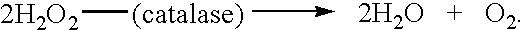Patents
Literature
139 results about "Substrate molecule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
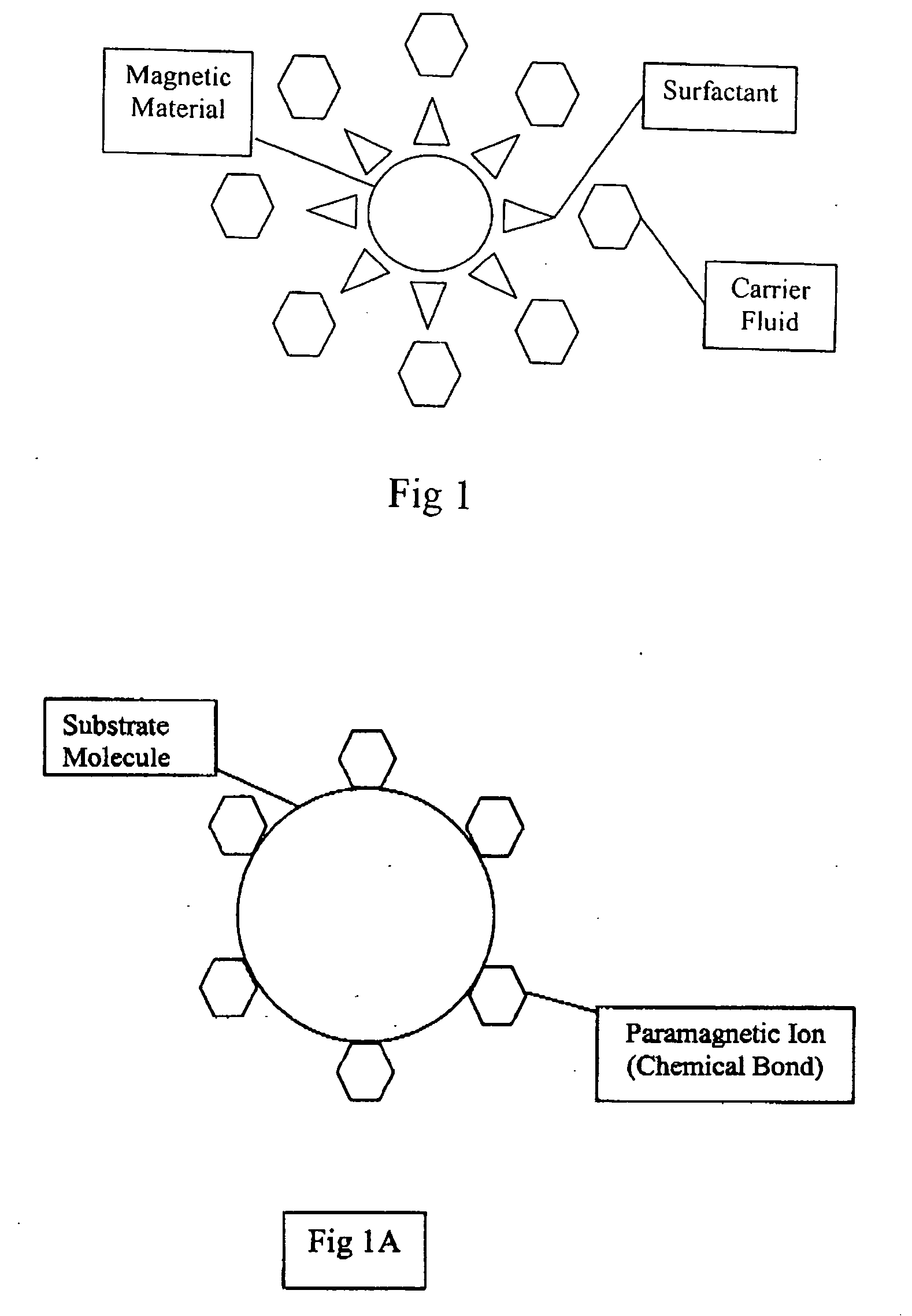
A substrate is a molecule acted upon by an enzyme. A substrate is loaded into the active site of the enzyme, or the place that allows weak bonds to be formed between the two molecules. An enzyme substrate complex is formed, and the forces exerted on the substrate by the enzyme cause it to react, and become the product of the intended reaction.
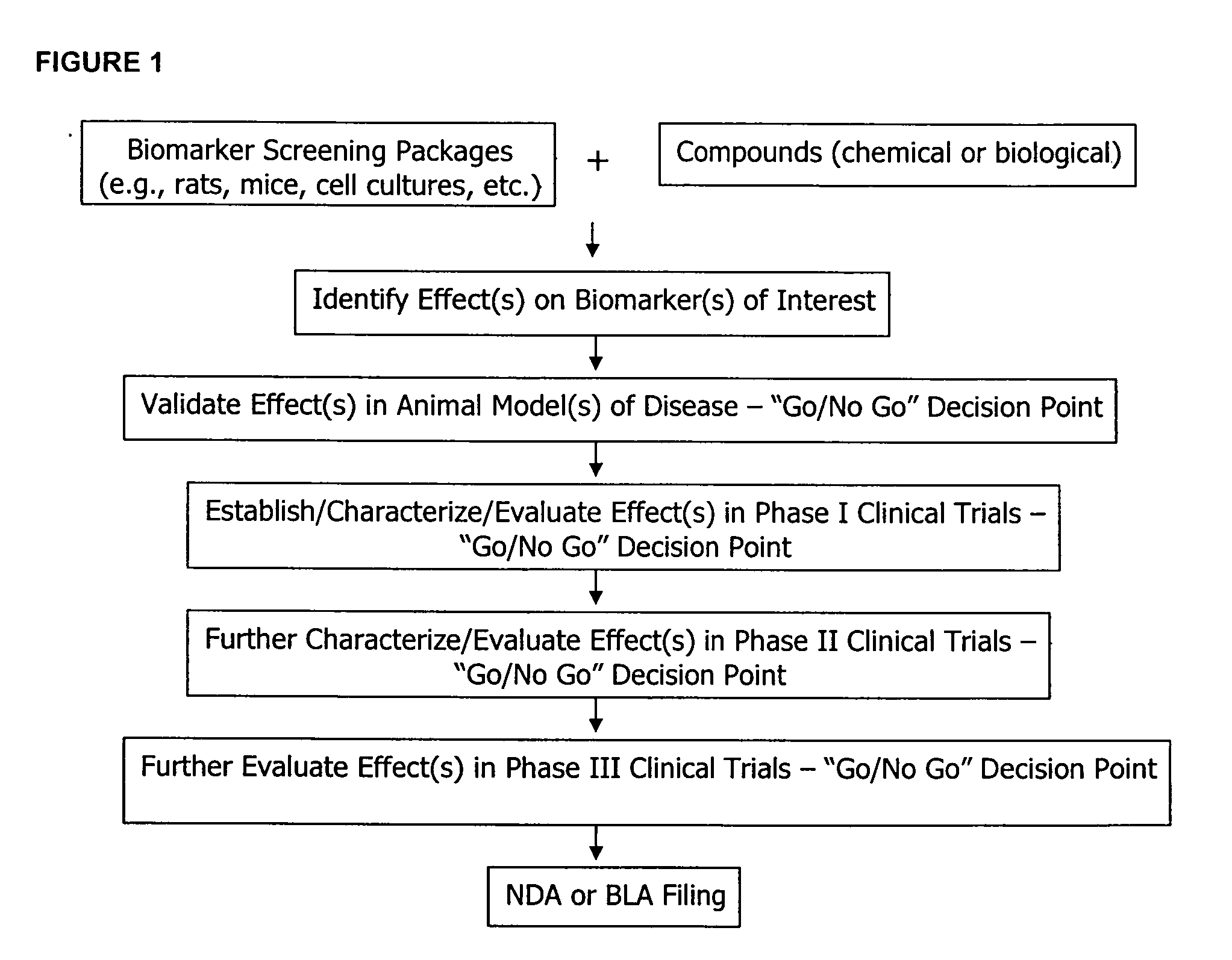
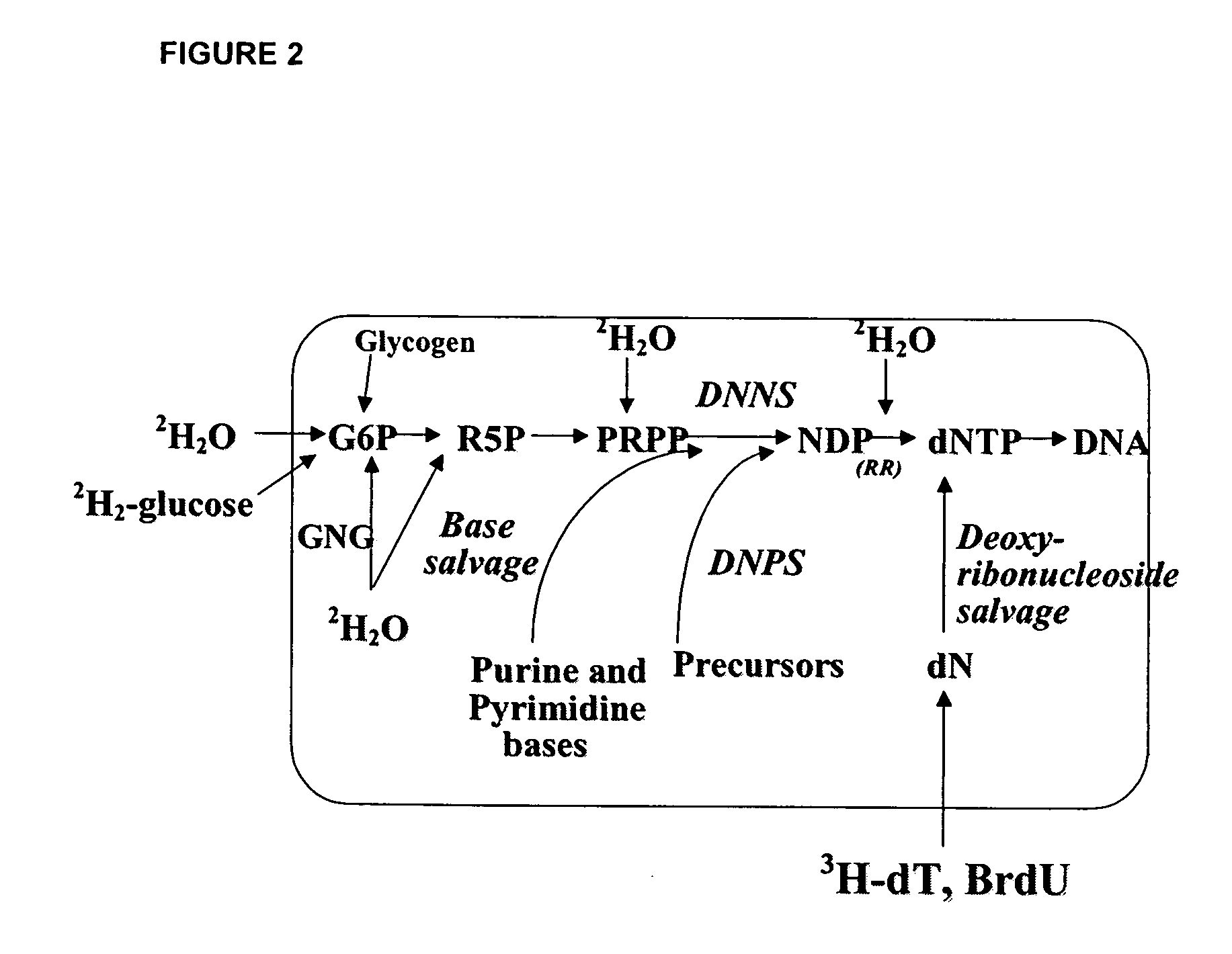
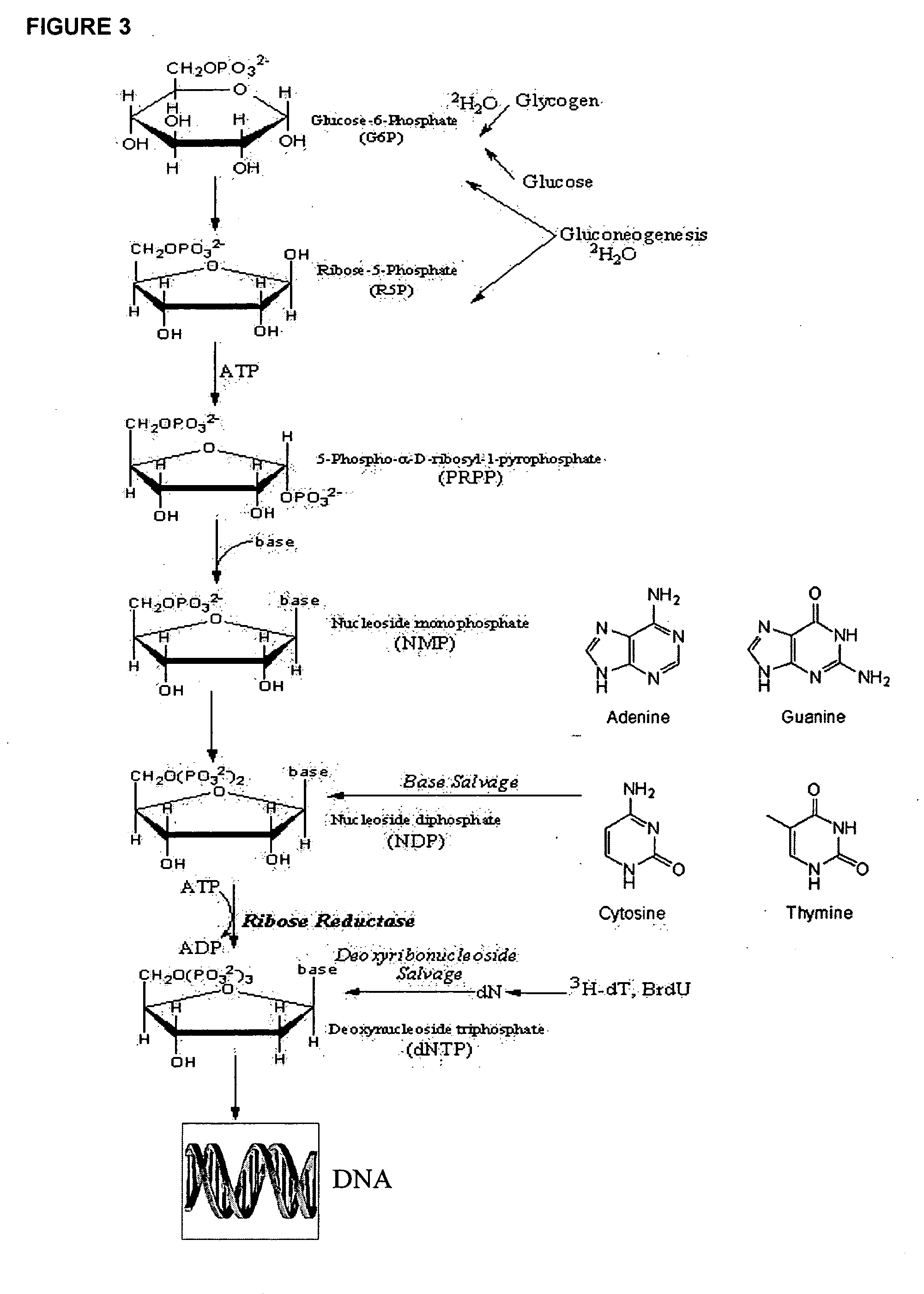
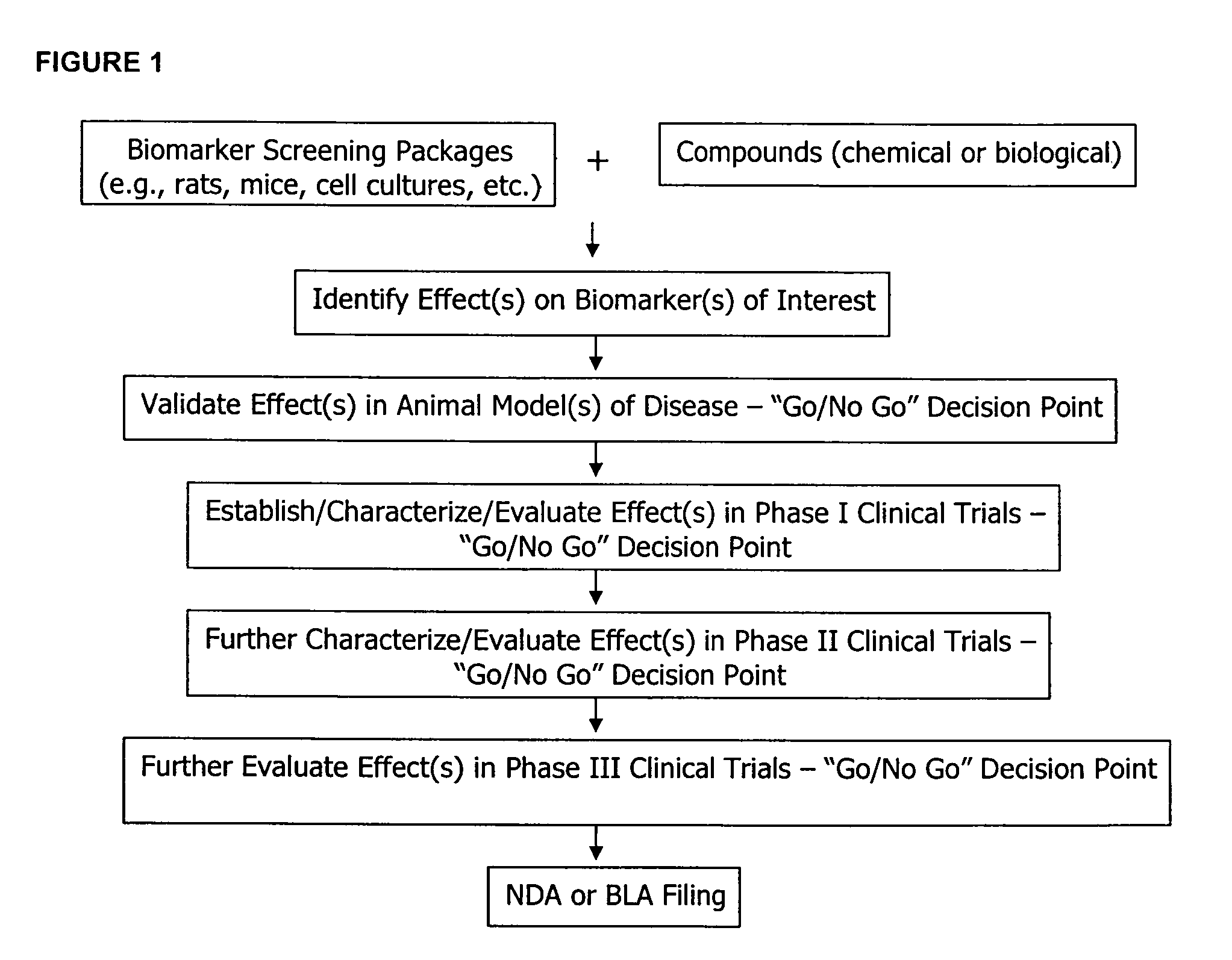
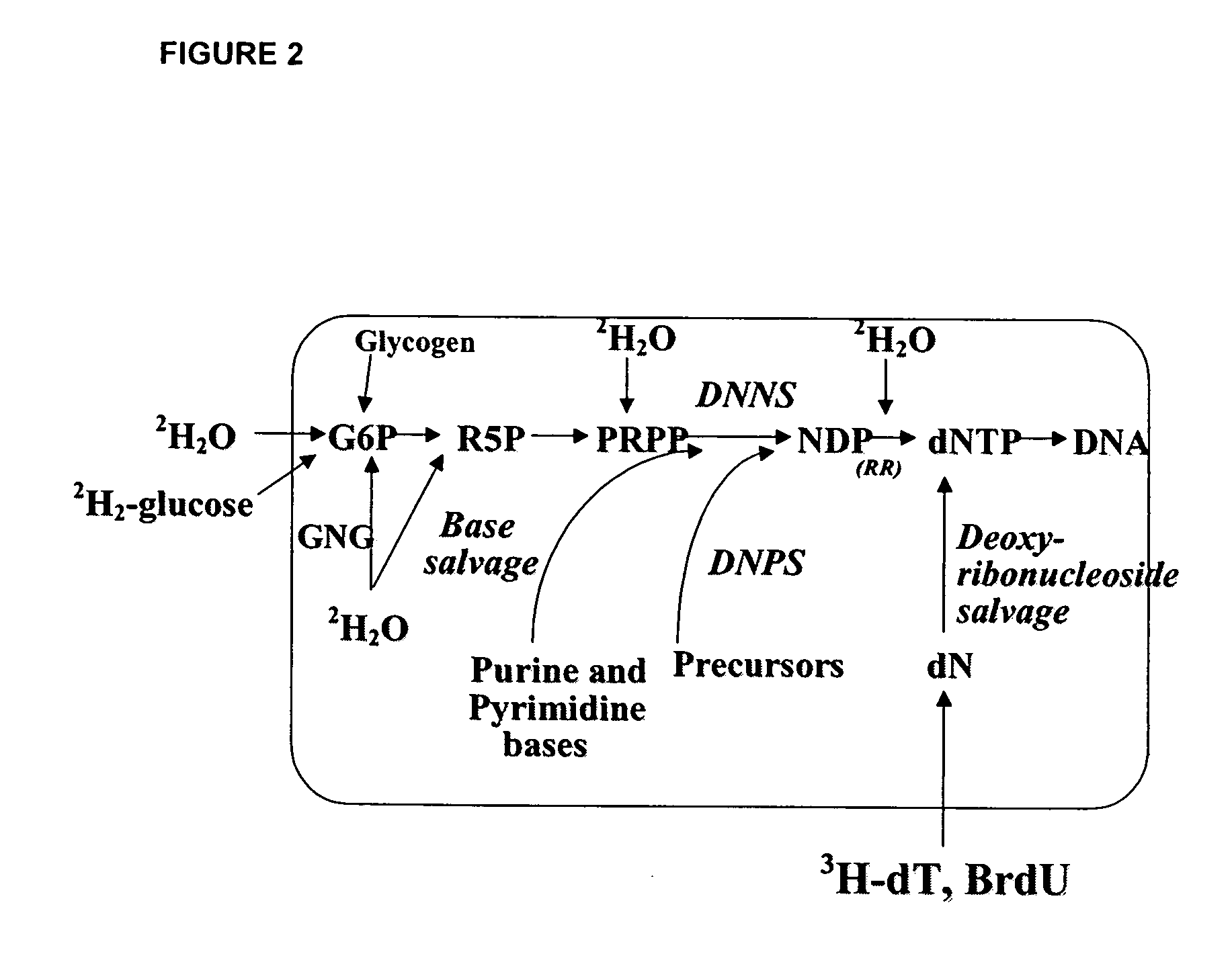
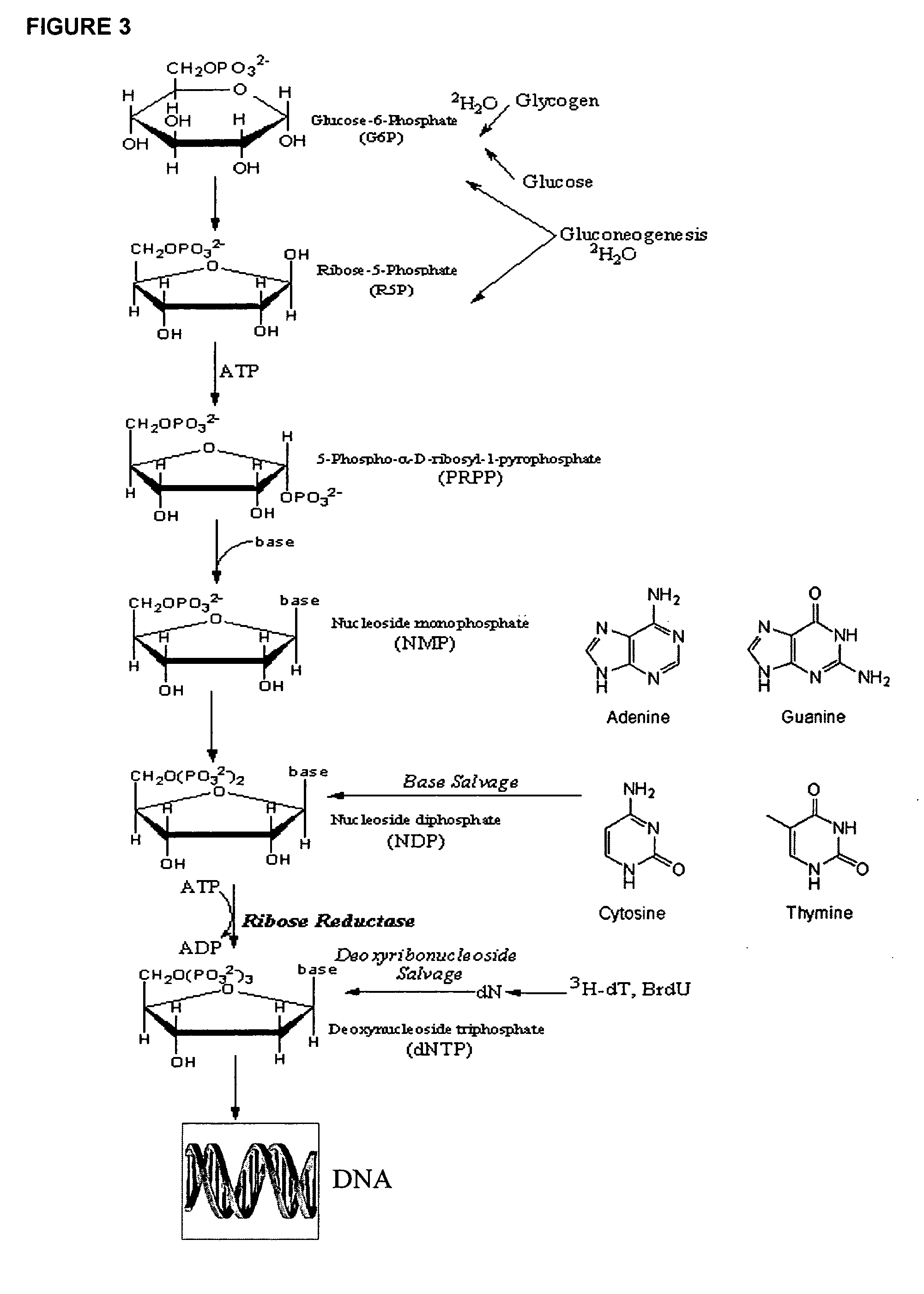
Molecular flux rates through critical pathways measured by stable isotope labeling in vivo, as biomarkers of drug action and disease activity
The methods described herein enable the evaluation of compounds on subjects to assess their therapeutic efficacy or toxic effects. The target of analysis is the underlying biochemical process or processes (i.e., metabolic process) thought to be involved in disease pathogenesis. Molecular flux rates within the one or more biochemical processes serve as biomarkers and are quantitated and compared with the molecular flux rates (i.e., biomarker) from control subjects (i.e., subjects not exposed to the compounds). Any change in the biomarker in the subject relative to the biomarker in the control subject provides the necessary information to evaluate therapeutic efficacy of an administered drug or a toxic effect and to develop the compound further if desired. In one aspect of the invention, stable isotope-labeled substrate molecules are administered to a subject and the label is incorporated into targeted molecules in a manner that reveals molecular flux rates through one or more metabolic pathways of interest. By this method, a comparison between subjects and control subjects reveals the effects of the chemical entity or entities on the biomarkers. This, in turn, allows for the identification of potential therapeutic uses or toxicities of the compound. Combinations of compounds can also be systematically evaluated for complementary, synergistic, or antagonistic actions on the metabolic pathways of interest, using the methods of the present invention as a strategy for identifying and confirming novel therapeutic or toxic combinations of compounds.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for the preparation of an immobilized protein ultrathin film reactor and a method for a chemical reaction by using an immobilized protein ultrathin film reactor
InactiveUS6107084AImprove responseEasy to spreadBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical reactionMolecular level
A method for the preparation of an immobilized protein ultrathin film reactor by immersing a solid support alternately into an aqueous solution of protein, and into an aqueous solution of polyion charged oppositely to said protein and preparing a structurally controlled ultrathin film of mono- or multi- protein layers on a said solid support with precision at molecular level. And a method for chemical reaction of a substrate by preparing an immobilized protein ultrathin film reactor composed of multiple layers of protein on a solid support by above mentioned method, and initiating a chemical change of the substrate molecules using obtained immobilized protein ultrathin film reactor.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Paramagnetic liquid interface
InactiveUS20070100457A1Improve rheologyExtended durationFinger jointsWrist jointsArticular surfacesEngineering
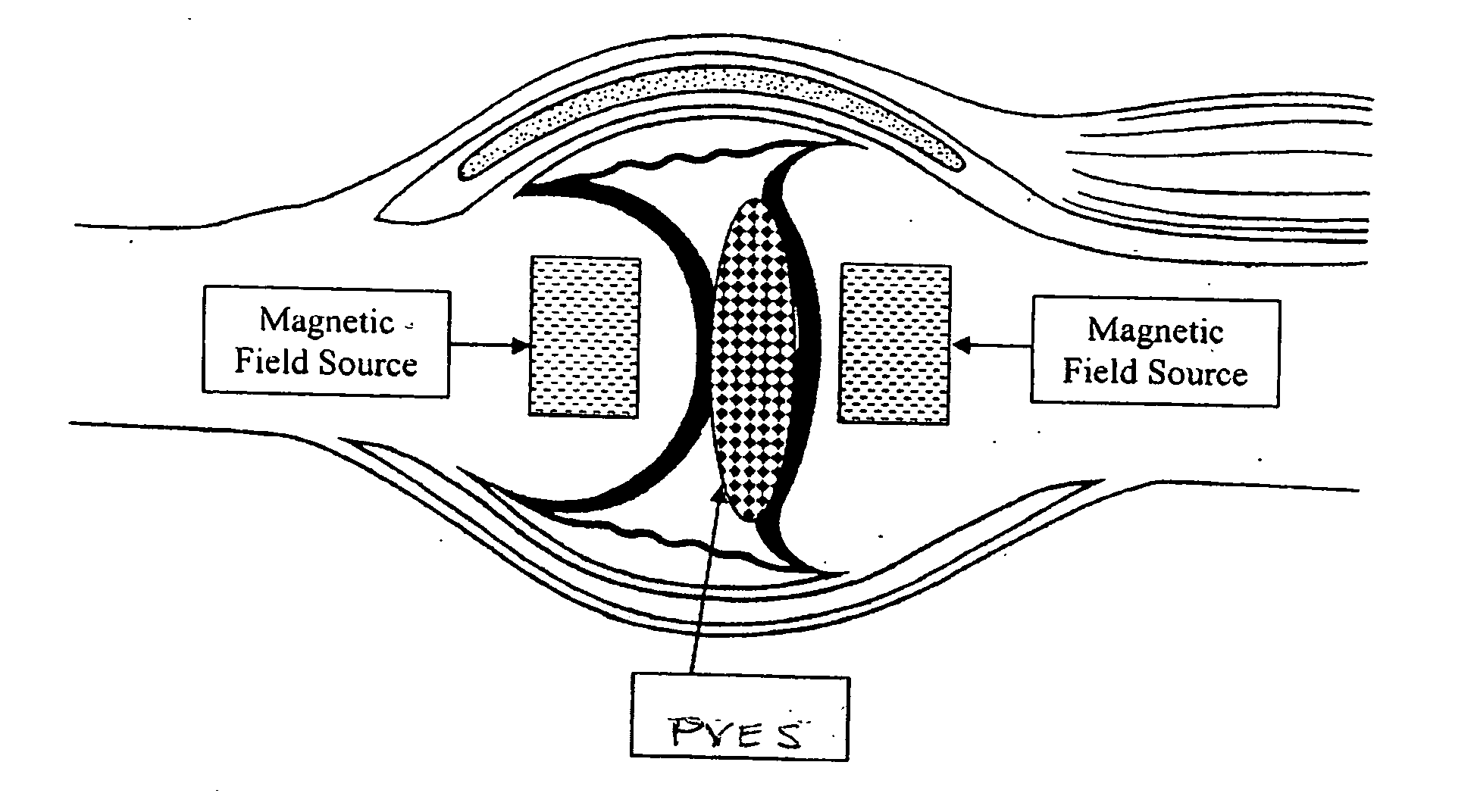
Natural joint interfaces wear out and / or are damaged causing pain and disability. They can be currently replaced by artificial surfaces made of materials or in the near future by magnetic fields. They would benefit from a PVES (paramagnetic visco-viscoelastic supplement) that can replace or augment natural joint interfaces or augment total joint replacements. Joint replacement components can be modular and would benefit from a PVES to decrease wear and damp impact between modular parts of a single component. The PVES is a dynamic interface allowing components to be less rigid. Energy transmission is reduced. PVES can act as an interface between natural damaged joint surfaces obviating the need for classic total joint replacement or between the surfaces of artificial joint components to improve or supplement their function. These PVES can be controlled by magnetic fields with respect to their location, physical properties, loads, etc. PVES are typically made of paramagnetic ions and a substrate molecule. One such PVES can be made of gadolinium ions and hyaluronic acid to form gadolinium hyaluronate.
Owner:HYDE EDWARD R JR
Method for synthesizing a specific, surface-bound polymer uniformly over an element of a molecular array
InactiveUS6936472B2Reduce synthesisMaterial nanotechnologyLibrary screeningMolecular arrayComputational chemistry
A method for specifically and uniformly synthesizing desired polymers within molecular array elements. Droplets containing a reactive monomer are successively applied to the elements of a molecular array in order to synthesize a substrate-bound polymer. Application of an initial droplet, having a first volume, defines the position and size of a molecular array element. Subsequent droplets are applied, to add successive reactive monomers to growing nascent polymers within the molecular array element, with covering volumes so that, even when application of the subsequent droplets is misregistered, the entire surfaces of the elements of the molecular array are exposed to the subsequently applied droplets. Following application of initial droplets, the surface of the molecular array is exposed to a solution containing a very efficient capping agent in order to chemically cap any unreacted nascent growing polymers and any unreacted substrate molecules.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Detection of biomolecules by sensitizer-linked substrates
InactiveUS20070112180A1High affinityDetection is limitedMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysSubstrate molecule
Methods and compositions for detecting and characterizing target biomolecules using sensitizer-linked substrate molecules are disclosed. High throughput screening assays and therapeutic applications of the inventions are also included.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Detection of biomolecules by sensitizer-linked substrates
InactiveUS7105310B1High affinityDetection is limitedMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysHigh flux
Methods and compositions for detecting and characterizing target biomolecules using sensitizer-linked substrate molecules are disclosed. High throughput screening assays and therapeutic applications of the inventions are also included
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Molecular flux rates through critical pathways measured by stable isotope labeling in vivo, as biomarkers of drug action and disease activity
The methods described herein enable the evaluation of compounds on subjects to assess their therapeutic efficacy or toxic effects. The target of analysis is the underlying biochemical process or processes (i.e., metabolic process) thought to be involved in disease pathogenesis. Molecular flux rates within the one or more biochemical processes serve as biomarkers and are quantitated and compared with the molecular flux rates (i.e., biomarker) from control subjects (i.e., subjects not exposed to the compounds). Any change in the biomarker in the subject relative to the biomarker in the control subject provides information to evaluate therapeutic efficacy of an administered drug or a toxic effect and to develop the compound further if desired. In one aspect of the invention, stable isotope-labeled substrate molecules are administered to a subject and the label is incorporated into targeted molecules in a manner that reveals molecular flux rates through metabolic pathways of interest.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
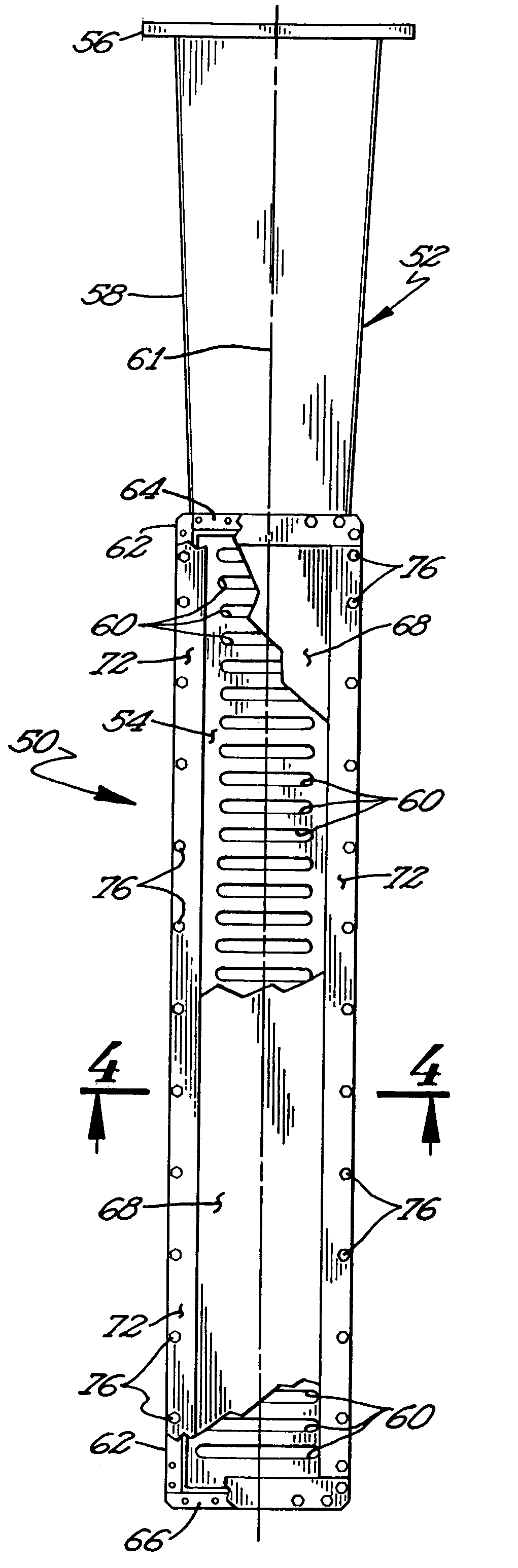
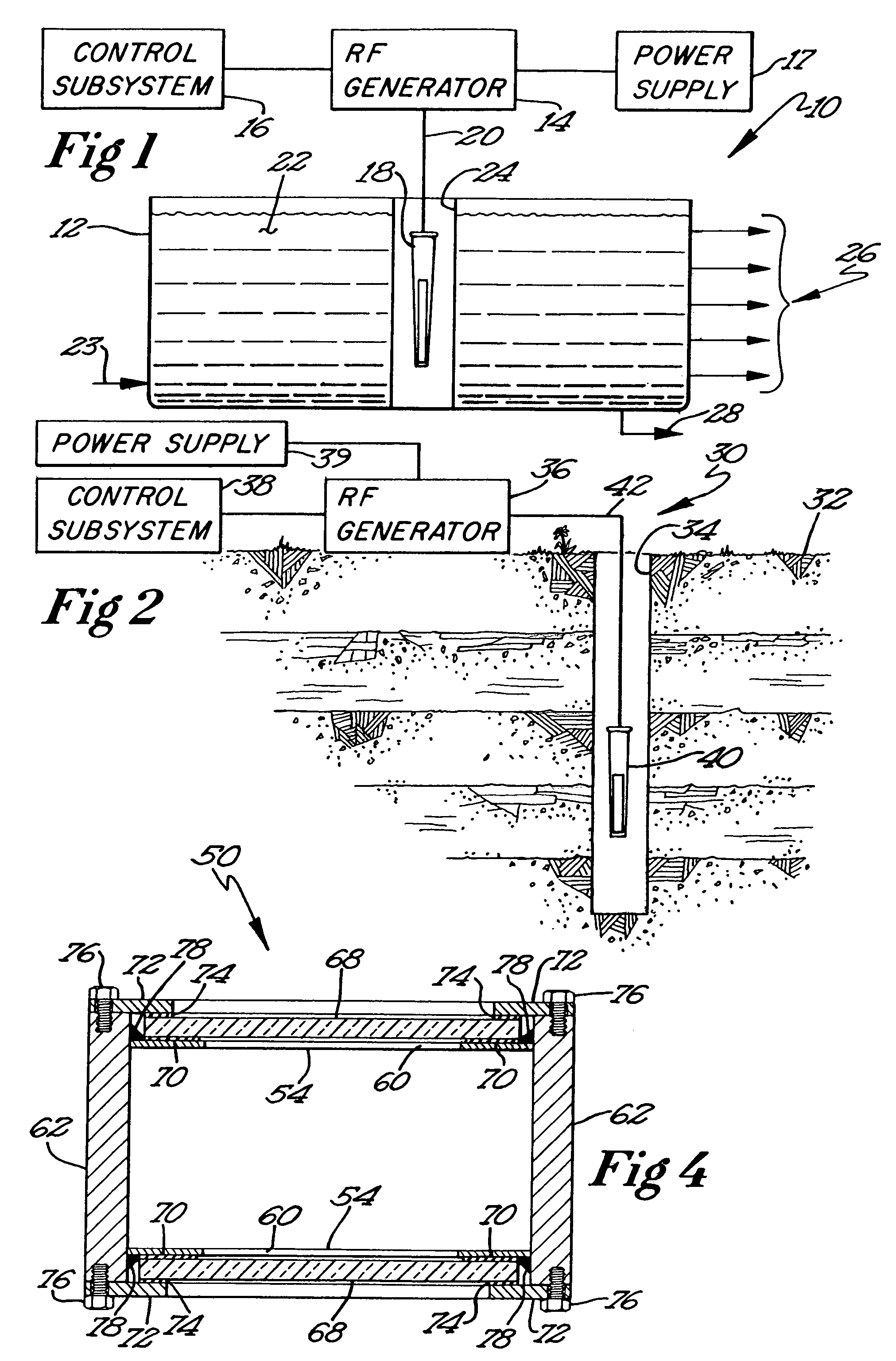
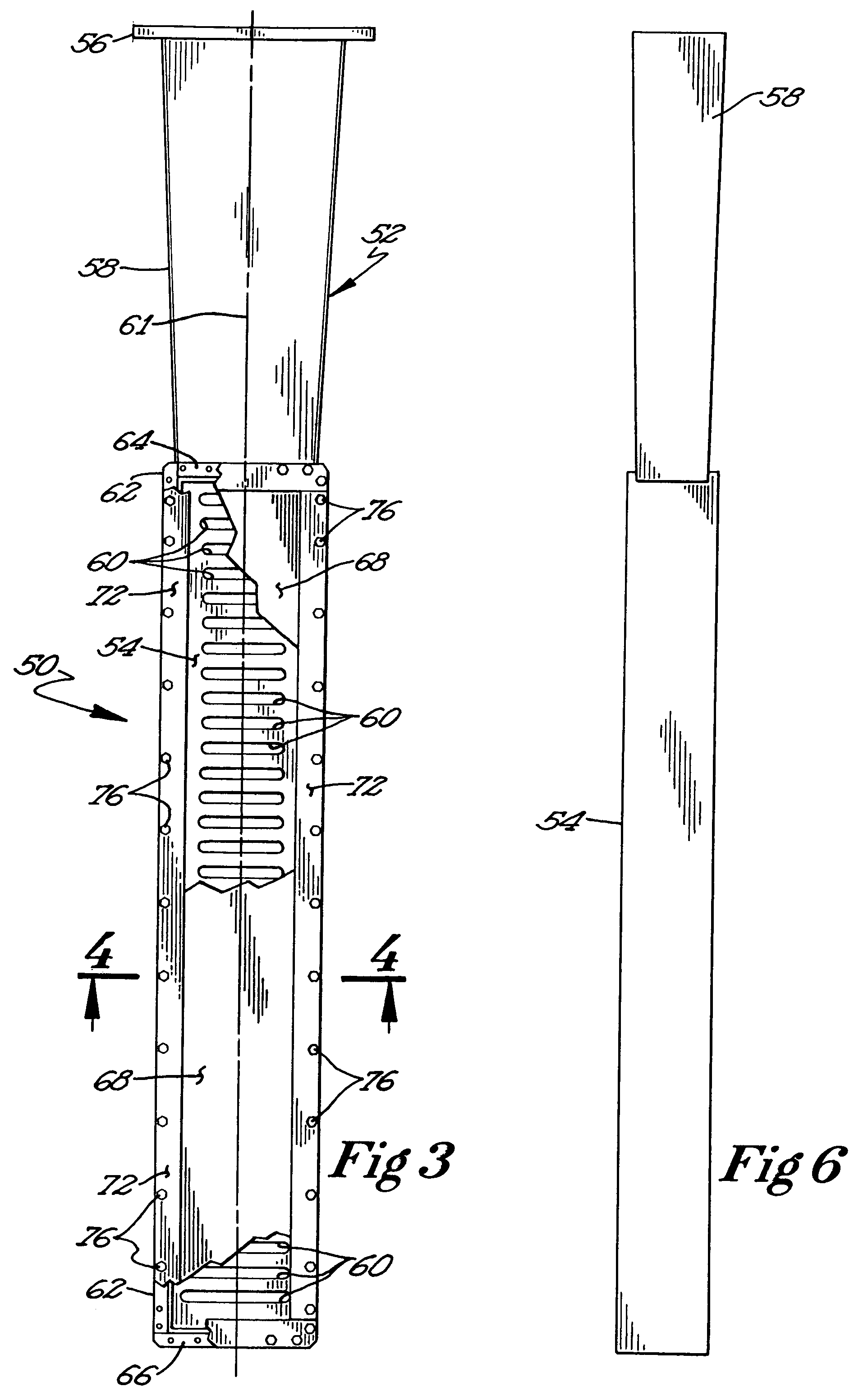
Microwave demulsification of hydrocarbon emulsion
InactiveUS7486248B2Promote demulsificationEfficiently delivers microwave energyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSubaqueous/subterranean adaptionEmulsionMicrowave
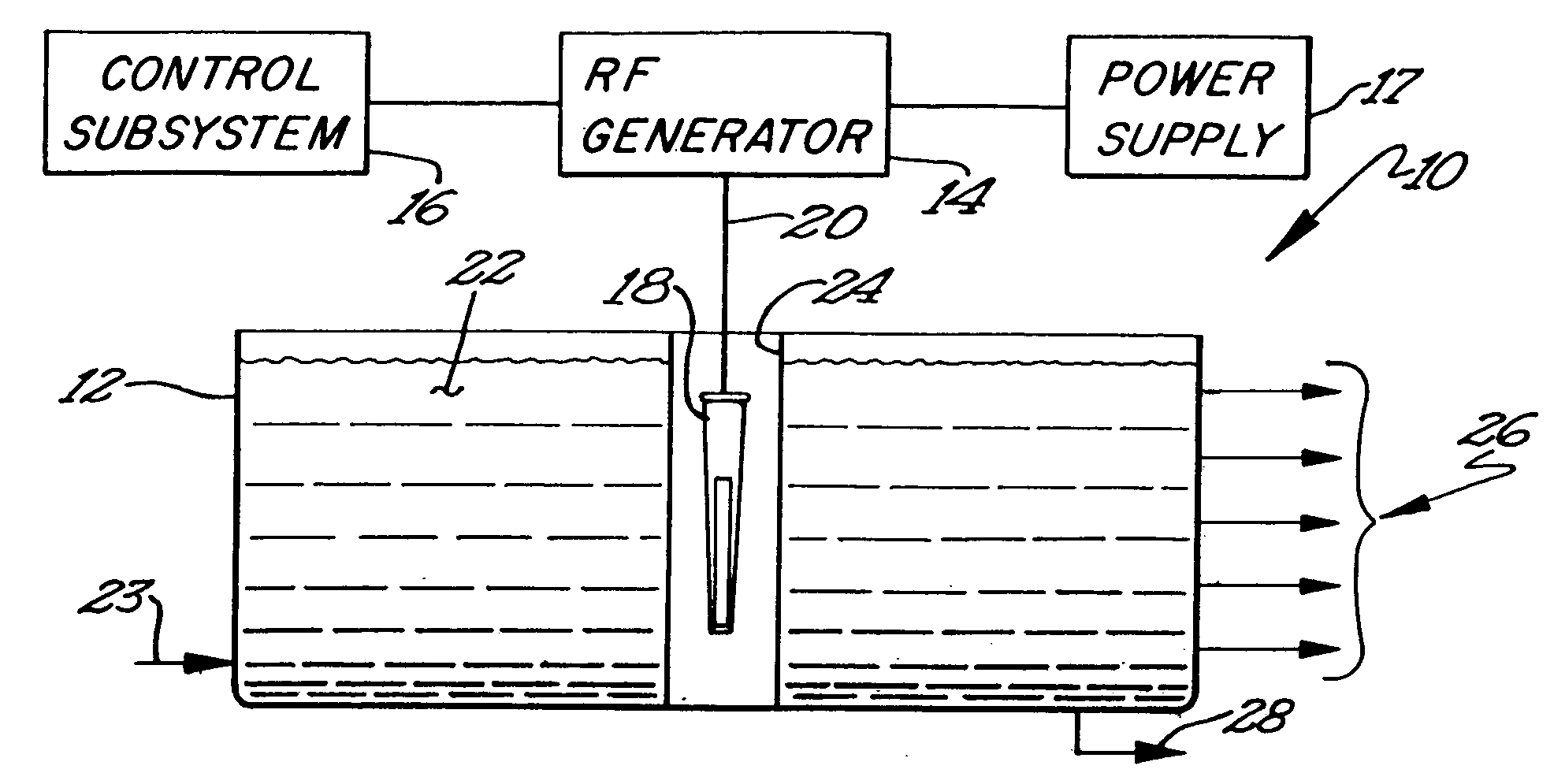
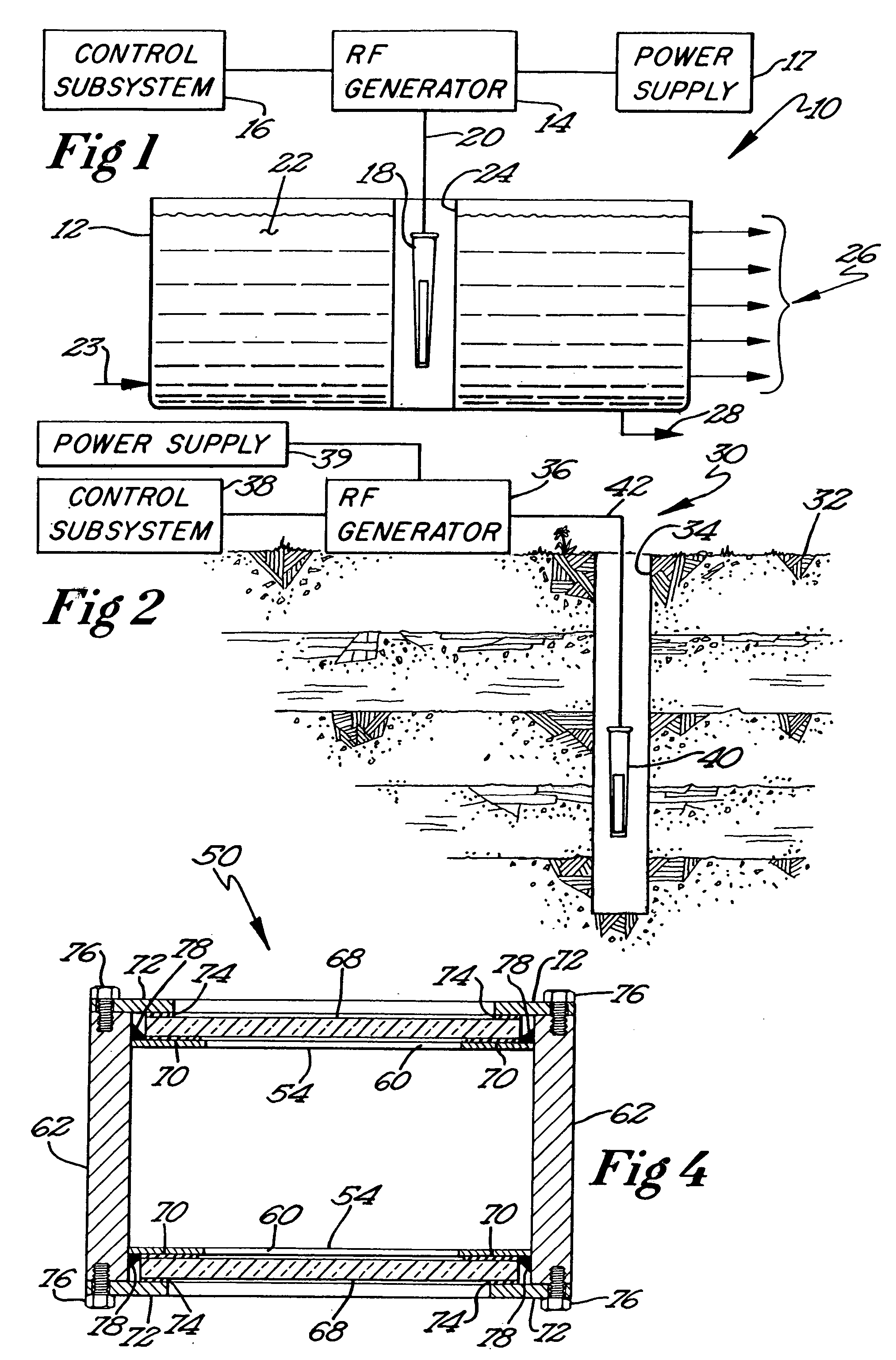
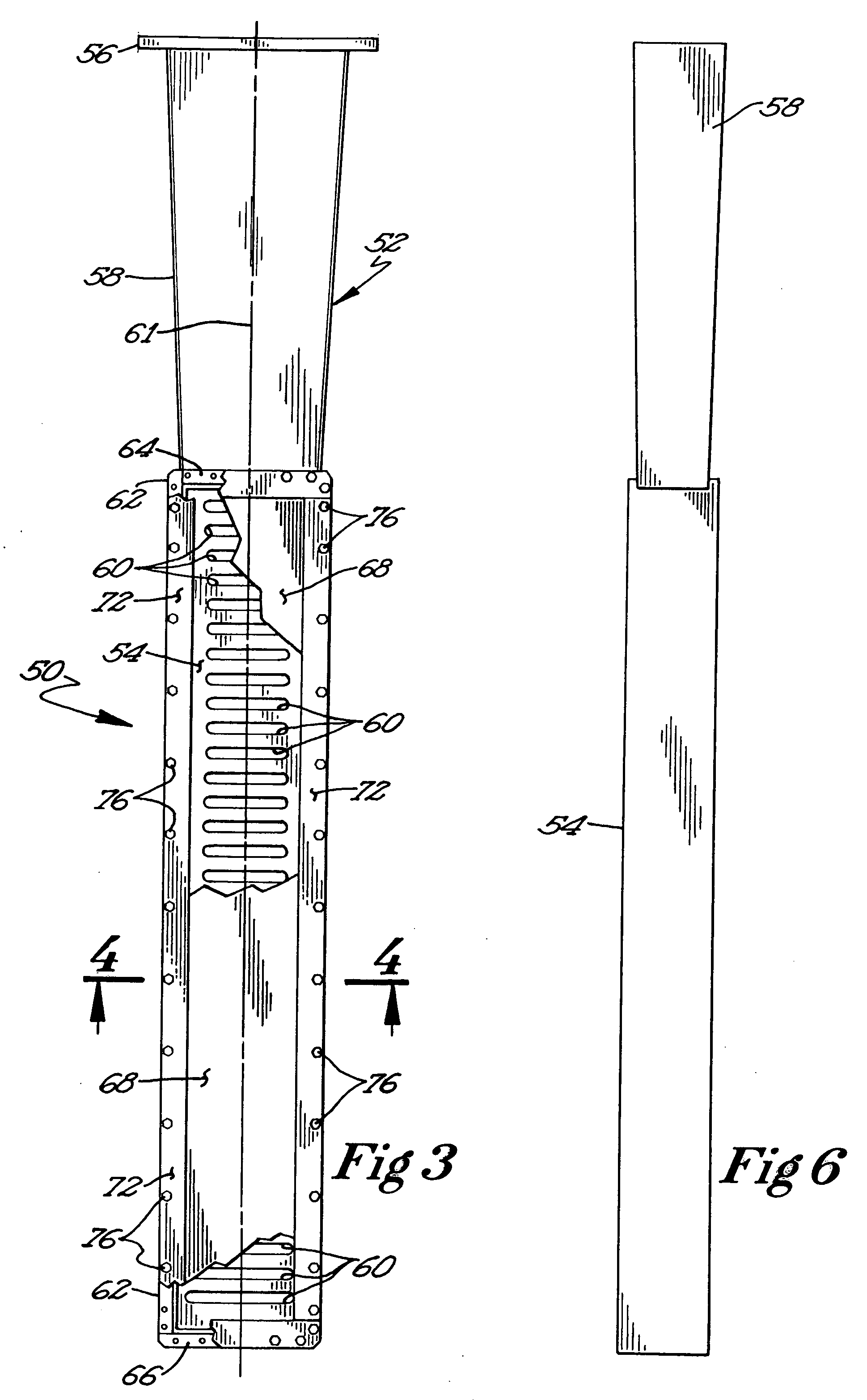
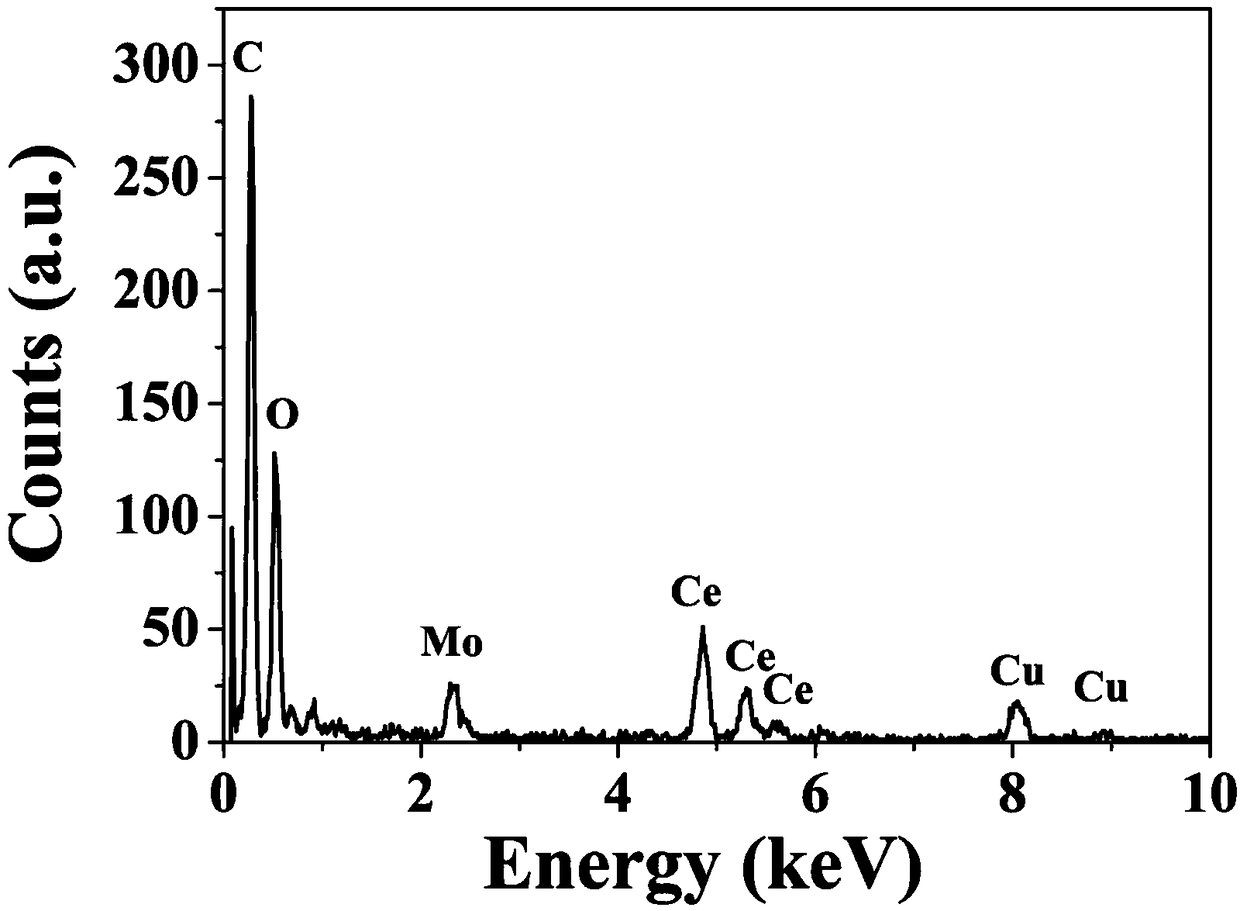
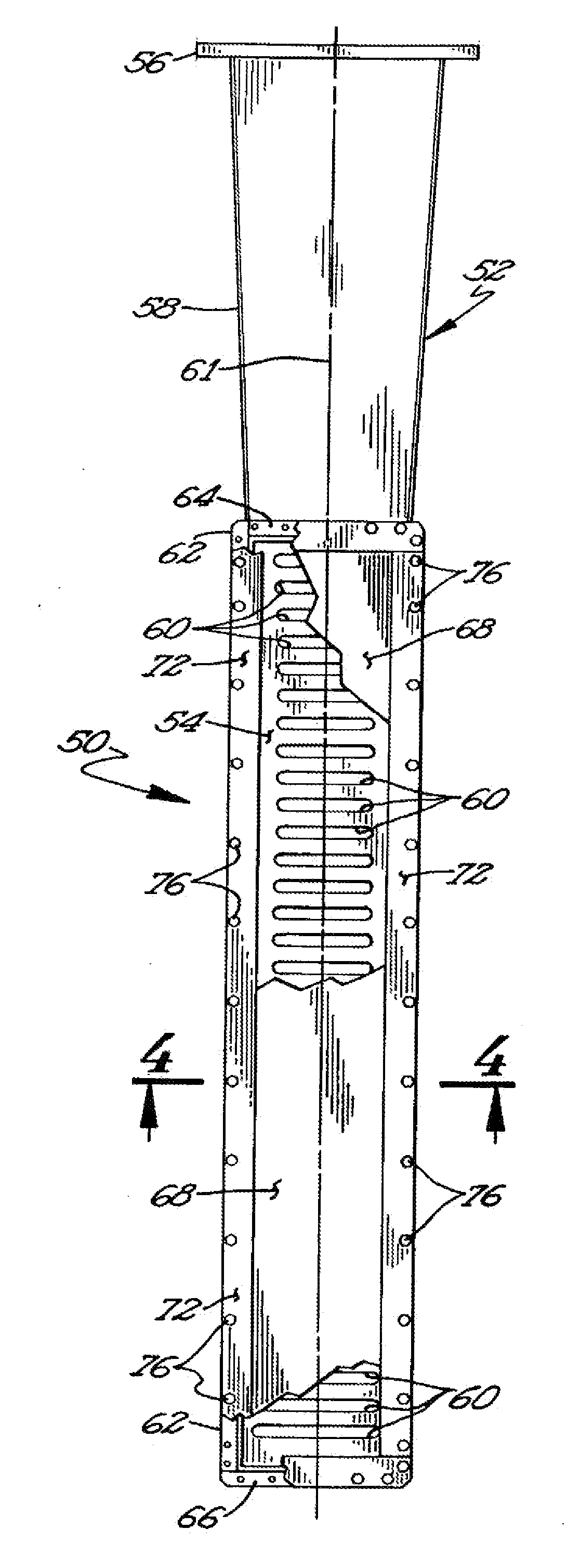
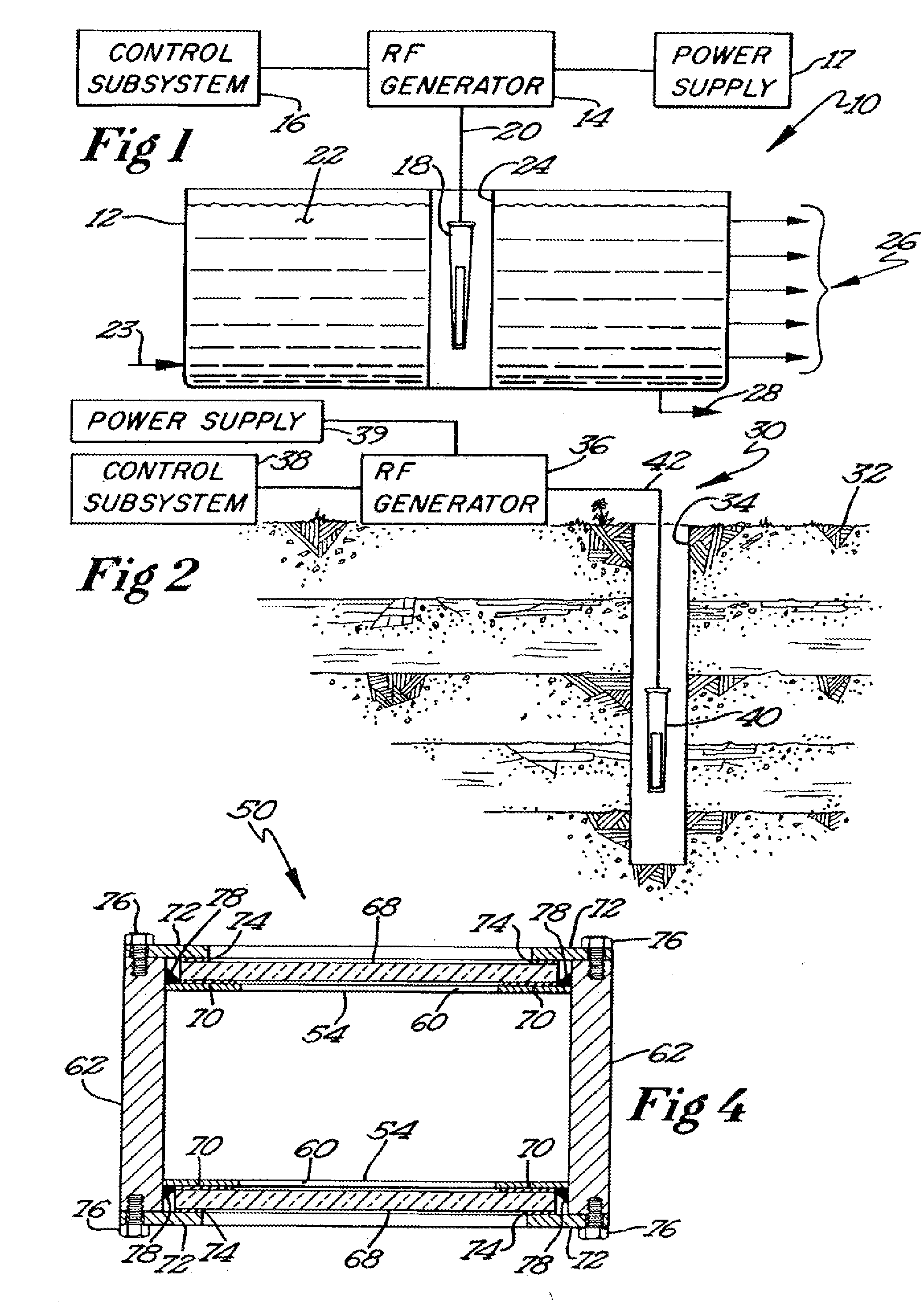
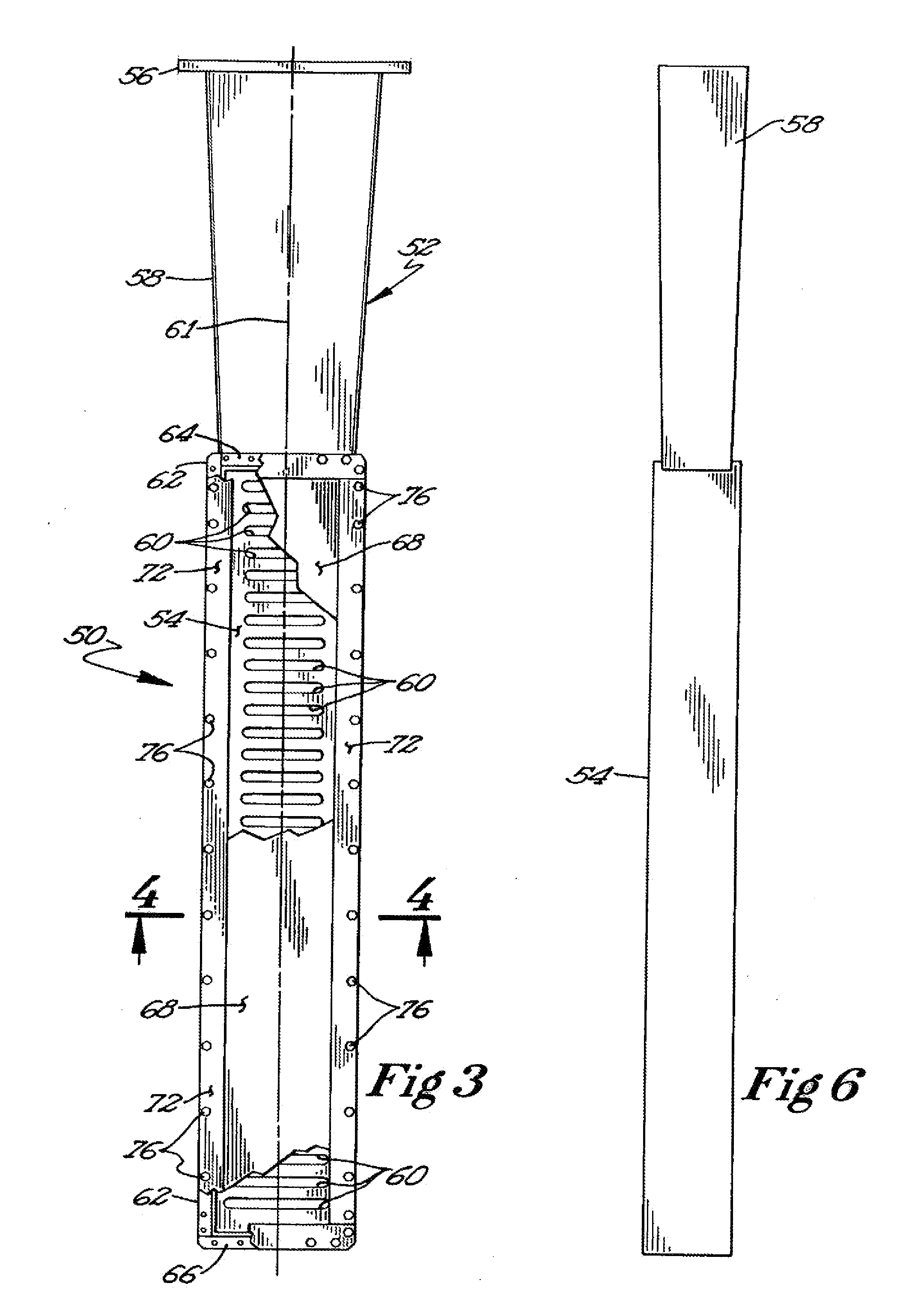
Recovery of hydrocarbons, such as petroleum products, from a liquid or solid substrate is facilitated by the use of microwave energy to energize and separate molecular bonds between the hydrocarbons and the substrate. A radio frequency (RF) applicator delivers microwave energy to a treatment volume containing an emulsion of a hydrocarbon and a substrate. Delivering the microwave energy to the emulsion facilitates separation of the hydrocarbon and substrate molecules into layers. Hydrocarbons and other products can then be recovered from their respective layers. The treatment volume may be located either above or below ground. The RF applicator may include an antenna body with slots formed substantially parallel to one another in a substantially horizontal orientation. The RF applicator efficiently delivers microwave energy into the treatment volume. Substantially all of the power supplied to the RF applicator is radiated, with very little power reflected internally within the RF applicator.
Owner:INTEGRITY DEV
Preparation method and applications of multi-level pore structure metal organic framework material
ActiveCN110256683AAdvantages of preparation methodAperture controllableOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsEther preparation from oxiranesN dimethylformamideSynthesis methods
The invention provides a preparation method and applications of a multi-level pore structure metal organic framework material. The preparation method comprises: mixing a metal salt, an organic ligand, N,N-dimethylformamide, water and carboxylic acid, uniformly stirring, carrying out a hydrothermal reaction, cooling to a room temperature after completing the hydrothermal reaction, carrying out centrifugation, and purifying to prepare the multi-level pore structure metal organic framework material. According to the present invention, the prepared multi-level pore structure metal organic framework material has characteristics of stable performance and controlled and uniform pore size; and phosphotungstic acid is loaded in the mesoporous channel of the metal organic framework material through an in-situ synthesis method, the original framework structure can be remained after the loading, and the presence of the mesopores allows the contact between the large substrate molecule and the active site so as to extend the application range of the multi-level pore structure metal organic framework material.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Detection method for activity of carboxylesterase and activity of carboxylesterase inhibitor
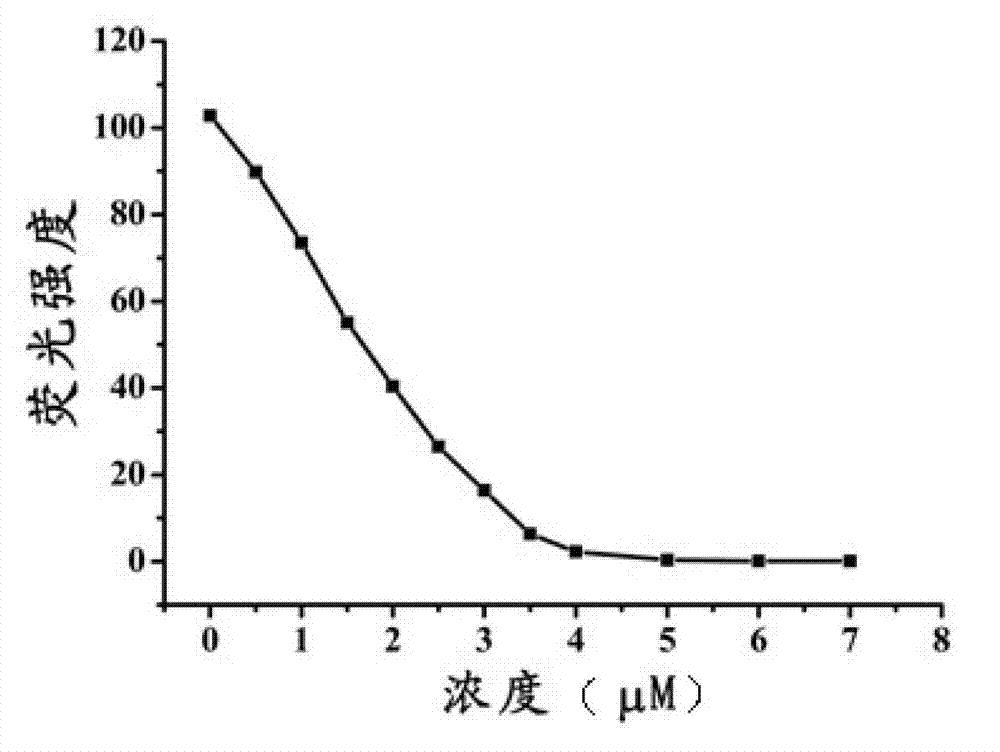
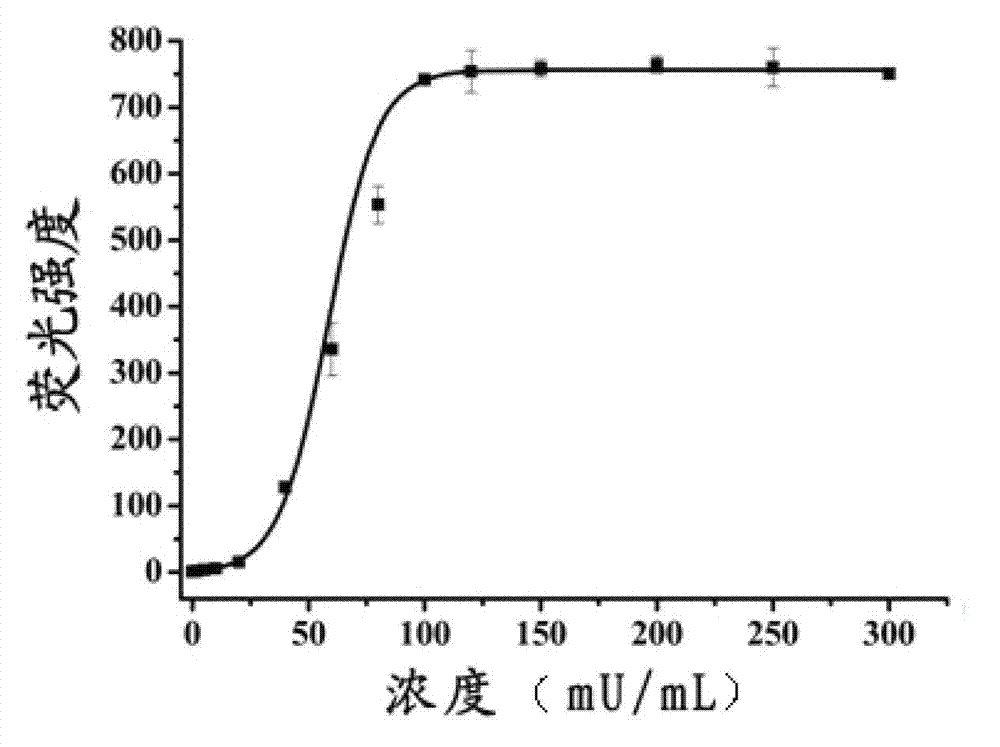
ActiveCN102788776AAvoid generatingHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceHydrolysis
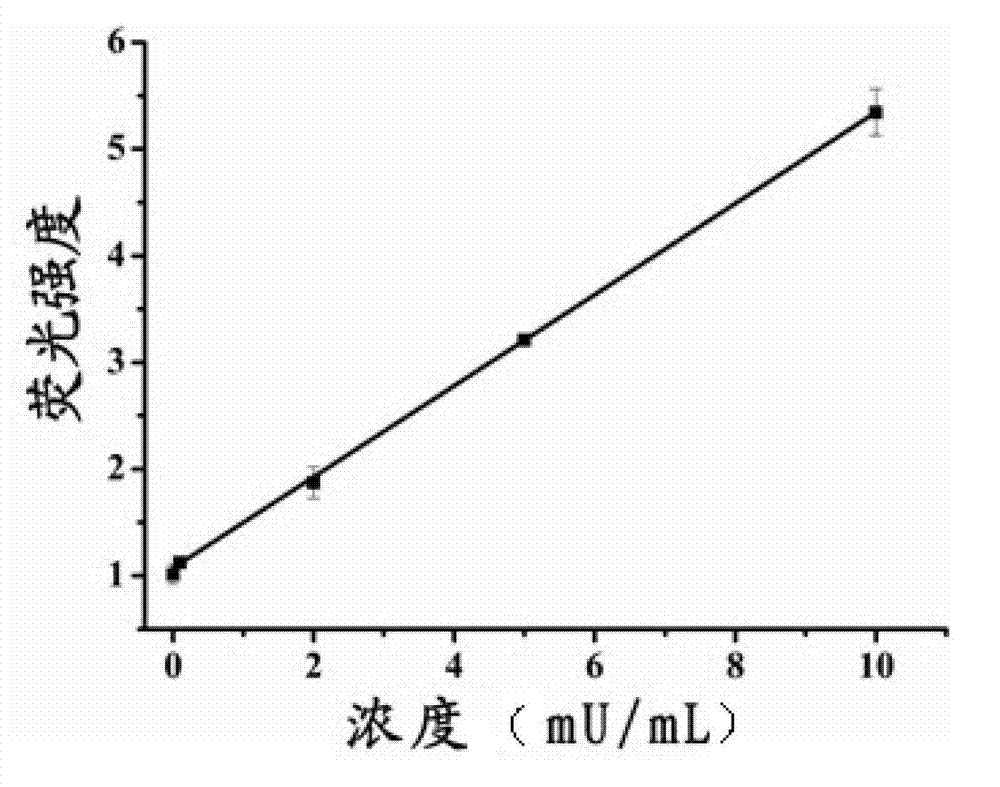
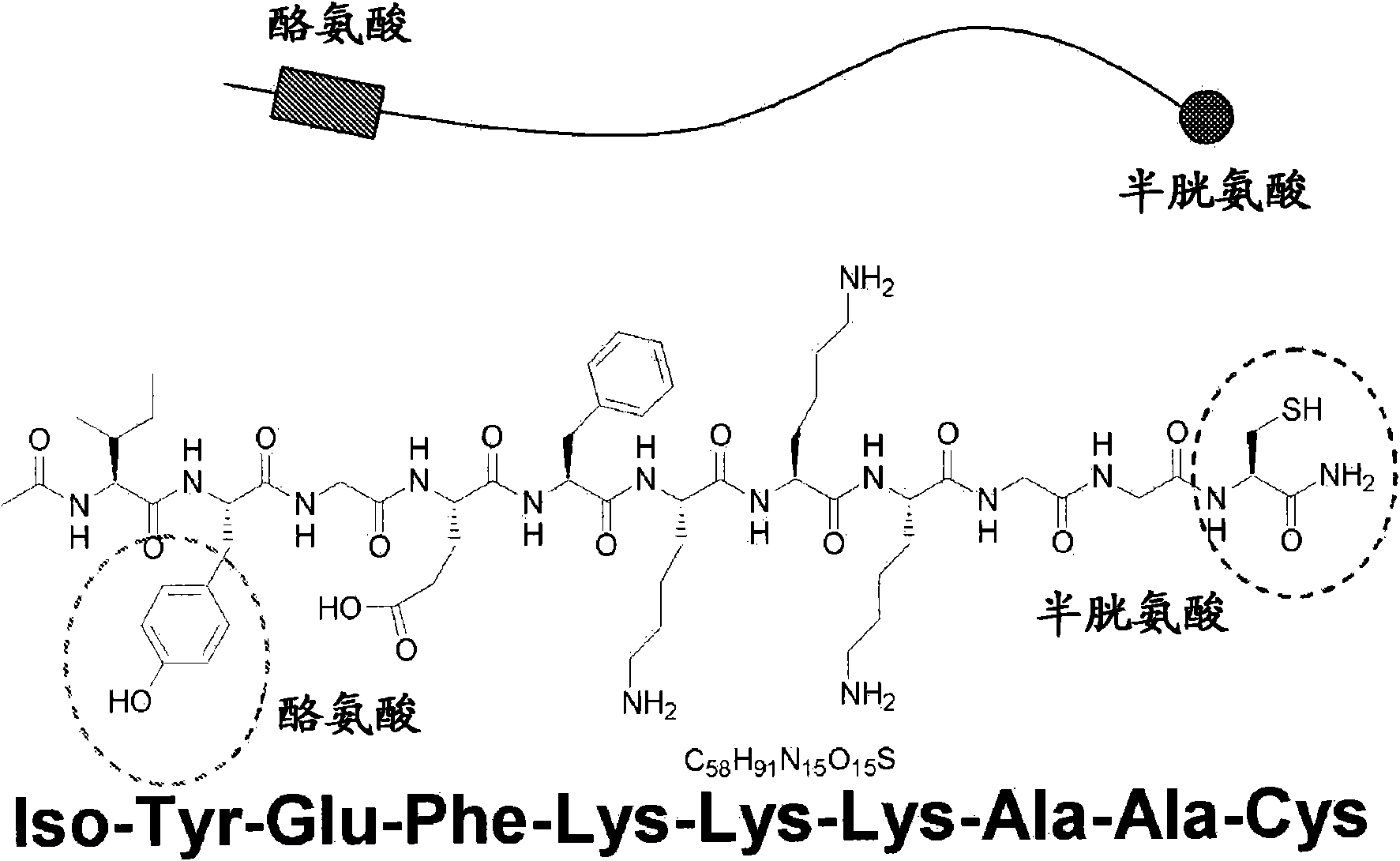
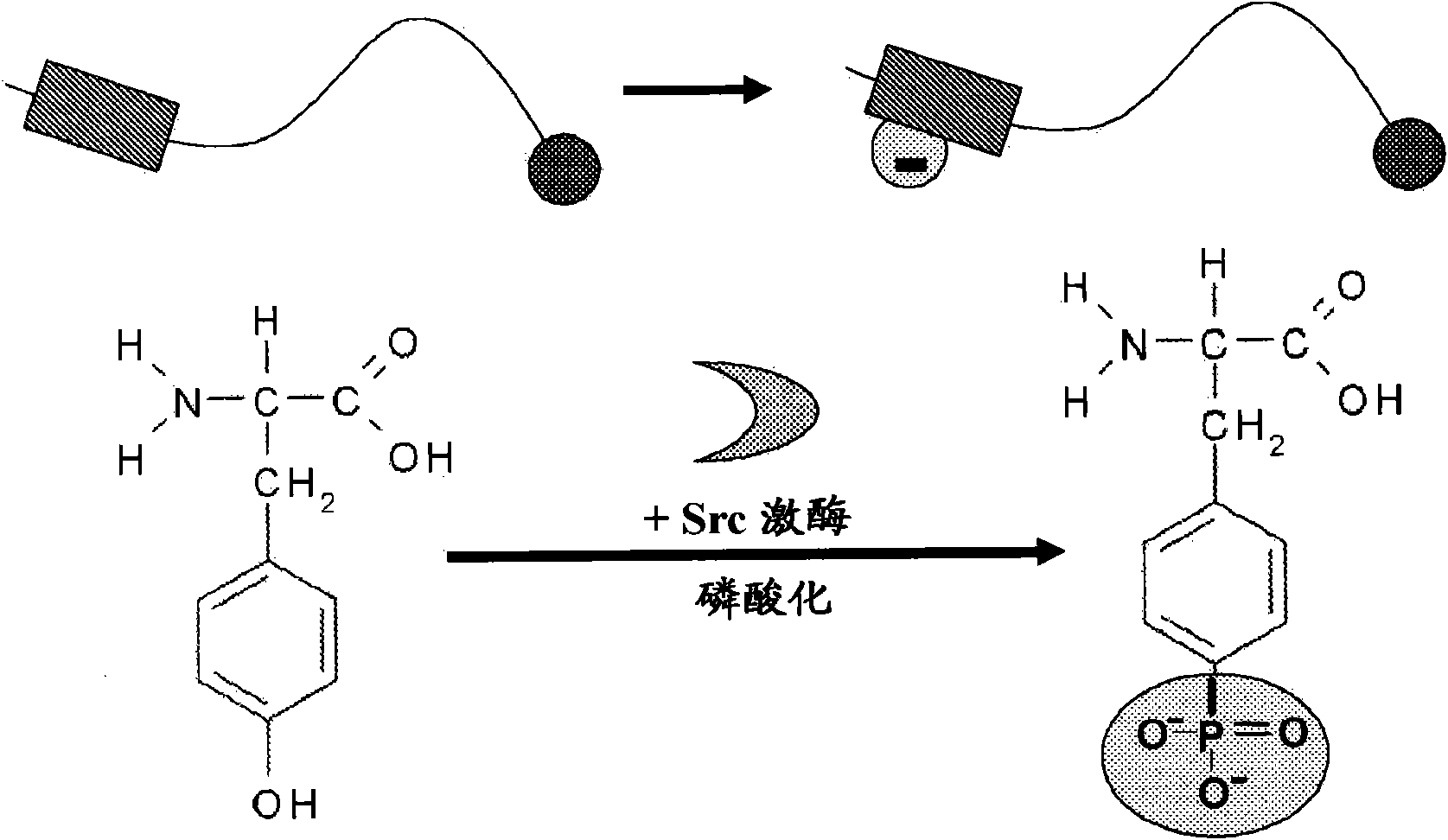
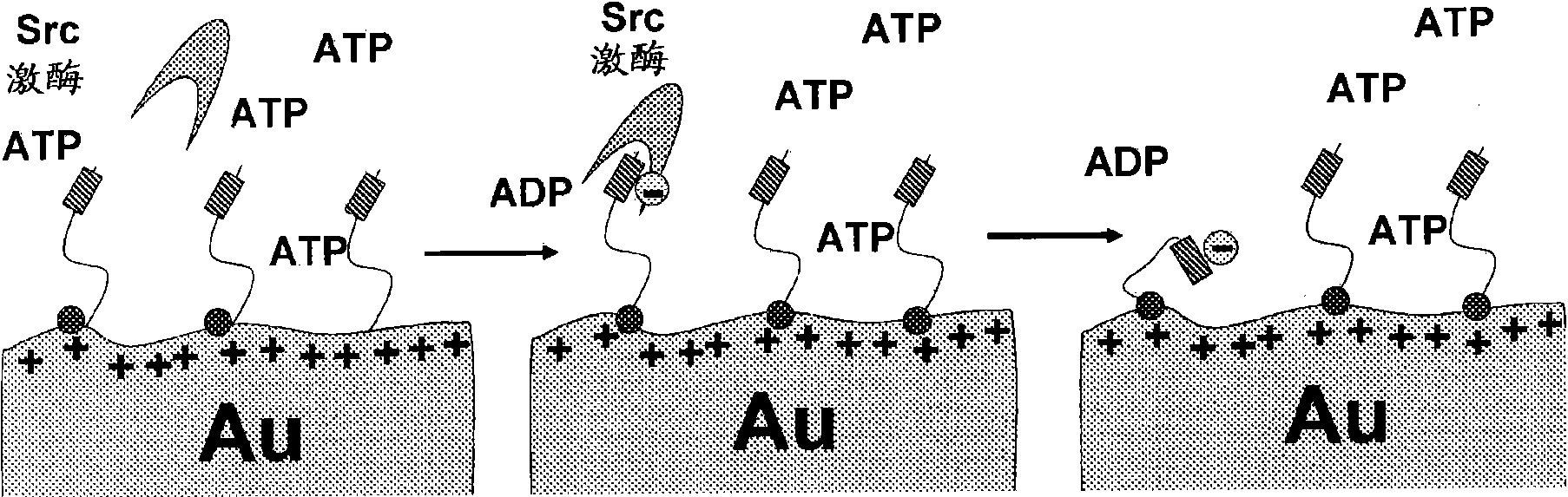
The invention discloses a detection method for the activity of carboxylesterase and the activity of a carboxylesterase inhibitor, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The detection method solves the problems of lower sensitivity, frequent occurrence of false positive signals, complex method, expensive price and long consumed time in the existing enzyme activity detection method. The detection method comprises the following steps of: reacting substrate molecules and carboxylesterases with different concentrations so as to obtain a hydrolysis product; and mixing the obtained hydrolysis product, silver nitrate solution, polyanion solution and a micromolecule probe with positive charges, and carrying out fluorescence detection on the activity of the carboxylesterase. The invention also provides a detection method for the activity of the carboxylesterase inhibitor. The method has higher sensitivity, and the detection limit is 0.05mU / mL, and is lower than that of the existing certain detection method by 1 or 2 order of magnitudes; and simultaneously, experiments prove that the method has good selectivity, simpleness and convenience and low cost.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Sers-based, single step, real-time detection of protein kinase and/or phosphatase activity
This invention provides novel compositions and methods for the detection, and / or quantification, of the presence and / or activity of one or more kinases and / or phosphatases. In certain embodiments this invention a device for the detection of kinase and / or phosphatase activity where the device comprises a Raman active surface comprising features that enhance Raman scattering having attached thereto a plurality of kinase and / or phosphatase substrate molecules.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Microwave demulsification of hydrocarbon emulsion
InactiveUS20050024284A1Promote demulsificationEfficiently delivers microwave energySubaqueous/subterranean adaptionSlot antennasEmulsionPetroleum product
Recovery of hydrocarbons, such as petroleum products, from a liquid or solid substrate is facilitated by the use of microwave energy to energize and separate molecular bonds between the hydrocarbons and the substrate. A radio frequency (RF) applicator delivers microwave energy to a treatment volume containing an emulsion of a hydrocarbon and a substrate. Delivering the microwave energy to the emulsion facilitates separation of the hydrocarbon and substrate molecules into layers. Hydrocarbons and other products can then be recovered from their respective layers. The treatment volume may be located either above or below ground. The RF applicator may include an antenna body with slots formed substantially parallel to one another in a substantially horizontal orientation. The RF applicator efficiently delivers microwave energy into the treatment volume. Substantially all of the power supplied to the RF applicator is radiated, with very little power reflected internally within the RF applicator.
Owner:INTEGRITY DEV
Protein molecule electronic device based on nanopore structure
InactiveCN104312914AOvercoming Sequencing BiasRead longBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsProtein moleculesProtein-protein complex
The invention relates to a protein molecule electronic device based on a nanopore structure. The protein molecule electronic device is a mono-enzyme biosensor which can be used for detecting a substrate molecule with extremely low concentration in a solution and sequencing the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of the single molecule. The protein molecule electronic device belongs to a third-generation DNA sequencing apparatus. The protein molecule electronic device based on the nanopore structure is characterized in that 1) the solution is divided into two parts by virtue of a solid structure with a nanochannel, wherein the solutions at the two sides of the solid structure are communicated by virtue of the nanochannel; 2) a protein molecule or a protein complex molecule is fixed in the nanochannel; 3) electrodes are respectively put in the two solutions separated by virtue of the solid structure, and resistance of the protein molecule in the nanochannel is detected by detecting current between the electrodes; and 4) the dynamic features of protein conformation are determined according to the changes of a current value passing through the protein molecule, and the information of the protein-catalyzed reaction substrate is obtained.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Amphiphilic type rare earth polyacid catalytic material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102935381AImprove catalytic performanceWith hydrophilic and lipophilic propertiesOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsIon exchangeRare earth
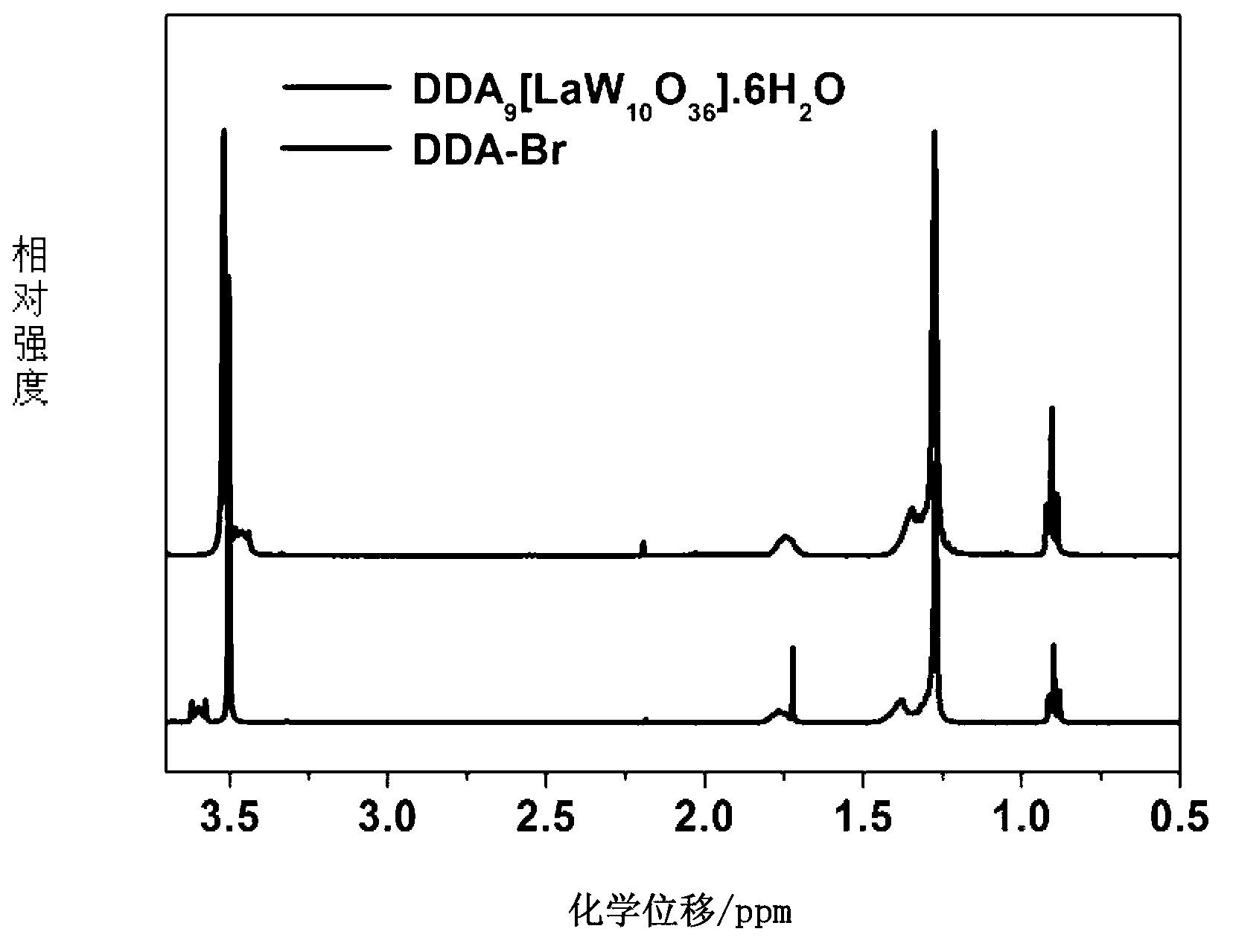
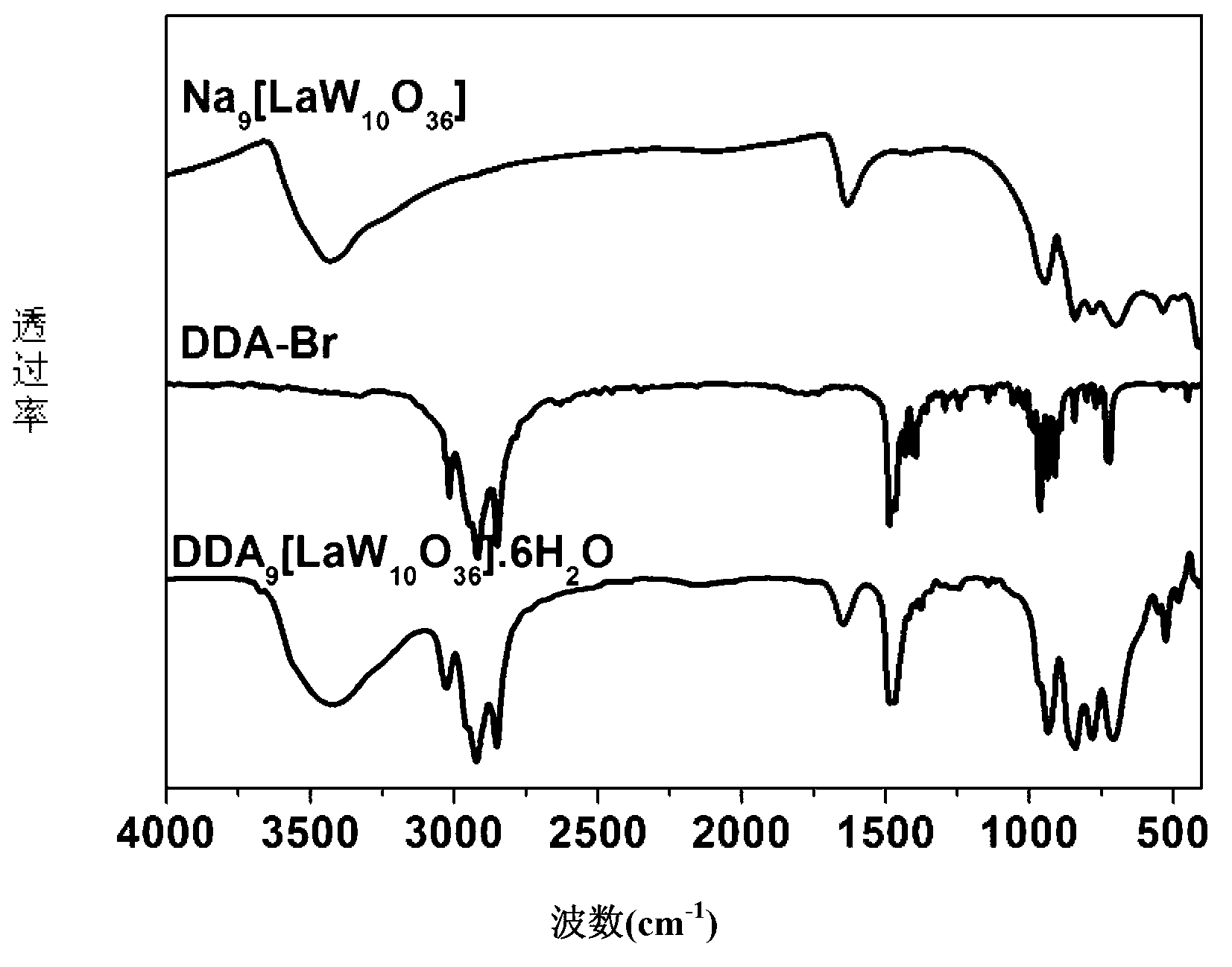
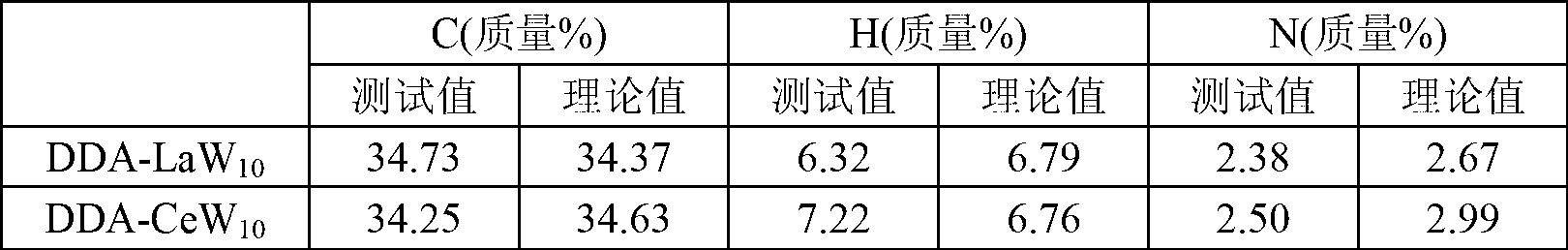
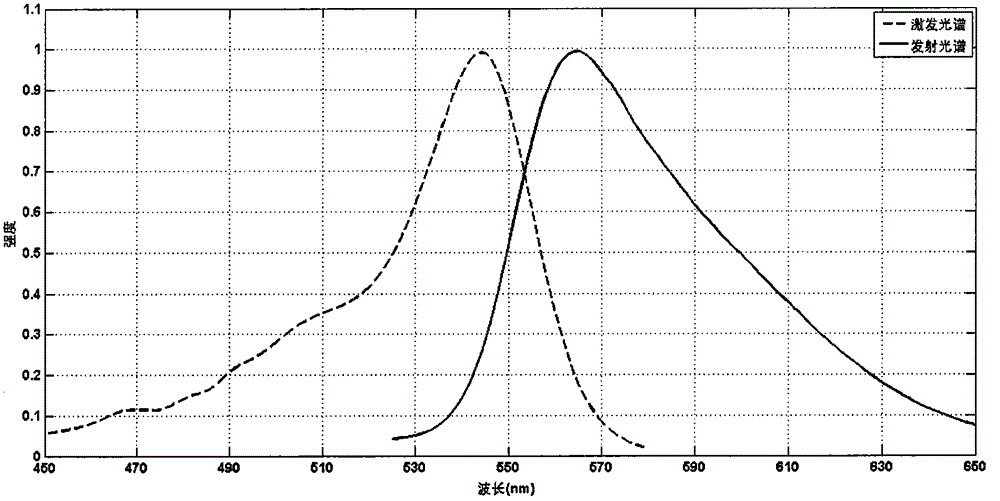
The invention relates to an amphiphilic type rare earth polyacid catalytic material and a preparation method and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of organic and inorganic composite materials. A chemical general formula is DDA9[MW10O36].Nh2o, and preparation steps comprise firstly preparing rare earth polyacid; preparing a polyacid solution; and wrapping the rare earth polyacid by using a cationic surface active agent through ion exchange reaction. The catalytic agent has good catalytic performance caused by lewis acid-base property specific to the rare earth polyacid, and introduction of the cationic surface active agent enables the catalytic agent to have hydrophilic and oleophilic characters. Simultaneously surface active agent groups in the catalytic agent quicken contact between substrate molecules and hydrogen peroxide and central polyacid portions. The amphiphilic type polyacid catalytic agent is used for enolic epoxidation reaction with a hydrogen peroxide water solution to serve as a hydrogen peroxide, and the amphiphilic type polyacid catalytic agent has high catalytic activity and high selectivity of epoxy products.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
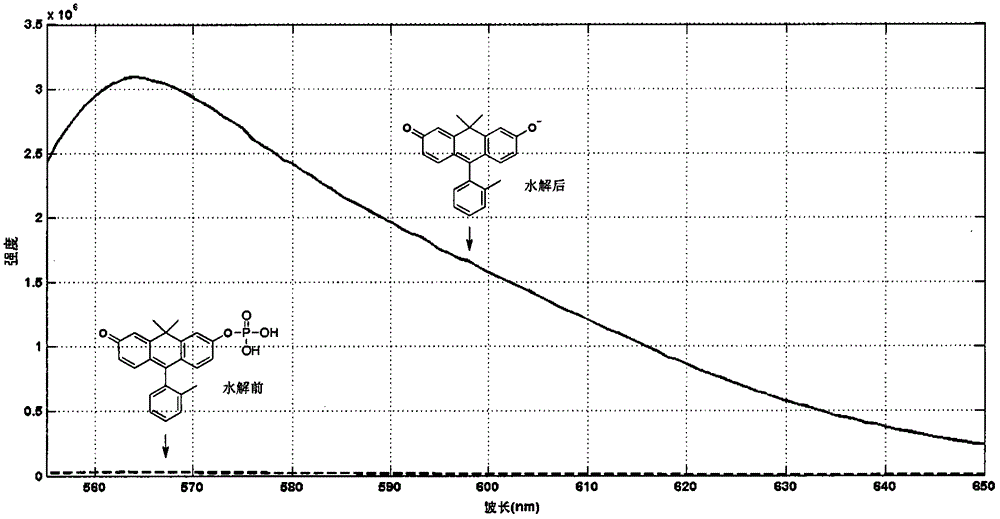
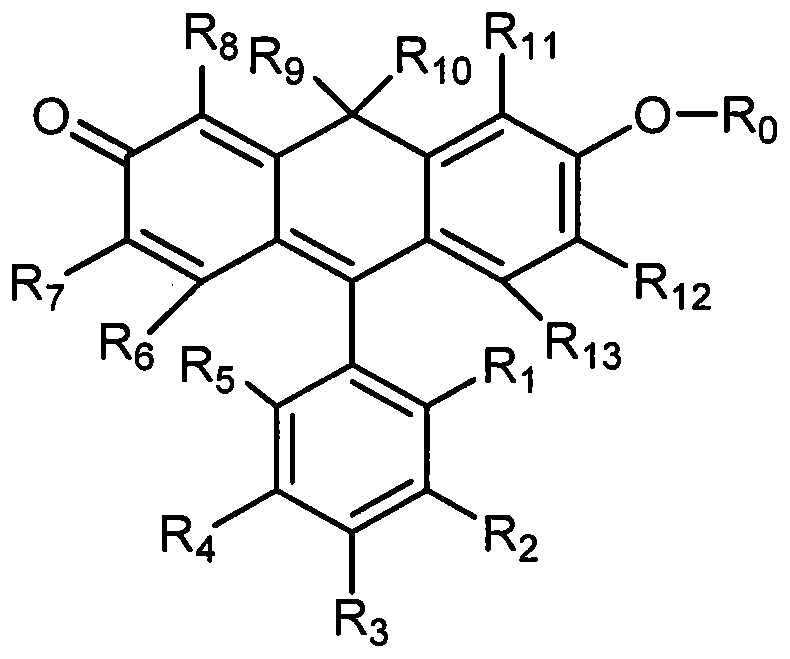
Anthracene fluorescent dye synthesis and application
ActiveCN105315698AHigh absorbance coefficientHigh quantum yieldAnthracene dyesLuminescent compositionsQuantum yieldAnthracene
The invention provides a novel fluorescent dye structure and a synthesis method thereof. The anthracene structure fluorescent dye of the type has a high light absorption coefficient similar to that of fluorescein molecules, a high quantum yield and the like and meanwhile has more bathochromic-shift excitation wavelength and emission wavelength. The synthesis method is simple and economical and suitable for large-scale synthesis and group modification of a molecular structure. According to the anthracene fluorescent dye synthesis and application, phosphatase substrate molecules with a fluorescent generation property can be obtained through phosphorylation modification conducted on the molecules, and wide biological application prospect is achieved.
Owner:CYGNUS BIOSCI BEIJING CO LTD
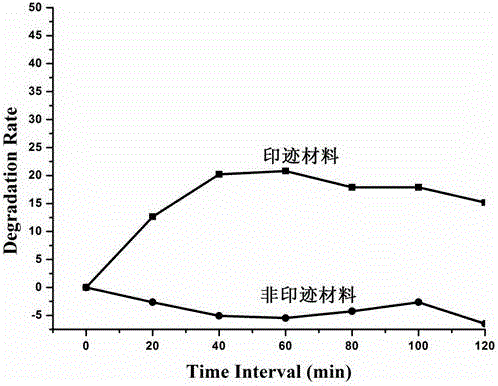
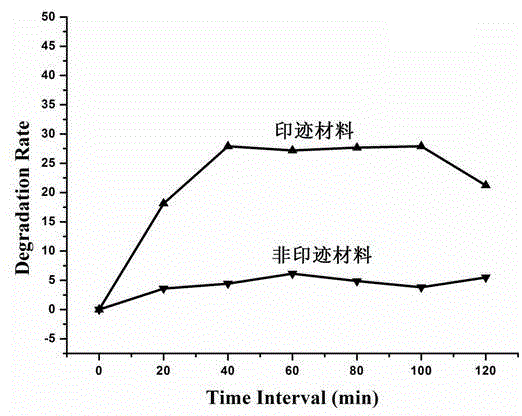
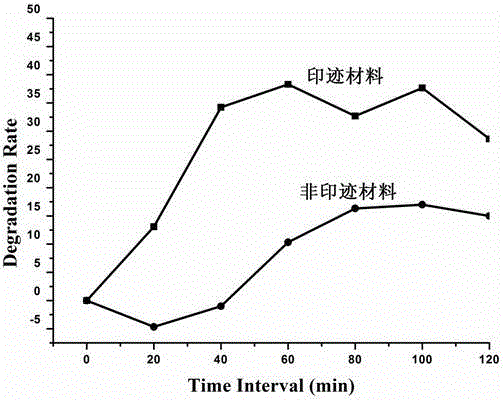
Preparation method of molecular imprinting photocatalytic composite material based on 3D graphene/BiOI
ActiveCN104971748AStrong specific and selective degradation abilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationPolypyrroleGraphite
The invention discloses a preparation method of a molecular imprinting photocatalytic composite material based on 3D graphene / BiOI. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, preparing a BiOI nano sphere; then modifying a polypyrrole molecular layer with a substrate molecular imprinting hole on the surface of the sphere; compounding the sphere with graphene to form a 3D graphene / BiOI molecular imprinting composite photocatalyst. The photocatalytic material obtained by the method has efficient selectivity and degrading performance, and has a wide application prospect in the field of managing organic pollutant wastewater.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Novel transferase and amylase, process for producing the enzymes, use thereof, and gene coding for the same
The invention provides a novel transferase that acts on a saccharide, as a substrate, composed of at least three sugar units wherein at least three glucose residues on the reducing end are linked alpha-1,4 so as to transfer the alpha-1,4 lingages to a alpha-1,alpha-1 linkages; a process for producing the transferase; a gene coding for the same; and a process for producing an oligosaccharide by using the same. Also provided are a novel amylase that has a principal activity of acting on a saccharide, as a substrate, composed of at least three sugar units wherein at least three sugar units on the reducing end side are glucose units and the linkage between the first and the second glucose units is alpha-1,alpha-1 while the linkage between the second and the third glucose units is alpha-1,4 so as to liberate alpha,alpha-trehalose by hydrolyzing the alpha-1,4 linkage and another activity of hydrolyzing the alpha-1,4 linkage within the molecular chain of the substrate and that liberates disaccharides and / or monosaccharides as the principal final products; a process for producing the amylase; a gene coding for the same; and a process for producing alpha,alpha-trehalose by using a combination of the transferase and the amylase.
Owner:KIRIN BEER KUBUSHIKI KAISHA
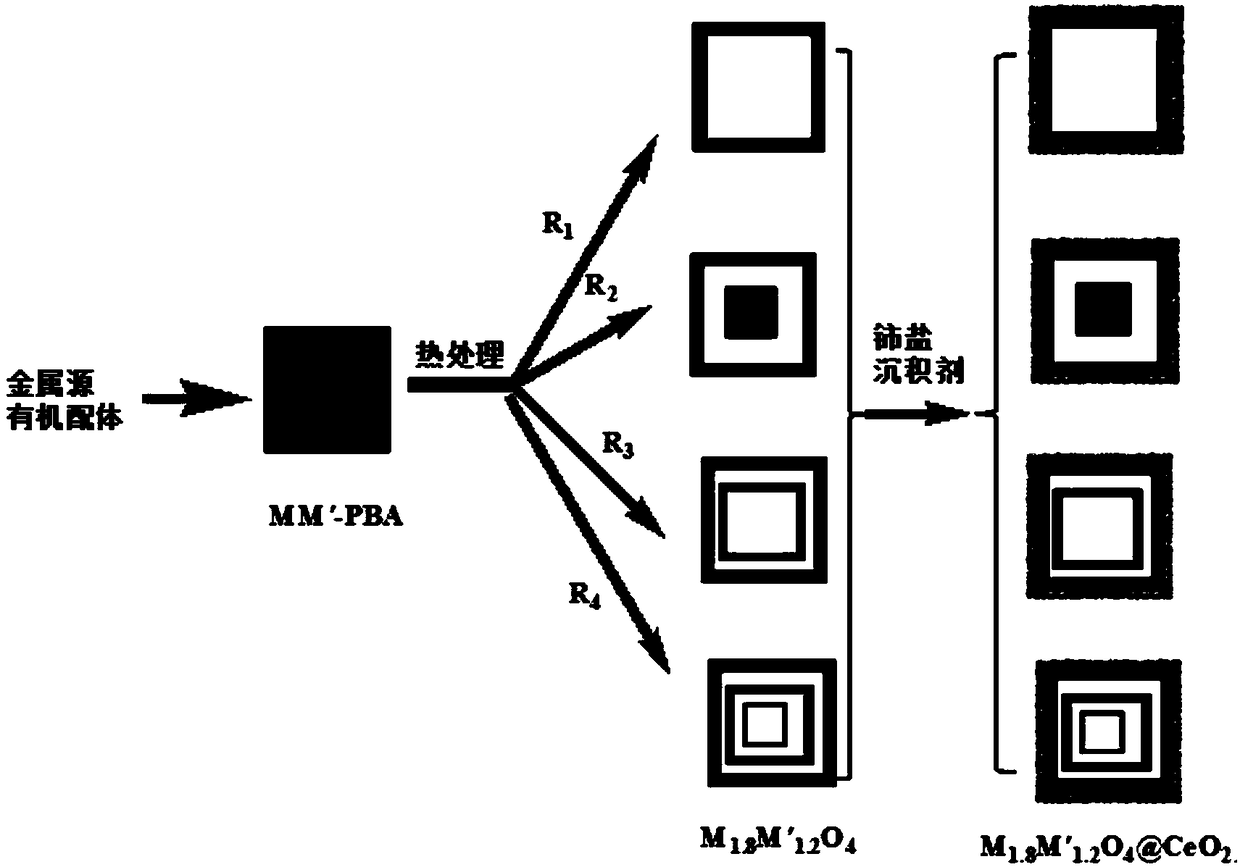
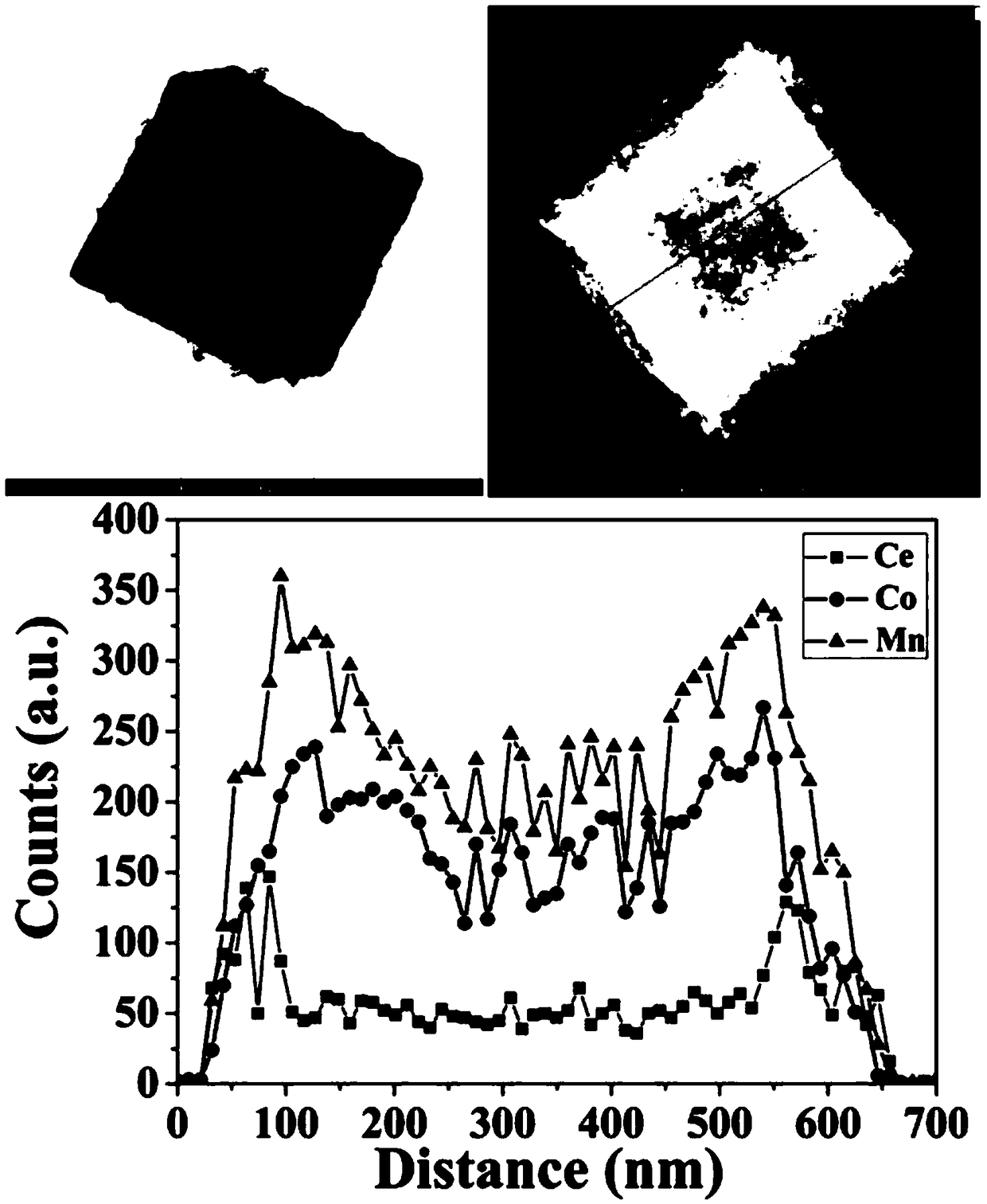
Multi-shell-layer hollow-core-shell cubic structure type M1.8M'1.2O4@CeO2 composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109364936AUniform shape and sizeGood dispersionHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCatalyst activation/preparationCavitationCatalytic oxidation
The invention discloses a multi-shell-layer hollow-core-shell cubic structure type M1.8M'1.2O4@CeO2 composite material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of firstly synthesizing a uniformly dispersed Prussian blue-similar metal organic framework material MM'-PBAs cubic structure, roasting MM'-PBAs at a high temperature under a specific condition so as to obtain a multi-shell-layer transition metal multiple oxide M1.8M'1.2O4 hollow cubic box based on an unbalanced thermal treatment method, and assembling a thickness-controllable CeO2 shell layer formedby nanometer crystals to the surface of M1.8M'1.2O4, so as to obtain the M1.8M'1.2O4@CeO2 core-shell cubic box. The process is simple, mild in condition and high in yield, a multi-shell-layer hollow structure material is directly obtained without use of a template or additional cavitation; the prepared material has a hollow structure and is large in specific surface area, meanwhile, the internal space can be effectively utilized by virtue of the multi-layer hollow structure, the contact area between substrate molecules and the material is increased, and more active sites are exposed, so that the catalytic oxidation performance is excellent.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Stoichiometry measurements for the parameterization of absolute rate models for cytochrome P450 metabolism
InactiveUS20030054430A1Microbiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesAbsolute rateReactive site
Systems and method are provided for modeling substrate molecules so that the various pathway reaction rates, and thus their overall reaction rates and metabolic properties, can be predicted. The current invention provides various systems and methods for stoichiometrically measuring the pathway reaction rates, both directly and indirectly. By repeating this for a class or several classes of substrate molecules, a general model of pathway reaction rates can be developed by correlating observed pathway reaction rates to the actual structural descriptors of the molecules, in particular, features around the reactive sites. The model can then be used to predict and design substrates according to desired metabolic characteristics. The systems and methods are particularly applicable to metabolism of substrate molecules by the cytochrome P450 enzymes.
Owner:ARQULE INC +1
Preparation method of aptamer biosensor for detecting thrombin
InactiveCN103926283AImproving Performance in Assaying ThrombinMaterial electrochemical variablesImpedance responseElectrochemistry
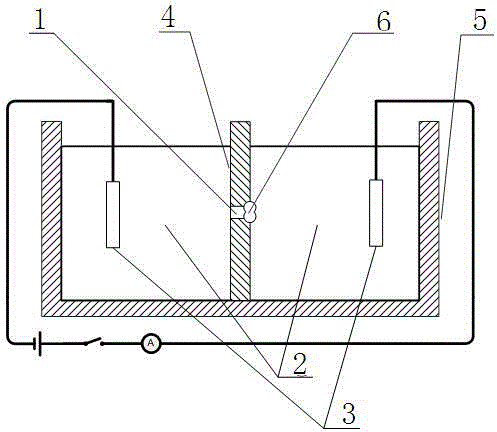
The invention relates to a preparation method of an aptamer biosensor for detecting thrombin. The method is characterized in that a hydrotalcite-carbon nanotube composite nano material modified electrode is prepared through a simple one-step electrodeposition method, and then the aptamer is loaded onto the surface of the hydrotalcite-carbon nanotube composite nano material modified electrode by adopting a strong static adsorption effect to prepare an aptamer modified electrode. By utilizing the synergistic effect of the hydrotalcite-carbon nanotube composite nano material and a specificity binding effect of the aptamer on a substrate, the thrombin can be sensitively, accurately and specifically detected. Other substrate molecules can be detected only by changing the sequence of the aptamer. The aptamer biosensor is suitable for determining the thrombin by utilizing the electrochemical impedance method. The appended drawing is the impedance response drawing of the aptamer biosensor for the thrombin.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Naked-eye differentiable isocarbophos rapid colorimetric detection method
ActiveCN106323958AHigh detection sensitivityGood choiceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsDiimineHemin
The invention discloses a method for specifically detecting isocarbophos in a catalytically colorimetric mode through interaction of a random ssDNA sequence, Hemin and a target in a NaH2PO4 buffer solution. Reagents adopted for the method mainly comprise the random ssDNA sequence, Hemin, H2O2 and 3,3',5,'5-tetramethyl benzidine (TMB). When the random ssDNA sequence and Hemin are firstly incubated for a certain time, the random ssDNA sequence can cover the surface of Hemin, the activity of Hemin for catalytically oxidizing TMB is restrained temporarily, N atoms in substrate molecules lose one electron, the color of the system is remarkably changed into light blue or blue from colorless originally, and at the moment, characteristic absorption peaks of a product are 370 nm and 650 nm. If isocarbophos is added into the system to jointly act for a certain time, the catalytic activity of hemin is greatly enhanced, substrate TMB loses two electrons and is changed into a diimine structure, at the moment, the color of the system is changed into yellow from blue, the characteristic absorption peak exists at the position of 450 nm, and the change amplitude of the light absorption value at the position of 450 nm and the concentration of isocarbophos are in direct proportion.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Preparation method for synthesizing Fe3O4(PAA)@C-Au core-shell-structured microspheres with one-step hydrothermal method
InactiveCN106040307ADoes not affect catalytic activityExcellent substrate adsorption capacityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationNano catalystNano composites
The invention provides a preparation method for synthesizing Fe3O4(PAA)@C-Au core-shell-structured microspheres with a one-step hydrothermal method, and belongs to the field of nano-composites. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing monodisperse PAA (polyacrylic acid) modified Fe3O4 magnetic microspheres with uniform particle size; (2) supporting a porous carbon layer and precious metal nanoparticles with high catalytic activity on the surfaces of the magnetic microspheres with the one-step hydrothermal method, and a supported precious metal nano-composite catalytic material is obtained. According to the method, the precious metal nano-catalytic material with high catalytic activity is supported on the surfaces of the magnetic microspheres with one step, the porous carbon layer provides a channel for conveying substrate molecules and transporting products, and promotes the collision probability of a catalytic activity center and the substrate molecules; by means of stable immobilization of the precious metal nanoparticles, the problems of proneness to running away, proneness to agglomeration and the like of the precious metal nano-catalyst in a using process are solved effectively; the nano-composite catalytic material prepared with the method has high catalytic efficiency and strong cycling stability. The method adopts a simple reaction process, and is short in process, pollution-free, little in energy consumption and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Supported PtAu catalyst and method for catalytic reduction of olefinic bonds or acetylenic bonds by using same
ActiveCN102976879ASimple preparation procedureMild reaction conditionsOrganic reductionOrganic compound preparationHydrogen atmosphereChloroauric acid
The invention relates to a supported PtAu catalyst and a method for catalytic reduction of olefinic bonds or acetylenic bonds by using same, and belongs to the technical field of heterogeneous catalysis. The supported PtAu catalyst is prepared by taking platinum acetylacetonate and chloroauric acid tetrahydrate as precursors and active carbon as a carrier, putting the two precursors into n-octadecylamine to prepare a bimetal PtAu through reduction, and loading the obtained bimetal PtAu on the active carbon. According to the method for catalytic reduction of the olefinic bonds or acetylenic bonds by using supported PtAu, halogenated aryl hydrocarbon is used as a substrate, the supported PtAu is used as a catalyst, and under a normal pressure hydrogen atmosphere at room temperature, the substrate and the catalyst are placed into an organic solvent to react so as to selectively reduce the olefinic bonds or acetylenic bonds in substrate molecules. The method has the advantages of simple preparation process of the catalyst, mild reaction condition, high catalyst activity, selectivity and stability and the like, so that highly selective reduction of the olefinic bonds or acetylenic bonds in a series of halogenated aryl hydrocarbon molecules.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Nano-structure-based protein unimolecular electronic device and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN106929565ARealize monitoringOvercoming Sequencing BiasMicrobiological testing/measurementThird generation sequencingNanostructure
The invention discloses a nano-structure-based protein unimolecular electronic device and preparation and application thereof; single protein or its complex molecules are fixed to a counter electrode at a nano hole, dynamical features of conformational fluctuation of the protein are characterized by detecting the electrical conductivity of the protein or its complex molecules in a solution, and the activity of the protein and the biochemical reactive process thereof with substrate molecules are detected. The nano-structure-based protein unimolecular electronic device may act as a third-generation sequencing method having great development potential, preparing special DNA sequencing libraries is not required, labeling nucleic acids is not required, ultra-long, continuous, quick and precise base reading can be performed, and ultralow-cost DNA sequencing and otherness can be achieved if a high-throughput molecular device is prepared.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
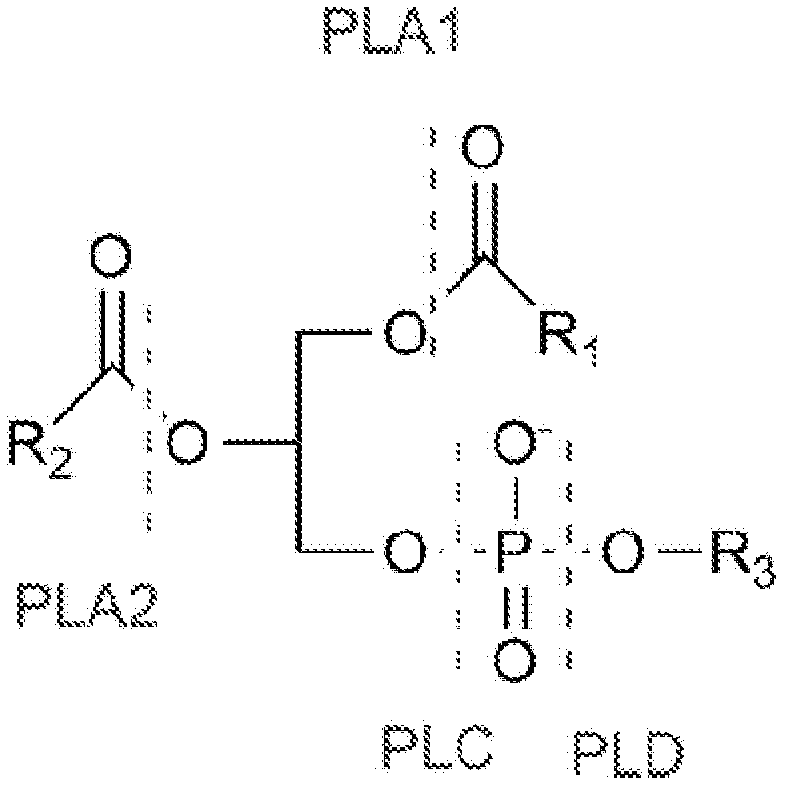
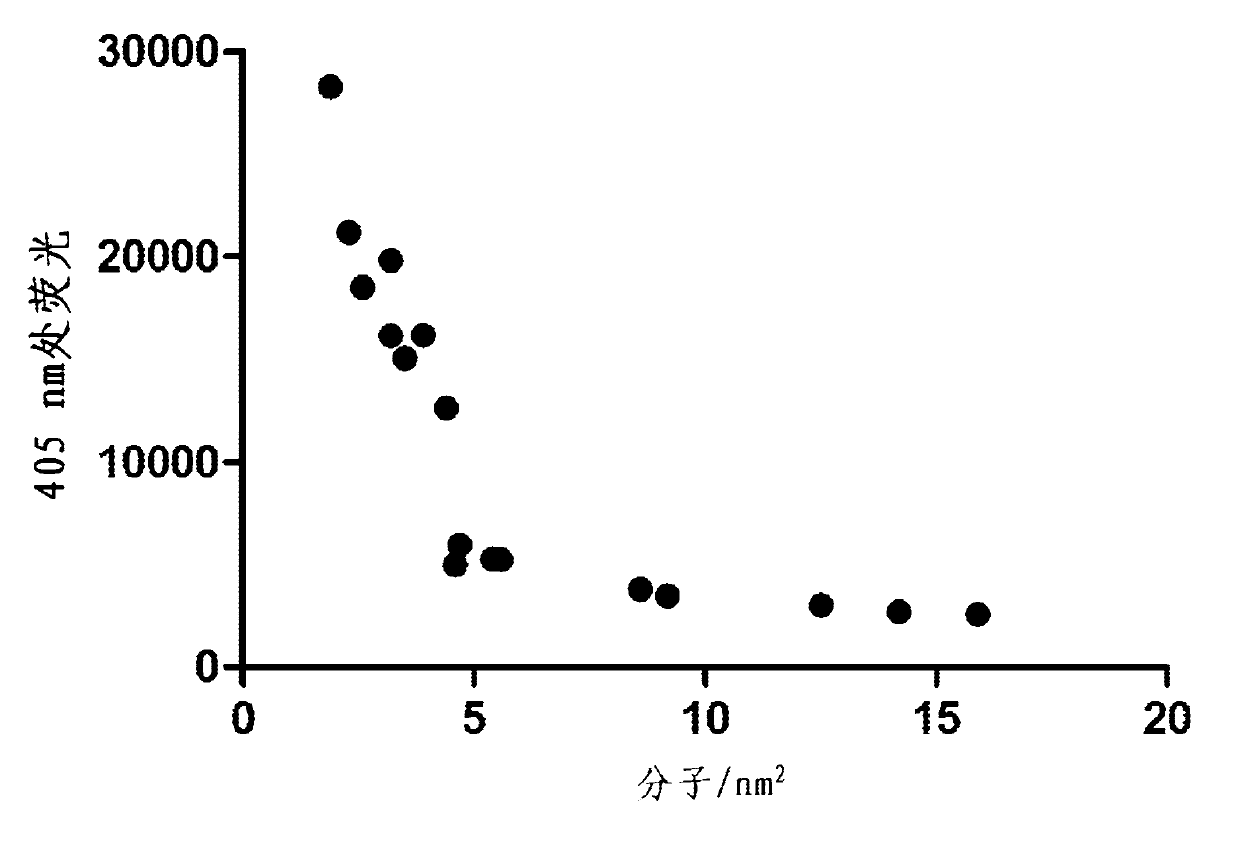
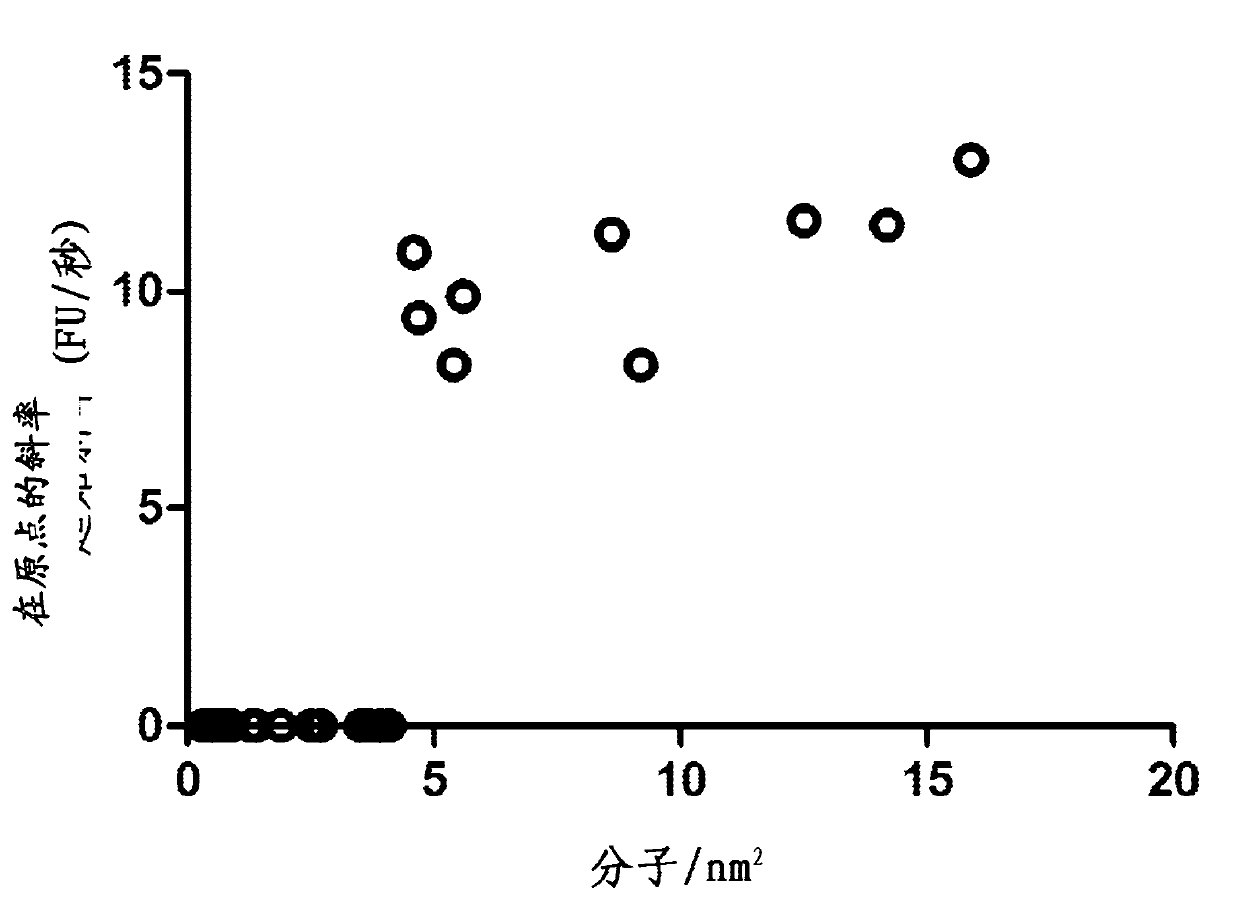
Enzymatic assay for the quantitative determination of phospholipase A1 or A2 activity in a sample
InactiveCN102388311ASensitivity advantageMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisQuantitative determinationFluorescence
The invention relates to a new method for measuring phospholipase A1 or A2 activity in a sample, using a solid phase coated with a fluorochrome-labelled phospholipase A1 or A2 substrate, wherein the molecular coverage is in the range from 8 to 30 fluorochrome-labelled phospholipase A1 or A2 substrate molecules / nm2, and kit for carrying out said method.
Owner:ATEROVAX
Method for preparing rare-earth transition metal composite oxide porous hollow spheres
InactiveCN109160544AEvenly distributedThickness is easy to controlMaterial nanotechnologyHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsRare earthCatalytic oxidation
The invention discloses a method for preparing rare-earth transition metal composite oxide porous hollow spheres and belongs to the field of inorganic nanometer materials and heterogeneous catalysis.The method comprises the following steps: 1, dissolving a rare-earth metal source and a transition metal source in a polyol medium, and synthesizing a solid spherical alkoxide precursor with excellentdispersion by adopting a solvothermal method; and 2, performing heat treatment on the precursor under specific conditions, and synthesizing the rare-earth transition metal composite oxide porous hollow spheres based on an unbalanced heat treatment method. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the raw material price is low, the hollow structure material is directly obtained, and the prepared rare-earth transition metal composite oxide porous hollow spheres have the advantages of being uniform in metal element dispersion, controllable in composition and size, capable ofrealizing porous distribution of the shell layer and controllable in thickness; and when the hollow spheres are applied to a catalytic reaction, the contact area between the substrate molecule and catalytic active sites can be greatly enlarged, the interface synergy among different components of the rare-earth transition metal oxides contributes to transmission of reactive oxygen species at the heterogenous interface and transfer of electrons, and the activity of the catalytic oxidation reaction is obviously improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Microwave demulsification of hydrocarbon emulsion
InactiveUS20090146897A1Promote demulsificationEfficiently delivers microwave energyRadiating element housingsSubaqueous/subterranean adaptionEmulsionMicrowave
Recovery of hydrocarbons, such as petroleum products, from a liquid or solid substrate is facilitated by the use of microwave energy to energize and separate molecular bonds between the hydrocarbons and the substrate. A radio frequency (RF) applicator delivers microwave energy to a treatment volume containing an emulsion of a hydrocarbon and a substrate. Delivering the microwave energy to the emulsion facilitates separation of the hydrocarbon and substrate molecules into layers. Hydrocarbons and other products can then be recovered from their respective layers. The treatment volume may be located either above or below ground. The RF applicator may include an antenna body with slots formed substantially parallel to one another in a substantially horizontal orientation. The RF applicator efficiently delivers microwave energy into the treatment volume. Substantially all of the power supplied to the RF applicator is radiated, with very little power reflected internally within the RF applicator.
Owner:INTEGRITY DEV
Synthetic method of amino-substituted cyclohexyl crown ether
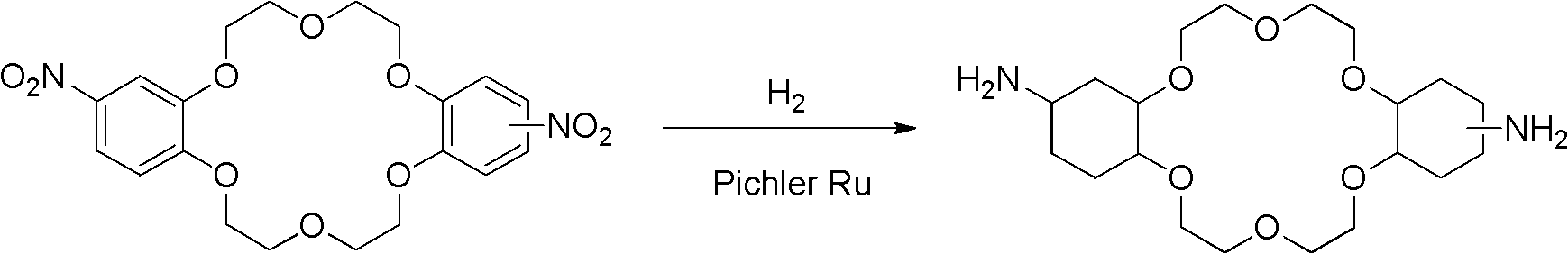
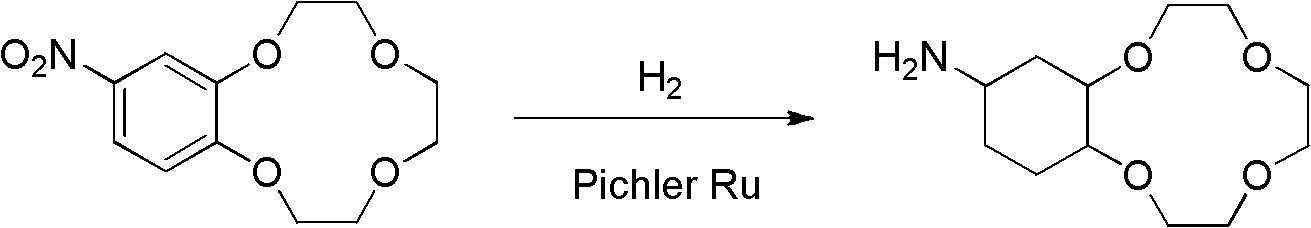
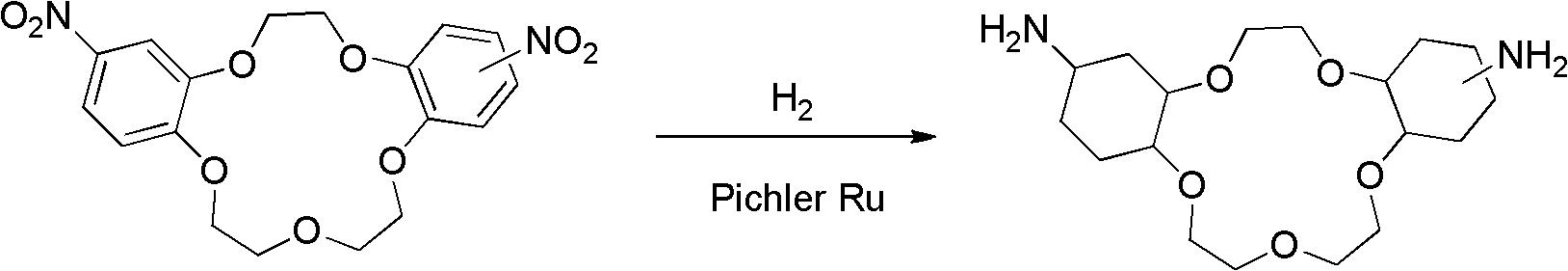
InactiveCN102558136AEasy to separateHigh catalytic activityOrganic chemistryChemical recyclingHigh pressureHigh activity
The invention discloses a synthetic method of amino-substituted cyclohexyl crown ether, which belongs to the technical field of synthetic technique of organic compound. The synthetic method uses nitro-substituted benzo crown ether as a substrate, uses high-activity Pichler ruthenium as a catalytic agent, uses high pressure hydrogen to achieve reduction of nitro and hydrogenation of phenyl group in substrate molecules simultaneously in one-step reaction, and accordingly obtains needed amino-substituted cyclohexyl crown ether products. The synthetic method enables the existing two-step reaction to be merged in a same system, and operation is greatly simplified. The temperature and the pressure of the needed reaction are relative mild, occurrence of side reaction is well avoided, and purity of obtained products is guaranteed. The ruthenium catalytic agent is high in catalytic activity, while cost is relatively lower than that of rhodium, platinum and the like, and the synthetic method has the cost advantage. Simultaneously, after reaction ends, the catalytic agent can be well separated and recycled.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
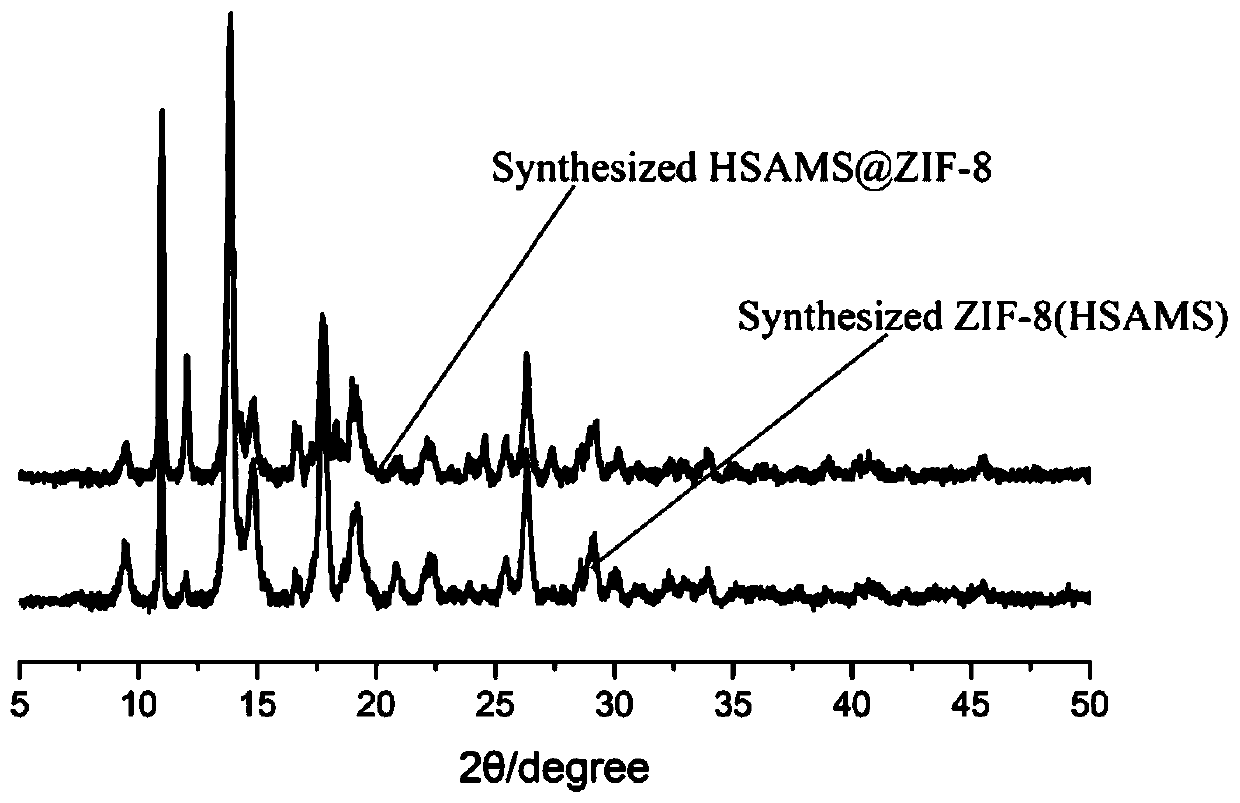
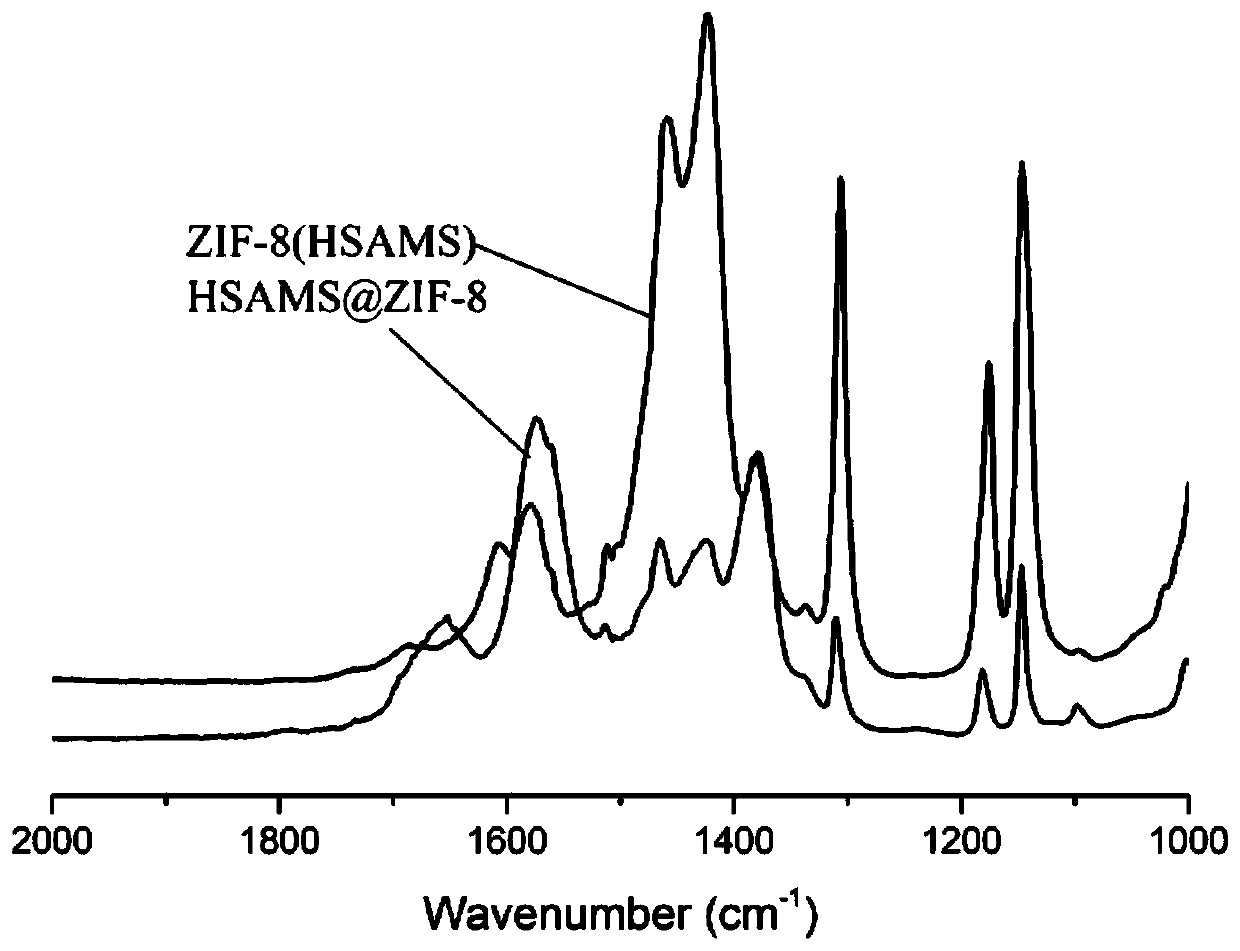
Preparation method of ZIF-8/enzyme composite material
ActiveCN111411102ADoes not affect activityImprove cycle performanceOn/in organic carrierOn/in inorganic carrierProtective enzymesActive center
The invention relates to a preparation method of a ZIF-8 / enzyme composite material. The preparation method comprises the steps of regulating the concentration of a precursor to enable a ZIF-8 crystalto grow on the surface of an enzyme in a lamellar structure, mixing a metal salt water solution with a mixed solution of a ligand water solution and the enzyme, performing stirring at room temperaturefor a period of time, and separating out a solid product, and thereby obtaining the ZIF-8 / enzyme composite material. Different from a composite material obtained through a traditional method, the method does not depend on ducts of ZIF-8 to diffuse substrate molecules, and a large-size substrate makes contact with the active center of the enzyme through gaps between ZIF-8 lamellar structures, so that a catalytic reaction is completed. ZIF-8 nanoflowers growing on the surface of the enzyme can well protect the enzyme from reacting under harsh conditions, and meanwhile, the ZIF-8 / enzyme nanoflower composite material also has good circularity and storage capacity.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Softening method for edible areca catechu
PendingCN106538999AGood flexibilityAccelerate unpleasant flavor substancesFood ultrasonic treatmentFood ingredient as mouthfeel improving agentFiberUltrasonic assisted
The invention relates to a food processing process, in particular to a softening method for edible areca catechu. An ultrasonic-assisted enzymolysis method is adopted for softening areca catechu; ultrasonic waves can influence the enzymatic reactions, the mass transfer efficiency and the internal structure of areca catechu fibers by virtue of heating, mechanical mass transfer and cavitation; under a suitable process, the enzyme activity can be improve, the mobility of substrate molecules and enzyme molecules are enhanced, and the touch probability of the substrate molecules and the enzyme molecules is increased, so that the whole enzymolysis softening efficiency is improved, softening of areca catechu fibers is enhanced, the softness of areca catechu is improved, and the degree of damage on the oral cavity and teeth of a human body due to areca catechu is reduced; furthermore, due to the relation between soaking and ultrasound, unpleasant-flavor substances generated by areca catechu during enzymolysis can be accelerated.
Owner:湖南宾之郎实业集团有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com