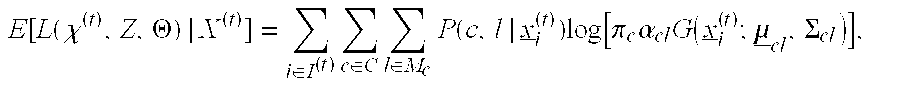Patents
Literature
3053 results about "System failure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A system failure can occur because of a hardware failure or a severe software issue, causing the system to freeze, reboot, or stop functioning altogether. A system failure may or may not result in an error being displayed on the screen.
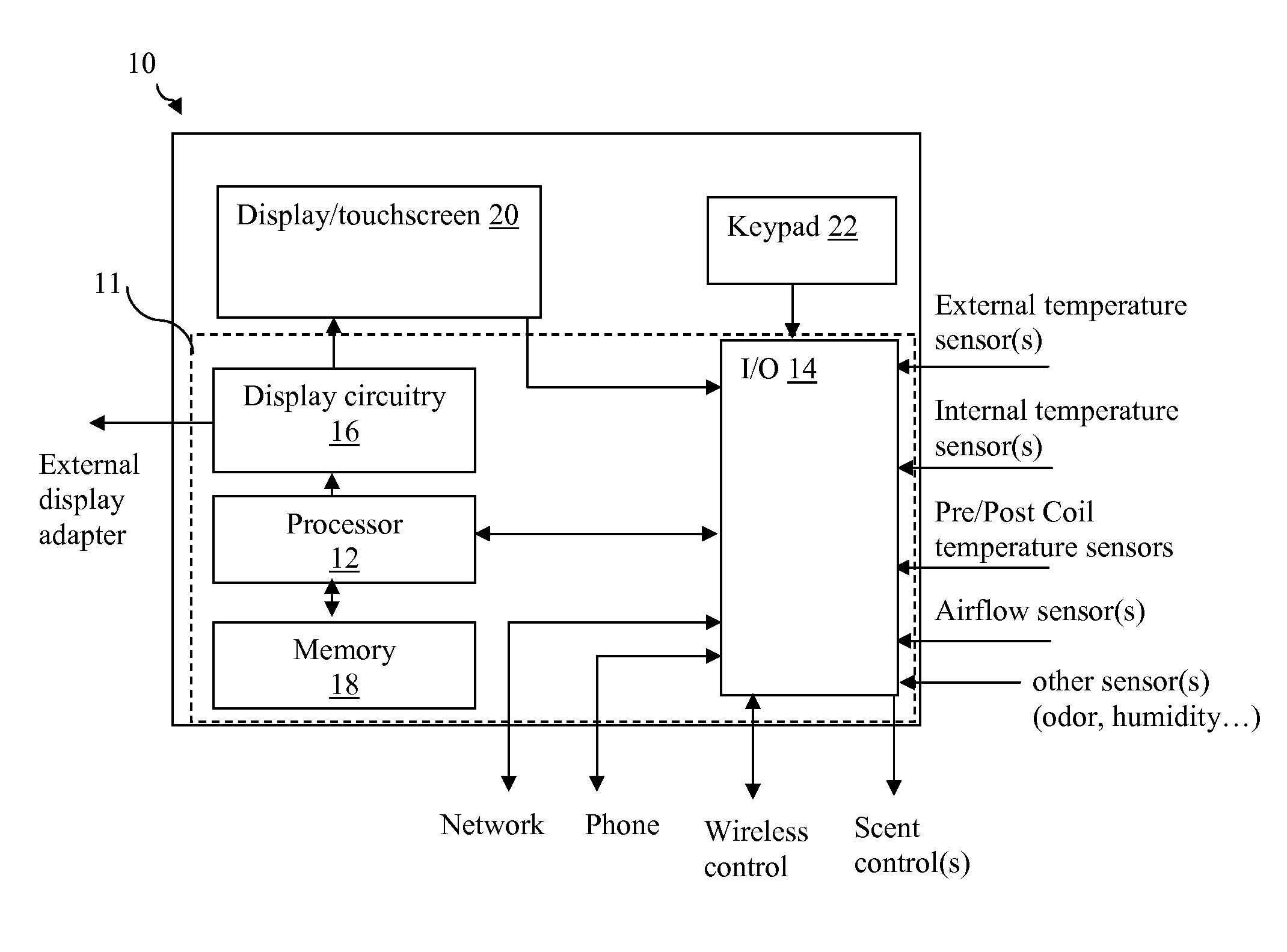
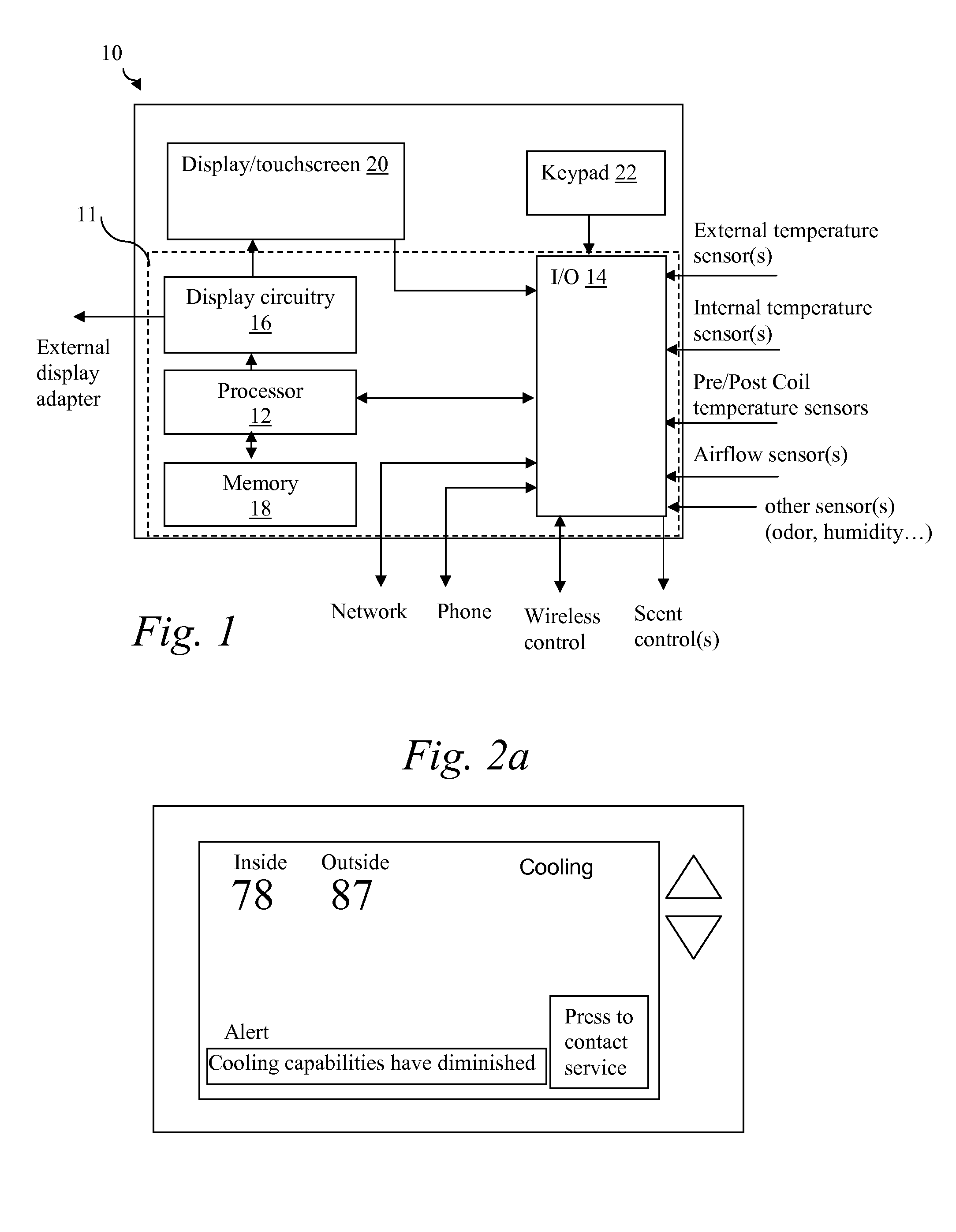
Thermostat
InactiveUS20100084482A1Energy efficient ICTSampled-variable control systemsTelecommunications linkRemote control
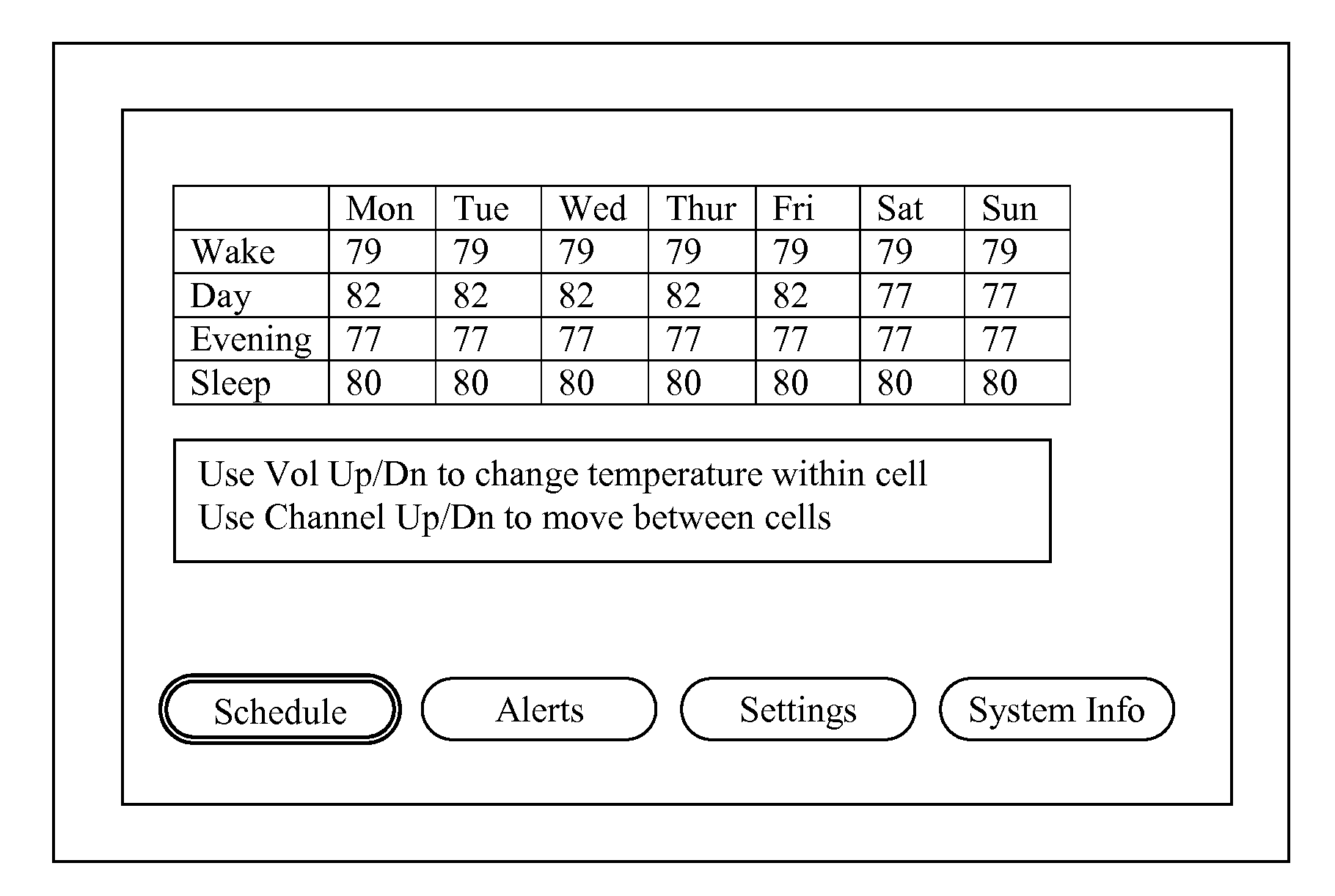
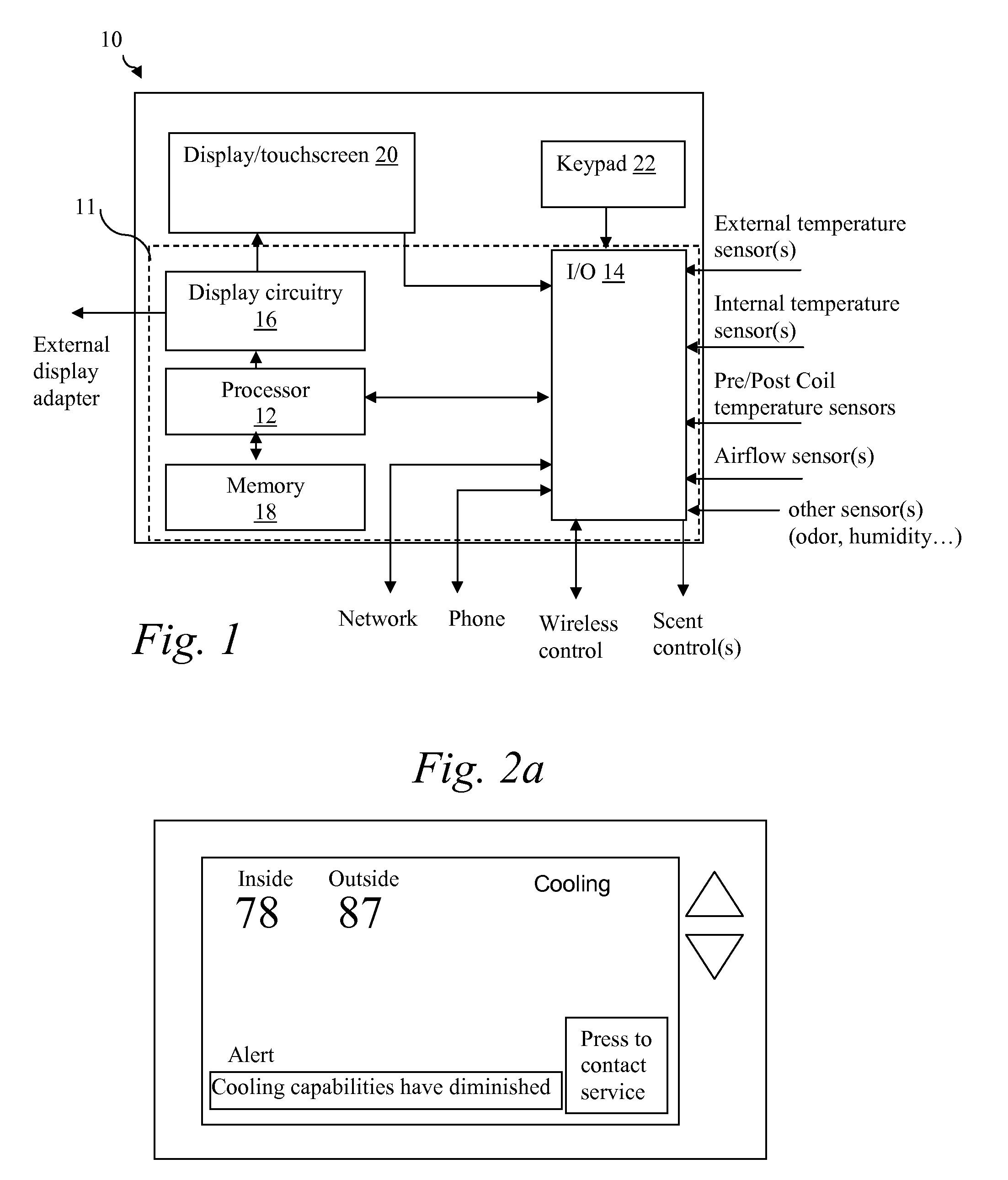
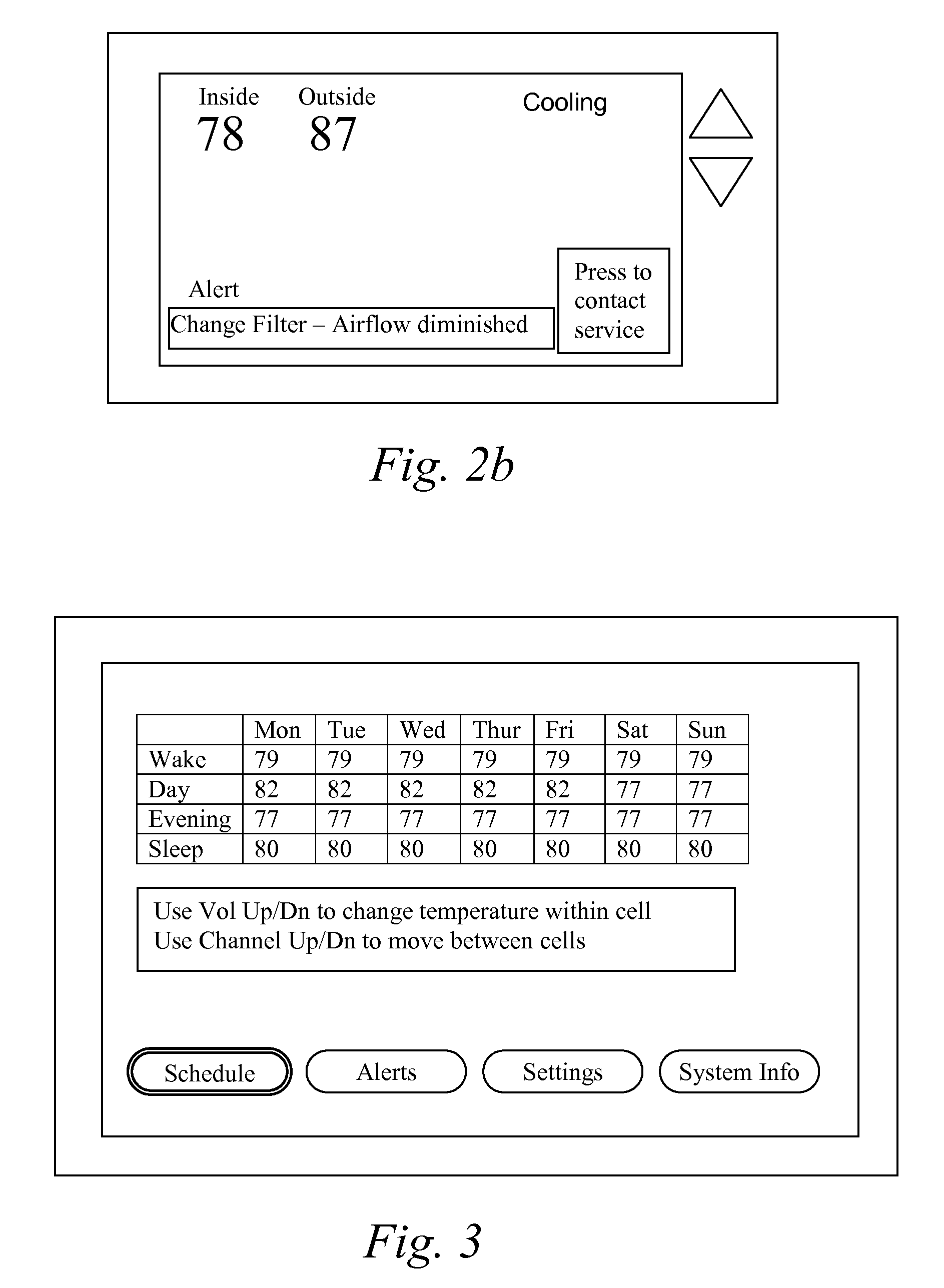
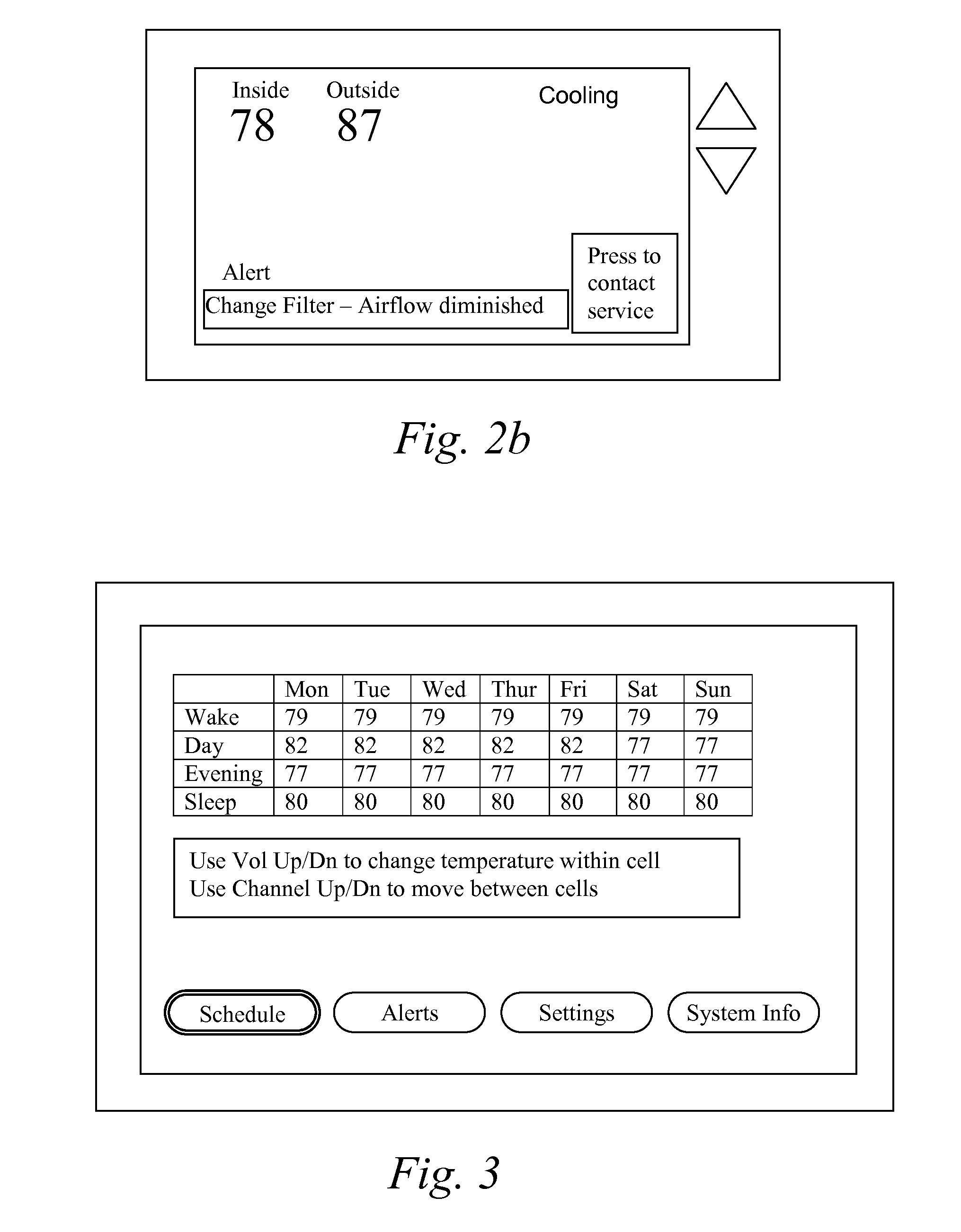
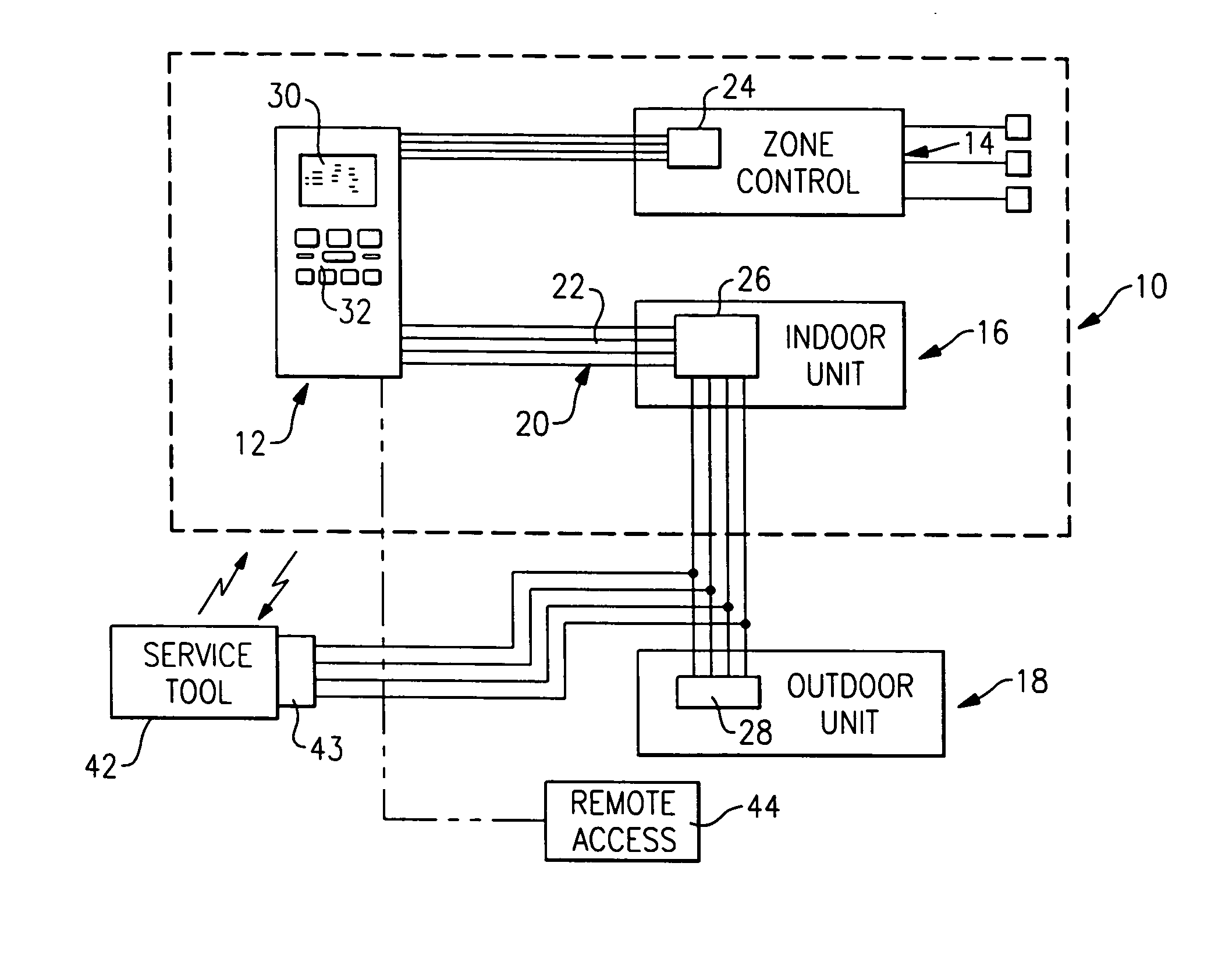
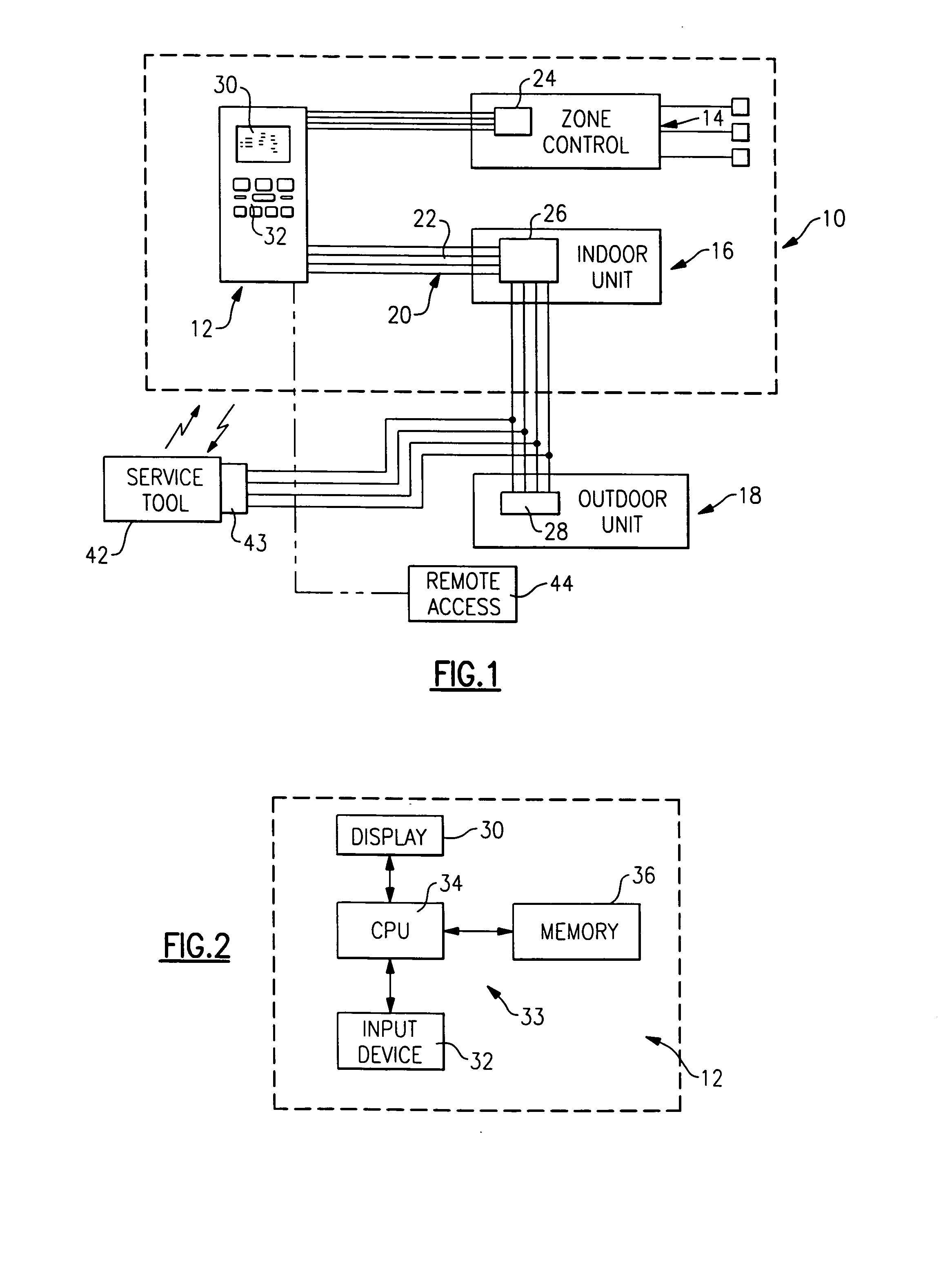
A thermostat includes an improved user interface, including automatic scheduling, remote control, system failure warning messages, and Energy Star compliance messages. Diagnostics can be provided without additional communication links to the thermostat. A sub-base accepts multiple thermostats and uses color coded terminals to ease installation. Glow-in-the dark features reduce power needs. In one embodiment, thermostats are coupled to AC power sources and communicate using wireless communications to control an HVAC system. A dampered system can be effected through a thermostat that communicates directly with zoned dampers.
Owner:PRO1 IAQ
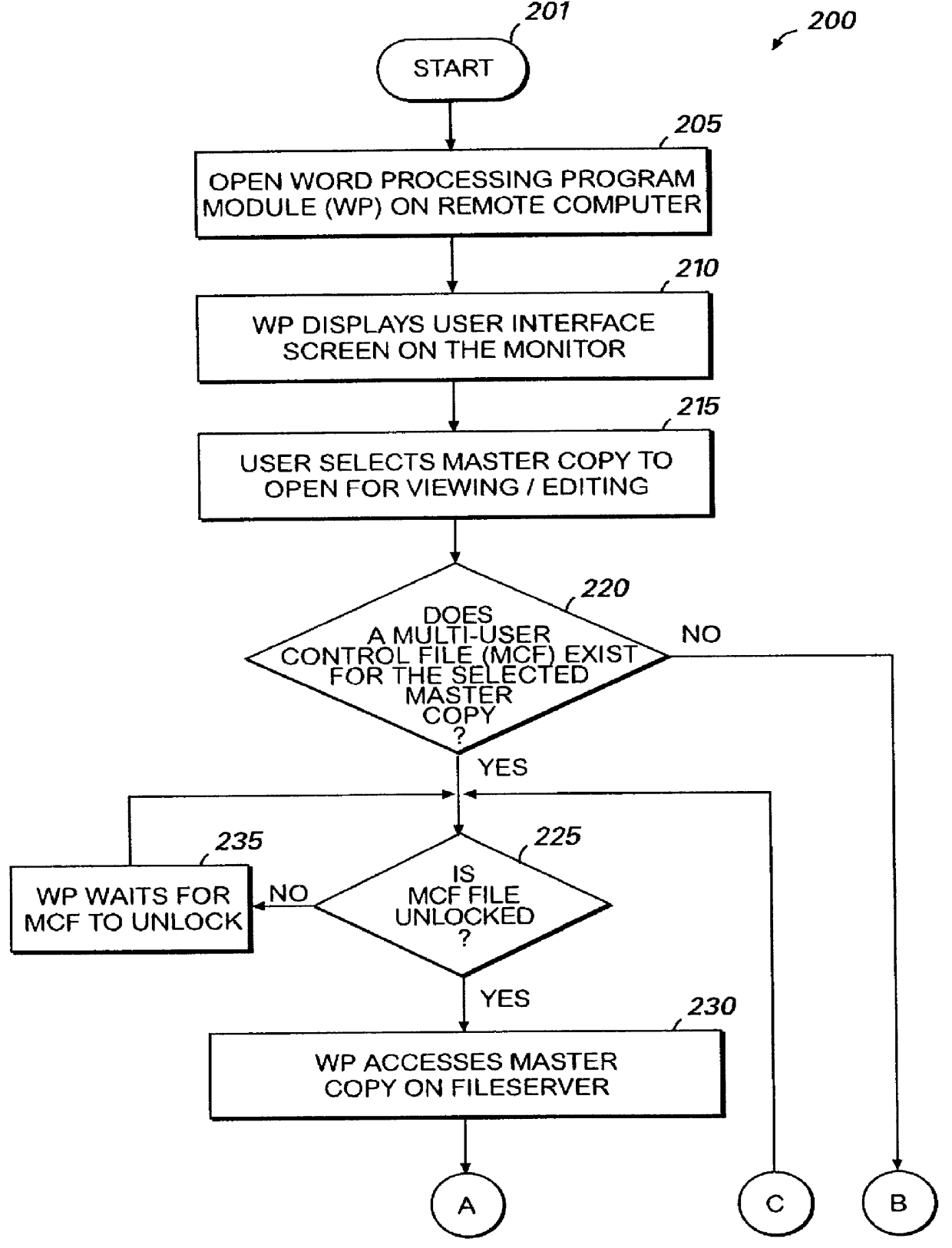
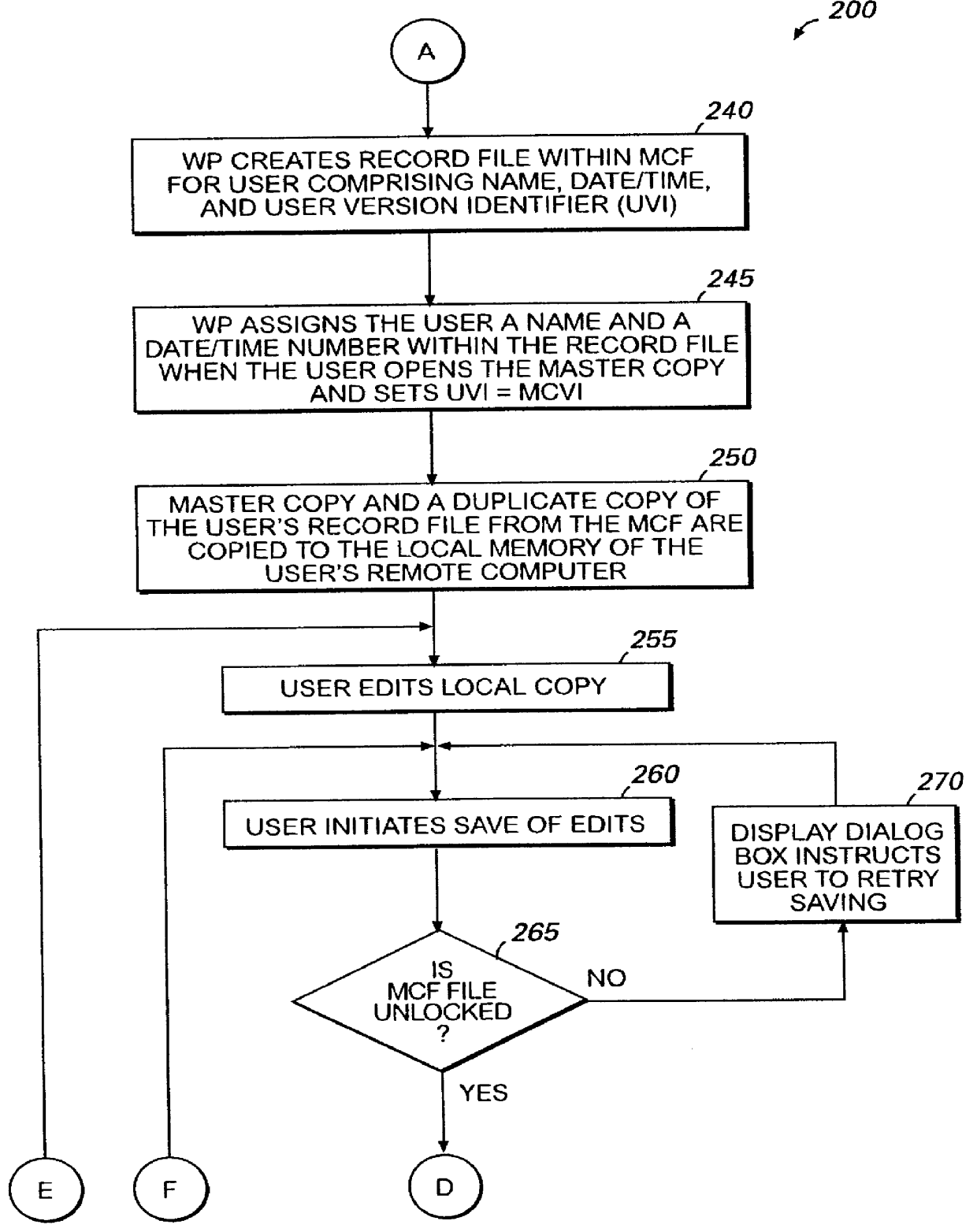
Computer implemented method for simultaneous multi-user editing of a document
InactiveUS6067551AEasily interfaceEasy to engageOffice automationSpecial data processing applicationsWord processingSystem failure
Word processing program module having a multi-user editing capability provided for by the utilization of a multi-user control file (MCF) that is created when a document is first accessed. The MCF is comprised of individual record files for the master copy of the document, and each user and includes an assigned name, a date / time number, and a version identifier number. The MCF facilitates the tracking of the version identifier numbers to control the timing and sequence of events when a user opens, saves, and / or closes a document. The MCF also facilitates the control of the reconciliation of documents that may be required when a user attempts to save as well as facilitates the performing of the necessary timing functions when conflict resolving is required before edits are saved. The MCF further facilitates the capability to automatically recover the multi-user editing environment from a system failure as well as to manually remove a user from the multi-user editing environment.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Thermostat
InactiveUS20070228183A1Energy efficient ICTTemperature control without auxillary powerTelecommunications linkRemote control
An thermostat 10 includes an improved user interface, including automatic scheduling, remote control, system failure warning messages, and Energy Star compliance messages. Diagnostics can be provided without additional communication links to the thermostat. A sub-base accepts multiple thermostats and uses color coded terminals to ease installation. Glow-in-the-dark features reduce power needs. In one embodiment, thermostats are coupled to AC power sources and communicate using wireless communications to control an HVAC system. A dampered system can be effected through a thermostat that communicates directly with zoned dampers.
Owner:PRO1 IAQ
Robust anomaly detection and regularized domain adaptation of classifiers with application to internet packet-flows
InactiveUS20120284791A1Maximize aggregate statistical significanceMaximizesMathematical modelsMemory loss protectionCredit cardAlgorithm
Sound, robust methods identify the most suitable, parsimonious set of tests to use with respect to prioritized, sequential anomaly detection in a collected batch of sample data. While the focus is on detecting anomalies in network traffic flows and classifying network traffic flows into application types, the methods are also applicable to other anomaly detection and classification application settings, including detecting email spam, (e.g. credit card) fraud detection, detecting imposters, unusual event detection (for example, in images and video), host-based computer intrusion detection, detection of equipment or complex system failures, as well as of anomalous measurements in scientific experiments.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
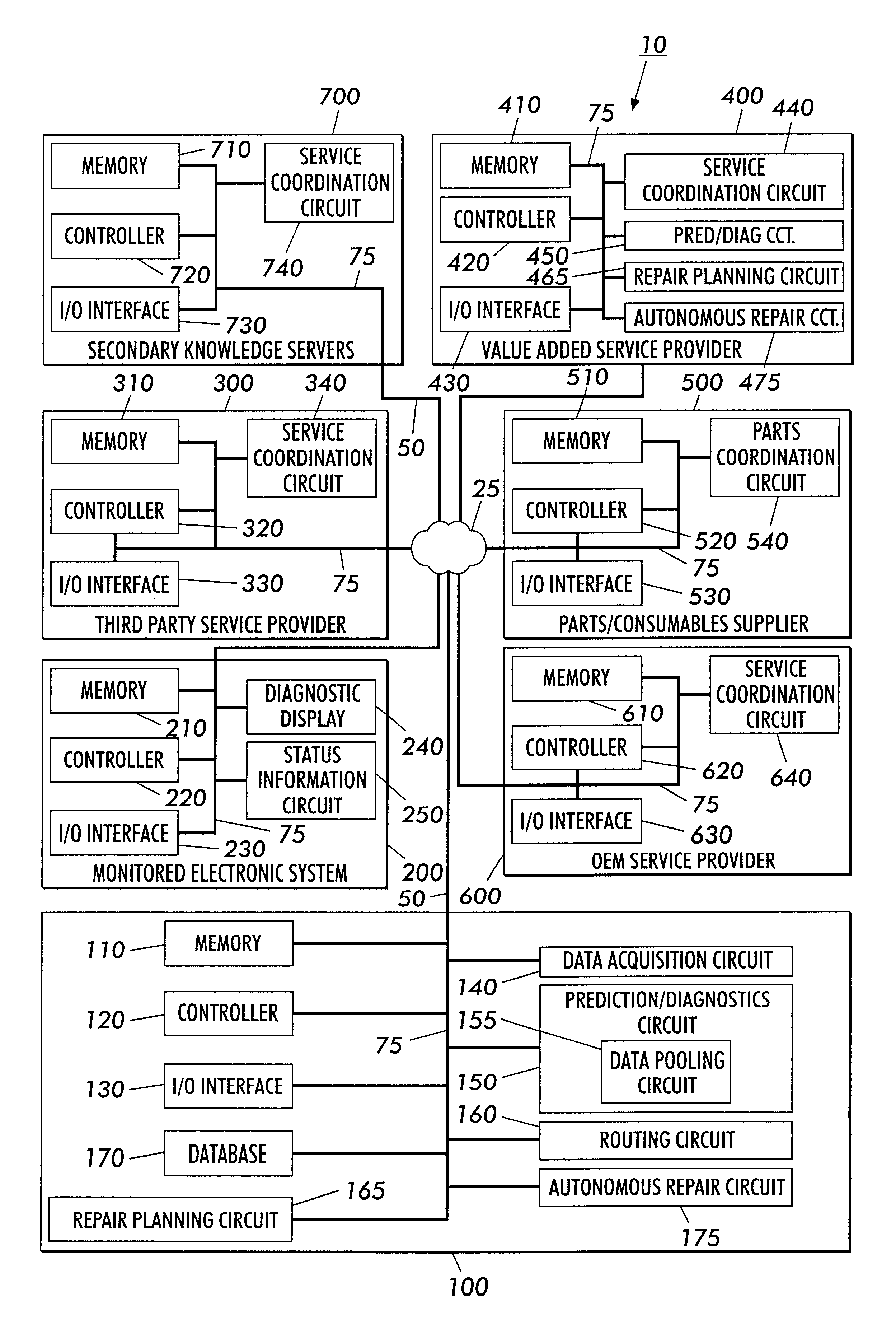
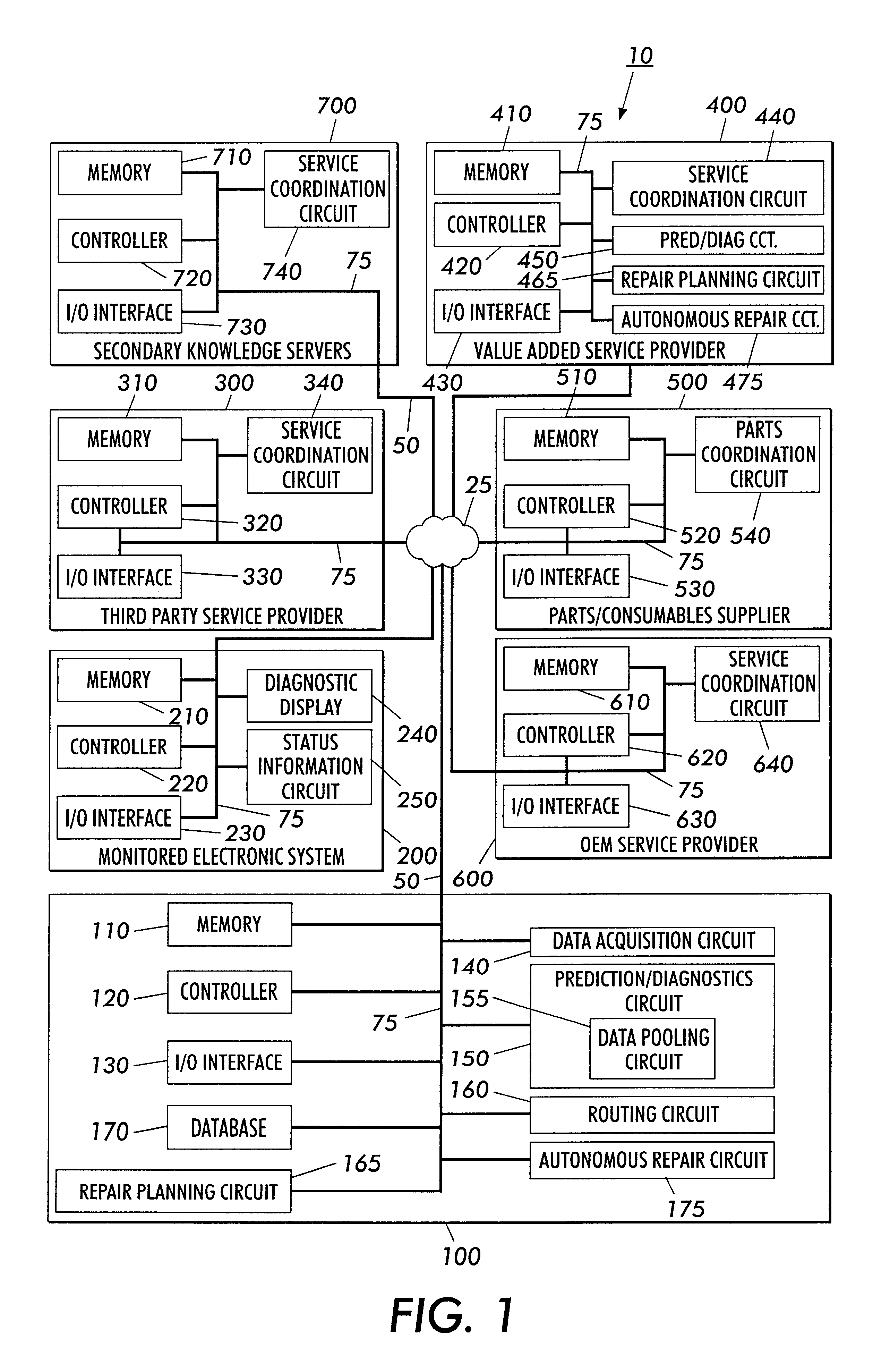
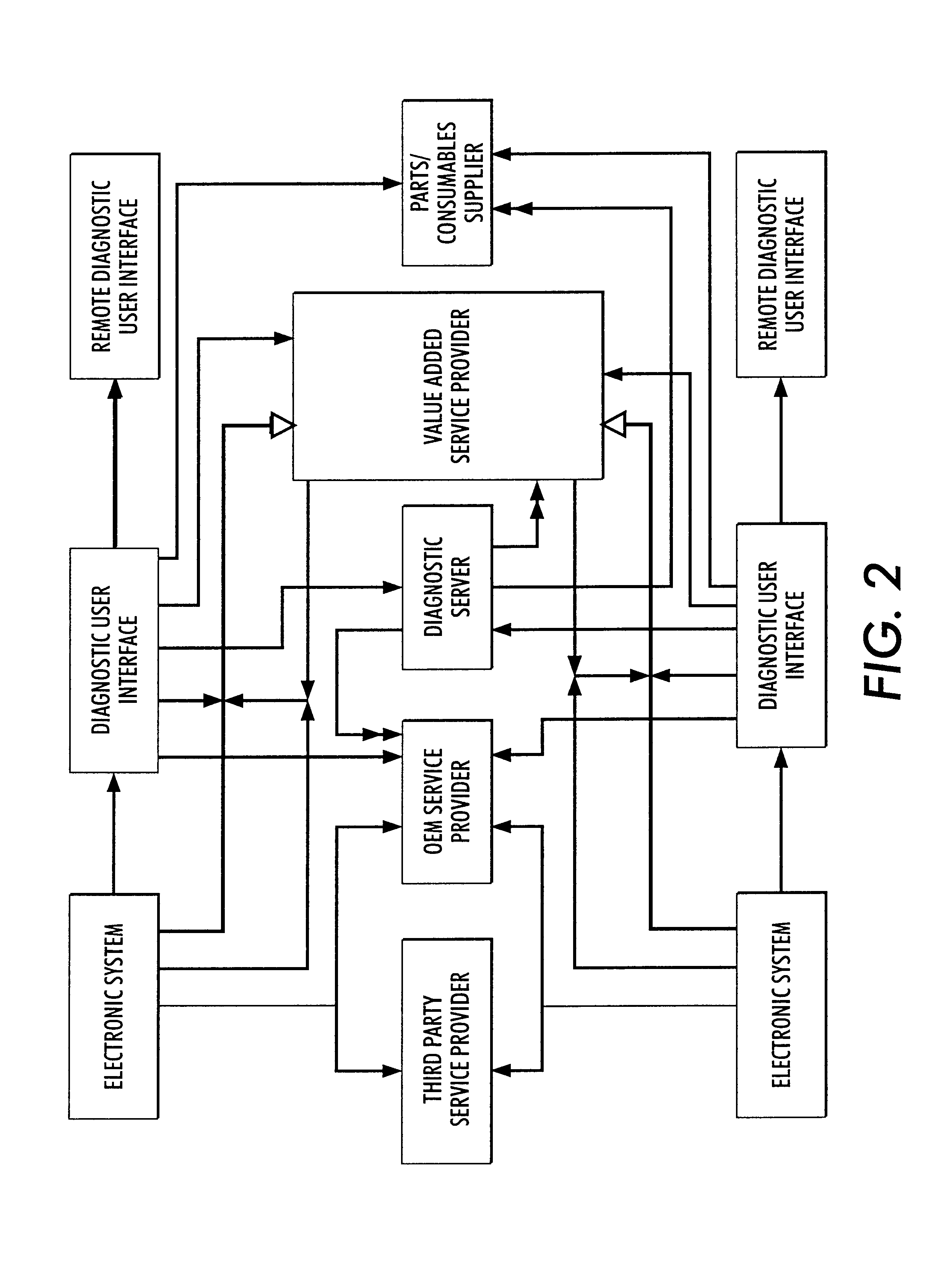
Systems and methods for failure prediction, diagnosis and remediation using data acquisition and feedback for a distributed electronic system
InactiveUS6892317B1Highly reliable actionHighly reliable responseData processing applicationsLogical operation testingPredictive systemsElectronic systems
By using monitoring data, feedback data, and pooling of failure data from a plurality of electronic devices, real-time failure prediction and diagnoses of electronic systems operating in a network environment can be achieved. First, the diagnostic system requests data on the state of a machine and / or its components and collections thereof as part of the machine's normal operation. Secondly, real-time processing of the data either at the machine site or elsewhere in the distributed network allows for predicting or diagnosing system failures. Having determined and / or predicted a system failure, a communication to one or more remote observers in the network allows the remote observers to view the diagnostic information and / or required action to repair the failure. Furthermore, interrogation of either the particular electronic system, or a database containing data on similar electronic systems by the diagnostic server allows the diagnostic server to refine original diagnoses based on this population data to achieve a comprehensive failure predication / diagnosing system.
Owner:LONGHORN HD LLC
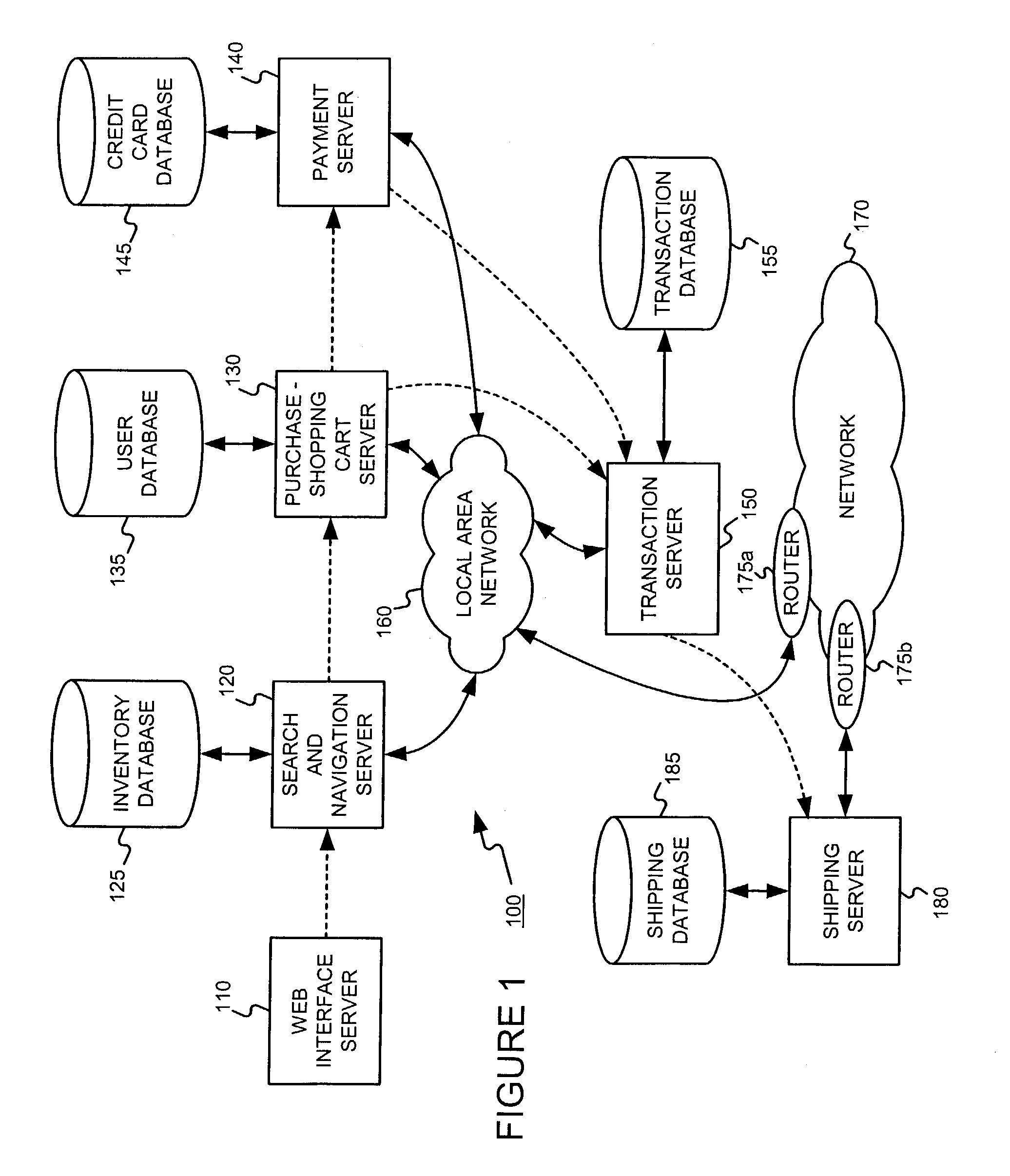
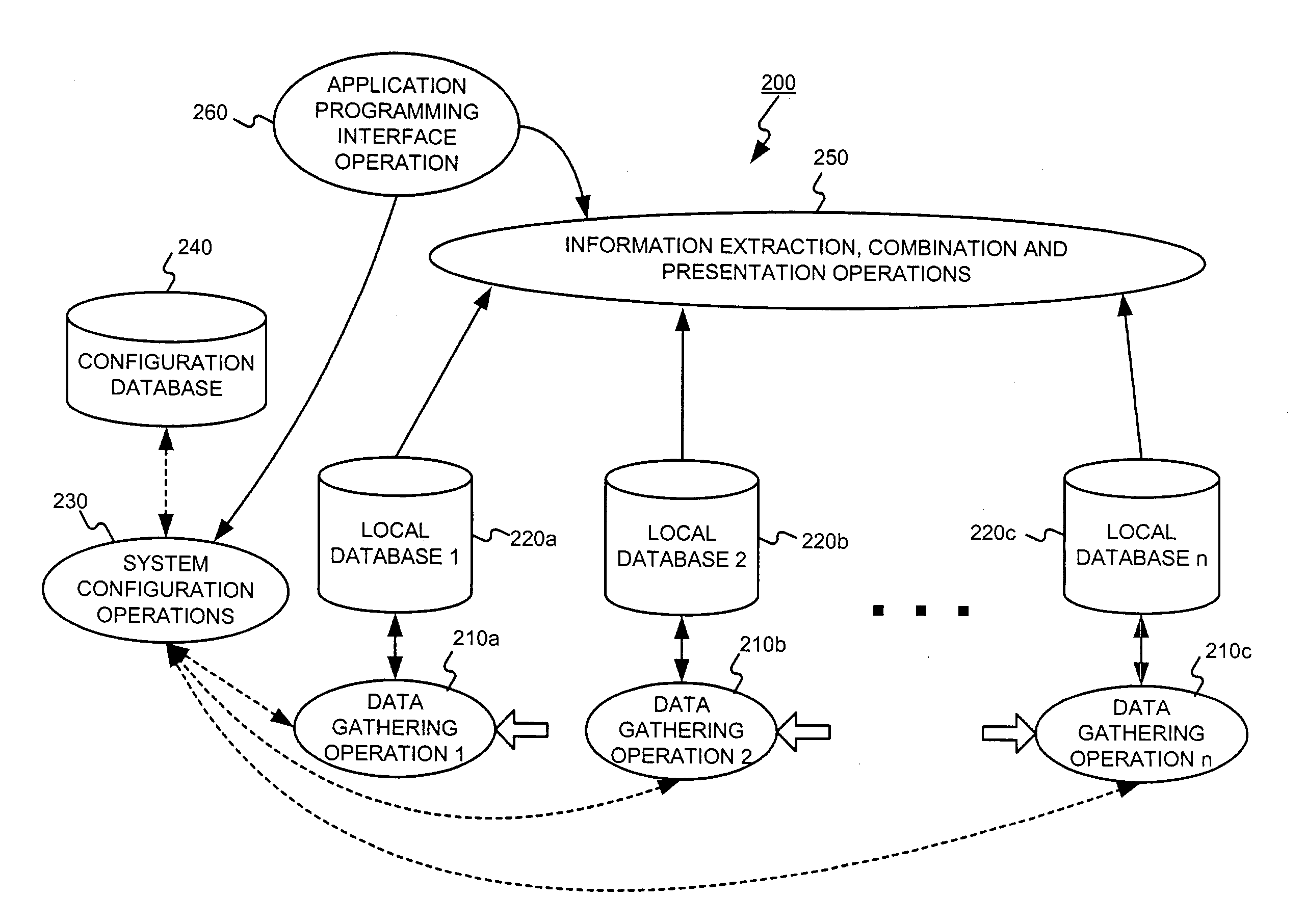
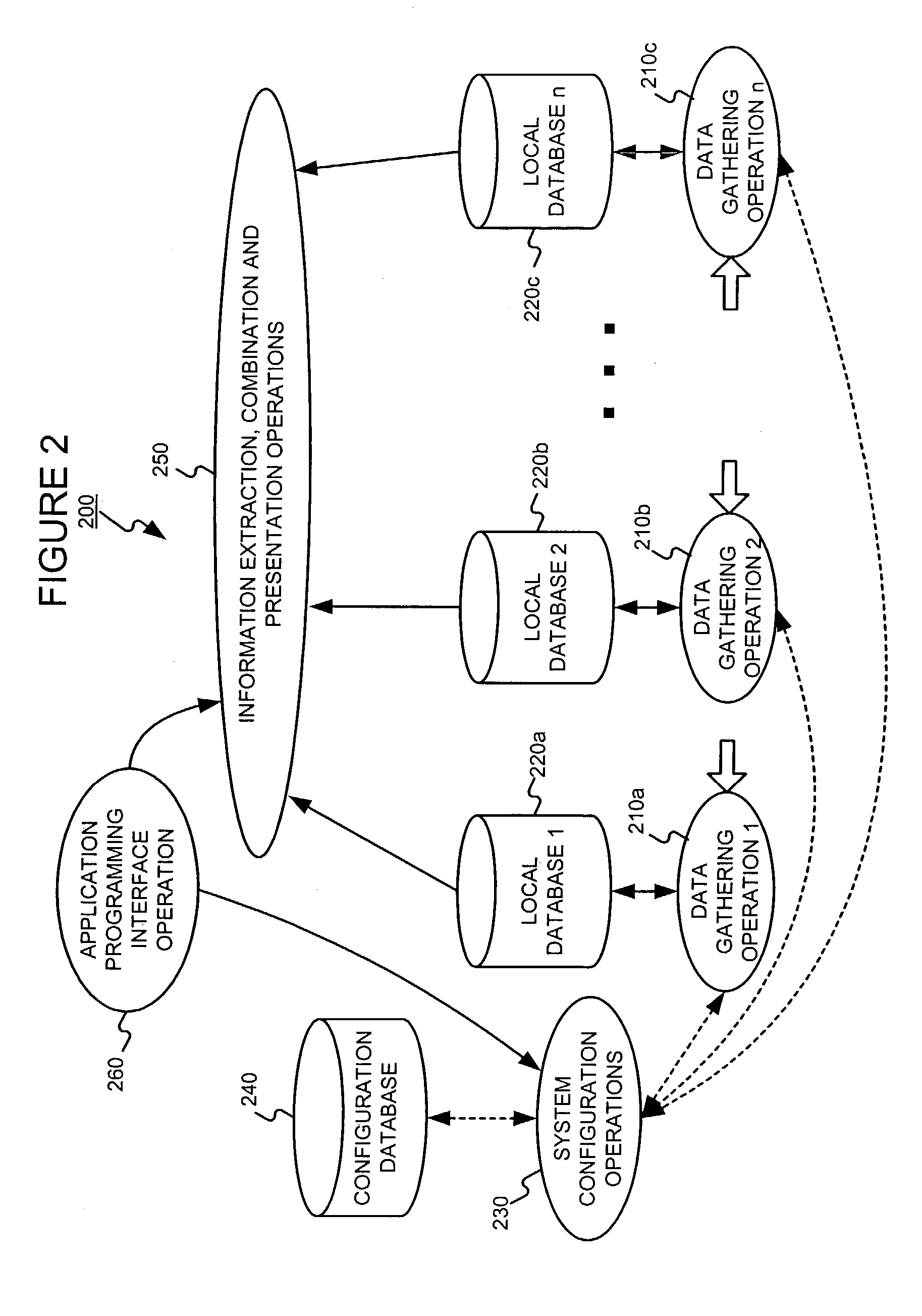
Distributed data gathering and storage for use in a fault and performance monitoring system
Combining system fault and performance monitoring using distributed data collection and storage of performance data. Storage requirements are relaxed and real-time performance monitoring is possible. Data collection and storage elements can be easily configured via a central configuration database. The configuration database can be easily updated and changed. A federated user model allows normal end users to monitor devices relevant to the part of a service they are responsible for, while allowing administrative users to view the fault and performance of a service in an end-to-end manner.
Owner:NETSCOUT SYSTEMS +1
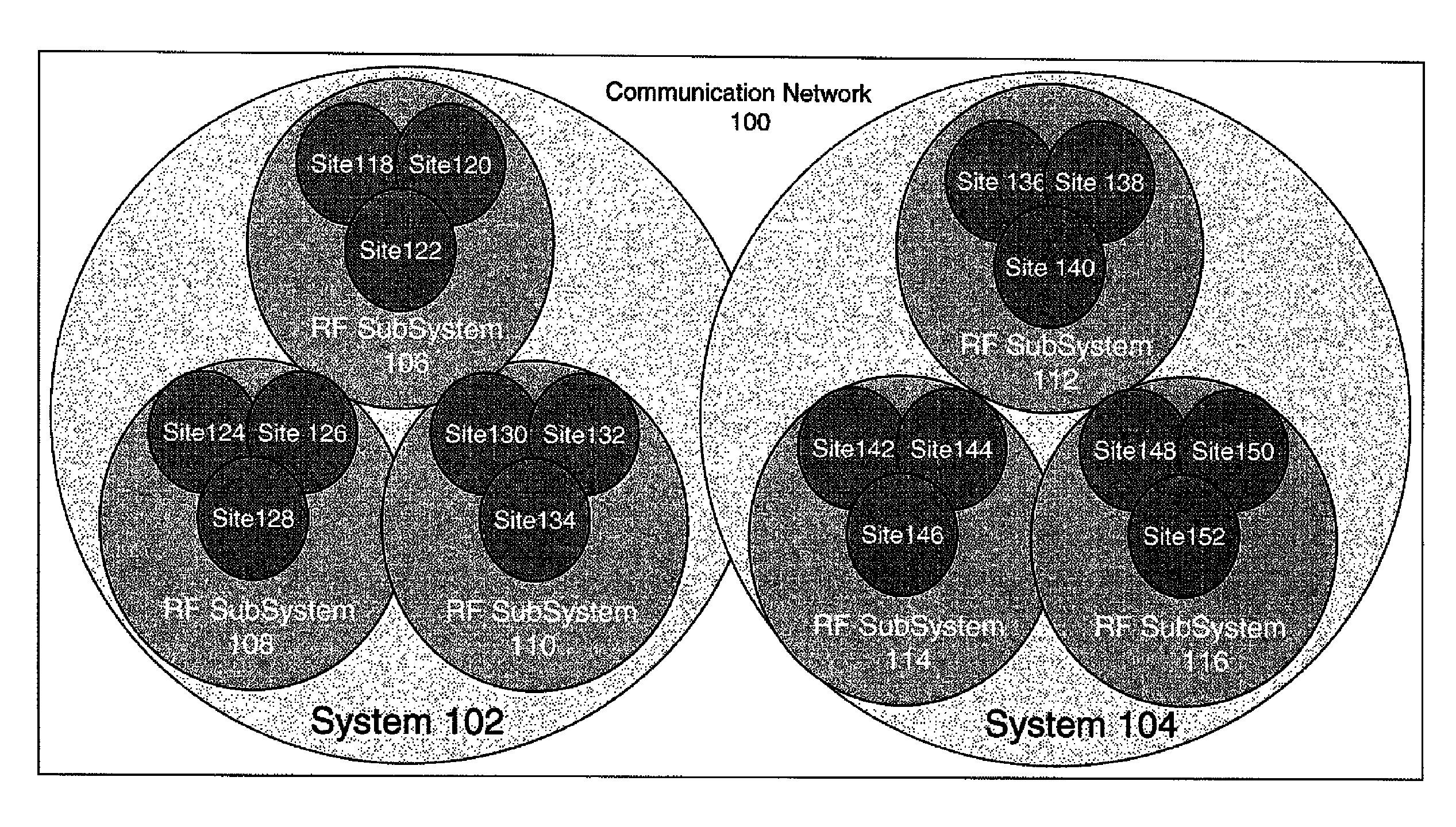
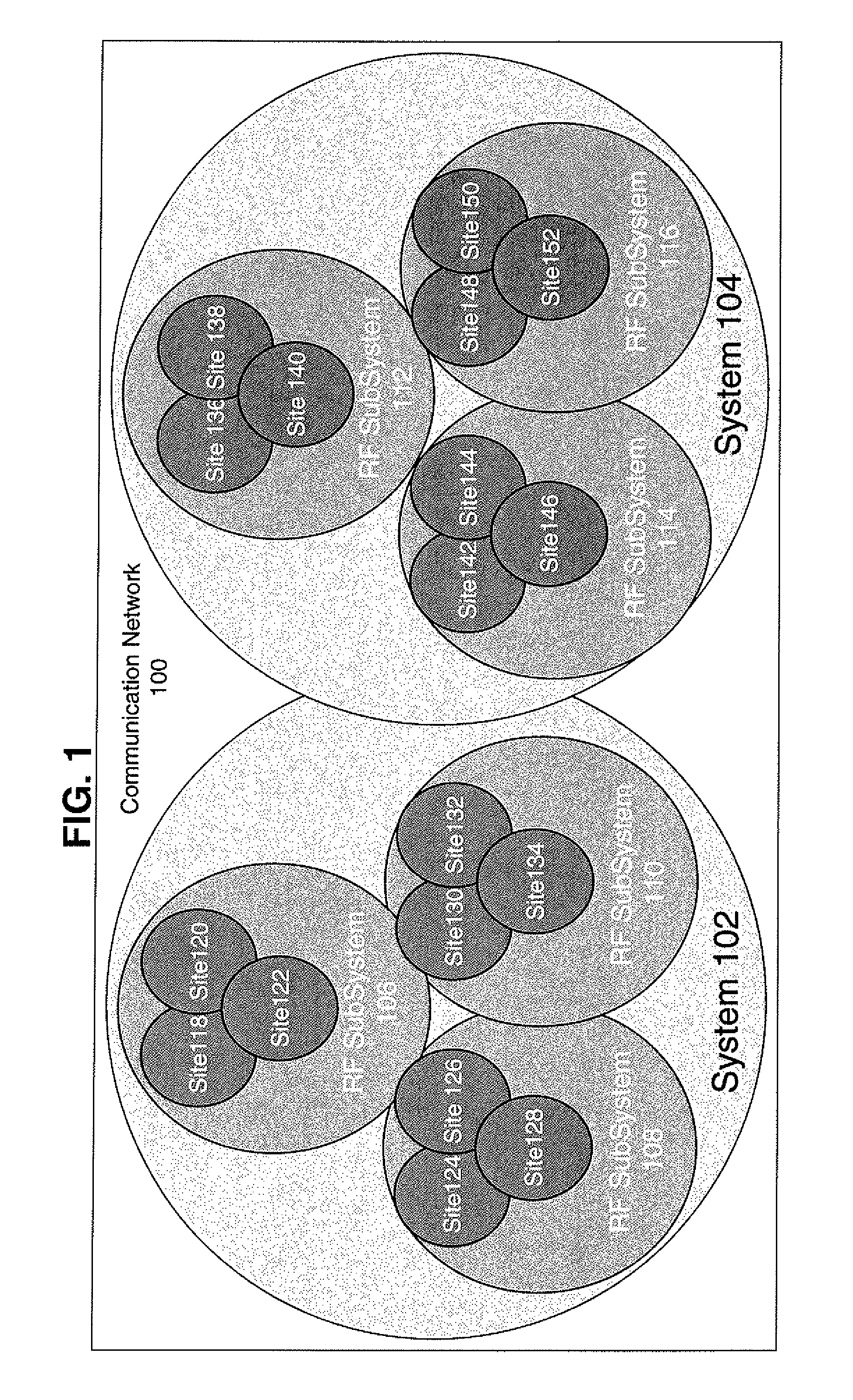
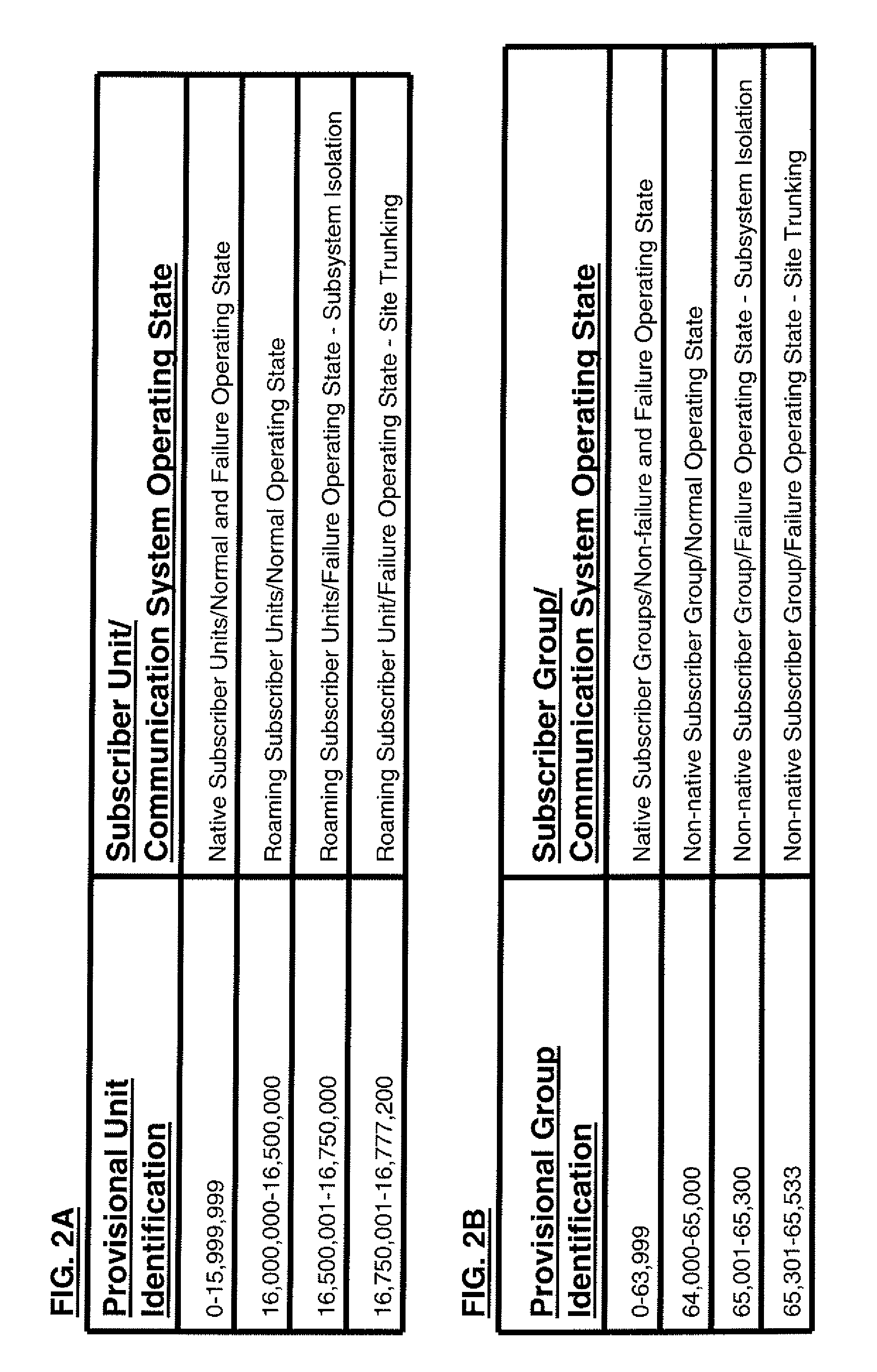
Method of assigning provisional identification to a subscriber unit and group
ActiveUS7970426B2Network traffic/resource managementBroadcast service distributionCommunications systemTrunking
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
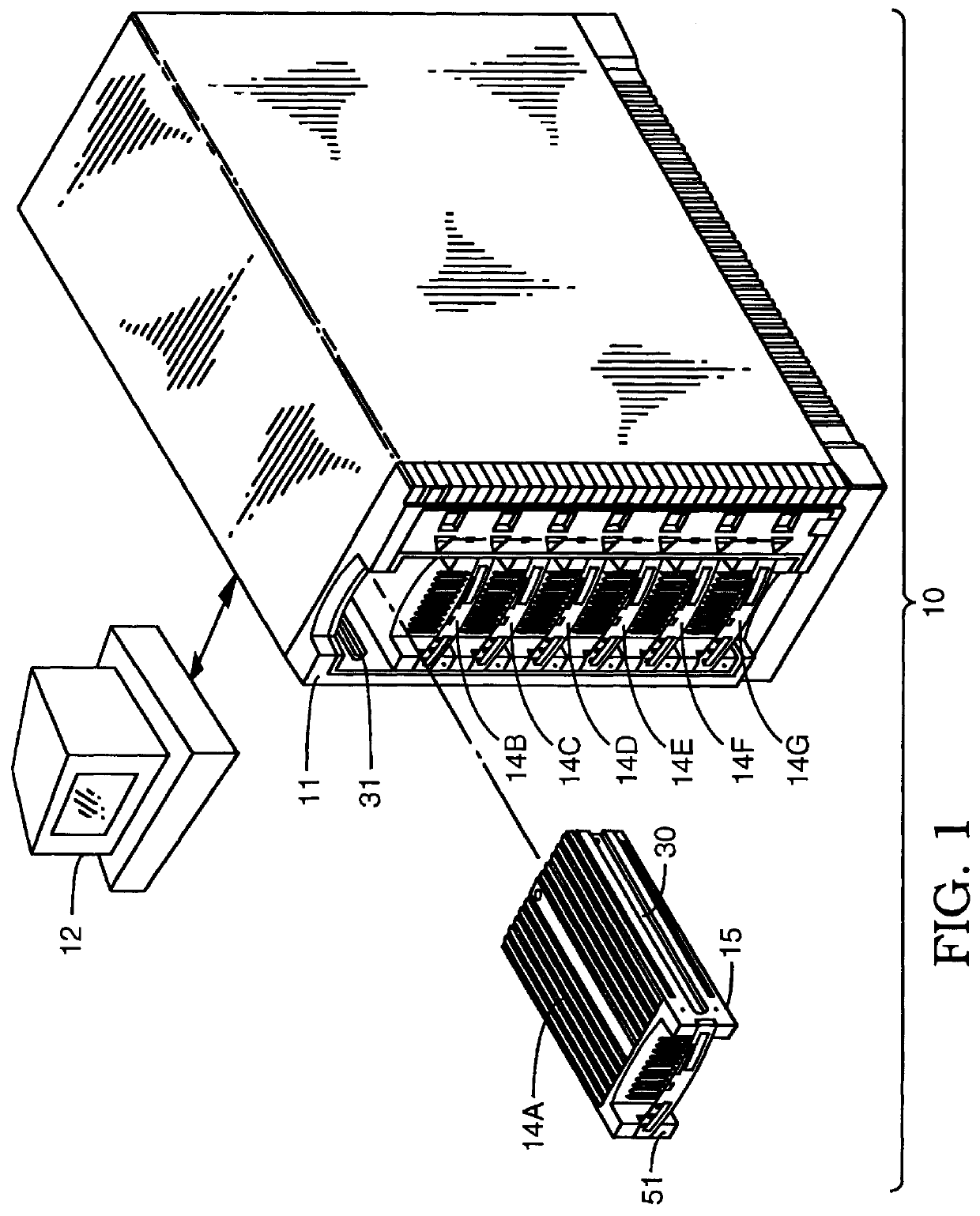
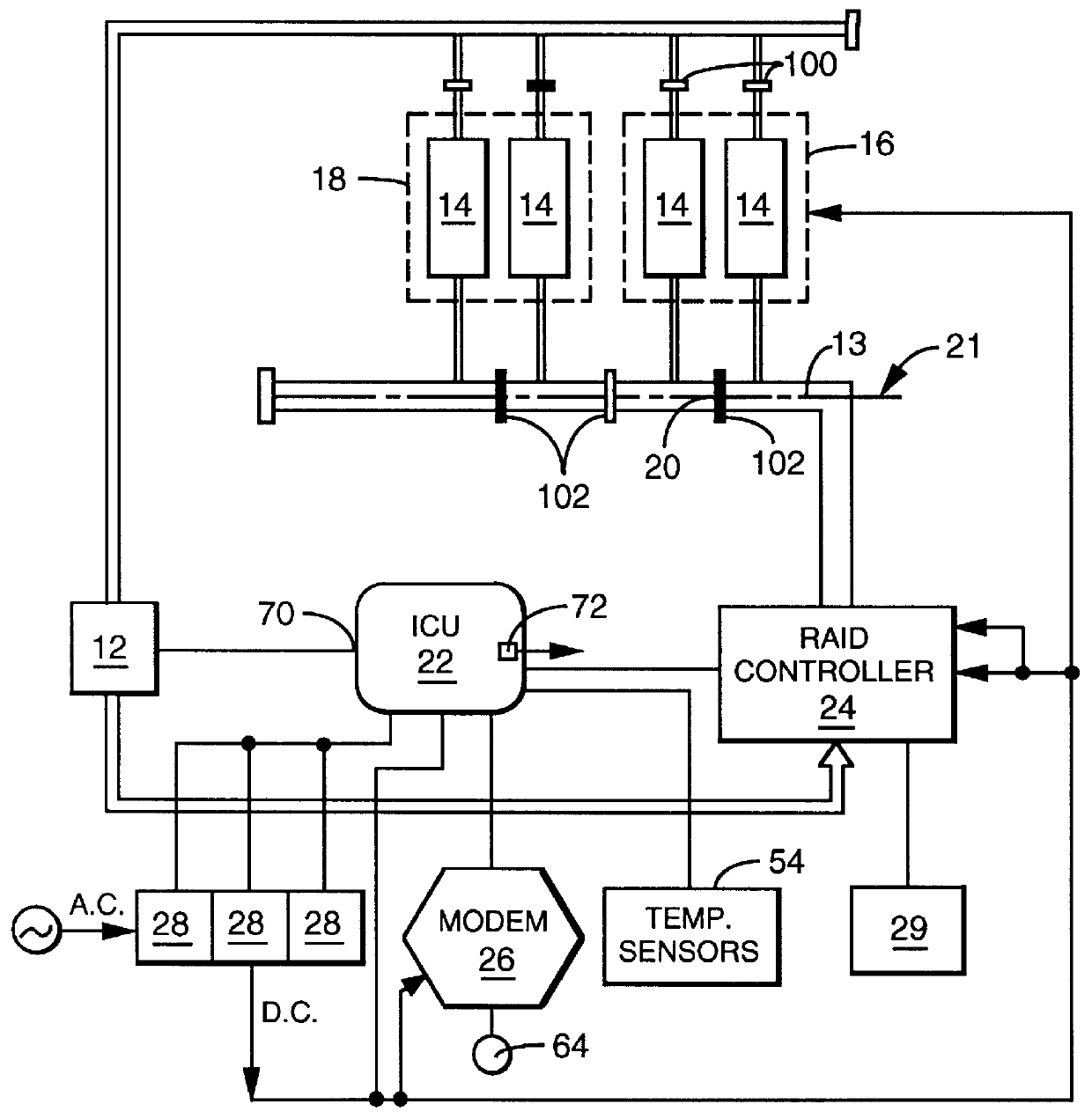
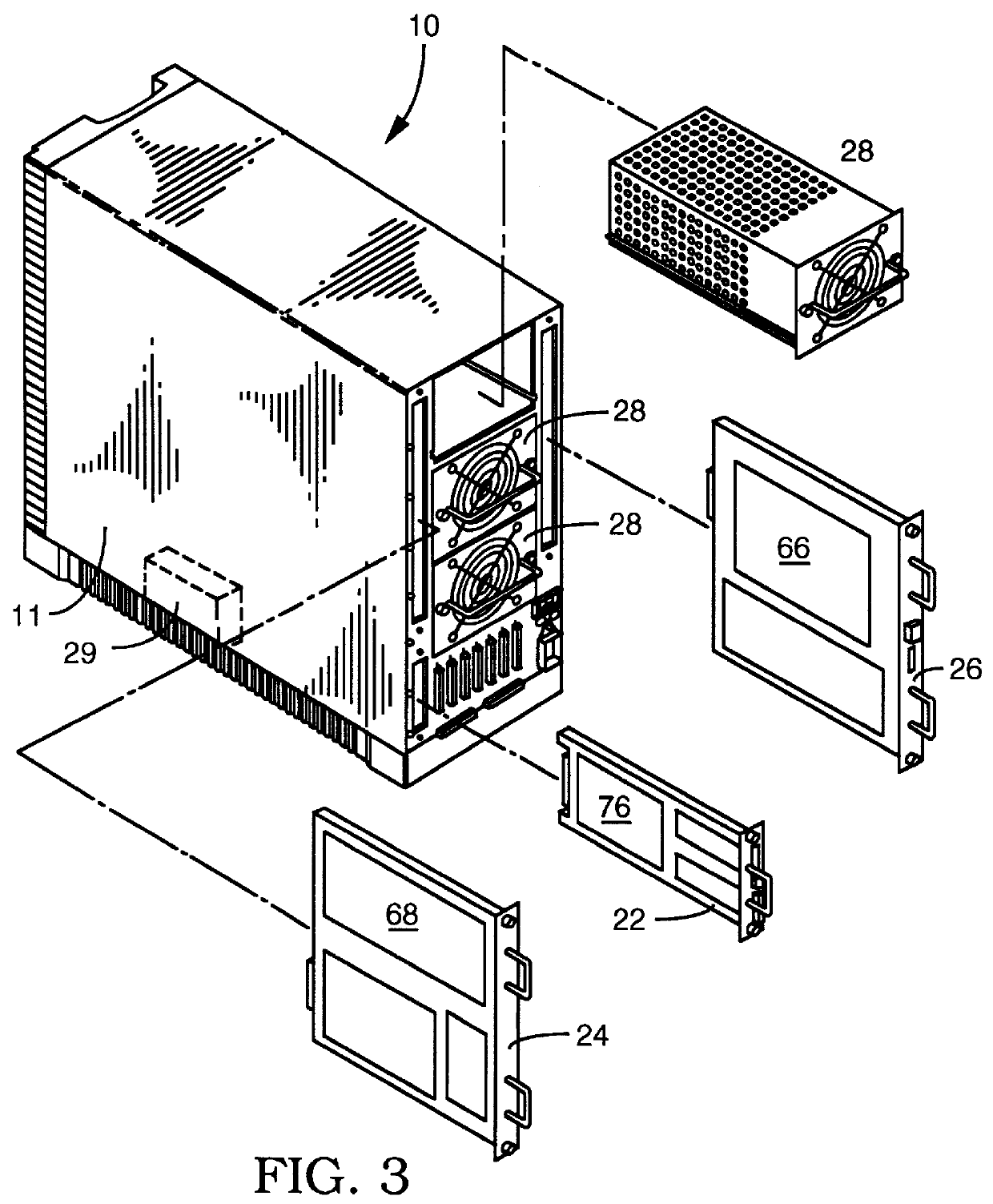
User configurable raid system with multiple data bus segments and removable electrical bridges
InactiveUS6076142ACarrier constructional parts dispositionError detection/correctionMass storageModem device
A user configurable RAID system designed to provide RAID functions as well as mass storage functions in a non-RAID mode. Flexibility is built into the system to allow the user to configure the SCSI bus to which removable drive modules are connected into one or more channels to define some of the drive modules in a RAID set and others as stand-alone drives which are independently operated or logically grouped and operated in a non-RAID mode. Removable internal SCSI bridges allow the SCSI bus to be configured into one or more channels. In the RAID mode, the system is configured to prevent a wrong drive from being removed from the system in the event of a drive failure. The system automatically unlatches only the failed drive. The RAID system includes an intelligent control unit ("ICU"), a RAID controller and a modem. The ICU allows the system administrator to access the RAID system Monitor Utility so that the status of the system may be monitored and its configuration changed. The ICU also monitors the failure status of the various components of the system. The ICU has a built-in pager feature that can be configured with the Monitor Utility to page the system administrator via the modem when a component or system failure is encountered. The RAID controller controls the functions of the RAID set as programmed and configured using the Monitor Utility. The Monitor Utility may be remotely accessed using a computer via the modem. Redundant removable power supply and fan units are provided to improve system integrity. The removable power supply and fan units are configured such when the unit is plugged into the system housing, the fan is first turned on and the power through the unit is allowed to stabilize before turning on the power supply to begin providing DC power to the components in the system. A set of manual release buttons are provided for manually unlatching the drive modules from the system housing. A locking mechanism is provided for simultaneously locking all the manual release buttons.
Owner:MICRONET TECH
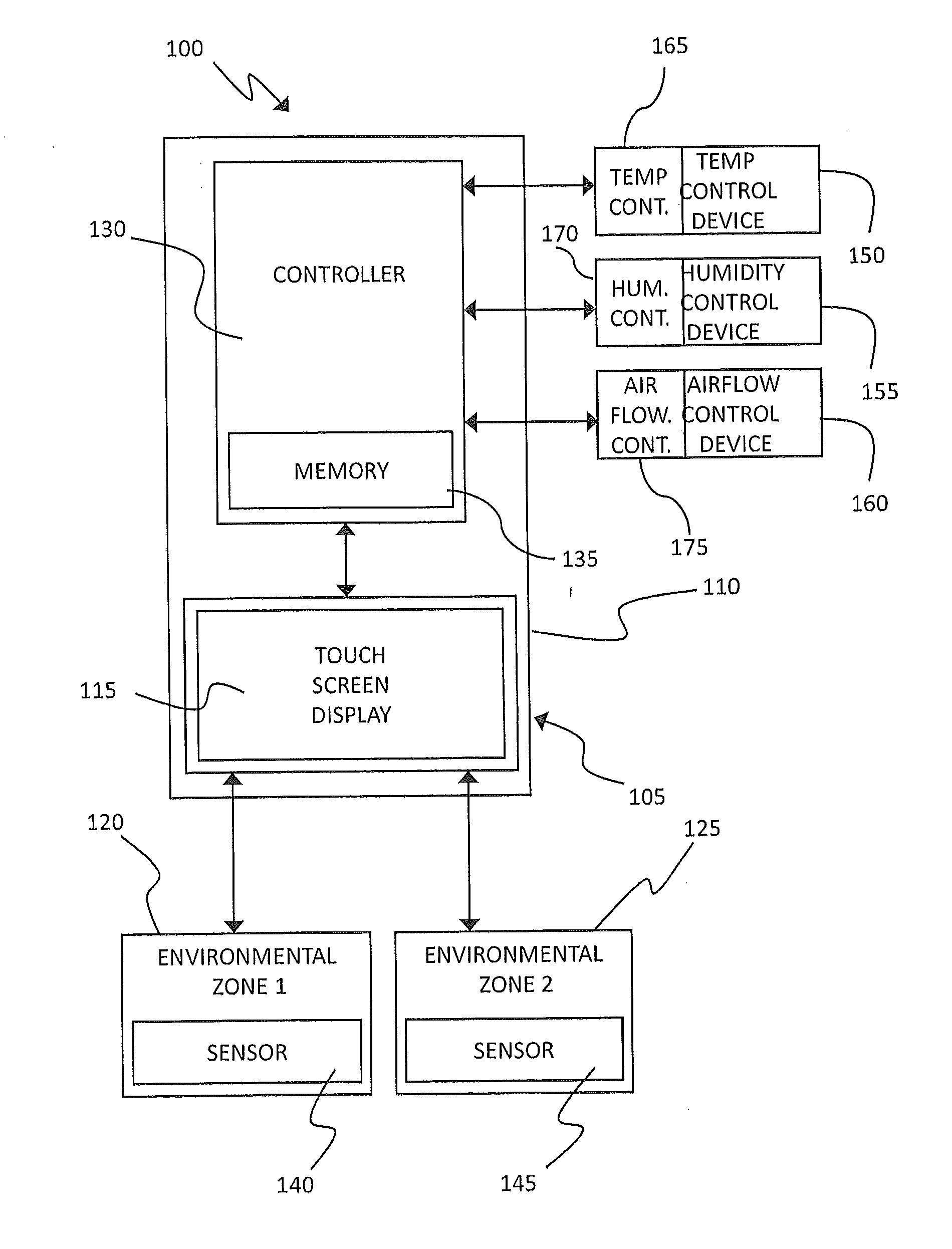
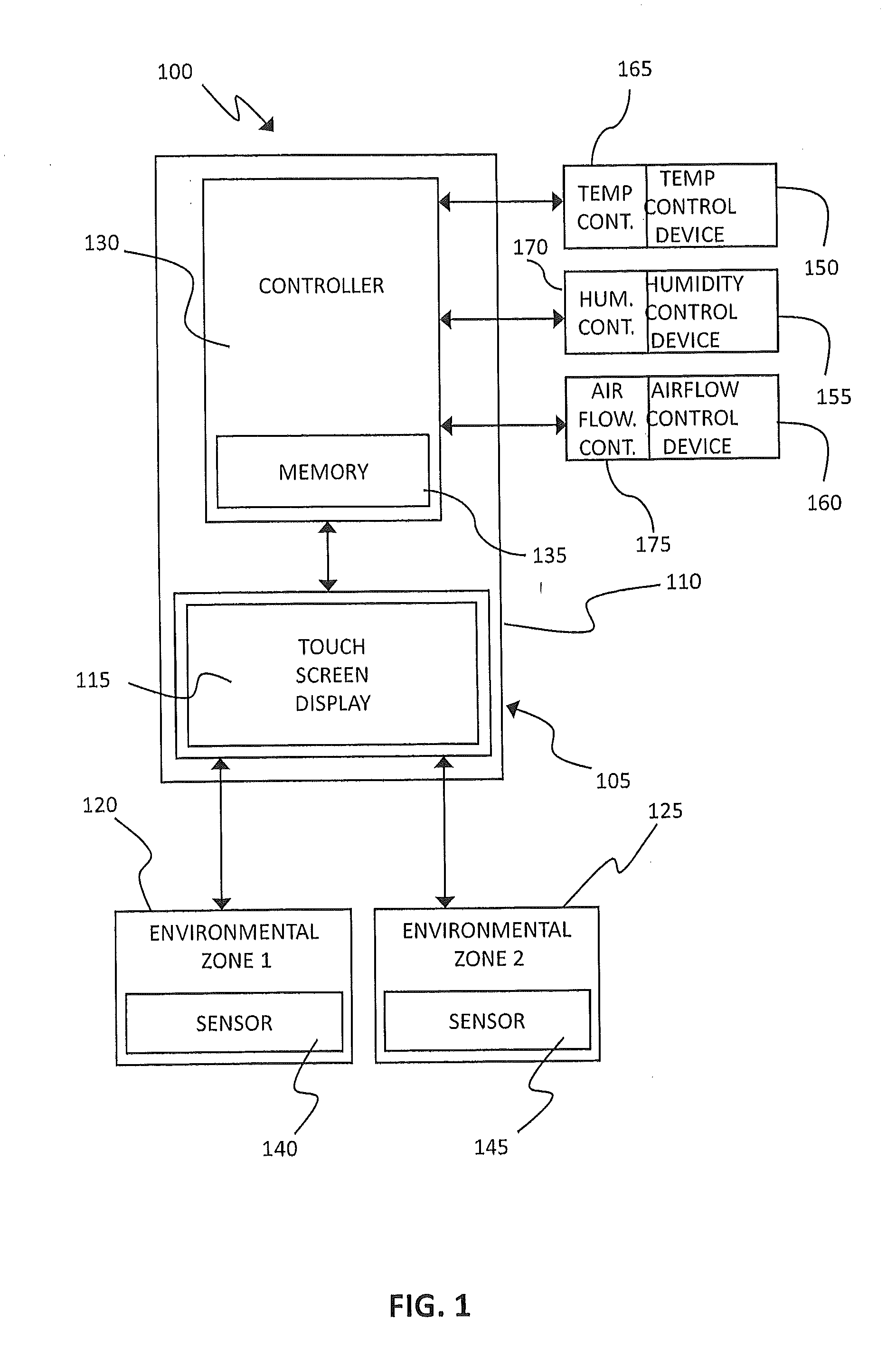
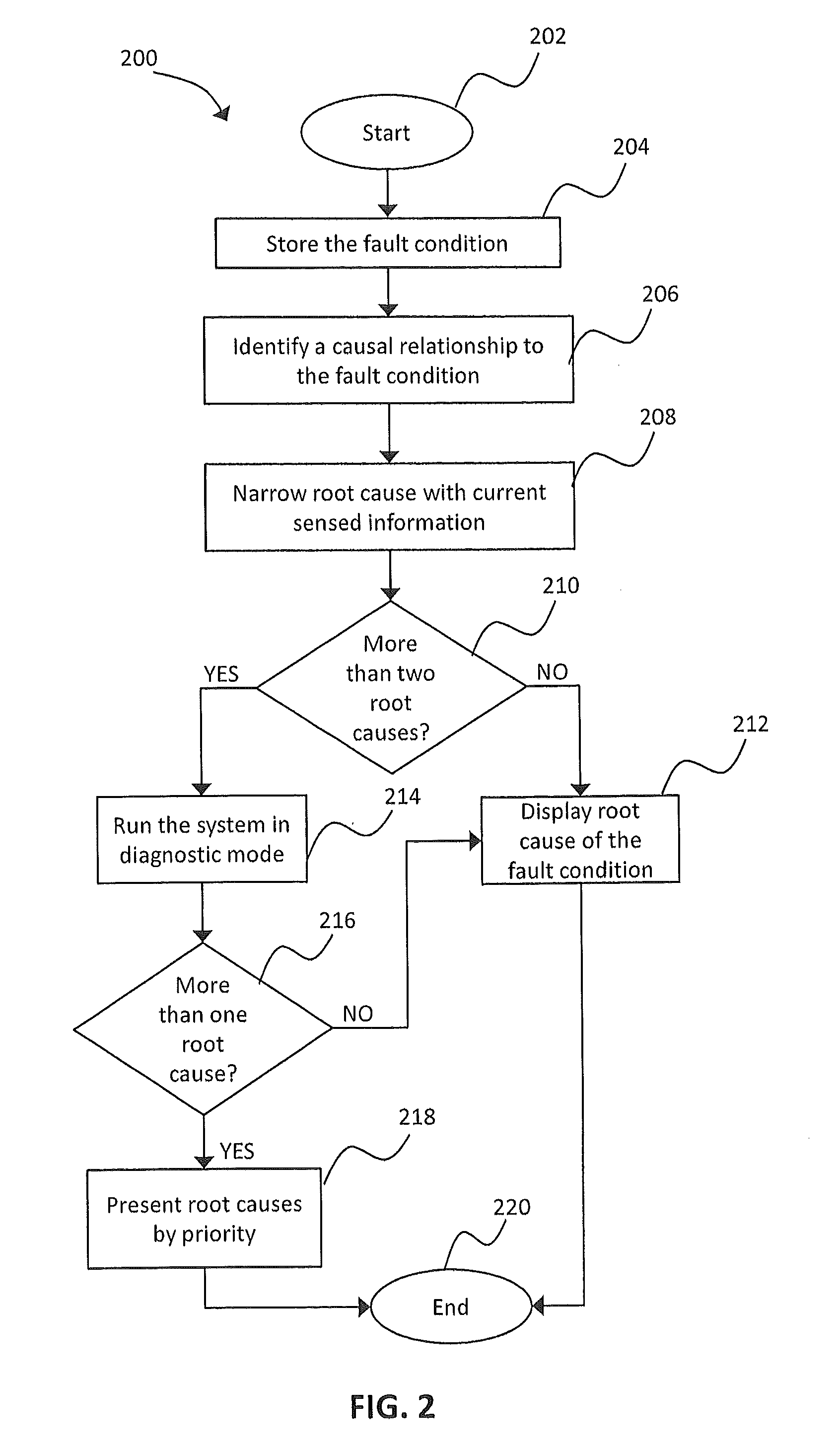
HVAC System Fault Root Cause Self-Determination
A method for self-determining a root cause of a system fault in a heating, ventilation, and cooling (HVAC) system includes receiving a fault message indicative of a fault condition in an operating characteristic of the HVAC system; determining a causal relationship between the fault condition and a predetermined list of root causes associated with the fault condition; receiving information indicative of operating conditions of the HVAC system; and eliminating at least one root cause that is unrelated to the fault condition in response to the receiving of the information.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
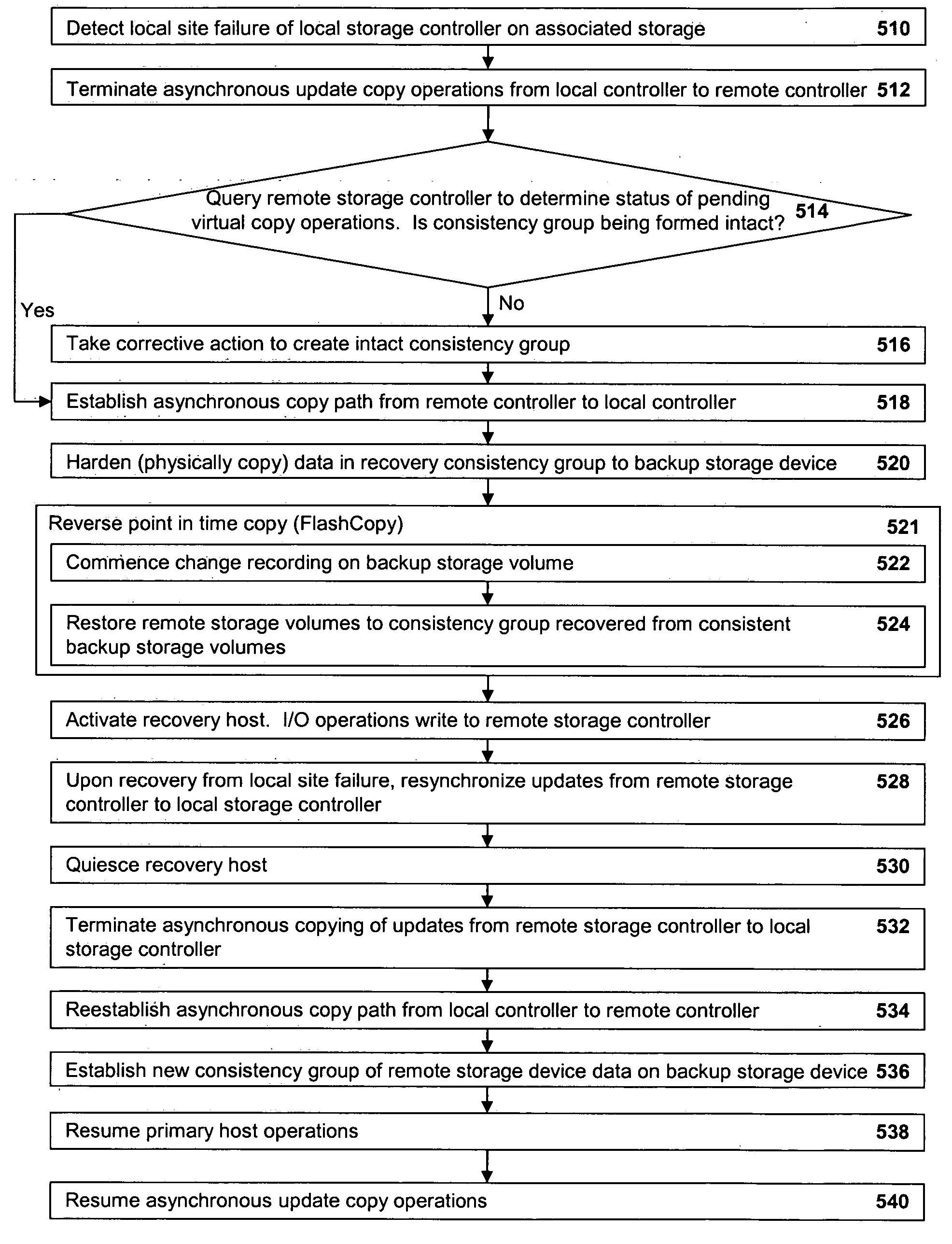
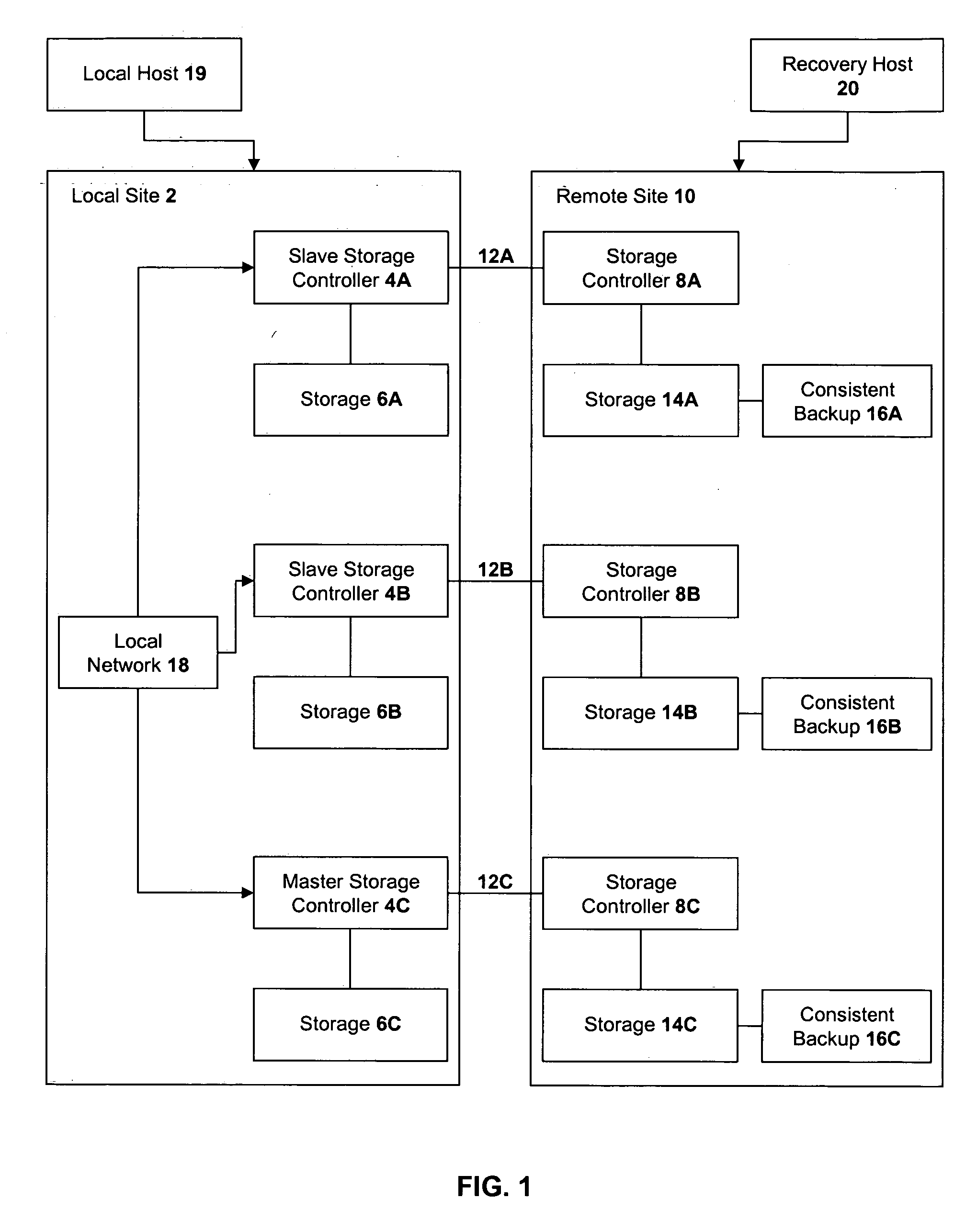
Method, system, and program for recovery from a failure in an asynchronous data copying system
InactiveUS20050071708A1Application downtime is minimizedMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionRecovery methodDevice form
A method of recovery from a data storage system failure in a data storage system having a host computer writing data updates to a local storage controller at a local site. The local controller is associated with a local storage device. The local storage controller is also configured to asynchronously copy the updates to a remote storage controller associated with a remote storage device at a remote site. In addition, the remote storage controller is configured to store a consistent point in time copy of the updates on a backup storage device. The consistent point in time copy is known as a consistency group. Upon detection of a failure associated with the local site, a determination is made whether a group of updates pending for storage on the backup storage device form an intact consistency group. If an intact consistency group has not formed, corrective action may be taken to create an intact consistency group. The recovery method further consists of synchronizing the remote storage device, initiating recovery operations and, upon recovery of the local site, resynchronization of the local storage device and the backup storage device to recovery consistency group without the need for full volume storage copies and while minimizing application downtime.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for automating the root cause analysis of system failures
InactiveUS20050210331A1Multiple digital computer combinationsNon-redundant fault processingRoot causeRoot cause analysis
A method for analyzing the root cause of system failures on one or more computers. An event is generated when a computer system detects a system failure. The cause of the failure is determined. The event, including the cause is transmitted from the computer system to a central repository. And the system failure is analyzed in the central repository.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
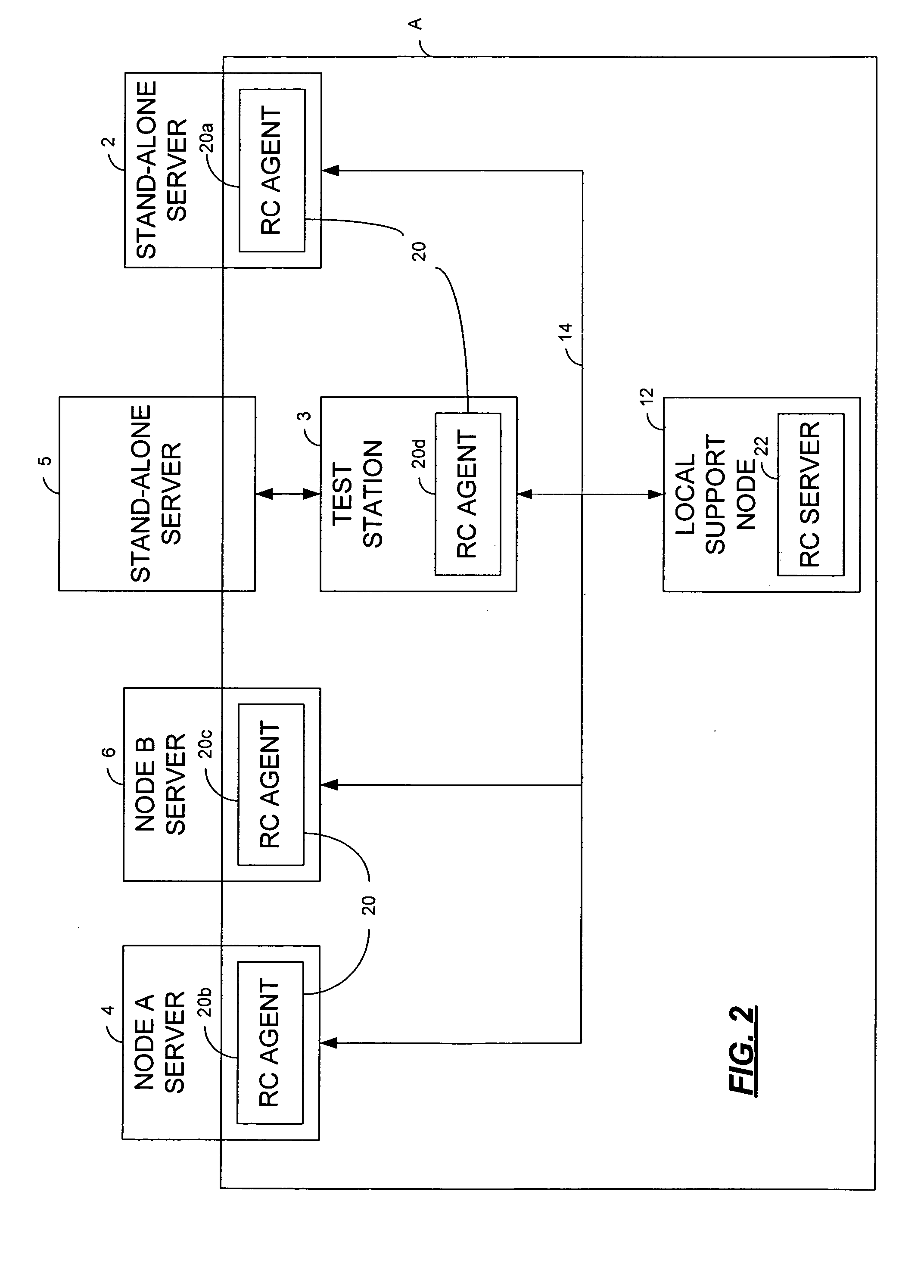
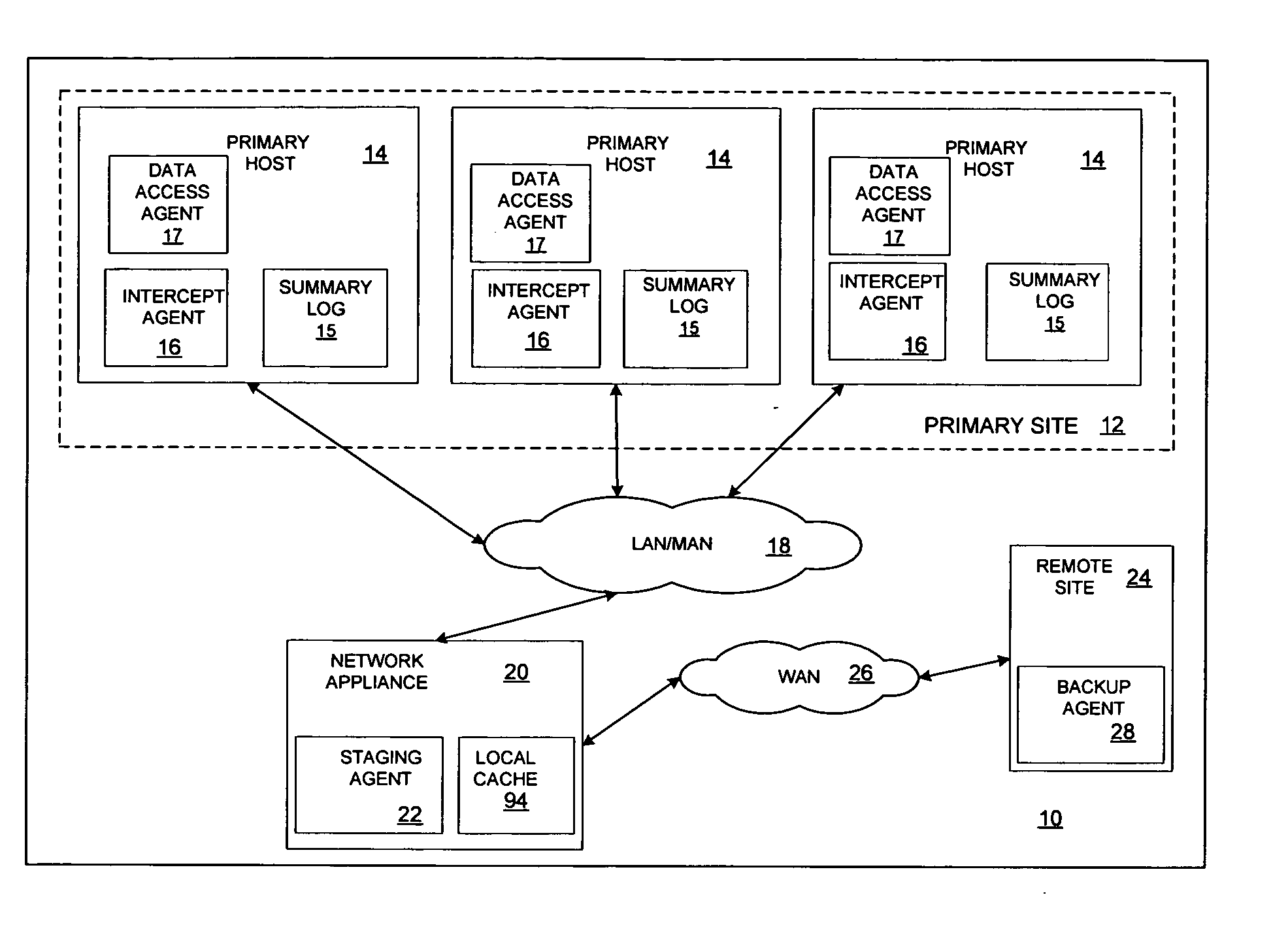
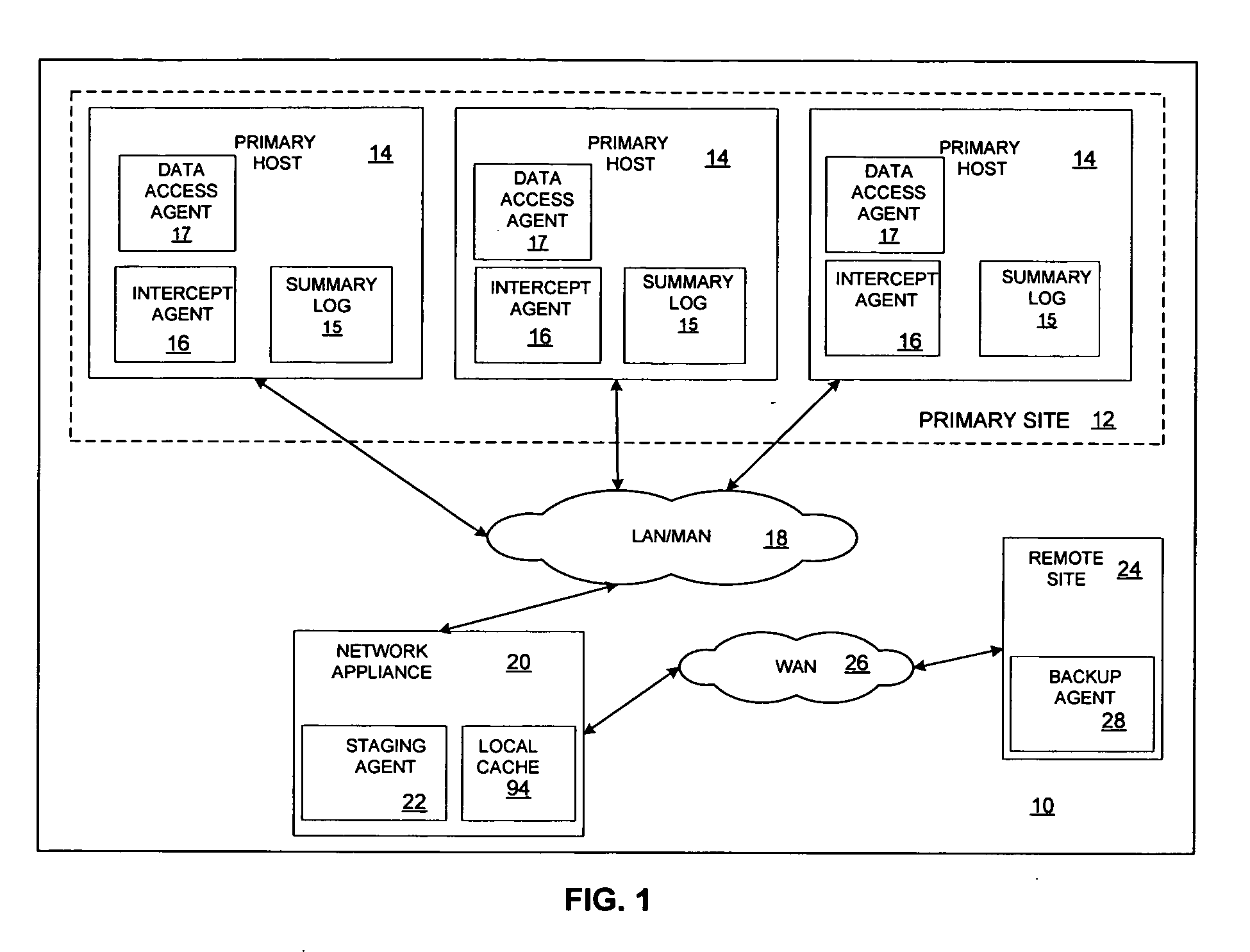
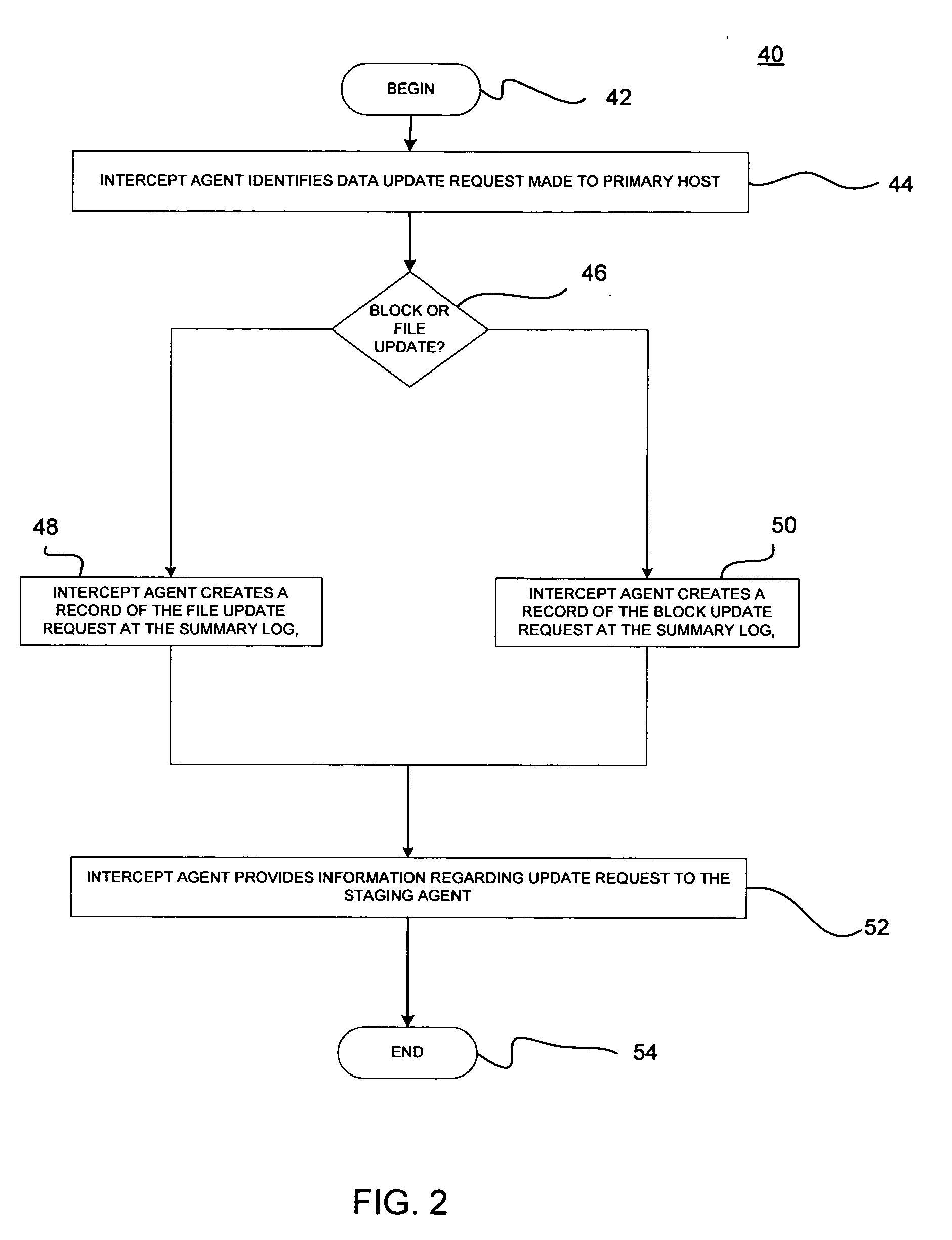
Minimizing resynchronization time after backup system failures in an appliance-based business continuance architecture
ActiveUS20050273654A1Minimize resynchronization timeMinimize timeMemory systemsRedundant hardware error correctionDowntimeSystem failure
A system for minimizing downtime in an appliance-based business continuance architecture is provided. The system includes at least one primary data storage and least one primary host machine. The system includes an intercept agent to intercept primary host machine data requests, and to collect information associated with the intercepted data requests. Moreover, at least one business continuance appliance in communication with the primary host machine and in communication with a remote backup site is provided. The appliance receives information associated with the intercepted data requests from the intercept agent. In addition, a local cache is included within the business continuance appliance. The local cache maintains copies of primary data storage according to the information received. Furthermore, the remote site is provided with the intercepted data requests via the business continuance appliance, wherein the remote site maintains a backup of the primary data storage.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
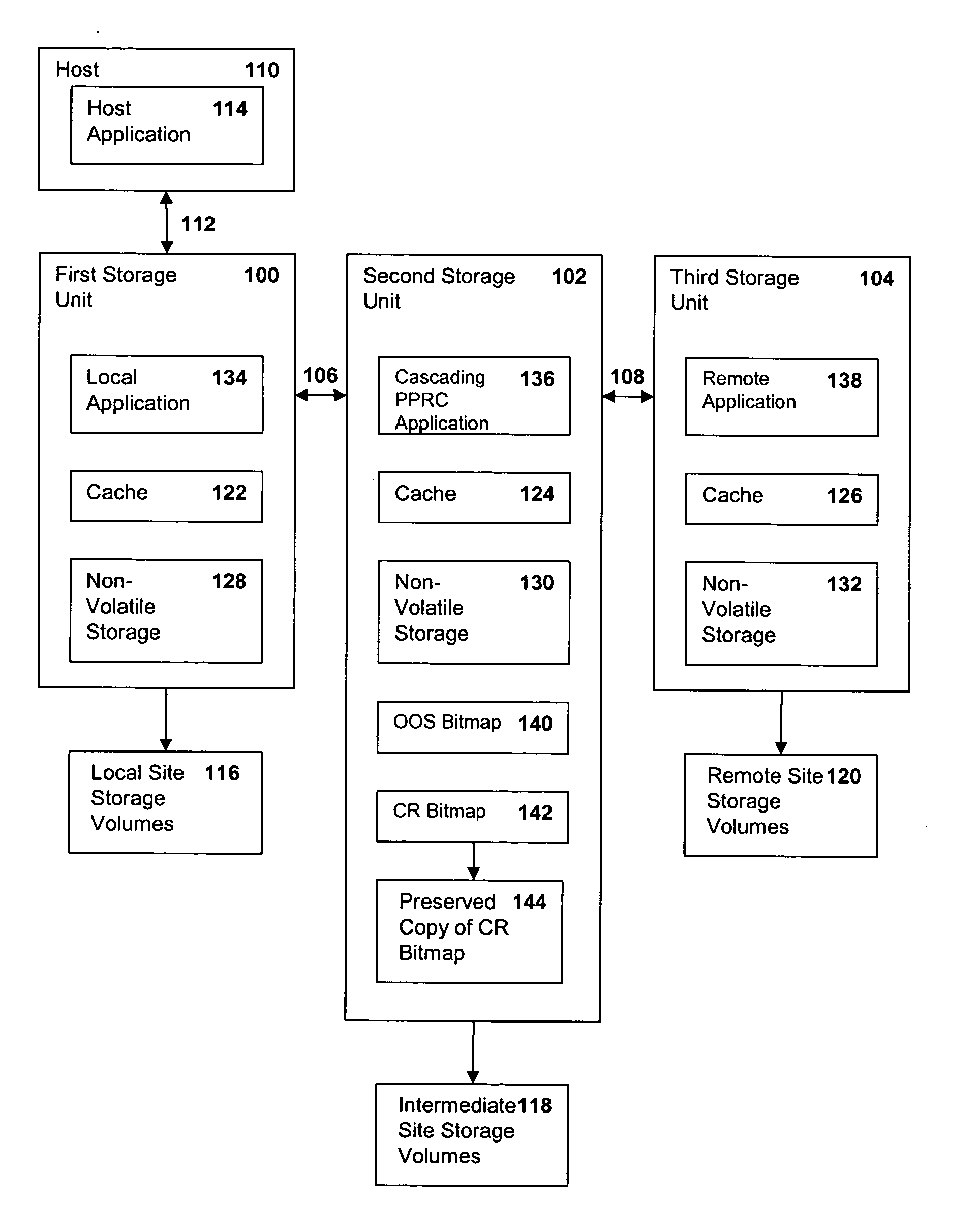
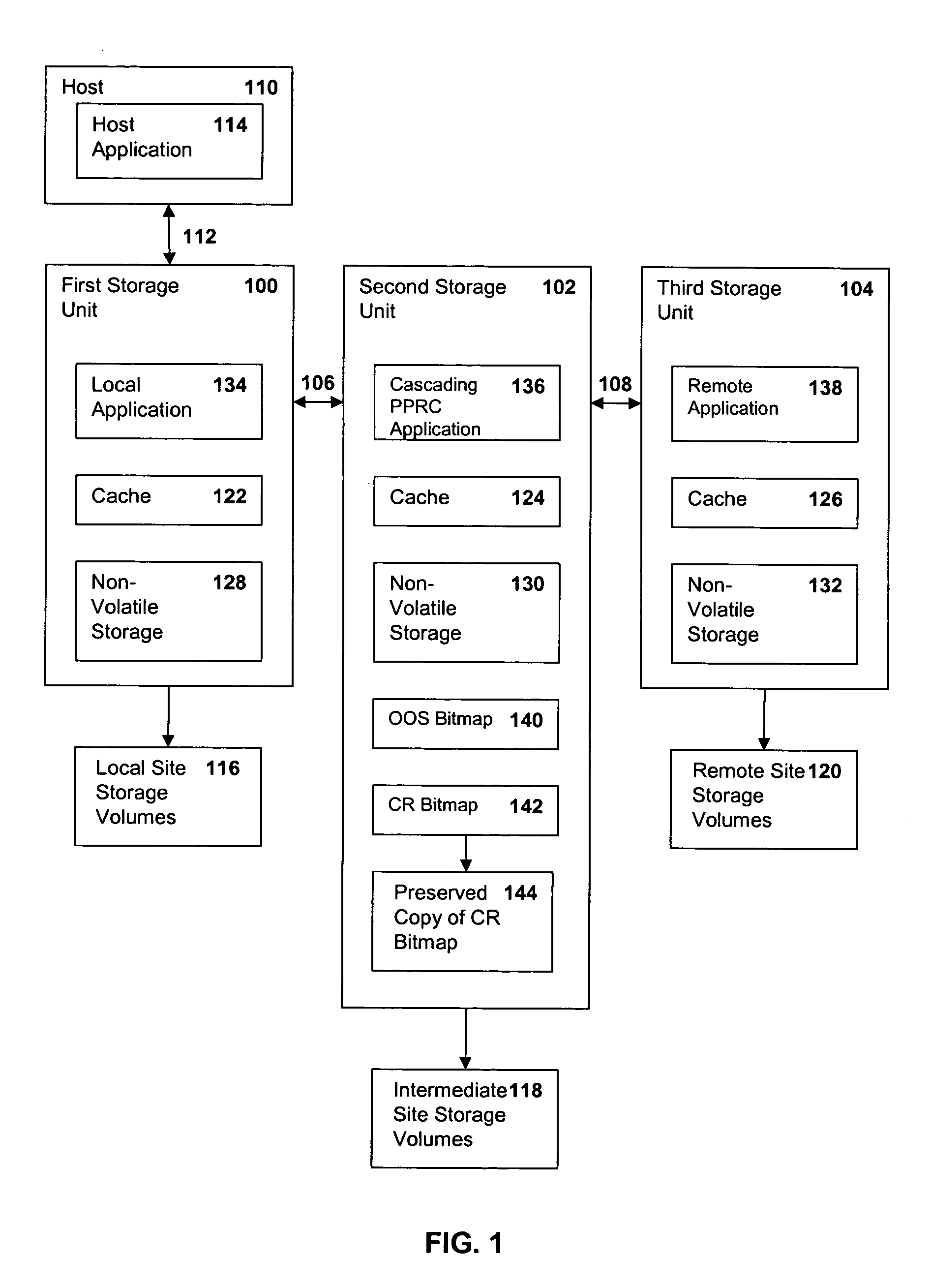
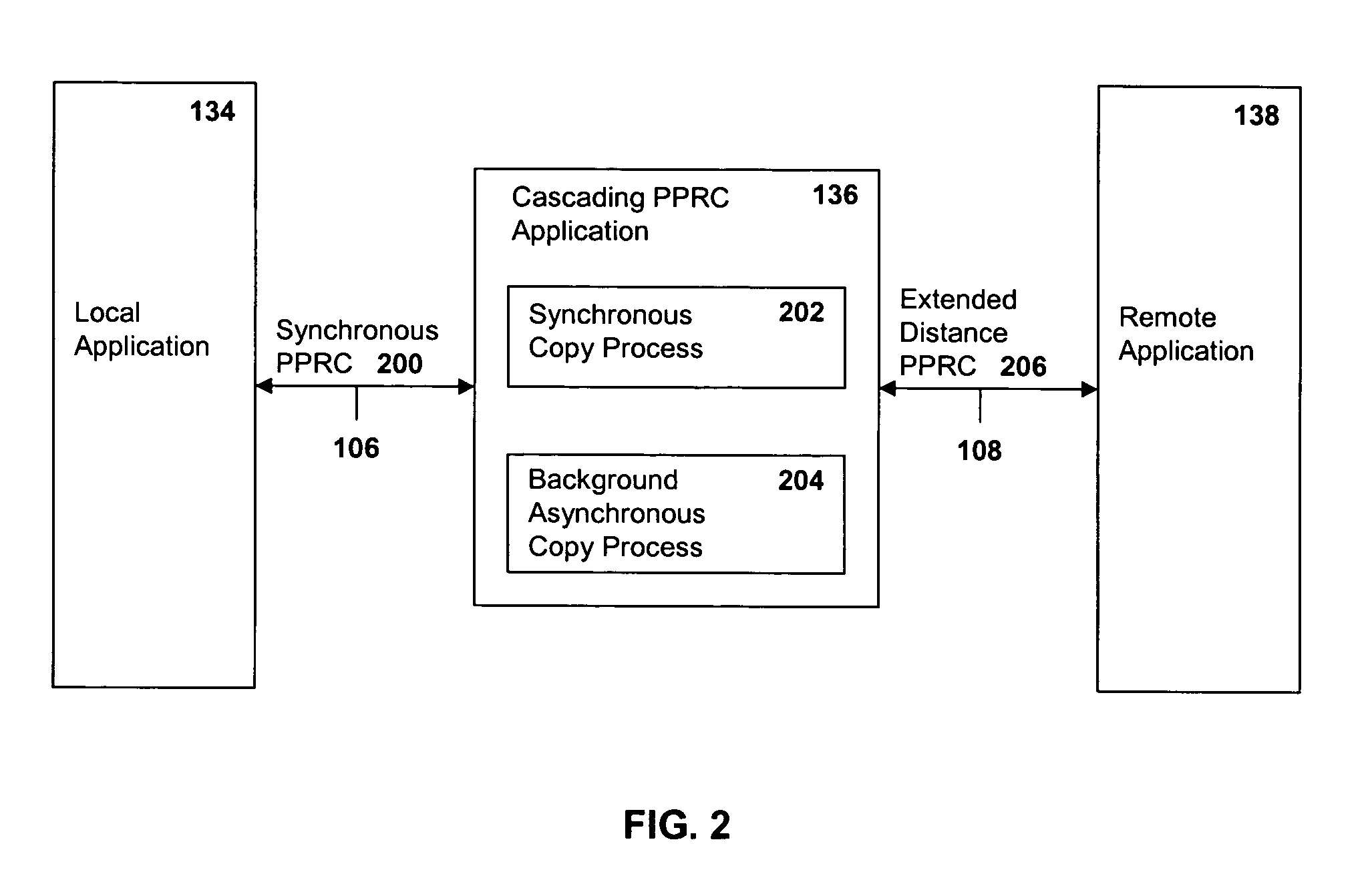
Method, system and article of manufacture for recovery from a failure in a cascading PPRC system
InactiveUS20050081091A1Application downtime is minimizedRedundant hardware error correctionData synchronizationControl store
A method of recovery from a data storage system failure in a data storage system having a host computer writing data to a first storage unit with a first storage controller synchronously mirroring the data to a second storage unit, and with a second storage controller asynchronously mirroring the data to a third storage unit. The method begins with the detection of a failure associated with the first storage unit. Upon detection of the error or failure associated with the first storage unit, the synchronous data mirroring relationship between the first storage unit and the second storage unit is terminated and the host is directed to write data updates directly to the second storage unit. Upon correction of the failure associated with the first storage unit, the asynchronous mirroring of data updates from the second storage unit to the third storage unit is suspended and synchronous mirroring of the data updates in a reverse direction, from the second storage unit to the first storage unit, is commenced. When a full duplex state is reached between the first storage unit and the second storage unit, the synchronous PPRC relationship with the first storage volume mirroring data to the second storage volume may be reestablished and host I / O writes to the first storage unit may be resumed.
Owner:IBM CORP
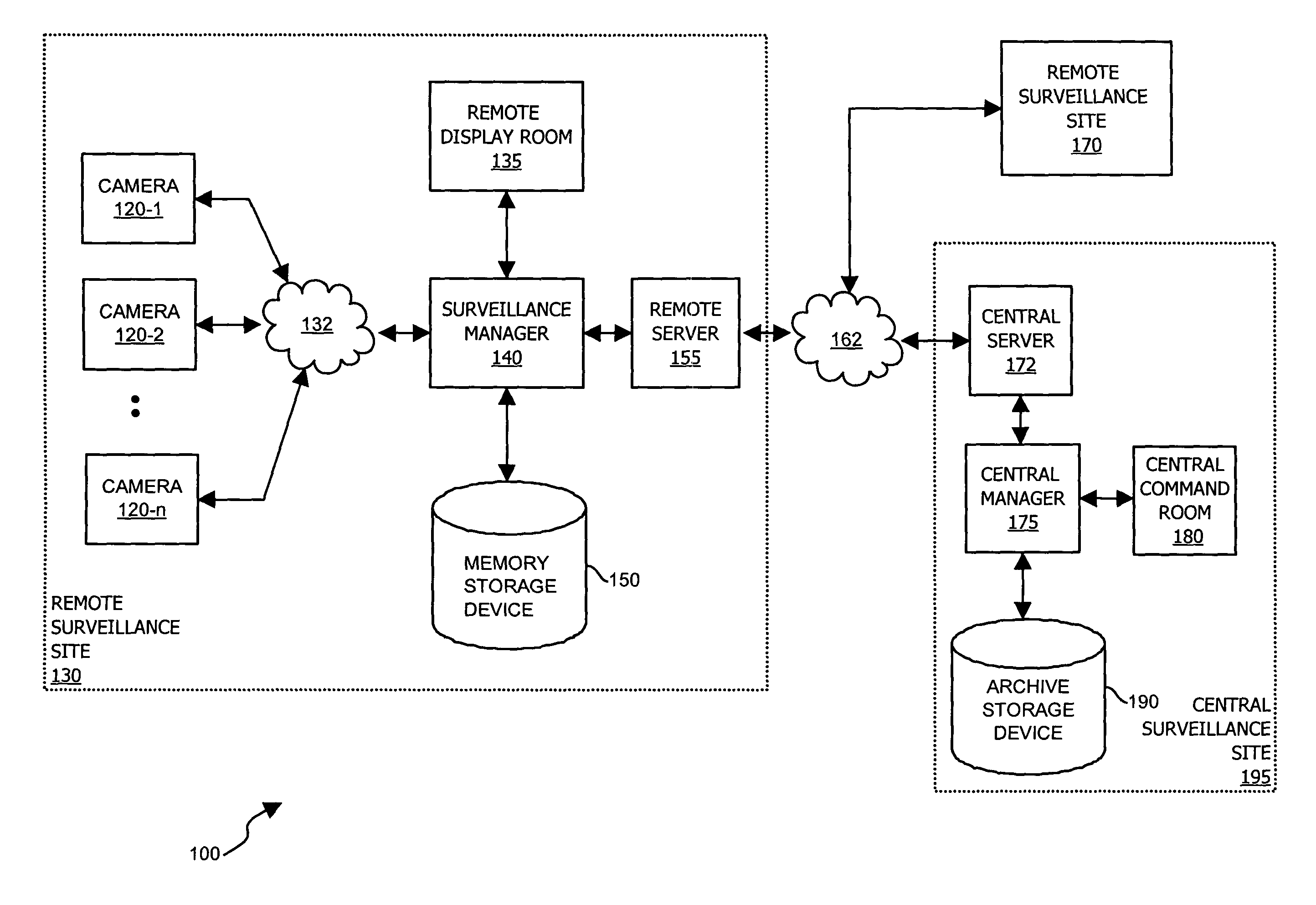
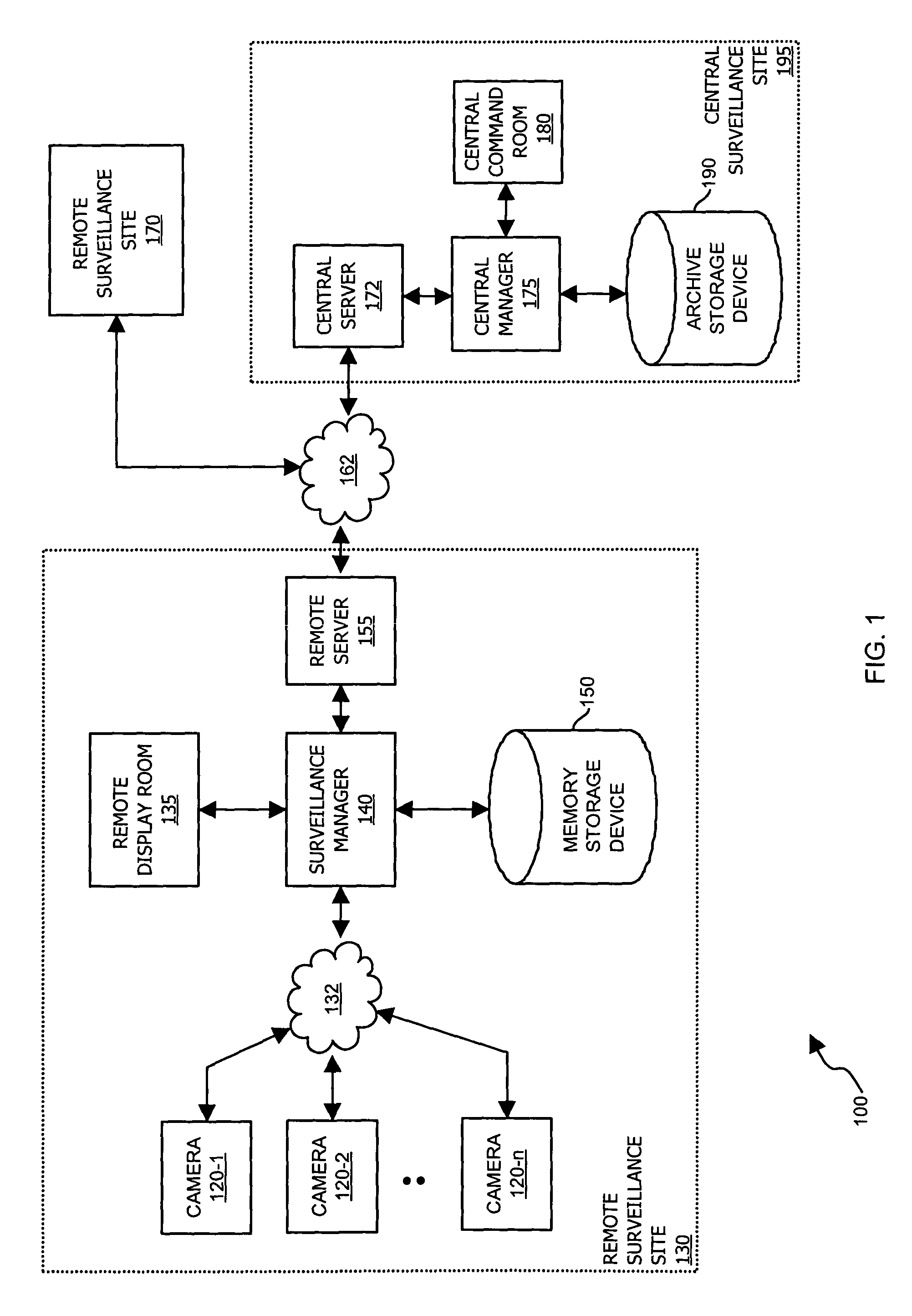
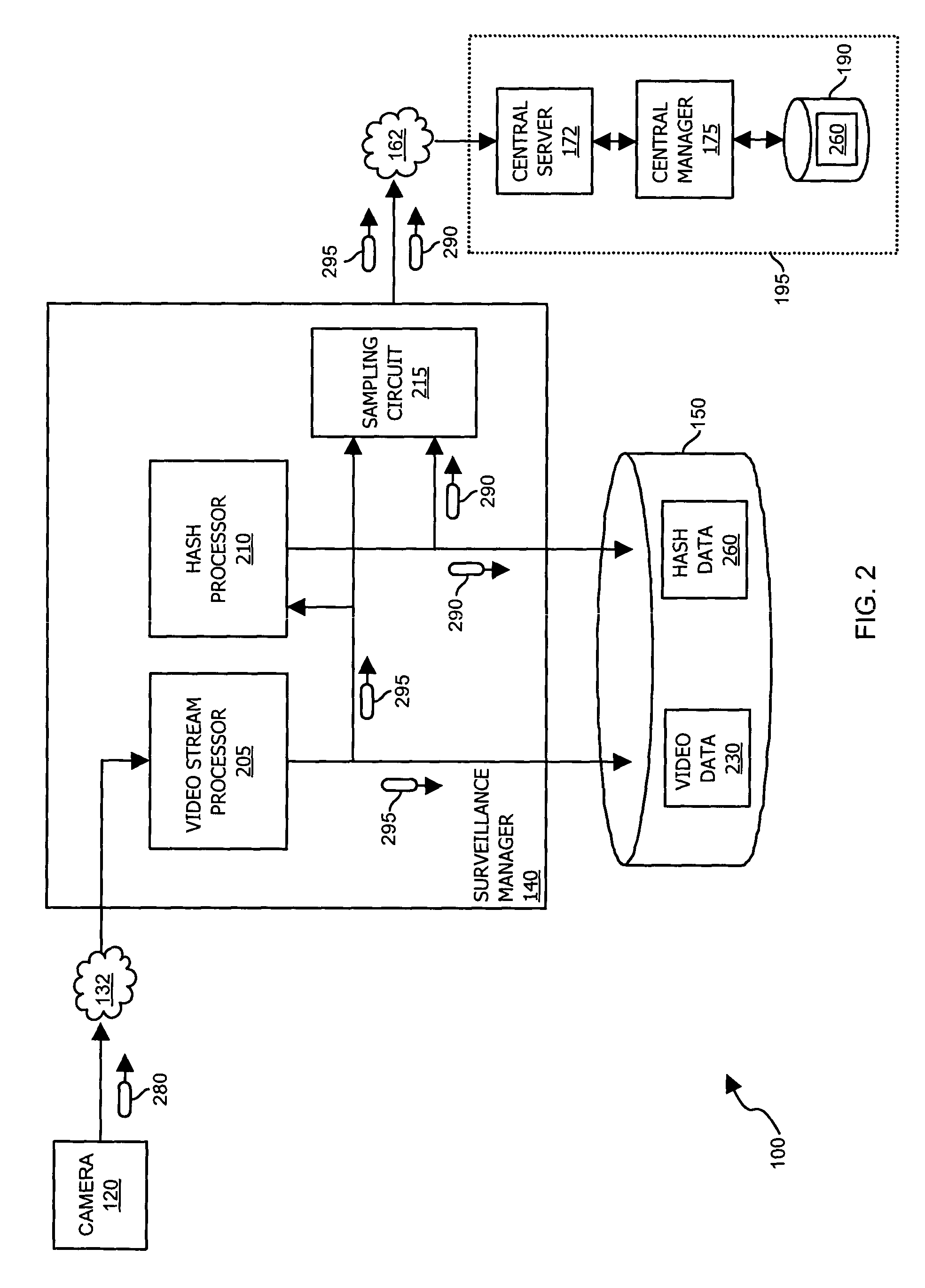
Methods and apparatus for use in surveillance systems
InactiveUS7508941B1Improve the level ofEasy to manageTelevision systemsBurglar alarmComputer hardwareControl signal
A control signal is provided to a video data acquisition system that generates video data. In response to receiving the control signal, the video data acquisition system modifies at least a portion of the video data to produce an output signal. Authenticity of the output signal from the video data acquisition system is verified by checking that the video data includes modifications according to the control signal. If the video data does not include such modifications, it is known that the video data acquisition system needs to be checked for tampering or system failures.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
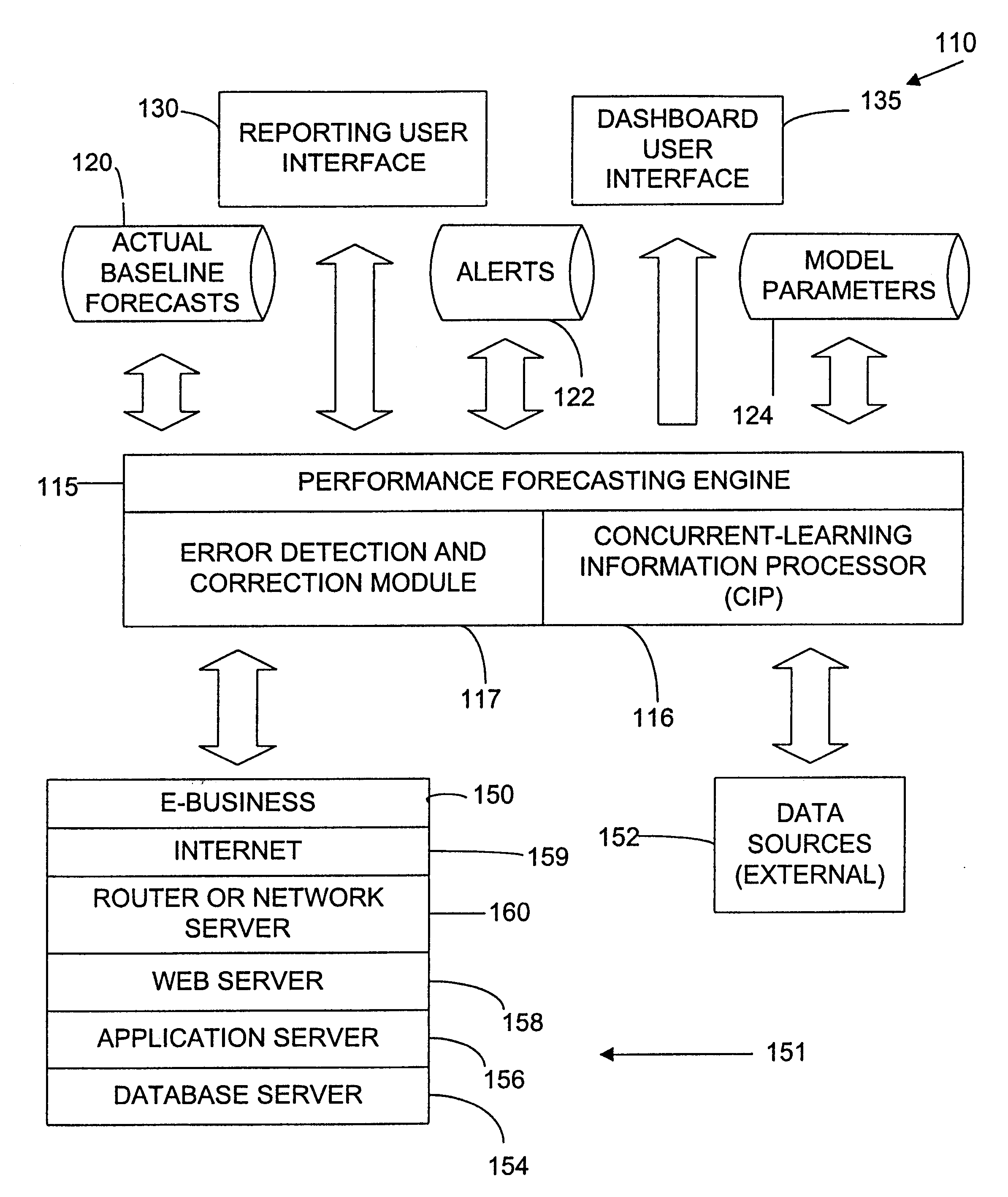
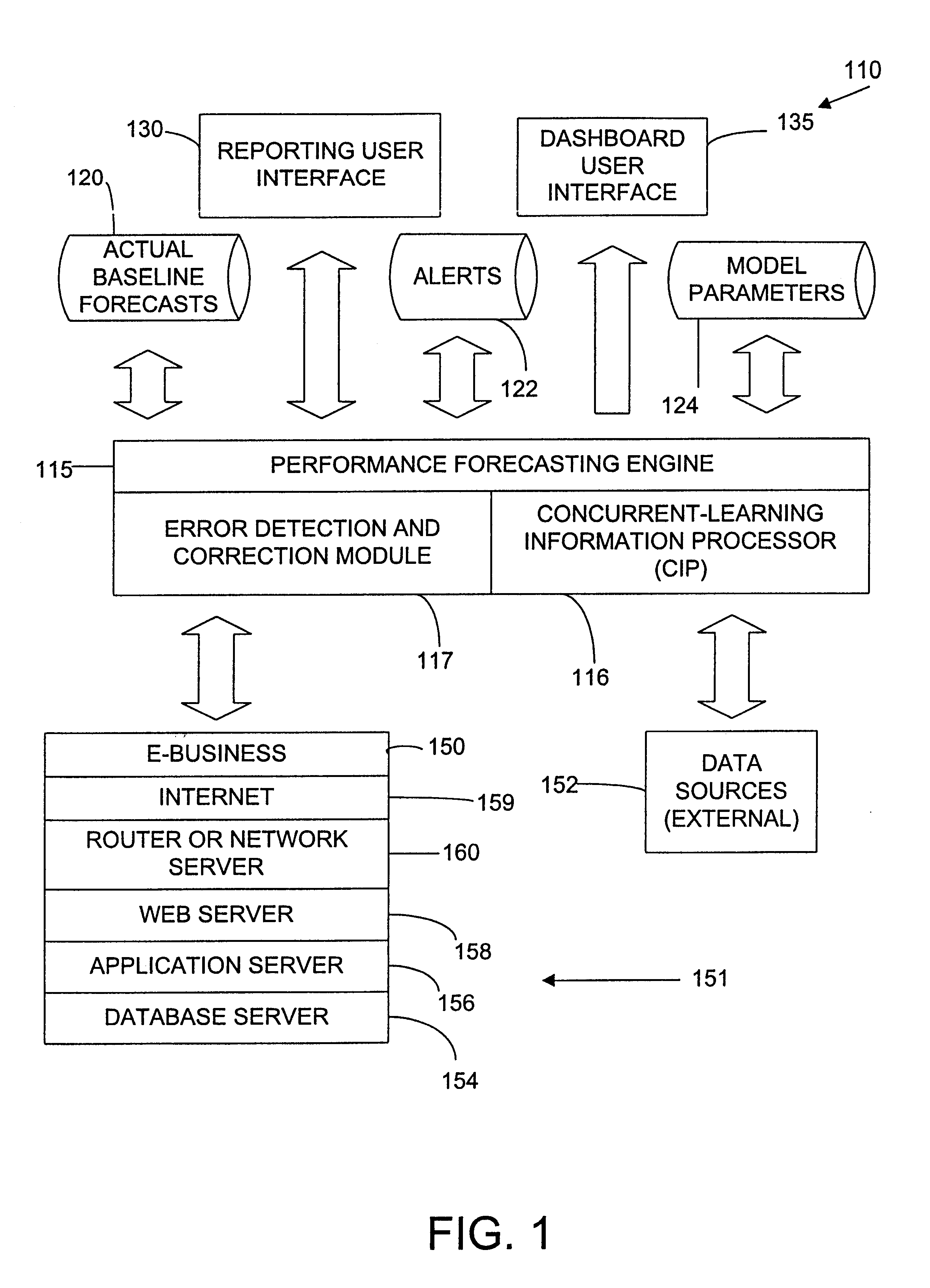
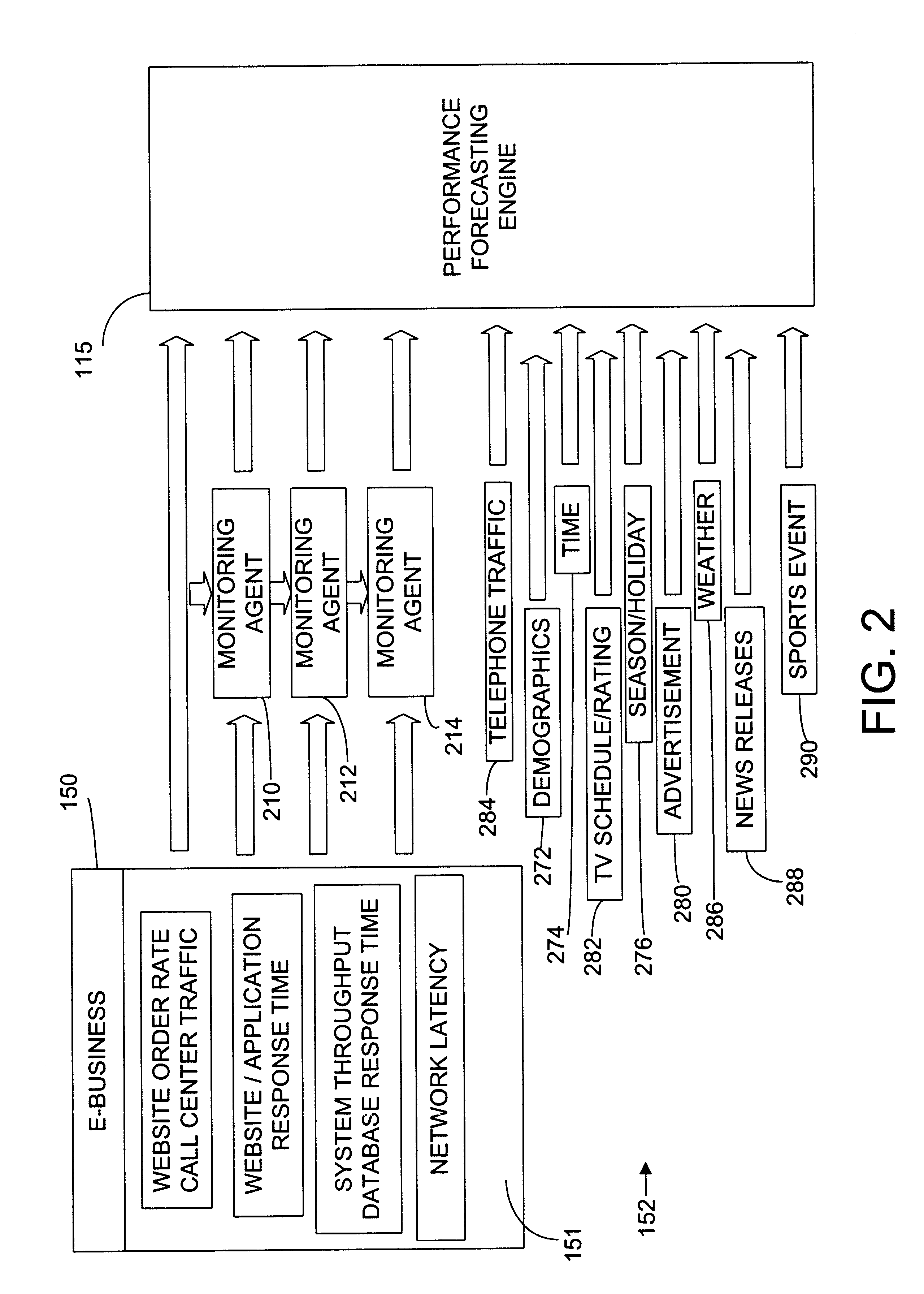
Enhanced computer performance forecasting system
ActiveUS6876988B2Accurate predictionEnsure correct executionDigital computer detailsHardware monitoringComputer performanceEngineering
A method and system for computing a performance forecast for an e-business system or other computer architecture to proactively manage the system to prevent system failure or slow response time. The system is adapted to obtain measured input values from a plurality of internal data sources and external data sources to predict a system's performance especially under unpredictable and dramatically changing traffic levels in an effort to proactively manage the system to avert system malfunction or slowdown. The performance forecasting system can include both intrinsic and extrinsic variables as predictive inputs. Intrinsic variables include measurements of the systems own performance, such as component activity levels and system response time. Extrinsic variables include other factors, such as the time and date, whether an advertising campaign is underway, and other demographic factors that may effect or coincide with increased network traffic.
Owner:NETUITIVE
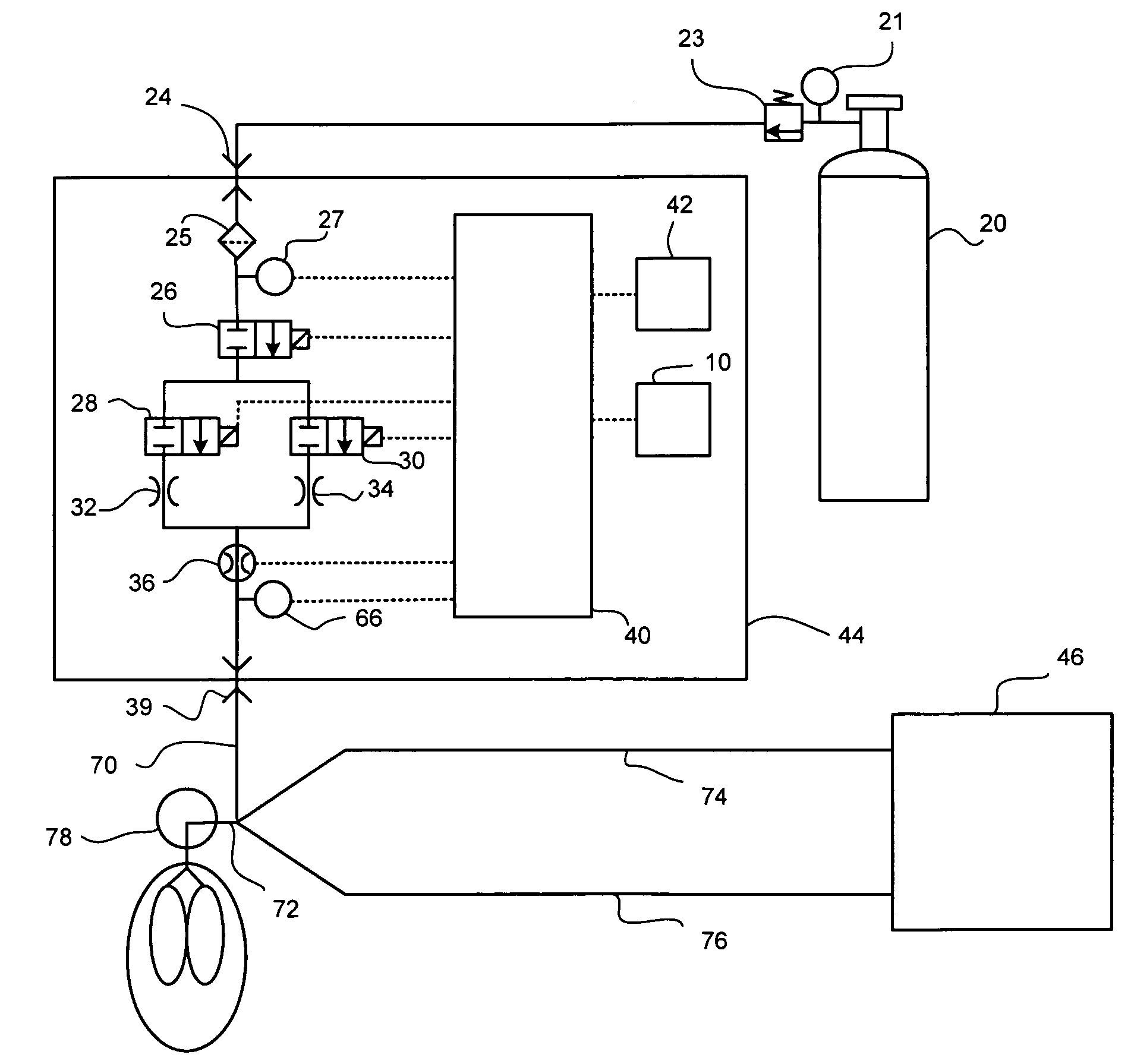
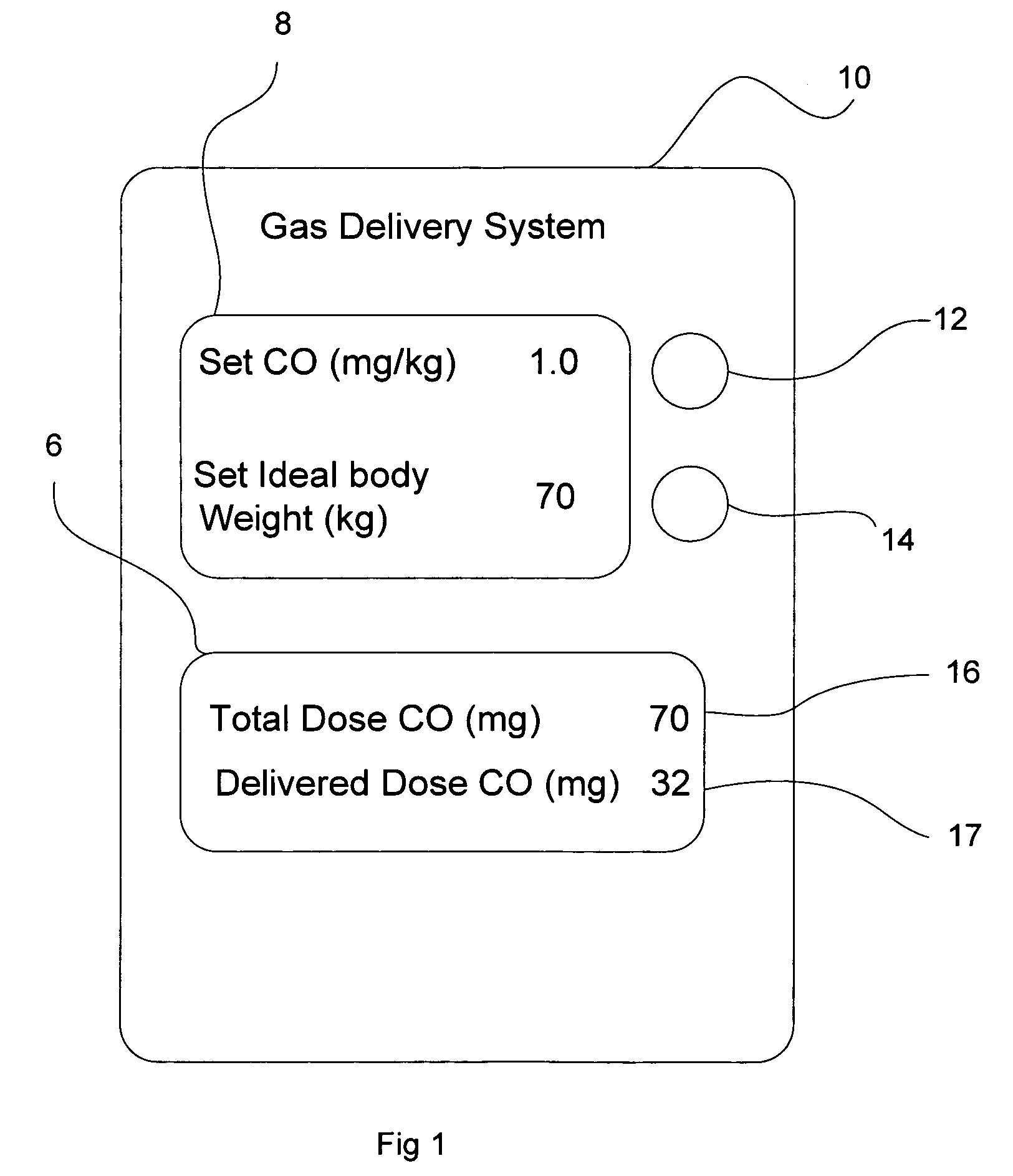
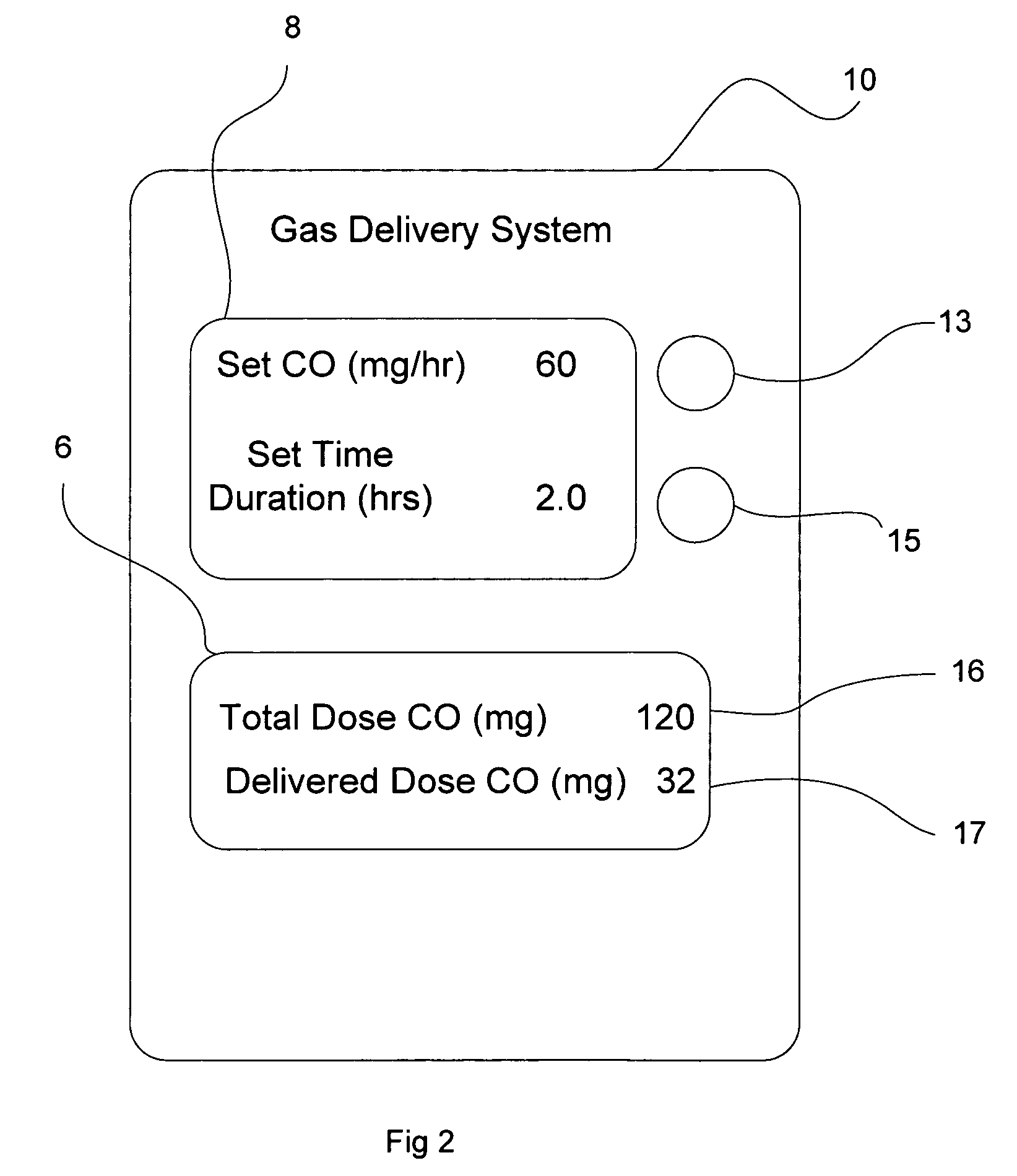
System and method of administering a pharmaceutical gas to a patient
ActiveUS7523752B2Tracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesControl systemProduct gas
A method and system for delivering a pharmaceutical gas to a patient. The method and system provide a known desired quantity of the pharmaceutical gas to the patient independent of the respiratory pattern of the patient. The preferred pharmaceutical gases are CO and NO, both of which are provided as a concentration in a carrier gas. The gas control system determines the delivery of the pharmaceutical gas to the patient to result in the known desired quantity (e.g. in molecules, milligrams or other quantified units) of the pharmaceutical gas being delivered. Upon completion of that known desired quantity of pharmaceutical gas over a plurality of breaths, the system can either terminate any further delivery of the pharmaceutical gas or can activate an alarm to alert the user that the known quantity has been delivered. The system also has alarm functions to alert the user of possible malfunctions of the system.
Owner:MALLINCKRODT HOSPITAL PRODUCTS IP LTD
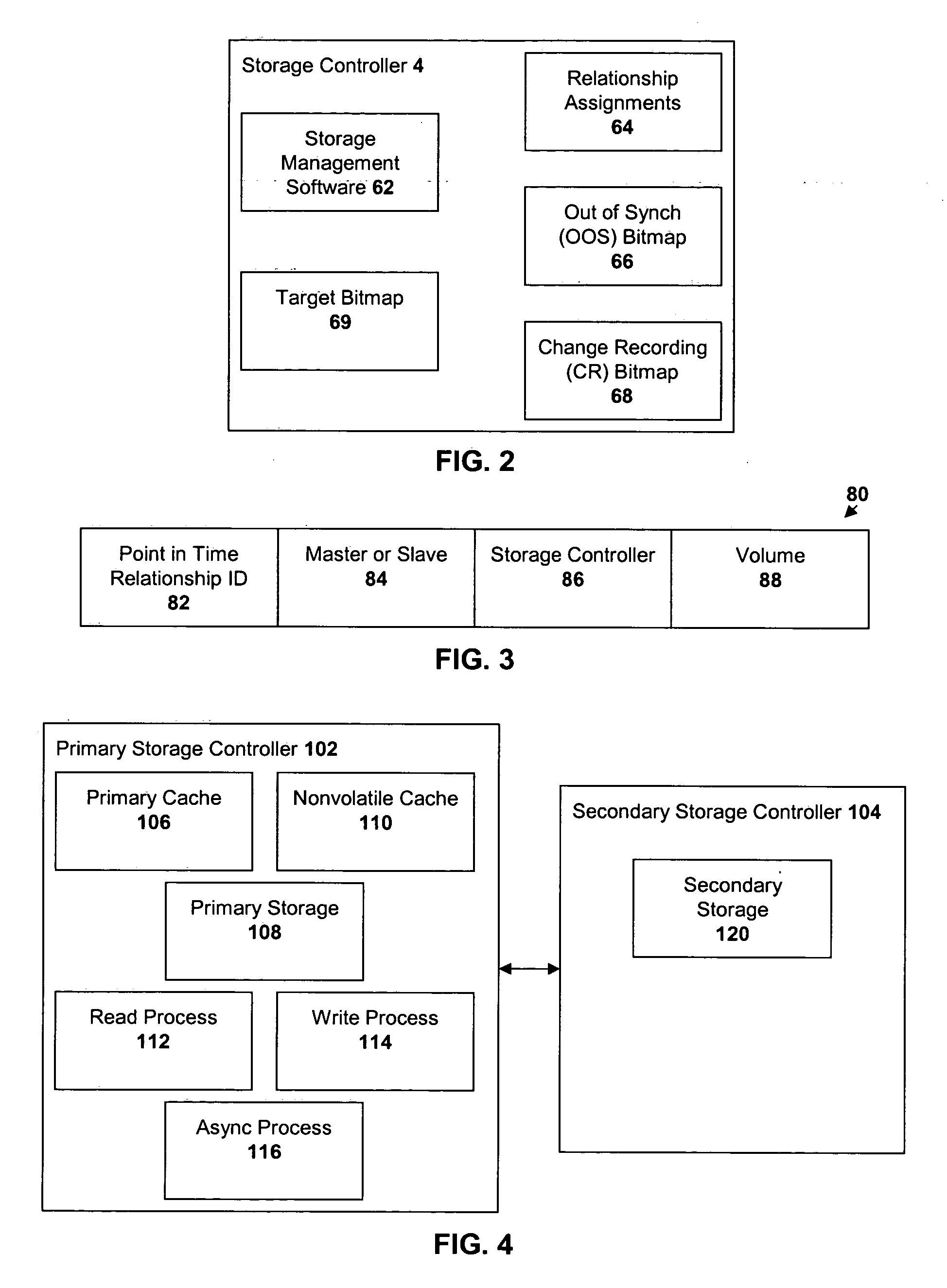
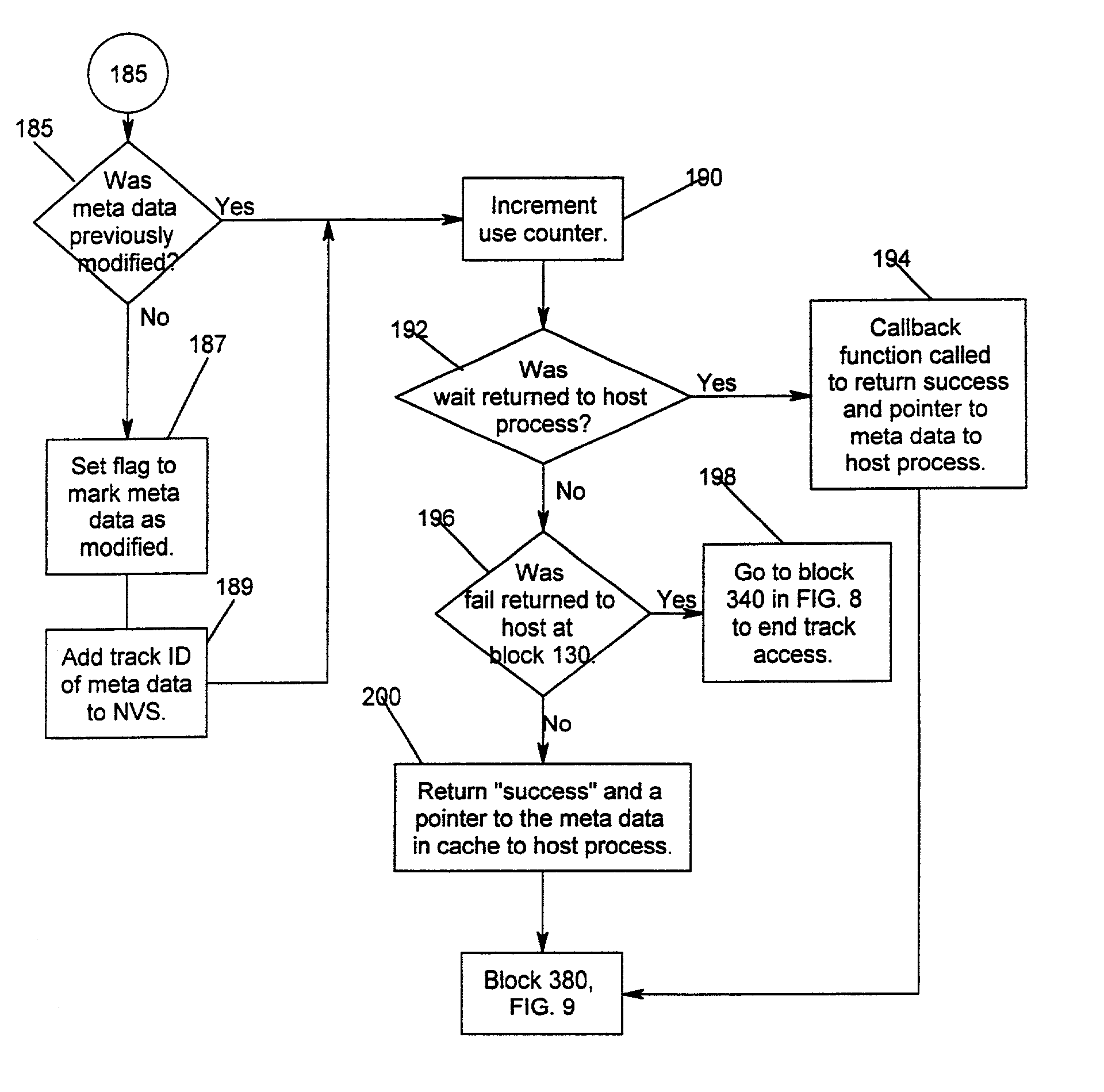
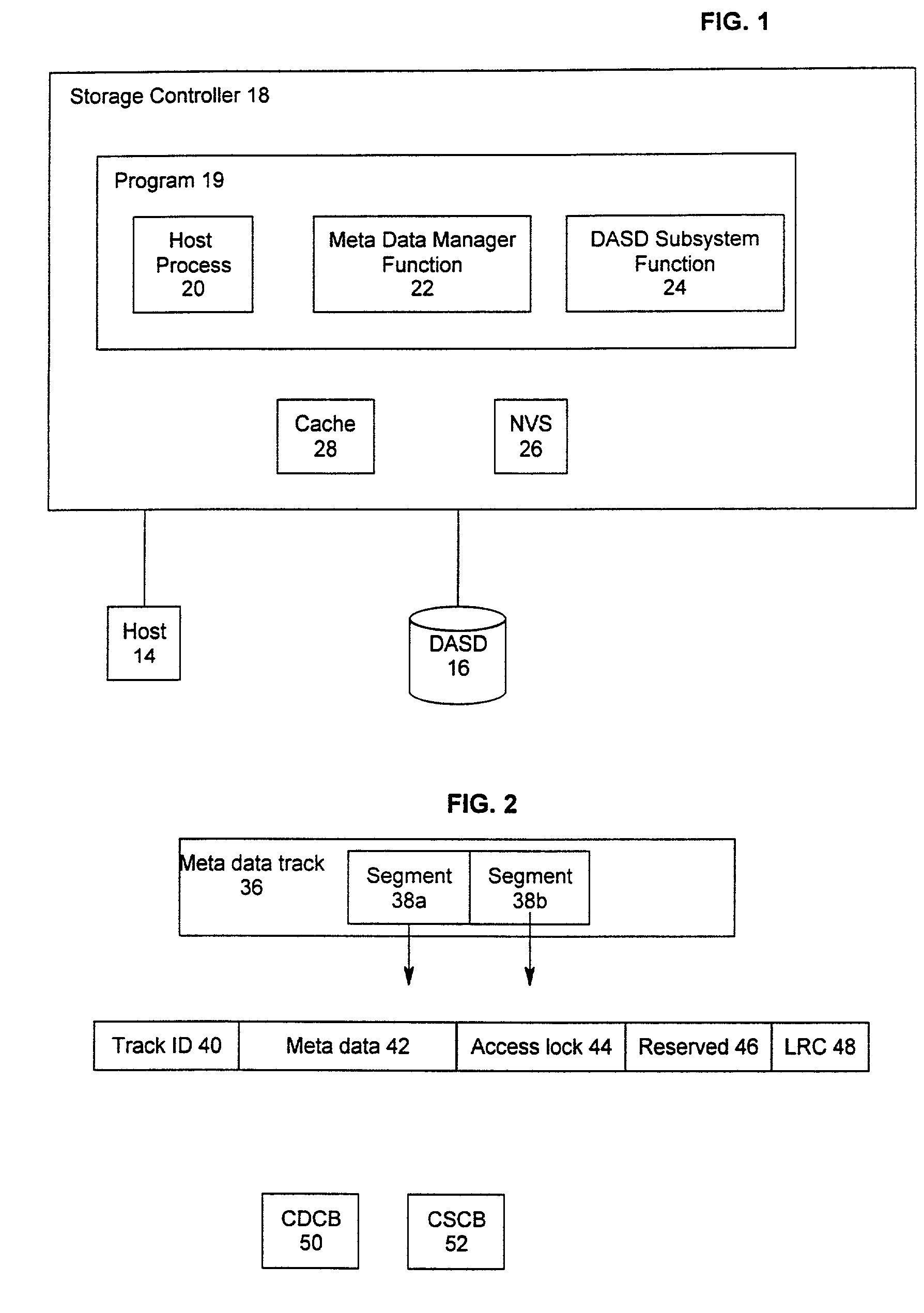
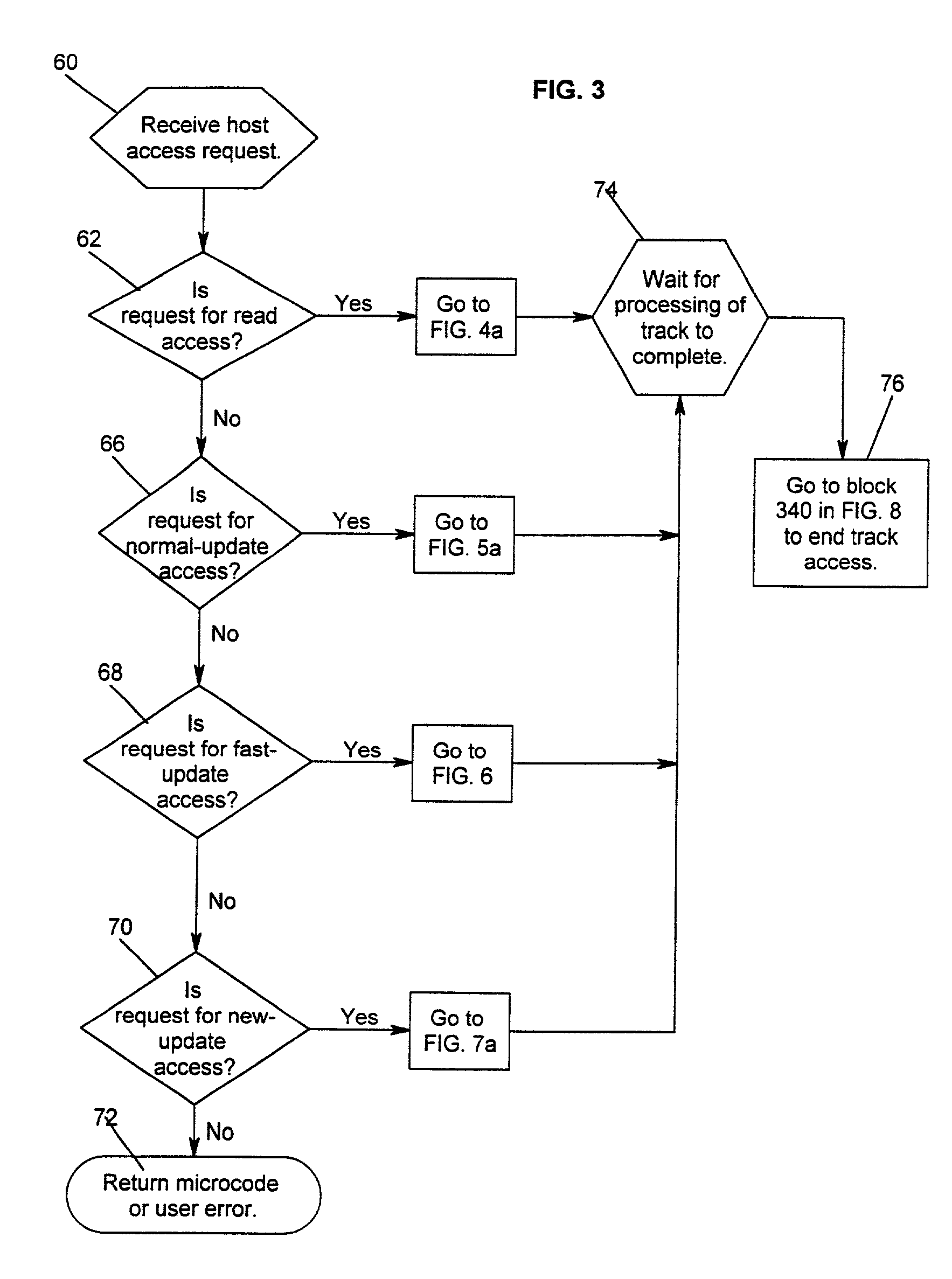
Method and system for recovery of meta data in a storage controller
InactiveUS6988171B2Data processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSystem failureComputer science
Disclosed is a method, system, and article of manufacture for processing modified meta data for data recovery operations. The meta data provides information on user data maintained in a storage device. The system determines whether meta data tracks maintained in a cache were modified and indicates in a non-volatile memory that the determined meta data tracks were modified. Data recovery operations may be initiated as a result of a system failure, such as a warmstart or coldstart recovery. During such data recovery operations, the system processes the non-volatile memory and the indications of modified meta data tracks therein to rebuild lost meta data tracks in the cache.
Owner:IBM CORP
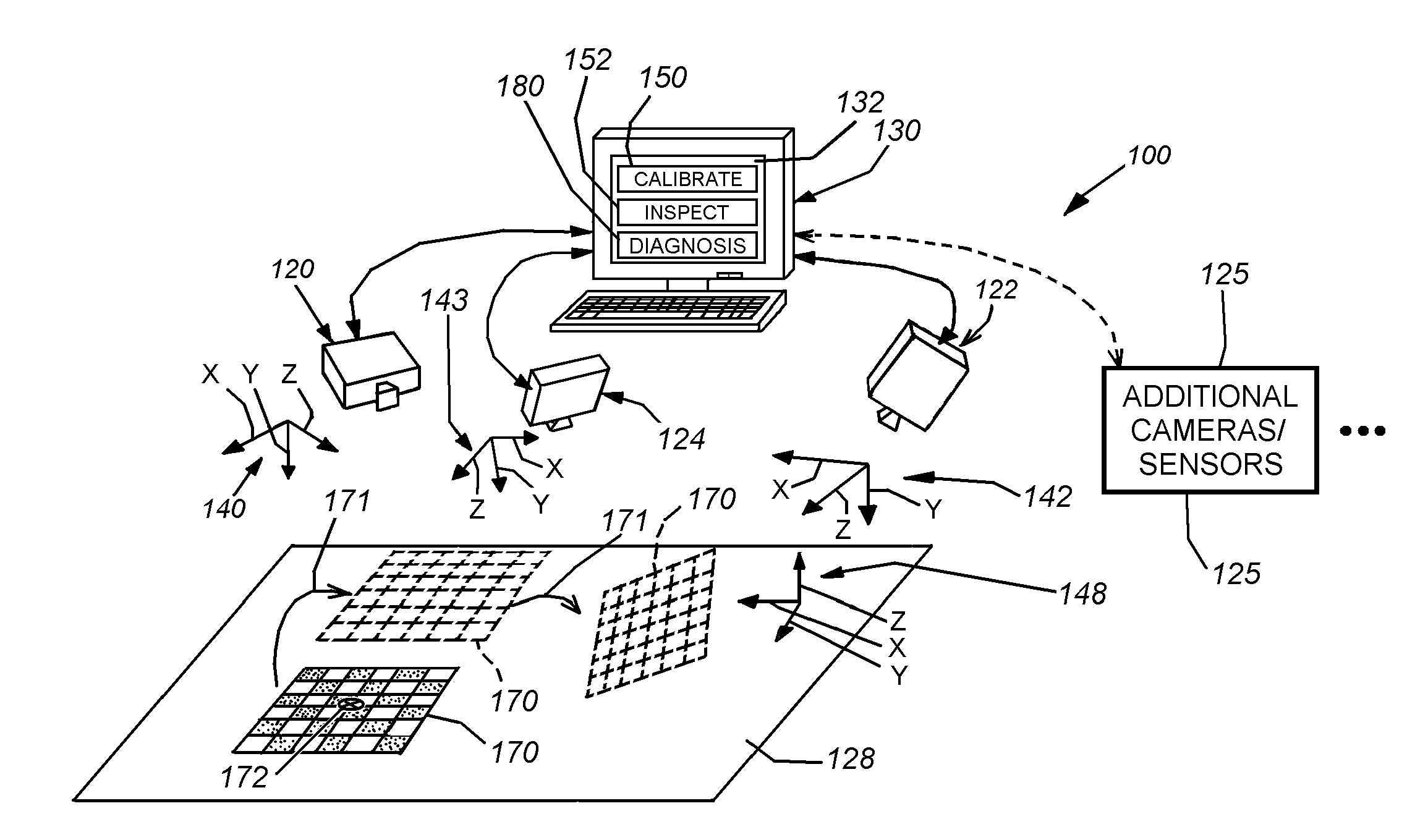
System and method for runtime determination of camera miscalibration
ActiveUS20110157373A1Faster and and diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisMulti cameraCamera auto-calibration
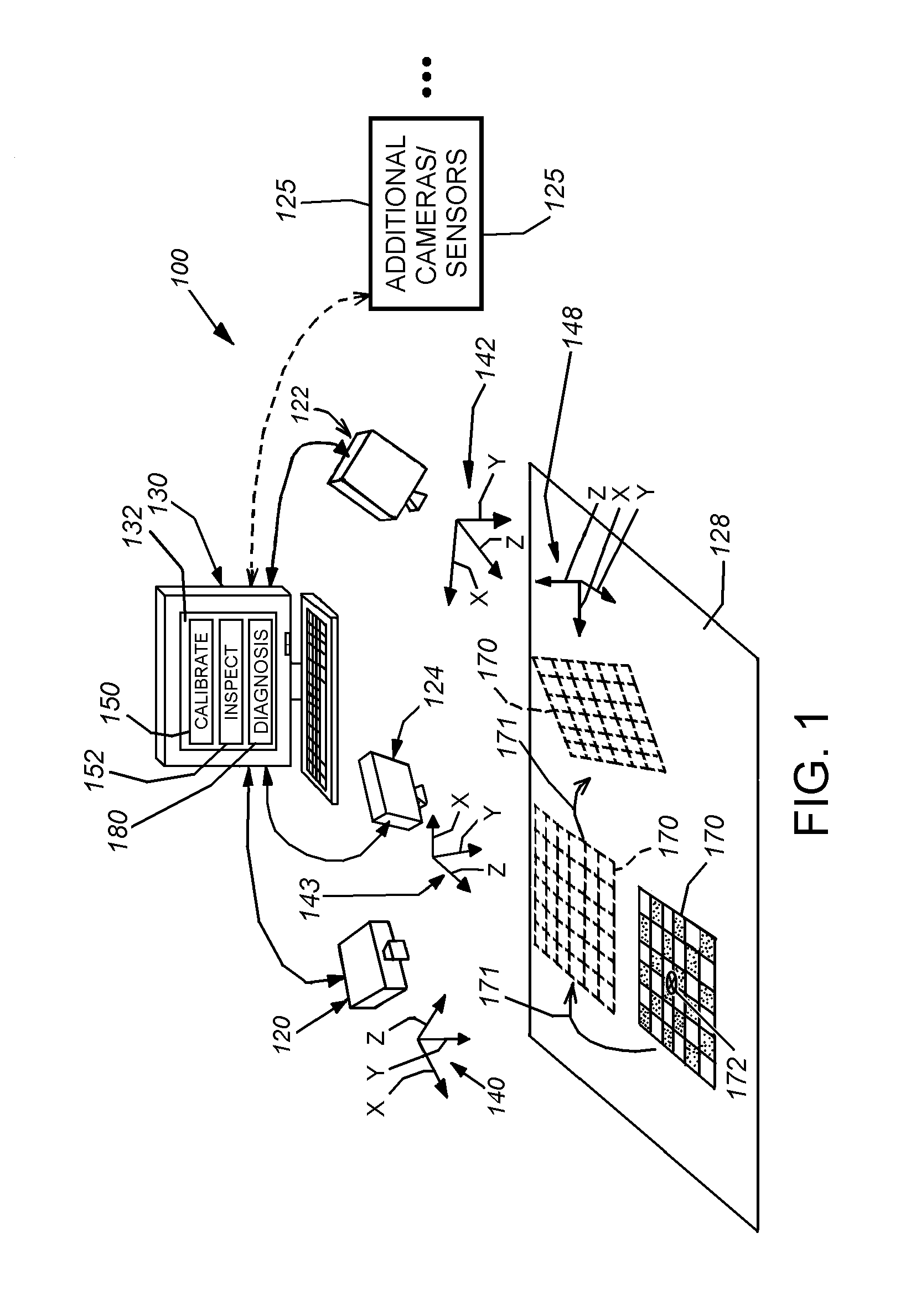
This invention provides a system and method for runtime determination (self-diagnosis) of camera miscalibration (accuracy), typically related to camera extrinsics, based on historical statistics of runtime alignment scores for objects acquired in the scene, which are defined based on matching of observed and expected image data of trained object models. This arrangement avoids a need to cease runtime operation of the vision system and / or stop the production line that is served by the vision system to diagnose if the system's camera(s) remain calibrated. Under the assumption that objects or features inspected by the vision system over time are substantially the same, the vision system accumulates statistics of part alignment results and stores intermediate results to be used as indicator of current system accuracy. For multi-camera vision systems, cross validation is illustratively employed to identify individual problematic cameras. The system and method allows for faster, less-expensive and more-straightforward diagnosis of vision system failures related to deteriorating camera calibration.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
Automated and self-adjusting data protection driven by business and data activity events
InactiveUS9632875B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsRetention periodSystem failure
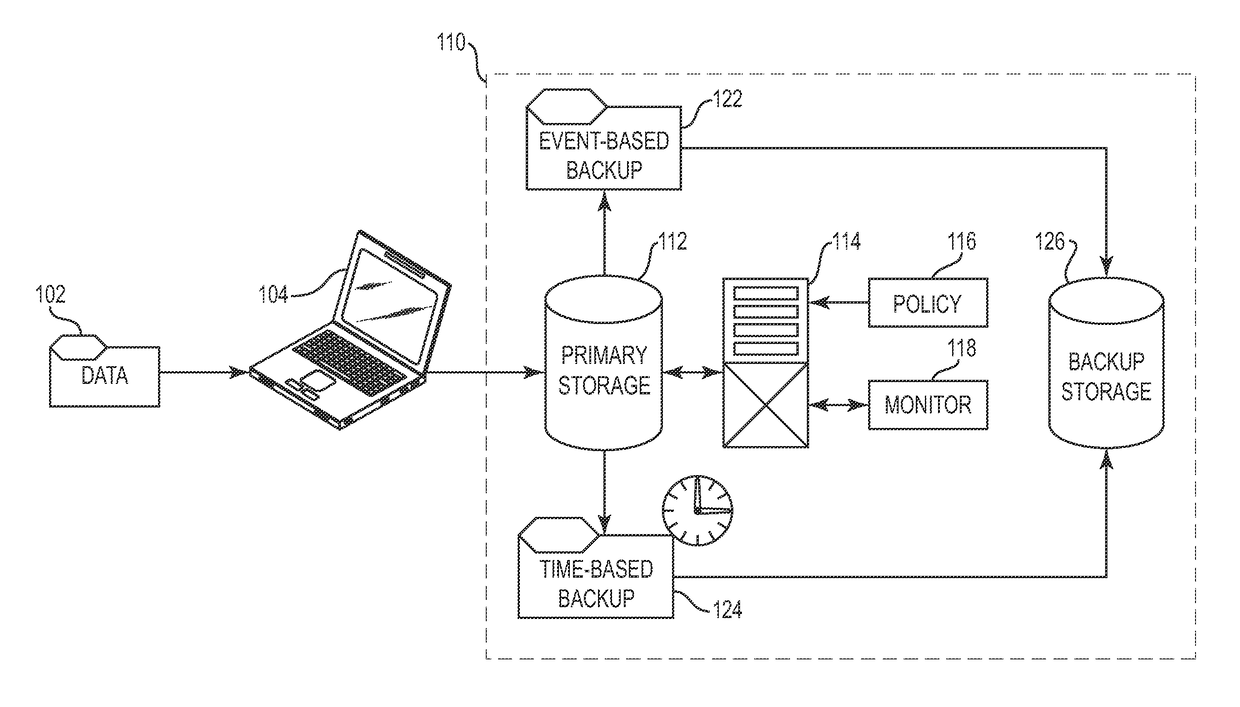
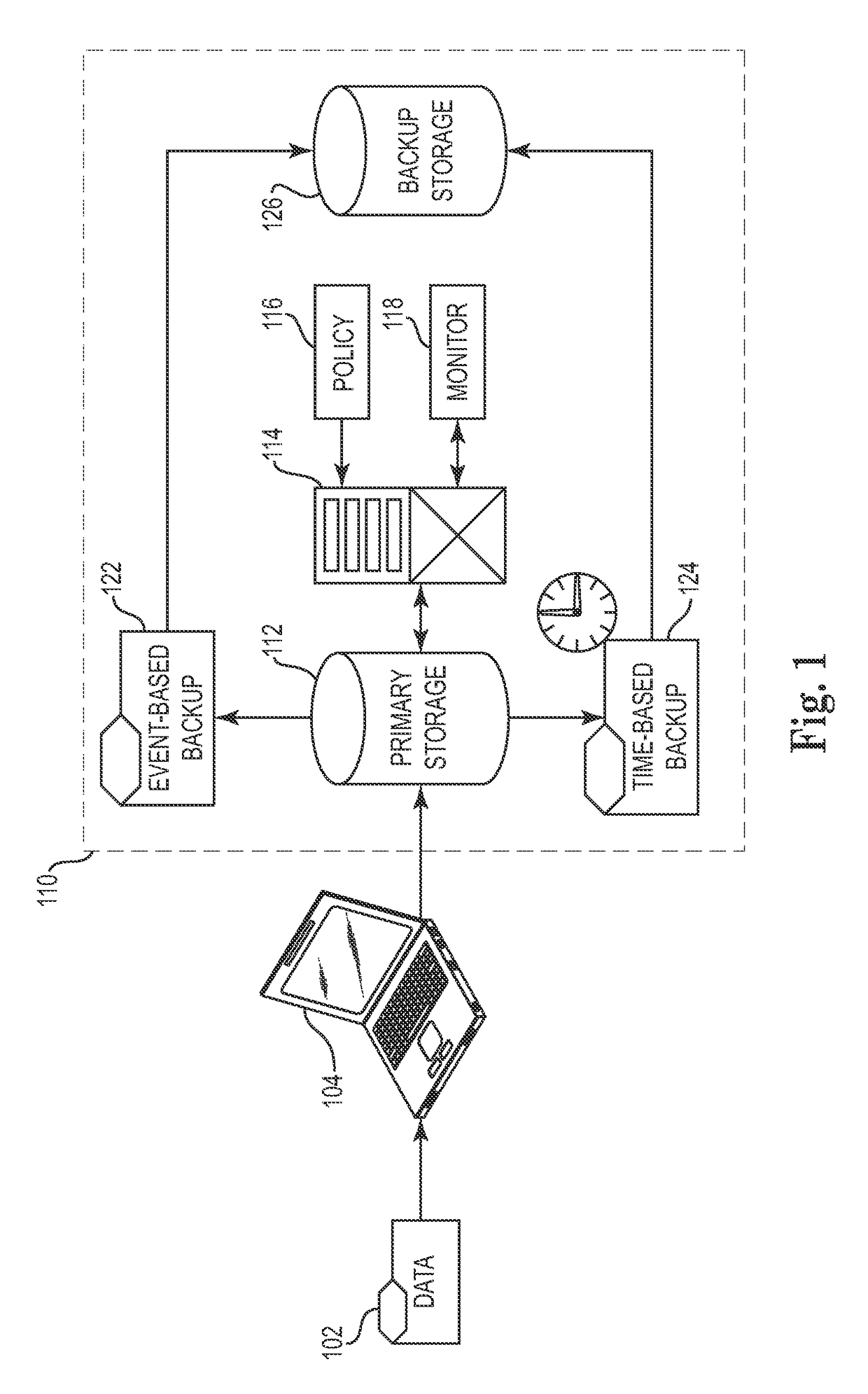
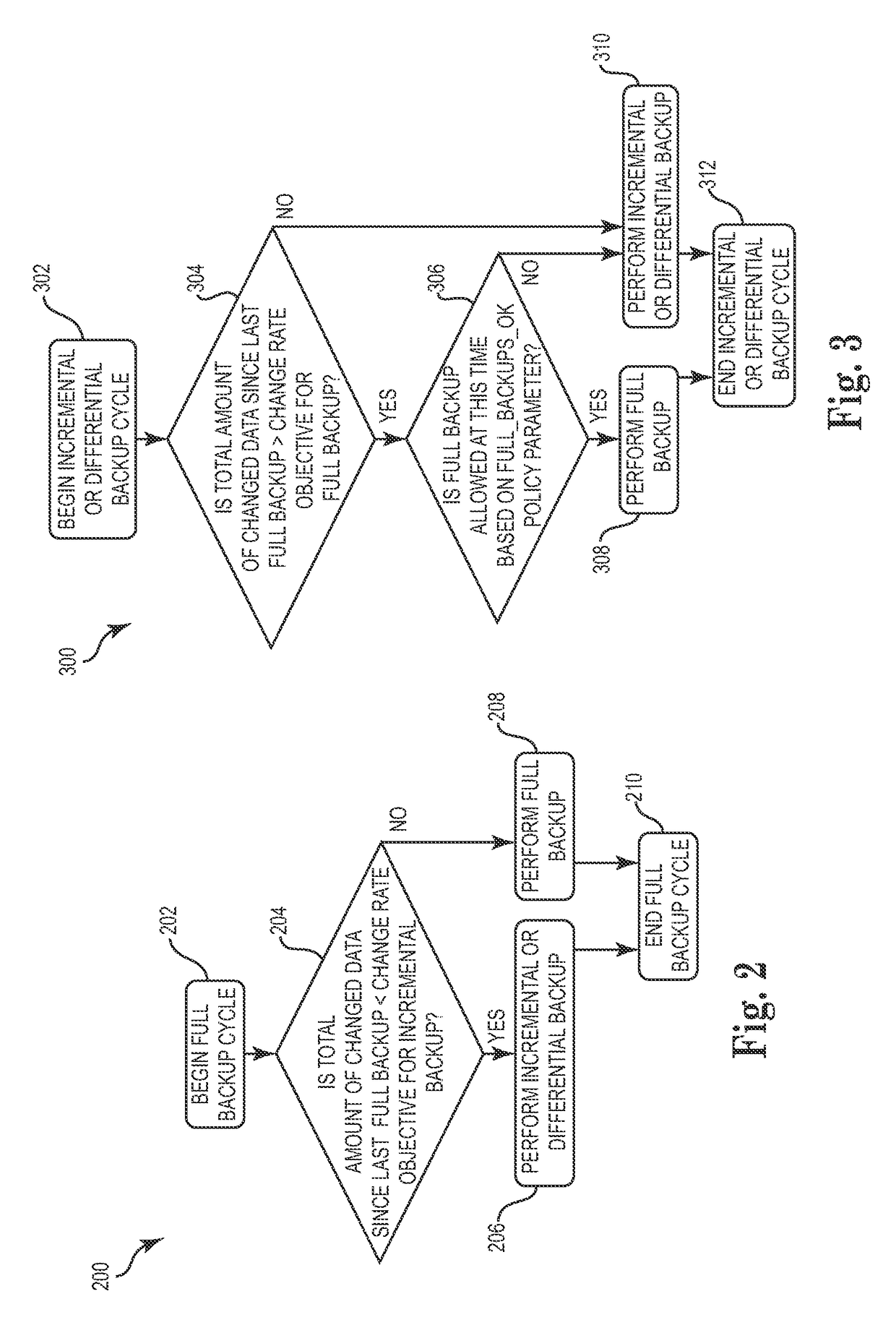
Techniques for adjusting the frequency of data backups and initiating event-driven backups in a storage system are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, a self-adjusting backup frequency, known as a “Change Rate Objective,” is defined to conduct or delay backups for one or more volumes in the storage system on the basis of an associated policy value. The Change Rate Objective may be tied to one or more business or data activity events, such as the amount and type of data changes since a last backup. The storage system may also be tailored to conduct or delay full or incremental backups on the basis of a Change Rate Objective that measures whether a full or incremental or differential backup is more appropriate. Various data or system failures, or data or business events may also be used to adjust the retention periods of continuous data protection (CDP) data and delay a rollup of CDP data.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
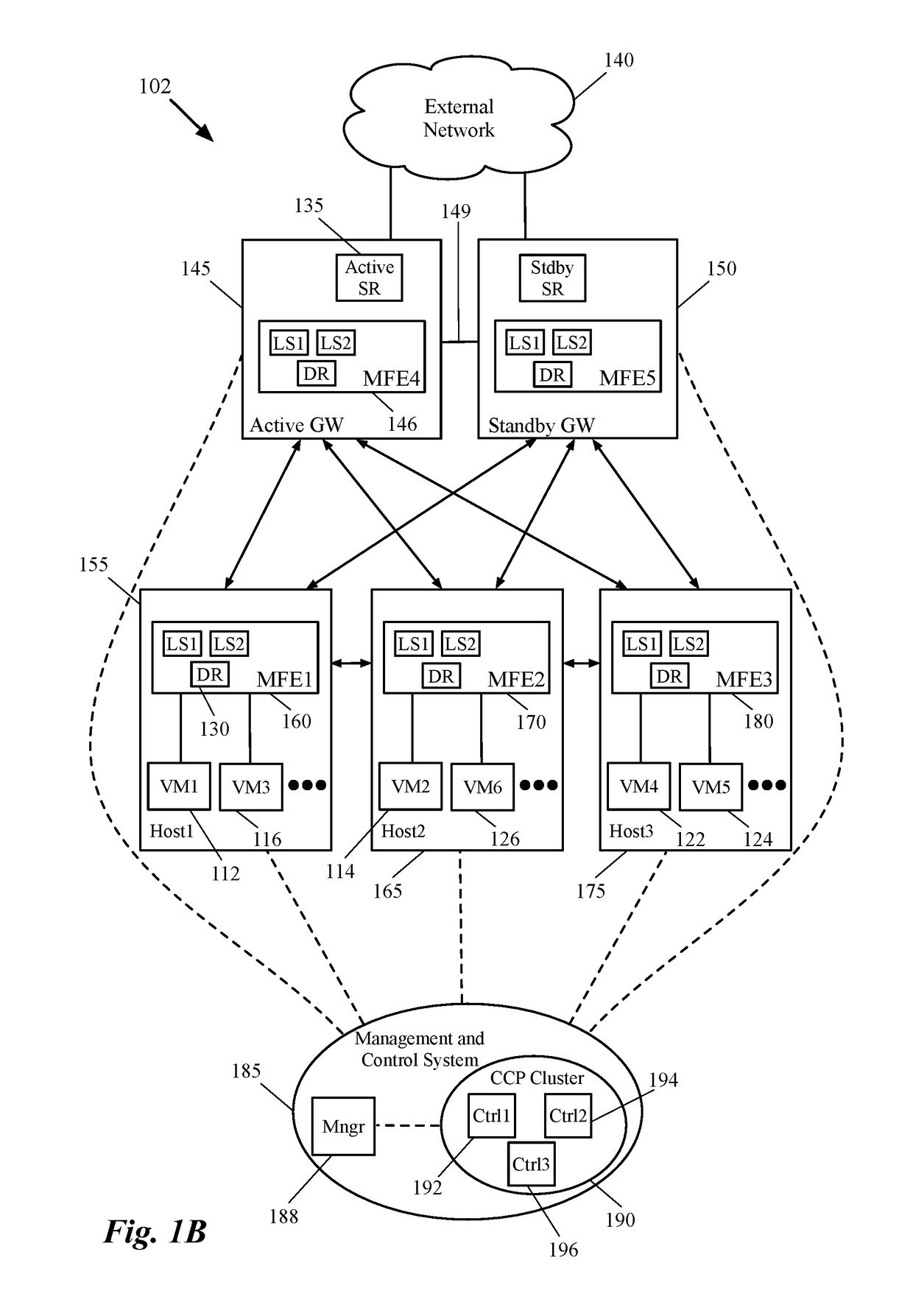
Dynamic recovery from a split-brain failure in edge nodes
ActiveUS20180176073A1Reduce the possibilityIncrease the number ofError detection/correctionSignal allocationActive edgeLoad Shedding
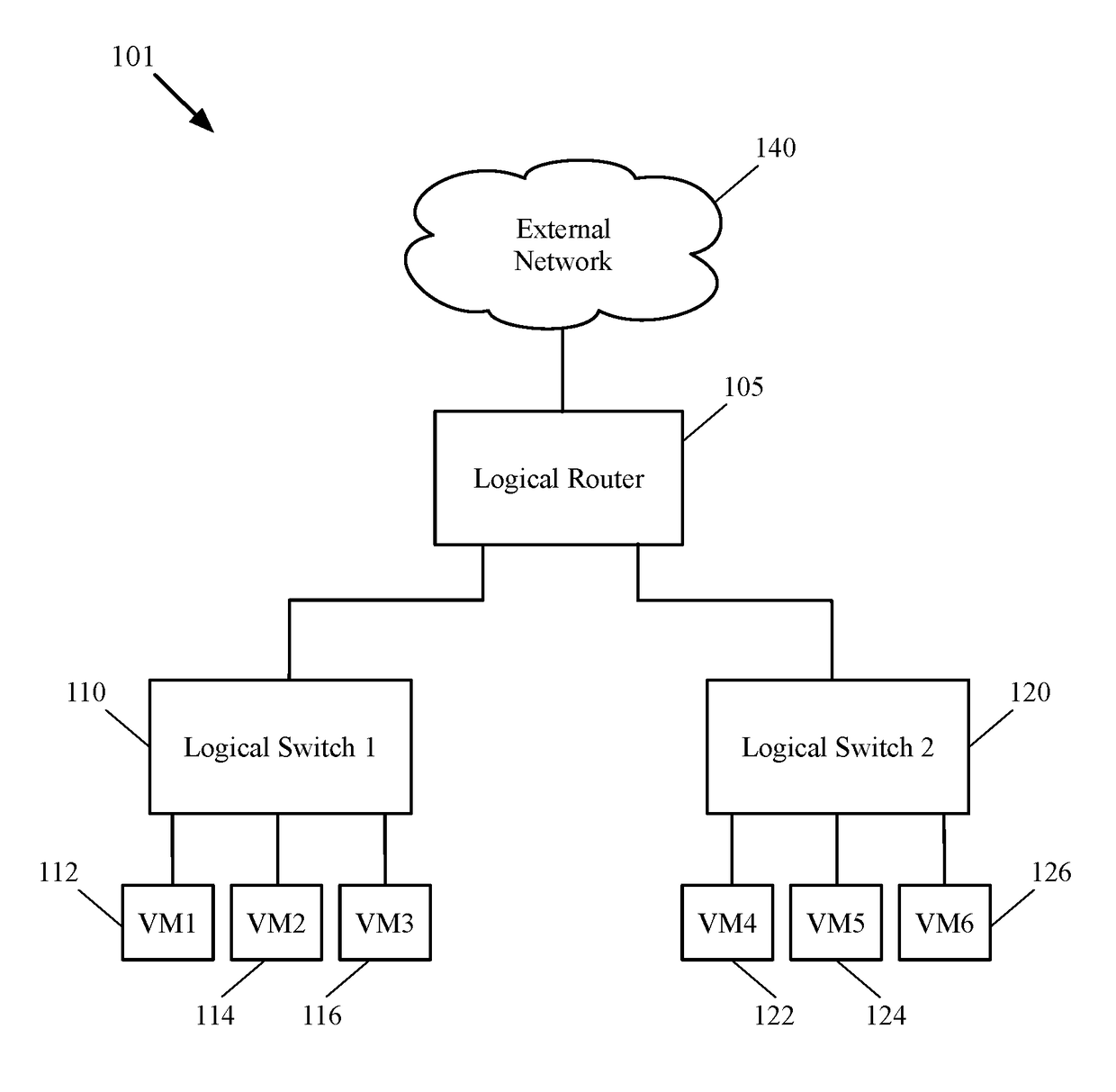
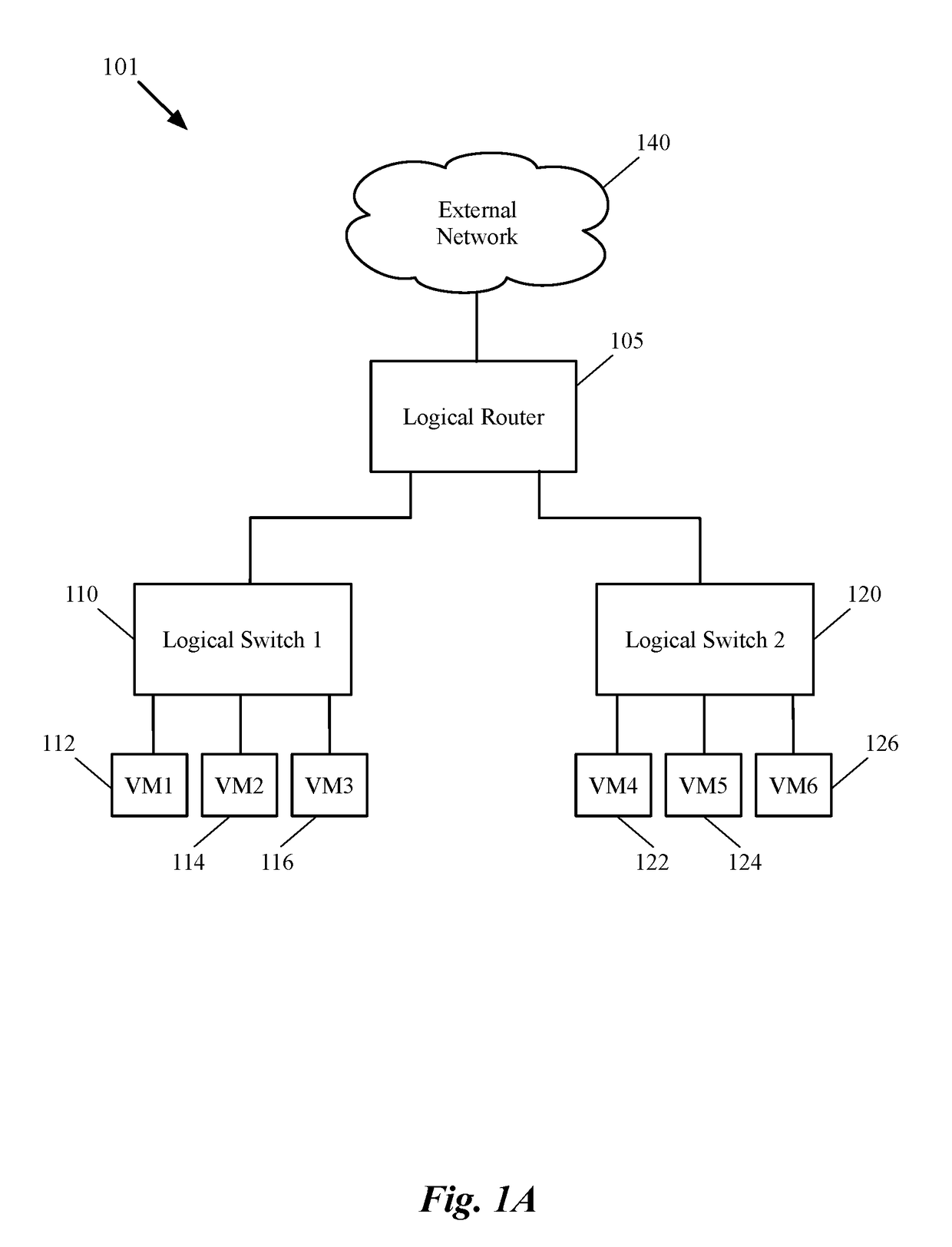
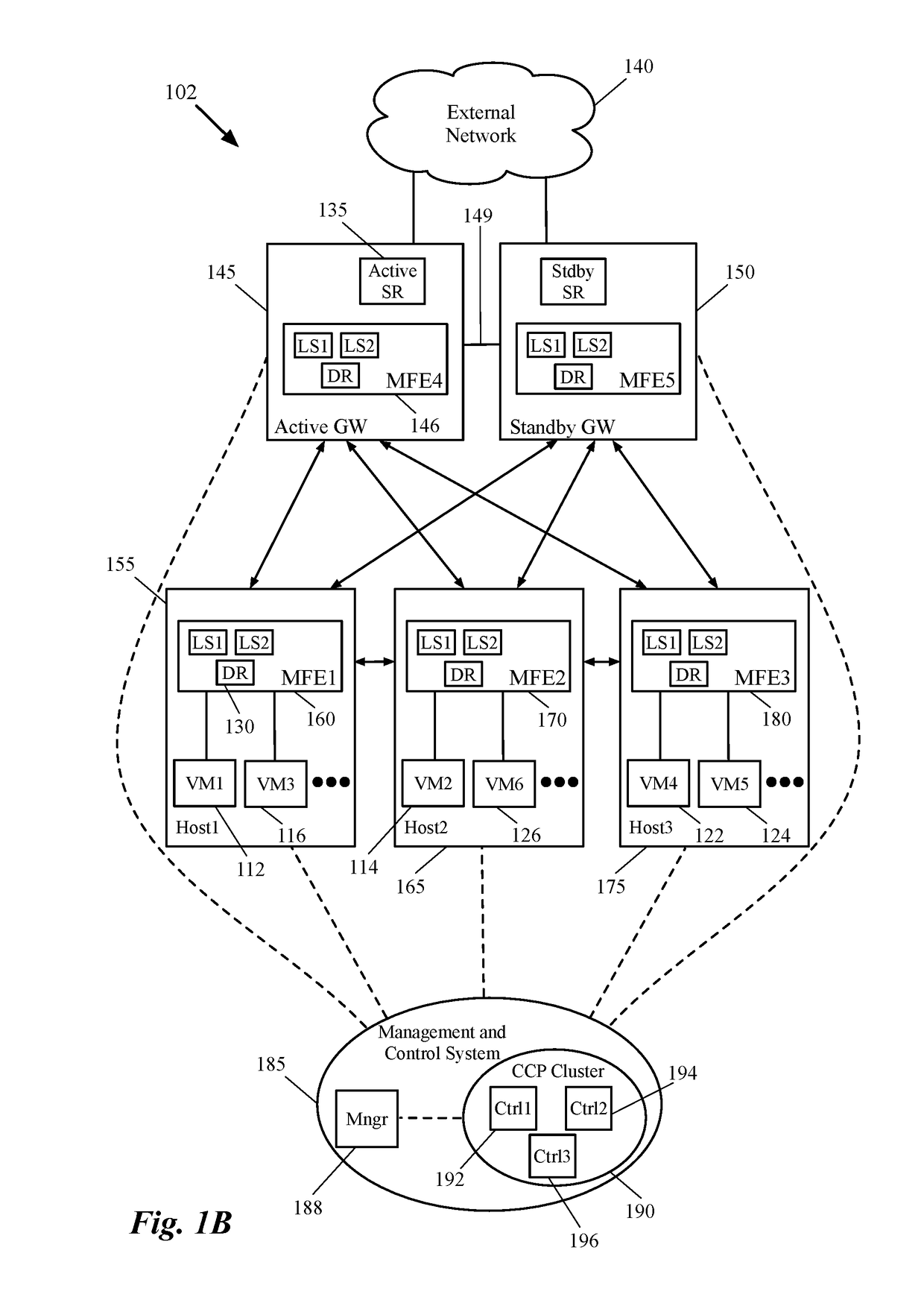
Some embodiments provide a method for employing the management and control system of a network to dynamically recover from a split-brain condition in the edge nodes of the network. The method of some embodiments takes a corrective action to automatically recover from a split-brain failure occurred at a pair of high availability (HA) edge nodes of the network. The HA edge nodes include an active machine and a standby machine. The active edge node actively passes through the network traffic (e.g., north-south traffic for a logical network), while the standby edge node is synchronized and ready to transition to the active state, should a failure occur. Both HA nodes share the same configuration settings and only one is active until a path, link, or system failure occurs. The active edge node also provides stateful services (e.g., stateful firewall, load balancing, etc.) to the data compute nodes of the network.
Owner:NICIRA
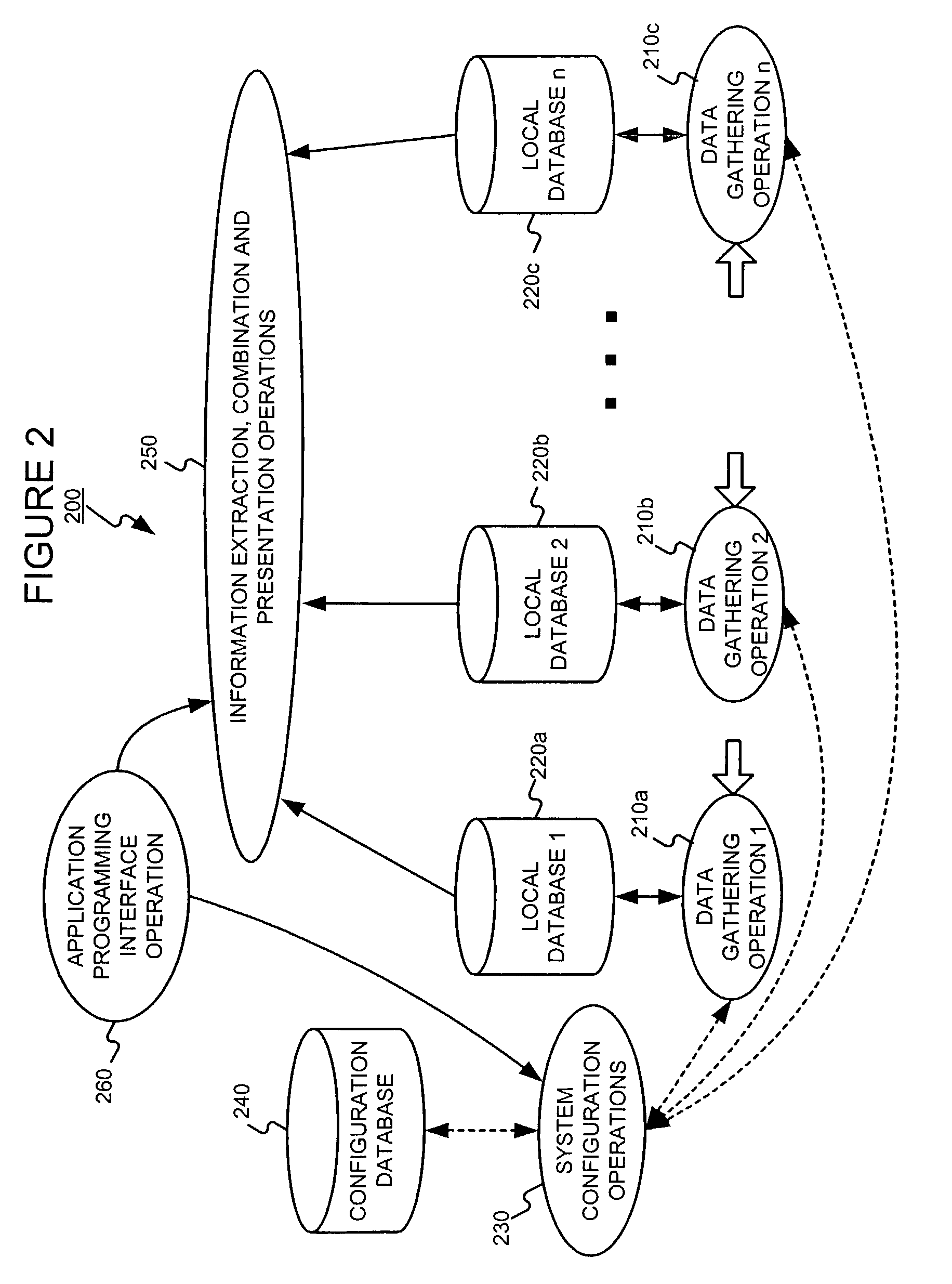
Administering users in a fault and performance monitoring system using distributed data gathering and storage
InactiveUS20040088404A1Digital computer detailsData switching networksMonitoring systemOptical performance monitoring
Combining system fault and performance monitoring using distributed data collection and storage of performance data. Storage requirements are relaxed and real-time performance monitoring is possible. Data collection and storage elements can be easily configured via a central configuration database. The configuration database can be easily updated and changed. A federated user model allows normal end users to monitor devices relevant to the part of a service they are responsible for, while allowing administrative users to view the fault and performance of a service in an end-to-end manner.
Owner:FIDELLA TECH
Apparatus and methods for detection of systematic defects
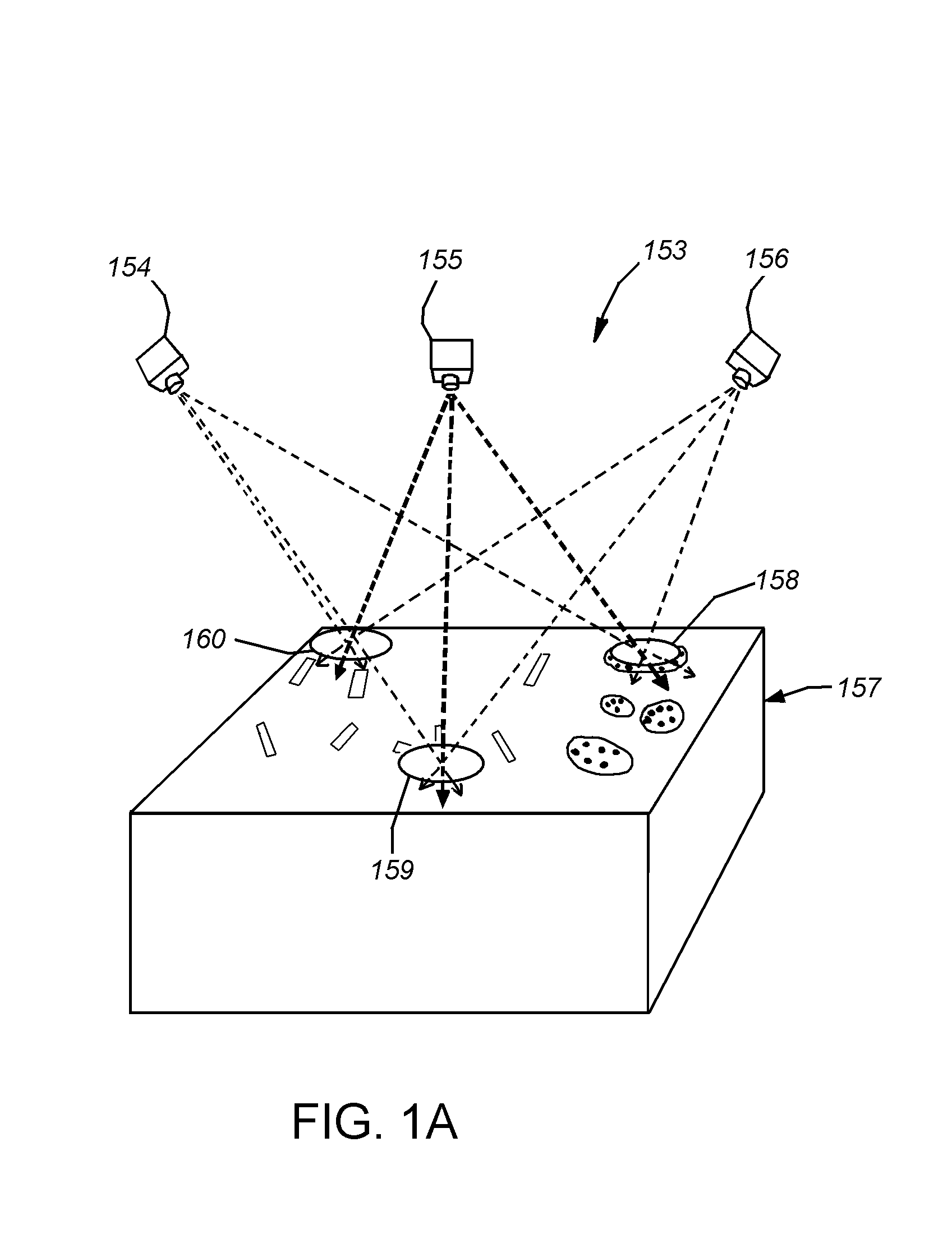
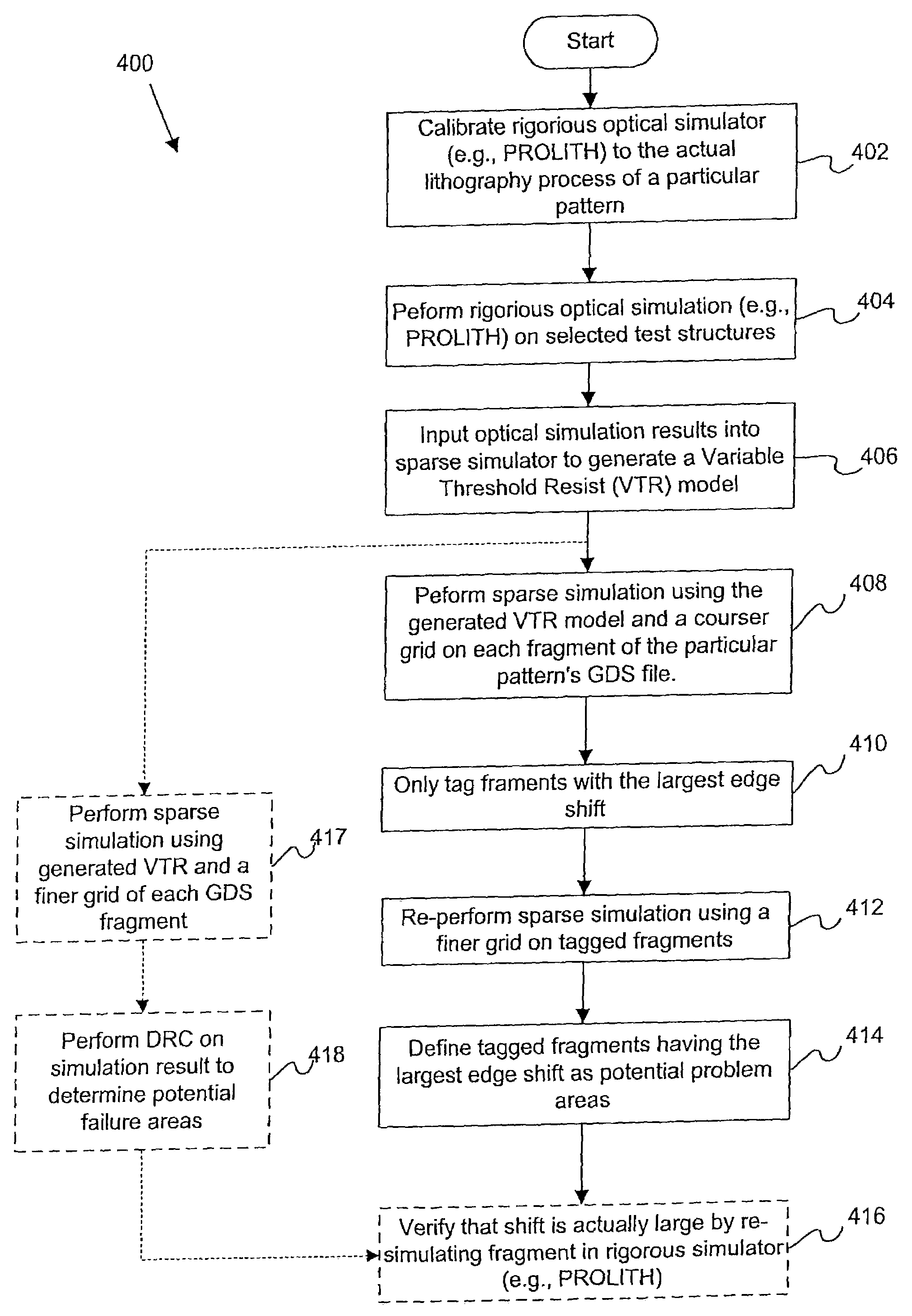
ActiveUS7280945B1Electrical testingComputation using non-denominational number representationResistSystem failure
Disclosed are mechanisms are provided for determining whether a particular integrated circuit (IC) pattern is susceptible to systematic failure, e.g., due to process fluctuations. In one embodiment, final resist patterns for such IC pattern are simulated using a sparse type simulator under various process settings. The sparse type simulator uses a model (e.g., a variable threshold resist model) for a particular photolithography process in which the IC pattern is to be fabricated. The model is generated from measurements taken from a plurality of simulated structures output from a rigorous type simulator. The simulated final resist patterns may then be analyzed to determine whether the corresponding IC pattern is susceptible to systematic failure. After an IC pattern which is susceptible to systematic failure has been found, a test structure may be fabricated from a plurality of IC patterns or cells. The cells of the test structure are arranged to have a particular pattern of voltage potential or brightness levels during a voltage contrast inspection. Mechanisms for quickly inspecting such test structures to thereby predict systematic yield of a product device containing patterns similar to the test structure cells are also disclosed.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Conditional data access after database system failure
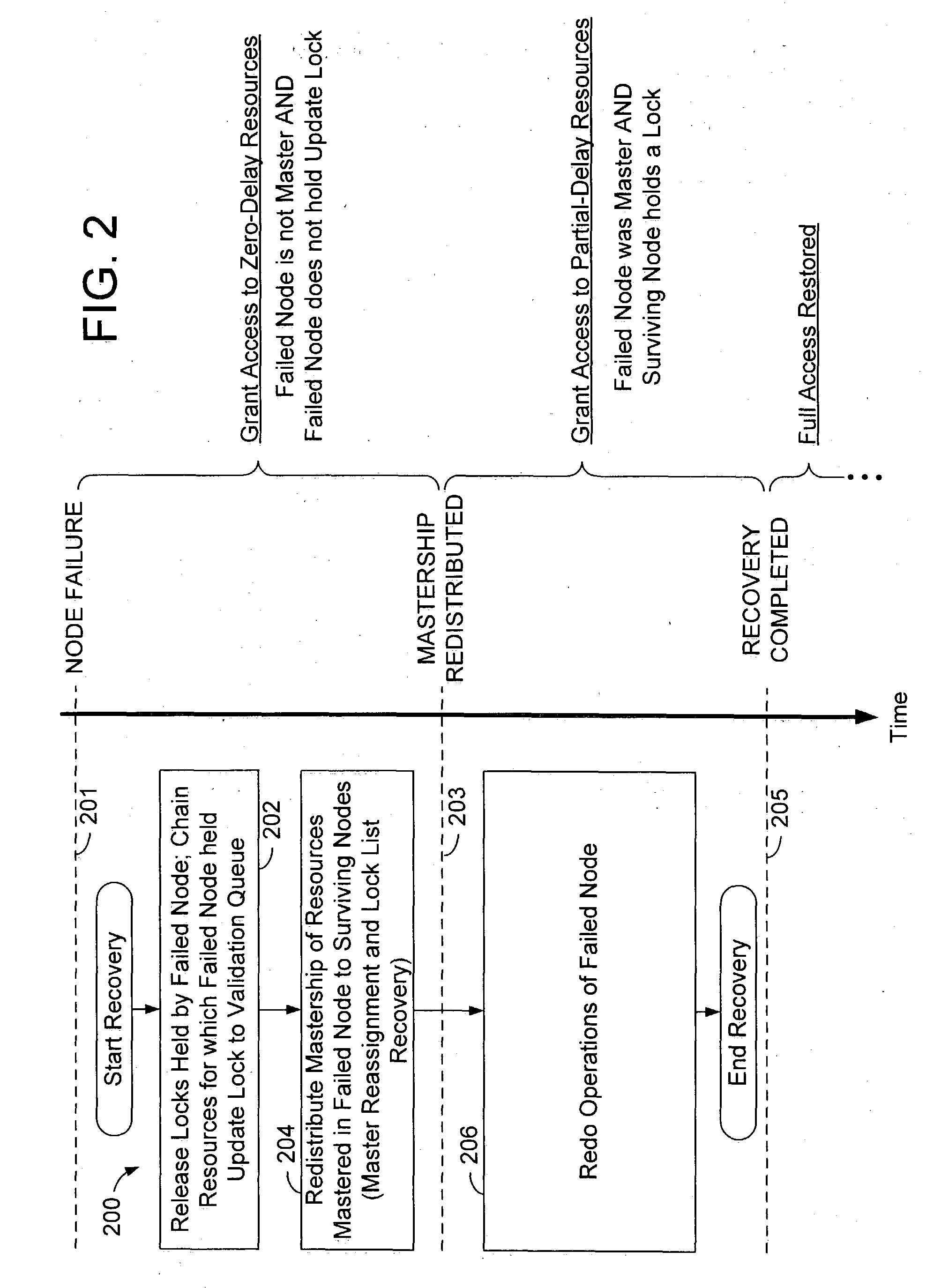
ActiveUS20050022047A1Digital data information retrievalRedundant operation error correctionData processing systemData access
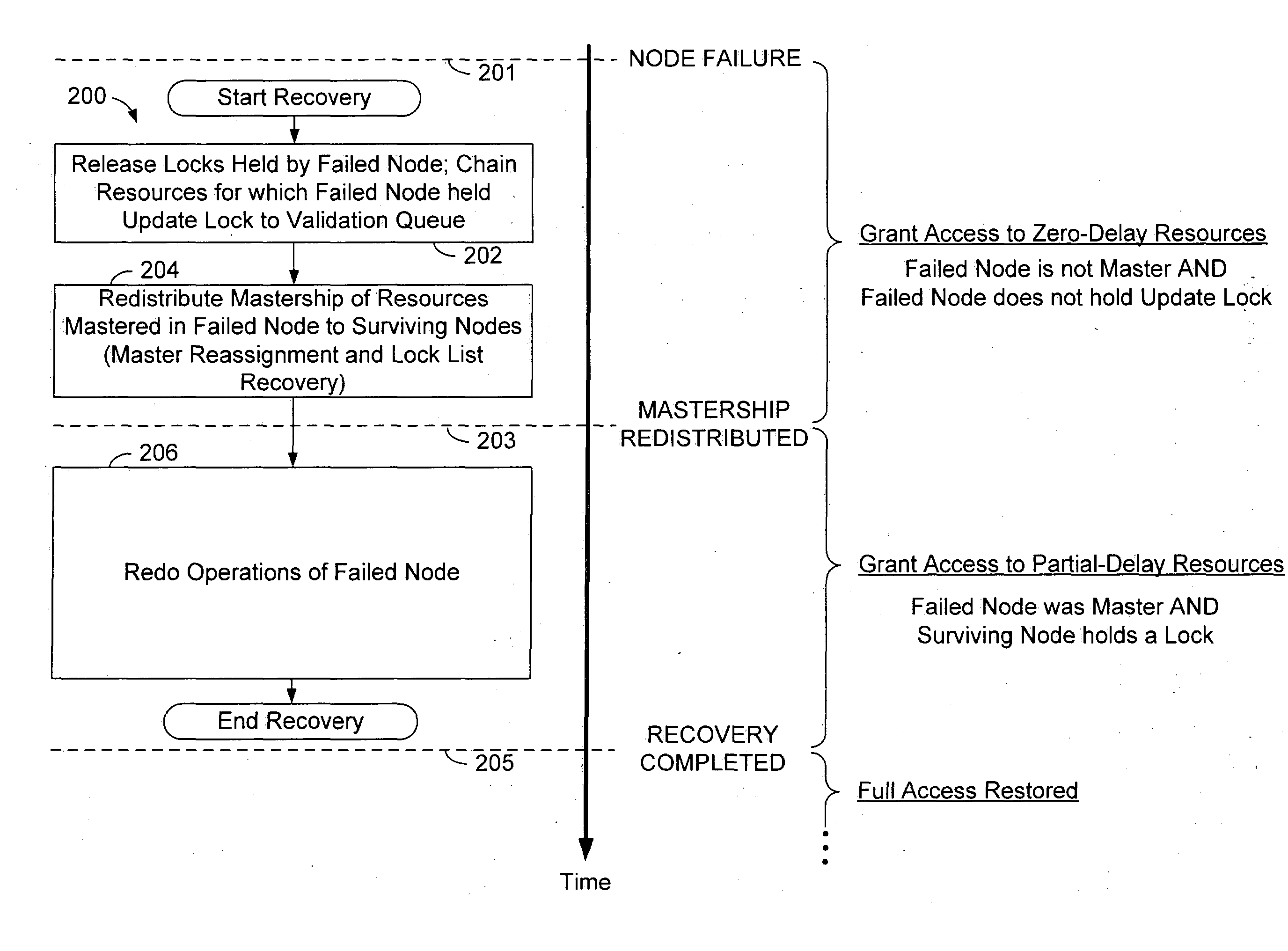
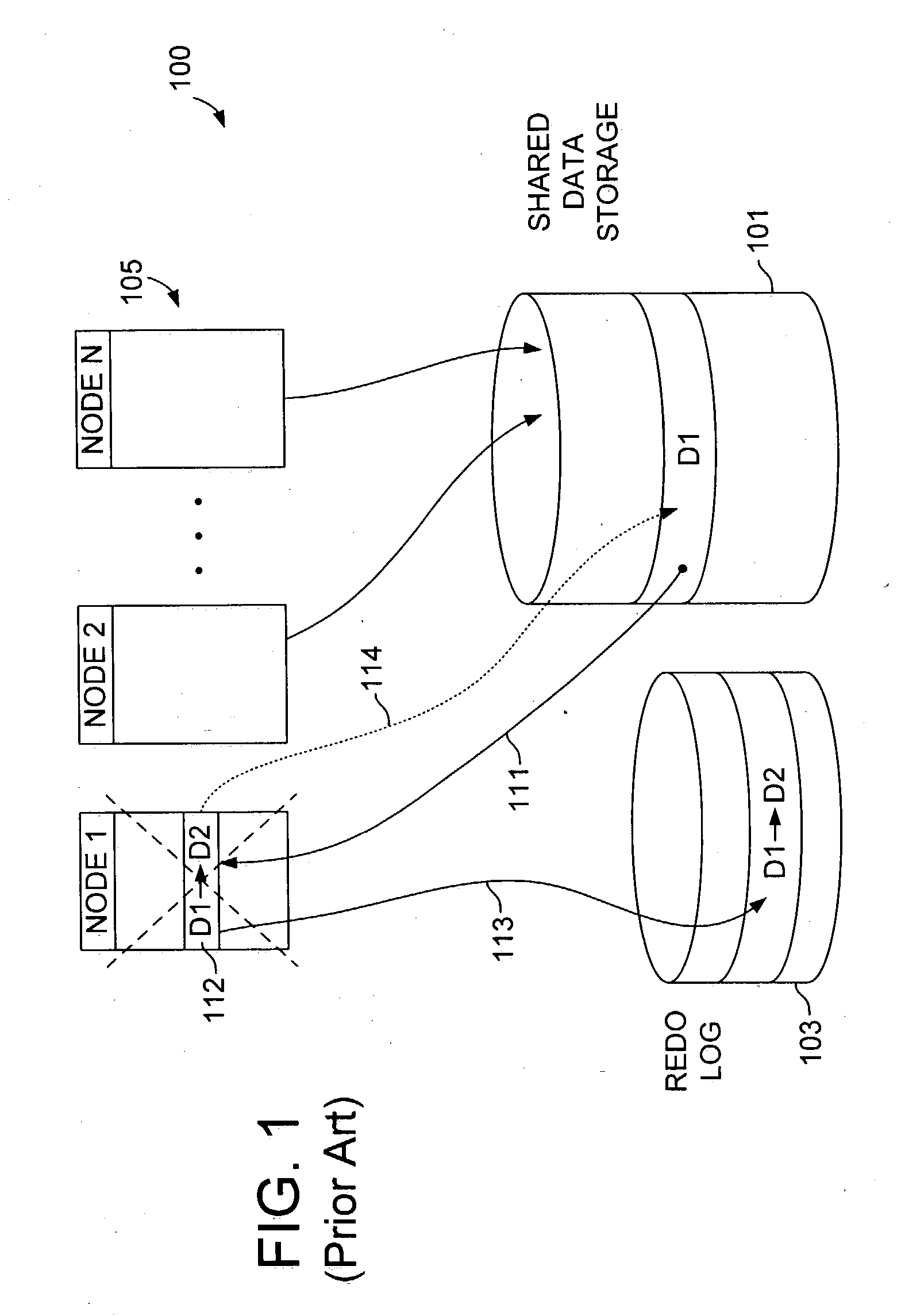
A method of operation within a data processing system that includes a plurality of processing nodes each having access to a set of shared resources. Failure of one of the processing nodes is detected, followed by receipt of a request to access a first resource of the set of shared resources. Access to the first resource is granted if the failed node was not responsible for controlling access to the first resource and did not have exclusive access to the first resource when the failure was detected.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and method for providing total real-time redundancy for a plurality of client-server systems
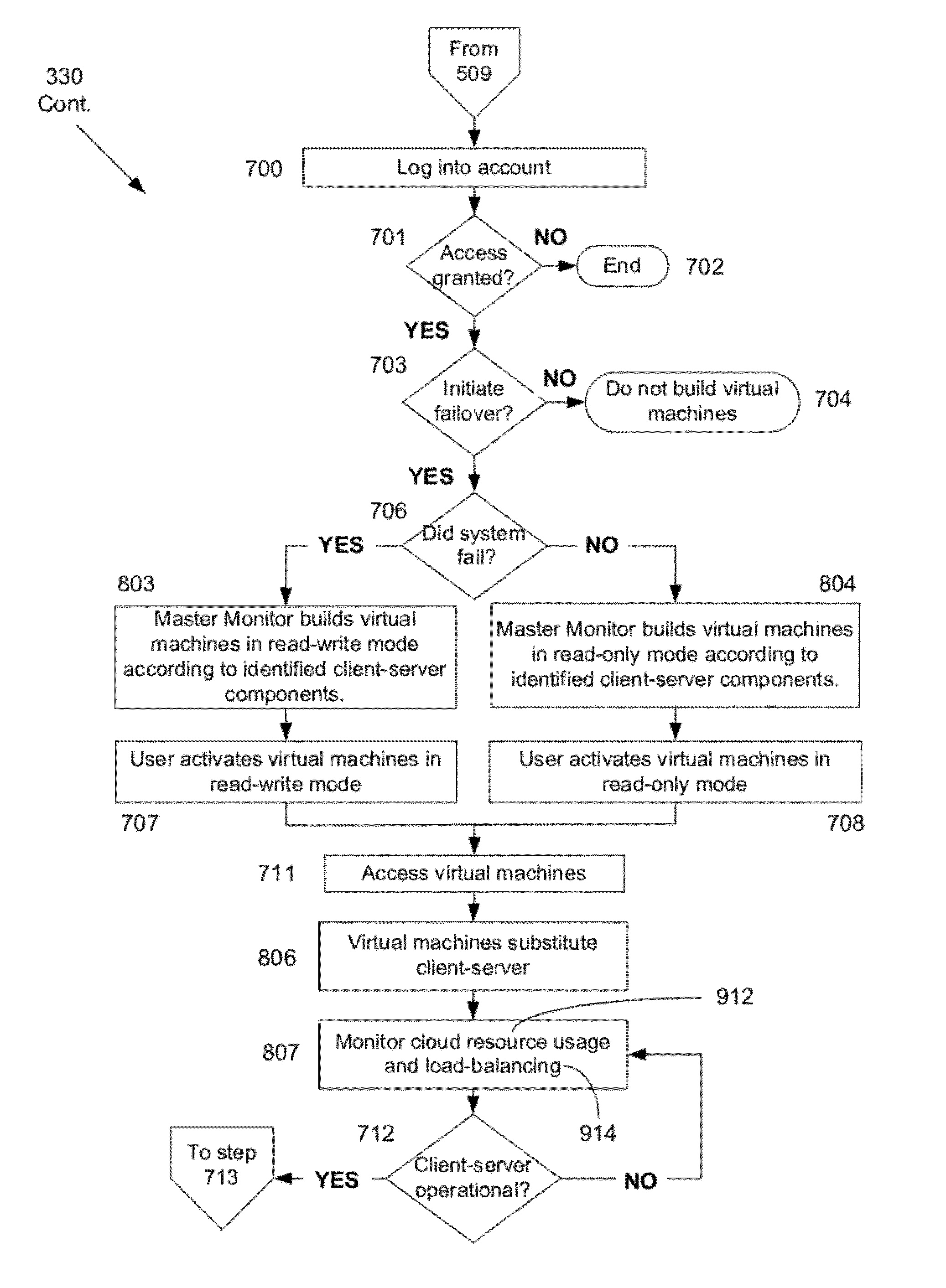
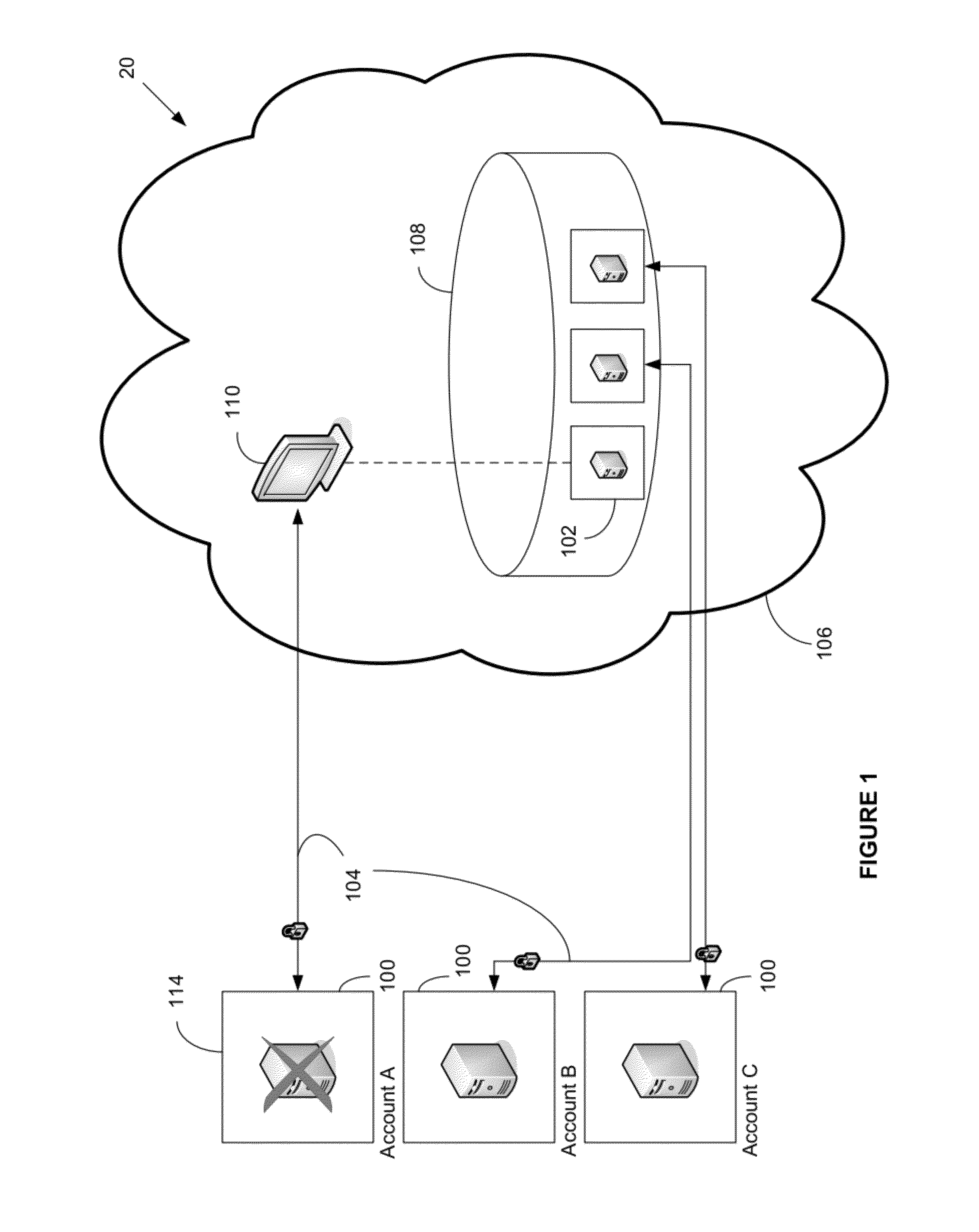
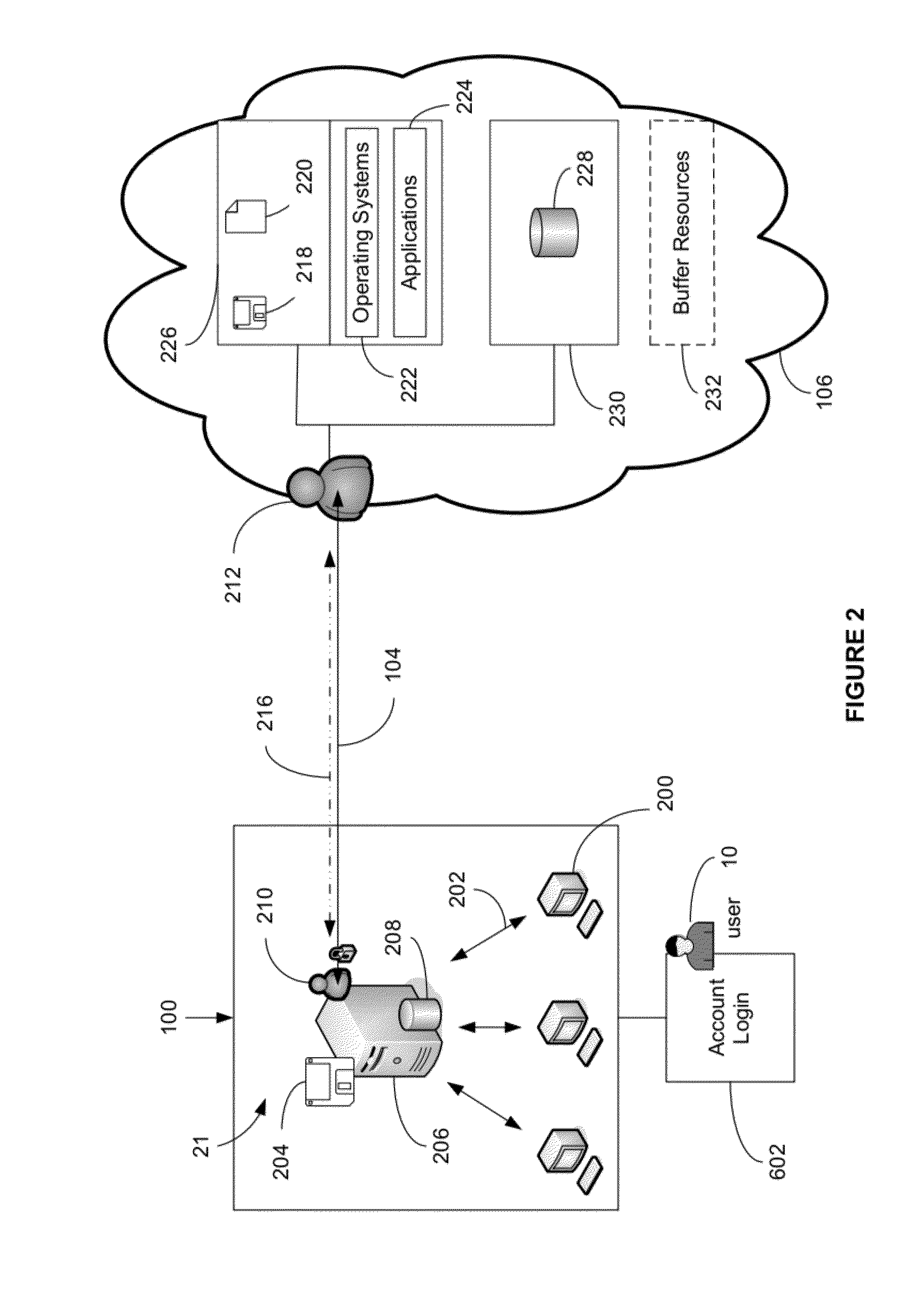
ActiveUS8103906B1Improve good performanceAvoid lostTransmissionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationScalable systemNetwork connection
An automated and scalable system for total real-time redundancy of a plurality of client-server systems, wherein, data is replicated through a network connection and operationally located on a virtual machine that substitutes for a failed client-server system, wherein the virtual machine is activated and installed on the cloud computing environment. Monitoring applications are installed on both the client-server systems and the cloud computing environment. System components are identified, a network connection is initiated, a heartbeat is established, data replication is automated, system failure is detected, failover is initiated, and subsequent client-server restoration is automated.
Owner:MASS IP LLC
Ordered record of system-wide fault in an HVAC system
ActiveUS20050159924A1Improve understandingRapid diagnosisElectric signal transmission systemsTemperatue controlSystem failureEmbedded system
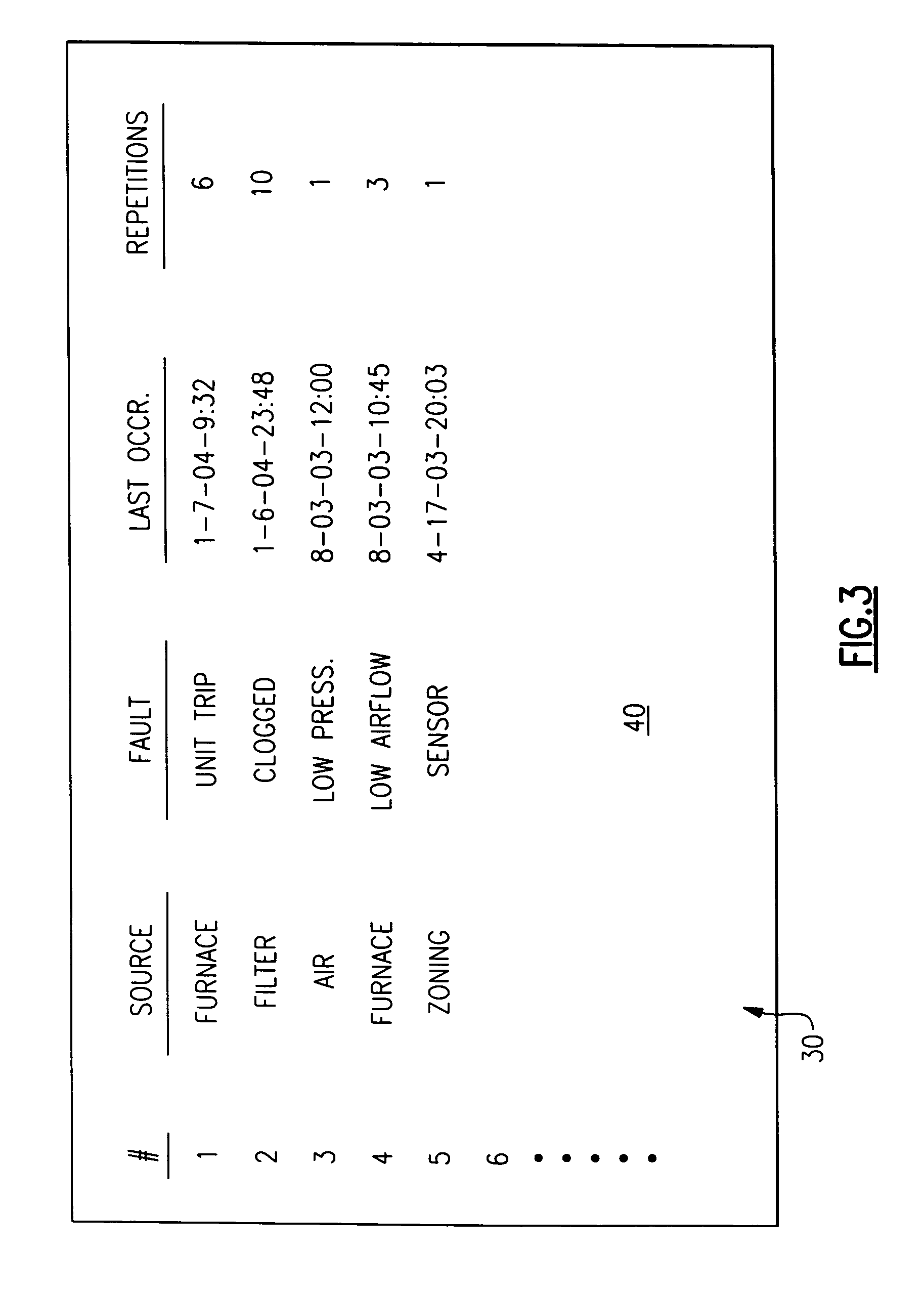
An HVAC system includes a central controller which communicates with a multiple of HVAC components over a digital communication bus. The central controller maintains an ordered fault list that includes the source of a fault, a description of the fault, the last occurrence of the fault, and the number of sequential occurrences, or repetitions across the entire HVAC system.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Dynamic recovery from a split-brain failure in edge nodes
ActiveUS10237123B2Reduce the possibilityIncrease the number ofSignal allocationData switching networksNODALTraffic capacity
Some embodiments provide a method for employing the management and control system of a network to dynamically recover from a split-brain condition in the edge nodes of the network. The method of some embodiments takes a corrective action to automatically recover from a split-brain failure occurred at a pair of high availability (HA) edge nodes of the network. The HA edge nodes include an active machine and a standby machine. The active edge node actively passes through the network traffic (e.g., north-south traffic for a logical network), while the standby edge node is synchronized and ready to transition to the active state, should a failure occur. Both HA nodes share the same configuration settings and only one is active until a path, link, or system failure occurs. The active edge node also provides stateful services (e.g., stateful firewall, load balancing, etc.) to the data compute nodes of the network.
Owner:NICIRA
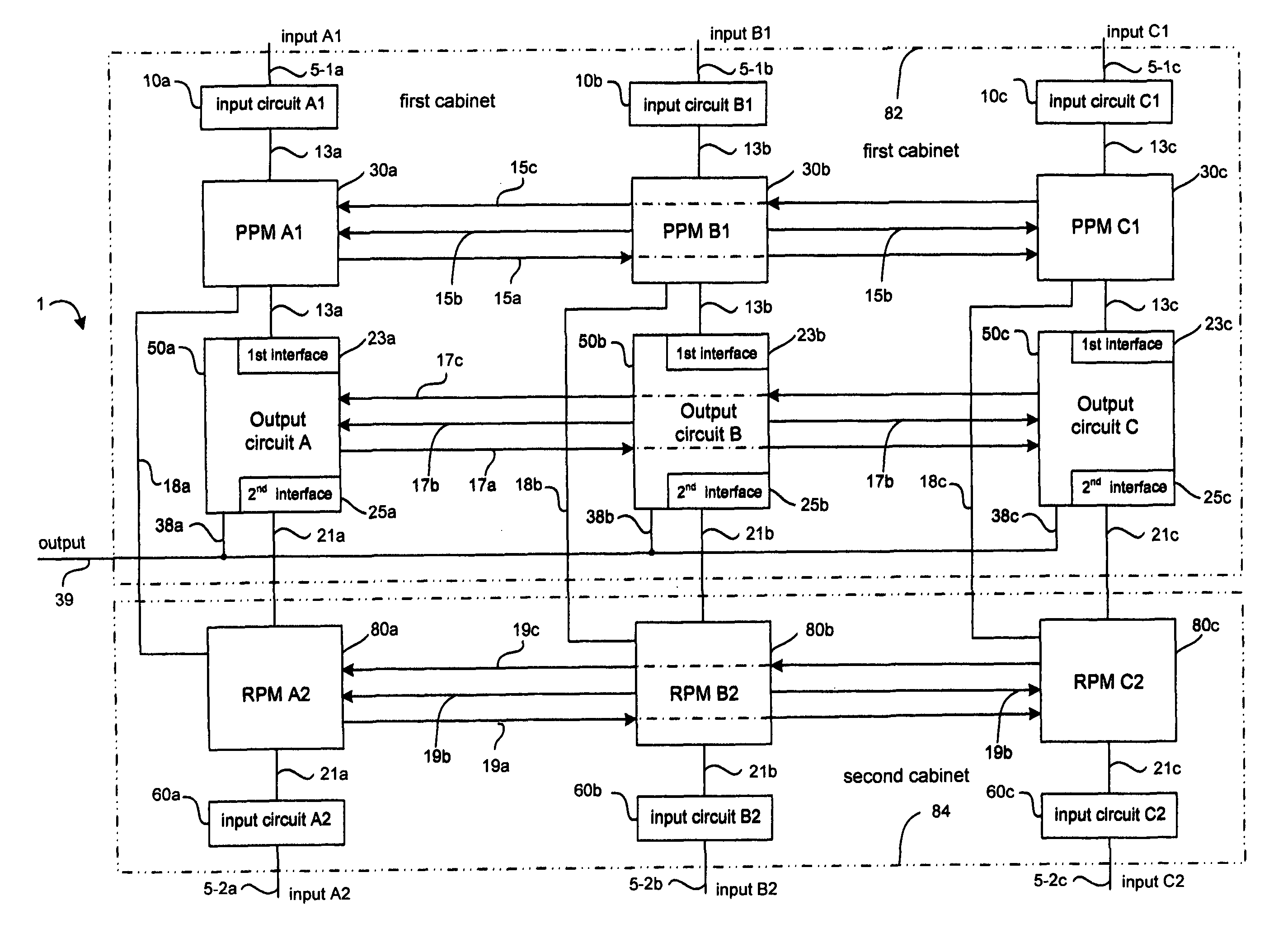
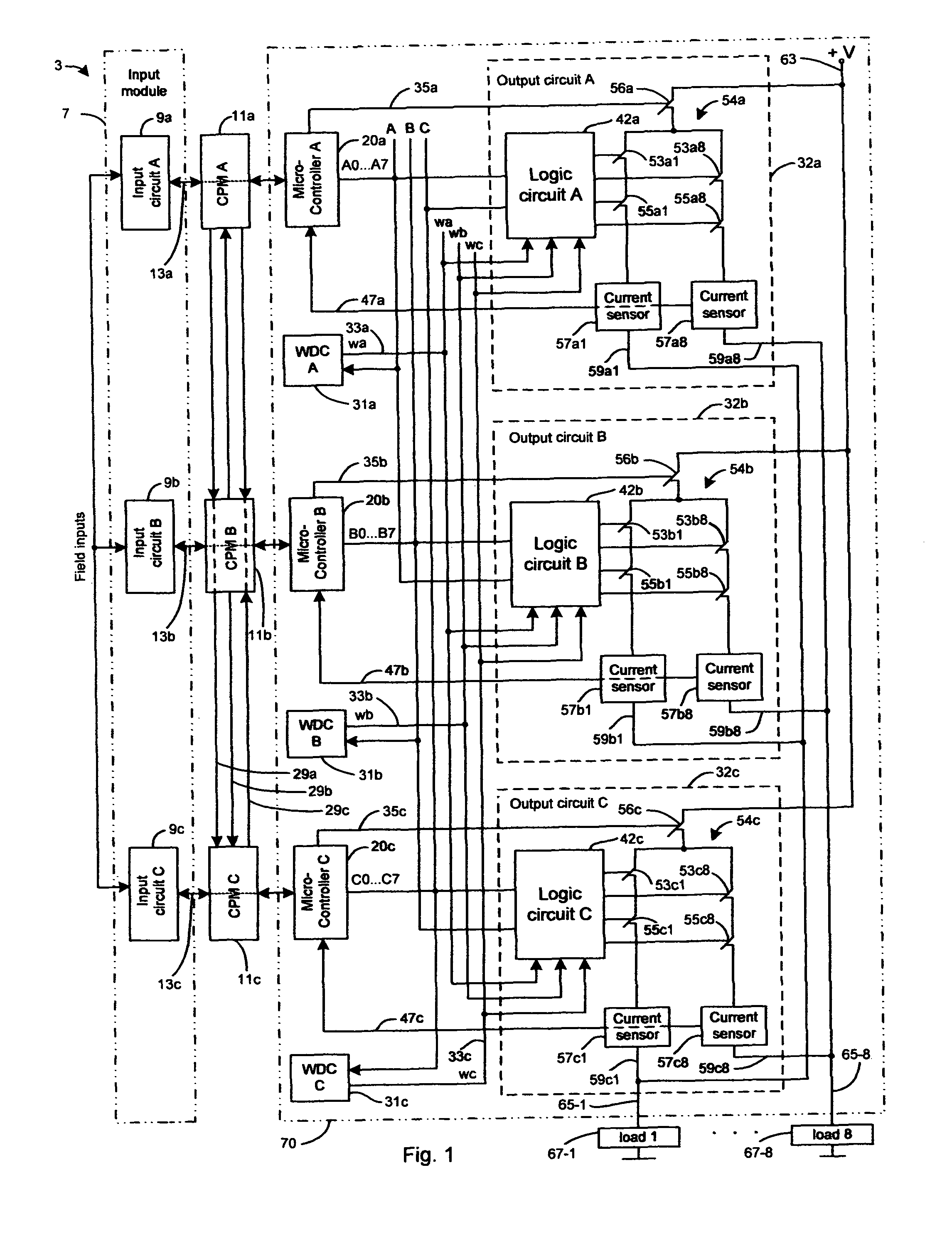
Multiple redundant computer system combining fault diagnostics and majority voting with dissimilar redundancy technology
InactiveUS7877627B1Failure can be causedReduce probabilityError detection/correctionExecution controlSystem failure
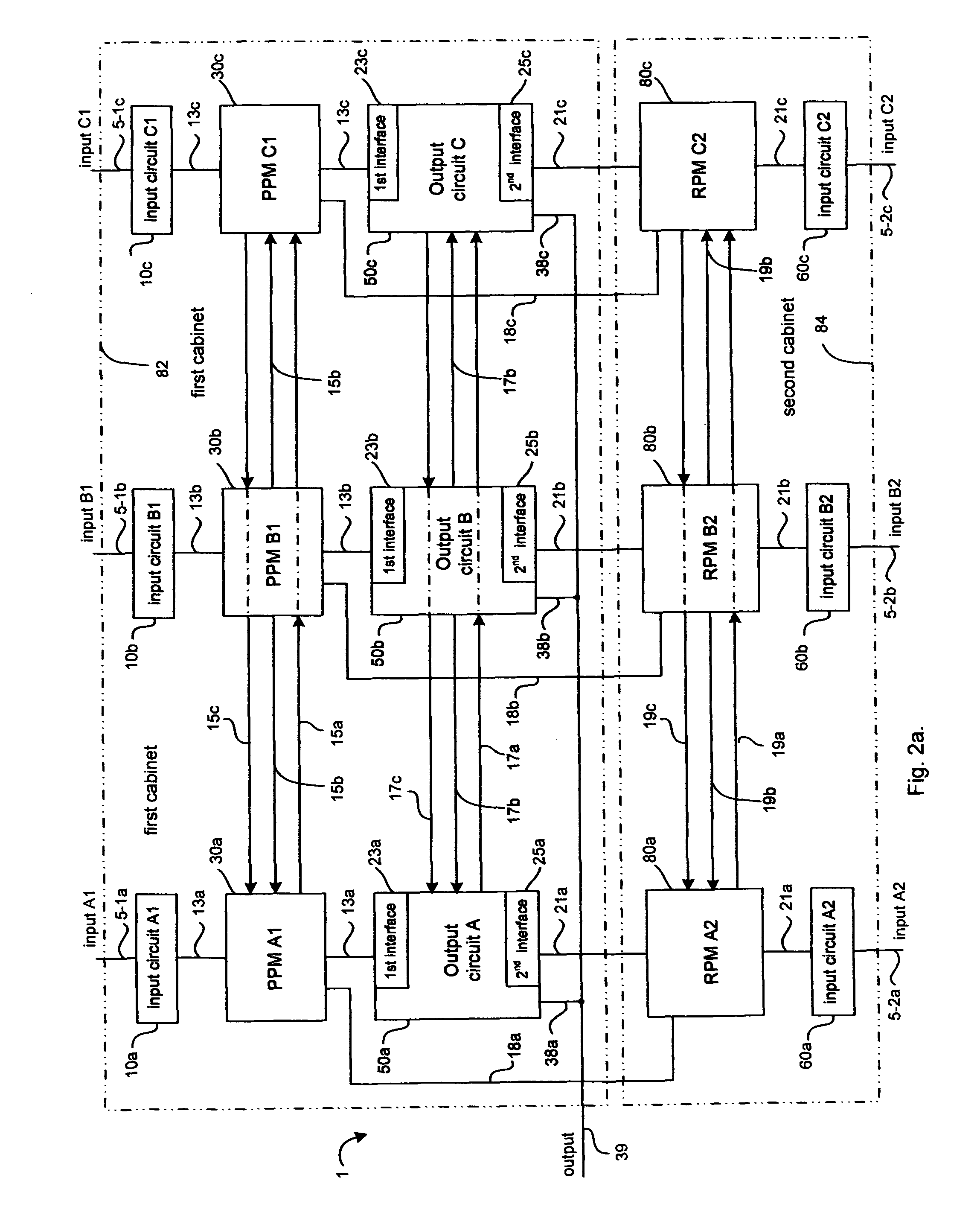
A multiple redundant computer system includes three primary processor modules (PPM) and three redundant processor modules (RPM) operating synchronously. Primary and redundant processor modules are dissimilar in hardware and software for decreasing the probability of a common cause system failure. Each primary and redundant processor module receives input data from associated primary and redundant input modules respectively, executes control program and transfers output data to an output module. The output module produces a system output as the result of 2-out-of-3 voting among output data generated by PPMs. In response to PPMs hard failures, the output module still produces the system output as the result of 2-out-of-3 voting among output data generated by any combination of the PPM and the RPM. As such, the system is able to operate properly even though five-out-of six processor modules have failed. The output module also compares output data that it has received from each pair of the associated PPM and RPM for detecting a disparity between said output data due to the occurrence of transient faults. Additionally, the output module produces the system output as the result of 2-out-of-2 and 1-out-of-1 voting upon the occurrence of disparity of output data generated by the associated PPM and RPM in one and two pairs of the associated PPM and RPM respectively.
Owner:SUPERCON
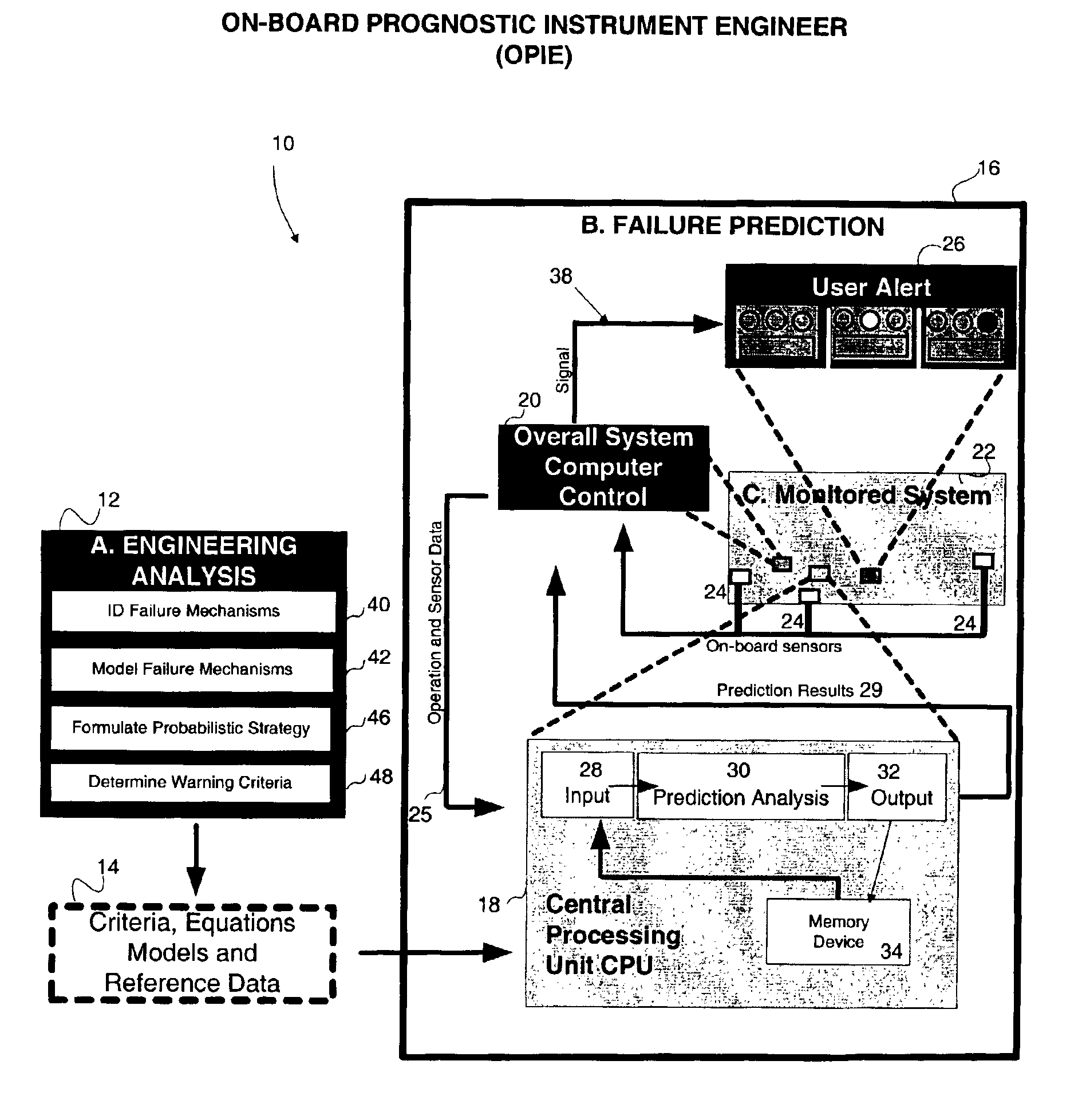
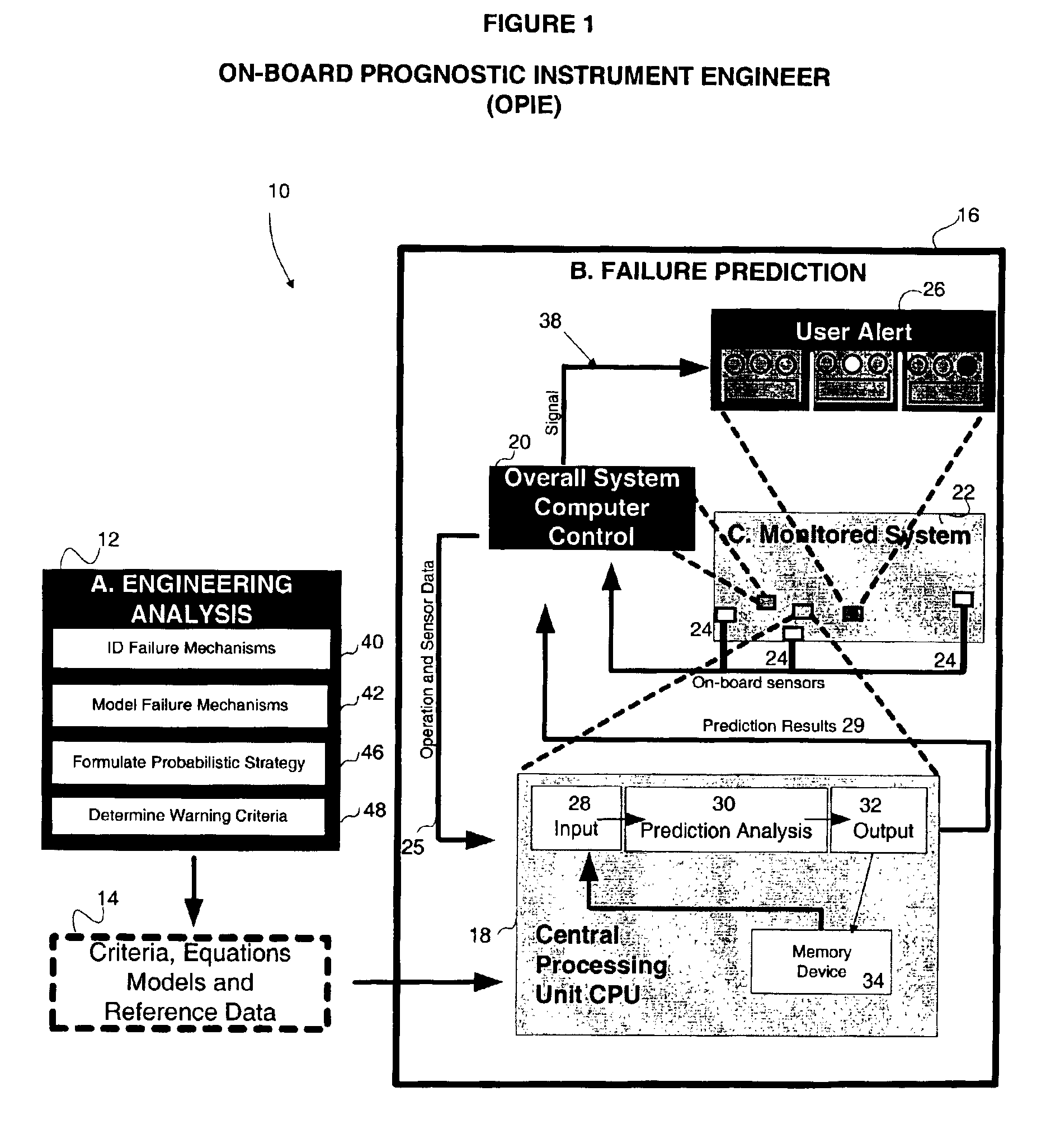
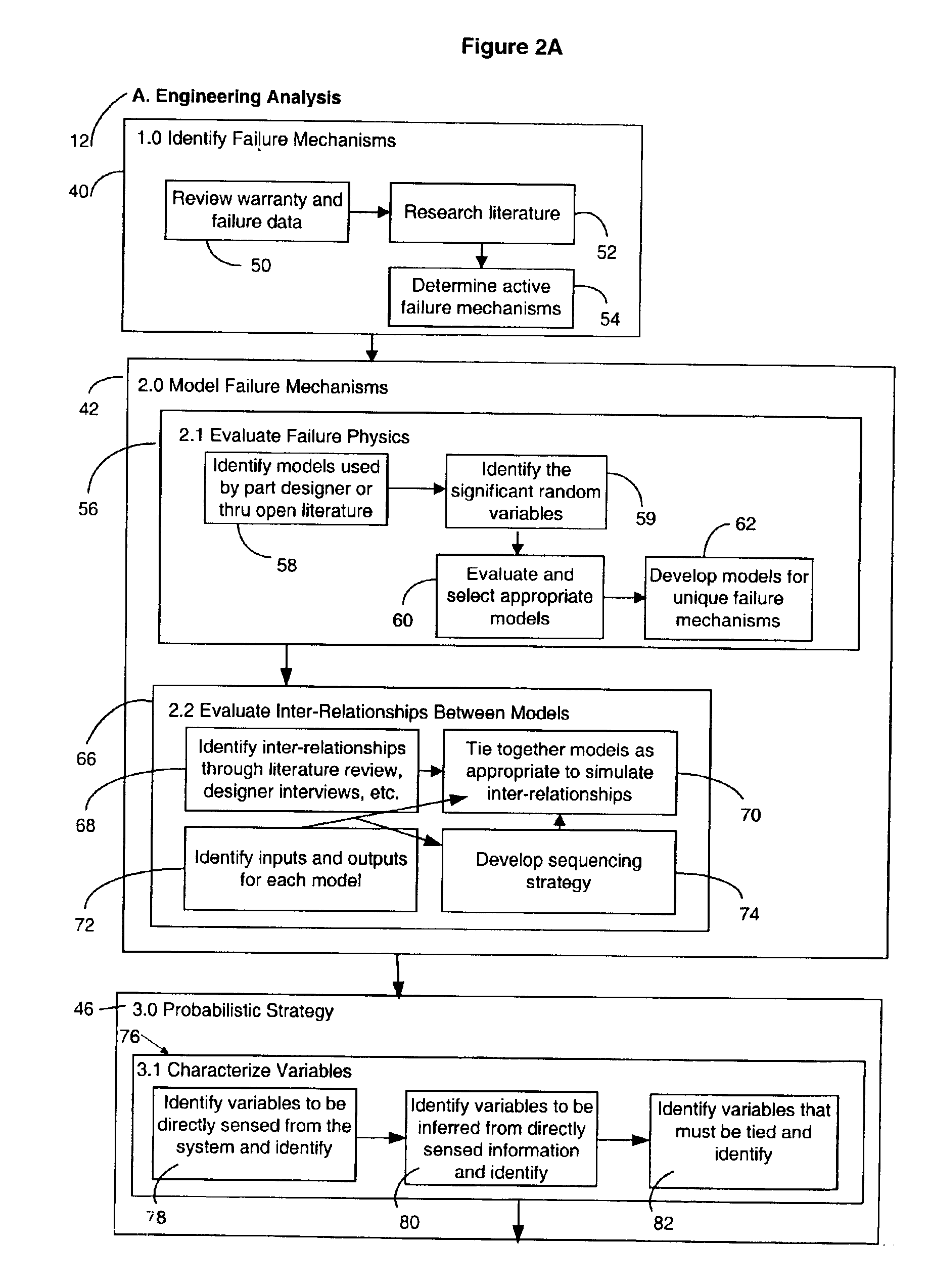
Method and apparatus for predicting failure in a system
The invention regards a system reliability or failure predicting apparatus and method that incorporates known information about system component failure into a system model and uses the model with or without other acquired system data to predict the probability of system failure. An embodiment of the method includes using probabilistic methods to create a system failure model from the failure models of individual system components, predicting the failure of the system based on the component models and system data, ranking the sensitivity of the system to the system variables, and communicating a failure prediction.
Owner:VEXTEC CORP
System and method for rapidly diagnosing bugs of system software
InactiveUS20090132860A1Improve efficiencyReduce difficultyError detection/correctionFault analysisFault management
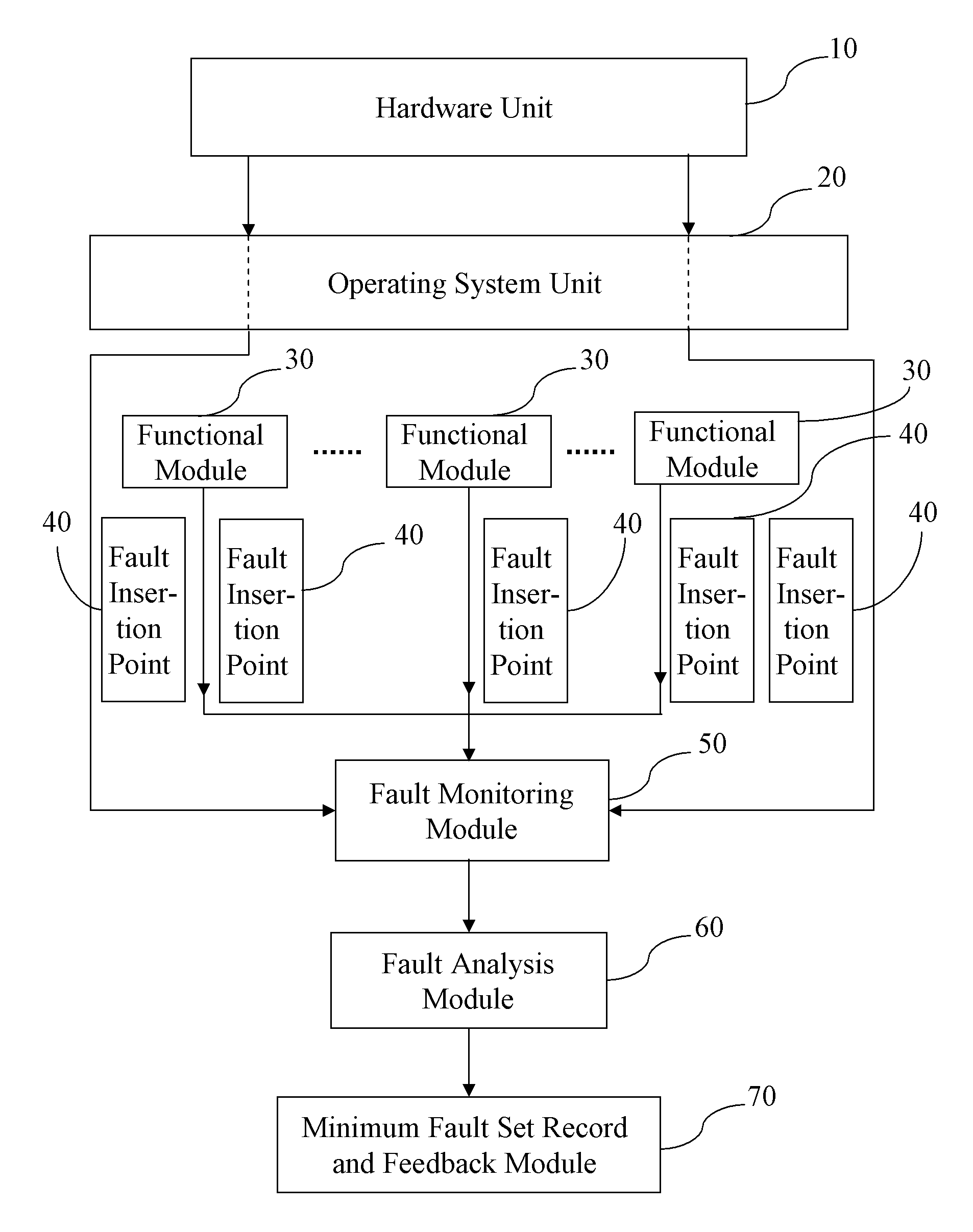
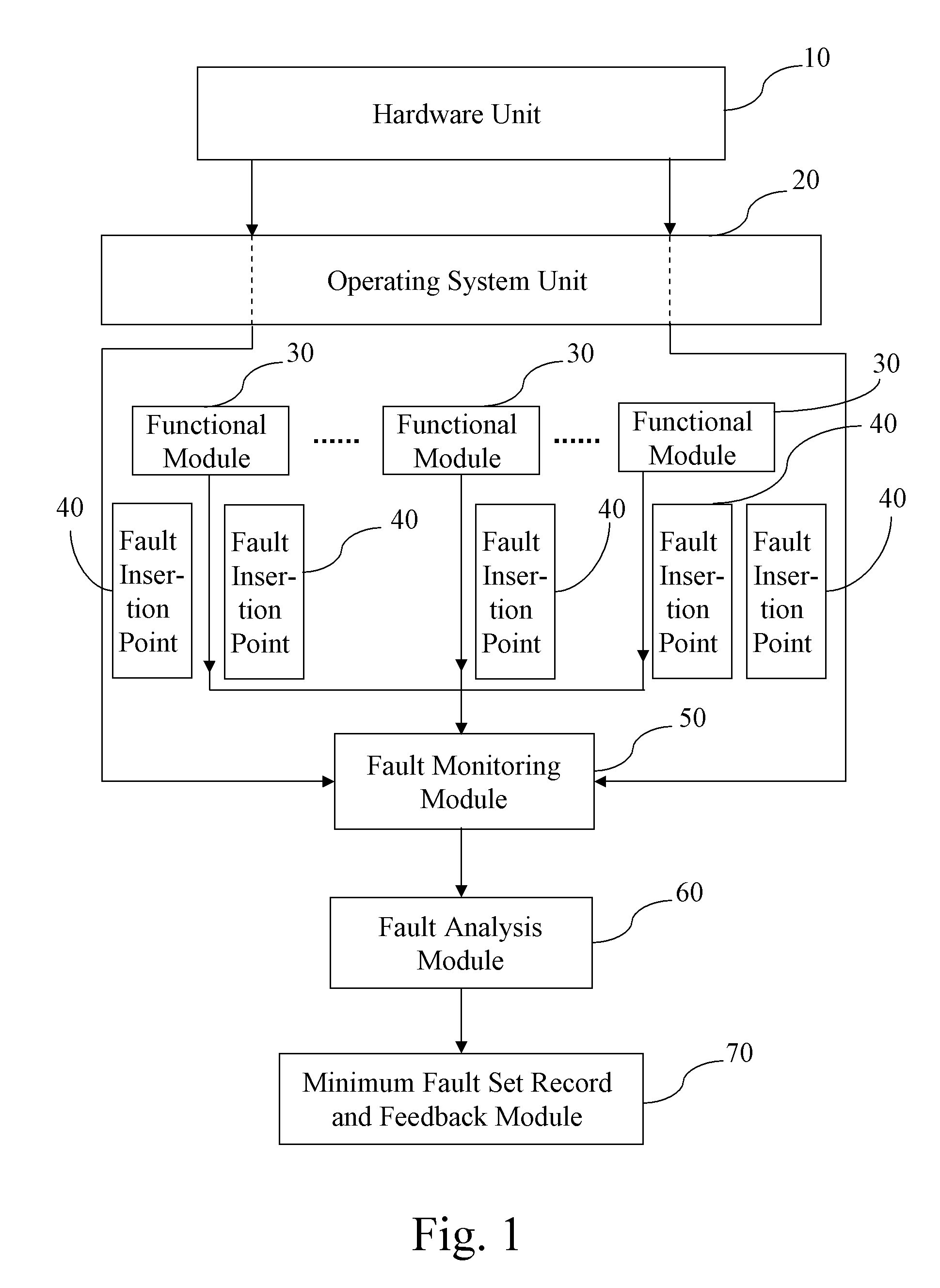
A system and a method for rapidly diagnosing bugs of system software are apply for rapidly localizing a system program fault that causes a system error and then feeding back to a subscriber. First, according to the subscriber's requirement, a program of system fault analysis standard is preset and written into the system. Next, a plurality of fault insertion points is added into a program module of the system according to the subscriber's requirement for the precision of the fault analysis result. Then, fault management information is generated at the fault insertion points during the running process of the system program, and the management information is monitored for collecting relevant system fault data. After that, the collected system fault data is analyzed in real time through the program of system fault analysis standard, so as to obtain the minimum fault set for causing the system error.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
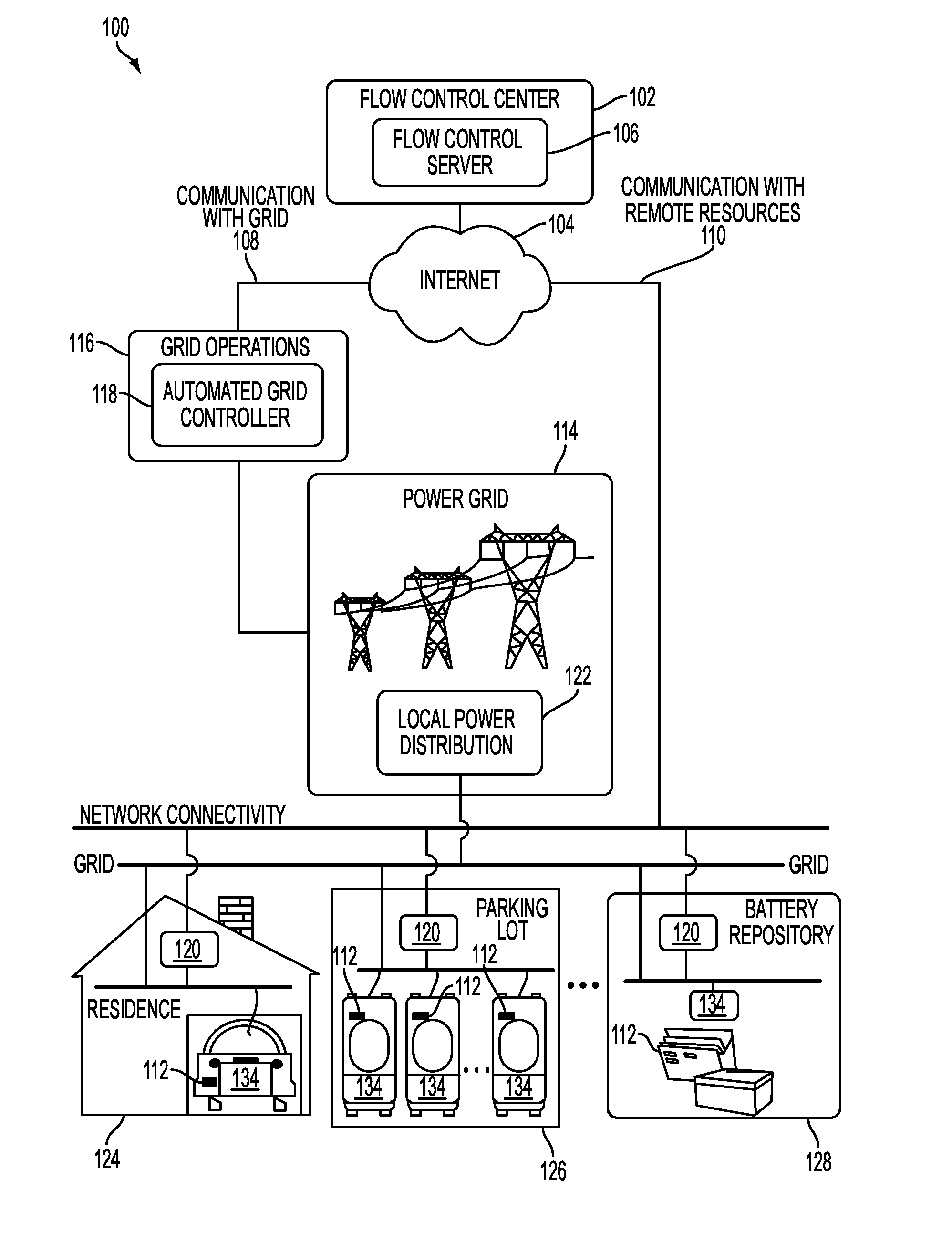
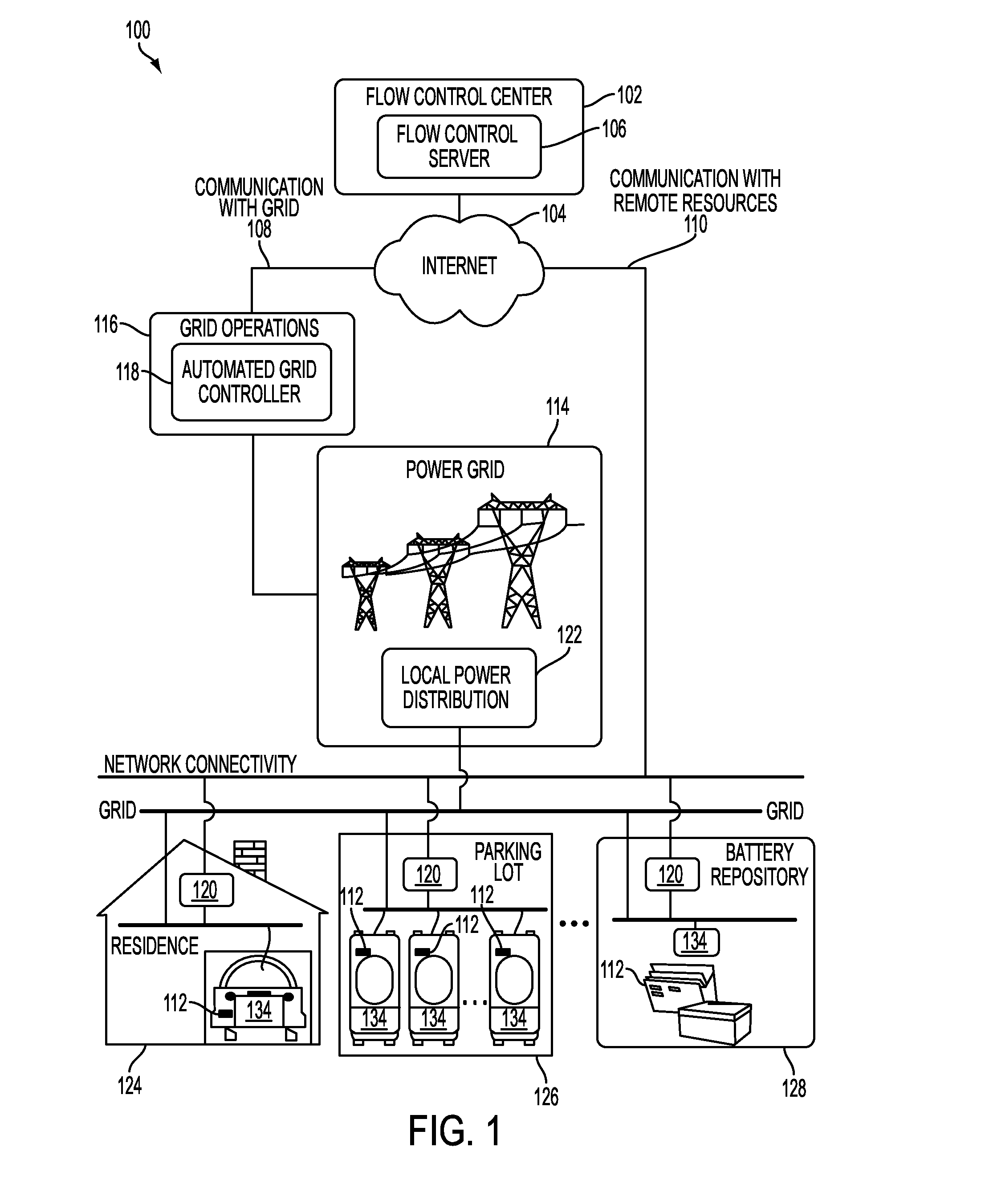
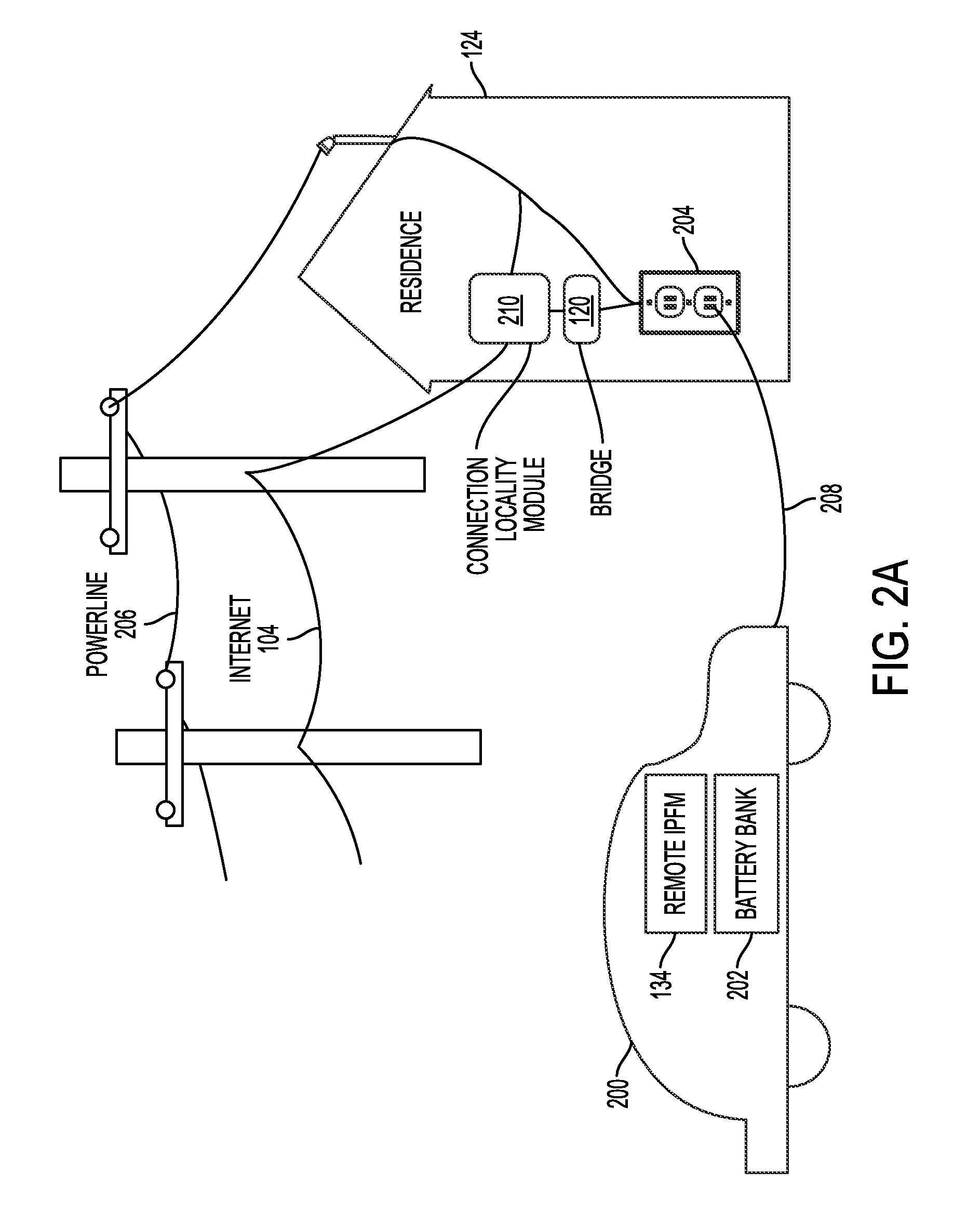
Systems and methods for electric vehicle power flow management
InactiveUS20110004358A1Low costBatteries circuit arrangementsLevel controlPower flowElectrical devices
Owner:GRIDPOINT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com