Patents
Literature
851 results about "Multi access" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition of multi-access in English: multi-access. adjective. (of a computer system) allowing the simultaneous connection of a number of terminals.
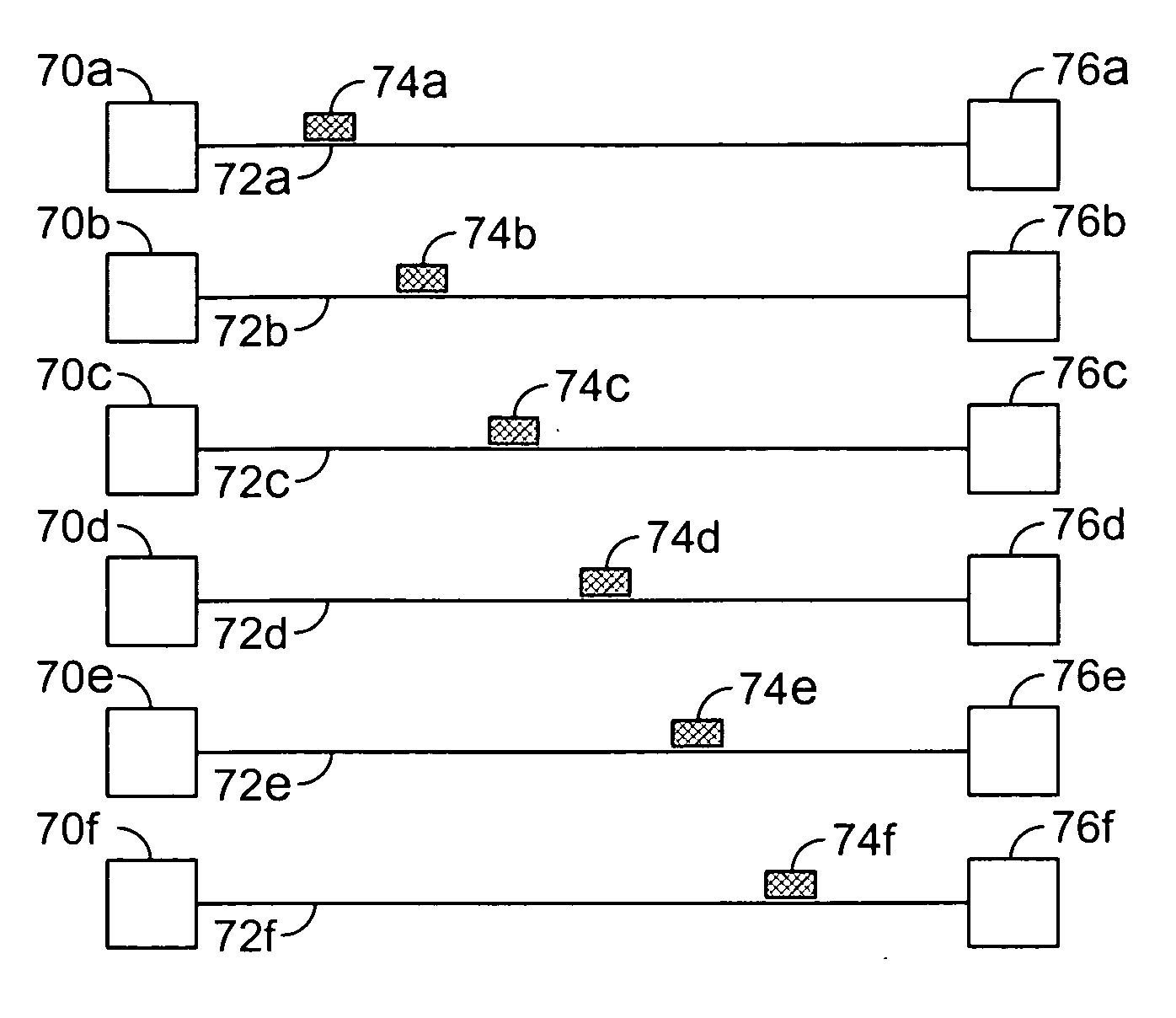
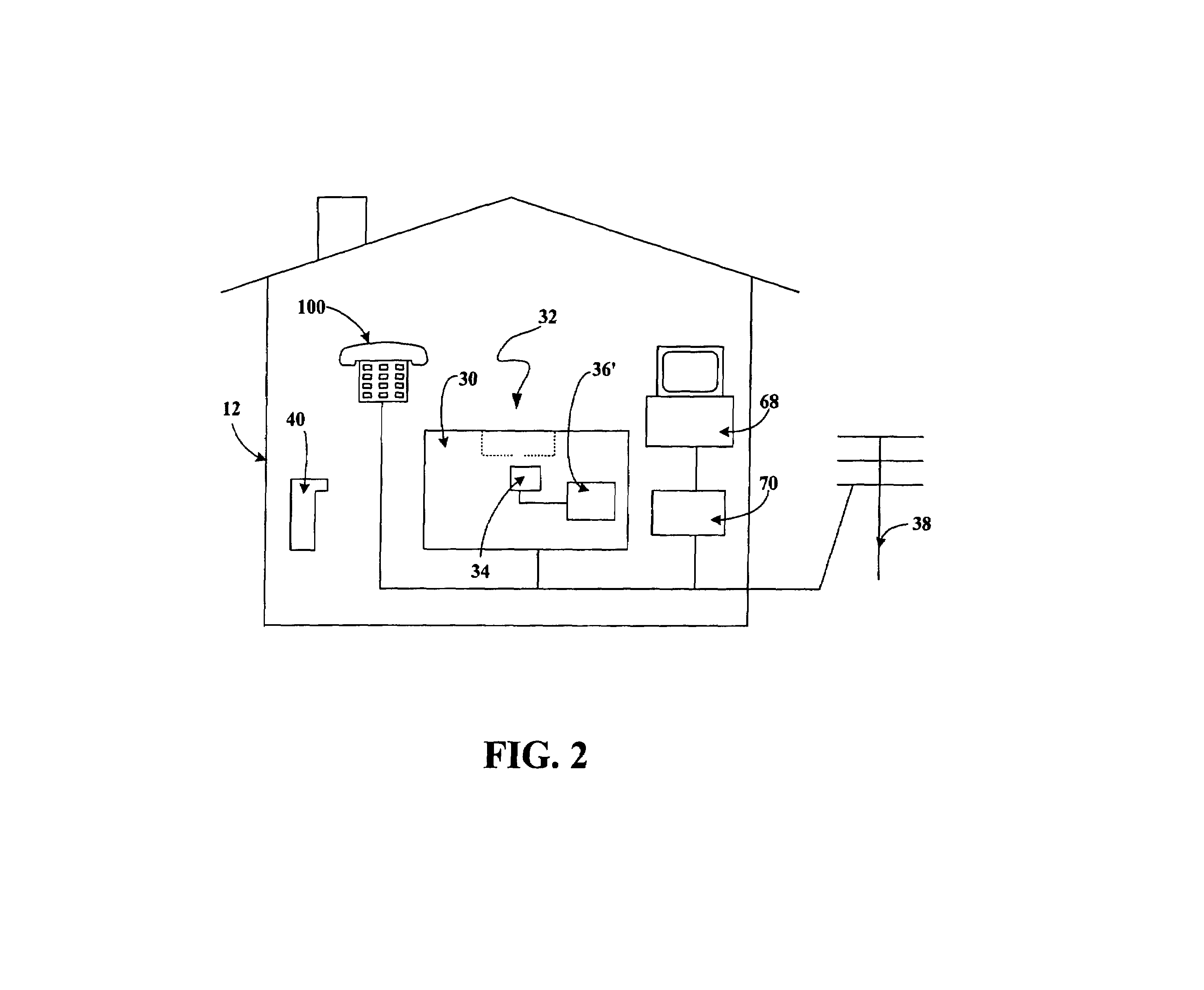
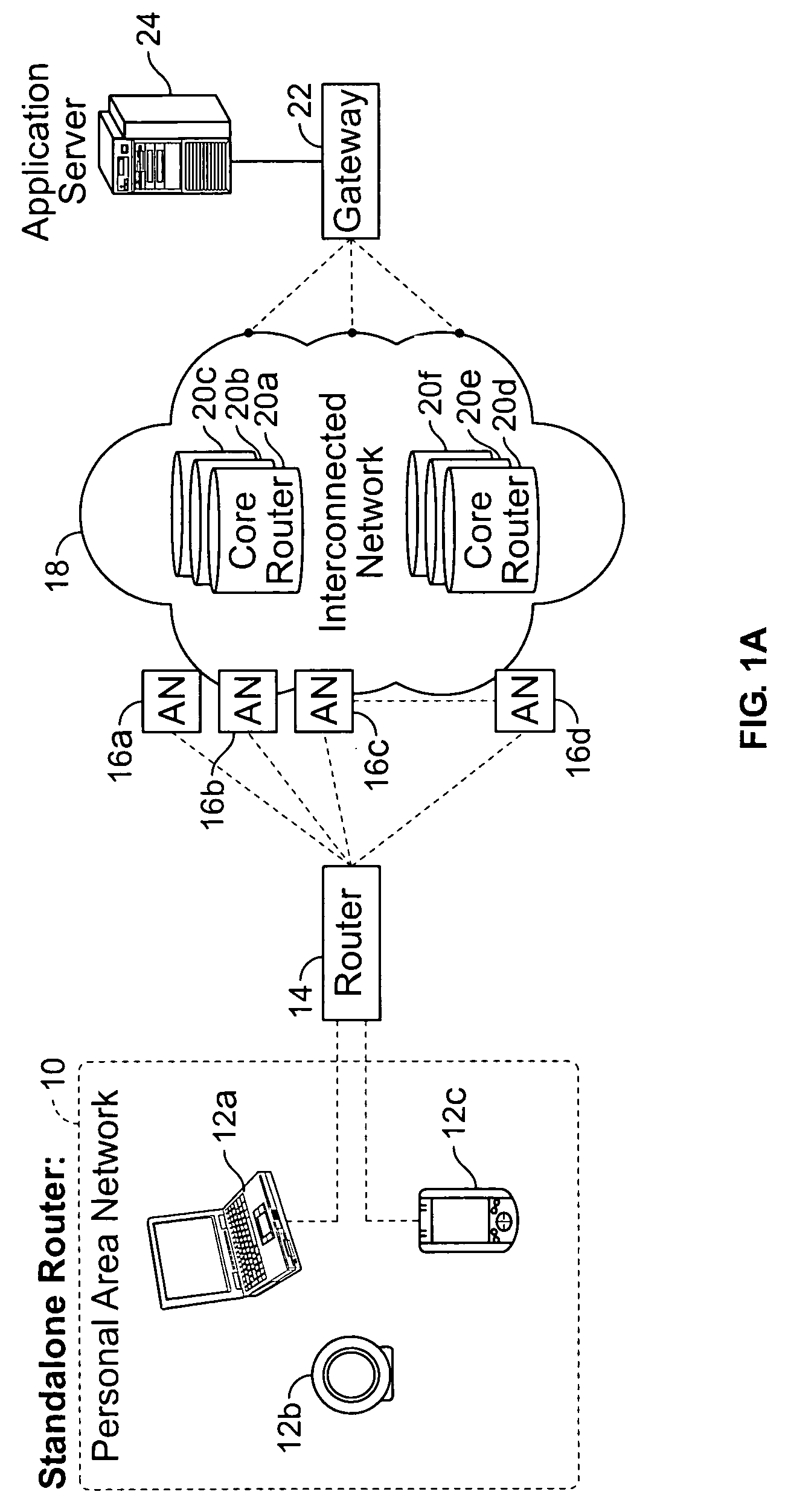
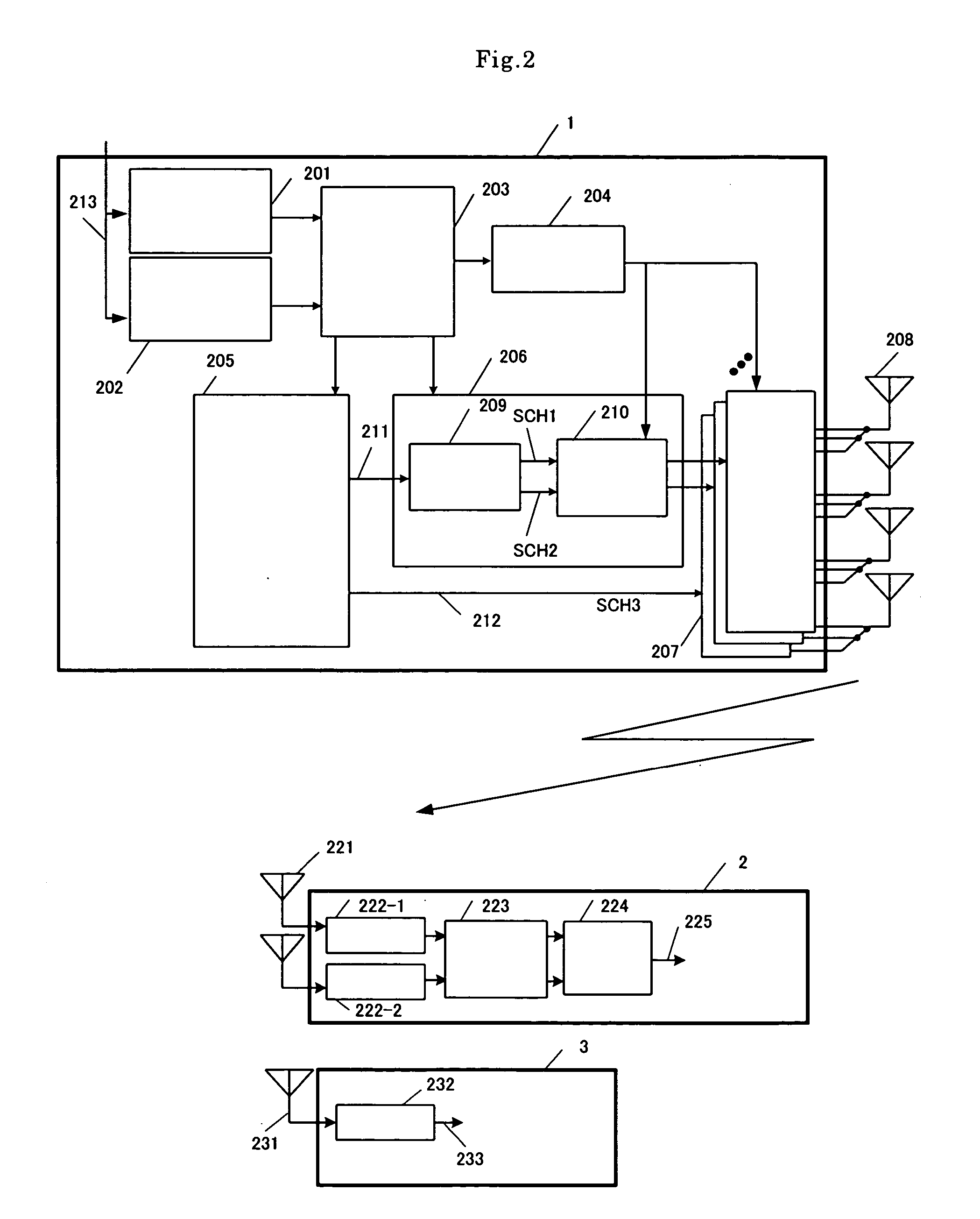
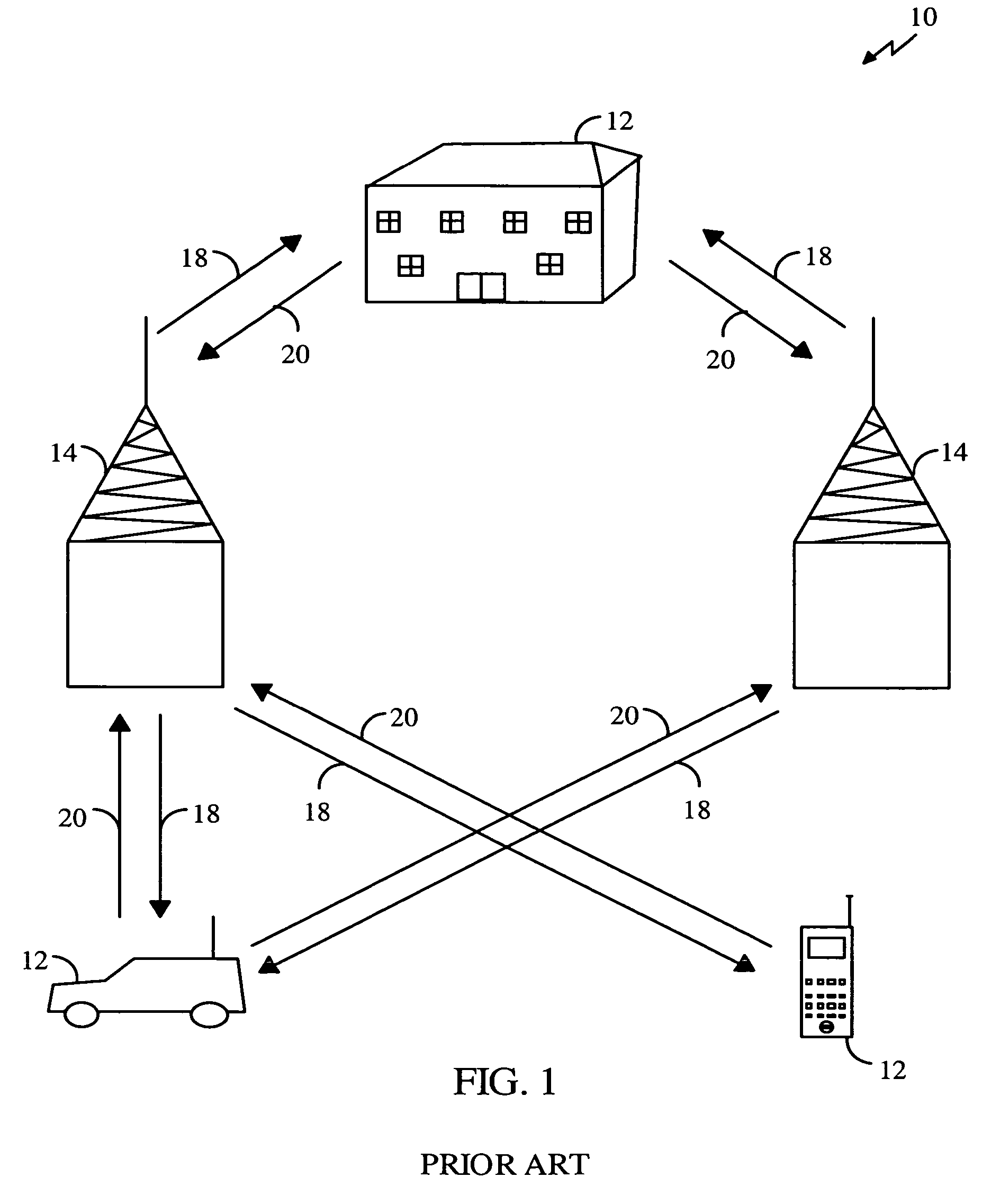
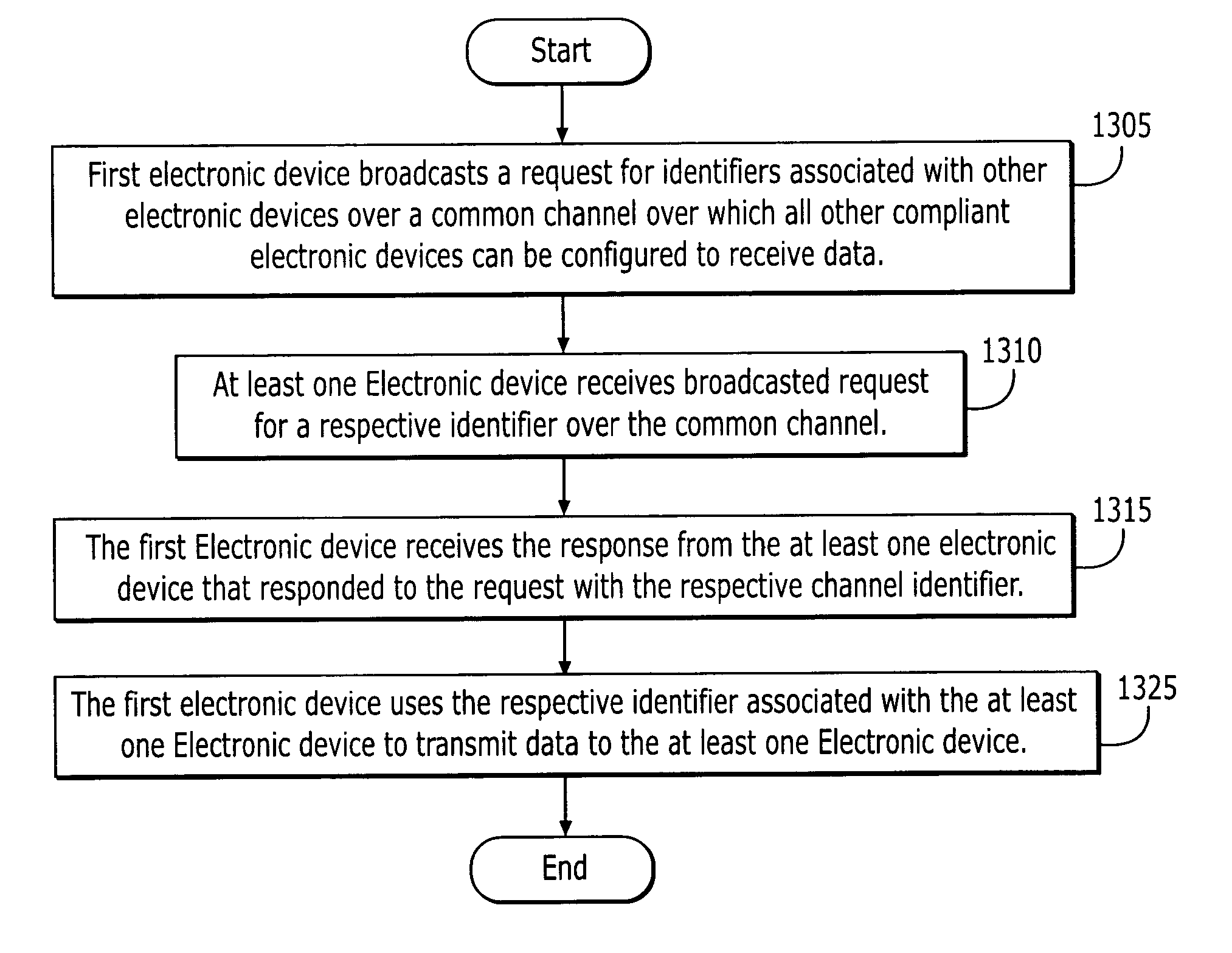
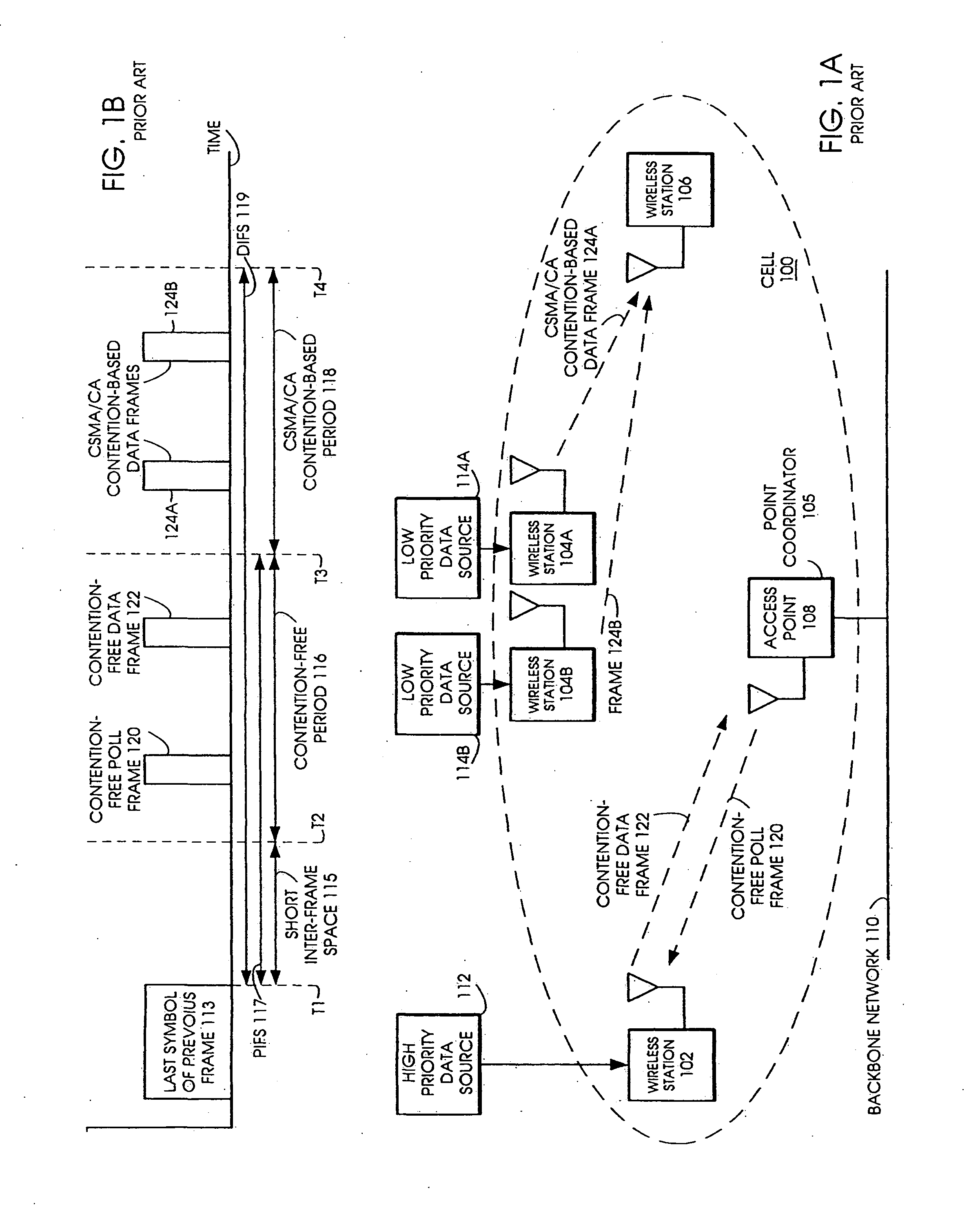
Multi-access terminal with capability for simultaneous connectivity to multiple communication channels
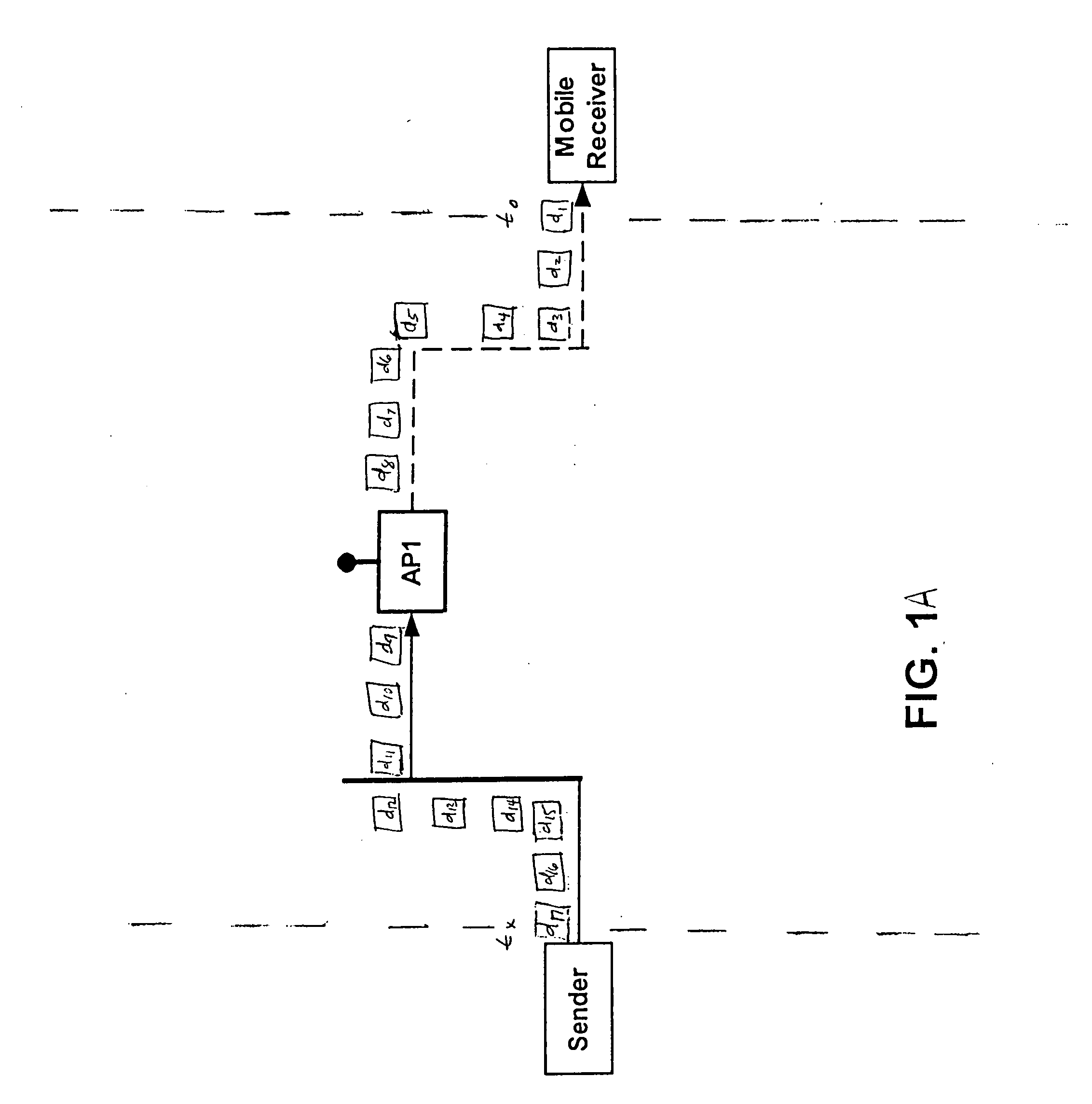
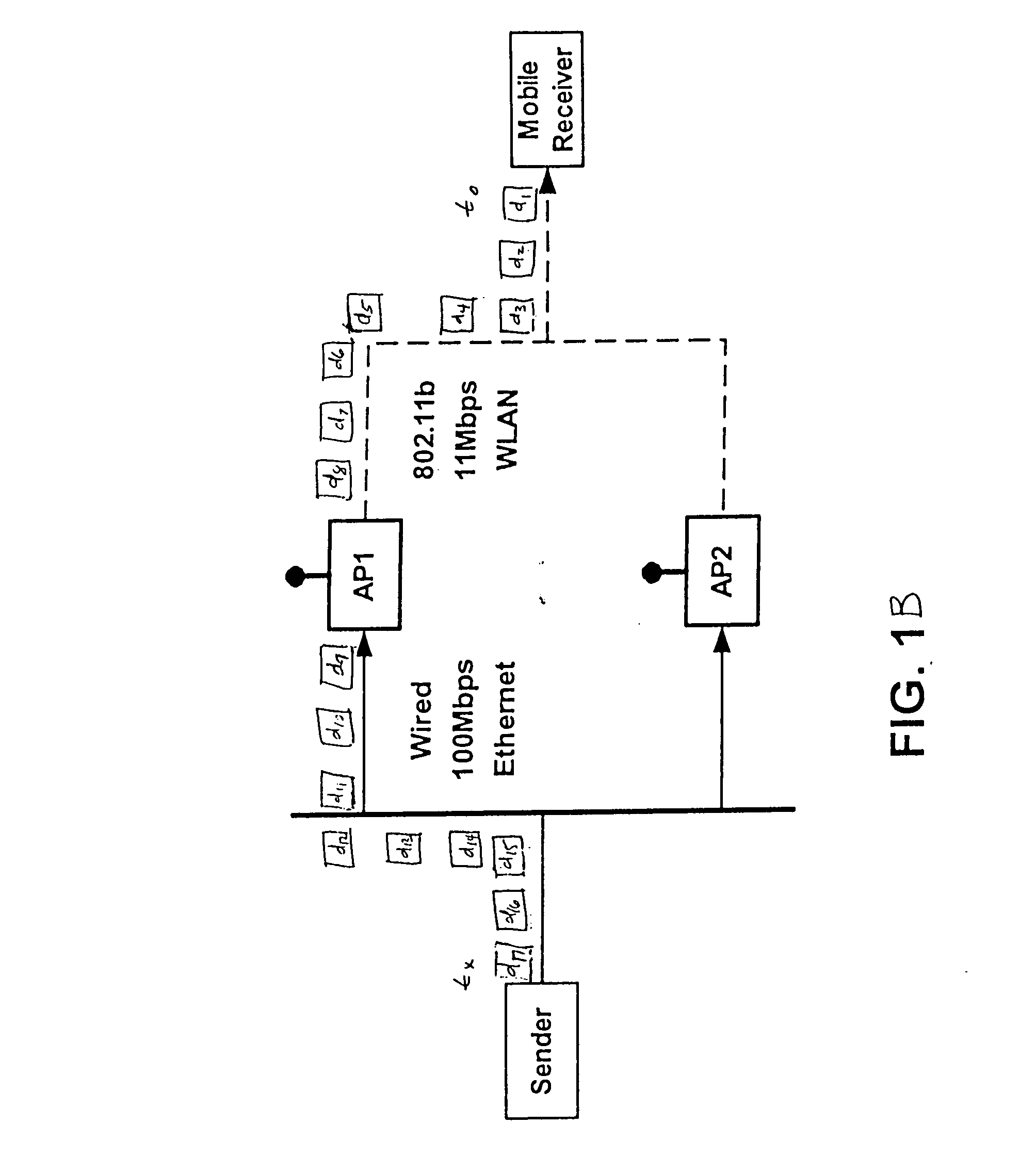
ActiveUS20060193295A1Improve reliabilityImprove behaviorNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexTransceiverOperational system
An apparatus is disclosed for permitting a mobile terminal having multiple, heterogeneous network connections (e.g., multiple wired or wireless transceivers of various types) to set up and maintain virtual connections over multiple networks to either the same or to multiple destinations. The mobile terminal can “load-share” traffic, i.e., it can distribute segments of traffic over a full set of heterogeneous networks, significantly improving the reliability and availability of communications. In a first embodiment, a mobile terminal is configured with multiple radio frequency (RF) transceivers. Operating system software is provided for dynamically establishing and maintaining traffic flow for user applications over multiple communications paths, and for automatically adapting to variations in the networking environment, application traffic flow requirements, end user preferences, or mobility. In a second embodiment, a software-defined radio is used to implement the physical layer protocols for each desired network, eliminating the need for multiple transceivers.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF STEVENS INST OF TECH THE
Multi-access mode electronic personal assistant
InactiveUS6895558B1Digital data information retrievalMultiplex communicationVocal responseData access
A system enables communication between server resources and a wide spectrum of end-terminals to enable access to the resources of both converged and non-converged networks via voice and / or electronically generated commands. An electronic personal assistant (ePA) incorporates generalizing / abstracting communications channels, data and resources provided through a converged computer / telephony system interface such that the data and resources are readily accessed by a variety of interface formats including a voice interface or data interface. A set of applications provides dual interfaces for rendering services and data based upon the manner in which a user accesses the data. An electronic personal assistant in accordance with an embodiment of the invention provides voice / data access to web pages, email, file shares, etc. A voice-based resource server authenticates a user by receiving vocal responses to one or more requests variably selected and issued by a speaker recognition-based authentication facility. Thereafter an application proxy is created.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Personal shopping system
The present invention relates to a personal shopping system for combined use in both the home of a user and a shopping establishment. The system includes a host computer which is coupled to a host modem and, optionally, to at least one wireless multi-access point. The portable terminal can be used in both the shopping establishment and the home of the user. It is configured to read bar codes associated with items related to shopping, and includes a memory, a bar code reader, a wireless transceiver, and a data interface. The data interface of the terminal communicates with a data interface of the shopping establishment kiosk cradle or directly with the shopping establishment's communications network.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
Channel equalization system and method
InactiveUS6904110B2Increase high performance and data rate capacityLow costMultiple-port networksChannel dividing arrangementsFiberEngineering
A system and method for delivering increases speed, security, and intelligence to wireline and wireless systems. The present invention increases channel capacity by using a parallel or multi-channel structure in such wireless and wireline at the edge or the core of. This new architecture of the present invention uses parallel bitstreams in a flexible way and distributed switching / routing technique, is not only to avoid the potential bottlenet of centralized switches, but also to increase speed with intelligence that is seamlessly integrating into the Fiber Optic Backbone such as WDM and SONET of the MAN / WAN network with a Real-time guarantees, different types of traffic (such as Stringent synchronous, isochronous, and asynchronous data messages) with different demands, and privacy & security of multi access and integrated services environment.
Owner:B C LEOW
Optimizing content and communication in multiaccess mobile device exhibiting communication functionalities responsive of tempo spatial parameters
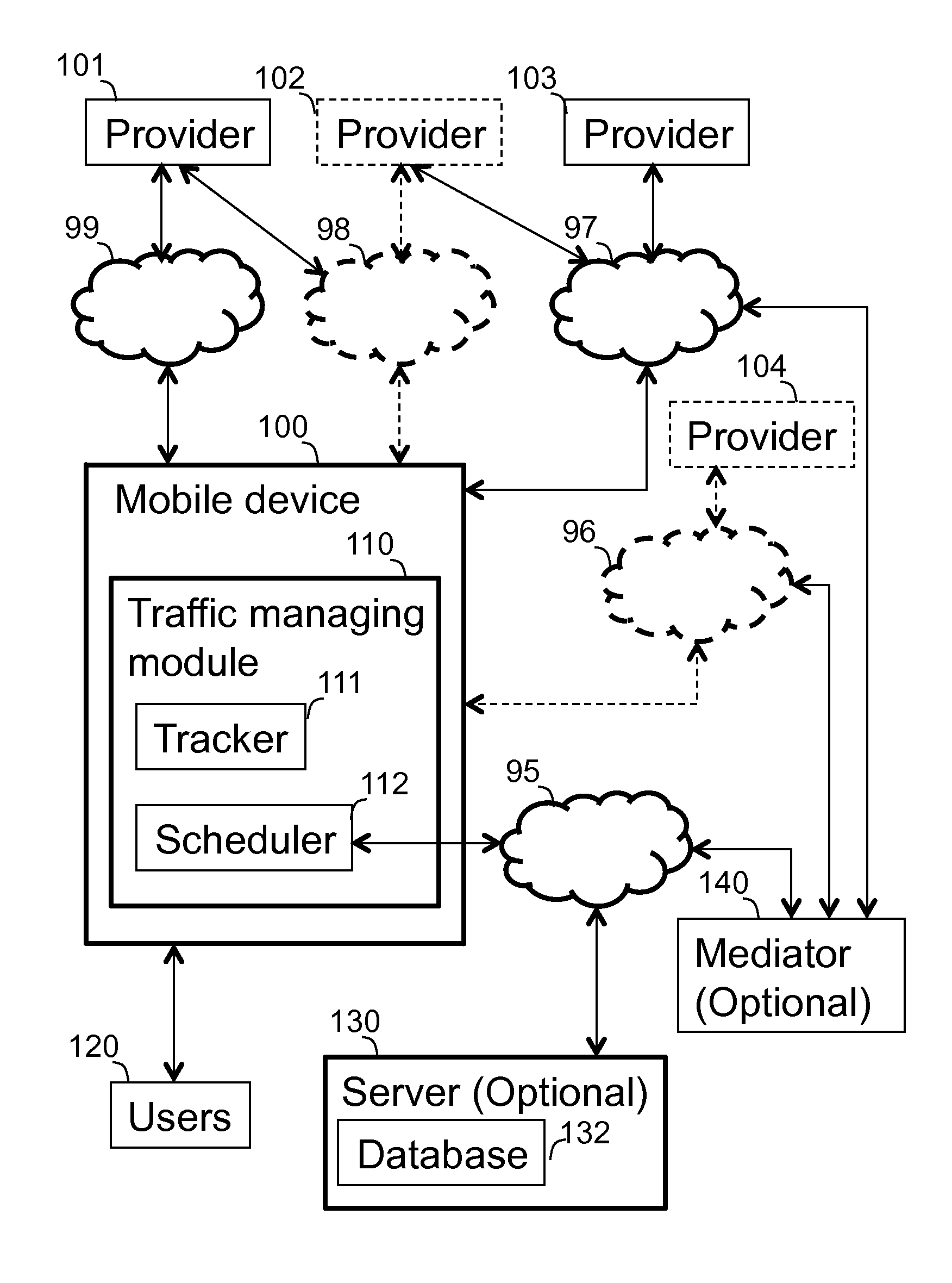
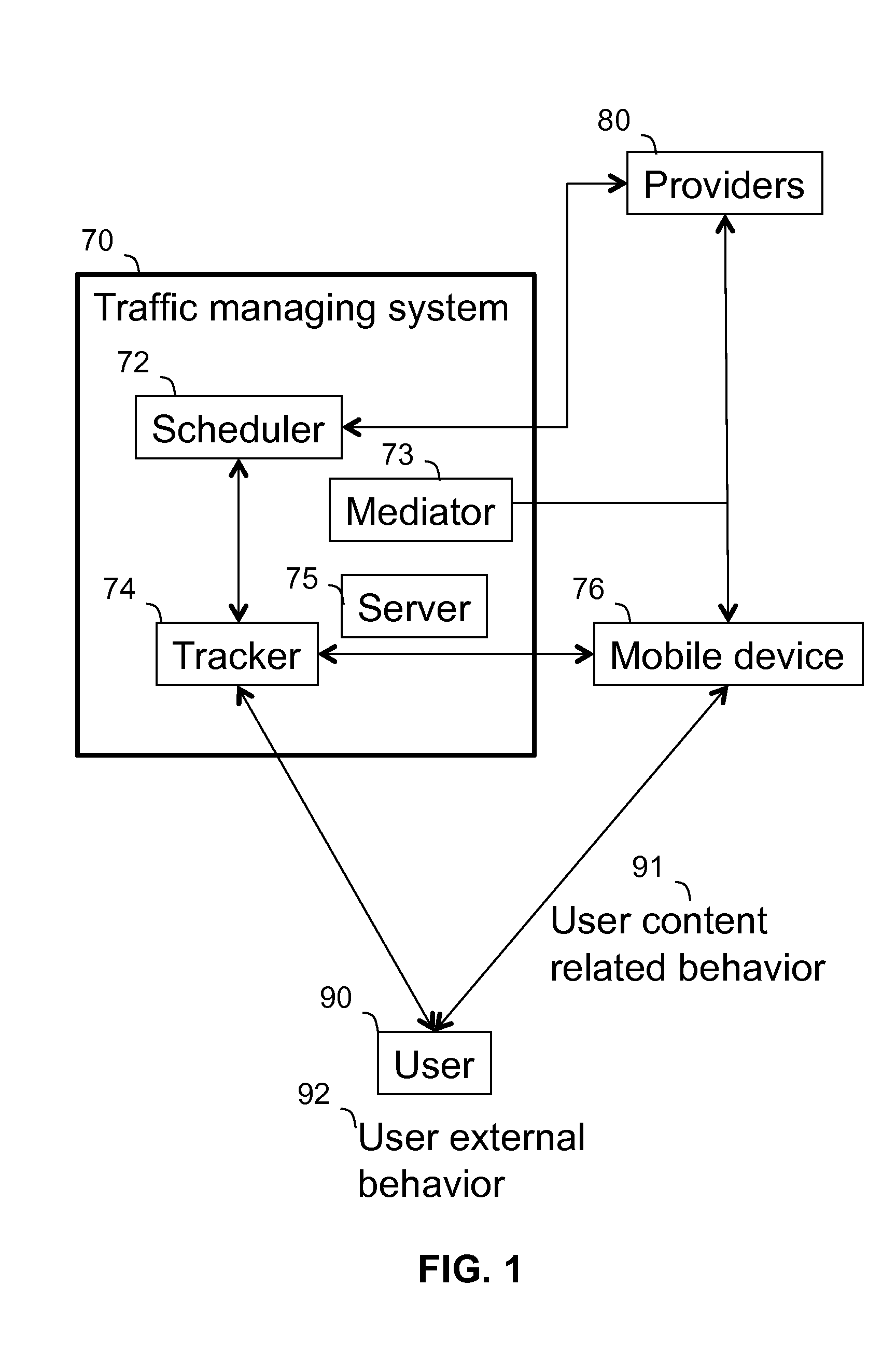
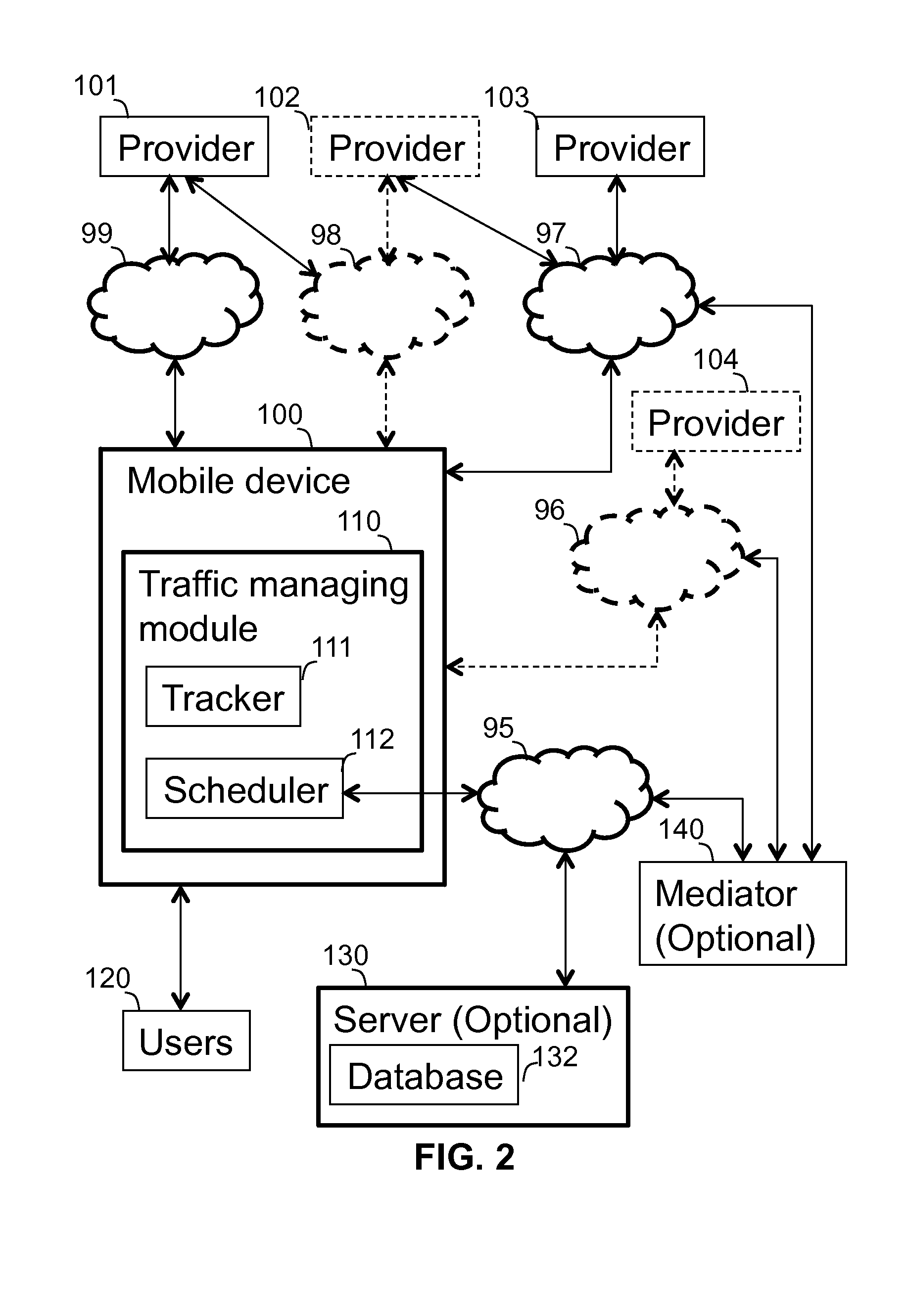
A content and traffic managing system operatively associated with and a computer implemented method of managing traffic of a mobile device exhibiting communication functionality. The mobile device is connectable to users and to content providers via communication links. The system tracks various parameters over time, and schedules communication, both in relation to predefined or projected content responsive of the following: users' content related behavior, users' communication behavior, users' external behavior, and parameters of communication links. The method comprises: (i) tracking users' content related behavior, communication behavior and users' external behavior over time; (ii) tracking parameters of communication links over time; (iii) scheduling and initiating communication related to predefined or projected content responsive of the above mentioned criteria at time slots selected such that the communication is performed in view of users' predefined or projected preferences in accordance with the parameters of communication links.
Owner:VELOCEE
Portable electronic terminal and data processing system
InactiveUS7171378B2Improve securityImprove programmabilityCredit registering devices actuationBuying/selling/leasing transactionsWireless transceiverModem device
The present invention relates to a personal shopping system for combined use in both the home of a user and a shopping establishment. The system includes a host computer which is coupled to a host modem and, optionally, to at least one wireless multi-access point. At least one shopping establishment kiosk cradle is employed to interface with a portable terminal which is also part of the system. The portable terminal can be used in both the shopping establishment and the home of the user. It is configured to read bar codes associated with items related to shopping, and includes a memory, a bar code reader, a wireless transceiver, and a data interface. The data interface of the terminal communicates with a data interface of the shopping establishment kiosk cradle. A home cradle for the portable terminal is also provided and is adapted to remain in the home of the user. It includes a home portable terminal-receiving station and a home data interface to communicate with the data interface of the portable terminal. A home data transfer circuit is also included to permit data exchange between the home data interface and the modem coupled to the host computer.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
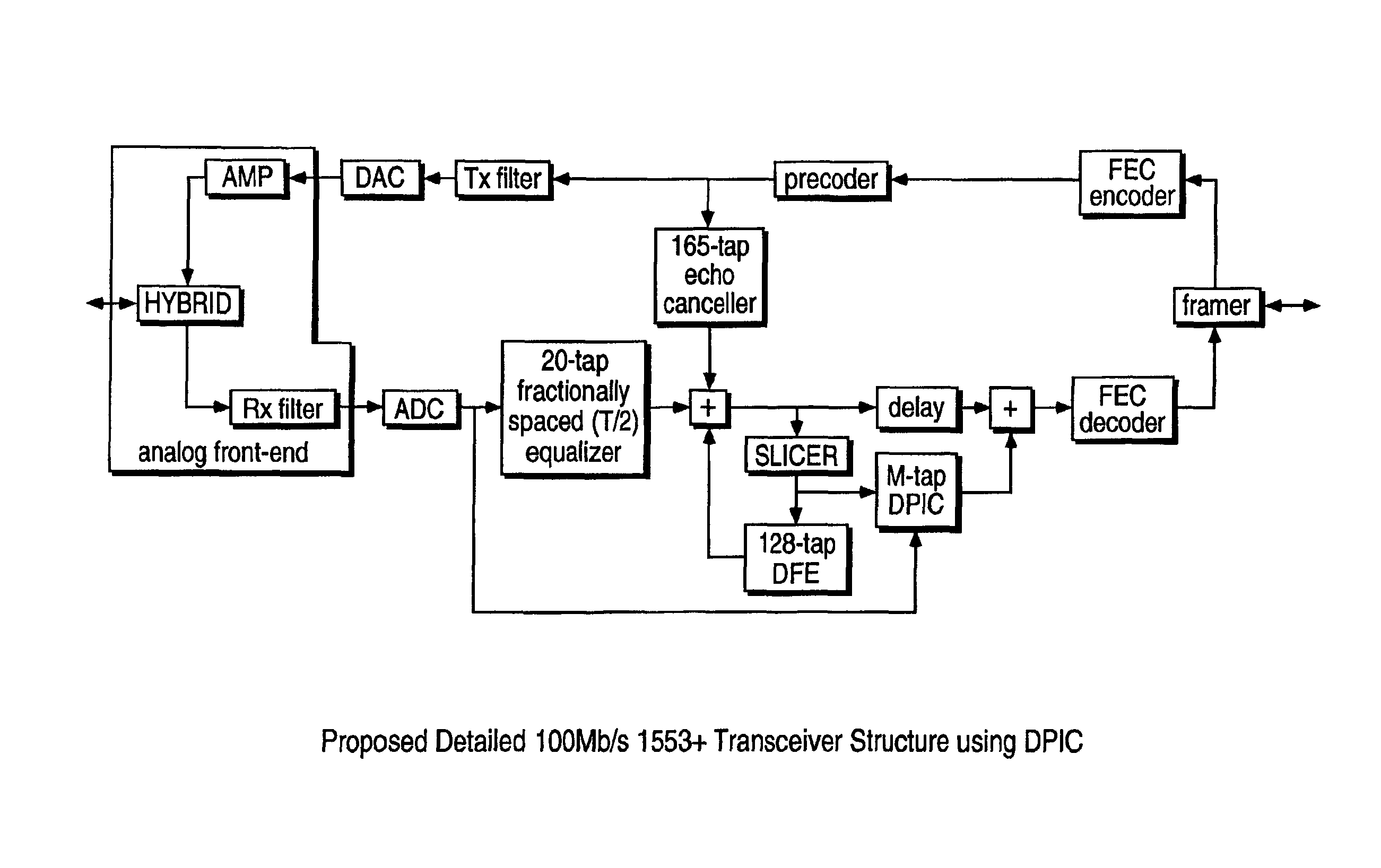
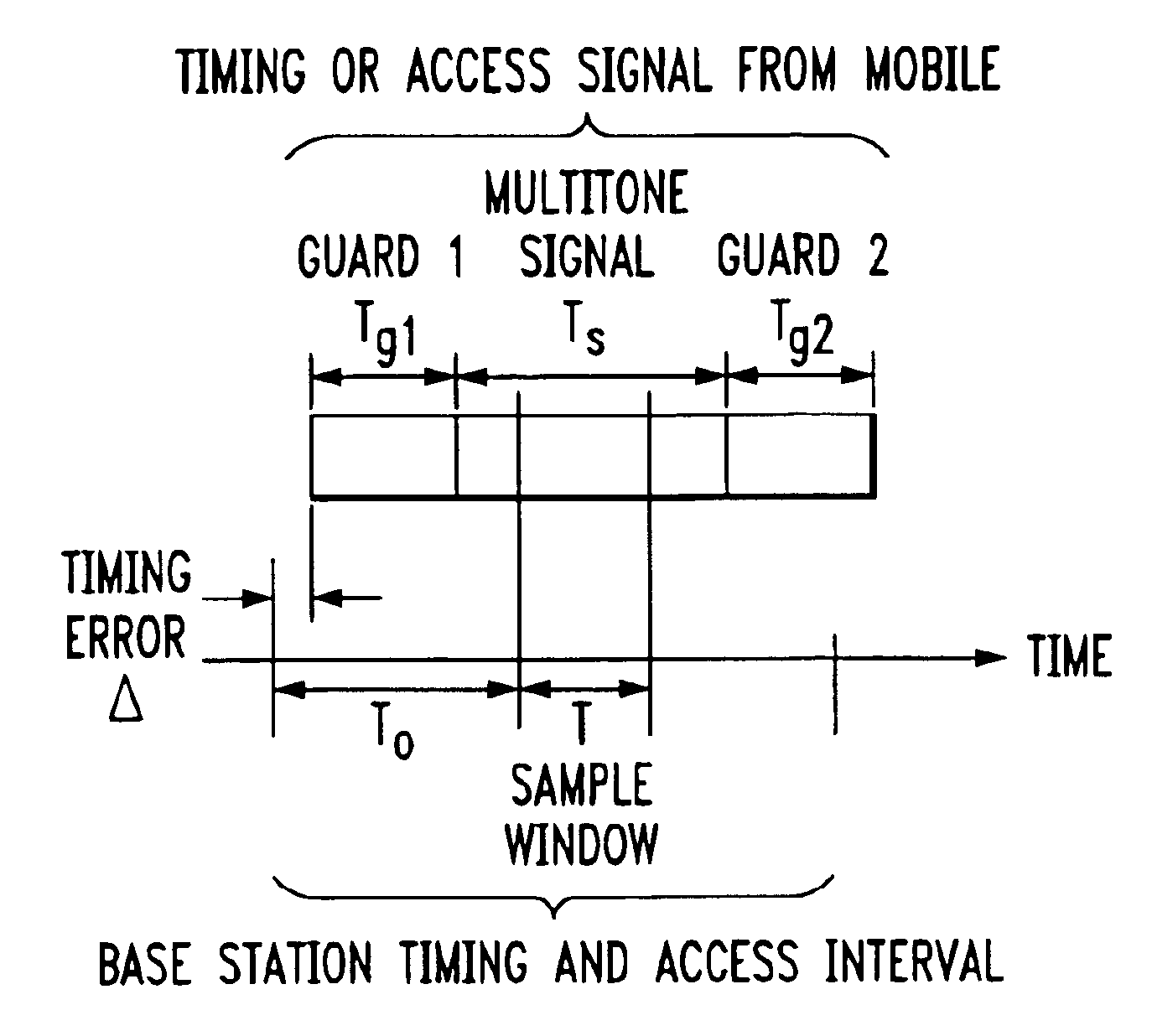
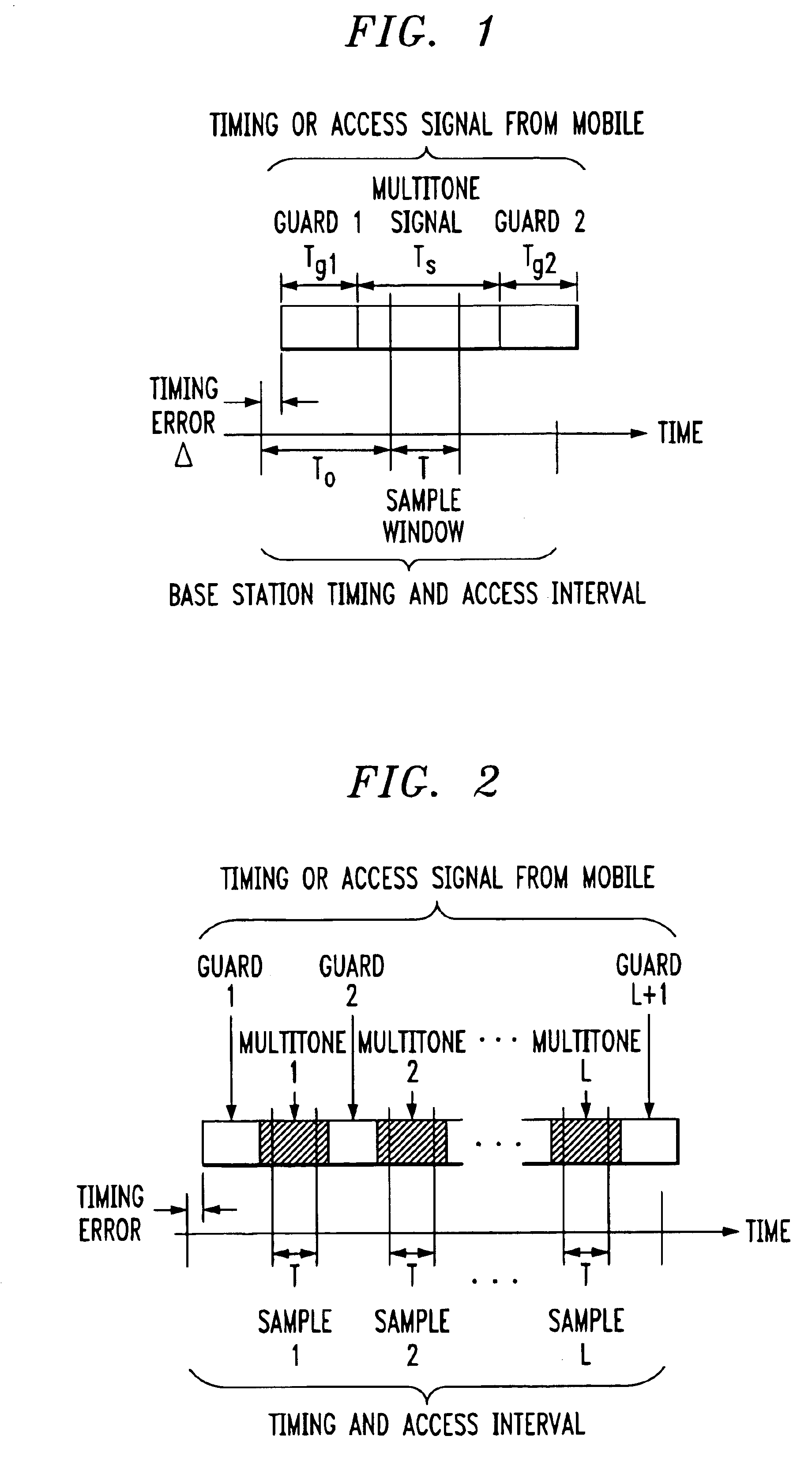
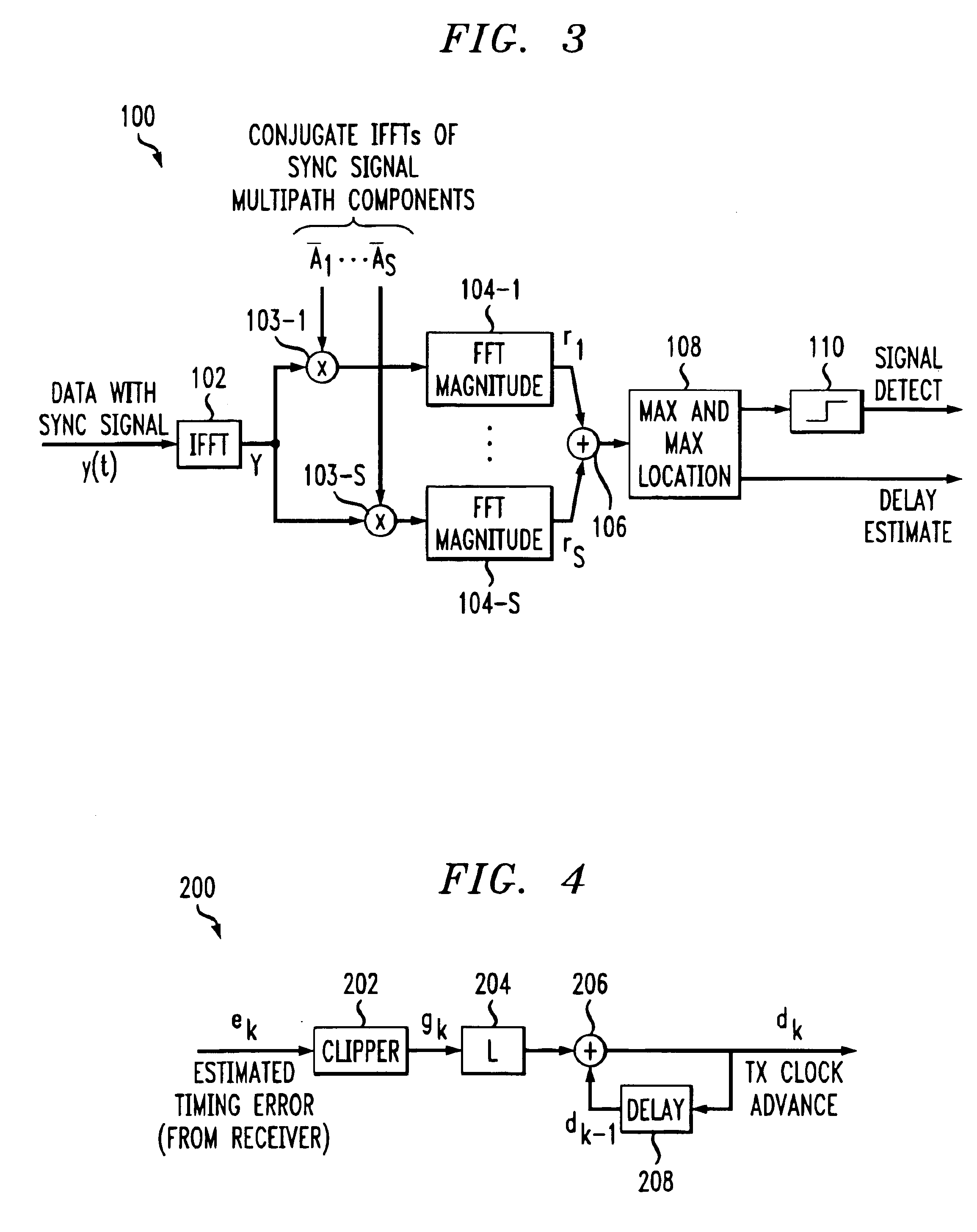
Signal construction, detection and estimation for uplink timing synchronization and access control in a multi-access wireless communication system
InactiveUS6922388B1Improve estimation accuracyGreat rangeTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexFourier transform on finite groupsCyclic prefix
Signal construction, detection and estimation techniques for use in uplink timing synchronization and access control in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexed (OFDM) wireless system or other type of wireless communication system. In accordance with an illustrative embodiment of the invention, timing and access signals to be transmitted in designated timing and access intervals are constructed from orthogonal multitone signals. The multitone signals may be similar to multitone signals used in OFDM data transmission, except that a cyclic prefix associated with reception of the signals in a base station is extended to cover the timing errors of mobile stations not yet synchronized. The invention also provides design techniques which optimize the time resolvability and peak-to-average ratio of the multitone signals, an efficient fast Fourier transform (FFT) based technique for maximum likelihood timing estimation, and a robust linear filtering technique for averaging timing estimates from different synchronizations.
Owner:GEMPLU
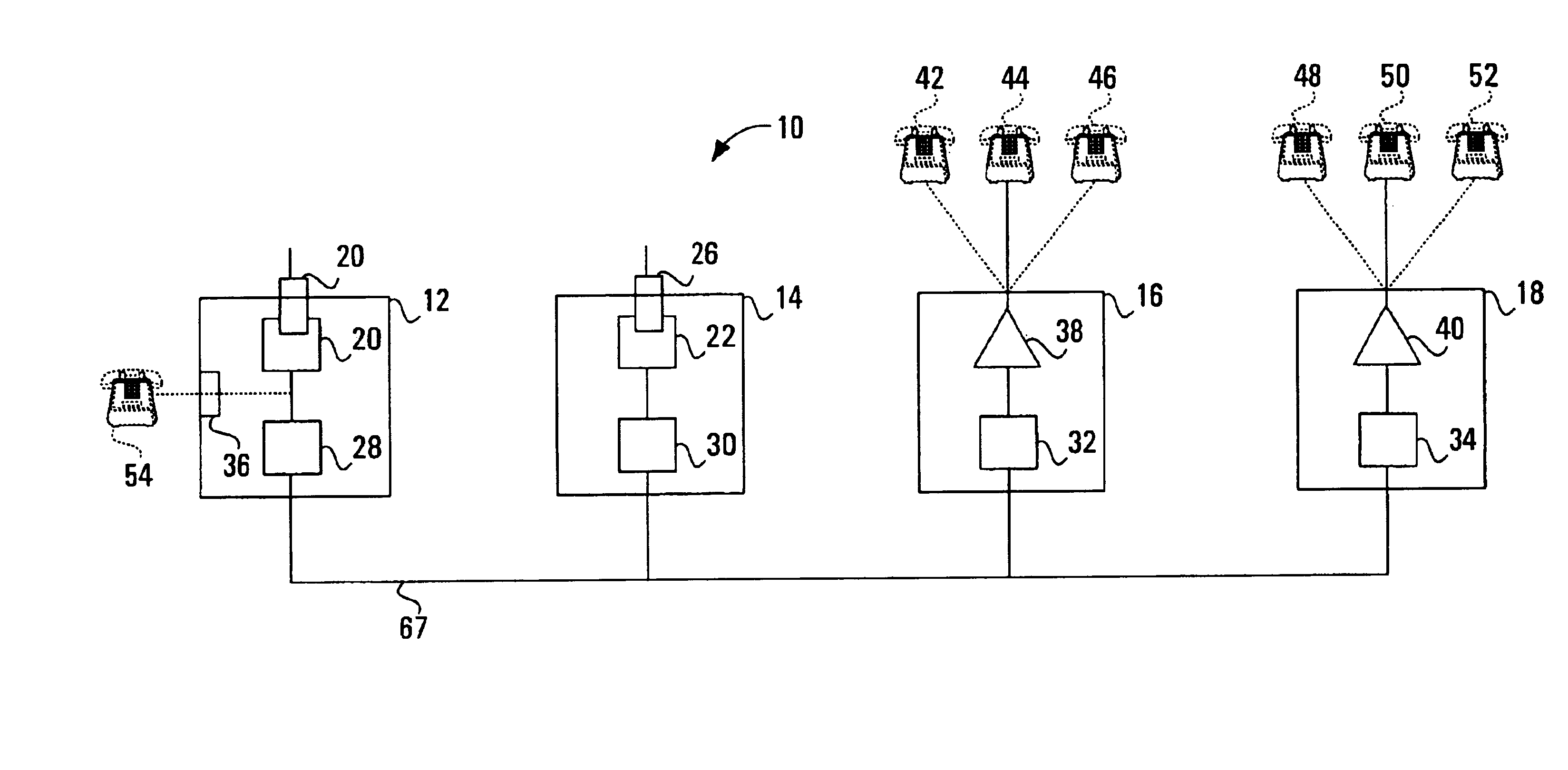
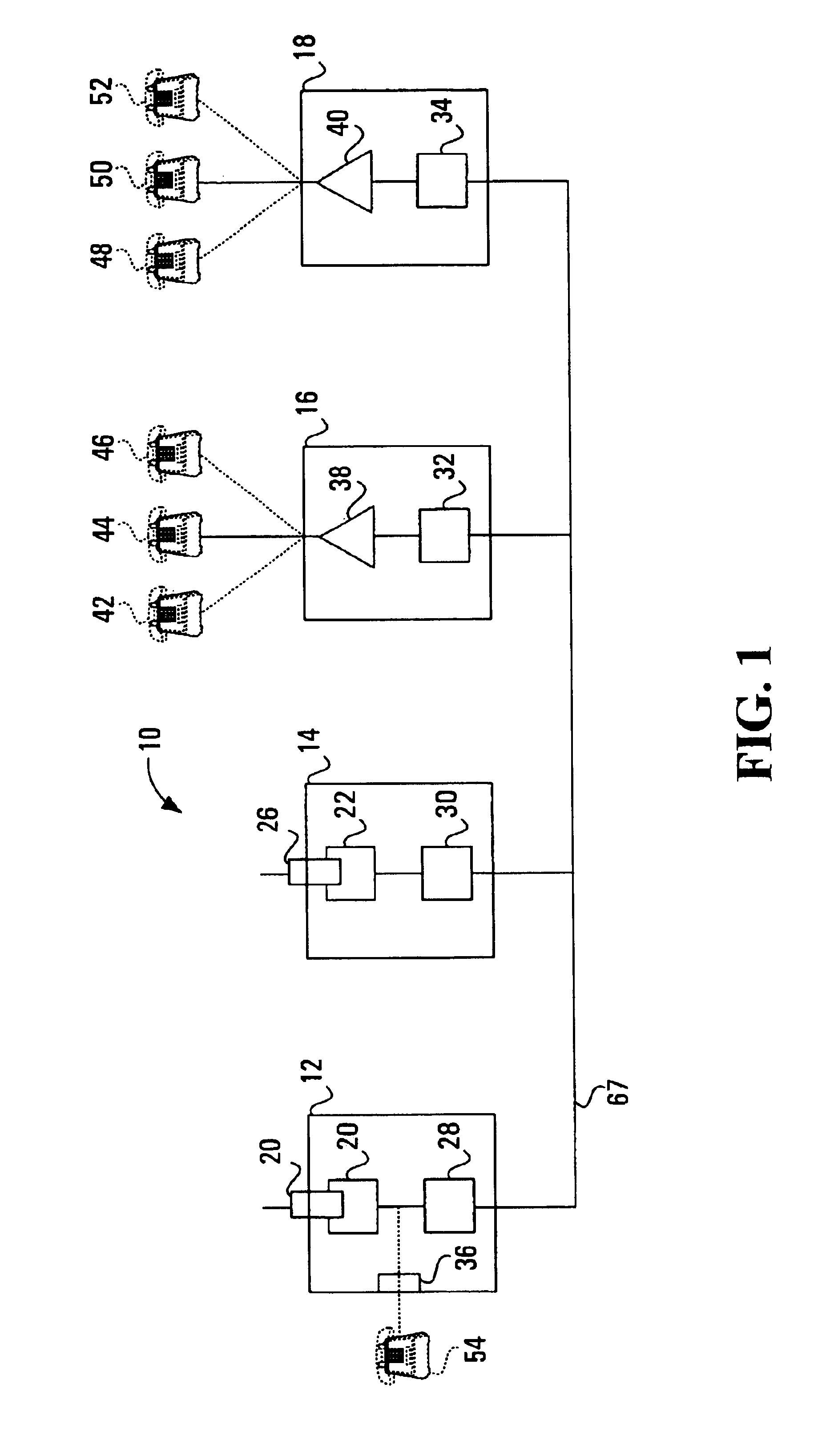
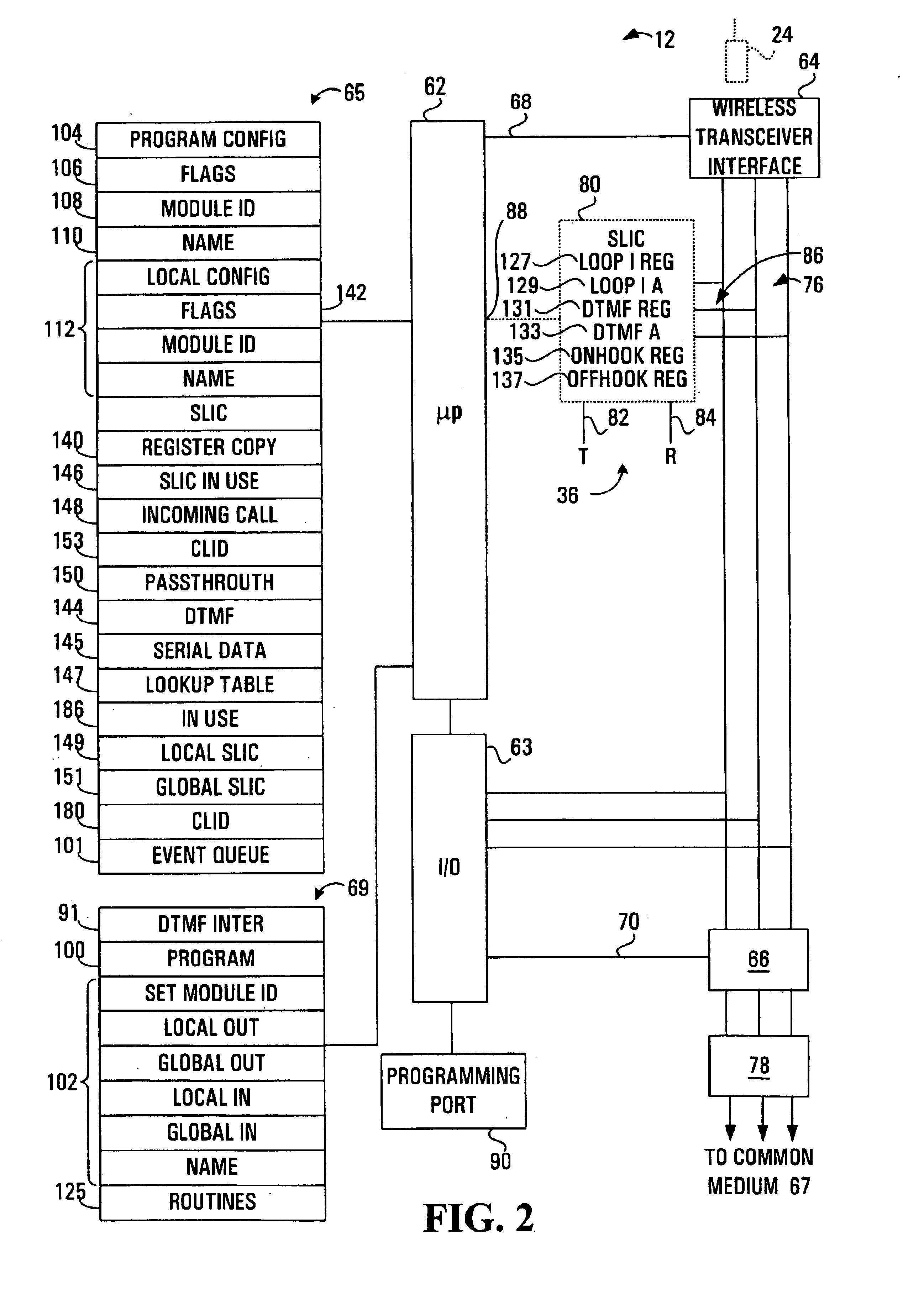
Communications unit, system and methods for providing multiple access to a wireless transceiver
InactiveUS7020488B1Eliminate needSpecial service for subscribersSubstation equipmentCommunication unitWireless transceiver
The present invention addresses the above need by providing a communications unit comprising a first wireless transceiver port operable to communicate with a first wireless transceiver operable to conduct wireless communications with a wireless base station; and a first expansion interface in communication with the first wireless transceiver port and operable to communicate with a second communications unit on a plurality of communications channels, to permit the second communications unit to access the first wireless transceiver. Effectively, a plurality of communications units of the type described above may be connected together to create a system for providing multiple access to a wireless transceiver, where the wireless transceiver may be a wireless transceiver on any of the so connected communications units. Using a system of this type, users may add the ability to add additional communications appliances and / or additional wireless communications paths to the system. Thus, the system is expandable and contractible and completely eliminates the need to connect communications appliances to land lines. In one embodiment the first expansion interface is operable to conduct communications with the second communications unit on time multiplex channels. Alteratively, such communications may be conducted on frequency multiplex channels.
Owner:EMBEDDED SYST PROD INTPROP LLC
Mobile wireless local network access device and method based on code division multi-address technology
InactiveCN101123553AEasy to set upBig spaceNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationInterface circuitsMulti access
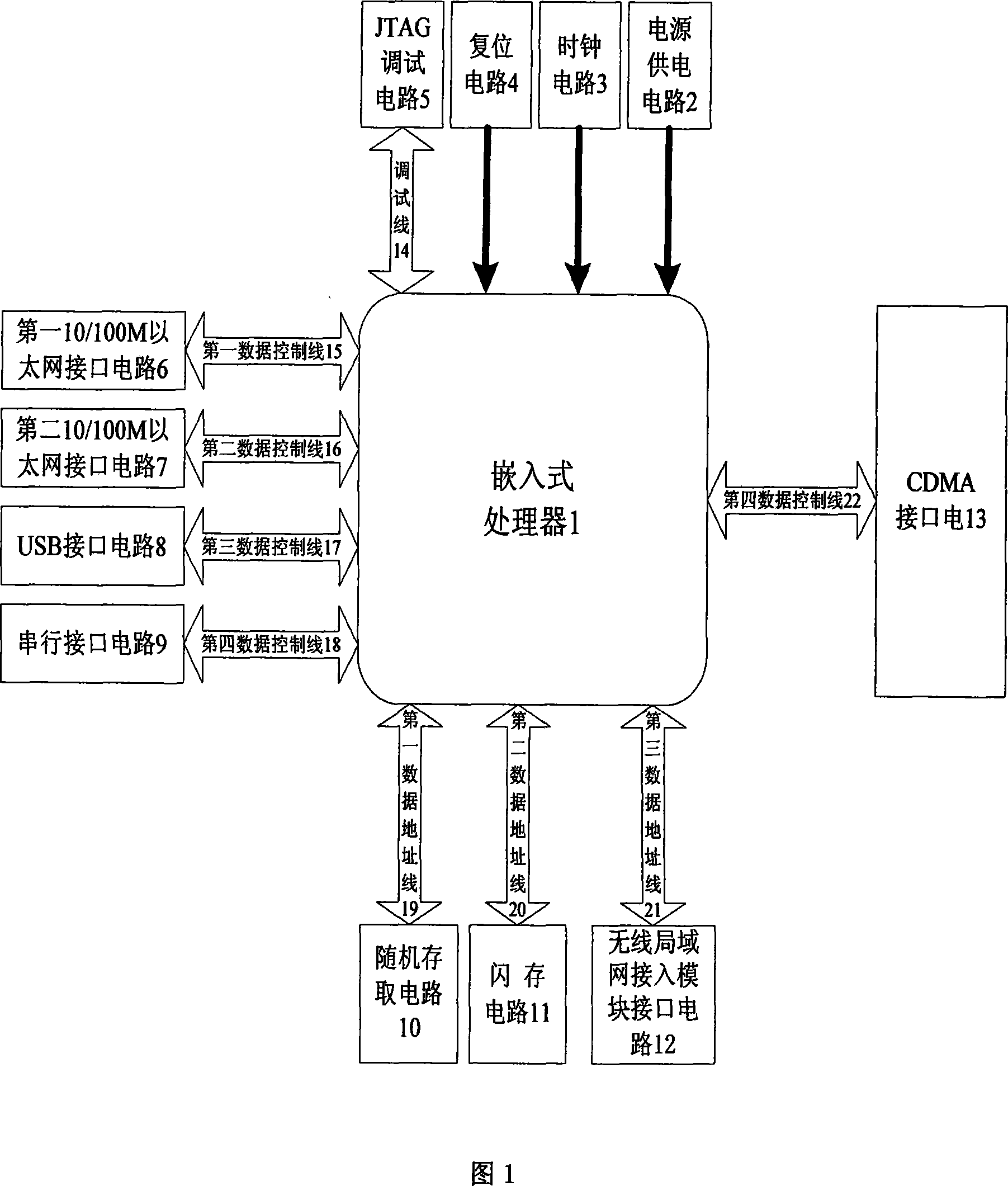
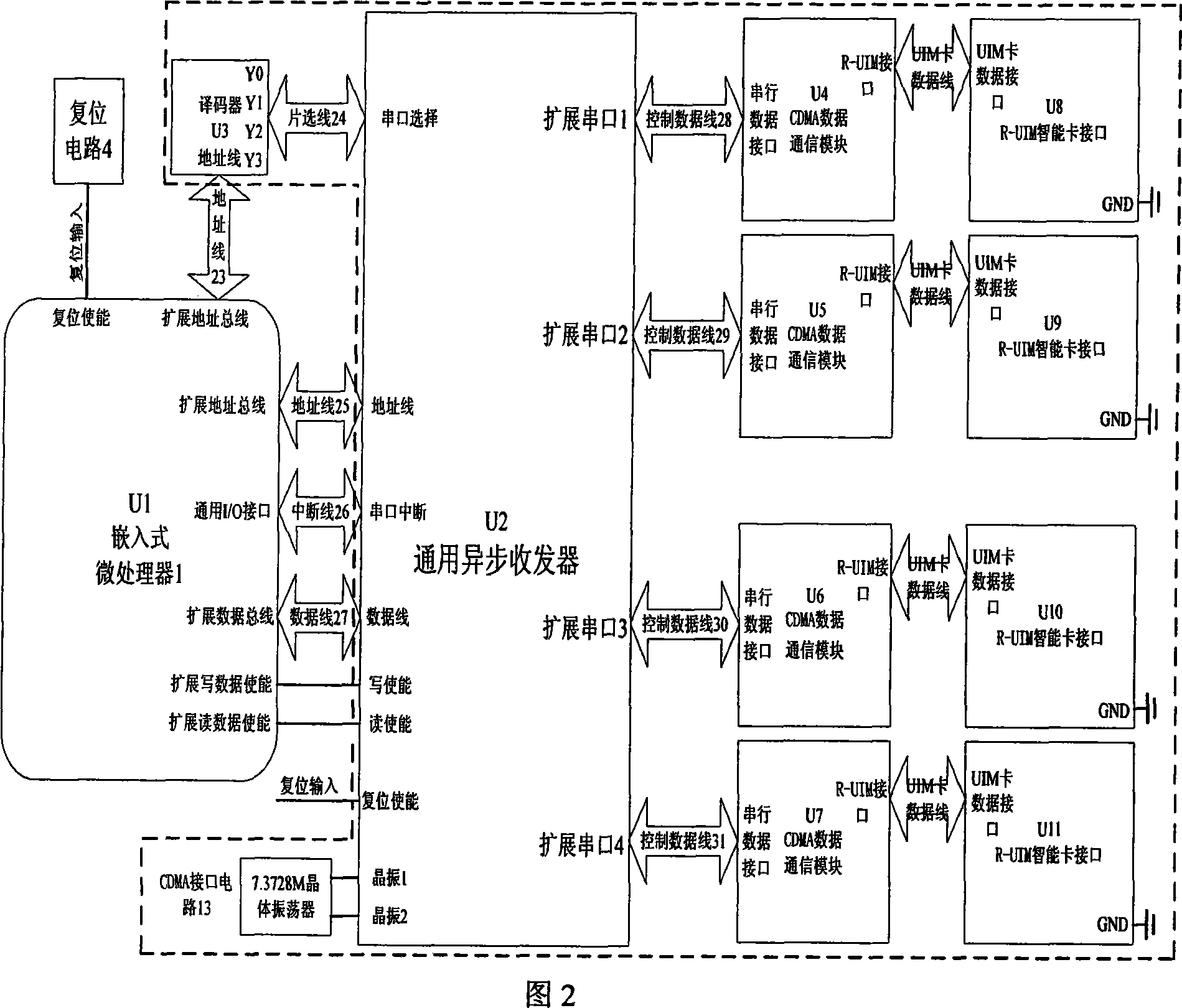
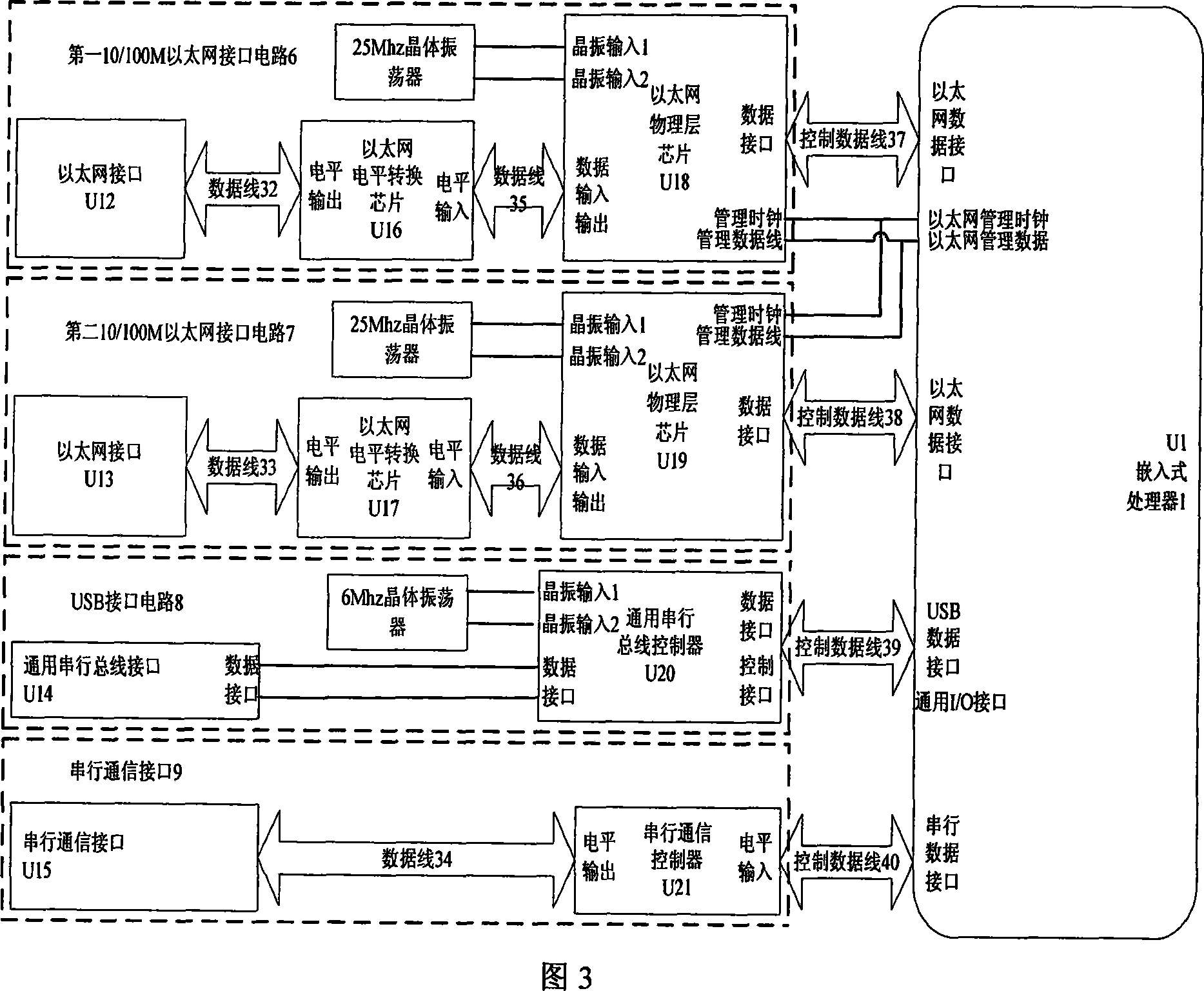
A method and a mobile wireless local area network access device based on Code Division Multiple Access technology relate to a method and a local area network access device, in particular to a method and a mobile wireless local area network access device based on Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) technology, wherein the device comprises an embedded hardware platform, a multi-access CDMA interface module circuit and a wireless local area network access module circuit. The embedded hardware platform comprises an embedded microprocessor, a power supply module circuit, a clock module circuit, a reset module circuit, a JTAG debug port, an Ethernet interface, a USB interface module circuit, a serial interface module circuit, a random access module circuit and a flash memory circuit. The multi-access CDMA interface module circuit comprises a serial interface extensive module circuit and one to four CDMA 2000 1X data links, each of which comprises a CDMA communication module circuit and a R-UIM intelligent card module circuit. The wireless local area network access module circuit comprises a MiniPCI interface circuit and a local area network wireless access module.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Multi-access terminal with capability for simultaneous connectivity to multiple communication channels
ActiveUS7539175B2Improve reliabilityImprove behaviorNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexOperational systemTransceiver
An apparatus is disclosed for permitting a mobile terminal having multiple, heterogeneous network connections (e.g., multiple wired or wireless transceivers of various types) to set up and maintain virtual connections over multiple networks to either the same or to multiple destinations. The mobile terminal can “load-share” traffic, i.e., it can distribute segments of traffic over a full set of heterogeneous networks, significantly improving the reliability and availability of communications. In a first embodiment, a mobile terminal is configured with multiple radio frequency (RF) transceivers. Operating system software is provided for dynamically establishing and maintaining traffic flow for user applications over multiple communications paths, and for automatically adapting to variations in the networking environment, application traffic flow requirements, end user preferences, or mobility. In a second embodiment, a software-defined radio is used to implement the physical layer protocols for each desired network, eliminating the need for multiple transceivers.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF STEVENS INST OF TECH THE
Radio communication system, radio communication method, and radio communication device
ActiveUS20050265470A1Efficient use ofFacilitate communicationSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityCommunications systemEngineering
In the environment of a communication area including a SDM-compatible mobile station for space division multiplex transmission and a SDM-uncompatible mobile station not compatible with space division multiplex transmission, a base station having a plurality of antennas and capable of adaptively changing directivity performs allocation of a mobile station which simultaneously performs space division multiplex transmission (SDM) and space division multiplex access (SDMA) by using a predetermined space division multiplex transmission evaluation criterion and a space division multi access evaluation criterion. By using this radio communication method, it is possible to use the spatial degree of freedom at its maximum and provide a radio communication system having an improved communication capacity.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
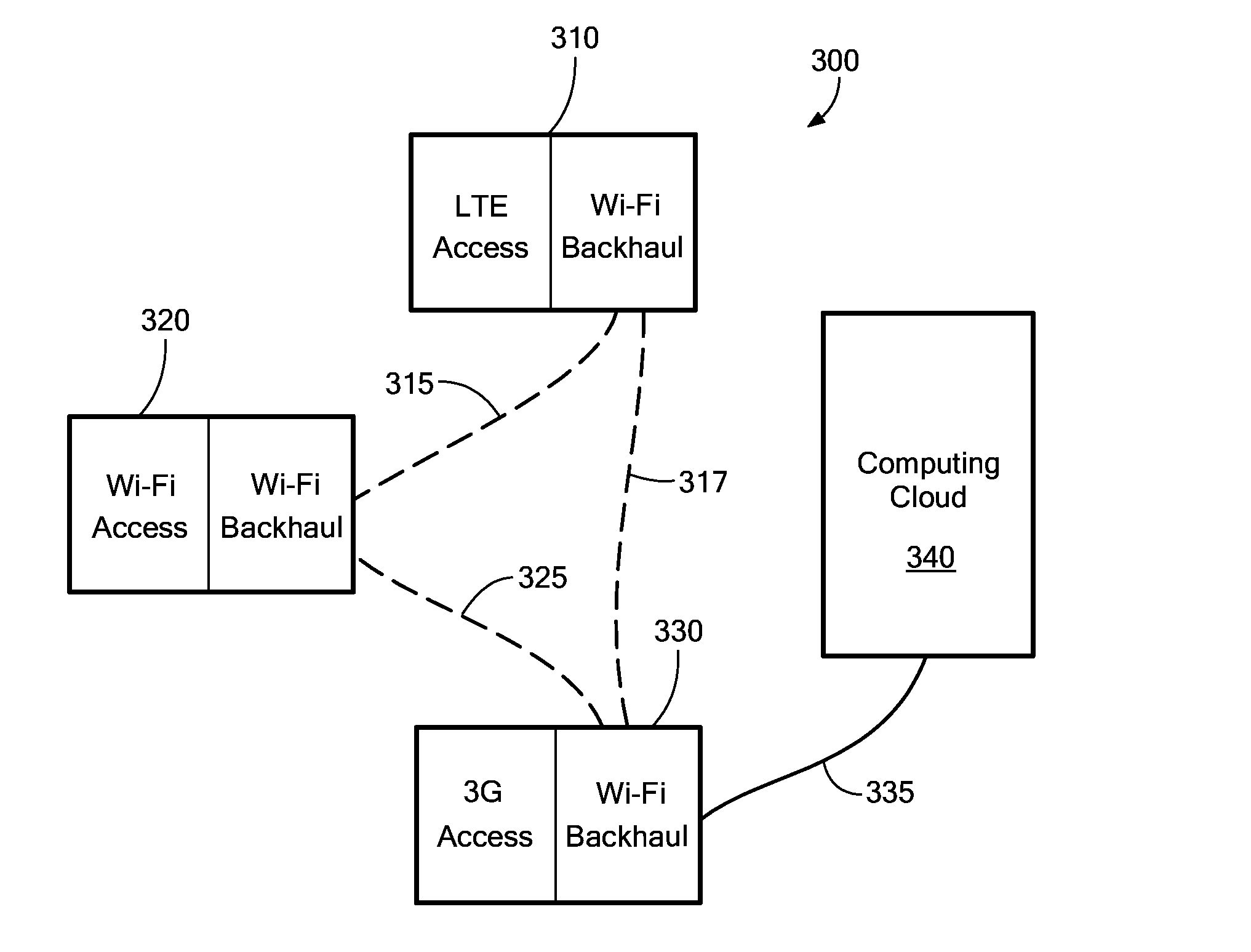
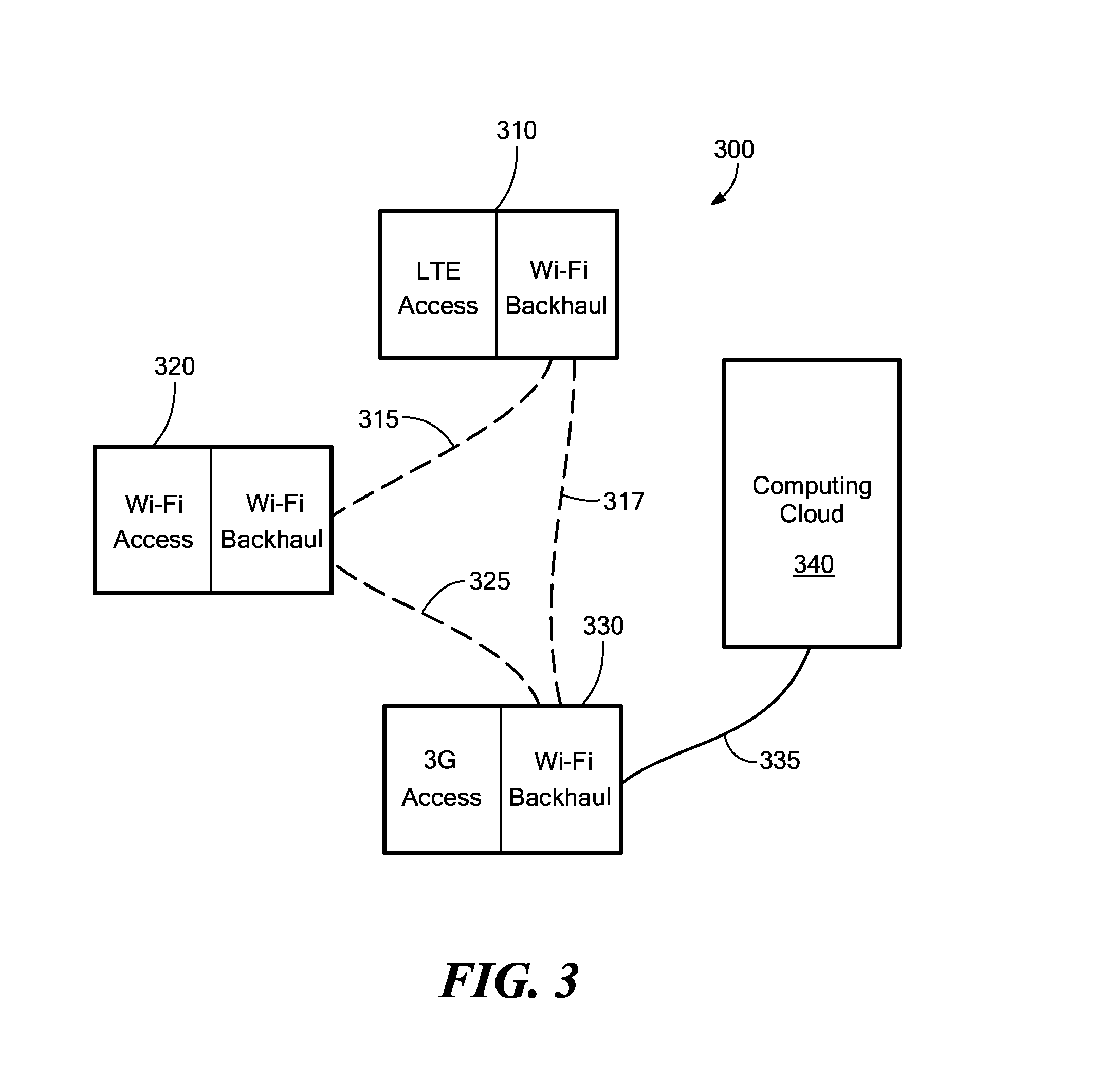
Dynamic Multi-Access Wireless Network Virtualization
ActiveUS20140133456A1Network topologiesWireless commuication servicesWireless network virtualizationMulti access
We disclose systems and methods of dynamically virtualizing a wireless communication network. The communication network is comprised of heterogeneous multi-RAT mesh nodes coupled to a computing cloud component. The computing cloud component virtualizes the true extent of the resources it manages and presents an interface to the core network that appears to be a single base station.
Owner:PARALLEL WIRELESS
Substrate processing apparatus
A semiconductor workpiece processing apparatus having a first chamber, a transport vehicle, and another chamber. The first chamber is capable of being isolated from an outside atmosphere. The transport vehicle is located in the first chamber and is movably supported from the first chamber for moving linearly relative to the first chamber. The transport vehicle includes a base, and an integral semiconductor workpiece transfer arm movably mounted to the base and capable of multi-access movement relative to the base. The other chamber is communicably connected to the first chamber via a closable opening of the first chamber. The opening is sized to allow the transport vehicle to transit between the first chamber and the other chamber through the opening.
Owner:BOOKS AUTOMATION US LLC
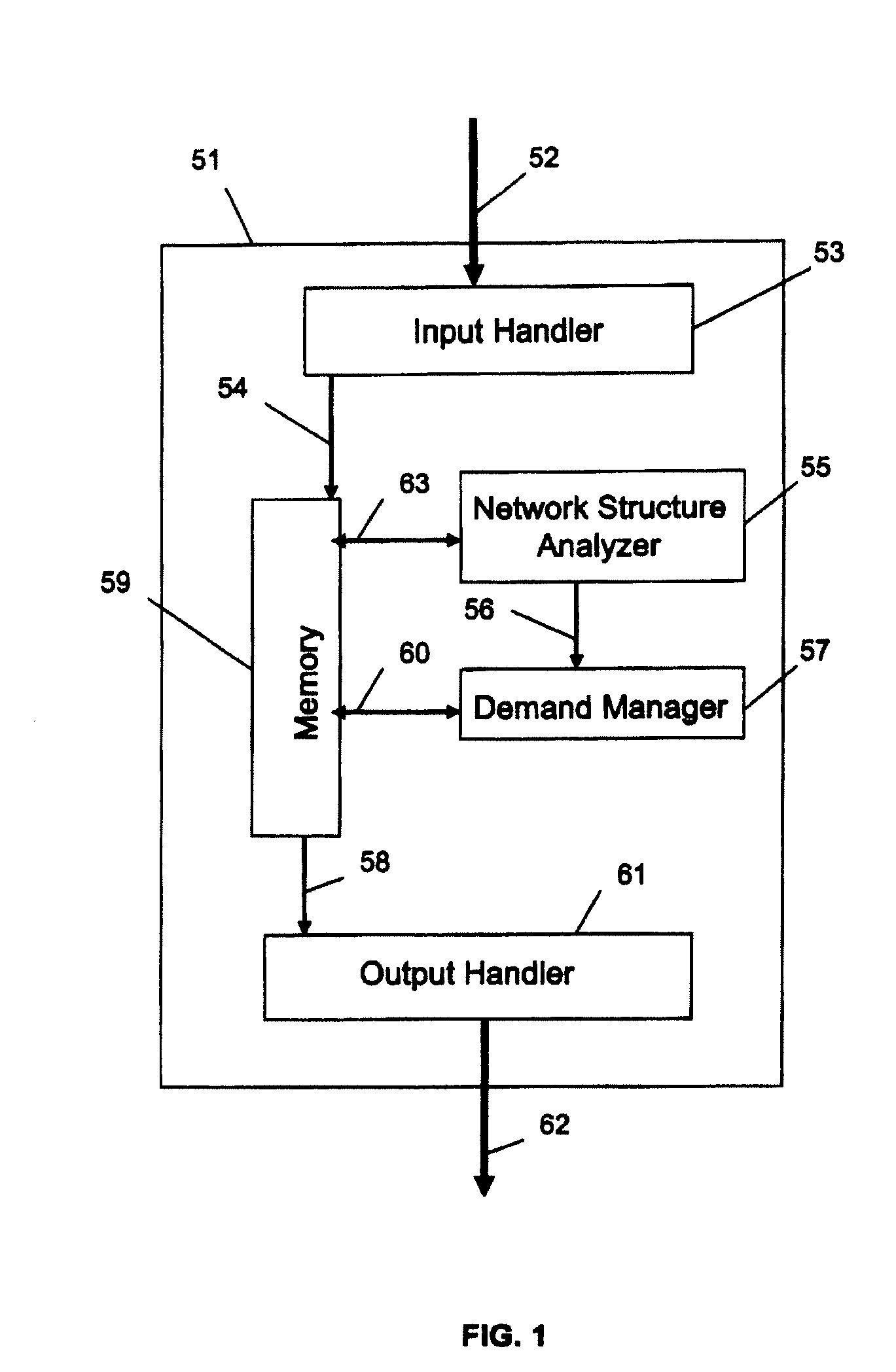
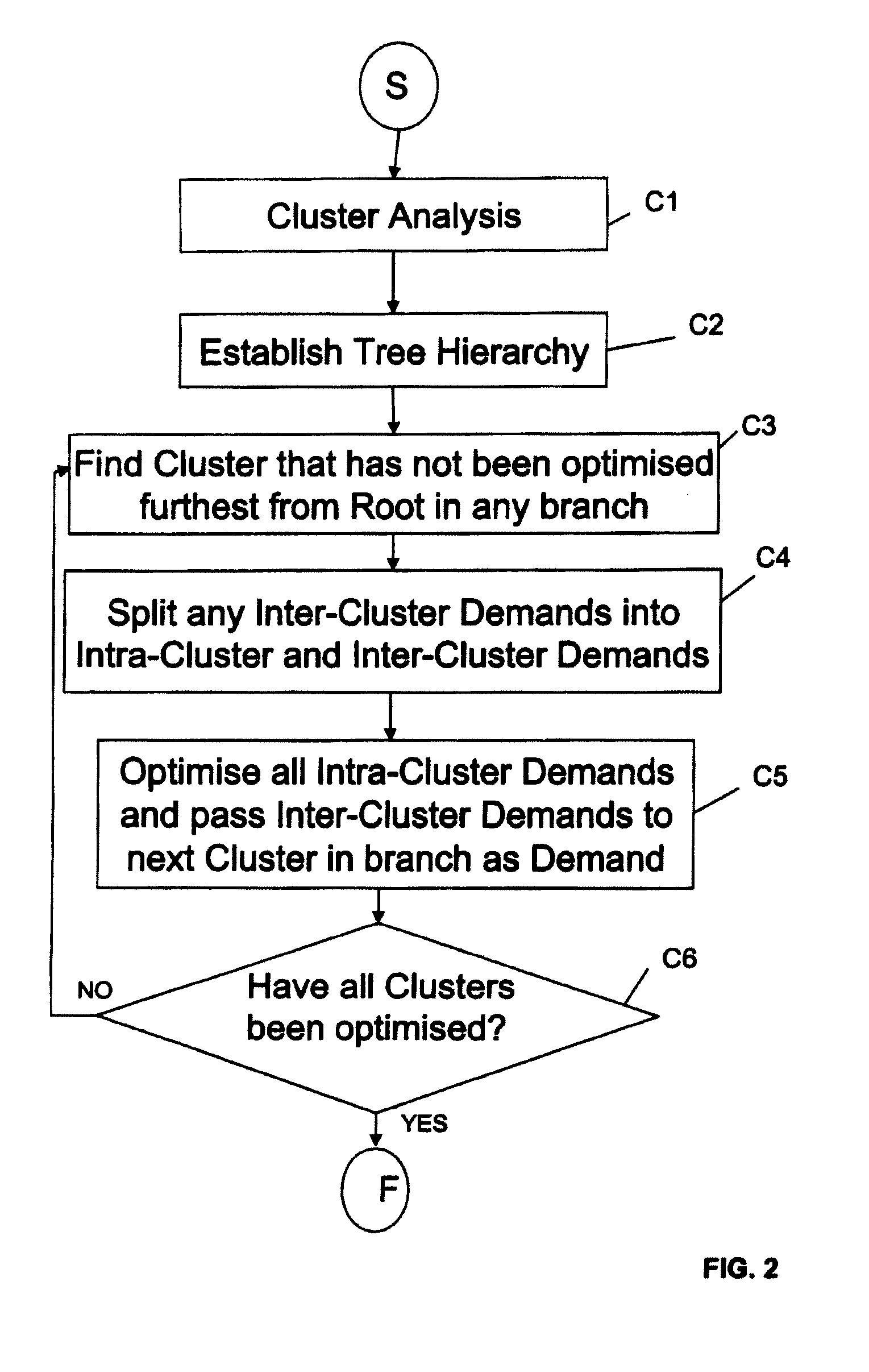
Method of Optimizing Routing of Demands in a Network
InactiveUS20070211637A1Optimizing routing of demandsError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCore componentMulti protocol
The present invention relates to a method for optimization of demands in a packet switched communication network, especially, though not exclusively, for the optimization of demands in a Multi Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) packet switched communication network. The present invention provides a method to enable network nodes, such as routers to be clustered into components, with the components organised in a hierarchical fashion, and with the network “core” at the root of this hierarchy. Demands that originate or terminate at components outside the core, but that traverse the core, are temporarily replaced by demands that originate and terminate within the core component. Having optimized the resulting set of demands it is then shown how to use the solution to satisfy the original demands. Multi-access networks cause some complications, and these are taken into account. Also, further demand replacement methods have been developed that take into account complex access situations, In particular, as mentioned, the case has been considered, where there is an existing partitioning of the routers, e.g. into core and access routers, which needs to be respected.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
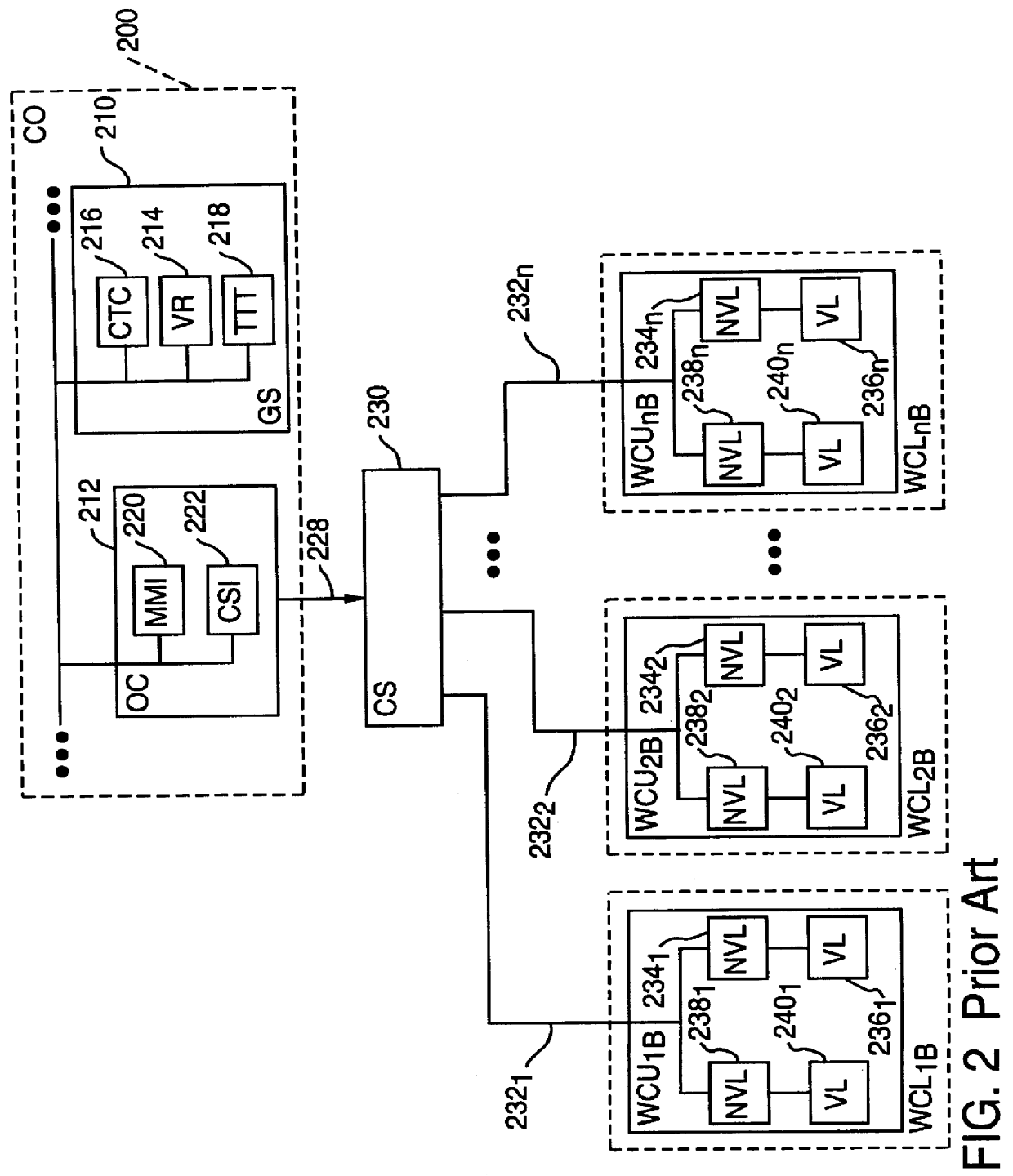
System for distributed automatic train supervision and control
InactiveUS6032905ARailway traffic control systemsRoute devices for controlling vehiclesCarrier signalEngineering
A system for supervising and controlling the movement of a railway vehicle is provided, wherein a plurality of wayside controller units are each distributed to a plurality of wayside controller locations by a multi-access carrier, such as a fiber LAN or IEEE 802.3 Ethernet, for instance, such that supervisory and control operations may be communicated between each of the wayside controller units with a multi-access protocol on the multi-access carrier. The present invention replaces the use of a serial-link protocol for point-to-point communication with a multi-access protocol on a multi-access carrier. In a preferred embodiment, a computer-based control system may be connected through the multi-access carrier, so that communication is achieved solely with multi-access protocols. Related art Centralized traffic control (CTC) functions may be eliminated from a global services (GS) block of the central office (CO) and implemented as Distributed Traffic Control functions that are distributed to the wayside controller units.
Owner:ANSALDO STS USA INC
Physically and electrically-separated, data-synchronized data sinks for wireless systems
Owner:PLANTRONICS
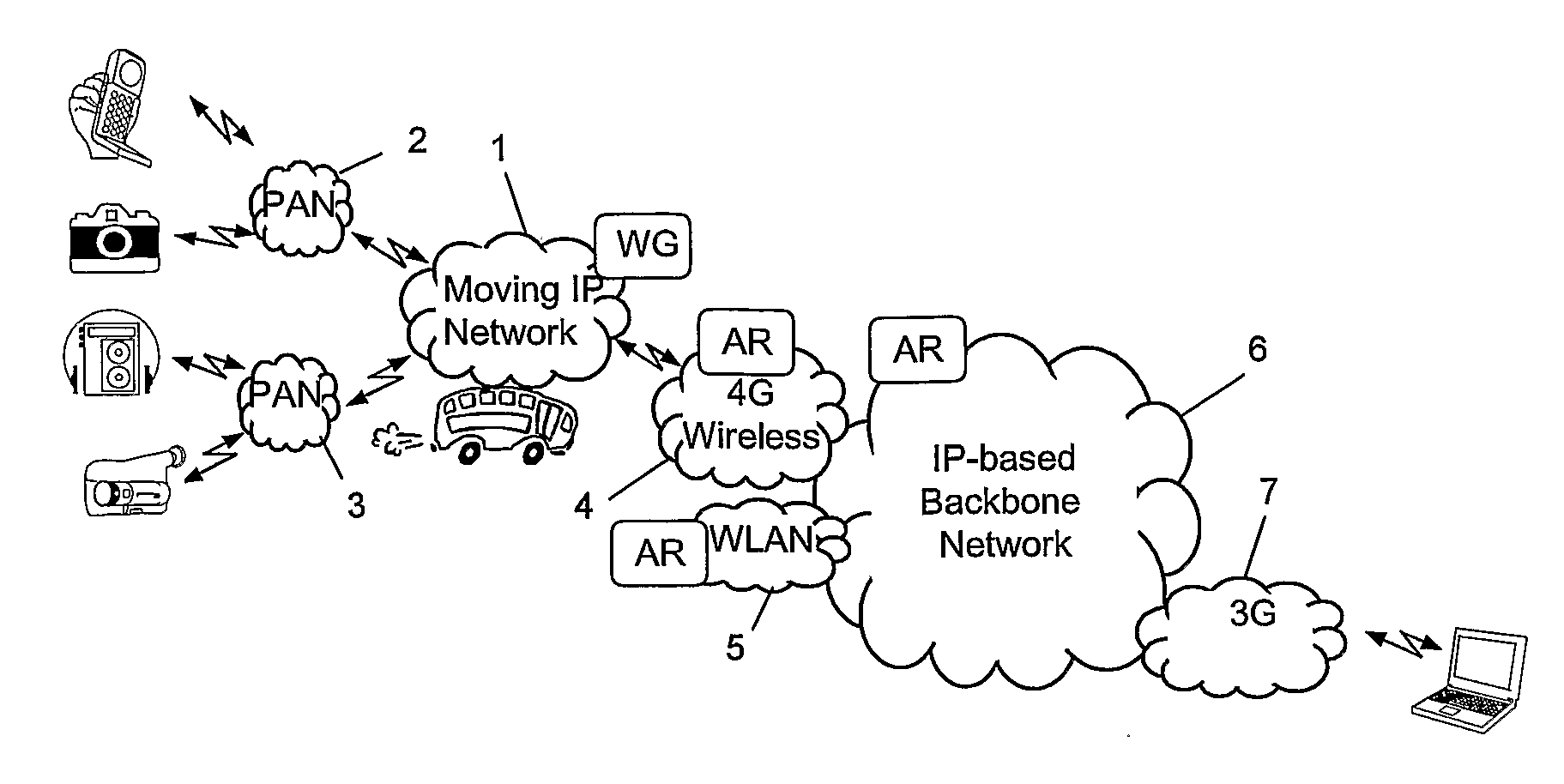
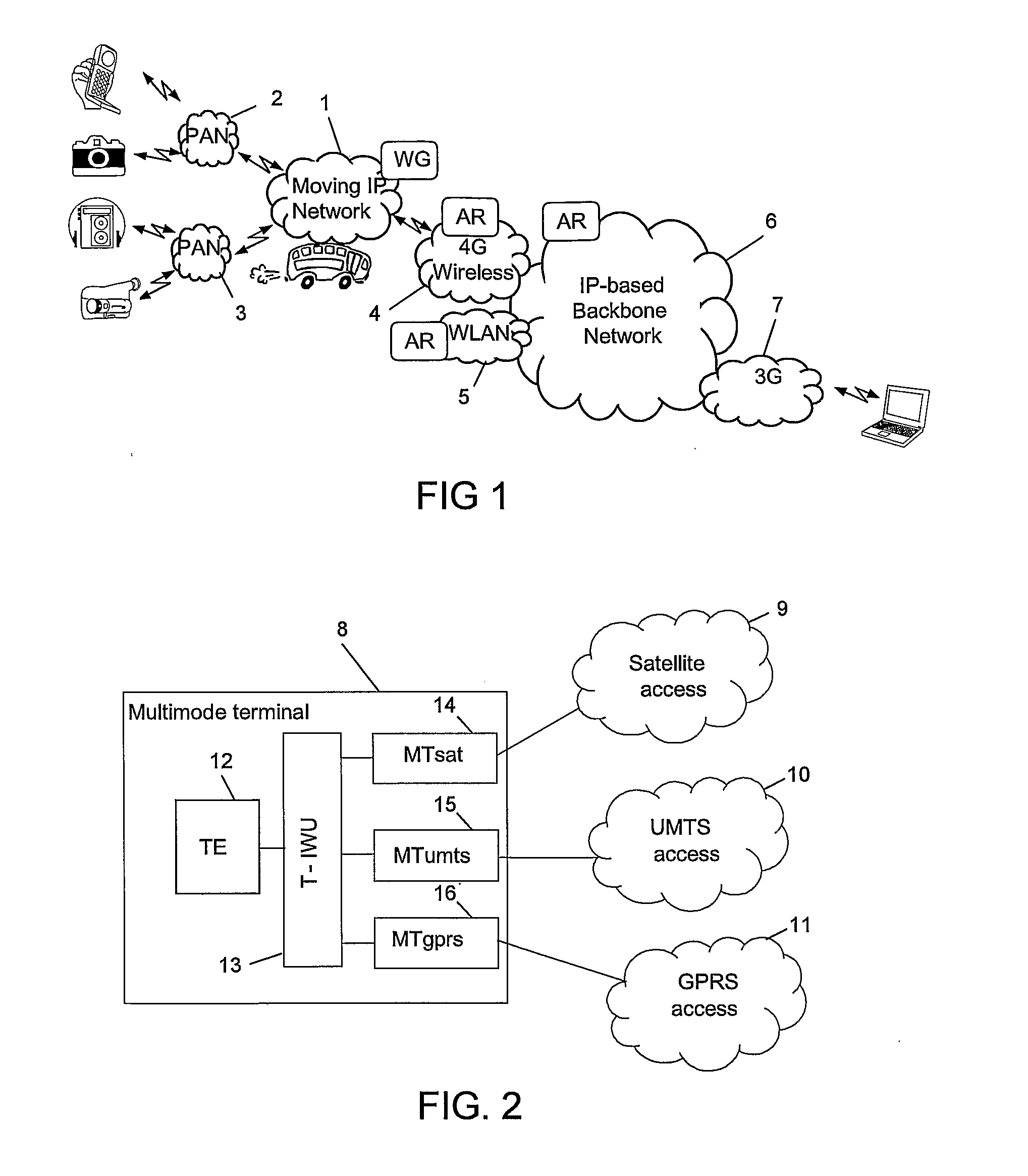
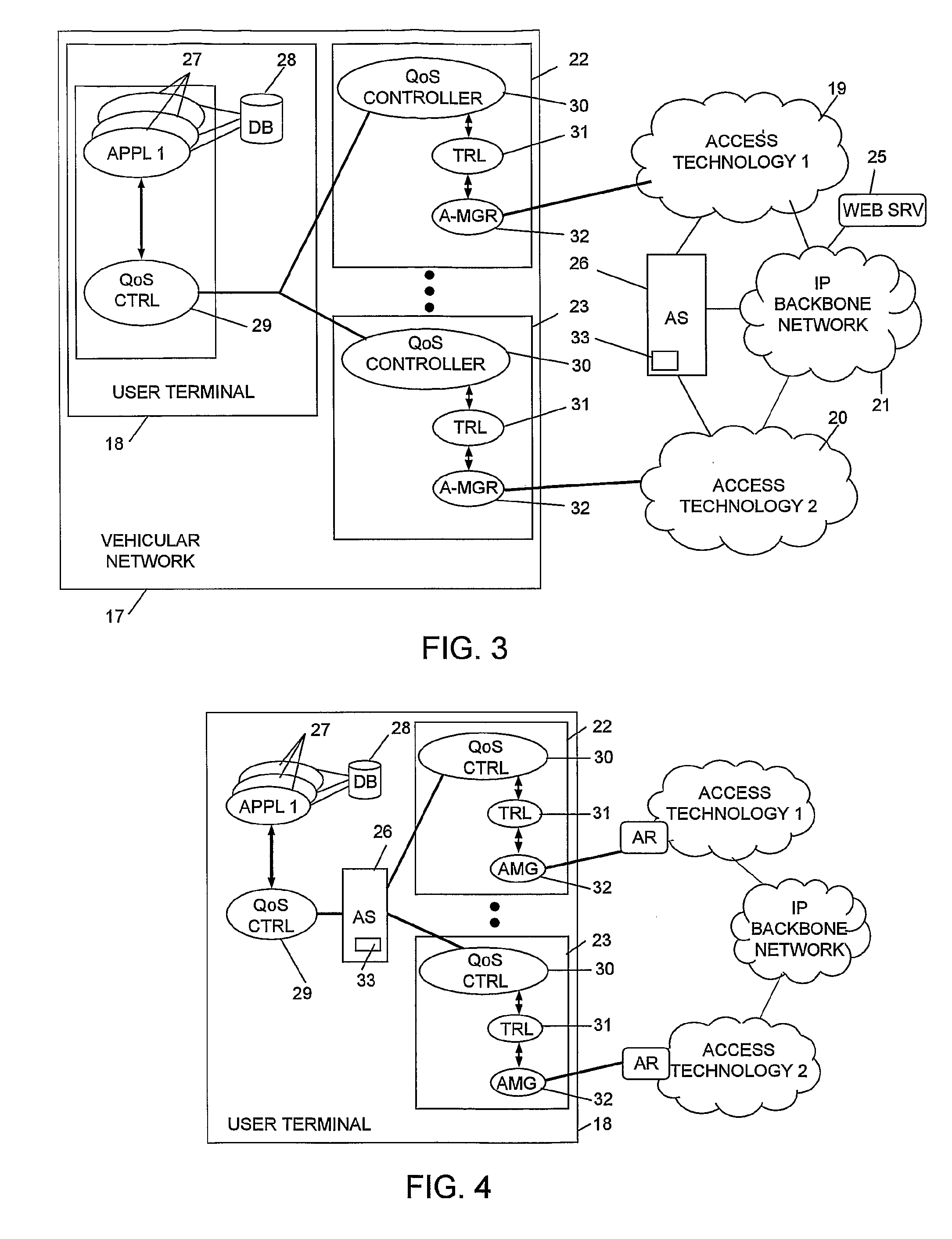
System and Method for Multi-Access
InactiveUS20070217349A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionAccess networkRadio access network
A system and a method allowing a user terminal (18) in a network to simultaneously access a plurality of radio based access networks (19, 20) of diverse access technologies. Characteristic features of the invention are access selection adapters (22, 23), each one associated with a respective radio based access network, and an access technology independent access selector (26). An access adapter has means (32) for receiving access technology dependant information from its respective access network and means (31) for translating the information into access technology independent status information. The access selector comprises an access selection algorithm (33) interacting with applications (27) resident in the user terminal and with each access adapter for selection of a radio access network based on an individual QoS profile associated with each respective application and on said access technology independent status information. The invention also relates to a method for service scheduling.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
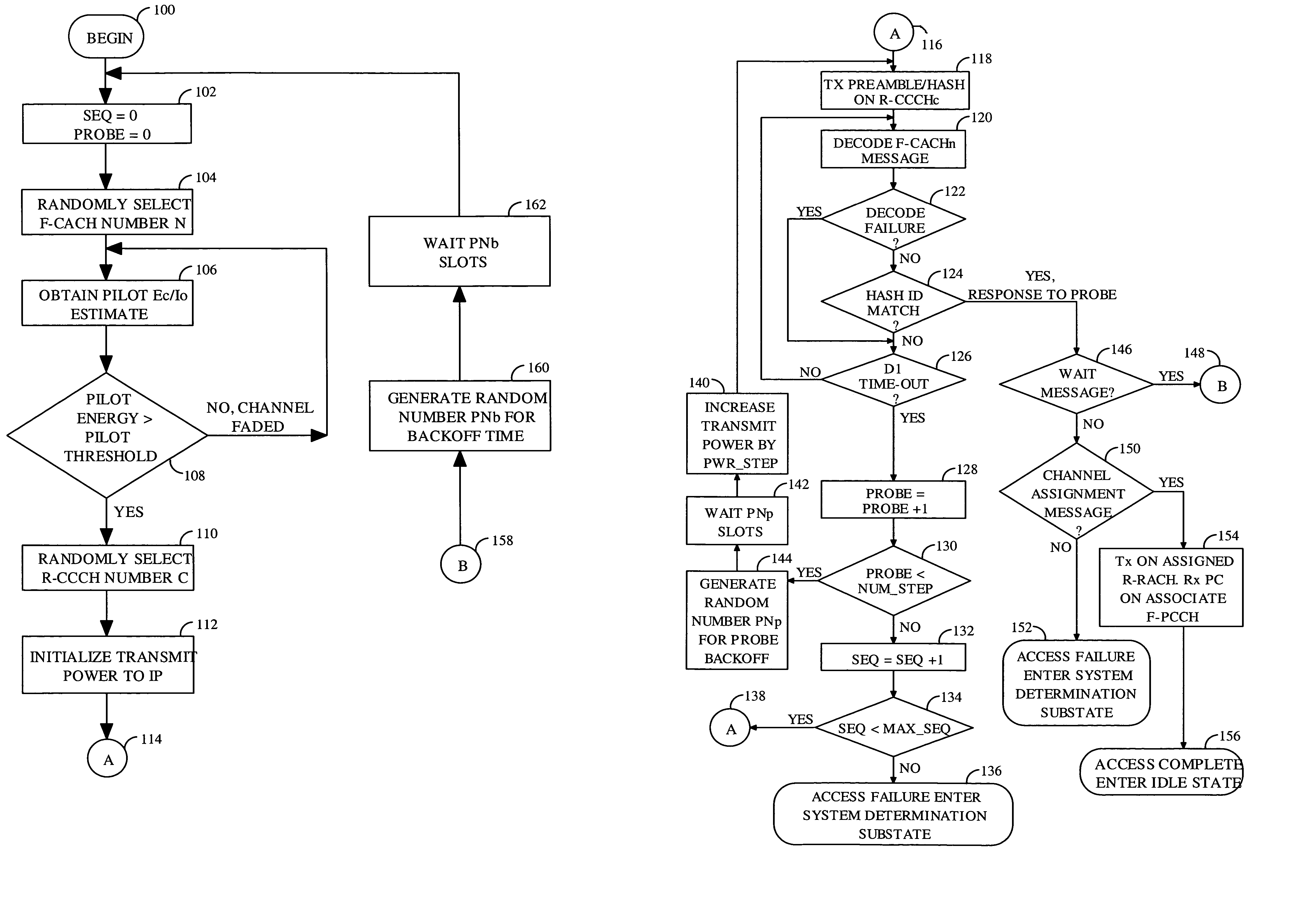
Reservation multiple access
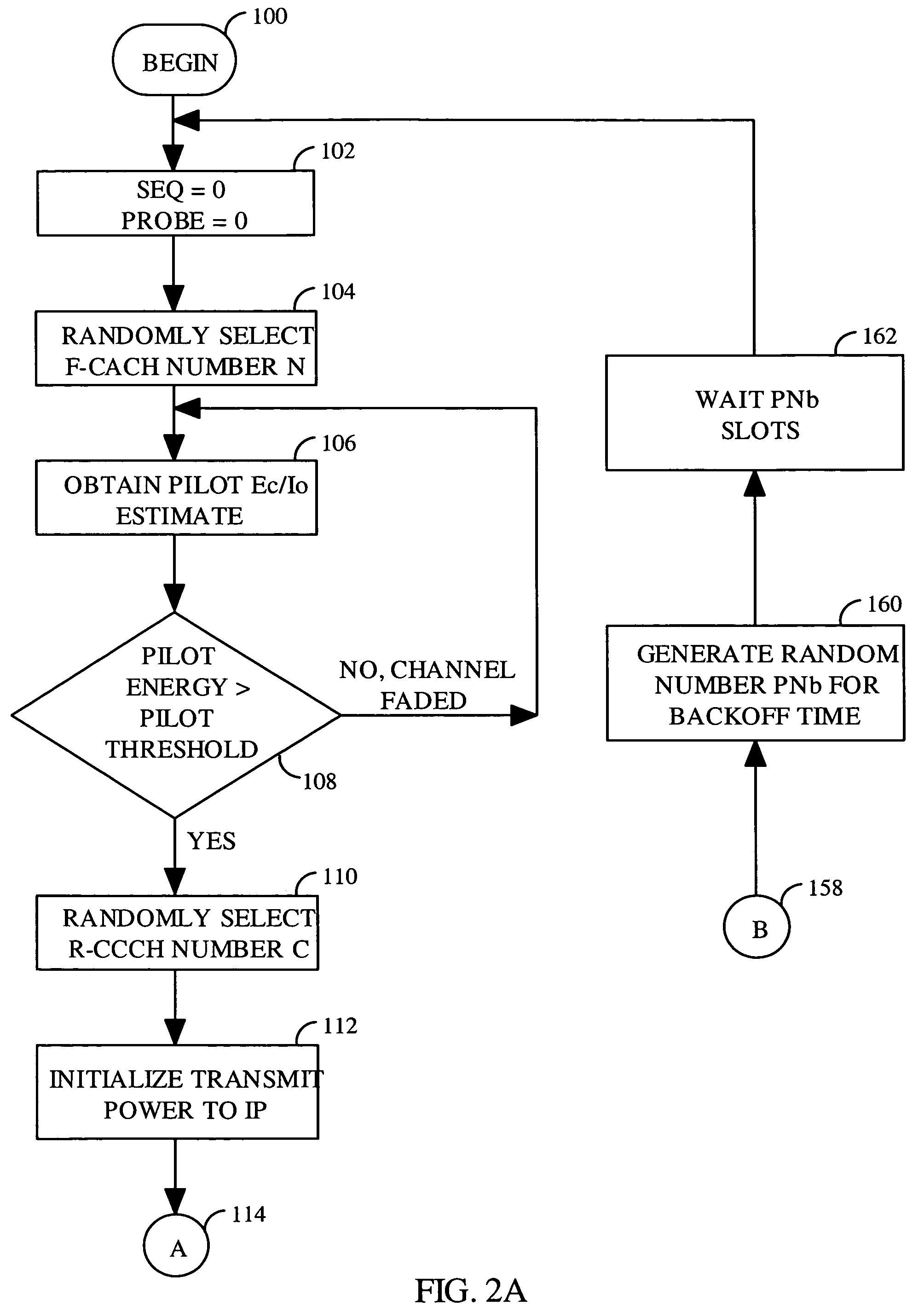
InactiveUS6987982B2Fast disablingPower managementTransmission control/equalisingHash functionTelecommunications
A mobile station accesses a base station by randomly selecting a first reverse link common control channel from a set of random access channels. The mobile station transmits a request portion of an access probe over the first reverse link common control channel. The request portion is subject to collision with other signals. The request portion comprises a hash identification which is derived from a uniquely identifying number using a hash function. The hash identification quasi-uniquely identifies the mobile station. The mobile station receives a channel assignment message from the base station designating the hash identification and a reserved access channel. The reserved access channel provides communication with a low probability of contention. The mobile station transmits a message portion of the access probe over the reserved access channel.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
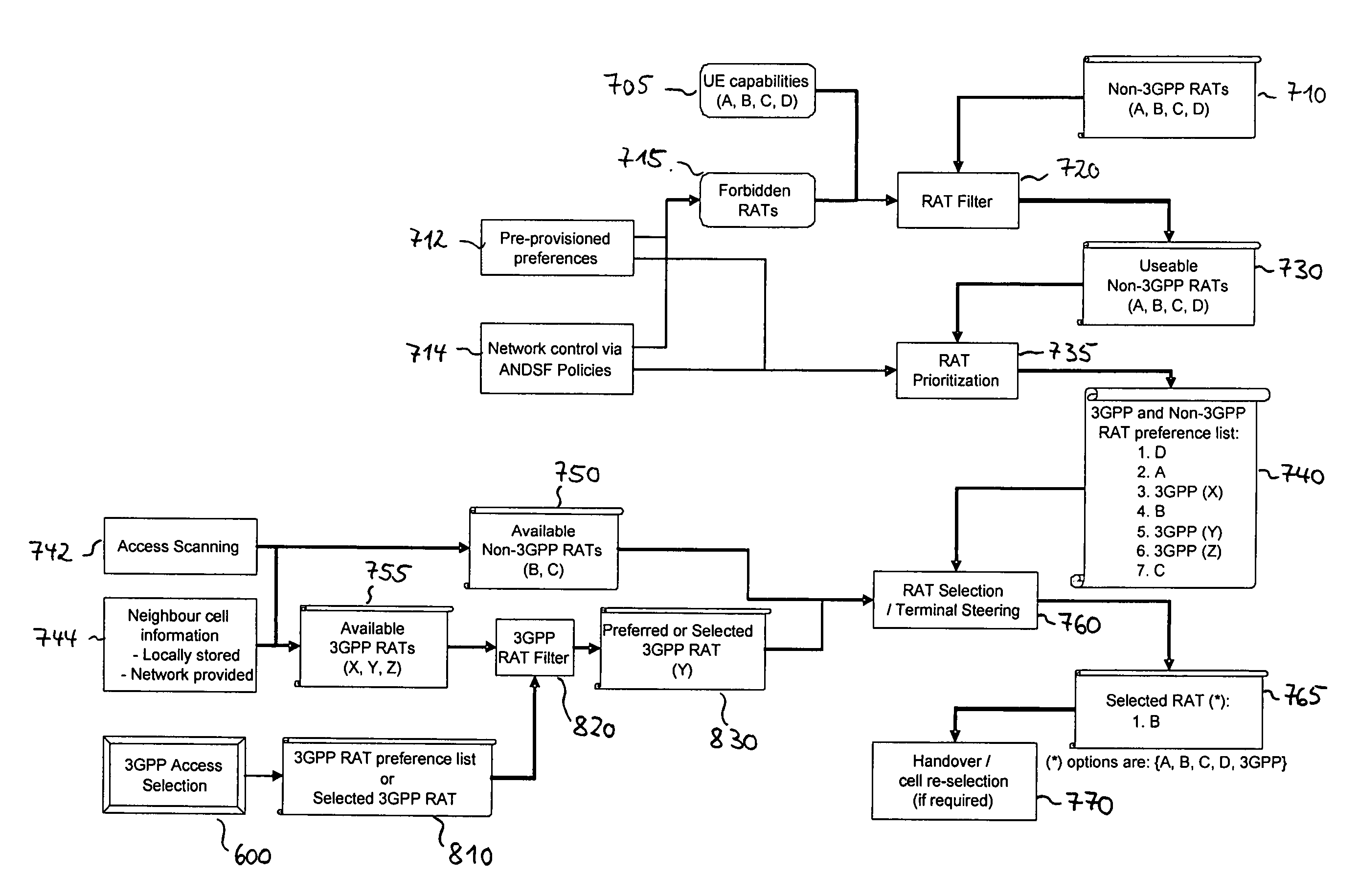
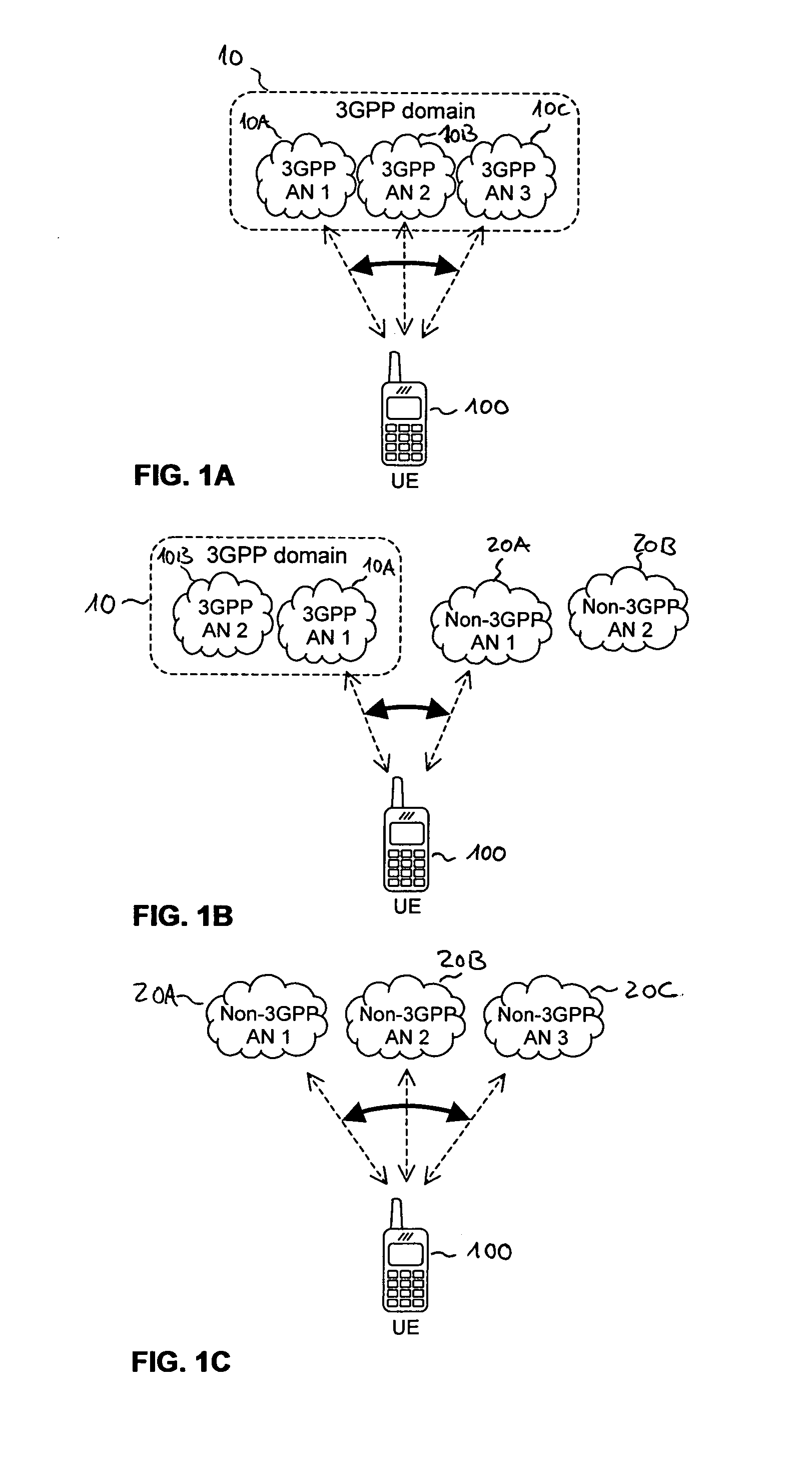
Access Network Selection in Multi-Access Network Environment
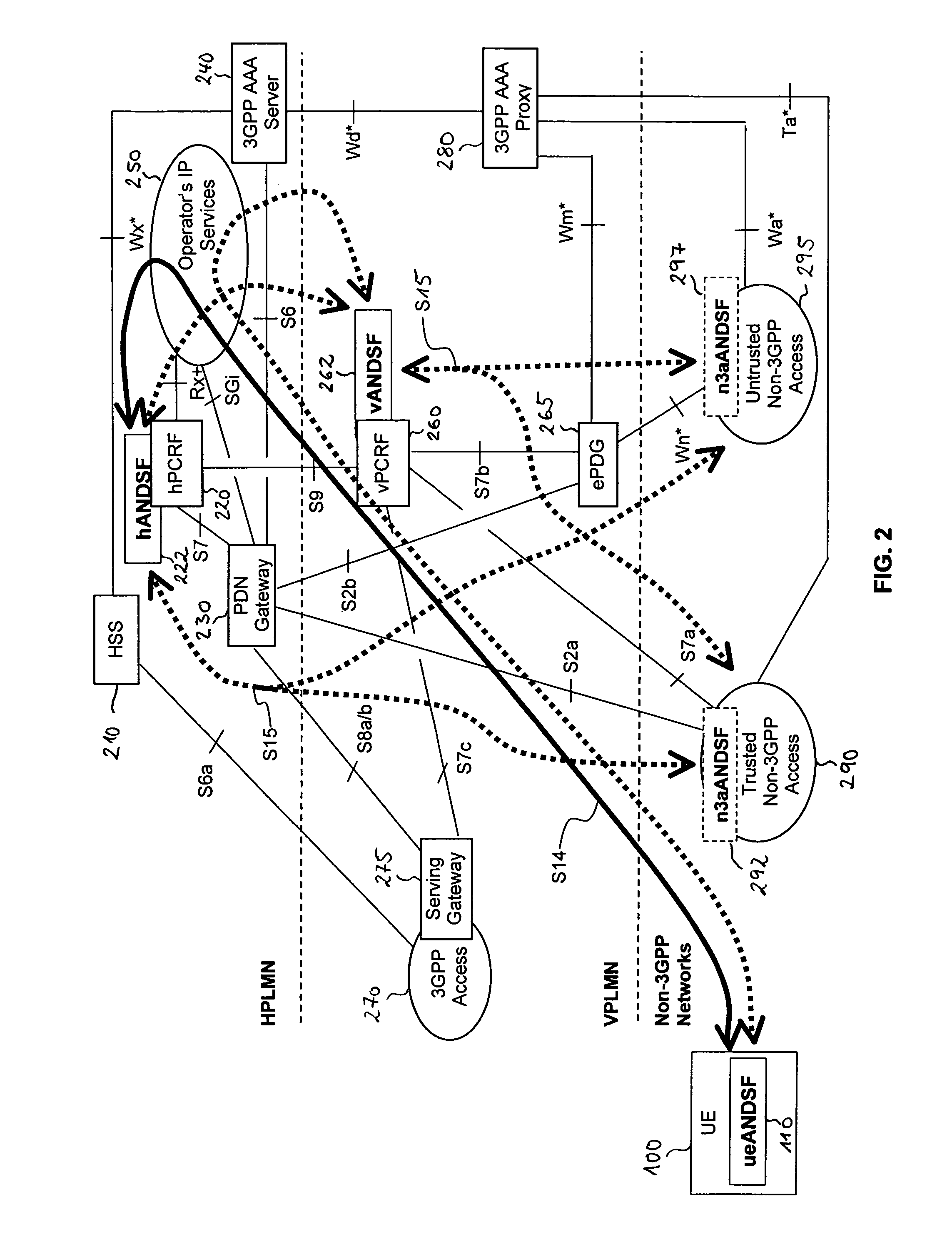
ActiveUS20110110300A1Avoiding undesired access selection loopAvoid choiceAssess restrictionWireless commuication servicesAccess networkMulti access
Novel techniques of access network selection in multi-access network environment are provided, which allow for avoiding access selection loops for independent access selection processes. The multi-access network environment provides a first access selection function, e.g. a 3GPP access selection function, and a second access selection function, e.g. an ANDSF based access selection function. At least a portion of the first access selection function (565) may be implemented by a network component (560). At least a portion of the second access selection function (110) may be implemented by a user equipment (100), e.g. a mobile terminal. According to the proposed concepts, a selection priority information of the first access selection function (565) is made available to the second access selection function (110).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Addressing scheme for a multimedia mobile network
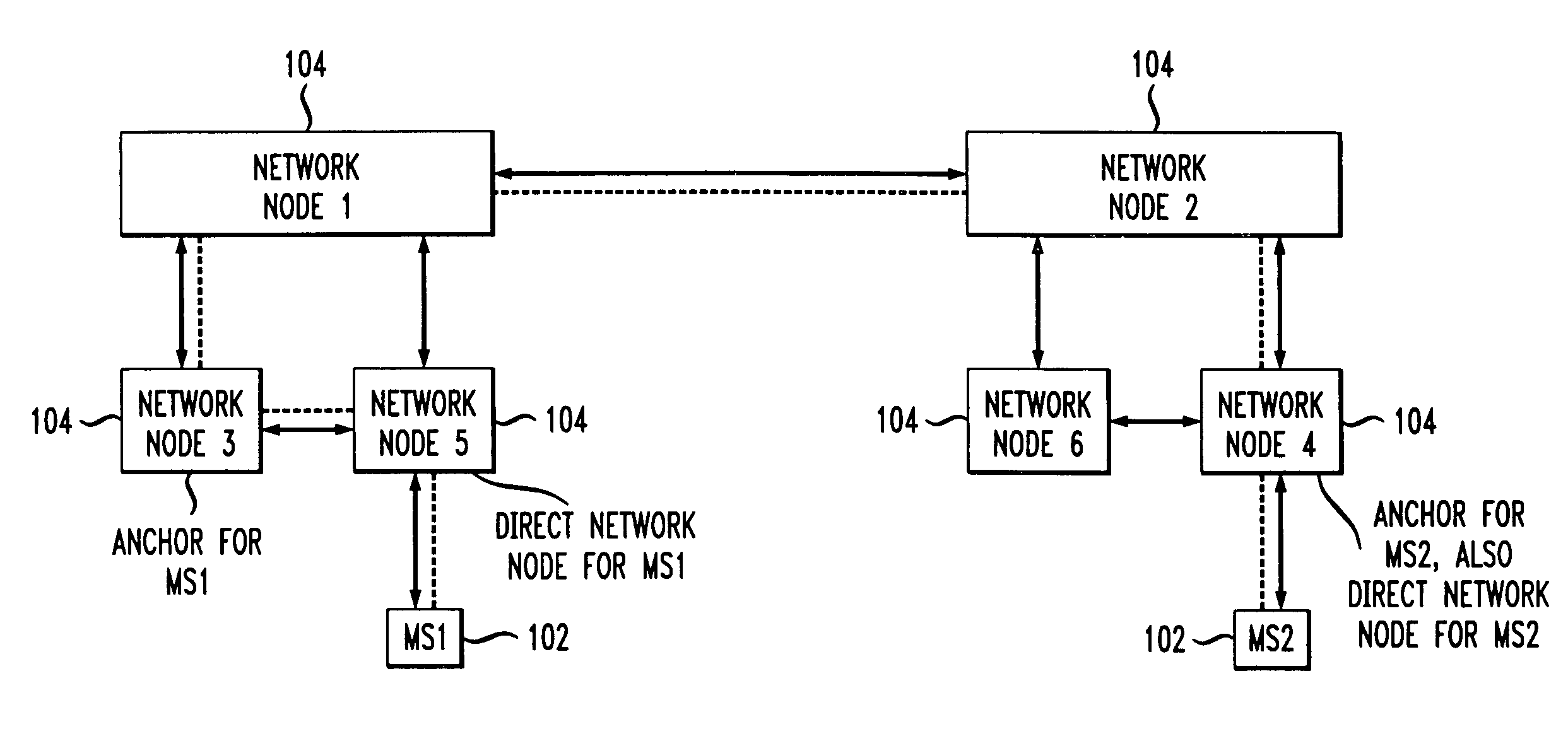
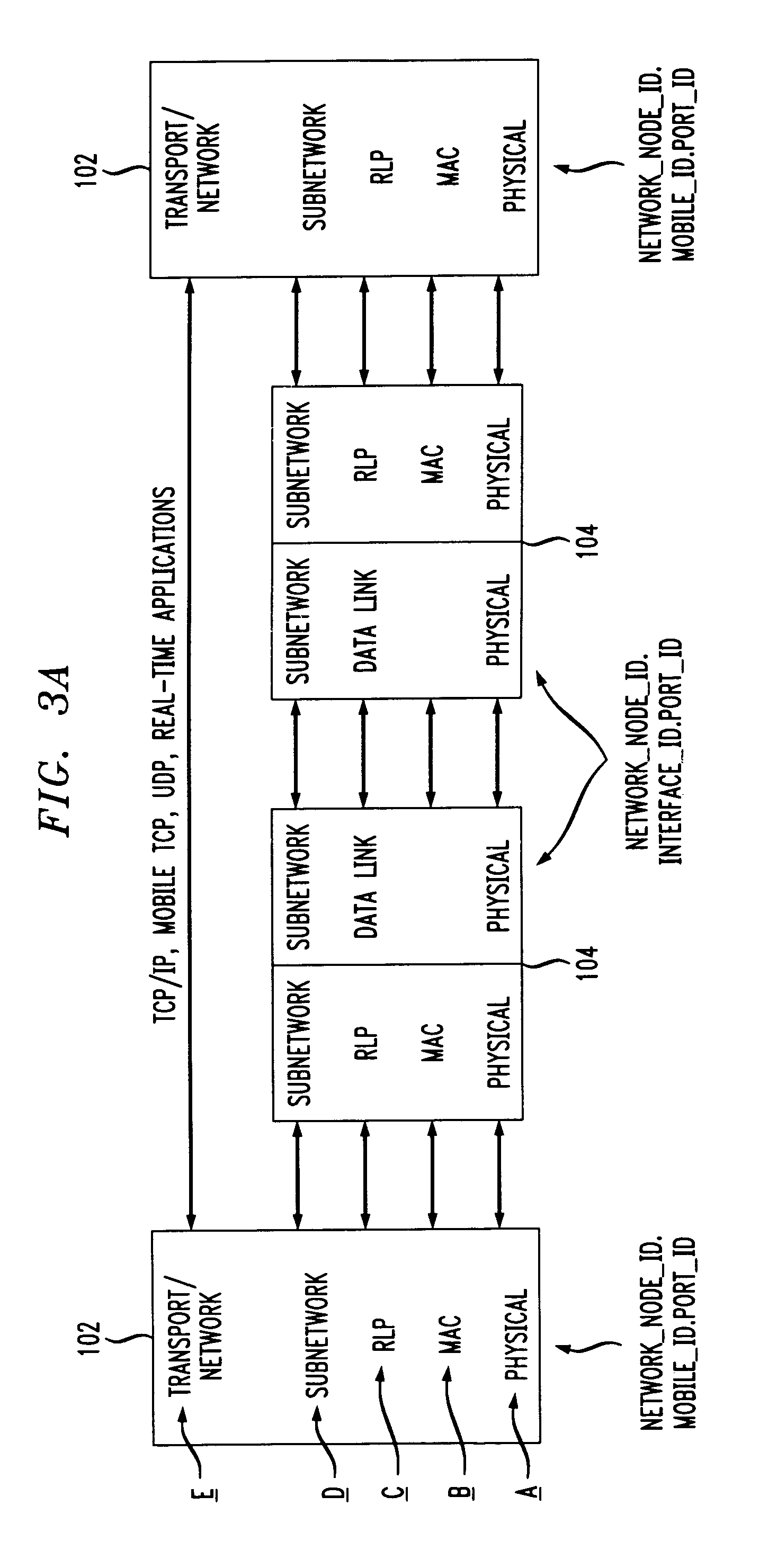
InactiveUS6947398B1Optimize packet routingReduce movementTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationCommunications systemUnique identifier
An addressing scheme for a packet-based multiaccess mobile communications system, which includes a plurality of mobile user stations and a plurality of network nodes, is provided. In such addressing scheme, each mobile station is assigned an address which is a combination (preferably, a concatenation) of a unique identifier of a network node with which the mobile station is currently associated and an identifier of the mobile station. The network node identifiers may be uniquely assigned by a network administrator, while the identifiers of the mobile stations may, for example, be set to a universal MAC address assigned to the station. The address may also include a port identifier which indicates the particular application flow associated with the accompanying packets. Similarly, each network node is assigned an address which is a combination (preferably, a concatenation) of its network node identifier and, preferably, an interface identifier. The address may also include a port identifier.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
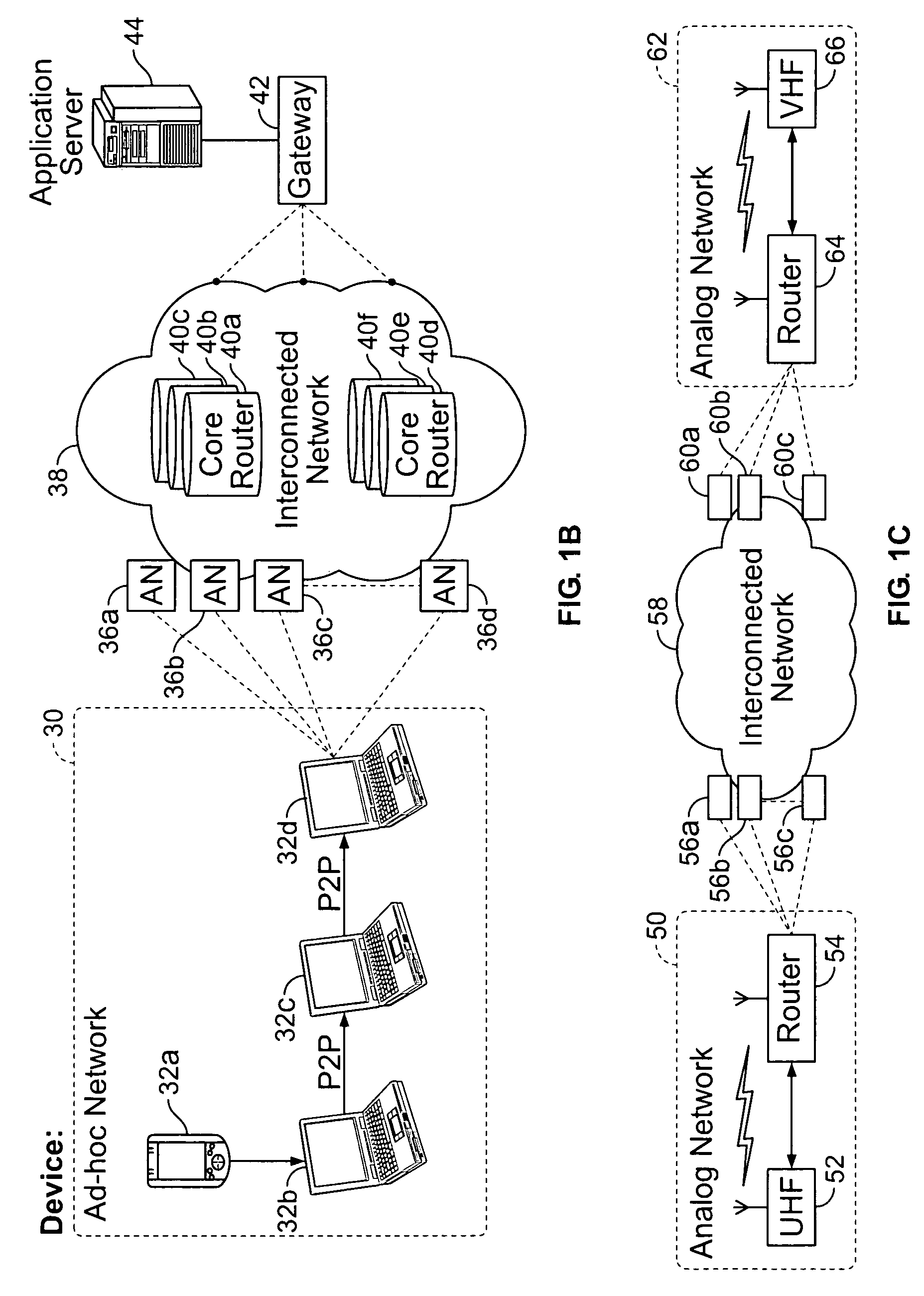
Methods and electronic devices for wireless ad-hoc network communications using receiver determined channels and transmitted reference signals
InactiveUS20040110508A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission path divisionCommunications systemWireless ad hoc network
Electronic devices for communicating in wireless ad-hoc networks and multiple access systems (such as mobile radio telephone communications systems) are disclosed. For example, a disclosed transmitter can transmit data to a first receiver in an ad-hoc wireless network (or multiple access system) over a first channel and can, further, transmit data to a second receiver in the ad-hoc wireless network (or multiple access system) over a second channel that is separate from the first channel, where the first and second channels are determined by the respective receivers which will receive the first and second transmitted data. Accordingly, communications between transmitters and different receivers in the ad-hoc wireless network (or multiple access system) can be carried on simultaneously. Related receivers as well as methods, computer program products, and systems for communicating are also disclosed.
Owner:ERICSSON TECH LICENSING
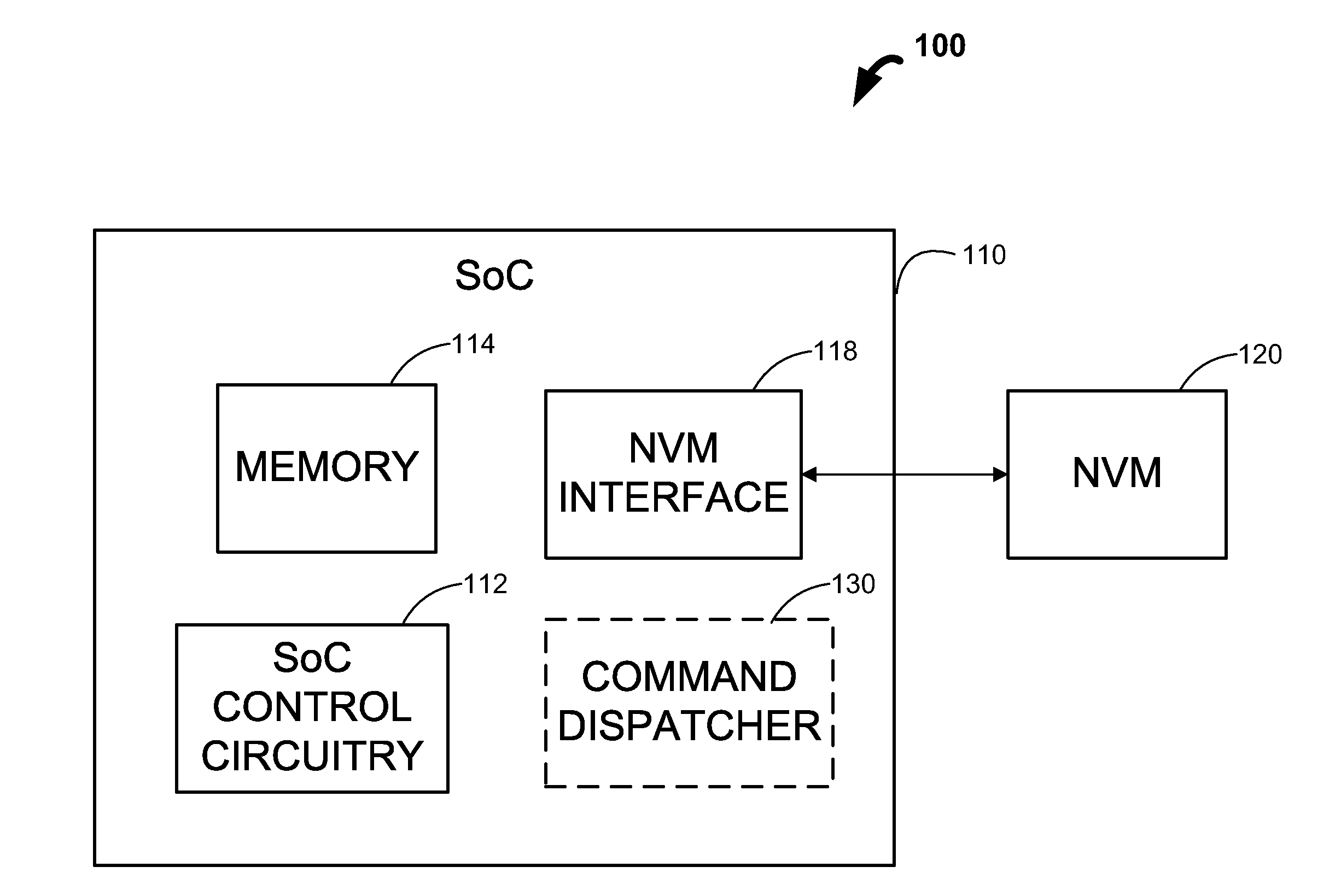
Selectively combining commands for a system having non-volatile memory
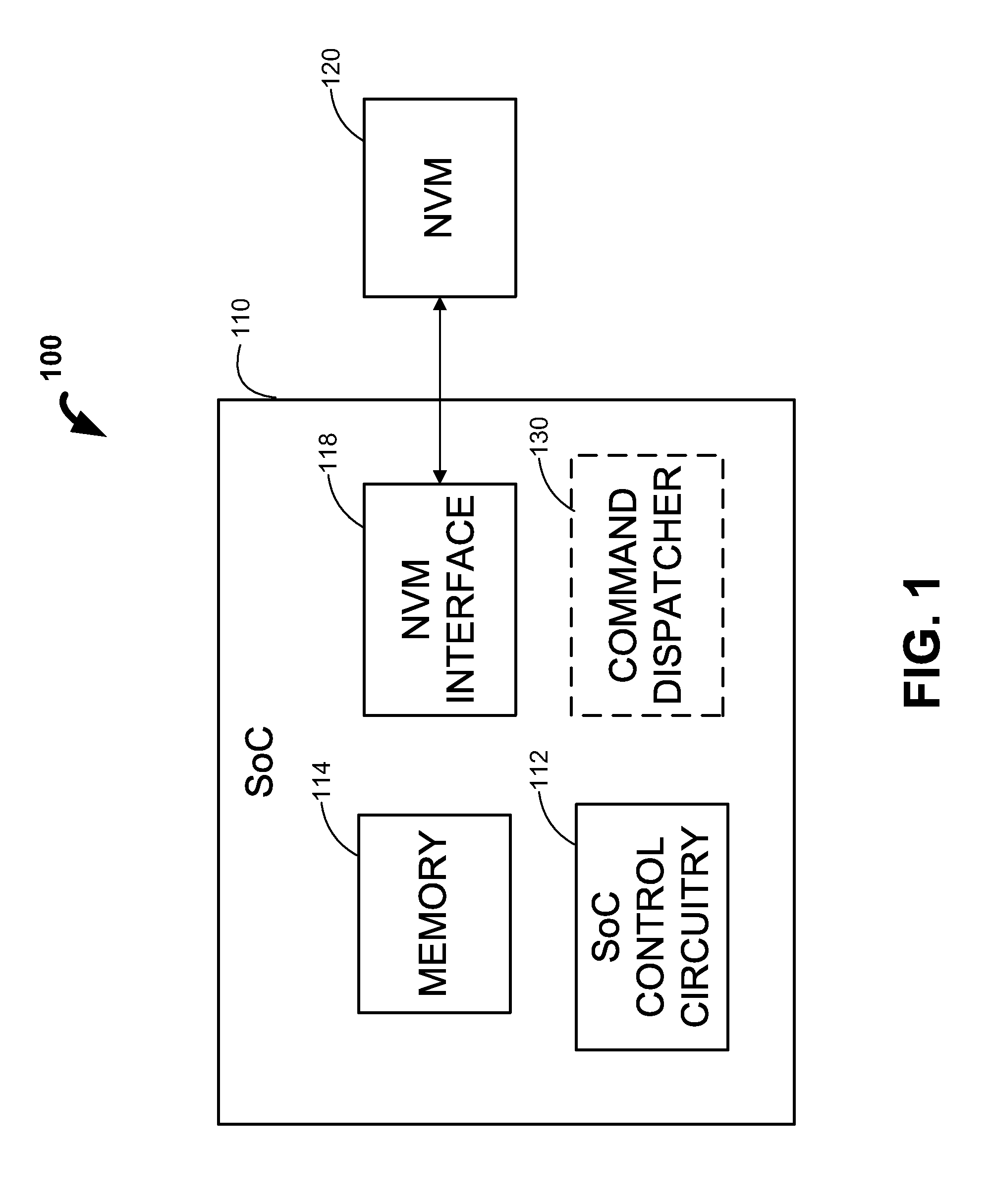
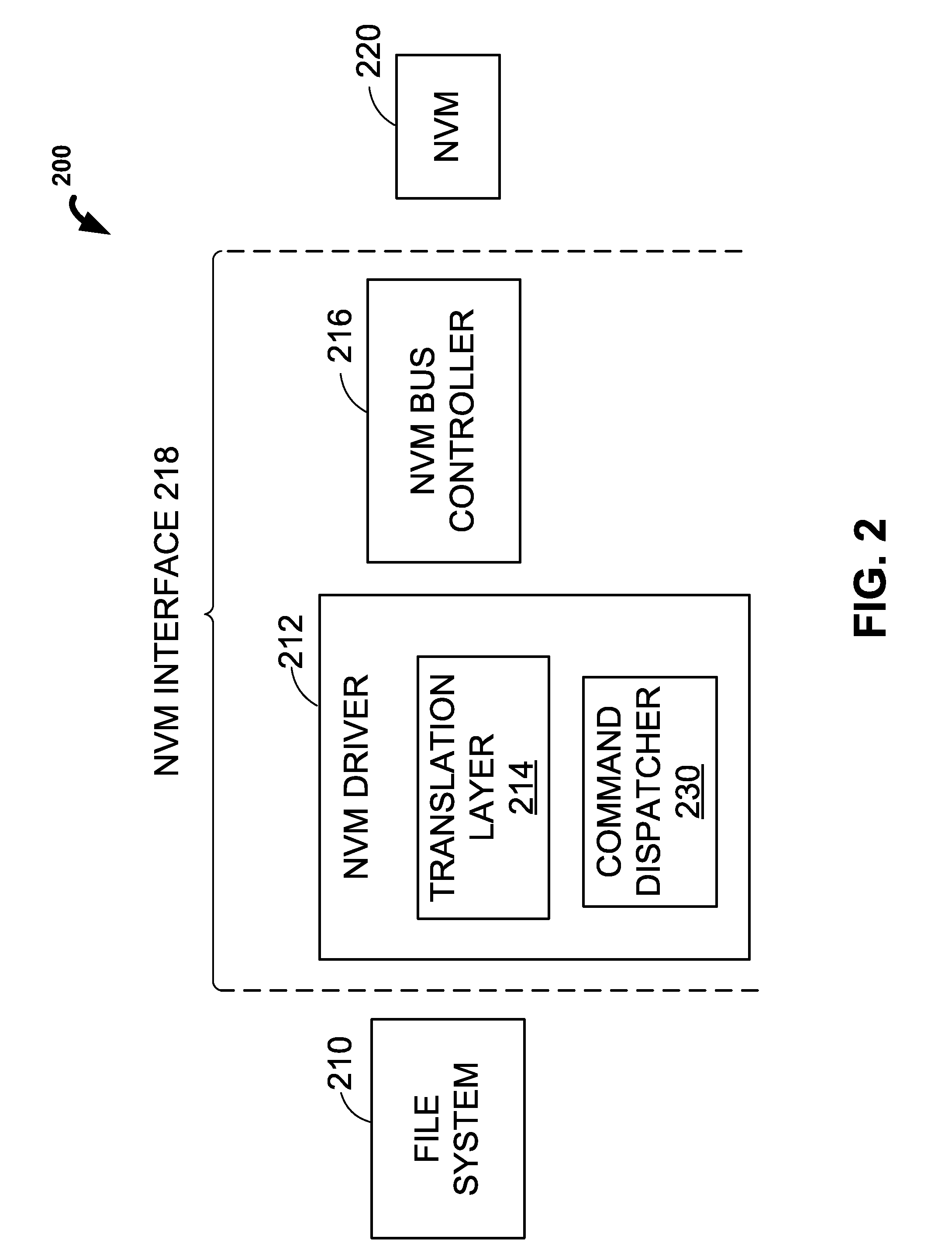
InactiveUS20120084484A1Reduce consumptionReduce overheadMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTMulti accessNon-volatile memory
Systems and methods are disclosed for selectively combining commands for a system having non-volatile memory (“NVM”). In some embodiments, a command dispatcher of a system can receive multiple commands to access a NVM for a period of time. After receiving the multiple commands, the command dispatcher can determine a set of commands that are naturally combinable. In some embodiments, the command dispatcher can select commands that are fairly distributed across different chip enables (“CEs”) and / or buses. After selecting the set of commands, the command dispatcher can combine the set of commands into a multi-access command. Finally, the command dispatcher can dispatch the multi-access command to the NVM.
Owner:APPLE INC
Tiered contention multiple access (TCMA): a method for priority-based shared channel access
InactiveUS20070019664A1Minimizing chanceLower latencySynchronisation arrangementError preventionService-level agreementClass of service
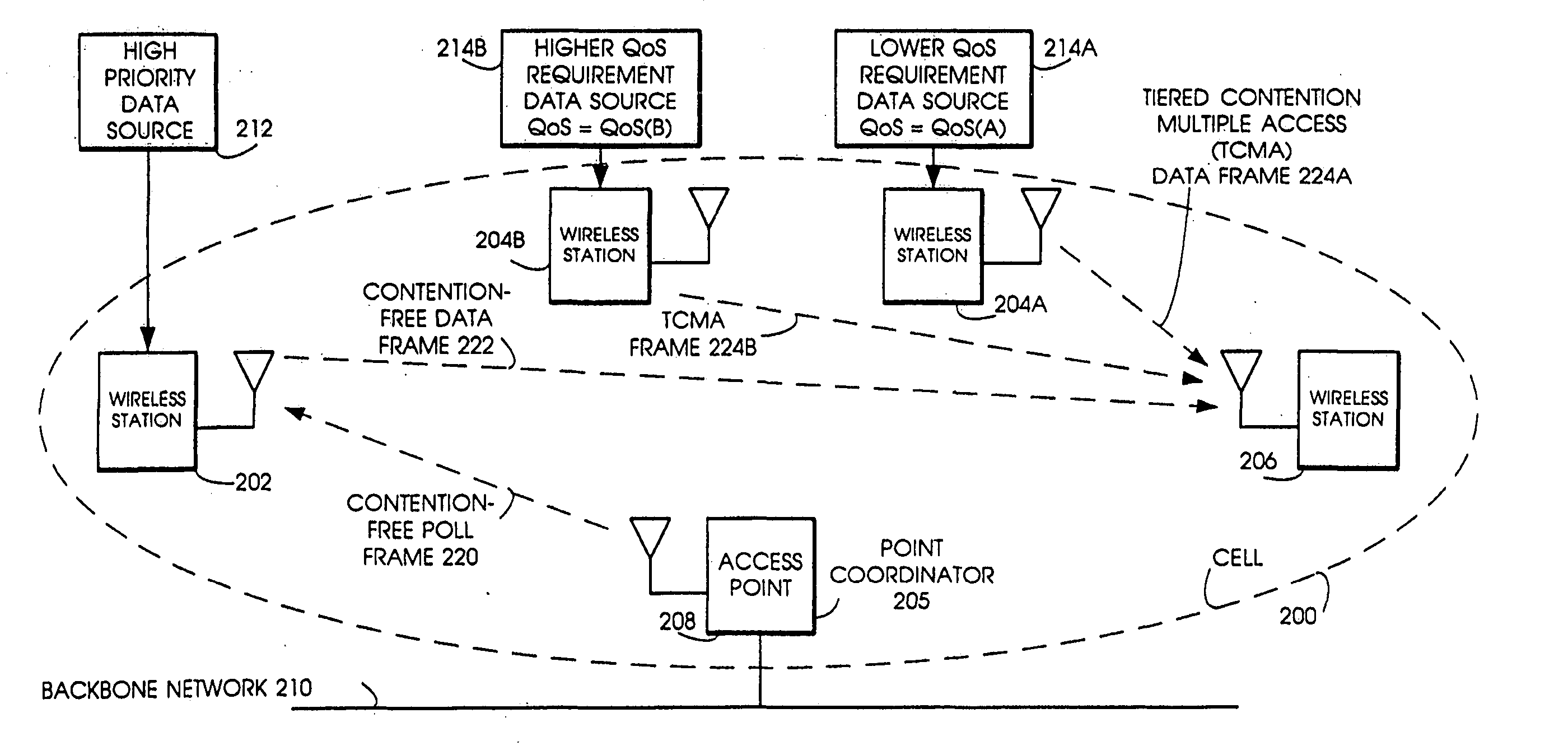
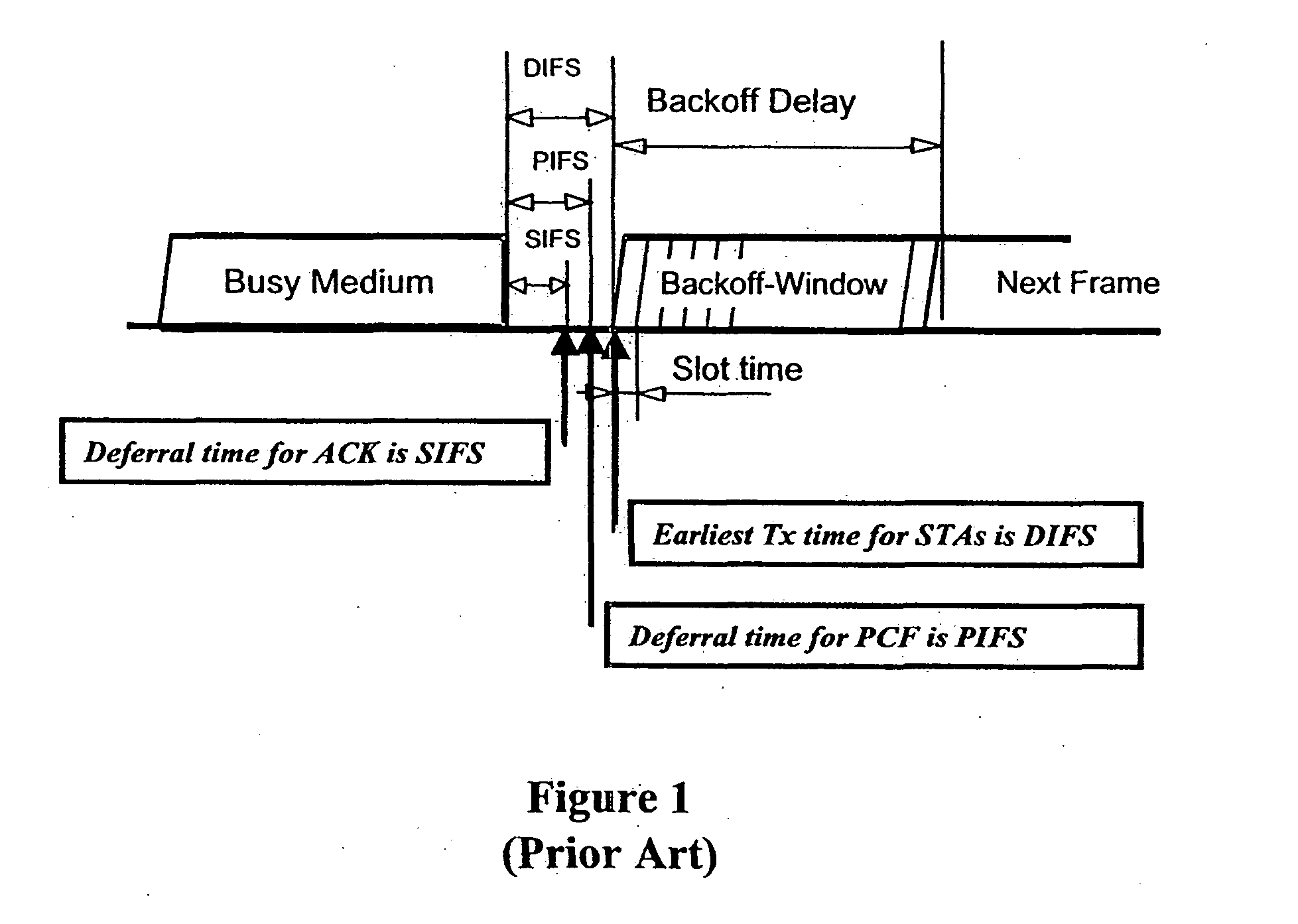
Quality of Service (QoS) support is provided by means of a Tiered Contention Multiple Access (TCMA) distributed medium access protocol that schedules transmission of different types of traffic based on their service quality specifications. In one embodiment, a wireless station is supplied with data from a source having a lower QoS priority QoS(A), such as file transfer data. Another wireless station is supplied with data from a source having a higher QoS priority QoS(B), such as voice and video data. Each wireless station can determine the urgency class of its pending packets according to a scheduling algorithm. For example file transfer data is assigned lower urgency class and voice and video data is assigned higher urgency class. There are several urgency classes which indicate the desired ordering. Pending packets in a given urgency class are transmitted before transmitting packets of a lower urgency class by relying on class-differentiated urgency arbitration times (UATs), which are the idle time intervals required before the random backoff counter is decreased. In another embodiment packets are reclassified in real time with a scheduling algorithm that adjusts the class assigned to packets based on observed performance parameters and according to negotiated QoS-based requirements. Further, for packets assigned the same arbitration time, additional differentiation into more urgency classes is achieved in terms of the contention resolution mechanism employed, thus yielding hybrid packet prioritization methods. An Enhanced DCF Parameter Set is contained in a control packet sent by the AP to the associated stations, which contains class differentiated parameter values necessary to support the TCMA. These parameters can be changed based on different algorithms to support call admission and flow control functions and to meet the requirements of service level agreements.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
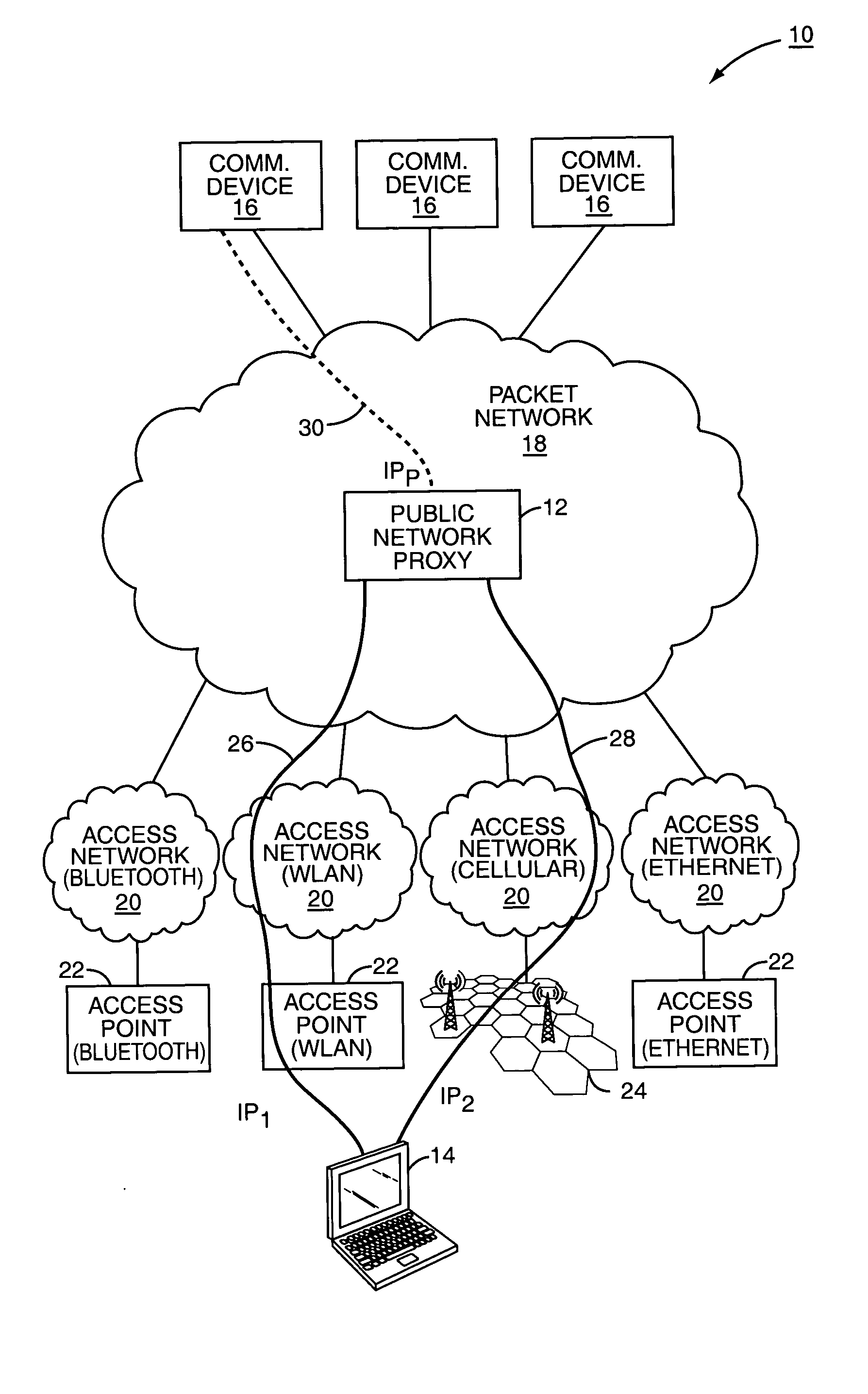
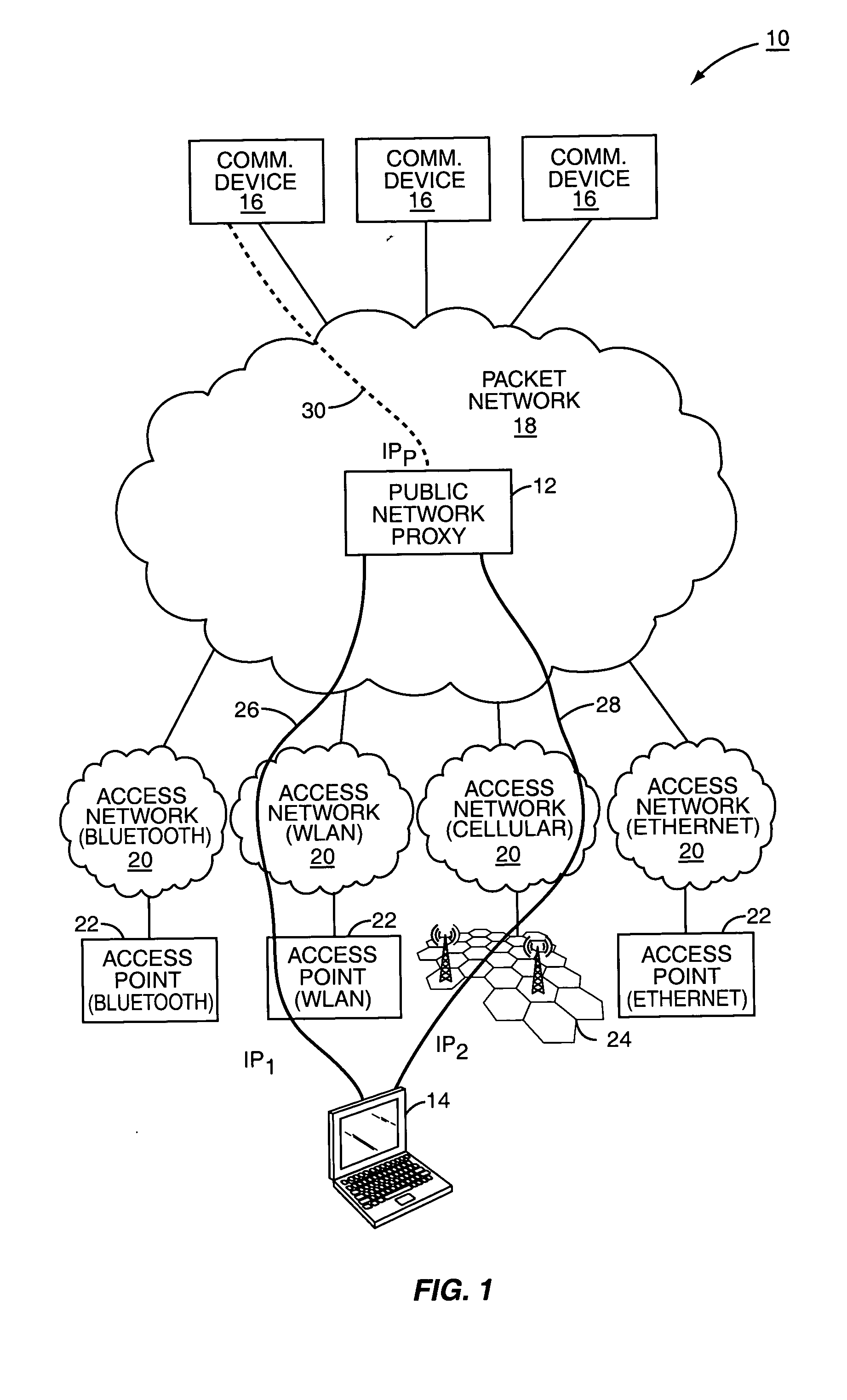
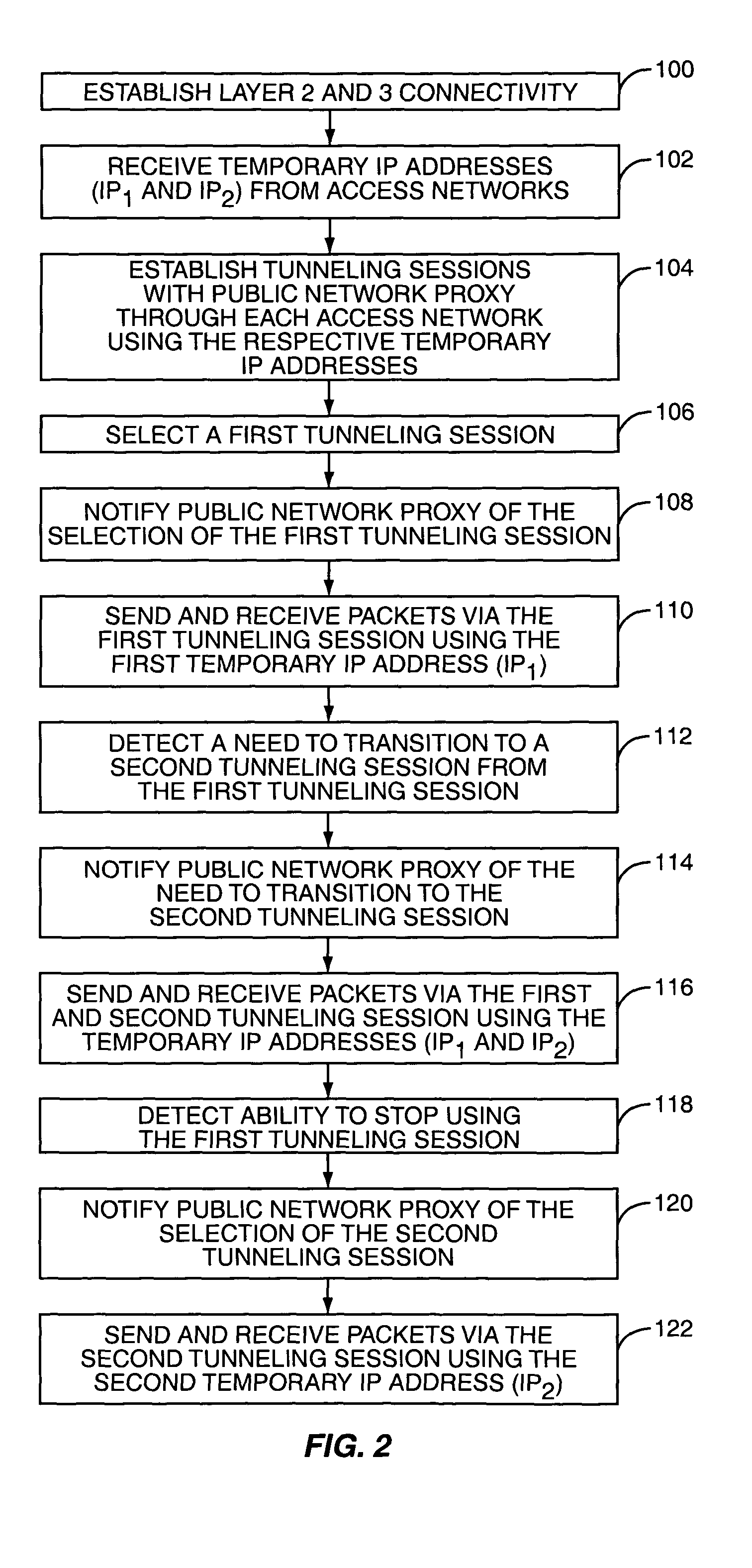
Mobility in a multi-access communication network
ActiveUS20050025163A1Facilitate communicationEffective controlError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsAccess networkPublic network
The present invention provides a terminal capable of establishing multiple communication sessions with a public network proxy through different access networks. The terminal actively communicates with the public network proxy to control which of the multiple communication paths are active, as well as control the transition from actively using one communication path to using another. The public network proxy facilitates data and voice sessions between the terminal and any number of other communication devices. In one embodiment, the communication sessions are reserved tunneling sessions, and the terminal cooperates with the public network proxy to effectively control how many tunneling sessions are established, how many tunneling sessions are active at any given time, and the transition from one tunneling session to another for active communications. Each of the communication or tunneling sessions may be established over different access networks using different communication technologies and protocols.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
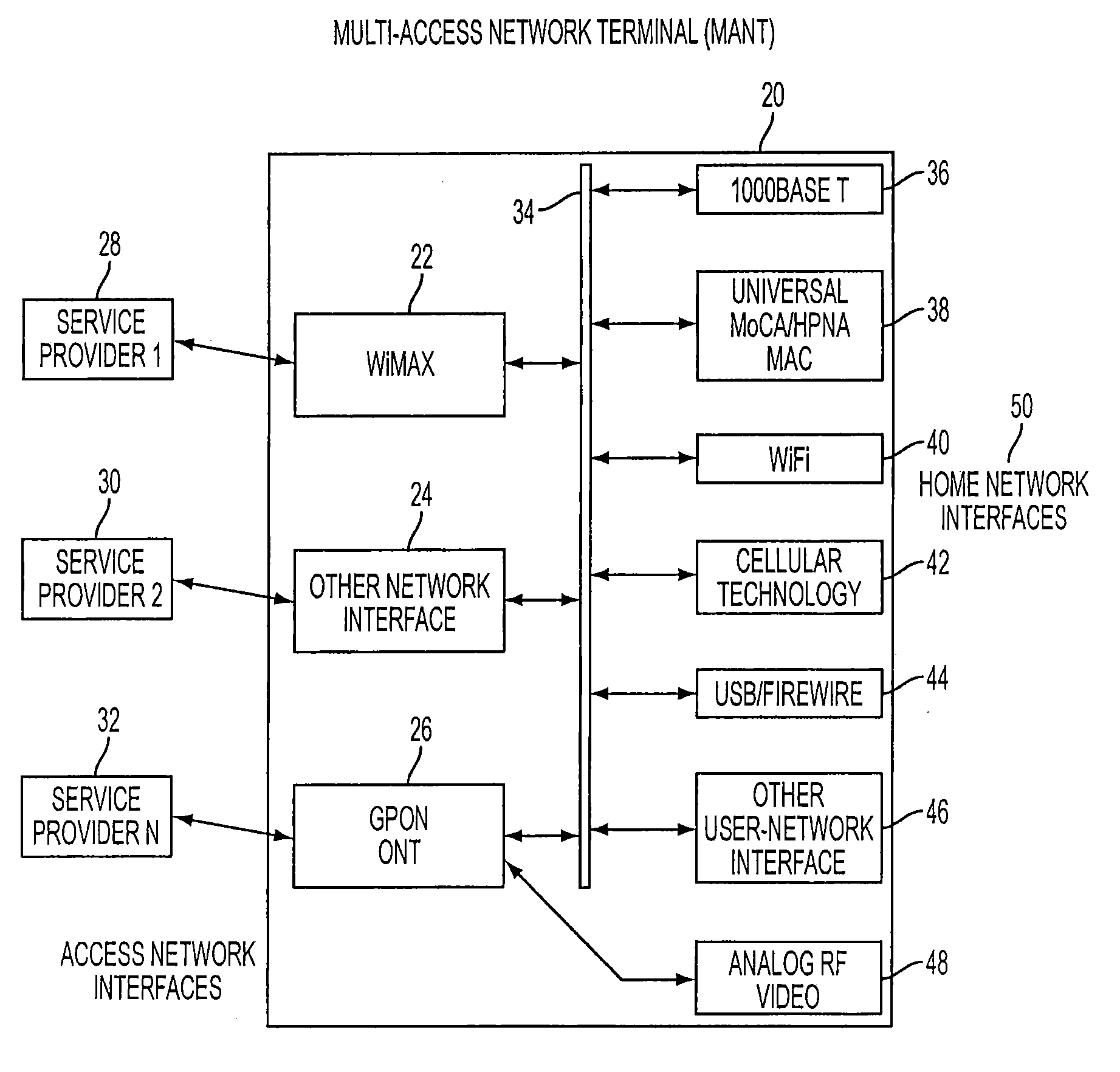
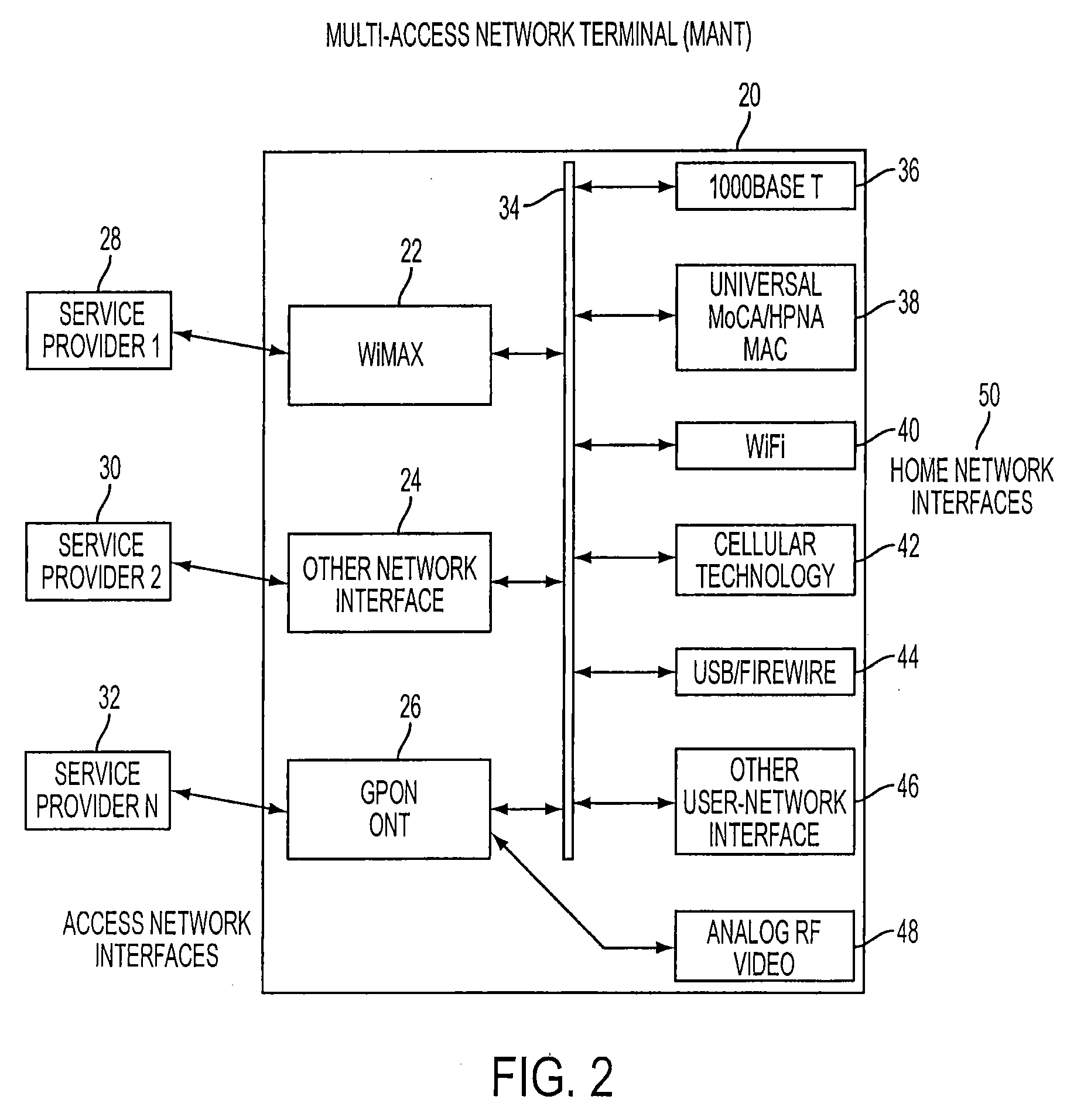
Multi-access network terminal, communication method, service-providing method, and revenue-receiving method
InactiveUS20090047016A1Solve problemsOptical multiplexData switching networksCommunication interfaceNetwork termination
A multi-access network terminal includes first and second communication interfaces. The first interface is configured to communicate with a first service provider providing services to a user through the first interface with a first type of signal and / or a first type of communications protocol. The second interface is configured to communicate with the first service provider providing services to the user through the second communication interface using a second type of signal and / or a second type of communications protocol. Alternatively, the second interface is configured to communicate with a second service provider providing services to the user through the second communication interface using the first or second type of signal and / or the first or second different type of communications protocol.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
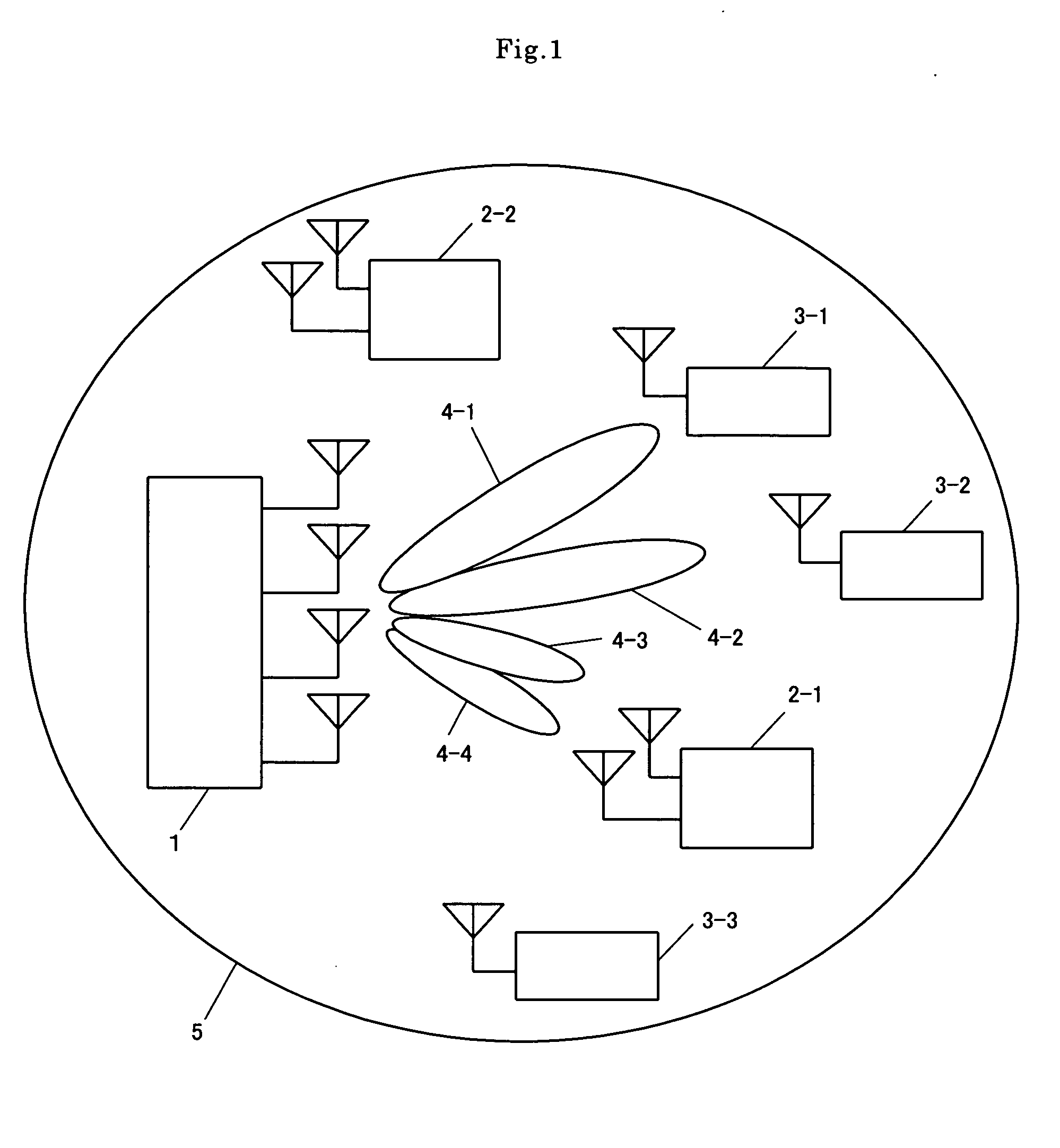
Systems and methods for multi-access point transmission of data using a plurality of access points
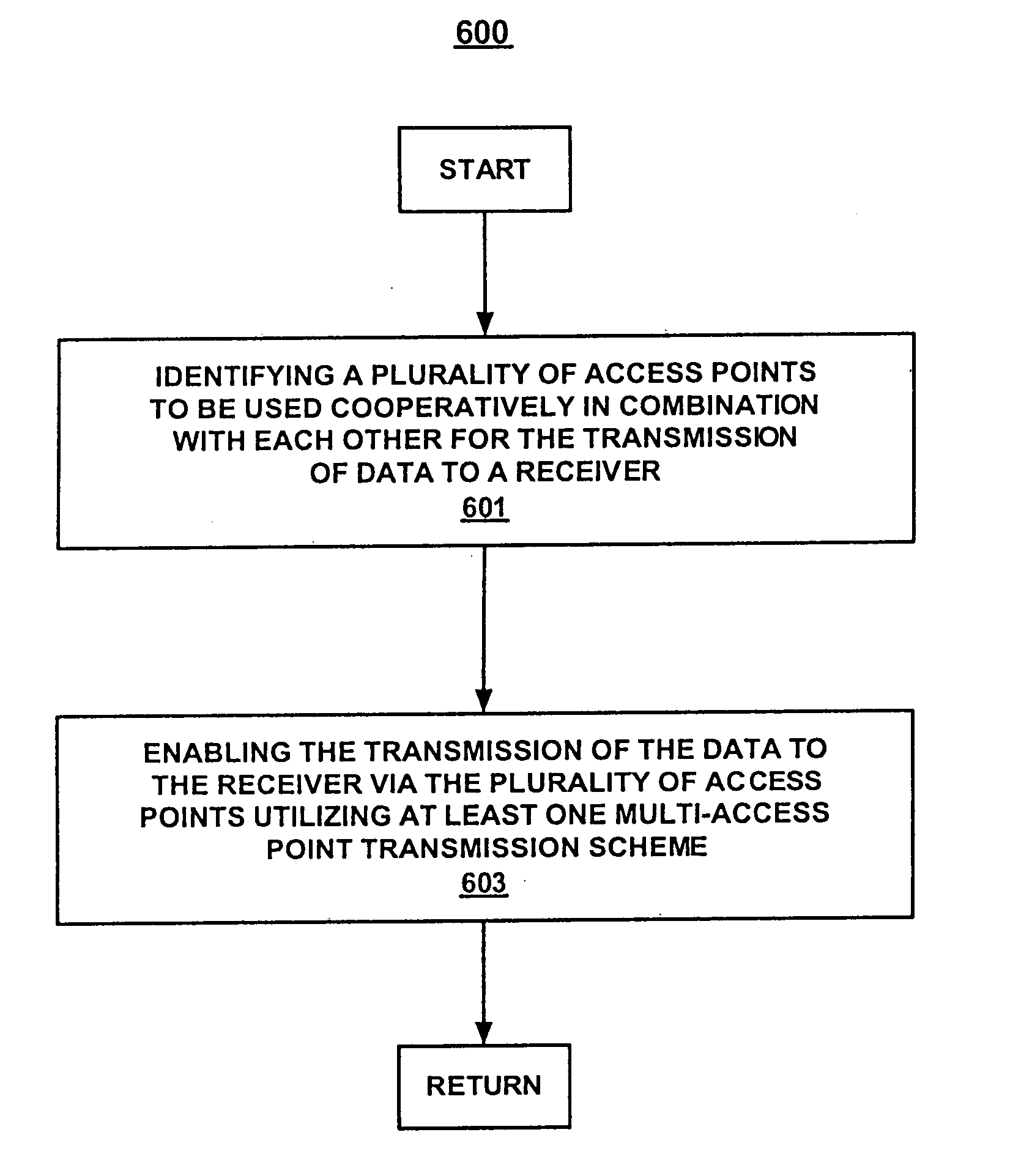
InactiveUS20050169209A1Spatial transmit diversityNetwork traffic/resource managementCombined useData transmission
Methods and systems for multi-access point transmission of data using a plurality of access points are disclosed. Methods include identifying a plurality of access points to be used cooperatively in combination with each other for the transmission of data to a receiver. The transmission of the data to the receiver via the plurality of access points is enabled utilizing at least one multi-access point transmission scheme.
Owner:MEIZU TECH CO LTD
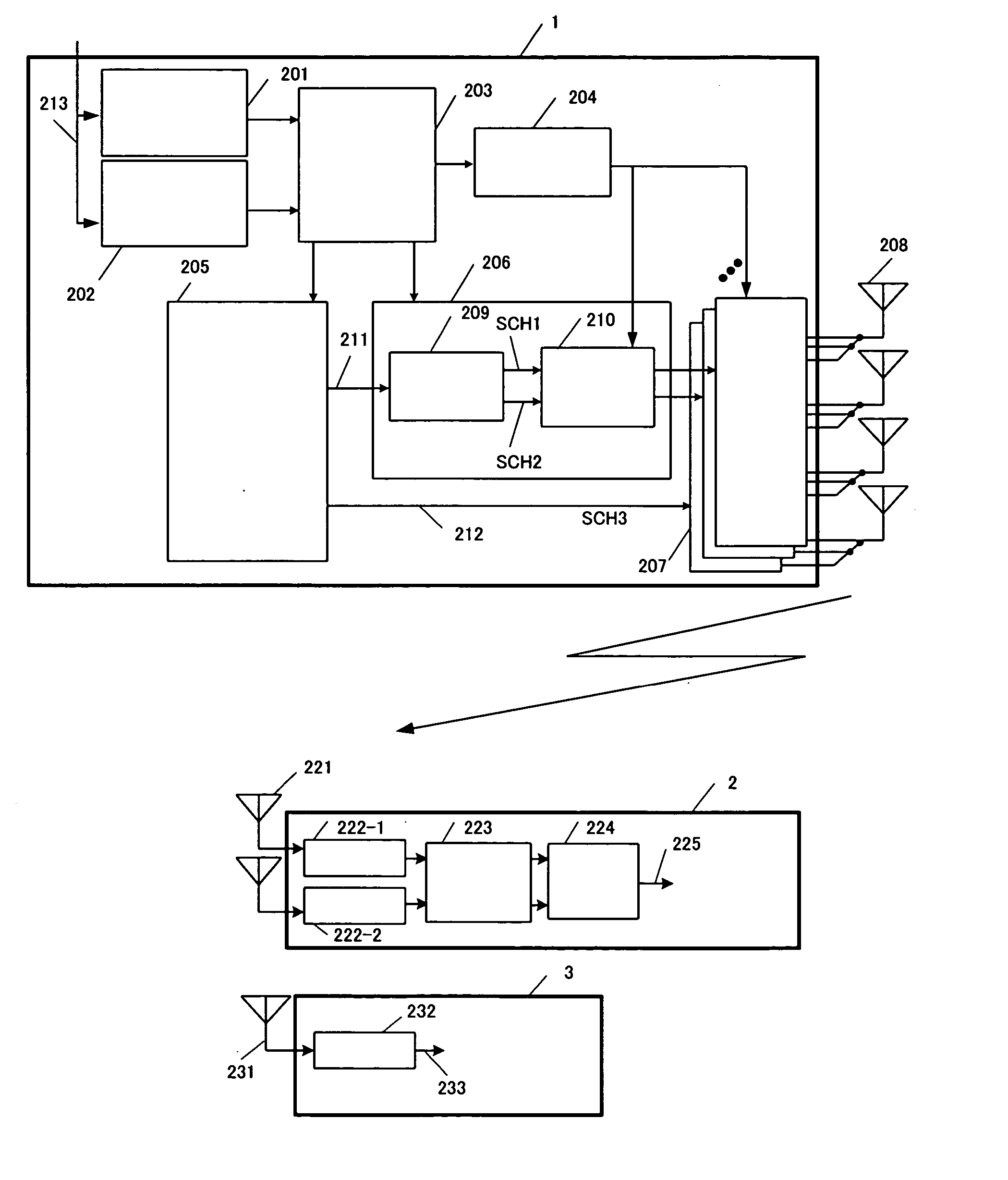
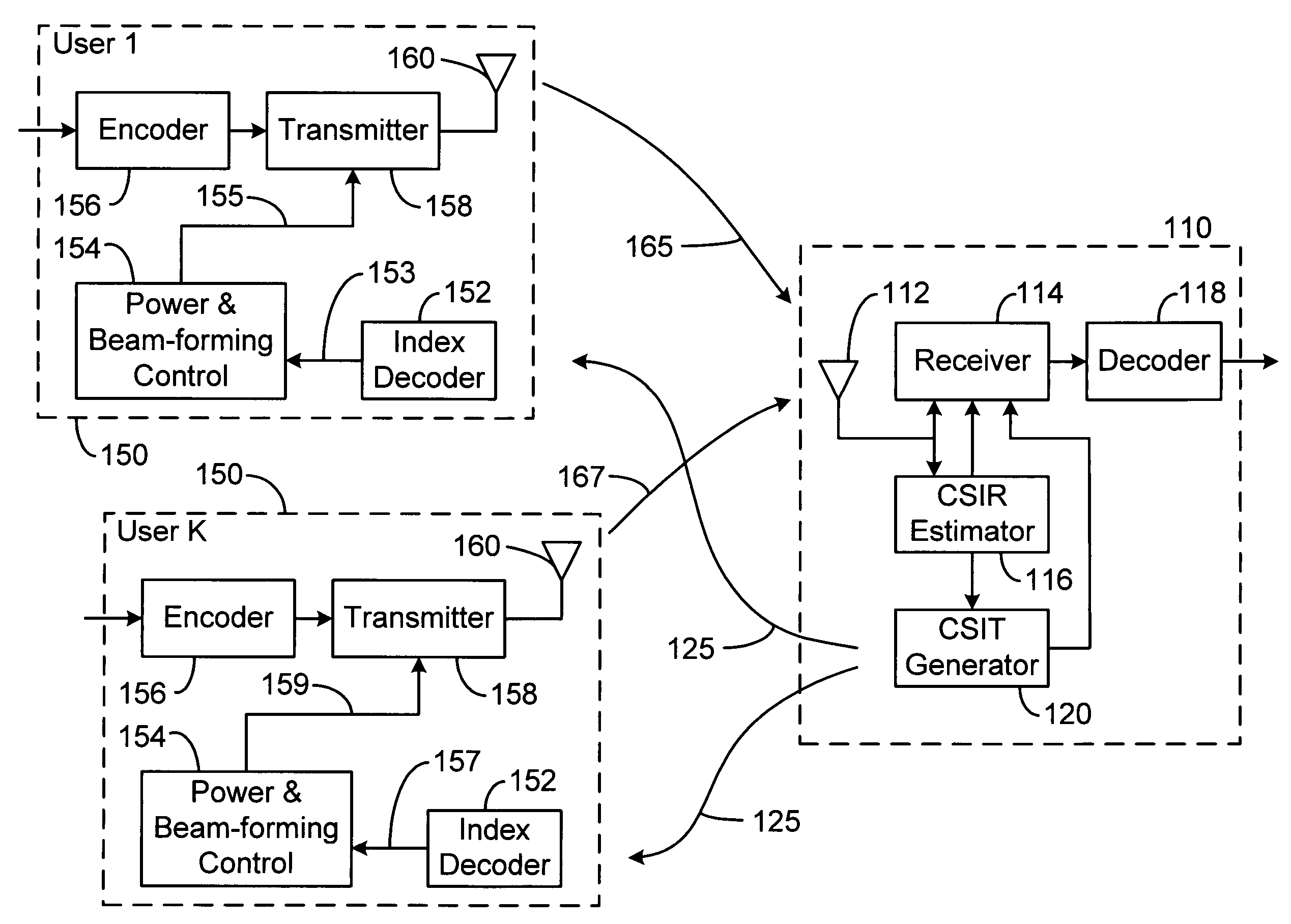
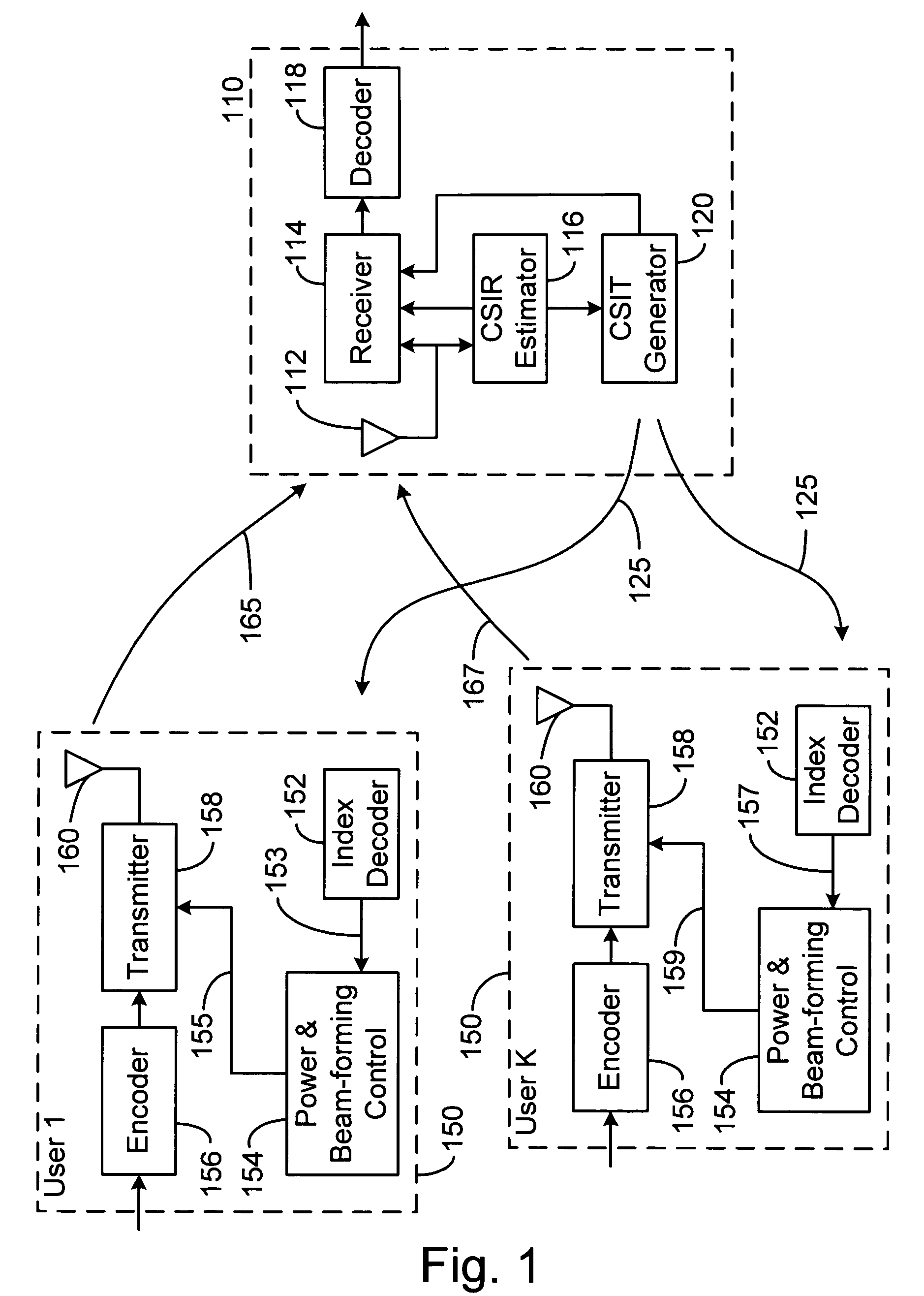
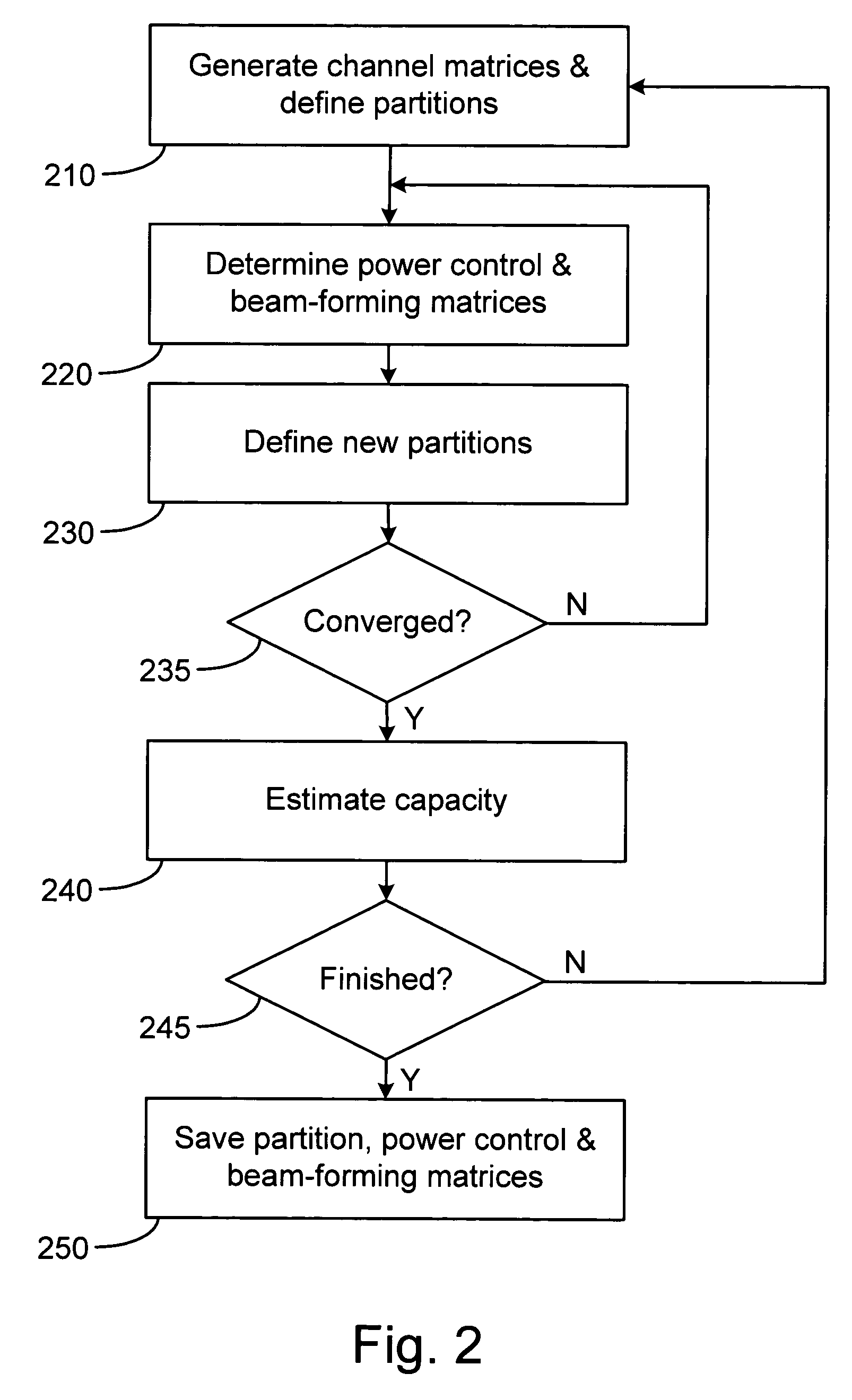
System and method for multi-access MIMO channels with feedback capacity constraint
ActiveUS7257167B2Radio wave direction/deviation determination systemsBaseband system detailsData streamFormation matrix
Systems and methods of MIMO wireless communication system with partial feedback are disclosed. In one embodiment, a base station estimates the channel matrices of the K mobile units and transmits an index value corresponding to each of the estimated channel matrix. Each mobile unit selects a power control matrix and beam-forming matrix based on the received index value and transmits its data stream to the base station using the selected power control and beam-forming matrix. A method for generating the sets of power control matrices, beam-forming matrices, and partitions of the channel matrix space is disclosed.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
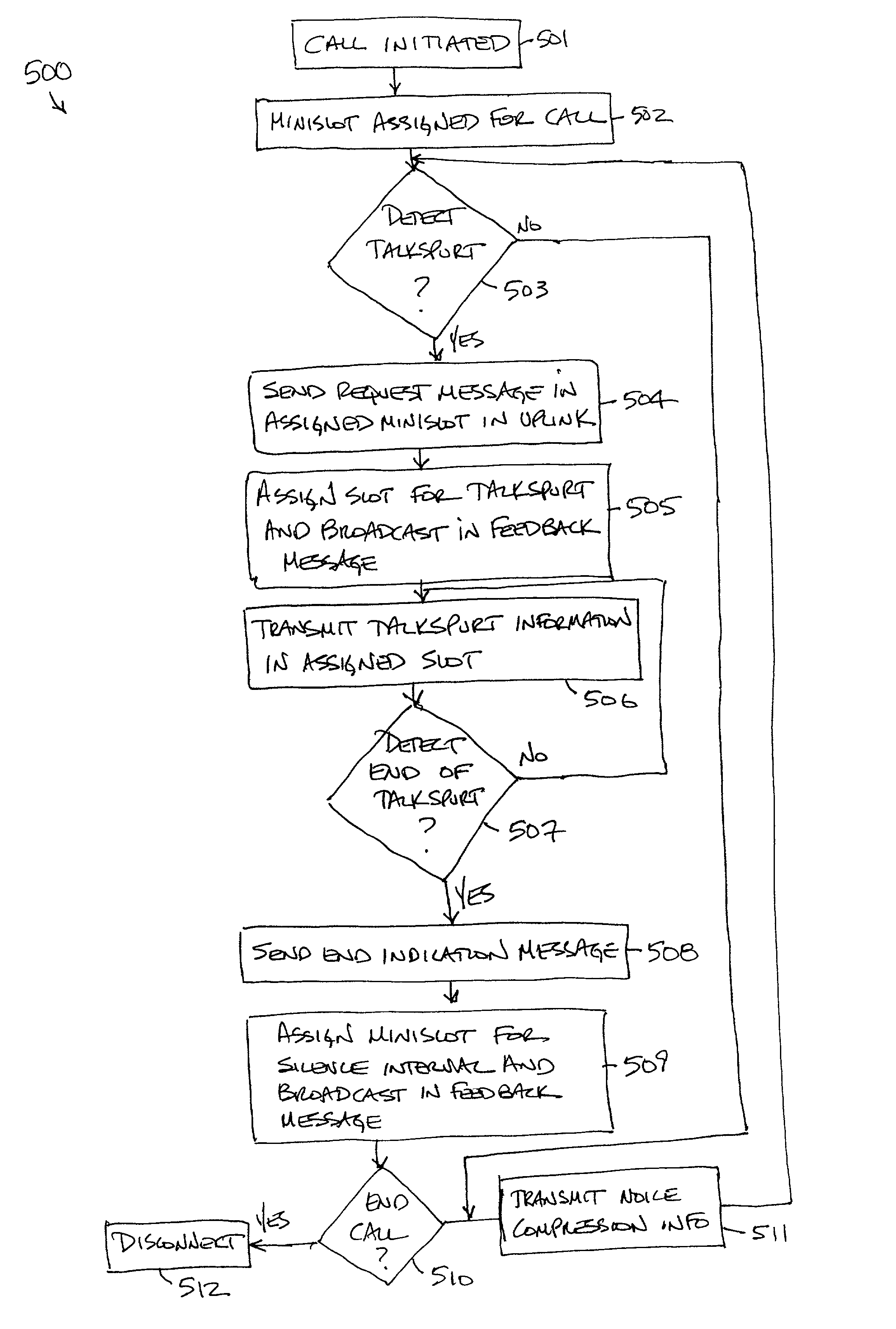
Voice-data integrated multiaccess by self-reservation and stabilized aloha contention
InactiveUS6963545B1Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexNetwork Communication ProtocolsAloha
A multiple access communication protocol that includes an uplink and a downlink channel is disclosed. The uplink channel has a plurality of frames, such that each frame has a first selectable number of minislots and a second selectable number of slots. A reservation request of a first type is sent into a first selected minislot of a selected frame of the uplink channel when information of a first type is to be sent. The reservation request of the first type requests an assignment for at least one slot for transmitting information of the first type in at least one frame that is subsequent to the selected frame. A reservation request of a second type is sent into a second selected minislot of the selected frame when the second selected minislot is available in the selected frame and when information of a second type is to be sent. The reservation request of the second type requests an assignment of at least one slot for transmitting information of the second type in at least one frame that is subsequent to the selected frame, and contends for the second selected minislot based on a pseudo-Bayesian Aloha algorithm. The downlink channel contains a feedback message that occurs prior to the end of the selected frame of the uplink channel. The feedback message includes minislot assignment information for sending reservation requests of the first and the second type and slot assignment information for transmitting information of the first and the second type, minislot contention information for the reservation requests of the second type sent in the selected frame, and reservation backlog information for an estimated number of reservation requests of the second type pending at a beginning of the selected frame.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
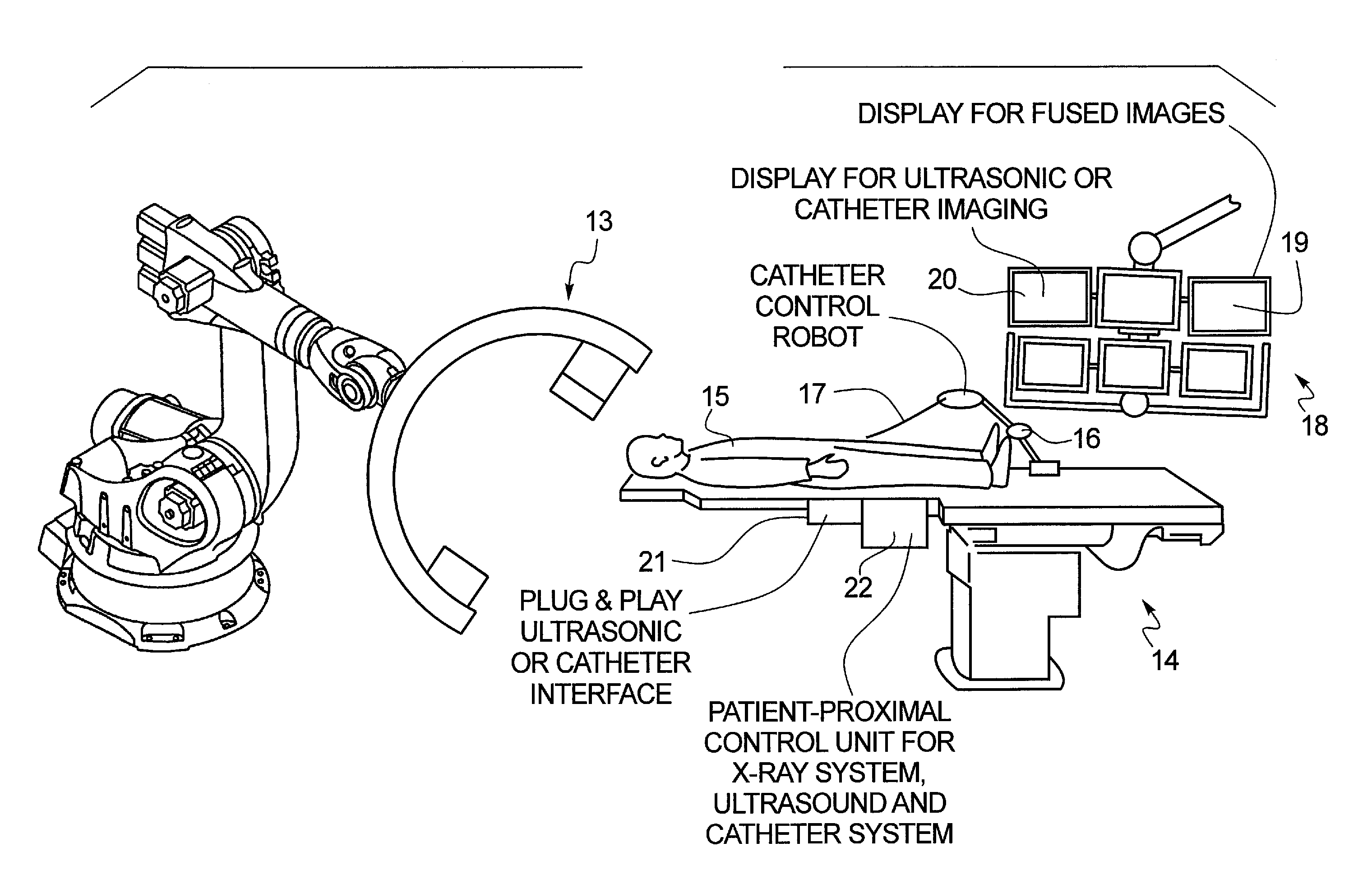
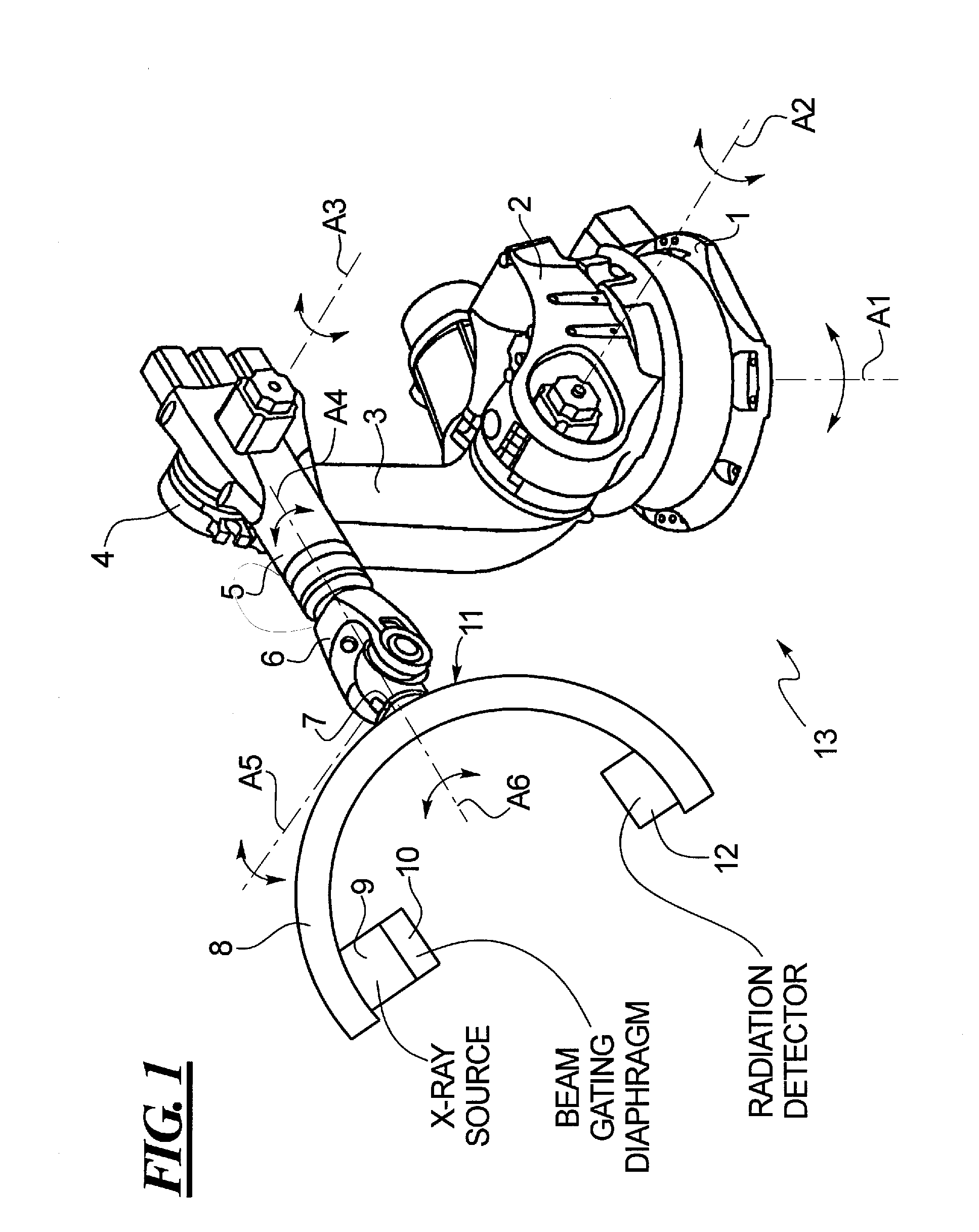
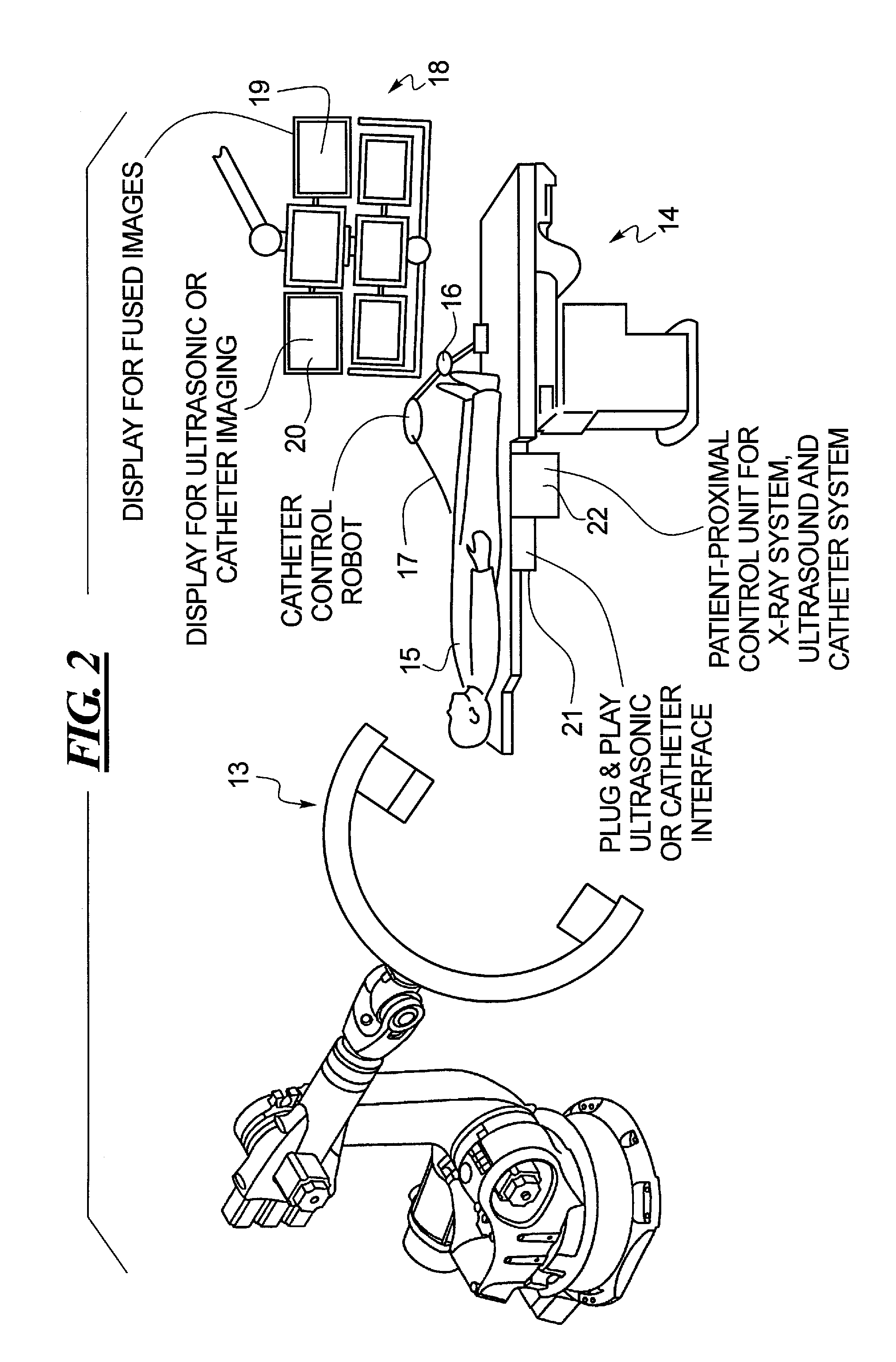
Method and apparatus for conducting an interventional procedure involving heart valves using a robot-based x-ray device
ActiveUS20090234444A1Improved imaging supportAdd supportUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHeart valvesSoft x rayEllipse
In a method and an apparatus for conducting minimally-invasive procedures involving heart valves at least one multi-access articulated x-ray imaging robot is employed that allows a radiation detector carried by the robot to be moved in arbitrary paths, such as in circle, an ellipse, or along a spiral, around a patient in order to generate multiple projection exposures of the relevant region of the patient during the procedure. An image processor reconstructs a 3D image from the projection exposures substantially in real time during the procedure, and the 3D image is displayed to operating personnel during the procedure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
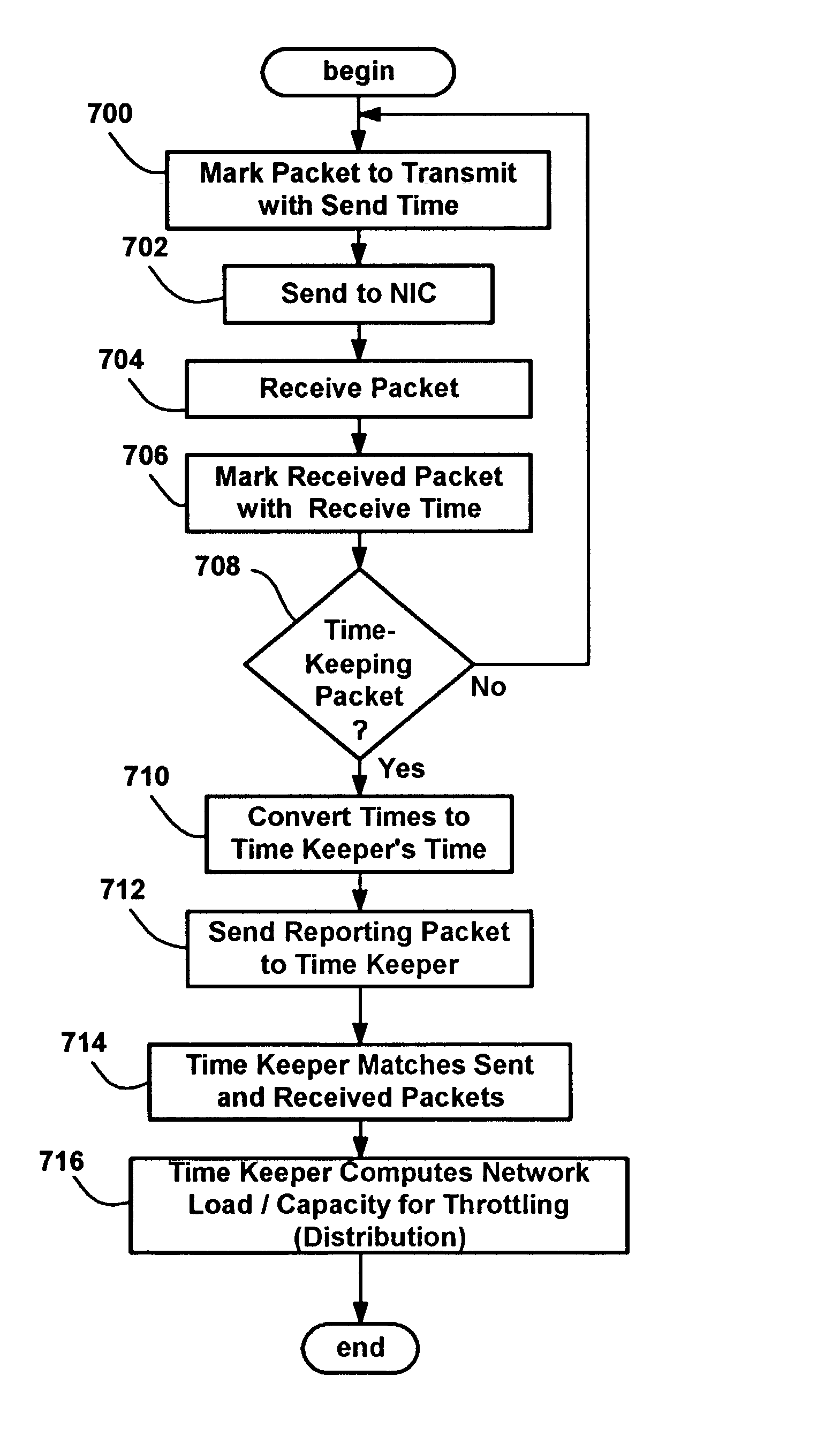
Method and system for measuring load and capacity on a variable capacity channel
InactiveUS7296083B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsOperational systemArrival time
A method and system are presented for determining the loading and capacity on a variable capacity channel by measuring the times at which packets are enqueued for transmission, and have their transmission completed, or by measuring these times in addition to the arrival times of the packets. The times may be measured using a device driver or other operating system component. The measurement may be performed in a centralized or distributed fashion for multi-access or point to point channels.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com