Patents
Literature
684 results about "Reference genome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
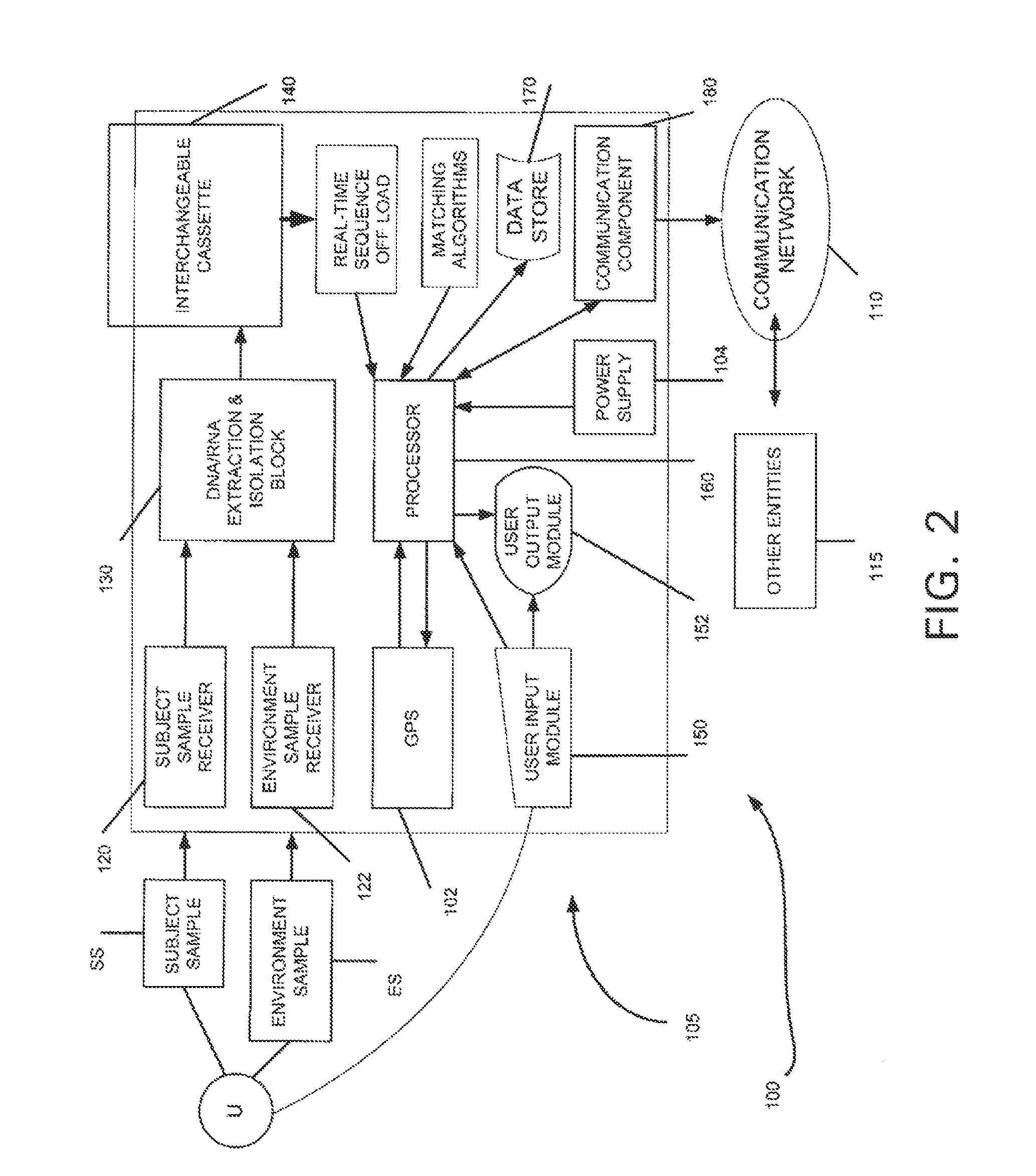
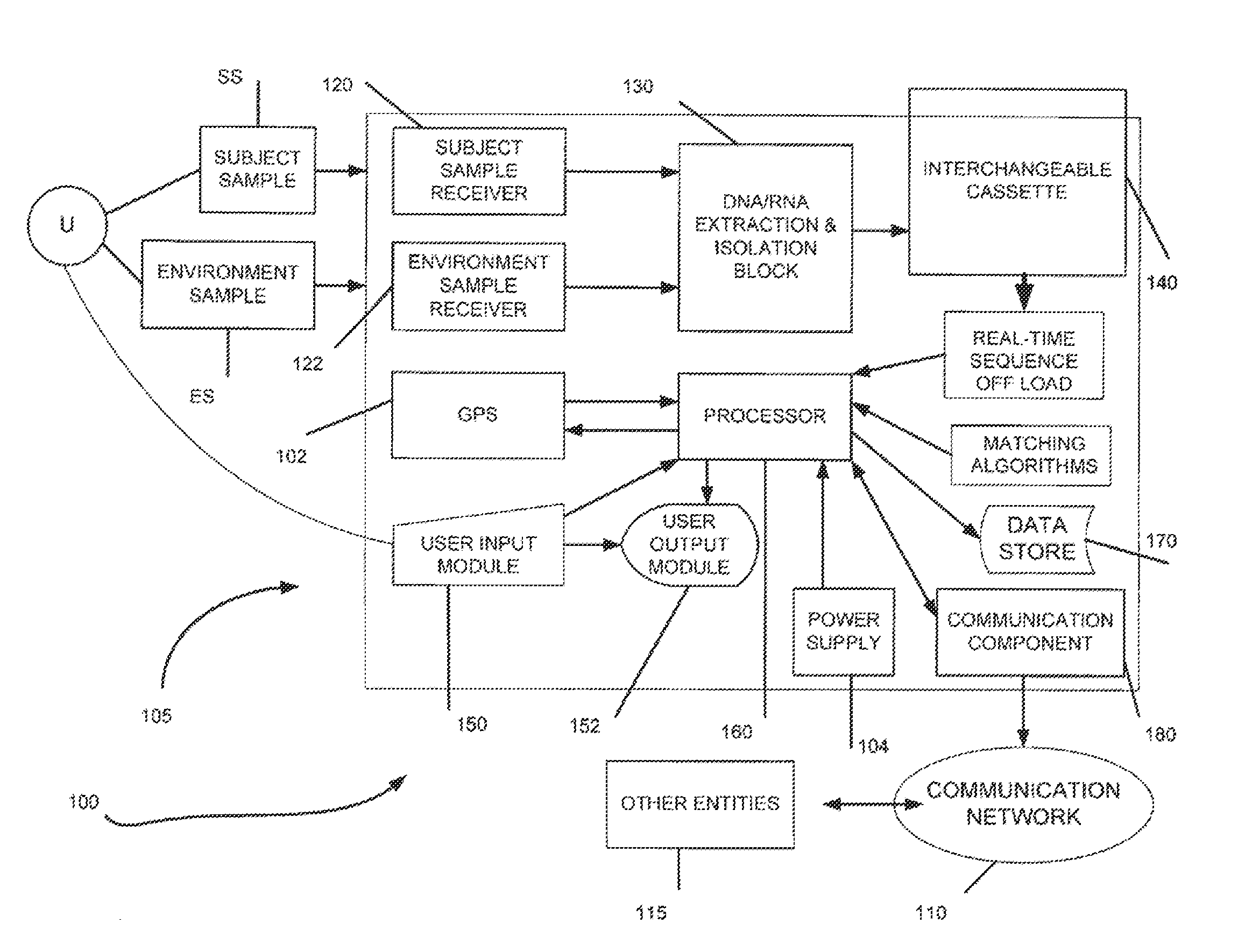
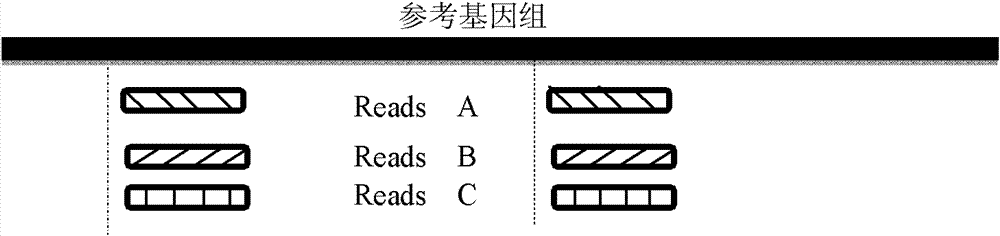
A reference genome (also known as a reference assembly) is a digital nucleic acid sequence database, assembled by scientists as a representative example of a species' set of genes. As they are often assembled from the sequencing of DNA from a number of donors, reference genomes do not accurately represent the set of genes of any single person. Instead a reference provides a haploid mosaic of different DNA sequences from each donor. For example, GRCh37, the Genome Reference Consortium human genome (build 37) is derived from thirteen anonymous volunteers from Buffalo, New York. The ABO blood group system differs among humans, but the human reference genome contains only an O allele (although the other alleles are annotated).
Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)
InactiveUS6335167B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingComparative genomic hybridization
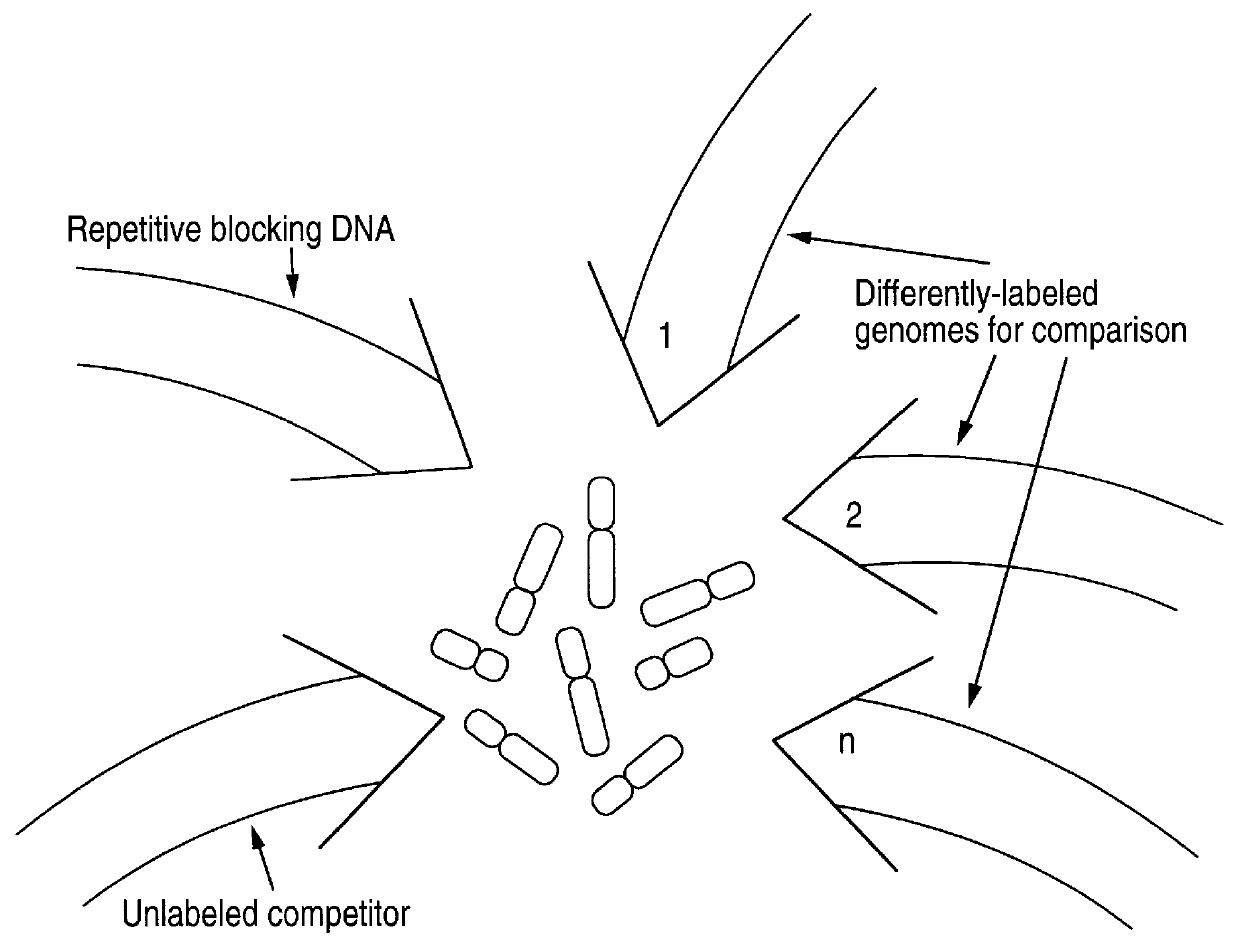
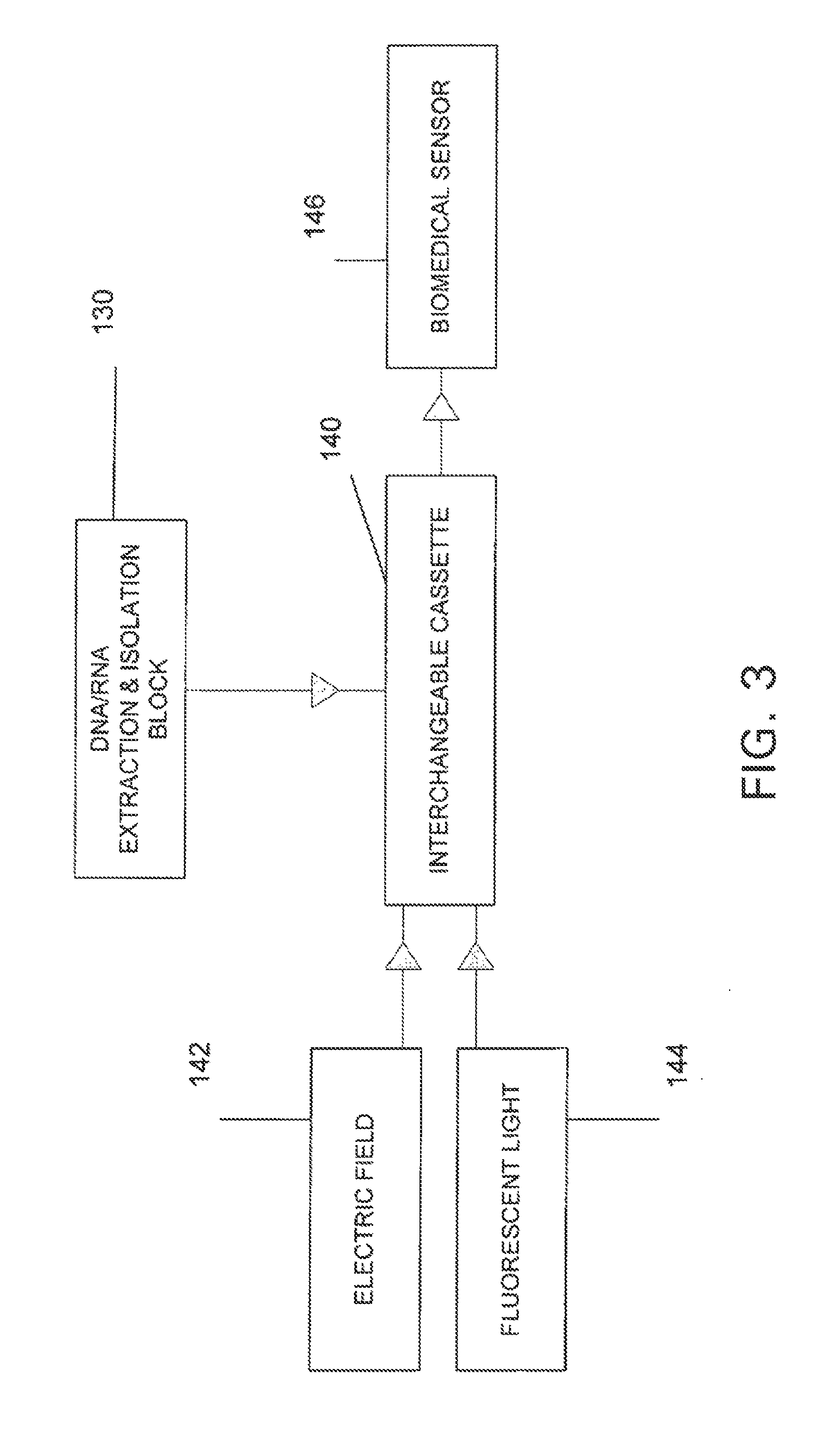
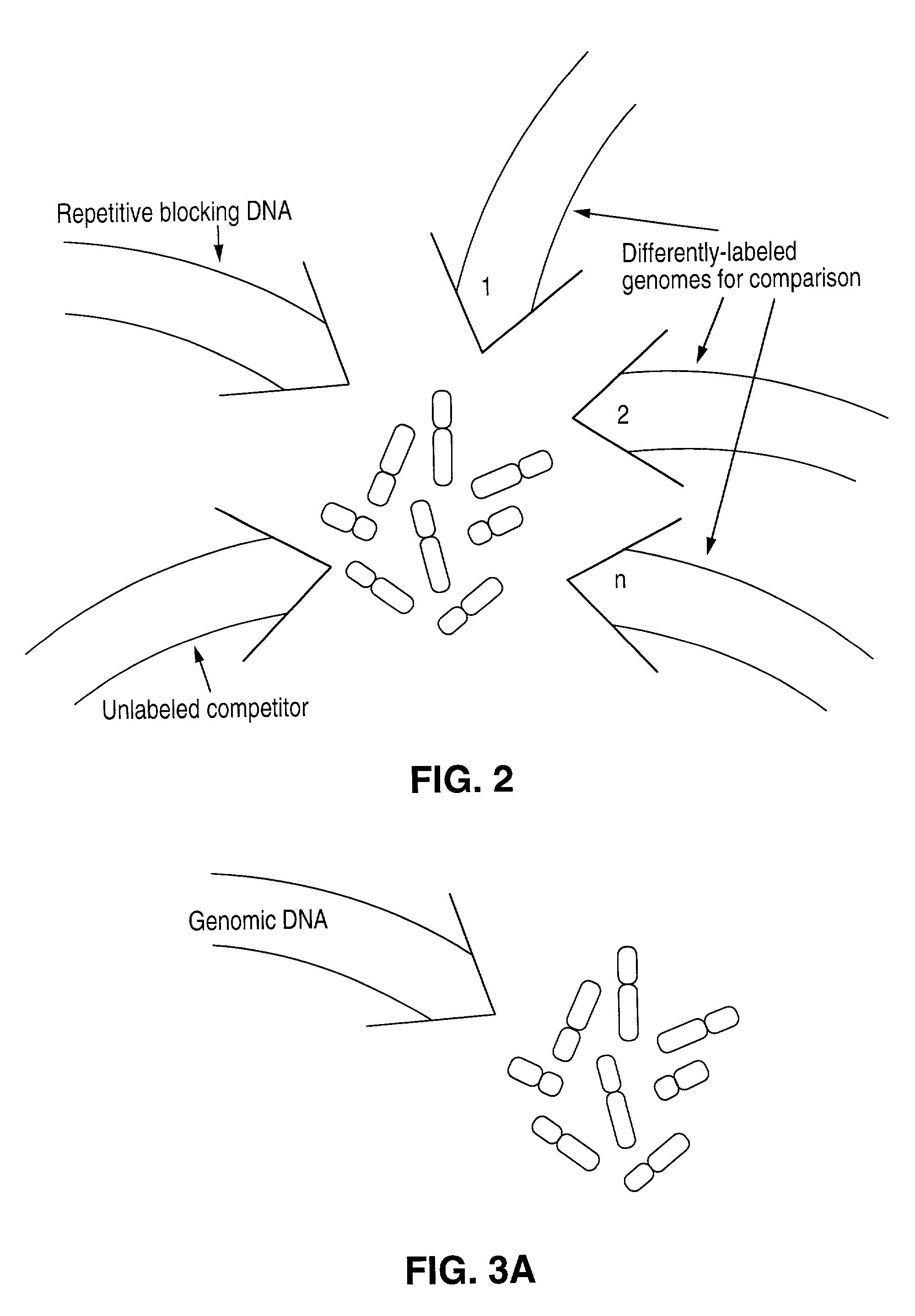
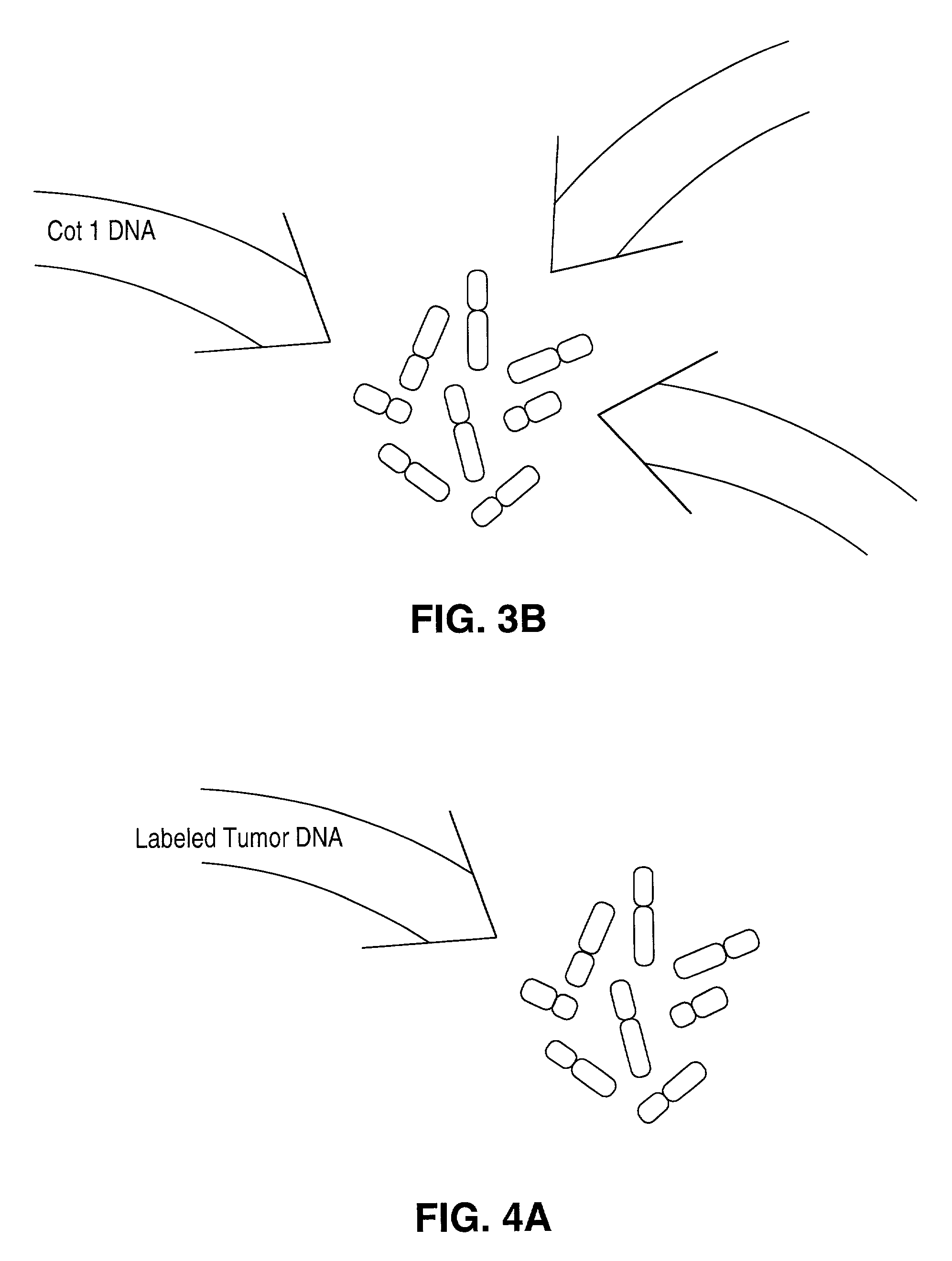
Disclosed are new methods comprising the use of in situ hybridization to detect abnormal nucleic acid sequence copy numbers in one or more genomes wherein repetitive sequences that bind to multiple loci in a reference chromosome spread are either substantially removed and / or their hybridization signals suppressed. The invention termed Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH) provides for methods of determining the relative number of copies of nucleic acid sequences in one or more subject genomes or portions thereof (for example, a tumor cell) as a function of the location of those sequences in a reference genome (for example, a normal human genome). The intensity(ies) of the signals from each labeled subject nucleic acid and / or the differences in the ratios between different signals from the labeled subject nucleic acid sequences are compared to determine the relative copy numbers of the nucleic acid sequences in the one or more subject genomes as a function of position along the reference chromosome spread. Amplifications, duplications and / or deletions in the subject genome(s) can be detected. Also provided is a method of determining the absolute copy numbers of substantially all RNA or DNA sequences in subject cell(s) or cell population(s).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Direct identification and measurement of relative populations of microorganisms with direct DNA sequencing and probabilistic methods
ActiveUS8478544B2Quick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenomic SegmentProbabilistic method
Owner:COSMOSID INC
Direct identification and measurement of relative populations of microorganisms with direct DNA sequencing and probabilistic methods
ActiveUS20120004111A1Quick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenomic SegmentProbabilistic method
The present invention relates to systems and methods capable of characterizing populations of organisms within a sample. The characterization may utilize probabilistic matching of short strings of sequencing information to identify genomes from a reference genomic database to which the short strings belong. The characterization may include identification of the microbial community of the sample to the species and / or sub-species and / or strain level with their relative concentrations or abundance. In addition, the system and methods may enable rapid identification of organisms including both pathogens and commensals in clinical samples, and the identification may be achieved by a comparison of many (e.g., hundreds to millions) metagenomic fragments, which have been captured from a sample and sequenced, to many (e.g., millions or billions) of archived sequence information of genomes (i.e., reference genomic databases).
Owner:COSMOSID INC
Using Haplotypes to Infer Ancestral Origins for Recently Admixed Individuals
InactiveUS20140067355A1Analogue computers for chemical processesProteomicsPattern recognitionProgenitor
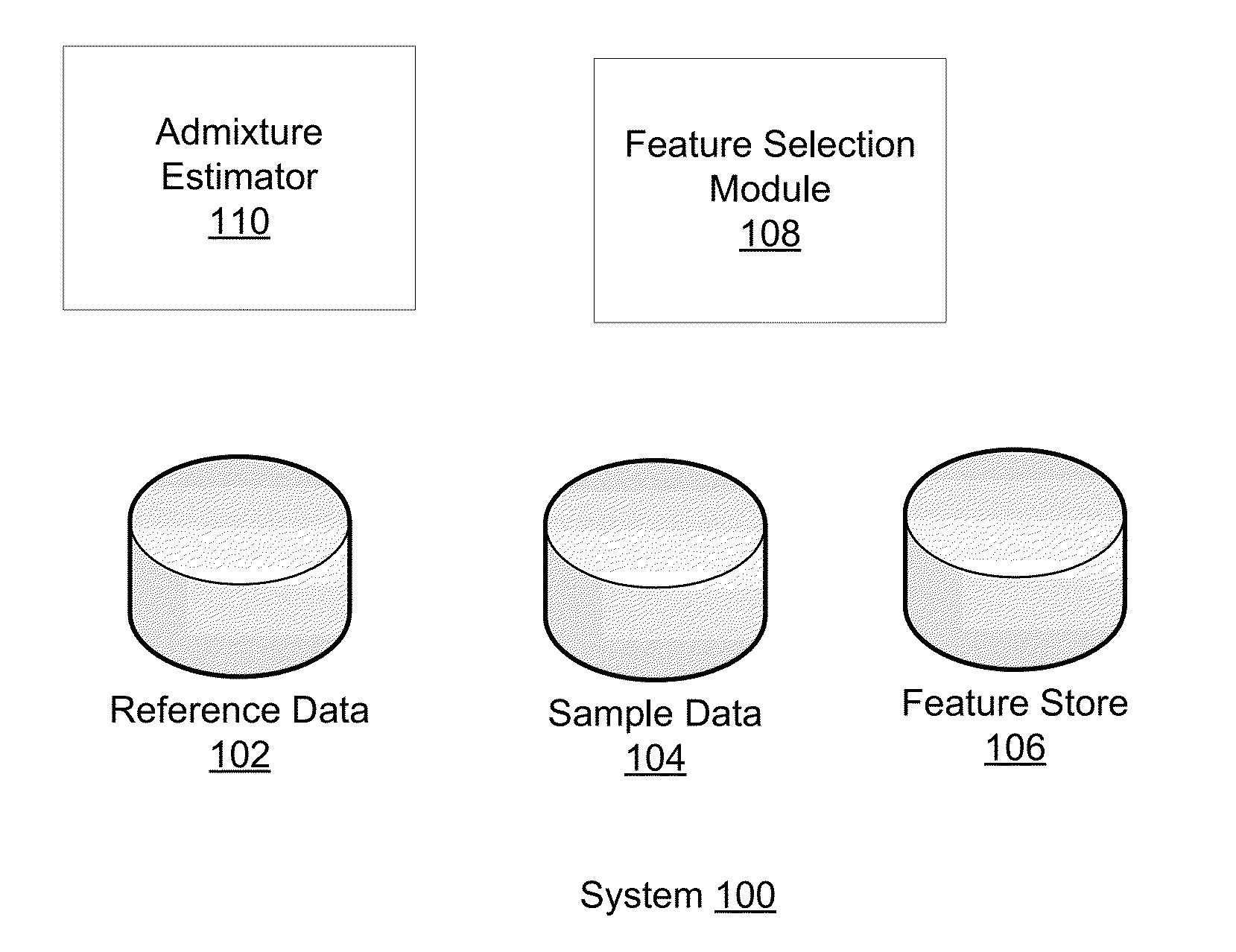
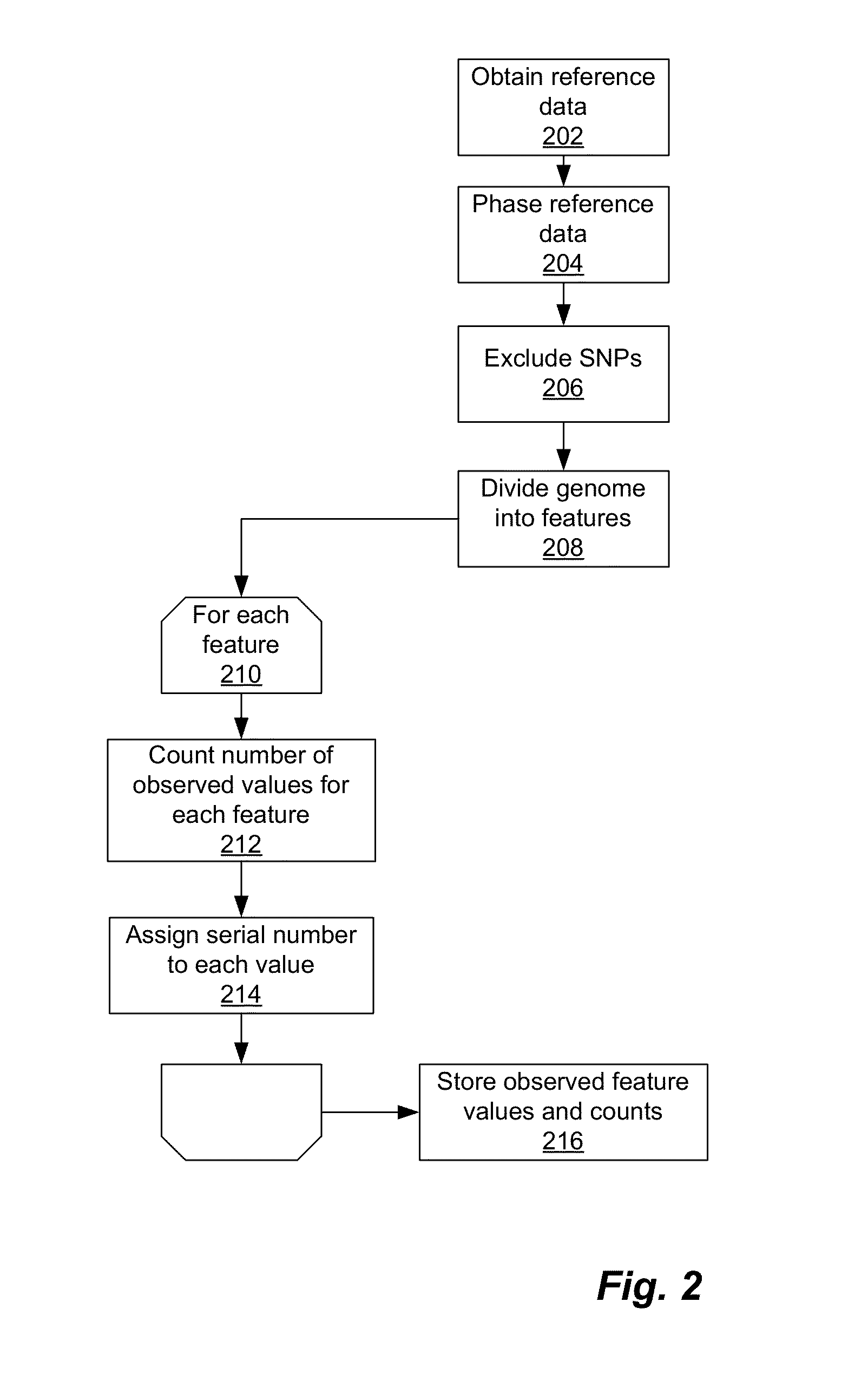
Phased haplotype features are used to infer an individual's ancestry. Reference genomic data is obtained for individuals of known ancestral origin. Haplotype features are identified based on consecutive SNPs from each individual. Sample genomic data is obtained for an individual of unknown ancestral origin. The data is phased and divided into features analogous to the features in the reference data. An admixture estimator then performs an admixture estimation based on the observed feature values in the sample data and the reference data. The estimation indicates a contribution of each of the known populations to the genome of the sample individual.
Owner:ANCESTRY COM DNA
System and methods for indel identification using short read sequencing
ActiveUS8165821B2Reduce in quantityReduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesParallel computingShort read
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Sequencing sequence mapping method and sequencing sequence mapping system
ActiveCN103336916ARealize quantitative analysisSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsProlongationComputer science
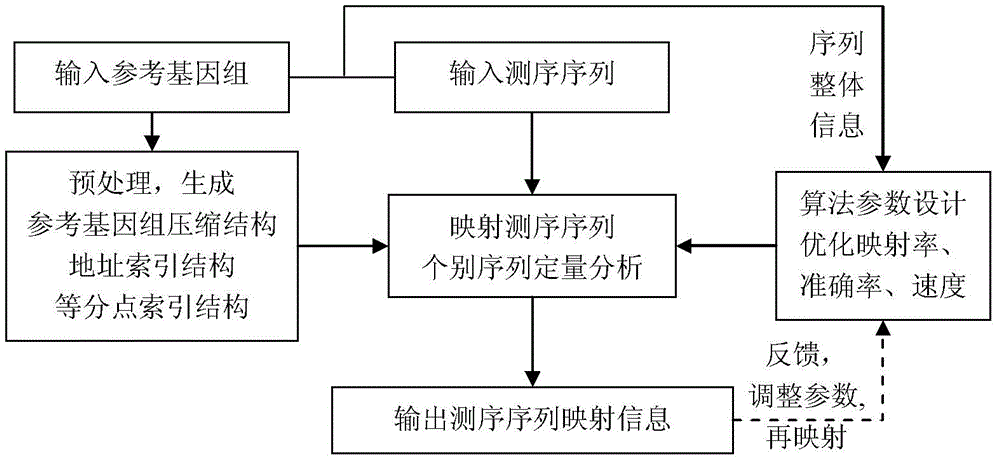
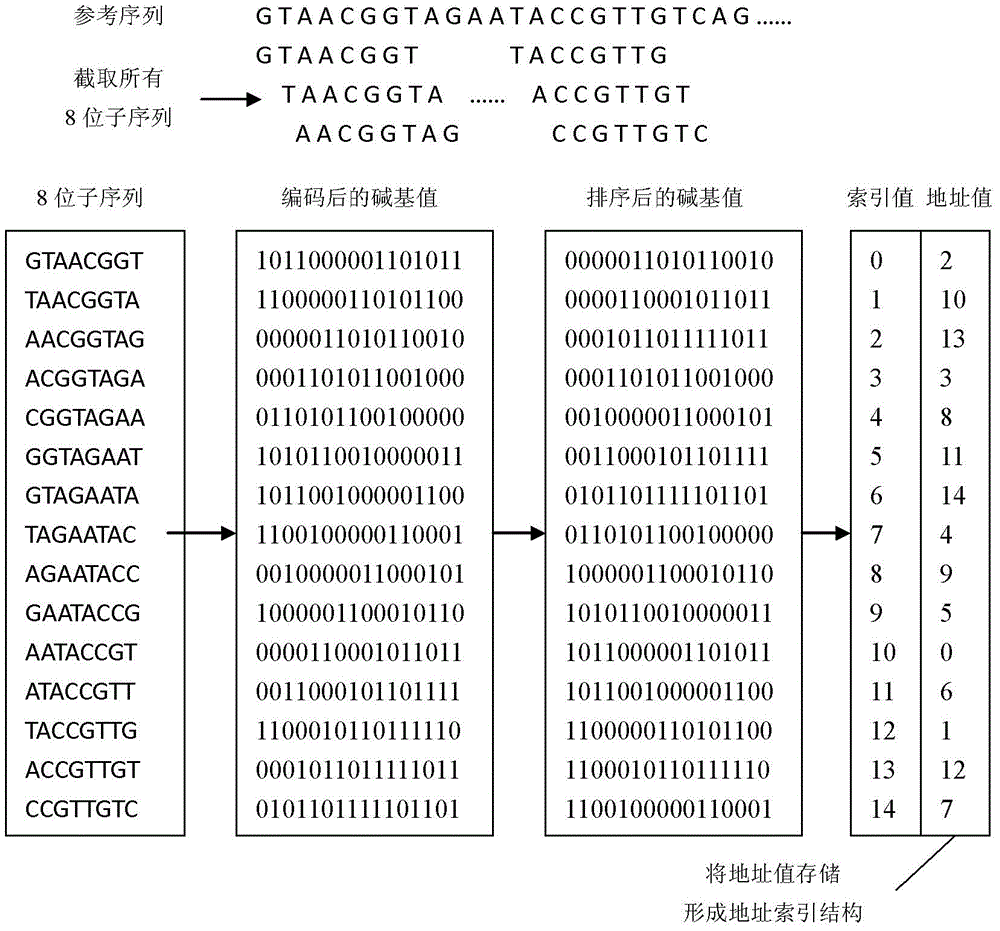
The invention discloses a sequencing sequence mapping method and sequencing sequence mapping system. The method comprises the steps that pretreatment is performed on a reference genome so as to generate a reference genome compression structure, an address index structure and a halving point index structure; the reference genome compression structure stores the whole reference genome in a compression mode, the address index structure address stores address values of all subsequences in the reference genome based on a certain sequence, and the halving point index structure is used for storing positions, where part of the address values exists, in the address index structure and used for achieving initial positioning of a sequencing sequence in an acceleration mode; based on the characteristics of the reference genome, the whole information of the sequencing sequence and the polymorphic occurrence conditions of a belonged specie of the sequencing sequence, an algorithm parameter is mapped according to probabilistic design so that the requirements for sensitivity, specificity and a mapping speed can be met or compromised. The structure is obtained through pretreatment, all sequencing sequences are mapped on the reference genome through subsequence positioning, prolongation based on the self-matching function and the step of quantitative analysis.
Owner:ACAD OF MATHEMATICS & SYSTEMS SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for detecting variation of copy numbers of genomes
ActiveCN105574361AIncreased sensitivityImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsGC-contentBiology
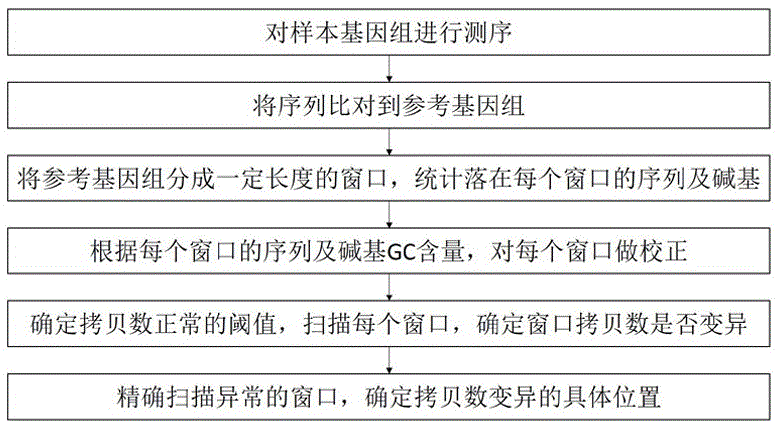
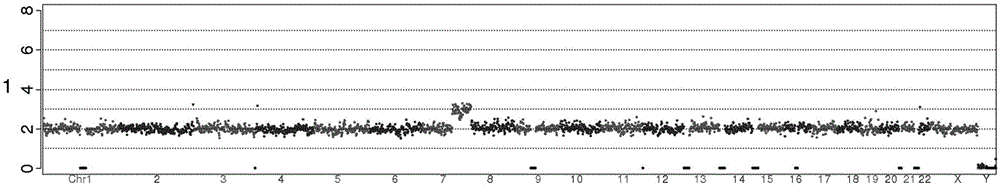
The invention relates to a method for detecting the variation of copy numbers of genomes. The method specifically comprises the following steps: sequencing sample genomes to obtain genome sequences; aligning the sequences to a reference genome to obtain the positions of the sequences on the genome; dividing the reference genome into windows with a certain length and carrying out statistics on the sequences and basic groups falling on the windows; correcting the windows according to the sequences and GC contents of the basic groups; determining threshold values with normal copy numbers, scanning the windows and determining whether the copy numbers of the windows varies; and precisely scanning the abnormal windows to determine the precise breakpoints and then determine the specific variation position of the copy numbers. According to the method, the sensitivity of the detection for the variation of the copy numbers of the genomes can be improved through utilizing three mean values, carrying out window correction, determining the threshold values with normal copy numbers, precisely scanning the abnormal windows and determining the precise breakpoints and the specific variation positions of the copy numbers; and the method is easy, simple and feasible to operate, high in efficiency, low in cost and beneficial for popularization and application.
Owner:YIKON GENOMICS SHANGHAI CO LTD
Proton-based transcriptome sequencing data comparison and analysis method and system
InactiveCN104657628AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilitySpecial data processing applicationsDifferentially expressed genesSingle-nucleotide polymorphism
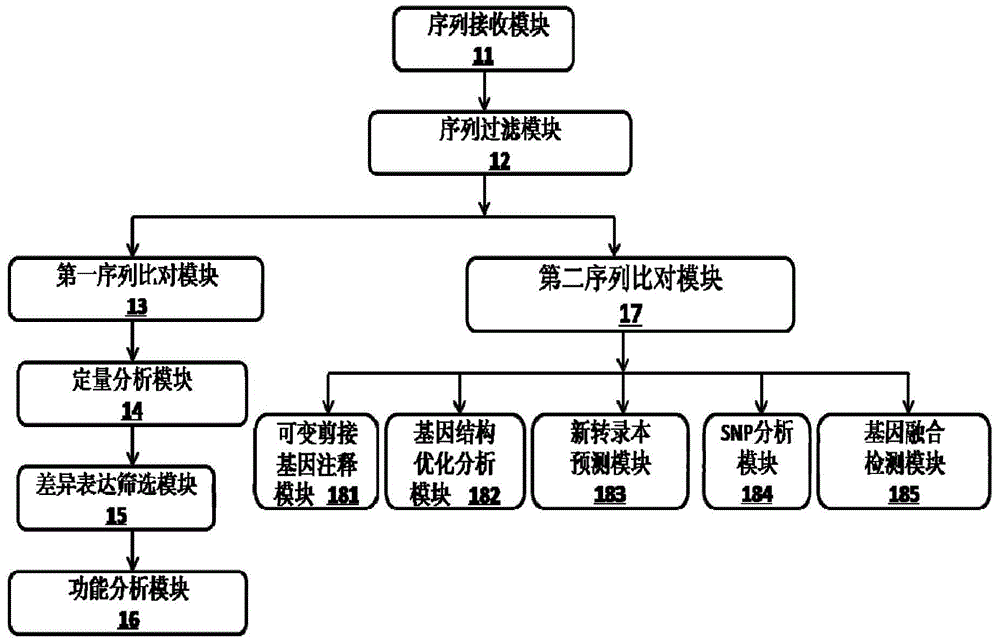
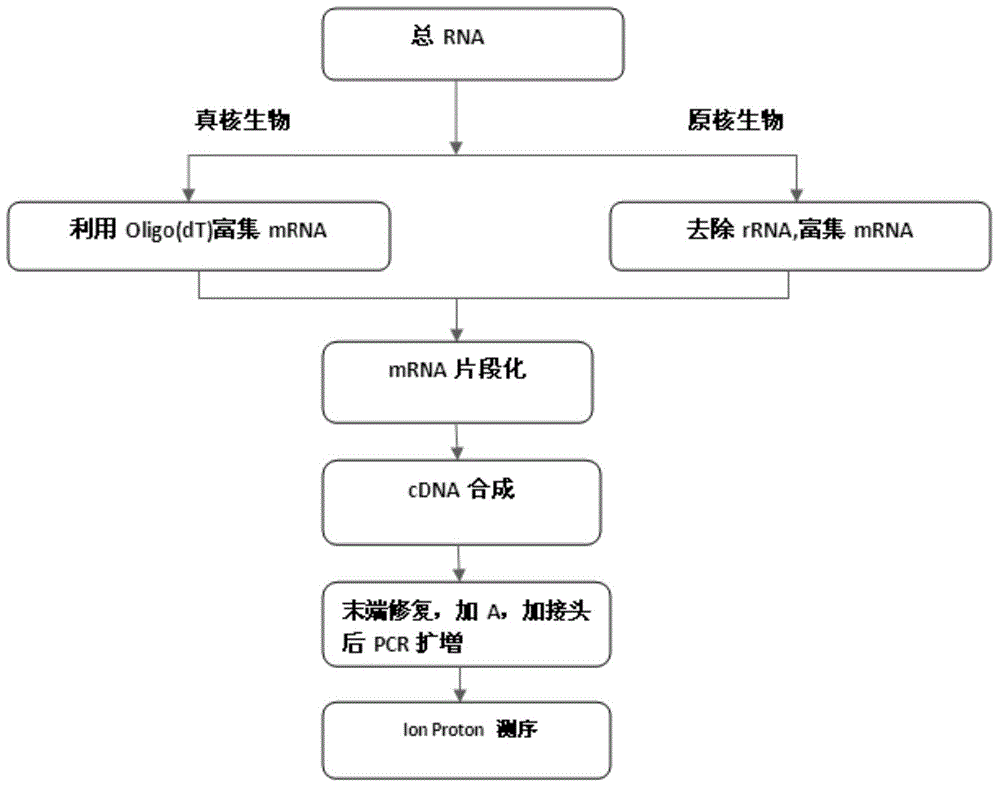
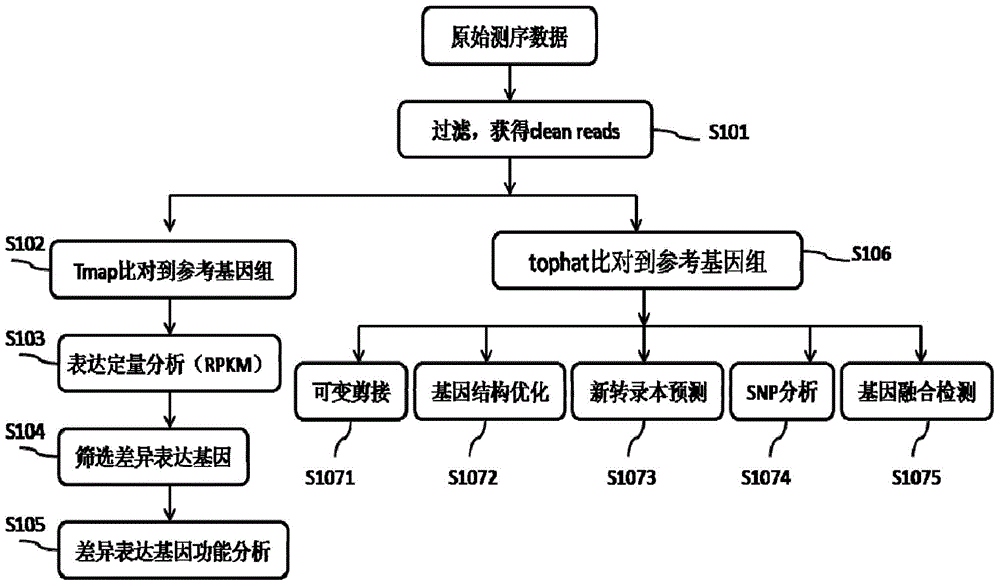
The invention provides a Proton-based transcriptome sequencing data comparison and analysis method and system. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring original sequencing data of at least two transcriptomes of a certain species by virtue of a Proton sequencing platform; filtering unqualified data to obtain clean reads; performing first-step analysis and second-step analysis, wherein the first-step analysis comprises the steps of comparing the clean reads with a reference genome of the species respectively, performing transcript quantitative analysis, screening significantly differently expressed genes and performing significantly differently expressed gene function analysis; the second-step analysis comprises the steps of comparing the clean reads to the reference genome of the species respectively, performing alternative splicing analysis, performing gene structure optimization analysis, performing new transcript prediction, performing SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) analysis and performing gene fusion detection. According to the method and the system, the transcriptome sequencing data comparison and analysis accuracy and reliability can be improved.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
Method for single cell classification and screening and device therefor
ActiveCN102952854AAvoid marked actionsImprove accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReference genesData set
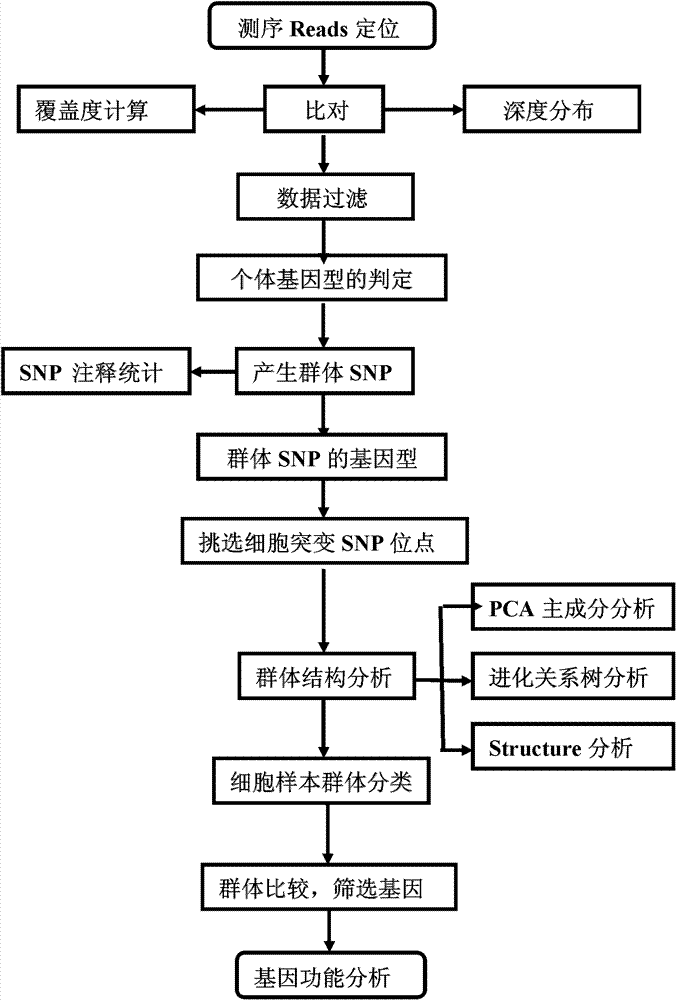
The invention provides a method for single cell classification and screening and a device therefor. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out comparison of reads obtained by sample sequencing and a reference genome, carrying out data filtration of a comparison result, determining a consistent genotype of all single cell samples according to filtered data, saving the consistent genotype of the all single cell samples into a SNP data set, extracting genotype files of loci corresponding to reference genome SNP data set positions from the saved SNP data set, selecting a cell mutation SNP locus, and carrying out cell classification and functional gene screening according to a genotype file of the cell mutation SNP locus. The method and the device avoid cell marking, solve the problem that the traditional single cell classification method can not realize classification of a certain cell subset having no corresponding specific markers, realize complete analysis of genetic variation information of a single cell genome, and greatly improve the accuracy of cell subset classification.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
Methods and apparatus for sorting data
ActiveUS20150220532A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsGenomic dataData sorting
A computer implemented system for genomic data sorting, comprising alignment and position mapping. The system maps each read to a position on the reference genome with which the read is associated, followed by sorting these reads by their mapped positions.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
Method and device for detecting somatic cell SNP
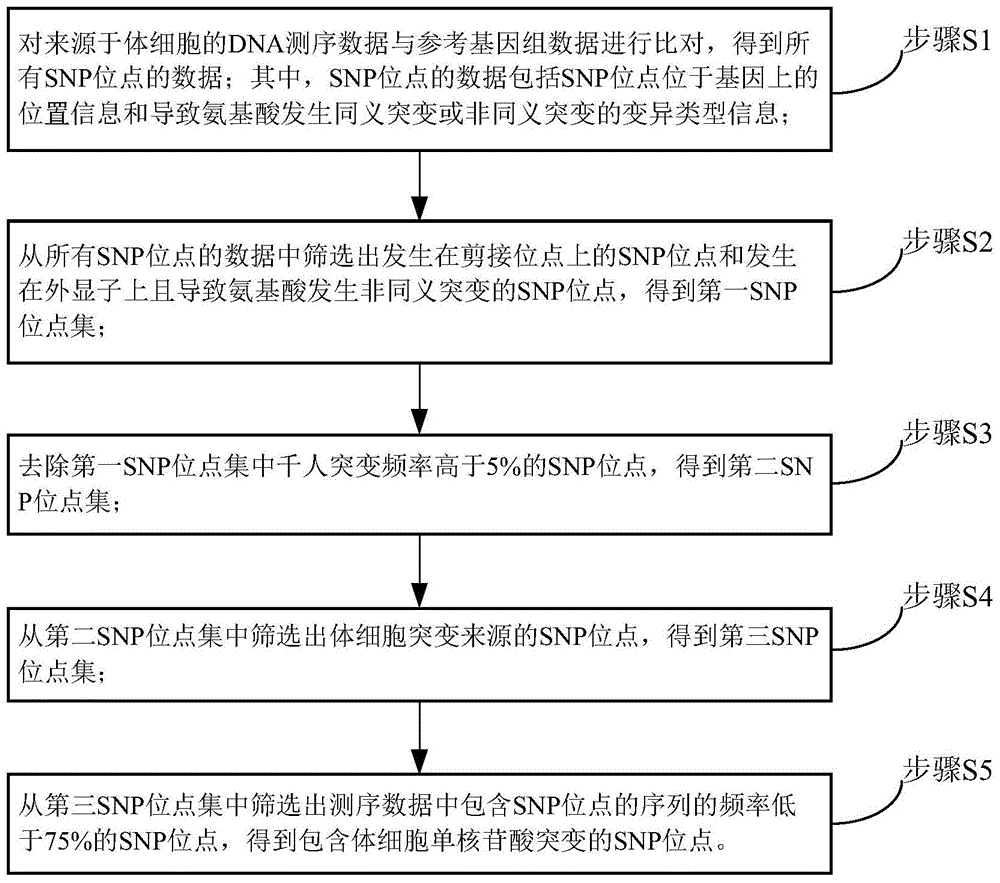
ActiveCN104462869ARealize detectionSimple methodBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMutation frequencySimple sample
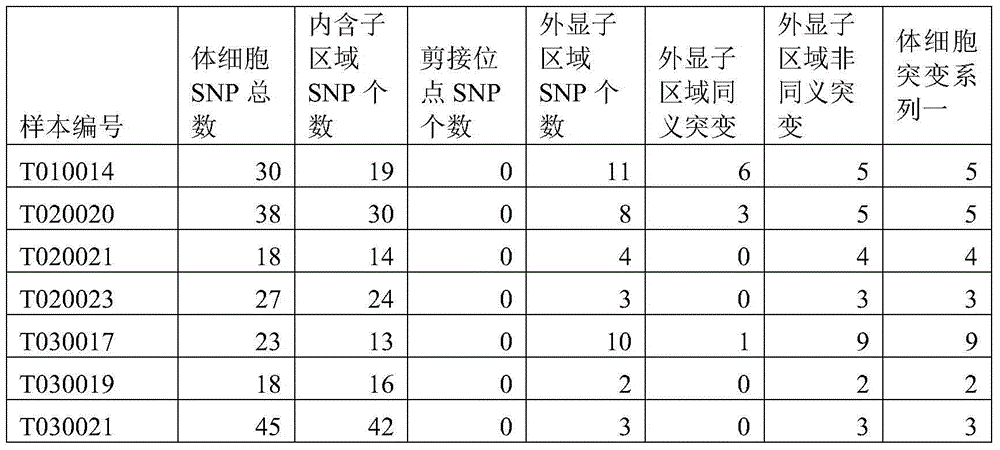
The invention discloses a method and device for detecting somatic cell SNP. The method comprises the steps of S1, comparing DNA sequencing data of somatic cells with reference genome data to obtain data of all SNP loci; S2, screening out SNP loci which occur on splicing loci and SNP loci which occur on exons and cause nonsynonymous mutation of amino acid to obtain a first SNP locus set; S3, removing SNP loci with the thousand-people mutation frequency higher than 5% in the first SNP locus set to obtain a second SNP locus set; S4, screening out SNP loci which are resources of somatic cell mutation from the second SNP locus set to obtain a third SNP locus set; S5, screening out SNP loci with the frequency of supporting sequences lower than 75% from the third SNP locus set to obtain SNP loci containing somatic cell SNP. By means of the method, somatic cell mutation can be detected through simple samples, and therefore the cost is lowered.
Owner:天津诺禾致源生物信息科技有限公司
Lossless compression of DNA sequences
ActiveUS20150227686A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementLossless compressionHistogram
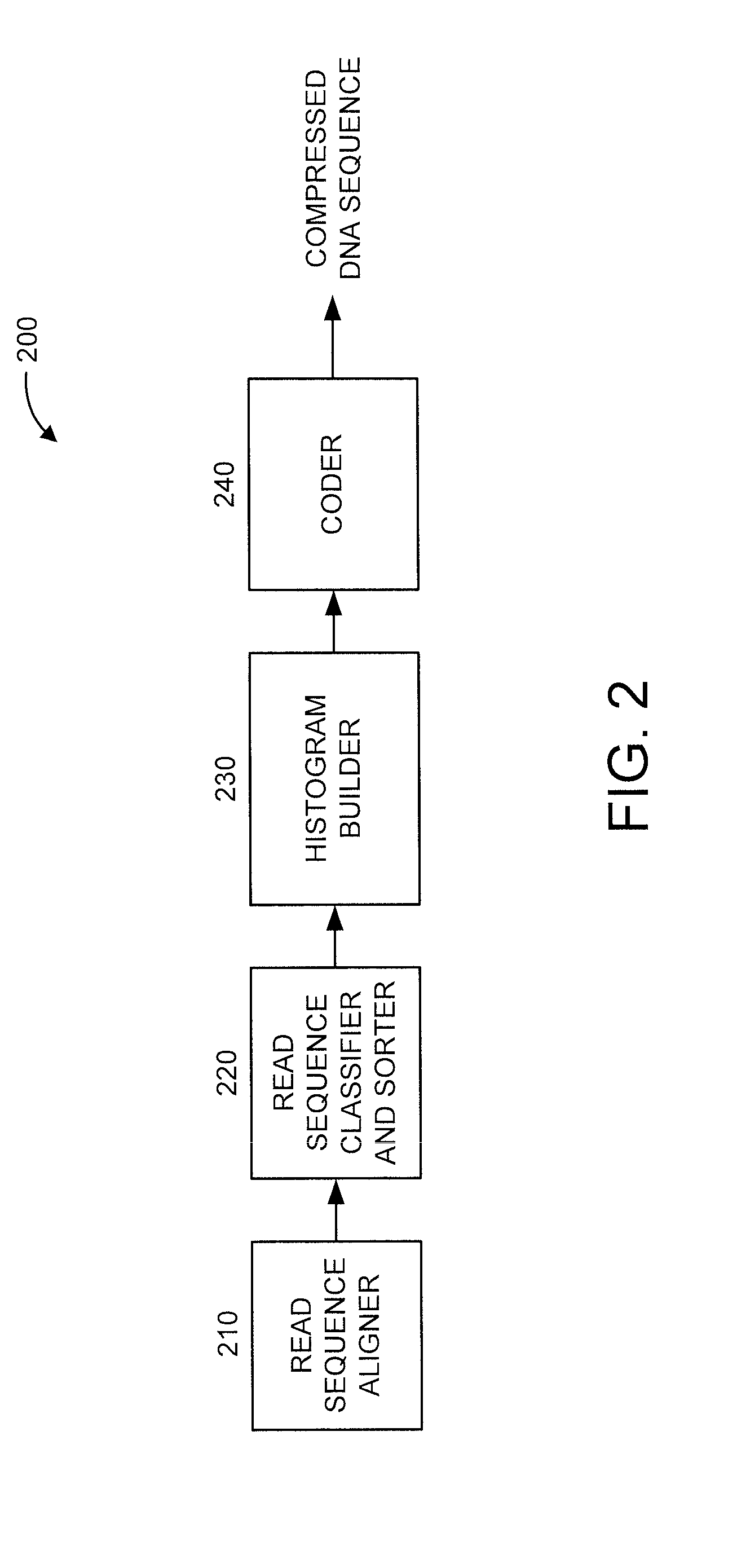
There is provided an apparatus and a processor-implemented method. The method includes aligning a reference genome with a plurality of DNA sequences. Each of the plurality of DNA sequences has a respective plurality of bases. The method further includes classifying and sorting the plurality of read sequences based on respective numbers of mismatched bases within the plurality of read sequences to obtain a plurality of re-arranged DNA sequences. The method also includes building a histogram based on respective positions of mismatched bases within the plurality of re-arranged DNA sequences. The method additionally includes coding at least some of the plurality of re-arranged DNA sequences based on the histogram.
Owner:IBM CORP
Combinatorial DNA Screening
The present disclosure relates to methods for detecting unique genetic signatures derived from markers such as, for example, mutations, somatic or germ-line, in nucleic acids obtained from biological samples. The sensitivity of the methods provides for detection of mutations associated with a disease, e.g., cancer mutations, or with inherited disease, e.g., an autosomal recessive disease, in a noninvasive manner at ultra-low proportions of sequences carrying mutations to sequences carrying normal, e.g., non-cancer sequences, or a reference sequence, e.g., a human reference genome.
Owner:MYRIAD WOMENS HEALTH INC
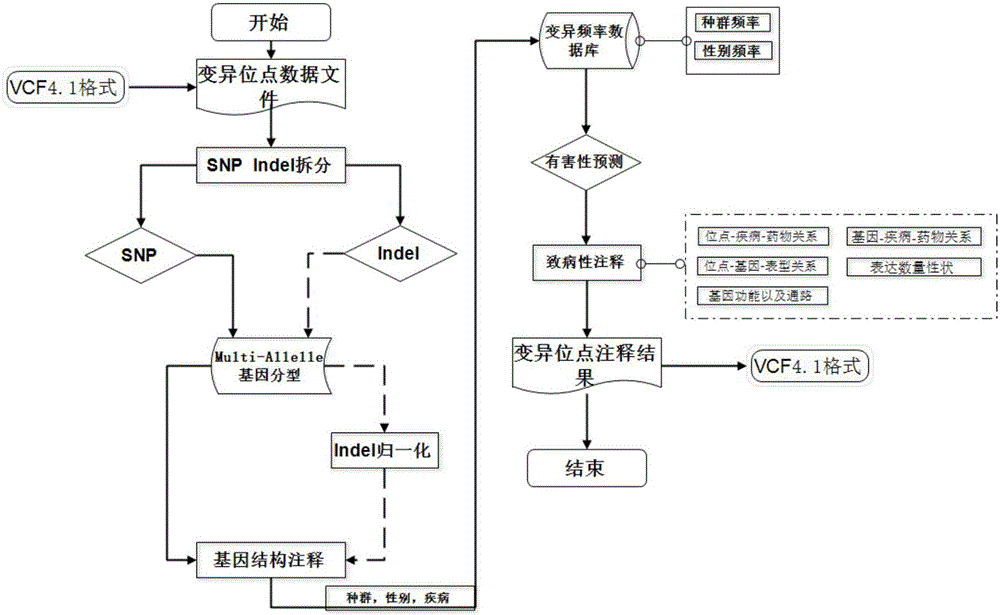
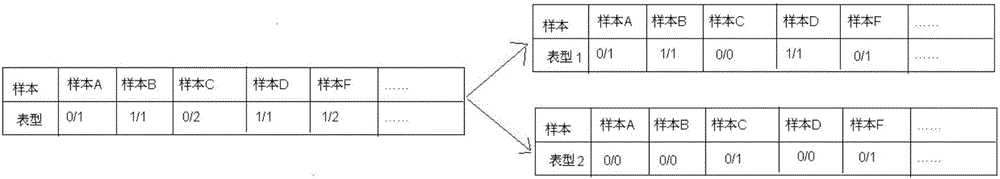
Annotation method and annotation system of whole-genome variant data
InactiveCN106156538AAccurate NotesSolve the screening puzzleProteomicsGenomicsReference genesAllele frequency
The invention discloses an annotation method and an annotation system of whole-genome variant data. The method comprises the following steps of S1, creating a variant data file, wherein the variant data are stored according to a national standard VCF format as an input file; S2, performing multi-allele genotyping, firstly performing genotype judgment, representing a basic group which is consistent with a reference genome by zero, and representing the basic groups which are inconsistent with the reference gene group by 1, 2, 3,..., then performing SNP and InDel multi-allele type resolution so that the allele type is represented by zero and one; S3, causing InDel generation position normalization, namely performing InDel generation position normalization according to a left justification and simplification normalization method; and S4, performing annotation, namely performing gene structure annotation, allele frequency annotation, variable site harm prediction and pathogenicity annotation. The annotation method and the annotation system improve integrity and accuracy of annotation information.
Owner:天津诺禾医学检验所有限公司
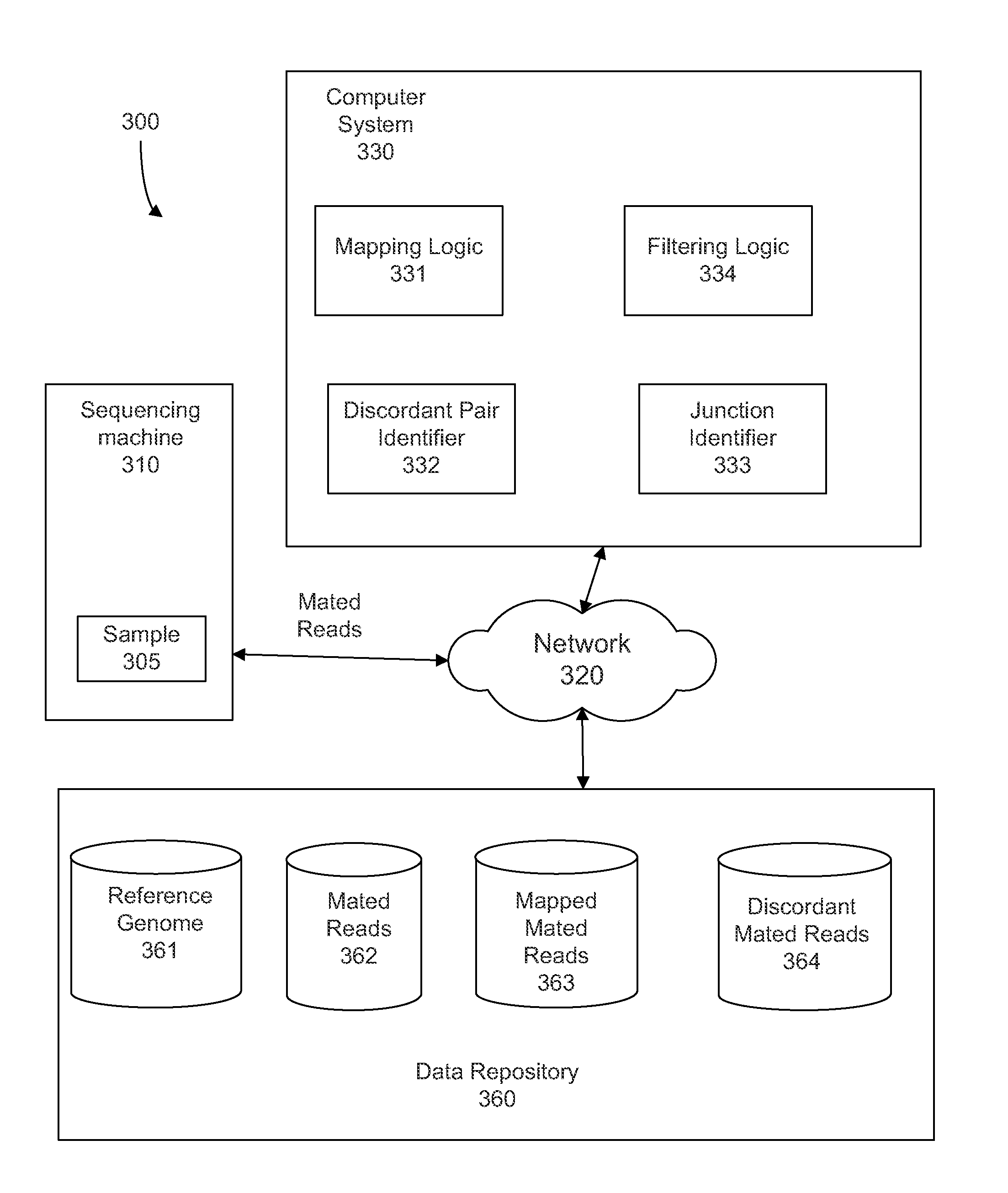
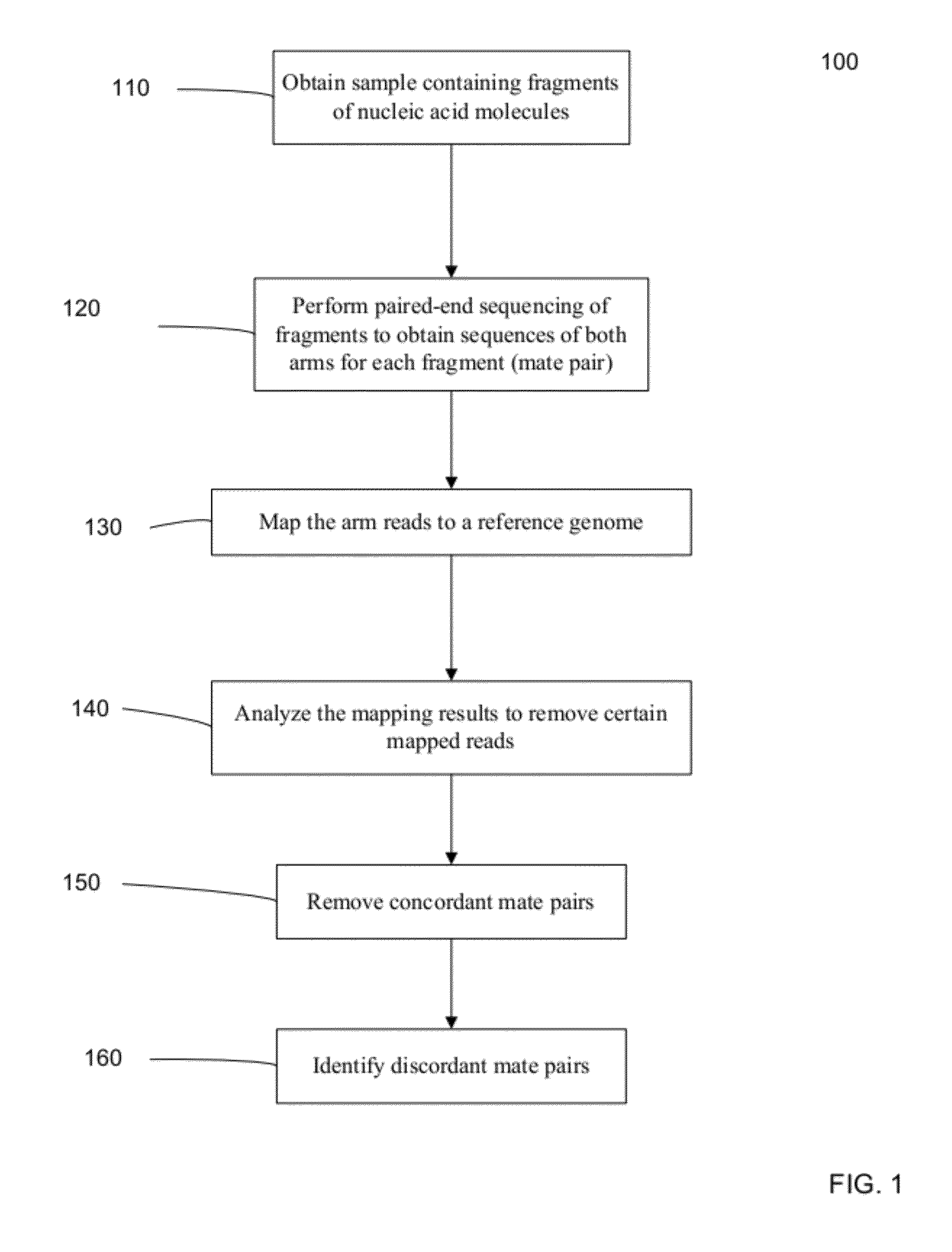
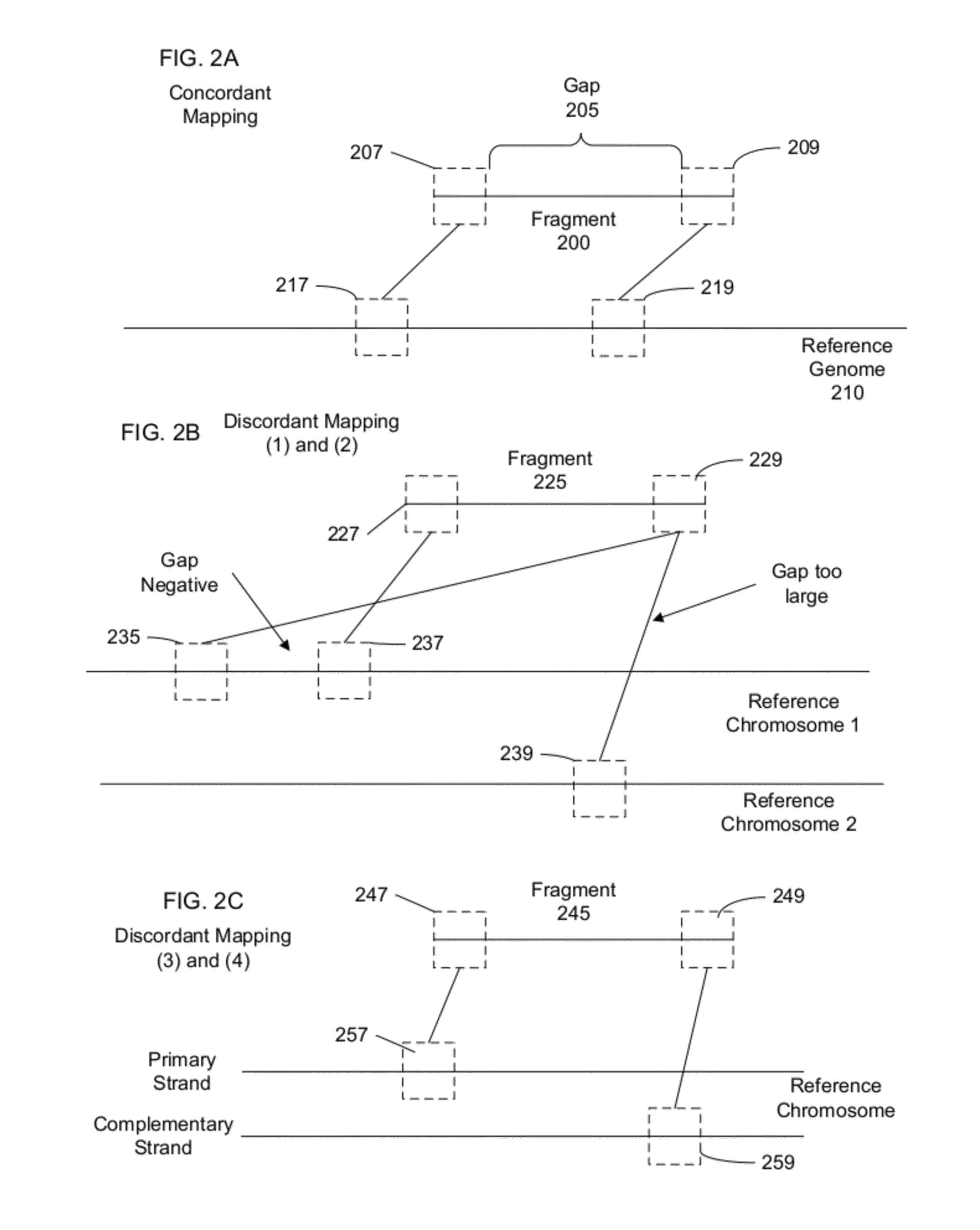
Identifying rearrangements in a sequenced genome
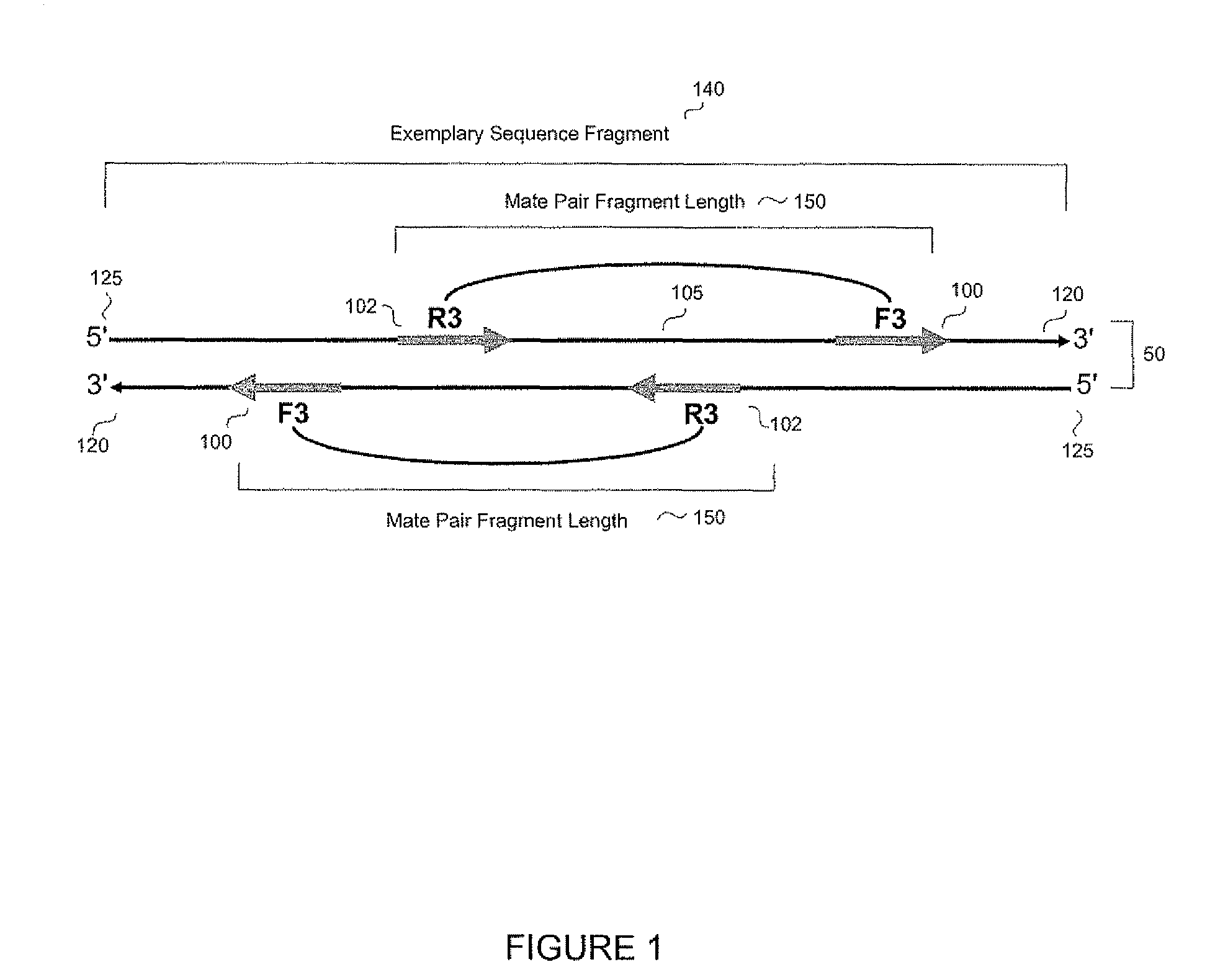
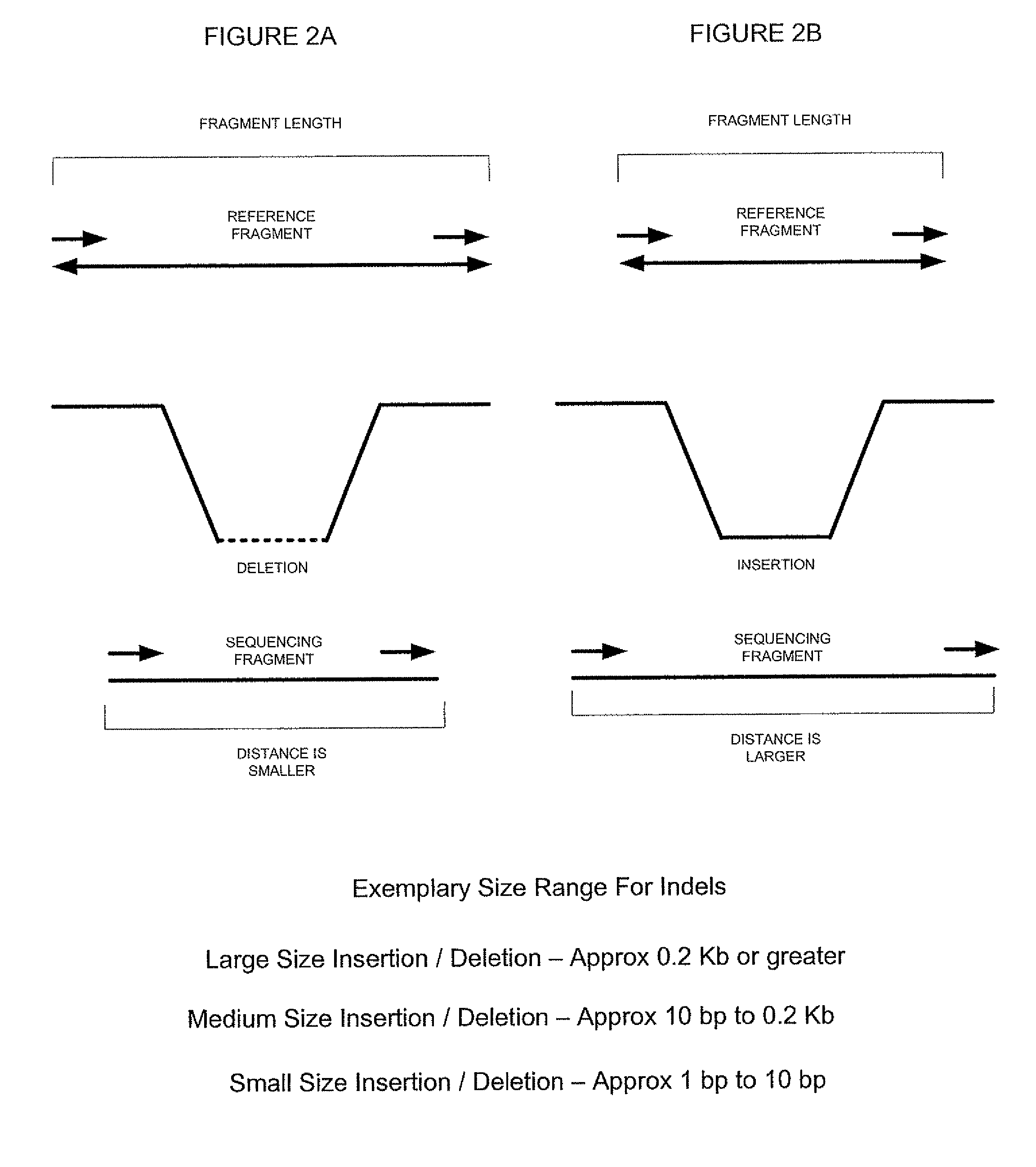
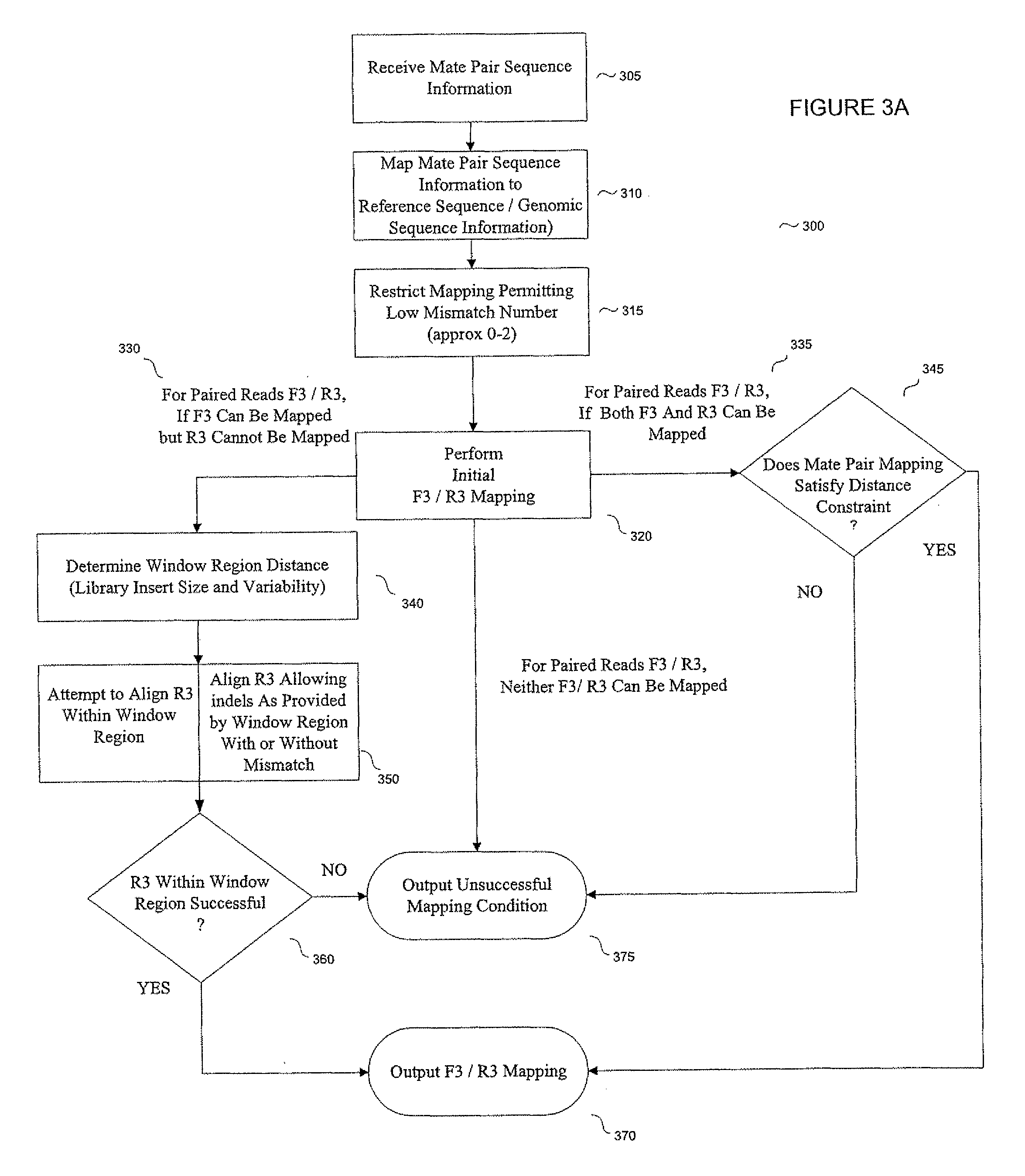
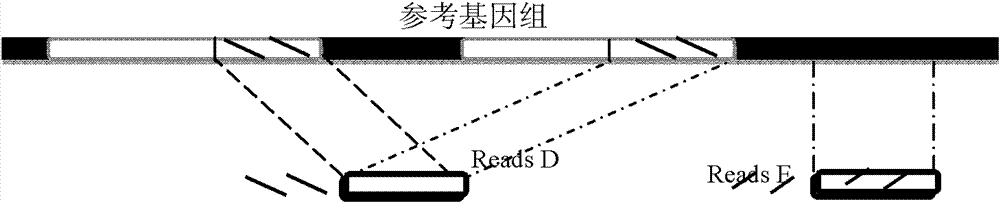
Methods, apparatuses, and systems for identification of junctions (e.g., resulting from large-scale rearrangements) of a sequenced genome with respect to a human genome reference sequence is provided. For example, false positives can be distinguished from actual junctions. Such false positives can result from many sources, including mismapping, chimeric reactions among the DNA of a sample, and problems with the reference genome. As part of the filtering processes, a base pair resolution (or near base pair resolution) of a junction can be provided. In various implementations, junctions can be identified using discordant mate pairs and / or using a statistical analysis of the length distributions of fragments for local regions of the sample genome. Clinically significant junctions can also be identified so that further analysis can be focused on genomic regions that may have more of an impact on the health of a patient.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Genomic coordinate system
InactiveUS20100330557A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingReference patternsAnalysis method
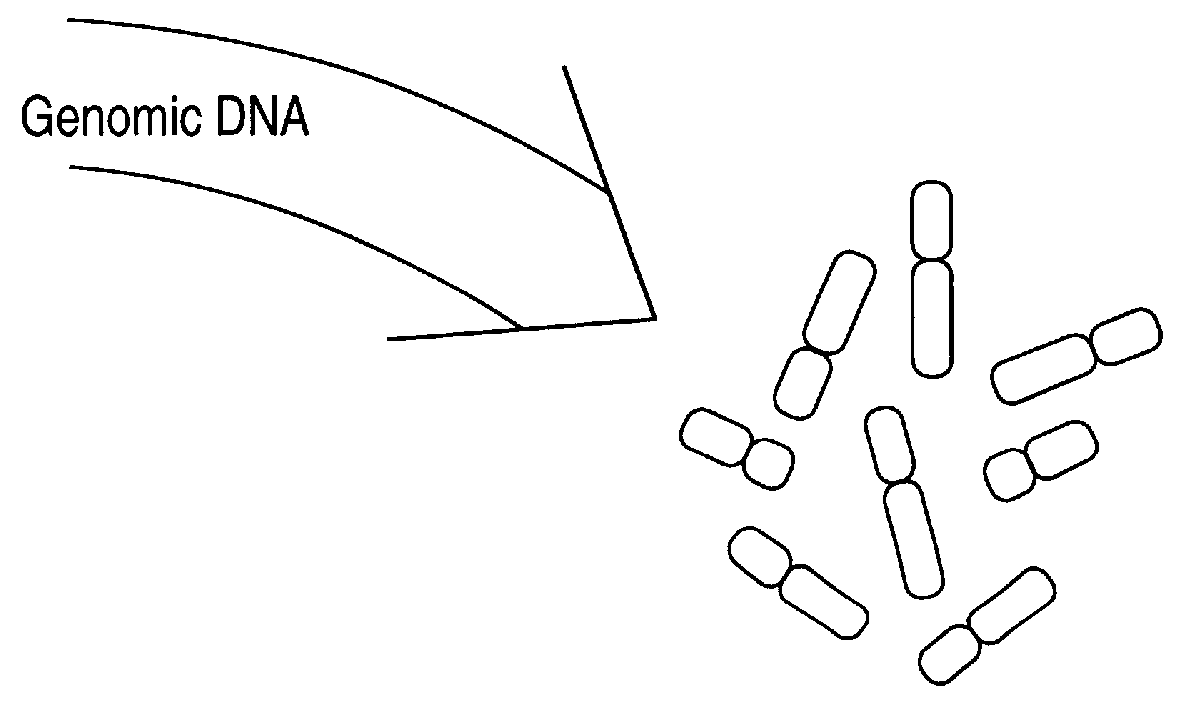
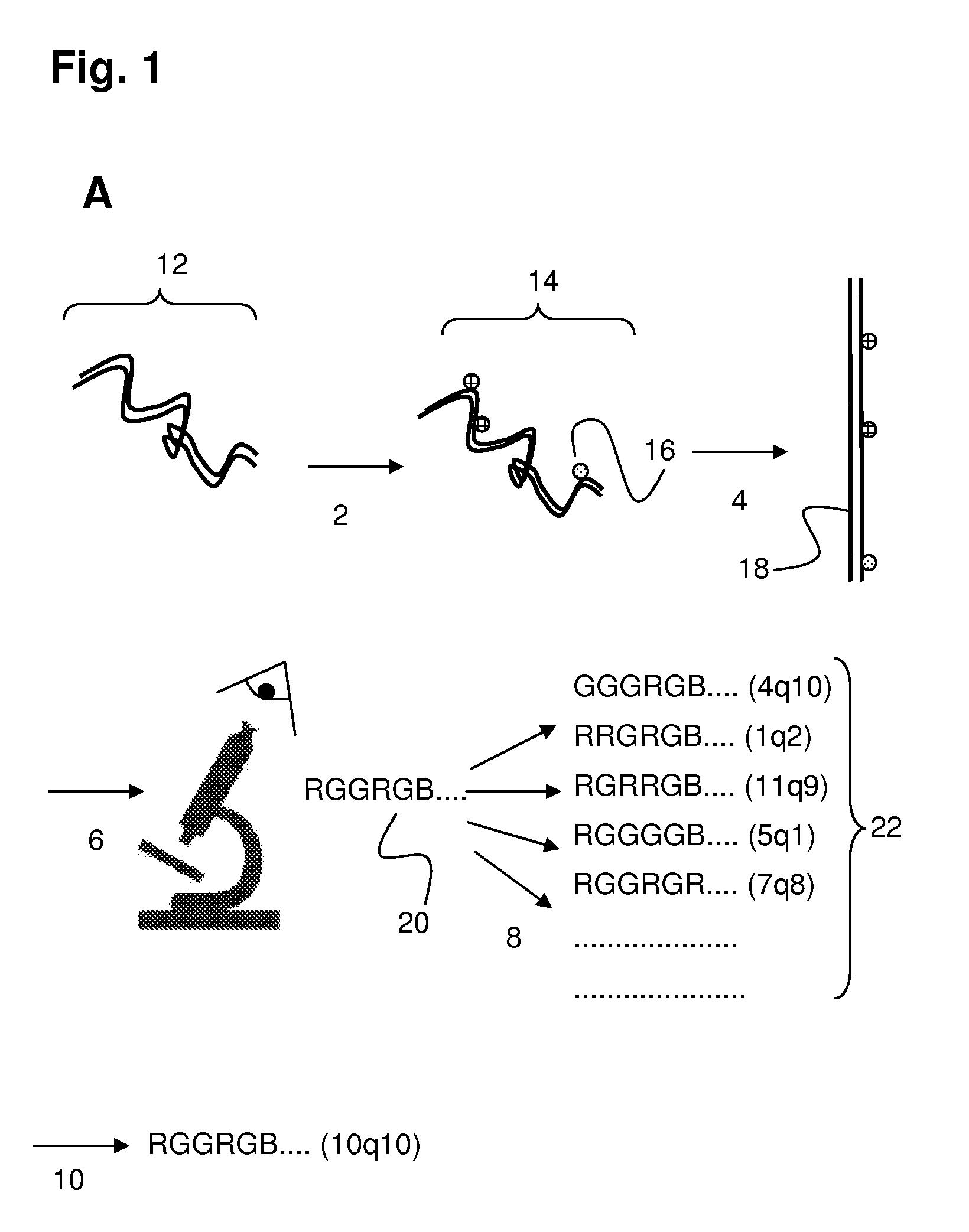
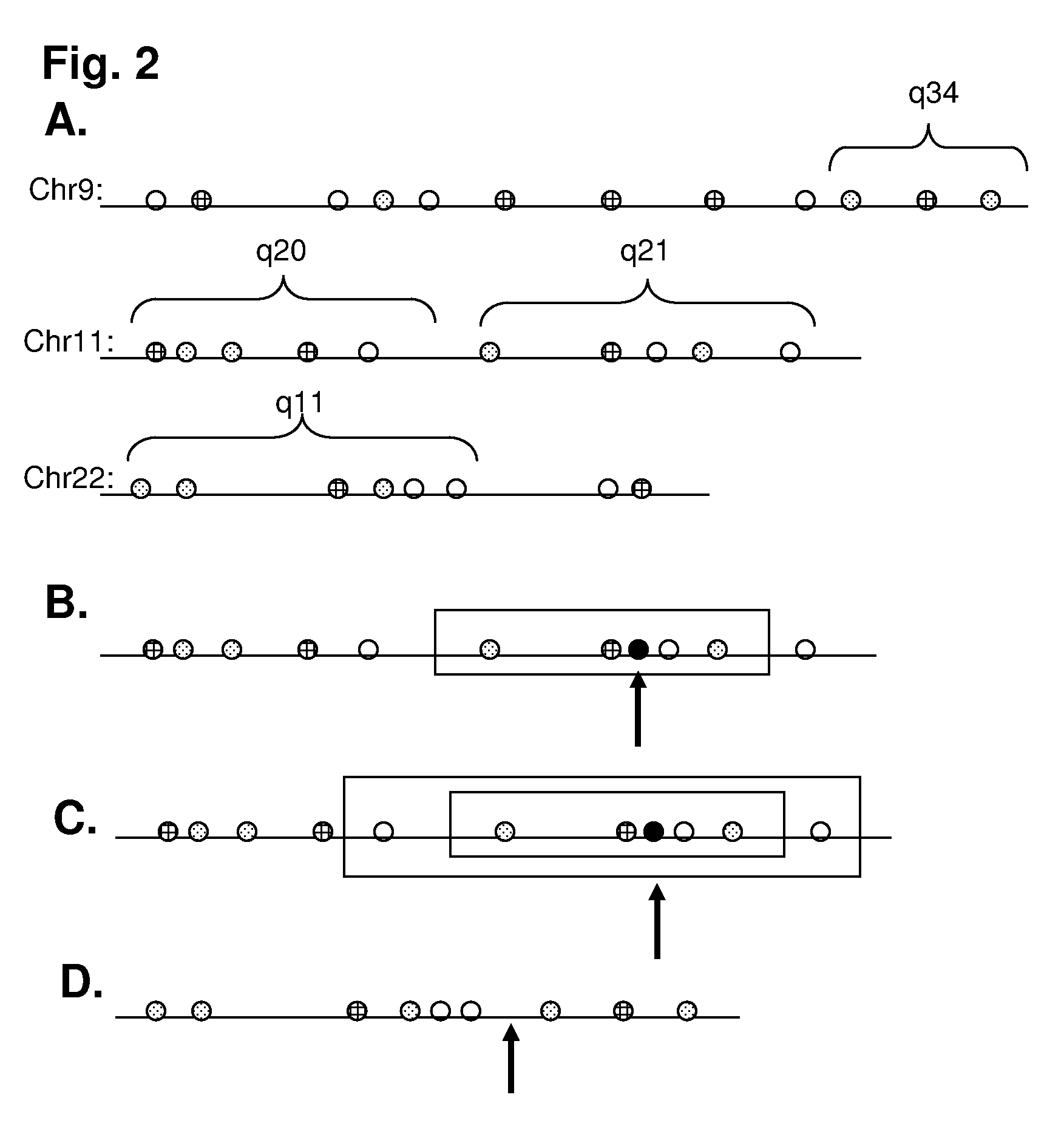
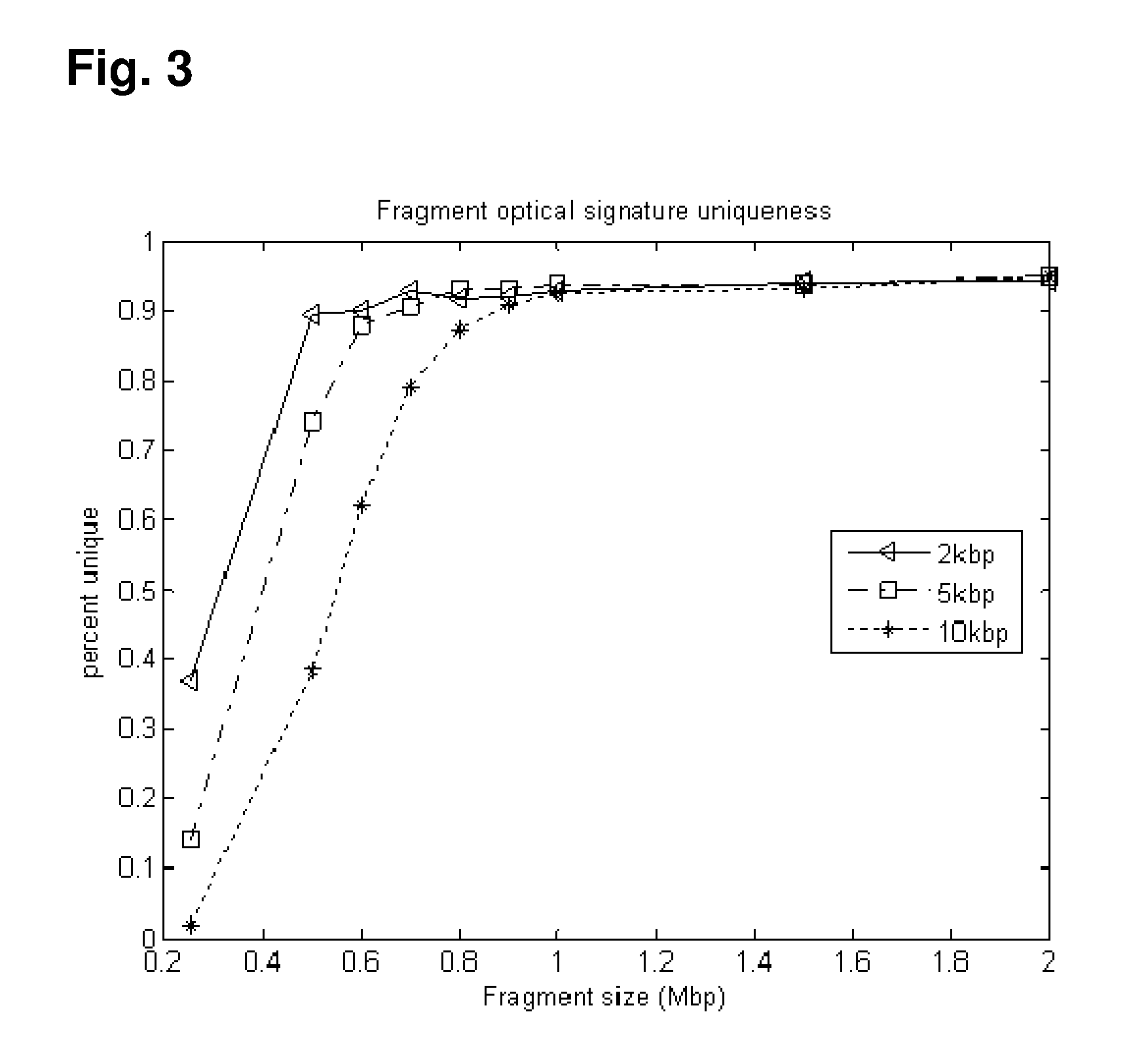
A method of sample analysis is provided. In certain embodiments, the method comprises: a) site-specifically labeling a test genome with at least two different labels to produce a labeled genome labeled at a plurality of discrete sites across the genome; b) stretching a nucleic acid of the labeled genome to produce a linear pattern of the different labels along a region of a stretched nucleic acid; c) reading the labels along the region to provide a test pattern comprising a sequence of colors emitted by the labels; d) comparing the test pattern to a plurality of reference patterns obtained from a reference genome, in which the reference patterns are mapped to corresponding genomic locations in the reference genome; and e) identifying one or more reference patterns that match the test pattern, thereby mapping a location for the region in the test genome.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method and device for quick contrast and analysis of short sequence for second-generation sequencing
ActiveCN106295250AImprove time and efficiencyFaster thanSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsReference genesArray data structure
The invention discloses a method and a device for quick contrast and analysis of a short sequence for second-generation sequencing, which can solve the problems of low contrast efficiency and high memory occupation ratio of sequencing data. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) short sequence obtained by sequencing, and respectively mapping and encoding the DNA short sequence by a first hash algorithm and a second hash algorithm, so as to respectively obtain a first index and a second index; according to a preset index query library, the first index and the second index, contrasting the DNA short sequence and a reference gene group, wherein the index query library consists of an unit structure array, and each unit structure comprises value and index 2; storing the array index offset of each unit structure as the corresponding index 1, namely the index value corresponding to the structure array, wherein K is the length of segment sequence; according to the contrast result, when the contrast result is correct, obtaining the value of the K-mer segment contrasted with the corresponding DNA short sequence, and determining the chromosome number of the corresponding DNA short sequence and the site on the chromosome.
Owner:北京普康瑞仁医学检验所有限公司
Detection of chromosoal abnormalities associated with breast cancer
InactiveUS7094534B2Avoid saturationHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingComparative genomic hybridization
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method, system, and apparatus for compactly storing a subject genome
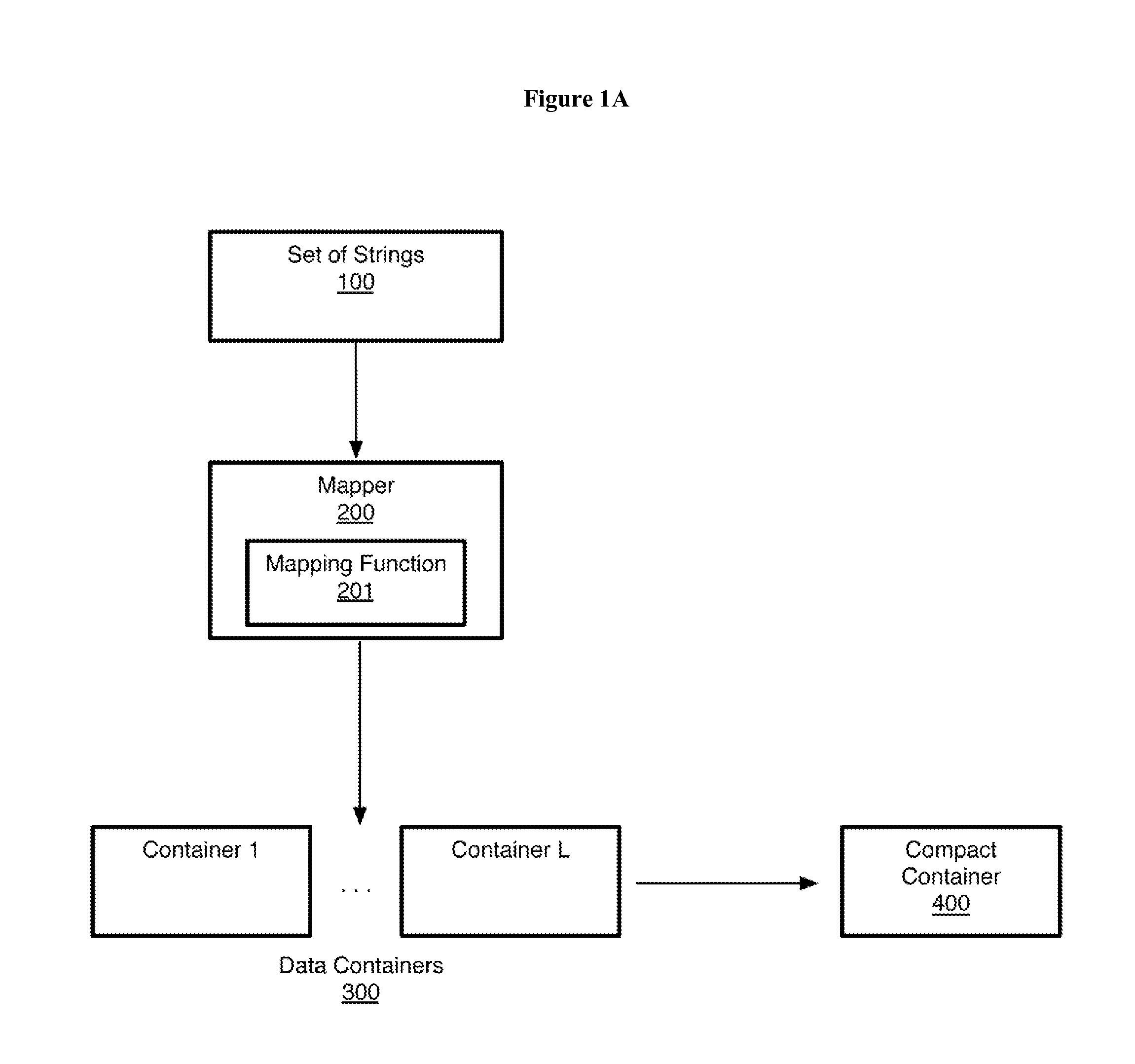
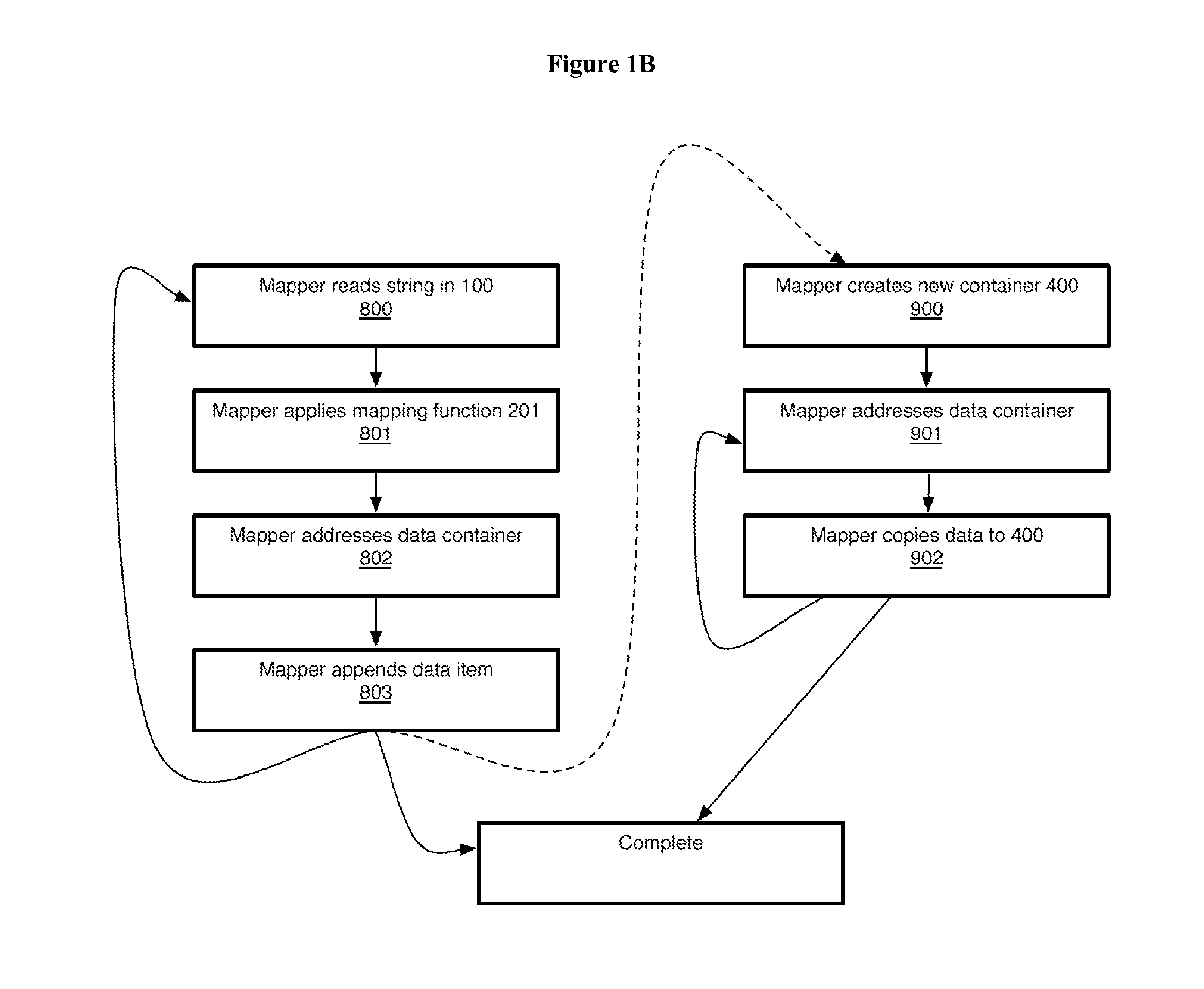
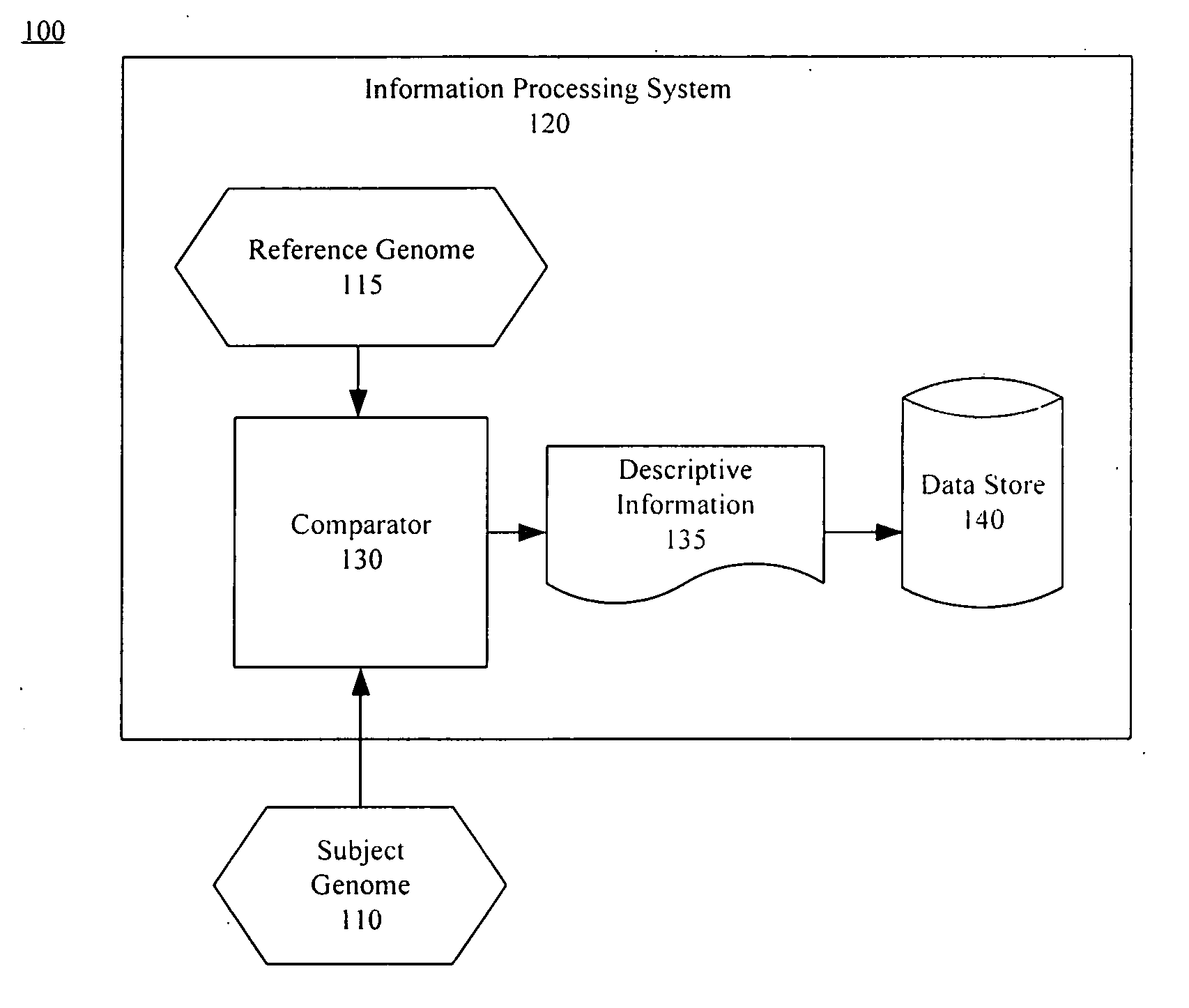
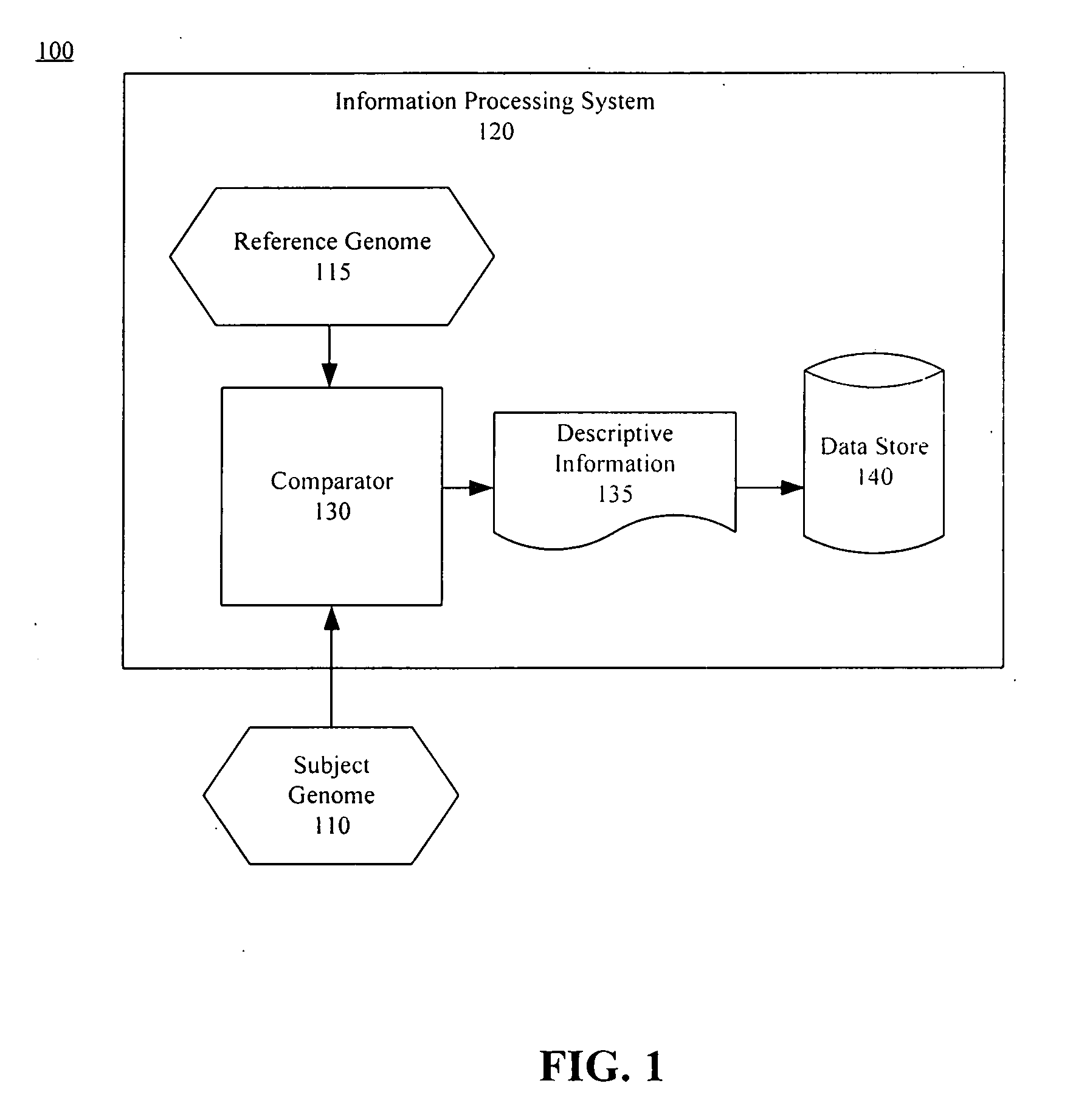
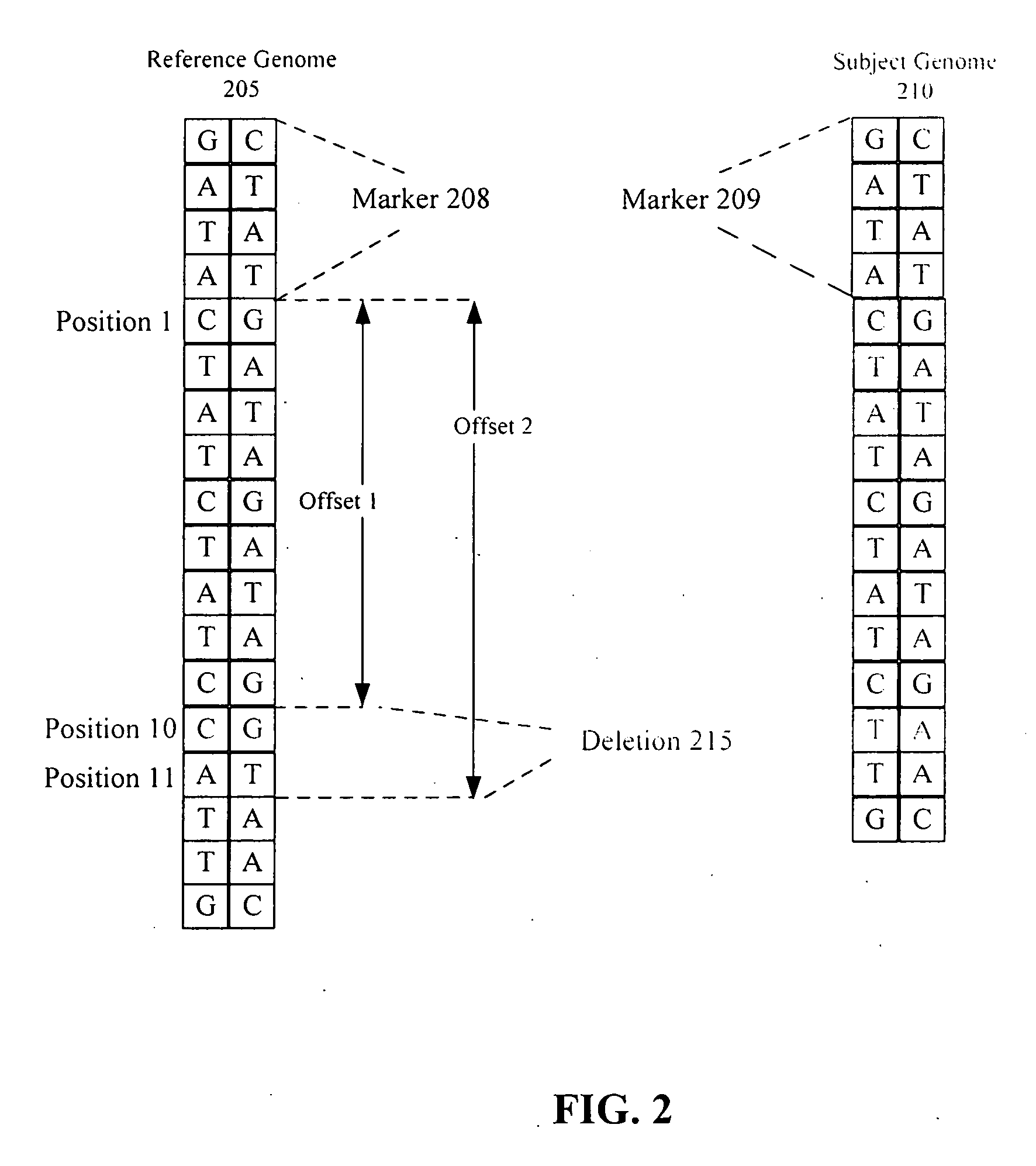
ActiveUS20050267693A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingSubject specificReference genome
A method of representing a subject genome can include comparing the subject genome to a base reference genome and identifying a difference between the subject genome and the base reference genome. The method can further include assigning one or more items of descriptive information to the difference, and compiling the items into a data set, where the data set represents the subject genome.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Parallel rapid matching method and system for stored DNA sequence
InactiveCN106096332ARun fastImprove efficiencyProgram initiation/switchingHybridisationTheoretical computer scienceFASTA format
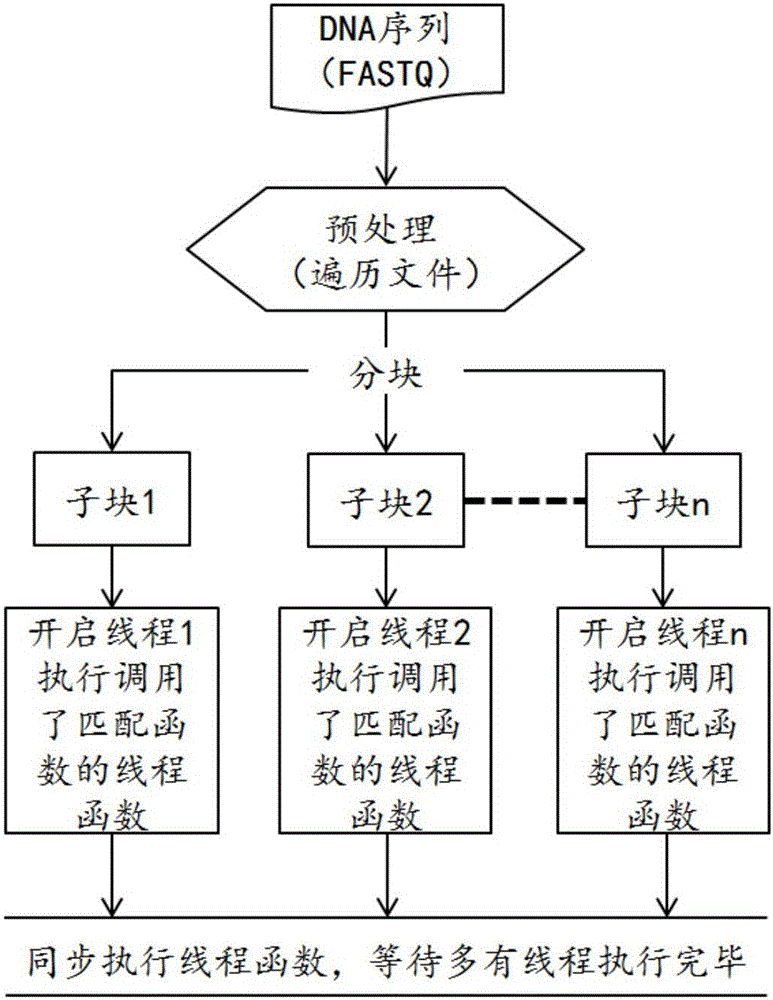
The invention provides a parallel rapid matching method and system for a stored DNA sequence. The parallel rapid matching method and system are applied to compressed storage for a DNA sequence. The method comprises the steps that a Hash index is built, wherein the Hash index is built based on a reference genome of a prefix for the FASTA format, all kmers of the designated prefix are found, a Hash index table is built with the kmers as key values, and each table stores corresponding kmer appearing position; a file is segmented, wherein the DNA sequence file with the FASTQ format is input and segmented; multithread processing is carried out, wherein multiple threads are started for processing multiple tasks determined by the number of threads, the multiple sub blocks call a matching function rapidly positioned based on the kmer Hash index at the same time, the sub blocks are matched into the target reference genome with the FASTA format in parallel, and the purpose of compressed storage is achieved by substituting the original DNA sequence with a storage matching result.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Detection device and method for gene fusion
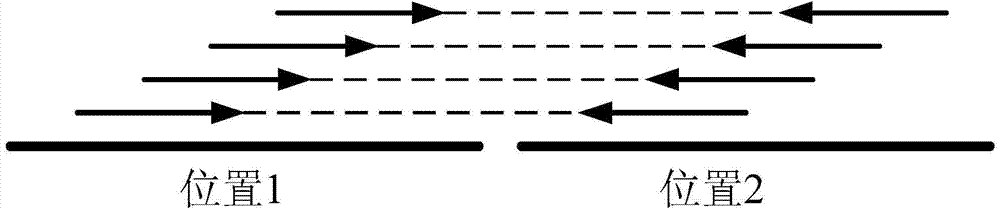
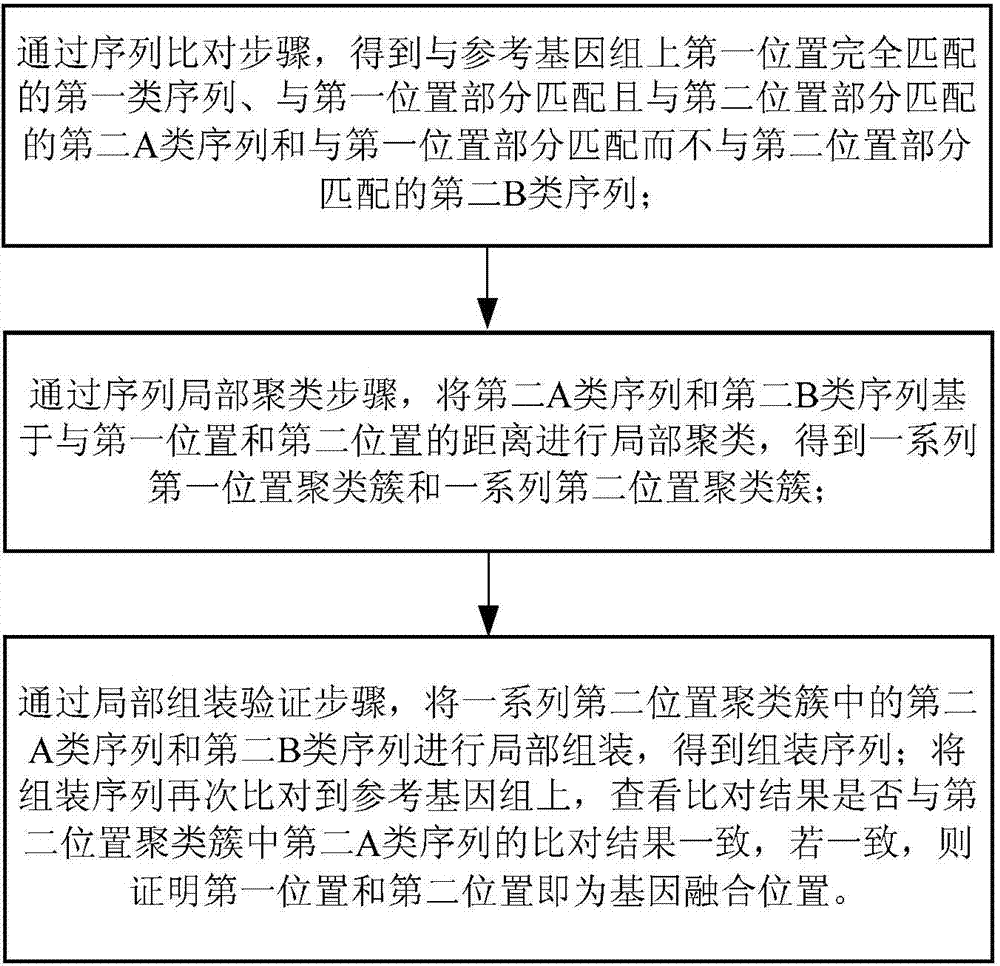
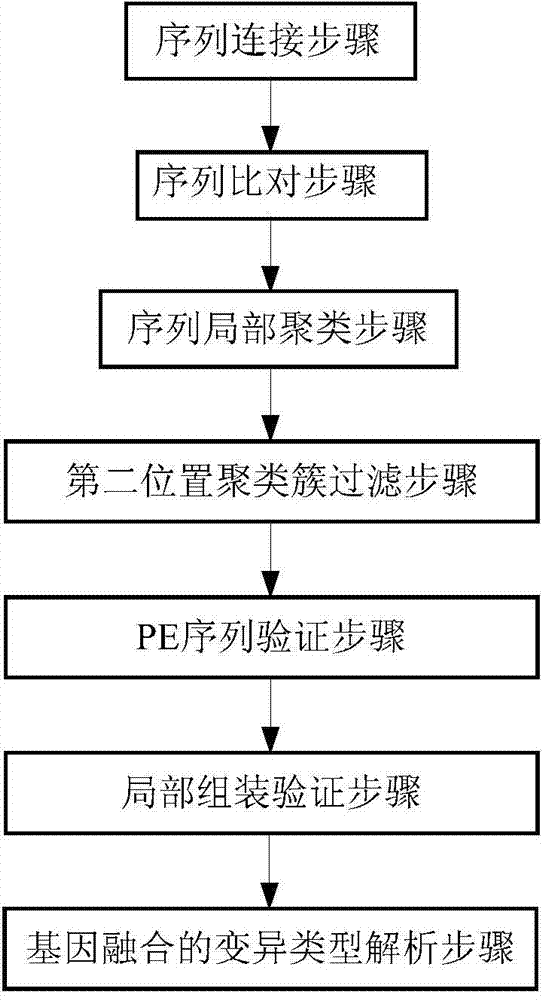
ActiveCN104298892AReduce false positive rateSpecial data processing applicationsTrue positive rateLocal sequence
The invention discloses a detection device and method for gene fusion. The detection method is executed between sequence alignment and local assembly verification and comprises the step of local sequence clustering. The method for local sequence clustering comprises the steps that local clustering is conducted on a second A type sequence which is partially matched with a first position and is also partially matched with a second position of a reference genome and a second B type sequence which is partially matched with the first position and is not partially matched with the second position based on the distance between the first position and the second position, so that a series of first position clusters and a series of second position clusters are obtained; local assembly is conducted on second A type sequences and second B type sequences in the series of second position clusters, so that an assembly sequence is obtained; the assembly sequence is compared with the reference genome again, whether the comparison result of the assembly sequence is consistent with a comparison result for second A type sequences in the second position clusters is checked, if yes, it is proved that the first position and the second position are the gene fusion positions. According to the detection method, the true positive rate is high, and the result is more reliable.
Owner:天津诺禾致源生物信息科技有限公司
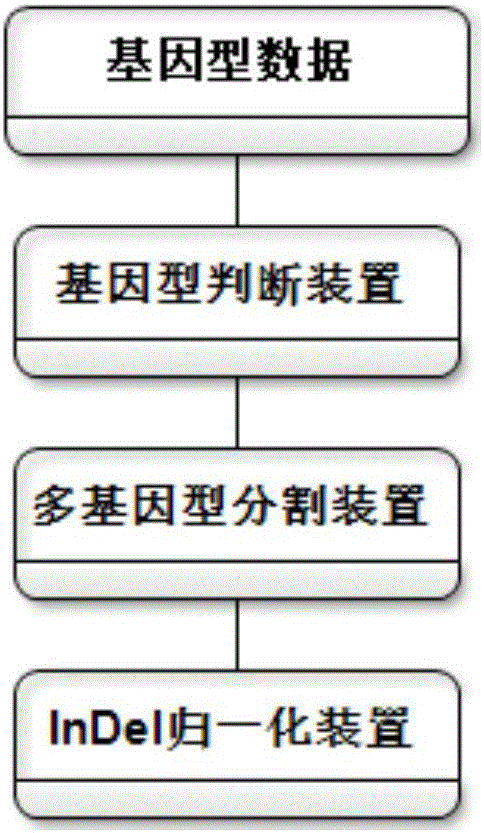
Method for detection of insertion deletion mutation based on second generation sequencing, device and storage medium
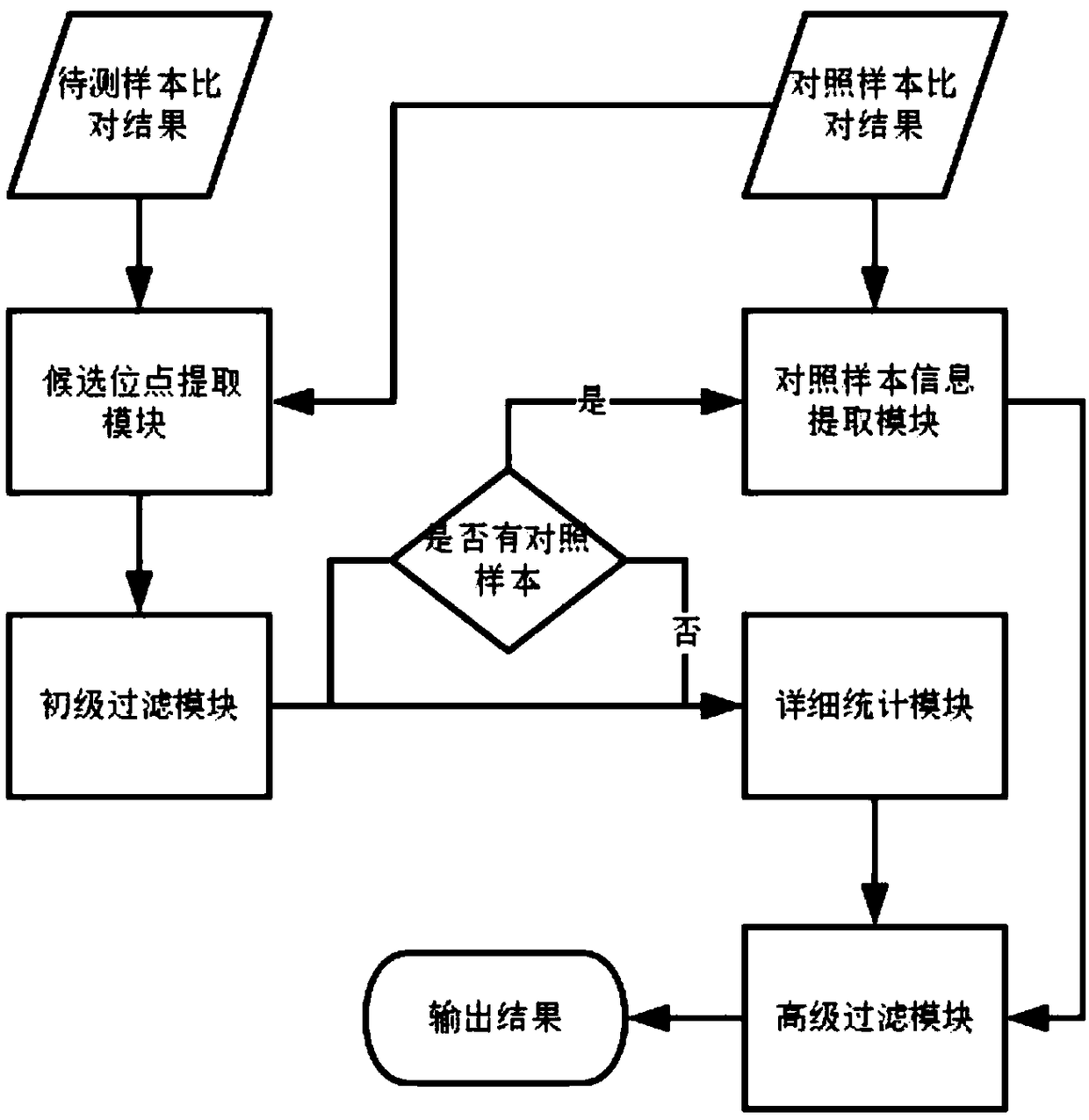
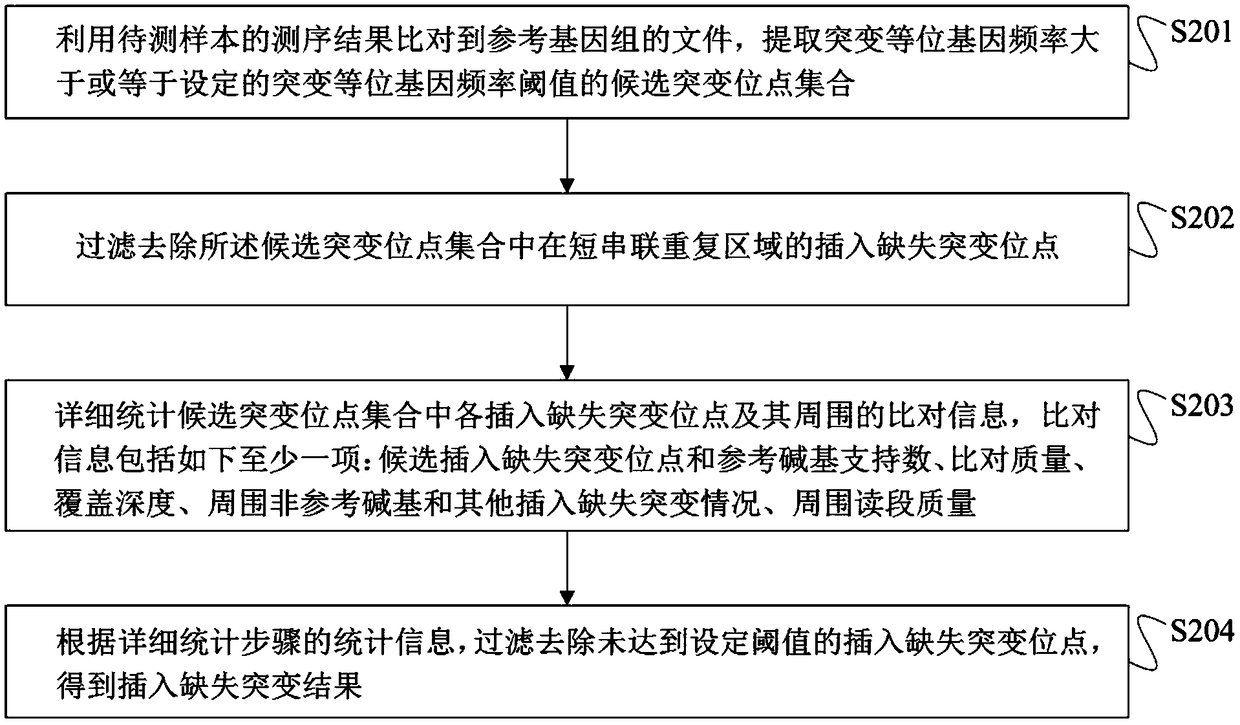
ActiveCN108690871AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsInsertion deletionAllele frequency
The present application discloses a method for detection of insertion deletion mutation based on second generation sequencing, a device and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps:comparing a sample to be tested with a file of a reference genome to extract a set of candidate mutation sites with mutation allele frequency being greater than or equal to a threshold; filtering to remove sites in a short tandem repeat region; making detail statistics of comparison information of the mutation sites and comparison information surrounding the mutation sites, wherein the comparisoninformation includes InDel site and reference base support number, comparison quality, coverage depth, surrounding non-reference base and other insertion deletion mutations, surrounding read quality;and filtering to remove sites that do not reach the set threshold according to statistical information to obtain mutation results. The method does not require partial assembly, and filters second-generation sequencing data in advance to quickly eliminate most of false positive results caused by the comparison, reduces detection running time and computing resources, improves detection efficiency, has strong sensitivity and specificity, and can quickly and accurately detect InDel mutations.
Owner:深圳裕策生物科技有限公司
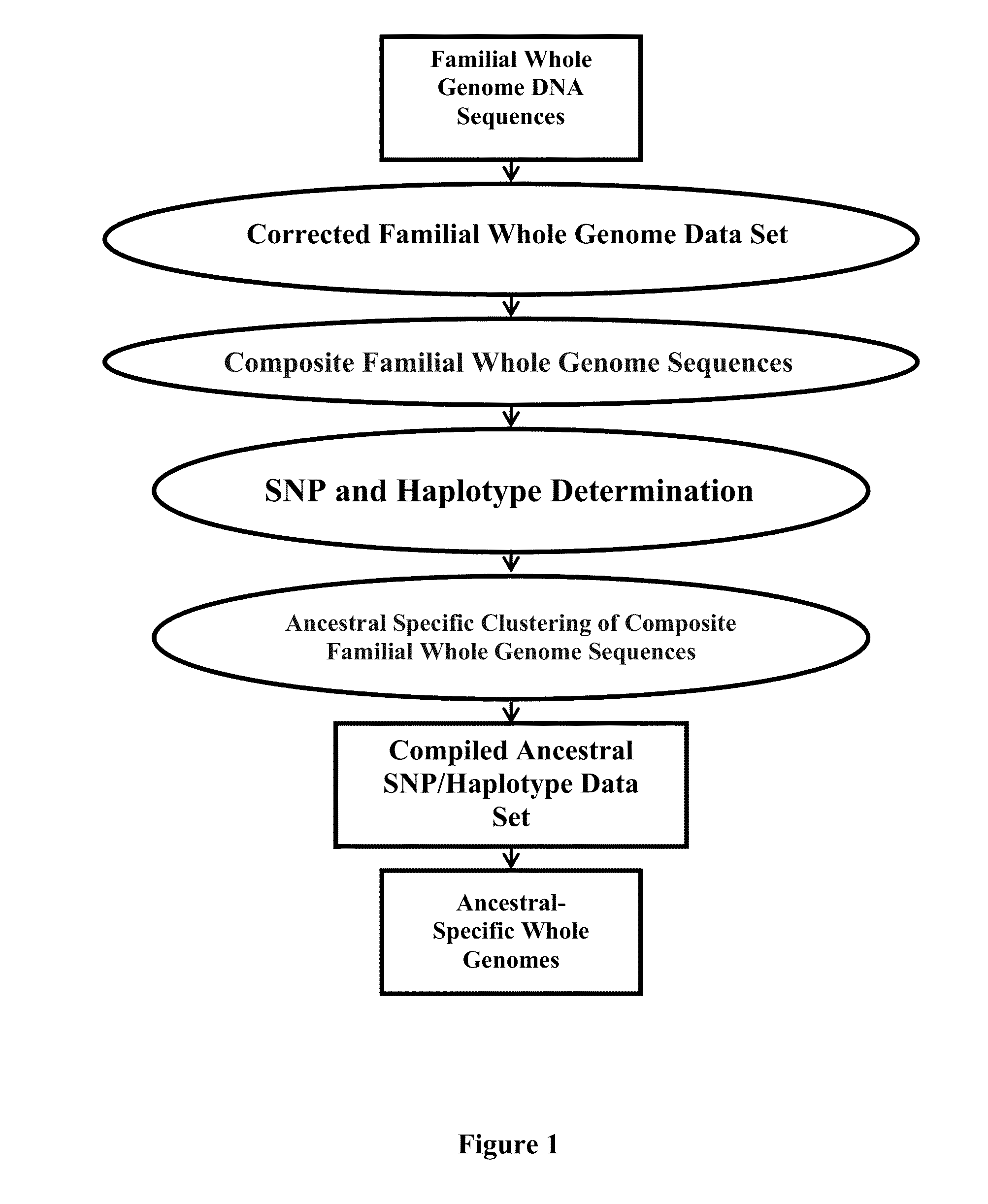
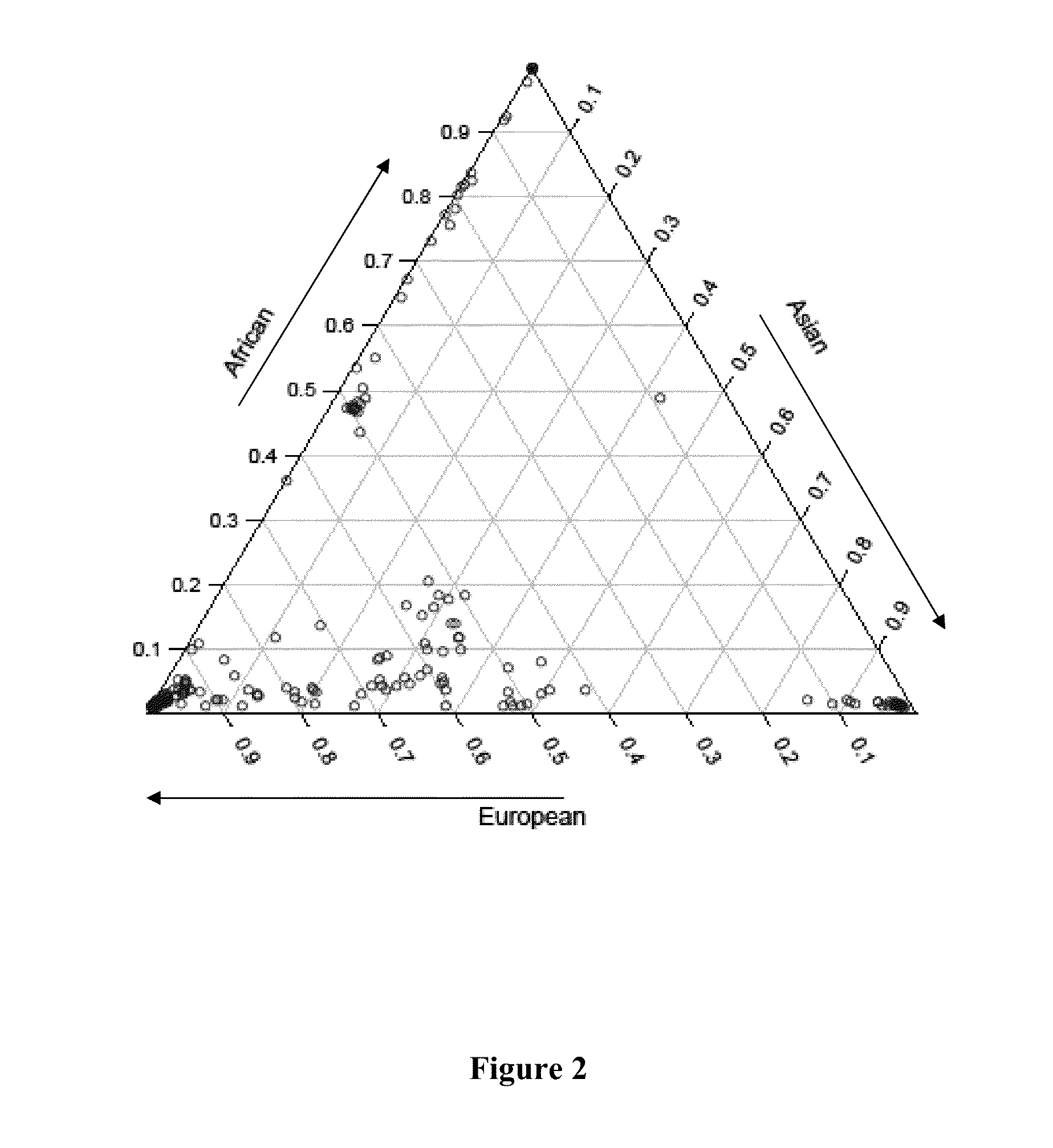
Ancestral-Specific Reference Genomes And Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20140067280A1Improve accuracyImprove targetingProteomicsGenomicsWhole genome sequencingMarker Discovery
Ancestry has a significant impact on the major and minor alleles found in each nucleotide position within the genome. Due to mechanisms of inheritance, ancestral-specific information contained within the genome is conserved within members of an ancestry. For this reason, individuals within a specific ancestry are more likely to share alleles in their genomes with other members of the same ancestry. Functionally, the combination of alleles at all positions within a group of individuals defines that group as having a common ancestry. Moreover, the aggregation of differences between alleles at all positions distinguishes one ancestry from another. The genomic similarities and differences between ancestries provides a mechanism to generate reference genomes that are specific for each ancestry. Reference genomes that are specific to an ancestry can be used to increase the accuracy of whole genome sequencing, DNA-based diagnostics and therapeutic marker discovery and in a variety of real-world DNA-based applications.
Owner:INOVA HEALTH SYST
Gene analysis annotation method and device
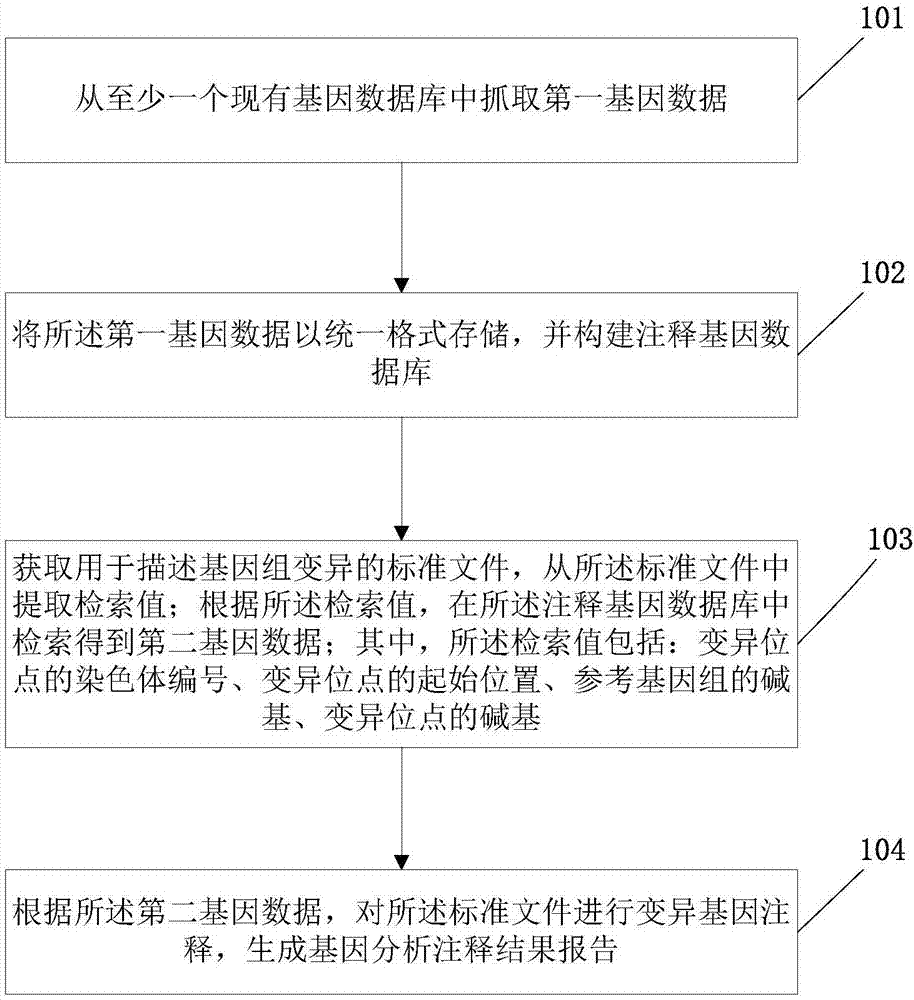
ActiveCN107194208AAccurate annotation of genetic analysisEfficient annotation of gene analysisBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsGene AnnotationChromosome number
The invention discloses a gene analysis annotation method and device. The method comprises the following steps that: capturing first gene data from at least one existing gene database; storing the first gene data in a uniform format, and constructing an annotation gene database; obtaining a standard file used for describing genome variation, and extracting a retrieval value from the standard file; according to the retrieval value, carrying out retrieval in the annotation gene database to obtain second gene data, wherein the retrieval value comprises the chromosome number of a variation site, the starting position of the variation site, the basic group of a refereed genome and the basic group of the variation site; and according to the second gene data, carrying out gene annotation on the standard file, and generating a gene analysis annotation result report. By use of the method, the gene analysis annotation can be accurately and efficiently carried out.
Owner:UNITED ELECTRONICS
A method and system for intelligently interpreting and reporting genetic variation of monogenic diseases
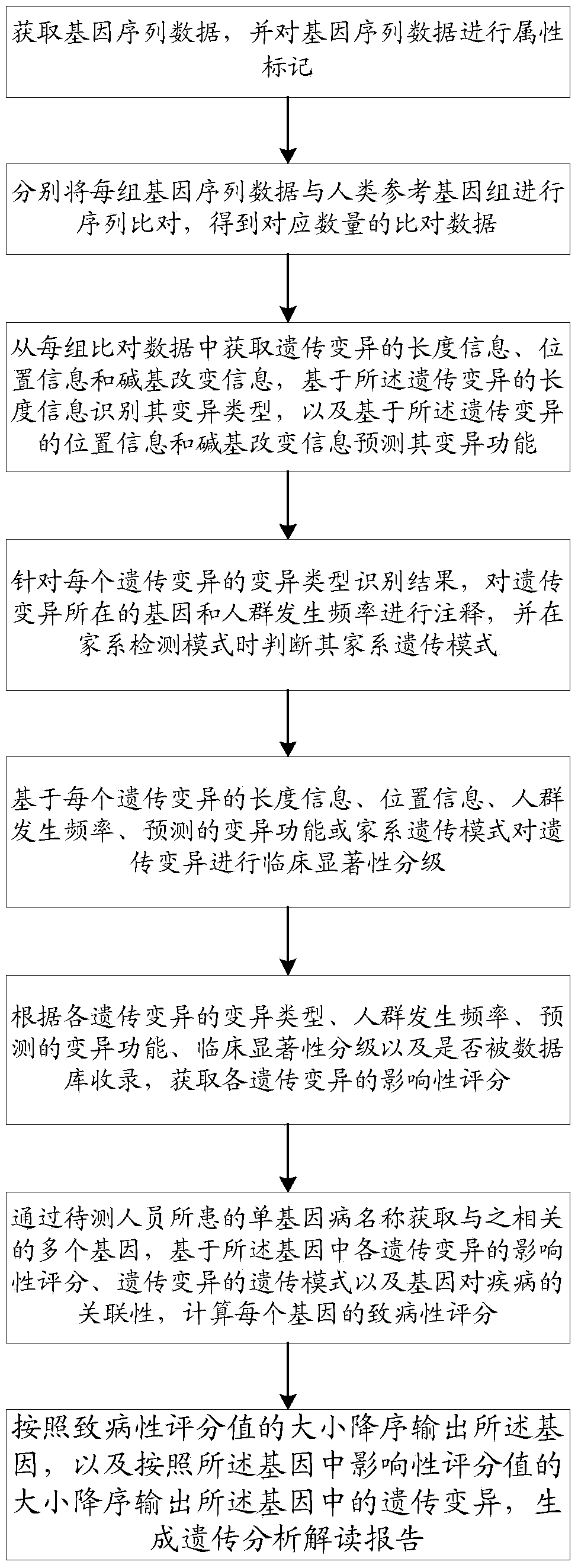
ActiveCN109086571ARealize full automationReduce workloadSpecial data processing applicationsCrowdsSequence alignment
The invention discloses a method and a system for intelligently interpreting and reporting the genetic variation of a single gene disease, which can automatically analyze the genetic variation resultbased on the original sequence data of a gene of a patient, and provide a professional genetic variation analysis report, thereby improving the diagnosis and treatment efficiency of the genetic variation. The method comprises the following steps of: gene sequence data is acquired and attribute marking is performed on the gene sequence data; sequence alignment of each set of gene sequence data withhuman reference genome is performed to obtain corresponding amount of alignment data; based on the length information of genetic variation, the variation type is identified, and the variation function is predicted based on the position information and base change information of genetic variation. According to the identification results of each genetic variation type, the gene and population frequencies of genetic variation were annotated, and the family genetic pattern was judged when the family detection mode was used. The system comprises the method proposed in the technical proposal.
Owner:国家卫生健康委科学技术研究所
Detection method for genomic copy number variation and device comprising same
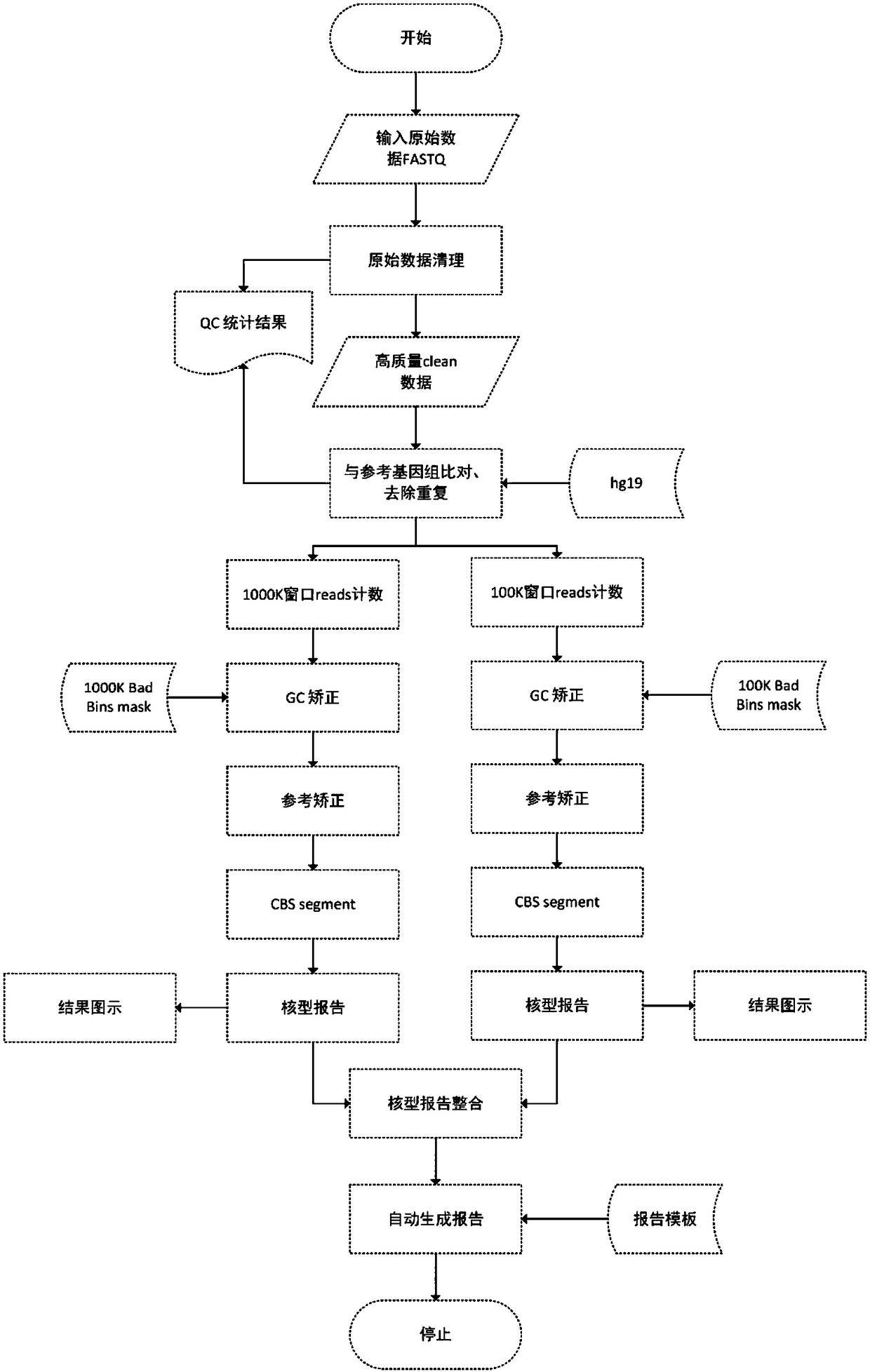
The invention provides a detection method for genomic copy number variation and a device comprising the method. The method comprises the following steps: inputting original data, cleaning quality control, aligning sequences to a reference genome, calculating a unique alignment sequence number by using windows of different sizes, performing GC correction and reference correction, shielding undetectable areas, segmenting CBS, integrating karyotype reports and generating reports, a complete set of the detection methods and devices is established through experimental exploration and optimization,through successive application of the specific sequential steps, the step of the reference correction is creatively adopted, and the windows with different sizes are used for performing alignment andintegration, the steps cooperate mutually, and finally the sensitivity and specificity are improved, so that the detection accuracy and result forms can conform to clinical demands, and the detectionmethod for the genomic copy number variation and the device comprising the method are high in automation degree, easy to expand, high in detection accuracy, capable of lowering the cost of data analysis, and extremely high in application value.
Owner:YIKON GENOMICS SHANGHAI CO LTD
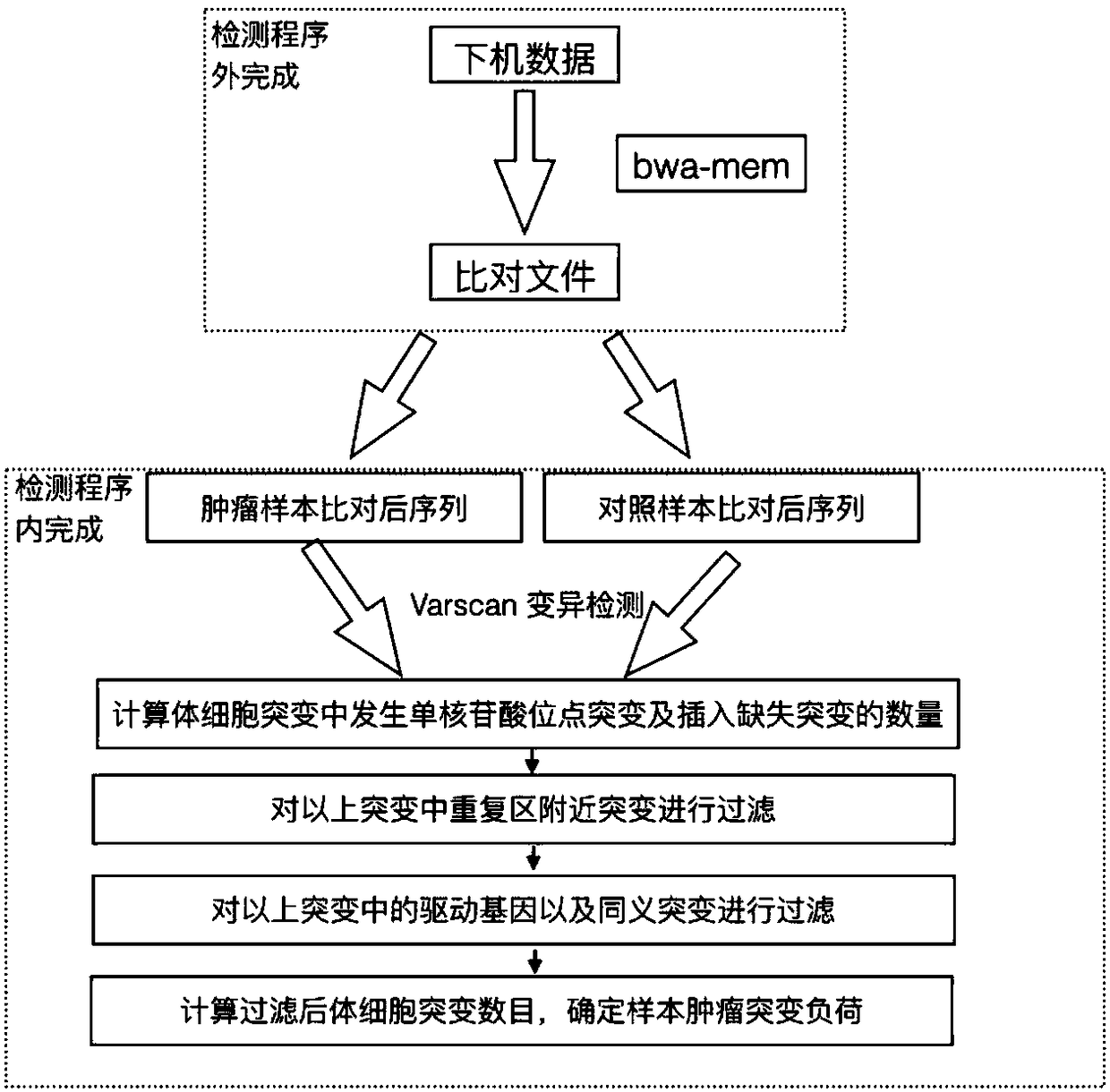
Method and device for detecting tumor mutation load based on single sample
ActiveCN111321140AAccurate detectionReduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsHuman tumorData set
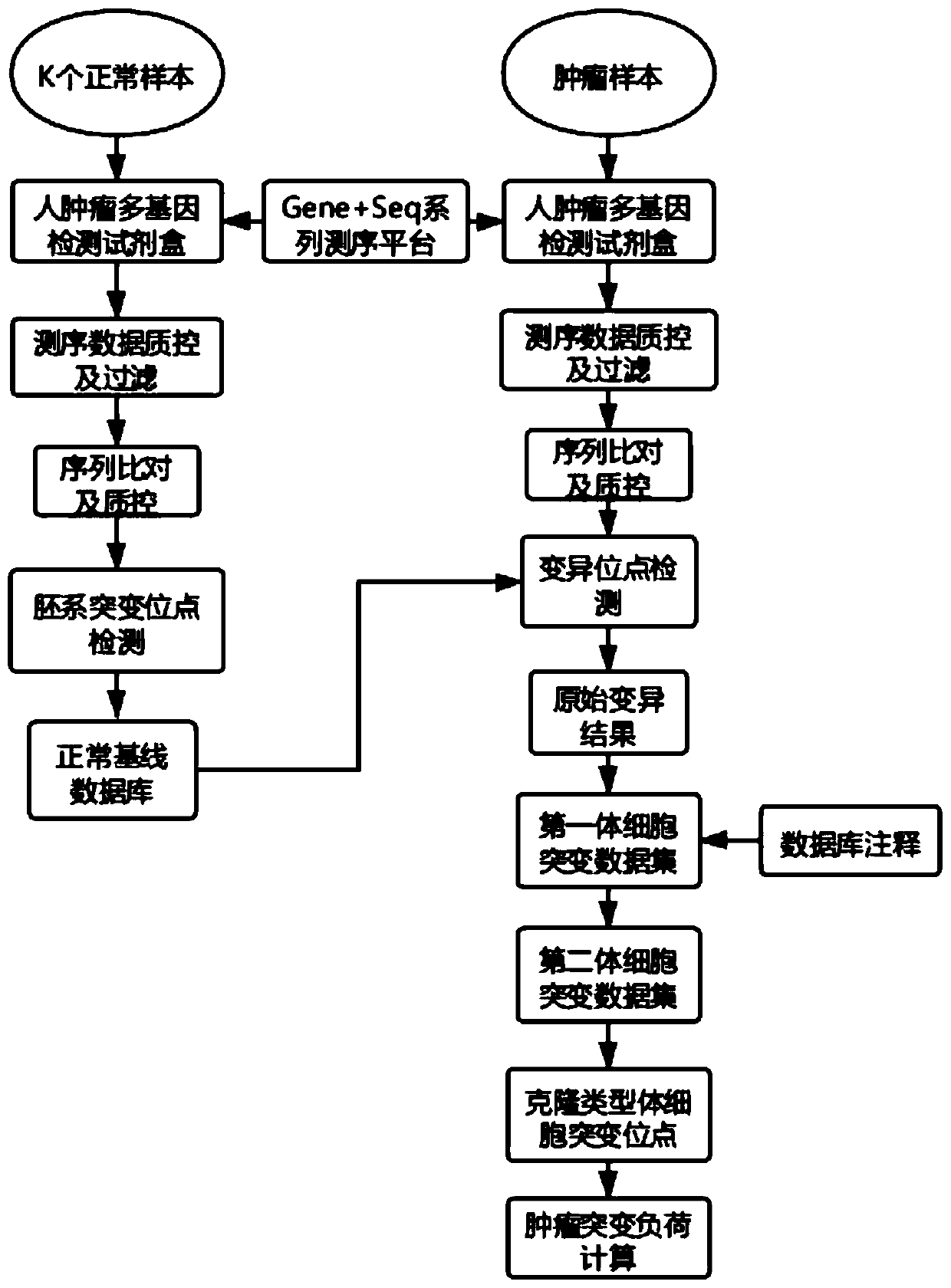
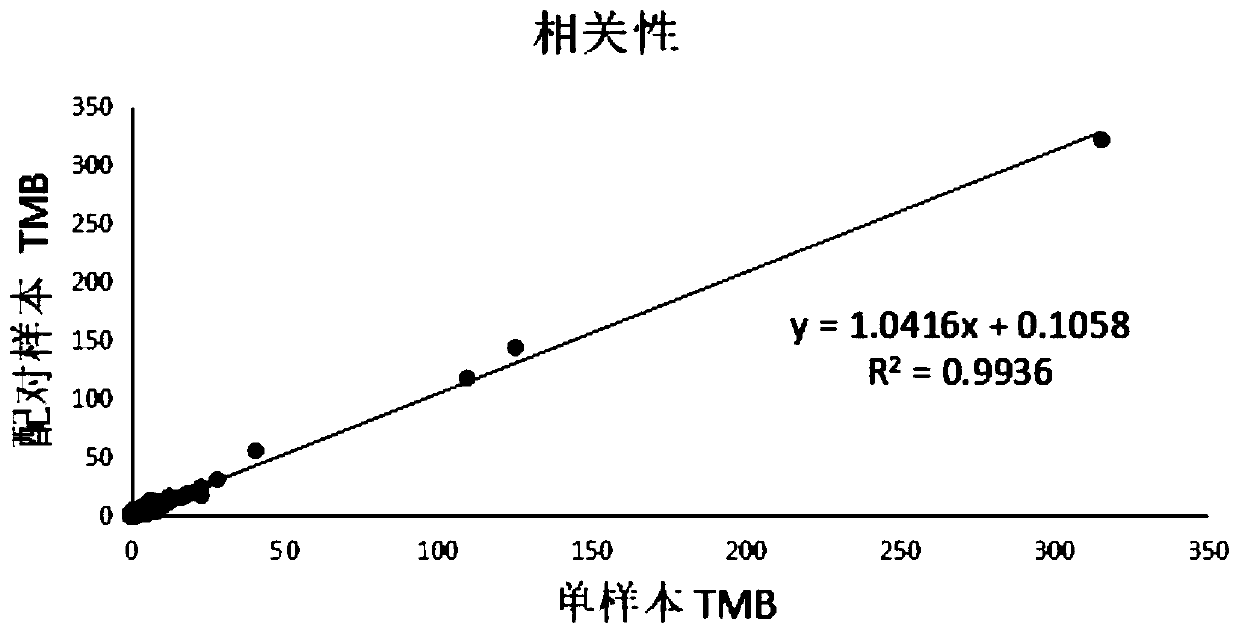
The invention relates to the field of biomedicine, in particular to a method and a device for detecting tumor mutation load based on a single sample. According to the device, a probe combination comprises probes that capture the exon region of a gene shown in Table 1, an intron promoter fusion breakpoint region of a gene shown in Table 2, and a coding region region of a gene shown in Table 3. A human tumor polygene detection kit comprises the probe combination. The TMB detection method based on the single sample comprises the following steps: access to target area of the tumor samples under test sequencing data, with the reference genome comparison, based on comparing the results obtained, detecting mutation loci, filtering original variable results with normal sample normal baseline database coincidence loci, filtering the high frequency reproductive mutation locus of a first cell mutation data set, screening the clonal somatic cell mutation locus of a second somatic cell mutation data set and calculating TMB. This method can accurately detect TMB of tumor samples without pairing samples.
Owner:苏州吉因加生物医学工程有限公司 +1
Reference genome and de novo assembly combination based next-generation sequencing data assembly method
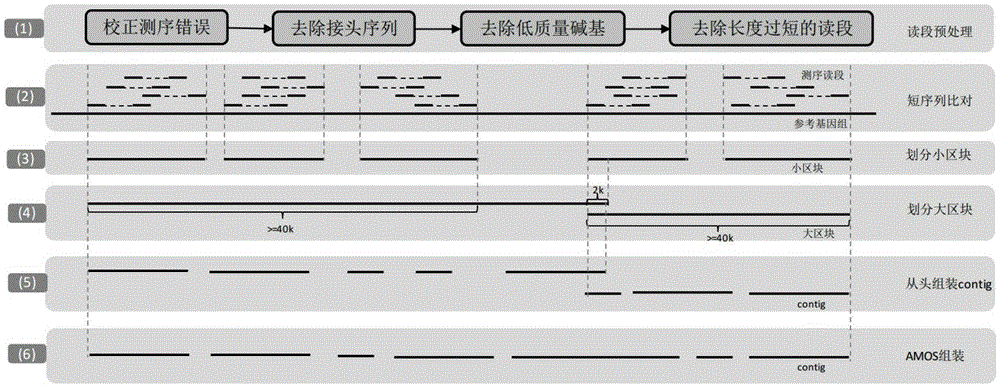
InactiveCN105303068AQuality improvementImprove continuitySpecial data processing applicationsReference genomeSequencing data
The invention relates to a reference genome and de novo assembly combination based next-generation sequencing data assembly method. Two policies based on reference genome assembly and genome de novo assembly are combined for overcoming the disadvantages of the two policies, and the advantages of the two policies are fully utilized. The method comprises: firstly, obtaining a genome sequence relatively high in continuity and accuracy by utilizing the reference genome based policy; secondly, obtaining a genome subjected to de novo assembly by utilizing the de novo assembly policy, wherein the genome is relatively good in performance of specific sequence assembly of species; and finally, integrating the two genomes to generate a genome relatively high in accuracy, continuity and integrity.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method and device for detecting tumor mutational load by using high-throughput sequencing data
InactiveCN108588194AStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMutation detectionA-DNA
The invention discloses a method and device for detecting a tumor mutational load by using high-throughput sequencing data. The method comprises the steps that a to-be-detected sample is pretreated and a DNA is extracted; according to a target area capture principle, a probe is used for capturing tumor related genes; sequencing is carried out through a high-throughput method to obtain sequencing information; low-quality sequences are filtered out, a checkout process is used for detection, the checkout process comprises that a high-throughput sequencing sequence is compared to a reference genome by using a comparison software, a non-compared sequence forms a soft truncation, according to the compared position, sorting is carried out, and an index is established; mutation detection is carried out on a compared sequence, the detected mutation is annotated by using a RMSK database, a repetitive area is removed on the annotation, driver genes and same sense mutation are filtered, and the number of the filtered somatic cell mutations is calculated to determine the sample tumor mutational load. By applying the technical scheme, the detection precision is higher, and the effect is better.
Owner:天津诺禾致源生物信息科技有限公司
System and method for real-time personalization utilizing an individual's genomic data
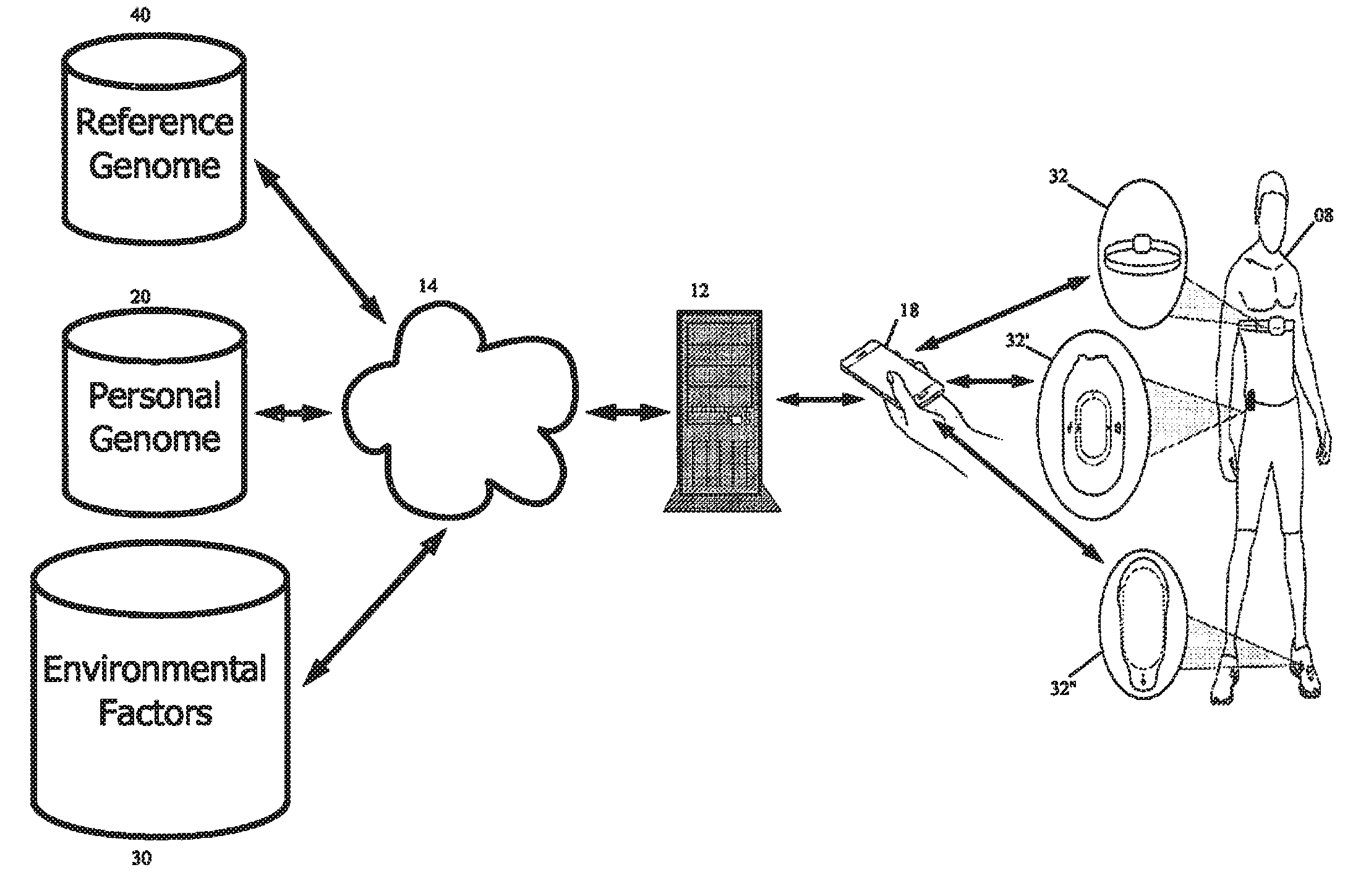
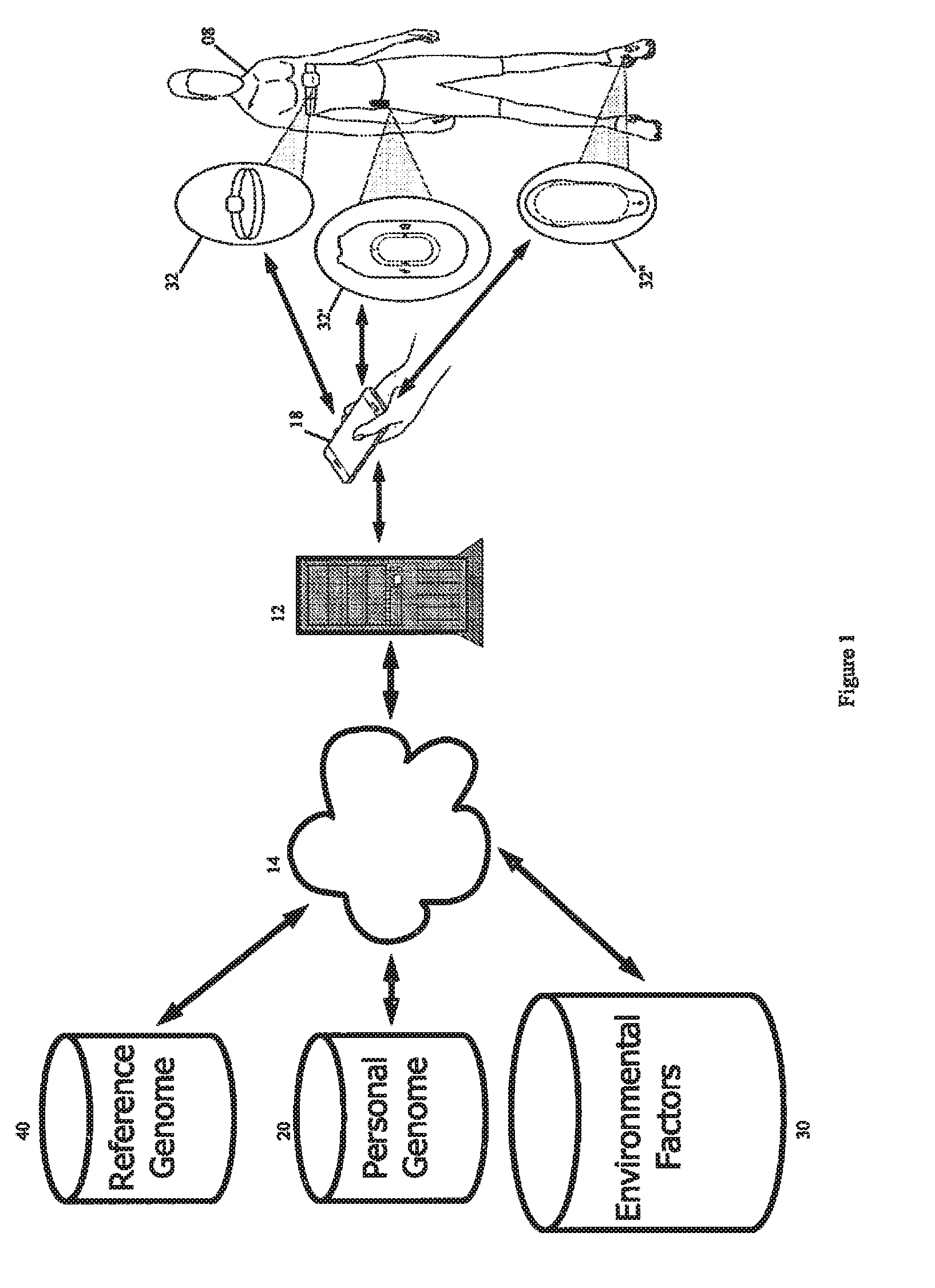
The principles of the present invention provide methods and systems for processing personal biological data for real time or near real time application. An exemplary system includes a received reference genome and a received personal genome. The genomes are accessed over a network by one or more servers. Input from one or more sensors associated with an individual or remote from the individual is used in conjunction with the individual's genomic data or the results of the comparison of the individual's genetic data and the reference genome(s) to provide real-time or near real-time suggestions, recommendations, warnings and the like in view of the sensor data and genomic data. An exemplary method includes receiving the personal genome and optionally selecting a suitable reference genome. The system compares the personal genome to the reference genome, of parts thereof, for one or more selected genotype(s) and / or phenotype(s) corresponding to a condition of concern in order to determine the differences between the reference genome and the personal genome. A sensor corresponding either directly or indirectly to the selected condition of concern is selected and optimum values for the sensor are calculated. The sensor is placed in proximity with the individual and the output is monitored. Alerts and reporting are presented in response to the sensor output. The present invention concerns systems and methods for analysis of biological data and integration of such data into everyday life.
Owner:SEQUENCING COM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com