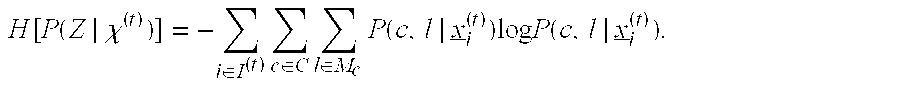Patents
Literature
1120 results about "Complex system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A complex system is a system composed of many components which may interact with each other. Examples of complex systems are Earth's global climate, organisms, the human brain, infrastructure such as power grid, transportation or communication systems, social and economic organizations (like cities), an ecosystem, a living cell, and ultimately the entire universe.
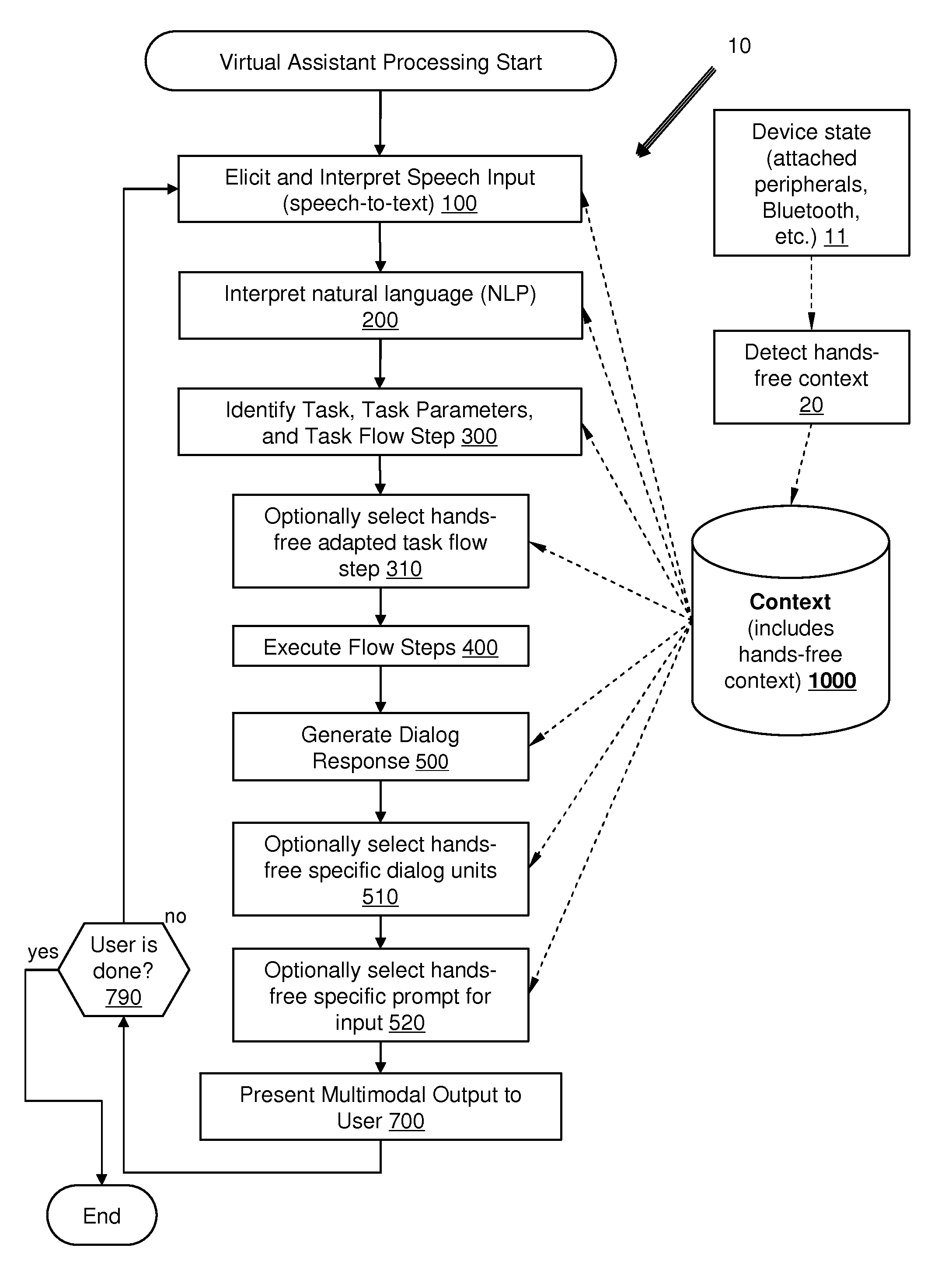
Automatically Adapting User Interfaces For Hands-Free Interaction
ActiveUS20120022872A1Reduce the burden onAdjusting operationNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionHands freeComplex system
A user interface for a system such as a virtual assistant is automatically adapted for hands-free use. A hands-free context is detected via automatic or manual means, and the system adapts various stages of a complex interactive system to modify the user experience to reflect the particular limitations of such a context. The system of the present invention thus allows for a single implementation of a complex system such as a virtual assistant to dynamically offer user interface elements and alter user interface behavior to allow hands-free use without compromising the user experience of the same system for hands-on use.
Owner:APPLE INC
Robust anomaly detection and regularized domain adaptation of classifiers with application to internet packet-flows
InactiveUS20120284791A1Maximize aggregate statistical significanceMaximizesMathematical modelsMemory loss protectionCredit cardAlgorithm
Sound, robust methods identify the most suitable, parsimonious set of tests to use with respect to prioritized, sequential anomaly detection in a collected batch of sample data. While the focus is on detecting anomalies in network traffic flows and classifying network traffic flows into application types, the methods are also applicable to other anomaly detection and classification application settings, including detecting email spam, (e.g. credit card) fraud detection, detecting imposters, unusual event detection (for example, in images and video), host-based computer intrusion detection, detection of equipment or complex system failures, as well as of anomalous measurements in scientific experiments.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Interactive education tool
An interactive education tool for graphically representing components of a complex system. When the user selects a displayed component of the system, the tool provides educational information relating to the selected component. A user may then “drill-down” further into the display of the system in order to obtain additional information regarding the selected component.
Owner:AT&T WIRELESS SERVICES
RFID systems and methods for automatically detecting and/or directing the physical configuration of a complex system
ActiveUS8138925B2Less timeAvoid excessive errorServersAutomatic card filesInformation processingRadio frequency
A radio-frequency identification (RFID)-based configuration detection system for automatically detecting, directing, and / or configuring the physical configuration of a complex system constituted by a set of one or more types of mateable components. The RFID configuration detection system utilizes a set of mateable RFID tags arranged so that each mateable component includes at least one mateable RFID tag. Each RFID tag includes information about its associated component and is arranged so that when the components are mated, their associated RFID tags also are mated. The system uses at least one RFID reader to read RFID tag signals from the RFID tags. The RFID tag signals provide information about mating status of the component, as well as information about components themselves. An information processing system operably connected to the RFID reader receives and process information concerning the number and type of mated connections and thus the configuration. Changes to the configuration, such as mated connections being unmated, can be tracked to provide real-time configuration information.
Owner:FIBER MOUNTAIN INC
Network models of complex systems
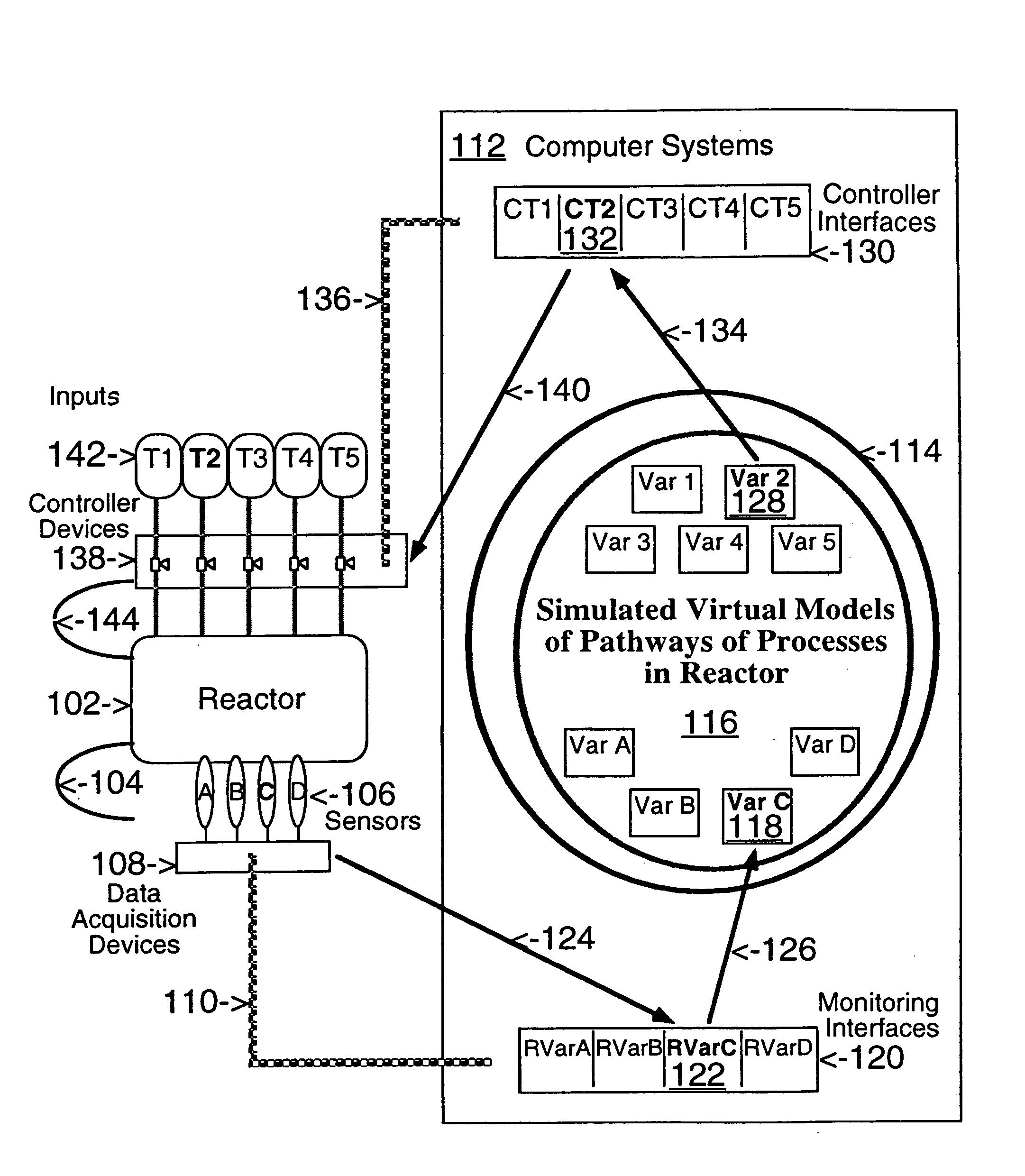
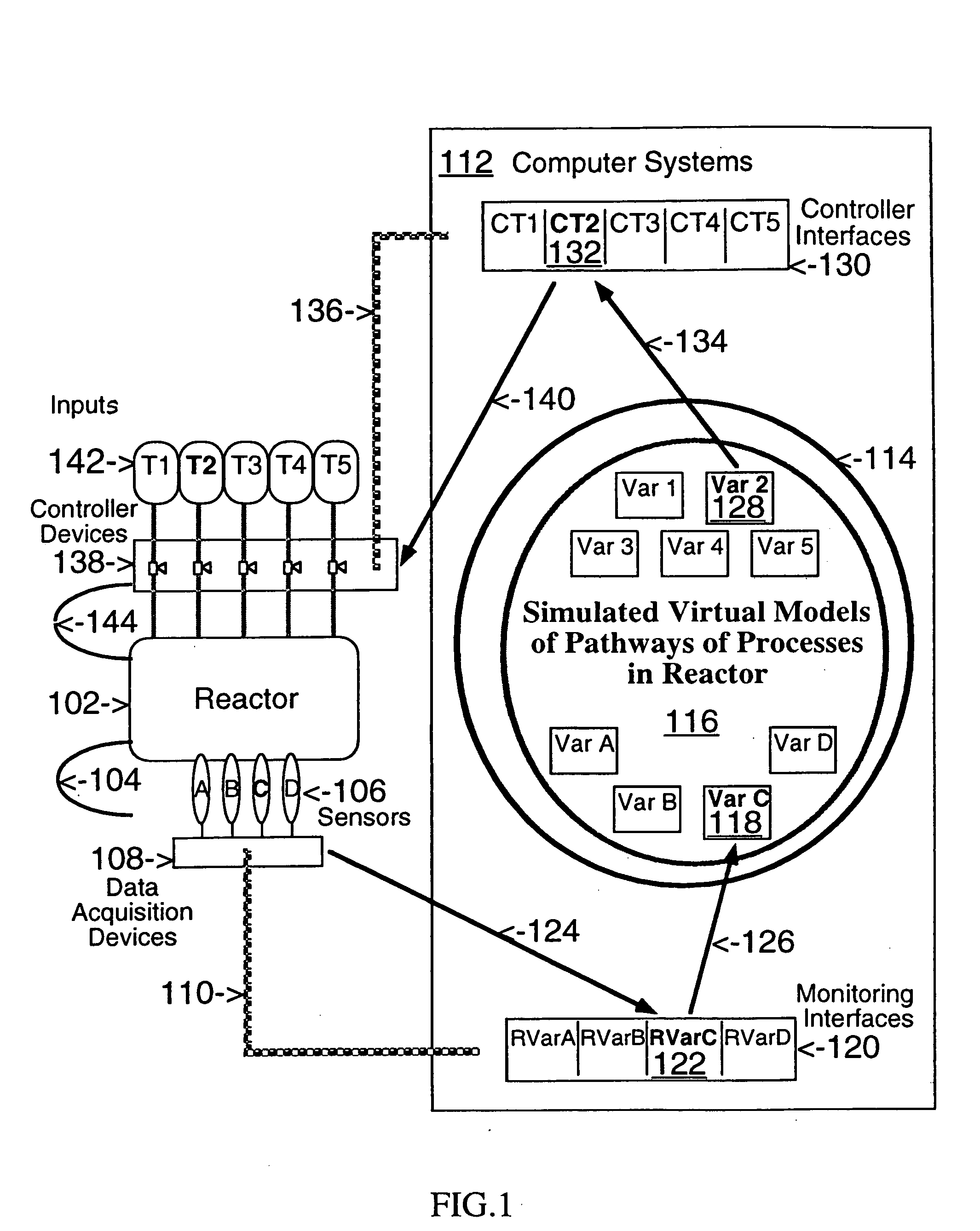
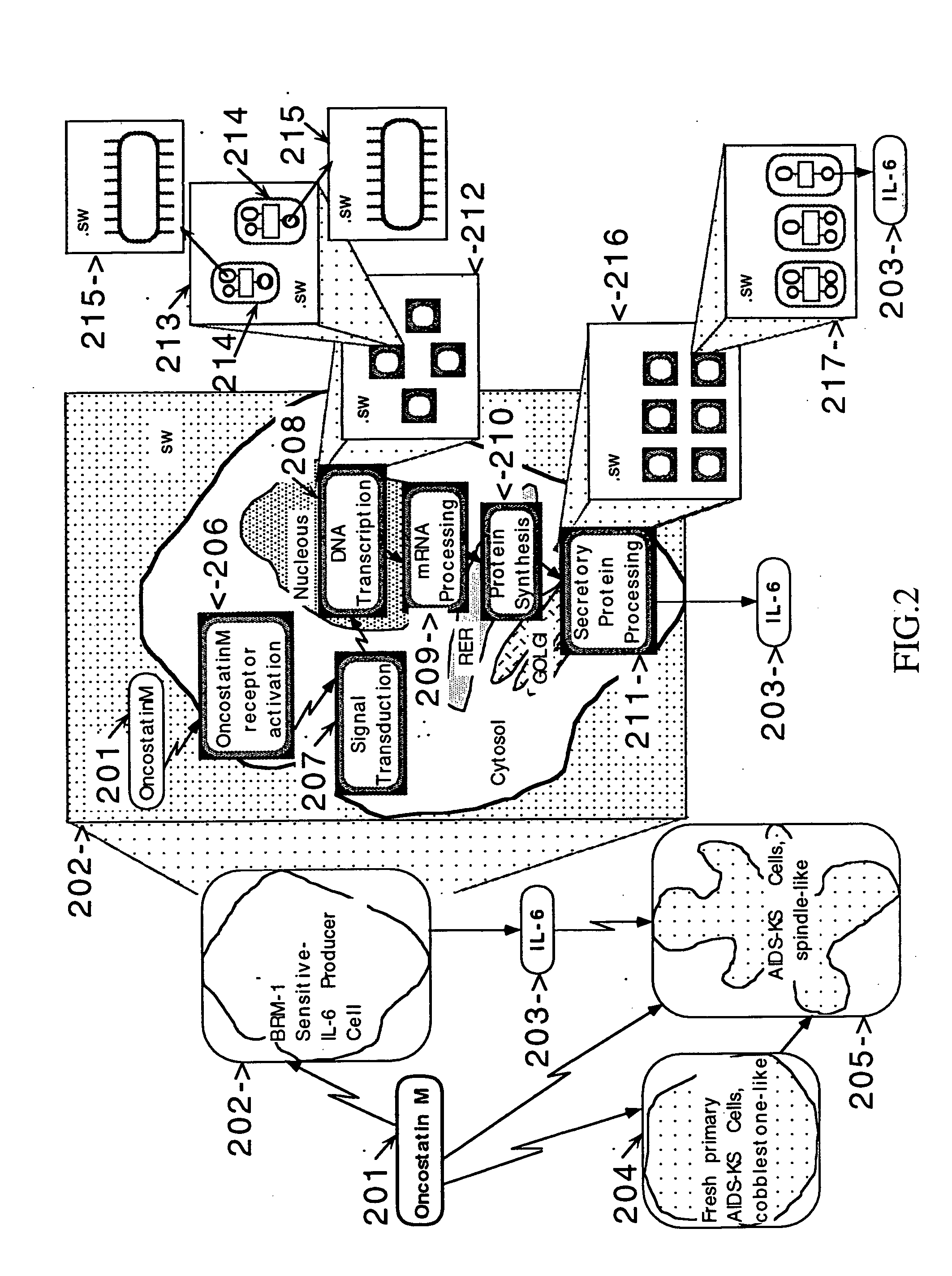
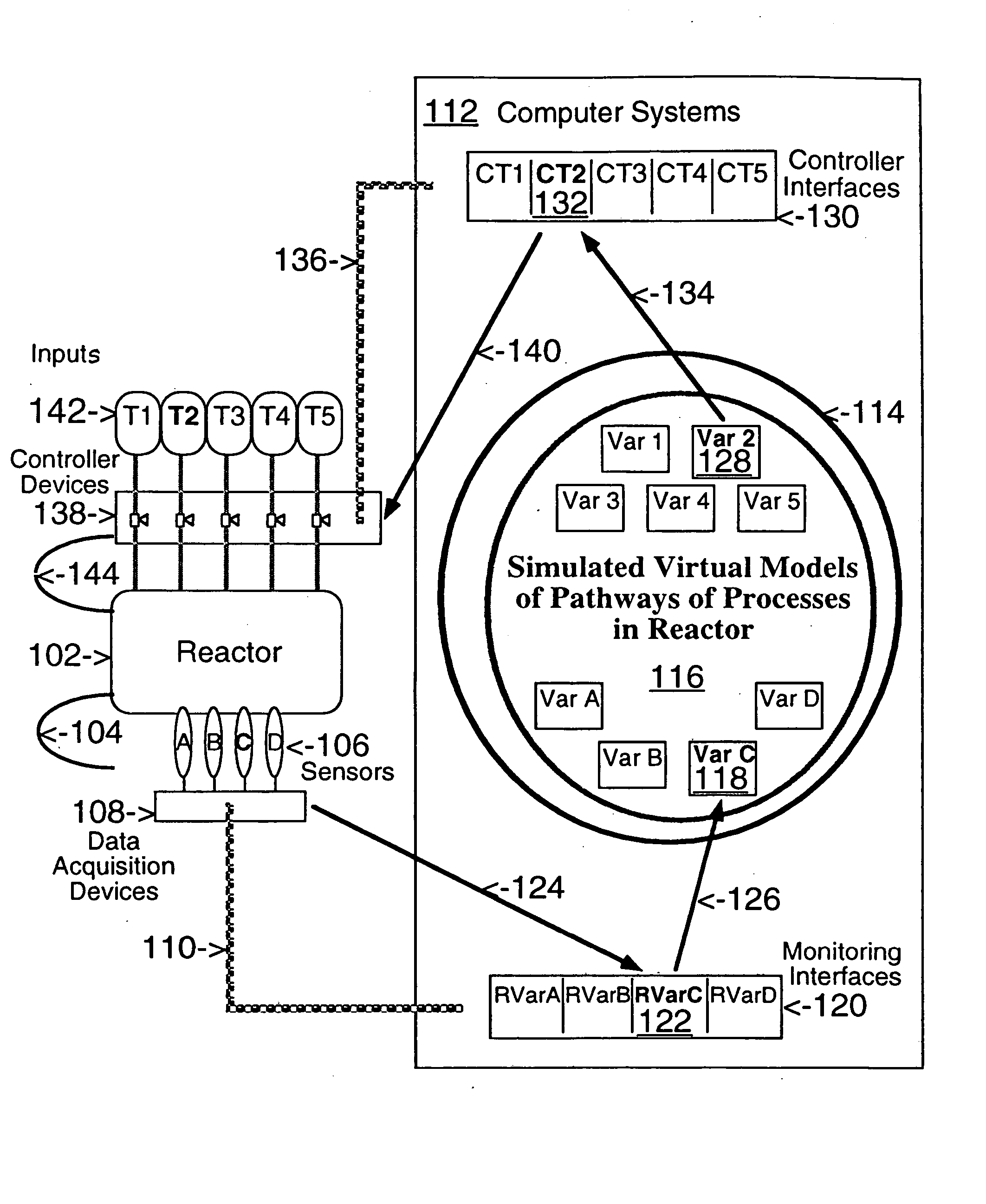
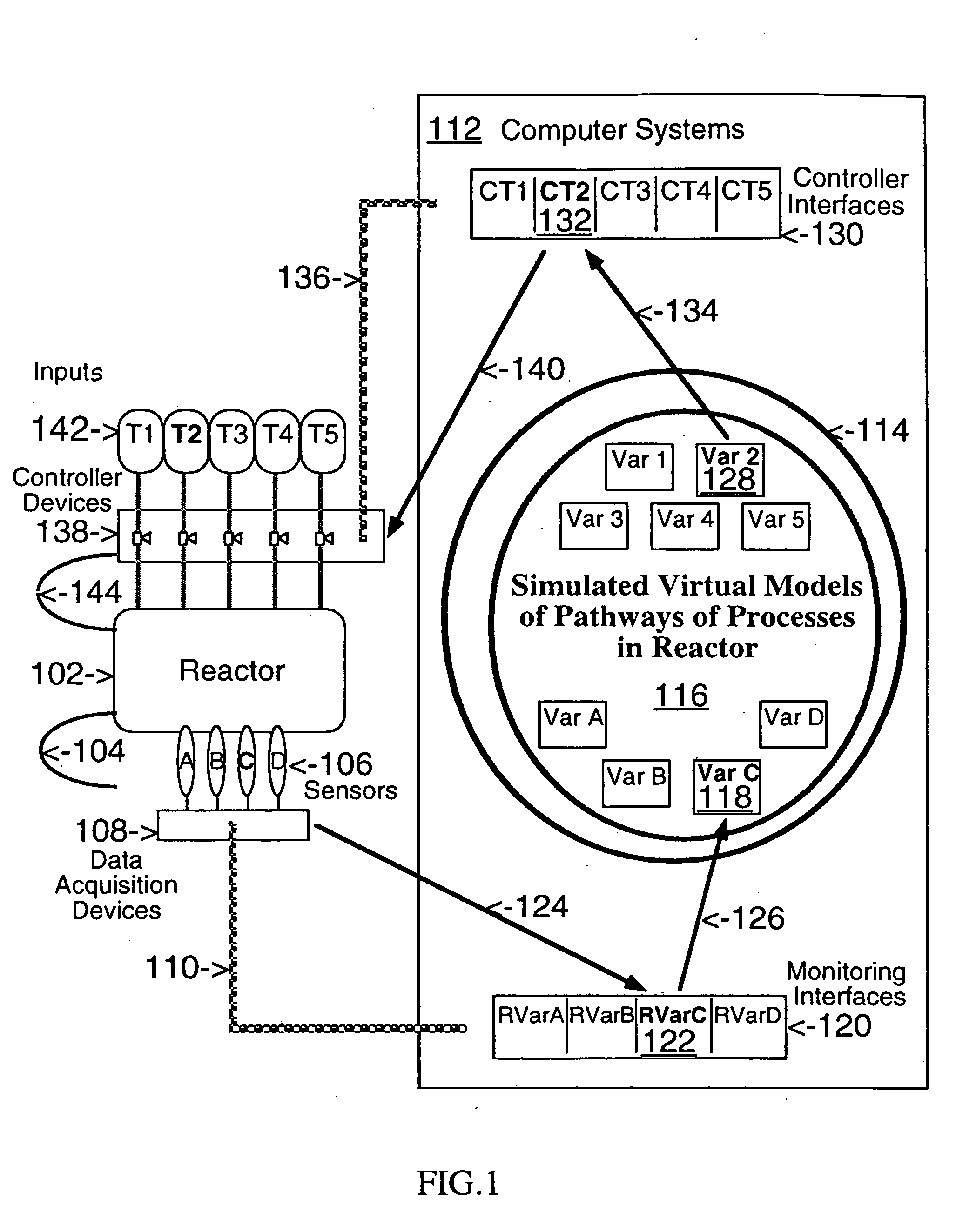
This invention describes computer based virtual models of complex systems, together with integrated systems and methods providing a development and execution framework for visual modeling and dynamic simulation of said models. The virtual models can be used for analysis, monitoring, or control of the operation of the complex systems modeled, as well as for information retrieval. More particularly, the virtual models in the present implementation relate to biological complex systems. In the current implementation the virtual models comprise building blocks representing physical, chemical, or biological processes, the pools of entities that participate in those processes, a hierarchy of compartments representing time-intervals or the spatial and / or functional structure of the complex system in which said entities are located and said processes take place, and the description of the composition of those entities. The building blocks encapsulate in different layers the information, data, and mathematical models that characterize and define each virtual model, and a plurality of methods is associated with their components. The models are built by linking instances of the building blocks in a predefined way, which, when integrated by the methods provided in this invention, result in multidimensional networks of pathways. A number of functions and graphical interfaces can be selected for said instances of building blocks, to extract in various forms the information contained in said models. Those functions include: a) on-the-fly creation of displays of interactive multidimensional networks of pathways, according to user selections; b) dynamic quantitative simulations of selected networks; and c) complex predefined queries based on the relative position of pools of entities in the pathways, the role that the pools play in different processes, the location in selected compartments, and / or the structural components of the entities of those pools. The system integrates inferential control with quantitative and scaled simulation methods, and provides a variety of alternatives to deal with complex dynamic systems and with incomplete and constantly evolving information and data.
Owner:INTERTECH VENTURES
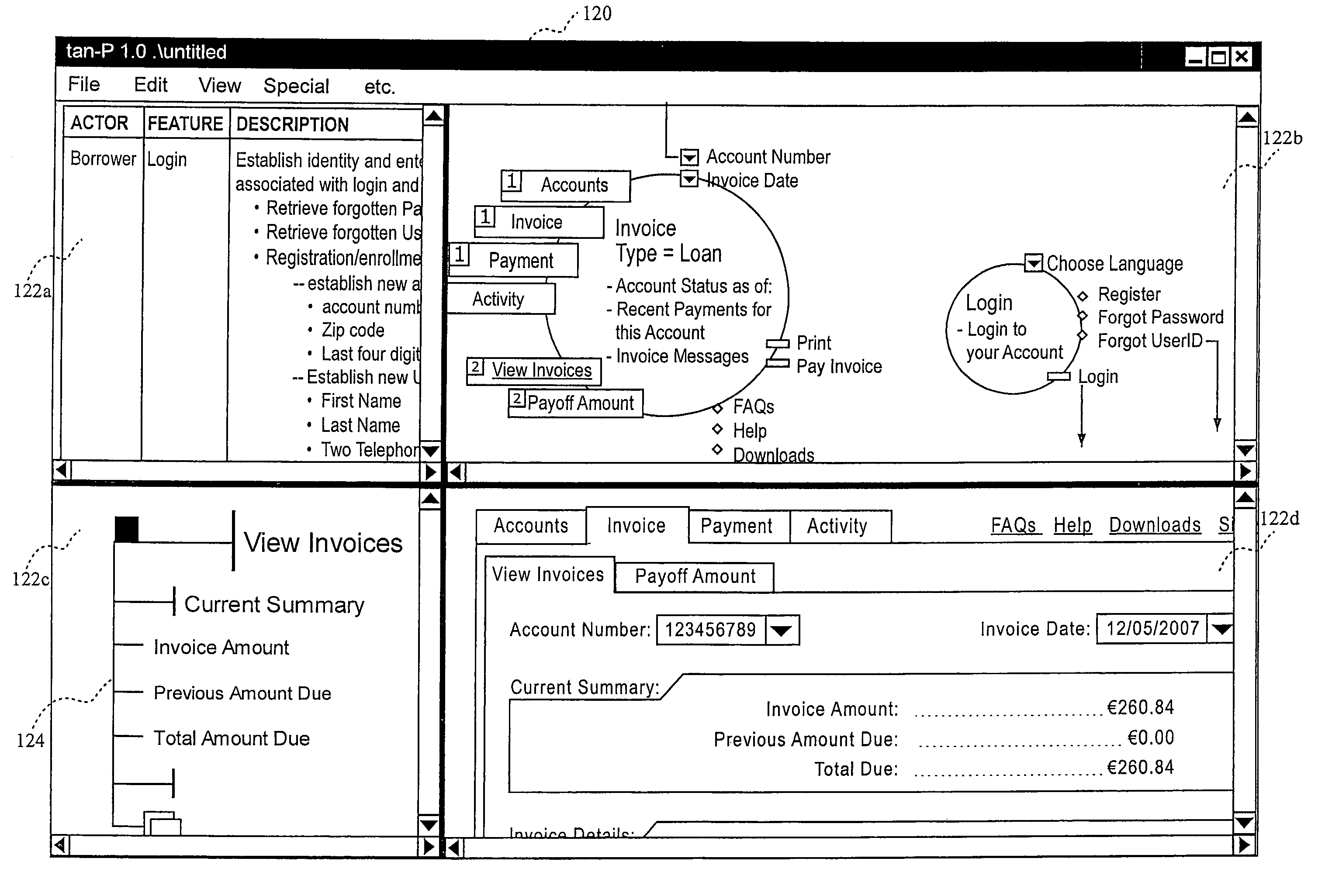
Design tool and methodology for enterprise software applications
ActiveUS7644390B2Easy to createEfficient communicationProgram documentationDesign optimisation/simulationProject managementApplication software
A system for creating and viewing simulation models that are used for managing requirements and design specifications for complex systems. Users simultaneously collaborate on the description of a complex system such as an enterprise software project throughout its life cycle. User interfaces, designed to assist in the visualization of a particular form of knowledge, allow users to describe the complex system with simple interactive elements. Information in all perspectives is presented so that it is legible and discernable to a non-technical audience. Multi-dimensional data structures record all the resulting information, creating a simulation model of the complex system, and the tasks required for construction and maintenance. Tasks are driven from the specifications not as a separate activity, but as part of the same activity to facilitate project management by allowing decisions to be tracked virtually throughout the simulation model.
Owner:KHODABANDEHLOO PAYMAN +1
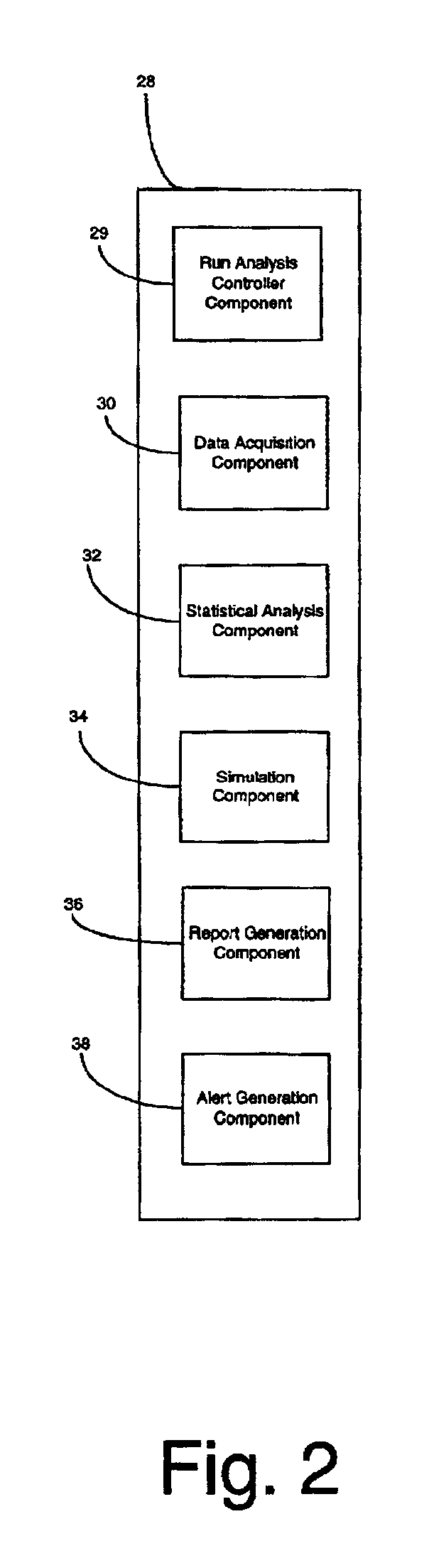
System, method and computer product for performing automated predictive reliability
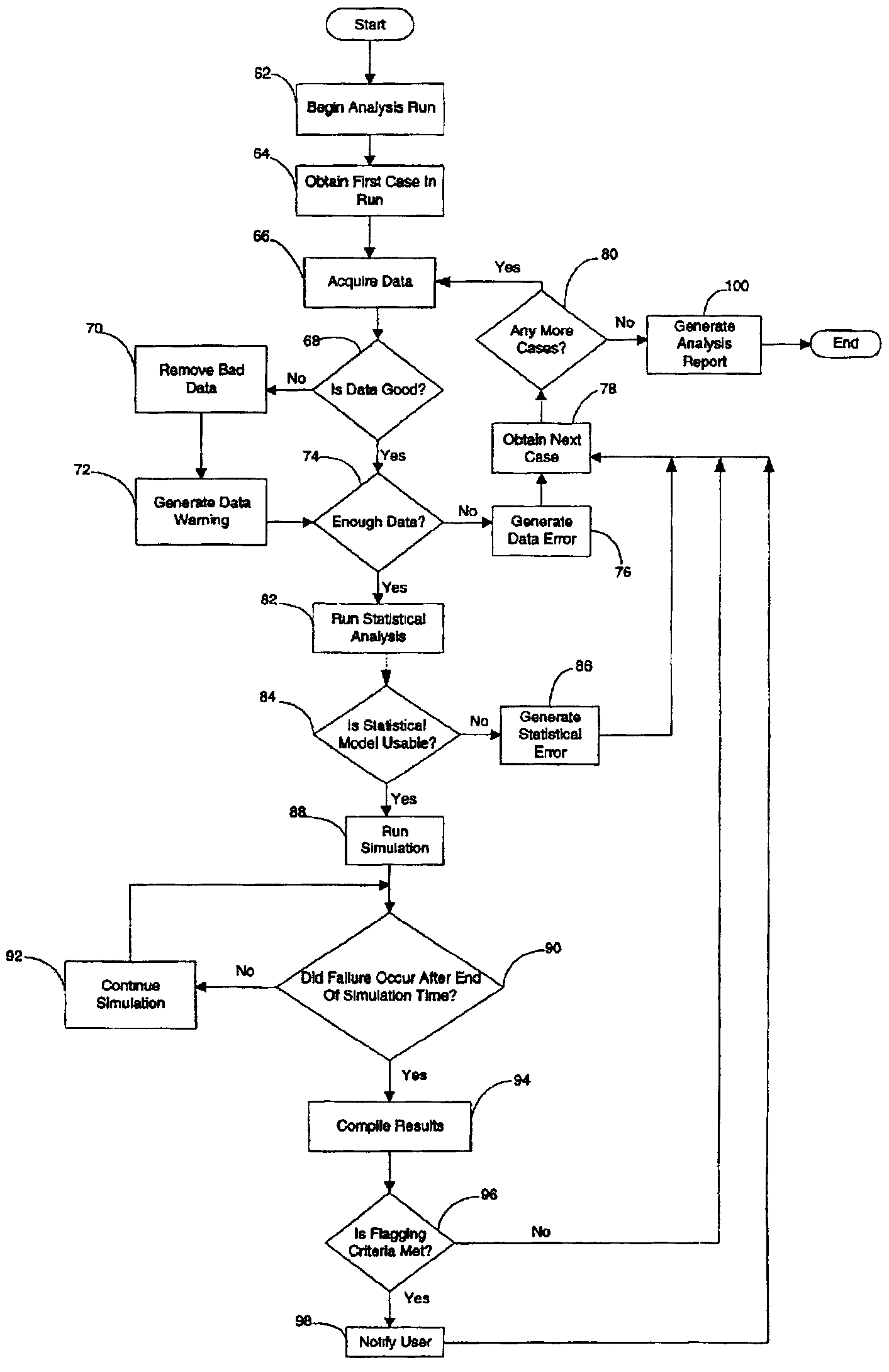
System, method and computer product for performing automated predictive reliability. A data acquisition component acquires service data for a complex system from a data repository. A statistical analysis component generates a statistical model for the service data. A simulation component predicts the reliability of the complex system according to the statistical model. An alert generation component generates alerts when predicted failures determined by the simulation component exceed predetermined alert criteria. A report generation component generates a summary of the analysis performed in the data acquisition, statistical analysis and alert generation components.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
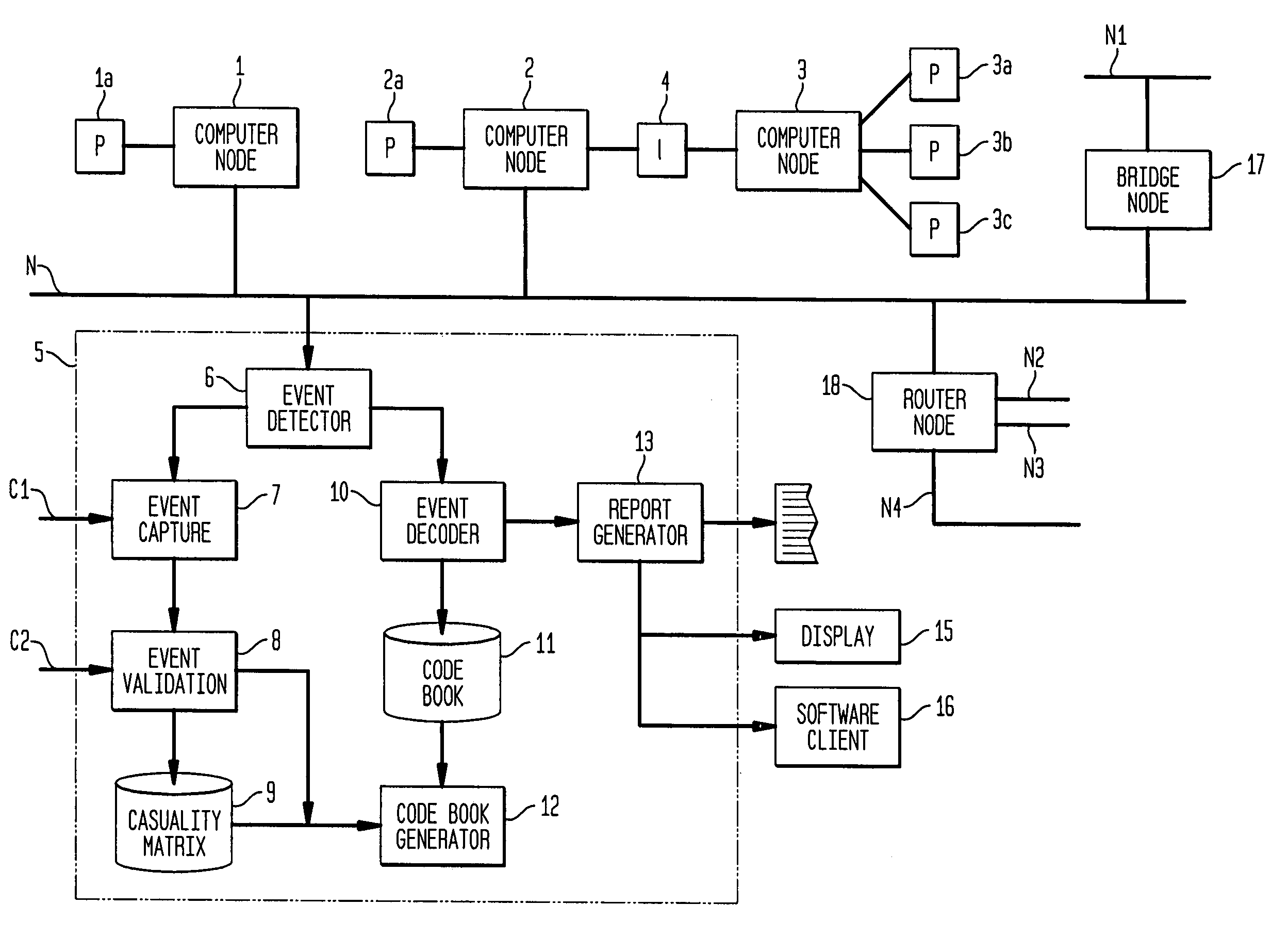
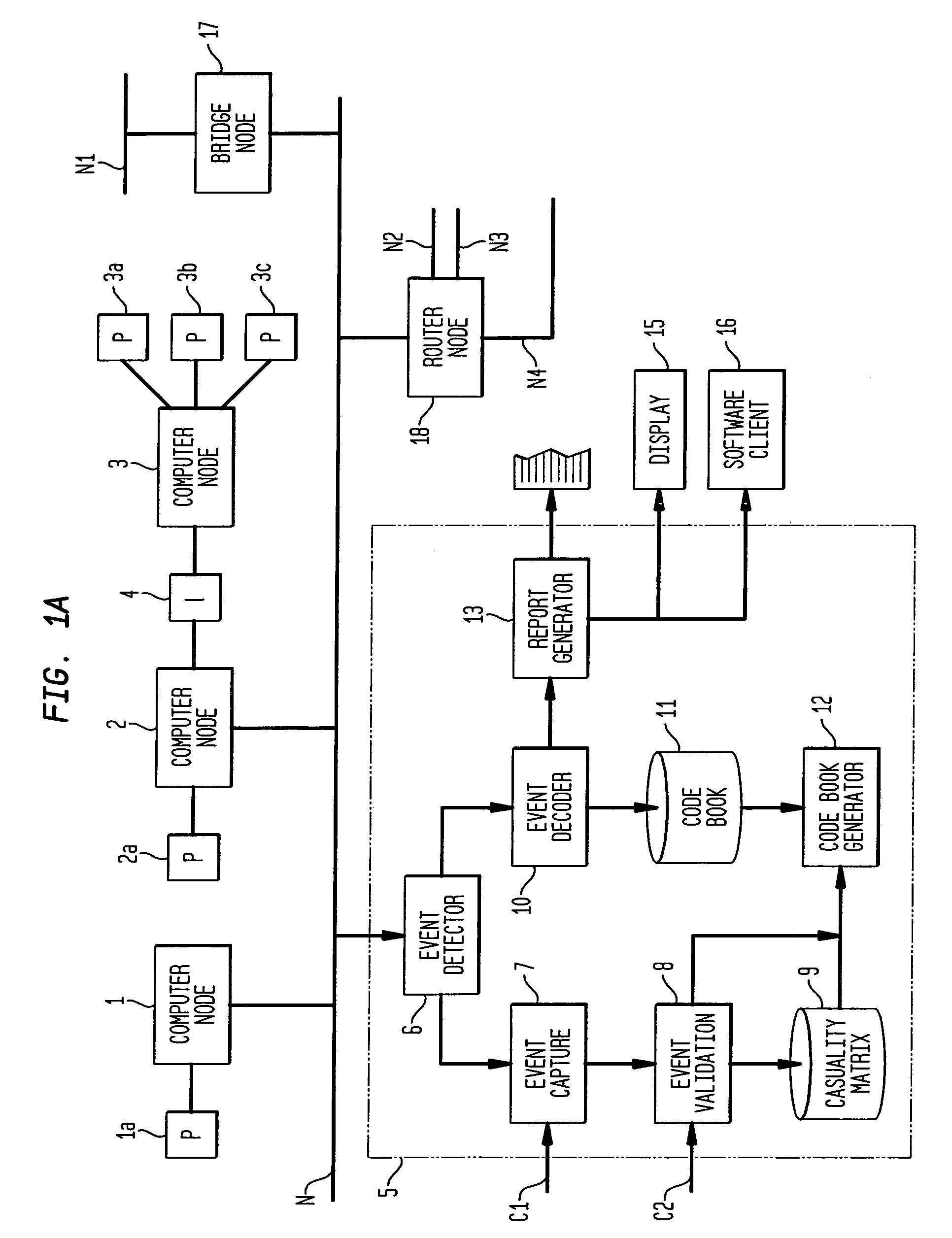
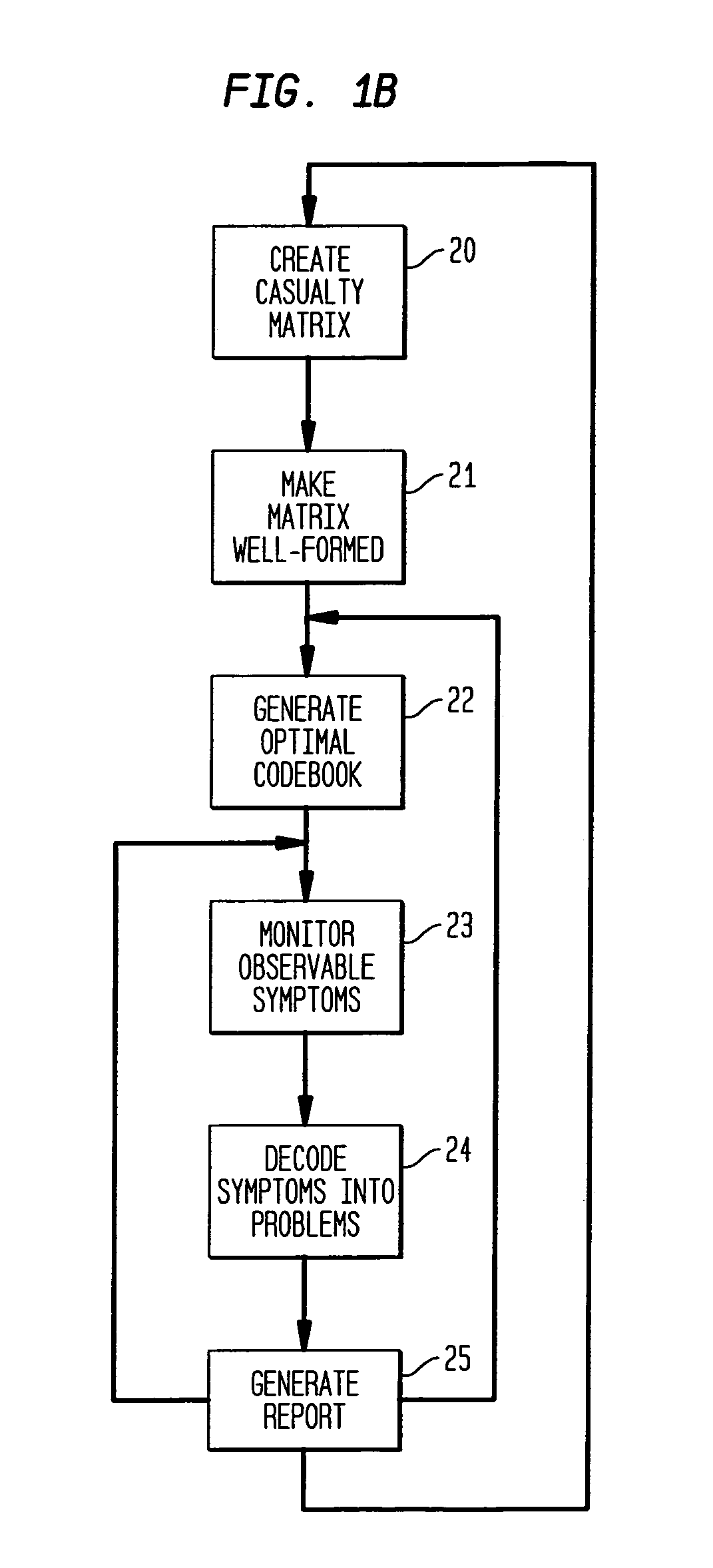
Apparatus and method for event correlation and problem reporting
InactiveUS7107185B1Effective monitoringImprove efficiencyNuclear monitoringDigital computer detailsComplex systemComputer science
A computer implemented method on a computer readable media is provided for determining the source of a problem in a complex system of managed components based upon symptoms. The problem source identification process is split into different activities. Explicit configuration non-specific representations of types of managed components, their problems, symptoms and the relations along which the problems or symptoms propagate are created that can be manipulated by executable computer code. A data structure is produced for determining the source of a problem by combining one or more of the representations based on information of specific instances of managed components in the system. Computer code is then executed which uses the data structure to determine the source of the problem from one or more symptoms.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Dynamic adaptive distributed computer system
InactiveUS20050177593A1Most efficientOptimizes adaptive self-organizing operationDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsSearch analyticsComplex system
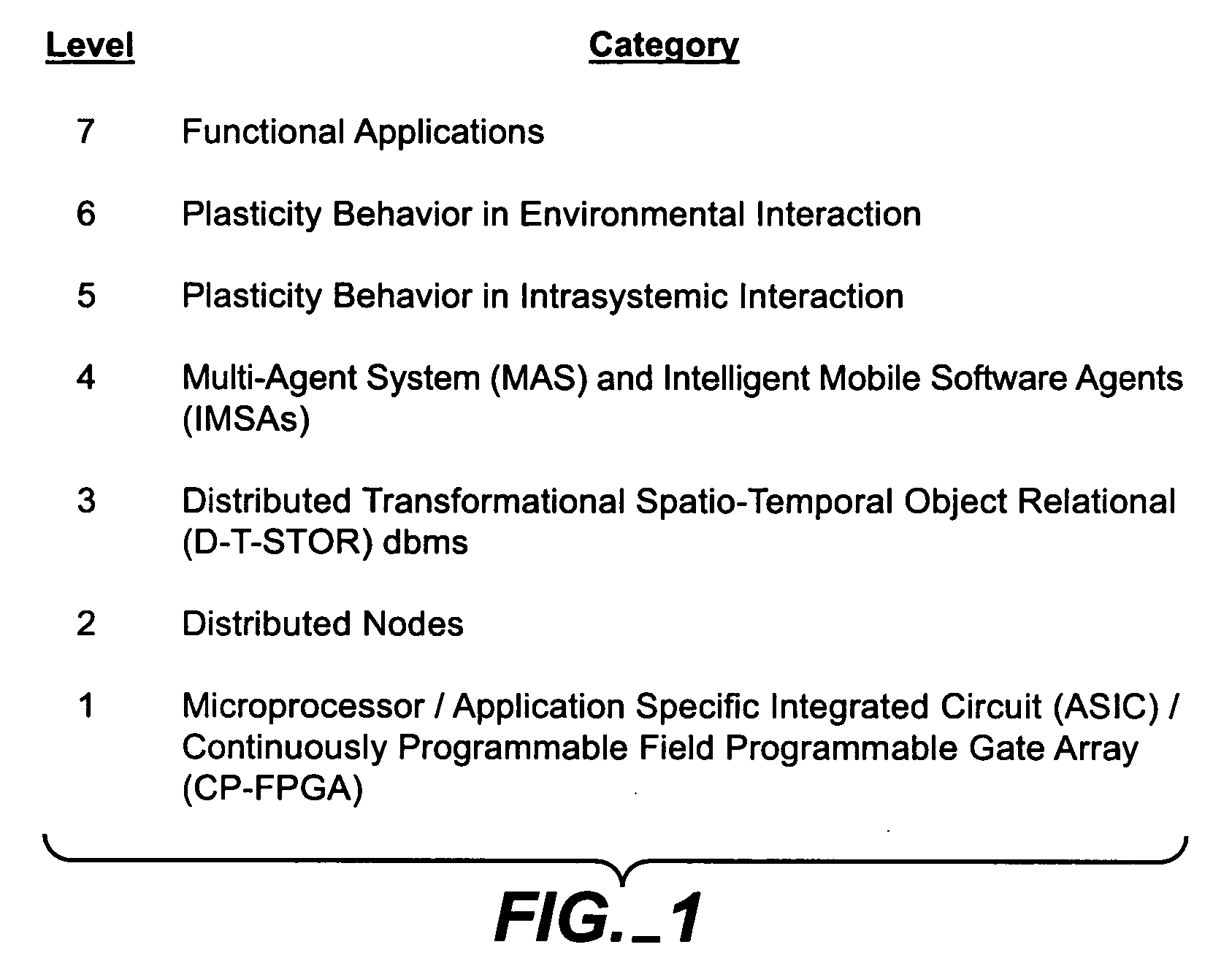
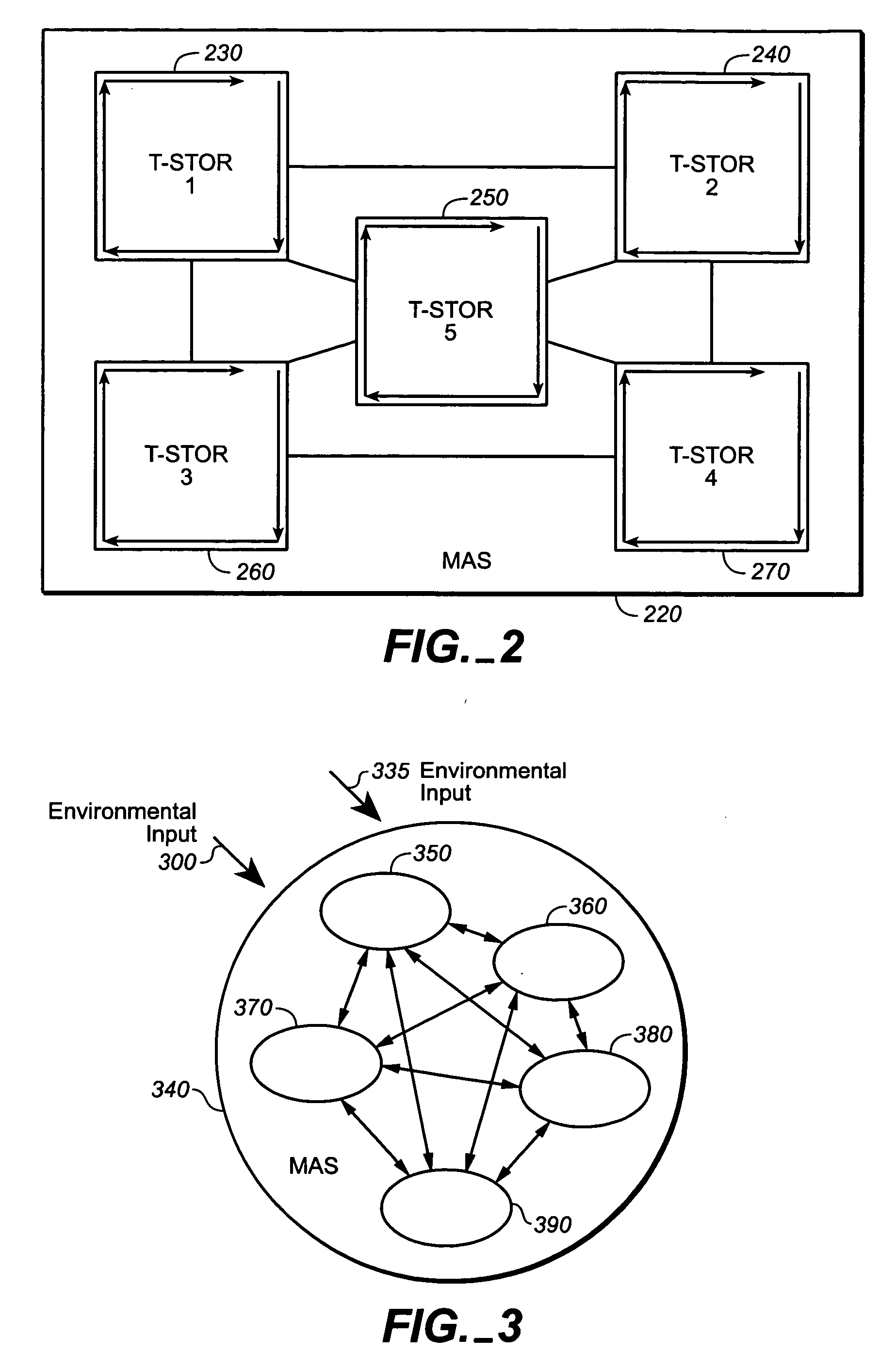
A system, methods and apparatus are described involving the self-organizing dynamics of networks of distributed computers. The system is comprised of complex networks of databases. The system presents a novel database architecture called the distributed transformational spatio-temporal object relational (T-STOR) database management system (dbms). Data is continuously input, analyzed, organized, reorganized and used for specific commercial and industrial applications. The system uses intelligent mobile software agents in a multi-agent system in order to learn, anticipate, and adapt and to perform numerous functions, including search, analysis, collaboration, negotiation, decision making and structural transformation. The system links together numerous complex systems involving distributed networks to present a novel model for dynamic adaptive computing systems, which includes plasticity of collective behavior and self-organizing behavior in intelligent system structures.
Owner:SOLOMON NEAL
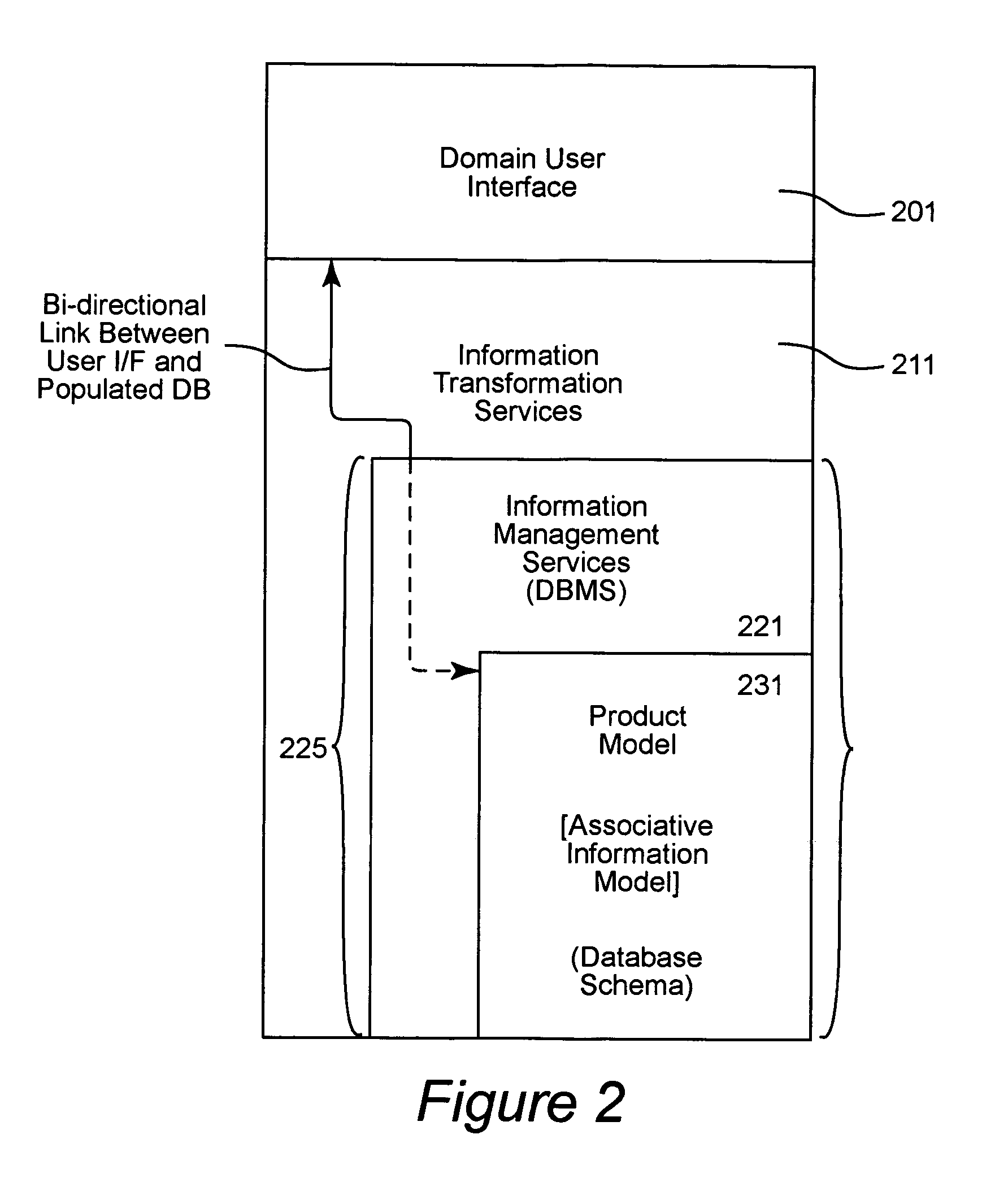
Product catalog for use in a collaborative engineering environment and method for using same
InactiveUS6959268B1Easy to useImprove visibilityMultiple digital computer combinationsOffice automationInformation dispersalSubject-matter expert
A collaborative engineering environment (CEE) enables the effective capture, management, communication, and exploitation of all product related information to a project team. The systematic employment of this information offers substantial improvements in productivity, cost savings, cycle time reductions, product integrity, and lifetime supportability of the system. Advanced CEE capabilities exploit and leverage the engineering, architectural and technological expertise of enterprise subject matter experts (domain experts) across multiple complex systems development and integration activities. The CEE provides a tightly coupled process automation using reusable product elements for coupling information with engineering processes and ensuring adherence to repeatable and traceable engineering processes. A product catalog provides a single information management point for intrinsic complex product characteristics and facilitates the propagation of that information to engineering teams incorporating the complex product into their system designs. The intrinsic complex product characteristics are augmented with implementation specific information to fully describe the complex product in the system design.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
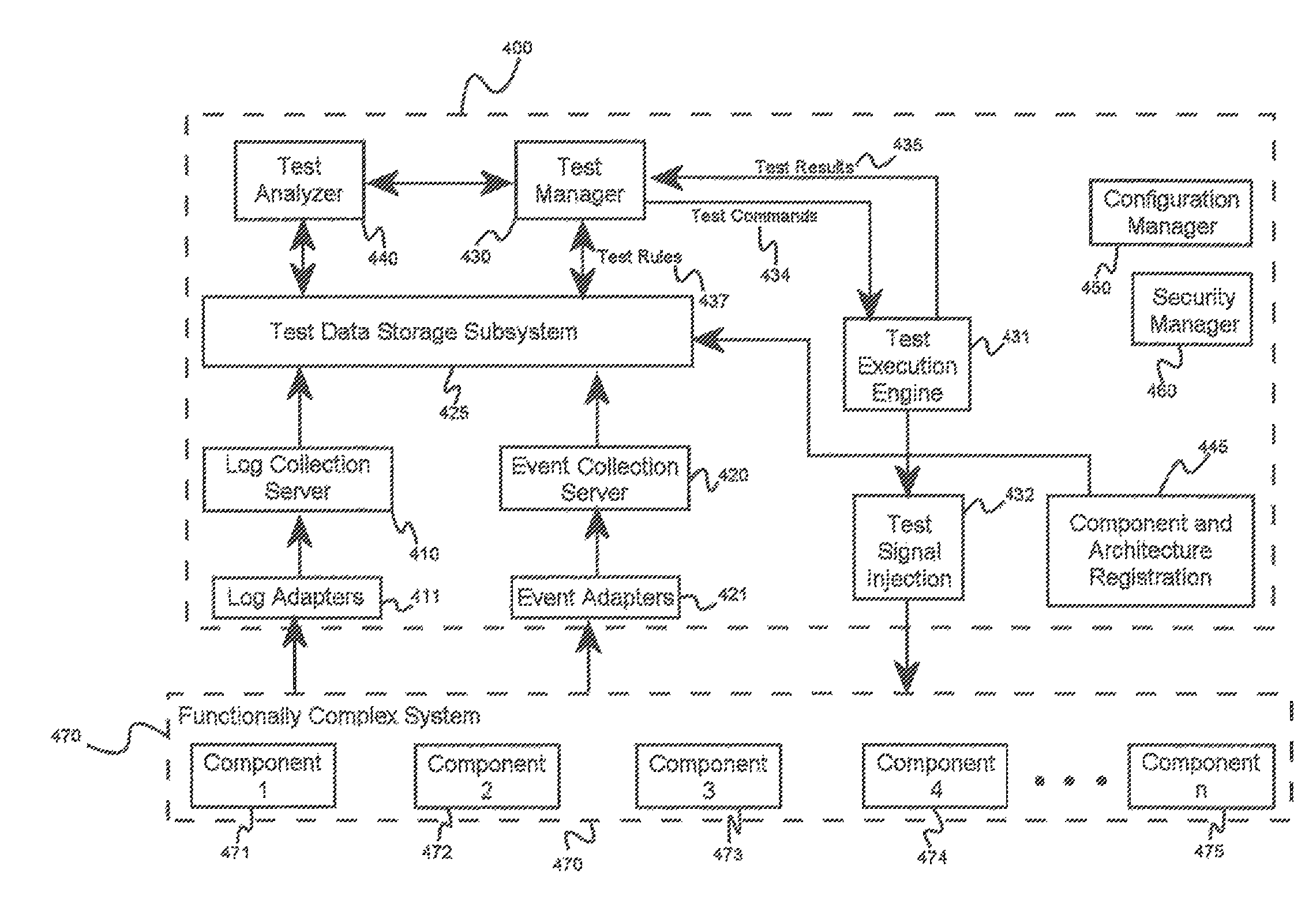
System and methods for automated testing of functionally complex systems
ActiveUS8418000B1Avoid mistakesNon-redundant fault processingTransmissionComputer hardwareAnomalous behavior
A system for automated testing of functionally complex systems, comprising a test manager module operating on a server computer, a test data storage subsystem coupled to the test manager module and adapted to store at least test results, a test execution module operating on a server computer, and a test analysis module operating on a server computer and adapted to receive test data from the test data storage subsystem. The test manager module causes tests to be executed by the test execution engine, and on detection of an anomalous test result, the test manager module at least causes additional testing to be performed and causes the test analysis module to analyze the results of at least some of the additional testing in order to isolate at least one component exhibiting anomalous behavior.
Owner:BFACTOR LLC
Asset tracking within and across enterprise boundaries
InactiveUS6237051B1Hand manipulated computer devicesSpecial service for subscribersRelational databaseGeolocation
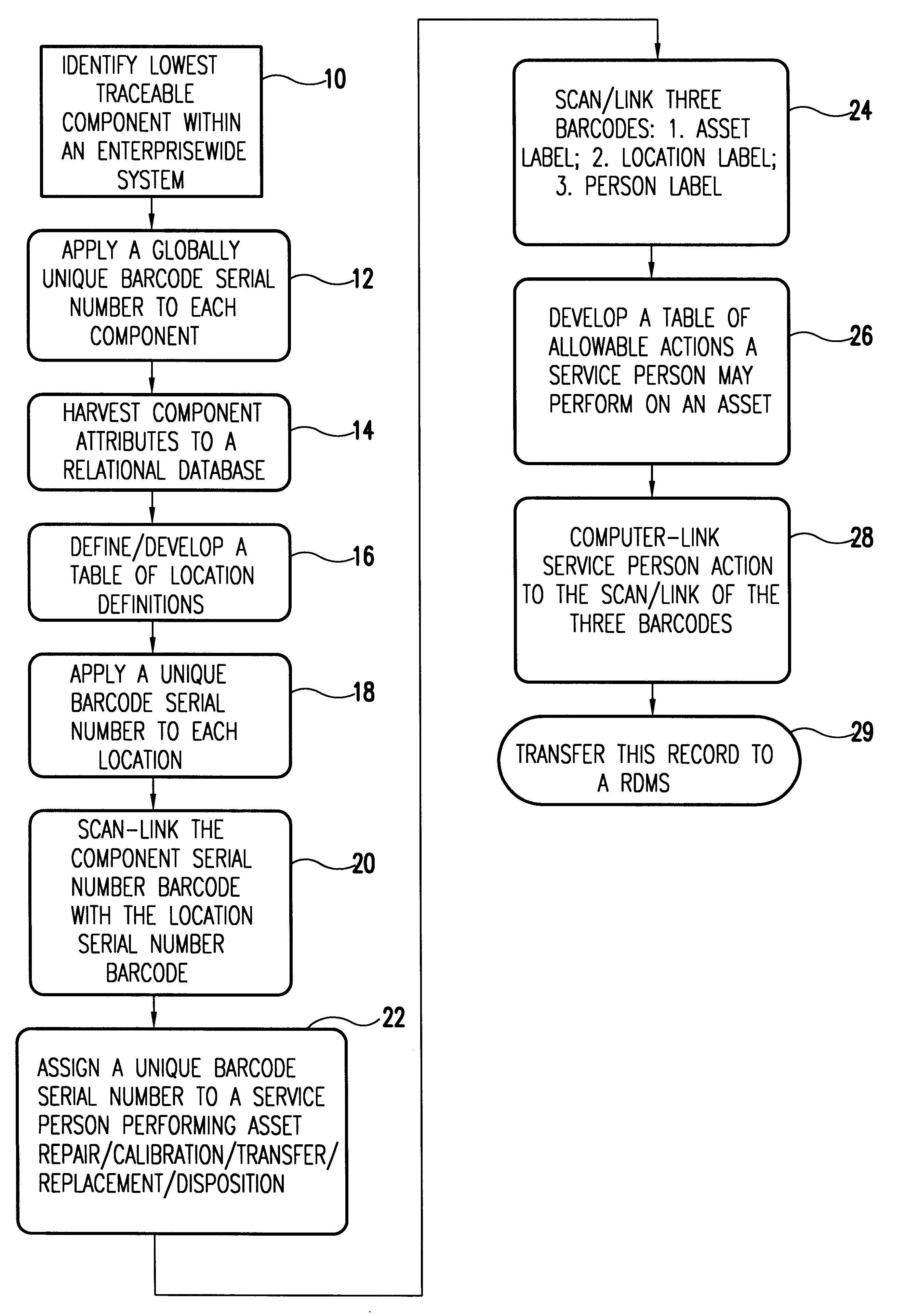
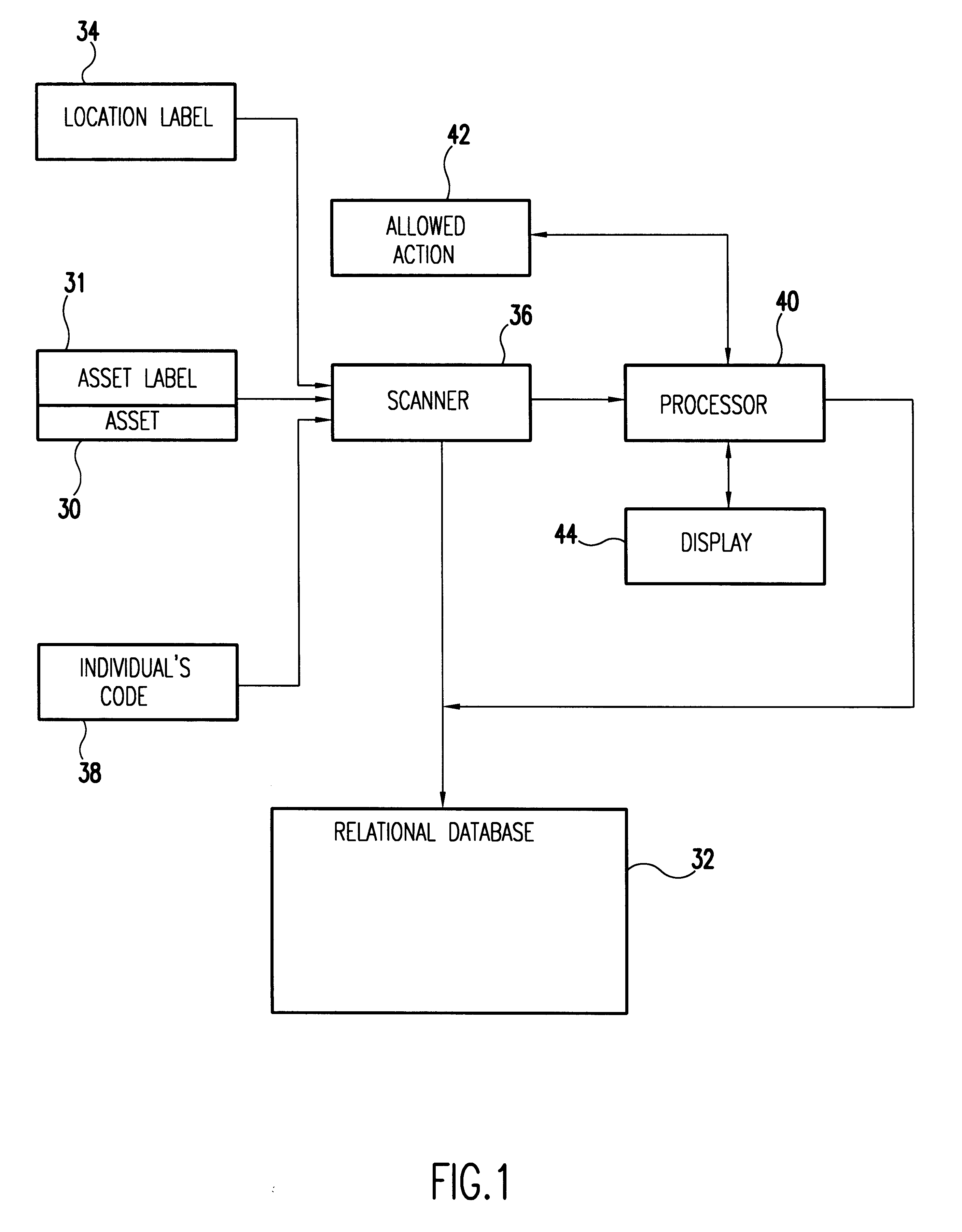
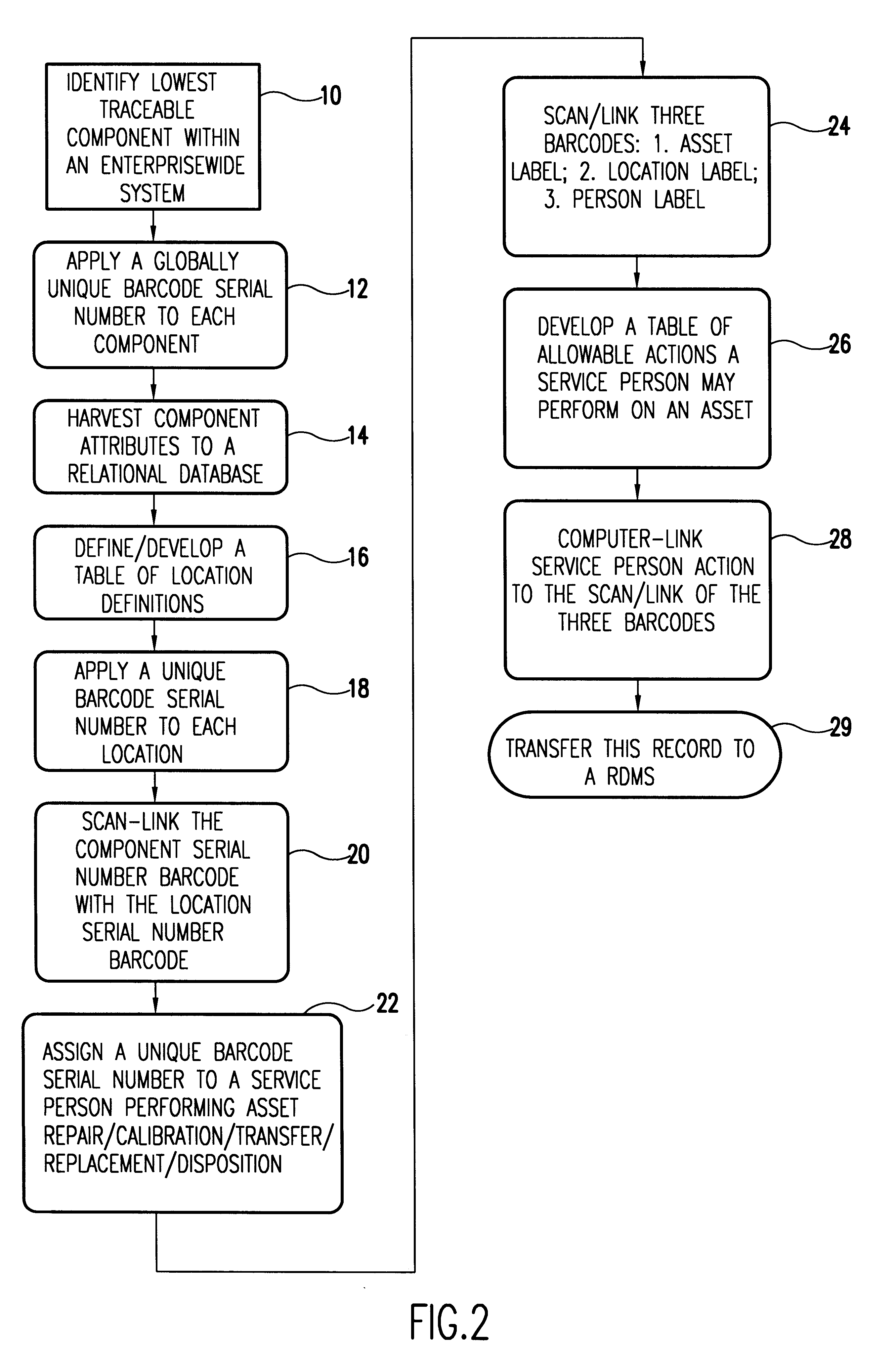
A unique data label is affixed to each tracked asset and a unique data label for each location in the enterprise, both real and virtual locations. Location history data of the asset is related to other asset data in a relational data base. Assets typically include system components down to the least repairable / replaceable unit (LRU). The data label, in the preferred embodiment of the invention, is a code label using a code that ensures each label is unique to the asset or location to which it is attached. Here the word location is an inclusive term. It includes the geographical location and the identity of the building in which the asset is housed. Location also includes the identity of the system of which a component is a part and, if relevant, location within the system. It includes also any real or virtual location of interest for subsequent analysis and is ultimately defined by the nature of the system being tracked.People assigned to install, upgrade, maintain, and do other work on the system are identified and this identifying data is entered into the data base along with each activity performed on the system and its components. Preferably, in response to a scanned asset label, a menu of allowable activities is presented so that the person assigned to do a task associated with the asset can easily make entries into the data base of the code assigned to the task performed. With asset data, asset location, and task record (including the person performing the task), entered into the relational data base, it is relatively easy to track the components of complex systems in a large enterprise over time and build complex relational records.
Owner:RATEZE REMOTE MGMT LLC +1
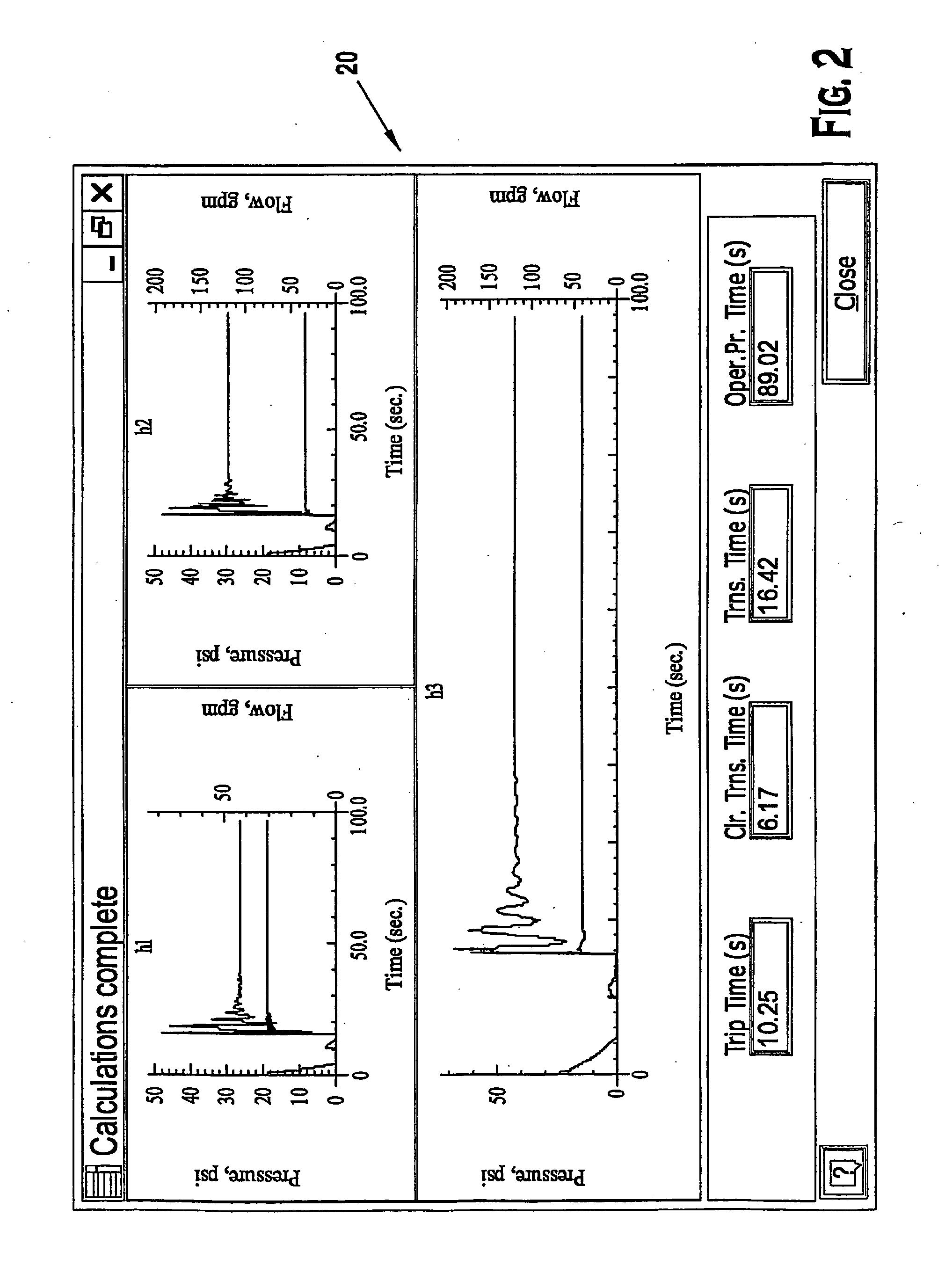
Complex system serviceability design evaluation method and apparatus
InactiveUS7249284B2Facilitate establishingEase of evaluationFault responseRegistering/indicating quality control systemsService modelField replaceable unit
A technique is provided for designing and evaluating service models for components, functions, subsystems and field replaceable units in a complex machine system. At a component or item level, each model identifies various items, failure modes, and so forth which may be the root cause of anticipated serviceable events or faults. The design tools permit numerous interfaces to be used in the design of service models, and in the evaluation of the degree to which the models address detectability and isolation capabilities for the root causes of serviceable events and faults.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYSTEMS INC
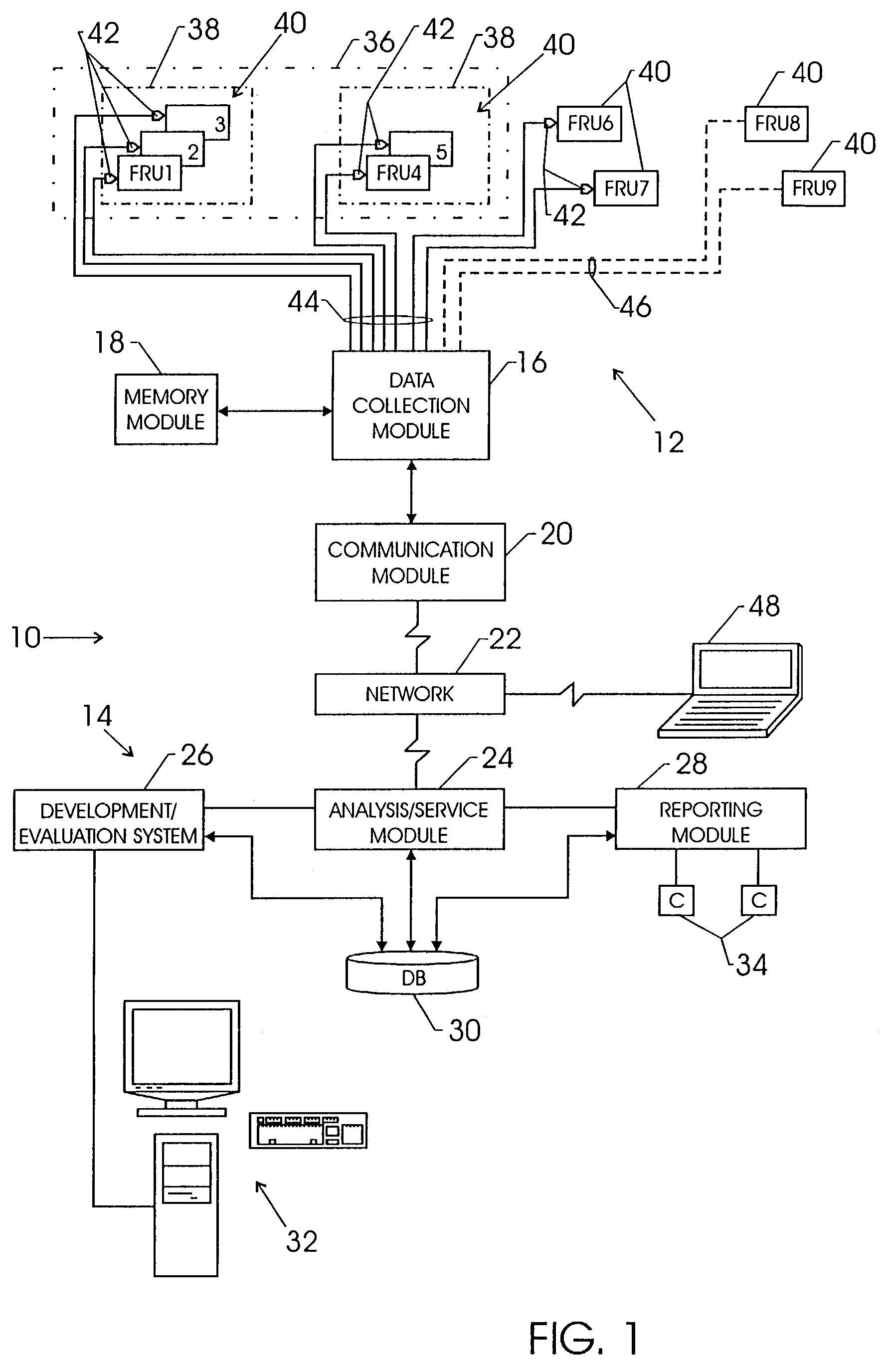
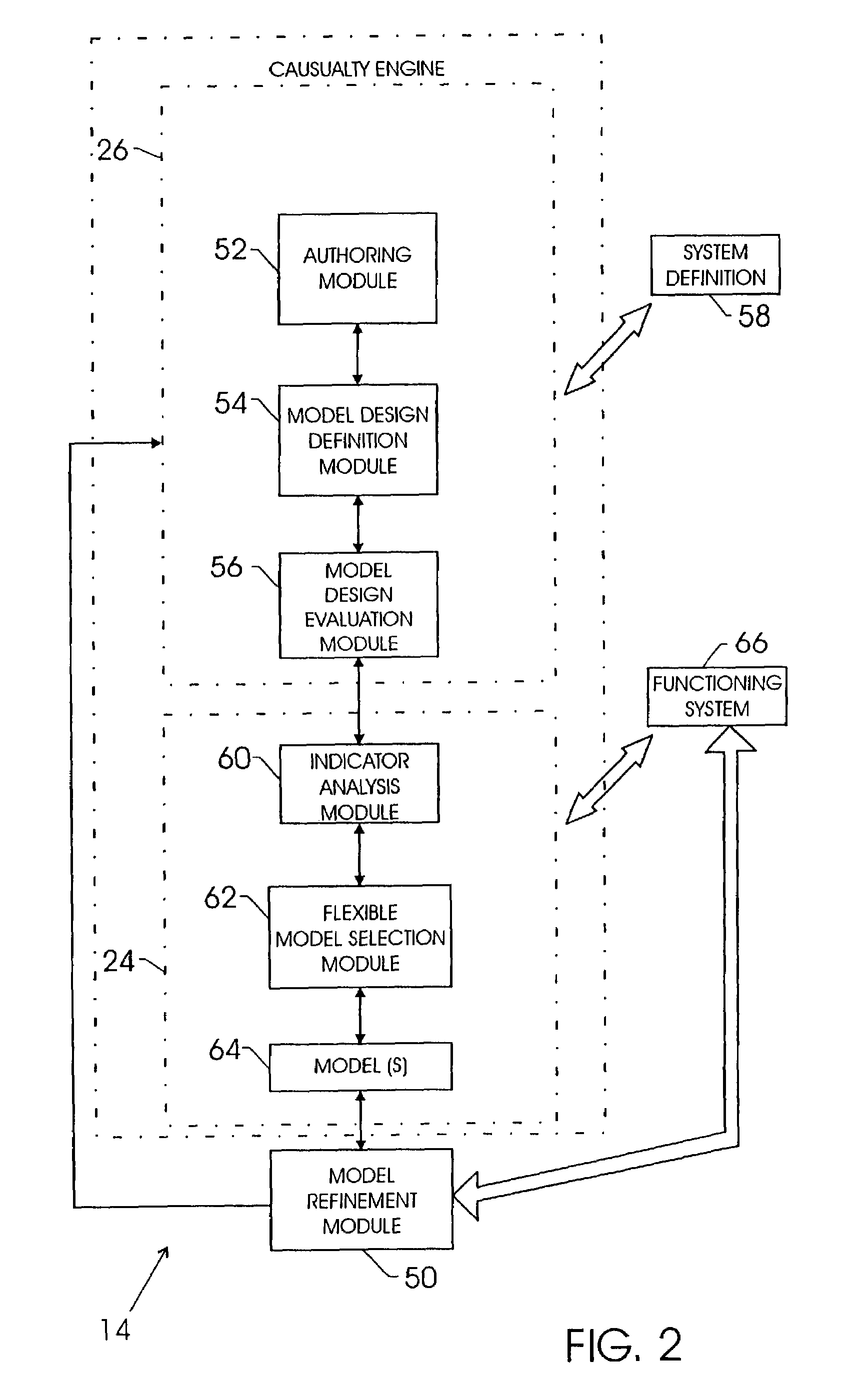
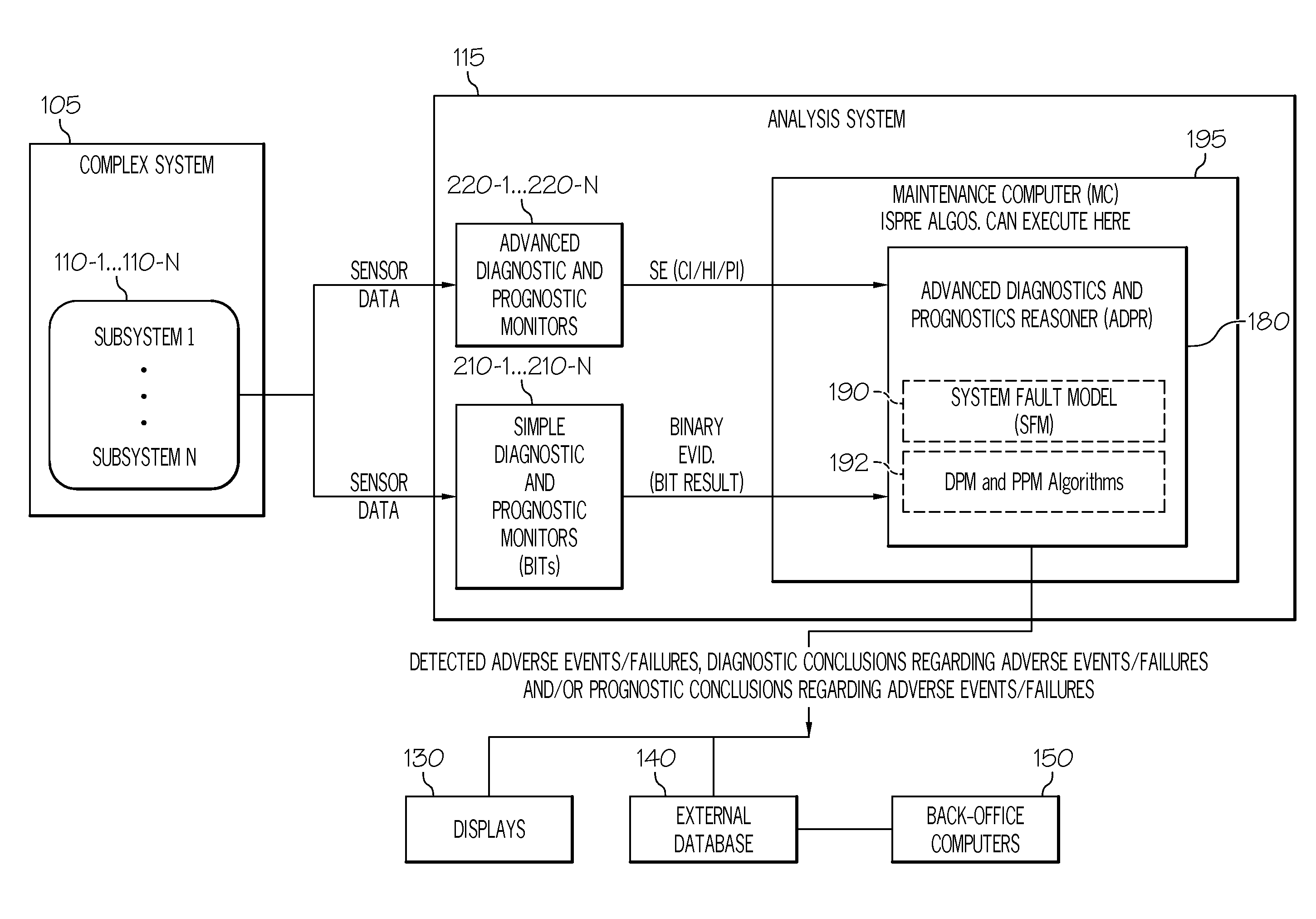
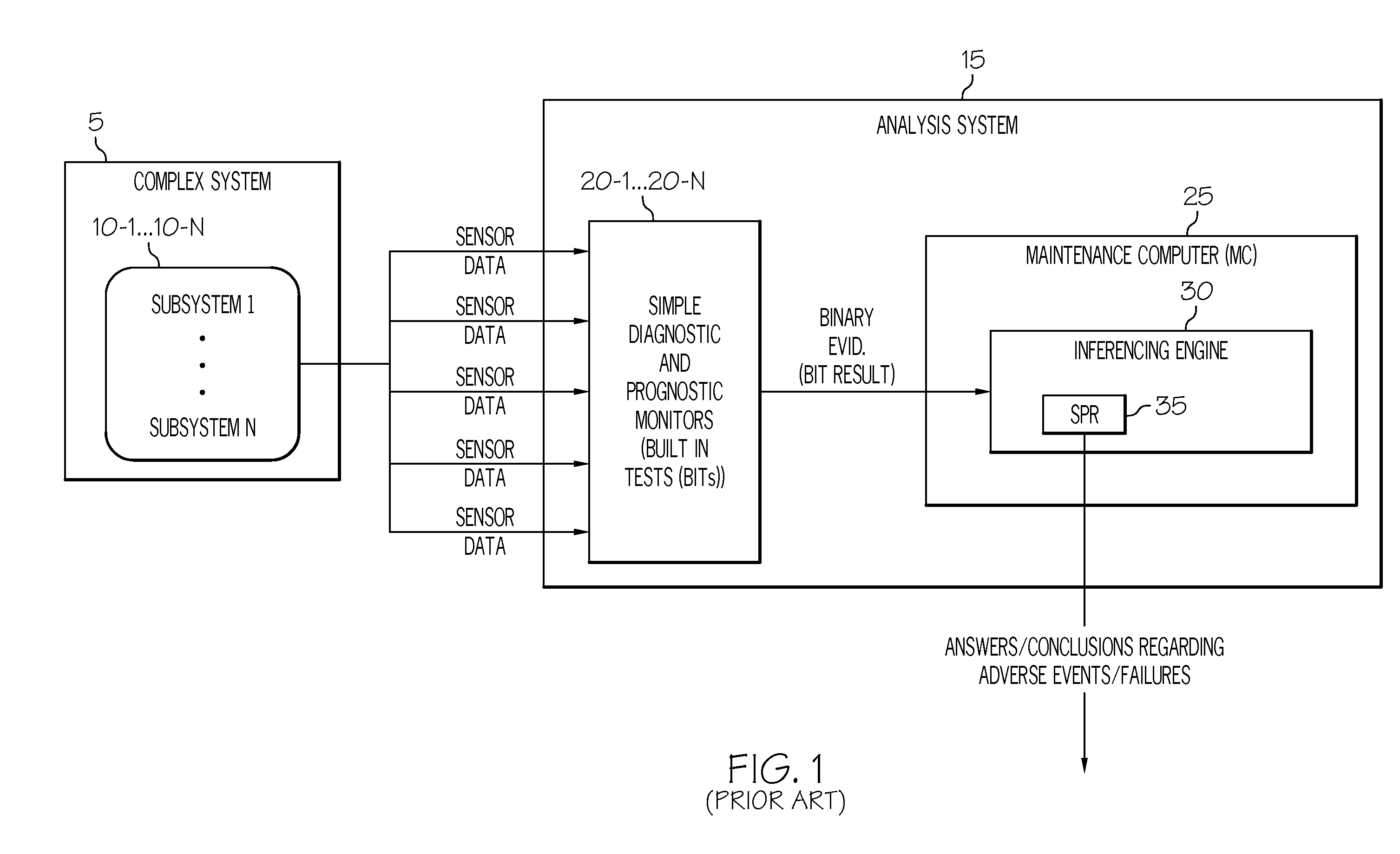
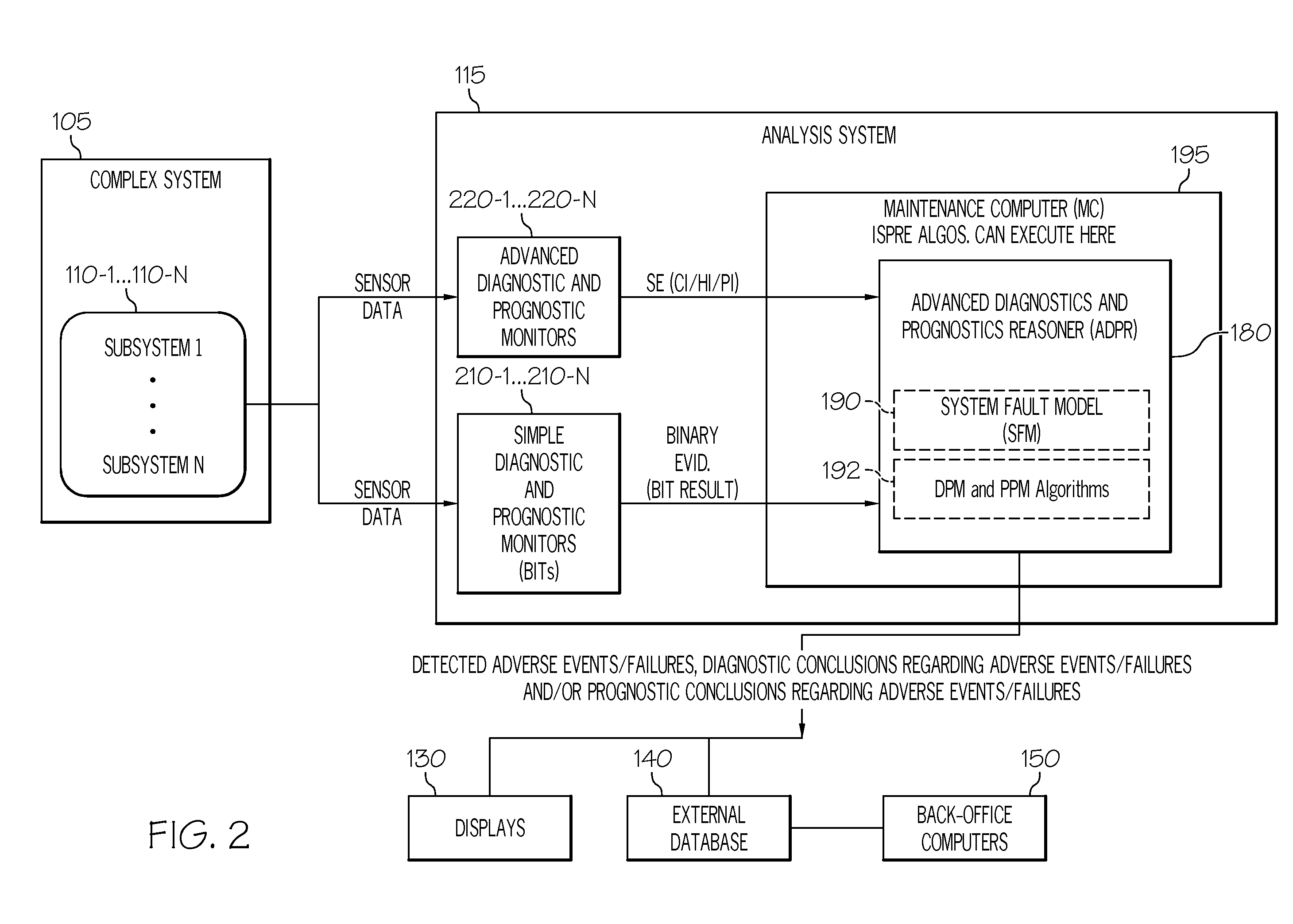
Methods systems and apparatus for analyzing complex systems via prognostic reasoning
ActiveUS20110118905A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesStatistical relationSystem failure
Methods and apparatus are provided for analyzing a complex system that includes a number of subsystems. Each subsystem comprises at least one sensor designed to generate sensor data. Sensor data from at least one of the sensors is processed to generate binary evidence of a sensed event, and complex evidence of a sensed event. The complex evidence has more sophisticated mathematical properties than the binary evidence. The complex evidence comprises one or more of: a condition indicator (CI), a health indicator (HI), and a prognostic indicator (PI). A system fault model (SFM) is provided that defines statistical relationships between binary evidence, complex evidence, and an underlying failure mode (FM) that is occurring in the complex system. The binary evidence and the complex evidence are processed to identify failure modes taking place within one or more of the subsystems. Based on the binary evidence and the complex evidence and the SFM, diagnostic conclusions can be generated regarding adverse events that are taking place within the complex system, and prognostic conclusions can be generated regarding adverse events that are predicted to take place within the complex system.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Automatically adapting user interfaces for hands-free interaction
InactiveCN103959751AEasy to operateOperation regulationDevices with voice recognitionSubstation equipmentHands freeComplex system
A user interface for a system such as a virtual assistant is automatically adapted for hands-free use. A hands-free context is detected via automatic or manual means, and the system adapts various stages of a complex interactive system to modify the user experience to reflect the particular limitations of such a context. The system of the present invention thus allows for a single implementation of a complex system such as a virtual assistant to dynamically offer user interface elements and alter user interface behavior to allow hands-free use without compromising the user experience of the same system for hands-on use.
Owner:APPLE INC
Fault predicting and diagnosing method suitable for dynamic complex system
InactiveCN102208028AOvercome the drawbacks of harsh restrictionsImprove general performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionPrediction intervalSystem failure
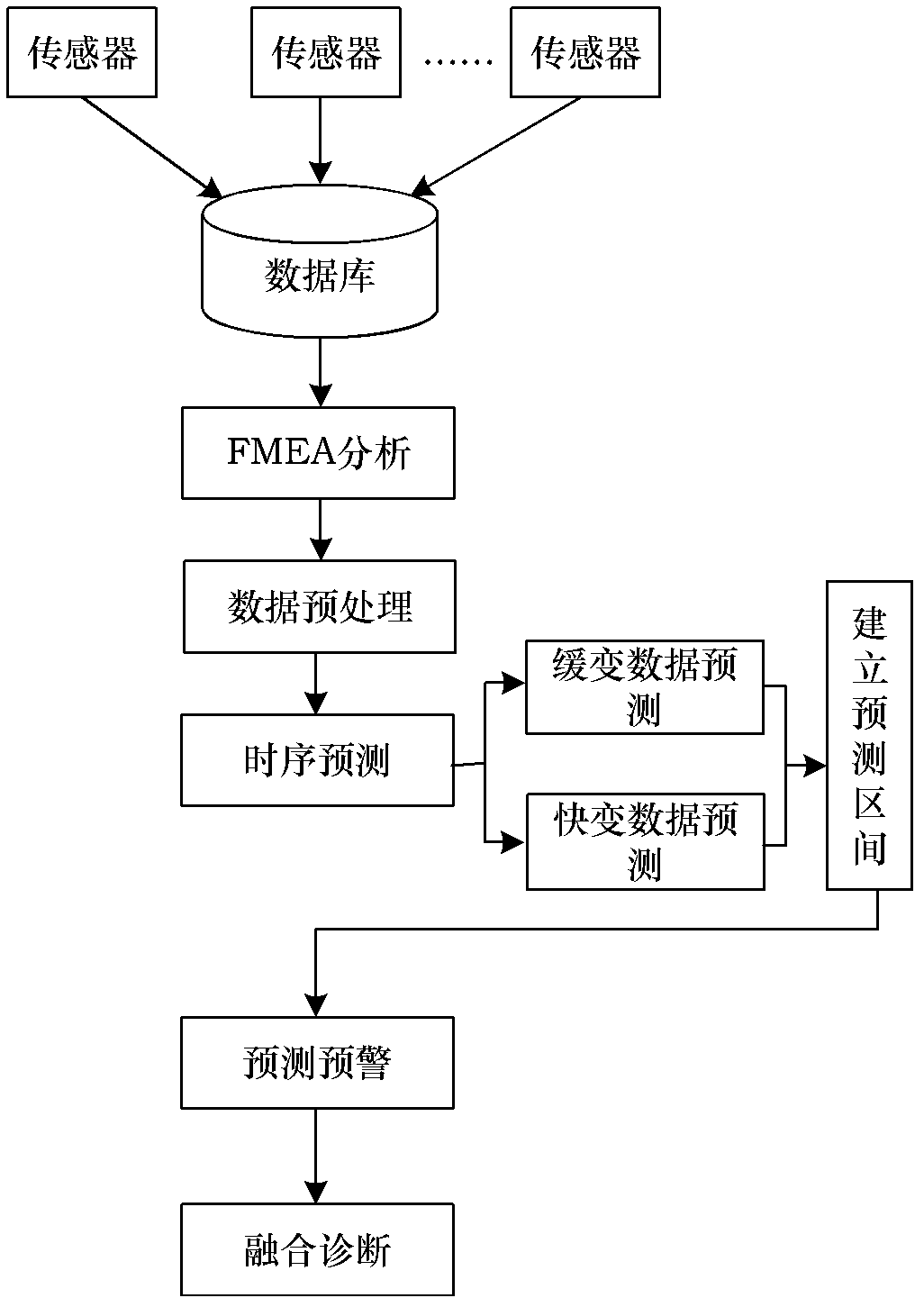
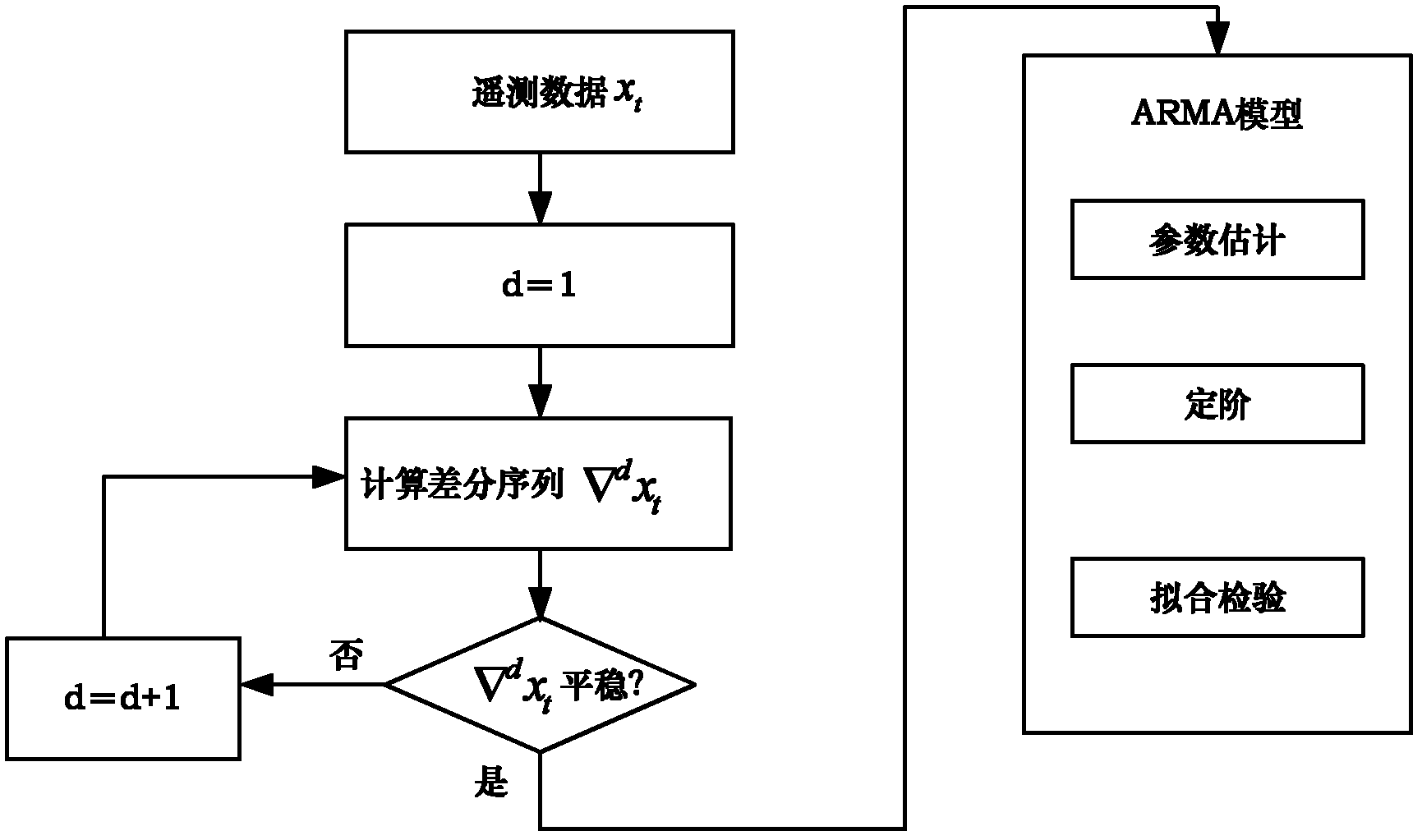
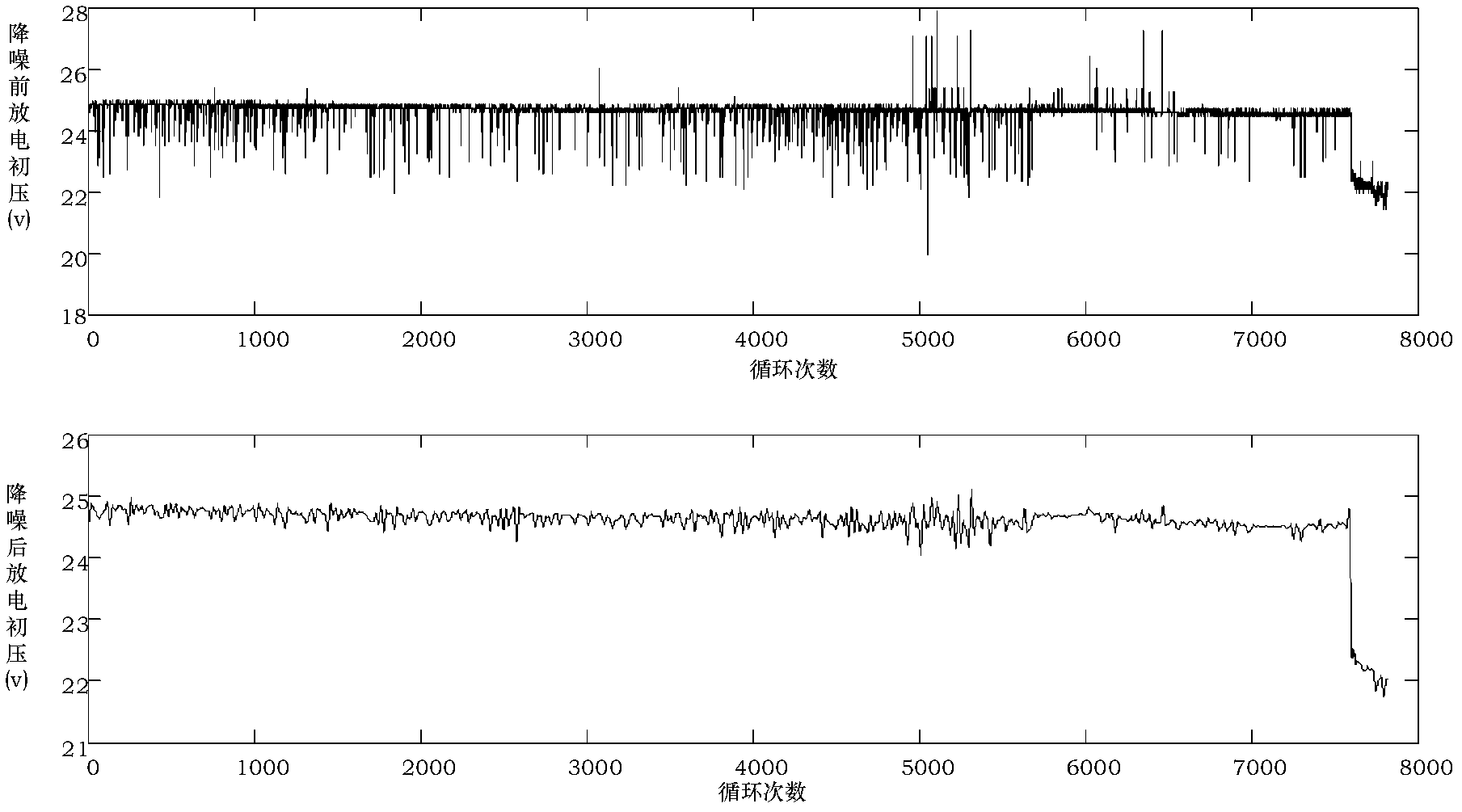
The invention provides a fault predicting and diagnosing method suitable for a dynamic complex system. The method can be applied in the field of fault prediction and diagnosis of dynamic complex systems of spacecrafts and the like. The method comprises the following steps of: performing failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) on the dynamic complex system to obtain a main fault mode and corresponding performance detection parameters, dividing the performance detection parameters into slowly variable data and fast variable data, pre-processing the performance detection parameters, establishingan autoregressive moving average model (ARMA) aiming at the slowly variable data to perform time sequence prediction, establishing a multi-resolution wavelet neural network aiming at the fast variable data to perform time sequence prediction, performing fault early warning on the time sequence prediction results by establishing a prediction interval model, and performing fault diagnosis by establishing a D-S (Dempster-Shafer) evidence theory-based multi-signal fusion model. The method can be used for predicting and diagnosing the faults of the dynamic complex system with high precision, and has strong universality.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
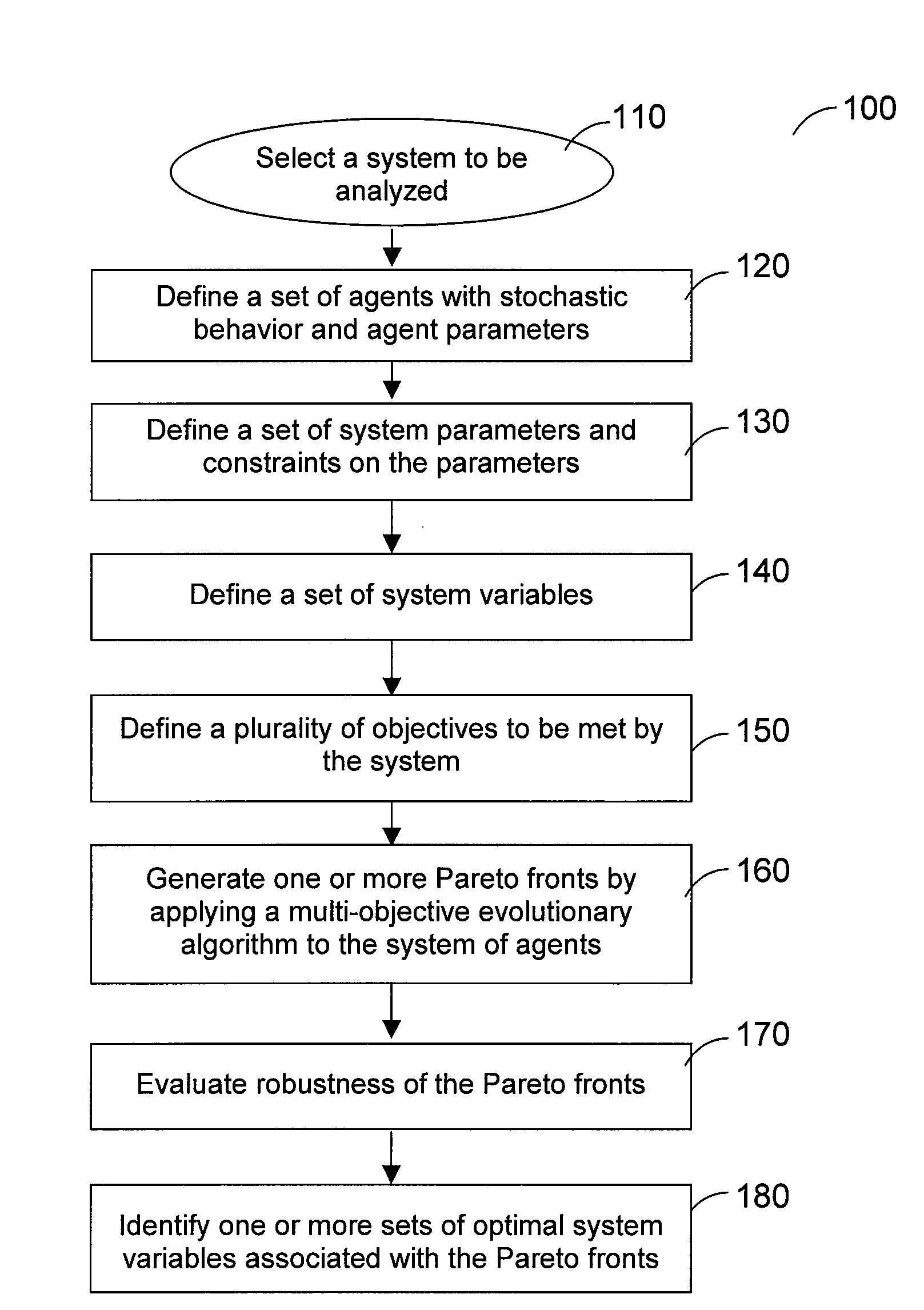
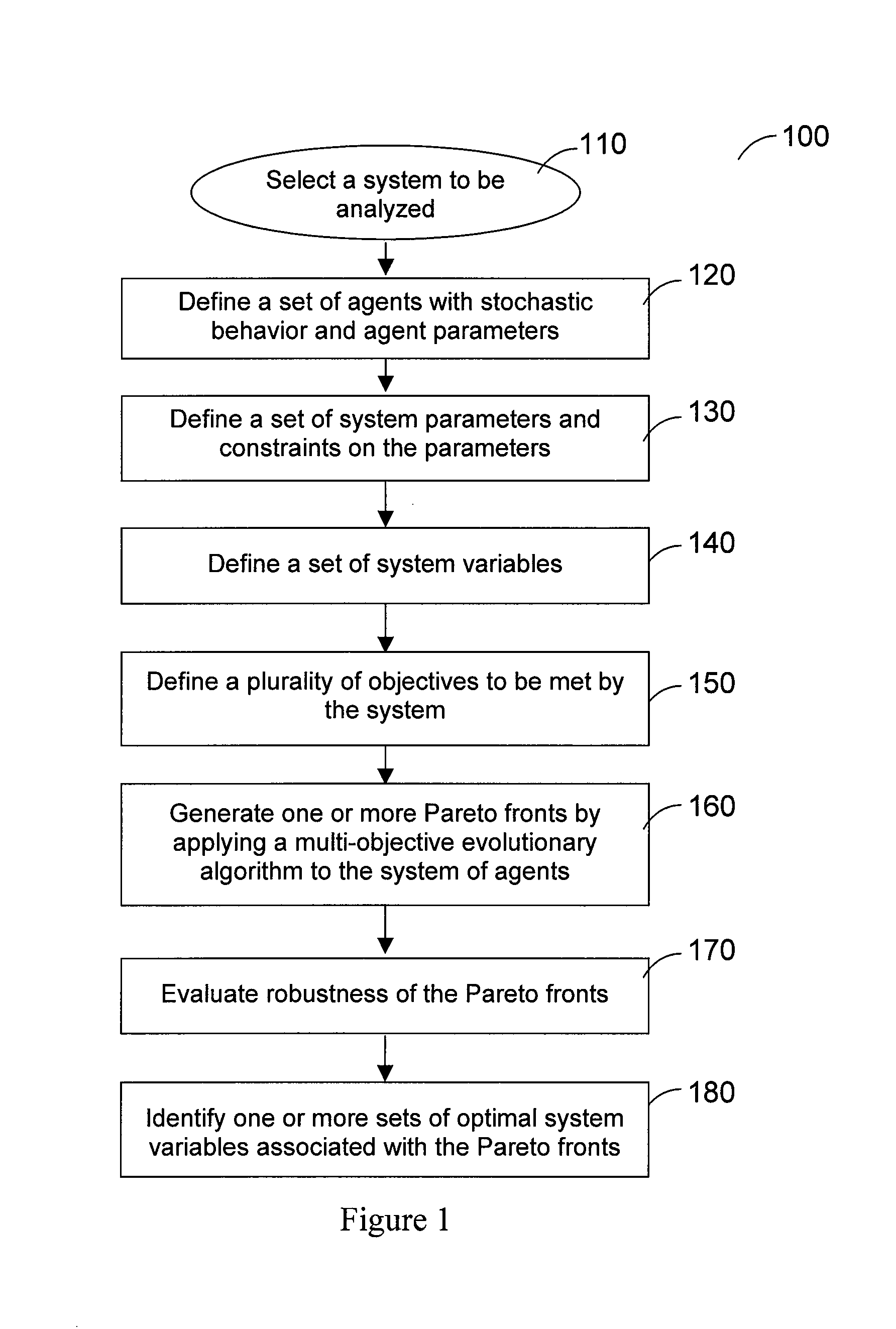
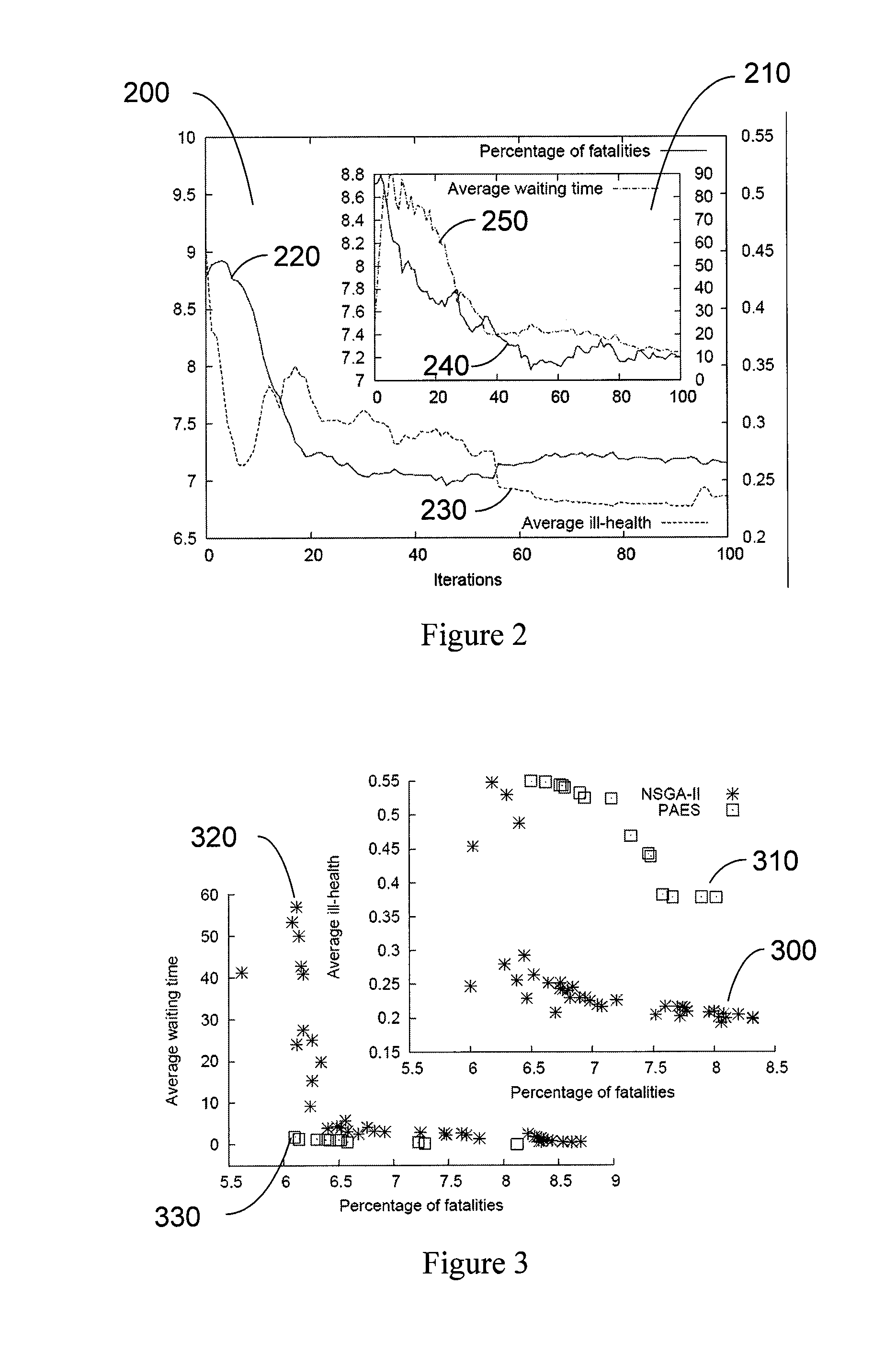
System, method, and computer-accessible medium for providing a multi-objective evolutionary optimization of agent-based models
InactiveUS20080215512A1Easy to analyzeDigital computer detailsElectric digital data processingProblem descriptionAlgorithm
Agent-based models (ABMs) / multi-agent systems (MASs) are one of the most widely used modeling-simulation-analysis approaches for understanding the dynamical behavior of complex systems. These models can be often characterized by several parameters with nonlinear interactions which together determine the global system dynamics, usually measured by different conflicting criteria. One problem that can emerge is that of tuning the controllable system parameters at the local level, in order to reach some desirable global behavior. According to one exemplary embodiment t of the present invention, the tuning of an ABM for emergency response planning can be cast as a multi-objective optimization problem (MOOP). Further, the use of multi-objective evolutionary algorithms (MOEAs) and procedures for exploration and optimization of the resultant search space can be utilized. It is possible to employ conventional MOEAs, e.g., the Nondominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II) and the Pareto Archived Evolution Strategy (PAES), and their performance can be tested for different pairs of objectives for plan evaluation. In the experimental results, the approximate Pareto front of the non-dominated solutions is effectively obtained. Further, a conflict between the proposed objectives can be seen. Additional robustness analysis may be performed to assist policy-makers in selecting a plan according to higher-level information or criteria which is likely not present in the original problem description.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
System and method for evaluation of fluid flow in a piping system
A method to model a complex system of pipes. The model takes into account the physical processes in a tree-type piping system and provides for an accurate modeling of a real world tree-type piping system. In a preferred embodiment, a computer program is provided for analyzing models of dry pipe systems. The computer program includes a user interface and a computational engine. The user interface allows a model of a dry pipe system to be defined and the computational engine determines a liquid flow time through the model of the dry pipe system. The computational engine provides a verification of the liquid flow time in a model of a referential dry pipe system within 20% of an actual liquid flow time in the referential dry pipe system.
Owner:TYCO FIRE PRODS LP
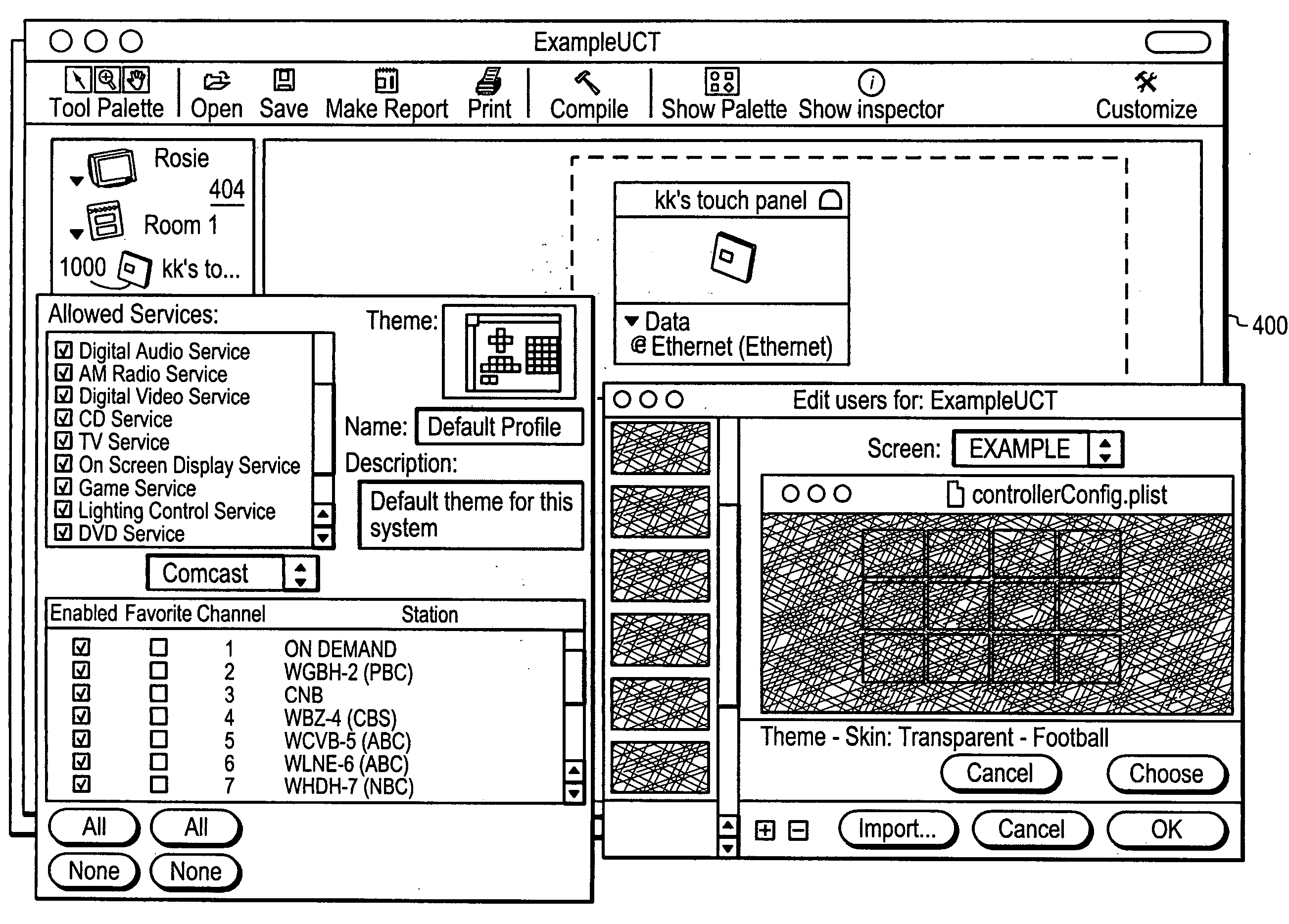
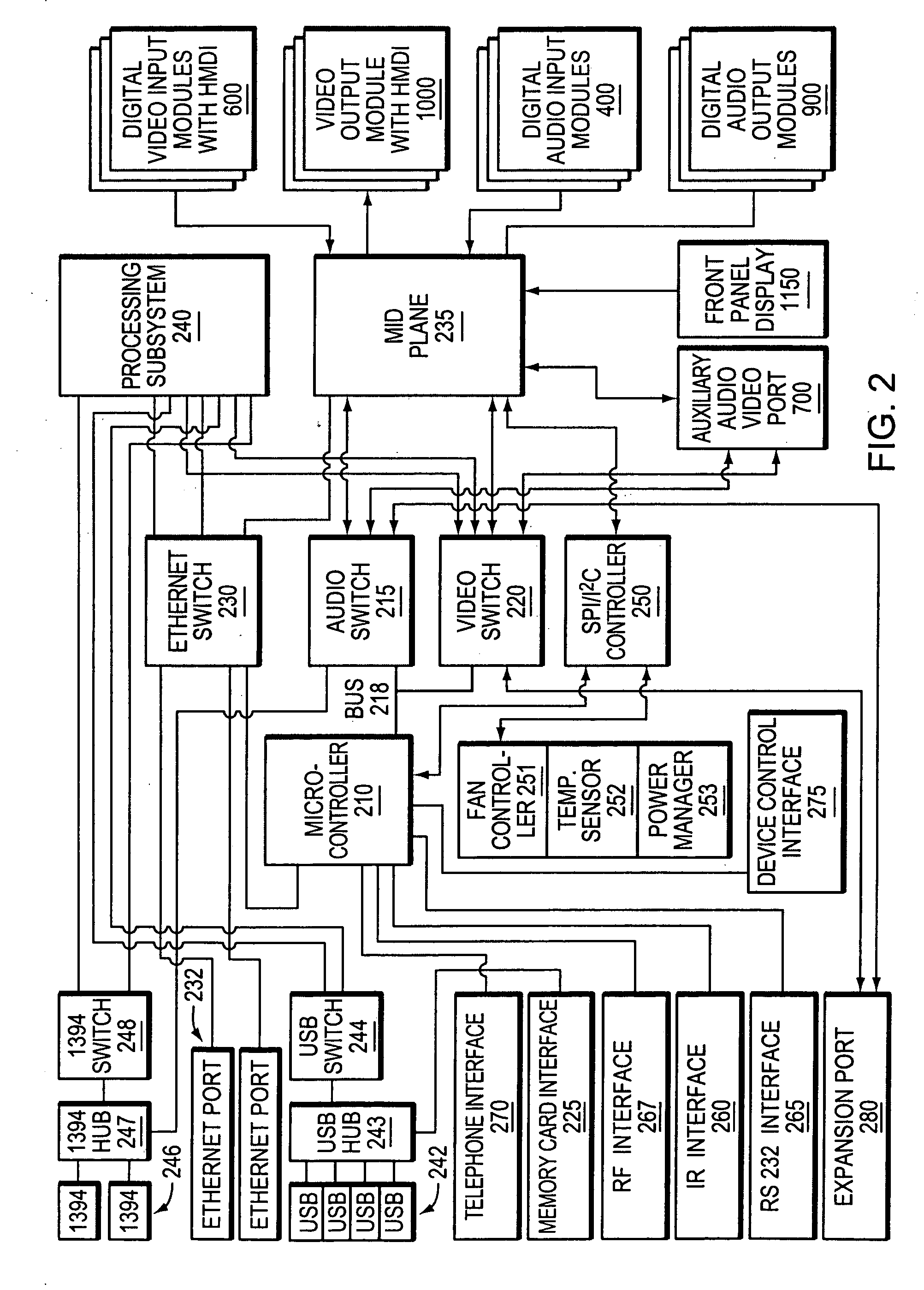
Programming environment and metadata management for programmable multimedia controller
ActiveUS20080127063A1Television system detailsTemperature control using digital meansGraphicsGraphical user interface
A multimedia controller, based on a general purpose computer, which is capable of interfacing with, controlling or managing a wide variety of audio, video, telecommunications, data communications or other devices. A configuration tool, based on a graphical user interface, provides a simple, schematic way to configure even highly complex systems having numerous components or devices which are to be interconnected with or interfaced to the multimedia controller. A user interface programming tool enables a user to customize the appearance and functionality of a graphical user interface to the multimedia controller. A metadata manager automatically collects metadata that is available within the multimedia controller, automatically detects the presence of new media and collects metadata from it, and may also access web resources to locate additional pertinent metadata.
Owner:SAVANT SYST INC
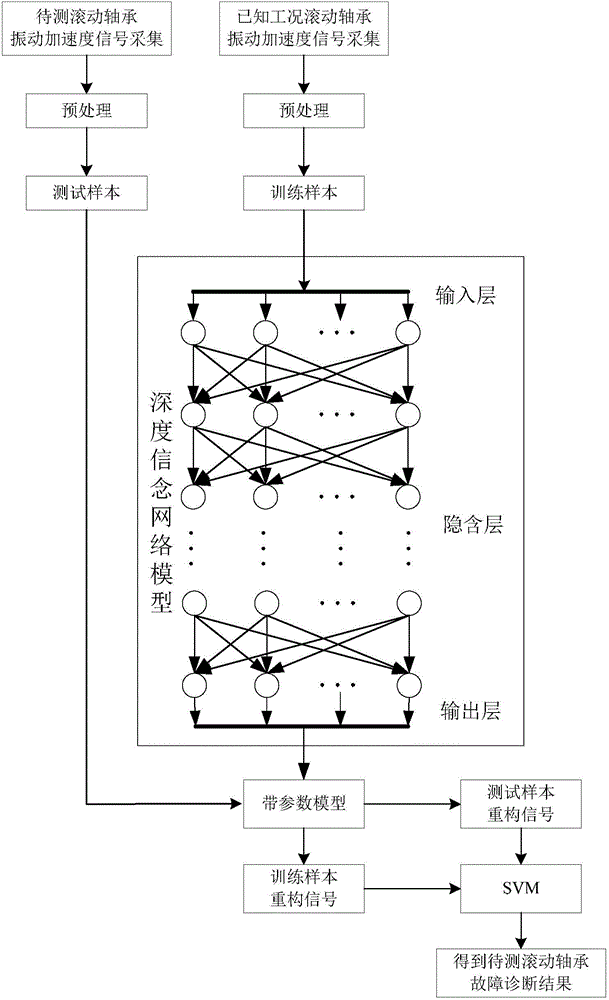
Fault diagnosis method for rolling bearing based on deep learning and SVM (Support Vector Machine)
InactiveCN104616033ASave human effortSolve the problem of local optimum solutionCharacter and pattern recognitionAviationDeep belief network
The invention provides a fault diagnosis method for a rolling bearing based on a deep learning and SVM (Support Vector Machine). The method comprises using a manure learning algorithm in a deep belief network theory to complete a characteristic extraction task needed by fault diagnosis; automatically extracting the substantive characteristics of data input independent of manual selection from simple to complicate, from low to high, and automatically digging abundant information concealed in known data; in addition, classifying and identifying a test sample by adopting an SVM classification method, seeking and finding a global minimum of a target function through an effective method previously designed, so as to solve the problem that a deep belief network may be trapped into a locally optimal solution. According to the fault diagnosis method for the rolling bearing based on the deep learning and SVM provided by the invention, the accuracy and effectiveness of the fault diagnosis method for a rolling bearing can be improved, and a new effective way can be provided to solve the accuracy and effectiveness of the fault diagnosis method, therefore the fault diagnosis method can be extensively applied complex systems in chemistry, metallurgy, electric power, aviation fields and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
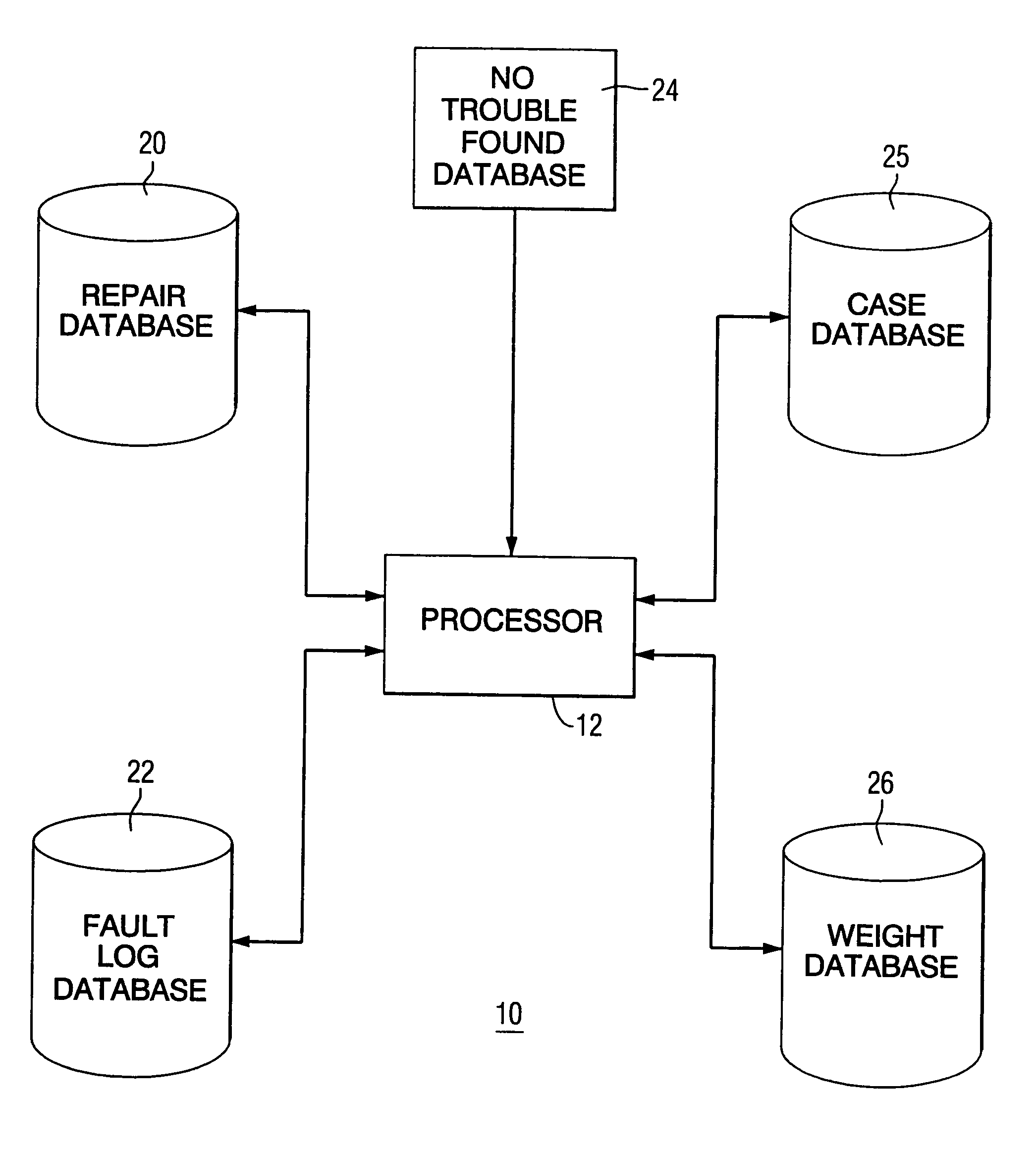
Method and apparatus for diagnosing difficult to diagnose faults in a complex system
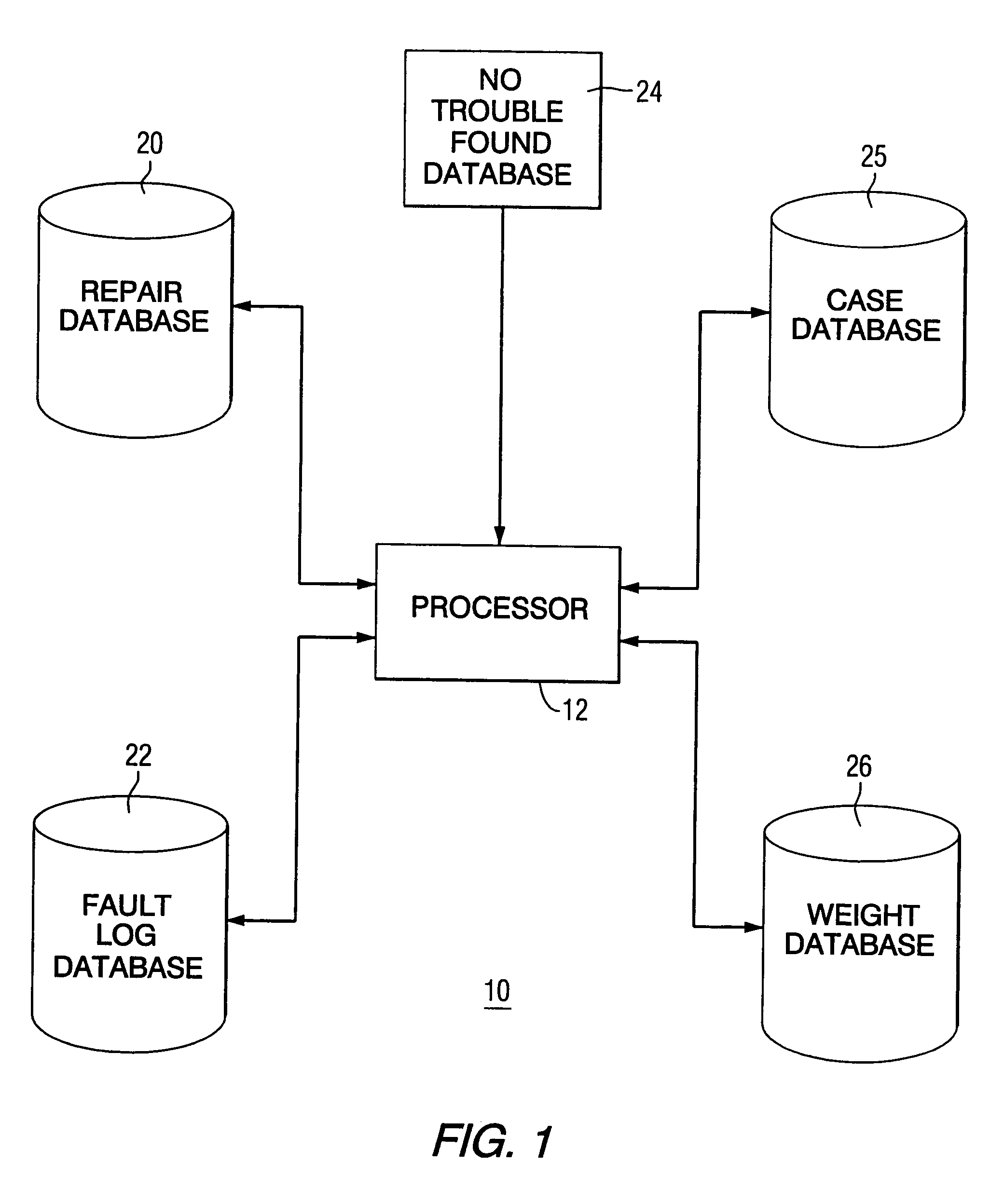
A method and apparatus for determining the root cause of no trouble found events in a machine is disclosed. The actual faults occurring during a predetermined time interval prior to the no trouble found event are analyzed and correlated with the no trouble found events in an effort to identify those actual faults that have a high correlation with each no trouble found event. If a high correlation is not found, then the no trouble found event is analyzed off-line to determine the root cause.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
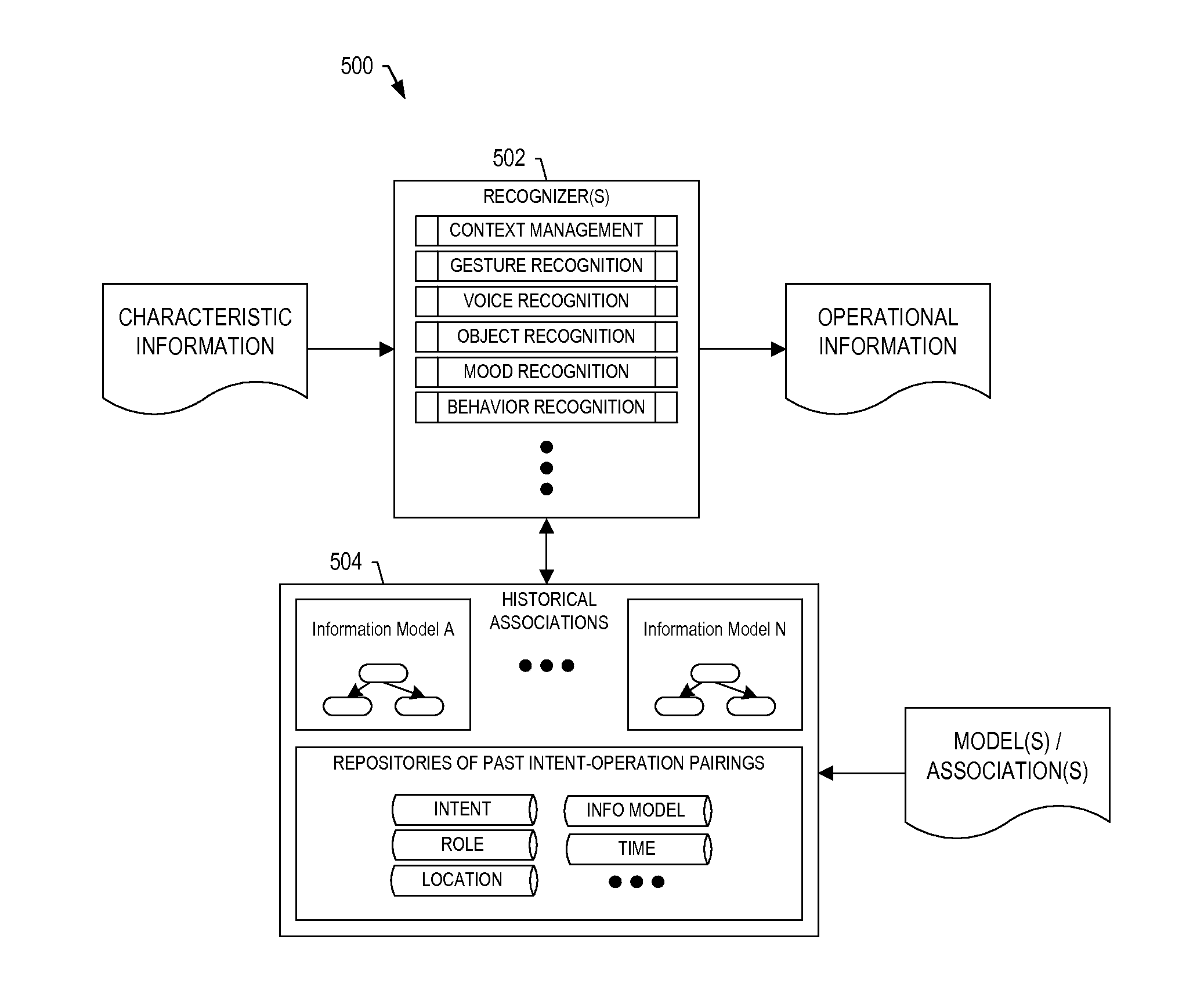
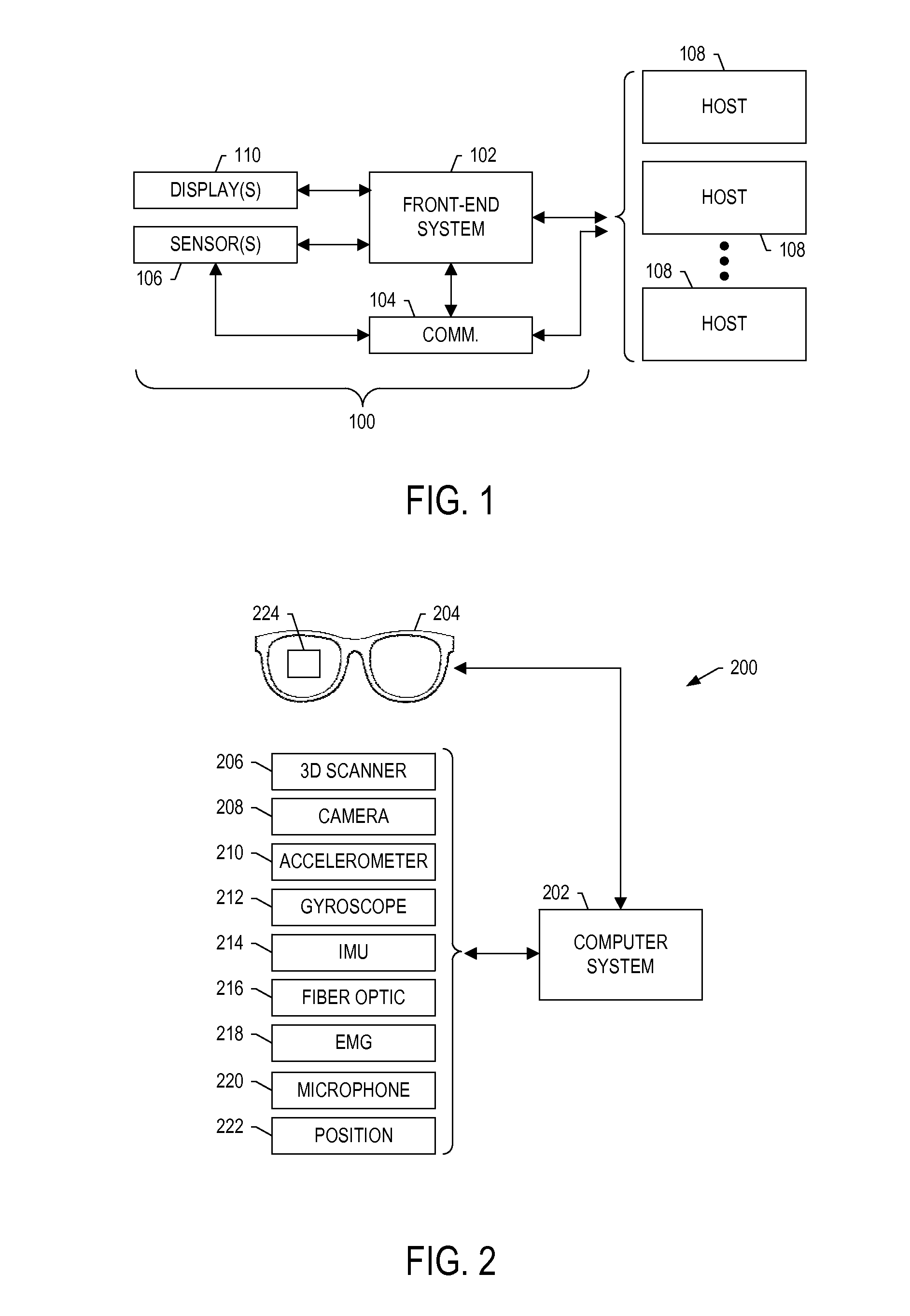
Tracking a user to support tasks performed on complex-system components
ActiveUS20140354529A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsEnd systemDisplay device
A system is provided that includes sensors(s) configured to provide sensed input including measurements of motion and / or orientation of a user during performance of a task to work a complex-system component. The system includes a front-end system configured to process the sensed input including the measurements to identify a known pattern that indicates a significance of the sensed input from which to identify operations of an electronic resource. The front-end system is configured to form and communicate an input to cause the electronic resource to perform the operations and produce an output. The operations include determination of an action of the user during performance of the task, or calculation of a process variable related to performance of the task, from the measurements. And the front-end system is configured to receive the output from the electronic resource, and communicate the output to a display device, audio output device or haptic sensor.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Advanced real-time grid monitoring system and method
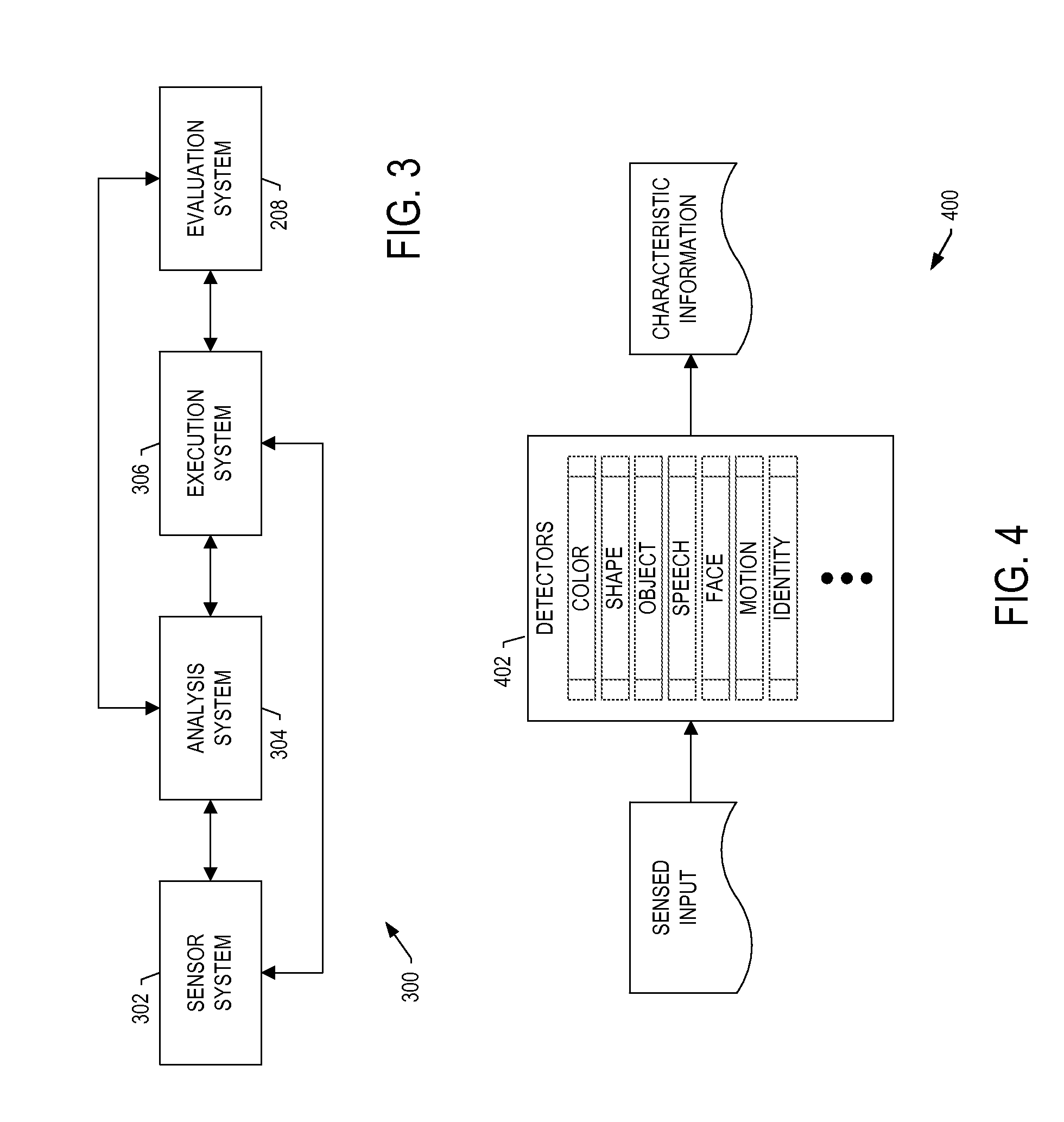
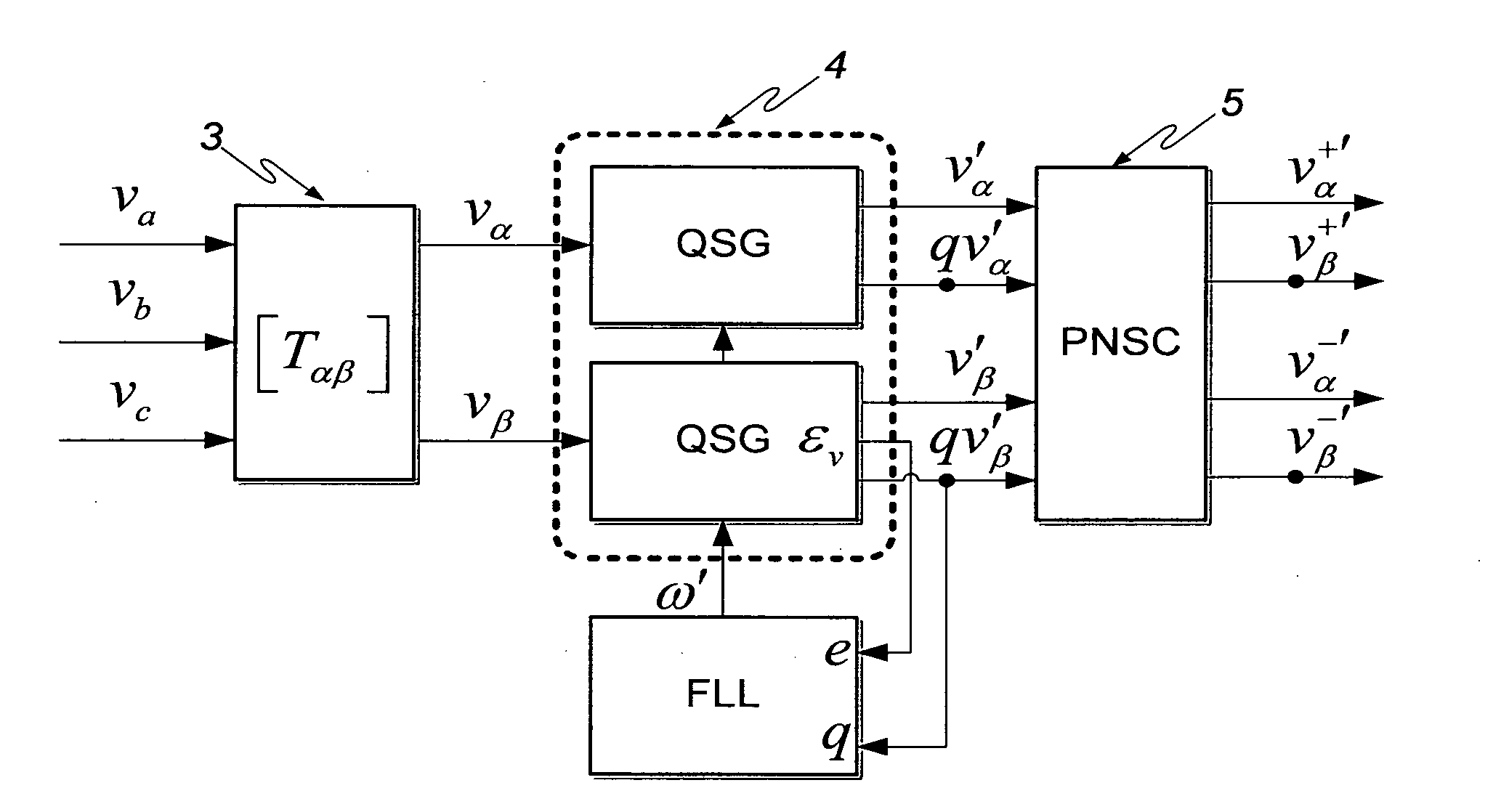
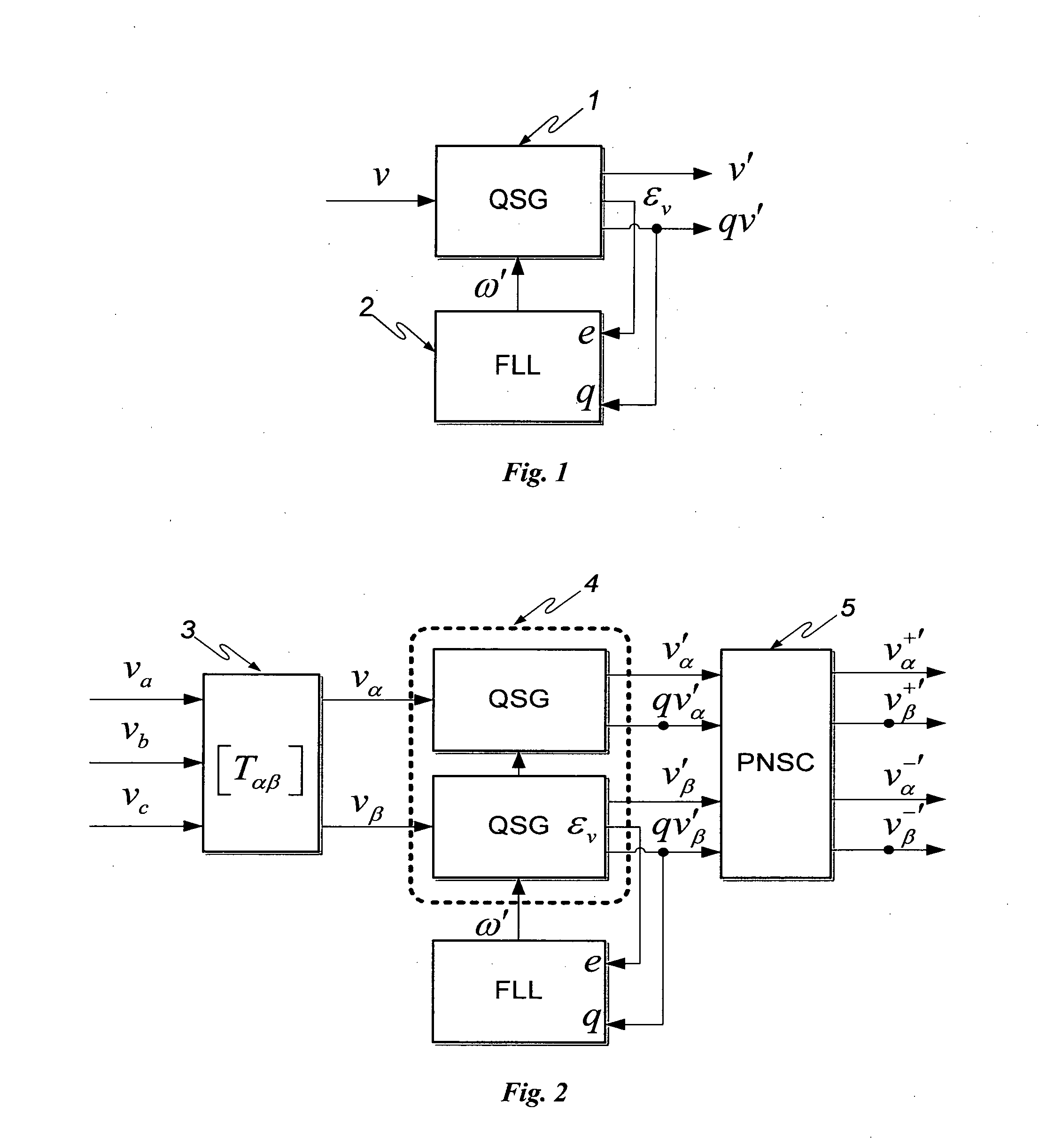
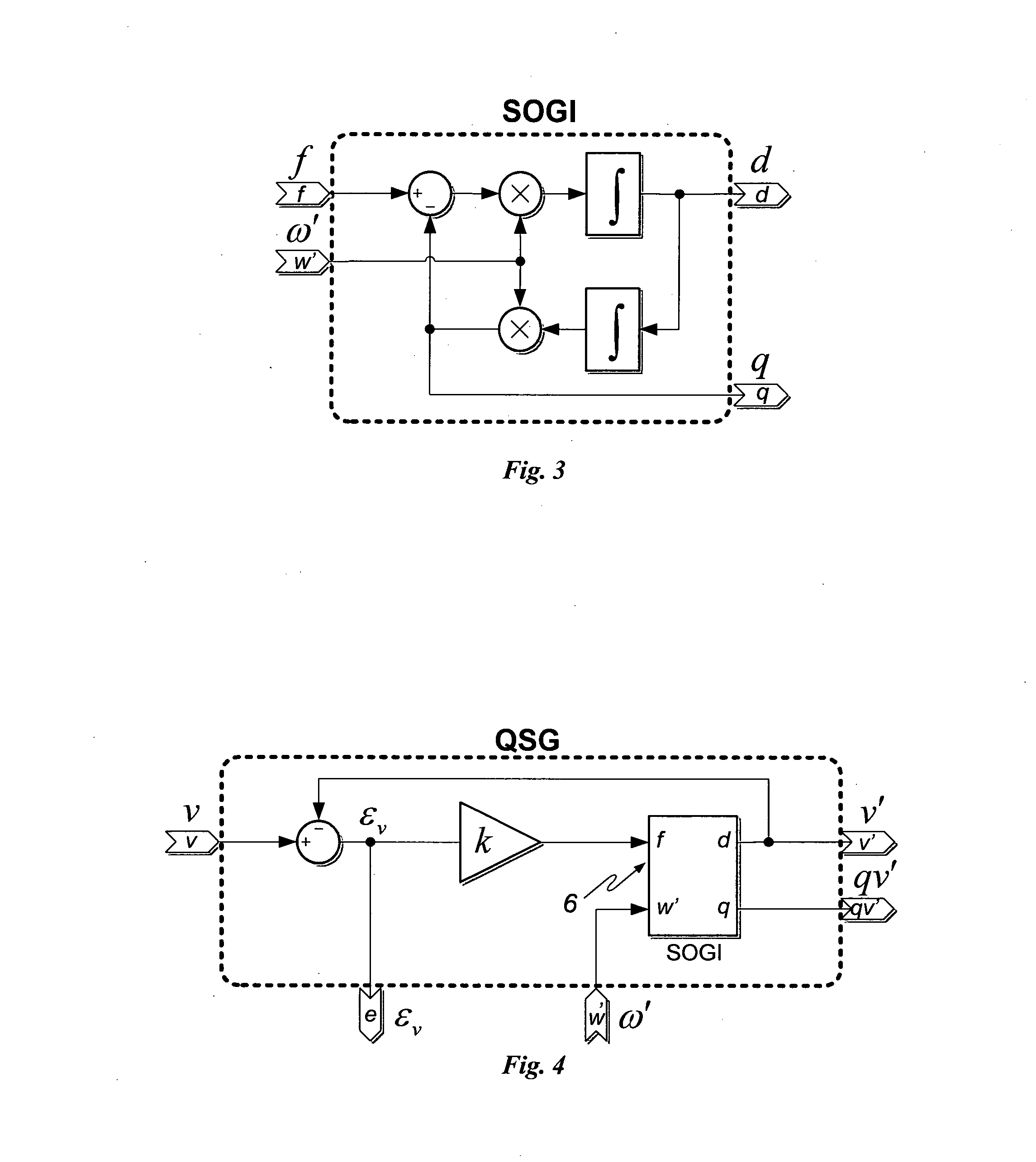
ActiveUS20100213925A1Efficient and robustIncreased computational burdenCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage-current phase anglePower qualityElectric power system
This invention deals with an advanced Real-time Grid Monitoring System (RTGMS) suitable for both single-phase and three-phase electric power systems. This invention provides an essential signal processing block to be used as a part of complex systems either focused on supervising and diagnosing power systems or devoted to control power processors interacting with the grid. This invention is based on a new algorithm very suitable for real-time characterization of the grid variables under distorted and unbalanced grid conditions. The main characteristic of this invention is the usage of a frequency-locked loop, based on detecting the grid frequency, for synchronizing to the grid variables. It results in a very robust system response in relation to existing technique based on the phase-angle detection since grid frequency is much more stable variable than the grid voltage / current phase-angle, mainly during grid faults. Moreover, the algorithm supporting this invention is very efficient and can be implemented in regular industrial microprocessors. These features make the RTGMS object of this invention ideal to be applied in the control of distributed generation systems (DGS), flexible AC transmission systems (FACTS), power quality conditioners (PQC) and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). In all these systems, the fast and precise real time detection of the voltage and / or current sequence components under grid fault conditions is a crucial matter.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
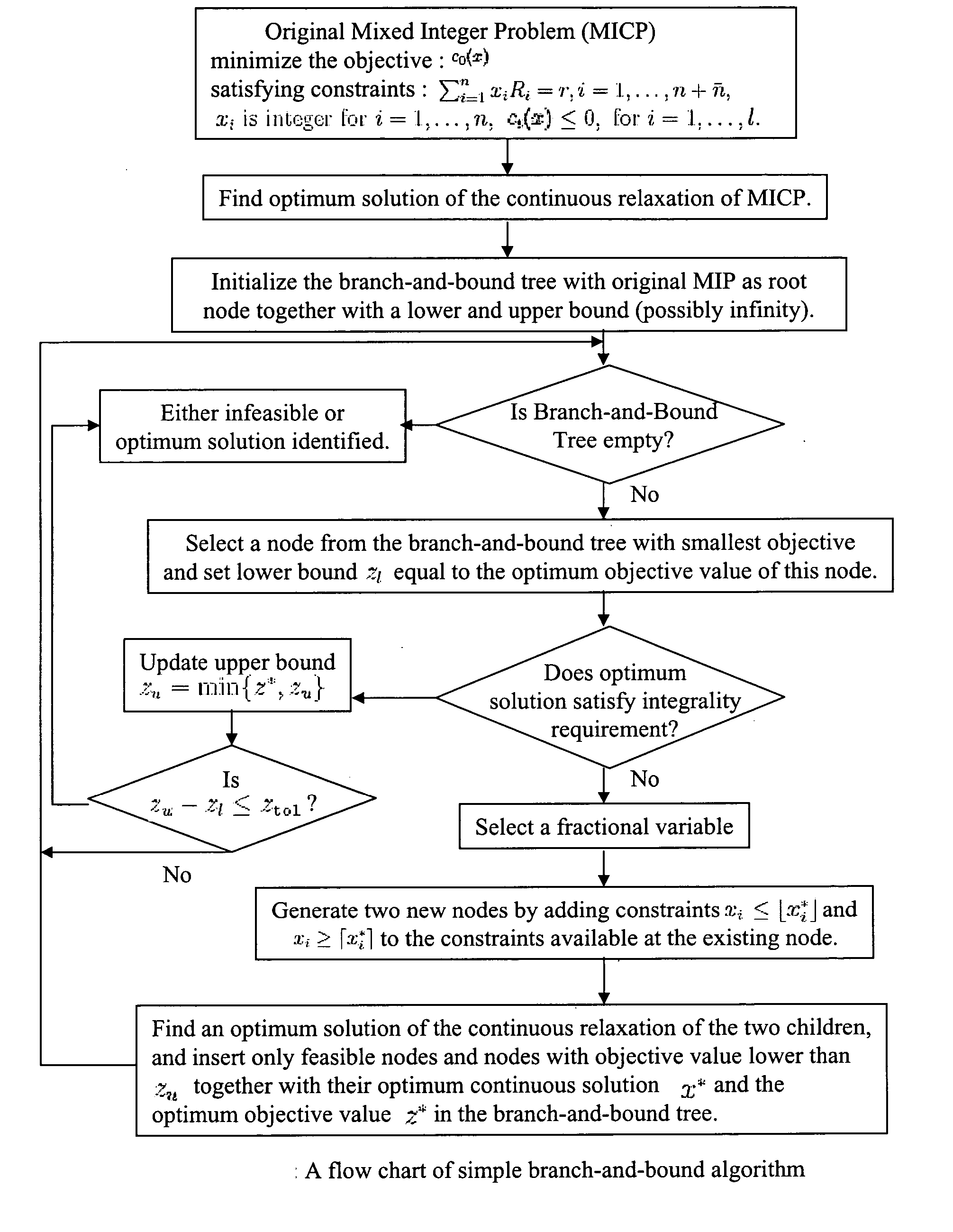
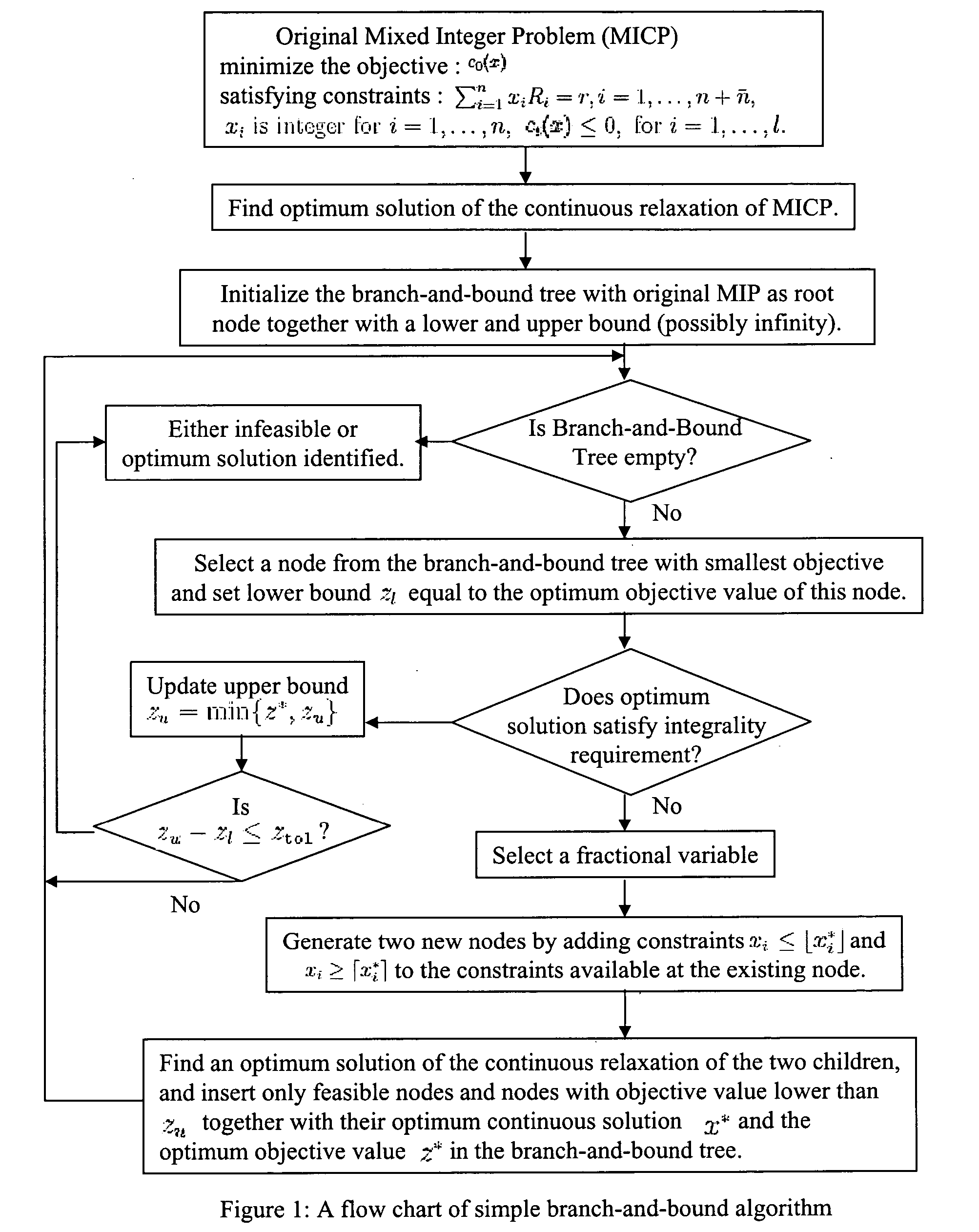
Generalized branching methods for mixed integer programming
InactiveUS20060112049A1Simple methodKnowledge representationComplex mathematical operationsLattice basisTheoretical computer science
A method and system using branching on hyperplanes and half-spaces computed from integral adjoint and / or kernel or dual lattice basis for solving mixed integer programs within specified tolerance. It comprises steps of: (1) preprocessing to ensure feasibility and linear objective; (2) computing adjoint and / or kernel lattice basis of the equality constraint coefficient matrix, or its transformed sub-matrix; (3) generating a generalized-branch-and-cut tree; (4) selecting a node and adding new constraints or approximating existing constraints; (5) processing a node to update lower and upper bounds, deleting nodes, or removing variables; (6 optional) computing an ellipsoidal approximation of continuous relaxation of (5); (7 optional) computing new lattice basis; (8) partitioning the set in (4) generating two or more nodes; (9) repeating (5-8) till termination. Such can be applied to problems in marketing management, data mining, financial portfolio determination, product design optimization, and other complex systems where optimization of system is desired.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
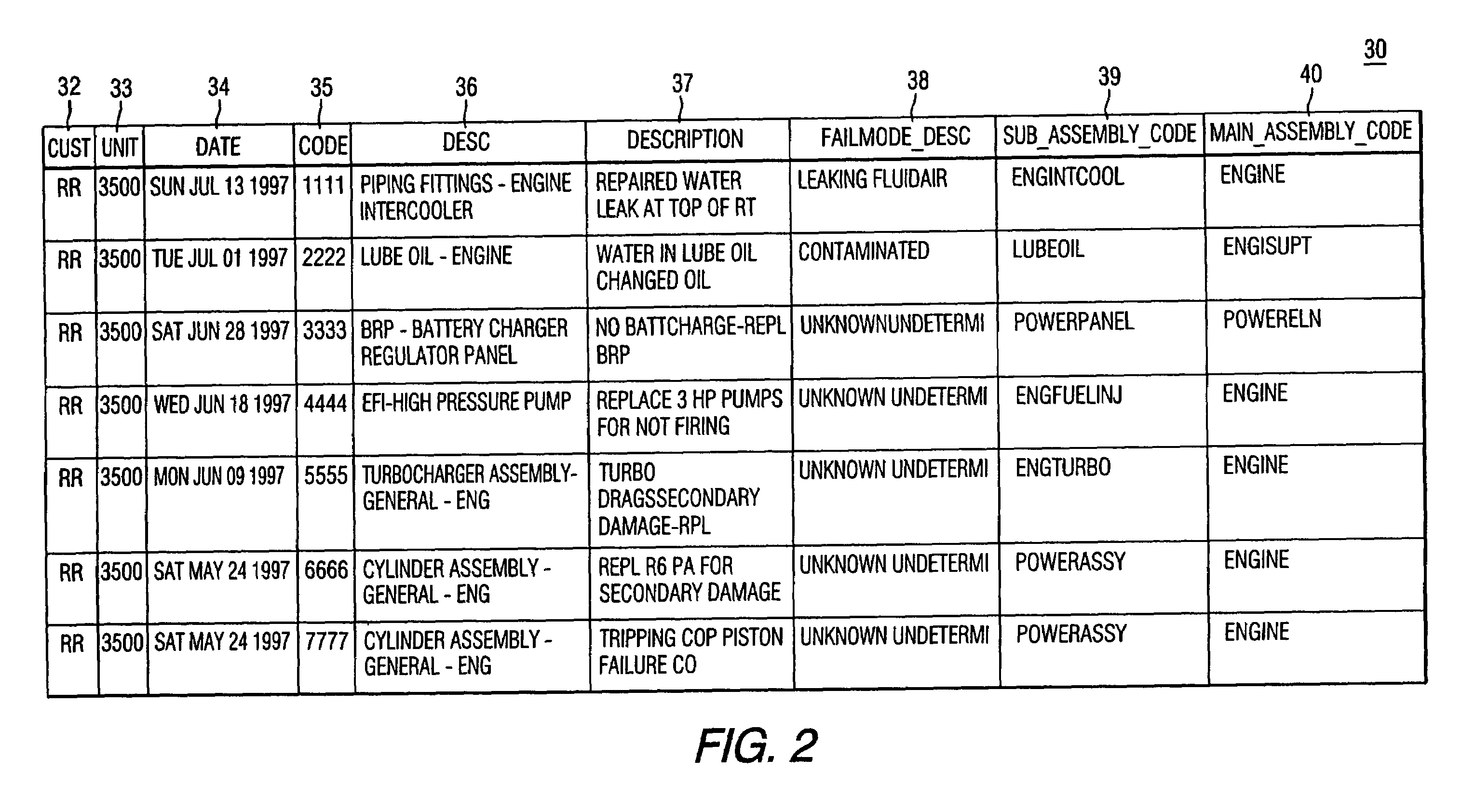
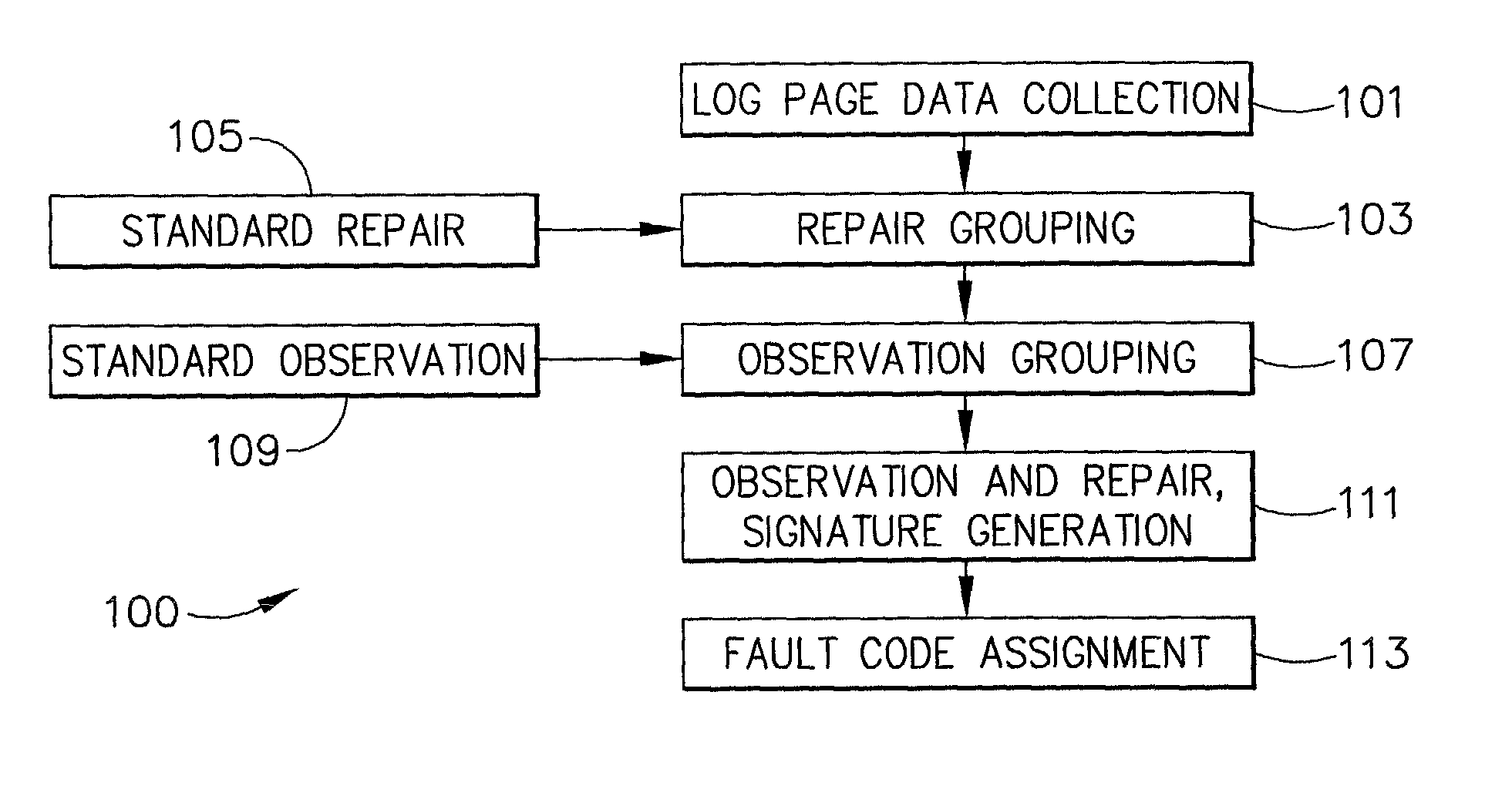
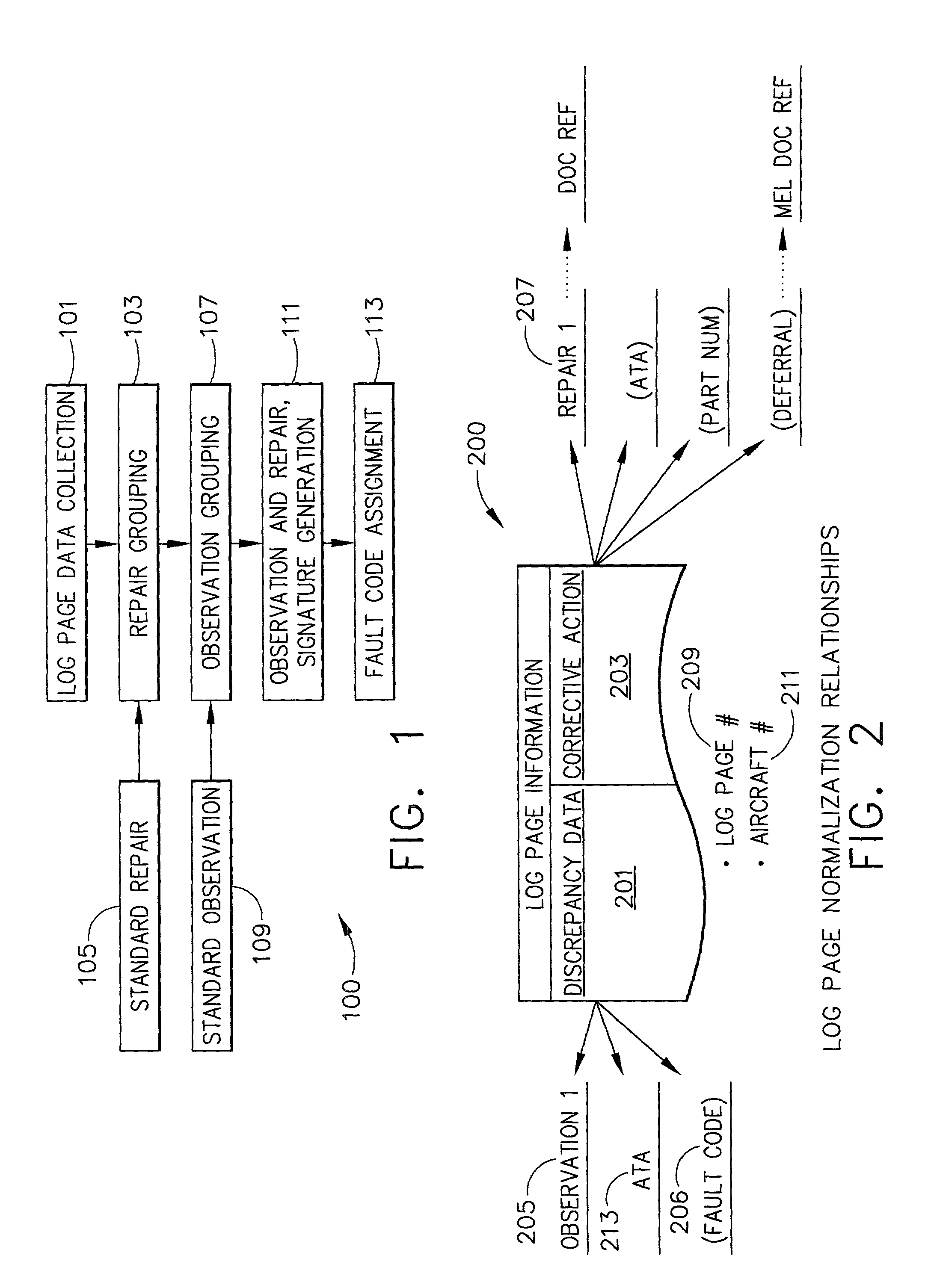
Method and apparatus for developing fault codes for complex systems based on historical data
ActiveUS7260505B2Easy maintenanceSimplify serviceVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesComplex systemAssociated observation
A method of developing fault codes for complex systems based on historical data that in one aspect is a software program arranged to be installed and to operate on a processor to process the historical data in order to facilitate development of the fault codes, the software program resulting in the processor performing the method including: grouping the historical data into a plurality of observations and a plurality of repairs; analyzing the plurality of repairs to determine associated observation signatures, each of the observation signatures being one or more of the observations; and assigning a fault code to each observation signature.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
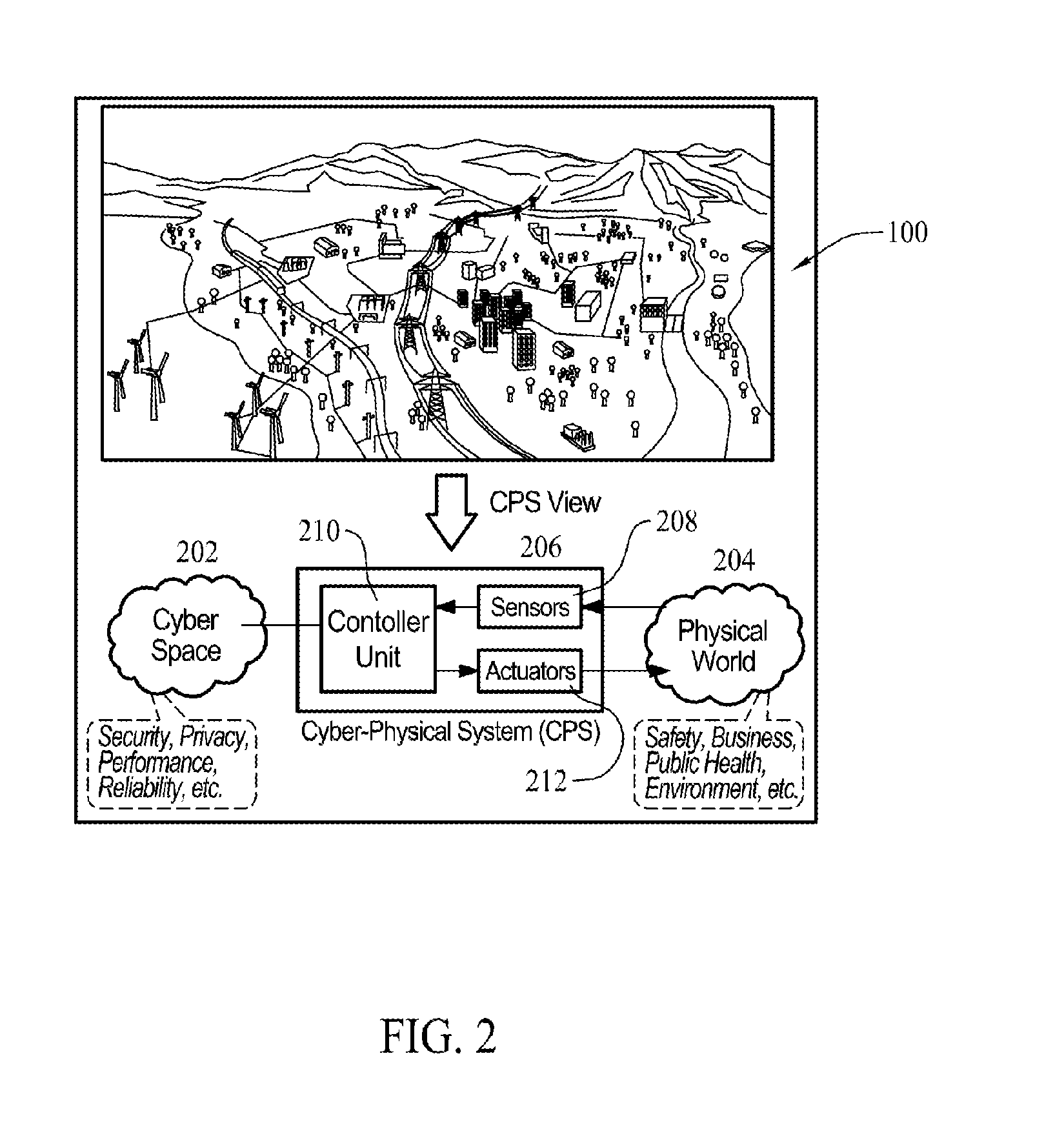
Methods and systems for cyber-physical security modeling, simulation and architecture for the smart grid
ActiveUS20130198847A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionInteractive softwarePhysical security
A computer-implemented method for use in evaluating at least one threat to a complex system includes identifying one or more physical components of the complex system and modeling the one or more physical components with interactive software multi-agents. The multi-agents are programmed to monitor and control at least one function of the modeled physical components. One or more threats to a target of the complex system are identified. Each threat is defined as a cyber threat or physical threat and the target is defined as a cyber component or physical component. The method includes simulating an attack on the complex system by the identified threat and assessing an impact of the attack on the complex system.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
System and method for turbine engine fault detection using discrete event system modeling
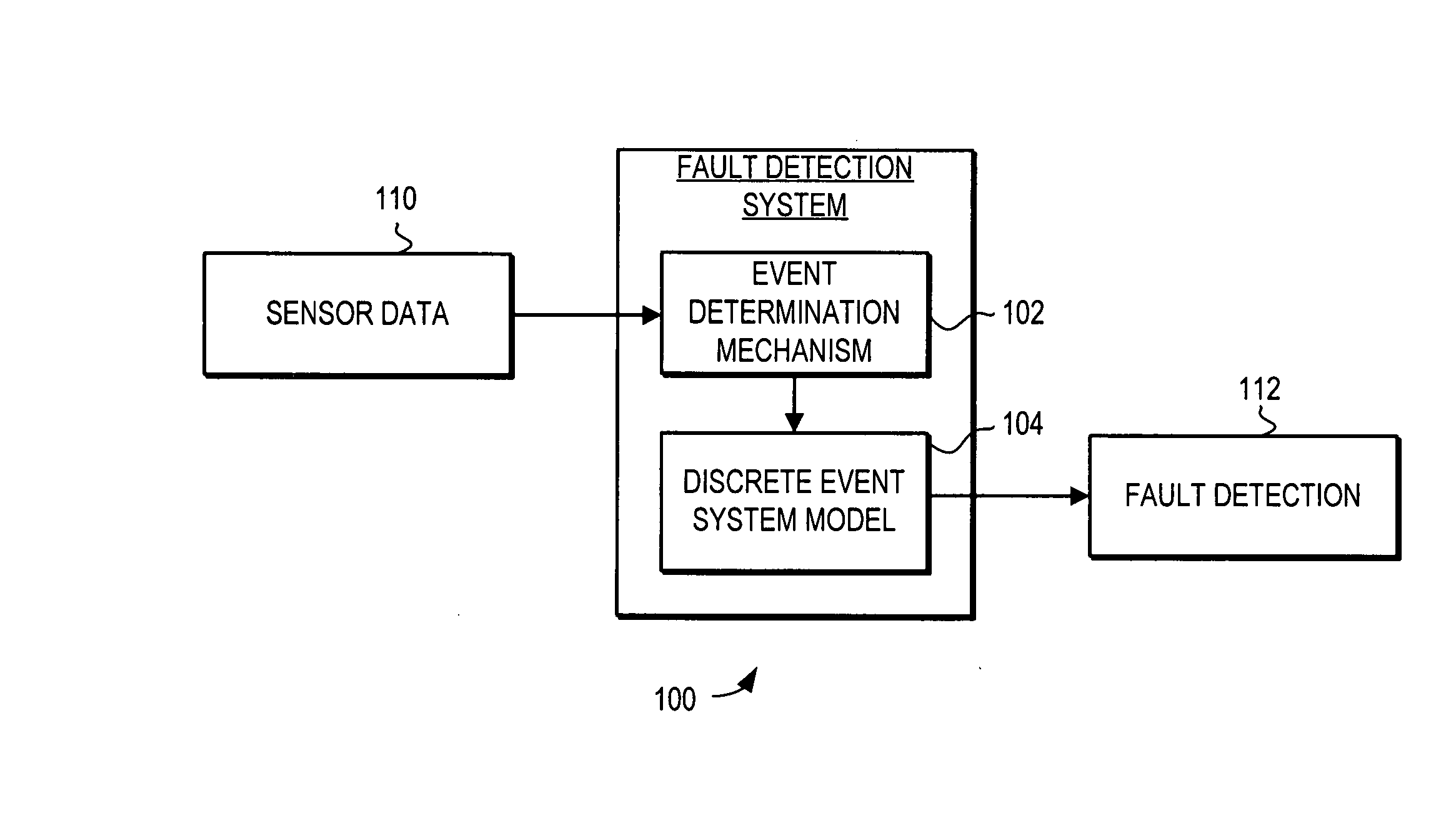
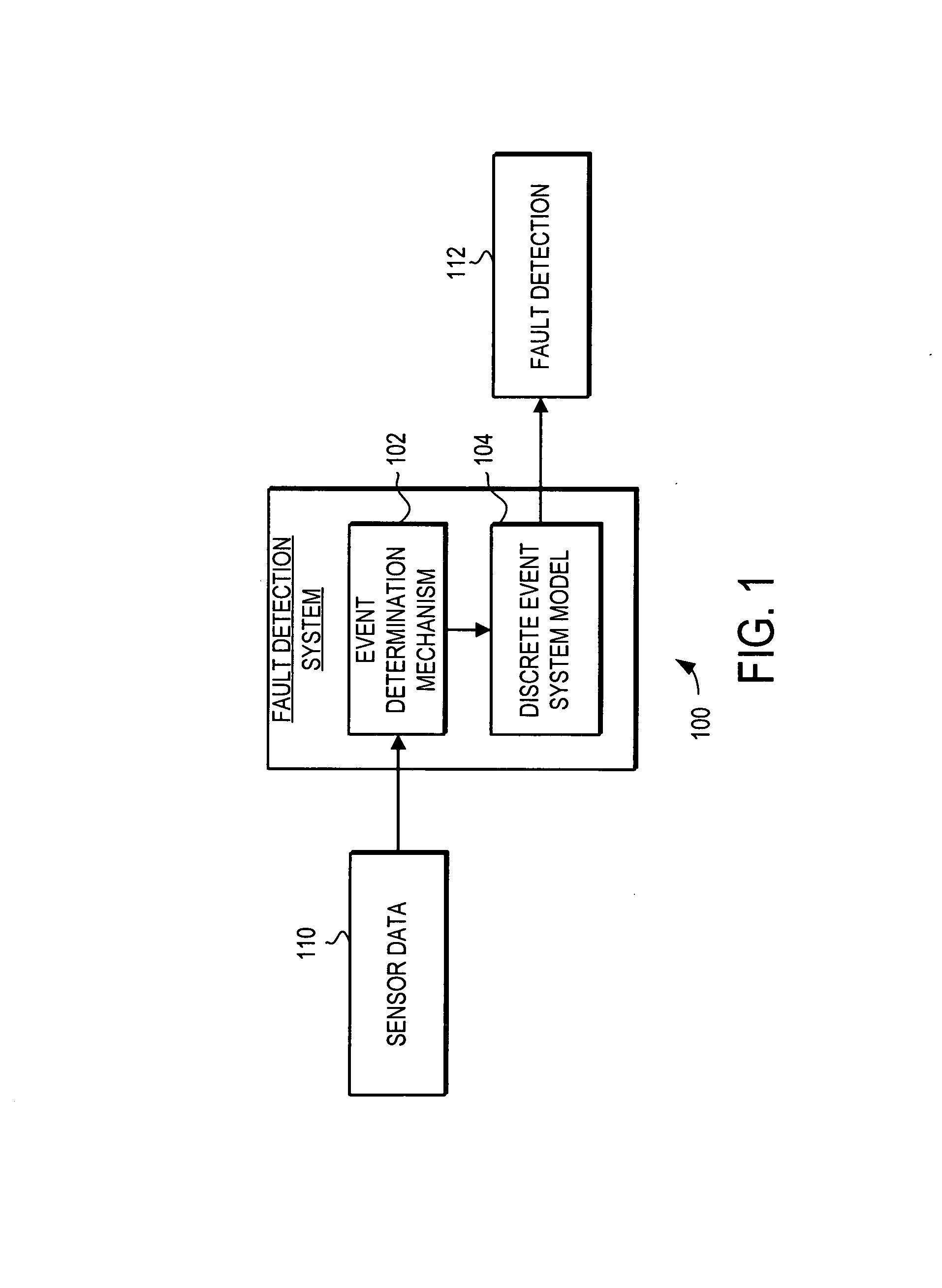
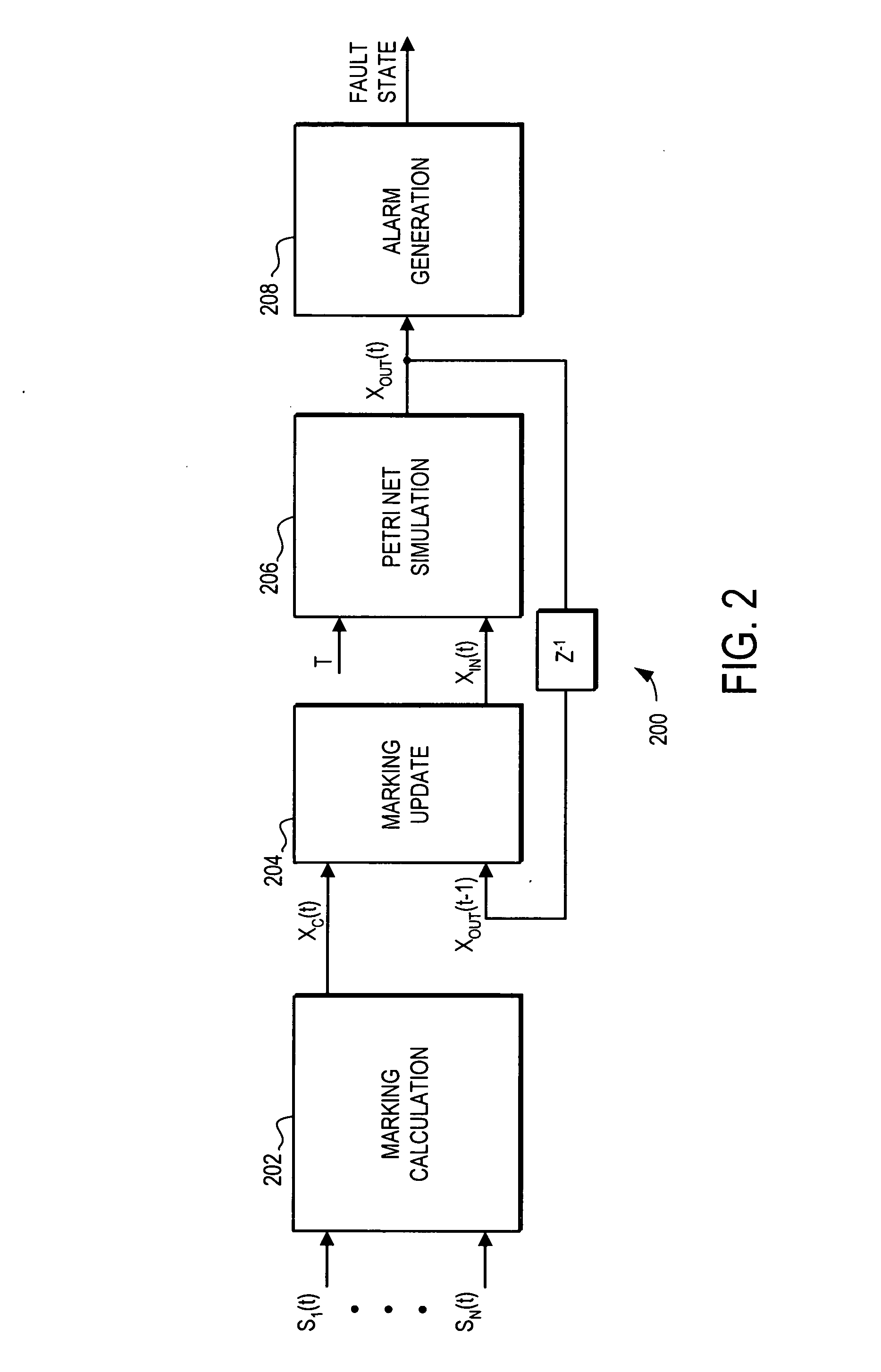
ActiveUS20070260390A1Improved fault diagnosisImproved prognosisVehicle testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesTurbineComplex system
A system and method is provided for fault detection in a turbine engine. The fault detection system and method uses discrete event system modeling to provide improved fault diagnosis and prognosis. The fault detection system and method receives sensor taken at multiple dynamic events occurring in different time windows. An event determination mechanism evaluates the received sensor data to determine if specified events have occurred. Indications of the occurrence of specified events are then passed to a discrete event system model. The discrete event system model analyzes the timing and sequencing of the event occurrences to determine if a fault has occurred. This method does not require a detailed modeling of the system, and thus can be applied to complex systems such as turbine engines.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Reactive component reduction system and methods for the use thereof
ActiveUS7896292B2Reduce riskMinimizes ventingUsing liquid separation agentIndirect heat exchangersGas phaseEngineering
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided simplified systems and methods for catalytically deactivating, removing, or reducing the levels of reactive component(s) from the vapor phase of fuel storage tanks. The simple apparatus described herein can be utilized to replace complex systems on the market. Simply stated, in one embodiment of the invention, the vapor phase from the fuel tank is passed over a catalytic bed operated at appropriate temperatures to allow the reaction between free oxygen and the fuel vapor by oxidation of the fuel vapor, thus deactivating reactive component(s) in the gas phase.
Owner:PHYRE TECH
Element management system with data-driven interfacing driven by instantiation of meta-model
InactiveUS7366989B2Easy accessSpecial service for subscribersDigital computer detailsTelecommunications networkElement management system
A network element management system which can exploit the customized interface features of a variety of versions of a variety of complex system products from a variety of manufacturers. This is done by maintaining a meta-model, which is not itself a model until instantiated, of the possible known product configurations to be interfaced to. Once the meta-model is instantiated, it provides configuration parameters which the interface program uses to build a correct configuration for the management and / or monitoring interface. This is particularly advantageous in the preferred embodiment of a telecommunications network element management system, but also has potential applicability to other large “supersystem” applications.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
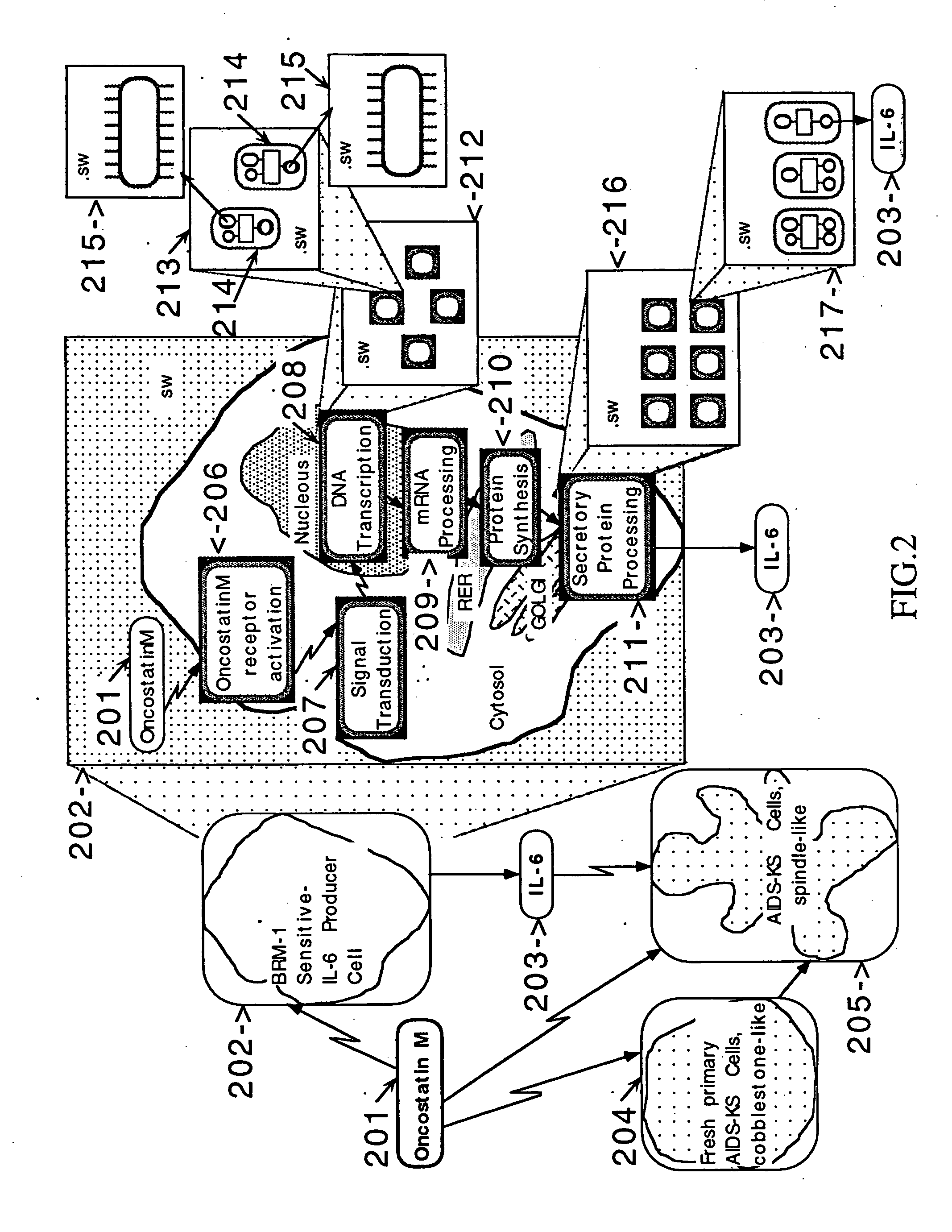
Network models of biological complex systems
This invention describes computer based systems and methods for modeling and simulation of complex biological systems from the cellular, or subcellular, to the organism and population level, for using said models to predict functions of components of the biological systems and to simulate physiological and pathological states at the various levels, and for using said models in drug development for testing in a computer system substances for possible use as therapeutics by simulating their effects on the physiological and pathological states.
Owner:INTERTECH VENTURES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com