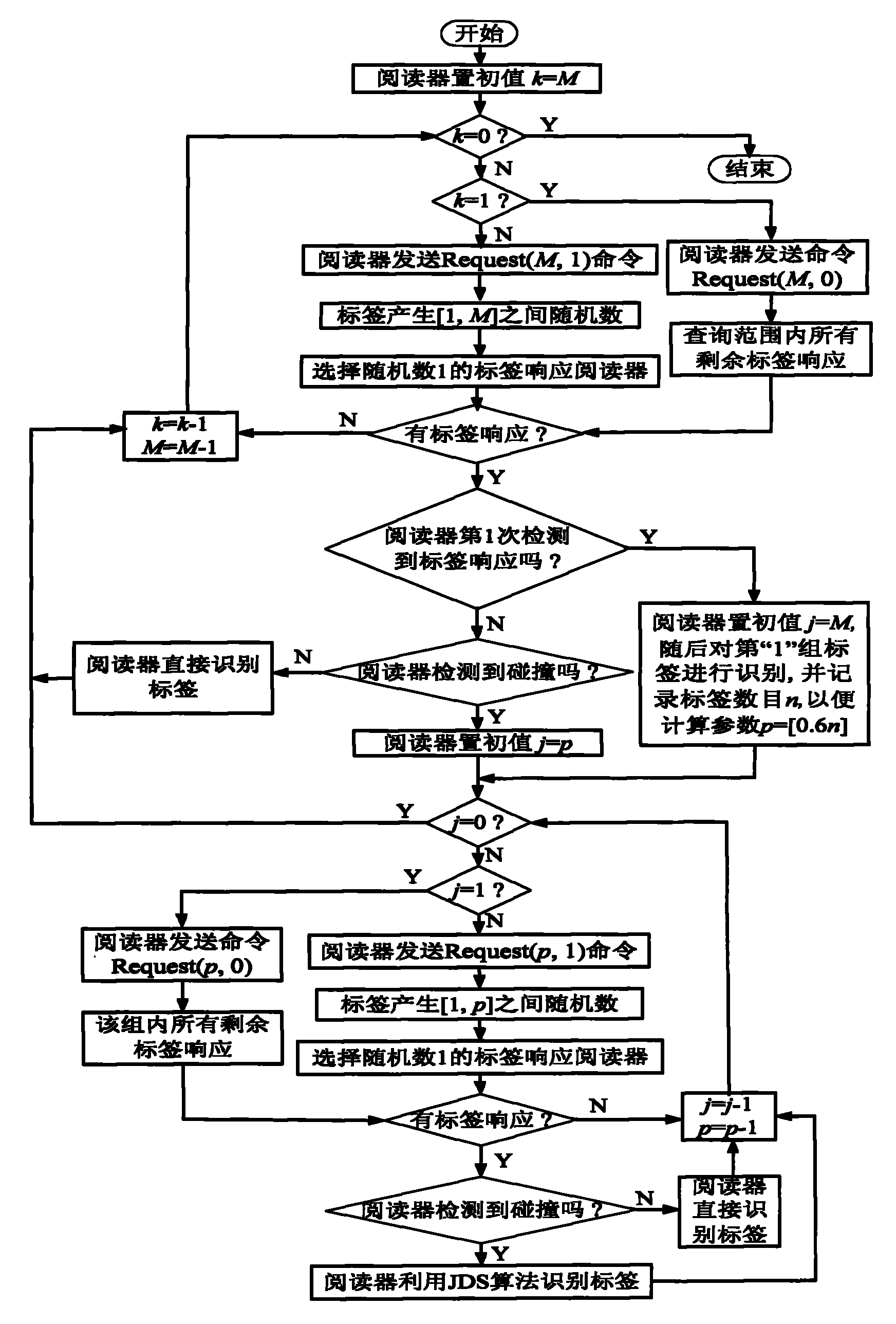
Multi-label anti-collision method based on grouping mechanism and jumping dynamic binary recognition
ActiveCN101866413AReduce the probability of collisionReduce the number of response readersSensing record carriersPattern recognitionAloha
The invention discloses a multi-label anti-collision method based on a grouping mechanism and jumping dynamic binary recognition used in an RFID system. The method comprises a label estimation phase and a label recognition phase, wherein in the label estimation phase, labels are grouped randomly, a first group of labels are recognized by adopting the jumping dynamic binary algorithm, and then the estimation of the quantity of unrecognized labels are completed according to the characteristics that the quantity of each group of labels are in accordance with even distribution; in the label recognition phase, a second grouping quantity, i.e. the optimal grouping conducted on the rest groups of labels is determined; in the recognition process, jumping dynamic binary algorithm is adopted to recognize collision labels, so as to recognize all the labels. The invention combines the advantages of binary tree algorithm and Aloha algorithm, thus greatly reducing the quantity of collision labels in the early and later phases of recognition. The invention has simple structure, rapid recognition speed, low complexity and label power consumption, thus being applicable to RFID system.
Owner:盐城市鹤业实业投资有限公司
Method for selecting one or more transponders
InactiveUS20060044114A1Reliable and time-efficient selectionSolve bulkyMemory record carrier reading problemsRadio transmissionNumber timesAloha
A method and device for selecting one or more transponders, in particular backscatter-based transponders, from a plurality of transponders by a base station, which method is based on a slotted ALOHA method, in which the base station defines numbered time slots and a random number generated in a given transponder determines a time slot when the transponder transmits its transponder-specific identification to the base station. The random number is generated in a given transponder with the aid of a random number generator, the relevant random number generator is switched into a counter operating mode after reception of a selection command transmitted by the base station, while a count state of the random number generator is decremented or incremented when the base station transmits the start of a time slot, the relevant transponder transmits a transponder-specific identification to the base station if the count state of its random number generator is equal to a predetermined value, and the relevant random number generator is then switched back into the operating mode for random number generation.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Method for underwater acoustic sensor network Aloha protocol
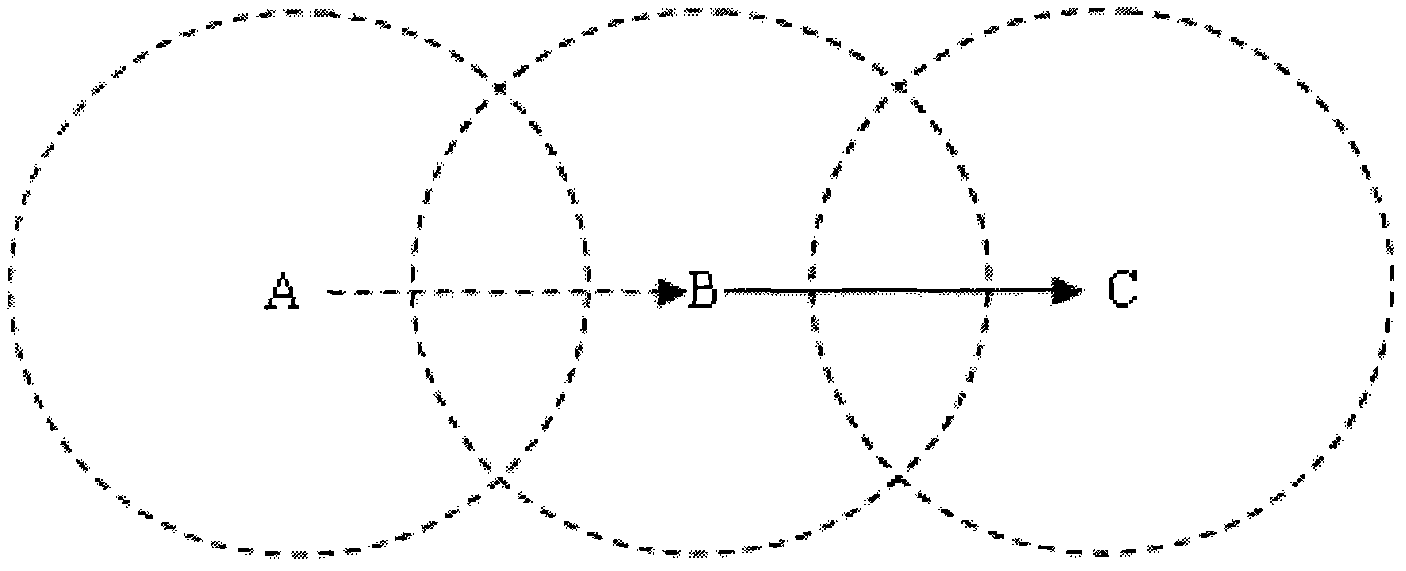
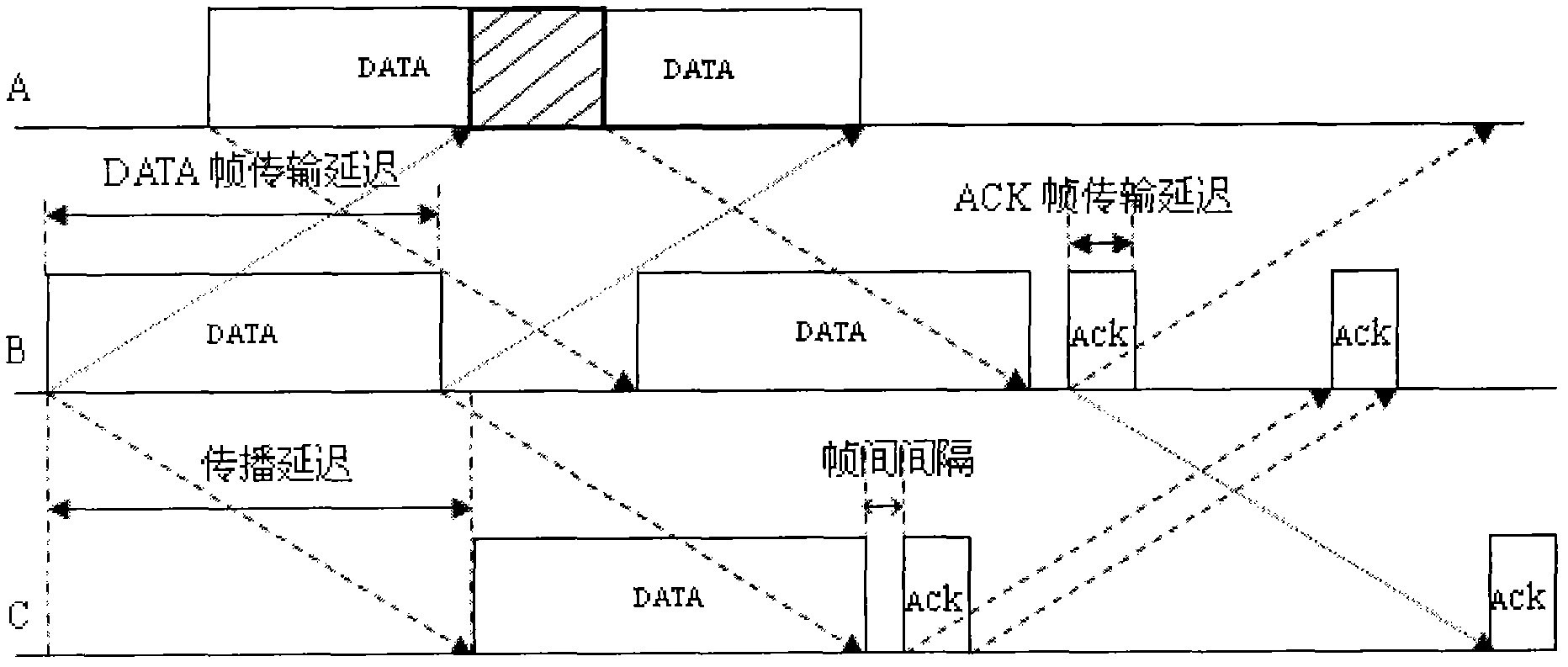
InactiveCN101982944AError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork topologiesPropagation delayInformation transmission
The invention relates to a method for an underwater acoustic sensor network Aloha protocol, which adopts a semiduplex communication mode and comprises the following steps: a node enters in the communication process after network initiation, channel monitoring is performed before data is transmitted, information transmission is performed when the channel is in an idle state, before confirmation information arrives, long propagation delay of an underwater acoustic channel is adopted to monitor information of other nodes, and channel monitoring is performed by adopting withdrawal gaps in the withdrawal process under a data conflict state, thus realizing conflict-free communication between one node and multiple nodes at the same time.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Self-adaptive competition window adjusting method based on interference analysis
InactiveCN102811498AReduce idlingIncrease profitWireless communicationInterference (communication)Round complexity
The invention discloses a self-adaptive competition window adjusting algorithm based on interference analysis and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The method is suitable for a time slot Aloha mechanism and comprises the steps of: determining a competition window value and back-off time, namely counting collision times and successful times in a period, acquiring corresponding channel busy indexes according to the counted values, and updating the competition window value according to the channel busy indexes when a next period begins; and determining back-off time, namely performing interference analysis on all nodes, determining a neighboring node number of each node and accordingly acquiring a quantile, and choosing the back-off time according to the quantile values when the nodes are successfully sent or collided. According to the self-adaptive competition window adjusting algorithm, the interference analysis is used for choosing the back-off time, so that the algorithm is low in complexity, and network time delay and collision probability are effectively reduced, and throughout performance is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
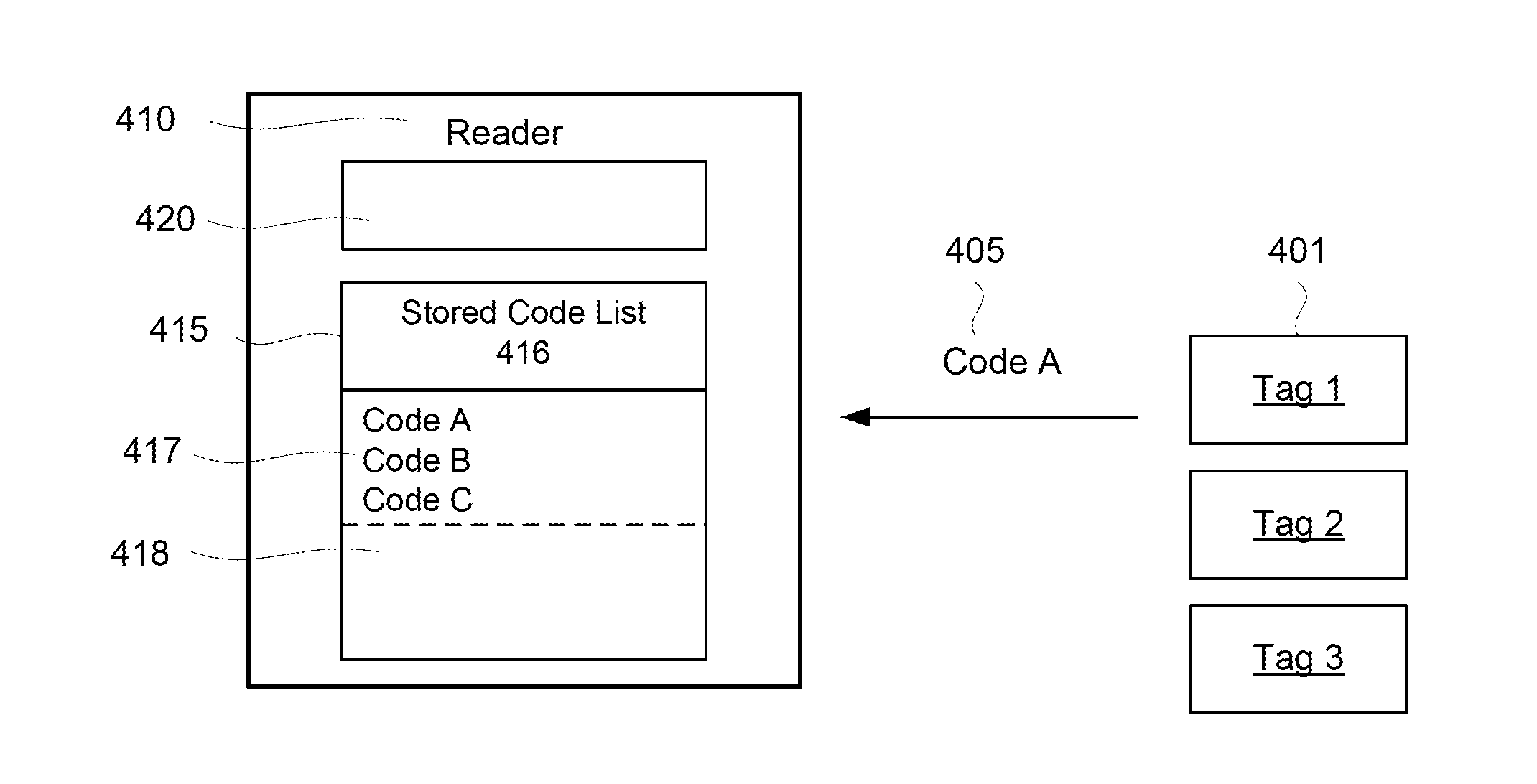
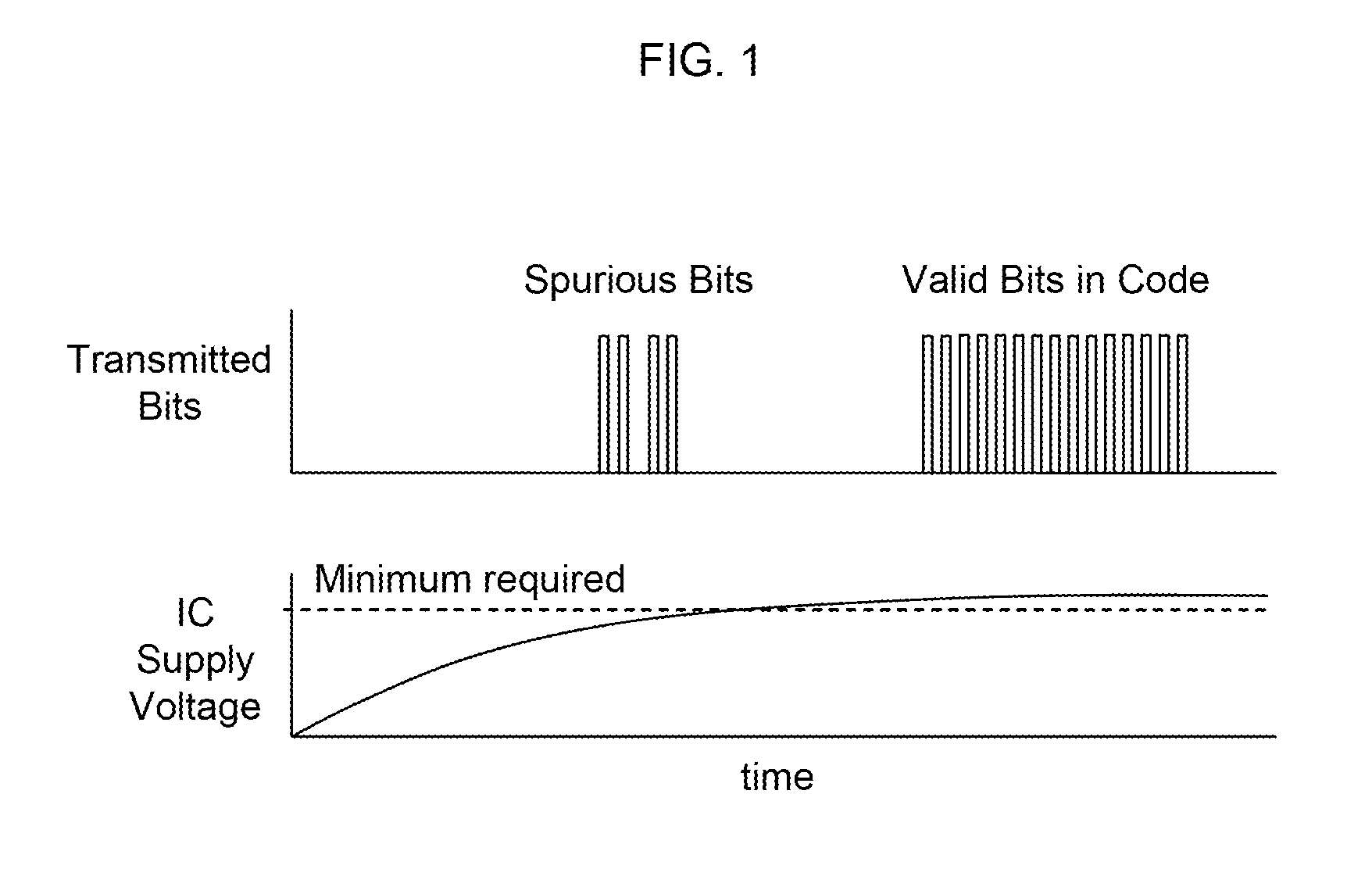
Methods and Systems for Validating Code from a Wireless Device
InactiveUS20110018692A1Reliable methodReadily apparentError preventionSensing detailsIntegrated circuitAloha
Methods, algorithms, architectures, circuits, and / or systems for managing POR-less integrated circuits are disclosed. The method of validating code from a wireless device can include: (i) broadcasting a signal from a reader to the wireless device, (ii) reading a code transmitted, re-radiated, and / or backscattered from the wireless device, the code having a predetermined quality, characteristic, and / or property, (iii) comparing the code to a reference quality, characteristic, and / or property, and (iv) validating the code when the predetermined quality, characteristic, and / or property matches the reference quality, characteristic, and / or property. Embodiments of the present invention can advantageously provide a reliable approach for validating integrated circuits that do not incorporate a POR circuit, and which therefore may transmit spurious bits of data upon being energized. In addition, embodiments of the present invention advantageously allow an Aloha-type anti-collision function to be implemented in a reader based on POR-less integrated circuits.
Owner:ENSURGE MICROPOWER ASA
Method and arrangement in a radio communication system
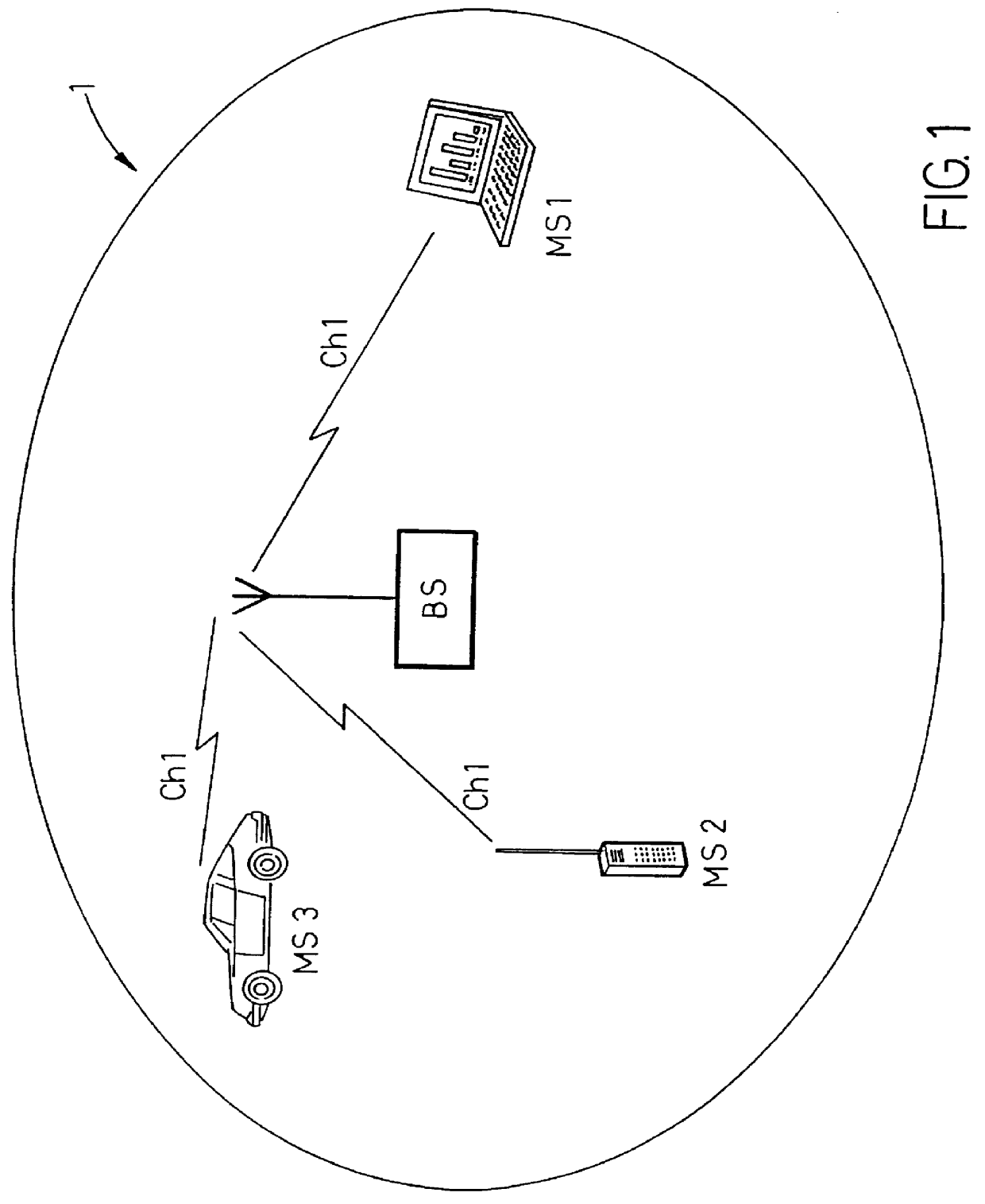
InactiveUS6097717AReduce delaysReduce loadNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesCommunications systemAloha
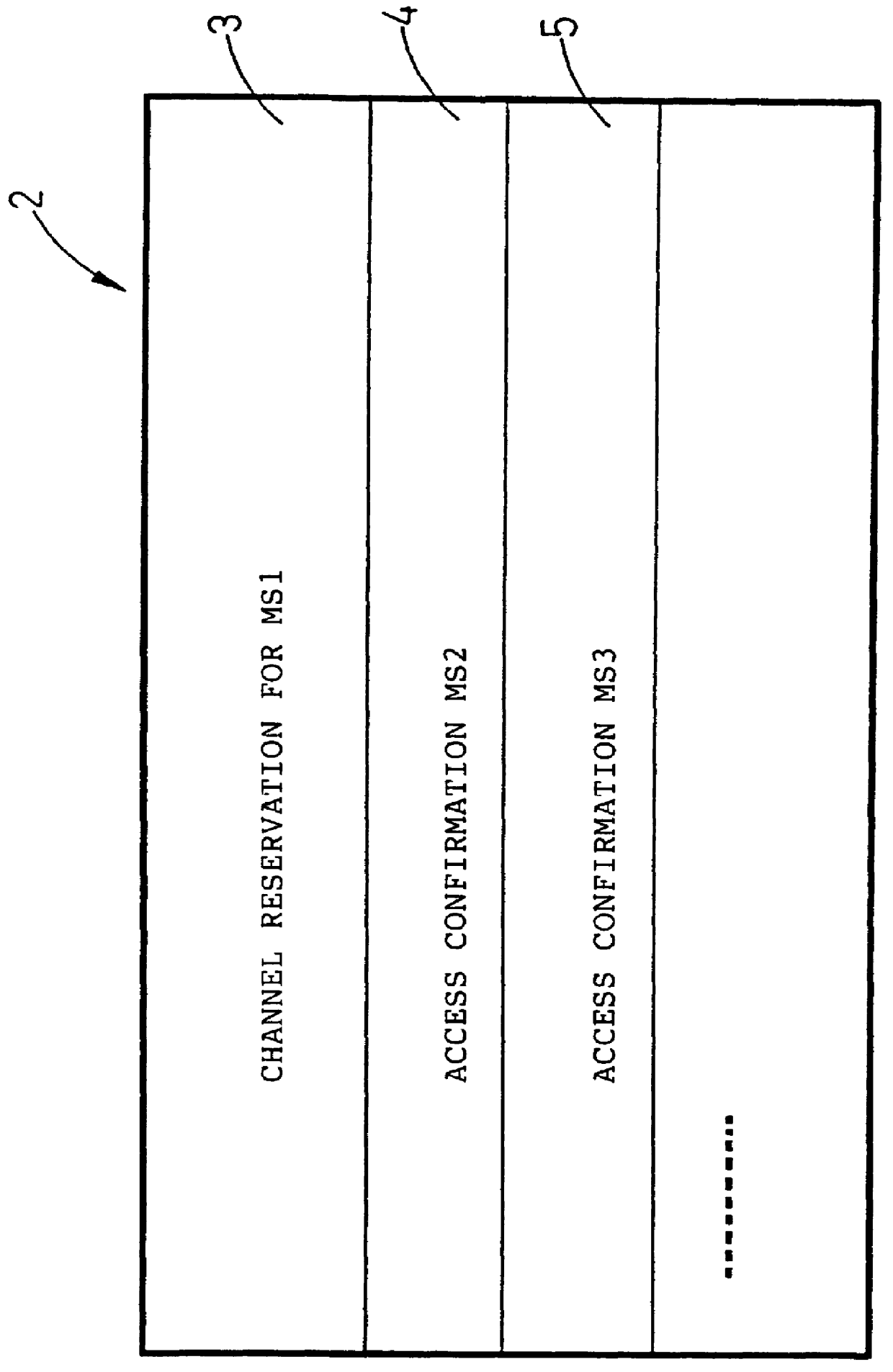
PCT No. PCT / SE96 / 00299 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 28, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 28, 1998 PCT Filed Mar. 7, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 31077 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 3, 1996The present invention concerns a process in a radio communication system which is arranged for packet data transmission according to a message-synchronized ALOHA protocol with reservation. Mobile stations in the system are arranged to send access requests to a base station during a reservation phase in a mobile radio system which uses this protocol. The base station is arranged to receive and comply with the access request from a first mobile station by sending thereto a channel reservation message (2) comprising a channel reservation (3). The base station is further arranged to receive access requests from at least a second mobile station for which channel reservation momentarily cannot be carried out. According to the process of the invention an access request received from the second mobile station is confirmed when channel reservation cannot be carried out in the usual manner. The confirmation is sent in the form of an access confirmation (4, 5) which is included in the same channel reservation message (2) as the channel reservation (3) for the first mobile station.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
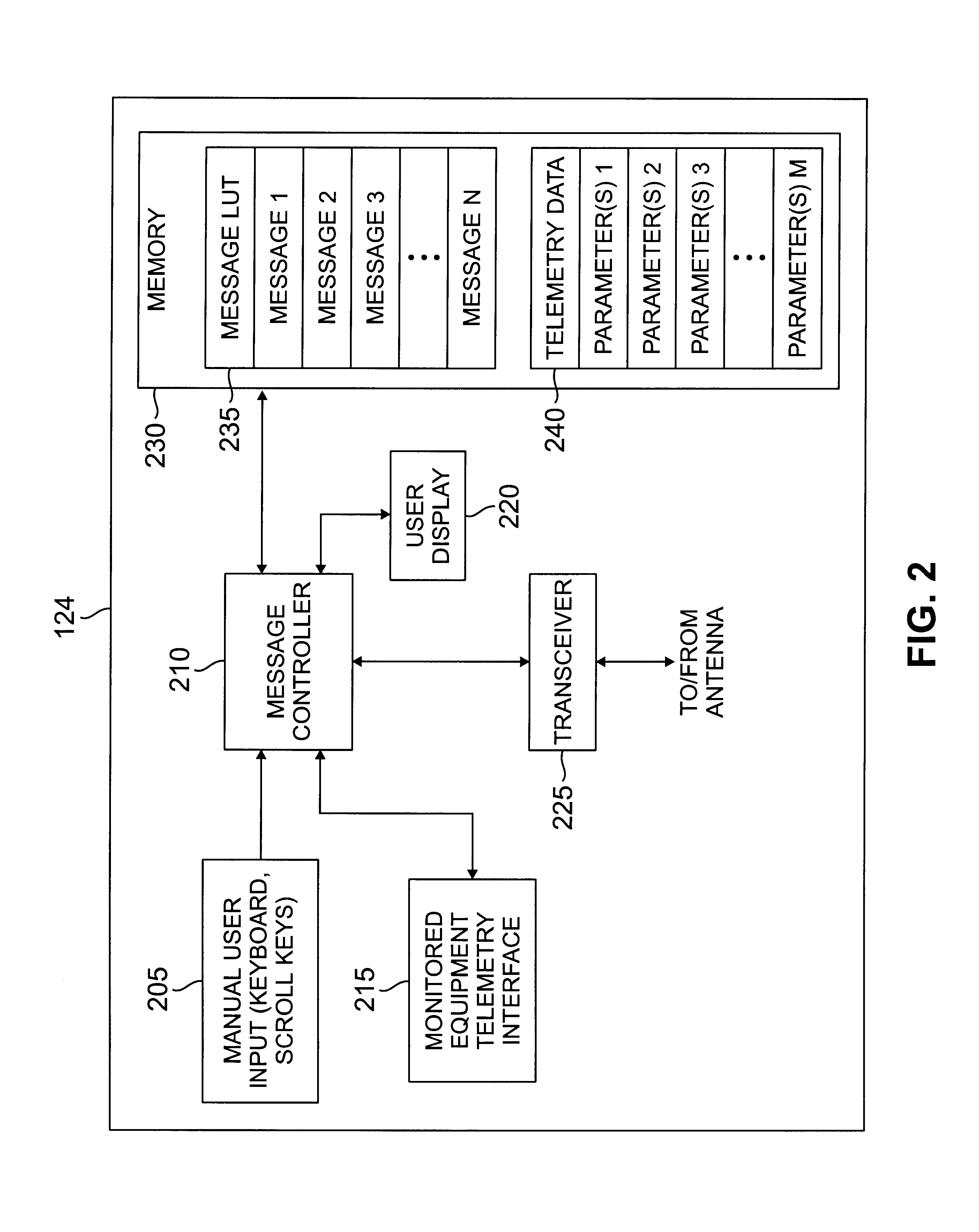
System and method for transmitting subscriber data in a narrowband advanced messaging system using unscheduled message time slots
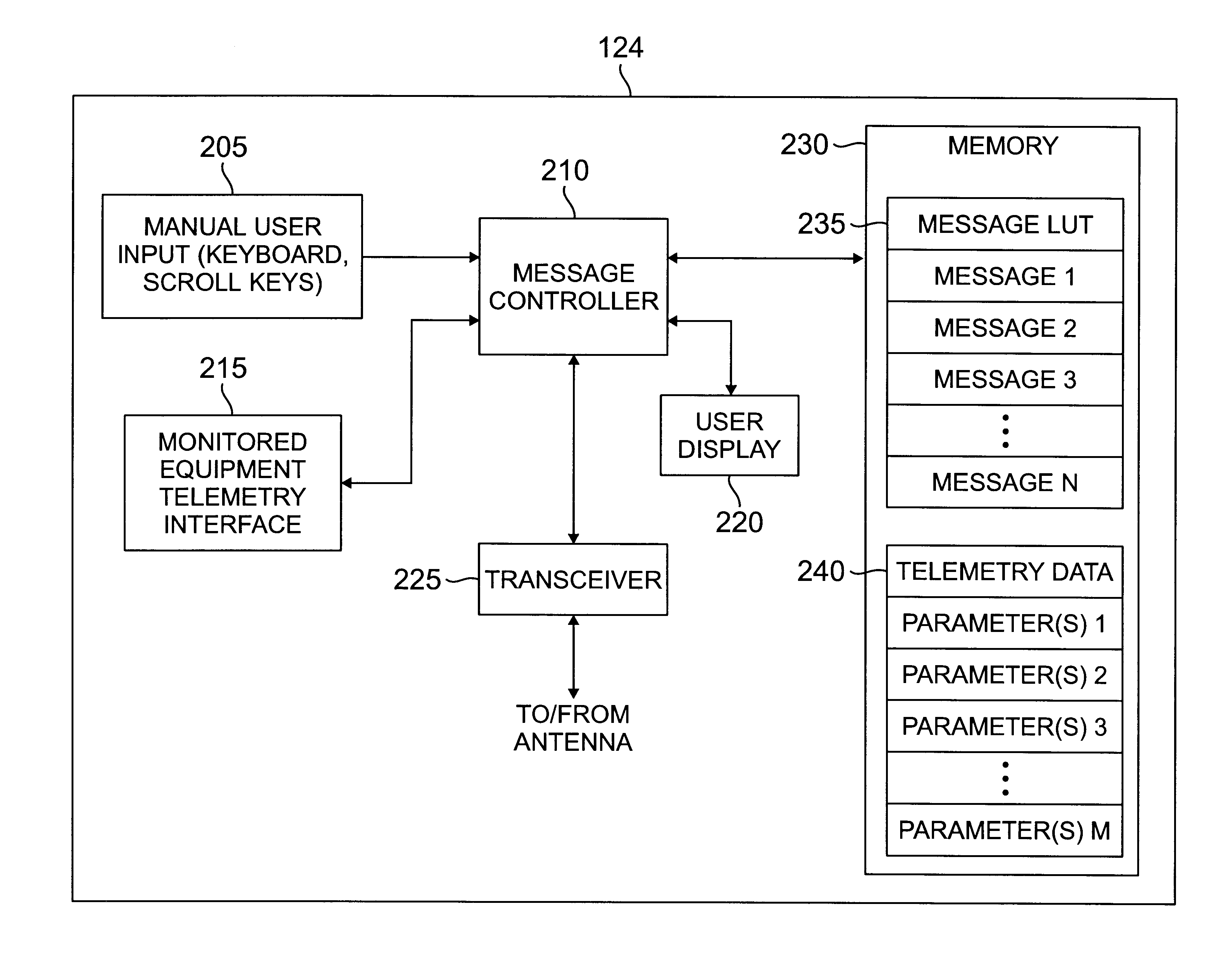
There is disclosed for use in a narrowband wireless messaging network, a subscriber communication unit that uses a miscellaneous ALOHA message to transmit predefined messages and / or formatted telemetry data to a base station. The subscriber communication unit comprises a transceiver for receiving messages from the base station in a forward channel and transmitting messages to the base station in a reverse channel. The reverse channel is divided into a plurality of scheduled transmission time slots and a plurality of unscheduled transmission time slots of the ALOHA type. A message controller receives input data generated by the subscriber communication unit and translates the input data into a reverse channel message capable of being transmitted in an available unscheduled time slot, such as a miscellaneous ALOHA message time slot.
Owner:USA MOBILITY WIRELESS INC
Label anti-collision algorithm based on RFID
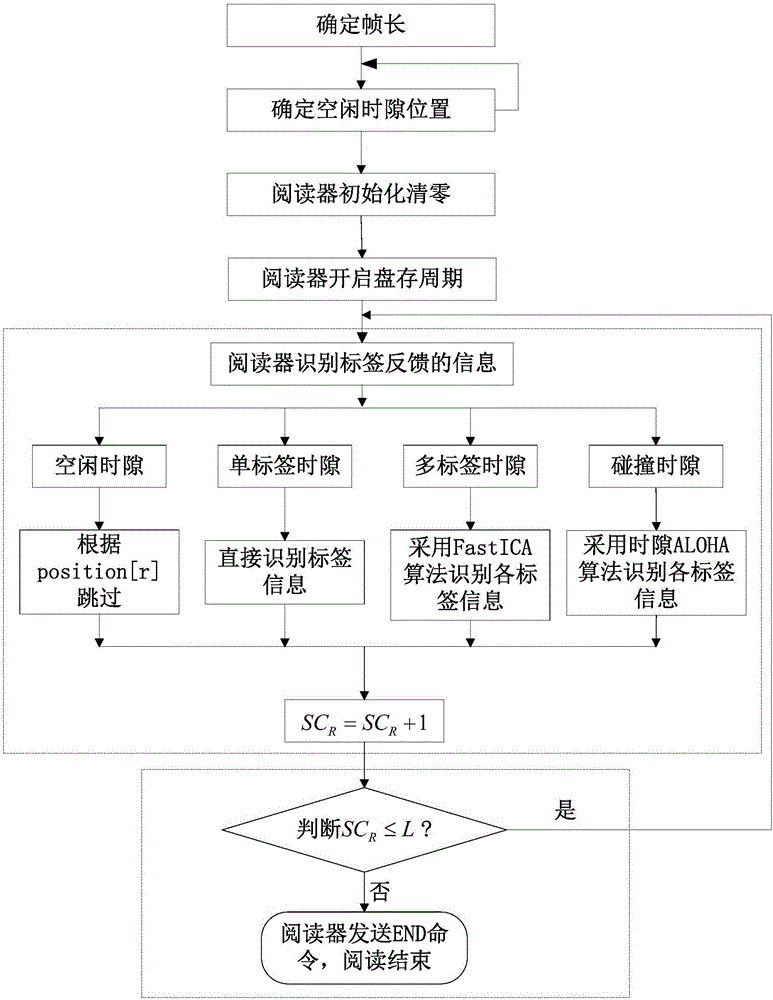
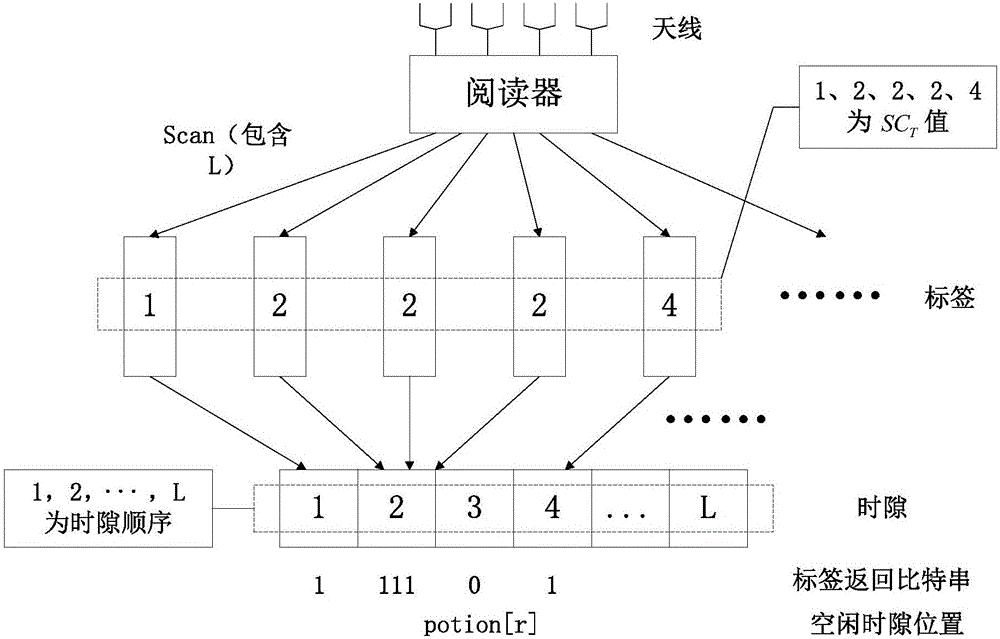
ActiveCN106778425AReduce running timeImprove efficiencySensing by electromagnetic radiationAlohaRunning time
The invention relates to a label anti-collision algorithm based on RFID. The algorithm includes the steps that 1, the frame length L is determined; 2, the positions of free timeslots are determined, wherein a reader sends a scanning instruction Scan including frame length L information to a label group within the recognizable range, time slot preview inventory taking is started, and the positions of the free timeslots are determined according to 1-bit information fed back by labels to the reader; 3, the reader is initialized and reset; 4, the reader starts an inventory taking period; 5, the reader recognizes the information fed back by the labels; 6, the current value SCR of a reader timeslot counter and the frame length L are compared to complete label recognition, wherein if SCR is smaller than or equal to L, the step 5 is executed again, if SCR is larger than L, it is shown that all the labels are recognized, the reader sends an ending instruction END, and the reading process is finished. A large number of free timeslots existing in an ALOHA algorithm are avoided through preprocessing, and the operating time of the algorithm is shortened; ID information of multiple labels can be read in one timeslot at the same time, and therefore the efficiency of the algorithm is improved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Control channel for a wireless digital subscriber line system
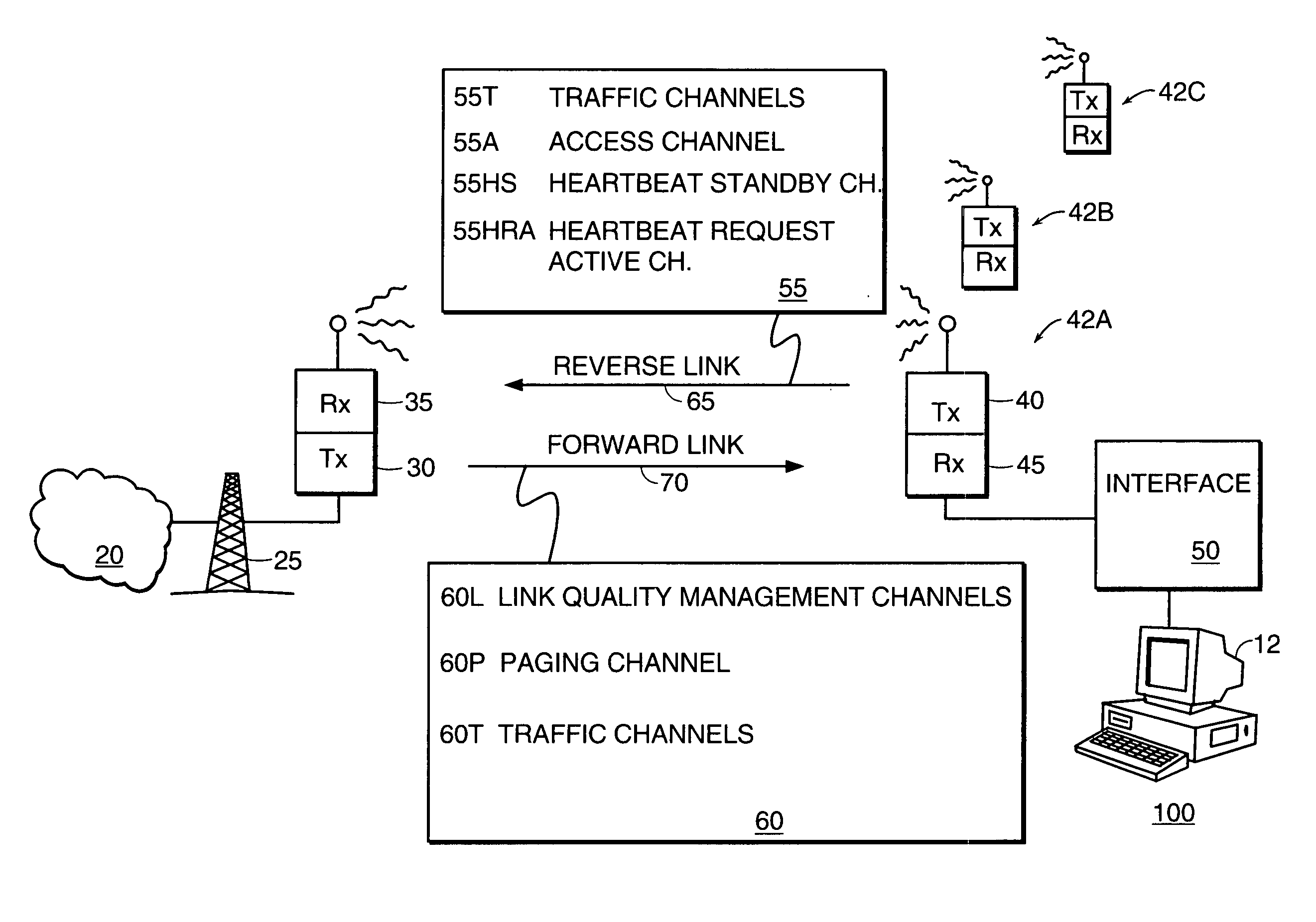
InactiveUS7170943B1Modulated-carrier systemsTime-division multiplexDigital subscriber lineCommunications system
A user control channel for a wireless digital subscriber line systems and the like, or other communications systems which can benefit from a control channel which provides a low data rate connection between stations on an ongoing basis, makes efficient use of transmission capacity in the communications systems. In one embodiment, the user control channel has a structure employing slotted frames, and a user can be assigned multiple slots, a single slot or less than a single slot (sharing slots with other users) to meet the data transmission needs of the user. Also, one or more slots can be designated as random access slots which users can access via an Aloha-like or other random access protocol as needed.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Access control method and device
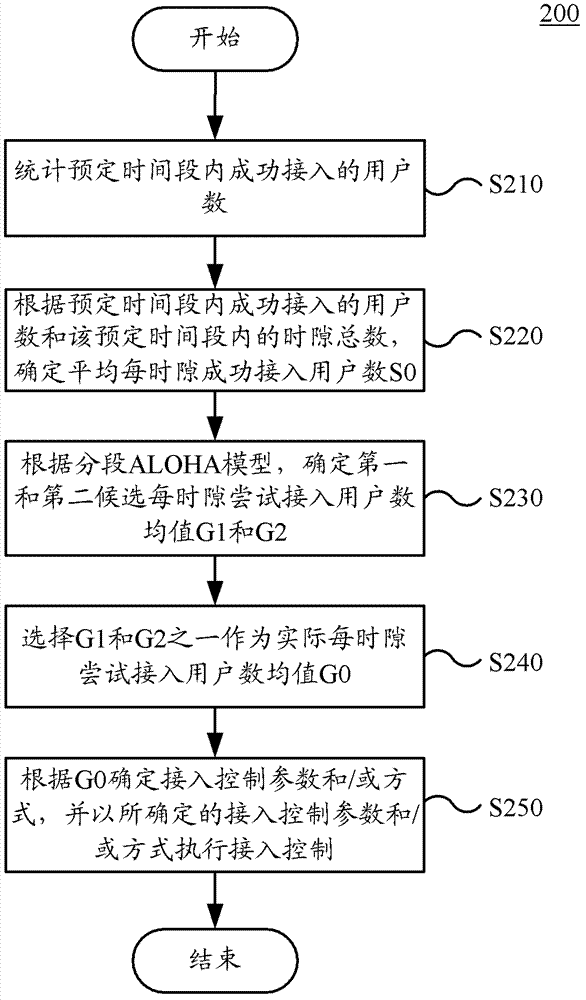
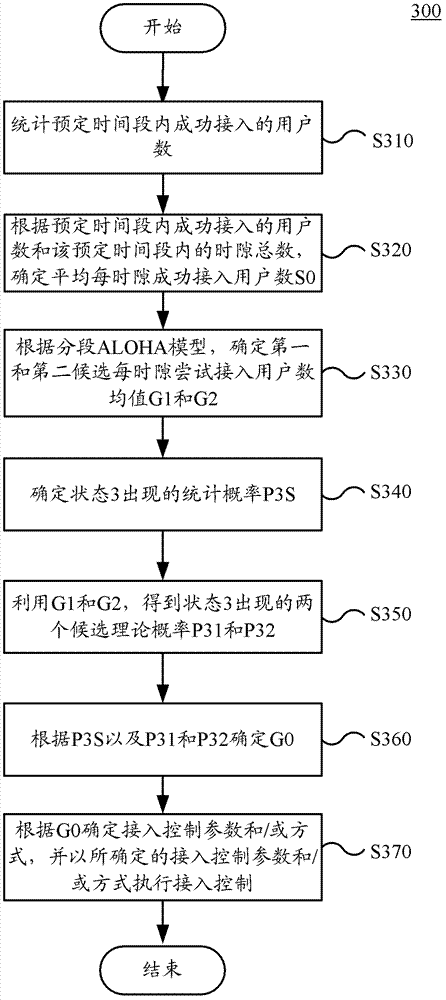
The embodiment of the invention provides an access control method and an access control device. The method comprises the following steps of: counting the number of users accessed successfully within the preset time period; determining the number of users accessed successfully each time slot on average according to the number of users accessed successfully in the preset time period and the total number of time slots within the preset time period; based on a slotted ALOHA model, determining the average value of the number of users tried to be accessed each time slot of a first candidate and a second candidate which correspond to the number of users accessed successfully each time slot on average; selecting one of the average values of the numbers of users tried to be accessed each time slot of the first candidate and the second candidate; and determining the accessed control parameters and / or modes according to the average value of the number of users tried to be accessed each time slot actually, and carrying out access control according to the determined access control parameters and / modes. The method and the device provided by the embodiment of the invention can determine the average value of the number of users tried to be accessed, and the access control modes or parameters are arranged accordingly, thus the access control is carried out effectively, and the jamming of an access network and a core network is reduced.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
Multichannel MAC protocol implementation method in service-intensive type vehicle-mounted network
ActiveCN105119680AEfficient use ofImprove throughputTime-division multiplexTransmission path multiple useReliable transmissionAloha
The invention discloses a multichannel MAC protocol implementation method in a service-intensive type vehicle-mounted network, and belongs to the field of vehicle-mounted wireless communication. The method comprises the steps: distributing a DS-ALOHA control channel access protocol and a service channel time slot, wherein the DS-ALOHA control channel access protocol employs a TDMA mechanism; introducing the concept of cluster; collecting and transmitting safety information through the cluster, thereby enabling the safety information in the network to be transmitted safely in real time; meanwhile, distributing the access of a service channel through the cluster, thereby reducing the collision among nodes, and improving the utilization rate of a business channel. The method just needs to use a single antenna to achieve the multi-channel communication, and more effectively uses wireless channel resources. Meanwhile, compared with a multi-antenna scheme, the method reduces the production cost, and reduces the energy consumption caused by the detection of safety information. The method can guarantee the reliable transmission of the safety information under the service intensive network, and improves the throughput of the system for the service information.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Anti-collision system and method for reducing the collision of data transmitted by RFID tags
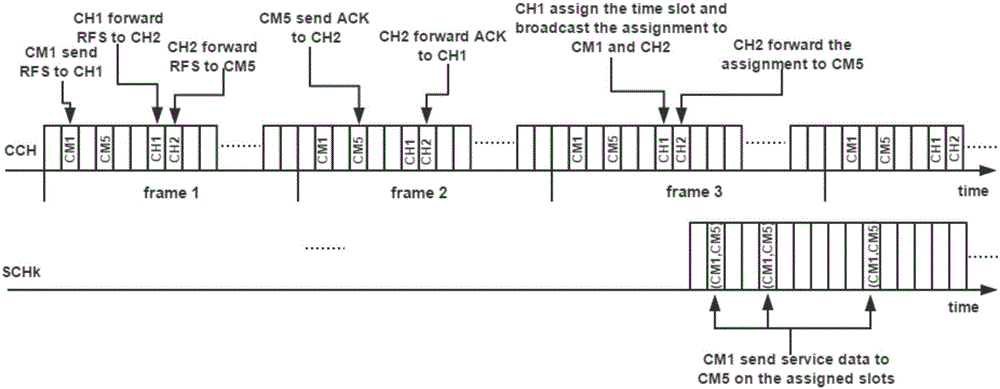
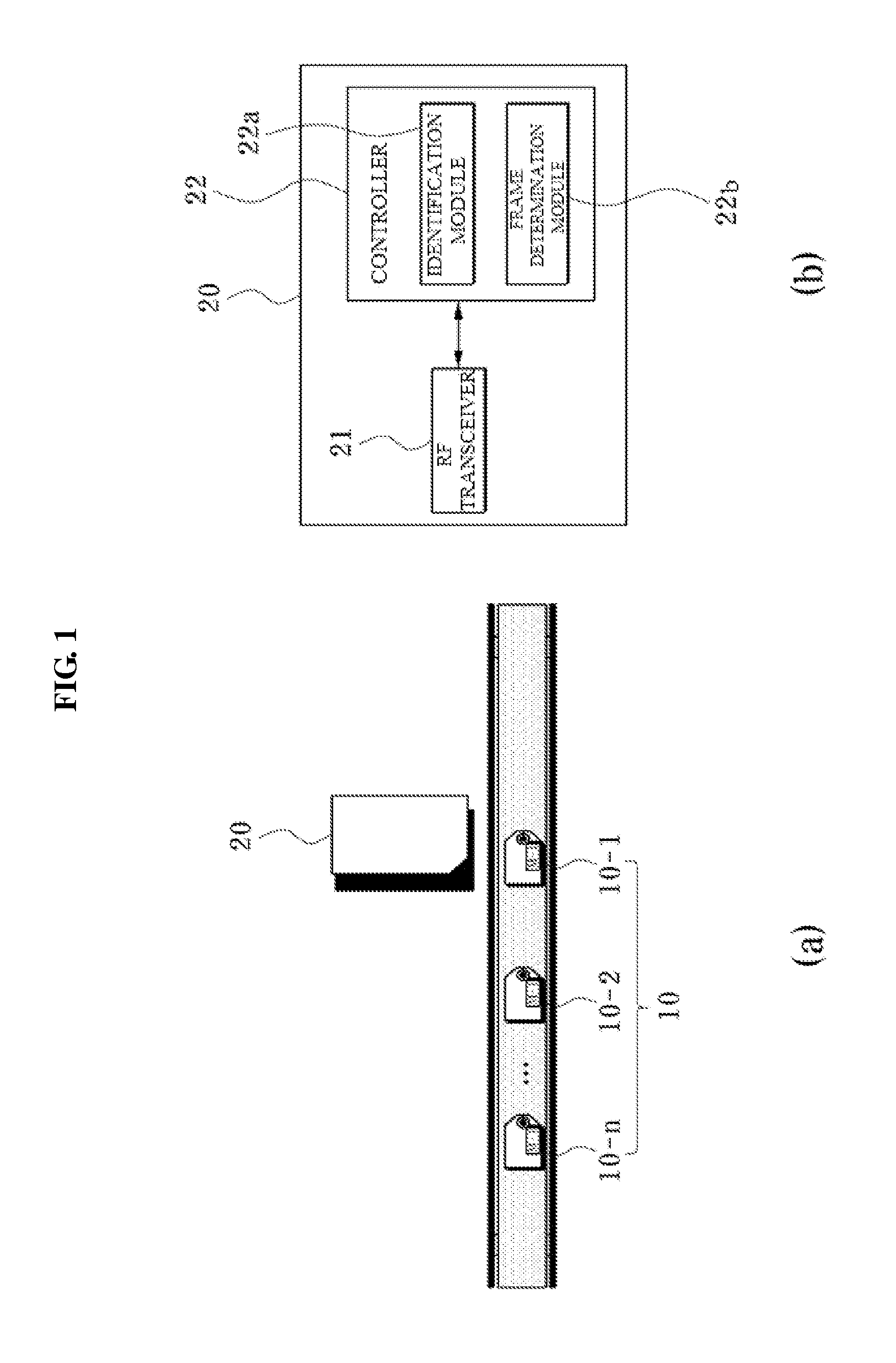
ActiveUS20130093571A1Reduce data conflictsReduce collisionSensing detailsCo-operative working arrangementsComputer hardwareFrame based
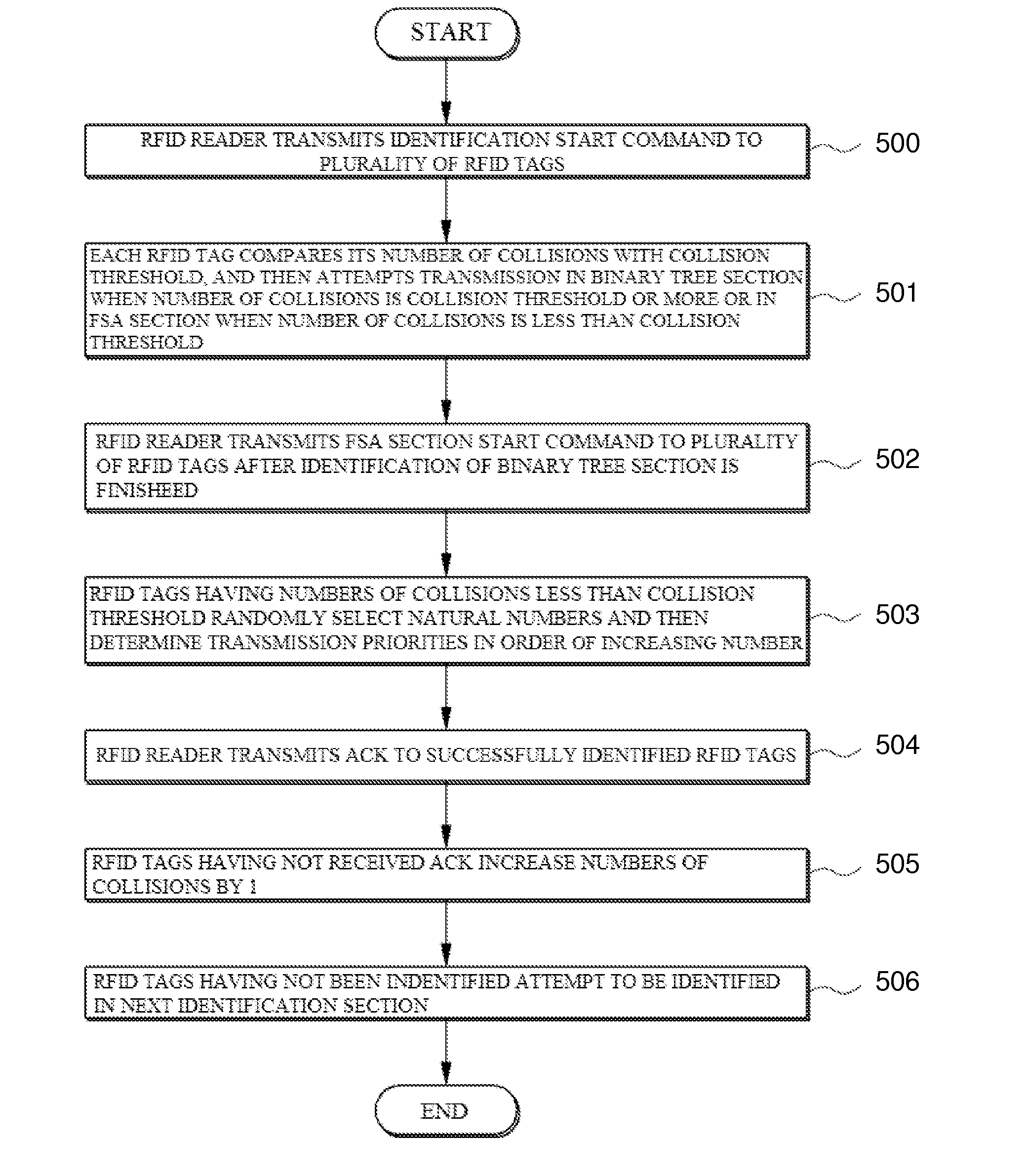
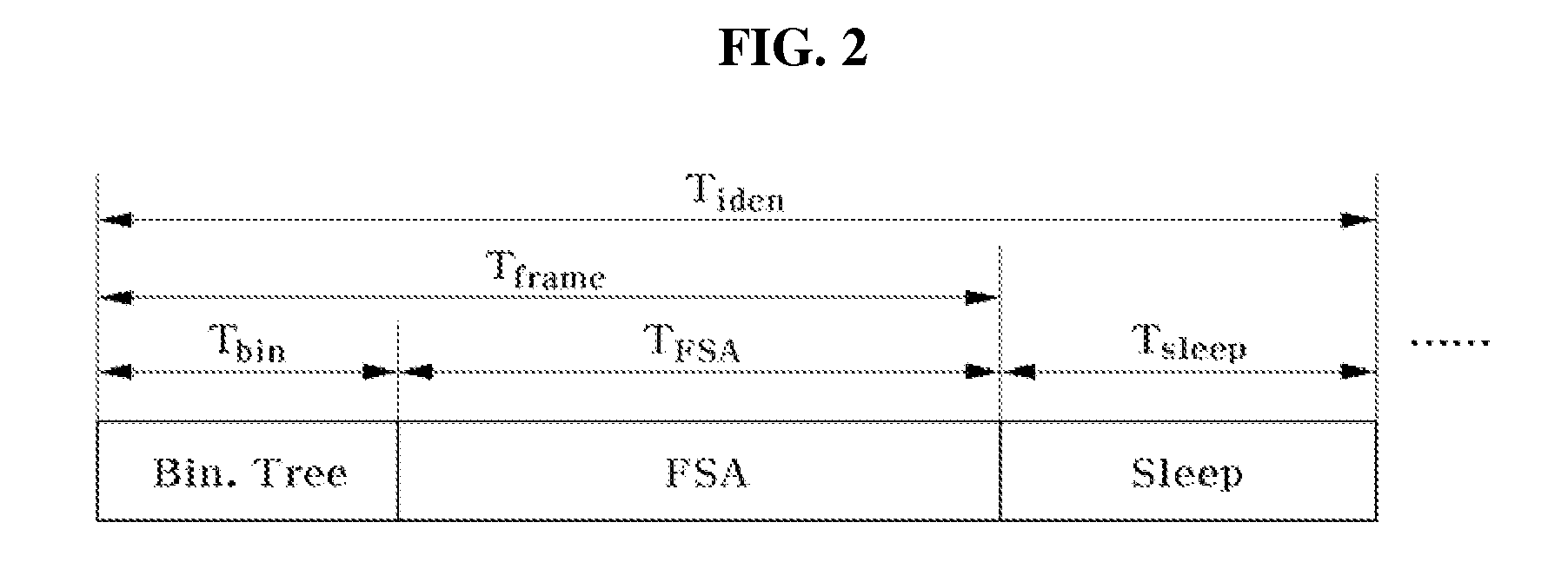
Provided are an anti-collision system and method which address the mobility of radio frequency identification (RFID) tags. An RFID reader may transmit an identification start command to identify a plurality of RFID tags in an identification area of the RFID reader. The RFID tags compare the number of collisions of each RFID tag receiving the identification start command with a collision threshold Cth and attempt to be identified in a binary tree section of a frame or in a framed slotted ALOHA (FSA) section of the frame based on the comparison.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com