Patents
Literature
5492results about "Computation using non-denominational number representation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optimization of microgrid energy use and distribution
ActiveUS20100179704A1Optimize energy distributionOptimize energy useBatteries circuit arrangementsLevel controlPersonalizationMicrogrid
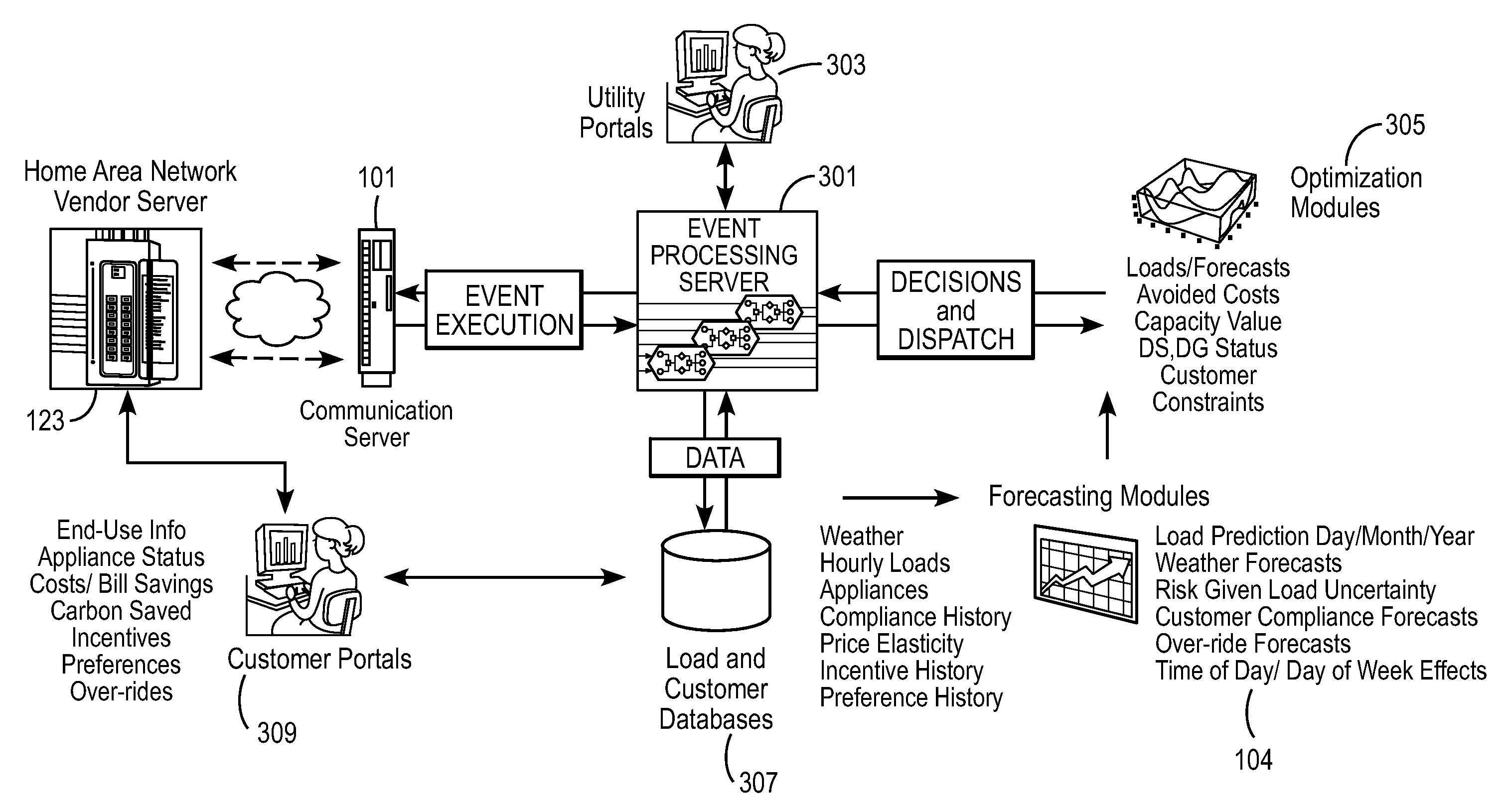
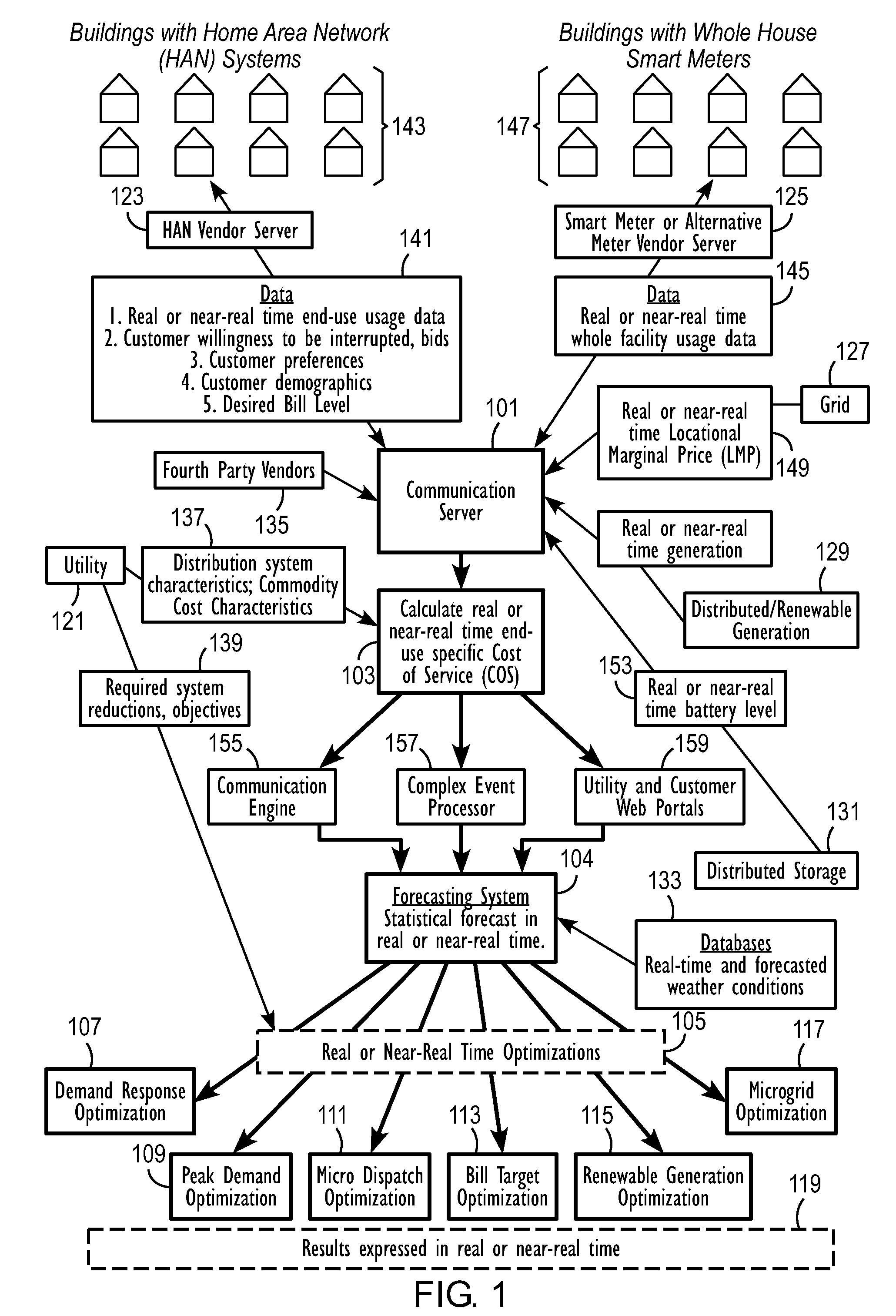
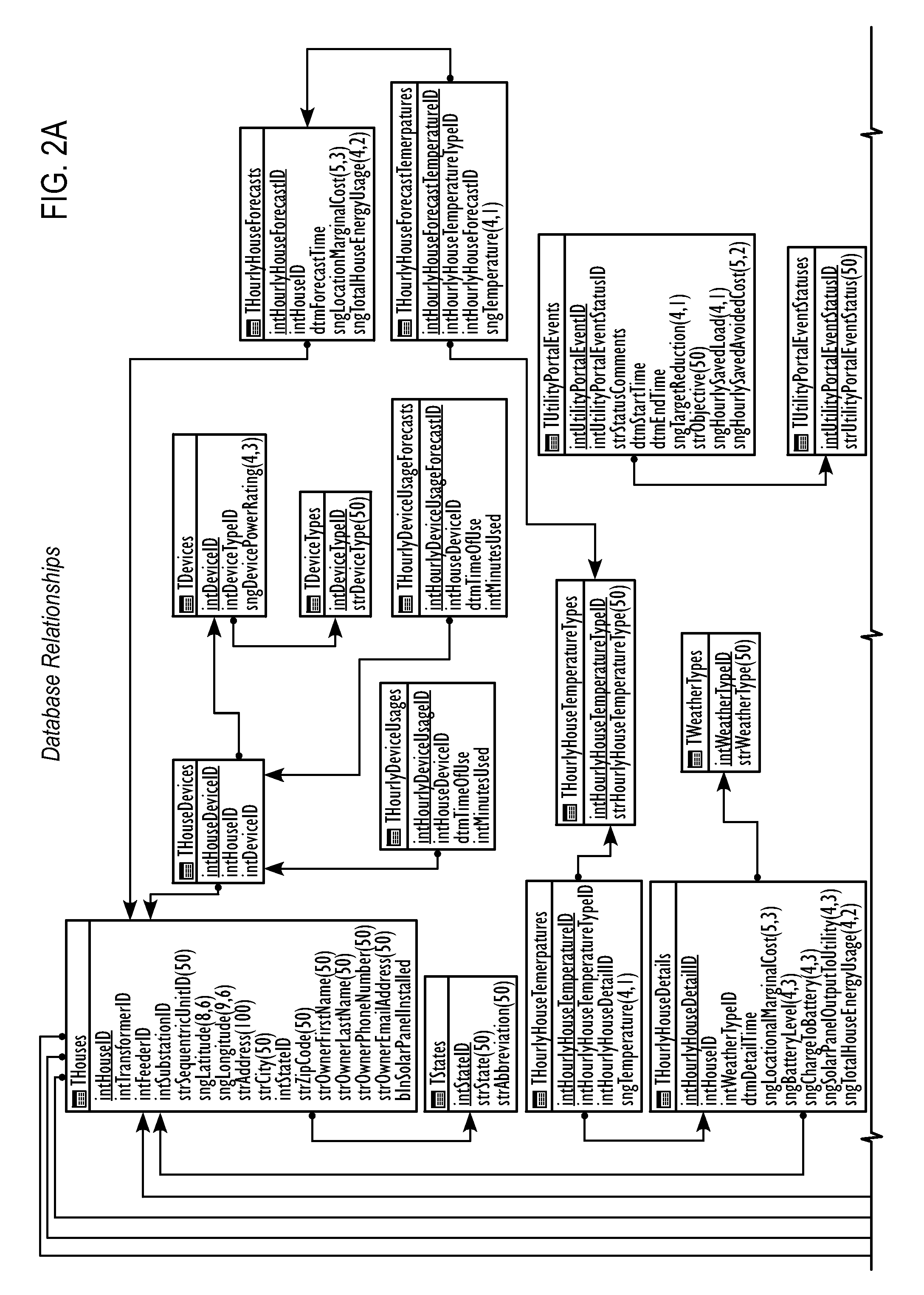
An energy distribution may include a server and one or more databases. The system may communicate with an energy provider to receive energy provider data, at least one information collector to receive information collector data such as individualized energy usage data, customer preferences, and customer or location characteristics, and the one or more databases for receiving data for optimization. The system may calculate a cost of service or avoided cost using at least one of the individualized energy usage data and a system generation cost at a nearest bus. The system may also forecast individualized demand by end-use, individualized demand by location, energy prices, or energy costs. The system may optimize energy distribution, energy use, cost of service, or avoided cost using the forecasted individualized demand by end-use, the forecasted individualized demand by location, the forecasted energy prices, and the forecasted energy costs.
Owner:INTEGRAL ANALYTICS
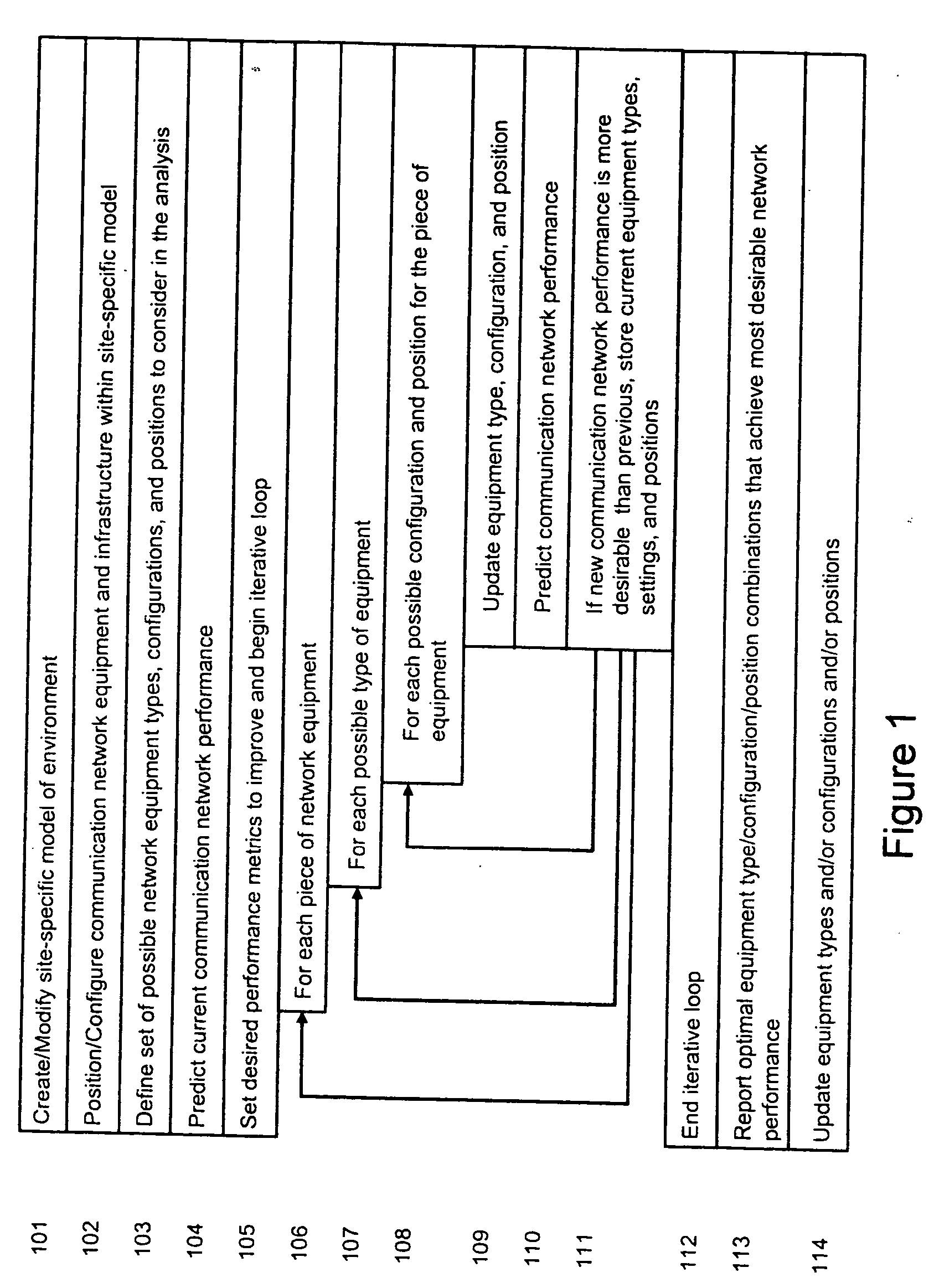
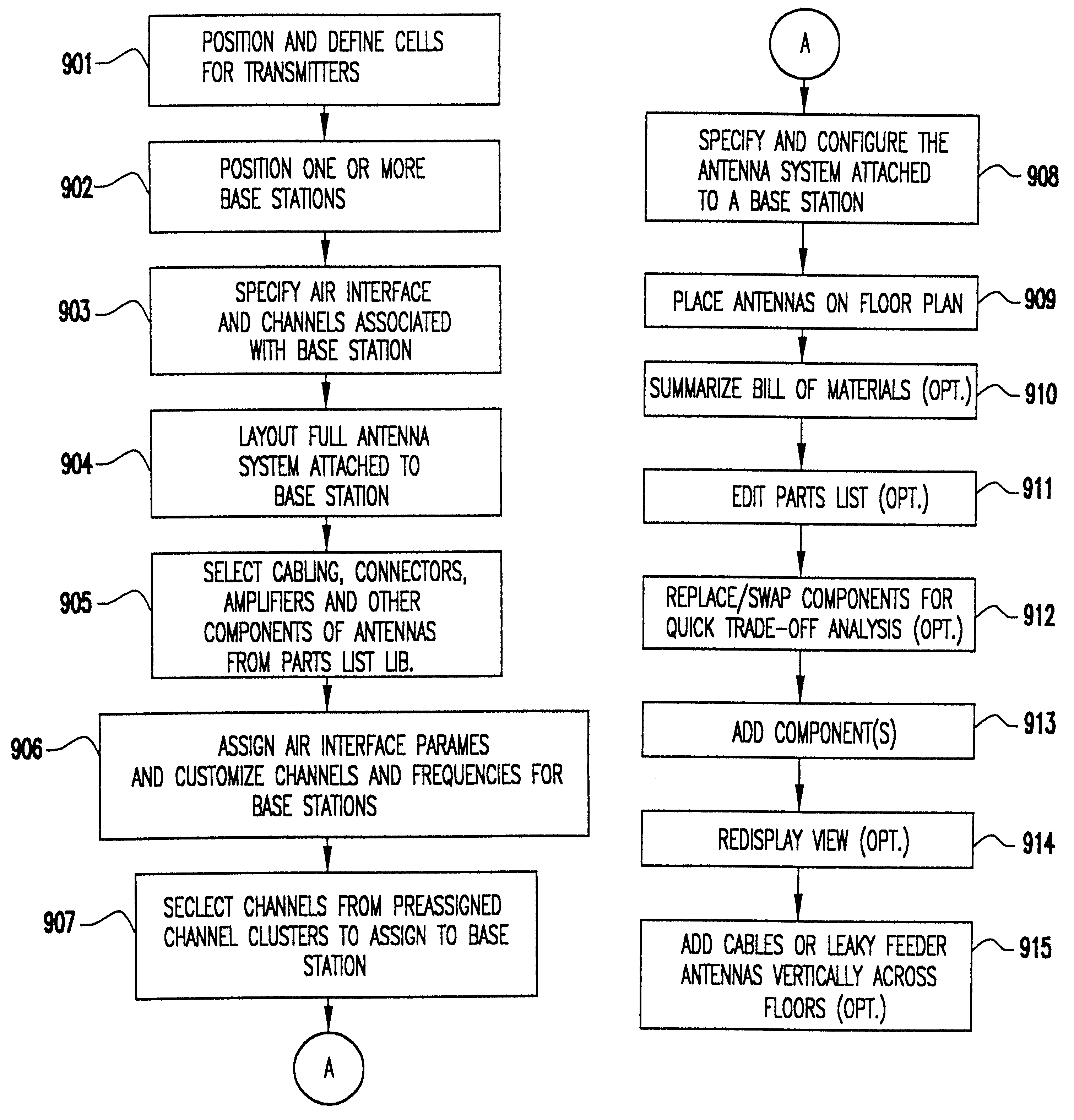
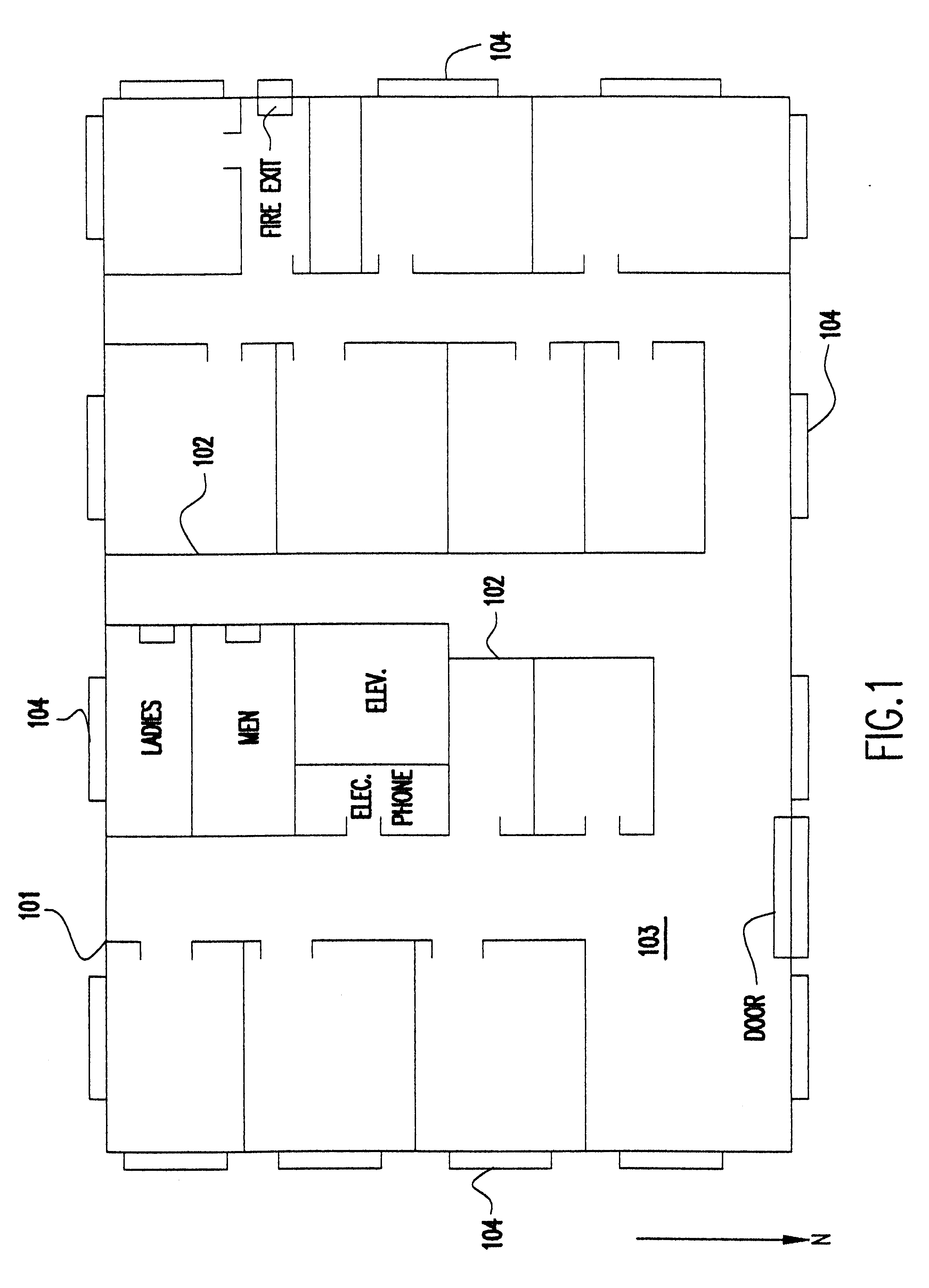
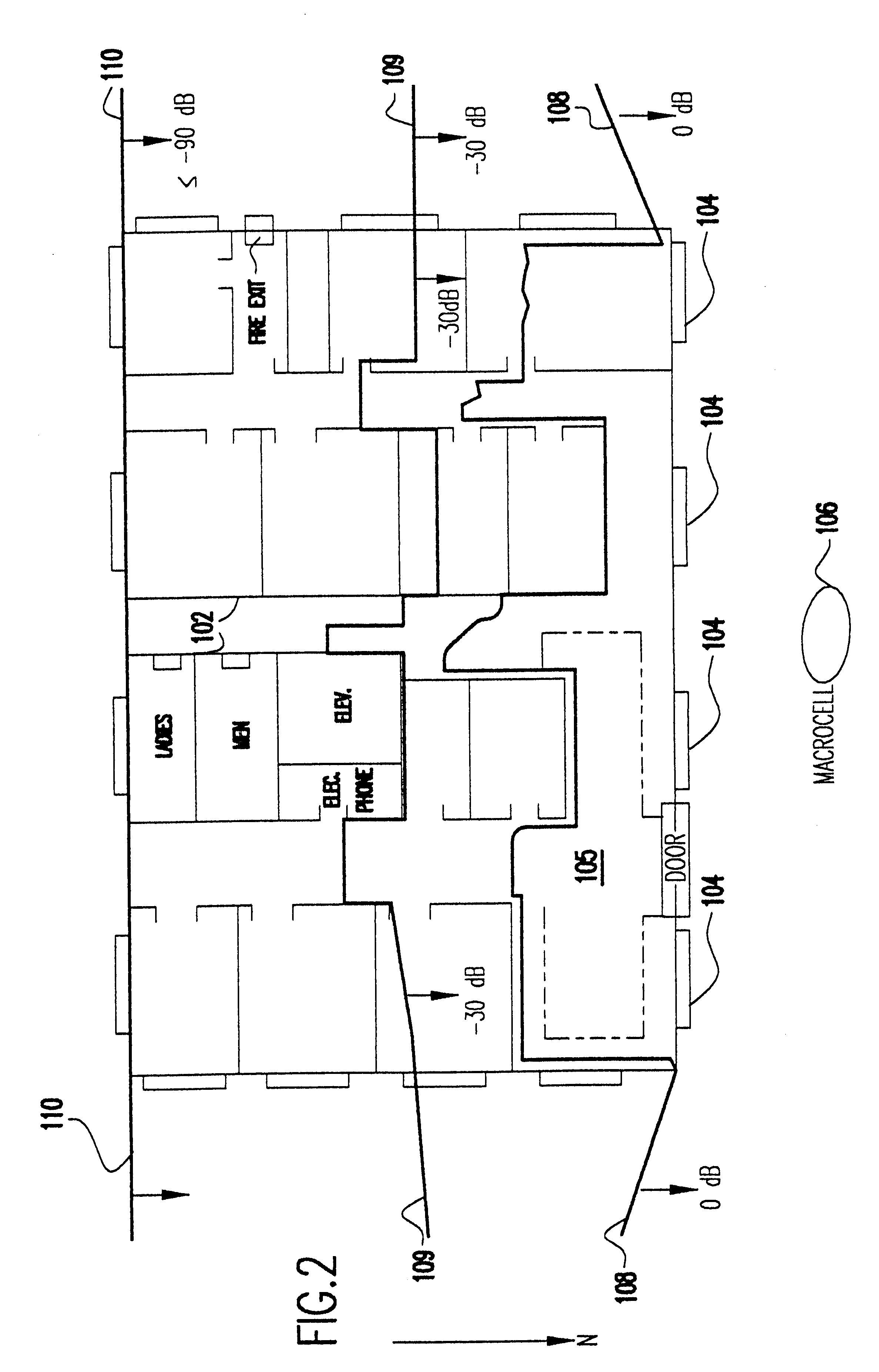
System and method for automated placement or configuration of equipment for obtaining desired network performance objectives and for security, RF tags, and bandwidth provisioning
ActiveUS20040236547A1Significant valueEasy to explainGeometric CADData taking preventionHard disc driveThe Internet
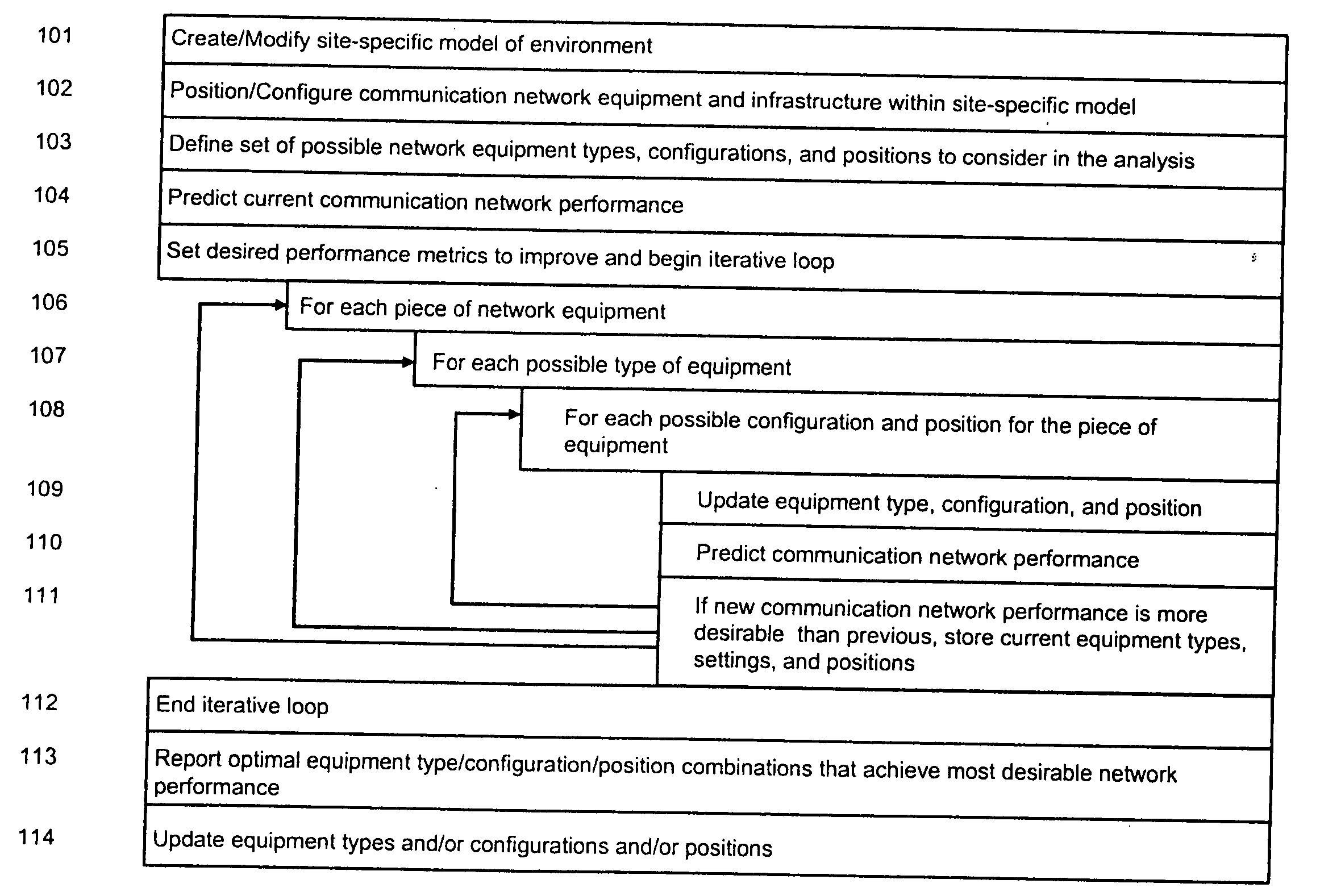
A method is presented for determining optimal or preferred configuration settings for wireless or wired network equipment in order to obtain a desirable level of network performance. A site-specific network model is used with adaptive processing to perform efficient design and on-going management of network performance. The invention iteratively determines overall network performance and cost, and further iterates equipment settings, locations and orientations. Real time control is between a site-specific Computer Aided Design (CAD) software application and the physical components of the network allows the invention to display, store, and iteratively adapt any network to constantly varying traffic and interference conditions. Alarms provide rapid adaptation of network parameters, and alerts and preprogrammed network shutdown actions may be taken autonomously. A wireless post-it note device and network allows massive data such as book contents or hard drive memory to be accessed within a room by a wide bandwidth reader device, and this can further be interconnected to the internet or Ethernet backbone in order to provide worldwide access and remote retrieval to wireless post-it devices.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Three dimensional multibody modeling of anatomical joints
InactiveUS6161080AEasy to modifyPerson identificationAnalogue computers for chemical processesData selectionDimensional modeling
The present invention relates to a method of generating a three dimensional representation of one or more anatomical joints, wherein the representation comprises two or more movable bodies and one or more links, comprising the steps of inputting anatomically representative data of two or more movable bodies of the selected joint or joints; selecting one or more link types responsive to the representative data of the bodies; selecting link characteristics responsive to each selected link type; generating an equilibrium condition responsive to interaction between the bodies and the links; and displaying a three dimensional representation of the selected joint or joints responsive to the data generated from the equilibrium condition of the anatomical joint or joints. The present invention further relates to a system for generating a three dimensional representation of one or more anatomical joints, and a method of planning surgery of one or more anatomical joints.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
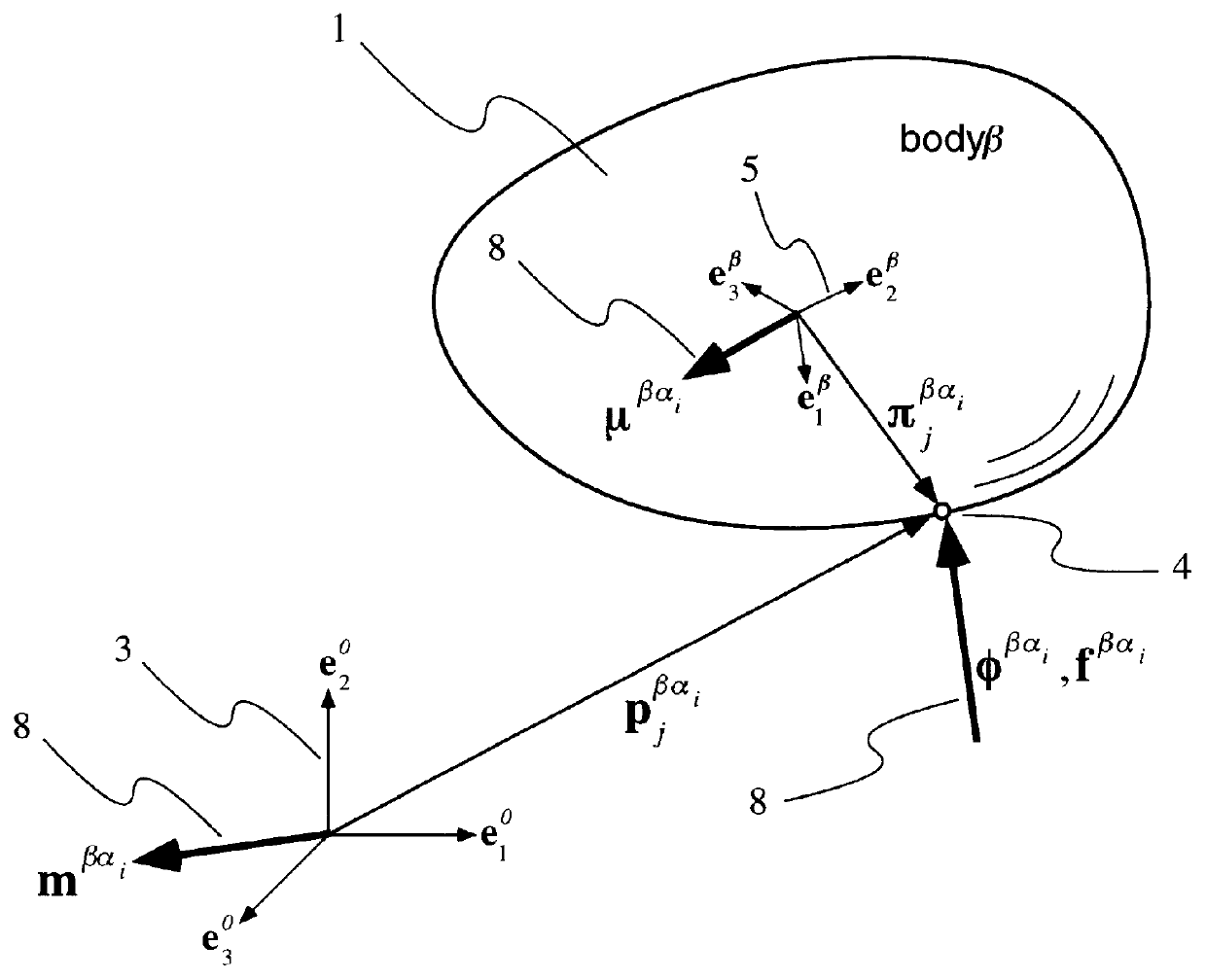
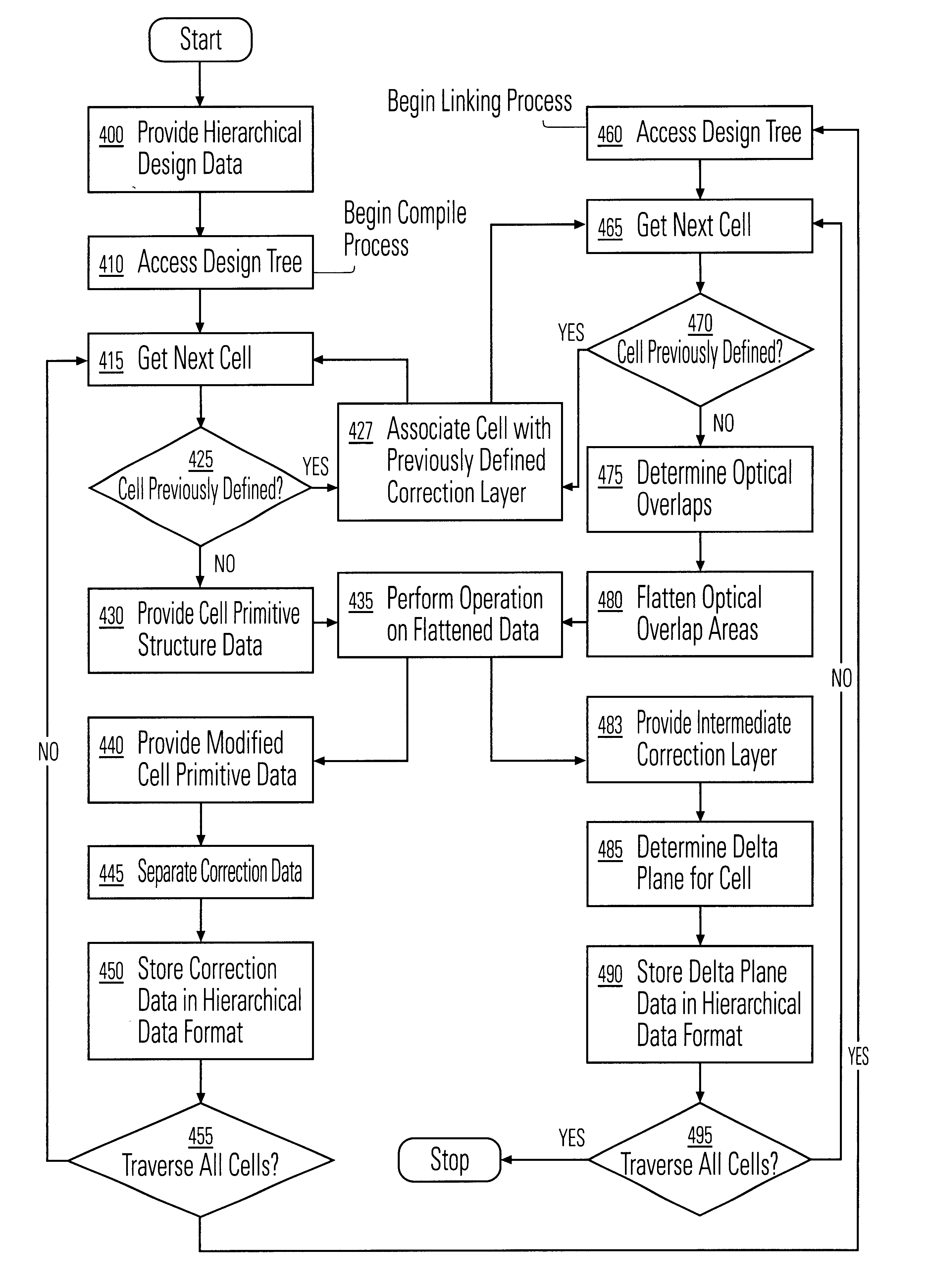
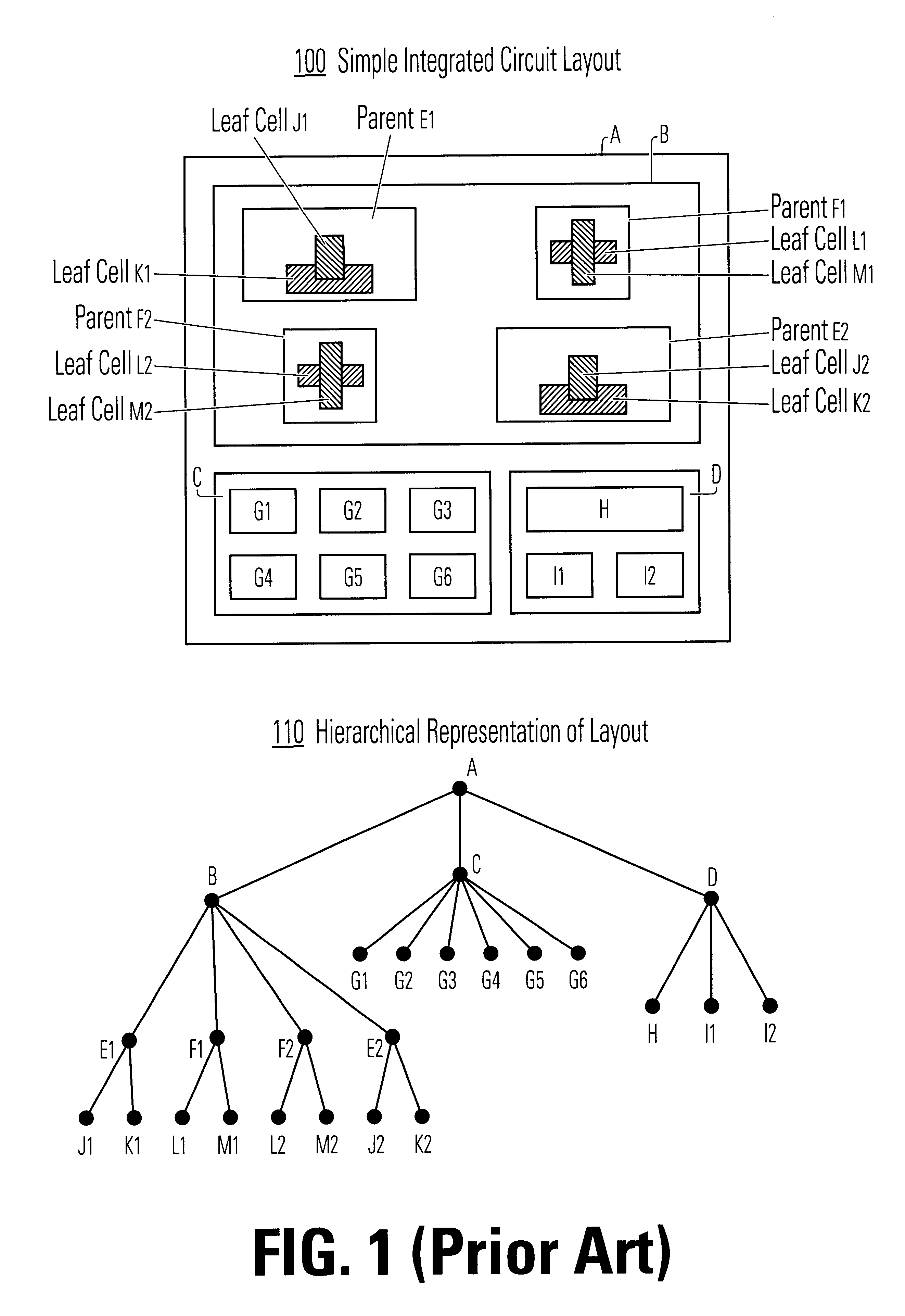
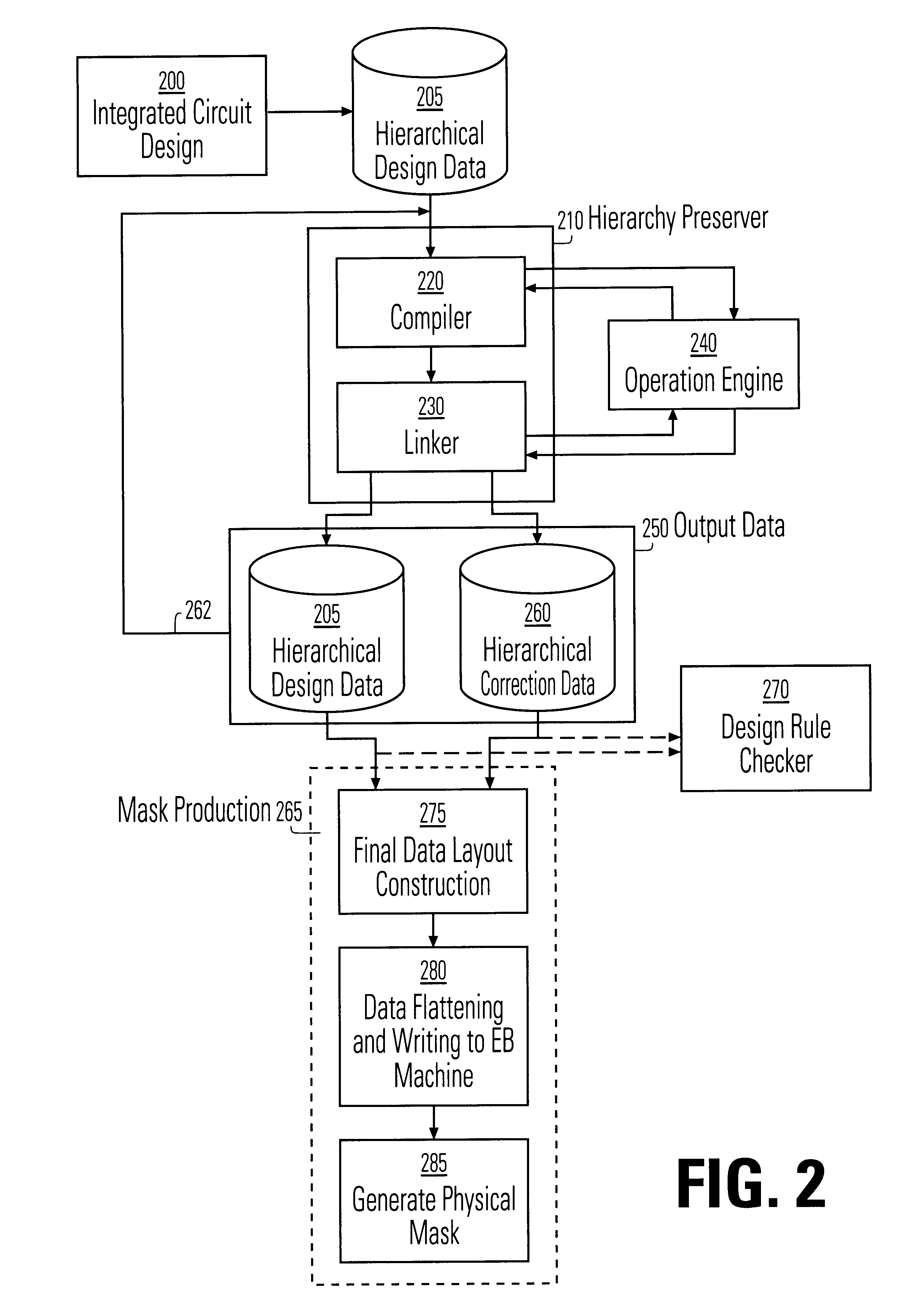
Data hierarchy layout correction and verification method and apparatus
InactiveUS6370679B1Computation using non-denominational number representationOriginals for photomechanical treatmentComputer architectureValidation methods
A method and apparatus for the correction of integrated circuit layouts for optical proximity effects which maintains the original true hierarchy of the original layout is provided. Also provided is a method and apparatus for the design rule checking of layouts which have been corrected for optical proximity effects. The OPC correction method comprises providing a hierarchically described integrated circuit layout as a first input, and a particular set of OPC correction criteria as a second input. The integrated circuit layout is then analyzed to identify features of the layout which meet the provided OPC correction criteria. After the areas on the mask which need correction have been identified, optical proximity correction data is generated in response to the particular set of correction criteria. Finally, a first program data is generated which stores the generated optical proximity correction data in a hierarchical structure that corresponds to the hierarchical structure of the integrated circuit layout. As the output correction data is maintained in true hierarchical format, layouts which are OPC corrected according to this method are able to be processed through conventional design rule checkers with no altering of the data.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
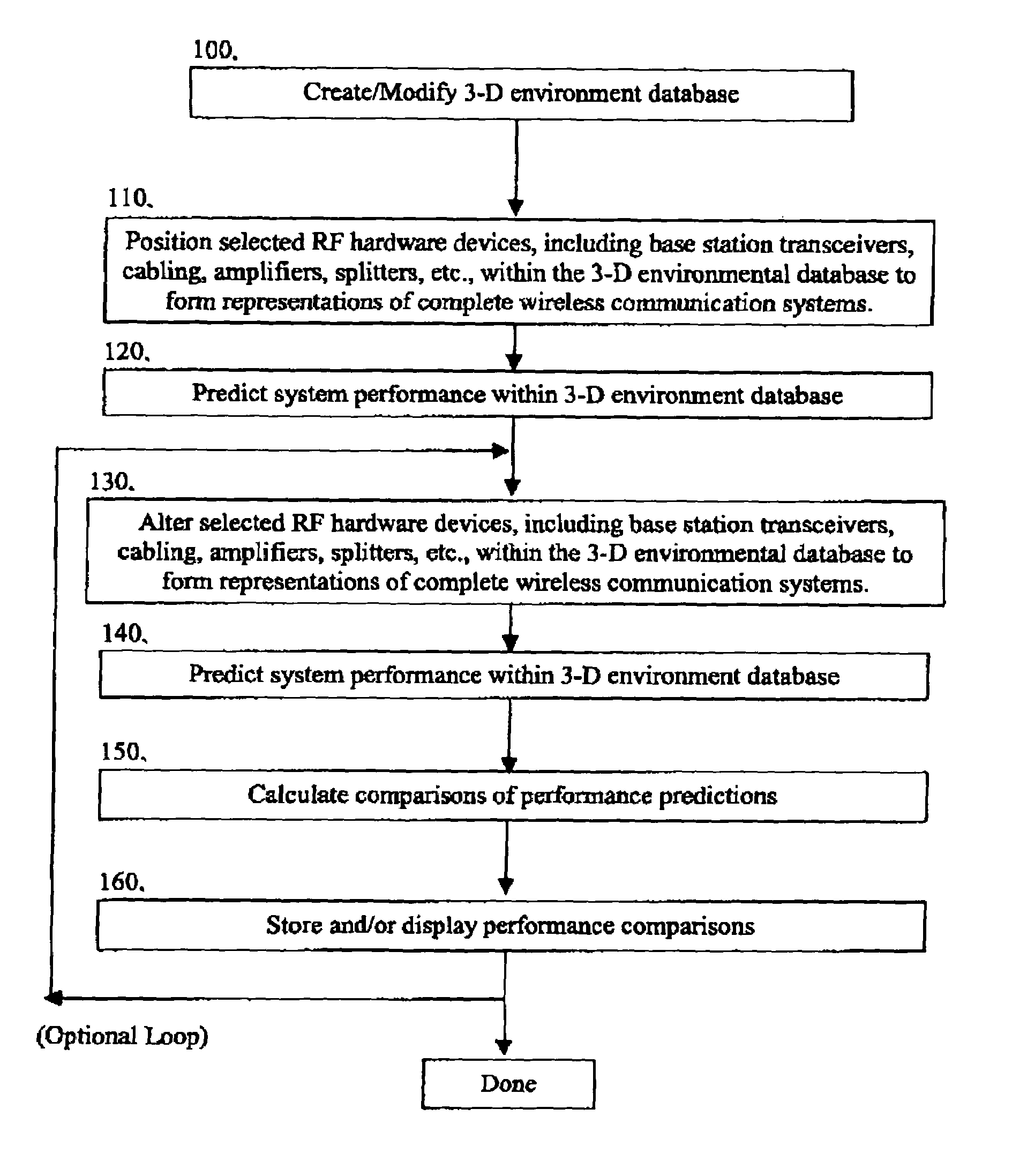
Method and system for automated optimization of antenna positioning in 3-D
InactiveUS6317599B1Quick fixSignificant valueMachines/enginesComputation using non-denominational number representationEngineeringRadio frequency
A method for engineering management and planning for the design of a wireless communications network in three-dimensions (3-D) combines computerized organization, database fusion, and radio frequency (RF) site-specific planning models. The method enables a designer to keep track of wireless system performance throughout the process of pre-bid design, installation and maintenance of a wireless system. Using a database of information that defines the desired environment, predictions of antenna coverage, system coverage and interference, and other wireless system performance criteria, such as frame error rate and network throughput, can be made. Watch points are created to ensure, in real time, that any modifications to the design of the wireless system do not degrade the performance of the system with respect to the watch point locations.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Simulation gridding method and apparatus including a structured areal gridder adapted for use by a reservoir simulator
InactiveUS6106561AHigh simulationSimulation results are accurateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingComputation using non-denominational number representationHorizonTriangulation
A Flogrid Simulation Gridding Program includes a Flogrid structured gridder. The structured gridder includes a structured areal gridder and a block gridder. The structured areal gridder will build an areal grid on an uppermost horizon of an earth formation by performing the following steps: (1) building a boundary enclosing one or more fault intersection lines on the horizon, and building a triangulation that absorbs the boundary and the faults; (2) building a vector field on the triangulation; (3) building a web of control lines and additional lines inside the boundary which have a direction that corresponds to the direction of the vector field on the triangulation, thereby producing an areal grid; and (4) post-processing the areal grid so that the control lines and additional lines are equi-spaced or smoothly distributed. The block gridder of the structured gridder will drop coordinate lines down from the nodes of the areal grid to complete the construction of a three dimensional structured grid. A reservoir simulator will receive the structured grid and generate a set of simulation results which are displayed on a 3D Viewer for observation by a workstation operator.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
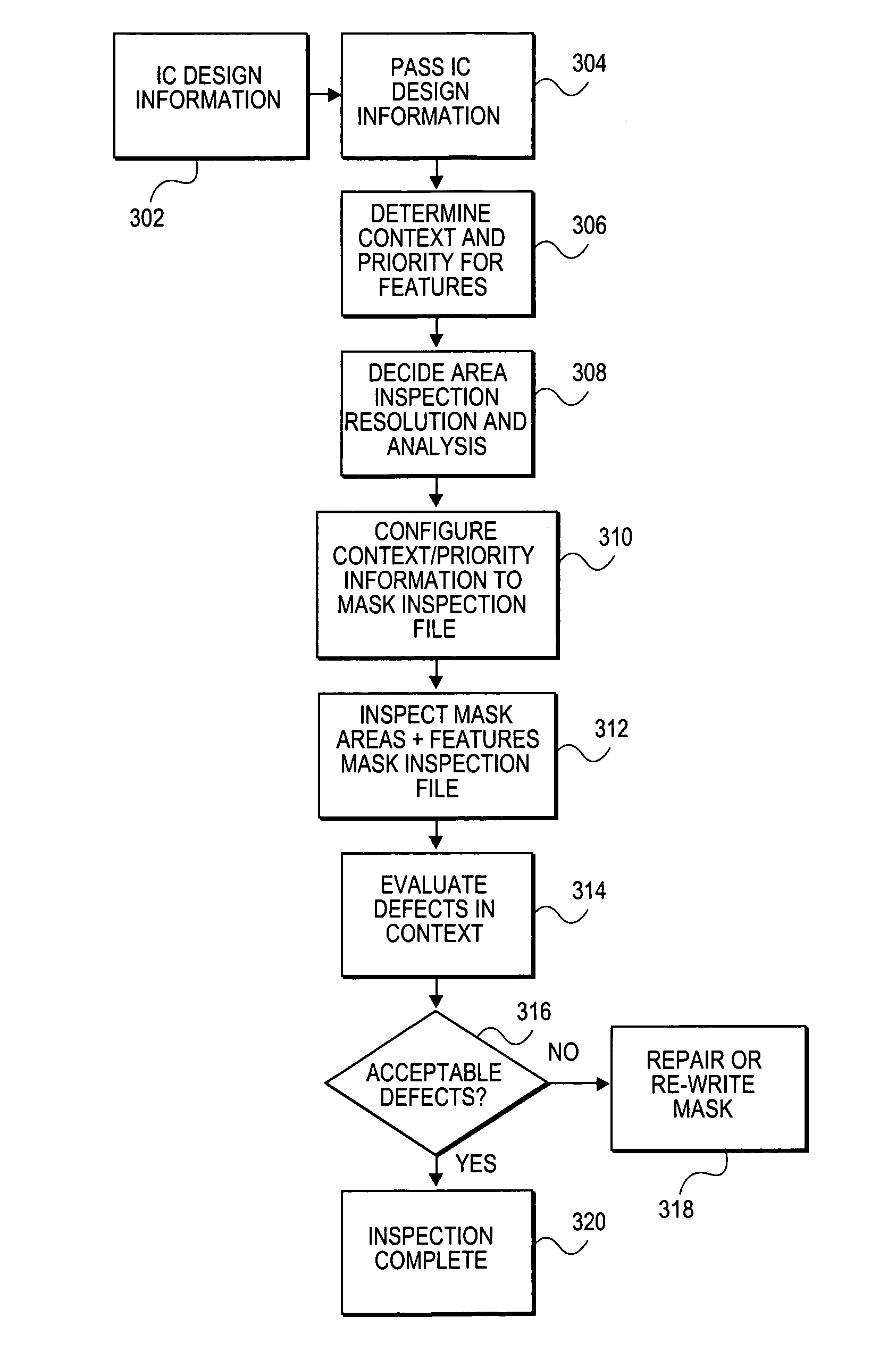
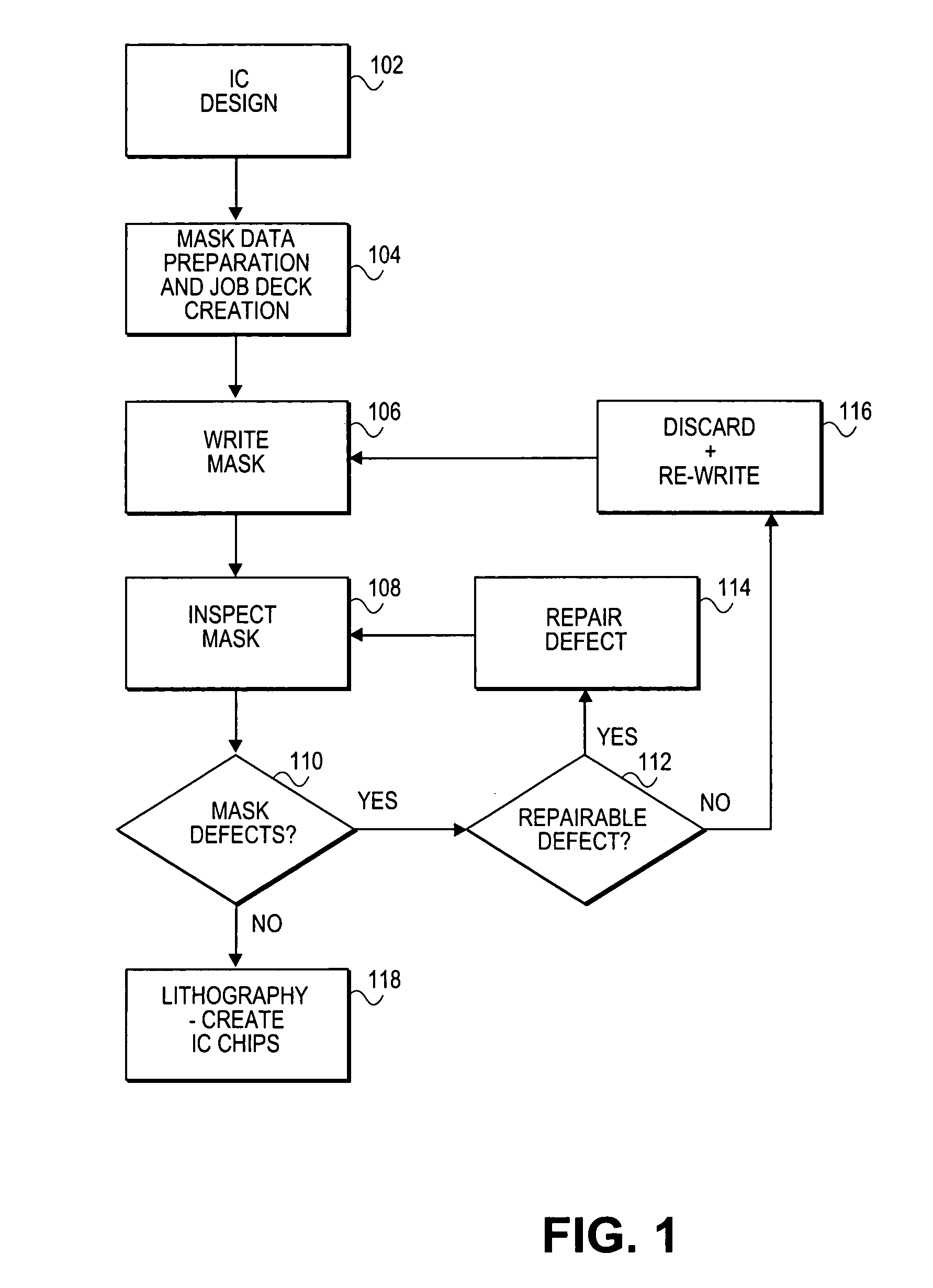
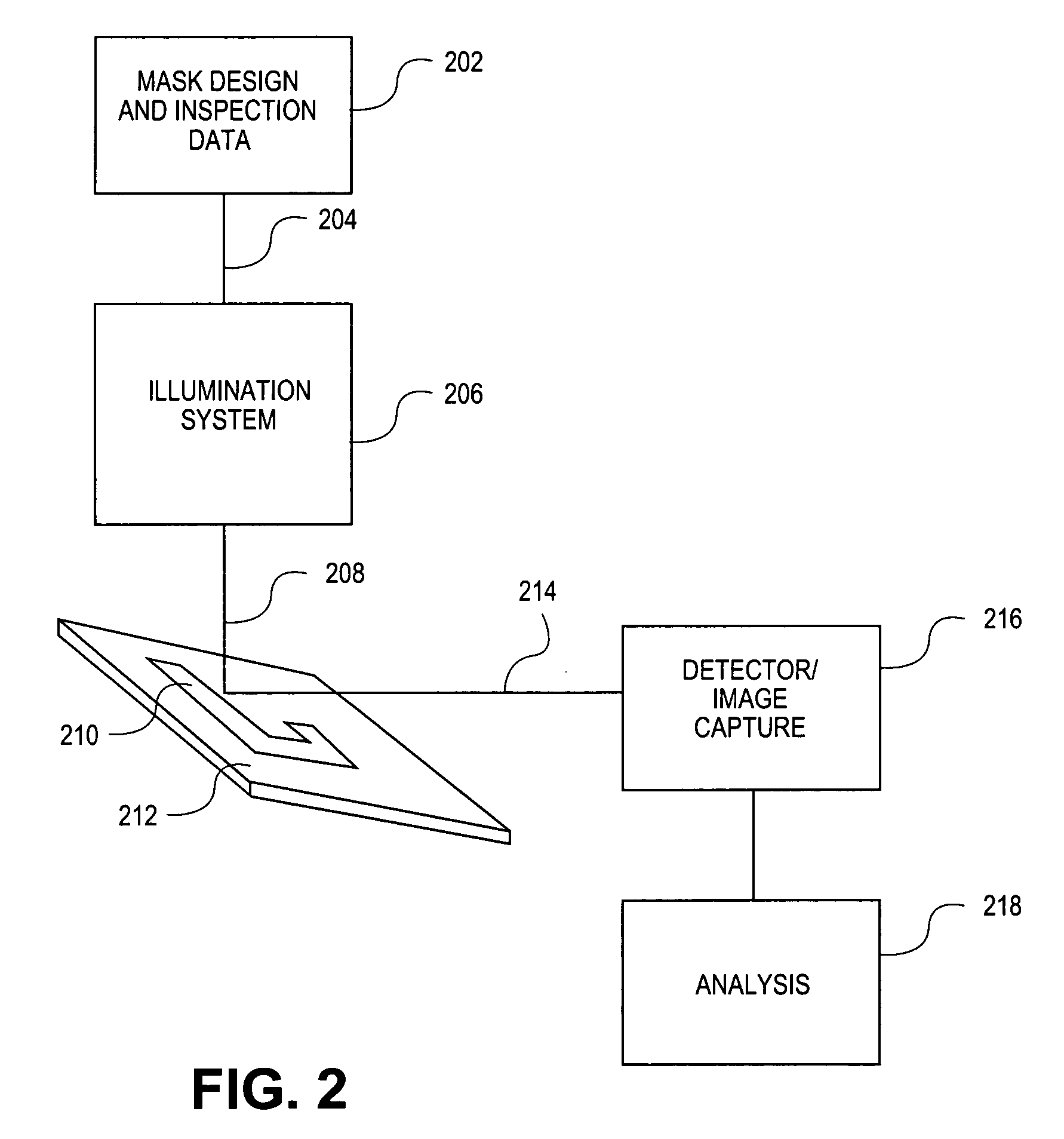
Method and system for context-specific mask inspection
InactiveUS7231628B2Electrical testingCharacter and pattern recognitionMask inspectionContext specific
A method for inspecting lithography masks includes generating integrated circuit design data and using context information from the integrated circuit design data to inspect a mask.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
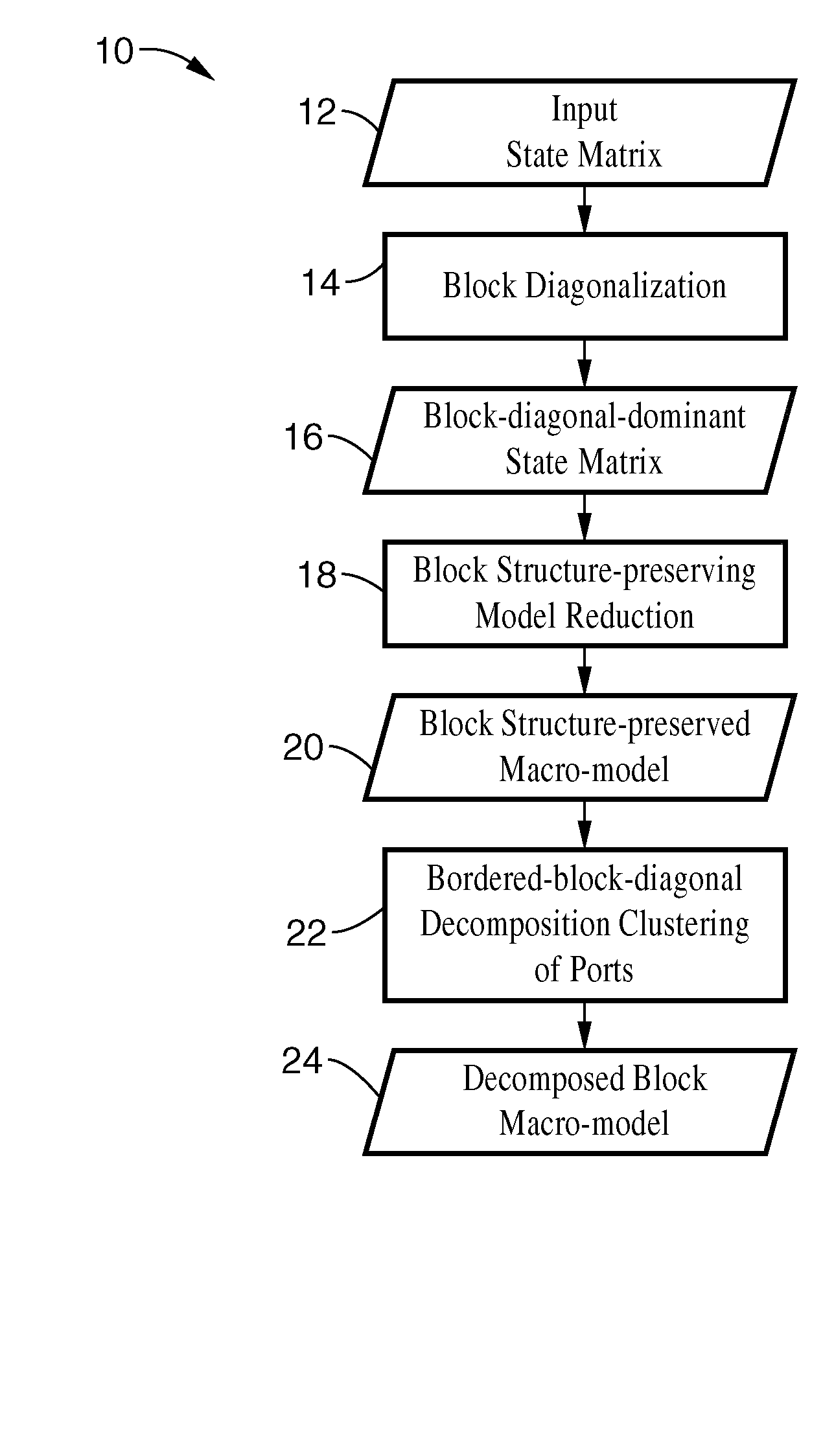
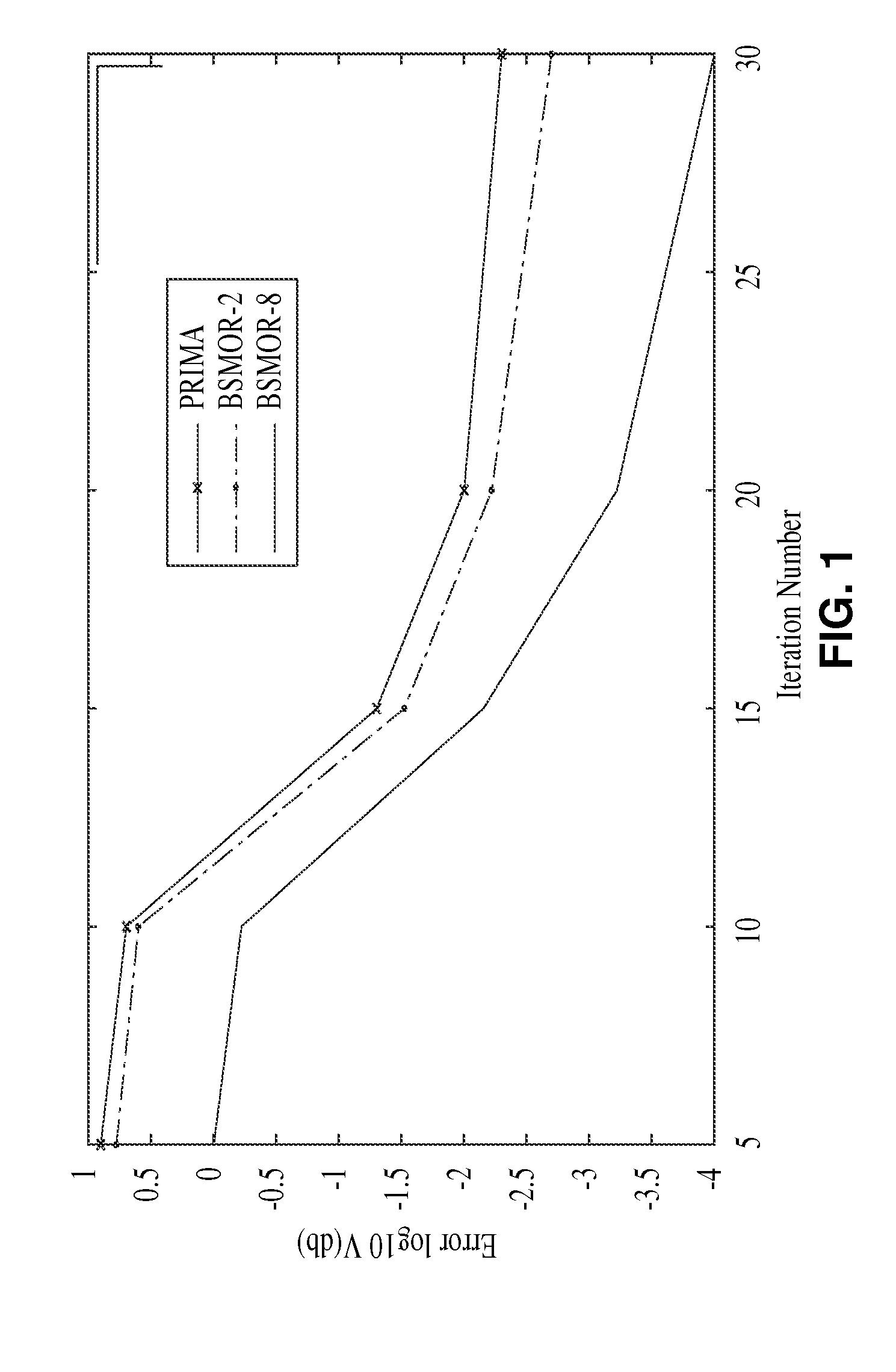
Structured and parameterized model order reduction
InactiveUS20080072182A1Reduce redundancyNon-uniformity is constantDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputation using non-denominational number representationStructured modelOrder reduction
Model-order reduction techniques are described for RLC circuits modeling the VLSI layouts. A structured model order reduction is developed to preserve the block-level sparsity, hierarchy and latency. In addition, a structured and parameterized model order reduction is developed to generate macromodels for design optimizations of VLSI layouts. The applications are thermal via allocation under the dynamic thermal integrity and via stapling to simultaneously optimize thermal and power integrity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for the evolutionary design of biochemical reaction networks
The present invention relates to methods for achieving an optimal function of a biochemical reaction network. The methods can be performed in silico using a reconstruction of a biochemical reaction network of a cell and iterative optimization procedures. The methods can further include laboratory culturing steps to confirm and possibly expand the determinations made using the in silico methods, and to produce a cultured cell, or population of cells, with optimal functions. The current invention includes computer systems and computer products including computer-readable program code for performing the in silico steps of the invention.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
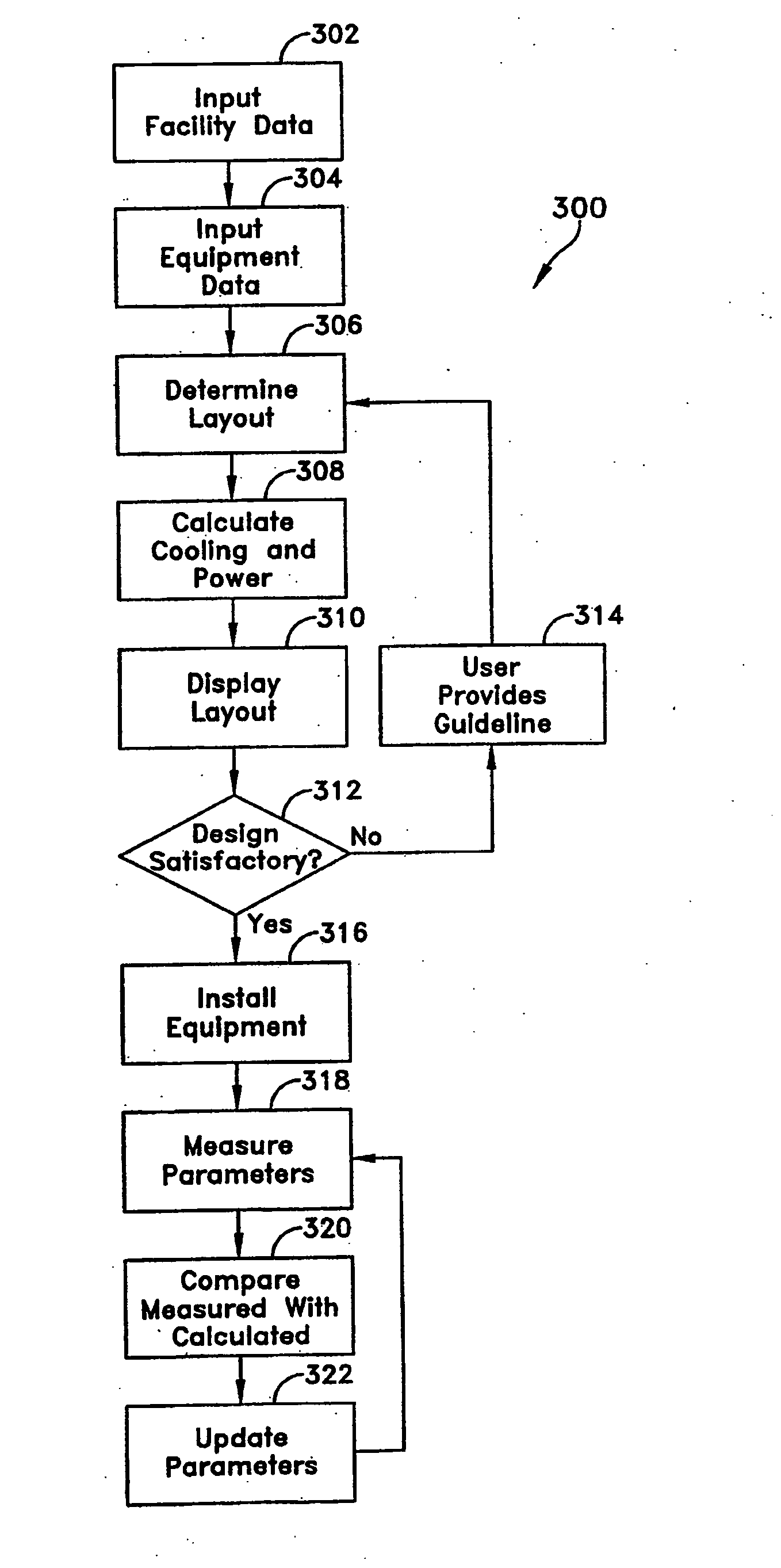
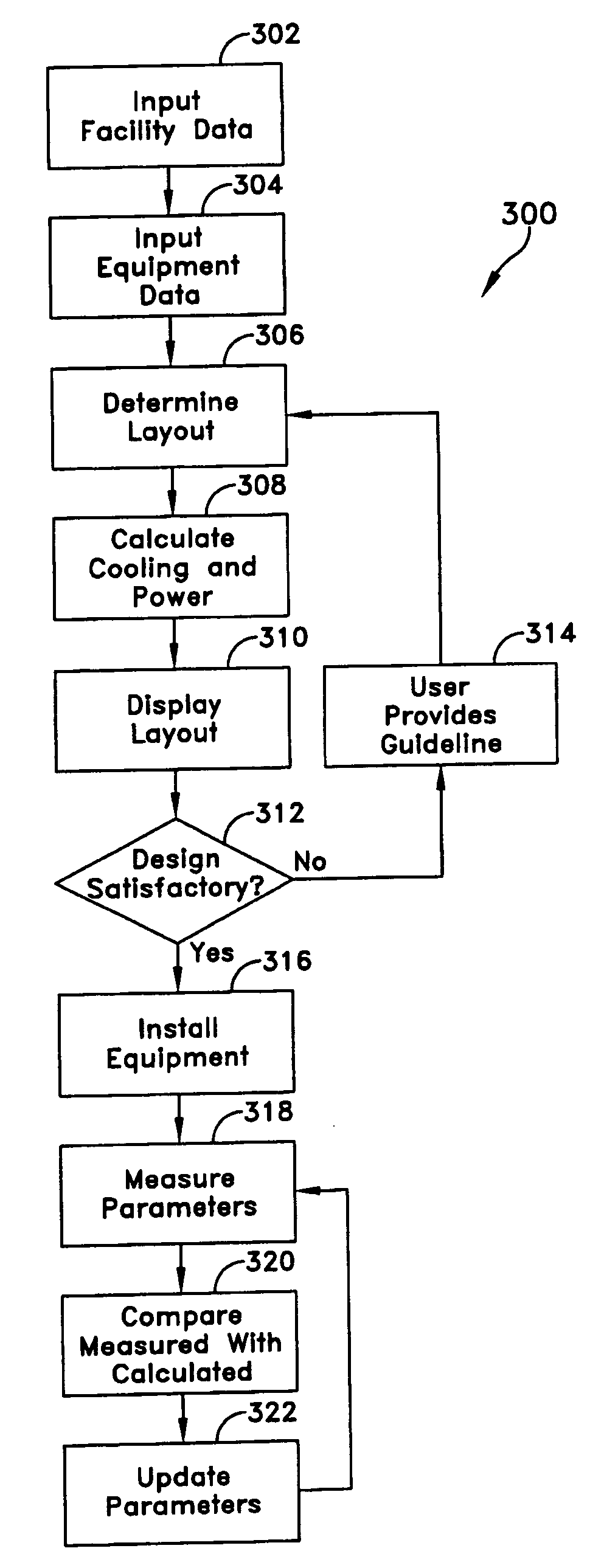
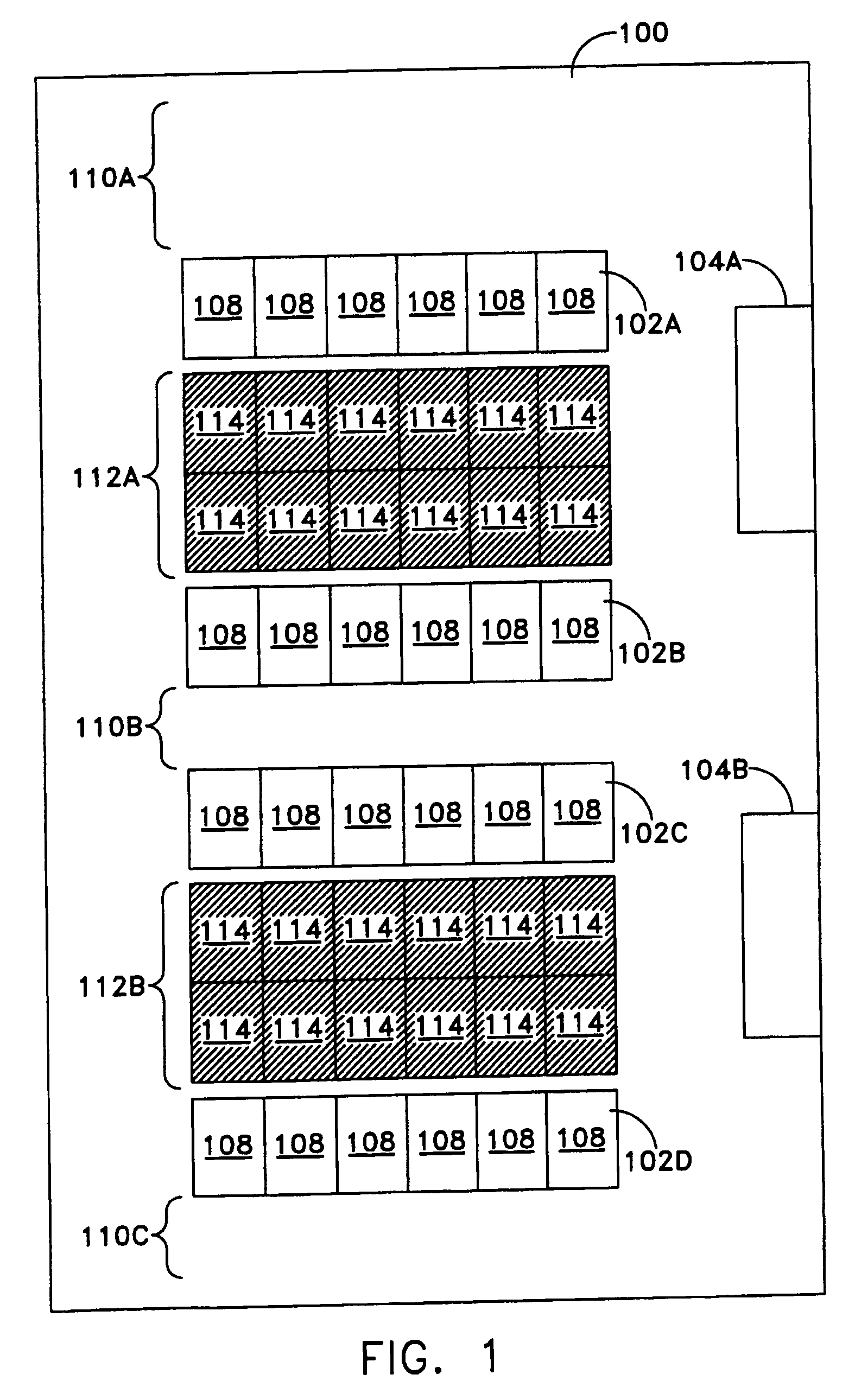
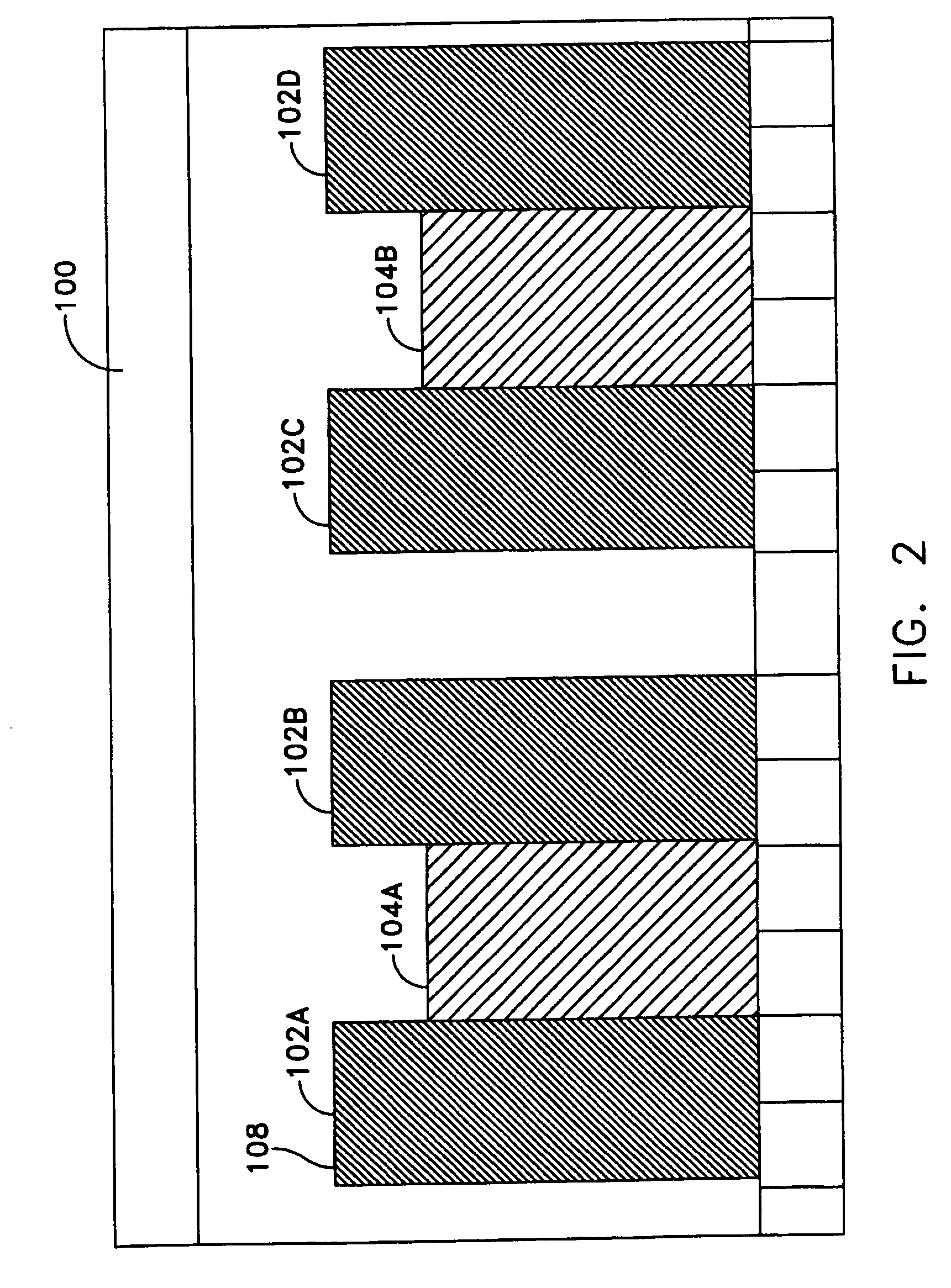
Methods and systems for managing facility power and cooling
Systems and methods are provided for determining data center cooling and power requirements and for monitoring performance of cooling and power systems in data centers. At least one aspect provides a system and method that enables a data center operator to determine available power and cooling at specific areas and enclosures in a data center to assist in locating new equipment in the data center.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IT CORP
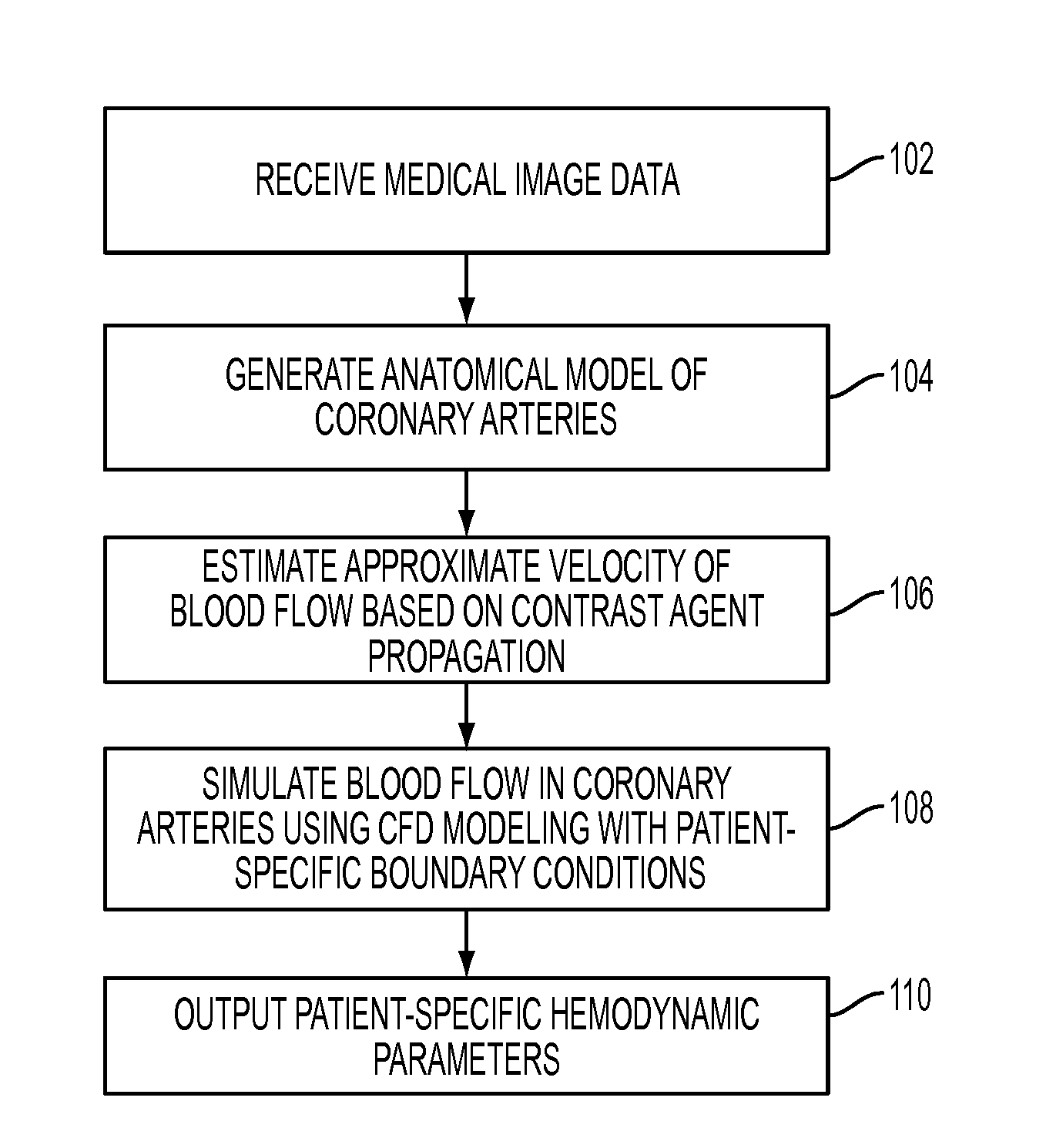
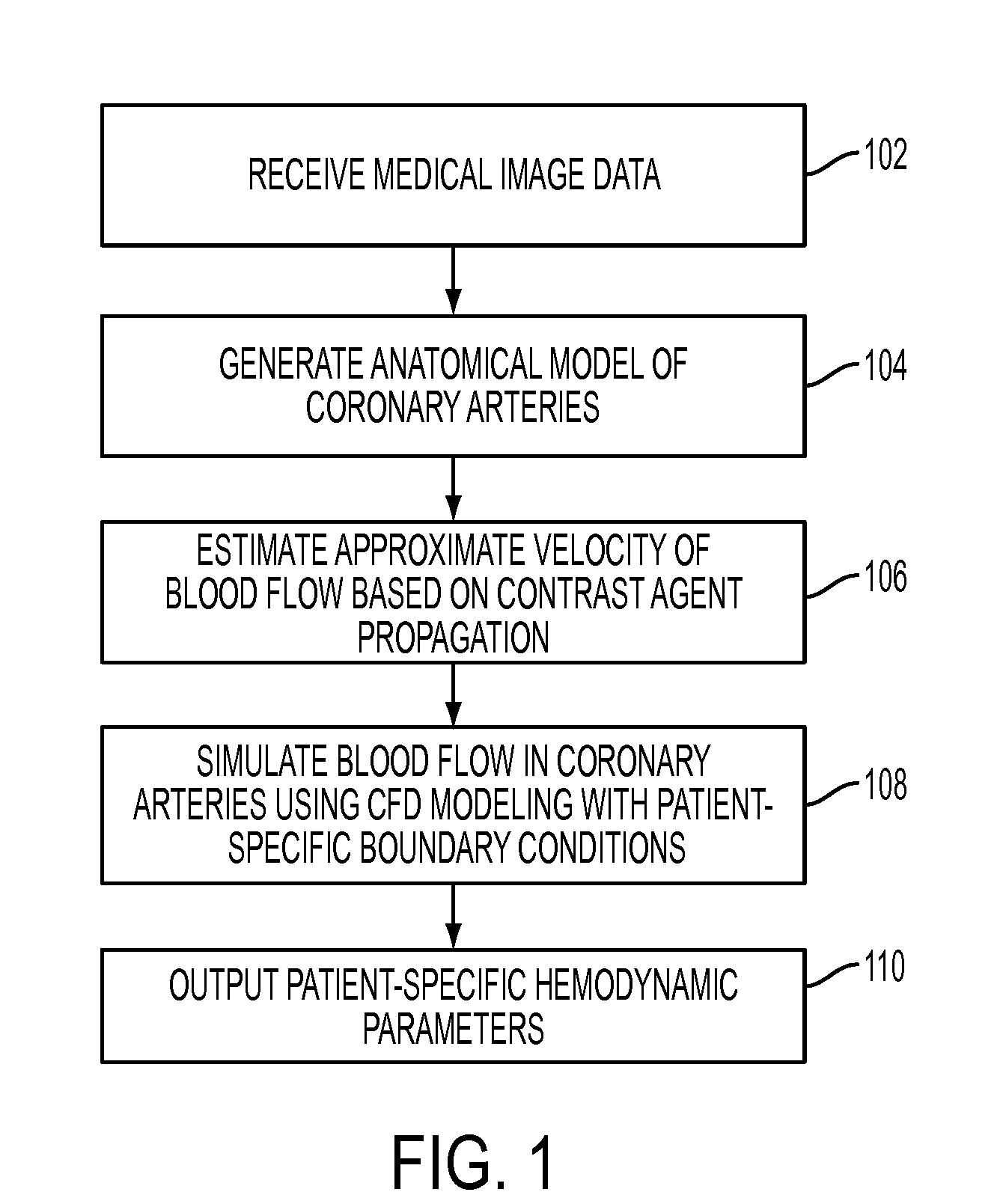
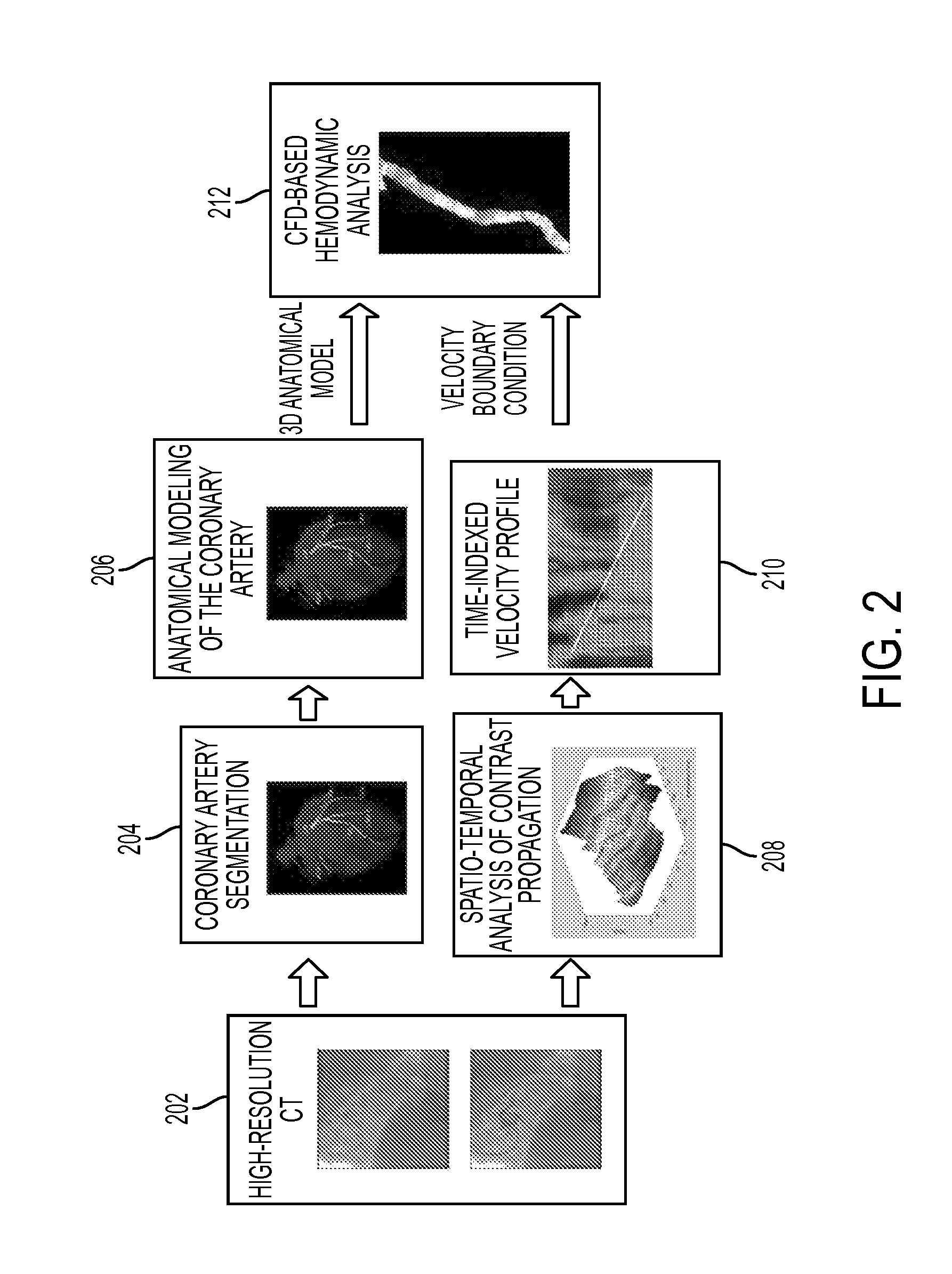
Method and System for Non-Invasive Assessment of Coronary Artery Disease
A method and system for non-invasive patient-specific assessment of coronary artery disease is disclosed. An anatomical model of a coronary artery is generated from medical image data. A velocity of blood in the coronary artery is estimated based on a spatio-temporal representation of contrast agent propagation in the medical image data. Blood flow is simulated in the anatomical model of the coronary artery using a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation using the estimated velocity of the blood in the coronary artery as a boundary condition.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Systems and methods for backing up data files
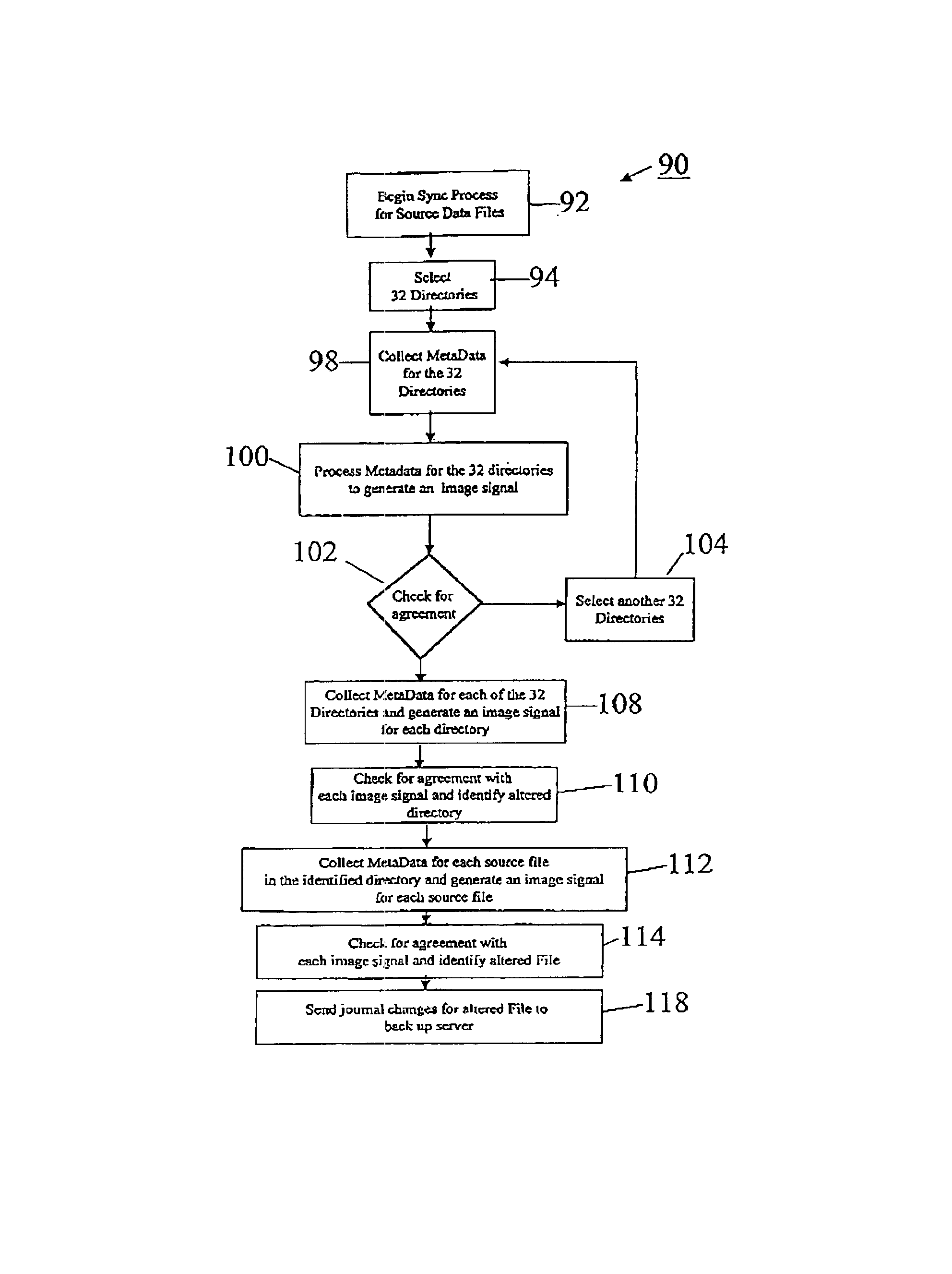
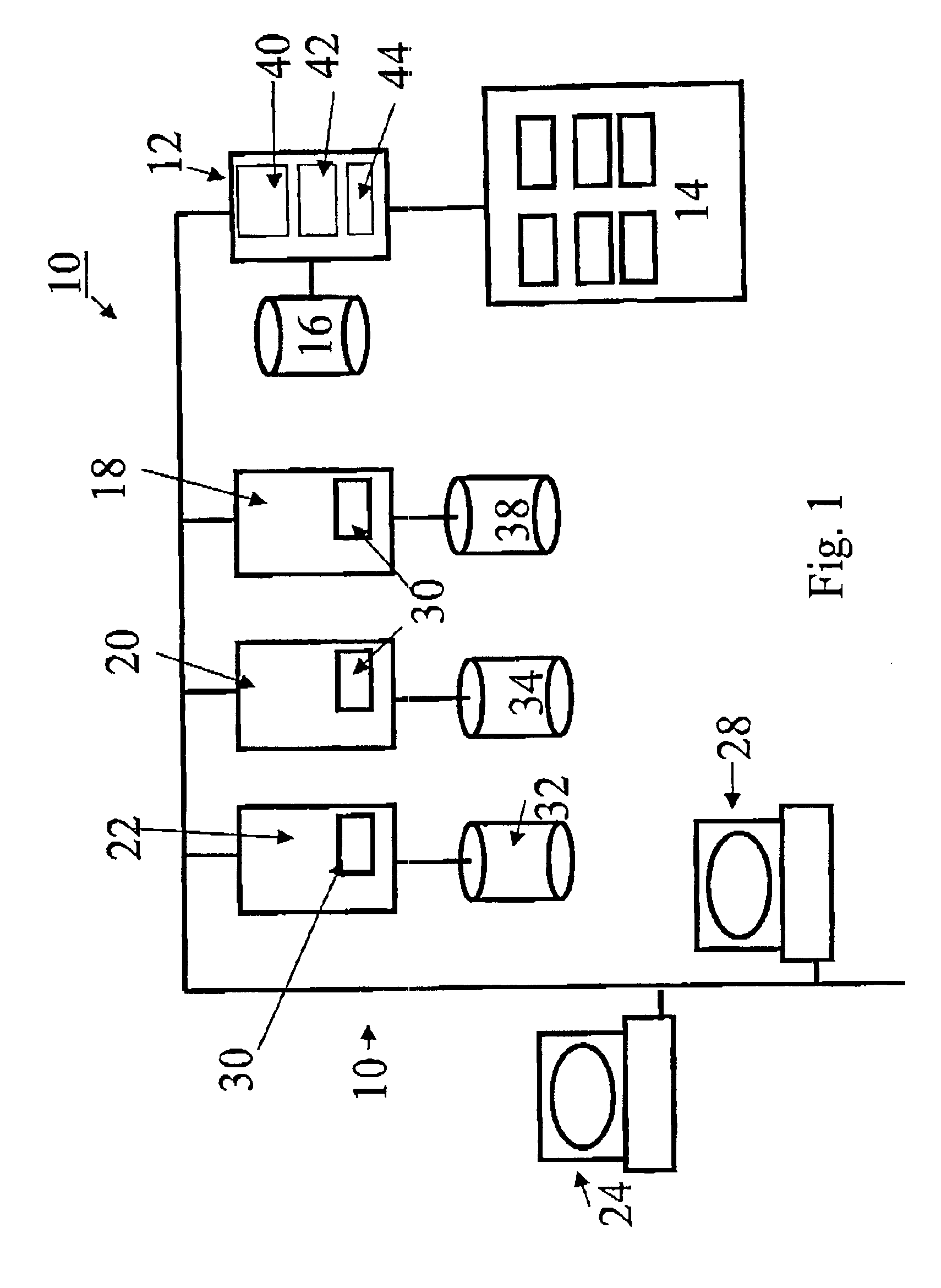
InactiveUS6847984B1Provide integrityReduce demandData processing applicationsError detection/correctionBaseline dataData file
The invention provides systems and methods for continuous back up of data stored on a computer network. To this end the systems of the invention include a synchronization process that replicates selected source data files data stored on the network and to create a corresponding set of replicated data files, called the target data files, that are stored on a back up server. This synchronization process builds a baseline data structure of target data files. In parallel to this synchronization process, the system includes a dynamic replication process that includes a plurality of agents, each of which monitors a portion of the source data files to detect and capture, at the byte-level, changes to the source data files. Each agent may record the changes to a respective journal file, and as the dynamic replication process detects that the journal files contain data, the journal files are transferred or copied to the back up server so that the captured changes can be written to the appropriate ones of the target data files.
Owner:KEEPITSAFE INC
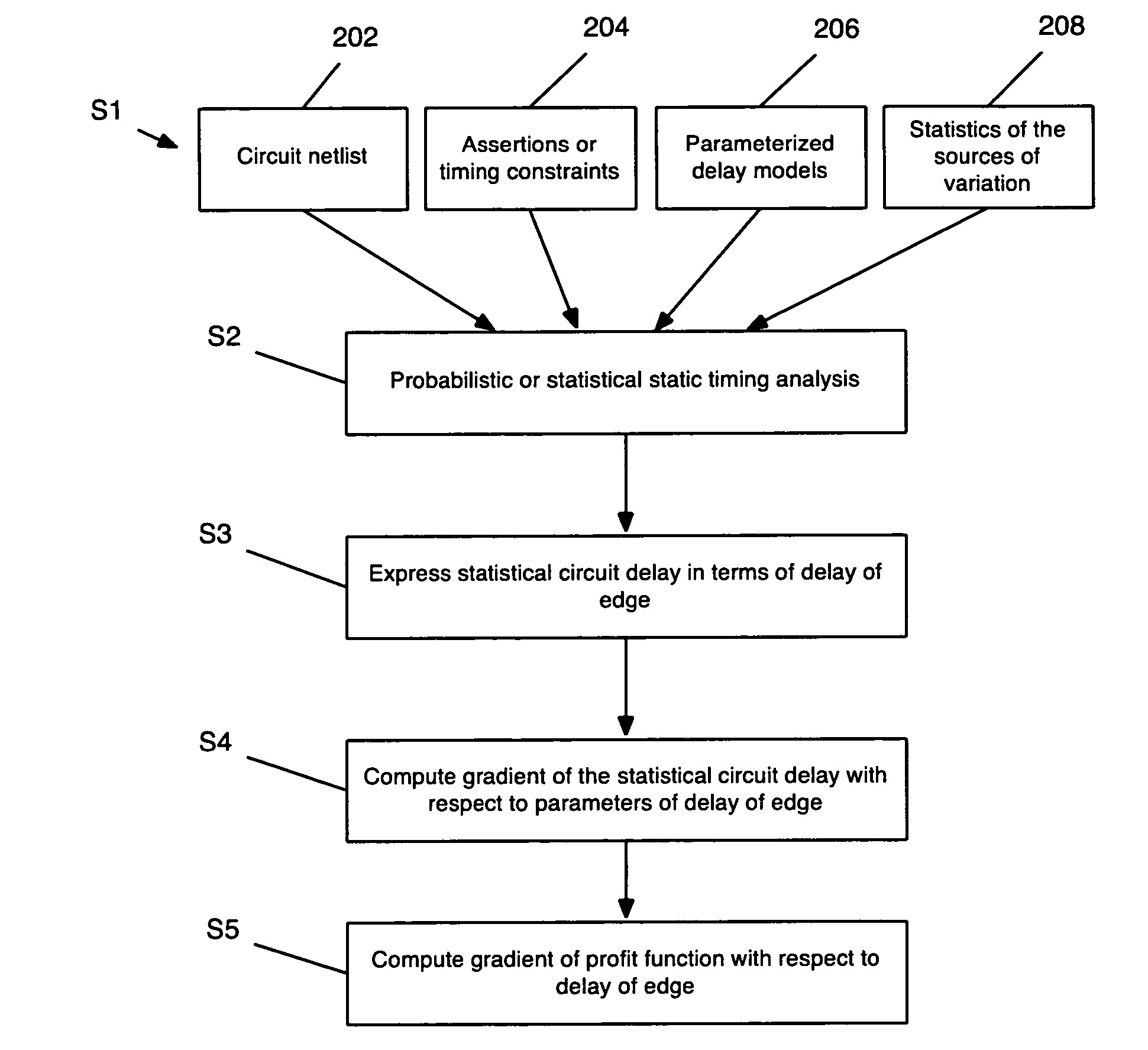
Method, system, and program product for computing a yield gradient from statistical timing
InactiveUS7480880B2Geometric CADComputation using non-denominational number representationCircuit delayComputer science
The invention provides a method, system, and program product for determining a gradient of a parametric yield of an integrated circuit with respect to parameters of a delay of an edge of a timing graph of the circuit. A first aspect of the invention provides a method for determining a gradient of a parametric yield of an integrated circuit with respect to parameters of a delay of an edge of a timing graph of the circuit, the method comprising: conducting a statistical timing analysis; expressing a statistical circuit delay in terms of a delay of the edge; and computing a gradient of the statistical circuit delay with respect to parameters of the delay of the edge.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Compact folded-optics illumination lens
The present embodiments provide for apparatuses, and methods for manufacturing apparatuses to convert a first distribution of an input radiation to a second distribution of output radiation. The apparatus can be defined in some embodiments by generating a two-dimensional representation of three active optical surfaces including calculating a segment of first, entry and second surfaces based on first second, and third generalized Cartesian ovals, respectively, and successively repeating the calculating of the segments of the first and second surfaces, and rotationally sweeping the two-dimensional representation about a central axis providing a three-dimensional representation. In some embodiments, portion of the first and / or second surfaces can be totally internally reflective.
Owner:LIGHT ENGINE
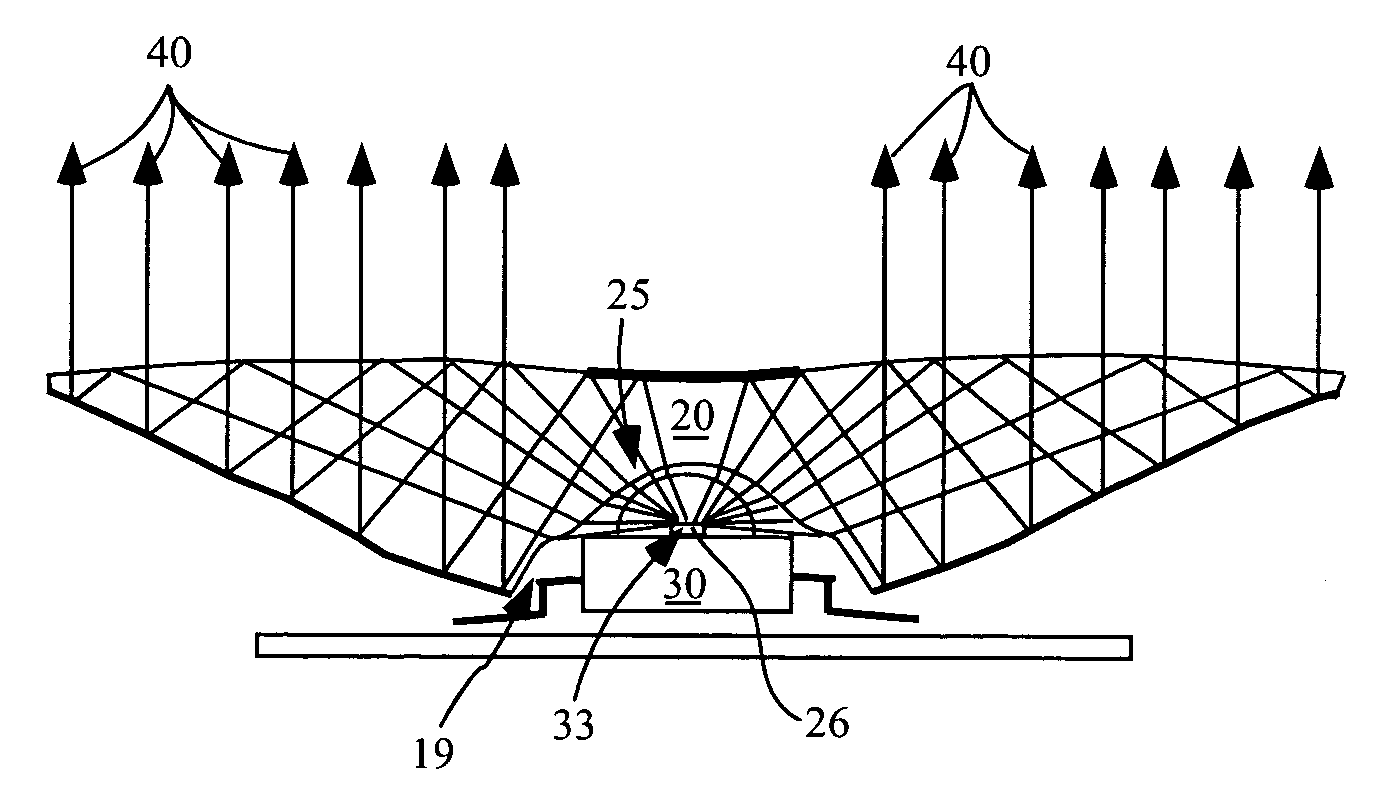
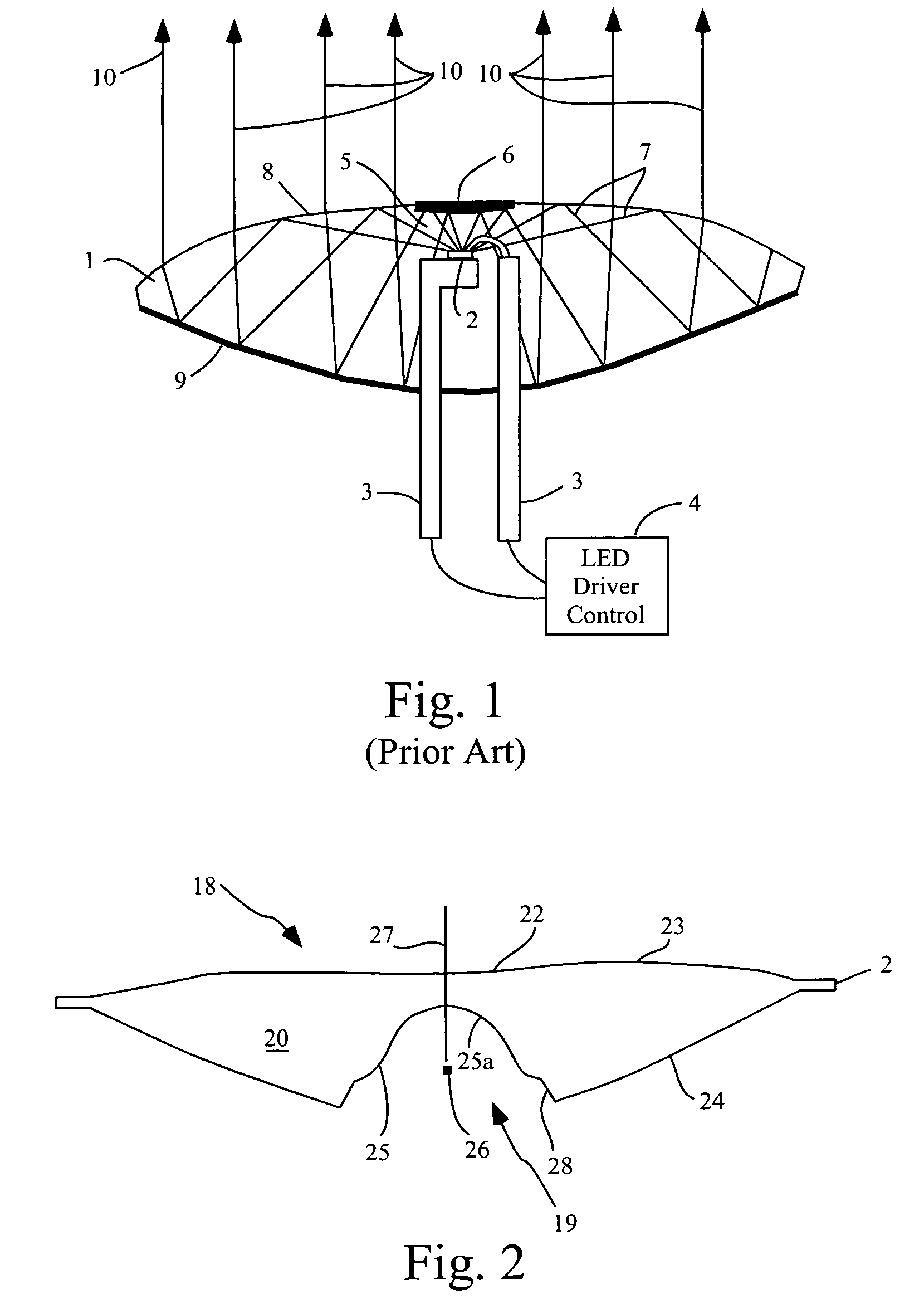
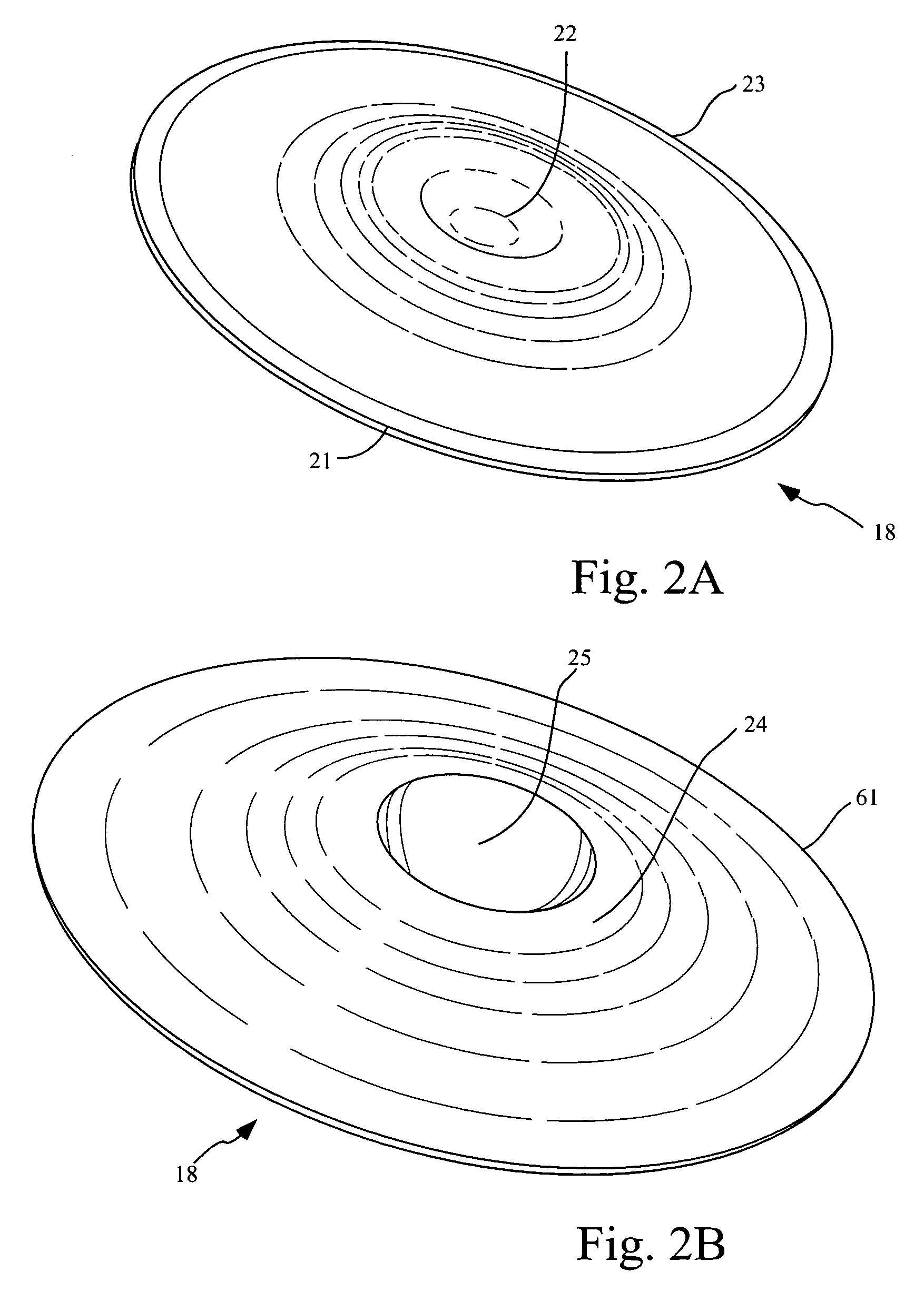
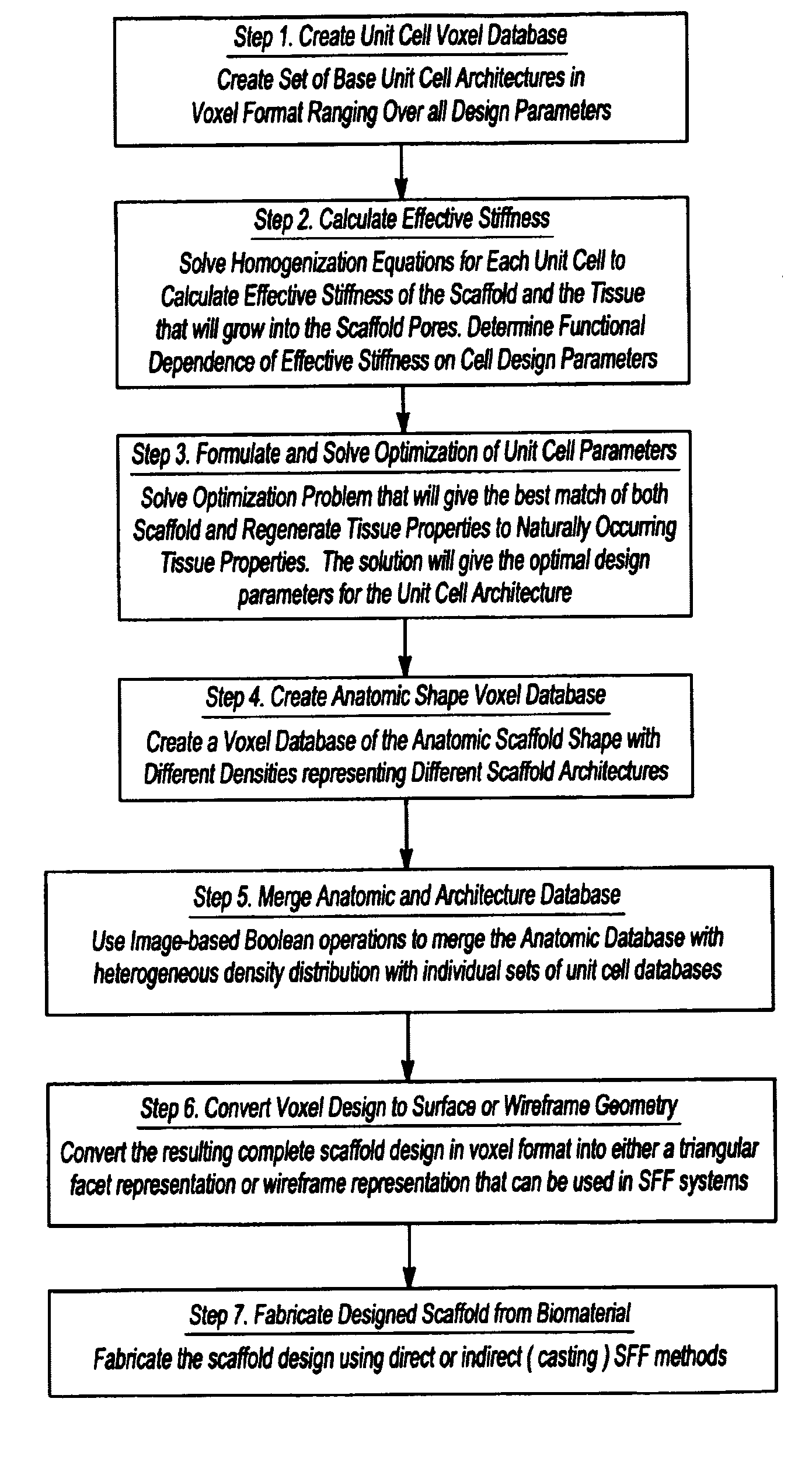
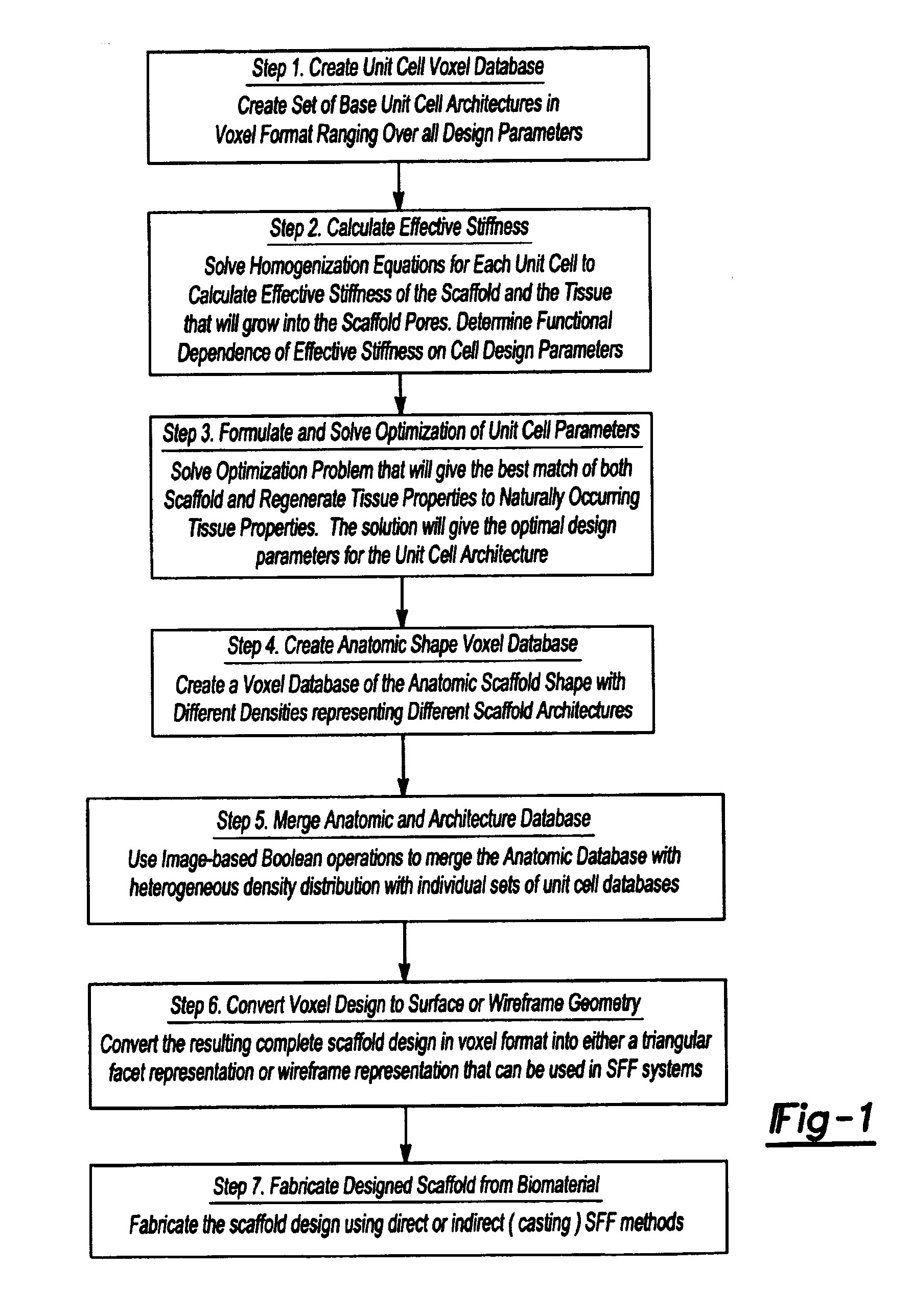
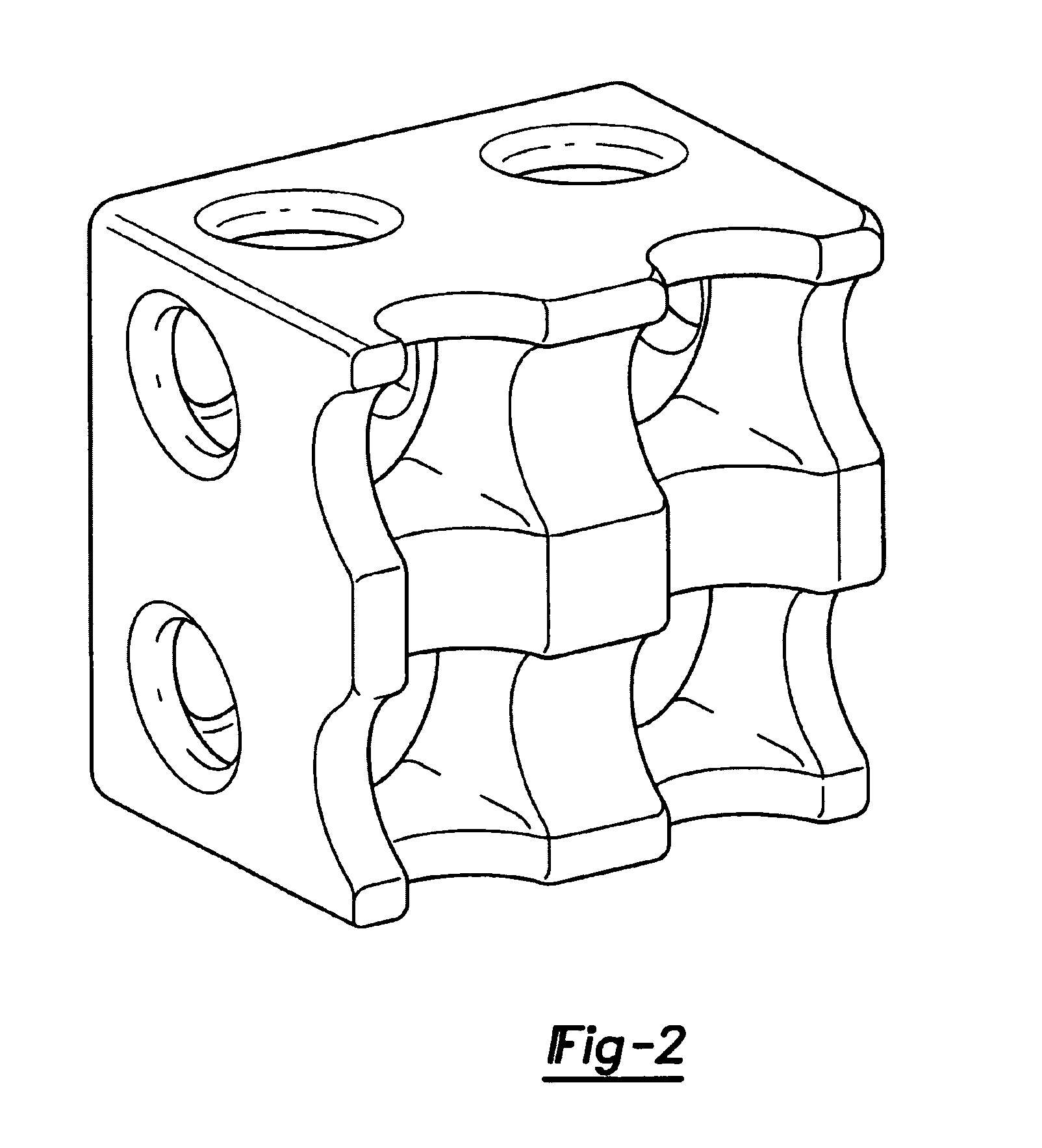
Design methodology for tissue engineering scaffolds and biomaterial implants
A design methodology is provided for creating biomaterial scaffolds optimized for in vivo function with any 3D anatomic shape. The method creates all designs using voxel based design techniques. It also provides for optimization of implant and scaffold microstructure to best match functional and biofactor delivery (including cells, genes and proteins) requirements. The voxel based design techniques readily allow combination of any scaffold or implant microstructure database with any complex 3D anatomic shape created by CT or MRI scanners. These designs can be readily converted to formats for layered manufacturing or casting.
Owner:HOLLISTER SCOTT J +2
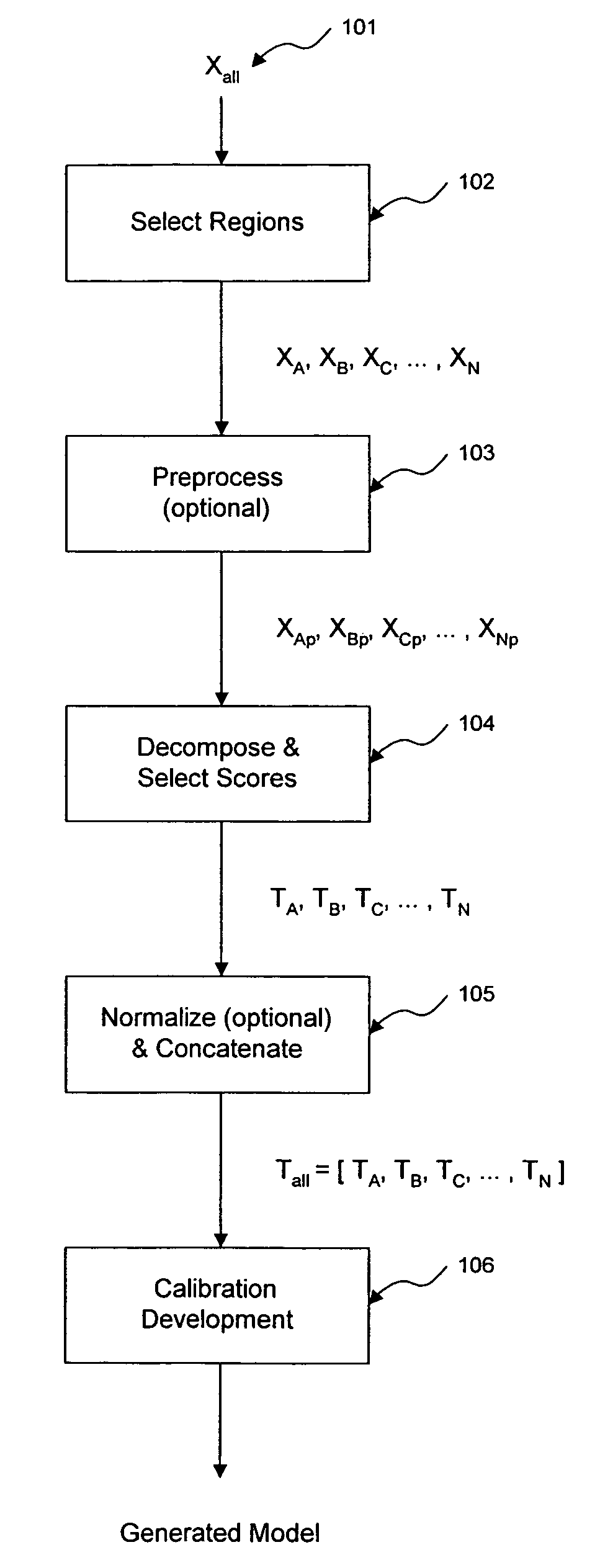
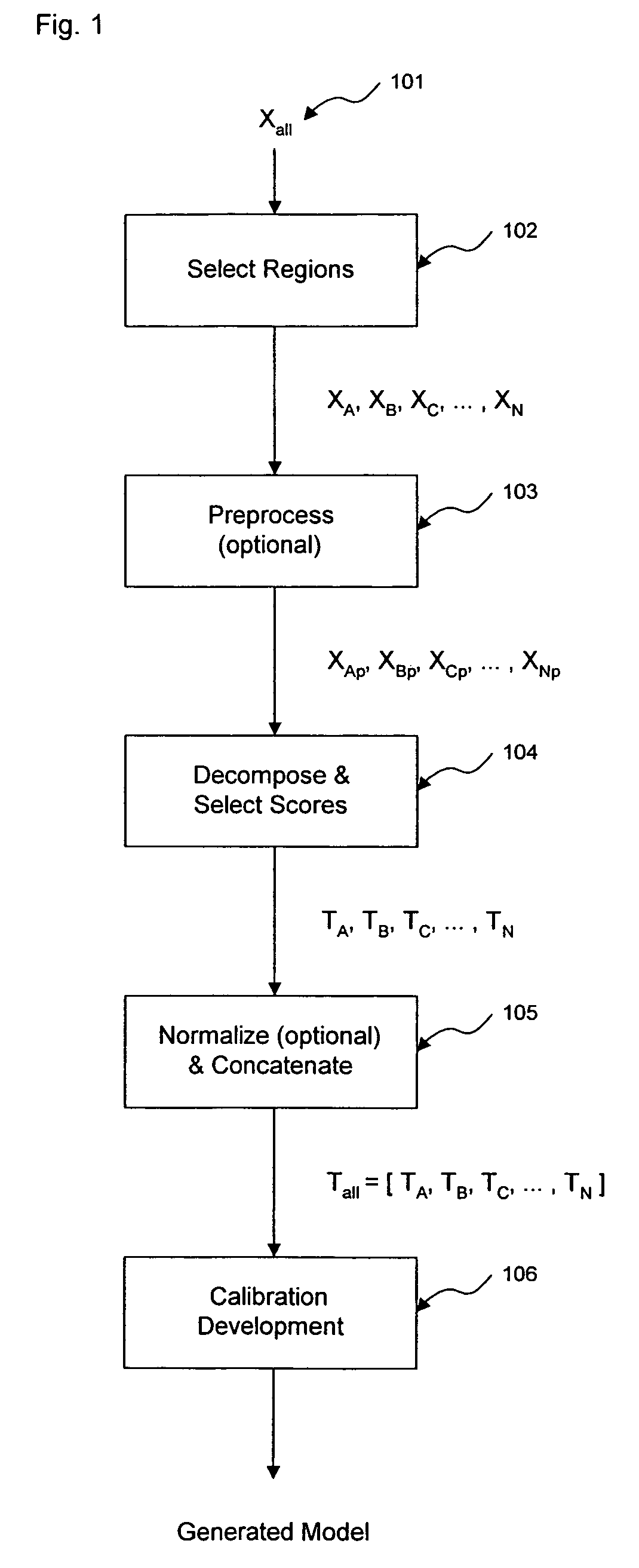
Method and apparatus for enhanced estimation of an analyte property through multiple region transformation
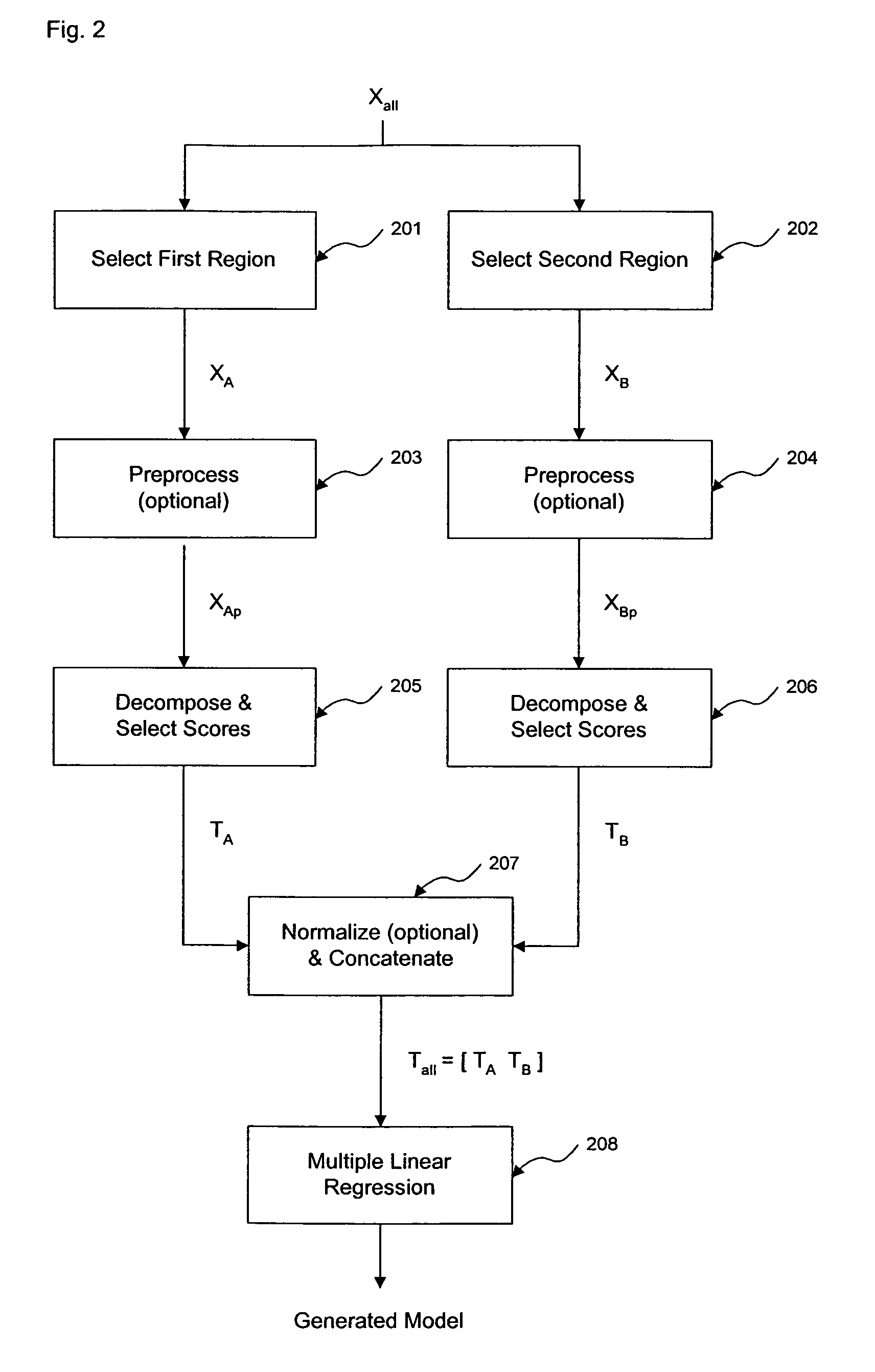
ActiveUS7620674B2Computation using non-denominational number representationDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalyteDecomposition
The invention comprises transformation of a section of a data block independently of the transformation of separate or overlapping data blocks to determine a property related to the original matrix, where each of the separate or overlapping data blocks are derived from an original data matrix. The transformation enhances parameters of a first data block over a given region of an axis of the data matrix, such as signal-to-noise, without affecting analysis of a second data block derived from the data matrix. This allows for enhancement of analysis of an analyte property, such as concentration, represented within the original data matrix. A separate decomposition and factor selection for each selected data matrix is performed with subsequent score matrix concatenization. The combined score matrix is used to generate a model that is subsequently used to estimate a property, such as concentration represented in the original data matrix.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
Methods and systems for managing facility power and cooling
Systems and methods are provided for determining data center cooling and power requirements and for monitoring performance of cooling and power systems in data centers. At least one aspect provides a system and method that enables a data center operator to determine available power and cooling at specific areas and enclosures in a data center to assist in locating new equipment in the data center.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IT CORP
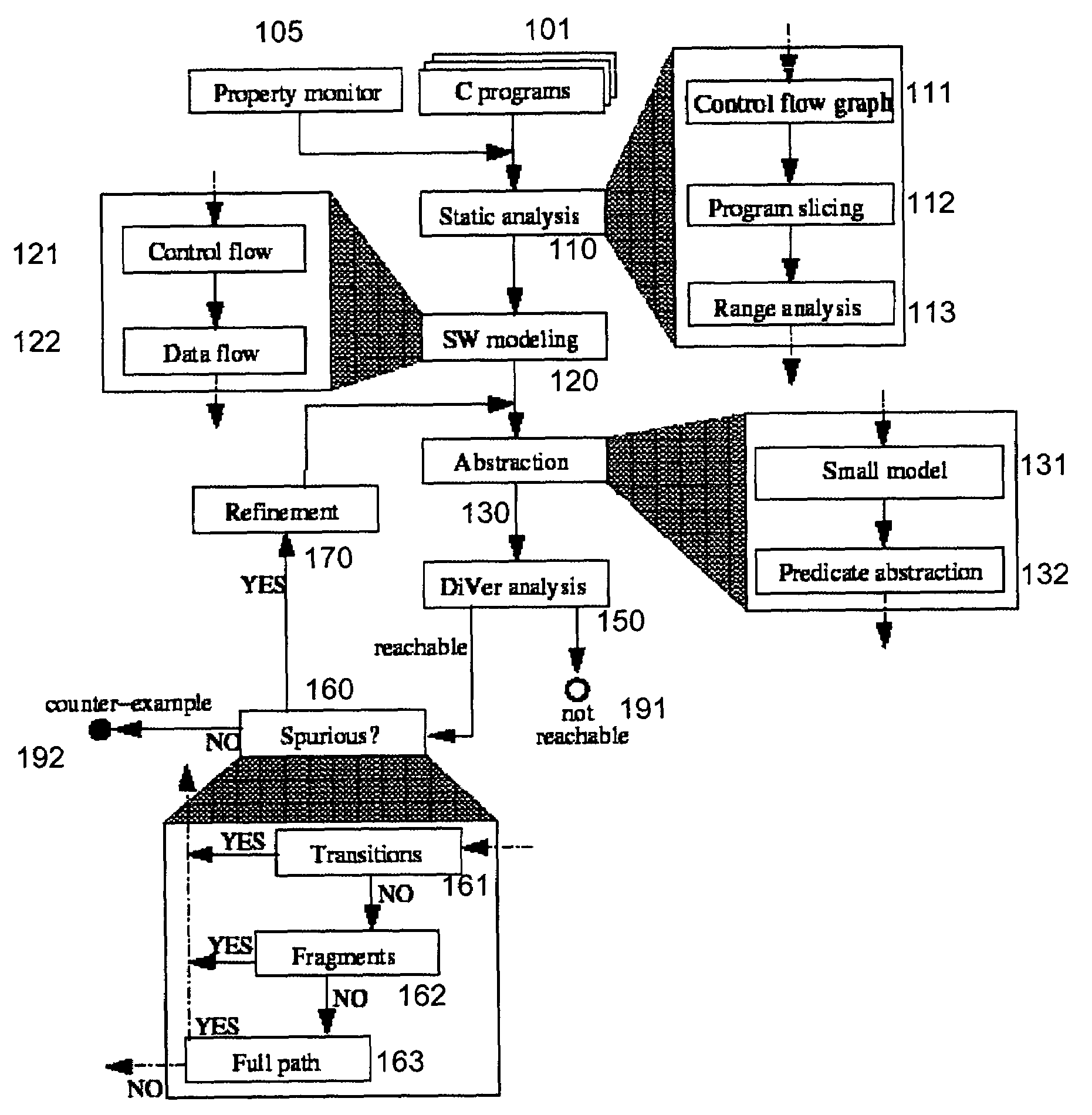
System and method for modeling, abstraction, and analysis of software
ActiveUS7346486B2Improve verification efficiencyImprove translationError detection/correctionComputation using non-denominational number representationBasic blockSoftware
A system and method is disclosed for formal verification of software programs that advantageously translates the software, which can have bounded recursion, into a Boolean representation comprised of basic blocks and which applies SAT-based model checking to the Boolean representation.
Owner:NEC CORP
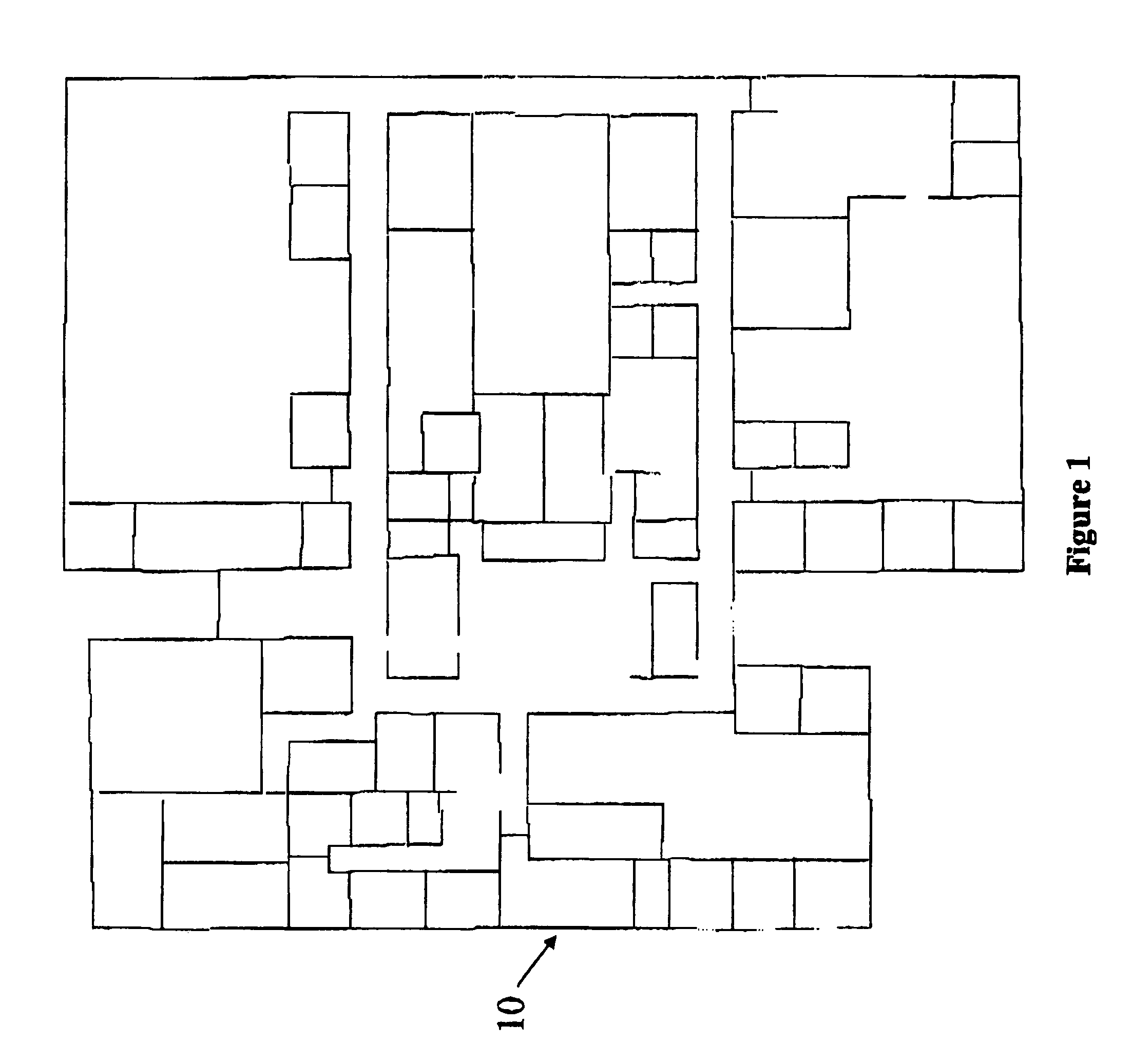
System and method for efficiently visualizing and comparing communication network system performance
InactiveUS7246045B1Easy to displayDrawing from basic elementsReceivers monitoringTerrainCommunications system
A method for visualizing and efficiently making comparisons of communication system performance utilizing predicted performance, measured performance, or other performance data sets is described. A system permits visualizing the comparisons of system performance data in three-dimensions using fluctuating elevation, shape, and / or color within a three-dimensional computer drawing database consisting of one or more multi-level buildings, terrain, flora, and additional static and dynamic obstacles (e.g., automobiles, people, filing cabinets, etc.). The method enables a design engineer to visually compare the performance of wireless communication systems as a three-dimensional region of fluctuating elevation, color, or other aesthetic characteristics with fully selectable display parameters, overlaid with the three-dimensional site-specific computer model for which the design was carried out.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Method for modelling customised earpieces
InactiveUS20040107080A1Easy to placeAdditive manufacturing apparatusHearing aid design aspectsSpeech identificationHeadphones
The present invention relates to a method for computer-controlled modelling of customised earpieces. These earpieces include housings for hearing aids, wireless or connected communication devices (headsets, mobile phones, personal agents), loud speakers, tinnitus masking devices, devices recording vibrations in the skull and transforming these into audio signals, voice recognition devices, earplugs, noise blockers with selective frequencies or sound levels, Man Machine Interface (MMI) products that enable clear communication even in the noisiest environments, or products related to wireless Internet applications. All these earpieces may be worn in the user's meatus and / or auditory canal. The invention also relates to a computerised system for manufacturing such customised earpieces. In particular, the invention is directed to a computerised system that models an earpiece based on a three-dimensional replica of the user's meatus and / or auditory canal.
Owner:3SHAPE AS
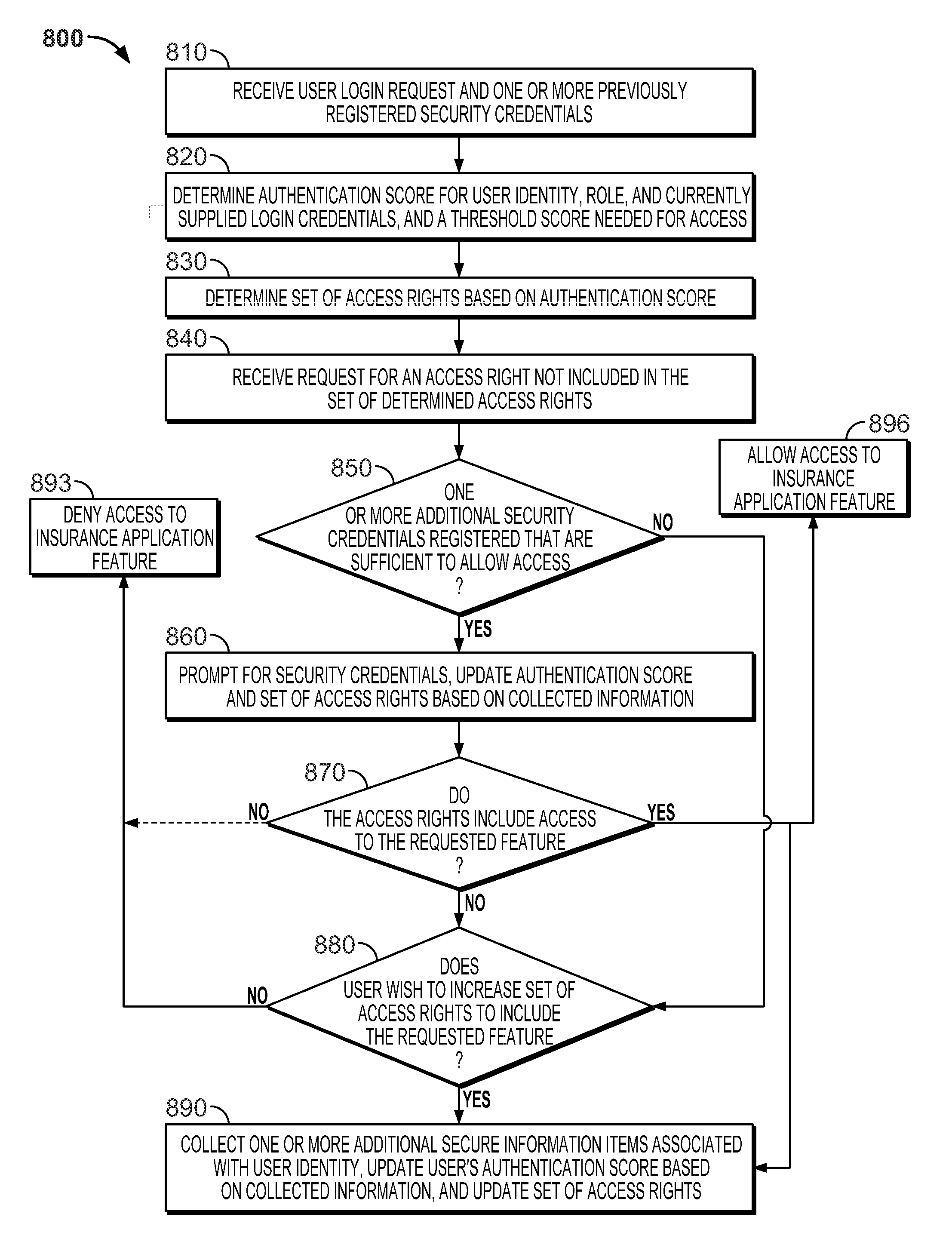
System and method for providing dynamic insurance portal transaction authentication and authorization
ActiveUS8918306B2Secure and accurate self-registrationSimpler and flexible interfaceFinanceDigital data protectionElectronic accessAuthorization
Systems and methods are disclosed herein for managing electronic access to a plurality of computerized insurance services. A network interface is configured to receive a user identity provided by a user remote to the system and an access request from the user to access a selected computerized insurance service from the plurality of computerized insurance services. A memory stores computer executable instructions which, when executed by a processor, cause the system to determine a set of access rights for the user based on the user identity and an insurance-related role associated with the user identity and allow the user to access the selected computerized insurance service according to the access request only if the access requested is included in the determined set of access rights. At least two of the computerized insurance services are implemented on substantially different information platforms.
Owner:HARTFORD FIRE INSURANCE
Method for tuning patient-specific cardiovascular simulations
ActiveUS20100017171A1Improve understandingImprove representationMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesReduced modelComputing Methodologies
Computational methods are used to create cardiovascular simulations having desired hemodynamic features. Cardiovascular modeling methods produce descriptions of blood flow and pressure in the heart and vascular networks. Numerical methods optimize and solve nonlinear equations to find parameter values that result in desired hemodynamic characteristics including related flow and pressure at various locations in the cardiovascular system, movements of soft tissues, and changes for different physiological states. The modeling methods employ simplified models to approximate the behavior of more complex models with the goal of to reducing computational expense. The user describes the desired features of the final cardiovascular simulation and provides minimal input, and the system automates the search for the final patient-specific cardiovascular model.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Interactive, internet supported health and fitness management system
A wellness system monitors the controlled progress of patients under surveillance and includes a server base station which is generally off-site, a web-site interface and a local station at the point-of-use, which is generally a health or fitness center. A unique data base is created for each user and goals and objectives may be set with progress monitored. Typically, the user will respond to a survey or questionnaire to populate his specific database. This is combined with a professional assessment and an automated measurement of vital statistics such as weight, blood pressure and body composition as measured at the local station. Other data may be entered manually such as height, age and the like. In a more comprehensive system the invention is designed to monitor other data such as cholesterol and blood glucose, as well. The locally input data may be updated at will by the user or on behalf of the user by professional personnel.
Owner:VIRGIN PULSE INC
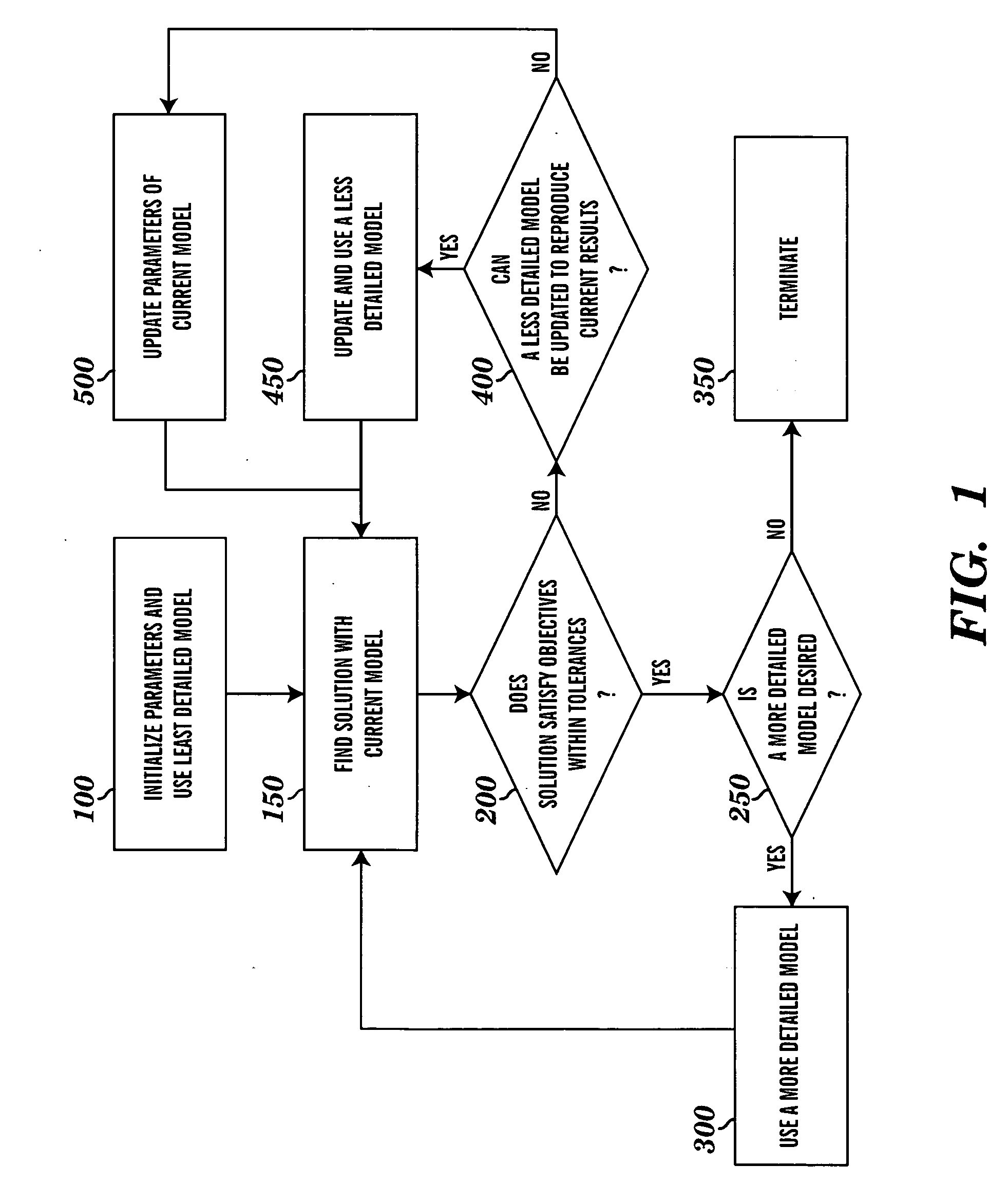
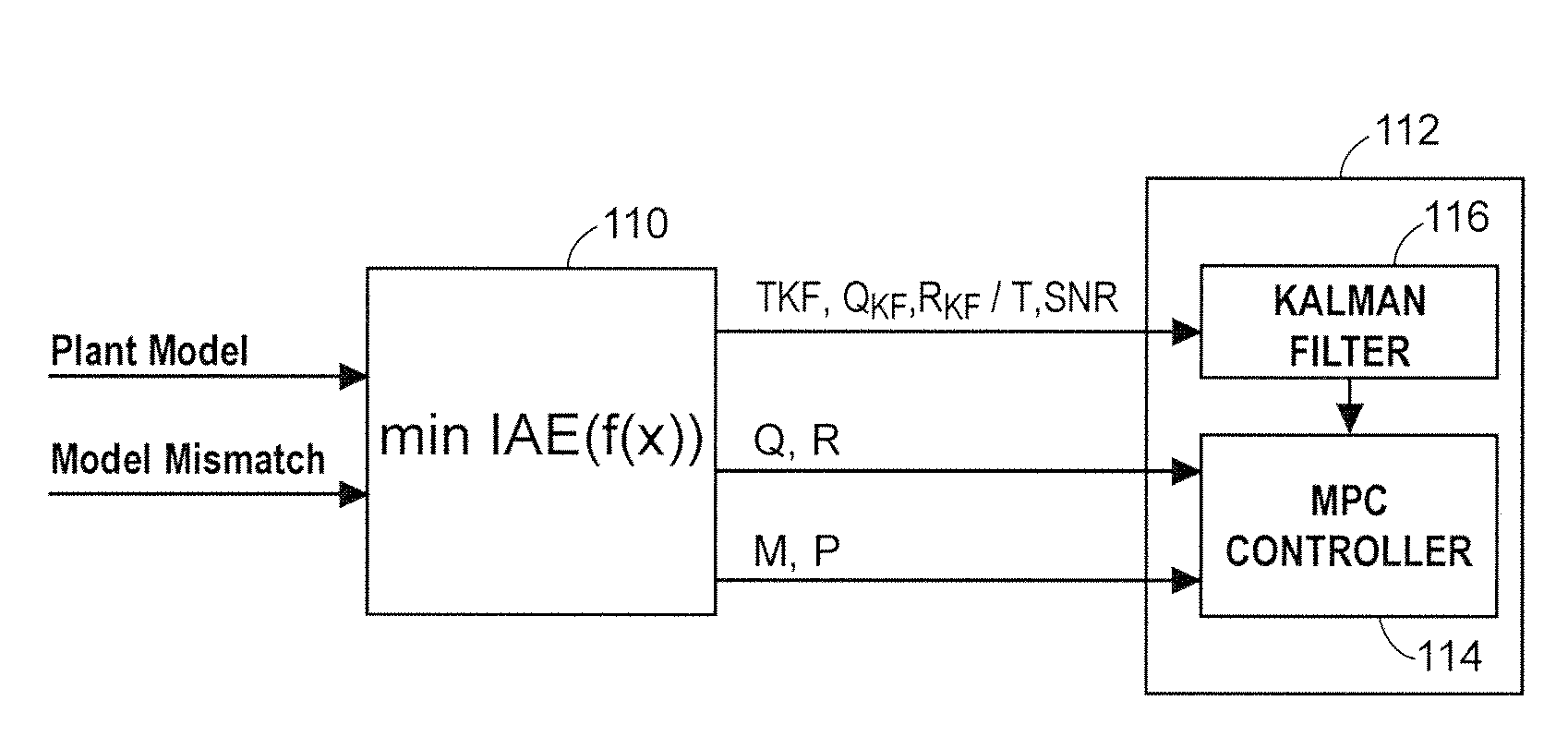
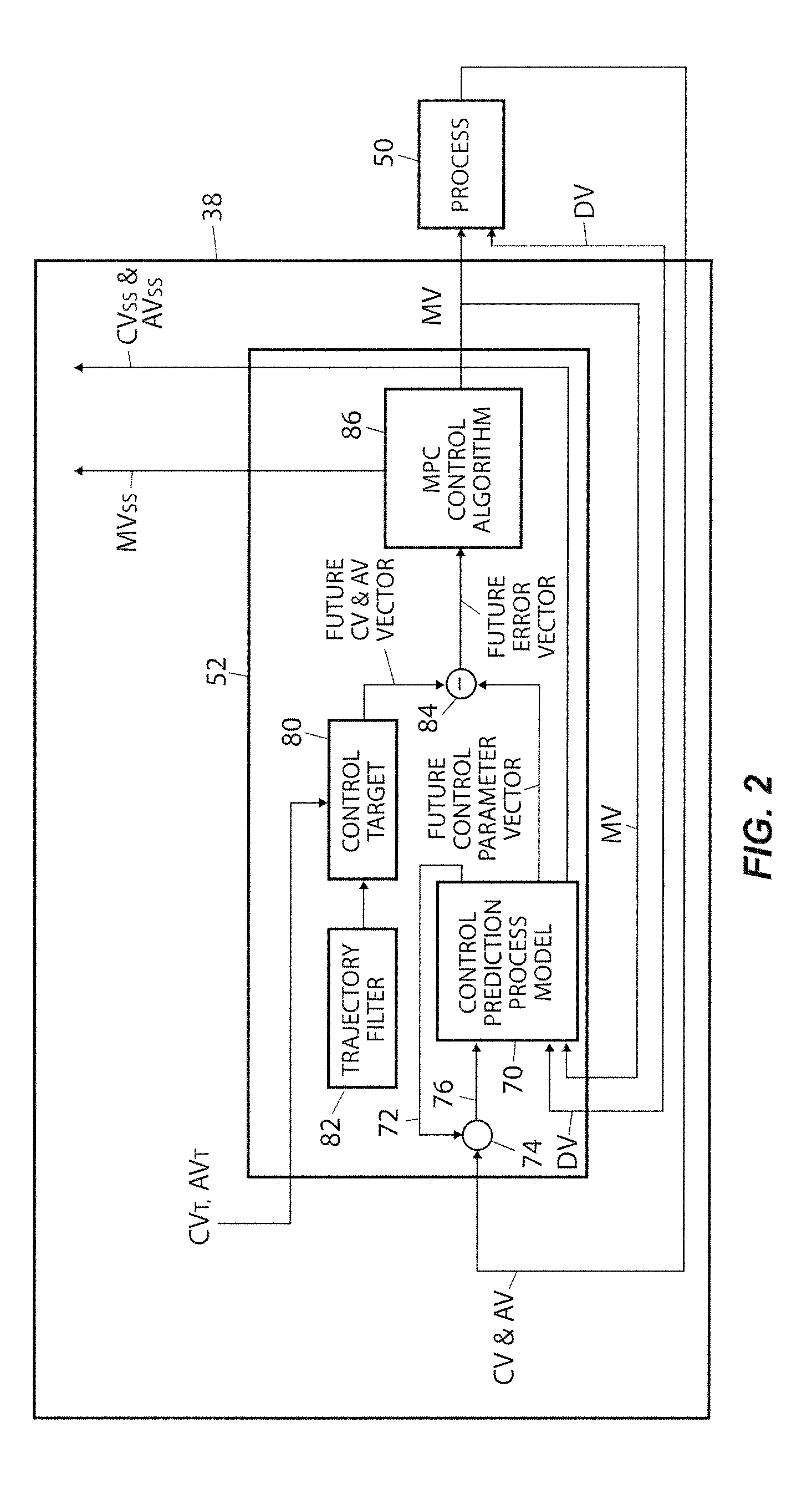
Robust adaptive model predictive controller with tuning to compensate for model mismatch
ActiveUS20090198350A1Improve immunityImprove performanceComputer controlSimulator controlClosed loopPredictive controller
An MPC adaptation and tuning technique integrates feedback control performance better than methods commonly used today in MPC type controllers, resulting in an MPC adaptation / tuning technique that performs better than traditional MPC techniques in the presence of process model mismatch. The MPC controller performance is enhanced by adding a controller adaptation / tuning unit to an MPC controller, which adaptation / tuning unit implements an optimization routine to determine the best or most optimal set of controller design and / or tuning parameters to use within the MPC controller during on-line process control in the presence of a specific amount of model mismatch or a range of model mismatch. The adaptation / tuning unit determines one or more MPC controller tuning and design parameters, including for example, an MPC form, penalty factors for either or both of an MPC controller and an observer and a controller model for use in the MPC controller, based on a previously determined process model and either a known or an expected process model mismatch or process model mismatch range. A closed loop adaptation cycle may be implemented by performing an autocorrelation analysis on the prediction error or the control error to determine when significant process model mismatch exists or to determine an increase or a decrease in process model mismatch over time.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
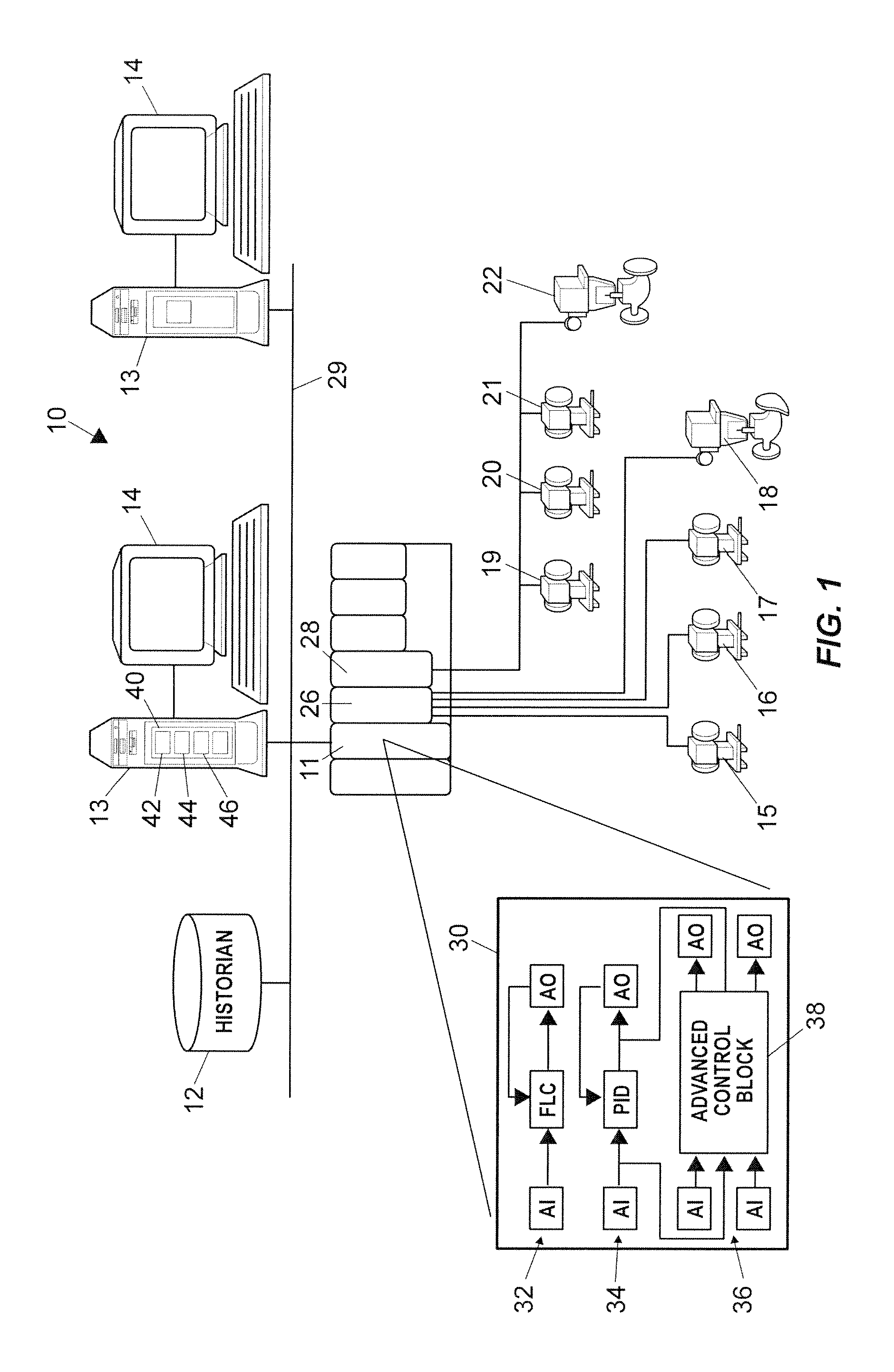
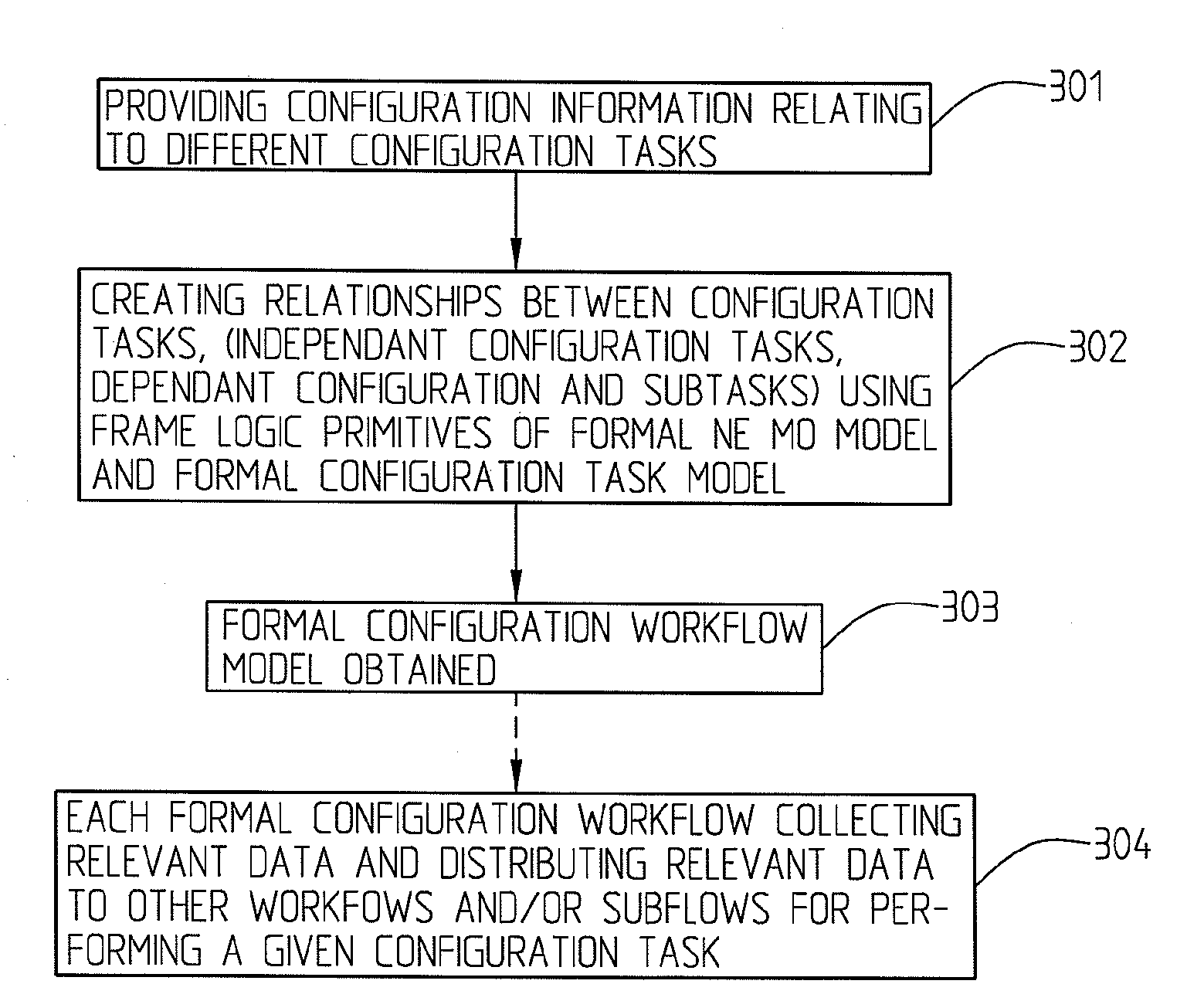
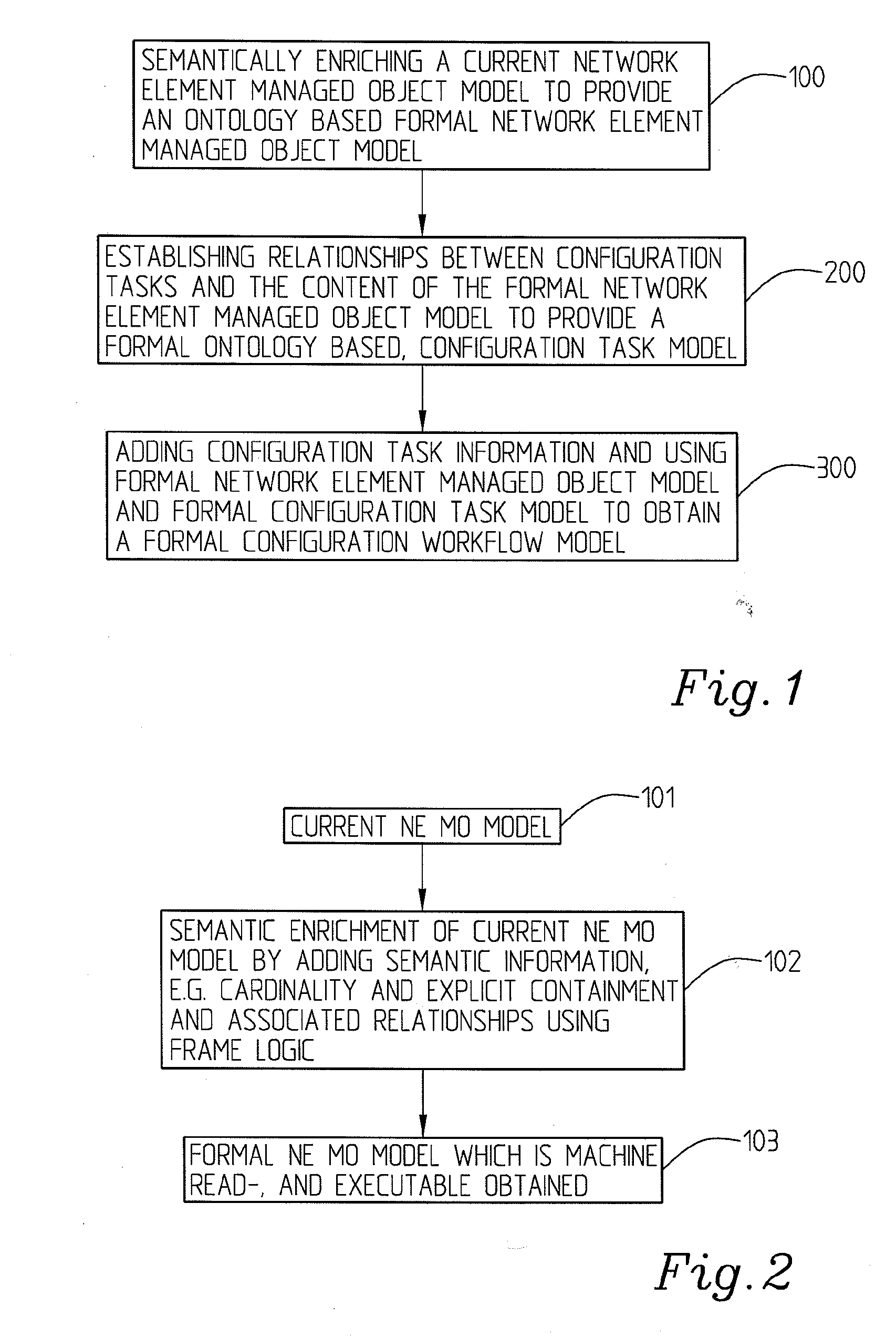
Method and a System Relating to Network Management
InactiveUS20080294418A1OptimizationReduce the amount requiredData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork managementManaged object
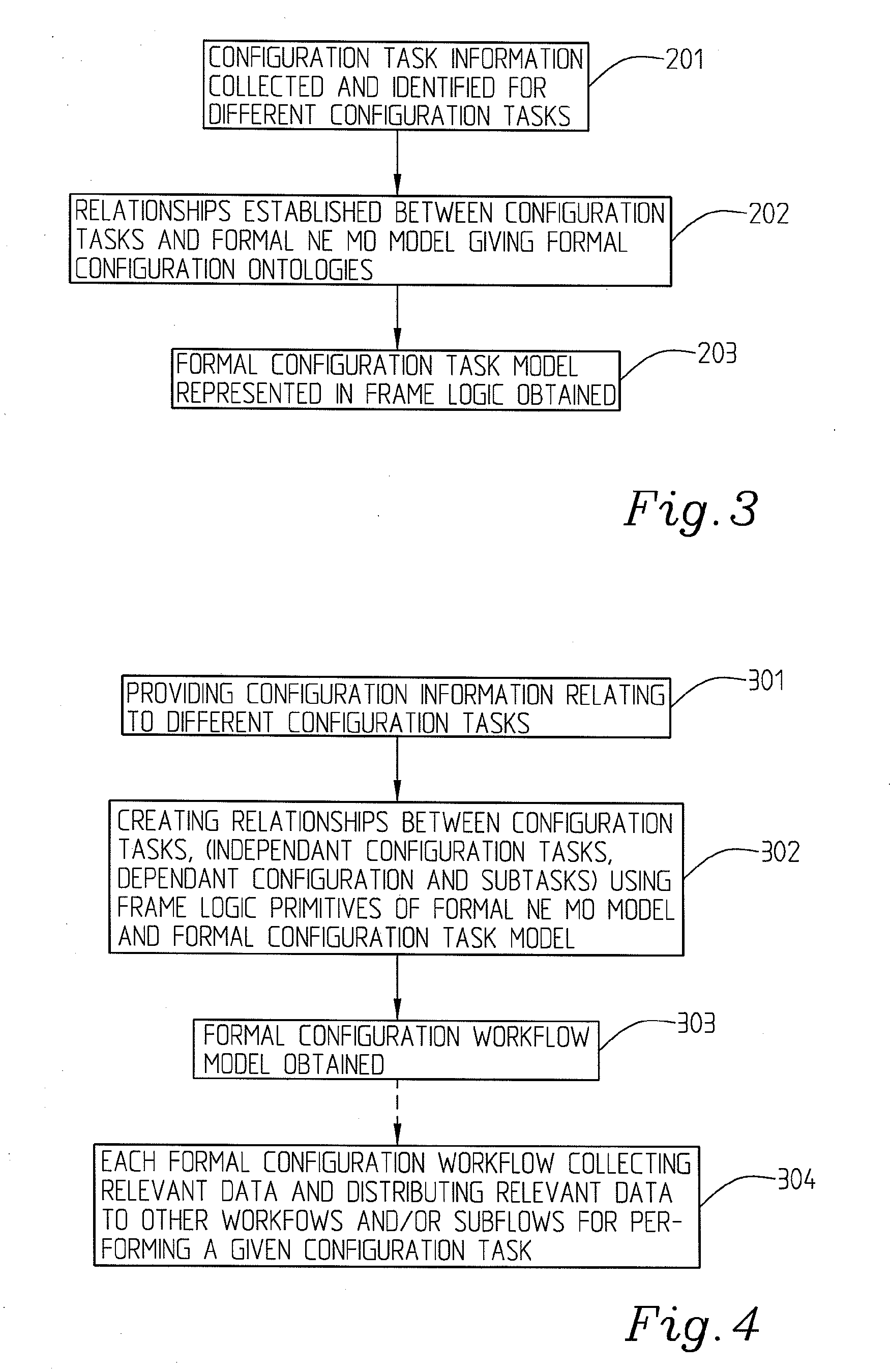
The present invention relates to a method for network management comprising configuration of control protocols between network elements in a network represented through a current, static, network element object model comprising a number of managed objects with attributes and instances and representing resources. It comprises the steps of: transforming the current network element object model to a machine readable and executable formal network element object model; identifying configuration tasks needed for the configuration of the relevant control protocols; modelling a formal configuration task model using information about the configuration tasks and the formal network element object model; building a formal configuration workflow model using the formal network element object model and the formal configuration task model, said formal configuration workflow model defining the relationships between different configuration tasks required for performing or completing a number of given actions or to achieve a number of given goals.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method a designing, engineering modeling and manufacturing orthotics and prosthetics integrating algorithm generated predictions
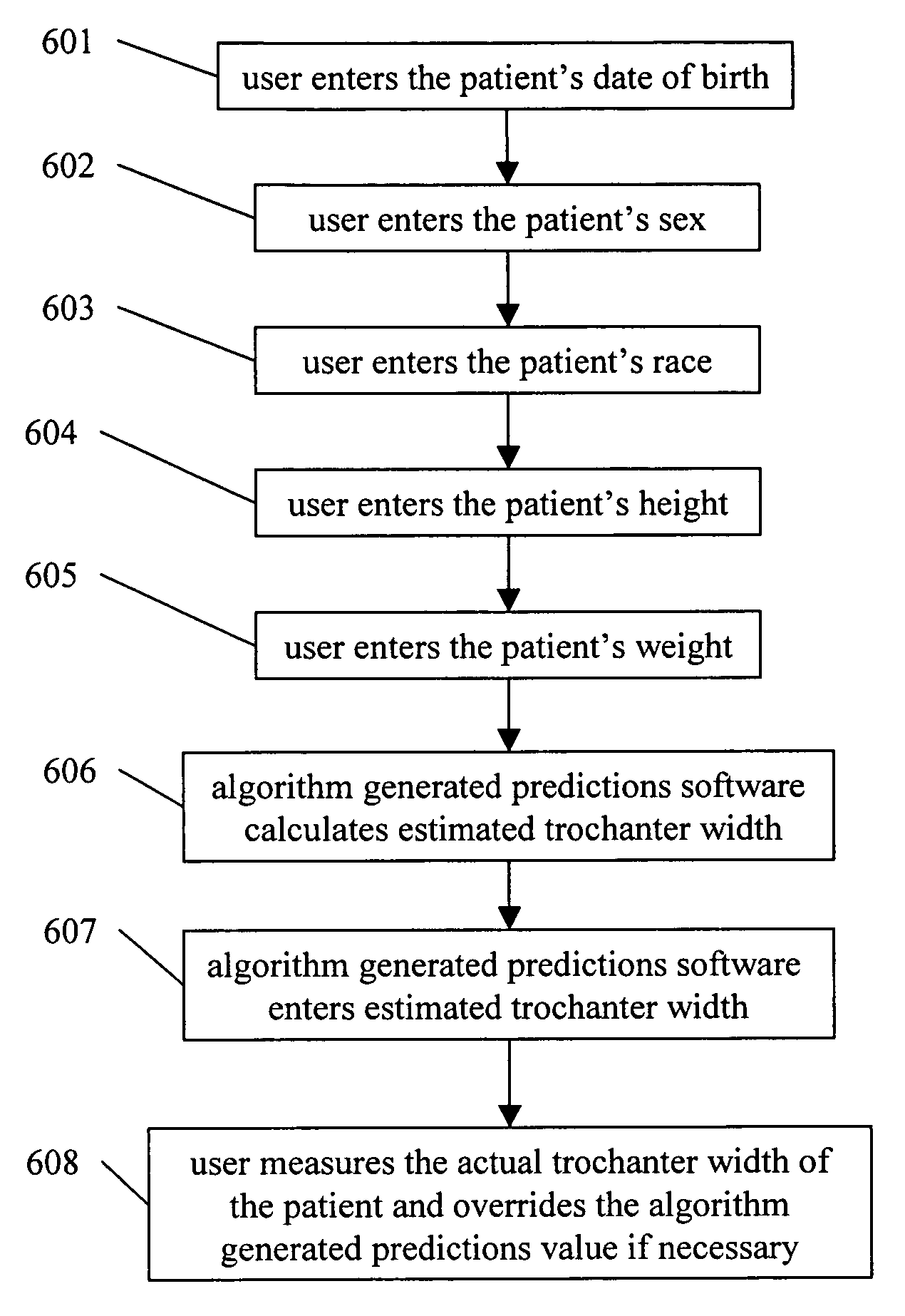
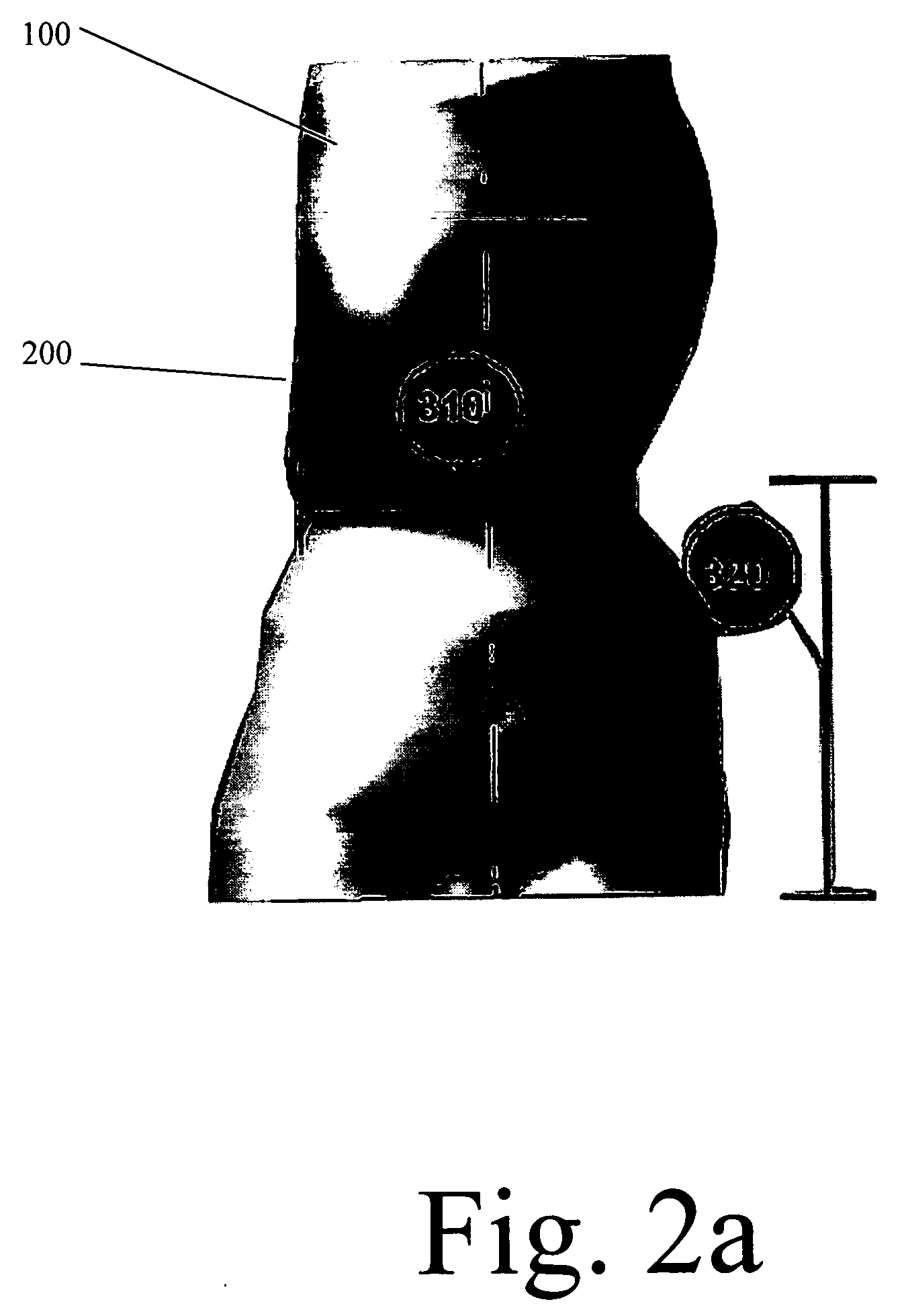
InactiveUS20060100832A1More accurateMore scientificComputation using non-denominational number representationProsthesisComputer Aided DesignPhysical model
The present invention represents an advancement on the current processes involved in designing, engineering, modeling and manufacturing of orthotic and prosthetic devices. Orthotic and prosthetic computer aided design software has the option to apply measurements to a template to create a patient specific model. The use of algorithm generated predictions (also referred to as “AGP”) software takes this functionality and makes it more scientific. Algorithm generated predictions is the process of predicting the appropriate size and shape data through the use of complex algorithms. Certain key pieces of data are entered into the software that then calculates the appropriate dimensions and the appropriate computer aided design template. The dimensions are then applied to the computer aided design template. The computer aided design software modifies the templates by reducing and enlarging areas as necessary and a custom computer aided design model is created that can then be transformed into a physical model for the manufacture of the device.
Owner:BOWMAN GERALD DAVID
System and Method for Monitoring and Controlling Underground Drilling
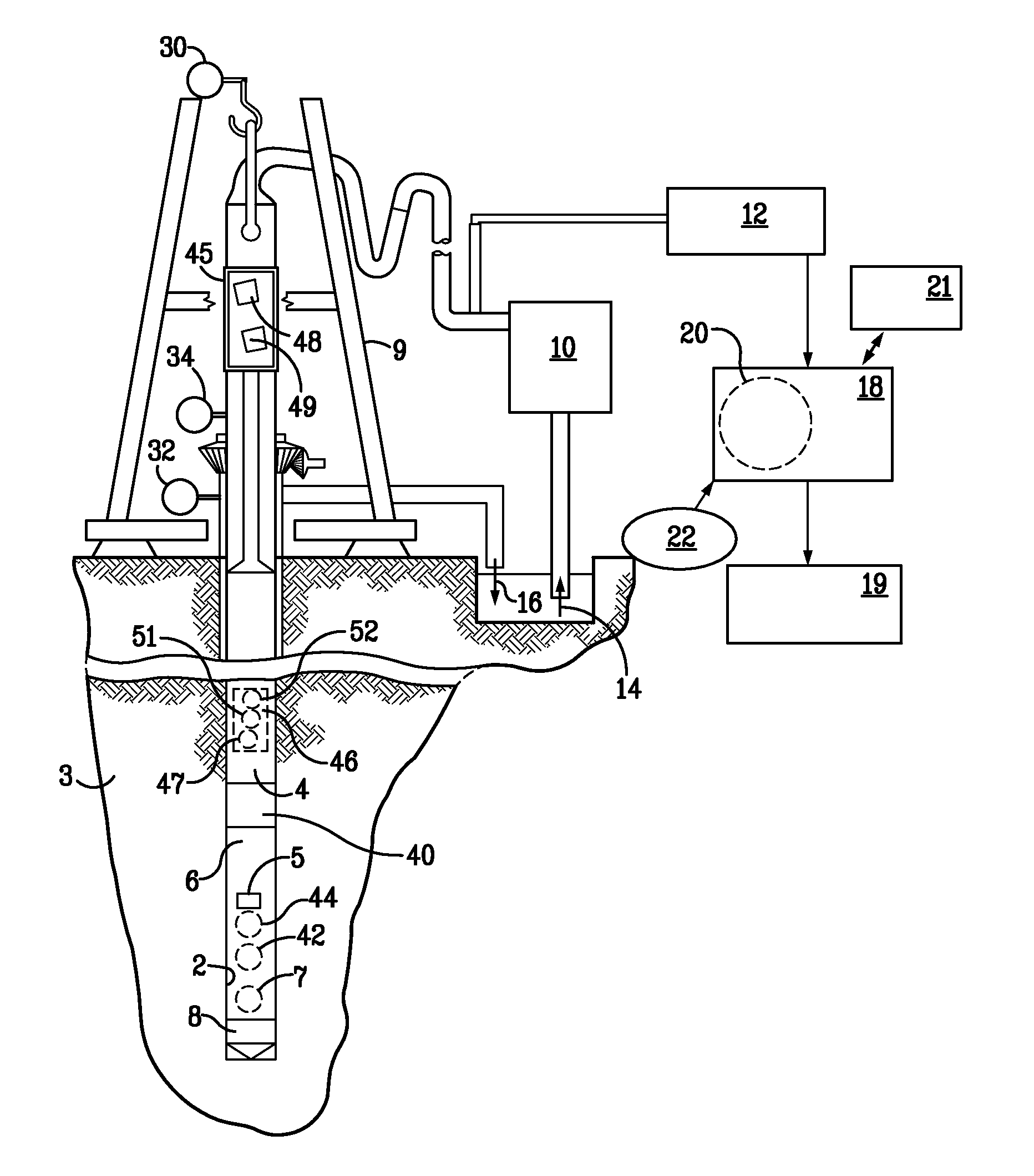
ActiveUS20110186353A1Reduce the differenceVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingFinite element techniqueResonance
A system and method for monitoring underground drilling in which vibration is monitored by creating a model of the drill string using finite element techniques or finite difference techniques and (i) predicting vibration by inputting real time values of operating parameters into the model, and then adjusting the model to agree with measured vibration data, (ii) predicting the weight on bit and drill string and mud motor speeds at which resonance will occur, as well as when stick-slip will occur, so that the operator can avoid operating regimes that will result in high vibration, (iii) determining vibration and torque levels along the length of the drill string based on the measured vibration and torque at one or more locations, (iv) determining the remaining life of critical components of the drill string based on the history of the vibration to which the components have been subjected, and (v) determining the optimum drilling parameters that will avoid excessive vibration of the drill string.
Owner:APS TECH
Automated systems and methods for generating statistical models
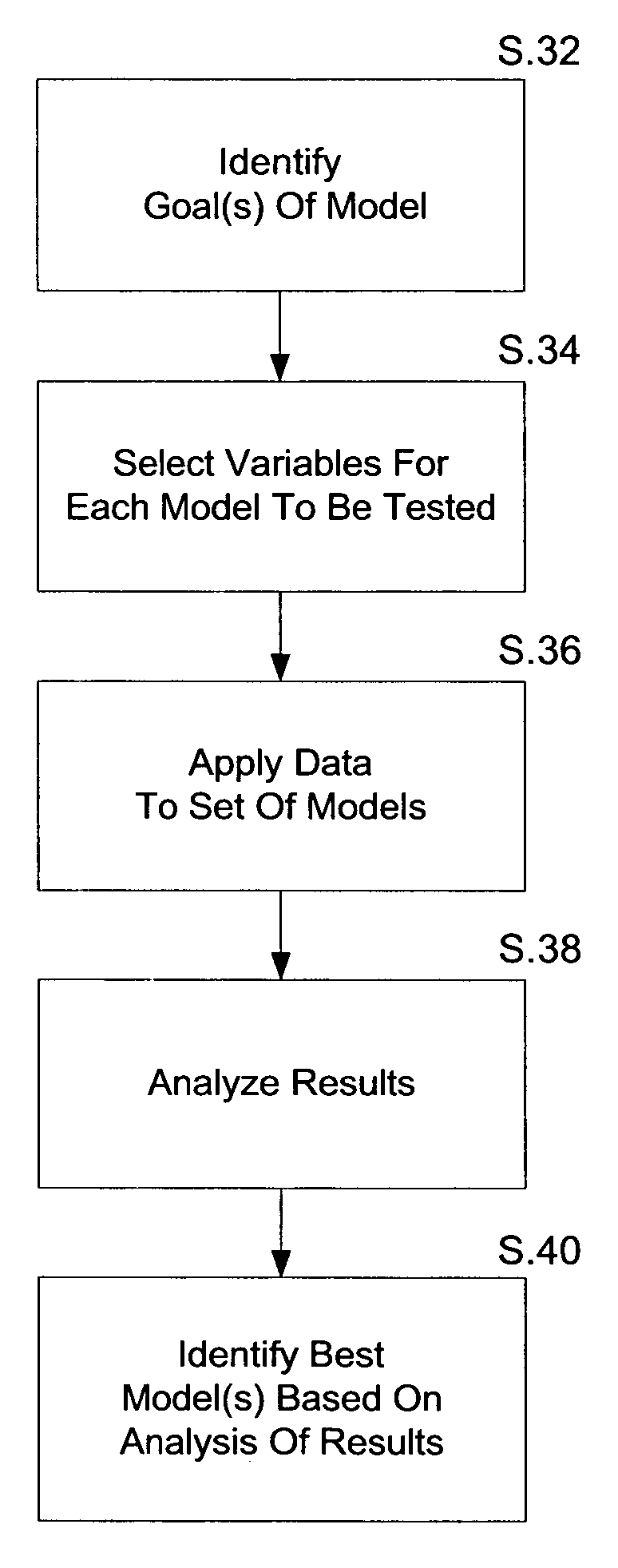
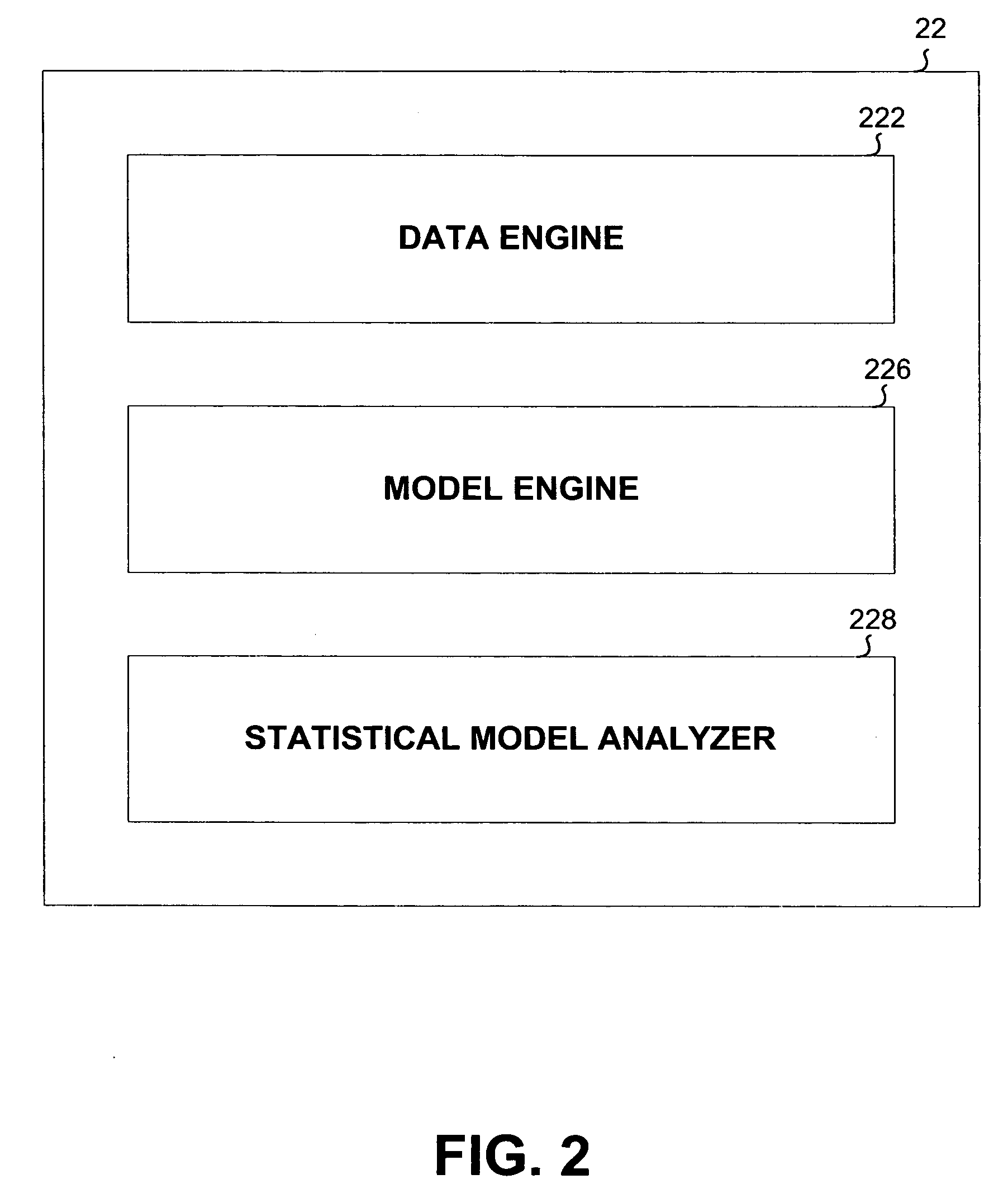
InactiveUS20060241923A1Quality improvementOvercome disadvantagesFinanceCharacter and pattern recognitionGoal selectionComputer science
Systems and methods are disclosed for generating statistical models. Such systems and methods may utilize a database comprising data representing a plurality of variables. To generate a statistical model, a set of variables may be selected in accordance with a goal of the model. Using the database, the selected set of variables may then be applied to a plurality of statistical model types and the results from each statistical model type may be analyzed. Finally, at least one of statistical model may be identified based on the analysis of the results.
Owner:CAPITAL ONE FINANCIAL
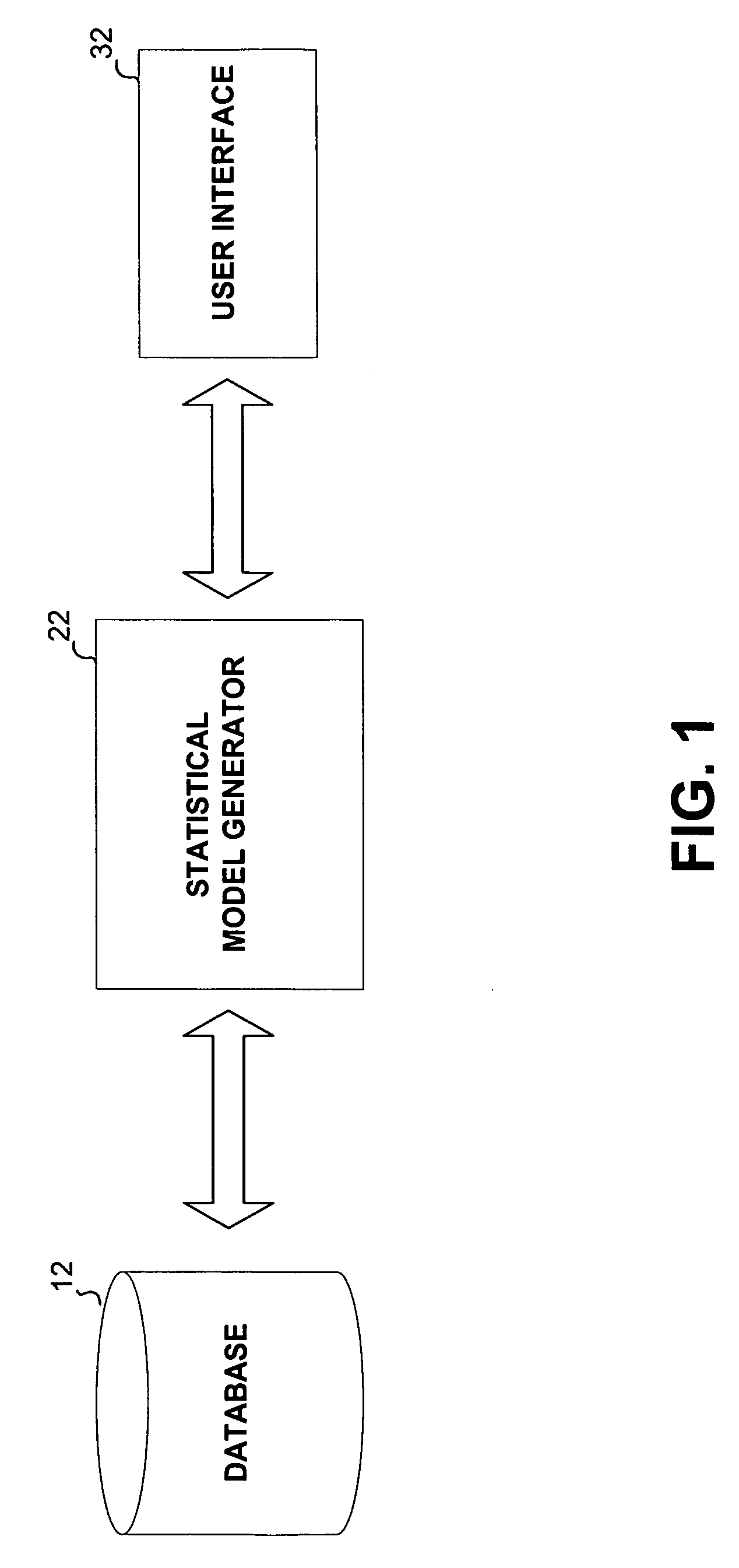
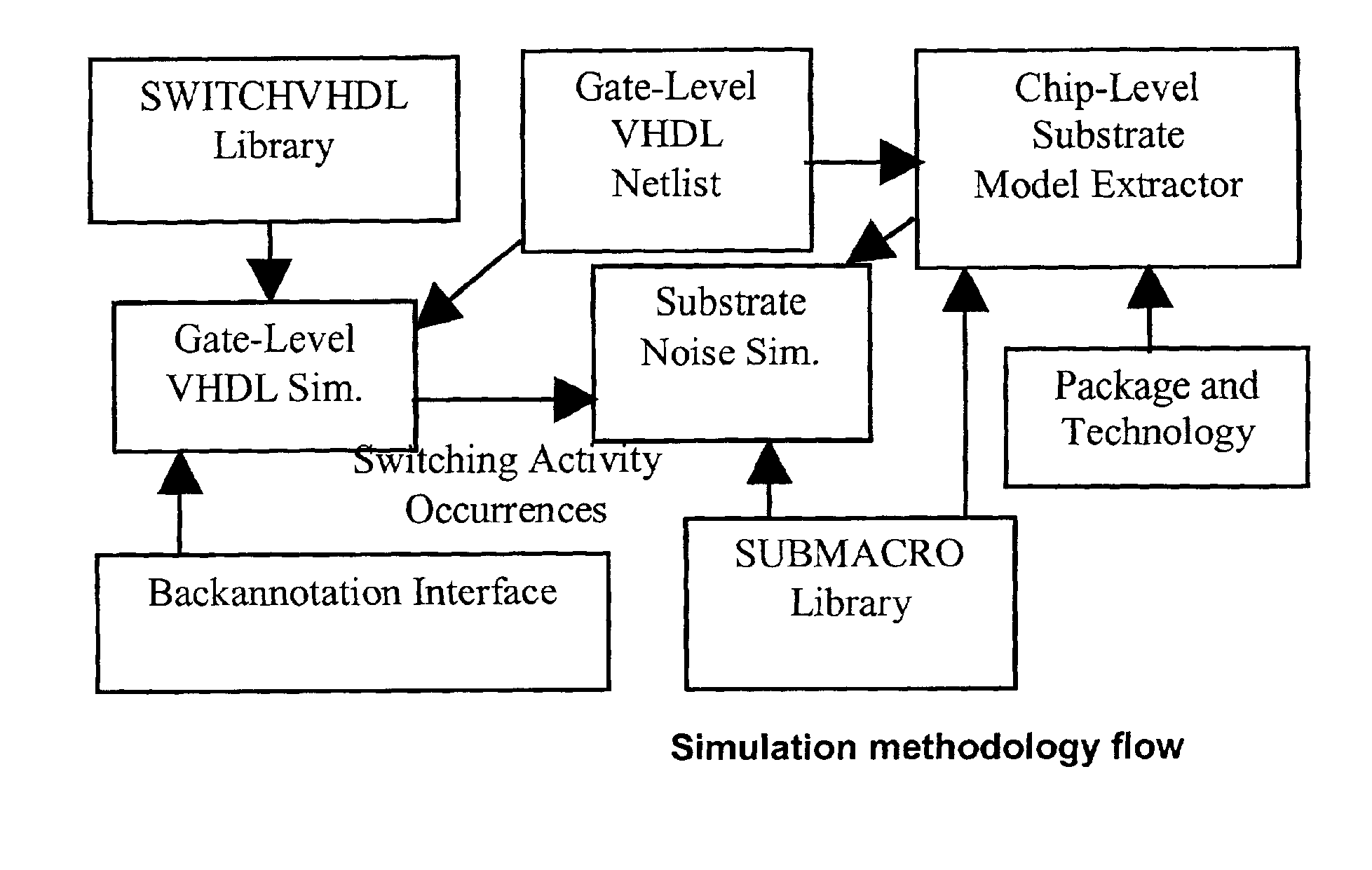
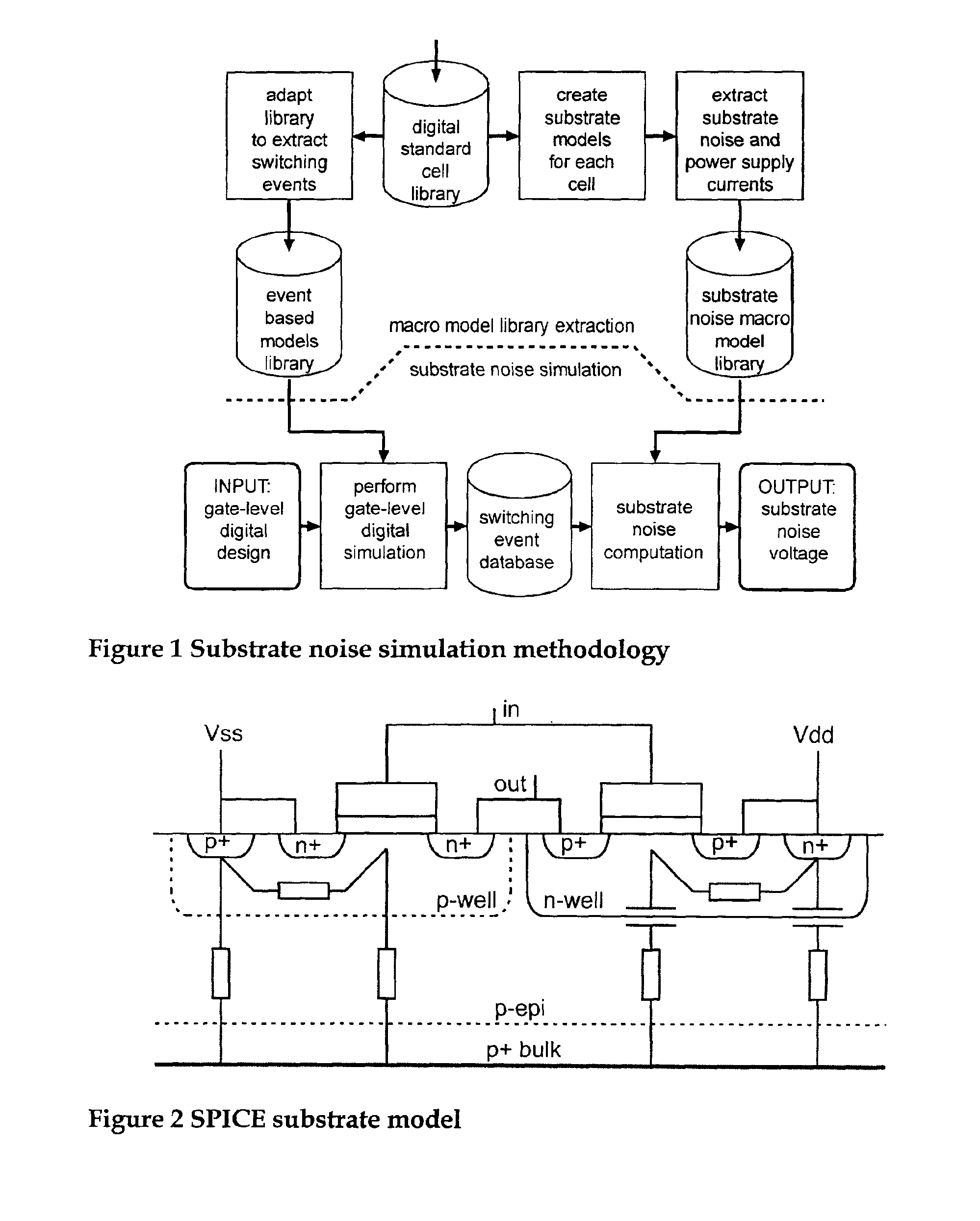
Method, apparatus and computer program product for determination of noise in mixed signal systems
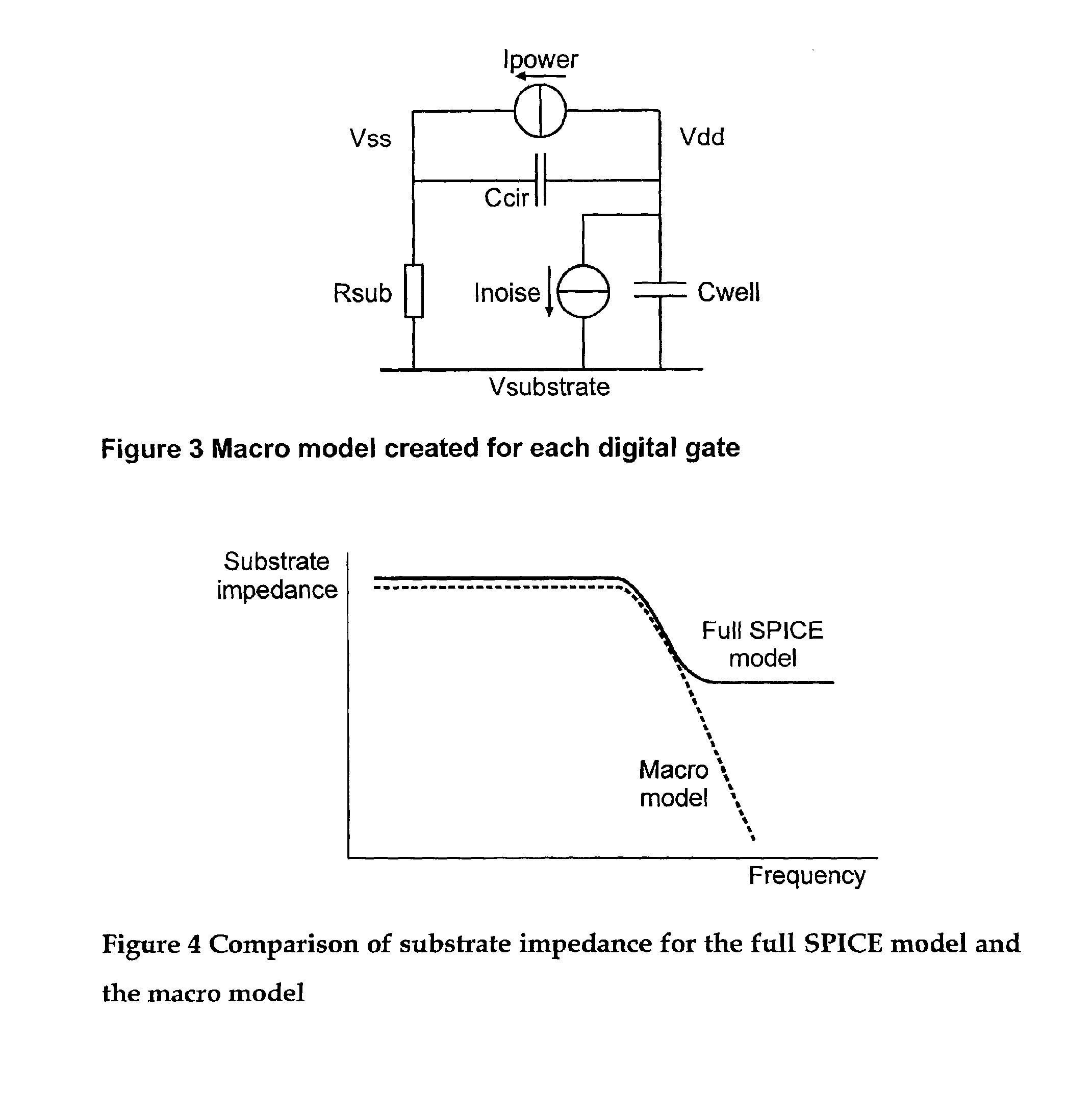
InactiveUS6941258B2Fast and accurate determinationAnalogue computers for electric apparatusDetecting faulty computer hardwareEngineeringSignaling system
A simulation system is described for computing the overall signal generated in a substrate by a digital system comprising a plurality of gates associated with the substrate, wherein each gate is configured to perform a switching event. Output of a transistor-level model is compared with output of a lumped circuit model for each gate and the substrate, and signal contributions from each gate and switching event are determined based on the comparison. The system determines switching event signals for each of the plurality of gates. The signal contributions and the switching event signals are combined, and a combined lumped circuit model is derived based on a combination of lumped circuit models of the plurality of gates. The overall signal is computed based on the combined gate signal contributions and switching event signals, which are configured as an input to the combined lumped circuit model.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Signal differentiation system using improved non-linear operator
InactiveUS6952662B2Guaranteed bandwidthAccurate signal differentiation determinationNuclear monitoringDigital computer detailsEngineeringLinearity
A system for detecting subtle differences in a signal in a set of linearly and / or non-linearly related signals that characterize a sensor-instrumented machine, process or living system. The system employs an improved similarity operator for signal differentiation. Signals or data representative of several linearly and / or non-linearly related parameters that describe a machine, process or living system are input to the inventive system, which compares the input to acceptable modeled states. If one or more of the input signals or data are different than expected, given the relationships between the parameters, the inventive system will indicate that difference. The system can provide expected parameter values, as well as the differences between expected and input signals; or the system can provide raw measures of similarity between the collection of input signals and the collection of acceptable modeled states. The system can be embodied in software or in a micro-controller.
Owner:SMARTSIGNAL CORP
Popular searches
Load forecast in ac network Analogue computers for control systems Buying/selling/leasing transactions Material dimension control Complex mathematical operations Power network operation systems integration Energy storage Power supply for data processing Ac network load balancing Control using feedback
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com