Systems and methods for electric vehicle power flow management
a technology for electric vehicles and power flow management, applied in non-electric variable control, process and machine control, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of increasing energy waste, grid instability, and difficulty in moving away from carbon-intensive forms of electricity, so as to reduce the cost of providing power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028]Reference will now be made in detail to the embodiments of the present invention, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings.
[0029]Overview
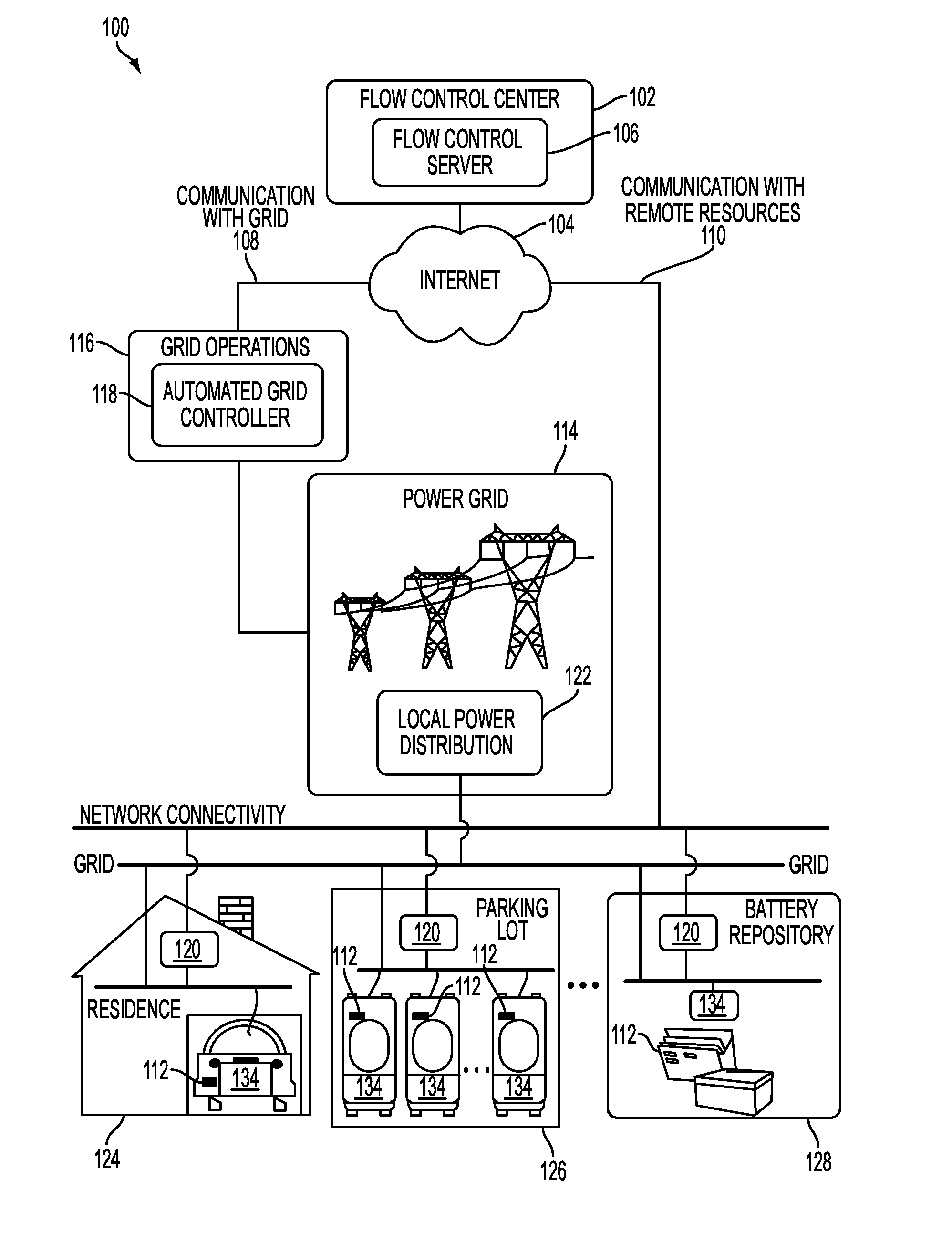
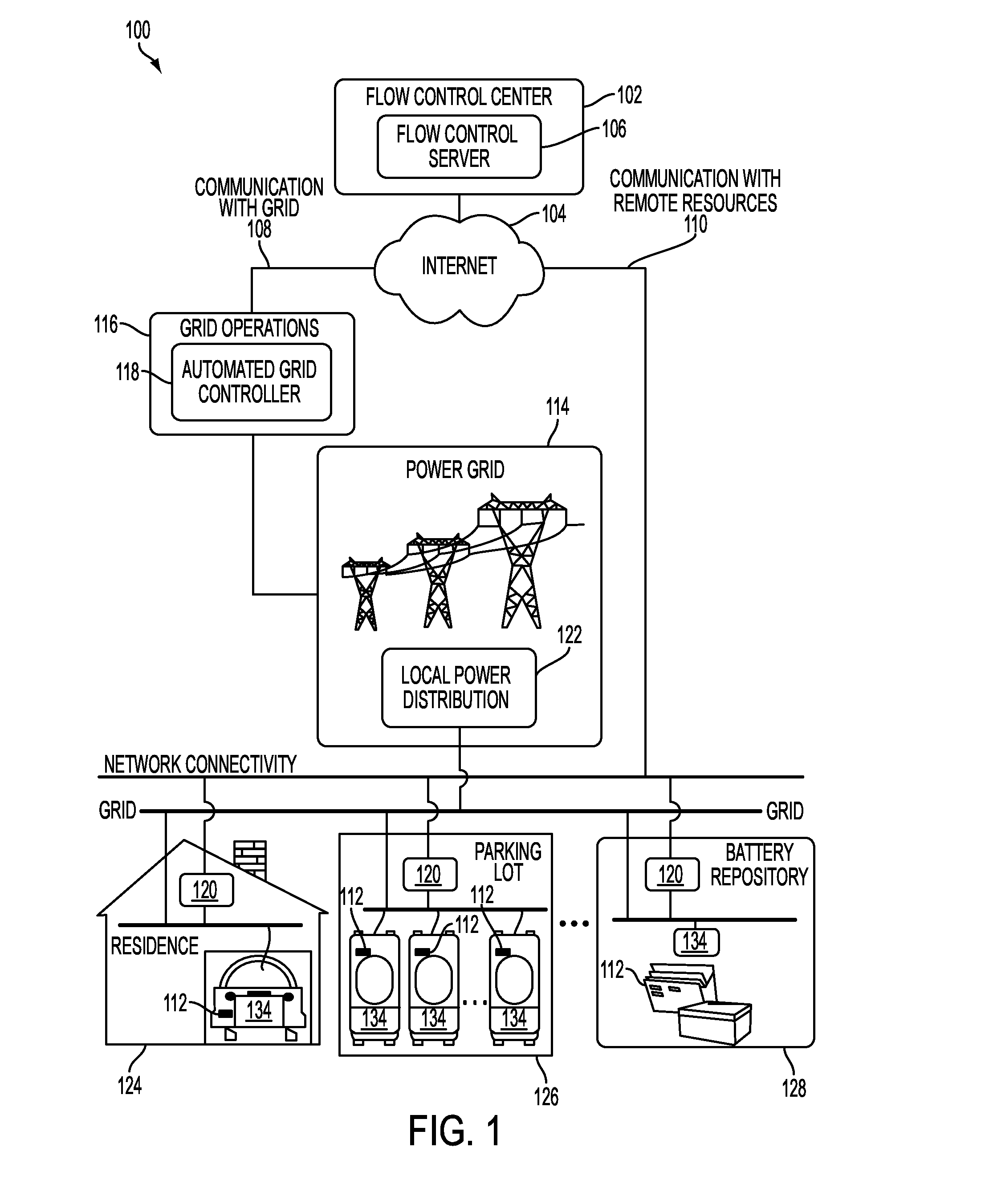
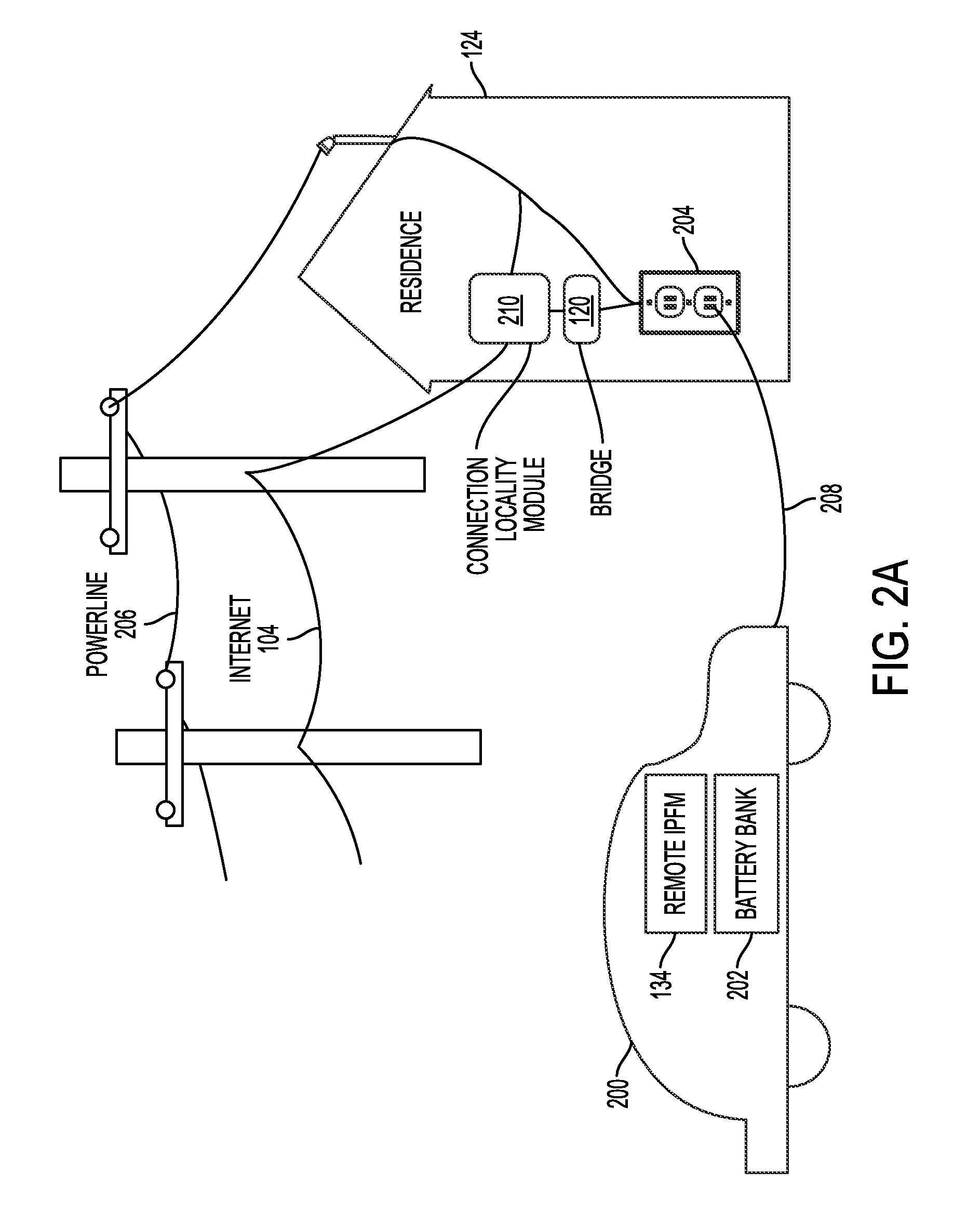
[0030]Described herein is a power aggregation system for distributed electric resources, and associated methods. In one implementation, a system communicates over the Internet and / or some other public or private networks with numerous individual electric resources connected to a power grid (hereinafter, “grid”). By communicating, the system can dynamically aggregate these electric resources to provide power services to grid operators (e.g. utilities, Independent System Operators (ISO), etc).
[0031]“Power services” as used herein, refers to energy delivery as well as other ancillary services including demand response, regulation, spinning reserves, non-spinning reserves, energy imbalance, reactive power, and similar products.
[0032]“Aggregation” as used herein refers to the ability to control power flows into and out of a s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com