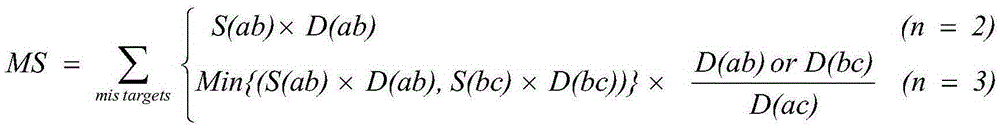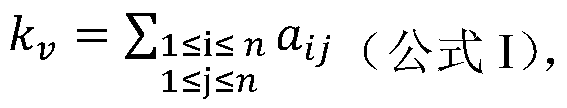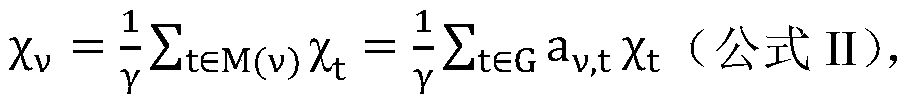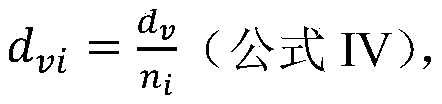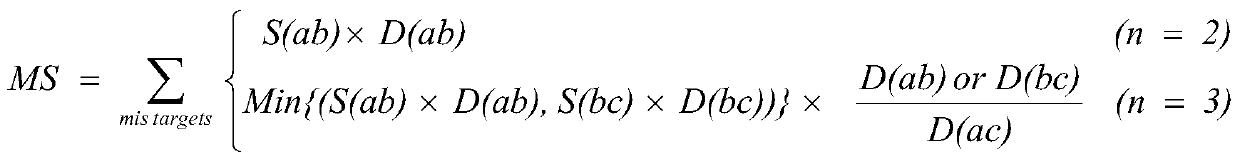Patents
Literature
59 results about "Gene Annotation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
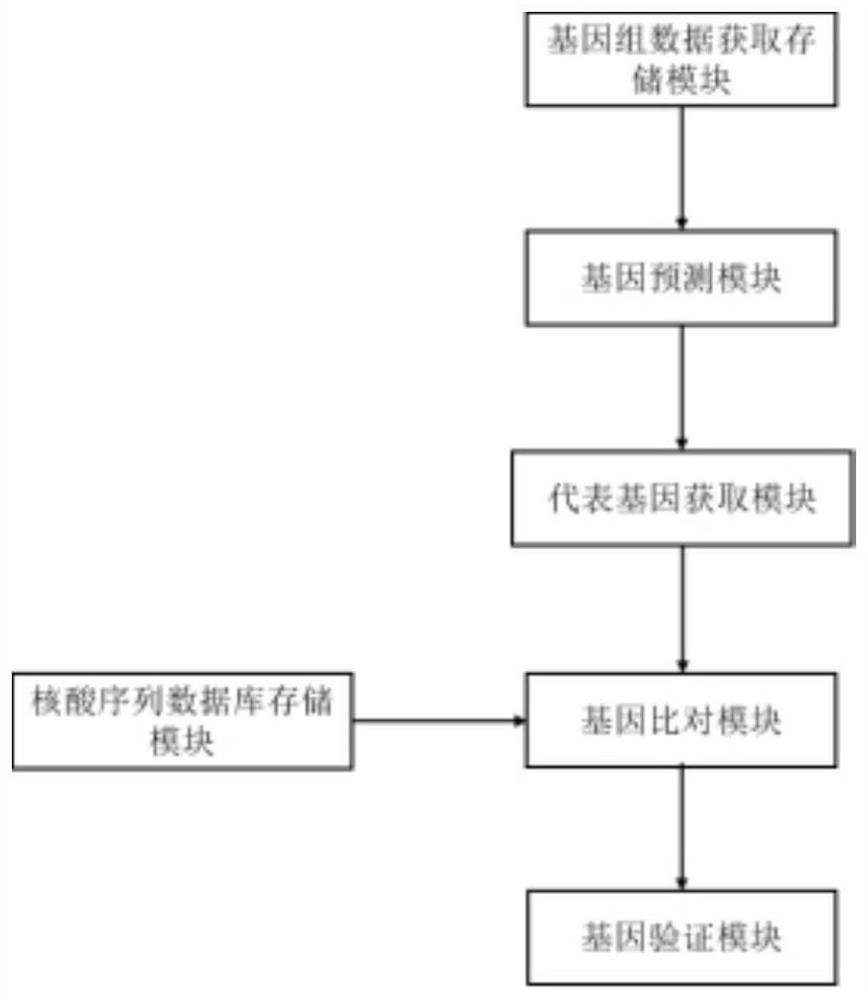
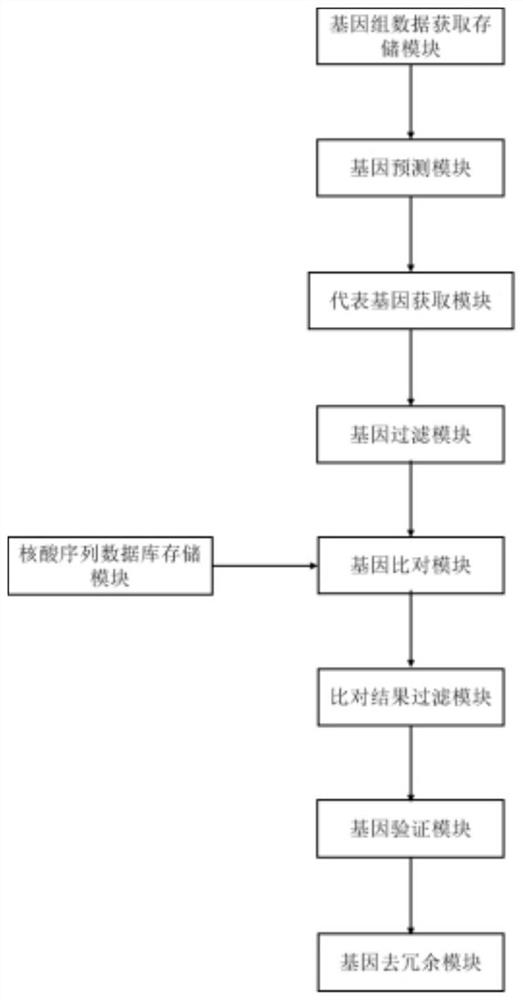
The addition of descriptive information about the function or structure of an RNA or DNA SEQUENCE to its record in a database (NUCLEIC ACID DATABASES.)
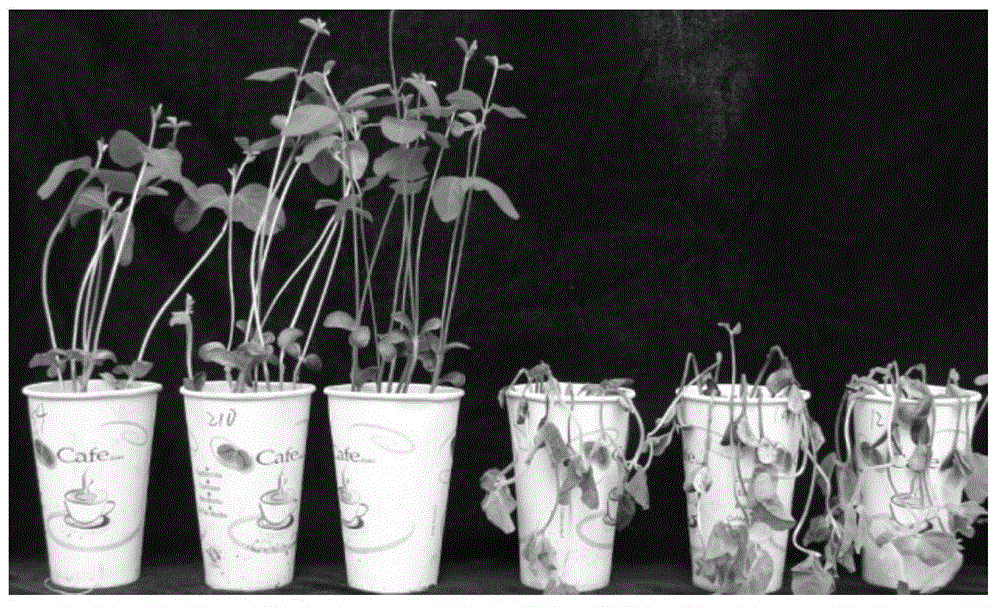
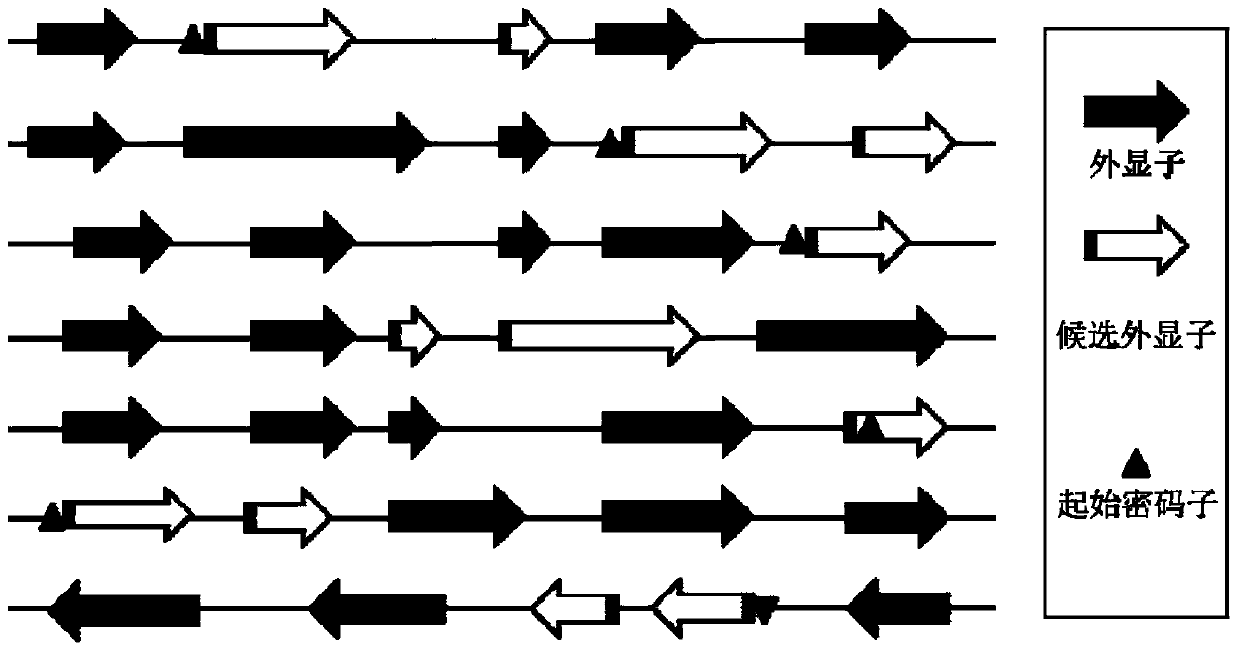
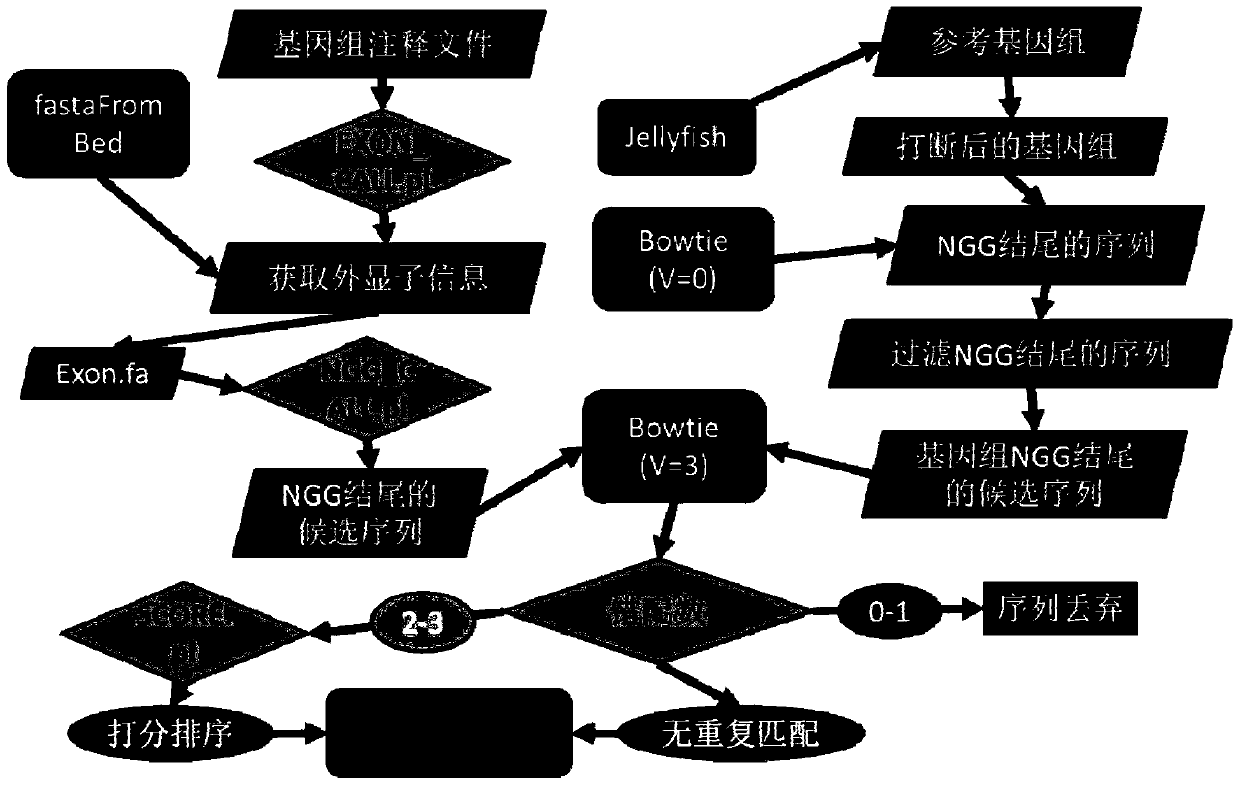
CRISPR-Cas9 system sgRNA action target screening method and apparatus
ActiveCN106845151ALow costOvercome costsSpecial data processing applicationsProtein nucleotide librariesScreening methodGene Annotation
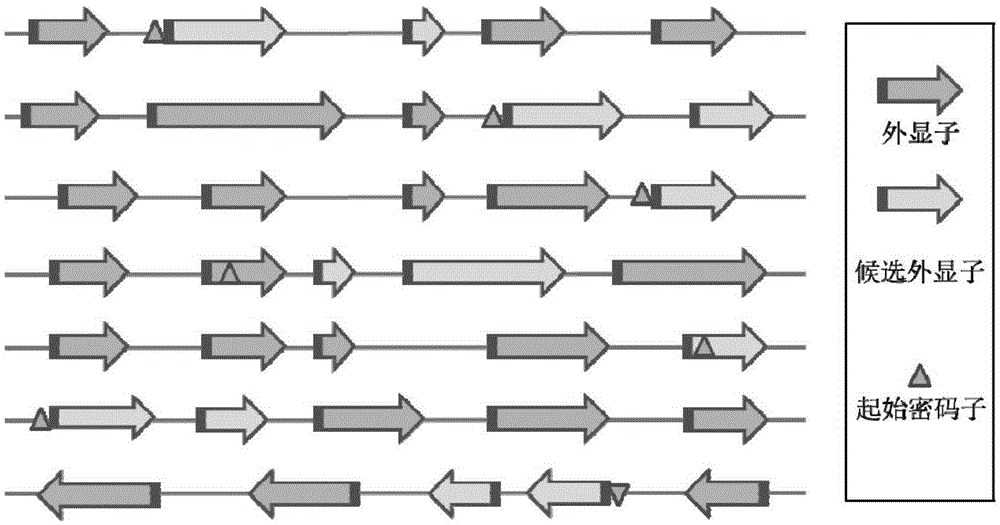
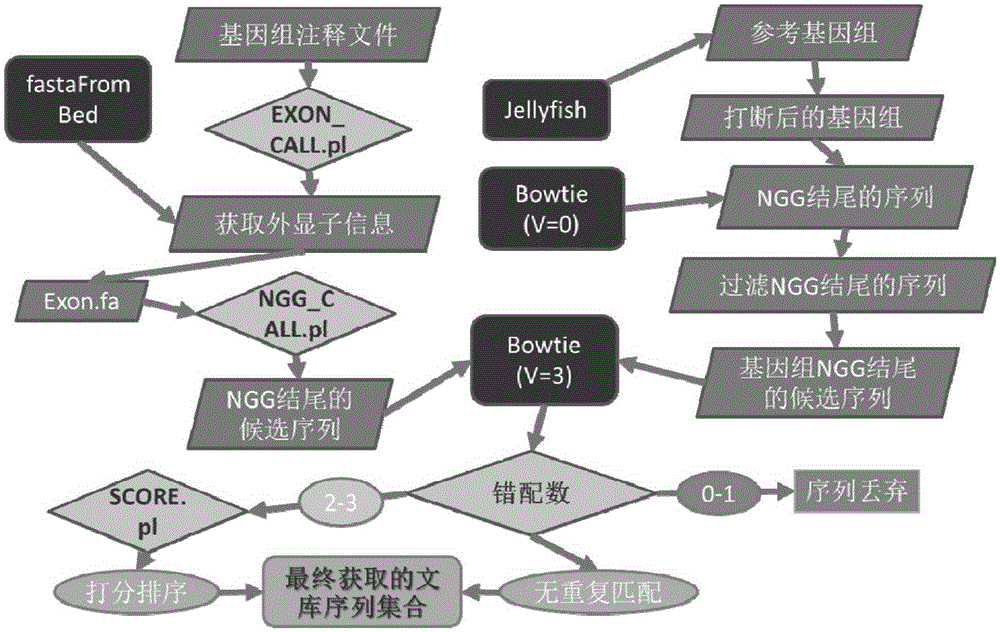
The invention relates to a CRISPR-Cas9 system sgRNA action target screening method. The method comprises the steps of (1) obtaining segments with 5'-Nx-NGG-3' sequences (x is an integer ranging from 19 to 22 and N represents A / T / C / G) in genomes by utilizing whole genome sequences and gene annotation information of published species to serve as candidate targets of CRISPR-Cas9 system sgRNA; (2) fragmenting the genomes into fragments of 22-25bp and screening sequences ending with NGG and non-repeated on the genomes; and (3) comparing the sequences of the candidate targets in the step (1) with the screened sequences in the step (2), and performing screening and sorting on corresponding optimal sequences according to mismatch information and a selection formula to obtain an optimal genome sgRNA action target set. The invention furthermore provides an apparatus used for realizing the screening method. The method is suitable for all species with known genomes and gene annotation information, and a universal sgRNA sequence set of whole genome level of the species is quickly and efficiently obtained to build a gene knockout mutant library or a gene knockout animal model.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
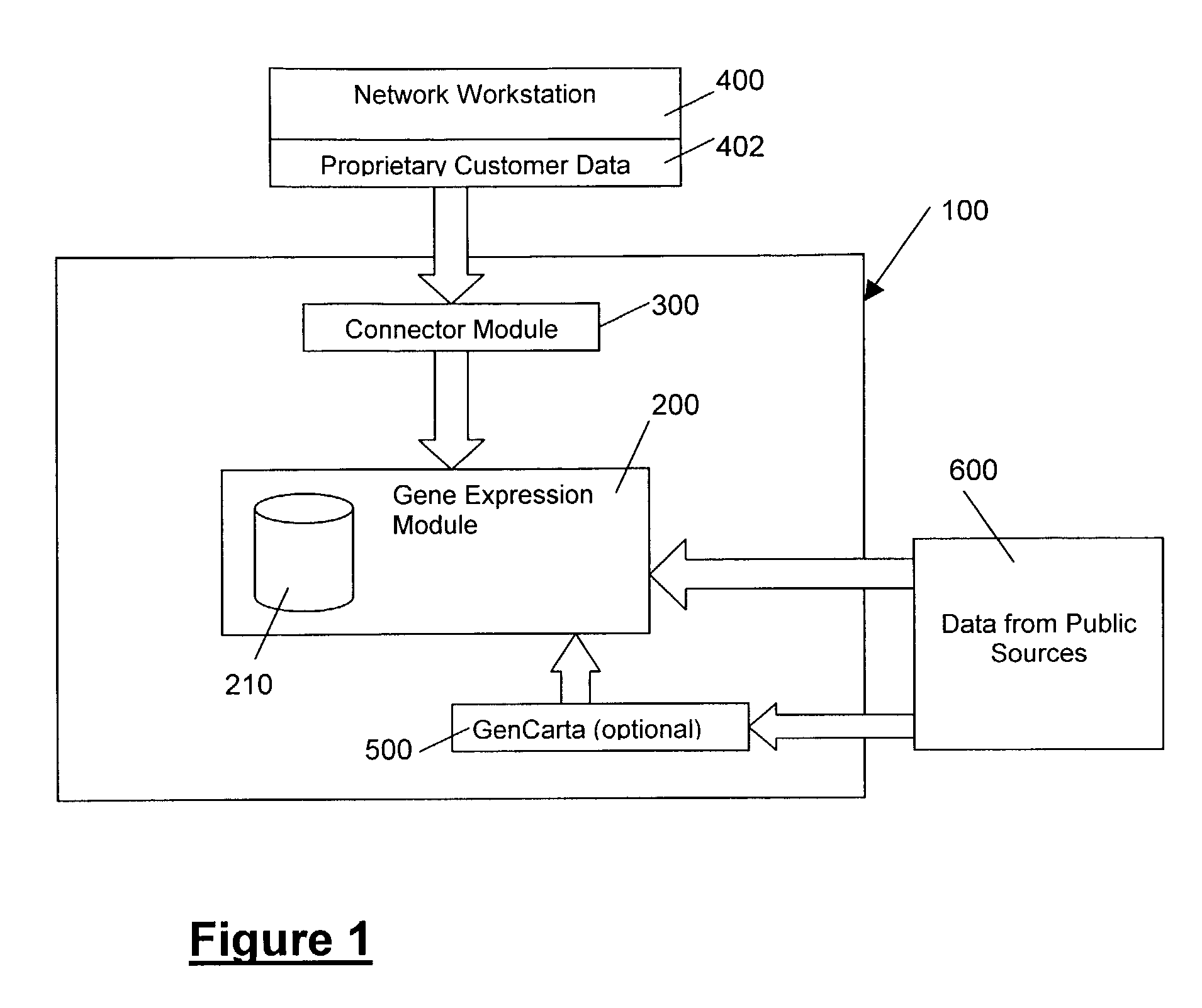
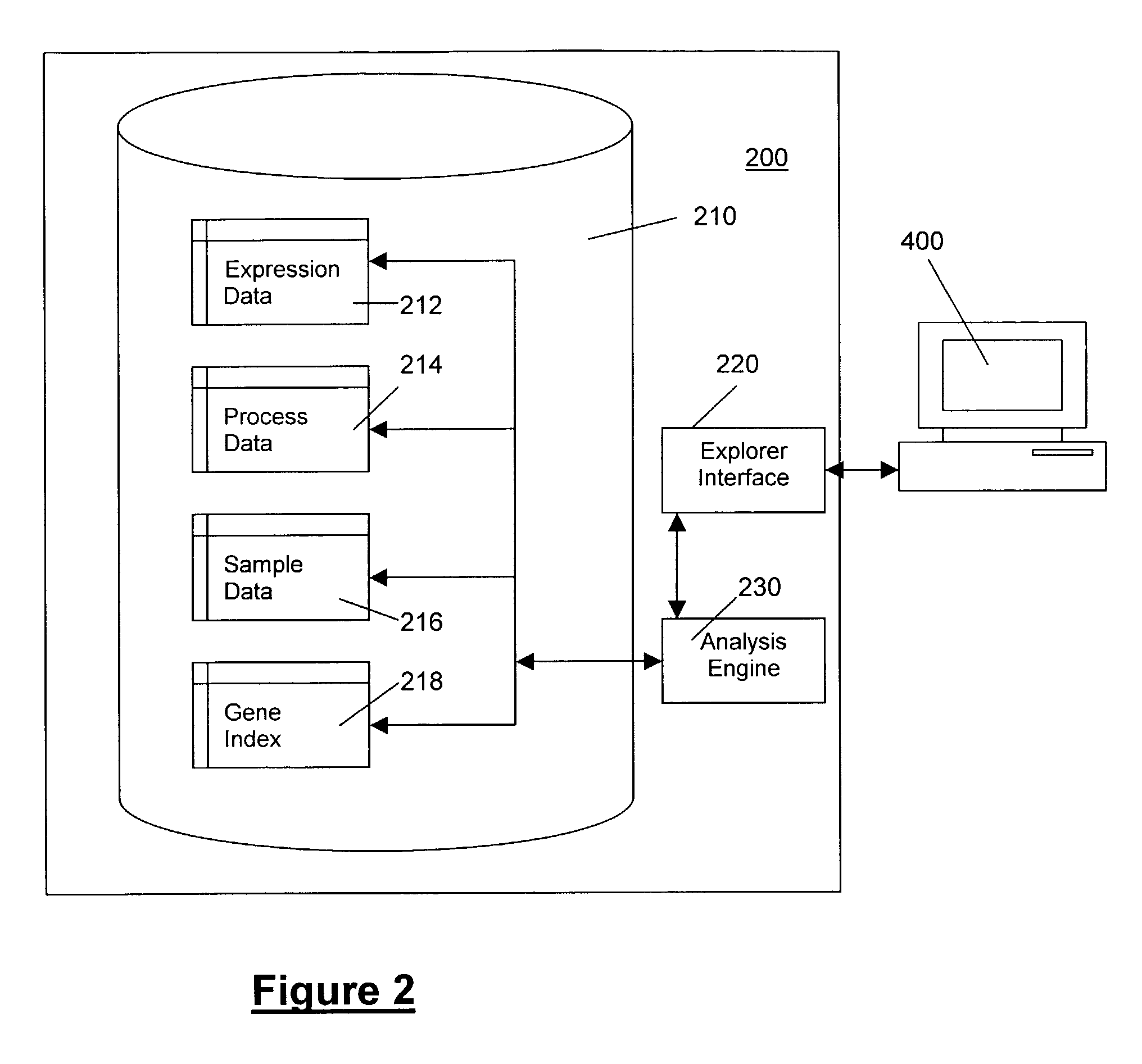
Methods and systems for efficient comparison, identification, processing, and importing of gene expression data
The present invention provides systems and methods for analyzing gene expression, gene annotation, and sample information in a relational format supporting efficient exploration and analysis, including comparative differential expression analysis, expression pattern matching, and mapping of external attributes or identifiers to internal representations of gene fragments or samples.
Owner:OCIMUM BIO SOLUTIONS
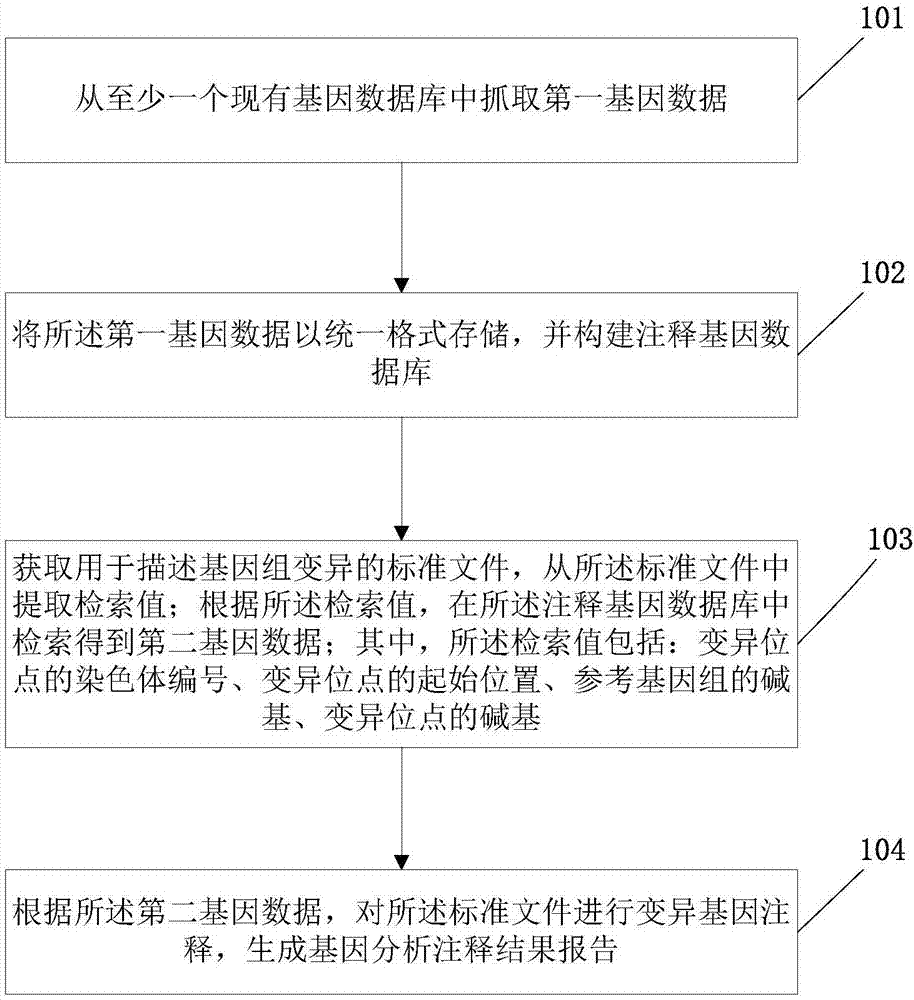
Gene analysis annotation method and device
ActiveCN107194208AAccurate annotation of genetic analysisEfficient annotation of gene analysisBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsGene AnnotationChromosome number
The invention discloses a gene analysis annotation method and device. The method comprises the following steps that: capturing first gene data from at least one existing gene database; storing the first gene data in a uniform format, and constructing an annotation gene database; obtaining a standard file used for describing genome variation, and extracting a retrieval value from the standard file; according to the retrieval value, carrying out retrieval in the annotation gene database to obtain second gene data, wherein the retrieval value comprises the chromosome number of a variation site, the starting position of the variation site, the basic group of a refereed genome and the basic group of the variation site; and according to the second gene data, carrying out gene annotation on the standard file, and generating a gene analysis annotation result report. By use of the method, the gene analysis annotation can be accurately and efficiently carried out.
Owner:UNITED ELECTRONICS
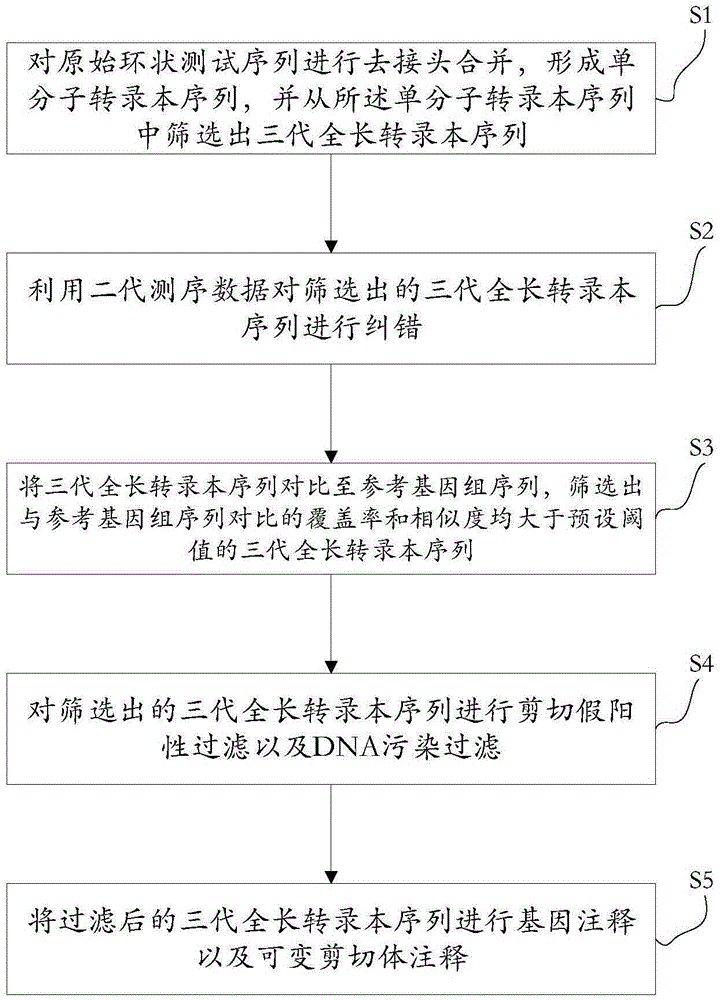
Method for detecting variable spliceosome in third generation full-length transcriptome
ActiveCN105389481AEfficient access to shear structuresPerfect commentSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsReference genome sequenceGene model
The invention discloses a method for detecting a variable spliceosome in a third generation full-length transcriptome. The method comprises the following steps: merging original annular test sequences with joints removed to form a monomolecular transcript sequence, and screening a third generation full-length transcript sequence; comparing the third generation full-length transcript sequence with a reference genome sequence, and screening a third generation full-length transcript sequence having coverage and similarity with the reference genome sequence larger than preset thresholds; carrying out splicing false positive filtration and DNA contamination filtration on the screened third generation full-length transcript sequence; and carrying out gene annotation and variable spliceosome annotation on the filtered third generation full-length transcript sequence. An overlong read length of a third generation sequencing technology mentioned in the method disclosed by the invention is large enough to cover most RNA, the third generation full-length transcript sequence can be obtained by SMRT sequencing transcriptomes without being assembled, and a splicing structure of a gene can be effectively obtained by third generation transcriptome sequencing, and more perfect gene model annotation can be constructed.
Owner:嘉兴菲沙基因信息有限公司
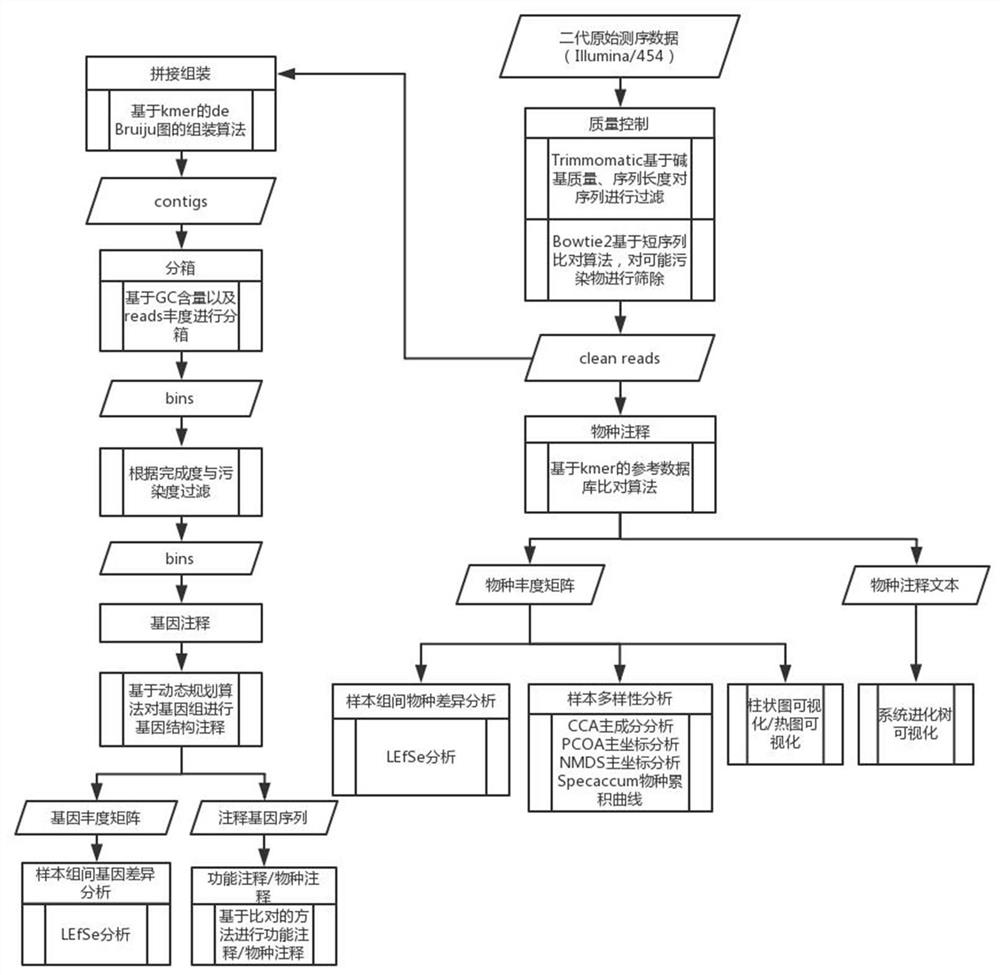
Metagenome data analysis method based on next-generation sequencing technology
PendingCN112071366ASolve incomplete problemsThe analysis process is reasonableCharacter and pattern recognitionHybridisationGenomicsContig
The invention discloses a metagenome data analysis method based on a next-generation sequencing technology, which comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out quality control on original sequencing data to obtain clean reads; (2) performing species annotation on the clean reads subjected to the quality control; (3) performing statistical analysis on the sample diversity based on a species abundance matrix; (4) performing statistical analysis on species with significant differences among sample groups based on the species abundance matrix; (5) splicing and assembling the clean reads to obtain a contigs sequence; (6) packaging the contigs obtained by splicing and assembling into boxes to obtain bins; (7) carrying out gene annotation on the bins subjected to boxing; (8) performing statistical analysis on the genes with significant differences among the sample groups based on the gene abundance matrix; and (9) based on the gene annotation result, performing function and species annotation on the sequence. A whole process from metagenome next-generation sequencing data processing to species composition analysis, gene composition analysis and function annotation is provided, an accurate analysis result is provided for researchers, and the metagenomics problem is comprehensively analyzed.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for detecting chromosome microdeletion and micro-duplication of human embryo
ActiveCN104745718AHigh sensitivityLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementEmbryoChromosome microdeletion
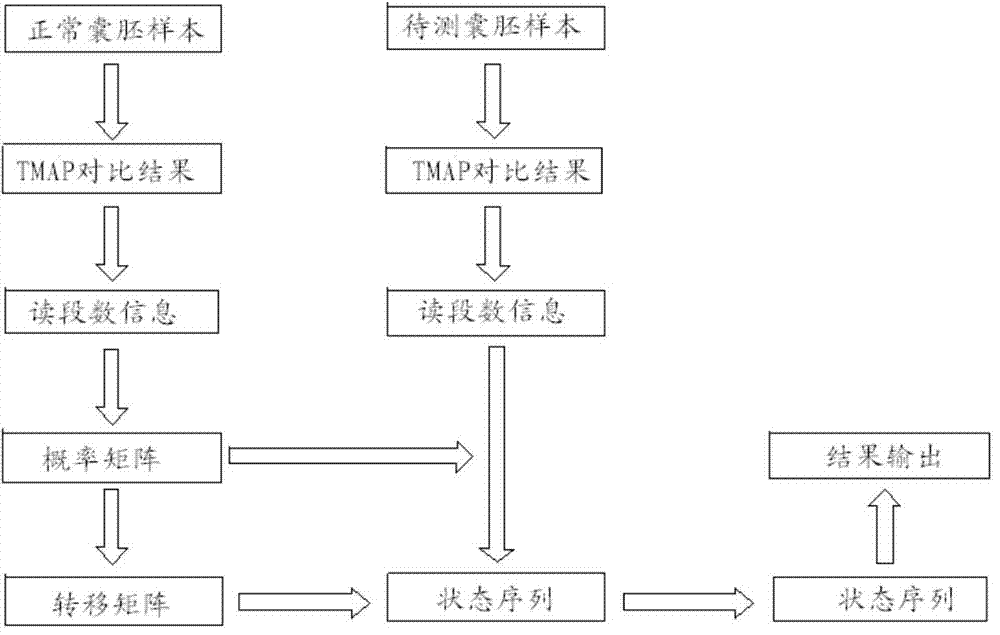
The invention relates to a method for detecting chromosome microdeletion and micro-duplication of a human embryo. The method comprises the following steps of performing whole genome amplification on cells cultured in vitro, interrupting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecules, and sequencing DNA fragments to obtain sequencing reads; comparing the sequencing reads with a reference sequence, and positioning the sequencing reads on the reference sequence; screening non-repeated areas of the reference sequence, and reserving the non-repeated areas; establishing a matrix of read number in windows through normal samples, analyzing the data of the normal samples, performing statistics on the read number of all the windows in the non-repeated areas, and establishing a probability matrix of the read number and chromosome enpeoids; calculating the copy number, i.e., the A / B / C state, of loci; selecting m continuous loci, i.e., the A state, as micro-duplication loci, and selecting m continuous loci, i.e., the C state, as microdeletion loci; contrasting the micro-duplication loci and the microdeletion loci with the existing CNV (copy number variation) and disease database, performing basic gene annotation and gene function analysis which relates to deletion parts, and annotating with a microdeletion syndrome disease type.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGYI KANGWEI MEDICAL INSTR
Novel cucumber SNP molecular marker
InactiveCN104988142AHelp with positioningMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPolymorphism analysisCell stress
The invention discloses a novel cucumber SNP molecular marker. The mark number of the novel cucumber SNP molecular marker is SLAF7695. According to the novel cucumber SNP molecular marker, the simplified genome depth sequencing technology is utilized, 73100 SLAF labels are obtained totally, 5355 polymorphic markers of three types including SNP, EPSNP and INDEL are obtained through polymorphic analysis, and 140 different markers closely related to cucumber powdery mildew resistance are obtained and mainly concentrated on the first chromosome and the sixth chromosome. Two candidate areas related to powdery mildew resistance characters are successfully located, seven special markers closely linked with cucumber powdery mildew resistance are obtained, 28 genes and related annotation information are obtained through gene annotation, and five genes are related to the functions of defense response, harm response, toxin catabolism, cell stress response and the like. The novel cucumber SNP molecular marker provides a theoretical foundation for exploration of cucumber powdery mildew resisting mechanism and molecular marker assisted selective breeding.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Network modeling for drug toxicity prediction
InactiveUS20160306948A1Chemical property predictionDrug and medicationsNetwork modelDrug side effect
A computational systems pharmacology framework consisting of statistical modeling and machine learning based on comprehensive integration of systems biology data, including drug target data, protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks, and gene ontology (GO) annotations, and reported drug side effects, can predict drug toxicity or drug adverse reactions (ADRs). Biomolecular network and gene annotation information can significantly improve the predictive accuracy of ADR of drugs under development. The use of PPI networks can increase prediction specificity, and the use of GO annotations can increase prediction sensitivity.
Owner:MEDEOLINX
Growth-related molecular marker in C-type scavenger receptor of Litopenaeusvannamei and application
ActiveCN109055580AImprove selection efficiencyImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCandidate Gene Association StudyReceptor for activated C kinase 1
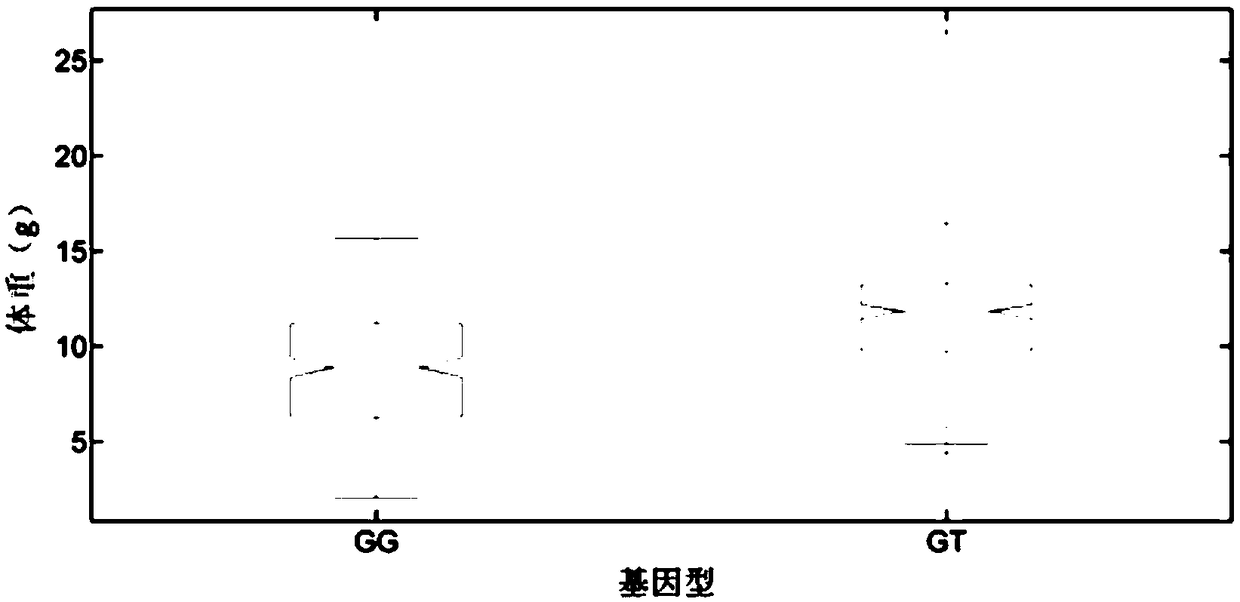
The invention belongs to the technical field of aquatic breeding, and particularly relates to a growth-related molecular marker in a C-type scavenger receptor gene (LvSRC) of Litopenaeusvannamei and application thereof to genetic breeding of the Litopenaeusvannamei. A batch of markers related to shrimp growth traits are positioned in the genomic level through genome-wide association analysis, a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) marker (LvSRC-211-G / T) positioned in a coding region of the LvSRC gene is further screened through gene annotation and by a candidate gene association analysis method, and the genotype of the marker is significantly correlated to the shrimp growth traits (P is smaller than 10<-6>). The marker is positioned at a 211bp position on the LvSRC gene and belongs to G / Ttype mutation, and the GT genotype of the marker is a distinct growth-dominant genotype. The marker provided by the invention can be used as the shrimp breeding molecular marker for assisting in genetic selection of the shrimp growth traits.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
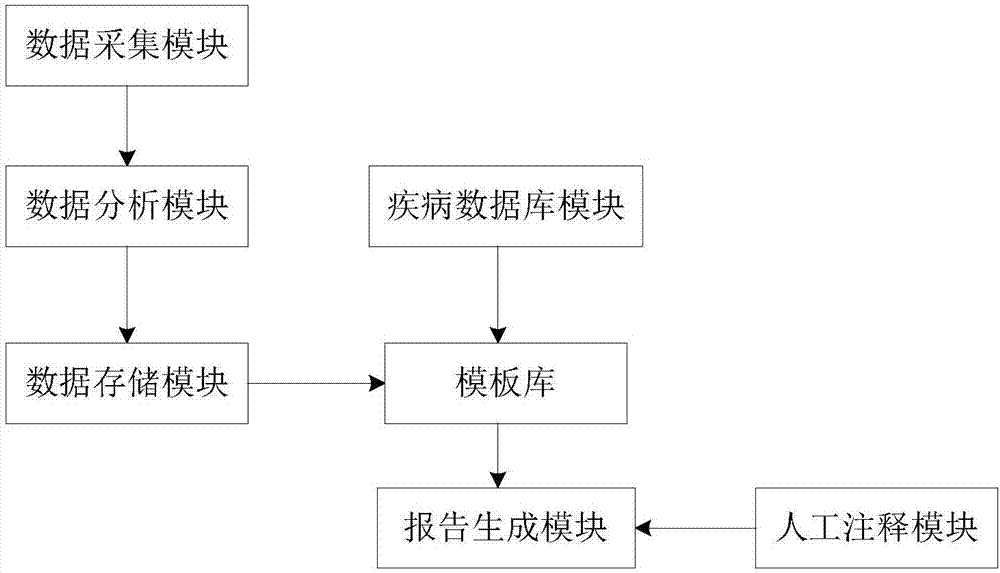
Health data analysis report generating system and method based on gene sequence analysis
InactiveCN107978345ASimplify the generation processSimplify the linkHealth-index calculationHybridisationSequence analysisManual annotation
The invention relates to a health data analysis report generating system and method based on gene sequence analysis. The system comprises a diseases database module, a manual annotation module, a dataacquisition module, a data analysis module, a data storage module, a template library and a report generation module, wherein the data acquisition module, the data analysis module, the data storage module, the template library and the report generation module are sequentially connected, the diseases database module is connected with the template library, and the manual annotation module is connected with report generation module. According to the system, a health analysis report is generated by the aid of a mode combining an automatic retrieval diseases database with a manual annotation supplementary information, contents are automatically, conveniently and rapidly searched by a computer, labor is saved, a health analysis report generating link is simplified, Chinese version of gene annotation databases is absent at present, a computer system cannot automatically capture data, the contents of the report can be more all-round by the aid of manual annotation, understanding of readers isfacilitated, and practical application requirements are met.
Owner:江苏医联生物科技有限公司
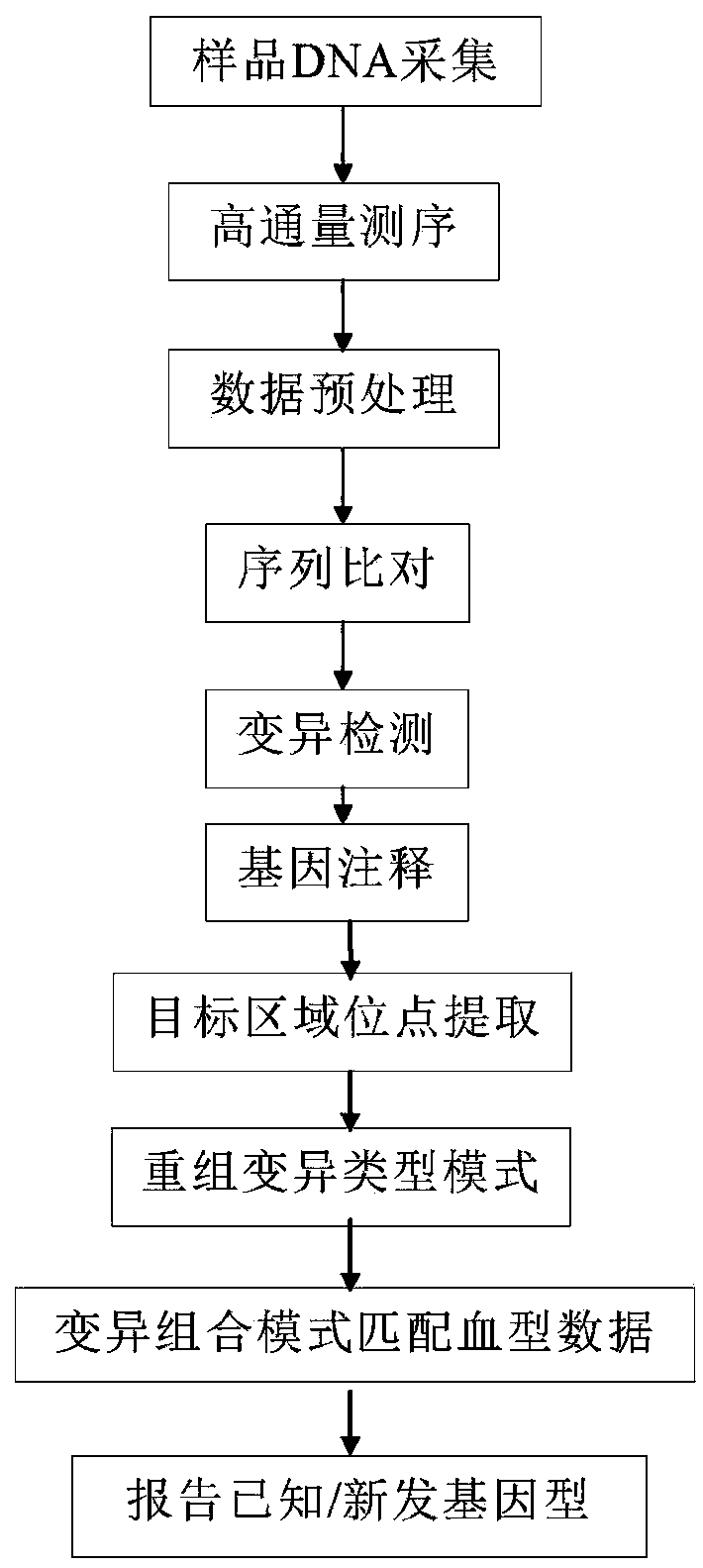
Method for analyzing human blood group genotype based on high-throughput sequencing, and application thereof
The invention discloses a method for analyzing the human blood group genotype based on high-throughput sequencing, and belongs to the field of bioinformatics. In the method, first high-throughput sequencing data of human blood sample DNA are obtained, and further the sequencing data are processed through sequence comparison, mutation detection, and gene annotation to complete the analysis and verification of the blood group genotype. The invention establishes a whole gene sequencing blood typing cloud platform for the first time, the NGS technology is used to reveal the molecular mechanism ofhuman GPA, GPB, and GPE, complex GP (A-B-A), GP (B-A-B), and GP (A-B) fragments are sequenced and analyzed, polymorphism characteristics of glycoprotein heterozygous genes are analyzed in detail and the corresponding glycoprotein molecular type is determined through BWA / GATK and other bioinformatics software, mutant genes are overexpressed and an antigenic type of the MNS system is verified, and thereby difficult problems of clinical blood transfusion reactions and the diagnosis and treatment of immune diseases caused by heterozygous glycoprotein polymorphism molecules are solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN BLOOD CENT
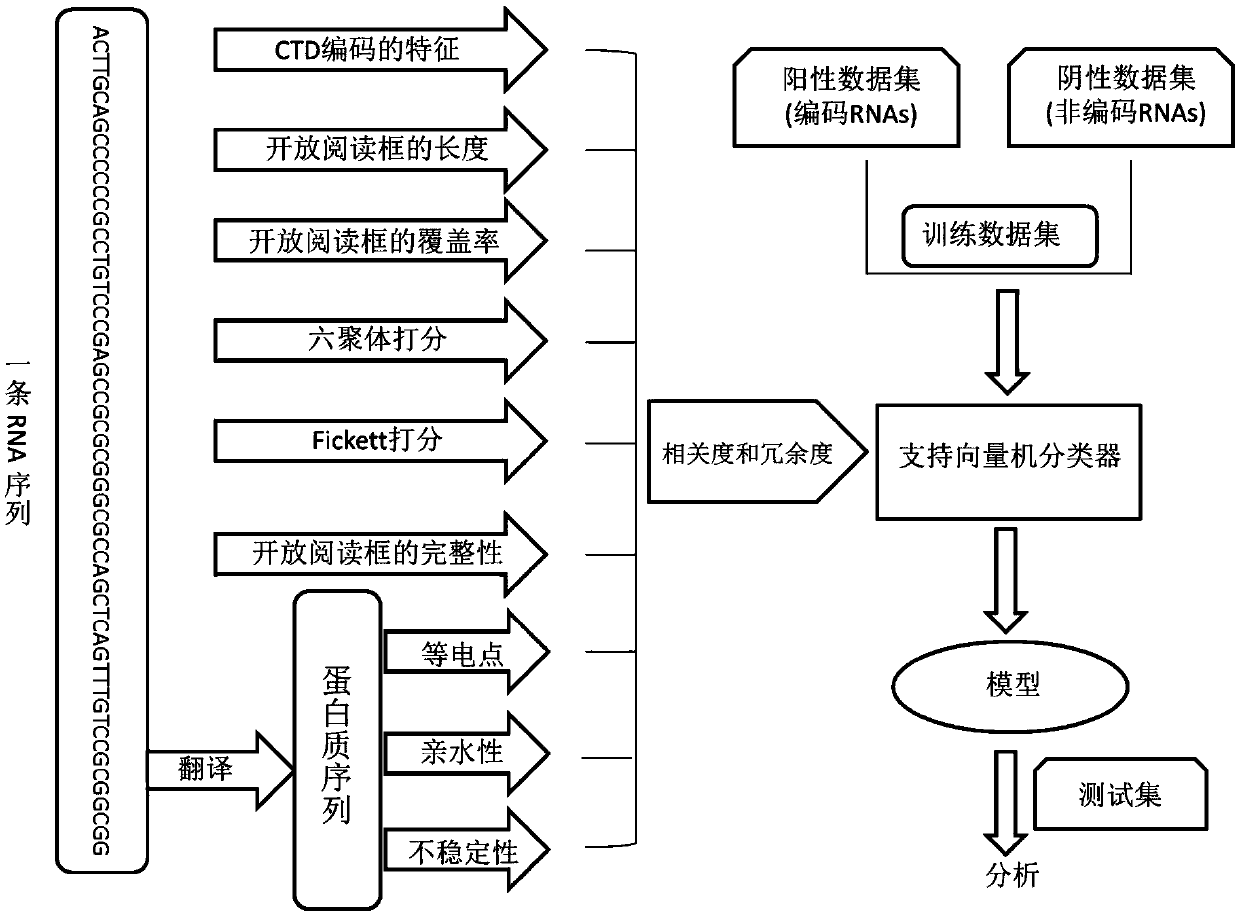
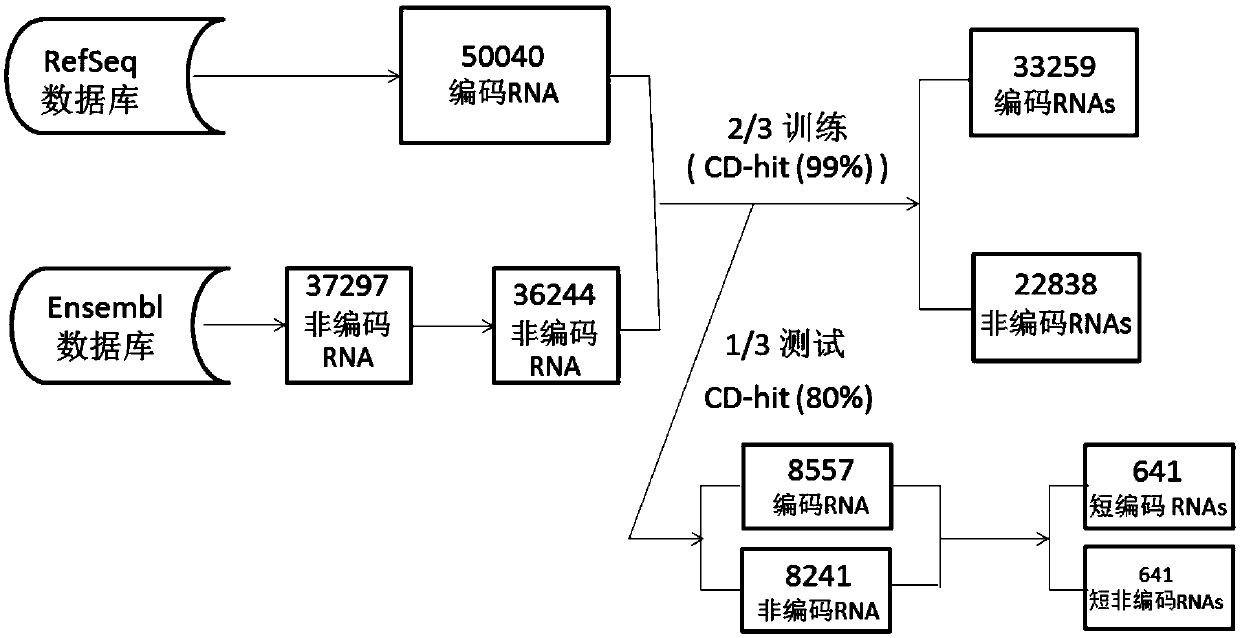
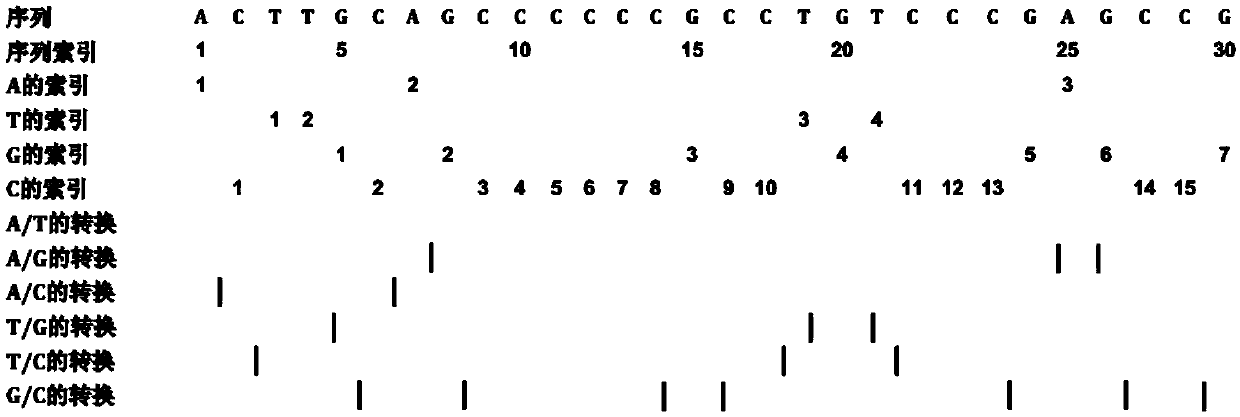
Method for predicting RNA coding potential
ActiveCN109599149AImprove accuracyReduce dependenceBioinformaticsInstrumentsFeature vectorSupport vector machine
The invention belongs to the field of gene annotation and in particular relates to a method for predicting RNA coding potential. The method (named as CPPred) comprises the following steps: by integrating multiple sequence characteristics, particularly describing global distribution of RNA by using CTD; taking redundancy and relevance among candidate characteristics as standards, and combining a characteristic increasing selection method to select an optimum characteristic set to serve as a characteristic vector; establishing a prediction model by a support vector machine (SVM); finally, acquiring the prediction result according to a to-be-predicted RNA sequence characteristic vector. The prediction method provided by the invention is equivalent to a current existing method (having accuracyreaching 90% or higher) while predicting a long RNA sequence, while the method is obviously better than the current existing method while predicting a short RNA sequence.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
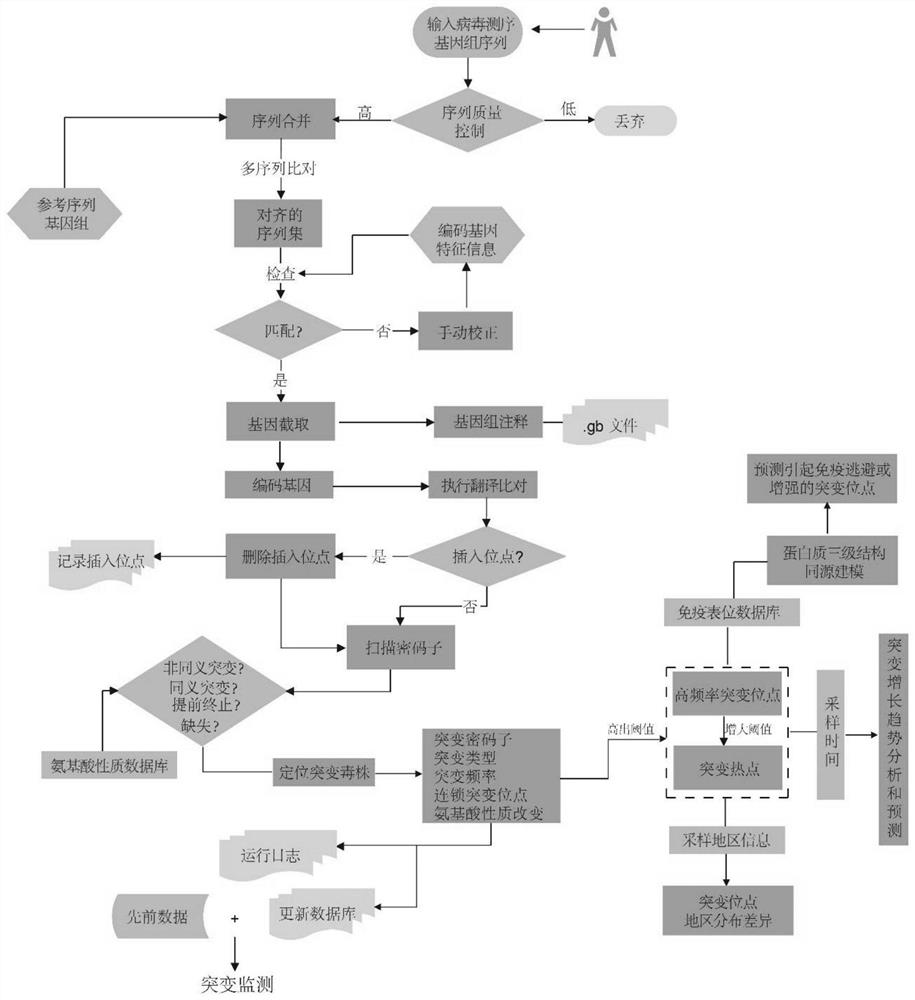
Method and system for analyzing and monitoring viral genome variation
ActiveCN113593639AQuick Batch AnnotationRealize analysisBiostatisticsProteomicsVirus strainBiomedicine
The invention belongs to the field of bioinformatics and biomedicine, and particularly relates to a method and a system for analyzing and monitoring viral genome variation. According to the method, after sequence comparison, whole-gene annotation is carried out to obtain coding gene information, translation comparison is carried out, mutation types are analyzed according to a genetic codon table, mutation sites, types and frequencies of genomes are obtained, high-frequency mutation sites are counted, virus strains at different times and in different areas are collected, and the distribution characteristics of the high-frequency mutation sites in time and regions are analyzed, and the high-frequency mutation sites located at the immune epitopes and nearby the immune epitopes are screened so as to realize virus genome variation analysis and monitoring.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Virus integrated DNA enrichment method, sequencing data analyzing method and device
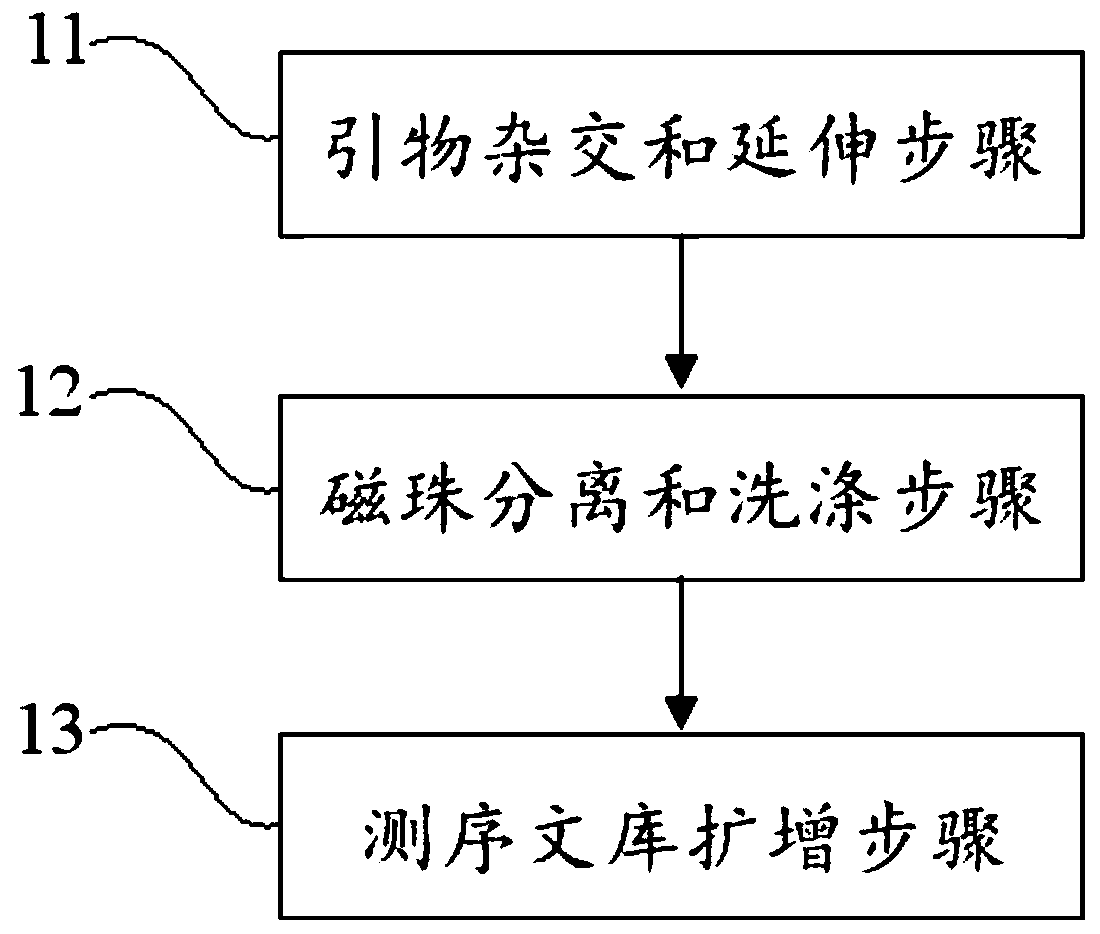
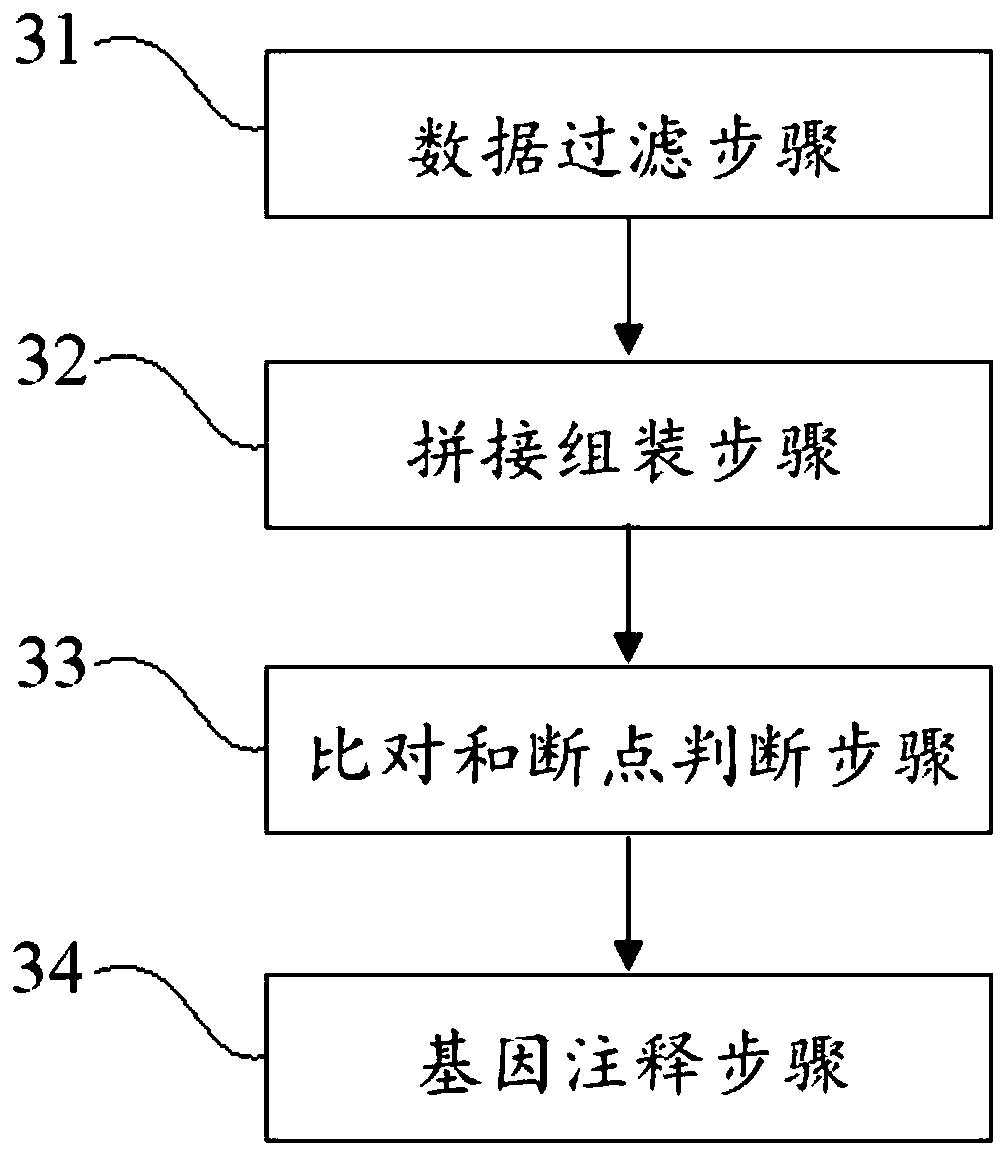
PendingCN110273028AReduce data volumeIncreased sequencing depthMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMagnetic beadEnrichment methods
The application discloses a virus integrated DNA enrichment method, a sequencing data analyzing method and a device. The enrichment method of the application comprises the steps of primer hybridizing and extending, magnetic bead separating and washing. The sequencing data analyzing method disclosed by the application comprises the steps of data filtering, splicing and assembling, comparing and breakpoint judging and gene noting. According to the enrichment method disclosed by the application, specific primers are adopted for extending virus genome target genes so as to replace a long probe, so that the cost is low, the efficiency is high, the specificity is high, and the enrichment time is shortened. Compared with a complete genome, the sequencing data analyzing method disclosed by the application can save data amount, can obtain higher sequencing depth, can obtain more virus DNA breakpoint information and integration position information on the host genome, and can obtain clonal integration events supported by more reads, and besides, can detect non-clonal integration supported by single reads, so as to construct a comprehensive prospect integrated on the host genome.
Owner:SHENZHEN HAPLOX BIOTECH
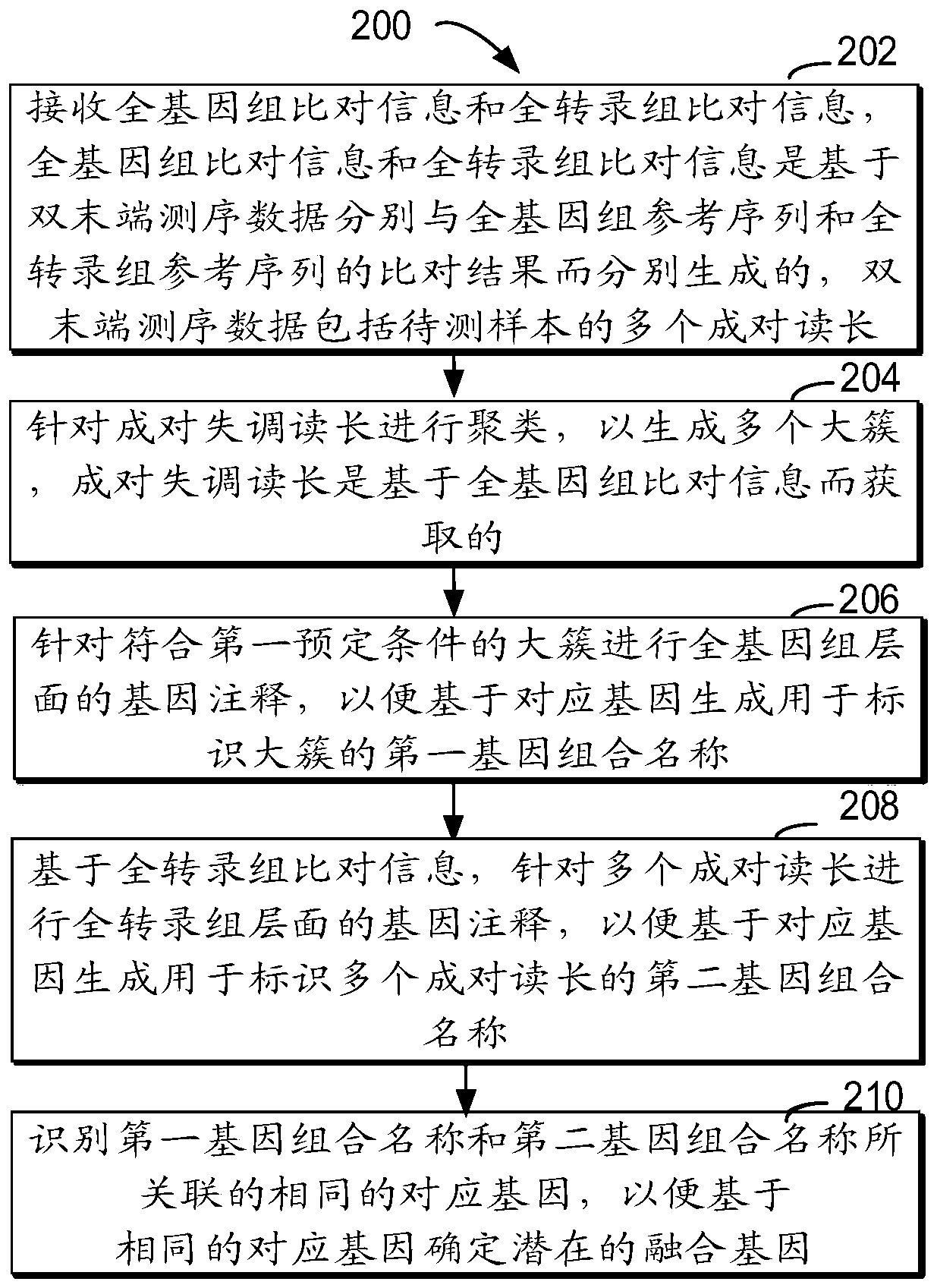
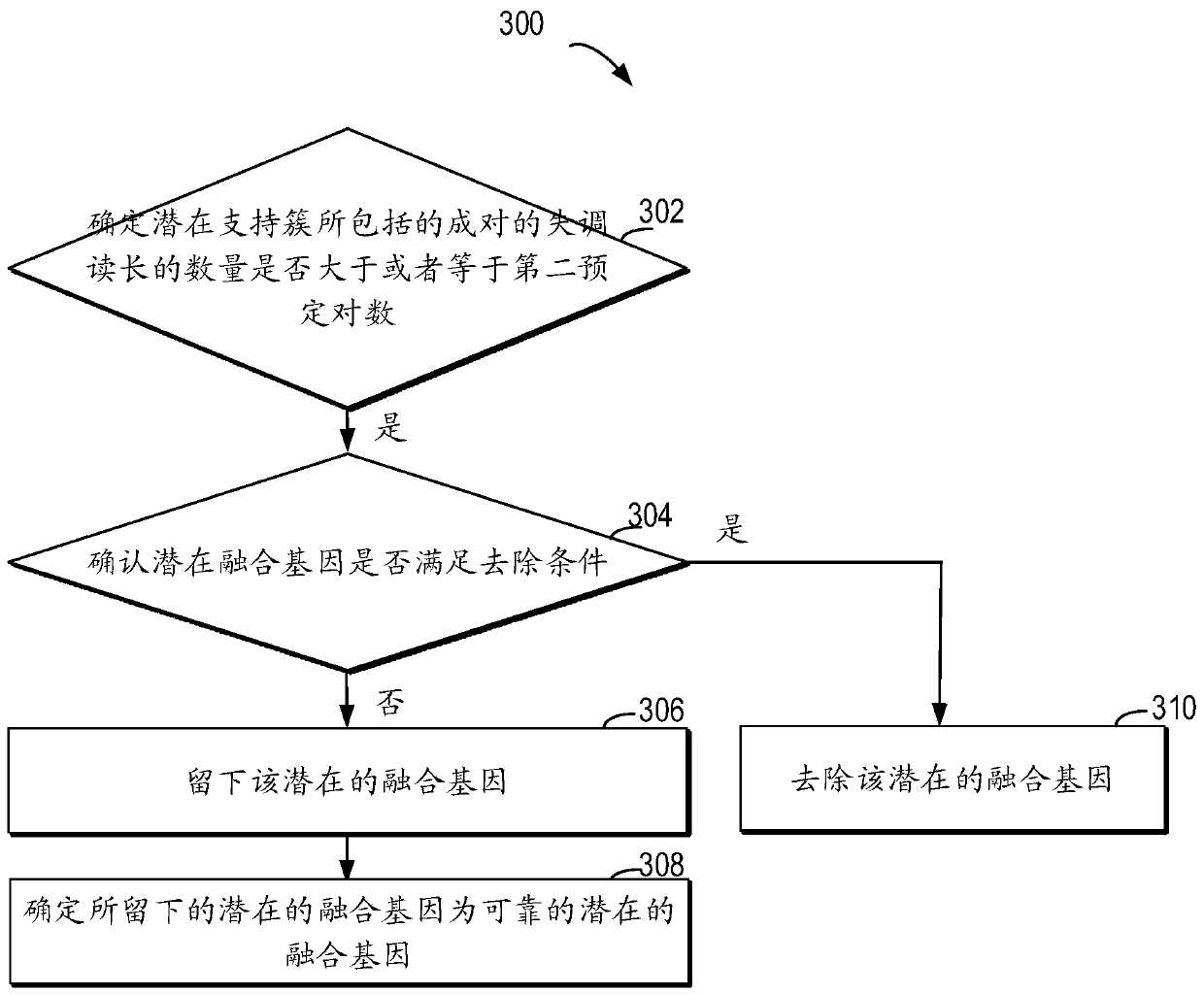
Method for detecting RNA level gene fusion, electronic device, and computer storage medium
ActiveCN111292809AQuick and correct identificationBiostatisticsProteomicsGenome alignmentGene Annotation
The invention relates to a method for detecting RNA level gene fusion, electronic equipment and a computer storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: receiving whole genome comparison information and whole transcriptome comparison information; clustering the paired maladjusted read lengths to generate a plurality of large clusters; carrying out whole-genome-level gene annotation onthe large clusters meeting a first preset condition so as to generate first gene combination names for identifying the large clusters based on the corresponding genes; based on the whole transcriptomecomparison information, performing whole transcriptome-level gene annotation on the plurality of paired read lengths so as to generate a second gene combination name for identifying the plurality ofpaired read lengths based on the corresponding gene; and identifying the same corresponding genes associated with the first gene combination name and the second gene combination name so as to determine the same corresponding genes as potential fusion genes. The method is beneficial to rapid and correct recognition of false positive results, and the false positive results of a gene fusion detectionresult can be obviously reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI ORIGIMED CO LTD +1
Construction method and system of microbial gene database
ActiveCN114121167AQuick searchQualitatively accurateBioinformaticsInstrumentsGenetic DatabasesGenomic data
Owner:SHENZHEN AIMIGENE TECH CO LTD
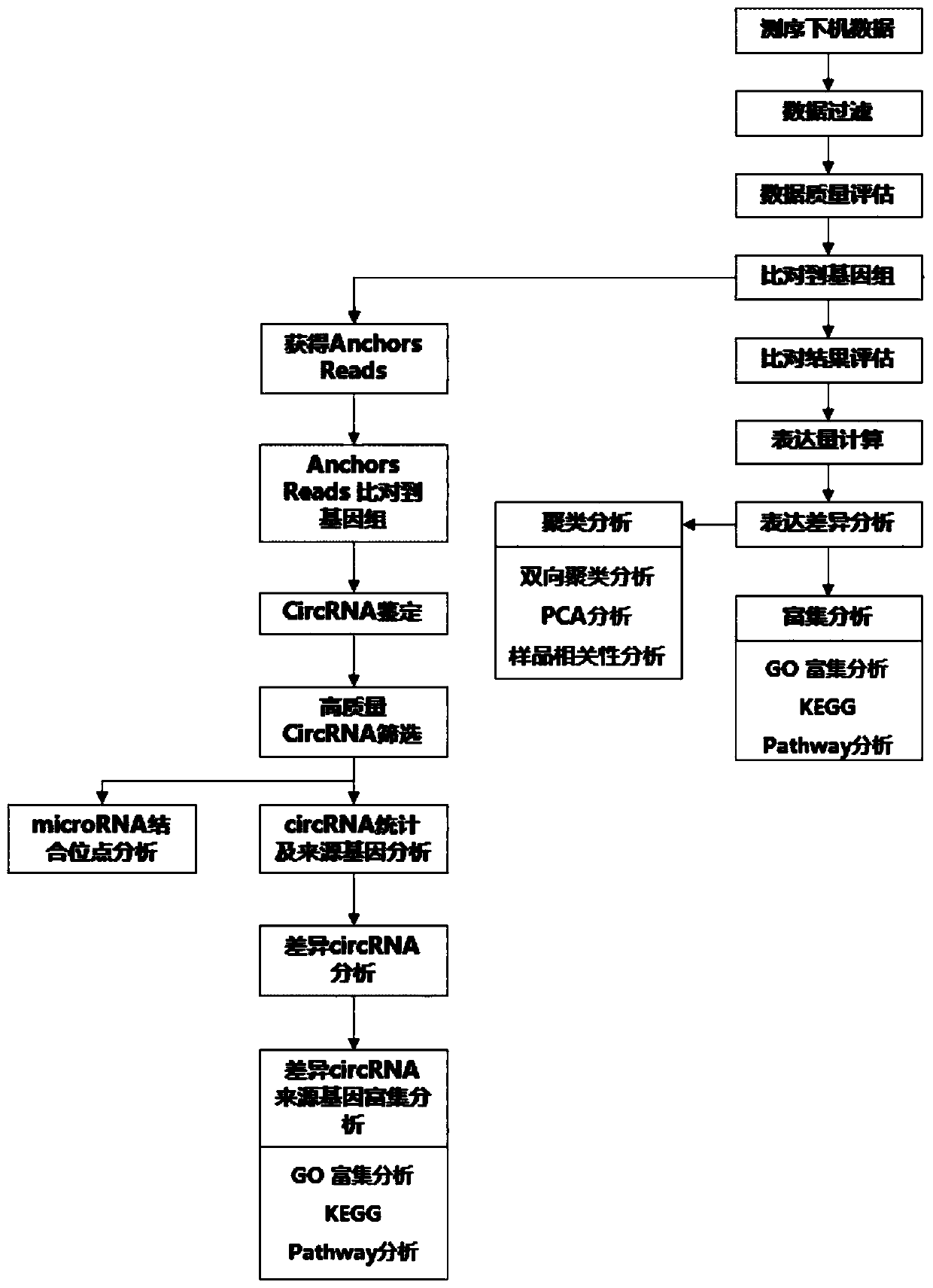
Circular RNA identification and expression quantification analysis method
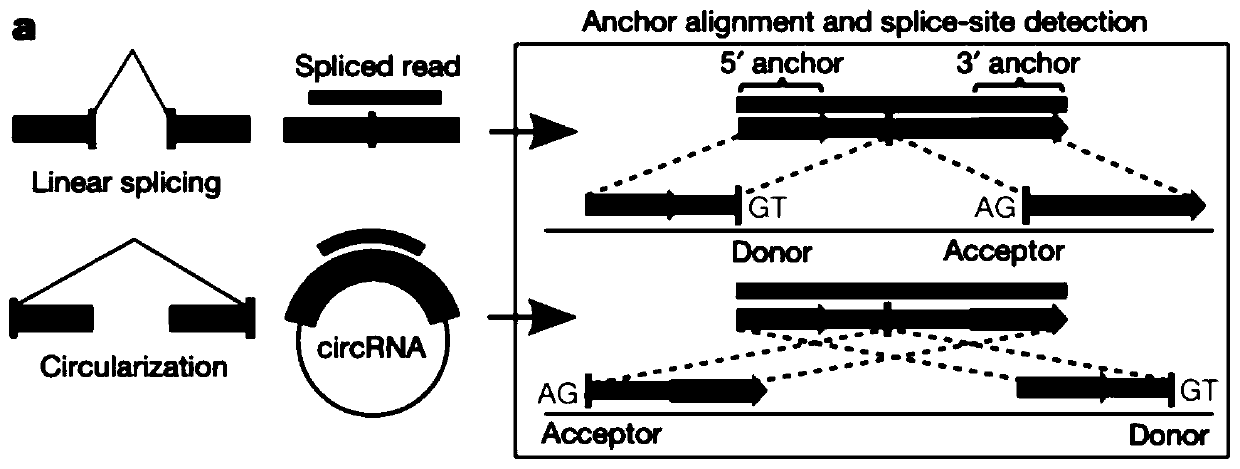
The invention discloses a circular RNA identification and expression quantification analysis method, which is characterized by comprising a series of a sequencing data filtering step, a sequencing data comparison step, a circular RNA connection point identification step, a difference analysis step, a gene annotation step and an enrichment analysis step. The analysis method provided by the invention can help to discover new circRNA information, and further performs circular RNA identification and expression quantitative analysis.
Owner:SHANGHAI PASSION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for identifying esophageal squamous cell carcinoma markers on basis of network index difference analysis
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioinformatics, and relates to a method for identifying esophageal squamous cell carcinoma markers on the basis of network index difference analysis. The method comprises the following steps of processing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma gene sample data and normal gene sample data to construct an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma gene interactionnetwork and a normal gene interaction network; using a network module identification method to find out key community structures in the two networks, and performing gene function enrichment analysison the key community structures; extracting same nodes from the two networks, and retaining nodes linked to the same nodes to obtain the two simplified networks; using a global index and a local modular index, analyzing the two simplified networks to obtain genes related to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; combining a gene function enrichment analysis result with gene annotations and functionalreferences to finally determine candidate markers for diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. A method for studying the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma markers on the basis of gene network difference analysis is further perfected.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Computation method for annotating semantic similarity by gene
InactiveCN101359349AHelpful for evaluationEasy constructionSpecial data processing applicationsGene ontologyGene Annotation
The invention provides a computation method of gene annotation semantic similarity. The method establishes correlation between the gene and the gene body node through the gene body correlation file provided by the gene body association; then the semantic similarity of the gene body node is firstly computed; the gene annotation semantic similarity is computed finally according to the semantic similarity of the gene body node. The computation method has the advantages of computing the gene annotation semantic similarity automatically and in large quantity.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Molecular marker coseparated from soybean epidemic disease resisting gene RpsZS18, and application thereof
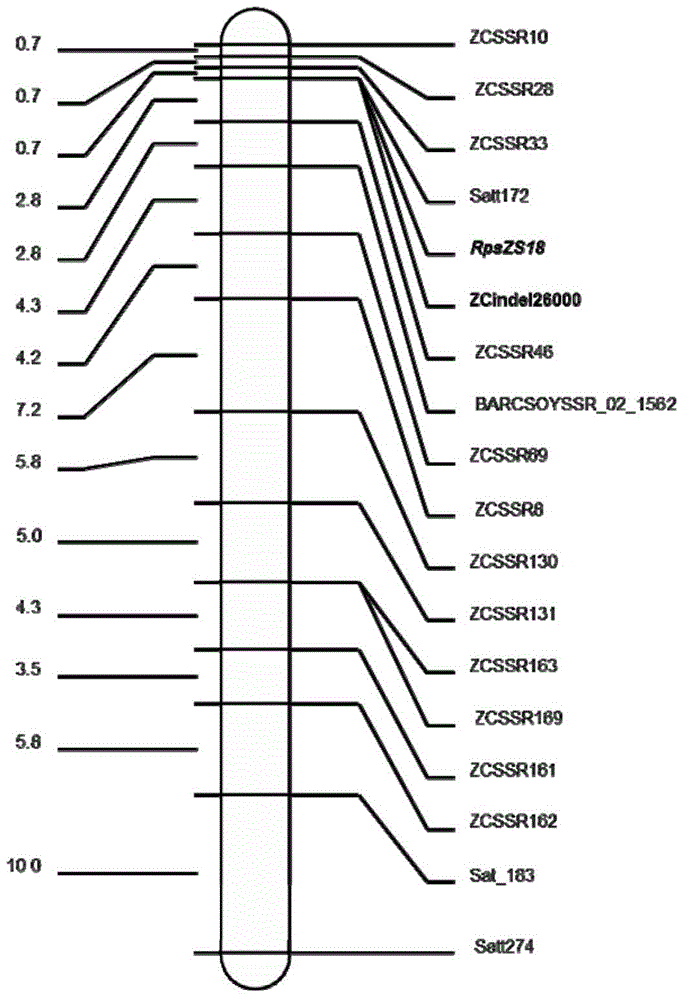
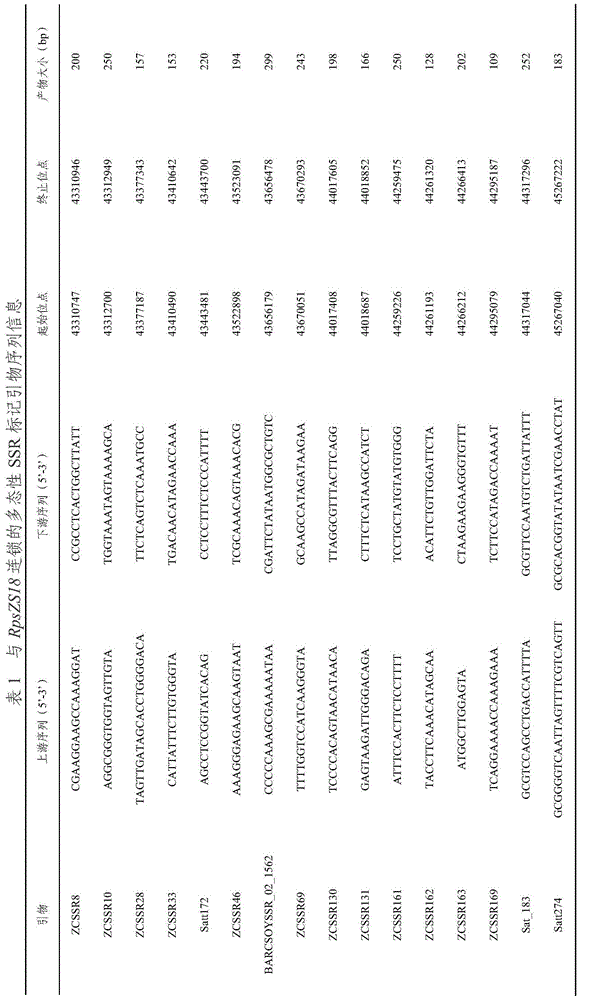
InactiveCN105462963AReduce yield lossClear structural featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCandidate Gene Association StudyGenome
The invention provides a molecular marker ZCindel246000 coseparated from a soybean epidemic disease resisting gene RpsZS18, and an application thereof. The marker is positioned between the SSR markers ZCSSR33 and ZCSSR46 of a soybean No.2 chromosome, and has a genetic distance of 0cM to the gene RpsZS18. A new SSR marker is exploited by using a soybean SSR marker in an interval and using a soybean genome sequence according to a preliminary positioning result with an F3 column generated through hybridizing and selfing disease resisting variety Zaoshu 18 used as a male parent and a susceptible variety Williams used as a female parent as a mapping colony, and a disease resisting gene contained in the Zaoshu 18 is finely positioned. The disease resisting gene RpsZS18 is positioned between the ZCSSR33 (0.7cM) and ZCSSR46 (2.8cM) of the No.2 chromosome, and is coseparated from an SSR marker Satt172. An RpsZS18 candidate gene is predicated according to gene note in the new positioning interval, the Indel marker ZCindel24600 is exploited according to the candidate gene site sequence difference predicated by resistant and susceptible parents, a colony verification result shows that the marker is a coseparated marker, and the Indel marker can be used in auxiliary breeding of soybean epidemic disease resistance.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
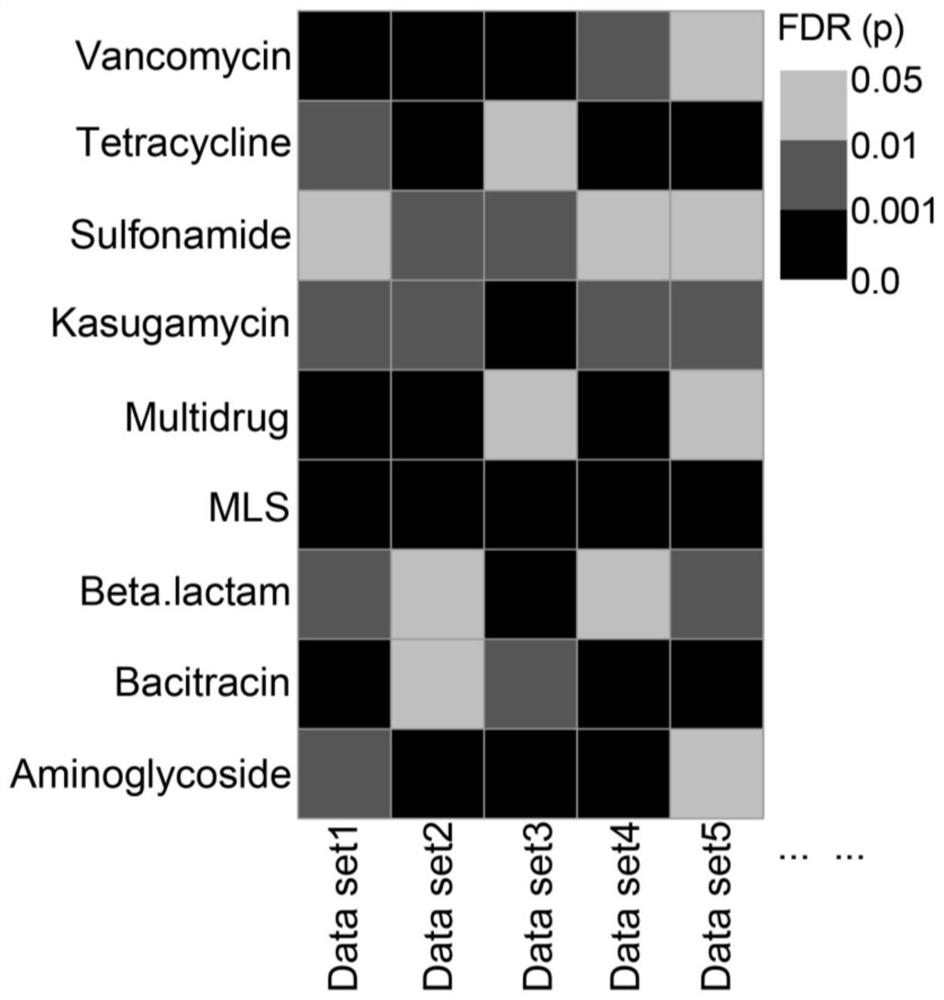
Antibiotic drug resistance gene influence factor and difference analysis method
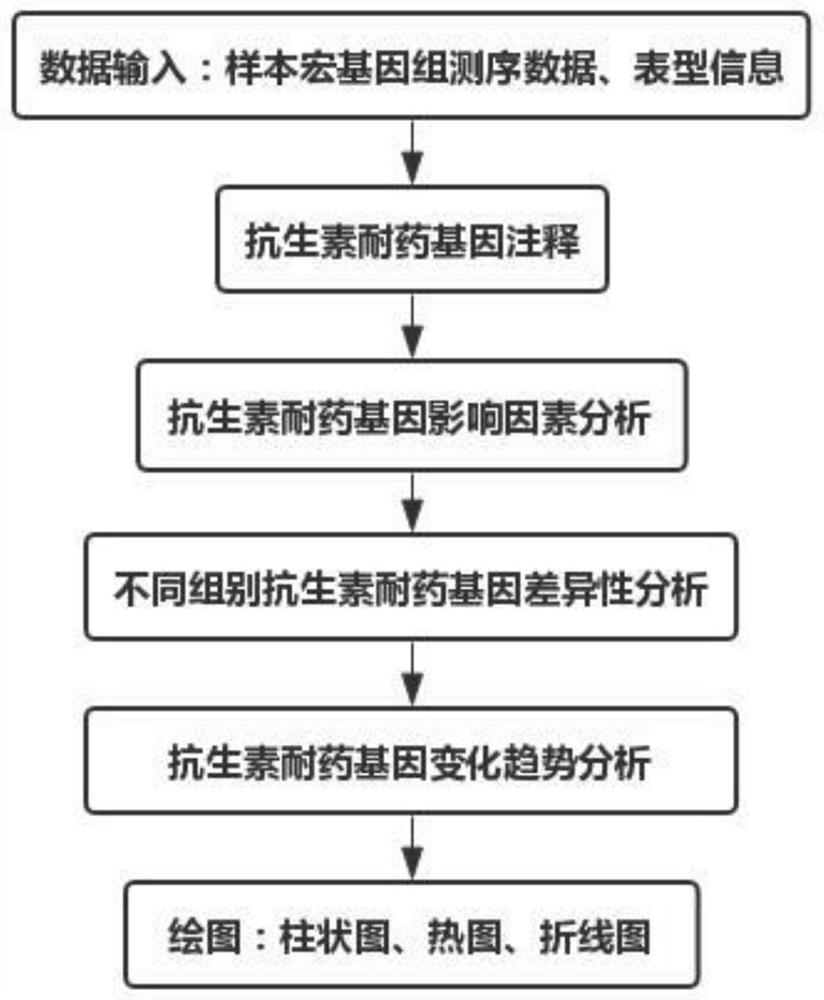
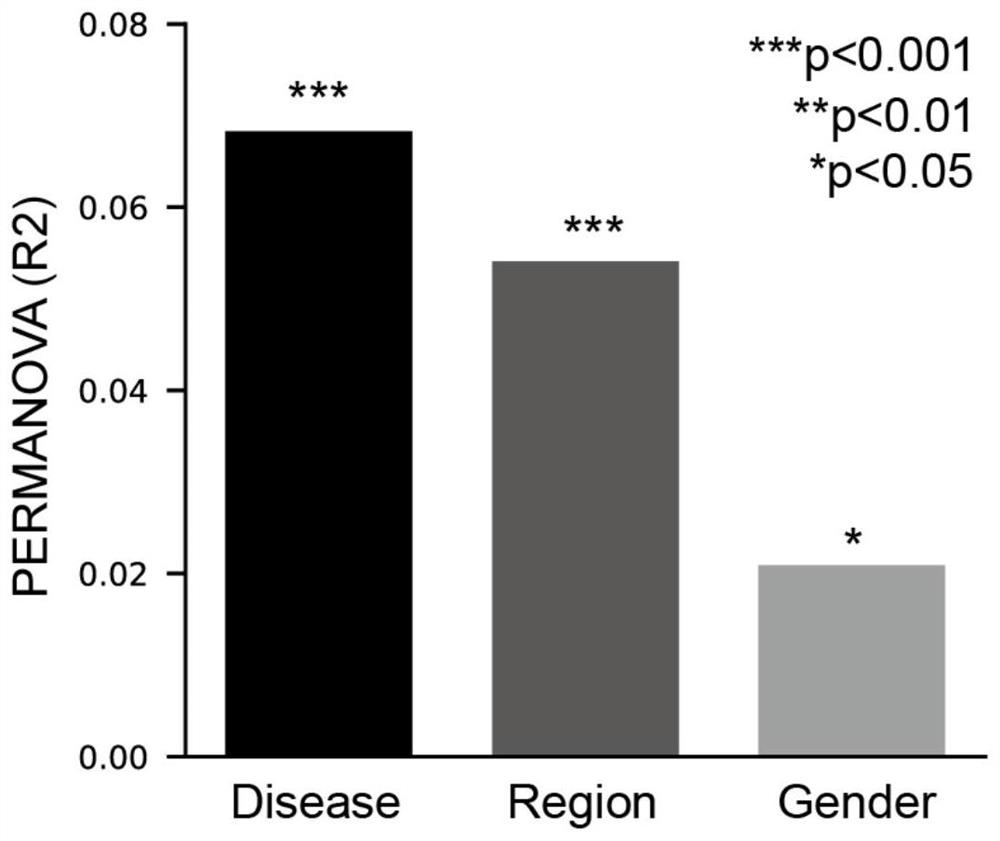
PendingCN112802552AReliable analysisImprove reliabilityDrug referencesSequence analysisData setResistant genes
The invention discloses an antibiotic drug resistance gene influence factor and difference analysis method. The method comprises the following steps: inputting sample metagenome data and phenotype information of a corresponding sample; annotating the antibiotic drug-resistant gene to obtain an antibiotic drug-resistant gene abundance file; performing antibiotic drug resistance gene influence factor analysis: performing PERMANOVA analysis to obtain a phenotype which has obvious influence on the antibiotic drug resistance gene; carrying out antibiotic drug resistance gene difference analysis: carrying out two-group mean value comparison by utilizing Wilcoxon test and FDR correction, and carrying out more than two-group mean value comparison by utilizing Kruscal-Wallis test, multiple comparison in a PMCMR packet and FDR correction; and judging the change trend of the content of the antibiotic resistance gene. The antibiotic reference database is better adapted to increase of antibiotic resistance sequences, and the multi-module combinatorial analysis method enables analysis of antibiotic resistance genes to be more comprehensive and systematic; and meanwhile, a data set splitting and recombining method is used for obtaining an intersection of multi-data-set analysis results, so that the reliability of the results is improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Gene alternative splicing analysis method
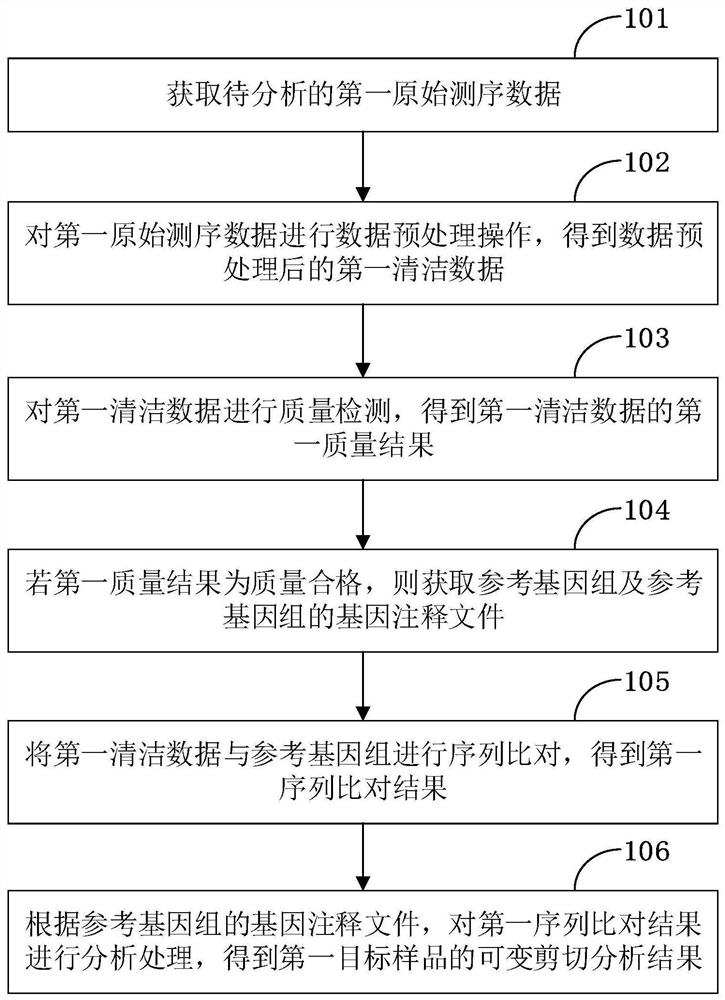
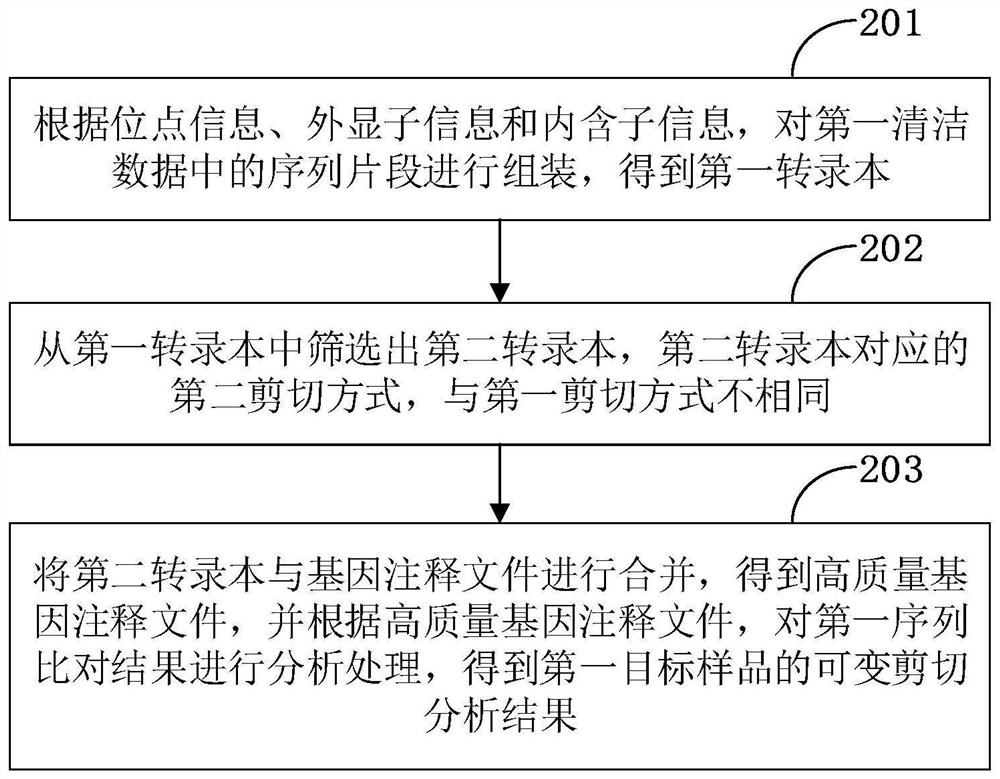
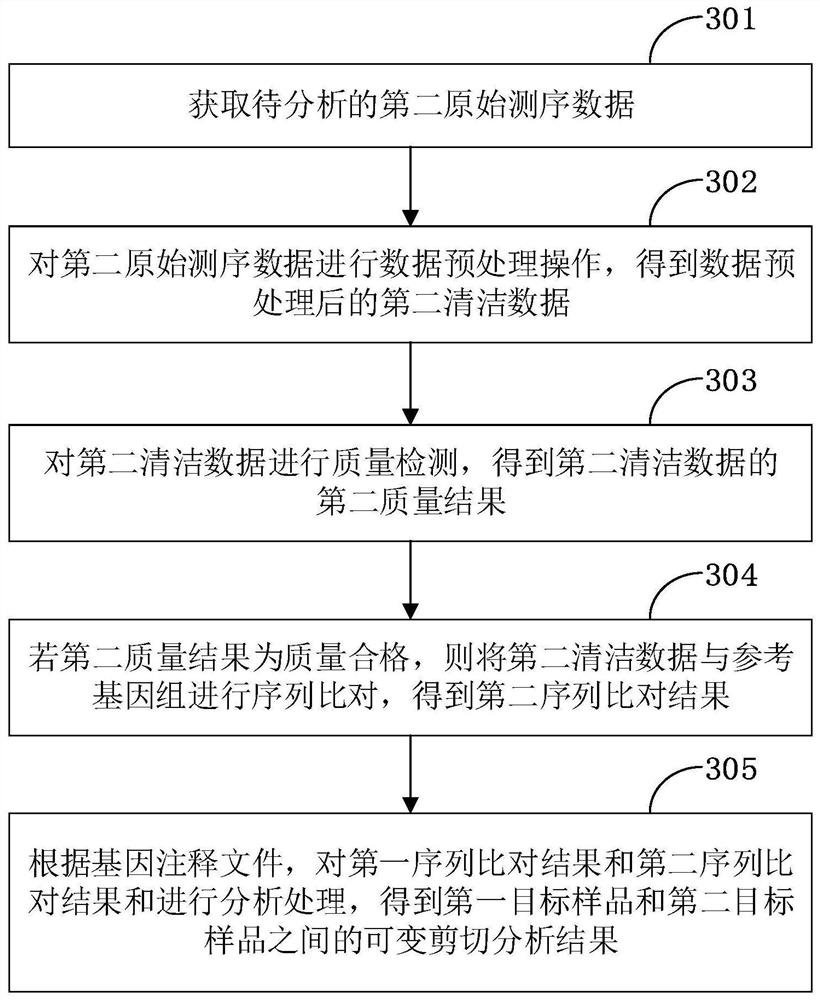
The invention is applicable to the technical field of biological information, and provides a gene alternative splicing analysis method. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring first original sequencing data to be analyzed; performing data preprocessing operation on the first original sequencing data to obtain first clean data after data preprocessing; performing quality detection on the first cleaning data, and if the first quality result is that the quality is qualified, obtaining a reference genome and a gene annotation file of the reference genome; performing sequence alignmenton the first cleaning data and the reference genome to obtain a first sequence alignment result; and analyzing the first sequence comparison result according to the gene annotation file of the reference genome to obtain an alternative splicing analysis result of the first target sample. According to the embodiment of the invention, the analysis of the alternative splicing condition of a mature transcript and the analysis of the differential alternative splicing of the transcript under specific conditions are realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV +1
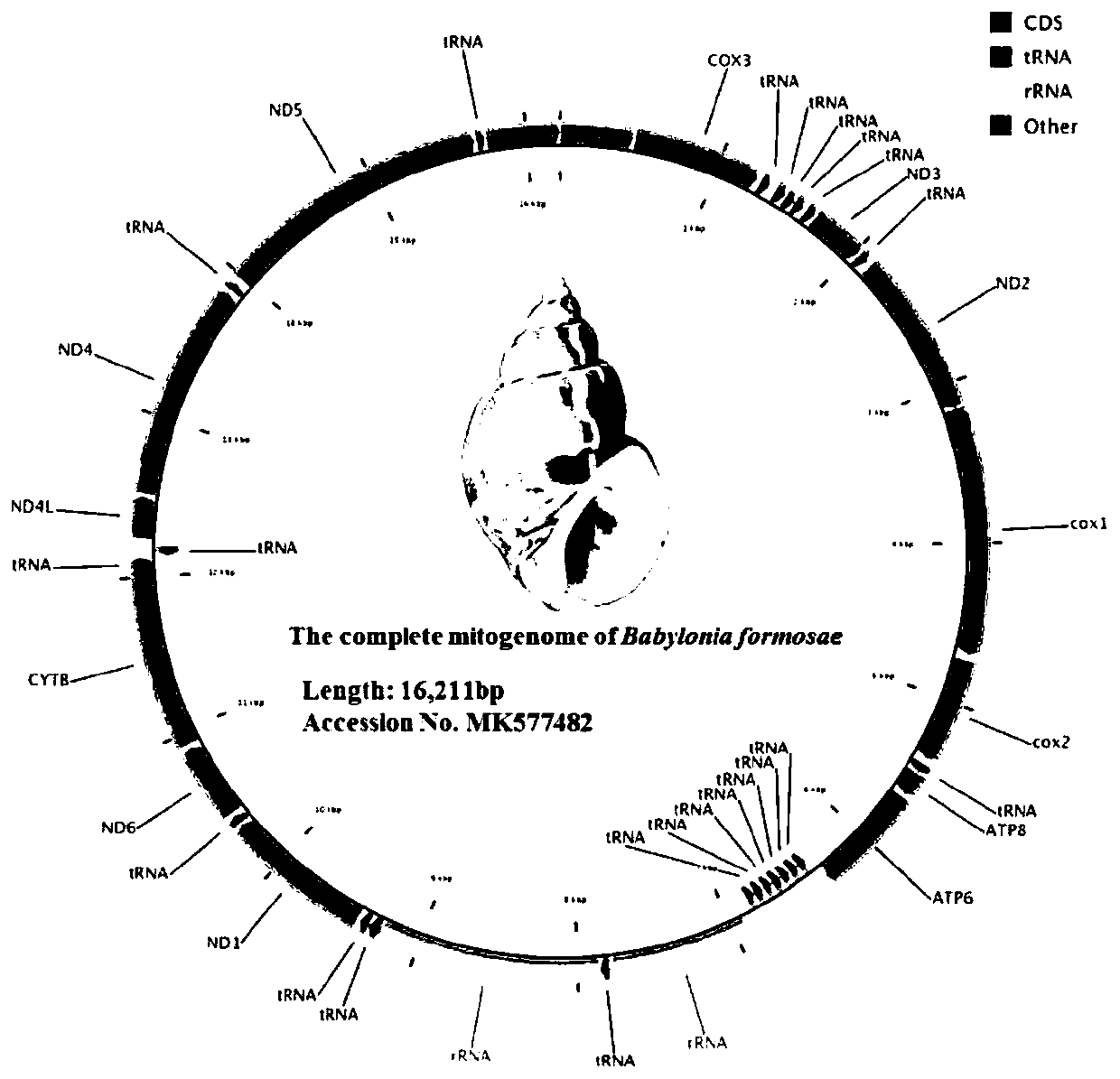
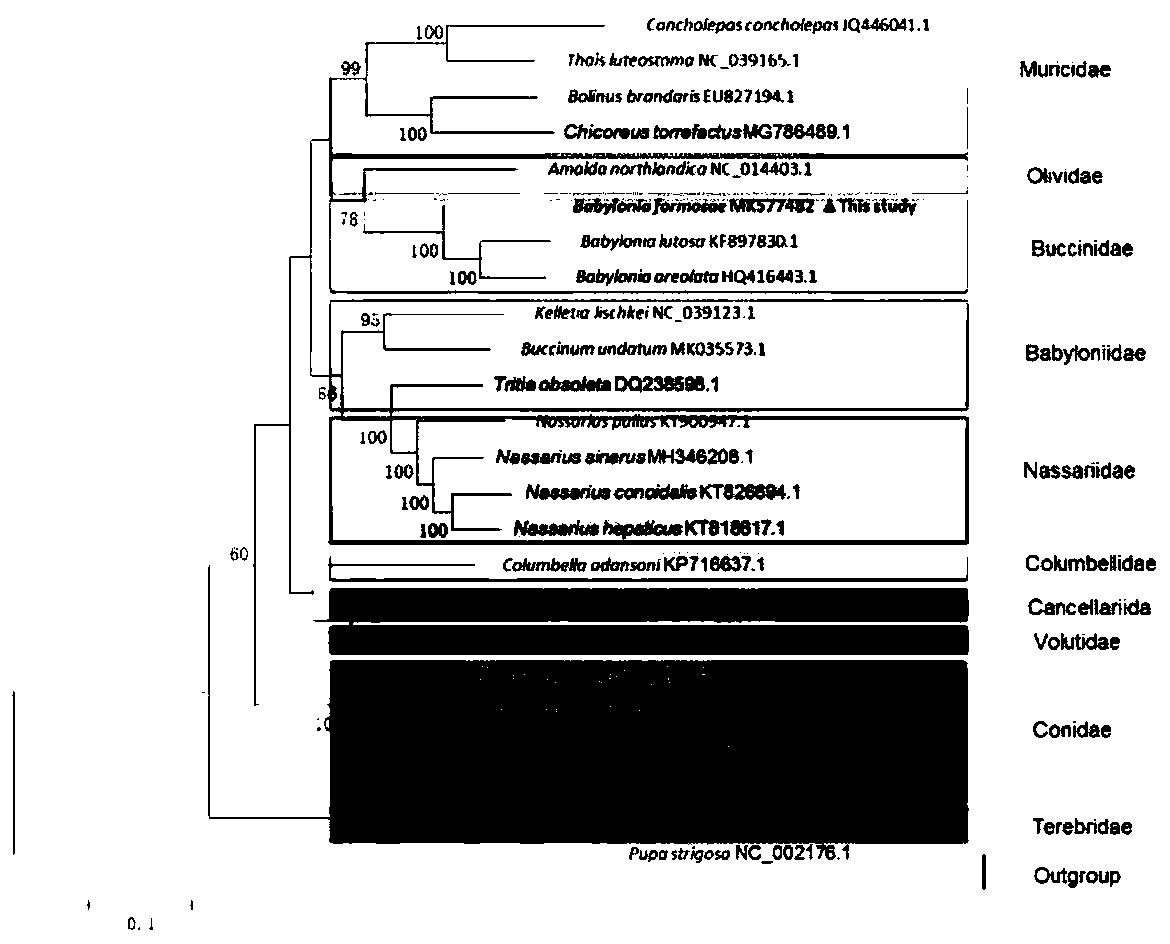
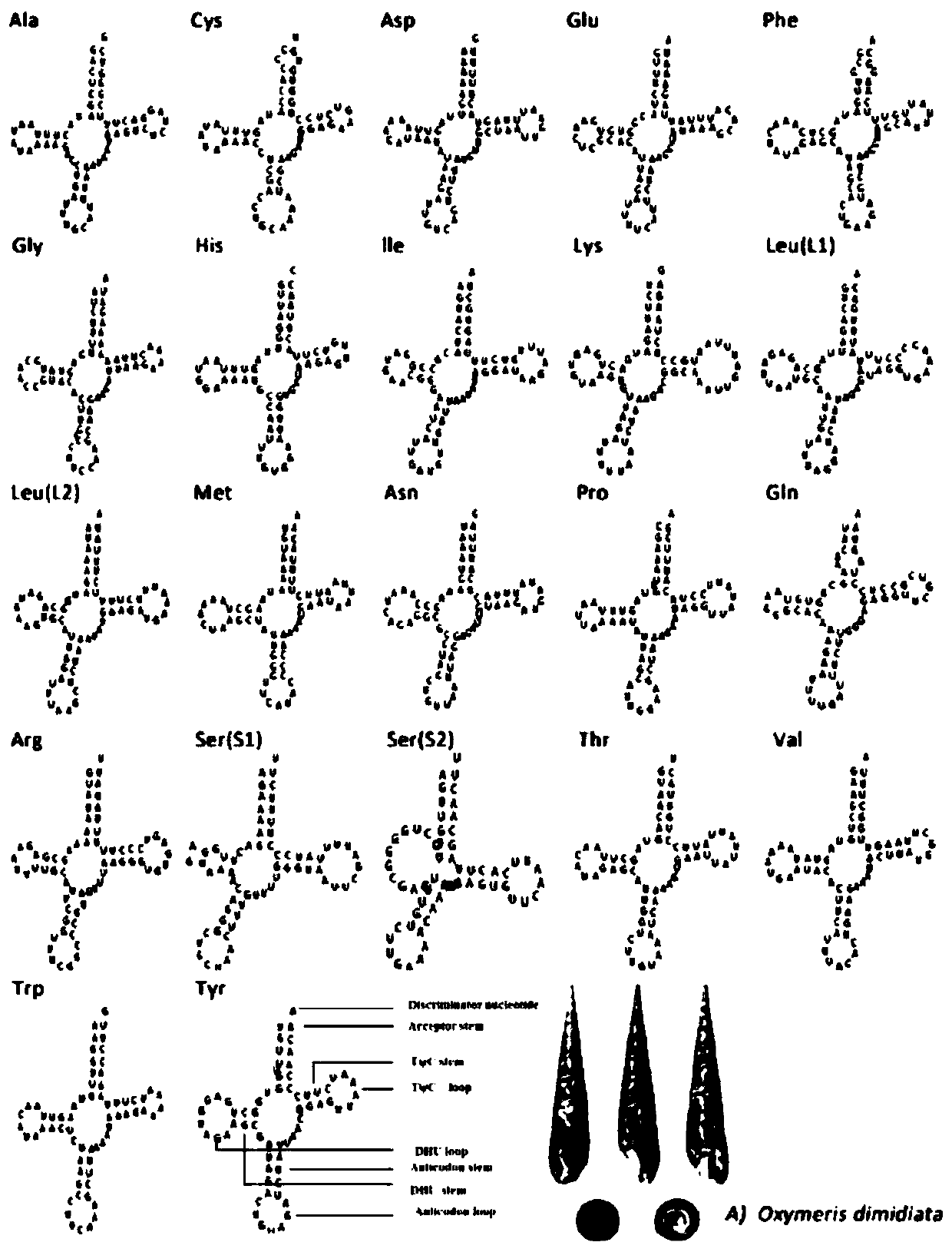
Method for analyzing phylogenetic development of babylonia formosae based on complete mitochondrial genomes
PendingCN110714063AFixedAnalysis is convenient and effectiveMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsNucleotideCaenogastropoda
The invention discloses a method for analyzing phylogenetic development of babylonia formosae based on complete mitochondrial genomes, and relates to the field of analysis of the phylogenetic development of the babylonia formosae. The method for analyzing phylogenetic development of the babylonia formosae based on the complete mitochondrial genomes comprises the following steps: 1) sample collection: collecting babylonia formosae extracting mitochondrial genomes DNA; 2), disrupting and purifying the mitochondrial genomes DNA and then building a DNA sequencing library; 3), obtaining a DNA cluster; 4), sequencing the babylonia formosae mitochondrial genomes DNA; 5), comparing the babylonia formosae mitochondrial genomes with other babylonias having known sequences, and then noting encoded protein genes; and 6), comparing a nucleotide sequence of each gene of the babylonia formosae extracting mitochondrial genomes DNA and an amino acid sequence deduced by the nucleotide sequence with other caenogastropoda species, and performing series connection and then analyzing the phylogenetic development. According to the phylogenetic analysis method of the babylonia formosae based on the complete mitochondrial genomes disclosed by the invention, based on the complete mitochondrial genomes, the phylogenetic development of the babylonia formosae is analyzed, complete data of the complete mitochondrial genomes of the babylonia formosae are obtained, and thus, phylogenetic development is performed, and analysis is performed conveniently and effectively.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
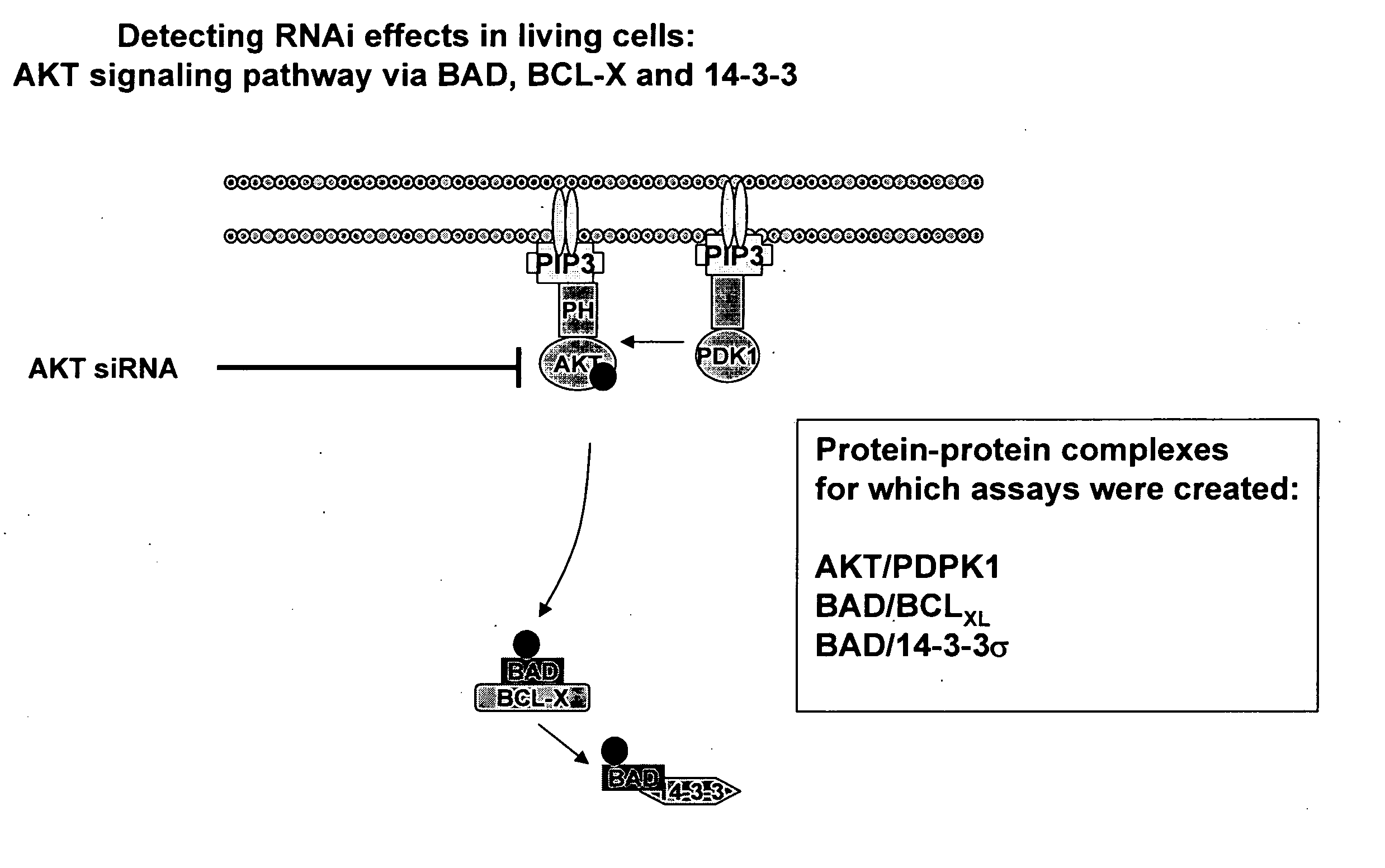
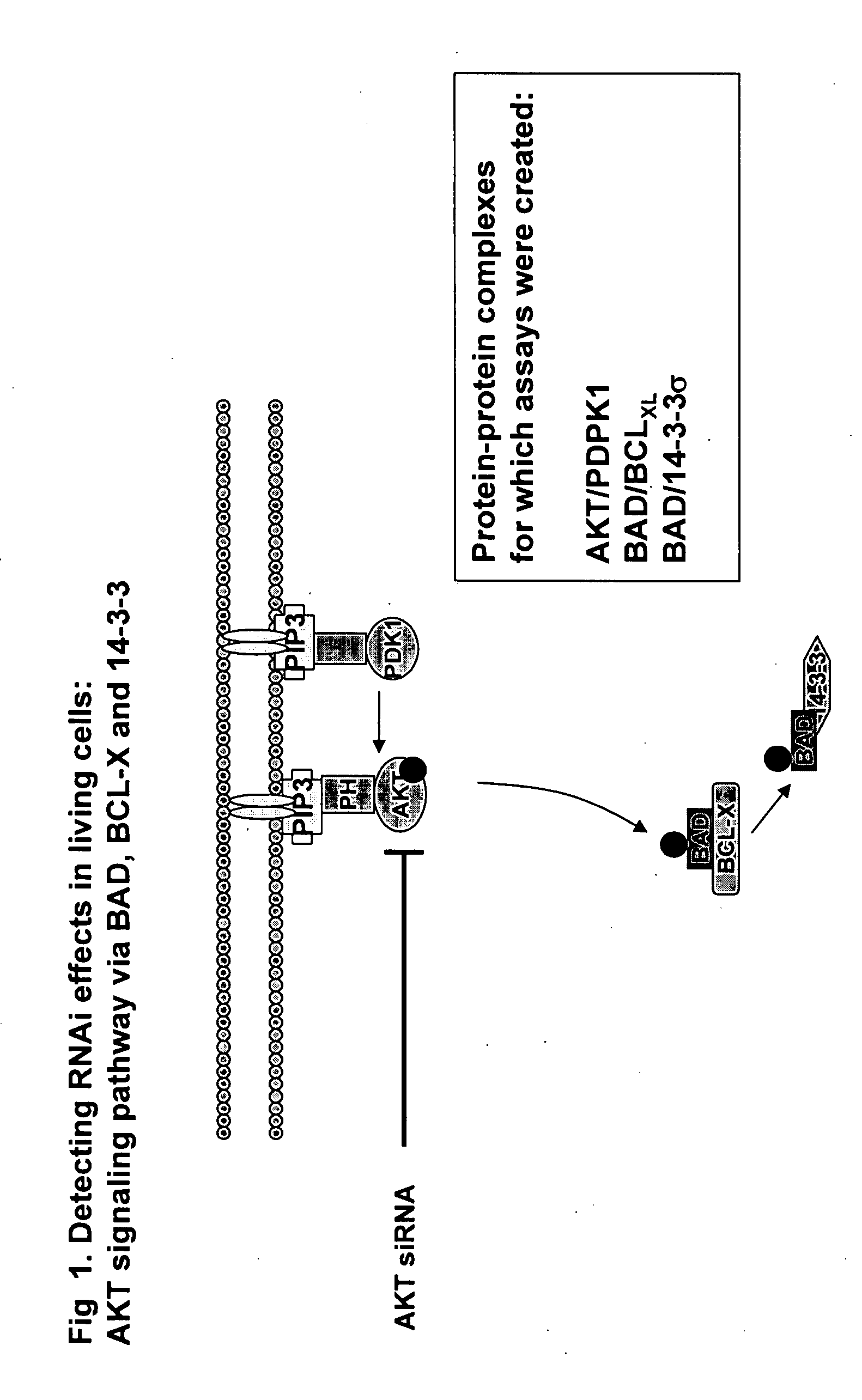
Monitoring gene silencing and annotating gene function in living cells
InactiveUS20080064040A1Direct effectSuitable for applicationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingFluorescenceProtein translocation
The cell-based assays described in the present invention can be used to directly assess the sensitivity and specificity of the gene annotation reagent against its target, and to determine if a non-targeted gene participates in a pathway of interest or is functionally linked to another gene or protein. The combination of annotation reagents with such cell-based assays is useful for mapping genes (proteins) into cellular pathways on a genome-wide scale. Preferred assay embodiments include fluorescence or luminescence assays in intact (live or fixed) cells. Such fluorescence or luminescence assays include high-throughput or high-content assays for protein activity, subcellular localization, post-translational modifications, or interactions of proteins. Suitable assays may include protein-protein interaction assays; protein translocation assays; and post-translational modification assays. The invention can be used to assess the efficacy of any gene silencing experiment, to determine the level of gene silencing that is achieved, and to map novel genes into biochemical pathways, and to identify novel pharmaceutical targets. The results also demonstrate the feasibility of employing this strategy in genome-wide functional annotation efforts.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Gene annotation method and system
ActiveCN101894211BHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsConserved sequenceGene Annotation
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
Development method of strawberry functional gene linked SSR marker
PendingCN112349347AHigh polymorphismCo-dominantMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsFragariaMicrosatellite
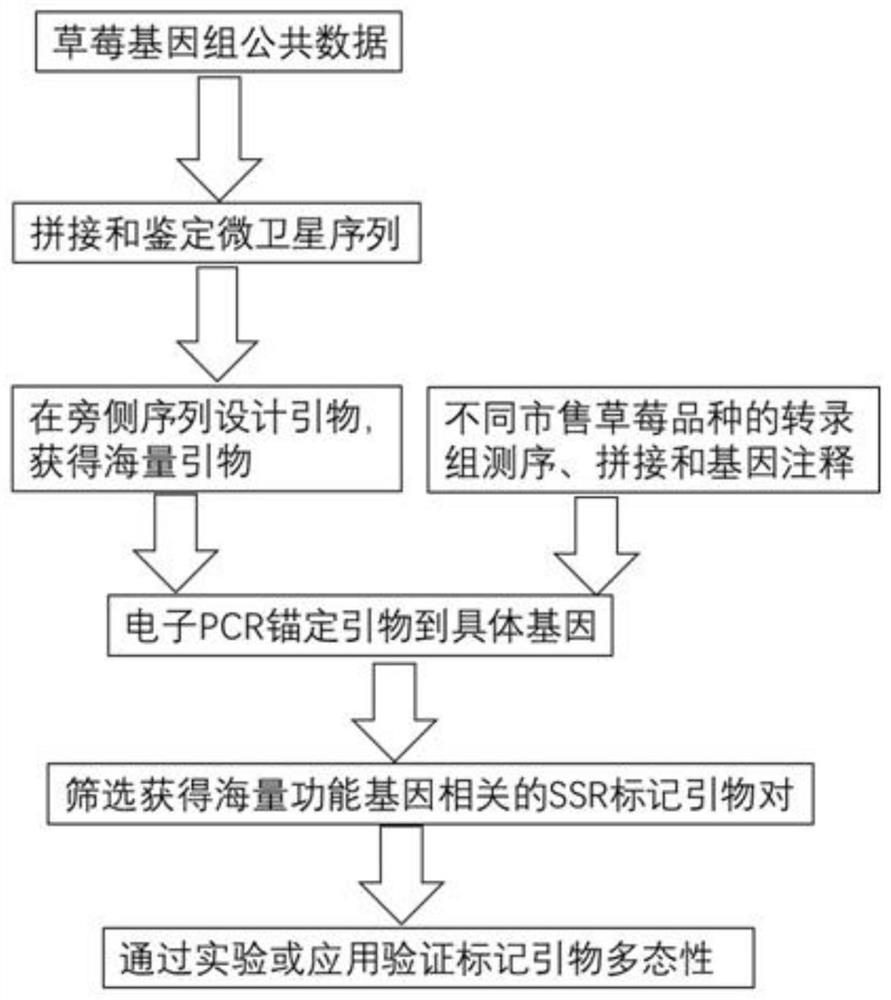
The invention discloses a development method of a strawberry functional gene linked SSR marker. The development method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring strawberry genome public data; (2) performing quality control processing on the data, assembling and splicing the processed sequences, and identifying a microsatellite sequence; (3) designing primers on a flanking sequence of the microsatellite sequence; (4) performing transcriptome sequencing, splicing and gene annotation of different strawberry varieties; and (5) carrying out electronic PCR anchoring on primers to specific genes.The SSR marker of the method has the advantages of high polymorphism, good codominance, good repeatability and the like. 2468 SSR markers and primers thereof are provided for strawberries, and the markers are all related to functional genes, so that a favorable tool is provided for strawberry breeding and gene mining related to agricultural traits.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE OF AGRI & FORESTRY
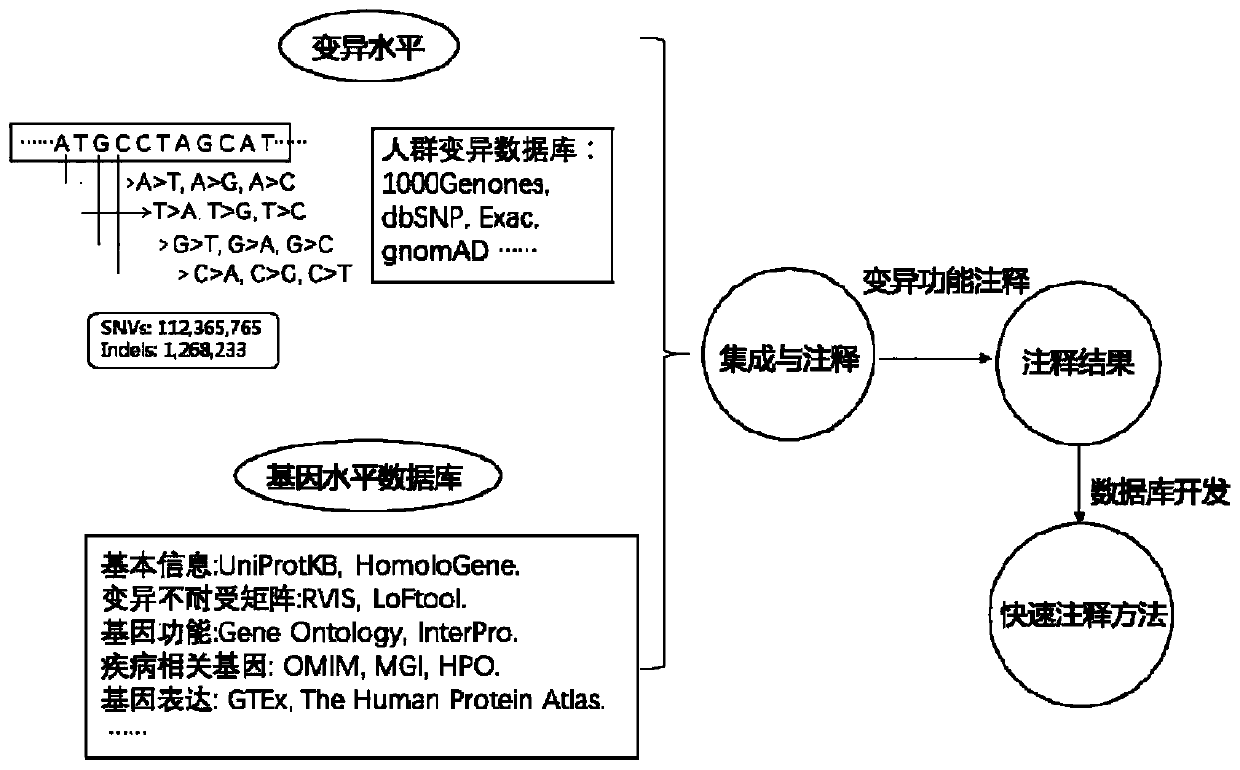
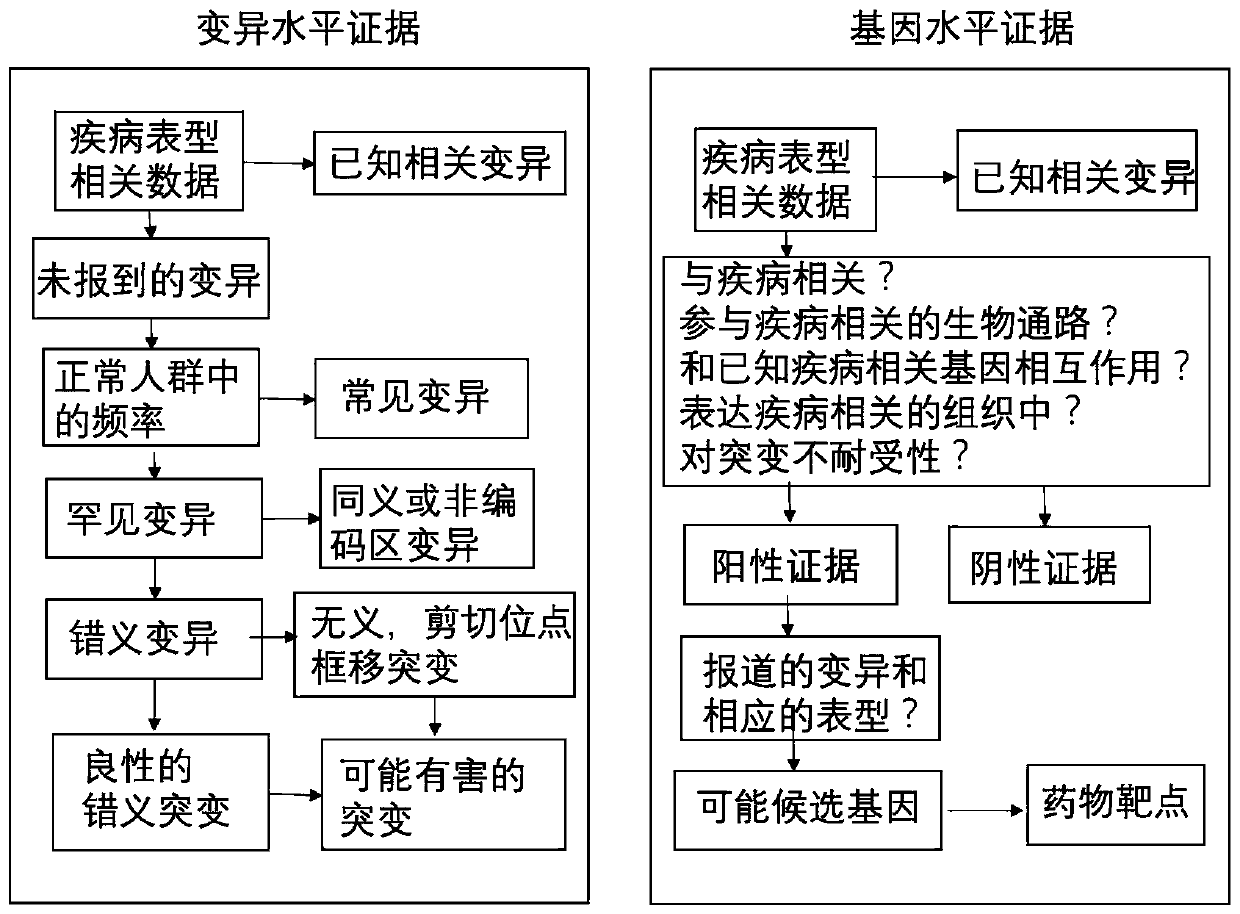
Method for quickly annotating gene mutations of human beings
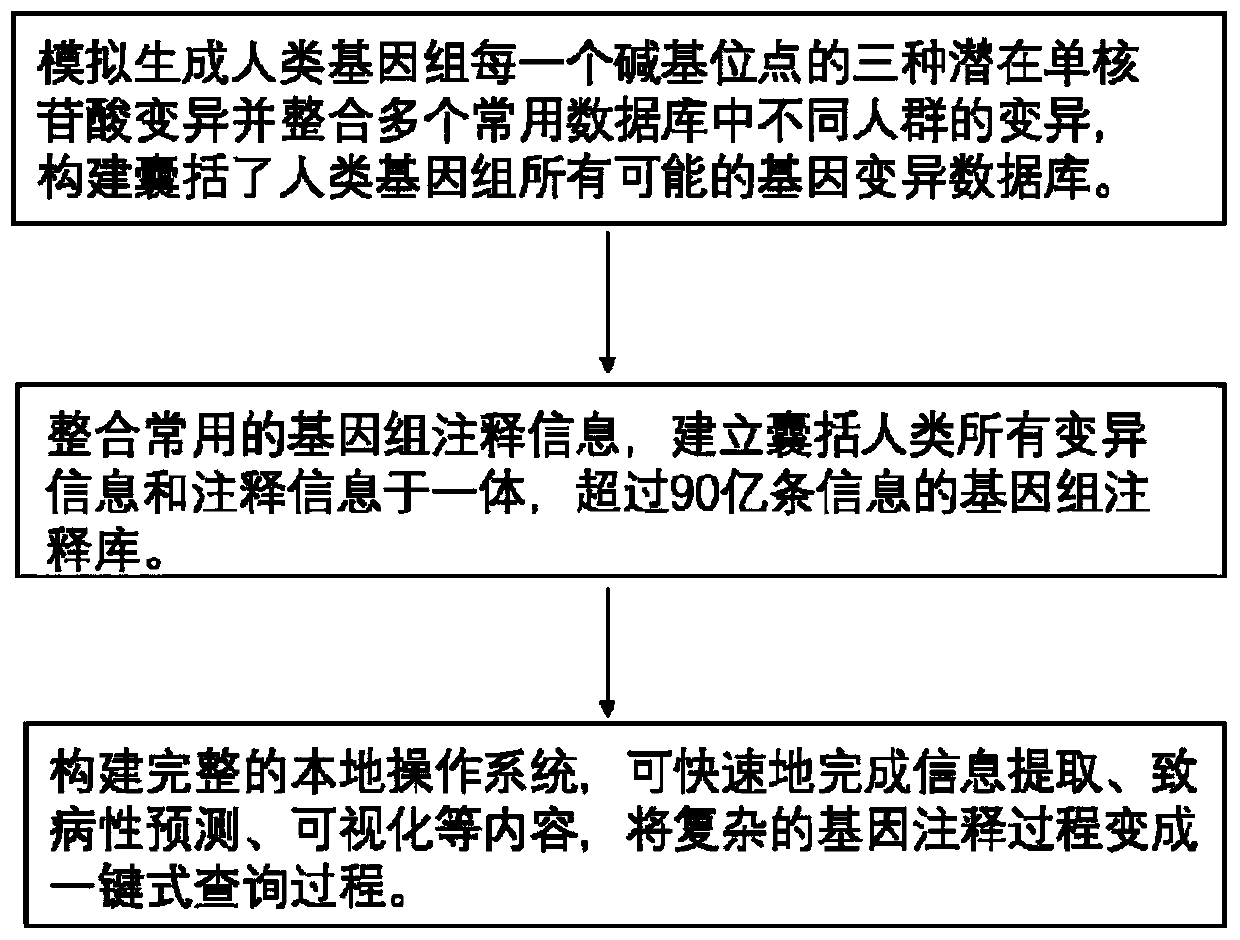
The invention is applicable to the technical field of medical genetics, and provides a novel method for quickly annotating genes and mutations by constructing an information query database with complete annotations. The method comprises the following steps: (1) simulating to generate three potential mononucleotide variations of each base site of a human genome, and integrating the variations of different populations in a plurality of common databases to construct a database including all possible gene variations of the human genome; (2) further integrating common genome annotation informationon the basis, and establishing a genome annotation library including all variation information and annotation information of human beings into a whole and more than 9 billion pieces of information; and (3) quickly completing information extraction, pathogenicity prediction, visualization and other content in a query mode according to the database. According to the method, a complex gene annotationprocess is changed into a one-stop query process, so that the problems of non-uniform formats, complicated operation and low efficiency caused by matching different gene variations in multiple databases one by one are avoided.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
Identification method of markers of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma based on difference analysis of network indicators
ActiveCN108108589BHigh precisionFill in the gaps in the analysisProteomicsGenomicsOncogeneCancer research
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioinformatics, and relates to a method for identifying esophageal squamous cell carcinoma markers on the basis of network index difference analysis. The method comprises the following steps of processing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma gene sample data and normal gene sample data to construct an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma gene interactionnetwork and a normal gene interaction network; using a network module identification method to find out key community structures in the two networks, and performing gene function enrichment analysison the key community structures; extracting same nodes from the two networks, and retaining nodes linked to the same nodes to obtain the two simplified networks; using a global index and a local modular index, analyzing the two simplified networks to obtain genes related to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; combining a gene function enrichment analysis result with gene annotations and functionalreferences to finally determine candidate markers for diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. A method for studying the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma markers on the basis of gene network difference analysis is further perfected.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Method and system for quickly comparing whole genome annotation intervals
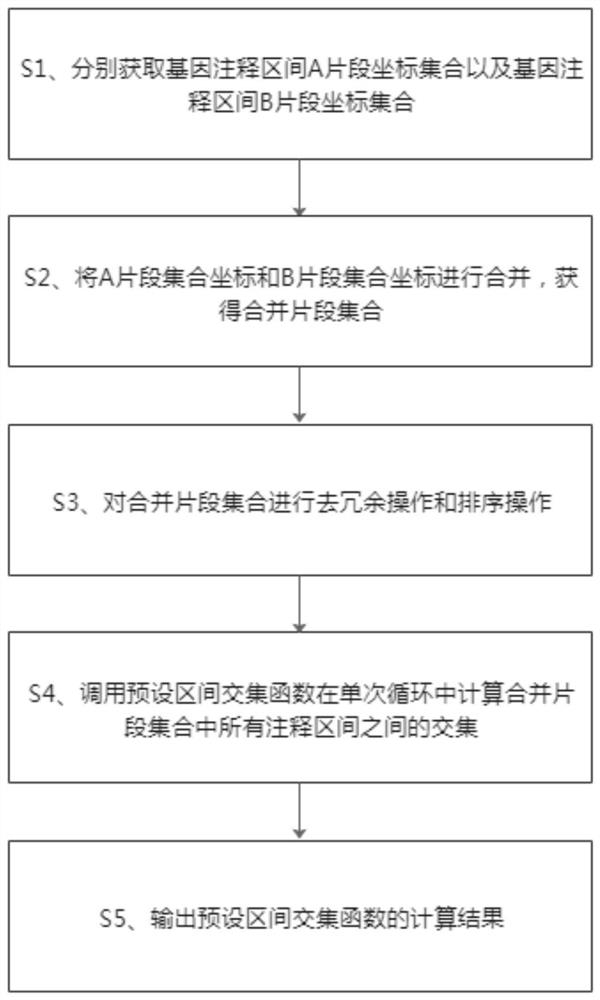
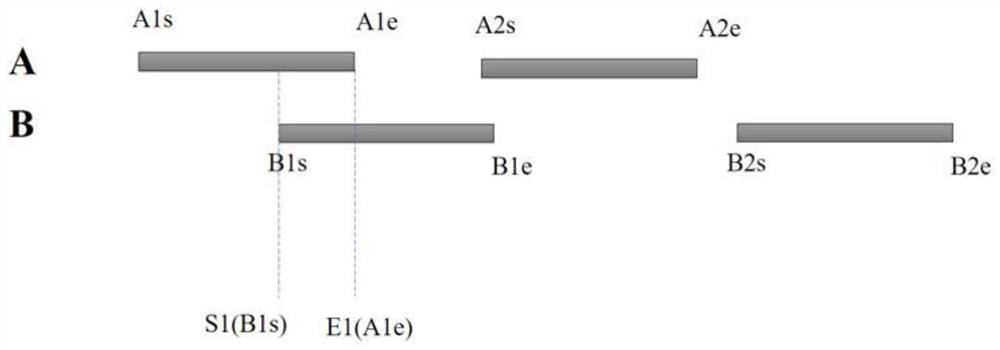
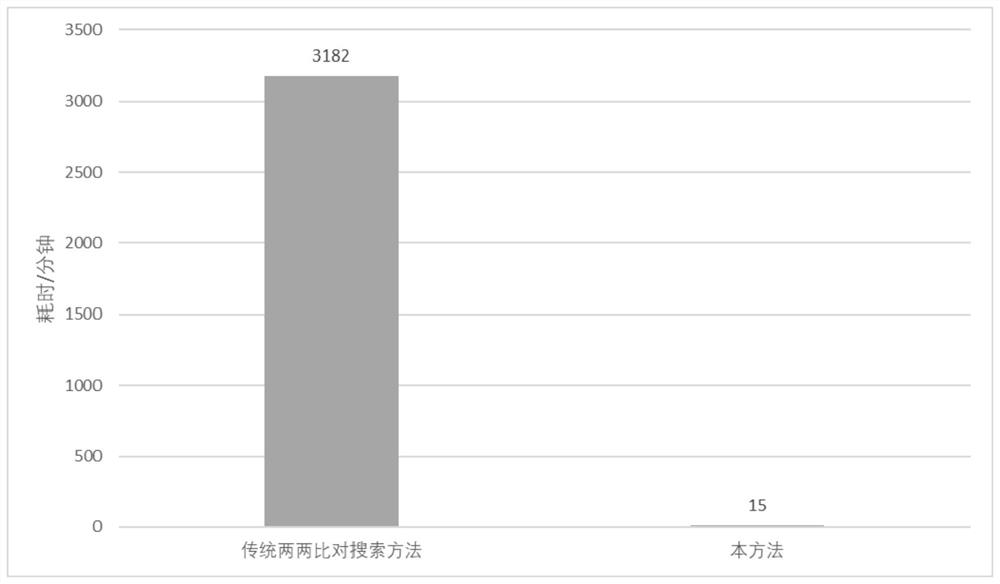
The invention provides a method and a system for quickly comparing whole genome annotation intervals. The method comprises the following steps: S1, respectively obtaining a gene annotation interval A fragment coordinate set and a gene annotation interval B fragment coordinate set; s2, combining the coordinates of the fragment set A and the coordinates of the fragment set B to obtain a combined fragment set; s3, performing redundancy elimination operation and sorting operation on the combined fragment set; s4, calling a preset interval intersection function to calculate the intersection of all the annotation intervals in the merged fragment set in a single cycle; and S5, outputting a calculation result of the preset interval intersection function. According to the method, the intersection of different types of gene annotation intervals can be rapidly calculated, and compared with a traditional comparison method, the method is simple in implementation logic, small in calculation amount, accurate in judgment and beneficial to improvement of comparison efficiency.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Method and device for screening sgRNA targets in CRISPR-Cas9 system
The invention relates to a CRISPR-Cas9 system sgRNA action target screening method. The method comprises the steps of (1) obtaining segments with 5'-Nx-NGG-3' sequences (x is an integer ranging from 19 to 22 and N represents A / T / C / G) in genomes by utilizing whole genome sequences and gene annotation information of published species to serve as candidate targets of CRISPR-Cas9 system sgRNA; (2) fragmenting the genomes into fragments of 22-25bp and screening sequences ending with NGG and non-repeated on the genomes; and (3) comparing the sequences of the candidate targets in the step (1) with the screened sequences in the step (2), and performing screening and sorting on corresponding optimal sequences according to mismatch information and a selection formula to obtain an optimal genome sgRNA action target set. The invention furthermore provides an apparatus used for realizing the screening method. The method is suitable for all species with known genomes and gene annotation information, and a universal sgRNA sequence set of whole genome level of the species is quickly and efficiently obtained to build a gene knockout mutant library or a gene knockout animal model.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com