Method for detecting variable spliceosome in third generation full-length transcriptome
A detection method and cutting body technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of redundant gene annotation results, wrong positioning of cutting sites, and lack of them, so as to improve the credibility Accurate, perfect annotation, high reliability effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
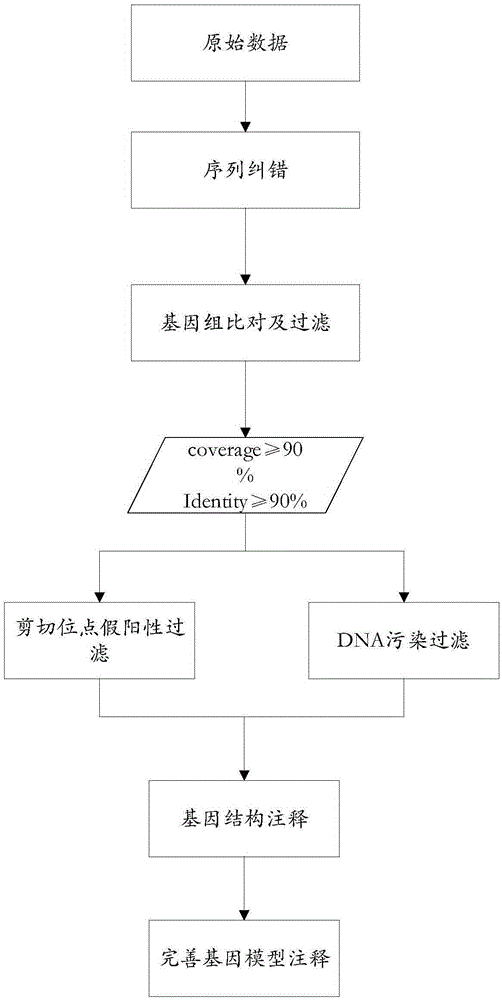
[0044] Example 1. A method for detecting alternatively spliced bodies in the three-generation full-length transcriptome. The following combination figure 1 with figure 2 This embodiment will be described.
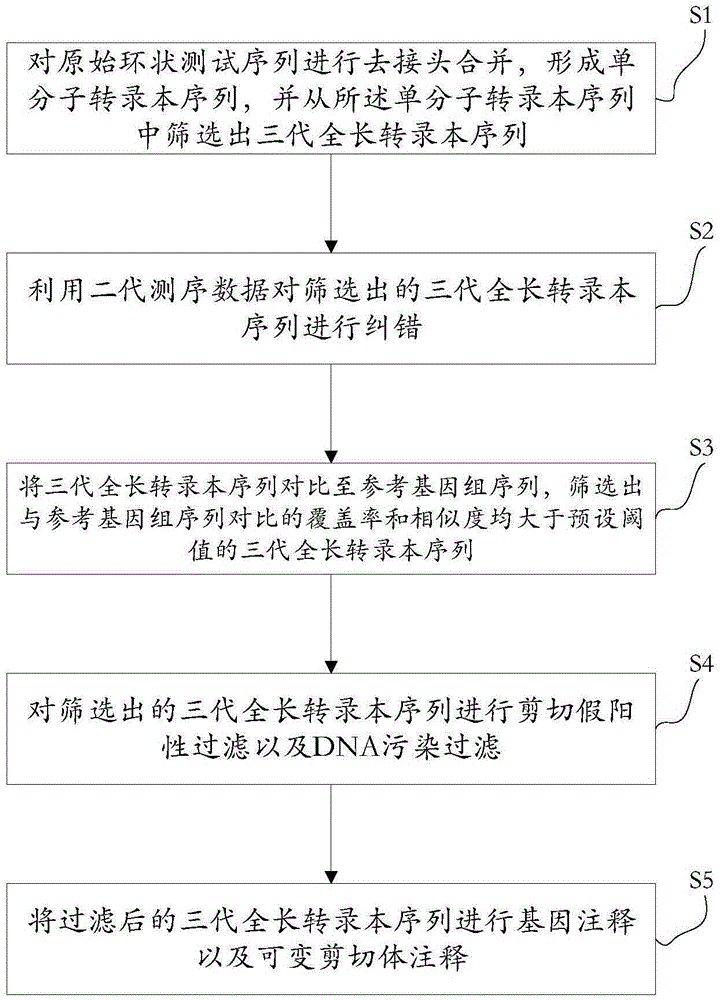
[0045] see figure 1 , S1. Using the SMRT process to dejoin and merge the original circular test sequences to form a single-molecule transcript sequence, and screen three generations of full-length transcript sequences from the single-molecule transcript sequence.
[0046] Specifically, using the SMTR_AnalysisIsoSeq process, the original circular sequencing sequence was de-jointed, and the de-joined sequencing sequences were combined to form a high-quality single-molecule transcript sequence, and three generations of full-length transcripts were screened from the single-molecule transcript sequence. Long transcript sequences.
[0047] S2. Using the next-generation sequencing data to correct errors in the screened third-generation full-length transcript sequences.
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com