Patents
Literature
683 results about "Service-level agreement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
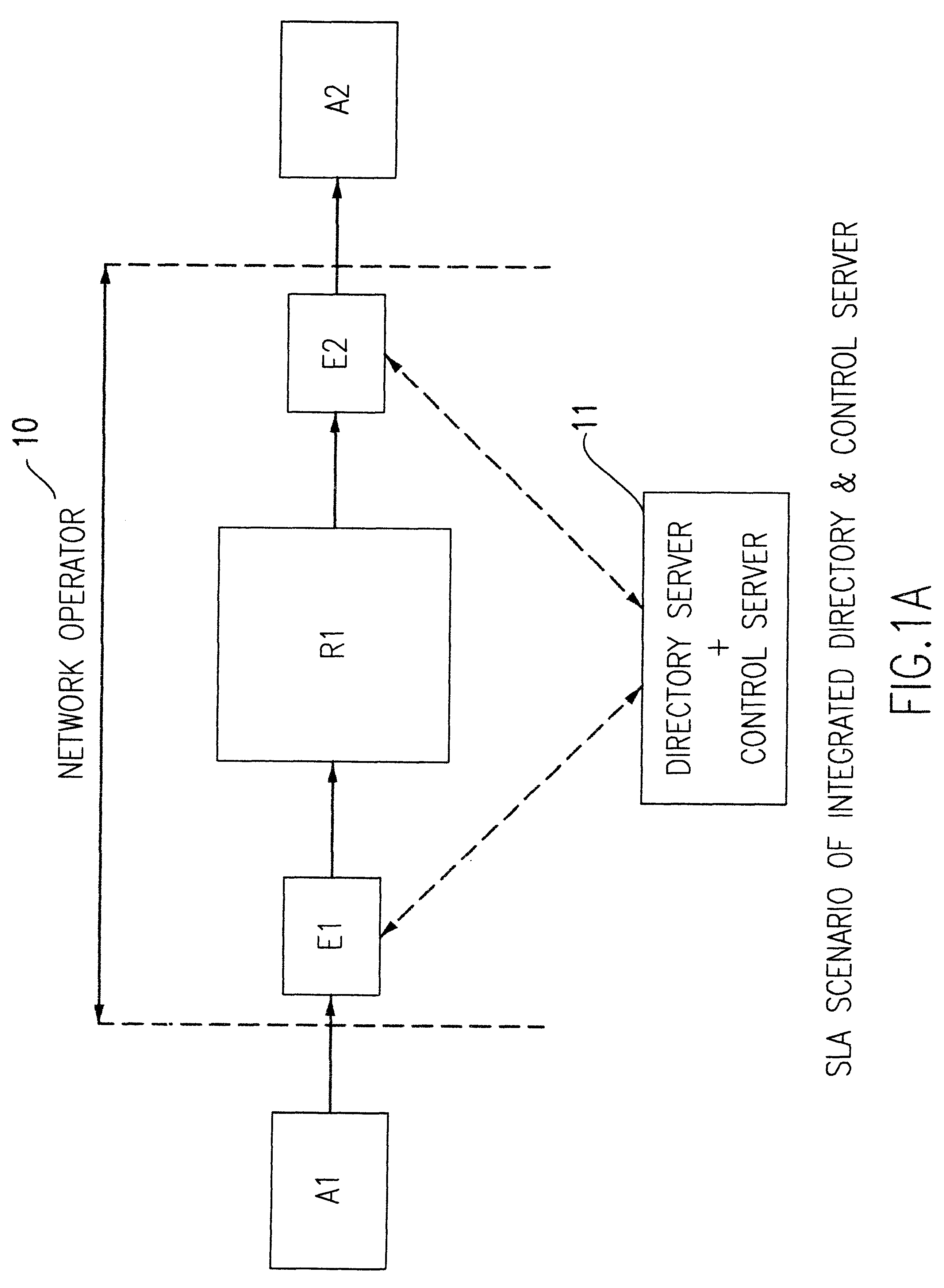
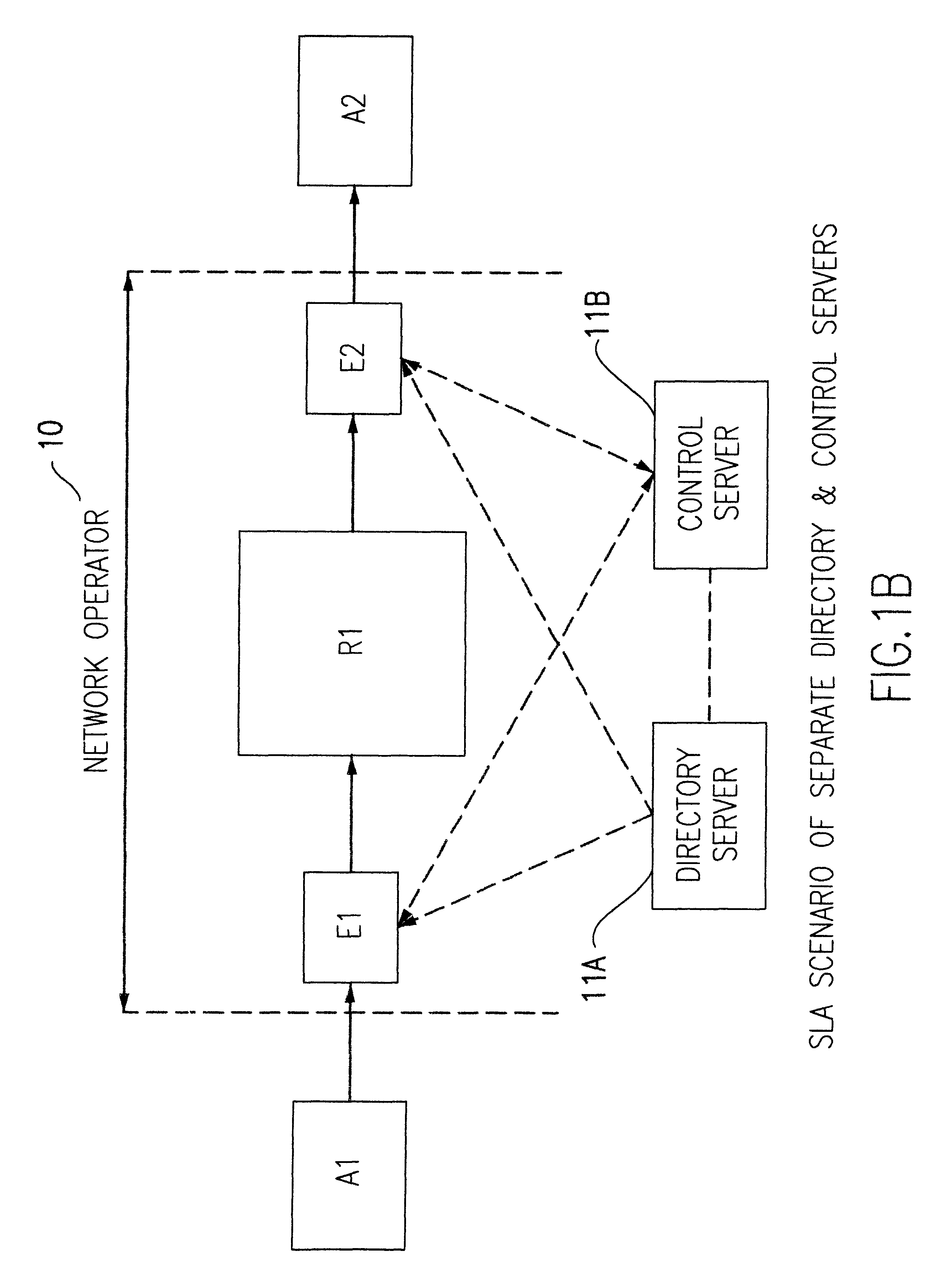
A service-level agreement (SLA) is a commitment between a service provider and a client. Particular aspects of the service – quality, availability, responsibilities – are agreed between the service provider and the service user. The most common component of SLA is that the services should be provided to the customer as agreed upon in the contract. As an example, Internet service providers and telcos will commonly include service level agreements within the terms of their contracts with customers to define the level(s) of service being sold in plain language terms. In this case the SLA will typically have a technical definition in mean time between failures (MTBF), mean time to repair or mean time to recovery (MTTR); identifying which party is responsible for reporting faults or paying fees; responsibility for various data rates; throughput; jitter; or similar measurable details.
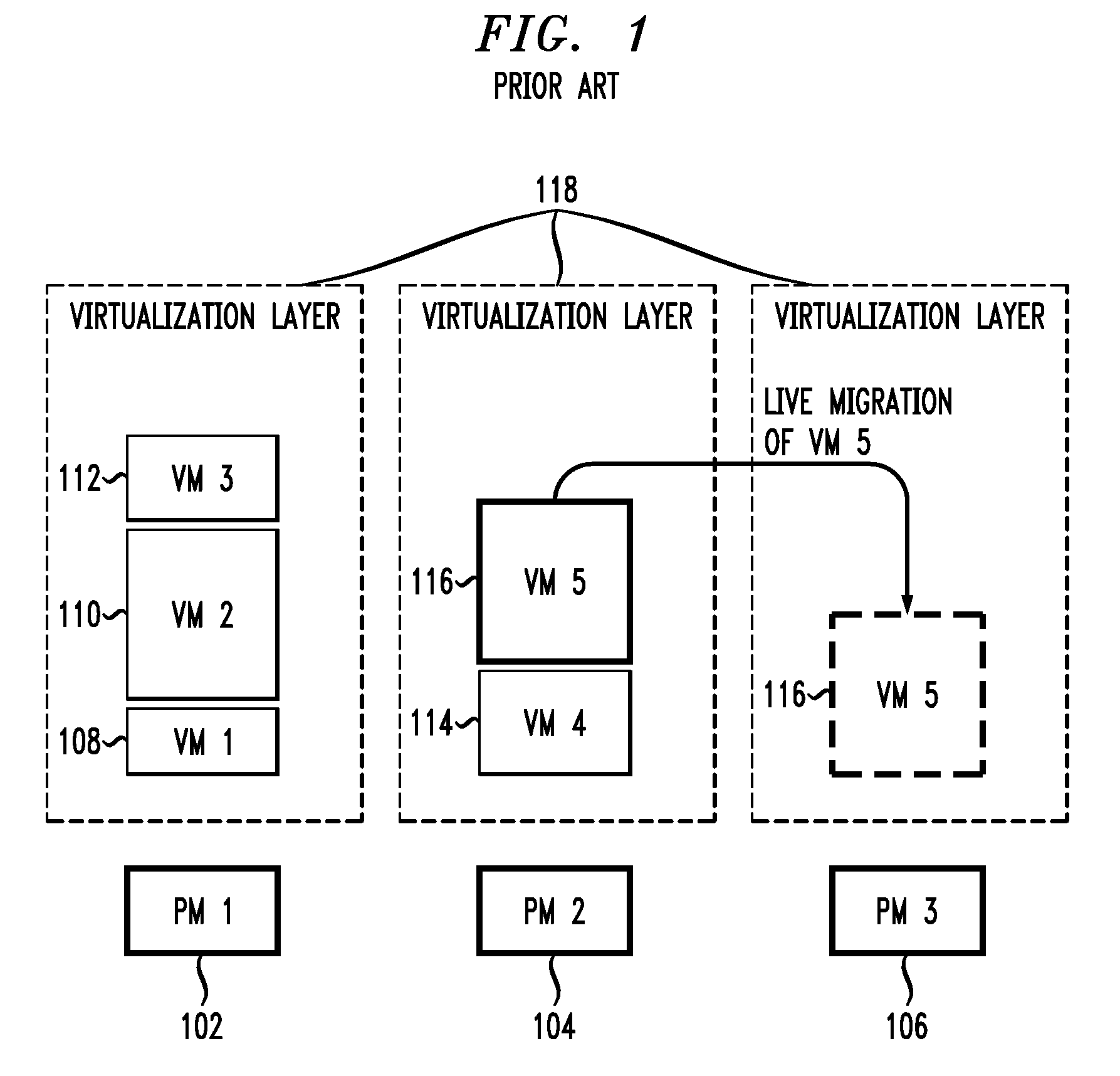
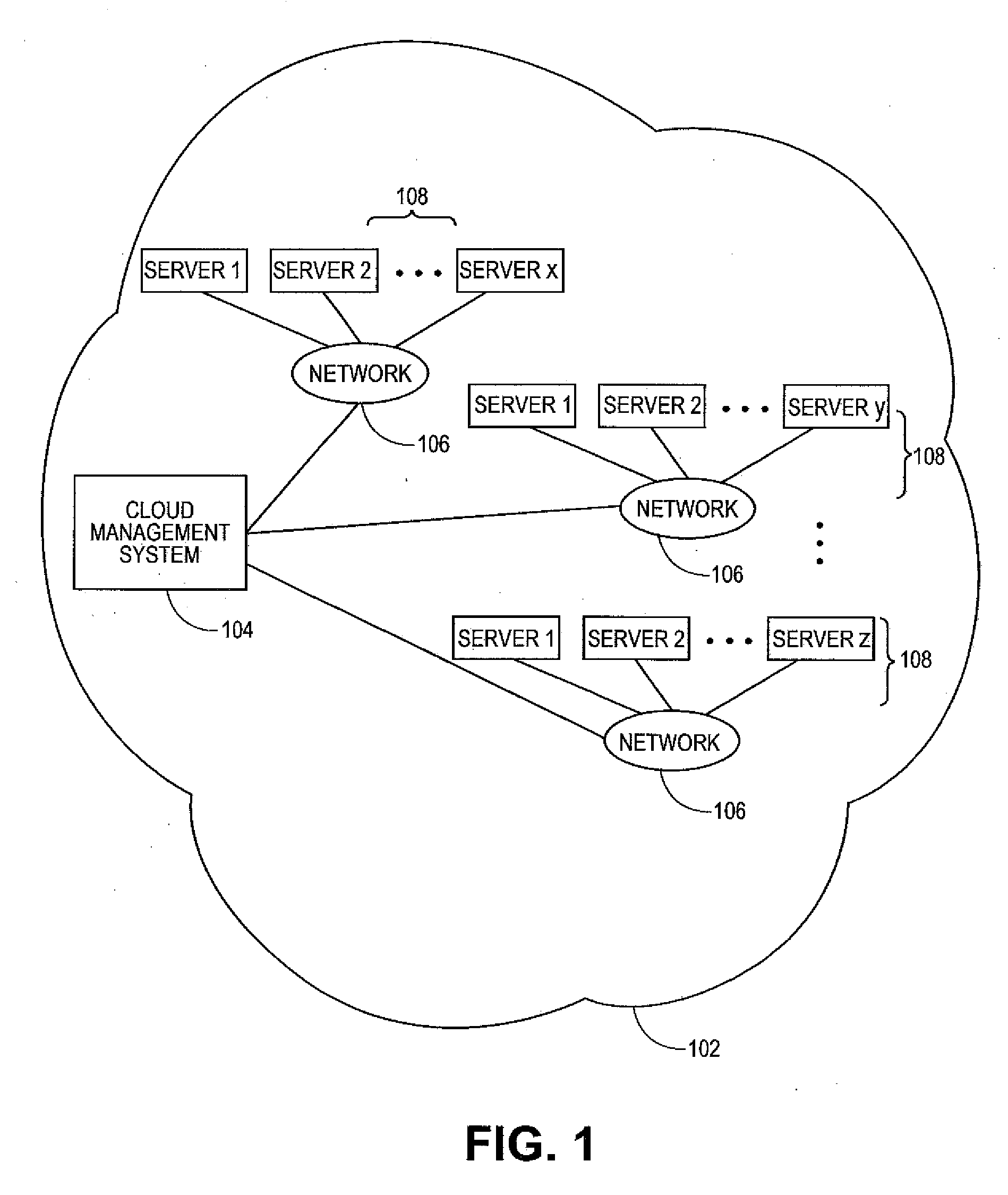
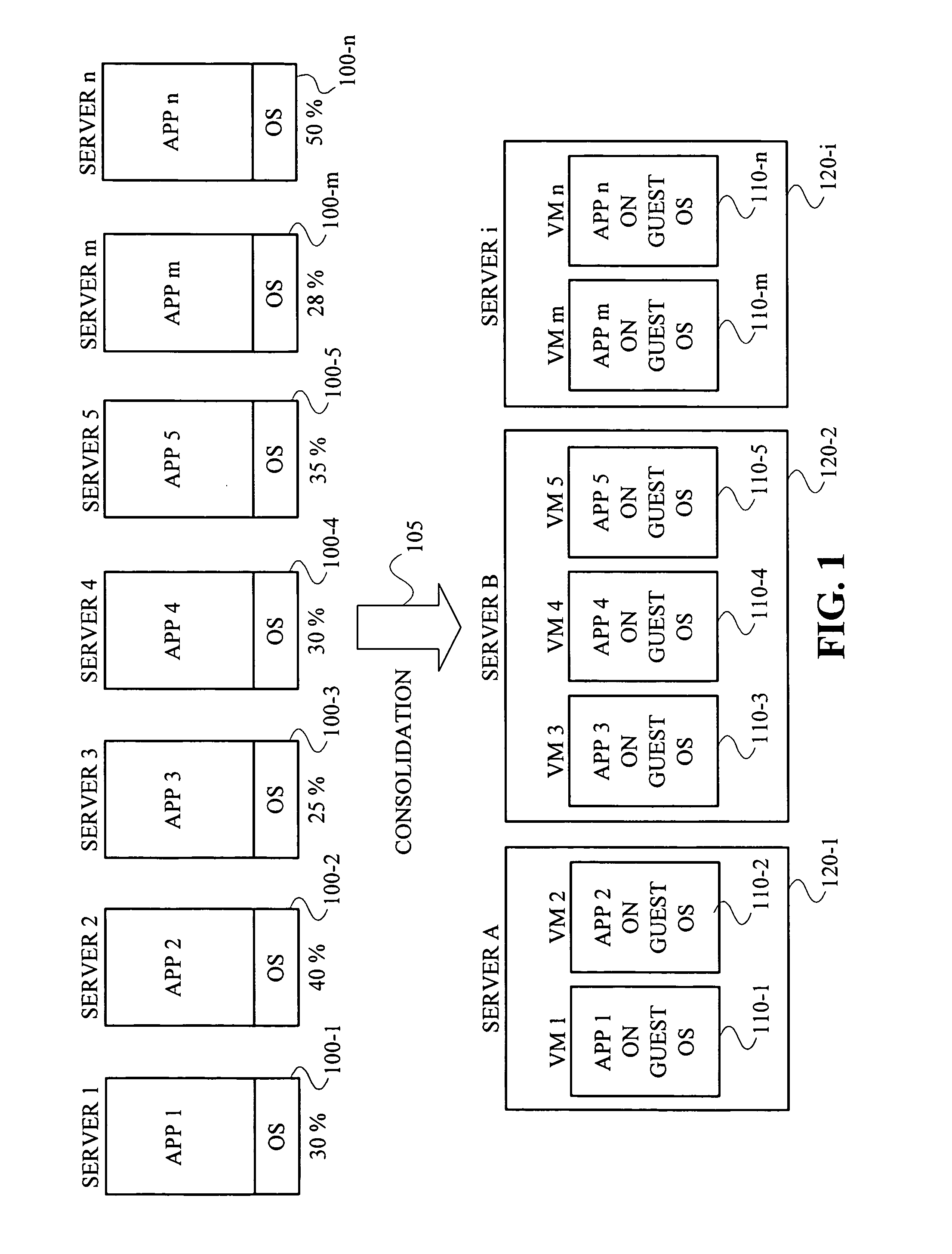
Dynamic resource allocation for virtual machines
InactiveUS20140007097A1Increase the amount of resourcesReduce the amount of solutionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsFailoverService-level agreement
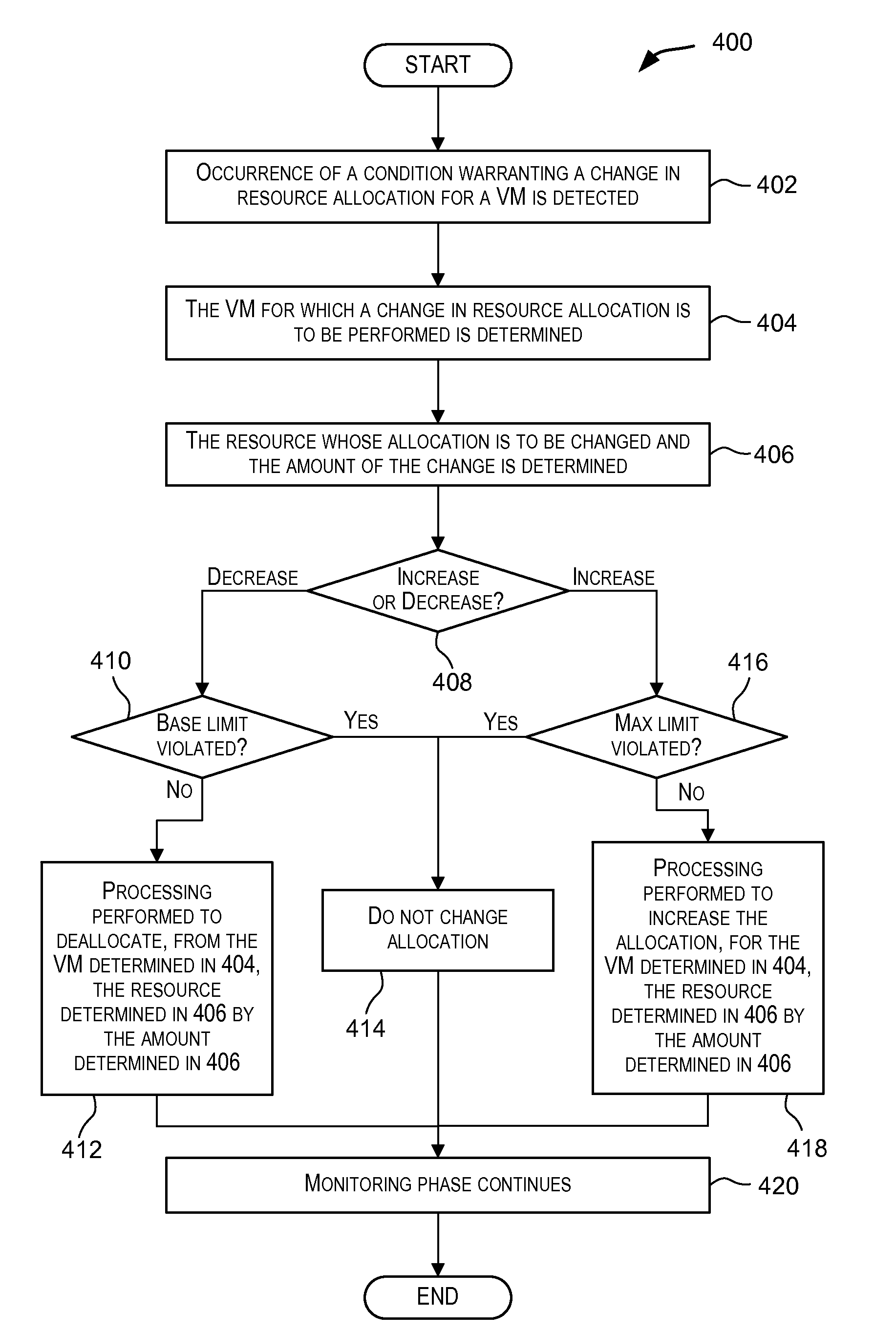
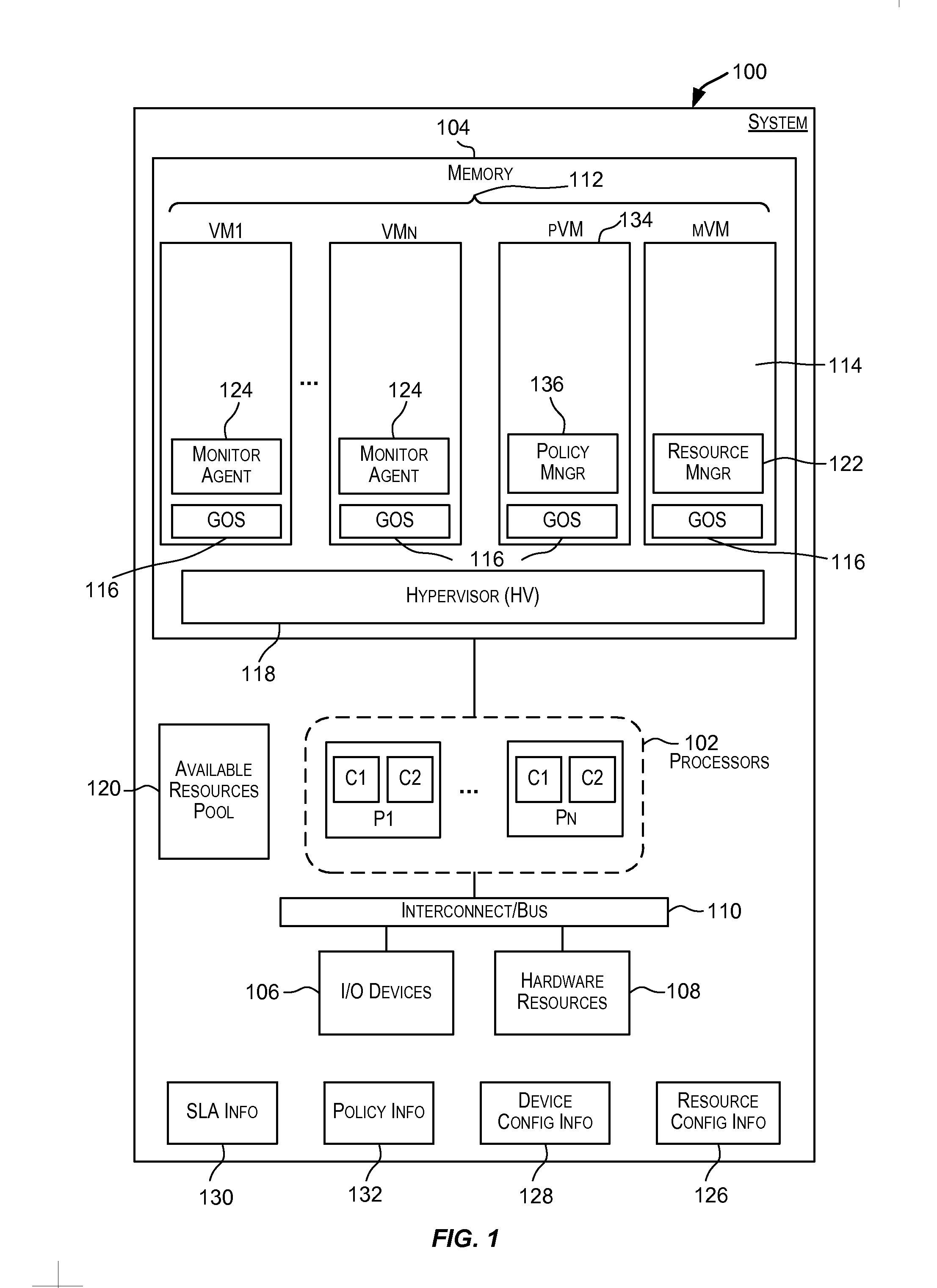
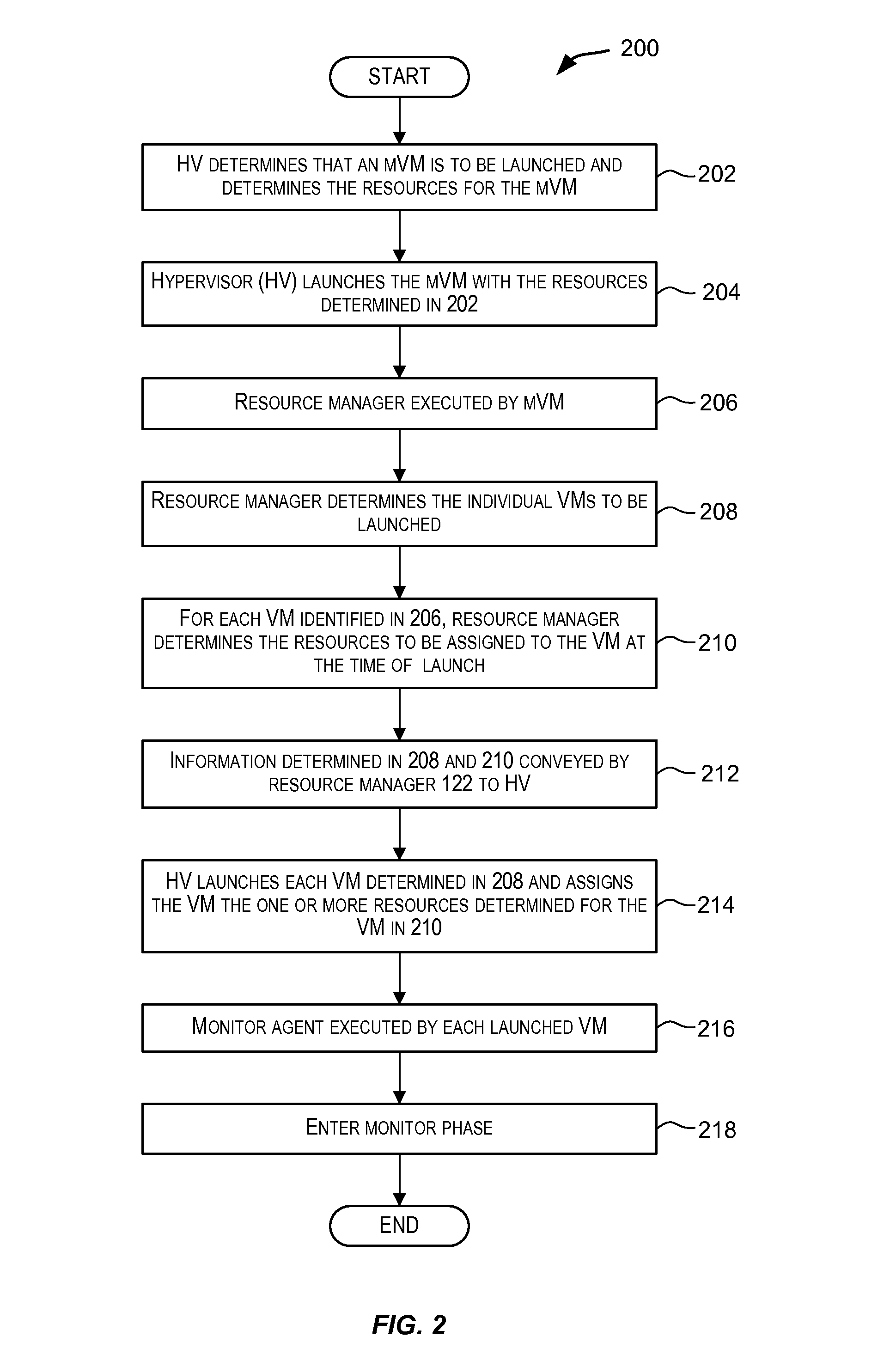
Certain embodiments enable resources assigned or allocated to an operating virtual machine (VM) to be modified while the VM is operating and without having to stop, restart, or reboot the VM. The modification may correspond to increasing or decreasing the amount of a resource being assigned to the VM. In this manner, resources assigned to a VM at the time of creation of the VM are not static and can instead be dynamically changed while the VM is operating without having to stop, reboot, or restart the VM. In some embodiments, the changes to the resources allocated to one or more VMs provided for a user (e.g., a customer) may be made according to or in response to a Service Level Agreement (SLA) entered into by the user, in response to an event such as a failover or switchover event, and the like.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Architecture for supporting service level agreements in an IP network
InactiveUS6459682B1Effective controlOptimizationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLoss rateTraffic capacity
A method of controlling packet traffic in an IP network of originating, receiving and intermediate nodes to meet performance objectives established by service level agreements. Traffic statistics and performance data such as delay and loss rates relating to traffic flows are collected at intermediate nodes. A control server processes the collected data to determines data flow rates for different priorities of traffic. A static directory node is used to look up inter-node connections and determine initial traffic classes corresponding to those connections. The rates are combined with the initial traffic classes to define codes for encoding the headers of packets to determine their network priority.
Owner:IBM CORP
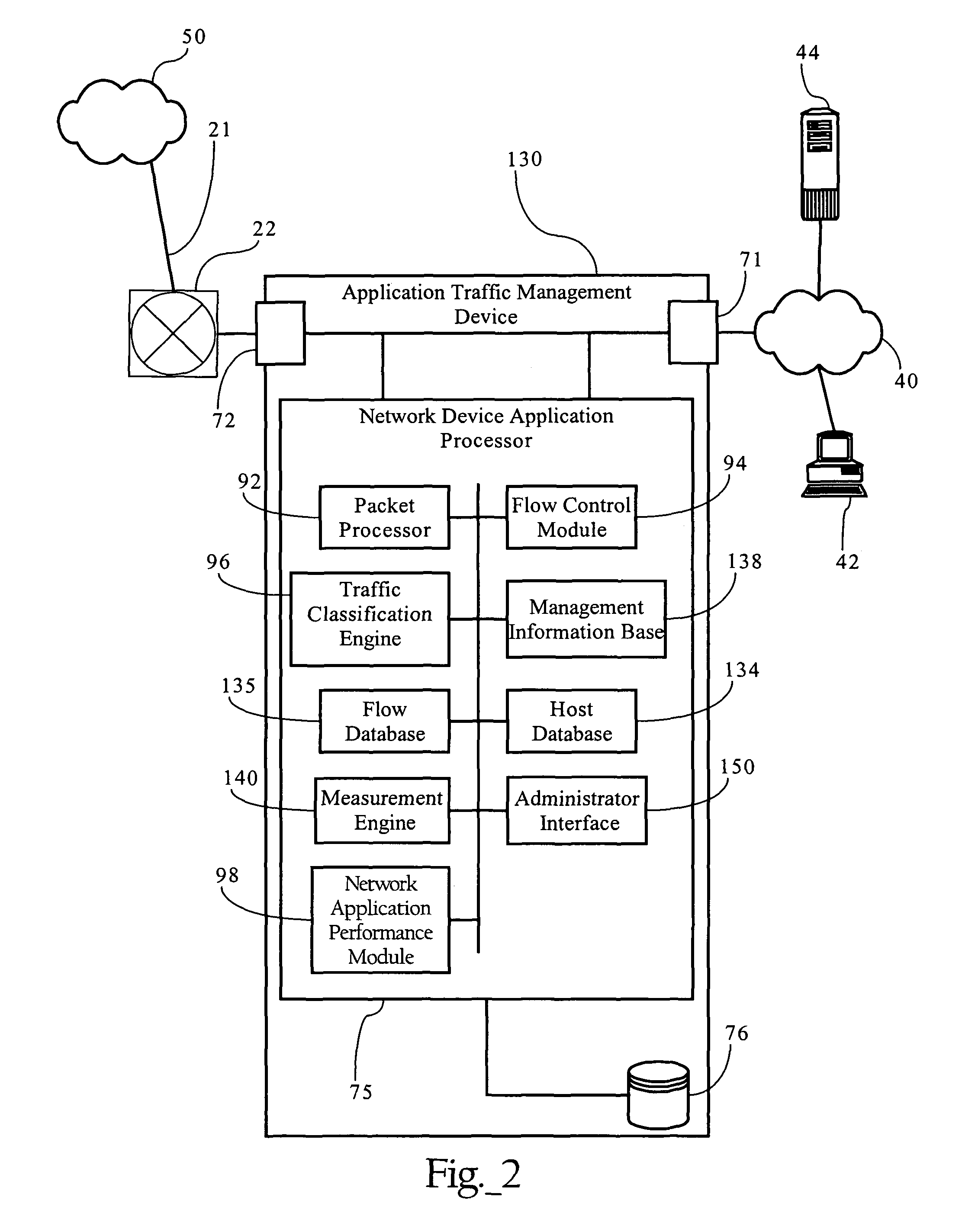
Adaptive correlation of service level agreement and network application performance
InactiveUS7822837B1Easy to useReduce network loadDigital computer detailsData switching networksService-level agreementWeb tracking
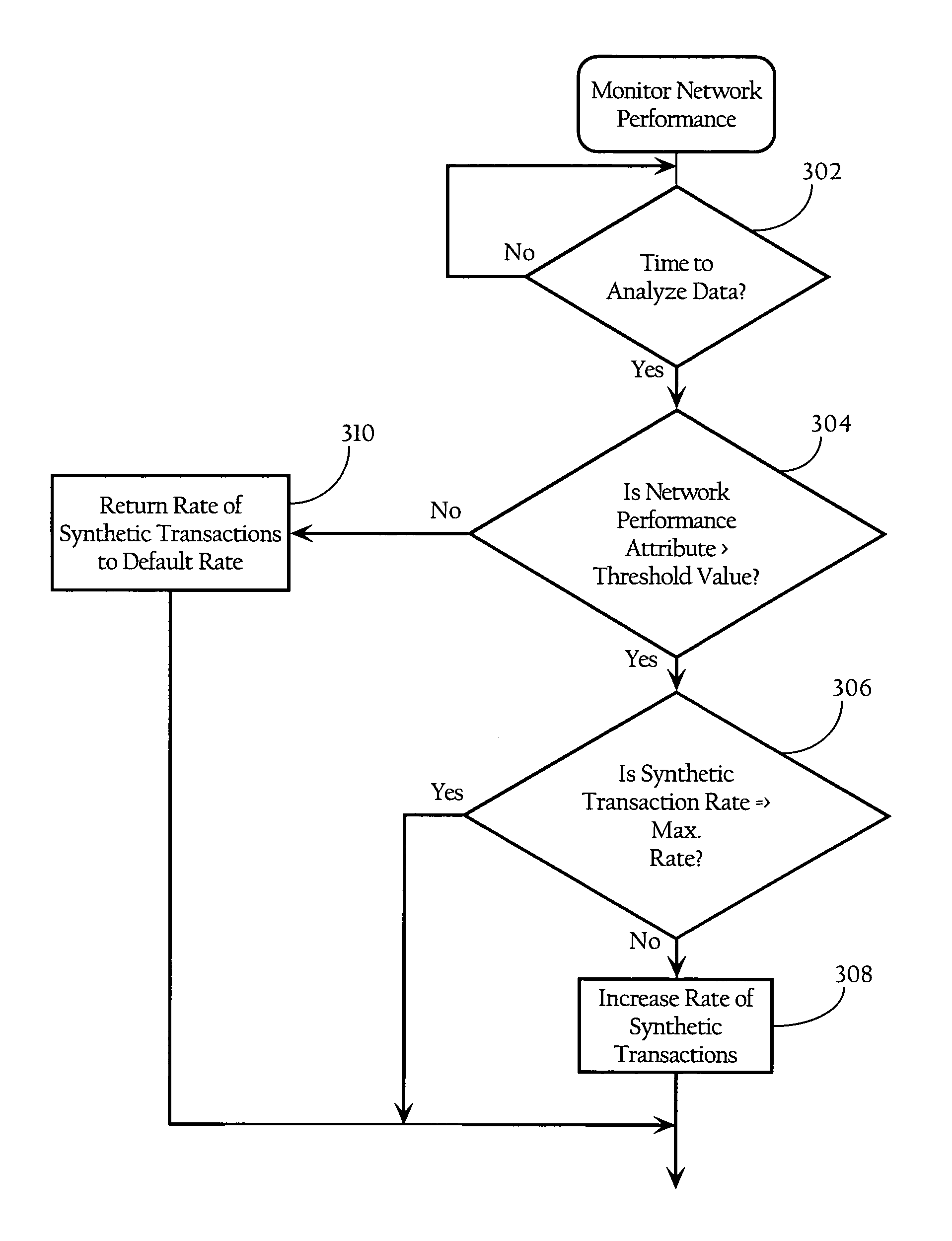
Methods, apparatuses and systems directed to adaptive monitoring of network application performance. In one implementation, the present invention improves processes used by enterprises to track, manage, and troubleshoot performance of network applications across distributed networks. In one implementation, the present invention allows for a network application performance monitoring scheme that tracks end-to-end performance of selected network applications on a passive basis, while selectively engaging more invasive (synthetic) approaches to tracking performance and troubleshooting issues when needed.
Owner:CA TECH INC
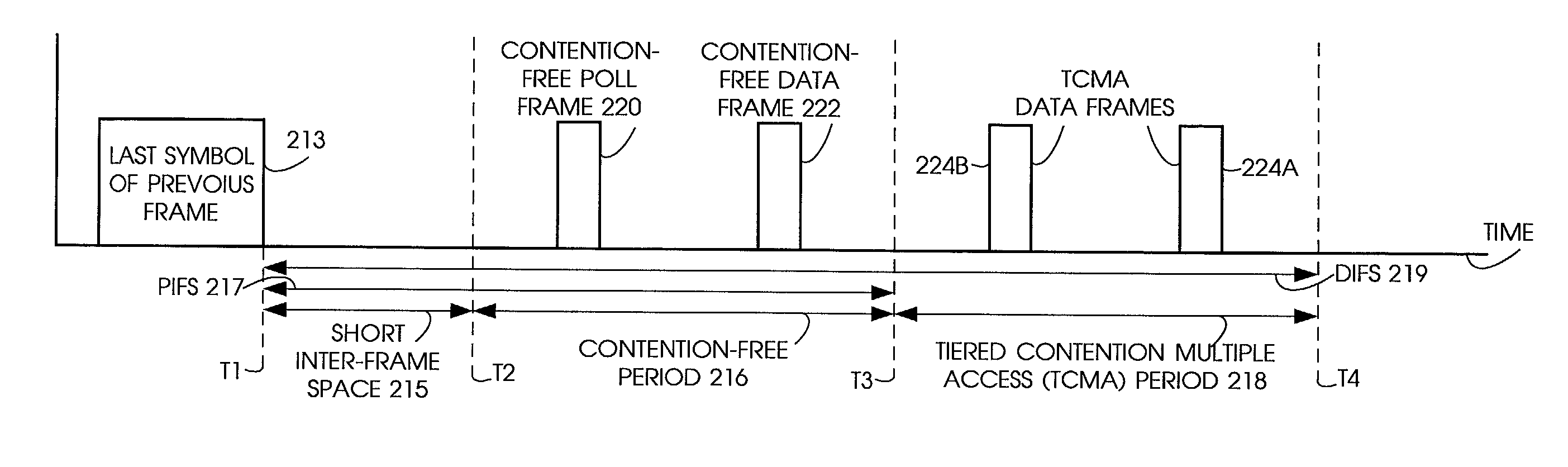
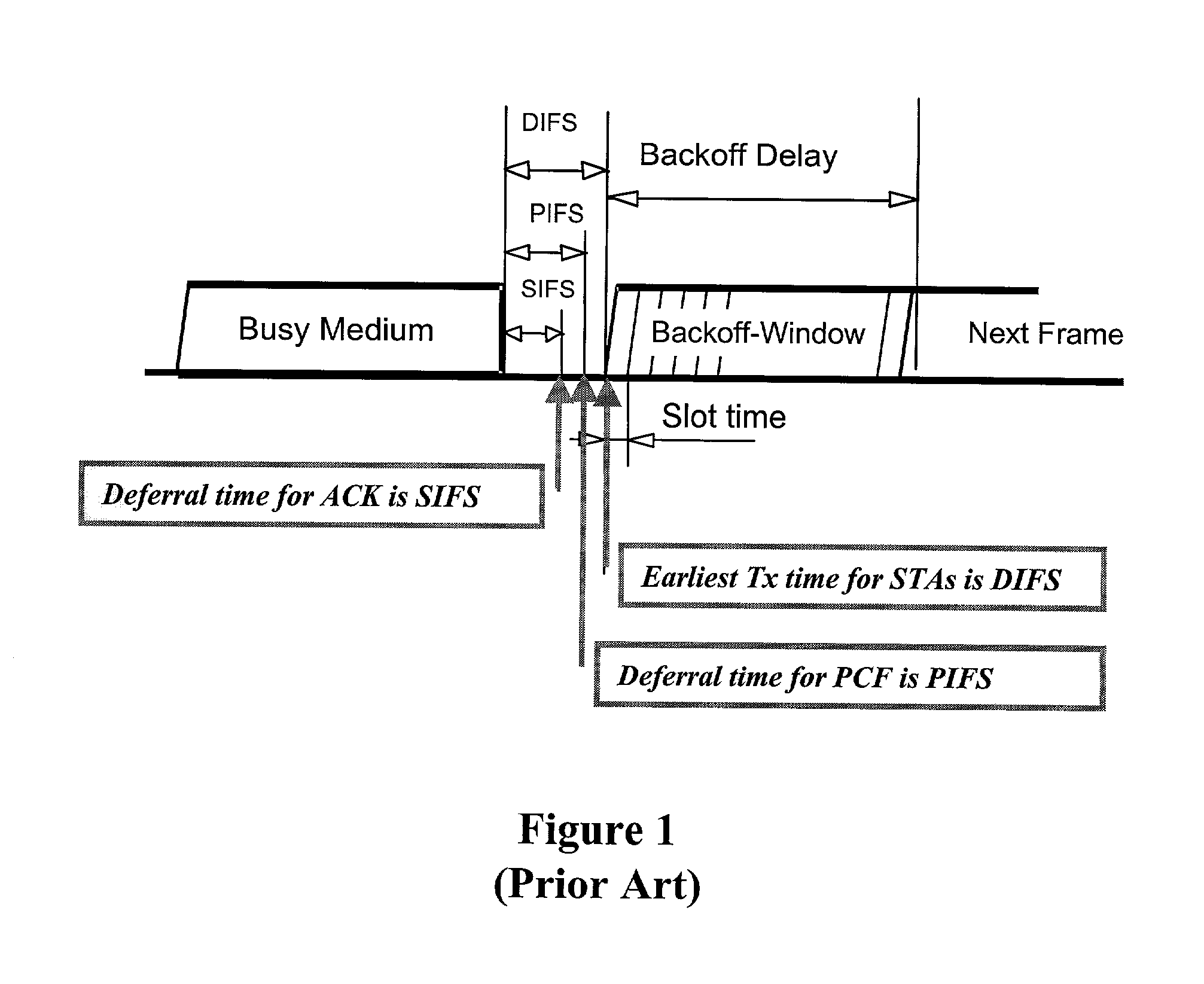
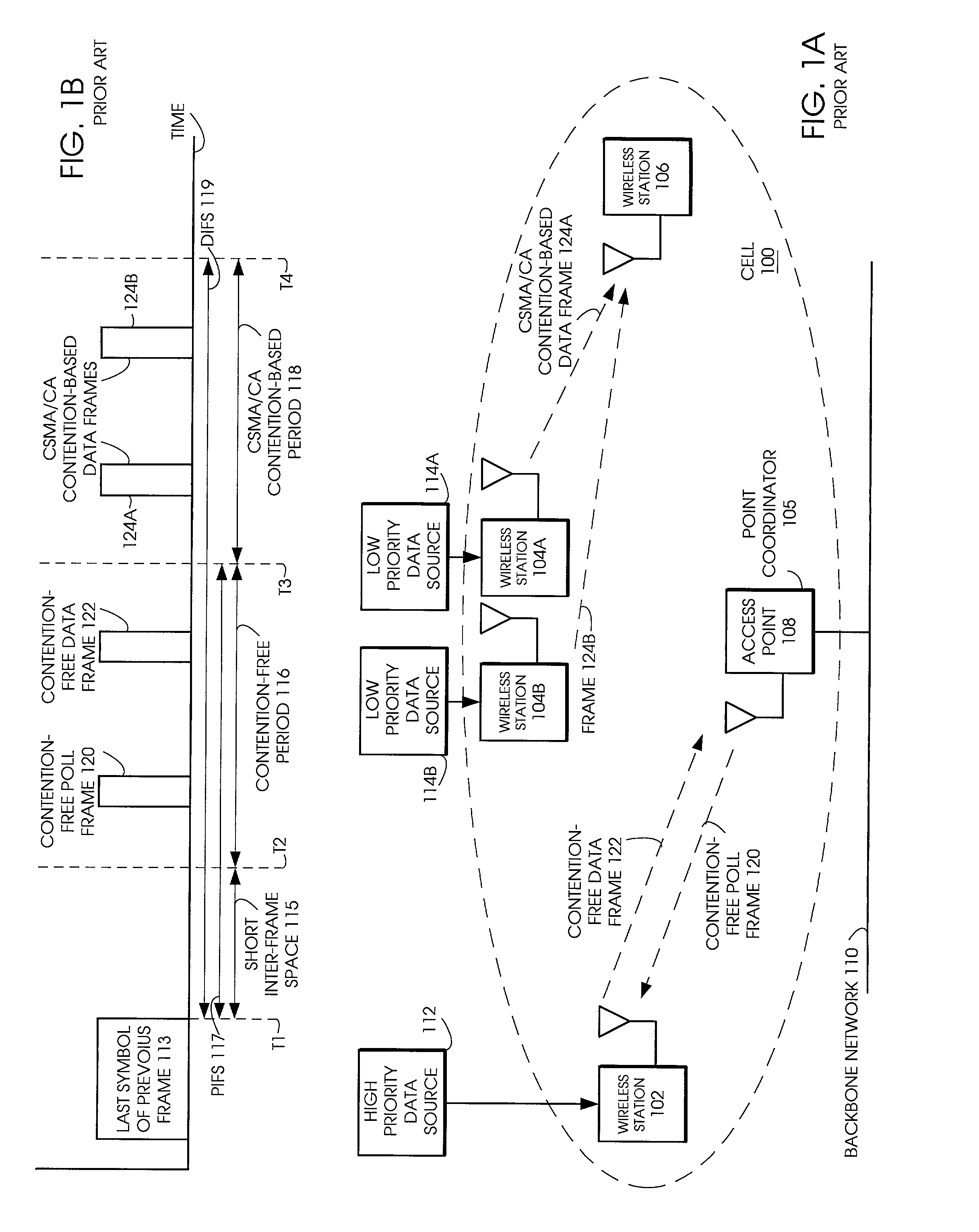
Tiered contention multiple access (TCMA): a method for priority-based shared channel access
ActiveUS7095754B2Minimizing chanceLower latencySynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementService-level agreementIdle time
Quality of Service (QoS) support is provided by means of a Tiered Contention Multiple Access (TCMA) distributed medium access protocol that schedules transmission of different types of traffic based on their service quality specifications. In one embodiment, a wireless station is supplied with data from a source having a lower QoS priority QoS(A), such as file transfer data. Another wireless station is supplied with data from a source having a higher QoS priority QoS(B), such as voice and video data. Each wireless station can determine the urgency class of its pending packets according to a scheduling algorithm. For example file transfer data is assigned lower urgency class and voice and video data is assigned higher urgency class. There are several urgency classes which indicate the desired ordering. Pending packets in a given urgency class are transmitted before transmitting packets of a lower urgency class by relying on class-differentiated urgency arbitration times (UATs), which are the idle time intervals required before the random backoff counter is decreased. In another embodiment packets are reclassified in real time with a scheduling algorithm that adjusts the class assigned to packets based on observed performance parameters and according to negotiated QoS-based requirements. Further, for packets assigned the same arbitration time, additional differentiation into more urgency classes is achieved in terms of the contention resolution mechanism employed, thus yielding hybrid packet prioritization methods. An Enhanced DCF Parameter Set is contained in a control packet sent by the AP to the associated stations, which contains class differentiated parameter values necessary to support the TCMA. These parameters can be changed based on different algorithms to support call admission and flow control functions and to meet the requirements of service level agreements.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
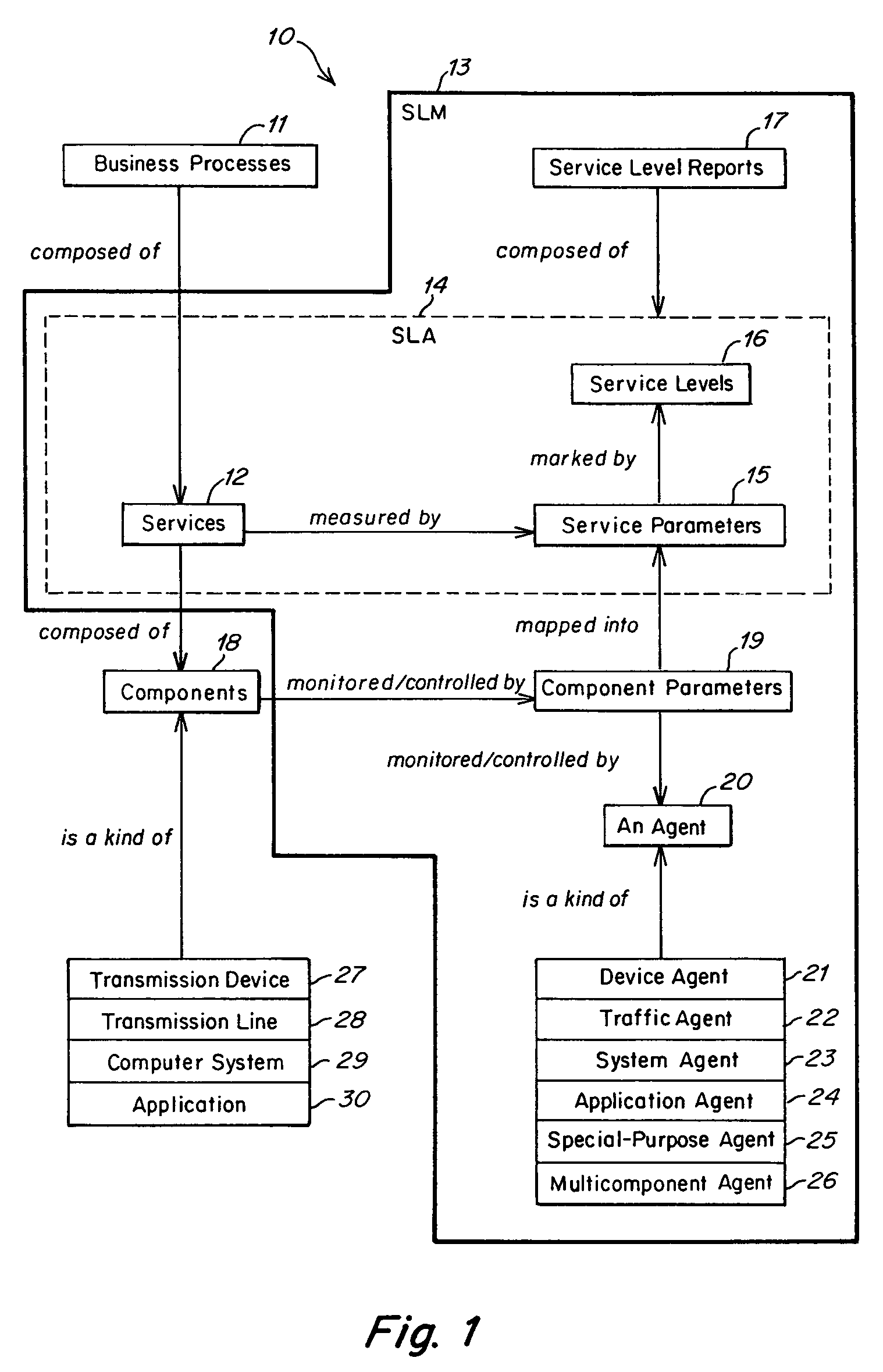
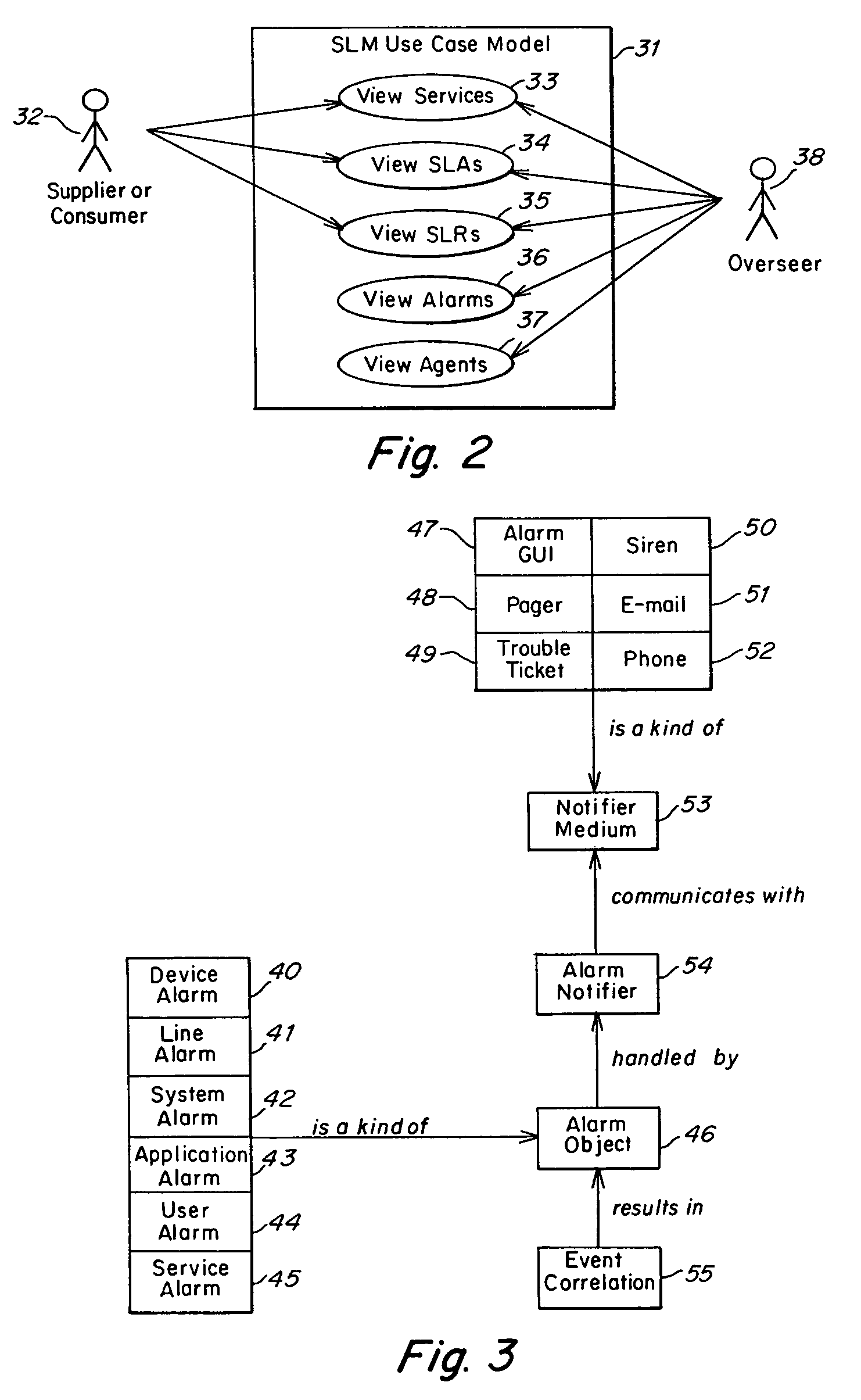
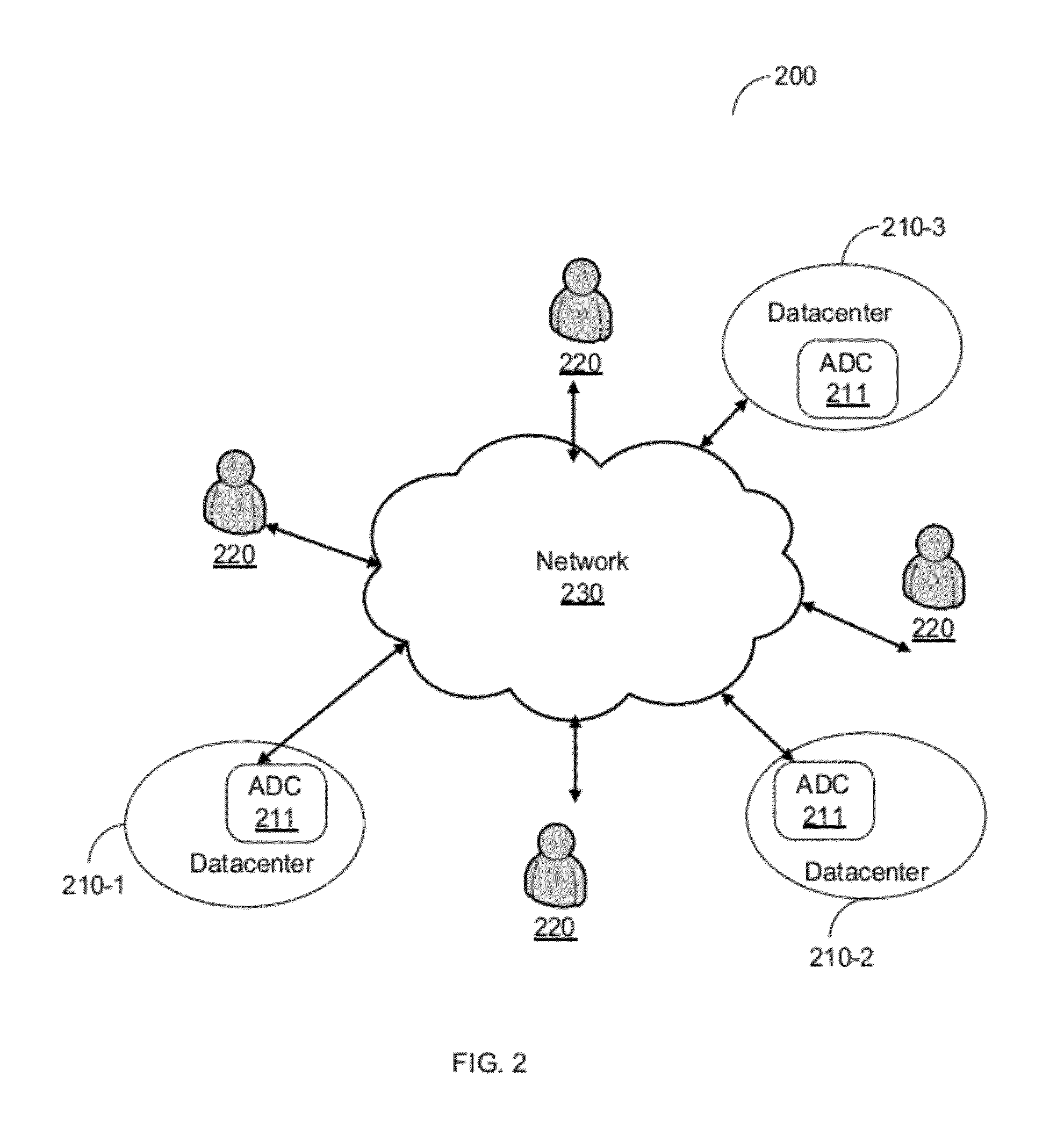
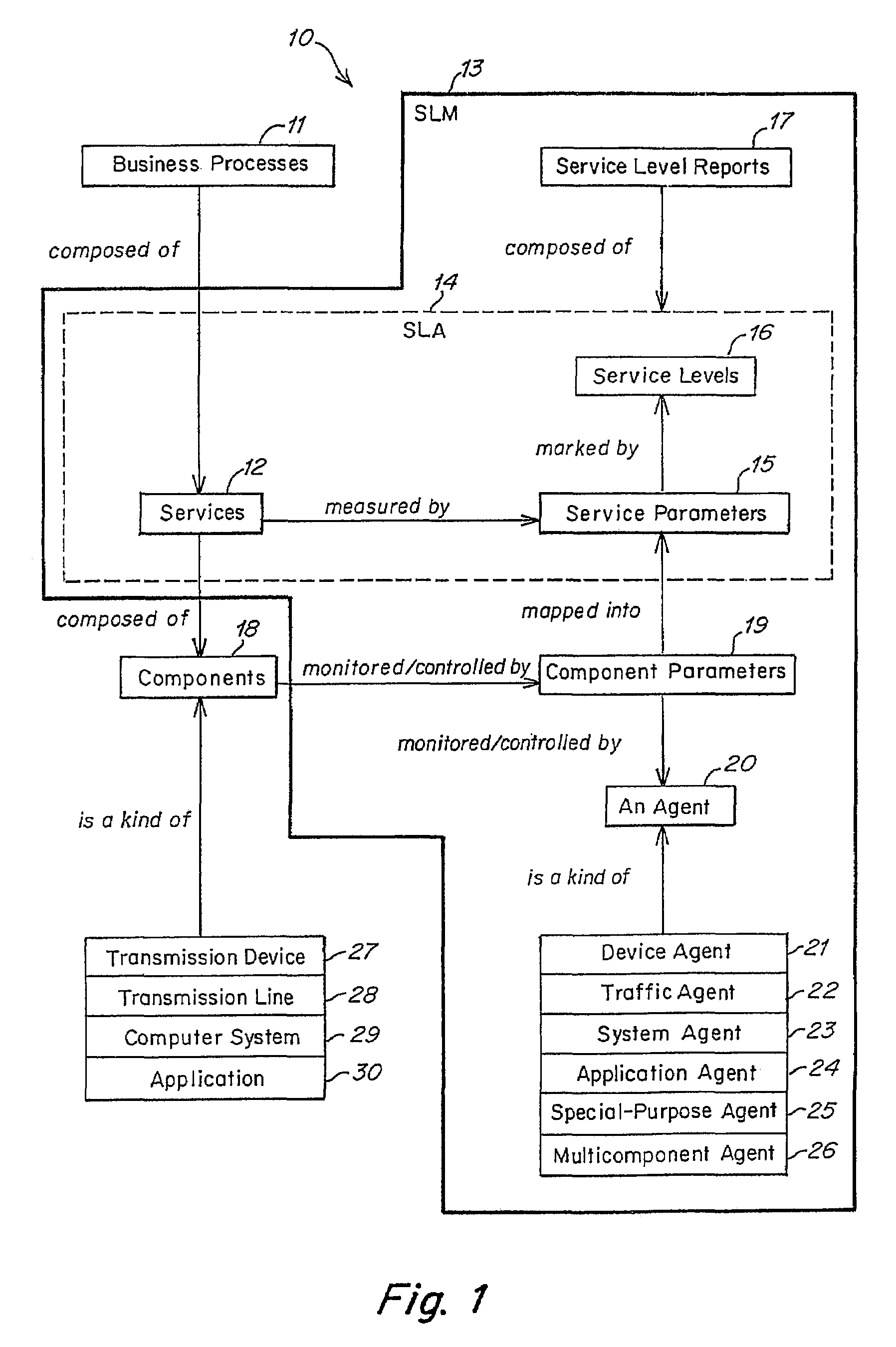
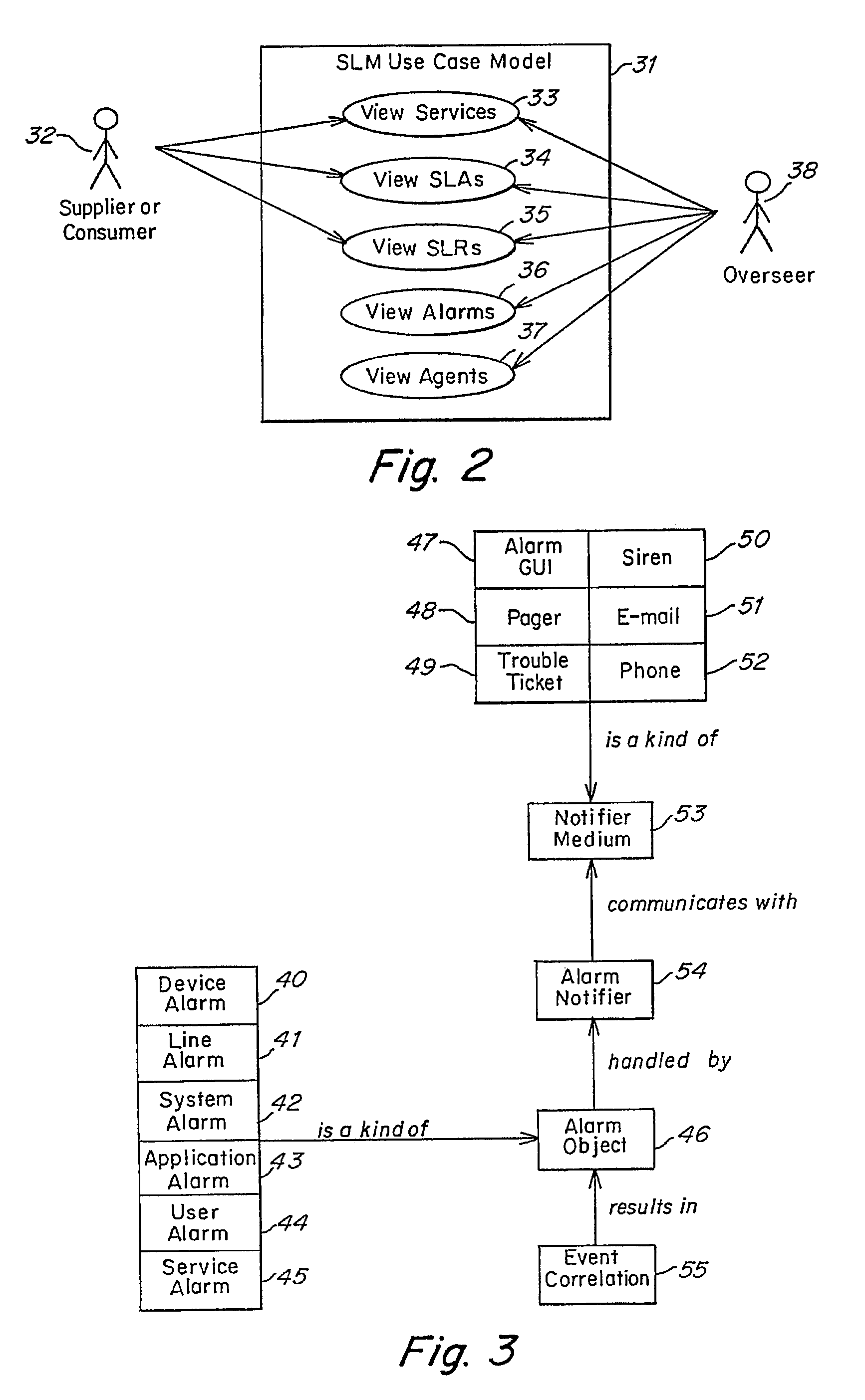
Method and apparatus for component to service mapping in service level management (SLM)
Owner:COMP ASSOC THINK INC
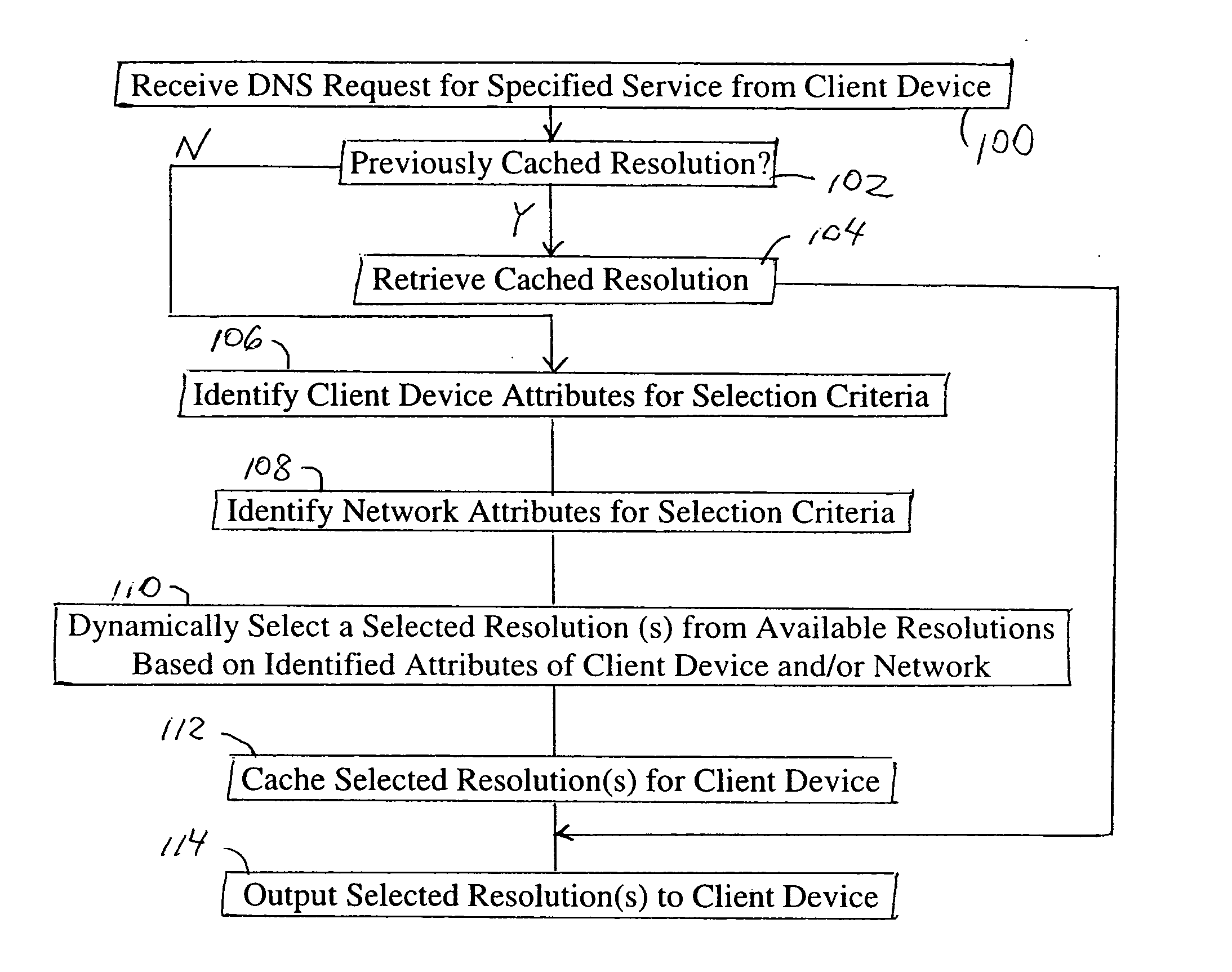
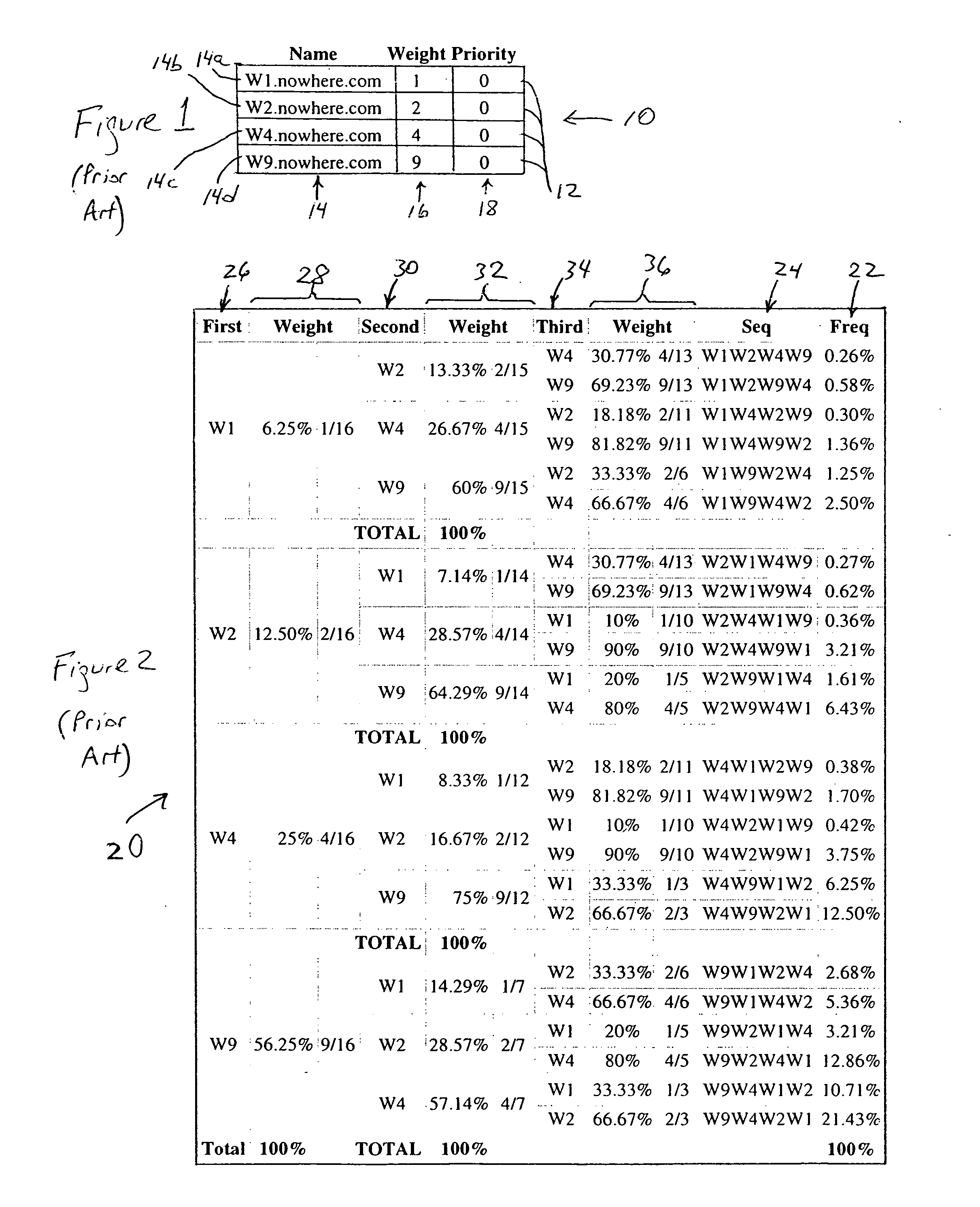
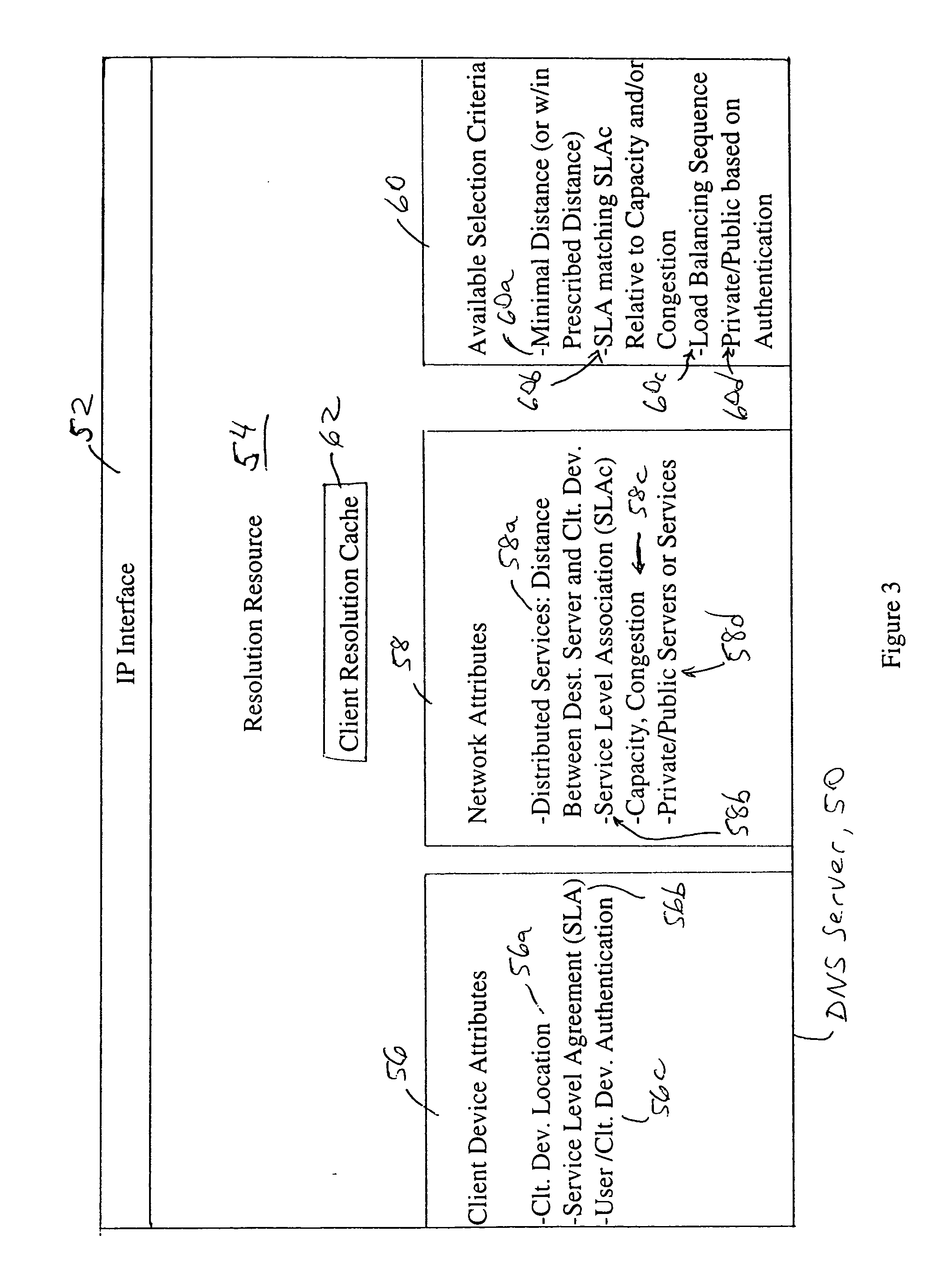
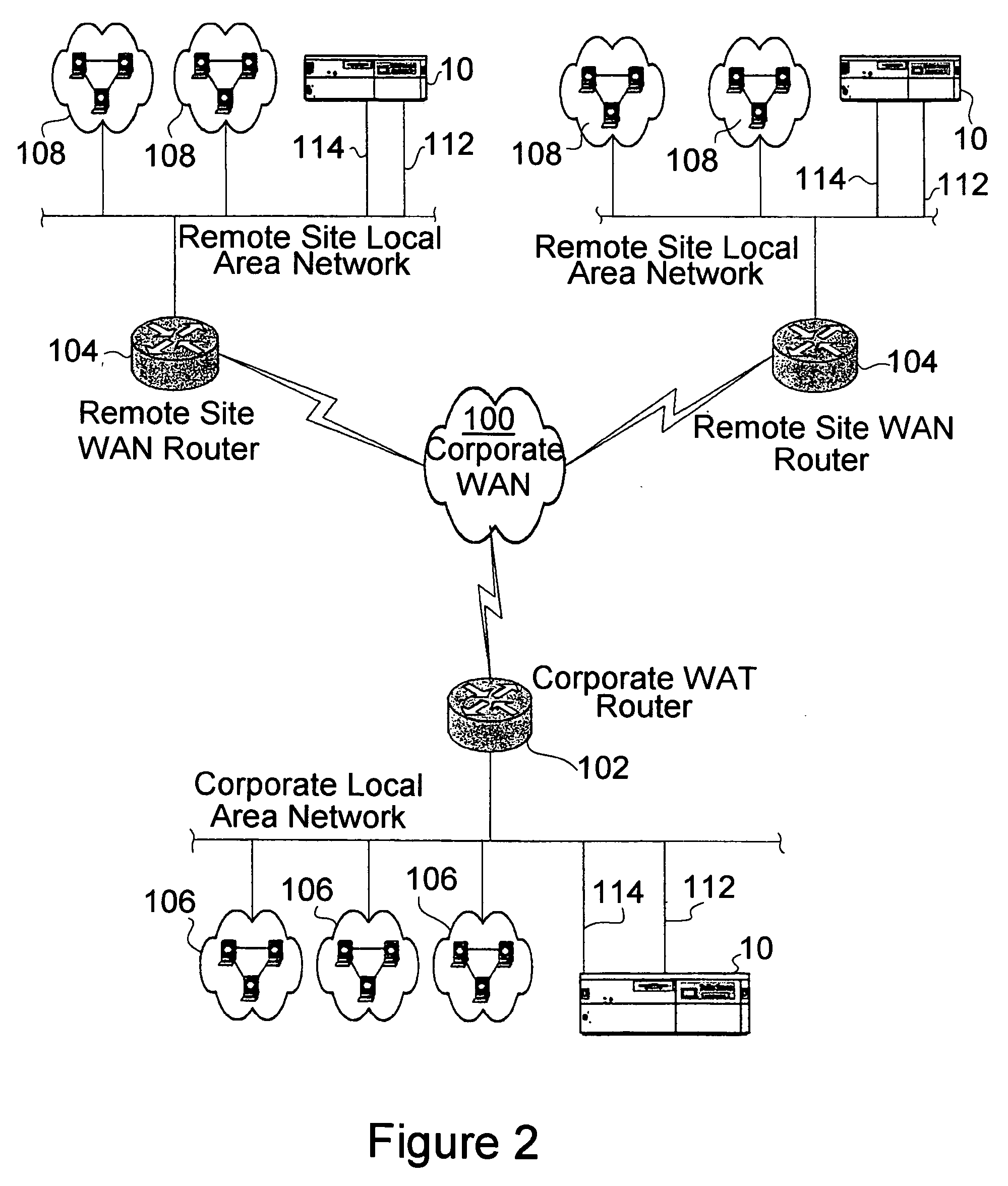
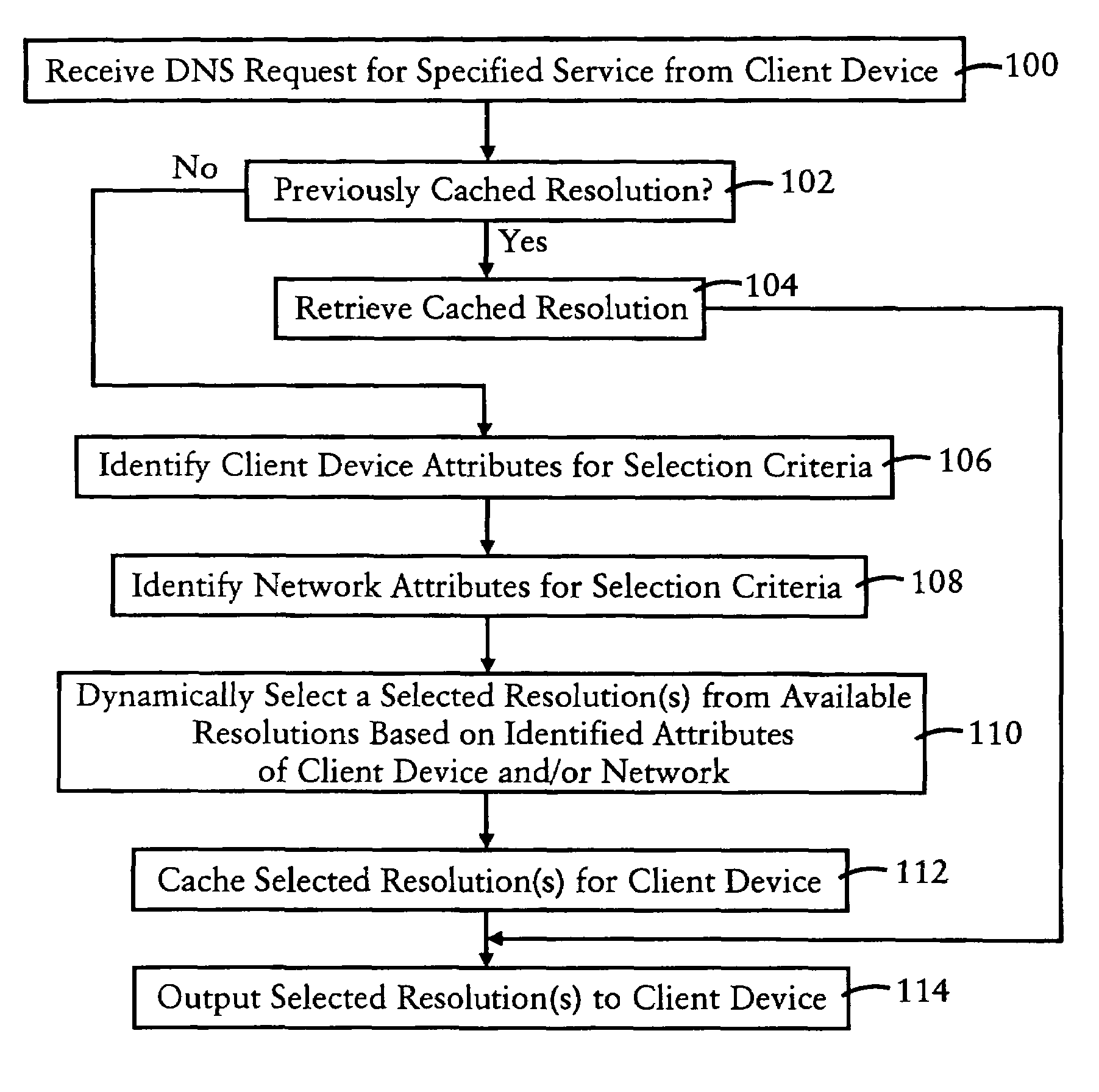
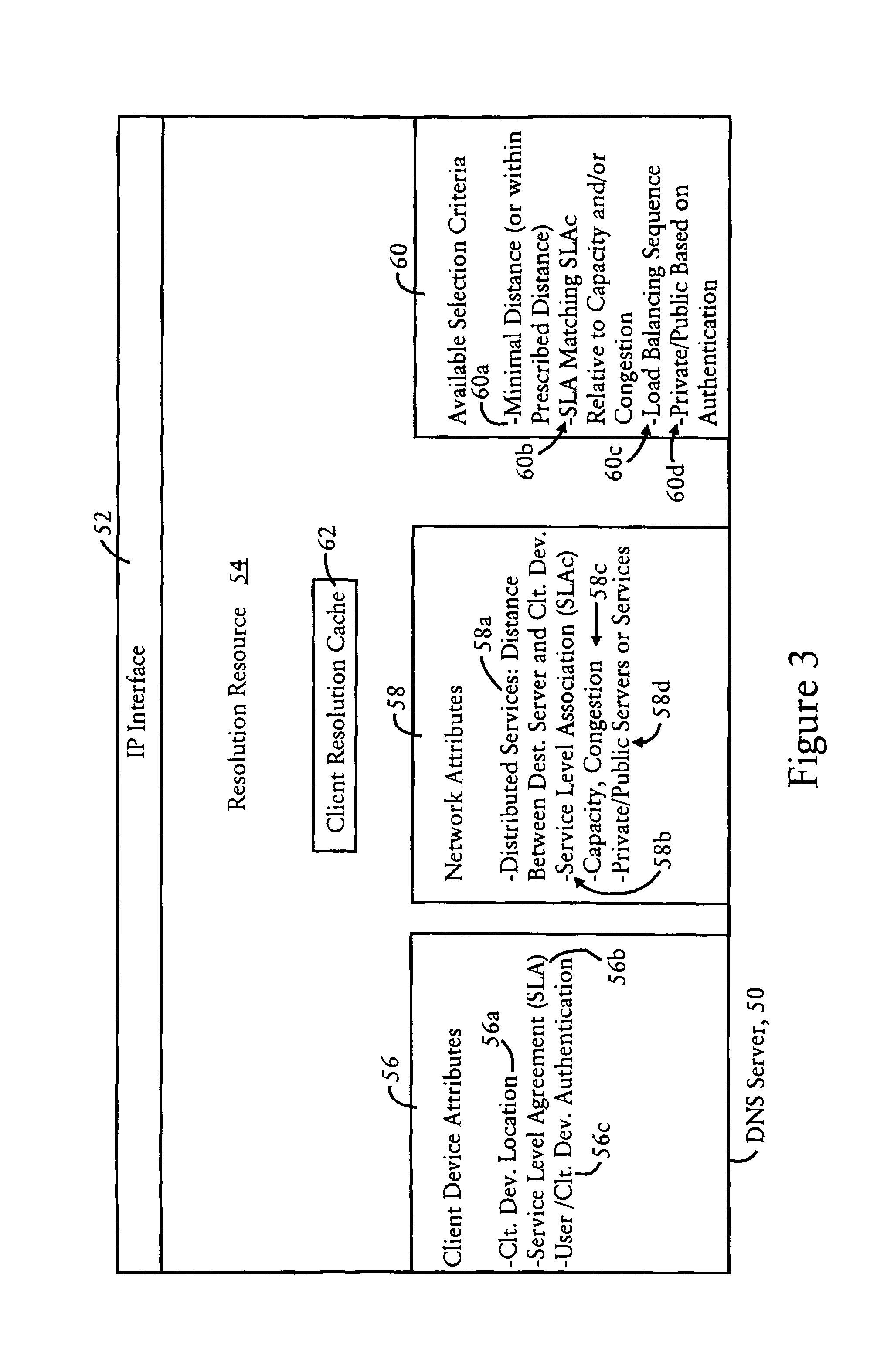
Arrangement in a server for providing dynamic domain name system services for each received request
ActiveUS20060129665A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsService-level agreementLoad Shedding
A Domain Name System (DNS) server is configured for dynamically selecting, for a client device, a selected resolution from available resolutions, the selected resolution identifying at least one destination for the specified service. The dynamic selection of the selected resolution is based on an attribute of the client device and / or a determined attribute of the network. Hence, the selected resolution directs the client device to a specific server based on prescribed selection criteria, for example service level agreements, the location of the client device, network performance or detected congestion conditions, authentication of the user of the client device, etc. The selected resolution also can be for enforcement of load balancing policies.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
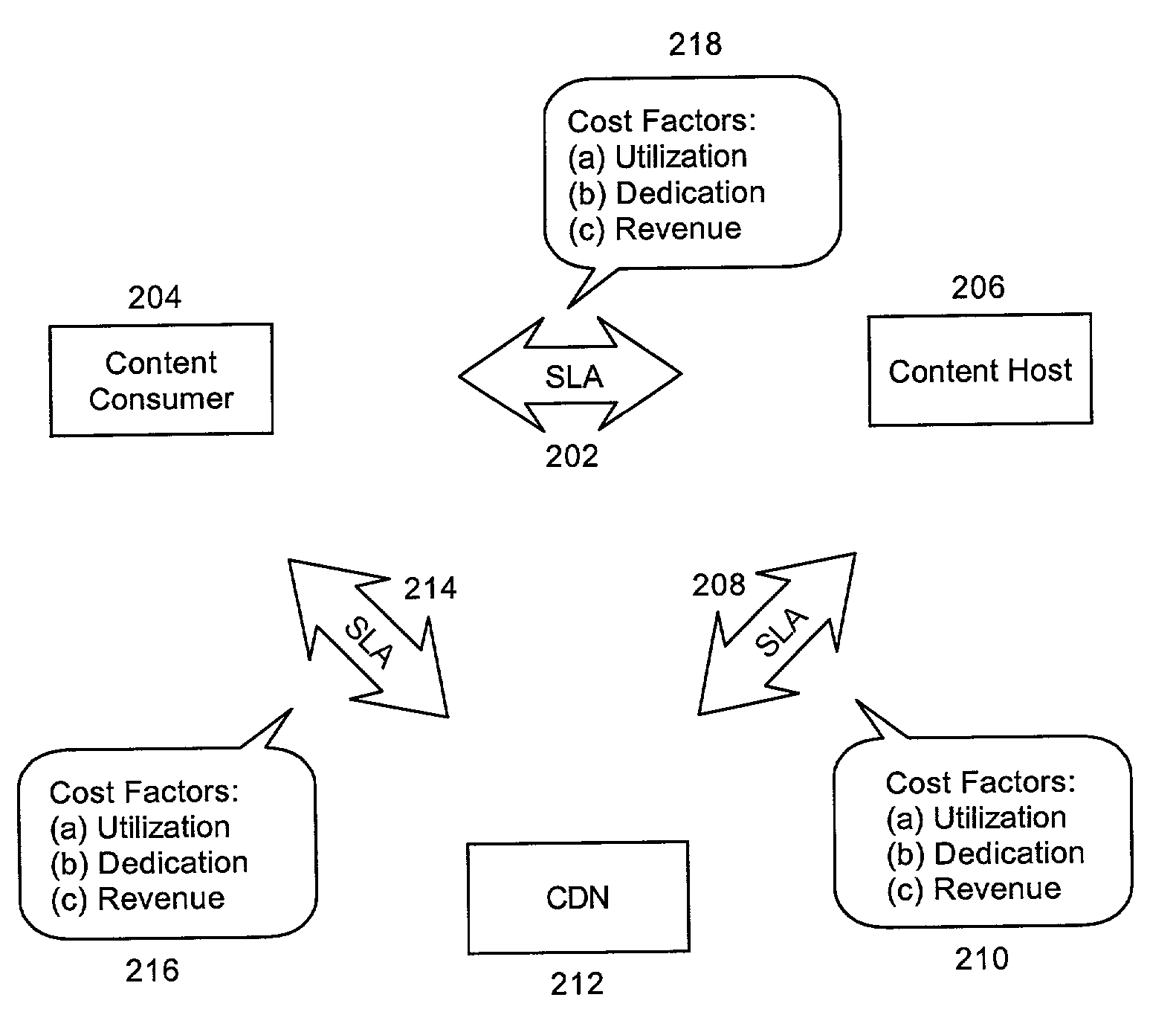
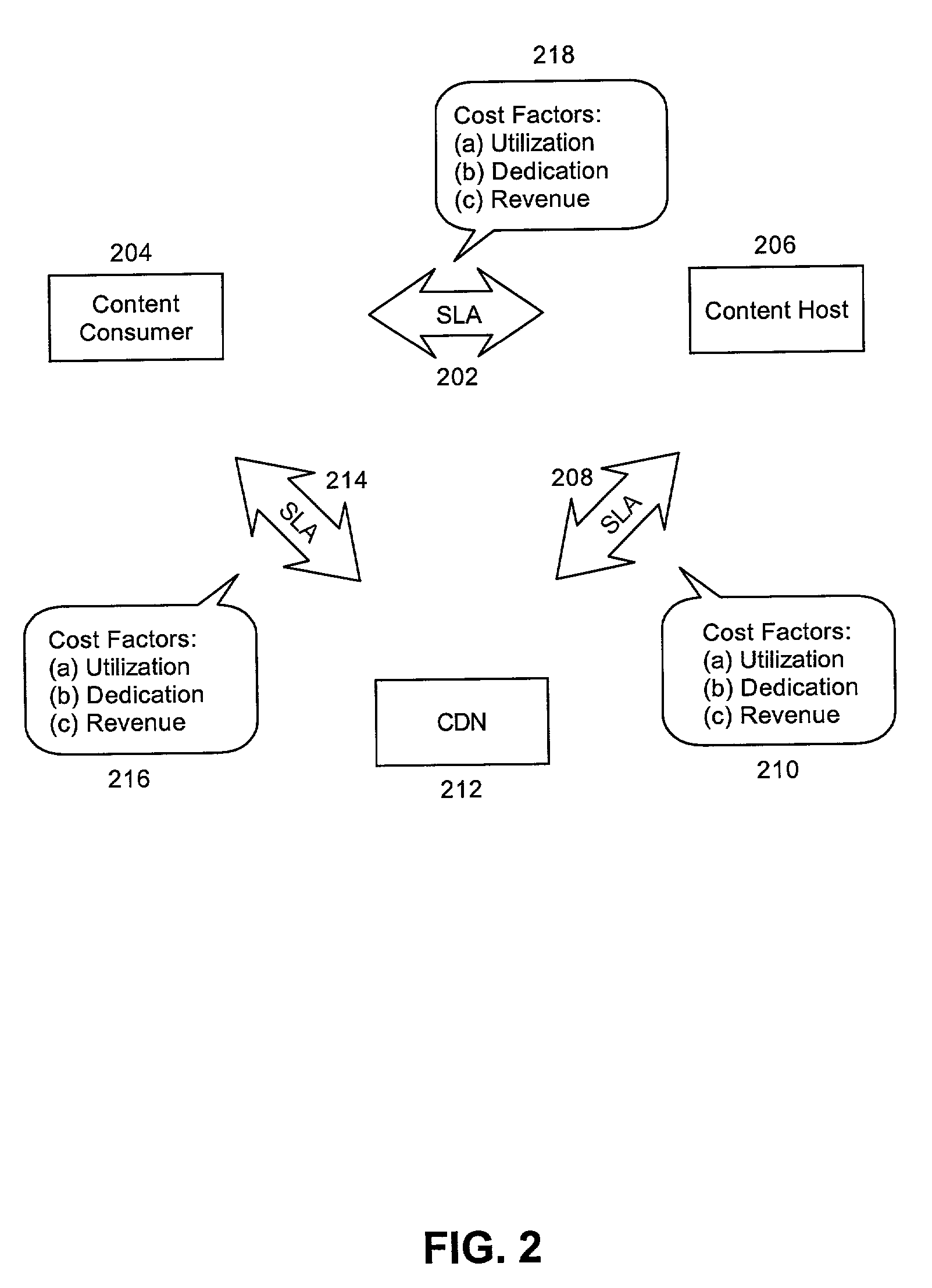
Multi-tier service level agreement method and system
ActiveUS7099936B2Overcome limitationsMultiple digital computer combinationsResourcesService-level agreementEdge server
A method for managing multi-tier SLA relationships. The method can include first computing costs of utilizing edge server resources in a CDN, costs of dedicating content host resources in a content host in lieu of the utilization, and prospective revenues which can be generated by the content host providing services based on the resources to content consumers. Minimum QoS levels can be identified which must be maintained when providing the services to the content consumers according to QoS terms in established SLAs between the content host and individual ones of the content consumers. Finally, a new SLA can be established between the content host and the CDN. Importantly, the new SLA can include QoS terms for selectively allocating resources in the CDN. Moreover, the QoS terms can optimize revenues generated by the content host providing services based on the selective allocation of resources and the computed costs.
Owner:IBM CORP
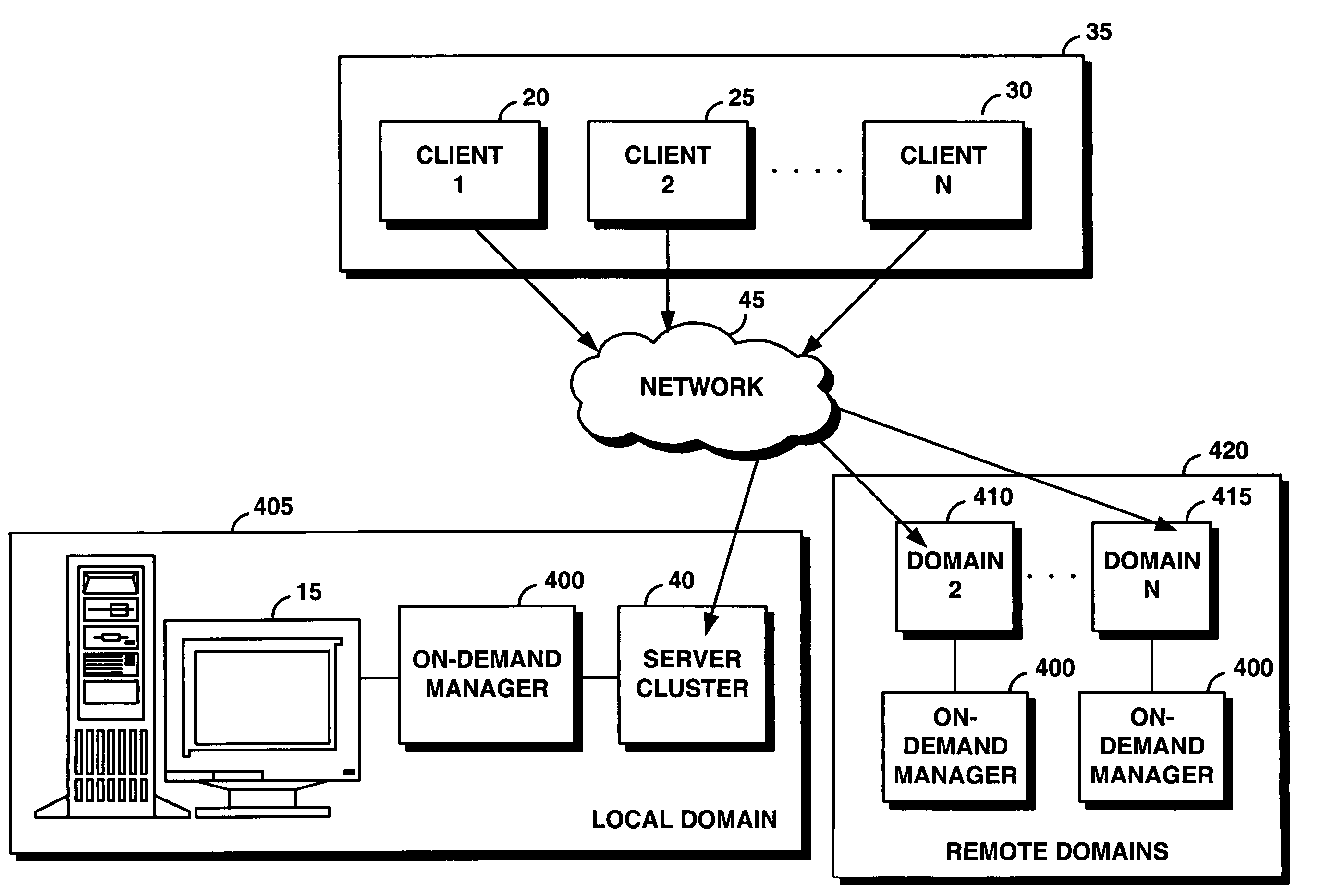
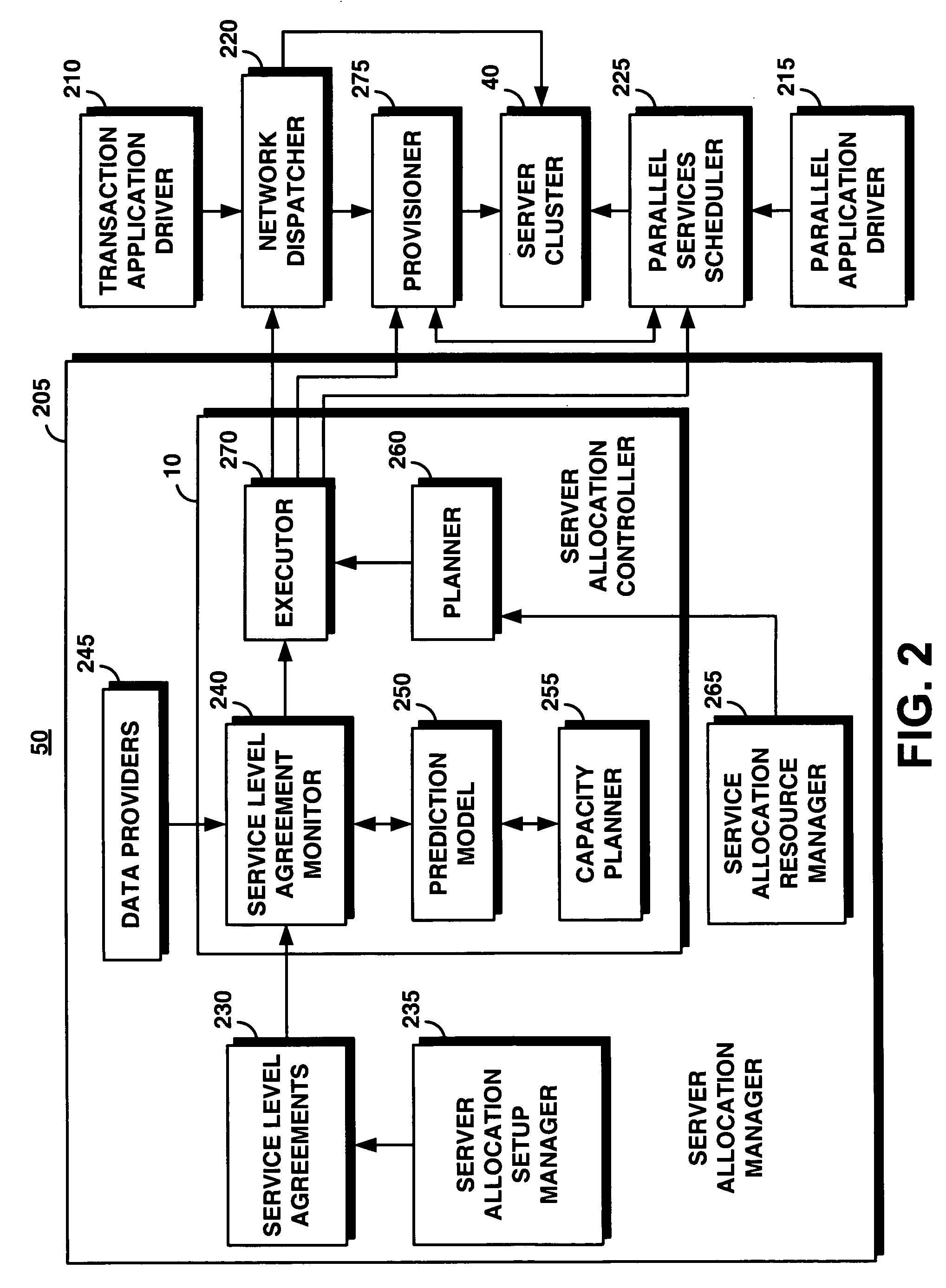
System and method for supporting transaction and parallel services across multiple domains based on service level agreenments
InactiveUS20050165925A1Facilitates dynamic allocationResource allocationDigital computer detailsService-level agreementData processing system
An on-demand manager provides an improved distributed data processing system for facilitating dynamic allocation of computing resources among multiple domains based on a current workload and service level agreements. Based on a service level agreement, the on-demand manager monitors and predicts the load on the system. If the current or predicted load cannot be handled with the current system configuration, the on-demand manager determines additional resources needed to handle the workload. If the service level agreement violations cannot be handled by reconfiguring resources at a domain, the on-demand manager sends a resource request to other domains. These other domains analyze their own commitments and may accept the resource request, reject the request, or counter-propose with an offer of resources and a corresponding service level agreement. Once the requesting domain has acquired resources, workload load balancers are reconfigured to allocate some of the workload from the requesting site to the acquired remote resources.
Owner:IBM CORP
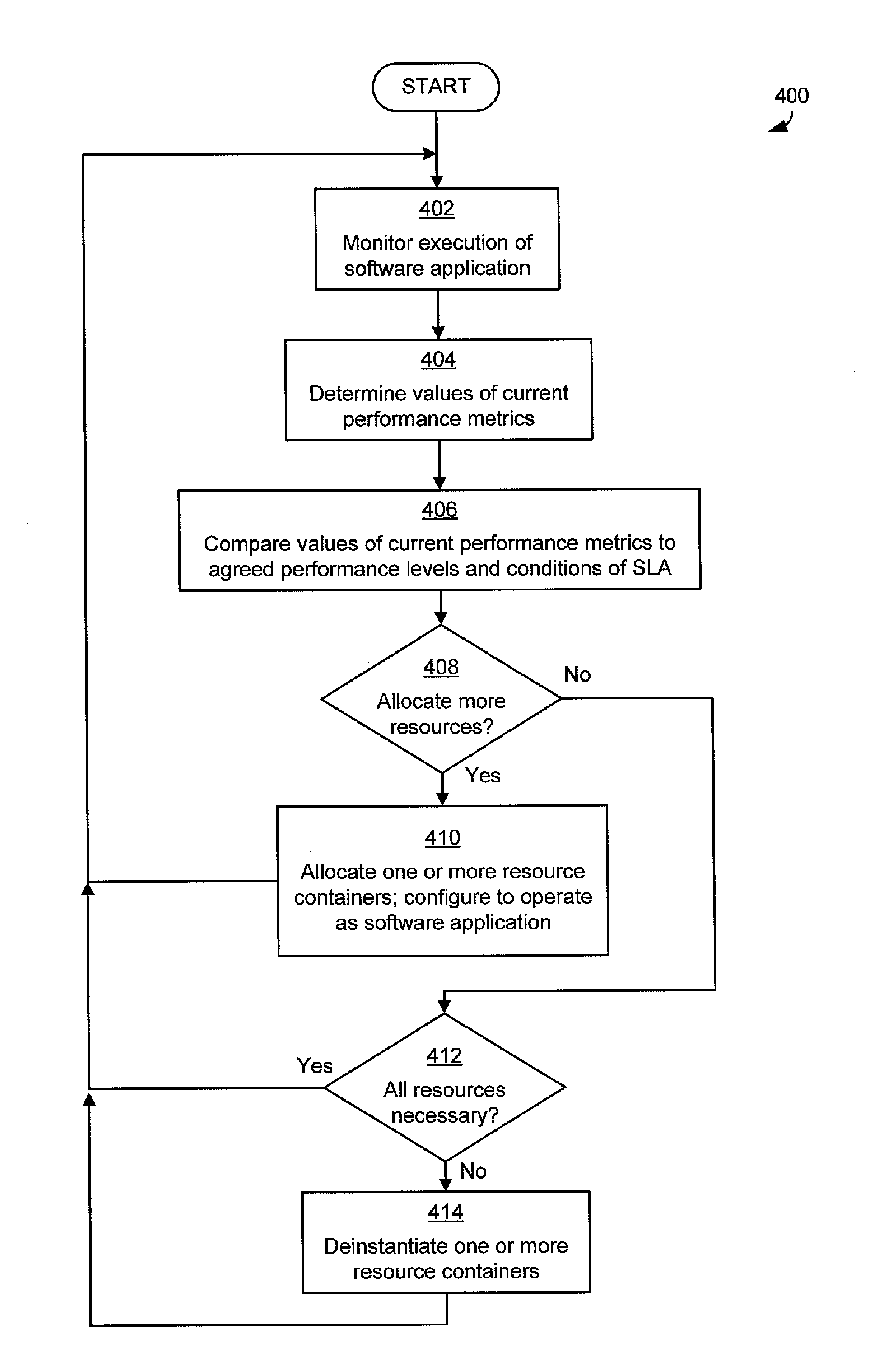
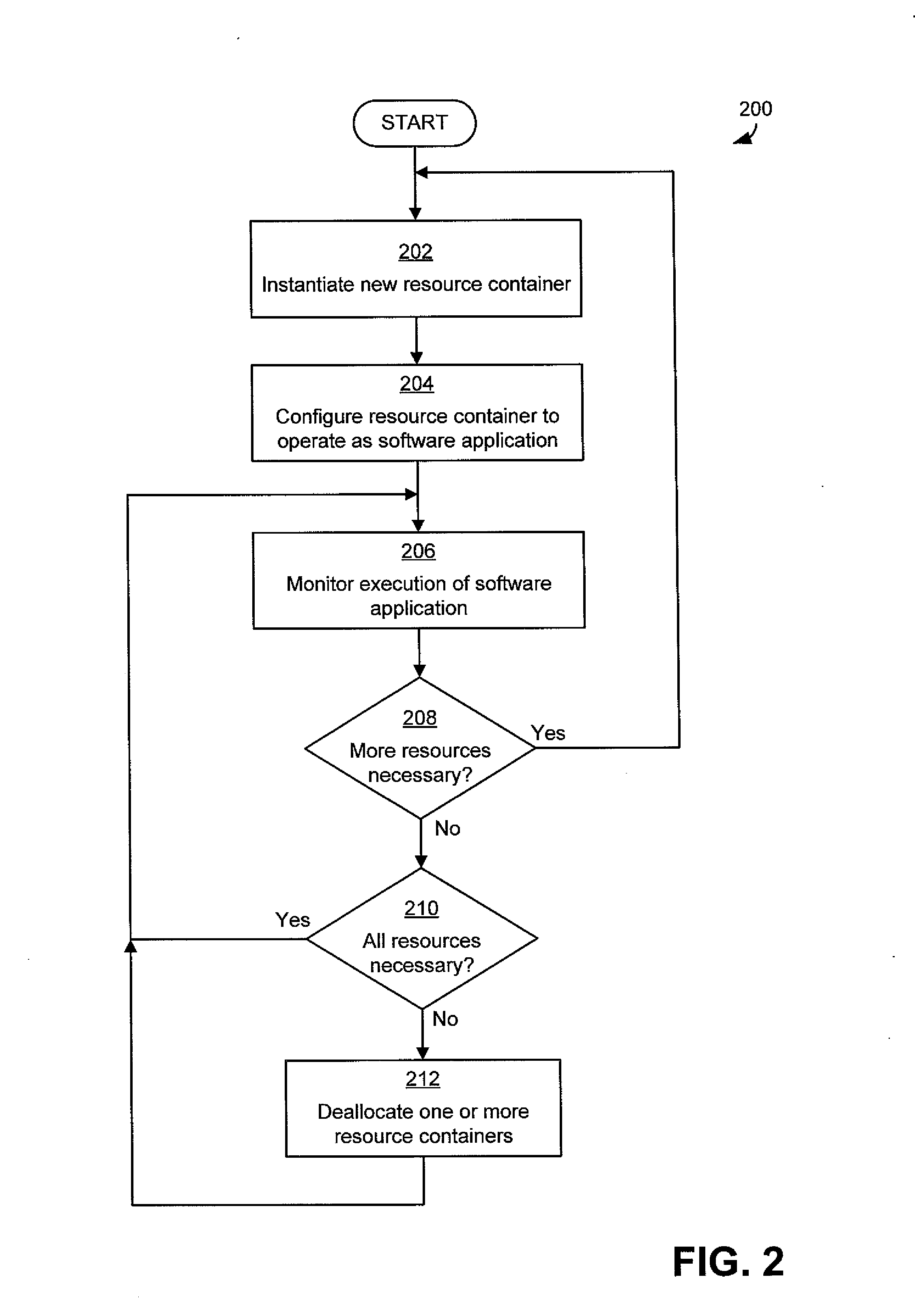
Resource management for cloud computing platforms
ActiveUS20120331113A1Reduce complexityGood flexibilityDigital computer detailsProgram controlService-level agreementService level requirement
A system for managing allocation of resources based on service level agreements between application owners and cloud operators. Under some service level agreements, the cloud operator may have responsibility for managing allocation of resources to the software application and may manage the allocation such that the software application executes within an agreed performance level. Operating a cloud computing platform according to such a service level agreement may alleviate for the application owners the complexities of managing allocation of resources and may provide greater flexibility to cloud operators in managing their cloud computing platforms.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
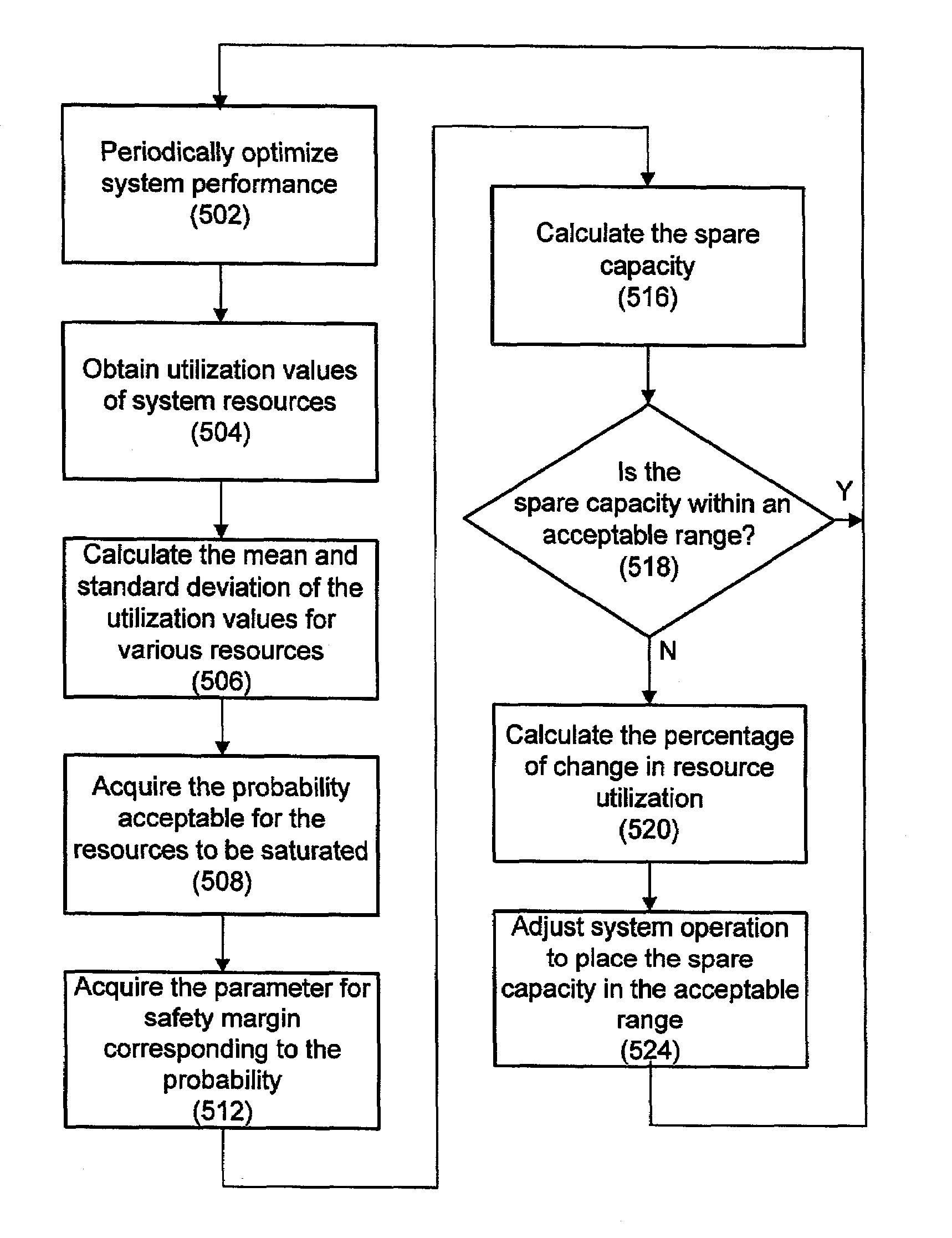
Managing power consumption based on utilization statistics
InactiveUS6996728B2Save powerEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementService-level agreementResource depletion
The present invention, in various embodiments, provides techniques for managing system power. In one embodiment, system compute loads and / or system resources invoked by services running on the system consume power. To better manage power consumption, the spare capacity of a system resource is periodically measured, and if this spare capacity is outside a predefined range, then the resource operation is adjusted, e.g., the CPU speed is increased or decreased, so that the spare capacity is within the range. Further, the spare capacity is kept as close to zero as practical, and this spare capacity is determined based on the statistical distribution of a number of utilization values of the resources, which is also taken periodically. The spare capacity is also calculated based on considerations of the probability that the system resources are saturated. In one embodiment, to maintain the services required by a Service Level Agreement (SLA), a correlation between an SLA parameter and a resource utilization is determined. In addition to other factors and the correlation of the parameters, the spare capacity of the resource utilization is adjusted based on the spare capacity of the SLA parameter. Various embodiments include optimizing system performance before calculating system spare capacity, saving power for system groups or clusters, saving power for special conditions such as brown-out, high temperature, etc.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Proactive network analysis system
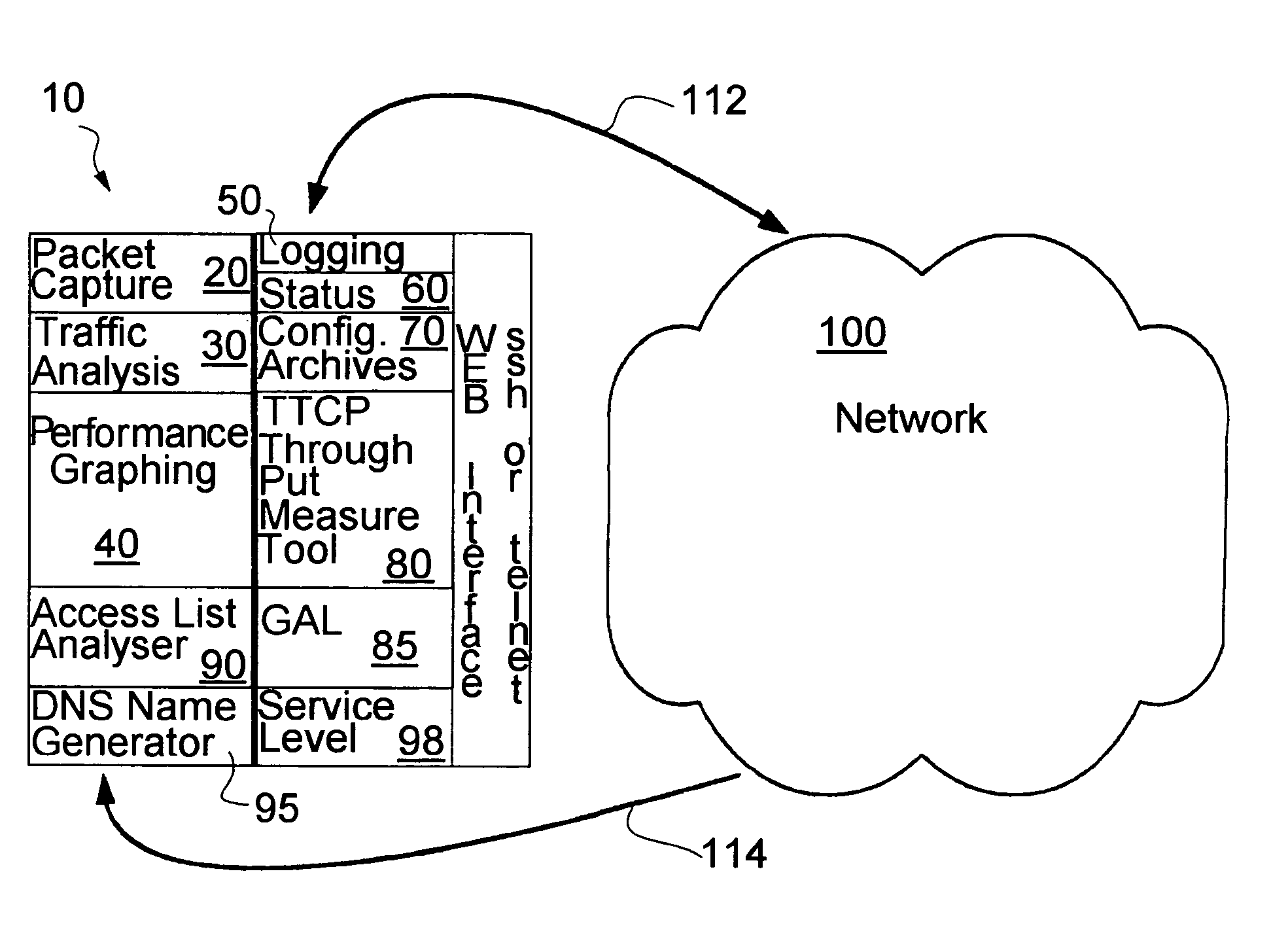
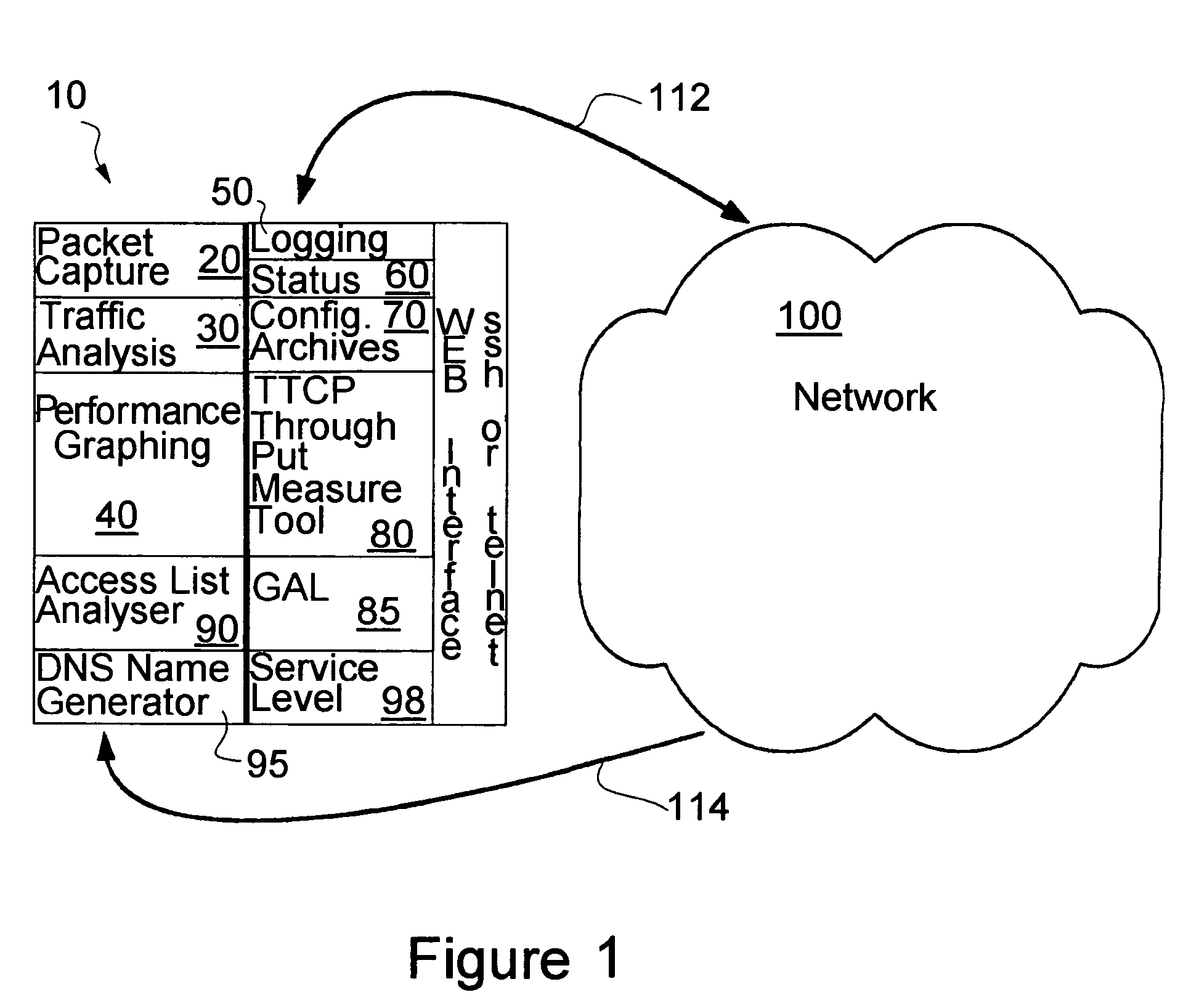
A proactive network analysis system is a single unit for diagnosing network problems, measuring network performance, and monitoring network status in a comprehensive manner. The system is a compilation of individual tools including a distributed network packet capture data stream collector; a traffic analyzer; a performance graphing unit; a syslog recorder analyzer and archiving unit; a system availability monitor; a device configuration archiving unit; and a throughput measurement tool. The system can further provide an access list generator, an access list analyzer, a router DNS name generator and a service level agreement measurement device.
Owner:SOLUTIONS4NETWORKS
Arrangement in a server for providing dynamic domain name system services for each received request
ActiveUS7499998B2Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsDomain nameService-level agreement
A Domain Name System (DNS) server is configured for dynamically selecting, for a client device, a selected resolution from available resolutions, the selected resolution identifying at least one destination for the specified service. The dynamic selection of the selected resolution is based on an attribute of the client device and / or a determined attribute of the network. Hence, the selected resolution directs the client device to a specific server based on prescribed selection criteria, for example service level agreements, the location of the client device, network performance or detected congestion conditions, authentication of the user of the client device, etc. The selected resolution also can be for enforcement of load balancing policies.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
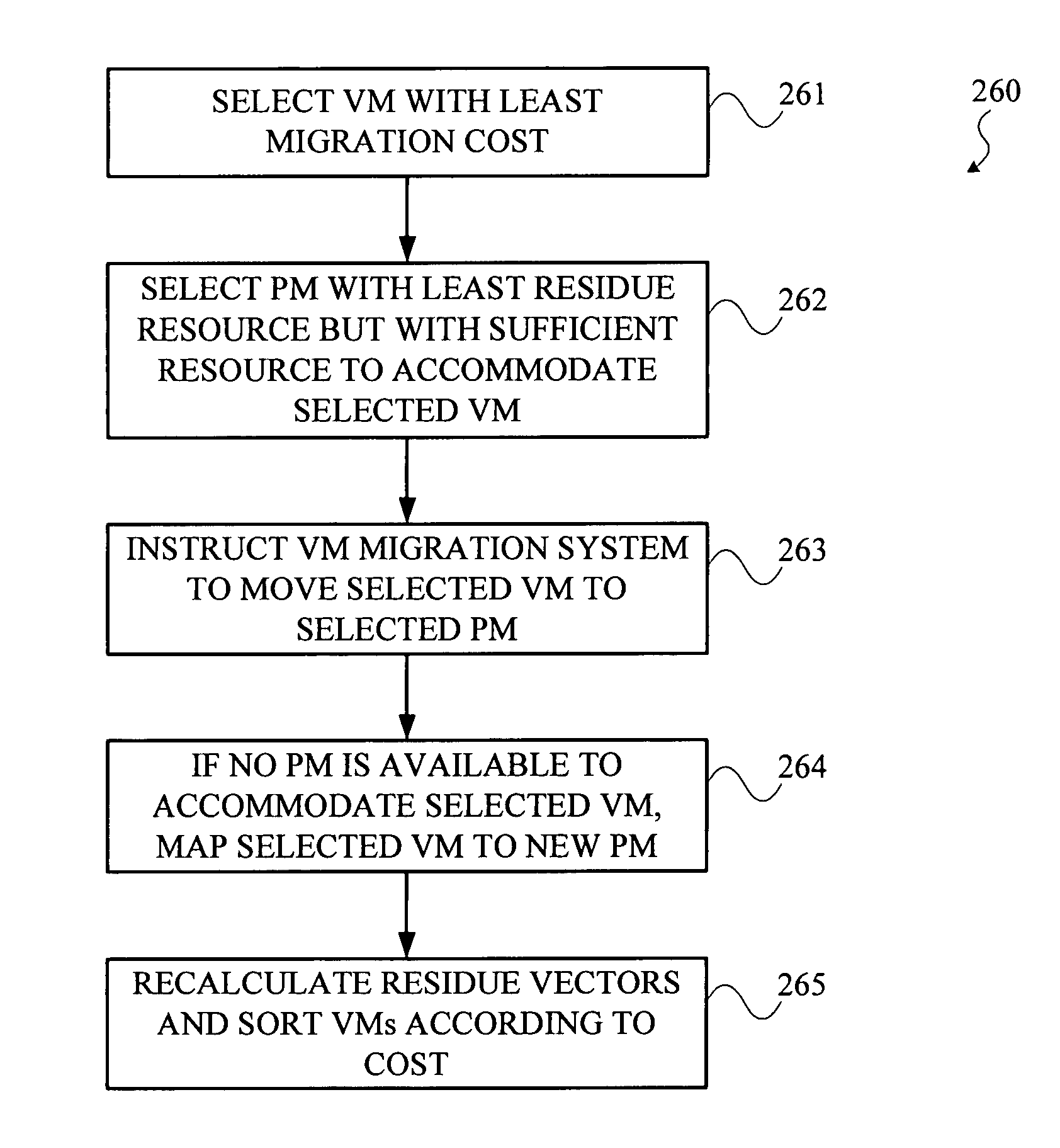
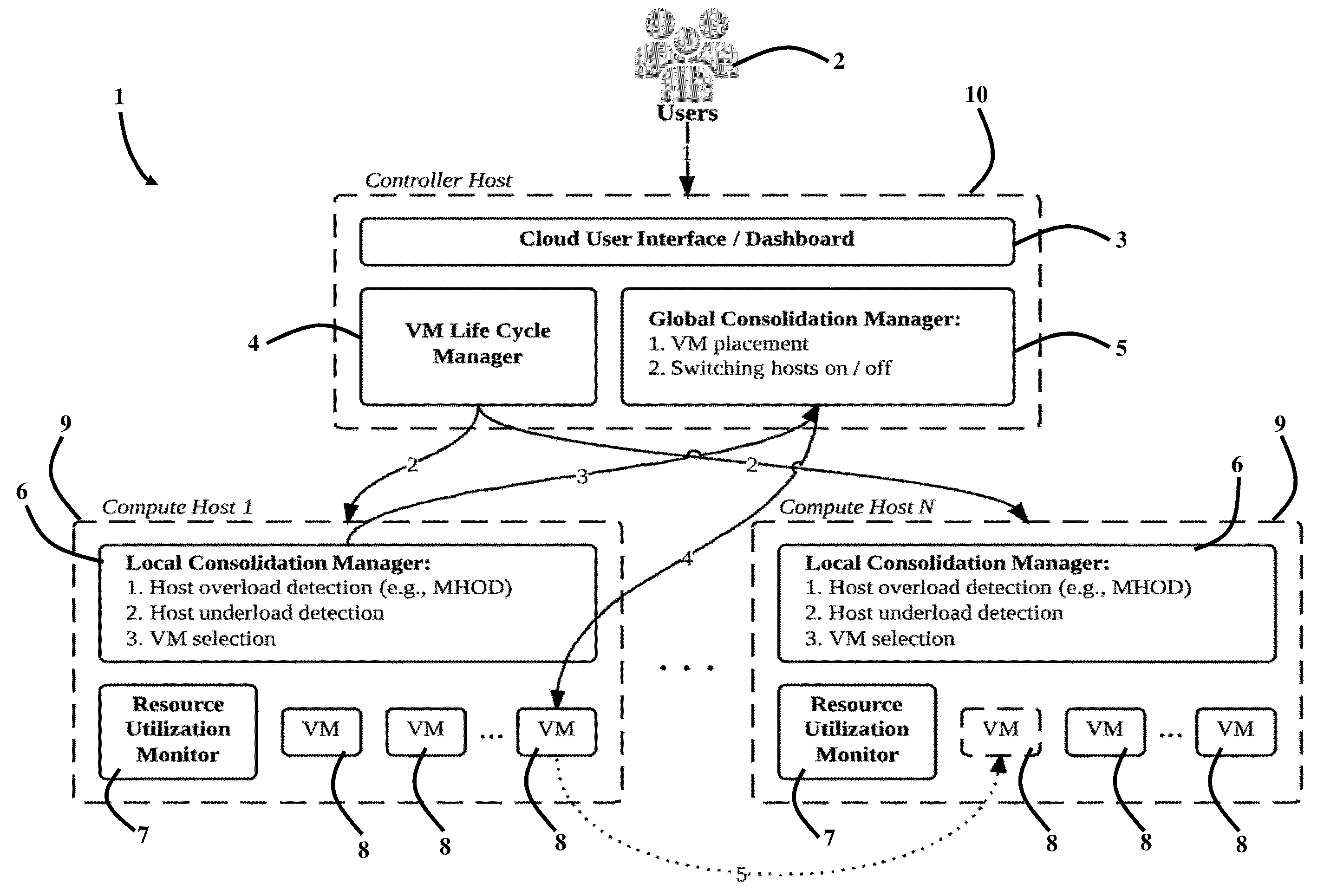
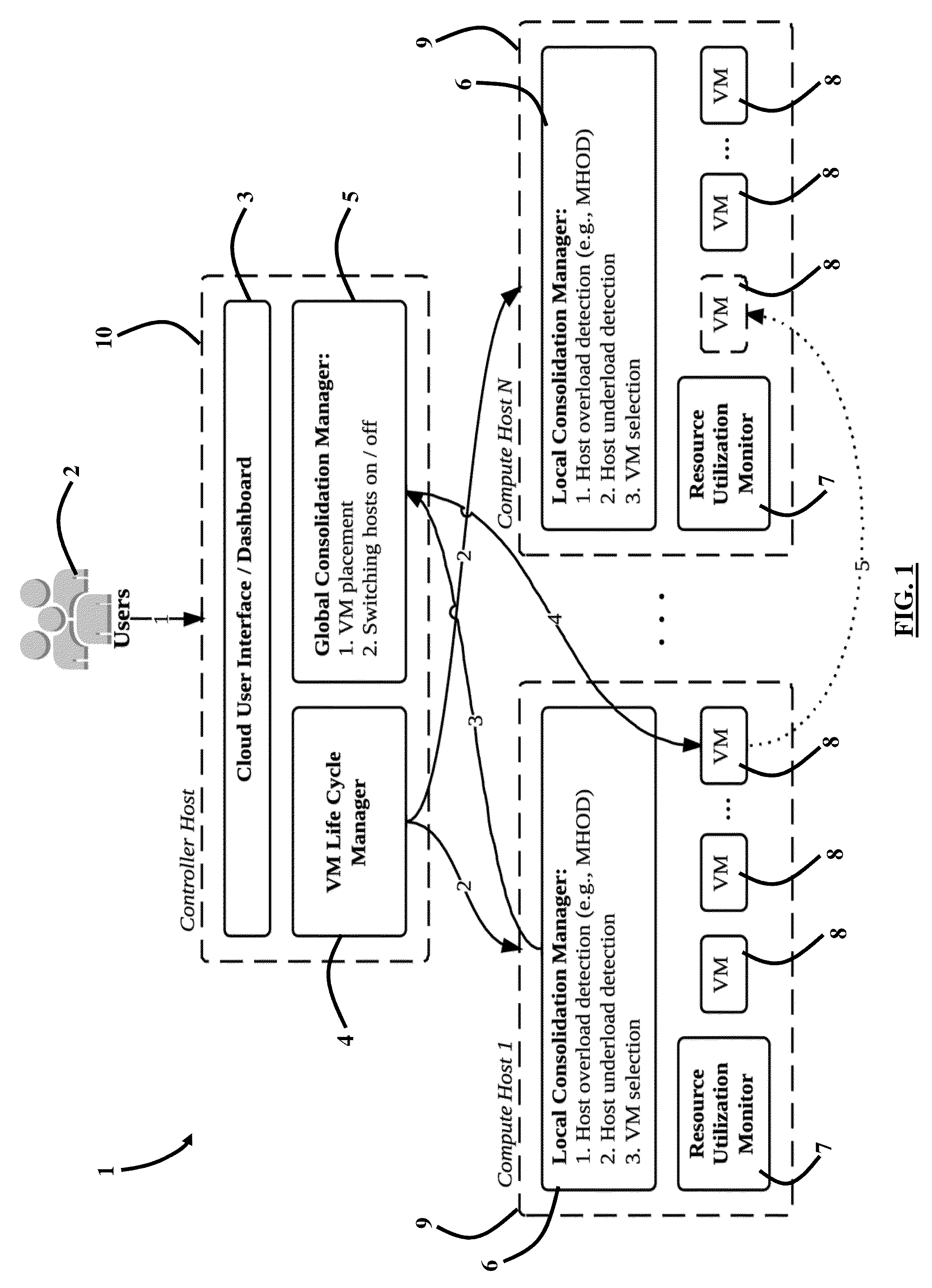
DYNAMIC PLACEMENT OF VIRTUAL MACHINES FOR MANAGING VIOLATIONS OF SERVICE LEVEL AGREEMENTS (SLAs)
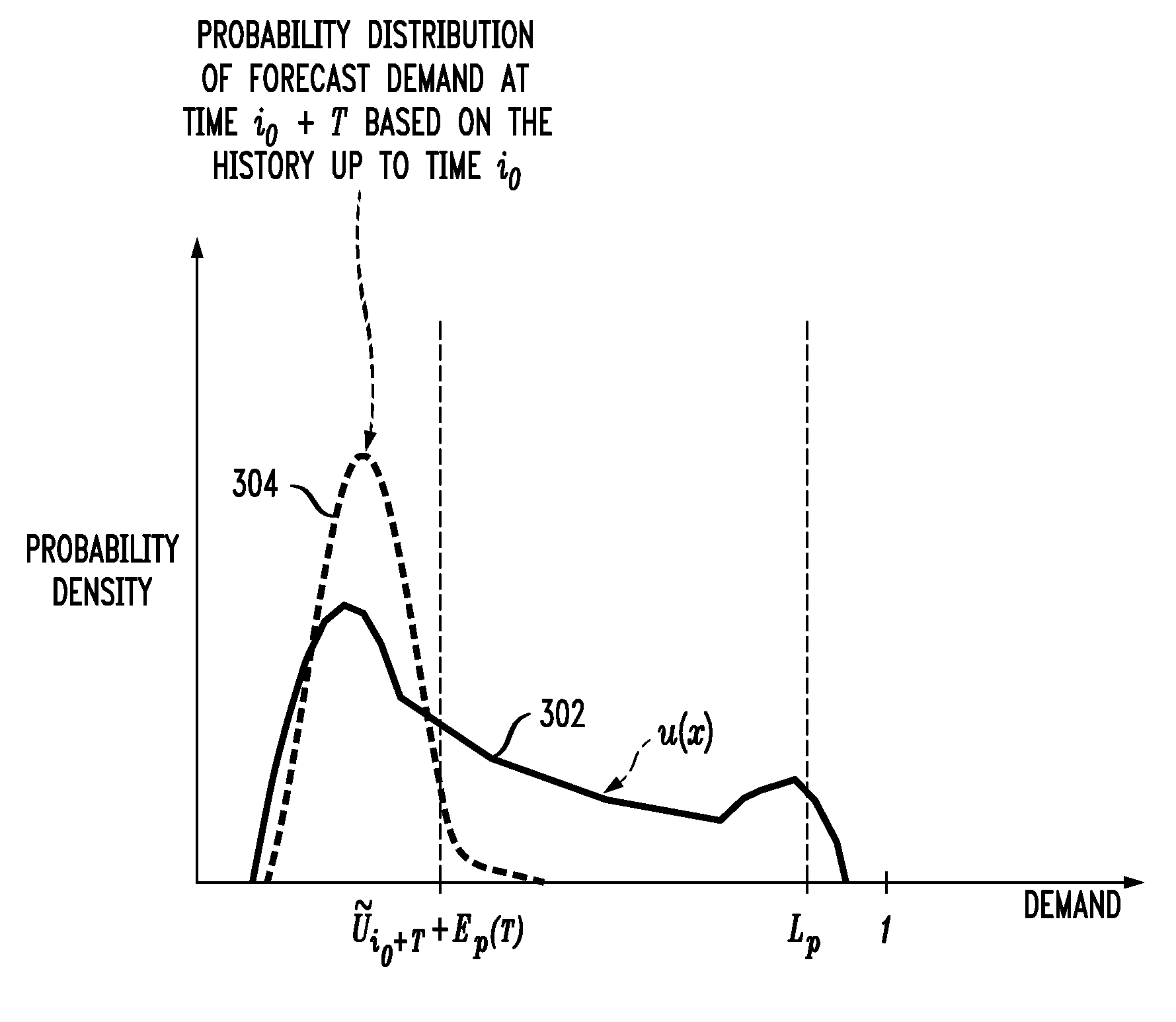
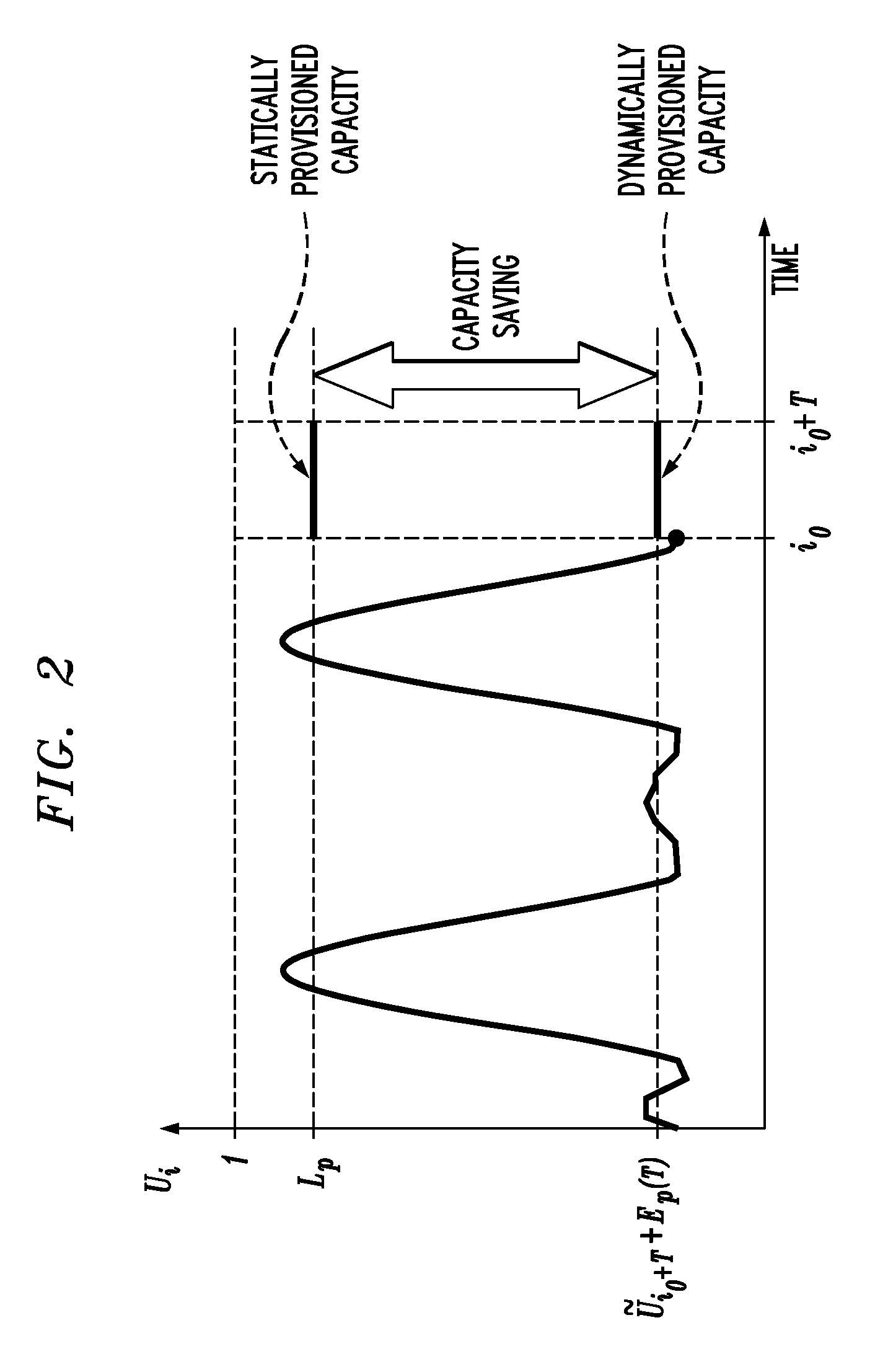
InactiveUS20080295096A1Reduce the amount requiredReducing of rate of serviceForecastingMultiprogramming arrangementsService-level agreementBusiness forecasting
Historical data is measured for a computer server system. Future demand for service in the computer server system is forecast based on the historical data, and the mapping of virtual machines to physical machines is updated based on the forecast of the future demand. Measurement, forecasting, and placement modules can be employed.
Owner:IBM CORP
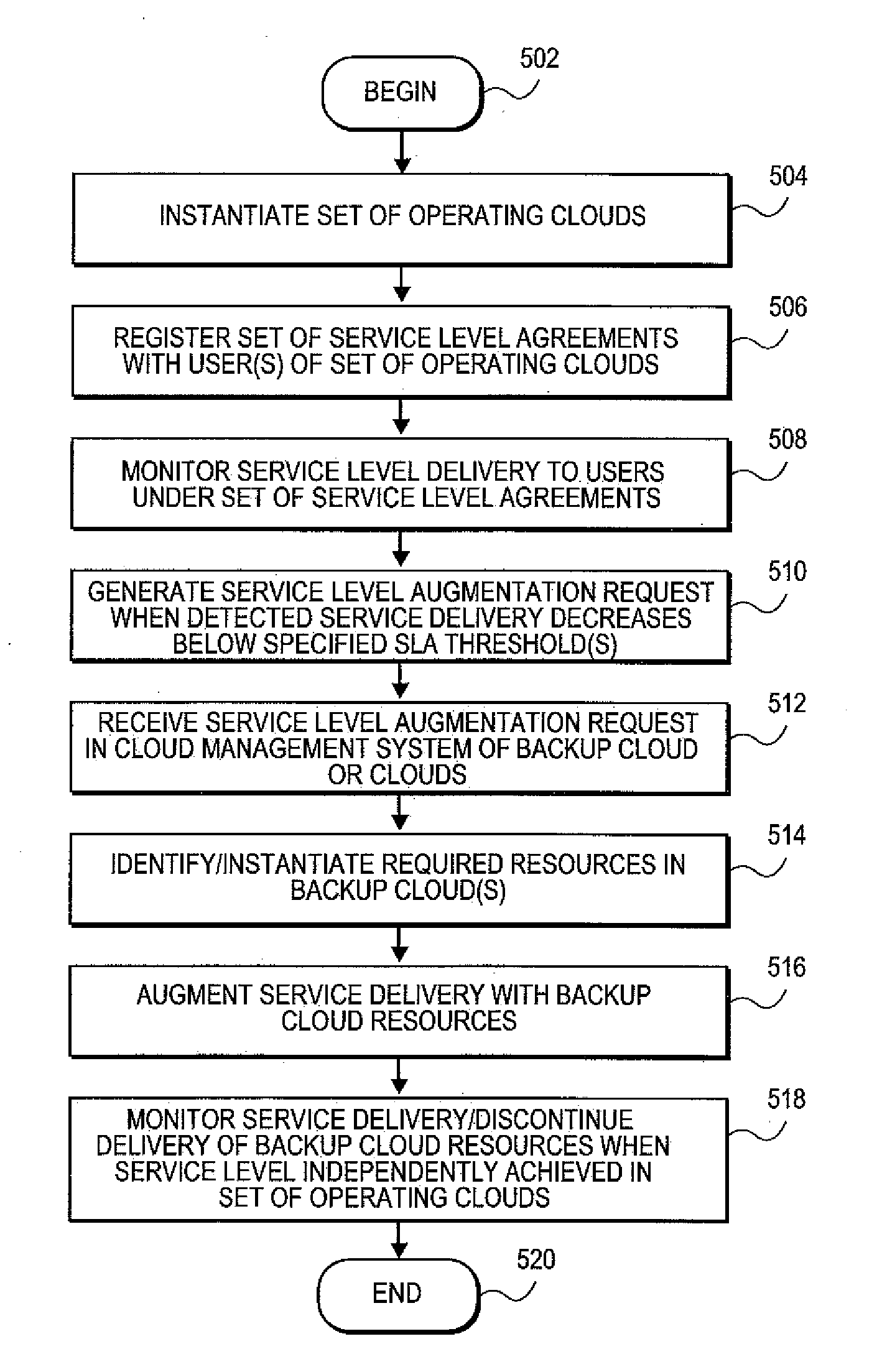
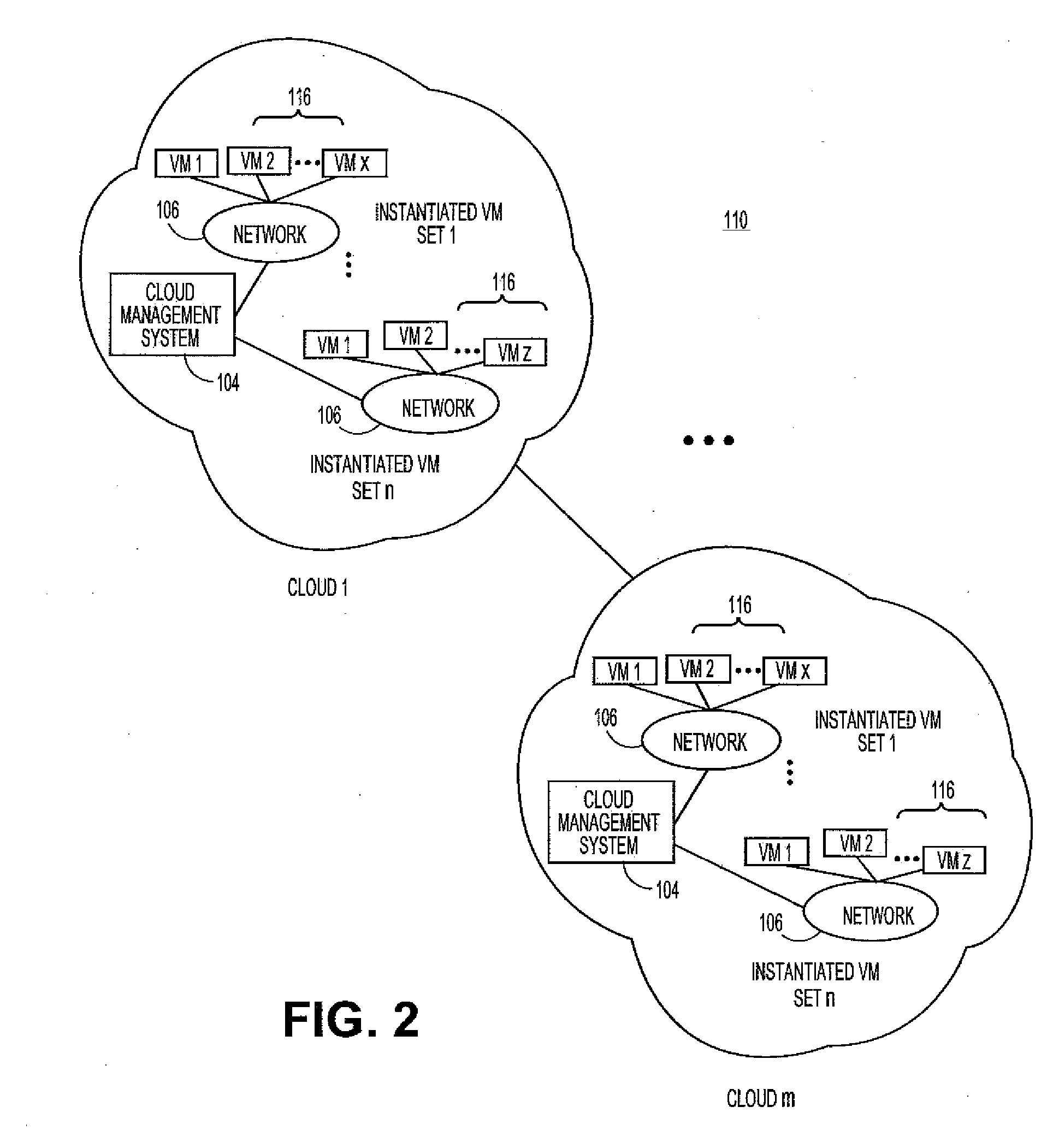
Systems and methods for service level backup using re-cloud network
Embodiments relate to systems and methods for service level backup using a re-cloud network. A set of operating clouds can support one or more users. In embodiments, the one or more users can accept service based on a service level agreement (SLA), according to which the user is assured a certain level of service or support from the cloud, such as a minimum amount of uptime, a minimum amount of processor cycles or network bandwidth, or other guaranteed parameters of the usage of their virtual machine. In embodiments, the set of operating clouds in which the user's service is supported can be configured to communicate a service level augmentation request to a backup cloud to request additional resources to maintain the delivery of one or more SLA-specified support to one or more users. In embodiments, the backup cloud network can in turn be nested with other backup clouds or resources.
Owner:RED HAT
Method and system for efficient deployment of web applications in a multi-datacenter system
ActiveUS20120136697A1Easy to deployDigital computer detailsTransmissionService-level agreementWeb application
A system for computing an optimal deployment of at least one web application in a multi-datacenter system comprising a collector for collecting performance measurements with regard to a web application executed in the multi-datacenter system and grouping the performance measurements according to locations of a plurality of clients accessing the web application; a data repository for maintaining at least a performance table including at least the performance measurements grouped according to the plurality of client locations and a service level agreement (SLA) guaranteed to clients in the plurality of client locations; and an analyzer for processing at least information stored in the performance table for generating a recommendation on an optimal deployment of the web application in at least one combination of datacenters in the multi-datacenter system by computing an expected SLA that can be guaranteed to the clients in each combination of datacenters.
Owner:RADWARE
Time-based monitoring of service level agreements
A Time-Based Service Monitoring mechanism for monitoring Service Level Agreements (SLAs) over specific time intervals is described. To provide for the time-based monitoring of service, data is received for defining one or more tests for monitoring the level of network service that is being provided to a particular customer. Based on the received data, information is created and stored that defines a specific time range for when the one or more tests are to be enforced. The one or more tests are distributed to one or more agents that are configured to communicate with devices that are associated with the network. The devices are then configured to perform the one or more tests within the specific time range. Based on the results, the customer is provided information indicating whether they are receiving the level of service that has been guaranteed by the service provider over the specific time intervals.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
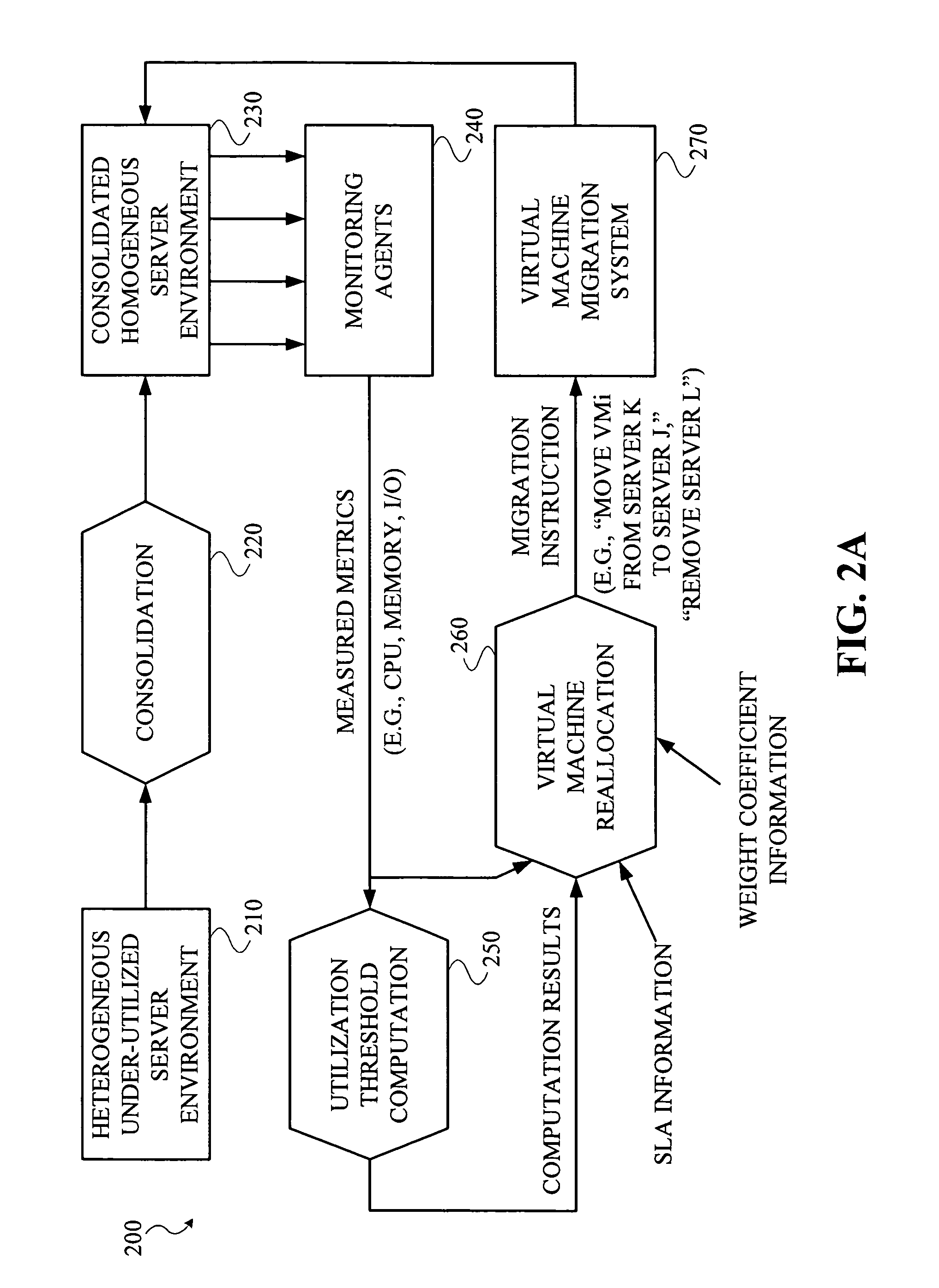
Systems and methods for dynamically managing virtual machines
InactiveUS20070204266A1Software simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsService-level agreementDynamic management
Techniques for dynamic management of virtual machine environments are disclosed. For example, a technique for automatically managing a first set of virtual machines being hosted by a second set of physical machines comprises the following steps / operations. An alert is obtained that a service level agreement (SLA) pertaining to at least one application being hosted by at least one of the virtual machines in the first set of virtual machines is being violated. Upon obtaining the SLA violation alert, the technique obtains at least one performance measurement for at least a portion of the machines in at least one of the first set of virtual machines and the second set of physical machines, and a cost of migration for at least a portion of the virtual machines in the first set of virtual machines. Based on the obtained performance measurements and the obtained migration costs, an optimal migration policy is determined for moving the virtual machine hosting the at least one application to another physical machine.
Owner:SERVICENOW INC
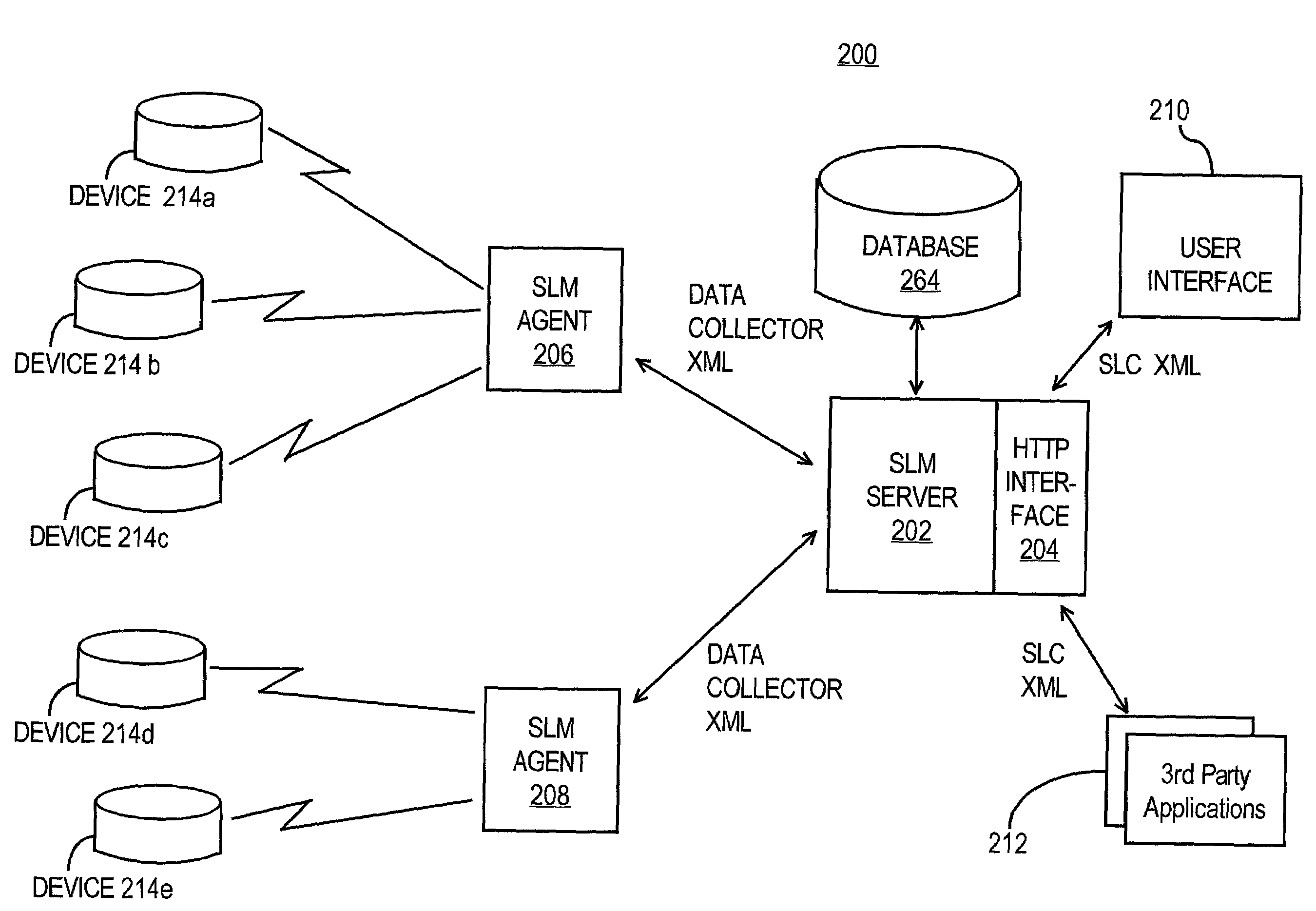
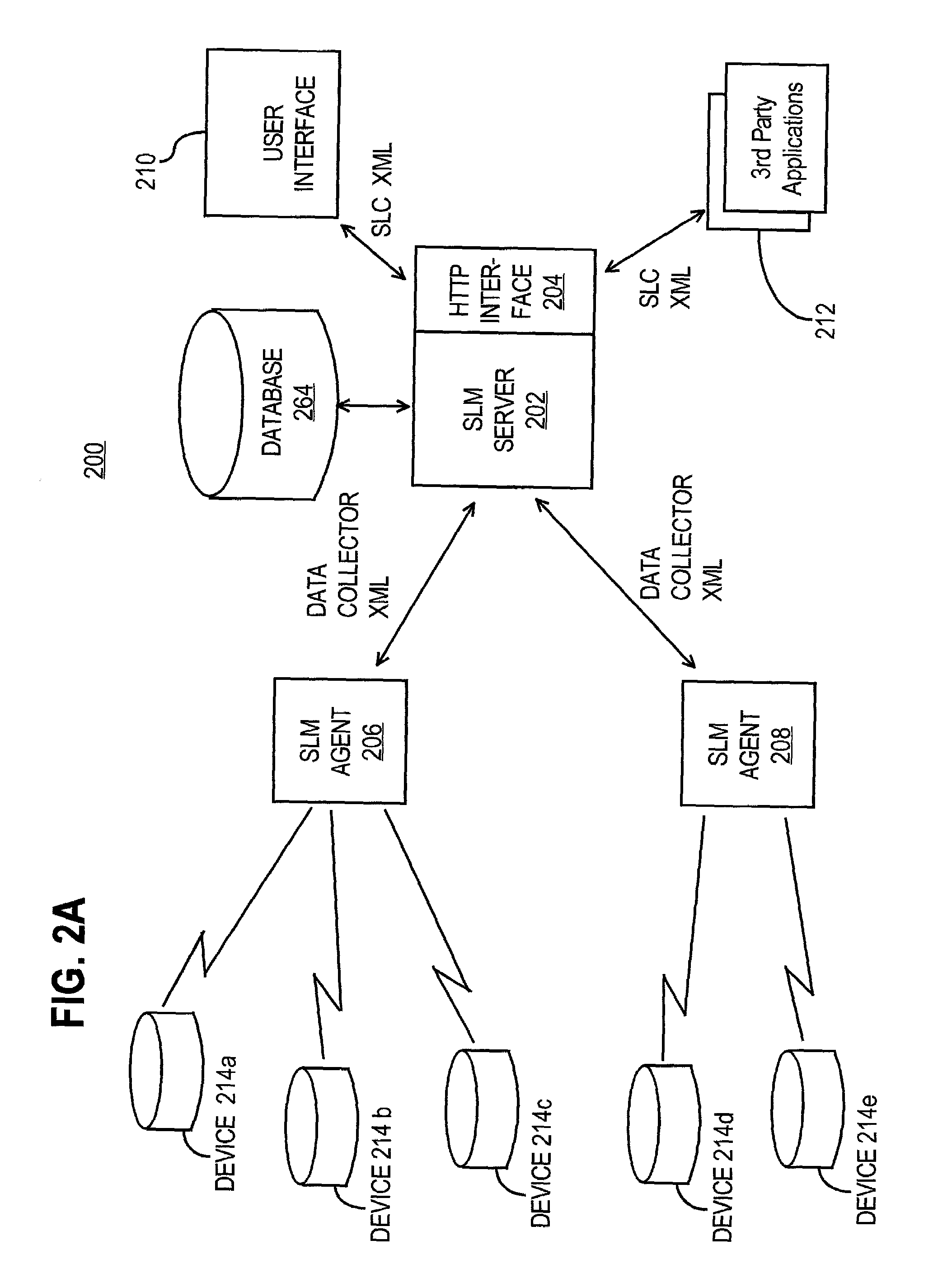
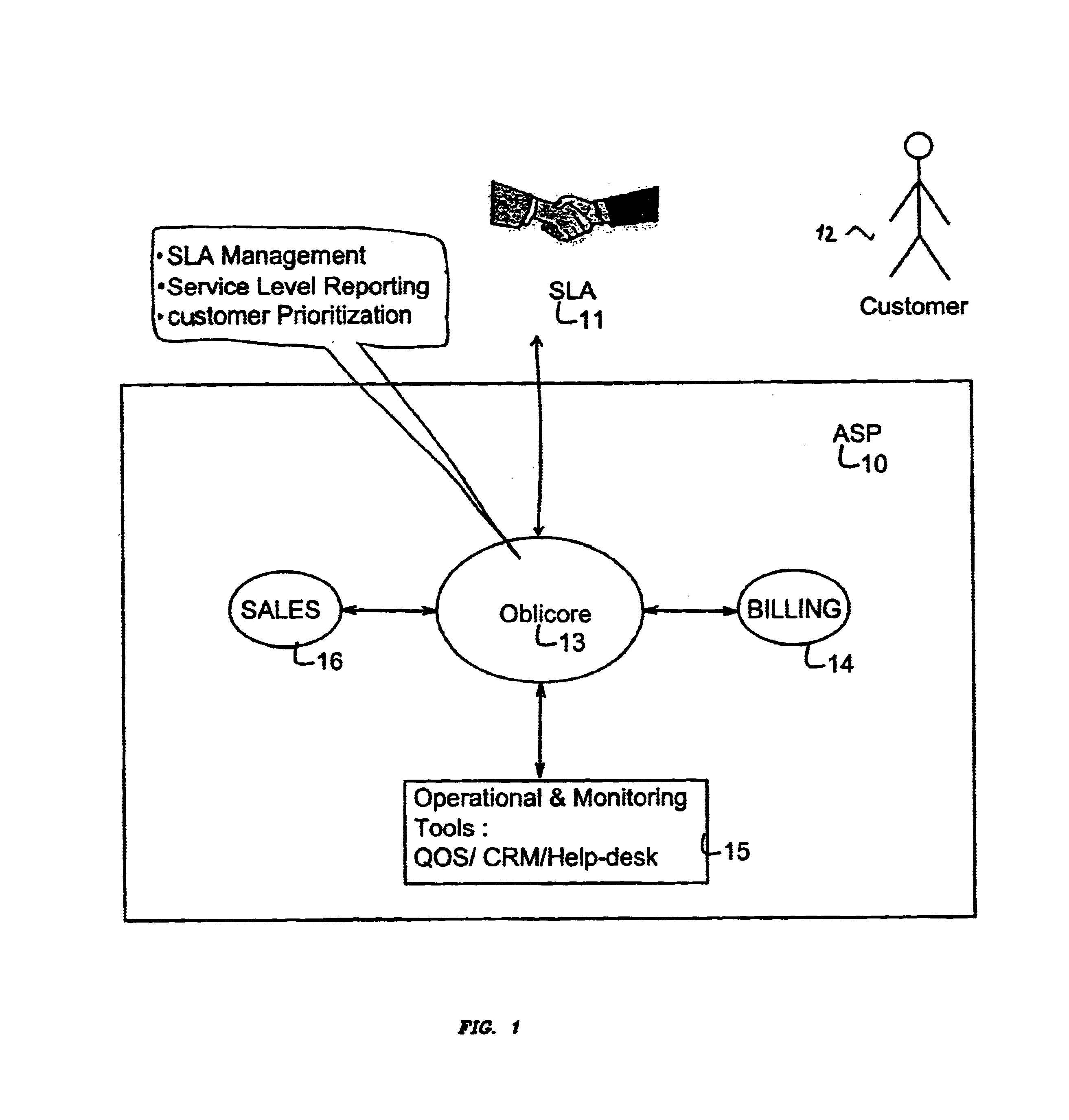
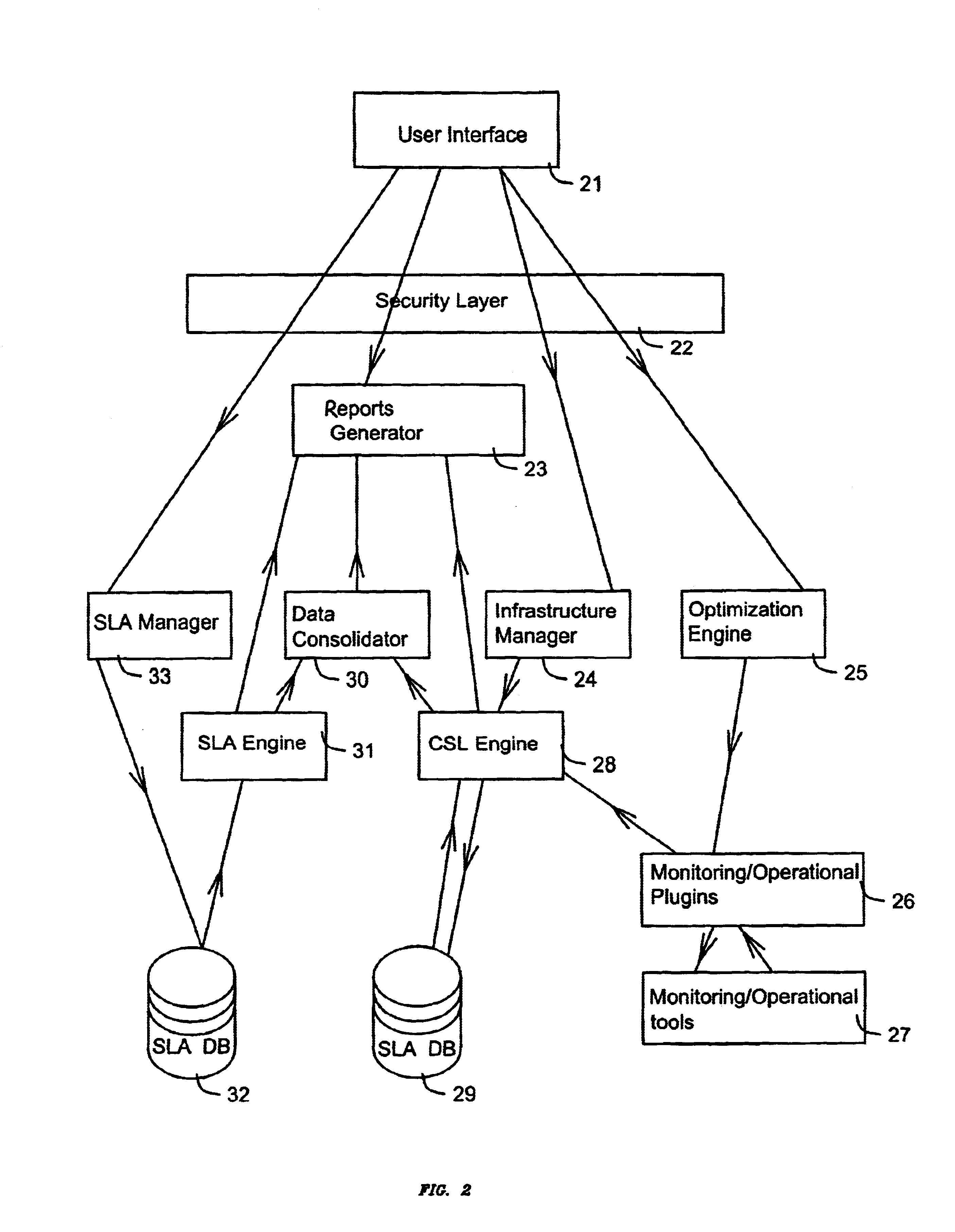
System use internal service level language including formula to compute service level value for analyzing and coordinating service level agreements for application service providers
InactiveUS6925493B1Accurately monitored and controlledMaximum flexibilityDigital computer detailsHardware monitoringService-level agreementCustomer relationship management
The present invention describes a system for automatically monitoring and managing Service Level Agreements on behalf of Service Providers (such as Application Service providers). The system is based on a specialized SLA language that can translate complex or simple Service Level Agreements into measurable and controllable criterion. The system enables Application Service providers to set up customized Service Level Agreements with customers, and monitor, modify and control all aspects of these agreements, including billing, sales, Customer Relation Management, customer support and Quality of Service. The technology on which the present invention is based is a formula driven language that translates Service Level Agreement details into commands. As such these details can be tracked and processed to produce detailed reports and summaries.
Owner:CA TECH INC
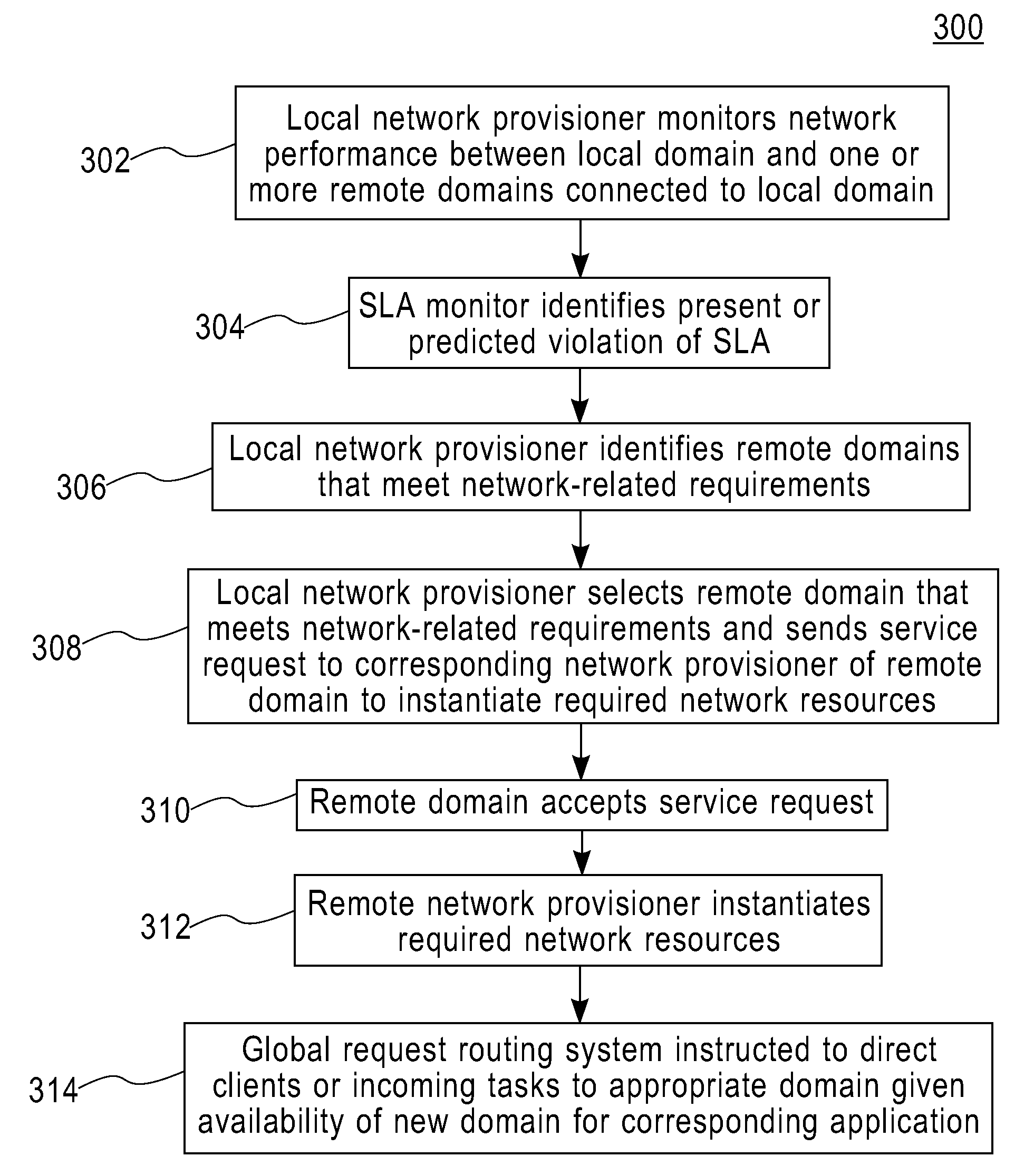
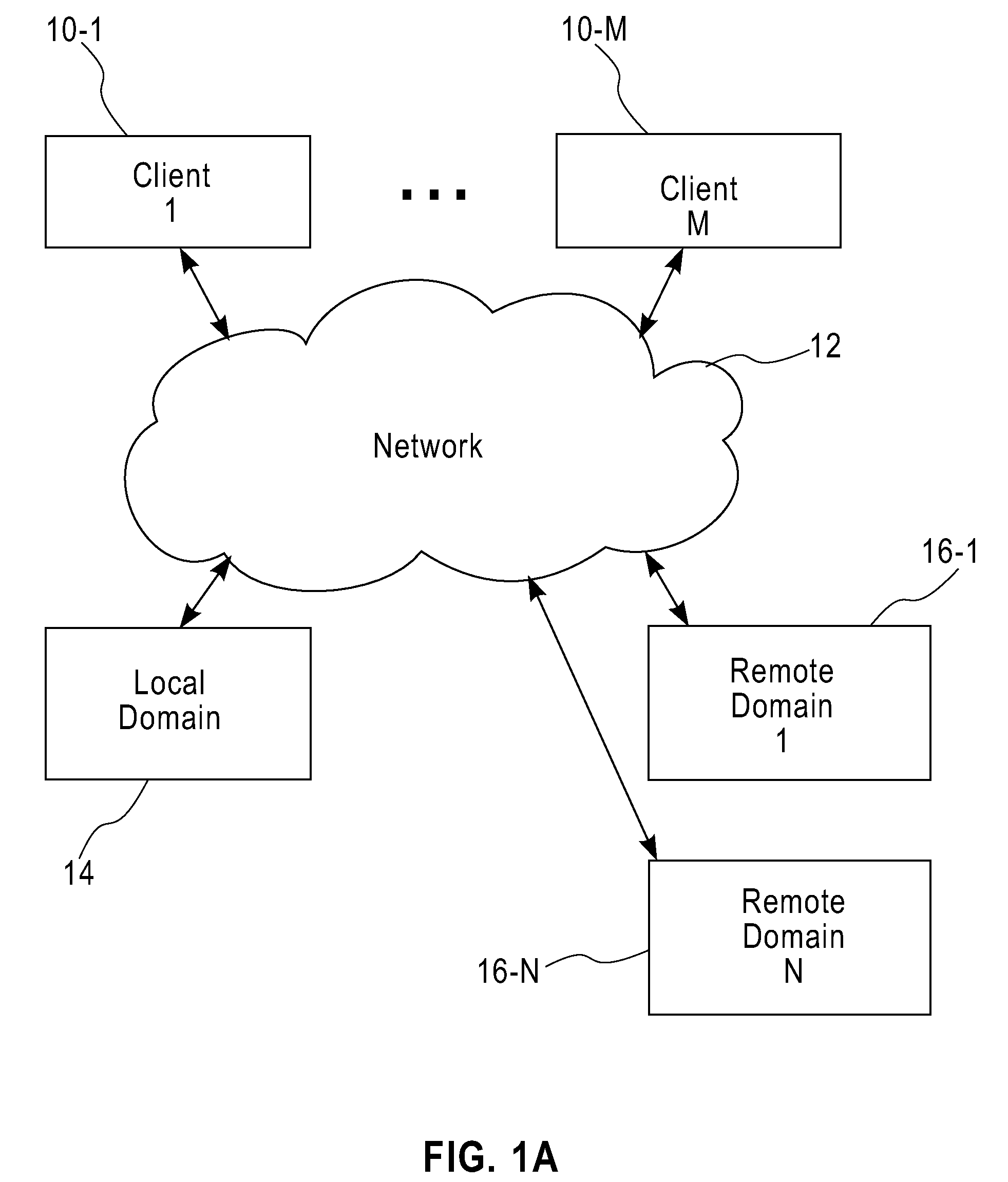
Method and apparatus for network distribution and provisioning of applications across multiple domains
ActiveUS20080240150A1Error preventionTransmission systemsService-level agreementAdministrative domain
Techniques are disclosed for network distribution and provisioning of applications, such as transactional applications and parallel applications, across multiple administrative domains that ensure compliance with service level agreements. For example, a method of provisioning one or more resources in a distributed computing network to ensure compliance with a service level agreement associated with a computer application includes the following steps. Network performance is monitored between a local domain and one or more cooperating domains connected to the local domain by network paths. A present or predicted violation of the service level agreement is identified based on at least a portion of results of the monitoring step. One or more cooperating domains are selected that can effect compliance with the service level agreement by instantiating one or more network resources within at least one of the selected cooperating domains in response to a request from the local domain. Reconfiguration of the local domain is effectuated to allow the computer application to make use of the one or more newly instantiated network resources within the selected cooperating domain.
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
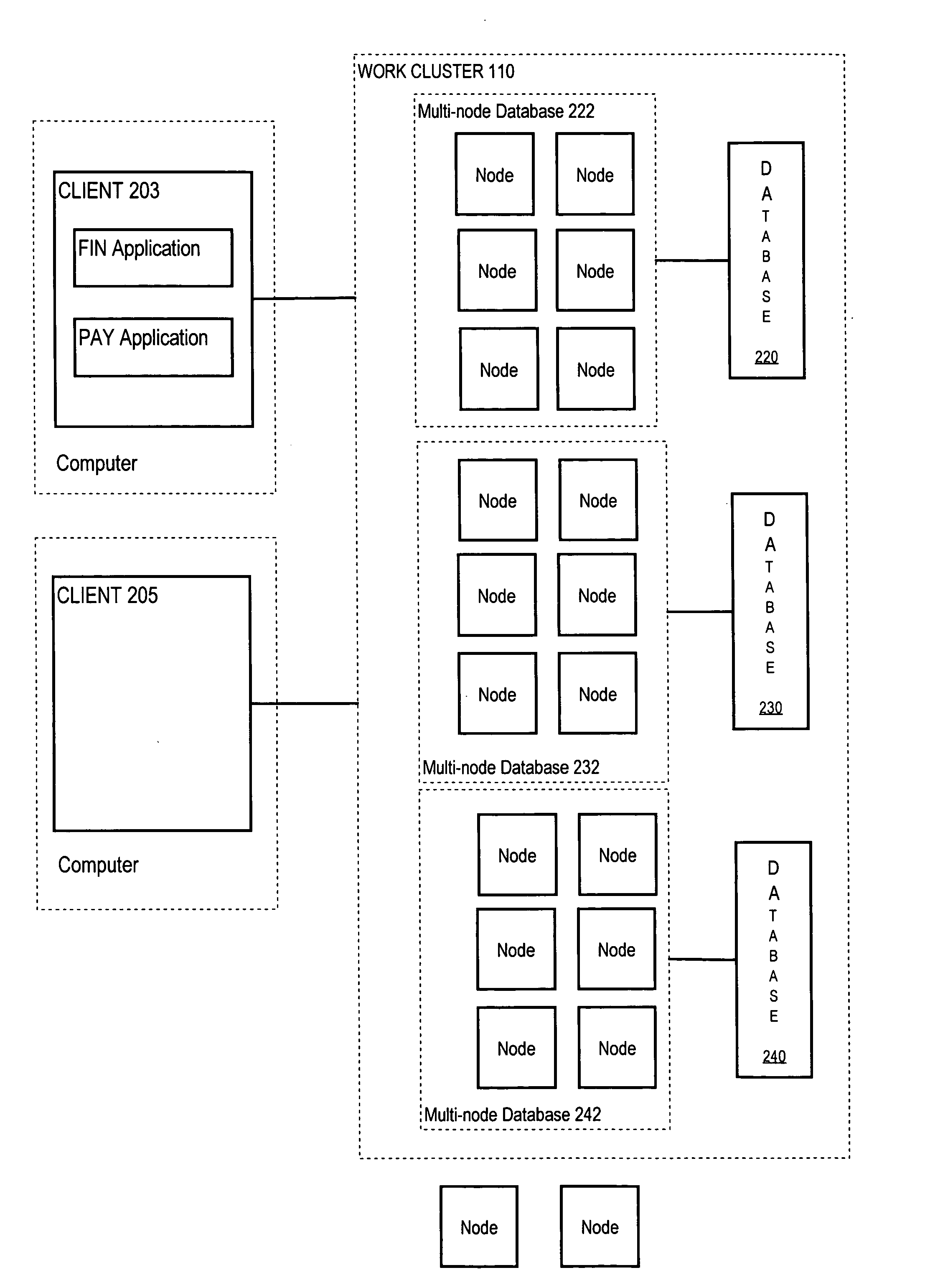
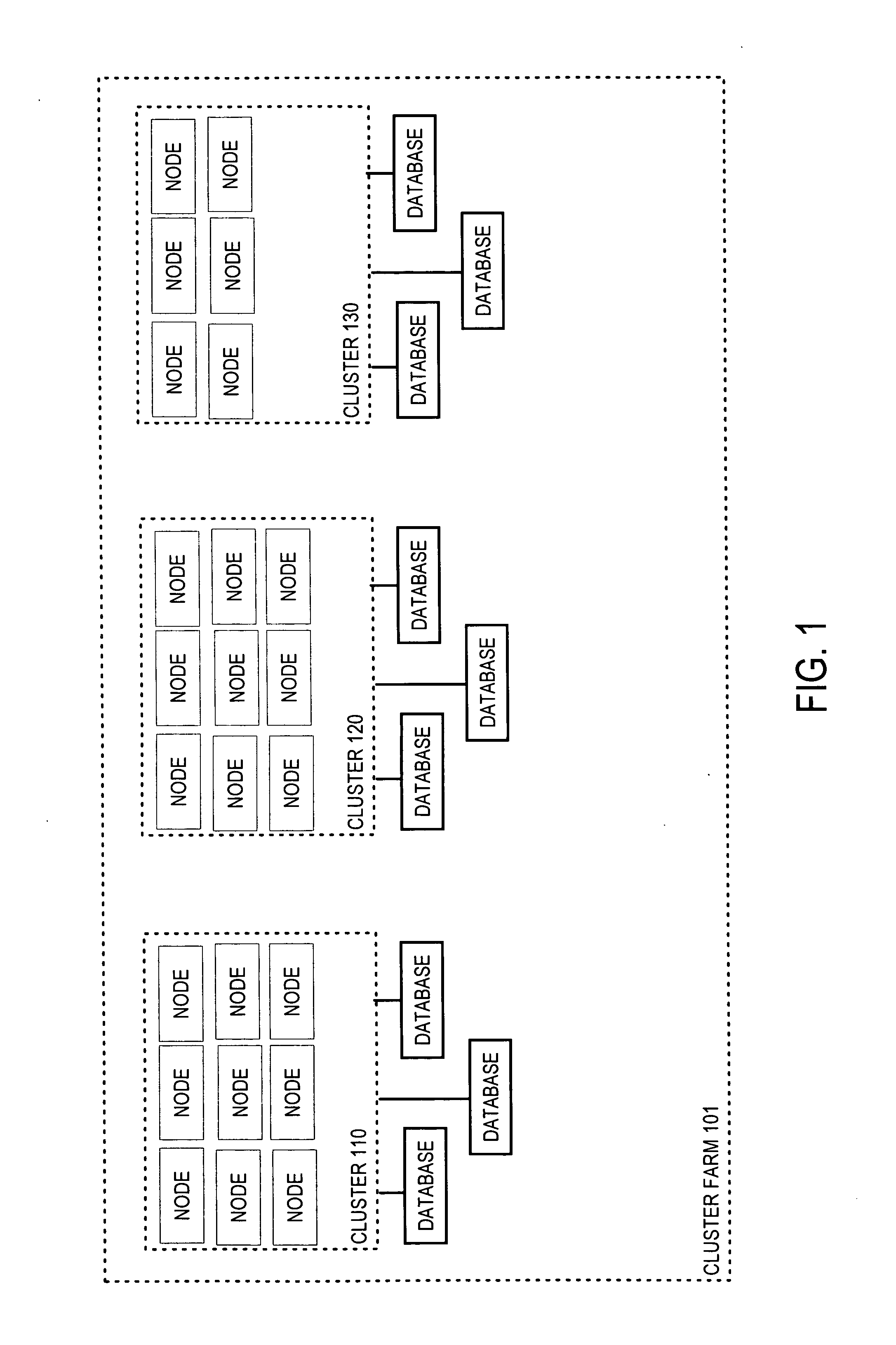
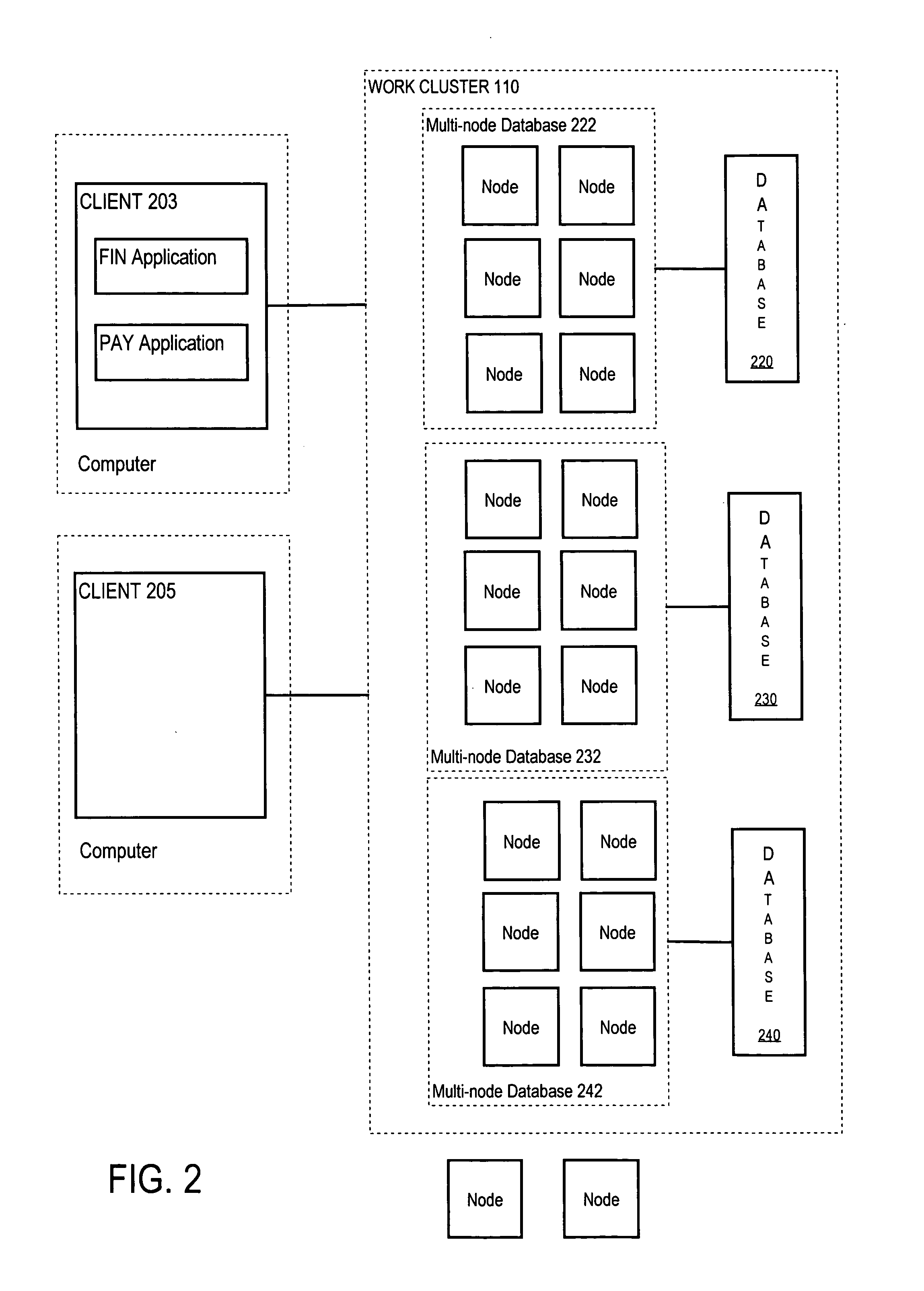
Hierarchical management of the dynamic allocation of resources in a multi-node system
ActiveUS20050038834A1Error detection/correctionMultiprogramming arrangementsService-level agreementDatabase server
Approaches are used for efficiently and effectively managing the dynamic allocation of resources of multi-node database systems between services provided by the multi-node database server. A service is a category of work that is hosted on the database server. The approaches manage allocation of resources at different levels. For services that use a particular database, the performance realized by the services is monitored. Resources assigned to the database are allocated between these services to ensure performance goals for each are met. Resources assigned to a cluster of nodes are allocated between the databases to ensure that performance goals for all the services that use the databases are met. Resources assigned to a farm of clusters are assigned amongst clusters based on service level agreements and back-end policies. The approach uses a hierarchy of directors to manage resources at the different levels.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Methods and systems for providing quality of service in packet-based core transport networks
InactiveUS7599290B2Effective carryFair sharingEnergy efficient ICTError preventionService-level agreementTraffic capacity
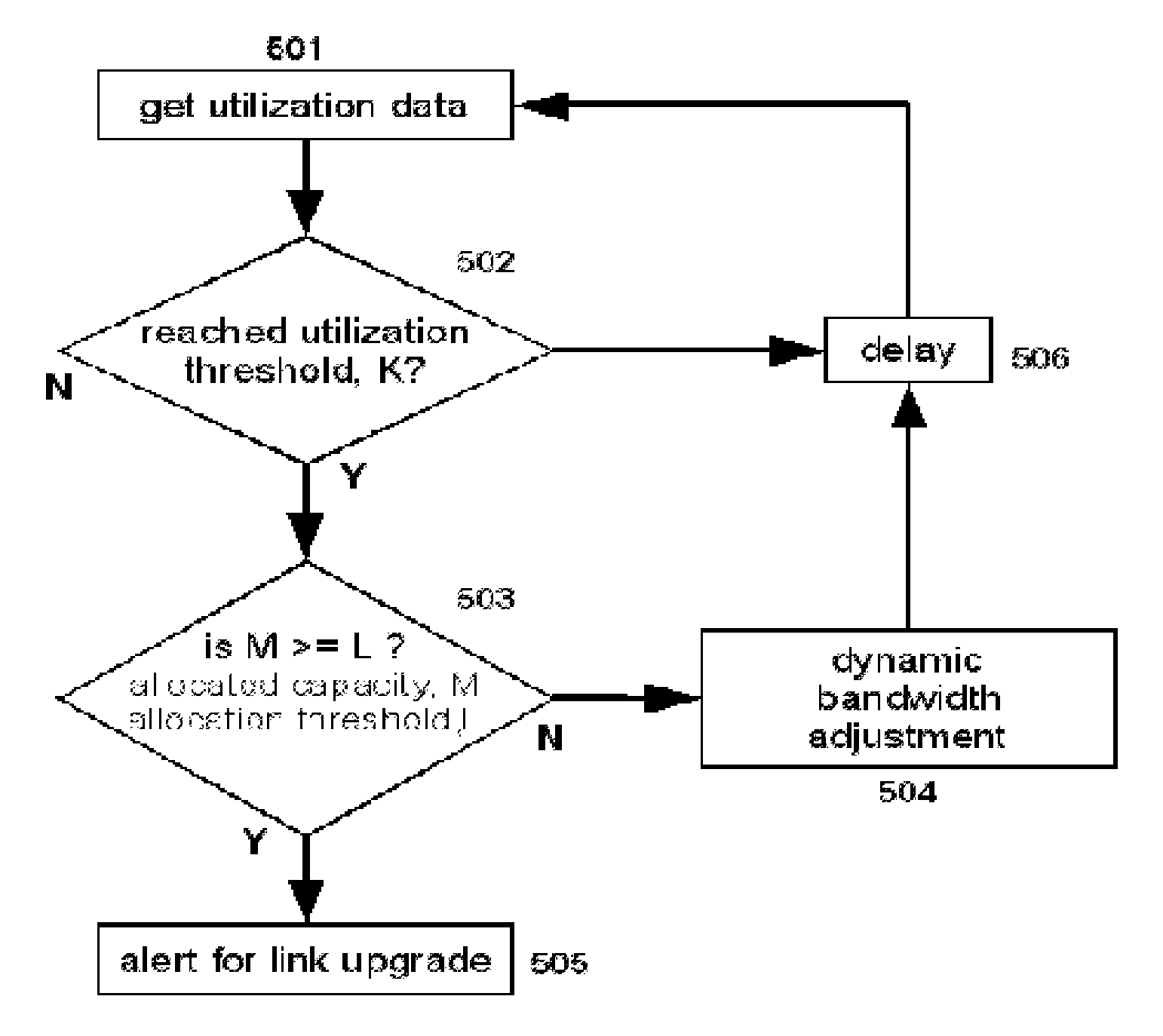
Methods and systems for providing necessary and sufficient quality-of-service (QoS), in a packet-based core transport network that utilizes dynamic setting of bandwidth management pipes or thresholds to obviate link congestion are disclosed. Congestion avoidance is a necessary and sufficient requirement in order to guarantee Quality of Service (QoS) in packet-based core networks.A typical network is composed of a plurality of backbone links connecting edge nodes where backhaul links are aggregated. The backhaul links connect the backbone links to the remote sites serving the subscribers. In order to enforce bandwidth management policies, Access Controllers, which perform traffic shaping, are situated on each remote site.In the event of a violation of certain link threshold settings, dynamic adjustment of the bandwidth management policies on affected Access Controllers is enforced. Various algorithms in determining the correlation between the link nearing congestion and the source or destination of traffic streams are also discussed. This invention implements a feedback control loop wherein probes at various points in the network checks for congestion states to guide bandwidth management threshold decisions in order to maintain the condition of non-congestion throughout the network. Capacity planning and congestion avoidance mechanisms work hand-in-hand to fulfill Service Level Agreements (SLA).
Owner:LATITUDE BROADBAND
Method and apparatus for maintaining a workload service level on a converged platform
ActiveUS20130311989A1Fault responseSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationService-level agreementComputerized system
A management server is provided in a computer system having one or more hosts, one or more storage systems and one or more switches, the hosts having a plurality of virtual machines, each virtual machine being defined according to a service level agreement. The management server is operable to manage the virtual machines and resources associated with the virtual machines; receive a notification of an event from a node in the computer system; determine if the event affects a service level agreement for any of the virtual machines defined in the computer system, the service level agreements listing required attributes for the corresponding virtual machines; allocate a new resource for a virtual machine whose service level agreement is affected by the event; and move the virtual machine whose service level agreement is affected by the event to the newly allocated resource.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
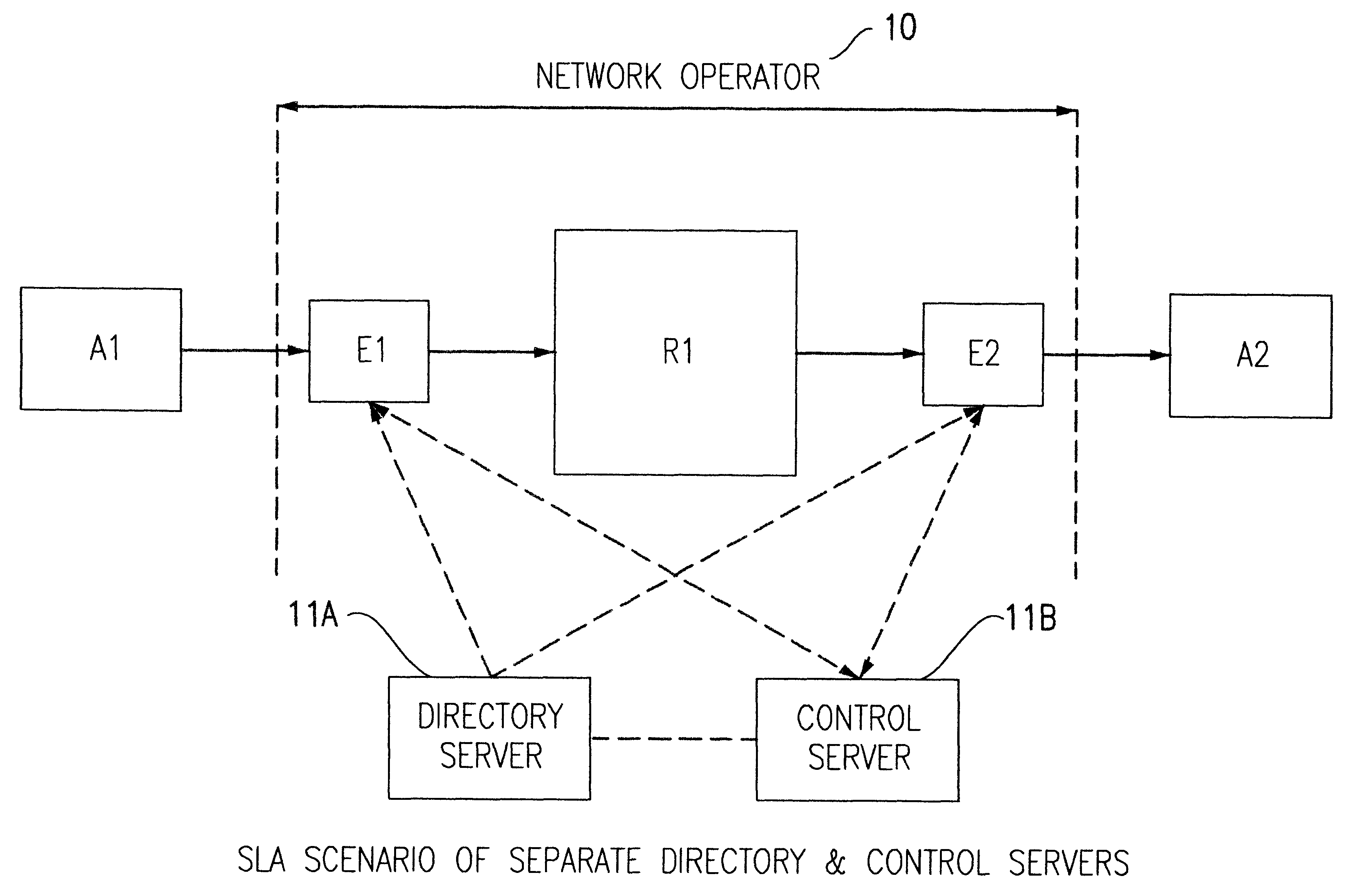
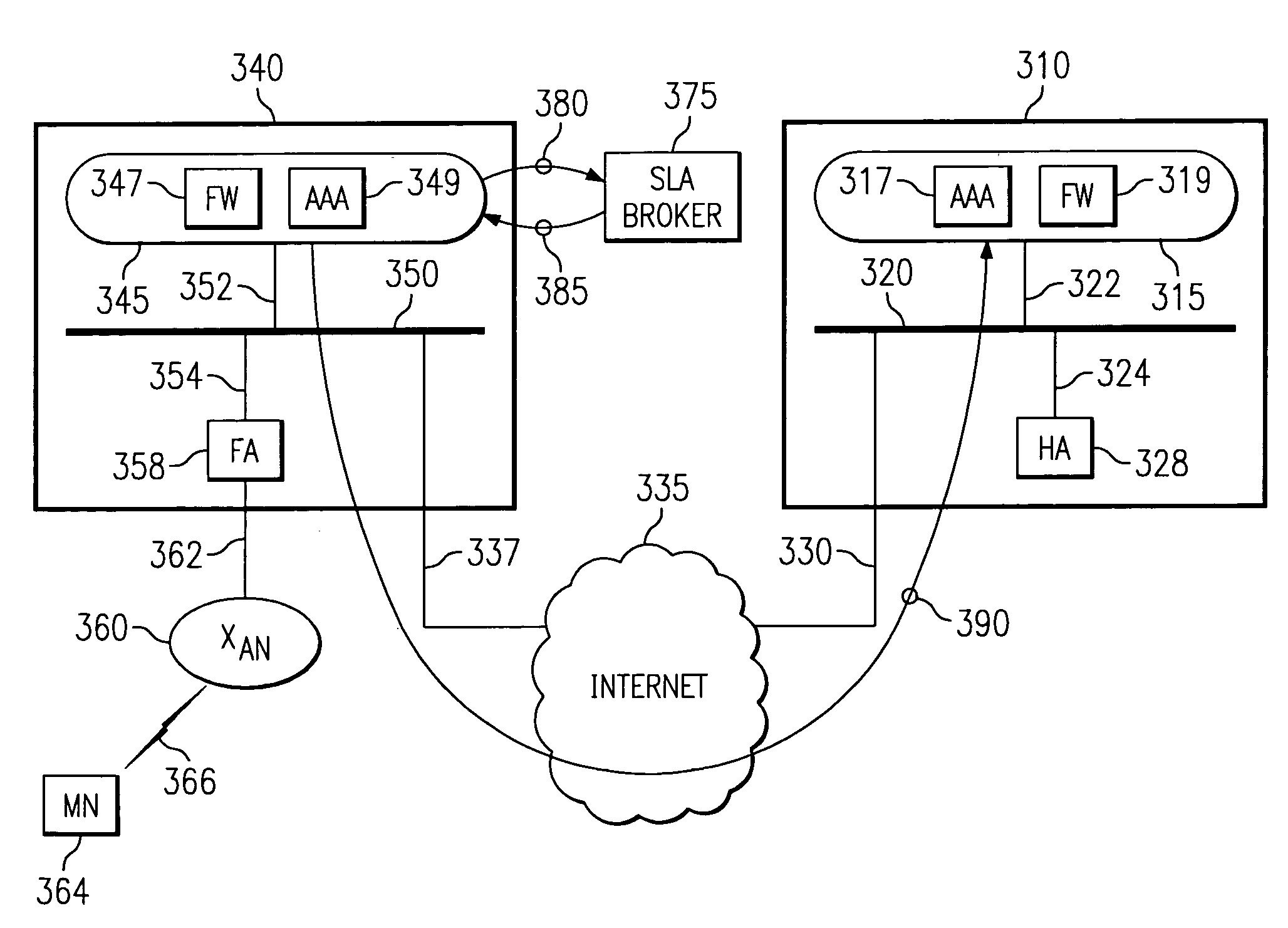
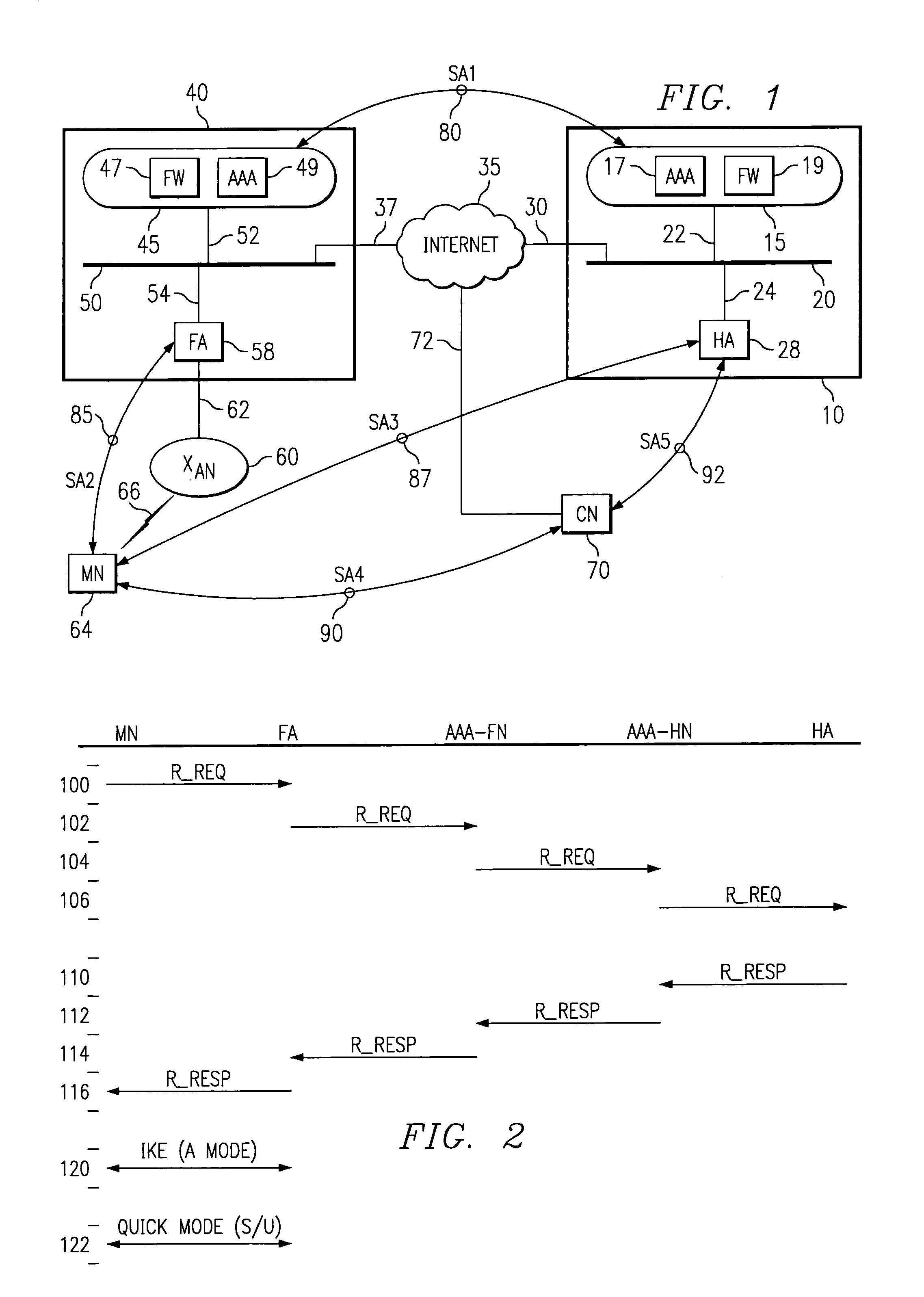
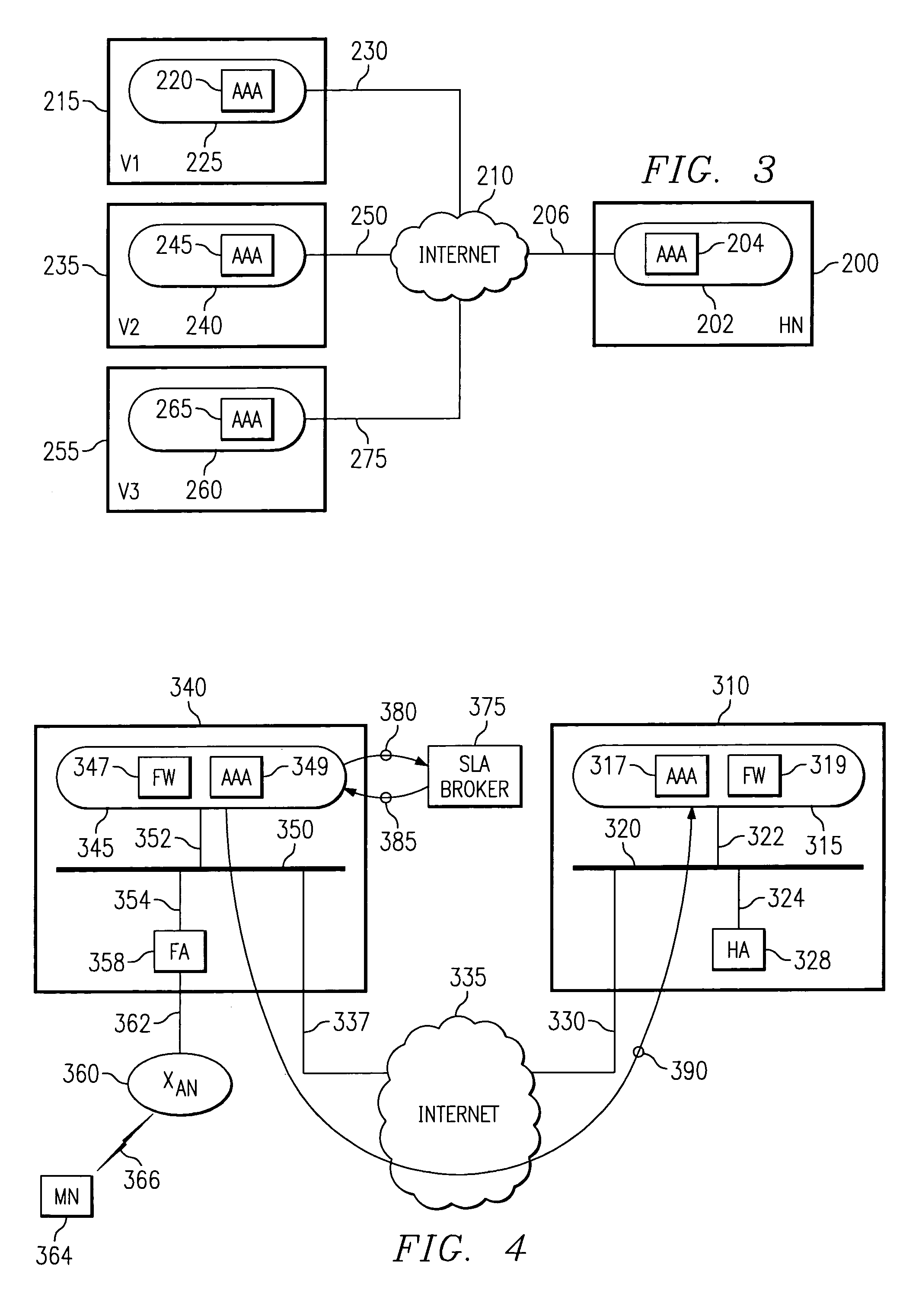
Security framework for an IP mobility system using variable-based security associations and broker redirection
InactiveUS7174018B1Improve securityPromote large-scale roamingWireless network protocolsSecret communicationService-level agreementSecurity association
In an IP-based mobile communications system, the Mobile Node changes its point of attachment to the network while maintaining network connectivity. Security concerns arise in the mobile system because authorized users are subject to the following forms of attack: (1) session stealing where a hostile node hijacks session from mobile node by redirecting packets, (2) spoofing where the identity of an authorized user is utilized in an unauthorized manner to obtain access to the network, and (3) eavesdropping and stealing of data during session with authorized user. No separate secure network exists in the IP-based mobility communications system, and therefore, it is necessary to protect information transmitted in the mobile system from the above-identified security attacks.The present invention improves the security of communications in a IP mobile communications system by creating variable-based Security Associations between various nodes on the system, a Virtual Private Network supported by an Service Level Agreement between various foreign networks and a home network, and an SLA Broker to promote large-scale roaming among different SLAs supported by the SLA Broker or agreements with other SLA Brokers.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
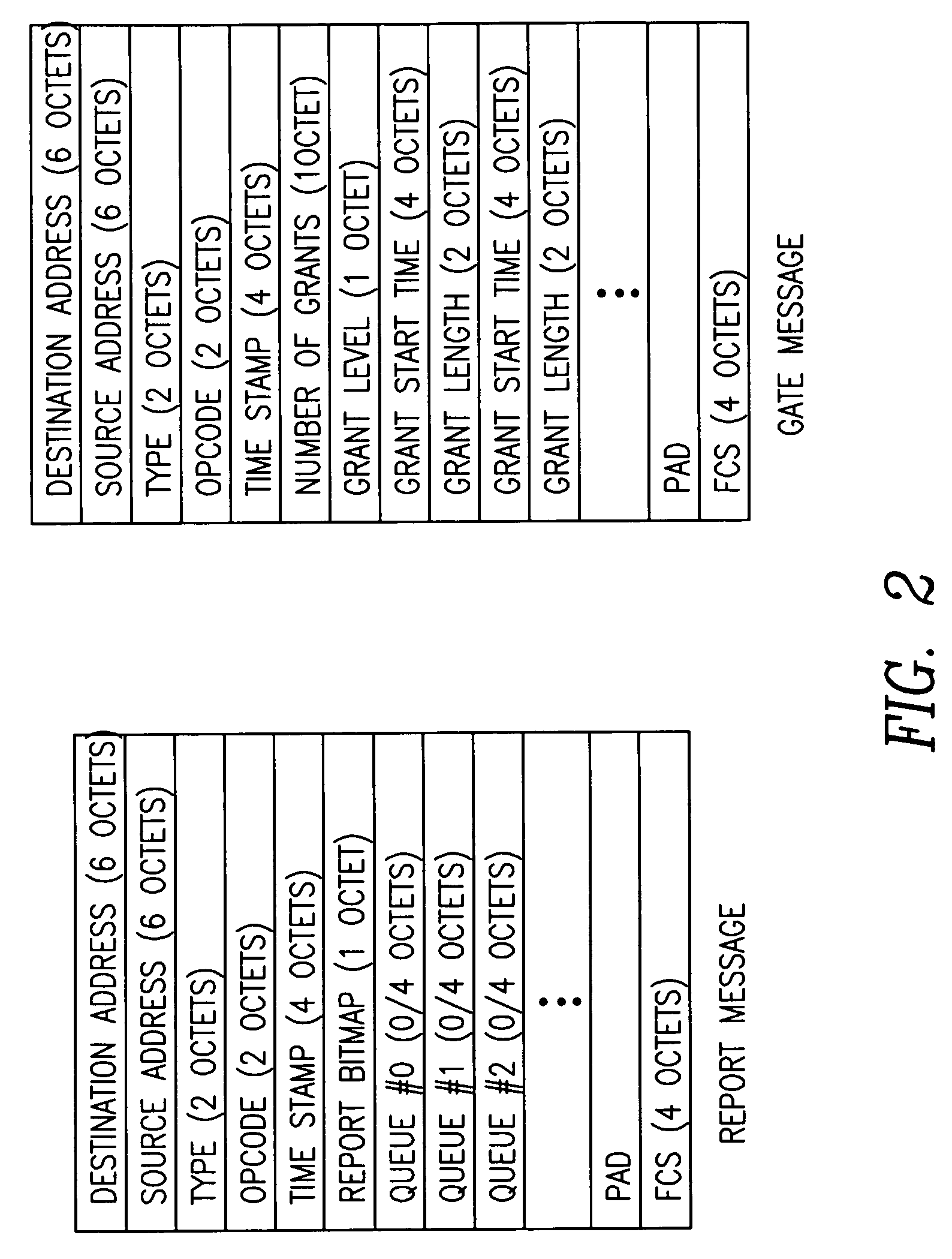
Dynamic bandwidth allocation and service differentiation for broadband passive optical networks
InactiveUS20060268704A1Effective bandwidthSpace complexityMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionService-level agreementTraffic prediction
A dynamic upstream bandwidth allocation scheme is disclosed, i.e., limited sharing with traffic prediction (LSTP), to improve the bandwidth efficiency of upstream transmission over PONs. LSTP adopts the PON MAC control messages, and dynamically allocates bandwidth according to the on-line traffic load. The ONU bandwidth requirement includes the already buffered data and a prediction of the incoming data, thus reducing the frame delay and alleviating the data loss. ONUs are served by the OLT in a fixed order in LSTP to facilitate the traffic prediction. Each optical network unit (ONU) classifies its local traffic into three classes with descending priorities: expedited forwarding (EF), assured forwarding (AF), and best effort (BE). Data with higher priority replace data with lower priority when the buffer is full. In order to alleviate uncontrolled delay and unfair drop of the lower priority data, the priority-based scheduling is employed to deliver the buffered data in a particular transmission timeslot. The bandwidth allocation incorporates the service level agreements (SLAs) and the on-line traffic dynamics. The basic limited sharing with traffic prediction (LSTP) scheme is extended to serve the classified network traffic.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
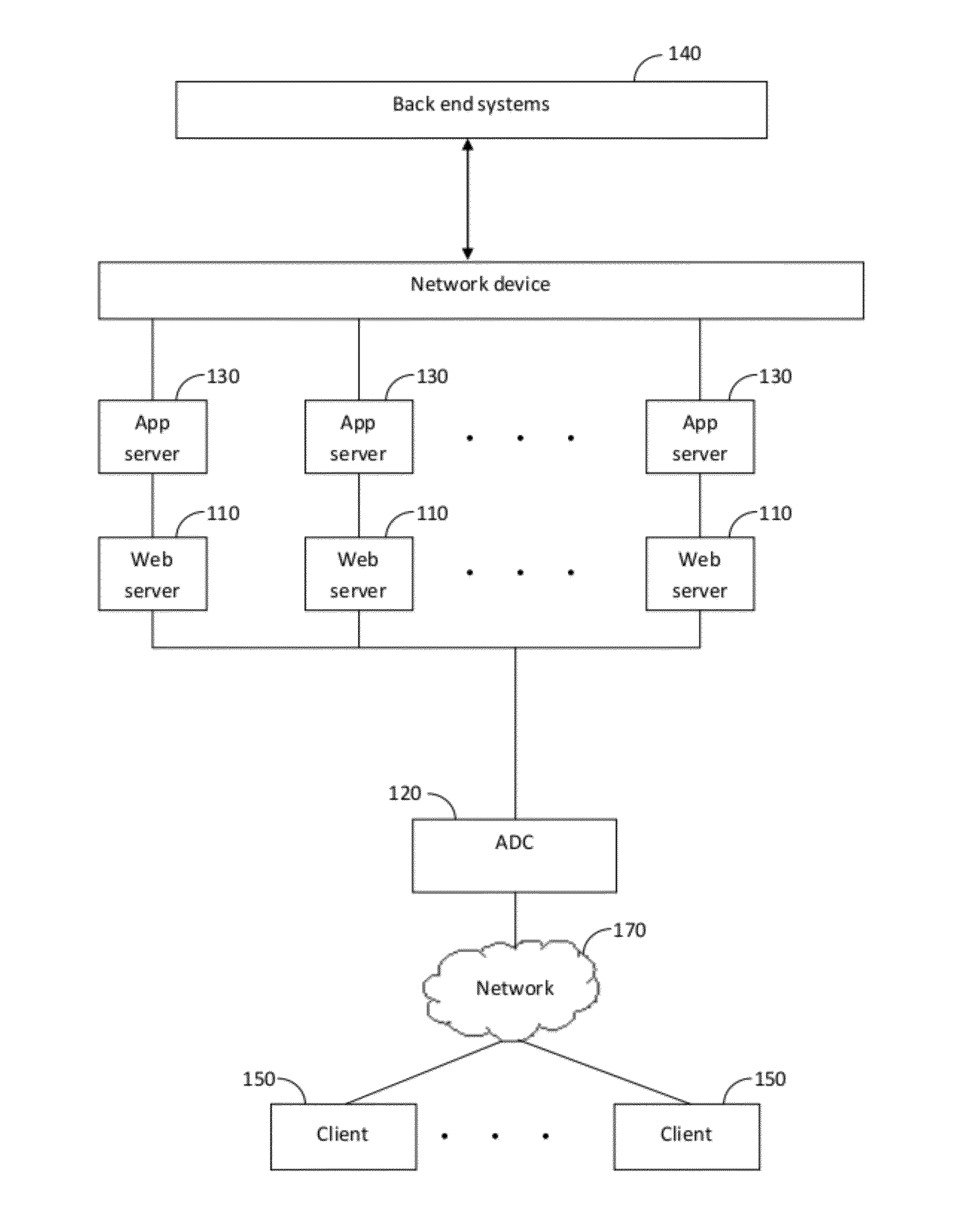
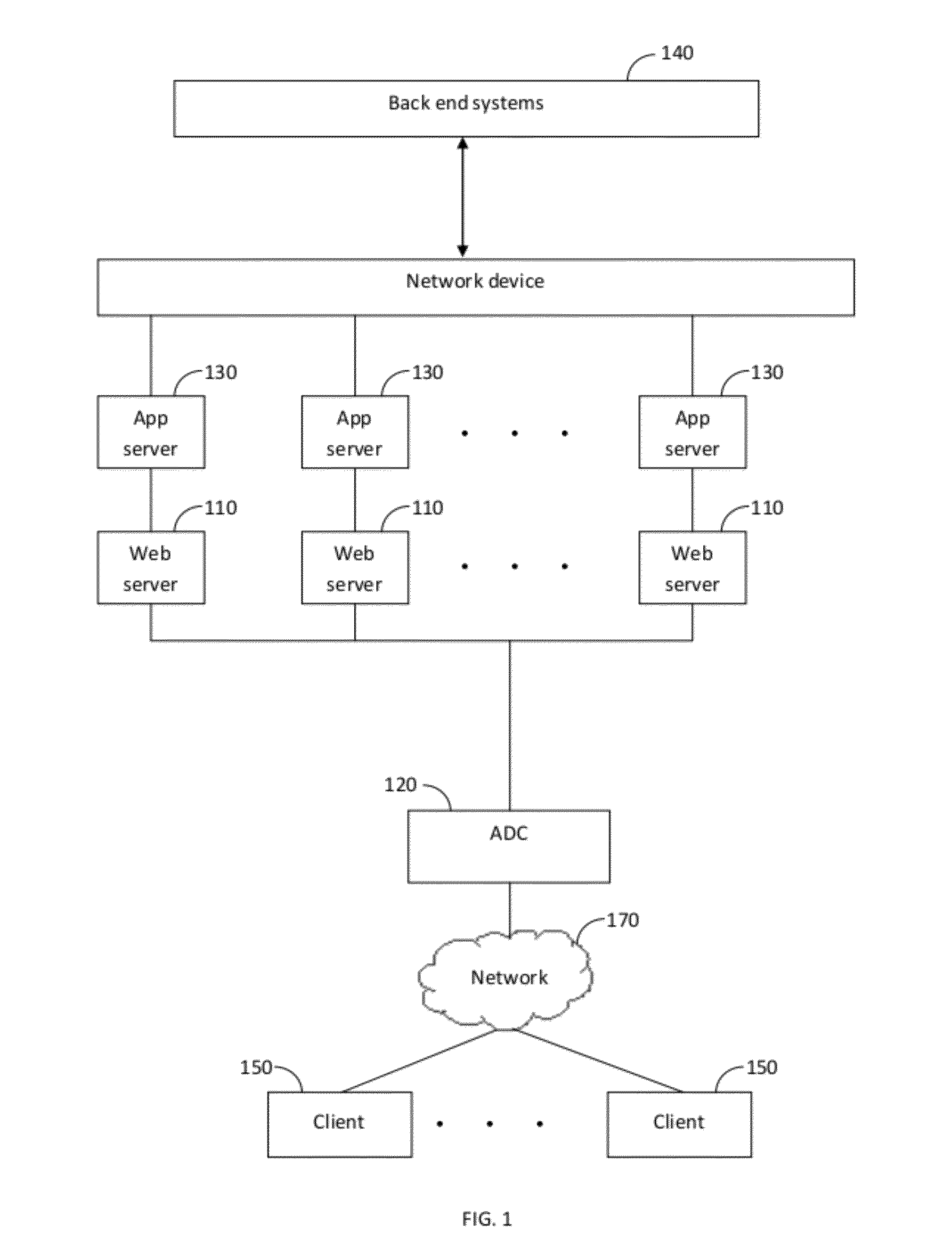
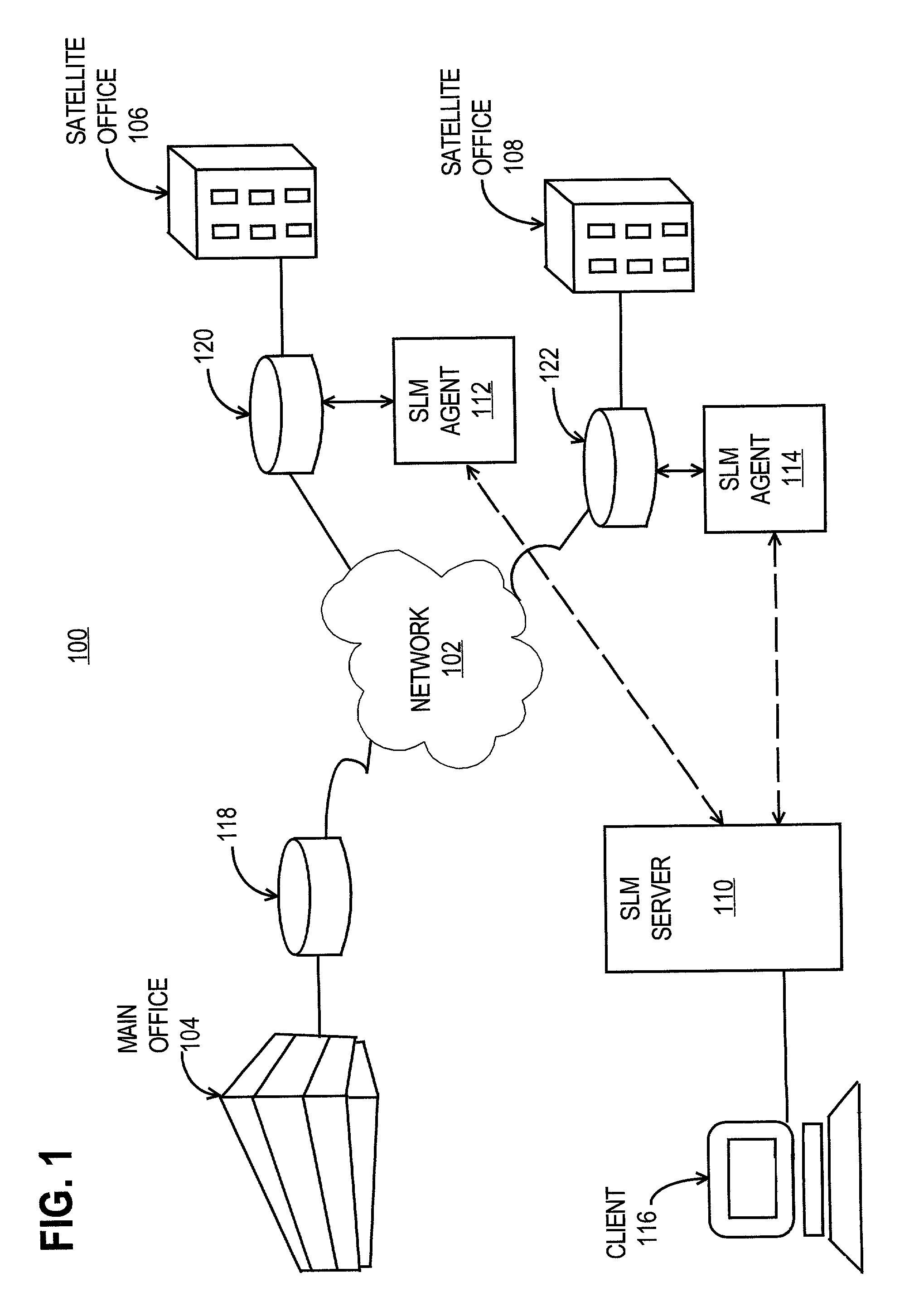
Method and apparatus for implementing a service-level agreement
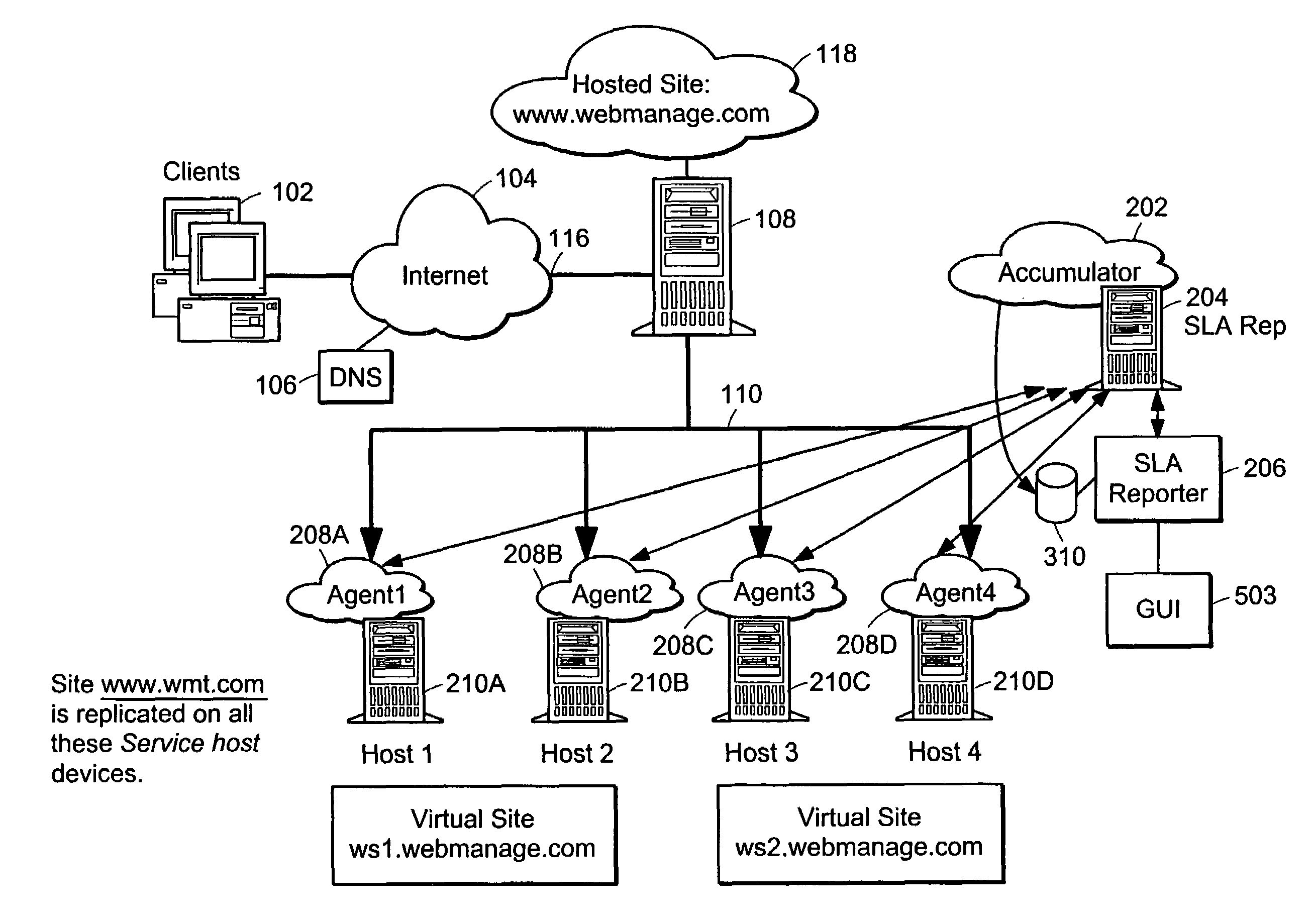
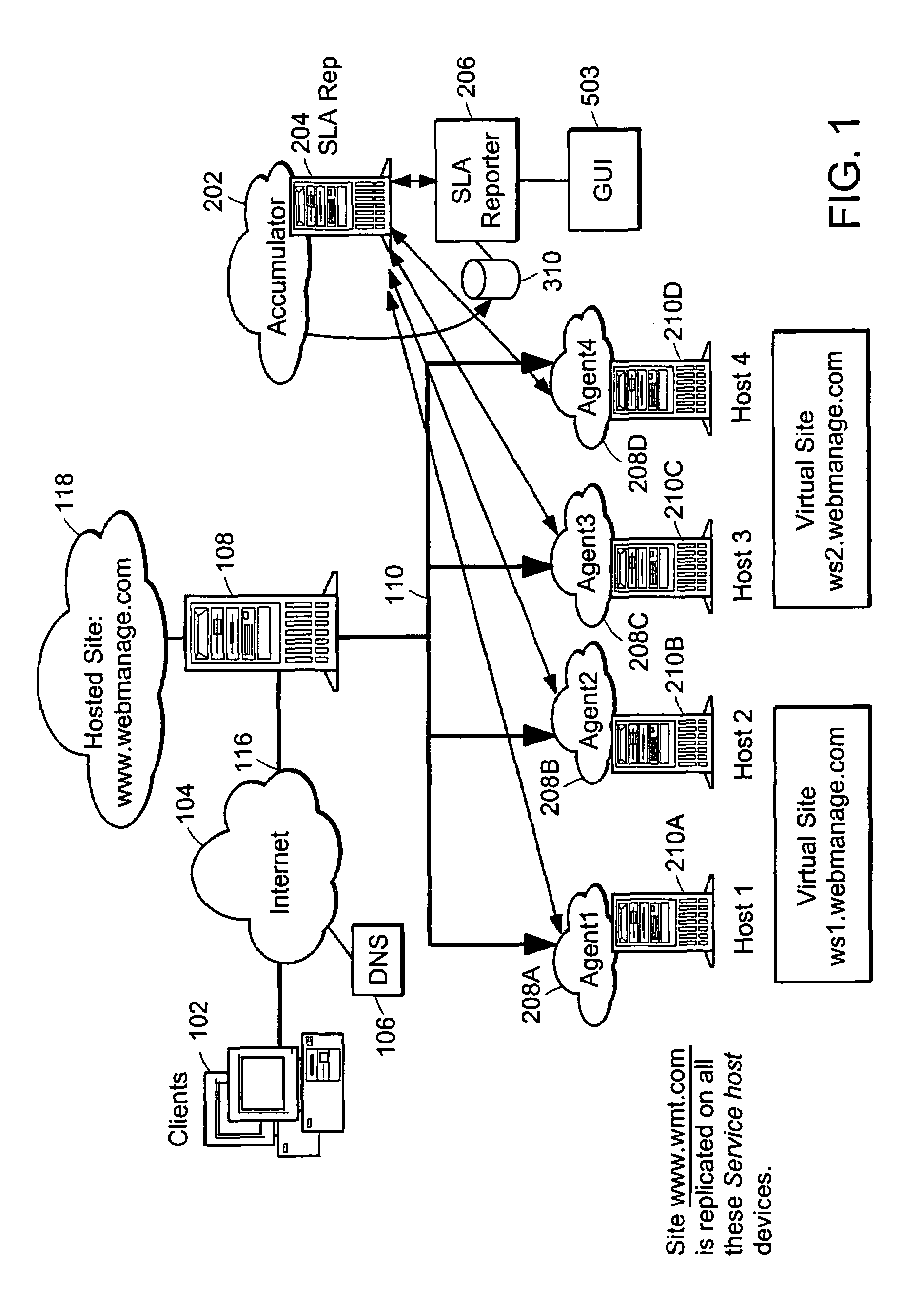
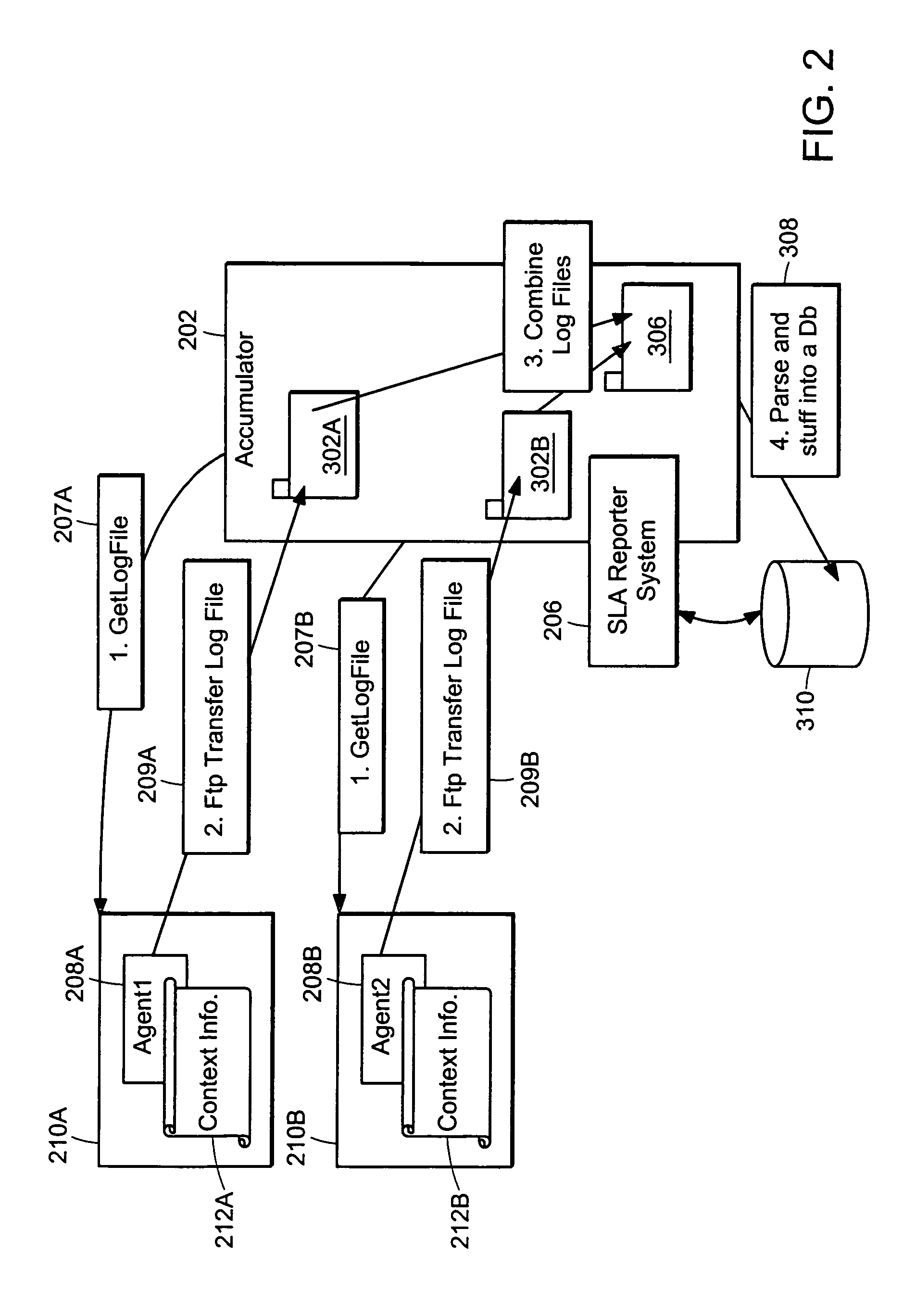
InactiveUS7058704B1Precise processingMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationWeb siteService-level agreement
A method and apparatus is provided for generating, collecting, and manipulating useful information for validating or defining SLAs of web servers on a network. Web servers comprising a web farm on the network are adapted for logging detailed runtime information regarding user transactions and performance parameters. An Accumulator device interacts with intelligent agents to collect and combine their log files, process the combined file and post information into a database. An operator enters committed performance parameters into an SLA Reporter system according to classes of users, classes of web sites being hosted on the web servers, classes of URLs, transaction, content and file type. When compared with the database, processing of SLA reports indicate how well the parameters of the SLAs are being met for users, web sites, classes, URL's and transactions, or other measurable elements. By generating, collecting, combining and processing in this manner, application-specific performance can be quickly and automatically evaluated with respect to parameters related to user satisfaction and detailed signals can be issued for cases in which remedial steps should be undertaken.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
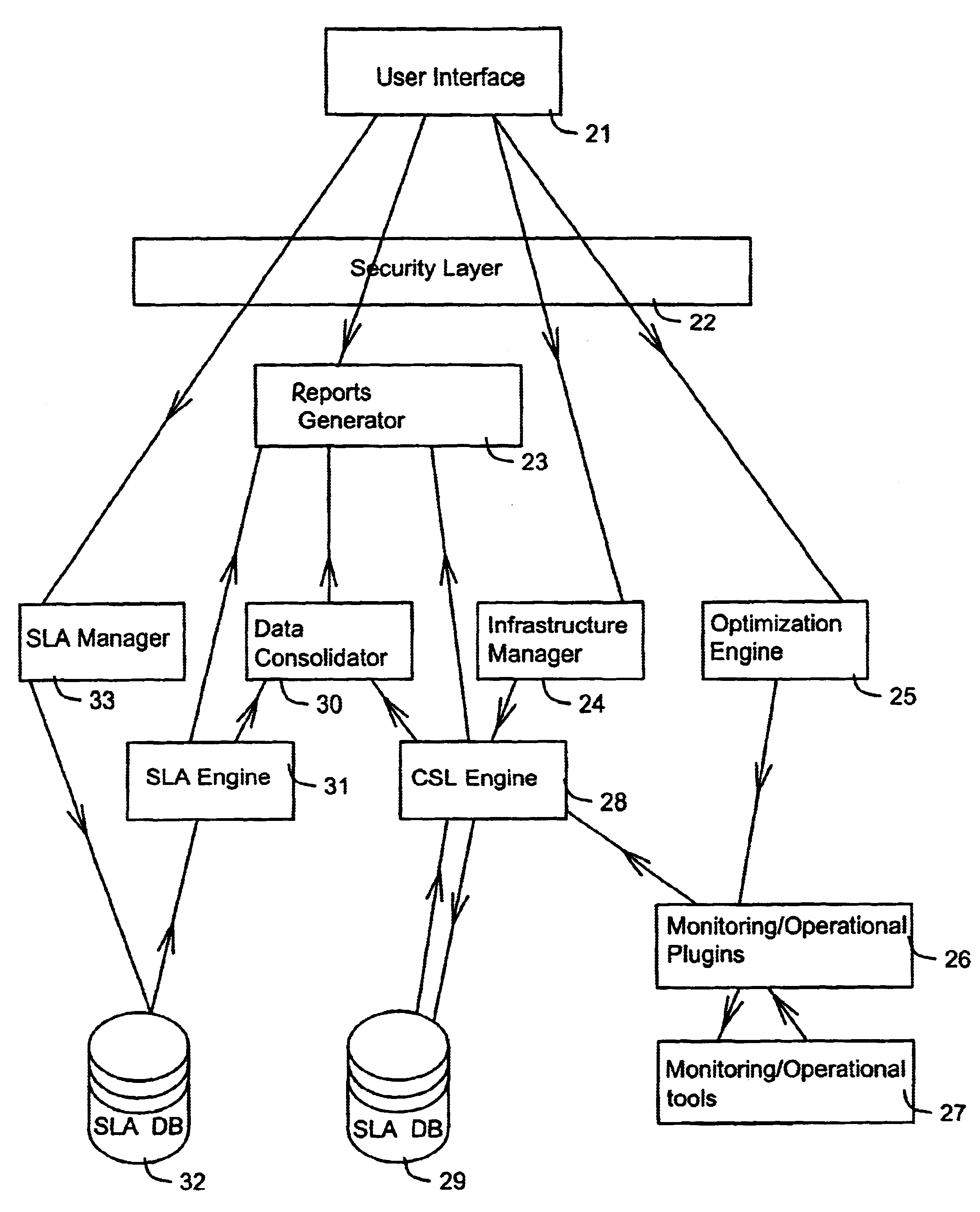
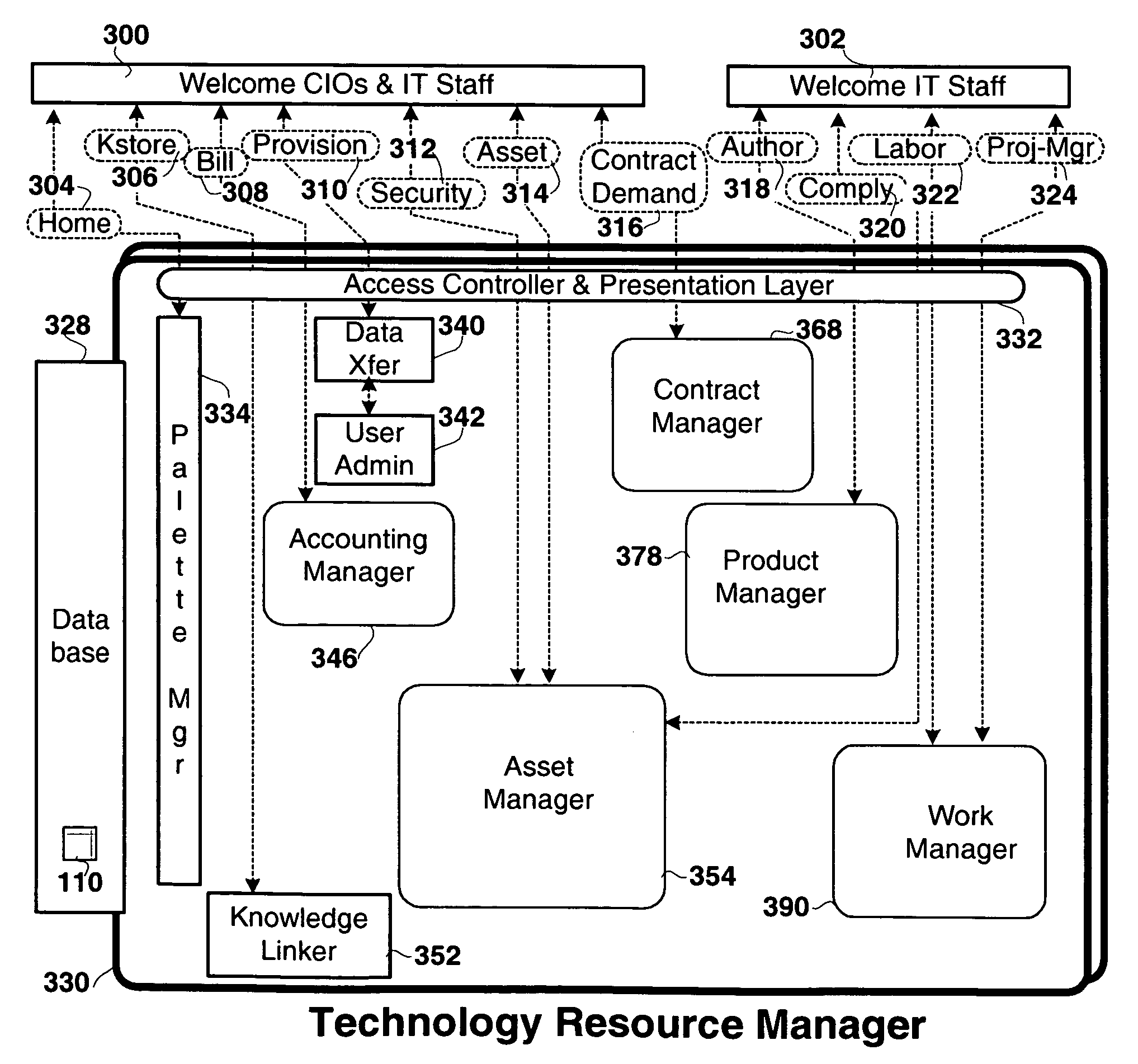
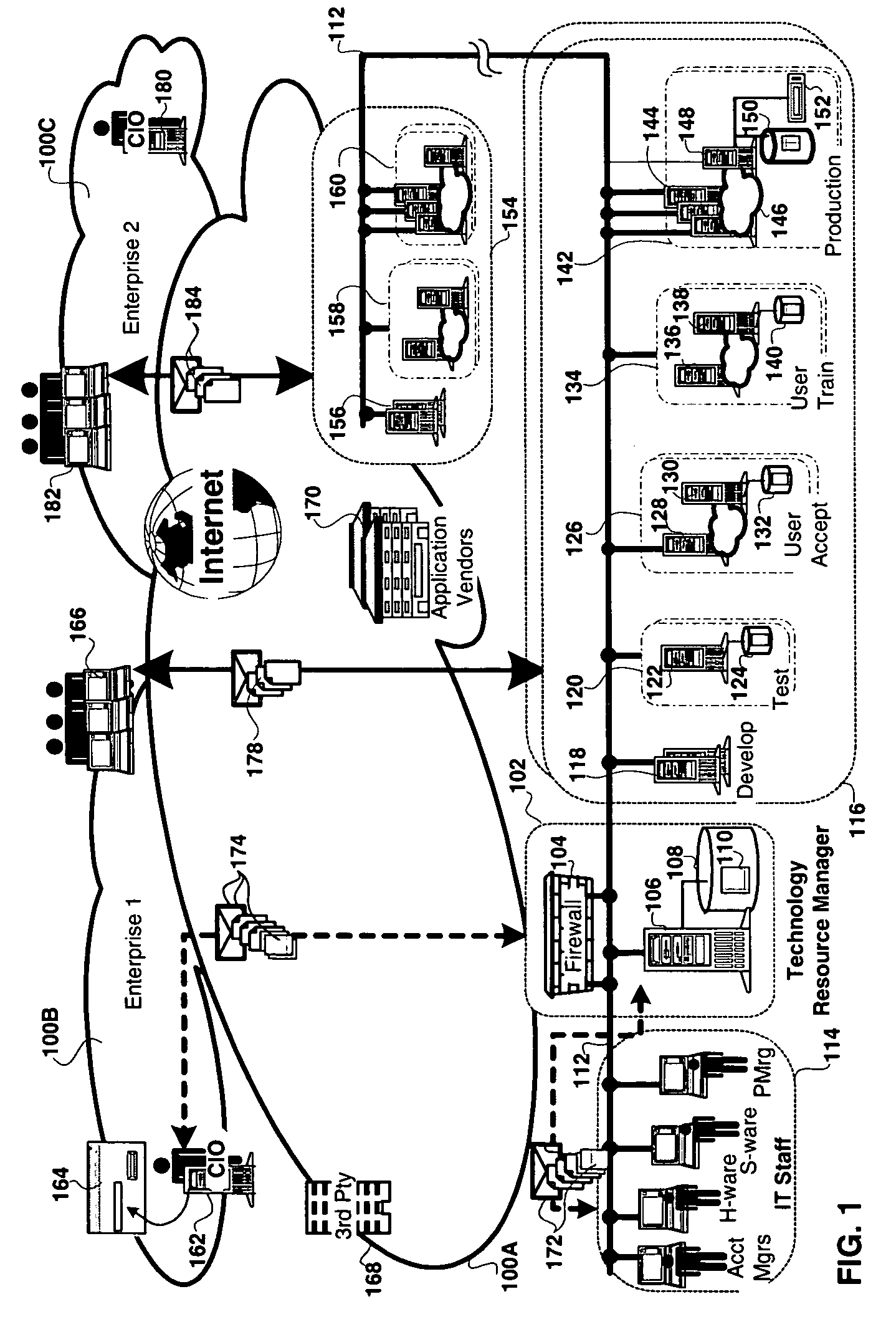
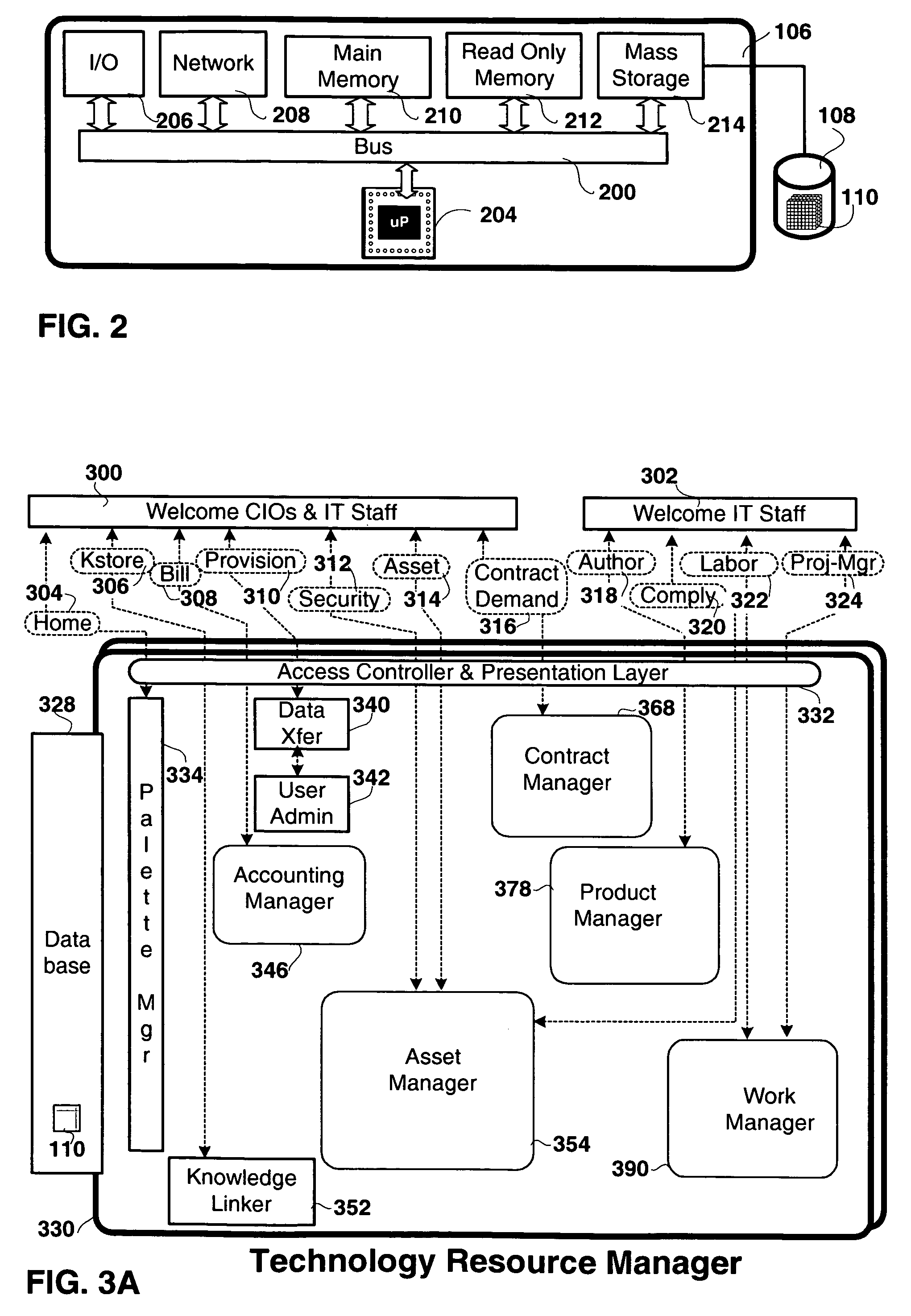
Method and apparatus for technology resource management
Apparatus, and associated methods, manage technology resources in hosted applications including: demand, service level agreements, assets both hardware and software, projects, labor, knowledge and provisioning. The apparatus includes an asset manager configured to couple to host servers and a network, to manage the host servers and software deployed thereon. In embodiments of the invention the asset manager: determines demand for new assets and allocates available assets to meet the demand; determines assets not in compliance with existing software licenses; determines which host servers have actual service level metrics which are not compliant with the target service level metrics; and determines availability of a patch or upgrade for selected software and instances of the selected software among the assets. In an embodiment of the invention the asset manager couples to a contract manager with the asset manager determining the assets for which actual monitored service level metrics violate contract service level metrics. In an embodiment of the invention the asset manager couples to a product manager and scans the host severs to determine which have actual security metrics which are not compliant with the target security metrics managed by the product manager. In an embodiment of the invention the asset manager couples with a product manager, a work manager and an accounting manager to compare the actual costs of the new assets from the accounting manager and the work manager with the price of the assets from the product record.
Owner:IBM CORP
Autonomic provisioning of netowrk-accessible service behaviors within a federted grid infrastructure
InactiveUS20040064548A1Avoiding expensive and inefficient over-commitmentDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsService-level agreementAuto-configuration
Methods, systems, computer program products, and a method of doing business are disclosed for autonomically provisioning network-accessible services in a decentralized network having a federated grid infrastructure. Autonomic, grid, and web services-related technologies, standards, and concepts are leveraged. More particularly, web service behaviors (augmented as grid services, according to preferred embodiments) are autonomically provisioned (i.e., dynamically distributed) via a grid of hosting services. In preferred embodiments, this dynamic distribution occurs in response to (and as a function of) external catalysts, such as algorithms that monitor designated resources (e.g., to proactively determine when the commitments in a utility service provider's service level agreements are in jeopardy).
Owner:IBM CORP
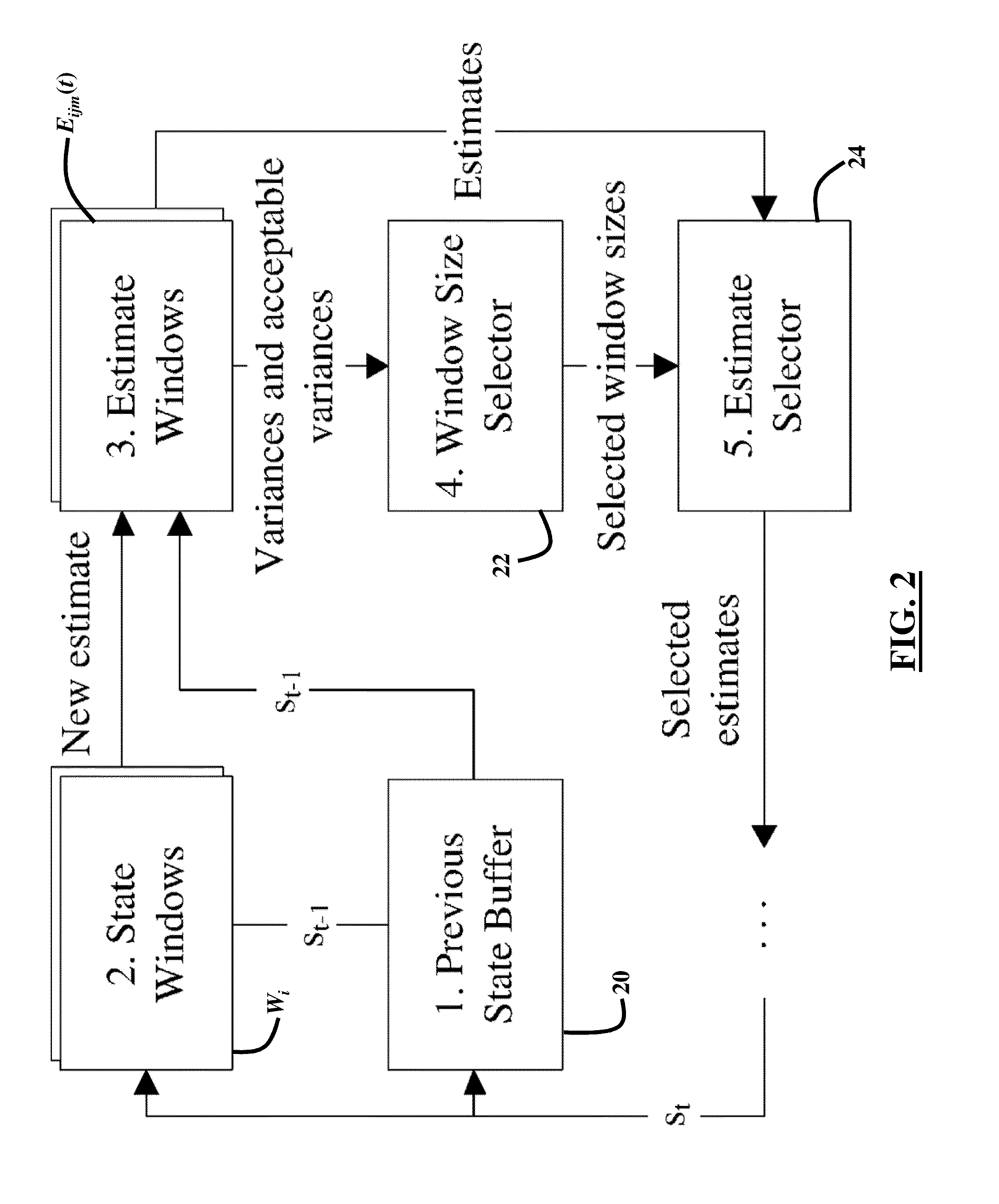
System, Method and Computer Program Product for Energy-Efficient and Service Level Agreement (SLA)-Based Management of Data Centers for Cloud Computing
ActiveUS20150039764A1Increase profitReduce energy consumptionDigital computer detailsProgram controlService-level agreementLevel of service
Improving the utilization of physical resources and reducing energy consumption in a cloud data center includes providing a plurality of virtual machines in the cloud data center; periodically reallocating resources of the plurality of virtual machines according to a current resource demand of the plurality of virtual machines in order to minimize a number of active physical servers required to handle a workload of the physical servers; maximizing a mean inter-migration time between virtual machine migrations under the quality of service requirement based on a Markov chain model; and using a multisize sliding window workload estimation process for a non-stationary workload to maximize the mean inter-migration time.
Owner:MANJRASOFT PTY LTD
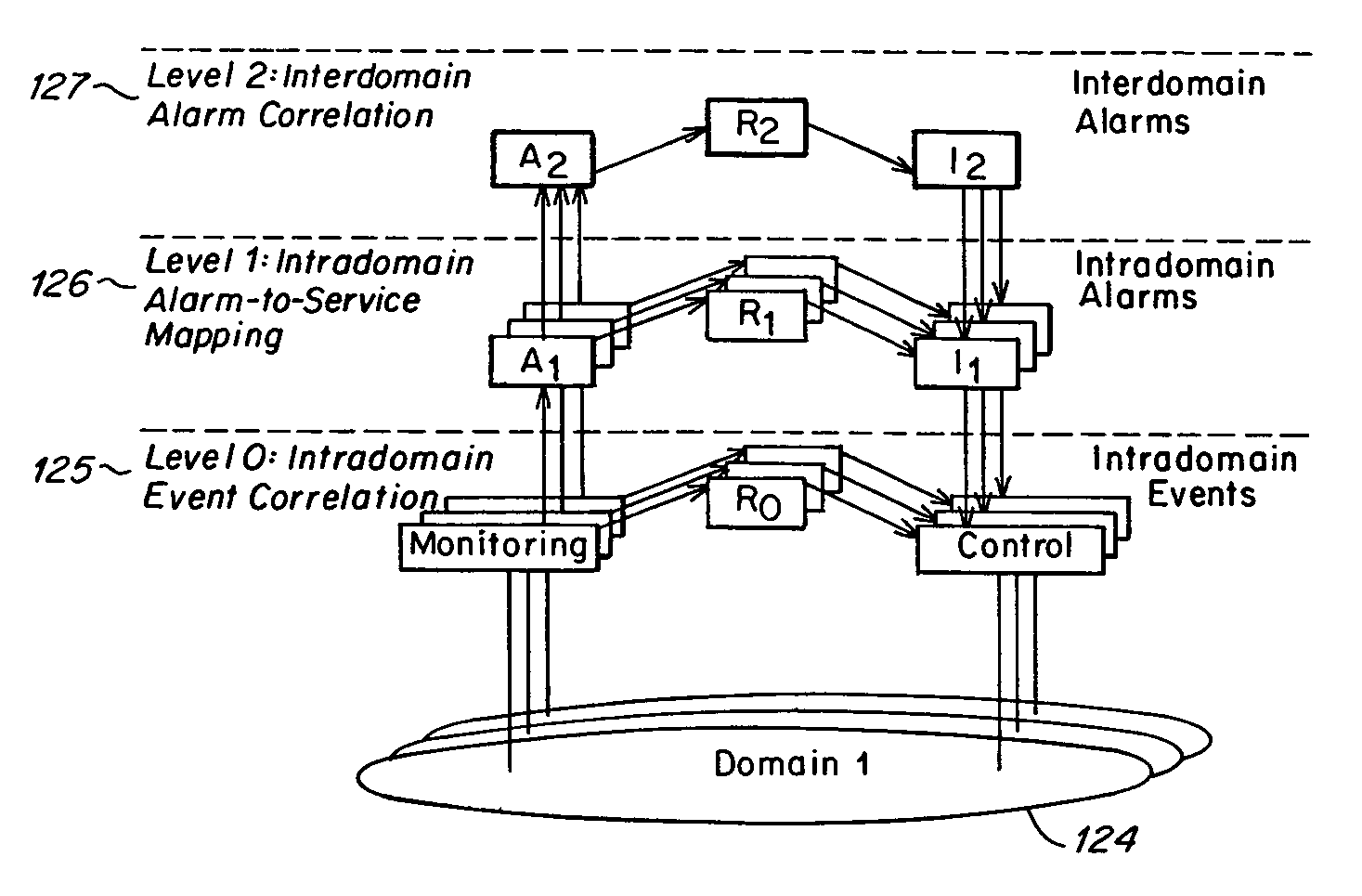
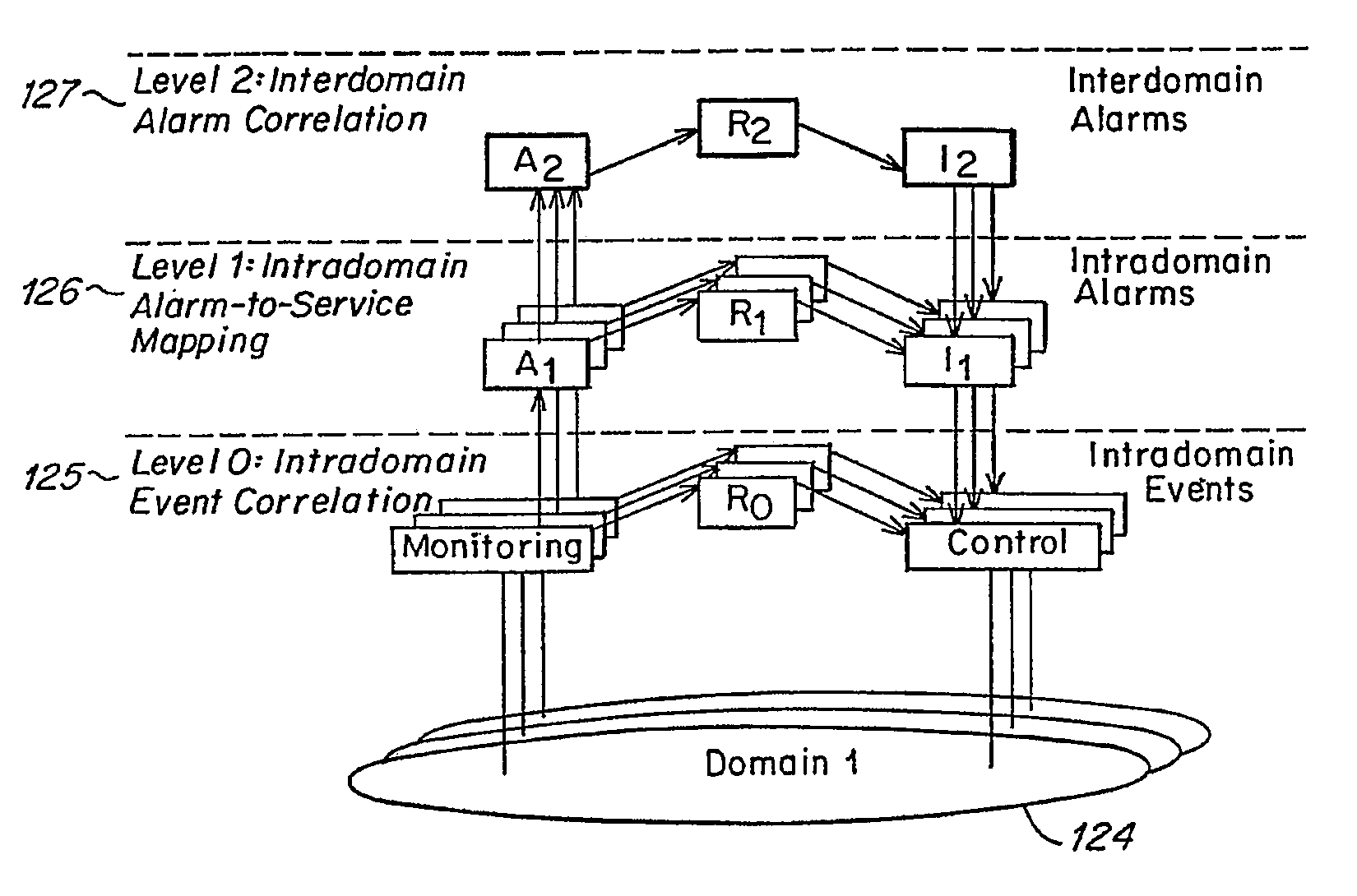
Method and apparatus for event correlation in service level management (SLM)
Method and apparatus for service level management, wherein business processes are composed of services. A state of the service is defined by one or more service parameters, and the service parameters depend upon performance of network components that support the service, e.g., component parameters. The state of the service may depend, for example, on a collection of service parameter values for availability, reliability, security, integrity and response time. A service level agreement is a contract between a supplier and a customer that identifies services supported by a network, service parameters for the services, and service levels (e.g., acceptable levels) for each service parameter.
Owner:COMP ASSOC THINK INC
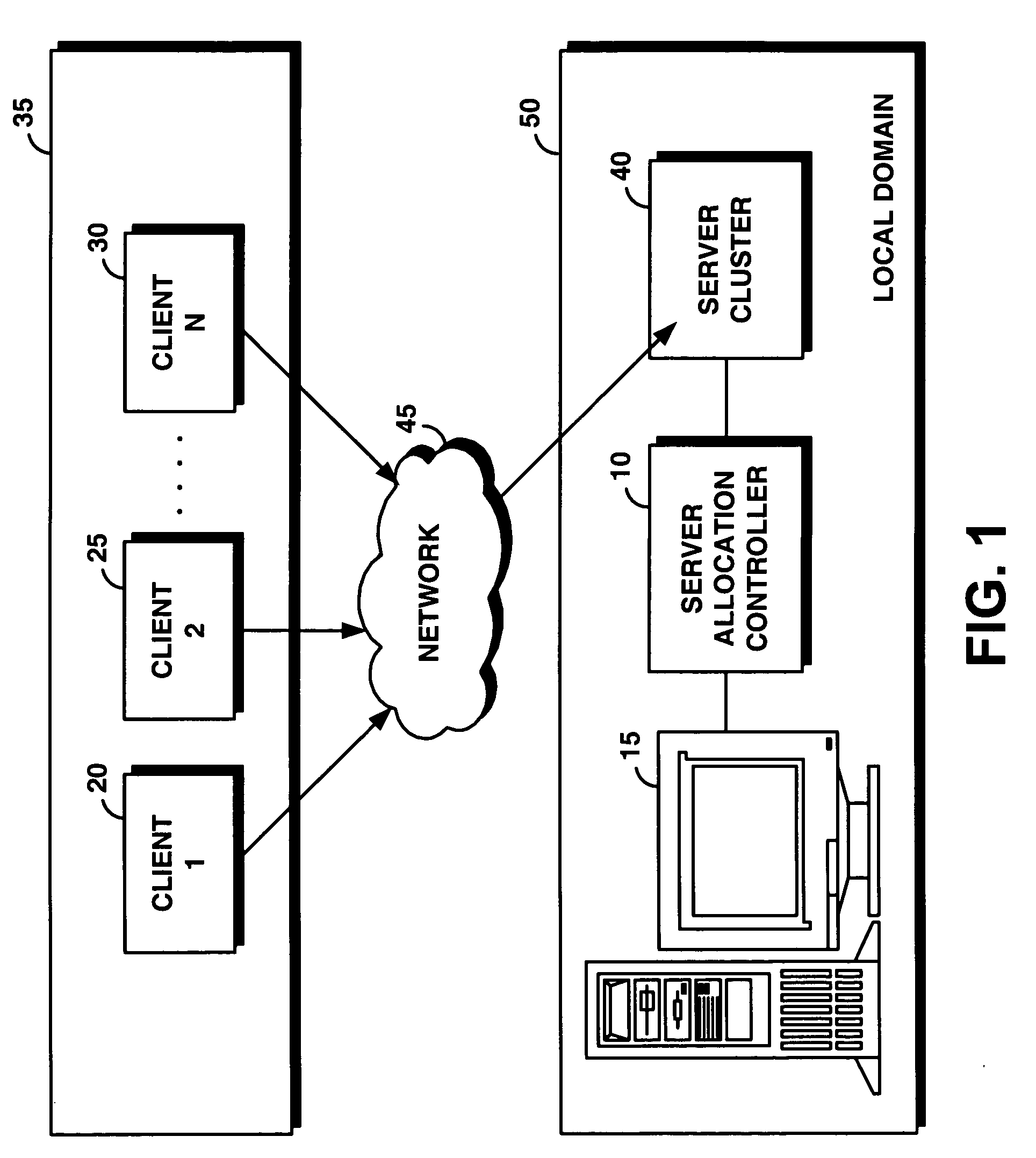
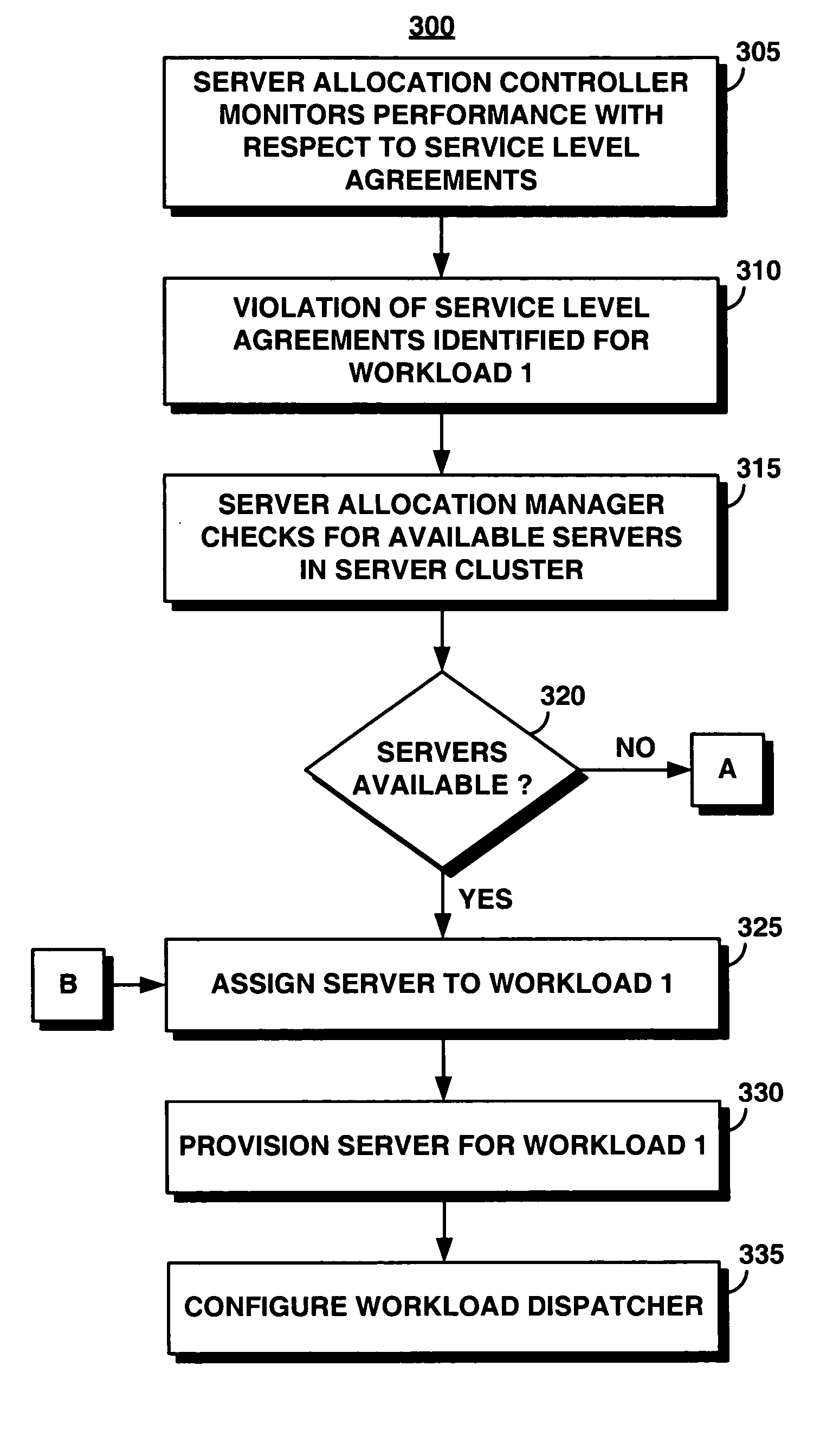
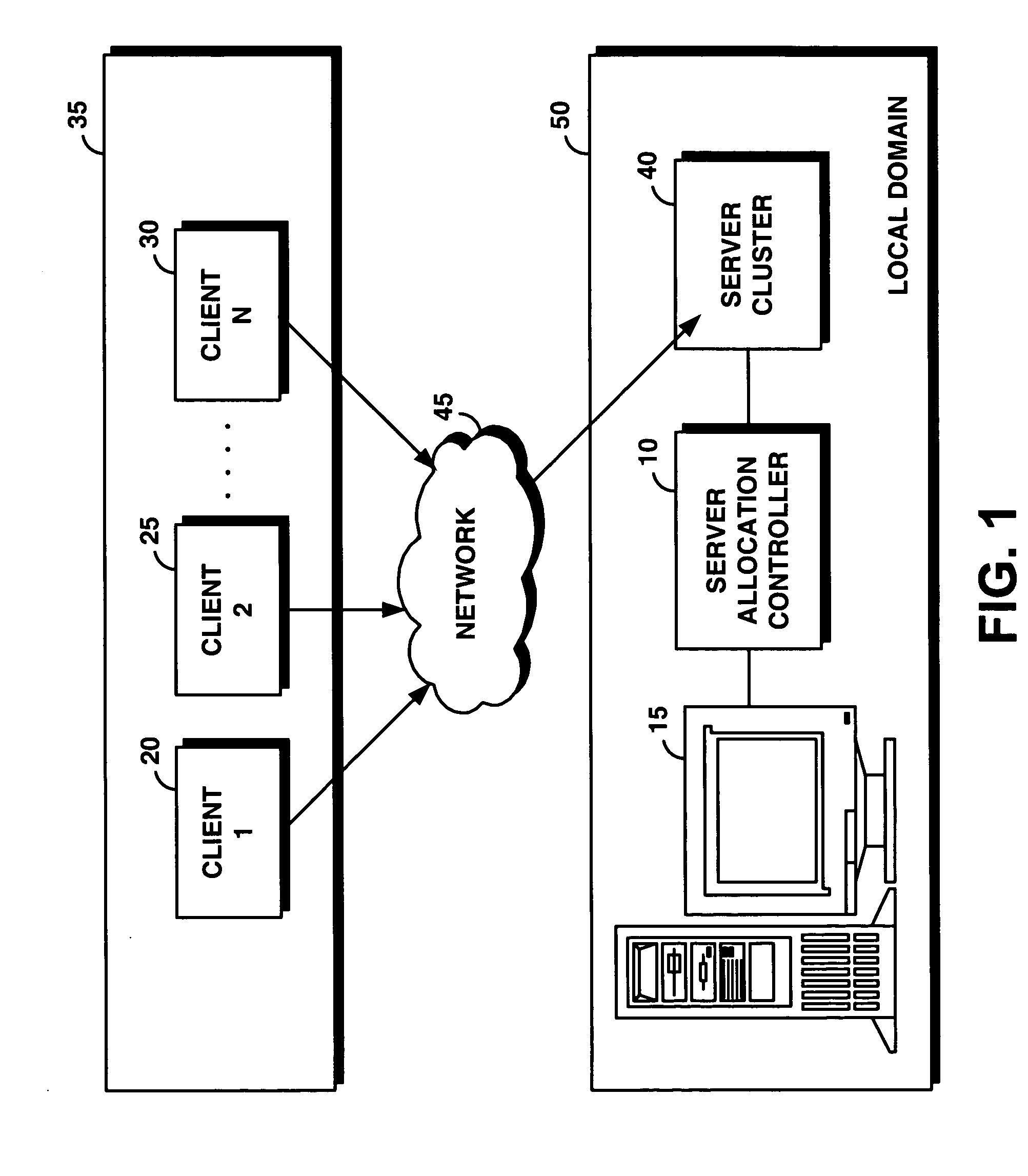
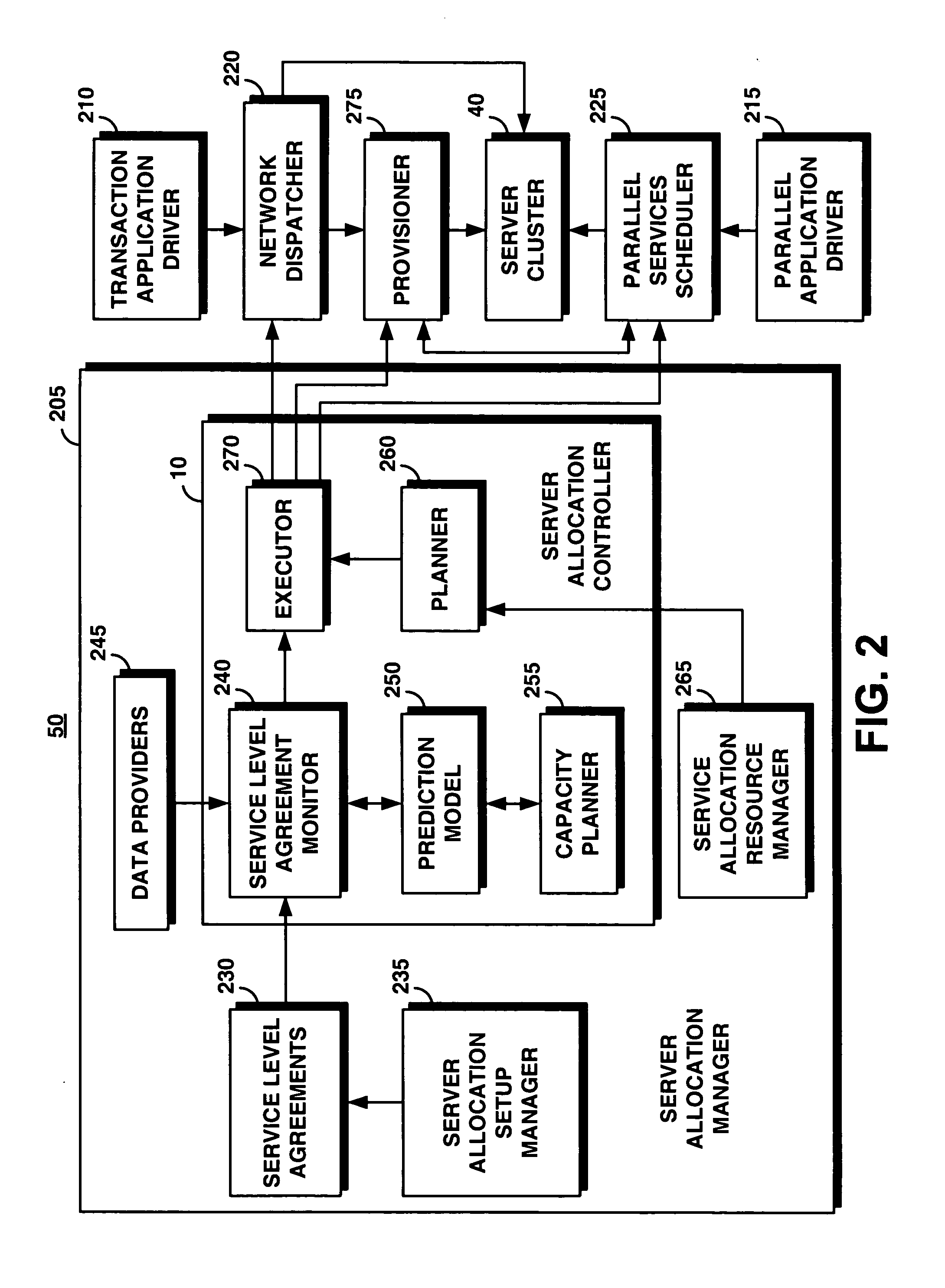
System and method for supporting transaction and parallel services in a clustered system based on a service level agreement
InactiveUS20050188075A1Facilitates dynamic allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionService-level agreementData processing system
A server allocation controller provides an improved distributed data processing system for facilitating dynamic allocation of computing resources. The server allocation controller supports transaction and parallel services across multiple data centers enabling dynamic allocation of computing resources based on the current workload and service level agreements. The server allocation controller provides a method for dynamic re-partitioning of the workload to handle workload surges. Computing resources are dynamically assigned among transaction and parallel application classes, based on the current and predicted workload. Based on a service level agreement, the server allocation controller monitors and predicts the load on the system. If the current or predicted load cannot be handled with the current system configuration the server allocation controller determines additional resources needed to handle the current or predicted workload. The server cluster is reconfigured to meet the service level agreement.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com