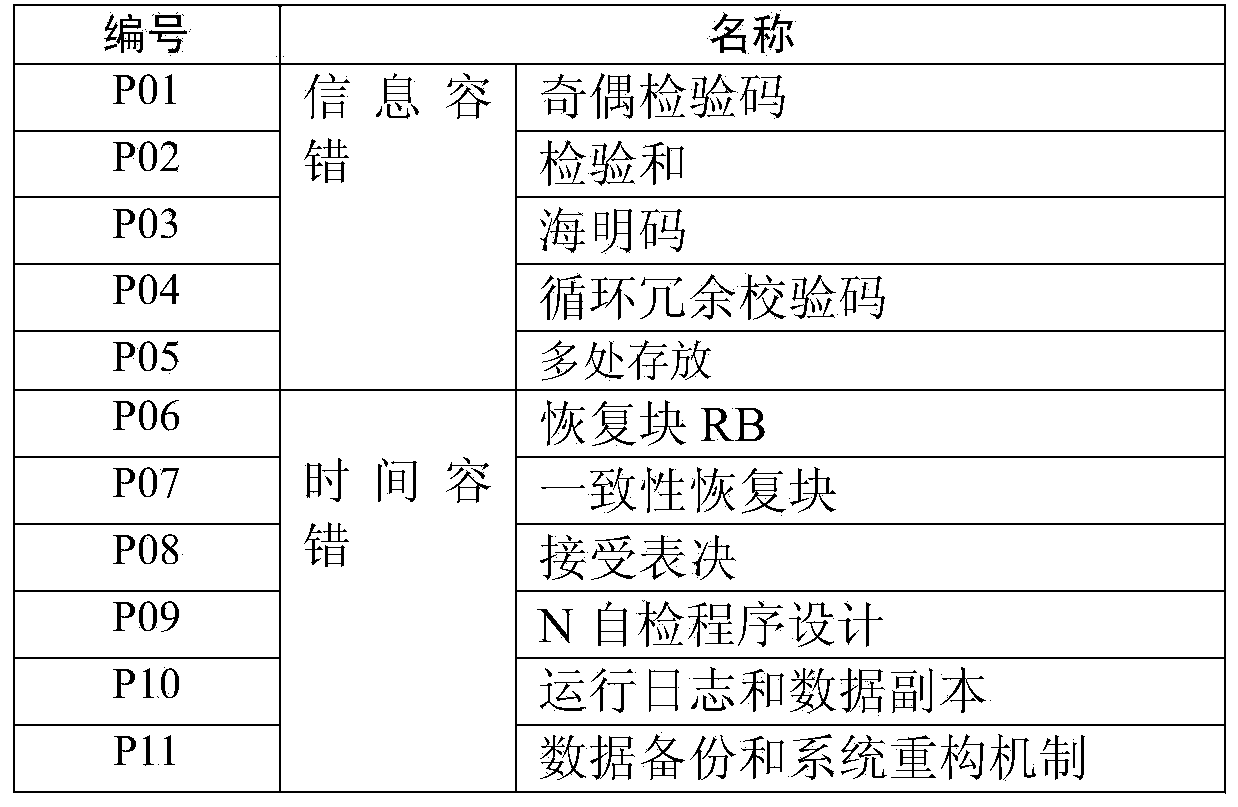
Patents
Literature
103 results about "Failure mode and effects analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA; often written with "failure modes" in plural) is the process of reviewing as many components, assemblies, and subsystems as possible to identify potential failure modes in a system and their causes and effects. For each component, the failure modes and their resulting effects on the rest of the system are recorded in a specific FMEA worksheet. There are numerous variations of such worksheets. A FMEA can be a qualitative analysis, but may be put on a quantitative basis when mathematical failure rate models are combined with a statistical failure mode ratio database. It was one of the first highly structured, systematic techniques for failure analysis. It was developed by reliability engineers in the late 1950s to study problems that might arise from malfunctions of military systems. An FMEA is often the first step of a system reliability study.
Fault predicting and diagnosing method suitable for dynamic complex system
InactiveCN102208028AOvercome the drawbacks of harsh restrictionsImprove general performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionPrediction intervalSystem failure
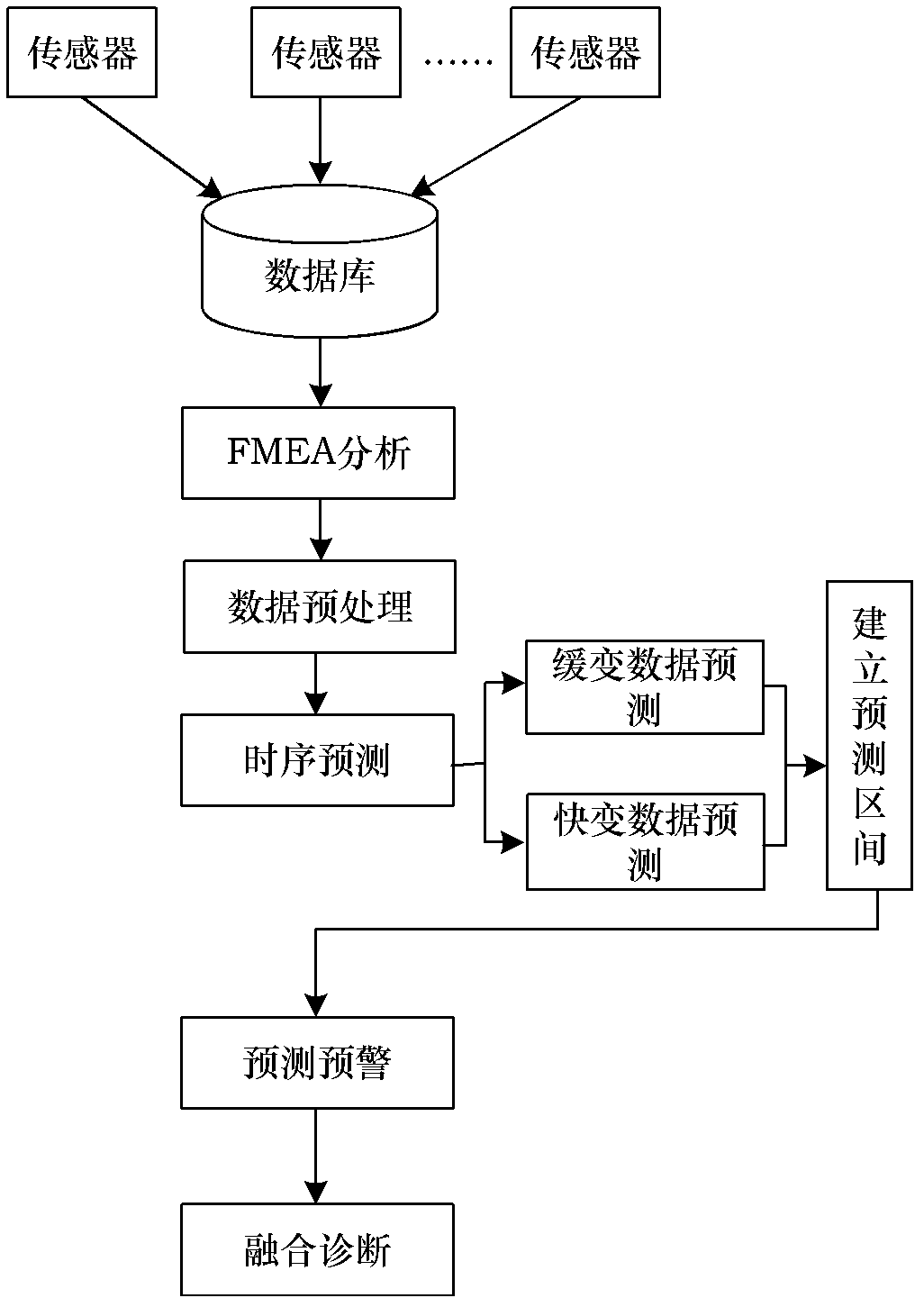
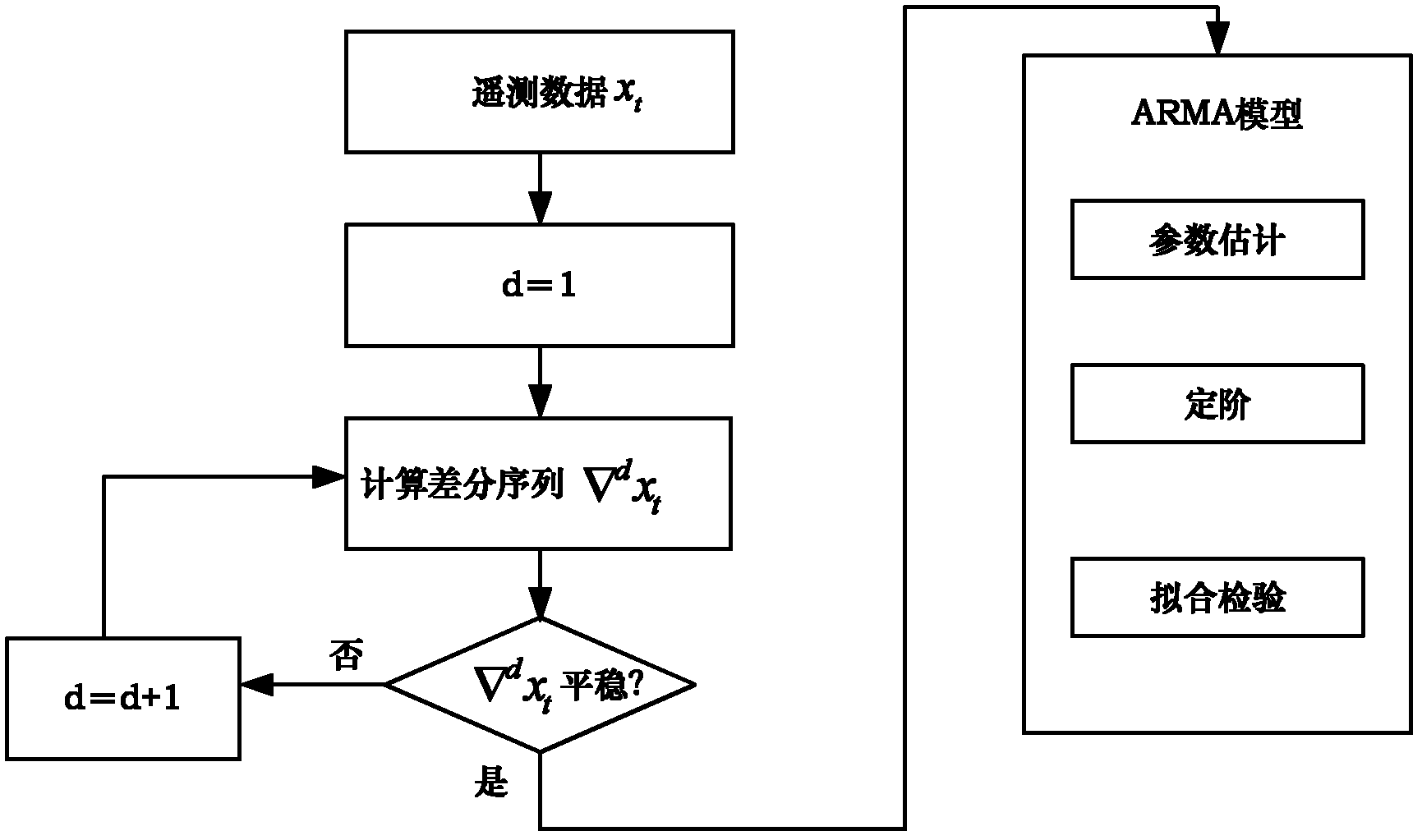
The invention provides a fault predicting and diagnosing method suitable for a dynamic complex system. The method can be applied in the field of fault prediction and diagnosis of dynamic complex systems of spacecrafts and the like. The method comprises the following steps of: performing failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) on the dynamic complex system to obtain a main fault mode and corresponding performance detection parameters, dividing the performance detection parameters into slowly variable data and fast variable data, pre-processing the performance detection parameters, establishingan autoregressive moving average model (ARMA) aiming at the slowly variable data to perform time sequence prediction, establishing a multi-resolution wavelet neural network aiming at the fast variable data to perform time sequence prediction, performing fault early warning on the time sequence prediction results by establishing a prediction interval model, and performing fault diagnosis by establishing a D-S (Dempster-Shafer) evidence theory-based multi-signal fusion model. The method can be used for predicting and diagnosing the faults of the dynamic complex system with high precision, and has strong universality.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Software FMEA (failure mode and effects analysis) method based on level dependency modeling
InactiveCN103473400AMeet system level FMEAMeet detailed level FMEASpecial data processing applicationsInfluence propagationReachability
The invention discloses a software FMEA (failure mode and effects analysis) method based on level dependency modeling. The method includes 1, understanding an object to be analyzed completely and deeply as required, and determining an analyzing target; 2, establishing a system-grade level dependency model by utilizing outline design as a reference; 3, selecting a module to be analyzed and determine a failure mode thereof, analyzing a failure influence propagation path and a failure reason tracing path to determine a failure reason and the failure influence and provide improvements according to system-grade level dependency model reachability node analysis; 4, selecting a detailed-grade FMEA analyzing object according to a system-grade FMEA result; 5 establishing a detailed-grade level dependency model on the basis of detailed design or a pseudo-code of the selected object to be analyzed; 6, selecting key variables to be analyzed according to the detailed-grade level dependency model; 7, determining a specific failure mode of the key variables to be analyzed, and analyzing producing reasons and failure influences of the variables and providing improvements according to detailed-grade level dependency model reachability node analysis.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A modeling method of hybrid fault early warning model and hybrid fault early warning model
InactiveCN102262690AGuarantee intrinsic safetySpecial data processing applicationsOperabilitySystem failure
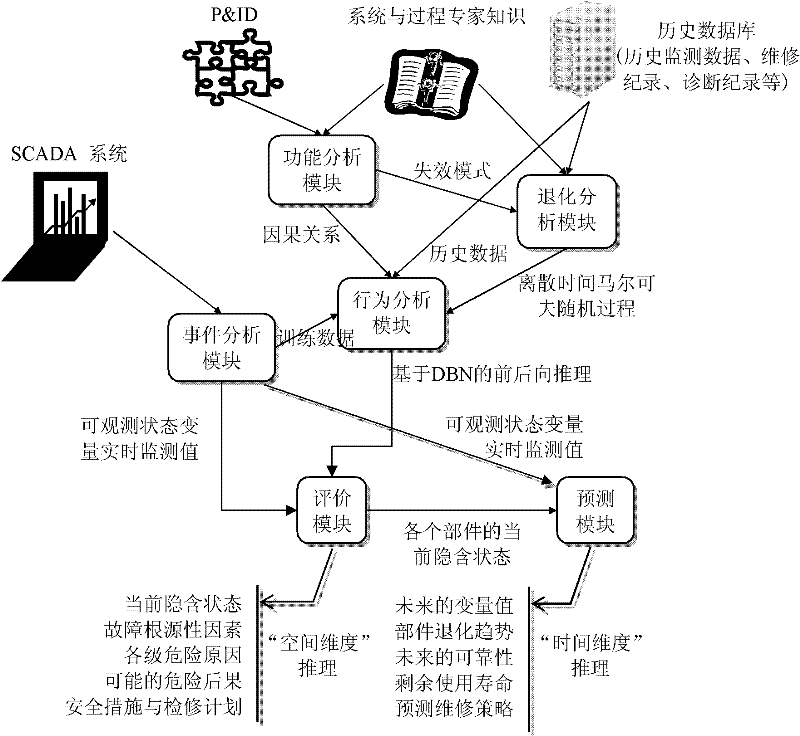
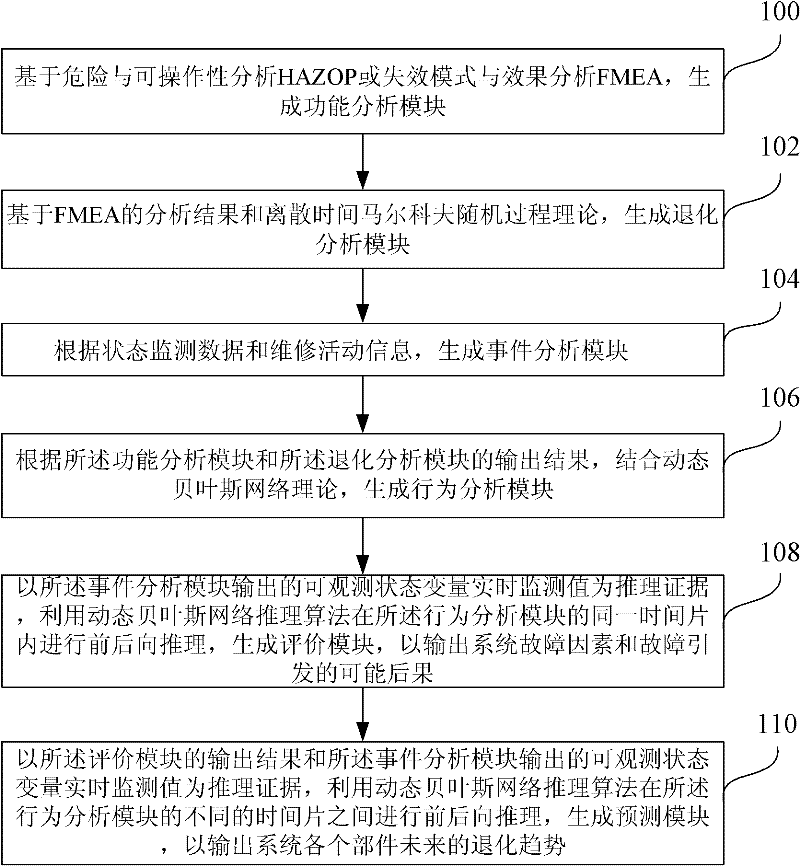
The embodiment of the invention provides a modeling method of an early warning model of mixed failures and a modeling system. The modeling method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: generating a function analyzing module on the basis of HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Analysis) or FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis); generating a degeneration analyzing module on the basis of FMEA analyzing results and a theory of stochastic processes; generating an accident analyzing module according to state monitoring data and maintenance action information; generating an action analyzing module according to output results of the function analyzing module and the degeneration analyzing module through combining a DBN (Dynamic Bayesian Network) theory; taking the output of the accident analyzing module as an inference evidence and utilizing a DBN inference algorithm to process forward and backward inferences in the same time period to generate an evaluating module for outputting factors and consequences of system failures; taking the output results of the evaluating module and the accident analyzing module as the inference evidence and utilizing the DBN inference algorithm to process forward and backward inferences in the different time periods to generate a predicating module for outputting prospective degeneration tendencies of each member of the system. The model provided by the invention can be used for tracking the failure factors of the system and inferring possible failure consequences and probability.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
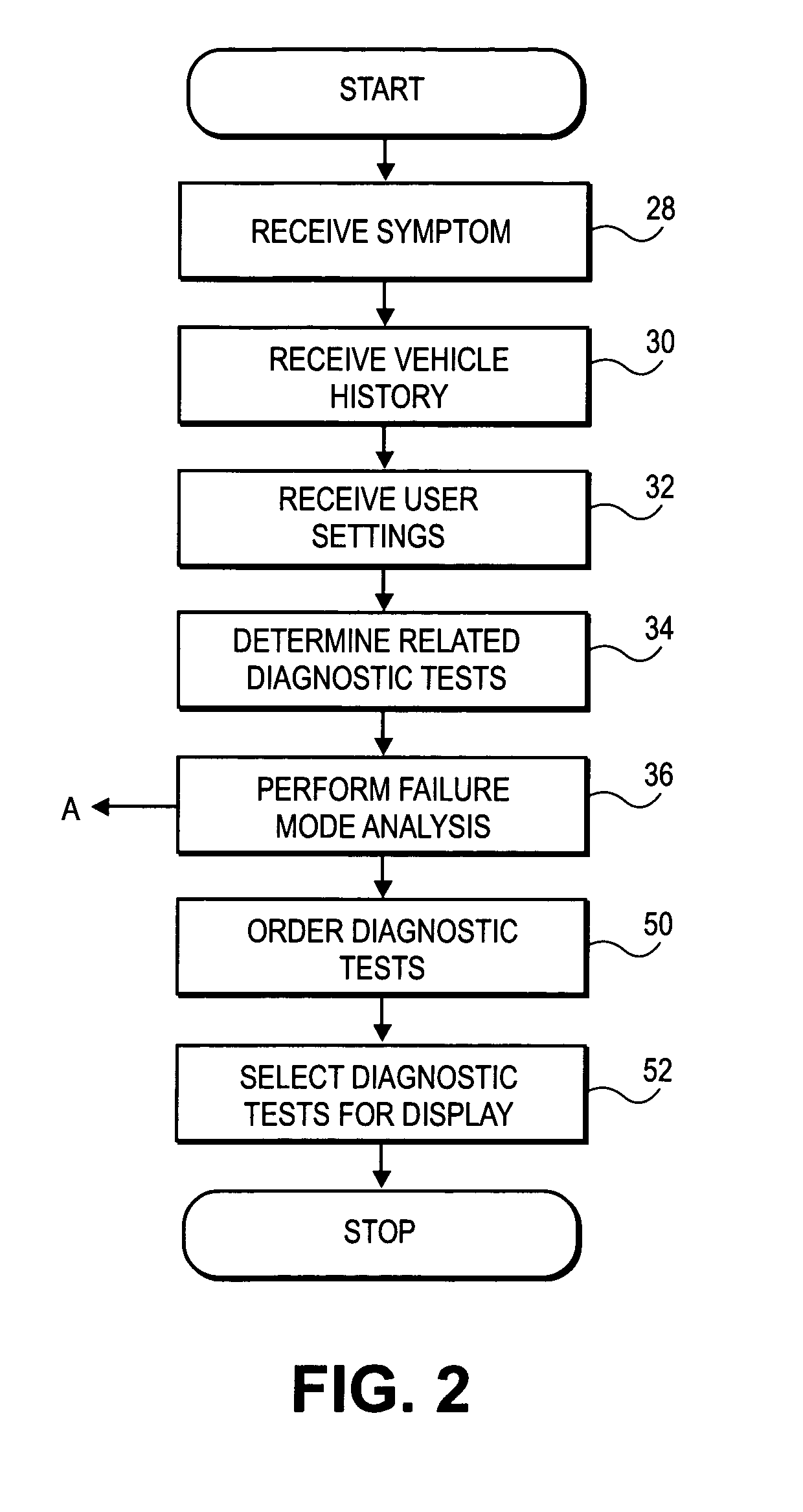
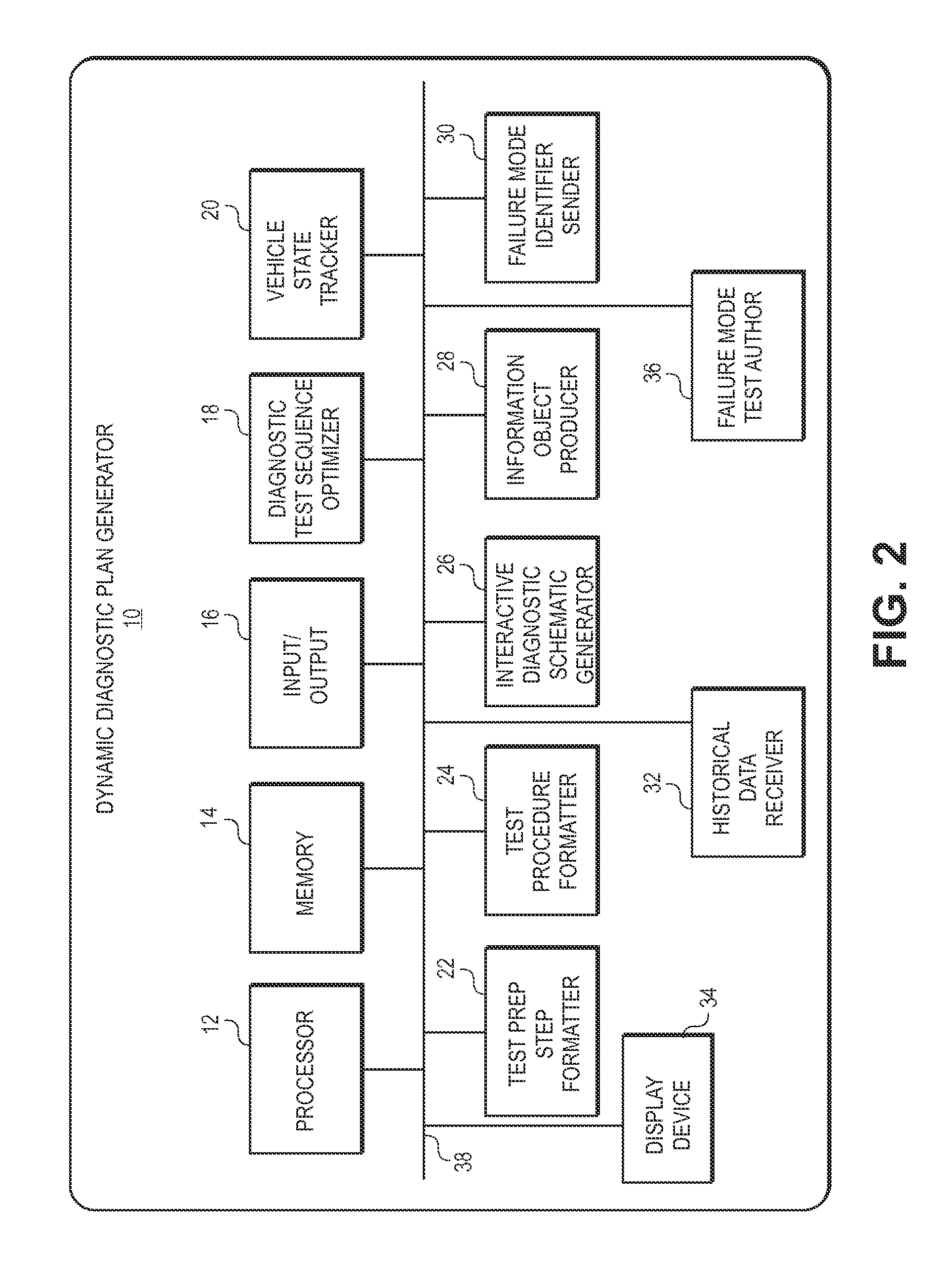
Dynamic decision sequencing method and apparatus for optimizing a diagnostic test plan
ActiveUS20070294001A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDiagnostic dataProgram planning
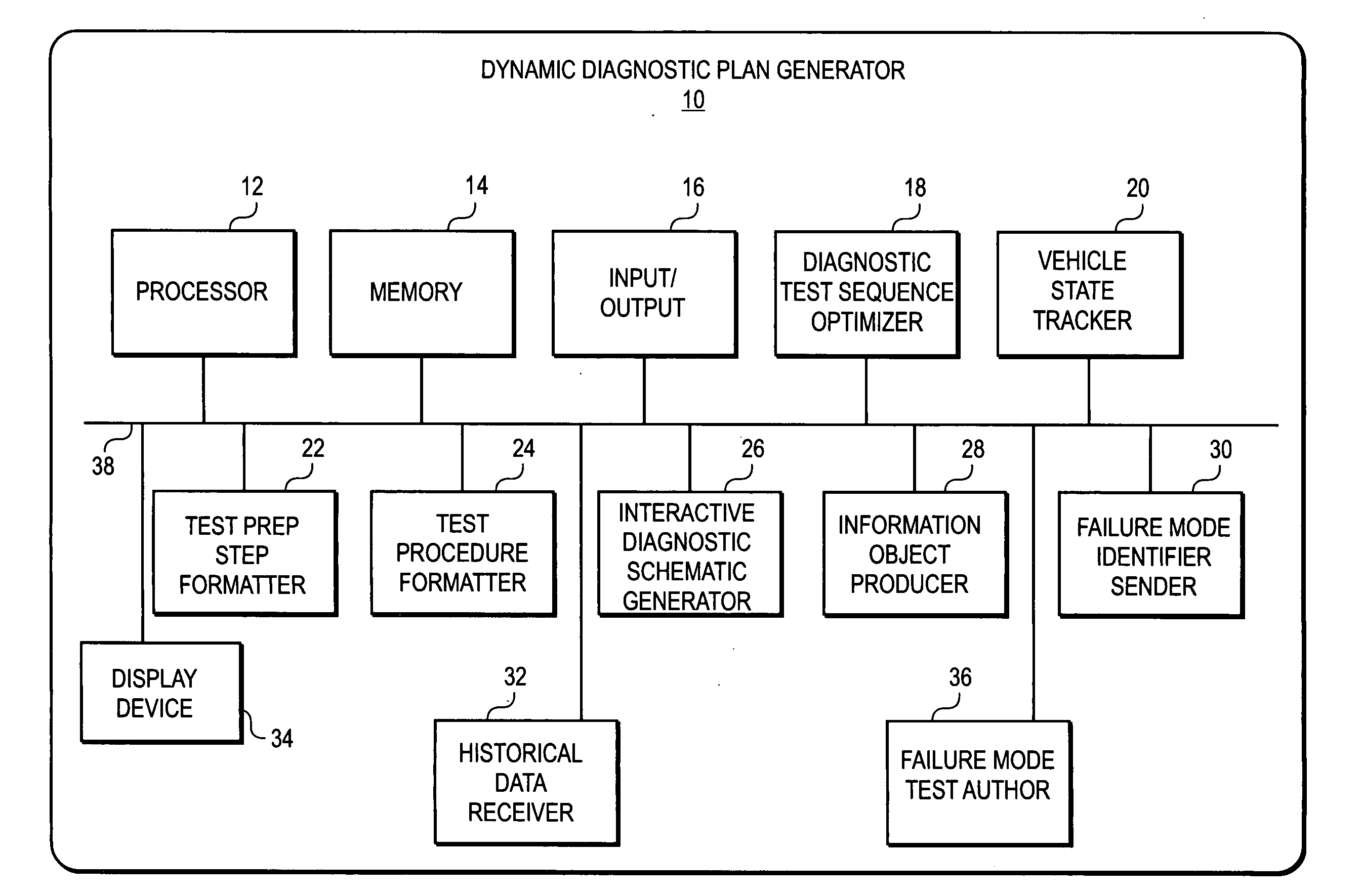
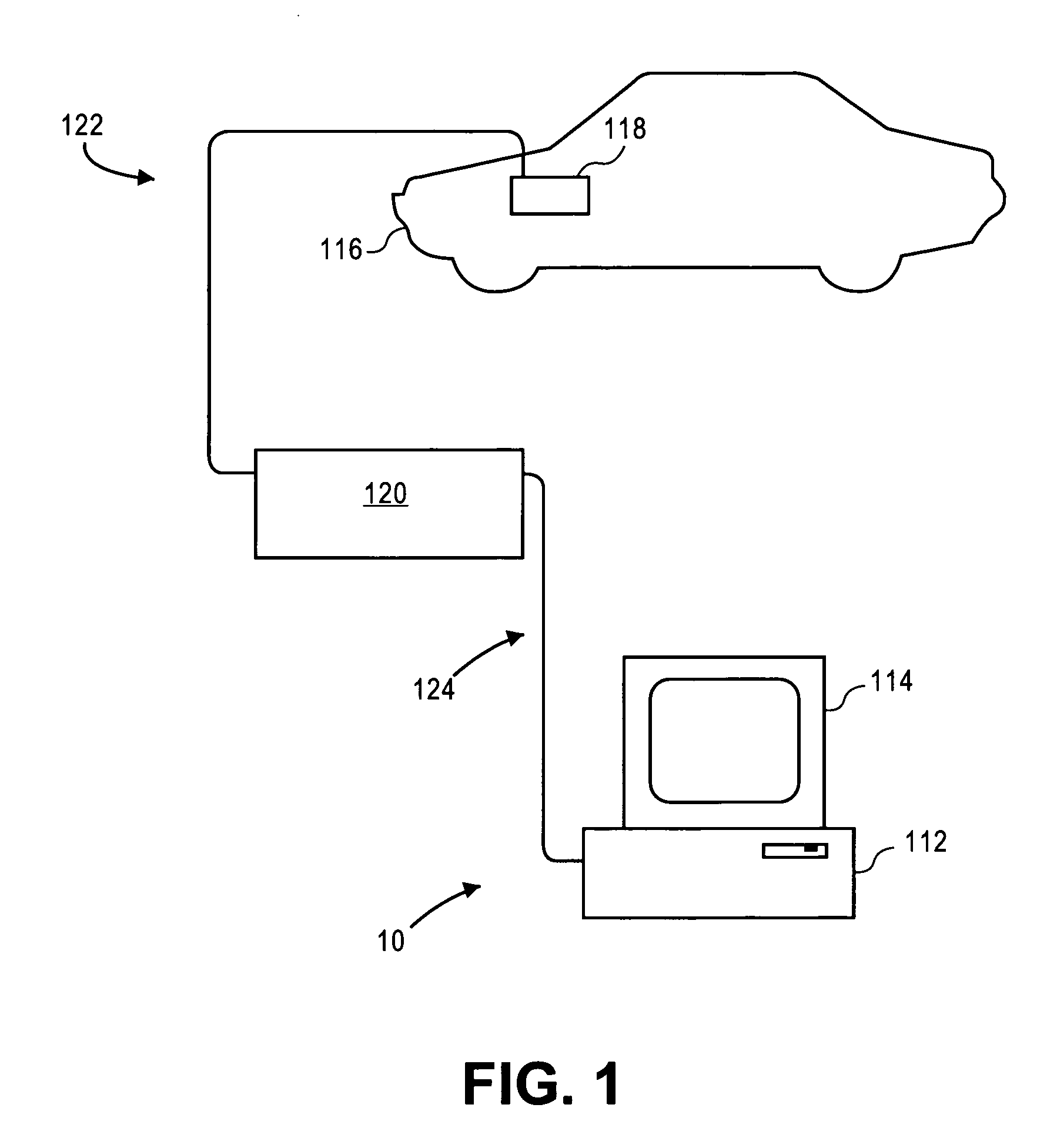
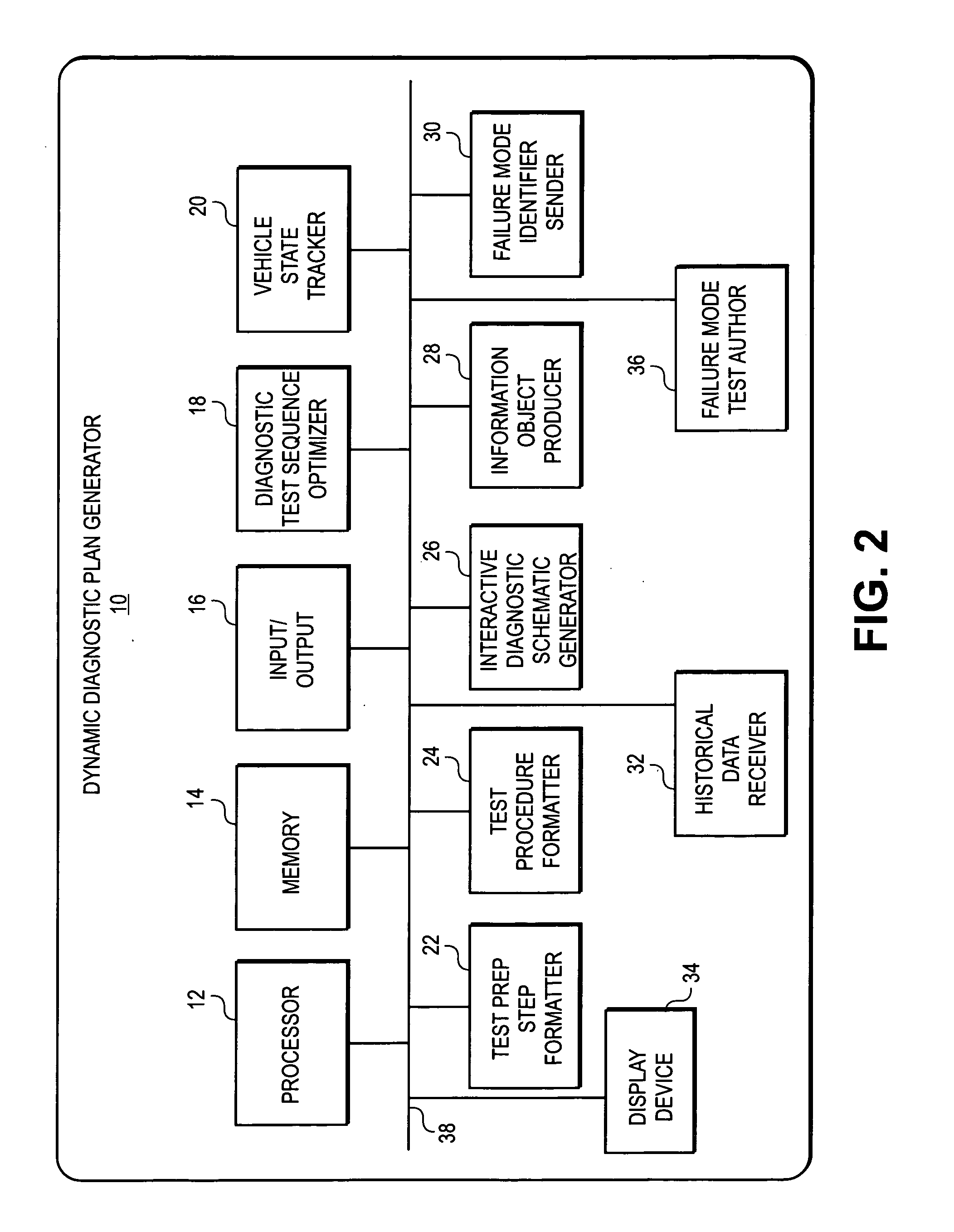
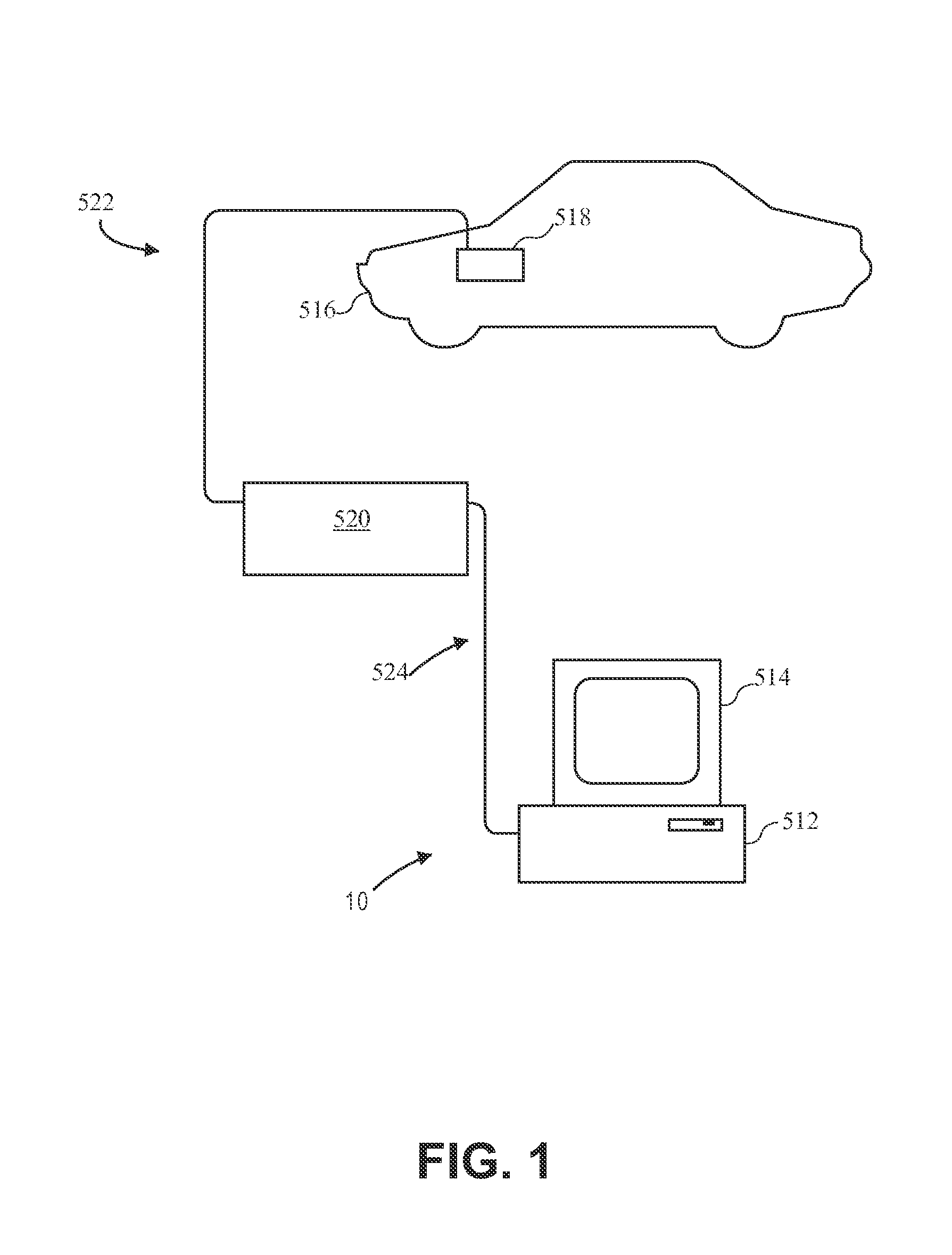
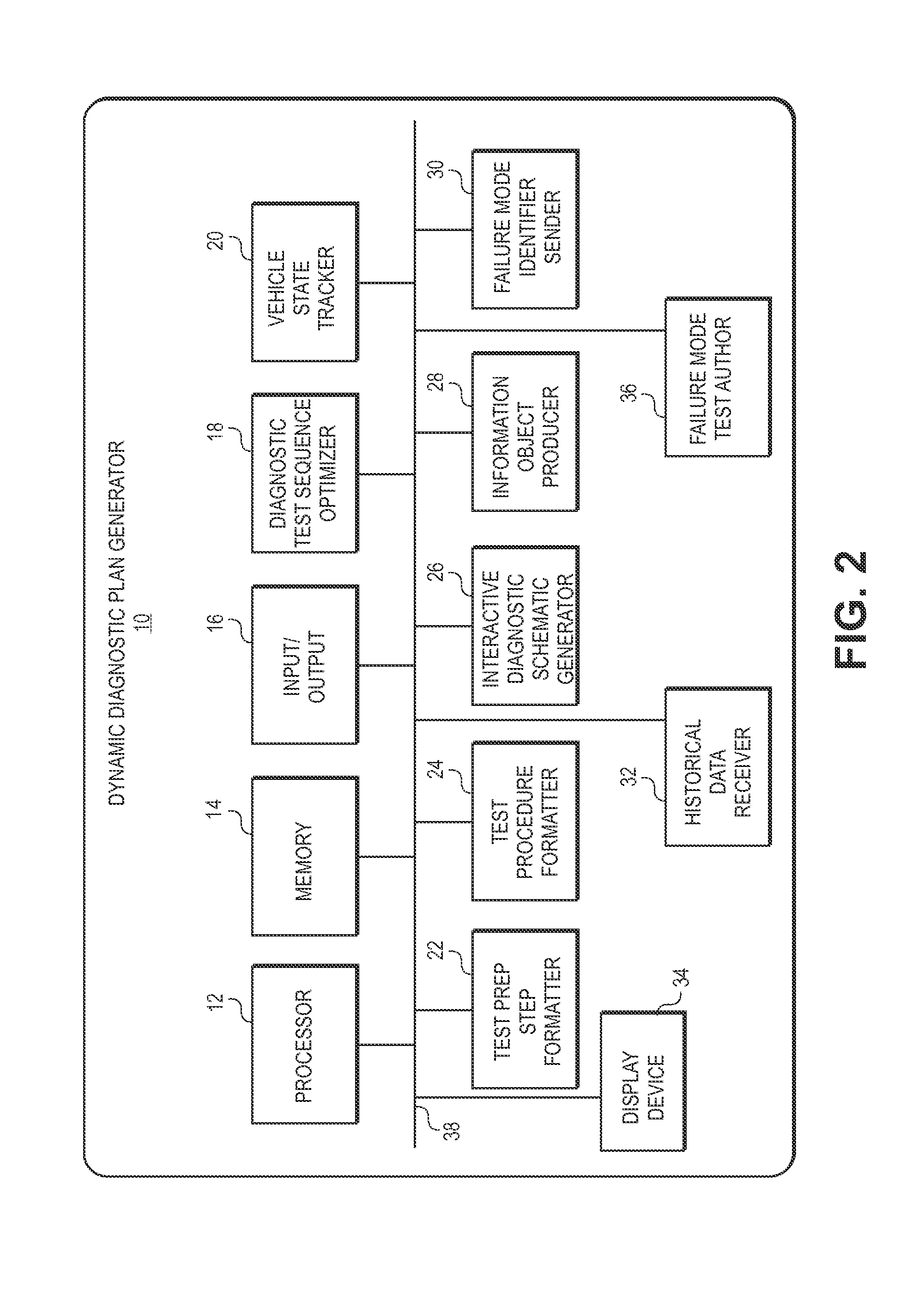
A dynamic diagnostic plan generator arranges diagnostic test procedures related to a vehicle symptom or operational problem in a sequence based on a probabilistic Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). The diagnostic plan generator also tracks a vehicle state, and provides instructions for test preparation steps and instructions for performing the diagnostic test procedures. The plan generator further generates schematic illustrations of the diagnostic test procedures, and creates a diagnostic data structure containing information related to the diagnostic test procedures. In addition, the diagnostic plan generator sends and receives information regarding actual failure mode occurrences, for example, to and from a central database. Furthermore, the diagnostic plan generator facilitates the creation of failure mode tests by an expert diagnostics author.
Owner:BOSCH AUTOMOTIVE SERVICE SOLUTIONS
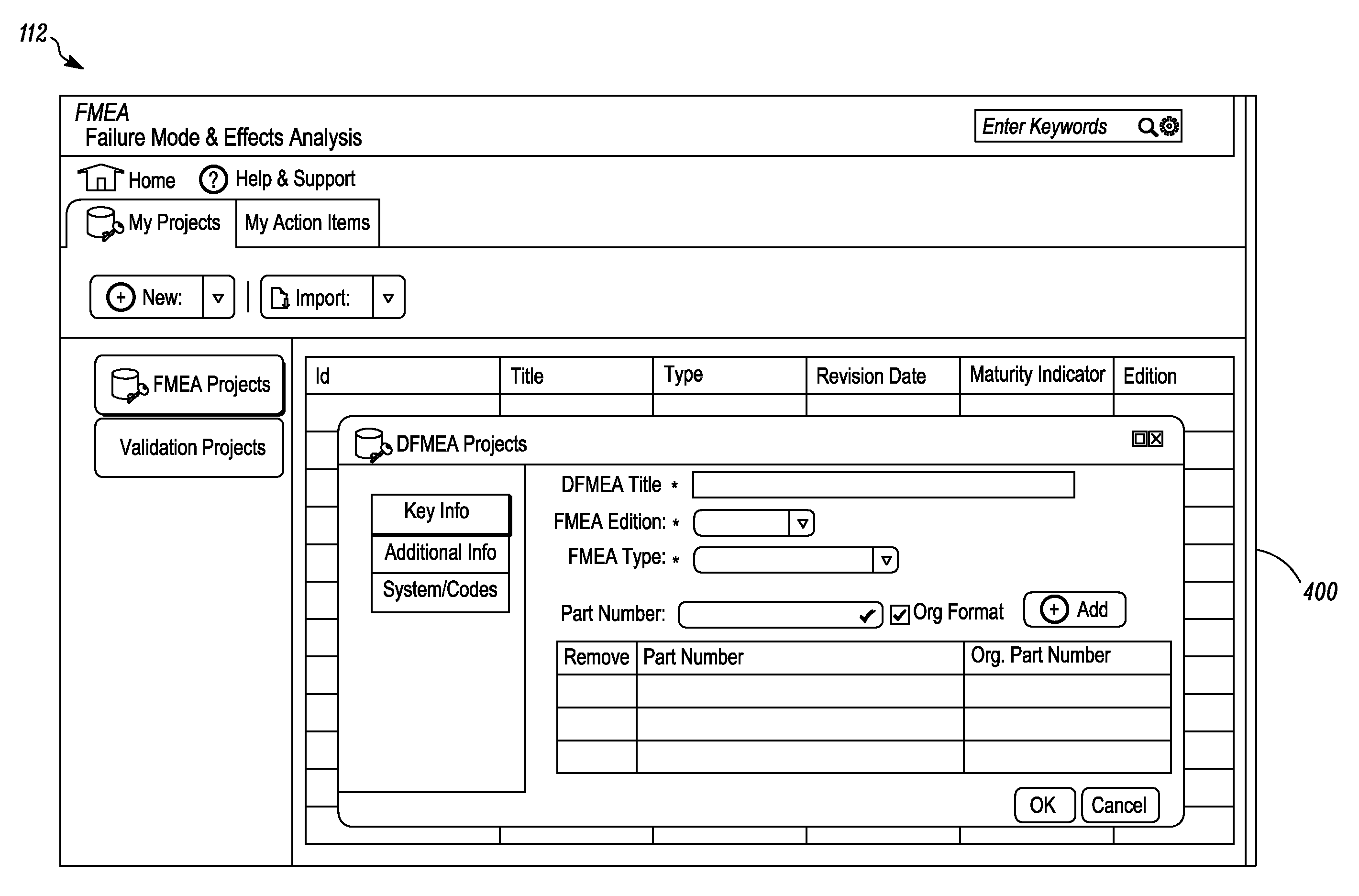
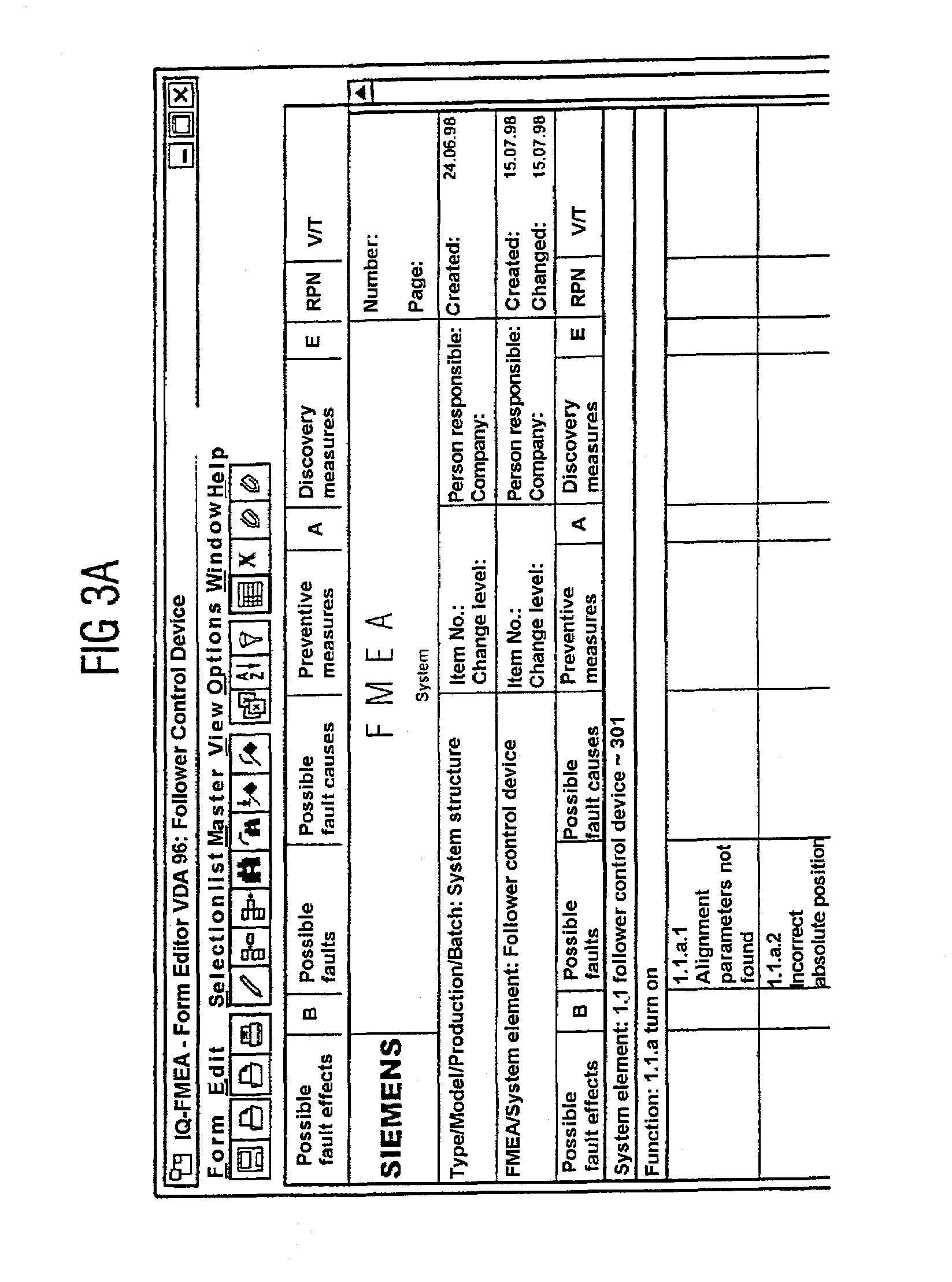
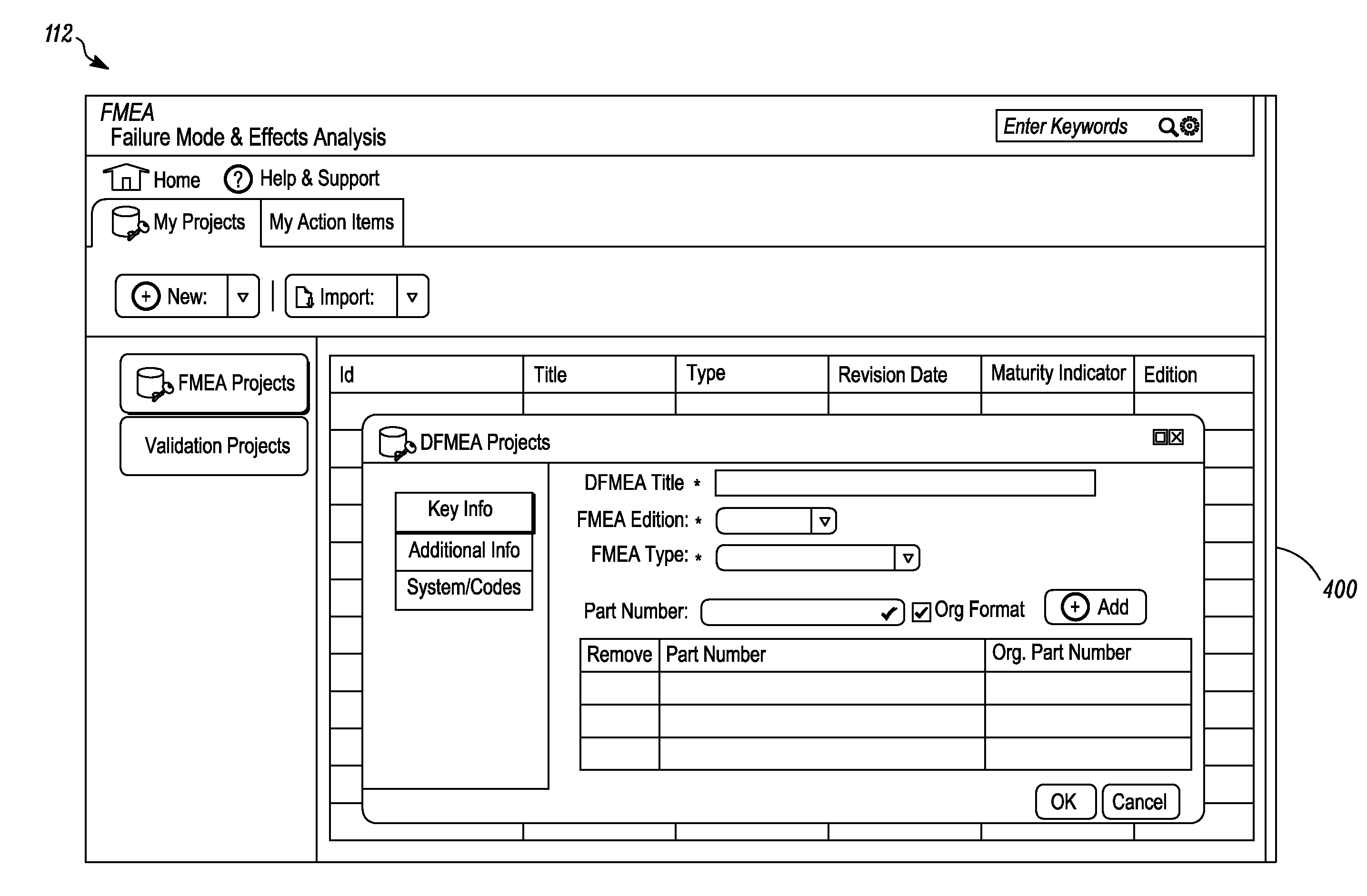
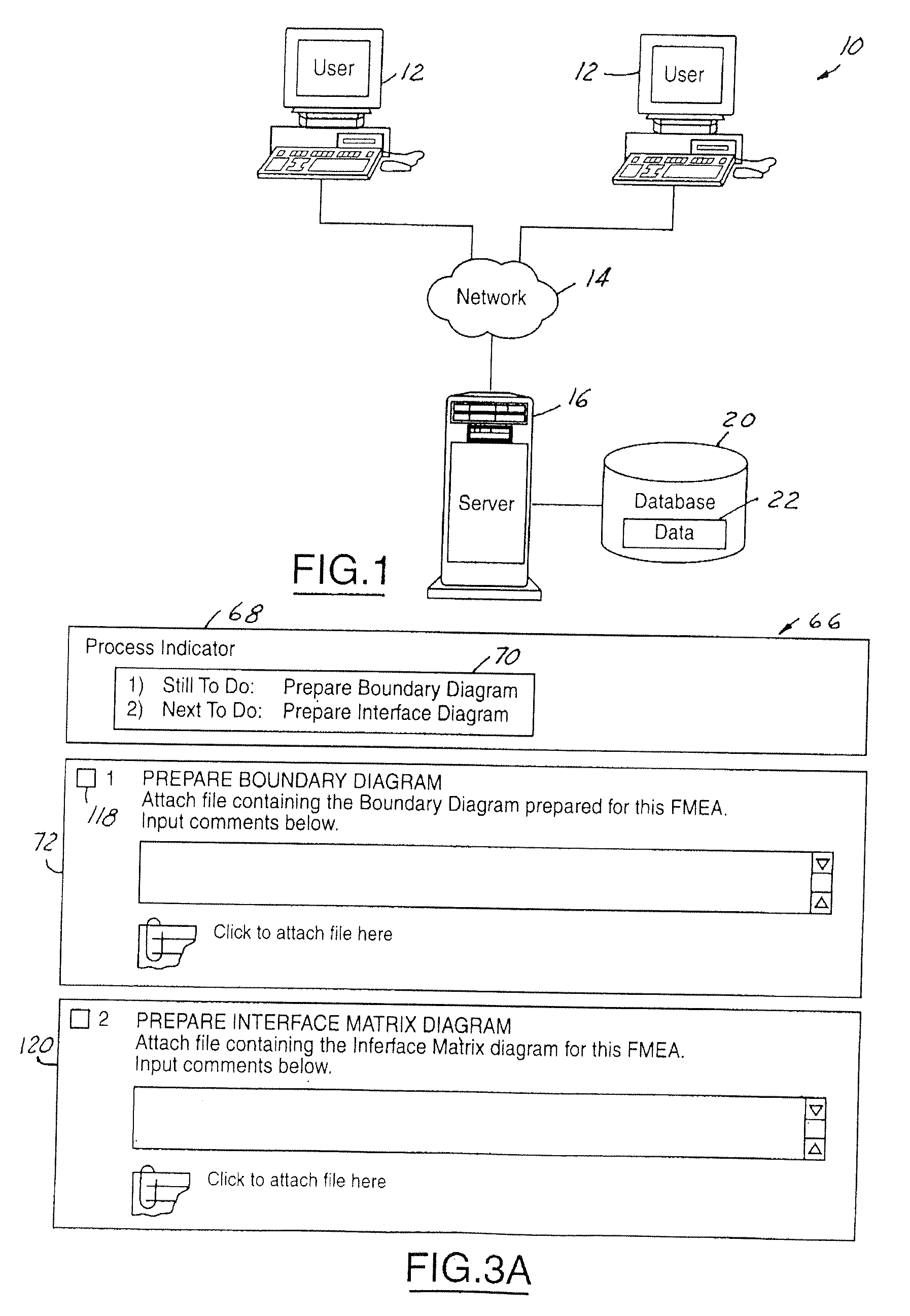
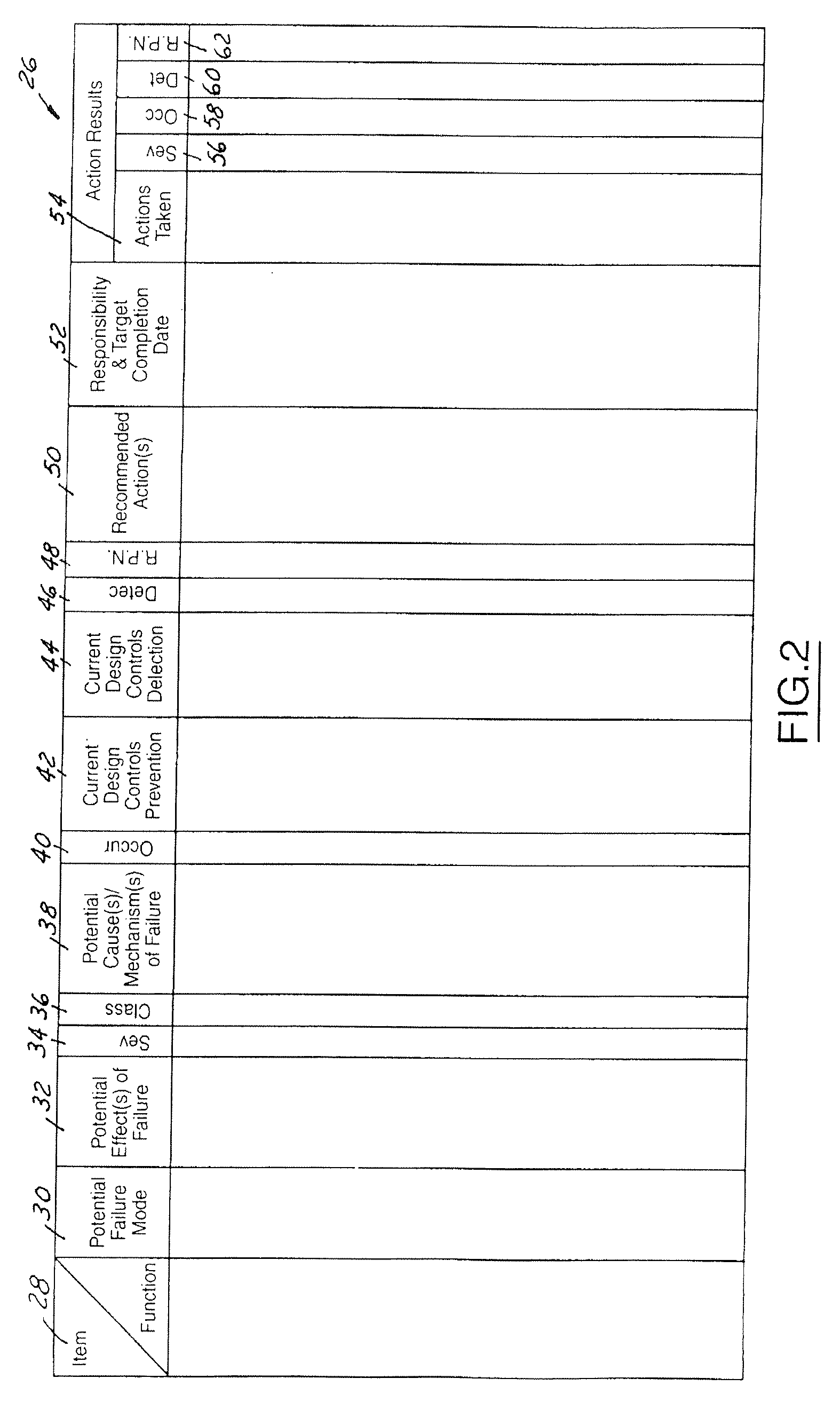
Graphical user interface for failure mode and effect analysis
A method to facilitate a failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA) project associated with one or more components or process during a product development cycle is provided. A real time FMEA status is viewable through a user interface which indicates the progress of the FMEA project. The method includes displaying on the user interface one or more information pages associated with sequential order of elements to be completed by one or more FMEA analysts. The method further involves receiving with an aid of the user interface textual inputs from the one or more FMEA analysts for the one or more information pages associated with the sequential orders of elements. The method further includes representing, to the one or more FMEA analysts, the sequential order of elements in a tree structure format. The information associated with the sequential order of elements is editable and is updated in real time.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
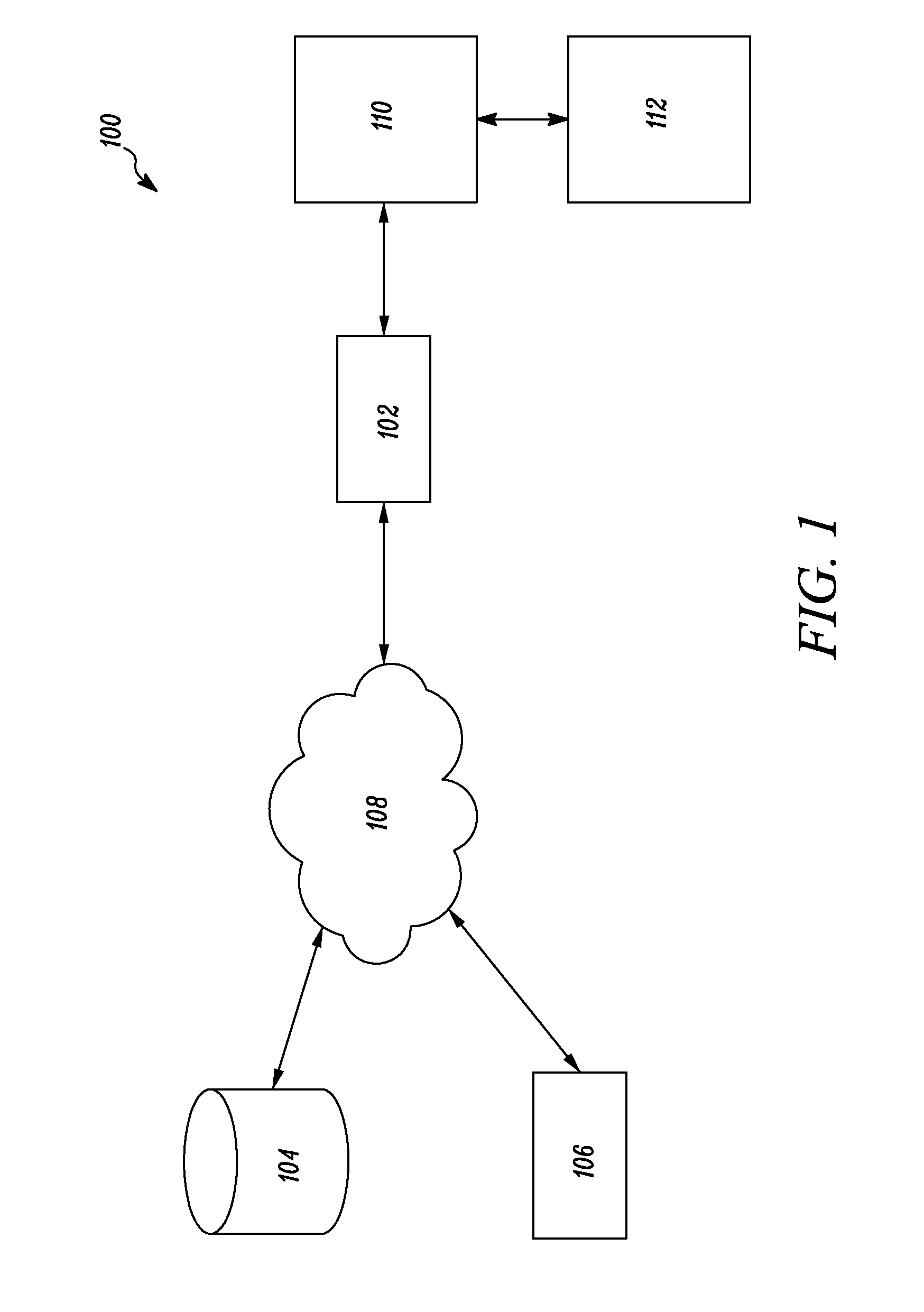
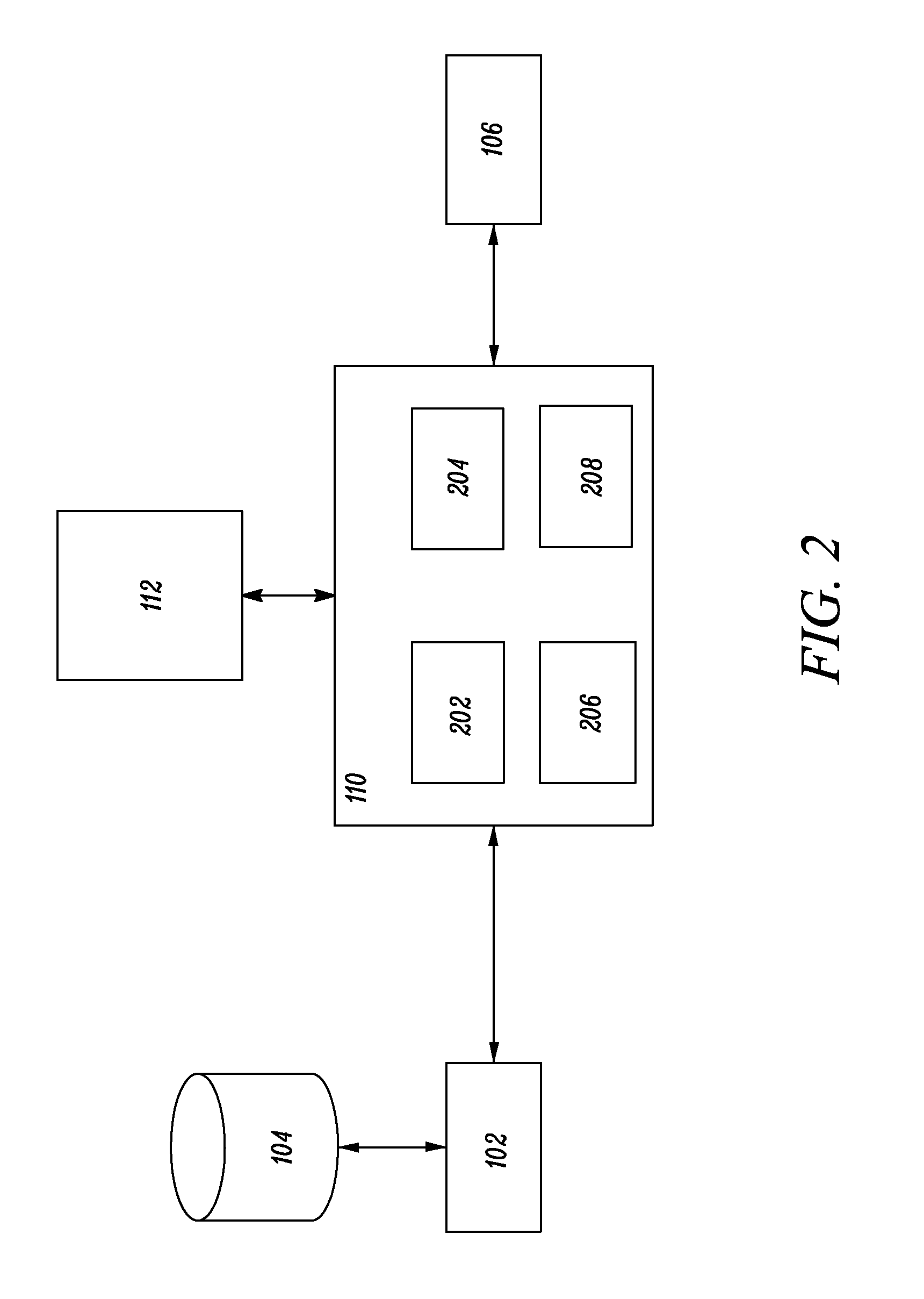
Method and system for determining a fault tree of a technical system, computer program product and a computer readable storage medium
InactiveUS7017080B1Reduce computational complexityImprove reliabilityLogical operation testingElectric testing/monitoringFrequency of occurrenceComputer science
The faults are described using a fault description which comprises data which have been determined using failure modes and effects analysis. The fault description is extended by information regarding the dependency of possible faults and the frequency of occurrence of said faults. The extended fault description is used to ascertain, for a prescribed fault event, the fault tree and the frequency of occurrence of the fault event.
Owner:IP EDGE LLC
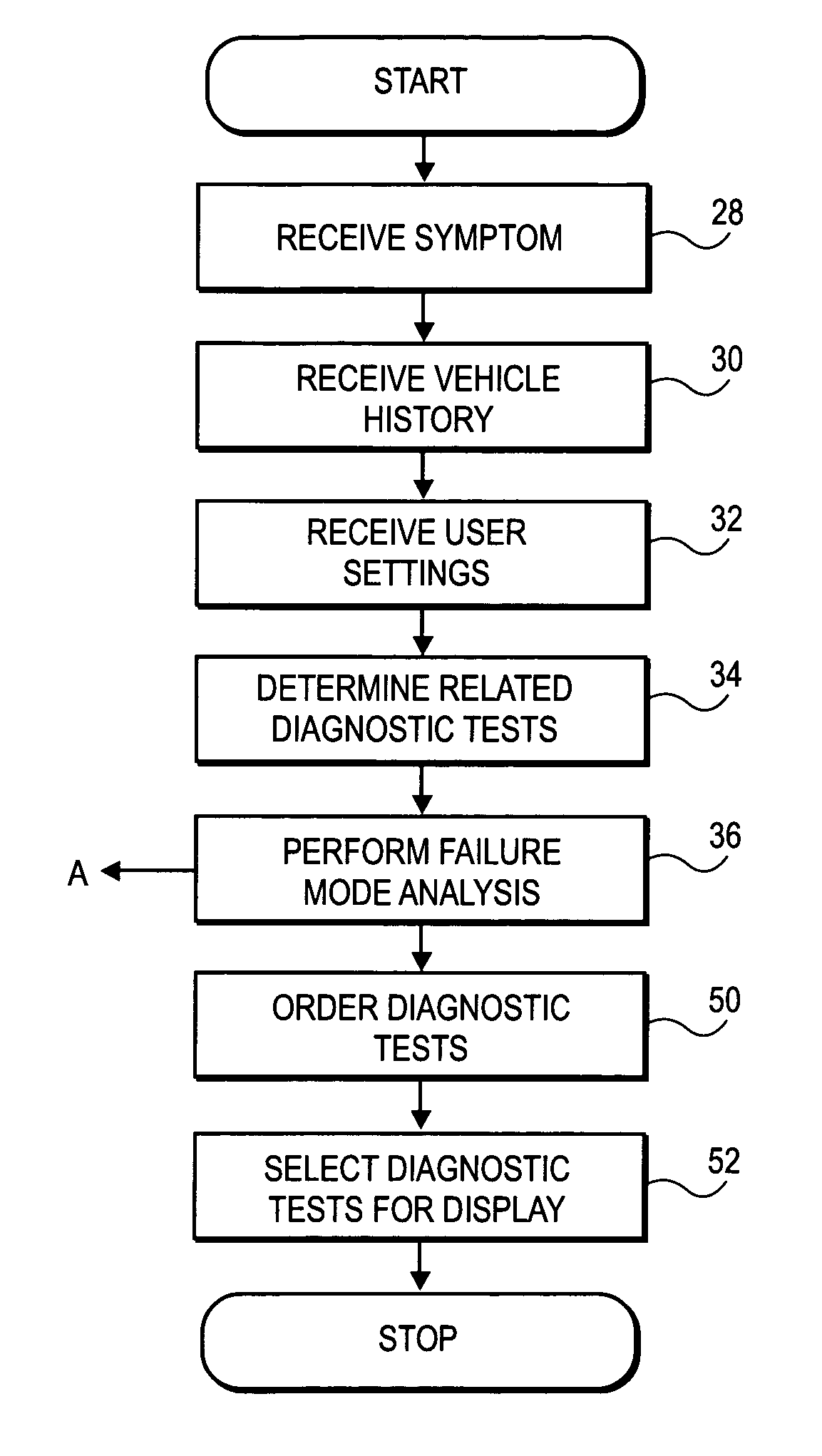
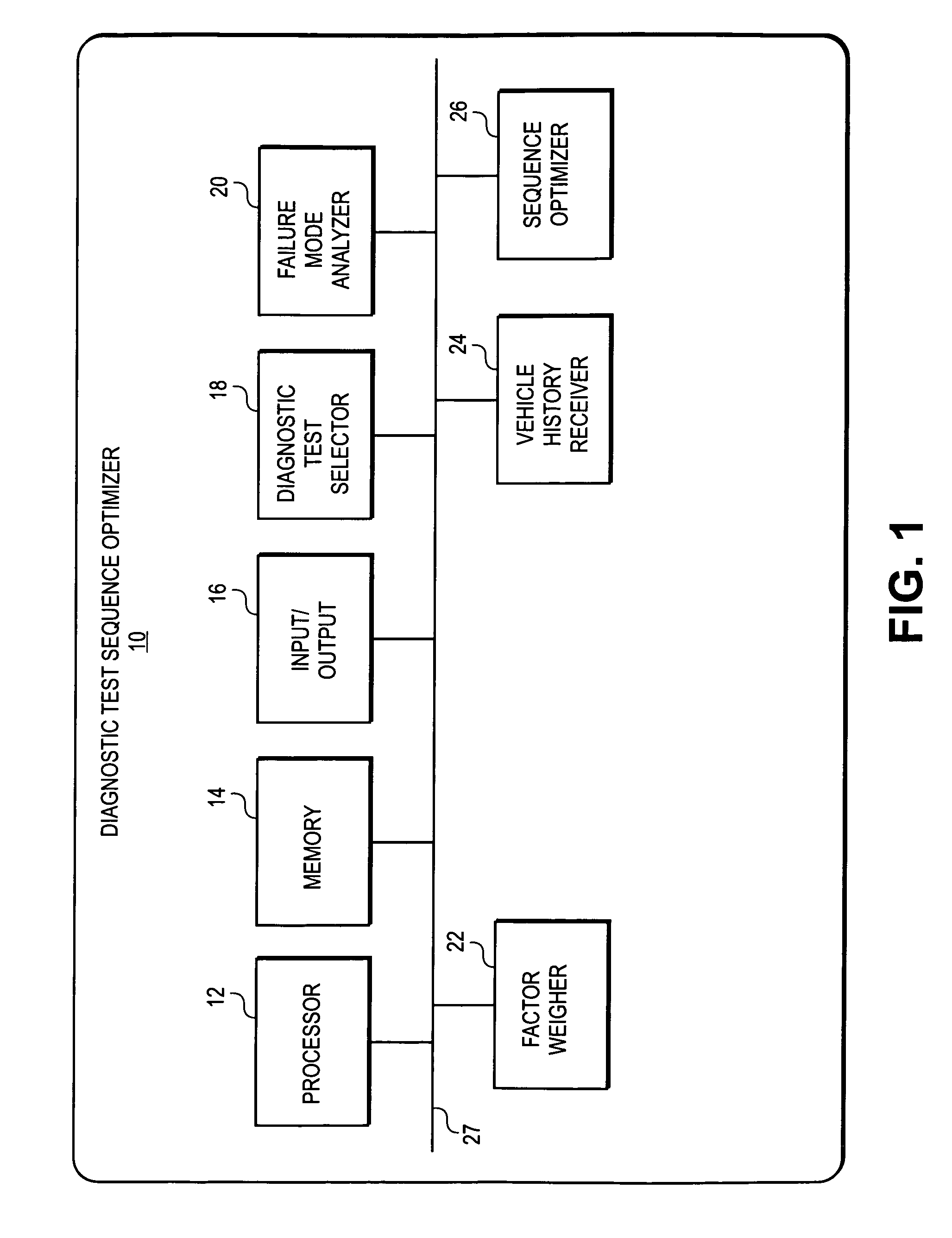
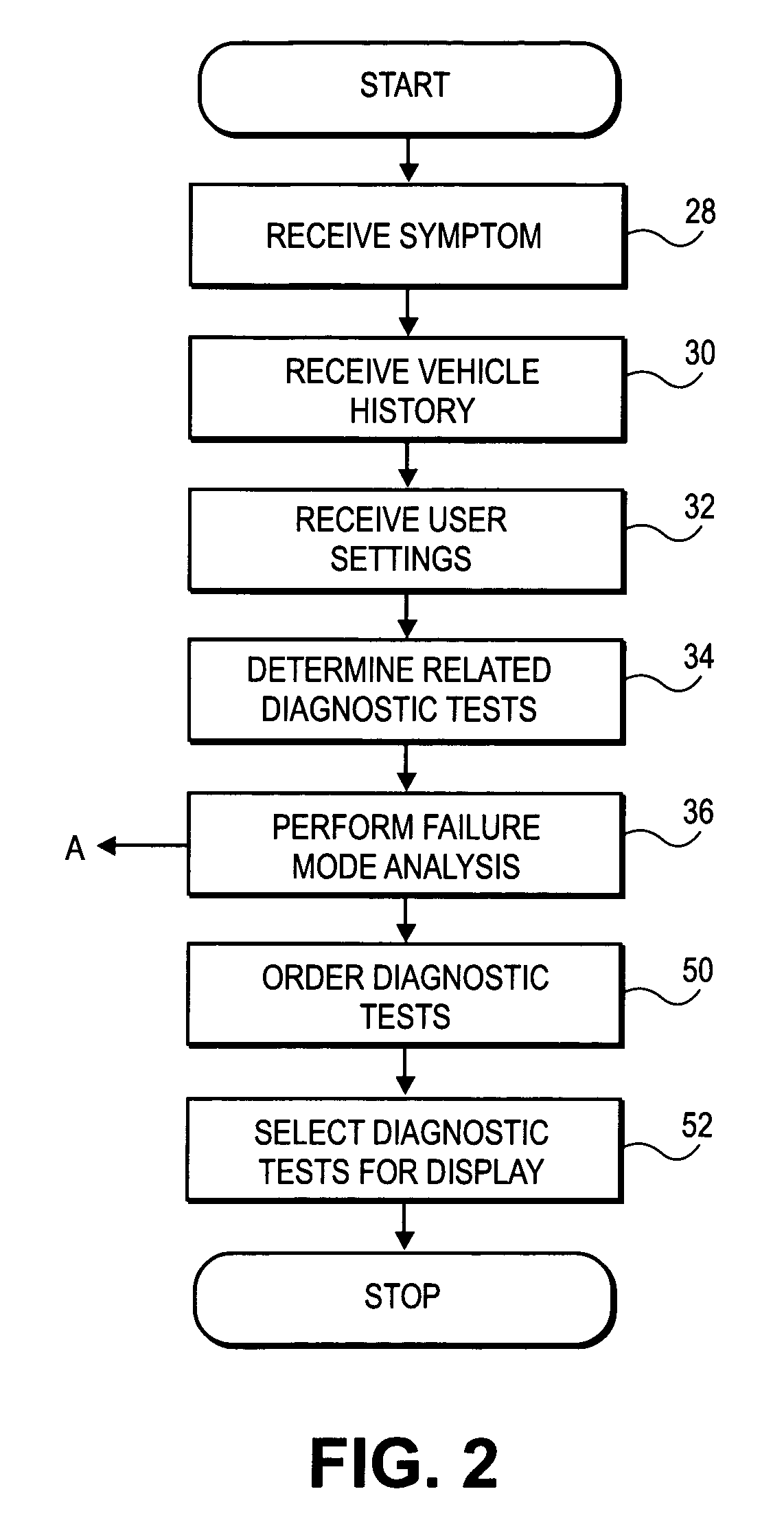
Diagnostic test sequence optimization method and apparatus
ActiveUS7865278B2Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDiagnostic programDiagnostic test
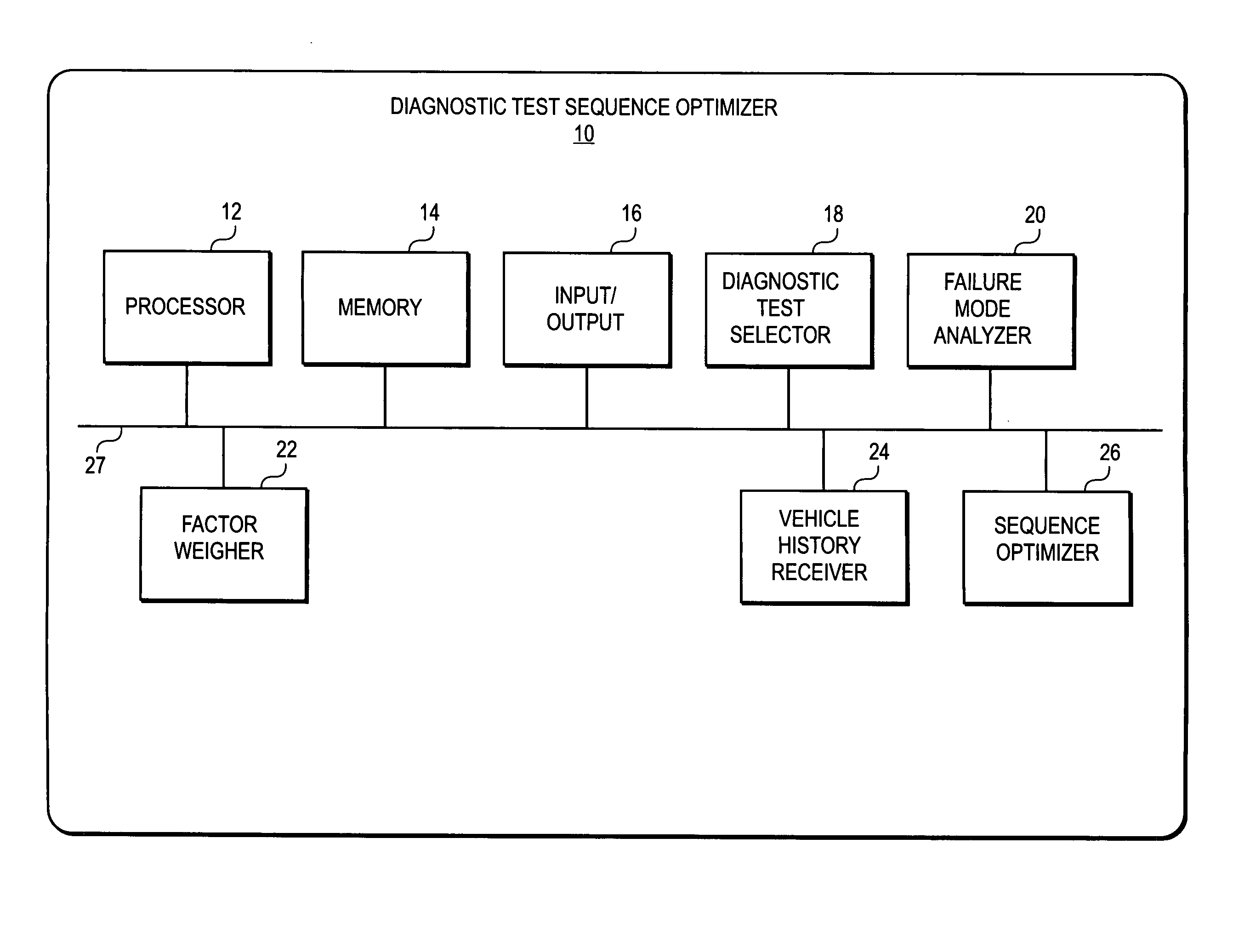
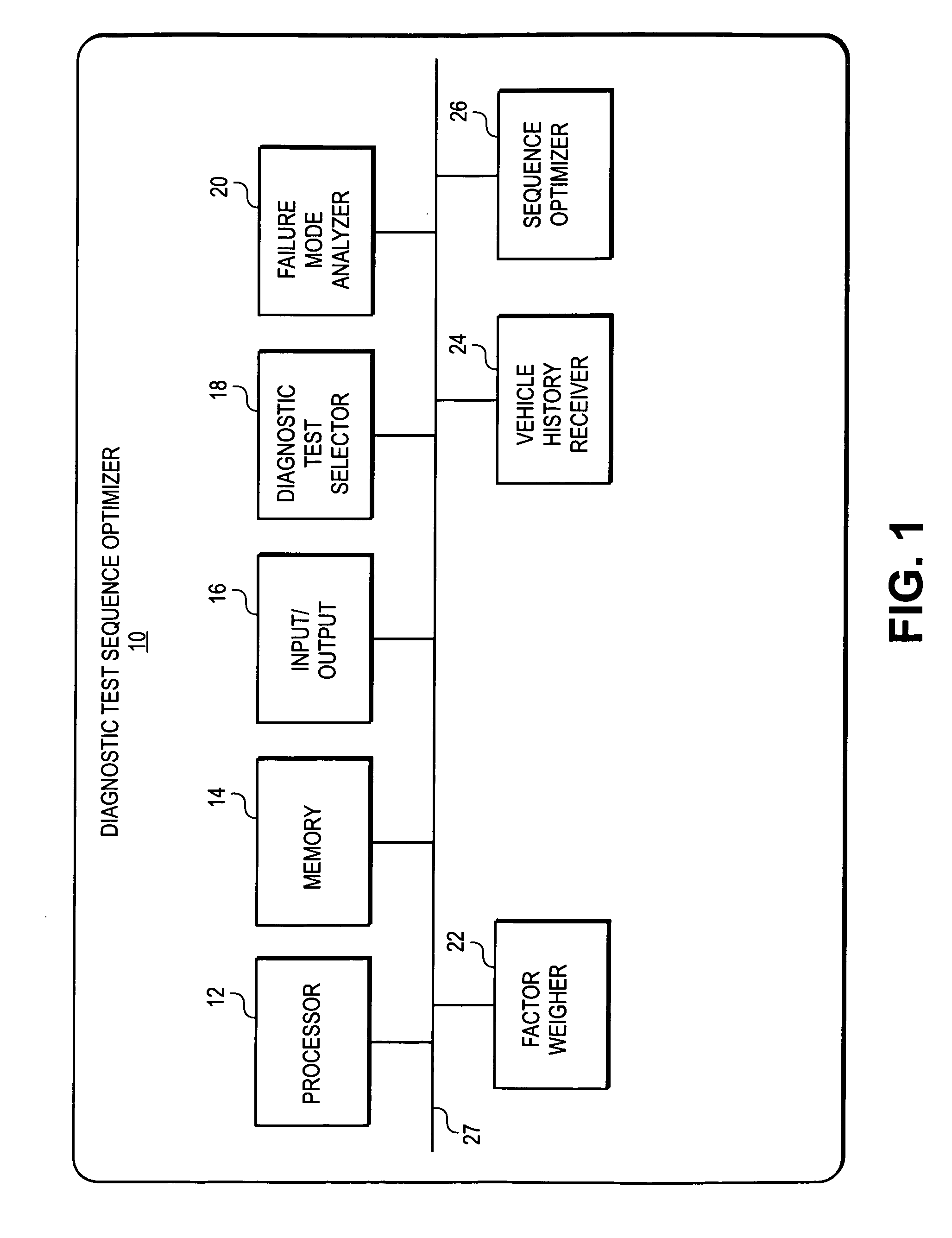
A diagnostic test sequence optimizer includes a diagnostic test selector that determines a group of diagnostic test procedures related to a specific symptom and vehicle type from a pool of diagnostic procedures. A failure mode analyzer then selects one or more factors that can affect resolution of a vehicle operational problem and performs a failure mode analysis to quantify a comparative utility of the individual tests, and a factor weighter assigns a weight to each of the factors. A vehicle receiver receives information regarding the history of the test subject vehicle, and a sequence optimizer places the diagnostic test procedures in an optimized sequence in accordance with the comparative utilities of the individual diagnostic procedures, user preferences and a Failure Mode and Effects Analysis compiled by the manufacturer of the vehicle.
Owner:BOSCH AUTOMOTIVE SERVICE SOLUTIONS
Targeted Equipment Monitoring System and Method for Optimizing Equipment Reliability
InactiveUS20110087517A1Easy to manageClear communicationGeometric CADFinanceGraphicsProgram planning
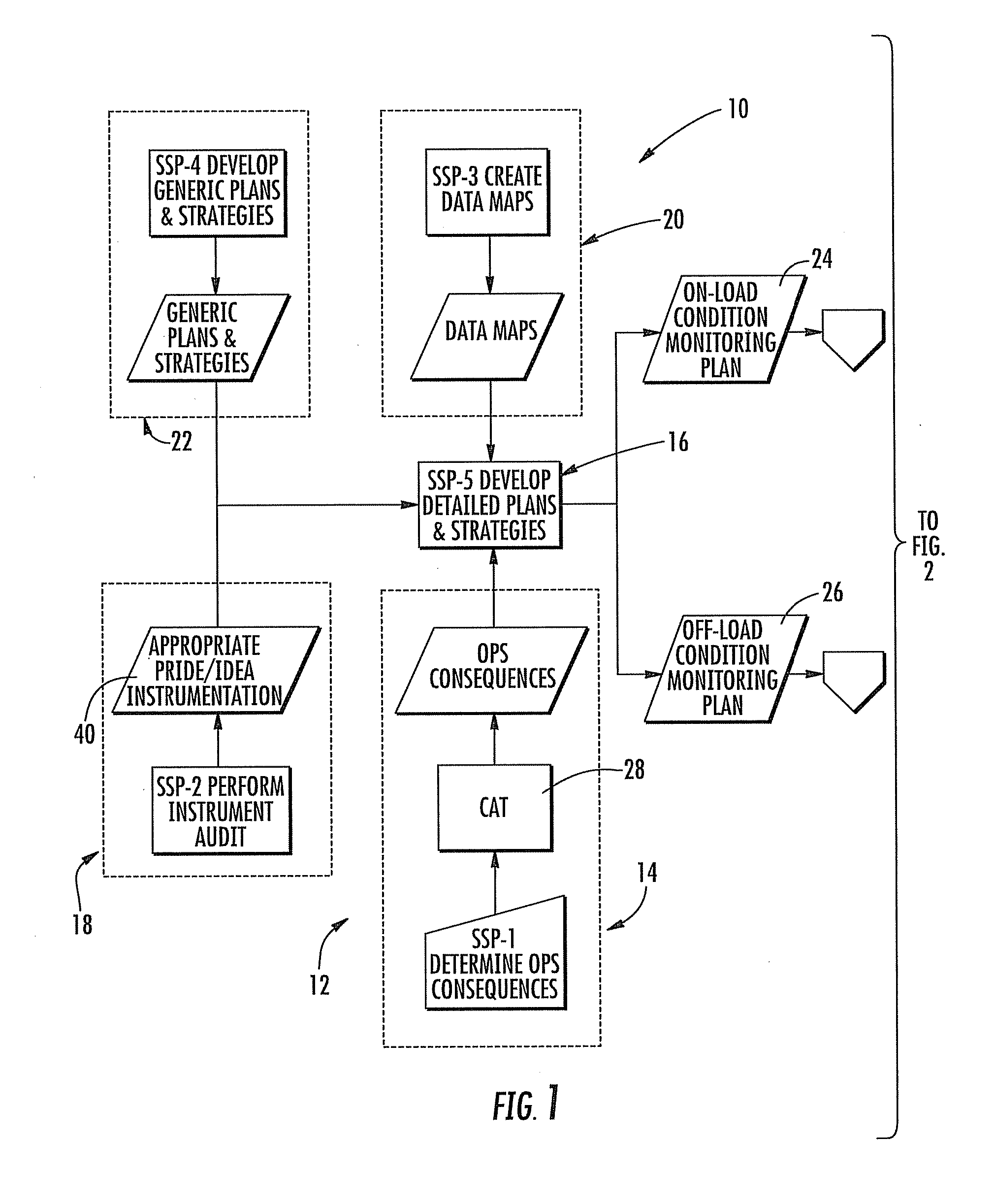
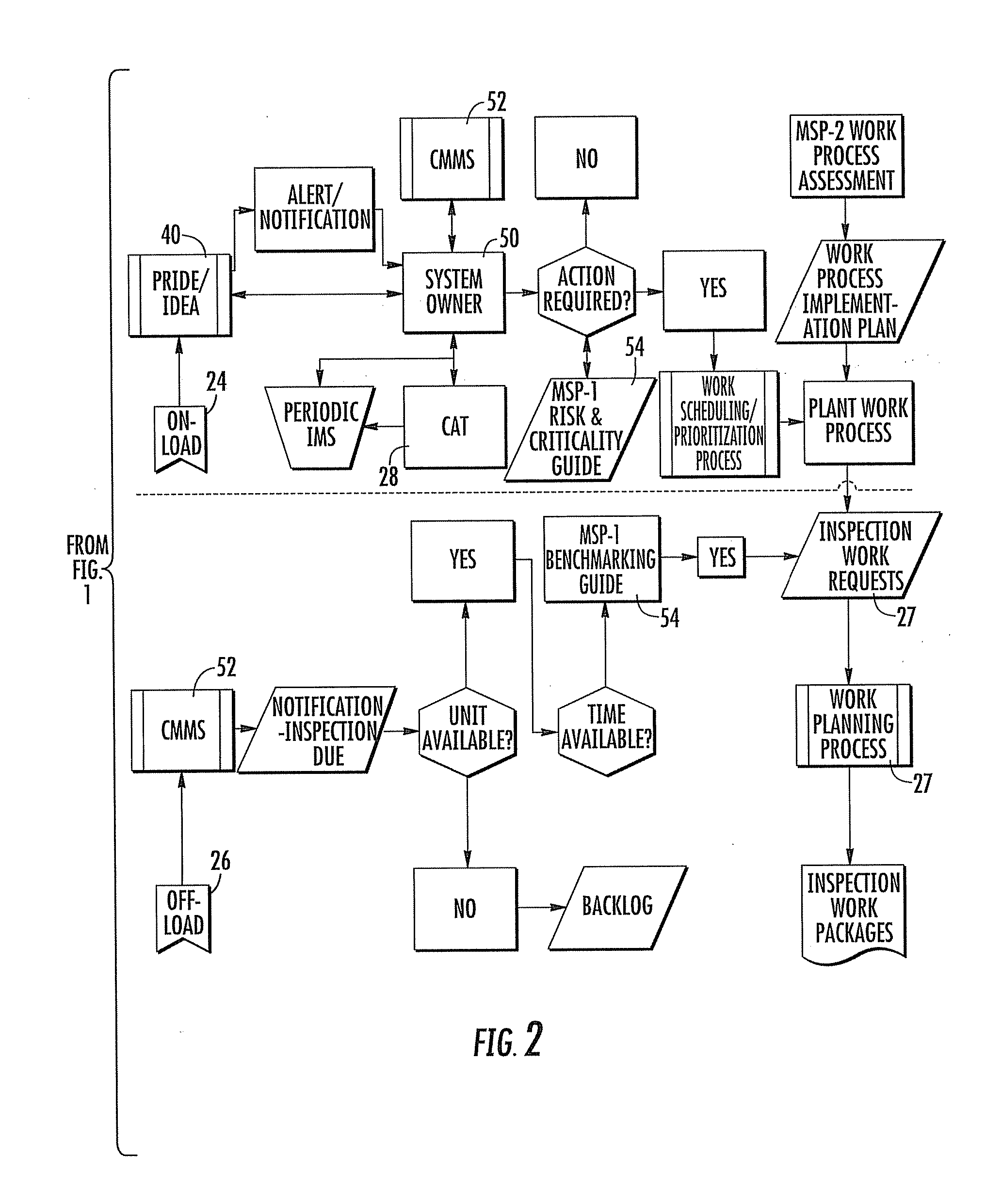
An operating strategy for effectively operating a system, such as a boiler system, is provided by quantifying operation of the system based on failure characteristics modeled in a computer processor performing failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) to forecast damage mechanisms from operational parameters. One method includes determining operational consequences from inherent damage impact of fixed operational parameters, enabling instruments for operation with the processor for monitoring and diagnosing potential damage mechanisms, forming a graphic component map sufficient for user review of preselected system locations, and developing macroscopic in-service and out-of-service condition monitoring plans for the system. Detailed condition monitoring plans are then created from the macroscopic plans by the processor classifying each damage mechanism as one of active, incipient, incidental and passive, and processing each classified damage mechanism based on industry and local historical data for providing yield indices and propensities as reference for the FMEA.
Owner:ABBOTT PATRICK D
Risk charts for failure mode and effect analysis
InactiveUS20120254710A1Easy to optimizeNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsComputer scienceUser interface
A method to facilitate a failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA) project associated with one or more components or process during a product development cycle is provided. The method includes displaying on the user interface one or more information pages associated with sequential order of elements to be completed by one or more FMEA analysts. The method further involves receiving with an aid of the user interface textual inputs from the one or more FMEA analysts for the one or more information pages associated with the sequential orders of elements. The method further includes developing a risk chart for tracking a risk mitigation progress for the FMEA project associated with the one or more components or process during the product development cycle. The risk charts include a Criticality Matrix Risk Chart (CMRC) and a Pro-active Reliability Risk Chart (PRRC).
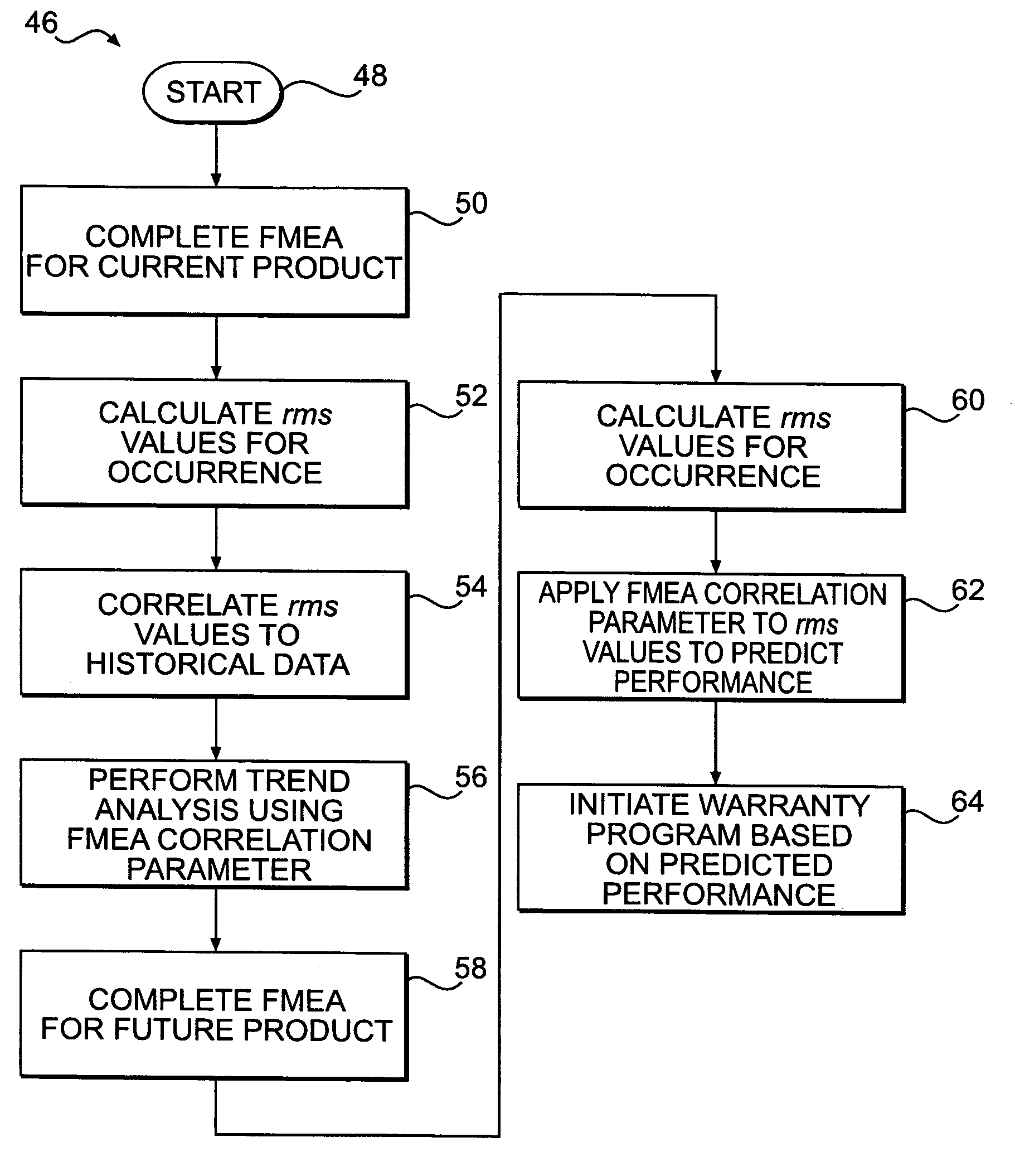
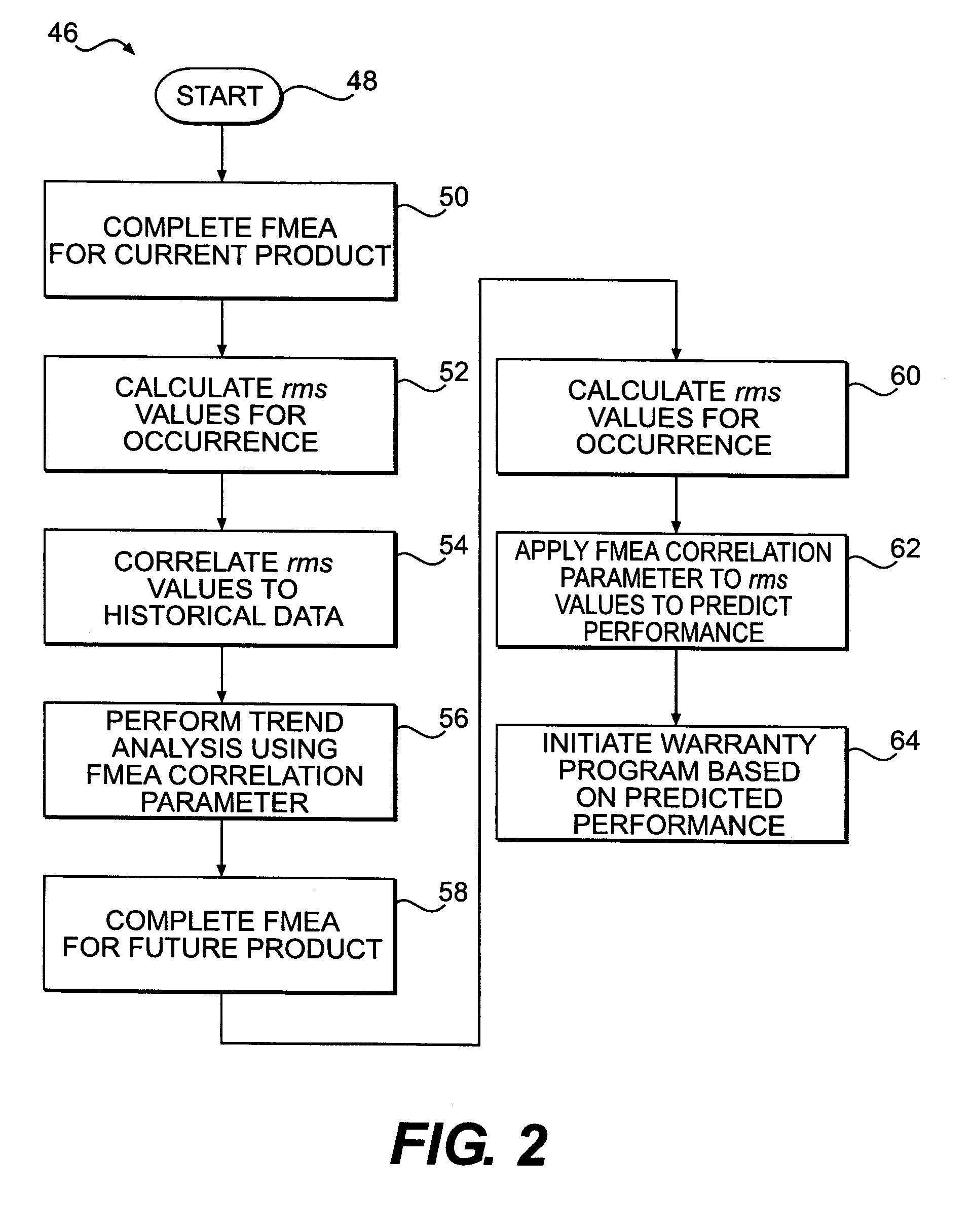
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
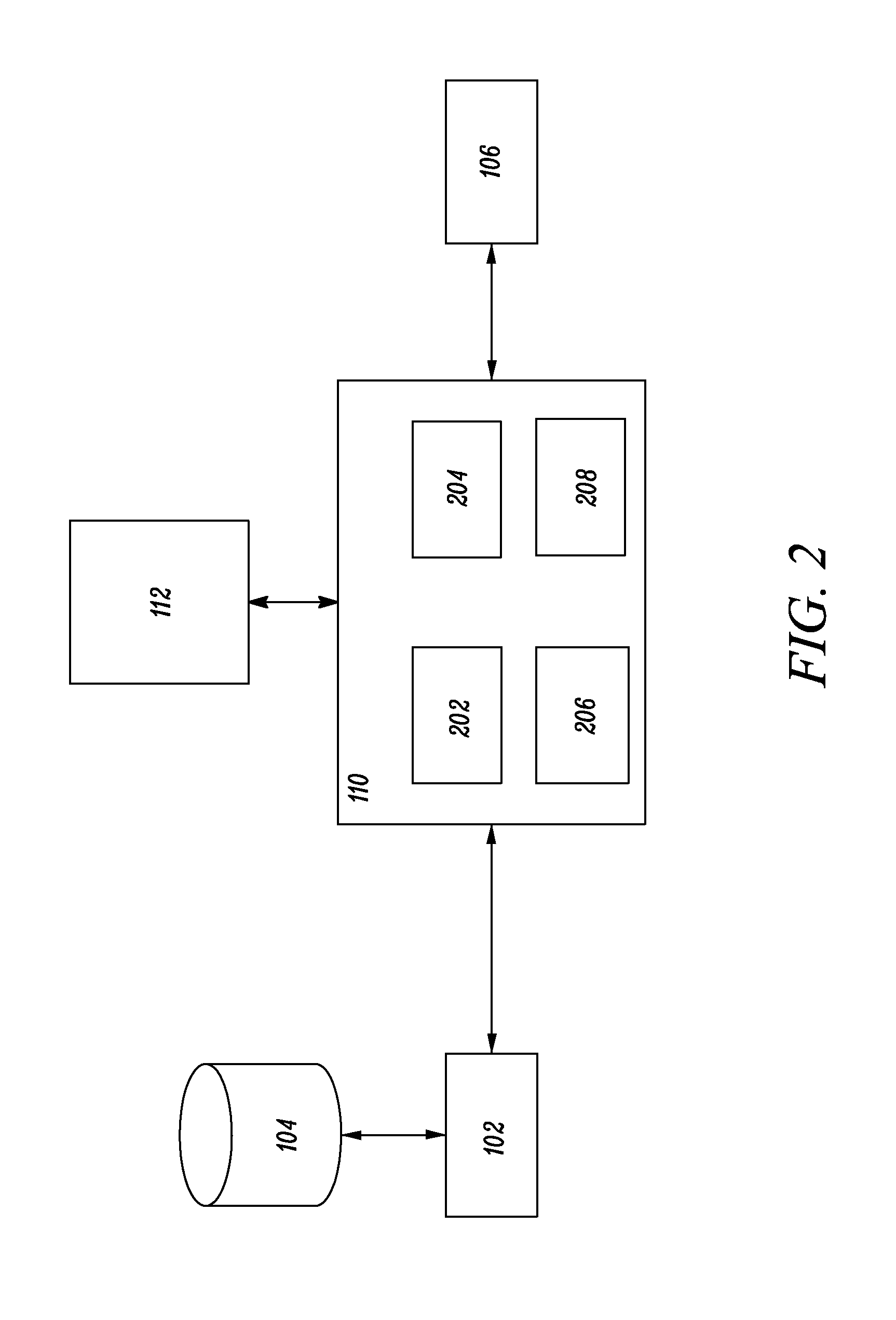
Method, system and computer product for performing failure mode and effects analysis throughout the product life cycle
A method for performing failure mode and effects analysis throughout the product life cycle. The method comprises receiving incident data from a requestor. The incident data includes a requestor product and a requestor fault mode. A shared failure mode and effects analysis database is accessed and searched for an existing entry that includes the incident data. The contents of the existing entry are transmitted to the requestor in response to locating an existing entry.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
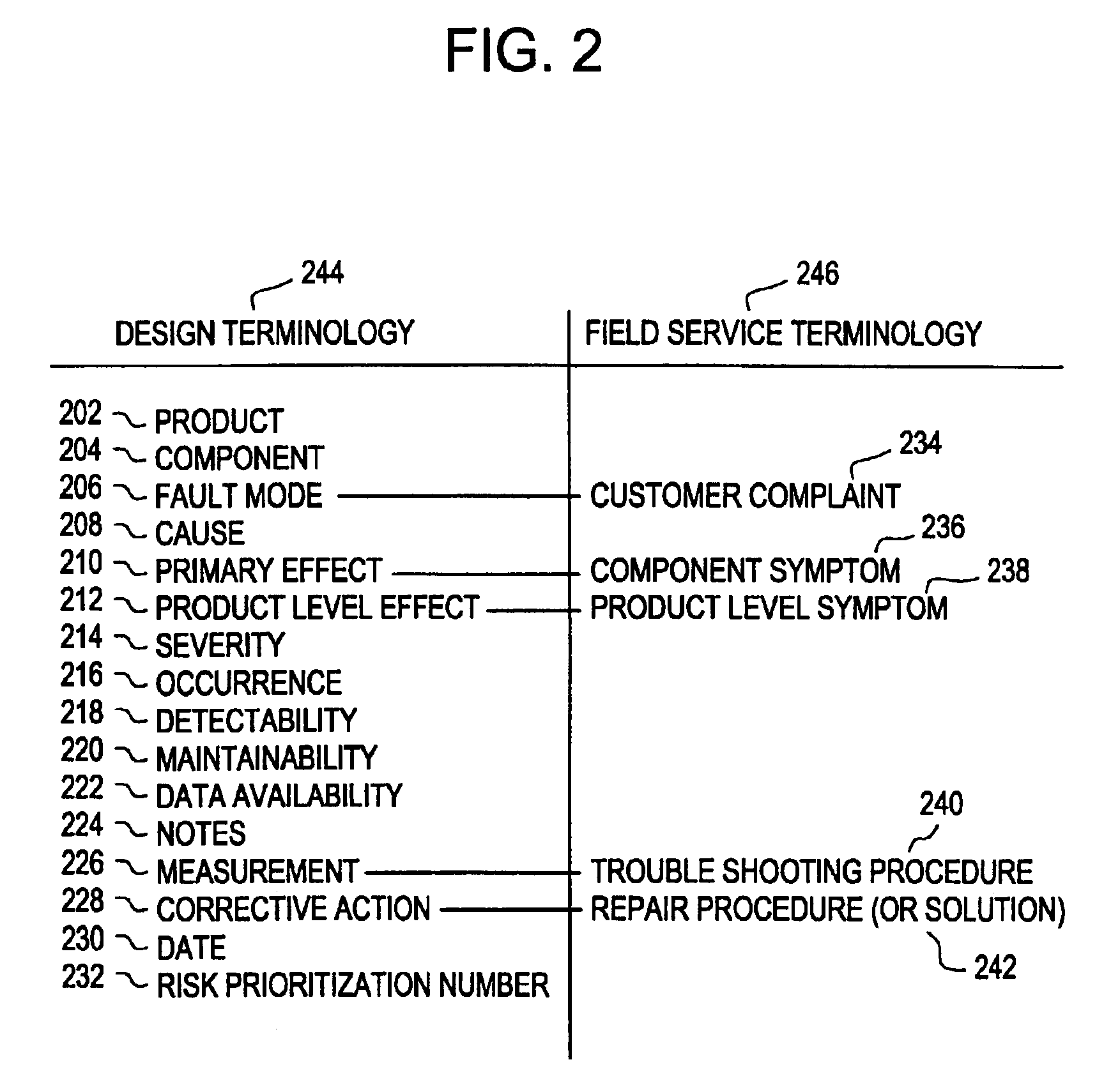
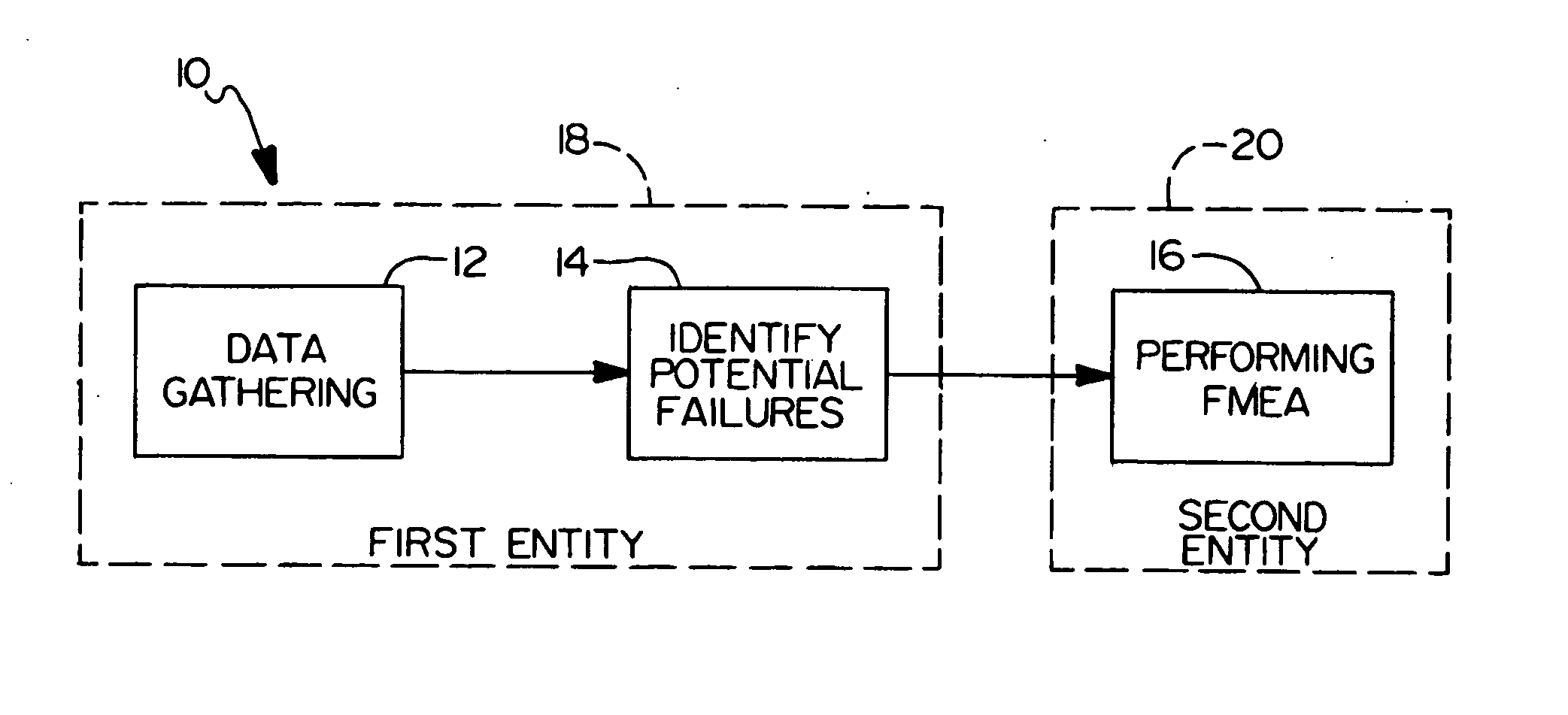
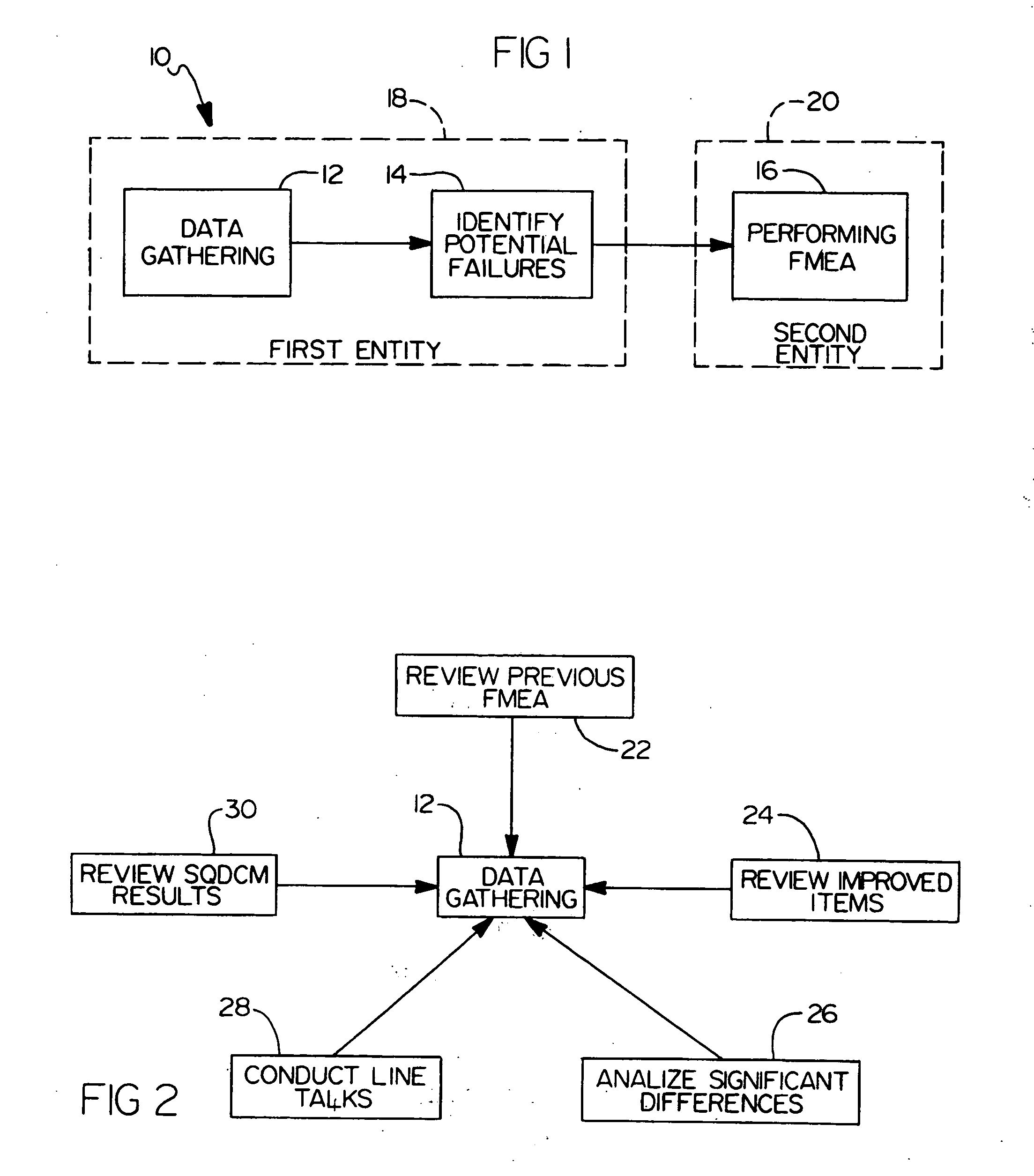
Method for performing failure mode and effects analysis
A method for performing failure mode and effects analysis of an intended process includes gathering data related to failures and deficiencies occurring in a similar process. Then, potential failures and deficiences are identified in the intended process by a first entity based on the gathered data. Finally, a failure mode and effects analysis is performed on the intended process by a second entity based on the potential failures identified by the first entity.
Owner:DAIMLER CHRYSLER CORP
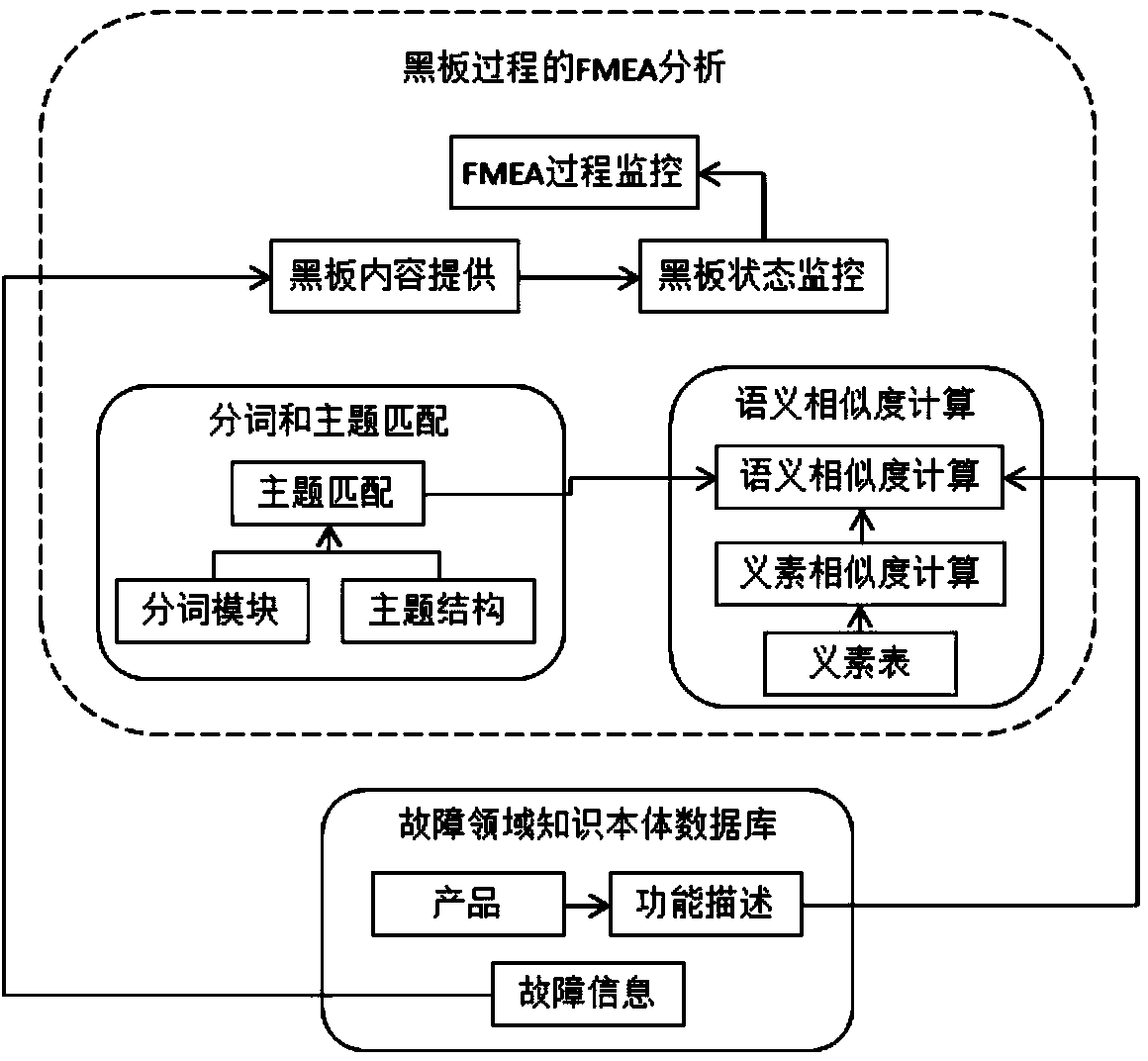
Failure knowledge storage and push method for FMEA (failure mode and effects analysis) process
ActiveCN104361026AQuality improvementQuick digWeb data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsComputer moduleAnalysis working
The invention relates to a failure knowledge storage and push method for the FMEA (failure mode and effects analysis) process. The failure knowledge storage and push method comprises four parts in eight steps: 1, creating a failure product storage module; 2, constructing a failure information storage module; 3, constructing a failure knowledge storage module based on the ontology theory; 4, constructing a word segment module for a failure mode description statement; 5, constructing a failure mode theme matching module; 6, enabling a semantic description model to describe a failure mode theme obtained in the step 2 of the part 2 by using a WDF (word description model); 7, calculating the semantic similarity of information in a failure database and the to-be-inquired fault mode theme; and 8, sequentially reasonably determining the fault mode, the fault reason and the fault influence of a designated product from the lowest indenture level to the initial indenture level of the product according to the step-by-step solution characteristics of the blackboard process. The failure knowledge storage and push method for the FMEA process achieves the effective storage and management and the efficient utilization of the history failure data, and completes the analysis work of the FMEA from the lowest indenture level to the initial indenture level.
Owner:北京可维创业科技有限公司
Method to facilitate failure modes and effects analysis
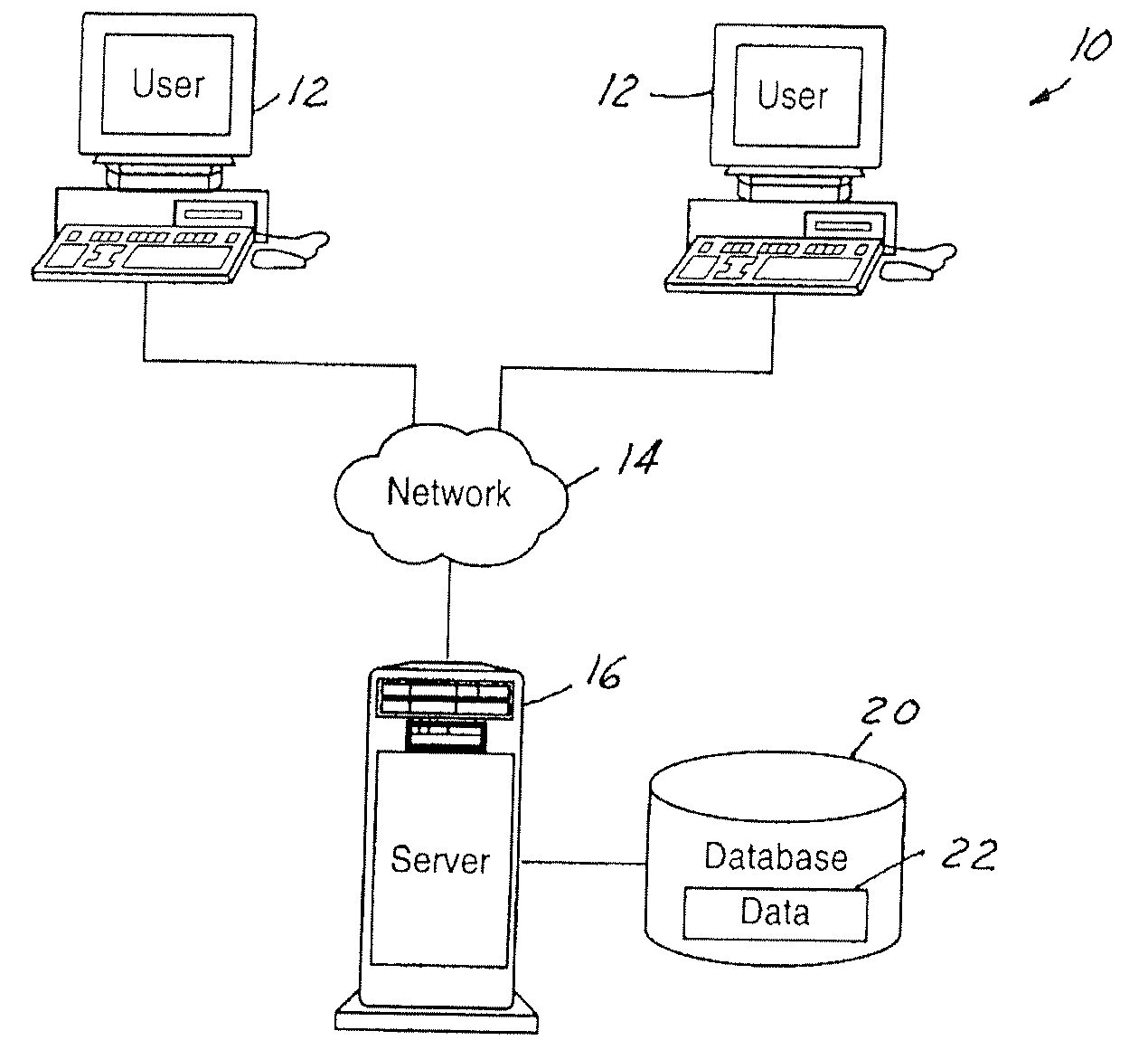
ActiveUS20050138477A1Promote generationProvide robustnessProgramme controlError detection/correctionGraphicsGraphical user interface
A method and system to facilitate failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA) of one or more components of a system. The FMEA is indicated with the generation of an FMEA form. A graphical user interface provides a sequential order of completion for a number of steps. The steps are followed to generate graphical representations which are to be completed by an FMEA analyst and received by the graphical user interface to facilitate generating the FMEA form.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
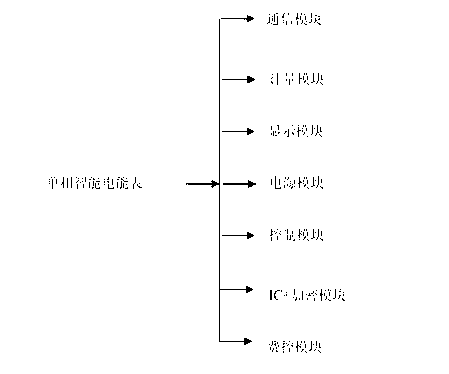
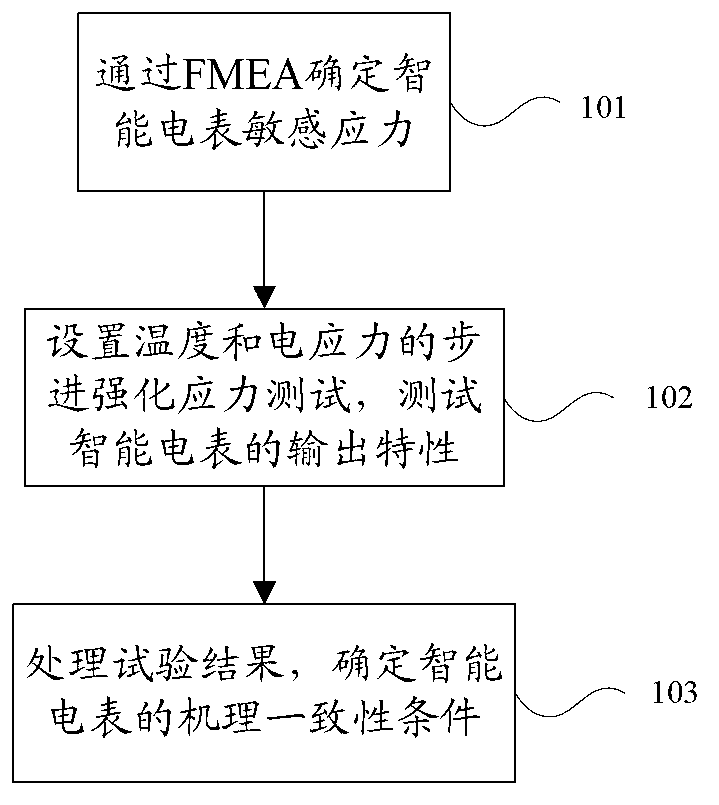
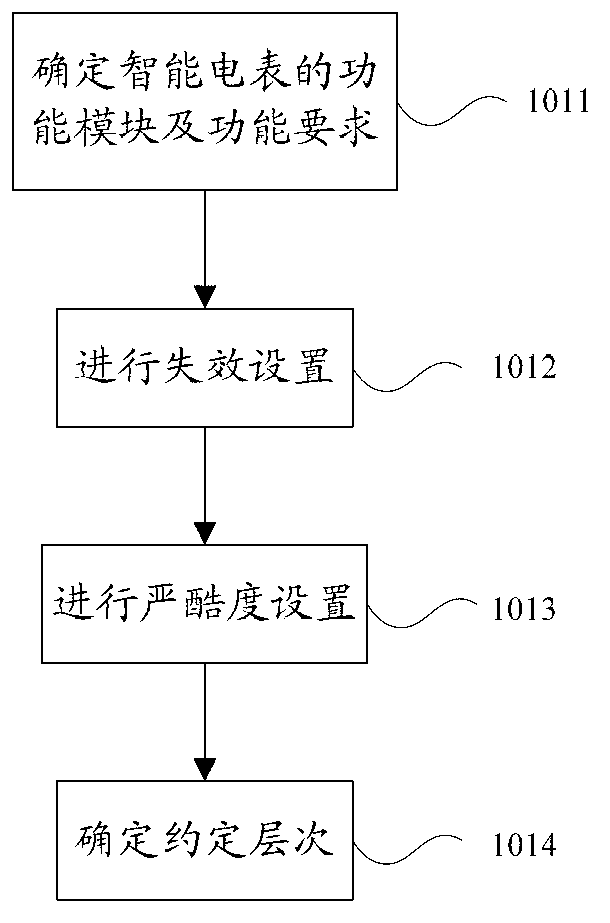
Multi-stress limit determination method for intelligent ammeter
ActiveCN102707257AHardened test data is scarceMake up for the flaws in processing intensive test dataElectrical measurementsSmall sampleElectric stress
The invention discloses a multi-stress limit determination method for an intelligent ammeter. The method comprises the following steps: determining the sensitive stress of the intelligent ammeter through FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis); respectively setting the stepping reinforcement stress tests of both temperature and electric stress; testing the output characteristics of the intelligent ammeter; processing the test result; and determining the mechanism consistency condition. The method provided by the invention is specially for determining the mechanism consistency of the intelligent ammeter and makes up the blank that a matched method specially researched and developed for the intelligent ammeter is unavailable in the present market. The conventional reinforcement test data of the intelligent ammeter is less, and can not be analyzed more accurately by adopting a traditional data processing method. The grey theory method provided by the invention can be used under the small-sample poor-information condition, thereby compensating defects when the reinforcement testing data is processed by the traditional method.
Owner:JIBEI ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY LIMITED CENT OF METROLOGY
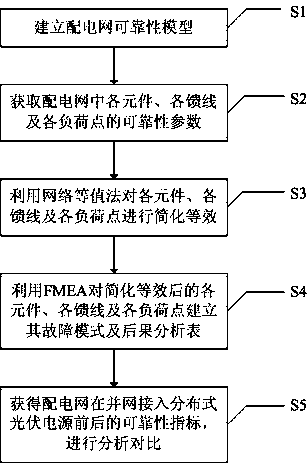
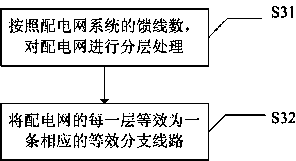
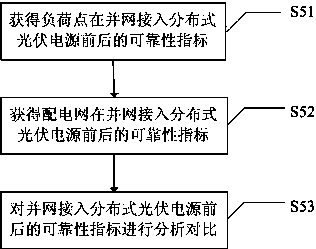
Network equivalent method based power distribution network reliability analysis method and system
ActiveCN104218604AImprove adaptabilityClear principleSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationConsequence analysisElectric power distribution
The invention discloses a network equivalent method based power distribution network reliability analysis method and system. The method includes the following steps: establishing a power distribution network reliability model; acquiring reliability parameters of each component, each feeder and each load point in a power distribution network; performing simplified equivalence on complicated units in the power distribution network by the aid of the network equivalent method; establishing a failure mode and a consequence analysis sheet of each load point, subjected to simplified equivalence, of the power distribution system by means of FMEA (failure mode and effects analysis); acquiring reliability parameters of the load points, and computing and comparing reliability indexes of the entire power distribution network before and after the power distribution network is combined with a grid and connected into a distributed photovoltaic power supply. The system comprises a reliability model establishing unit, a reliability parameter acquisition unit, a simplified equivalence unit, a failure mode and consequence analysis unit and an analysis comparison module. The network equivalent method based power distribution network reliability analysis method and system is clear in principle, simple in model, relative small in calculated amount, high in adaptability and easy to apply to practical engineering.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +2
Dynamic decision sequencing method and apparatus for optimizing a diagnostic test plan
ActiveUS20130185093A1Data processing applicationsMedical automated diagnosisDiagnostic dataDiagnostic test
A dynamic diagnostic plan generator arranges diagnostic test procedures related to a vehicle / power tool / patient symptom or operational problem in a sequence based on a probabilistic Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). The diagnostic plan generator also tracks a vehicle / power tool / patient state, and provides instructions for test preparation steps and instructions for performing the diagnostic test procedures. The plan generator further generates schematic illustrations of the diagnostic test procedures, and creates a diagnostic data structure containing information related to the diagnostic test procedures. In addition, the diagnostic plan generator sends and receives information regarding actual failure mode occurrences, for example, to and from a central database. Furthermore, the diagnostic plan generator facilitates the creation of failure mode tests by an expert diagnostics author.
Owner:BOSCH AUTOMOTIVE SERVICE SOLUTIONS +1
Diagnostic test sequence optimization method and apparatus
ActiveUS20070294000A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDiagnostic programDiagnostic test
A diagnostic test sequence optimizer includes a diagnostic test selector that determines a group of diagnostic test procedures related to a specific symptom and vehicle type from a pool of diagnostic procedures. A failure mode analyzer then selects one or more factors that can affect resolution of a vehicle operational problem and performs a failure mode analysis to quantify a comparative utility of the individual tests, and a factor weighter assigns a weight to each of the factors. A vehicle receiver receives information regarding the history of the test subject vehicle, and a sequence optimizer places the diagnostic test procedures in an optimized sequence in accordance with the comparative utilities of the individual diagnostic procedures, user preferences and a Failure Mode and Effects Analysis compiled by the manufacturer of the vehicle.
Owner:BOSCH AUTOMOTIVE SERVICE SOLUTIONS
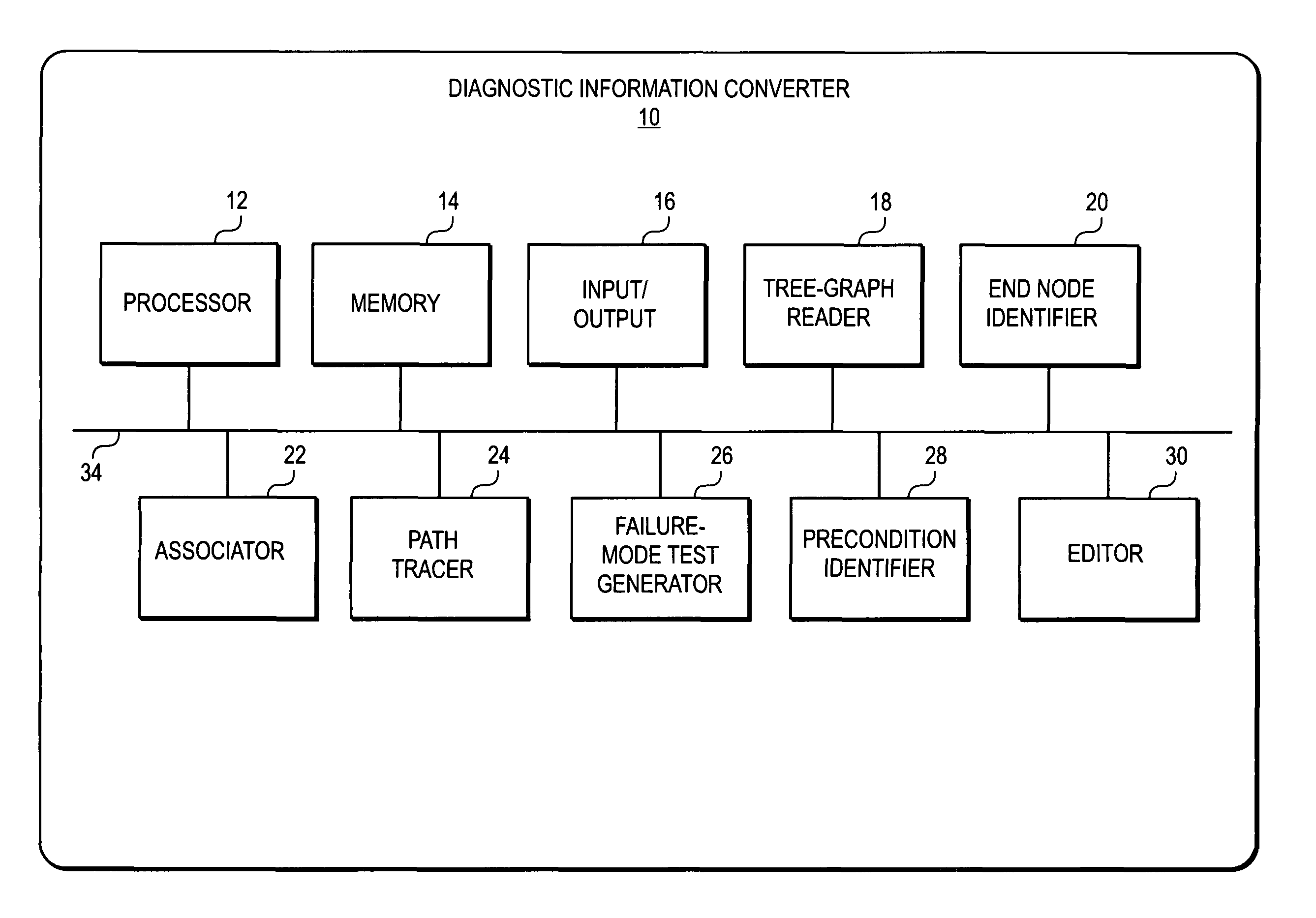
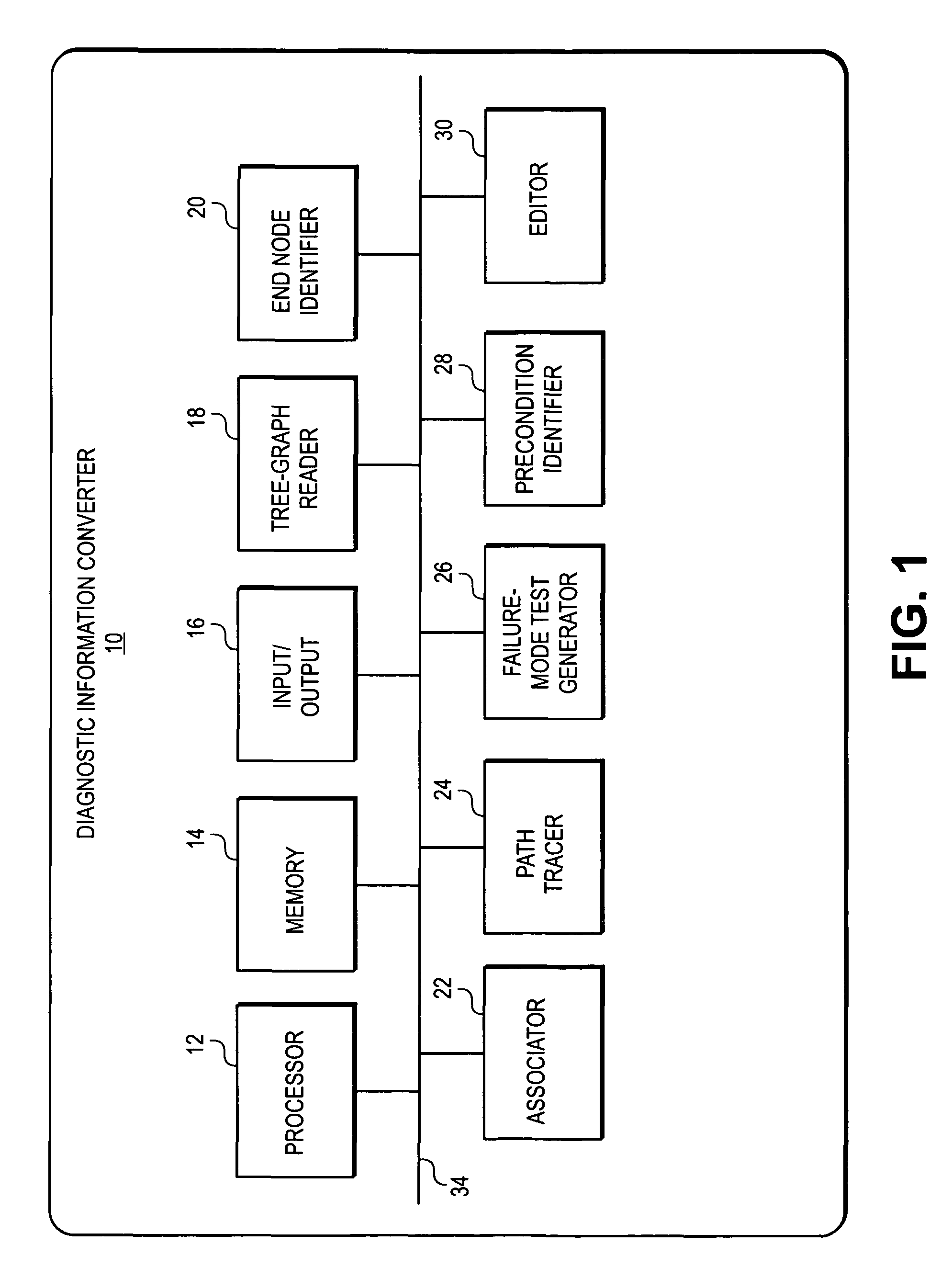
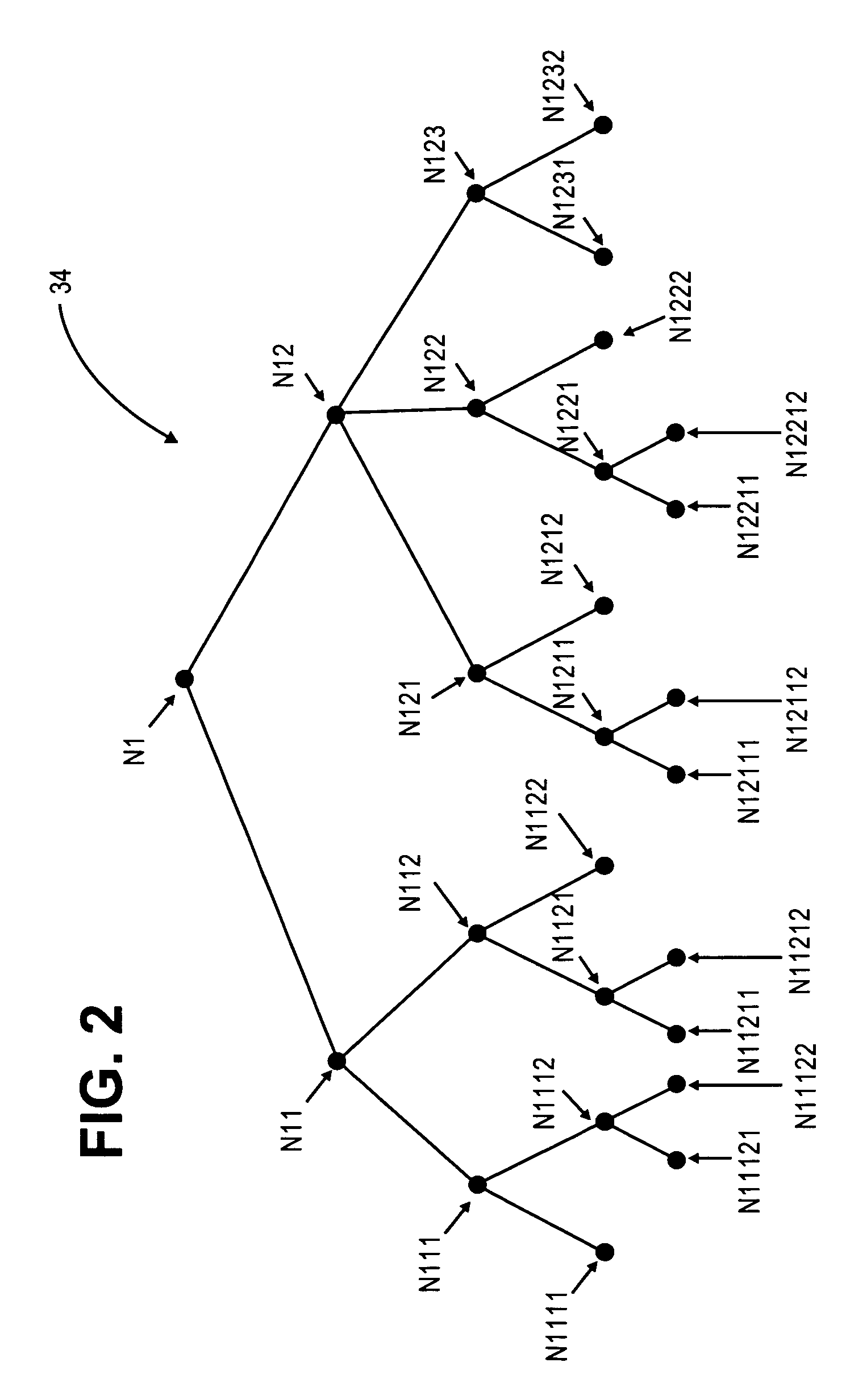
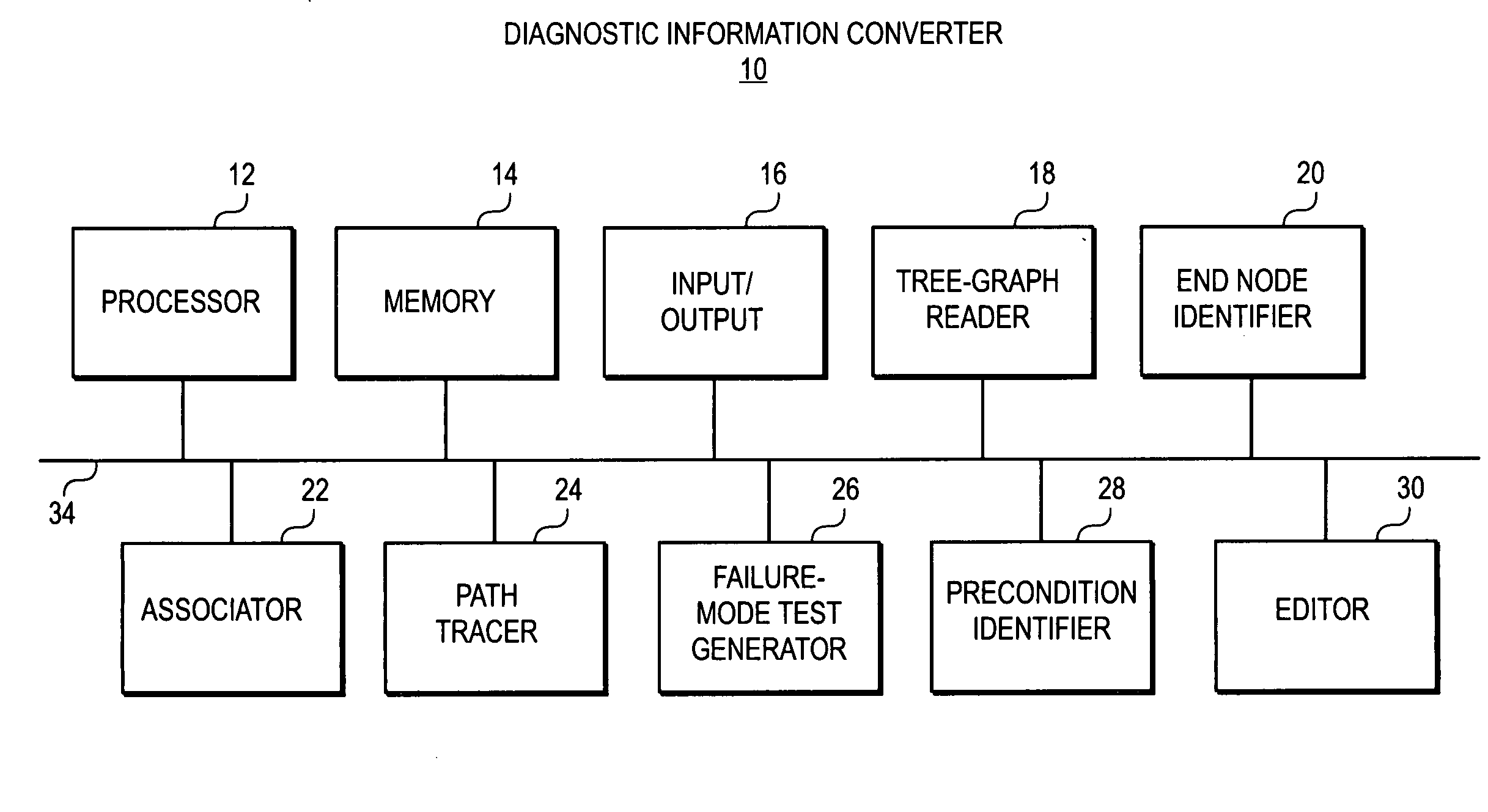
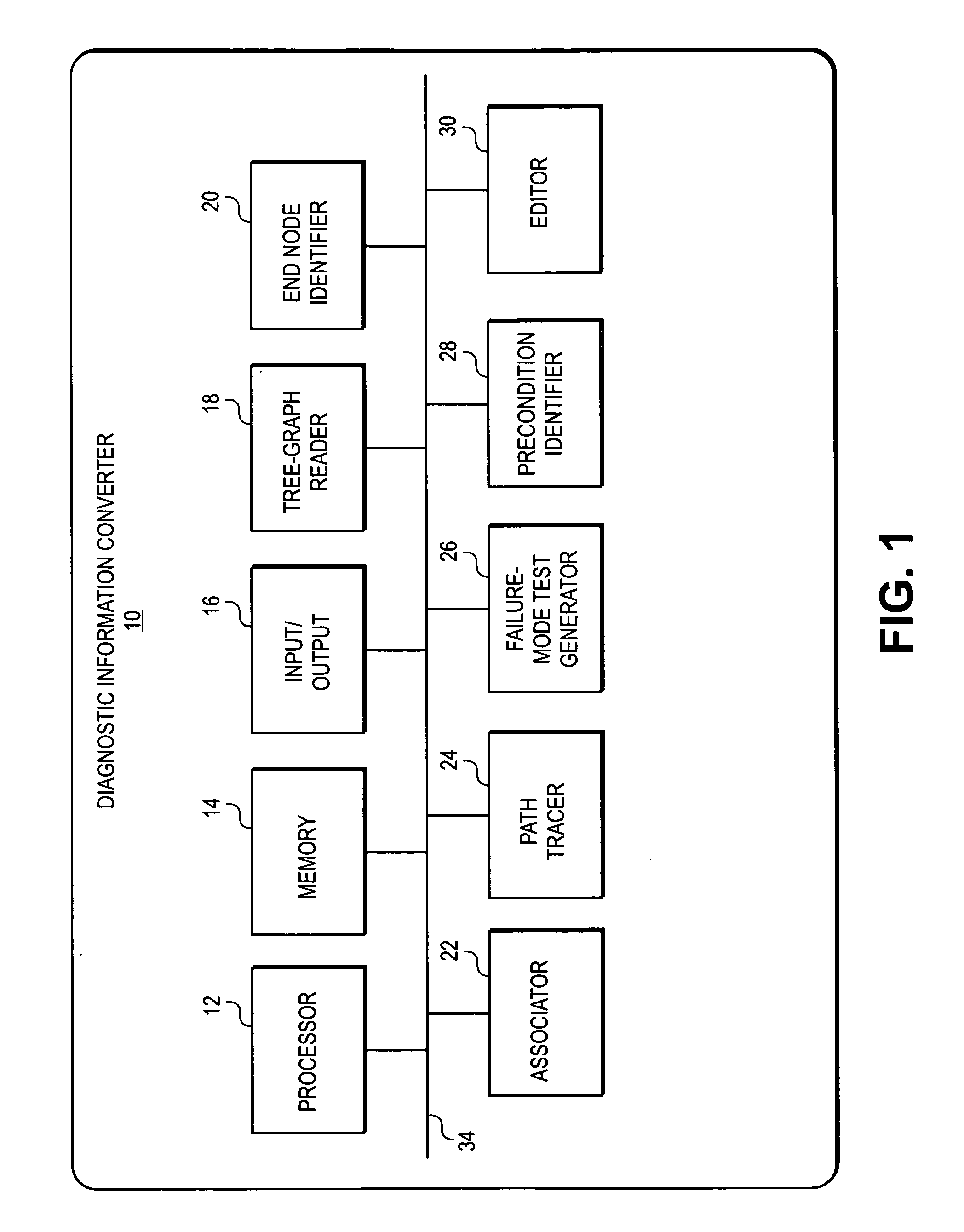
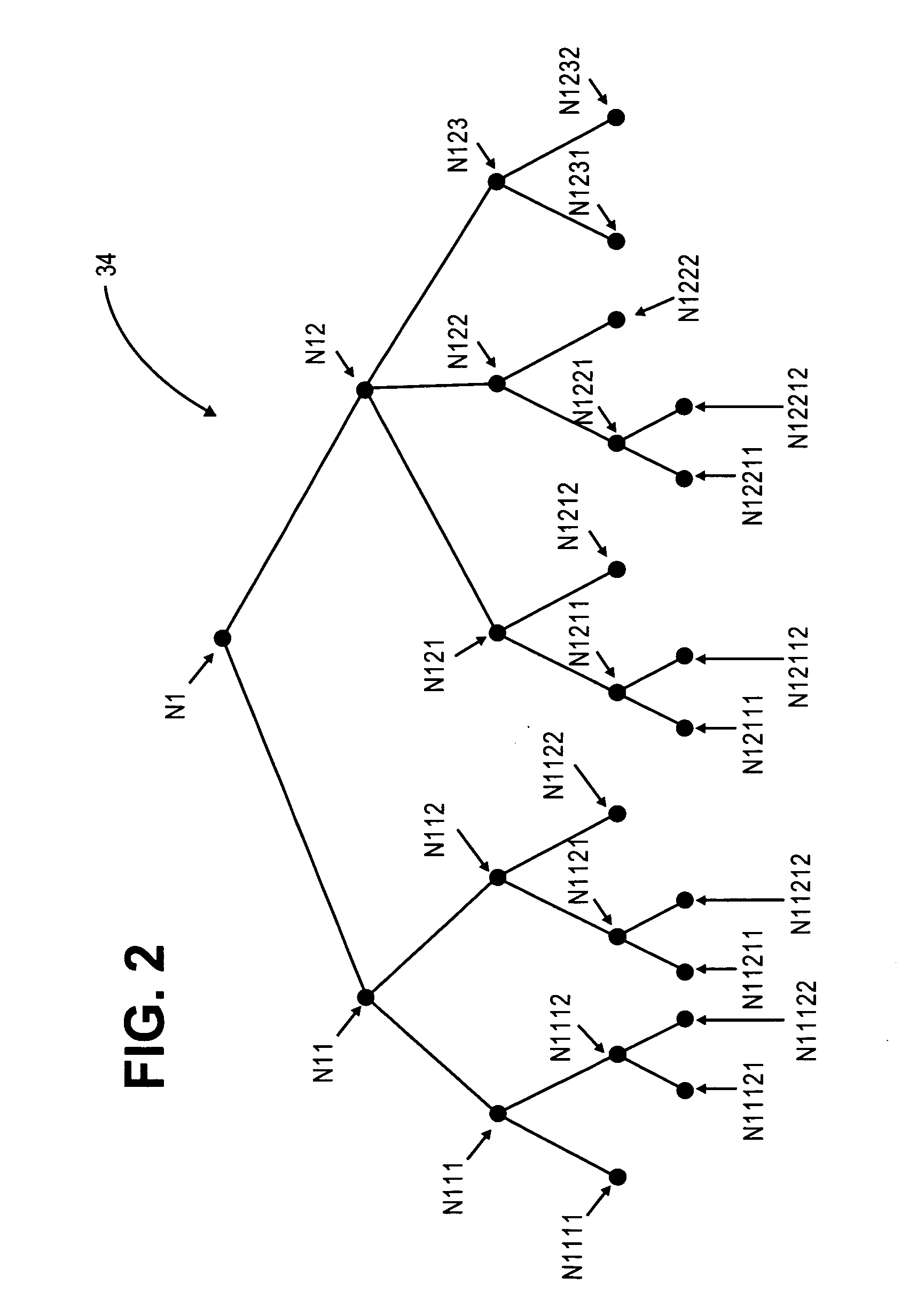
Conversion of static diagnostic procedure to dynamic test plan method and apparatus
A diagnostic information converter reads an existing static diagnostic procedure in the form of a tree graph and generates a diagnostic Failure Modes and Effects Analysis that can be used in the generation of a dynamic diagnostic test plan. The converter identifies the end nodes of the graph and associates a specific failure mode with each of the end nodes. In addition, the converter traces a unique path from each end node along successive branches through one or more intermediate nodes to the root node, and from each of the paths derives an initial failure mode test including the test steps corresponding to the root node, the intermediate nodes and the end node. The converter further identifies and annotates precondition nodes that correspond to a vehicle state or condition, rather than to an actual diagnostic test step and allows a user to edit the initial failure mode tests.
Owner:SPX CORP
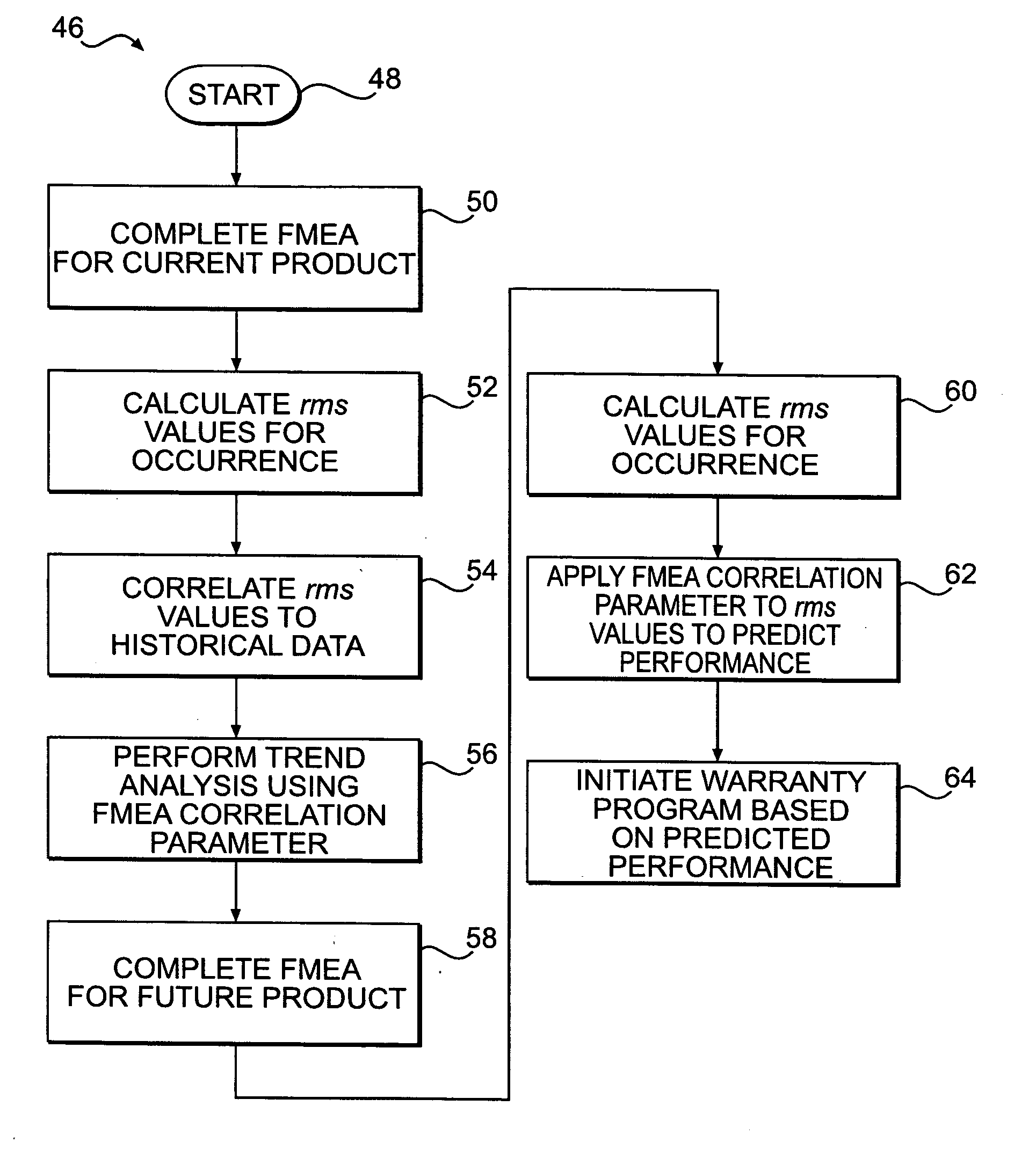
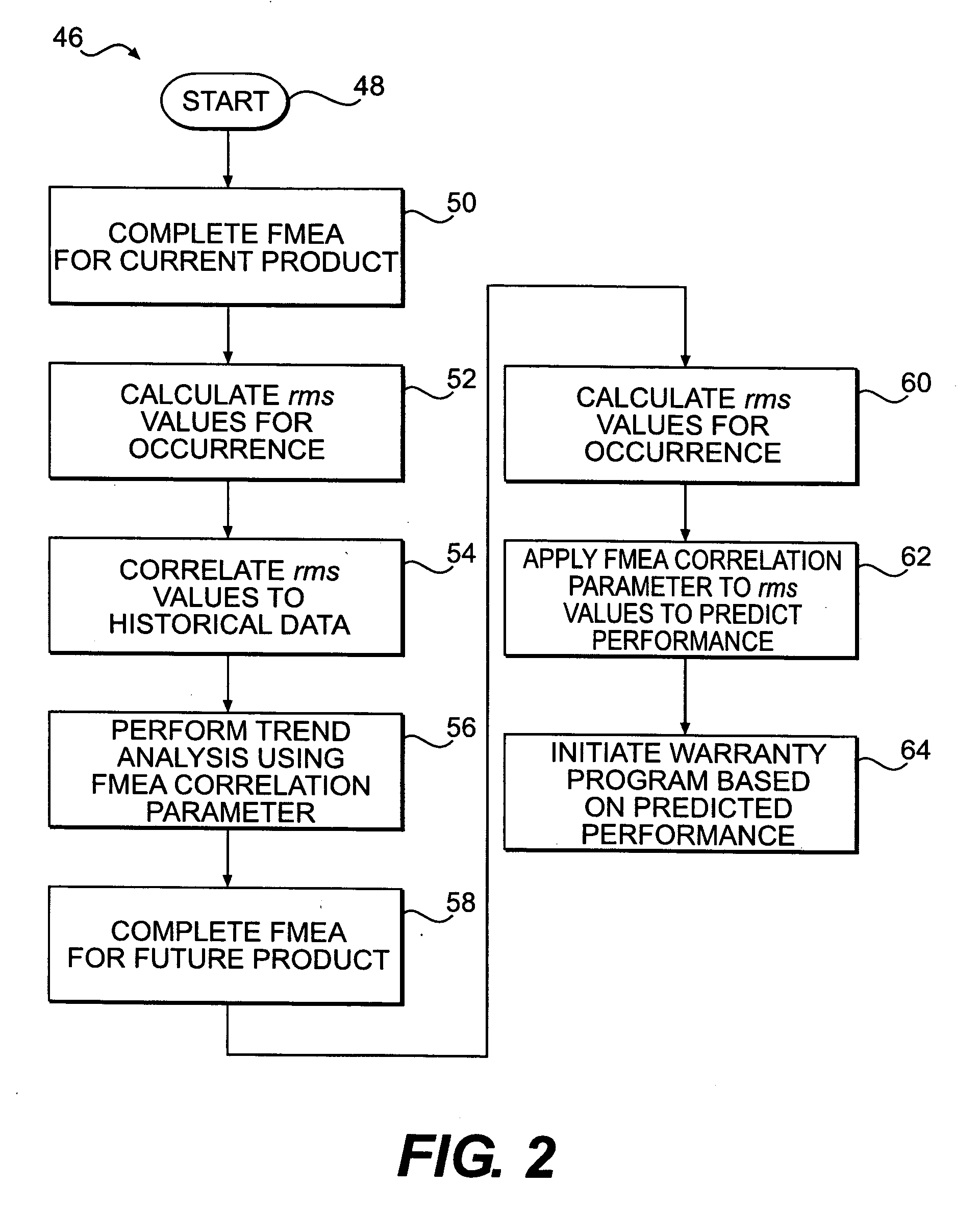
Method for predicting performance of a future product
InactiveUS20060271346A1Predictive performanceNuclear monitoringDigital computer detailsPredicting performanceComputer science
A method for predicting performance of a future product is disclosed. The method includes generating historical data for at least one product and generating a Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) for the at least one product. The method also includes determining a relationship between an FMEA indicator of the FMEA generated for the at least one product and the historical data for the at least one product. The method further includes generating an. FMEA for the future product and applying the determined relationship to the FMEA indicator from the FMEA generated for the future product to predict performance for the future product.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
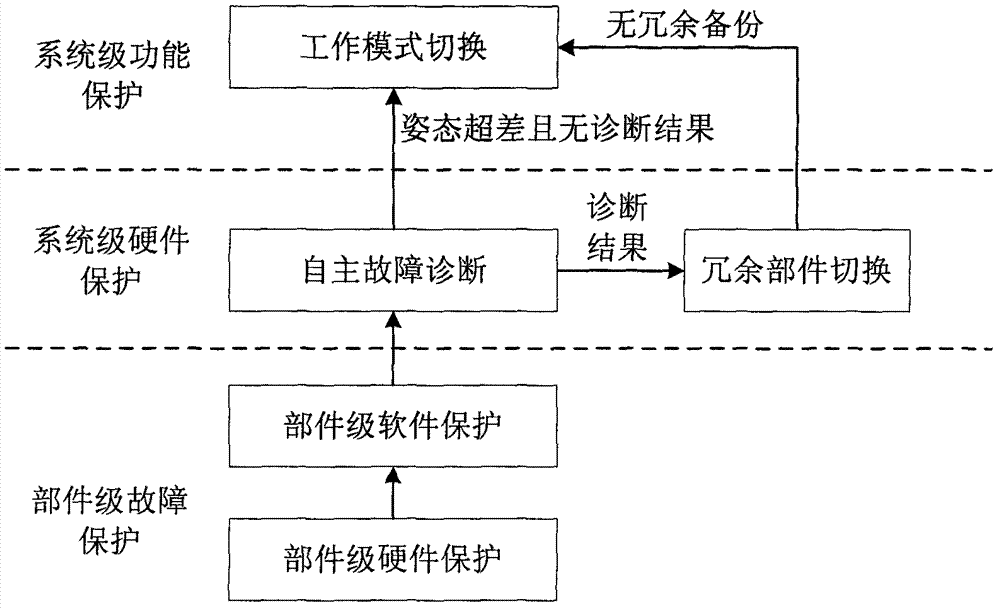
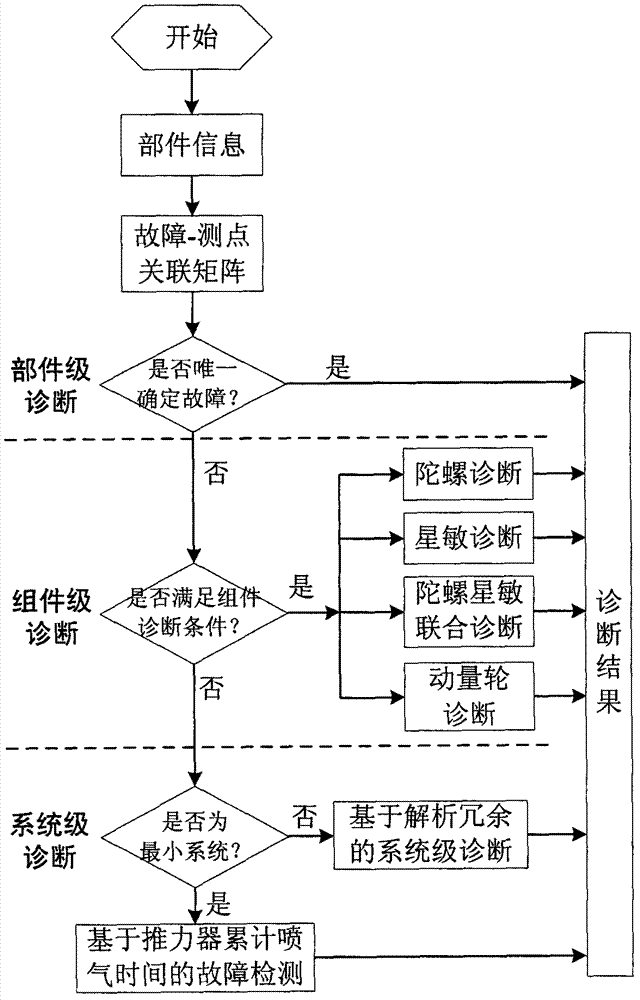
Automatic failure handling and protection method of deep space probe global navigation chart (GNC) system base on layered structure
ActiveCN103034232ACause harmReduce misdiagnosis rateElectric testing/monitoringSpace probeSelf locking
Disclosed is an automatic failure handling and protection method of a deep space probe global navigation chart (GNC) system base on a layered structure. The automatic failure handling and protection method of the deep space probe GNC system base on the layered structure comprises the steps of carrying out hardware protection to avoid a failure which can result in permanent damage or invalidation of other parts or other parts inside a part according to a result of failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), judging whether the data of measuring points are normal with an infrared ray method for other failures, marking the states of parts and handling the data and state information to a controller for analyzing of system-level failures; carrying out failure analyzing according to the state information and the data of the measuring points handed to the controller: if hardware redundancy or analysis redundancy exists, a failure part is switched to a normal redundancy part; if the hardware redundancy or the analysis redundancy dose not exist, the next step is carried out; switching to a counter-glow orientation mode when the prior step can not position a failure source or no redundant backup can replace the failure source and gesture is pretty poor and directing is out of control, switching off equipments not necessary for flying of a deep space probe to reduce power consumption, and switching off a self-locking valve and switching to a control-stop mode to reduce propellant consumption of the probe when the probe is out of control, a pushing system spray gas at random and star bodies roll.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
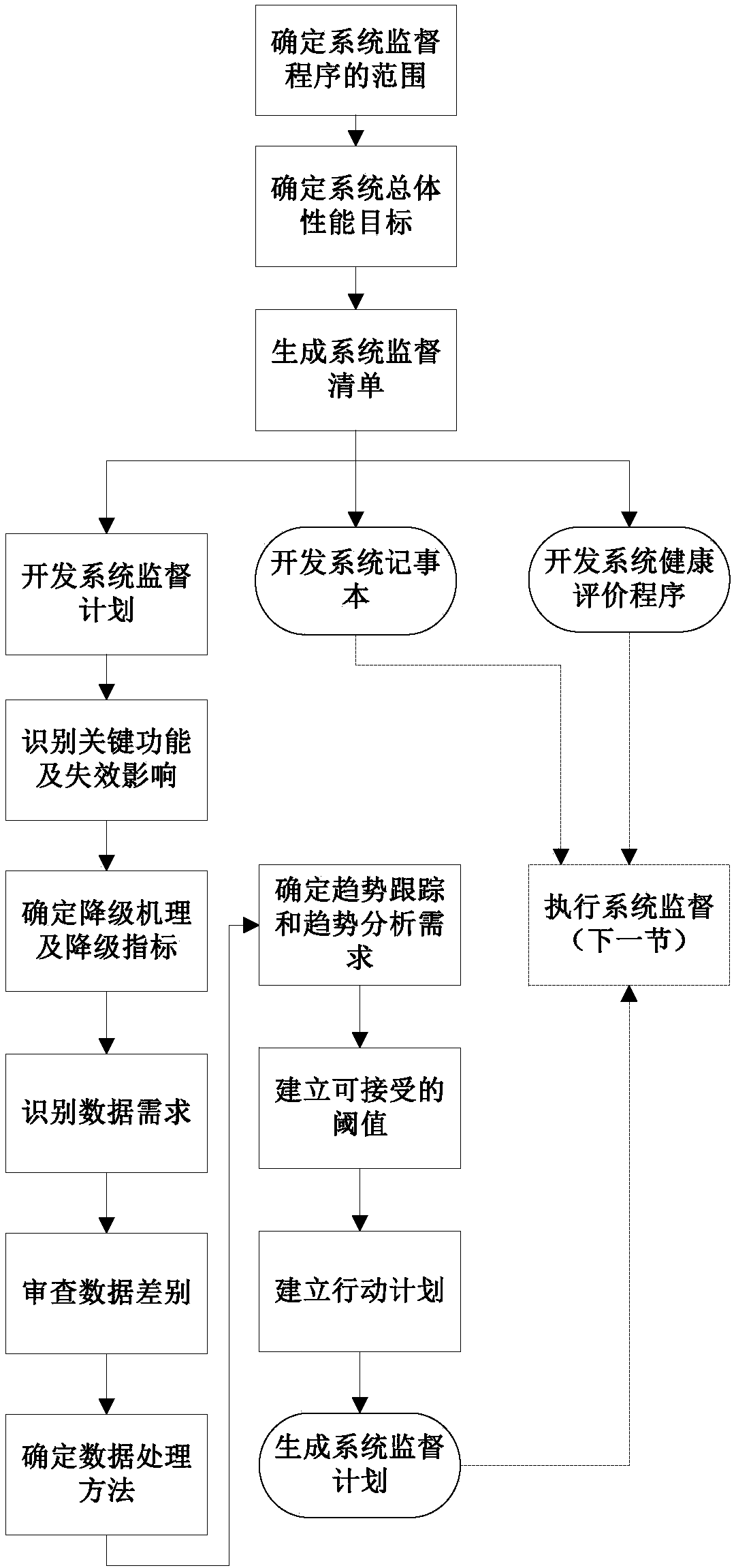
Nuclear power plant system supervision method based on ERDB
InactiveCN108256713AGuaranteed operational safetyImprove reliabilityResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsPower stationNuclear power
The invention relates to the technical field of nuclear power plant equipment reliability management, and specifically discloses a nuclear power plant system supervision method based on ERDB. The supervision method comprises the steps that 1 the supervision scope of a nuclear power plant system is determined to form a system supervision list; 2 the performance target level of the system supervision list is classified according to the health status of the nuclear power plant system or equipment; 3 a system notebook module is used to automatically generate and query the supervision data of the system; and 4 system supervision is carried out on the nuclear power plant system or equipment. According to the method, system and equipment important for nuclear safety and power generation are identified through system function analysis; through failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA), the degradation mechanism and monitoring parameters of the equipment are identified; the degradation of the equipment is found and predicted in advance through monitoring and trend analysis of the parameters; and corresponding corrective actions are taken in time to improve the reliability of the equipment toensure the safe operation of a power station.
Owner:CNNC NUCLEAR POWER OPERATION MANAGEMENT
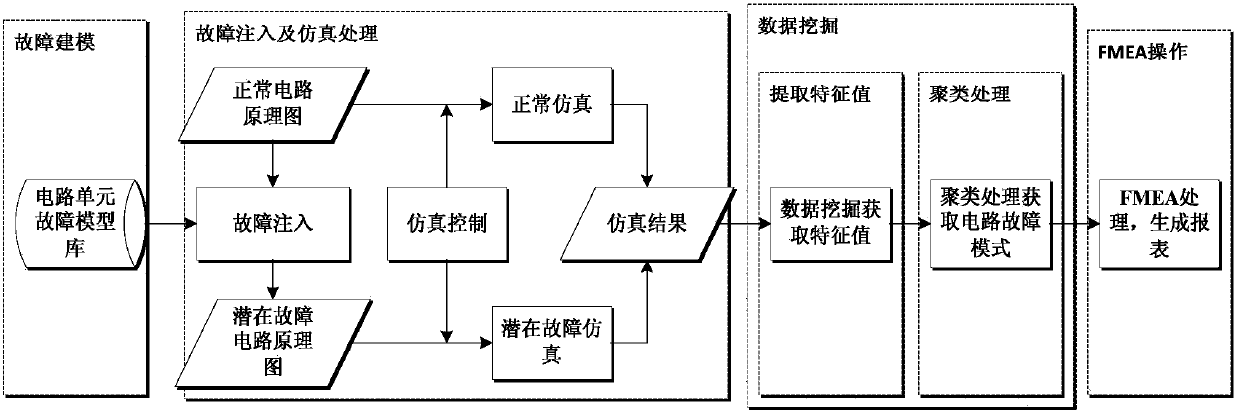
Data mining-based hardware circuit FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) method
The invention discloses a data mining-based hardware circuit FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) method. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a corresponding failure simulation model specific to the failure signature way of research elements, traversing each element in a normal circuit, injecting the failure model of each element, acquiring a potential failure circuit, and generating a normal circuit simulation result and failure circuit simulation results in a simulation tool; comparing each failure circuit simulation result with the normal circuit simulation result, extracting difference characteristic values, and acquiring the failure mode of the hardware circuit by means of clustering analysis of the difference characteristic values; finishing FMEA processing in combination with the failure mode of the hardware circuit according to an FMEA basic method in order to automatically generate a corresponding FMEA report. Through adoption of the data mining-based hardware circuit FMEA method, the requirements on the circuit function cognition and FMEA processing experience of FMEA personnel can be lowered to the maximum extent; the method is simple and efficient.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Product quality improvement feedback method
InactiveUS20140081442A1Avoid problemsSolve the real problemSpecial data processing applicationsInfluence analysisEffect analysis
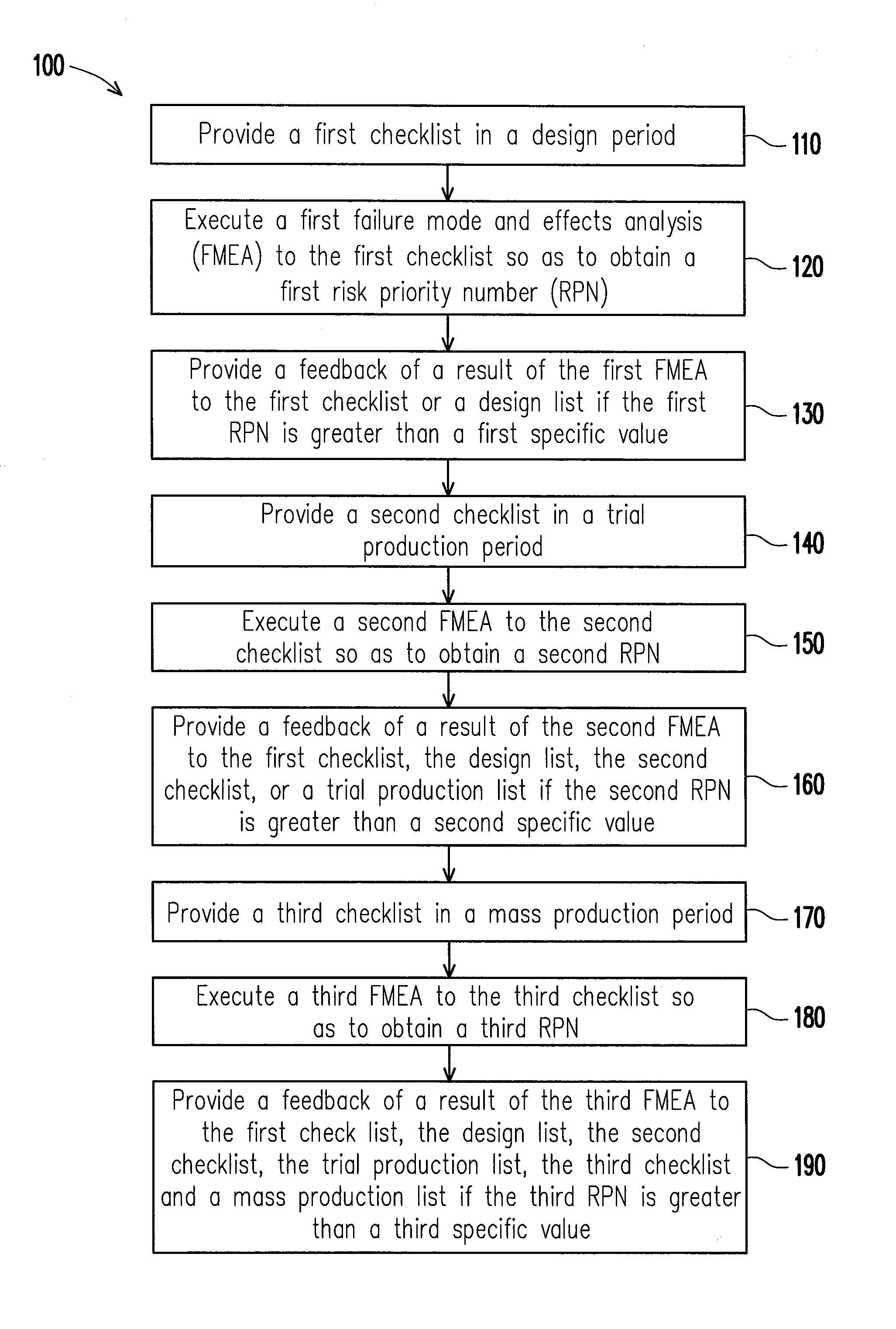
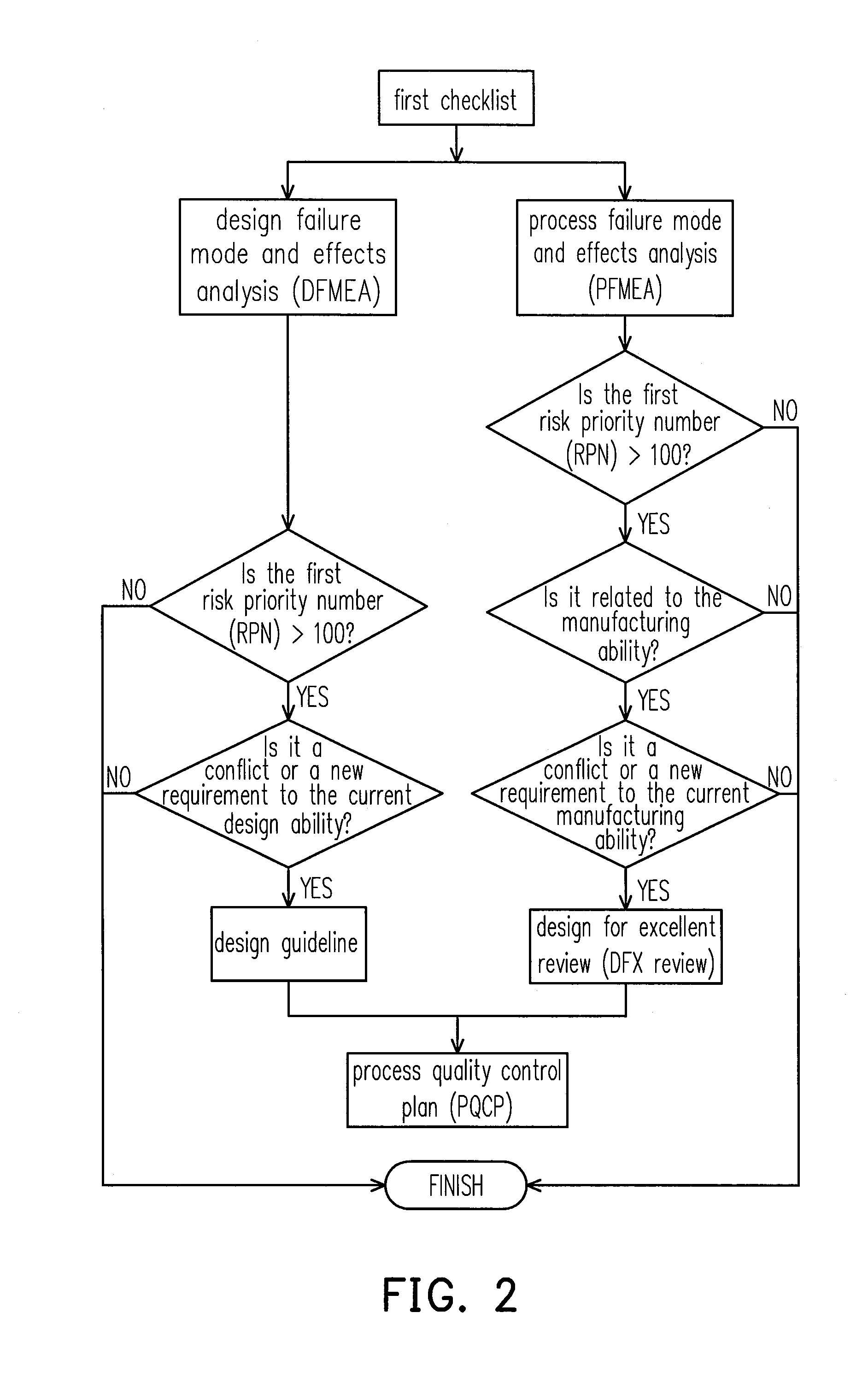
A product quality improvement feedback method is provided. The method includes the following steps. Provide a first checklist, a second checklist, and a third checklist in a design period, a trial production period, and a mass production period respectively. Execute a failure mode and effects analysis to the first checklist, the second checklist, and the third checklist so as to obtain a risk priority number respectively. When the first risk priority number is greater than a specific value, feedback each result of the failure mode and effects analyses to the first checklist, the second checklist, the third checklist, a design list, a trial production list or a mass production list.
Owner:ASKEY COMP
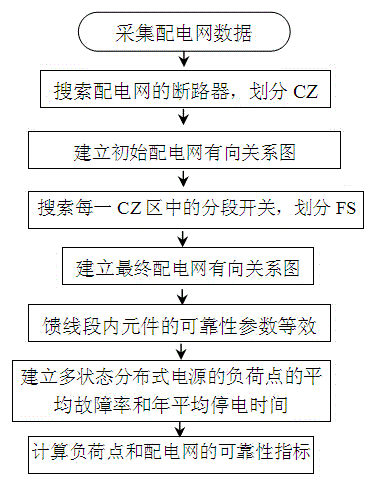
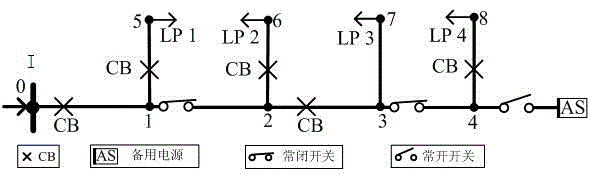
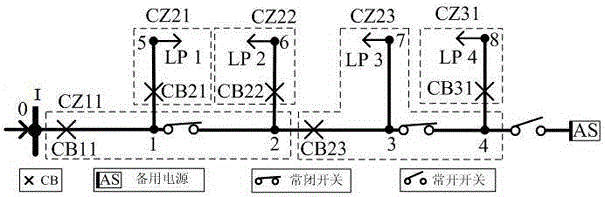
Directed relational graph-based power distribution network reliability evaluation method
ActiveCN104485660AFacilitate reliability assessmentAc network circuit arrangementsRelational graphElectric distribution network
The invention discloses a directed relational graph-based power distribution network reliability evaluation method. According to the method, a power distribution network is divided into protection zones (CZ) of different levels and feeder layers (FS) according to protection zones of circuit breakers in the power distribution network and segmental acting of disconnecting switches in feeders, so that a digraph of the power distribution network can be constructed; and the digraph can be conveniently applied to reliability evaluation of the power distribution network and can be directly applied to a power distribution network with a distributed power source; the greater an ASAI value is, the higher reliability is, and the smaller the SAIFI, SAIDI, CAIDI and AENS values are, the higher the reliability is, and therefore, the reliability of the power distribution network system can be evaluated. The directed relational graph-based power distribution network reliability evaluation method of the invention can be widely applied to the reliability evaluation of medium-voltage power distribution networks. With the directed relational graph-based power distribution network reliability evaluation adopted, defects of an existing failure mode and effect analysis method and blocking algorithm can be eliminated.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
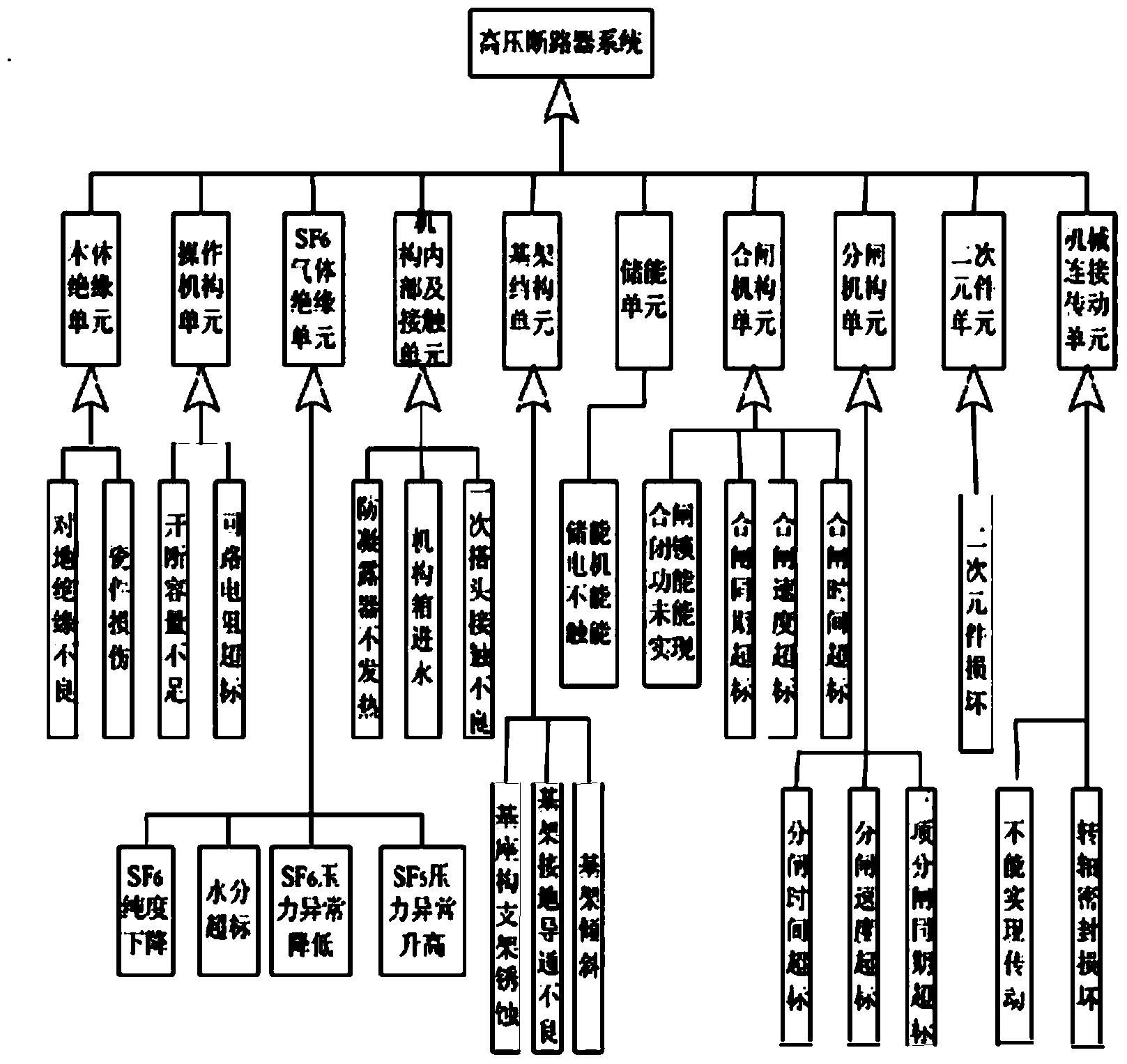
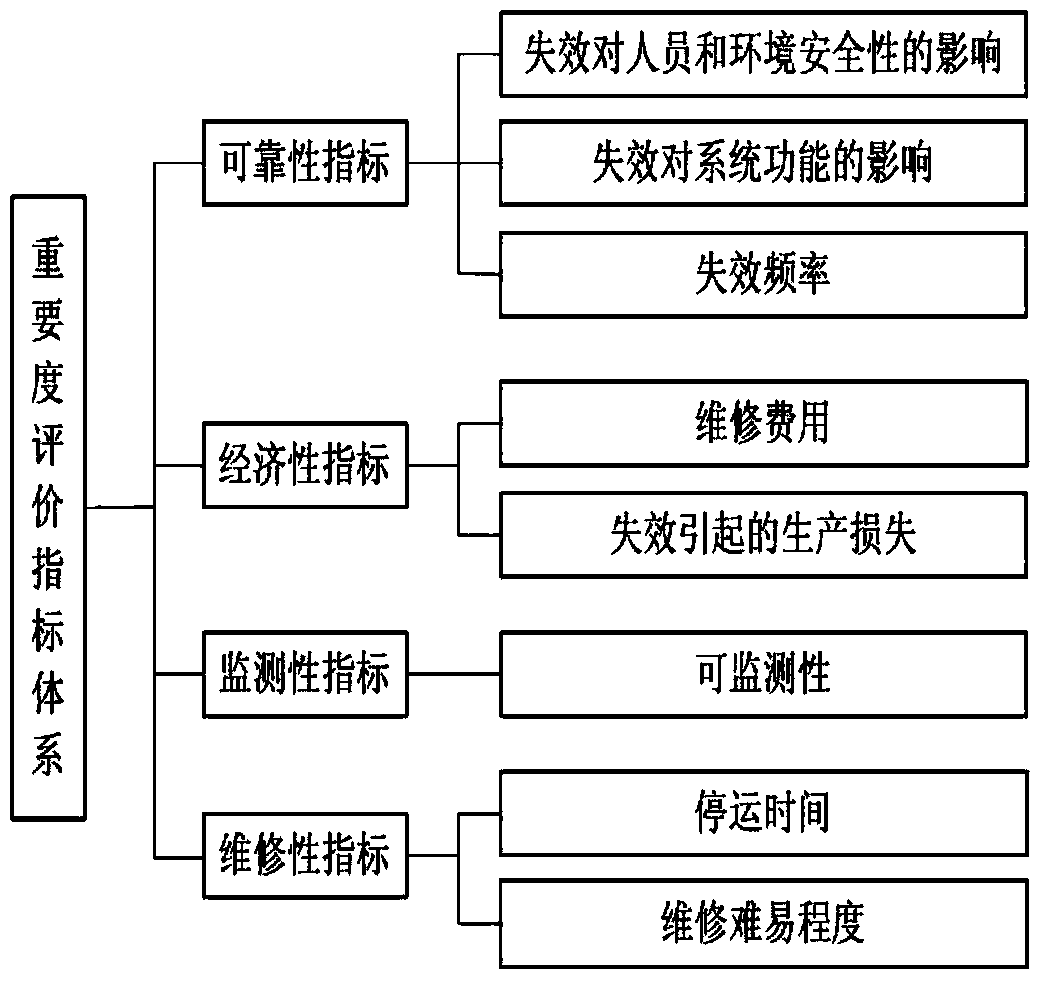
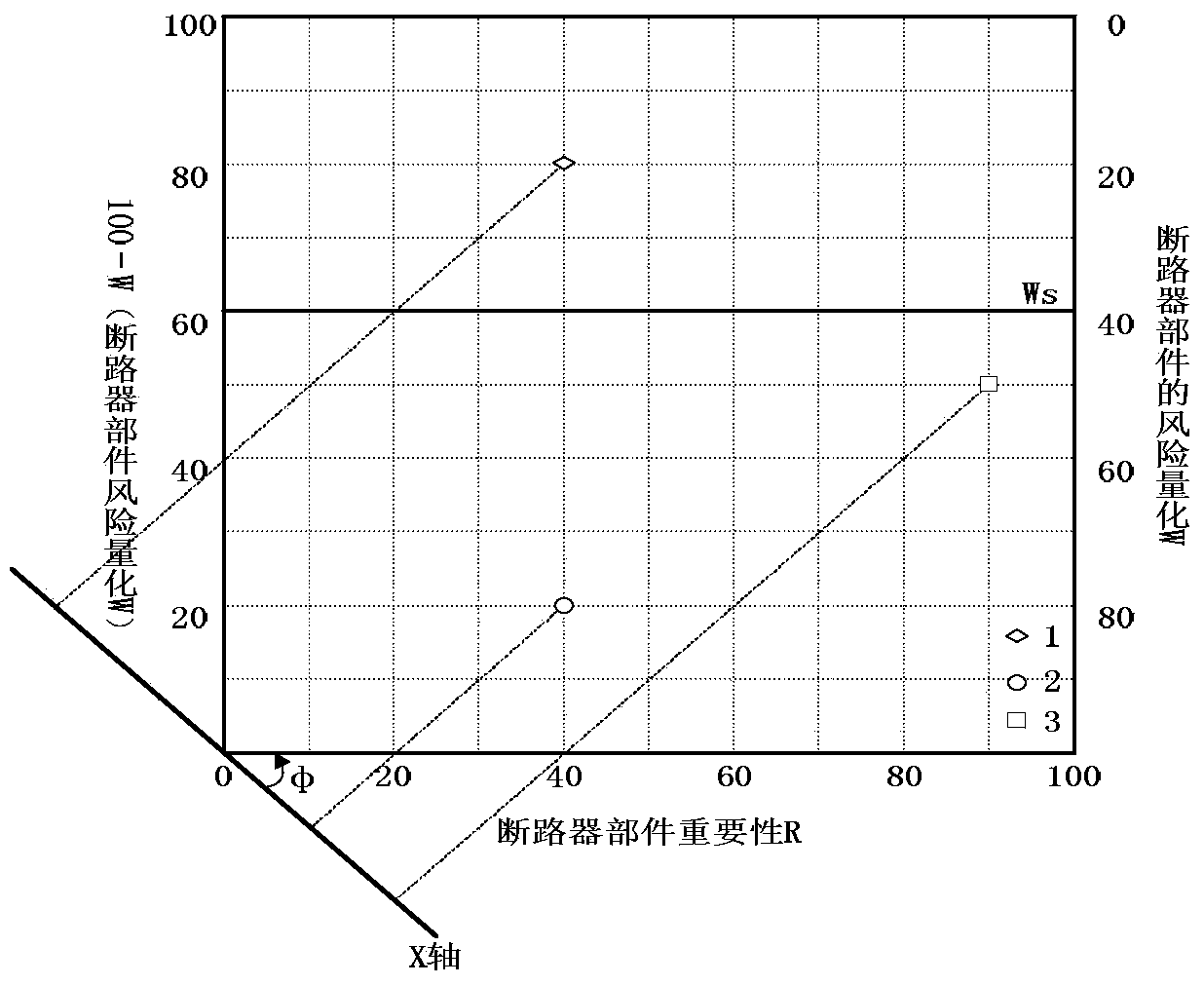
High-voltage circuit breaker component maintaining method
The invention discloses a high-voltage circuit breaker component maintaining method. The method comprises the following steps: performing module division on a circuit breaker by adopting an FMEA (failure mode and effect analysis) in combination with functions and components of the circuit breaker, establishing a risk assessment index system for a high-voltage circuit breaker component on the basis of risk assessment, and performing weight determining on risk assessment indexes by using an analytic hierarchy process; then establishing an importance level assessment index system for the circuit breaker component by applying risk quantification values of failure modes of a weighted grey relationship analysis model to obtain an importance level index of the circuit breaker component; establishing a two-dimensional relationship model between the failure risk degree and the importance of the component according to importance level indexes and the risk quantification values of the circuit breaker component, and taking the degree of urgency of needing maintaining equipment as an intermediate quantity to finally obtain a standard maintaining sequence value.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGXI POWER GRID CO LTD
Dynamic decision sequencing method and apparatus for optimizing a diagnostic test plan
A dynamic diagnostic plan generator arranges diagnostic test procedures related to a vehicle / power tool / patient symptom or operational problem in a sequence based on a probabilistic Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). The diagnostic plan generator also tracks a vehicle / power tool / patient state, and provides instructions for test preparation steps and instructions for performing the diagnostic test procedures. The plan generator further generates schematic illustrations of the diagnostic test procedures, and creates a diagnostic data structure containing information related to the diagnostic test procedures. In addition, the diagnostic plan generator sends and receives information regarding actual failure mode occurrences, for example, to and from a central database. Furthermore, the diagnostic plan generator facilitates the creation of failure mode tests by an expert diagnostics author.
Owner:BOSCH AUTOMOTIVE SERVICE SOLUTIONS +1
Conversion of static diagnostic procedure to dynamic test plan method and apparatus
ActiveUS20080005628A1Mathematical modelsError detection/correctionProgram planningDiagnostic information
A diagnostic information converter reads an existing static diagnostic procedure in the form of a tree graph and generates a diagnostic Failure Modes and Effects Analysis that can be used in the generation of a dynamic diagnostic test plan. The converter identifies the end nodes of the graph and associates a specific failure mode with each of the end nodes. In addition, the converter traces a unique path from each end node along successive branches through one or more intermediate nodes to the root node, and from each of the paths derives an initial failure mode test including the test steps corresponding to the root node, the intermediate nodes and the end node. The converter further identifies and annotates precondition nodes that correspond to a vehicle state or condition, rather than to an actual diagnostic test step and allows a user to edit the initial failure mode tests.
Owner:SPX CORP
Method for predicting performance of a future product
A method for predicting performance of a future product is disclosed. The method includes generating historical data for at least one product and generating a Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) for the at least one product. The method also includes determining a relationship between an FMEA indicator of the FMEA generated for the at least one product and the historical data for the at least one product. The method further includes generating an FMEA for the future product and applying the determined relationship to the FMEA indicator from the FMEA generated for the future product to predict performance for the future product.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
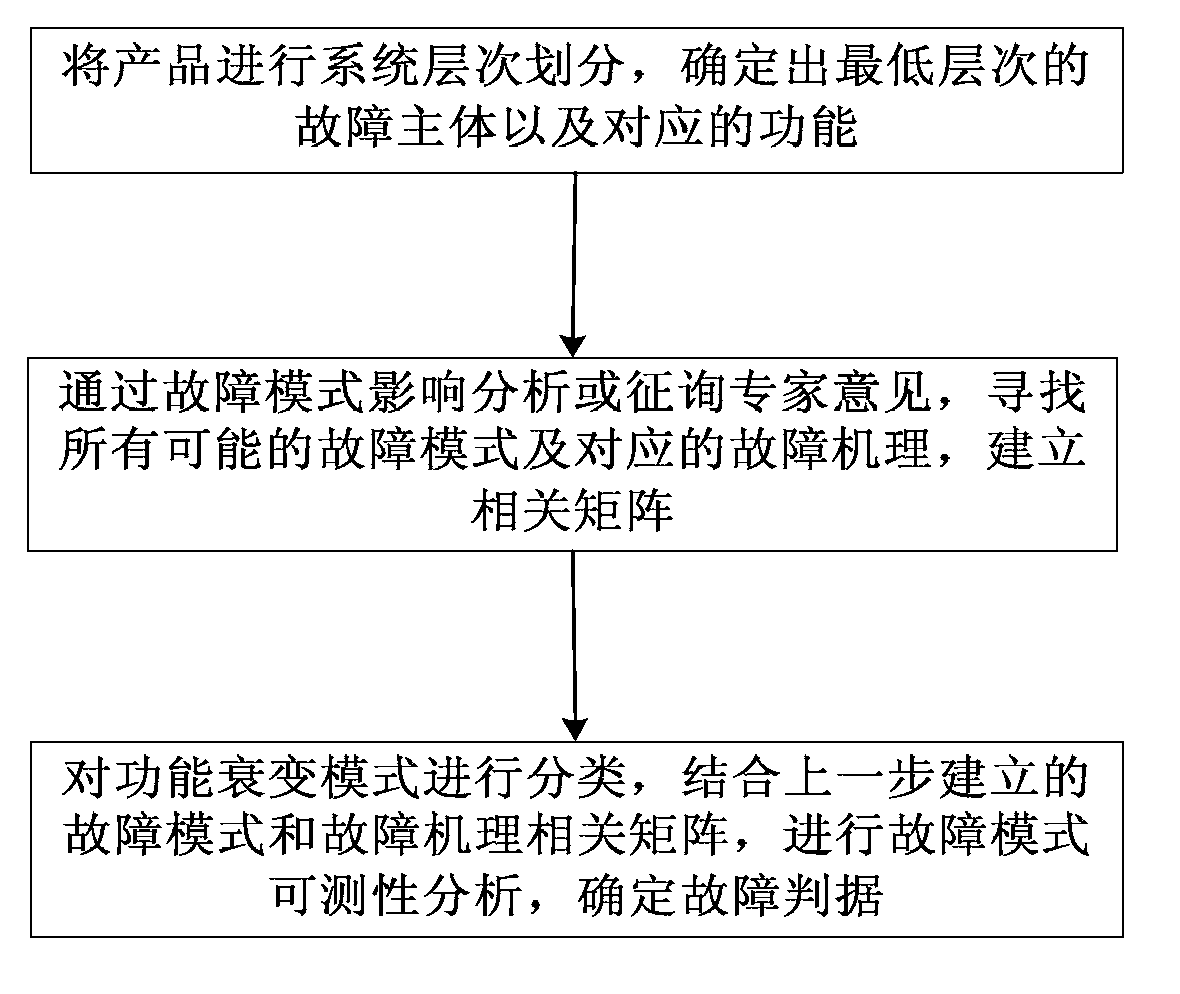
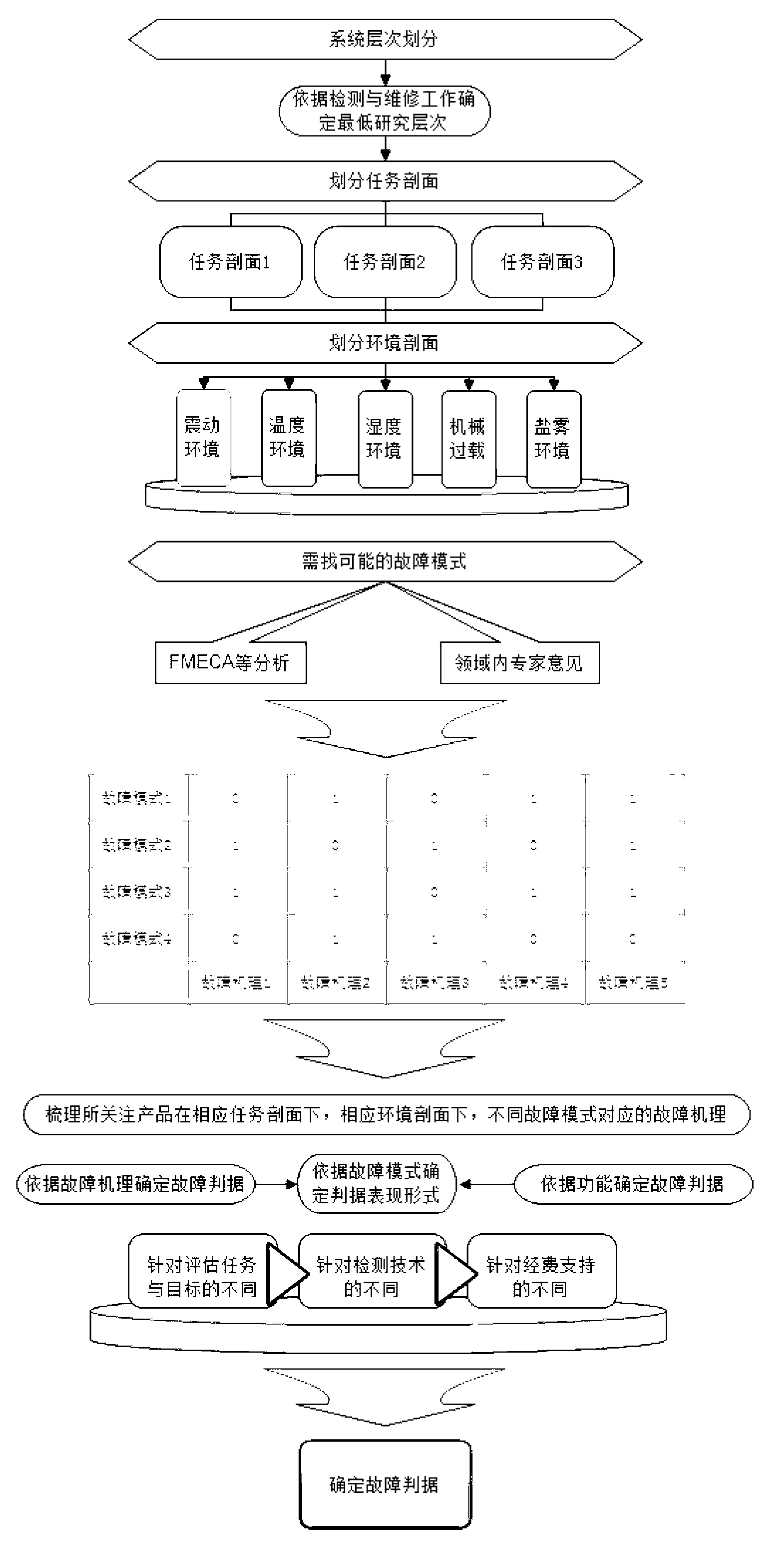
Failure criterion determination method based on function analysis and mechanism analysis
InactiveCN103268273ASimple designWide applicabilityFunctional testingExpert opinionTestability analysis
A failure criterion determination method based on function analysis and mechanism analysis includes a first step of carrying out system level division on products and determining fault bodies of the products at the lowest level and functions of the fault bodies, wherein the 'system level division' refers to the fact that a system is divided into subsystems and components in sequence until smallest analysis units, and the 'lowest level' refers to the fact that the lowest level which can meet technical requirements, a second step of searching possible failure modes and failure mechanisms according to failure mode impact analysis and consultation of expert opinions, analyzing related relations between the failure modes and the failure mechanisms, and building correlation matrixes of the failure modes and the failure mechanisms, and a third step of carrying out classification specific to different function decay modes, combining the established correlation matrixes of the failure modes and the failure mechanisms in the second step, inspecting whether the failure modes are measurable, and determining the failure criterion after classification and corresponding measurability analysis are finished. The failure criterion determination method is wide in applicability, capable of obtaining the appropriate failure criterion, and good in application value.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
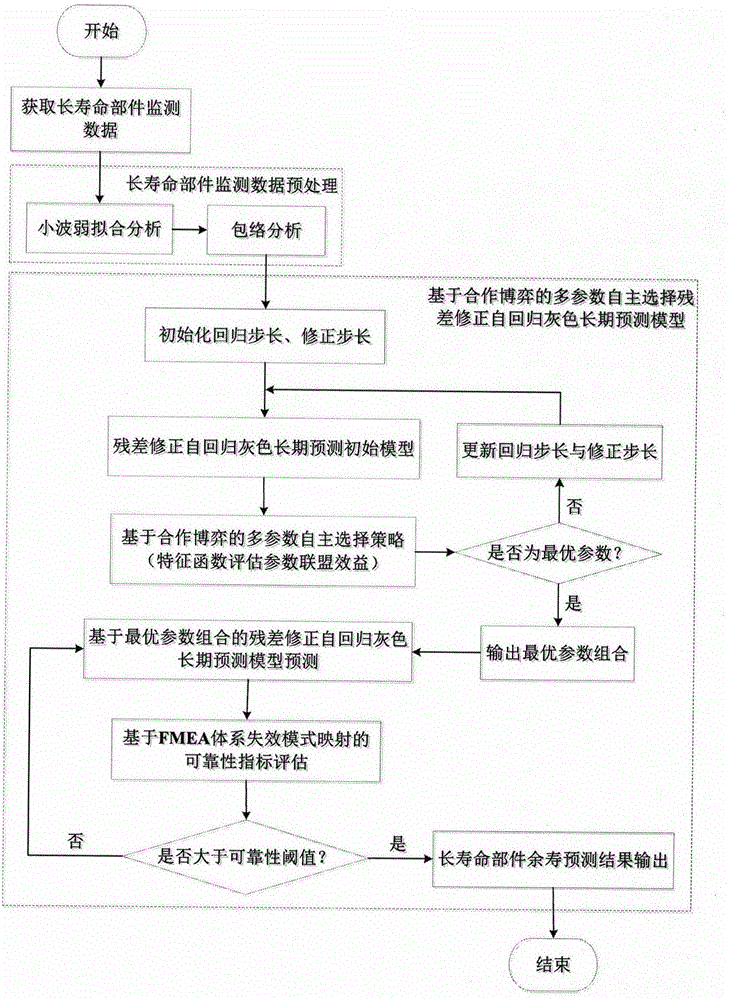
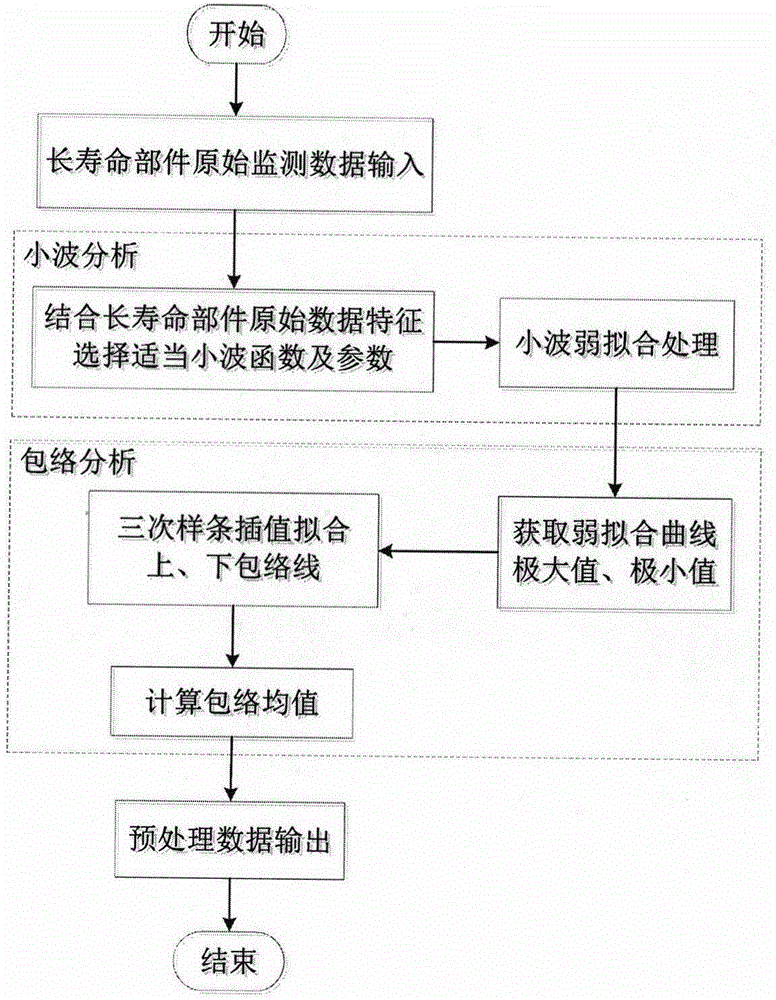
Limited data driving long-life part residual life prediction method
ActiveCN106201849AResolution timeSolve needsHardware monitoringComplex mathematical operationsPredictive methodsData-driven
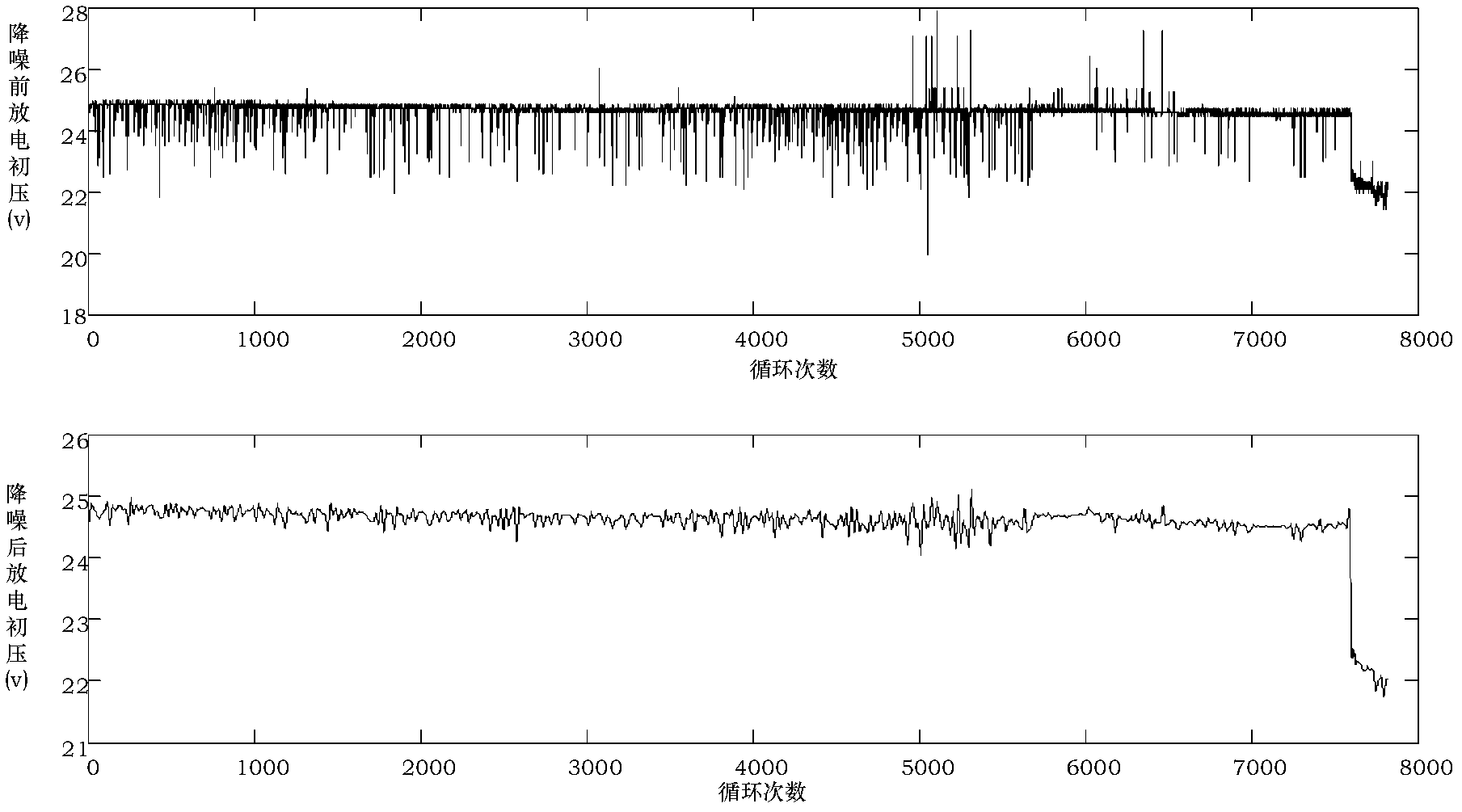
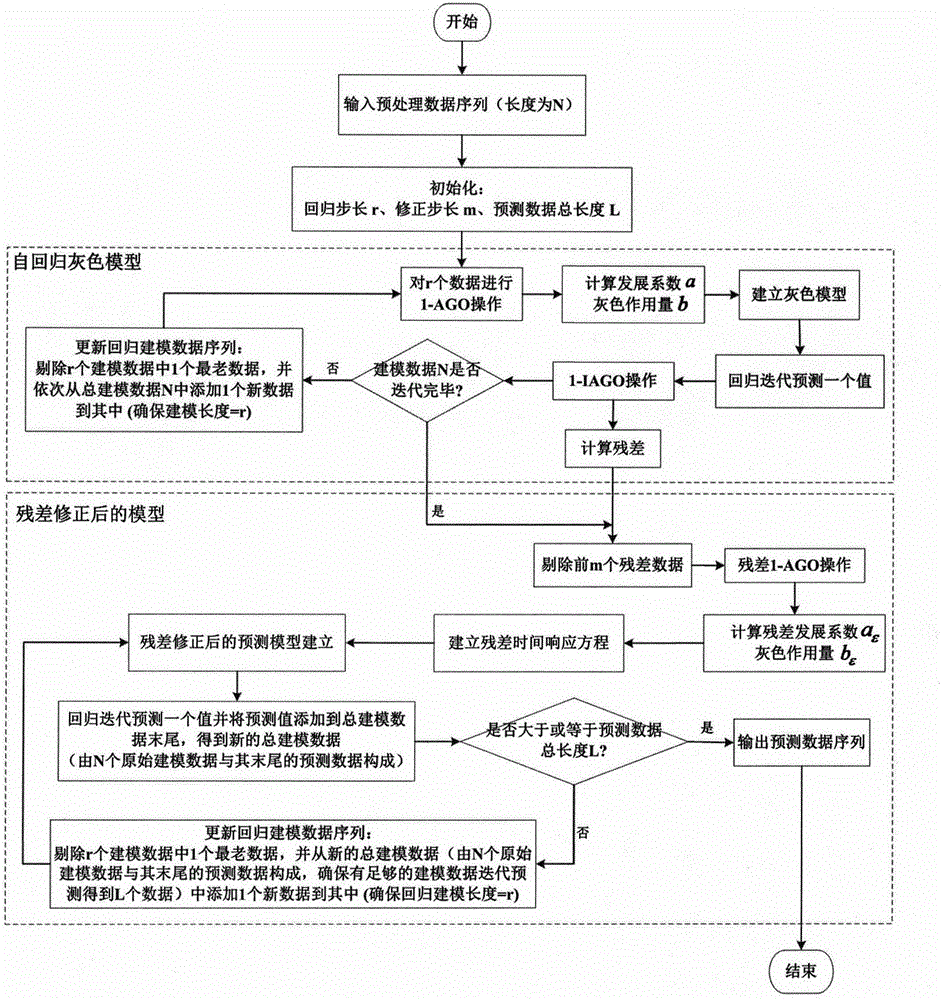
The invention discloses a limited data driving long-life part residual life prediction method comprising the following steps: using a wavelet-envelope to analyze and preprocess long life part history monitoring data, thus reducing data noises; building a multiparameter residual error correction autoregression gray long-term prediction model for the preprocessed data; using combined cooperate gaming to map autonomous selection optimal parameters; mapping a failure mode and a failure mode in an influence analysis system as reliability evaluation indexes of the prediction model, and thus real time evaluating prediction result reliability. The advantages are that the cooperate gaming and the residual error correction autoregression gray long-term prediction model are organically combined, thus fully utilizing long life part limited monitoring data, and solving a series of problems in the prior art that a conventional prediction method cannot respond in long time, is large in data amount demand, multiparameter selection depends on expert knowledge, and the prediction reliability cannot be evaluated in real time; the novel method can improve long-life part residual life prediction result reliability and accuracy under the limited data background; the method is suitable for residual life prediction of the highly reliable long life part with limited data and high test cost; the novel method has universality.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com