Patents
Literature
3856 results about "Amylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Amylase (/ˈæmɪleɪz/) is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (Latin amylum) into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large amounts of starch but little sugar, such as rice and potatoes, may acquire a slightly sweet taste as they are chewed because amylase degrades some of their starch into sugar. The pancreas and salivary gland make amylase (alpha amylase) to hydrolyse dietary starch into disaccharides and trisaccharides which are converted by other enzymes to glucose to supply the body with energy. Plants and some bacteria also produce amylase. As diastase, amylase was the first enzyme to be discovered and isolated (by Anselme Payen in 1833). Specific amylase proteins are designated by different Greek letters. All amylases are glycoside hydrolases and act on α-1,4-glycosidic bonds.
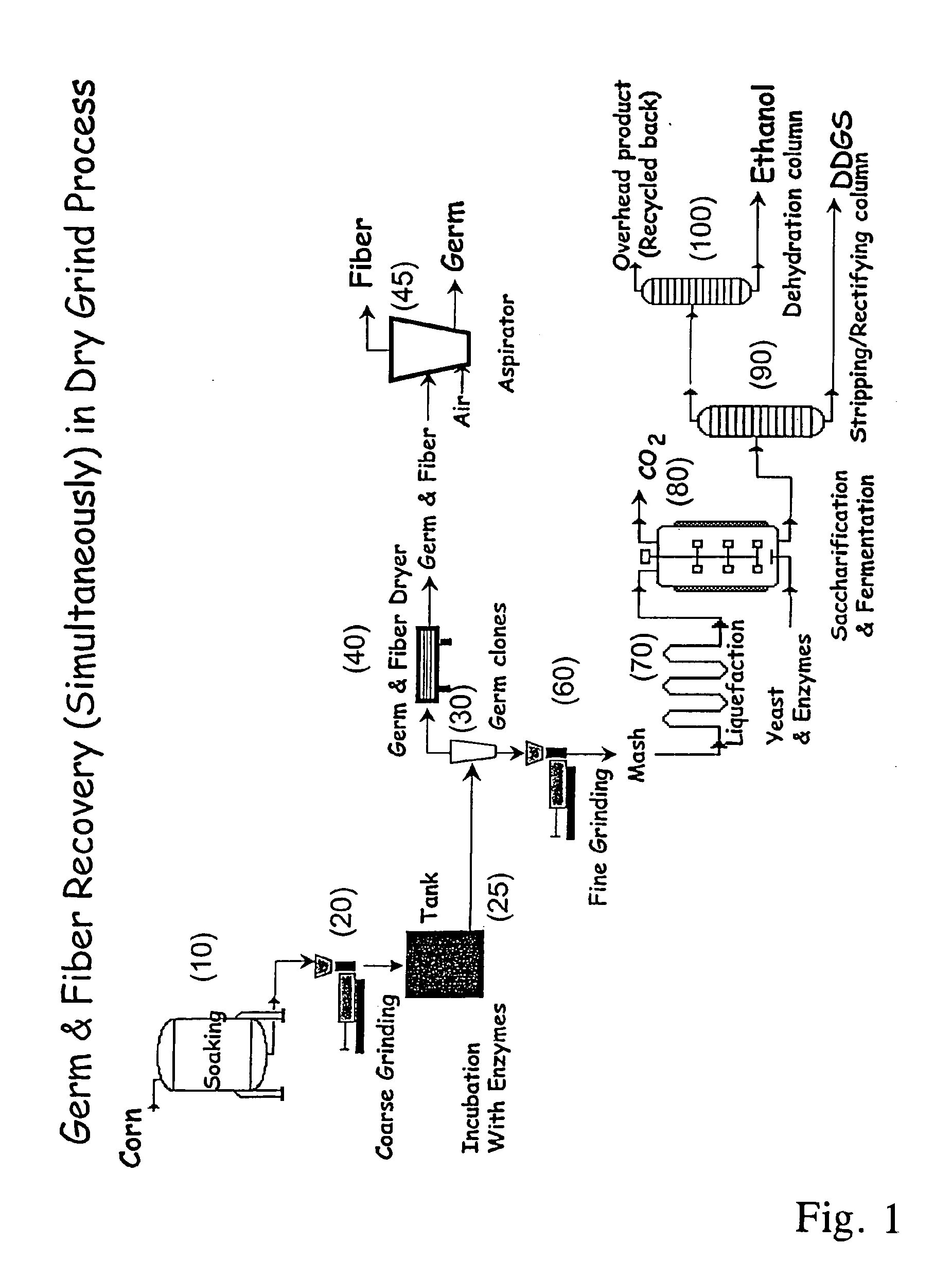
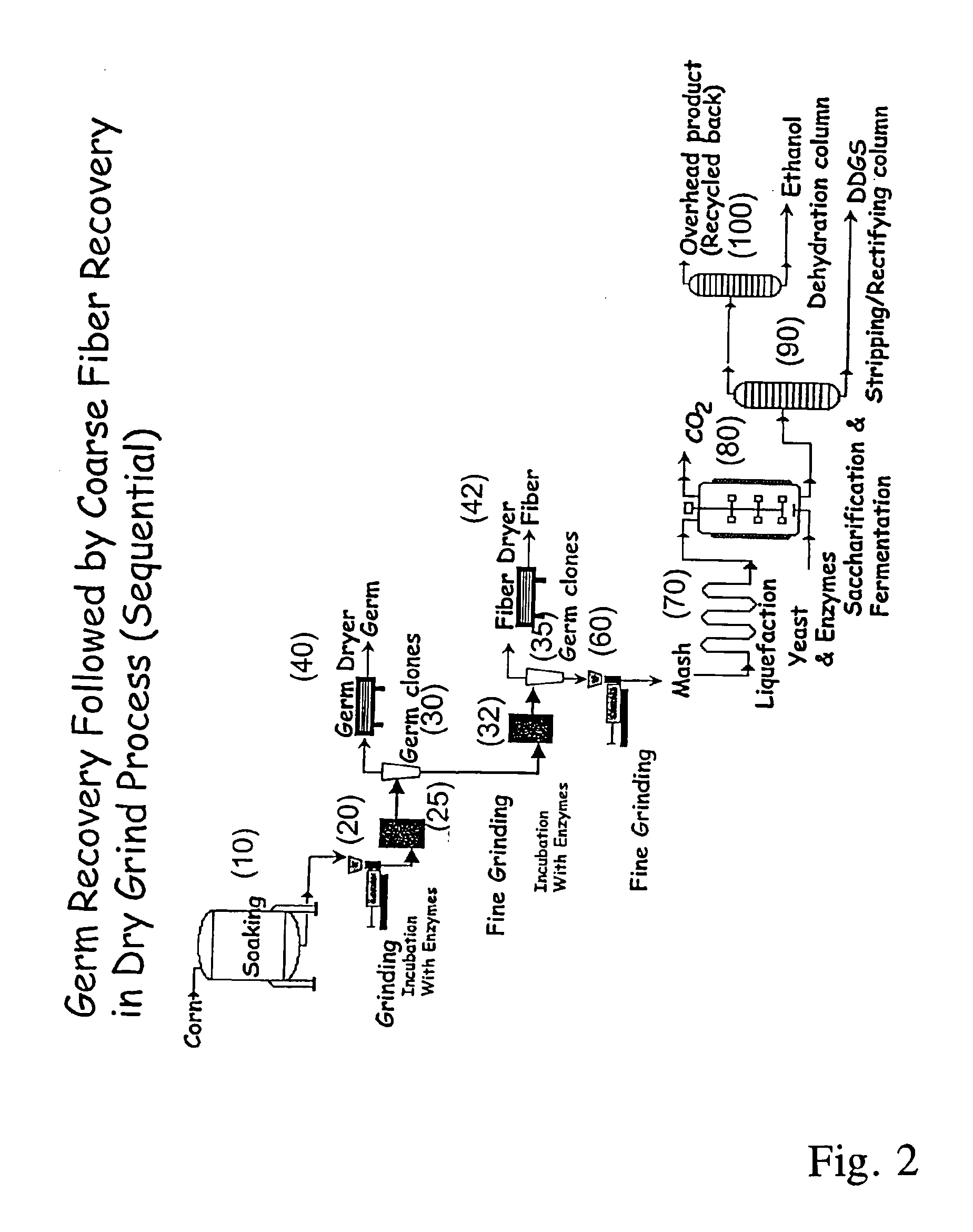
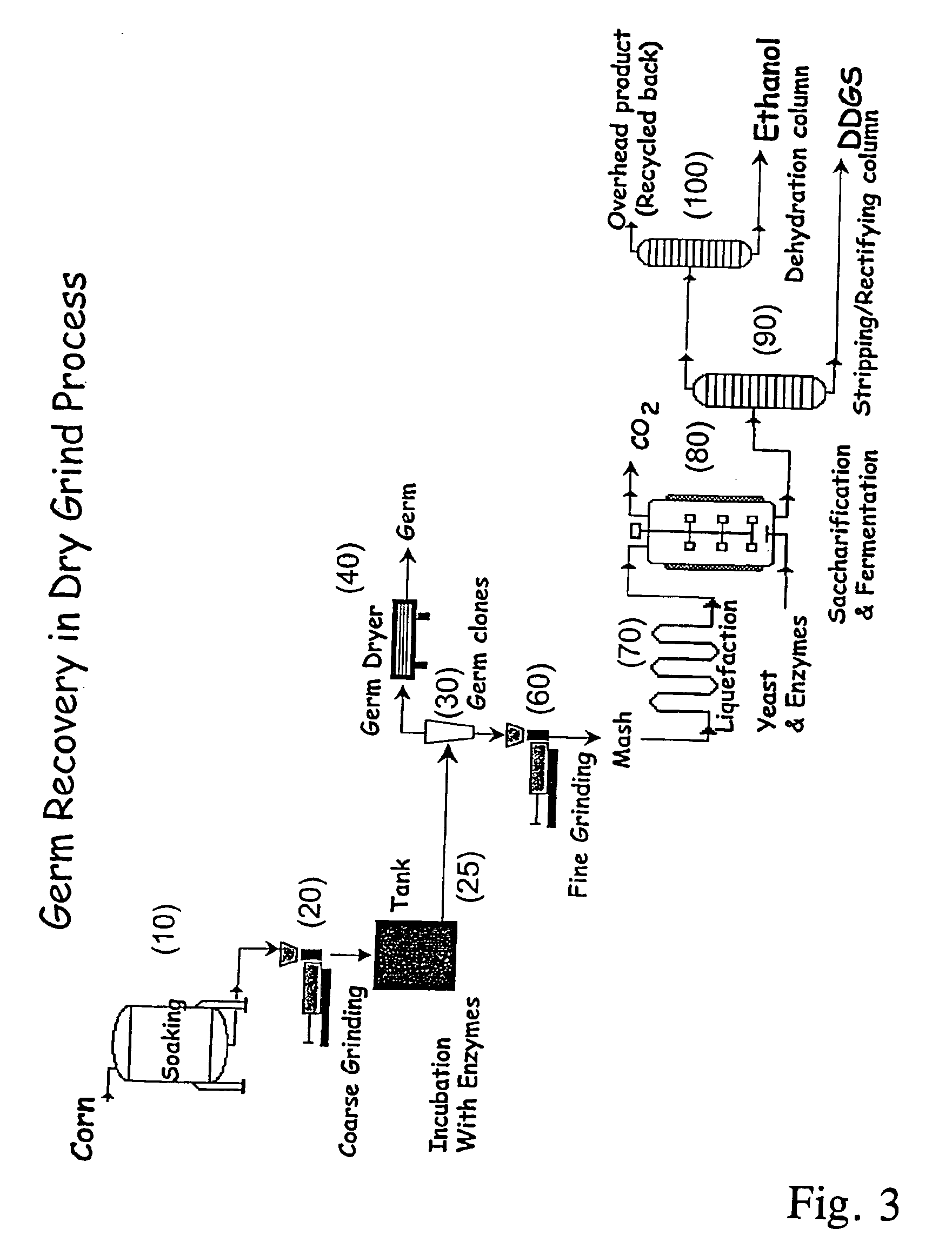
Processes for recovery of corn germ and optionally corn coarse fiber (pericarp)
A process for recovering corn germ and corn coarse fiber from corn in a dry grind process, involving soaking corn kernels in water to produce soaked corn kernels, grinding the soaked corn kernels to produce a ground corn slurry, and incubating the ground corn slurry with at least one enzyme (amylase(s), protease(s), cell wall degrading enzyme(s), or mixtures thereof, and optionally other enzyme(s)) to increase the specific gravity of the slurry to about 10-about 16 Baume so that the corn germ and corn coarse fiber floats to the top of the slurry, recovering the corn germ and the corn coarse fiber, and optionally producing ethanol from the slurry no longer containing the corn germ and corn coarse fiber. The process does not involve the addition of starch, a salt, a sugar syrup, or mixtures thereof to the slurry.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
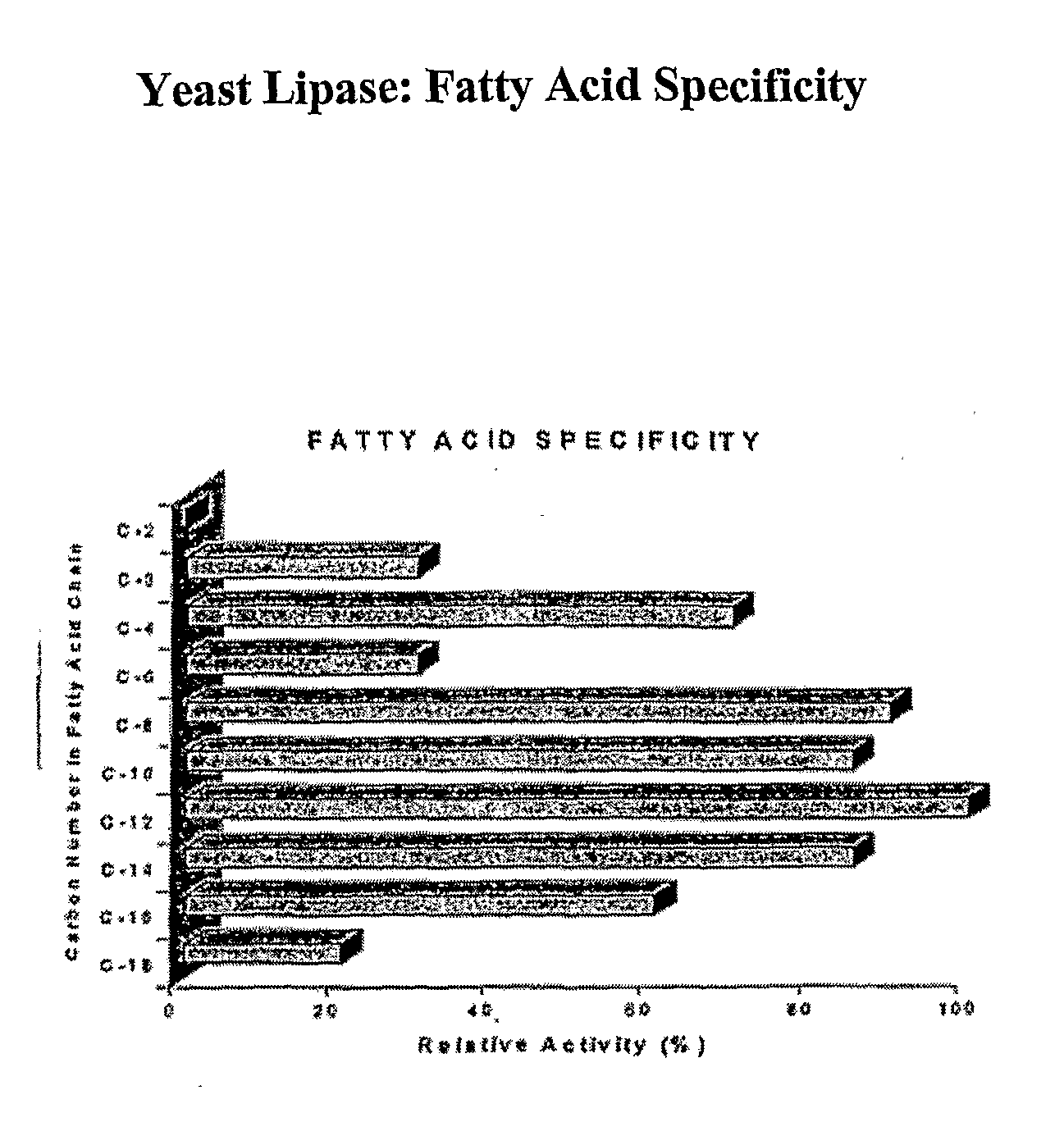
Composition With a Fungal (Yeast) Lipase and Method For Treating Lipid Malabsorption in Cystic Fibrous as Well as People Suffering From Pancreatic Lipase Insufficiency
The invention provides compositions and methods for treating pancreatic enzyme insufficiency, such as the pancreatic enzyme insufficiency associated with cystic fibrosis. The invention also provides compositions comprising lipase from Candida cylindracea, alone or in combination with amylase or amyloglucosidase, protease and / or lactase. Furthermore, the invention discloses methods for treating pancreatic enzyme insufficiency comprising administering compositions to patients in need thereof.
Owner:BIO CAT
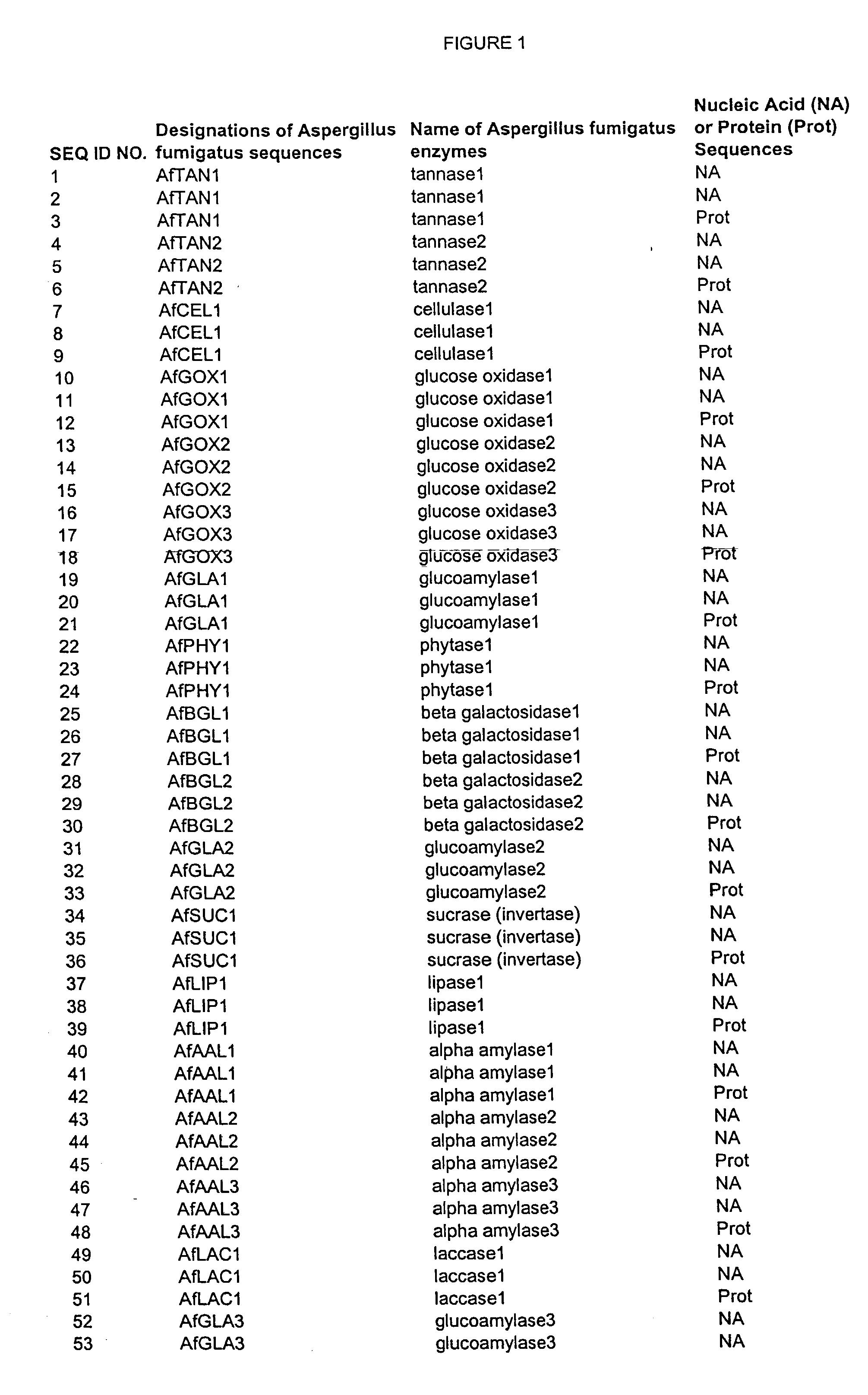
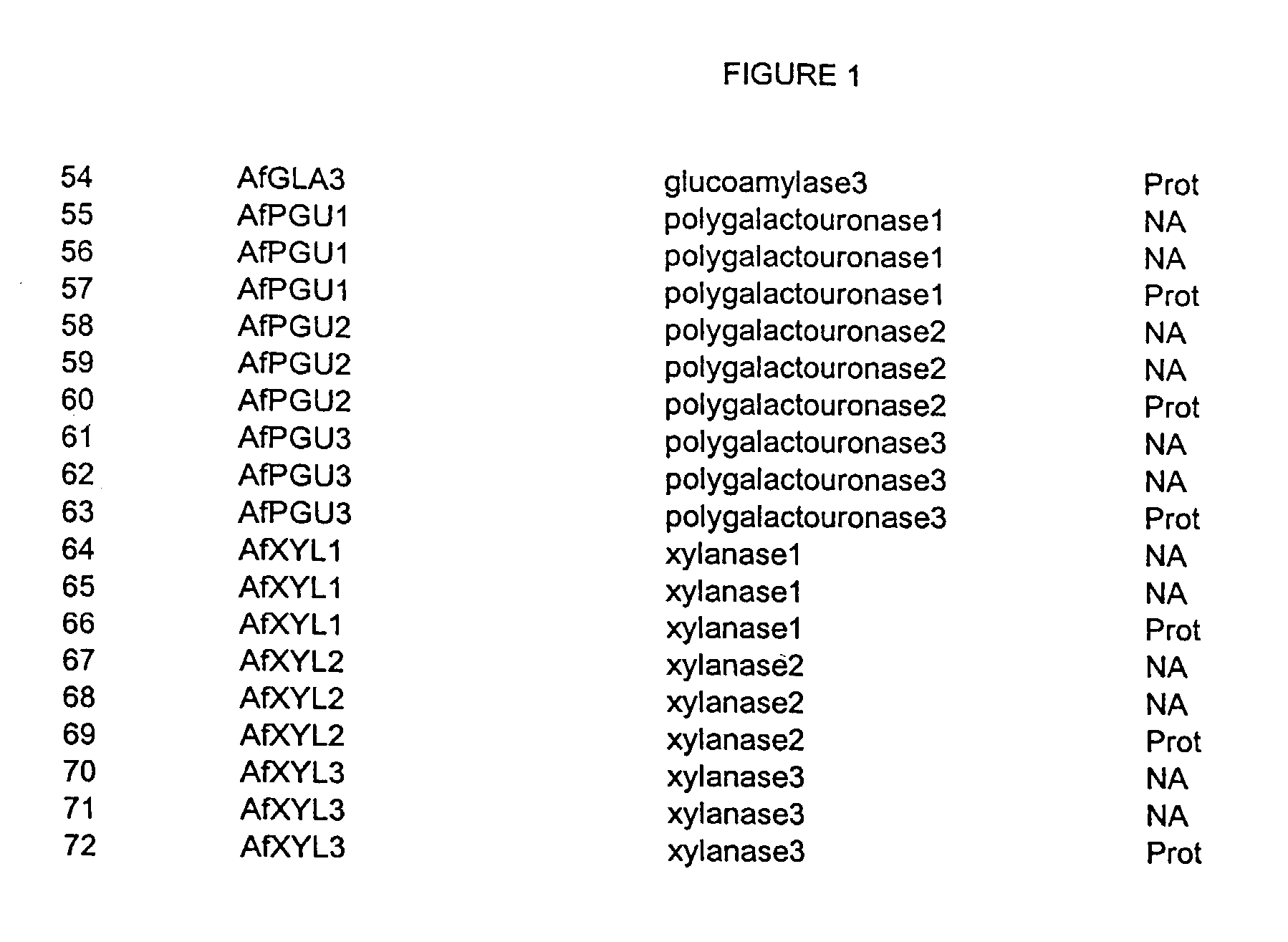
Nucleic acids of aspergillus fumigatus encoding industrial enzymes and methods of use
The present invention provides nucleotide sequences of Aspegillus fumigatus that encode proteins which exhibit enzyme activities. Vectors, expression constructs, and host cells comprising the nucleotide sequences of the enzyme genes are also provided. The invention further provides methods for producing the enzymes, and methods for modifying the enzymes in order to improve their desirable characteristics. The activities displayed by the enzymes of the invention include those of a tannase, cellulase, glucose oxidase, glucoamylase, phytase, beta-galactosidases, invertase, lipase, alpha-amylase, laccase, polygalacturonase or xylanase. The enzymes of the invention can be used in a variety of industrial processes. Enzymatically active compositions in various forms as well as antibodies to the enzymes and fragments thereof, are also provided.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Method of removing a biofilm
The present invention relates to a method of removing a biofilm, which comprises at least the following steps, carried out simultaneously or consecutively: a) a solution comprising an enzyme mixture containing at least one enzyme chosen from the group of proteases, at least one enzyme chosen from the group of esterases and an amylase is prepared; b) a solution comprising a detergent with an alkaline pH is prepared; and c) said solutions are applied, by washing or by circulation, to the surface to be treated. It also relates to a kit intended for removing a biofilm, which comprises the solutions defined above and the compositions comprising the said solutions.
Owner:KARINE MARION +1
Novel strain of bacillus amyloliquefaciens and its use
InactiveUS20100143316A1Inhibits pathogenic growthPromote biodegradationAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiotechnologyAmylase
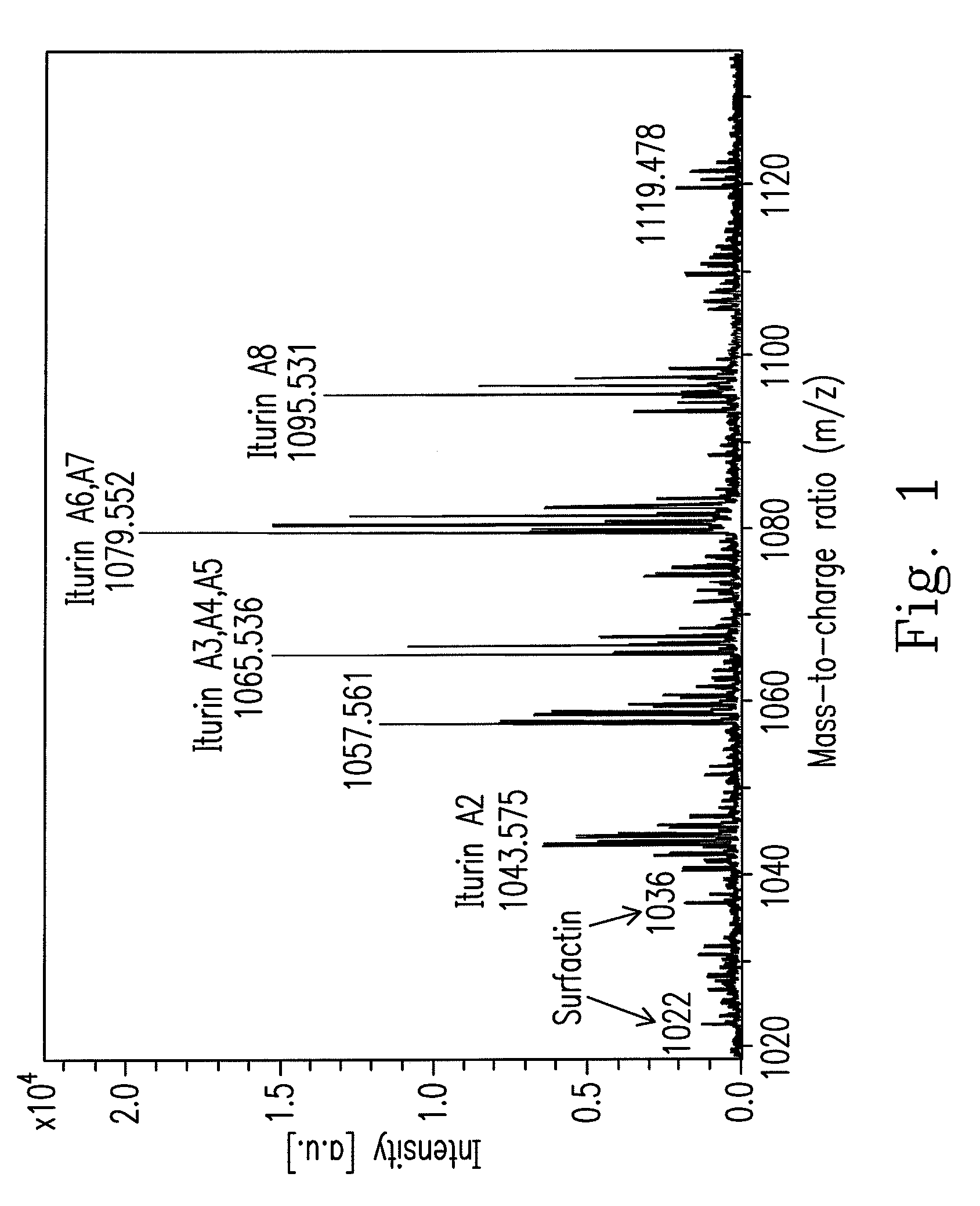
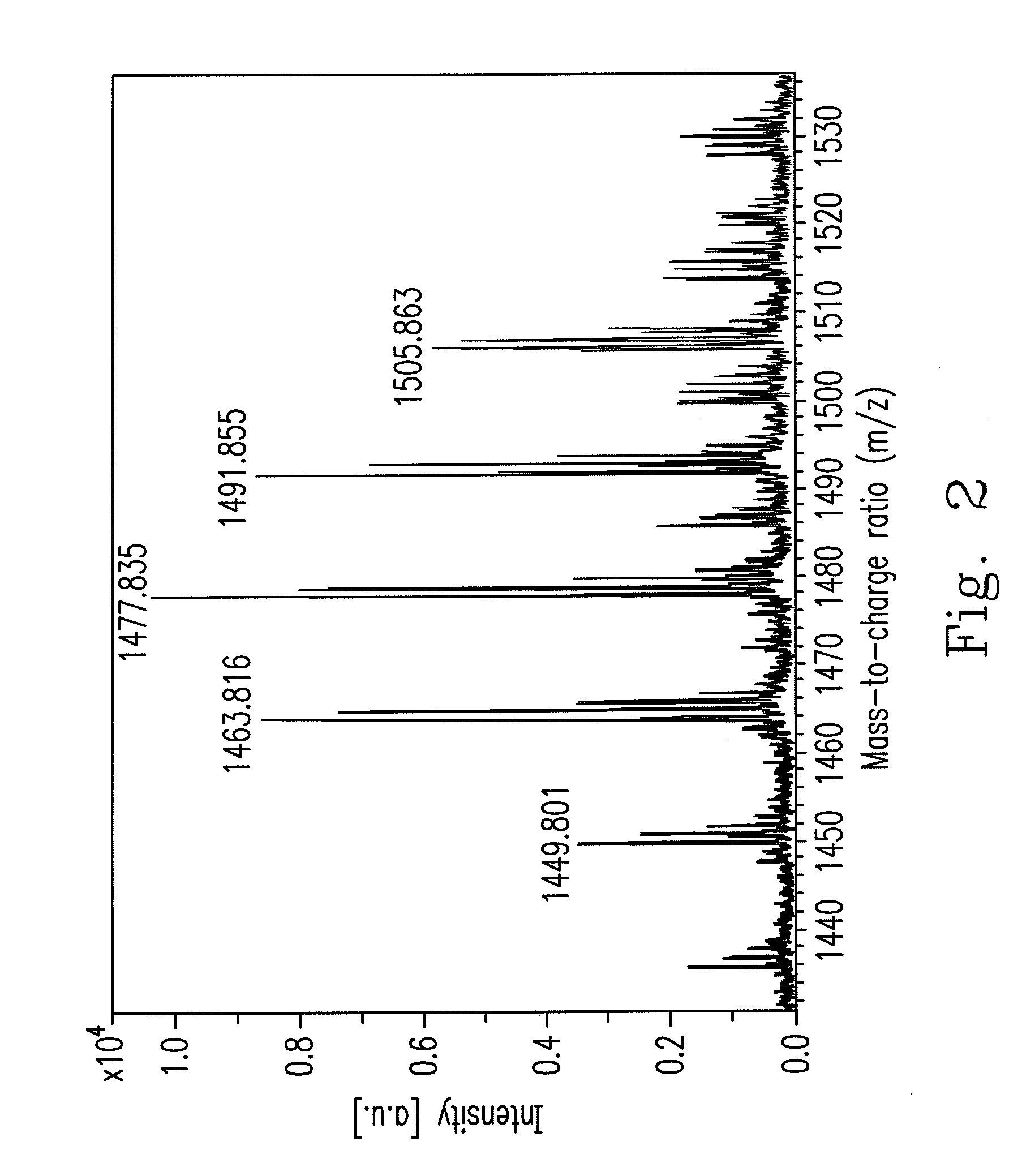
An isolated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 having an Accession No. of DSM 21836 is provided. This novel strain has unique 16S ribosomal RNA sequenced as SEQ ID NO:1 and produces amylase, protease, cellulase and lipase, fibrinolytic enzyme to show their biodegradation capacities. Further, B. amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 produces the antibiotic substances, such as iturin, fengycin and surfactin, and has antimicrobial capacity for inhibiting the fungal or bacterial growth. In conclusion, the novel strain of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 and its products can be applied in agriculture, wastewater treatment, food industry and chemical industry.
Owner:AGRI CHEM & TOXIC SUBSTANCES RES INST COUNCIL AGRI EXECUTIVE YUAN
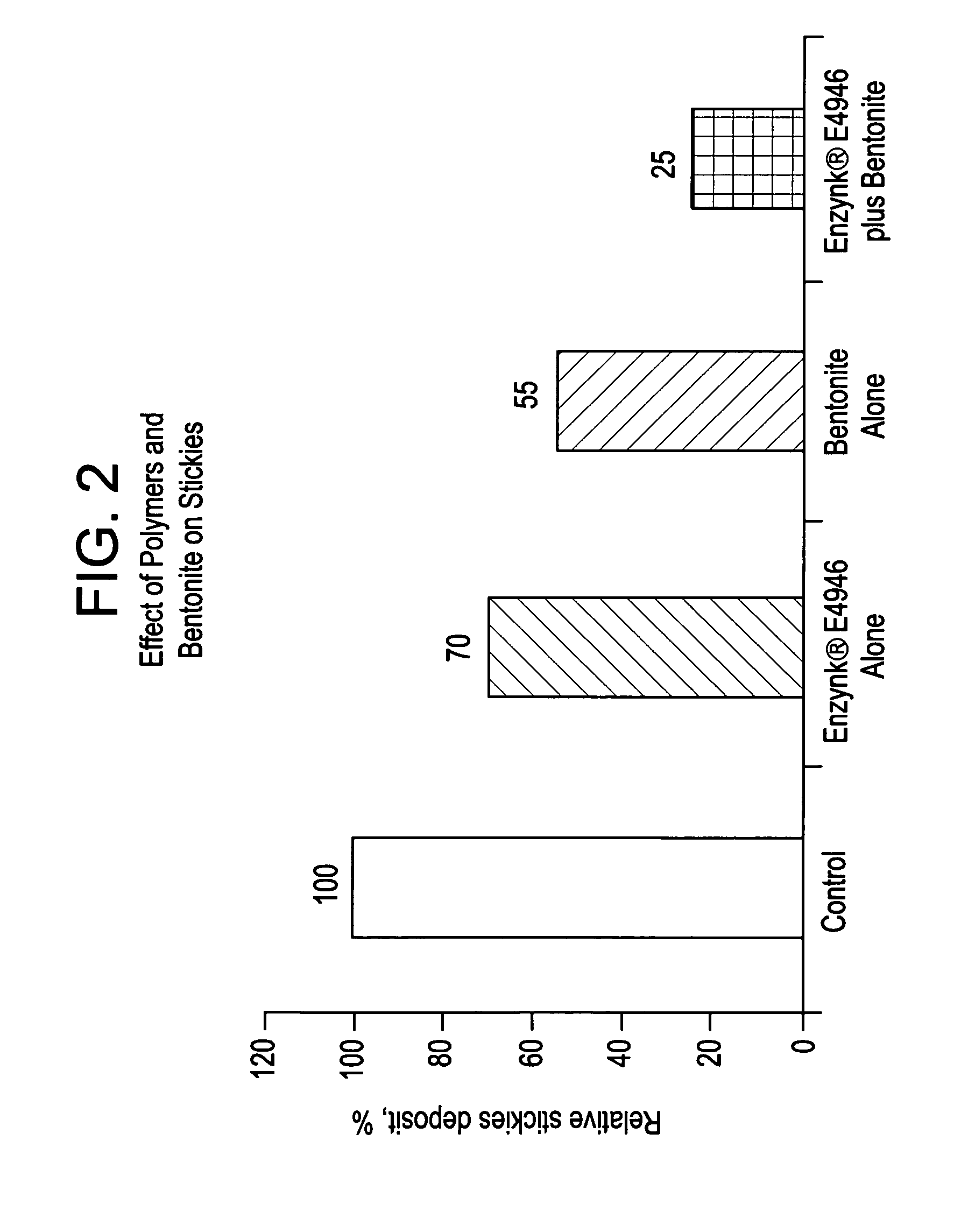
System for control of stickies in recovered and virgin paper processing
InactiveUS20060048908A1Good removal effectEasy to controlFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpMachine wet endPectinaseAmylase
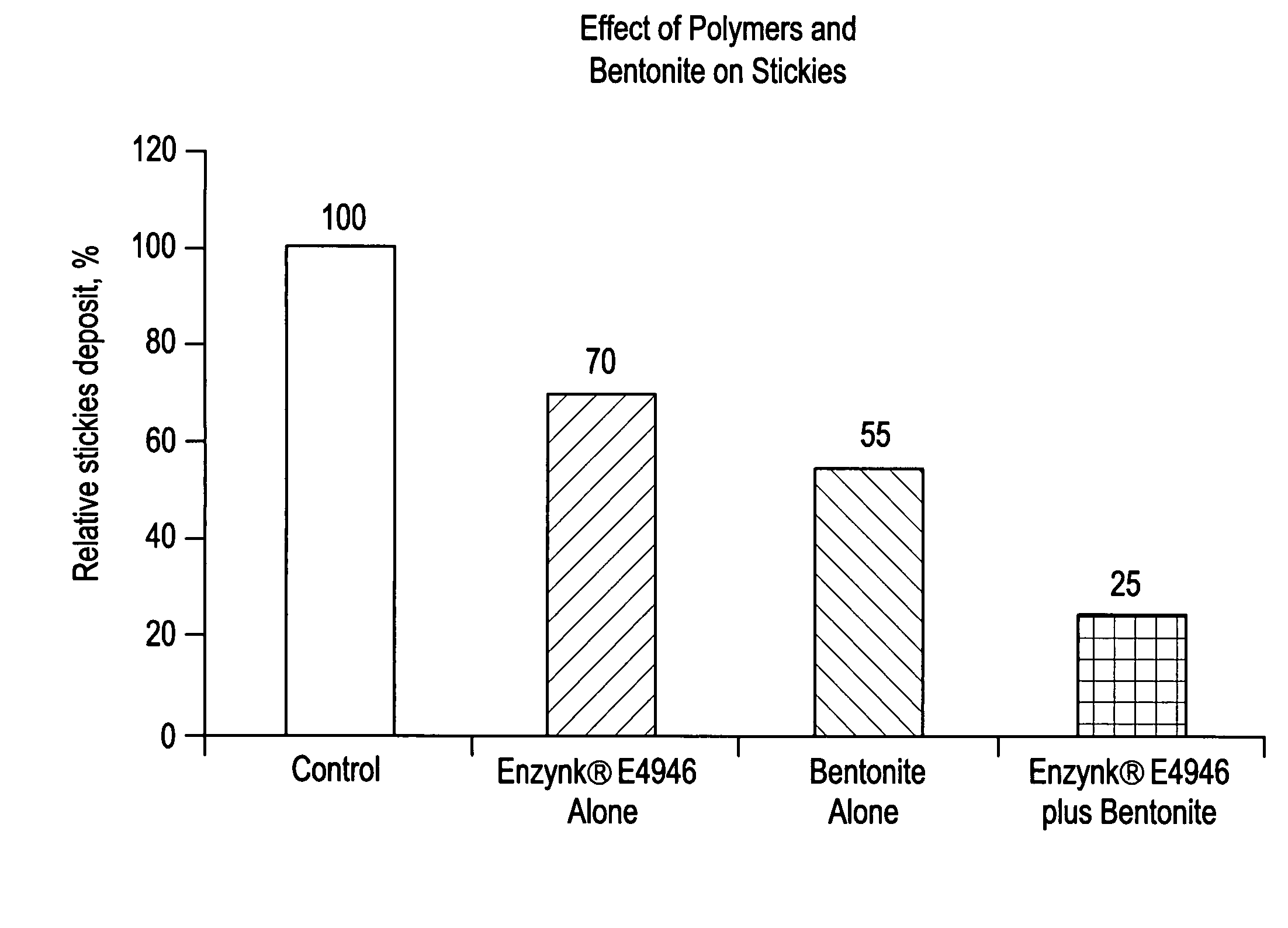
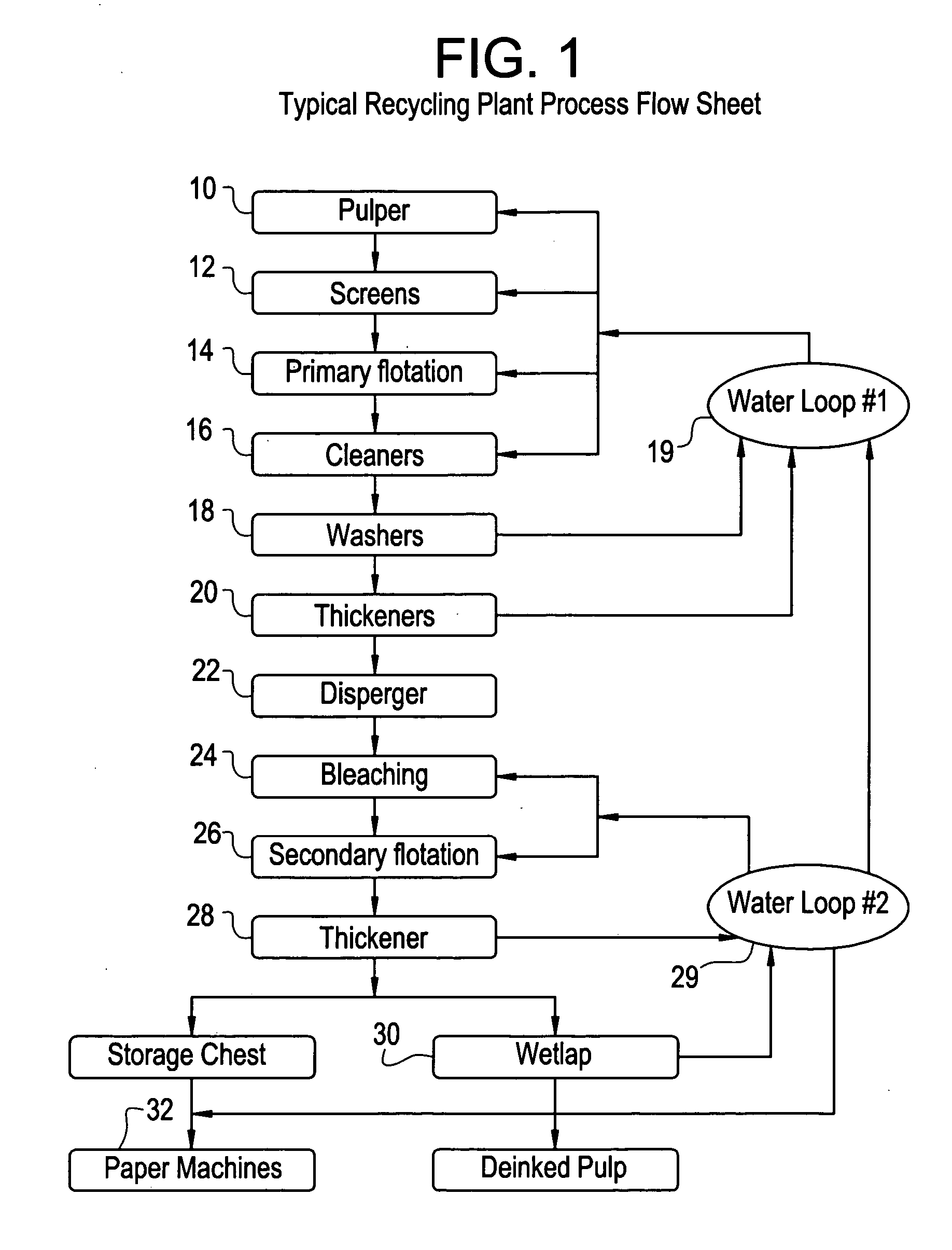
Enhanced removal and / or control of adhesives or sticky materials, “stickies”, from recovered paper stock or virgin pulp fibers is achieved using a combination of enzyme treatment with adsorbents and / or absorbents. Pulp stock to be treated is typically obtained from old magazines, newspapers, household waste, but may include corrugated boxes and office waste. Virgin pulps may include mechanical, chemical, or semi-chemical pulps. Enzymes typically include hydrolases such as cellulases, hemicellulases, pectinases, amylases, and lipases such as esterases, lyases such as pectate lyases, and oxidoreductases. Adsorbents include activated bentonite, microparticles, talc, clay and modified silica. Absorbents typically include water soluble polymers, dispersants, coagulatants and agglomerants.
Owner:ENZYMATIC DEINKING TECH LLC
Mutant alpha-amylases
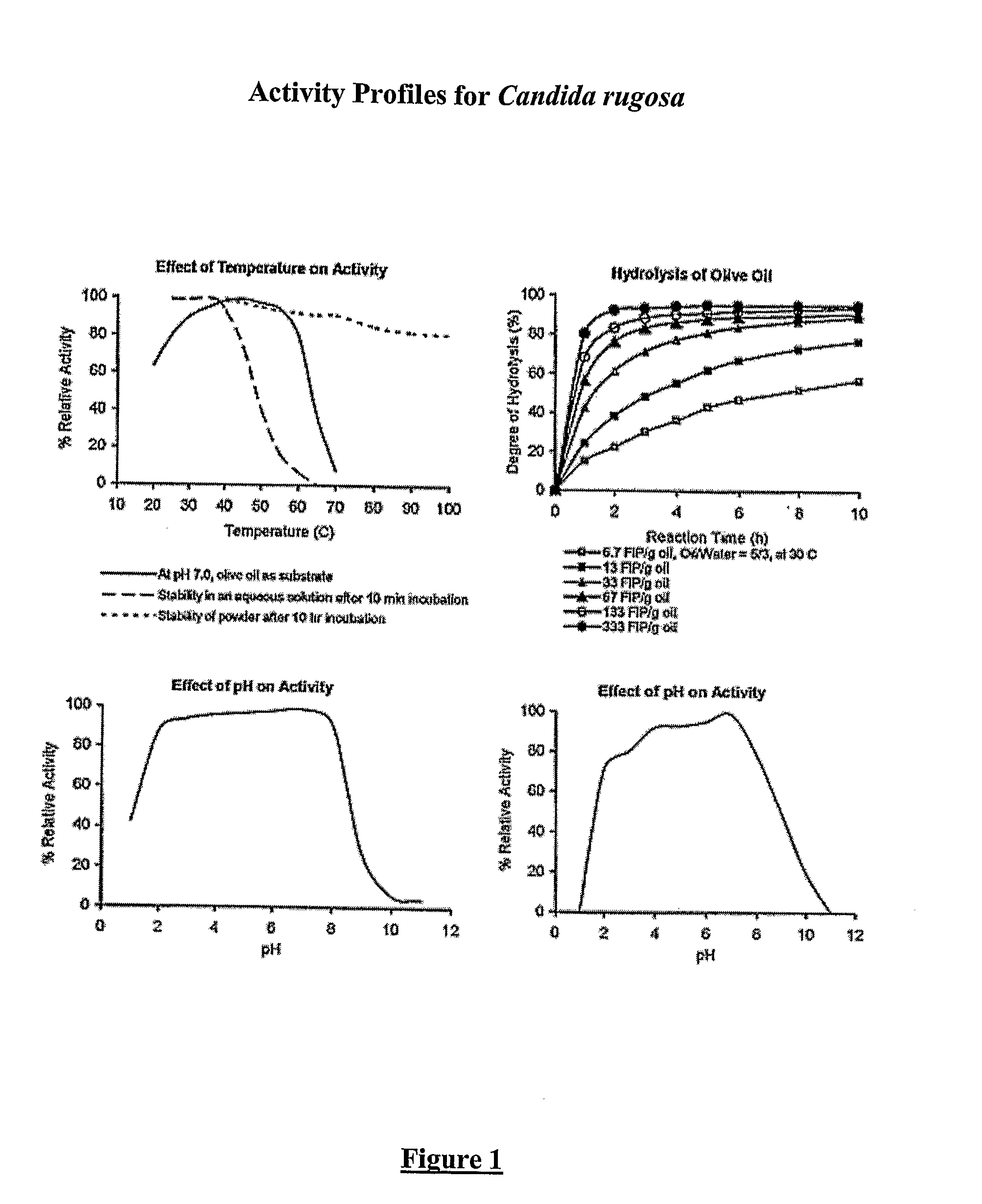
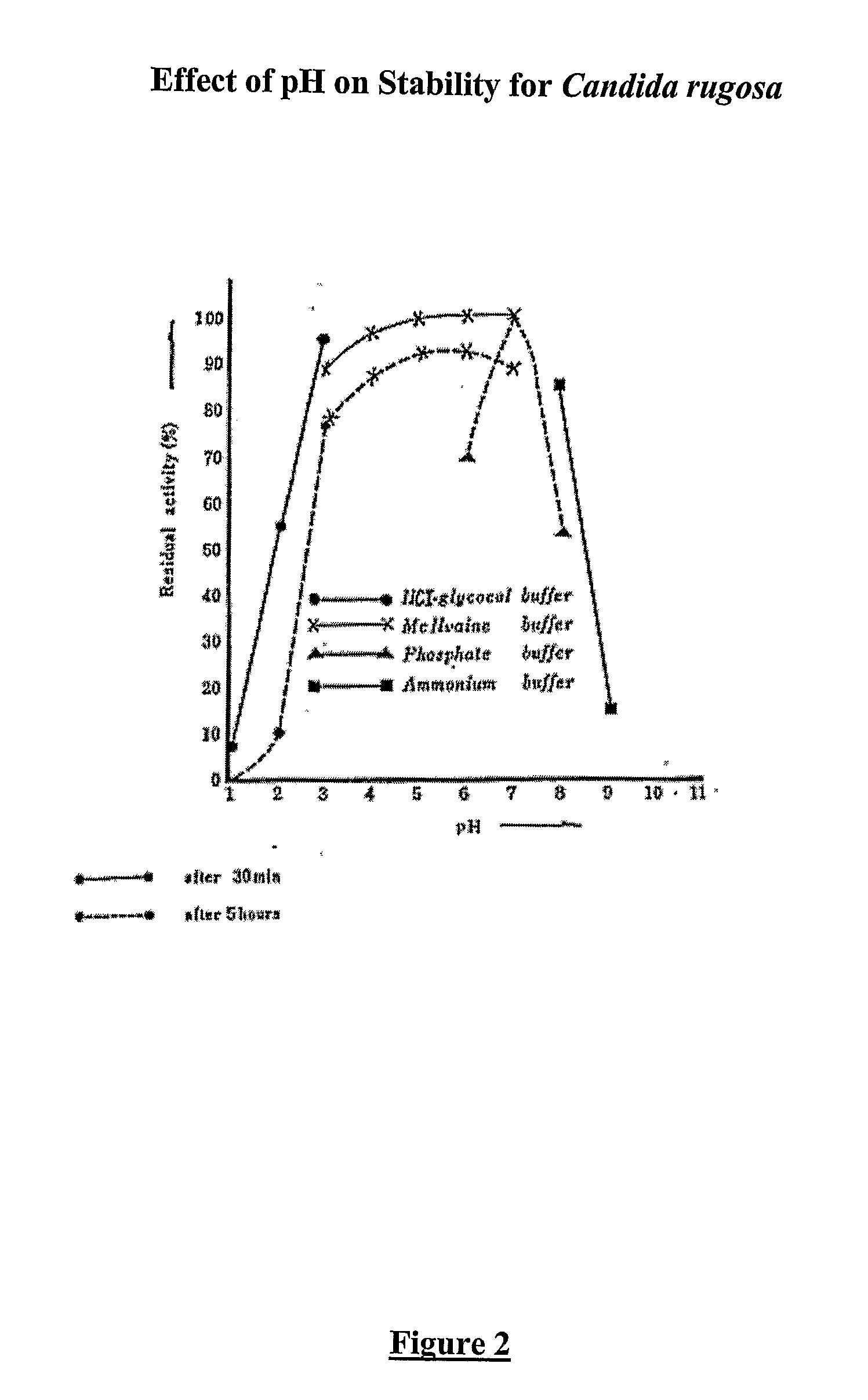
InactiveUS20060014265A1Improve stabilityViscosity of slurrySugar derivativesBacteriaAlpha-amylaseActivity profile
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Thermostable amylase polypeptides, nucleic acids encoding those polypeptides and uses thereof
This invention relates to amylase polypeptides, and nucleic acids encoding the polpypeptides and uses thereof. The amylases of the present invention have been engineered to have more beneficial qualities. Specifically, the amylases of the current invention show an altered thermostability.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Exo-specific amylase polypeptides, nucleic acids encoding those polypeptides and uses thereof
This invention relates to amylase polypeptides, and nucleic acids encoding the polpypeptides and uses thereof. The amylases of the present invention have been engineered to have more beneficial qualities. Specifically, the amylases of the current invention show an altered exospecifity.
Owner:BERG CASPER TUNE +9
Thermostable amylase polypeptides, nucliec acids encoding those polypeptides and uses thereof
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Compositions and methods for treating pancreatic insufficiency
InactiveUS7718169B2Stable enzyme componentEffective low dose treatment regimensPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemProteinase activityExocrine pancreatic insufficiency
The present invention relates to compositions for the treatment of conditions, including pancreatic insufficiency. The compositions of the present invention comprise lipase, protease and amylase in a particular ratio that provides beneficial results in patients, such as those afflicted with pancreatic insufficiency. This invention also relates to methods using such compositions for the treatment of pancreatic insufficiency. The compositions specifically comprise crosslinked Burkholderia cepacia lipase crystals, Aspergillus melleus protease crystals and amorphous Aspergillus oryzae amylase in a ratio of about 1:1:0.15 USP units.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Two-effects microbiological additives of forage specially used for ruminants
InactiveCN1559261AImproves rumen fermentationImprove payAnimal feeding stuffFood preparationBranFeed additive
A dual-effect microbial feed additive for ruminant is prepared through pulverizing corn, steaming, liquefying, saccharified, inoculating lactobacillus acidophilus and saccharomyce cerevisiae, fermenting to obtain living bacterium preparation, culturing bacillus subtilis, aspergillus oryzae and aspergillus niger in the culture medium prepared from corn, bran and soybean dregs, fermenting to obtain composite enzyme preparation, and proportionally mixing said living bacterium preparation with said composite enzyme preparation. It can promote the growth and health of ruminant and increase the utilization rate of feed.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA SILONG BIOTECH
Preparation method of rice noodles
ActiveCN103005299AControl the production processThe production process is easy to controlFood preparationRice flourAlpha-amylase
The invention discloses a preparation method of rice noodles. The preparation method comprises the steps of fermenting a raw material, resisting aging, grinding into pulp and steaming and further comprises the step of resisting aging secondarily after the steaming step, wherein the step of resisting aging secondarily comprises the substeps of contacting amylase with a rice slice obtained in the steaming step and putting aside the rice slice for 20-80 minutes at 30-80 DEG C; the amylase is alpha-amylase and / or beta-amylase; and the raw material is rice and / or unpolished rice. By the preparation method, the production process can be conveniently controlled, the rice noodles can be produced on a large scale, and the produced rice noodles are stable in quality and long in shelf life.
Owner:湖南金健米制食品有限公司
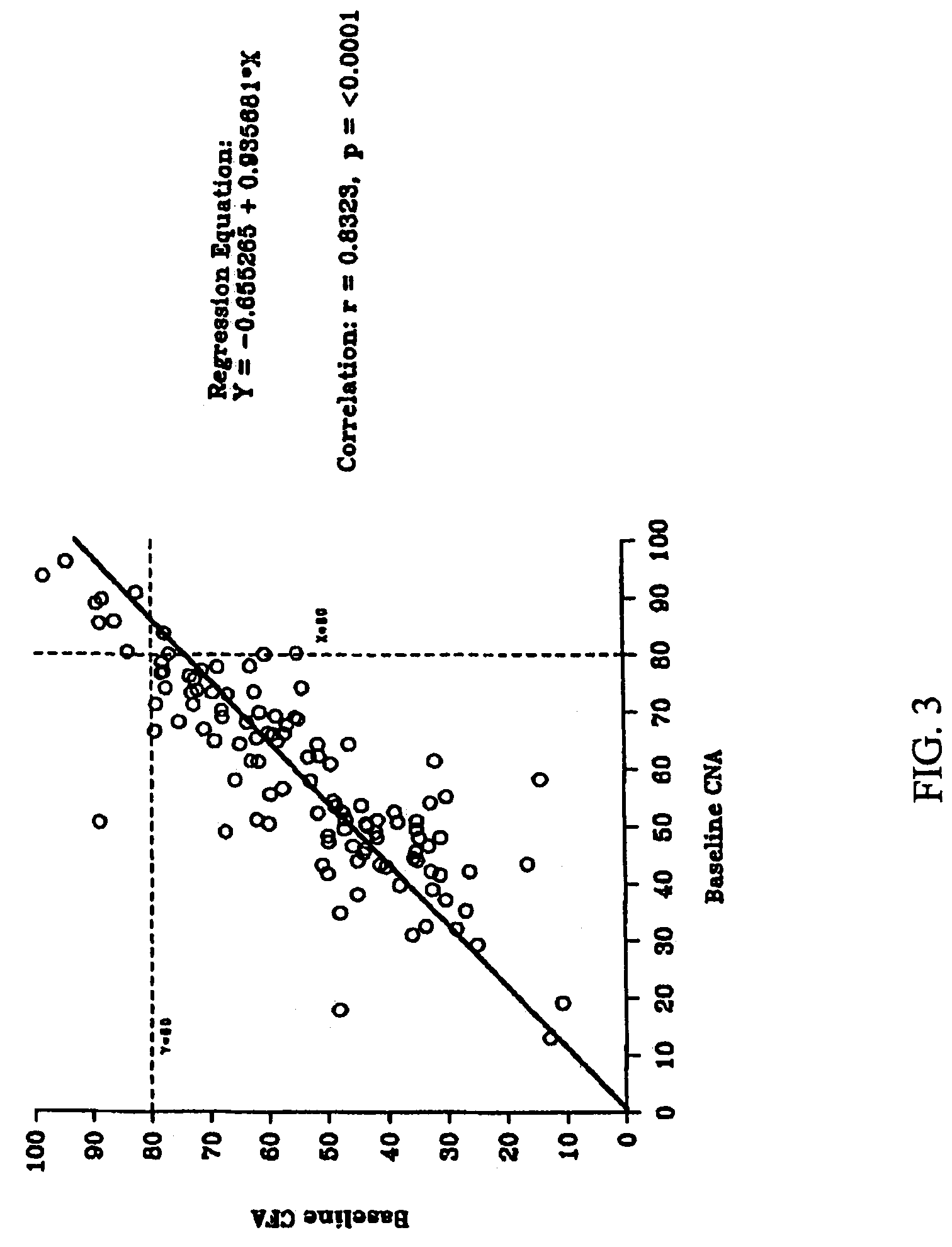
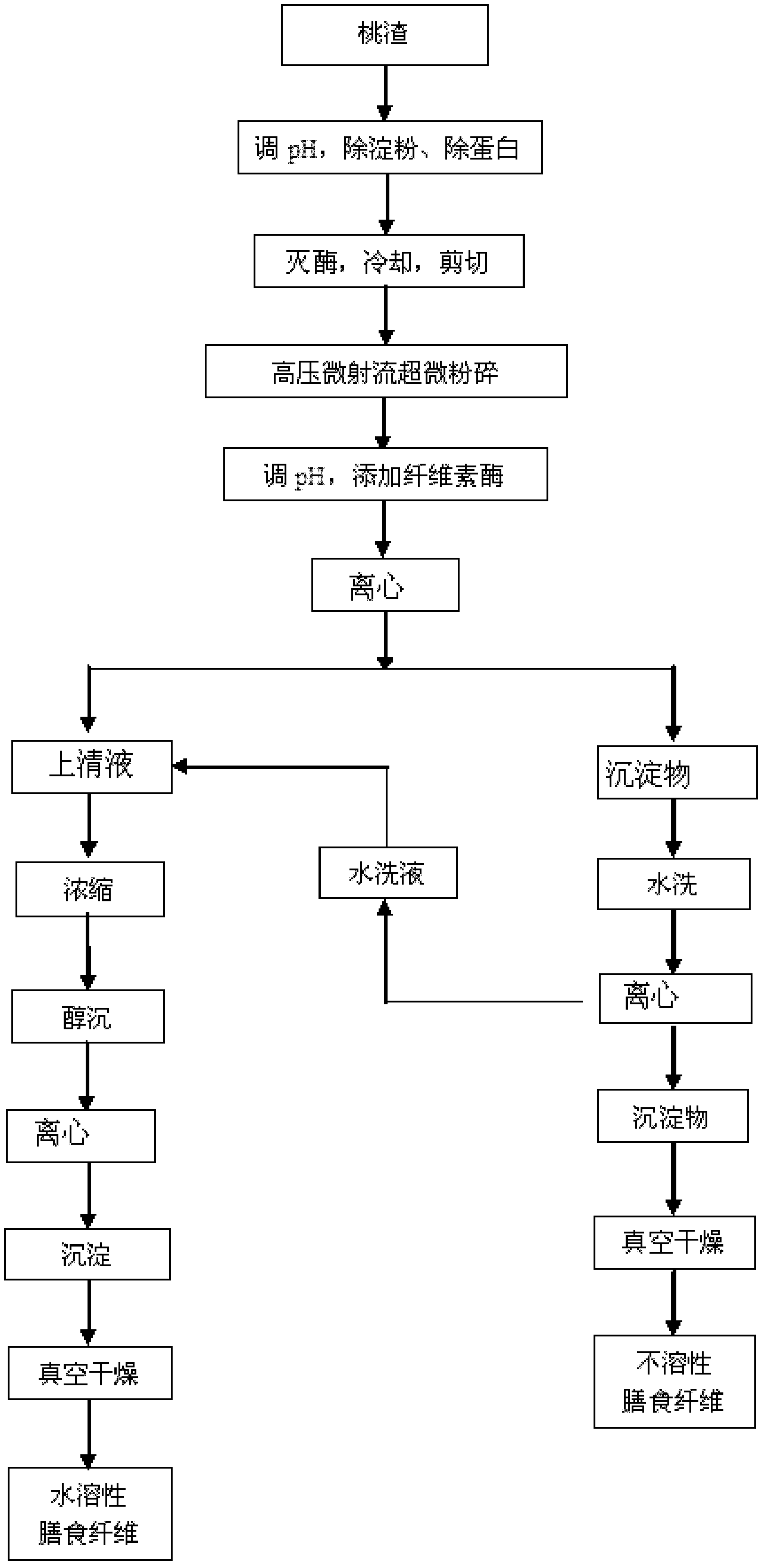
Method for extracting fruit dreg dietary fiber through high-pressure microfluidization ultramicro crushing and enzymolysis coupling
ActiveCN102524803AChange compositionChange structureFood preparationEthanol precipitationAlpha-amylase
The invention discloses a method for extracting fruit dreg dietary fiber through high-pressure microfluidization ultramicro crushing and enzymolysis coupling and belongs to the technical field of agricultural and sideline product waste deep processing. According to the method, water is added into peach dreg for dispersing the peach dreg, the pH is regulated, high-temperature-resistance alpha-amylase and protease are respectively used for enzymolysis for eliminating starch and protein, the peach dreg subjected to the enzymolysis is treated by a high-speed shearing instrument and is subjected to high-pressure microfluidization ultramicro crushing, then, cellulose is added for enzymolysis and centrifugation, filter liquid after enzymolysis and precipitates after enzymolysis are respectively obtained, the filter liquid is subjected to concentration, ethanol precipitation and vacuum drying to obtain high-activity water-soluble dietary fiber, and the precipitates are subjected to water washing and vacuum drying to obtain high-purity insoluble dietary fiber. Waste fruit dreg after the juice squeezing is utilized as raw materials, the fine and deep processing of agricultural and sideline products is realized, and the resource waste is reduced.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
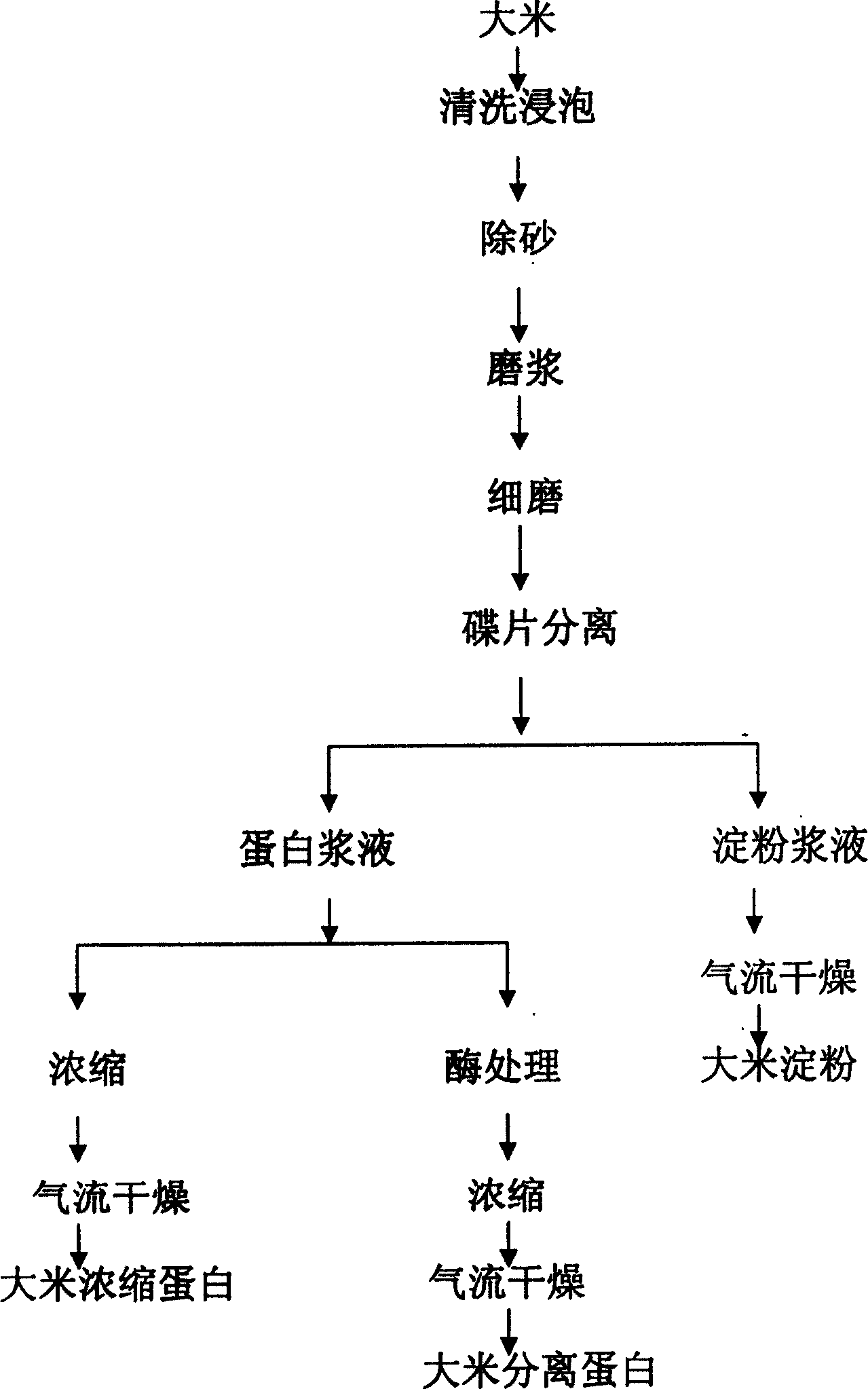
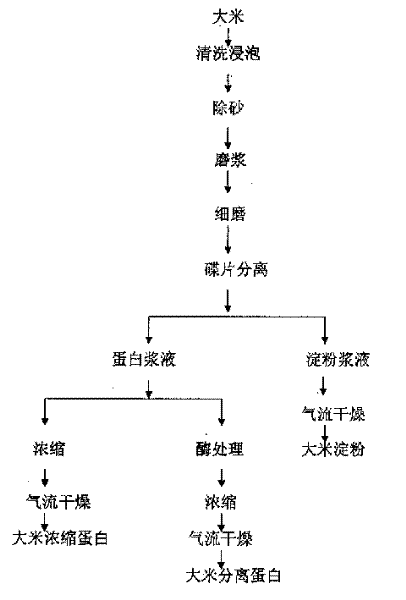
Method for extracting rice protein from rice
The present invention discloses a method for extracting rice protein from rice. Said method includes the following steps: cleaning rice, soaking, removing sand, grinding to make pulp, concentrating and drying rice protein; also includes the steps of fine-grinding rice pulp, adopting dished separating machine to make multistage separation and making the protein pulp undergo the process of enzyme treatment. The described enzyme treatment is characterized by that in the multistage separated and combined rice protein pulp the following enzymes are successively added to make reaction: adding 0.05%-0.2% of amylase, temp. is 60-70 deg.C and time is 40-60 min; adding 0.05%-0.2% of cellulase, temp. is 40-50 deg.C and time is 2-3 hr; and adding 0.1%-1% of lipase, temp. is 40-60 deg.C and time is 2-3 hr. Said method can implement industrial production of rice protein.
Owner:GAEA GEM RICE
Method for extracting refined cordycepin and cordycepin polysaccharide from cordyceps mititaris
ActiveCN101124988ALow costReduce pollutionSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationAmylaseAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates to a method for extracting the purificatory cordycepin and the cordyceps amylase from the cordyceps militaris, belonging to the fields of medicines and health protection and chemical engineering. The cordyceps militaris powder is extracted and filtrated by a cooling seep method, the filter residue is mixed with ethanol, the supersonic wave assists to extract and offcenter, the supernatant has the processes of concentration and alcohol-precipitating, then the alcohol-precipitated supernatant has the processes of decompression, concentration and elution, the eluted liquid has the processes of concentration and crystallization and recrystallization using the n-butyl alcohol, at last the purificatory amylase is obtained after freezing and drying. The preparation progress of the present invention only uses water and ethanol as the solvent, thus reducing the pollution, the resin is capable of being reused a plurality of times with low cost. The present invention fully exploits the biological activity ingredients of the cordyceps militaris, realizes the coextraction of the cordycepin and the cordyceps amylase, guarantees the biological activities of the cordycepin and the cordyceps amylase, farthest increases the utilization rate of the raw material to the largest extent, reduces the manufacturing cost. The present invention is suitable for the large-scale industrialized manufacture.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Bacillus subtilis capable of effectively degrading vomitoxin and application of bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN103243047AImprove degradation efficiencyStrong specificityBacteriaHydrolasesAdditive ingredientBacillus subtilis
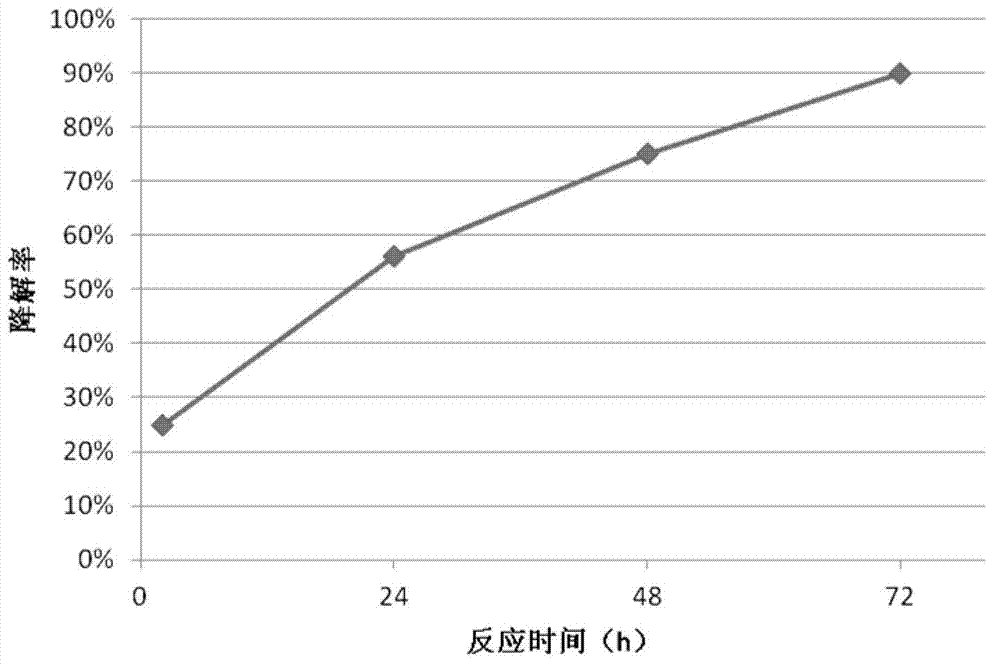
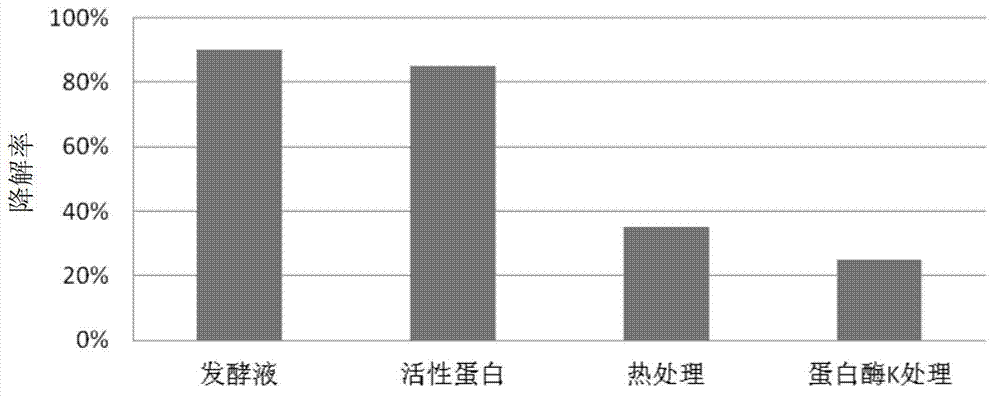
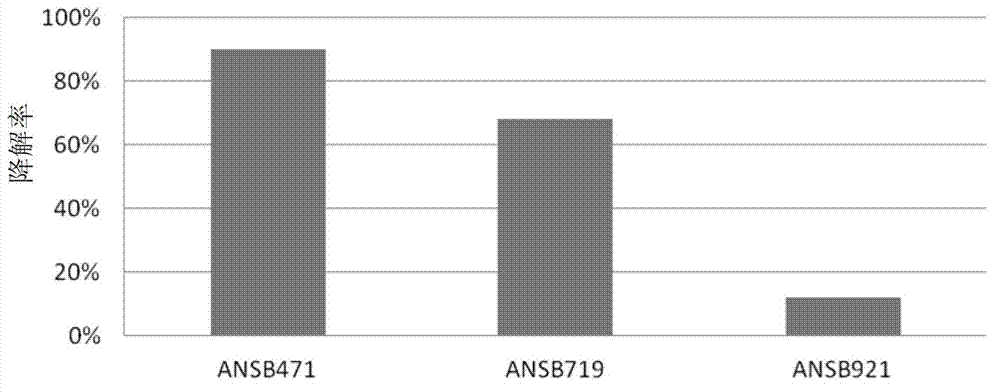
The invention provides Bacillus subtilis ANSB471 capable of effectively degrading vomitoxin in feed and an application of the Bacillus subtilis. The invention also relates to a cultural method of the Bacillus subtilis strain and a method for applying fermentation liquor of the strain to degradation on vomitoxin in the feed. After reacting for 72 hours, degradation rate of the bacillus subtilis ANSB471 on the vomitoxin in the feed is 95%, and the degradation rate on the vomitoxin is still about 90% after subculture. The strain also can secrete amylase and is high in enzyme activity, and utilization rate of animals on starch in the feed can be increased. The Bacillus subtilis ANSB471 has high vomitoxin degradation activity, strong specificity and mild effect and can not damage nutritional ingredients in the feed.
Owner:河南亿万中元生物技术有限公司
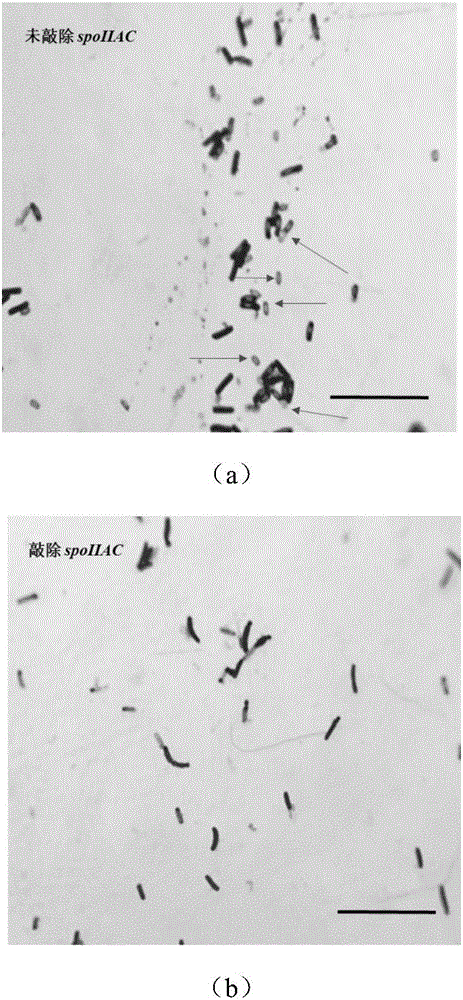
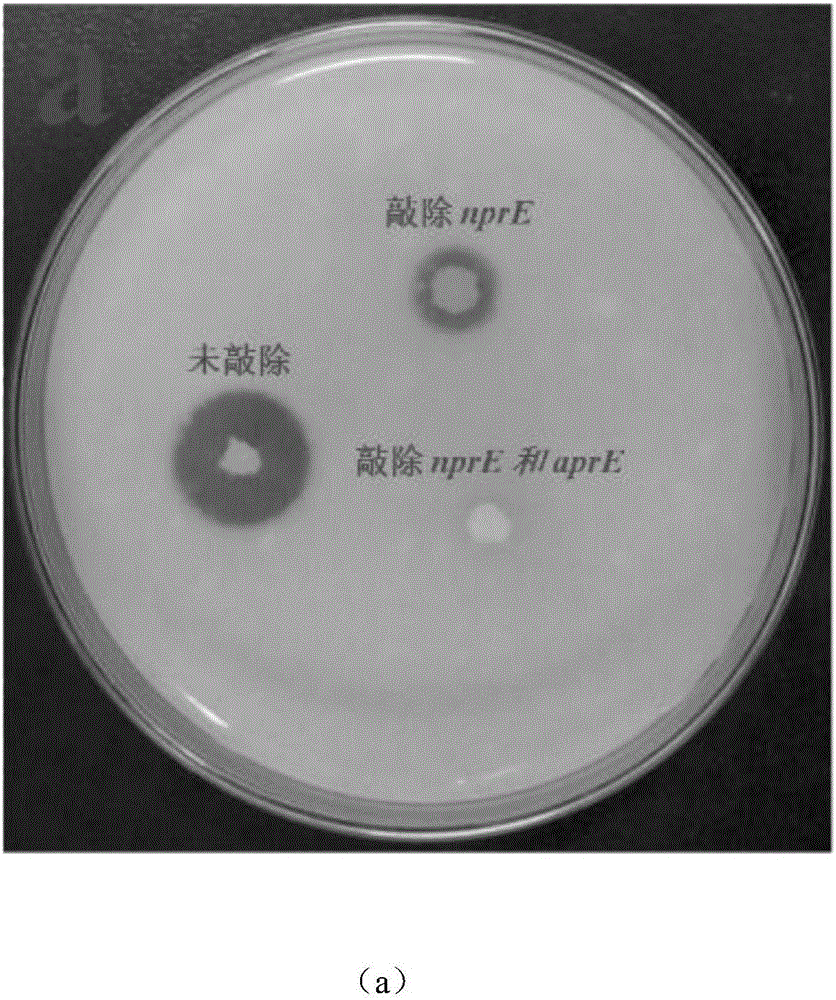
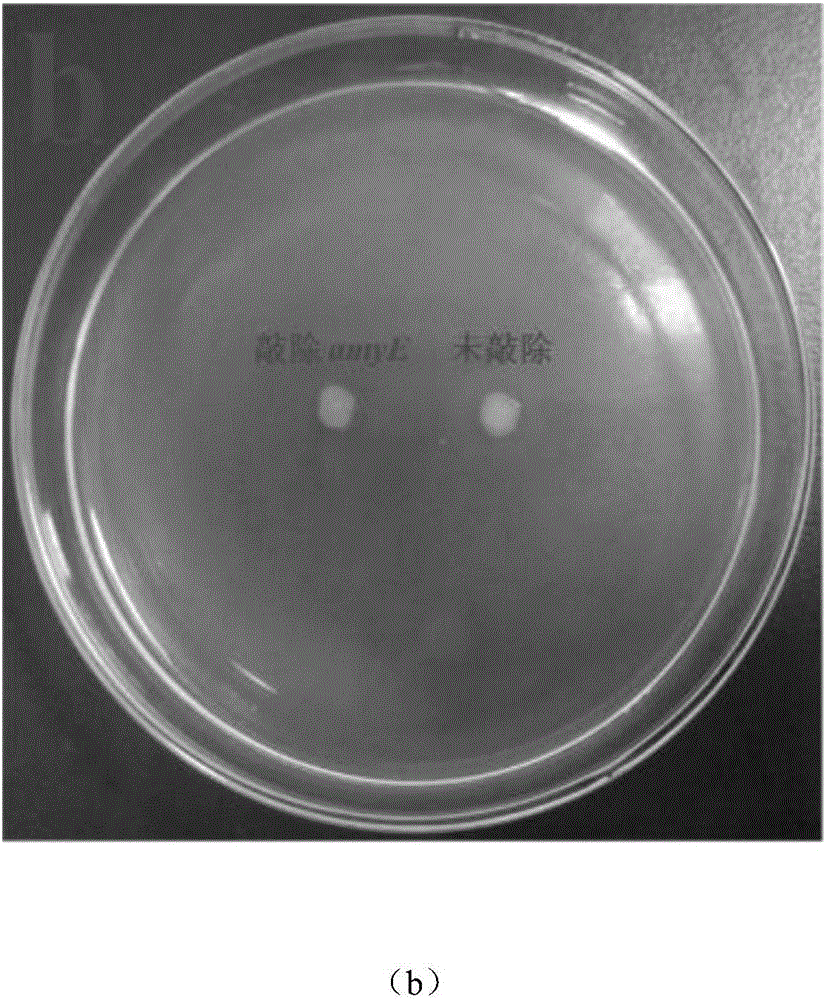
Bacillus subtilis for efficient exogenous protein expression and high density culture
Belonging to the technical field of bioengineering, the invention discloses a bacillus subtilis for efficient exogenous protein expression and high density culture. According to the invention, a screening and separation method is employed to acquire a bacillus subtilis with high protein expression quantity, and the six genes srfC, spoIIAC, amyE, nprE, aprE and bamA are knocked out to obtain B. subtilis WS5 with a preservation number of CCTCC M 2016536. The bacillus subtilis WS5 is adopted as the expression host for construction of a beta-CGTase genetically engineered bacterium. The beta-CGTase genetically engineered bacterium is subjected to 3L fermentor culture, foams produced in the fermentation process are obviously decreased, a mirror does not detect spore production, almost no extracellular amylase and protease exist in the culture process, after 70h of fermentation culture, the beta-CGTase enzyme activity reaches 270U / ml, and DCW reaches 70g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Compound enzyme preparation for fermentation of pu'er tea and application
InactiveCN102492665APromote decompositionImprove the unique quality of connotationHydrolasesPre-extraction tea treatmentBiotechnologyPhytase
The invention relates to a compound enzyme preparation for fermentation of pu'er tea, which is formed by compounding 10% to 20% of cellulase, 10% to 20% of pectinase, 5% to 15% of polyphenol oxidase, 5% to 10% of glucose oxidase, 5% to 10% glucoamylase, 5% to 10% xylanase, 5% to 10% of beta-glucanase, 5% to 10% of beta-mannase, 5% to 10% of tannase, 5% to 10% of acidic protease, 5% to 10% of lipase, 1% to 5% of alpha-amylase and 1% to 5% of phytase. By the aid of coordination of the enzyme system, polysaccharide and other substances in tea including cellulose and hemicellulose can be effectively decomposed, so that various physiochemical substances in cells can be dissolved. Meanwhile, oxidation and condensation of tea polyphenol, decomposition of protein, amino acid and carbonhydrate, a series of reactions of various products including polymerization and condensation and the like are accelerated and promoted.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Composition and method for making high-protein and low-carbohydrate food products
InactiveUS20050129823A1Effectively reducing the net carbohydrate total of the traditional productIncrease nutritionDough treatmentBaking mixturesAdditive ingredientProtein isolate
Conventional food compositions for use in making baked goods and extruded food products are improved by reducing the carbohydrate content. This is done by substituting the conventional flour in whole or in part by a combination of starch that is resistant to amylase digestion and / or from about 1-150 baker's percent of a first proteinaceous ingredient comprising at least about 70% by weight protein, and a second proteinaceous ingredient selected from the group consisting of (i) between about 0.5-100 baker's percent of a wheat protein isolate product; (ii), between about 0.5-100 baker's percent of a wheat protein concentrate product; (iii) between about 0.5-100 baker's percent of a devitalized wheat gluten product; (iv) between about 0.5-20 baker's percent of a fractionated wheat protein product; (v) between about 0.5-20 baker's percent of a deamidated wheat gluten product; (vi) between about 0.5-30 baker's percent of a hydrolyzed wheat protein product; and (vii) any combination of ingredients (i) to (vi).
Owner:MGP INGREDIENTS
Corps nutrient complex enzyme and use thereof
InactiveCN101434498AImprove immunityImprove disease resistanceEnzymesFertilizer mixturesAmylaseDisease
Owner:郝伟星
Polyzyme microbial growth-promoting additive for plants
InactiveCN101412648AEliminate negative effectsFully exploit potentialBiocideAnimal repellantsEcological environmentGrowth promoting
The invention relates to a multienzyme microorganism and plant growth promotion additive. An active regulator containing multienzyme microorganism and leavening, amylase, protease, cellulose, pectase and polyase are used as base stocks, are added with chitin, various elements and vitamins in micro quantity, amino acid and are added with a microorganism and leavening inoculum Em bacterial solution, are mixed and are fermented to prepare the multienzyme microorganism and plant growth promotion additive. The additive can effectively improve soil, strength land capacity, reduce plant diseases and insect pests, fully excavate the soil potential, bring organic nutritive compositions for plants, promote the healthy and rapid growth of the plants, remove negative influence of pesticide and fertilizer, protect soil and entironment, is beneficial for society and people, adopt waste utilization, and has low investment, low cost, rapid effect and good effect.
Owner:HUNAN YIKE BIOTECH DEV
Animal fur clean depilation and fur fiber loosing method for preparing leather and application thereof
ActiveCN101235421AEliminate pollution and other issuesFine grainPre-tanning chemical treatmentFiberEnzyme system
The invention provides a method for unhairing leather and loosening leather fiber without sodium sulfide and lime in a leather production process and the application of the method. The method is characterized in that a method for combining unhairing by non-sulfur (sodium sulfide) depilatory under the alkaline condition and enzyme fiber loosening under the under the non-lime (lime) alkaline swelling condition are adopted, the enzyme unhearing and the enzyme fiber loosening take protease, lipase, amylase and glucoamylase as a compound enzyme system. The method achieves the effects for unhairing and loosening the leather fiber through adopting the method for combining compound enzyme water immersion, compound enzyme unhairing, unhairing with sodium sulfide depilatory, expansion regulator-sodium hydroxide expansion and the enzyme unhairing under the alkaline condition and eliminates the pollution which is brought by the sodium sulfide and the lime in animal unhairing or leather fiber loosening procedures in the leather production process. The method of the invention is suitable for unhairing and leather fiber dispersed processing of various animal leather of leather with various usages.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Method of increasing content of resistant starch in rice through genome editing and sgRNA special for same
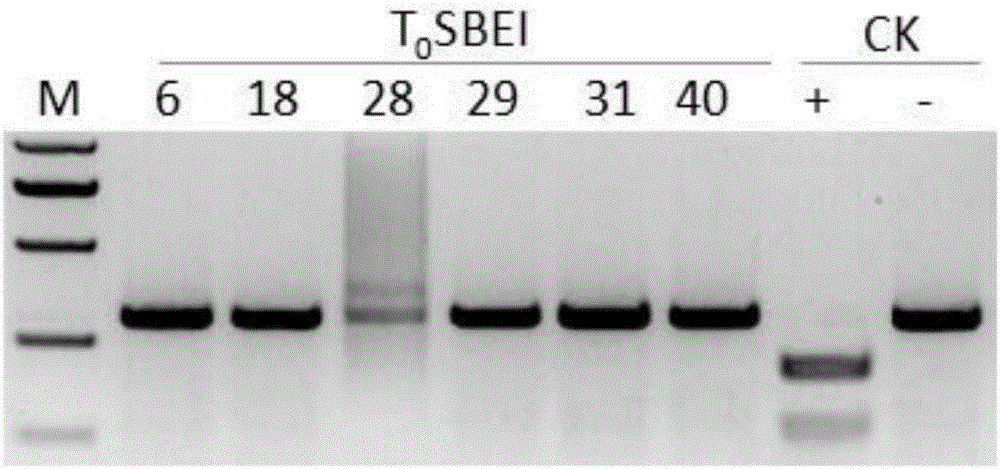
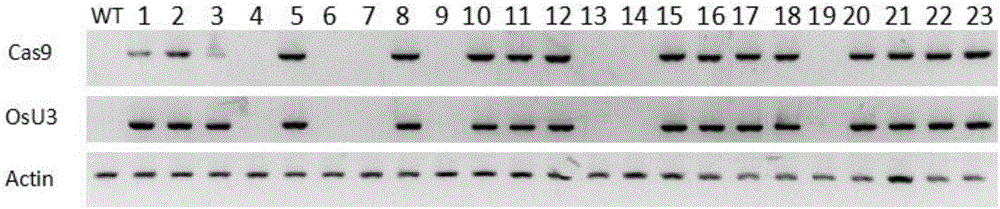
ActiveCN106086028AAddressing the lack of low-glycemic foodsAvoid problemsNucleic acid vectorPlant peptidesBiotechnologyAmylase
The invention discloses a method of increasing the content of resistant starch in rice through genome editing and sgRNA special for the same. The method provides a method of increasing the content of resistant starch and / or amylase in rice seeds. The method includes the following steps that expression of SBEIIb genes in the rice is inhibited; the SBEIIb genes are genes of encoding SBEIIb protein. The invention further provides a method of increasing the content of resistant starch in rice and includes the step of inhibiting the activity of the SBEIIb protein in the rice. By using the CRISPR / Cas9 technology, the rice SBEIIb genes are edited at fixed points, the rice SBEIIb genes are knocked off by causing frameshift mutation, and the new generation of new rice germplasm with the content of amylase and resistant starch obviously increased is obtained.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Vermicelli or bean vermicelli produced from non-alum arrow root/potato powder and method of processing the same
The invention relates to noodles or vermicelli made from alum-free arrowroot flour or sweet potato starch and a method for processing the same. The invention solves the problem of production of the noodles and the vermicelli without using alum as a food additive. The product of the invention comprises the following raw materials: potato starch 85-95, arrowroot flour 5-15, compound polysaccharides 0.10-0.50, and compound emulsifiers 0.15-0.40, wherein the compound polysaccharides comprise sodium alginate, xanthan gum and carrageenan, and the compound emulsifiers comprise molecular distilled mono glyceride, carboxymethylcellulose sodium and common salt. The method uses food-grade microbiological compound polysaccharides to replace alum used in the prior production formula and uses the compound food emulsifiers. The method uses amylopectase to reduce amylopectins in potato starch, a vacuum method to exhaust gas in starch pulp, steam to cure the starch pulp, a low temperature technology to age starch paste or sheet jelly and a rolling method to cut strips, and adopts gradient temperature rise and aeration drying to obtain high quality arrowroot flour noodles or vermicelli which are free from the alum, order in appearance, flexible, pure white and boilproof.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
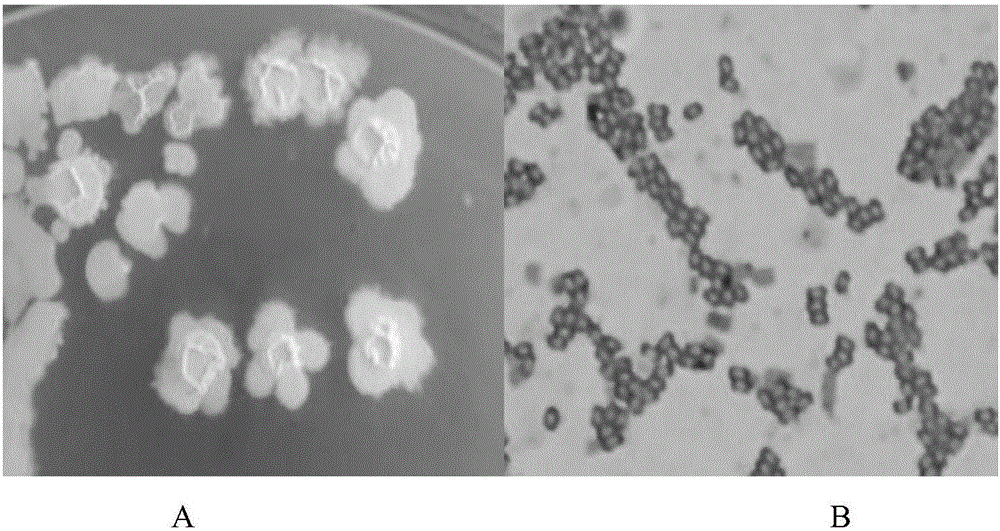
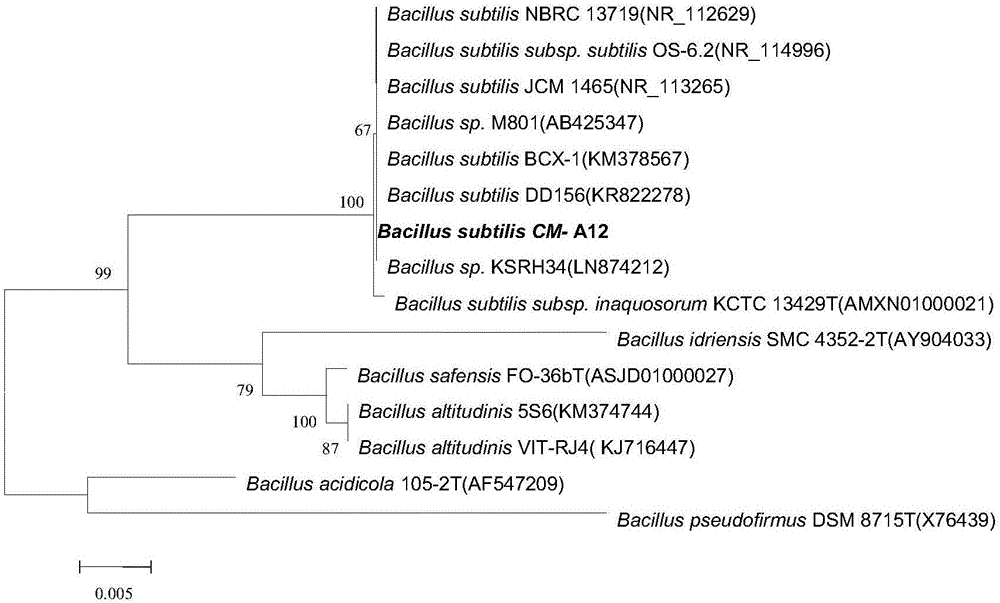
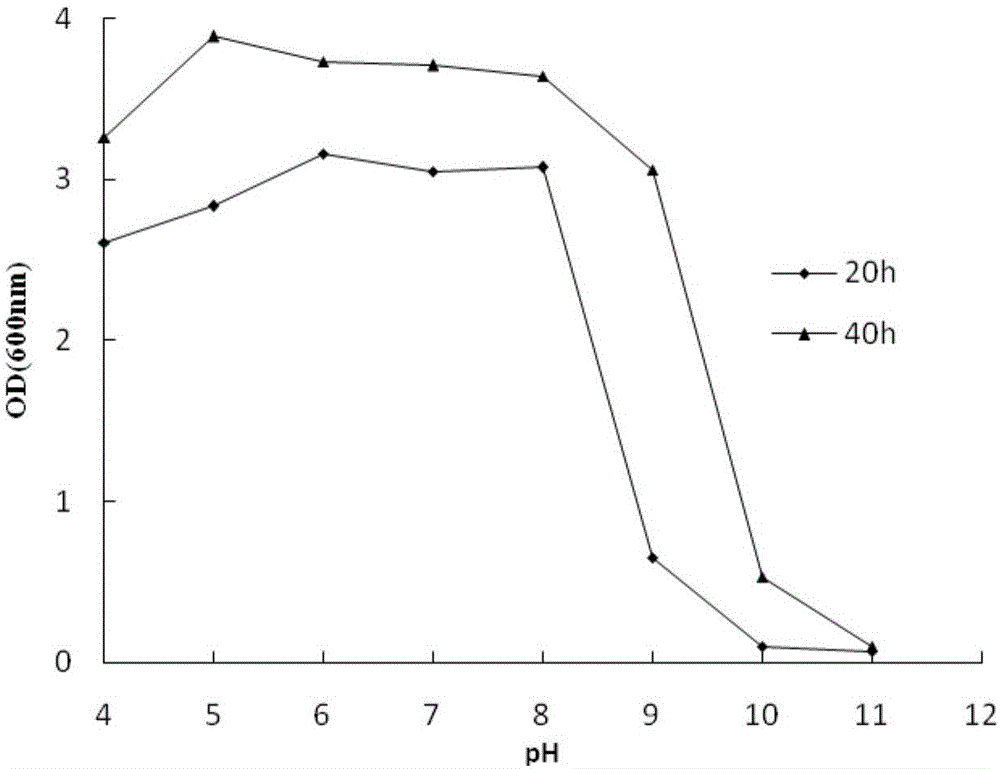
Bacillus subtilis strain and application thereof
ActiveCN106011034ASimple cultivation conditionsReduce CODImmobilised enzymesBacteriaMicroorganismWater quality
Belonging to the field of environmental microorganism application, the invention discloses a Bacillus subtilis strain and application thereof. The strain is named as Bacillus subtilis CM-A12, is currently preserved in China Center For Type Culture Collection (called CCTCC for short) with a preservation number of CCTCC NO:M 2015688, and the preservation date is November 23, 2015. The Bacillus subtilis strain provided by the invention has the advantages of simple cultivation condition, high temperature resistance, acid and alkali resistance, and high salinity resistance, can secrete protease, amylase and cellulase, and can effectively improve water quality and reduce COD and ammonia nitrogen in water.
Owner:浙江至美环境科技有限公司
Resistant starch-hydrocolloid blends and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080233260A1Improve functional propertiesHighly suitableMilk preparationAnimal feeding stuffResistant starchAlpha-amylase
Interacted starch products made up of resistant starch and hydrocolloid are provided which exhibit at least about 20% resistance to α-amylase digestion. The products are prepared by mixing together quantities of resistant starch and hydrocolloid in water with mixing and optional heating, followed by drying. Foods containing the interacted starch products are also disclosed.
Owner:MGPI PROCESSING
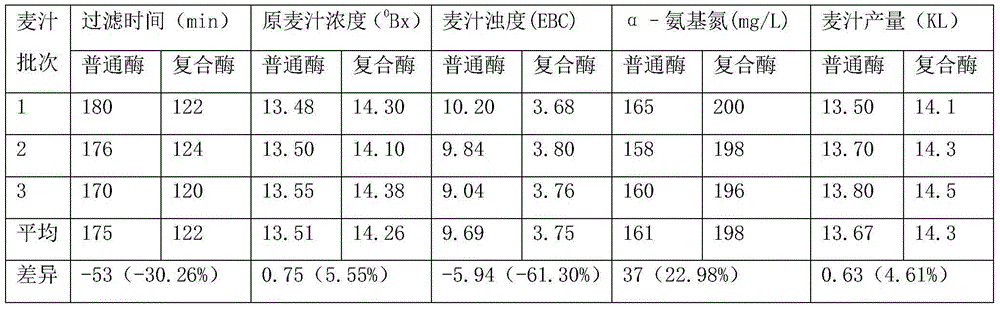
Fungal alpha-amylase-containing beer complex enzyme and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104651335AEnsure food safetyIncrease profitOxidoreductasesGlycosylasesAntioxidantAlpha-amylase
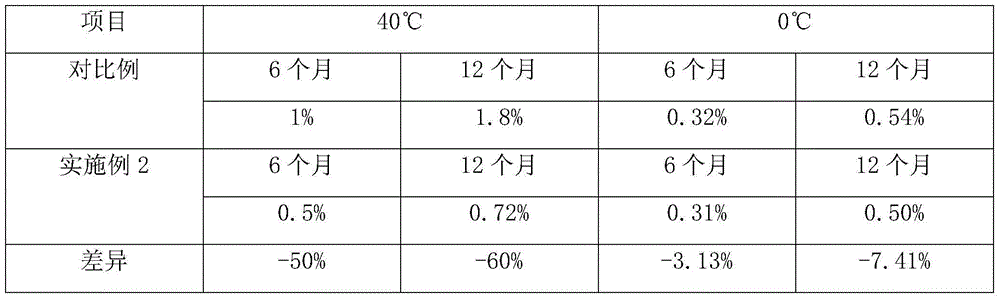
The invention discloses a fungal alpha-amylase-containing beer complex enzyme and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of enzyme preparation processing. The high-activity fungal alpha-amylase and other food grade enzyme preparations, plant extracts, antioxidants, protective agents, activating agents and the like can be scientifically compounded by taking concentrated maltase and concentrated malt juice powder as main raw materials; the prepared beer complex enzyme is complete in proteases, high in enzyme activity, difficult to deactivate, mellow in malt aroma, and capable of providing abundant nitrogen source for malt juice, wherein the activity of fungal alpha-amylase in fermenting liquor during the preparation of fungal alpha-amylase is 17000-21000 U / mL. The complex enzyme can be stored for 12 months under the conditions of 0DEG C and 40DEG C, the single enzyme activity loss in the complex enzyme are respectively 0.50% and 0.72%, the enzyme deactivation caused by environment change, and inappropriate operation methods during packaging, storage, transportation, use and the like can be effectively prevented, especially the enzyme deactivation caused by high temperature can be prevented.
Owner:湖南新鸿鹰生物工程有限公司
Method for extracting sweet potato dietary fibers
The invention discloses a method for extracting sweet potato dietary fibers, which belongs to the field of bioengineering and is easy in raw material getting, high in efficiency and environmental-friendly. The method comprises the steps of starch removal, enzymatic hydrolysis, centrifugation and dietary fiber extraction, wherein the insoluble dietary fiber extraction comprises insoluble dietary fiber extraction and soluble dietary fiber extraction; the insoluble dietary fiber extraction comprises the processes of centrifuging the enzymatically hydrolyzed mixed solution to obtain precipitates and supernatant separated from each other, soaking the obtained precipitate with ethanol and then carrying out suction filtration to obtain solids and filtrate, wherein the obtained solids are insoluble dietary fibers; and the soluble dietary fiber extraction comprises the processes of carrying out water bath to evaporate most of the moisture of the obtained supernatant and filtrate, then adding ethanol to carry out digestion so that flocculent precipitates appear in the supernatant and the filtrate, and separating the flocculent precipitates from the supernatant and filtrate, wherein the obtained flocculent precipitates are soluble dietary fibers.
Owner:李冉
Feed additive composition
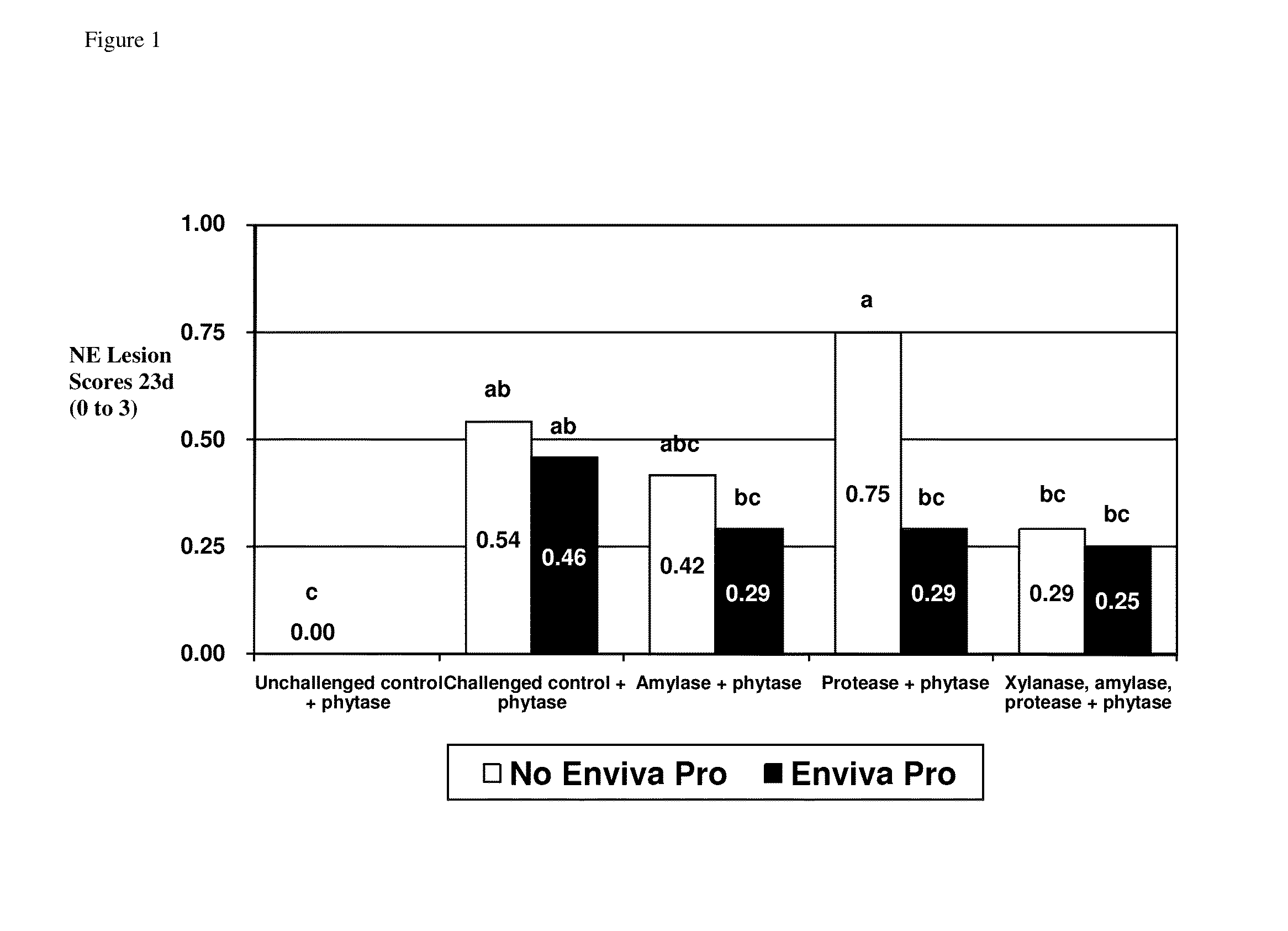
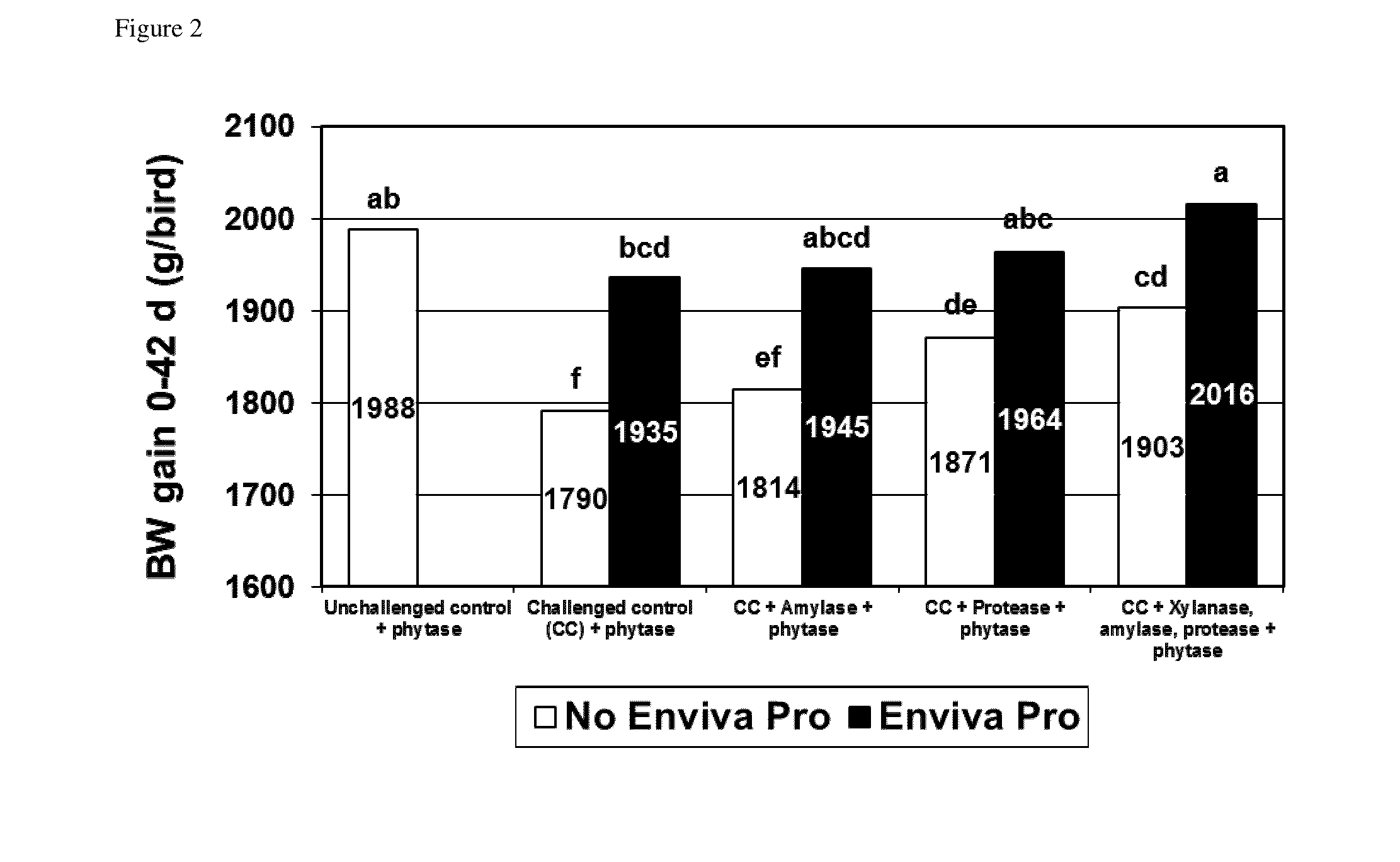
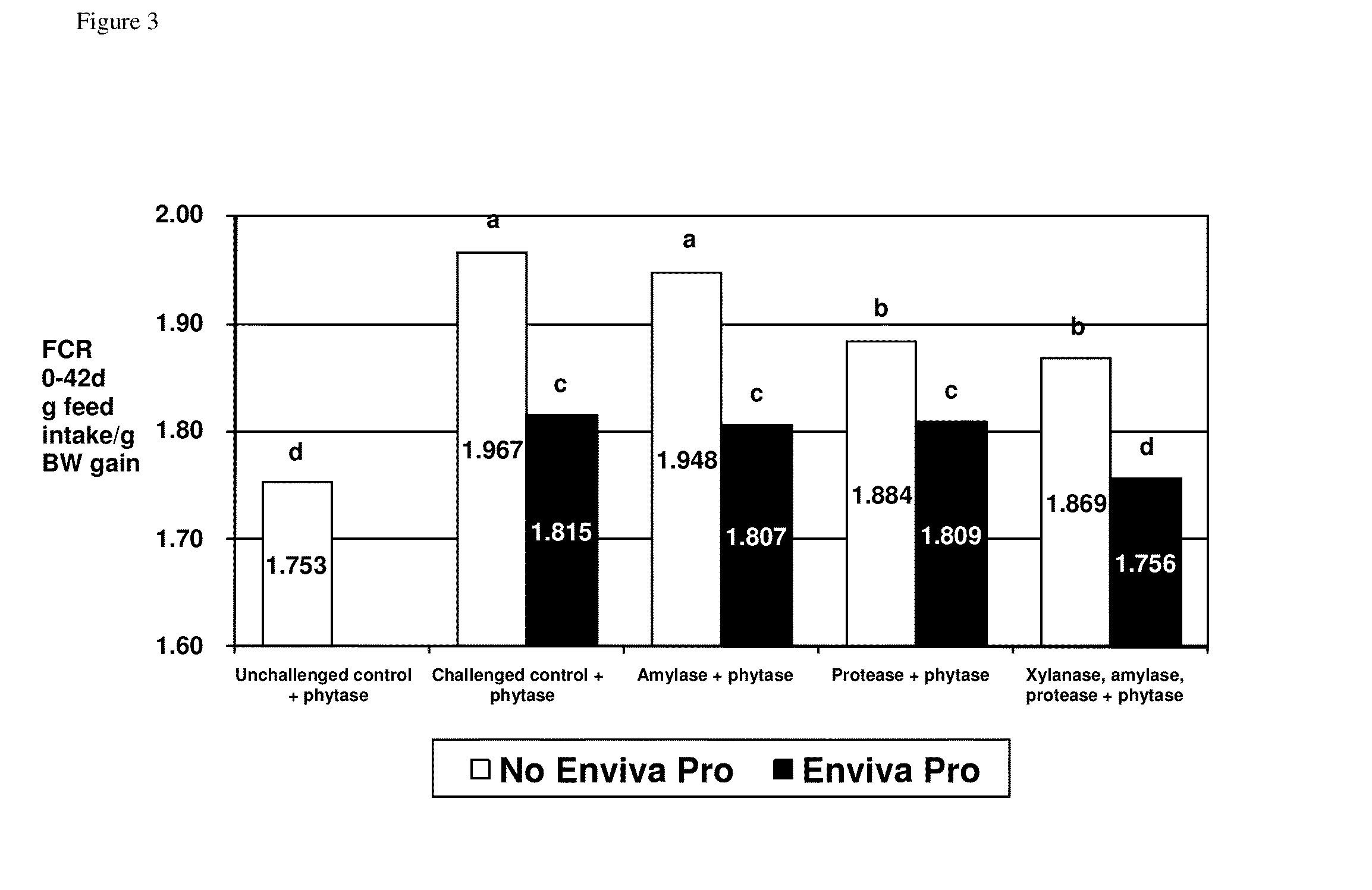
A feed additive composition comprising a direct fed microbial in combination with a protease, a xylanase, an amylase and a phytase, and a method for improving the performance of a subject or for improving digestibility of a raw material in a feed (e.g. nutrient digestibility, such as amino acid digestibility), or for improving nitrogen retention, or for avoiding the negative effects of necrotic enteritis or for improving feed conversion ratio (FCR) or for improving weight gain in a subject or for improving feed efficiency in a subject or for modulating (e.g. improving) the immune response of the subject or for promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract of a subject, which method comprising administering to a subject a direct fed microbial in combination with a protease, a xylanase, an amylase and a phytase.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com