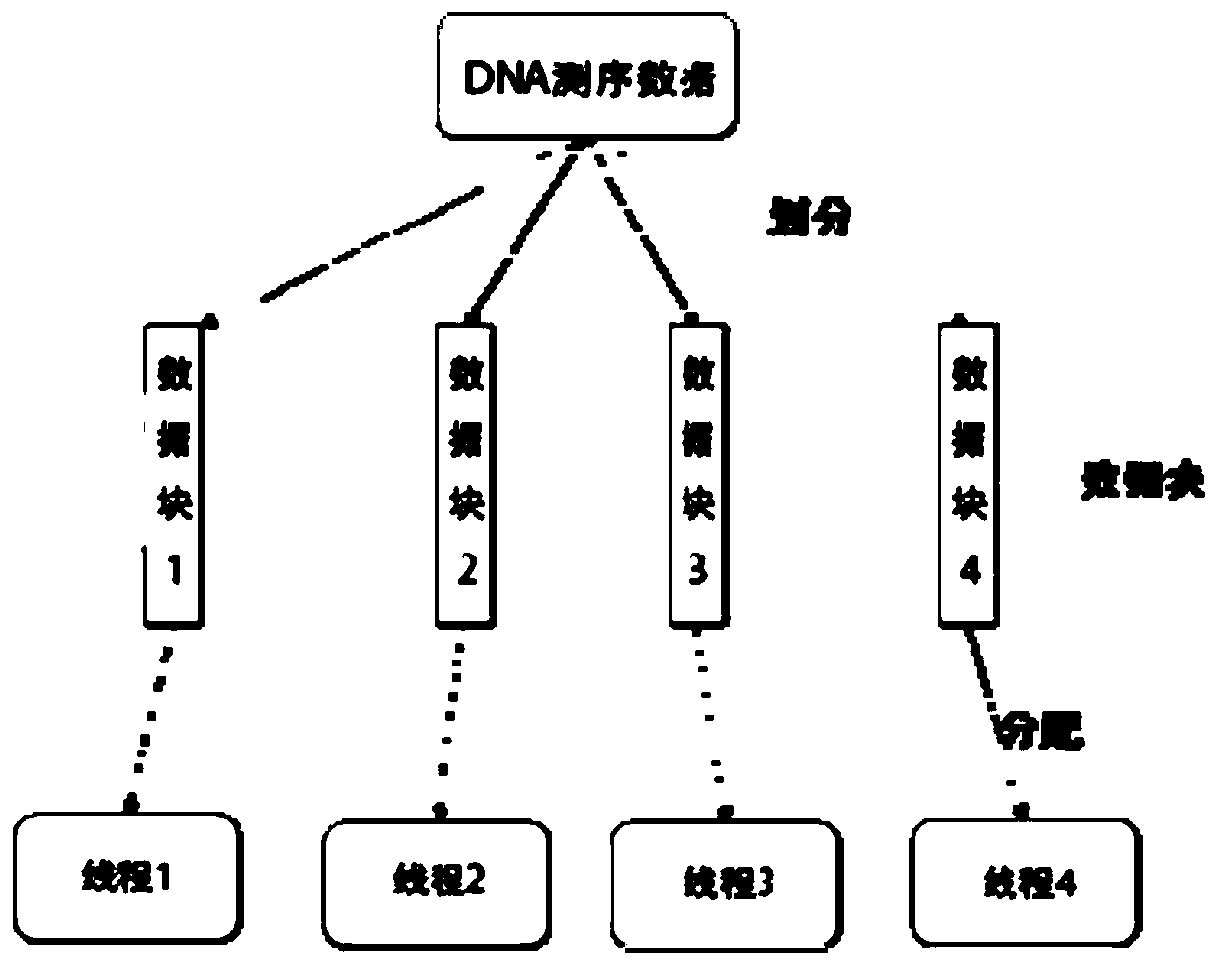
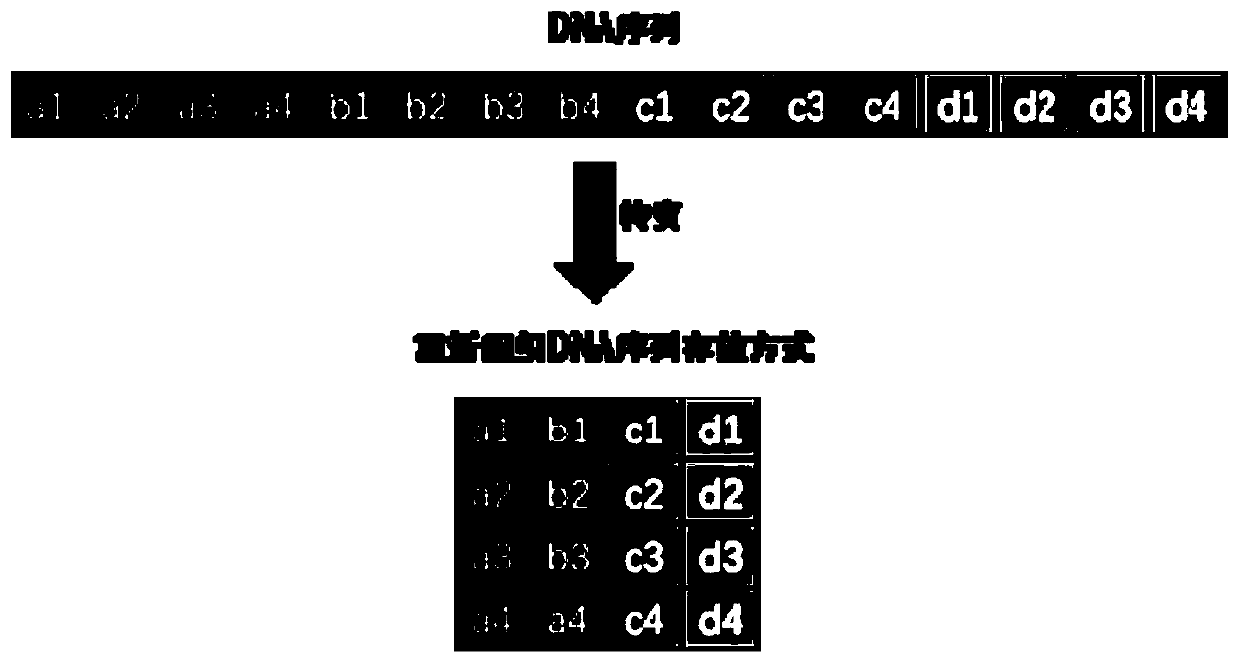
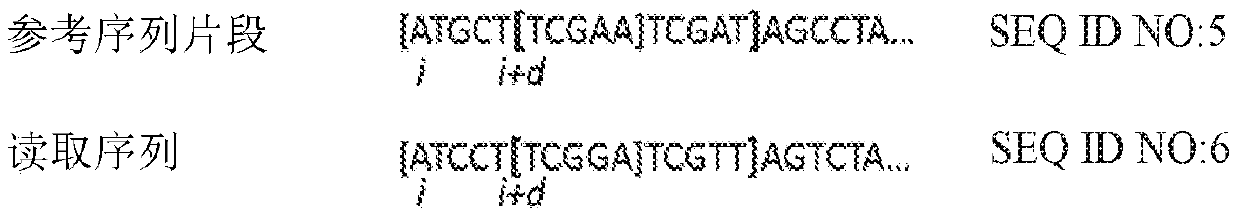Patents
Literature
55 results about "Third generation sequencing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Third-generation sequencing. Third-generation sequencing (also known as long-read sequencing) is a class of DNA sequencing methods currently under active development.
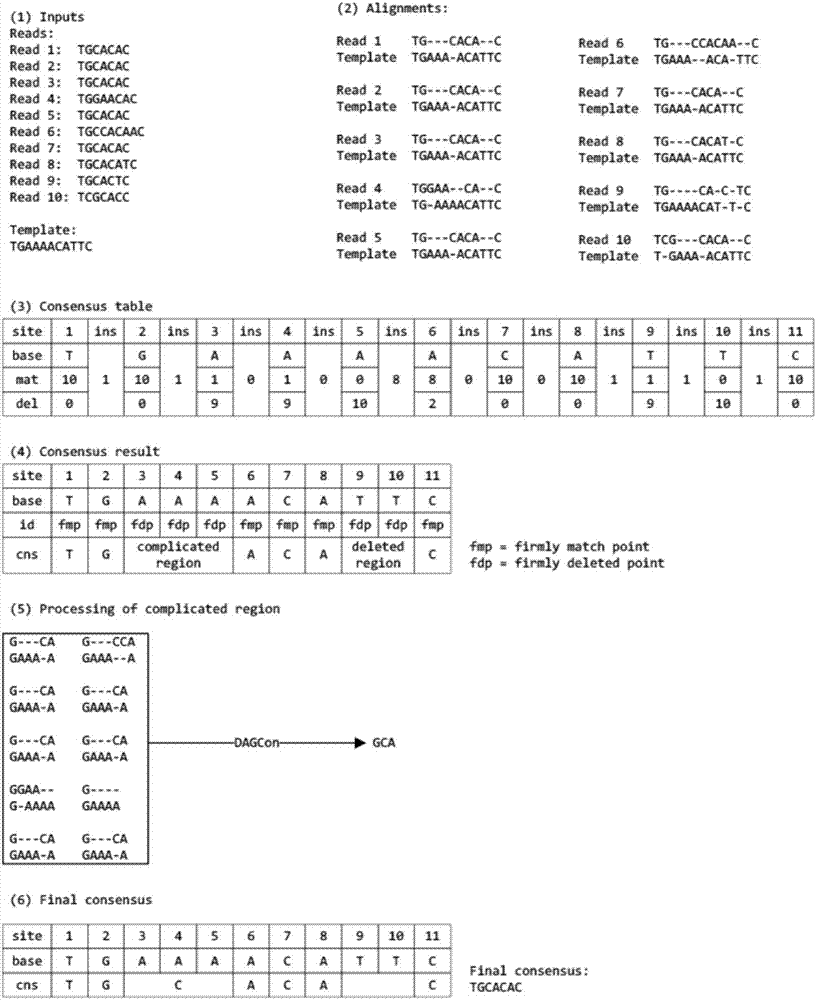
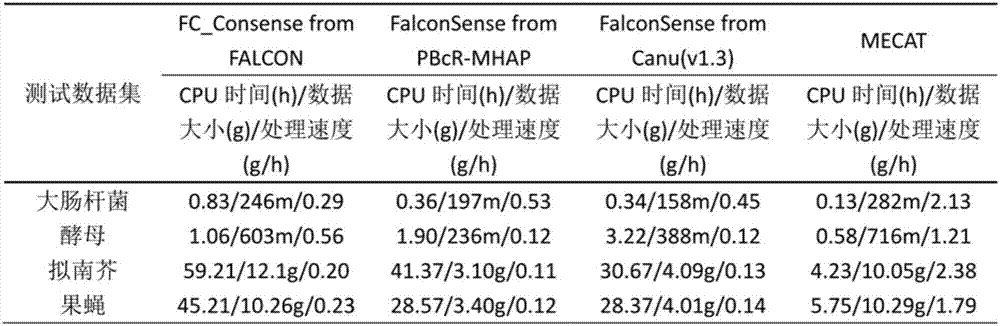
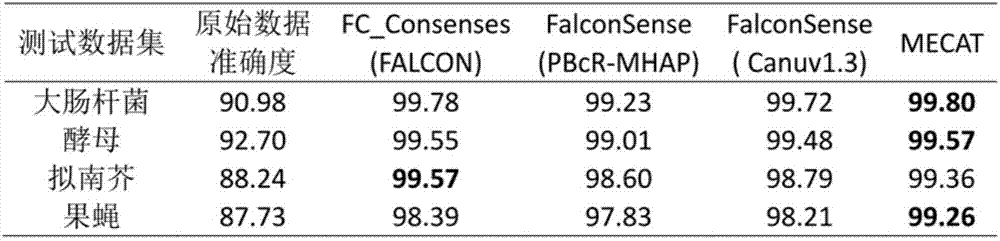
Method for detecting variable spliceosome in third generation full-length transcriptome
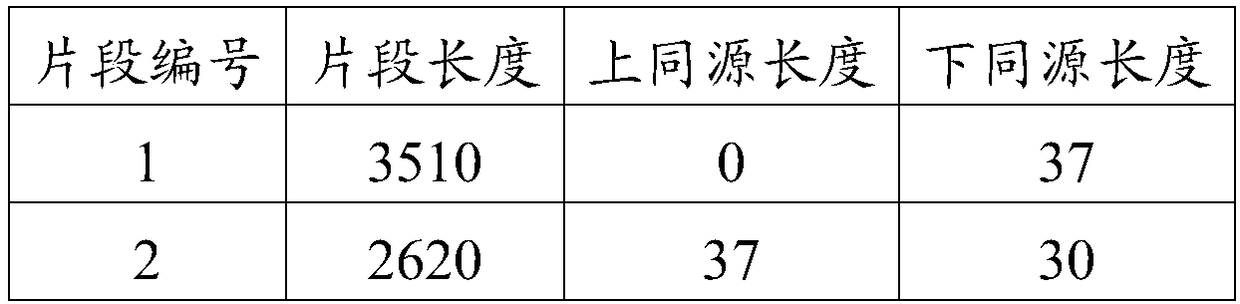
ActiveCN105389481AEfficient access to shear structuresPerfect commentSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsReference genome sequenceGene model
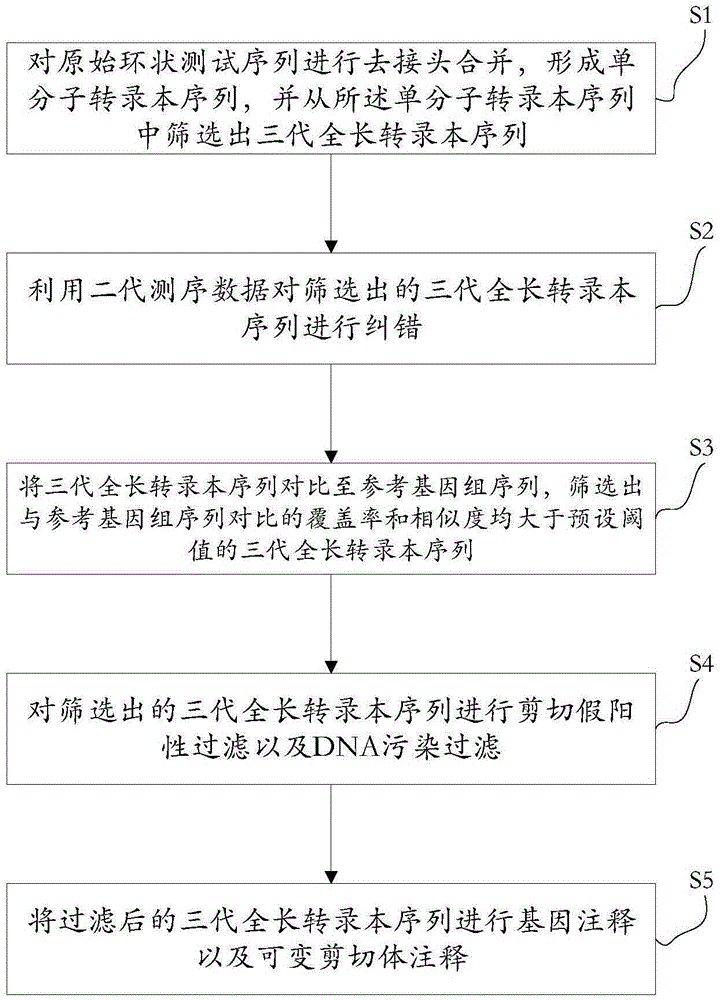
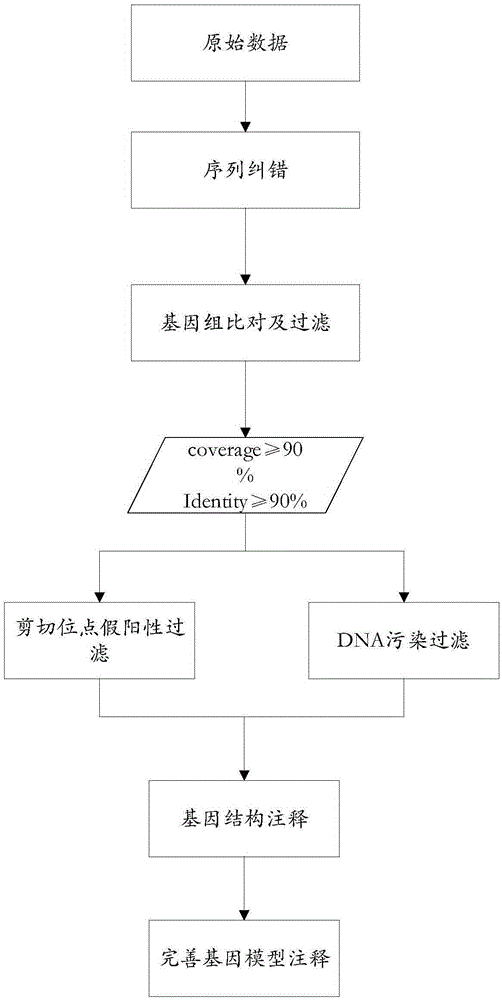
The invention discloses a method for detecting a variable spliceosome in a third generation full-length transcriptome. The method comprises the following steps: merging original annular test sequences with joints removed to form a monomolecular transcript sequence, and screening a third generation full-length transcript sequence; comparing the third generation full-length transcript sequence with a reference genome sequence, and screening a third generation full-length transcript sequence having coverage and similarity with the reference genome sequence larger than preset thresholds; carrying out splicing false positive filtration and DNA contamination filtration on the screened third generation full-length transcript sequence; and carrying out gene annotation and variable spliceosome annotation on the filtered third generation full-length transcript sequence. An overlong read length of a third generation sequencing technology mentioned in the method disclosed by the invention is large enough to cover most RNA, the third generation full-length transcript sequence can be obtained by SMRT sequencing transcriptomes without being assembled, and a splicing structure of a gene can be effectively obtained by third generation transcriptome sequencing, and more perfect gene model annotation can be constructed.
Owner:嘉兴菲沙基因信息有限公司
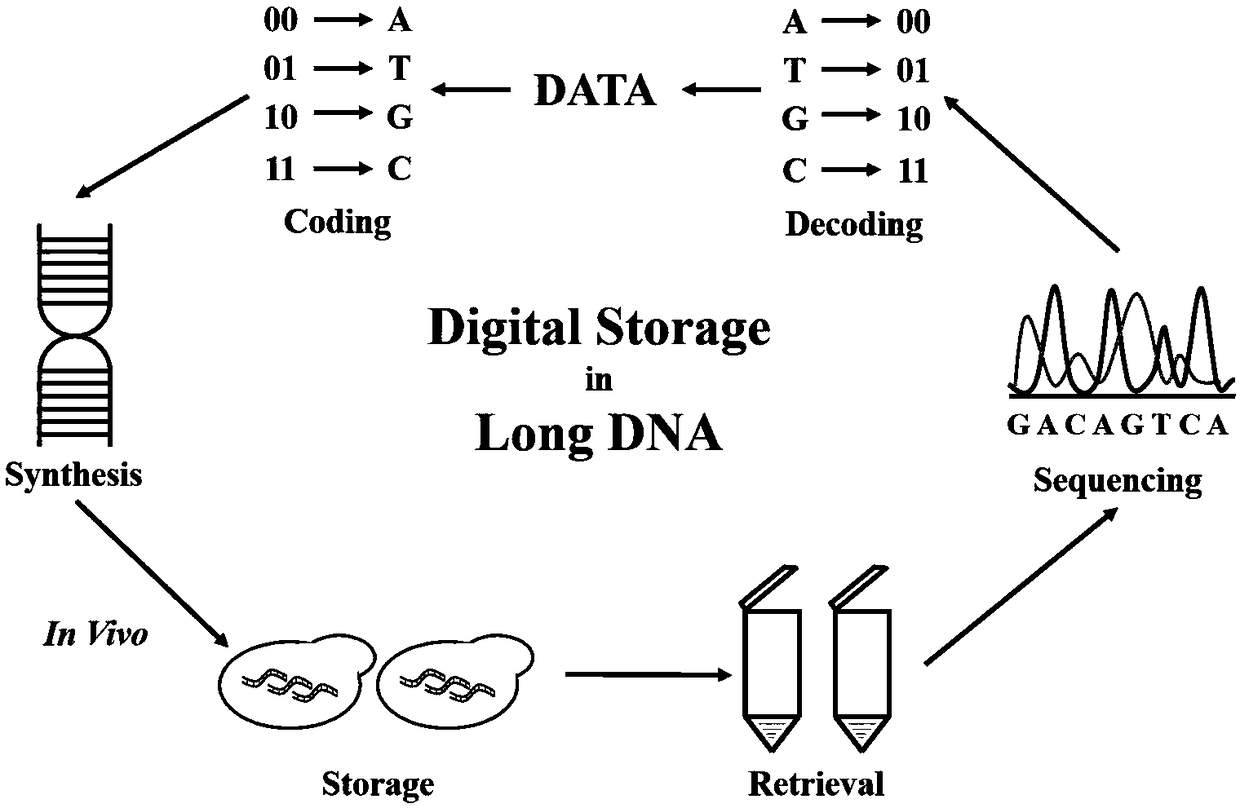
DNA-based Information Storage Method
ActiveCN109460822AIncrease load rateFast copyRedundant data error correctionDNA computersEscherichia coliA-DNA
The invention relates to the technical field of information storage, in particular to a DNA-based information storage method. A long sequence in vivo DNA information storage technique is provide. Themain goal is to construct a coding system with strong error correction mechanism based on LDPC and BCH codes, which can reduce the redundancy of primers and indexes by long sequence coding, and achieve a high actual carrying capacity (above 97%). The main goal is to construct a medium-length DNA sequence (above 1Kbp). Saccharomyces cerevisiae in vivo assembly system is used to assemble and store long sequences and preserve information, and the information can be replicated at low cost, high fidelity and high speed by model organisms such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Escherichia coli or Bacillus. At the same time, because of the existence of strong error correction system, the data in the bacterial cell can be reduced perfectly with low coverage (1-5 X) in the second generation and third generation sequencing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Protein molecule electronic device based on nanopore structure
InactiveCN104312914AOvercoming Sequencing BiasRead longBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsProtein moleculesProtein-protein complex
The invention relates to a protein molecule electronic device based on a nanopore structure. The protein molecule electronic device is a mono-enzyme biosensor which can be used for detecting a substrate molecule with extremely low concentration in a solution and sequencing the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of the single molecule. The protein molecule electronic device belongs to a third-generation DNA sequencing apparatus. The protein molecule electronic device based on the nanopore structure is characterized in that 1) the solution is divided into two parts by virtue of a solid structure with a nanochannel, wherein the solutions at the two sides of the solid structure are communicated by virtue of the nanochannel; 2) a protein molecule or a protein complex molecule is fixed in the nanochannel; 3) electrodes are respectively put in the two solutions separated by virtue of the solid structure, and resistance of the protein molecule in the nanochannel is detected by detecting current between the electrodes; and 4) the dynamic features of protein conformation are determined according to the changes of a current value passing through the protein molecule, and the information of the protein-catalyzed reaction substrate is obtained.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for detecting fusion gene based on transcriptome sequencing data
ActiveCN106650254AIncreased sequencing depthImprove efficiencyHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsThird generation sequencingTranscriptome Sequencing
The invention relates to a method for detecting a fusion gene based on transcriptome sequencing data. The method comprises the following steps of S1: performing second-generation transcriptome sequencing and third-generation transcriptome sequencing on a sample to obtain second-generation transcriptome sequencing data and third-generation transcriptome sequencing data; S2: comparing the third-generation transcriptome sequencing data with a reference genome, identifying FLNC reads possibly subjected to gene fusion and gene pairs possibly participating in fusion, extracting a sequence of the FLNC reads possibly subjected to the gene fusion, and judging a fusion position; and S3: comparing the second-generation transcriptome sequencing data with the FLNC reads possibly subjected to the gene fusion, obtained in the step S2, and identifying the gene pairs fused indeed according to logarithms of discordant paired-end reads and the number of junction reads in a comparison result and the number of the FLNC reads possibly subjected to the gene fusion. According to the method, the fusion gene is detected in combination with third-generation transcriptome sequencing and second-generation transcriptome sequencing, so that a result of detecting the fusion gene in combination with second-generation and third-generation sequencing support evidences is more reliable.
Owner:嘉兴菲沙基因信息有限公司
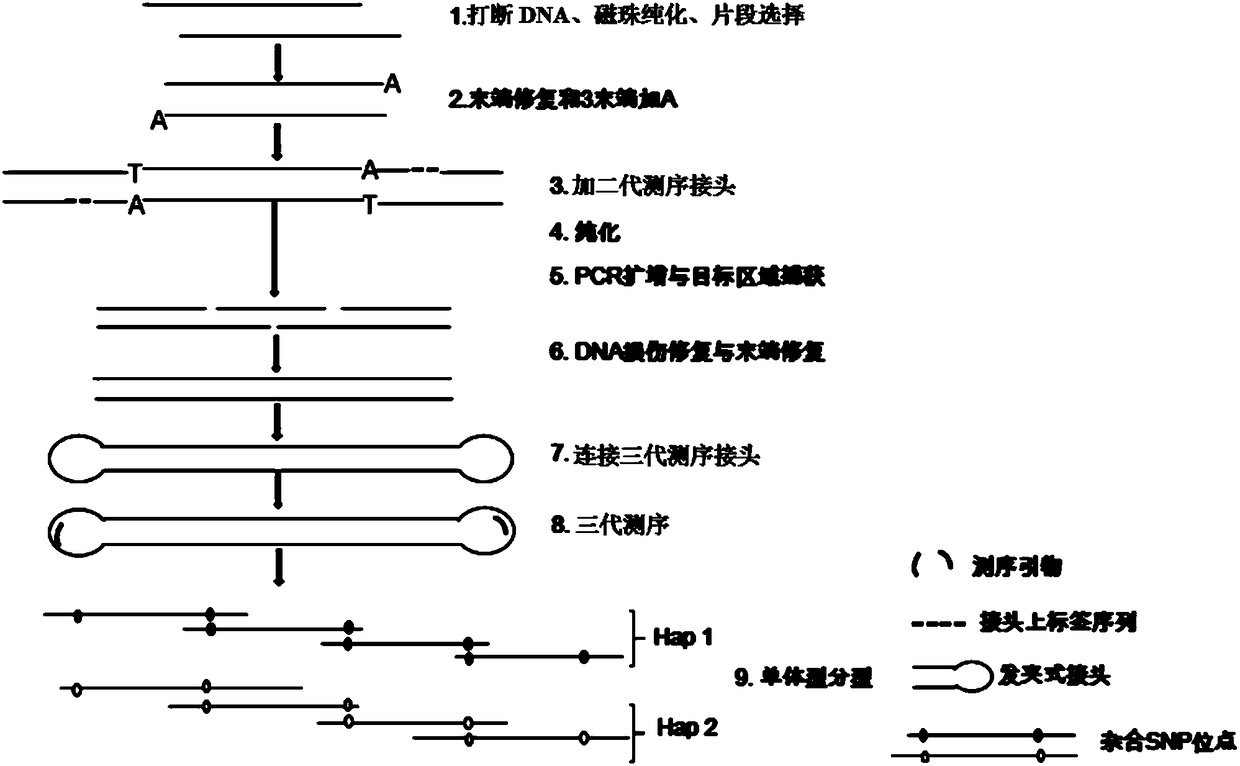
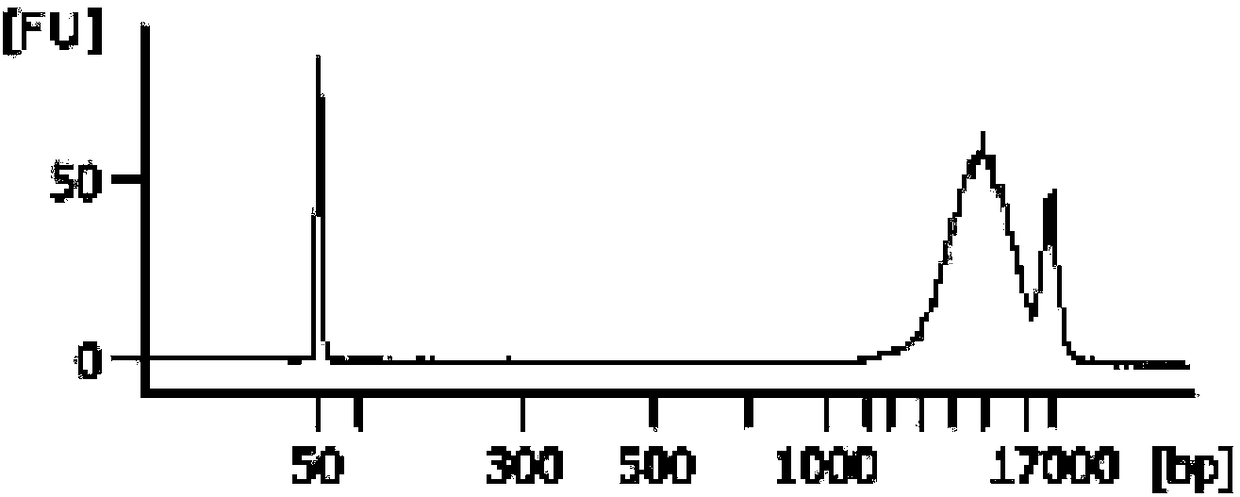
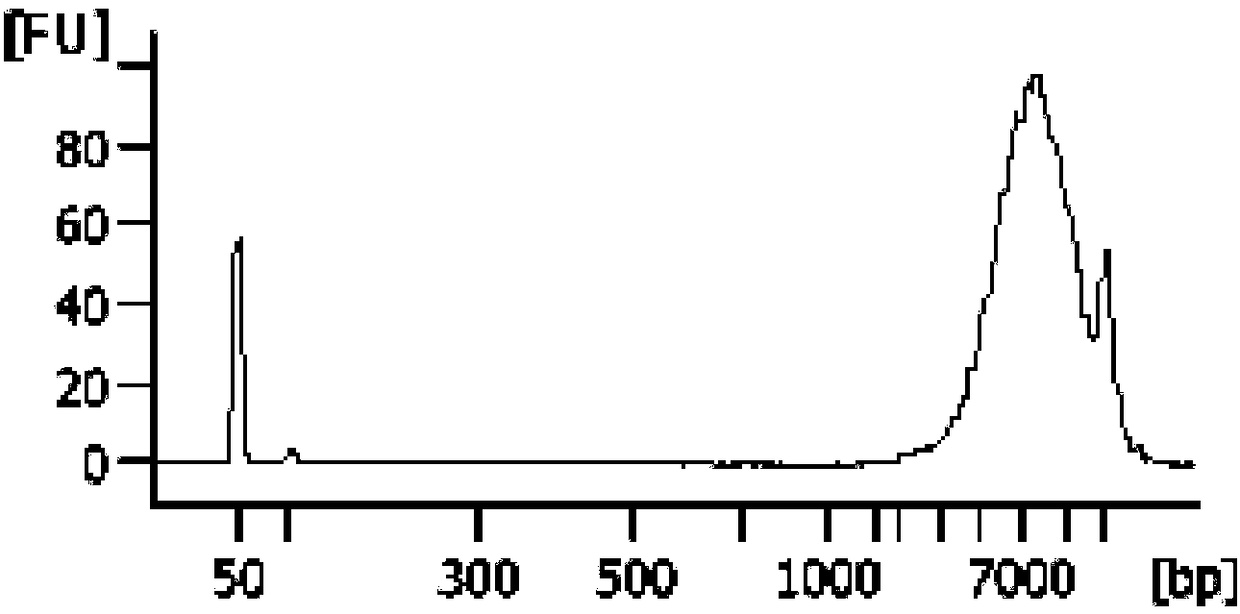
Building method of DNA large-fragment library for Pacbio platform and assay kit
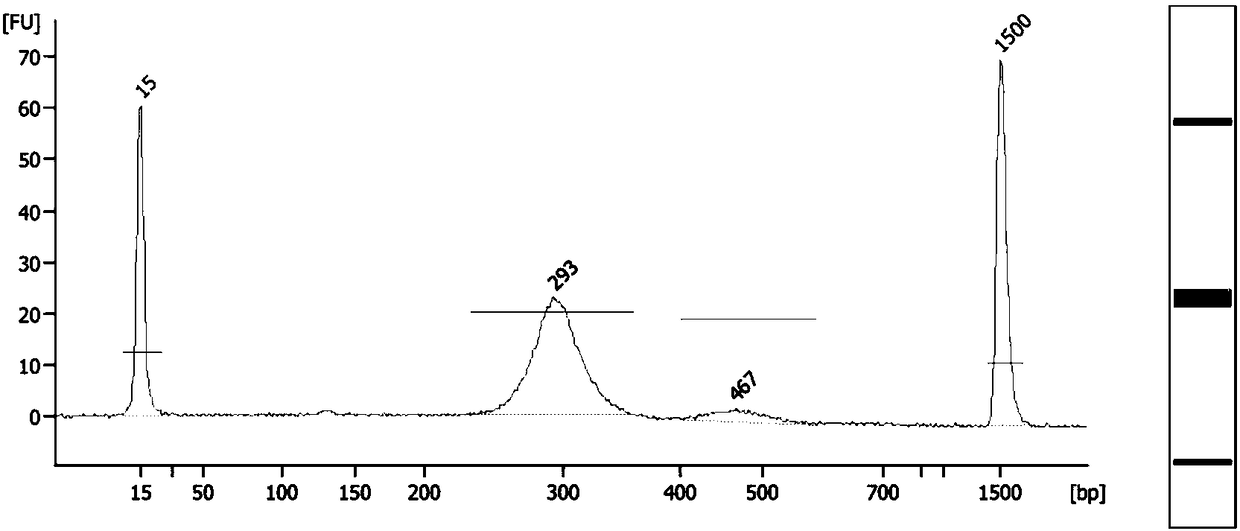
InactiveCN107794575ALow costEasy constructionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationElectrophoresisLarge fragment
The application discloses a building method of DNA large-fragment library for Pacbio platform and an assay kit. The building method includes subjecting broken DNA large fragments to VII enzyme treatment, sequentially carrying out primary DNA damage repairing and terminal repairing treatment, linker splicing treatment, exonuclease ExoIII and ExoVII double-digest treatment, subjecting products obtained by double-digest treatment to fragment separation through nucleic acid electrophoresis and a fragment recovery system, subjecting products obtained by the fragment separation to secondary DNA damage repairing, so as to obtain the DNA large-fragment library adaptable to the Pacbio platform. According to the building method of the DNA large-fragment library, the whole building process is carriedout without Pacbio library-building assay kit, library building cost is lowered greatly, and a material foundation is laid for promotion and application of the third-generation sequencing and Pacbionucleic acid sequencing platform.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
Method for detecting expansion of short tandem repeat
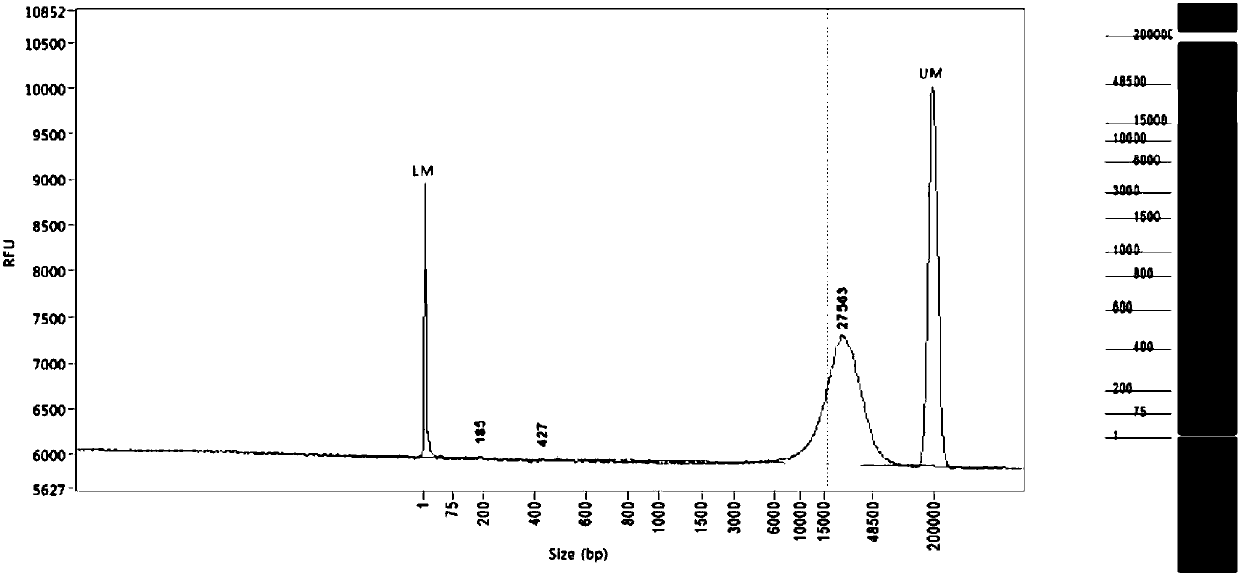
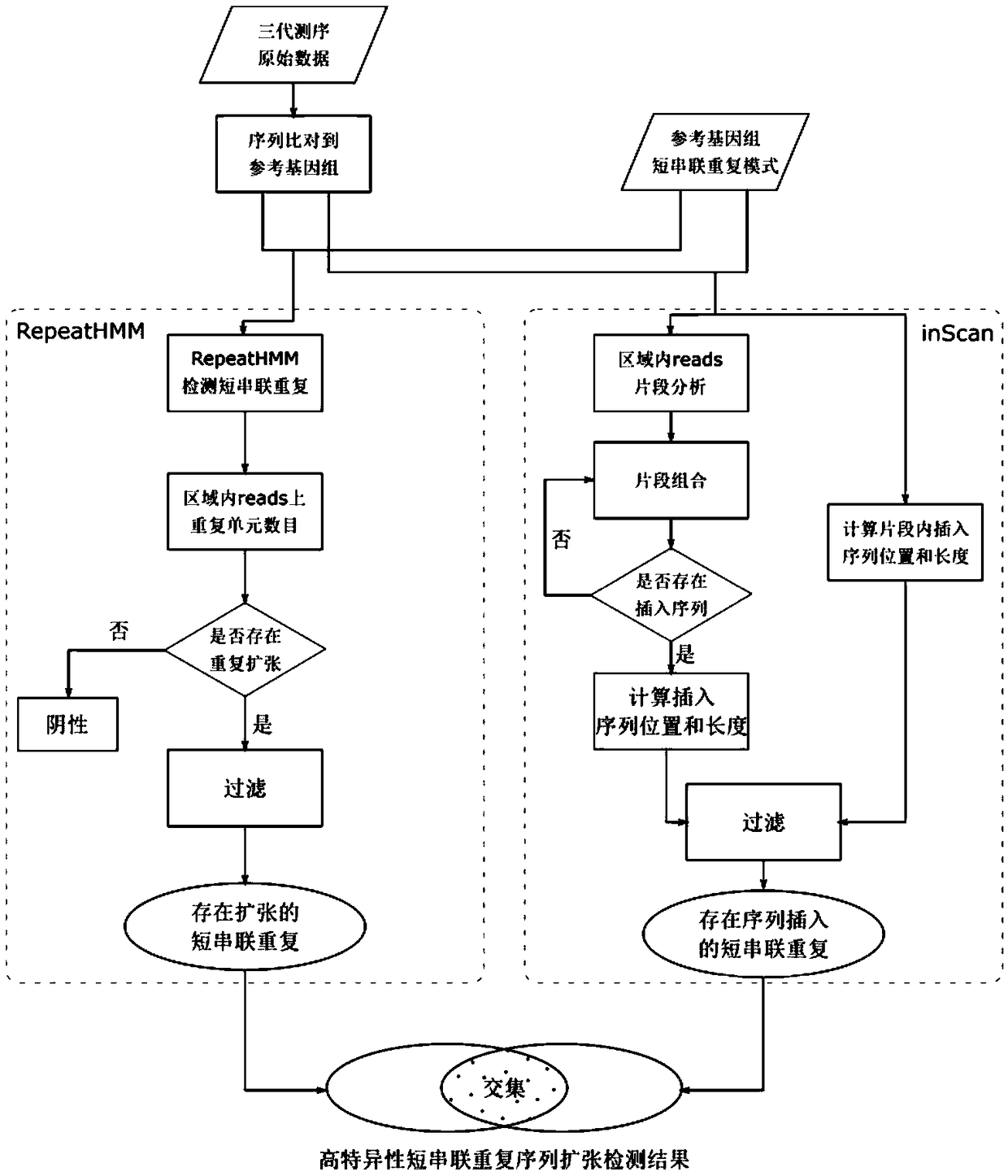
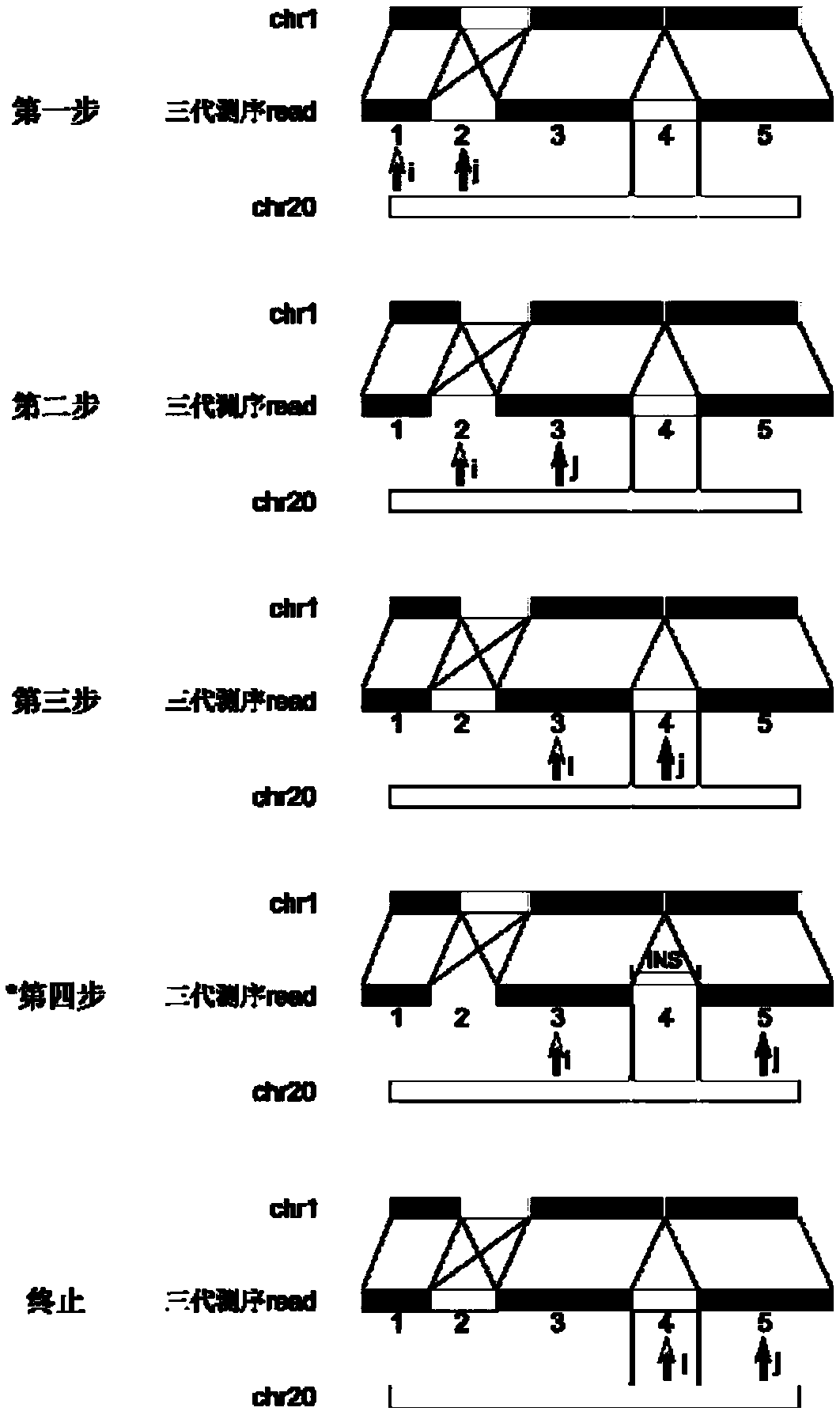
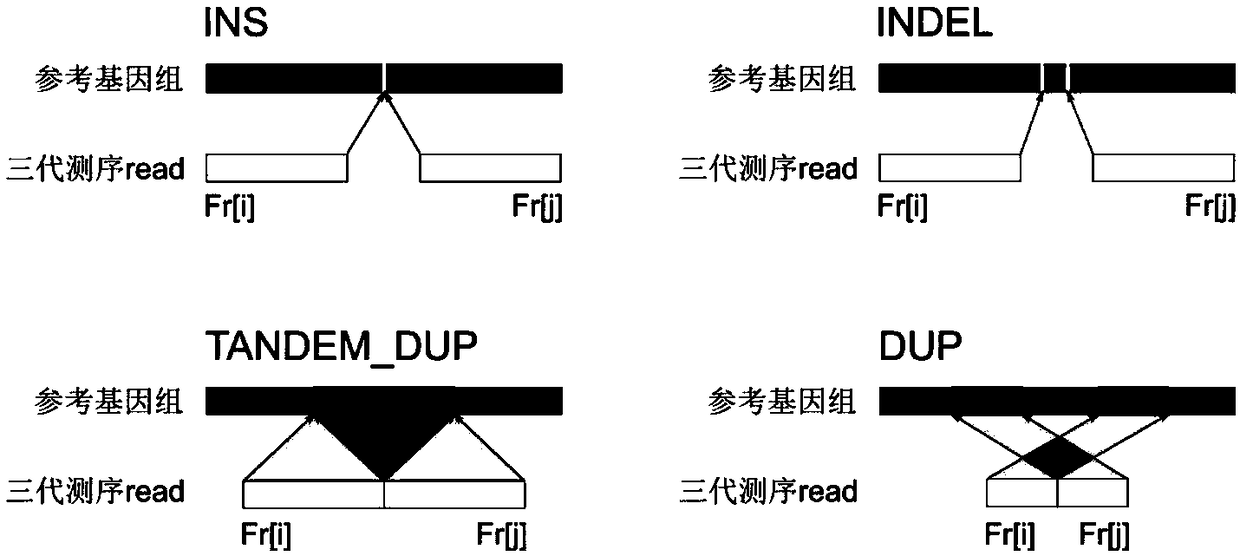
ActiveCN108660200AStrong specificityReduce false positivesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence InsertionsThird generation sequencing
The invention provides a method for detecting expansion of a short tandem repeat. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out sequence alignment; secondly, detecting short tandem repeat of third-generation sequencing data by RepeatHMM; thirdly, detecting sequence insertion of a short tandem repeat area by inScan; fourthly, calculating an intersection of RepeatHMM detection results and sequence insertion detection results of the short tandem repeat area. According to the method provided by the invention, the results of the sequence insertion and RepeatHMM short tandem repeatdetection are combined, so that the specificity of detecting the expansion of the short tandem repeat is improved.
Owner:BEIJING GRANDOMICS BIOTECH +1
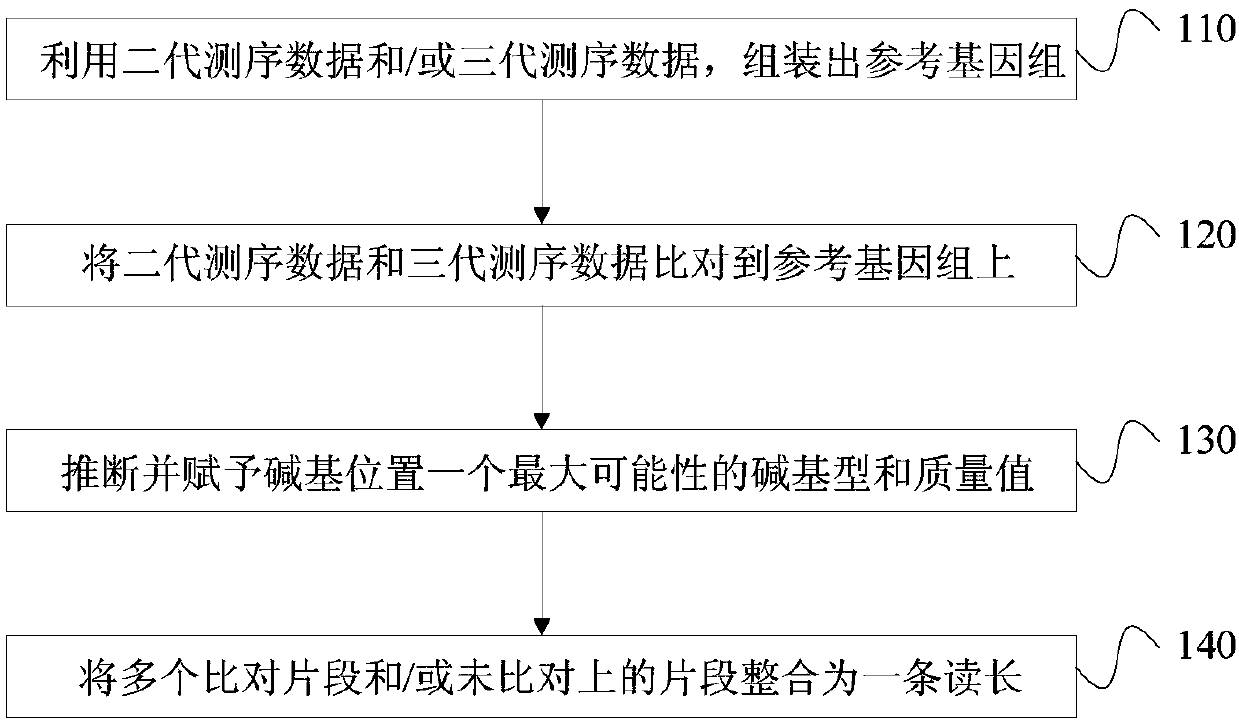
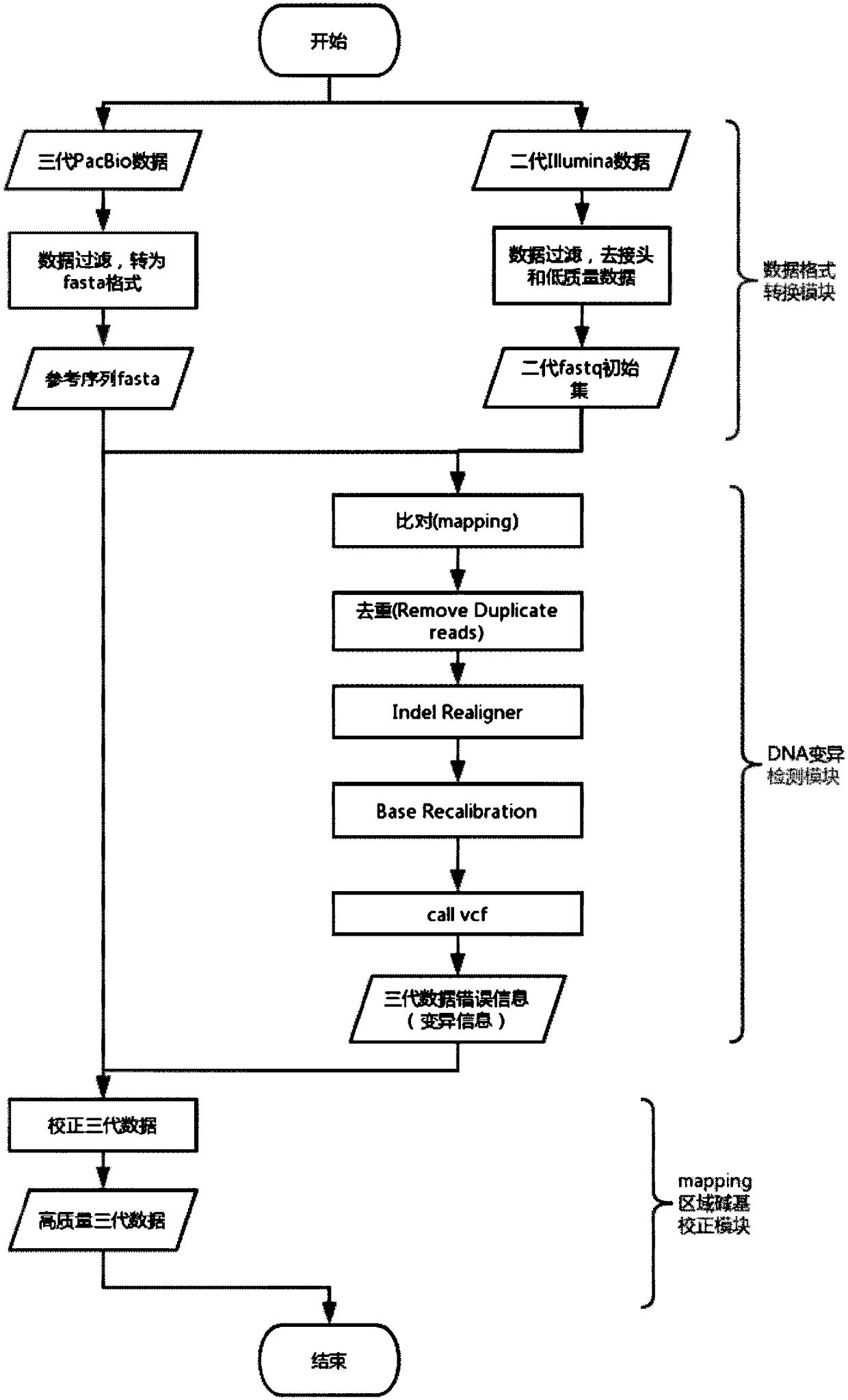
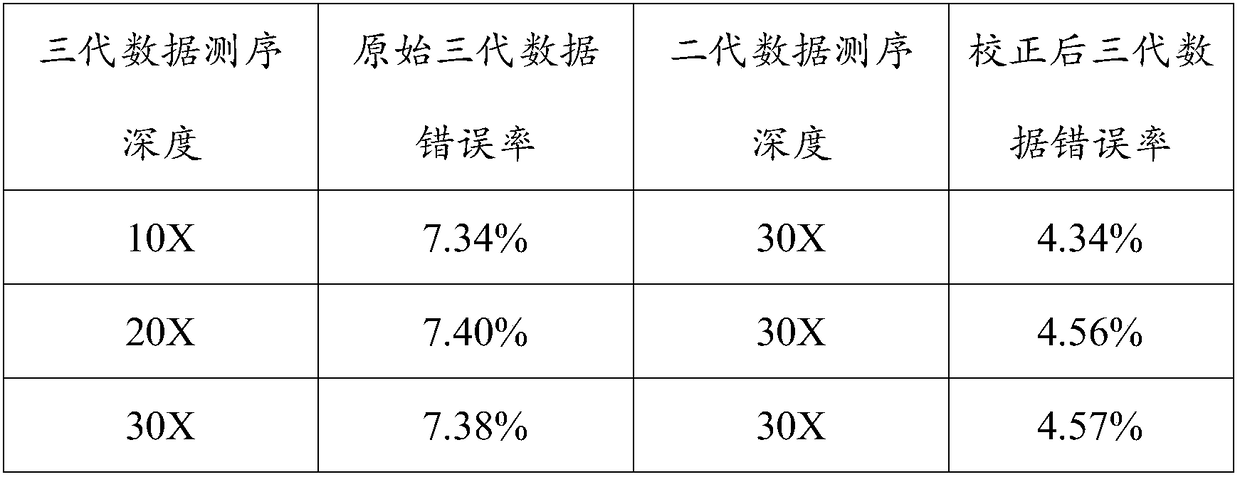
Third-generation sequencing data error correction method, third-generation sequencing data error correction device and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN108629156AImplement error correctionEasy to analyzeBiostatisticsSequence analysisThird generation sequencingData error
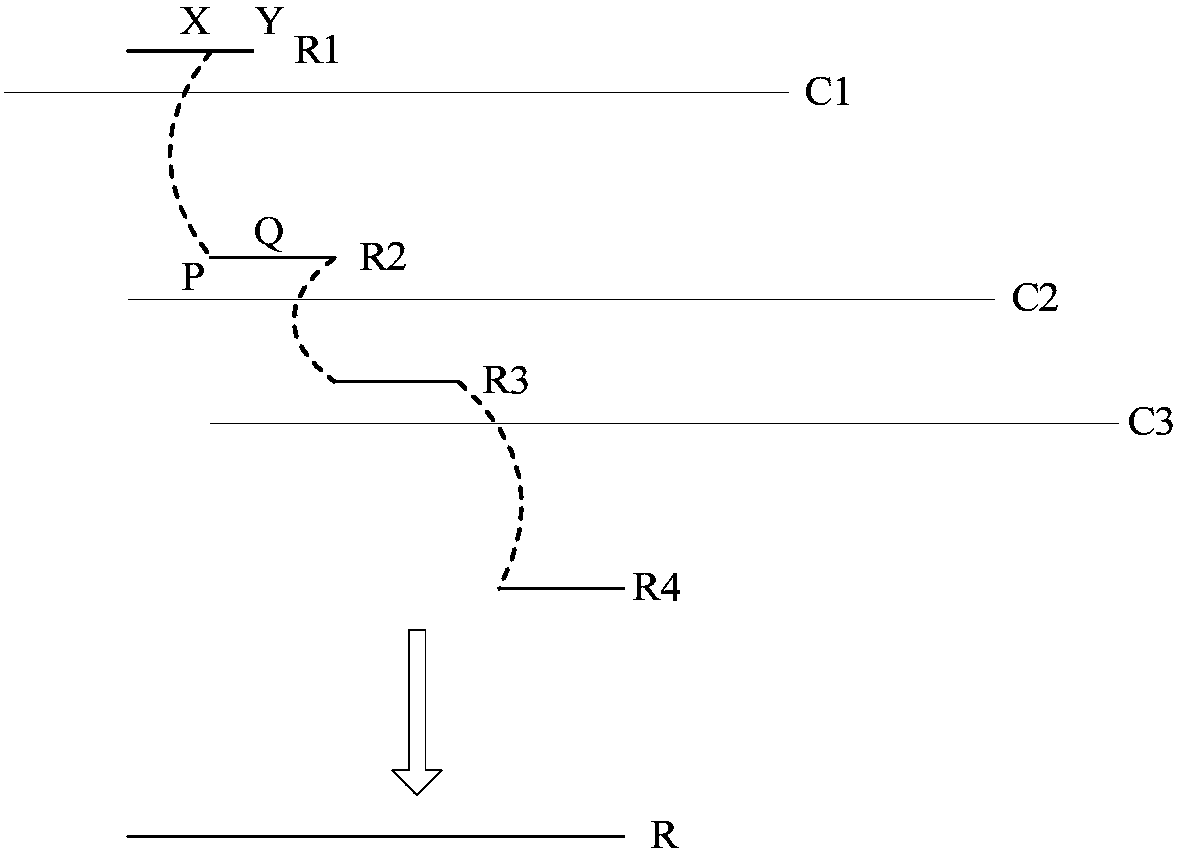
The invention discloses a third-generation sequencing data error correction method, which comprises the following steps of assembling a reference genome by using second-generation sequencing data and / or third-generation sequencing data; comparing the second-generation sequencing data and the third-generation sequencing data onto the reference genome; for each basic group position on each comparison segment in the third-generation sequencing data comparison result, deducing and giving a most possible basic group type and quality value to the basic group position; and for a plurality of comparison segments in a read length and / or unmatched segments, integrating the plurality of comparison segments and / or unmatched segments into the same read length. The method has the advantages that no limitation exists on the third-generation sequencing data depth; the error correction on the low-depth third-generation sequencing data can be realized; the additional data loss and length loss of the read length are not introduced; and a quality value system of the error correction result is introduced, so that the single basic group quality of the error correction result can be evaluated.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
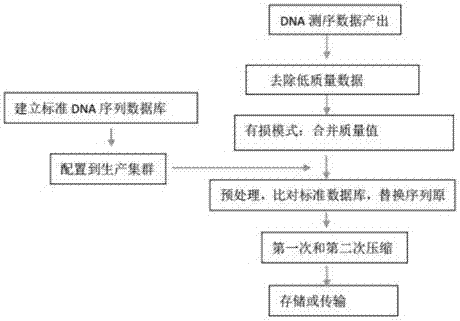
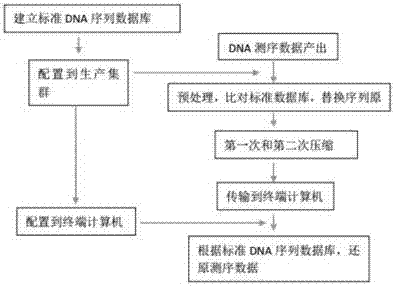
Gene sequencing data compression and transmission method
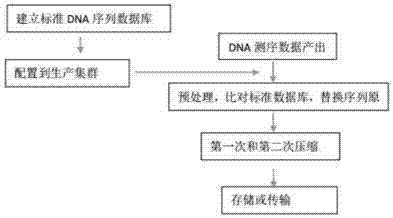
InactiveCN106971090ASave storage spaceImprove data transfer efficiencyHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsData compressionData capacity
The invention discloses a gene sequencing data compression and transmission method. The method comprises the following steps of A, establishing a standard DNA sequence database; B, deploying the standard DNA sequence database to a data processing device; C, preprocessing DNA sequencing data: comparing the DNA sequencing data with the standard DNA database one by one, generating a corresponding relationship, replacing an original text of the DNA sequencing data with numbers of the standard DNA database, and separately storing a part, different from the standard DNA database, of the DNA sequencing data; D, performing compression; and E, performing storage or transmission. The standard DNA sequence database is stored in the data processing device, so that a large amount of information contained in the DNA sequencing data can be represented by the numbers of the standard DNA database, and the data capacity after the step of preprocessing the DNA sequencing data is greatly reduced; through further compression, the capacity is smaller, so that the storage space of the DNA sequencing data is smaller, and the data transmission efficiency is higher; and the data in the method is matched with output data of a second-generation sequencing technology and even a third-generation sequencing technology.
Owner:首度生物科技(苏州)有限公司 +1
Third-generation data correction method based on DNA variation detection
ActiveCN108595915AReduce calibration costsFast calibrationProteomicsGenomicsGeneration rateThird generation sequencing
The invention provides a third-generation data correction method based on DNA variation detection and belongs to the field of bioinformation technology. According to the method, third-generation sequencing data is processed to serve as reference sequence data, then second-generation sequencing data is compared with the third-generation sequencing data after being processed, and a comparison file is obtained; and variation analytical detection is performed on the comparison file, variation information of the second-generation sequencing data relative to the third-generation sequencing data canbe obtained, and the variation information is utilized to complete correction of the third-generation sequencing data. The DNA variation detection method is applied to third-generation sequencing dataerror correction, the second-generation sequencing data and the third-generation sequencing data are combined in use, and therefore the cost of third-generation data correction is lowered; and a multithread thought is adopted in a program, so that the correction speed of the third-generation data is increased. Through the method, the problems of a high error rate and high cost in a third-generation sequencing technology are solved through a united correction technology, and a foundation is laid for subsequent third-generation sequencing data variation detection.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
Method and system for determining fetus alpha thalassemia gene haplotype
ActiveCN108048541AAvoid the risk of harming the fetusRelieve stressMicrobiological testing/measurementRelationship - FatherThalassemia
The invention relates to a method for determining a fetus alpha thalassemia gene haplotype. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a third-generation sequencing library according to ablood sample, wherein the blood sample is collected from blood samples of the father and mother of the fetus; performing the third-generation sequencing for the third-generation sequencing library, and obtaining a third-generation sequencing result; determining a father and mother alpha thalassemia gene haplotype according to the third-generation sequencing result; establishing a second-generationsequencing library according to a detection sample, wherein the detection sample is collected from a peripheral blood sample of a pregnant woman; performing the second-generation sequencing for the second-generation sequencing library, and obtaining a second-generation sequencing result; and determining the fetus alpha thalassemia gene haplotype according to the second-generation sequencing result as well as the father and mother alpha thalassemia gene haplotype.
Owner:GUANGZHOU JINGKE DX CO LTD
Third-generation sequencing sequence correction method based on local graph
InactiveCN107229842ASequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsApplication softwareThird generation sequencing
The invention relates to a third-generation sequencing sequence correction method based on a local graph and a system of the third-generation sequencing sequence correction method. The system comprises a two-two comparison module, a multi-sequence comparison module, a correction operation comparison module, a correction operation classification module, a consistent-area base position correction and complex-area local graph base sequence correction module and a module sequence correction division and defusion processing module, the two-two comparison module is connected with a single molecule real-time sequencing database and a nanopore sequencing database, and the single molecule real-time sequencing database and the nanopore sequencing database are input into the two-two comparison module separately. The precision of the third-generation sequencing sequence correction method and system can reach 99%, and the speed is 7-10 folds that of current application software.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN OPHTHALMIC CENT SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Nano-structure-based protein unimolecular electronic device and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN106929565ARealize monitoringOvercoming Sequencing BiasMicrobiological testing/measurementThird generation sequencingNanostructure
The invention discloses a nano-structure-based protein unimolecular electronic device and preparation and application thereof; single protein or its complex molecules are fixed to a counter electrode at a nano hole, dynamical features of conformational fluctuation of the protein are characterized by detecting the electrical conductivity of the protein or its complex molecules in a solution, and the activity of the protein and the biochemical reactive process thereof with substrate molecules are detected. The nano-structure-based protein unimolecular electronic device may act as a third-generation sequencing method having great development potential, preparing special DNA sequencing libraries is not required, labeling nucleic acids is not required, ultra-long, continuous, quick and precise base reading can be performed, and ultralow-cost DNA sequencing and otherness can be achieved if a high-throughput molecular device is prepared.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
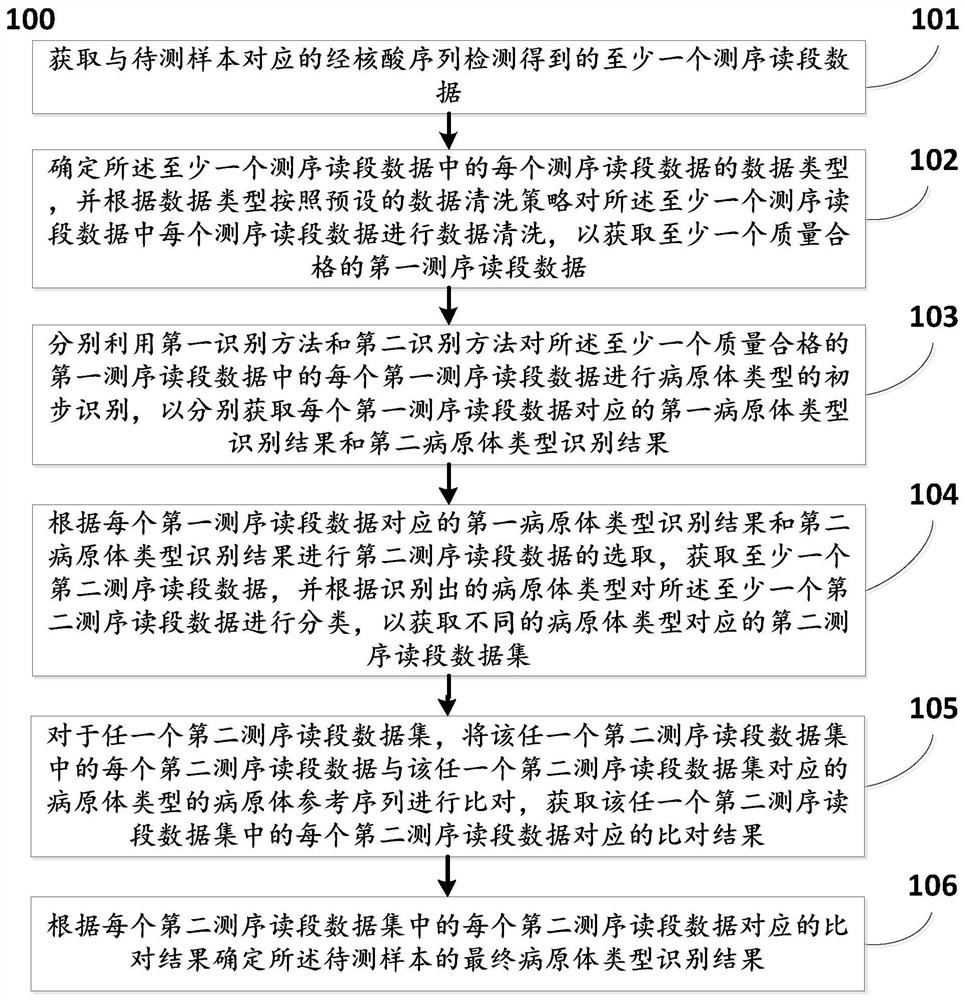
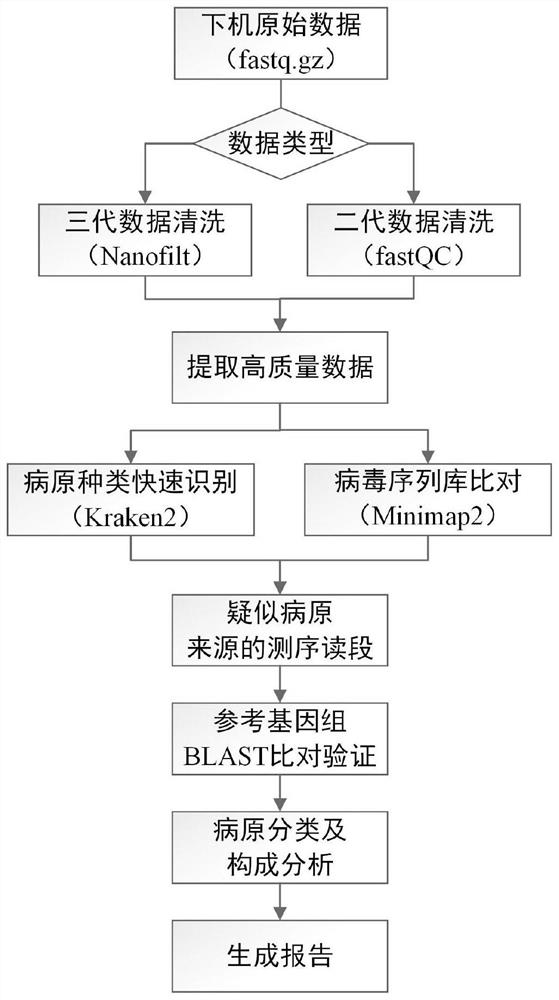
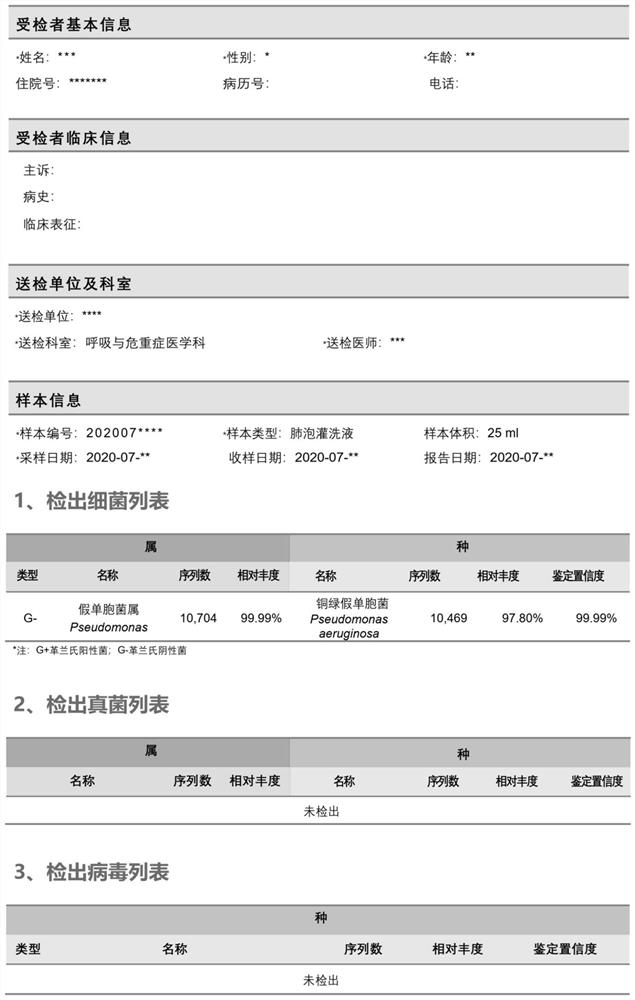
Method and system for automatically analyzing pathogen types
PendingCN113096737AMeet the needs of rapid pathogen detection and analysisEasy to handleProteomicsGenomicsThird generation sequencingShort read
The invention discloses a method and system for automatically analyzing pathogen types. The and comprises the following steps that: pathogen types of first sequencing read data of different data types of a to-be-detected sample are preliminarily judged through two different algorithms, and second sequencing read data are selected; then comparison verification and screening are performed on the identified second sequencing read data of the different pathogen types and corresponding pathogen reference sequences, and therefore, pathogen types existing in the to-be-detected sample can be determined. According to the method, long read length data generated based on a third-generation sequencing technology can be effectively processed, the calculation amount of accurate comparison is reduced, accurate analysis and report generation of typical third-generation metagenome or metatranscriptome data within 30 minutes can be achieved, and the requirement for rapid pathogen detection and analysis is met; and meanwhile, the method can be used for analyzing short read length data obtained by next-generation sequencing, and has relatively good data compatibility.
Owner:北京源生康泰基因科技有限公司
Noninvasive antenatal haplotype construction method based on long fragment DNA capturing and three-generation sequencing
ActiveCN108866154AAddressing the drawbacks of detectionReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationHaplotypeThird generation sequencing
A noninvasive antenatal haplotype construction method based on long fragment DNA capturing and three-generation sequencing includes the steps of creating a second-generation library of genomes DNA inperipheral blood of pregnant women and / or husbands of the pregnant women; capturing target genes and flank regions; creating a third-generation computer sequencing library, and performing third-generation sequencing to acquire the sequencing read length; extending from mutational sites of target genes on the sequencing read length to two ends so as to look up heterozygous SNP sites; when differentsequencing read length overlapping regions contain one or more same SNP sites, continuing to differentiate the haplotype towards two ends successfully until a section of region is not covered by thesequencing read length or the SNP sites detected by the sequencing read length are homozygous. The noninvasive antenatal haplotype construction method has the advantages that haplotype construction ofparent individuals is realized, and the defect that current common noninvasive antenatal detection based on parent-child family haplotype analysis is not applicable to family detection without acquisition of propositus samples is overcome.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD +1
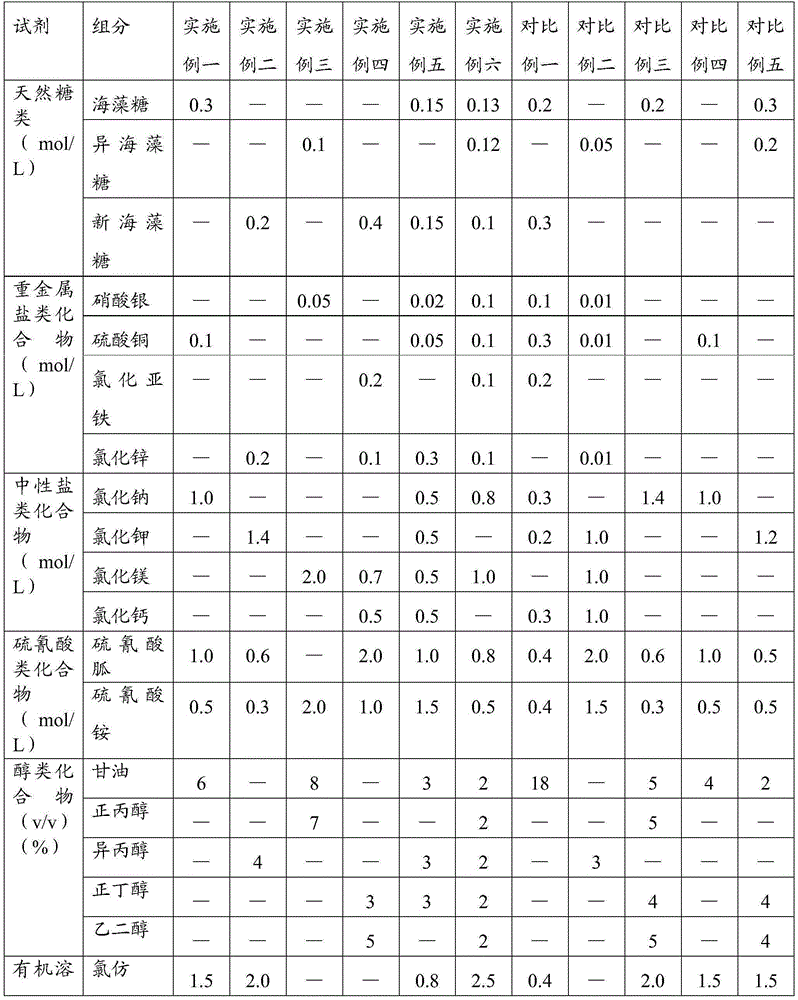
Reagent for simultaneous extraction of DNA and RNA, extraction method and application
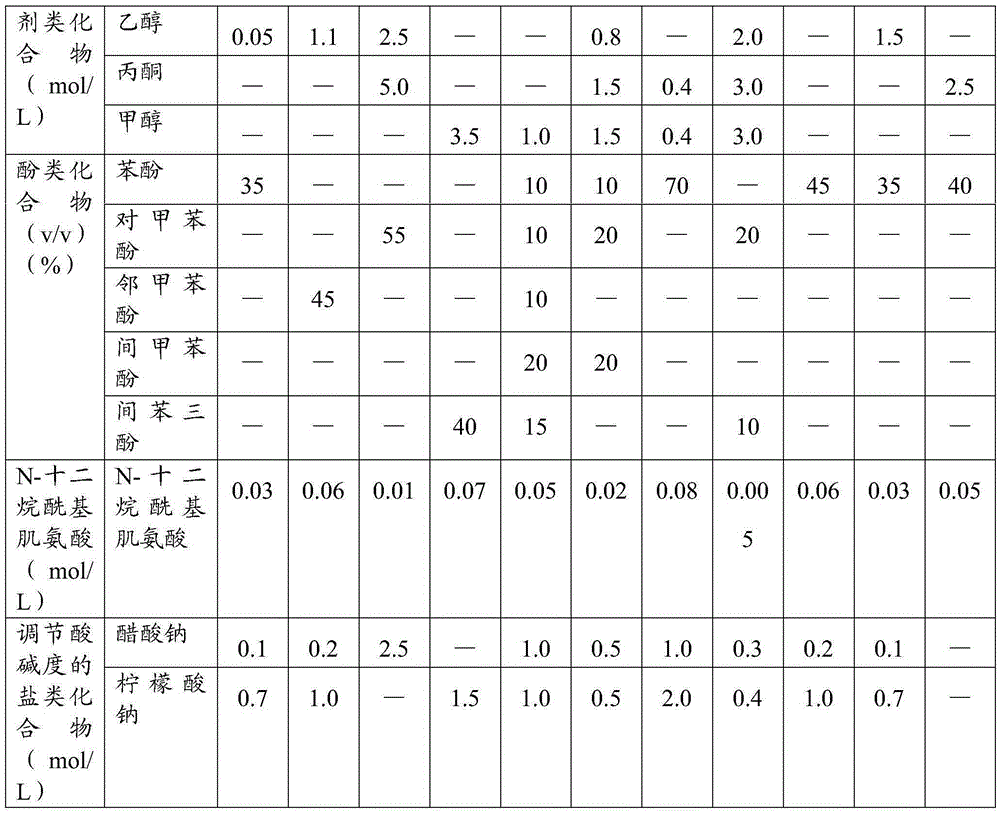
ActiveCN105385680AImprove protectionMeet the extraction requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationThird generation sequencingN-Lauroylsarcosine
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, in particular to a reagent for simultaneous extraction of DNA and RNA, a method for simultaneously extracting the DNA and the RNA and application of the reagent. The reagent comprises a natural saccharide compound, a heavy metal salt compound, a neutral salt compound, a thiocyanic acid compound, an alcoholic compound, an organic solvent compound, a phenolic compound, N-lauroylsarcosine and a salt compound used for adjusting the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. The reagent for extracting the DNA and the RNA is optimized, protection to the DNA and the RNA is enhanced, the whole extraction process can be conducted at room temperature, cooling treatment does not need to be conducted, and the needs of follow-up second-generation sequencing and third-generation sequencing can be completely met. The operation method is simple and rapid, the quantity demand of samples is less, and the purity and the concentration of extracted DNA and RNA are high.
Owner:天津脉络医学检验有限公司
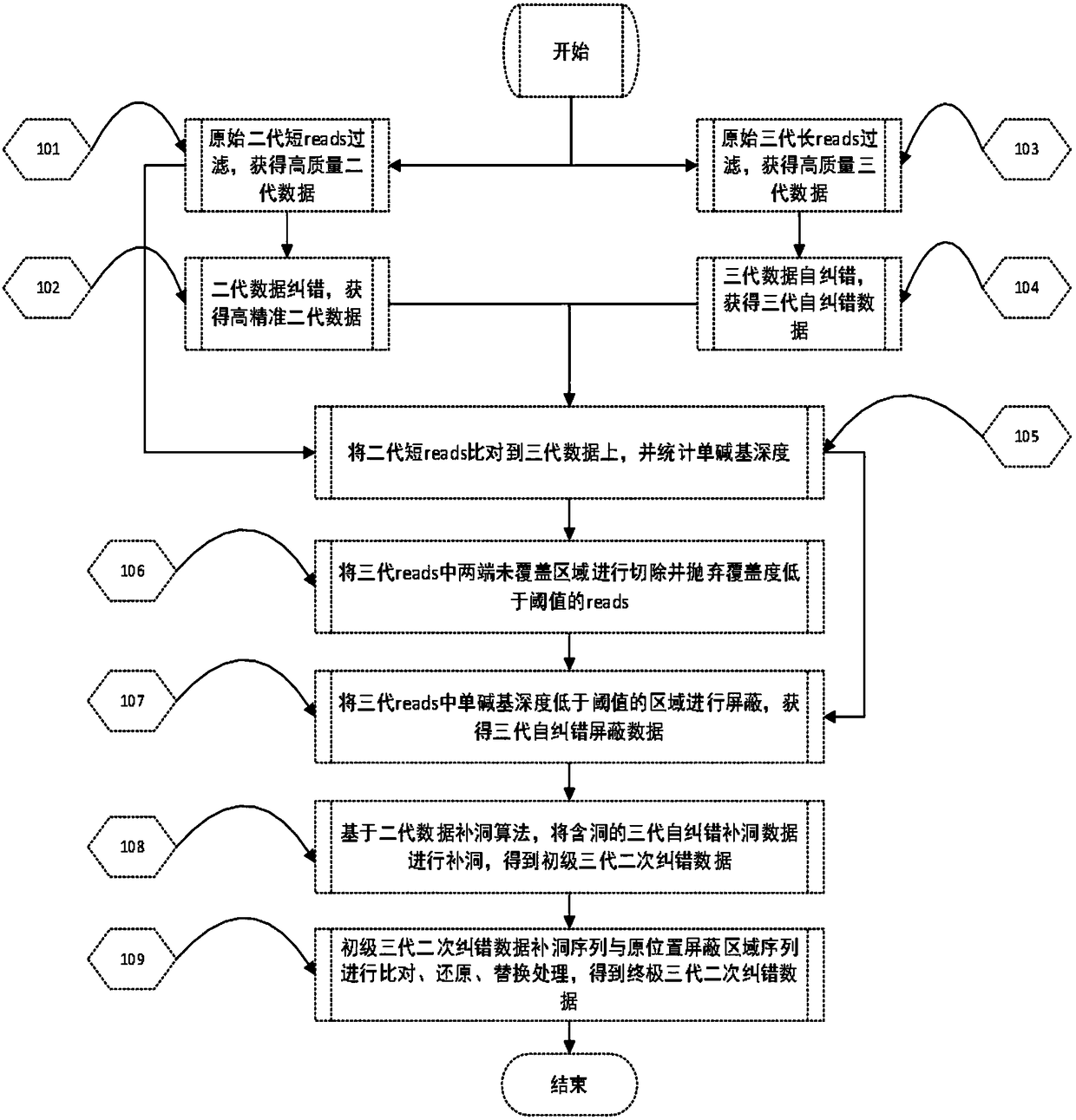
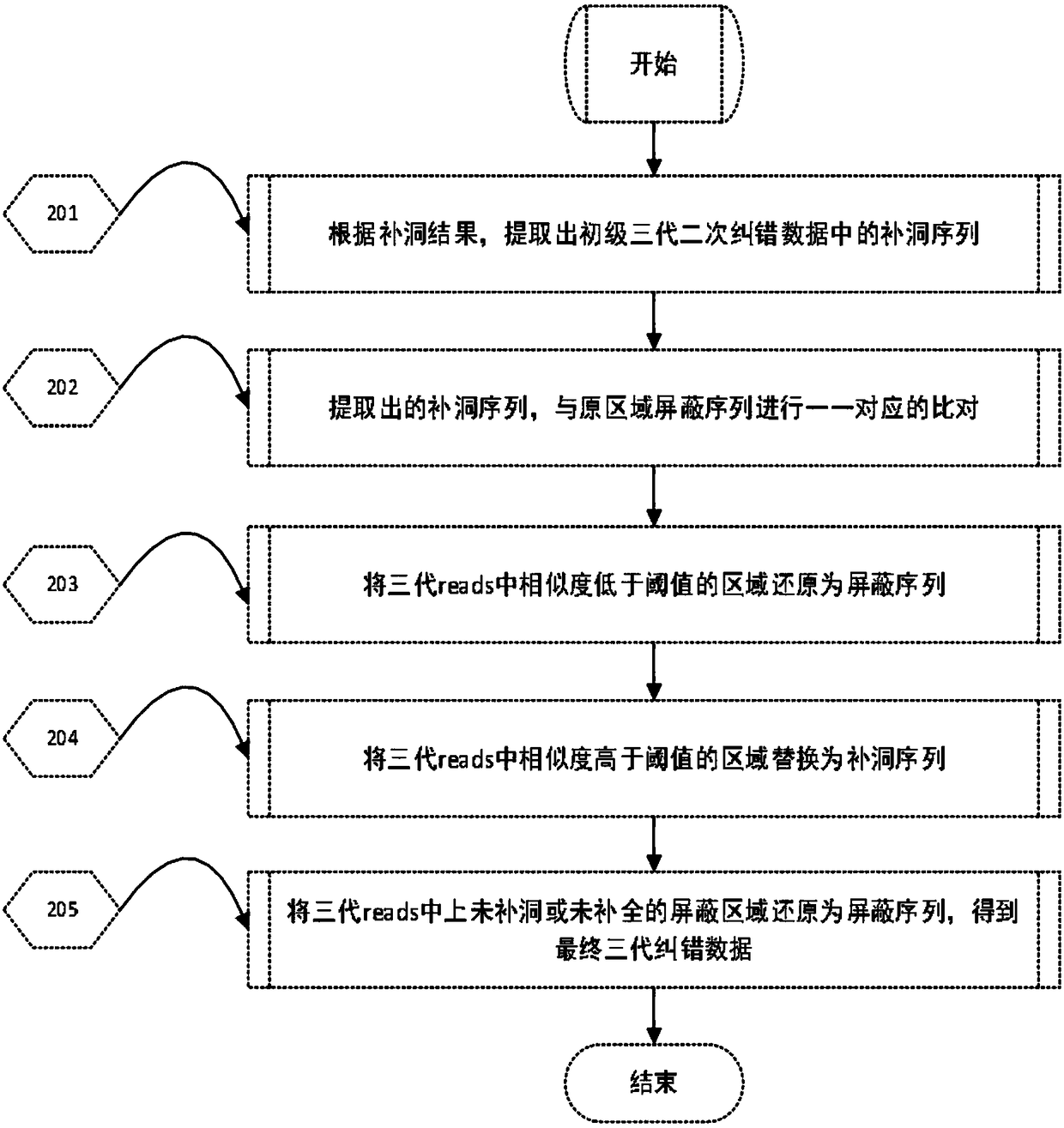
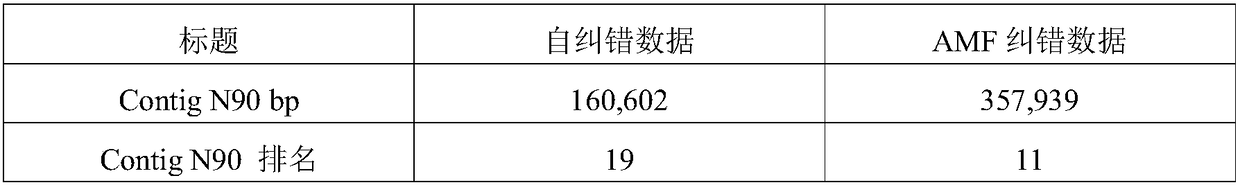
Processing method for nucleic acid third generation sequencing raw data and application thereof
ActiveCN108573127AImprove accuracyImprove throughputSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsThird generation sequencingRaw data
The invention discloses a processing method for nucleic acid third generation sequencing raw data and an application thereof. The processing method for the nucleic acid third generation sequencing rawdata includes comparing second generation short sequence data to third generation self-correcting data, obtaining the single-base covering depth of the third generation self-correcting data in a comparison result, shielding an area where the single-base covering depth is lower than the threshold as N, and adopting second generation sequencing hole filling software to fill the shielded area N to obtain the nucleic acid third generation sequencing data with low single-base error rate. According to the processing method for the nucleic acid third generation sequencing raw data, the second generation short sequence data is compared with third generation long sequence data, the second generation sequencing hole filling software is utilized to make up the shielded area N with the low single-base covering depth in the comparison result, the single-base error rate in the third generation sequencing data is effectively reduced, the sequencing quality is improved.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
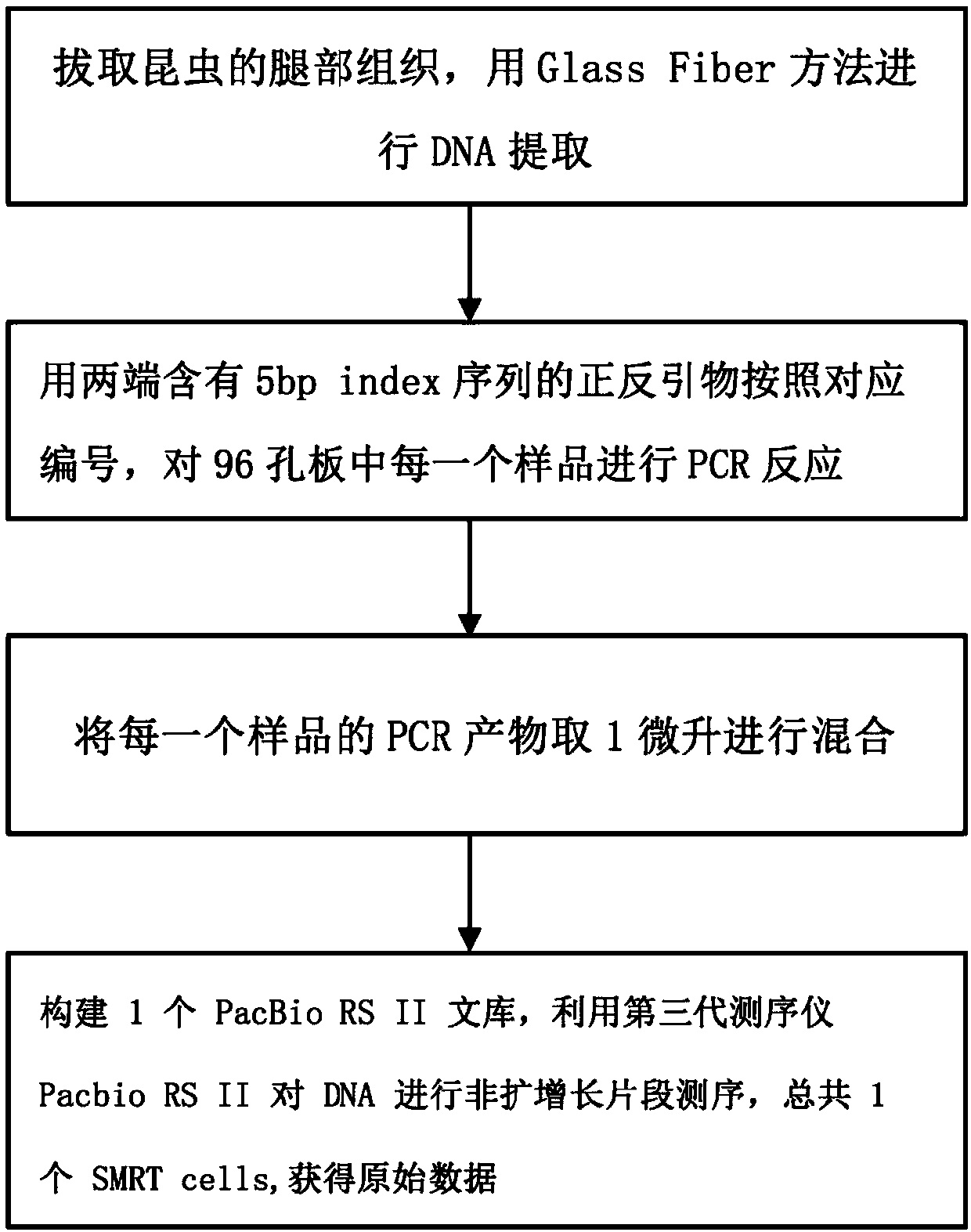
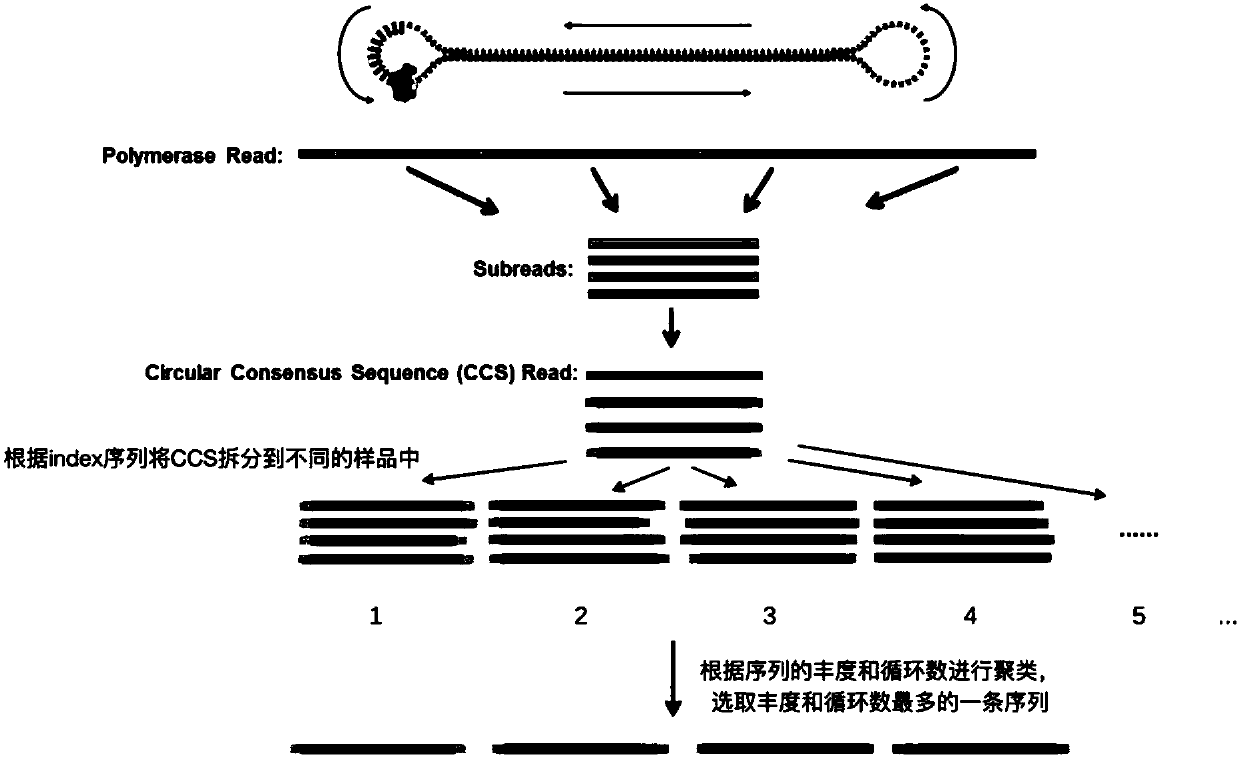
Method for obtaining bar code area of COI (C oxidase I) gene of insect in batched and high-accuracy ways by using PacBio monomolecule sequencing
InactiveCN107641646ASolve the problem of not being able to sequenceImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerNucleotide
The invention discloses a method for obtaining a bar code area of a COI (C oxidase I) gene of insect in batched and high-accuracy ways by using PacBio monomolecule sequencing. The method comprises thefollowing steps of (1) respectively performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) samples of a plurality of insects, wherein the forward primers sequentiallycomprise a forward label and a forward segment corresponding to the COI gene of the insect, and the reverse primers sequentially comprise a reverse label and a reverse segment corresponding to the COI gene of the insect; the forward segments in the forward primers are the same, and the reverse segments in the reverse primers are the same; the difference of at least two nucleotides exists betweenthe forward labels of every two forward primers; the difference of at least two nucleotides exists between the reverse labels of every two reverse primers; (2) respectively obtaining the amplified products after PCR amplification, and mixing, so as to obtain a mixed sample; (3) performing third-generation sequencing on the mixed sample. The method has the advantage that the important application and popularization value on obtaining the bar code area of the COI gene of the insect at high flux is realized.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD
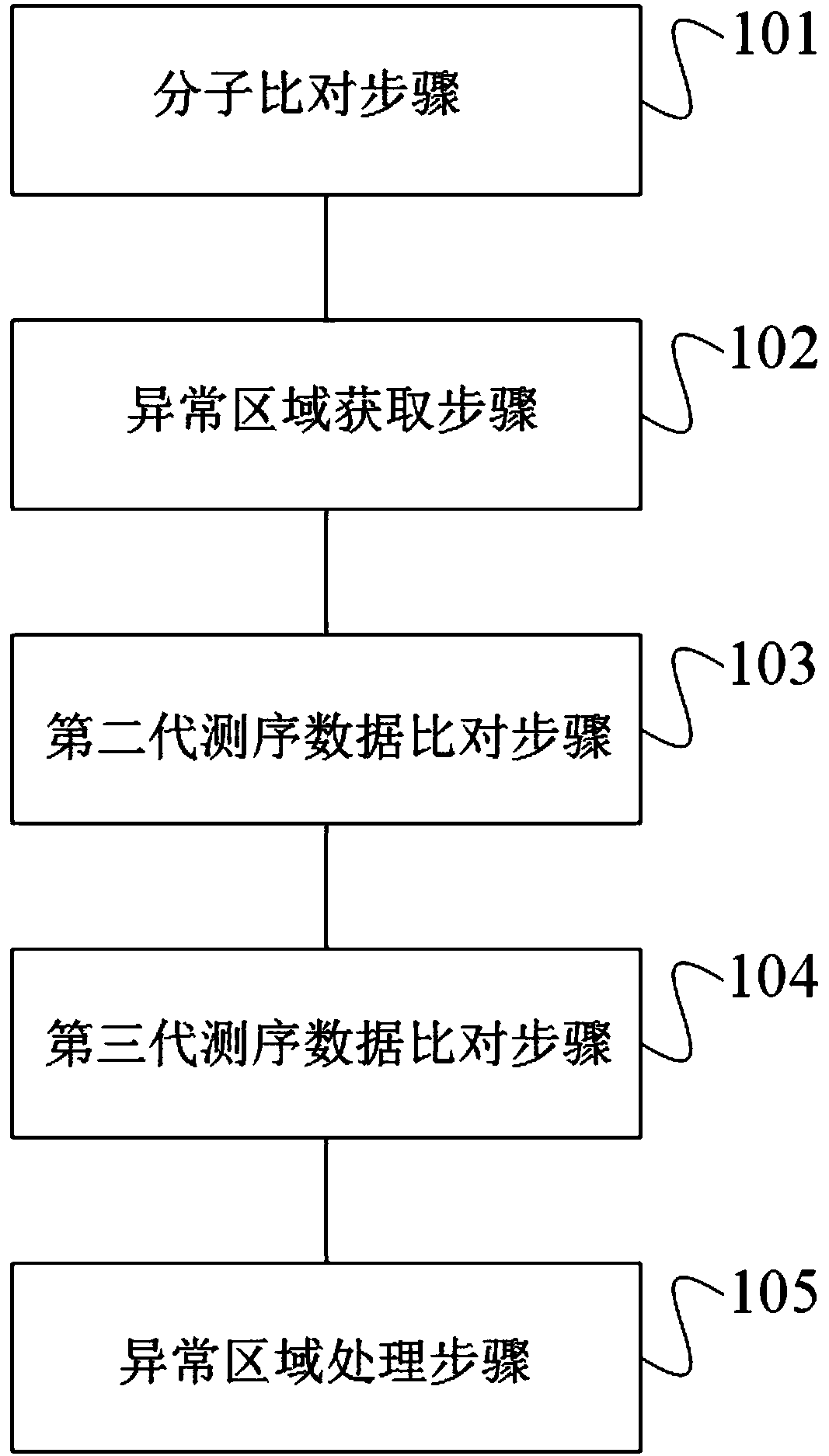
Method and device for repairing genome sequencing and assembling results, and storage medium
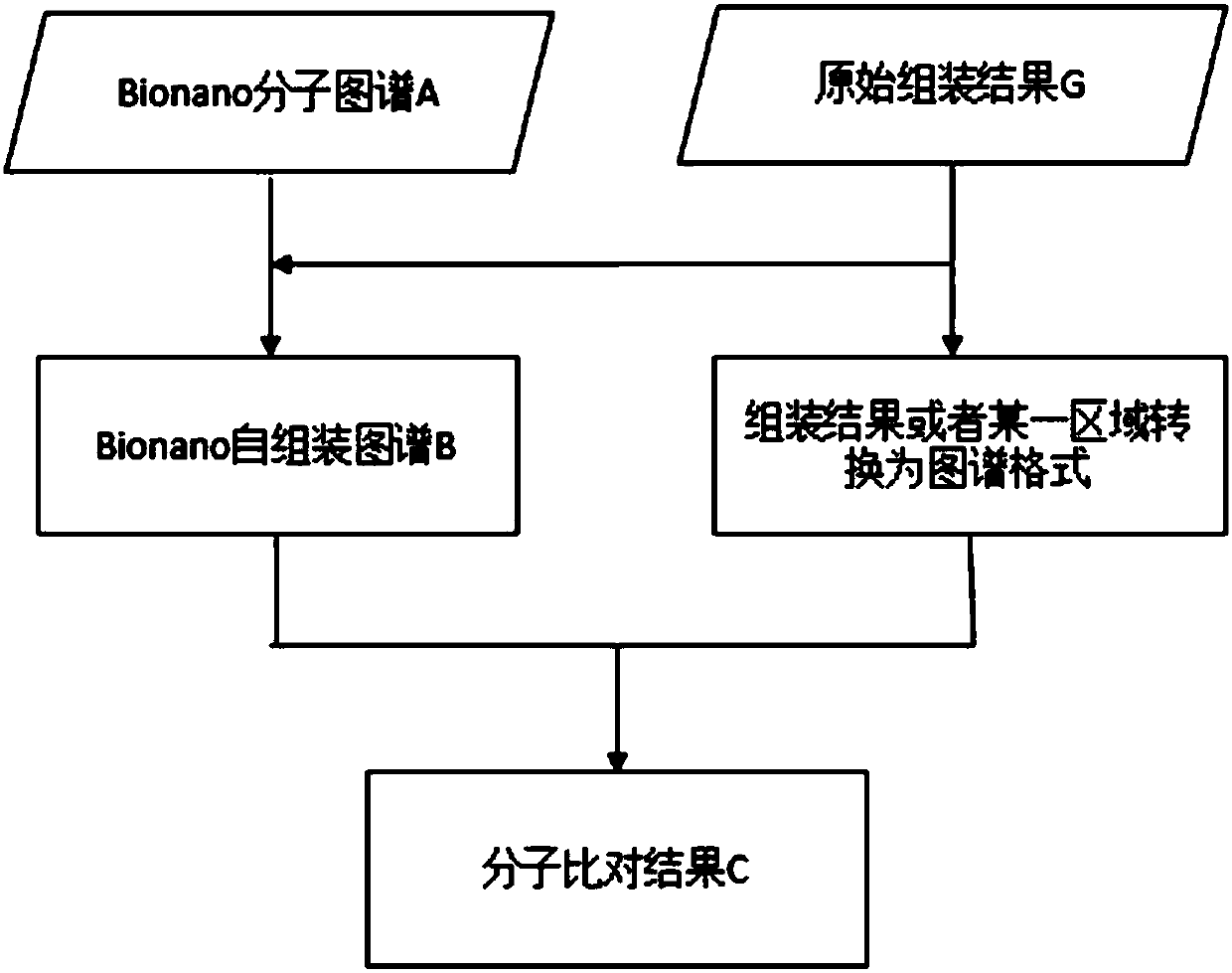
ActiveCN110310702AFix structural errorsImprove accuracySequence analysisHybridisationGenomic sequencingStructural error
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
Method for de novo assembly of genome by comprehensively applying third-generation ultra-long reads and second-generation linked reads
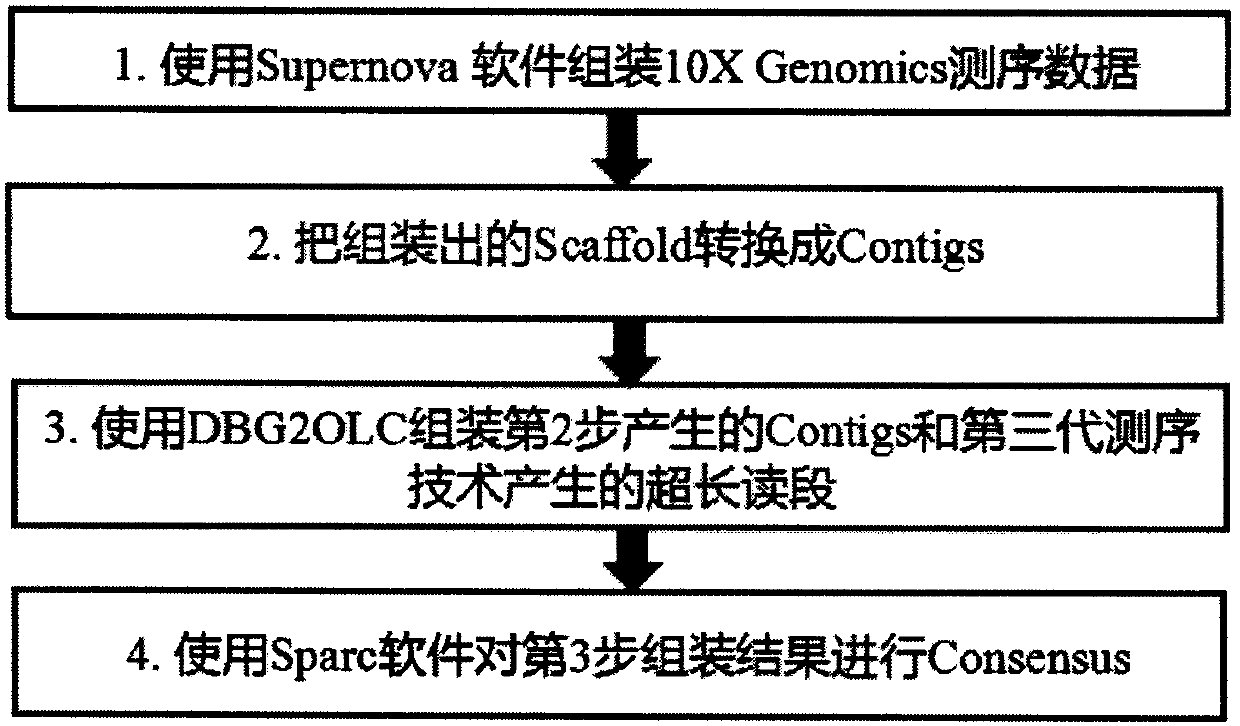
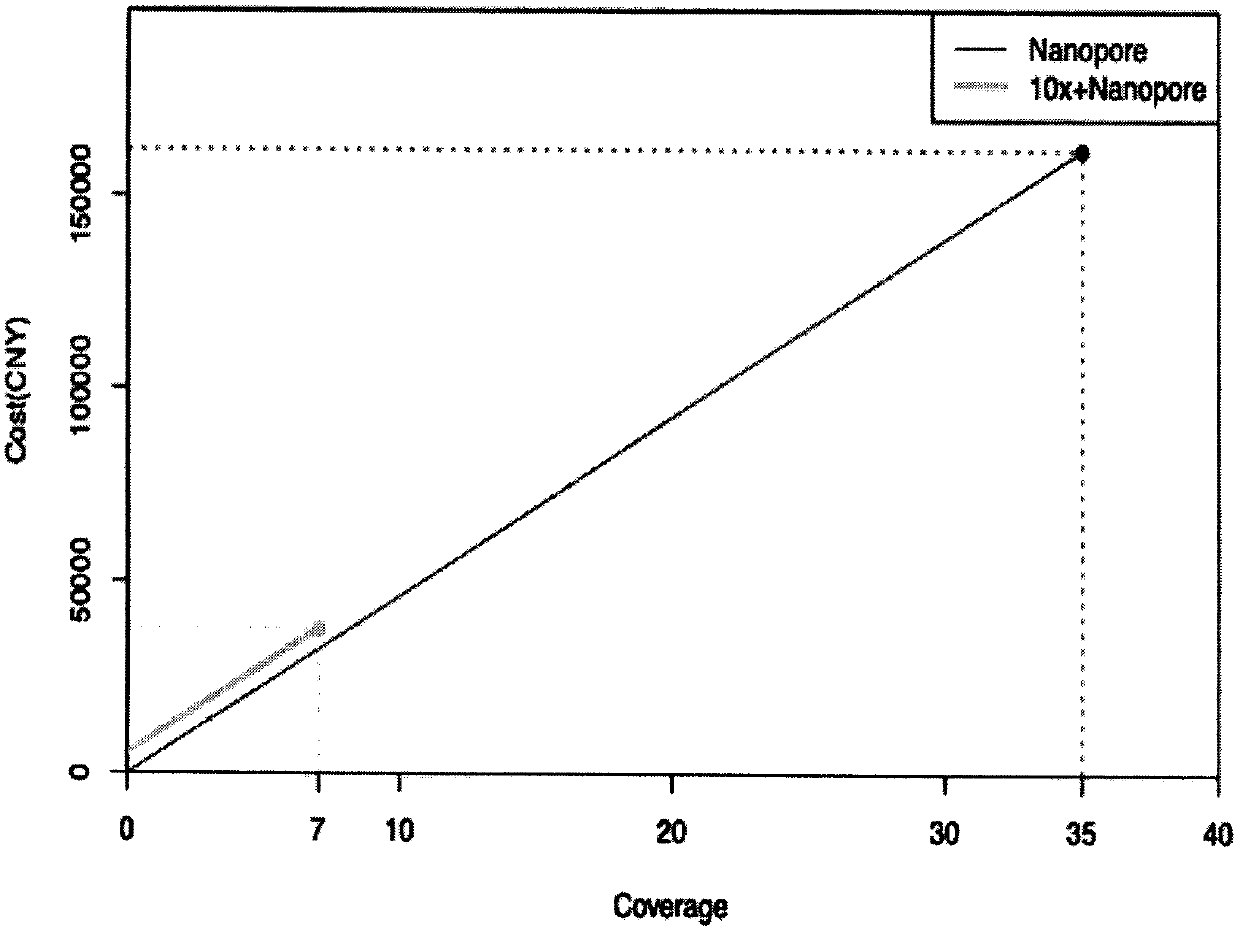
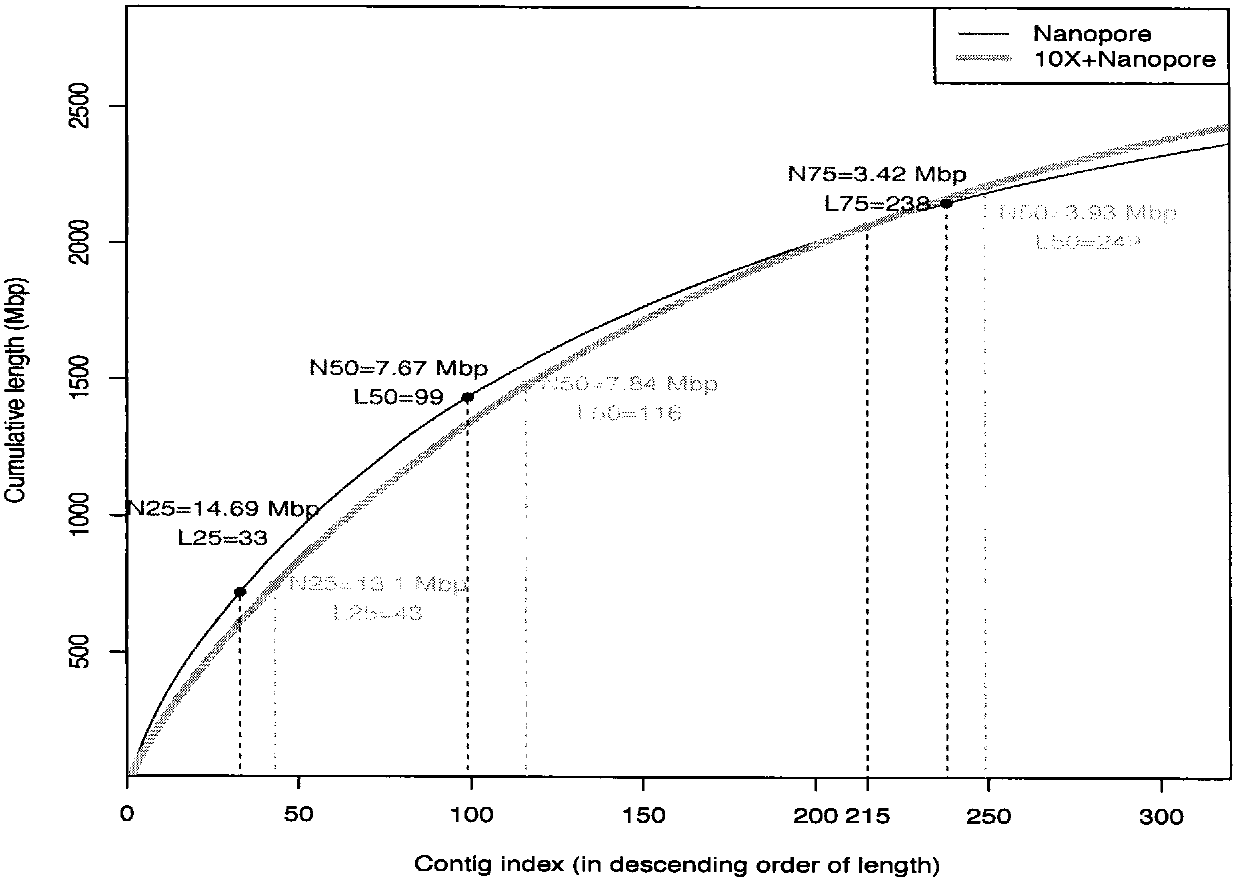
PendingCN110858503AQuality improvementHigh assembly resultsSequence analysisInstrumentsGenomicsGenomic sequencing
The invention discloses a method for high-efficiency and high-quality de novo assembly of a genome by comprehensively applying third-generation ultra-long reads and second-generation linked reads. Thethird-generation ultra-long reads are ultra-long reads generated by a third-generation sequencing technology Nanopore and PacBio which are most widely applied at present. The second-generation linkedreads are reads generated by a 10x Genomics sequencing platform. A high-quality genome sequence is assembled through high-efficiency hybrid assembly software. According to the method, the advantagesof the third-generation super-long reads and the second-generation linked reads are brought into full play and are integrated, and high-efficiency assembly software DBG2OLC and SPARC are combined, sothat the application cost of the third-generation sequencing technology is greatly reduced. The invention provides an efficient, reliable and economic method for large-scale and high-quality genome denovo assembly by applying the third-generation sequencing technology.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
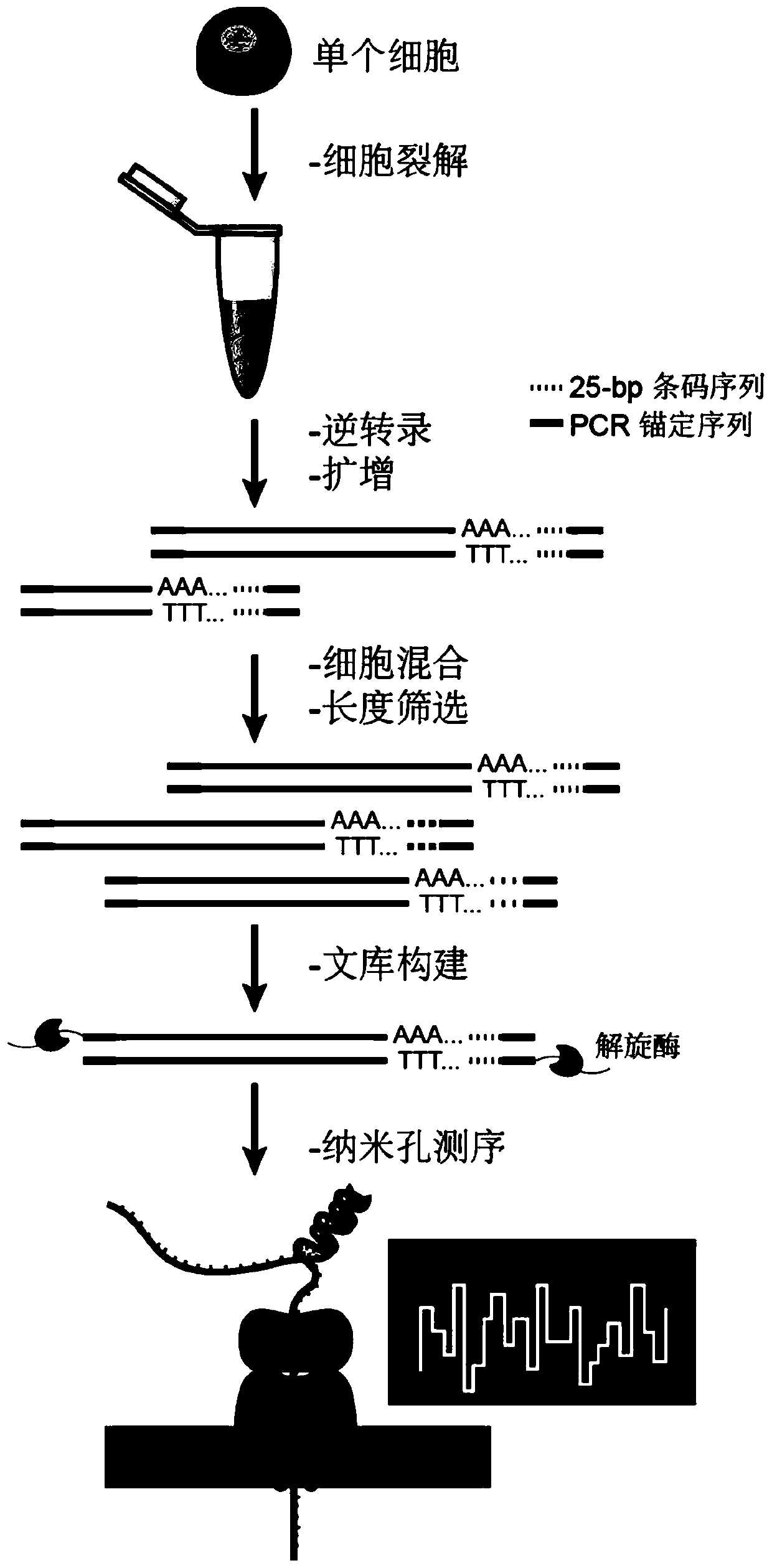
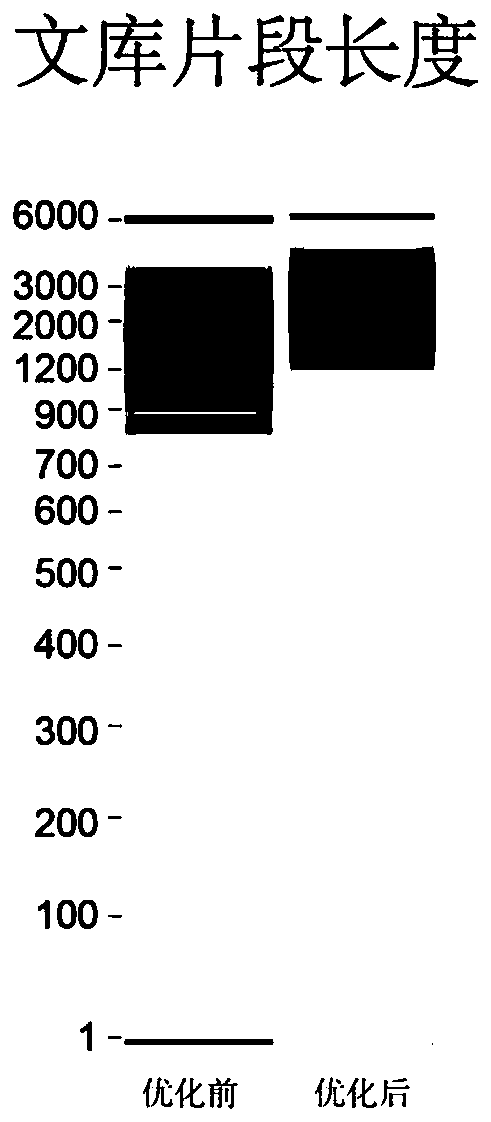
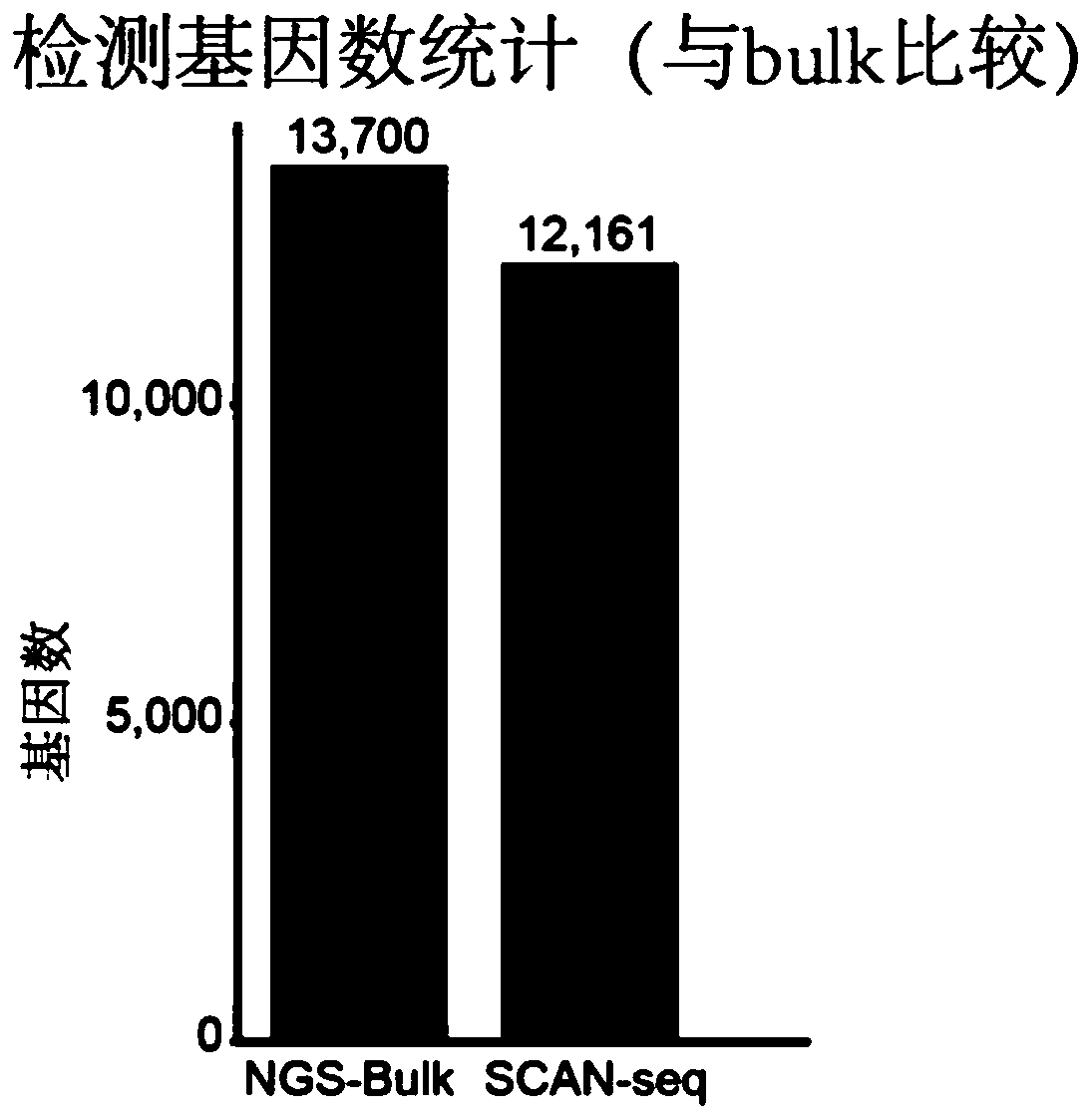
Single cell transcriptome sequencing method based on third-generation sequencing
ActiveCN111549099ASolve the technical problem of high demand for original samplesAchieving Precise SequencingMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle cell transcriptomeComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention provides a single-cell transcriptome sequencing method based on third-generation sequencing, which comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out reverse transcription on single-cell RNA by using a reverse transcription primer to obtain cDNA with a bar code; (2) carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on the cDNA with the bar code, and mixing obtained PCR amplification products with different single cell sources; or mixing cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) with barcodes from different single cell sources and then carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification; the reverse transcription primer sequentially comprises an anchoring sequence, a bar code sequence and poly dT from the 5'end to the 3 'end. According to the invention, a bar code sequence is added into a reverse transcription primer to carry out reverse transcription on single-cell full-length RNA; sequences of different single cell sources are marked, DNA amplification products of different sources are mixed to meet the requirement of a third-generation sequencing platform for the template amount, and accurate sequencing of a full-length transcript is achieved through the third-generation sequencing platform.
Owner:BIOISLAND LAB
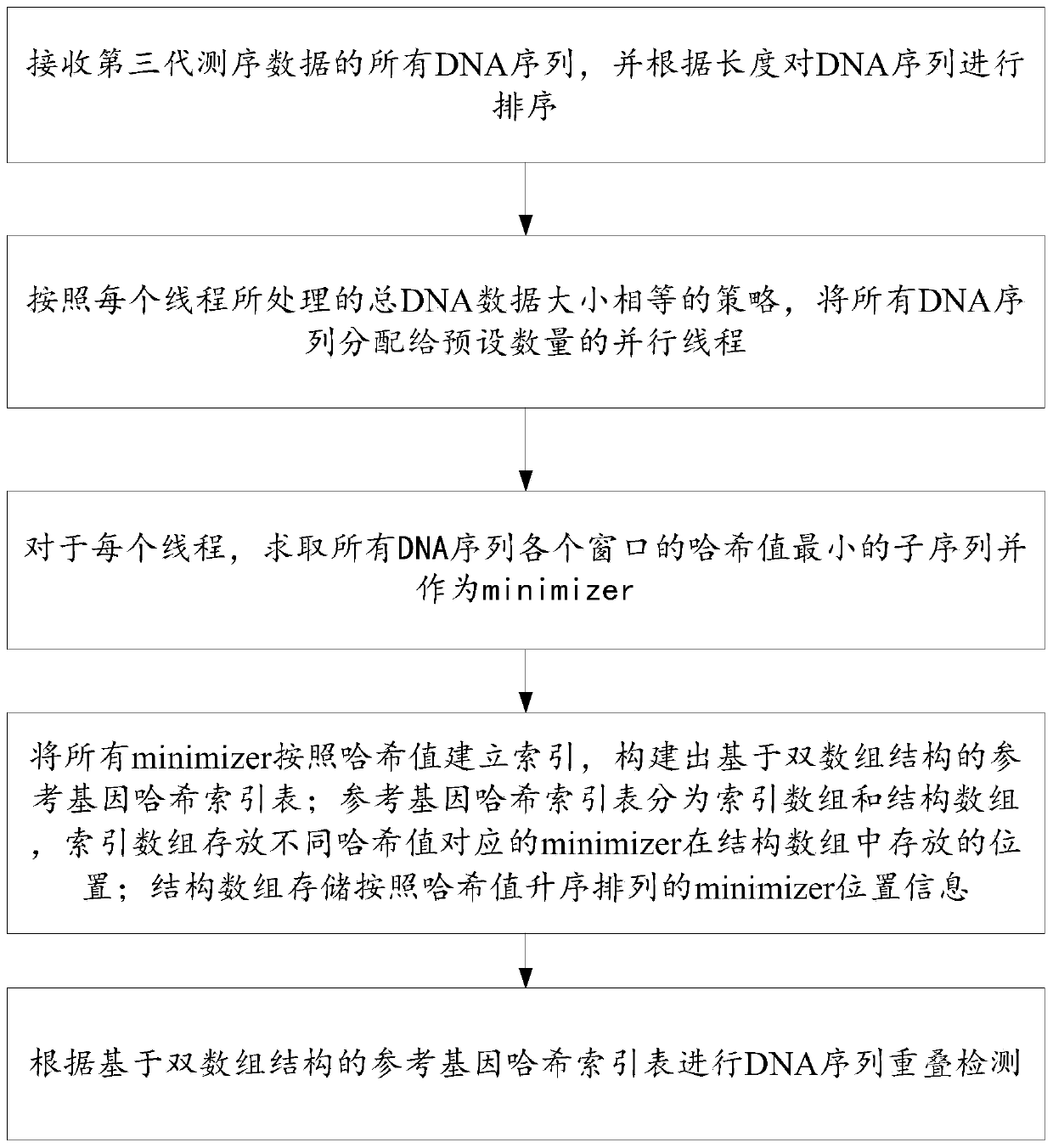
Three-generation sequencing data overlapping detection method and system
PendingCN111292805ALoad balancingGuaranteed speedupResource allocationSequence analysisReference genesAlgorithm
The invention provides a three-generation sequencing data overlapping detection method and system. The third-generation sequencing data overlapping detection method comprises the following steps: receiving all DNA sequences of third-generation sequencing data, and sorting the DNA sequences according to the length; allocating all DNA sequences to a preset number of parallel threads according to a strategy that the total DNA data processed by each thread is equal in size; for each thread, solving a sub-sequence with the minimum hash value of each window of all DNA sequences and taking the sub-sequence as a minimizer; establishing indexes for all the minimizers according to the hash values, and constructing a reference gene hash index table based on a double-array structure, wherein the reference gene hash index table is divided into two arrays, the index arrays store the storage positions of the minimizers corresponding to different hash values in the structure array, and the structure array stores the position information of the minimizers; and performing DNA sequence overlapping detection according to the reference gene hash index table based on the double-array structure. Sequencing data overlapping detection efficiency can be improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method and system for determining fetal beta thalassemia gene haplotype
ActiveCN108315404AAvoid the risk of harming the fetusRelieve stressMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsRelationship - FatherBeta thalassemia
The invention relates to a method for determining a fetal beta thalassemia gene haplotype. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a third-generation sequencing library based on a bloodsample, wherein the blood sample is taken from blood samples of fetal father and mother; performing third-generation sequencing on the third-generation sequencing library to obtain a third-generationsequencing result; determining father and mother beta thalassemia gene haplotypes according to the third-generation sequencing result; constructing a second-generation sequencing library based on a detection sample, wherein the detection sample is taken from peripheral blood samples of a pregnant woman; performing second-generation sequencing on the second-generation sequencing library to obtaina second-generation sequencing result; determining the fetal beta thalassemia gene haplotype according to the second-generation sequencing result and the father and mother beta thalassemia gene haplotypes.
Owner:GUANGZHOU JINGKE DX CO LTD
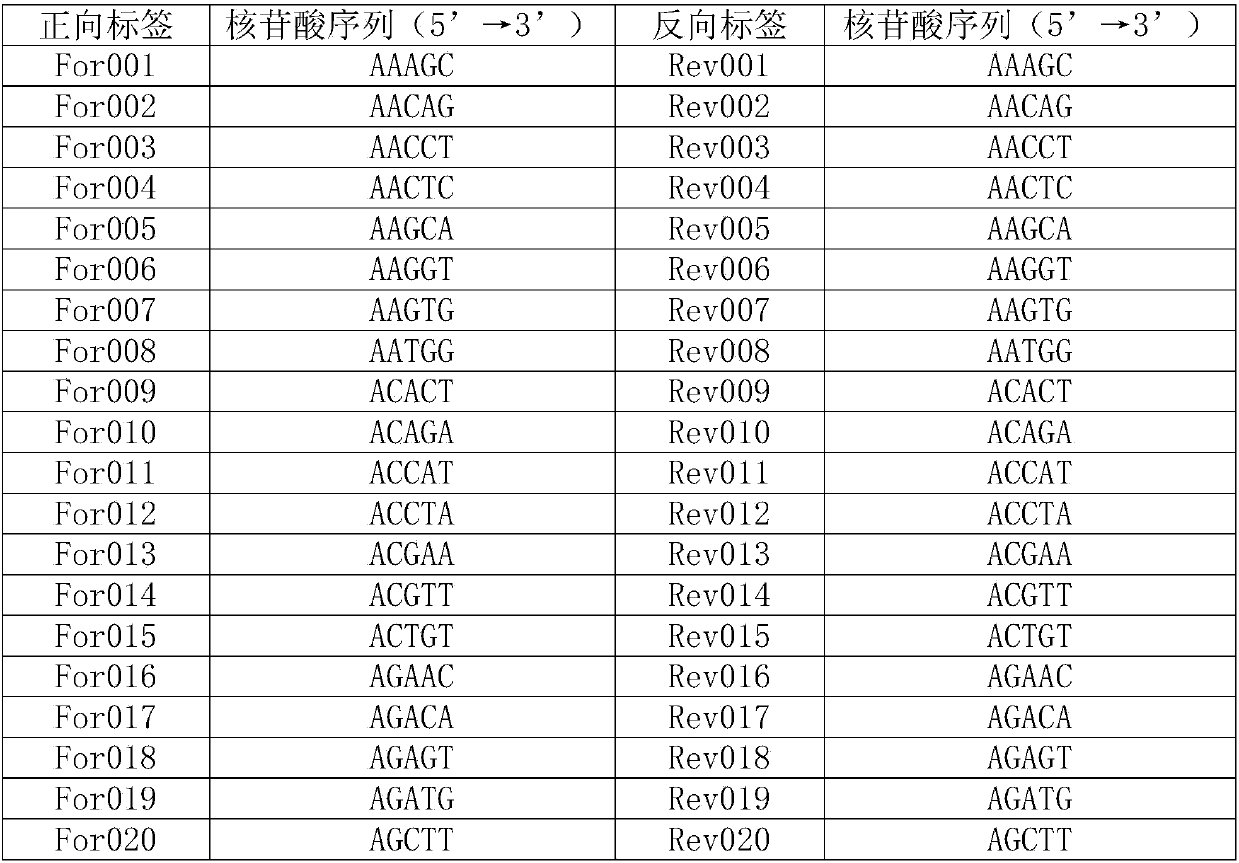
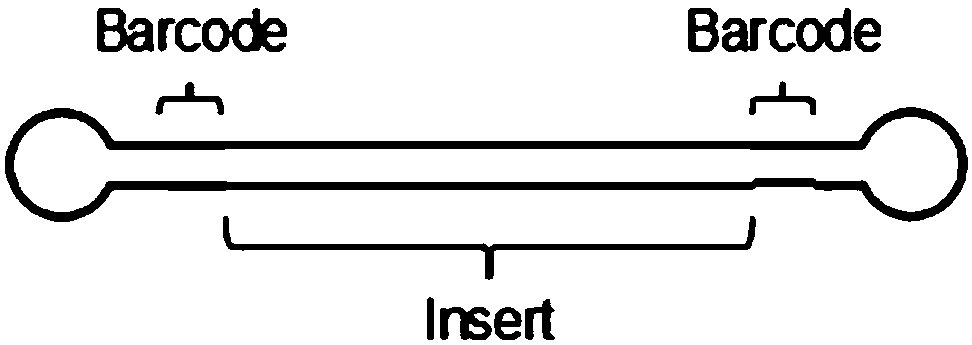
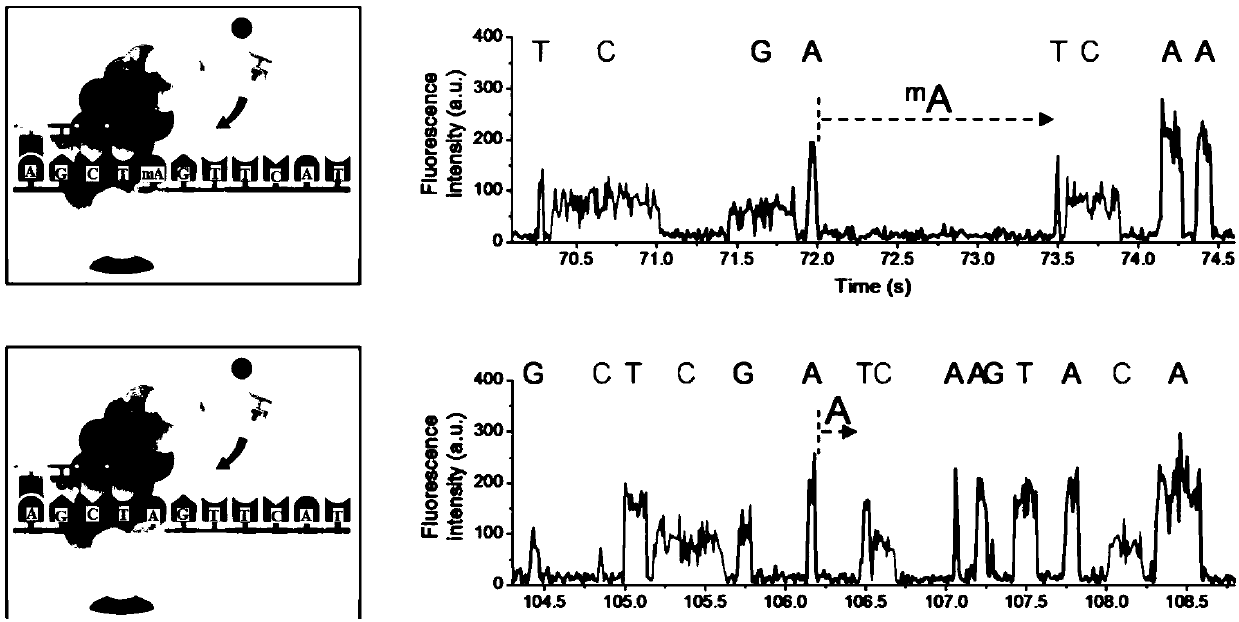
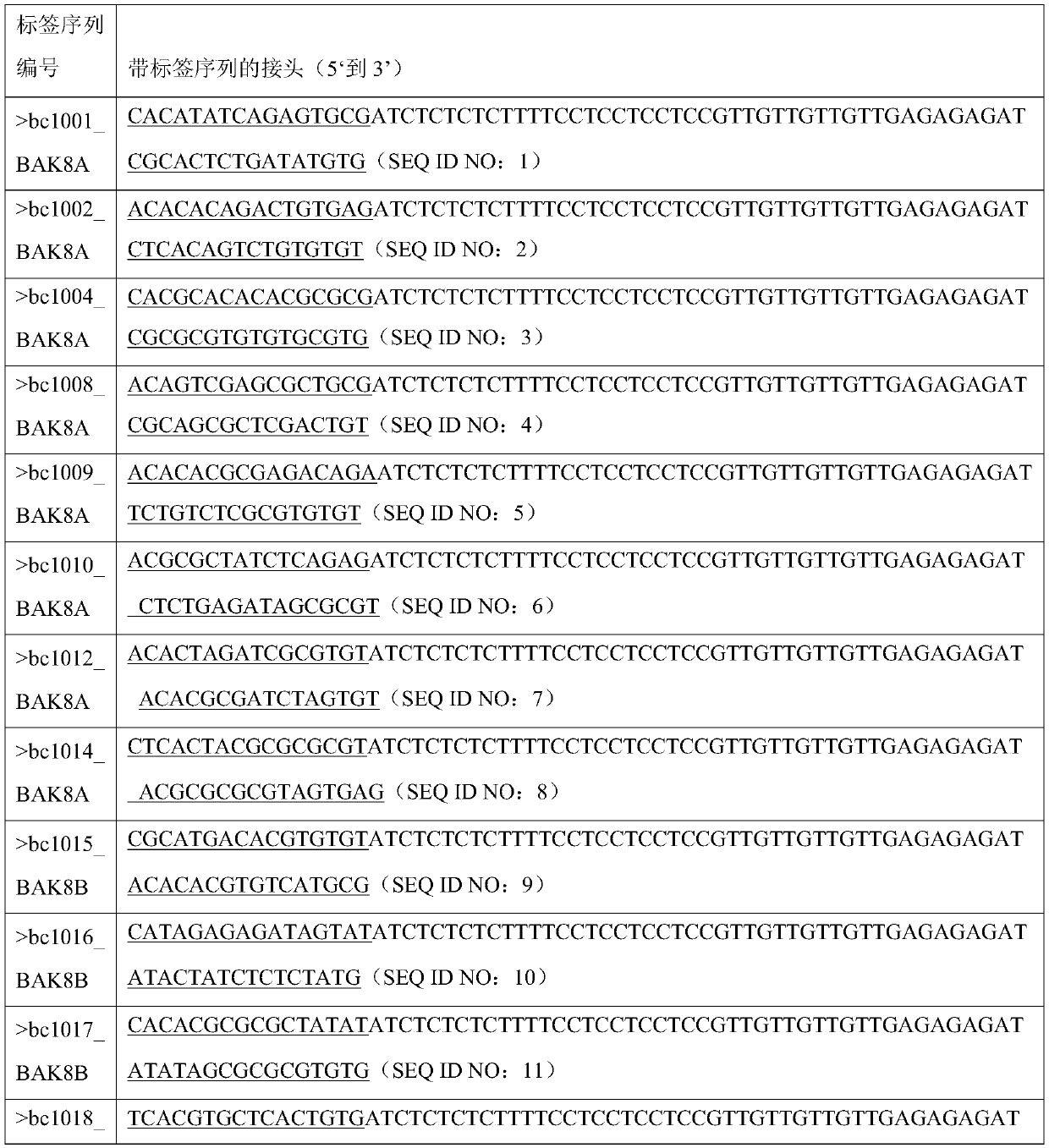
Barcode, linker sequence and kit for third-generation sequencing, and library construction method for third-generation sequencing
InactiveCN110938625AImprove split ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGeneticsBarcode
The invention provides a barcode, a linker sequence and a kit for third-generation sequencing, and a library construction method for the third-generation sequencing. The barcode is composed of a plurality of consecutive bases, wherein in the bases, at least part of the bases are methylated bases. The linker sequence includes the above barcode. The methylated barcode used in the invention can splitthird-generation sequencing data which cannot be split by a conventional splitting method, so that the splitting rate of the third-generation sequencing data is greatly improved; and the overall splitting rate of the third-generation sequencing data can reach about 85%.
Owner:WUHAN BGI CLINICAL LAB CO LTD
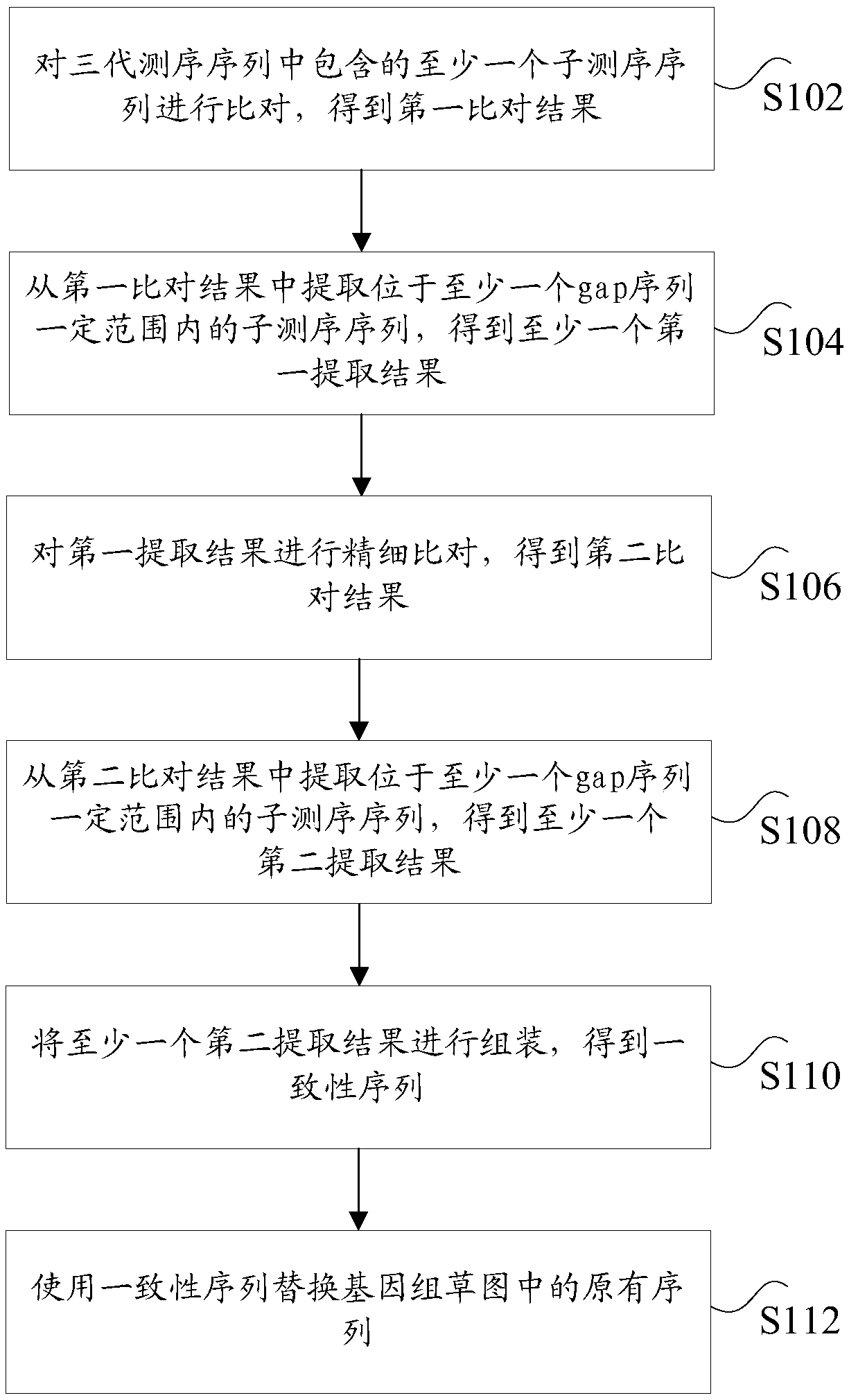
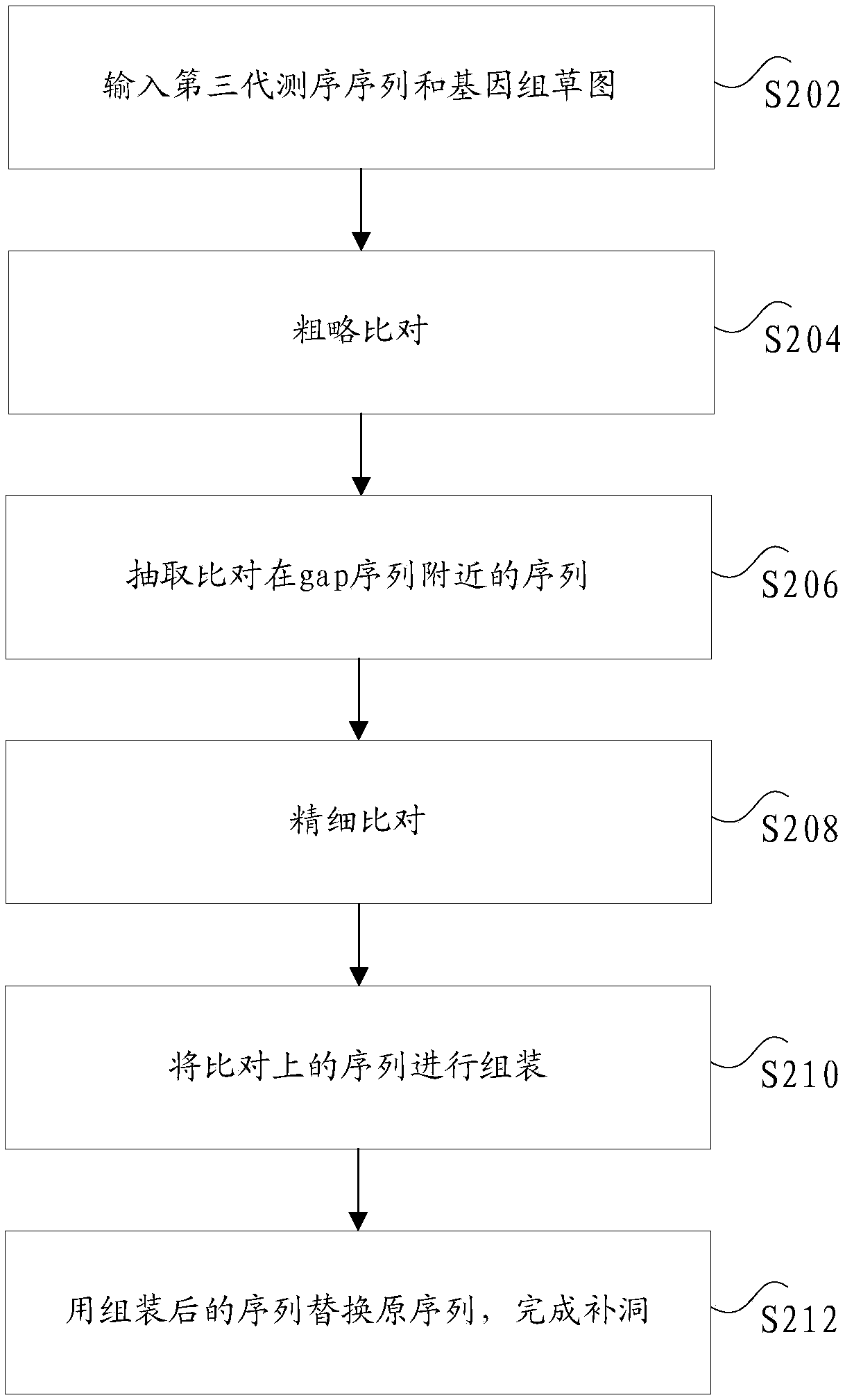
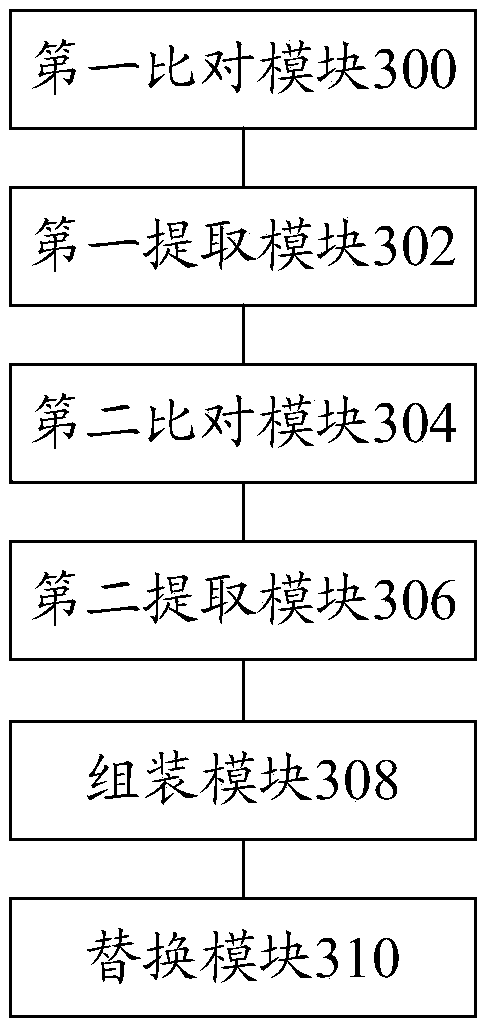
Hole filling method and device based on third-generation sequencing sequence
ActiveCN108763871AHigh speedReduce consumptionSpecial data processing applicationsResource consumptionThird generation sequencing
The invention discloses a hole filling method and device based on a third-generation sequencing sequence. The method includes the following steps: comparing at least one sub-sequencing sequence contained in a third-generation sequencing sequence to obtain a first comparison result; extracting a sub-sequencing sequence located within a certain range of at least one gap sequence from the first comparison result to obtain at least one first extraction result; performing fine comparison on the first extraction result to obtain a second comparison result; extracting a sub-sequencing sequence located within a certain range of the at least one gap sequence from the second comparison result to obtain at least one second extraction result; assembling the at least one second extraction result to obtain a consistent sequence; and replacing an original sequence in a genome sketch with the consistent sequence, wherein the gap sequence is an unknown sequence. According to the scheme of the invention, the technical problem that in the process of performing genome hole filling on sequencing data, the process of comparing the sequencing sequence has a low speed, and large resource consumption is caused can be solved.
Owner:BEIJING NOVOGENE TECH CO LTD
Third-generation sequencing phytoplankton genomic DNA extraction method and application thereof
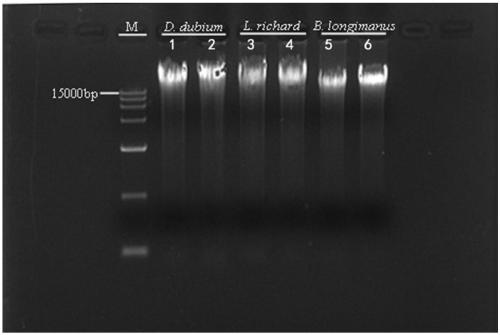
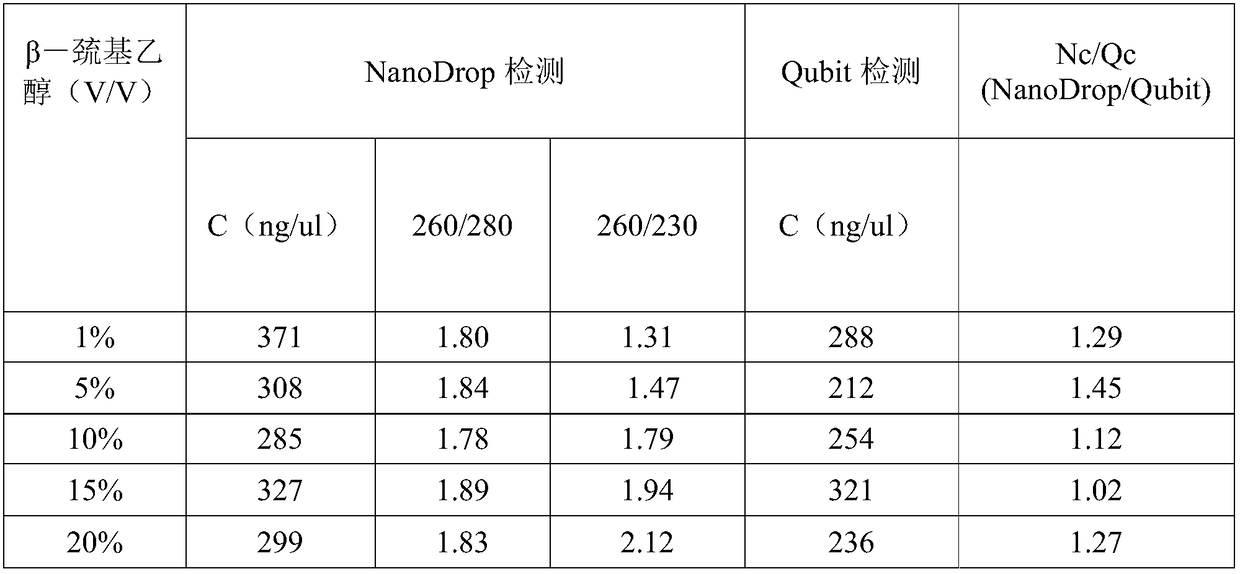
ActiveCN109337955AQuick collectionHigh purityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGenomic DNADigestion
The invention discloses a third-generation sequencing phytoplankton genomic DNA extraction method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding 18% to 20% (V / V) beta-mercaptoethanol to a buffer GA, then adding zooplankton, and grinding to obtain a tissue buffer solution; (2) adding protease PK to the tissue buffer for digestion, then adding RNase A, allowing standing still, centrifuging to obtain supernatant I, adding a solvent, centrifuging to obtain supernatant II, finally adding a buffer GB, mixing uniformly, and adding anhydrous ethanol to obtain a mixed solution; (3) adding the mixed solution to an adsorbent column CB3, rinsing and eluting to obtain phytoplankton genomic DNA. The method disclosed by the invention is simple, easy to operate, and capableof effectively removing pigments, and obtained phytoplankton genomic DNA fragments are complete, high in purity, and high in concentration, thereby being capable of providing the assurance for smoothimplementation of the third-generation sequencing of zooplanktons, especially cladocerans.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Third generation sequencing alignment algorithm
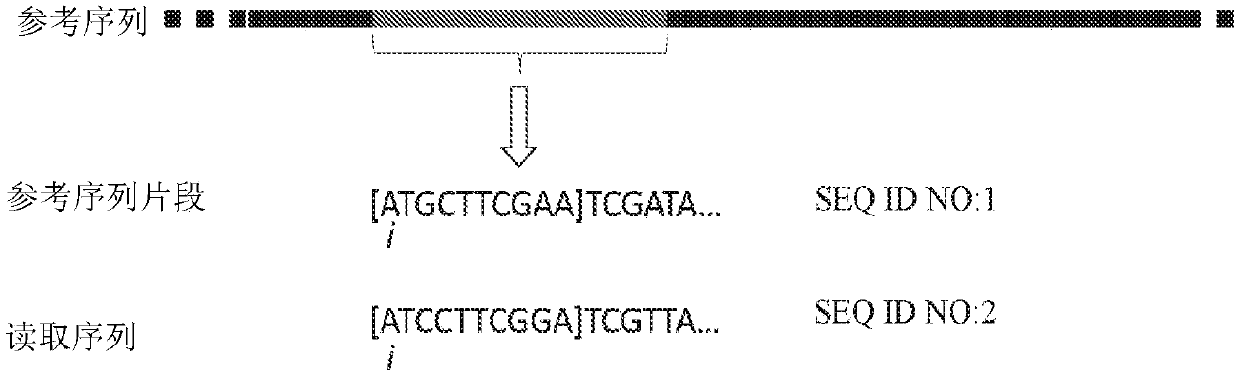
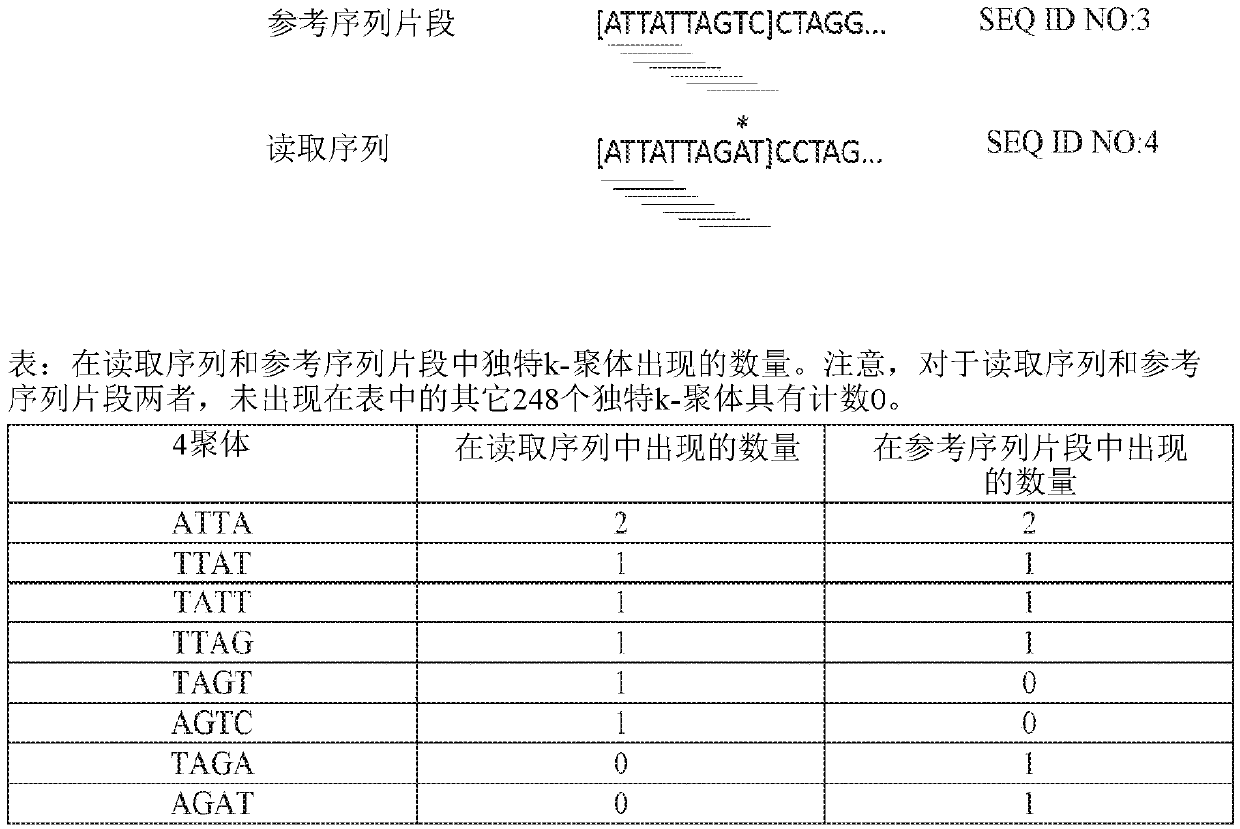
InactiveCN108699601AMicrobiological testing/measurementData visualisationSequence alignment algorithmAlgorithm
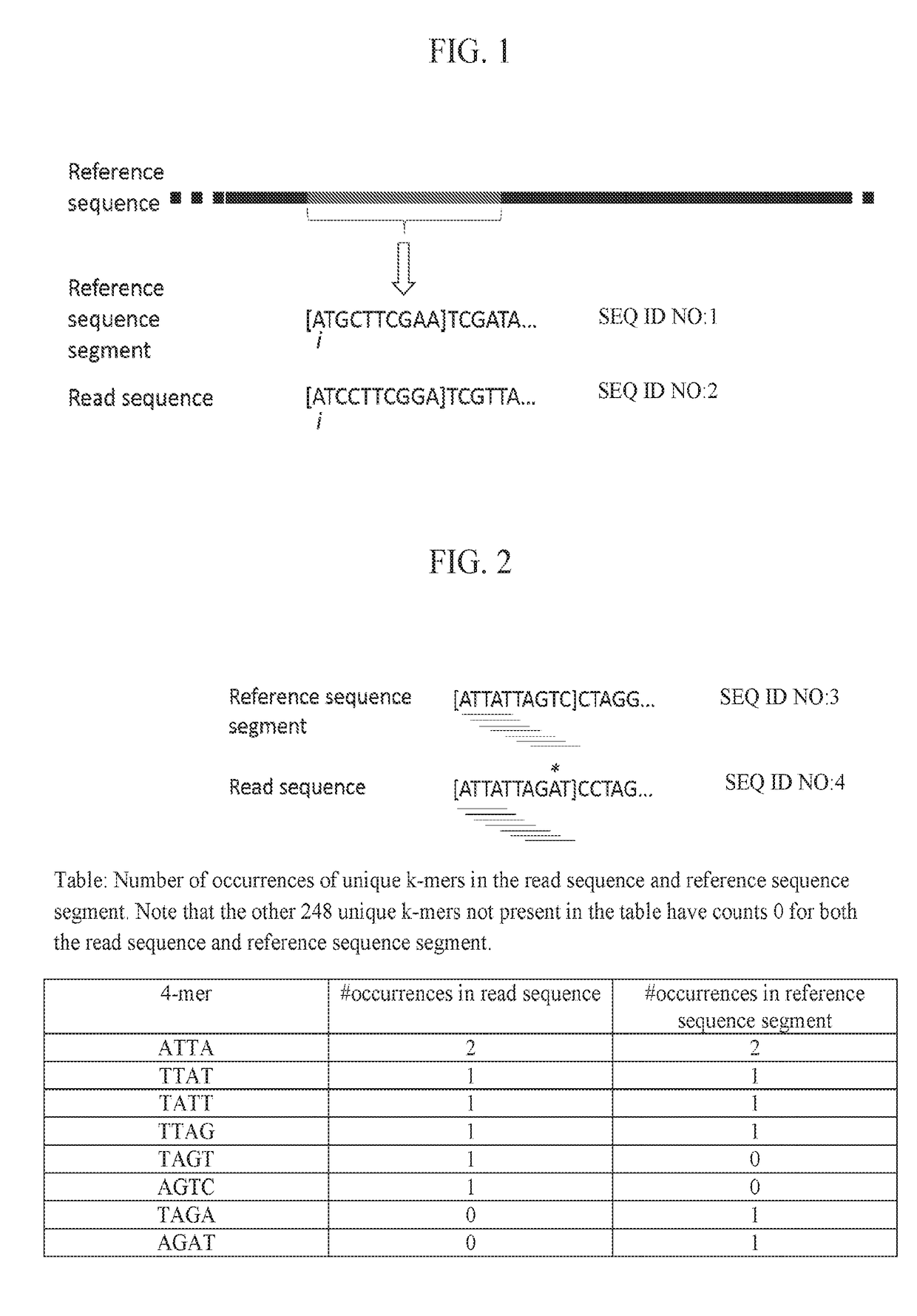
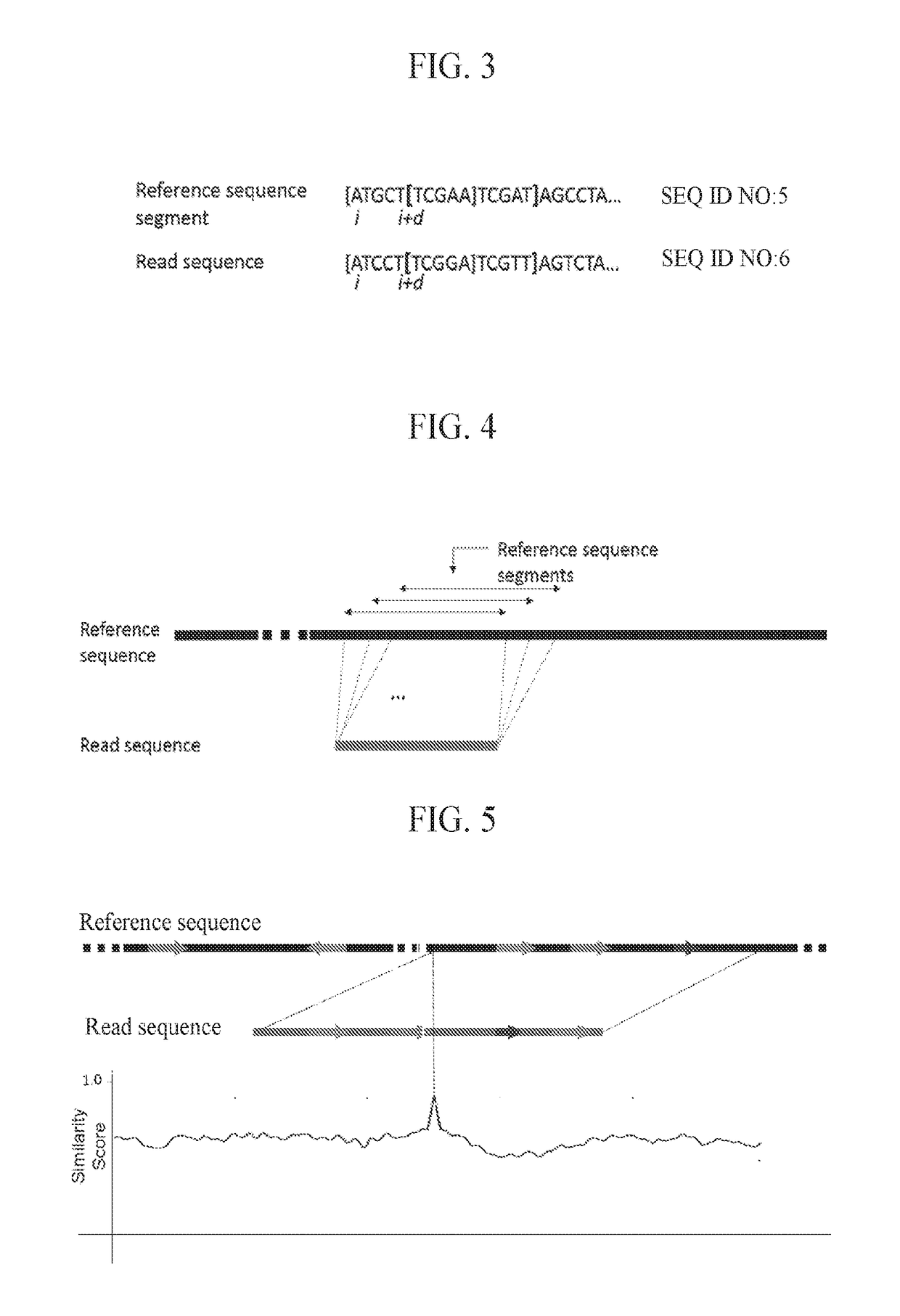
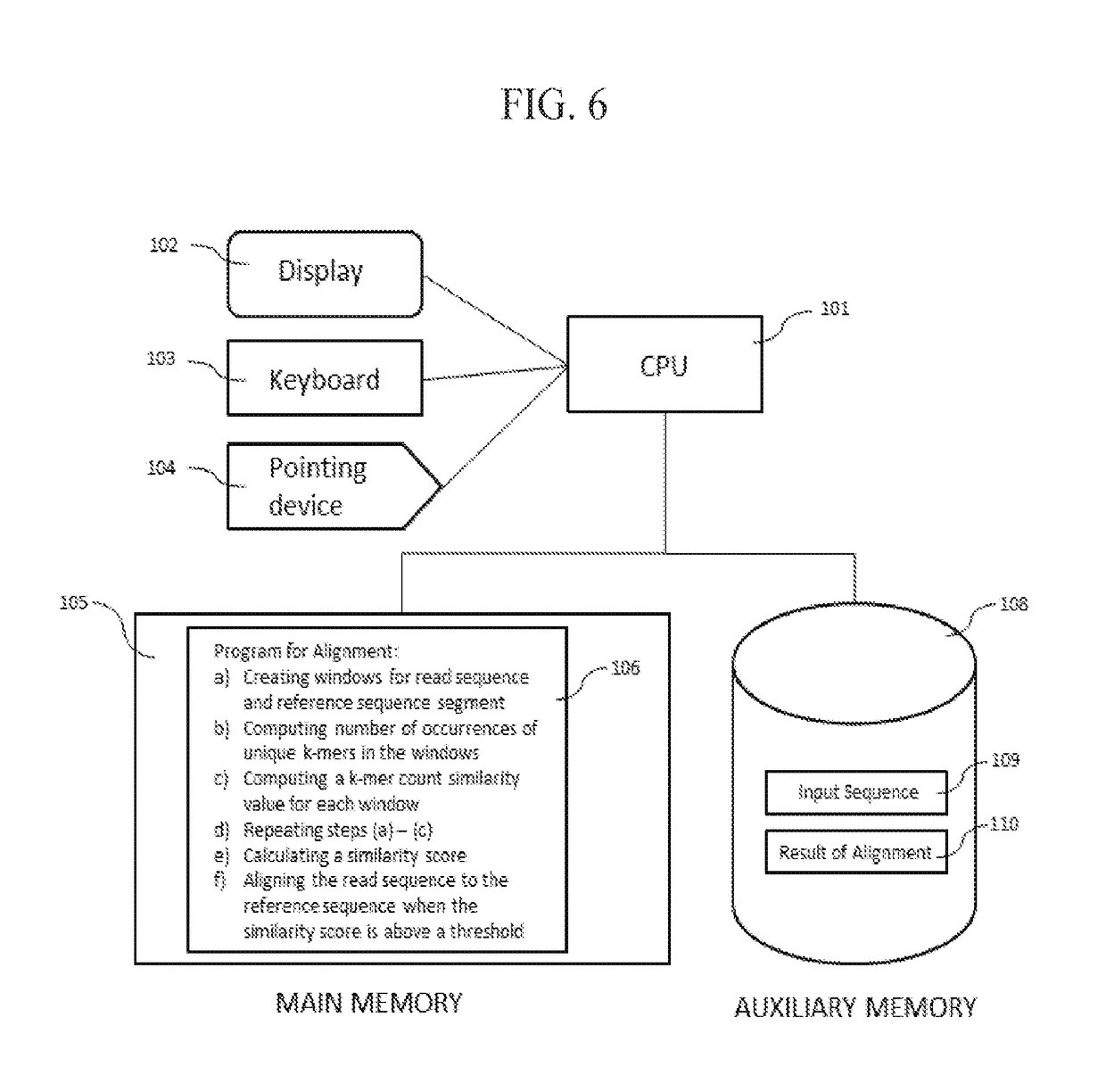
Methods, software, and systems for aligning a read sequence to a reference sequence are disclosed. In certain embodiments, the methods, software, and systems involve determining similarity of distribution of k-mers between a region of the read sequence and a region of the reference sequence in order to determine whether the region of the read sequence maps to the region of the reference sequence.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Fetus spinal muscular atrophy gene haplotype determining method and system
ActiveCN108070648AAvoid the risk of harming the fetusRelieve stressMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsHaplotypeThird generation sequencing
The invention relates to a fetus spinal muscular atrophy gene haplotype determining method and system. The method comprises the following steps of, on the basis of blood samples, structuring a three-generation sequencing library, wherein the blood samples are from parents of a fetus; performing third-generation sequencing on the three-generation sequencing library to acquire third-generation sequencing results; according to the third-generation sequencing results, determining spinal muscular atrophy gene haplotypes of the parents; based on detected samples, structuring a second-generation sequencing library, wherein the detected samples are peripheral blood samples of a pregnant mother; performing second-generation sequencing on the second-generation sequencing library to obtain second-generation sequencing results; according to the second-generation sequencing results and the spinal muscular atrophy gene haplotypes of the parents, determining the spinal muscular atrophy gene haplotypeof the fetus.
Owner:GUANGZHOU JINGKE DX CO LTD
Efficient method for actinomycete genome splicing
InactiveCN106778076AComplete splicing resultSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsGenomicsThird generation sequencing
The invention discloses an efficient method for actinomycete genome splicing. The method includes the steps that A, actinomycete is subjected to database building sequencing through a third-generation sequencing platform; B, the actinomycete is subjected to database building sequencing through a second-generation sequencing platform; C, stopping data of the third-generation sequencing platform is spliced; D, stopping data of the second-generation sequencing platform is spliced; E, the splicing results of the two platforms are subjected to collinearity analysis to obtain the connecting relationships between all sequences, and the sequences are connected depending on the relationships; F, the connecting result is corrected through the stopping data of the second-generation sequencing platform. According to the efficient method for actinomycete genome splicing, the advantages of third-generation sequencing and the advantages of second-generation sequencing are combined, the complete actinomycete genome splicing results are obtained, and the genomics basis is provided for revealing the physiological and biochemical characteristics and the metabolic rule of actinomycete genome splicing.
Owner:SHANGHAI PASSION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Third Generation Sequencing Alignment Algorithm
InactiveUS20190042696A1Massive throughputLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementData visualisationSequence alignment algorithmThird generation
Methods, software, and systems for aligning a read sequence to a reference sequence are disclosed. In certain embodiments, the methods, software, and systems involve determining similarity of distribution of k-mers between a region of the read sequence and a region of the reference sequence in order to determine whether the region of the read sequence maps to the region of the reference sequence.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Microbial detection system based on third-generation sequencing technology
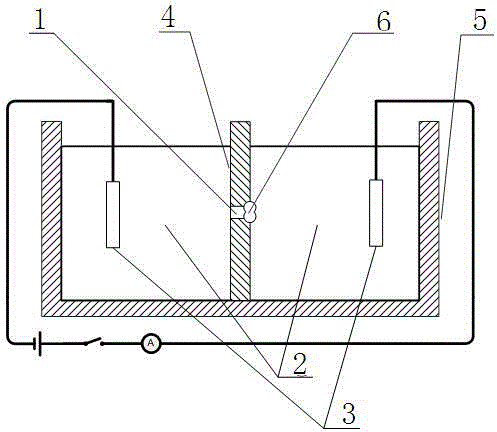
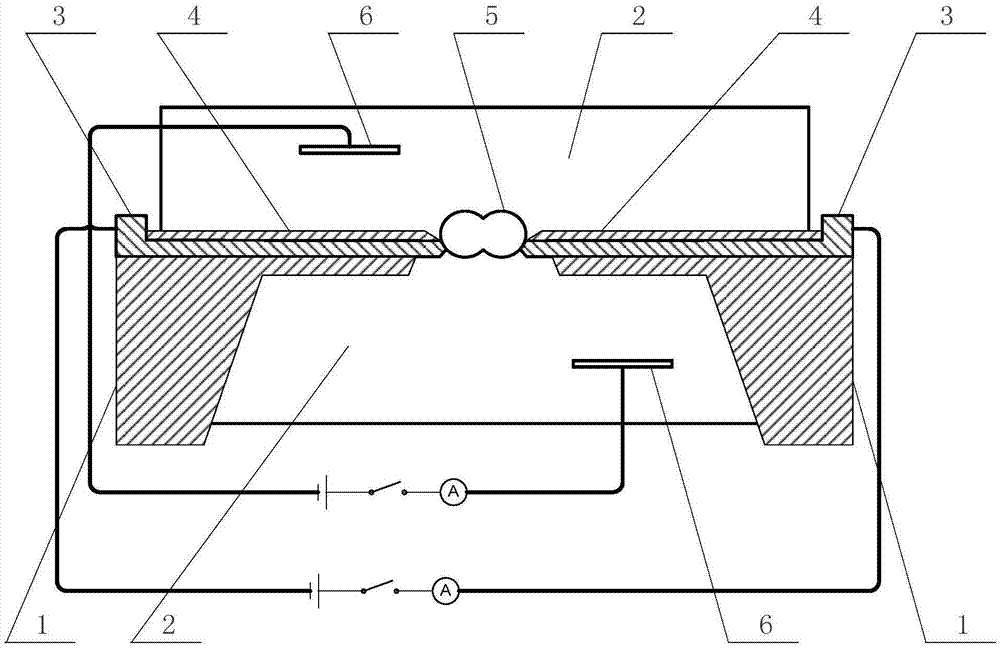
PendingCN113789257AAchieve acquisitionRealize exception judgmentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsData displayMicroorganism
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial detection, in particular to a microbial detection system based on a three-generation sequencing technology, which comprises a sample collection device, a sample vibrating device, a sample detection device and a data display device, a test liquid is arranged in the collection device, according to the present invention, an obtained microbial sample is detected by using the third-generation sequencing technology so as to achieve the obtaining of the detection result of the microbial sample; through intelligent identification processing of the detection result, abnormity judgment of the detection result is realized; according to the method, not only is the detection result of the microbial sample obtained, but also the abnormality judgment of the detection result is realized by performing intelligent identification processing on the detection result; and compared with the prior art, the method does not need to culture a microbial sample, and can realize collection of the detection result by adopting the third-generation sequencing technology, so that the time consumed by detection is greatly shortened, and meanwhile, the cost consumed by microbial detection is also effectively reduced.
Owner:厦门赛特奥斯生物技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com