Patents
Literature
837 results about "Reachability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In graph theory, reachability refers to the ability to get from one vertex to another within a graph. A vertex s can reach a vertex t (and t is reachable from s) if there exists a sequence of adjacent vertices (i.e. a path) which starts with s and ends with t. In an undirected graph, reachability between all pairs of vertices can be determined by identifying the connected components of the graph. Any pair of vertices in such a graph can reach each other if and only if they belong to the same connected component.
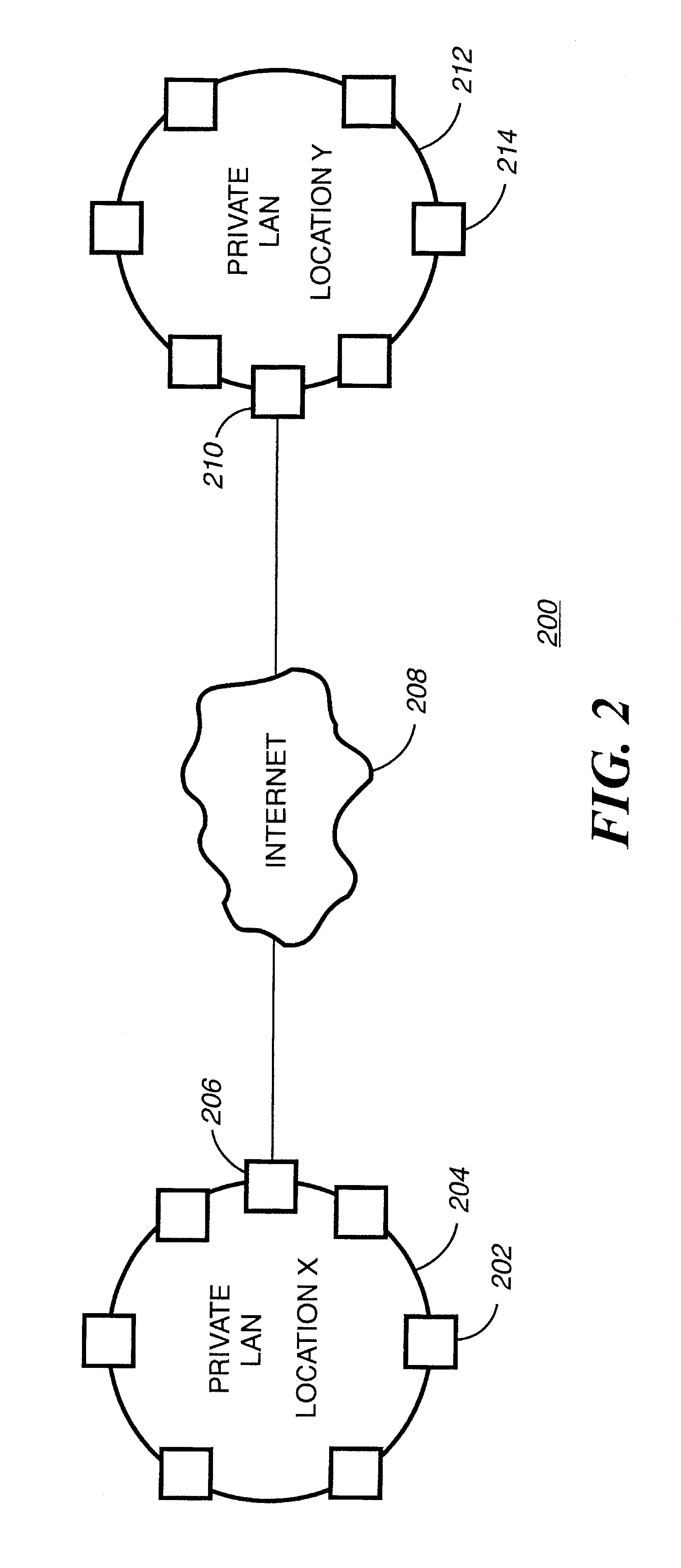
Virtual private network having automatic reachability updating
InactiveUS20050138204A1Easy to createCommunication securityEnergy efficient ICTDigital data protectionPrivate networkReachability
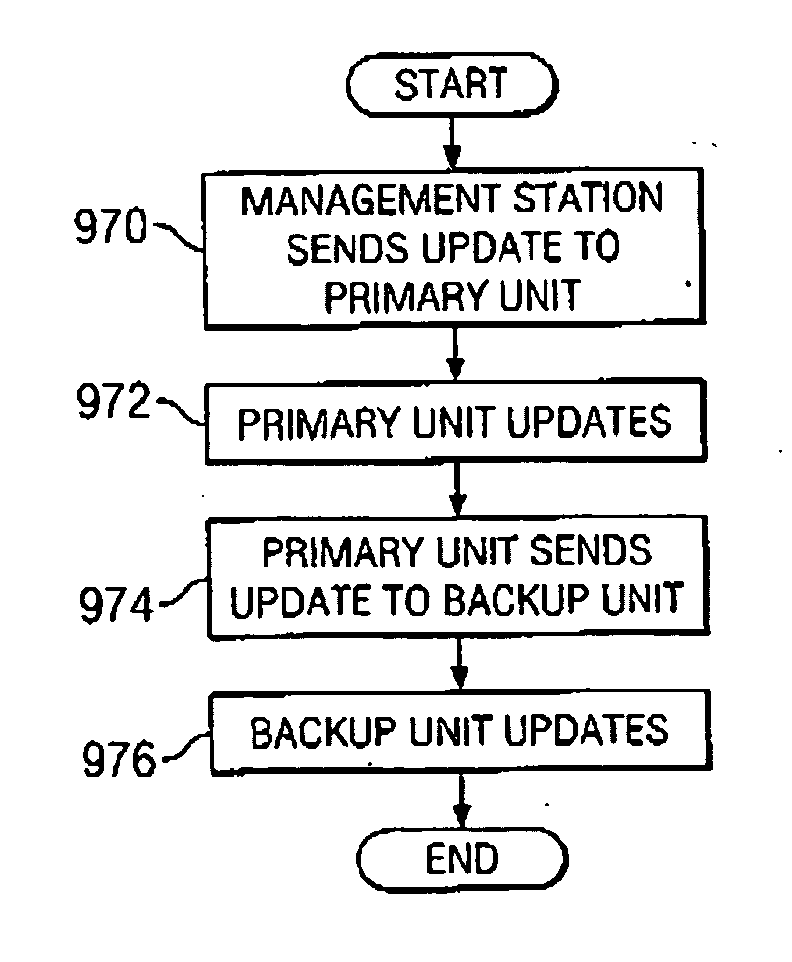
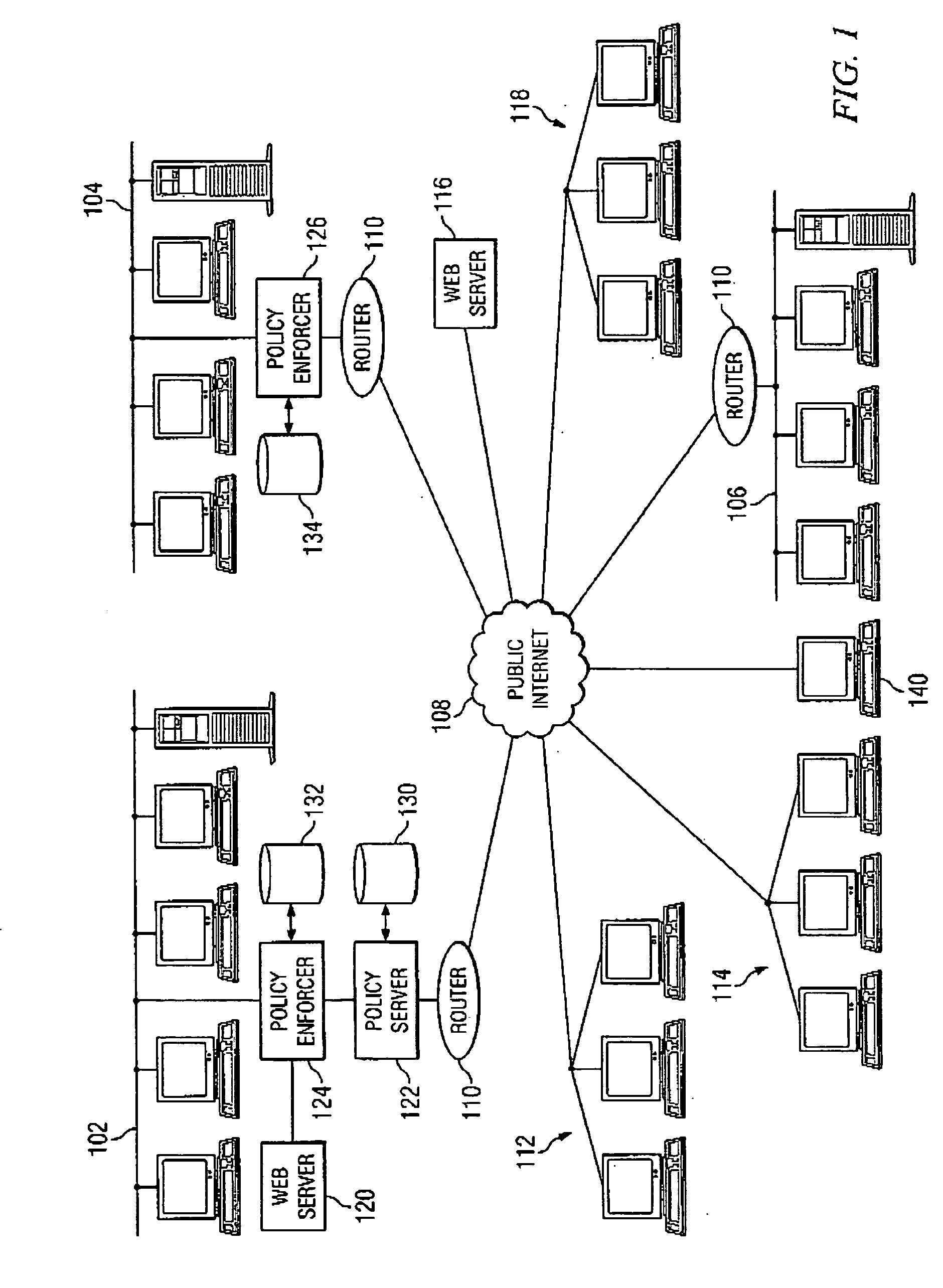
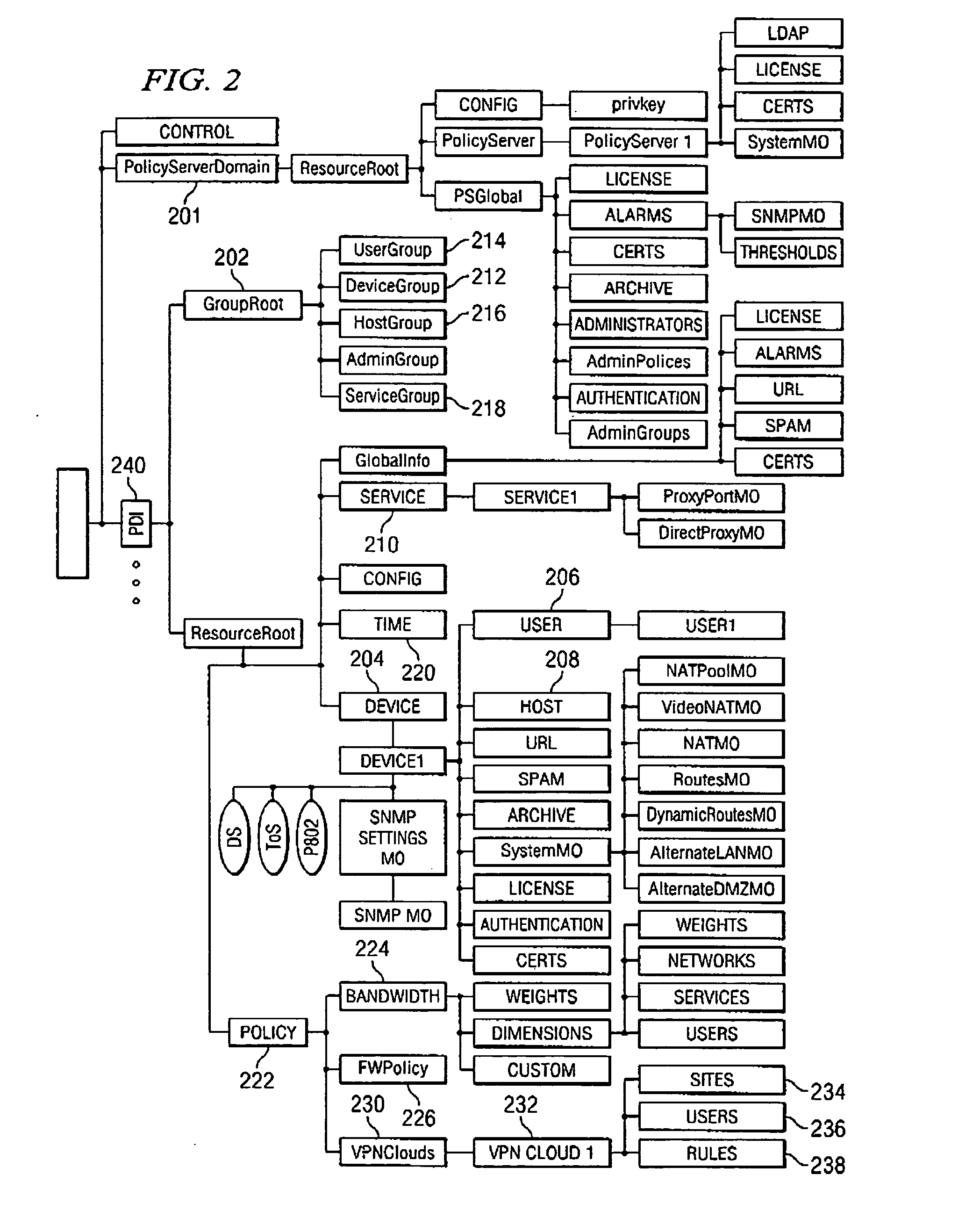
A unified policy management system for an organization including a central policy server and remotely situated policy enforcers. A central database and policy enforcer databases storing policy settings are configured as LDAP databases adhering to a hierarchical object oriented structure. Such structure allows the policy settings to be defined in an intuitive and extensible fashion. Changes in the policy settings made at the central policy server are automatically transferred to the policy enforcers for updating their respective databases. Each policy enforcer collects and transmits health and status information in a predefined log format and transmits it to the policy server for efficient monitoring by the policy server. For further efficiencies, the policy enforcement functionalities of the policy enforcers are effectively partitioned so as to be readily implemented in hardware. The system also provides for dynamically routed VPNs where VPN membership lists are automatically created and shared with the member policy enforcers. Updates to such membership lists are also automatically transferred to remote VPN clients. The system further provides for fine grain access control of the traffic in the VPN by allowing definition of firewall rules within the VPN. In addition, policy server and policy enforcers may be configured for high availability by maintaining a backup unit in addition to a primary unit. The backup unit become active upon failure of the primary unit.
Owner:IYER SHANKER V +3
Machine-to-machine gateway architecture and functionality
ActiveUS20110213871A1Easy to shareGood synchronizationService provisioningMultiple digital computer combinationsReachabilityData aggregator
A machine-to-machine (M2M) gateway (GW) includes reachability, addressing, and repository (RAR) capability. The GW maintains a local mapping table and local device application repository, performs data aggregation, address / name translation, provides event reporting and establishes GW reachability and wake-up time. The GW supports requests from M2M applications or other capabilities within the GW, and from a network and application (N&A) domain RAR. The GW may include an M2M device and M2M gateway management (MDGM) capability that receives management requests for an M2M device and functions as a network proxy. The MDGM accepts and processes requests from the N&A domain on behalf of the M2M device and performs management functions of the M2M device on behalf of the N&A domain. The MDGM may request the N&A domain for permission to interact with the M2M device, initiate an interaction for device management tasks with the M2M device, and report to the N&A domain.
Owner:DRNC HLDG INC
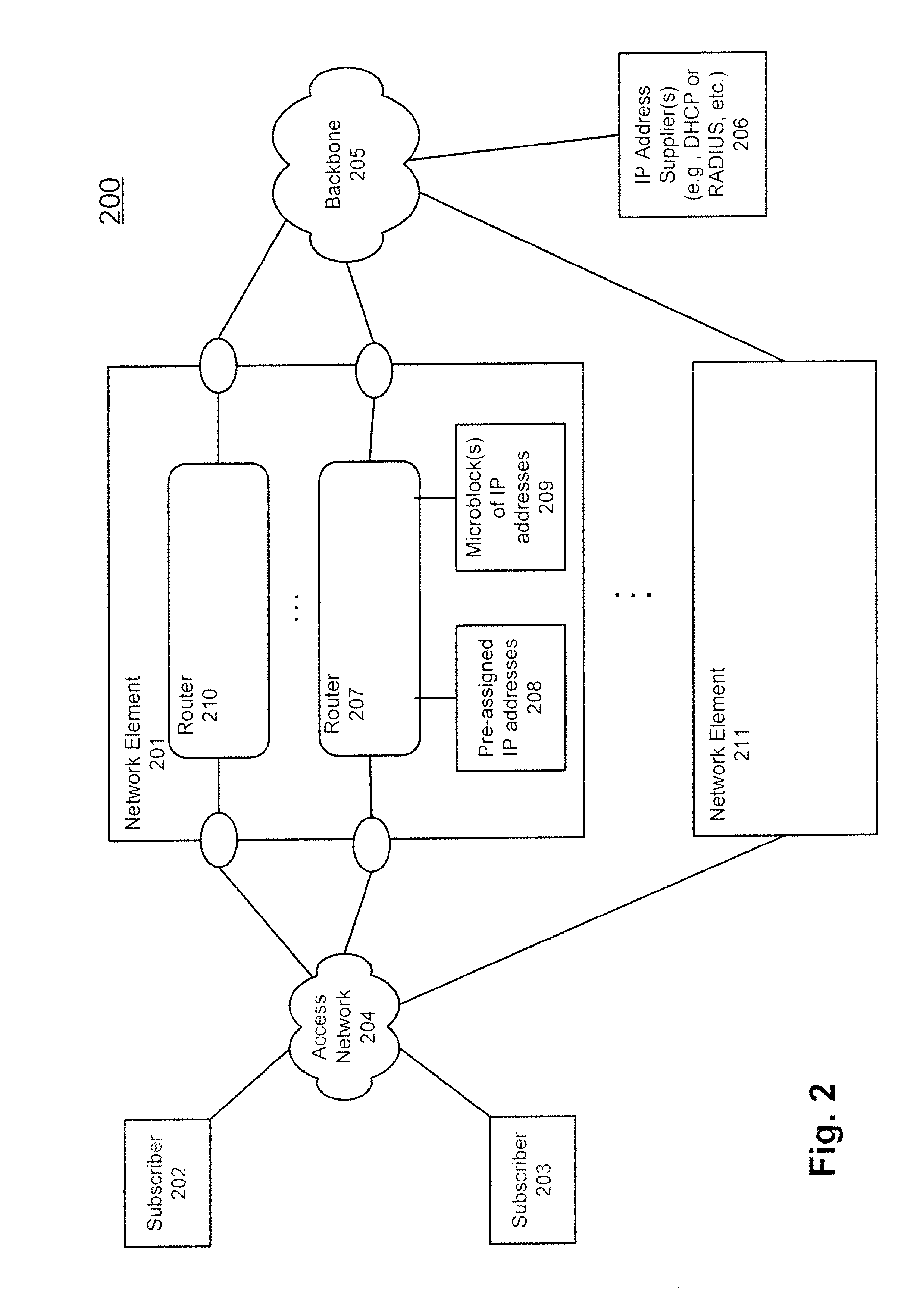
Use of IP address blocks with default interfaces in a router
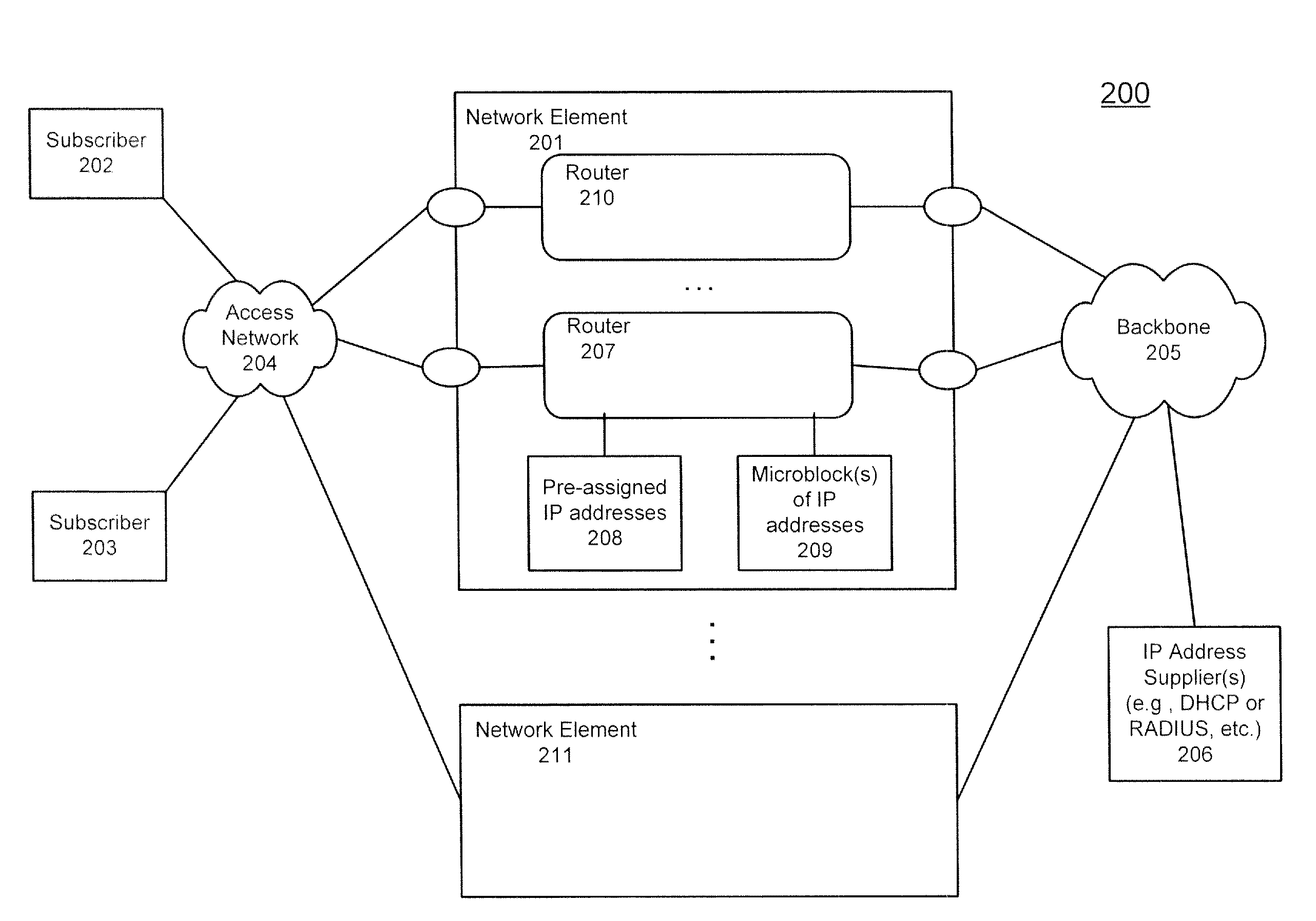
The use of IP address blocks with default interfaces in a router is described herein. According to one embodiment, an exemplary method includes in response to a request for a first IP address received from a first client at an interface of the network element, assigning the first client an IP address from a first block of IP addresses dynamically allocated from an IP address provider separated from a pool of statically preassigned IP addresses, if there is no IP address remained unassigned in the pool of statically preassigned IP addresses, and advertising reachability information in a network with respect to the first block of the IP addresses dynamically allocated from the IP address provider, such that other entities of the network are aware of the first block of the IP addresses. Other methods and apparatuses are also described.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
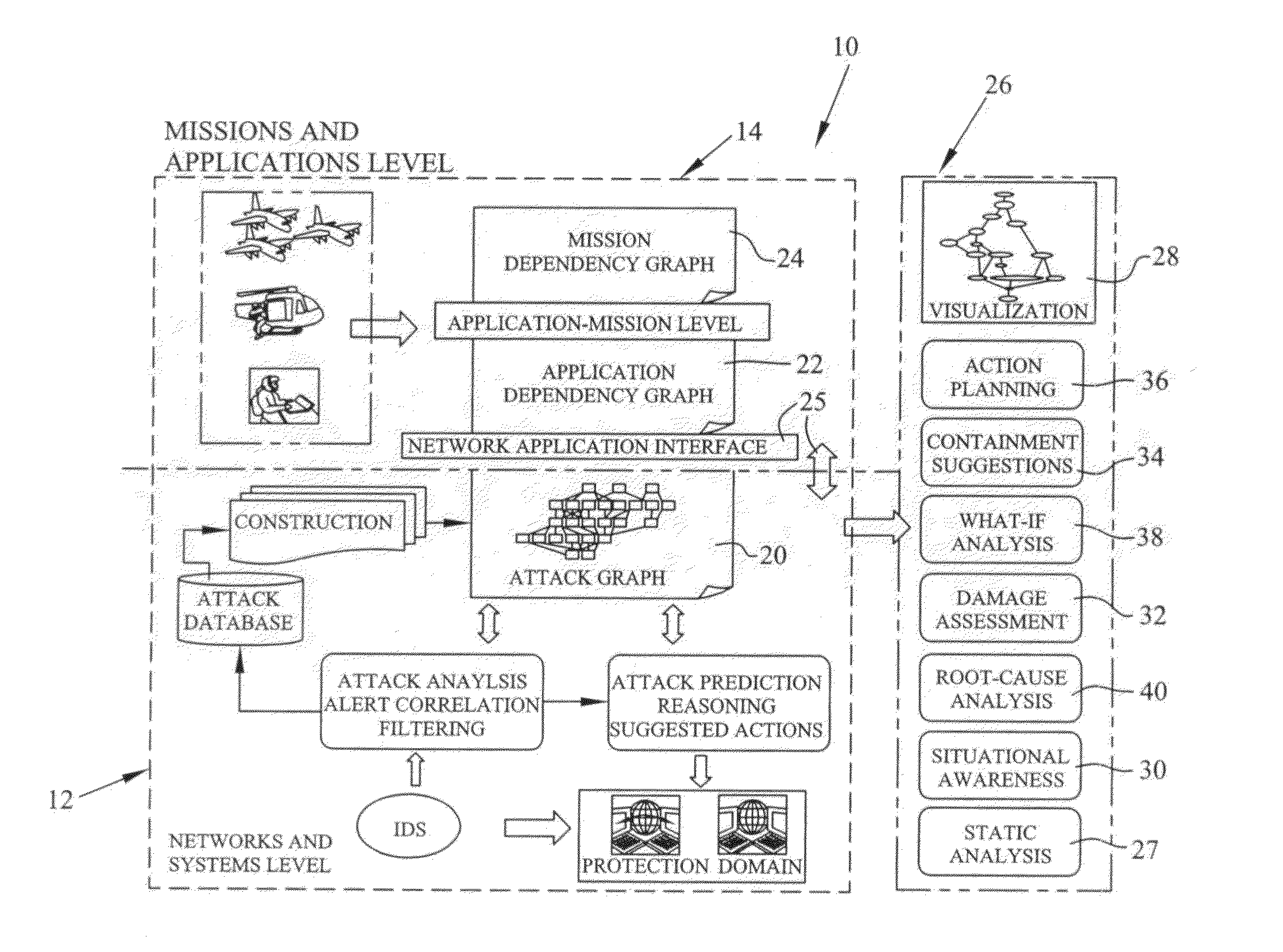
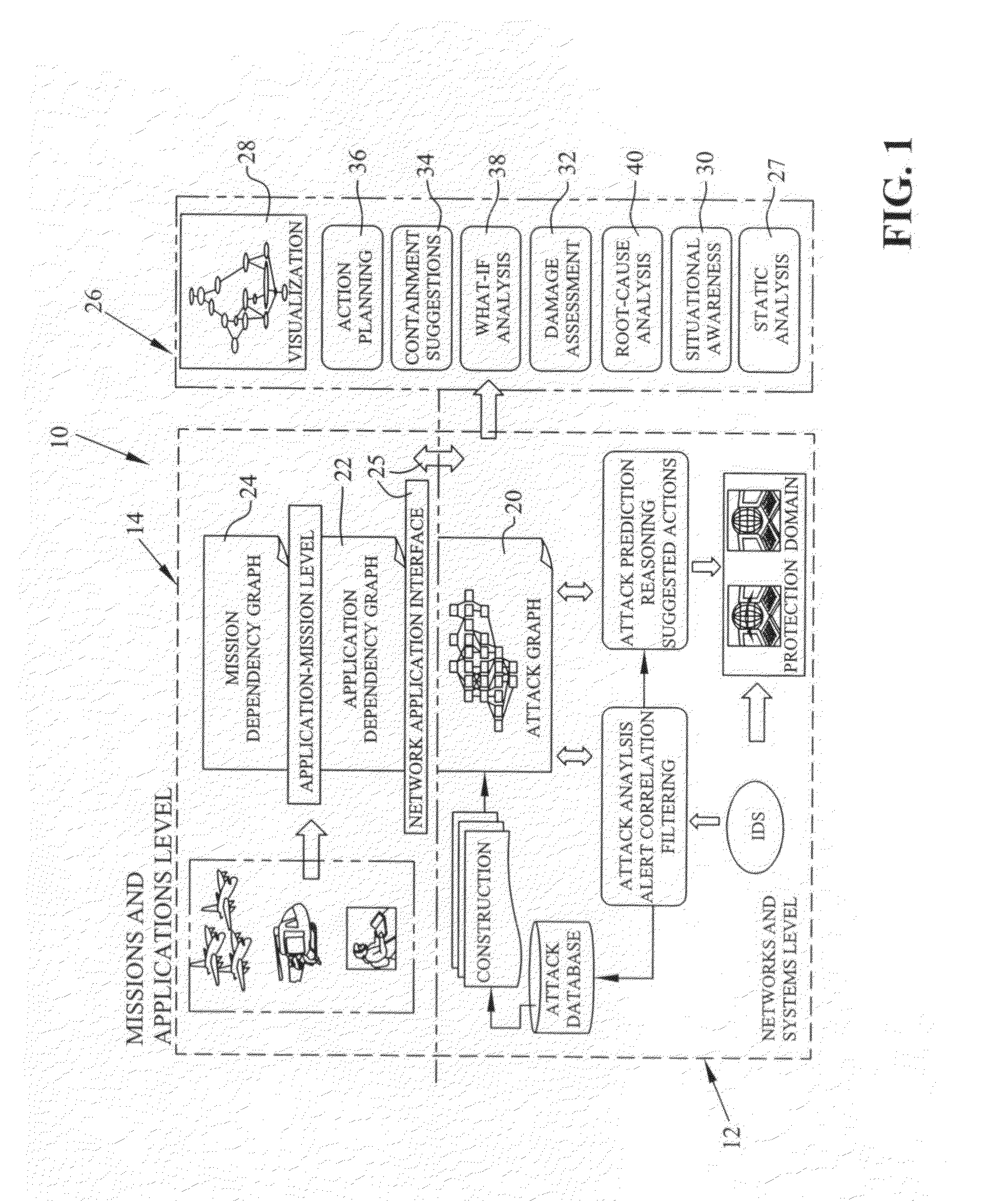
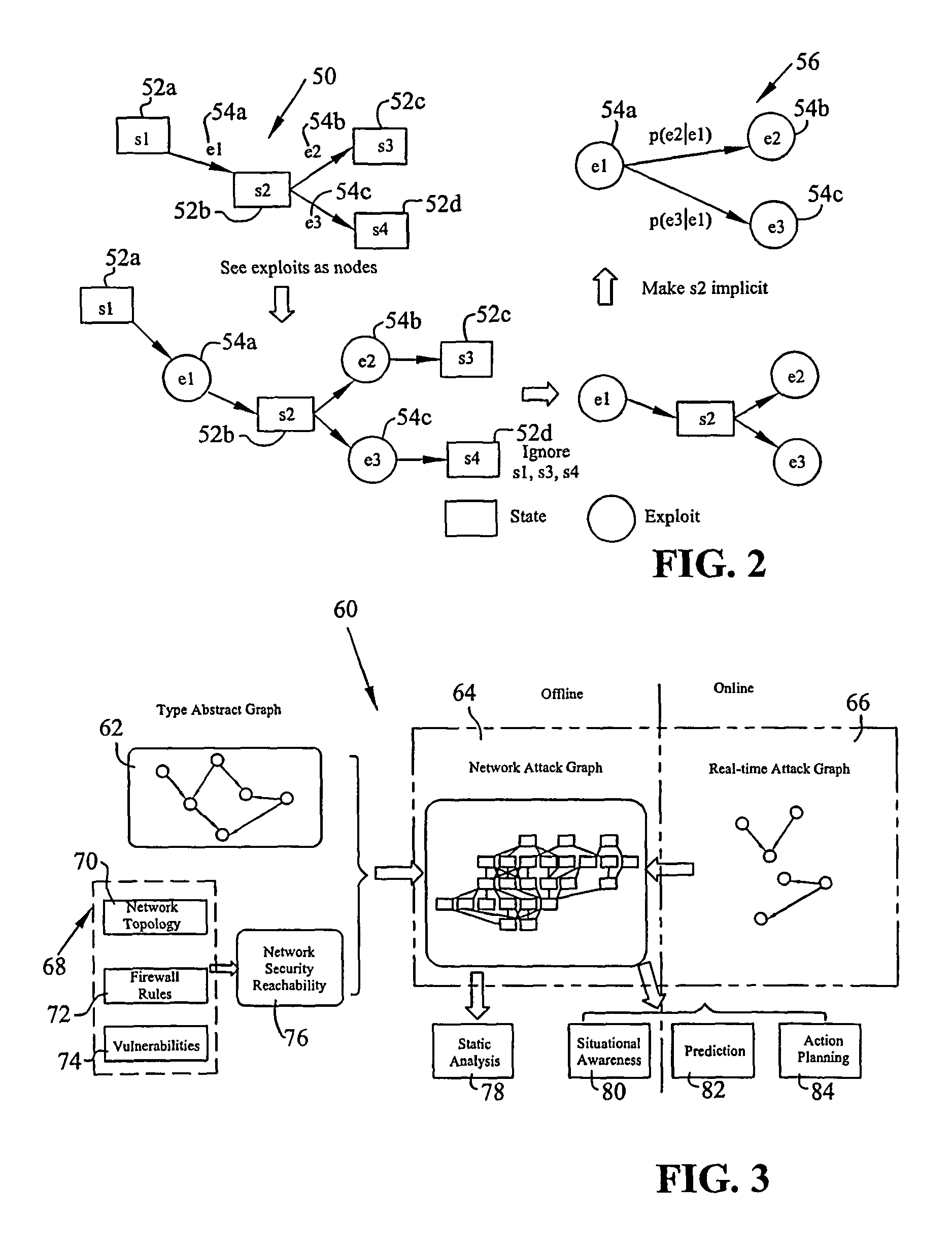
Graphical models for cyber security analysis in enterprise networks
ActiveUS8881288B1Accurate and efficientReduce and compress redundancyMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionGraphicsGaussian network model
A method of generating graphical models for providing security analysis in computer networks that in one embodiment includes the steps of generating a type abstract graph independent of particular networks that models abstract dependency relationships among attributes and exploits; generating network-specific attack graphs by combining the type abstract graph with specific network information; monitoring an intruder alert; and generating a real-time attack graph by correlating the intruder alert with the network-specific attack graph. The real-time attack graph can be generated using reachability checking, bridging, and exploit prediction based on consequence alerts and may further include the step of calculating the likelihood of queries using a Bayesian network model. The method may also include the steps of inferring unobserved attacks that may have been missed by intrusion detection sensors, and projecting on which hosts and using what exploits additional intruder attacks may occur. The method may further include the step of comparing alternate actions by computation, wherein the alternate actions include the step of patching some vulnerabilities, and wherein the specific network information includes network topology. The specific network information may also include firewall rules.
Owner:INTELLIGENT AUTOMATION LLC
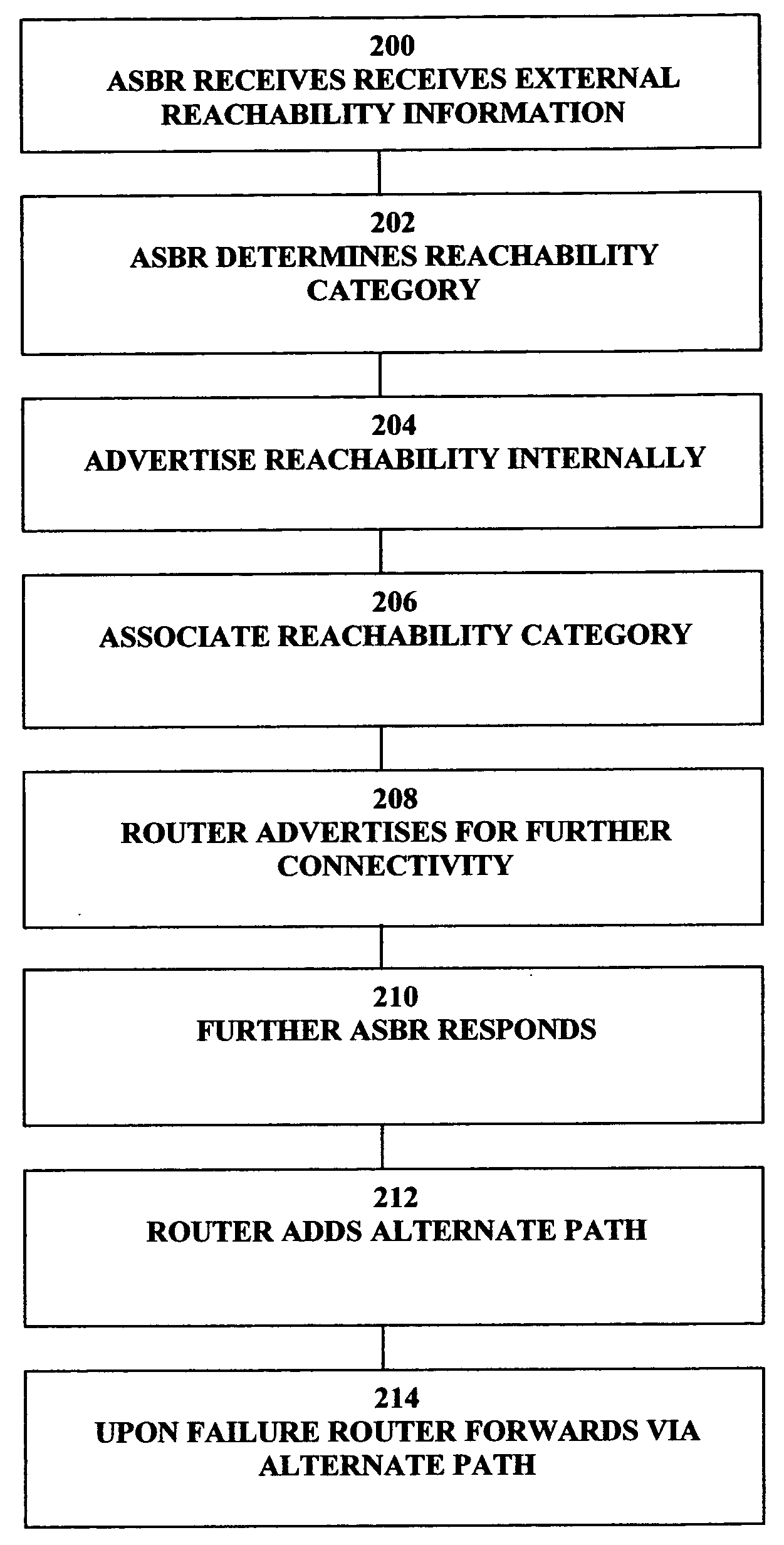
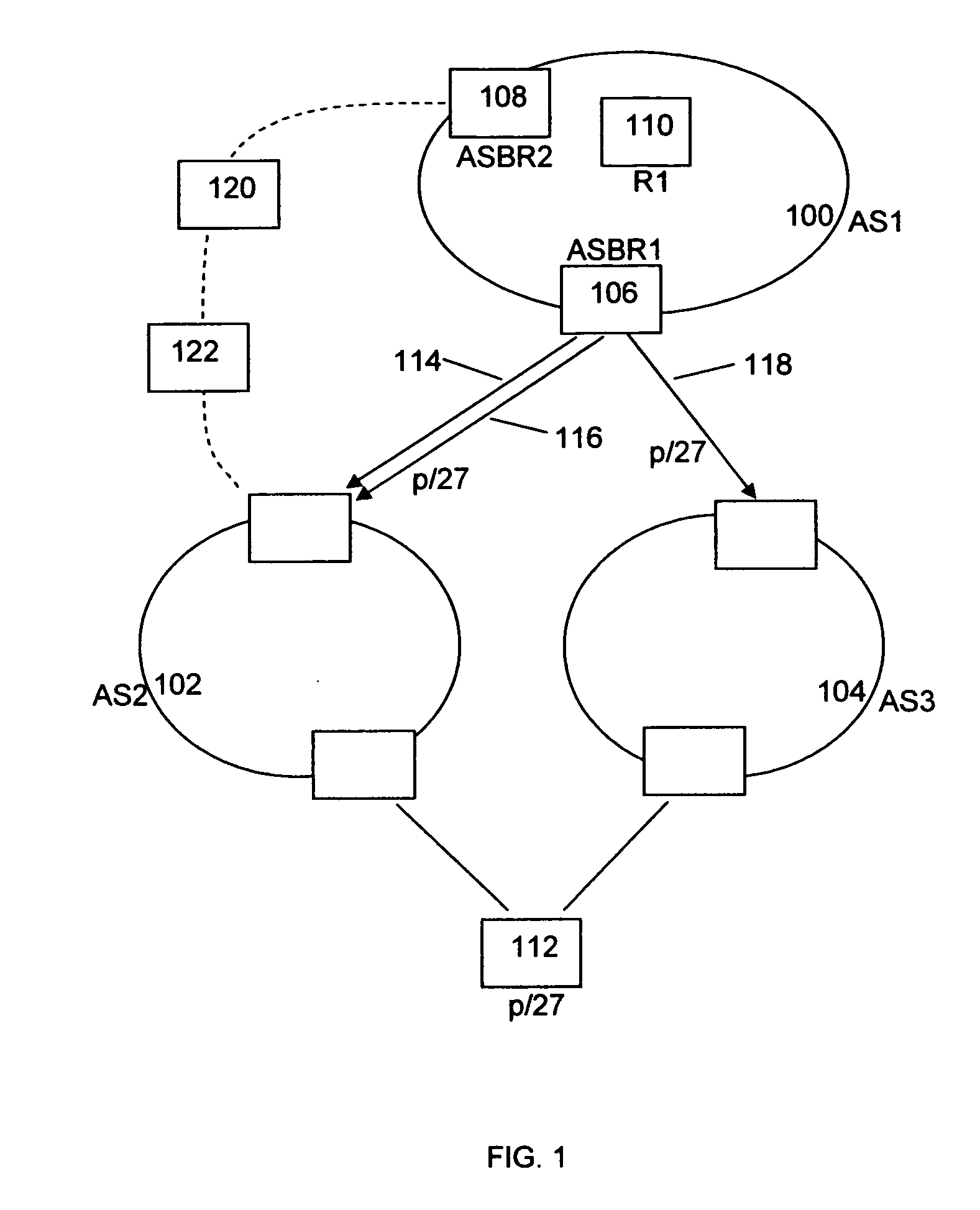
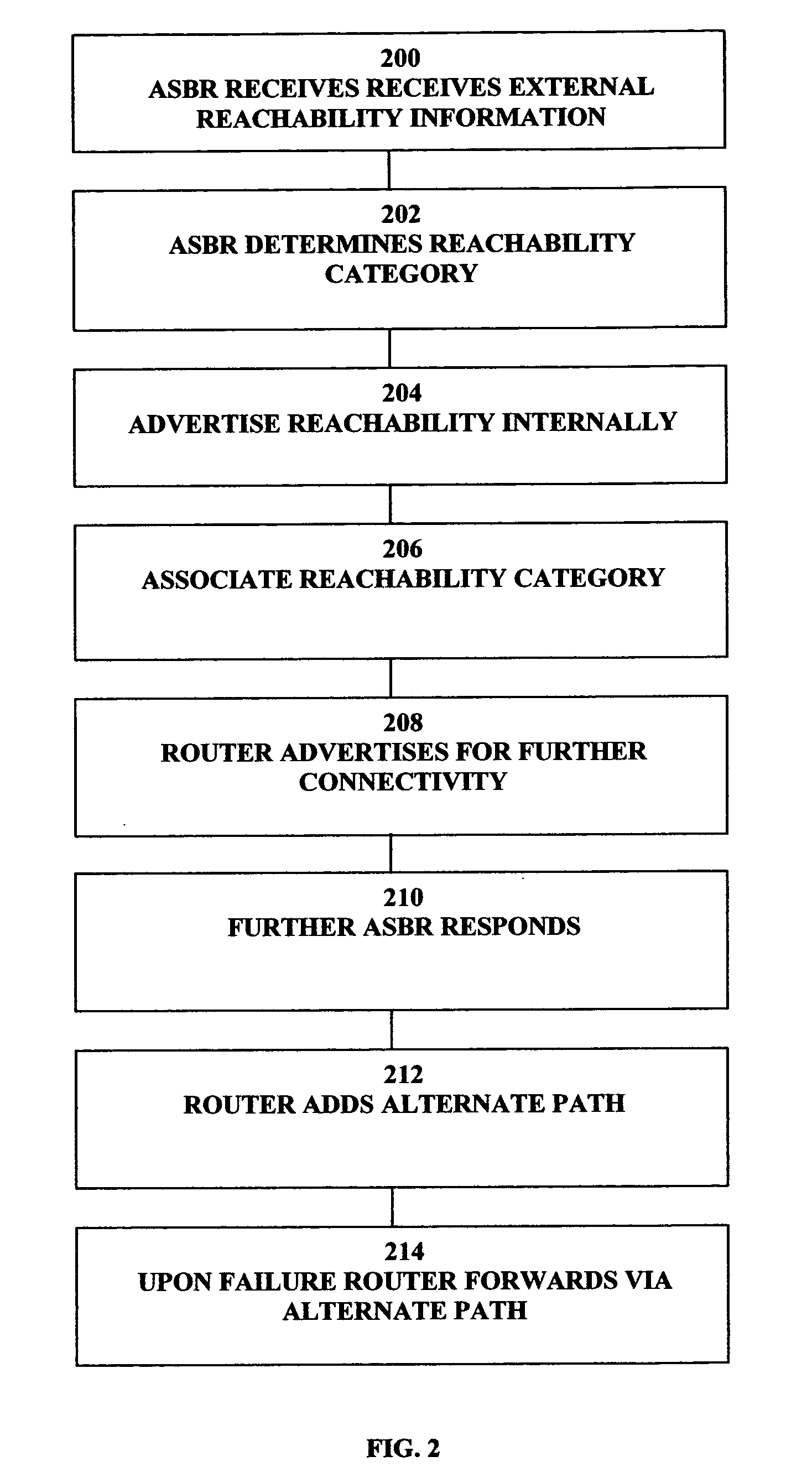
Providing reachability information in a routing domain of an external destination address in a data communications network
An apparatus for providing reachability in a routing domain of a data communications network having as components nodes and links therebetween for a routing domain—external destination address is described. The apparatus is arranged to advertise destination address reachability internally to nodes in the routing domain and associate a reachability category with said internal advertisement of said destination address reachability.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
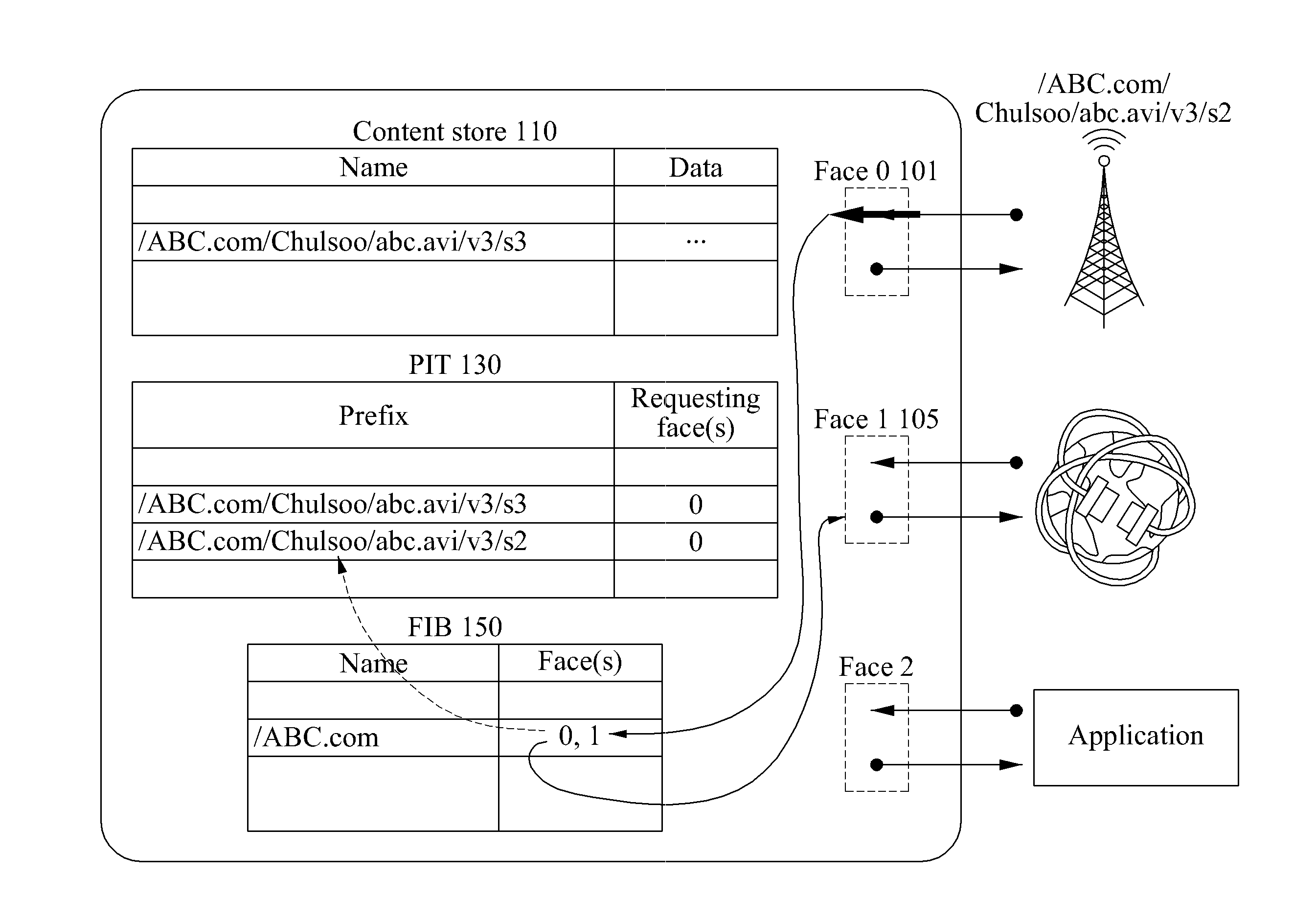
Communication method of content router to control traffic transmission rate in content-centric network(CCN), and content router
ActiveUS20130182568A1Transmission rate is limitedError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic volumeReachability
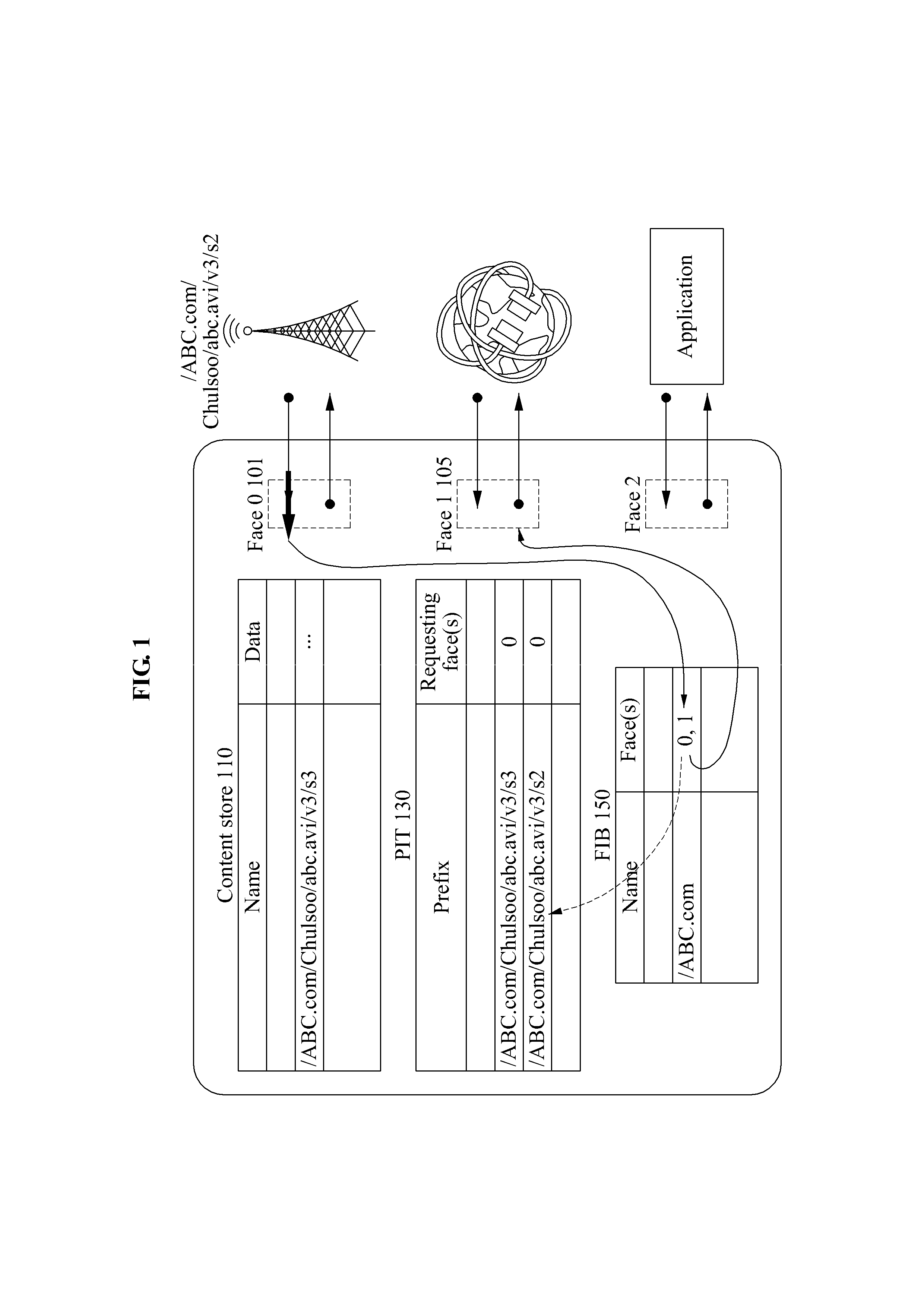
A communication apparatus and method of a content router control a traffic transmission rate in a content-centric network (CCN), and the content router. In the communication method and the content router, a congestion of a network may be predicted, a warning signal indicating the congestion may be added to an interest packet, and the interest packet with the warning signal may be transmitted. Additionally, a traffic transmission rate may be controlled by adjusting a data packet transmission time based on a value of a marked field of a PIT. The PIT is set by receiving an interest packet to which a warning signal is added. Thus, the communication apparatus and method thereof provide reachability, while maintaining stability of network routing.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
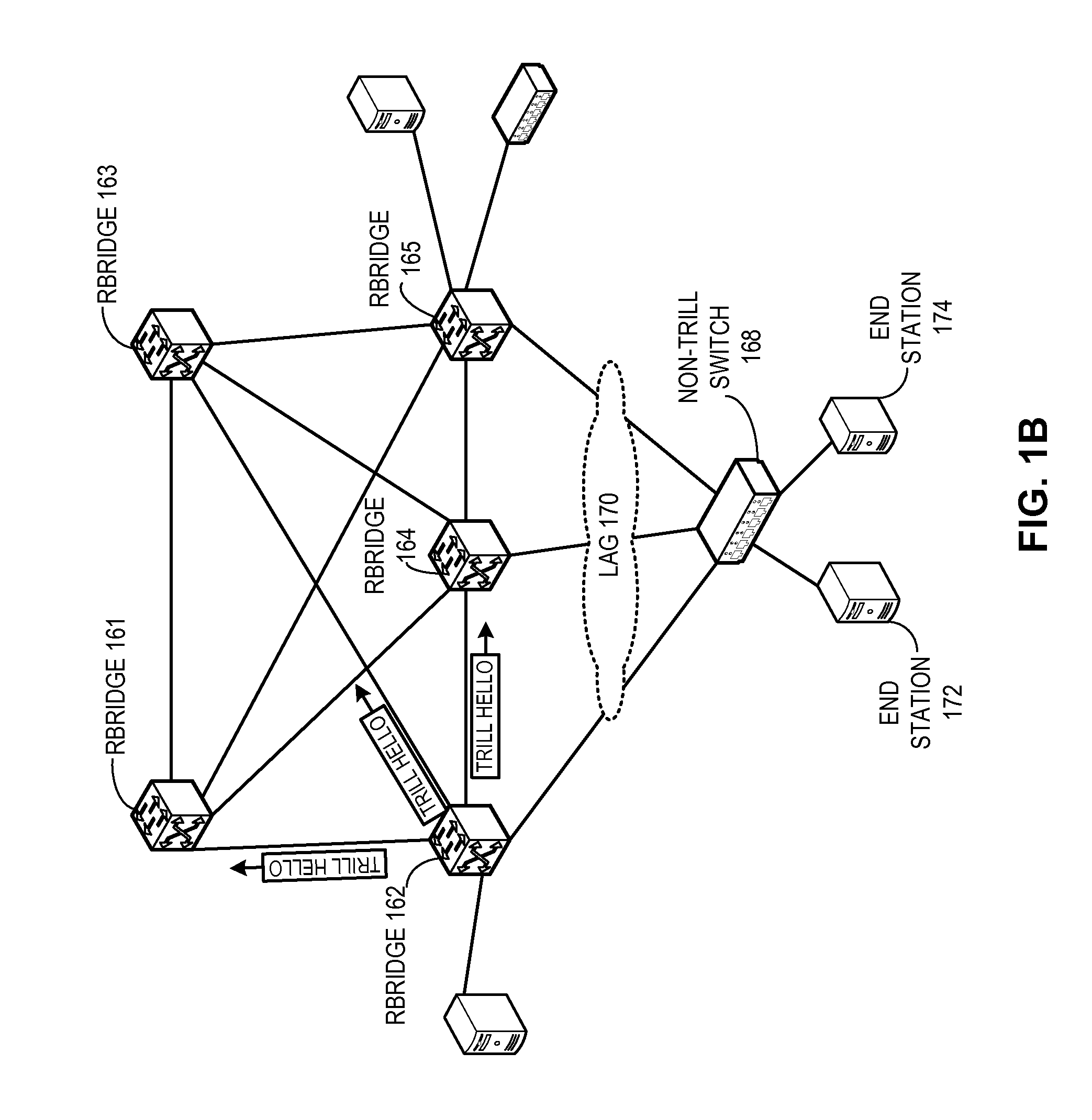
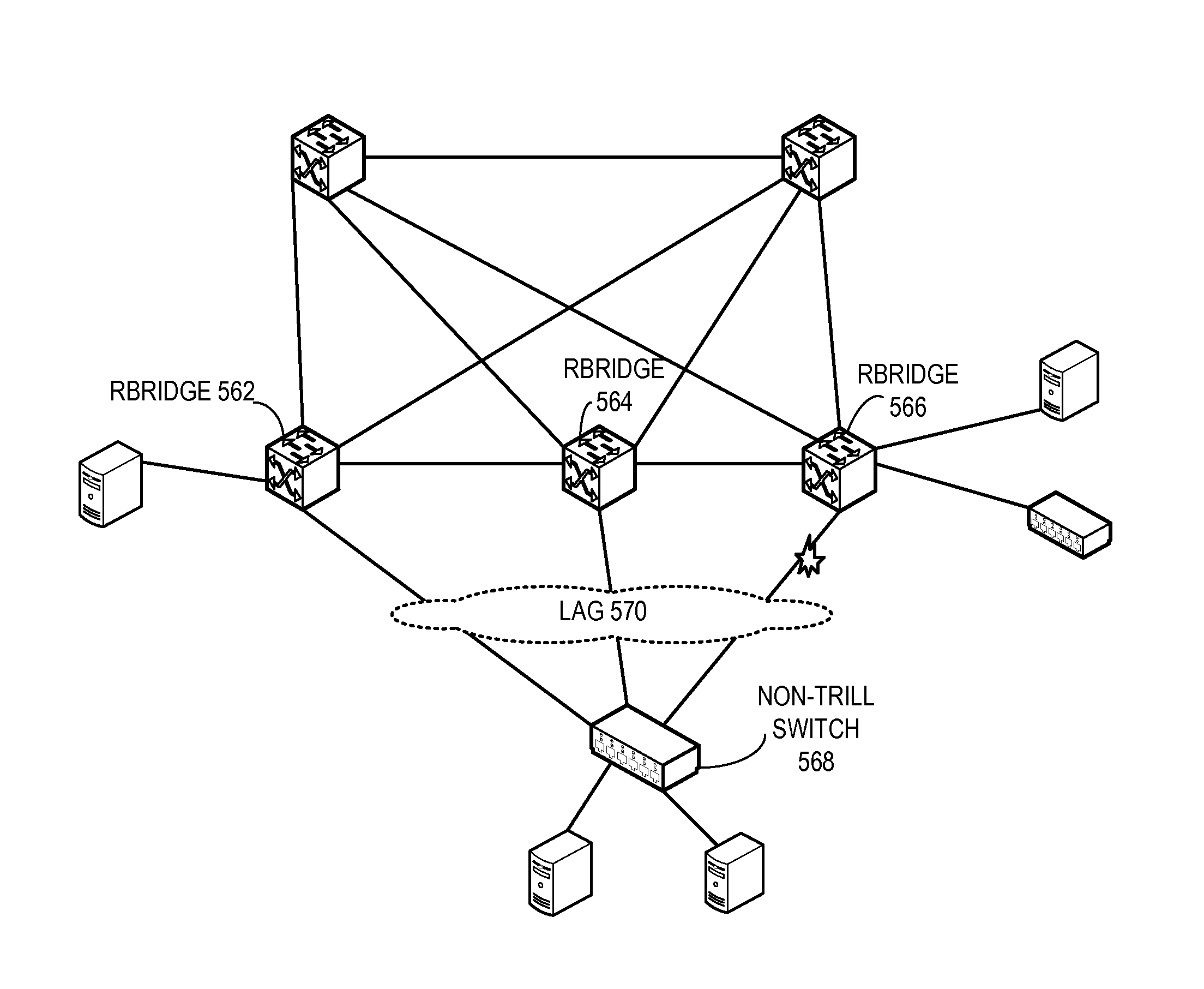
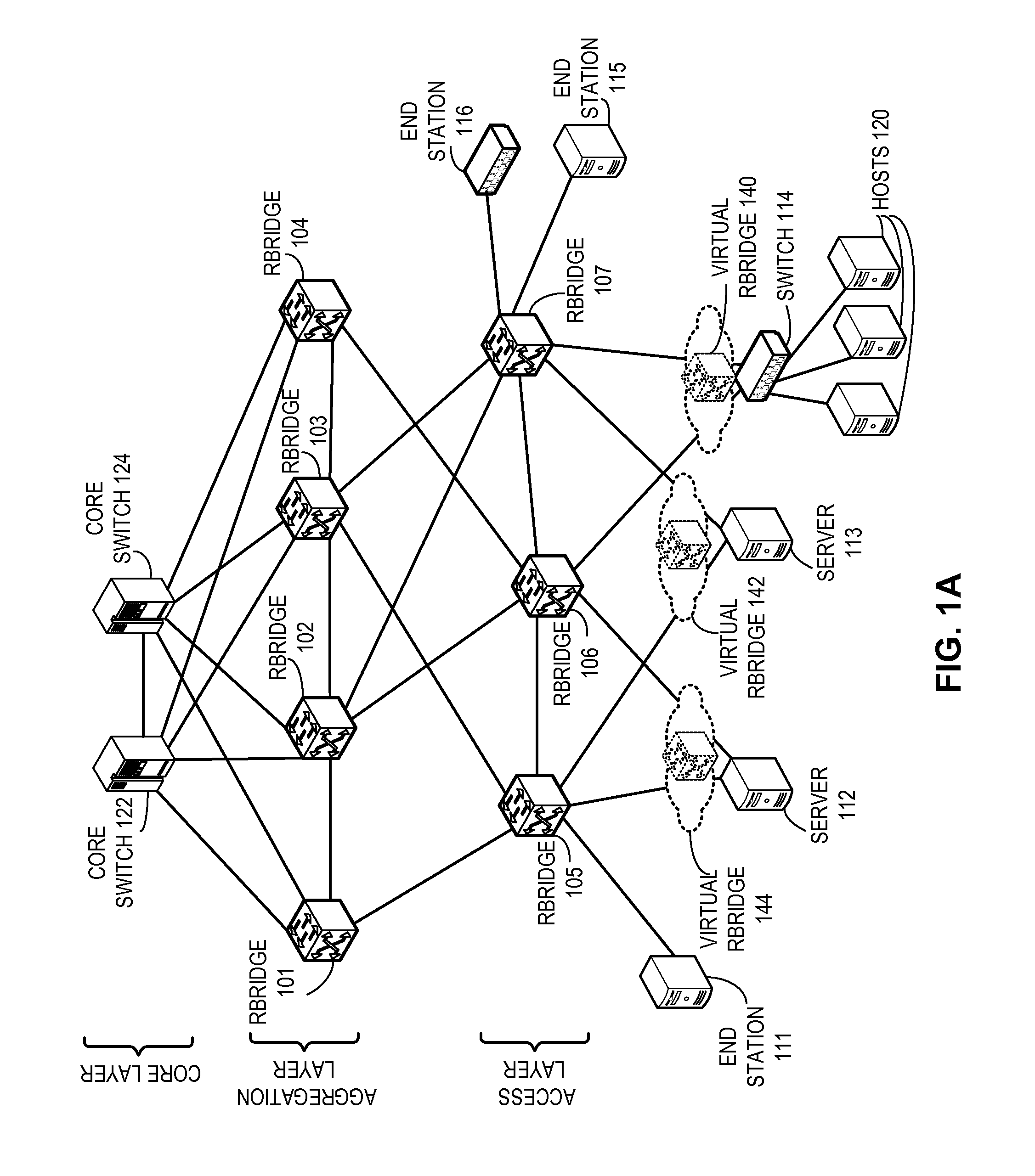
Method and system for extending routing domain to non-routing end stations
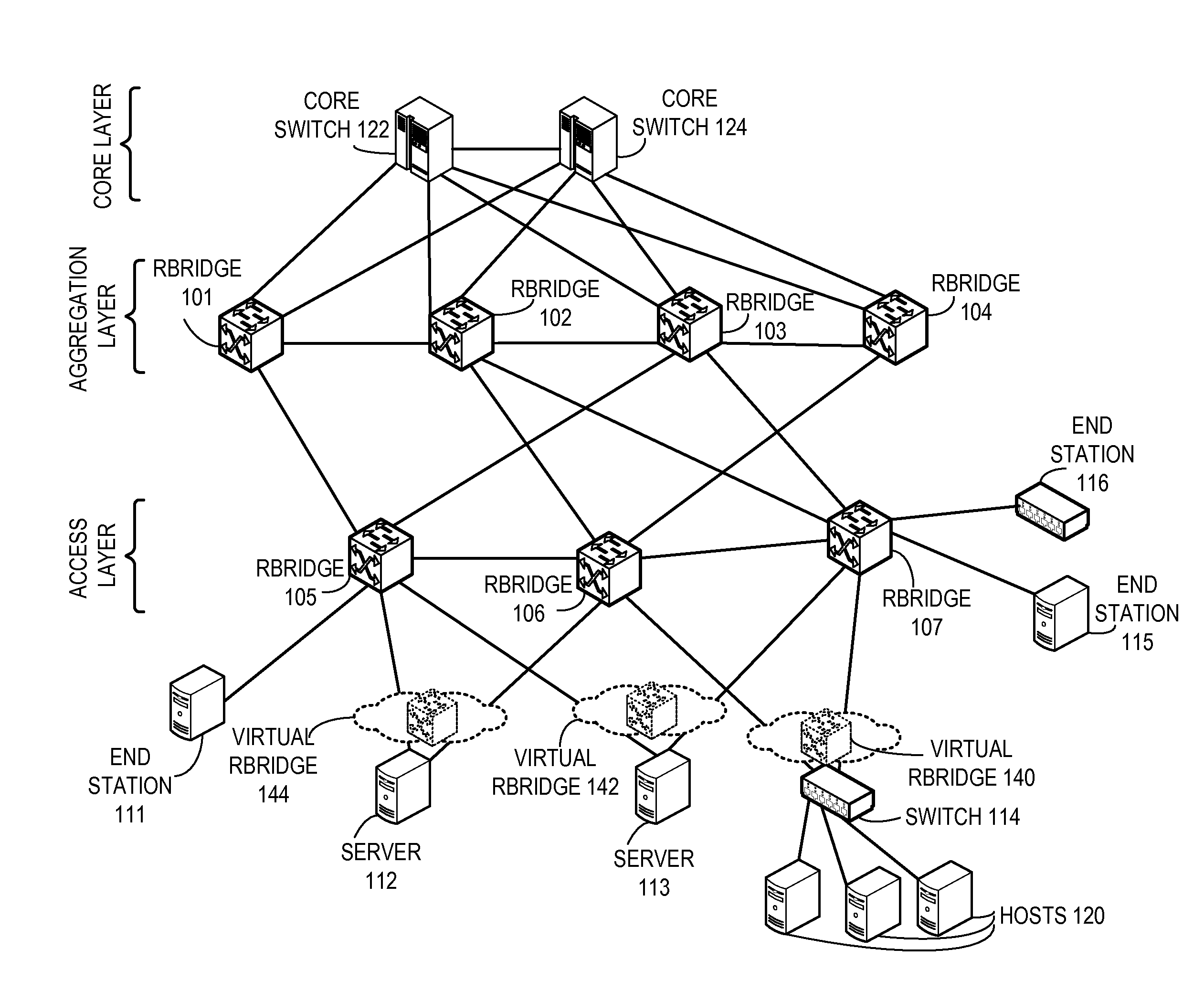
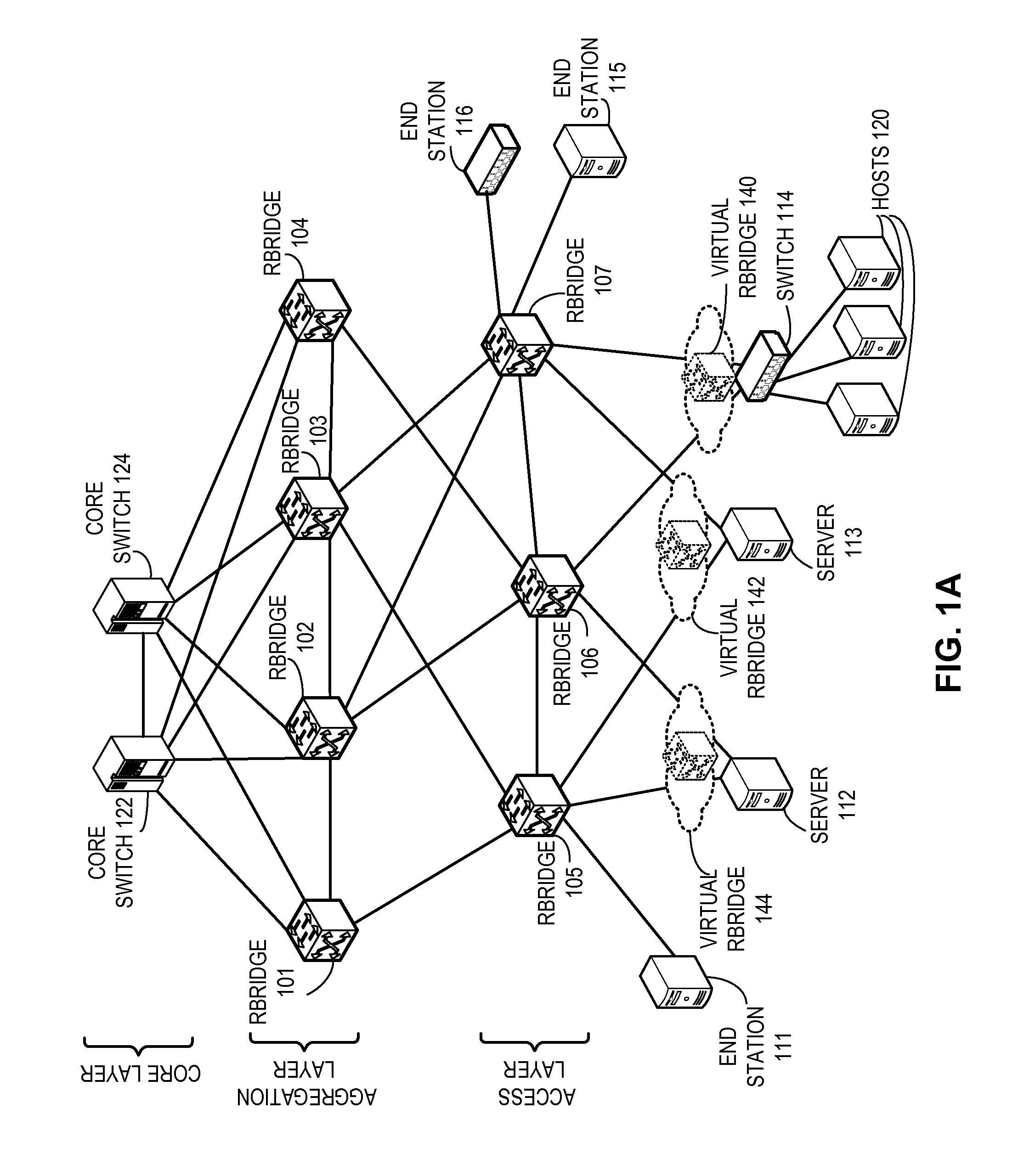
ActiveUS20110235523A1Optimize allocationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsReachabilityRouting domain
A system is provided for facilitating assignment of a virtual routing node identifier to a non-routing node. During operation, the system assigns to a non-routing node coupled to a switch a virtual routing node identifier unique to the non-routing node. In addition, the system communicates reachability information corresponding to the virtual routing node identifier to other switches in the network.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Boarder Gateway Protocol Signaling to Support a Very Large Number of Virtual Private Networks
InactiveUS20150003458A1Data switching switchboardsNetworks interconnectionBorder Gateway Protocol24-bit
Disclosed herein are example embodiments for Boarder Gateway Protocol (BGP) signaling in virtual private network (VPN) communications. For example, a first network element may encode Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) information in a Network Layer Reachability Information (NLRI) label field that is longer than 24 bits, and transmit a BGP update message comprising a BGP attribute to a second network element. The BGP attribute comprises the NLRI and a specific Subsequent Address Family Identifier (SAFI) value. The specific SAFI value signals to the second network element, upon reception of the BGP update message by the second network element, that the NLRI label field is more than 24 bits long.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
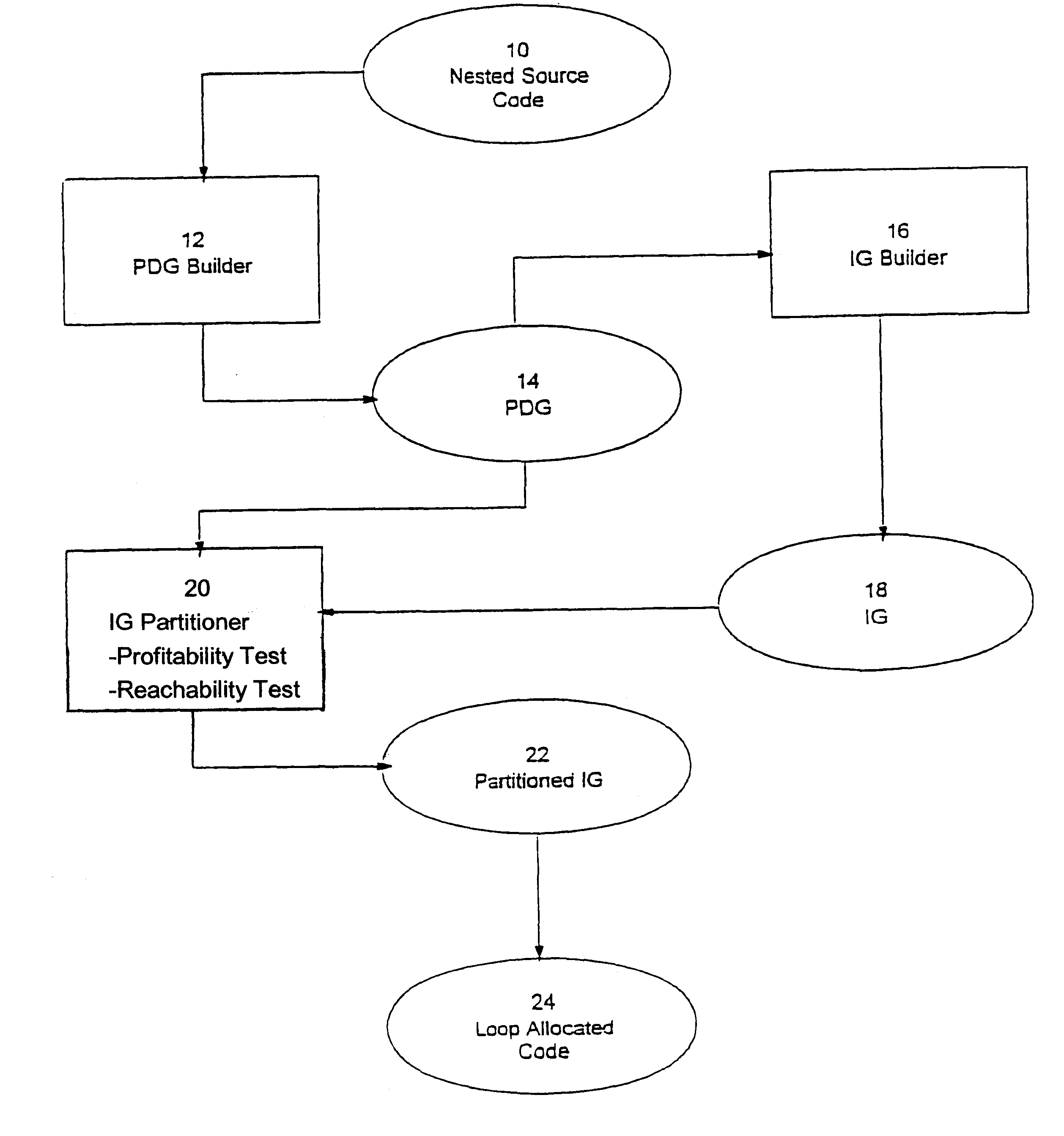
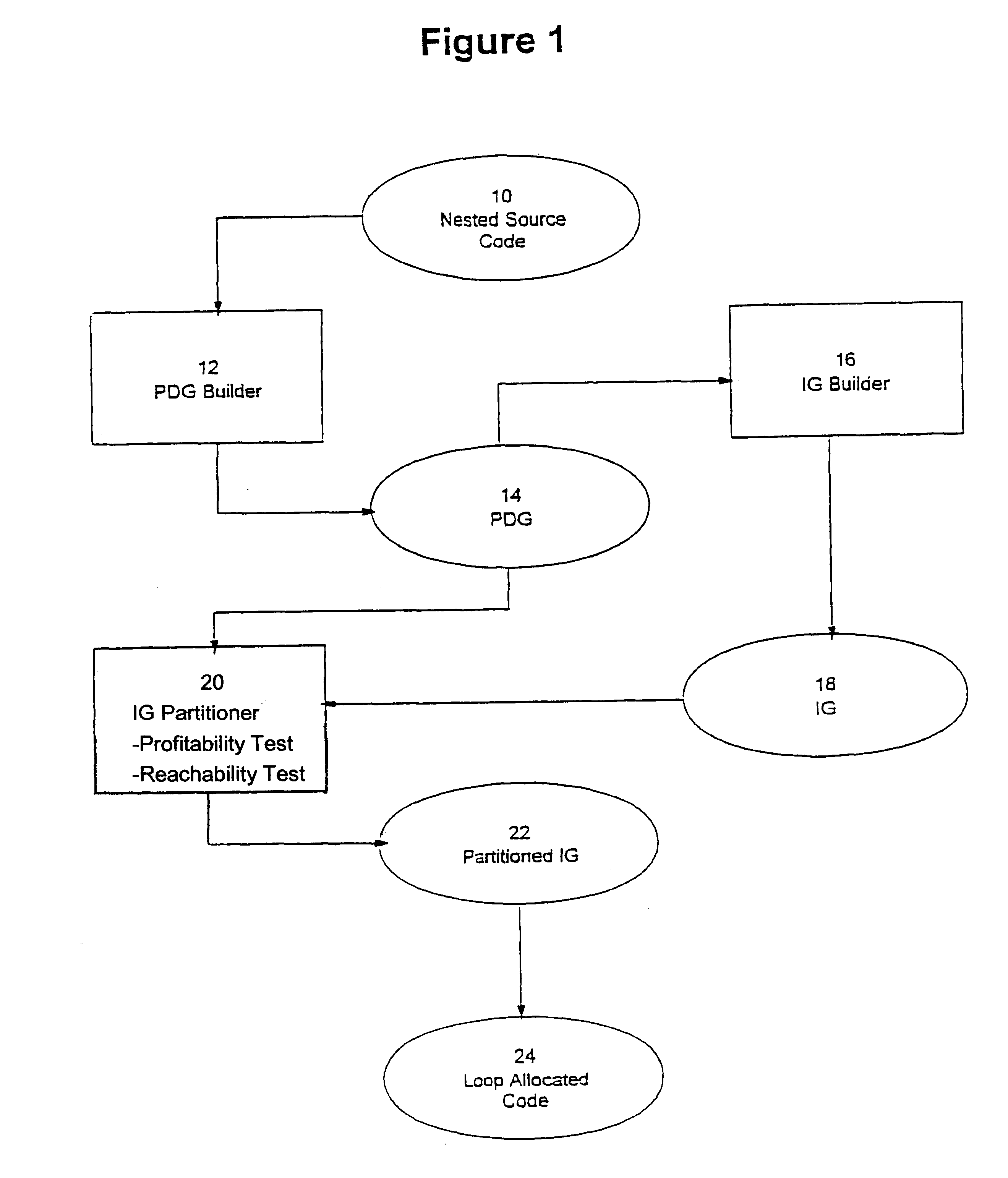
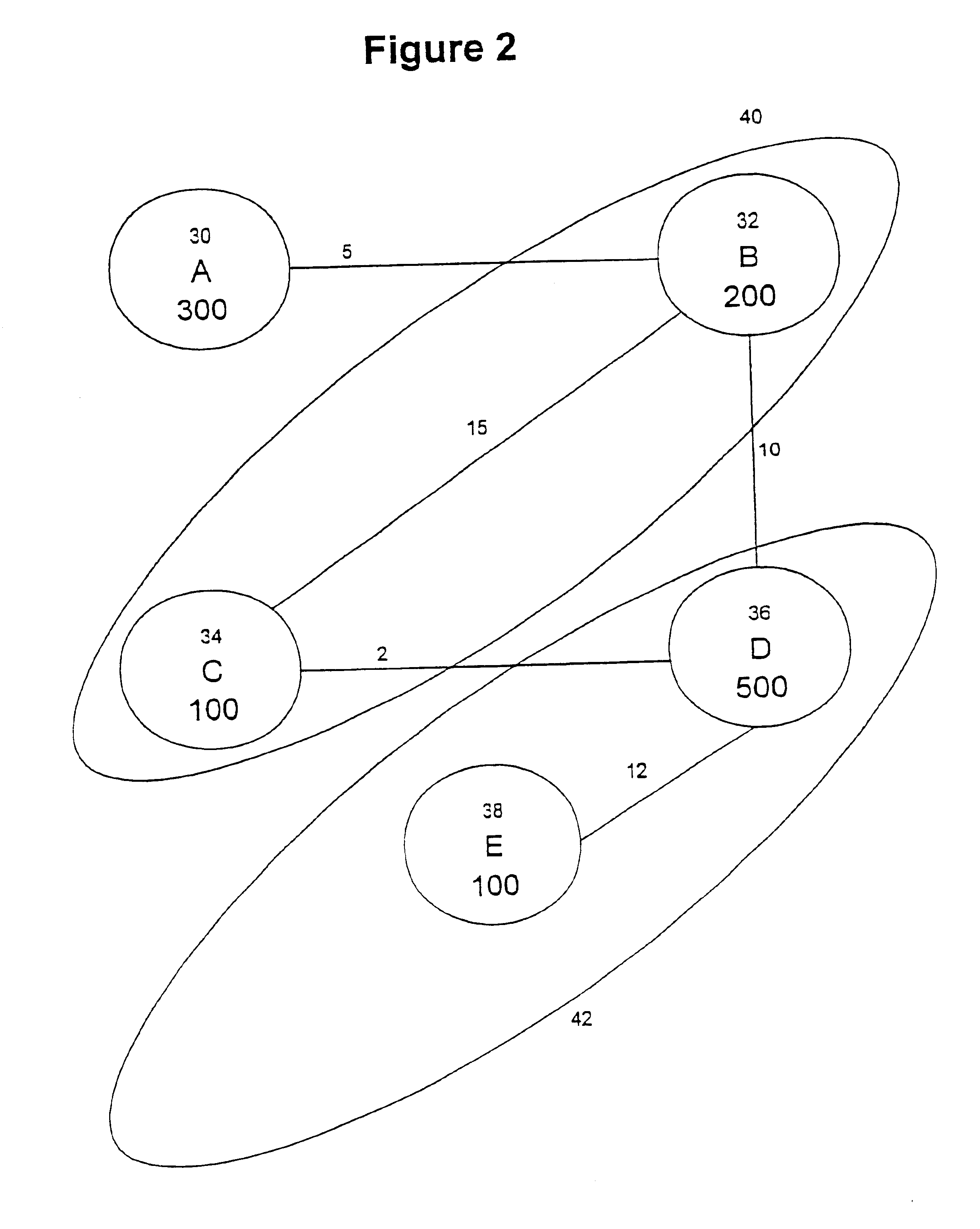
Loop allocation for optimizing compilers
Loop allocation for optimizing compilers includes the generation of a program dependence graph for a source code segment. Control dependence graph representations of the nested loops, from innermost to outermost, are generated and data dependence graph representations are generated for each level of nested loop as constrained by the control dependence graph. An interference graph is generated with the nodes of the data dependence graph. Weights are generated for the edges of the interference graph reflecting the affinity between statements represented by the nodes joined by the edges. Nodes in the interference graph are given weights reflecting resource usage by the statements associated with the nodes. The interference graph is partitioned using a profitability test based on the weights of edges and nodes and on a correctness test based on the reachability of nodes in the data dependence graph. Code is emitted based on the partitioned interference graph.
Owner:IBM CORP
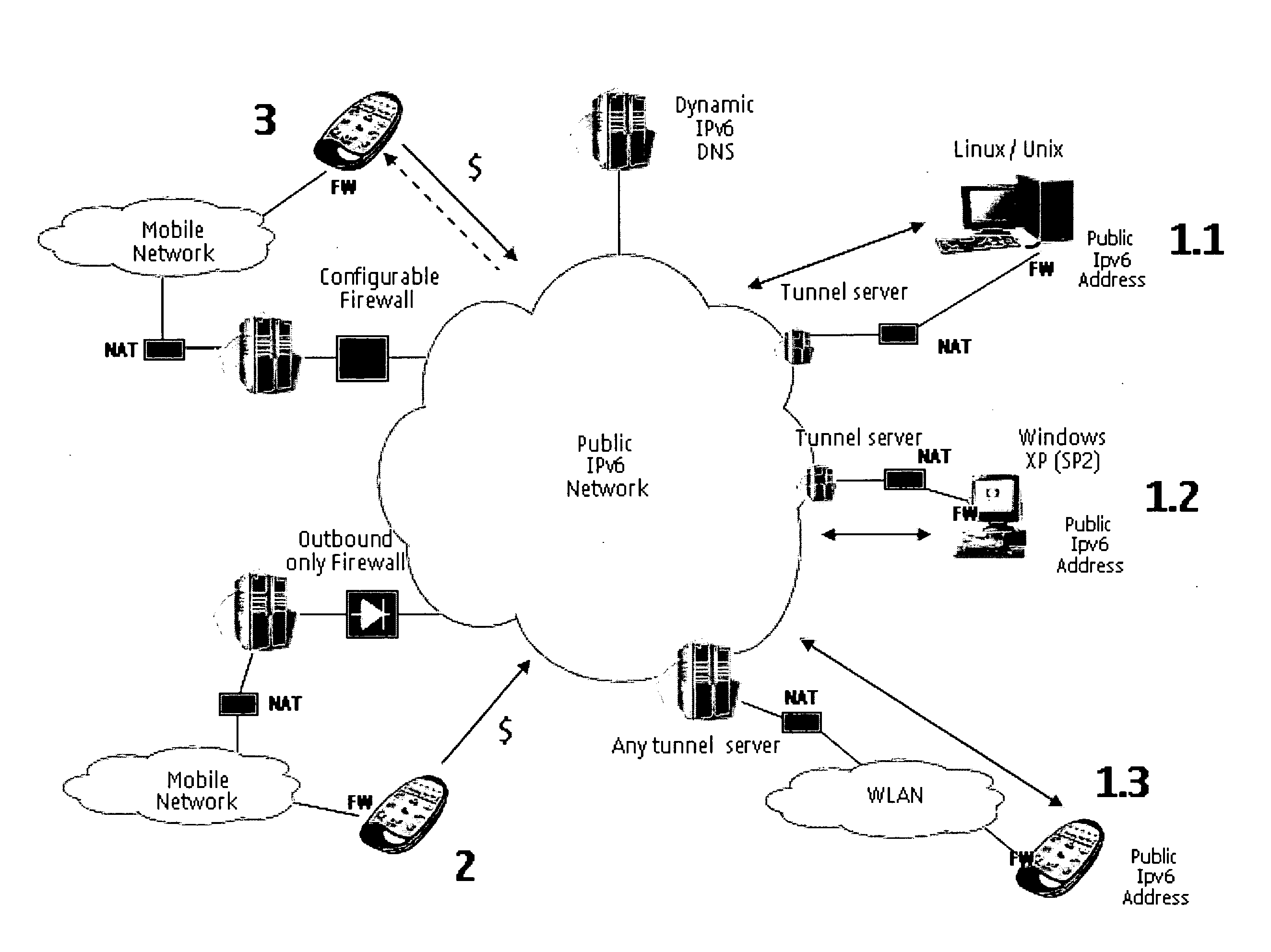
Terminal reachability
InactiveUS20070297430A1Data switching by path configurationSecurity arrangementReachabilityComputer science
A communication network for providing seamless peer-to-peer connectivity between nodes of different communication network environments, the communication network comprising at least one tunneling server comprising an access unit for providing access to the communication network and an addressing unit for assigning a dynamic address of a first addressing scheme routable in the communication network to a node connecting itself to the tunneling server, the node having a fixed address of a second addressing scheme, and storing at runtime an association between the fixed address of the second addressing scheme and the dynamic address of the first addressing scheme.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
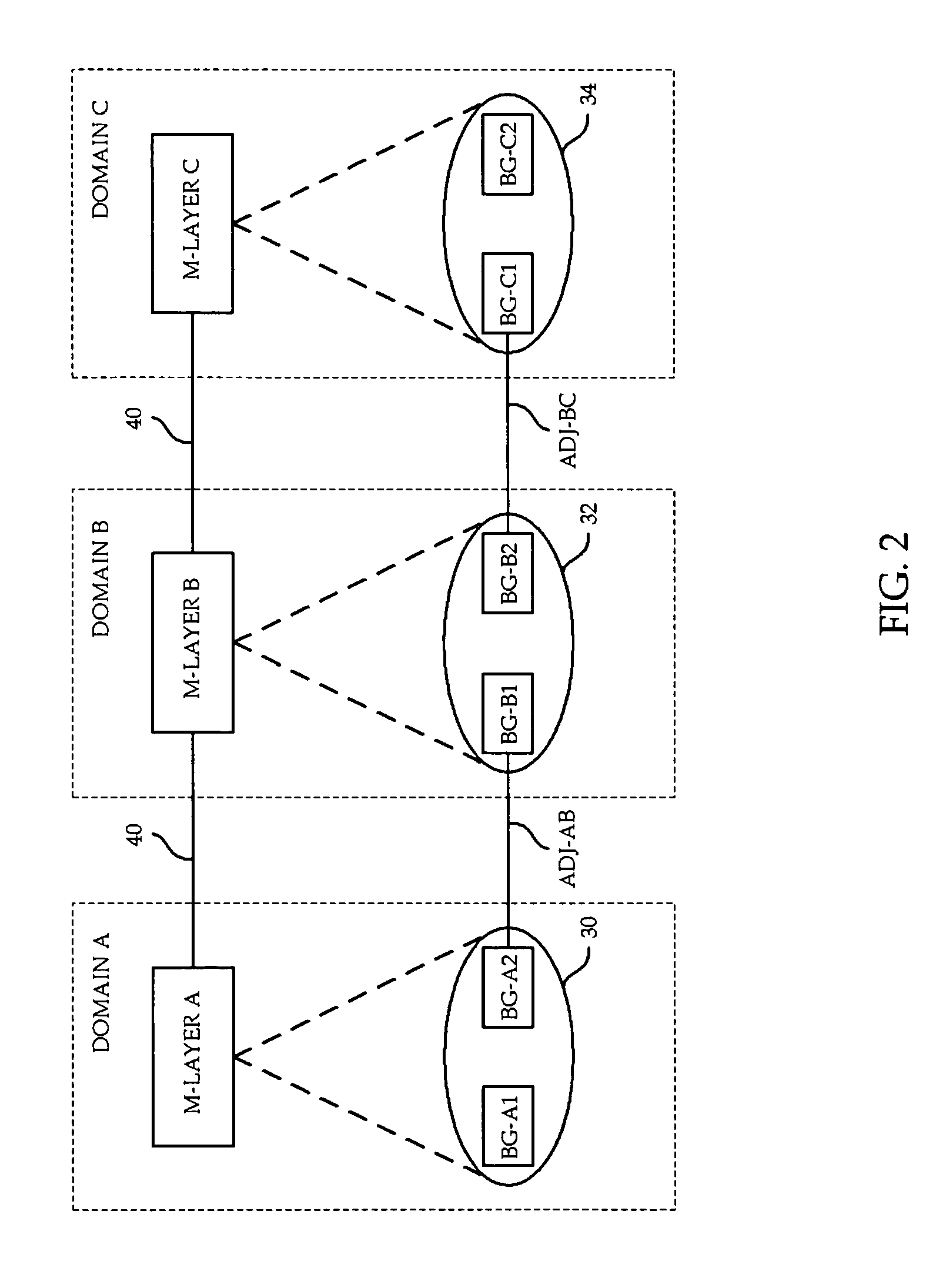
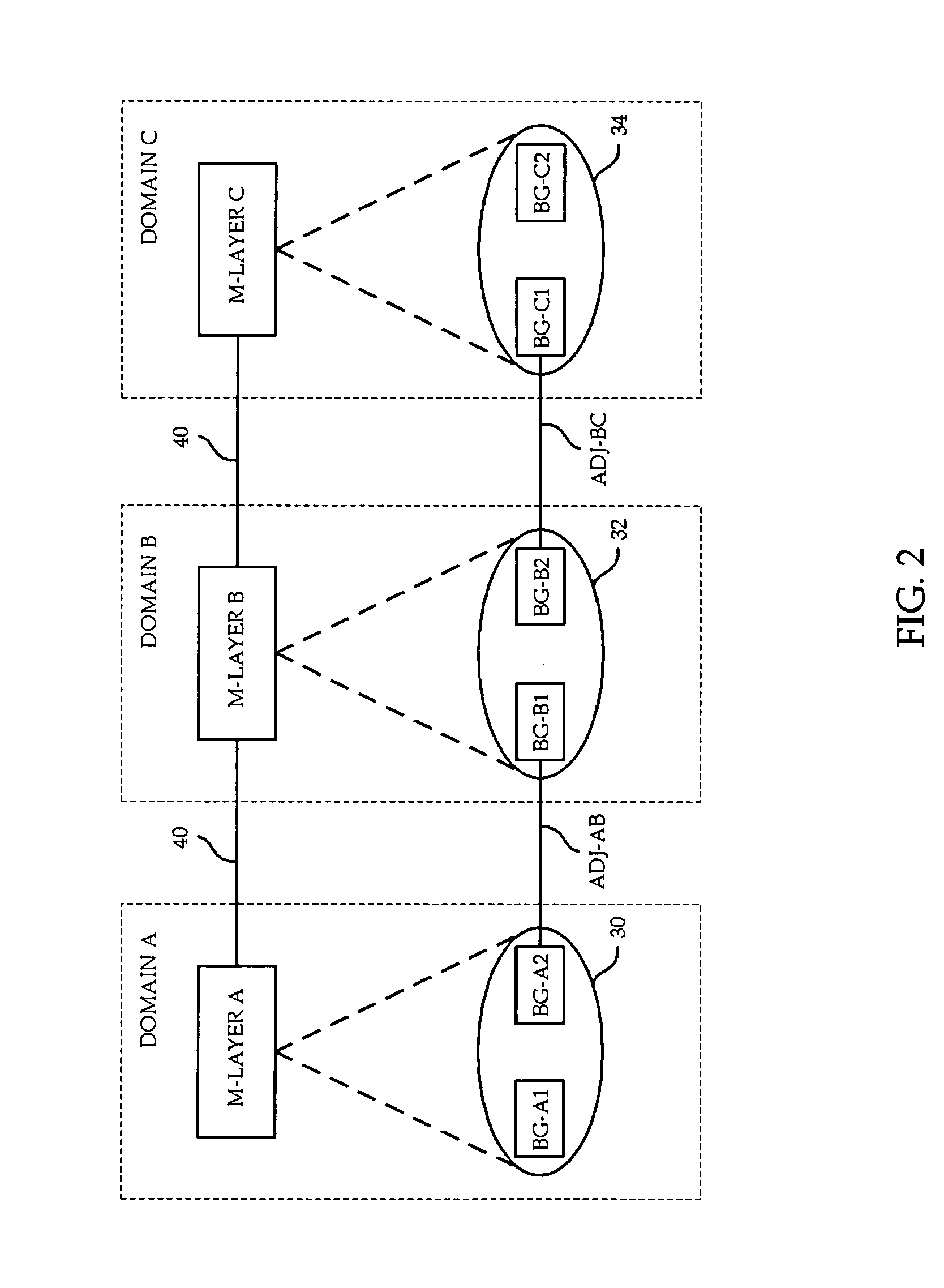
Open service discovery and routing mechanism for configuring cross-domain telecommunication services
ActiveUS20050259655A1Alleviating issue of trust and privacy restrictionScalability problems are significantly reduced or eliminatedData switching by path configurationService domainReachability
Apparatus and method are provided for distributing service domain reachability information across domain boundaries, thereby allowing domain management systems to determine routing for cross-domain services even when the domains have different technologies or administrators. A Service Domain Manager within each domain advertises to neighbouring domains which services it supports. A domain which receives such advertisements forwards the advertisement on to other domains. Each SDM builds a routing information table which specifies the service, the domain, the next hop, and optionally user defined metrics. The routing information table does not include end-point addresses, in order to keep the size of the table manageable. In this way, the NMS of each domain obtains an end-to-end view of service routes.
Owner:RPX CORP
Architecture for configuration and management of cross-domain network services
ActiveUS20050262232A1Minimum manual configurationData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsReachabilityNetwork service
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Modelling network to assess security properties
ActiveUS20070136788A1Random number generatorsUser identity/authority verificationRich modelReachability
A method of assessing a network uses a model (450) having nodes (100, 110) to represent parts of the network infrastructure and the application services, and having links to represent how the nodes influence each other. Dependencies or effects of the application services are found by determining paths through the nodes and links of the model (530). Such assessment can be useful for design, test, operations, and diagnosis, and for assessment of which parts of the infrastructure are critical to given services, or which services are dependent on, or could have an effect on a given part of the infrastructure. The dependencies or effects can encompass reachability information. The use of a model having links and nodes can enable more efficient processing, to enable larger or richer models. What changes in the dependencies or effects result from a given change in the network can be determined (830).
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Secure tunnel establishment upon attachment or handover to an access network
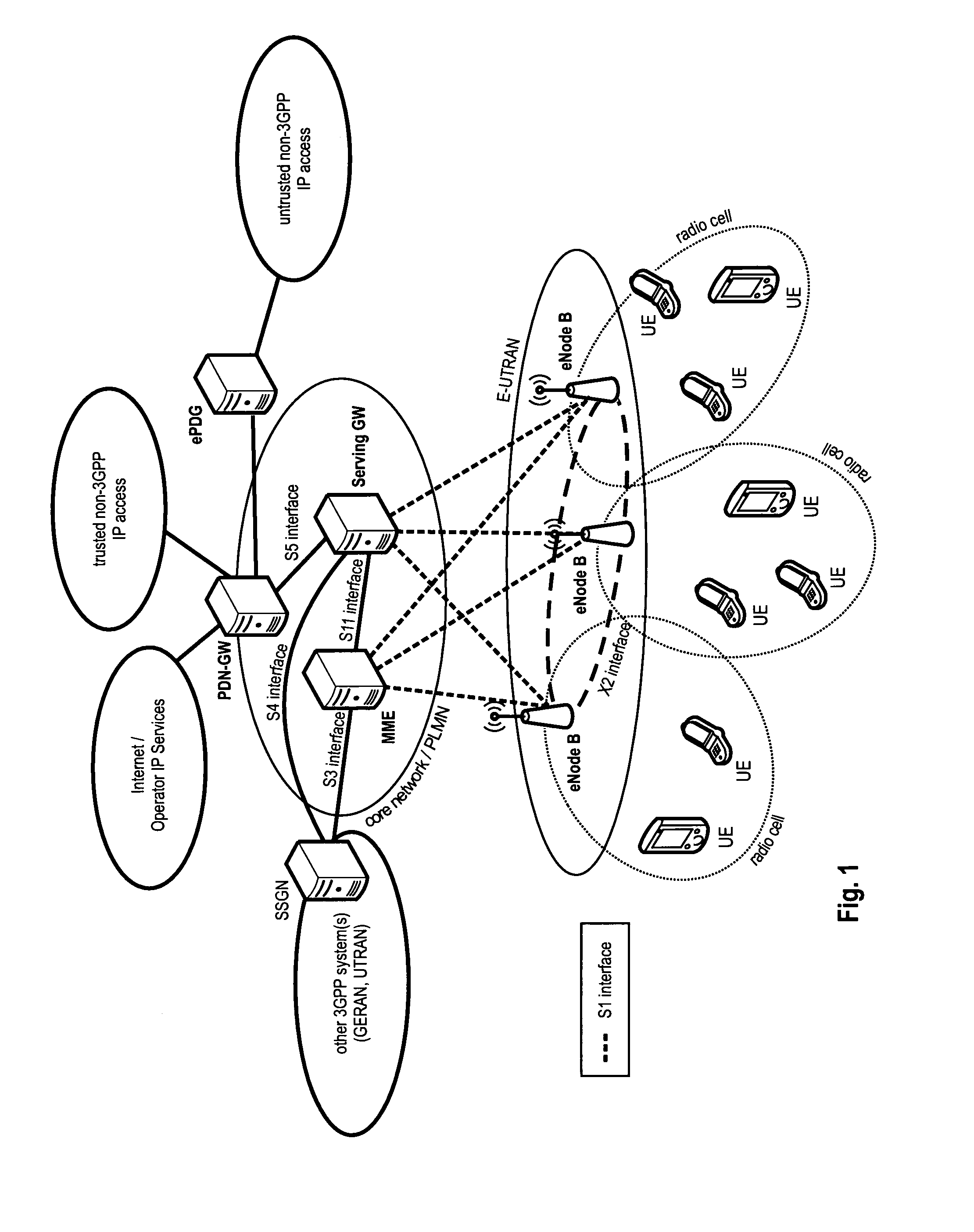
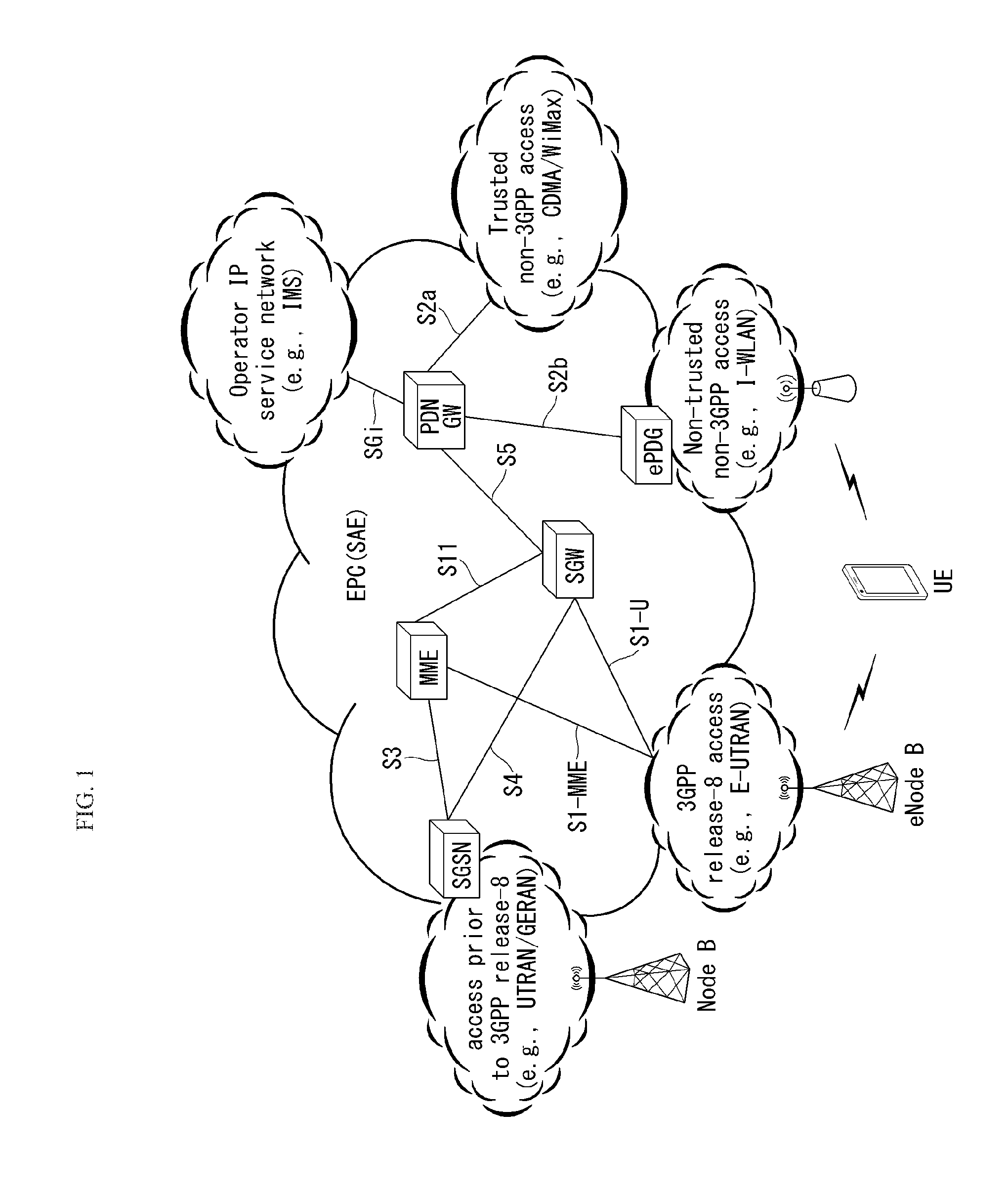
ActiveUS20110261787A1Reduce delaysFacilitate fast establishmentConnection managementWireless network protocolsAccess networkReachability
The invention relates to a method, mobile node and computer-readable medium for establishing (or pre-establishing) a secure tunnel to an ePDG to prepare for a mobile node attachment or handover to another access network. To reduce the delay of a handover or upon attachment of a mobile node to an access network implied by mechanisms to discover a ePDG, the mobile node maintains a reachability list that can be consulted to identify an ePDG or ePDGs that are reachable in the target access network, i.e. to which the mobile node may establish a secure tunnel. If the mobile node can identify a reachable ePDG for a given access network from the reachability list, the mobile node (pre-)establishes a secure tunnel to the ePDG upon attaching to the given access network. In alternative solutions DNS, DHCP or other mechanism can be used to provide the mobile node with information on ePDGs in its vicinity.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
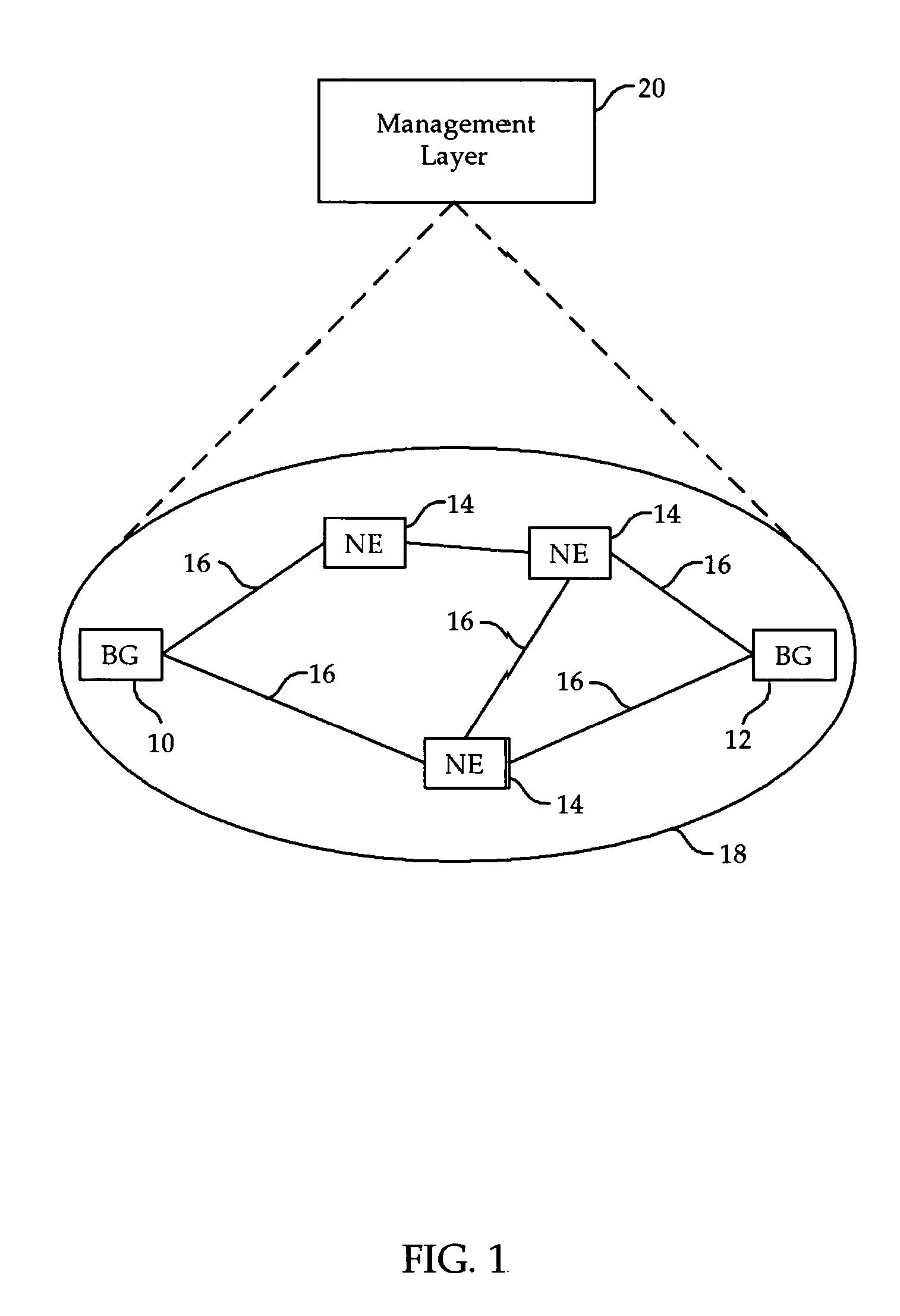
Methods and systems for exchanging reachability information and for switching traffic between redundant interfaces in a network cluster
InactiveUS6954794B2Shorten the timeQuick switchSpecial service provision for substationTime-division multiplexTraffic capacityRouting table
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
Method for planning path for mobile robot based on environmental modeling and self-adapting window
InactiveCN101738195ASolve the problem of generating obstacle avoidance paths in real timeThe problem of real-time generation of obstacle avoidance paths satisfiesInstruments for road network navigationSpecial data processing applicationsSimulationLocal environment
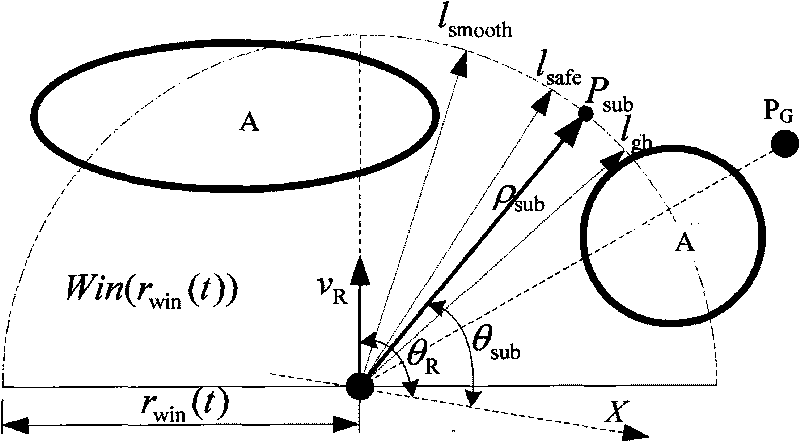
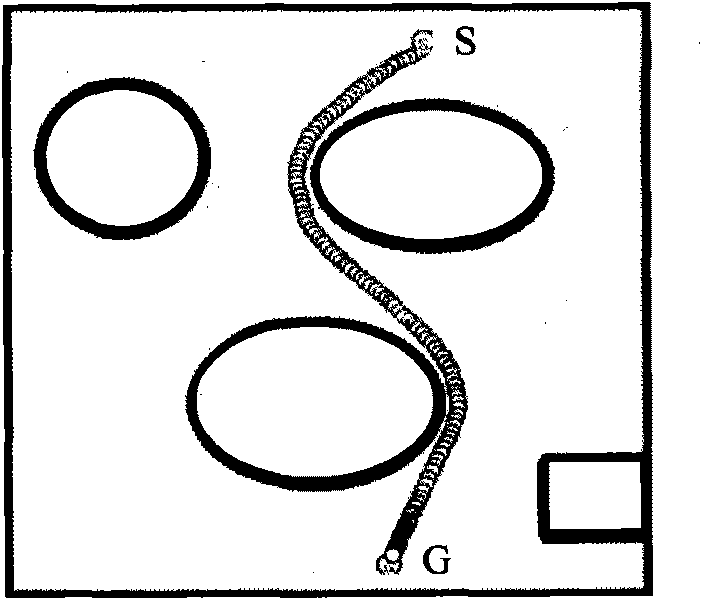
The invention relates to a method for planning a path for a mobile robot based on environmental modeling and a self-adapting window, which relates to a method for planning a real-time path for the mobile robot. The method comprises the following steps of: performing modeling and analysis on a multiple constraint local environment; performing passable analysis; performing safety analysis; performing motion smoothness analysis; performing goal-directed analysis; and performing path planning by adopting the self-adapting window. Because the method has better environmental suitability and obstacle avoiding capacity, the method obtains good safety and reachability, has high calculation real-time property, so the method solves the problem that the mobile robot generates an obstacle avoidance path in real time in an uncertain complex environment, provides a path selection method with optimized integration, better meets the requirements on obstacle avoidance for the mobile robot, realizes the real-time path planning and control of the robot, and provides an effective collision-less path planning method for the navigation application of the mobile robot.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
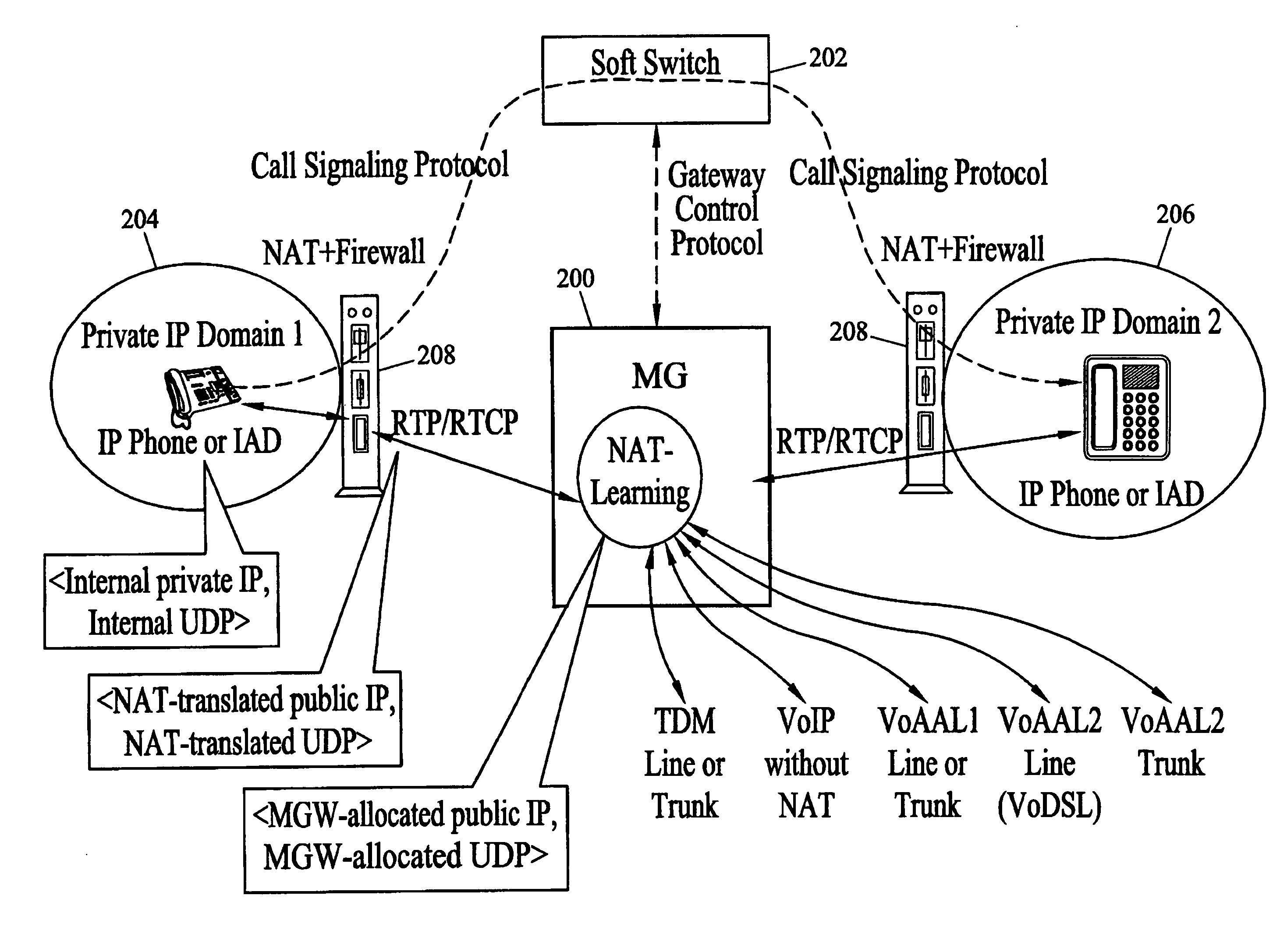
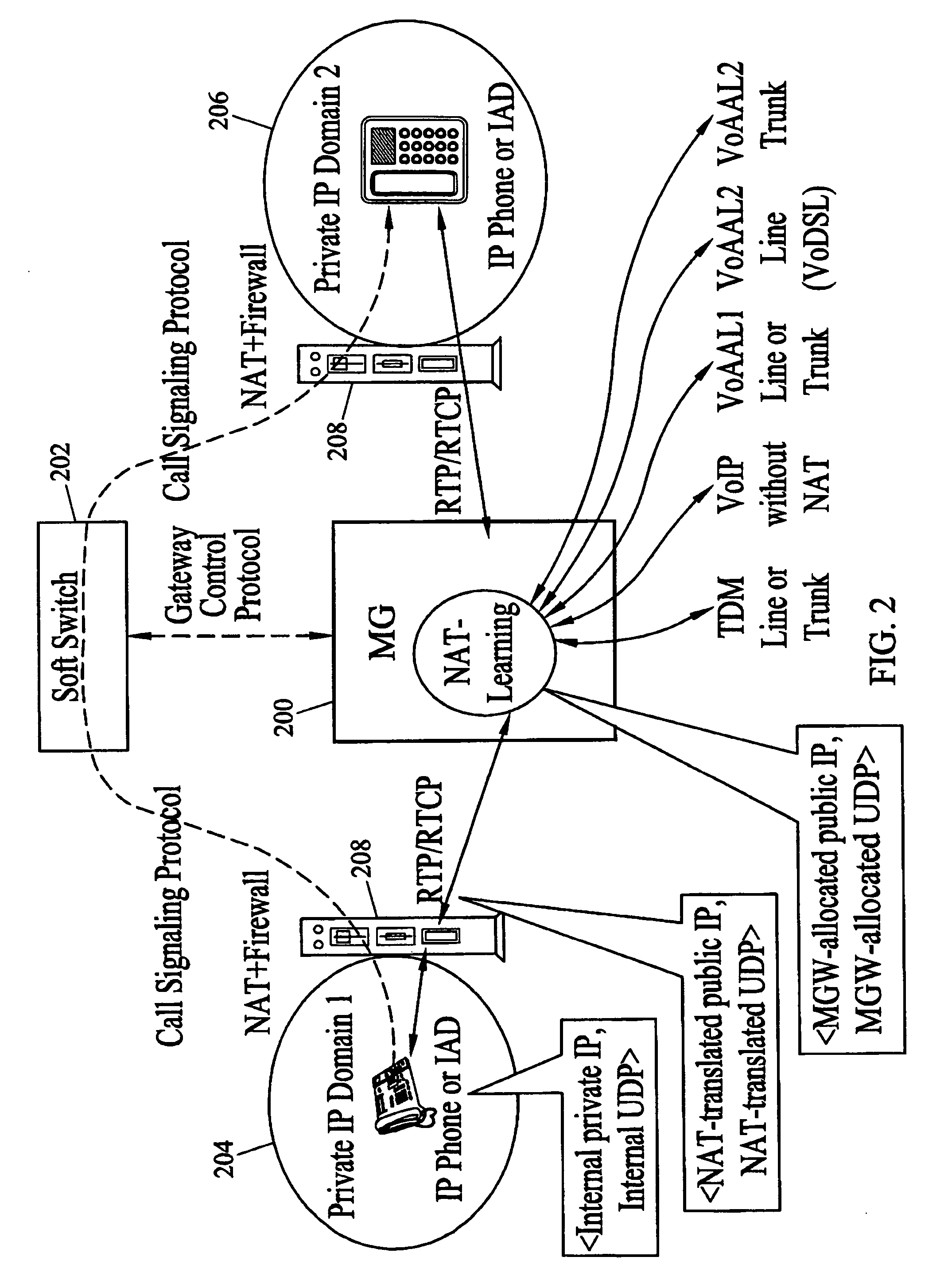
Methods and systems for per-session network address translation (NAT) learning and firewall filtering in media gateway
ActiveUS20050076108A1Network security is highHigh levelFrequency-division multiplex detailsData switching by path configurationIp addressReachability
Methods and systems for per-session NAT learning and firewall filtering are disclosed. Media packets associated with a call / session are received and processed at a media gateway. For the first few received media packets associated with a session, the media gateway uses various unique methods to learn the actual source IP address and UDP port assigned to the remote communication terminal by its customer-premises Network Address Translators (NATs) to the media flows of the current session. After the remote IP and UDP are learned, the media gateway reconfigures its firewall filtering function to check both the dynamically learned remote IP and UDP and the locally assigned IP and UDP of the current session. The per-session NAT learning function removes reachability issues in VoIP deployment, and the per-session firewall filtering function enhances security protection in VoIP deployment.
Owner:GENBAND US LLC
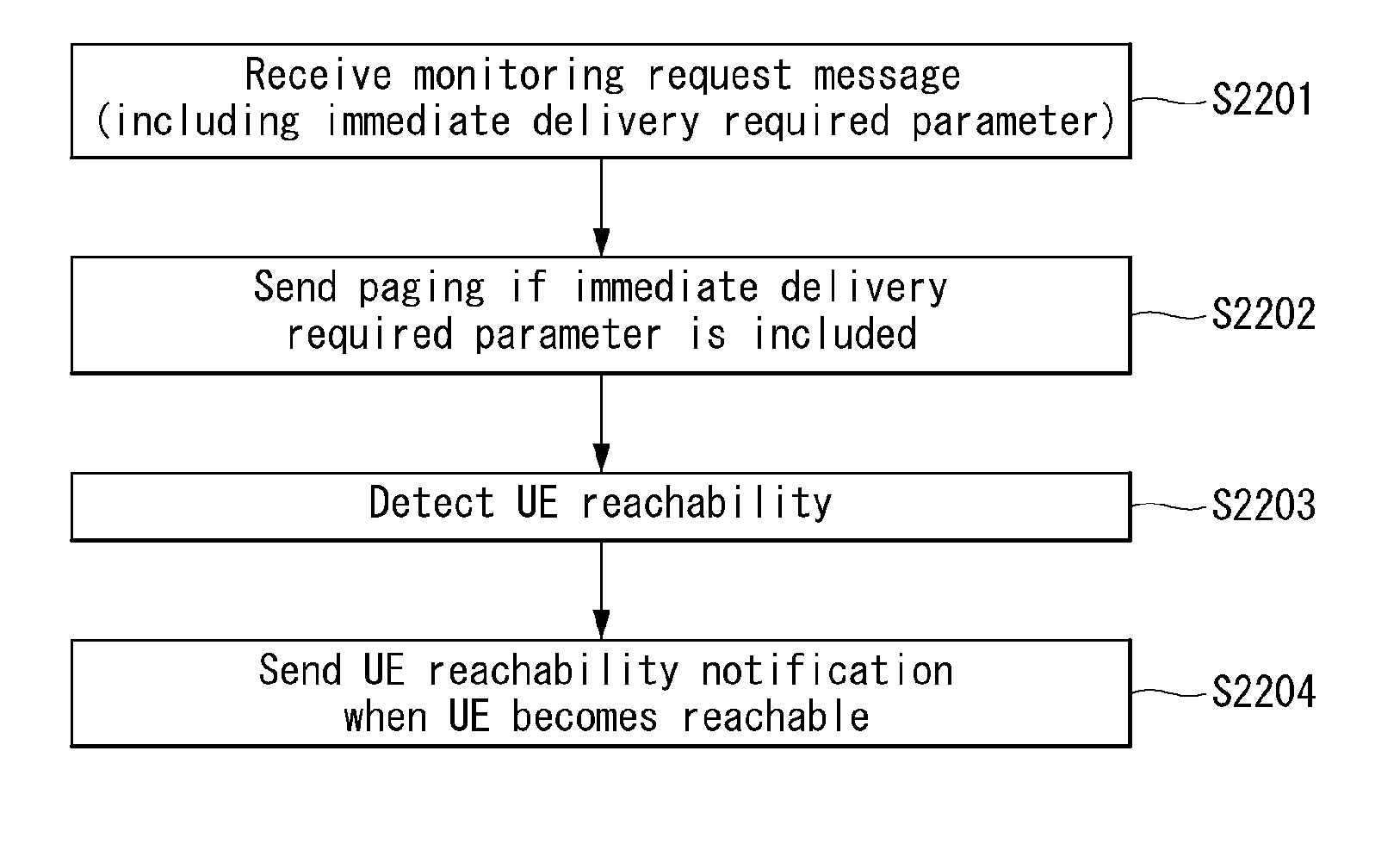
Method and apparatus for monitoring user equipment reachability in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20160286385A1Effective serviceExtended Discontinuous ReceptionConnection managementNetwork data managementCommunications systemReachability
Disclosed herein are a method and apparatus for monitoring UE reachability in a wireless communication system. A method for monitoring UE reachability may include receiving, by a Mobility Management Entity, a monitoring request message for UE reachability including a maximum response time from a Home Subscriber Server, detecting, by the MME, the UE reachability if it is expected that paging is able to be transmitted to UE when extended Discontinuous Reception is applied to the UE, and sending, by the MME, a UE reachability notification to a Service Capability Exposure Function before a next paging occasion of the UE, wherein the maximum response time may indicate a time during which the UE maintains a reachable state so that downlink data is reliably delivered to the UE, and wherein an occasion when the UE reachability notification is transmitted may be determined by taking into consideration the maximum response time.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and system for extending routing domain to non-routing end stations
A system is provided for facilitating assignment of a virtual routing node identifier to a non-routing node. During operation, the system assigns to a non-routing node coupled to a switch a virtual routing node identifier unique to the non-routing node. In addition, the system communicates reachability information corresponding to the virtual routing node identifier to other switches in the network.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
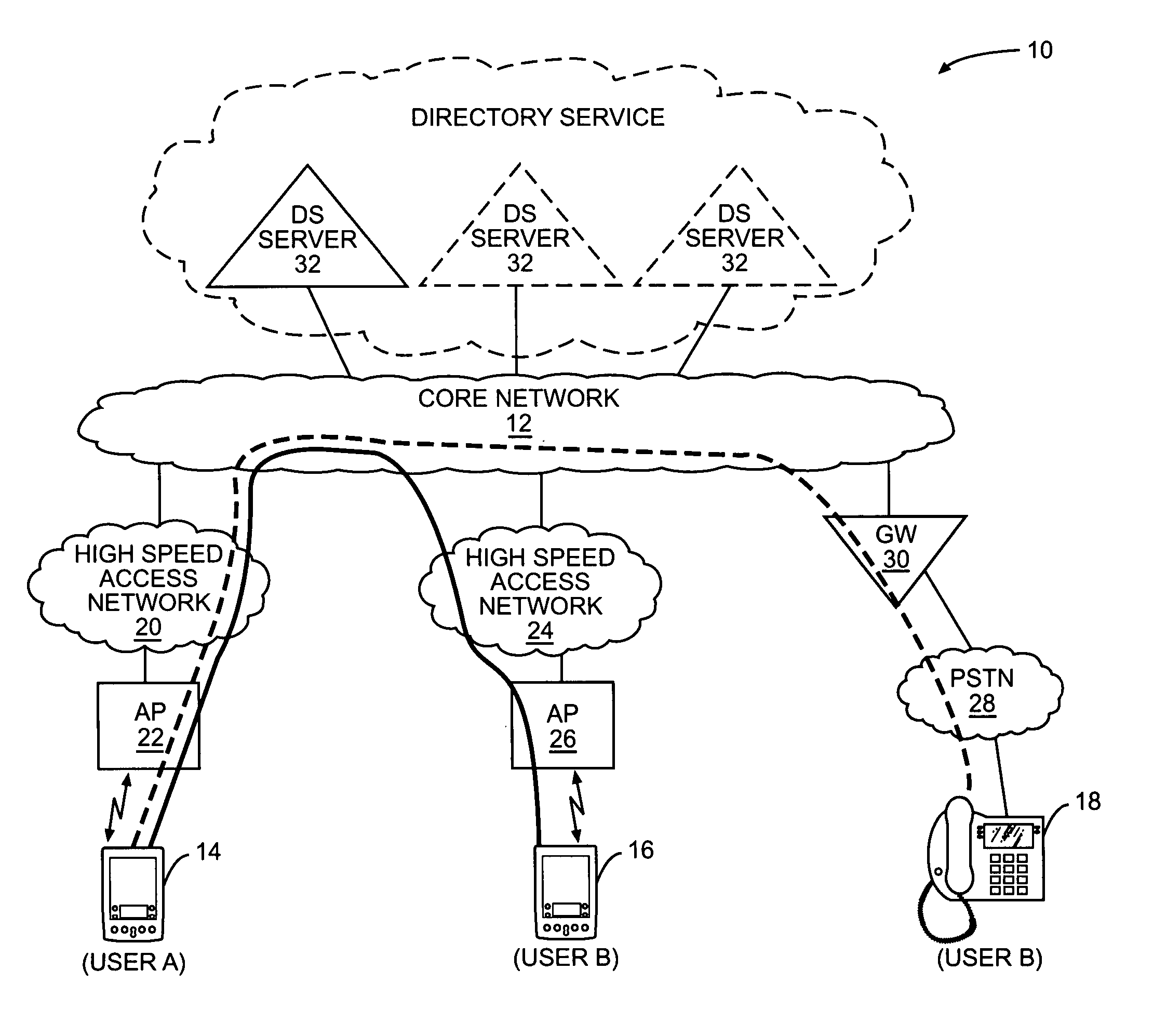
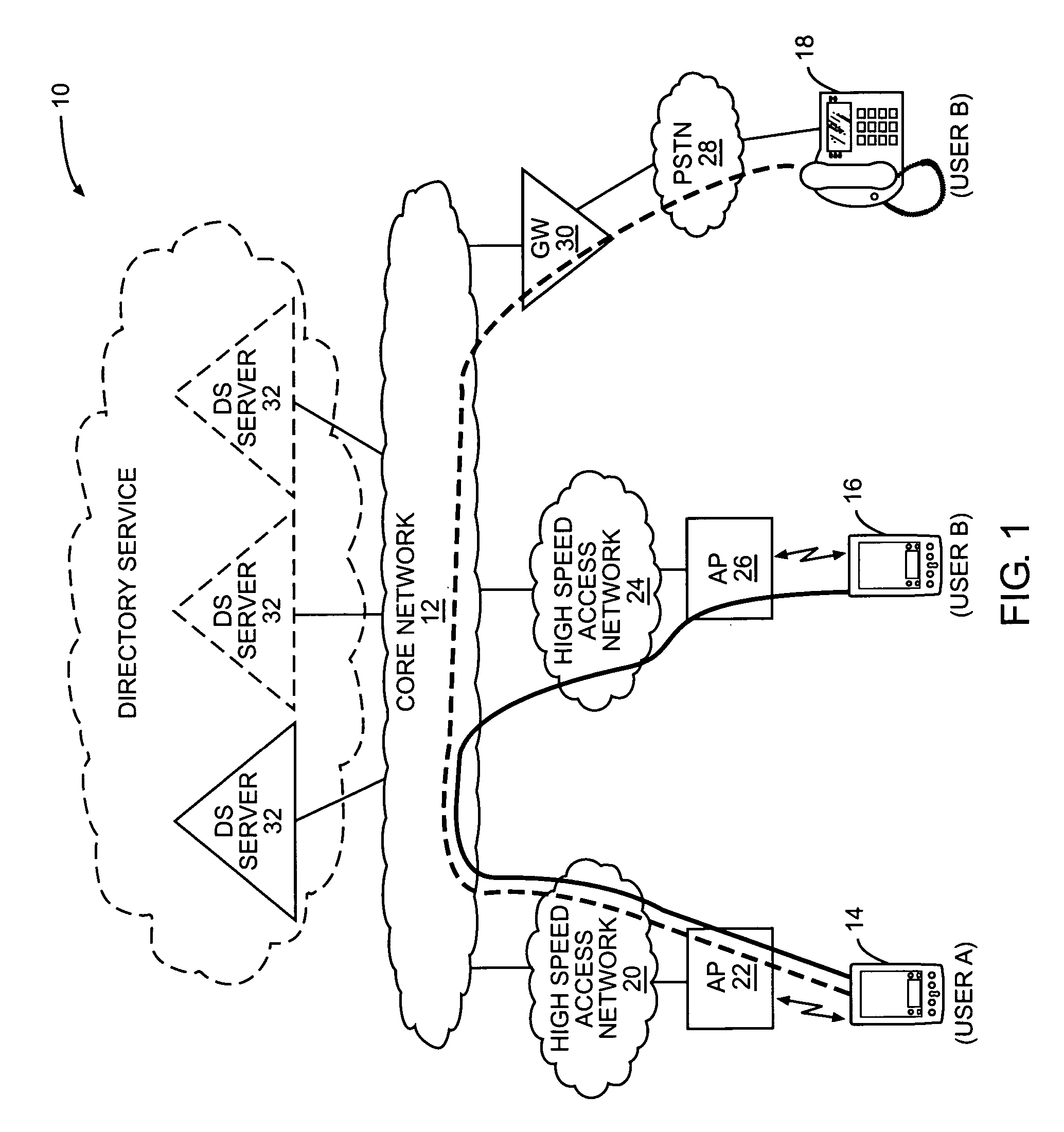
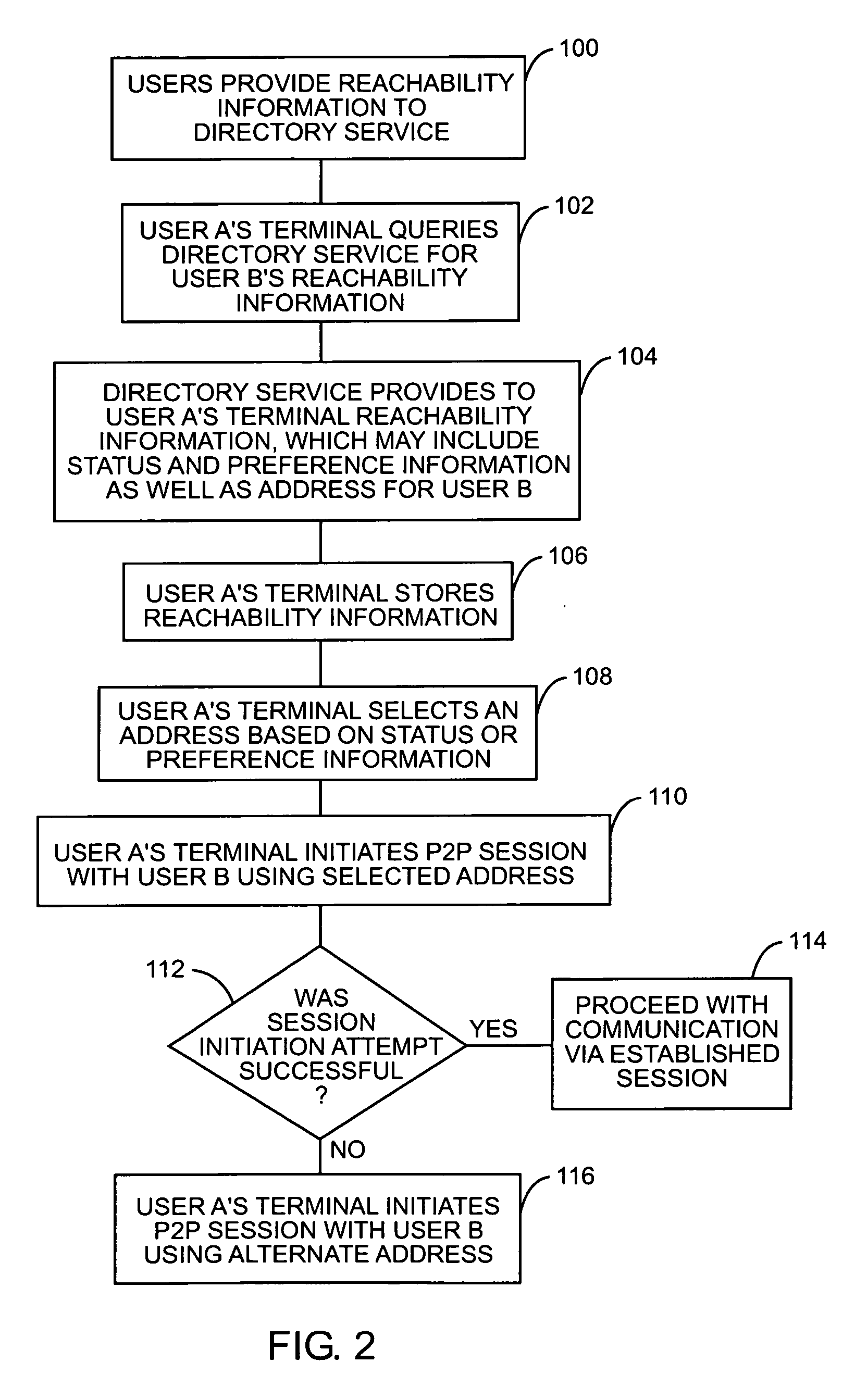
Using reachability information to facilitate peer-to-peer communications
ActiveUS20070025270A1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsRelevant informationReachability
The present invention allows originating endpoints to obtain reachability information from a directory service, which collects contact and related information from available users. When initiating a peer-to-peer communication session to an endpoint of a destination user, the originating endpoint will access the directory service to obtain reachability information for the destination user. The reachability information may contain one or more addresses, one of which will be a peer-to-peer communication session address. From the reachability information, the originating terminal will determine an appropriate address to initiate communications with the destination user. The reachability information may identify multiple addresses, where only certain of the addresses may be peer-to-peer communication addresses and other addresses may be used to establish other types of sessions through disparate types of networks.
Owner:APPLE INC
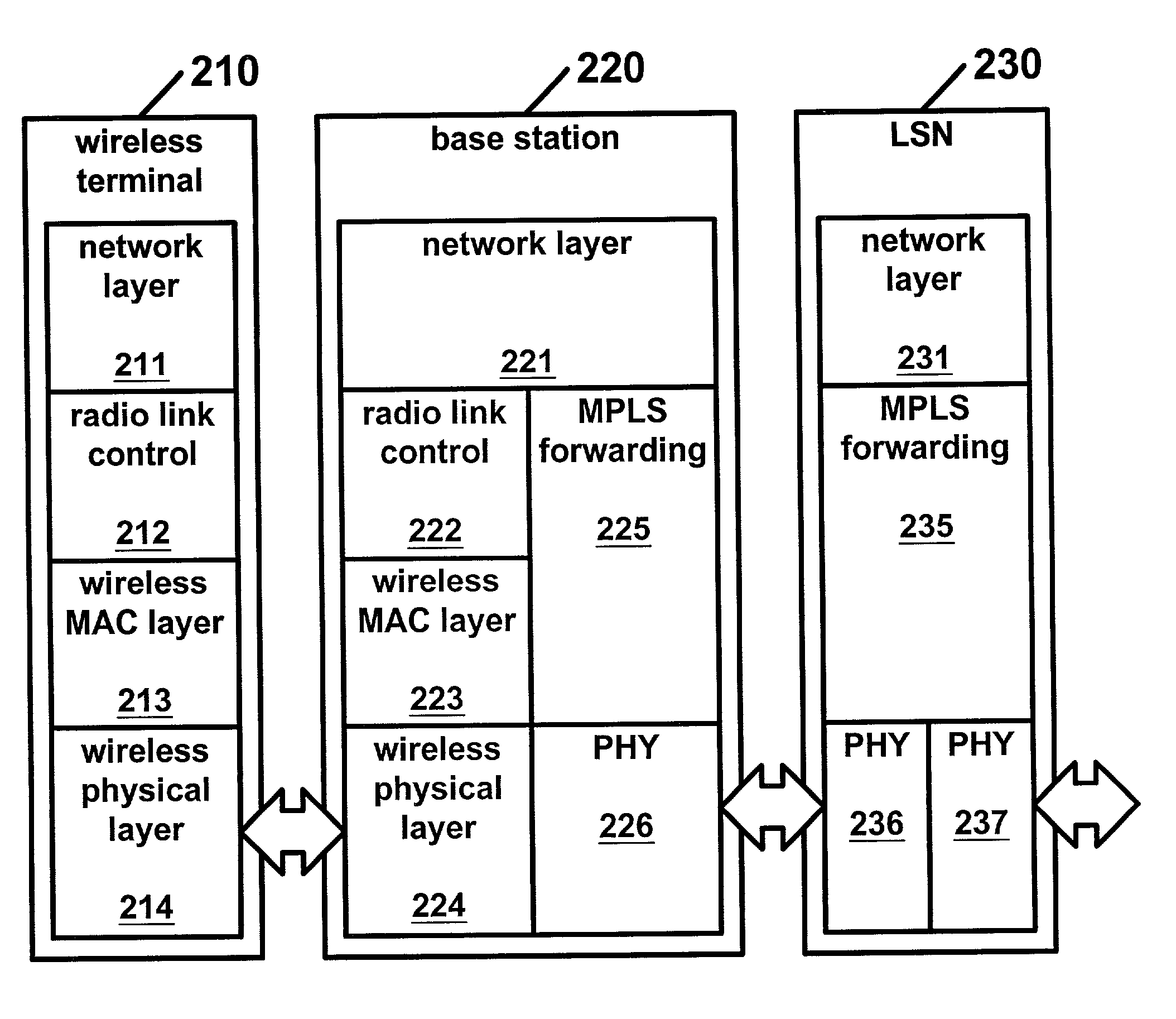
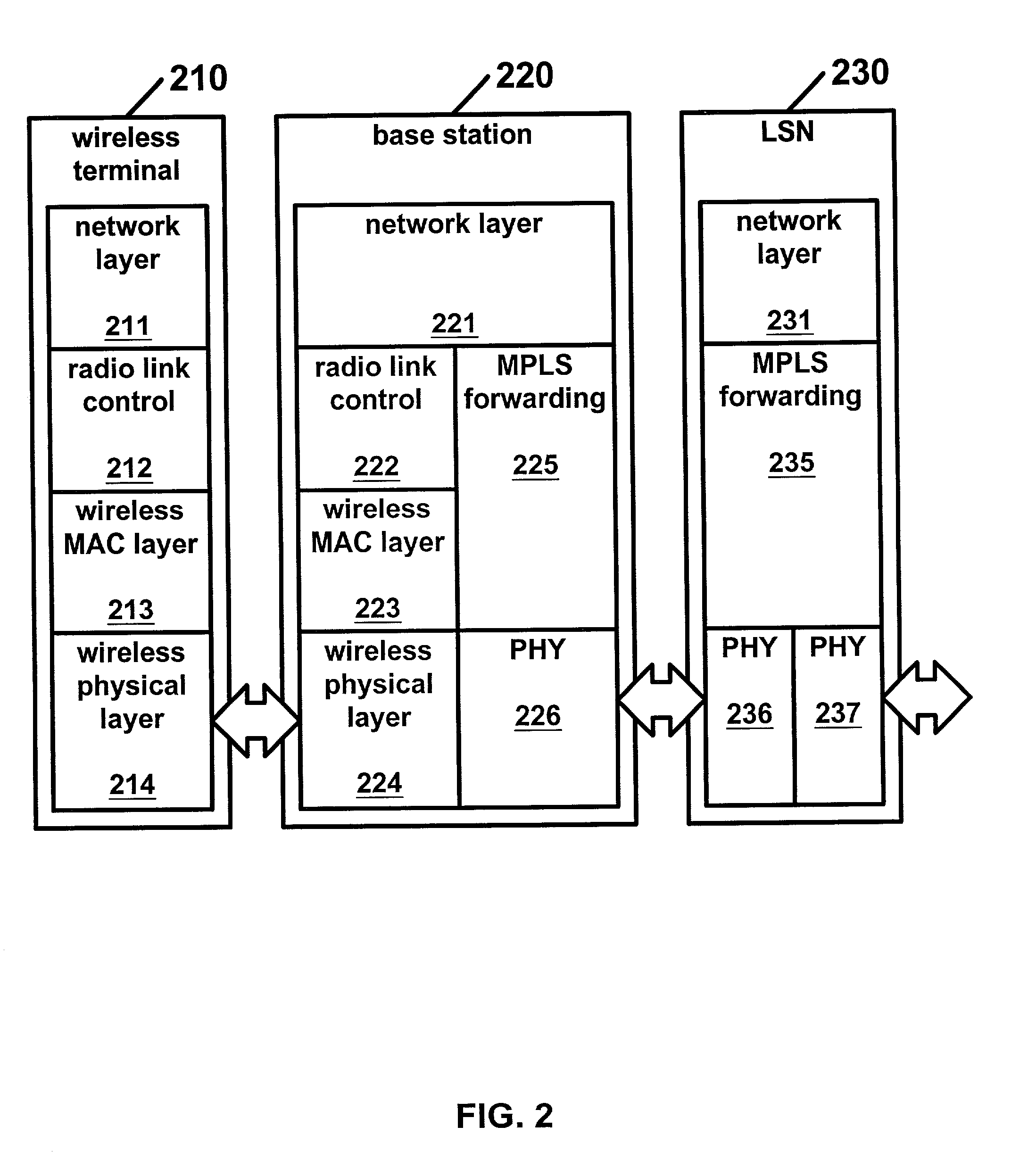
Wireless label switched packet transfer network
ActiveUS7061896B2Minimal requirementProvide benefitsNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesWireless mesh networkMulti link
A method and apparatus to support a hierarchical architecture which integrates wireless mobile terminals into networks such as the Internet. This architecture provides for efficient packet transfers over mobile wireless networks by efficiently allocating wireless resources. Label Switched packet forwarding facilitates traffic engineering and internetworking by attaching short fixed length labels to communications packets at an entry node to a wireless network to provide an efficient path to an exit node of the same wireless network. Forwarding mechanisms and limited broadcasting of reachability information are used in managing and routing the communications packets through the wireless mobile network. The present invention also supports multiple radio links between a mobile and a multiplicity of base stations. Multi-link techniques are used to affect an efficient packet transfer and admission policy.
Owner:RPX CORP
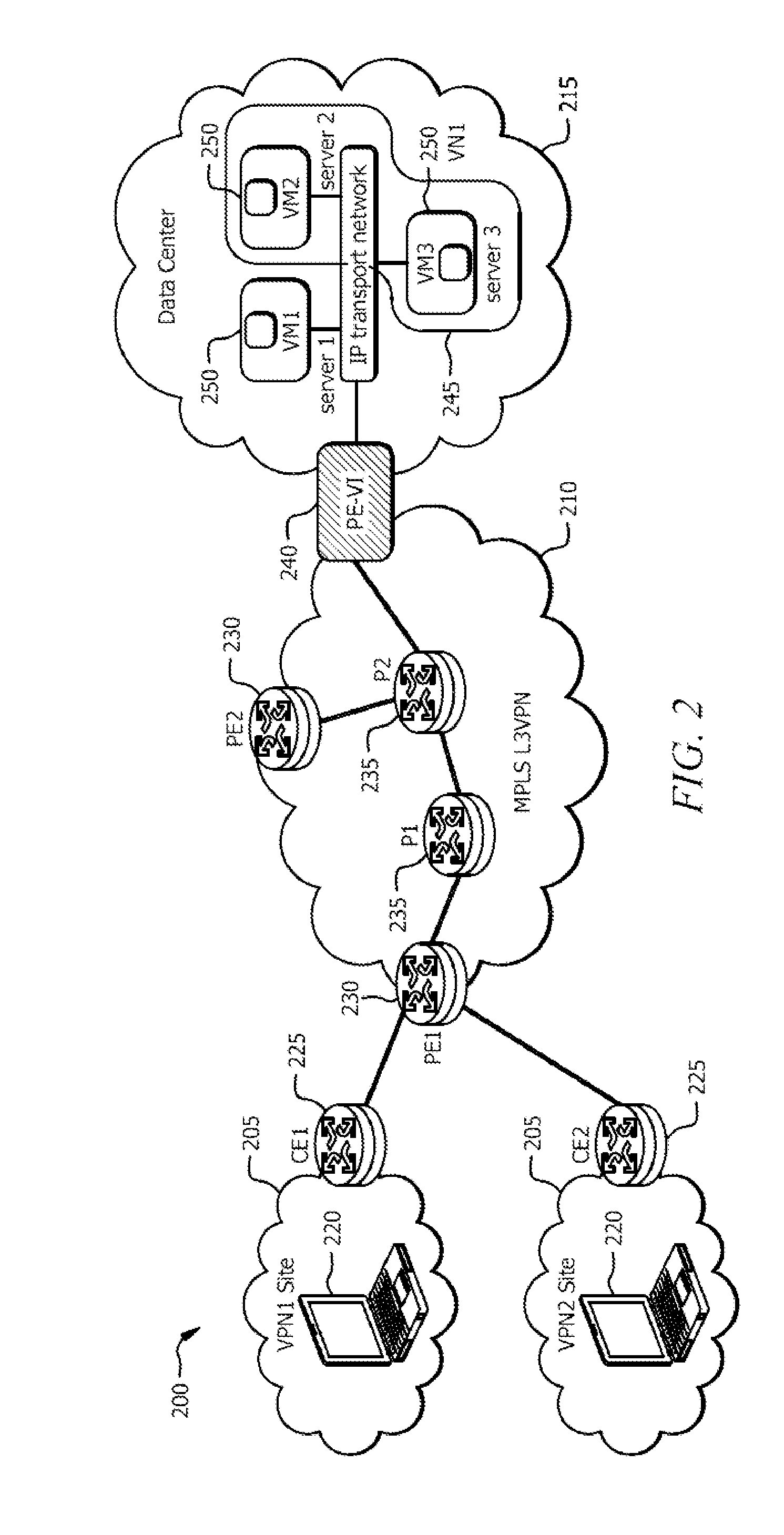
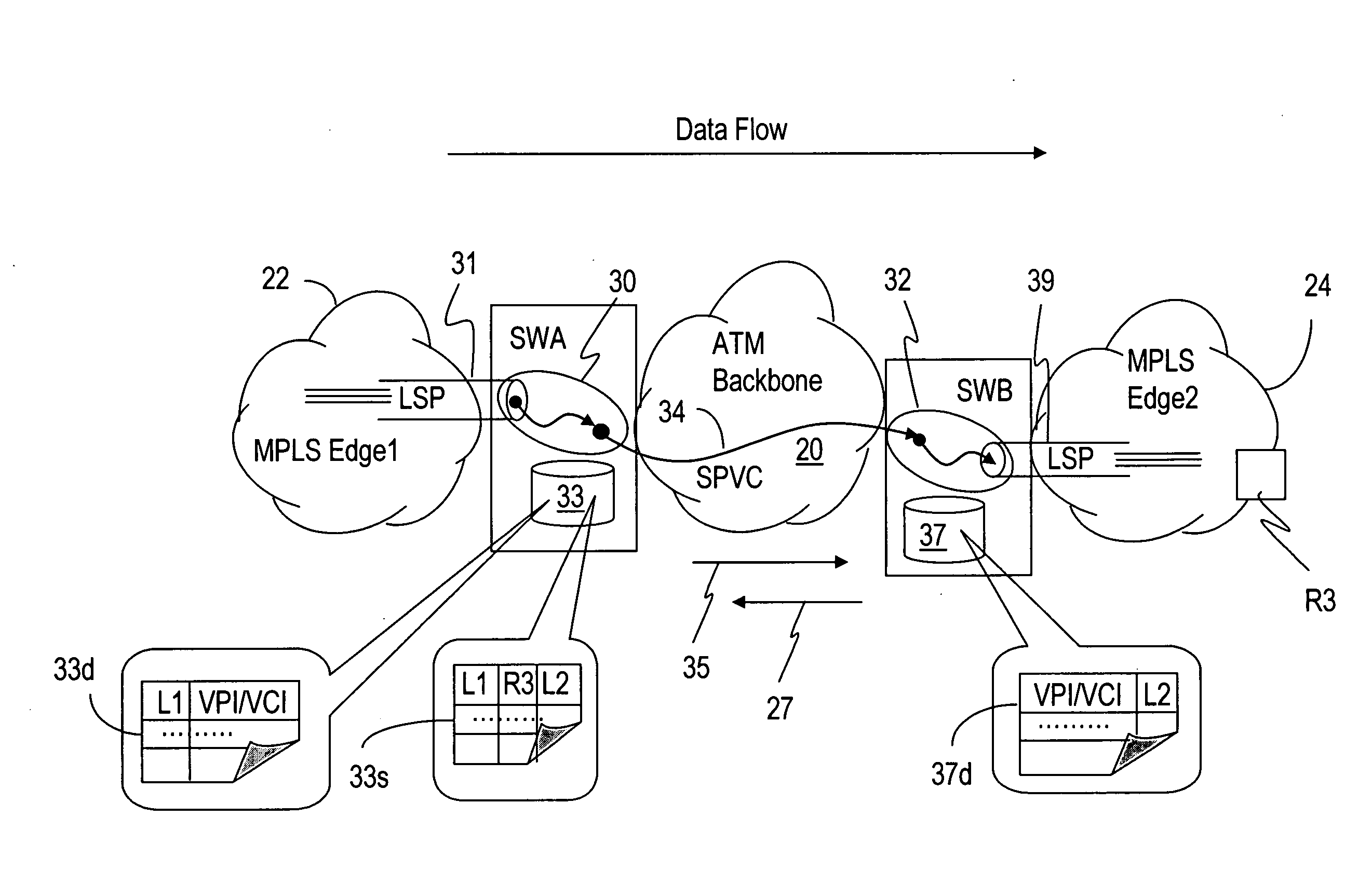
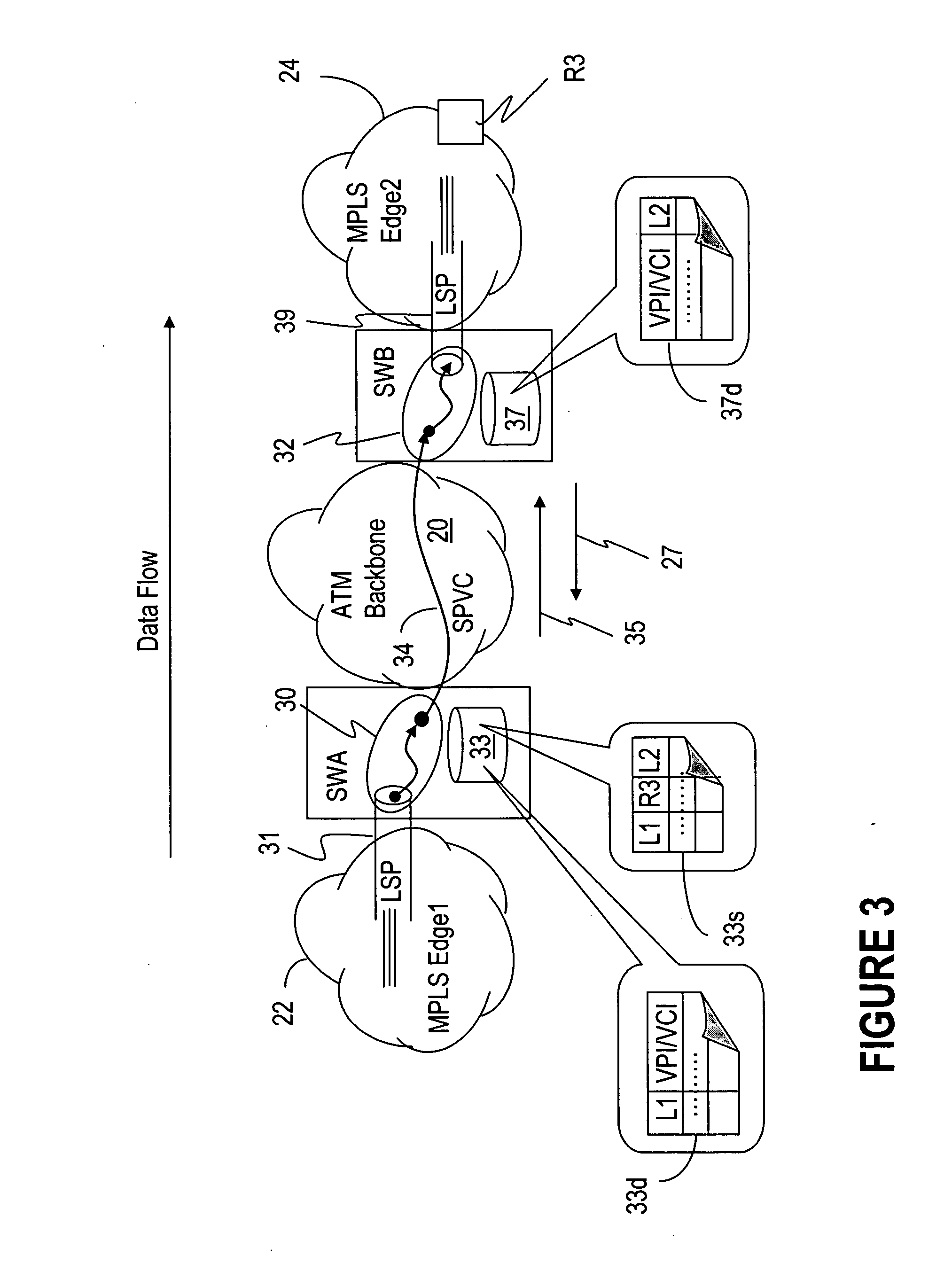
Extending IP/MPLS services reachability over ATM backbone networks
The invention enables an LSP or embedded LSPs to be mapped directly to an SPVC and carried over the ATM network. A unidirectional SPVC is established by associating it to a particular ingress LSP at the SPVC source endpoint on a multi-service switch, and to an egress LSP on the SPVC destination endpoint on another multi-service switch. The information necessary to establish the SPVC is appended in the SPVC setup message and includes LSP specific information such as the far end router ID and LSP label information, be it transport label or the full label stack. The information in the modified setup message is then used by the destination endpoint to find and connect the SPVC to the correct LSP. Incoming traffic from the LSP is switched to the SPVC at the source endpoint. The SPVC carries this traffic through the ATM network, and then the traffic is switched to the egress LSP when it emerges from the ATM network at the destination endpoint.
Owner:SOUND VIEW INNOVATIONS
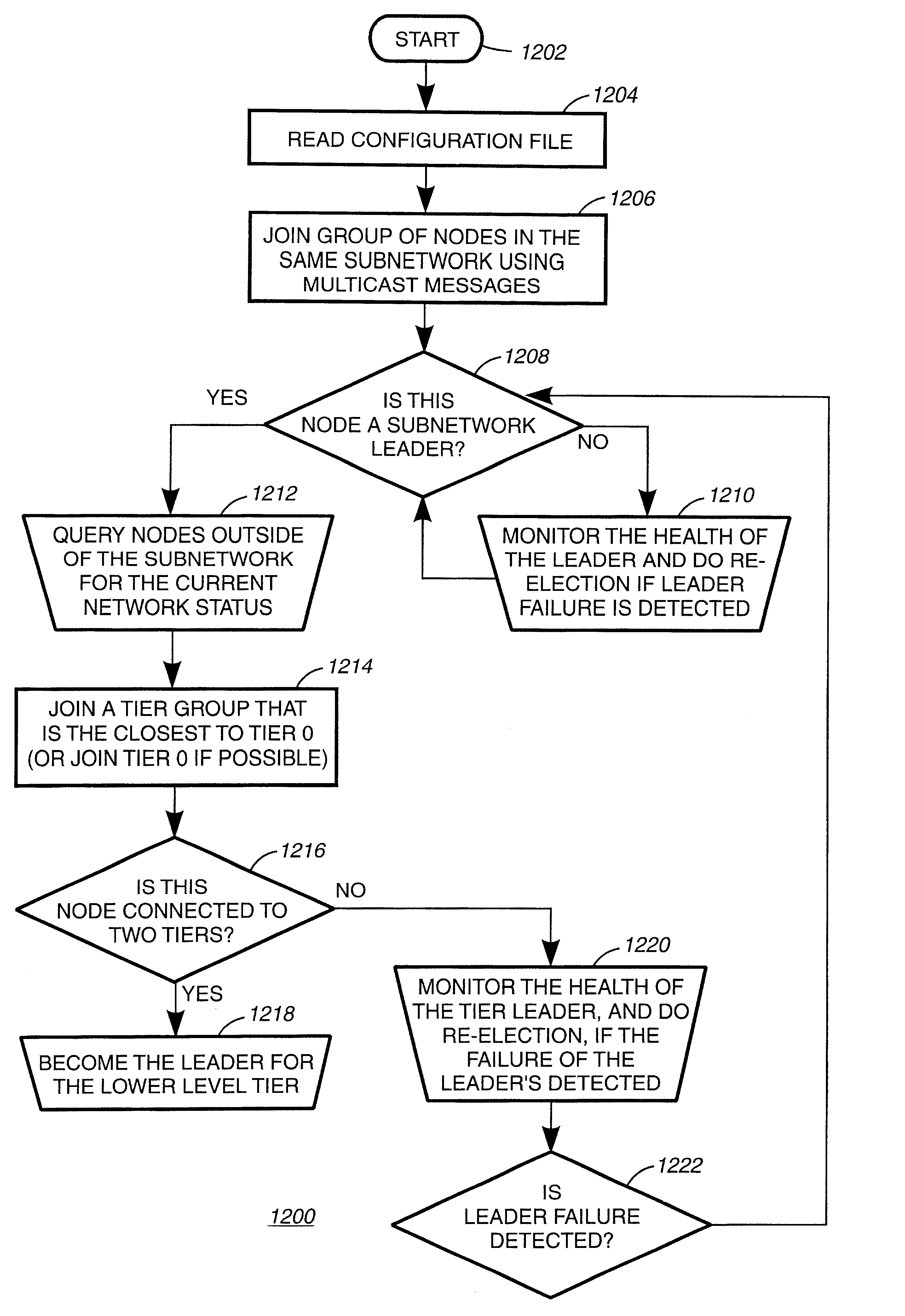
Method and apparatus for fault tolerant tunneling of multicast datagrams
InactiveUS6732189B1Special service provision for substationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork addressReachability
A method for maintaining the reachability of IP multicast communications across a communications network with one or more subnetworks wherein each subnetwork comprises at least one node coupled thereto and a node identified as a subnetwork leader and the communications network comprises one node identified as a network leader. The method comprising the steps of: receiving a host address list containing a list of all the network addresses of the nodes in a network including at least two subnetworks, and a node in each subnetwork identified as a subnetwork leader; using the host address list for determining which subnetworks the subnetwork leaders are associated therewith. The reachability of at least one subnetwork leader in the network is periodically monitored. And if at least one subnetwork leader for one of the subnetworks in the network become multicast unreachable, then at least one node in the subnetwork associated with the subnetwork leader that has become multicast unreachable performing the steps of: electing a new subnetwork leader for a multicast unreachable subnetwork associated with the subnetwork. leader that has become unavailable; and establishing a connection using IP tunneling between a newly elected subnetwork leader for the multicast unreachable subnetwork with at least one other subnetwork leader in the network. In another embodiment, a apparatus and computer readable medium is disclosed to carry out the above method.
Owner:IBM CORP
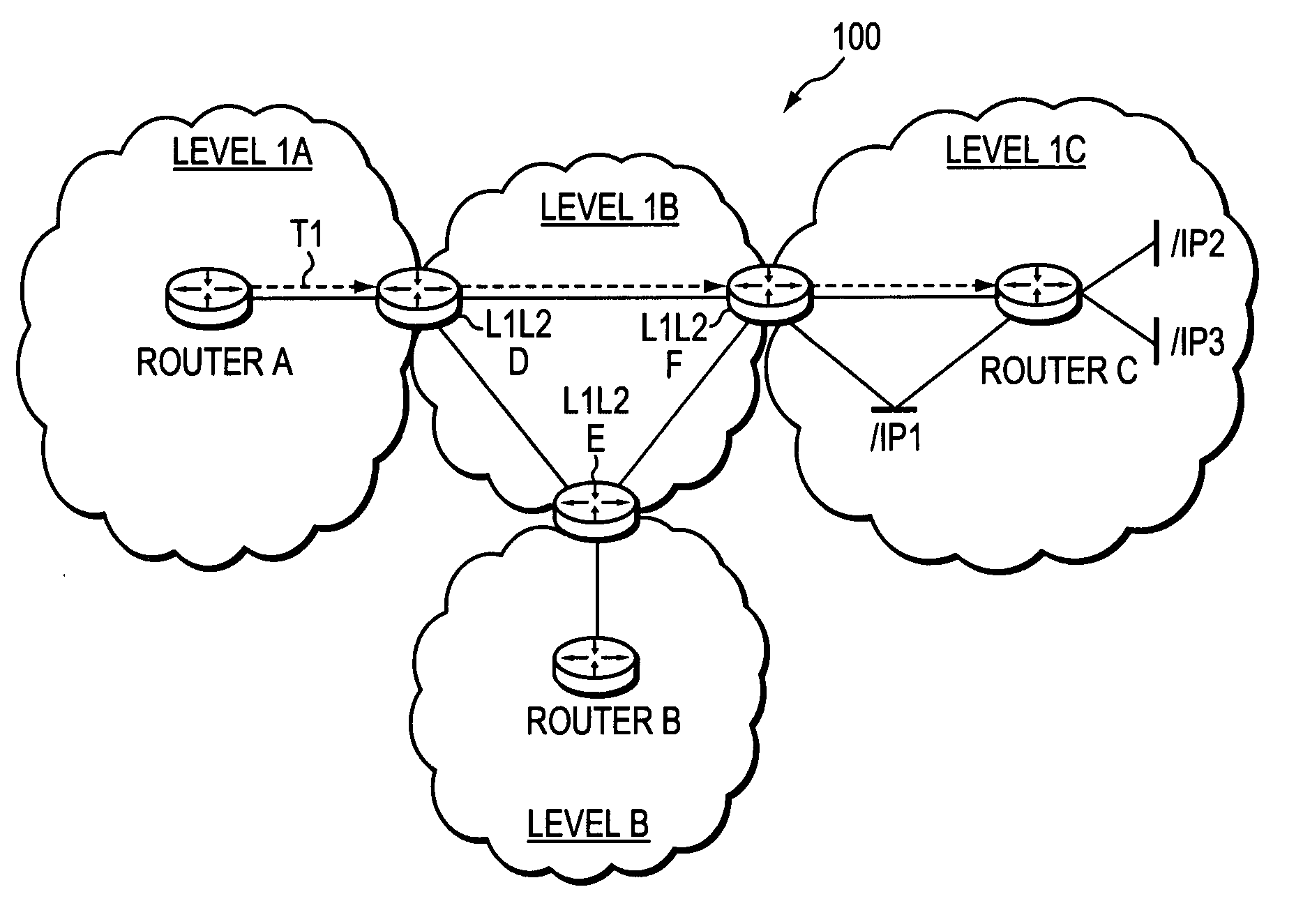
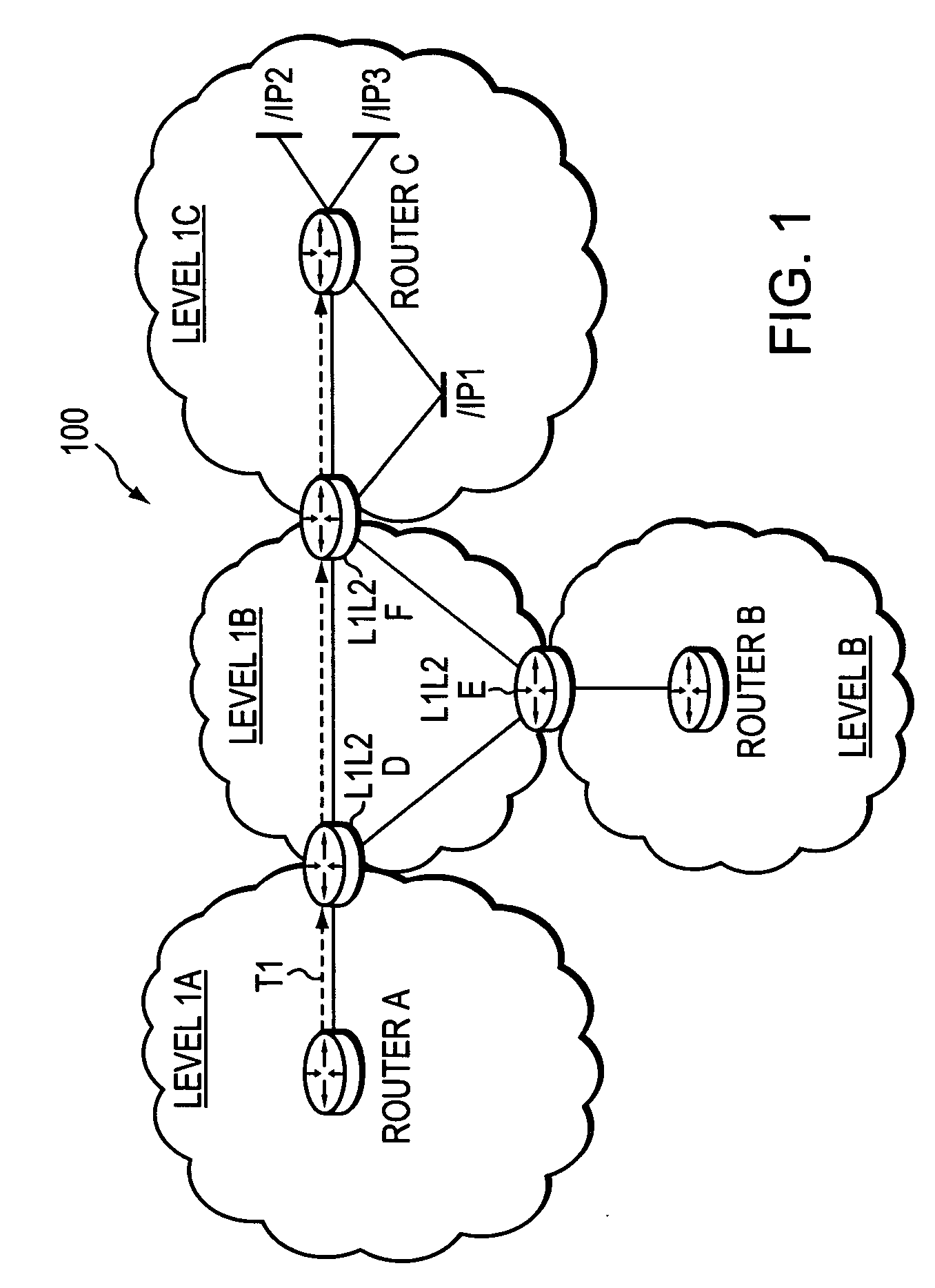
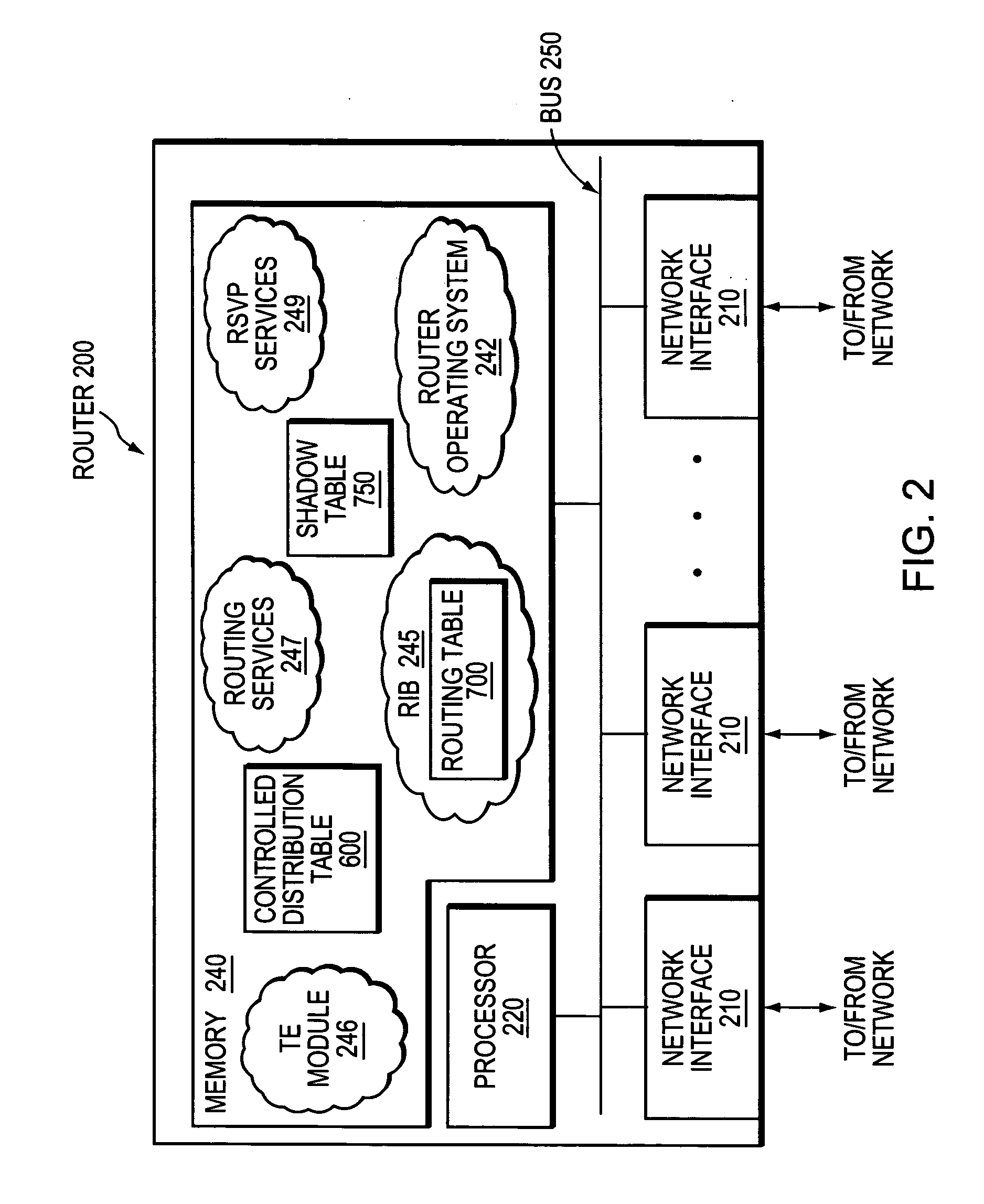
Controlled distribution of inter-area routing information
InactiveUS20070058568A1Limit excess distributionData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityRouting table
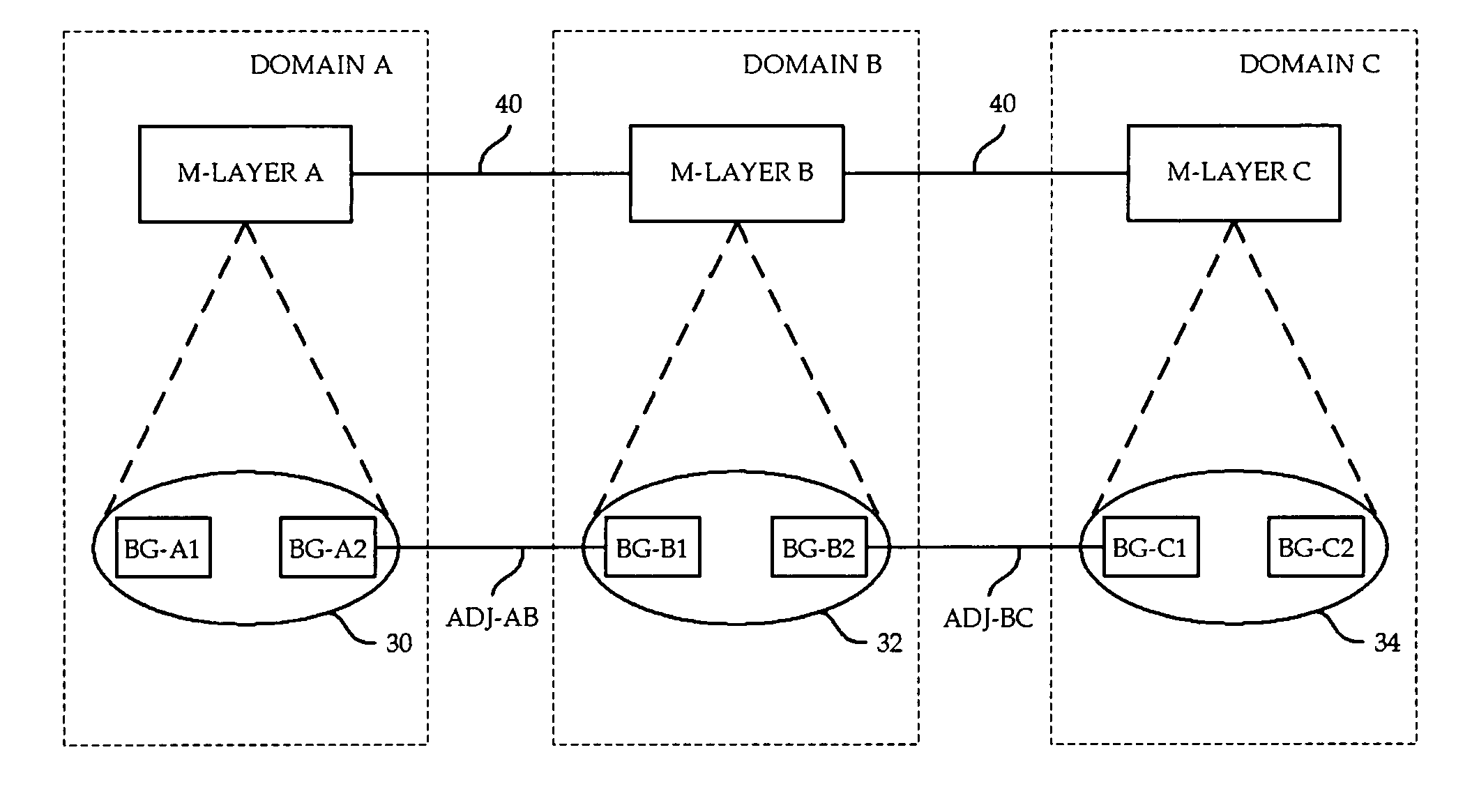
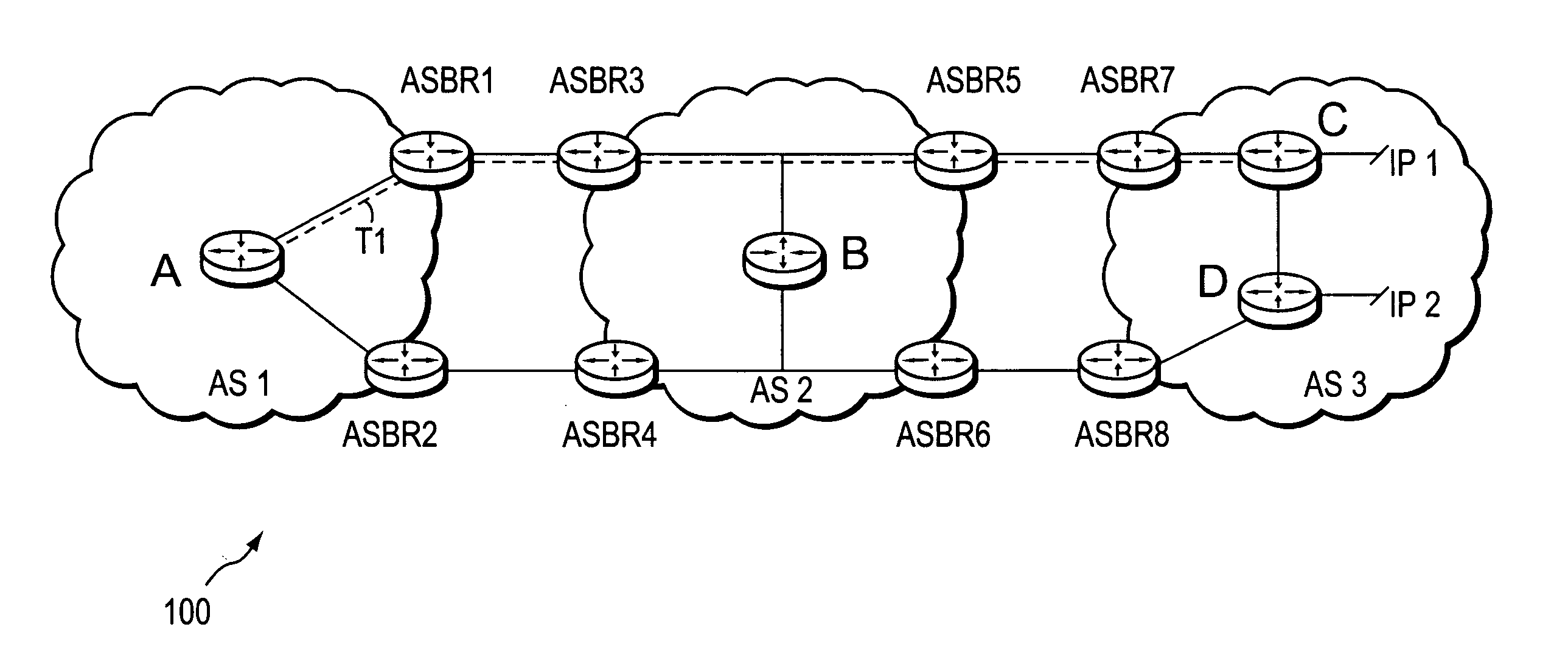
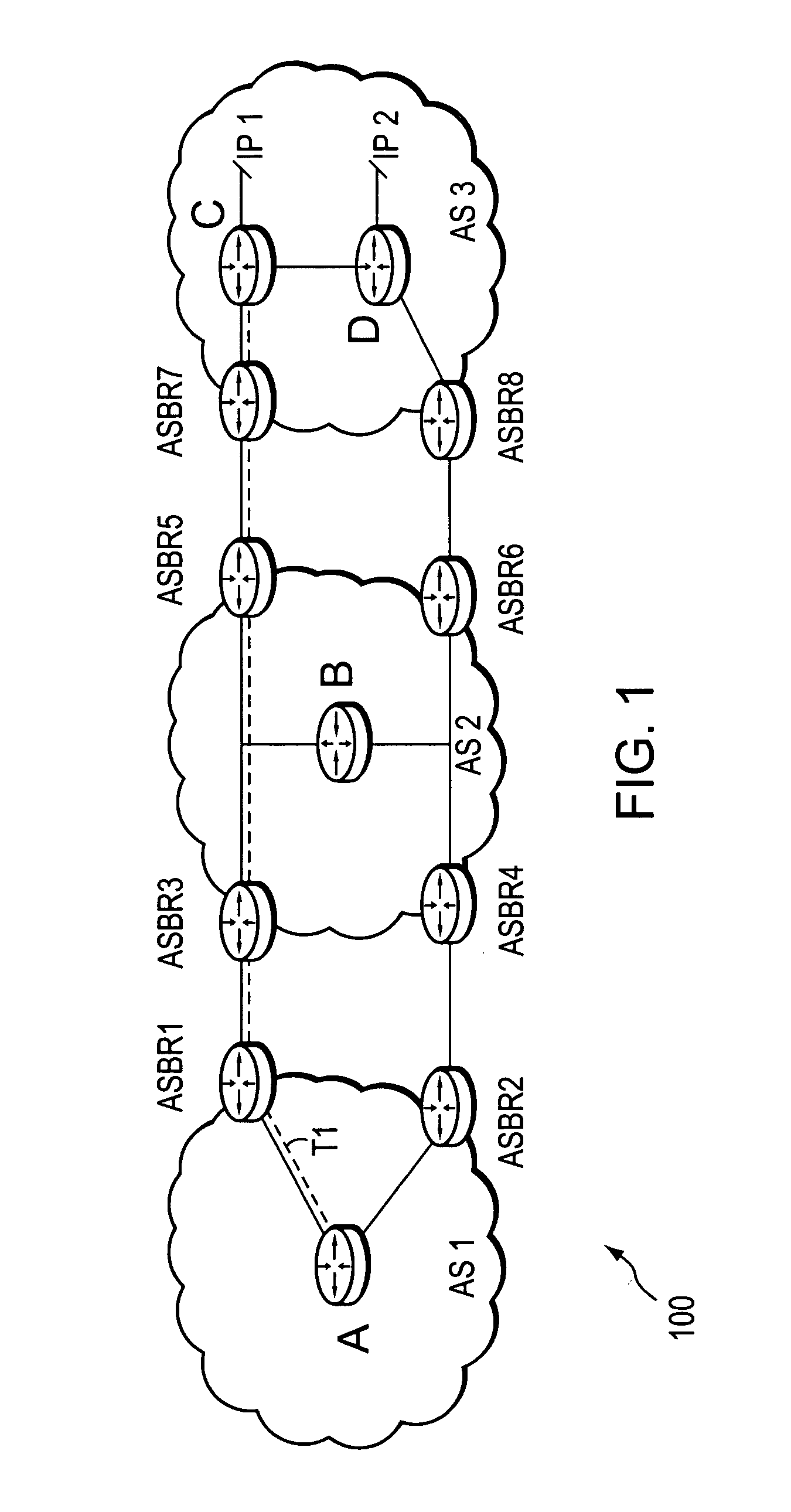
A technique controls distribution of reachability information for a tail-end node of a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) to a head-end node of the TE-LSP in a computer network. The TE-LSP preferably spans multiple domains of the network such that the tail-end node resides in a domain (“tail-end domain”) that is different (remote) from the domain of the head-end node (“head-end domain”). According to the inter-domain information distribution technique, the head-end node requests the remote reachability information from the tail-end node, which may employ an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) to transmit the information to a border router of the tail-end domain. The tail-end domain border router then shares this information with at least a head-end domain border router. The head-end node thereafter requests that the head-end domain border router release the reachability information into the head-end domain. The head-end node uses the remote information to calculate routes, i.e., address prefixes and associated attributes, reachable from the tail-end node for insertion into its routing table.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Dynamic retrieval of routing information for inter-AS TE-LSPs
A technique dynamically triggers an exchange of reachability information between a tail-end (remote) domain target node (e.g., a tail-end node) of a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) and a local domain head-end node of the TE-LSP in a computer network. The inter-domain information retrieval technique is illustratively based on triggering a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) session whereby at least a portion of the reachability, i.e., routing, information of the tail-end node is transmitted to the head-end node of the TE-LSP in accordance with BGP. Specifically, once a TE-LSP is established between the head-end node and the tail-end node, the head-end node triggers the tail-end node, e.g., through extensions to a request / response signaling exchange, to establish the BGP session. Establishment of the BGP session enables transmission of the routing information from the tail-end node to the head-end node. The head-end node uses the routing information to calculate routes, i.e., address prefixes and associated attributes, reachable from the tail-end node for insertion into its routing table.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
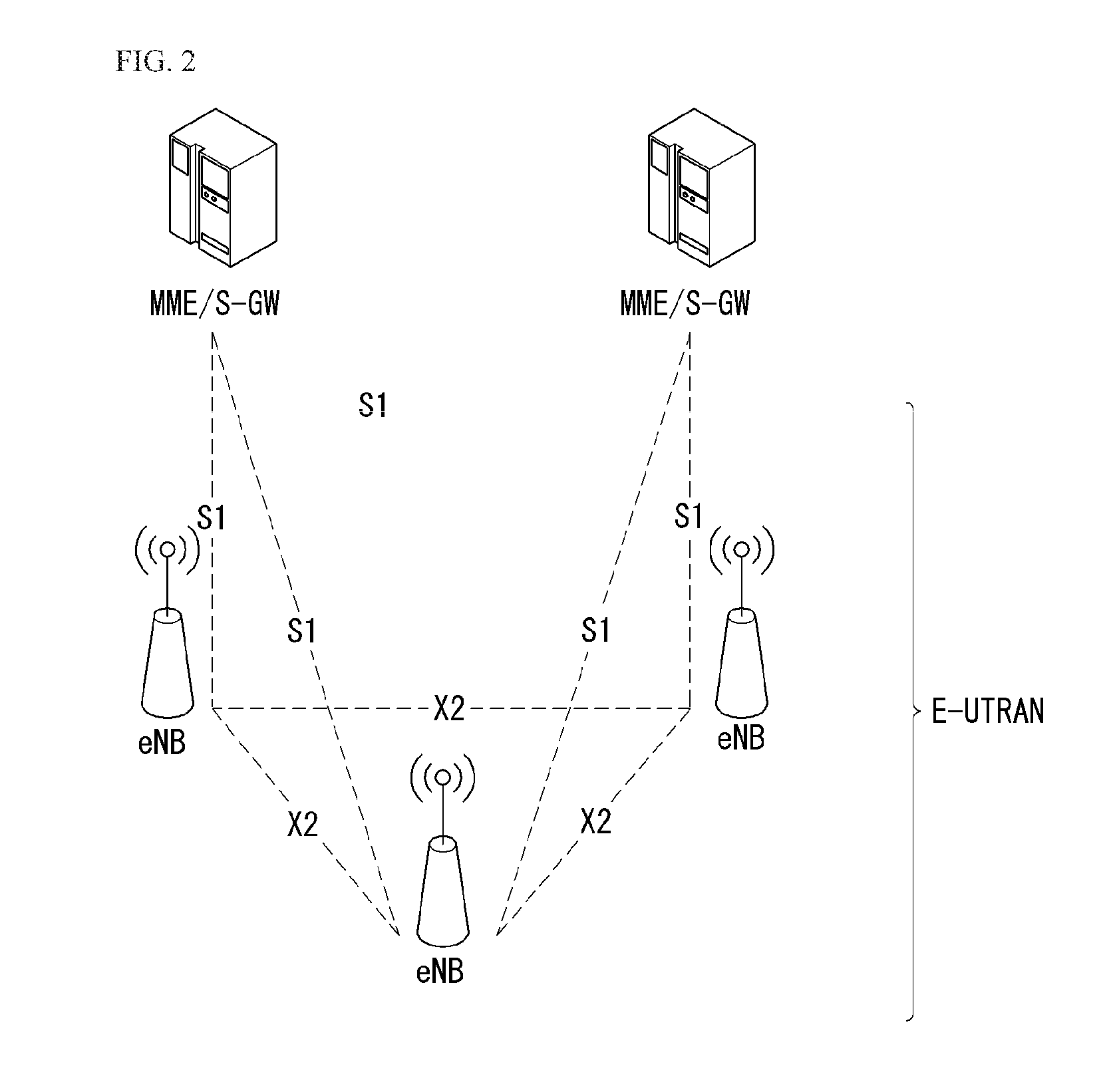
Advanced link tracking for virtual cluster switching
ActiveUS20110299402A1Facilitates advanced link trackingError preventionTransmission systemsReachabilityVirtual cluster
One embodiment of the present invention provides a switch system. The switch includes a port that couples to a server hosting a number of virtual machines. The switch also includes a link tracking module. During operation, the link tracking module determines that reachability to at least one end host coupled to a virtual cluster switch of which the switch is a member is disrupted. The link tracking module then determines that at least one virtual machine coupled to the port is affected by the disrupted reachability, and communicates to the server hosting the affected virtual machine about the disrupted reachability.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
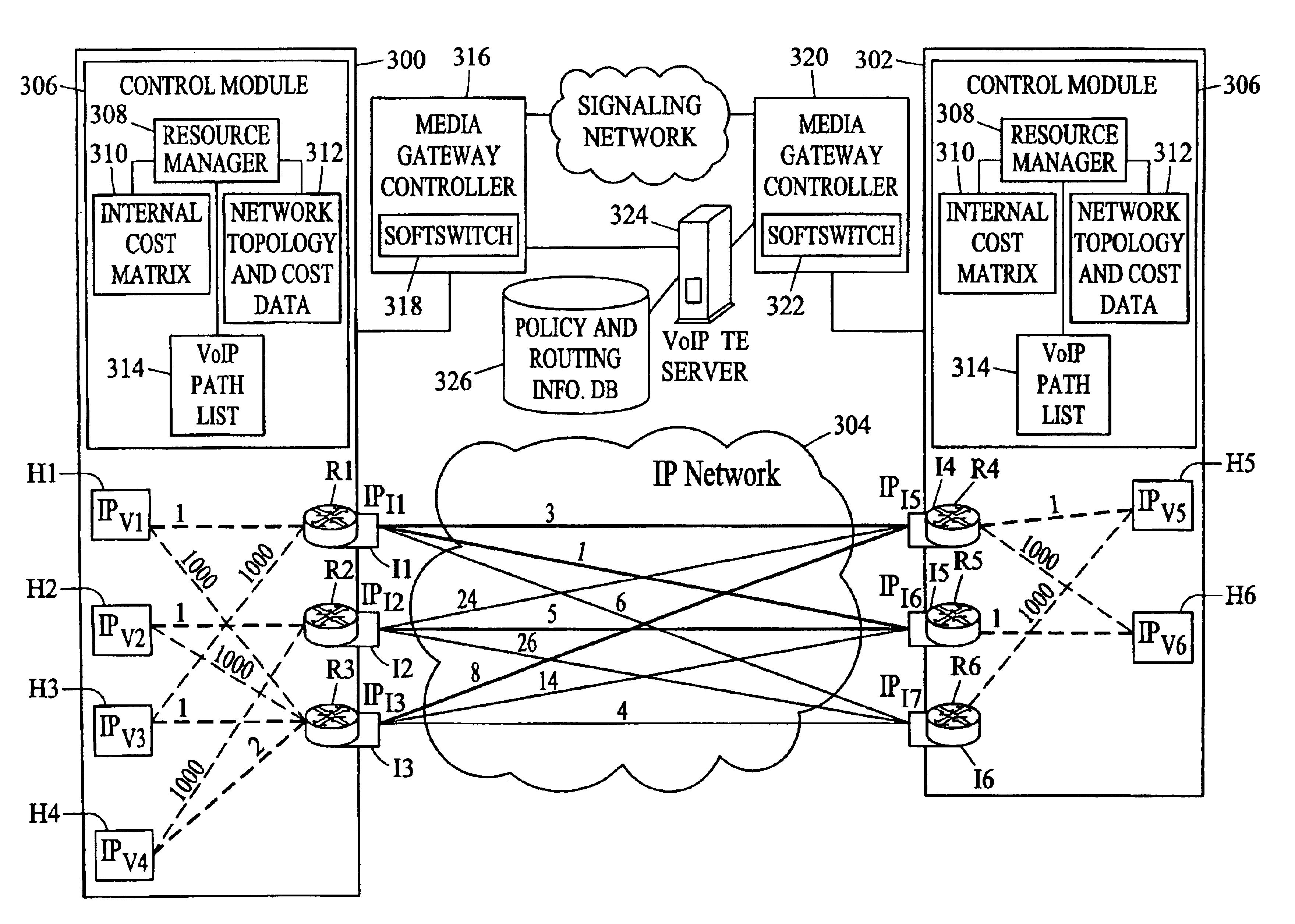
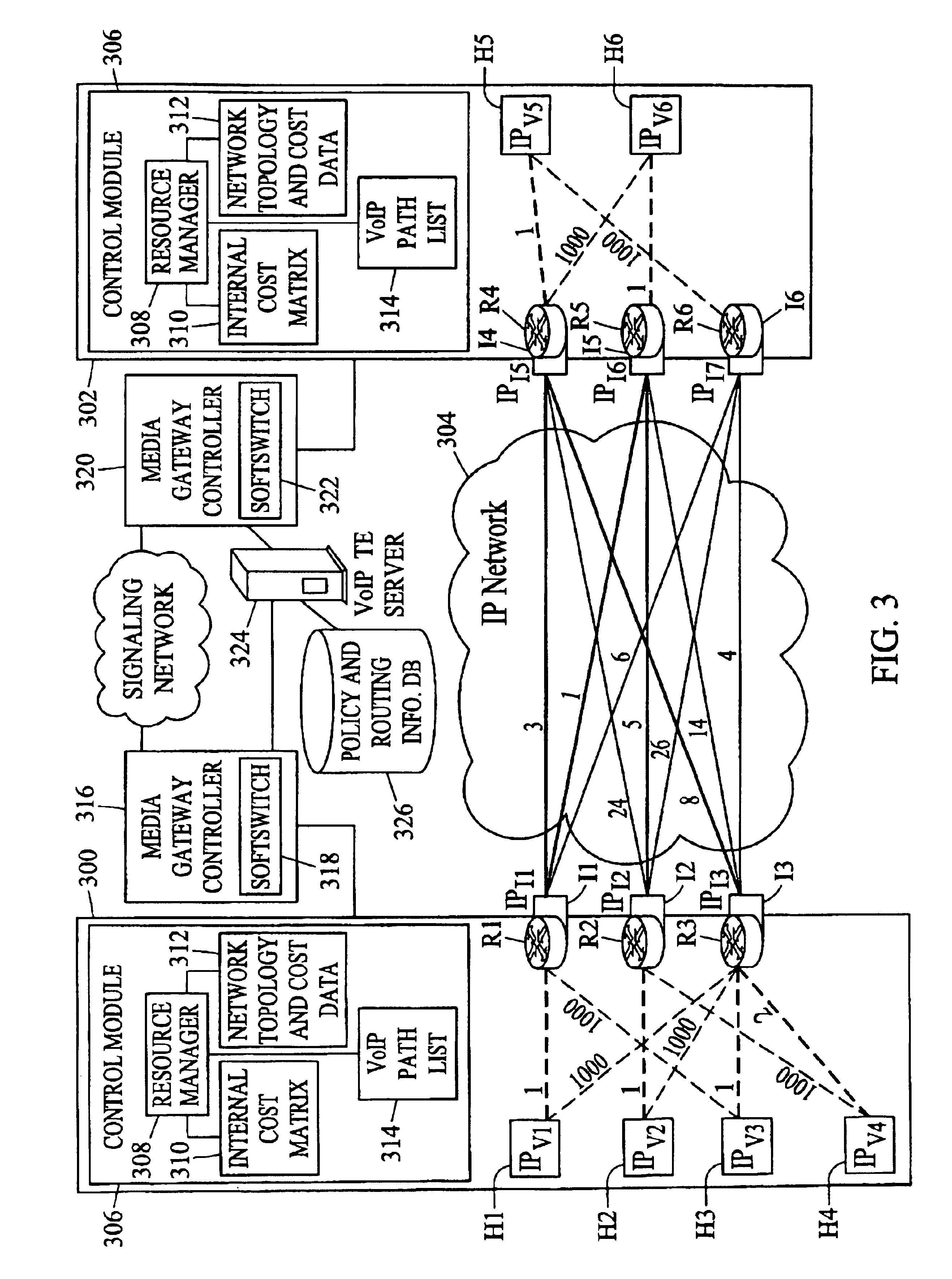
Methods, systems, and computer program products for voice over IP (VoIP) traffic engineering and path resilience using network-aware media gateway
InactiveUS6956820B2End-to-end network resilienceError preventionTransmission systemsInternet traffic engineeringRouting table
Methods and systems for providing voice over IP traffic engineering and path resilience using a network-aware media gateway are provided. In a media gateway, voice over IP hosts are assigned a first set of IP addresses. Network interfaces in the media gateway are assigned a second set of IP addresses that differ from the first set of IP addresses. Per-interface routers advertise reachability information from at least one of the voice over IP hosts via multiple interfaces and participate in network routing protocols to generate per interface routing tables. Voice over IP path lists may be generated based on the per interface routing tables. Internal costs may be assigned to the associations between the voice over IP hosts and the interfaces based on traffic engineering criteria.
Owner:GENBAND US LLC
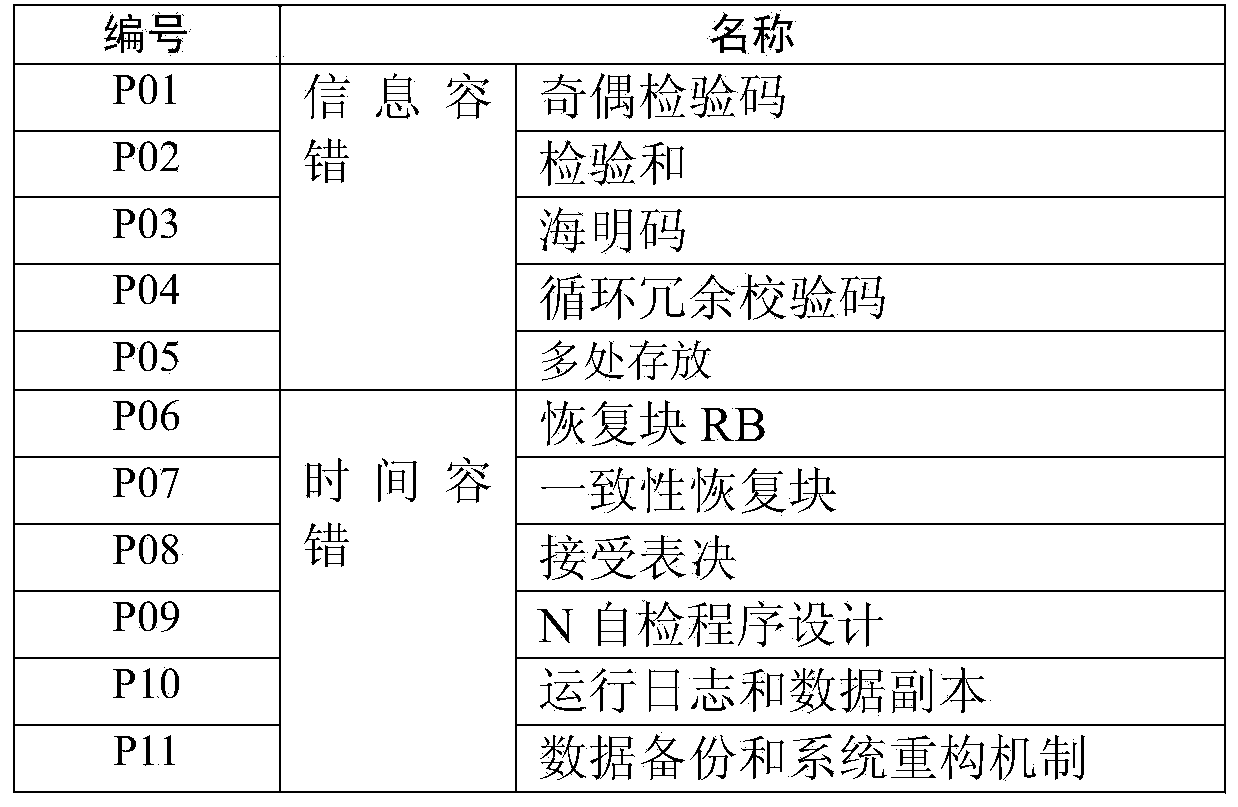
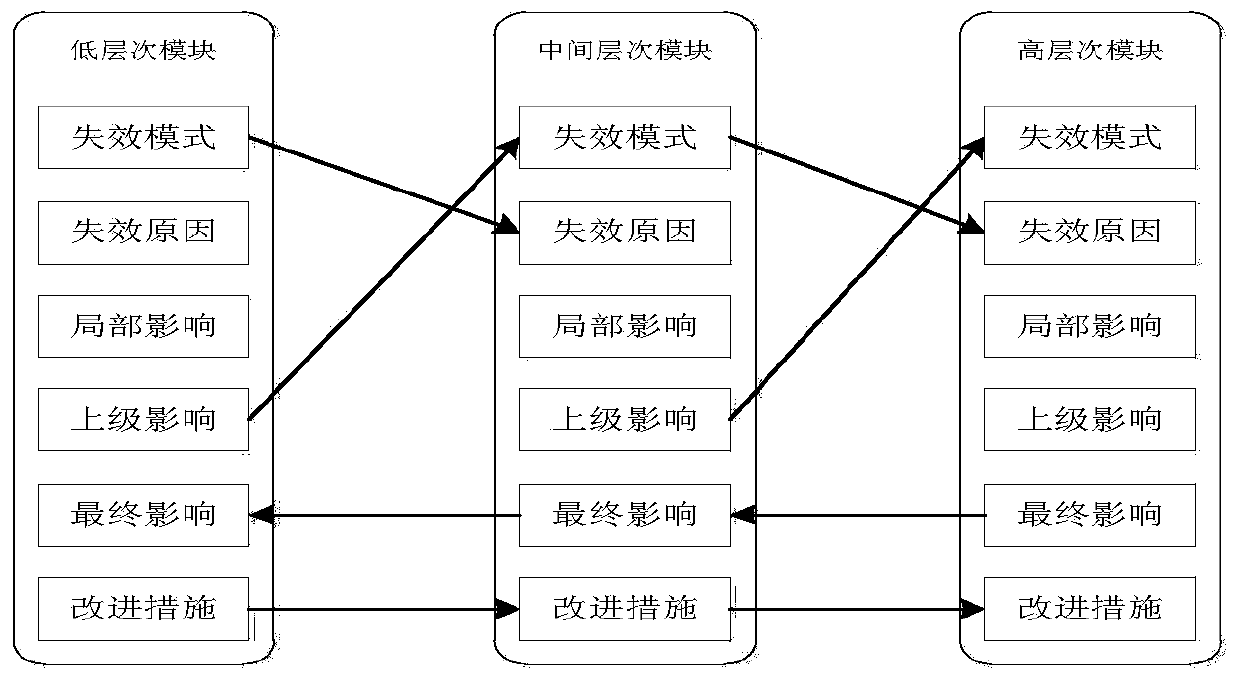
Software FMEA (failure mode and effects analysis) method based on level dependency modeling
InactiveCN103473400AMeet system level FMEAMeet detailed level FMEASpecial data processing applicationsInfluence propagationReachability
The invention discloses a software FMEA (failure mode and effects analysis) method based on level dependency modeling. The method includes 1, understanding an object to be analyzed completely and deeply as required, and determining an analyzing target; 2, establishing a system-grade level dependency model by utilizing outline design as a reference; 3, selecting a module to be analyzed and determine a failure mode thereof, analyzing a failure influence propagation path and a failure reason tracing path to determine a failure reason and the failure influence and provide improvements according to system-grade level dependency model reachability node analysis; 4, selecting a detailed-grade FMEA analyzing object according to a system-grade FMEA result; 5 establishing a detailed-grade level dependency model on the basis of detailed design or a pseudo-code of the selected object to be analyzed; 6, selecting key variables to be analyzed according to the detailed-grade level dependency model; 7, determining a specific failure mode of the key variables to be analyzed, and analyzing producing reasons and failure influences of the variables and providing improvements according to detailed-grade level dependency model reachability node analysis.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Technique for using OER with an ECT solution for multi-homed sites
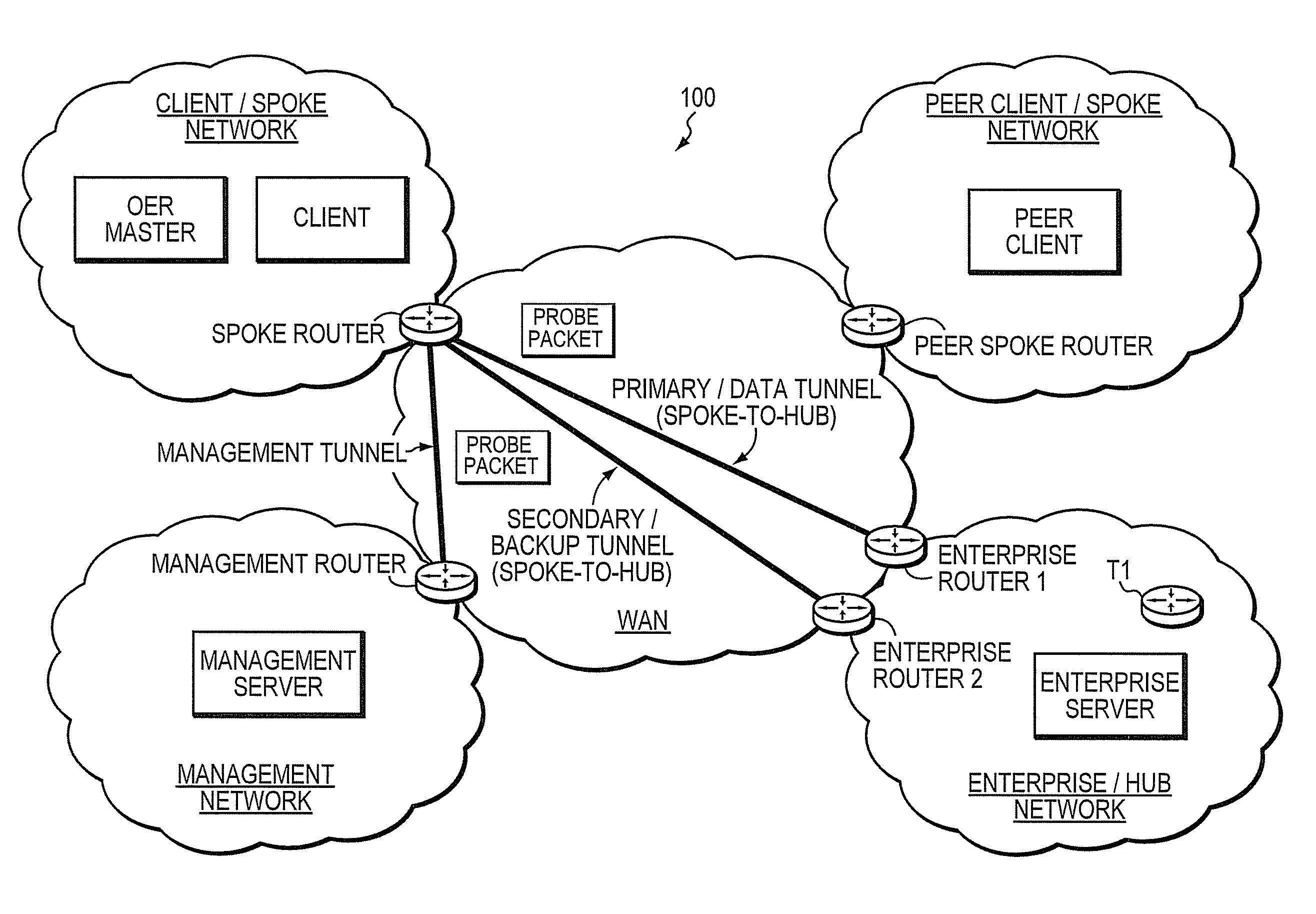
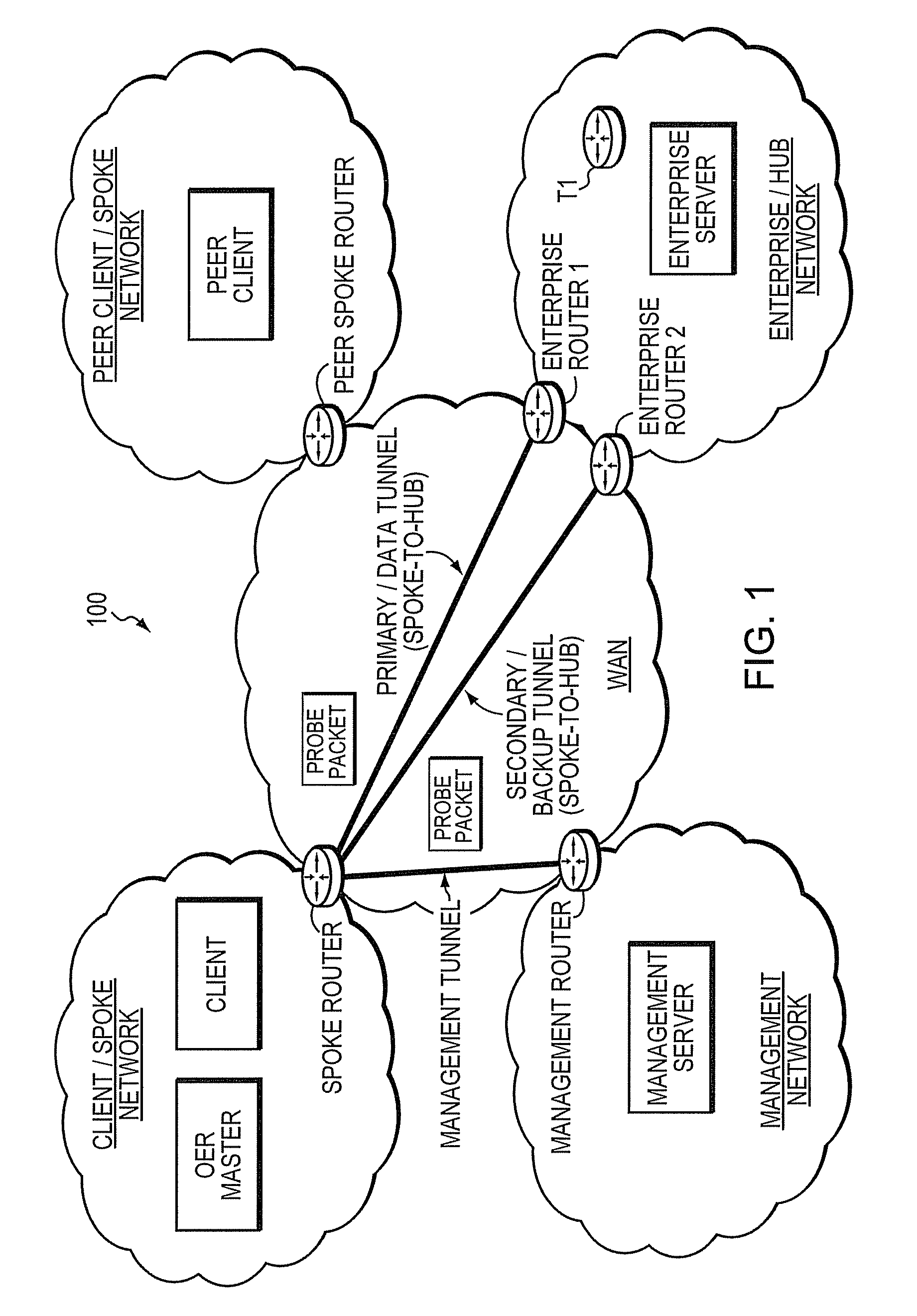
ActiveUS8260922B1Extended run timeImprove usabilityDigital computer detailsTransmissionTraffic capacityReachability
A technique dynamically utilizes a plurality of multi-homed Virtual Private Network (VPN) tunnels from a client node to one or more enterprise networks in a computer network. According to the technique, a VPN client node, e.g., a “spoke,” creates a plurality of multi-homed VPN tunnels with one or more servers / enterprise networks, e.g., “hubs.” The spoke designates (e.g., for a prefix) one of the tunnels as a primary tunnel and the other tunnels as secondary (backup) tunnels, and monitors the quality (e.g., loss, delay, reachability, etc.) of all of the tunnels, such as, e.g., by an Optimized Edge Routing (OER) process. The spoke may then dynamically re-designate any one of the secondary tunnels as the primary tunnel for a prefix based on the quality of the tunnels to the enterprise. Notably, the spoke may also dynamically load balance traffic to the enterprise among the primary and secondary tunnels based on the quality of those tunnels.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
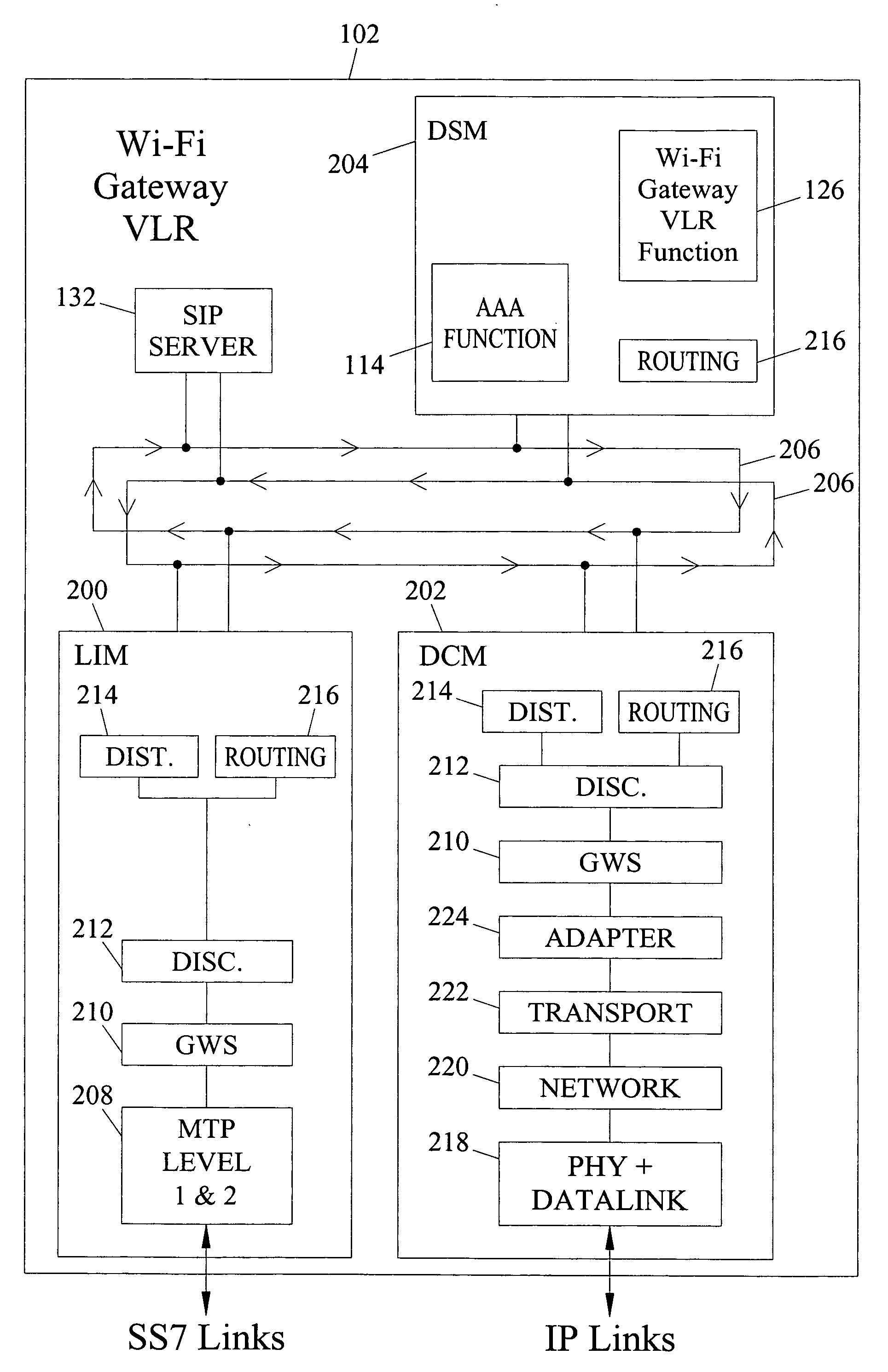
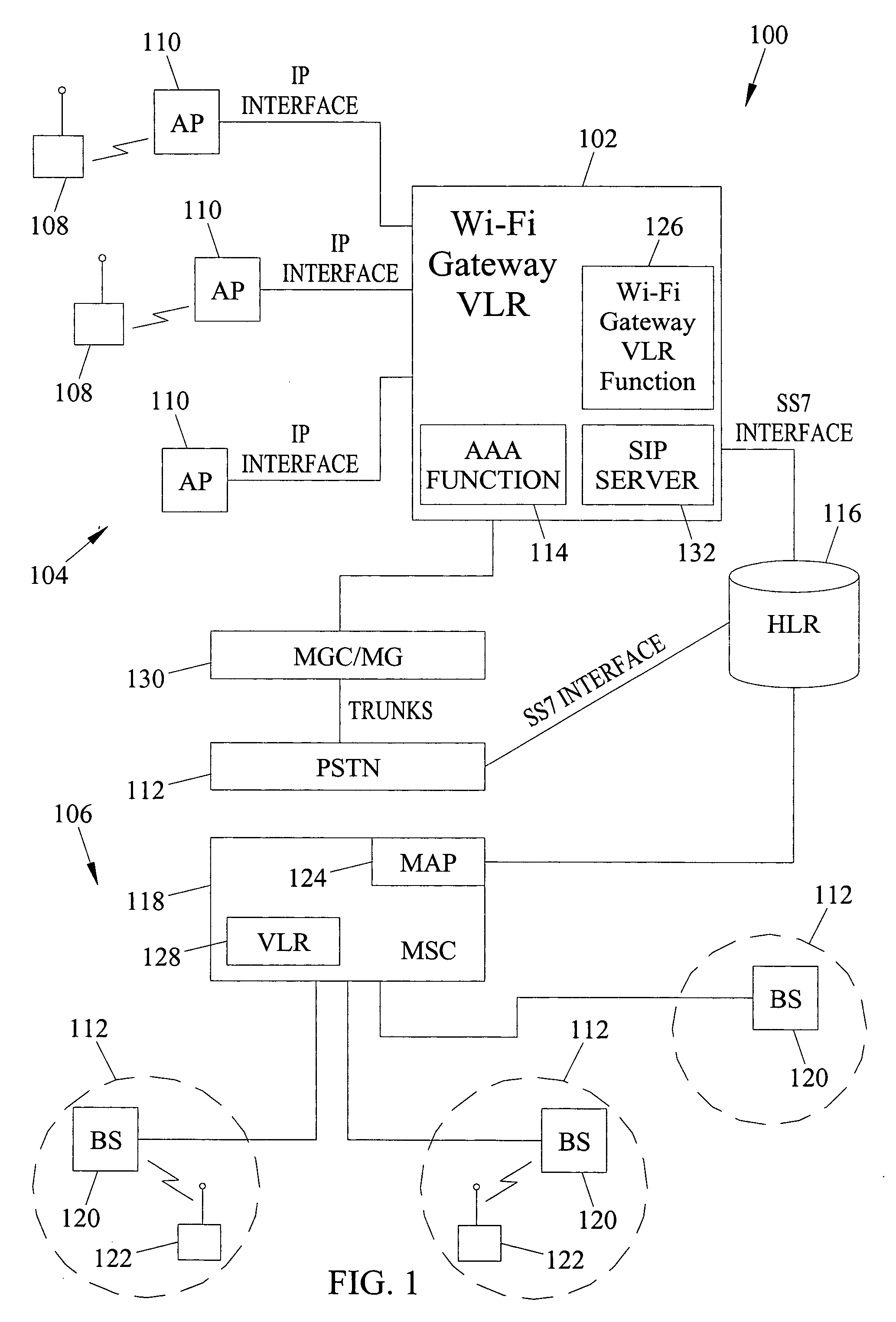
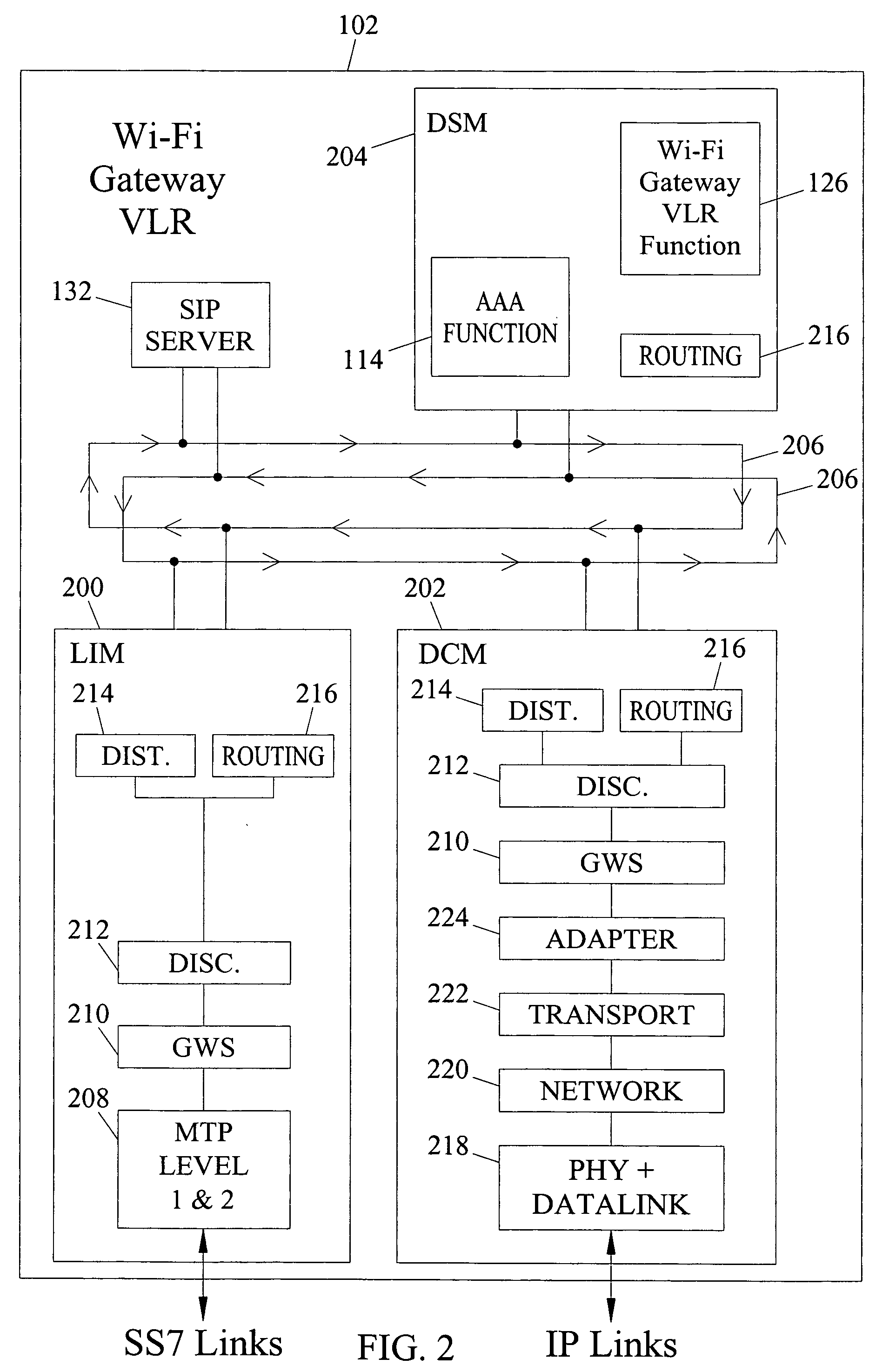
Methods, systems, and computer program products for providing wireless-fidelity (WI-FI) gateway visitor location register (VLR) functionality
Methods, Systems, and Computer Program Products for Providing Wireless-Fidelity (Wi-Fi) Gateway Visitor Location Register (VLR) Functionality. A method is disclosed herein for providing Wi-Fi gateway VLR functionality for an access point in a Wi-Fi network. The steps of the method can occur at a Wi-Fi gateway VLR that can perform VLR functions for at least one access point in a Wi-Fi network. The VLR functions can include receiving a registration request from a subscriber located in a service area of an access point in the Wi-Fi network. Further, the VLR functions can include authenticating the subscriber with a home location register (HLR) associated with the cellular network. The VLR functions can also include receiving information associated with the subscriber from the HLR. The Wi-Fi gateway VLR can store the information associated with the subscriber and maintain Wi-Fi reachability information for sending media packets to the subscriber in the Wi-Fi network.
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com