Patents
Literature
166 results about "In silico" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
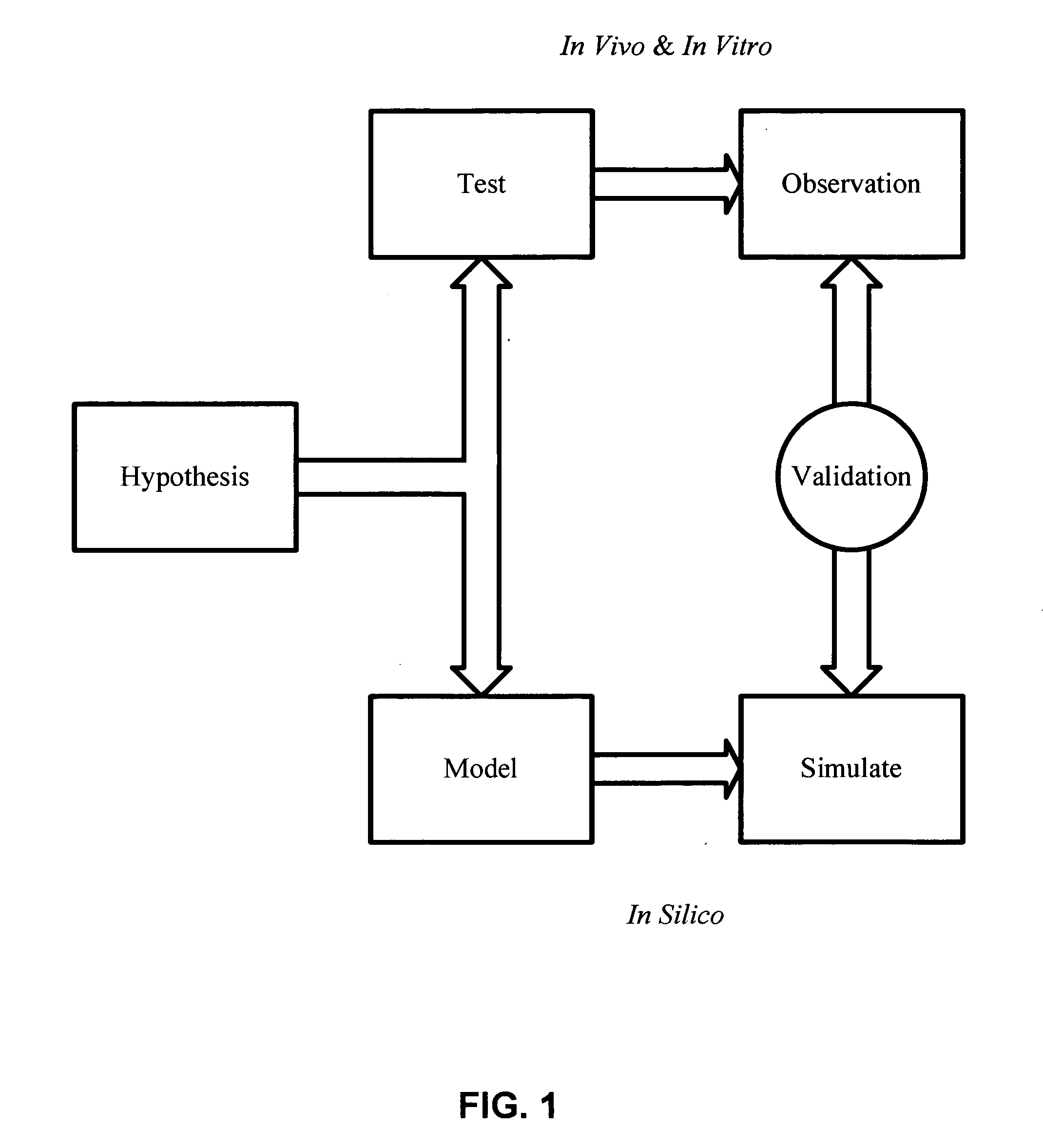
In silico (Pseudo-Latin for "in silicon", alluding to the mass use of silicon for computer chips) is an expression meaning "performed on computer or via computer simulation" in reference to biological experiments. The phrase was coined in 1989 as an allusion to the Latin phrases in vivo, in vitro, and in situ, which are commonly used in biology (see also systems biology) and refer to experiments done in living organisms, outside living organisms, and where they are found in nature, respectively.
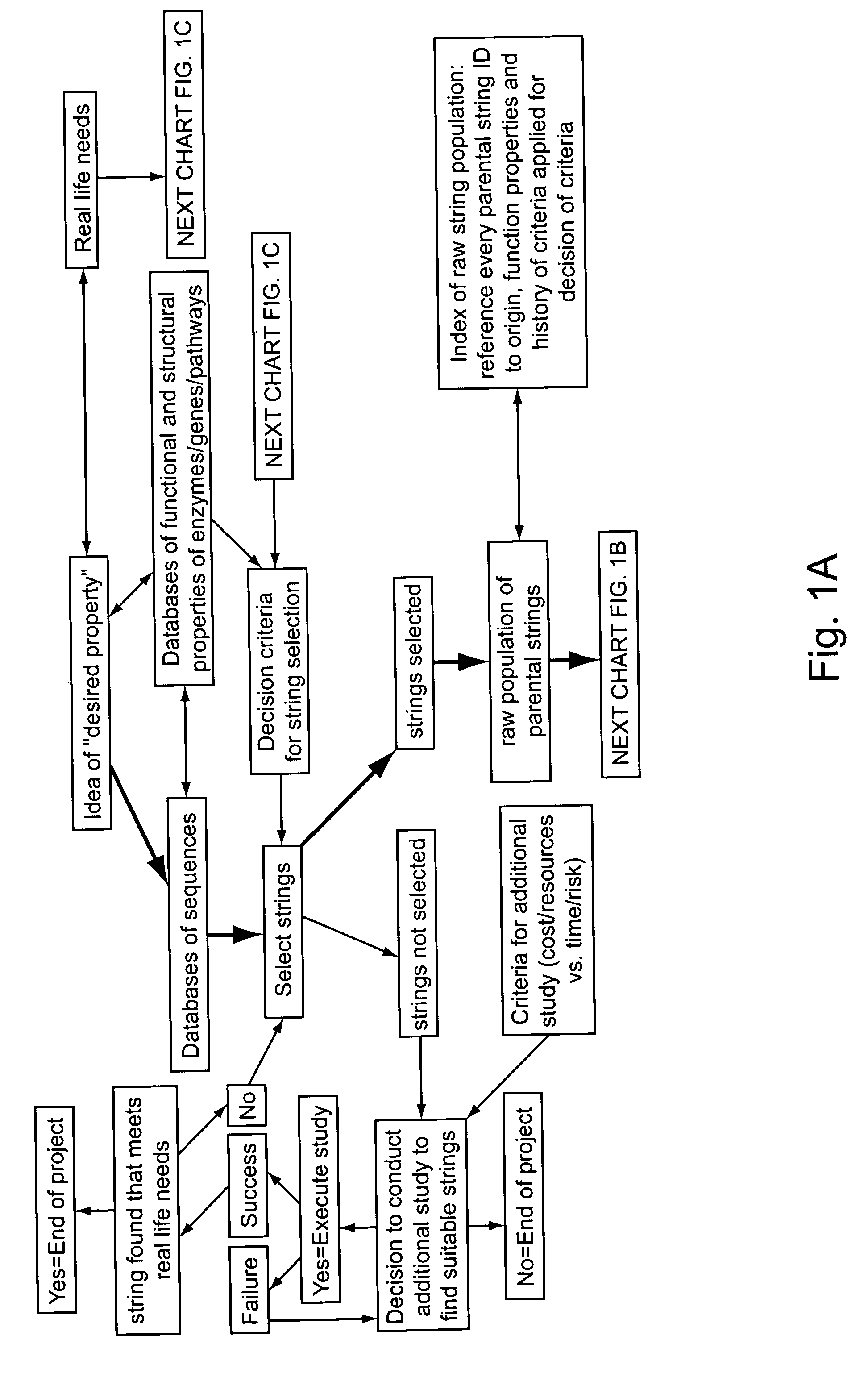
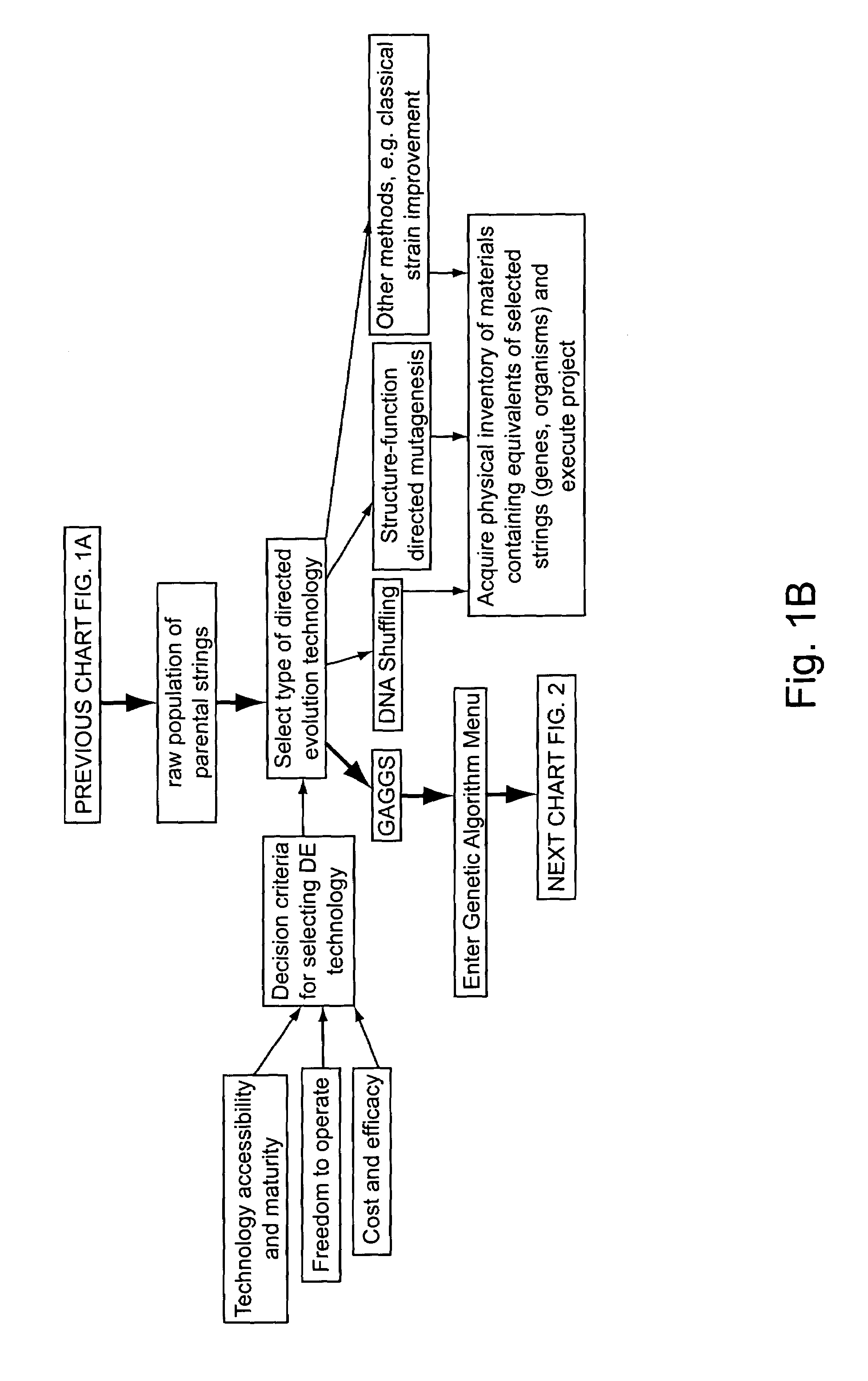
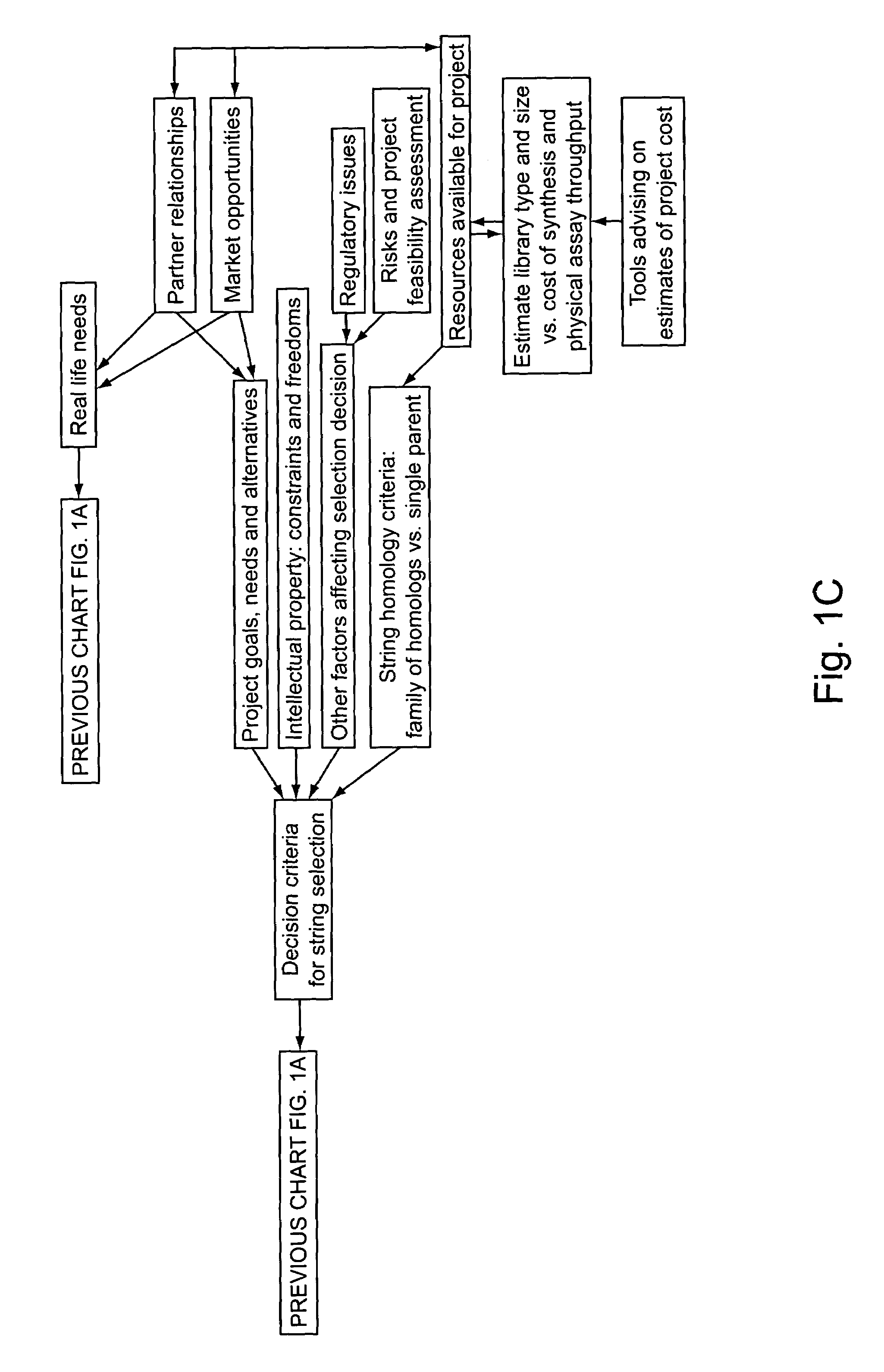
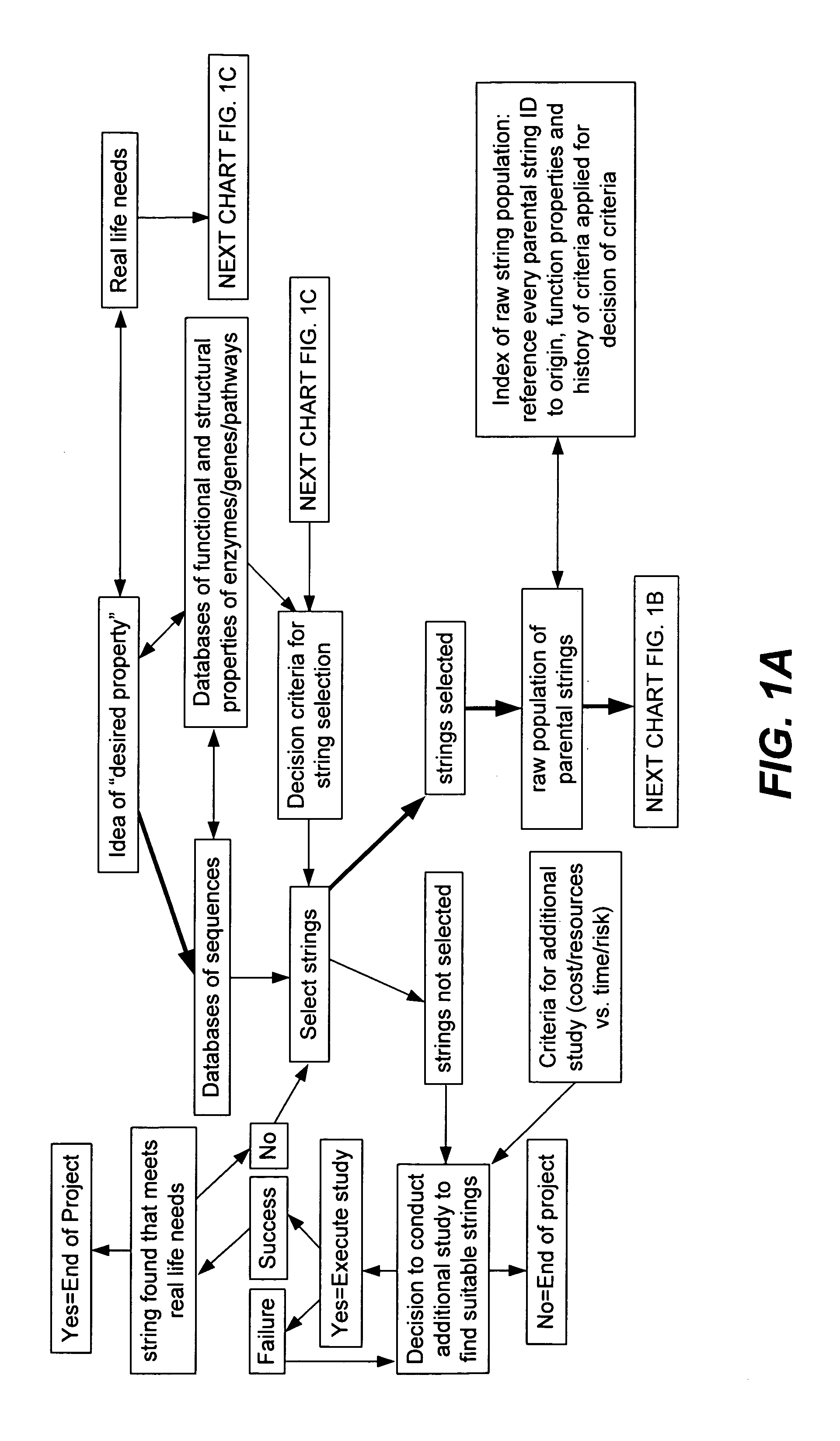
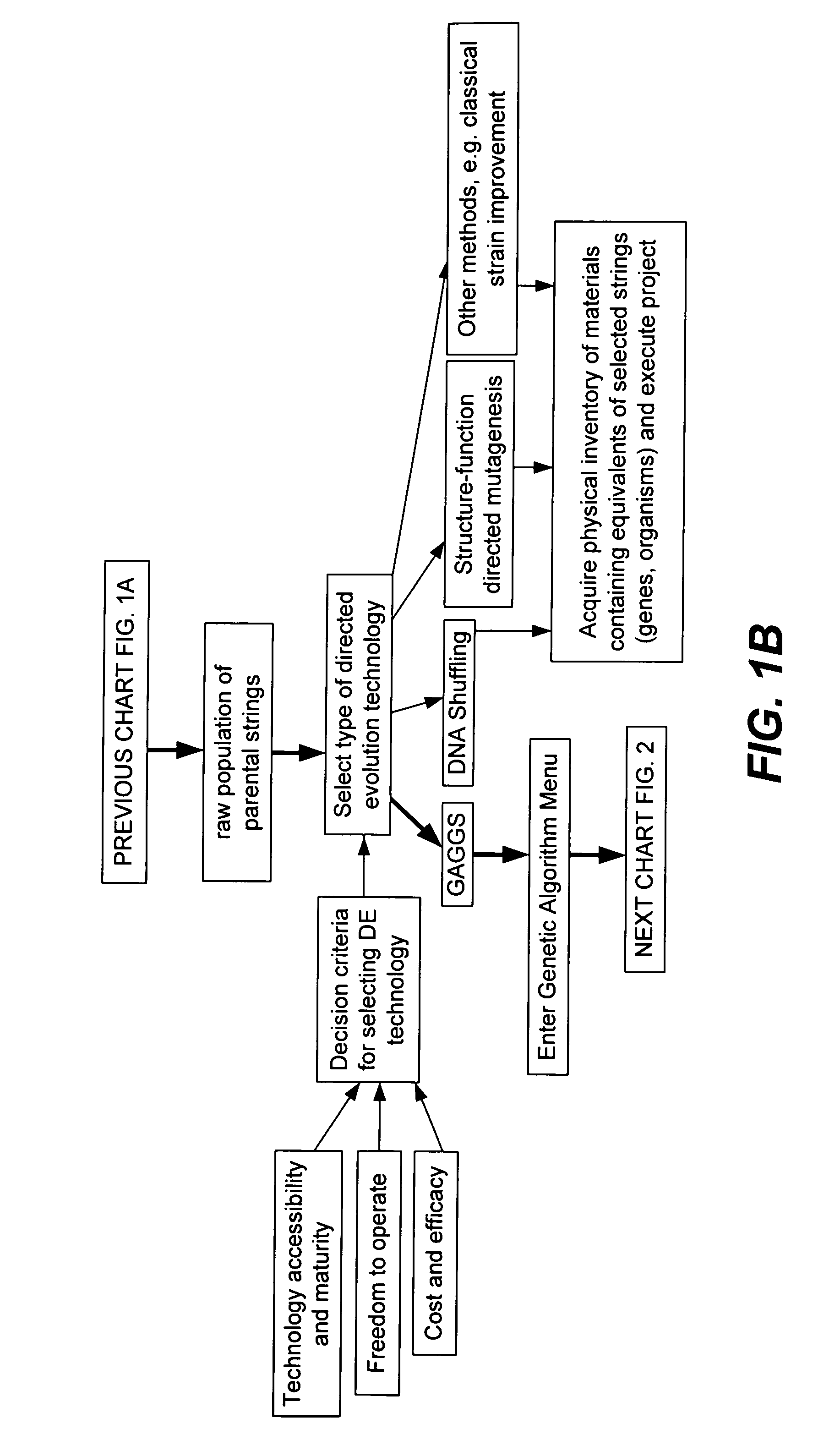
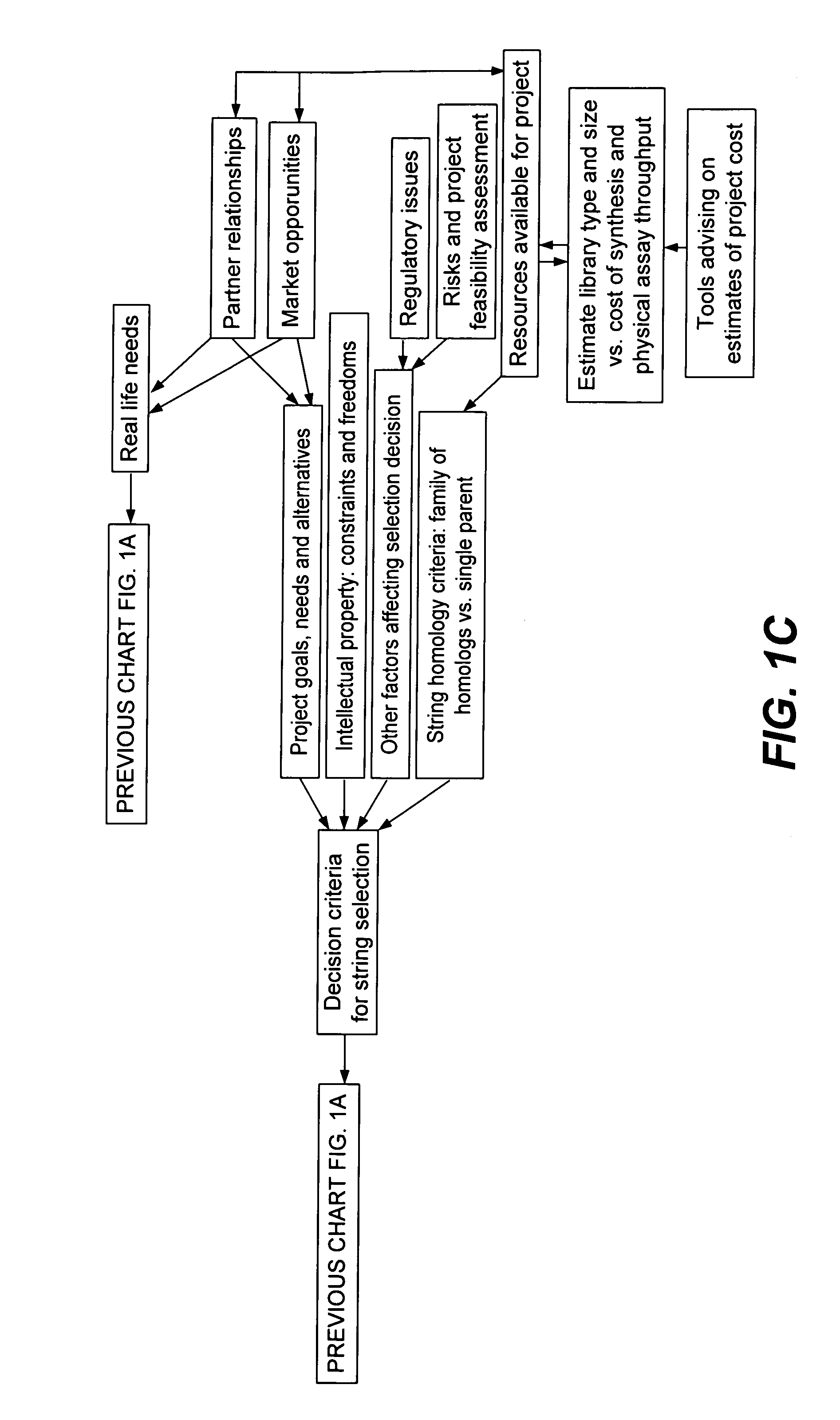
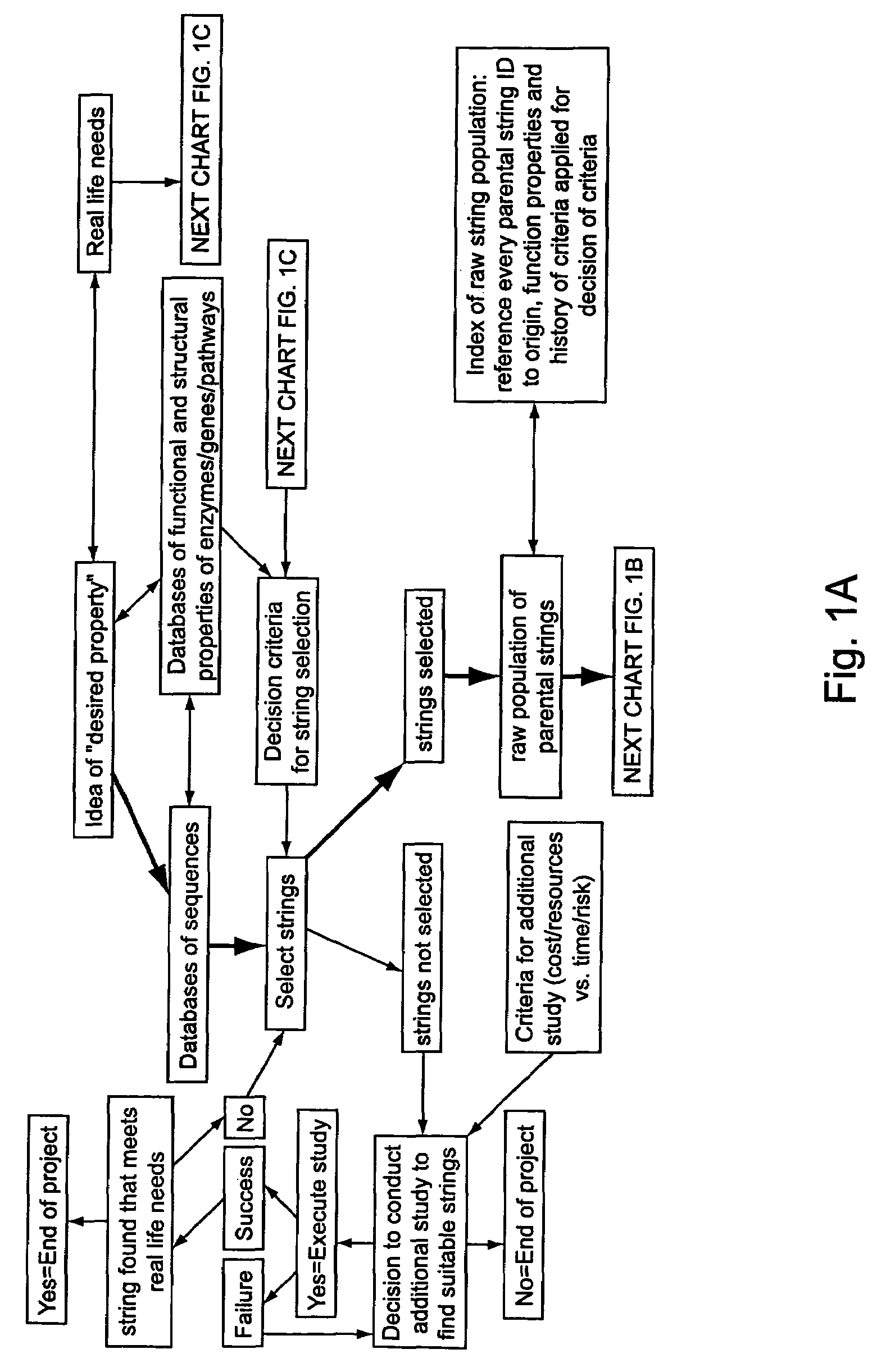
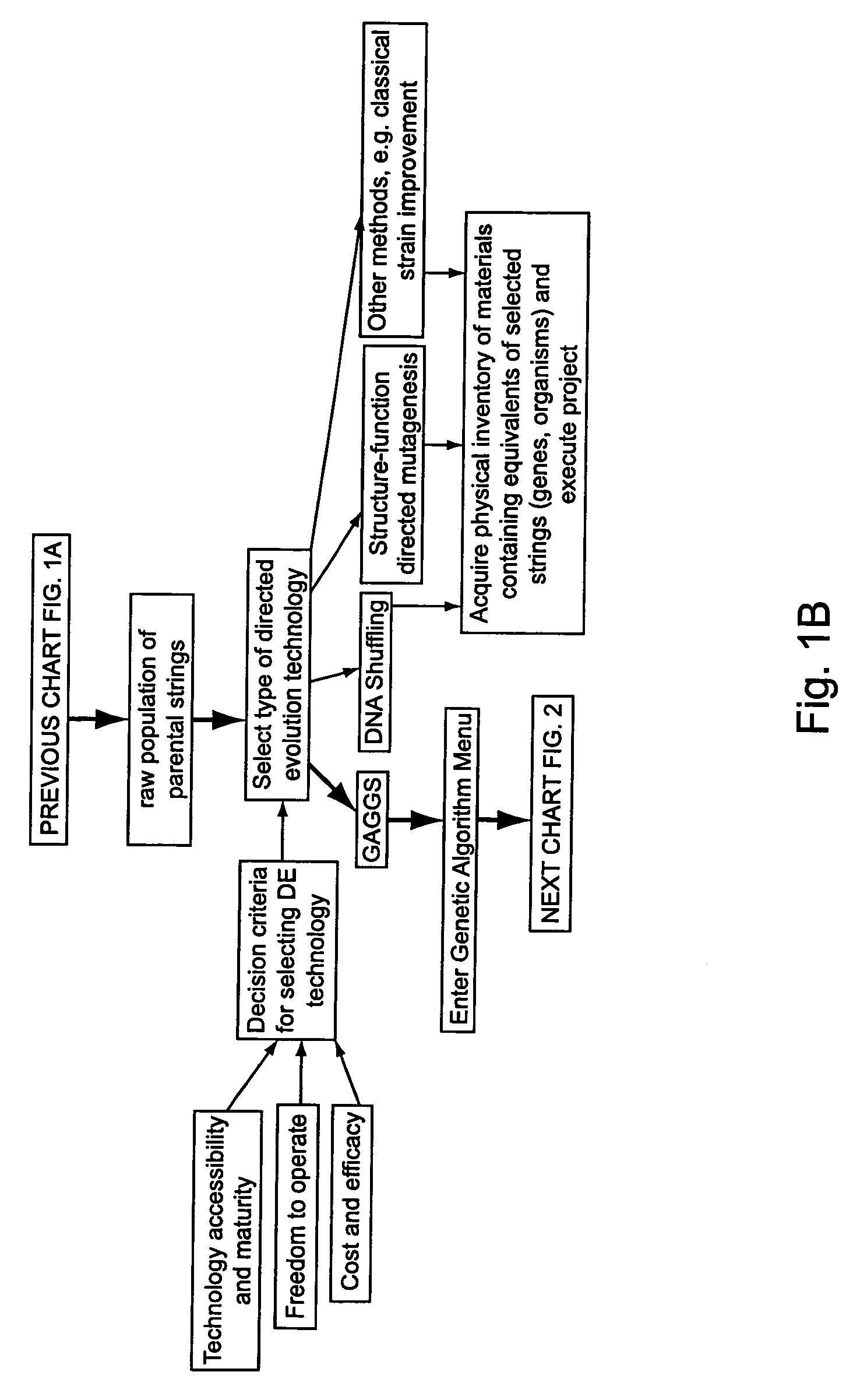
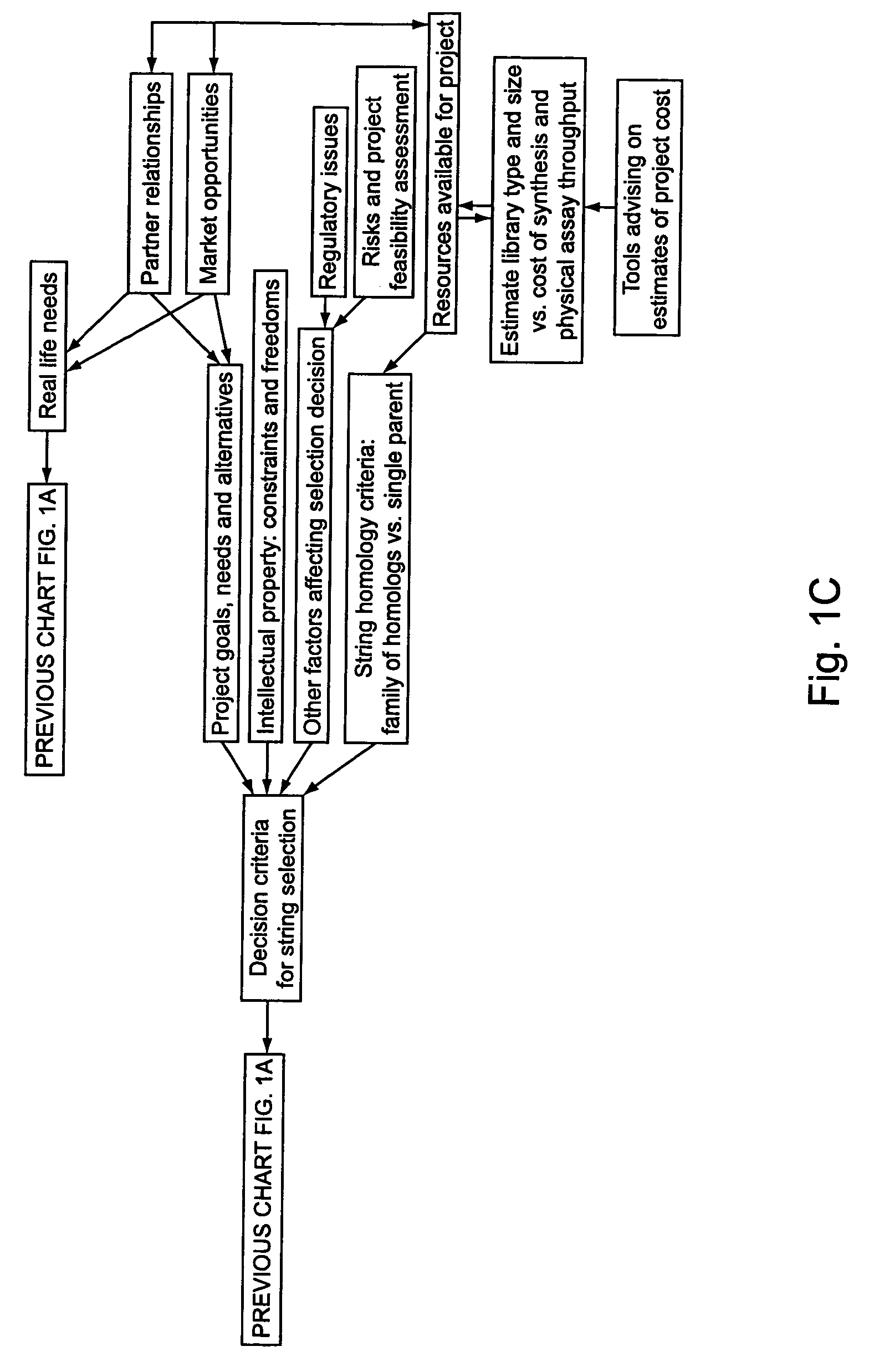
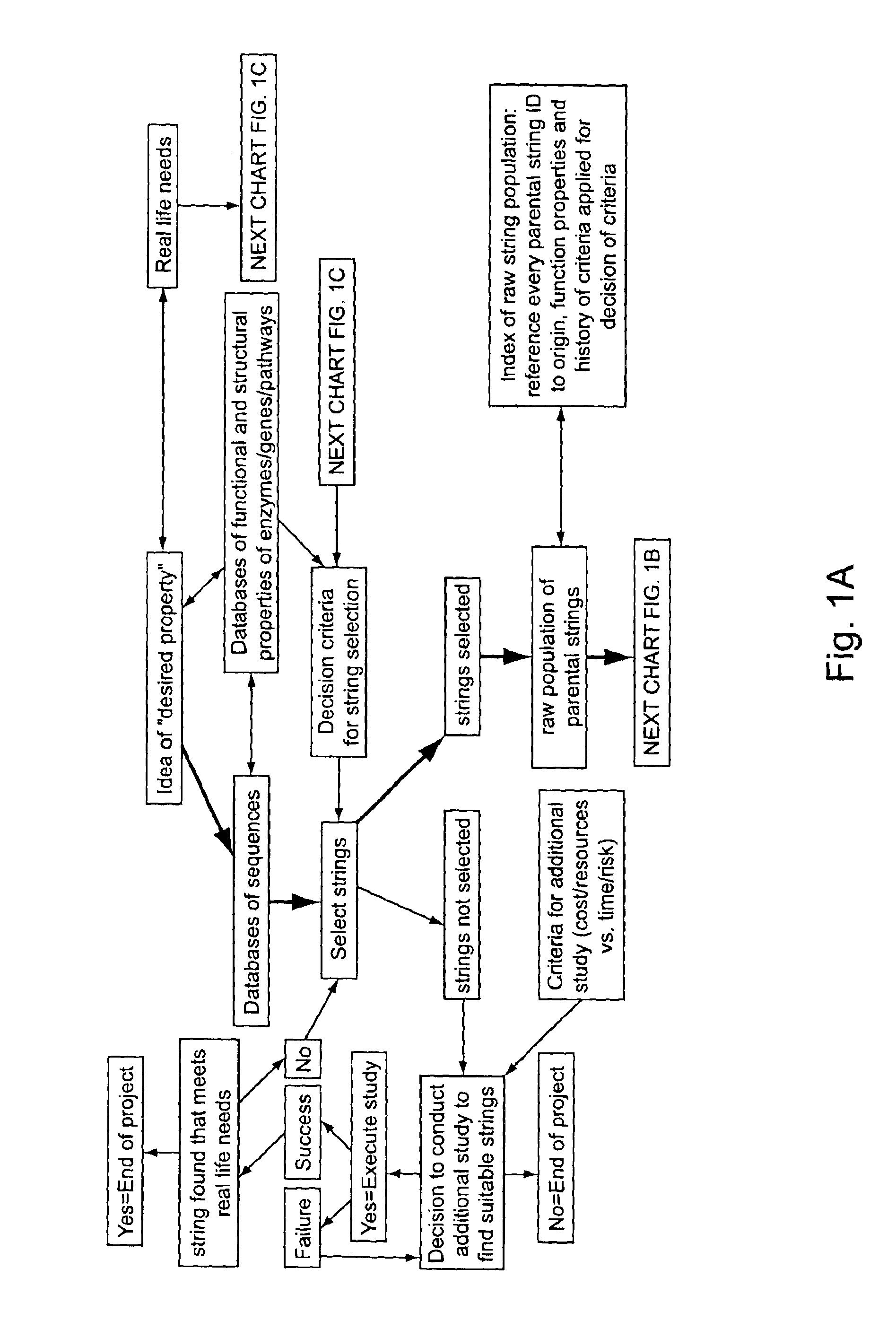
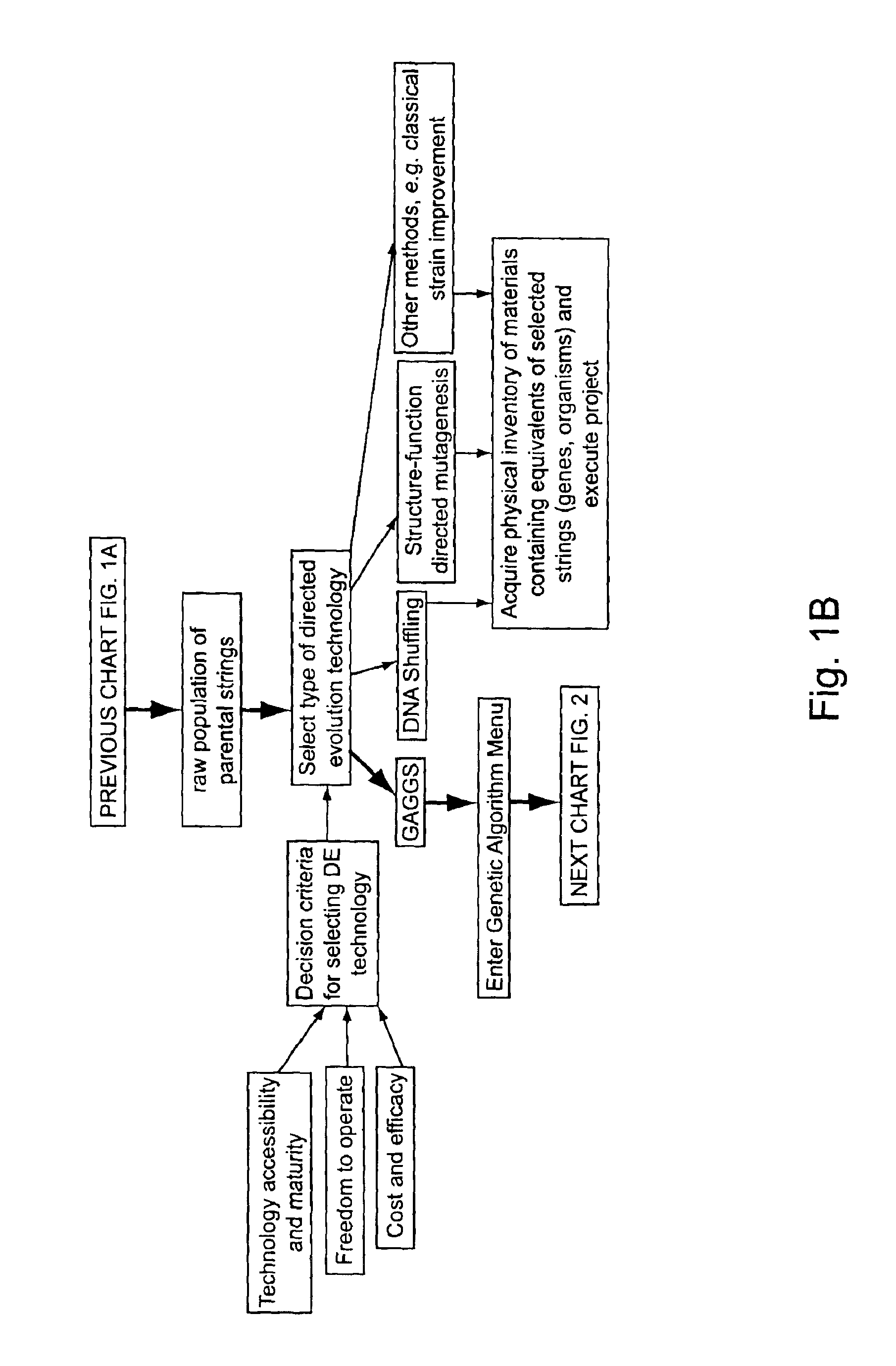
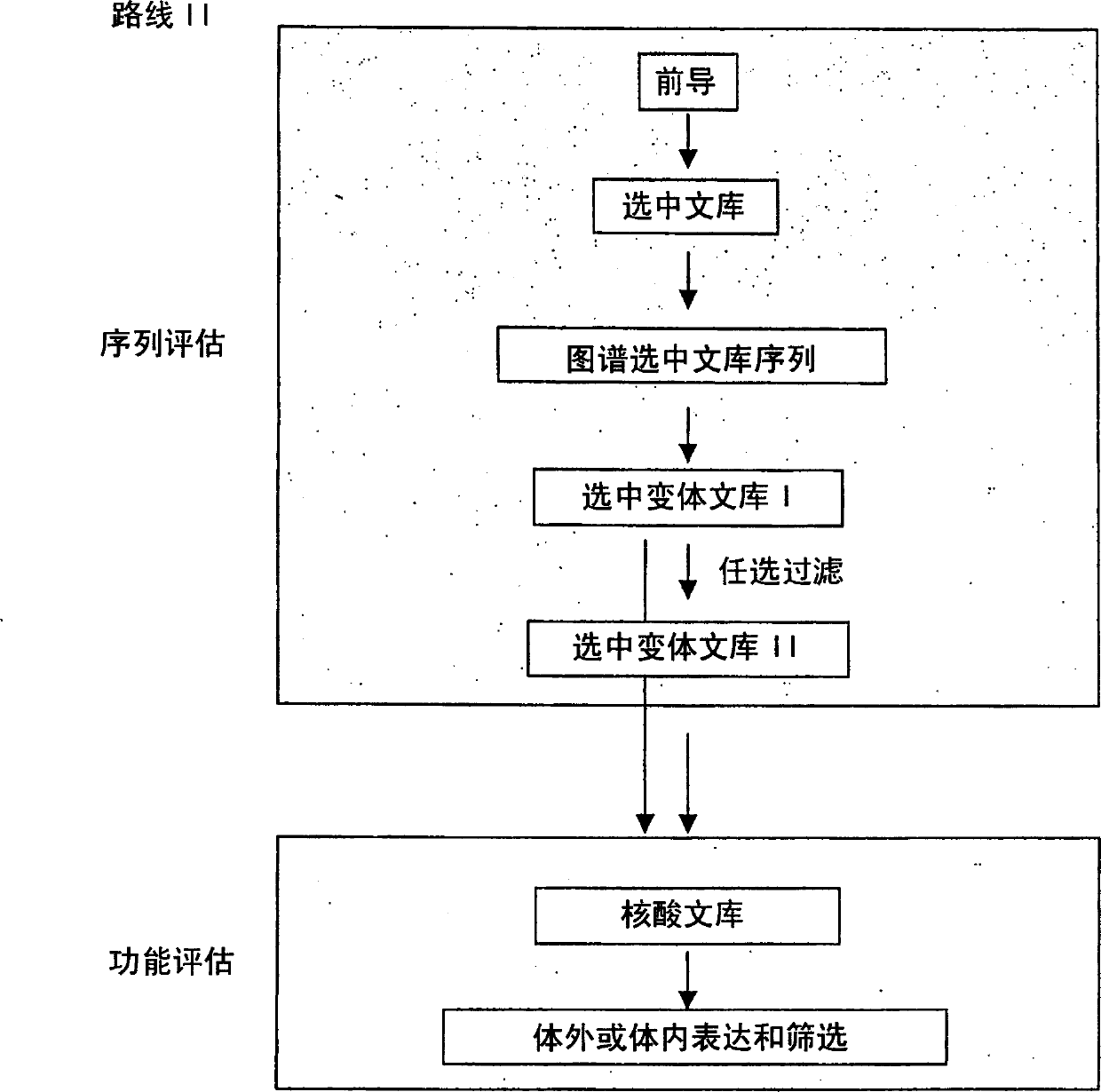
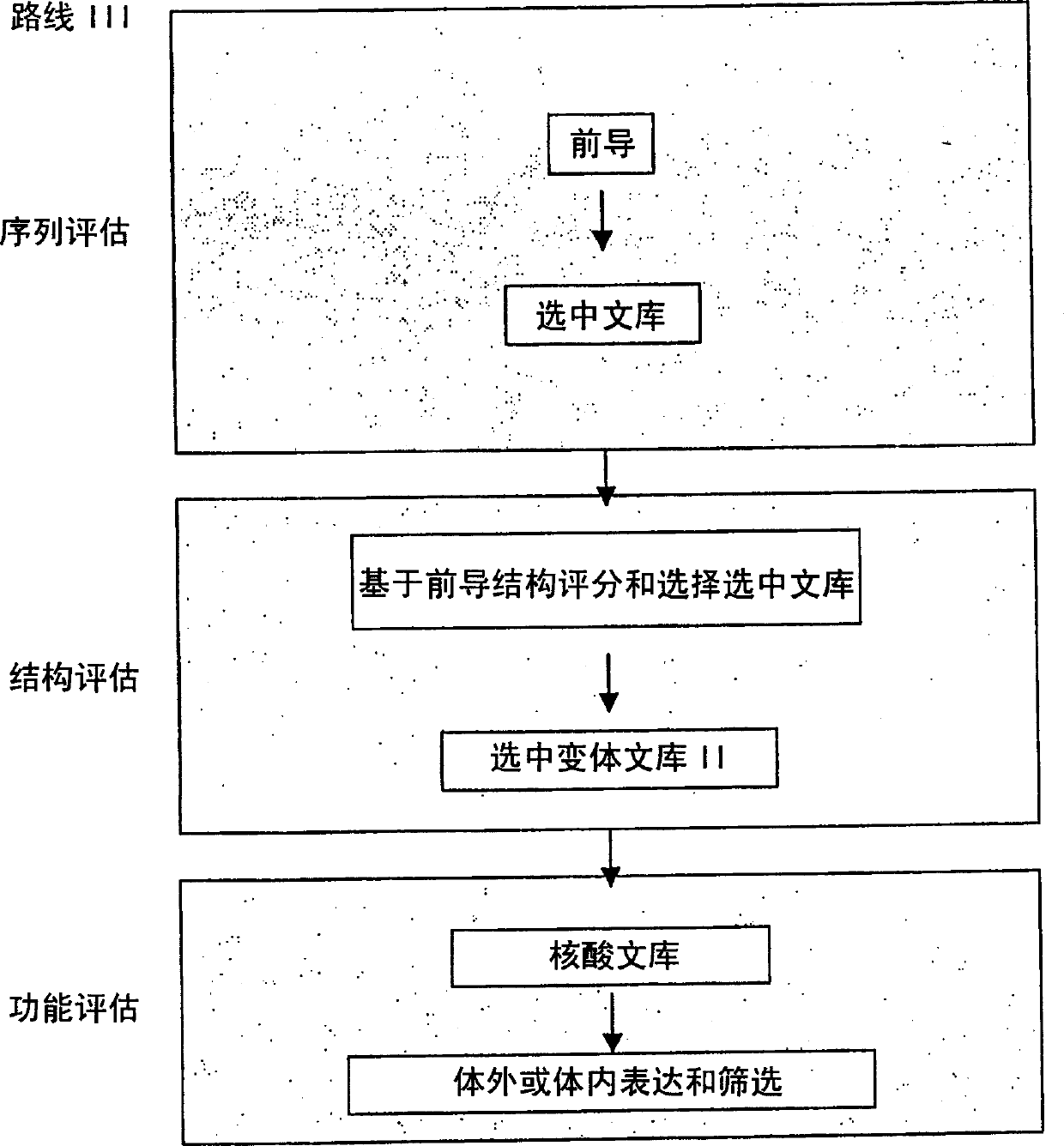
Methods for making character strings, polynucleotides and polypeptides having desired characteristics
InactiveUS7024312B1Simplifies overall synthesis strategyLow levelPeptide/protein ingredientsBiostatisticsPolynucleotideIn silico
“In silico” nucleic acid recombination methods, related integrated systems utilizing genetic operators and libraries made by in silico shuffling methods are provided.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
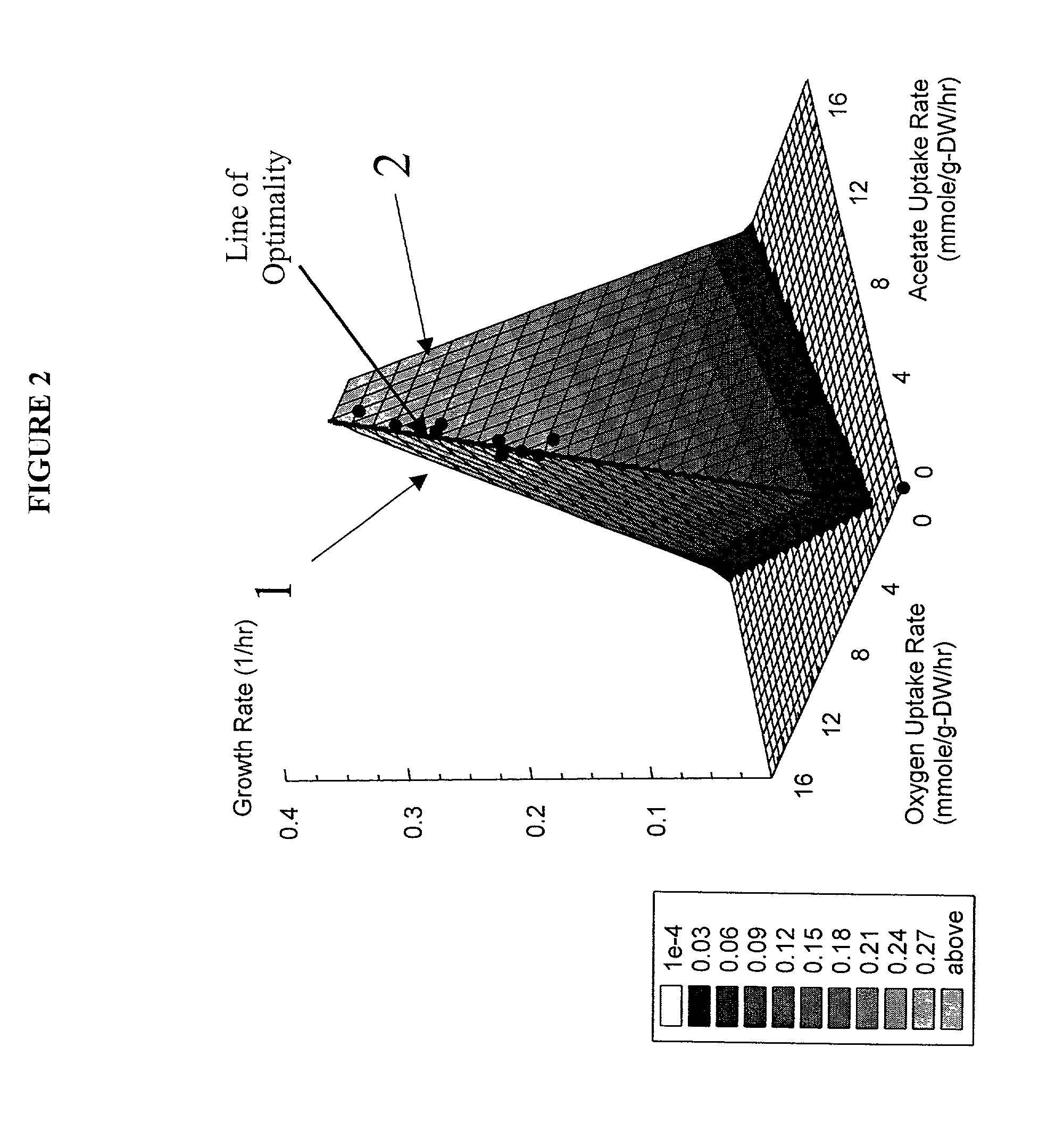
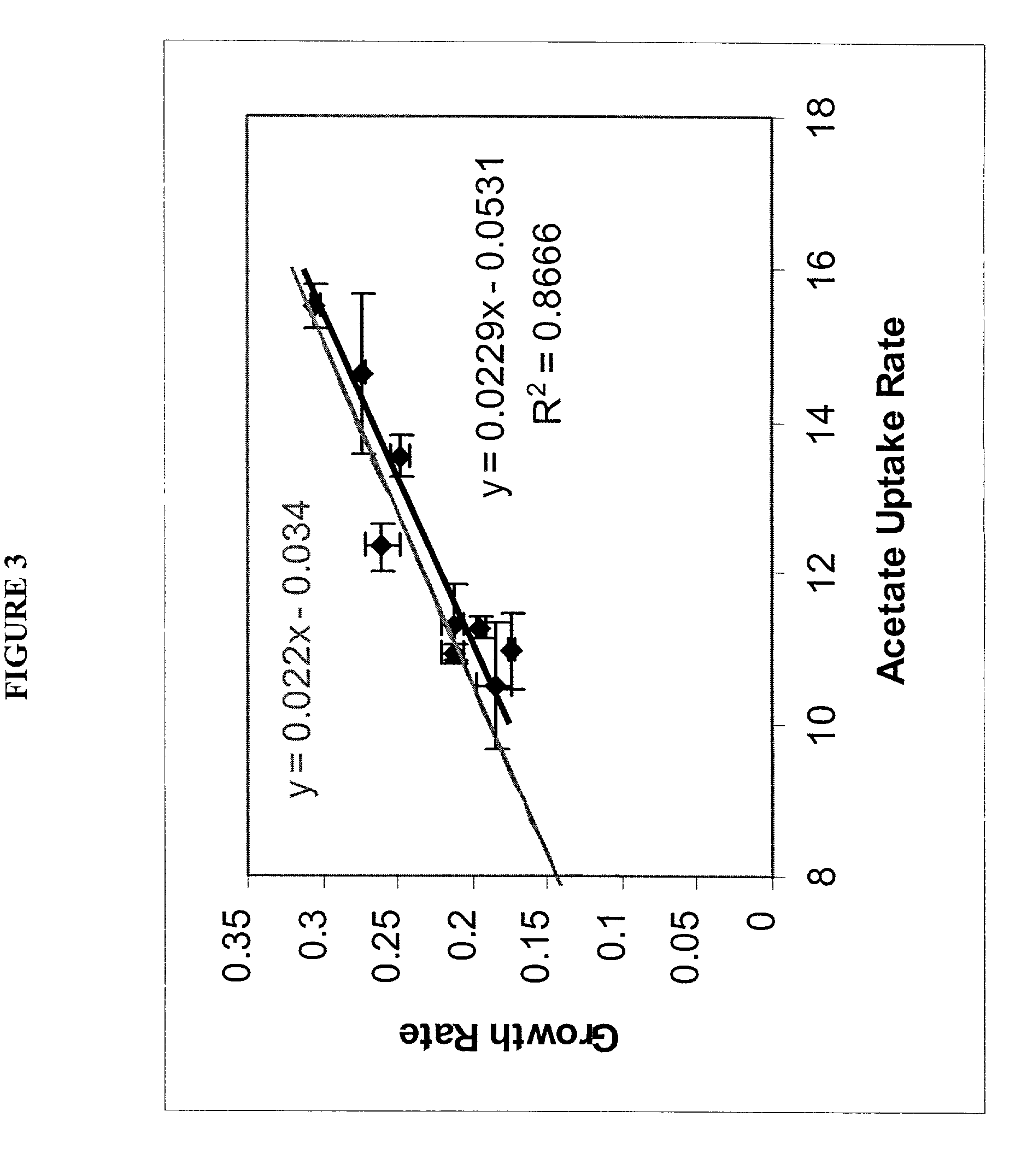
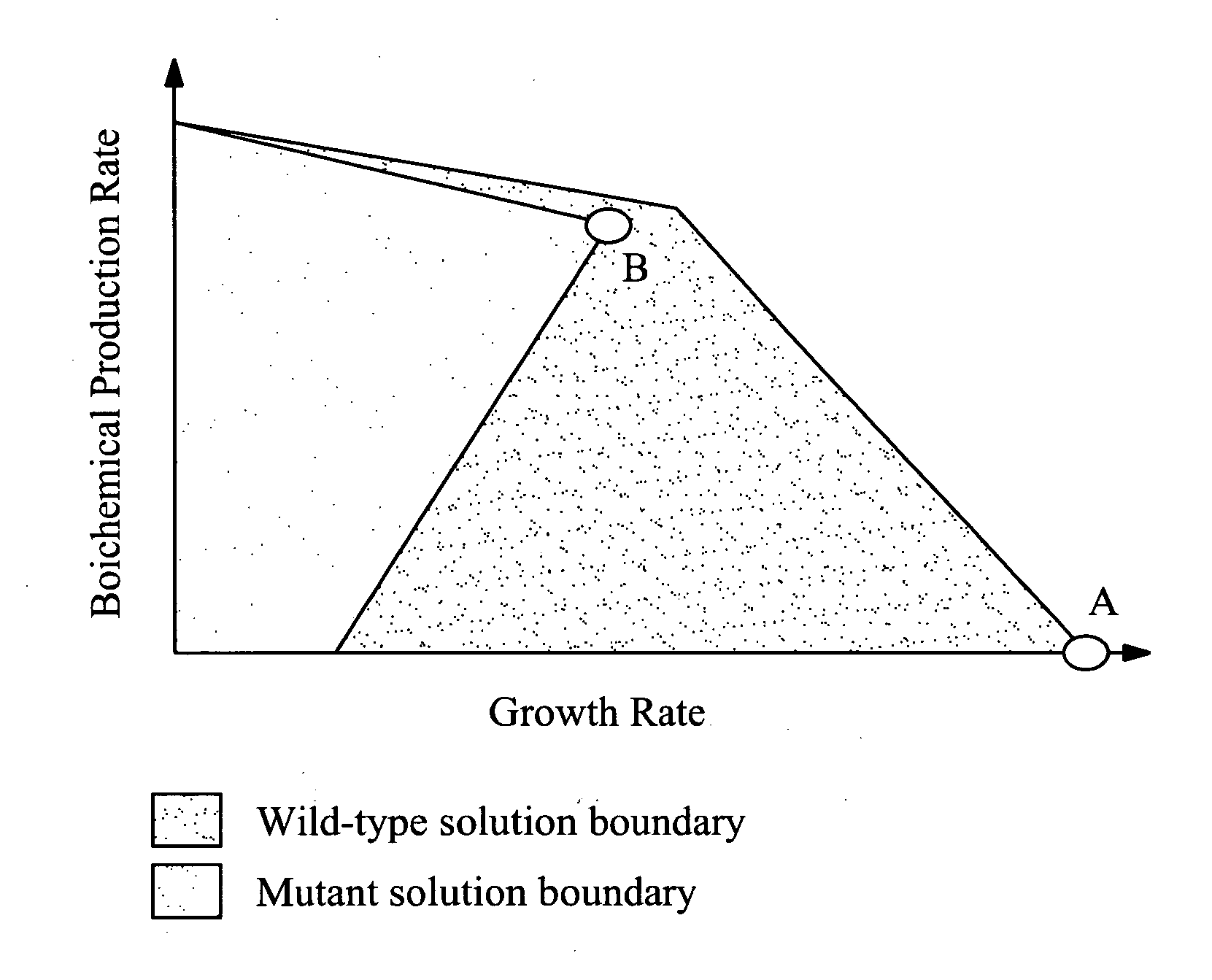
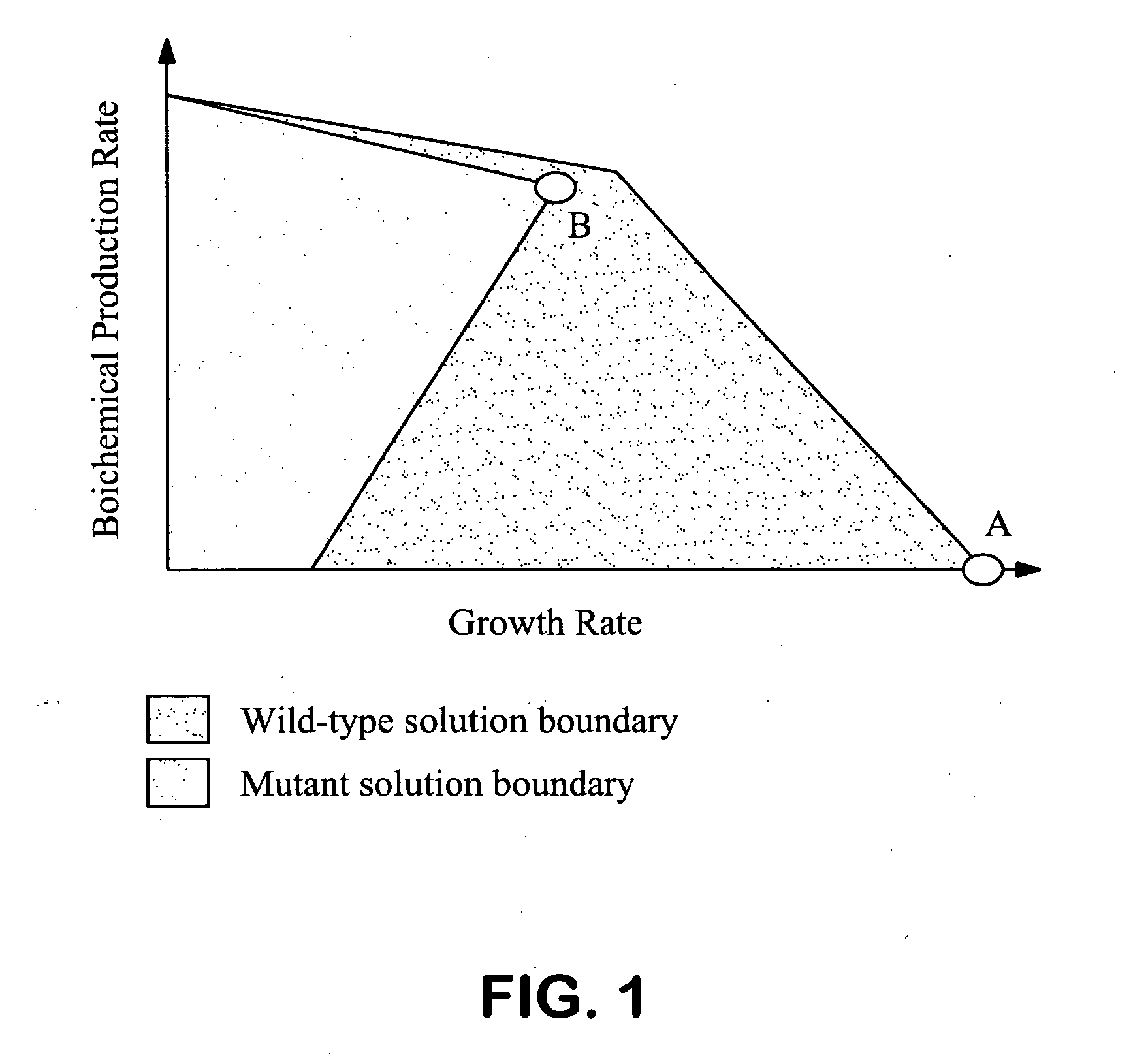
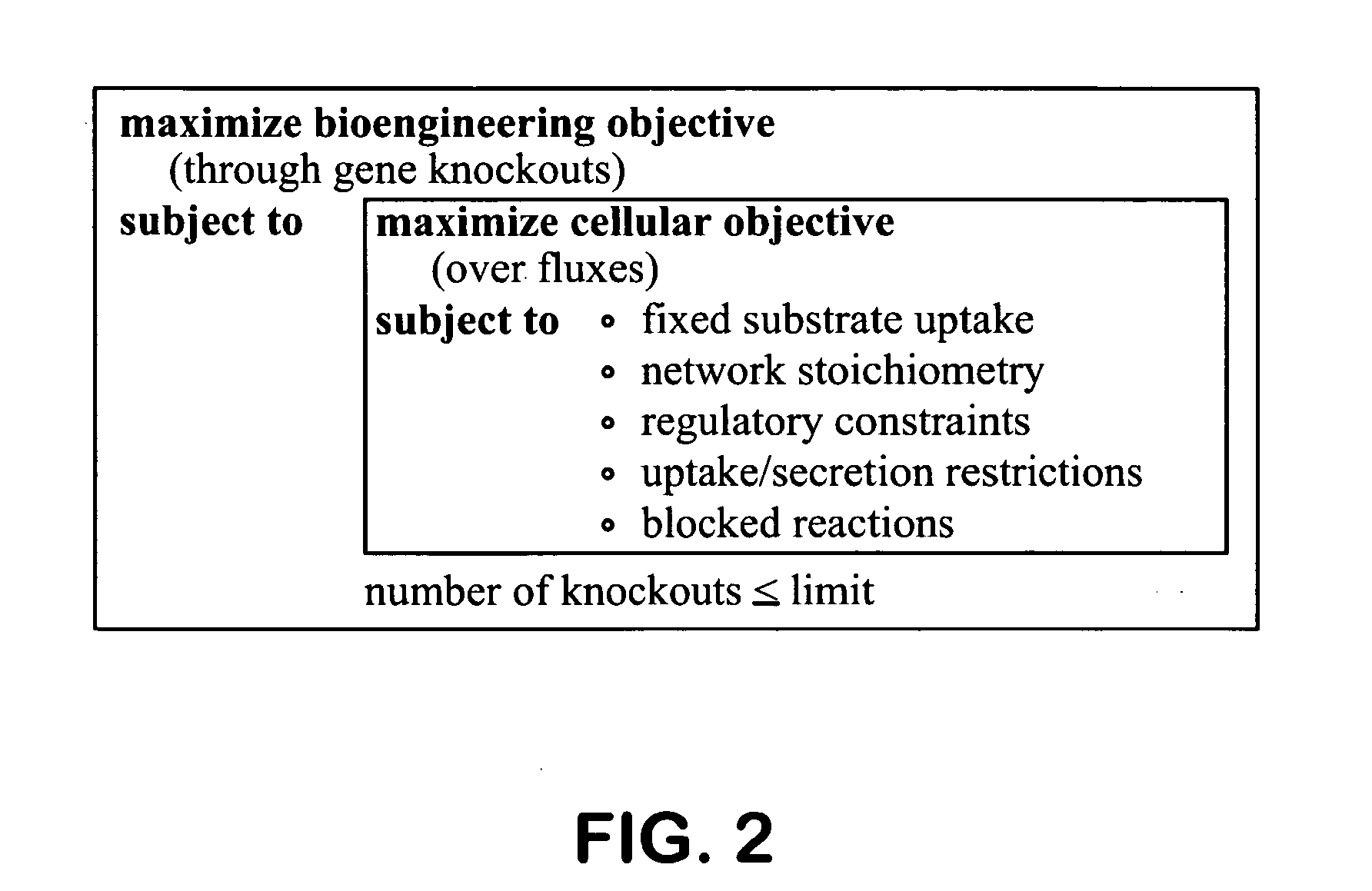
Method for the evolutionary design of biochemical reaction networks
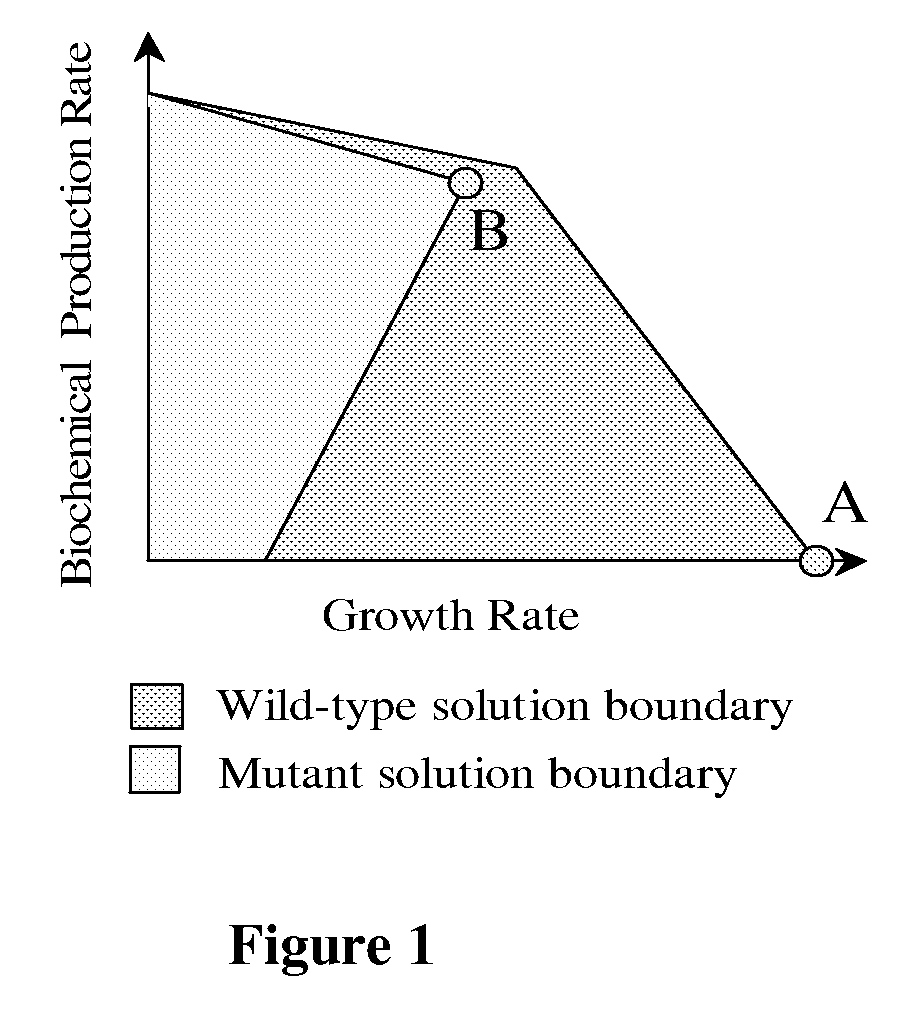
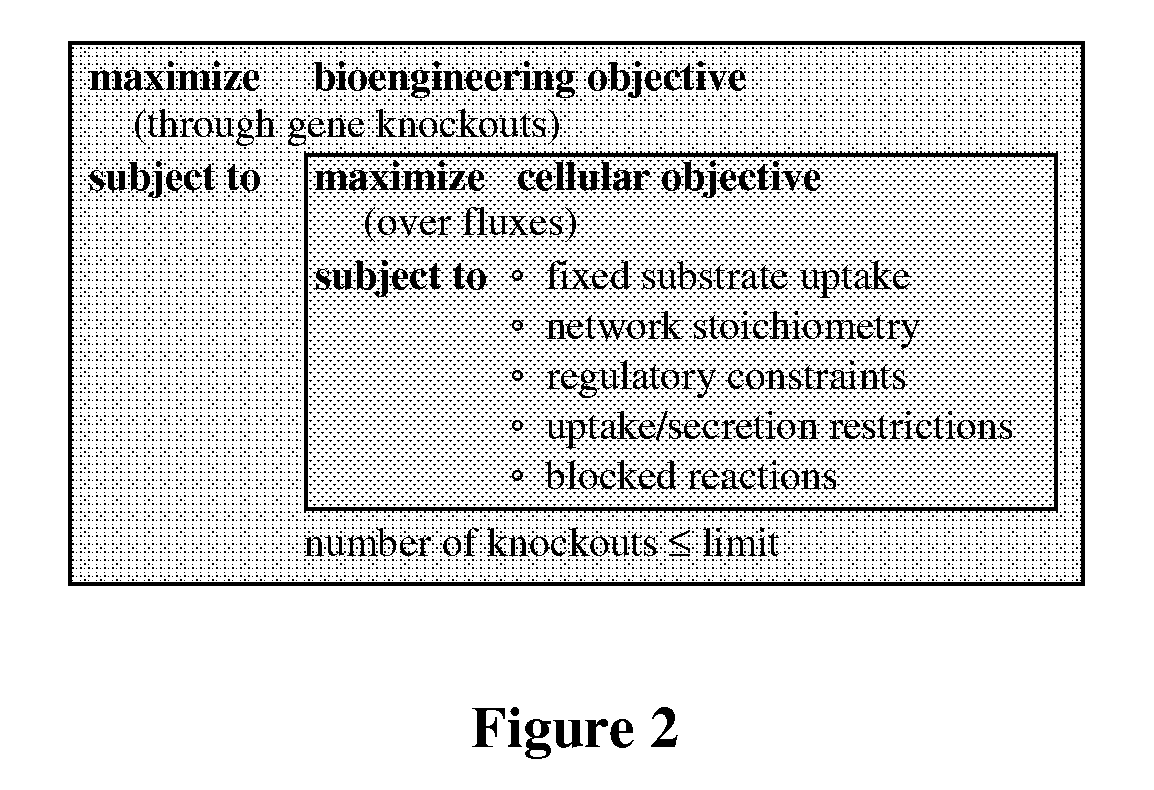
The present invention relates to methods for achieving an optimal function of a biochemical reaction network. The methods can be performed in silico using a reconstruction of a biochemical reaction network of a cell and iterative optimization procedures. The methods can further include laboratory culturing steps to confirm and possibly expand the determinations made using the in silico methods, and to produce a cultured cell, or population of cells, with optimal functions. The current invention includes computer systems and computer products including computer-readable program code for performing the in silico steps of the invention.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for making character strings, polynucleotides and polypeptides having desired characteristics
“In silico” nucleic acid recombination methods, related integrated systems utilizing genetic operators and libraries made by in silico shuffling methods are provided.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Identifying oligonucleotides for in vitro recombination
“In silico” nucleic acid recombination methods, related integrated systems utilizing genetic operators and libraries made by in silico shuffling methods are provided.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
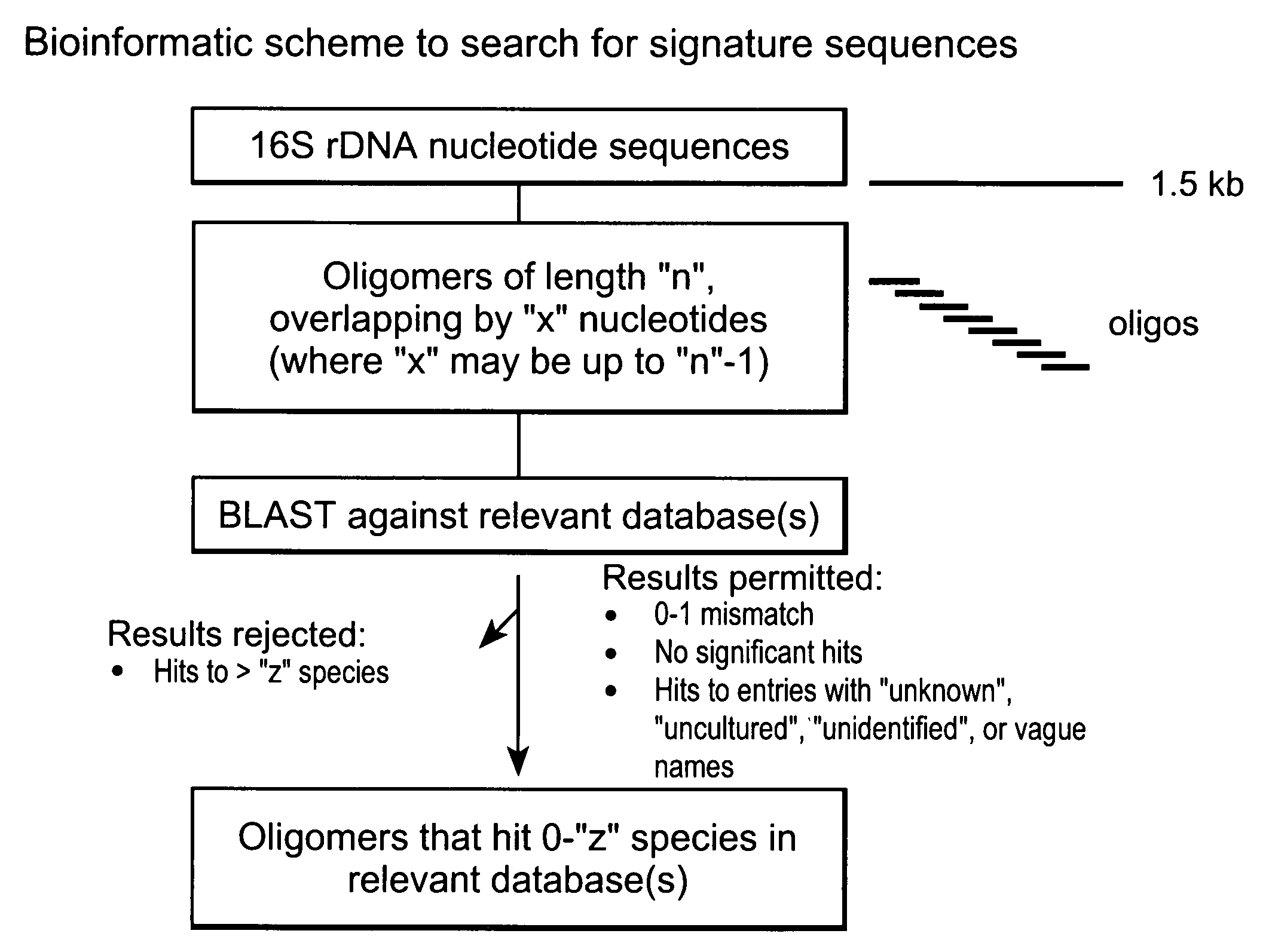
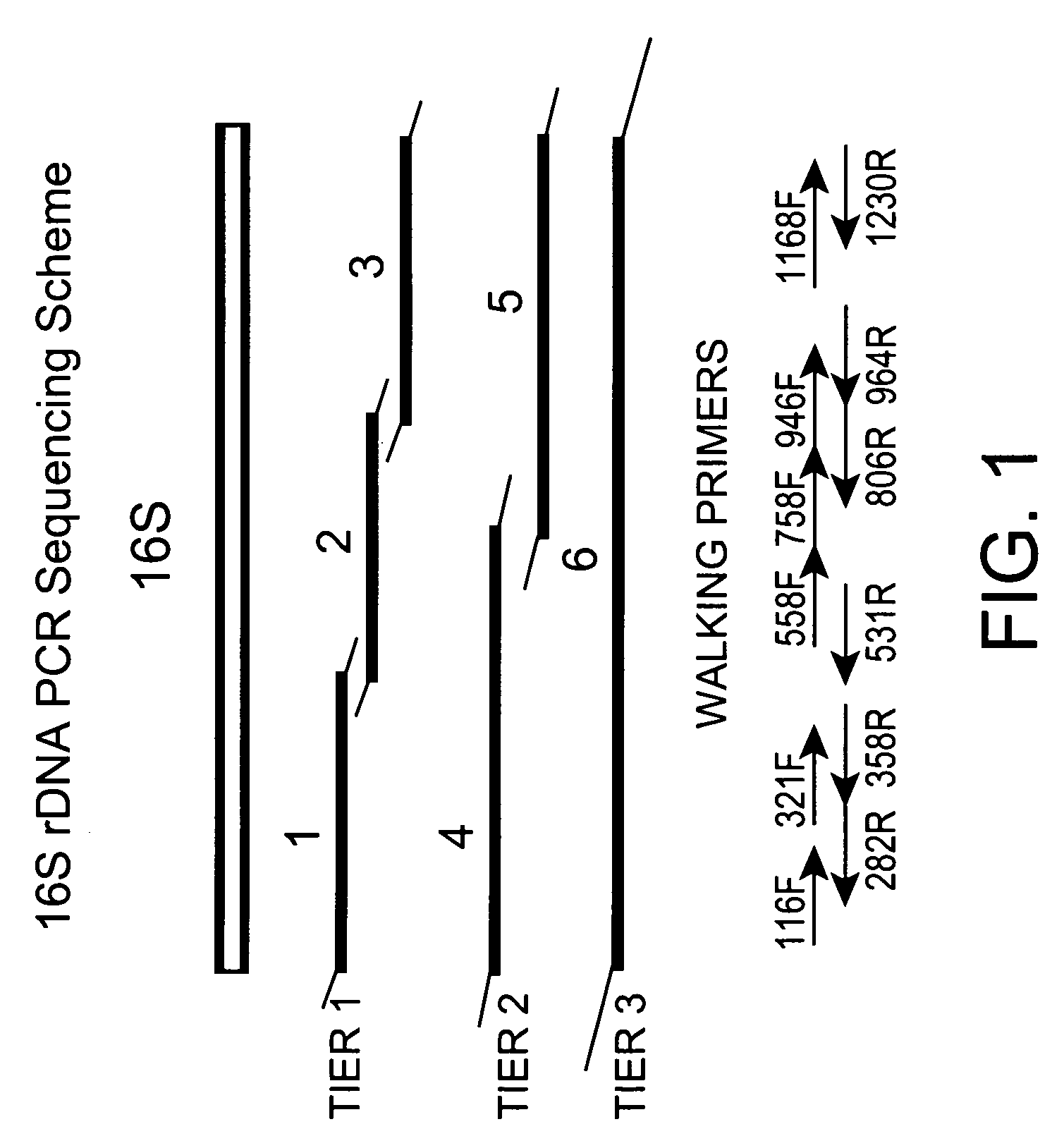
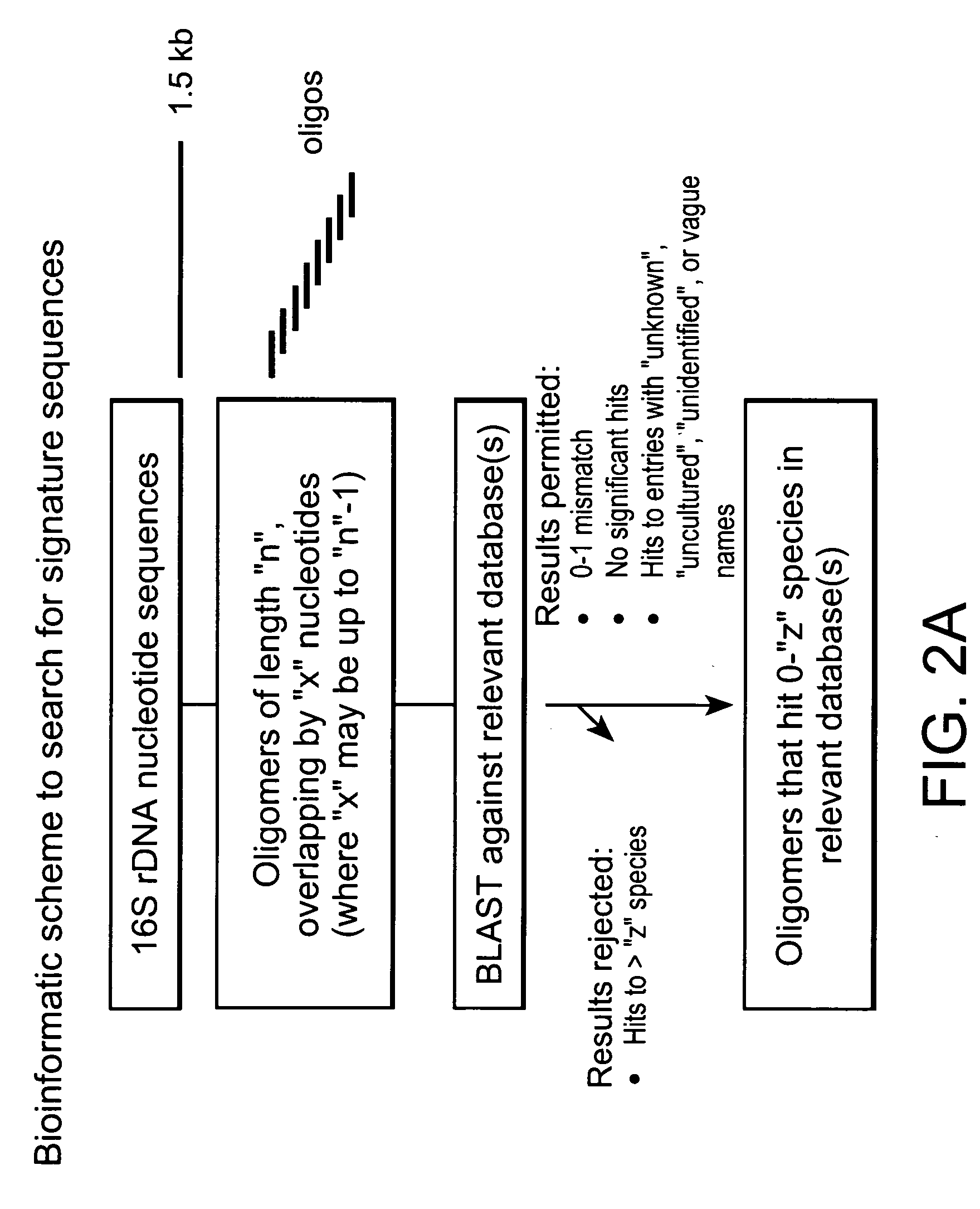
Genus, group, species and/or strain specific 16S rDNA sequences
InactiveUS20060046246A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismStrain specificity
Materials and methods for identifying unique sites in bacterial 16S and 23S rDNA are provided, as well as specific unique sequences of 16S rDNA in select bacteria. The distinguishing moieties will enable rapid differentiation between families, genera, groups, species, strains, subspecies, and isolates of microorganisms. Such differentiation can be performed by using rapid screening kits in combination with in silico analysis for diagnostic, prognastic, epidemiologic, phylogenetic, and other purposes.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX INC +1
Methods and organisms for the growth-coupled production of succinate
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microorganism comprising one or more gene disruptions encoding an enzyme associated with growth-coupled production of succinate when an activity of the enzyme is reduced, whereby the one or more gene disruptions confers stable growth-coupled production of succinate onto the non- naturally occurring microorganism. Also provided is a non-naturally occurring microorganism comprising a set of metabolic modifications obligatory coupling succinate production to growth of the microorganism, the set of metabolic modifications comprising disruption of one or more genes selected from the set of genes comprising: (a) adhE, ldhA; (b) adhE, ldhA, acka-pta; (c) pfl, ldhA; (d) pfl, ldhA, adhE; (e) acka-pta, pykF, atpF, sdhA; (f) acka-pta, pykF, ptsG, or (g) acka-pta, pykF, ptsG, adhE, ldhA, or an ortholog thereof, wherein the microorganism exhibits stable growth-coupled production of succinate. Additionally provided is a non-naturally occurring microorganism having the genes encoding the metabolic modification (e) acka-pta, pykF, atpF, sdhA that further includes disruption of at least one gene selected from pyka, atpH, sdhB or dhaKLM; a non-naturally occurring microorganism having the genes encoding the metabolic modification (f) ackA-pta, pykF, ptsG that further includes disruption of at least one gene selected from pykA or dhaKLM, or a non-naturally occurring microorganism having the genes encoding the metabolic modification (g) ackA-pta, pykF, ptsG, adhE, ldhA that further includes disruption of at least one gene selected from pykA or dhaKLM. The disruptions can be complete gene disruptions and the non-naturally occurring organisms can include a variety of prokaryotic or eukaryotic microorganisms. A method of producing a non-naturally occurring microorganism having stable growth-coupled production of succinate also is provided. The method includes: (a) identifying in silico a set of metabolic modifications requiring succinate production during exponential growth, and (b) genetically modifying a microorganism to contain the set of metabolic modifications requiring succinate production.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Methods for making character strings, polynucleotides and polypeptides having desired characteristics
“In silico” nucleic acid recombination methods, related integrated systems utilizing genetic operators and libraries made by in silico shuffling methods are provided.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
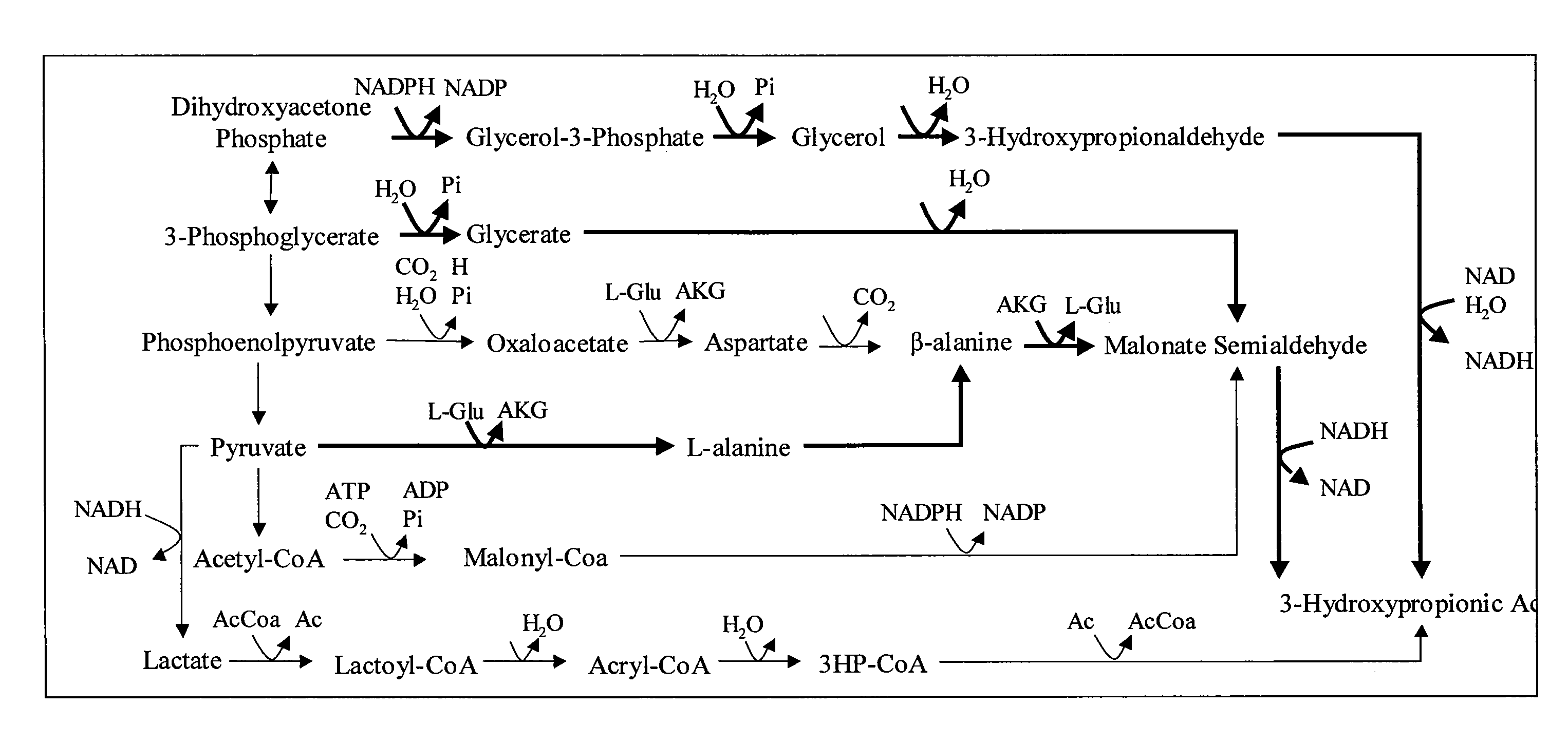
Methods and Organisms for Growth-Coupled Production of 3-Hydroxypropionic Acid
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microorganism having one or more gene disruptions, the one or more gene disruptions occurring in genes encoding an enzyme obligatory coupling 3-hydroxypropionic acid production to growth of the microorganism when the gene disruption reduces an activity of the enzyme, whereby the one or more gene disruptions confers stable growth-coupled production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid onto the non-naturally occurring microorganism. Also provided is a non-naturally occurring microorganism comprising a set of metabolic modifications obligatory coupling 3-hydroxypropionic acid production to growth of the microorganism, the set of metabolic modifications having disruption of one or more genes including: (a) the set of genes selected from: (1) adhE, ldhA, pta-ackA; (2) adhE, ldhA, frdABCD; (3) adhE, ldhA, frdABCD, ptsG; (4) adhE, ldhA, frdABCD, pntAB; (5) adhE, ldhA, fumA, fumB, fumC; (6) adhE, ldhA, fumA, fumB, fumC, pntAB; (7) pflAB, ldhA, or (8) adhE, ldhA, pgi in a microorganism utilizing an anaerobic β-alanine 3-HP precursor pathway; (b) the set of genes selected from: (1) tpi, zwf; (2) tpi, ybhE; (3) tpi, gnd; (4) fpb, gapA; (5) pgi, edd, or (6) pgi, eda in a microorganism utilizing an aerobic glycerol 3-HP precursor pathway; (c) the set of genes selected from: (1) eno; (2) yibO; (3) eno, atpH, or other atp subunit, or (4) yibO, atpH, or other atp subunit, in a microorganism utilizing a glycerate 3-HP precursor pathway, or an ortholog thereof, wherein the microorganism exhibits stable growth-coupled production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid. The disruptions can be complete gene disruptions and the non-naturally occurring organisms can include a variety of prokaryotic or eukaryotic microorganisms. A method of producing a non-naturally occurring microorganism having stable growth-coupled production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid is further provided. The method includes: (a) identifying in silico a set of metabolic modifications requiring 3-hydroxypropionic acid production during exponential growth, and (b) genetically modifying a microorganism to contain the set of metabolic modifications requiring 3-hydroxypropionic acid production.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
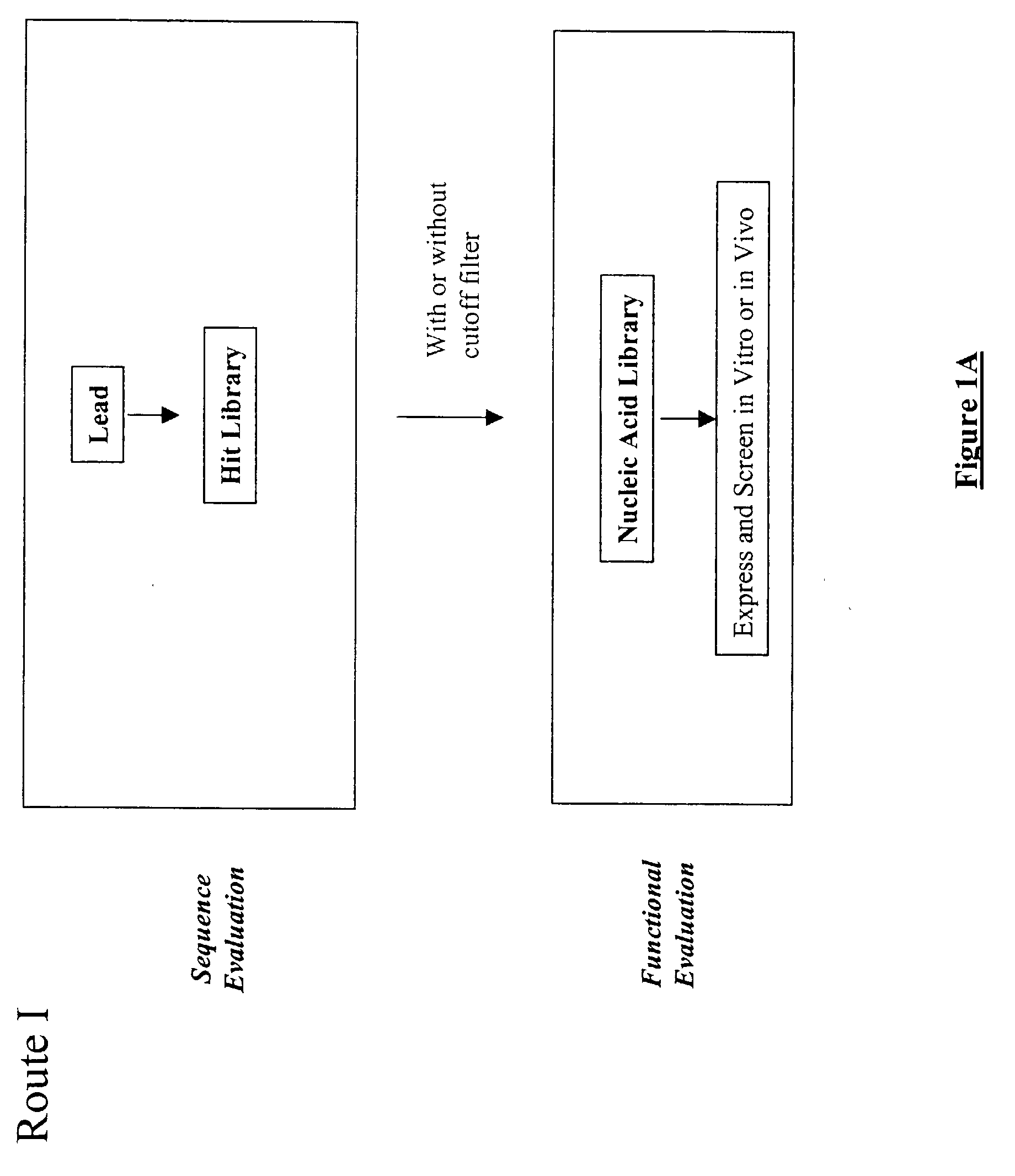
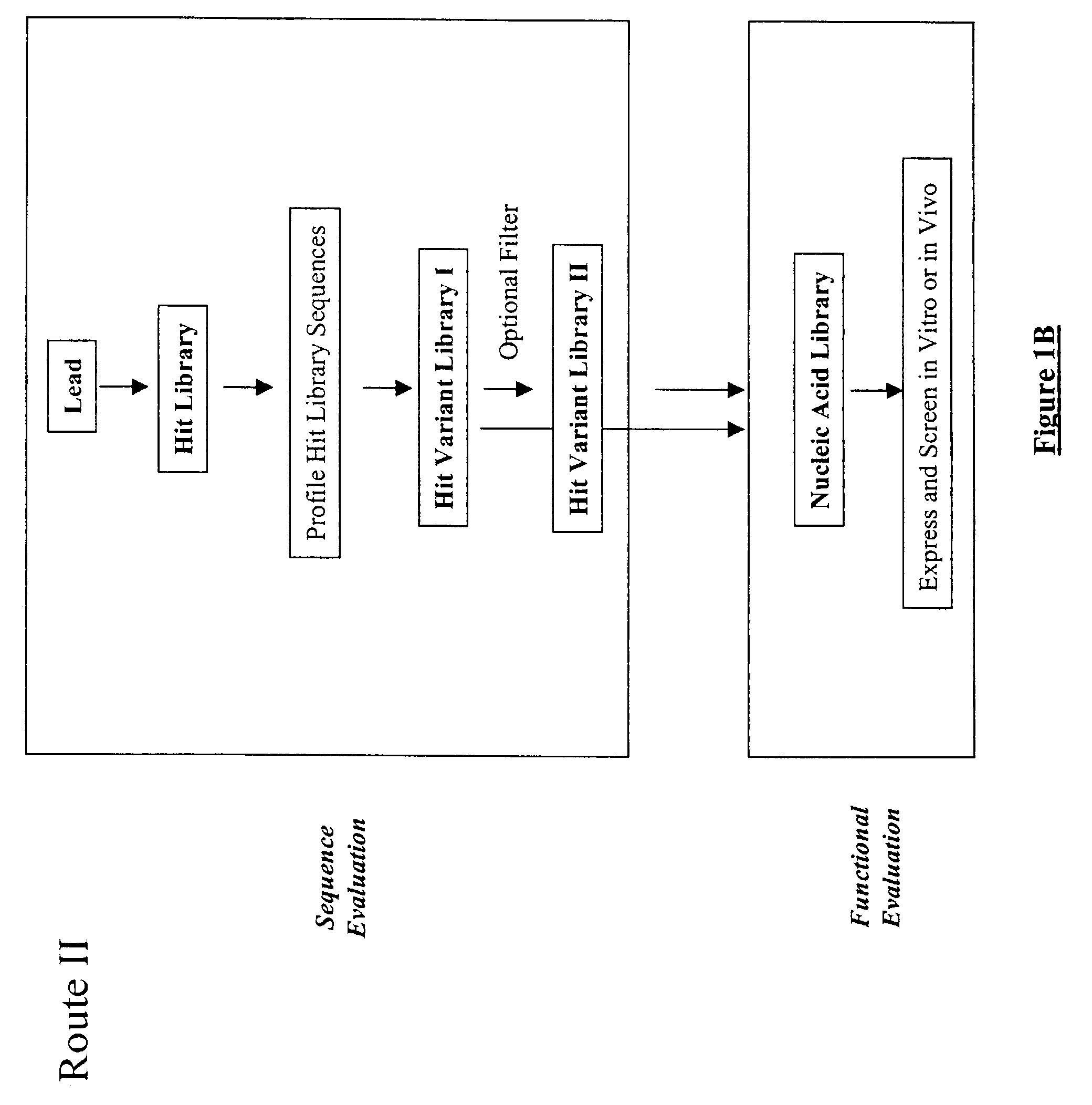
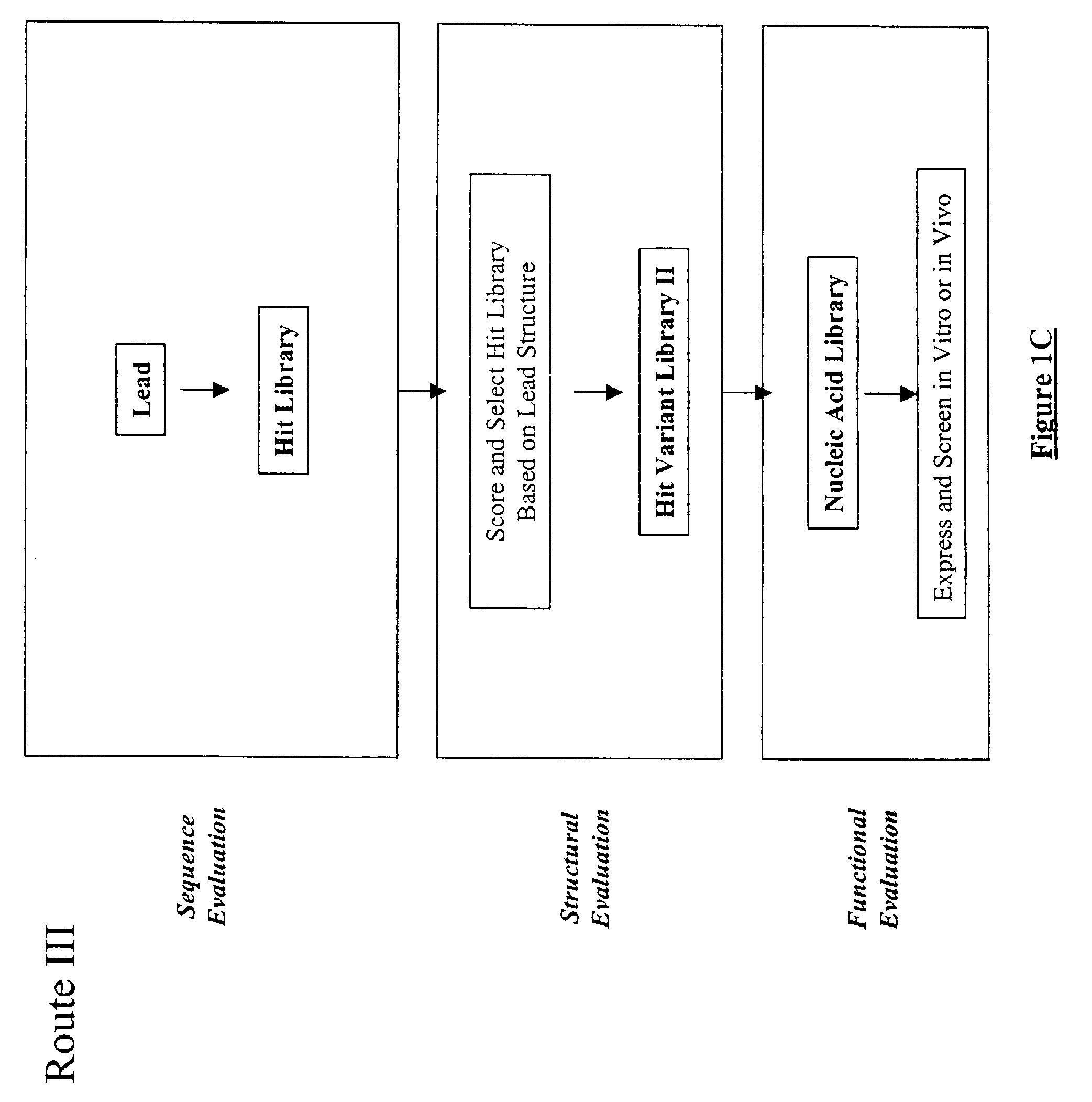
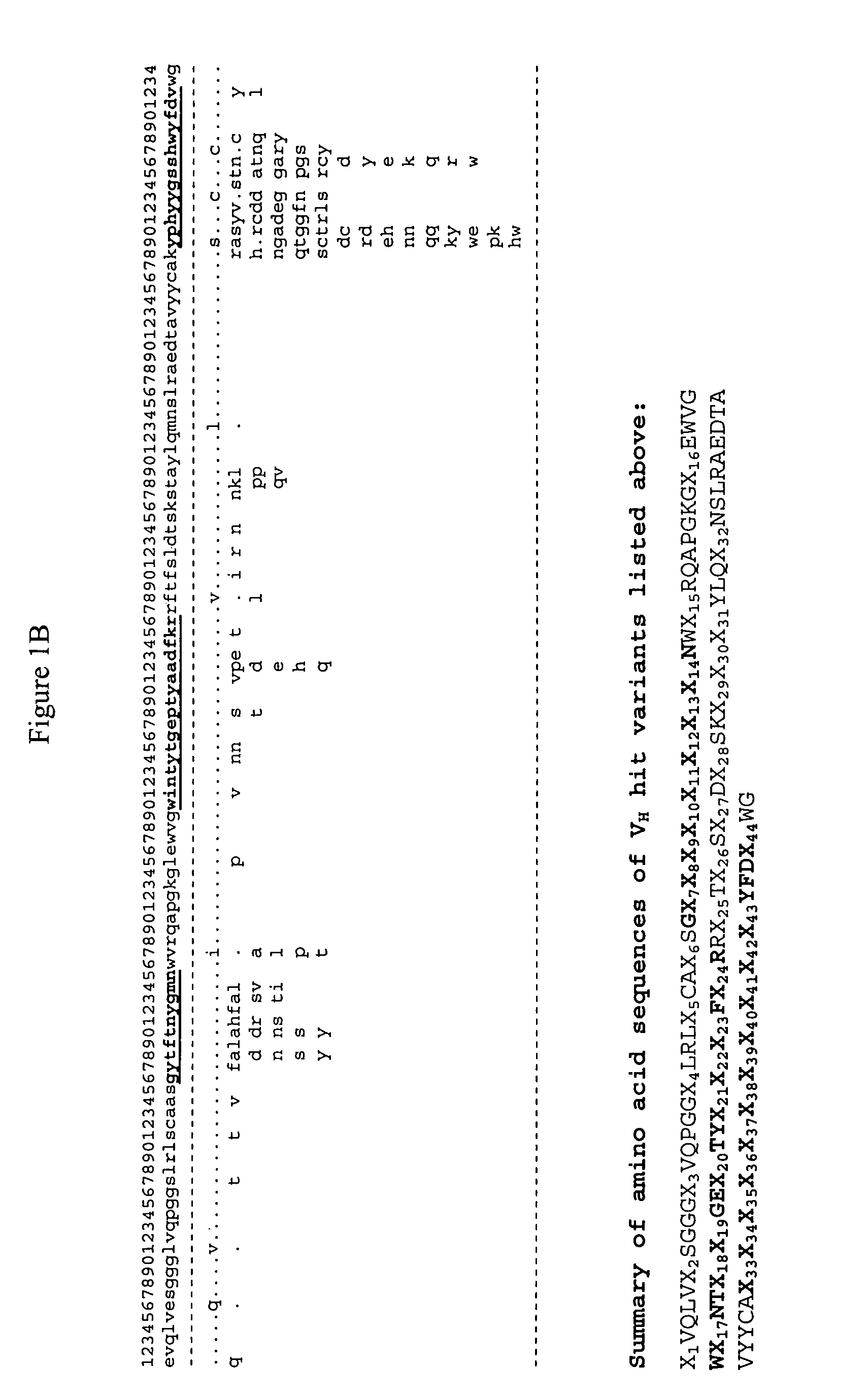
Generation and affinity maturation of antibody library in silico
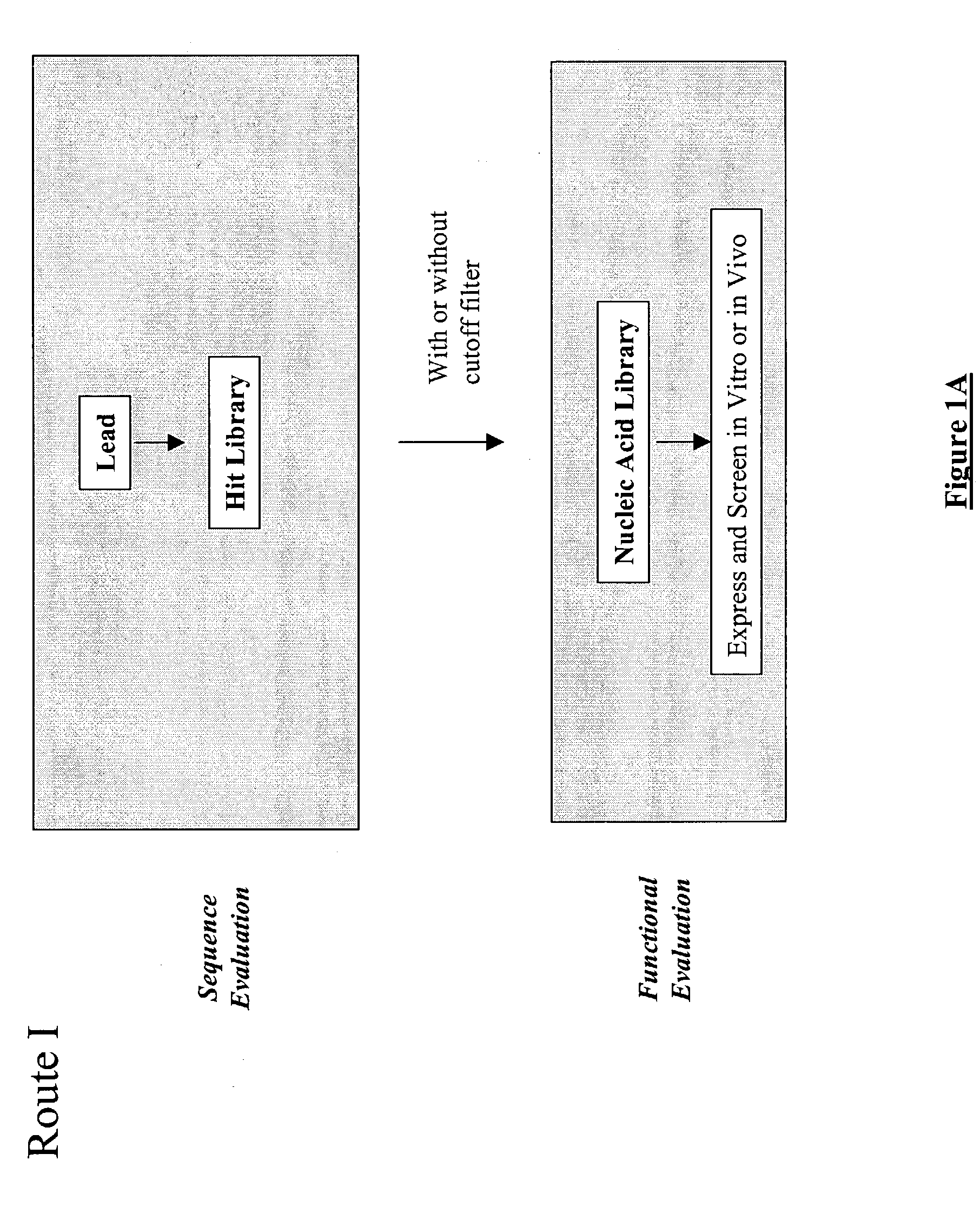
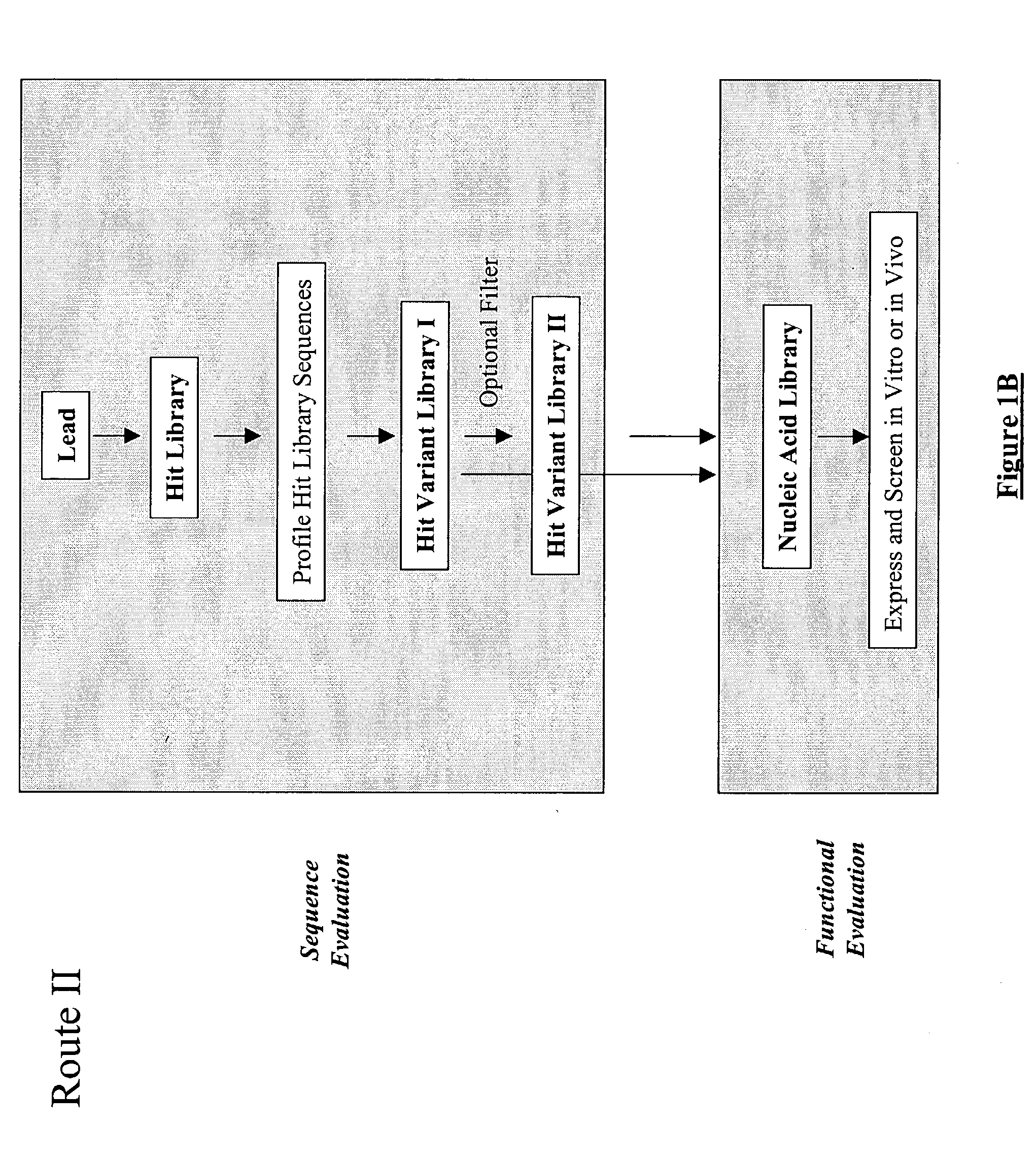
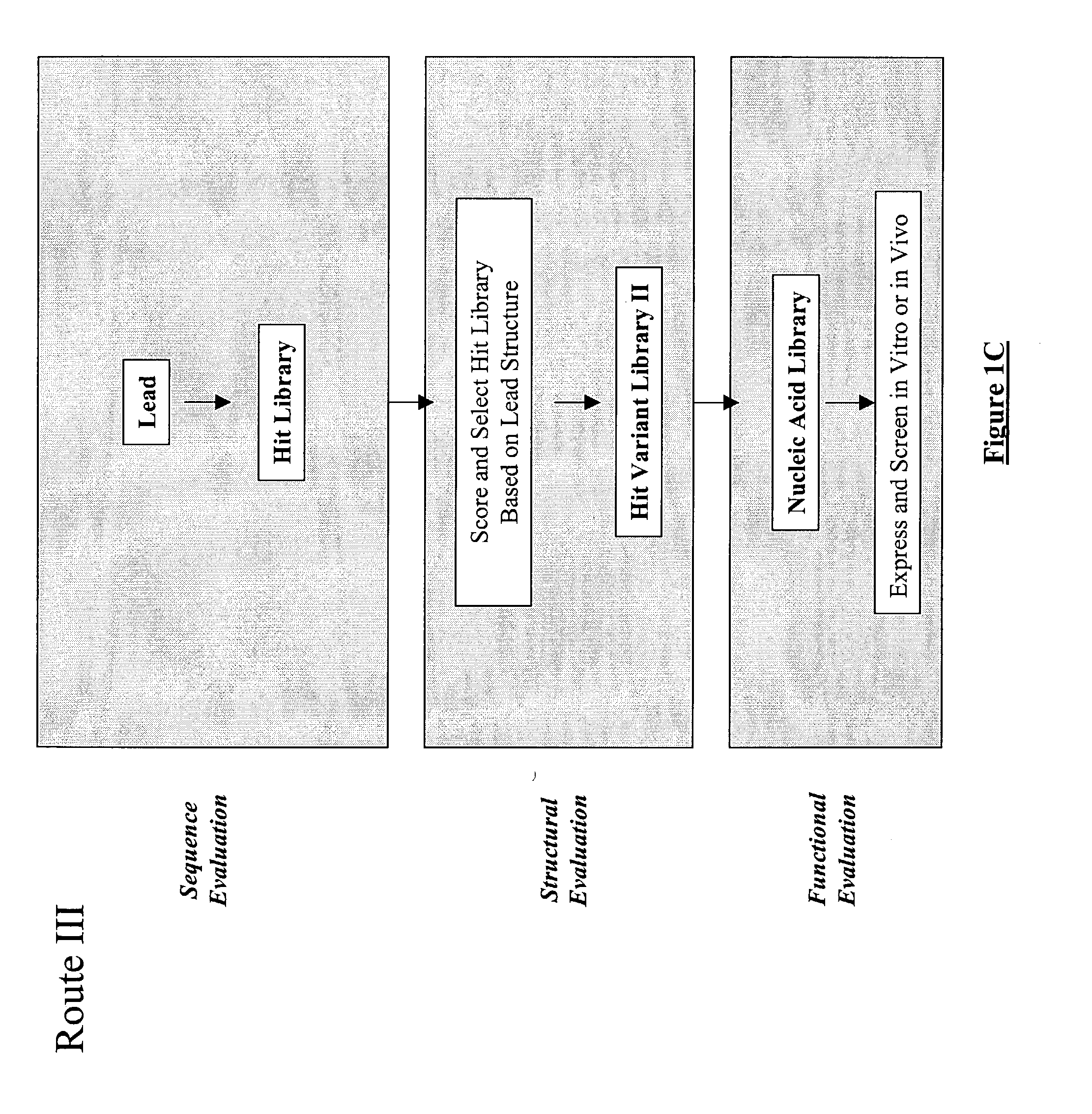
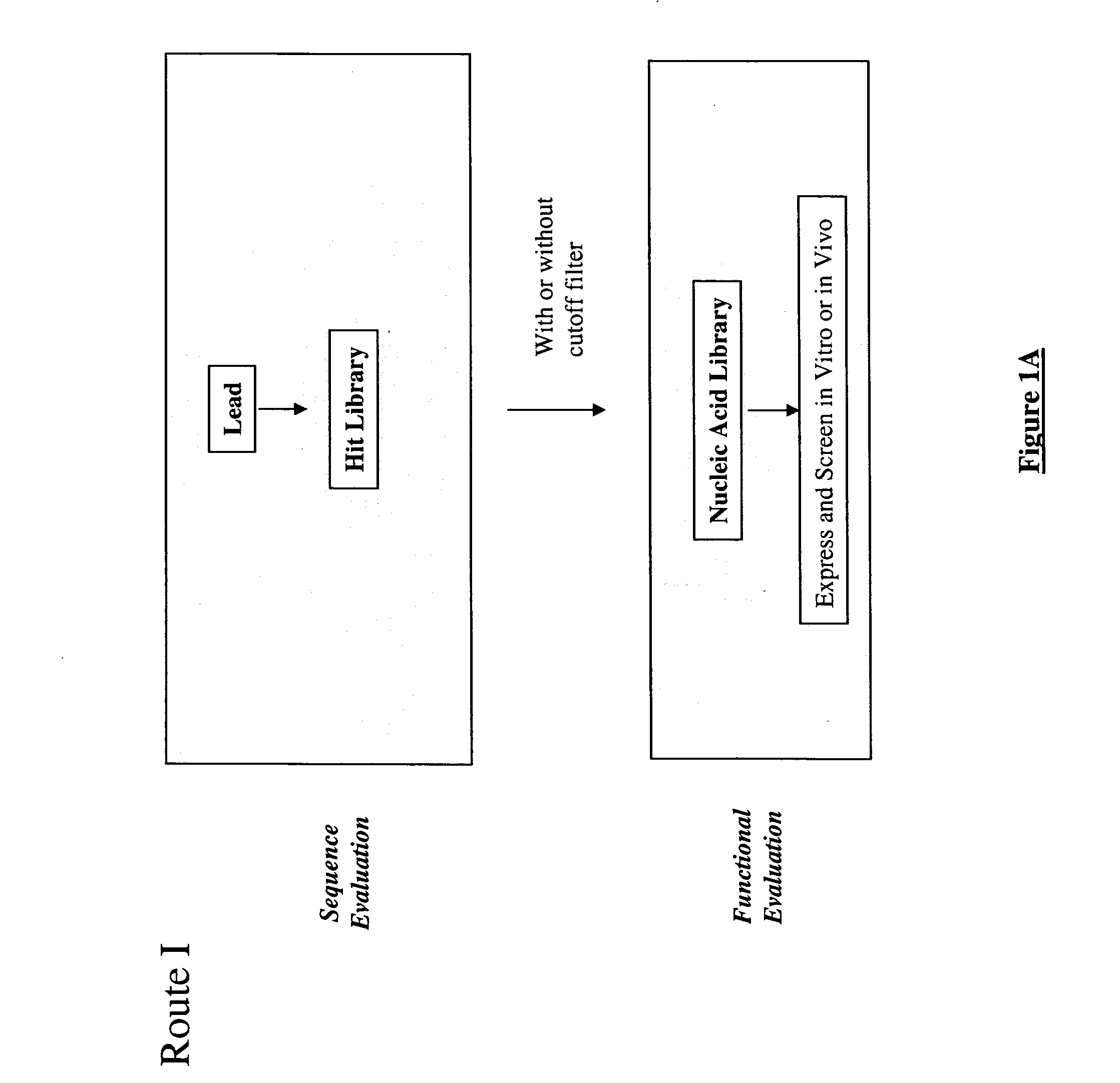
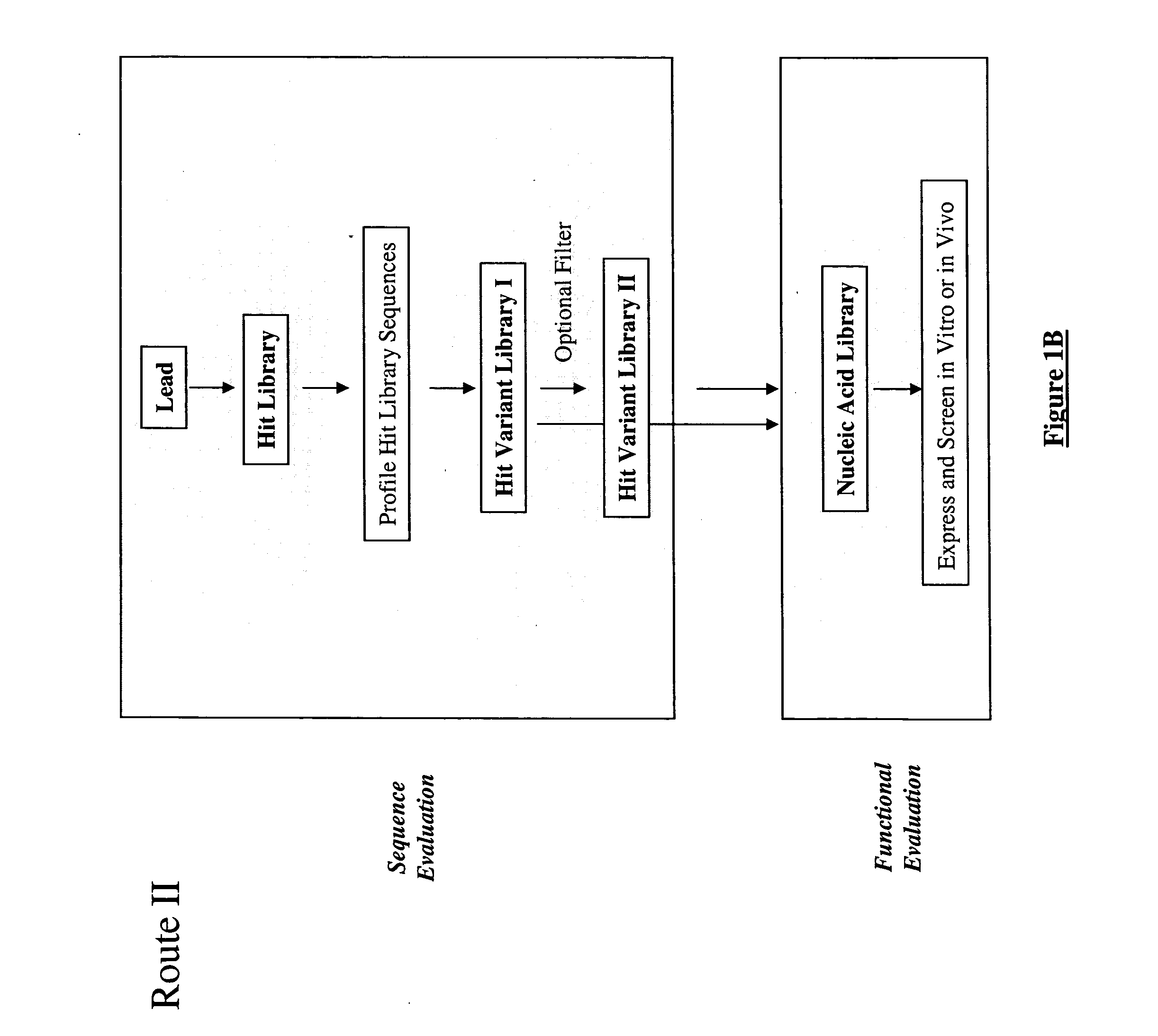
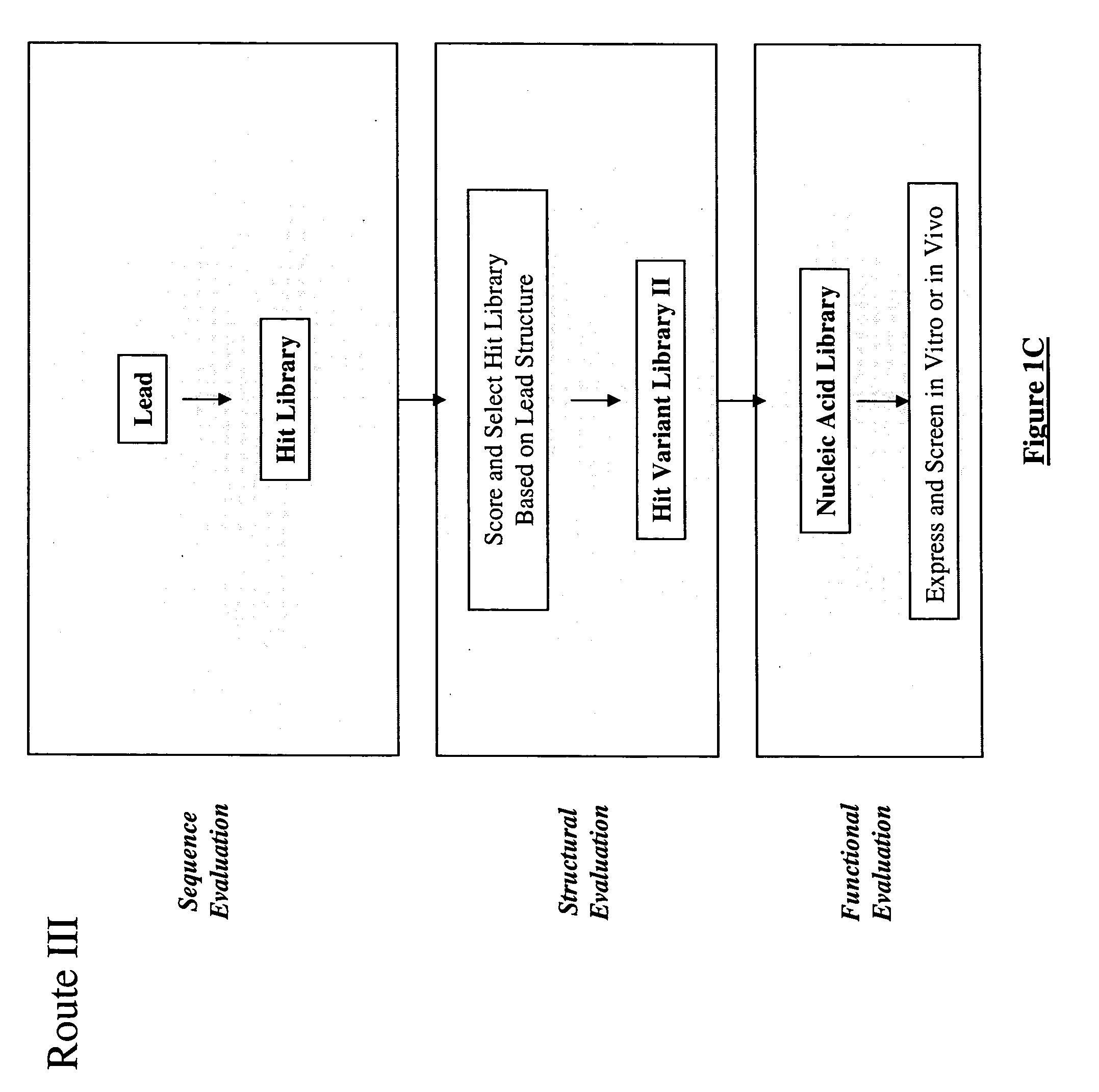
The present invention provides a methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as improved binding affinity towards biologically and / or therapeutically important target molecules. The process is carried out computationally in a high throughput manner by mining the ever-expanding databases of protein sequences of all organisms, especially human. In one embodiment, a method is provided for constructing a library of antibody sequences based on the amino acid sequence of a lead antibody. The method comprises: providing an amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) of a lead antibody; identifying the amino acid sequences in the CDRs of the lead antibody; selecting one of the CDRs in the VH or VL region of the lead antibody; providing an amino acid sequence that comprises at least 3 consecutive amino acid residues in the selected CDR, the selected amino acid sequence being a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence with a plurality of tester protein sequences; and selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 15% sequence identity with the lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library. The hit library of antibody sequences can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant antibodies that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead antibody.
Owner:ABMAXIS
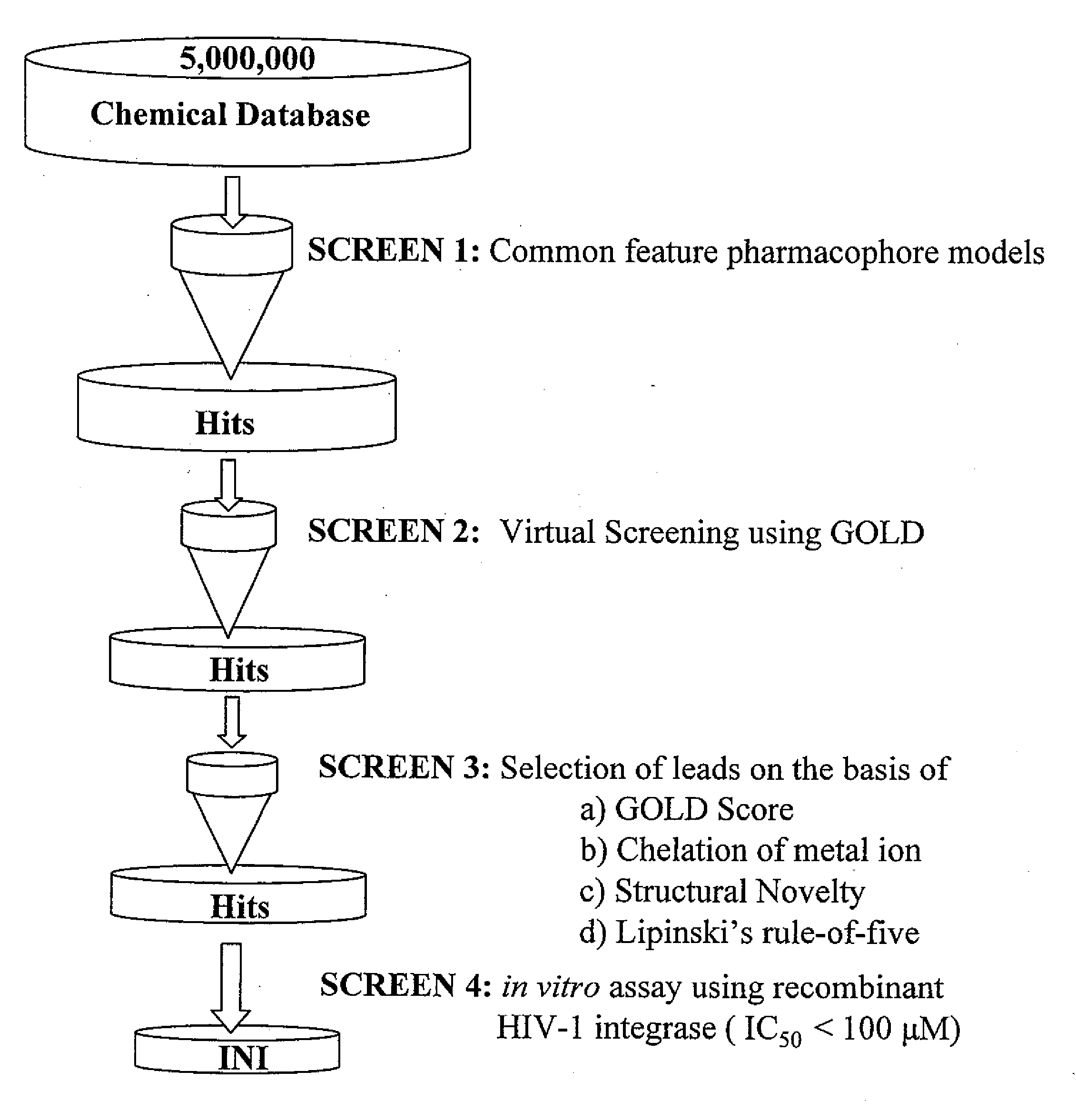
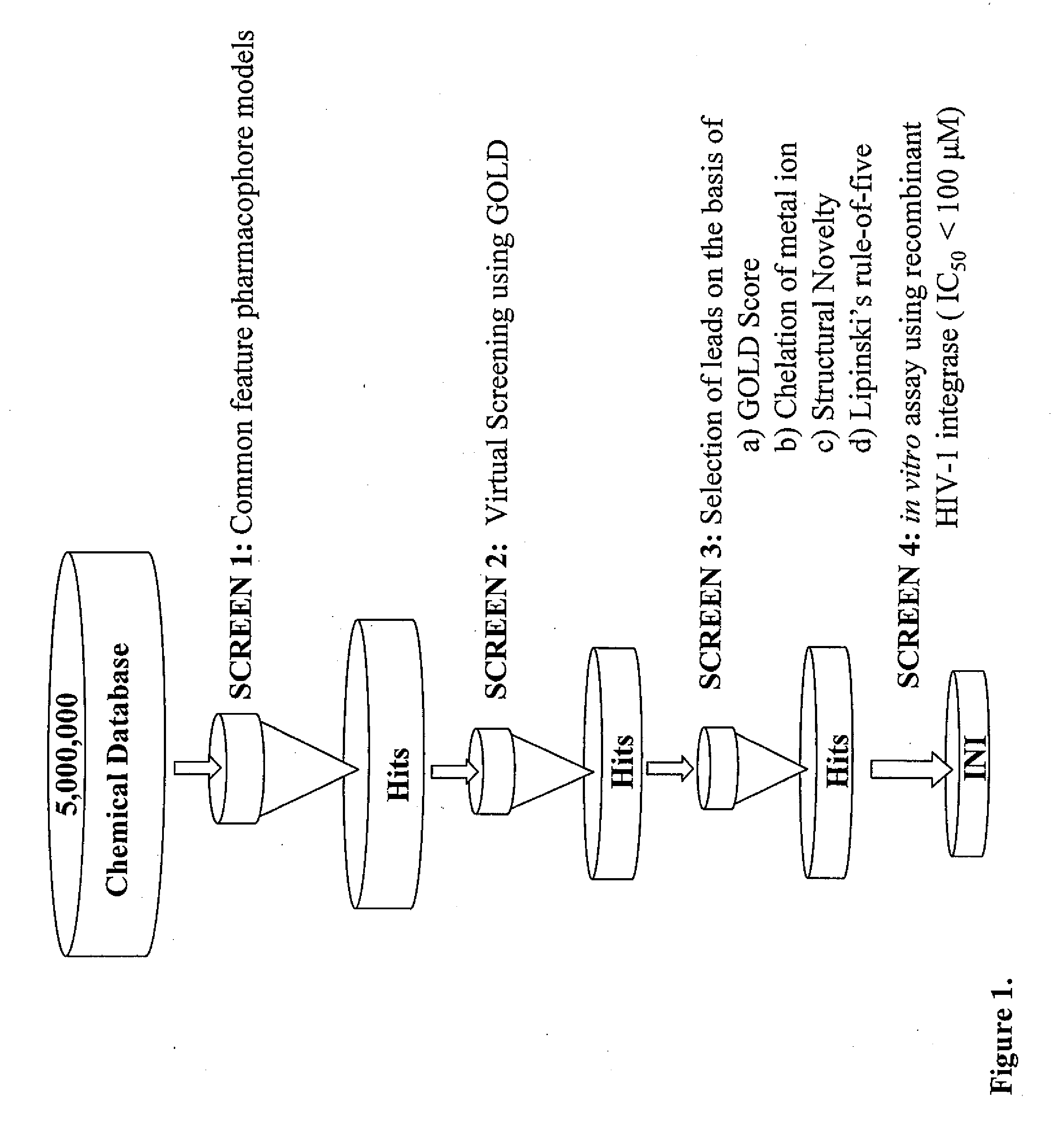
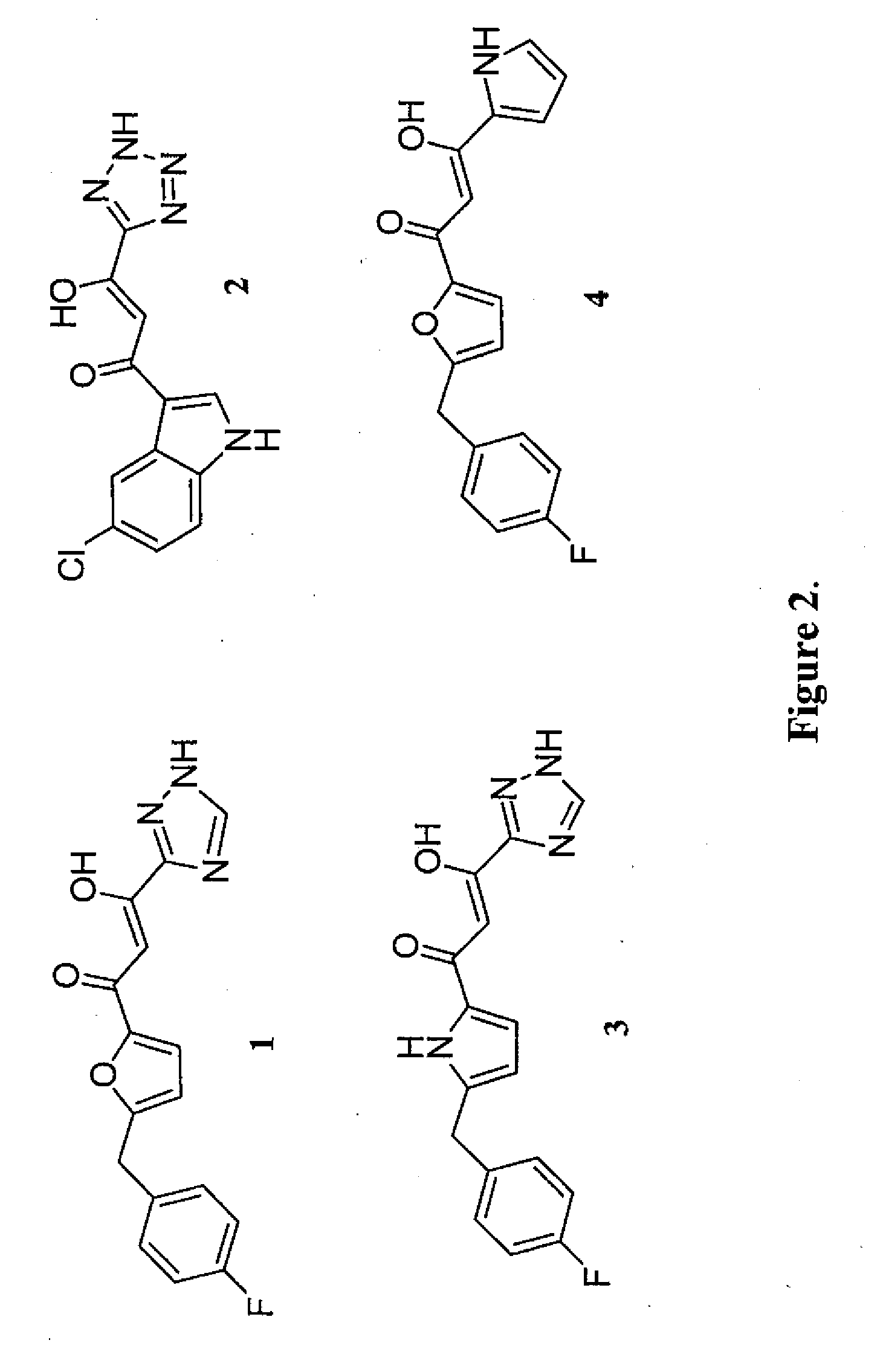
Compounds with hiv-1 integrase inhibitory activity and use thereof as Anti-hiv/aids therapeutics
Pharmacophore models to be used in drug design and discovery are provided. An in silico protocol and in vitro assays are presented. Compounds and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts with HIV-1 integrase inhibitory and anti-HIV activity and use thereof in the treatment of HIV / AIDS and related infections either alone or in combination with all the known antiretroviral therapeutics are described.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
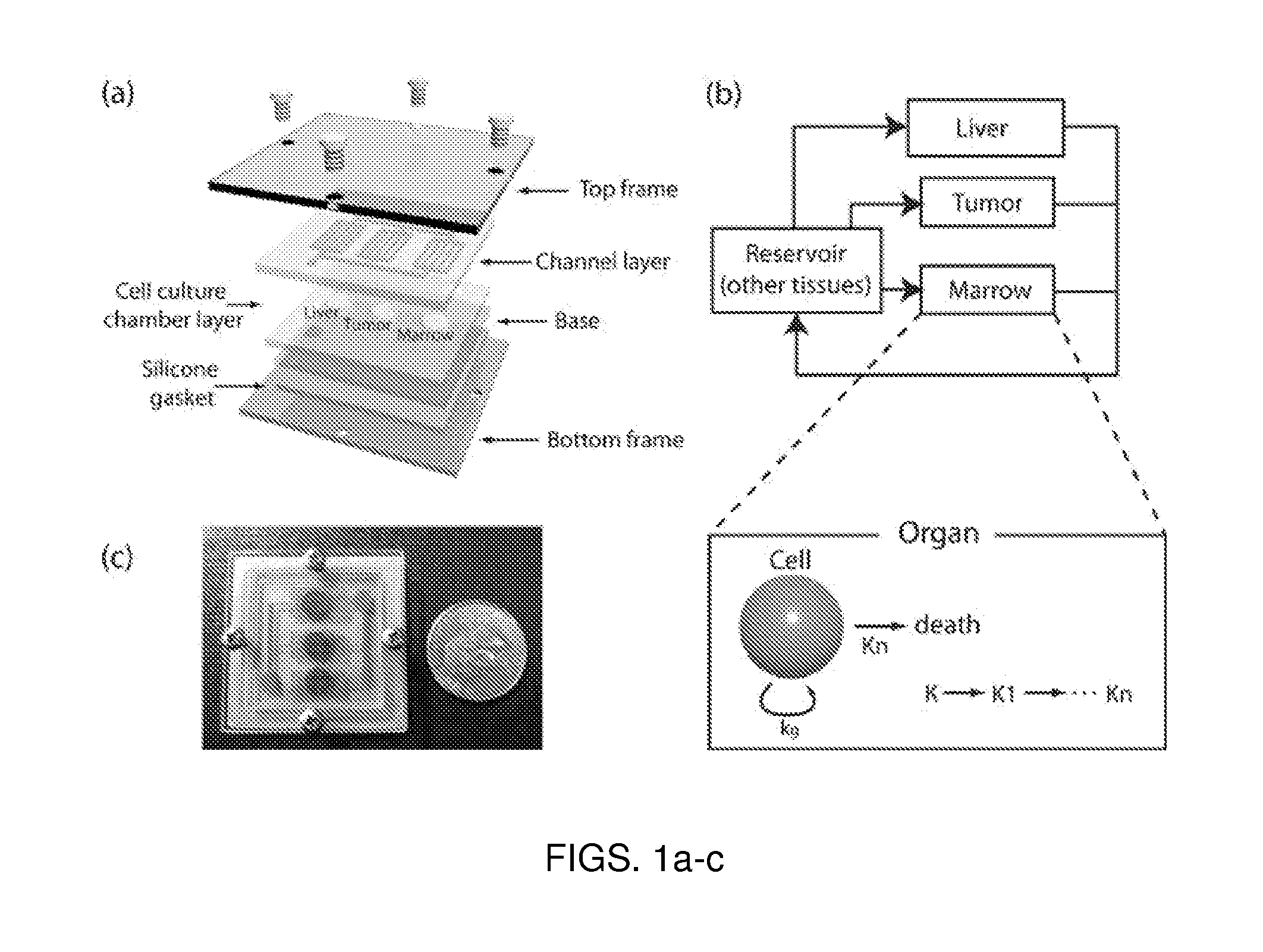
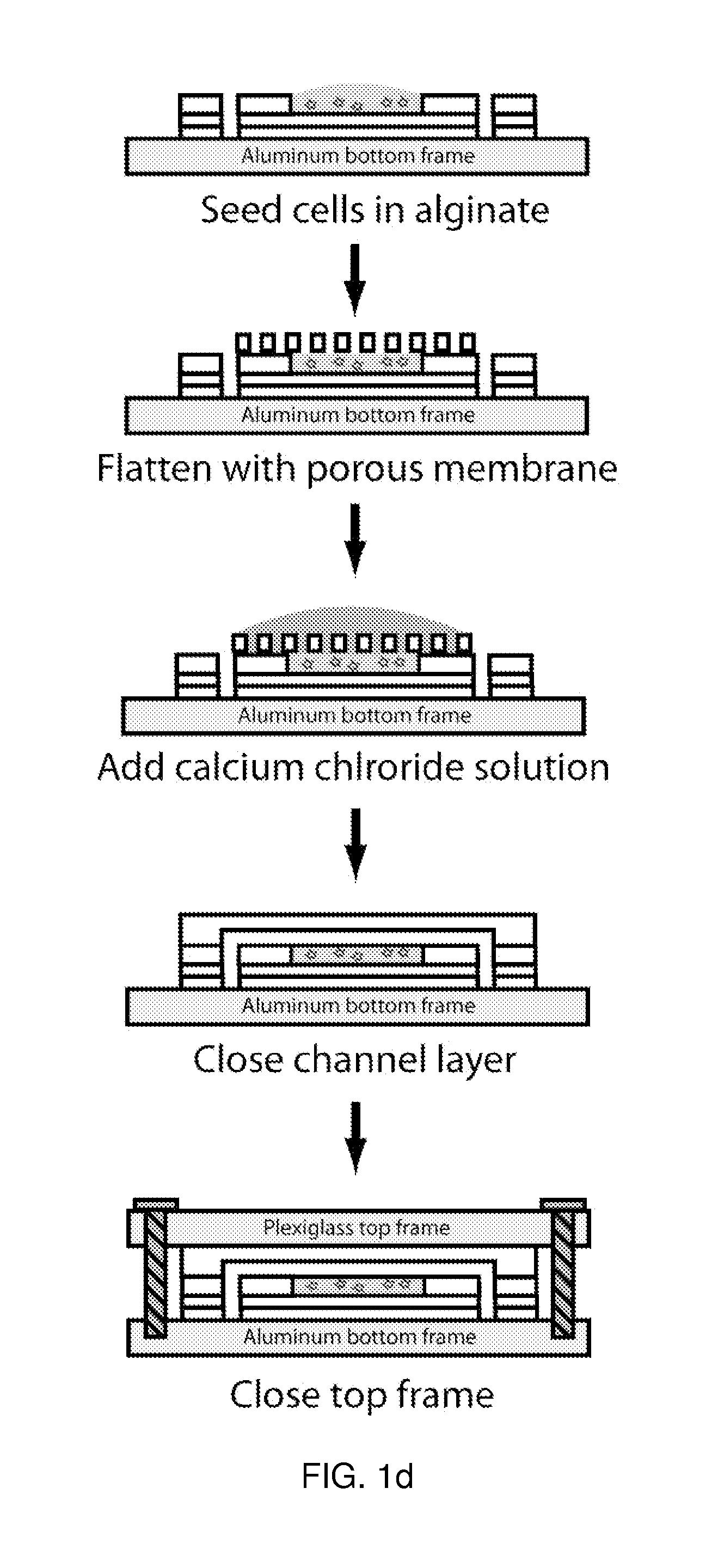
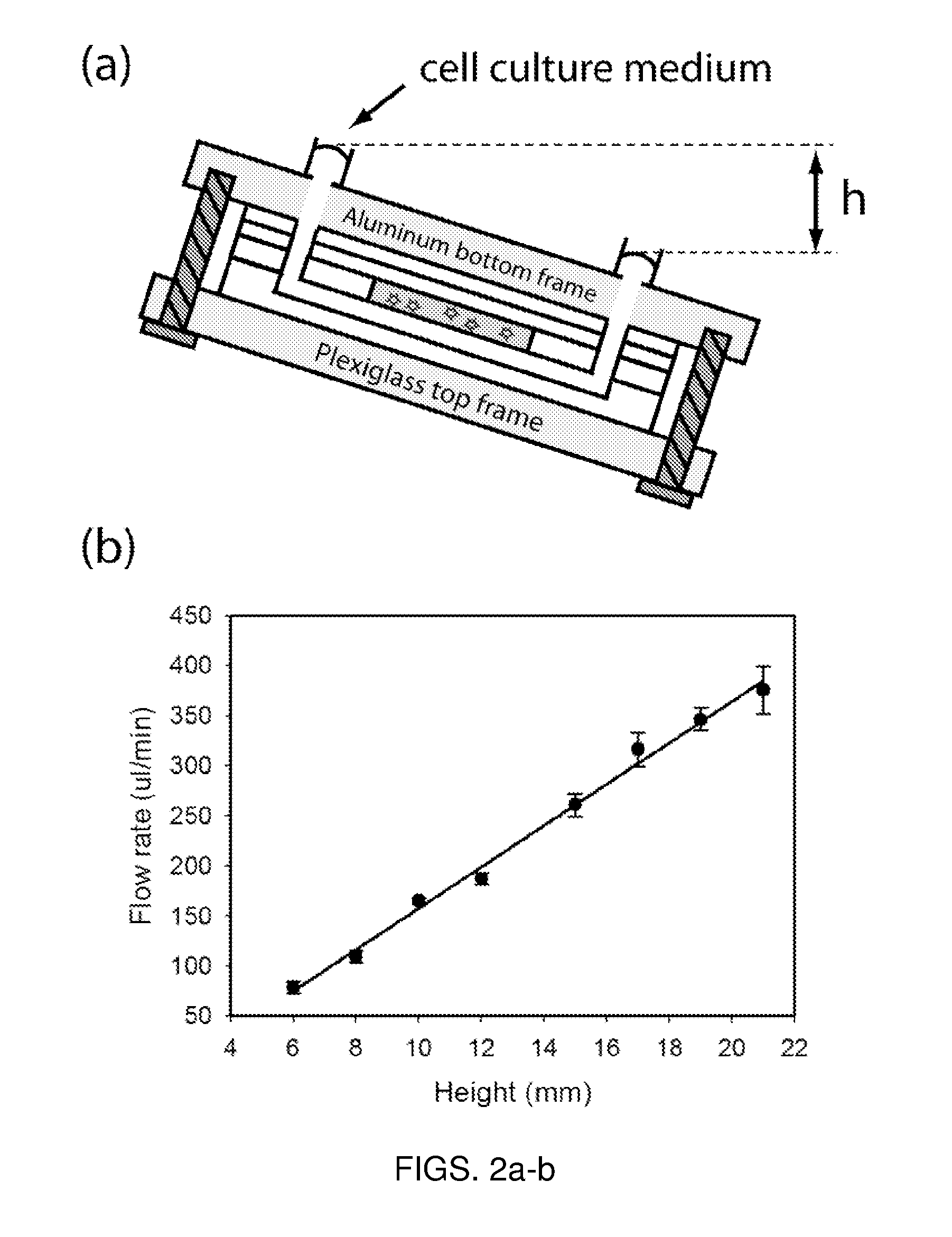
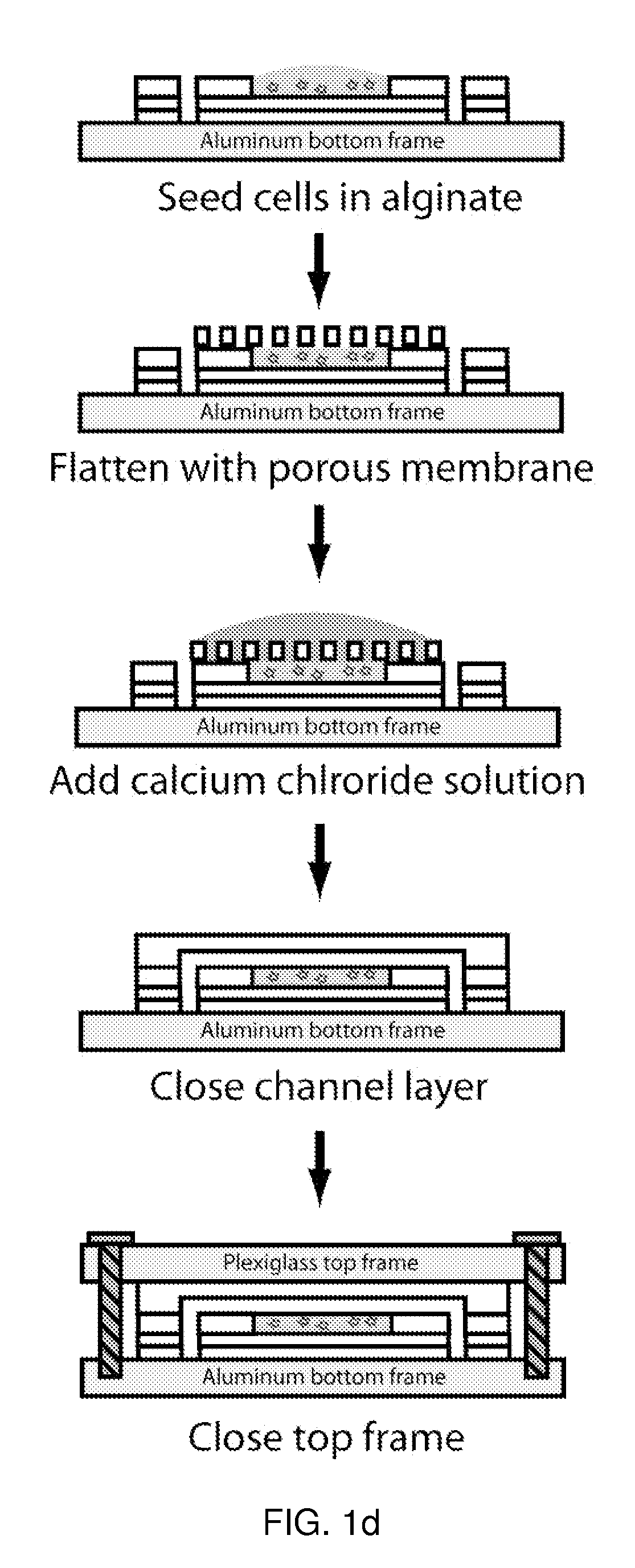
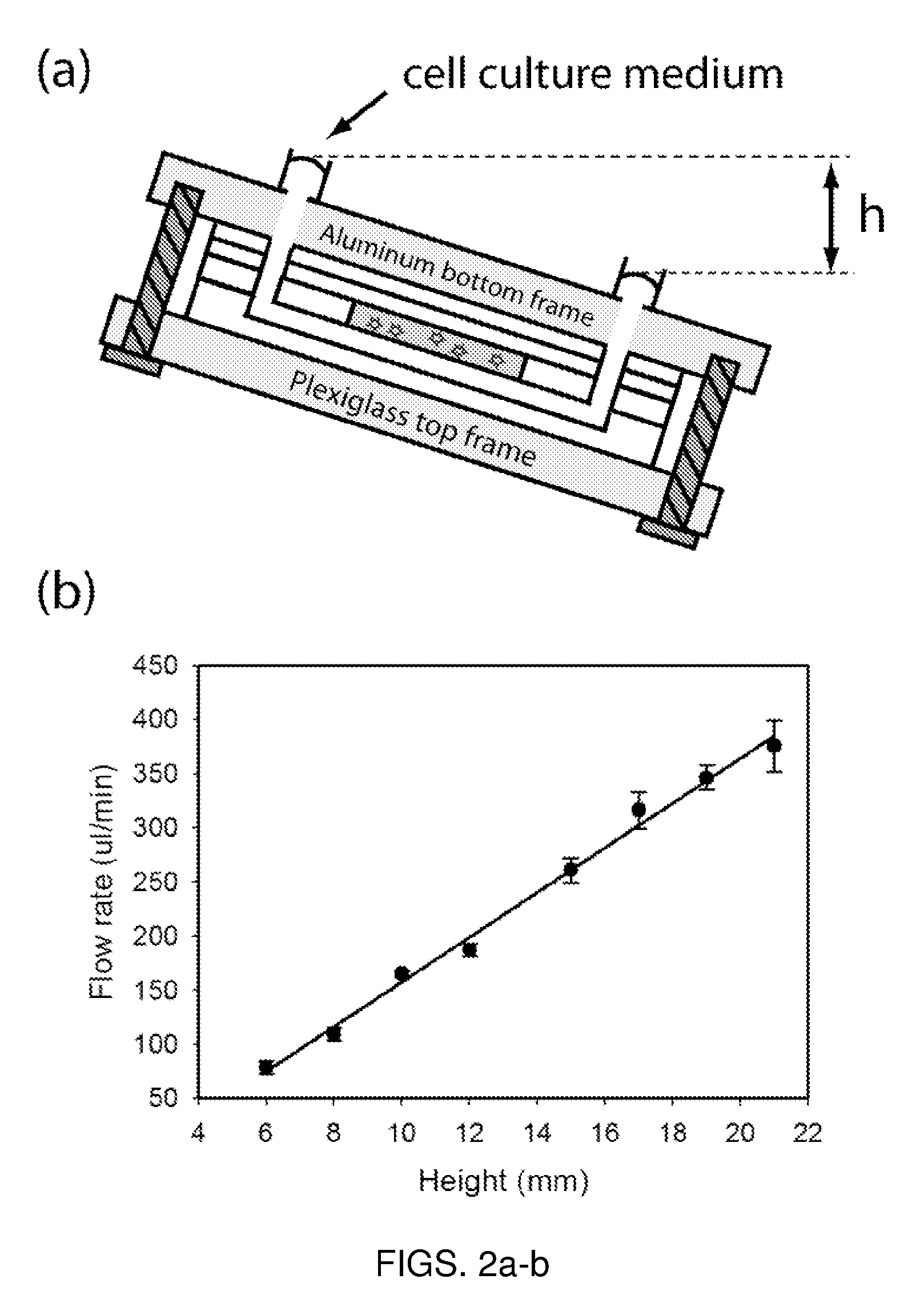
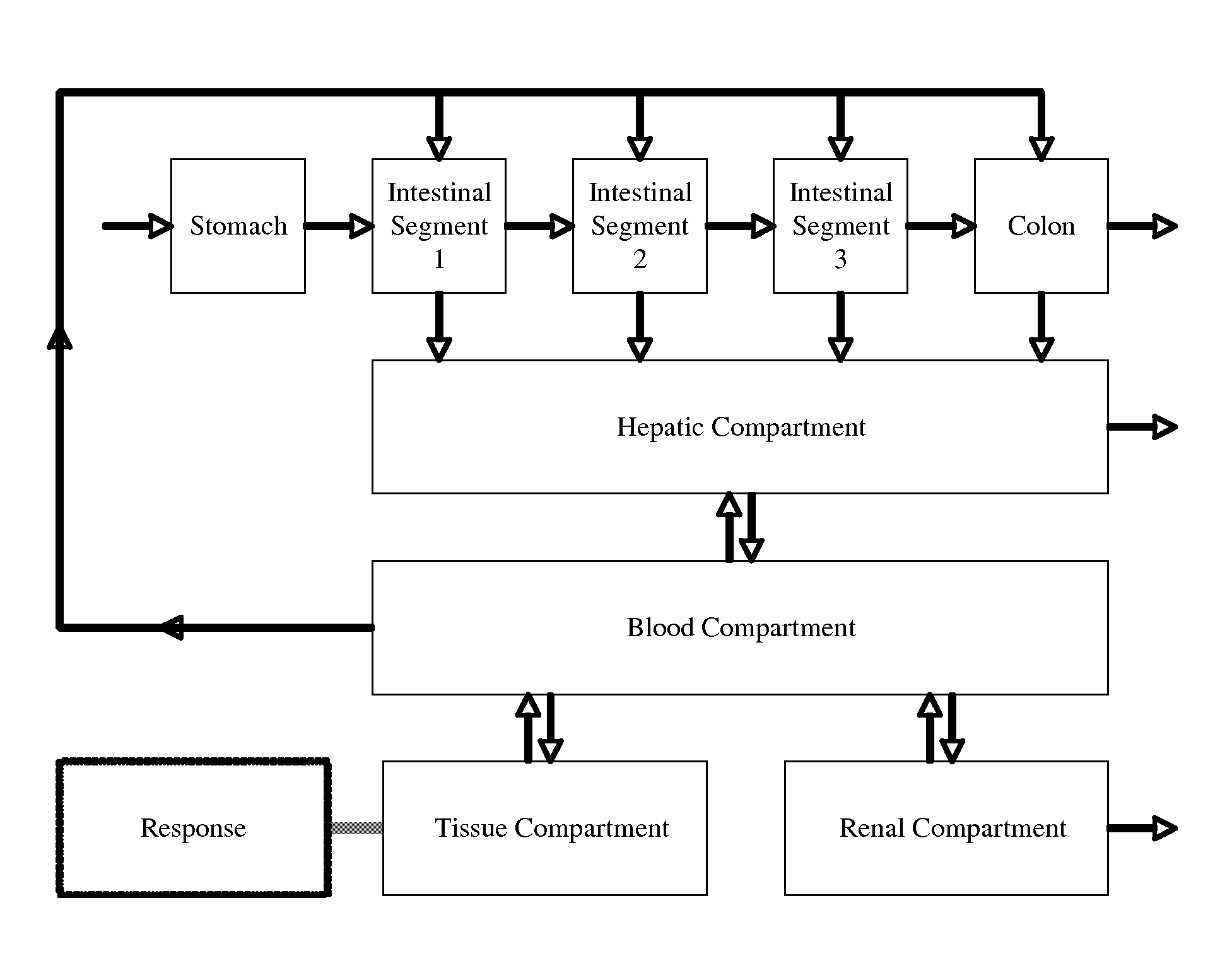
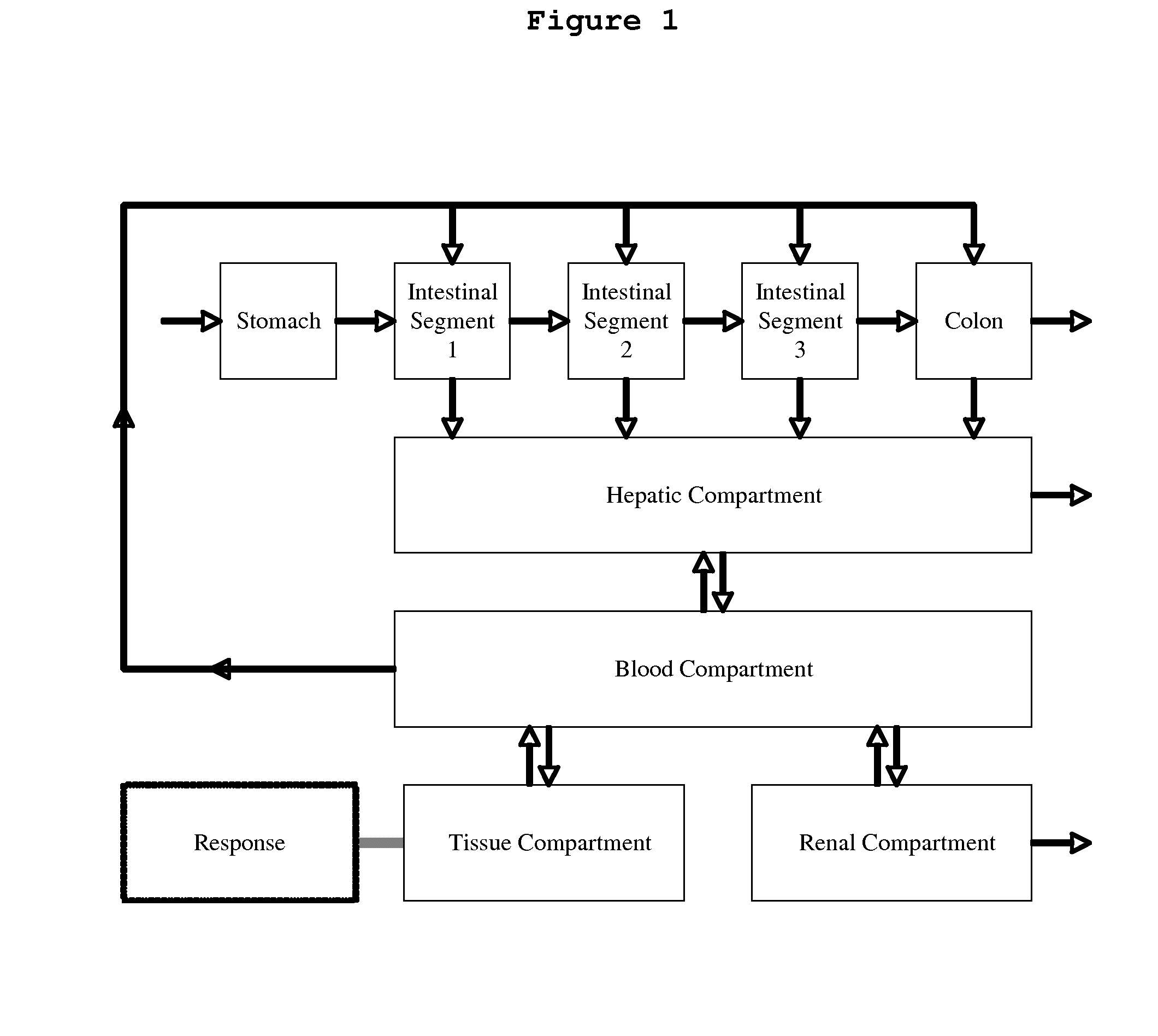
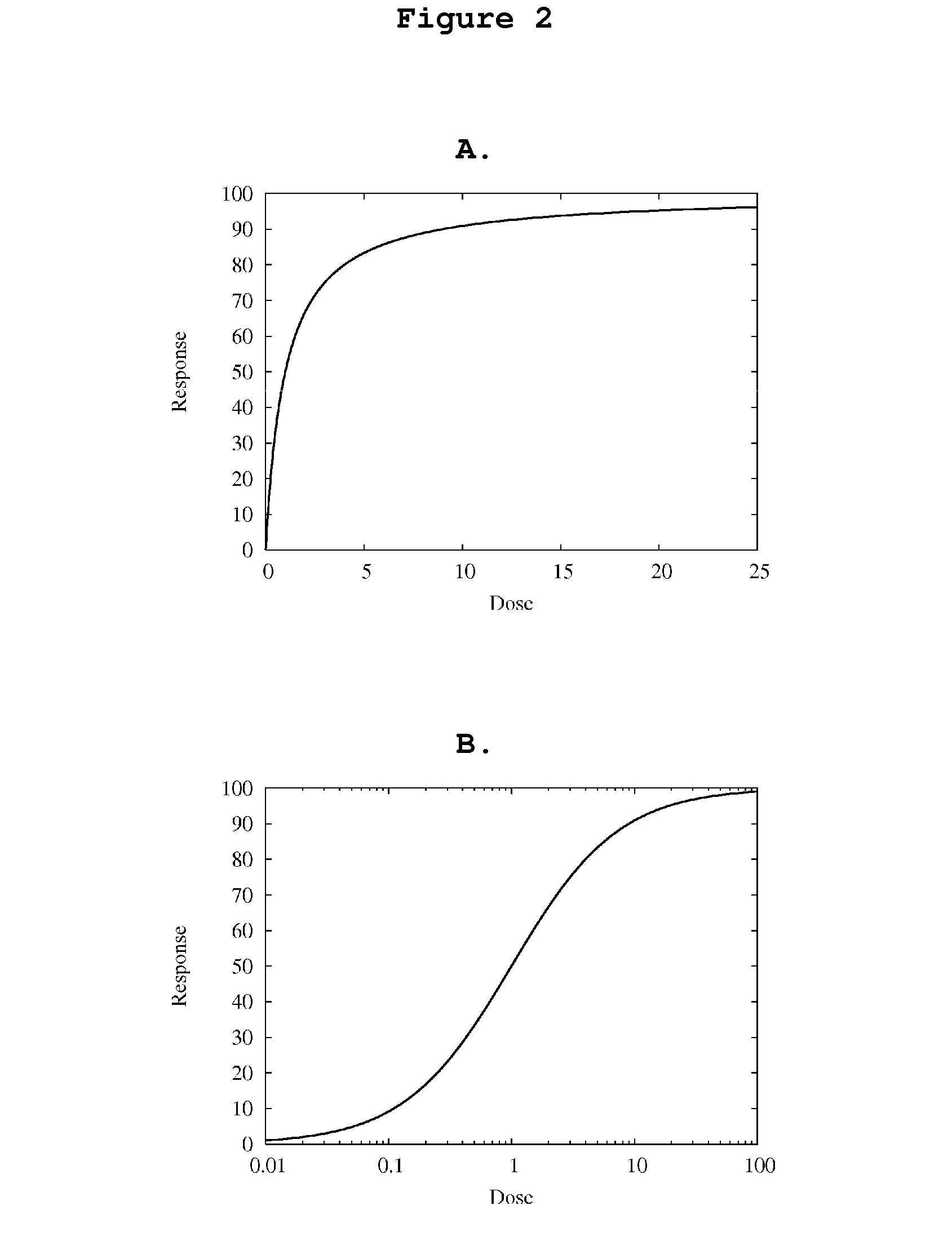
Microfluidic device for pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic study of drugs and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120135452A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningTissues typesMicrofluidic channel
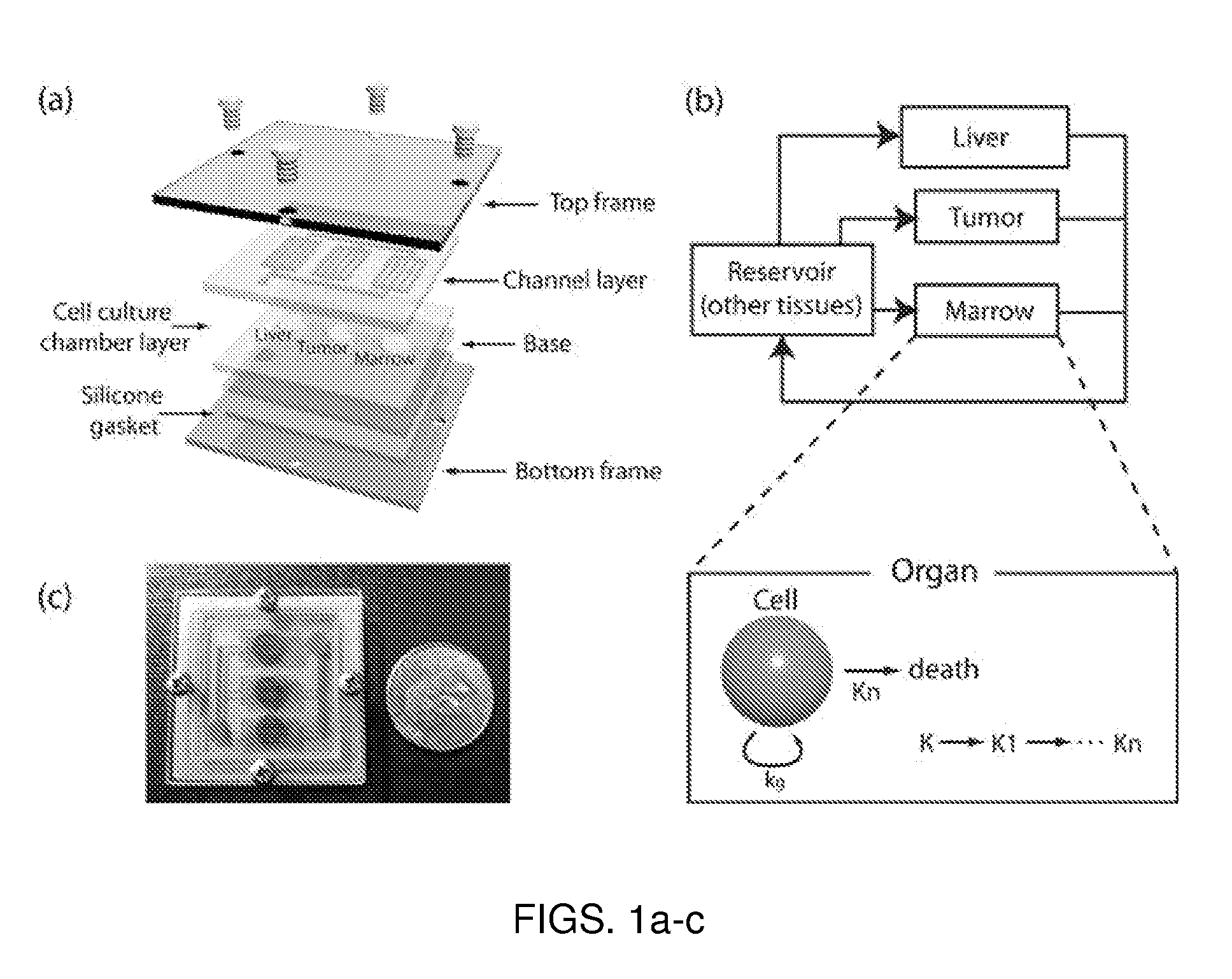
A microfluidic device for culturing cells, termed a microscale cell culture analog (μCCA), is provided. The microfluidic device allows multiple cell or tissue types to be cultured in a physiologically relevant environment, facilitates high-throughput operation and can be used for drug discovery. The microfluidic device uses gravity-induced fluidic flow, eliminating the need for a pump and preventing formation of air bubbles. Reciprocating motion between a pair of connected reservoirs is used to effect the gravity-induced flow in microfluidic channels. Bacterial contamination is reduced and high throughput enabled by eliminating a pump. The microfluidic device integrates a pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) model to enable PK-PD analyses on-chip. This combined in vitro / in silico system enables prediction of drug toxicity in a more realistic manner than conventional in vitro systems.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Humanized antibodies against vascular endothelial growth factor
InactiveUS7667004B2High binding affinityInhibit cell proliferationPeptide librariesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiabetic retinopathyAntigen
Methods are provided for designing and selecting antibodies against human antigens with high affinity and specificity in silico and in vitro. In some particular embodiments, methods are provided for designing and selecting humanized or fully human antibodies against vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) with high affinity and specificity. In another aspect of the invention, monoclonal antibodies against VEGF are provided. In particular, humanized or human anti-VEGF monoclonal antibodies are provided with ability to bind to human VEGF with high affinity, inhibit VEGF-induced proliferation of endothelial cells in vitro and inhibit VEGF-induced angiogenesis in vivo. These antibodies and their derivative can be used in a wide variety of applications such as diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases such as cancer, AMD, diabetic retinopathy, and other diseases derived from pathological angiogenesis.
Owner:ABMAXIS
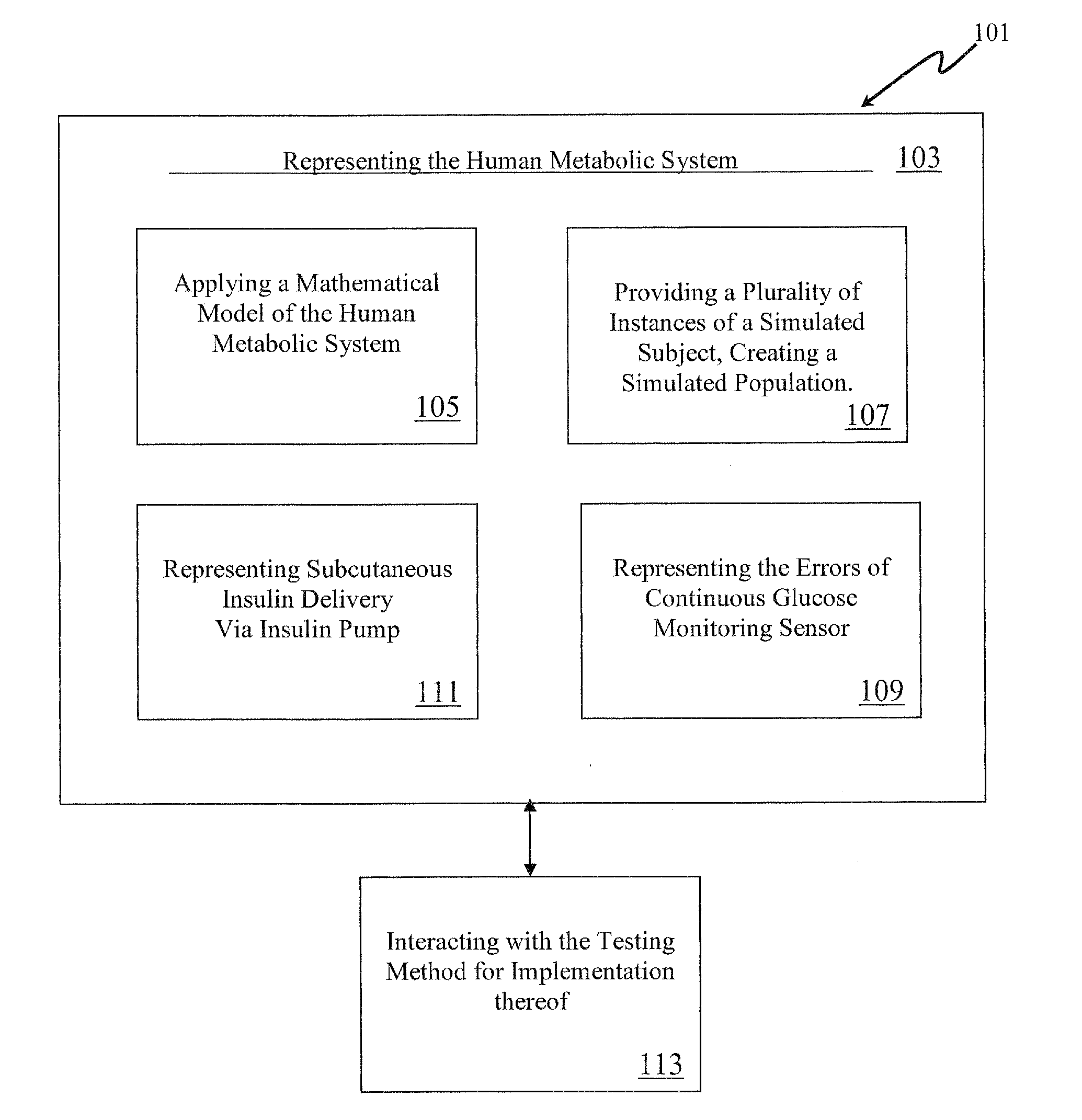
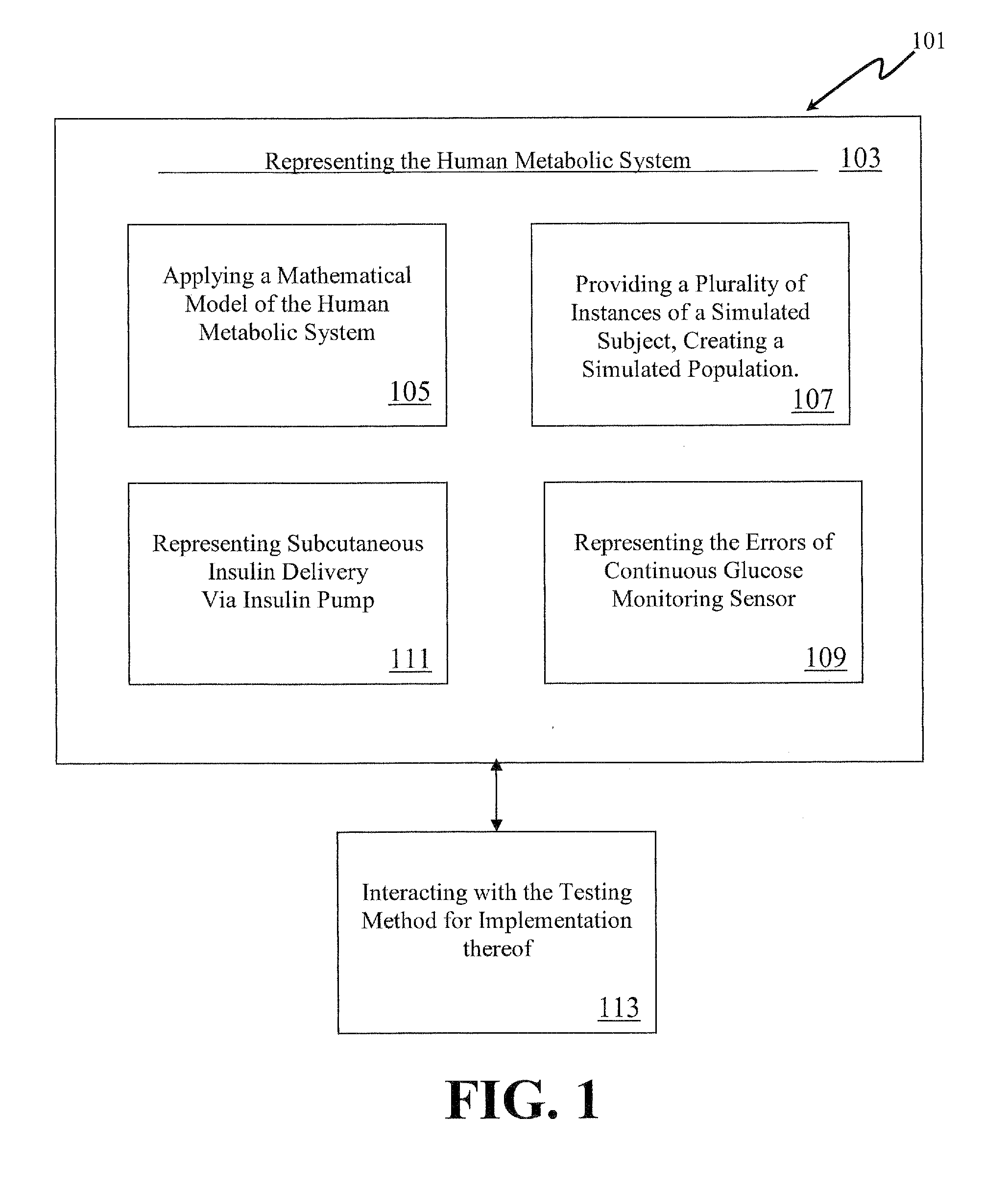
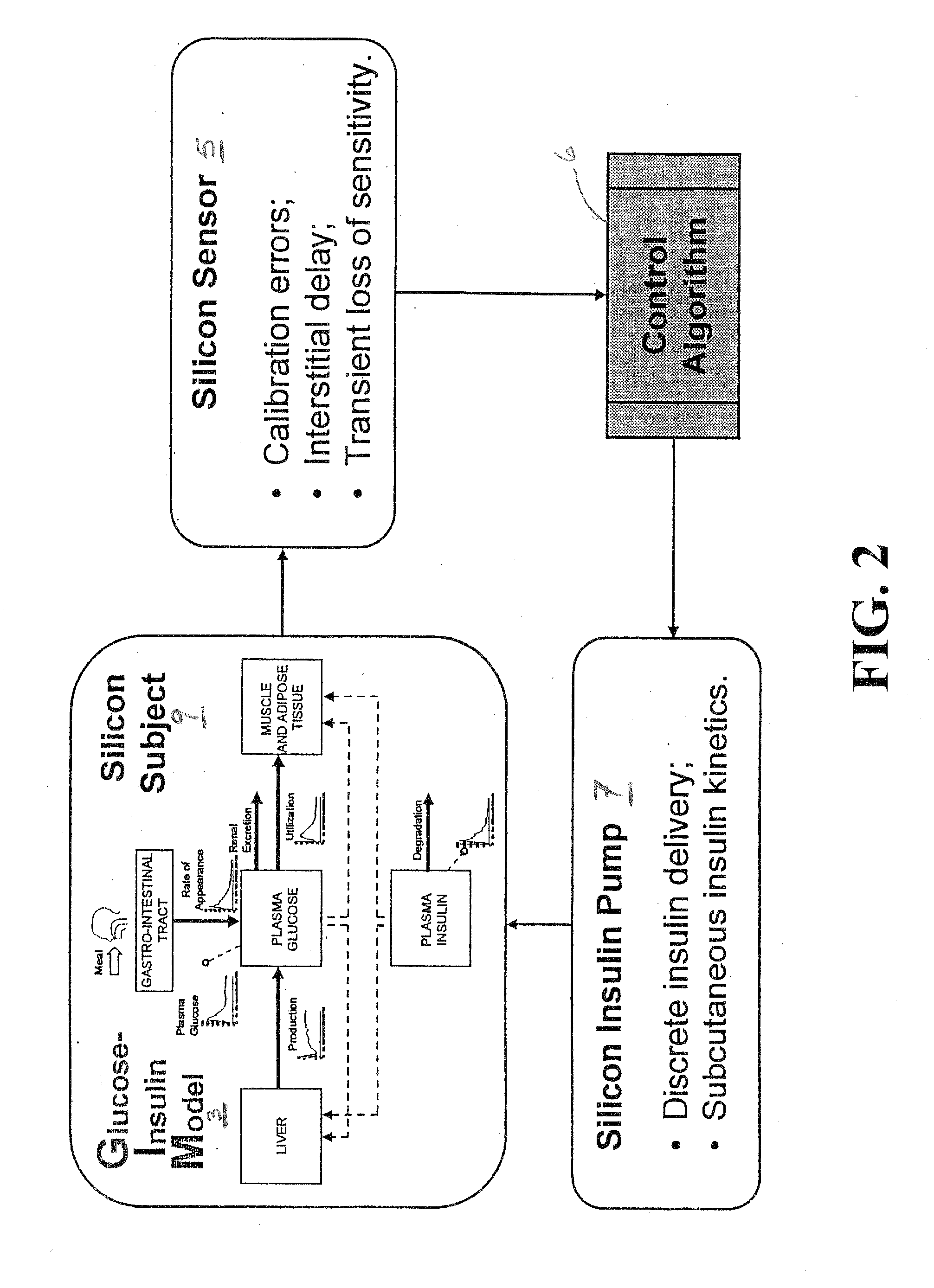
Method, System and Computer Simulation Environment for Testing of Monitoring and Control Strategies in Diabetes
A simulation environment for in silico testing of monitoring methods, open-loop and closed-loop treatment strategies in type 1 diabetes. Some exemplary principal components of the simulation environment comprise, but not limited thereto, the following: 1) a “population” of in silico “subjects” with type 1 diabetes in three age groups; 2) a simulator of CGM sensor errors; 3) a simulator of insulin pumps and discrete insulin delivery; 4) an interface allowing the input of user-specified treatment scenarios; and 5) a set of standardized outcome measures and graphs evaluating the quality of the tested treatment strategies. These components can be used separately or in combination for the preclinical evaluation of open-loop or closed-loop control treatments of diabetes.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
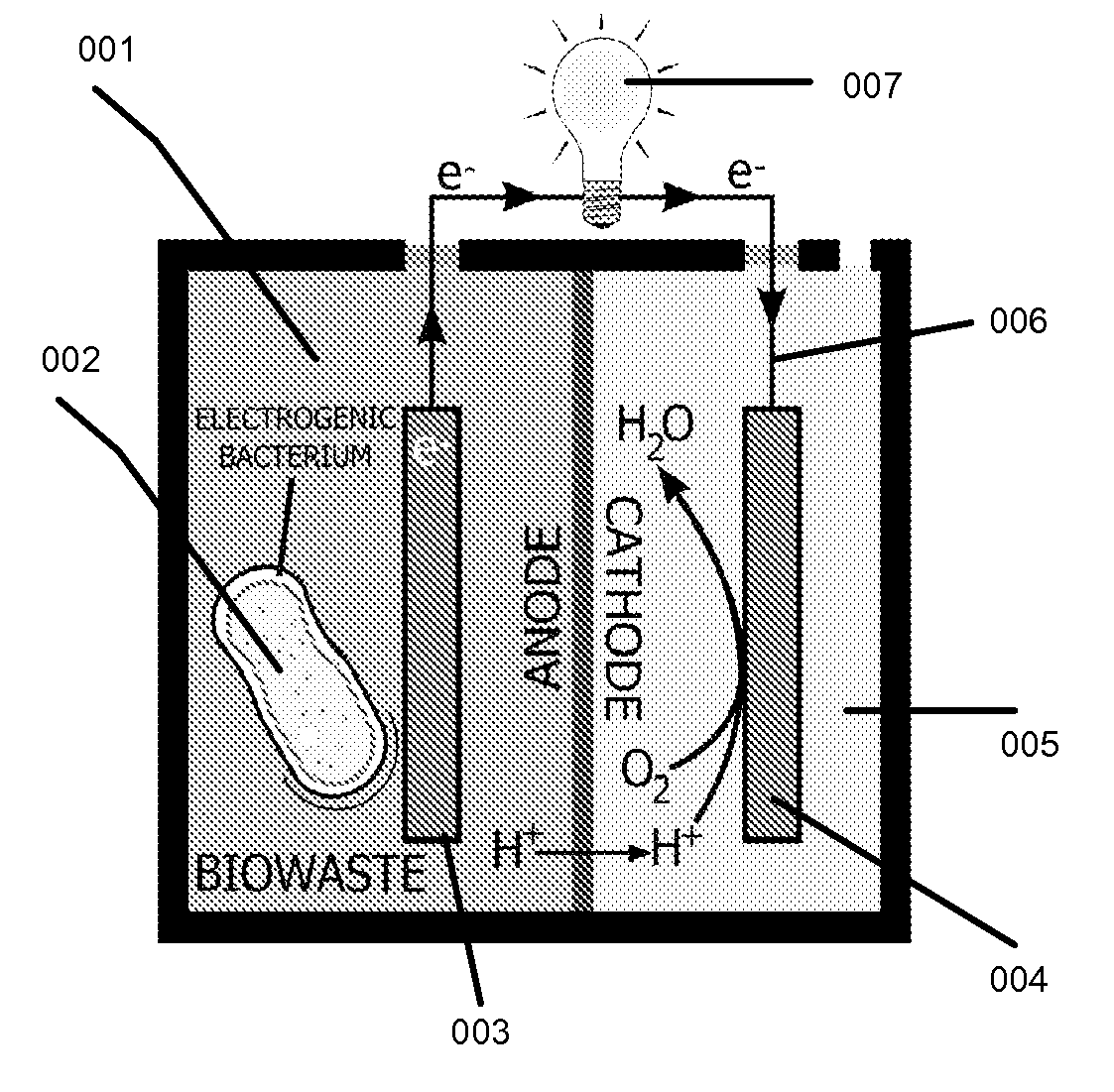
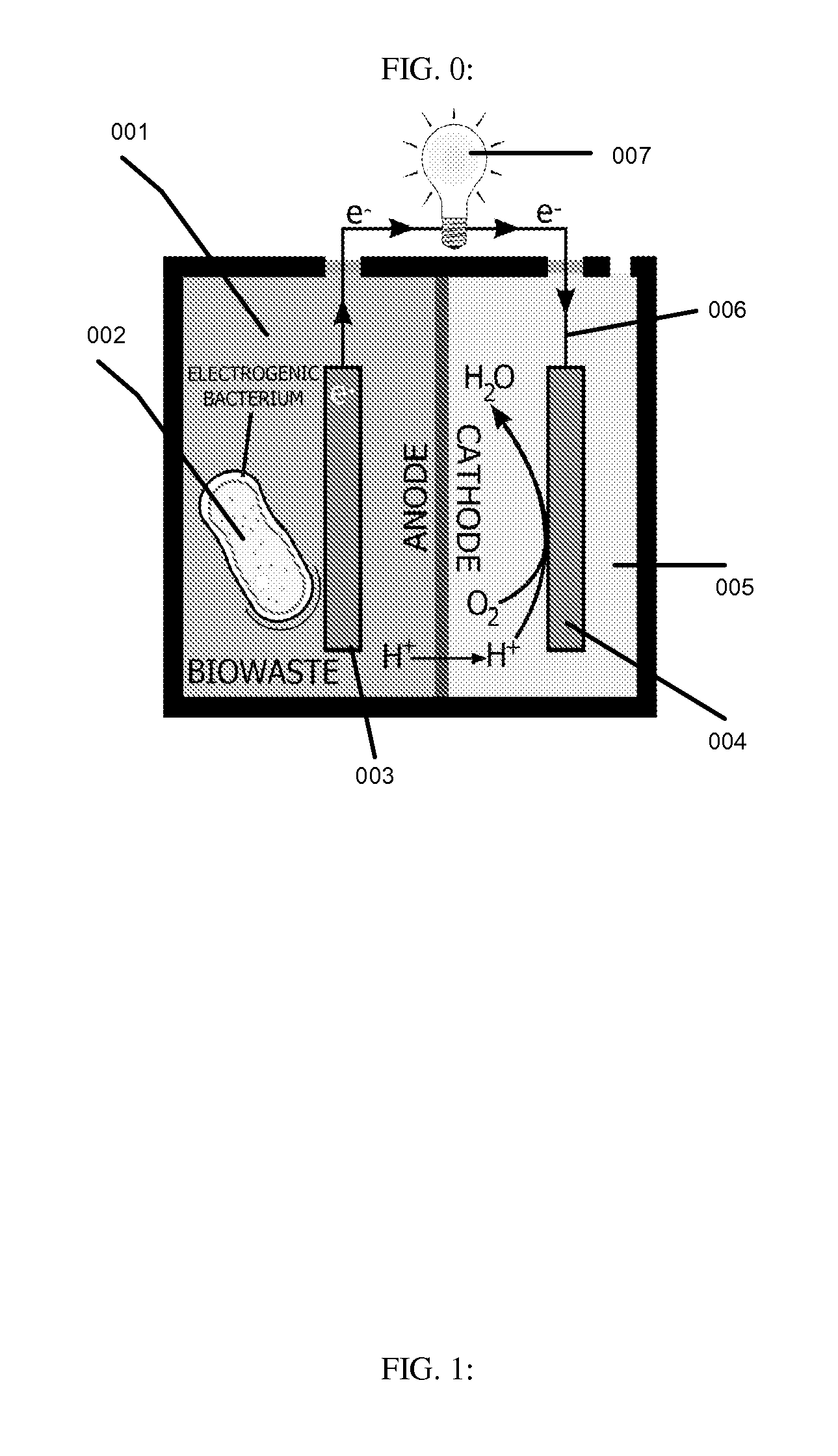
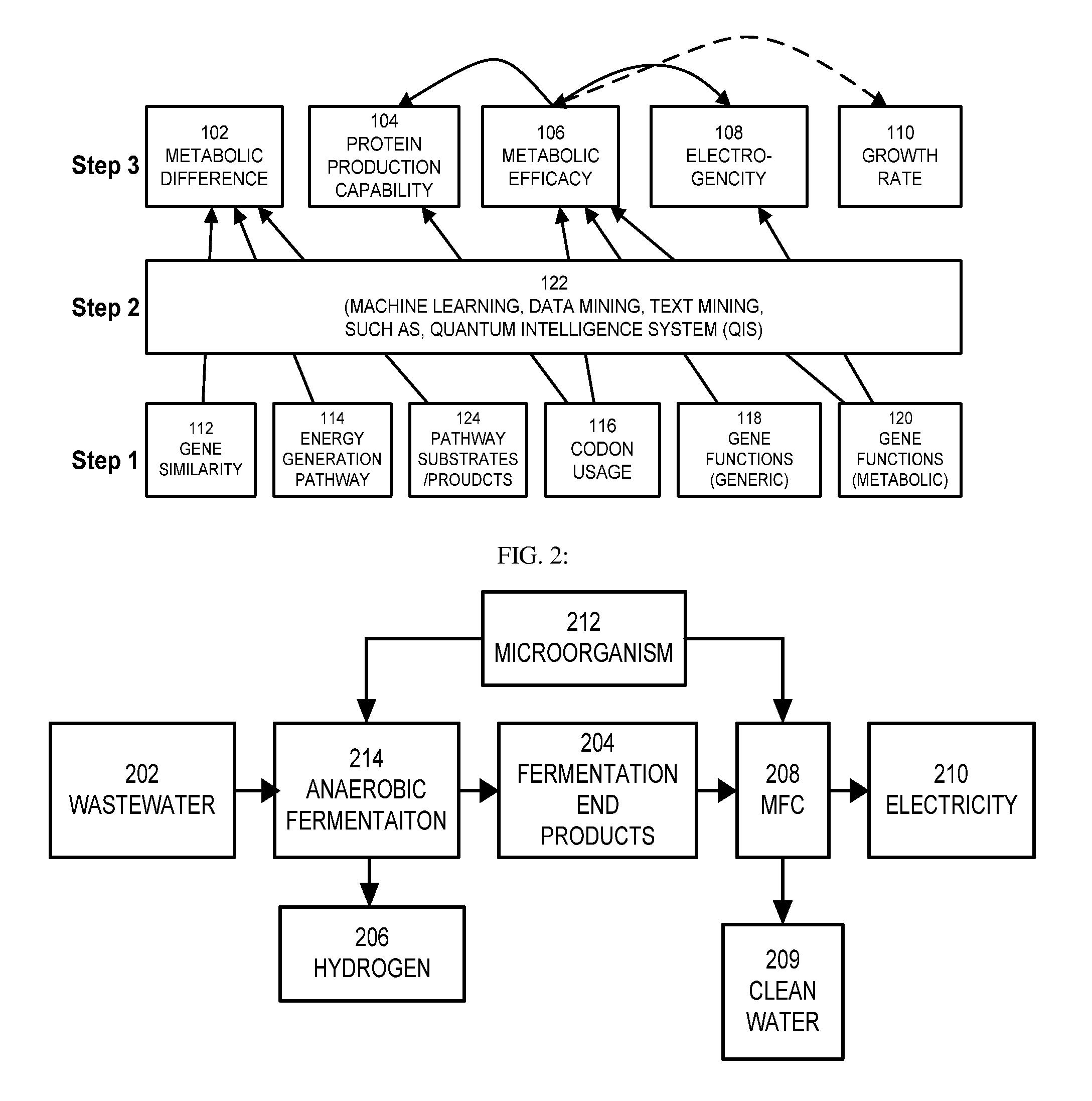
Using knowledge pattern search and learning for selecting microorganisms
InactiveUS20080090736A1Recover clean energyMost efficientMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningScreening methodClean energy
This invention is to use knowledge pattern learning and search system for selecting microorganisms to produce useful materials and to generate clean energy from wastes, wastewaters, biomass or from other inexpensive sources. The method starts with an in silico screening platform which involves multiple steps. First, the organisms' profiles are compiled by linking the massive genetic and chemical fingerprints in the metabolic and energy-generating biological pathways (e.g. codon usages, gene distributions in function categories, etc.) to the organisms' biological behaviors. Second, a machine learning and pattern recognition system is used to group the organism population into characteristic groups based on the profiles. Lastly, one or a group of microorganisms are selected based on profile match scores calculated from a defined metabolic efficiency measure, which, in term, is a prediction of a desired capability in real life based on an organism's profile. In the example of recovering clean energy from treating wastewaters from food process industries, domestic or municipal wastes, animal or meat-packing wastes, microorganisms' metabolic capabilities to digest organic matter and generate clean energy are assessed using the invention, and the most effective organisms in terms of waste reduction and energy generation are selected based on the content of a biowaste input and a desired clean energy output. By selecting a microorganism or consortia of multiply microorganisms using this method, one can clean the water and also directly generate electricity from Microbial Fuel Cells (MFC), or hydrogen, methane or other biogases from microorganism fermentation. In addition, using similar screening method, clean hydrogen can be recovered first from an anaerobic fermentation process accompanying the wastewater treatment, and the end products from the fermentation process can be fed into a Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC) process to generate clean electricity and at the same time treat the wastewater. The invention can be used to first select the hydrogenic microorganisms to efficiently generate hydrogen and to select electrogenic organisms to convert the wastes into electricity. This method can be used for converting wastes to one or more forms of renewable energies.
Owner:QUANTUM INTELLIGENCE
Generation and selection of protein library in silico
The present invention provides a methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as improved binding affinity towards biologically and / or therapeutically important target molecules. The process is carried out computationally in a high throughput manner by mining the ever-expanding databases of protein sequences of all organisms, especially human. In one embodiment, a method for constructing a library of designed proteins, comprising the steps of: providing an amino acid sequence derived from a lead protein, the amino acid sequence being designated as a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence with a plurality of tester protein sequences; and selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 15% sequence identity with the lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library; and forming a library of designed proteins by substituting the lead sequence with the hit library. The library of designed proteins can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant proteins that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead protein, such as an antibody against therapeutically important target.
Owner:ABMAXIS
Programmable iterated elongation: a method for manufacturing synthetic genes and combinatorial DNA and protein libraries
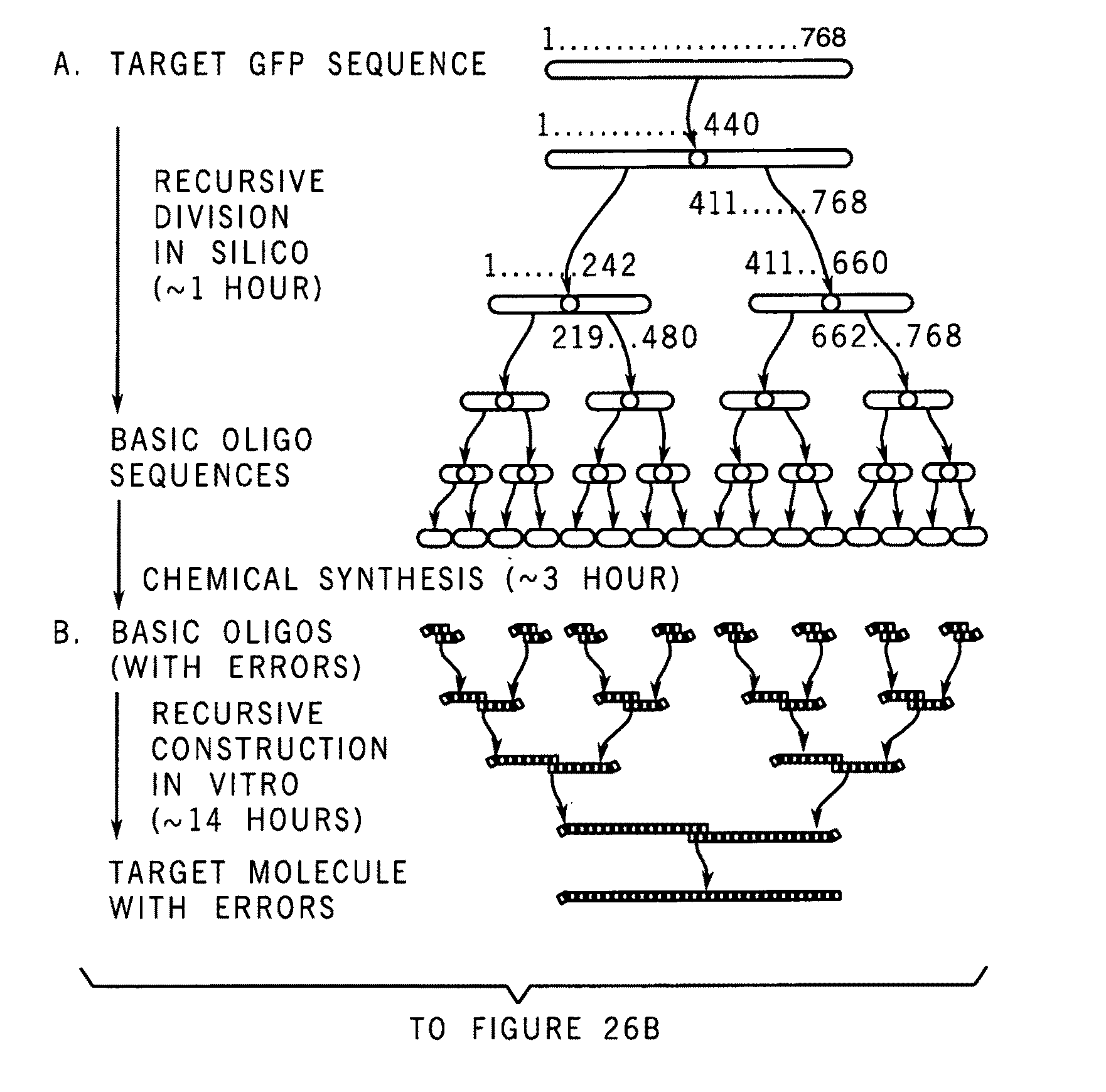
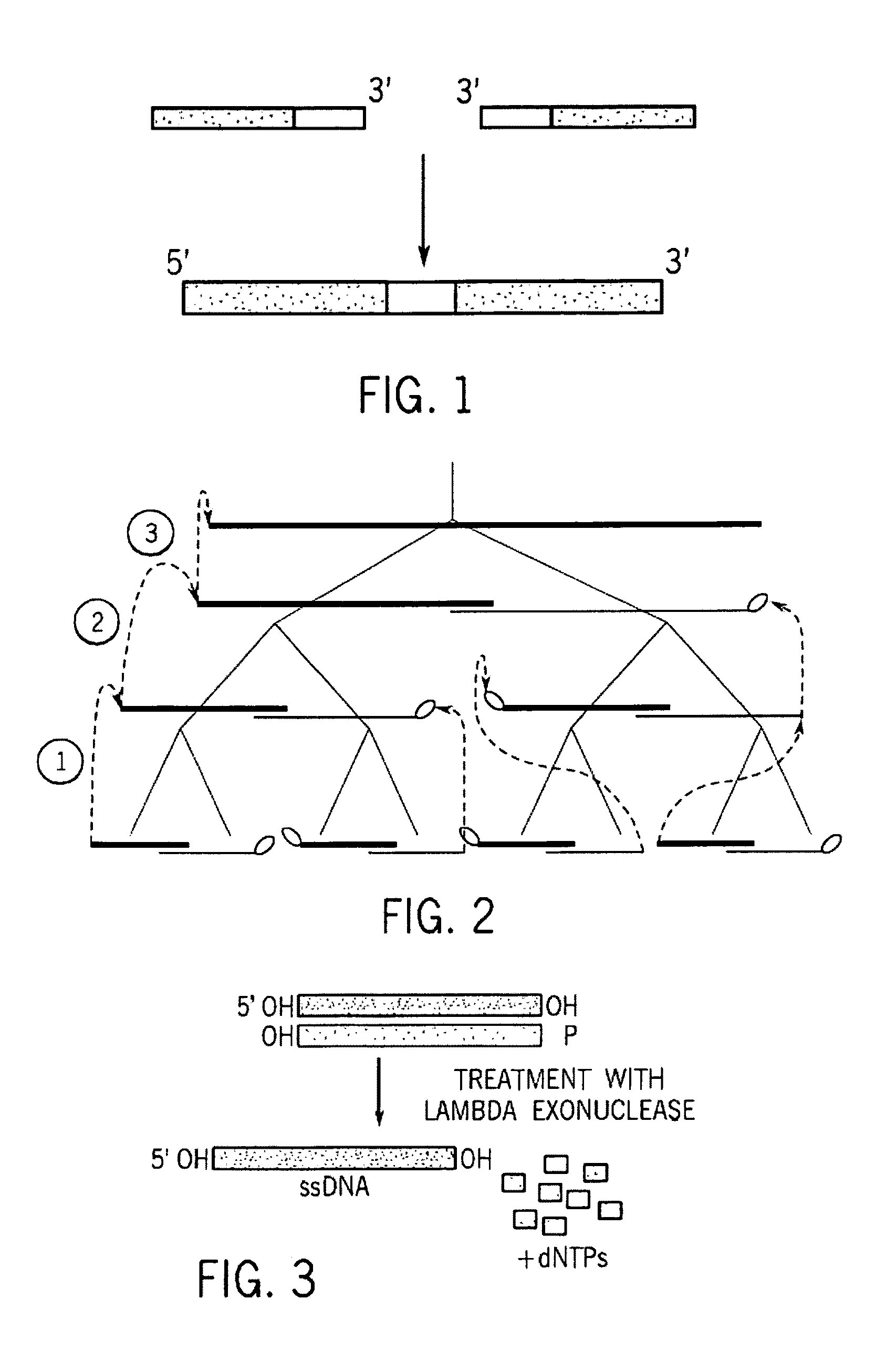
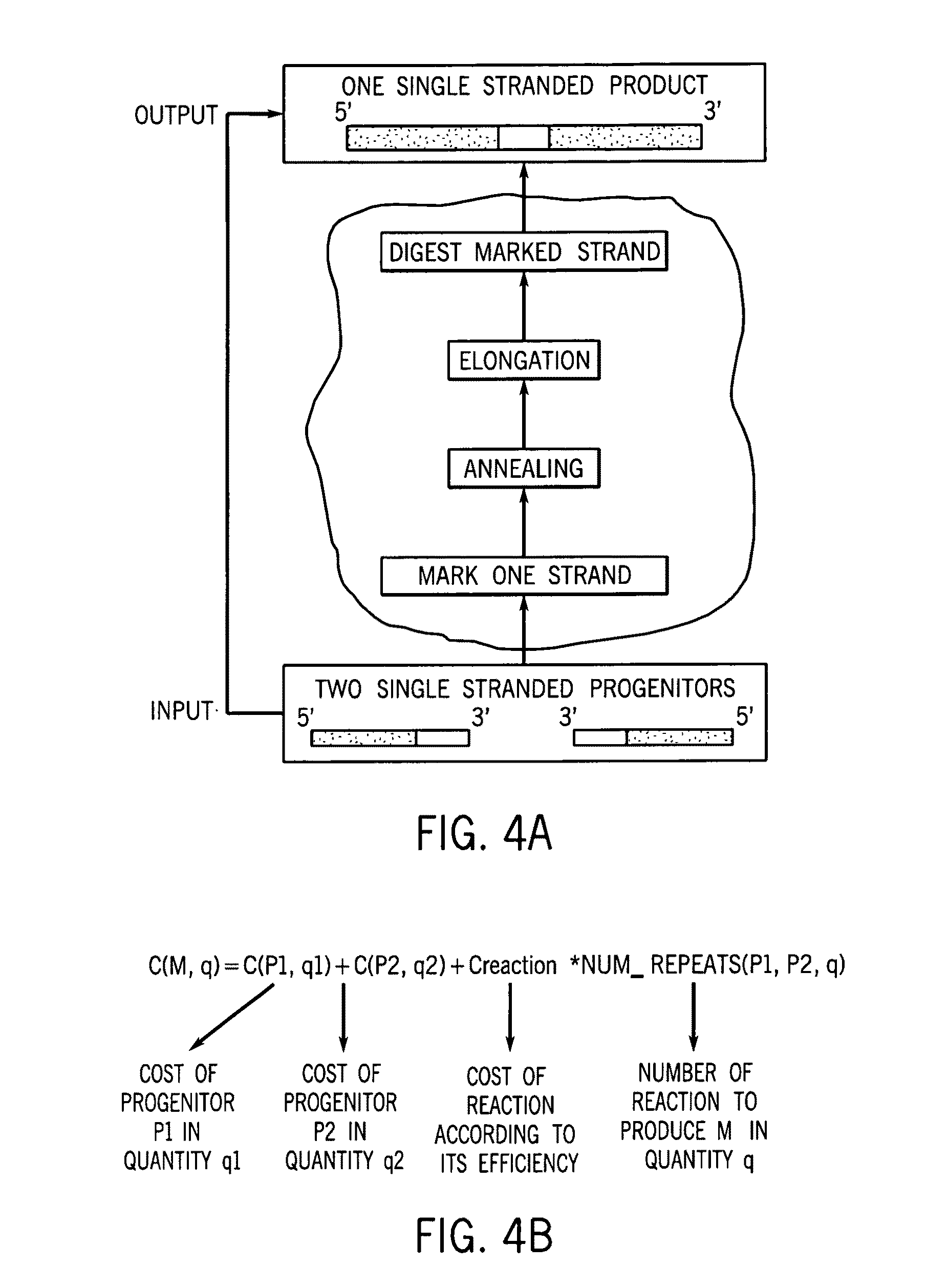
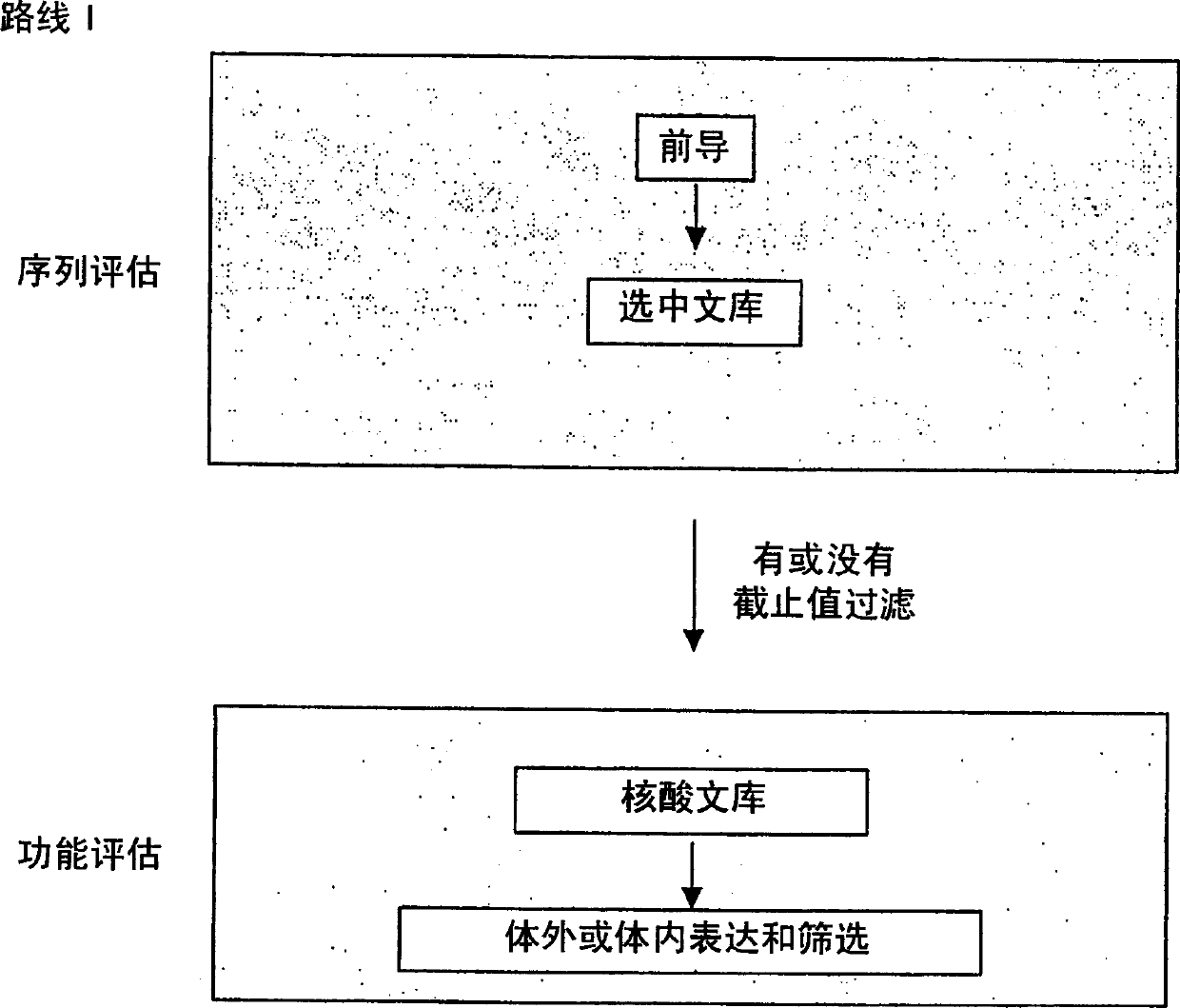
A method for manufacturing synthetic genes and combinatorial DNA and protein libraries, termed here Divide and Conquer-DNA synthesis (D&C-DNA synthesis) method. The method can be used in a systematic and automated way to synthesize any long DNA molecule and, more generally, any combinatorial molecular library having the mathematical property of being a regular set of strings. The D&C-DNA synthesis method is an algorithm design paradigm that works by recursively breaking down a problem into two or more sub-problems of the same type. The division of long DNA sequences is done in silico. The assembly of the sequence is done in vitro. The D&C-DNA synthesis method protocol consists of a tree, in which each node represents an intermediate sequence. The internal nodes are created in elongation reactions from their daughter nodes, and the leaves are synthesized directly. After each elongation only one DNA strand passes to the next level in the tree until receiving the final product. Optionally and preferably, error correction is performed to correct any errors which may have occurred during the synthetic process.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Generation and selection of protein library in silico
The present invention provides methods for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimal proteins with desired biological functions, such as improved binding affinity for biologically and / or therapeutically important target molecules. The method is performed in silico in a high-throughput fashion by mining the ever-expanding database of protein sequences in all living things, especially humans. In one embodiment, a method of constructing a designer protein library comprises the steps of: providing an amino acid sequence derived from a lead protein, referred to as a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence with a plurality of test protein sequences; Select at least two peptide fragments having at least 15% sequence identity with the leader sequence from each test protein sequence, and the selected peptide fragments form a selection library; a library of designed proteins is formed by replacing the leader sequence with the selection library. Libraries of designed proteins can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to generate libraries of recombinant proteins that can be screened for new or improved functions relative to lead proteins, such as antibodies against a therapeutically important target.
Owner:埃博马可西斯公司
Multi-scale complex systems transdisciplinary analysis of response to therapy
Described herein are methods and systems to measure dynamics of disease progression, including cancer growth and response, at multiple scales by multiple techniques on the same biologic system. Methods and systems according to the invention permit personalized virtual disease models. Moreover, the invention allows for the integration of previously unconnected data points into an in silico disease model, providing for the prediction of disease progression with and without therapeutic intervention.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Predicting hemostatic risk; dependence on plasma composition
InactiveUS20090298103A1Improve the level ofFaster rateMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMedicinePlasma composition
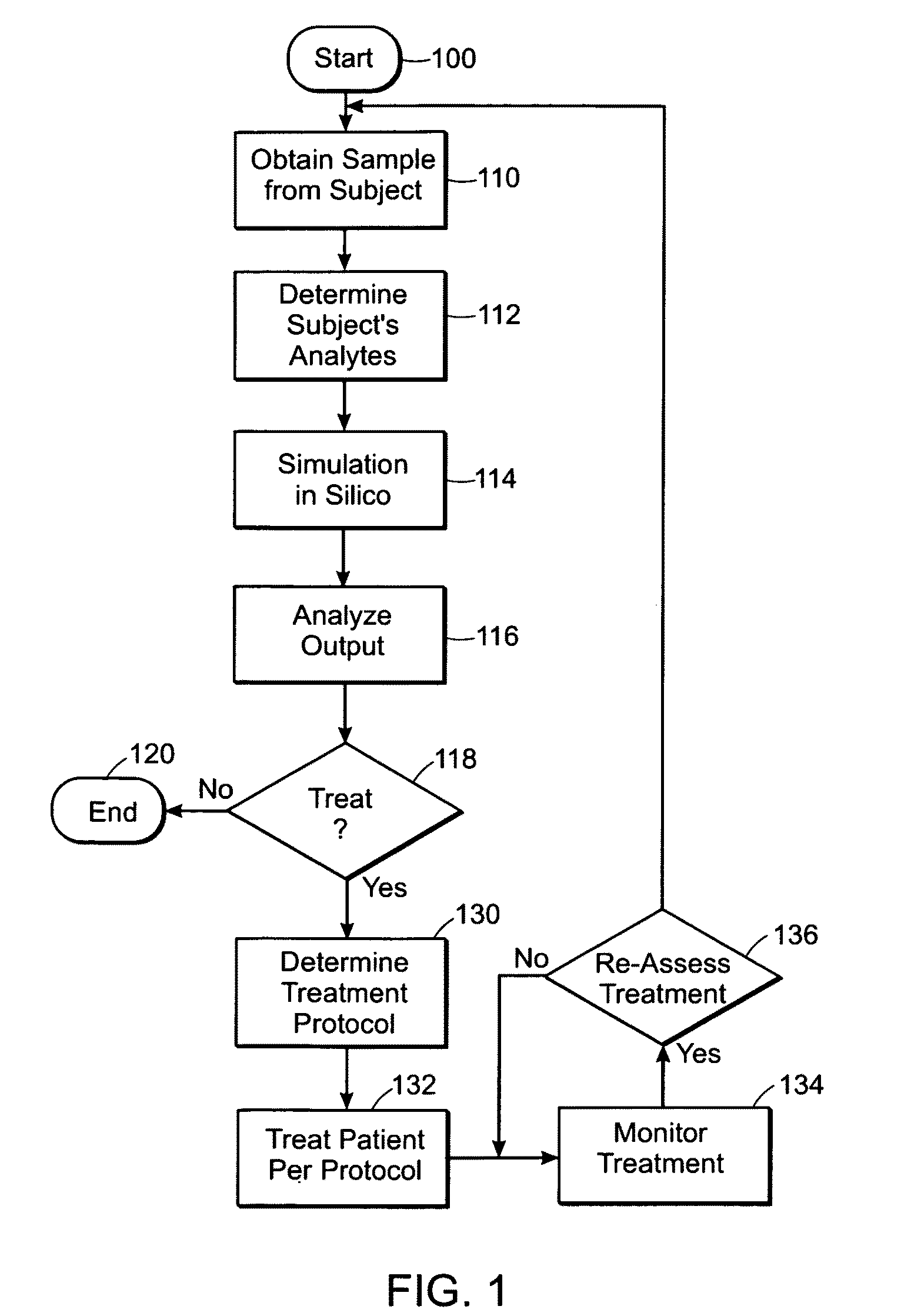
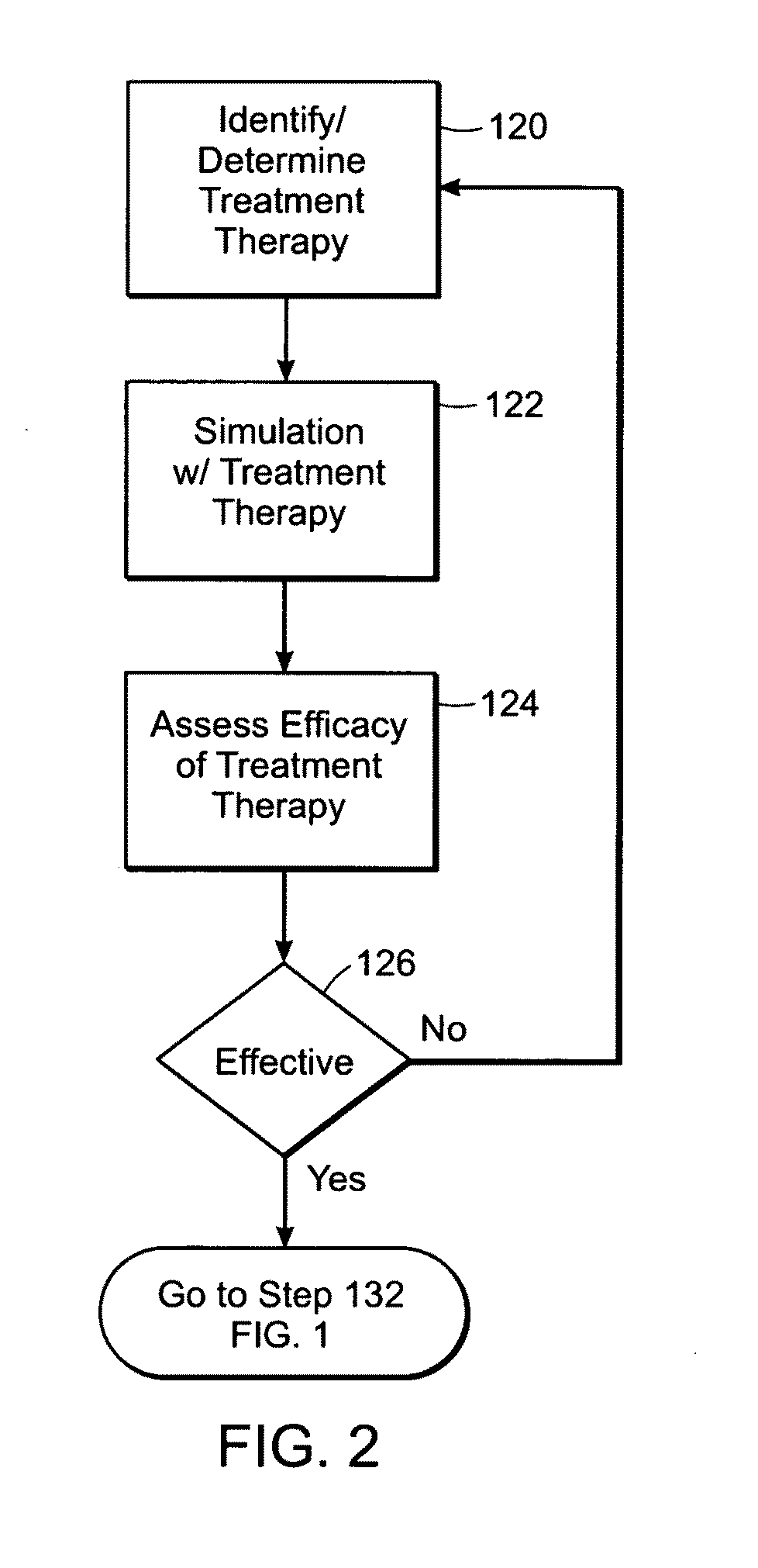
Featured are methods for assessing hemostatic risk including the risk for ACS. Such methods include acquiring blood / plasma composition based on a biological sample obtained from a subject, determining parameters associated with blood clotting, simulating in silico blood clotting using the determined parameters and comparing the results of such simulation to a reference and to determine the hemostatic risk from said comparing. In further embodiments, such methods further include selecting a treatment regime or protocol based on the results of such comparing. In yet further embodiments, such methods further include assessing the efficacy of medicants, drugs and the like of a given treatment protocol such as by simulating in silico the application of such medicants, drugs and the like.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VERMONT
Microfluidic device for pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic study of drugs and uses thereof
ActiveUS8748180B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningTissues typesMicrofluidic channel
A microfluidic device for culturing cells, termed a microscale cell culture analog (μCCA), is provided. The microfluidic device allows multiple cell or tissue types to be cultured in a physiologically relevant environment, facilitates high-throughput operation and can be used for drug discovery. The microfluidic device uses gravity-induced fluidic flow, eliminating the need for a pump and preventing formation of air bubbles. Reciprocating motion between a pair of connected reservoirs is used to effect the gravity-induced flow in microfluidic channels. Bacterial contamination is reduced and high throughput enabled by eliminating a pump. The microfluidic device integrates a pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) model to enable PK-PD analyses on-chip. This combined in vitro / in silico system enables prediction of drug toxicity in a more realistic manner than conventional in vitro systems.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
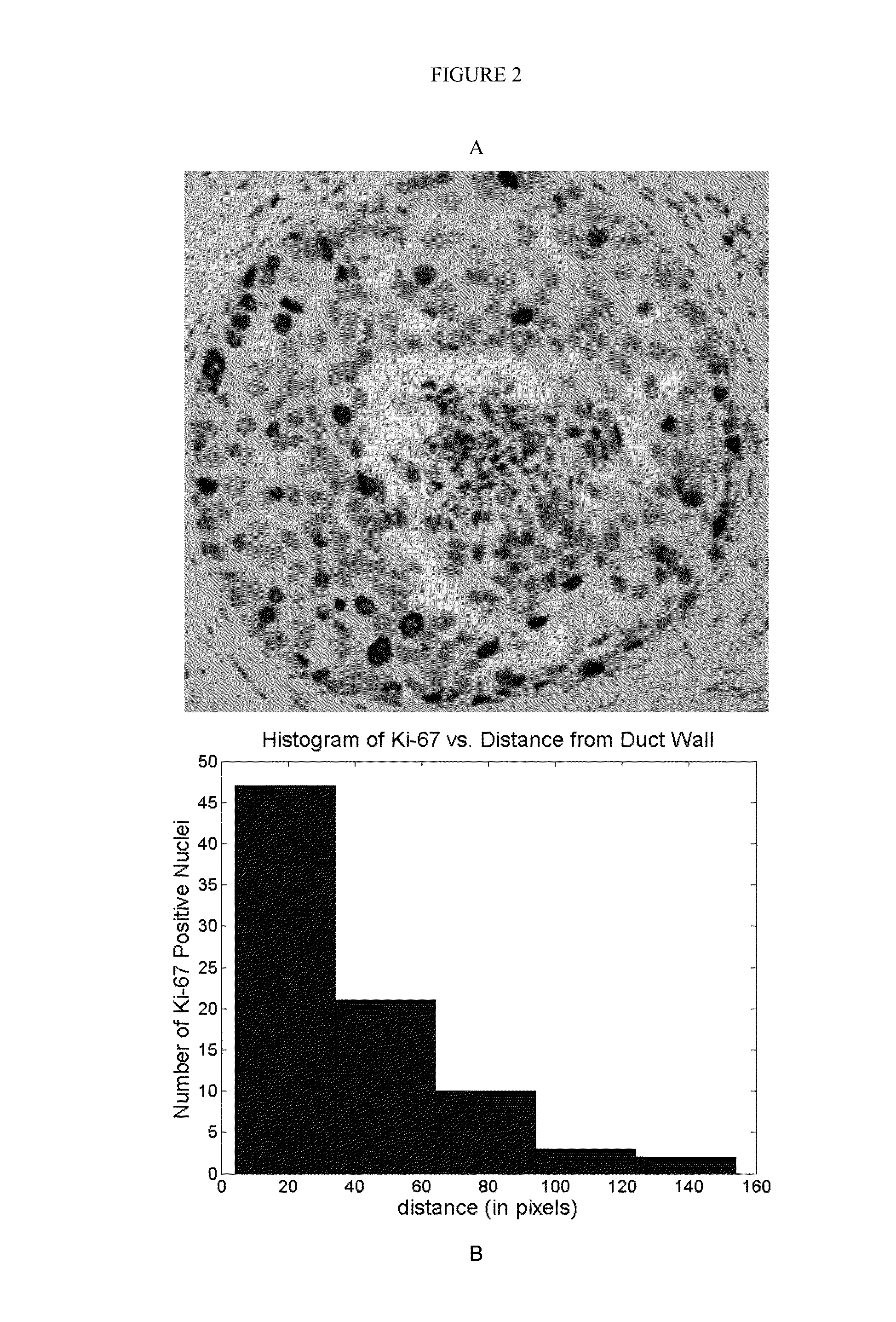
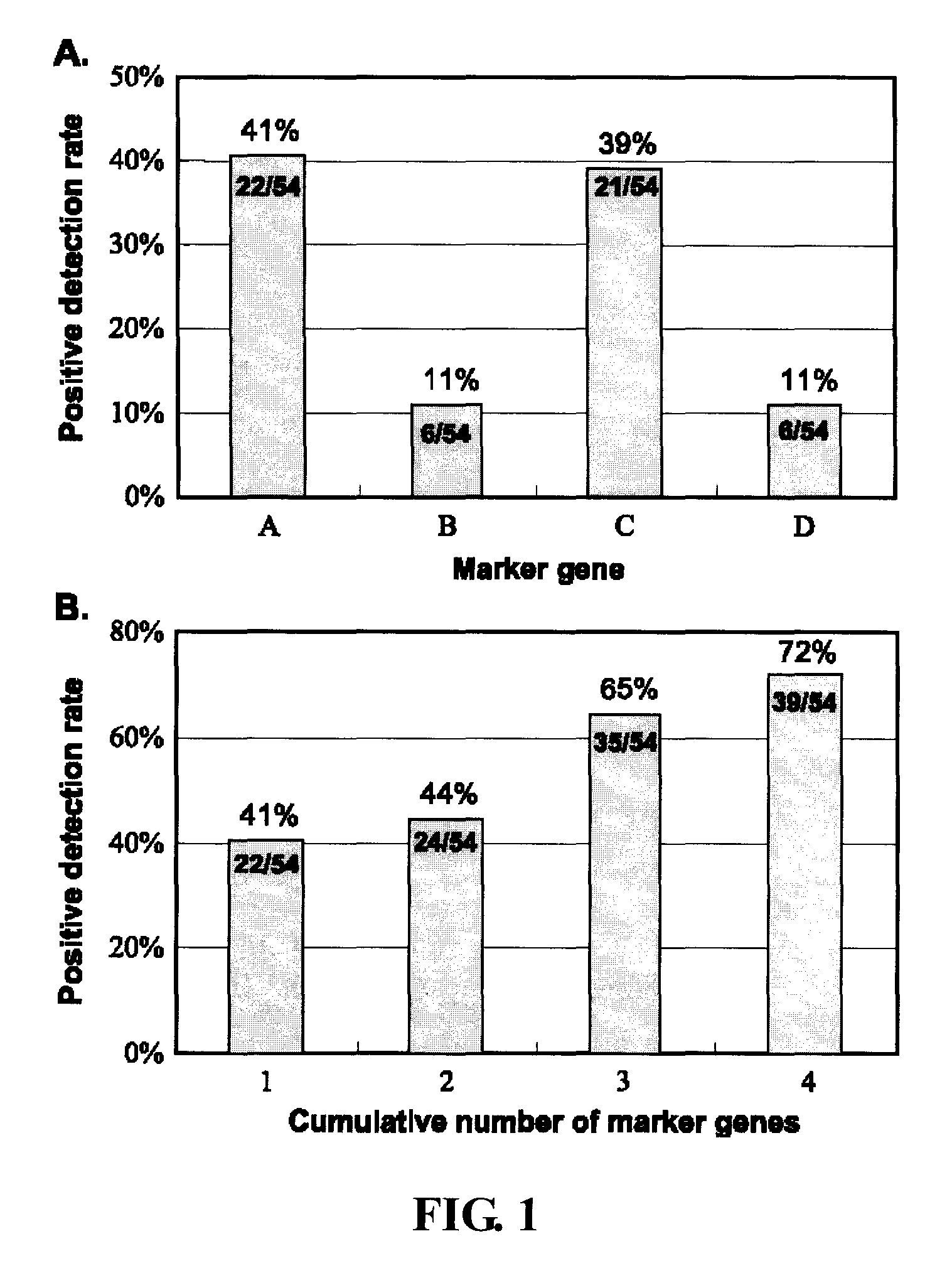
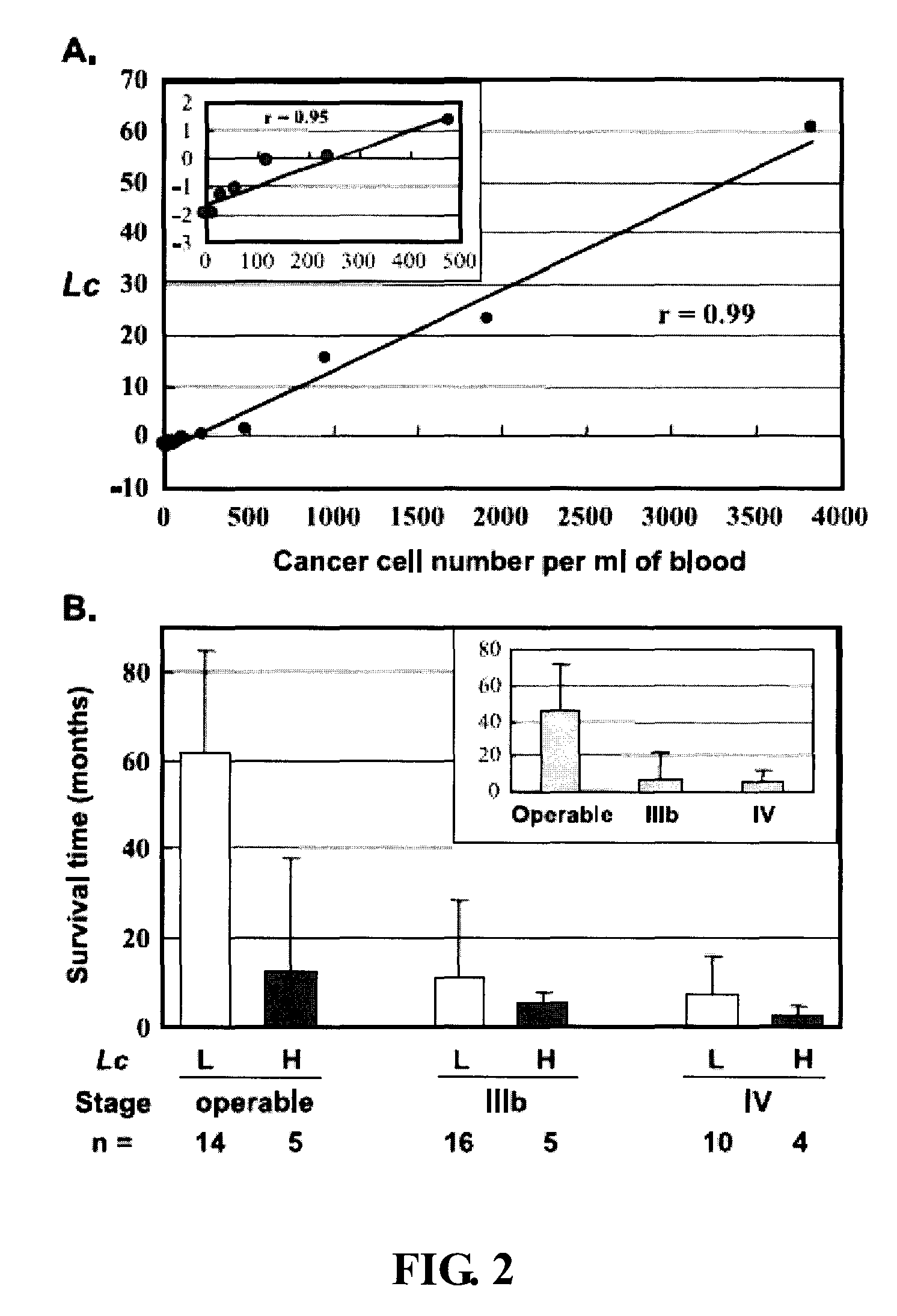
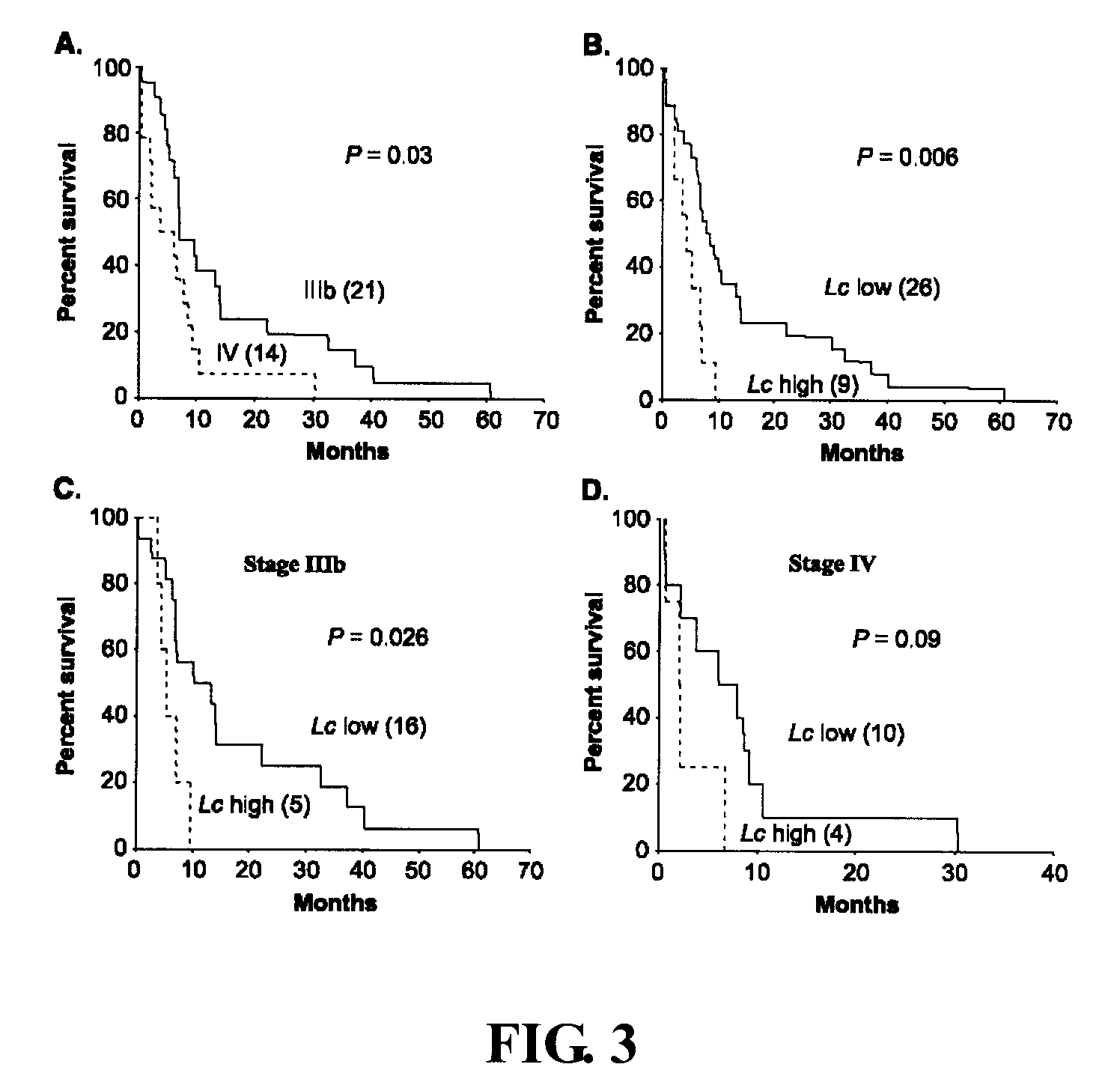
Rapid efficacy assessment method for lung cancer therapy
InactiveUS20070048750A1Rapid efficacy assessmentHigh correlationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSequence databaseEfficacy
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
Generation and selection of protein library in silico
InactiveUS20070037214A1High affinityImprove throughputPeptide librariesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIn vivoOrganism
The present invention provides a methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as improved binding affinity towards biologically and / or therapeutically important target molecules. The process is carried out computationally in a high throughput manner by mining the ever-expanding databases of protein sequences of all organisms, especially human. In one embodiment, a method for constructing a library of designed proteins, comprising the steps of: providing an amino acid sequence derived from a lead protein, the amino acid sequence being designated as a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence with a plurality of tester protein sequences; and selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 15% sequence identity with the lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library; and forming a library of designed proteins by substituting the lead sequence with the hit library. The library of designed proteins can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant proteins that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead protein, such as an antibody against therapeutically important target.
Owner:LUO PEIZHI +5
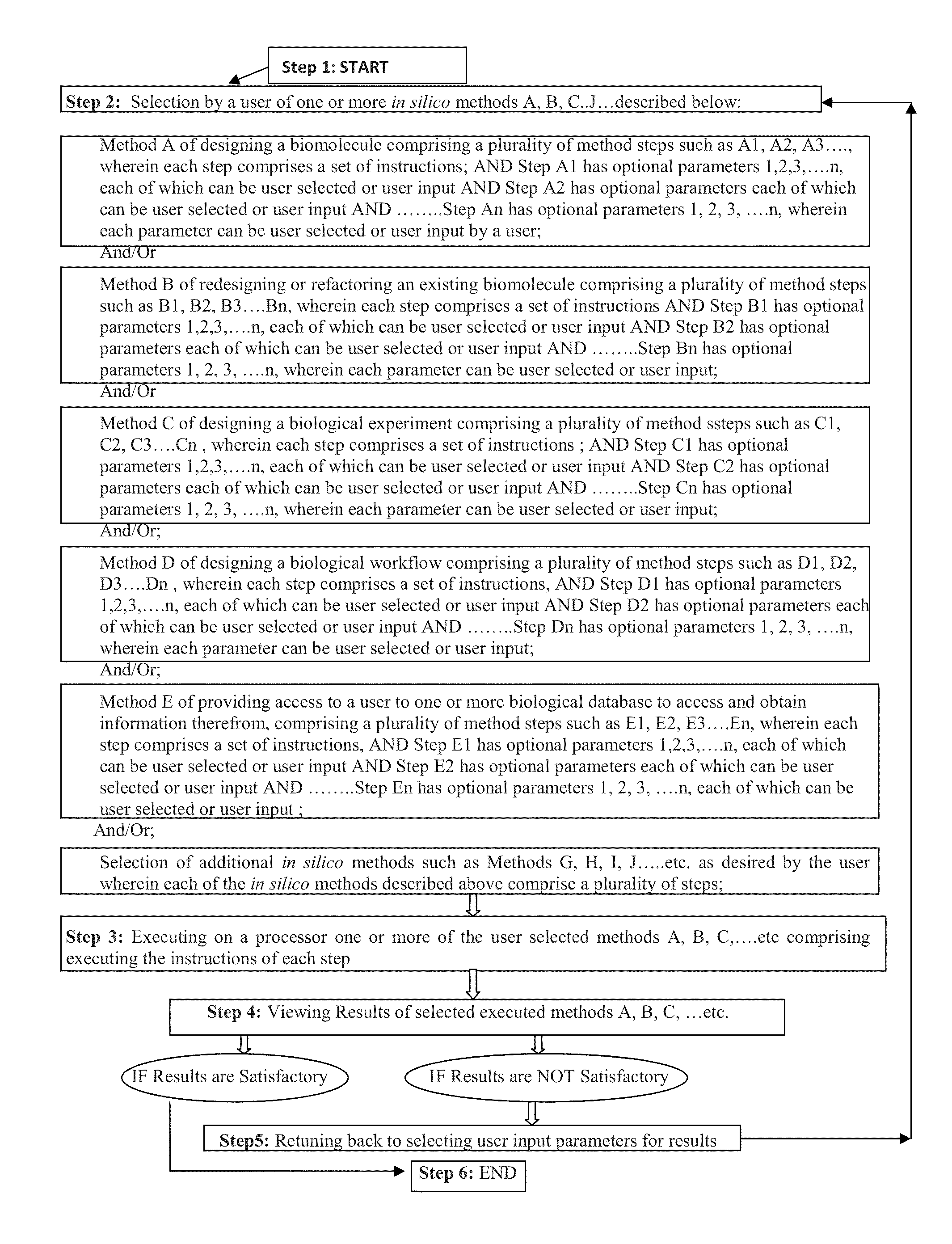
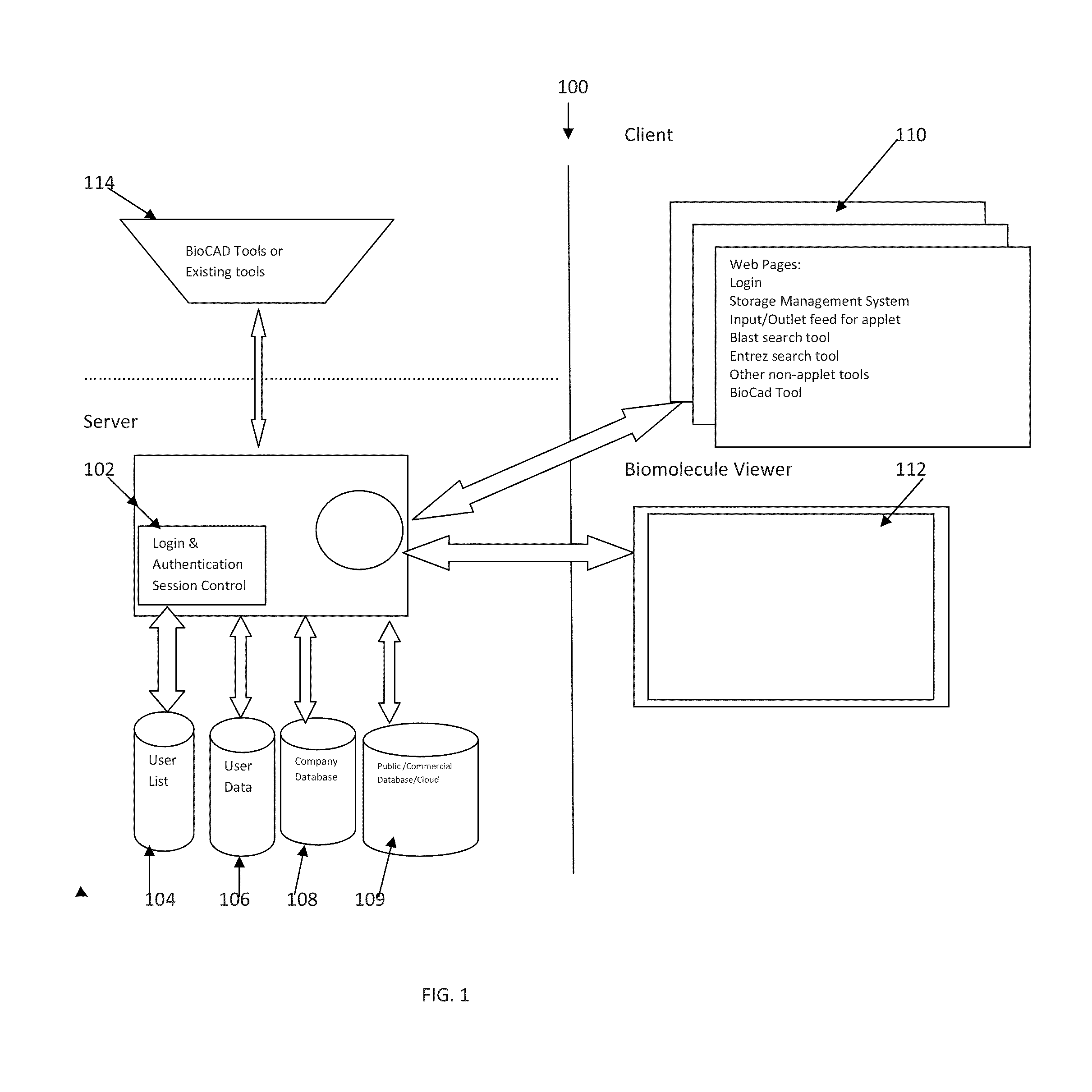
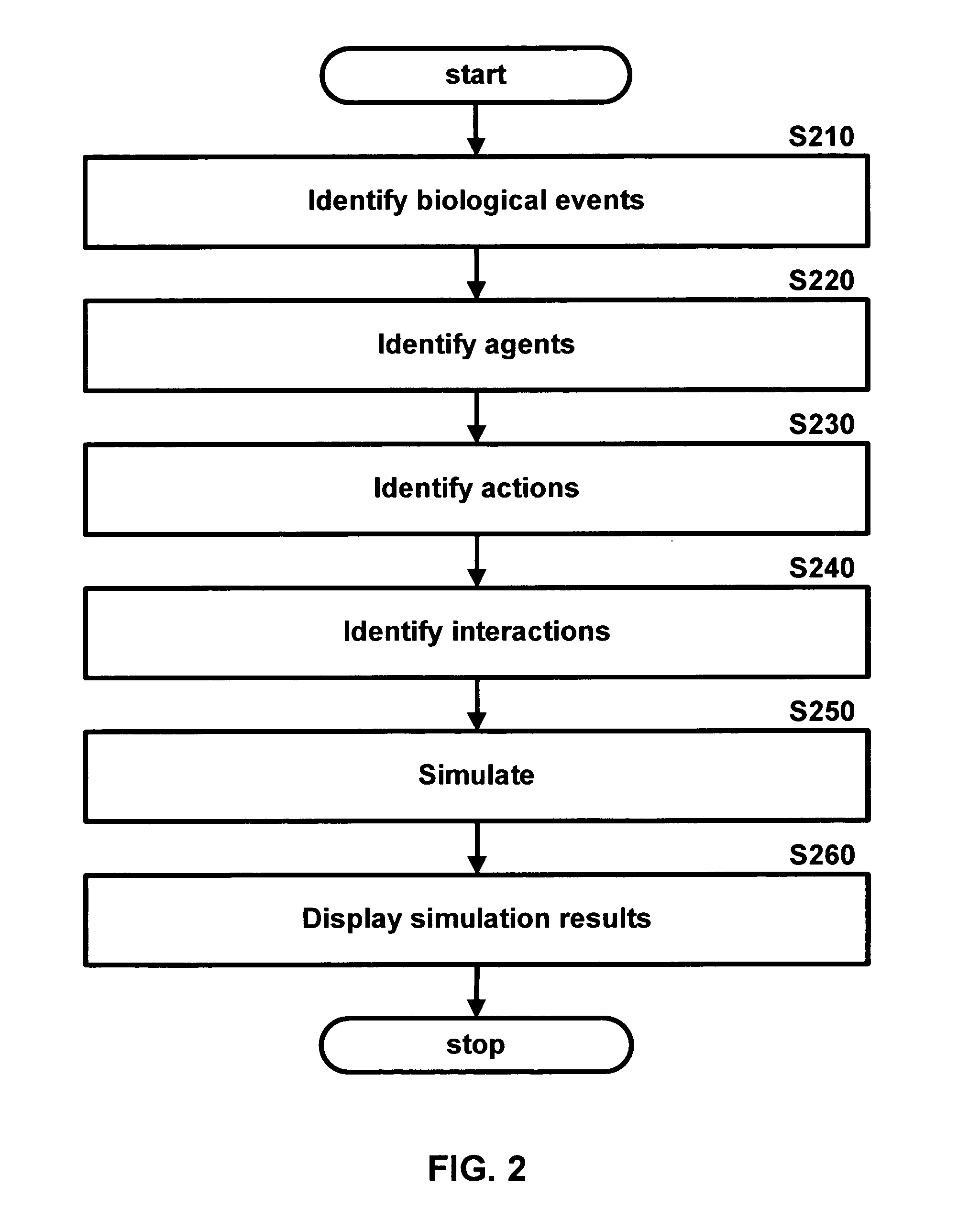
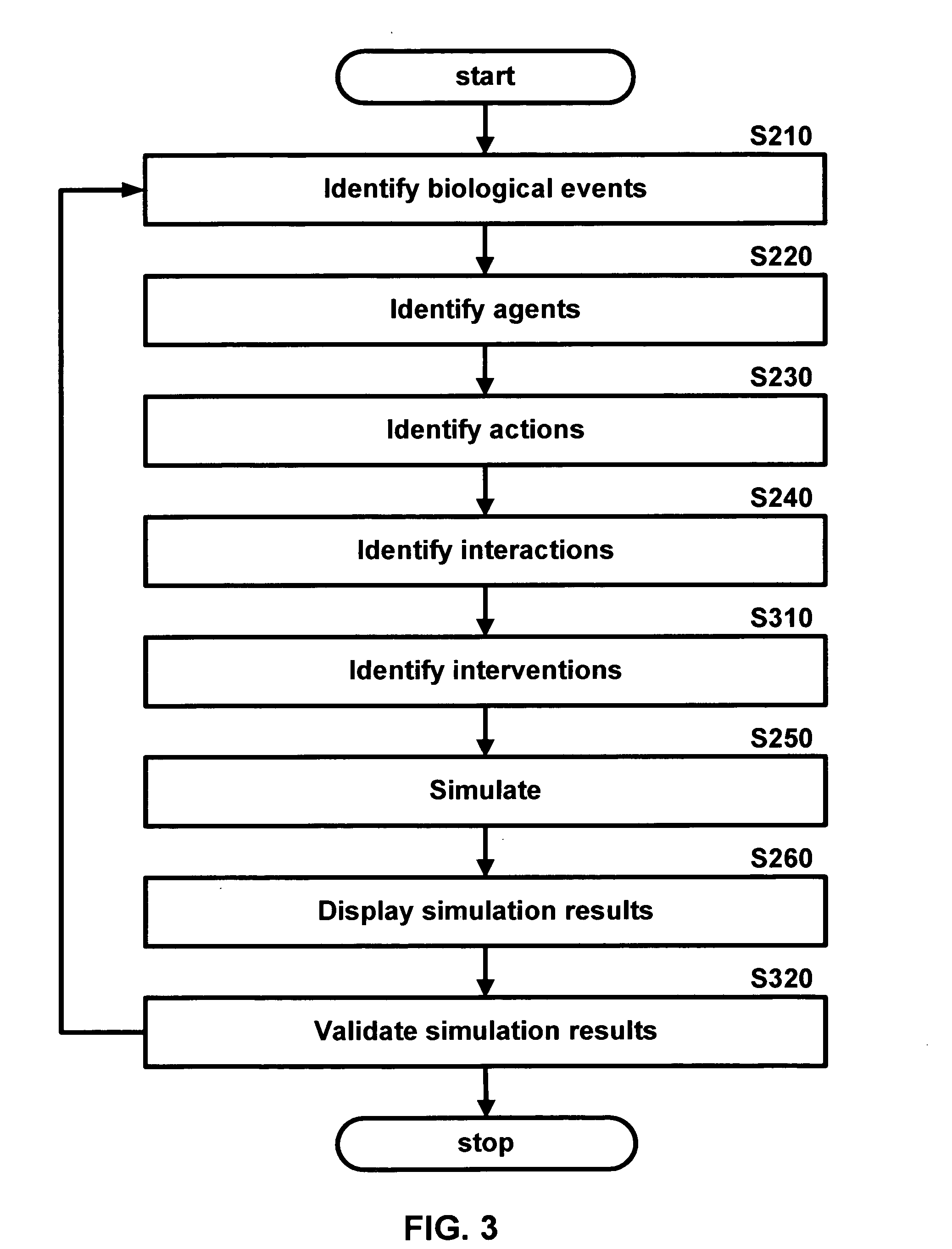
Methods and systems for in silico design
InactiveUS20140180660A1Improve upon and resolve issueSave resourcesData visualisationAnalogue computers for chemical processesUser inputComputerized system
Embodiments describe computer systems and computer programs for implementing BioCAD methods comprising one or more data models and one or more BioCAD tools, wherein the BioCAD tools enable users to design or refactor a biomolecule or to conduct a biological experiment in silico by user input of one or more components selected by the user from a database populated with information on components and scientific data of existing biomolecules and experiments. Data models of the programs are operable to manage development of the new biomolecule or experiment based on information in the databases. Computer programs also provide an output with information that enables the users to determine in silico if the newly designed or refactored molecule or biological experiment is satisfactory or not for its intended purpose in vitro and also provides the user the capability to re-design the biomolecule or experiment till it is satisfactory.
Owner:LIFE TECH HLDG PTE LTD
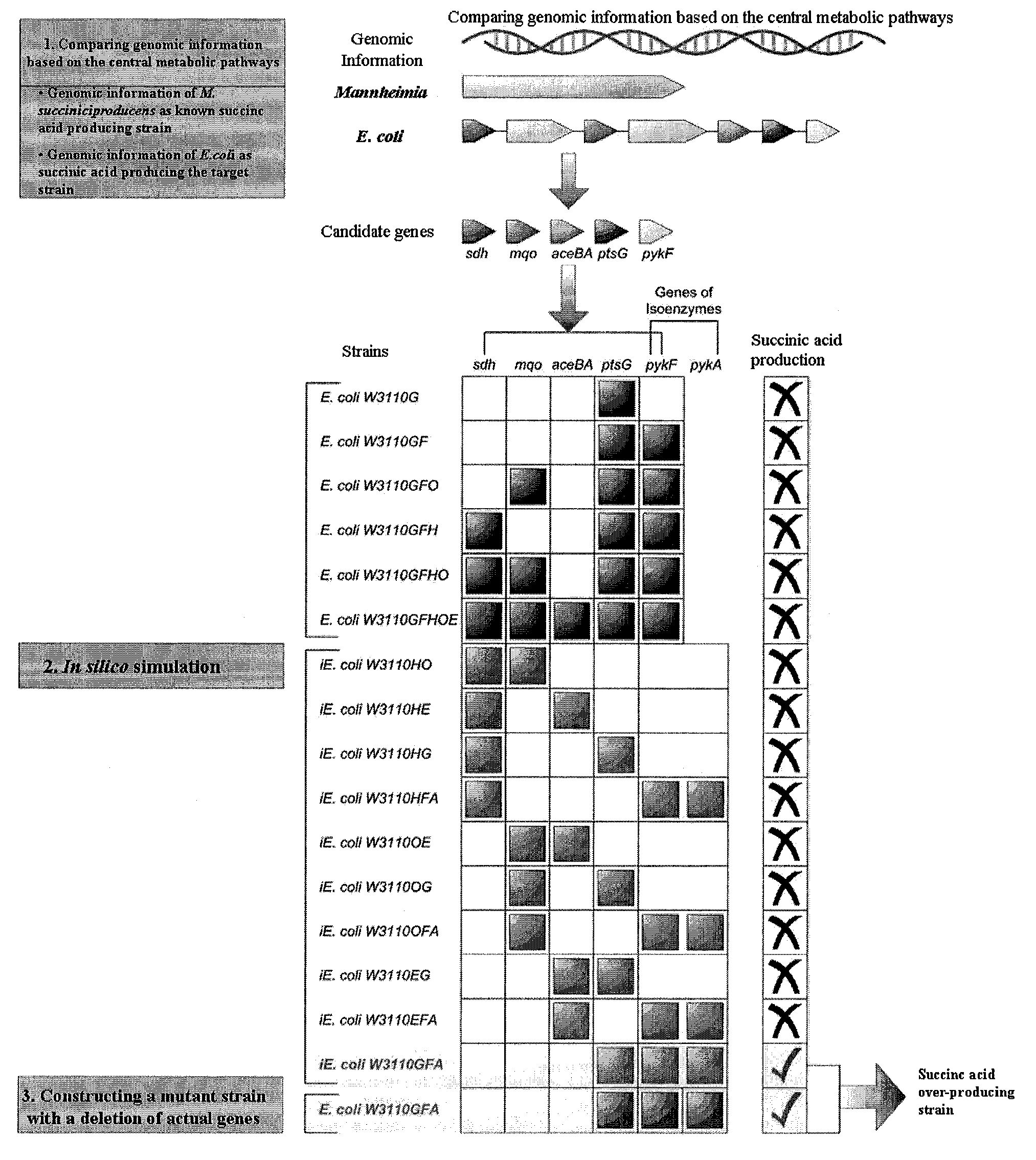
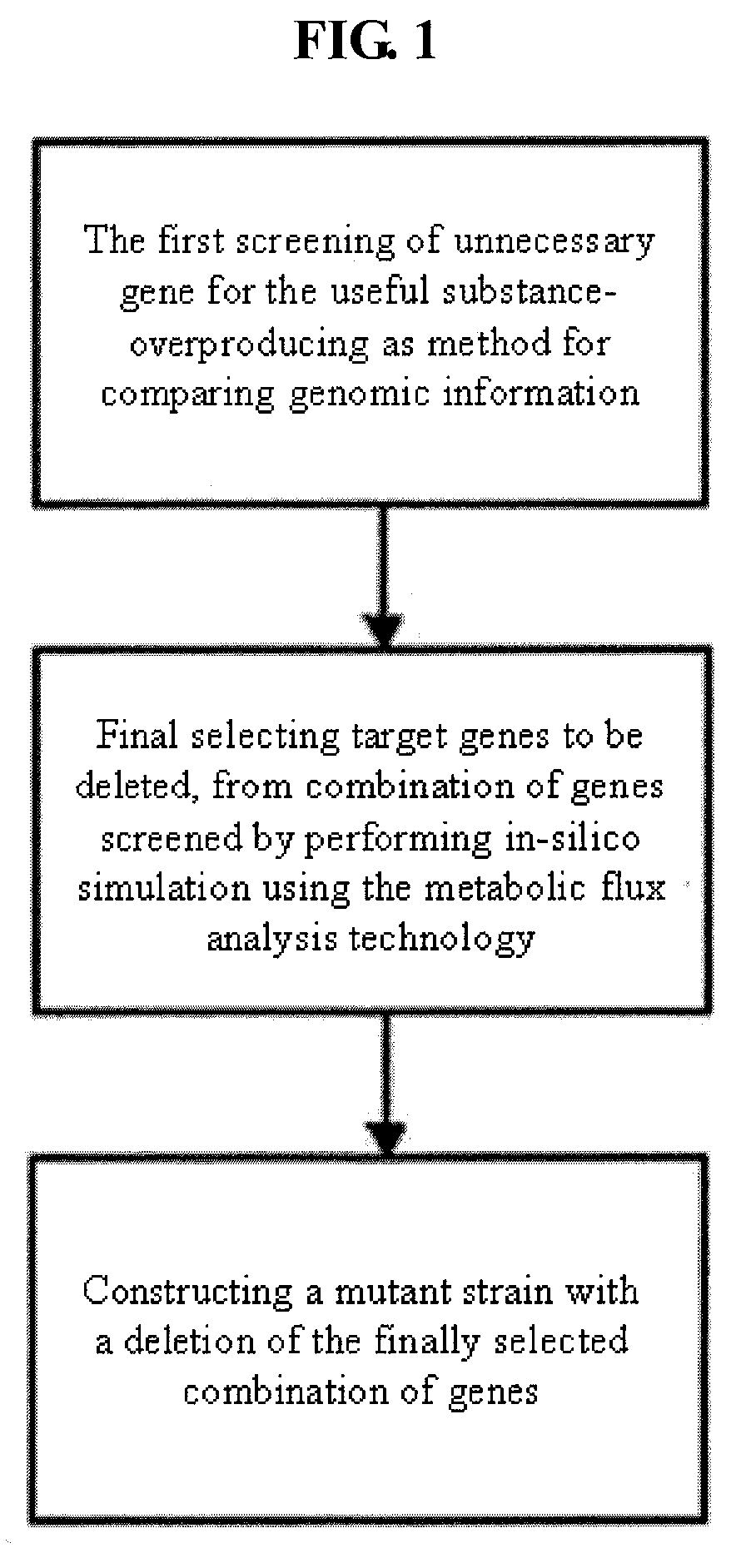
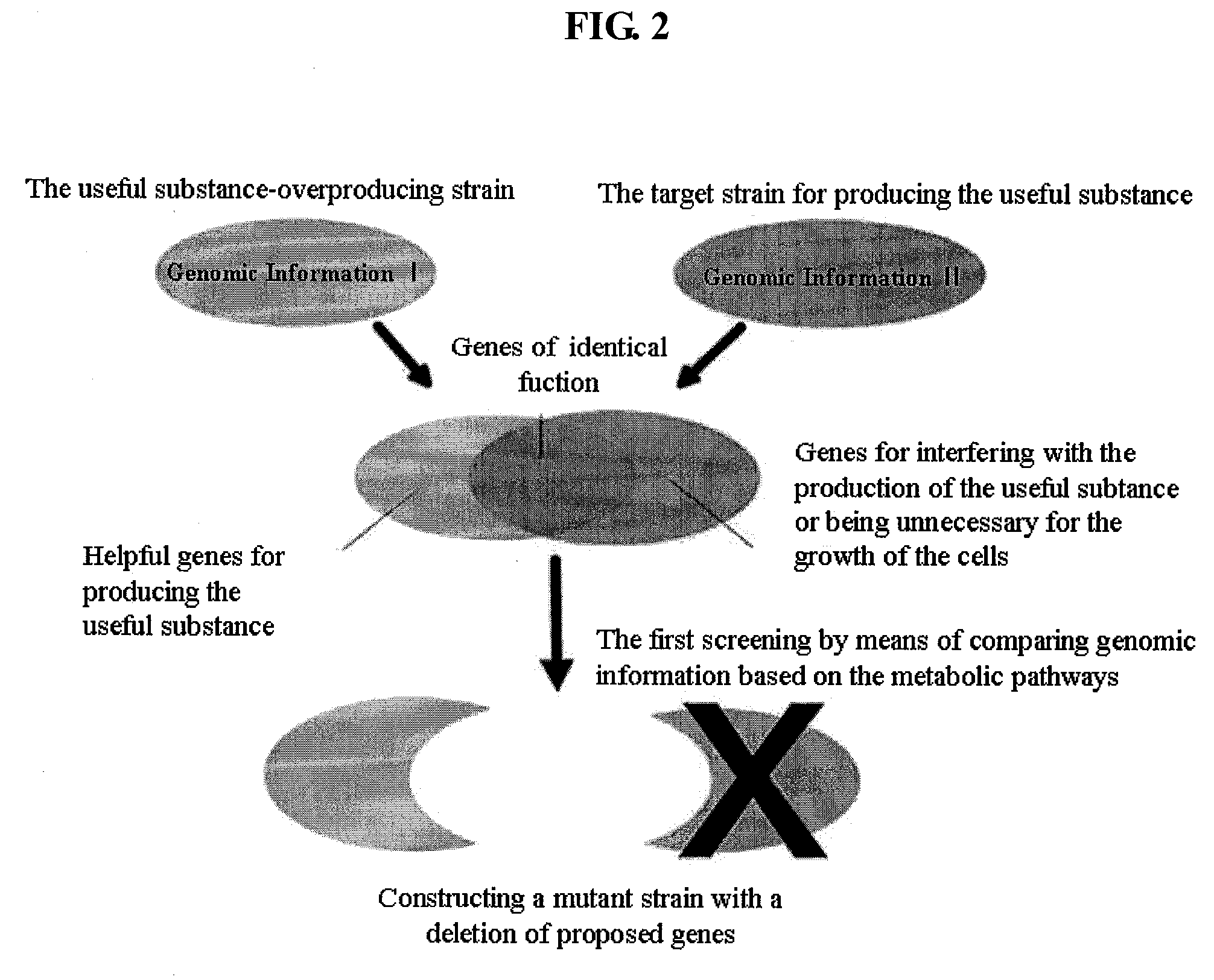
Method For Improving A Strain Based On In-Silico Analysis
InactiveUS20090075352A1Increase strainHigh yieldBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyCandidate Gene Association Study
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
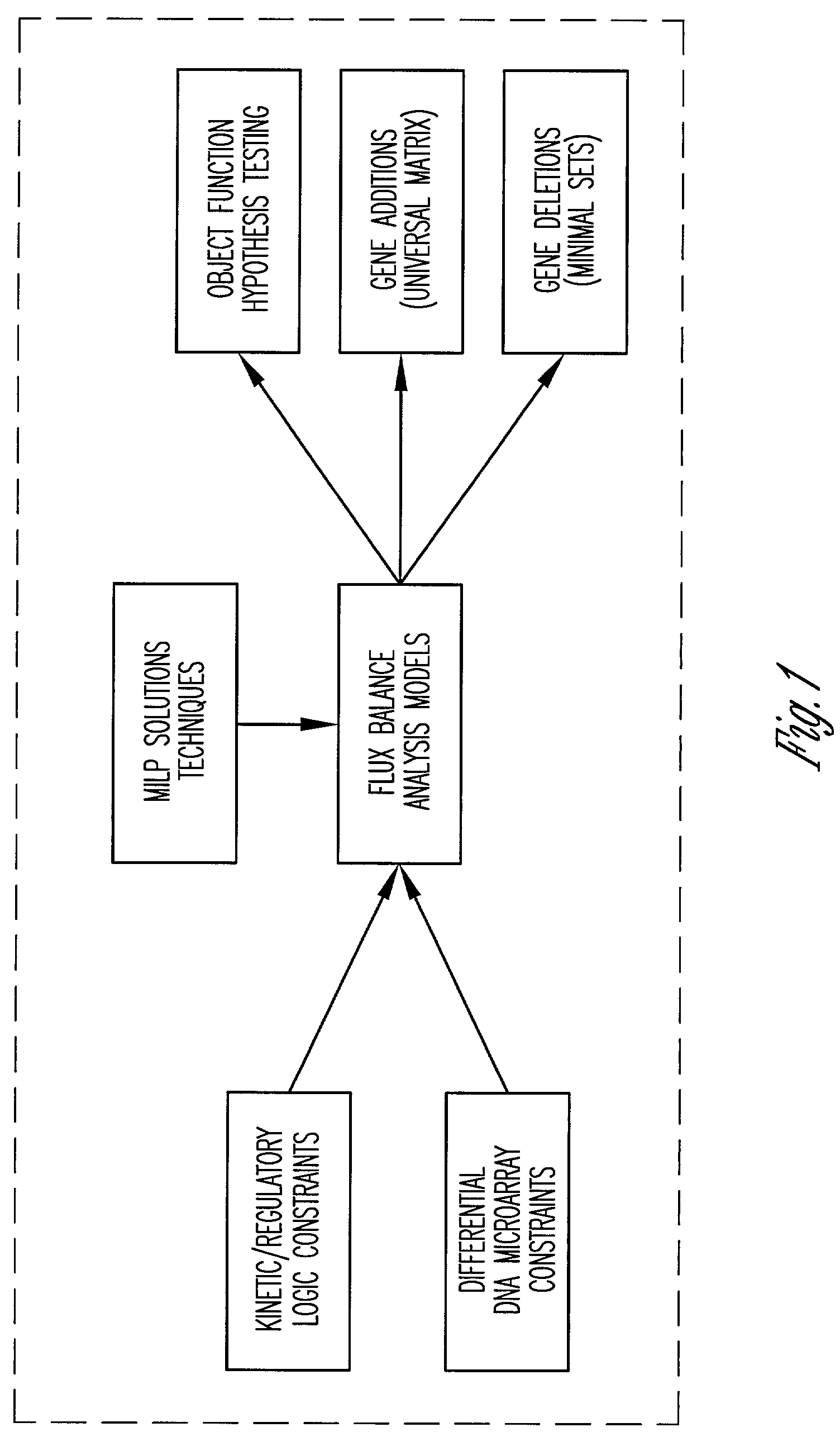
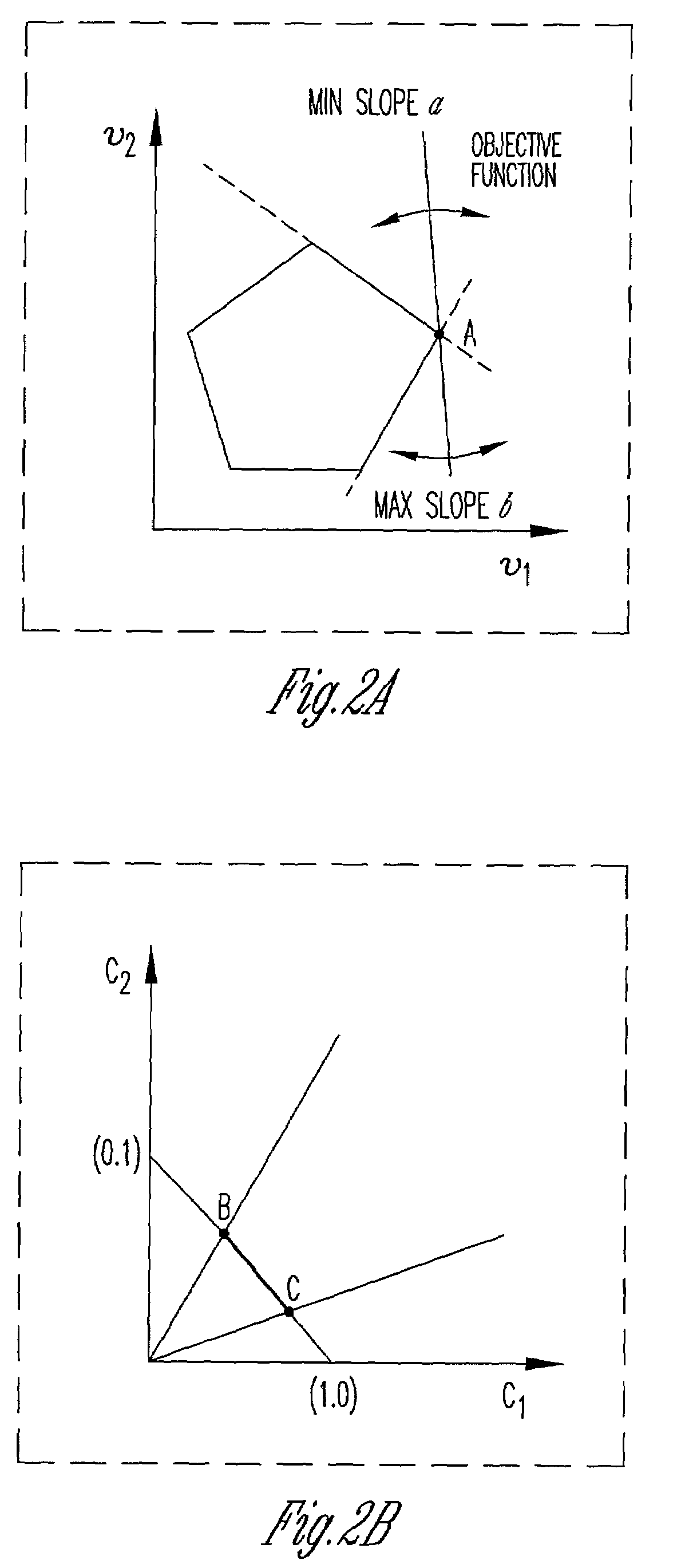
Method and system for modeling cellular metabolism
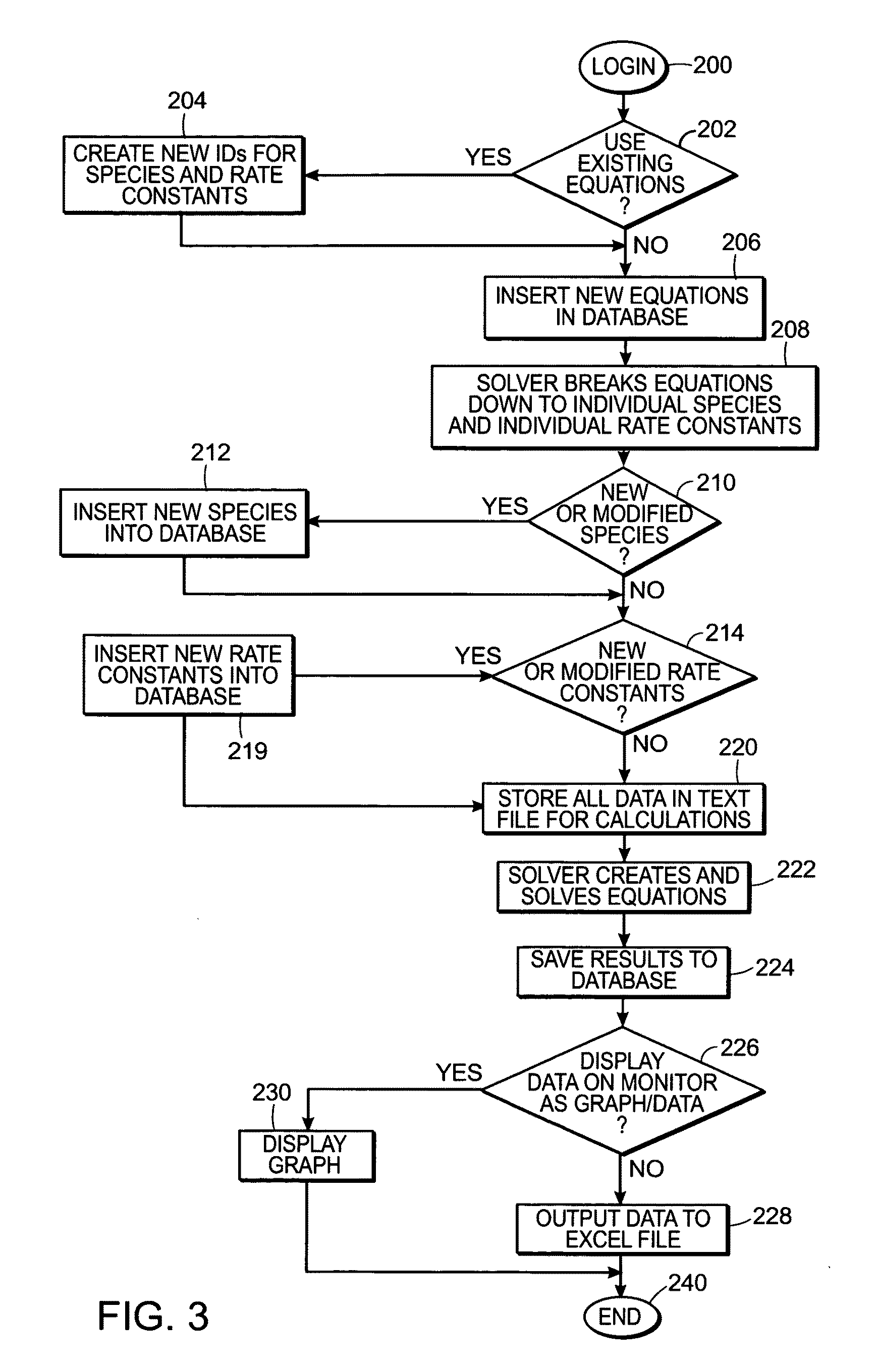
This invention relates to methods and systems for in silico or bioinformatic modeling of cellular metabolism. The invention includes methods and systems for modeling cellular metabolism of an organism, comprising constructing a flux balance analysis model, and applying constraints to the flux balance analysis model, the constraints selected from the set consisting of: qualitative kinetic information constraints, qualitative regulatory information constraints, and differential DNA microarray experimental data constraints. In addition, the present invention provides for computational procedures for solving metabolic problems.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Pharmaceutical Platform Technology for the Development of Natural Products
The present invention provides a set of in vitro and in silico methodologies for predicting in vivo pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of multiple components; the methodologies comprise mathematical models for solving multiple unknowns which are linearly independent and / or interacting with each other. The present invention can be applied to develop phytomedicines which contain multiple active ingredients without prior identification, isolation and purification of these components.
Owner:SINOVEDA CANADA INC
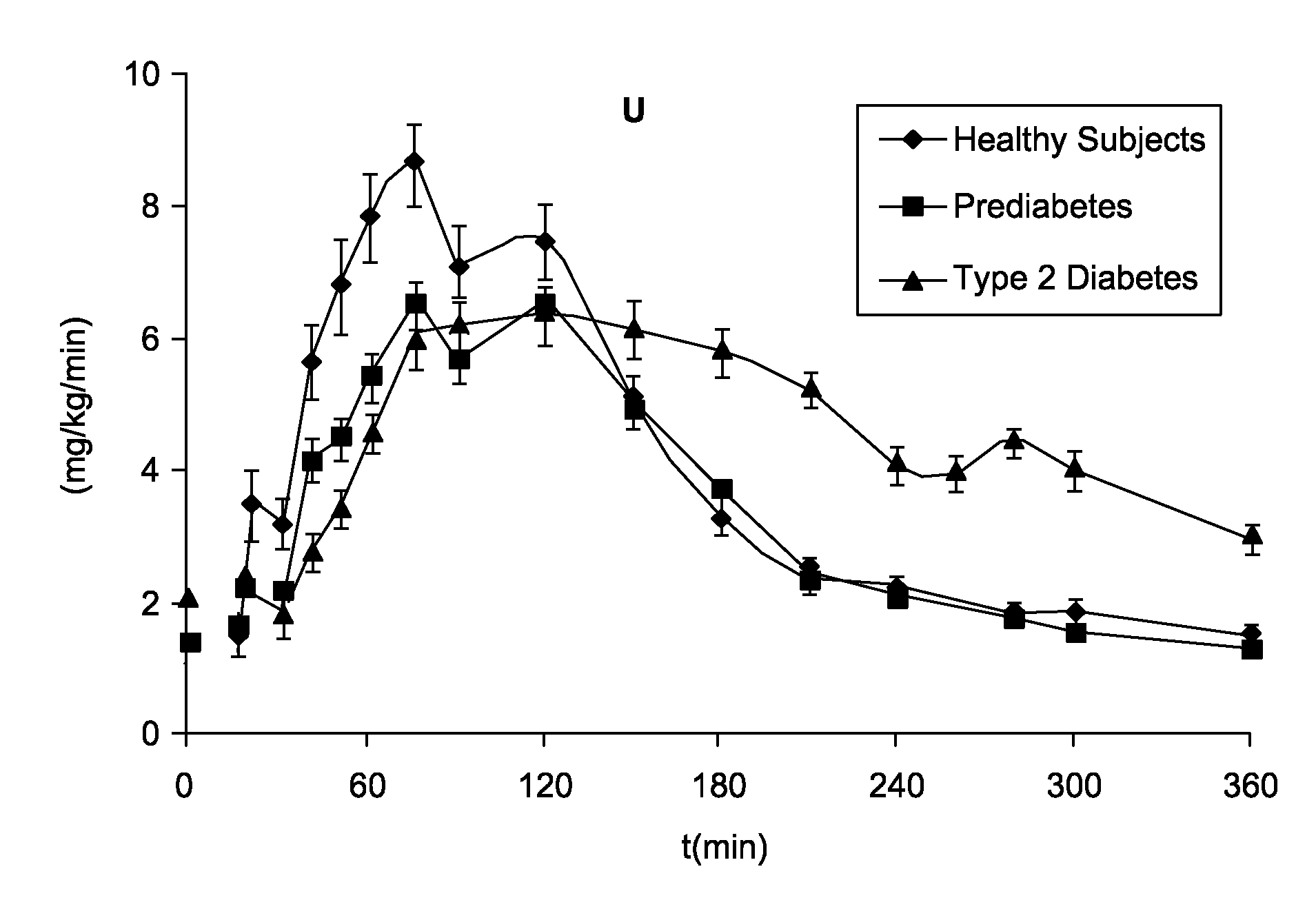
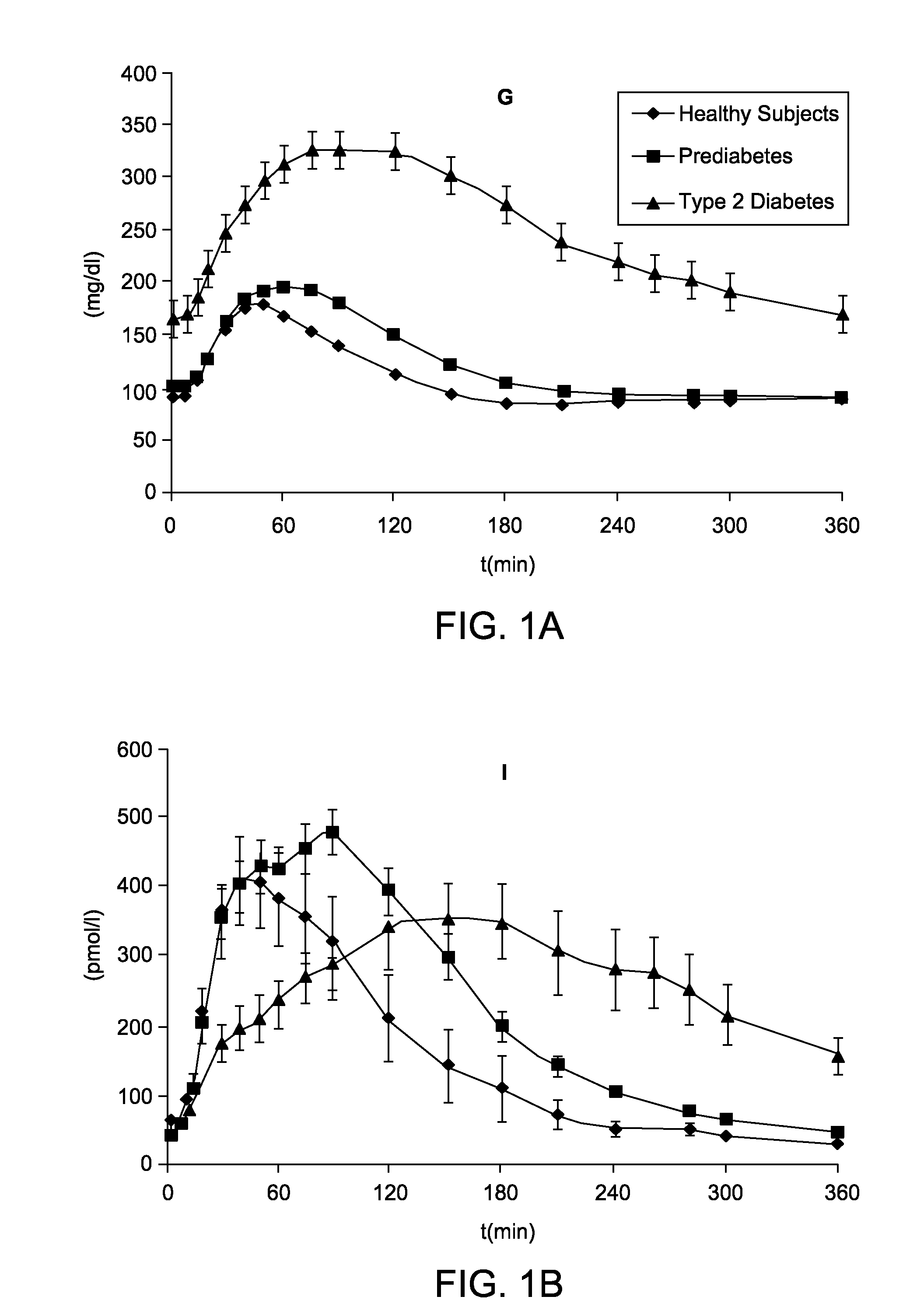
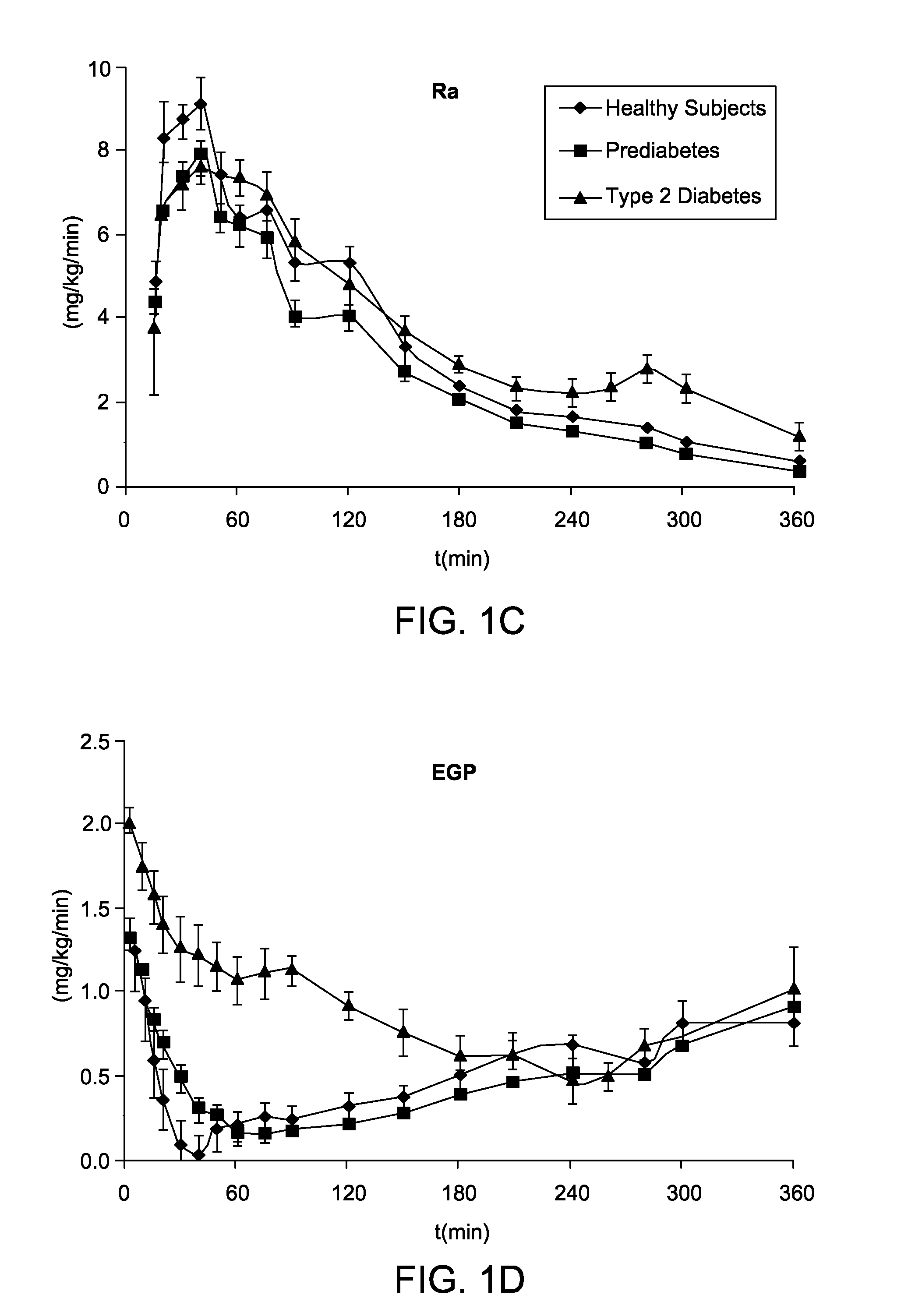
System, Method and Computer Simulation Environment For In Silico Trials in Pre-Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes
ActiveUS20120130698A1Provide informationIneffective treatmentMedical simulationMedical data miningGlucose utilizationModel dynamics
An electronic system is provided that simulates a glucose-insulin metabolic system of a T2DM or prediabetic subject, wherein the system includes a subsystem that models dynamic glucose concentration in a T2DM or prediabetic subject, including an electronic module that models endogenous glucose production (EGP(t)), or meal glucose rate of appearance (Ra(t>>, or glucose utilization (U(t)), or renal excretion of glucose (B(t)), a subsystem that models dynamic insulin concentration in said T2DM or prediabetic subject, including an electronic module that models insulin secretion (S(t)), an electronic database containing a population of virtual T2DM or prediabetic subjects, each virtual subject having a plurality of metabolic parameters, and a processing module that calculates an effect of variation of at least one metabolic parameter value on the glucose insulin metabolic system of a virtual subject by inputting the plurality of metabolic parameter values.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Computational modeling and simulating of host-pathogen interactions
InactiveUS20050055188A1Medical simulationEpidemiological alert systemsHost–pathogen interactionIn vivo
The present invention reveals a method for developing agent-based simulation systems that are capable for the modeling and simulation of a systematic and analytical approach to a host-pathogen interaction. This methodology may enable users to explore “what if” scenarios and develop predictive data that may be used in experimental design and the testing of hypotheses of disease states. Using an in silico testing environment, the in silico approach helps combine knowledge of disease states that may be obtained from various sources, such as in vitro studies and in vivo studies, without requiring users to perform all necessary experimentation.
Owner:NAVY SEC OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA OFFICE COUNSEL
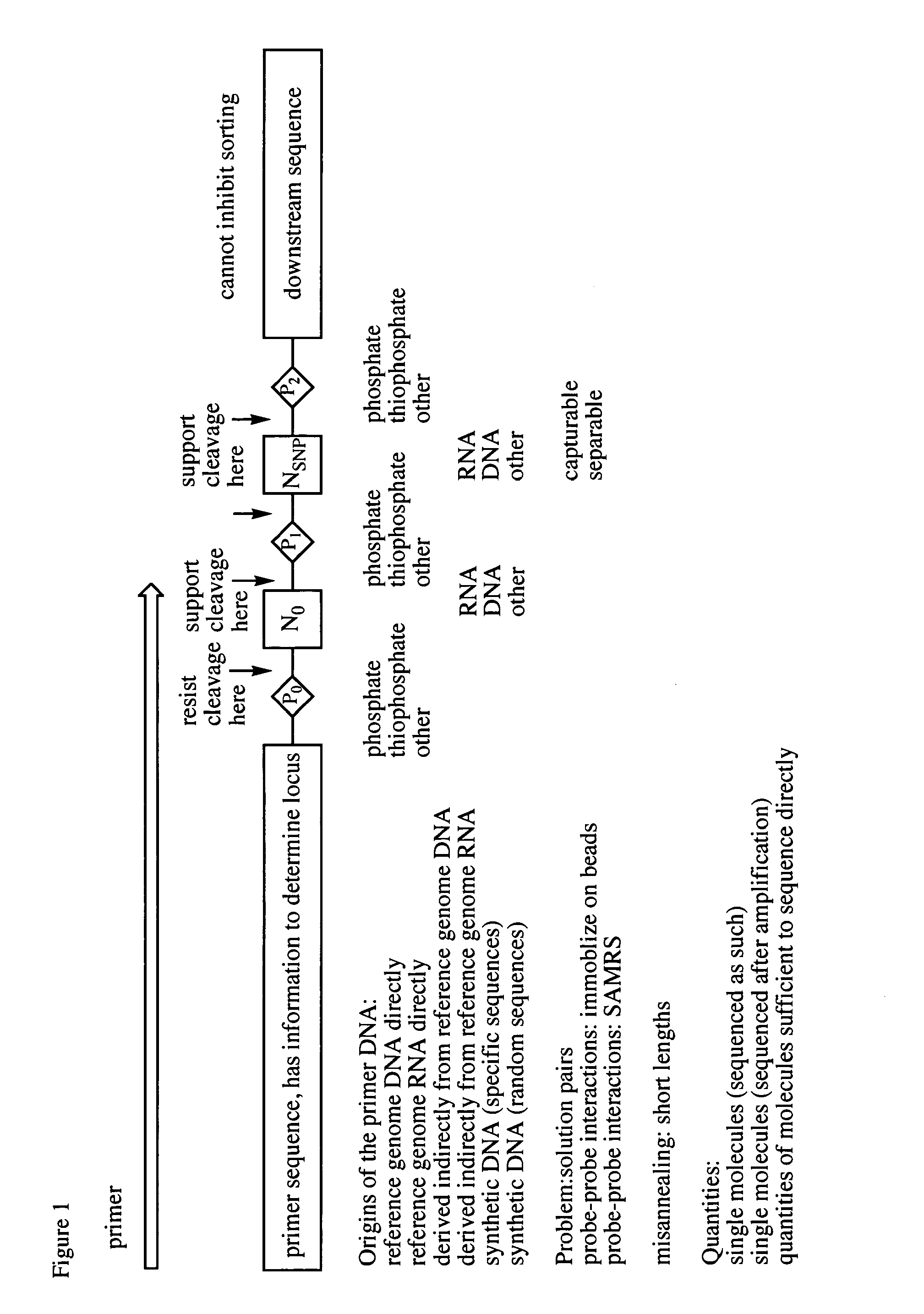
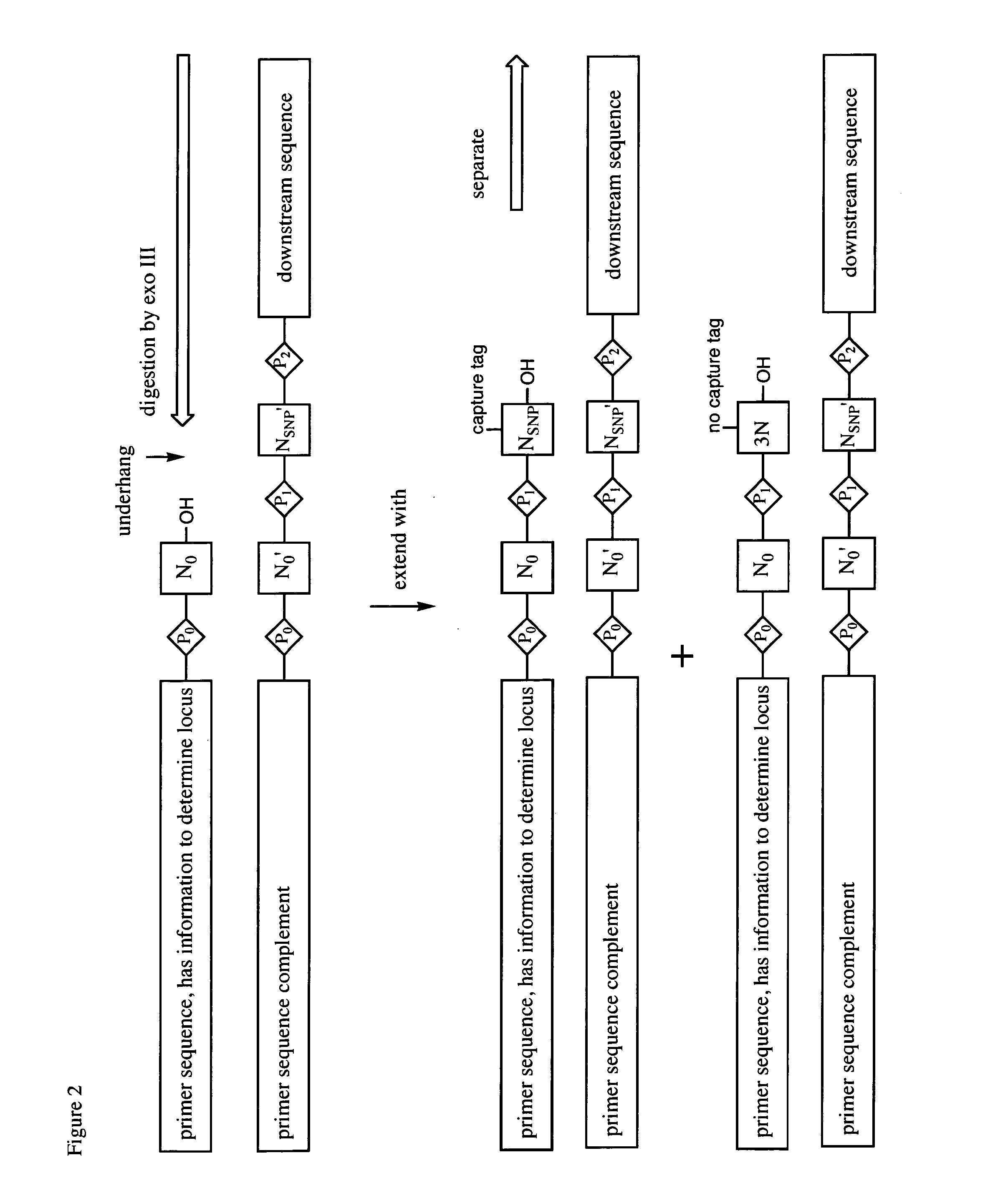
Differential detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms
This patent application claims processes and compositions of matter that enable the discovery of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that distinguish the genomes of two individual organisms in the same species, as well as that distinguish the paternal and maternal genetic inheritance of a single individual, as well as distinguish the genomes of cells in special tissues (e.g. cancer tissues) within an individual from the genomes of the standard cells in the same individuals, as well as the SNPs that are discovered using these processes and compositions. Two steps are essential to the invention disclosed in this application. The first step provides four sets of primers, which are designated “T-extendable”, “A-extendable”, “C-extendable”, and “G-extendable”. These primers, when targeted against a reference genome as a template, add (respectively) T, A, C, and G to their 3′-ends in a template-directed primer extension reaction. The second step presents these four primer sets, separately, to a sample of the target genome DNA under conditions where they bind to their complementary segments within the target DNA. Once bound, members of each primer set serve as primers for a template-directed primer extension reaction using the target genome as the template. If the template from the target genome presents the same templating nucleotide for the first nucleotide added in the extension reaction as the reference genome, then the T-extendable, A-extendable, C-extendable, and G-extendable primers will be extended (respectively) by T, A, C, and G. If, however, the template from the target genome presents a nucleotide different from the reference genome, then the T-extendable, A-extendable, C-extendable, and G-extendable primers will be extended (respectively) by not T, not A, not C, and not G (referred to here as “3N” or “3”, to indicate the other three nucleotides, where which of the other three is understood by context). In these cases, the primers have discovered a SNP, a difference between the target and reference genomes. Then, the T-extendable, A-extendable, C-extendable, and G-extendable primers that add (respectively) not-T, not-A, not-C, and not-G are separated or made otherwise physically distinct (through, for example, the use of irreversible terminators, such as 2′,3′-dideoxynucleosides) from those that added T, A, C, and G (respectively). Those that added T, A, C, and G (respectively) did not discover a SNP, and are discarded. The primers that added “not-T”, “not-A”, “not-C”, and “not-G” discovered a SNP, and presented in a mixture enriched (relative to those primers that did not discover a SNP) in a useful deliverable. Following these steps, the SNPs discoveries are realized by sequencing the extracted species. The information obtained from this sequencing allows the identification of the locus of the SNP in the in silico genome.
Owner:BENNER STEVEN A +2
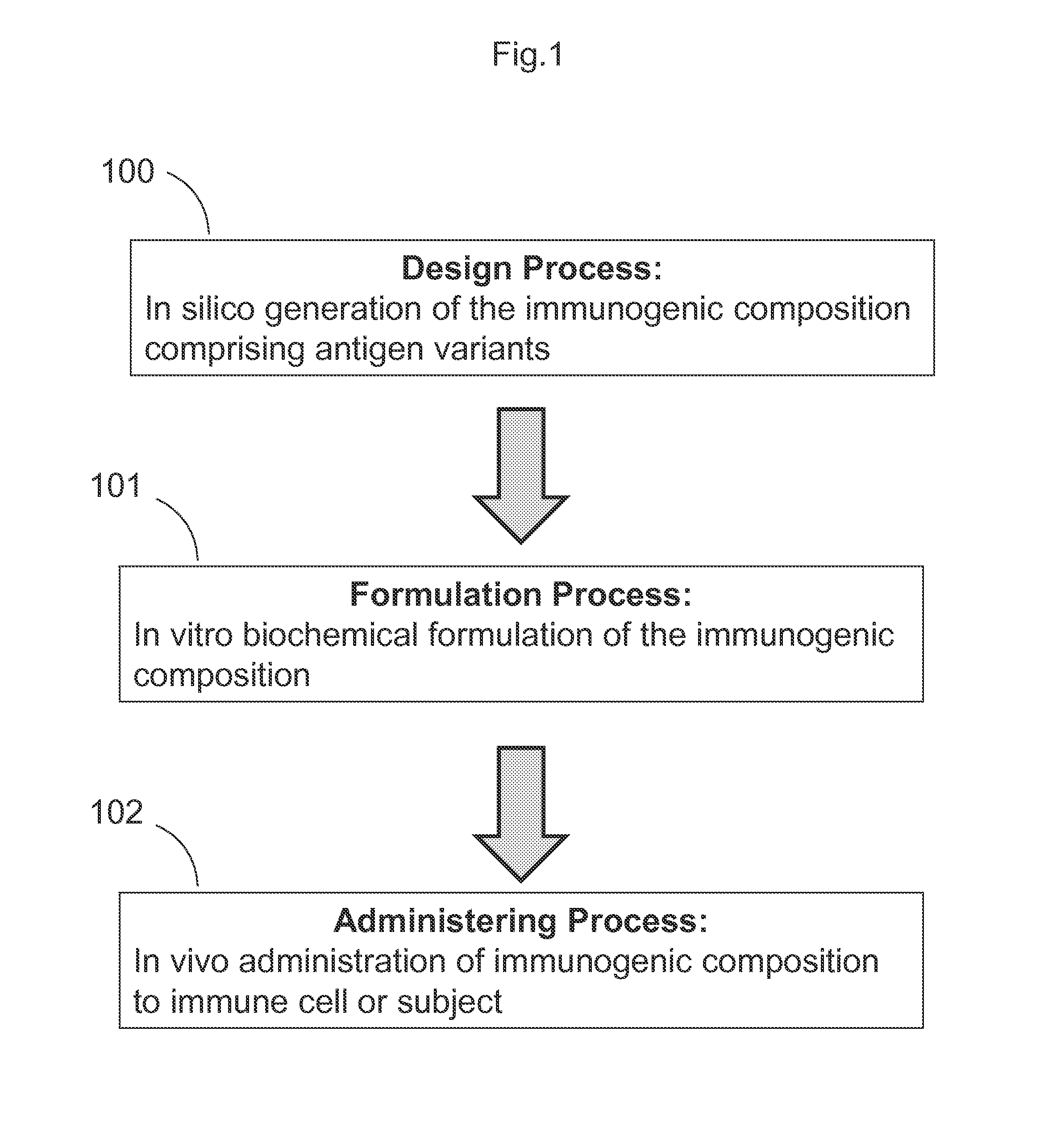
Epitope focusing by variable effective antigen surface concentration
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods for the generation of an antibody or immunogenic composition, such as a vaccine, through epitope focusing by variable effective antigen surface concentration. Generally, the composition and methods of the disclosure comprise three steps: a “design process” comprising one or more in silico bioinformatics steps to select and generate a library of potential antigens for use in the immunogenic composition; a “formulation process”, comprising in vitro testing of potential antigens, using various biochemical assays, and further combining two or more antigens to generate one or more immunogenic compositions; and an “administering” step, whereby the immunogenic composition is administered to a host animal, immune cell, subject or patient. Further steps may also be included, such as the isolation and production of antibodies raised by host immune response to the immunogenic composition.
Owner:CENTIVAX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com