Patents
Literature
396 results about "Local domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
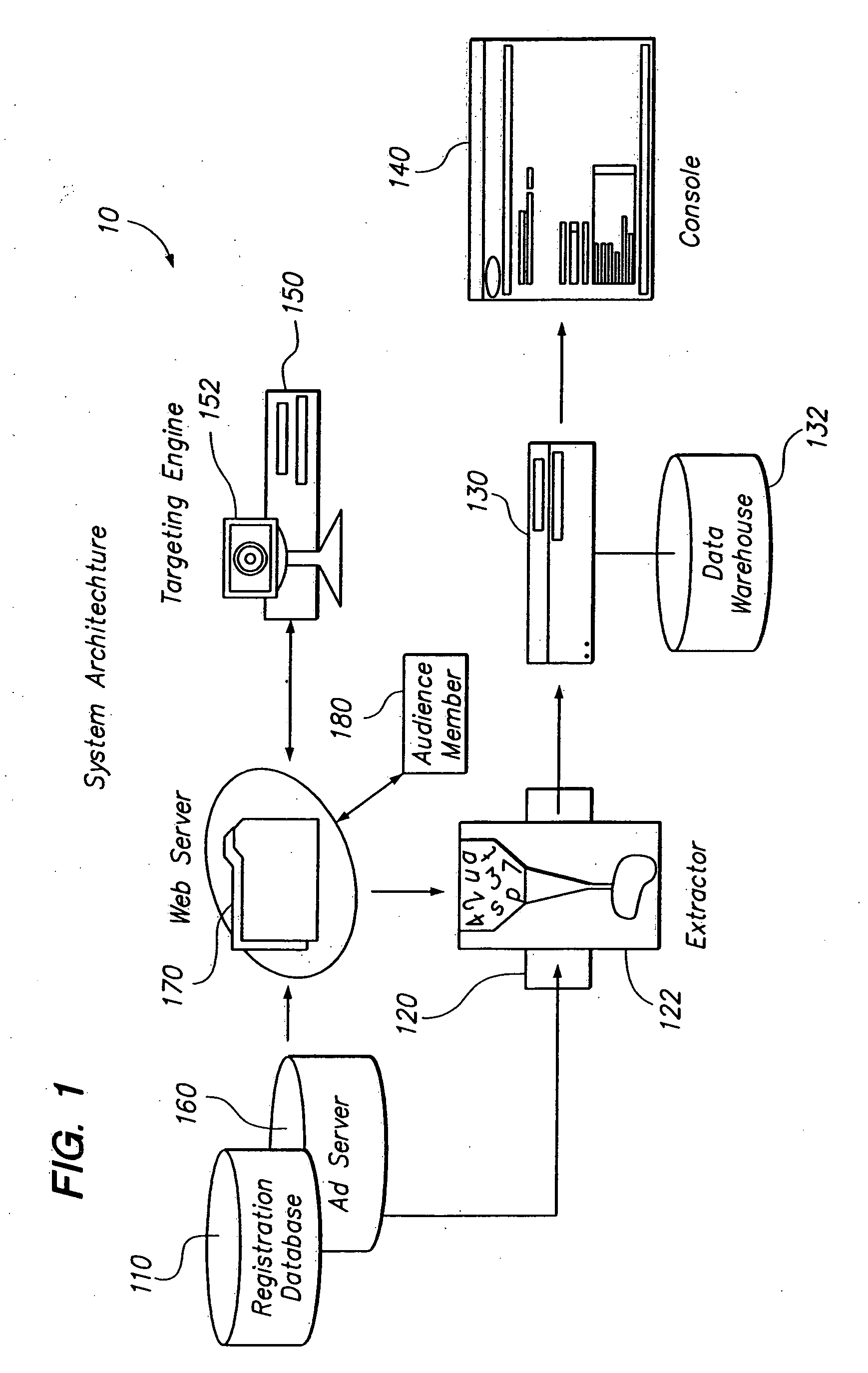
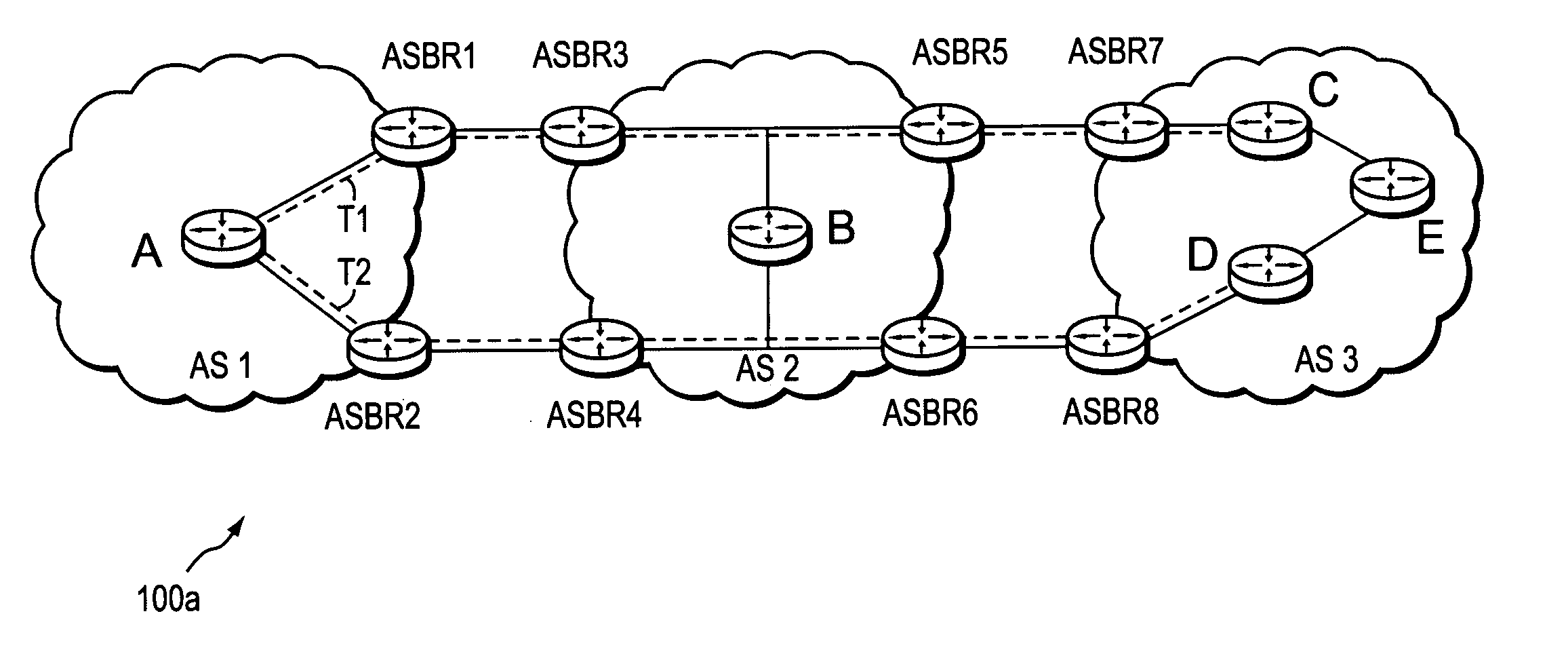
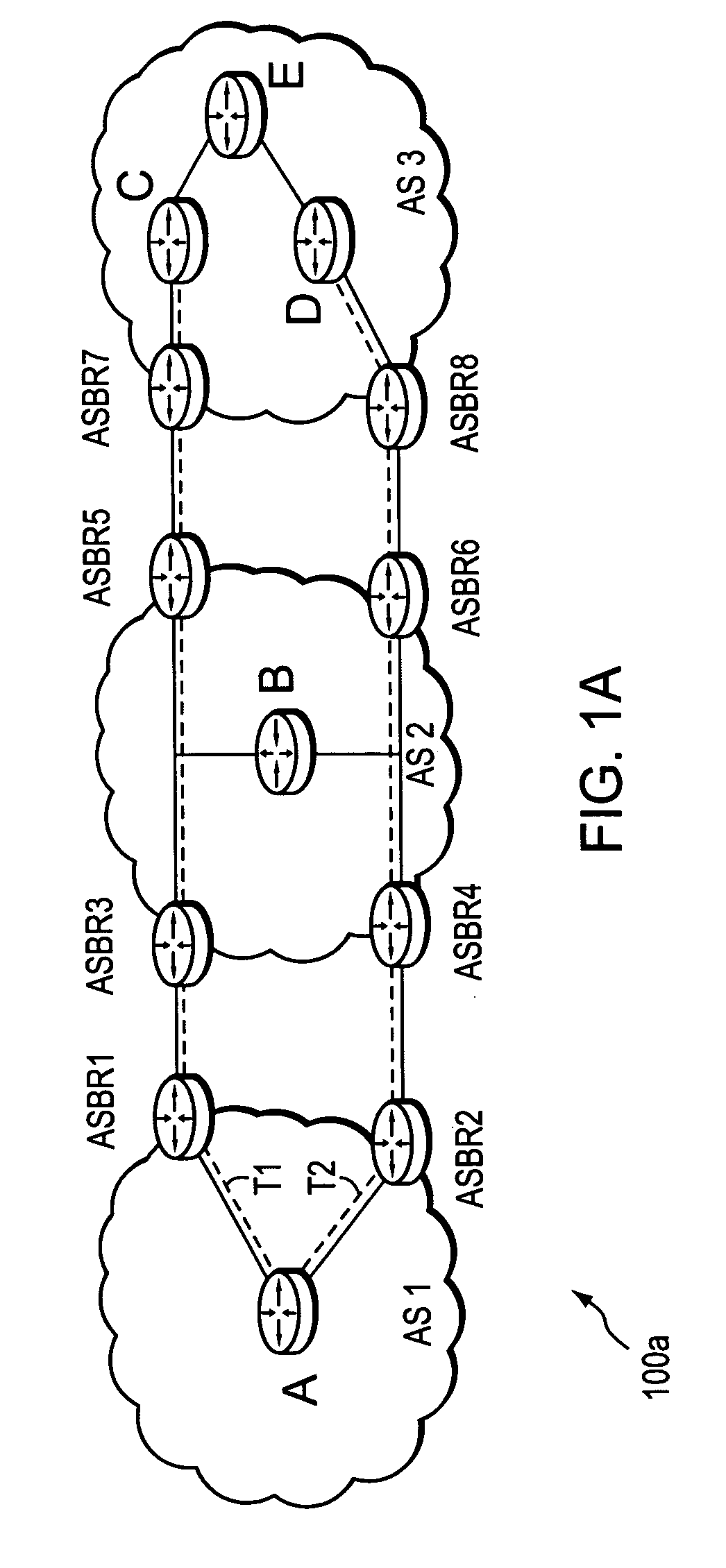
A local domain is a domain that belongs to your company. For example, if you work for a company called Acme Coffee Shop and you have registered AcmeCoffeeShop.com with InterNic, you need to specify acmecoffeeshop.com as a local domain. When Xeams is running in Stand-Alone mode emails sent for local domain stay in Xeams.
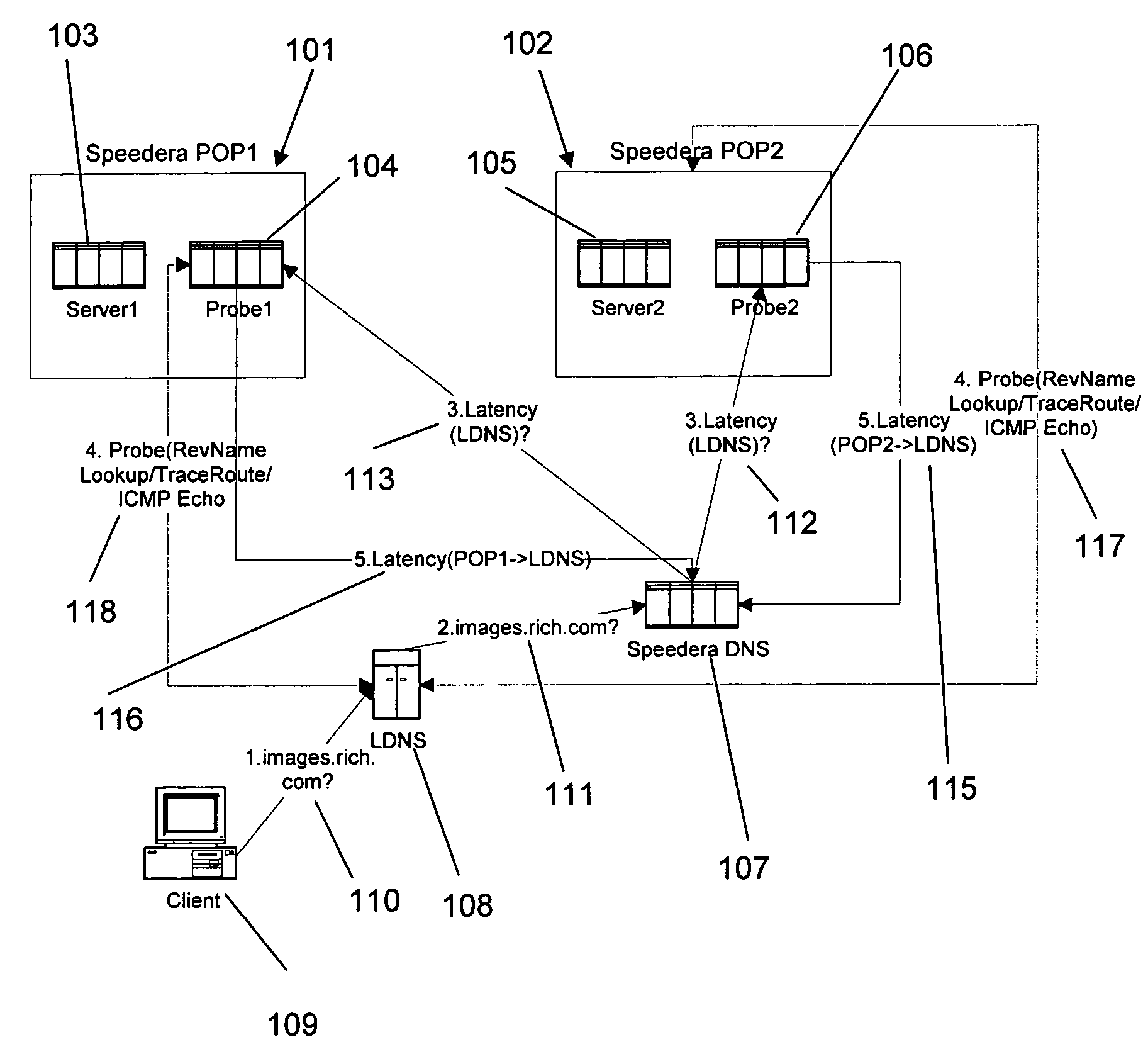
Method and apparatus for determining latency between multiple servers and a client
InactiveUS7058706B1Reduce network trafficAccurately determineDigital computer detailsData switching networksTraffic capacityName server
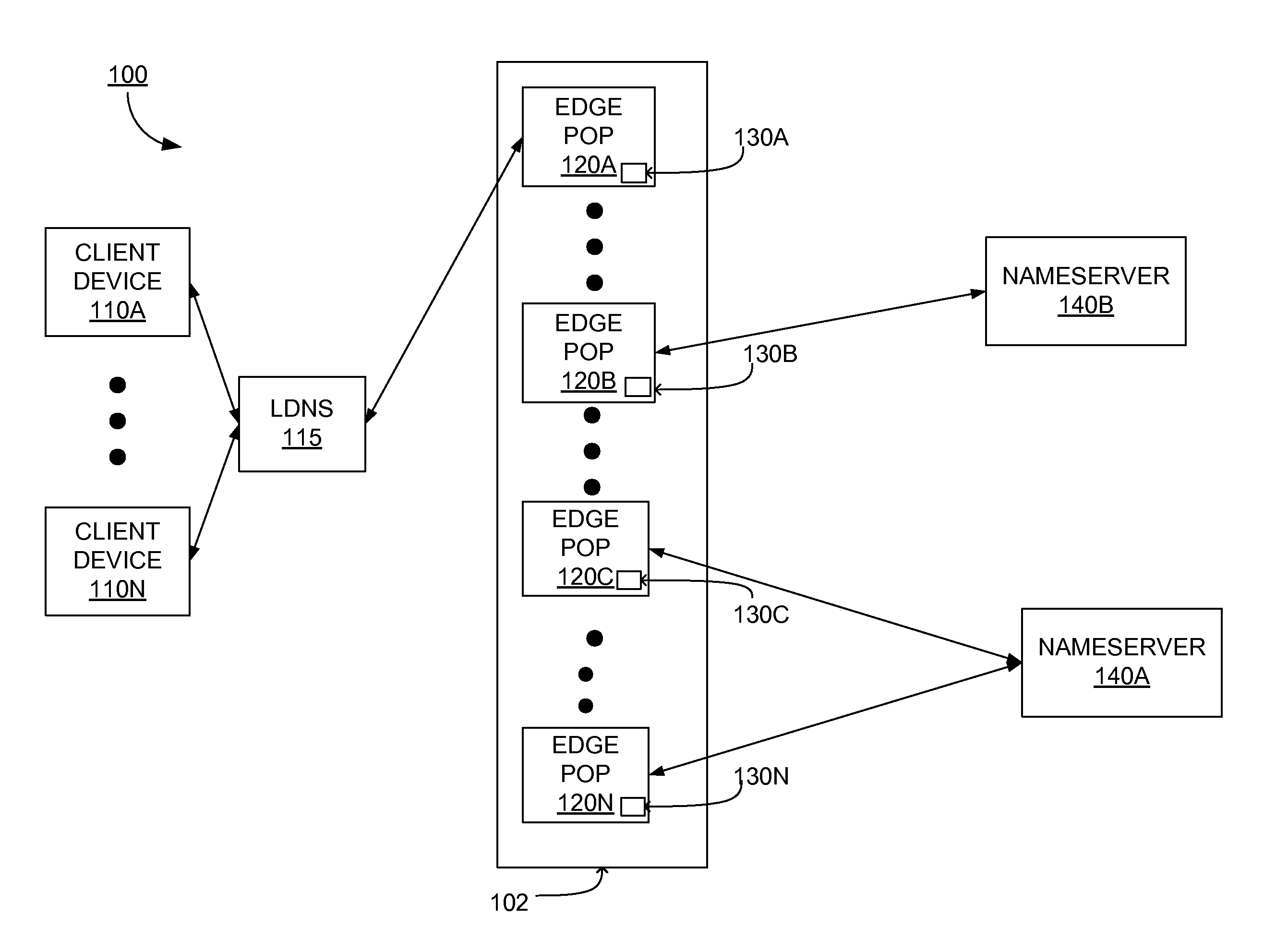
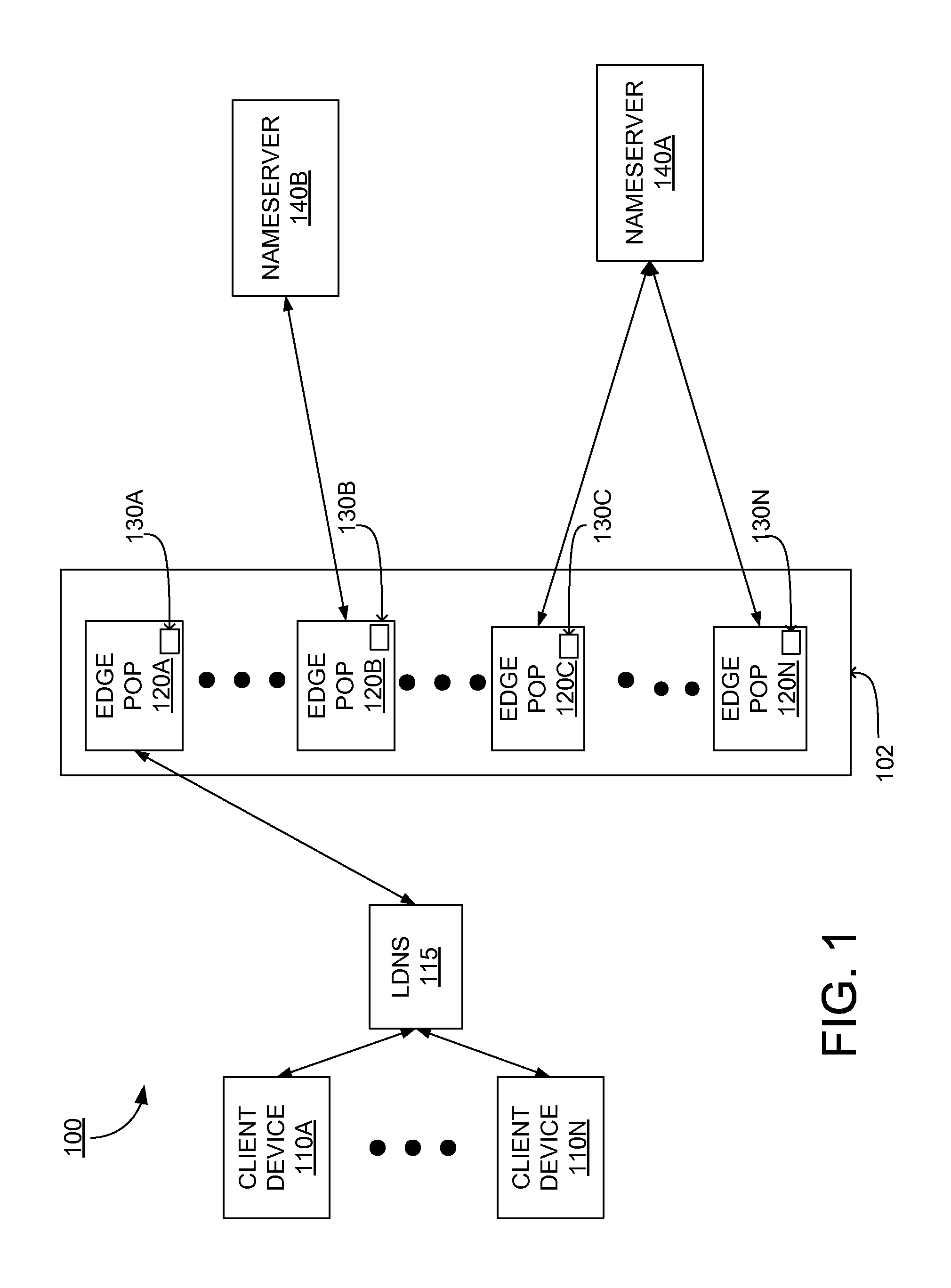
A method and apparatus for determining latency between multiple servers and a client receives requests for content server addresses from local domain names servers (LDNS). POPs that can serve the content are determined and sent latency metric requests. The content server receives the request for latency metrics and looks up the latency metric for the requesting client. Periodic latency probes are sent to the IP addresses in a Latency Management Table. The IP addresses of clients are masked so the latency probes are sent to higher level servers to reduce traffic across the network. The hop count and latency data in the packets sent in response to the latency probes are stored in the Latency Management Table and is used to determine the latency metric from the resident POP to the requesting client before sending the latency metric to the requesting server. The BGP hop count in the Latency Management Table is used for the latency metric upon the first request for an IP address. The latency metric is calculated for subsequent requests of IP addresses using the hop count and RTT data in the Latency Management Table. Latency metrics from POPs are collected and the inverse relationship of the hop counts in a weighted combination with the RTT are used to determine which latency metric indicates the optimal POP. The address of the optimal POP is then sent to the requesting LDNS.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Method and apparatus for direct frame switching using frame contained destination information
InactiveUS20050027881A1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationImage resolutionEmbedded system
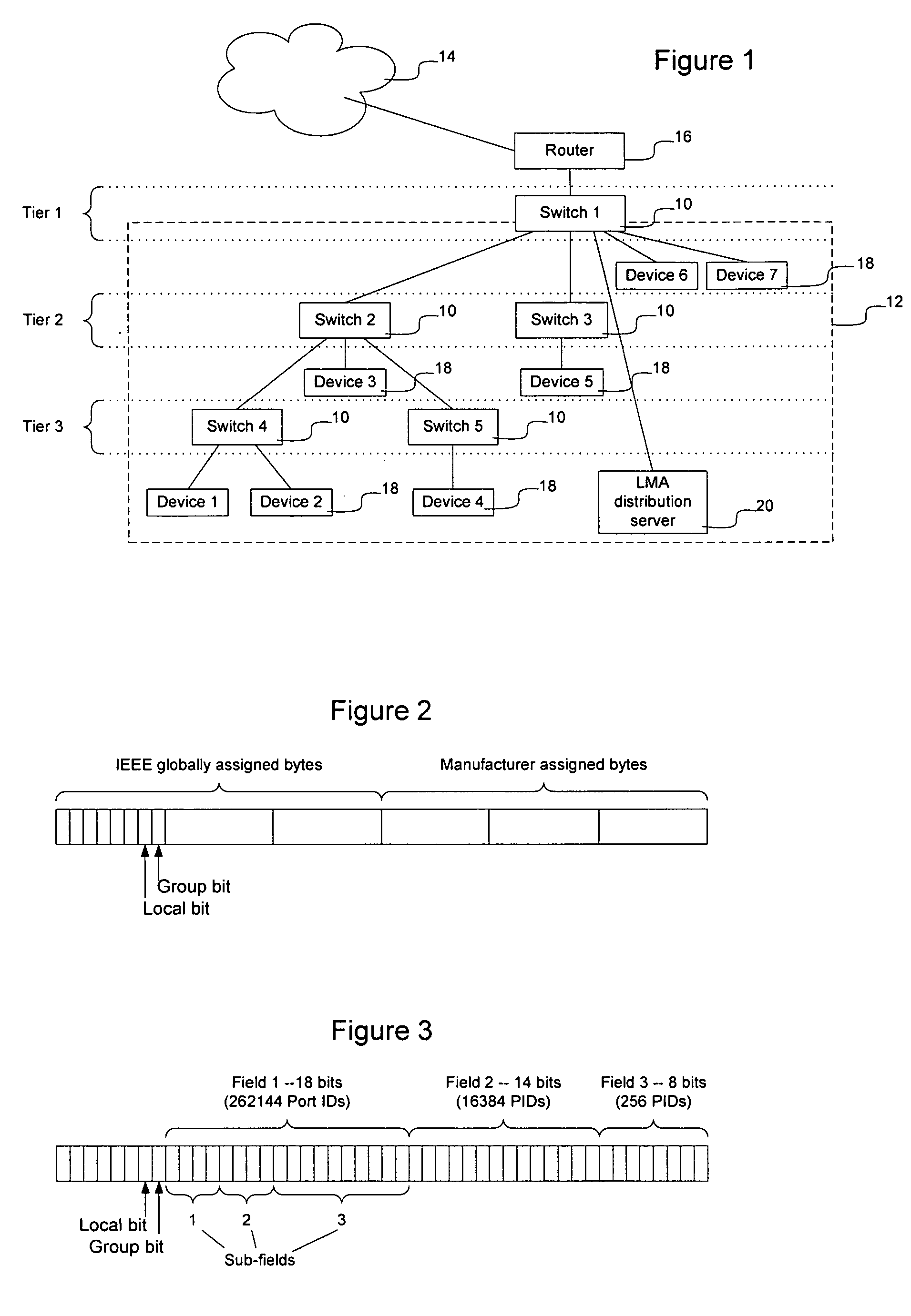
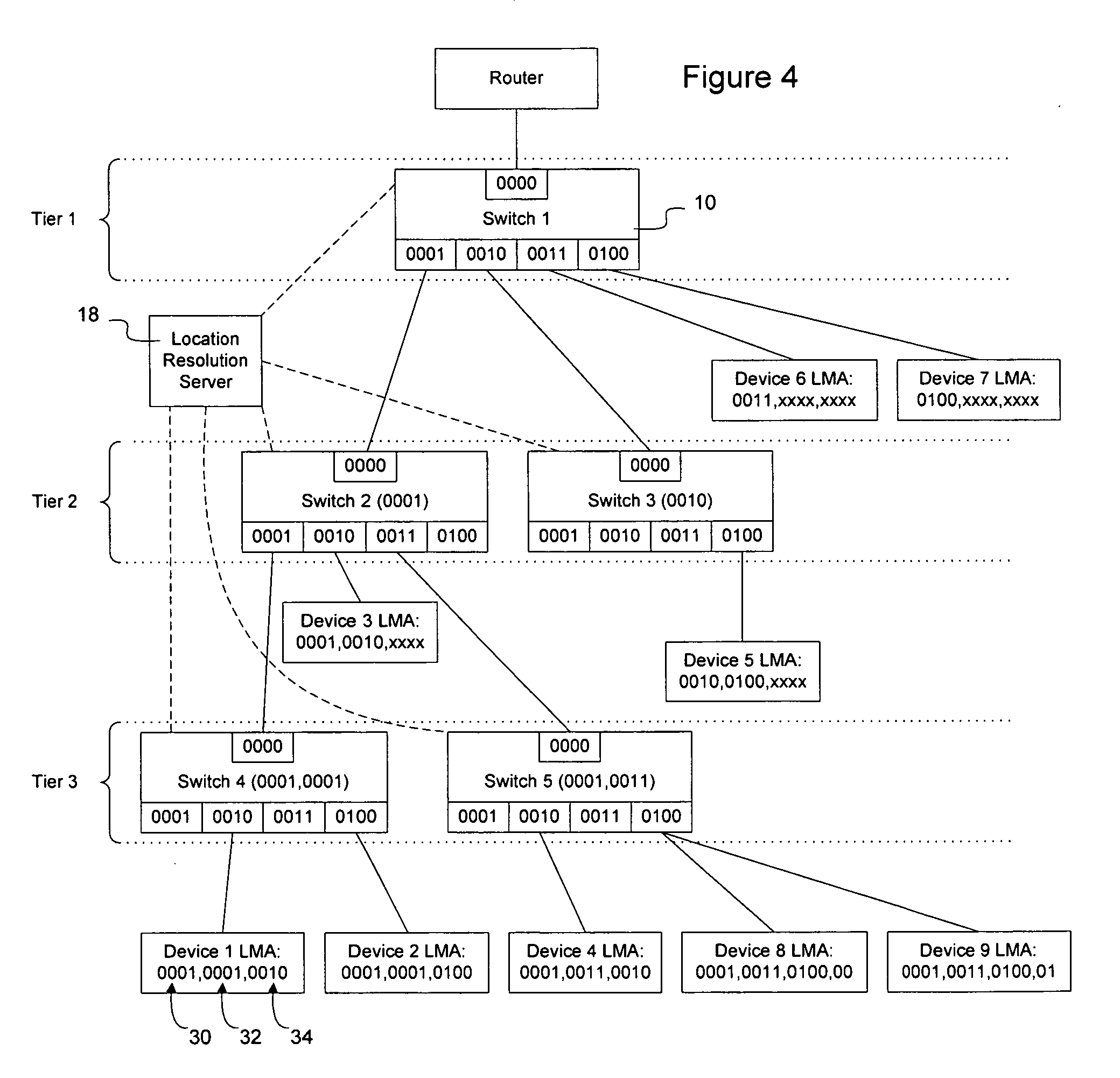
Frame contained destination information may be used by a switch to identify an appropriate output port for a given frame without performing a table access operation. This reduces the processing requirements of the switch to enable the switch to handle frames more efficiently. The frame contained destination information may be contained in the frame's local destination MAC addresses (DA) such that a portion of the DA directly indicates, for each switch that handles the frame, an output port for that switch. Different portions of the DA may be used by different switches, depending on where they are in the network hierarchy. Large switches may also use sub-fields within their allocated portion in the DA to identify internal switching components. A location resolution server may be provided to store and distribute IP and MAC addresses and respond to local ARP requests on the local domain.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Cname-based round-trip time measurement in a content delivery network
Round-trip time (RTT) for communication between an edge point of presence (POP) in a content delivery network (CDN) and a local domain name server (LDNS) is determined by resolution of a canonical name (CNAME) record. A first server in a first edge POP in a CDN receives a request to resolve a domain name from a LDNS and transmits a CNAME record including a timestamp indicating when the CNAME record was transmitted to the LDNS. The first server subsequently receives a request from the LDNS to resolve the CNAME record and determines a RTT time indicating the time needed for round-trip transmission between the LDNS and the first server based on the time when the request to resolve the CNAME request was received by the first server and the time indicated by the timestamp.
Owner:CDNETWORKS HLDG SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Determining address of closest edge server
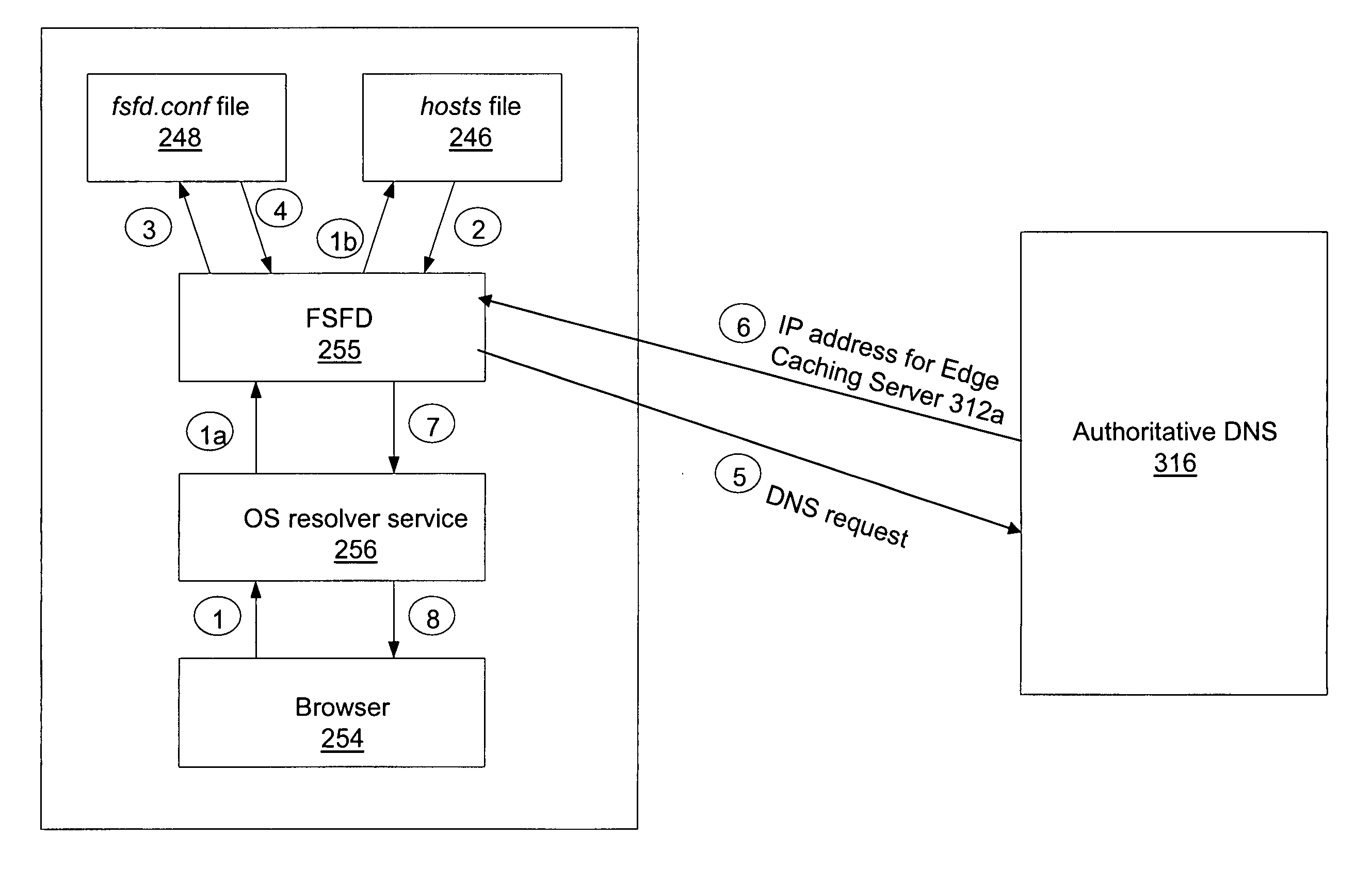
A method and system is presented for bypassing a local Domain Name Server (DNS) when using edge caching servers. Domain names of frequently used business applications that are known to rely upon edge servers, together with the corresponding authoritative DNSs, are listed in both local hosts file and user defined FSFD local configuration file fsfd.conf. When the client computer's browser attempts to resolve a domain name, a File System Filtering Driver (FSFD) in the client computer intercepts the browser's request. If the domain name which is being resolved is found in a local FSFD configuration file fsfd.conf, then the FSFD initiates a DNS request directly to the appropriate authoritative DNS whose IP address gets extracted from the fsfd.conf record, thus bypassing the local DNS. The authoritative DNS returns the IP address for an edge caching server that is topographically proximate to the client computer's browser.
Owner:LINKEDIN
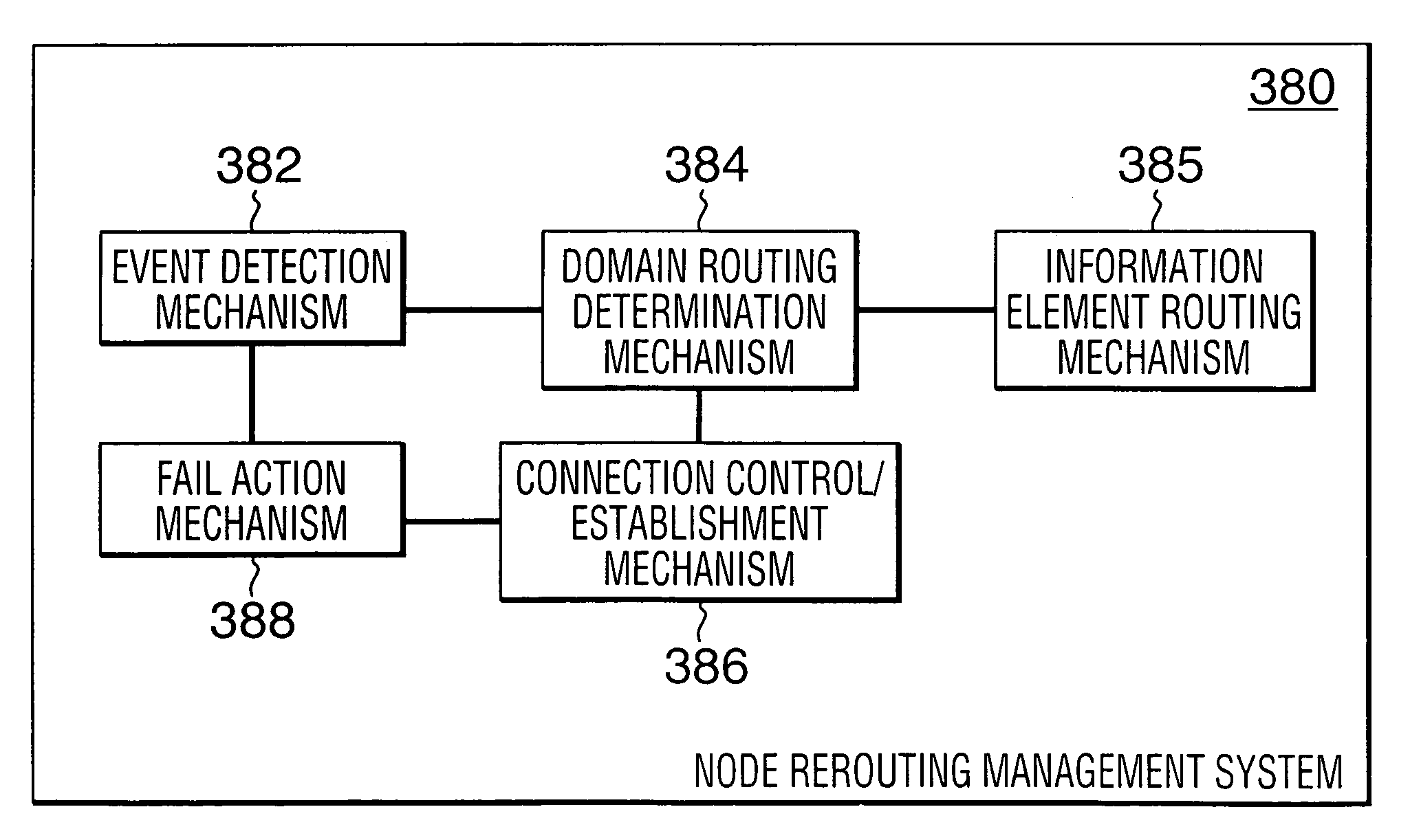
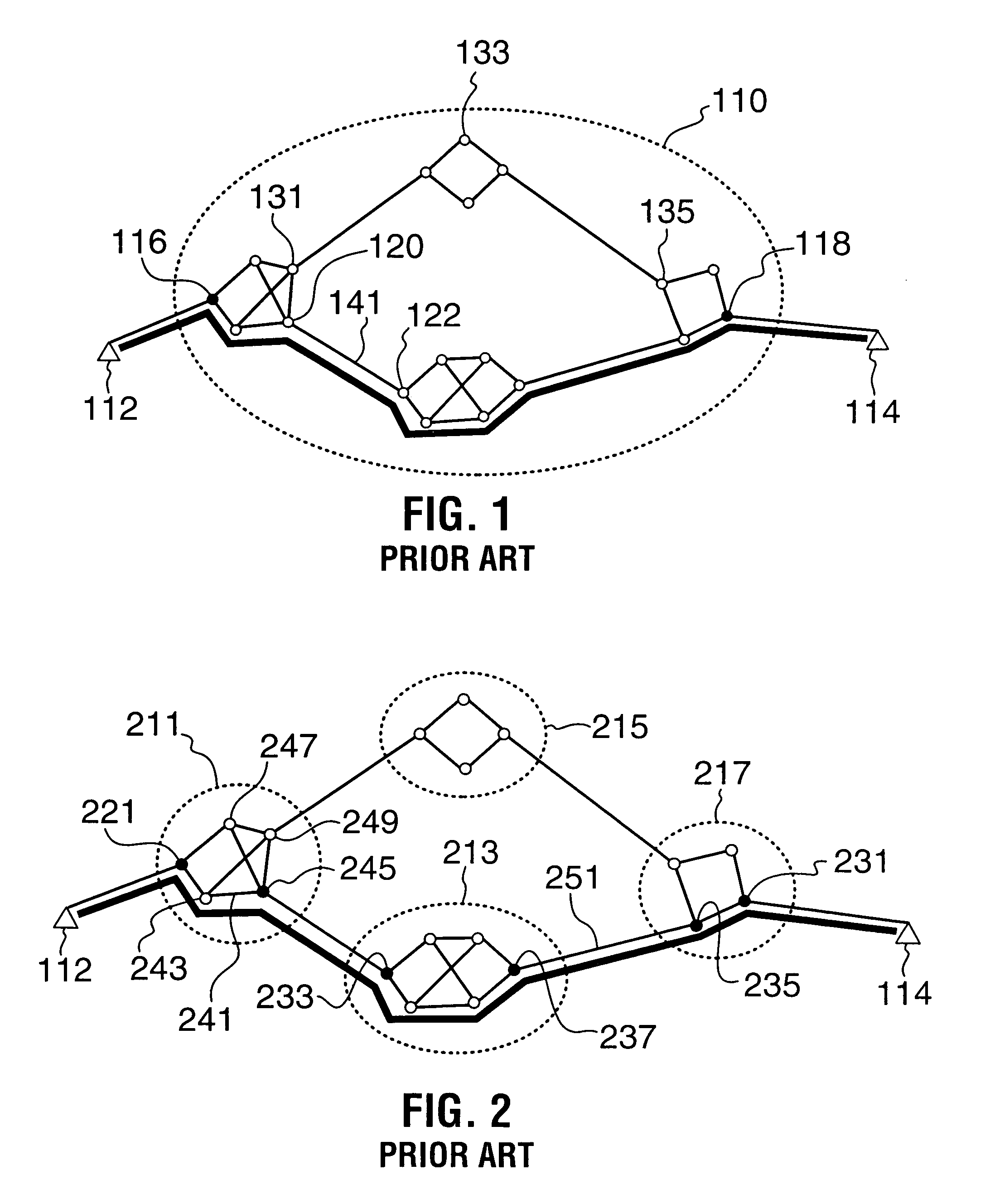
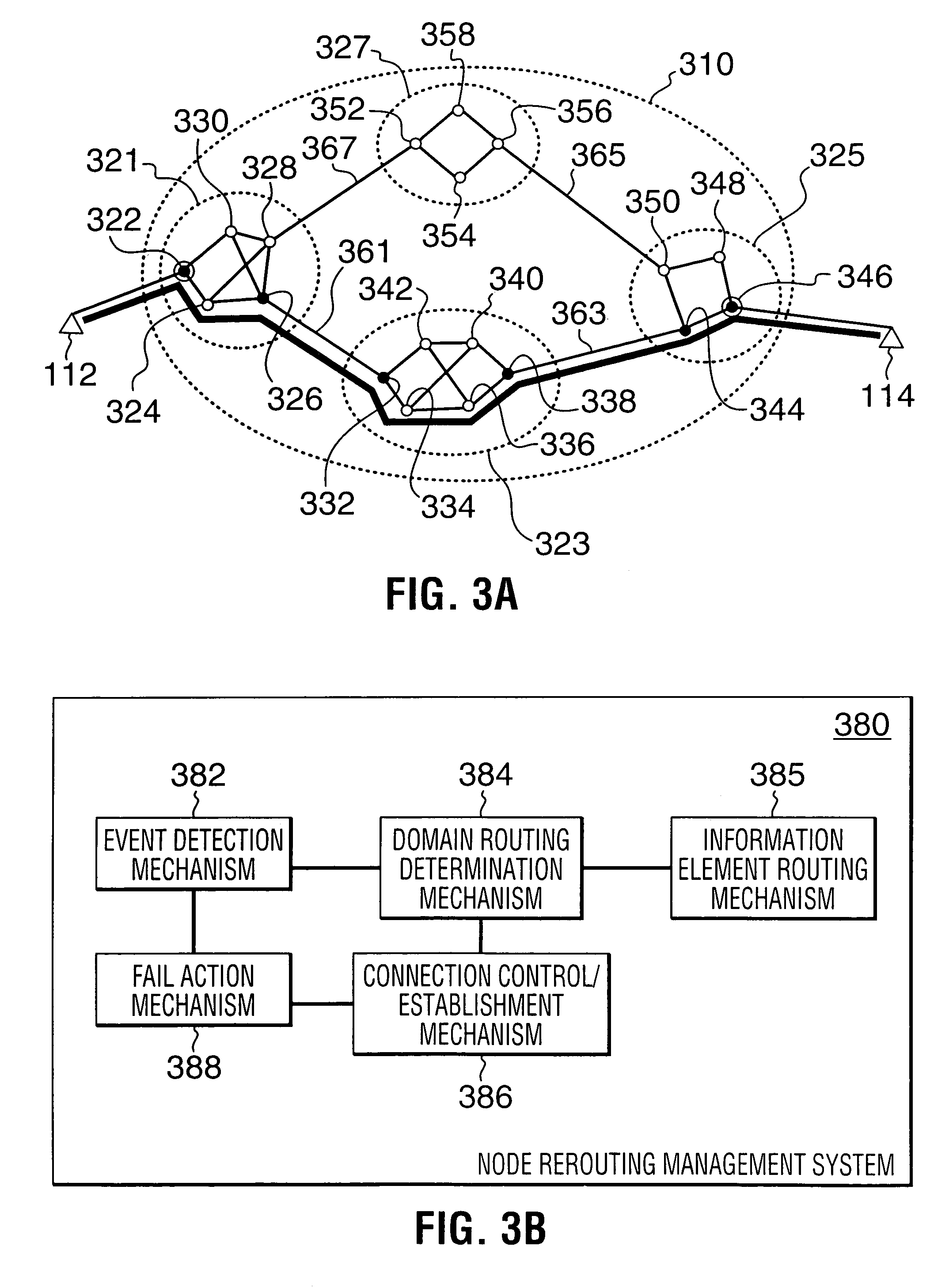
Rerouting in connection-oriented communication networks and communication systems
InactiveUS7180866B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionDouble faultCommunications system
A Private Network-Network Interface (PNNI) network including interconnected nodes is defined as a single rerouting domain (“global domain”) and the global domain is further defined by multiple divided domains (“local domains”). Each of the local domains is defined to include multiple nodes that are included in the network. Connection recovery and path optimization in the global domain (the entire PNNI network) are performed in accordance with a global rerouting protocol. The global rerouting protocol is a modification of the standard Domain-Based Rerouting (DBR) protocol, by adding information elements of domain identifier, rerouting for the global domain. The DBR protocol does not support the connection recovery from a link failure between local domains (“inter-domains”) and the global path optimization. The global rerouting method is capable of connection recovery and path optimization outside of any rerouting local domains. The global rerouting provides double fault recovery within the rerouting domain (“intra-domain”) as covered by the DBR and outside of the domains (“inter-domain”) or when the initial fault recovery within the domain has failed. Also, the global rerouting method provides maximum path optimization across all domains and within the rerouting local domain.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
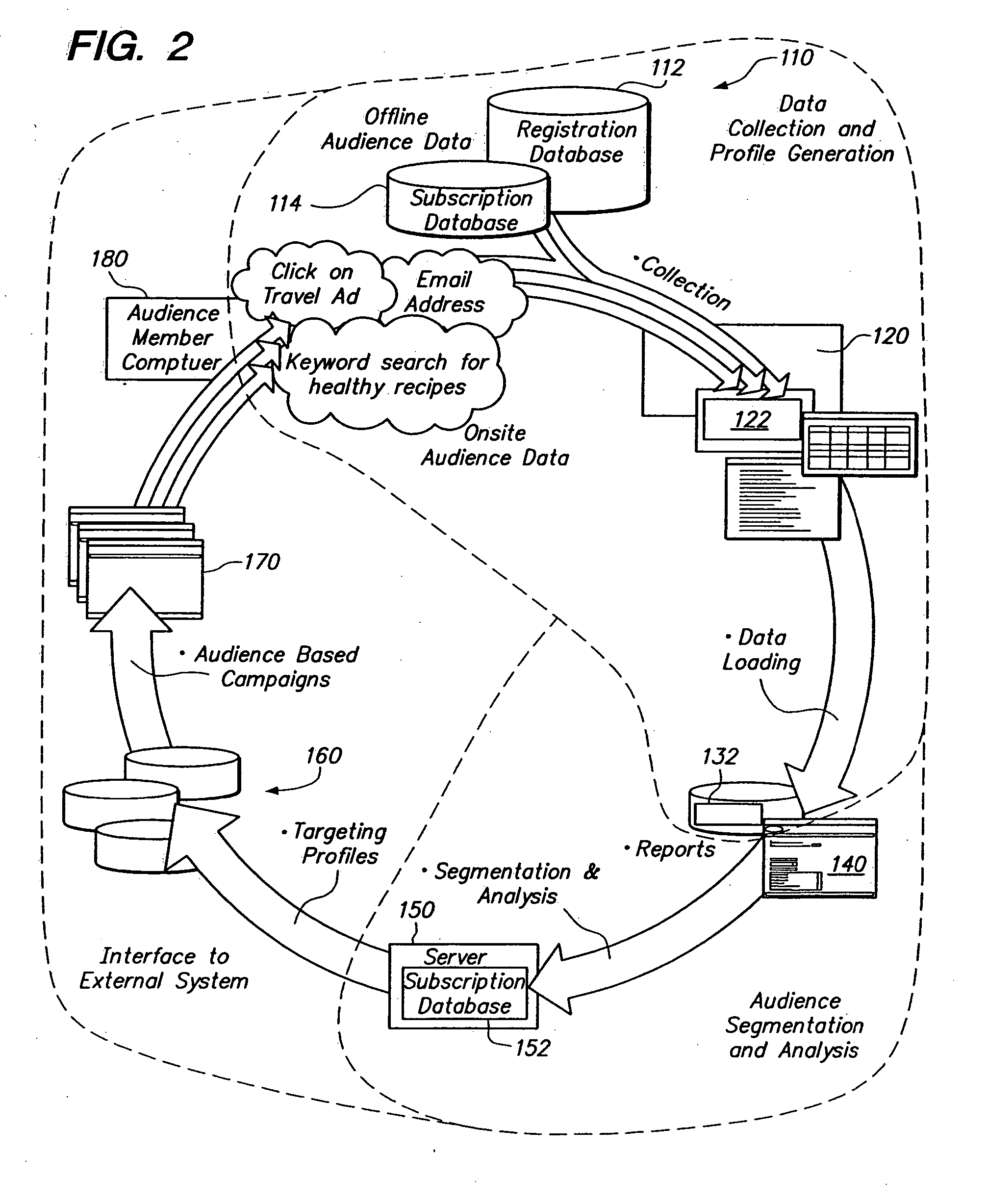
Network for matching an audience with deliverable content
ActiveUS20050166233A1Television system detailsBroadcast systems characterised by addressed receiversDistributed computingNetwork segment
Owner:YAHOO AD TECH LLC
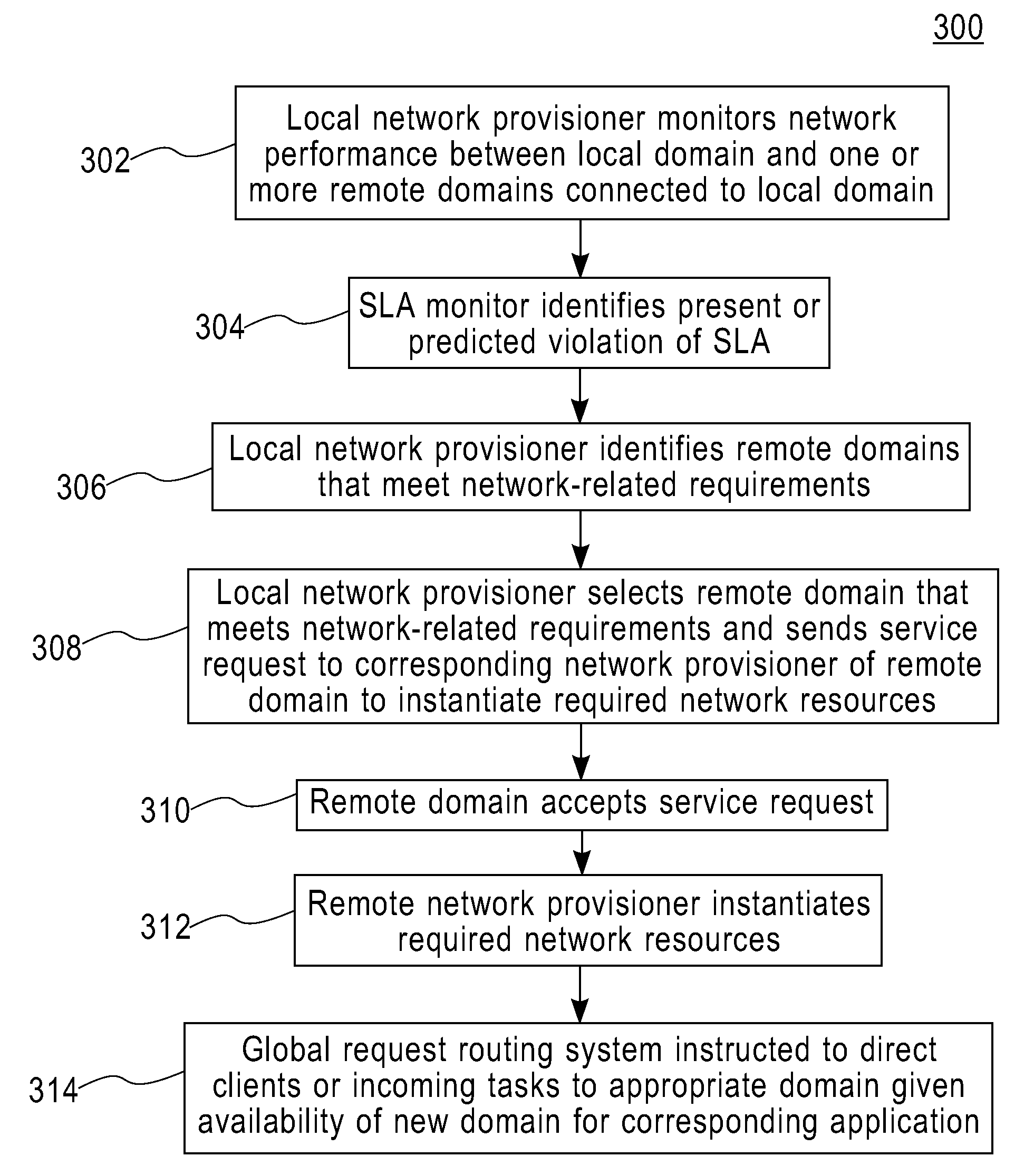
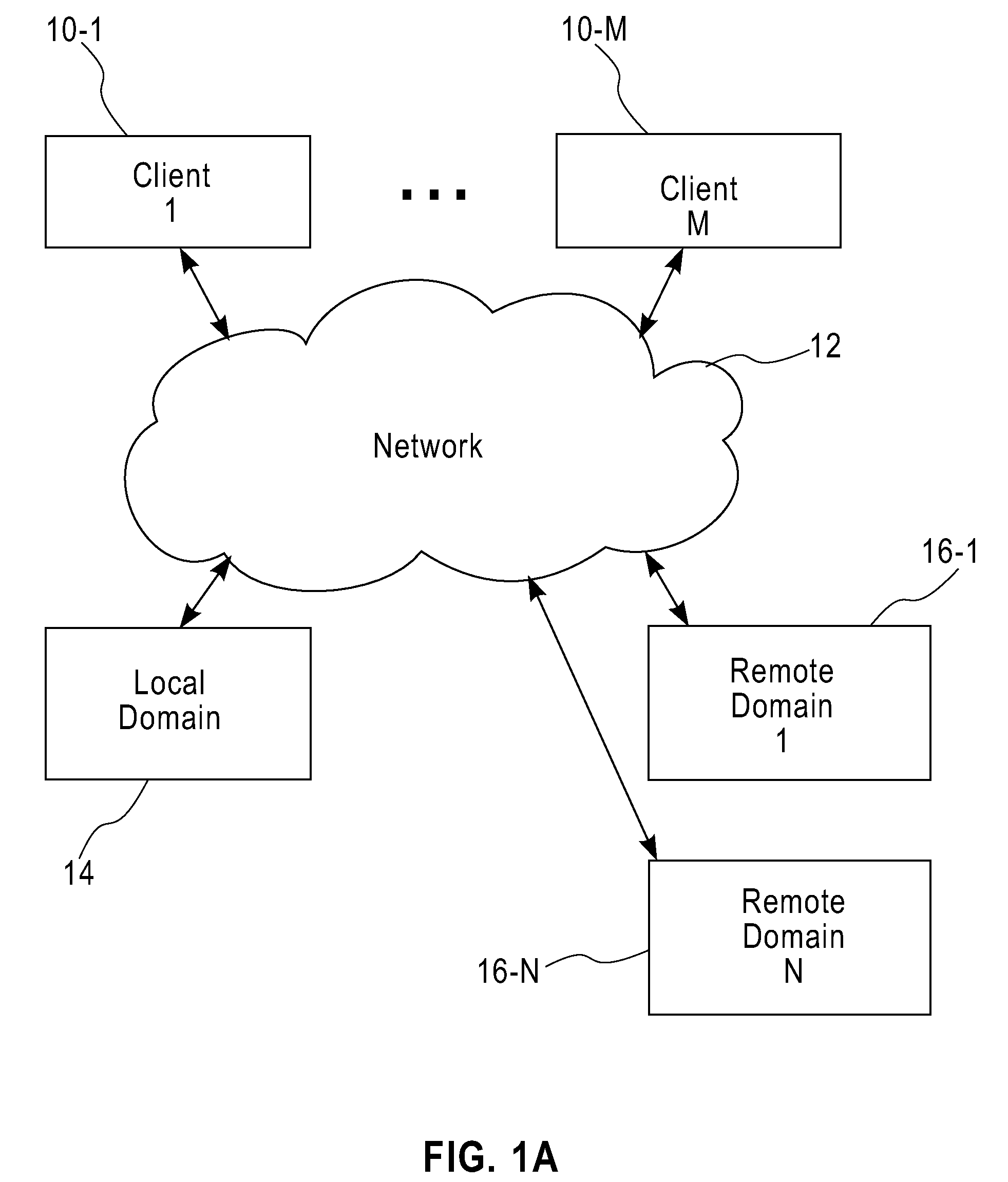
Method and apparatus for network distribution and provisioning of applications across multiple domains
ActiveUS20080240150A1Error preventionTransmission systemsService-level agreementAdministrative domain
Techniques are disclosed for network distribution and provisioning of applications, such as transactional applications and parallel applications, across multiple administrative domains that ensure compliance with service level agreements. For example, a method of provisioning one or more resources in a distributed computing network to ensure compliance with a service level agreement associated with a computer application includes the following steps. Network performance is monitored between a local domain and one or more cooperating domains connected to the local domain by network paths. A present or predicted violation of the service level agreement is identified based on at least a portion of results of the monitoring step. One or more cooperating domains are selected that can effect compliance with the service level agreement by instantiating one or more network resources within at least one of the selected cooperating domains in response to a request from the local domain. Reconfiguration of the local domain is effectuated to allow the computer application to make use of the one or more newly instantiated network resources within the selected cooperating domain.
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
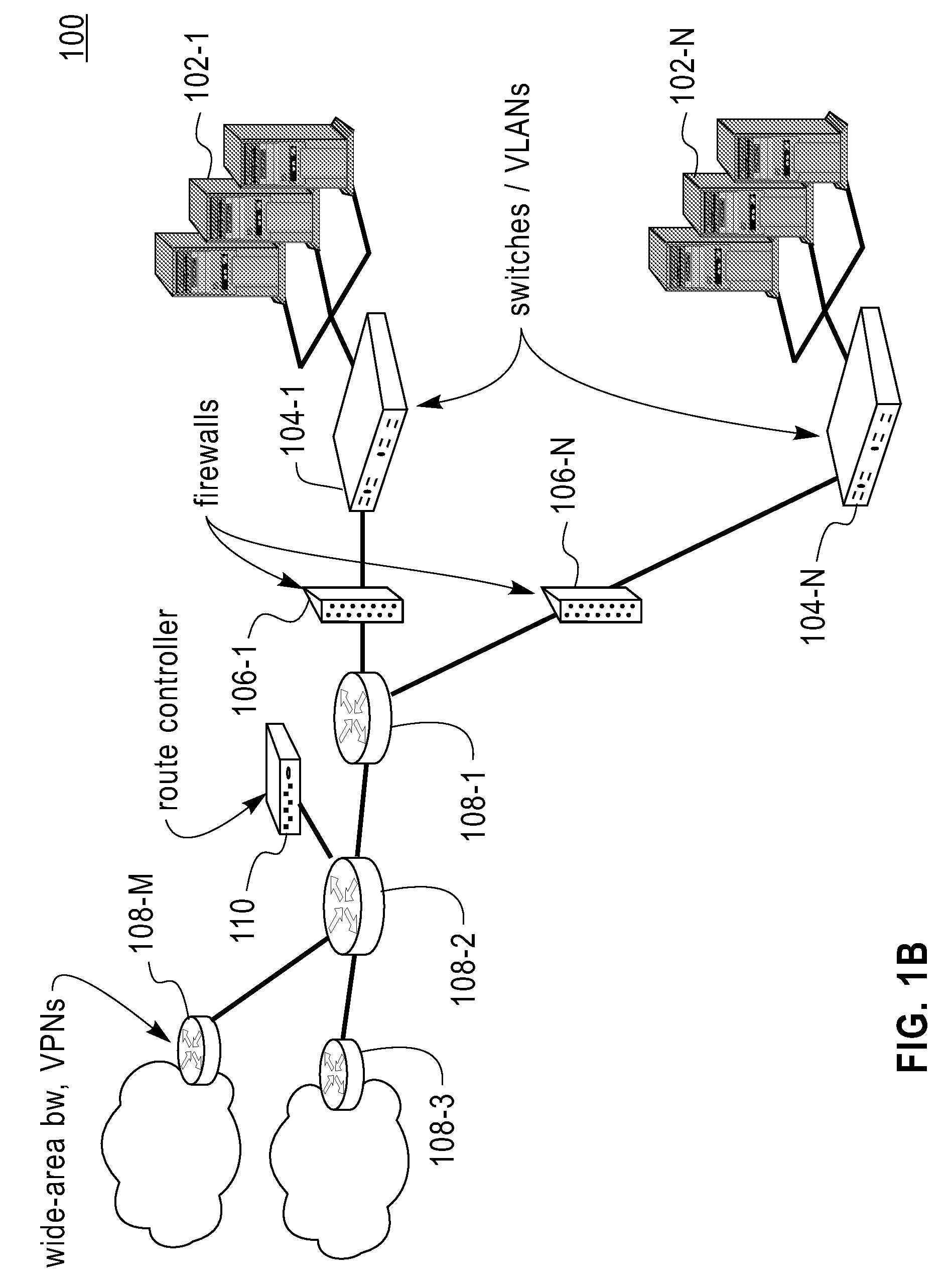
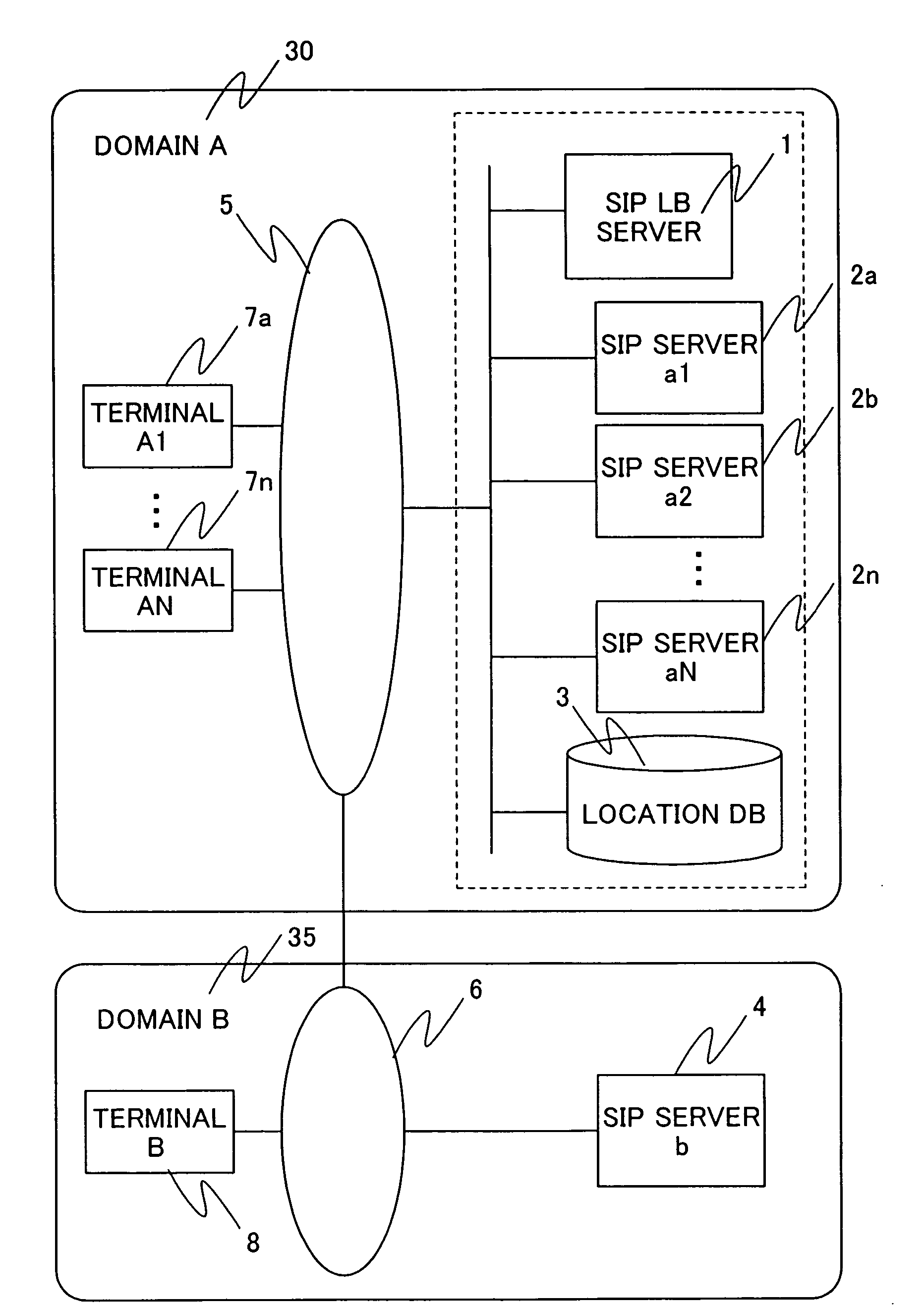
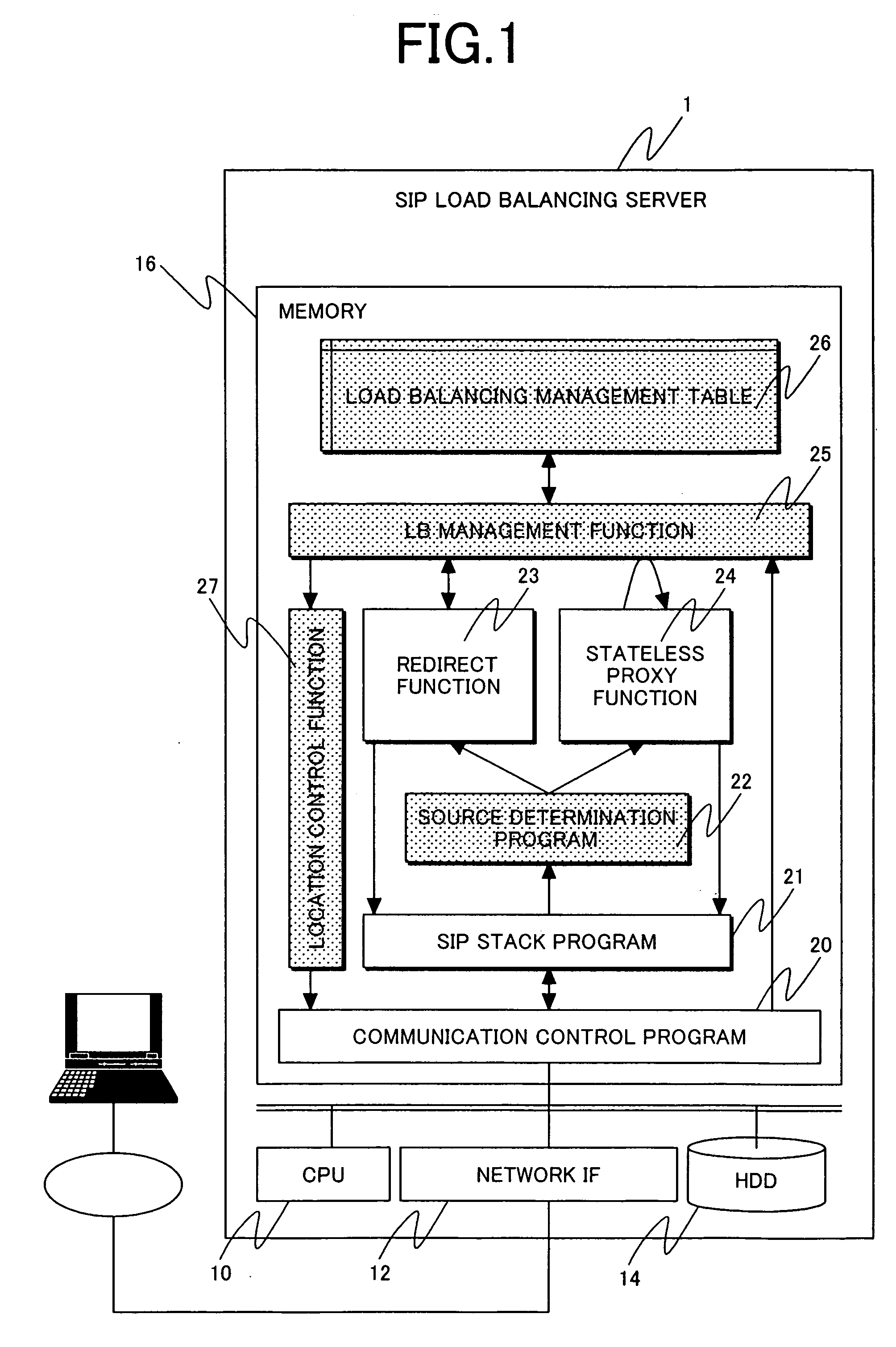
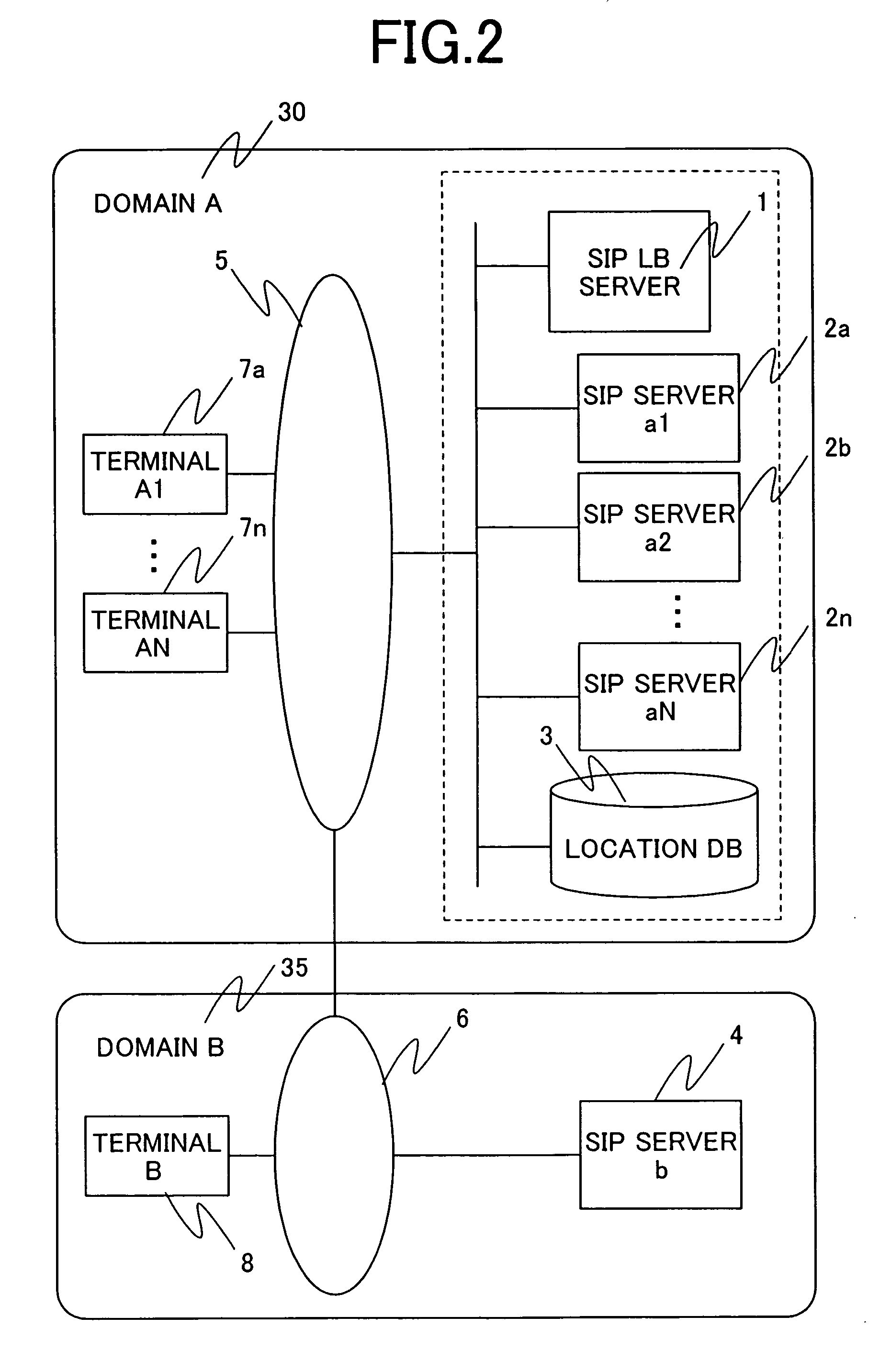
Load balancing server and system
InactiveUS20060242300A1Simple processReduce impactError preventionTransmission systemsSip serverLocal domain
When load balancing (LB) for SIP message communication is performed across multiple SIP servers, the number of messages that must be processed by an LB server is reduced. The SIP LB server includes an LB management means which, if the previous hop source of a received request message is a terminal in the local domain, determines which SIP server to serve the terminal, and a redirect function which notifies the message source terminal in the local domain of the address of the serving SIP server. The SIP LB server further includes an LB management table which, if the previous hop source of a received request message is other than a terminal in the local domain, is searched to find a SIP server serving communication with a destination terminal in the local domain, and a stateless forwarding function which statelessly forwards the received request message to the resolved SIP server address.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
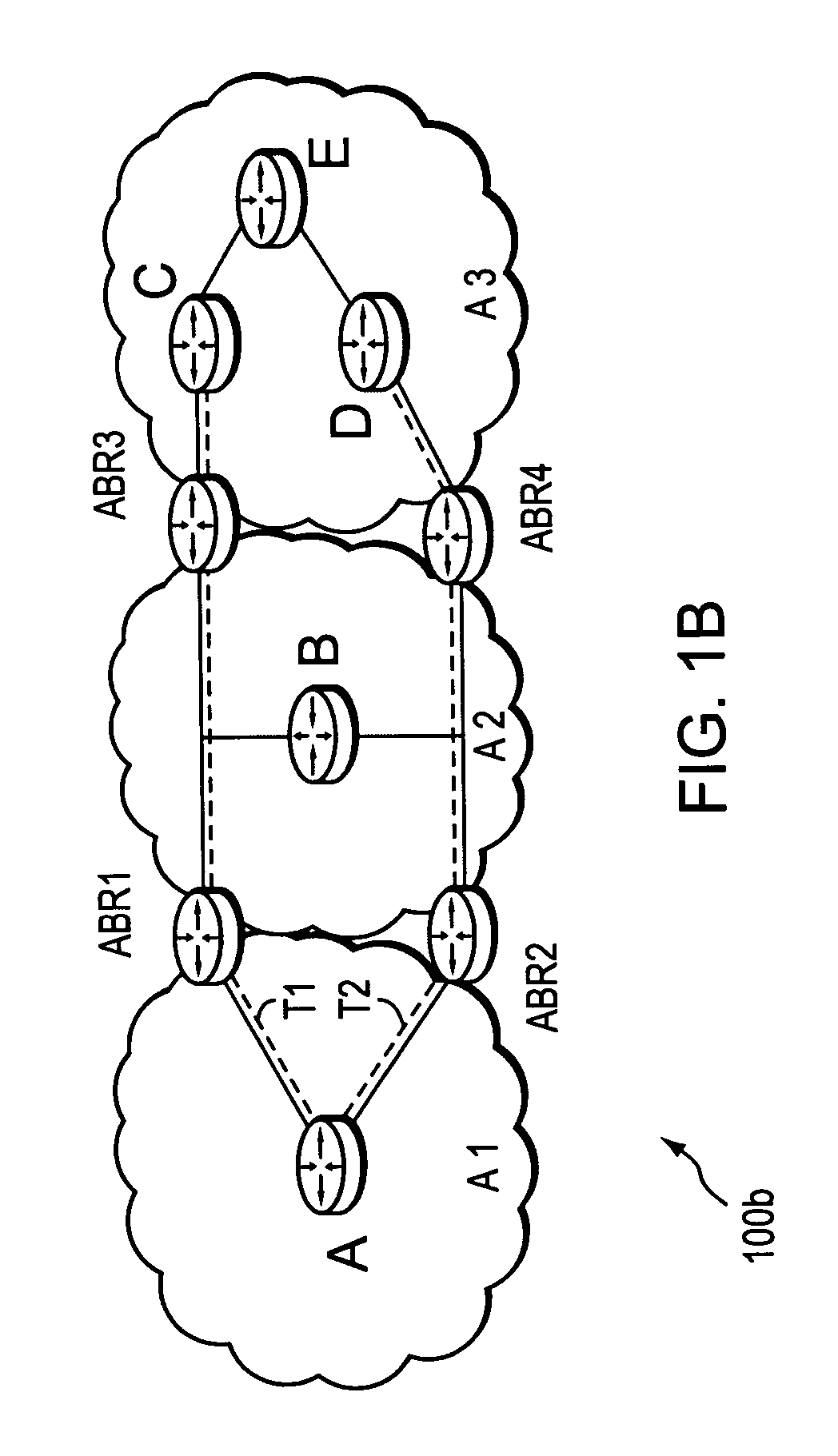
Computation of a shortest inter-domain TE-LSP across a set of autonomous systems
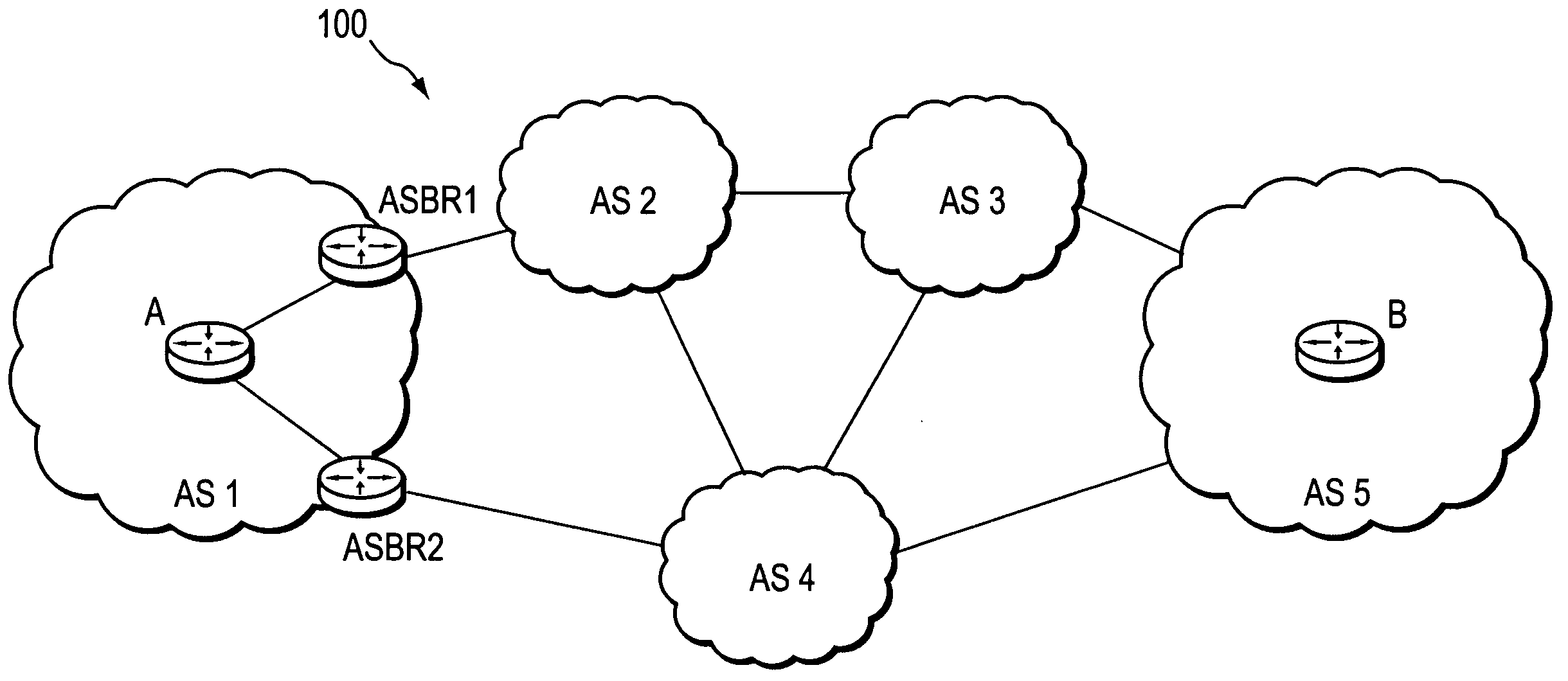
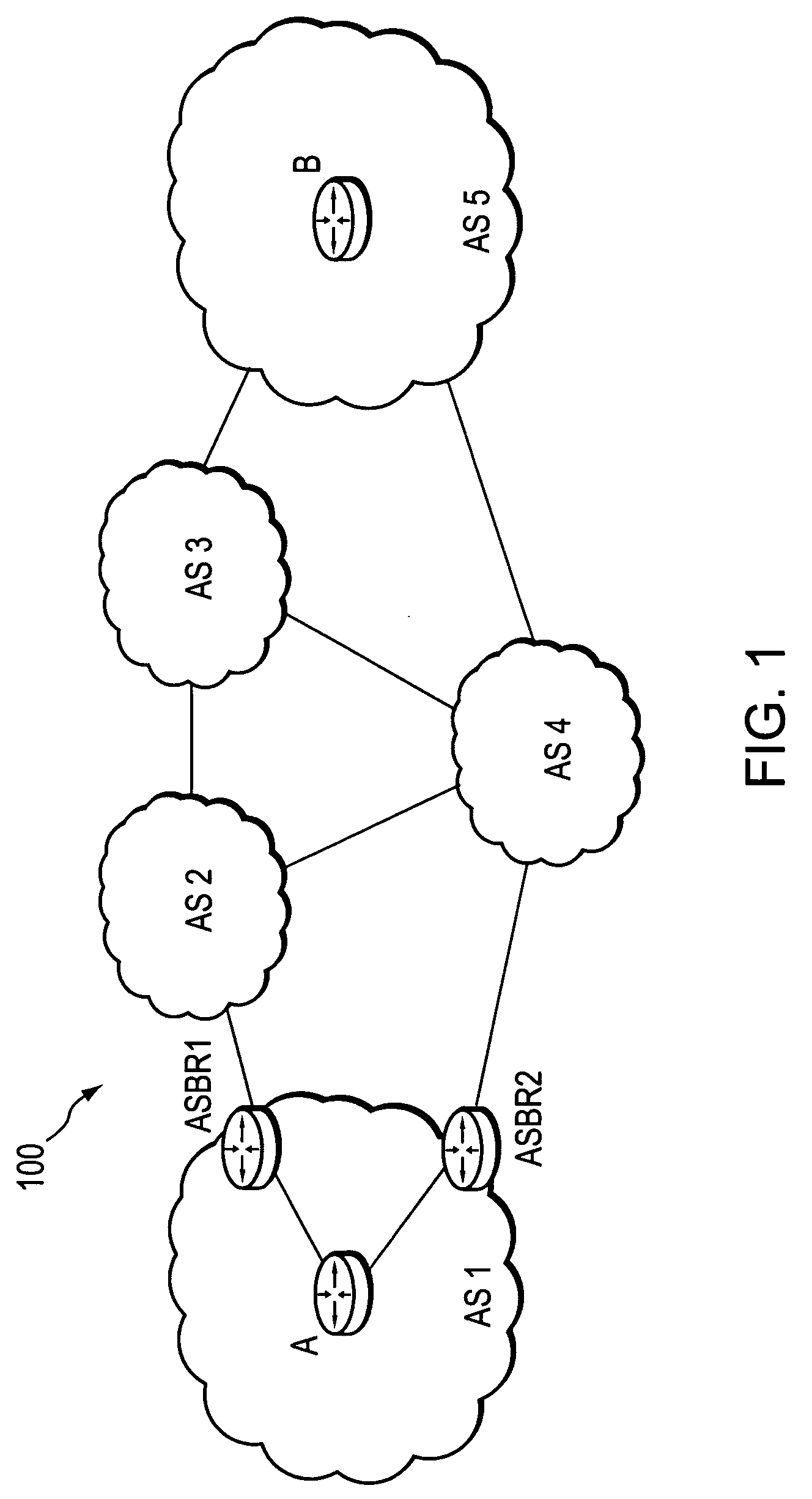
A technique calculates a shortest path for a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) from a head-end node in a local domain to a tail-end node of a remote domain in a computer network. The novel path calculation technique determines a set of different remote domains through which the TE-LSP may traverse to reach the tail-end node (e.g., along “domain routes”). Once the set of possible routes is determined, the head-end node sends a path computation request to one or more path computation elements (PCEs) of its local domain requesting a computed path for each domain route. Upon receiving path responses for each possible domain route, the head-end node selects the optimal (shortest) path, and establishes the TE-LSP accordingly.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
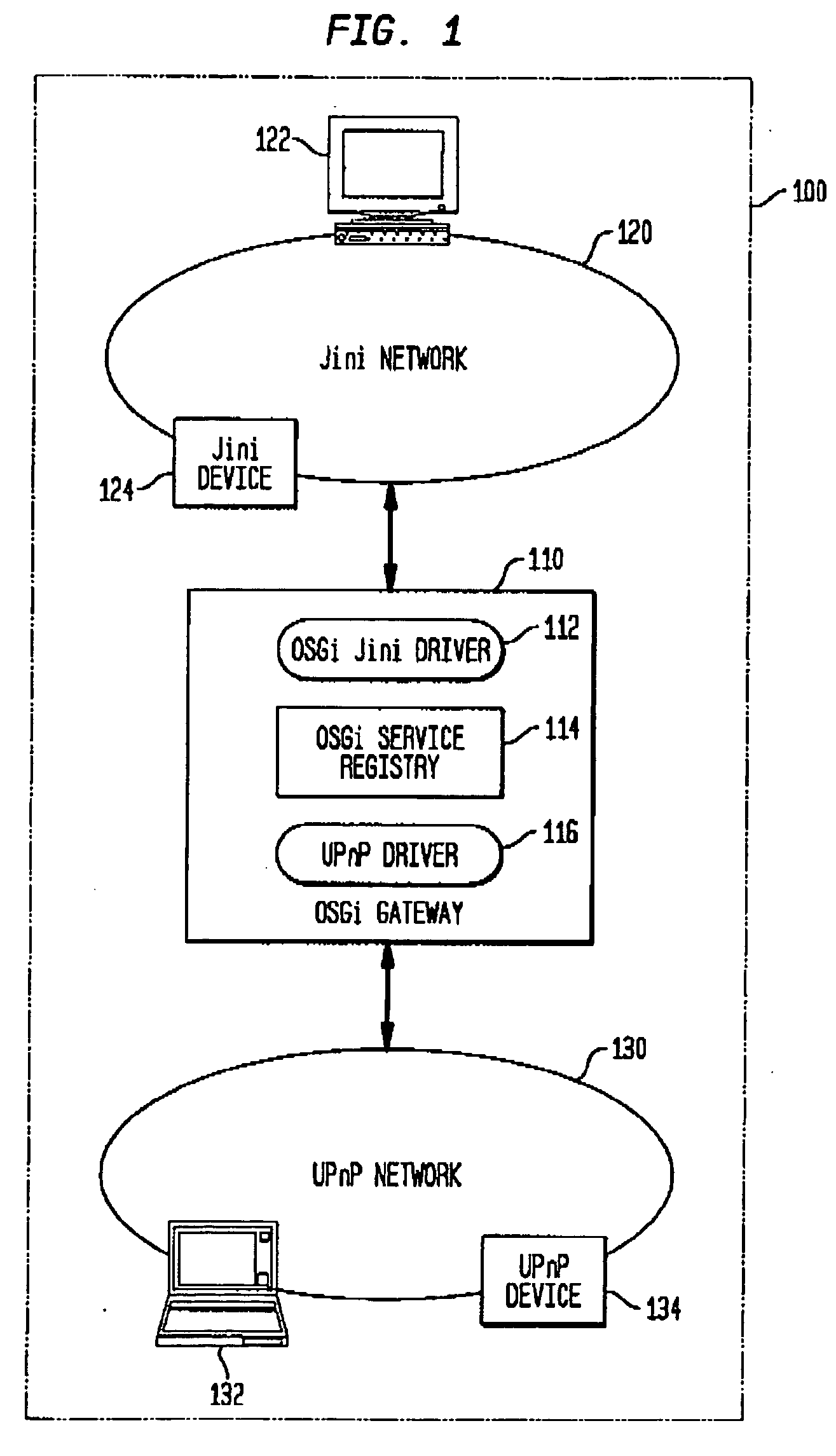
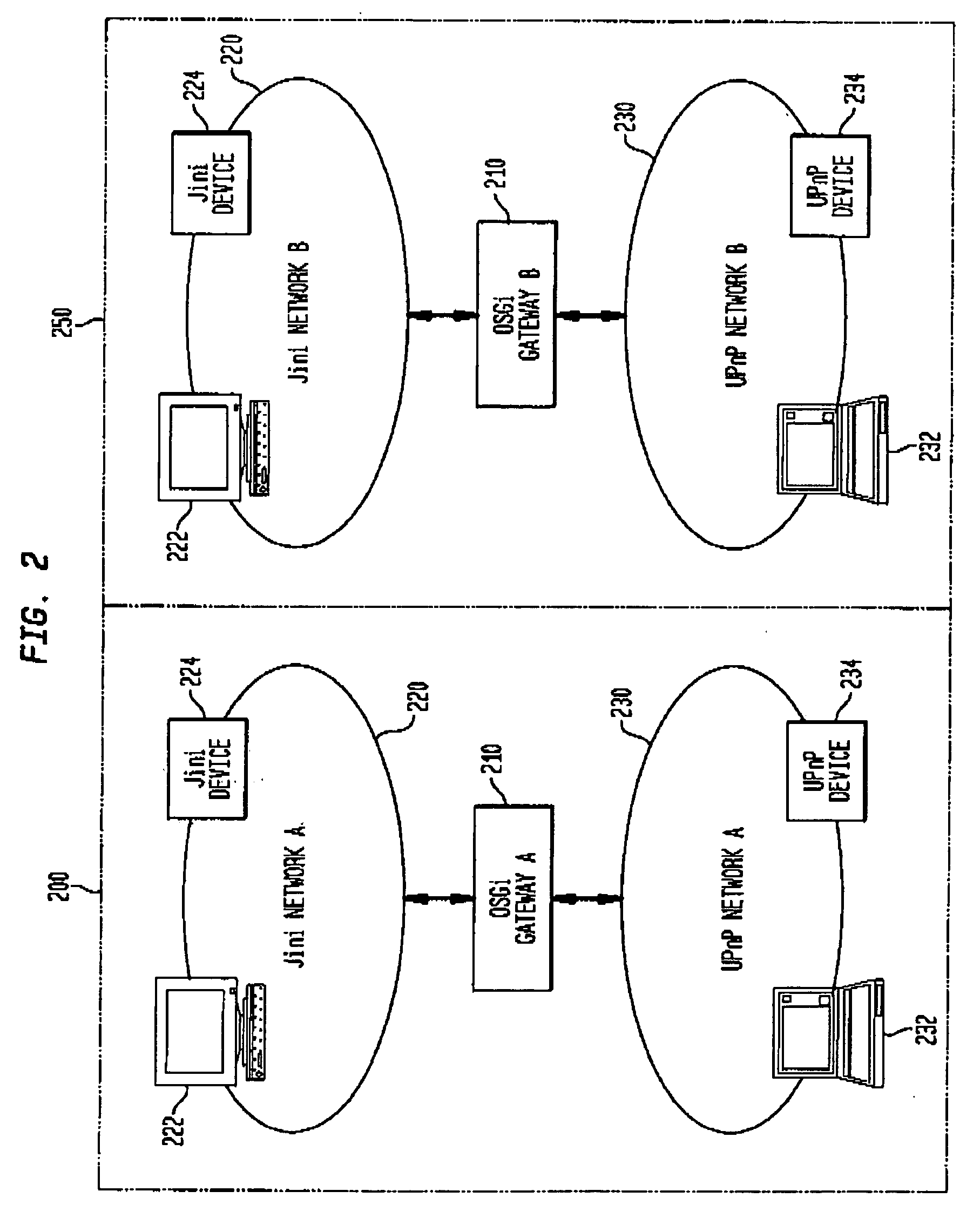
Bridging local device communications across the wide area
ActiveUS20050232283A1Multiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionsSession Initiation ProtocolBluetooth
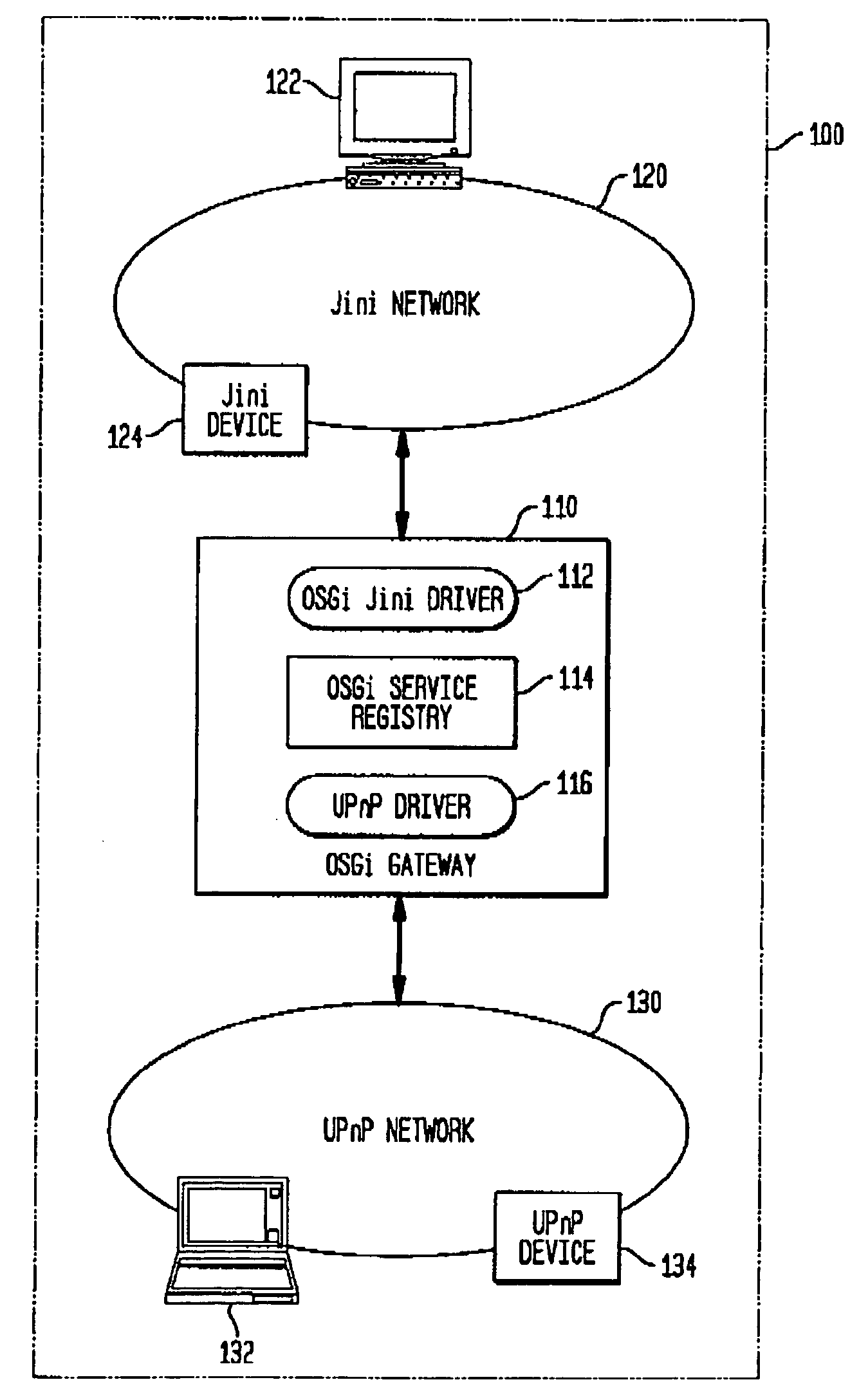
In a network of devices having a plurality of local domains, each local domain is likely to comprise a plurality of networks or communities of devices that communicate using a shared native protocol such as Jini, UPnP, Bluetooth, HAVi, WiFi, WiMAX or other standard architectures and protocols. The Open Services Gateway initiative (OSGi) created a platform and method for various networks to communicate with one another in a local domain. OSGi does not, however, solve the problems associated with communication across local domains. An instant messaging protocol such as Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and a remote services register are used to provide a means for communication between local devices in a plurality of local OSGi domains using native communications protocols.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES ASSETS 20
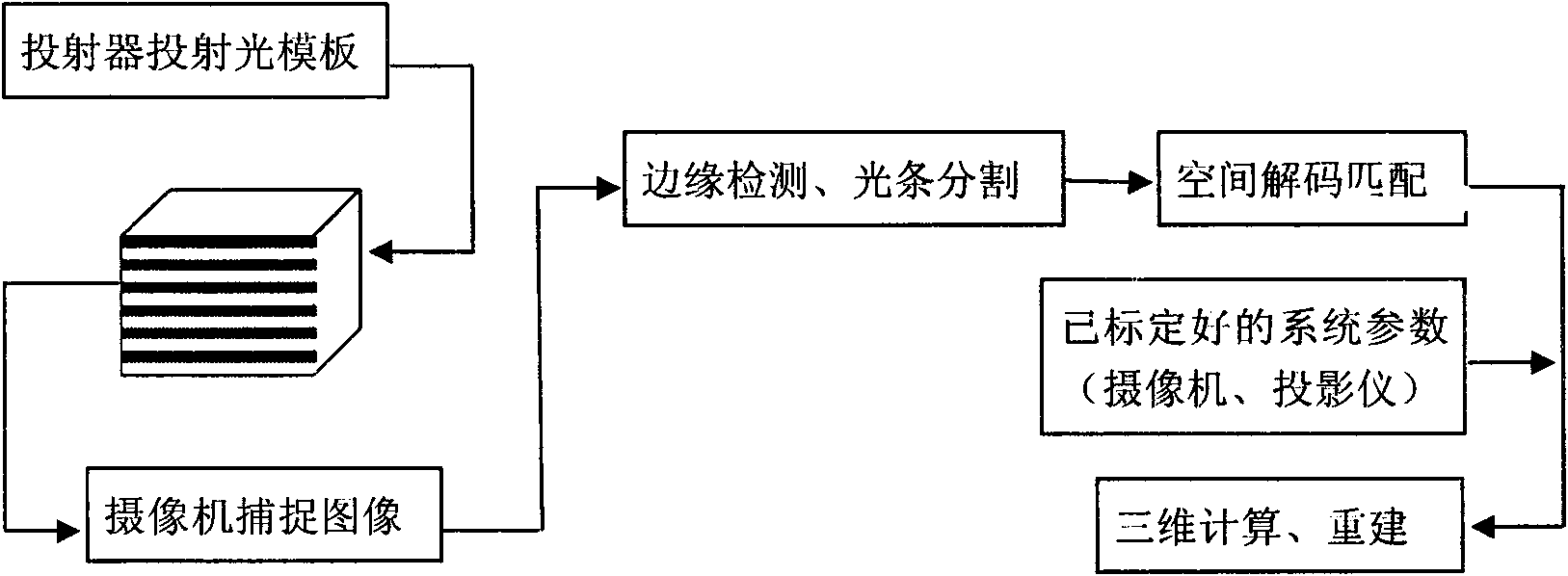
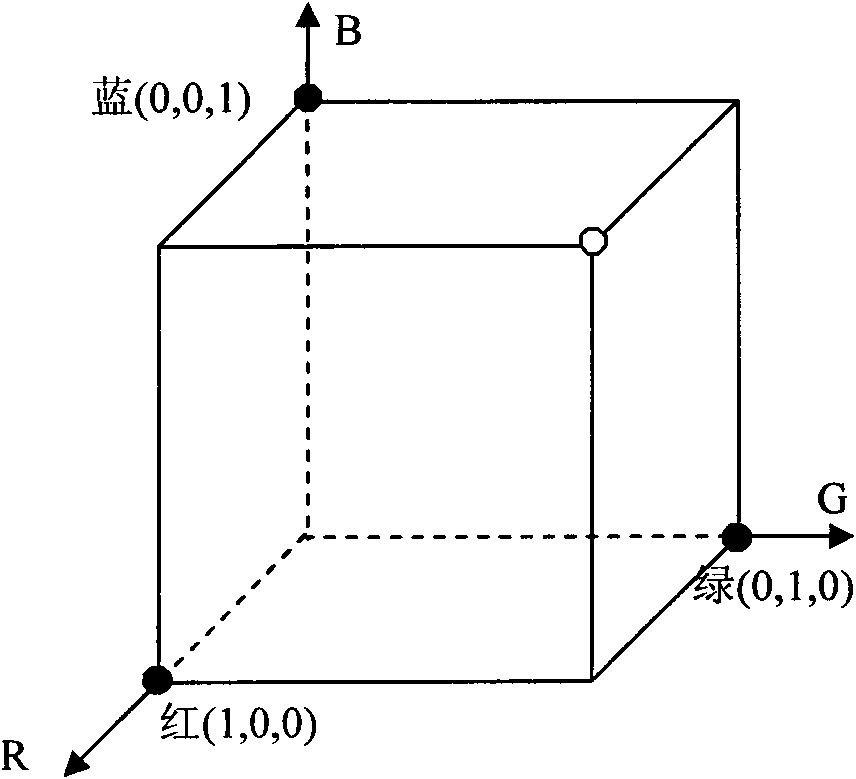
Three-dimensional reconstruction method based on coding structured light
ActiveCN101667303ASimple calculationImprove matching accuracyImage analysisUsing optical meansTemplate matchingFeature vector
The invention discloses a three-dimensional reconstruction method based on coding structured light, comprising the following steps: 1) projecting structured light to an object to be measured, and capturing an image modulated by the object to be measured by a camera; 2) matching an optical template, comprising: (2.1) positioning the optical strip boundary, scanning along each row of the image, determining a pixel point with strong gray variation as a candidate marginal point, and searching a local domain; and (2.2) matching the optical strip: adopting a color cluster method to build a color matching proper vector, comparing image color with a projected color, and defining Euclidean distance between the color proper vector and the cluster center to distribute the colors of red, green, blue and white of the candidate optical strip; and 3) using a calibrated system parameter for three-dimensional reconstruction of the object to be measured, determining the relation between a space point coordinate and the image coordinate point thereof by the calibrated conversion matrix parameter; and restoring three-dimensional spatial coordinate from the image coordinate of a feature point. The invention can simplify calculation process and has high matching precision and high reconstruction precision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
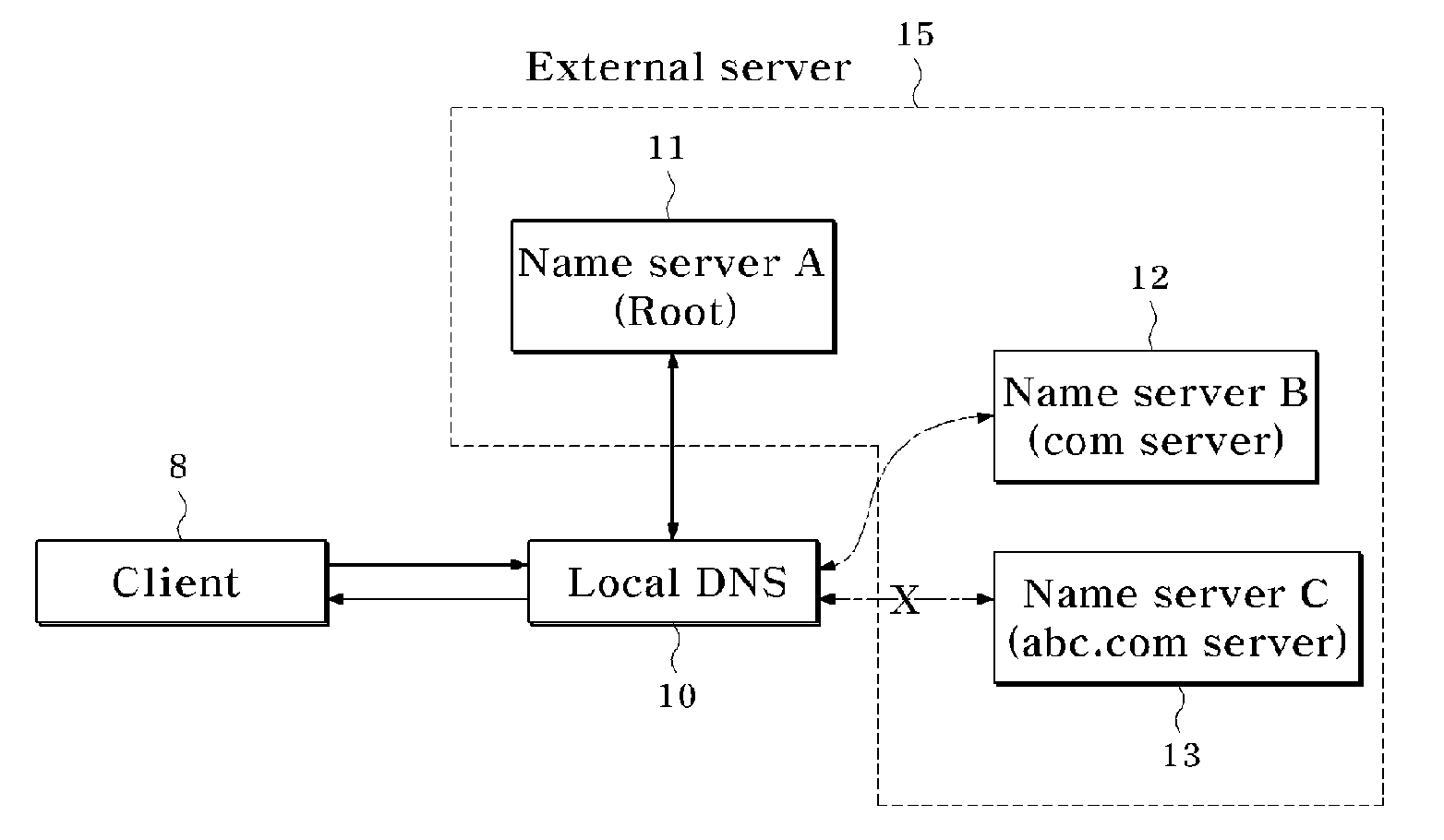
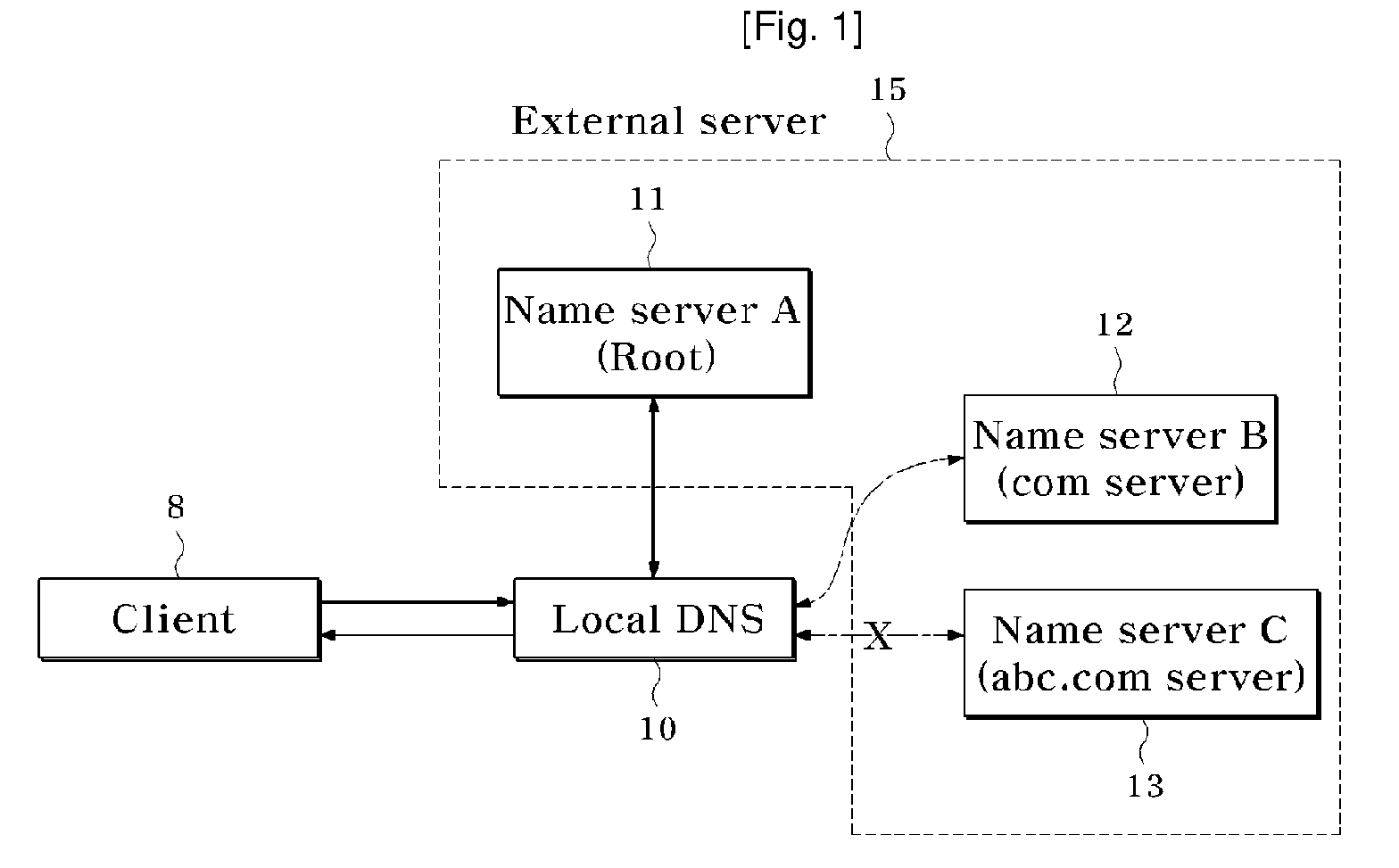
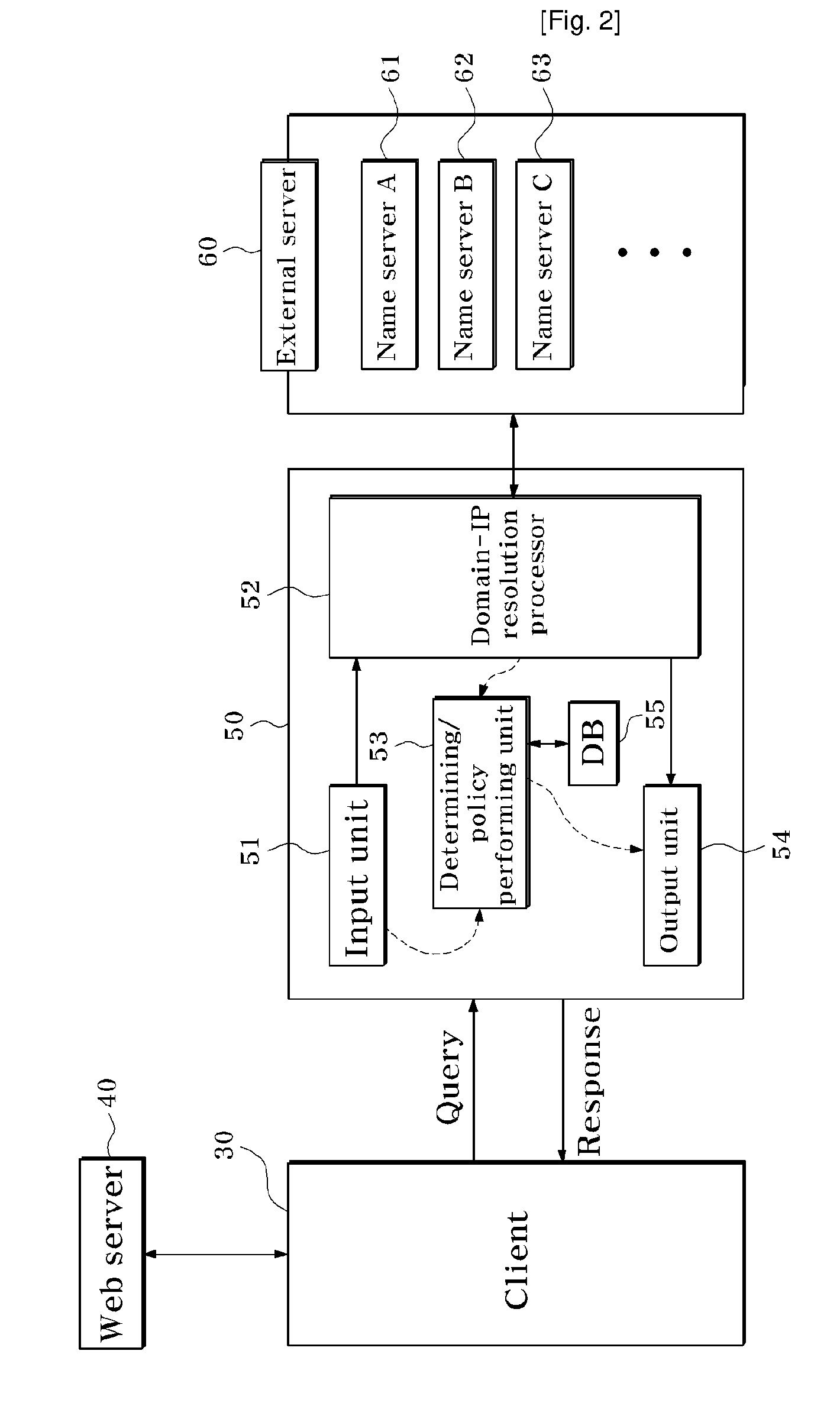
Local Domain Name Service System and Method for Providing Service Using Domain Name Service System
InactiveUS20090055929A1Quality improvementImprove system performanceSingle unit pavingsMemory loss protectionDomain nameClient-side
Provided is a local domain name system for querying an external server for a client-requested domain name and providing desired data to a user. A determination is made as to whether a special policy is to be applied to a client-input query through a test task. When a special policy is to be applied to the query, the special policy is performed to provide additional service to the client.
Owner:NETPIA COM
Inter-domain path computation technique
ActiveUS20060171320A1Computationally efficientOptimization pathError preventionTransmission systemsPath computation elementLabel switching
A technique computes a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) that spans multiple domains of a computer network from a head-end node of a local domain to a tail-end node of a remote domain. The novel inter-domain TE-LSP computation technique comprises a computation algorithm executed by the head-end node, which utilizes Path Computation Elements (PCEs) located within the remote domains (i.e., other than the local domain). Specifically, the head-end node requests path segments from a PCE in each of the remote domains, in which the path segments represent paths between all entry border routers to either all exit border routers of the particular remote domain (i.e., through the domain), or to the tail-end node. Upon receiving path segments from each remote domain, the head-end node combines the path segments with local domain information, and performs a forward path computation from the head-end node to the tail-end node to find the best (i.e., “shortest”) path.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Dynamic retrieval of routing information for inter-AS TE-LSPs
A technique dynamically triggers an exchange of reachability information between a tail-end (remote) domain target node (e.g., a tail-end node) of a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) and a local domain head-end node of the TE-LSP in a computer network. The inter-domain information retrieval technique is illustratively based on triggering a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) session whereby at least a portion of the reachability, i.e., routing, information of the tail-end node is transmitted to the head-end node of the TE-LSP in accordance with BGP. Specifically, once a TE-LSP is established between the head-end node and the tail-end node, the head-end node triggers the tail-end node, e.g., through extensions to a request / response signaling exchange, to establish the BGP session. Establishment of the BGP session enables transmission of the routing information from the tail-end node to the head-end node. The head-end node uses the routing information to calculate routes, i.e., address prefixes and associated attributes, reachable from the tail-end node for insertion into its routing table.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for managing integrated network locations
InactiveCN101123536AInterconnection arrangementsSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsReal-time computingLocal domain
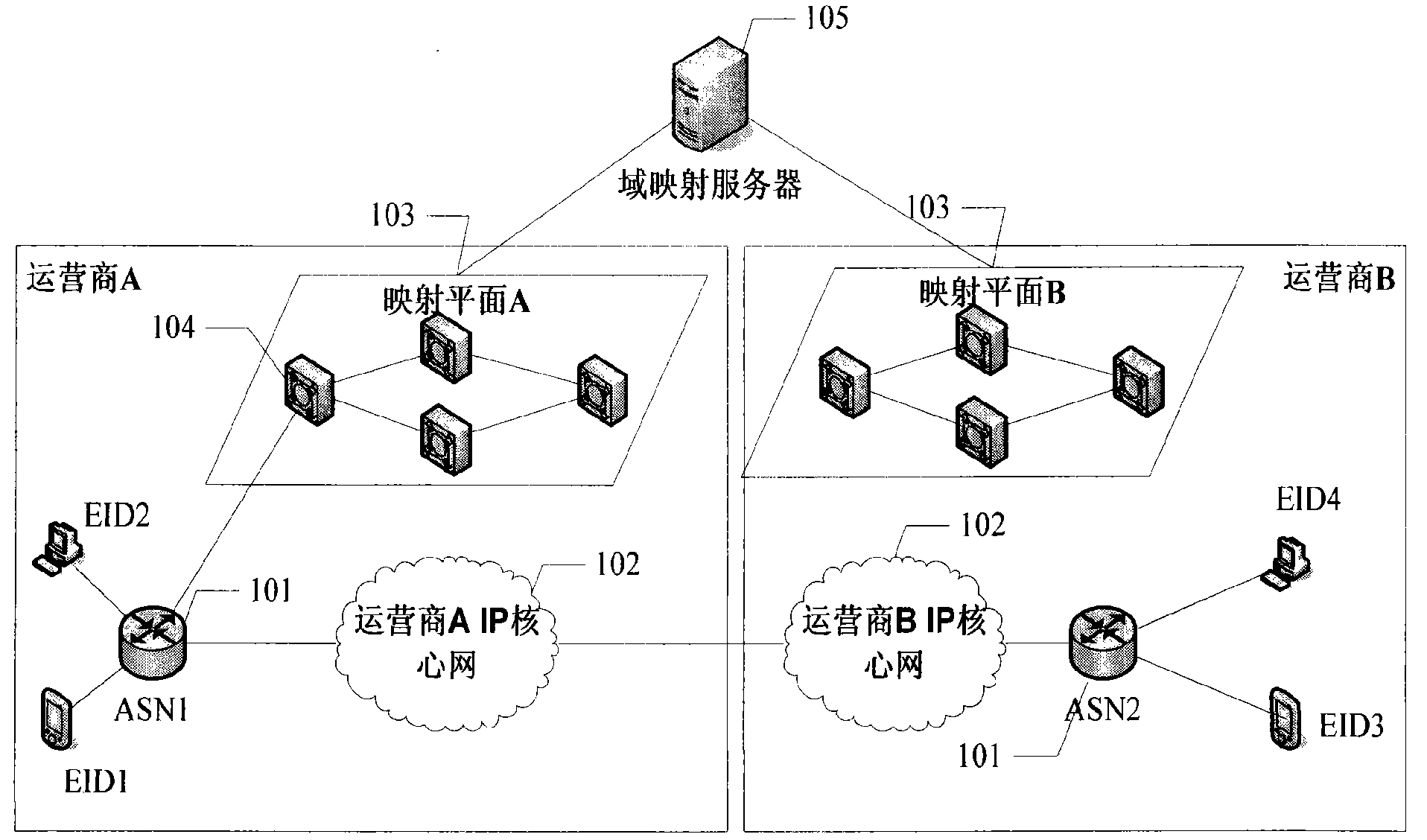
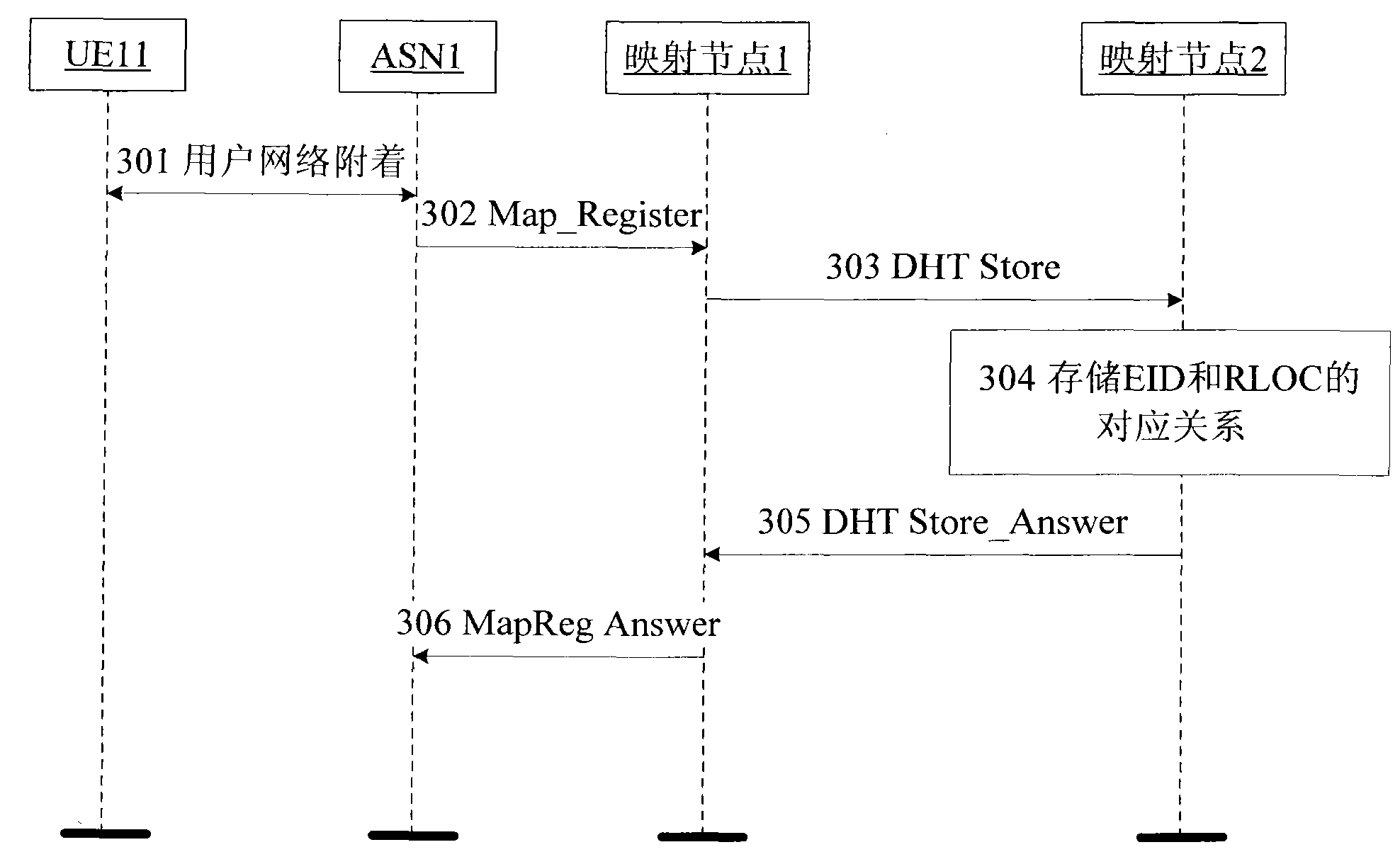
A method realizing the location management of an integrated network assigns location information for various types of terminals accessing the integrated network and finishes location registration by registering identities and location mapping of the terminals on a mapping server. When a terminal moves, a location update process is initiated toward the mapping server via an access router, and the update of terminal location information in the whole network is finished by means of information interaction among related entities. When a terminal initiates communication, the access router initiates a location query procedure toward the mapping server of the local domain, and by means of the cooperation of the mapping server of the local domain, the mapping server of the ownership domain of the destination terminal and the mapping server of the domain in which the destination terminal locates, the current location information of the destination terminal is obtained by query and returned to the access router of the source end to ensure that the access router can correctly initiate a communication connection.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
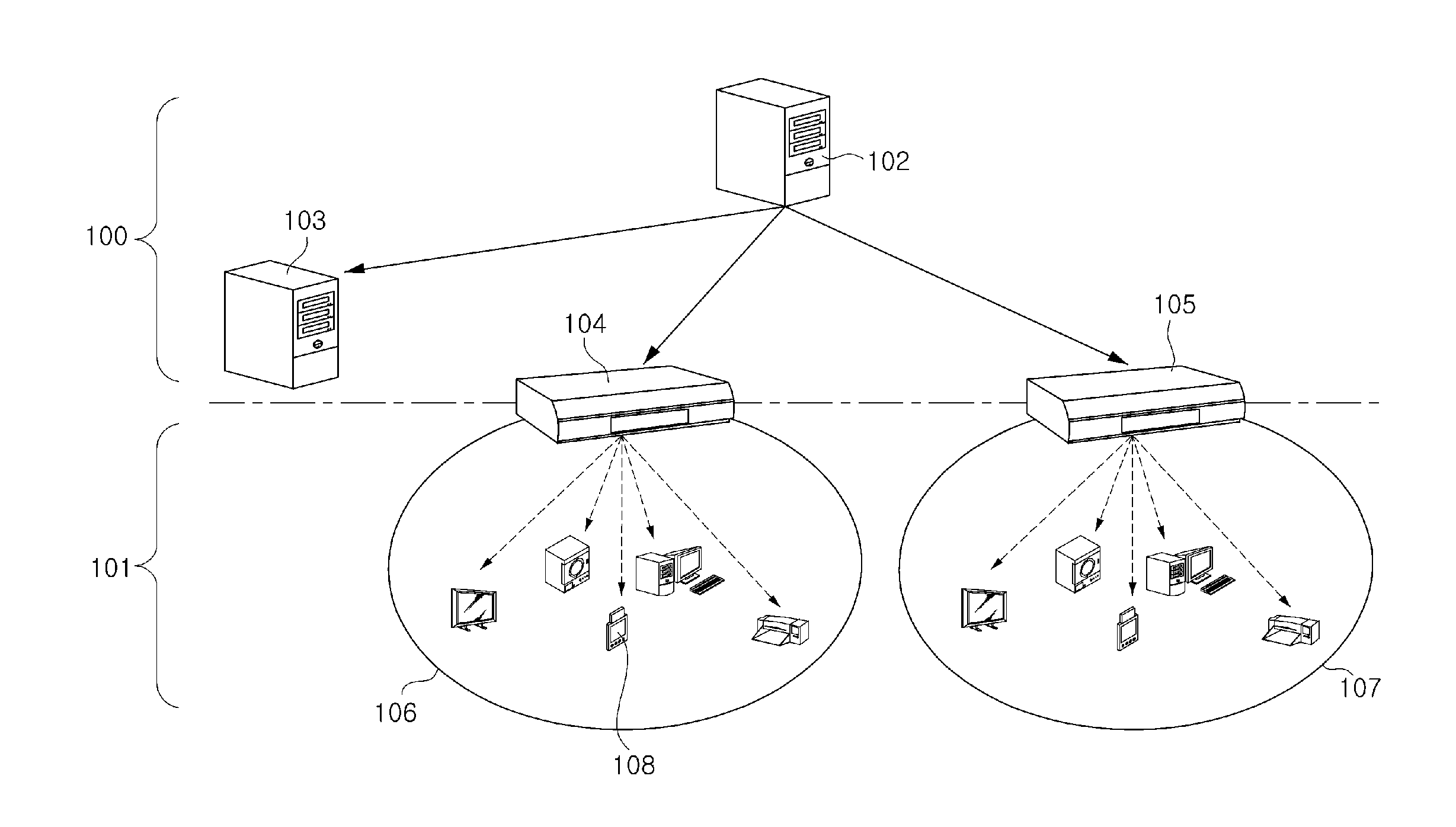
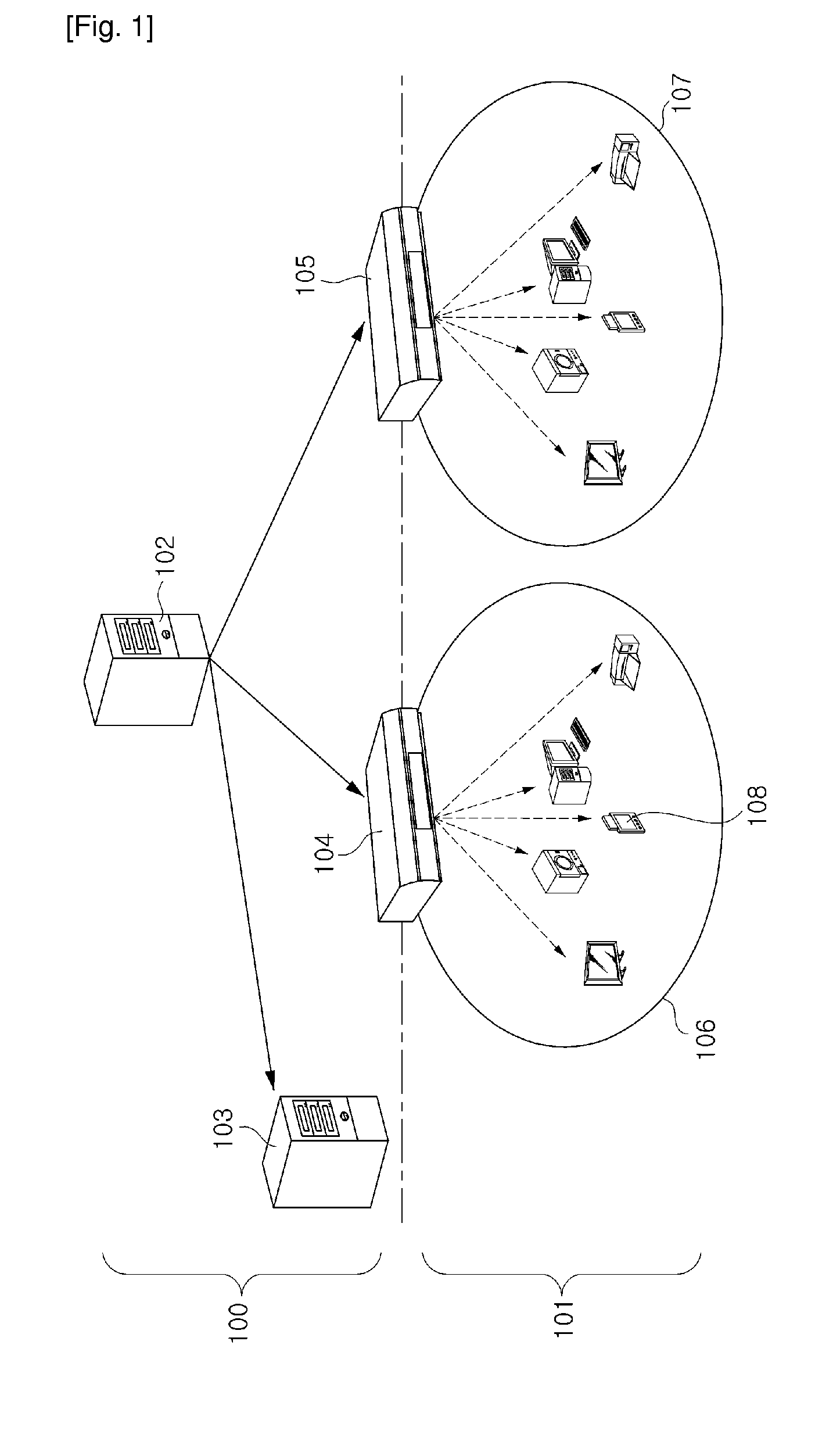
Method and apparatus for authenticating device in multi domain home network environment
InactiveUS20090240941A1Low costMinimizing interventionEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesPublic key for secure communicationDevice registerMulti domain
A device authentication method and device authentication apparatus in a multi domain home network environment are provided. The method includes registering a new device in each local domain and issuing a local domain certificate; making an agreement between local domains in order to authenticate a device registered to another local domain; when the device registered to the home local domain or another local domain requests a service, authenticating the device via communication inside the local domains, thereby minimizing a user's intervention, making it easier to use the apparatus, reducing a device operation with regard to a device having limited performance, and making it easier to extend the apparatus.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
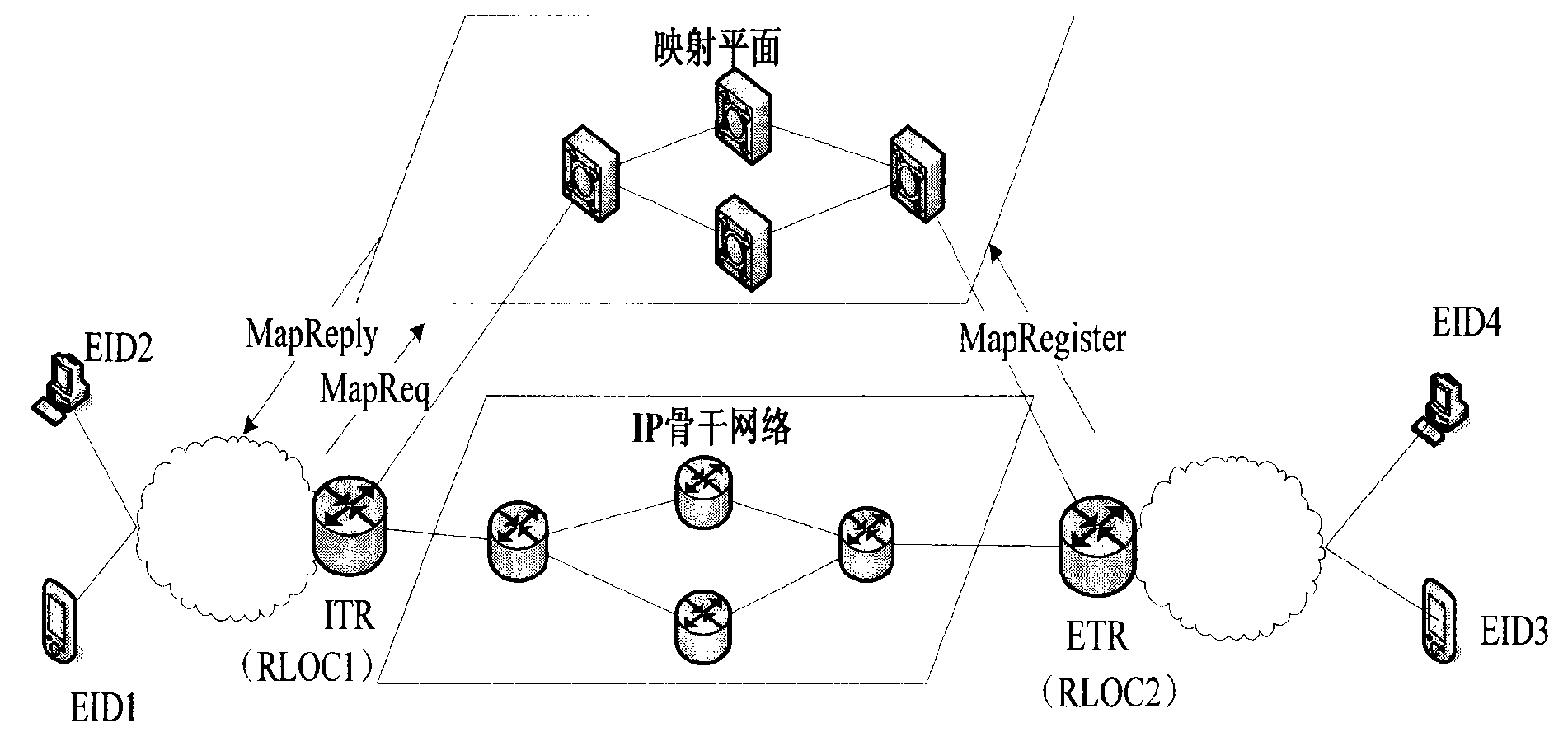
Address mapping system and data transmission method of identifier/locator separation network
ActiveCN101656765AQuick searchImprove routing efficiencyStore-and-forward switching systemsA domainData transmission
Owner:安盟鑫(江苏)办公用品有限公司
Methods and systems for processing network data packets
ActiveUS7386628B1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksReal-time computingLocal domain
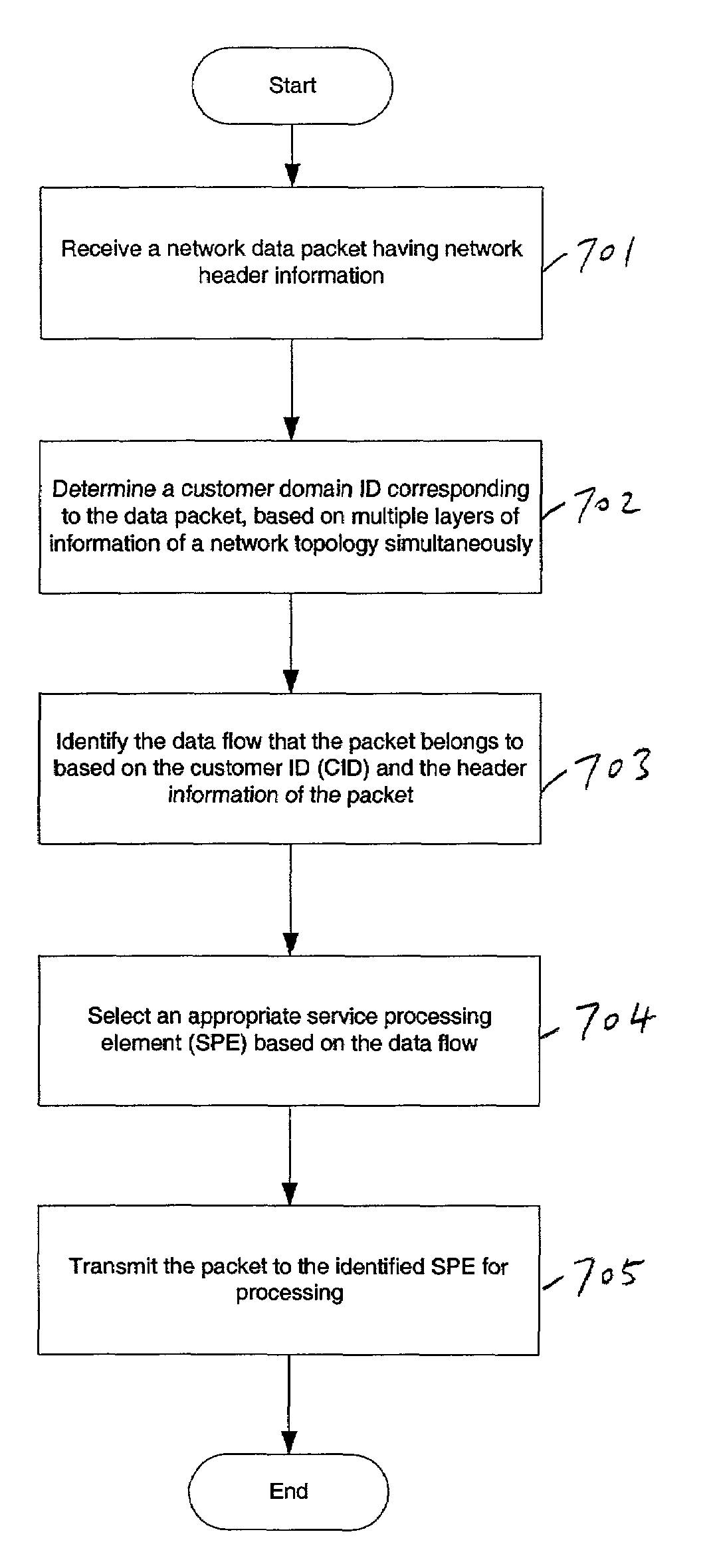
Methods and systems for identifying a local domain for a data packet received at an interface through a network are described herein. In one aspect of the invention, an exemplary method includes extracting the network protocol information from the data packet, determining a local domain ID based on multiple layers of network protocol information simultaneously, and assigning the local domain ID to the data packet. Other methods and systems are also described.
Owner:AVAYA MANAGEMENT LP
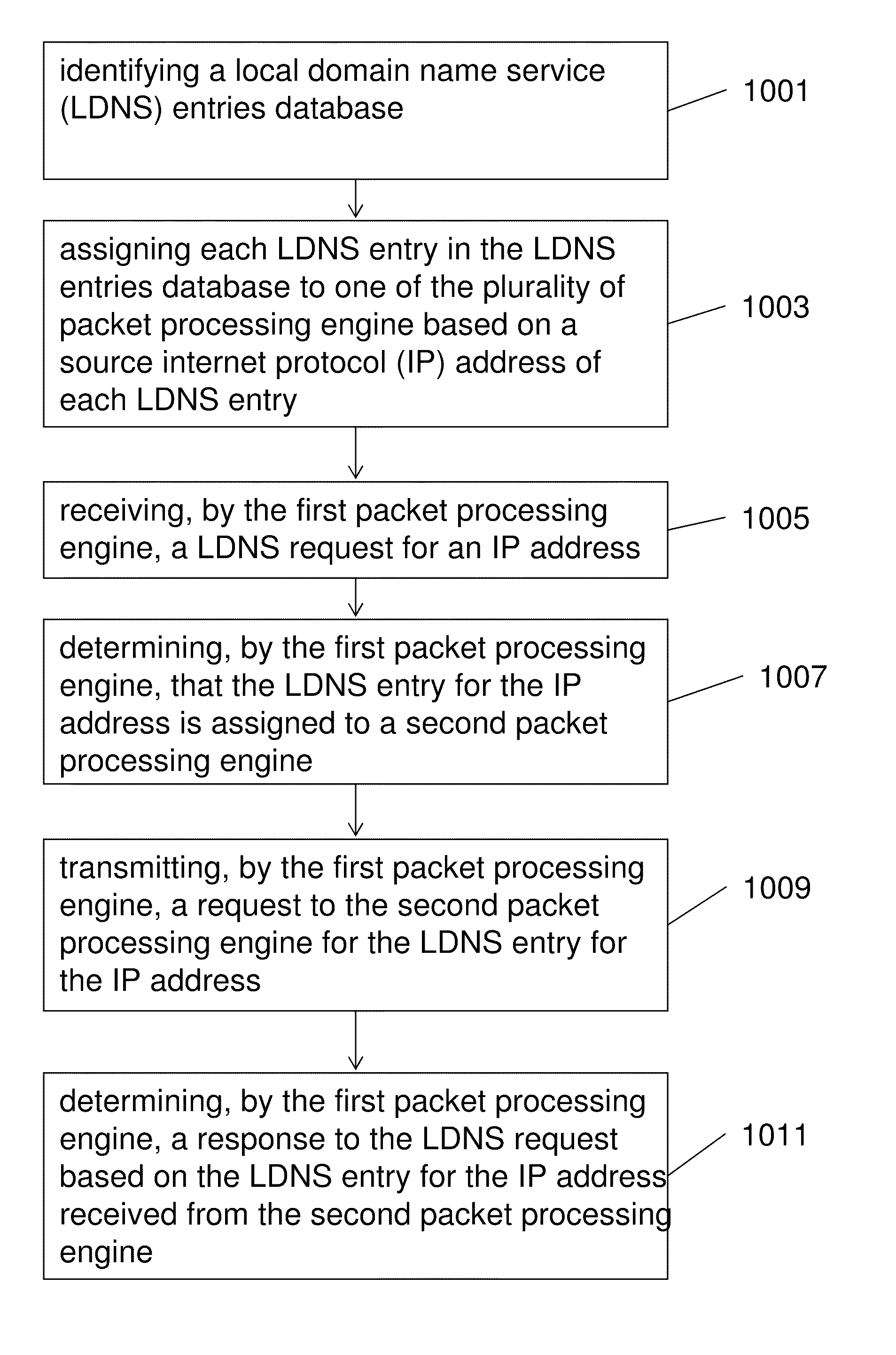
Systems and methods for managing dynamic proximity in multi-core GSLB appliance
The present invention is directed towards systems and methods for providing dynamic proximity load balancing via a multi-core intermediary device. An intermediary device providing global server load balancing (GSLB) identifies a local domain name service (LDNS) entries database and assigns each LDNS entry in the LDNS entries database to one of the plurality of packet processing engine base on a source internet protocol (IP) address of each LDNS entry. The first packet processing engine on the appliance receives a LDNS request for an IP address, determines that the LDNS entry for the IP address is assigned to a second packet processing engine of the plurality of packet processing engines, transmits a request to the second packet processing engine for the LDNS entry for the IP address, and determines a response to the LDNS request based on the LDNS entry for the IP address received from the second packet processing engine.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Inter-domain TE-LSP selection
InactiveUS20060120288A1Avoid errorsReduce riskError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityReachability
A technique selects a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) from among a plurality of TE-LSPs, each of which spans multiple domains of a computer network from a head-end node of a local domain to a tail-end node of a remote domain, in order to reach one or more address prefixes within the remote domain. The inter-domain TE-LSP selection technique comprises a selection algorithm executed by the head-end node and based on predetermined TE-LSP attributes (e.g., bandwidth, cost, etc.) and / or address prefix reachability attributes (e.g., cost from a tail-end node to the prefix) to select an appropriate inter-domain TE-LSP for the reachable address prefix. The selection algorithm is embodied in one of two modes: (i) a hierarchical selection mode, or (ii) a weighted selection mode. In addition, the technique comprises a load balancing aspect that cooperates with the selection algorithm to enable the head-end node to balance traffic loads among the multiple TE-LSPs based on the results of the selection algorithm.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
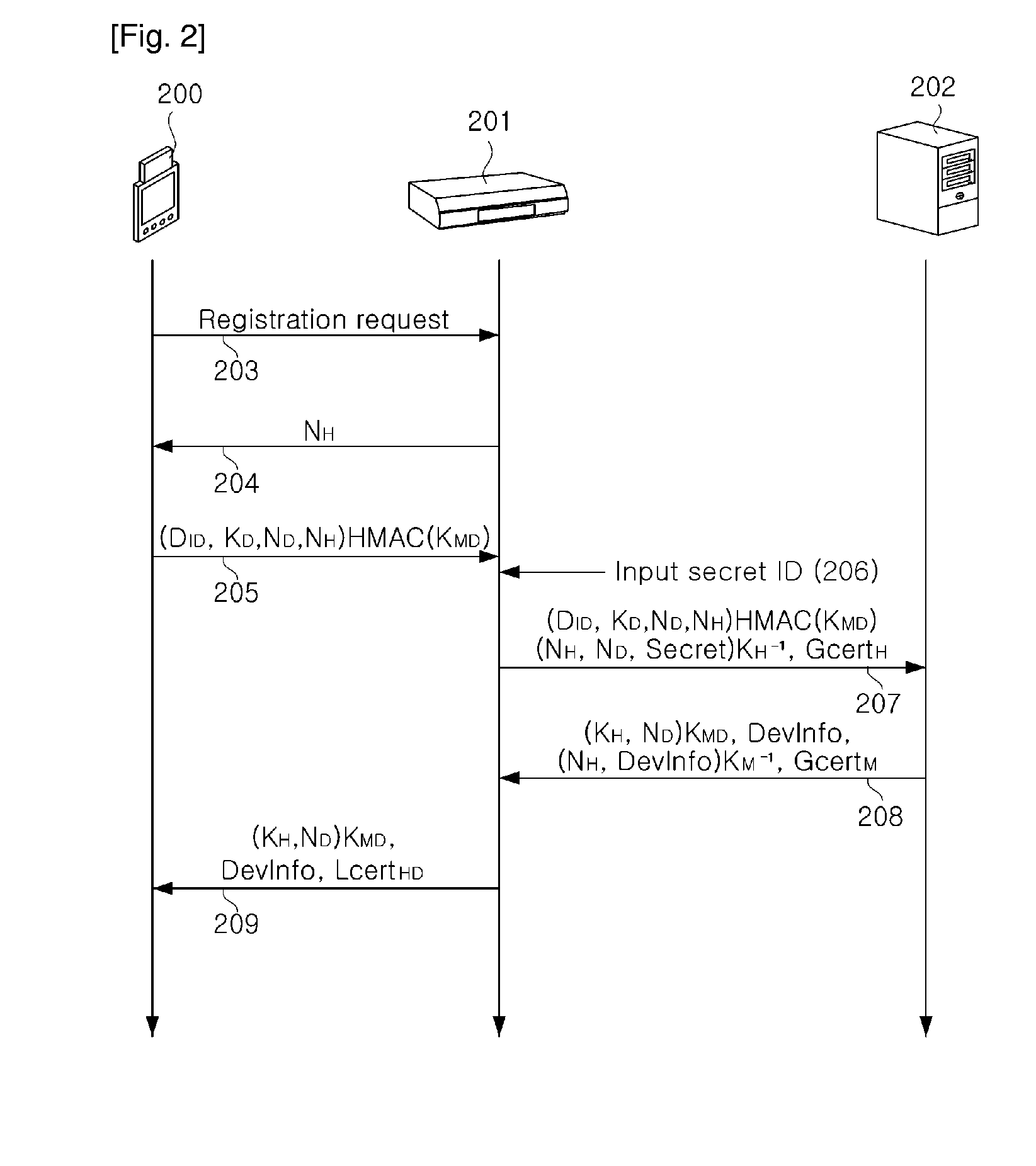
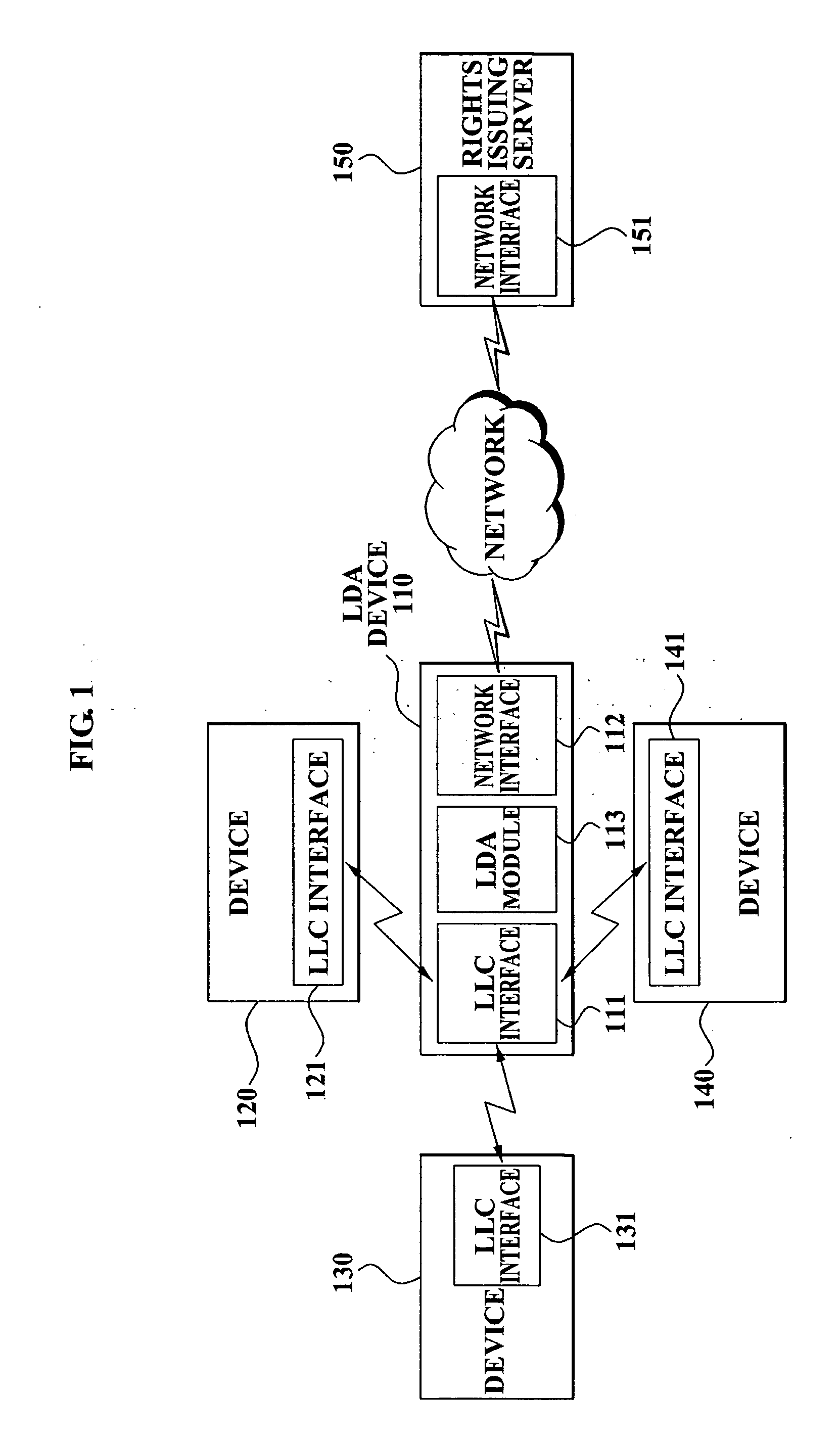
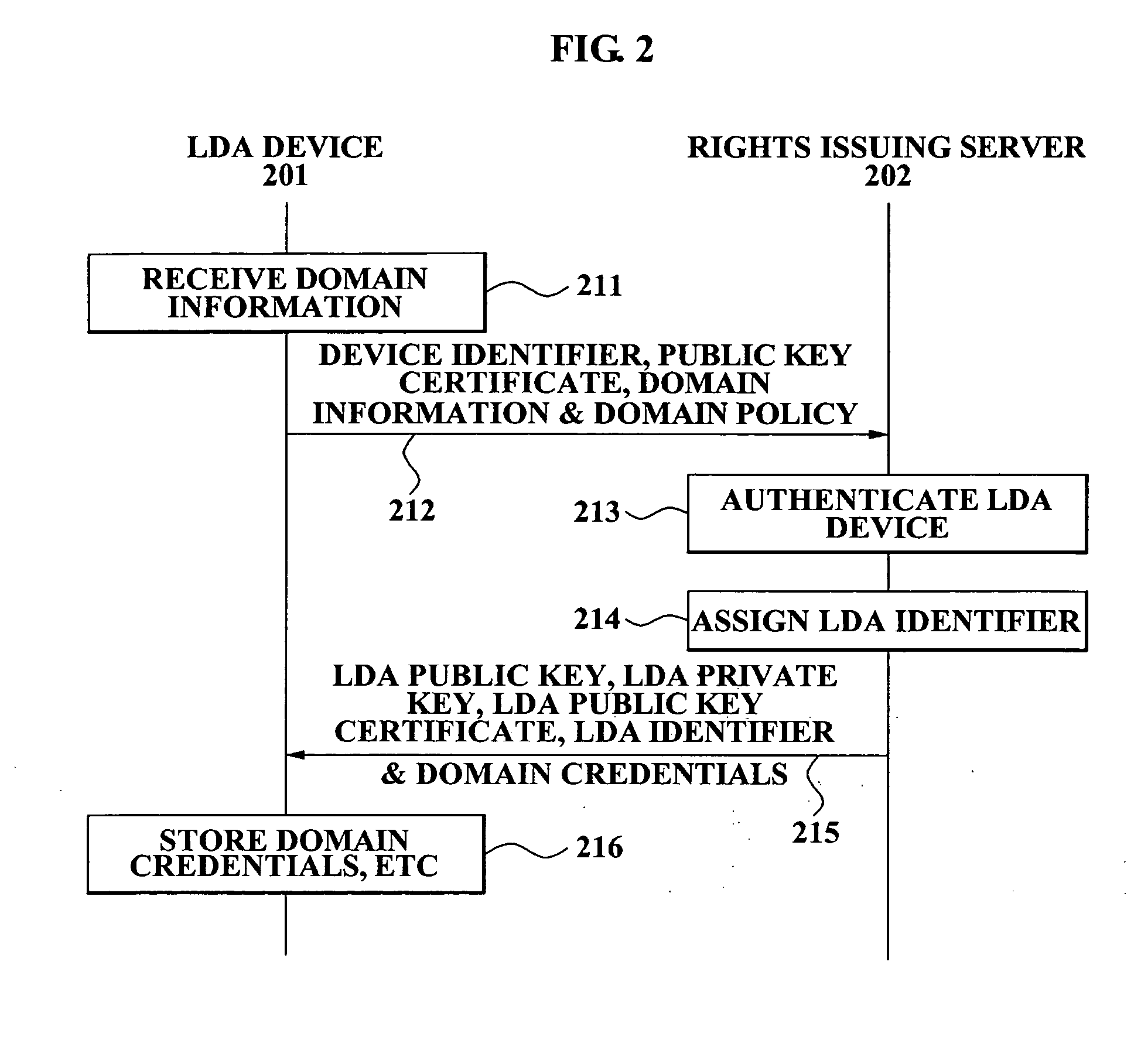
Method and apparatus for local domain management using device with local authority module
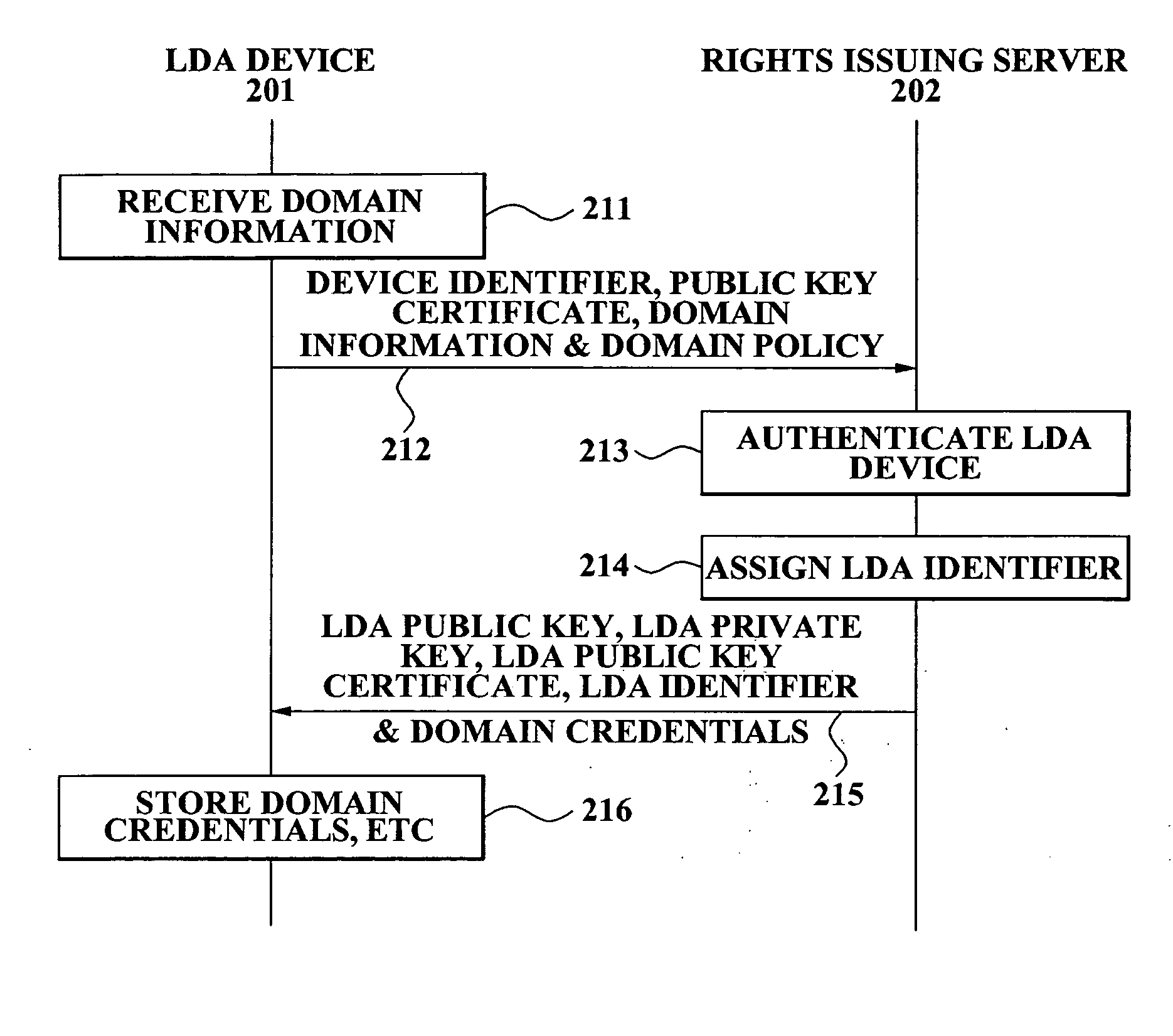
ActiveUS20070234432A1Grant an authorization quicklyEasily includedDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationA domainAuthentication information
A method and device for local domain management are provided and include a local domain authority device. The local domain authority (LDA) device includes a location limited channel (LLC) interface for transmitting and receiving information of devices which are positioned within a limited location and a (LDA) module for authenticating a device which is selected as a member of a domain from the devices, transmitting device authentication information corresponding to the domain, to the authenticated device via the LLC interface, and registering the authenticated device as a member of the domain. The method and device provide an easy and secure means for domain management.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
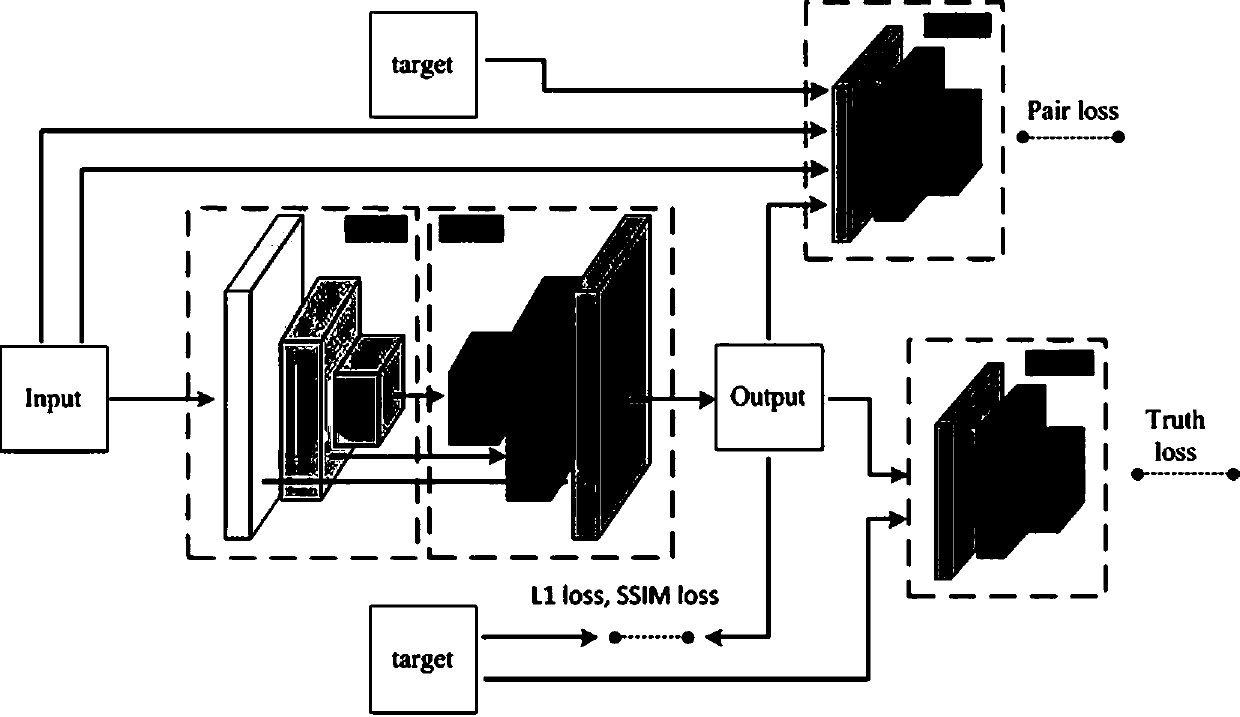
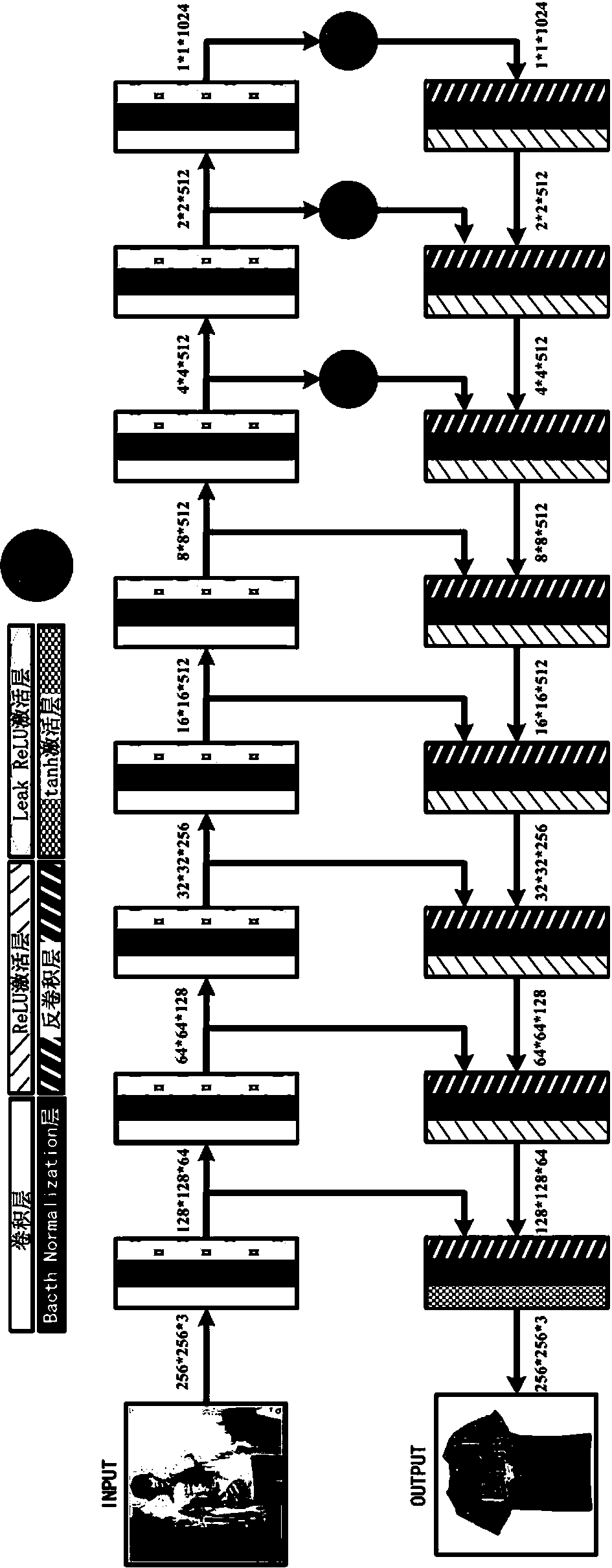
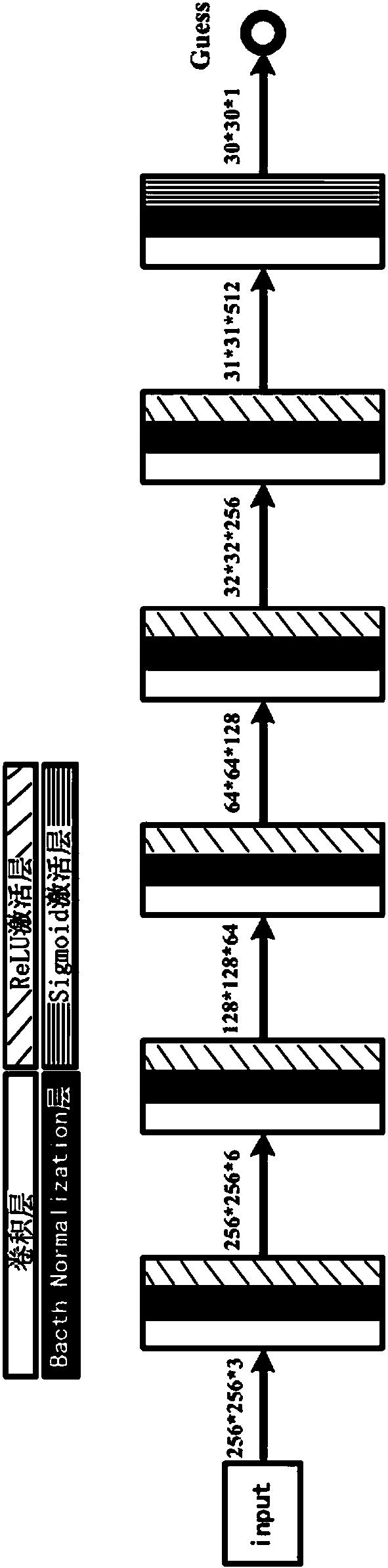
Image domain conversion network based on generative adversarial networks (GAN) and conversion method
ActiveCN108171320AImprove conversion performanceImprove reliabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesGenerative adversarial networkNetwork model
The invention discloses an image domain conversion network based on generative adversarial networks (GAN) and a conversion method. The image domain conversion network includes a U-shaped generative network, an authenticity authentication network and a pairing authentication network. An image domain conversion process mainly includes the following steps: 1) training the U-shaped generative network,and establishing a network model of the U-shaped generative network; and 2) normalizing a to-be-converted image, and then input the image into the network model established through the step 1) to complete image domain conversion of the to-be-converted image. According to the image domain conversion network, an image domain conversion task of a local region in the image can be achieved, image local-domain conversion quality is high, judgment ability of the network is high, stability of image conversion is high, and authenticity of a generated image is greatly improved.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
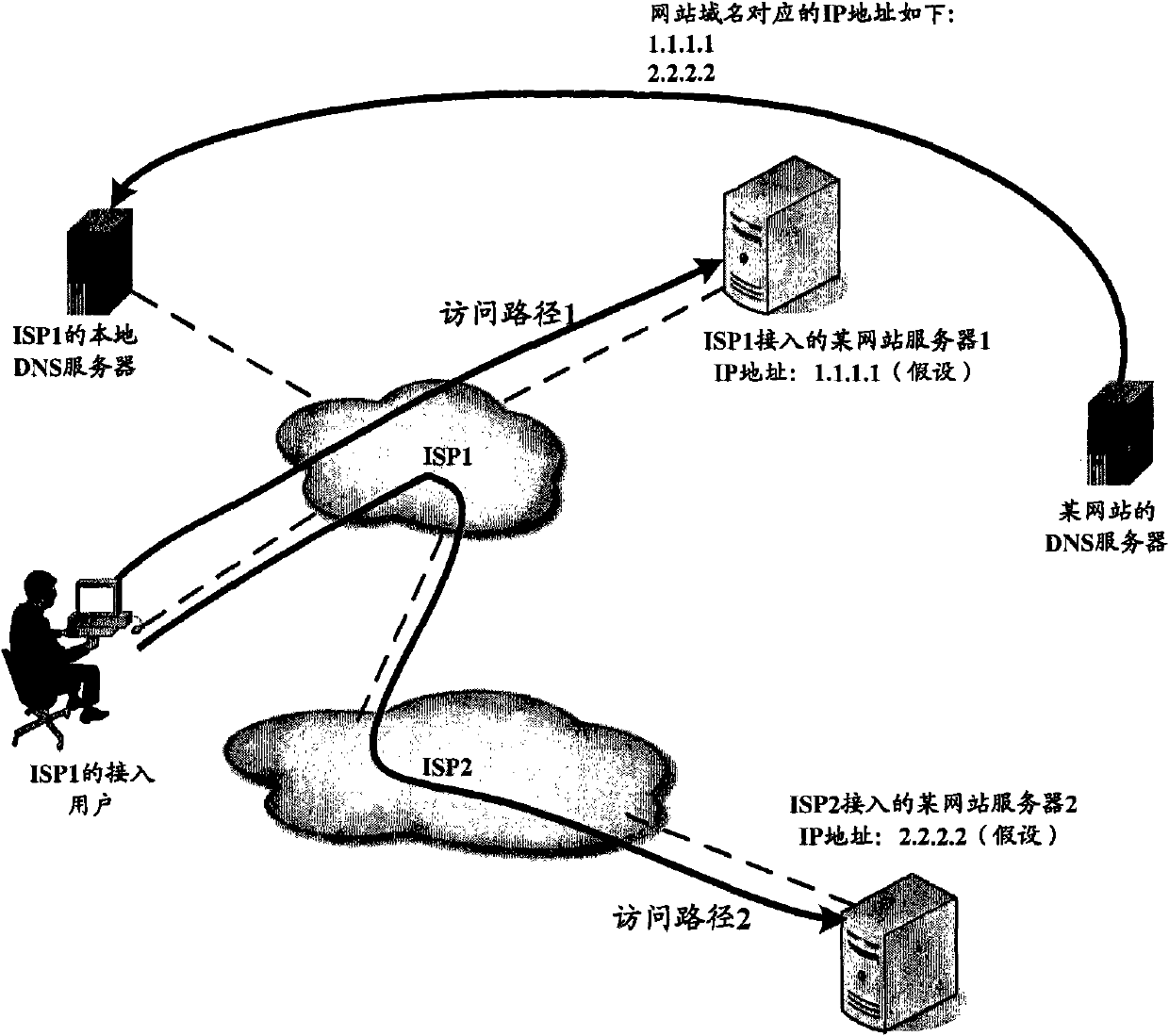
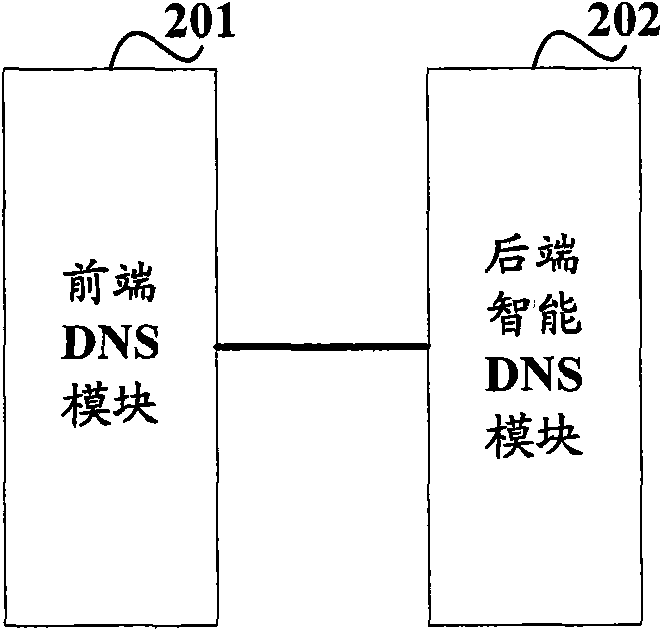
Domain name resolution method and system and DNS in IP network
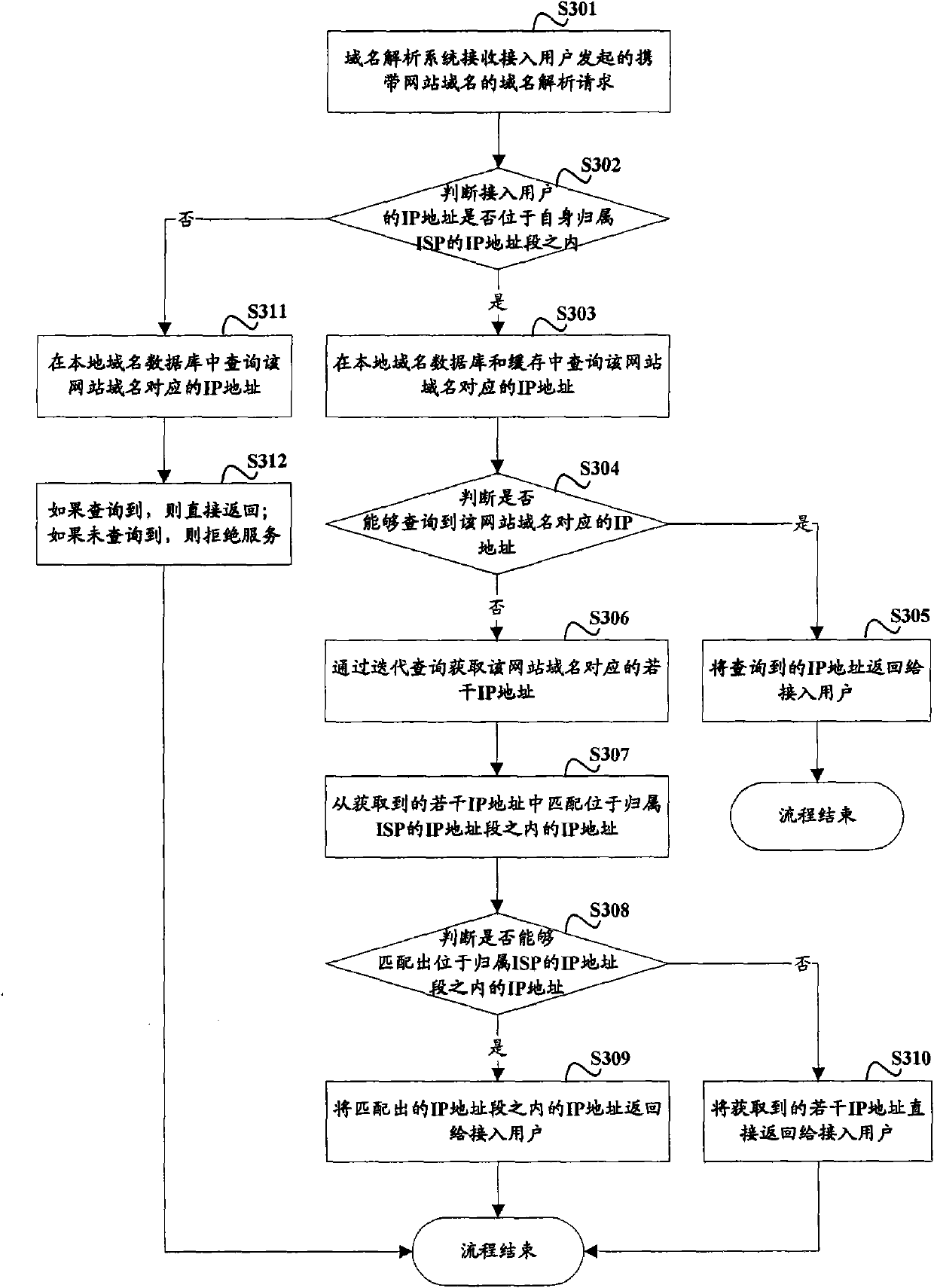
The invention discloses a domain name resolution method and a domain name resolution system in an Internet protocol (IP) network, which are used for solving the problems that: in an Internet service provider (ISP) provided with the access resource of a certain website, an access user of the ISP may access a website server accessed by another ISP, so that an access route is lengthened and packet loss and delay jitter are increased. The domain name resolution method in the IP network comprises the following steps that: when receiving a domain name resolution request carrying a website domain name initiated by the access user, the domain name resolution system queries an IP address which corresponds to the website domain name in a local domain name database and a cache; when the IP address which corresponds to the website domain name is not queried in the local domain name database and the cache, the domain name resolution system acquires a plurality of IP addresses which correspond to the website domain name through iterative query; and the domain name resolution system matches an IP address positioned in an IP address field of the ISP to which the domain name resolution system belongs in the plurality of acquired IP addresses and returns the IP address to the access user. The invention also provides the domain name resolution method and a domain name server (DNS) in the IP network.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GRP BEIJING
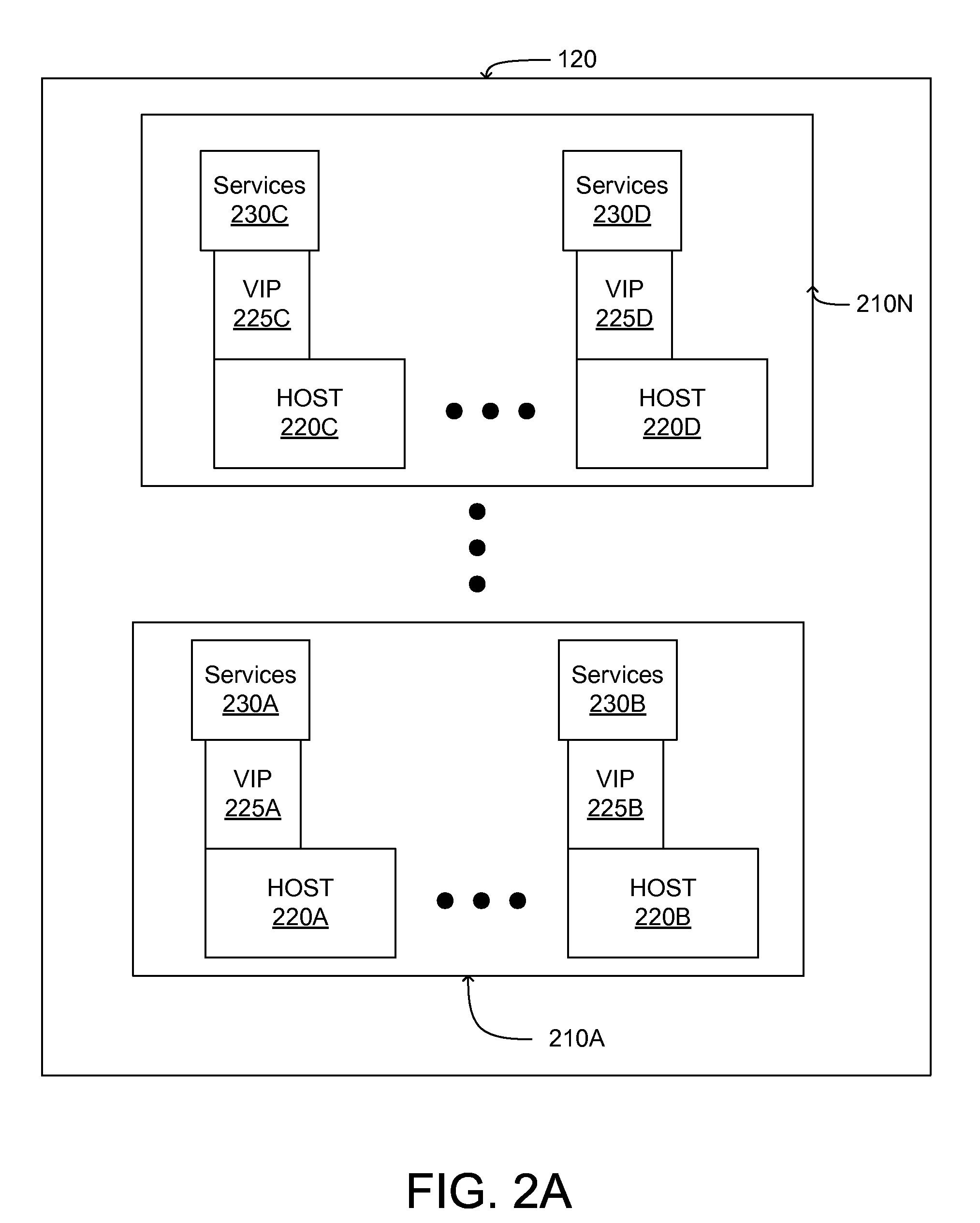
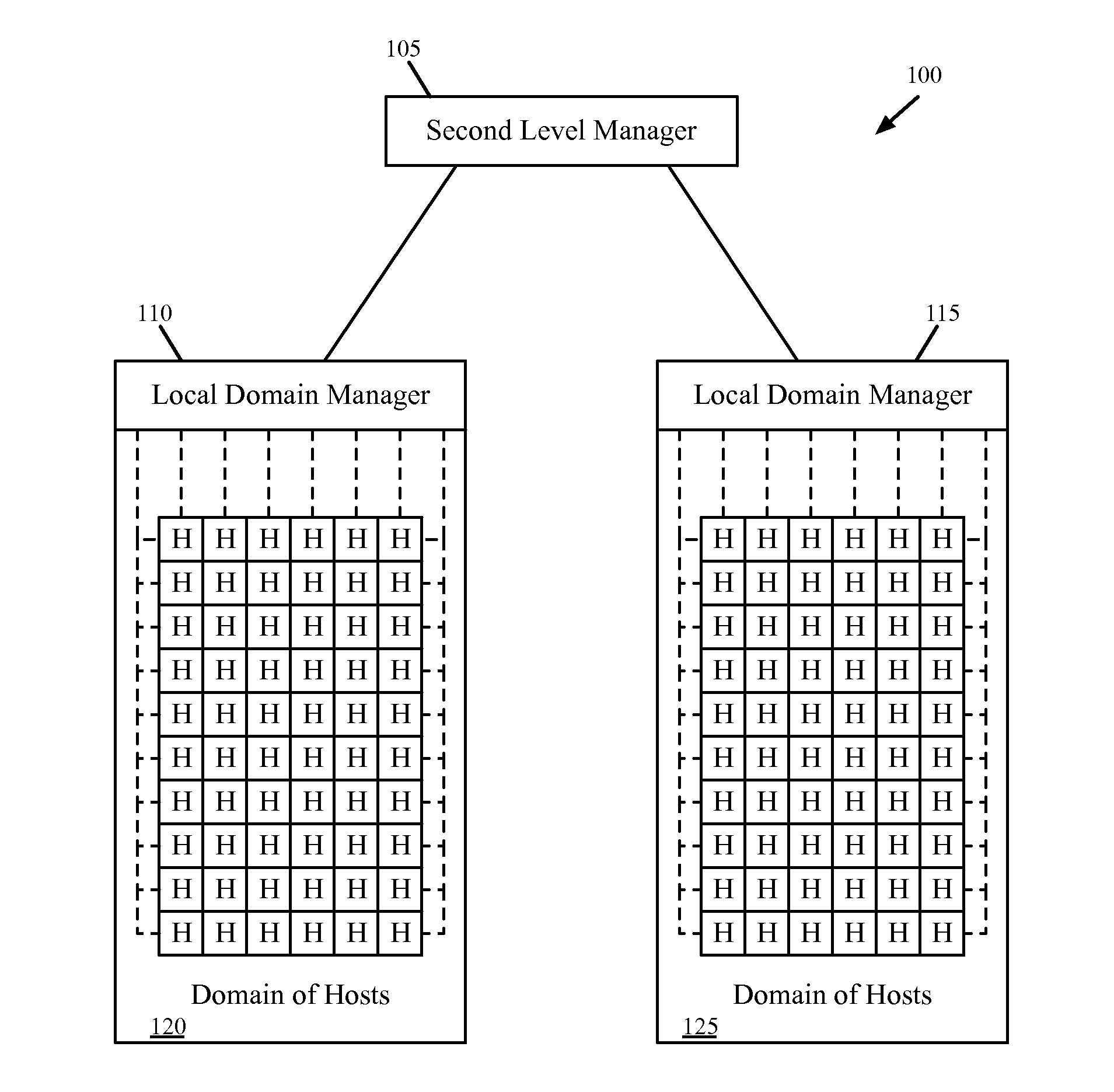
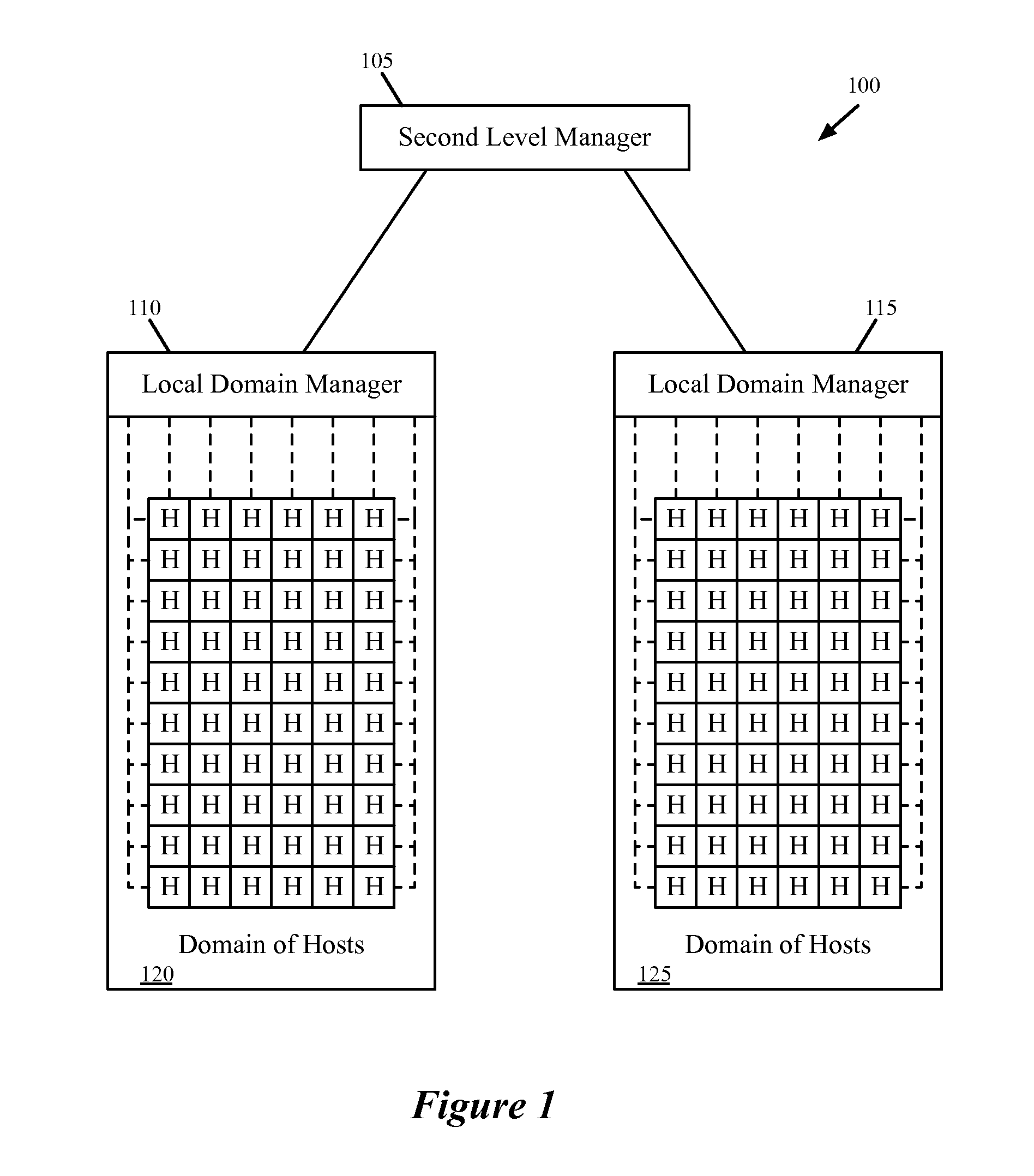
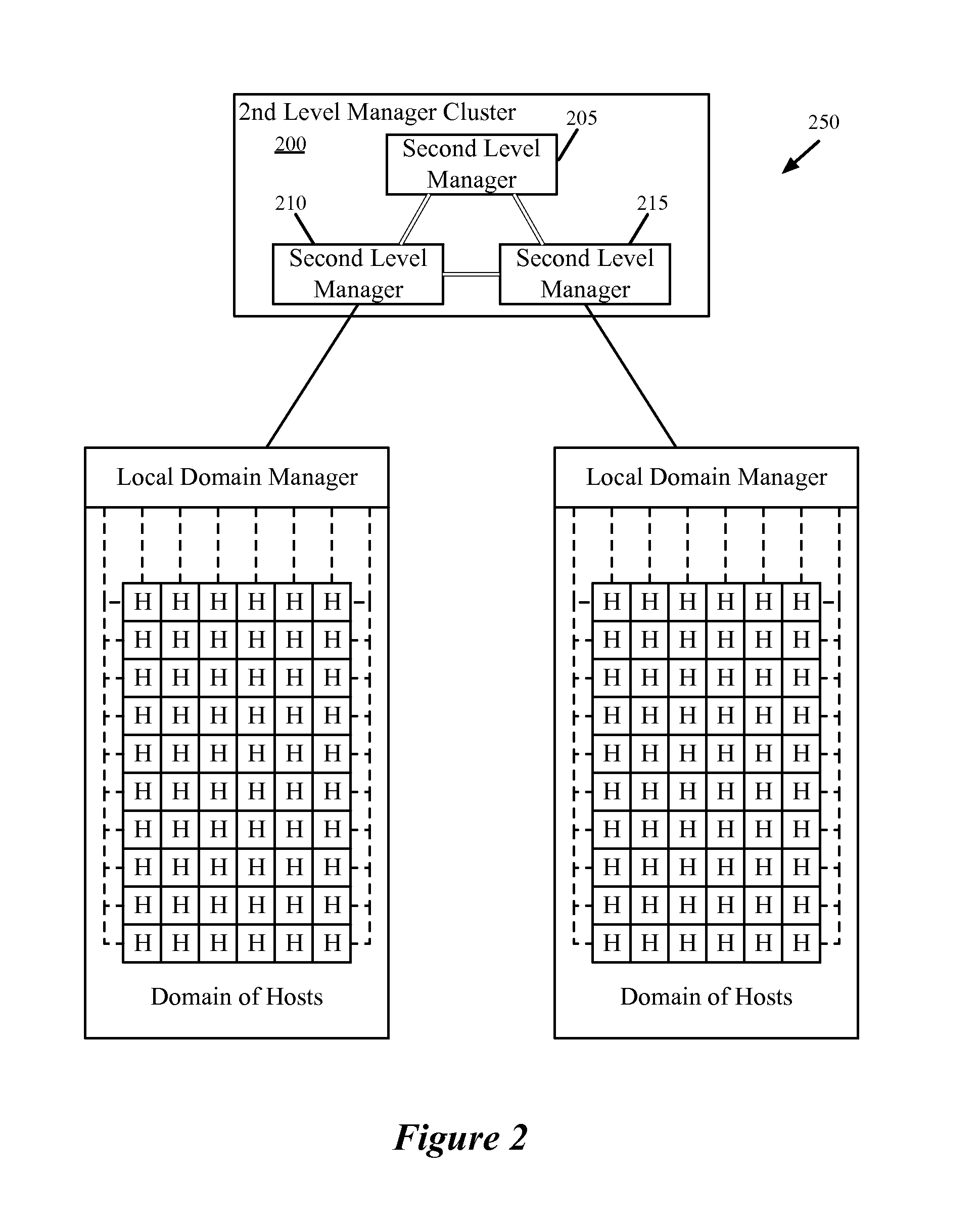
Hierarchical Network Managers
Some embodiments provide a network system that includes several host machines for hosting virtual machines, divided into several different domains. The network system includes several local domain management servers. A first local domain management server of a first domain is for (i) initiating creation of a set of distributed virtual switch ports associated with a particular logical network identifier on a host machine within its domain and (ii) attaching a first virtual machine on the host machine to a created port associated with the particular logical network identifier in order for the first virtual machine to send traffic over the logical network. The network system includes a second level management server for coordinating the use of logical network identifiers between multiple different logical domain management servers in order for the first virtual machine to communicate via the logical network with a second virtual machine in a second domain.
Owner:NICIRA
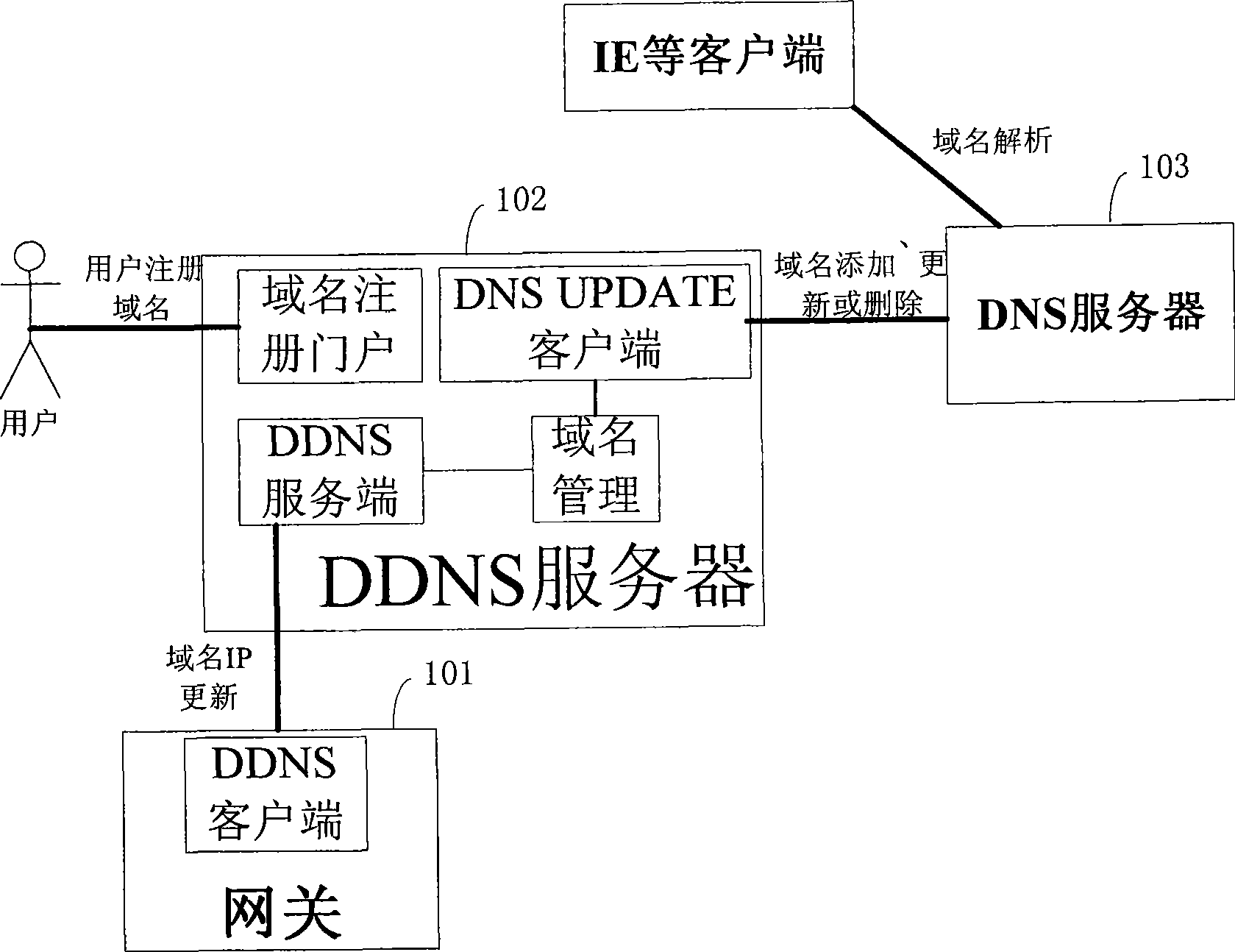
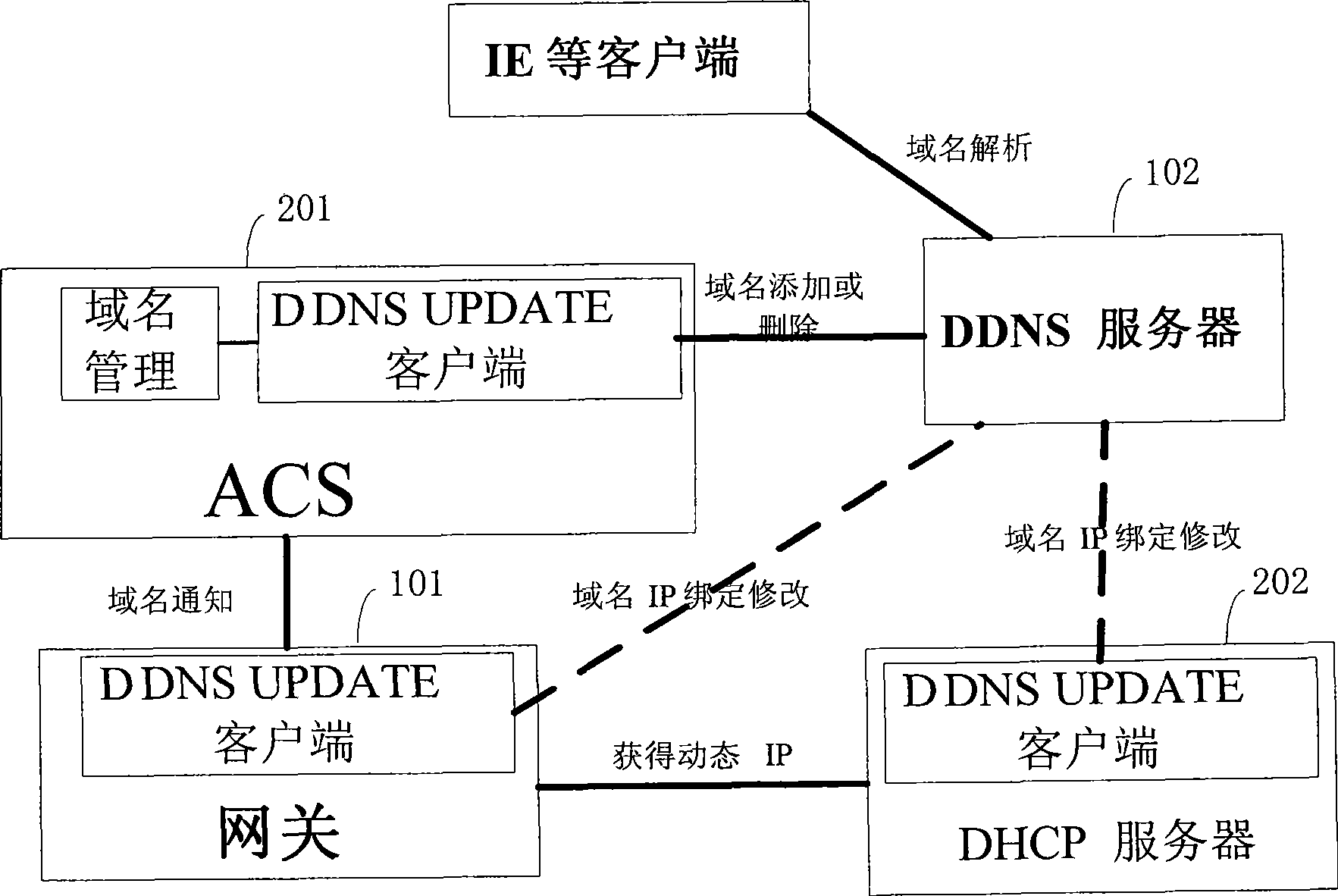
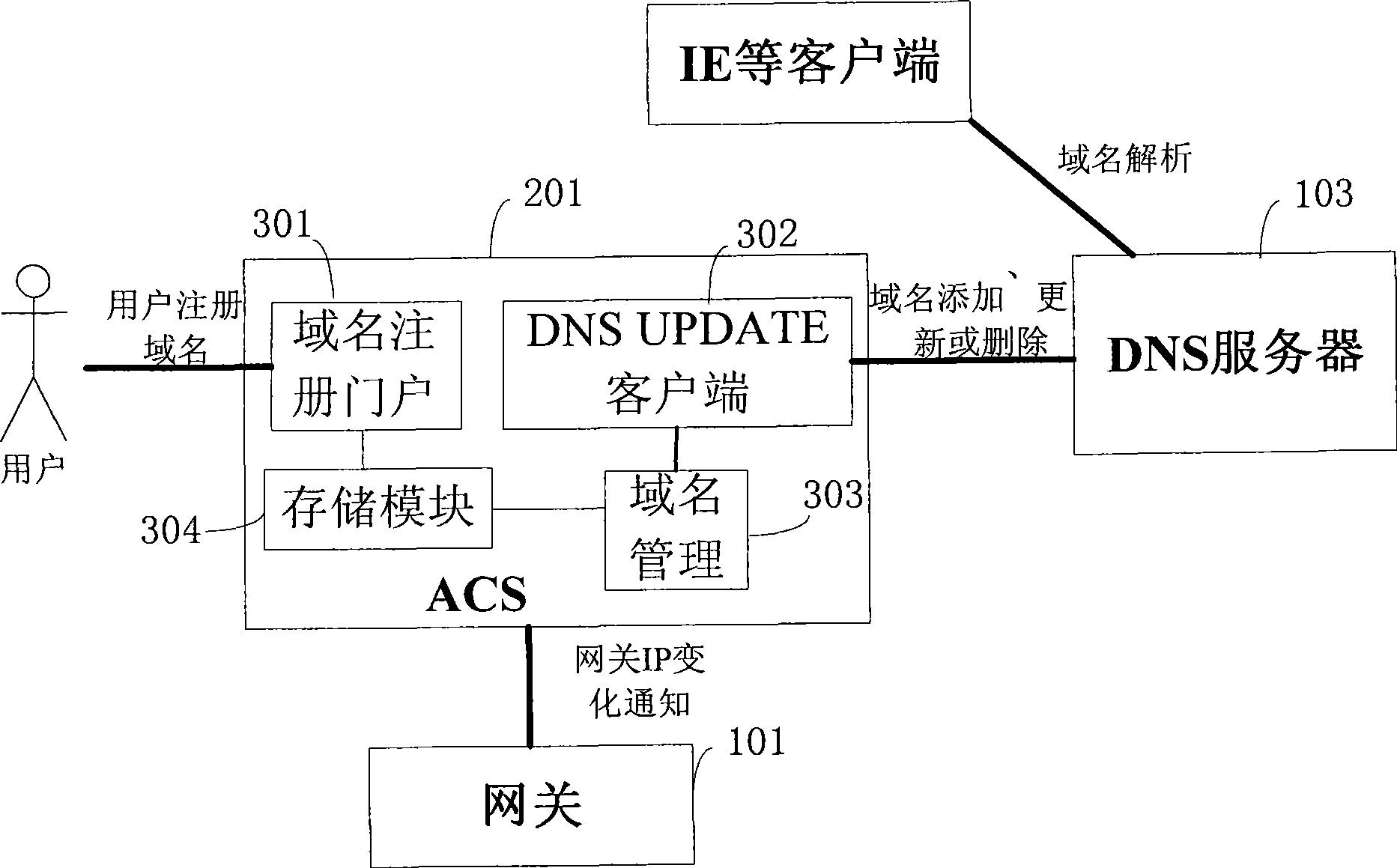
Method and apparatus for implementing dynamic domain name update
The invention discloses a method and equipment for realizing the updating of a dynamic domain name. The method comprises: a domain name storage table is saved in a gateway management system, wherein the domain name storage table comprises a domain name of gateway equipment and binding information of an IP address; the gateway management system finds that the domain name of the gateway equipment or the IP address is changed, the local domain name storage table is changed according to current changed situation; and the gateway management system sends the information of current changed situation to a DNS server of a domain name service system. The method only needs to add certain functional modules to an ACS server, does not need to reconstruct or upgrade relevant systems and can provide DDNS service for a gateway owner without needing the gateway to add any function to the DDNS service.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
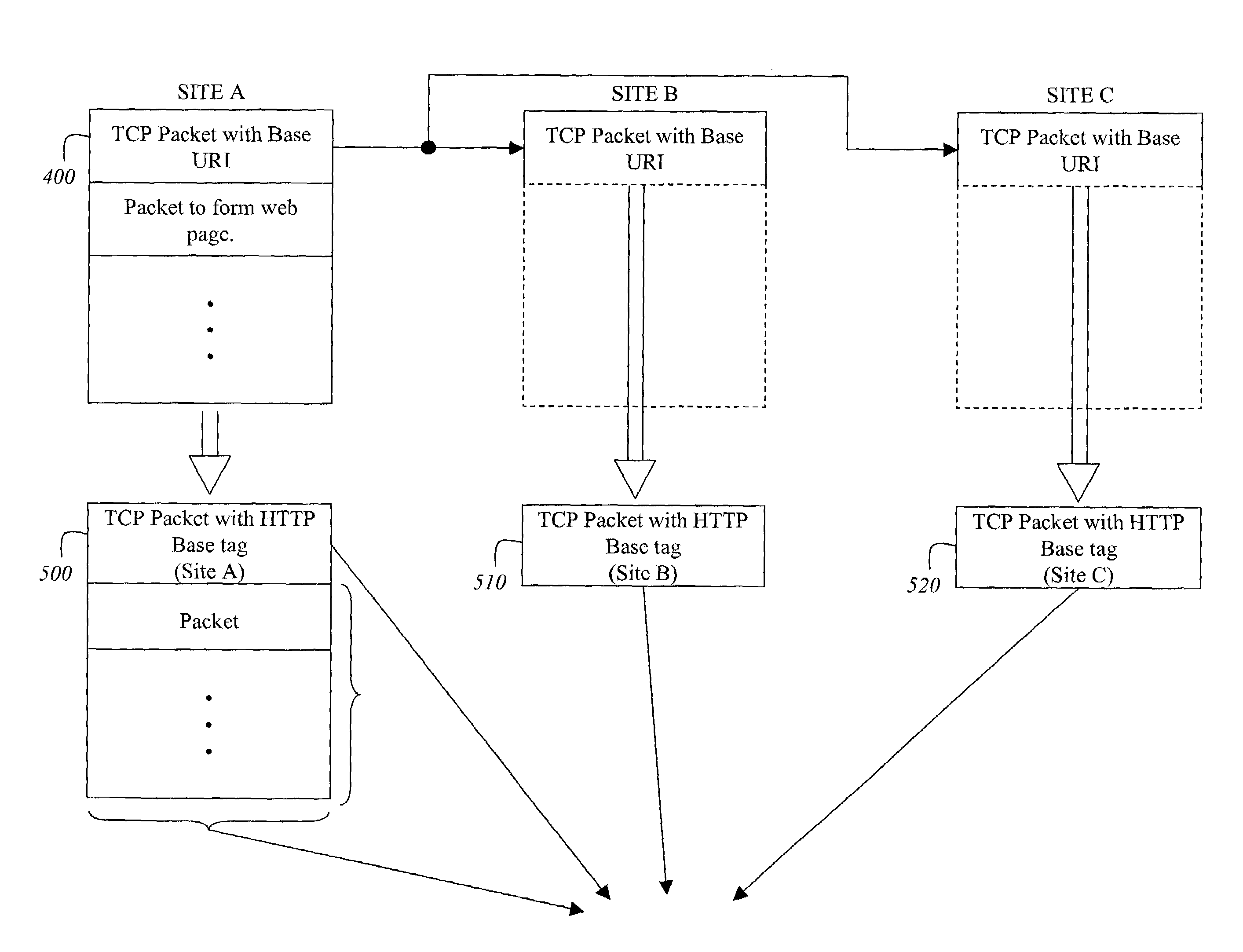
Method and apparatus for discovering client proximity using race type translations
ActiveUS7231458B2Optimize locationMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionWeb siteNetwork packet
A system and method for determining a chronometrically optimal web site location for access by a client based on proximity measurements on established connections that are a result of requests for actual content. In one embodiment, the technique involves a race condition between local domains each transmitting TCP packets loaded with a HyperText Markup Language (HTML) Base tag identifying that local domain. The earliest received TCP packet is incorporated into the TCP stream. In another embodiment, the technique involves a race condition between local domains each transmitting files having links to streaming media translated to point to its own local domain. The earliest received file is incorporated into the TCP stream while the others are discarded as TCP resends. In yet another embodiment, HTTP redirect operations are performed once for each grouping of links only the earliest redirect packet to reach the client is incorporated into the existing TCP stream.
Owner:RADWARE
Solving system specific to content distribution network
ActiveCN102932451AStrong complementarityAvoid inaccessibilityTransmissionContent distributionDistributed computing
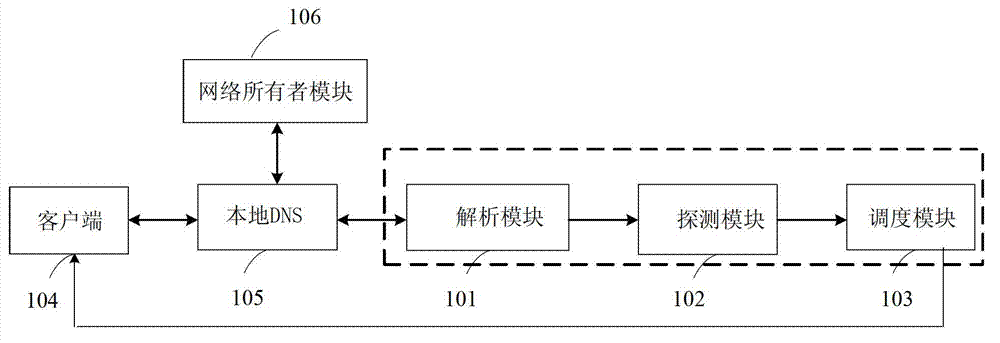
The invention discloses a solving system specific to content distribution network. The system is applied to clients, local domain name modules and all modules of websites. The system is characterized in that the system comprises an analysis module, a detection module and a scheduling module. The system has the advantage that the problems that in prior art, content distribution network (CDN) service providers are mutually isolated, the number of nodes and server distribution of a single CDN service provider can not overlay all networks and really stable and intelligent CDN service can not be supplied are solved.
Owner:北龙中网(北京)科技有限责任公司
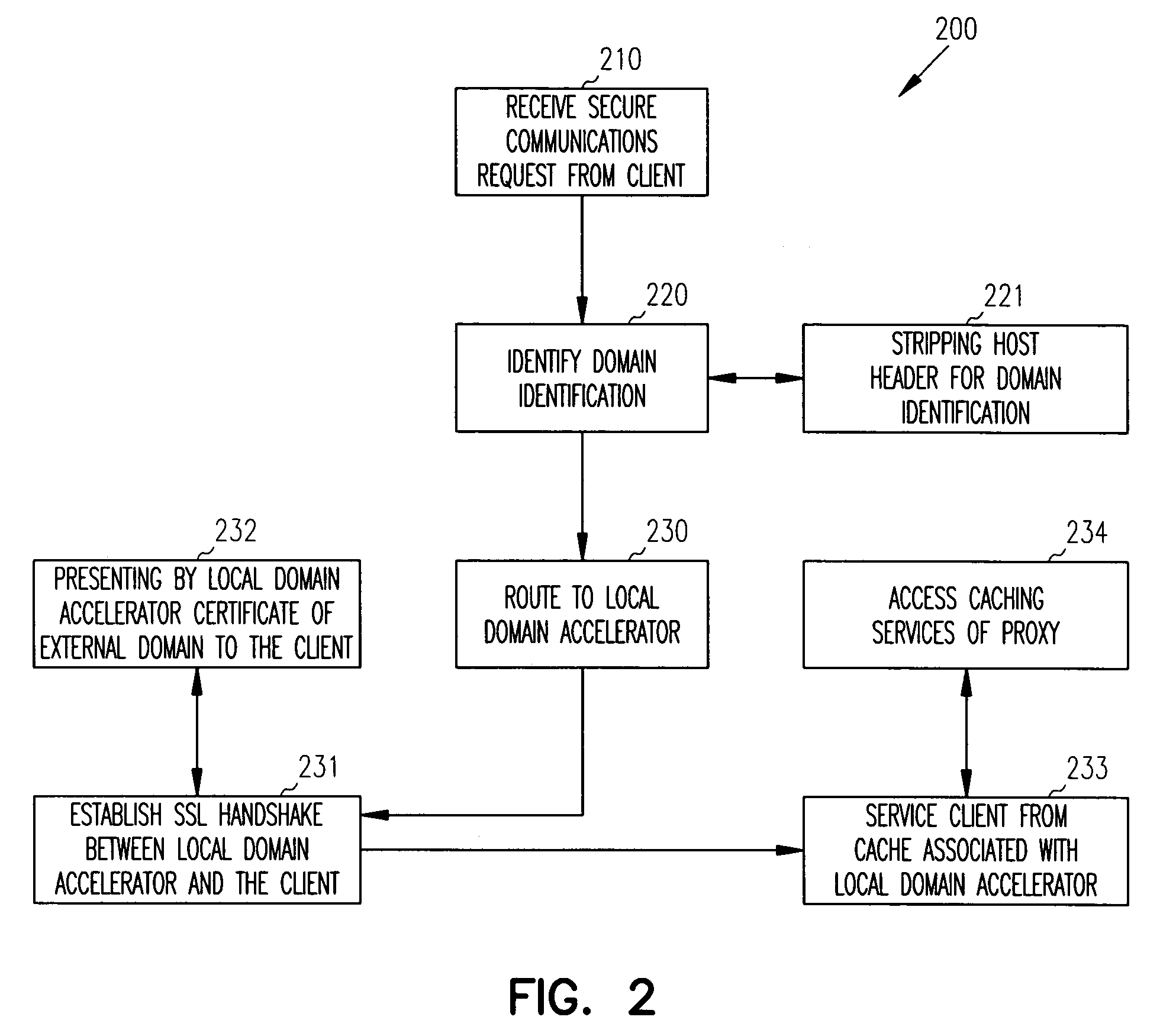
Techniques for securely accelerating external domains locally
InactiveUS7904951B1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlSecure communicationInternet privacy
Owner:RPX CORP
Content distribution implementation method and system
ActiveCN101984637AImprove experienceReduce interactionData switching networksContent distributionDomain name
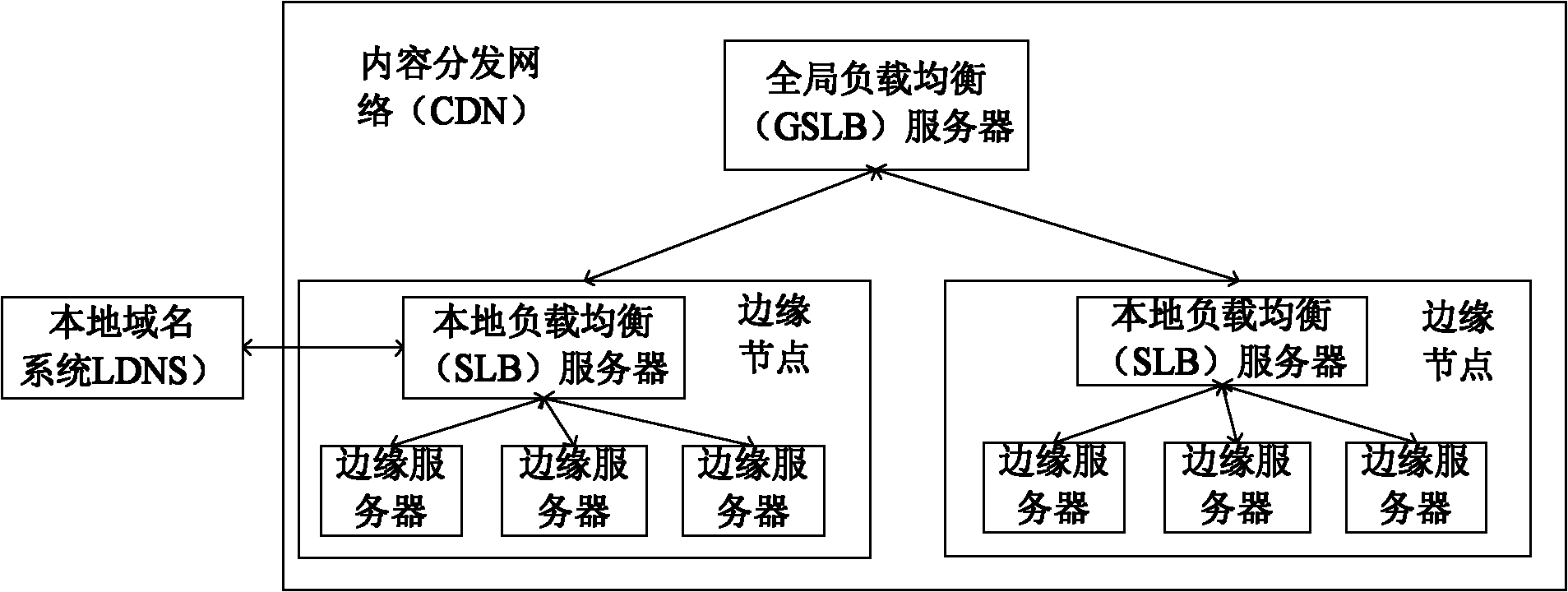
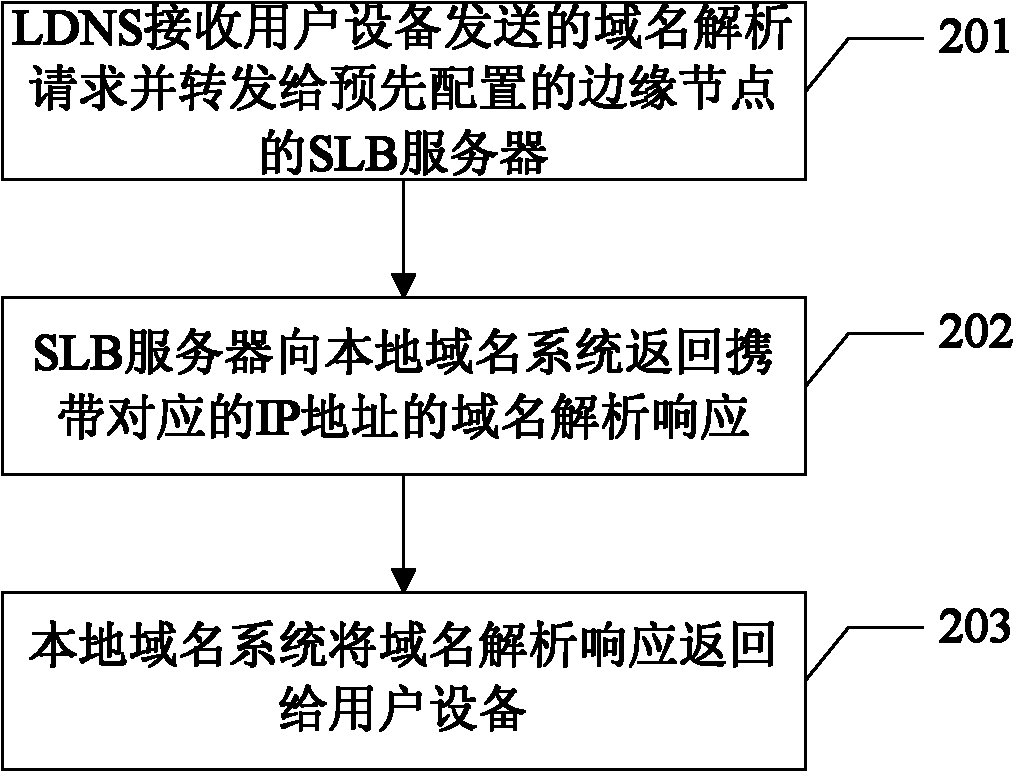
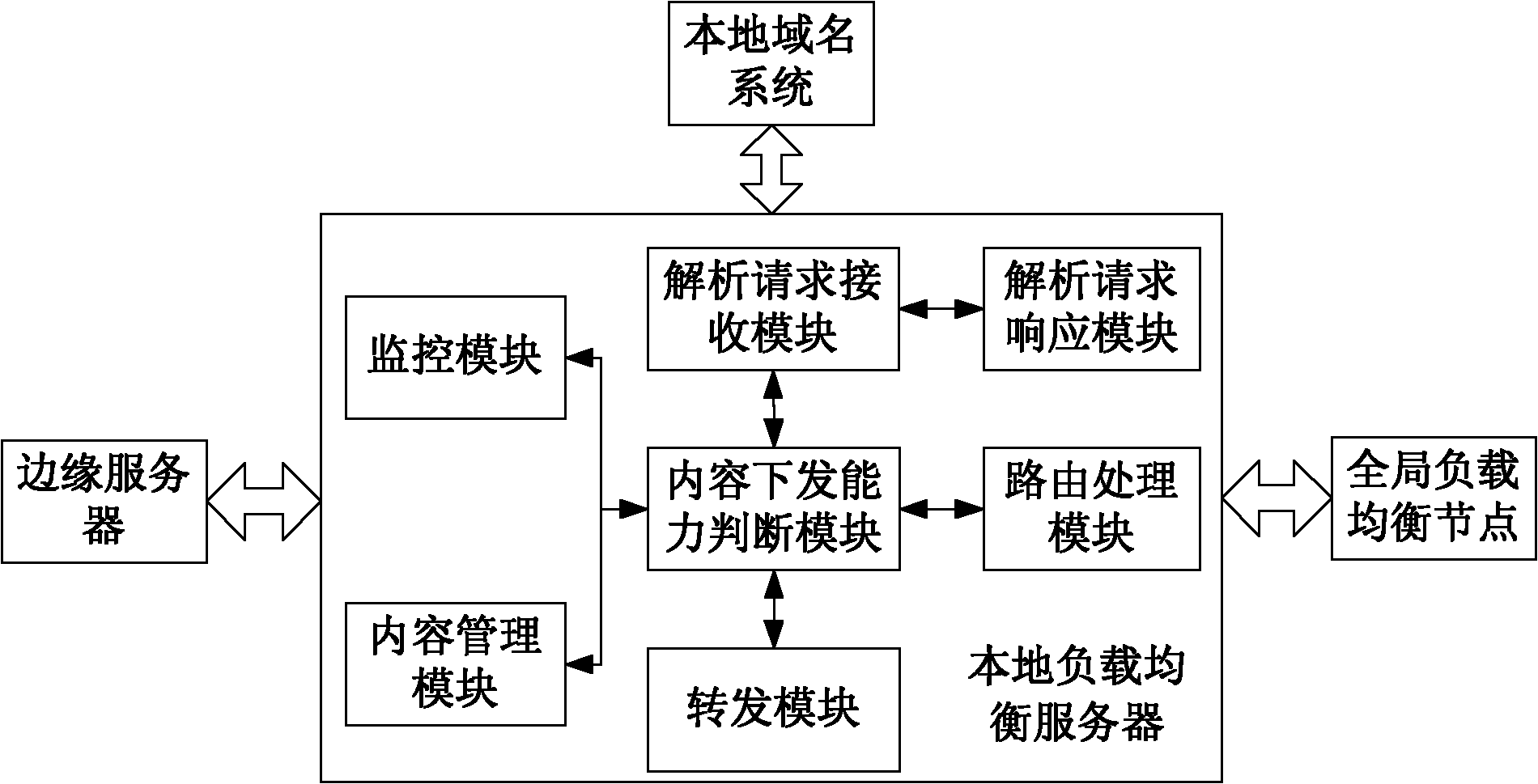
The invention relates to a content distribution implementation method and system, wherein the method comprises the following steps: a local domain name system (LDNS) receives a domain name resolution (DNS) request sent by user equipment, forwards the request to a local server load balance (SLB) server of a preset edge node; the SLB server returns a domain resolution response carrying the corresponding IP address to the LDNS; and the LDNS returns the domain resolution response to the user equipment. The method and system of the invention can quicken the process of the domain resolution.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Dynamic enforcement of MPLS-TE inter-domain policy and QoS
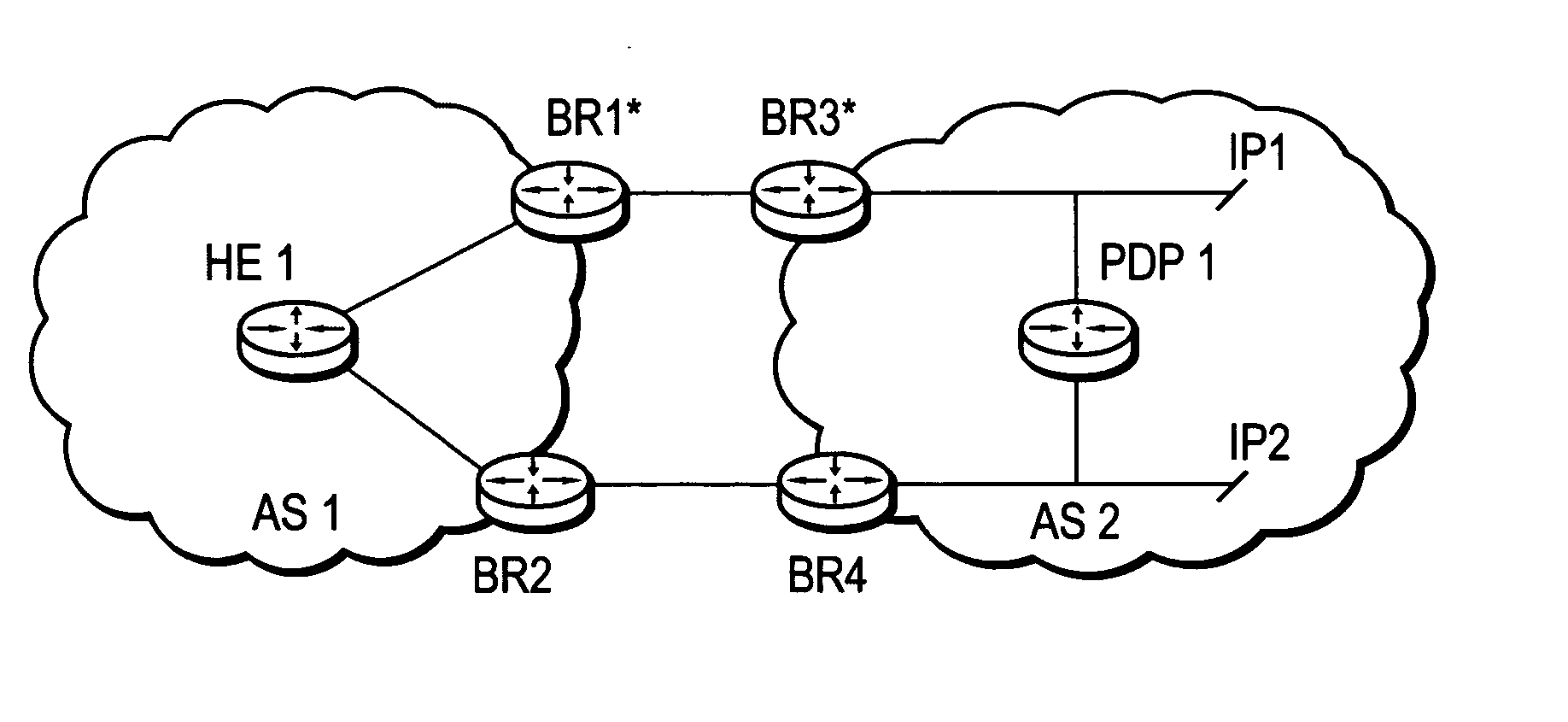
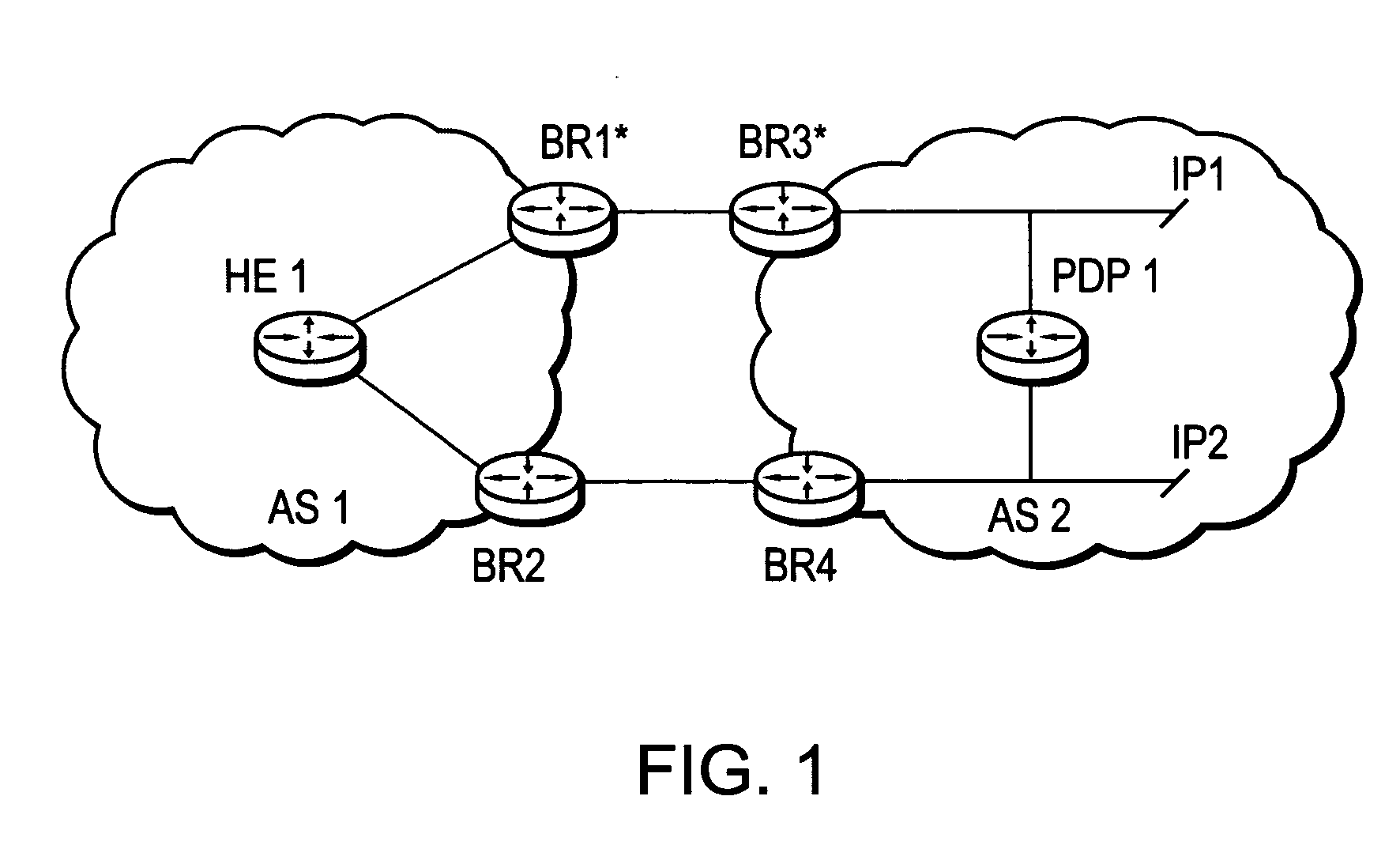
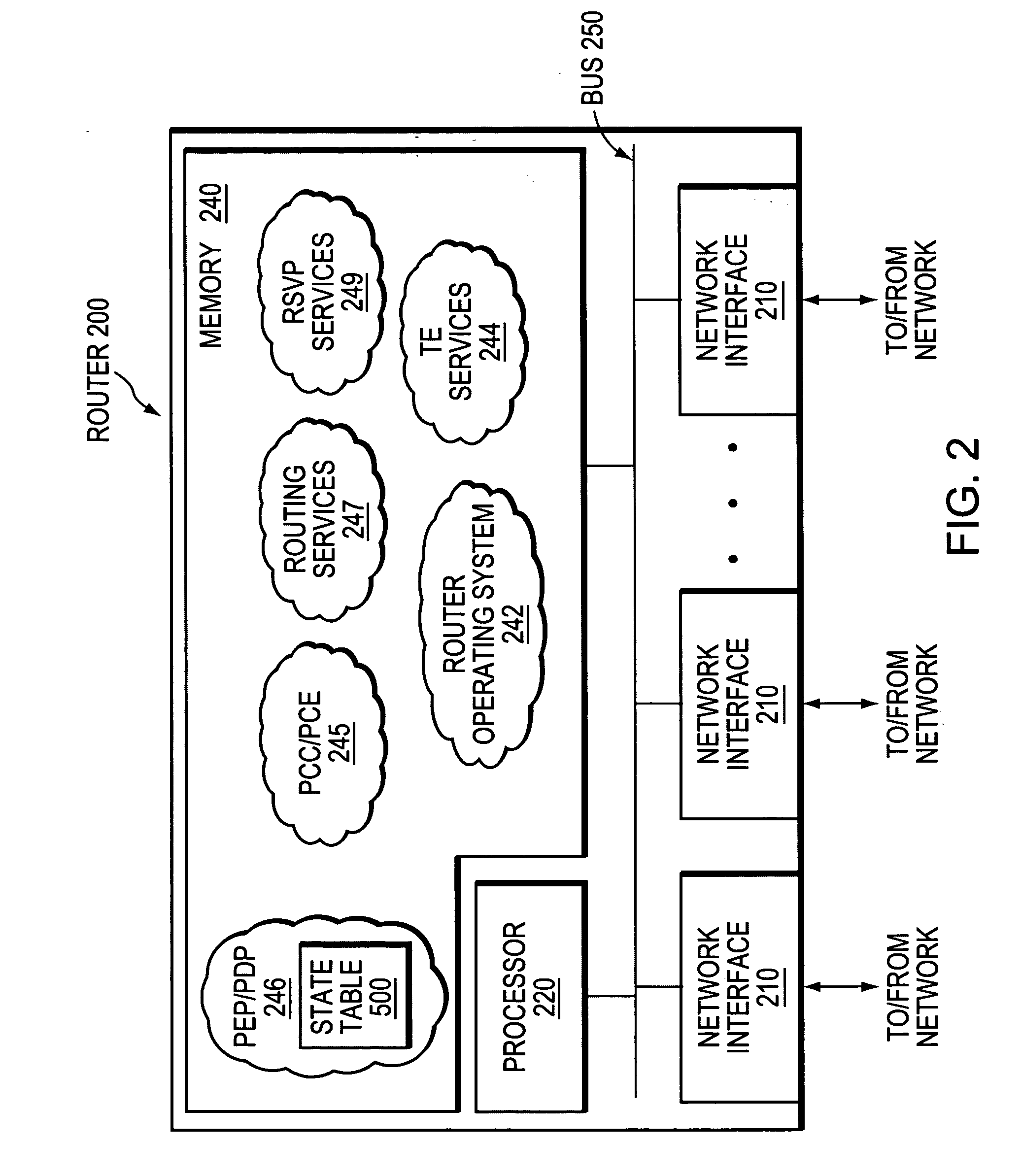
InactiveUS20070019558A1Efficient mechanismError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of servicePolicy decision
A technique dynamically enforces inter-domain policy and quality of service (QoS) for Traffic Engineering (TE) Label Switched Paths (LSPs) between a local domain and a remote domain in a computer network. According to the enforcement technique, a Path Computation Element (PCE) of the local domain receives a path computation request for an inter-domain TE-LSP from the remote domain, and triggers a policy verification procedure at a Policy Decision Point (PDP) of the local domain. The PDP determines whether the requested TE-LSP is allowed based on configured policy for the remote domain and previously established TE-LSPs from the remote domain. In the event the requested TE-LSP is allowed and subsequently established, a Policy Enforcement Point (PEP) along the TE-LSP, e.g., a border router of the local domain or a dedicated server, updates the PDP with the state of the TE-LSP. In response to the update, the PDP returns a QoS template indicating configured QoS guidelines the PEP must enforce for that TE-LSP. If the TE-LSP is eventually torn down, the PEP again updates the PDP with the state of the TE-LSP.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com