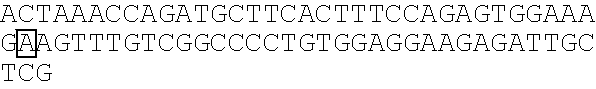Patents
Literature
81 results about "Nonsense mutation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
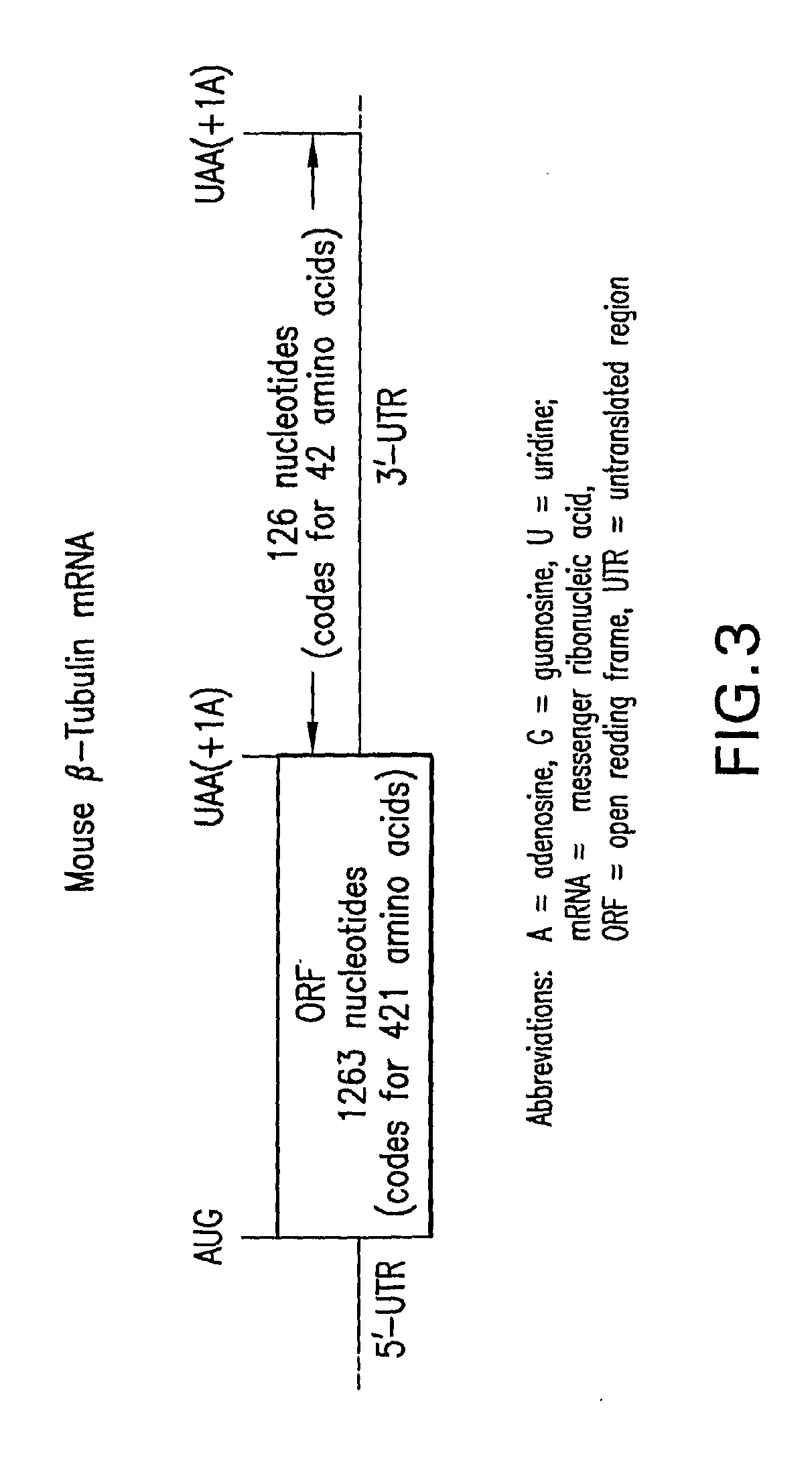
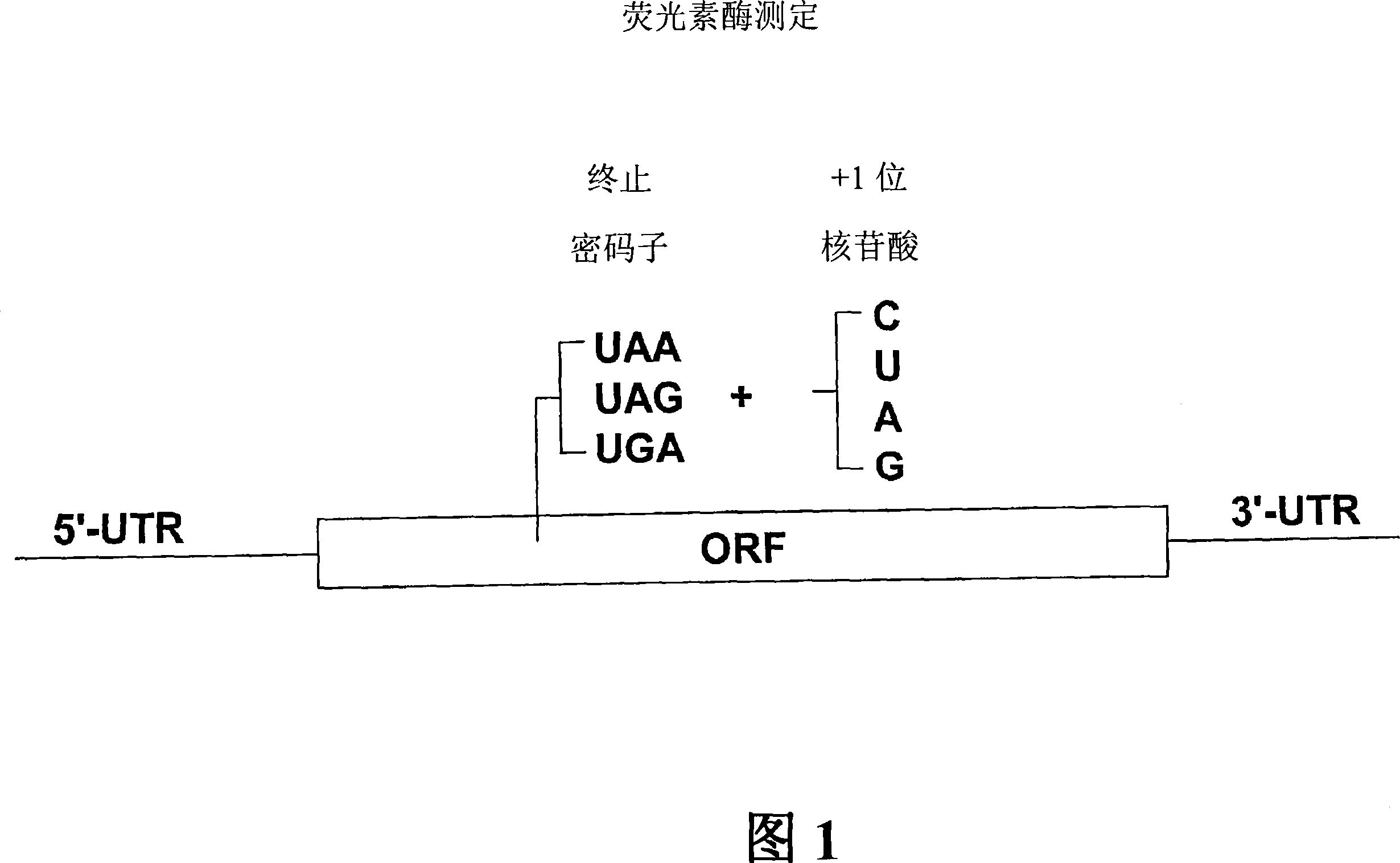
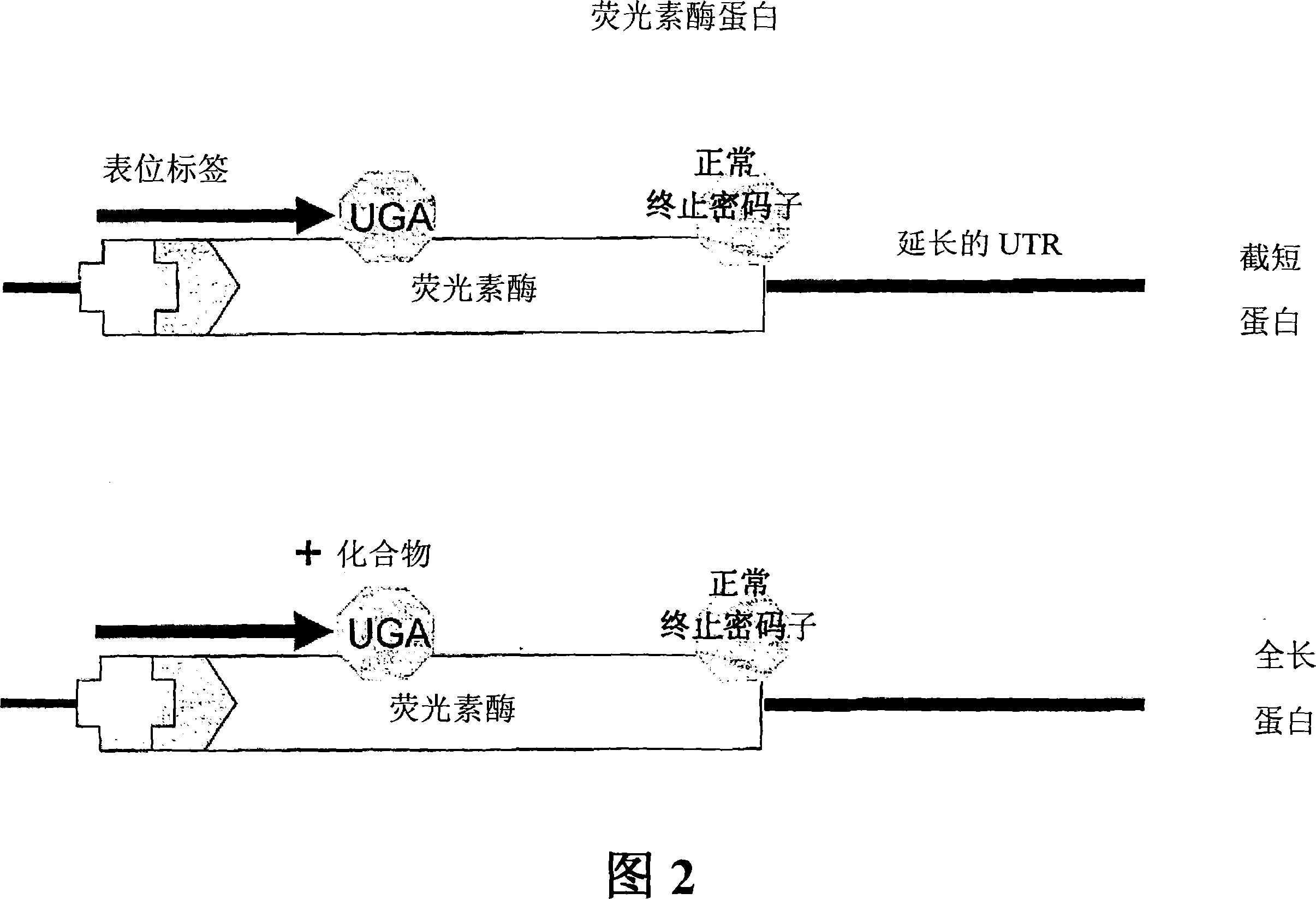
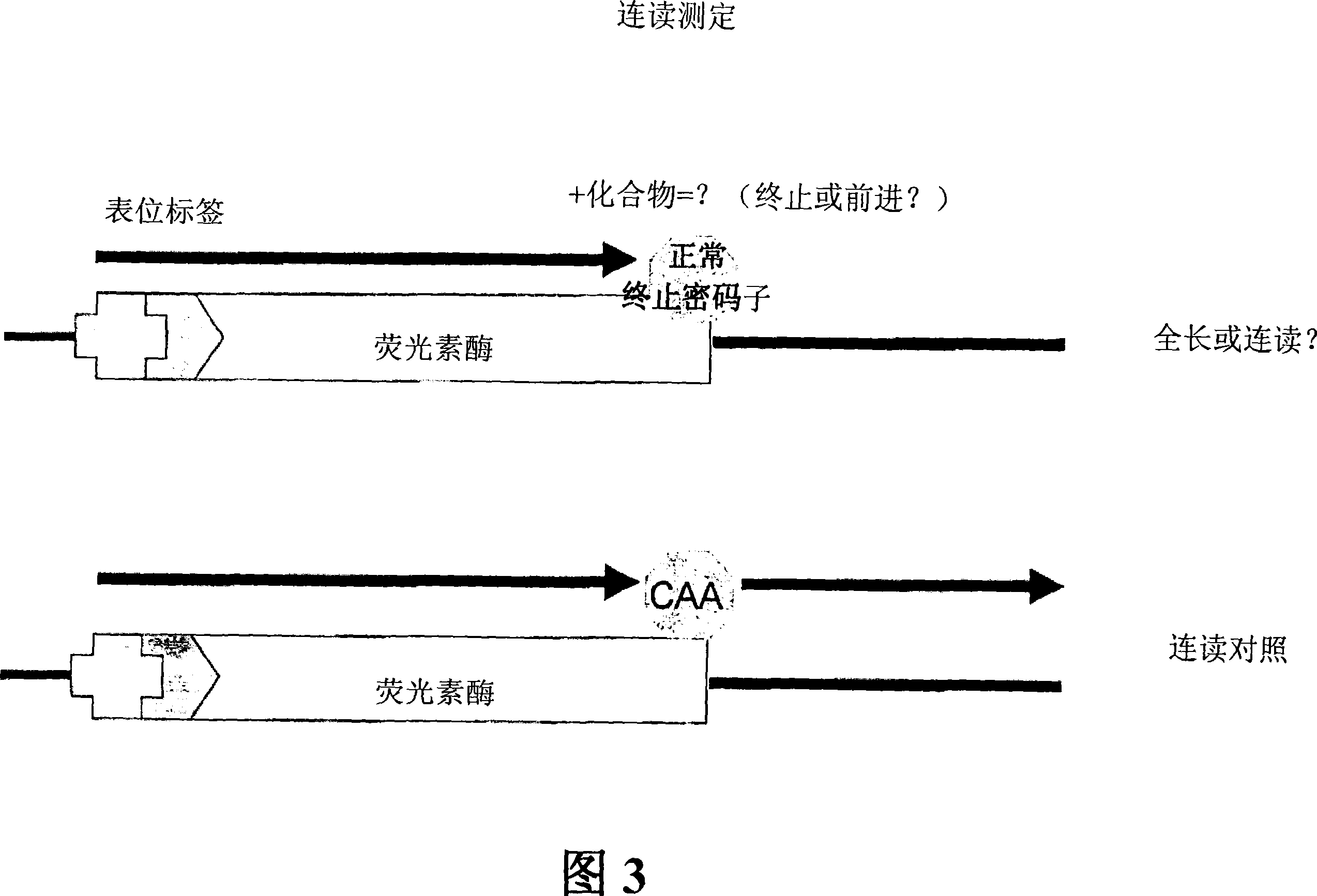
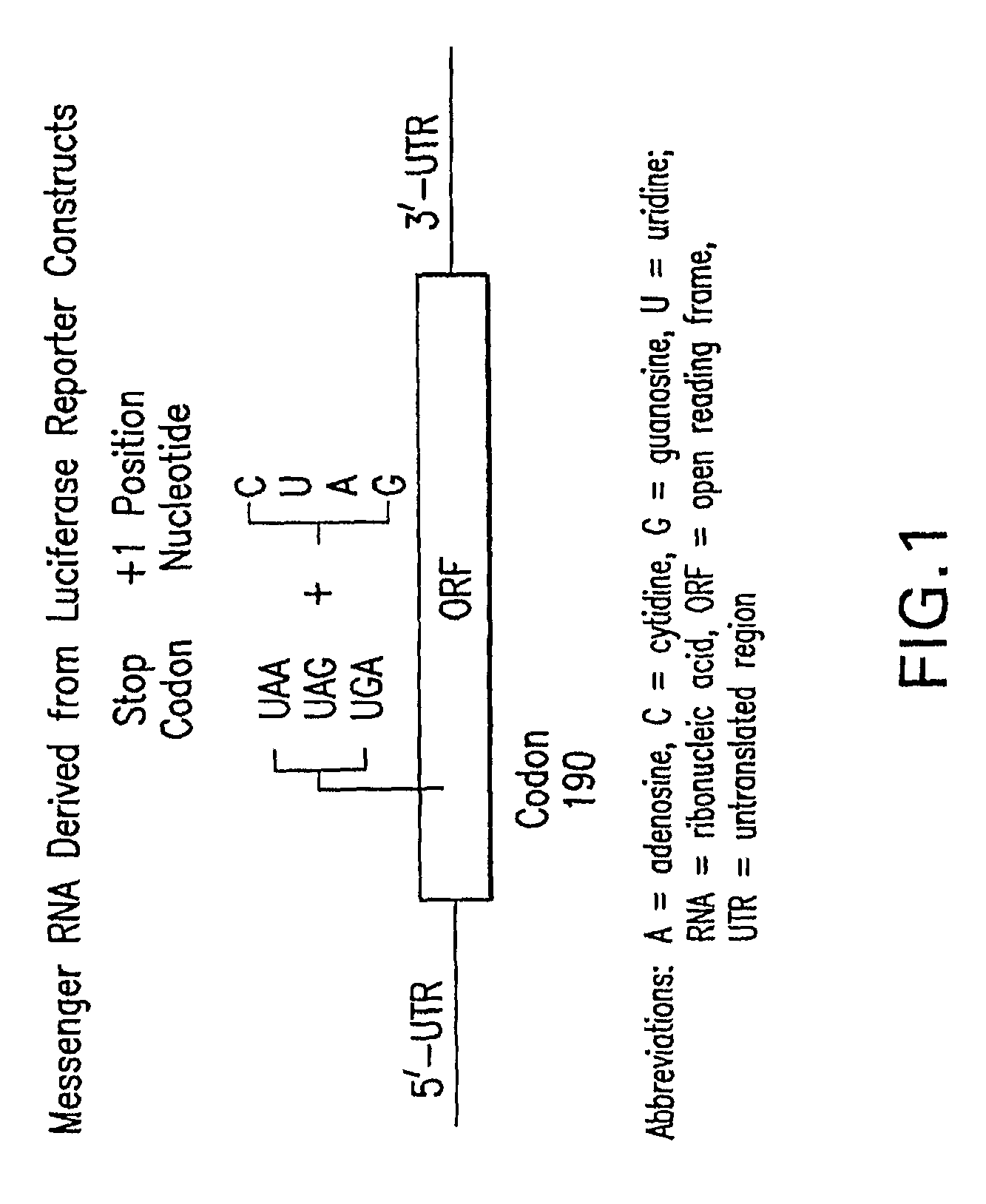
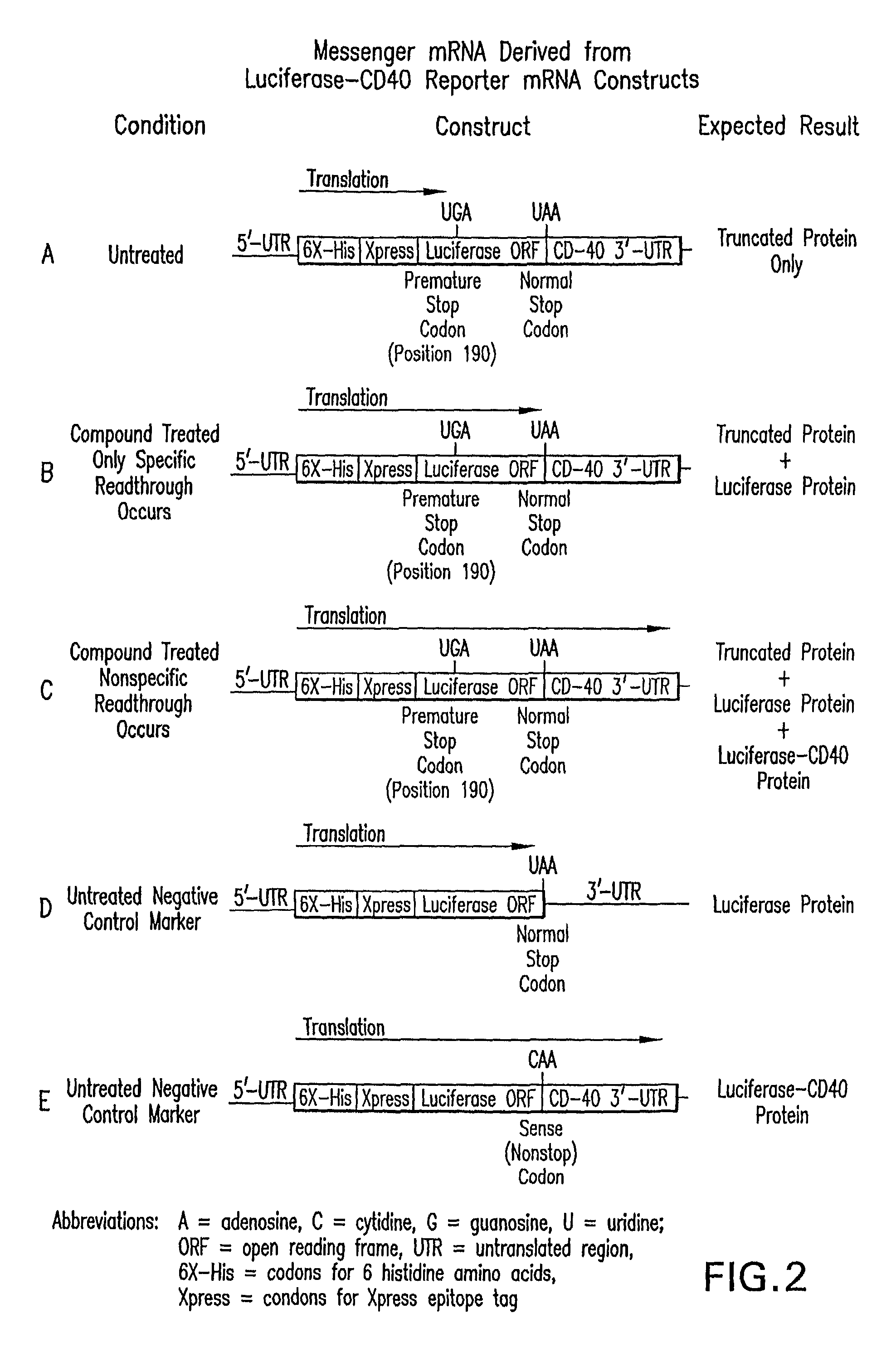
In genetics, a point-nonsense mutation is a point mutation in a sequence of DNA that results in a premature stop codon, or a point-nonsense codon in the transcribed mRNA, and in a truncated, incomplete, and usually nonfunctional protein product. The functional effect of a point-nonsense mutation depends on the location of the stop codon within the coding DNA. For example, the effect of a point-nonsense mutation depends on the proximity of the point-nonsense mutation to the original stop codon, and the degree to which functional subdomains of the protein are affected. A point-nonsense mutation differs from a missense mutation, which is a point mutation where a single nucleotide is changed to cause substitution of a different amino acid. Some genetic disorders, such as thalassemia and DMD, result from point-nonsense mutations.
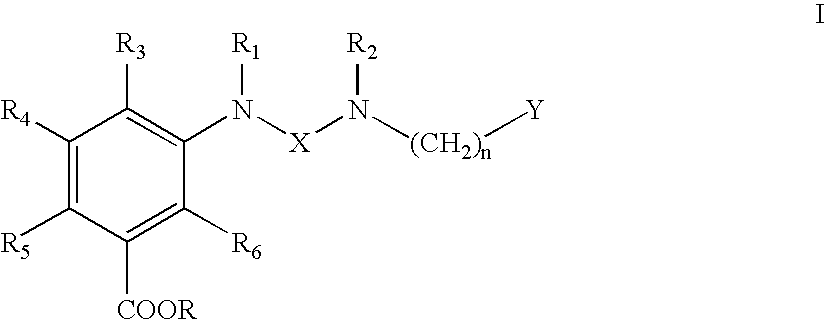
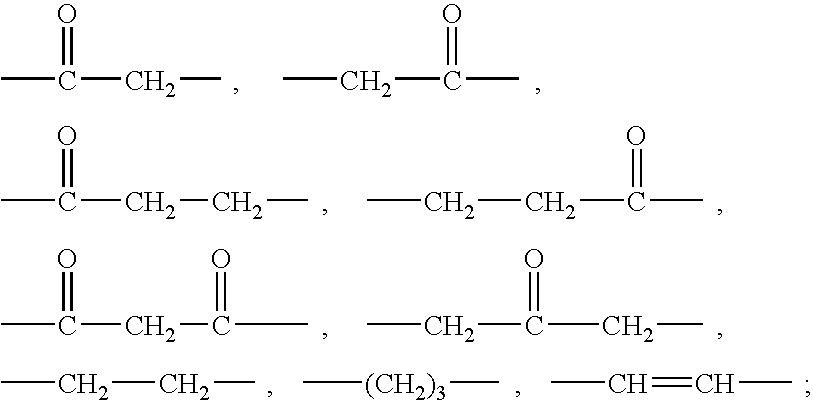
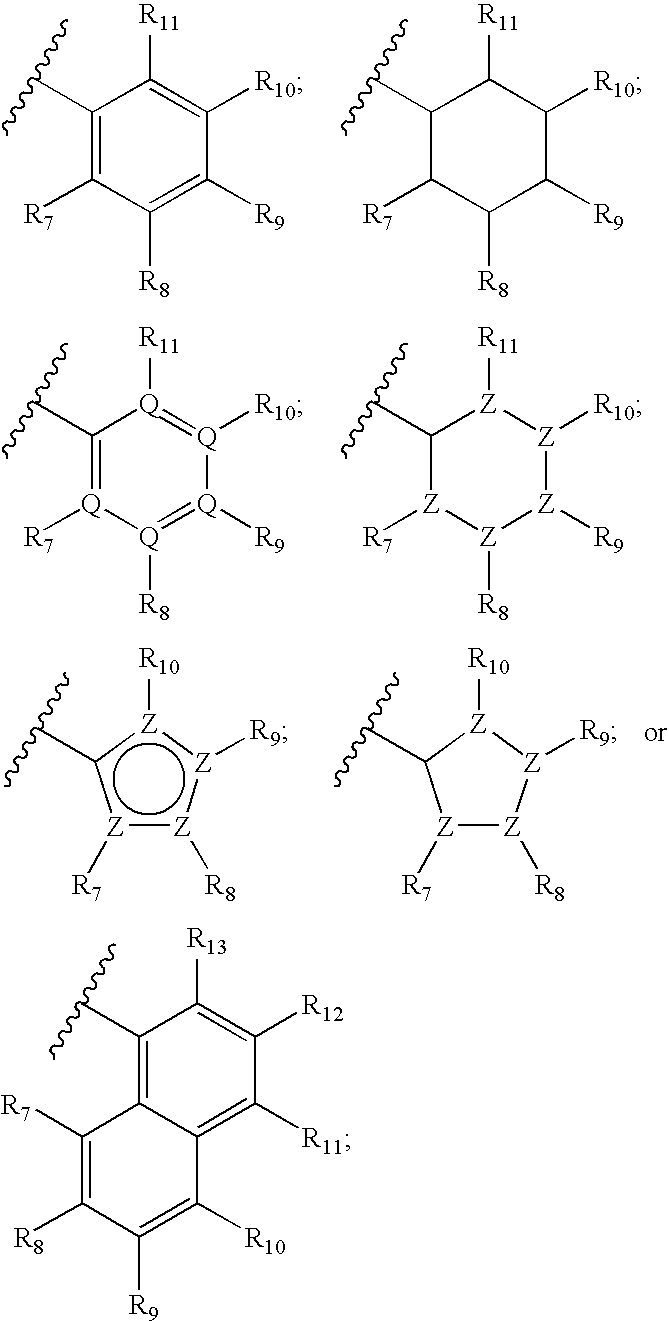
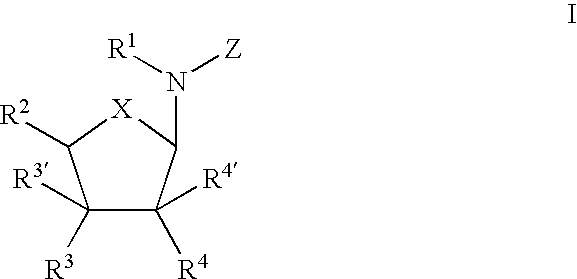
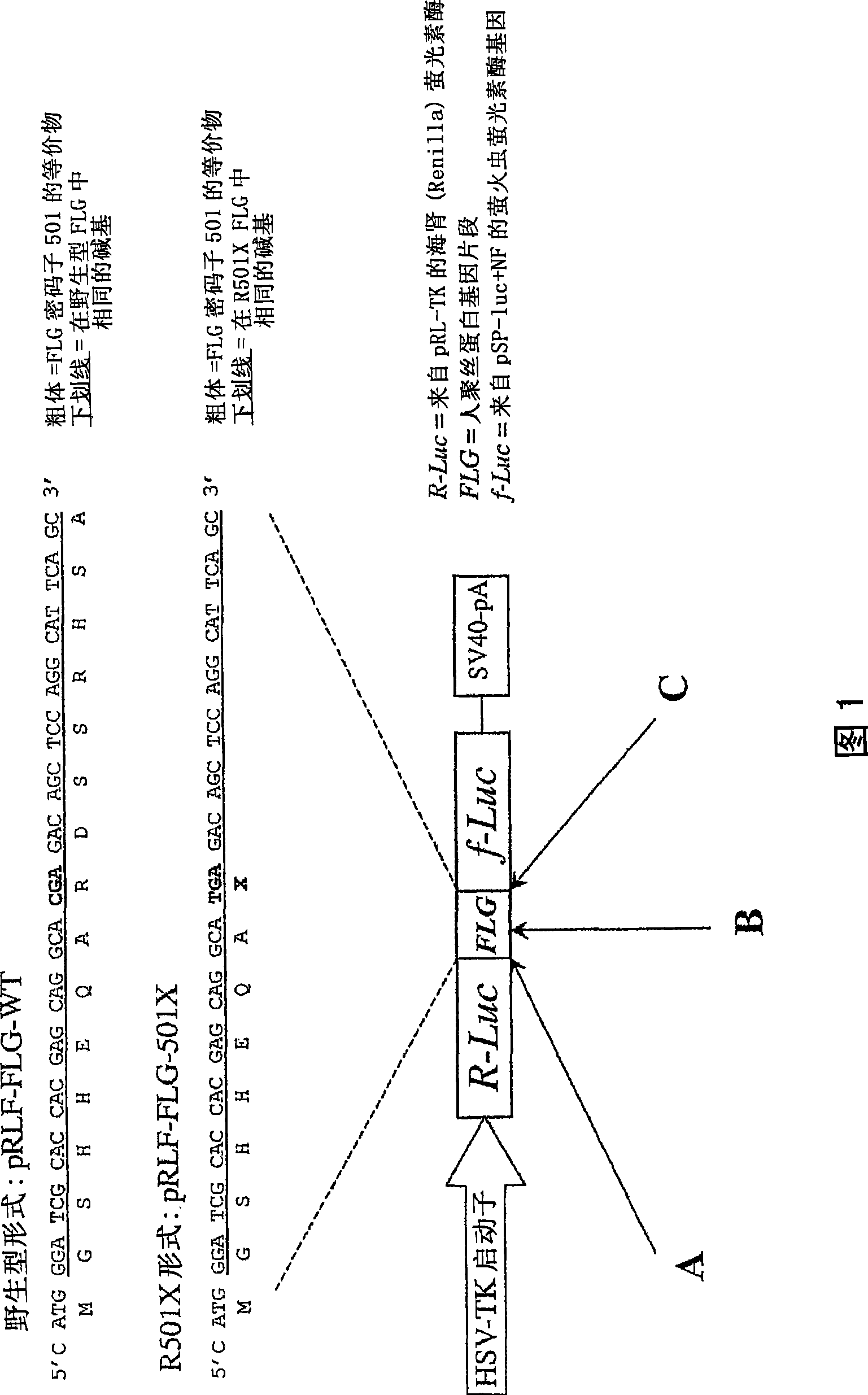
Ureido substituted benzoic acid compounds and their use for nonsense suppression and the treatment of disease
ActiveUS7405233B2Decreased amount of producedPromote readthrough of stop codonsAntibacterial agentsBiocideBenzoic acidDisease
The invention encompasses ureido substituted benzoic acid compounds, compositions comprising the compounds and methods for treating or preventing diseases associated with nonsense mutations of mRNA by administering these compounds or compositions.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Nonsense suppressor agents in treatment of cutaneous and gastrointestinal disorders
InactiveUS20050261210A1Suppresses genetic basisAdverse side-effectBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsDiseaseSuppressor
The invention features methods of treating a inherited or acquired cutaneous or gastrointestinal (GI) disorder caused by or having a symptom caused by a nonsense mutation by local administration of a nonsense suppressor agent (e.g., an aminoglycoside or nucleic acid encoding a suppressor tRNA) to the skin or intraluminal GI surface so as to provide for phenotypic suppression of the nonsense mutation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Use of nucleoside compounds for nonsense suppression and the treatment of genetic diseases
ActiveUS20060166926A1Minimizing spreadMinimizing worseningBiocideNervous disorderDisease causeNonsense mutation
The invention encompasses nucleoside compounds, compositions comprising the compounds and methods for treating or preventing diseases associated with nonsense mutations of mRNA by administering these compounds or compositions.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Methods for the production of functional protein from DNA having a nonsense mutation and the treatment of disorders associcated therewith
InactiveUS20110046136A1Eliminate riskImprove the quality of lifeBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to functional proteins encoded by nucleic acid sequences comprising a nonsense mutation. The present invention also relates to methods for the production of functional proteins encoded by nucleic acid sequences comprising a nonsense mutation and the use of such proteins for prevention, management and / or treatment of diseases associated with a nonsense mutation(s) in a gene.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Agents for Treating Diseases Caused by Nonsense Mutations
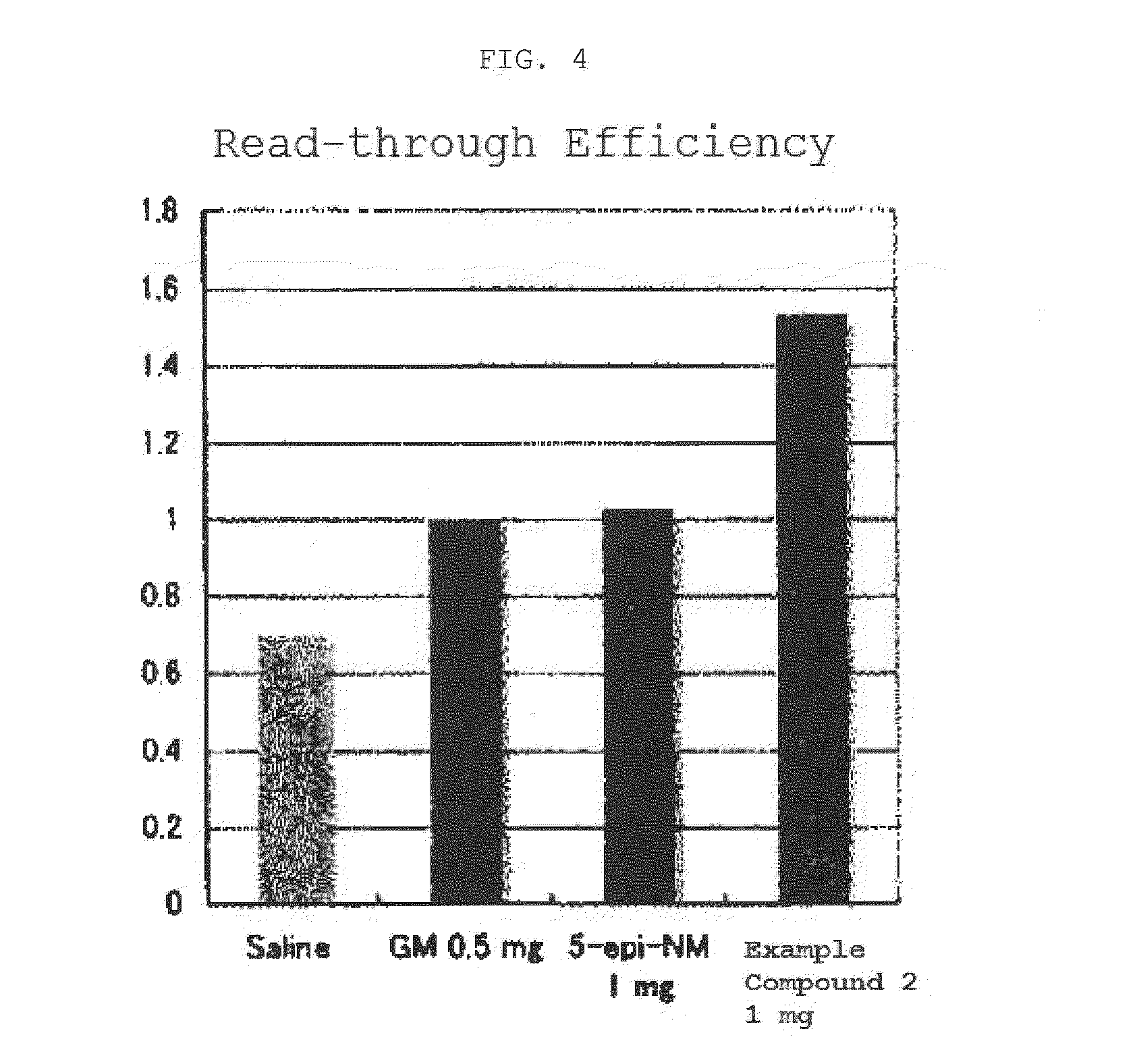
The present invention comprises compositions for treating diseases caused by nonsense mutations, including dipeptide antibiotics of Formula (I) shown below, such as negamycin. Unlike aminoglycoside antibiotics such as gentamicin, dipeptide antibiotics can induce the expression of mature proteins by readthrough nonsense mutations without generating serious side effects.
Owner:ARAKAWA MASAYUKI +1
Mutant lactobacillus bulgaricus strains free from beta-galactosidase activity
InactiveUS20050196388A1Increase capacityReduced post-acidificationBiocideMilk preparationBiotechnologyBeta-galactosidase activity
The invention concerns mutant L. bulgaricus strains bearing a nonsense mutation, in at least one of the sequences coding for the lactose operon, and free from β-galactosidase activity, and lactic starters comprising these strains. The strains and starters can be used to obtain fermented milk products from glucose-added milk.
Owner:DANONE
Nucleoside compounds and their use for treating cancer and diseases associated with somatic mutations
InactiveUS20040067900A1Promote readthroughDecreased amount of producedBiocideSugar derivativesDiseaseSomatic cell
The invention encompasses nucleoside compounds, compositions comprising the compounds and methods for treating or preventing diseases associated with nonsense mutations of mRNA by administering these compounds or compositions.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Pyrazole or triazole compounds and their use for the manufacture of a medicament for treating somatic mutation-related diseases
The present invention relates to methods, compounds, and compositions for treating or preventing diseases associated with nonsense mutations in an mRNA by administering the compounds or compositions of the present invention. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods, compounds, and compositions for suppressing premature translation termination associated with a nonsense mutation in an mRNA.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
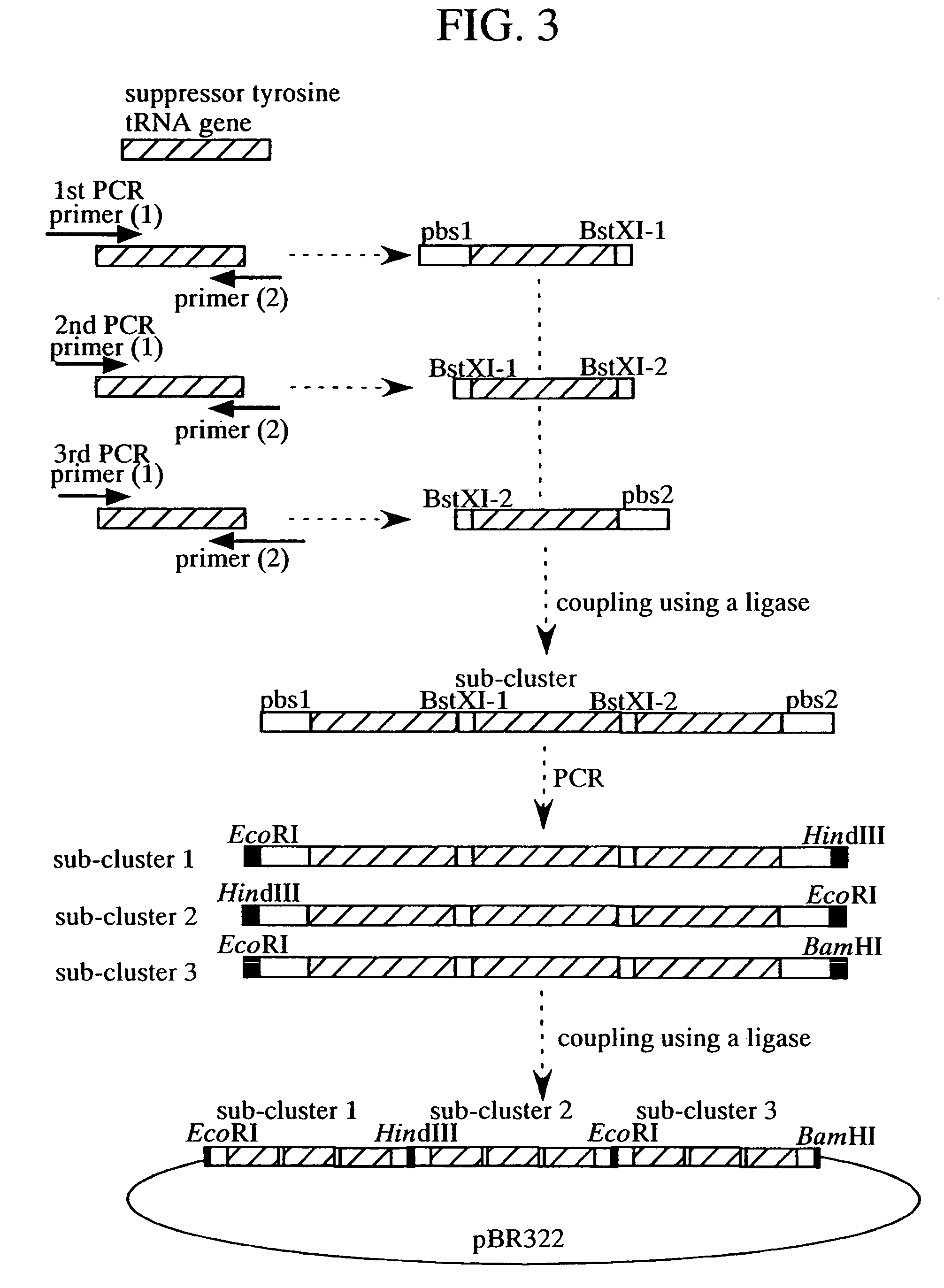
Method of expressing protein having unnatural amino acid integrated thereinto
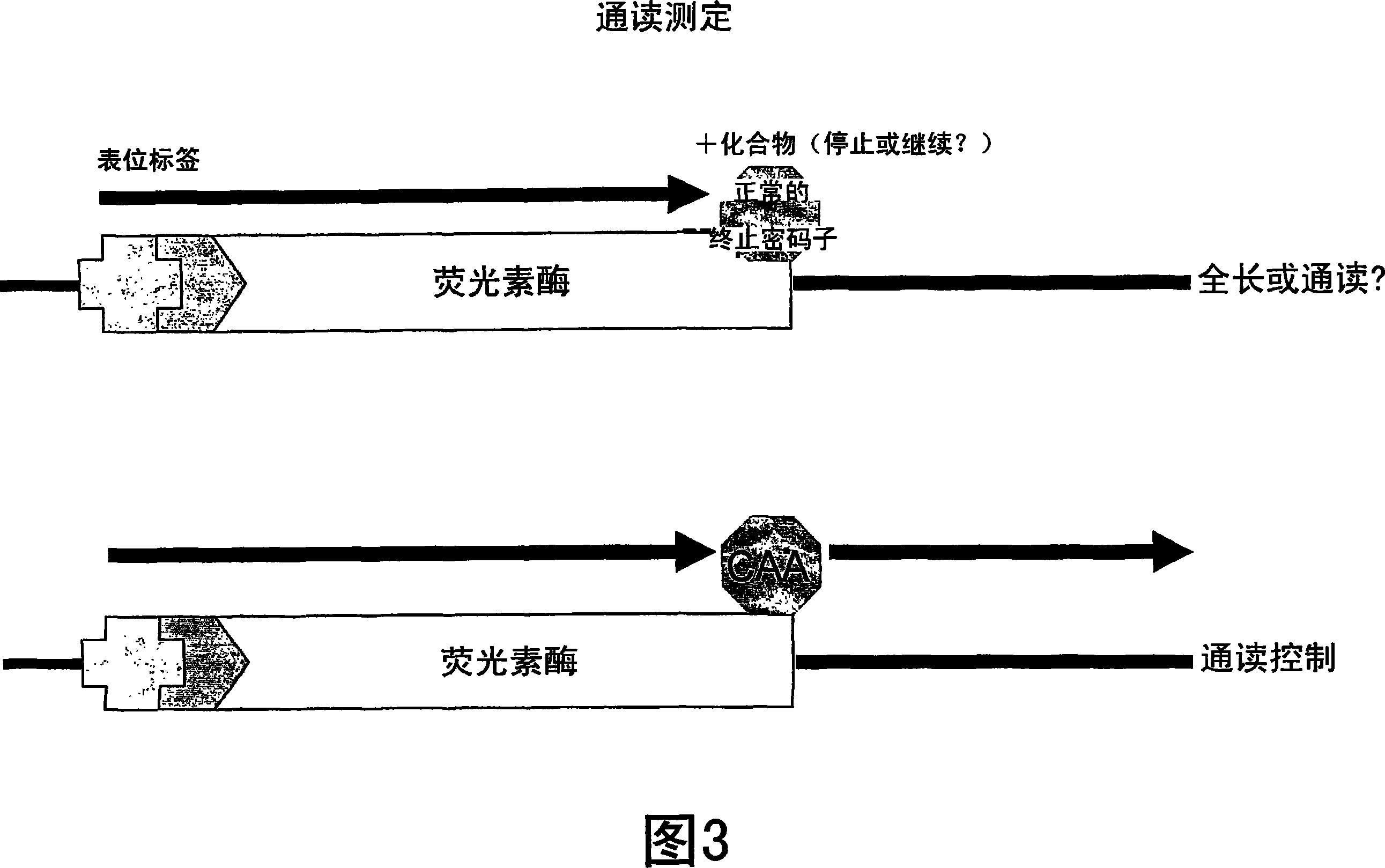
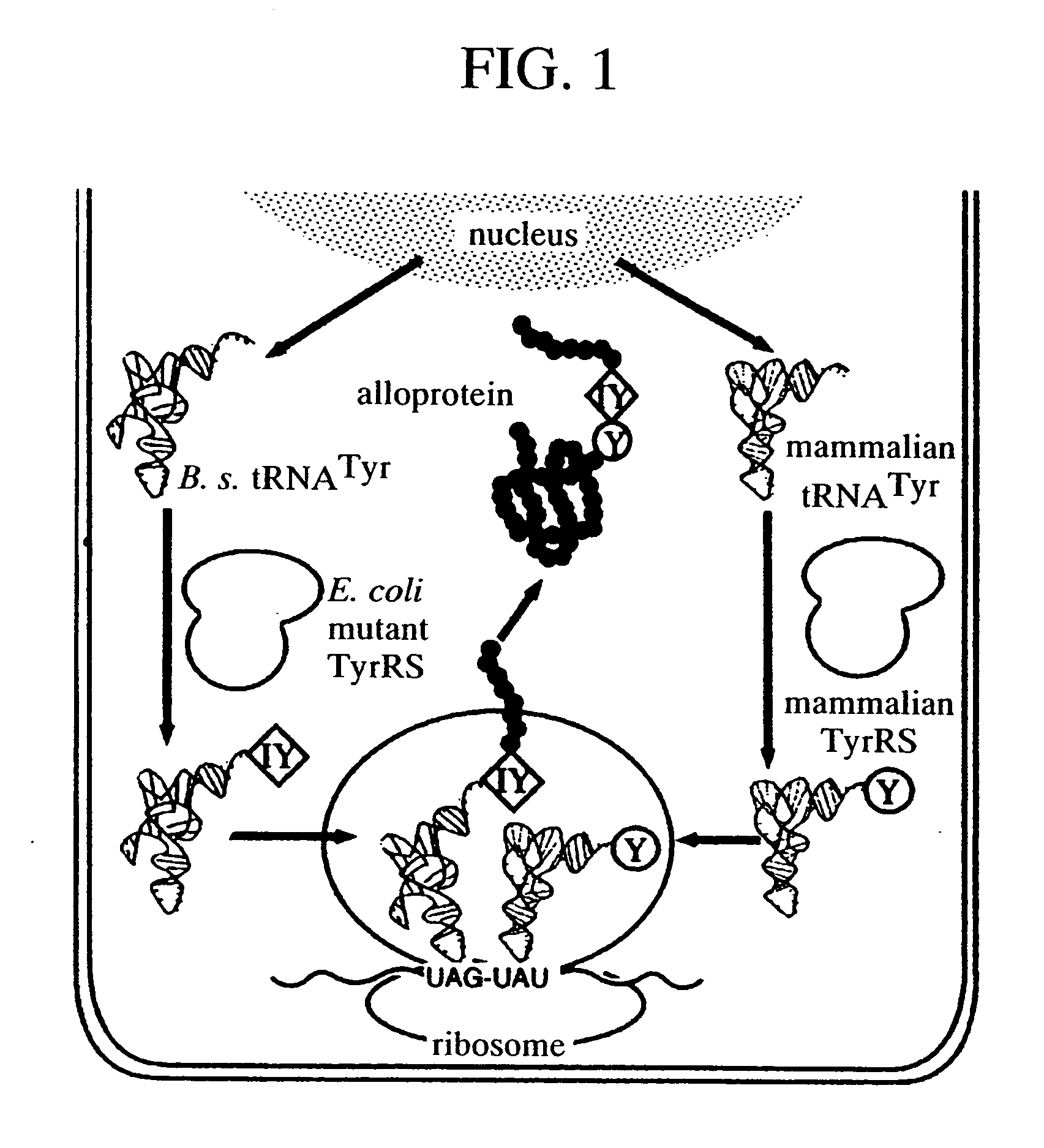
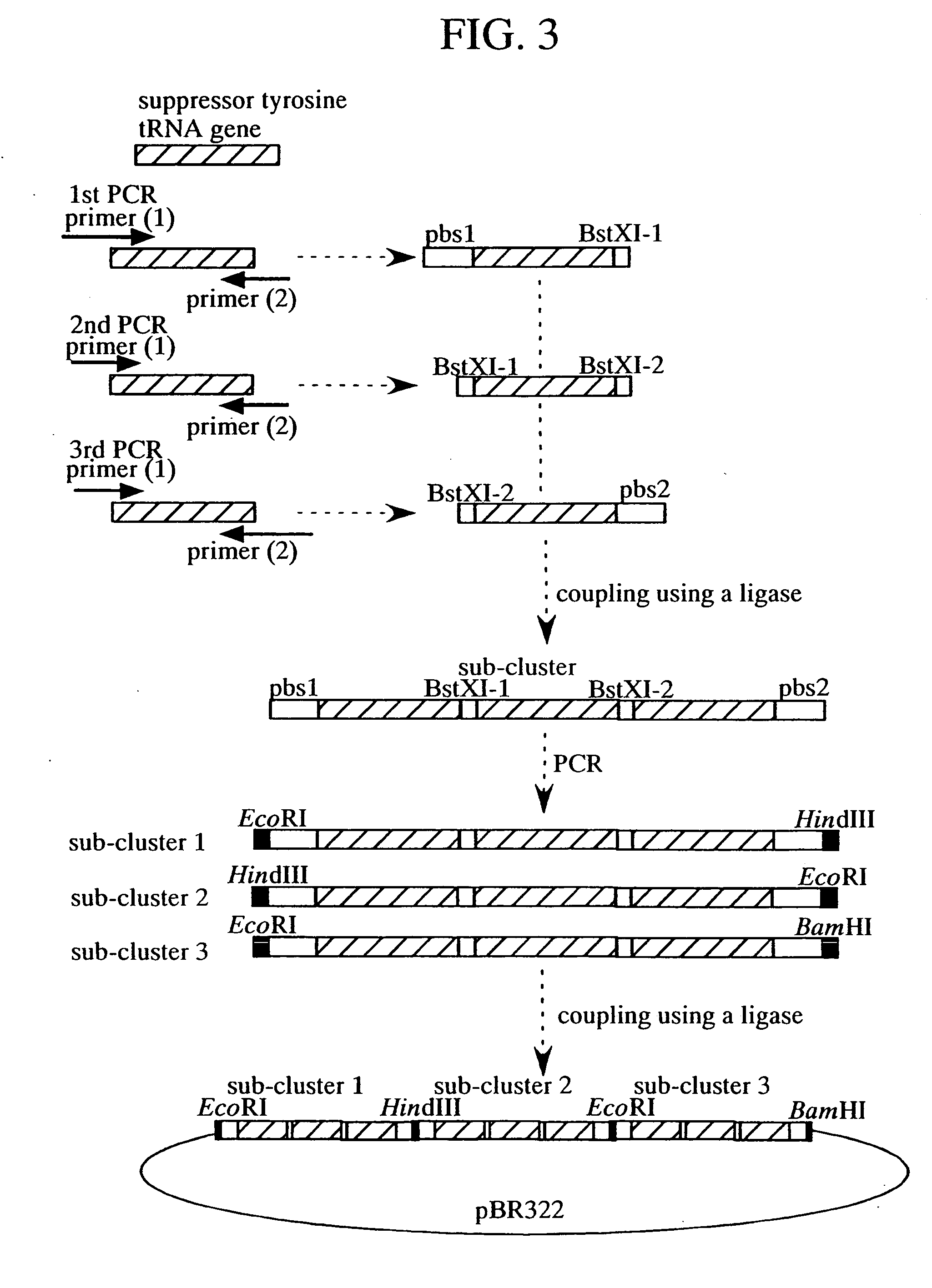
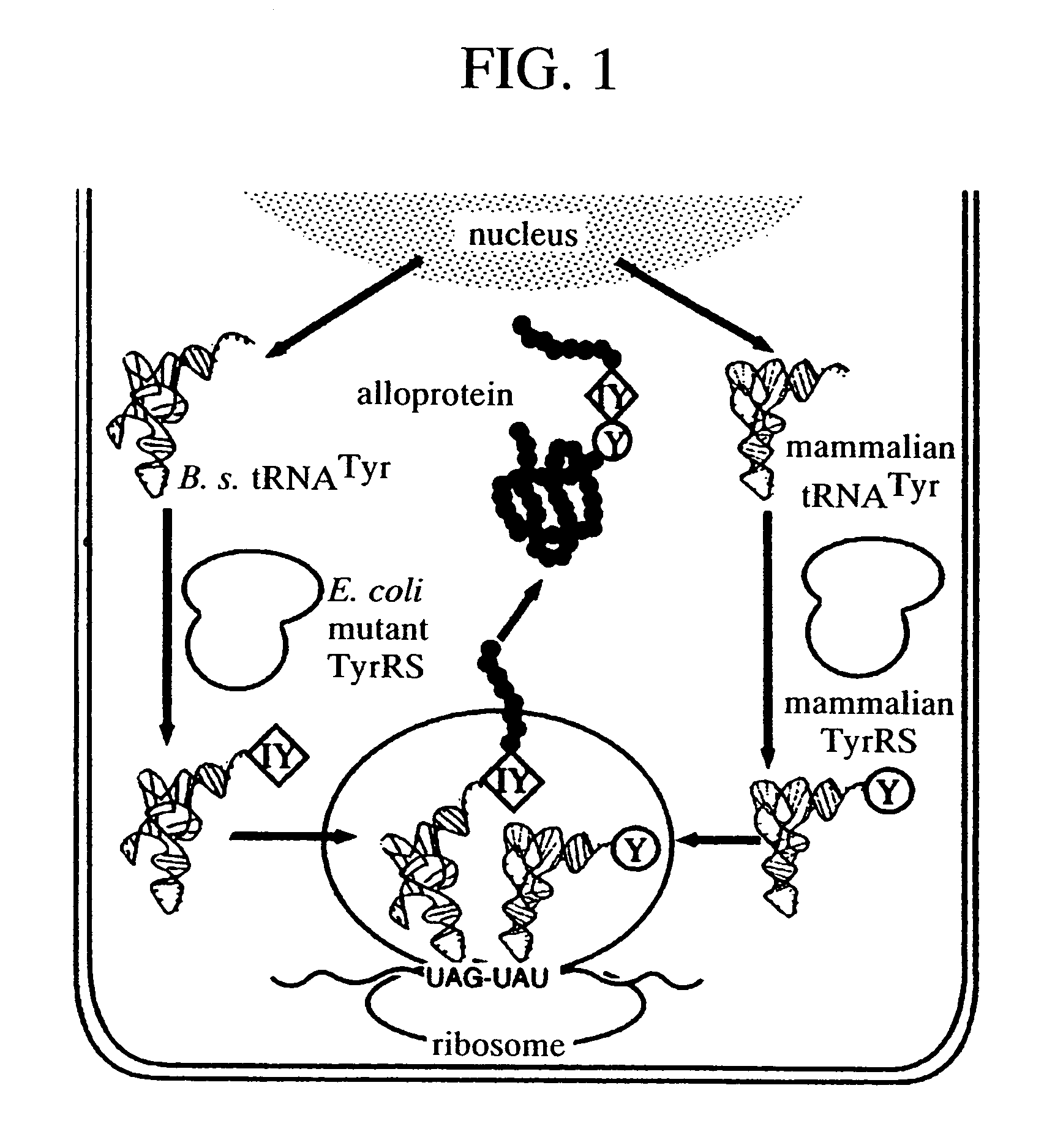
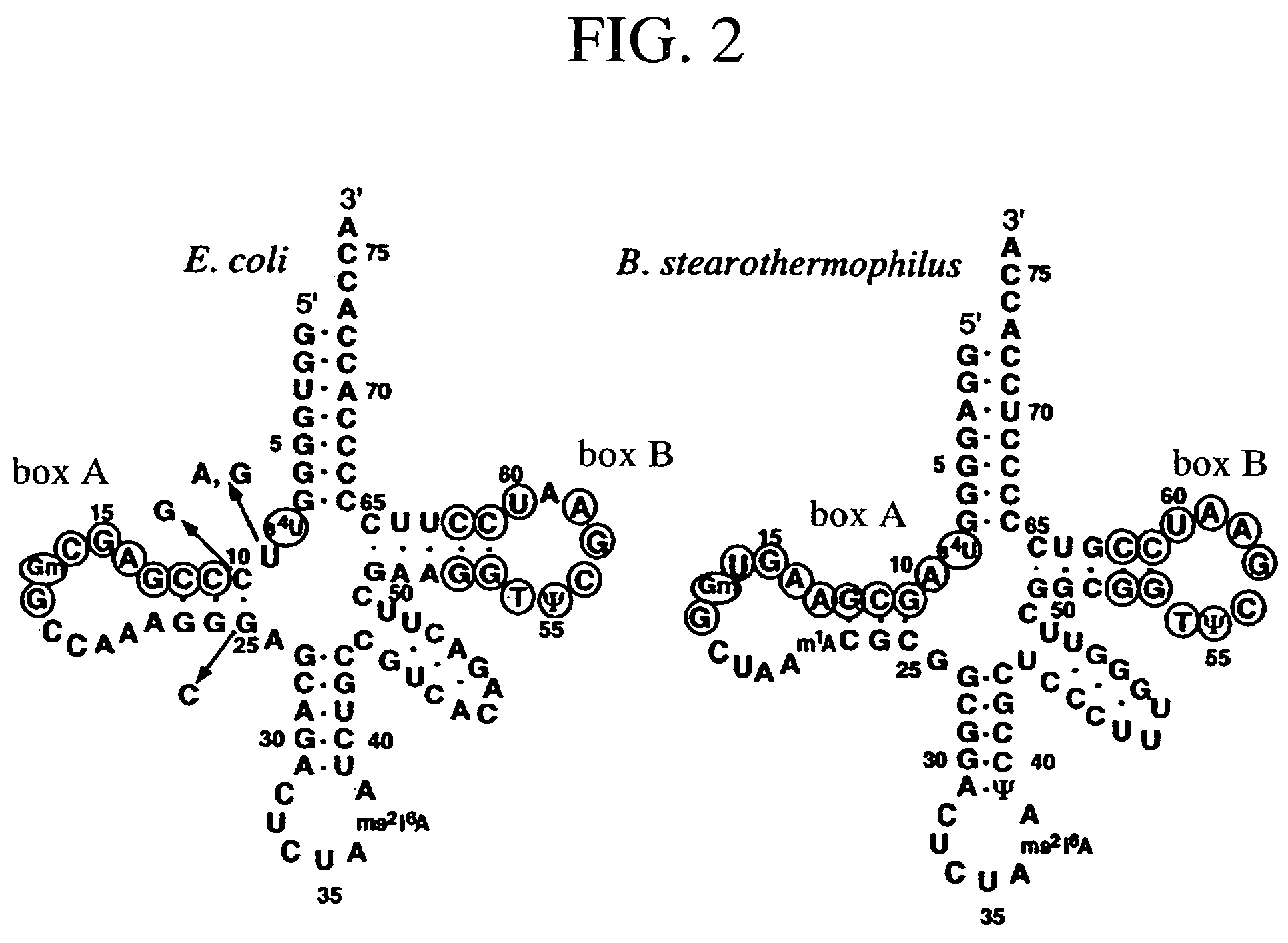
A method of expressing a protein having an unnatural amino acid integrated thereinto characterized by comprising expressing (A) a mutant tyrosyl tRNA synthase which is a mutant of Escherichia coli-origin tyrosyl tRNA synthase and has an elevated specificity for a unnatural tyrosine derivative compared with the specificity for tyrosine, (B) a suppressor tRNA originating in an eubacterium belonging to the genus Bacillus, Mycoplasma or Staphylococcus which is capable of binding to the above tyrosine derivative in the presence of the above mutant TyrRS, and (C) a desired protein gene having a nonsense mutation at a desired site in animal cells to thereby incorporate the above tyrosine derivative into the nonsense mutation site in the above protein.
Owner:RIKEN
Compounds and their use for treating somatic mutation-related diseases
The present invention relates to methods, compounds, and compositions for treating or preventing diseases associated with nonsense mutations in an mRNA by administering the compounds or compositions of the present invention. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods, compounds, and compositions for suppressing premature translation termination associated with a nonsense mutation in an mRNA.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
I type neurofibroma NF1 gene mutation nucleotide sequence related to cerebrovascular stenosis and application thereof
InactiveCN103045605AAt risk for cerebrovascular stenosisFungiBacteriaNormal peopleNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to an I type neurofibroma NF1 gene mutation nucleotide sequence related to cerebrovascular stenosis and application thereof. Compared with a corresponding nucleotide sequence contained in NF1, the nucleotide sequence related to cerebrovascular stenosis, which is disclosed by the invention, is mutated at the following position: c.541C>T; the mutation position is started from a first base in a gene coding region of NF1; and the mutation causes a patient to suffer from cerebrovascular stenosis. Research finds that the nonsense mutation exists in all NF1 family patients suffering from cerebrovascular stenosis, but does not exist in normal people in the NF1 family. The mutational site can provide basis for establishing a similar clinical symptom cerebrovascular stenosis animal model and is further used for carrying out super early diagnosis and prevention on the sporadic potential cerebrovascular stenosis of NF1 patients.
Owner:XUANWU HOSPITAL OF CAPITAL UNIV OF MEDICAL SCI
Method of expressing proteins comprising non-naturally-occurring amino acids
A method of expressing a protein having an unnatural amino acid integrated thereinto comprising expressing (A) a mutant tyrosyl tRNA synthase that is derived from Escherichia coli-origin tyrosyl tRNA synthase and has an elevated specificity for an unnatural tyrosine derivative compared with the specificity for tyrosine, (B) a suppressor tRNA originating in an eubacterium belonging to the genus Bacillus, Mycoplasma or Staphylococcus which is capable of binding to the above tyrosine derivative in the presence of the above mutant TyrRS, and (C) a desired protein gene having a nonsense mutation at a desired site in animal cells to thereby incorporate the above tyrosine derivative into the nonsense mutation site in the above protein.
Owner:RIKEN
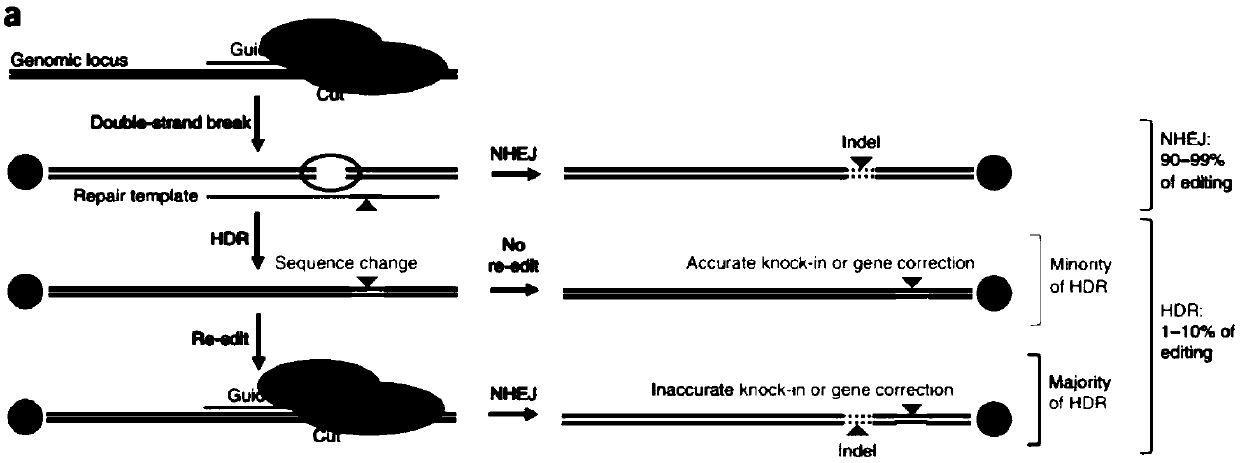
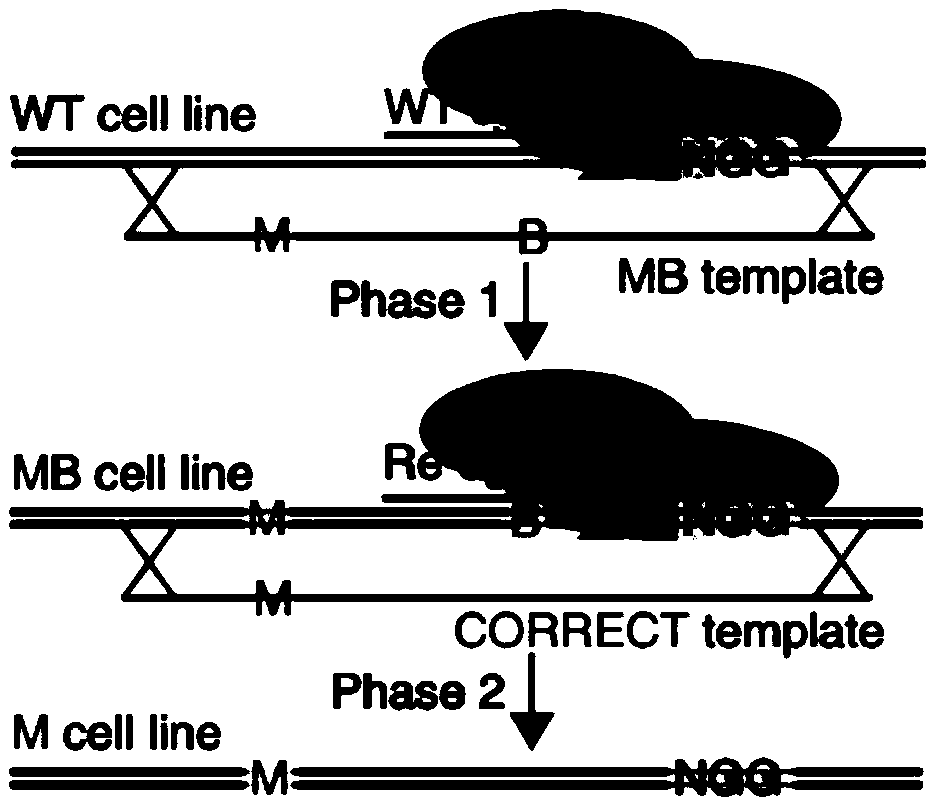
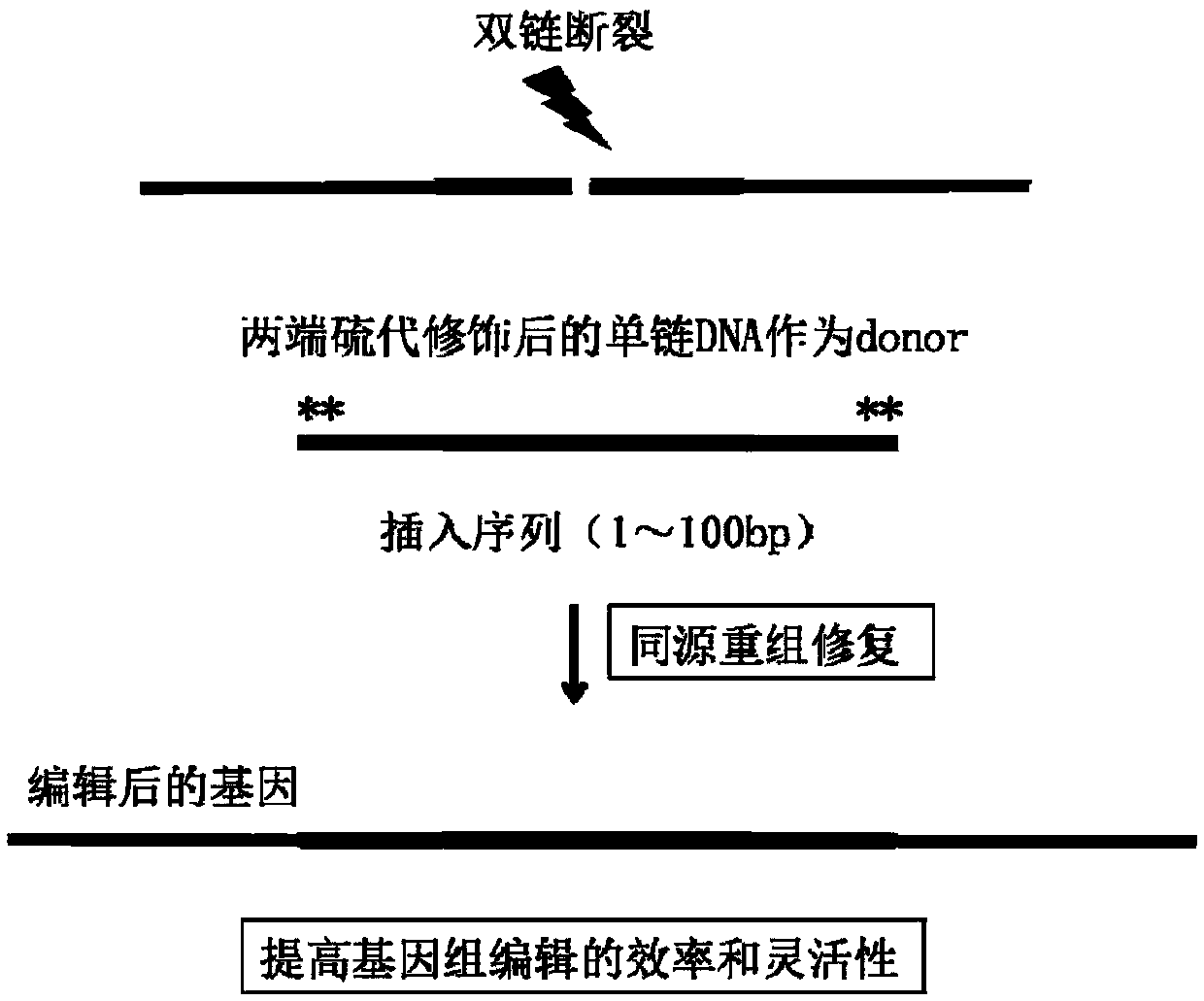
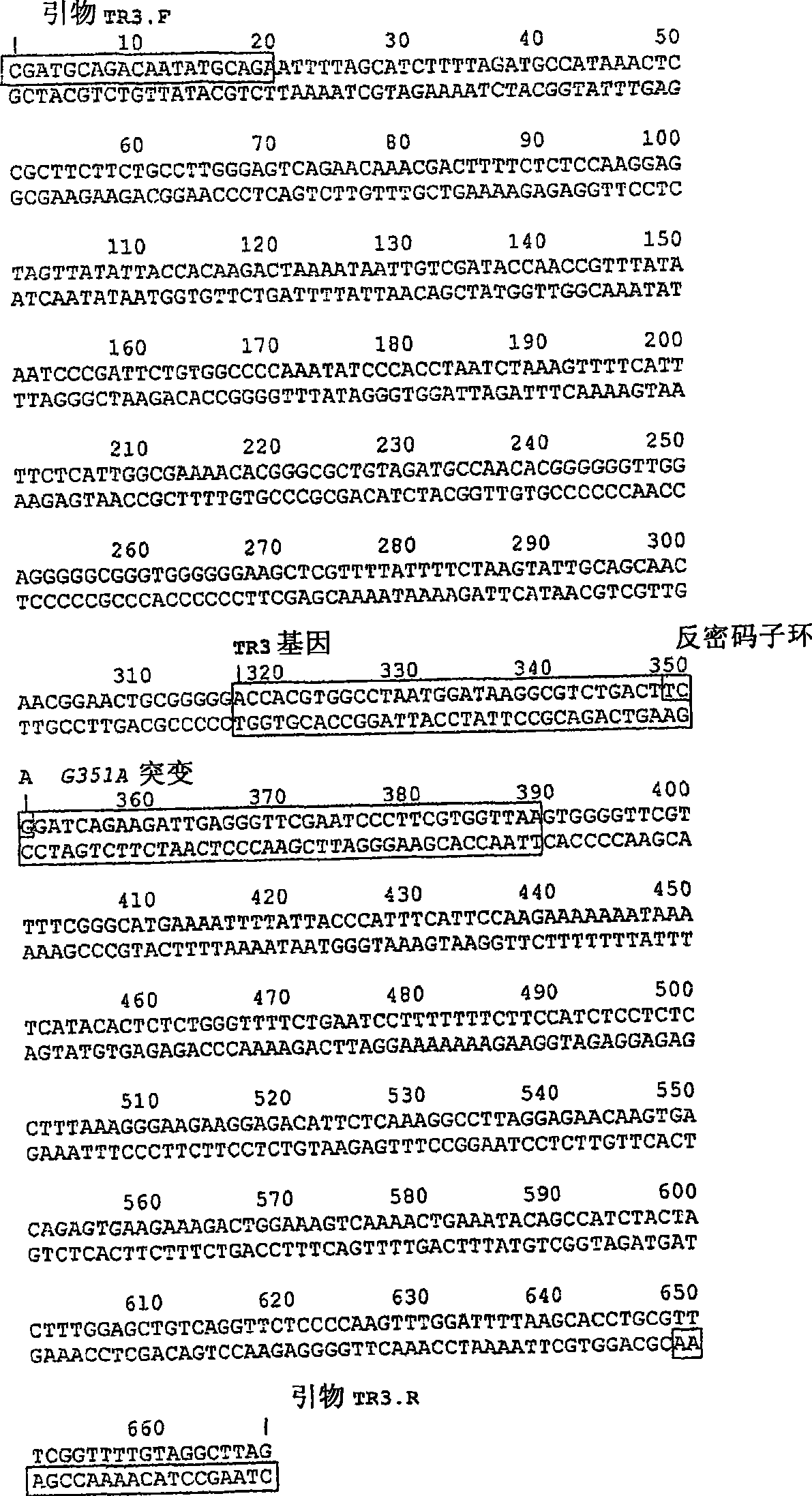
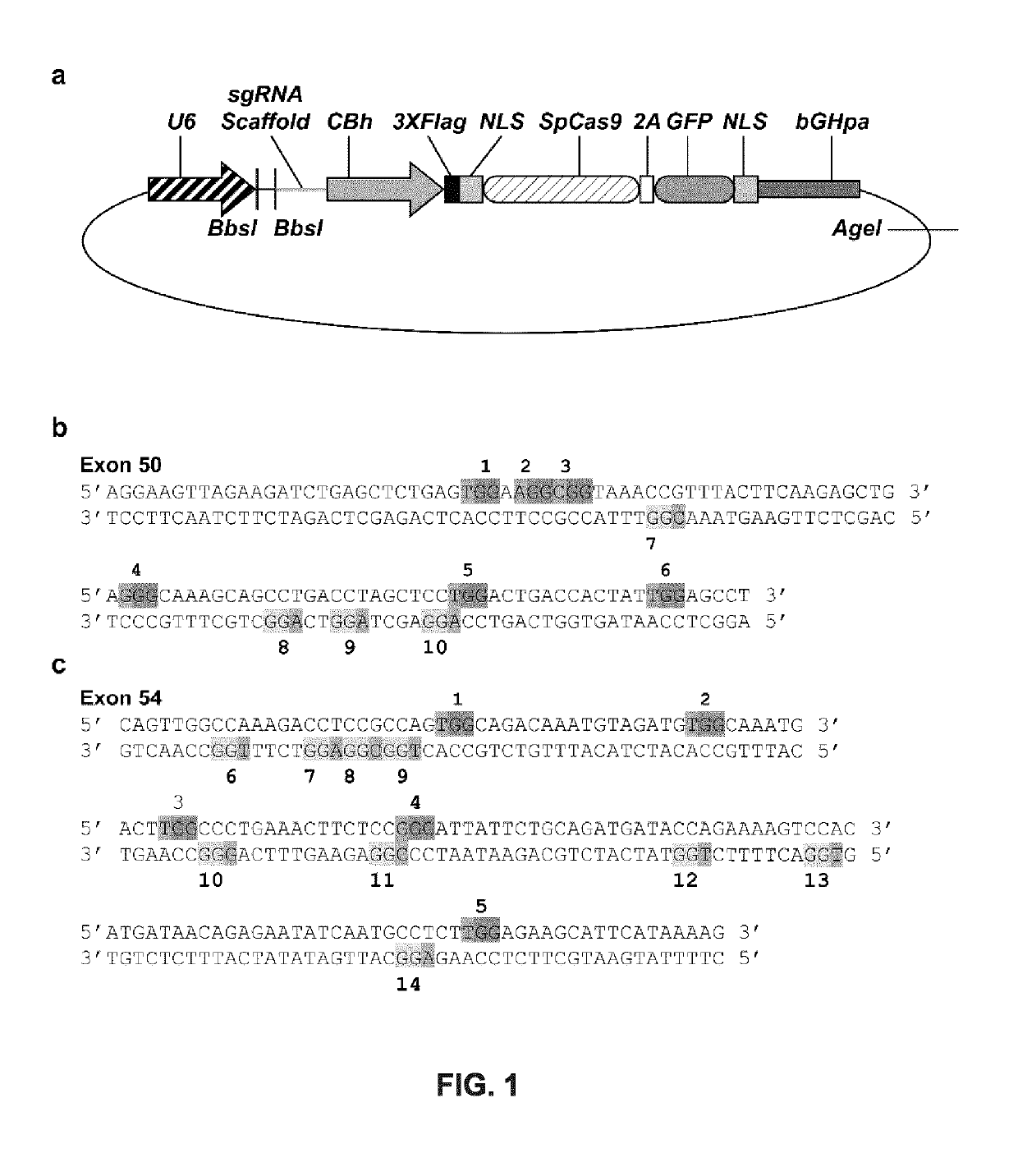
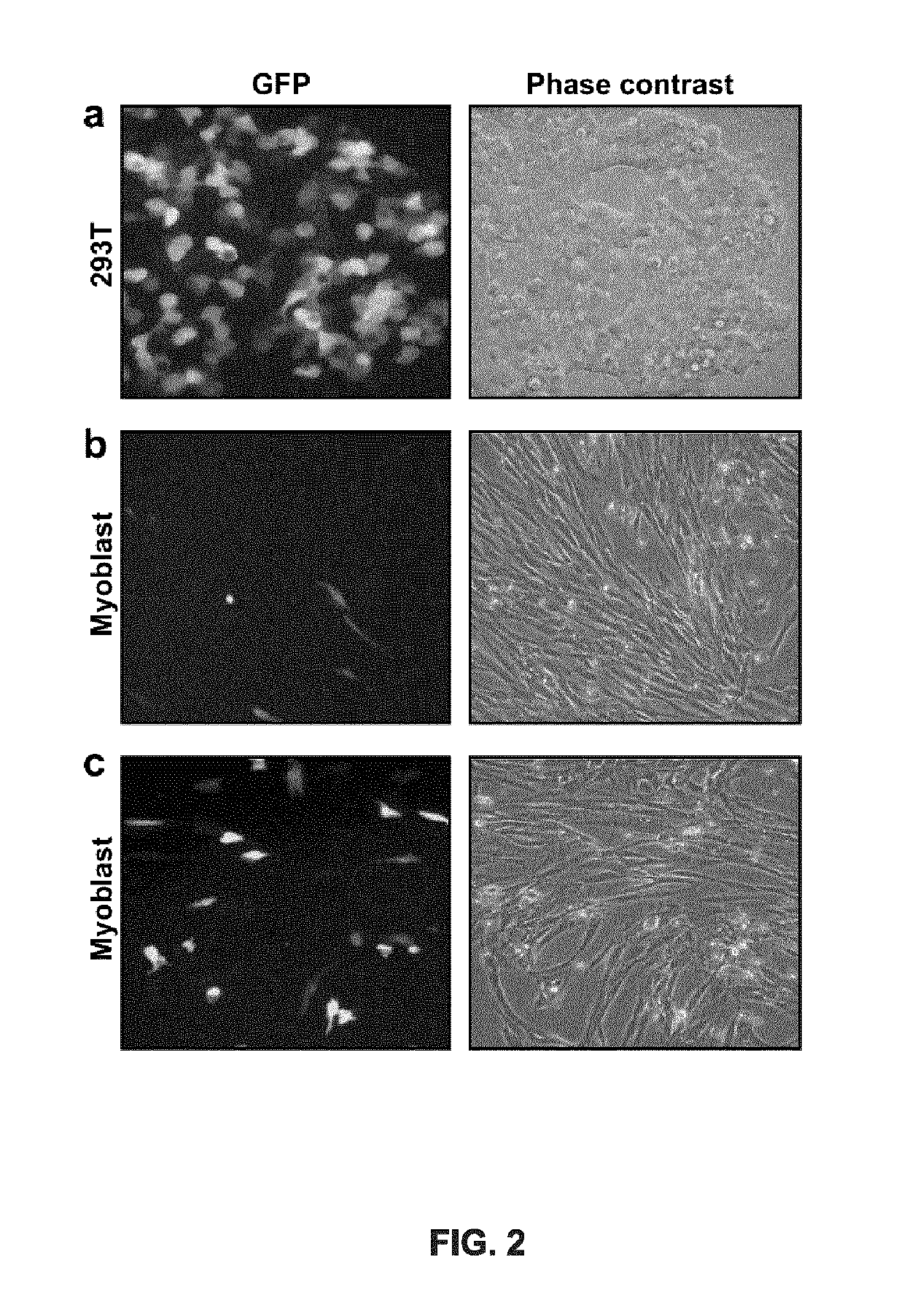
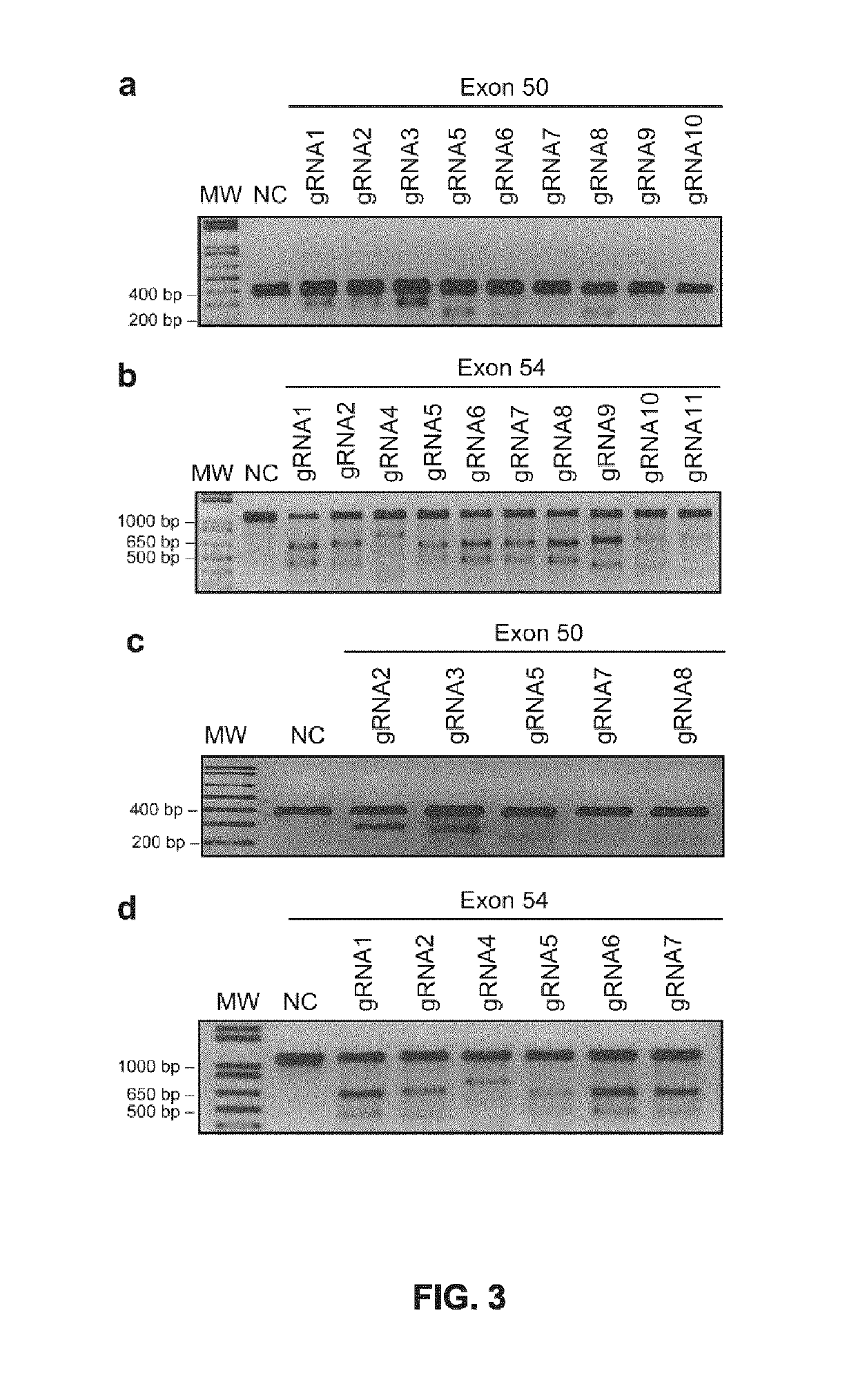
CRISPR single-base restoration system and application thereof
PendingCN109517845APrevent re-editingTo achieve the purpose of seamless repairStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorDiseaseWild type
The invention discloses a CRISPR single-base restoration system. The CRISPR single-base restoration system is capable of expressing eukaryotic expression vectors of sgRNA and Cas9 and single strandedoligonucleotide as a donor template, wherein the base sequence of single stranded oligonucleotide is basically the same as the base sequence between bases 30-60 on two sides of a to-be-restored singlebase, and the differences between the two base sequences are that the base corresponding to the to-be-restored single base is a non-mutation wild base, and nonsense mutation occurs on one side of theto-be-restored single base. The invention further discloses application of the CRISPR single-base restoration system in the preparation of drugs for treating beta thalassemia caused due to CD17A-T point mutation of a beta bead protein gene. According to the CRISPR single-base restoration system, a CRISPR / Cas expression plasmid and a donor are commonly transfected into cells, the traceless directional transformation of gene mutation sites in beta17 thalassemia is specifically induced in a 293TT cell, and the method has very important clinical application values in the execution of gene editingaccurate treatment on diseases based on single-gene point mutation.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Methods for the production of functional protein from DNA having a nonsense mutation and the treatment of disorders associated therewith
InactiveUS9289398B2Eliminate riskImprove the quality of lifeBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to functional proteins encoded by nucleic acid sequences comprising a nonsense mutation. The present invention also relates to methods for the production of functional proteins encoded by nucleic acid sequences comprising a nonsense mutation and the use of such proteins for prevention, management and / or treatment of diseases associated with a nonsense mutation(s) in a gene.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods for treating methylmalonic acidemia
InactiveUS20140343009A1Reduction and amelioration of severityImprove survivalBiocideOrganic chemistryPremature Stop CodonMessenger RNA
Methods for treating methylmalonic acidemia in which at least one allele of a gene associated with MMA (e.g., the MUT, MMAA, or MMAB gene) contains a mutation (e.g., nonsense mutation) that results in a premature stop codon in RNA encoded by an allele of the gene associated with MMA involving the administration of a compound that promotes readthrough of RNA (e.g., messenger RNA) containing a premature stop codon encoded by an allele of the gene associated with MMA are described. The compound can be administered as a single-agent therapy or in combination with one or more additional therapies to a human in need of such treatment.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
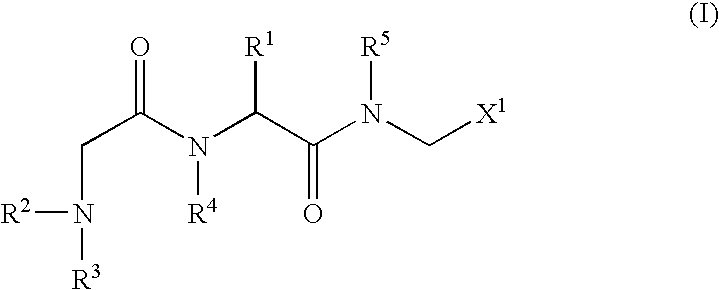
Method Of Treating Genetic Disease Caused By Nonsense Mutation
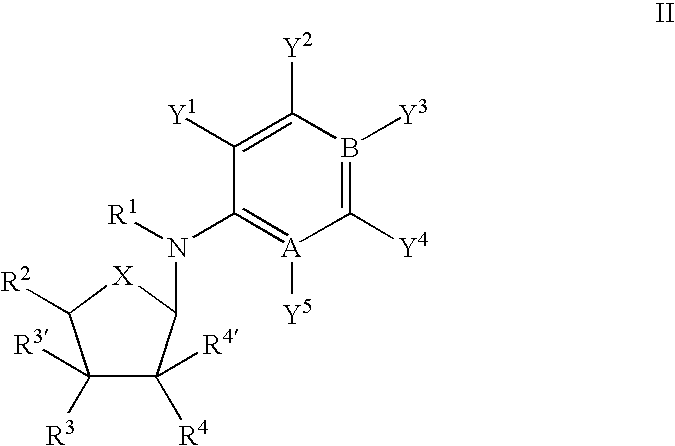
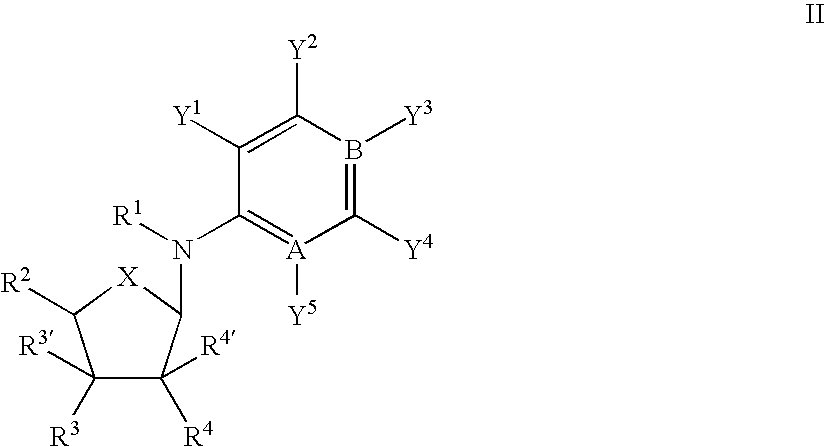
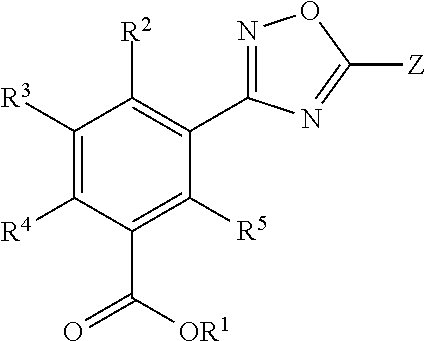
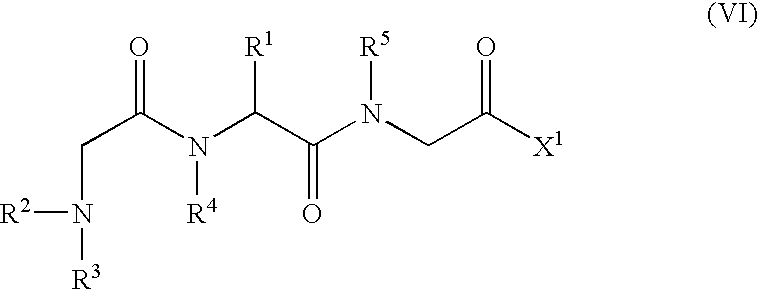
An object of the present invention is to provide compounds having read-through activity for use in treatment methods of genetic diseases caused by nonsense mutation, to provide pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compound, and to provide a treatment method of genetic diseases caused by nonsense mutation comprising administering the compound.The present invention can provide a method of producing wild type normal protein in a living body of a mammal from a gene with a premature termination codon being generated by a mutation, wherein the method comprises administering a compound expressed by the following formula (VI):(wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 and X1 in the formula are as defined in description) or the like to the mammal.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
Methods for treating epilepsy
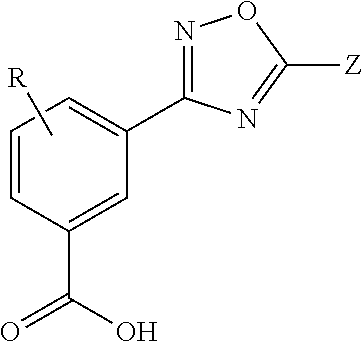
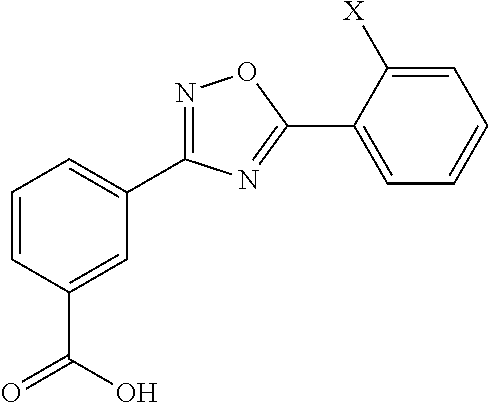
Provided herein are methods of treating, preventing, ameliorating or managing a nonsense mutation mediated epileptic disease, comprising administering a 1,2,4-oxadiazole benzoic acid to a patient having a nonsense mutation mediated epileptic disease. In particular, provided herein are methods of treating, preventing, ameliorating or managing a CDKL5 and / or SCN1A (Dravet syndrome) nonsense mutation mediated epileptic disease.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Truncated protein for reading through premature termination codons diseases by using inhibitory transfer ribonucleic acids (tRNAs)
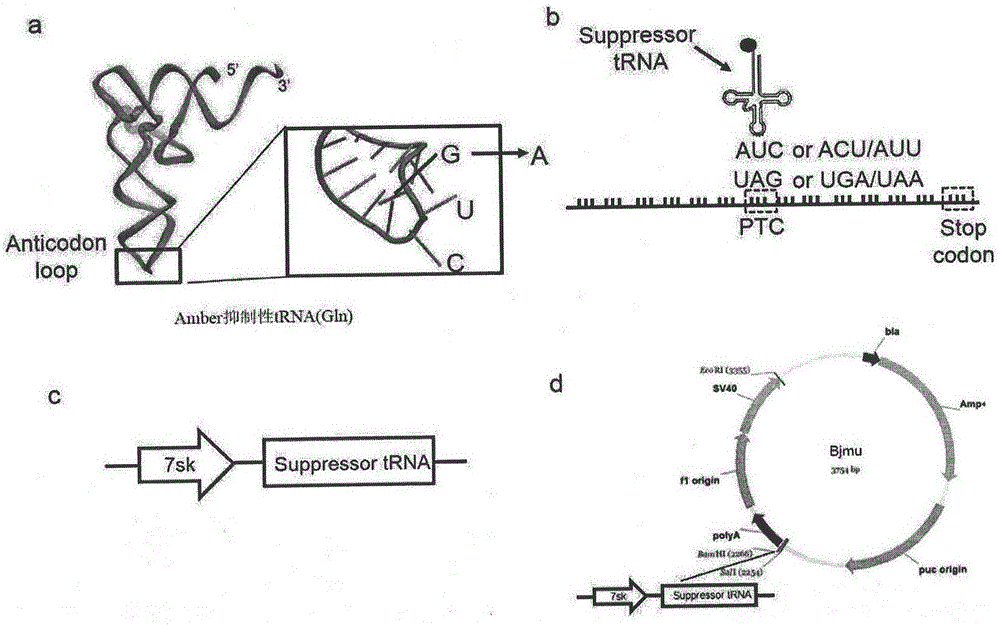
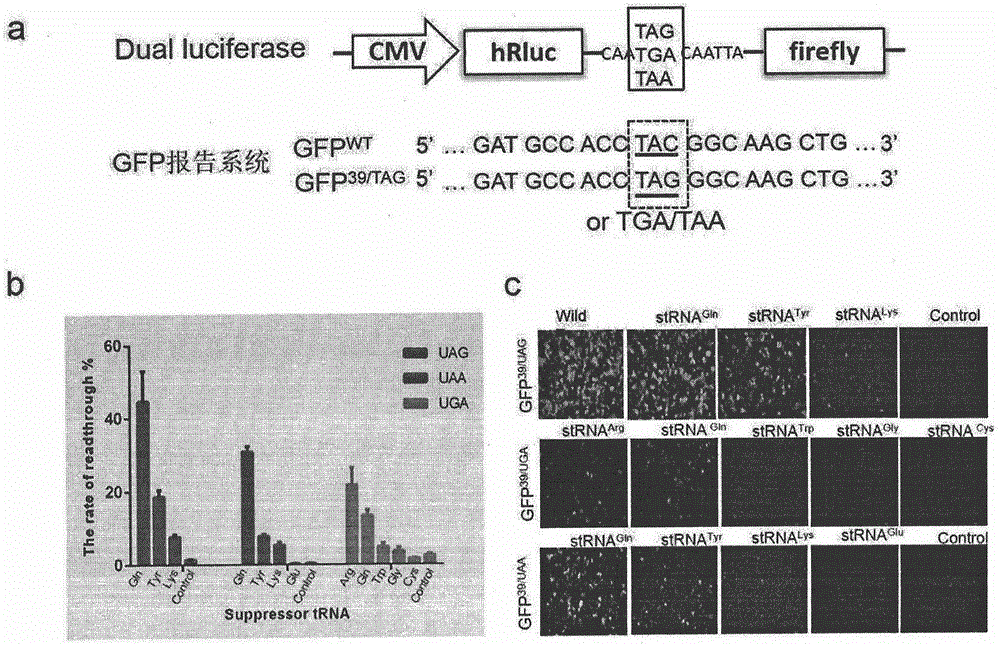
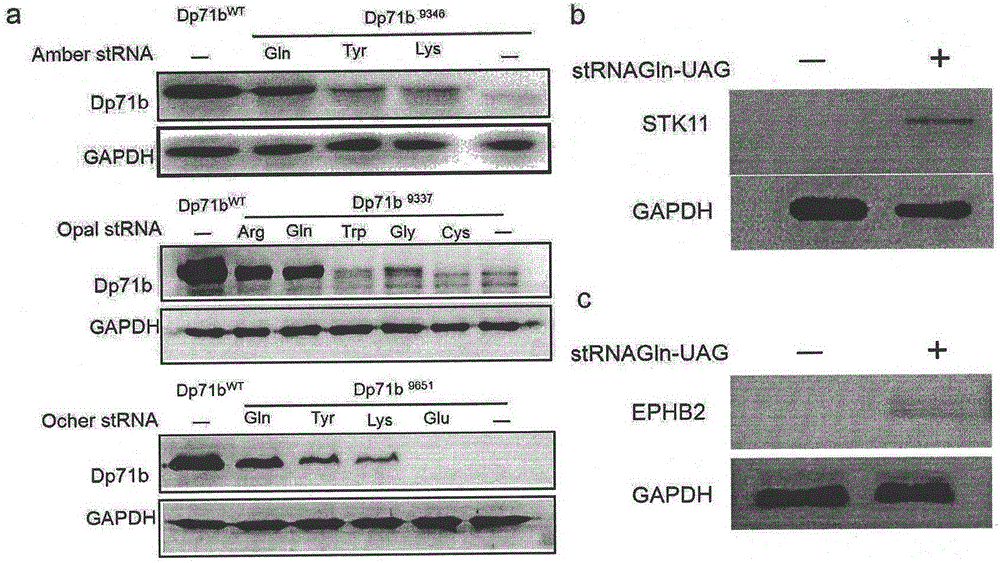
The invention relates to a truncated protein for prolonging a disease-causing gene nonsense mutant by establishing inhibitory transfer ribonucleic acids (tRNAs) so as to enable full-length functional proteins to be produced in mammalian cells and further restore the normal structure and function of the mutant. A nonsense mutation system related in the invention comprises disease-causing genes of single gene inheritance diseases and tumor suppressor genes in tumor cells. The invention mainly relates to constructing of nineteen inhibitory tRNAs corresponding three termination codons, a dystrophin protein is efficiently read through in the mammalian cells, and a nonsense mutant protein is read through in the tumor cells, so that a remarkable effect is achieved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
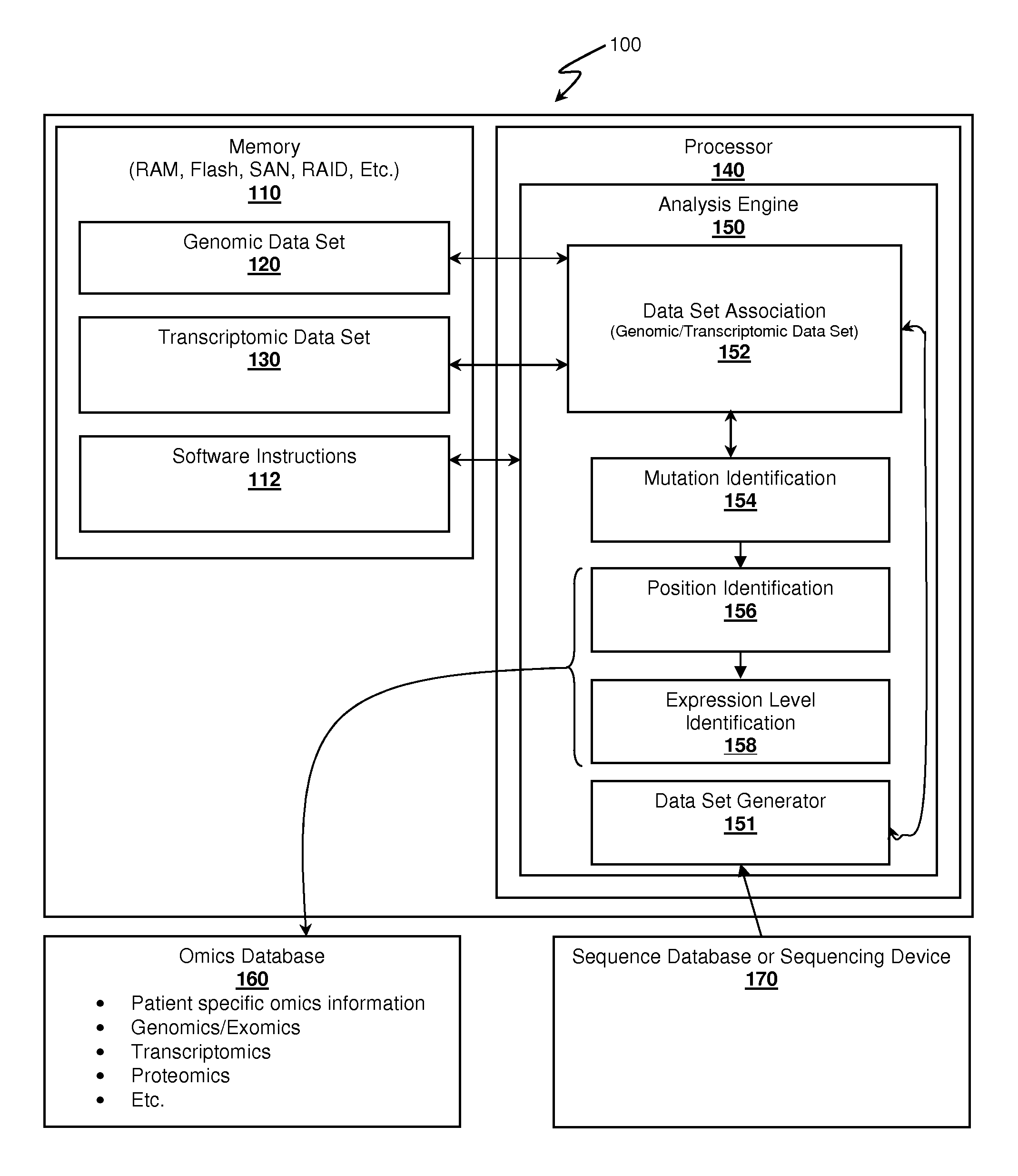
Systems and Methods For RNA Analysis In Functional Confirmation Of Cancer Mutations
Owner:FIVE3 GENOMICS
Compound having read-through activity
[Problem] Provision of a novel compound having read-through activity and a drug for the treatment of nonsense mutation-type disease containing this compound.[Solution] A compound represented by the following general formula (1):and a pharmaceutical composition containing this compound.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Prevention/treatment of ichthyosis vulgaris, atopy and other disorders
The present invention relates to the prevention / treatment of ichthyosis vulgaris (IV), atopy and potentially other disorders associated with loss-of-function mutations in the filaggrin gene sequence. The prevention / therapy is based on the use of agents which enable the host's translational machinery to read through a nonsense mutation found in a mutant allele of the filaggrin gene.
Owner:UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF DUNDEE
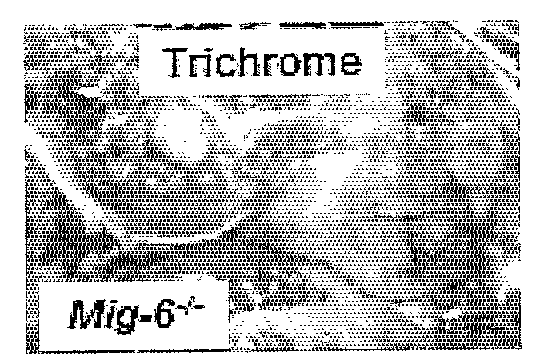
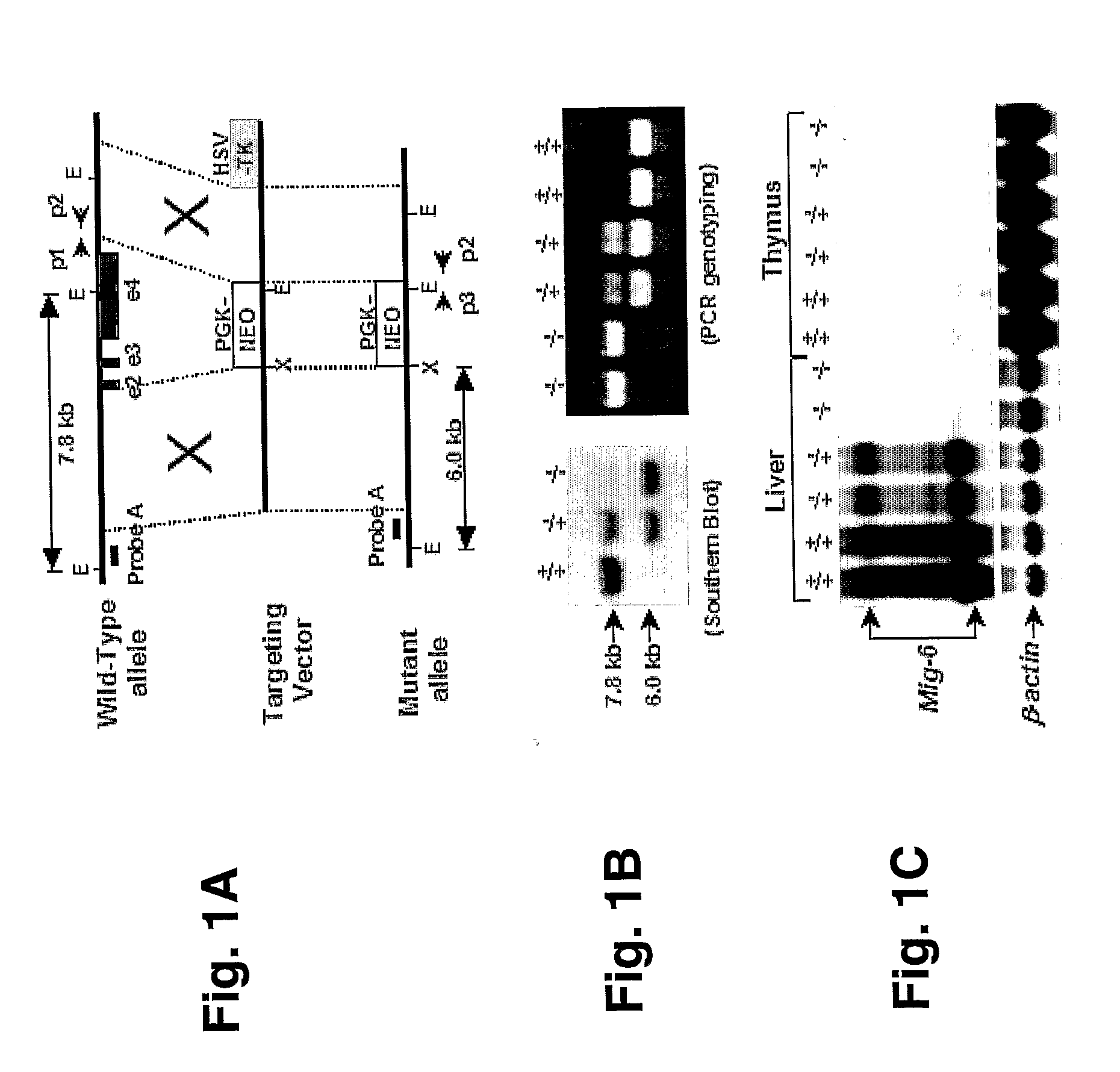
Mig-6 knockout mice and elucidation of association of mig-6 with early onset degenerative joint disease and role as a tumor suppressor
InactiveUS20110099644A1Reduce developmentIncreased tumorigenesisAnimal cellsSugar derivativesProgenitorDisease
The molecular mechanism underlying degenerative joint disease, also known as osteoarthritis (OA), is not fully understood. Disruption of mitogen inducible gene 6 (Mig-6) in mice by homologous recombination (KO mice) led to early onset OA as revealed by simultaneous enlargement and deformity of multiple joints, degradation of articular cartilage and the development of bony outgrowths or osteophytes within the joint space. The latter appeared to be derived from proliferation of mesenchymal progenitor cells followed by differentiation into chondrocytes. Because of the striking similarity to human OA, Mig-6 KO mice are a useful animal model for studying the mechanism of this disease and for testing new drugs or therapies for treating OA. These KO mice also developed epithelial hyperplasia, adenoma, and adenocarcinoma in organs such as lung, gallbladder, and bile duct. Mig-6 is therefore a tumor suppressor gene and is a candidate gene for the frequent Ip36 genetic alterations found in lung cancer. It can be used as a tumor biomarker as well as a target for cancer therapy. Mig-6 is located in human chromosome Ip36, a locus frequently associated with human lung cancer. Mig-6 is a negative regulator of EGF signaling, and like EGF, was induced by HGF / SF in human lung cancer cell lines. Frequently the receptors EGFR and Met were co-expressed, and Mig-6 was induced by both EGF and HGF / SF in a MAPK-dependent fashion. Not all tumor lines express Mig-6 in response to either EGF or HGF / SF. In these cases, missense and nonsense mutations in the Mig-6 coding region were found, as was evidence for Mig-6 transcriptional silencing.
Owner:VAN ANDEL RES INST
Methods for the production of functional protein from DNA having a nonsense mutation and the treatment of disorders associated therewith
InactiveUS20160199357A1Eliminate riskImprove the quality of lifeSenses disorderNervous disorderDiseaseNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to functional proteins encoded by nucleic acid sequences comprising a nonsense mutation. The present invention also relates to methods for the production of functional proteins encoded by nucleic acid sequences comprising a nonsense mutation and the use of such proteins for prevention, management and / or treatment of diseases associated with a nonsense mutation(s) in a gene.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods of modifying the dystrophin gene and restoring dystrophin expression and uses thereof
PendingUS20190248854A1Restoring correct reading frameSmall possible deletionHydrolasesMuscular disorderDystrophinBiology
Methods for modifying a dystrophin gene are disclosed, for restoring dystrophin expression within a cell having an endogenous frameshift or nonsense mutation within the dystrophin gene. The methods comprise introducing a first cut within an exon en or intron of the dystrophin gene creating a first exon end or intron end, wherein said first cut is located upstream of the endogenous frameshift or nonsense mutation; and introducing a second cut within an exon or intron of the dystrophin gene creating a second exon end or intron end, wherein said second cut is located downstream of the frameshift or nonsense mutation. Upon joining / ligation of said first and second exon ends or intron ends a hybrid exon or intron junction is created and dystrophin expression is restored, as the correct reading frame is restored. Reagents and uses of the method are also disclosed, for example to treat a subject suffering from muscular dystrophy.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
cSNP molecular marker detection kit and method for scylla paramamosain disease-resistant characters
ActiveCN106811526AHigh antibacterial activityStrong anti-Candida albicans functionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseNucleotide
The present invention relates to a cSNP molecular marker detection kit and a detection method for scylla paramamosain disease-resistant characters, relates to the technical field of molecule auxiliary disease resistance breeding in aquatic livestock, and particularly relates to a single nucleotide polymorphism cSNP molecular marker, capable of influencing disease resistance of blue crabs, in a cDNA sequence of scylla paramamosain SpALF6, as well as a detection kit and a detection method thereof. On a basis that a disease resistance factor SpALF6 of the scylla paramamosain is identified, by performing sequence comparison, it is found that 215th nucleotide in the cDNA sequence of SpALF6 and 222th nucleotide G of a variant of the SpALF6, namely SpALF6-V, are nonsense mutation for each other. In the invention, the mutation site is used as the basis, a convenient and practical molecular marker detection kit is built, and a matched RT-PCR detection method is provided; detection results can be used as important indicators for judging the disease resistance of the blue crabs, and the single nucleotide polymorphism cSNP molecular marker has the great importance in predicting of the disease resistance of the blue crabs and molecule auxiliary disease resistance breeding.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Compounds and their use for treating somatic mutation-related diseases
The present invention relates to methods, compounds, and compositions for treating or preventing diseases associated with nonsense mutations in an mRNA by administering the compounds or compositions of the present invention. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods, compounds, and compositions for suppressing premature translation termination associated with a nonsense mutation in an mRNA.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Human induced pluripotent stem cell and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113881637AArtificial cell constructsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsGerm layerReprogramming
The invention relates to a human induced pluripotent stem cell strain SXMUi002-A-1. The human induced pluripotent stem cell strain SXMUi002-A-1 is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the preservation number of the human induced pluripotent stem cell strain SXMUi002-A-1 is CGMCC No: 22359. The iPSC is obtained by extracting urine cells from urine of a B-type hemophilia patient carrying F9c.223C>T(p.R75X) nonsense mutation and reprogramming, and further research finds that the iPSC is similar to an embryonic stem cell in the aspects of cellular morphology, gene expression, proliferation and differentiation potential and has the potential of differentiating to three germ layers. The prepared human induced pluripotent stem cell strain SXMUi002-A-1 has important value for molecular mechanism research of hemophilia nonsense mutation, hemophilia detection, drug screening, gene therapy and other clinical application researches, and provides important resources.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV +1
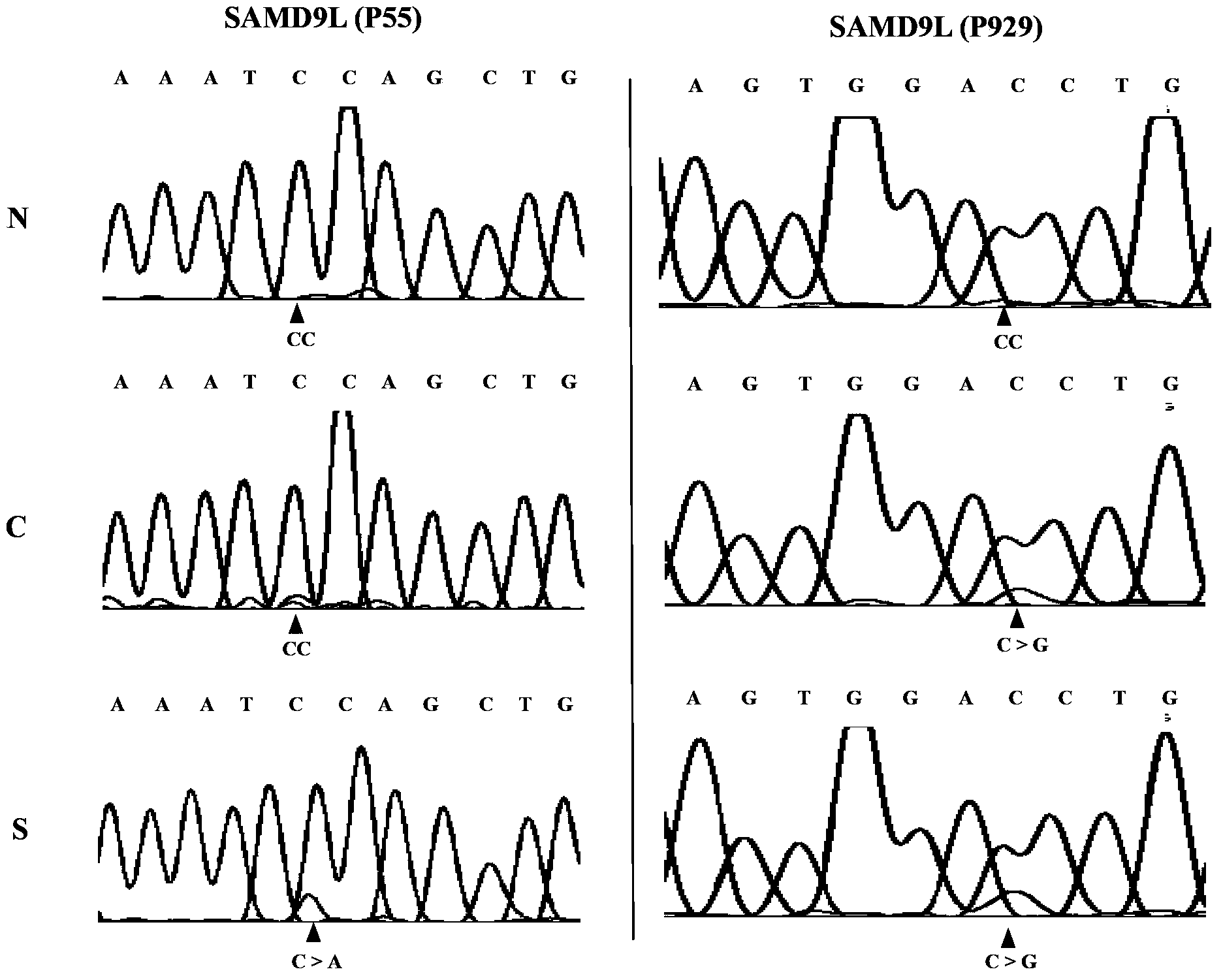
Applications of human SAMD9L gene and protein product encoded by human SAMD9L gene
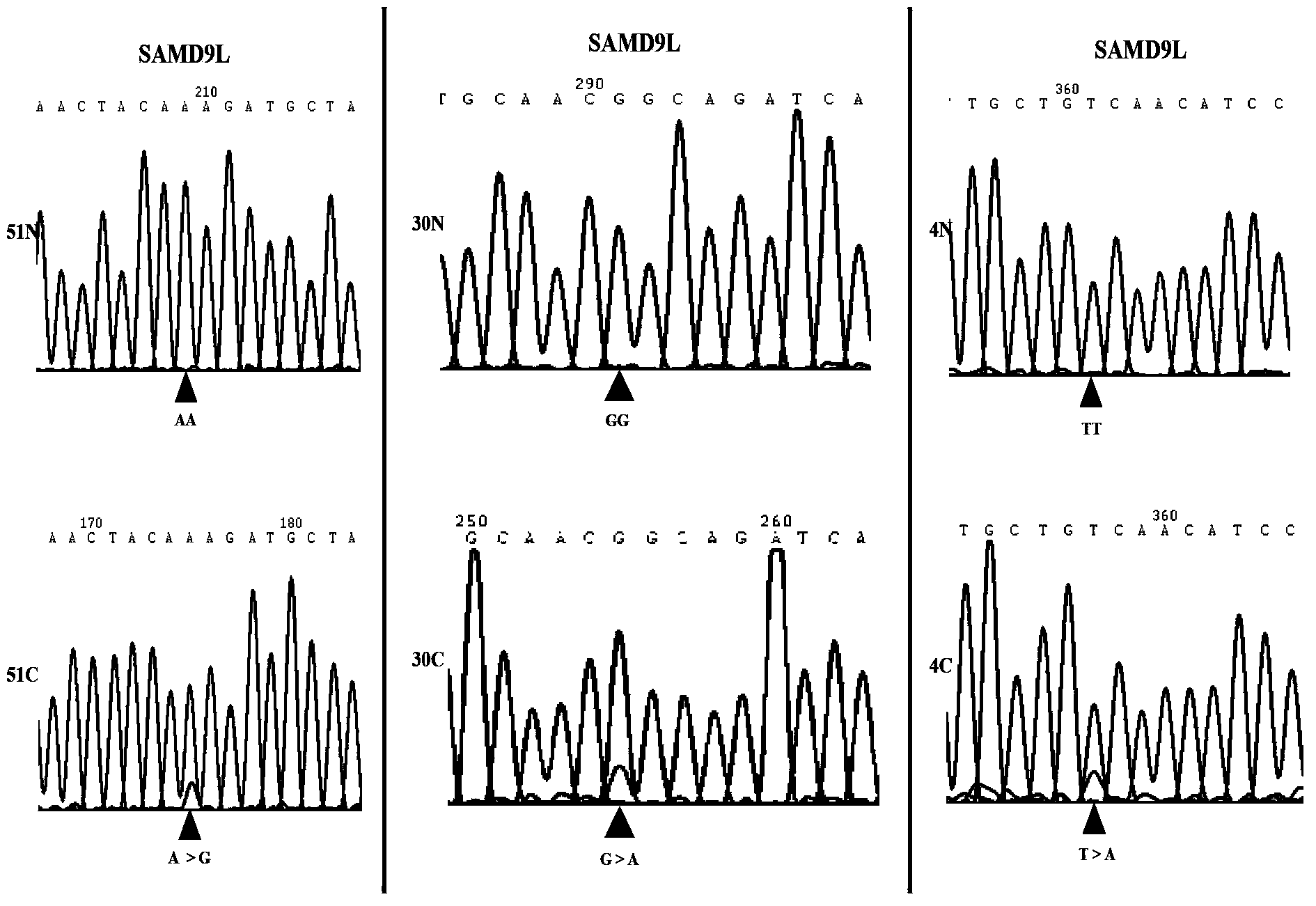
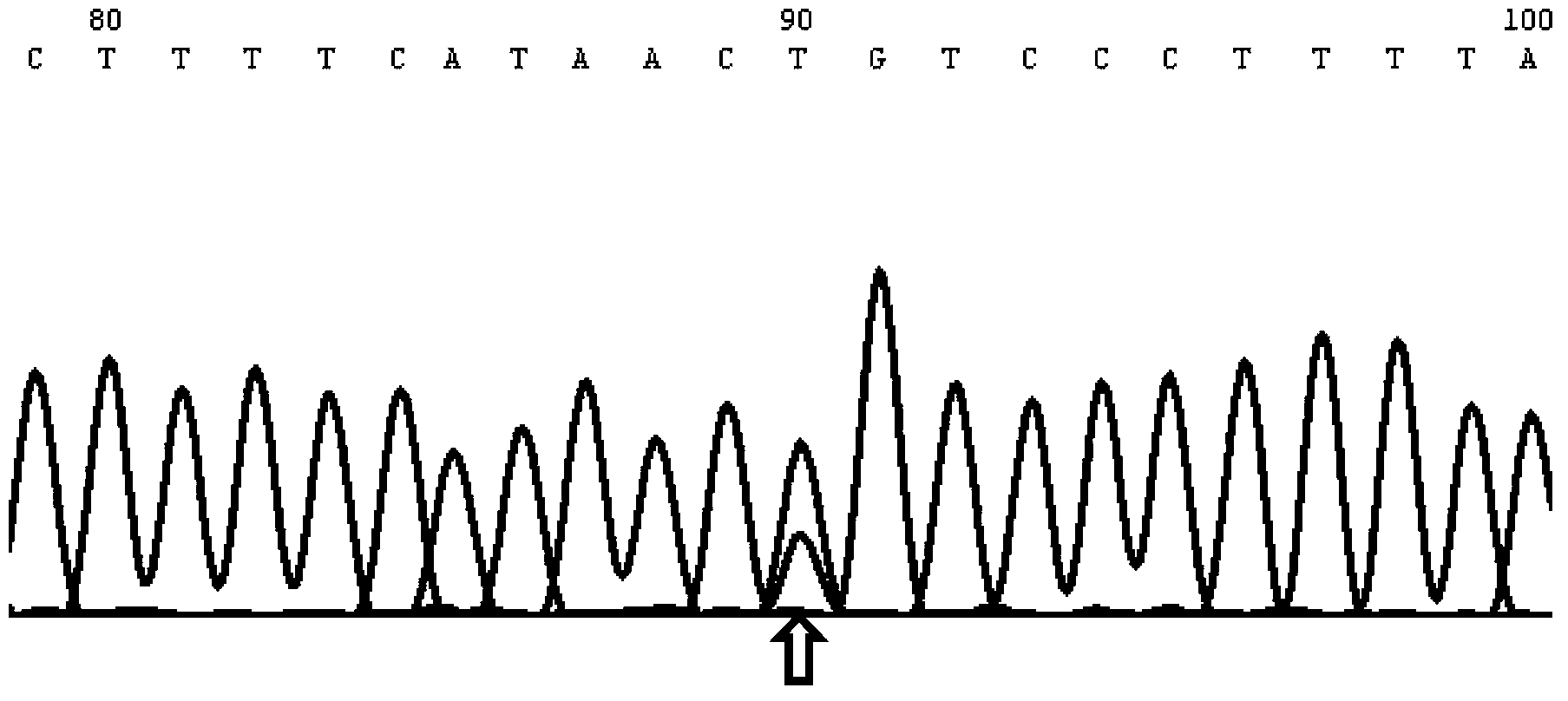
InactiveCN103571927AAccurate diagnosisRapid diagnosisPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementOpen reading frameLymphatic Spread
The present invention discloses applications of human SAMD9L gene and a protein product encoded by the human SAMD9L gene, wherein the SAMD9L gene sequence, especially the open reading frame sequence of the protein encoded by the human SAMD9L gene, generates missense mutation, nonsense mutation, frameshift mutation and other gene structure variations with different forms in tumors so as to be adopted as the specific marker gene for liver cancer diagnosis, such that liver cancer diagnosis is accurate and rapid. According to the present invention, the human SAMD9L protein can be applied on tumor patients so as to treat or alleviate related diseases caused by SAMD9L protein deletion, nonfunction or abnormality; and the human SAMD9L gene can be over-expressed in cancer cells through the transgenic technology, or the SAMD9L protein can be supplied through the in vitro supply manner to control cancer cell proliferation and metastasis so as to achieve the tumor treatment purpose.
Owner:CHINESE NAT HUMAN GENOME CENT AT SHANGHAI
Novel SMG-1
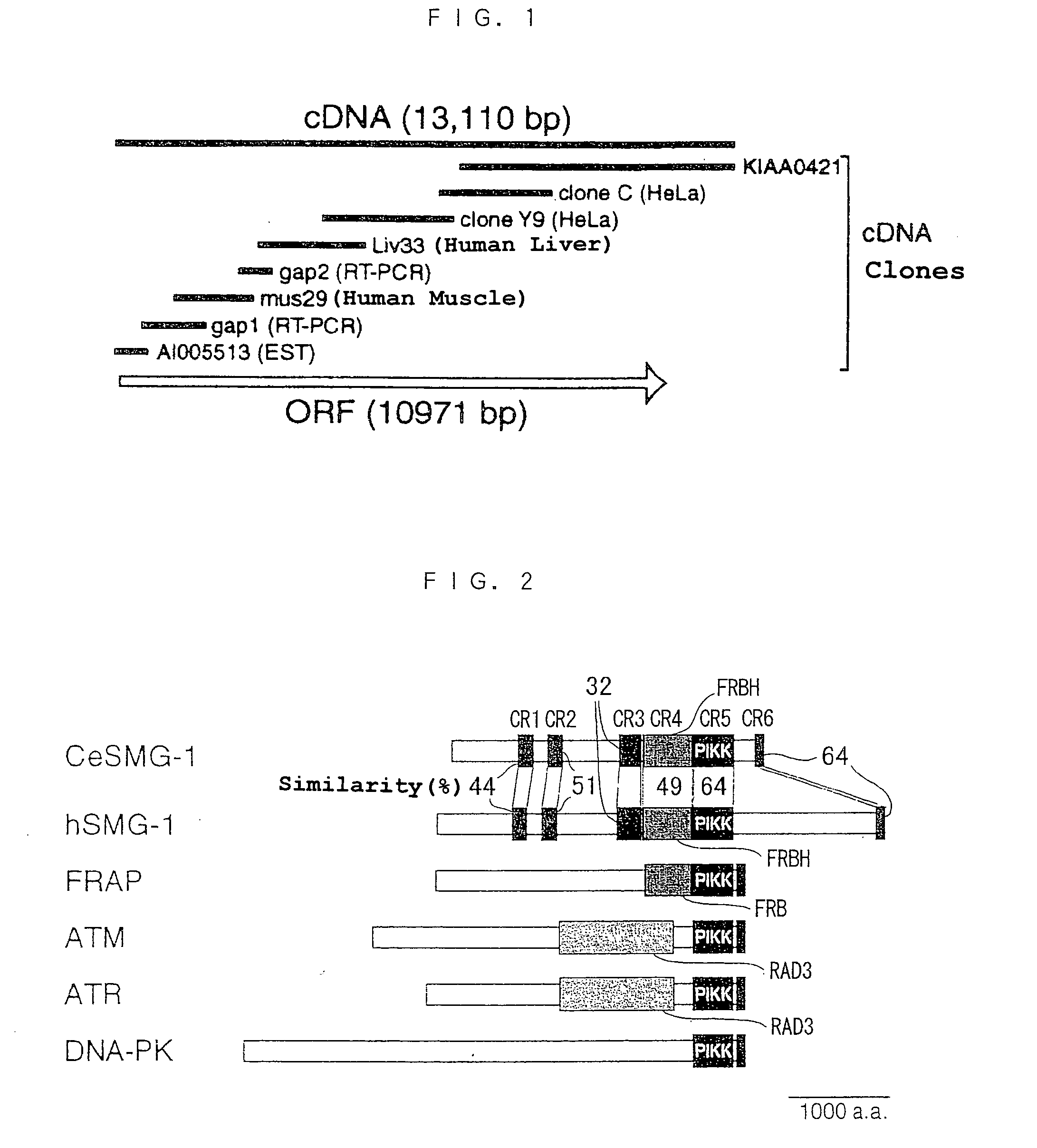
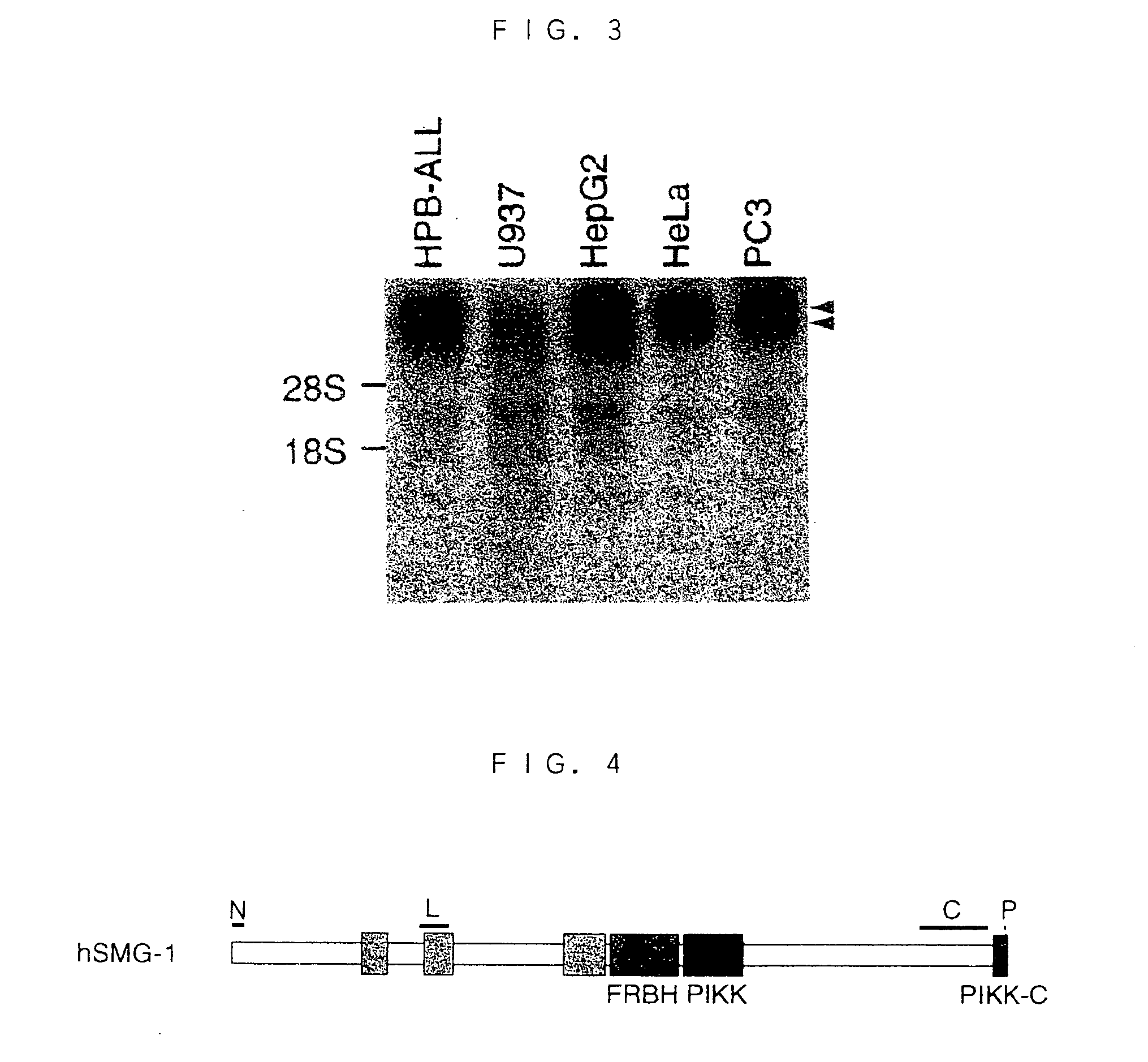
InactiveUS20040137592A1Alleviate gene mutationNew typeCompound screeningFungiDiseasePhosphatidyl inositol
A novel polypeptide and a novel polynucleotide encoding the same are disclosed. The polypeptide is SMG-1, a protein included in the phosphatidyl inositol kinase related kinase family, and is useful in constructing a screening system for agents of treating and / or preventing a disease caused by a premature translation termination codon generated by a nonsense mutation.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Methods for identification of alport syndrome
InactiveUS20070243538A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAlport syndromeLinkage Disequilibrium Mapping
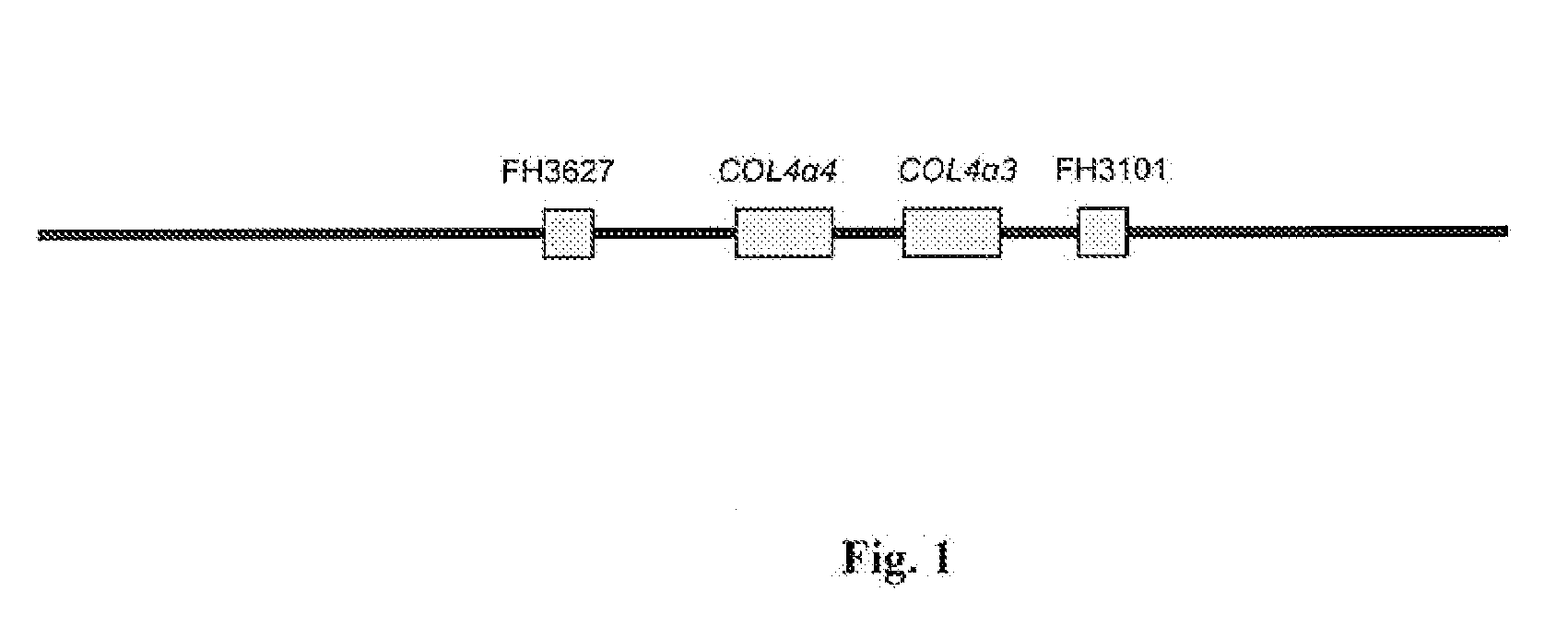
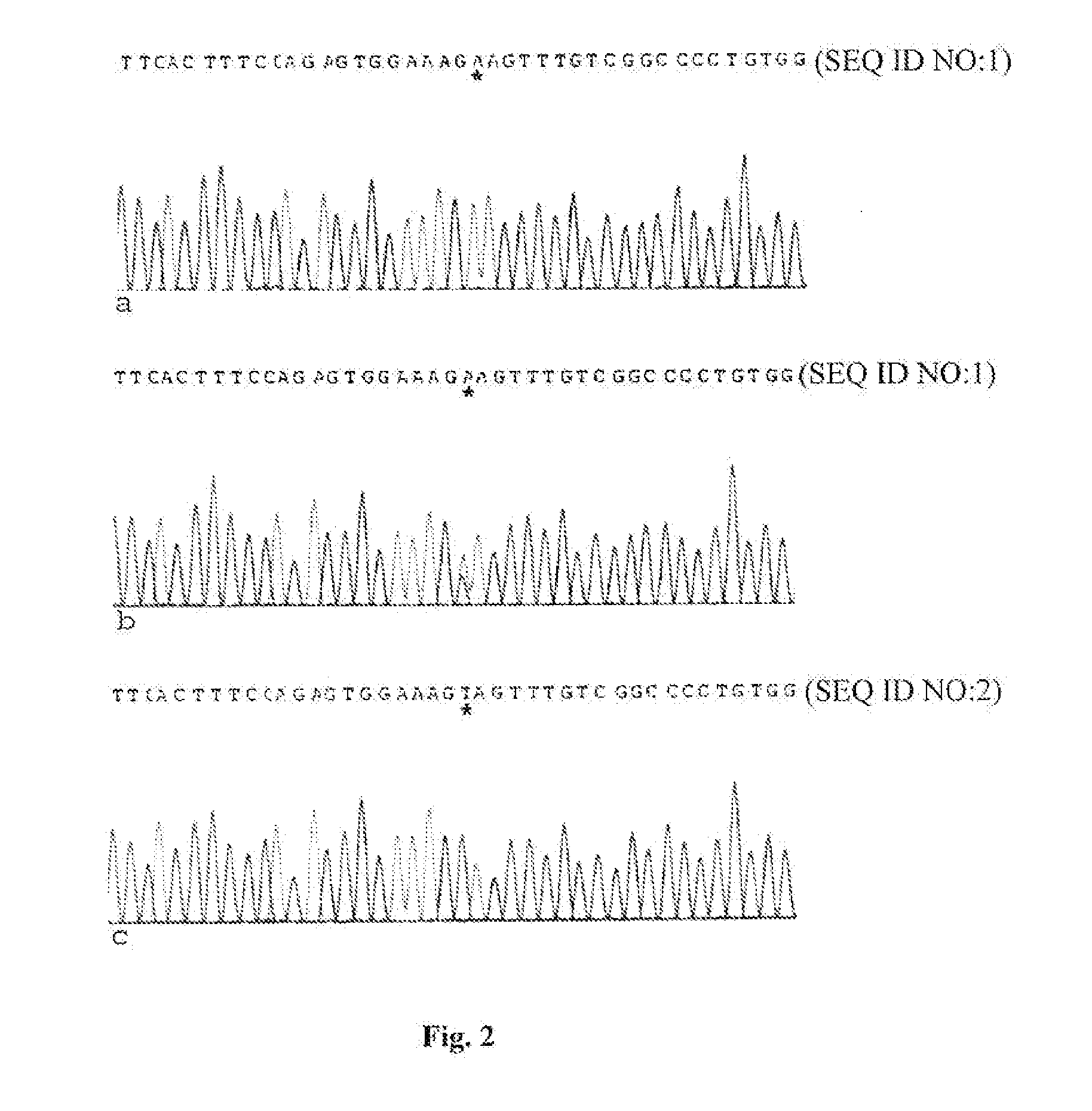
Animals with mutations in COL4α4 present with autosomal recessive Alport Syndrome (ARAS). Through sequencing of COL4α4, the mutation causative for ARAS in the English Cocker Spaniel (ECS) has been identified. The resulting protein is severely truncated due to a premature stop codon in exon 3. This nonsense mutation occurs in the 7S domain and also causes the loss of the entire collagenous and NC1 domains of the protein. Methods for the identification of animals that harbor a mutation in the COL4α4 gene are described. Mutations in the COL4α4 gene can be identified from any biological sample such as a cell or tissue that contains genomic DNA. Methods for identifying single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that are inherited with the disease are also described. A microsatellite marker that segregates with ARAS is also described that was identified using linkage disequilibrium mapping.
Owner:LEES GEORGE E +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com