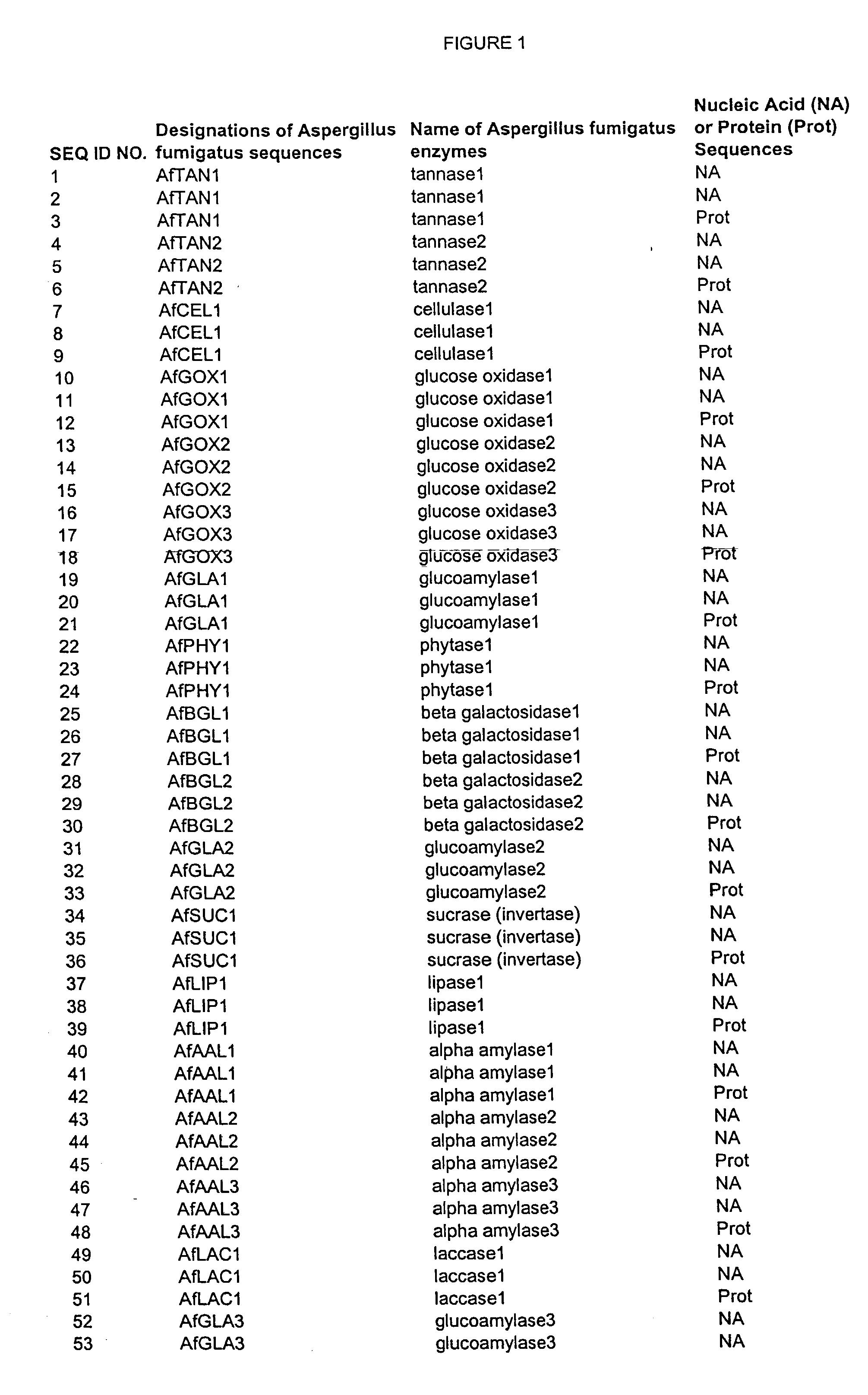
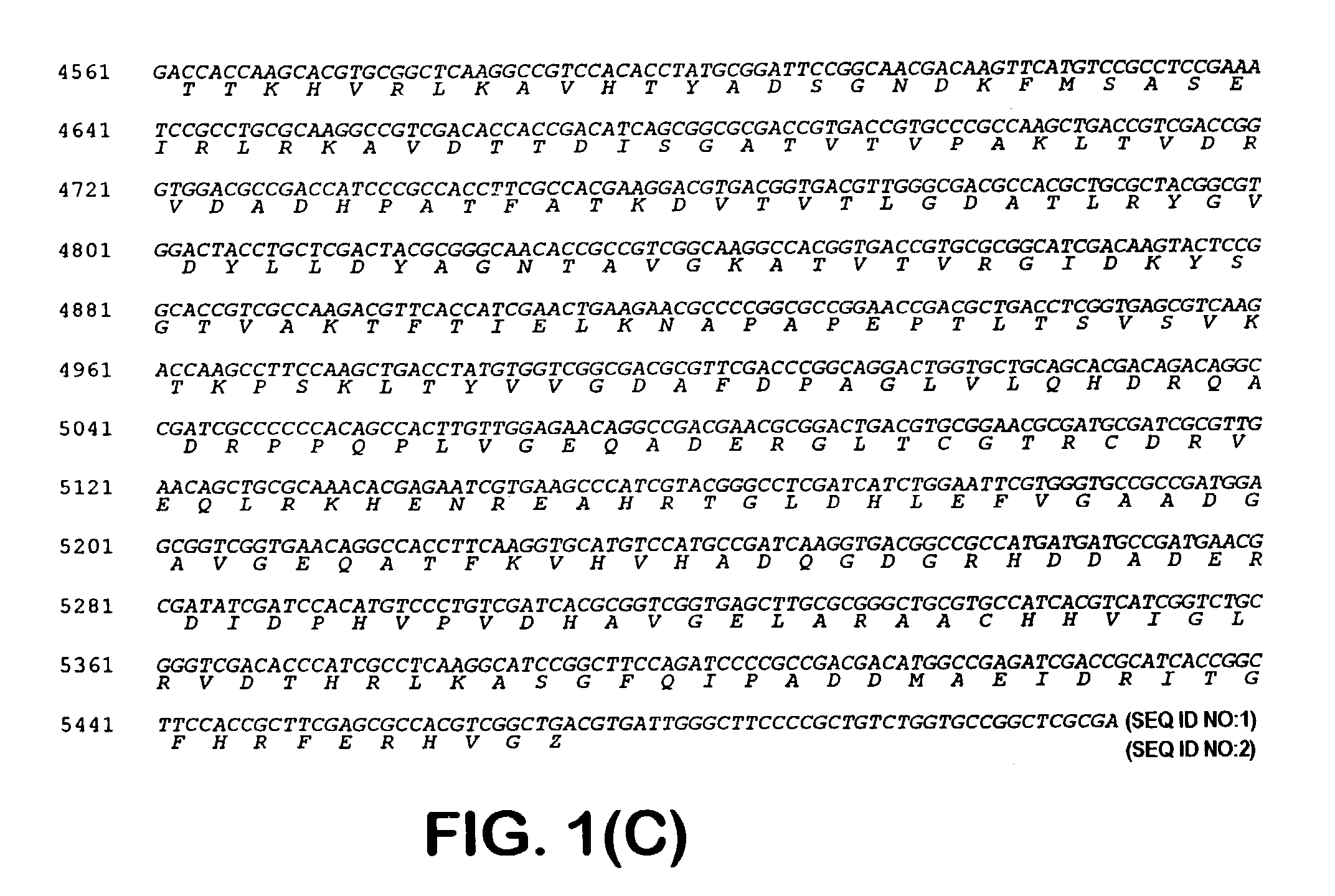
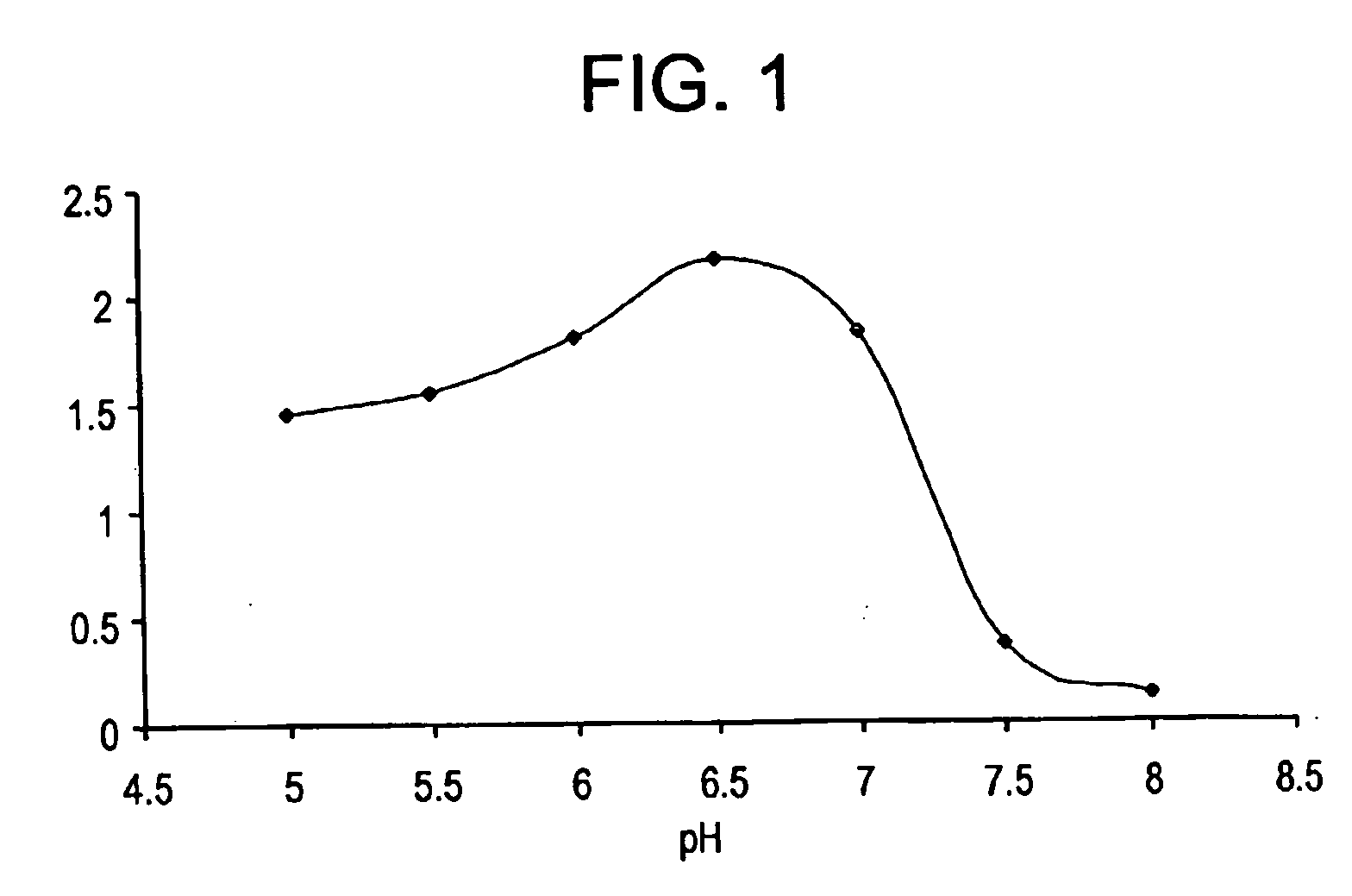
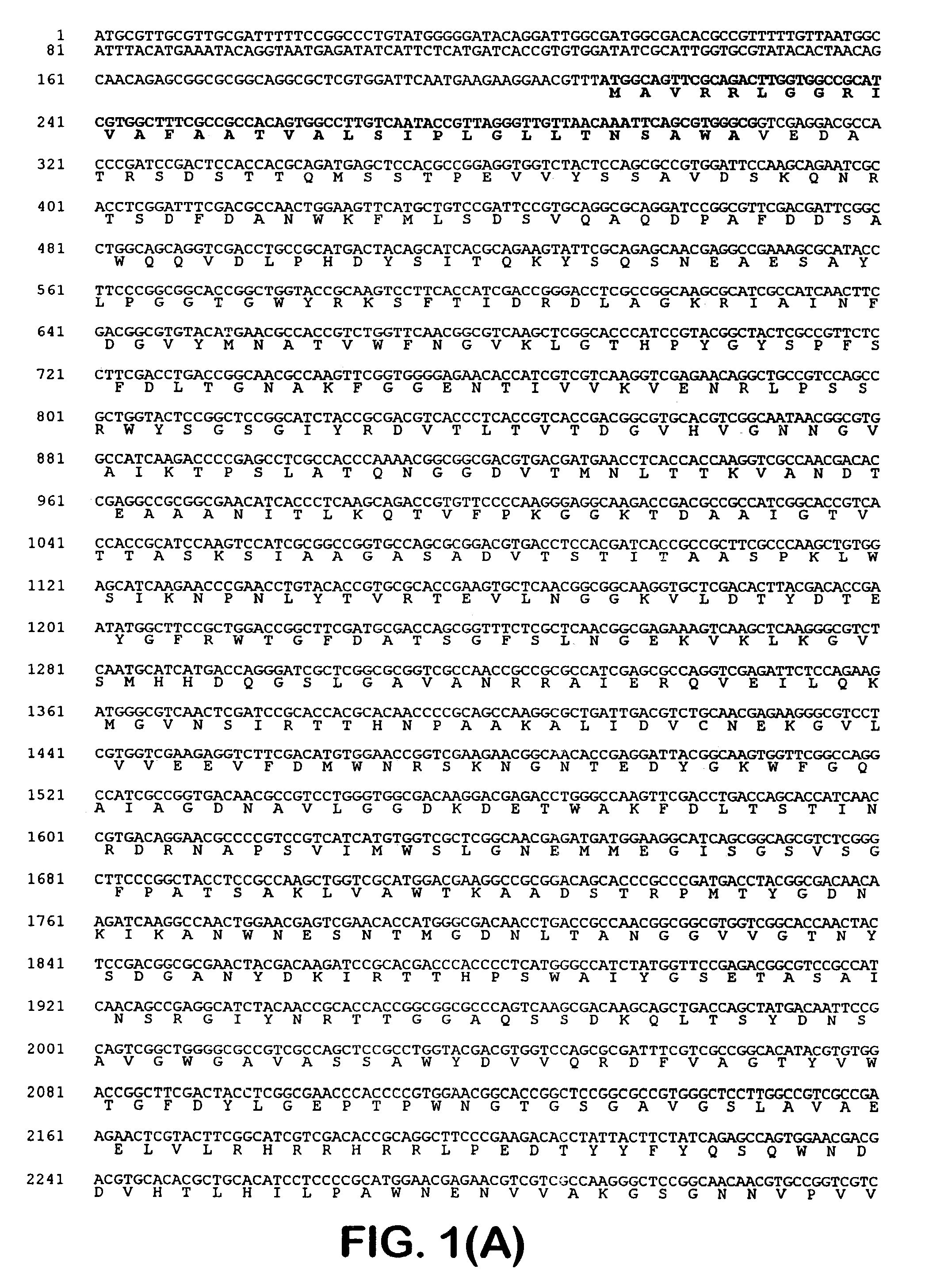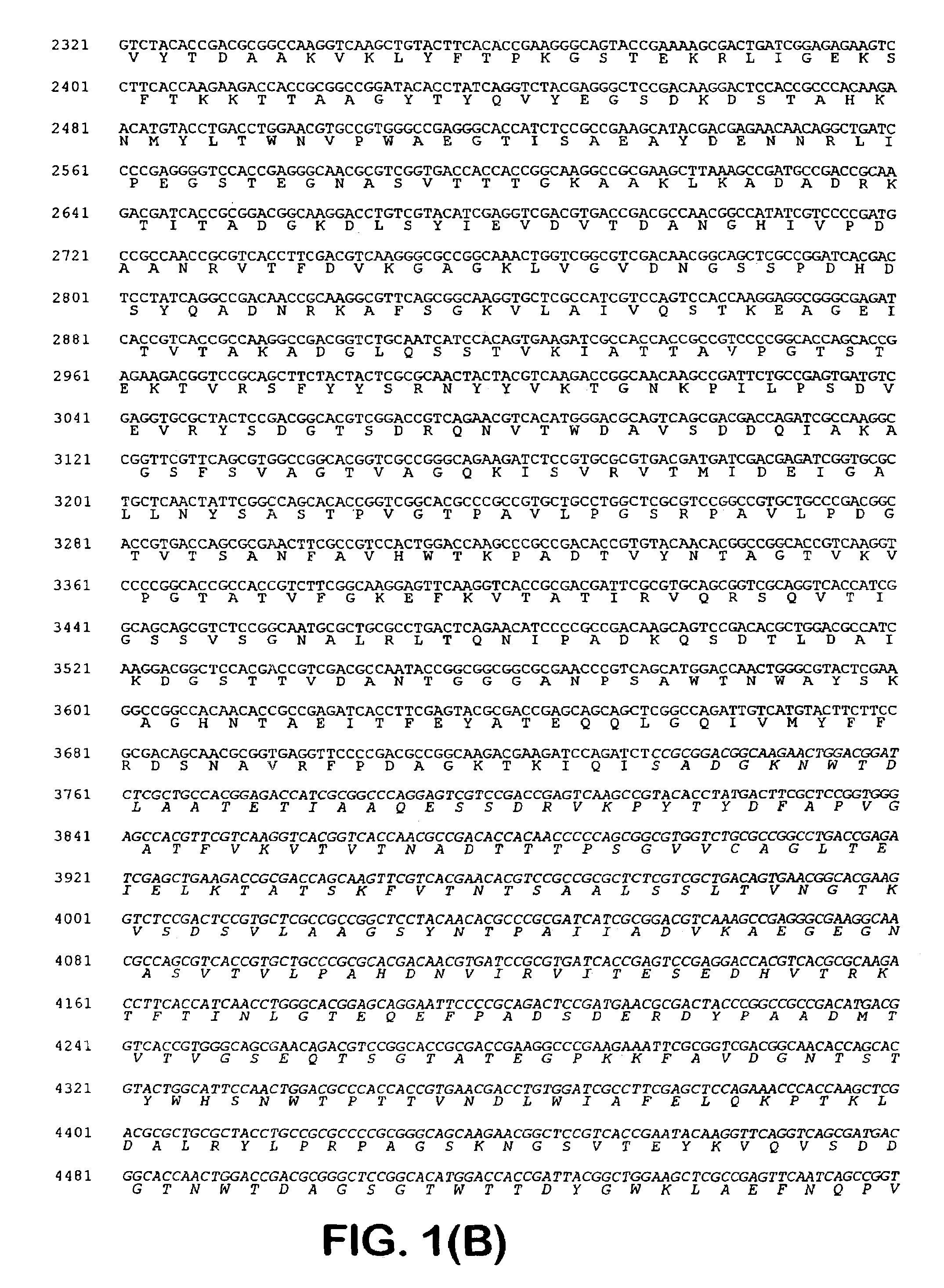Patents
Literature
524 results about "Galactosidases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Galactosidases are enzymes (glycoside hydrolases) that catalyze the hydrolysis of galactosides into monosaccharides. Galactosides can be classified as either alpha or beta. If the galactoside is classified as an alpha-galactoside, the enzyme is called alpha-galactosidase, and is responsible for catalyzing the hydrolysis of substrates that contain α-galactosidic residues, such as glycosphingolipids or glycoproteins. On the other hand, if it is a beta-galactoside, it is called beta-galactosidase, and is responsible for breaking down the disaccharide lactose into its monosaccharide components, glucose and galactose Both varieties of galactosidase are categorized under the EC number 3.2.1.
Nucleic acids of aspergillus fumigatus encoding industrial enzymes and methods of use
The present invention provides nucleotide sequences of Aspegillus fumigatus that encode proteins which exhibit enzyme activities. Vectors, expression constructs, and host cells comprising the nucleotide sequences of the enzyme genes are also provided. The invention further provides methods for producing the enzymes, and methods for modifying the enzymes in order to improve their desirable characteristics. The activities displayed by the enzymes of the invention include those of a tannase, cellulase, glucose oxidase, glucoamylase, phytase, beta-galactosidases, invertase, lipase, alpha-amylase, laccase, polygalacturonase or xylanase. The enzymes of the invention can be used in a variety of industrial processes. Enzymatically active compositions in various forms as well as antibodies to the enzymes and fragments thereof, are also provided.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
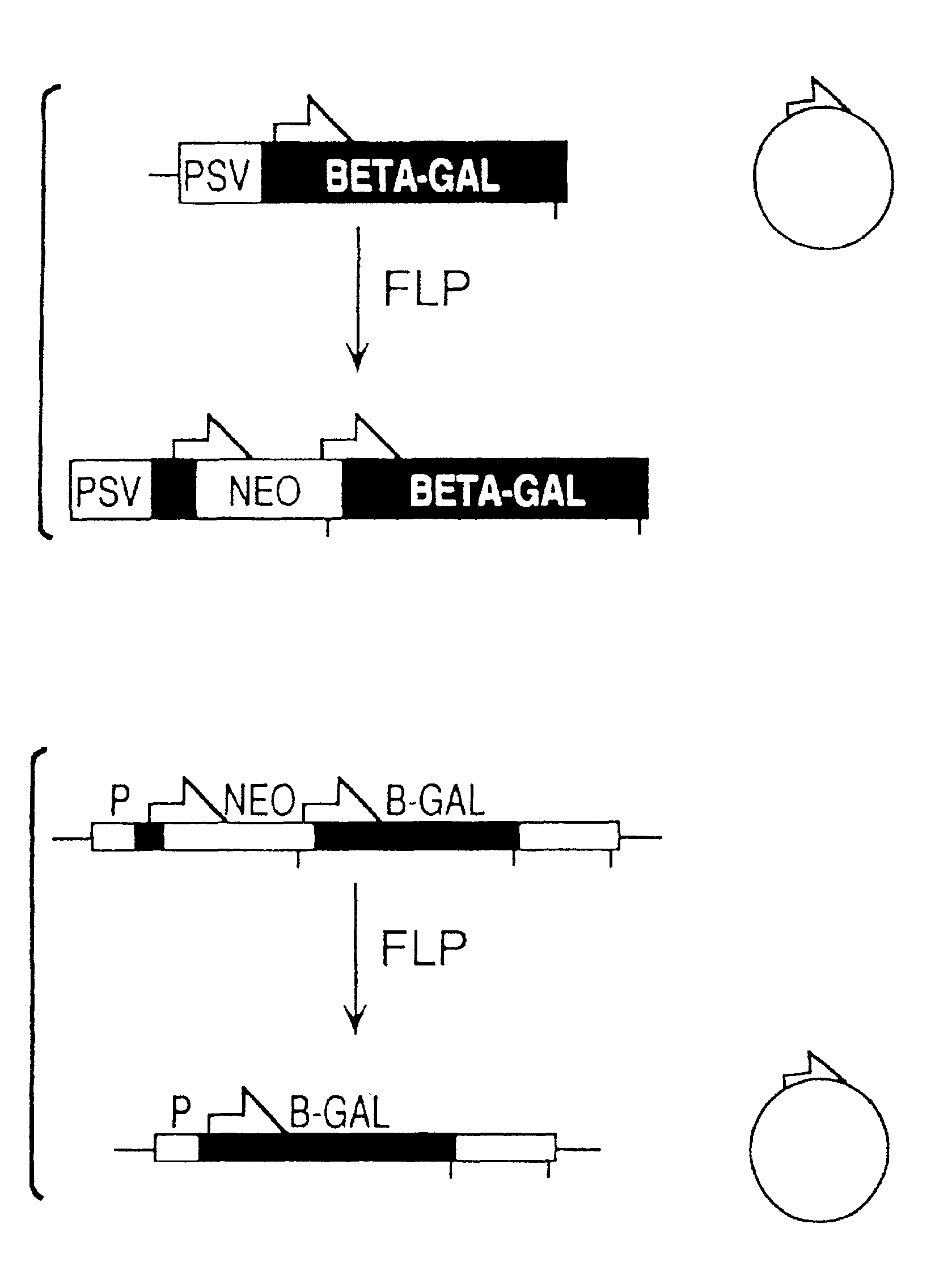
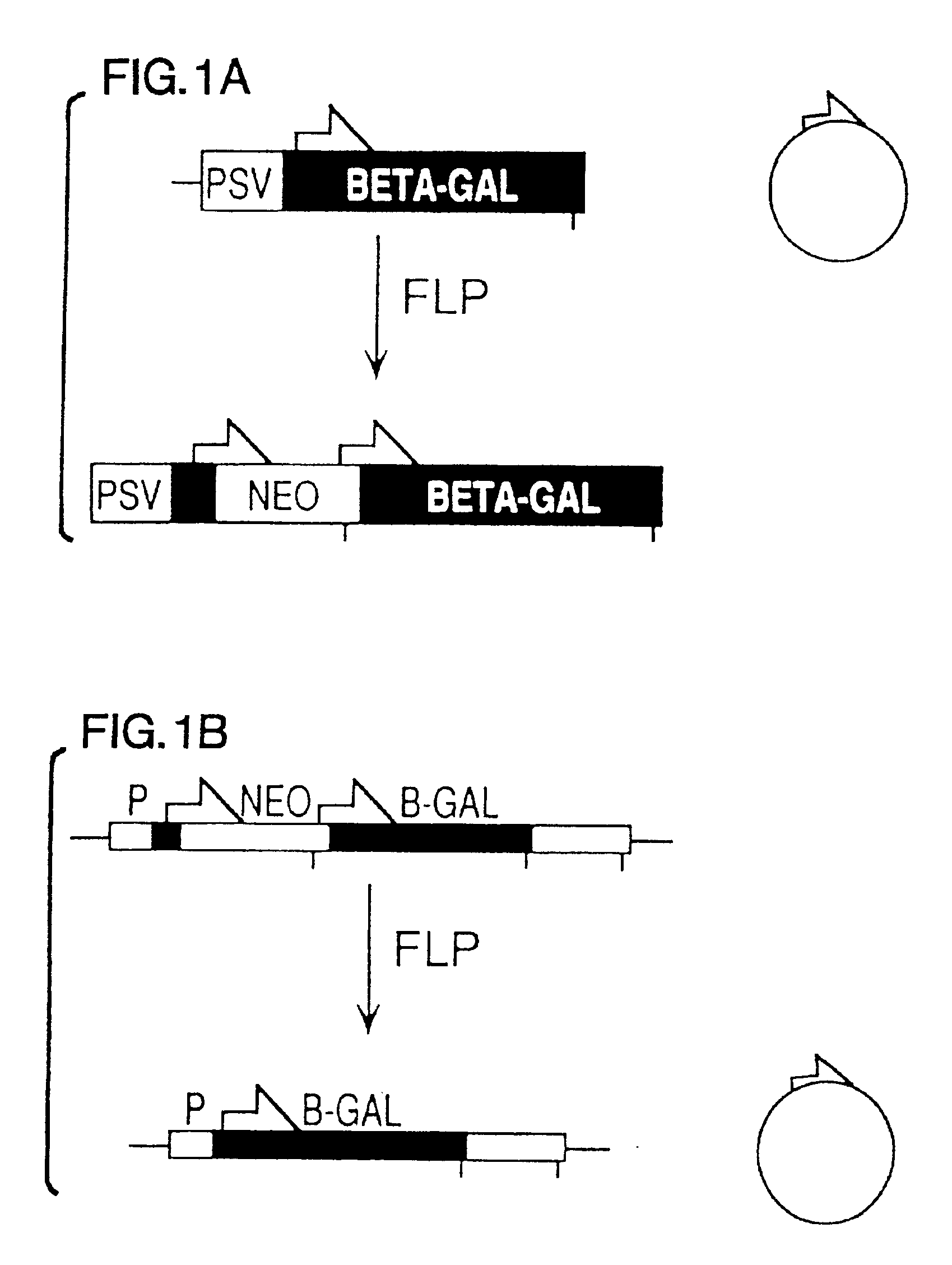
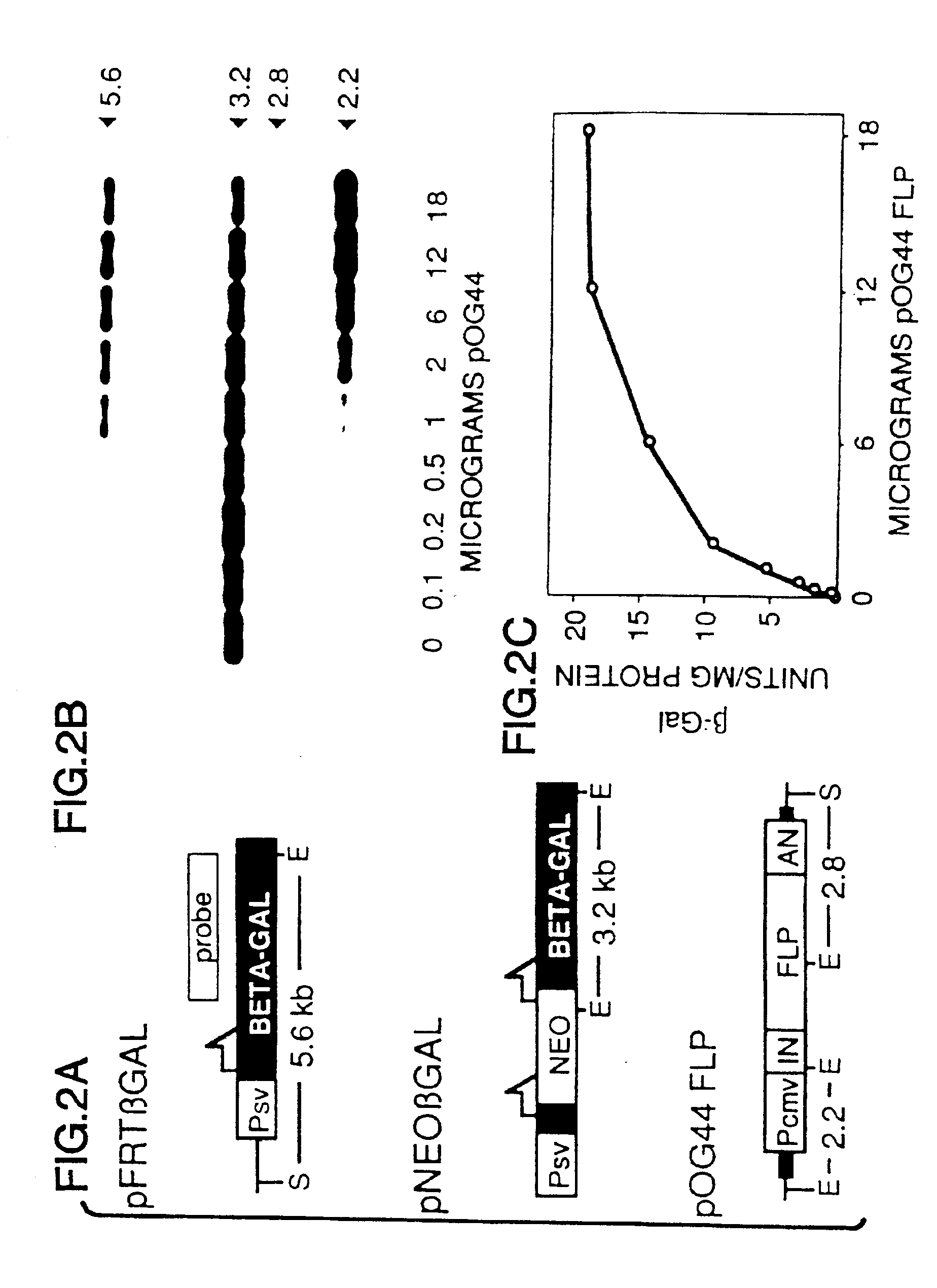
FLP-mediated gene modification in mammalian cells, and compositions and cells useful therefor
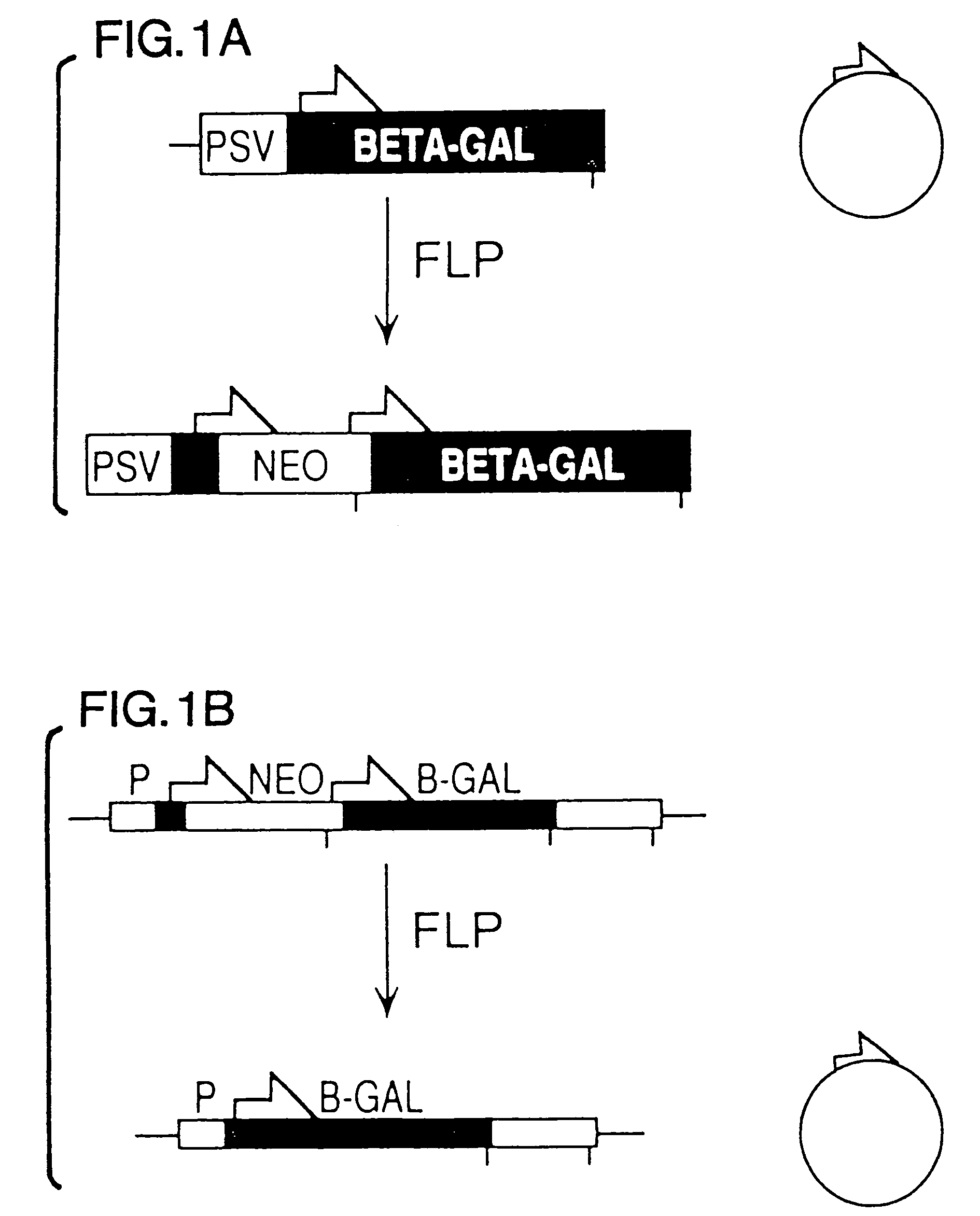
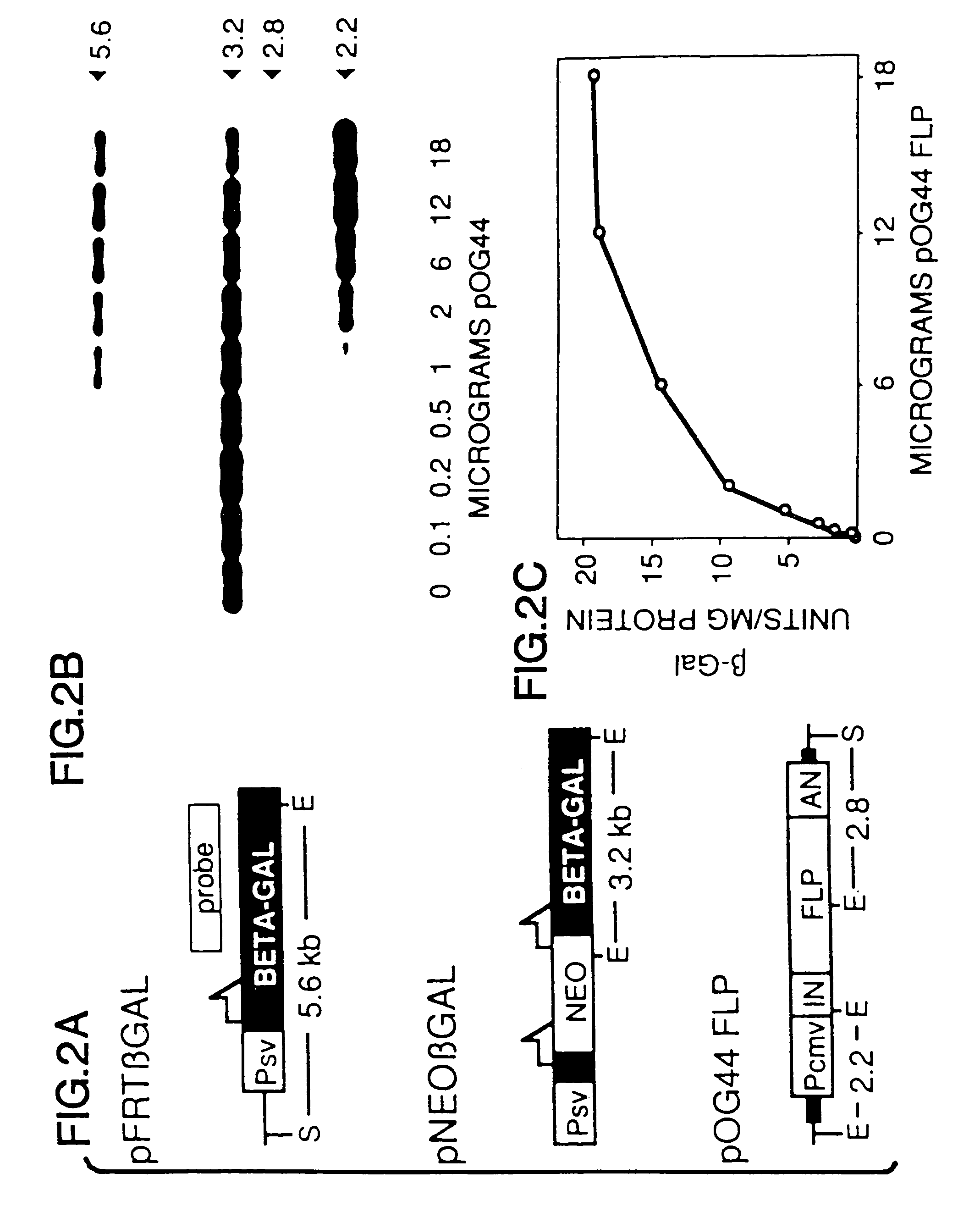
A gene activation / inactivation and site-specific integration system has been developed for mammalian cells. The invention system is based on the recombination of transfected sequences by FLP, a recombinase derived from Saccharomyces. In several cell lines, FLP has been shown to rapidly and precisely recombine copies of its specific target sequence. For example, a chromosomally integrated, silent β-galactosidase reporter gene was activated for expression by FLP-mediated removal of intervening sequences to generate clones of marked cells. Alternatively, the reverse reaction can be used to target transfected DNA to specific chromosomal sites. These results demonstrate that FLP can be used, for example, to mosaically activate or inactivate transgenes for a variety of therapeutic purposes, as well as for analysis of vertebrate development. The FLP recombination system of the present invention can be incorporated in transgenic, non-human mammals to achieve site-specific integration of transgenes, to construct functional genes or to disrupt existing genes.
Owner:CORN PROD DEV INC
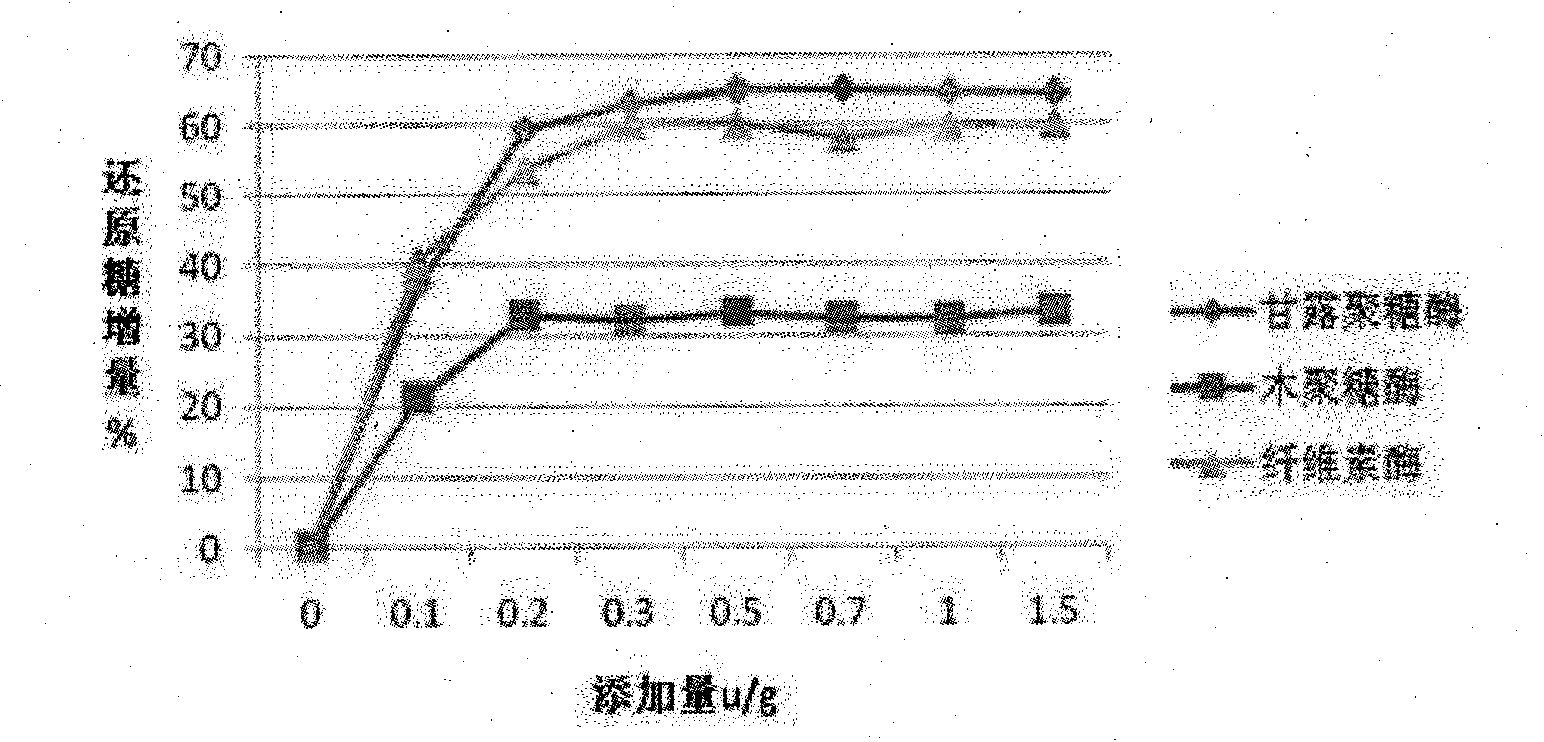
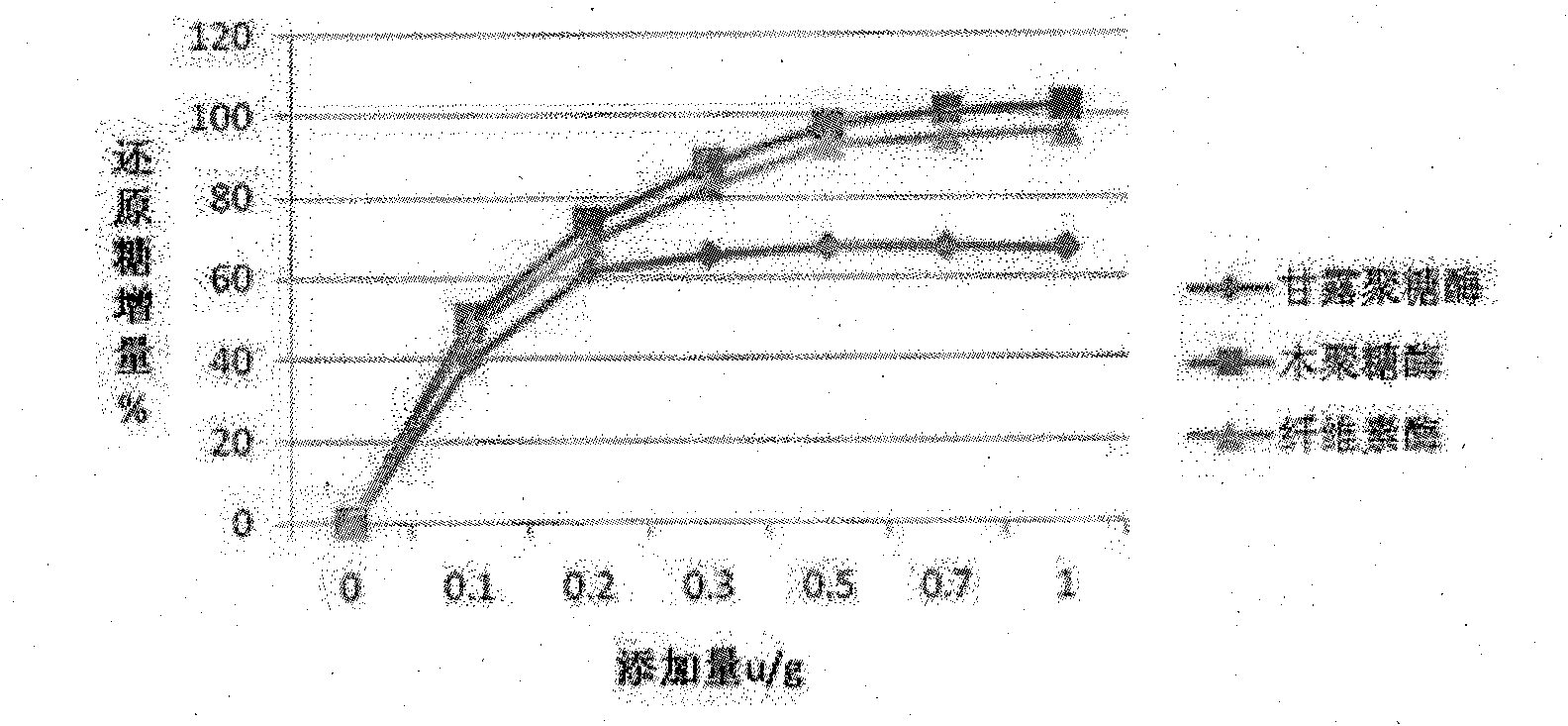
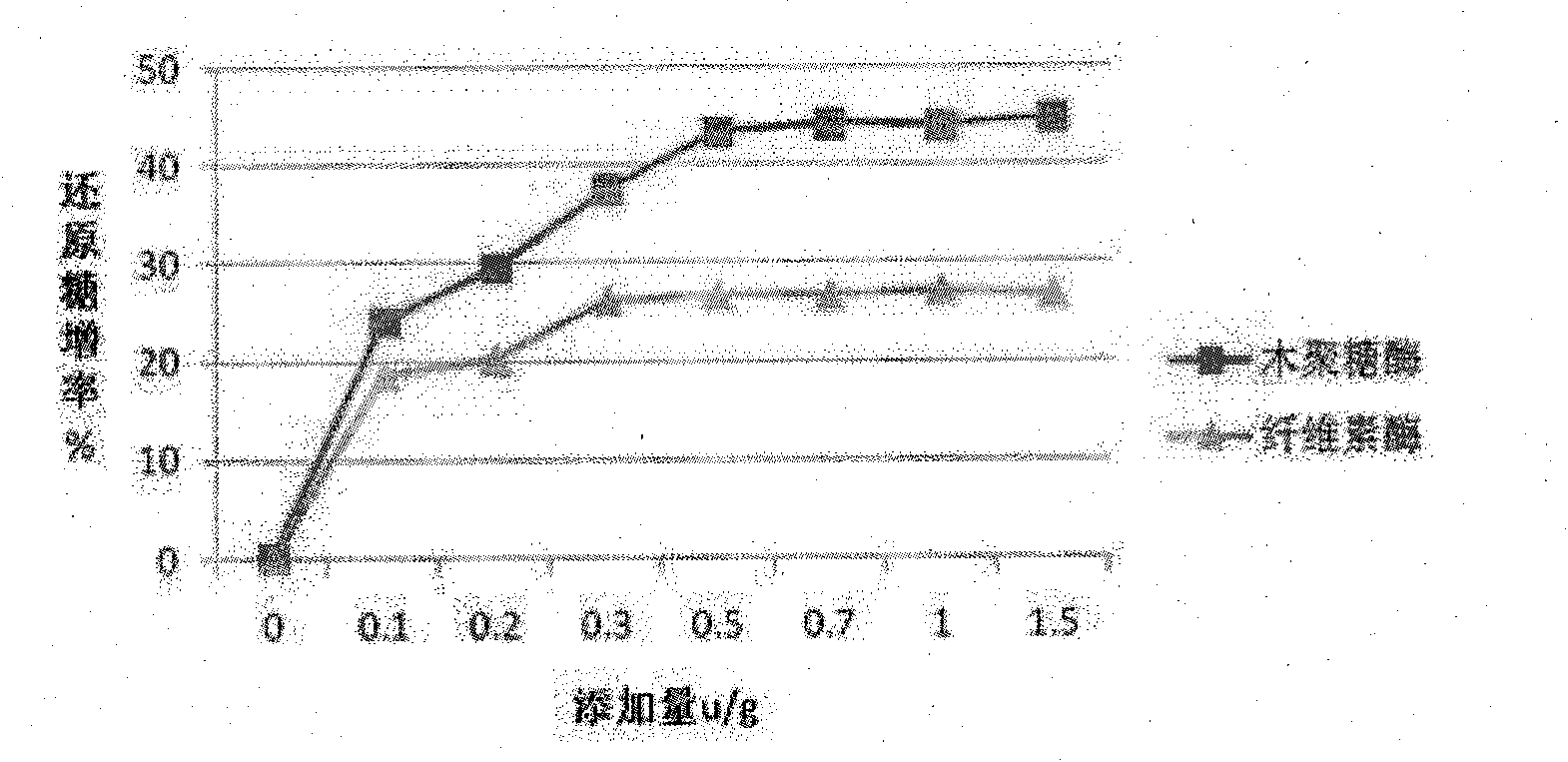
Complex enzyme for feed
InactiveCN101874547AIncrease profitSolve the problem of uncertain addition amountAnimal feeding stuffCellulosePectinase
The invention belongs to the technical field of feed additives, and in particular relates to complex enzyme for a feed. The complex enzyme comprises 7,500 to 15,000U / g of xylanase, 1,000 to 3,000U / g of mannose, 50 to 80U / g of galactosidase, 200 to 700U / g of cellulose, 500 to 1,500U / g of beta-glucanase, 150 to 1,000U / g of alpha-amylase, 2,000 to 10,000U / g of protease and 100 to 200U / g of pectinase. By adding corresponding enzyme preparations, the anti-nutrition function of the complex enzyme is reduced, the feed utilization is improved, and the animal production efficiency is improved, so the problems that the utilization rate of animal feed raw materials is low and the animal production performance is inhibited are effectively solved; meanwhile, the complex enzyme has the advantages of reasonable raw material mixing, good effect, and low overall cost.
Owner:JINAN TIANTIANXIANG
Method for producing complex micro-ecological preparation with microbial agents and enzyme
InactiveCN101690545ALess chance of growthGrow fastAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsMicrobial agentAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a method for producing a complex micro-ecological preparation with microbial agents and enzyme. According to the action principles and characteristics of every microbial strain, the method adopts scientific combination and adds enzyme preparations and acidifier to enable microorganisms in the product to grow rapidly and take dominance in fermented feed and animal bodies so as to reduce the growth opportunity of miscellaneous bacteria. The preparation comprises the following components: bacillus subtilis, lactobacillus plantarum, candida utilis yeast, lactobacillus acidophilus, protease, amylase, cellulase, xylanase, mannanase, galactosidase, pectinase and citric acid. As all strains of the product adopt liquid deep fermentation culture, the non-polluting property of the product is guaranteed. Liquid microbial agents ensure that the number of bacterial colonies of the product is more than 100 million and the product is free from the pollution of other miscellaneous bacteria, while solid microbial agents ensure that the number of bacterial colonies of the product is more than 1 billion and the proportion of miscellaneous bacteria to effective bacteria is not more than 0.0001. The preparation contains bacillus, lactic acid bacteria and yeast, can apply to the processes of making green-yellow storage feed, fermenting feed, soaking feed, and the like, can be directly added to feed for feeding, and can improve the growth performance of ruminant animals, poultry, pigs, aquatic products and special animals.
Owner:ZHAODONG SUN SHINE ENZYME
Method for increasing breast meat yields in poultry
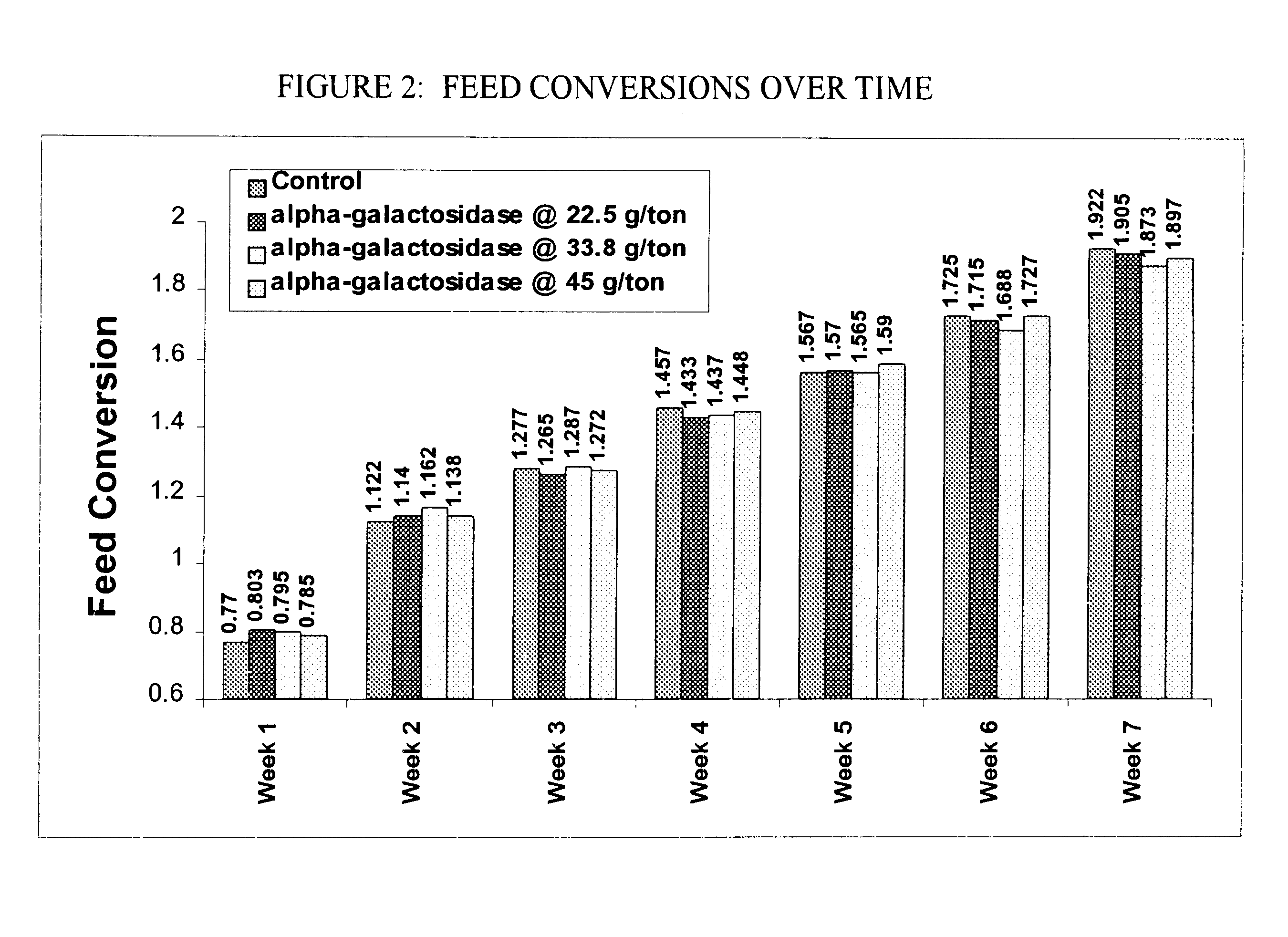
A poultry feed composition including protein, vitamins and minerals, and a source of carbohydrates from the group consisting of soybean meals and corn supplemented with an alpha-galactosidase that catalyzes the degradation of the galactoside. The addition of the alpha-galactosidase increases the ratio of gain to feed, increases the amount of white meat, or decreases the amount of fat deposited during growth of a chicken fed the feed composition, relative to the chicken fed on an identical feed composition absent the alpha-galactosidase.
Owner:KEMIN IND INC
Methods of treating fabry disease in patients having the G9331A mutation in the GLA gene
ActiveUS10537564B2Metabolism disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmacometricsPharmacological chaperone
Provided are methods of treating a patient diagnosed with Fabry disease and methods of enhancing α-galactosidase A in a patient diagnosed with or suspected of having Fabry disease. Certain methods comprise administering to a patient a therapeutically effective dose of a pharmacological chaperone for α-galactosidase A, wherein the patient has a splice site mutation in intron 4 of the nucleic acid sequence encoding α-galactosidase A. Also described are uses of pharmacological chaperones for the treatment of Fabry disease and compositions for use in the treatment of Fabry disease.
Owner:BPCR LLP
Galactosidase-treated prosthetic devices
InactiveUS20050221703A1Low immunogenicityBone implantSynthetic resin layered productsEpitopeMeniscus
Matrix material for a substantially immunologically-compatible meniscal augmentation device of biocompatible and partially bioresorbable fibers is prepared by treatment with ∝-galactosidase to eliminate ∝-Gal epitopes. Upon implantation into a segmental defect of a meniscus, the composite of the meniscal augmentation device and the meniscus establishes a scaffold adapted for ingrowth of meniscal fibrochondrocytes.
Owner:APERION BIOLOGICS
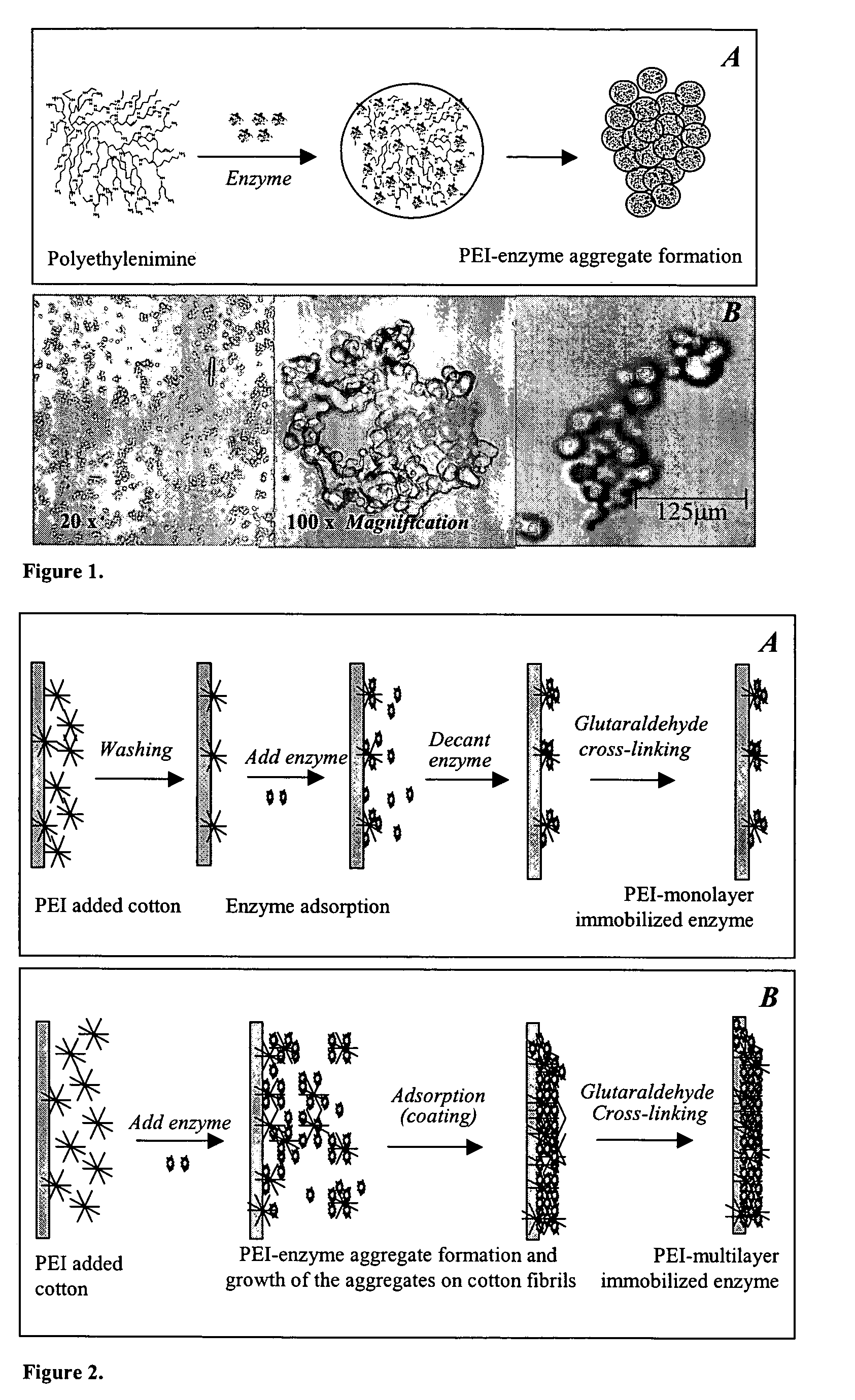
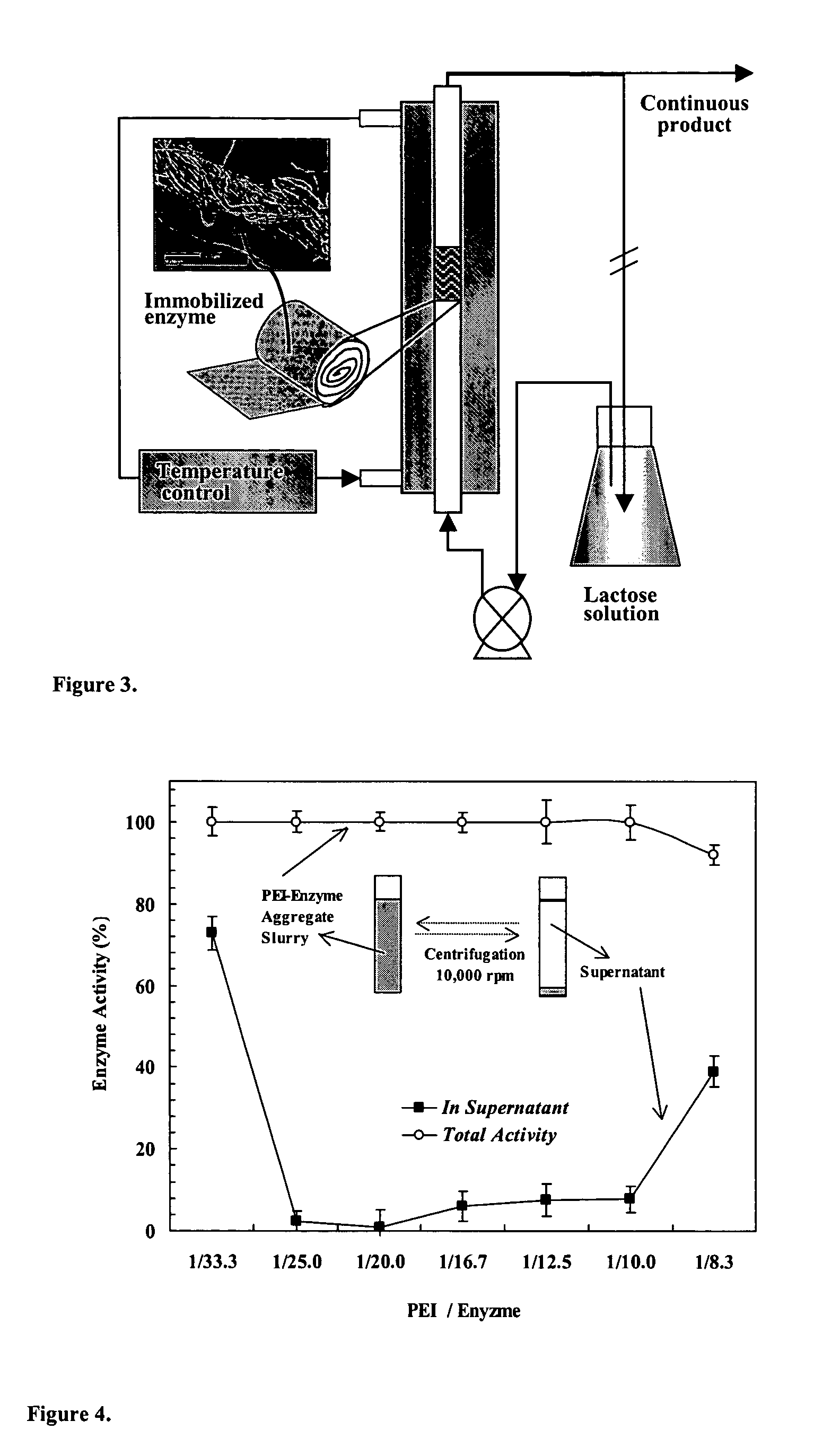
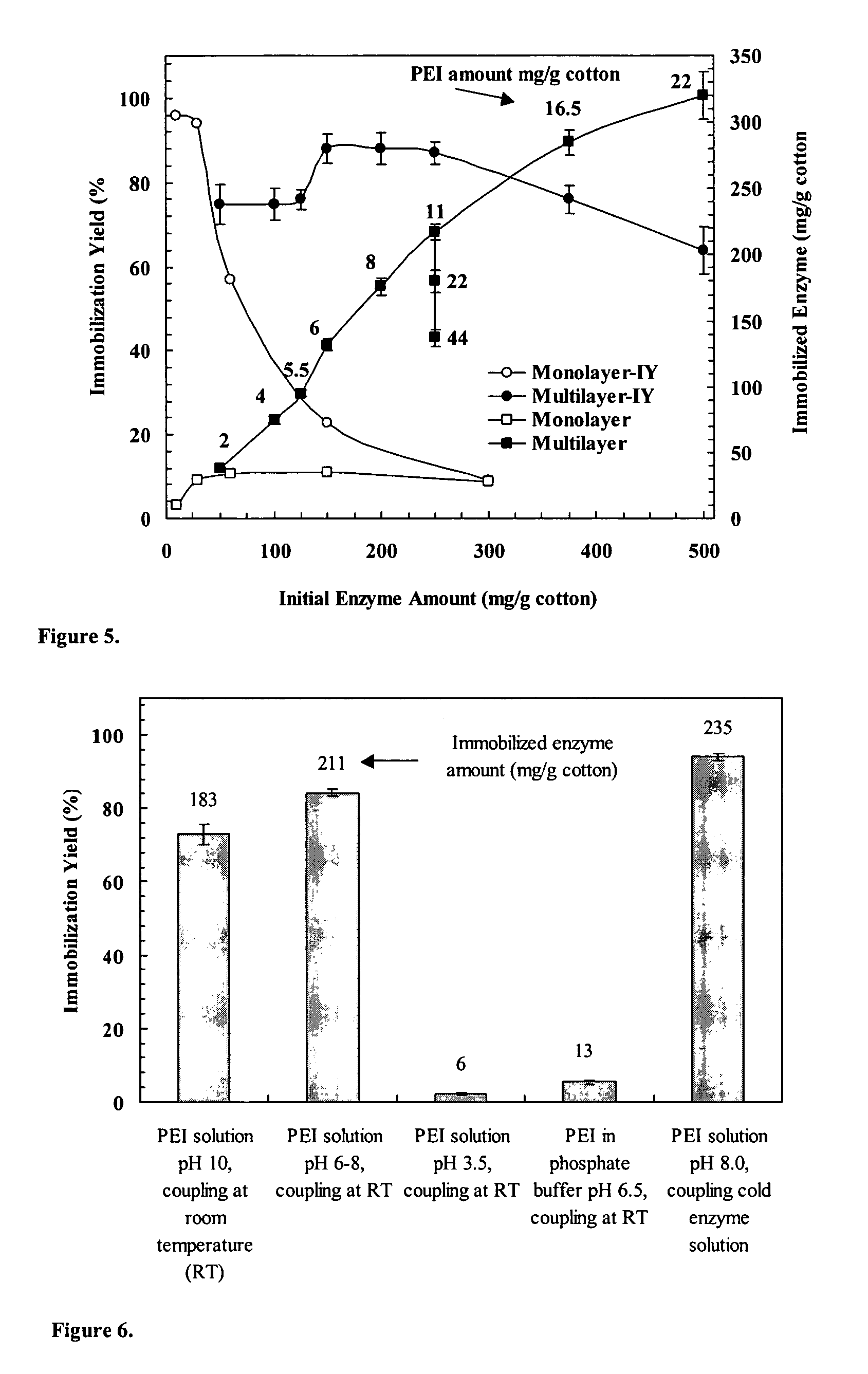
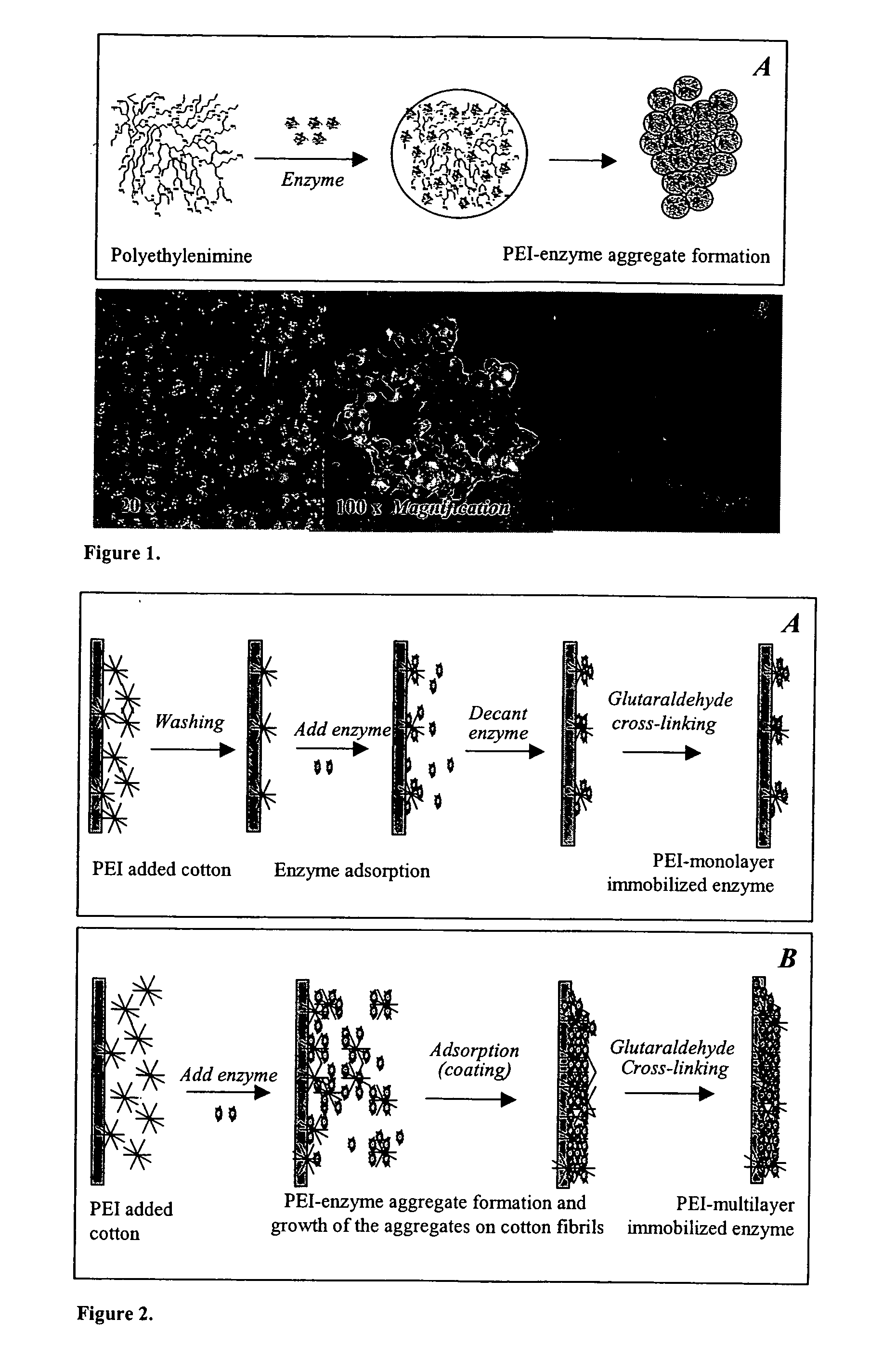
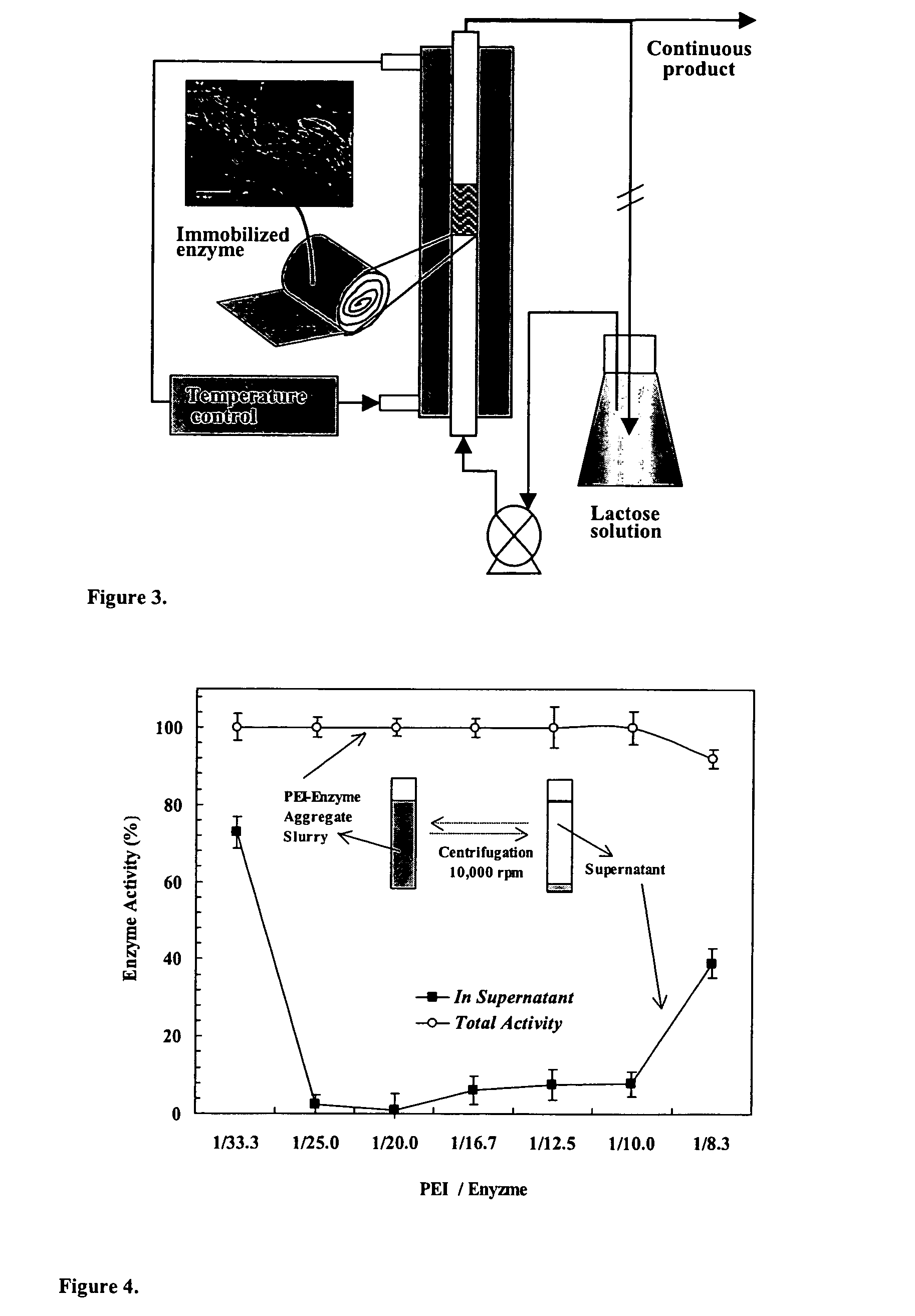
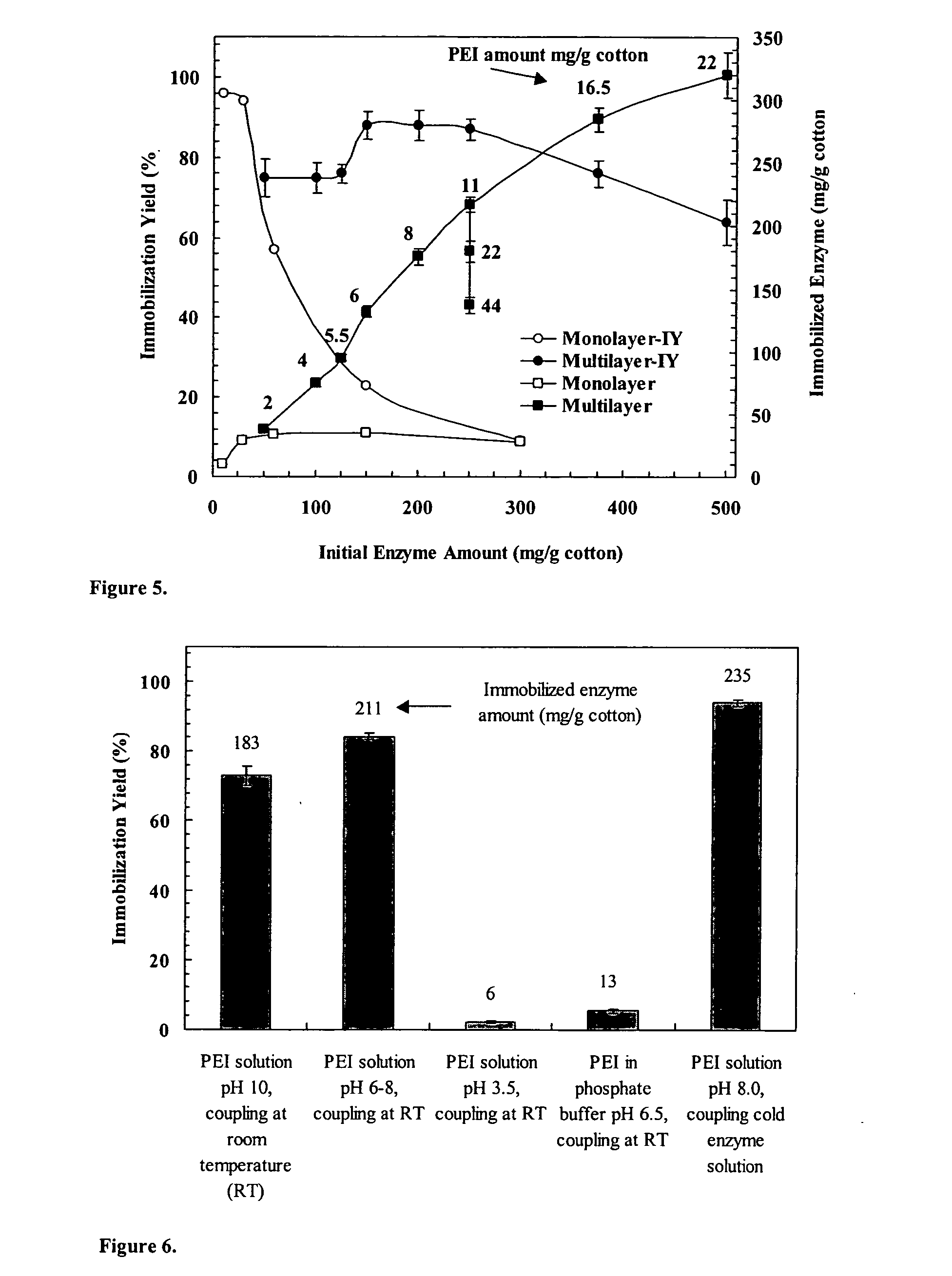
Immobilization of enzyme on a fibrous matrix
ActiveUS7166451B1The process is simple and clearHigh enzyme loadingOn/in organic carrierFermentationFiberCross-link
A multilayer enzyme immobilization process is provided comprising adsorbing a polyethyleneimine (PEI) solution in a fibrous matrix, and adding an enzyme to the fibrous matrix, which comprises a plurality of fibrils. The process further comprises forming at least two layers of PEI-enzyme aggregates on the fibrils, and cross-linking the multilayer PEI-enzyme aggregates. The process can further comprise washing the fibrils containing the cross-linked PEI-enzyme aggregates with distilled water and acetic acid buffer subsequent to cross-linking. However, the PEI-containing matrix is not washed prior to the addition of enzyme. The enzyme can be β-galactosidase and the fibrous matrix can be cotton cloth. The multilayer immobilized enzyme can be employed in a biocatalyst reactor for production of galacto-oligosaccharides from lactose and the hydrolysis of lactose to glucose and galactose.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Pharmaceutical composition for enzyme replacement therapy
ActiveUS20100291059A1Increase doseEffective absorptionSenses disorderSugar derivativesSide effectWild type
Owner:ALTIF LAB +1
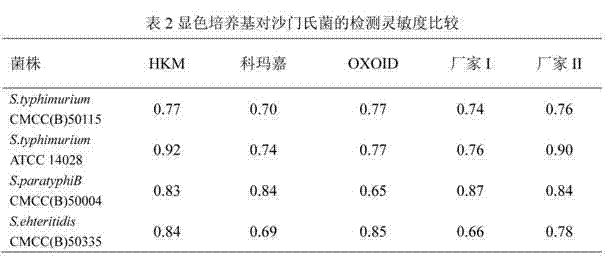
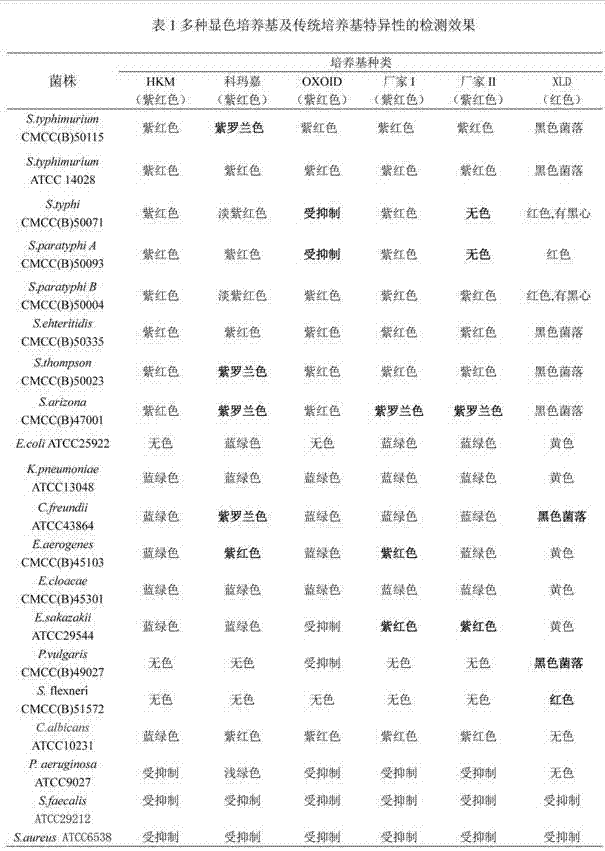
Plating media for the identification of Salmonella
InactiveUS7150977B2Reduce and eliminate responseElimination reactionMicrobiological testing/measurementAdditive ingredientBeta-Galactosidases
An isolation plating medium for the identification of Salmonella bacteria in a sample containing a plurality of different bacteria comprising a mixture of a carbohydrate capable of being a metabolic source for Salmonella bacteria and supporting colonies of Salmonella bacteria, a pH indicator dye that changes the color of the plating medium to a first color different from the color of the medium responsive to a change in the pH of the medium, a first substrate that does not react with Salmonella bacteria and injects color into the medium of a second color responsive to the presence of beta-galactosidase, the second color contrasting with the first color and the color of the medium, a second substrate that does not react with Salmonella bacteria and injects color into the medium of substantially the same color as the second color responsive to the presence of beta=galactosidase, and an ingredient for thickening the mixture in sufficient quantity to solidify the mixture.
Owner:R&F PROD
Short enzyme donor fragment
InactiveUS7135325B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFunctional activityOrganic compound
Short enzyme donor fragments of β-galactosidase are provided of not more than 40 amino acids, where the short fragments are used as a label and may be substituted with a wide variety of organic compounds, particularly polypeptides having independent functional activity. The enzyme donor finds use in competitive and non-competitive assays, monitoring intracellular events, or other processes where a sensitive non-interfering label is desired.
Owner:DISCOVERYX CORP
Method For The Detection Of Coliforms And In Particular Escherichia Coli
InactiveUS20070196884A1Detectable amountReduction of background fluorescenceMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBacteria coliformsLarge intestine
The invention is relative to a novel method for the detection of coliforms, which is based on the use of a mixture of amino acids to promote the expression of inducible enzymes, in absence of cell growth. This enzyme-inducing solution can be used for the rapid detection of the enzymes β-glucuronidase and / or β-galactosidase in a very small number of E. coli and / or total coliforms.
Owner:ISRIM S CONS A R L
Method for preparing rubusoside by catalytically hydrolyzing stevioside with beta-galactosidase
ActiveCN102250990AMild reaction conditionsHigh selectivityFermentationSimple Organic CompoundsSteviolmonoside
The invention relates to a method for preparing rubusoside by catalytically hydrolyzing stevioside with beta-galactosidase, belonging to the technical field of biosynthesis of organic compounds. In the invention, beta-galactosidase is utilized to selectively and catalytically hydrolyzing stevioside obtained from stevia so as to prepare the rubusoside. Thus, the invention has the advantages of high conversion rate, high speed, high selectivity, simple separation and clearing process and the like. The invention provides a new efficient and environment-friendly method for preparing rubusoside.
Owner:DONGTAI HIRYE BIOTECH CO LTD
FLP-mediated gene modification in mammalian cells, and compositions and cells useful therefor
A gene activation / inactivation and site-specific integration system has been developed for mammalian cells. The invention system is based on the recombination of transfected sequences by FLP, a recombinase derived from Saccharomyces. In several cell lines, FLP has been shown to rapidly and precisely recombine copies of its specific target sequence. For example, a chromosomally integrated, silent β-galactosidase reporter gene was activated for expression by FLP-mediated removal of intervening sequences to generate clones of marked cells. Alternatively, the reverse reaction can be used to target transfected DNA to specific chromosomal sites. These results demonstrate that FLP can be used, for example, to mosaically activate or inactivate transgenes for a variety of therapeutic purposes, as well as for analysis of vertebrate development. The FLP recombination system of the present invention can be incorporated in transgenic, non-human mammals to achieve site-specific integration of transgenes, to construct functional genes or to disrupt existing genes.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
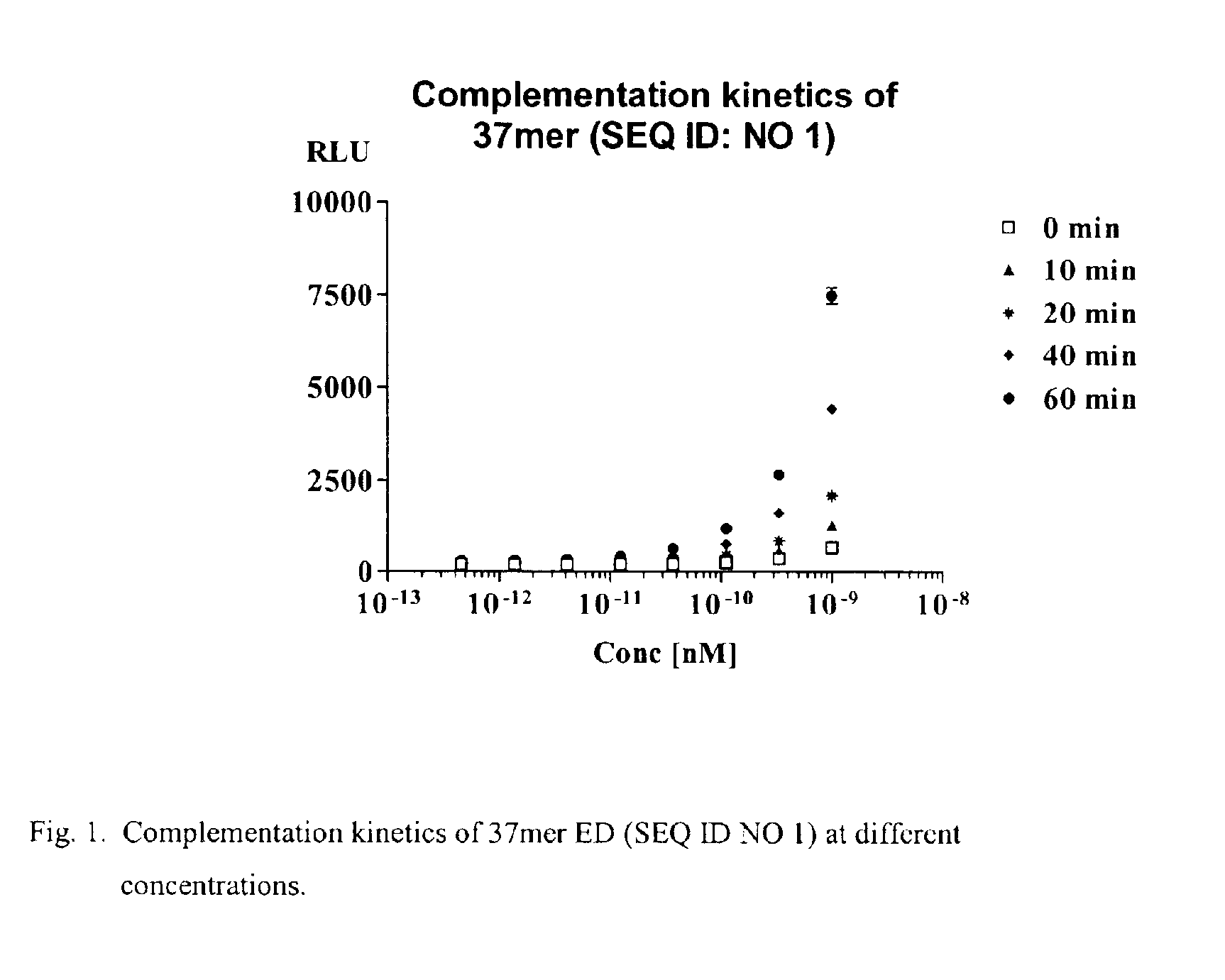
Detection of protein translocation by beta-galactosidase reporter fragment complementation
ActiveUS20050287522A1Precise and accurate monitoringMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBeta-GalactosidasesElisa assay
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting molecular translocations, particularly protein translocations within and between subcellular copartments, using at least two components that exhibit a localization-dependent difference in complementation activity. In particular, alpha-complementing β-galactosidase fragments are provided. These β-galactosidase reporter fragments display significantly enhanced enzymatic activity when one fragment is localized in a membrane. Methods for carrying out no-wash ELISA assays based on the reporter component system are also provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Beta-galactosidase mutant with high transglycosylation activity and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103881994AHigh transglycosidic activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationAspergillus oryzaeMutant
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and discloses a beta-galactosidase mutant with high transglycosylation activity. On the basis of removal of an amino acid sequence of beta-galactosidase of aspergillus candidus and aspergillus oryzae of a signal peptide, the beta-galactosidase mutant is obtained through fixed point saturated mutation of a unit point. The transglycosylation activity of the mutant is improved by above 15 percent in comparison of the transglycosylation activity of a wild type mutant. Meanwhile, the invention further discloses a DNA molecule for coding the mutant, a recombinant expression vector containing the DNA molecule and a host cell for expressing the DNA molecule. In addition, the invention further provides a method for preparing the beta-galactosidase mutant with high transglycosylation activity by adopting the recombinant expression vector, and application of the mutant, the DNA molecule, the recombinant expression vector and the host cell to the preparation of the beta-galactosidase.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for remodelling cell wall polysaccharide structures in plants
InactiveUS20030159178A1Reduce the ratioImprove gel propertiesSurgical adhesivesDead animal preservationReticulum cellNucleotide
Methods for providing transgenic plants and parts hereof that, relative to the wild type state, is modified in a complex cell wall polysaccharide structure including pectins and hemicelluloses, the modification being in the overall glycosidic linkage pattern or the monosaccharide profile, comprising transforming a plant cell with a nucleotide sequence that causes an altered production of a complex cell wall polysaccharide-modifying enzyme such as endo-rhamnogalacturonan hydrolase, an endo-rhamnogalacturonan lyase, an endo-galactanase, an endo-arabinanase, an arabinofuranosidase, a galactosidase such as a beta-galactosidase, a xylosidase and an exo-galacturosidase. The modification can occur in vivo or post harvest, in which latter case the modifying enzyme is separated in the growing plant from its substrate, e.g. by targeting the enzyme to the Golgi, the endoplasmic reticulum or a vacuole, or is in a form that is inactive in the plant. After harvest the enzyme is brought into contact with its substrate or it is activated to provide the desired post harvest modification of the cell wall polysaccharide. The transgenic plant materials have improved functionalities and are useful in food and feed manufacturing and as pharmaceutically or medically active substances.
Owner:POALIS
Immobilization of enzyme on a fibrous matrix
ActiveUS20070111289A1High enzyme loadingEasy loadingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCross-linkFiber
A multilayer enzyme immobilization process is provided comprising adsorbing a polyethyleneimine (PEI) solution in a fibrous matrix, and adding an enzyme to the fibrous matrix, which comprises a plurality of fibrils. The process further comprises forming at least two layers of PEI-enzyme aggregates on the fibrils, and cross-linking the multilayer PEI-enzyme aggregates. The process can further comprise washing the fibrils containing the cross-linked PEI-enzyme aggregates with distilled water and acetic acid buffer subsequent to cross-linking. However, the PEI-containing matrix is not washed prior to the addition of enzyme. The enzyme can be β-galactosidase and the fibrous matrix can be cotton cloth. The multilayer immobilized enzyme can be employed in a biocatalyst reactor for production of galacto-oligosaccharides from lactose and the hydrolysis of lactose to glucose and galactose.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Chromogenic medium for detecting salmonella
InactiveCN102827918AHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyActive agent
The invention discloses a chromogenic medium for detecting salmonella, which belongs to the fields of food safety and clinical microbiological detection. The culture medium contains agar, peptone, beef extract powder, sodium chloride, a surfactant, cholate, an enzyme inducer, an octoate enzyme chromogenic substrate, a beta-galactosidase chromogenic substrate, a hexosaminidase chromogenic substrate and robiocina. The chromogenic medium disclosed by the invention is used for detecting salmonella, has high detection sensitivity and high specificity, and can be used for initially identifying strains directly according to the color of a colony; the chromogenic medium has high operability, and suitable for treating large-reflux samples, and can be used for comprehensively, systematically and accurately detecting and initially identifying salmonella in food production, clinical disease diagnosis and the environment; and a new way is provided for rapid detection of microorganisms.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUANKAI MICROBIAL SCI & TECH
Rapeseed meal enzyme-linked micro-ecological preparation and solid fermentation method of rapeseed meal
The present invention discloses a rapeseed meal enzyme-linked micro-ecological preparation and a solid fermentation method of rapeseed meal. The preparation comprises ingredients: xylanase, beta-glucanase, galactosidase, beta-mannanase, cellulase, phytase, acid protease, neutral protease, papain, alkaline protease, amylase, lactic acid bacteria, bacillus, yeasts, starch and polysaccharides. The preparation is prepared by mixing the various enzyme preparations with the fermentation micro-organisms, reduces the use of an acidifier, reduces production costs, and at the same time enhances decomposition and detoxification effects of the preparation. A produced fermented rapeseed meal feed product is rich in 3-15% of lactic acid; glucosinolate is reduced by 80% or more and toxic effects on livestock and poultry are significantly reduced; crude proteins are increased by 1-2% and a consumption of non-protein materials is ensured; a small peptide content is increased to 15-25% and utilization of animals for feed proteins is effectively improved; and bitter substances in the rapeseed meal are effectively removed and a tannin degradation rate is 60% or more.
Owner:湖北华扬科技发展有限公司 +2
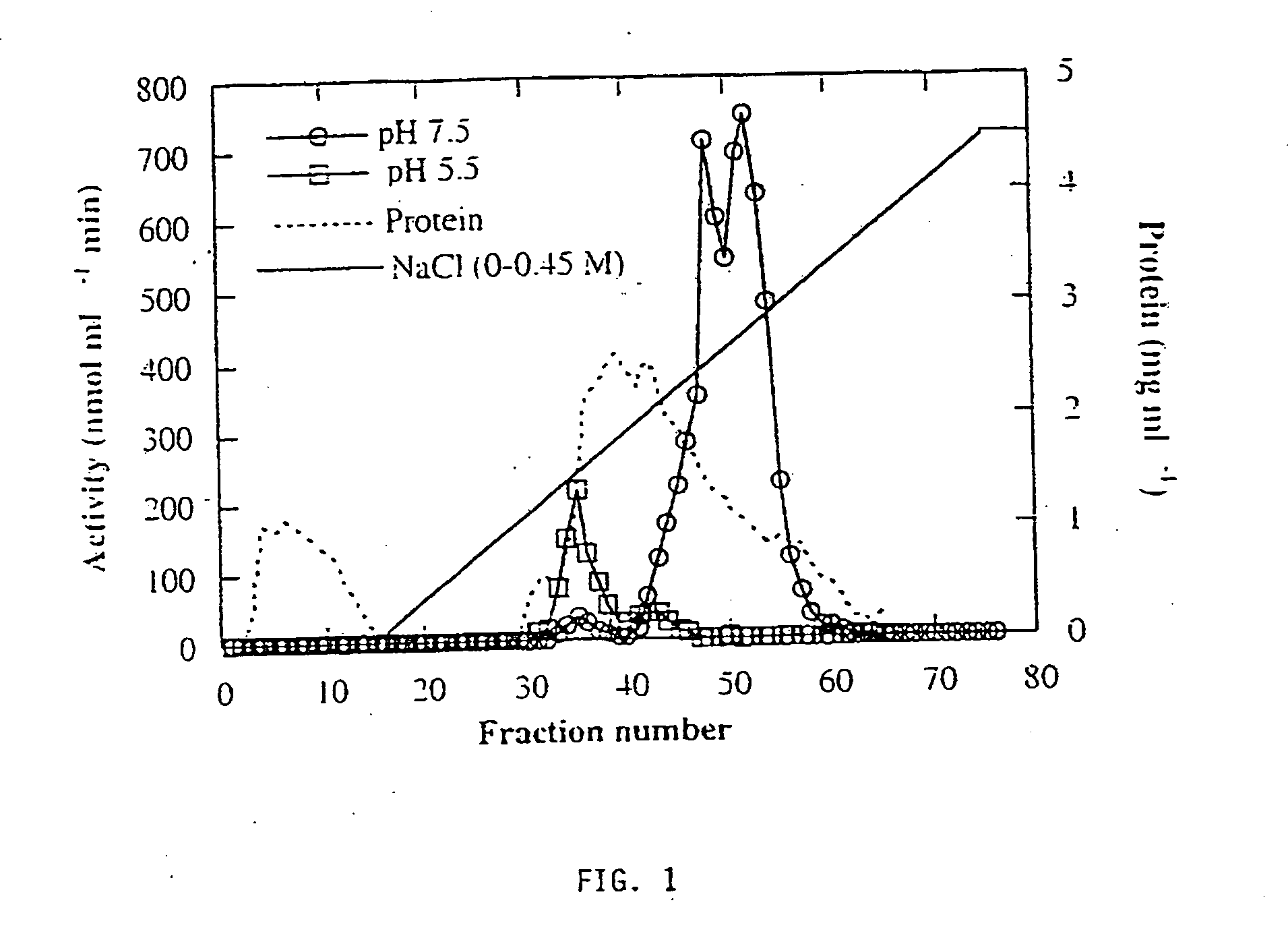
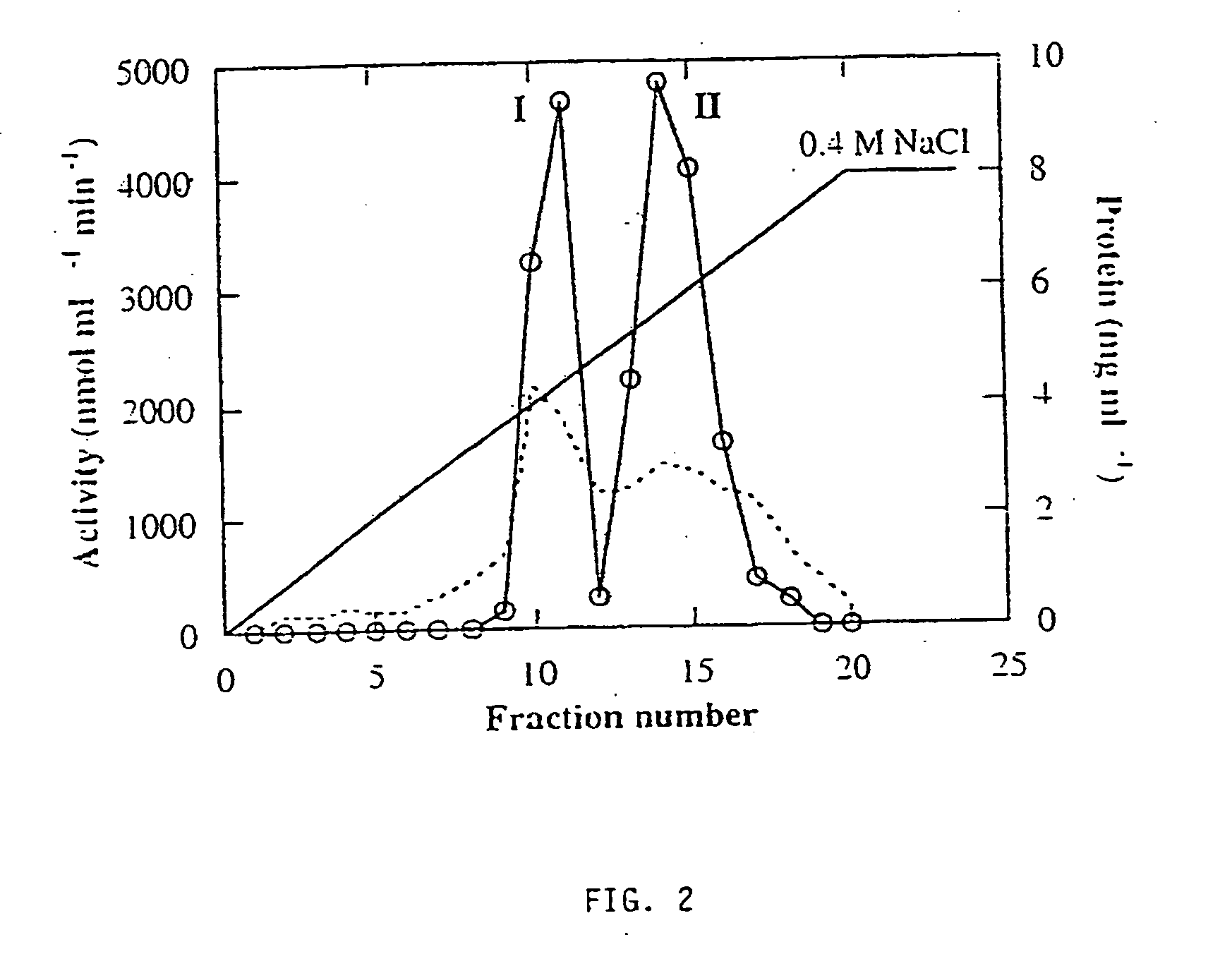
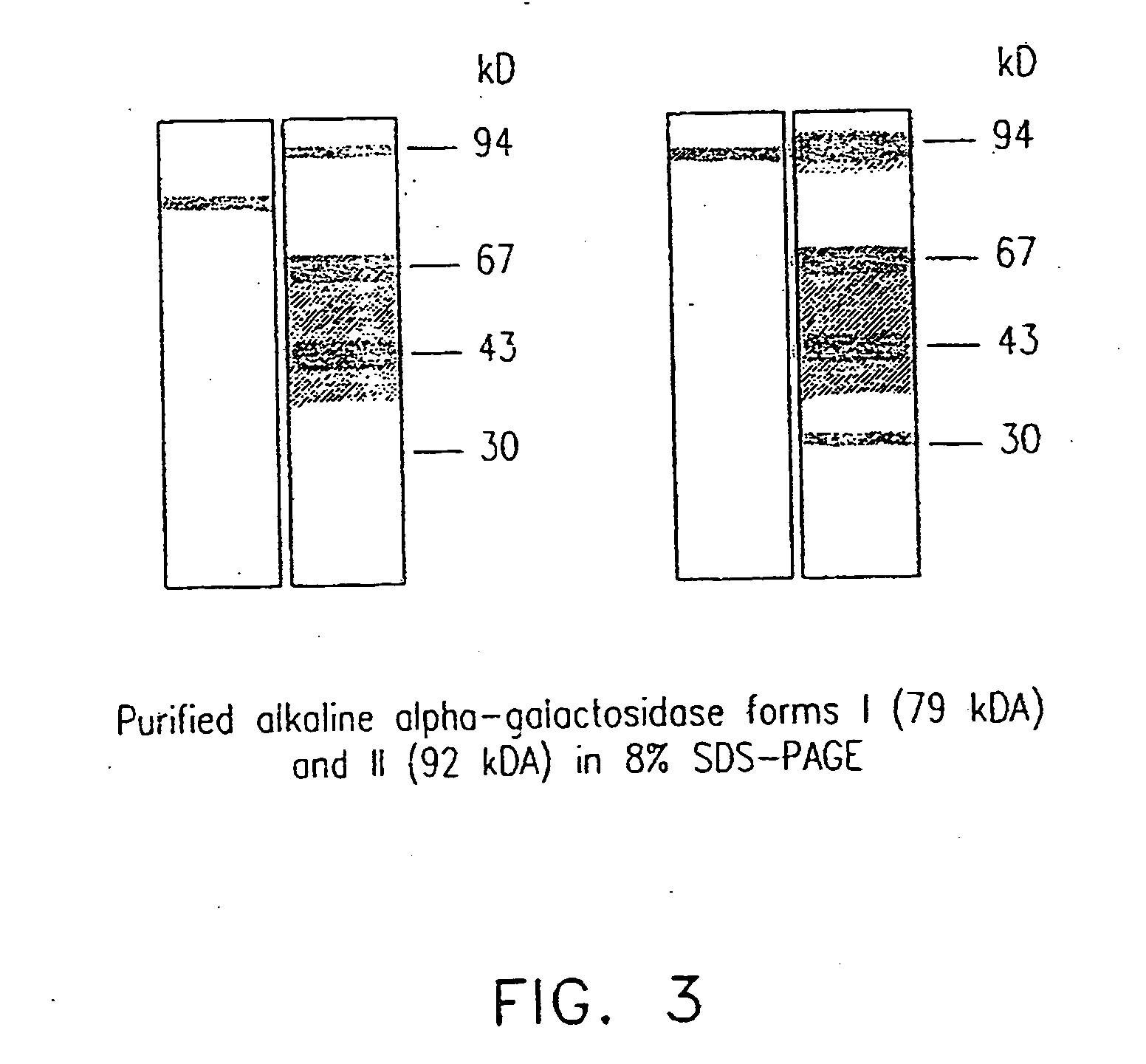
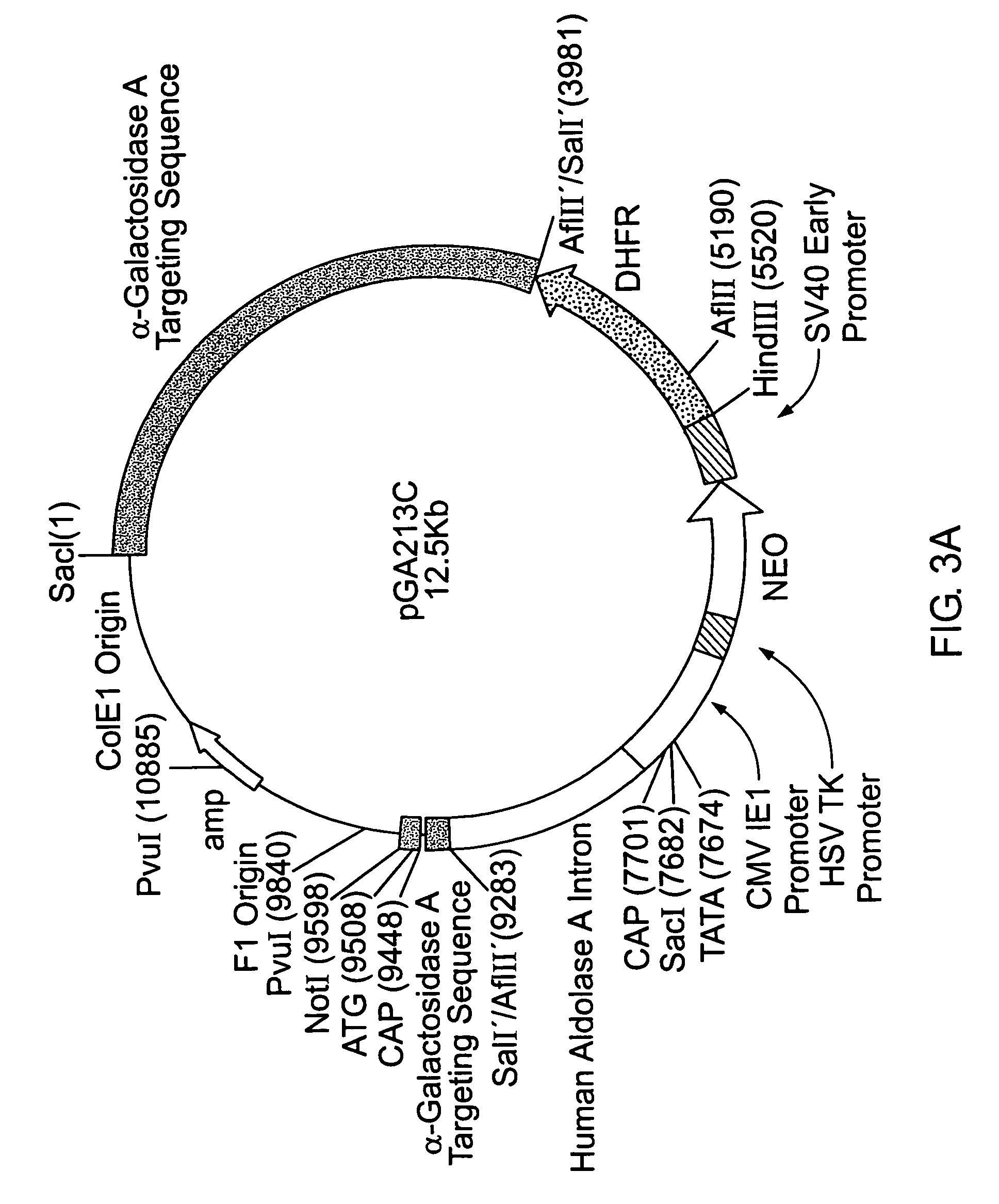
Plant-derived alkaline alpha-galactosidase
InactiveUS20070036883A1Hydrolyze raffinosePromote crystallizationMilk preparationPeptide/protein ingredientsLactoseSugar
There are provided novel plant-derived enzymes for hydrolysis of sugars and particularly an alkaline alpha-galactosidase which hydrolyzes a broad spectrum of galactosyl-saccharides such as melibiose, raffinose and stachyose and guar gum, at neutral to alkaline pH conditions.
Owner:STATE OF ISRAEL MINIST OF AGRI & RURAL DEV AGRI RES ORG (A R O) (VOLCANI CENT)
Treatment of α-galactosidase A deficiency
InactiveUS7833742B2Minimize frequencyCost-effectiveNervous disorderMammal material medical ingredientsΑ galactosidase aEndocrinology
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
High-quality enzymolysis-fermented bean pulp as well as preparation method and application thereof
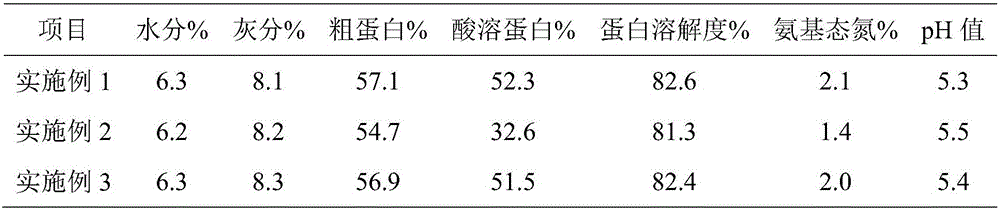
ActiveCN106615672AImprove digestibilityImprove palatabilityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffAntigenMetabolite
The invention relates to a high-quality enzymolysis-fermented bean pulp as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of crushing peeled bean pulp, sieving by virtue of an 80-mesh sieve, carrying out primary enzymolysis by virtue of alpha-galactosidase and glucoamylase, carrying out secondary enzymolysis by virtue of papain, carrying out enzyme deactivation, inoculating a compound strain of saccharomycetes, bacillus and lactic acid bacteria, sequentially carrying out aerobic fermentation and anaerobic fermentation to obtain a finished product, and carrying out spray drying on the finished product, so as to preserve active components to the greatest extent. The prepared enzymolysis-fermented bean pulp has the special fermentation flavor, the protein content is about 55%, the acid soluble protein content is more than 50%, antinutritional factors such as antigens are fundamentally eliminated, the components are stable, and the enzymolysis-fermented bean pulp has the characteristics of strong hydrophily, high water holding ratio and strong palatability and has an obviously food calling effect on aquatic animals; and the enzymolysis-fermented bean pulp is rich in functional small peptides, probiotics and metabolite of the probiotics, beneficial to the nutrient balance of intestinal tract of bred animals and is suitable for being added into feeds of piglets, poultries, pets, aquatic products and the like, the problem of trophic diarherra of the animals is solved, and the suggested use ratio is 2%-5%.
Owner:岳阳市展翔生物科技有限公司
Mutant lactobacillus bulgaricus strains free from beta-galactosidase activity
InactiveUS20050196388A1Increase capacityReduced post-acidificationBiocideMilk preparationBiotechnologyBeta-galactosidase activity
The invention concerns mutant L. bulgaricus strains bearing a nonsense mutation, in at least one of the sequences coding for the lactose operon, and free from β-galactosidase activity, and lactic starters comprising these strains. The strains and starters can be used to obtain fermented milk products from glucose-added milk.
Owner:DANONE
Enzyme isolated from a Bifidobacterium
InactiveUS7081355B2High transgalactosylatingImprove scalabilityFungiBacteriaBifidobacteriumDairy industry
The present invention concerns a new β-galactosidase with transgalactosylating activity isolated from Bifidobacterium bifidum and a truncated enzyme where the C-terminal end of the β-galactosidase protein has been deleted, resulting in an enzyme with a higher transgalactosylating activity than hydrolase activity. When lactose is used as a substrate, galacto-oligosaccharides are products of the transgalactosylase activity. Galacto-oligosaccharides enhance growth of health-promoting Bifidobacterium that may be used in a number of applications in the dairy industry.
Owner:ARLA FOODS AMBA
Blood cells having modified antigenicity
InactiveUS20050208655A1BacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementKinetic constantWhole blood product
This invention relates to enzymatic removal of type A and B antigens from blood group A, B, and AB reactive cells in blood products, and thereby converting these to non-A and non-B reactive cells. The invention further relates to using unique alpha N-acetylgalactosaminidases and alpha-galactosidases with superior kinetic properties for removing the immunodominant monosaccharides of the blood group A and B antigens and improved performance in enzymatic conversion of red blood cells. The preferred unique alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidases and alpha-galactosidases exhibit the following characteristics: (i) exclusive, preferred or no less than 10% substrate specificity for the type A and B branched polysaccharide structures relative to measurable activity with simple mono- and disaccharide structures and aglycon derivatives hereof; (ii) optimal performance at neutral pH with blood group oligosaccharides and in enzymatic conversion of cells; and (iii) a favorable kinetic constant Km with mono- and oligosaccharide substrates. The conversion methods of the invention use significantly lower amounts of recombinant glycosidase enzymes than previous and result in complete sero-conversion of all blood group A and B red cells.
Owner:ZYMEQUEST
Flavor enhancement semi-fermented fleece-flower root leaf tea and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103815102AReduce bitternessFacilitated releaseTea substituesCooking & bakingNutritive values
The invention discloses a flavor enhancement semi-fermented fleece-flower root leaf tea which is prepared by the following steps: (1) picking fresh leaves; (2) withering; (3) rocking of green leaves; (4) treating by exogenous enzyme for comprehensive flavor enhancement; (5) debitterizing and killing out; (6) mass rubbing; (7) baking by gross fire; (8) packed rolling; (9) baking by full fire; (10) drying. According to the preparation method of the flavor enhancement semi-fermented fleece-flower root leaf tea, galactosidase and water soluble chitosan are used for carrying out exogenous enzyme treatment on the fleece-flower root leaves for comprehensive flavor enhancement, so that the content of aromatic substances can be increased, and the free aroma can be locked on the leaves by the subsequent drying process so as to be avoided running away; the obtained flavor enhancement semi-fermented fleece-flower root leaf tea has the advantages of being green in color, elegant in flavor and durable in soaking, has very high nutritive value, medicinal value and health care effect, and is clear and elegant in mouthfeel; therefore, the flavor enhancement semi-fermented fleece-flower root leaf tea is a new semi-fermented tea, has very good application prospect, and has the advantages of being simple in preparation method, affordable and stable in product quality.
Owner:HUAINAN DONGSHEN AGRI PLANTING TECHCO
Chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7
ActiveCN102424832AHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyThio-
The invention discloses a chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7. The medium comprises agar, peptone, beef extract powder, sodium chloride, sorbitol, inositol, neutral red, beta-galactosidase chromogenic substrate, beta-glucuronidase chromogenic substrate, isopropyl-beta-D- thiogalactopyranoside, natrium taurocholicum, potassium tellurite and cefixime. The chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7 of the present invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity, direct bacterial strain discrimination according to colony color, short detection period and strong operationality, is suitable for treating high-reflux samples, is capable of comprehensively, systematically and accurately detecting and preliminarily identifying the esherichia coli O157:H7 in food production and environment, and provides a novel approach for rapidly detecting the microbes.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUANKAI MICROBIAL SCI & TECH
Cloning, expression and application of a β-glucosidase gene
ActiveCN102268421AImprove securityThe follow-up processing process is convenientFungiMicroorganism based processesBeta-glucosidaseHigh activity
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to a beta-glucosaccharase which can decompose lactose and has high activity under both high-temperature and low-temperature conditions, and a gene engineering bacterium capable of efficiently expressing secretion-type beta-glucosaccharase. The invention discloses a beta-glucosaccharase having an amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2, and constructs a gene engineering bacterium capable of efficiently secreting the beta-glucosaccharase. The gene engineering bacterium is collected in Common Microorganism Center of Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, and the collection number is CGMCC No.4891. The beta-glucosaccharase produced by the method disclosed by the invention has high activity of galactosidase, and can be applied to dairy industry; and meanwhile, the beta-glucosaccharase has stable activity within wide pH value range and temperature range.
Owner:山西恩泽生物技术有限公司
Fluorescence probe for detecting beta-galactosidase as well as preparation method and application of fluorescence probe
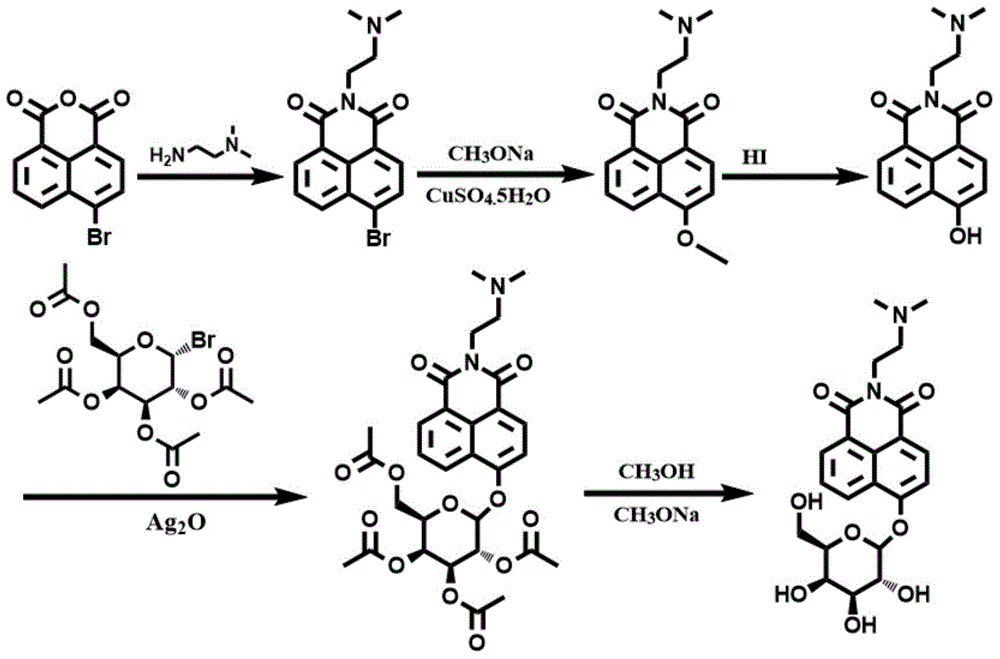
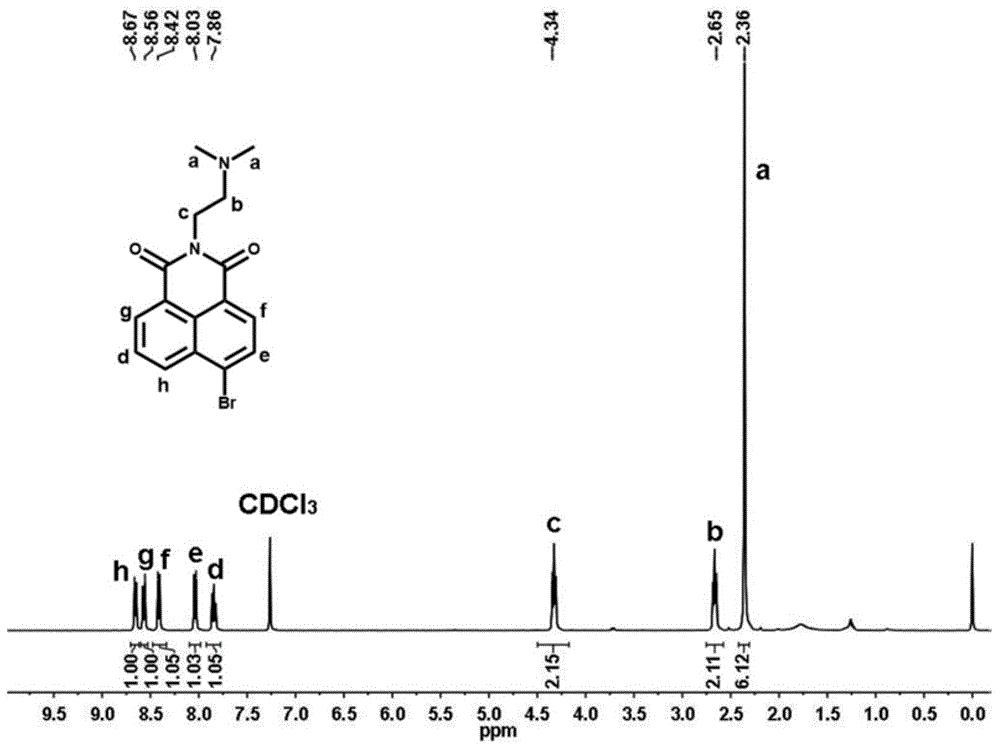
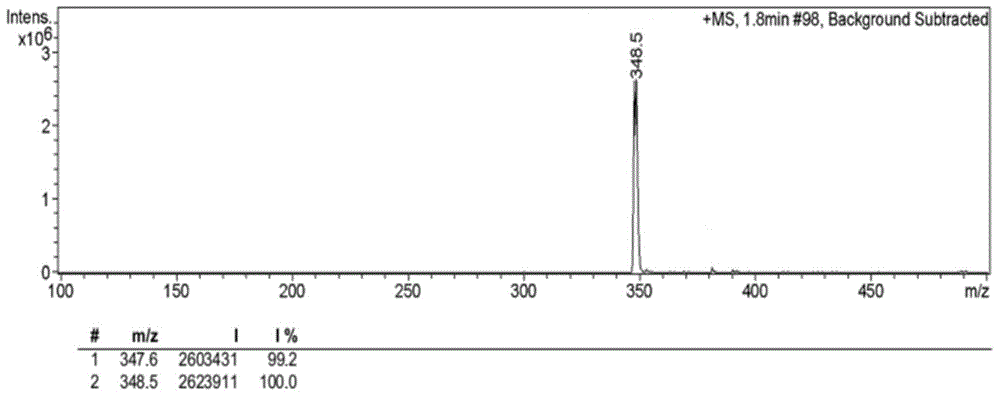
InactiveCN104946242AImprove detection accuracyHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesEthyl group
The invention belongs to the technical field of analysis and detection, and discloses a fluorescence probe for detecting beta-galactosidase as well as a preparation method and application of the fluorescence probe. The substrate of the fluorescence probe is 2-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl-6-(((3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxidation)-1H-benzisoquinoline diketone, and has a structural formula shown in the description. The fluorescence probe has the advantages that naphthalic anhydride is taken as a fluorophore of the substrate of the fluorescence probe, and lined with a galactose group which can respond to the specificity of beta-galactosidase; the ratio of double fluorescence signals being I554 / I445 is taken as a detection signal, and thus the detection accuracy is higher; under the condition of 1U / L enzyme concentration, obvious fluorescence alteration can be detected, and the lower detection limit is 0.35 U / L; the fluorescence probe is excited (418 nm) in a visible light region, so that the background interference can be eliminated to achieve a better detection effect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com