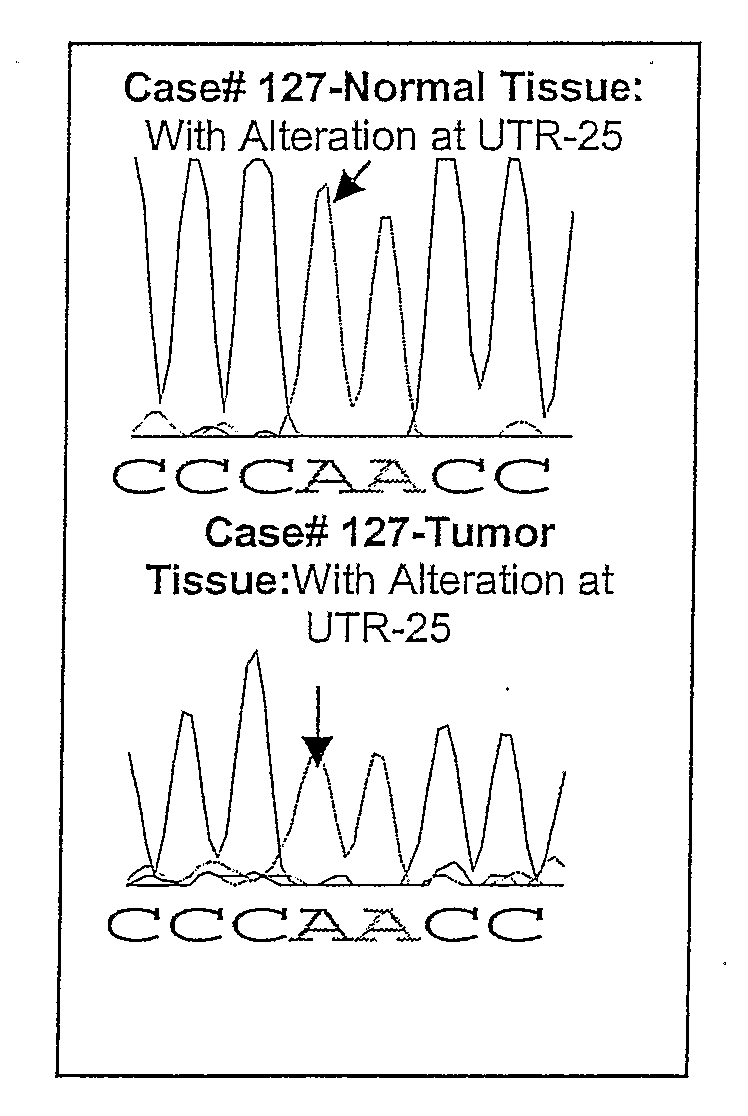
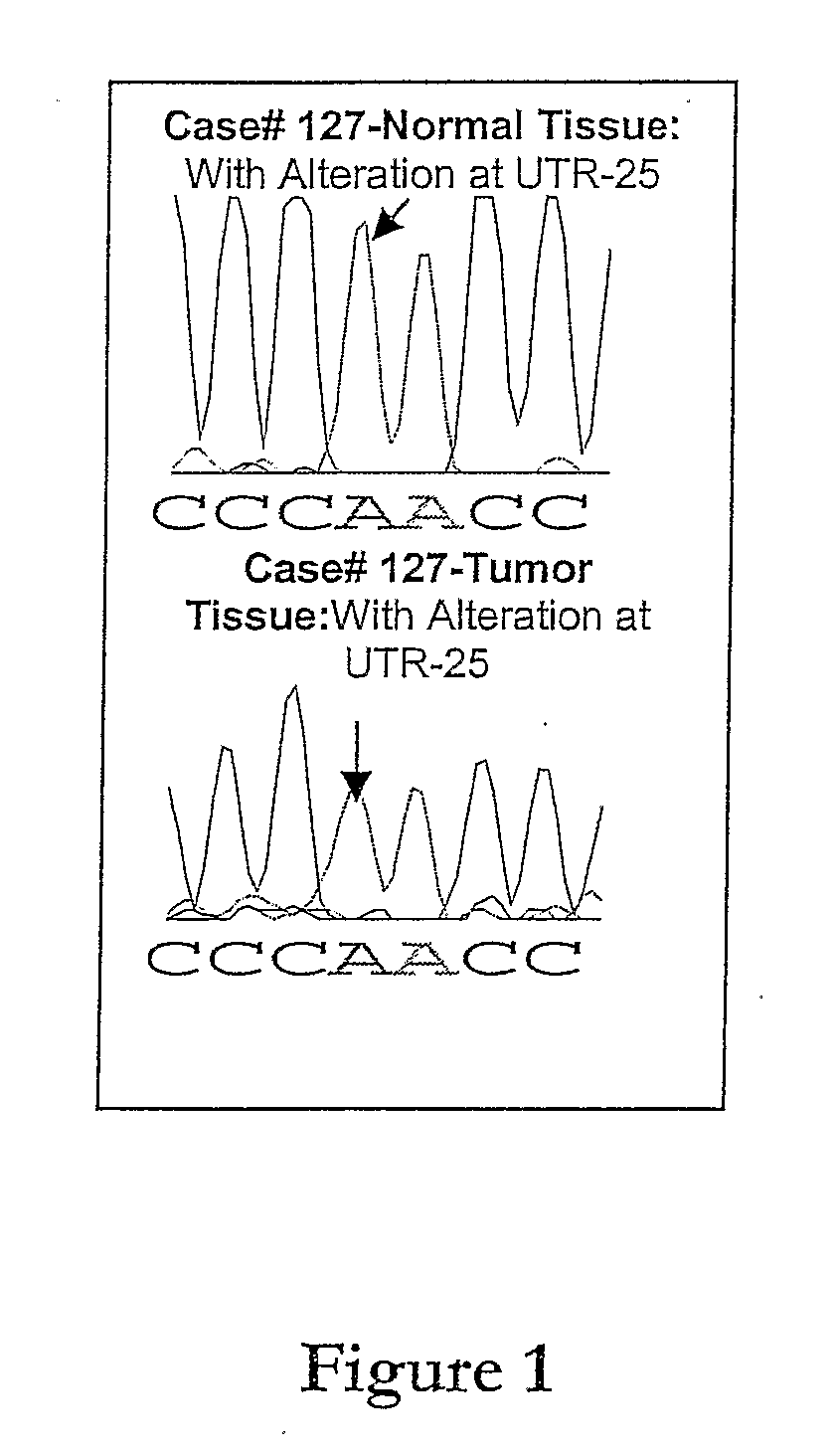
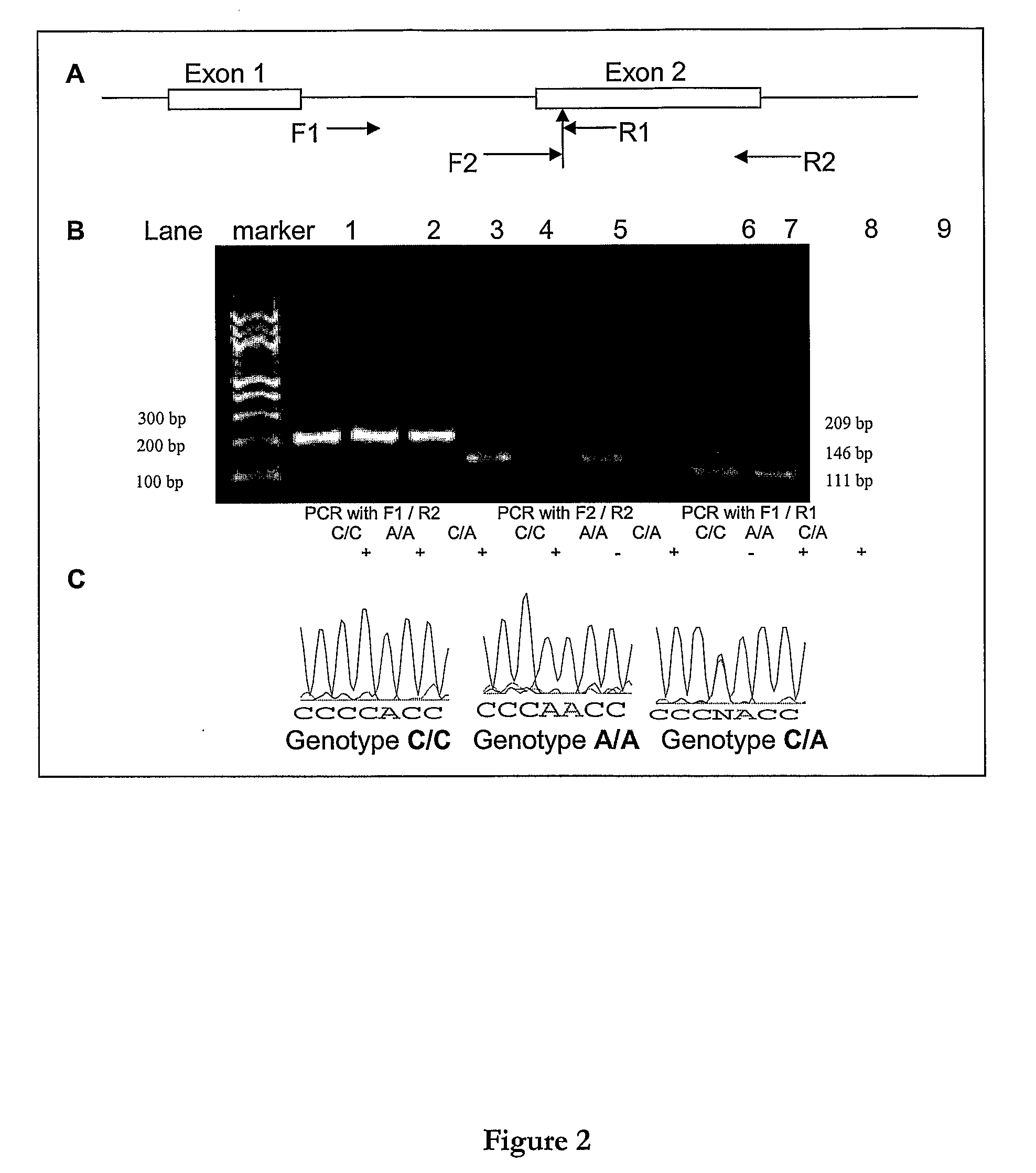
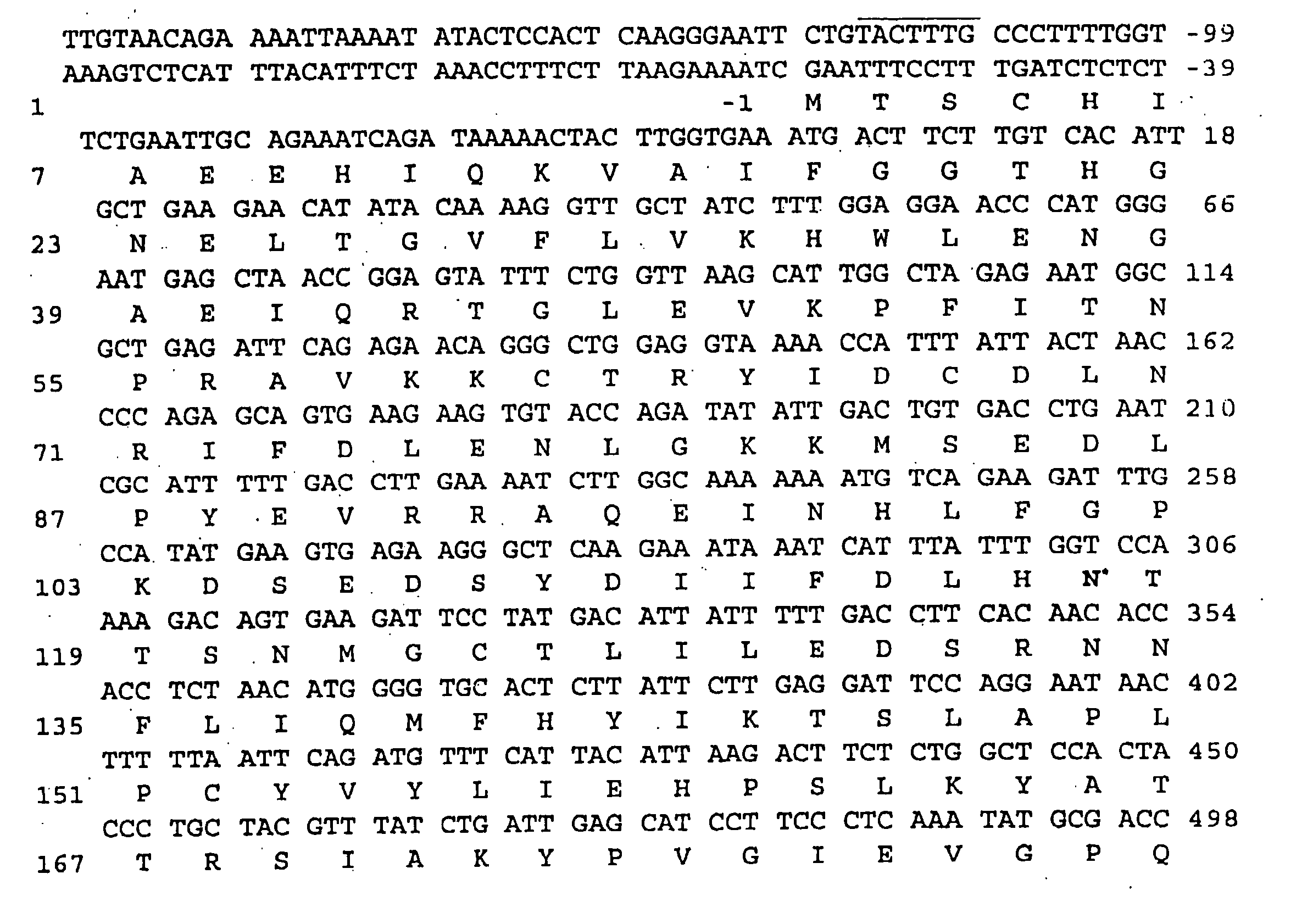
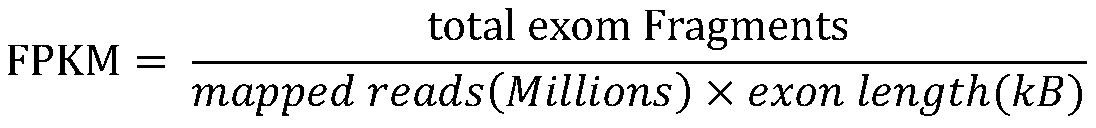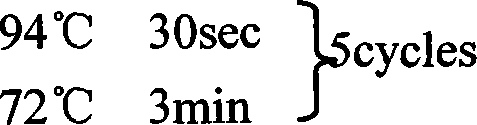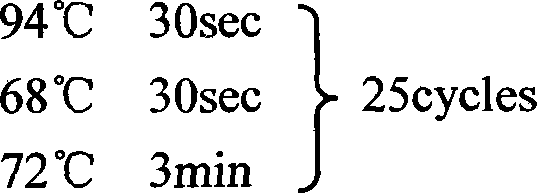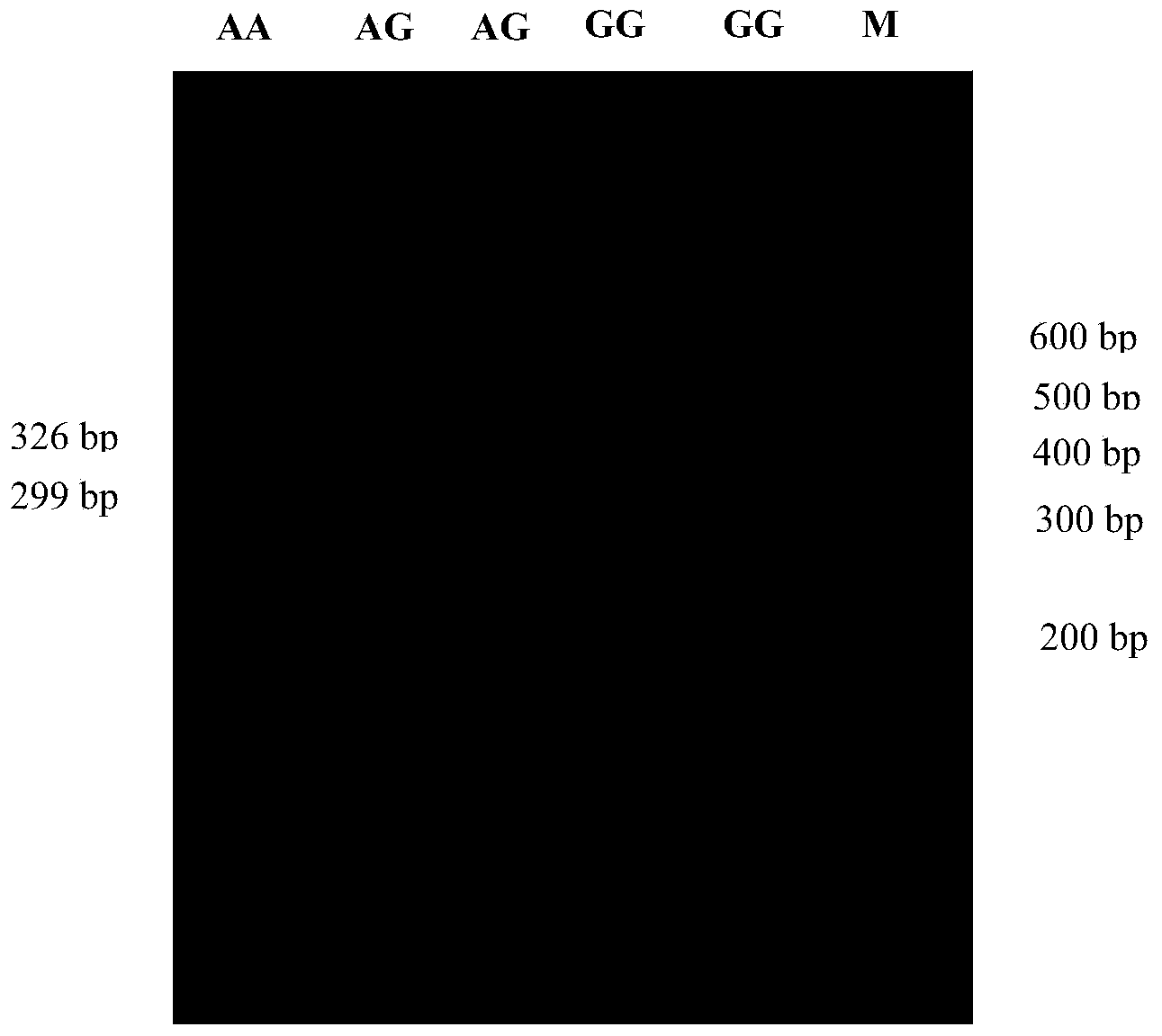Patents
Literature
67 results about "Missense mutation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In genetics, a missense mutation is a point mutation in which a single nucleotide change results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid. It is a type of nonsynonymous substitution.
Novel Missense Mutations and Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the Rabphillin-3A-Like Gene and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080311574A1Digital data processing detailsMicrobiological testing/measurementMissense mutationSingle-nucleotide polymorphism
The invention relates to methods and compositions of matter for determining or predicting aggressiveness of a subject's tumor, for determining a subject's predisposition to cancer, for diagnosing cancer in a subject, and for selecting a therapy for a subject with cancer. Also provided are methods and compositions of matter for determining a Rabphillin-3A-Like gene genotype in a subject and for characterizing a Rabphillin-3A-Like gene in a subject.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Aspartoacylase gene, protein, and methods of screening for mutations associated with canavan disease
Canavan disease, an autosomal recessive leukodystrophy, is caused by deficiency of aspartoacylase and accumulation of N-acetylaspartic acid in brain. Human aspartoacylase (ASP) cDNA spanning 1,435 bp has been cloned and expressed in E. coli. A base change, a854>c, has been found in 85% of the 34 Canavan alleles tested so far, which results in a missense glu285>ala mutation that is predicted to be part of the catalytic domain of aspartoacylase. The invention therefore provides nucleic acid sequences, genes, polypeptides, antibodies, vectors containing the gene, host cells transformed with vectors containing the gene, animal models for the disease, methods for expressing the polypeptide, genetic screening methods and kits, diagnostic methods and kits, methods of treating Canavan disease and methods of genetic therapy for the disease.
Owner:MIAMI CHILDRENS HOSPITAL RES INST
Protein Tyrosine Phosphate Mutations in Cancers
ActiveUS20080039417A1Growth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthCellular pathways
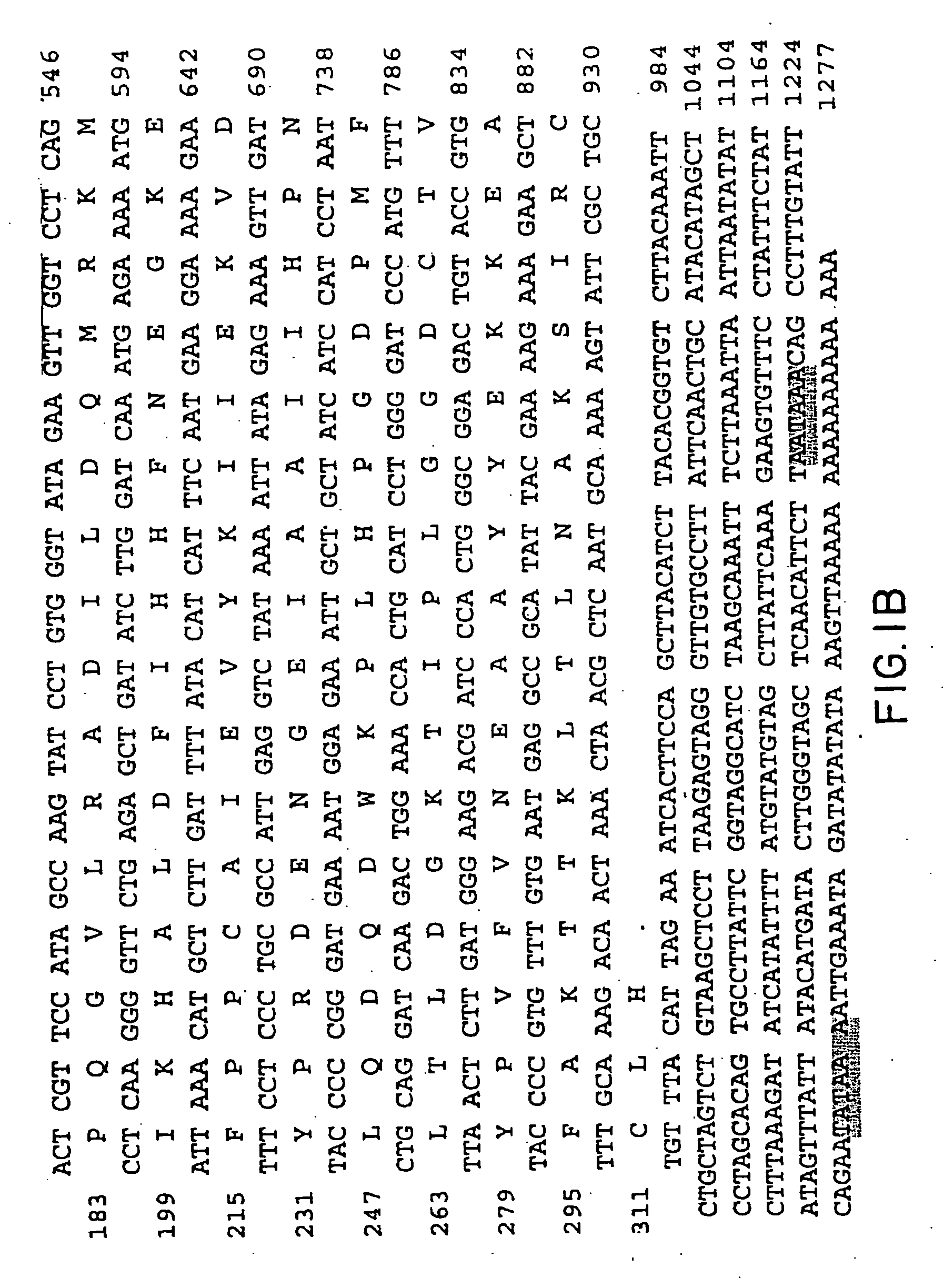
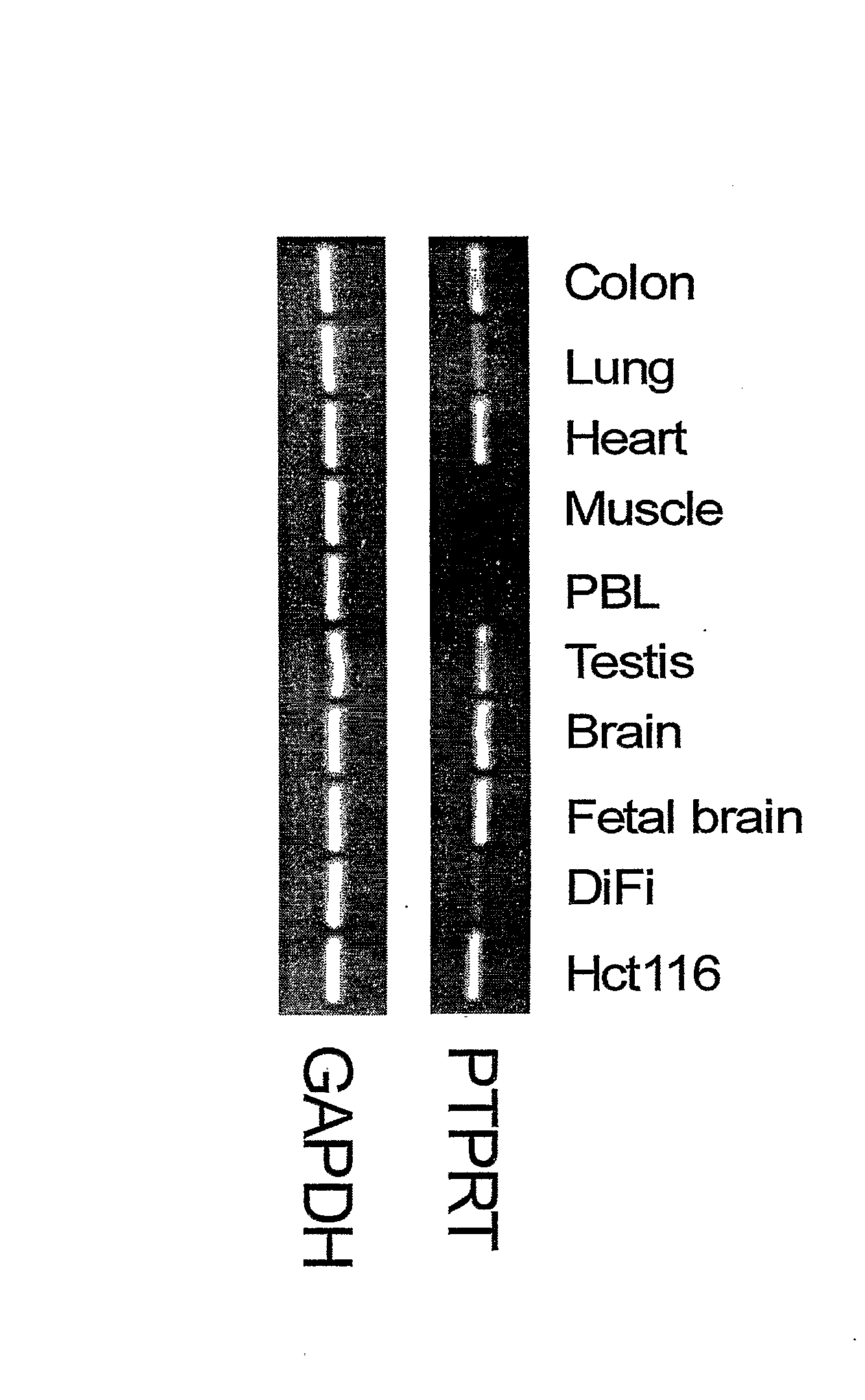
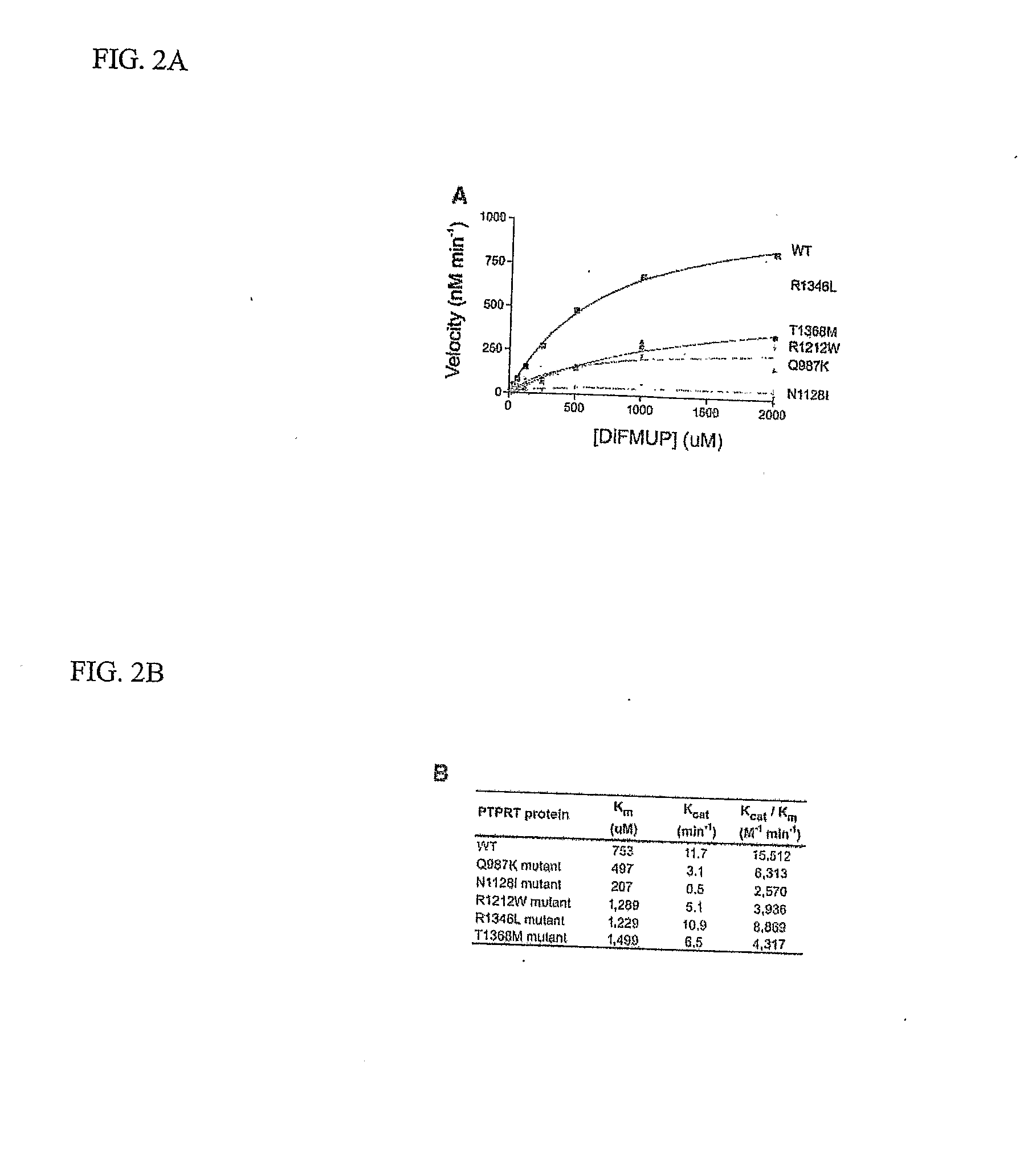
Tyrosine phosphorylation, regulated by protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) and kinases (PTKs), is important in signaling pathways underlying tumorigenesis. A mutational analysis of the tyrosine phosphatase gene superfamily in human cancers identified 83 somatic mutations in six PTPs (PTPRF, PTPRG, PTPRT, PTPN3, PTPN13, PTPN14) affecting 26% of colorectal cancers and a smaller fraction of lung, breast and gastric cancers. Fifteen mutations were nonsense, frameshift or splice site alterations predicted to result in truncated proteins lacking phosphatase activity. Five missense mutations in the most commonly altered PTP (PTPRP) were biochemically examined and found to reduce phosphatase activity. Expression of wild-type but not a mutant PTPRT in human cancer cells inhibited cell growth. These observations suggest that the tyrosine phosphatase genes are tumor suppressor genes, regulating cellular pathways that may be amenable to therapeutic intervention.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
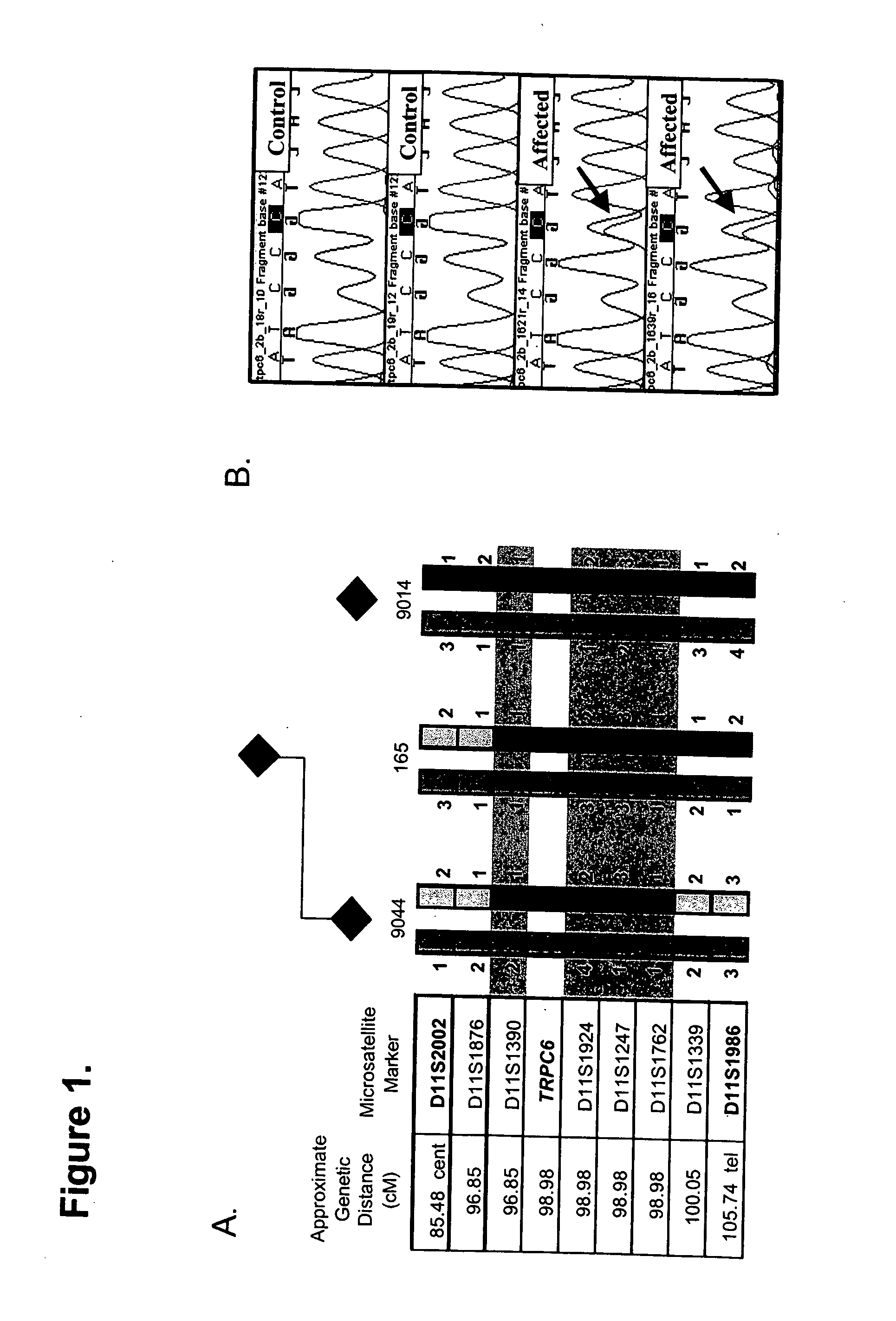
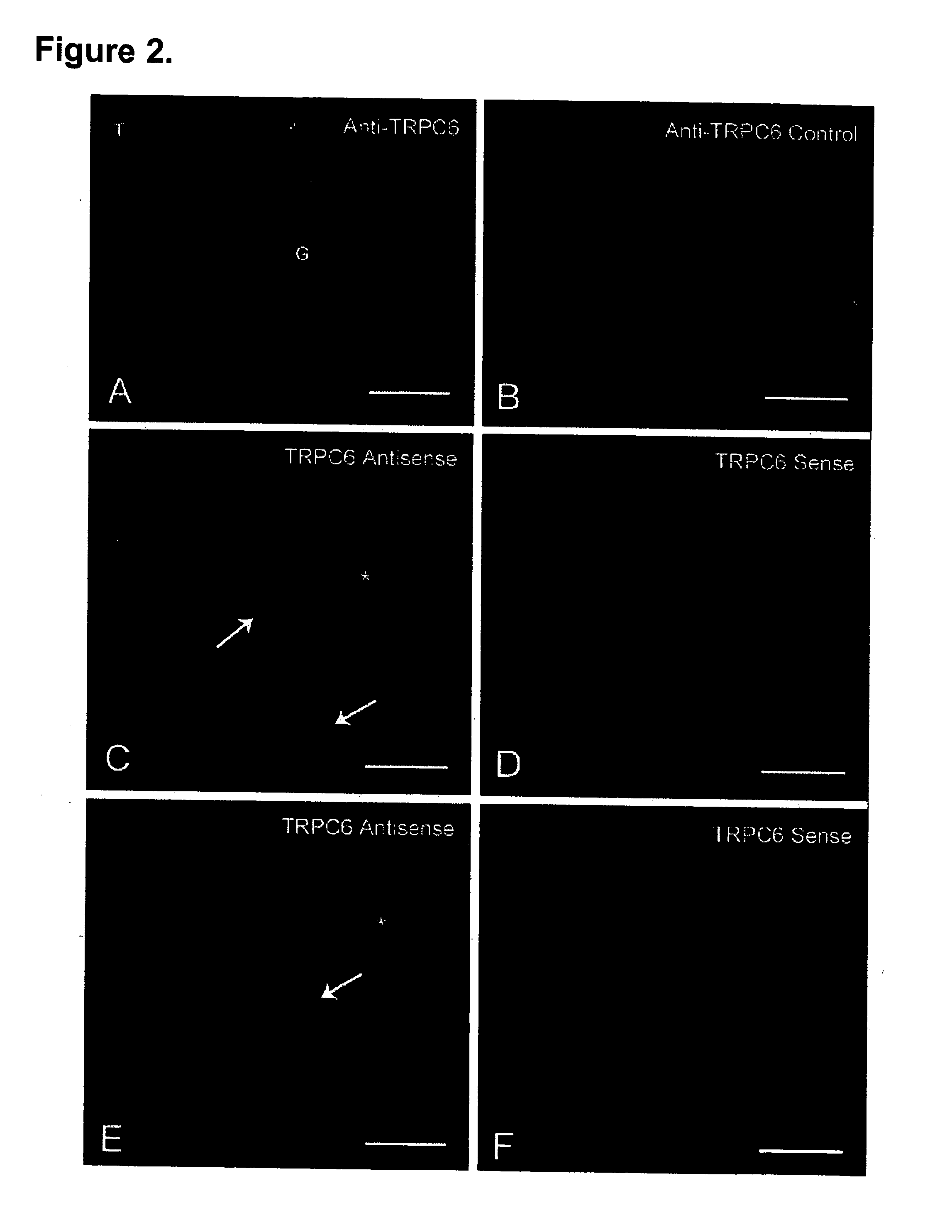
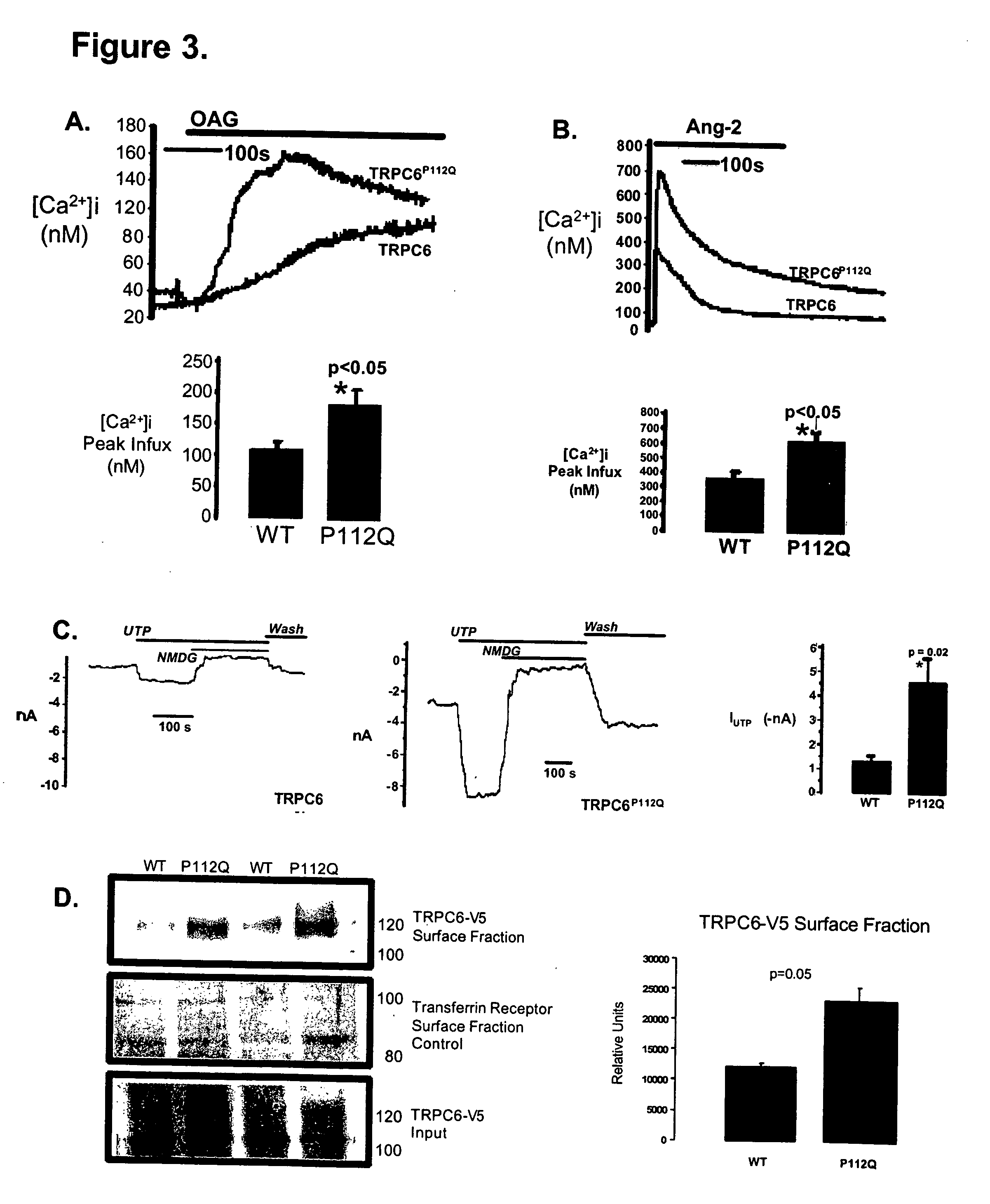
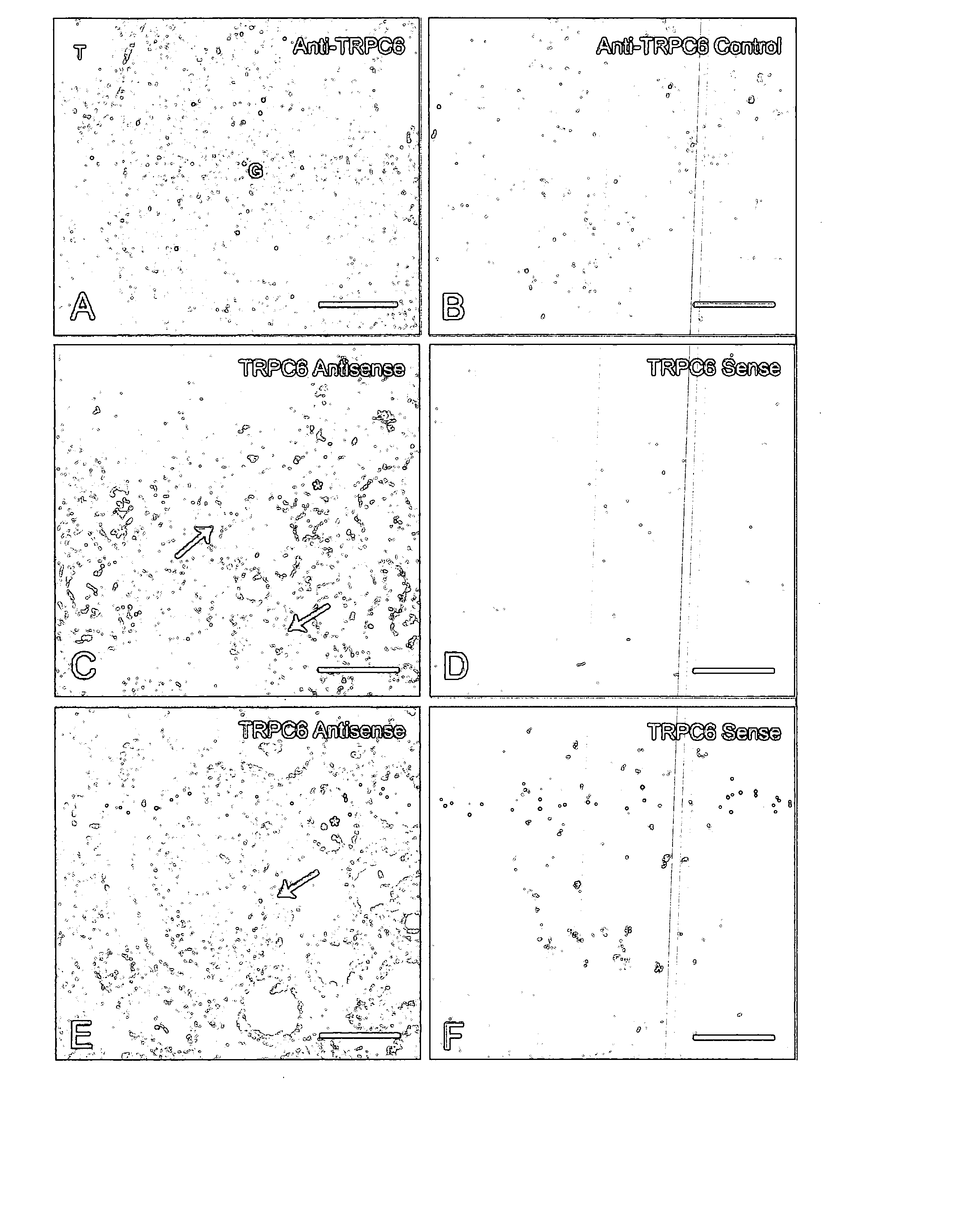
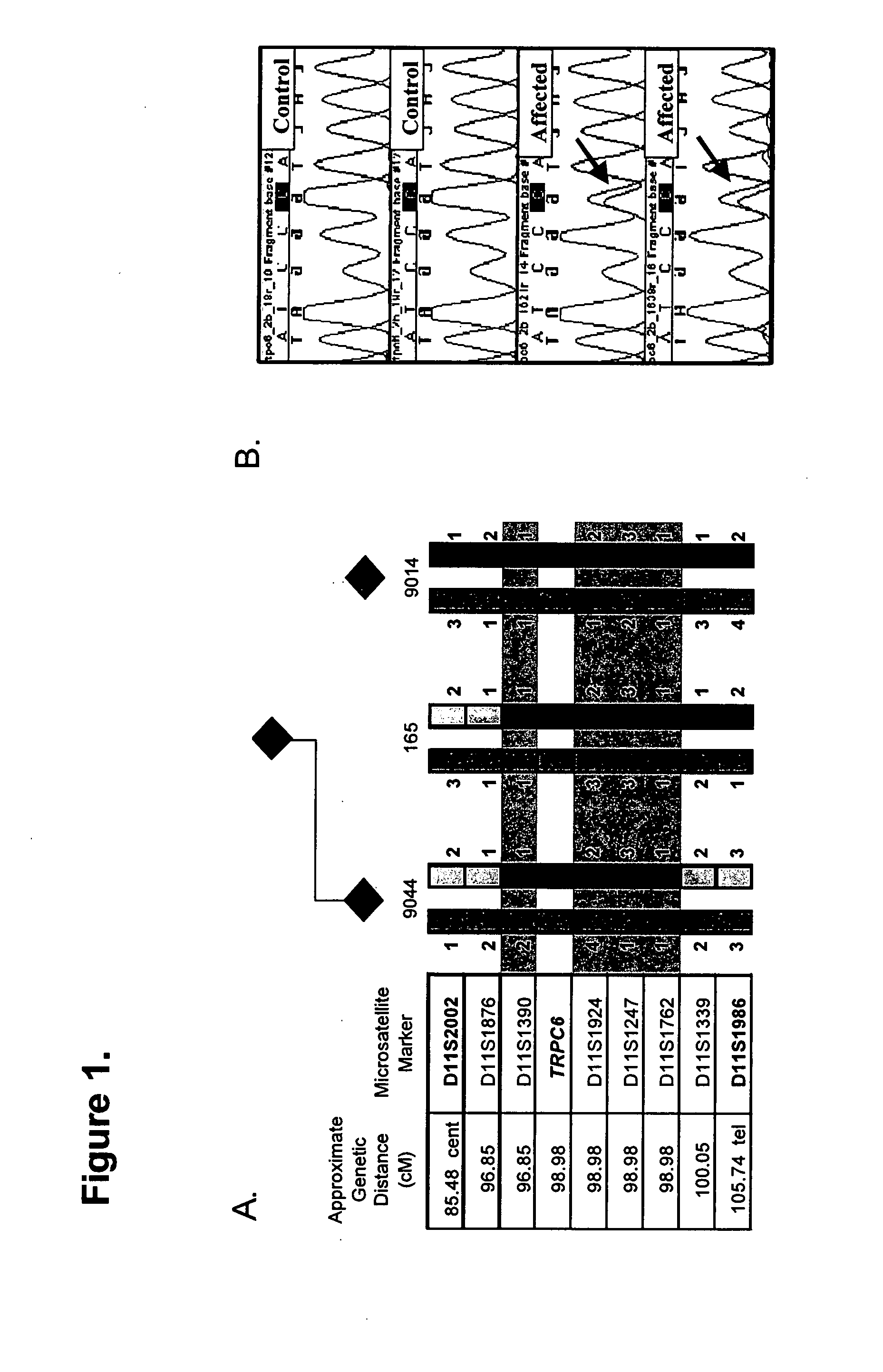
TRPC6 involved in glomerulonephritis
InactiveUS20060257500A1Calcium ion influx is thereby reducedCompound screeningBiocideEtiologyDisease
Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a kidney disorder of unknown etiology and up to 20% of patients on dialysis have this diagnosis. A large family with hereditary FSGS carries a missense mutation in the TRPC6 gene on chromosome 11q, encoding the ion channel protein Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel 6. The missense mutation is a P112Q substitution, which occurs in a highly conserved region of the protein, enhances TRPC6-mediated calcium signals in response to agonists such as angiotensin II, and alters the intracellular distribution of TRPC6 protein. Previous work has emphasized the importance of cytoskeletal and structural proteins in proteinuric kidney diseases. Our findings suggest a novel mechanism for glomerular disease pathogenesis.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
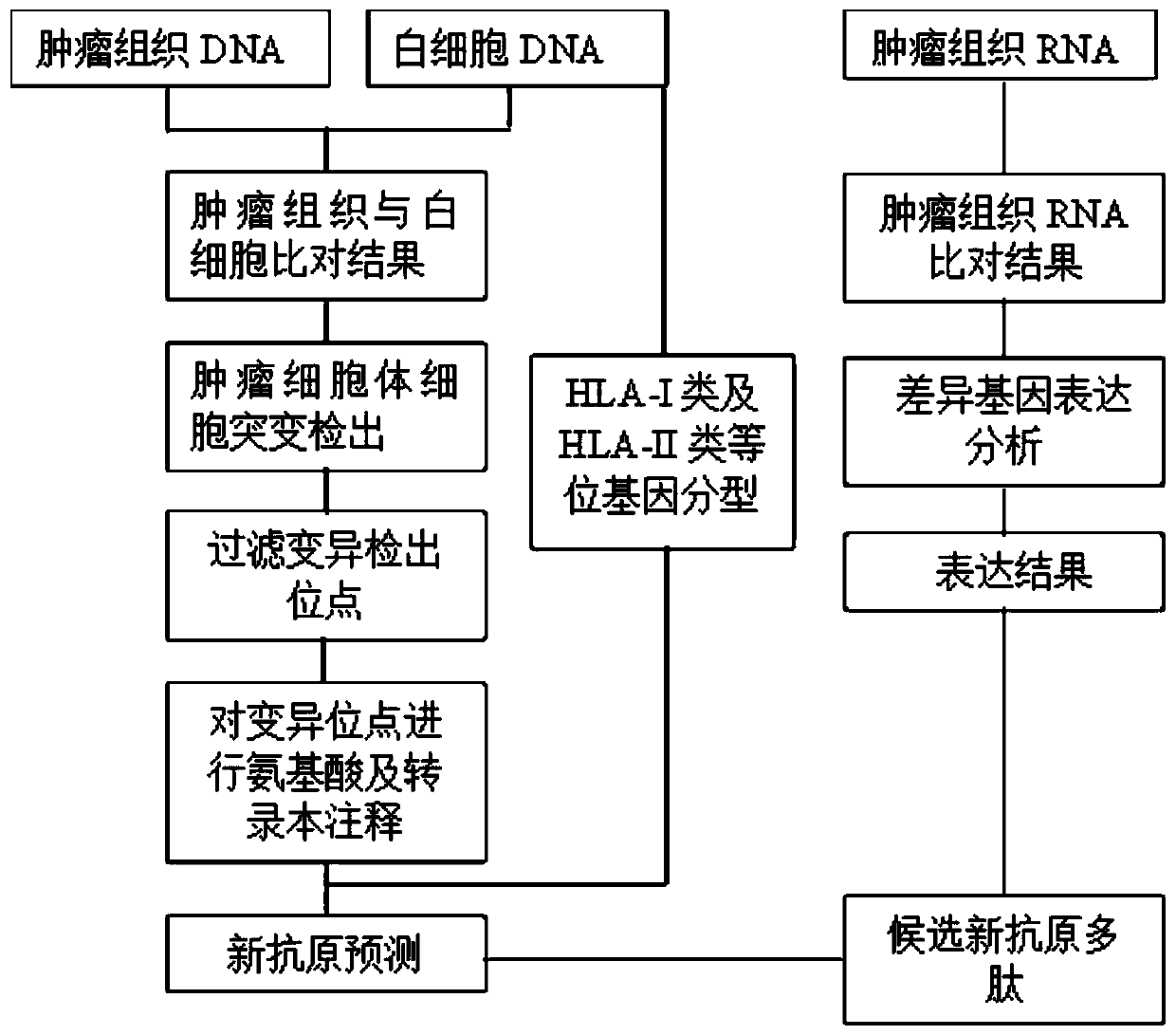
Method for predicting tumor neoantigen and its application
The invention discloses a method for predicting a tumor neoantigen and its application. The prediction method includes the following steps: S1, obtaining a tumor sample and a plasma leukocyte sample of a tumor patient, constructing a sequencing library, and performing whole genome, whole exome or targeted capture RNA, DNA sequencing; S2, using the plasma leukocyte DNA as a contrast, comparing thetumor sample DNA and detecting somatic mutation, filtering out a missense mutation site, and annotating the filtered missense mutation site; S3, using the plasma leukocyte DNA sequencing data to typeHLA-I and HLA-II alleles; and S4, predicting antigenic polypeptides that can bind to HLA-I and HLA-II alleles. The method of the present invention can more accurately screen out an antigen that can beexpressed genes and that can bind to HLA-I and HLA-II alleles and cause antitumor immune response.
Owner:BEIJING USCI MEDICAL LAB CO LTD
SLC39A7 gene as genetic label of pig fat deposition description and application thereof
The invention pertains to the technical field of pig genetics and breeding and assistant selection by molecular marker, in particular to a genetic marker for screening SLC39A7 gene of pig fat deposition trait. The genetic marker has a nucleotide sequence as shown in sequence table SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO. 2. A missense mutation of A250-G250 is shown in the place of 250bp in the SEQ ID NO.1, which causes the coded amino acid to be changed from arginine to glycine and causes polymorphism of HpaII-RFLP. The genetic marker of the invention is adopted to do relative analysis of relative fat deposition trait of foreign pig variety and local variety in China. The invention also discloses a detection method of SNP typing of a third exon in SLC39A7 gene and provides the novel genetic marker and the detection method for assistant selection by molecular marker.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Mitofusins, Fzo Homologs and functional derivatives thereof
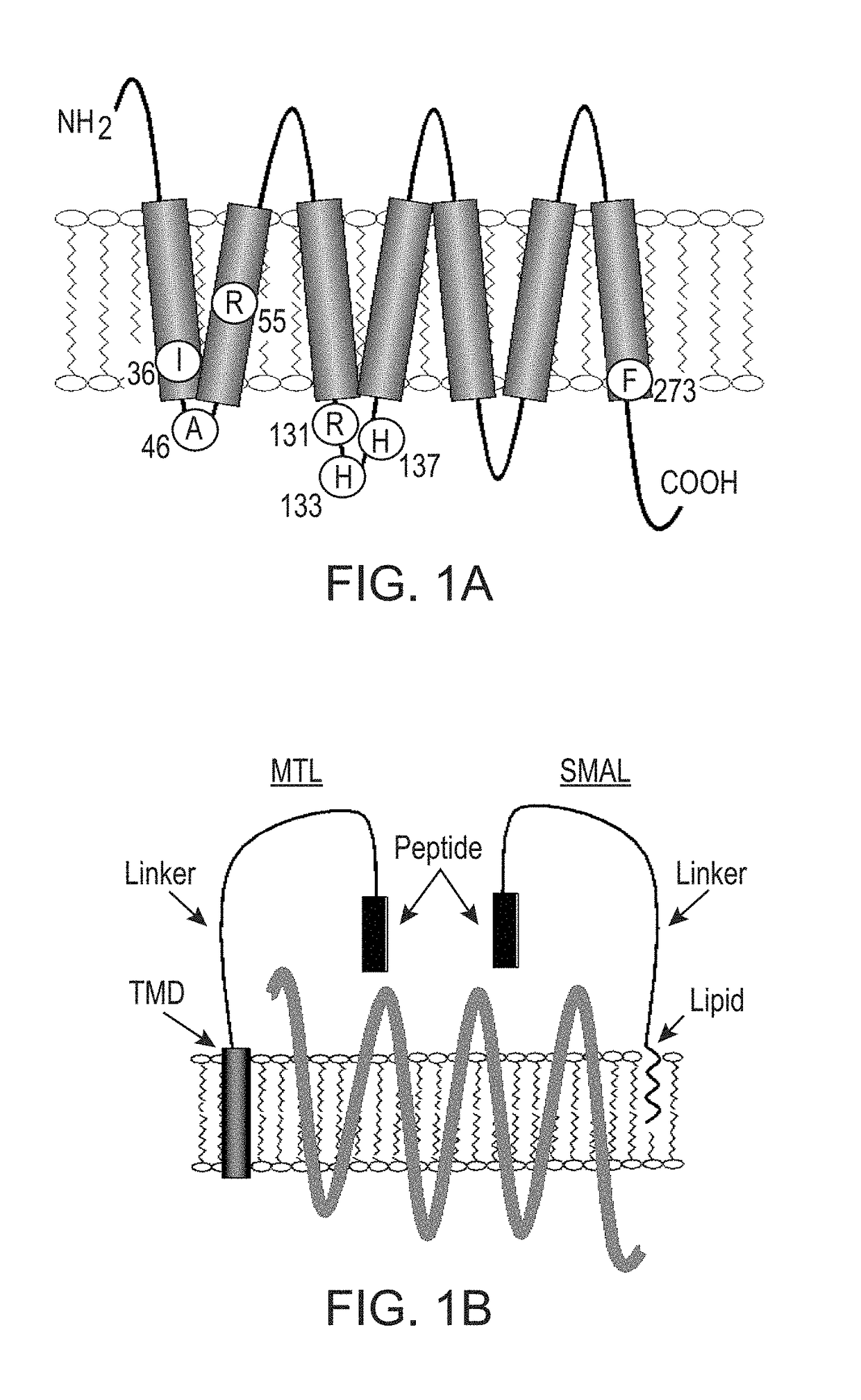
Mitofusin genes and encoded polypeptides are provided, including the Drosophila Fzo protein and its homologs from insects, other invertebrates, yeast, and vertebrates including mouse and humans. Mitofusins are large predicted GTPases with a predicted trans-membrane domain, coiled-coil regions, and a C-terminal region showing a high pI. The mitofusins are the first known protein mediator of mitochondrial fusion, and mediate developmentally regulated post-meiotic fusion of mitochondria. Missense mutations that alter conserved residues required for GTP binding in other GTPases inhibit the in vivo fusogenic activity of Fzo but do not affect its localization. Fusion proteins having amino acid sequences from mitofusin transmembrane regions localize to mitochondria. Mitofusins may be used in methods of identifying anti-insect and antifungal agents. Functional derivatives of mitofusins useful for such methods are described.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Detection of mutations in acta2 and myh11 for assessing risk of vascular disease
InactiveUS20110028331A1Increased riskMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningLower riskA-DNA
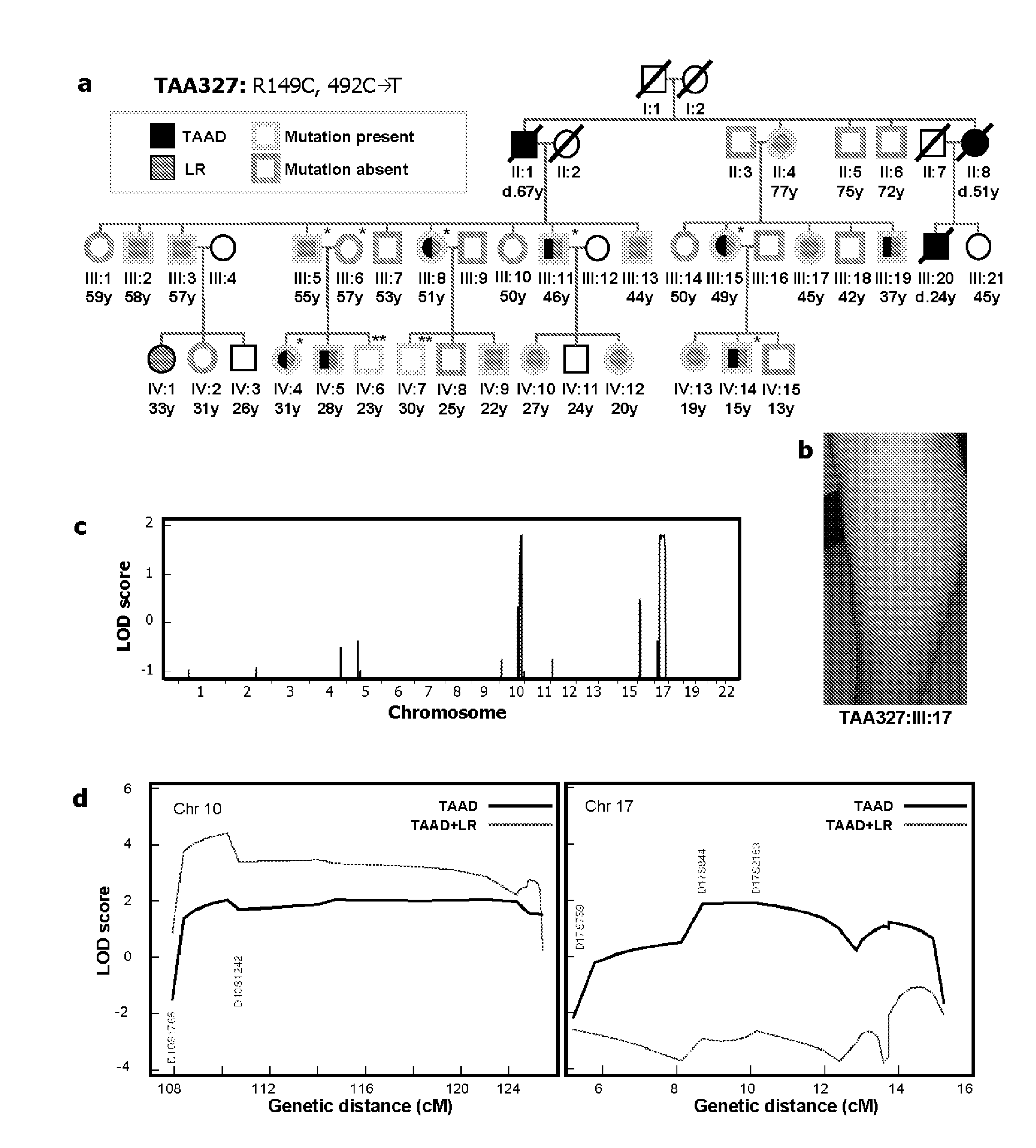
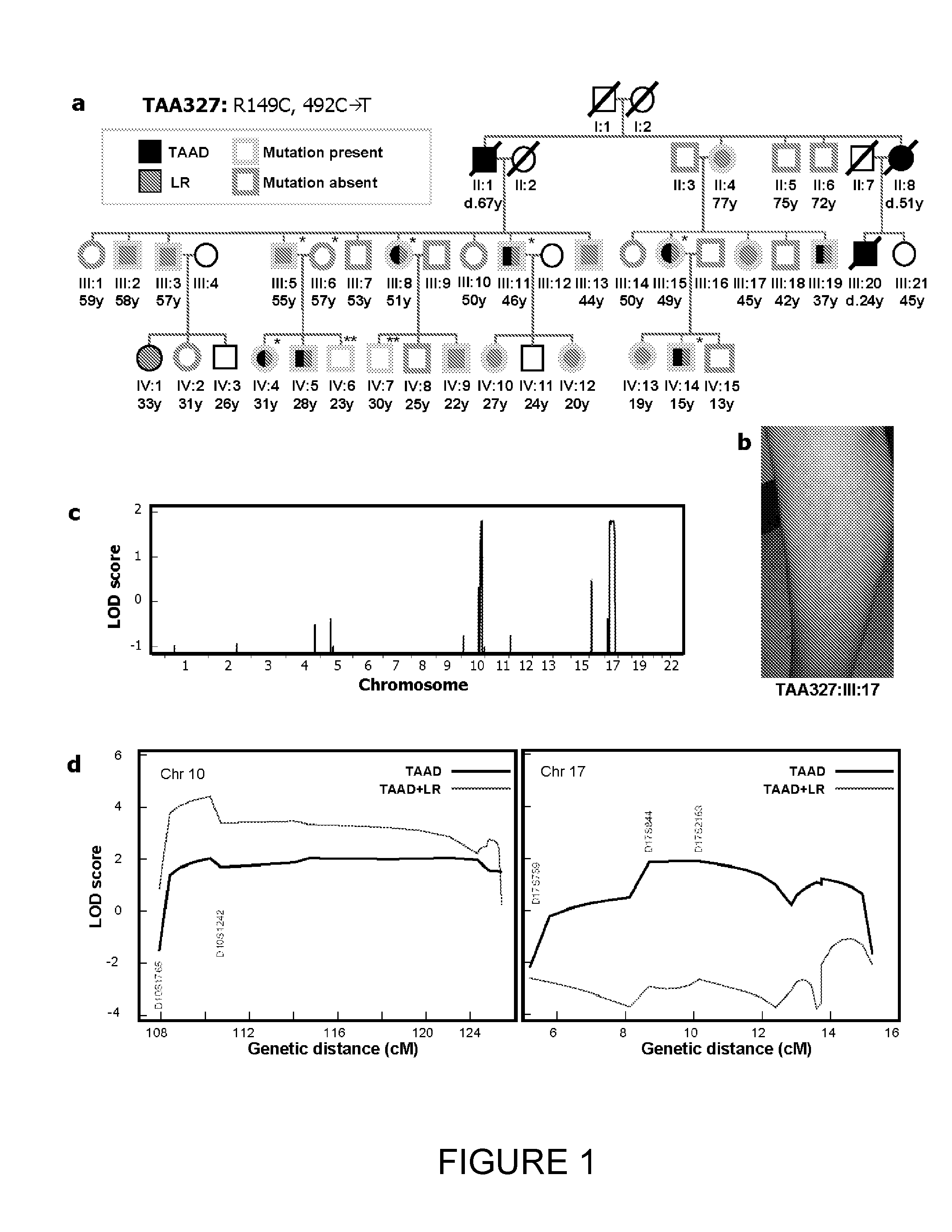
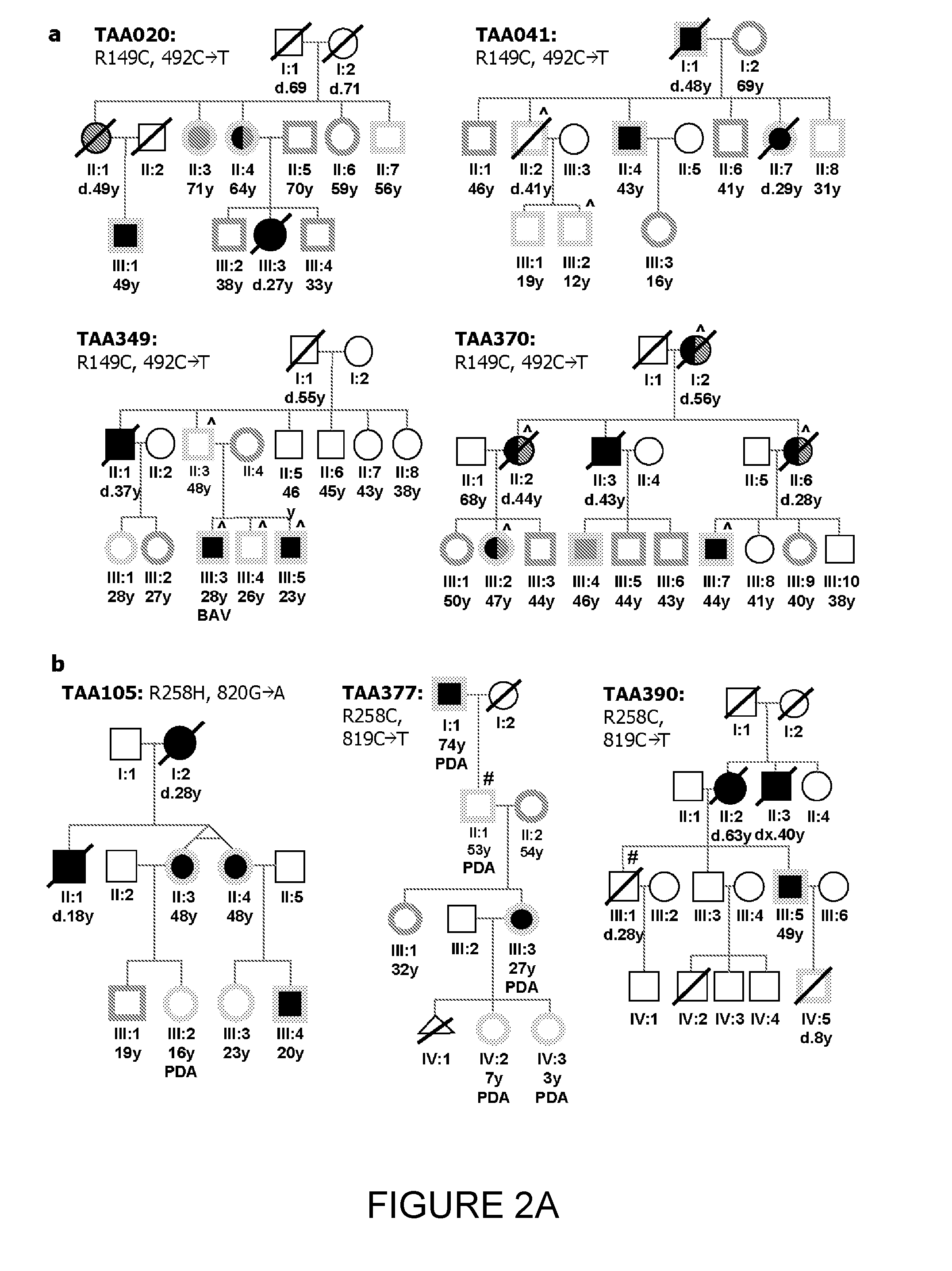
A method of detecting in an individual an increased risk of hyperplastic vasculomyopathy, or a vascular disease resulting therefrom is disclosed. The method comprises obtaining a DNA genome sample from the individual and detecting in the sample a missense mutation in a gene which is a component of a smooth muscle cell contractile unit. In some embodiments the gene is ACTA2 and in some embodiments the gene is MYH11. In some embodiments, the gene is sequenced and then compared to a panel of control gene sequences which are representative of the same gene in individuals without vascular disease or who are at low risk of developing hyperplastic vasculomyopathy, to detect any missense mutations in the gene. The presence of a missense mutation in the gene indicates an increased risk of hyperplastic vasculomyopathy.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Beta-catenin oligonucleotide microchip and method for detecting beta-catenin mutations employing same
InactiveUS20050176016A1Fast and reliableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBeta-cateninΒ catenin mutation
Owner:NAT CANCER CENT
New mutation of PEB (Phosphatidylethanolamine Binding Protein) virulence gene and application thereof
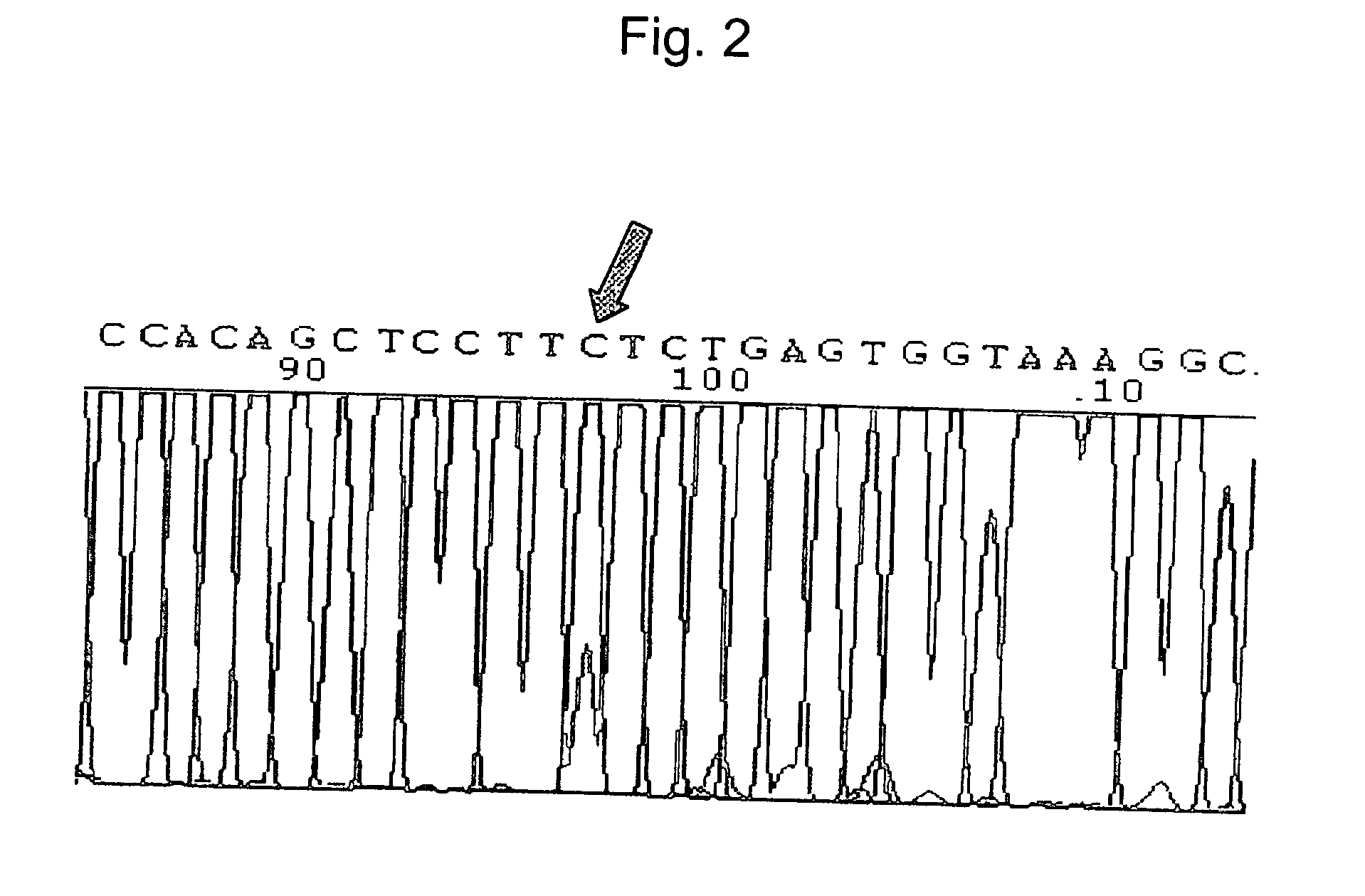
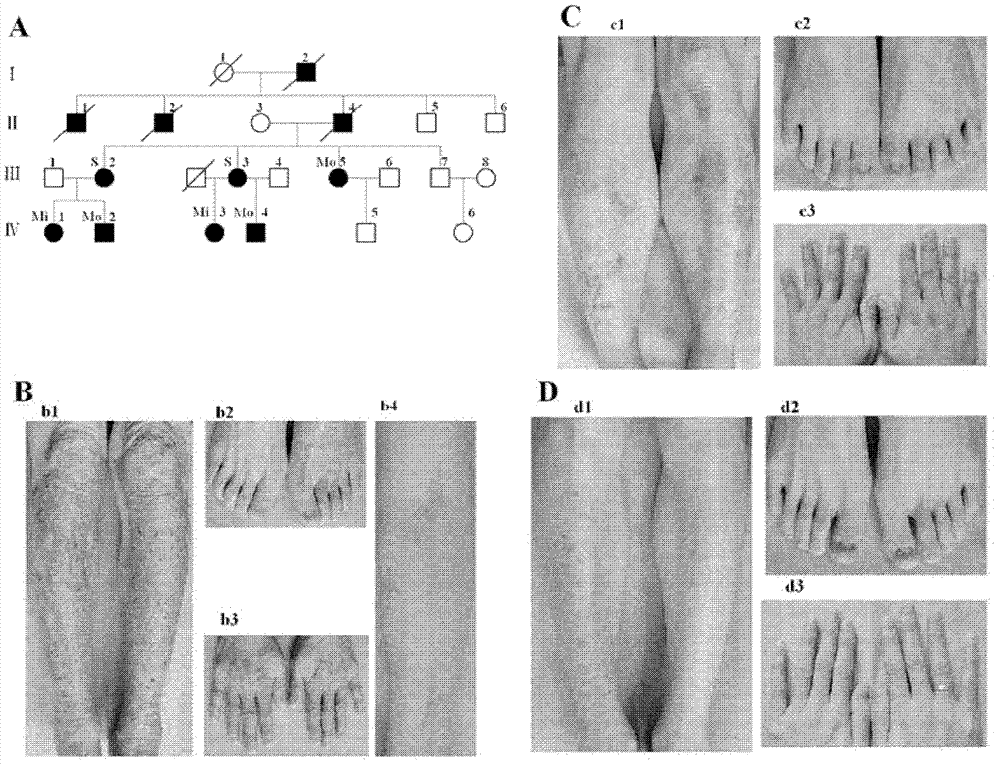
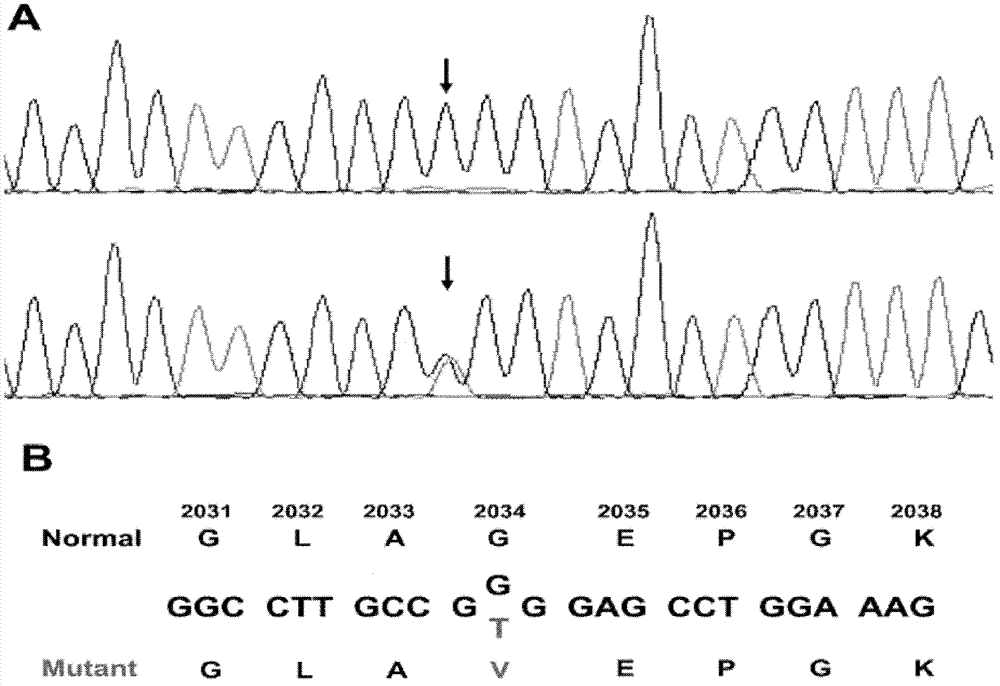
The invention relates to a new mutation of a PEB (Phosphatidylethanolamine Binding Protein) virulence gene and an application thereof. Specifically, a COL7A1 new mutation of a PEB virulence gene is found for the first time by virtue of large-scale screening by the inventor. The inventor takes PEB affected pedigree as a research target, performs exome sequencing and comparison on affected individuals and non-affected individuals in the pedigree and accidently finds a missense mutation (G>T) in the 73rd exon of the COL7A1 gene; due to the mutation, glycocoll Gly of the 2034th of the COLA1 protein is mutated as valine Val; the mutation is highly conservative in the patients; and by applying the mutation, the anterior epidenmoiysis bulbse can be detected.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
Lymphohematopoietic engineering using cas9 base editors
PendingUS20210040507A1Easily damagedGenetically modified cellsStable introduction of DNABase JEngineered genetic
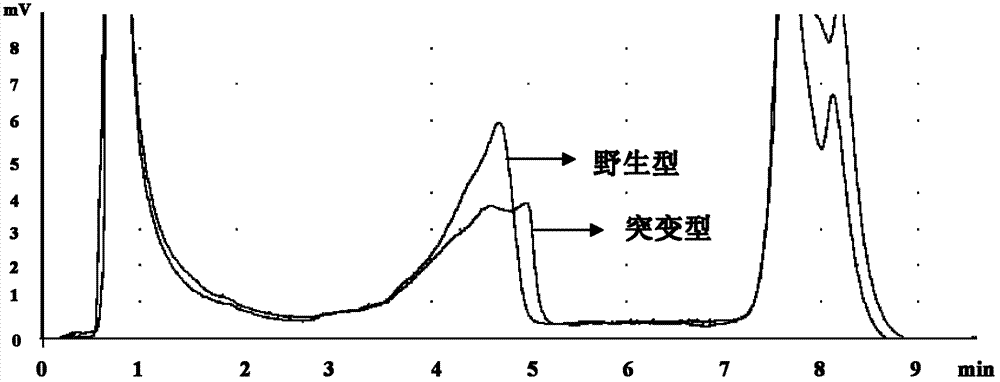
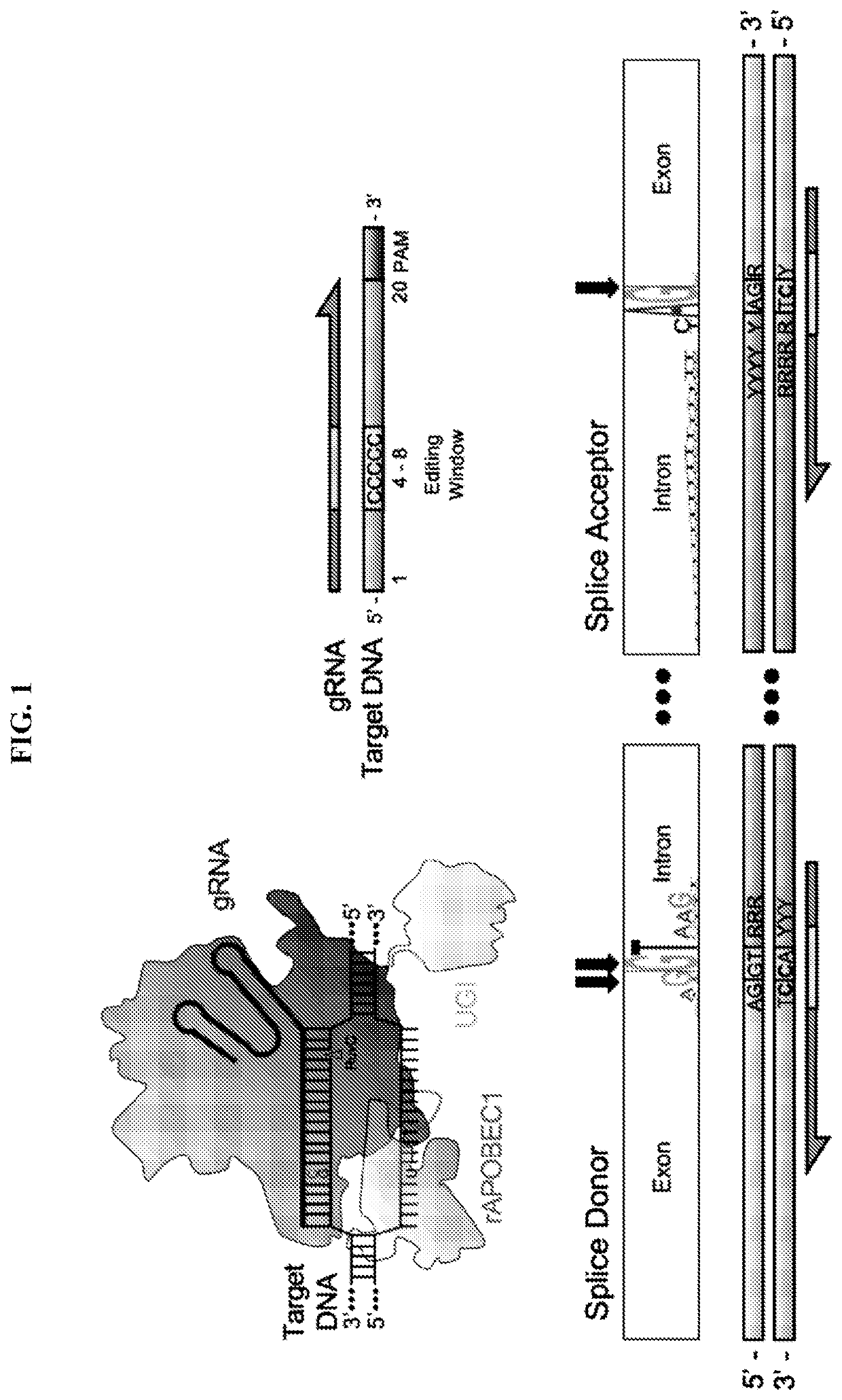
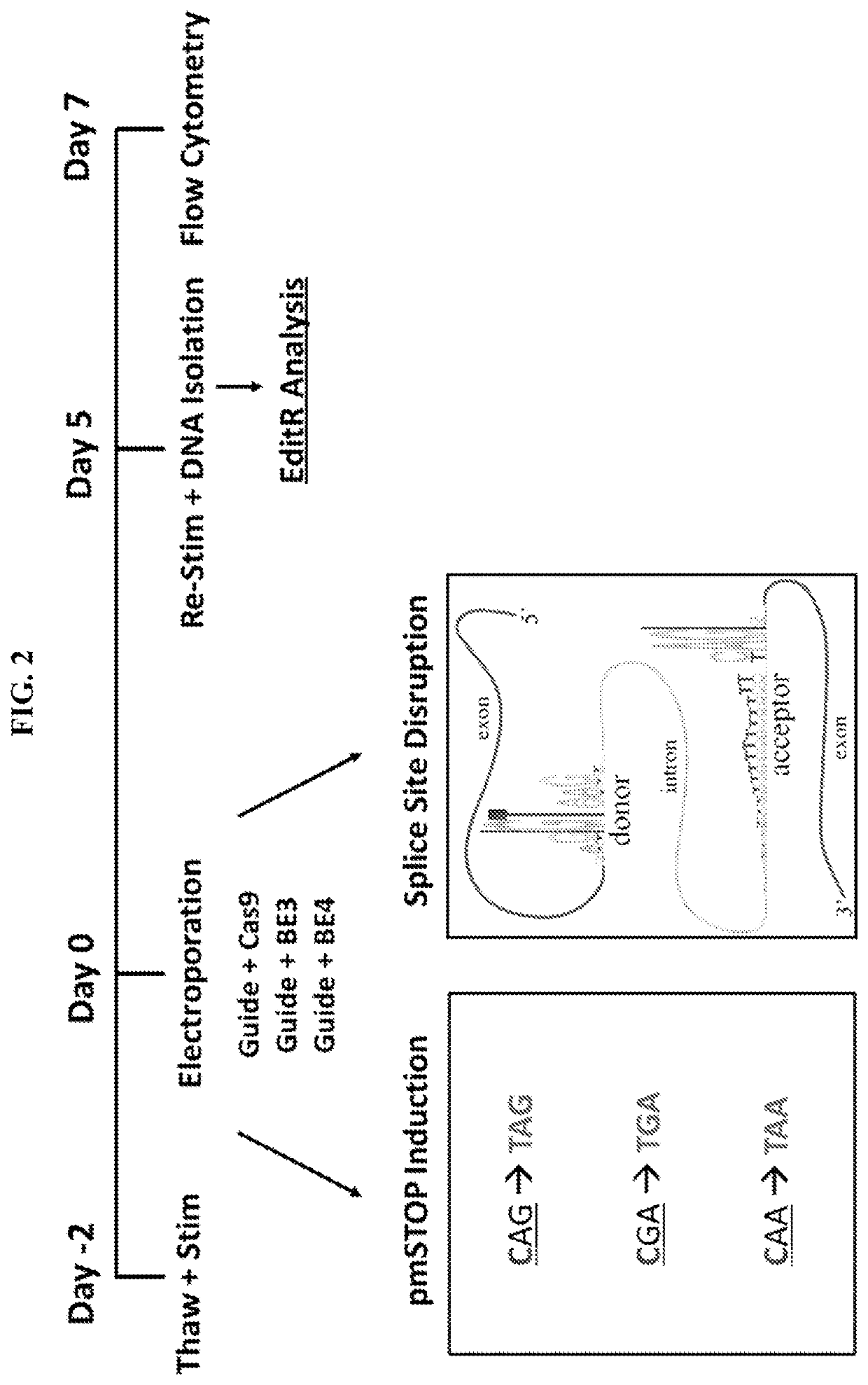
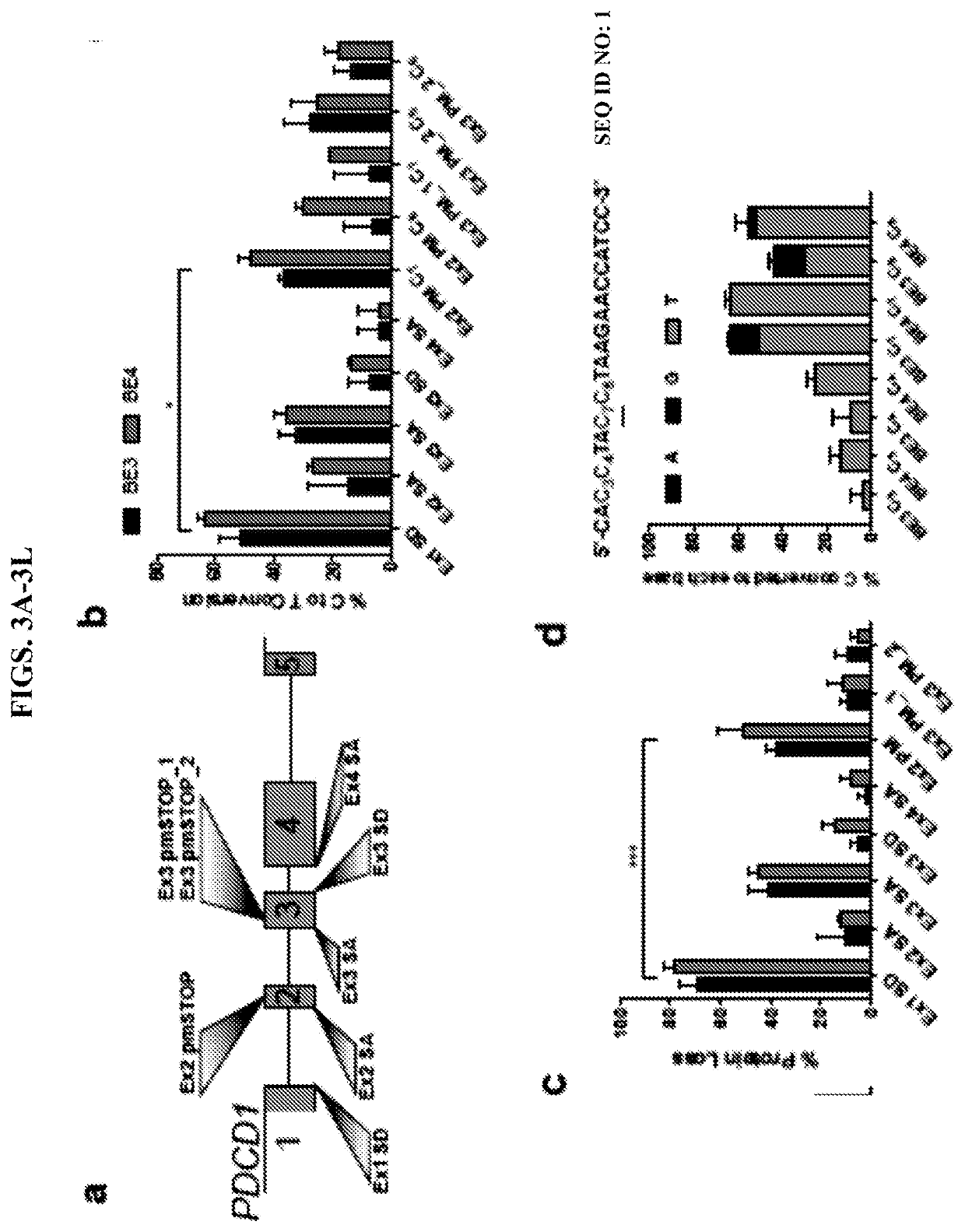
Provided herein are methods and systems for targeted gene disruption (knock-out, missense mutation) and targeted gene knock-in in mammalian cells using base editors and guide RNAs (gRNAs) designed to target splice acceptor-splice donor sites. Also provided herein are universally acceptable genetically engineered cells comprising targeted disruptions in immunotherapy-related genes and comprising a CAR / TCR for therapeutic applications.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Truncated crispr-cas proteins for DNA targeting
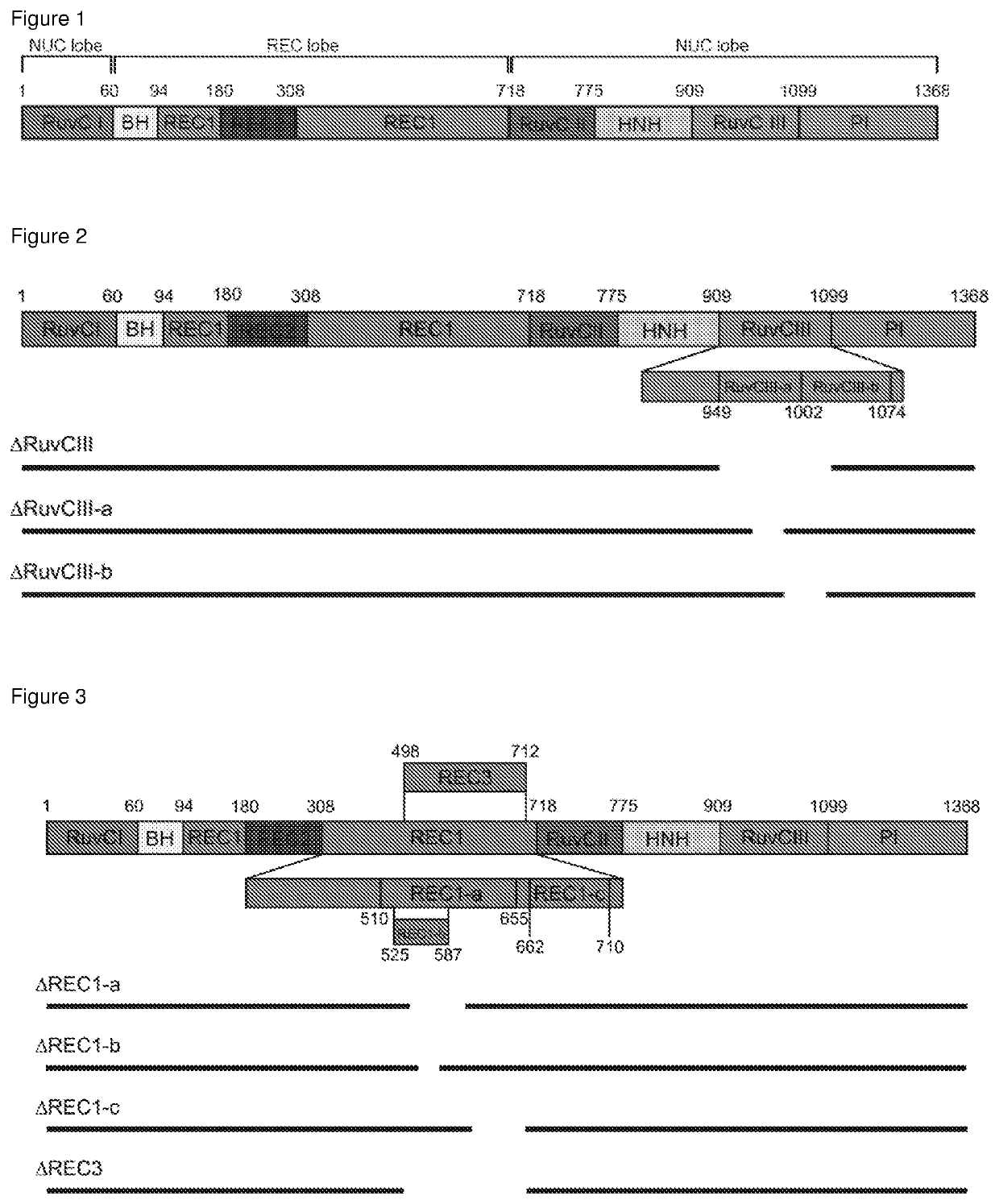
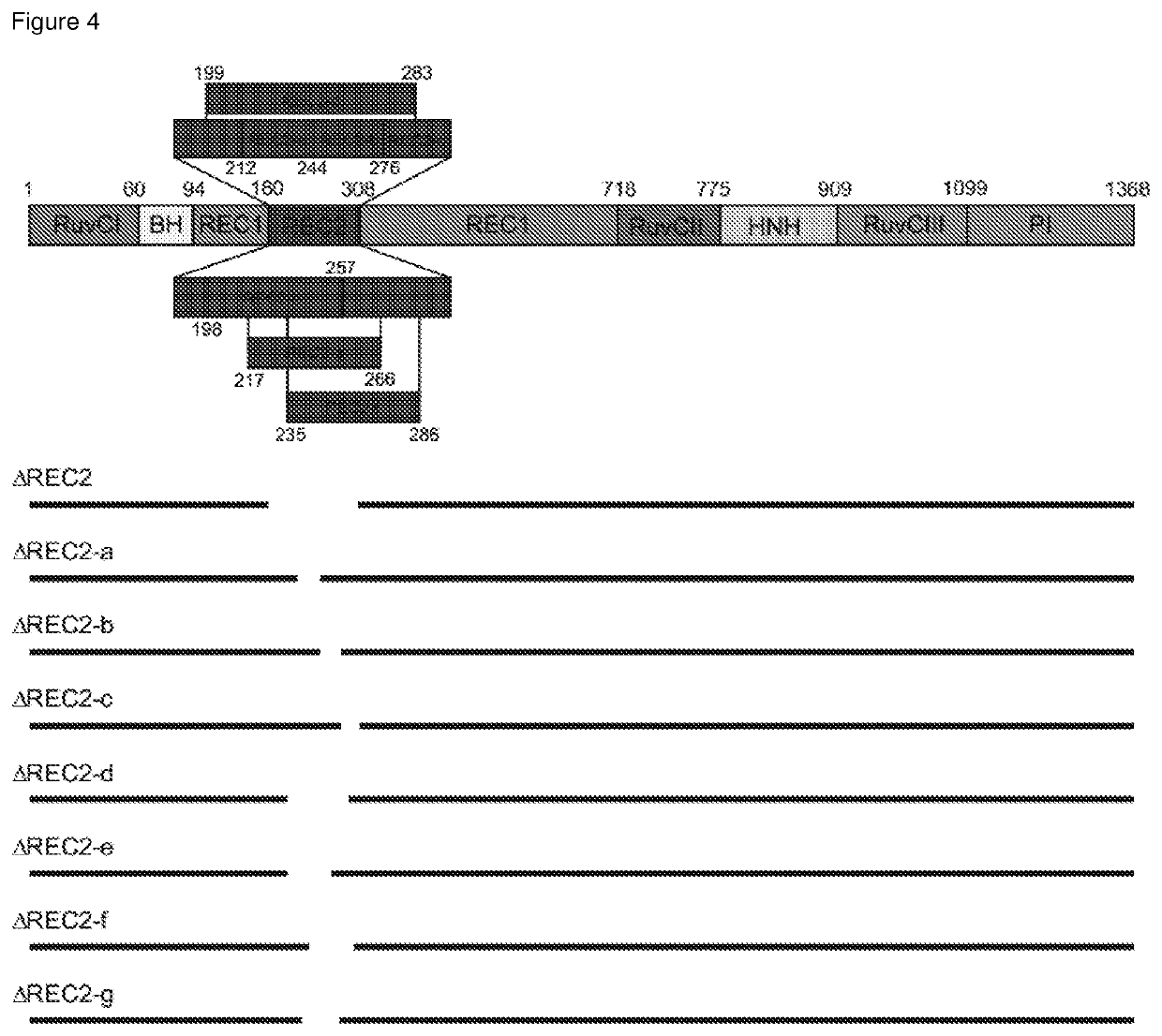
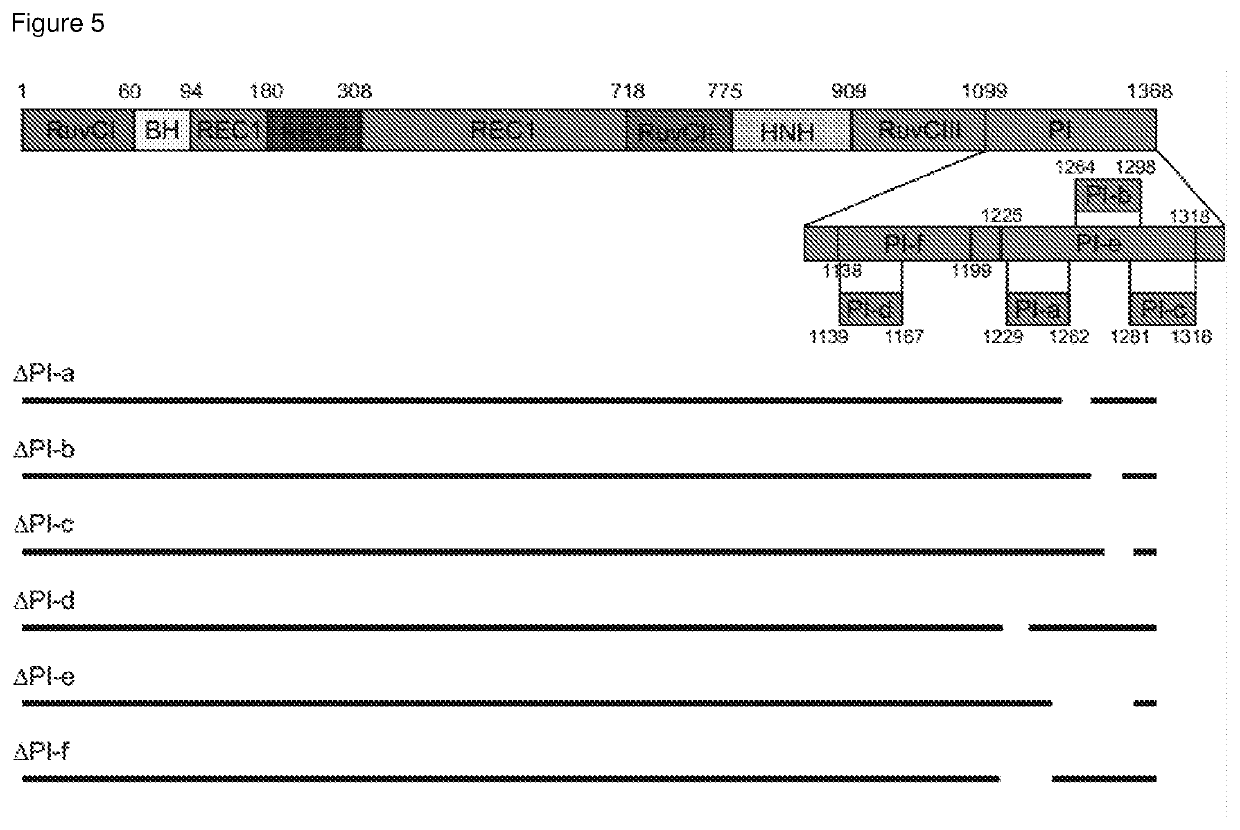
The present invention relates to a polypeptide comprising at least one at least one deletion selected from the group consisting of ΔHNH (Δ775-909), ARuvCIII-b (Δ1002-1074), AREC1-a (Δ510-655), AREC1-b (Δ525-587), AREC1-c (Δ662-710), AREC2 (Δ180-308), AREC2-a (Δ212-244), AREC2-b (Δ244-276), AREC2-c (Δ276-308), AREC2-d (Δ199-283), AREC2-e (Δ198-257), AREC2-f (Δ235-286), AREC2-g (Δ217-266), AREC3 (Δ498-712) and combinations thereof, wherein the position numbering is in accordance with SEQ ID NO: 1 encoding for S. pyogenes Cas9, and wherein the polypeptide has CRISPR-Cas DNA-binding activity. The polypeptide may further comprises a missense mutations selected from G12R, T13K, T13R, N14K, N497K, T657K, T657R, N767K, T770K, T770R, Q920K, Q920R, S1109R, D1135K, D1135R, S1338R and combinations thereof. Also claimed are nucleic acid molecules encoding for said polypeptides, compositions and method of site-directed engineering of a target DNA thereof.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV +1
TRPC6 involved in glomerulonephritis
ActiveUS20080038365A1Calcium ion influx is thereby reducedOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsZona glomerulosaDisease
Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a kidney disorder of unknown etiology and up to 20% of patients on dialysis have this diagnosis. A large family with hereditary FSGS carries a missense mutation in the TRPC6 gene on chromosome 11q, encoding the ion channel protein Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel 6. The missense mutation is a P112Q substitution, which occurs in a highly conserved region of the protein, enhances TRPC6-mediated calcium signals in response to agonists such as angiotensin II, and alters the intracellular distribution of TRPC6 protein. Previous work has emphasized the importance of cytoskeletal and structural proteins in proteinuric kidney diseases. Our findings suggest a novel mechanism for glomerular disease pathogenesis.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
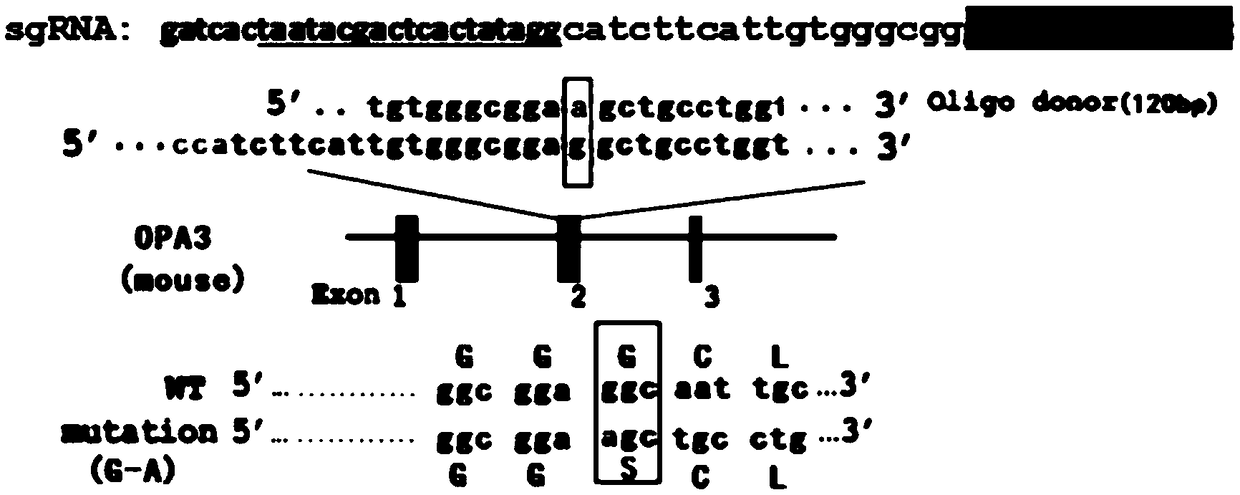
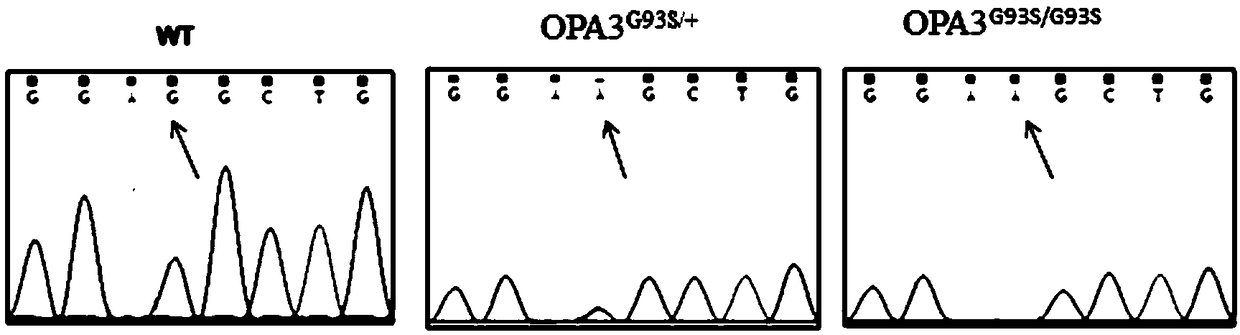
Construction method, construction kit and application of optic atrophy animal model
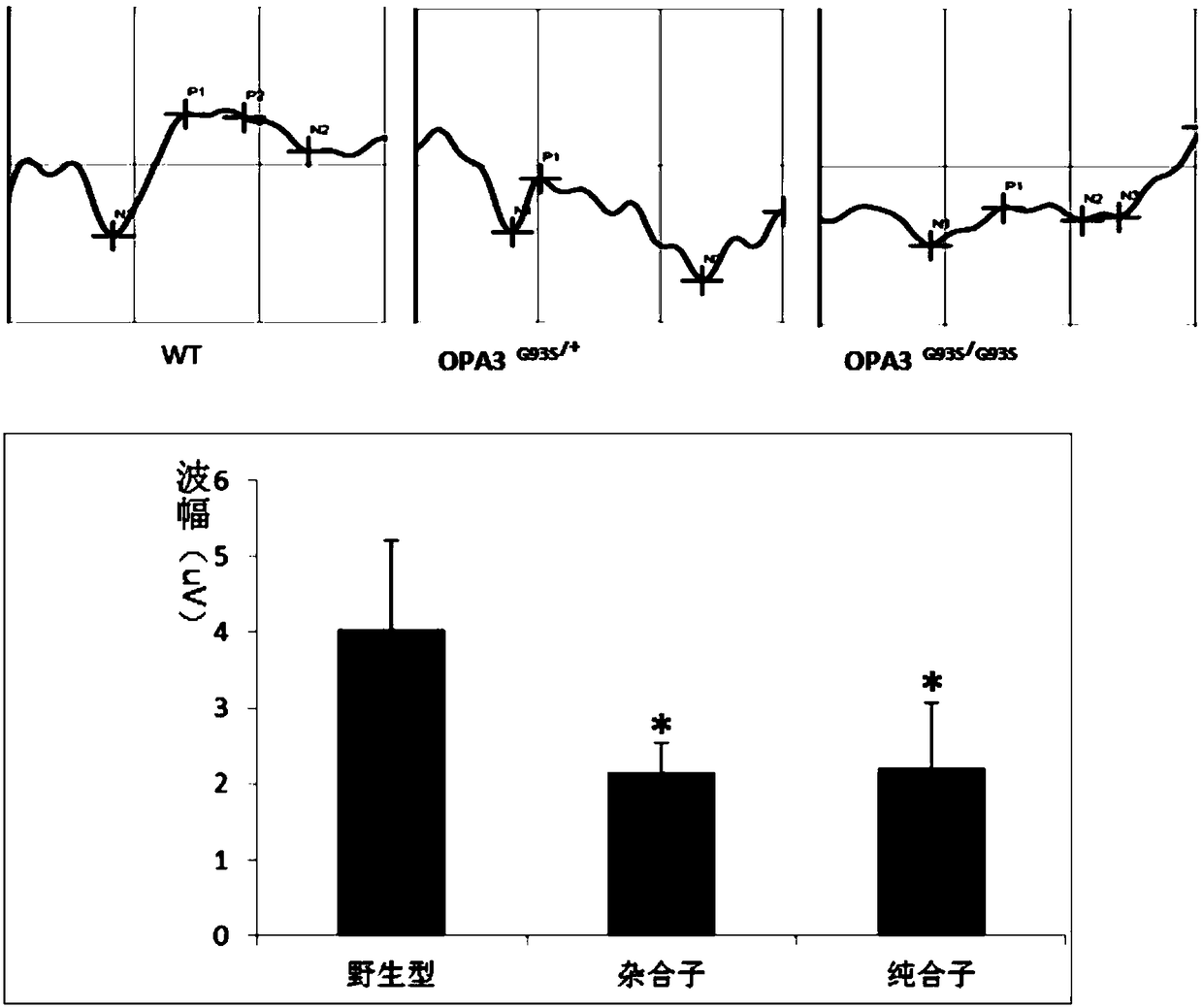
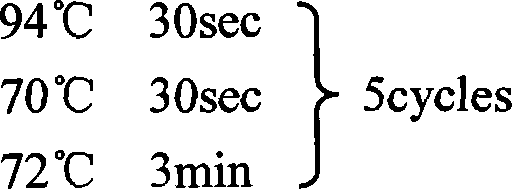
ActiveCN109022485AMany categoriesTypical features of optic atrophyNucleic acid vectorAnimals/human peptidesAtrophyExon
The invention discloses a construction method, a construction kit and an application of an optic atrophy animal model, and relates to the biotechnical field. The construction method is characterized in that a base at the 277th locus of an exon 2 of an animal OPA3 gene mutates from G to A to cause missense mutation, an amino acid residue mutating from G to S, of the 93rd position of an encoded OPA3protein, and an animal containing the mutation exhibits typical optic atrophy disease characteristics and can be used as the optic atrophy animal model. The animal model fills a gap in human autosomal dominant optic atrophy animal models, enriches the type of existing optic atrophy animal models, and facilitates the development of researches on ophthalmic diseases.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
DNA fragment related to pig polydactyly
The invention provides a DNA fragment relating to a swine polydactyly. The DNA fragment is one of the following polynucleotide: (1) the polynucleotide with the nucleotide sequence of SEQ NO.1 and SEQ NO.2; (2) the polypeptide polynucleotide with the encoding amino acid sequence of SEQ NO.2 and SEQ NO.4. The DNA fragment of the invention has a close relation with the development of swine limbs. The missense mutation of the former four codons of an Exon 16 directly results the polydactuly of swine toes. Therefore, the invention provides a method for detecting the development phenotype of the swine. The method adopts the following premiers to increase reverse transcription products of the general RNA of the swine: 5'-CGC CGT GGC TTG TAA CAT TCT CTG C-3', 5'-AAG CAG TGG TAT CAA CGC AGA GT-3'. The product of the normal swine is 197bp, the product of the pilydactyly swine is 636bp.
Owner:CHONGQING ACAD OF ANIMAL SCI
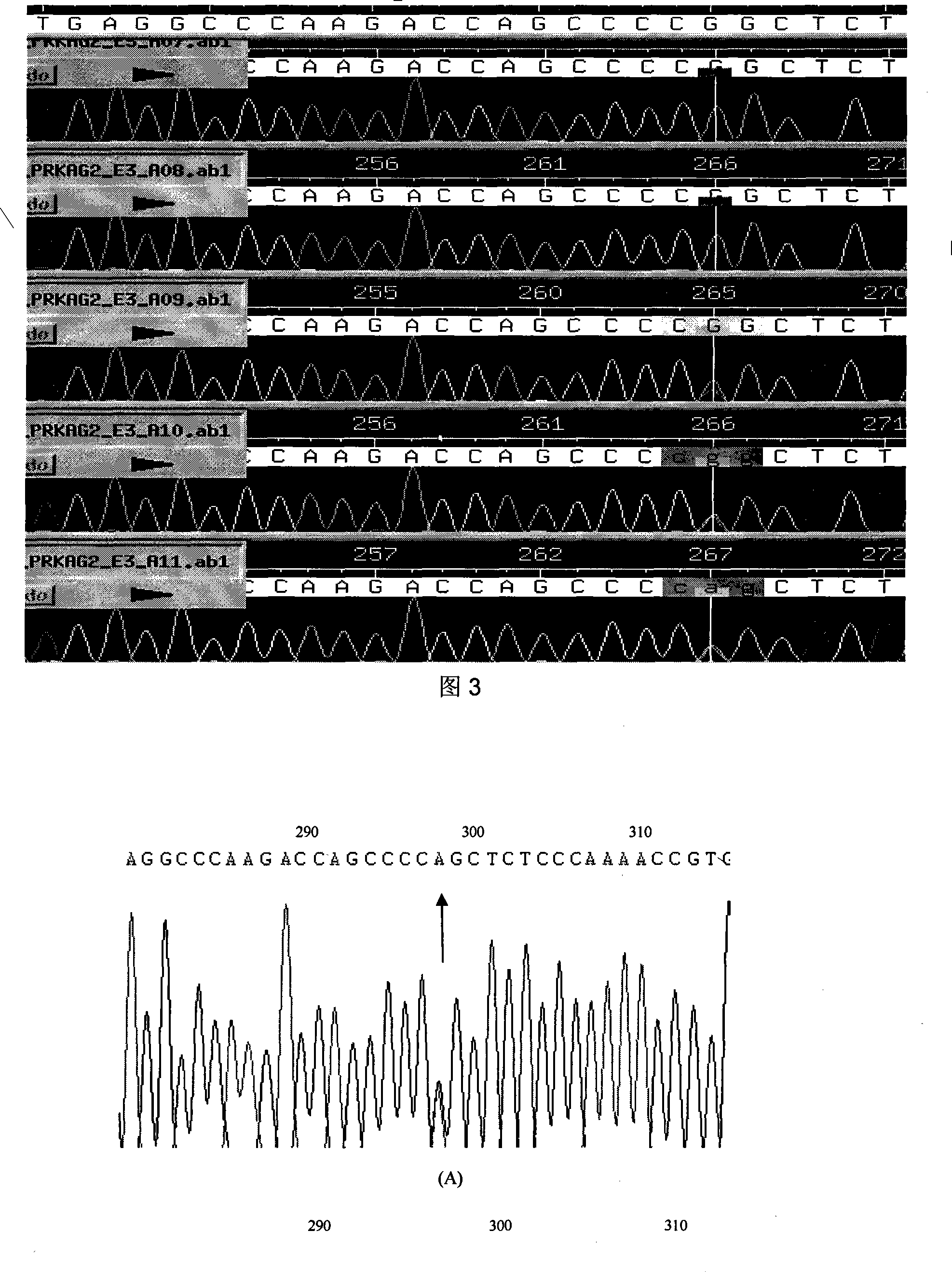
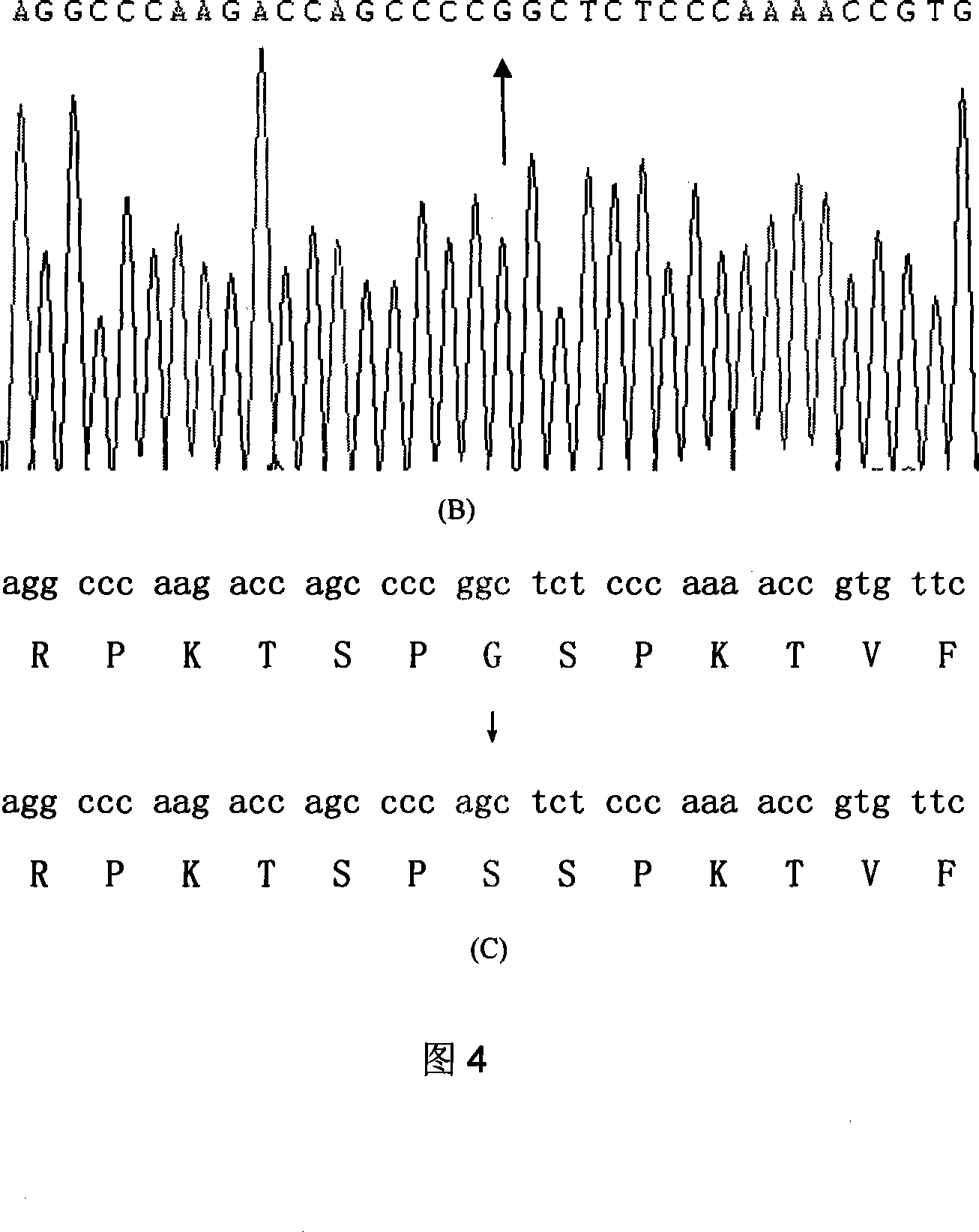
Hypertrophic type cardiomyopathy PRKAG2 gene mutation and detecting method thereof
InactiveCN101134961AMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringHypertrophic cardiomyopathyMolecular genetics
The present invention relates to PRKAG2 gene mutation of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and its detection method. The PRKAG2 gene mutation is the G-->A heterozygous mutation of the No. 298 place base in the 3rd exon of PRKAG2 gene, and causes the coded amino acid in No. 100 place to change from glycine (G) to serine (S). Its detection method includes the following steps: 1. extracting peripheral blood DNA; 2. in vitro PCR amplification of PRKAG2 gene exon; and 3. DNA sequencing analysis. The discovery of the PRKAG2 gene mutation can define the molecular genetic mechanism of Chinese familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy combined with conducting system abnormality and ventricle pre-exciting disease further.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY +1
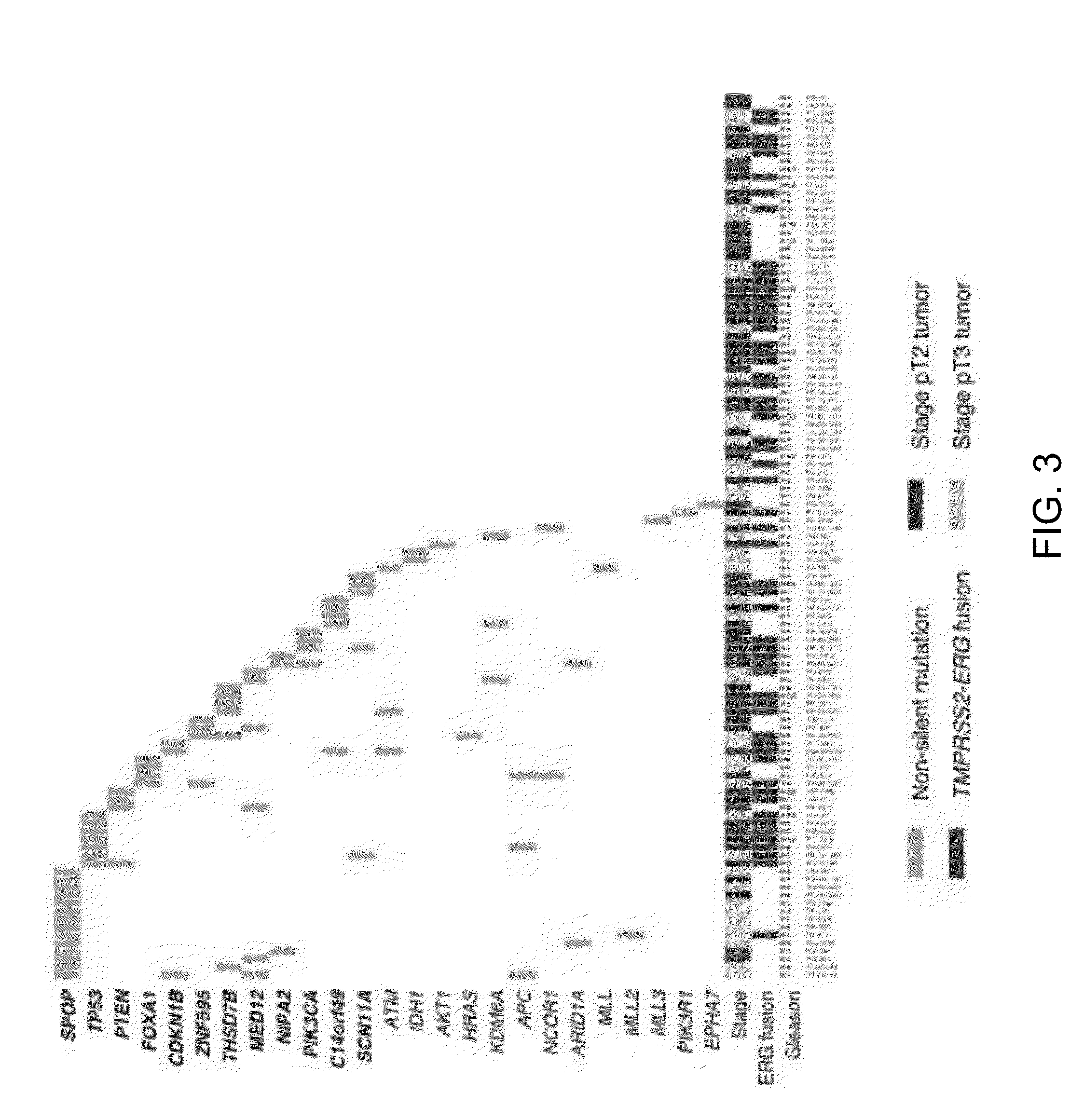
Recurrent spop mutations in prostate cancer
ActiveUS20130331279A1Specific detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationOncologyDisease progression
The invention relates generally to new prostate cancer markers, and particularly to a class of cancer marked by the presence of missense mutations in SPOP, an E3 ubiquitin ligase component. The invention provides methods and materials for detecting and diagnosing prostate cancer by detecting these mutations and may be useful in predicting disease progression and response to therapy.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
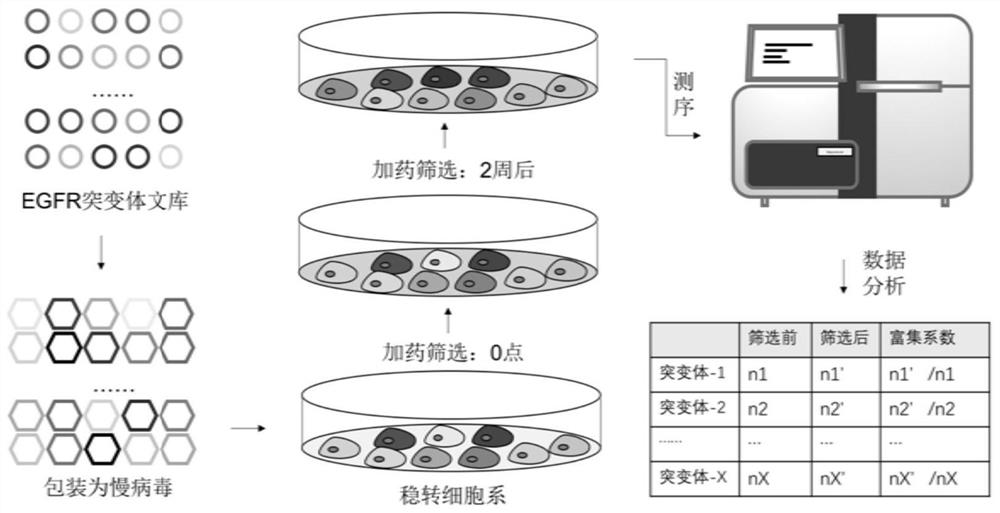
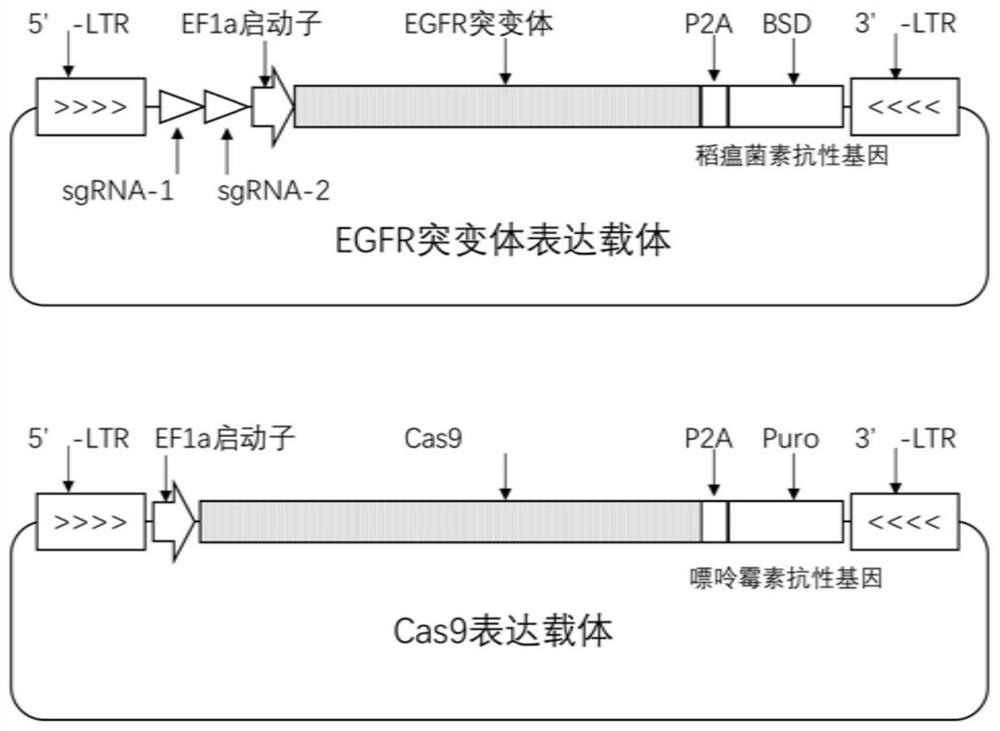
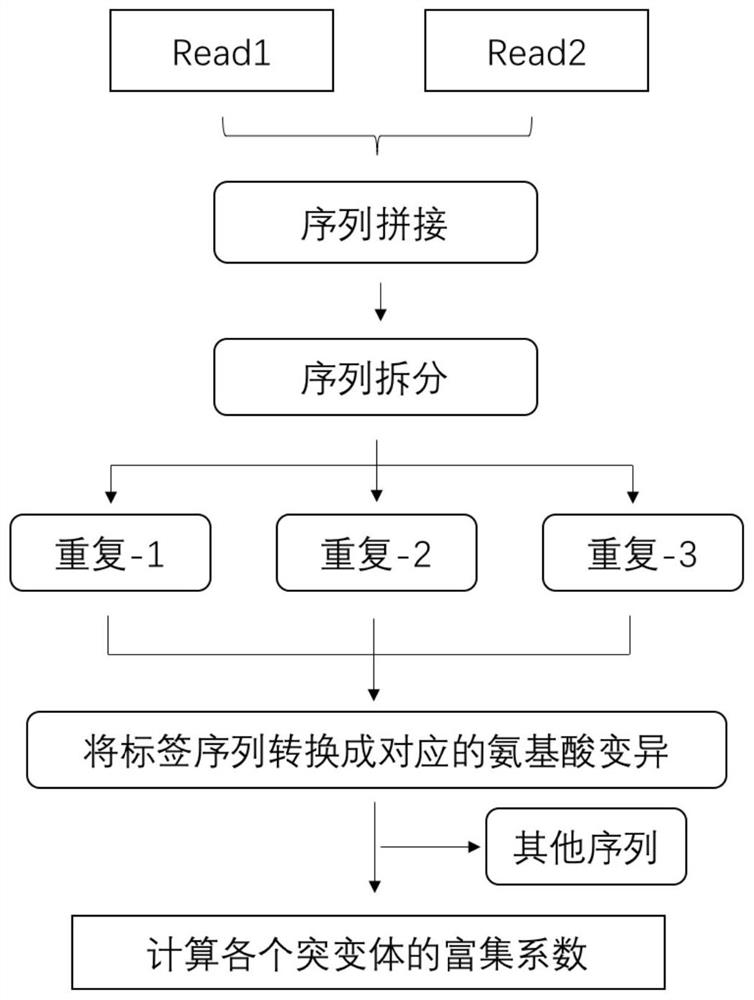
Human EGFR gene missense mutation molecular marker and application thereof in predicting drug resistance of targeted inhibitor
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine and gene detection, and particularly relates to a human EGFR gene missense mutation molecular marker and application thereof in predicting drug resistance of a targeted inhibitor. The molecular marker provided by the invention comprises 242 types of EGFR missense mutants related to the drug resistance of erlotinib, gefitinib and icotinib, and other 15 types of EGFR missense mutants related to the drug resistance of afatinib and osimertinib, and the mutants can be used for predicting the drug resistance of non-small cell lung cancer patients to targeted inhibitor treatment. According to the invention, a mutant library of EGFR gene tyrosine kinase functional regions is constructed by using a synthetic biology method, and the EGFR mutants are highly enriched in drug screening; the molecular marker can be clinically used as a potential molecular marker for predicting drug resistance of a lung cancer patient after the lung cancer patient is treated by a targeted inhibitor.
Owner:卫国朋
Method for rapidly detecting single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of bovine PNPLA3 (patatin like phospholipase domain-containing 3) gene and application of method
InactiveCN103805692AIncrease weightMicrobiological testing/measurementEnergy balancingEnzyme digestion
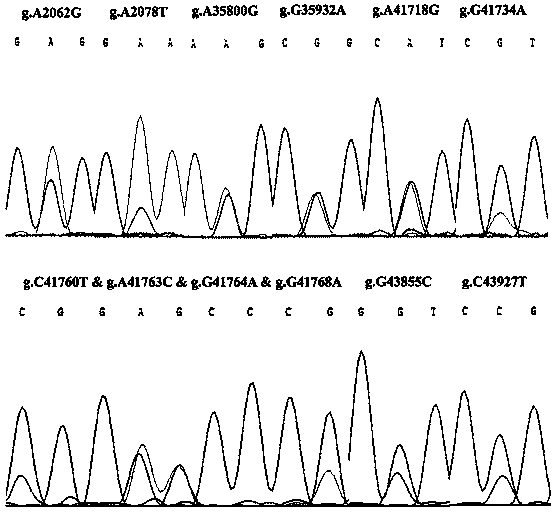
The invention discloses an RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) method for rapidly detecting single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of bovine PNPLA3 (Patatin Like Phospholipase Domain-Containing 3) gene. The RFLP method comprises the steps of by taking PNPLA3 gene-containing to-be-detected whole-genome DNA as a template, and human-designed primer pairs P1-P5 as primers, carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on the bovine PNPLA3 gene, and discovering 27 SNP loci; selecting four missense mutation loci and respectively designing primer pairs P2-Bg1I, P2-RsaI, P3-BmgT120I and P3-MspI; carrying out PCR amplification by using the four primer pairs, respectively performing enzyme digestion to the PCR amplified product by using the four restriction endonuclease, and then detecting the enzyme digestion product by using agarose gel electrophoresis, wherein the electrophoresis result shows the SNP at the 2062th locus, the 2078th locus, the 35800th locus and the 35932th locus of the PNPLA3 gene of the Qinchuan bovine gene. The PNPLA3 gene relates to the growth traits of weight, average daily gain and the like, the PNPLA3 gene has the activity of lipase and acyltransferase and plays an important role in aspects of maintaining energy balance, the detection method can be used for marker assisted selection (MAS) breeding of the growth traits of China cattle, thus being beneficial to fast setting cattle population with excellent genetic resources.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Inherited Mitochondrial Dna Mutations in Cancer
InactiveUS20080280294A1Increase chanceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementProstate cancerFhit gene
A method is provided for identifying a subject likely to have, or at risk of developing a disease condition correlated with increased reactive oxygen species (ROS), including cancer, by identifying in the subject a missense mutation in a nucleic acid of Complex III, IV and / or V of the OXPHOS system. This invention also provides a method of identifying a likelihood of having a heritable predisposition to cancer by detecting a homoplasmic missense mutation in non-tumor tissue of an OXPHOS system gene. This invention also provides a method for detecting likelihood of having cancer, predisposition to cancer, and likelihood of passing a predisposition to cancer to progeny involving identifying in non-tumor tissue of the subject a missense mutation in a complex III, IV and / or V gene of the mitochondrial OXPHOS system. The mutation may be a nuclear or mitochondrial mutation. The invention has been exemplified with respect to prostate cancer. When the mutation is homoplasmic in non-tumor tissue this is an indication it is an inherited and inheritable trait, and that the subject is likely to pass on the mutation to her progeny in the case of mutations in mitochondrial DNA or his or her progeny in the case of mutations in nuclear DNA. Both homoplasmic and heteroplasmic mutations in non-tumor tissue can indicate the presence of cancer.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
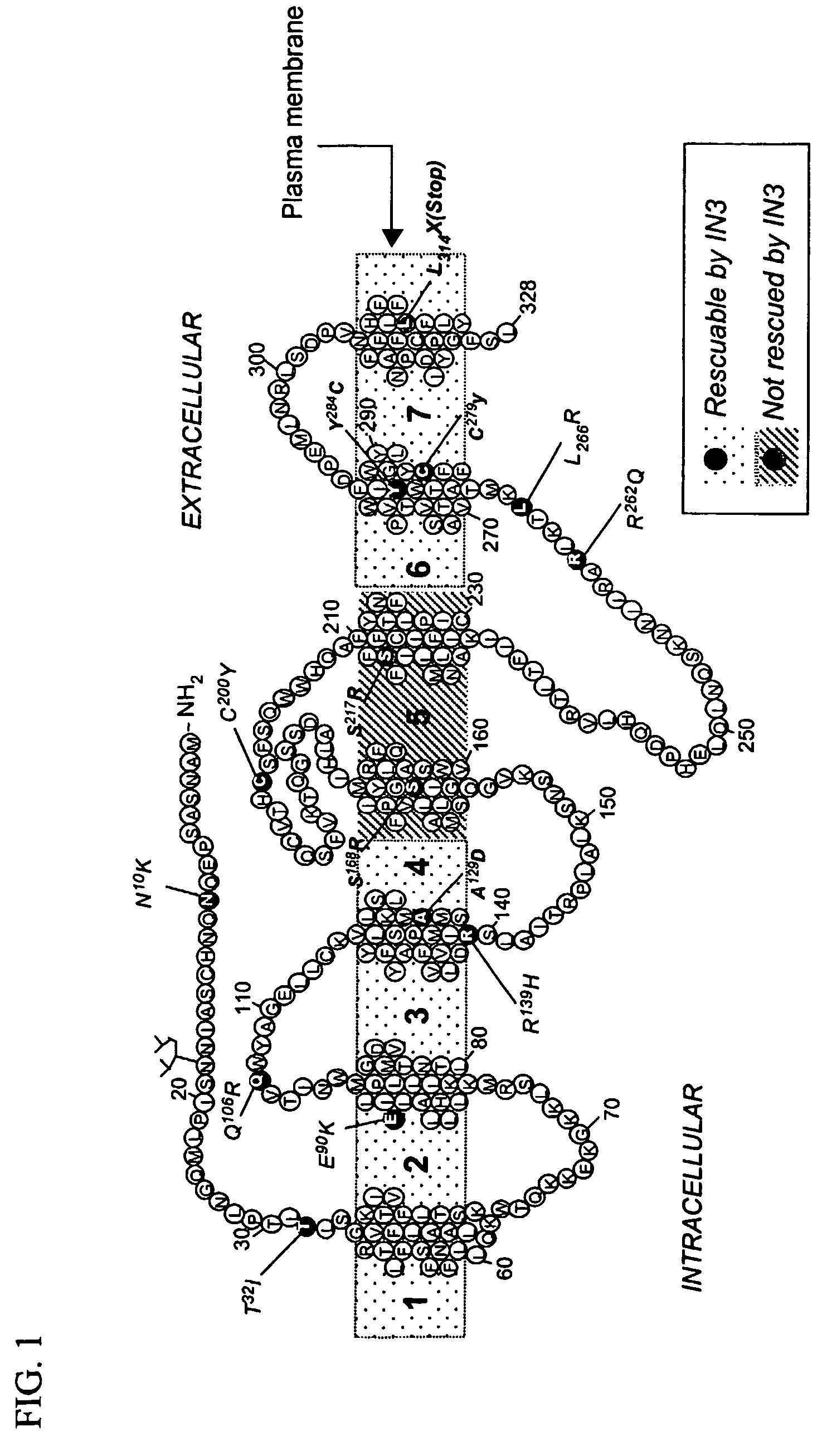
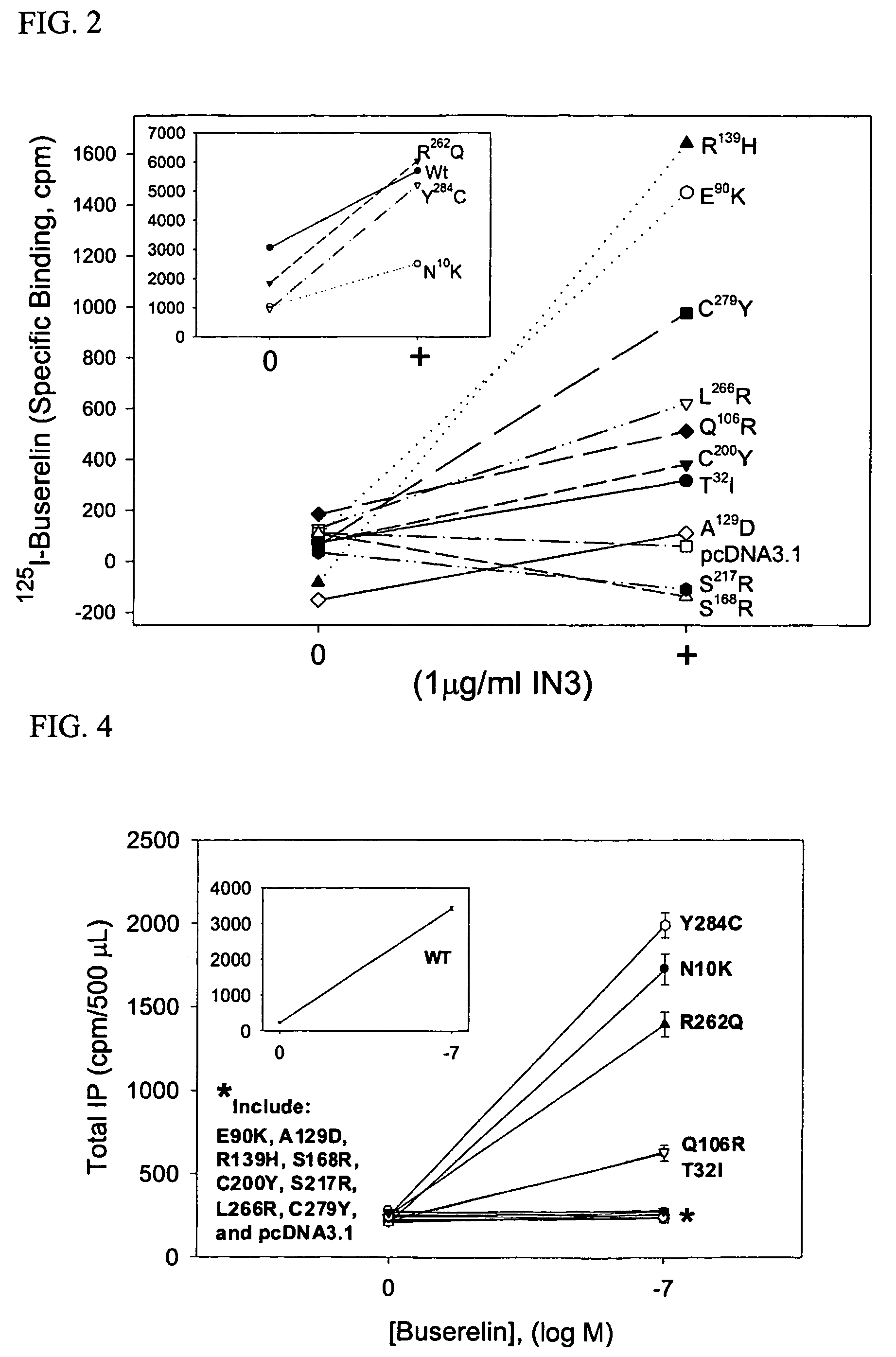
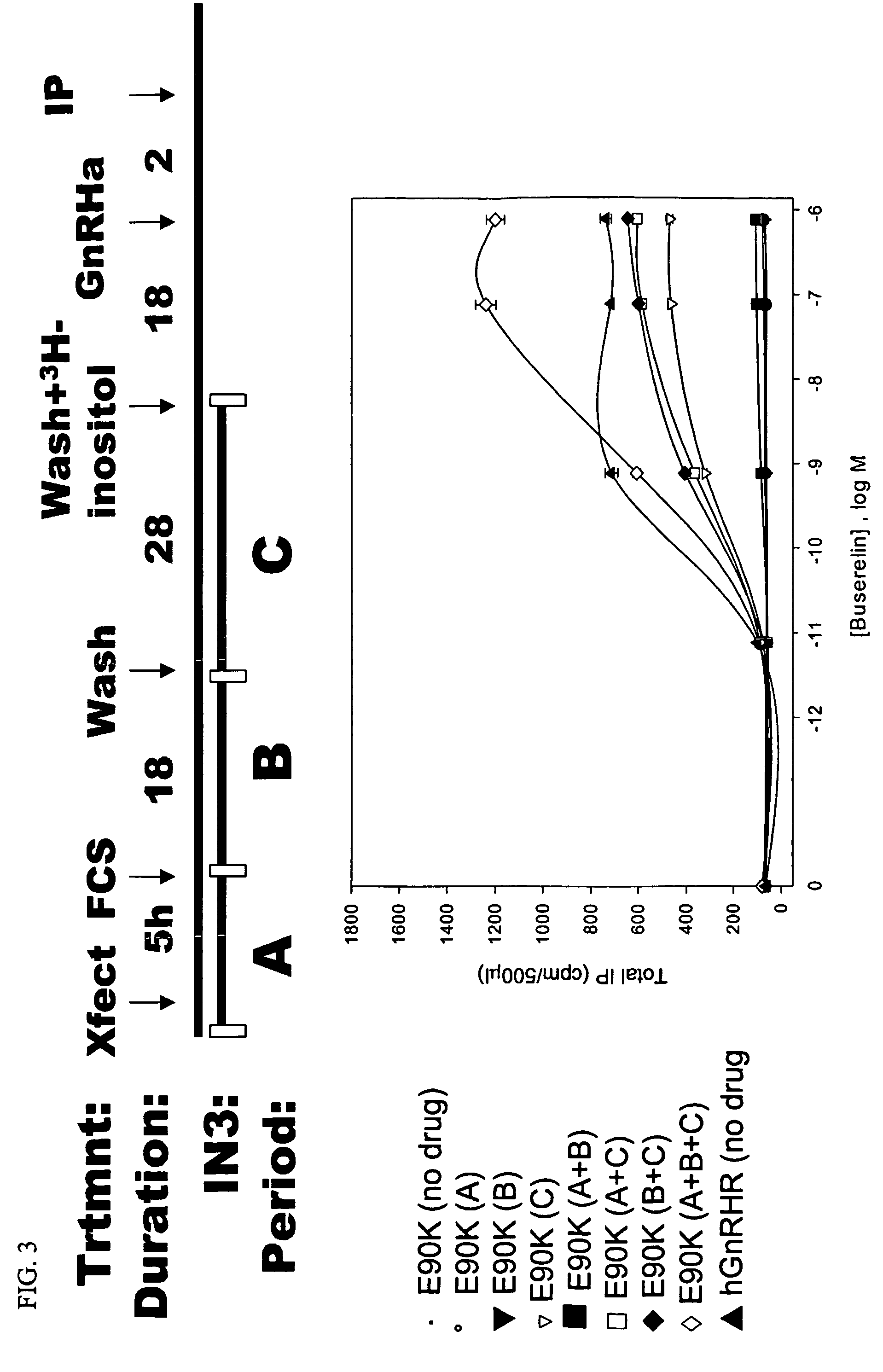
Rescue of gonadotropin releasing hormone receptor mutants
InactiveUS7695917B2Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsGonadotropin-releasing hormone receptorMutant
Herein disclosed is a method of rescuing gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor (GnRHR) mutants with IN3 or a mimetic thereof. IN3 significantly rescues 11 missense mutations as assessed by radioligand binding and by IP production. Such rescue occurred despite widely disparate loci along the receptor. In addition, many altered GnRH receptors (terminally truncated, internal deletions, or lacking the ability to form bridges to form tertiary structure) were rescued with IN3.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
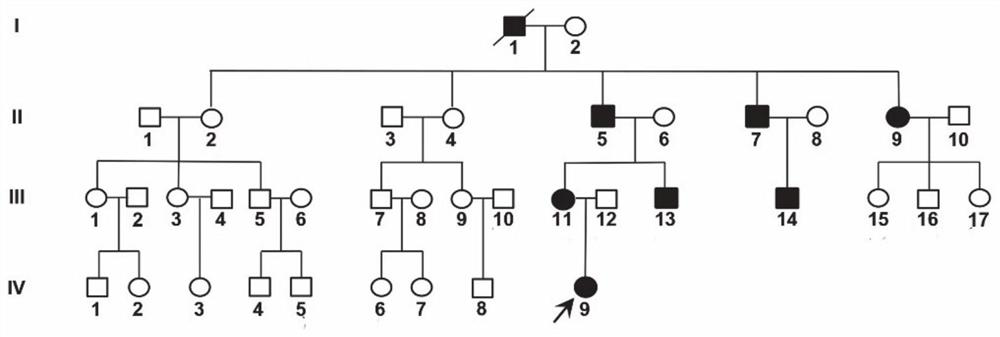
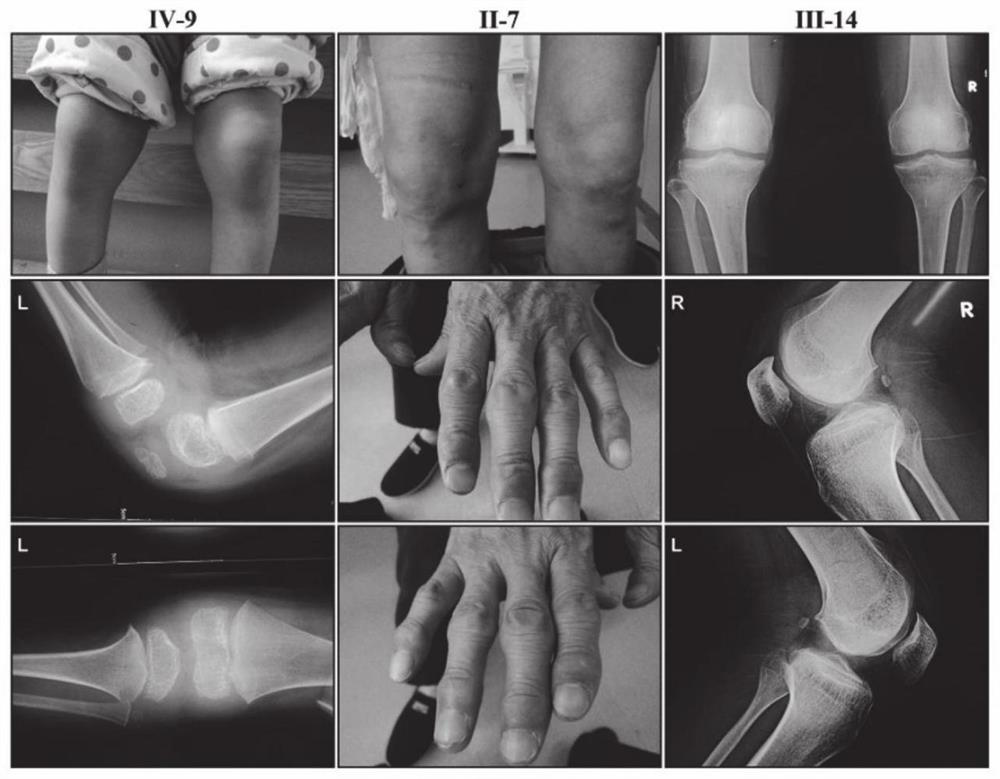
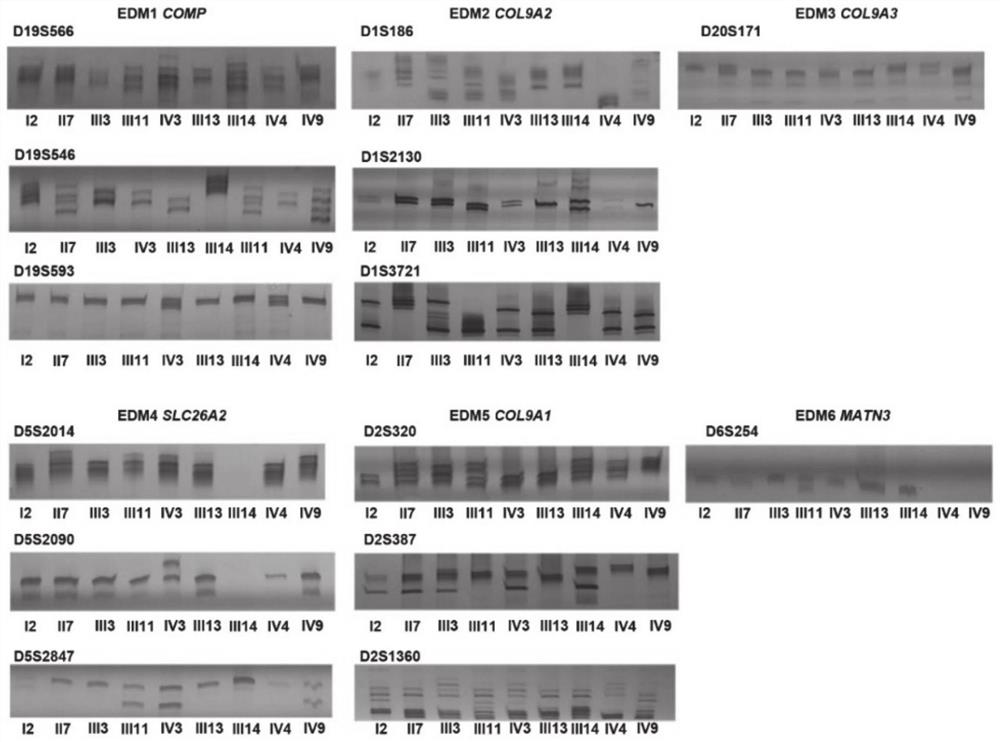
Application of Smoc2 gene and SNP marker thereof in multiple epiphyseal dysplasia
PendingCN112522390AThe value of good practical applicationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEarly warning modelBiomedicine
The invention provides an application of a Smoc2 gene and an SNP marker thereof in multiple epiphyseal dysplasia, and relates to the technical field of biomedicine. According to the invention, a family with skeletal dysplasia is collected in Shandong, and final screening tests prove that SMOC2 c.1076T is greater than G; and p.L359R missense mutation is pathogenic mutation of a family with autosomal dominant multiple epiphyseal dysplasia, and the SMOC2 gene is a new pathogenic gene of the multiple epiphyseal dysplasia. A new pathogenic theoretical basis is provided for revealing a multiple epiphyseal dysplasia occurrence mechanism, and a foundation is laid for developing a disease early warning model suitable for people in China, so that the Smoc2 gene has good practical application value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Anti-PCV (porcine circovirus) diseased pig screening SERPINA1 molecular marker breeding method and application thereof
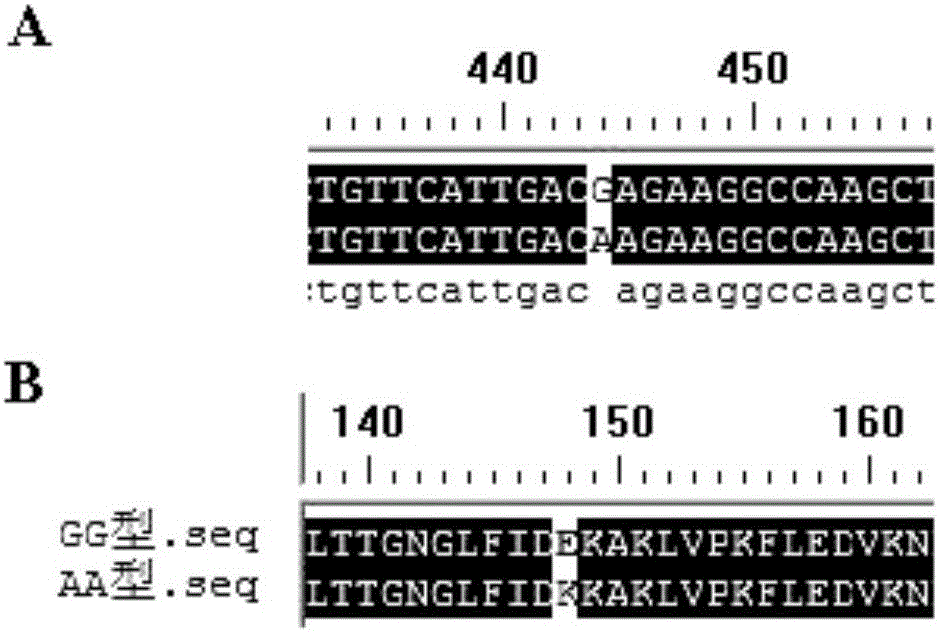
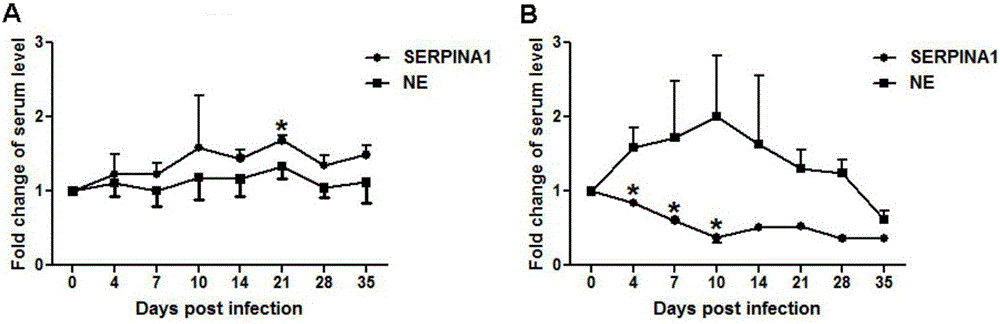
The invention relates to the field of molecular genetics, in particular to a molecular marking method for a mutation site of a coding region of a porcine SERPINA1 gene and application of the method to anti-PCV (porcine circovirus) pig breeding. The inventor finds that SERPINA1 coding regions of different varieties of pigs have multiple mutations, wherein a G>A mutation exists at the 445th base of the coding region to further cause a missense mutation: glutamic acid>lysine. Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay shows that an AA type individual has highest SERPINA1 serum content, an AG type individual has the second highest SERPINA1 serum content and a GG type individual has the lowest SERPINA1 serum content in a healthy state. After infection with PCV2, the SERPINA1 serum content of the GG type individual rapidly increases, while the content of the AG type and AA type individuals rapidly decreases, and such a result is consistent with that a Laiwu pig population with a higher anti-PCV capability is more likely to comprise GG type pigs compared with a western population and an mRNA expression level of the SERPINA1 gene is high. Obviously, a genotype of the 445th site of a coding region of an SERPINA1 gene in a porcine genome can be detected as a molecular marker associated with an anti-PCV character of a pig, so that the method is convenient, rapid and free of environmental influence, and early breeding can be implemented.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Compounds and methods for treating pain
ActiveUS20180319842A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsG protein-coupled receptorOcular inflammation
The present disclosure relates to, among other things, compounds and methods for treating neuropathic pain, ocular pain, ocular inflammation, and / or dry eye and methods of detecting mutations in specific G-protein coupled receptors, such as missense mutations, and determining the extent to which these mutations alter the pharmacological response of the G-protein coupled receptor.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE +1
SNP molecular marker related to residual feed intake of pigs and application thereof
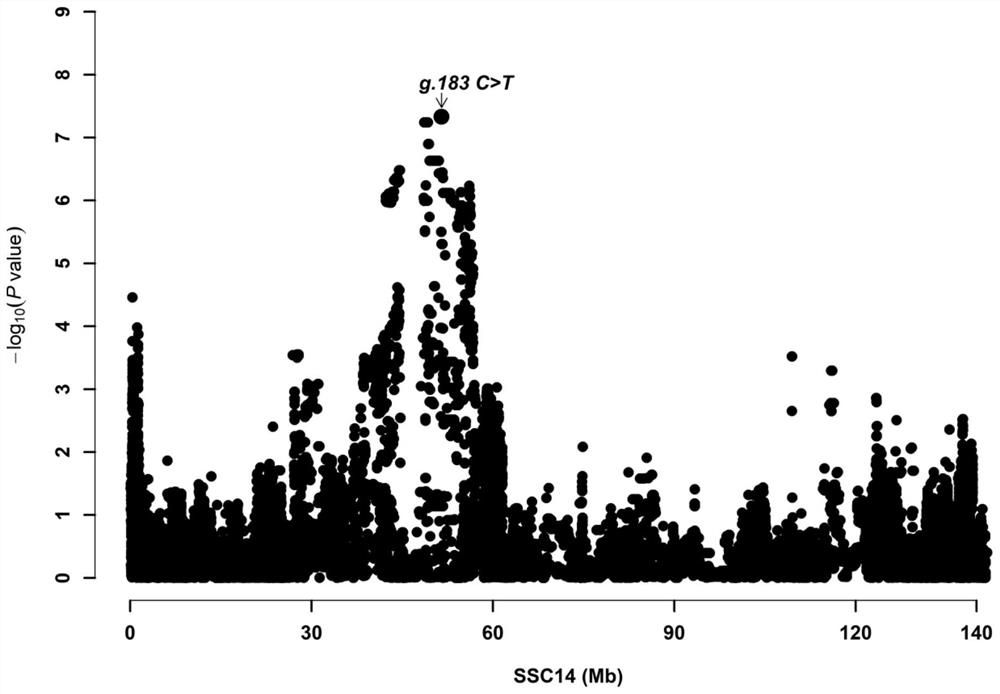
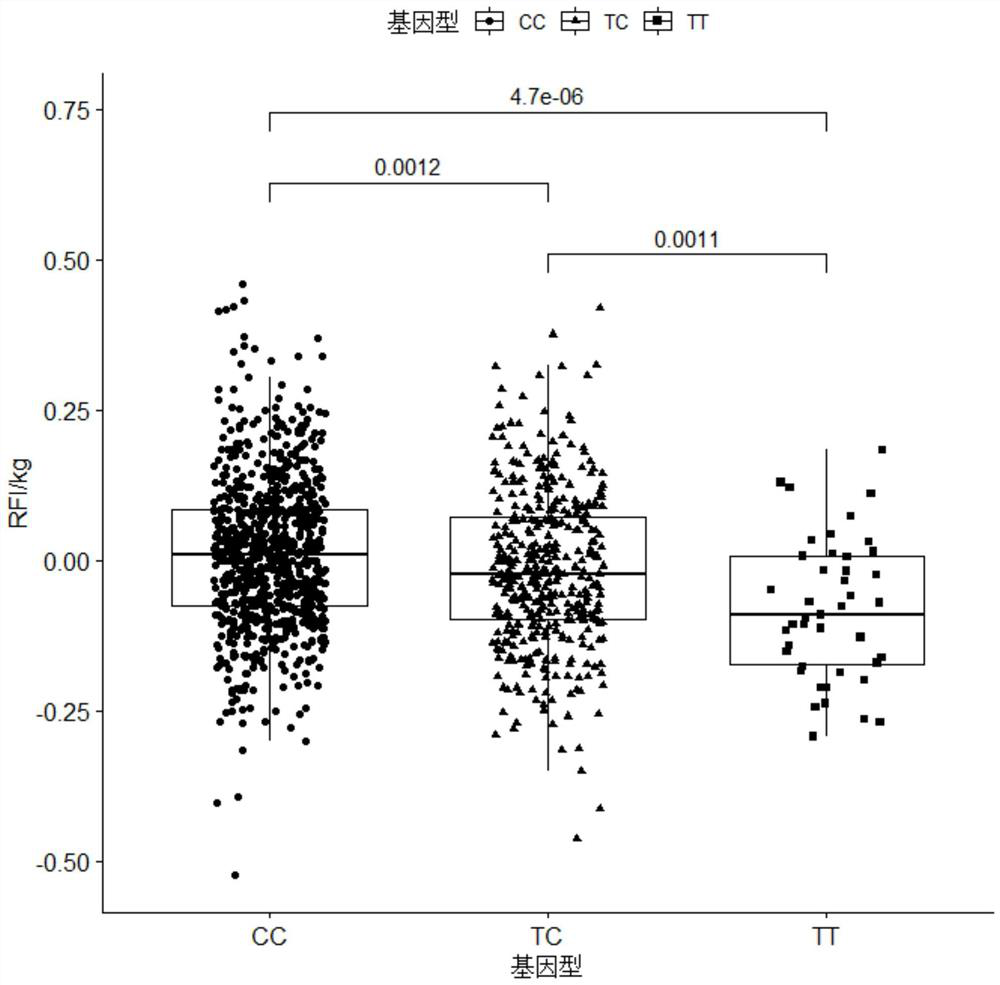
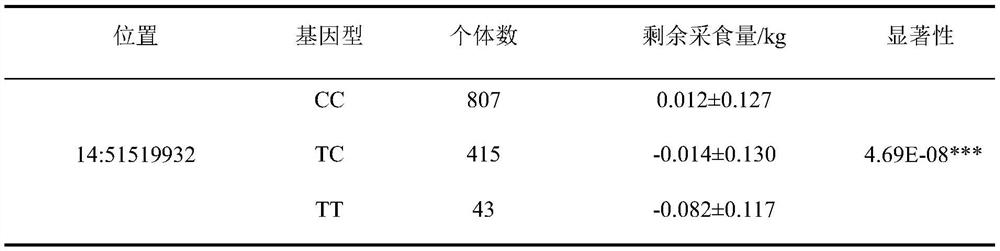
ActiveCN113584181AAccelerating progress in genetic improvementReduced feed intakeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAnimal scienceNucleotide
The invention provides an SNP molecular marker related to residual feed intake of pigs, the site of the SNP molecular marker is the 51519932th nucleotide site on chromosome 14 of international pig reference genome version 11.1, the site is a missense mutation site on a gene CCDC188, and the basic group of the site is T or C. By optimizing the dominant alleles of the SNP, the frequency of the dominant alleles can be increased generation by generation, the remaining feed intake of the boars can be reduced, the excellent boars with the characters can be bred, and the genetic improvement progress of the boars can be accelerated, so that the economic benefit of breeding of the boars can be effectively improved.
Owner:WENS FOOD GRP CO LTD +1
Marker assisting epilepsy diagnosis and detection kit of marker
ActiveCN108192969AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMolecular levelBiomarker (petroleum)
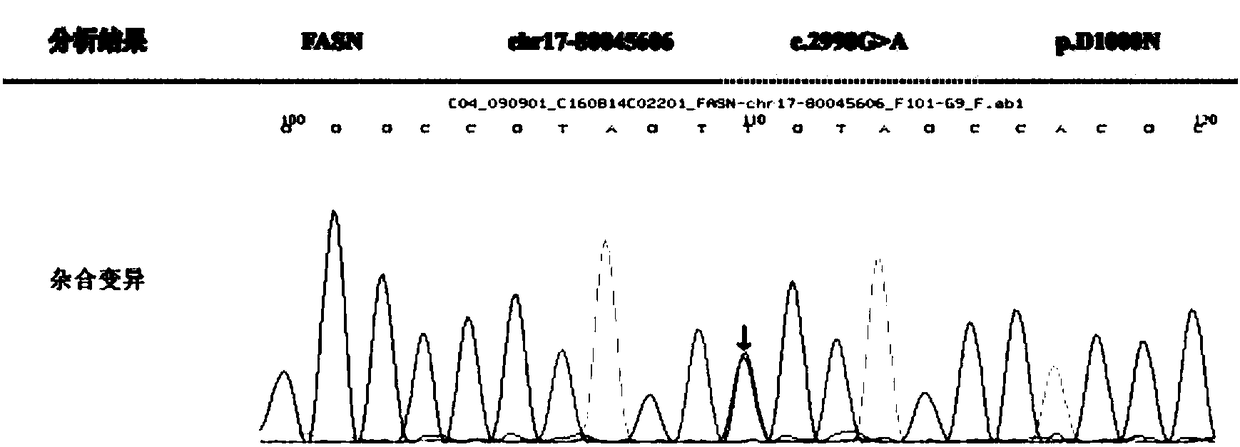
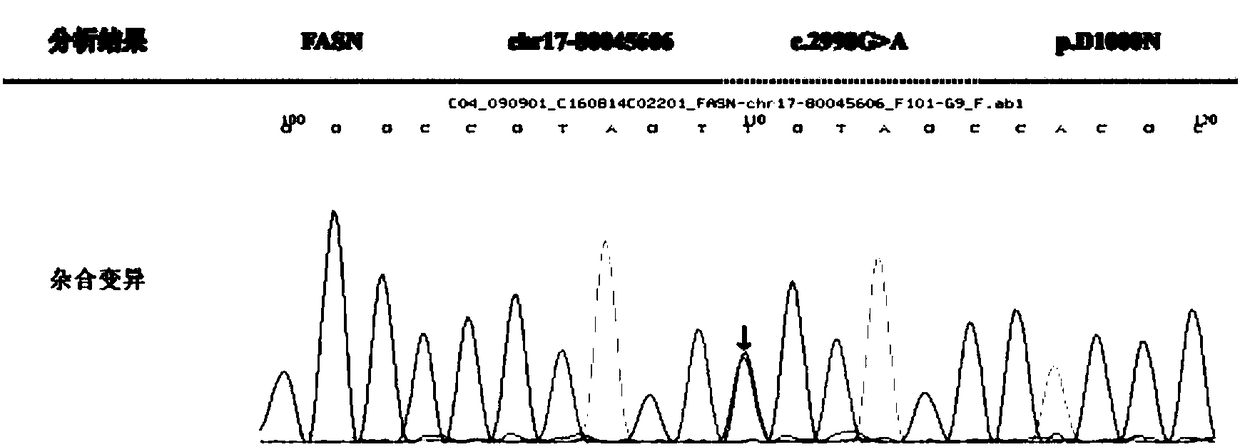
The invention discloses a marker assisting epilepsy diagnosis and a detection kit of the marker, and relates to the field of epilepsy diagnosis. According to the research, it is found from detection on an FASN gene of a member of an epilepsy family patient that the FASN gene of the member of the epilepsy family patient has a mutation c.G2998A, the gene mutation causes that the 1,000 amino acidof the corresponding FASN protein mutates into asparagine (N) from aspartic acid (D) and is a missense mutation. An nucleic acid molecule containing the c.G2998A mutation or protein containing a mutation p.D1000N can both serve as a biomarker of epilepsy diagnosis, and the rapid and reliable detection assistance marker is provided for epilepsy diagnosis on the molecular level.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Maker assisting in epilepsy diagnosis and detection kit thereof
InactiveCN108517358AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMolecular levelBiomarker (petroleum)
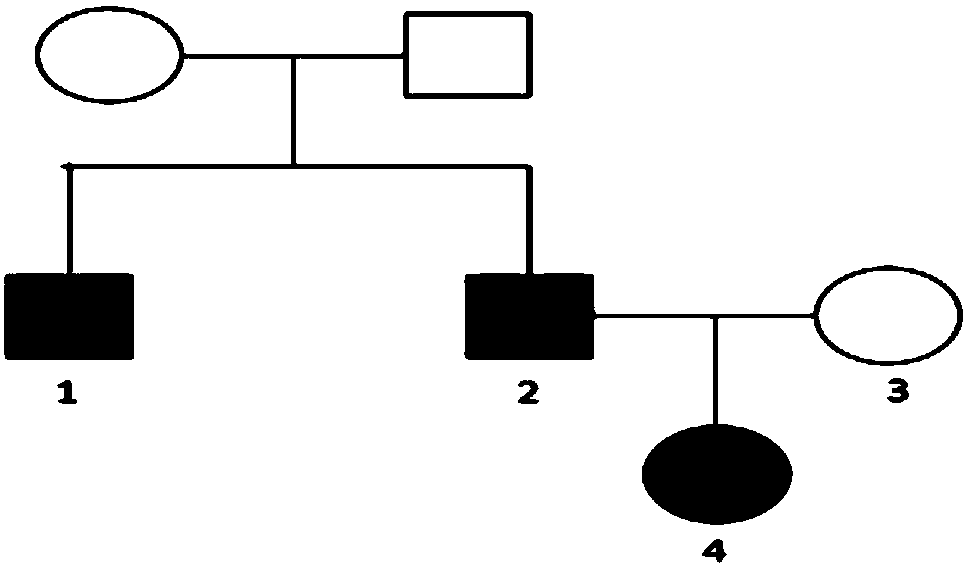
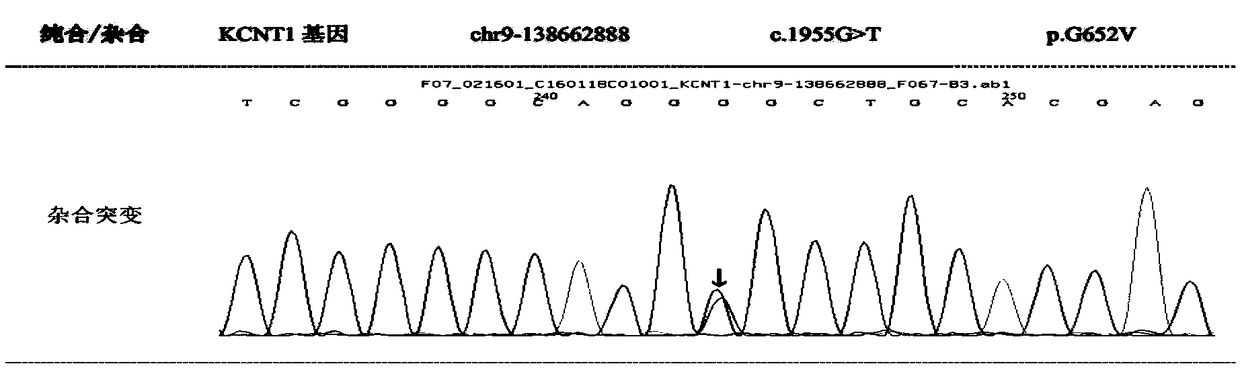
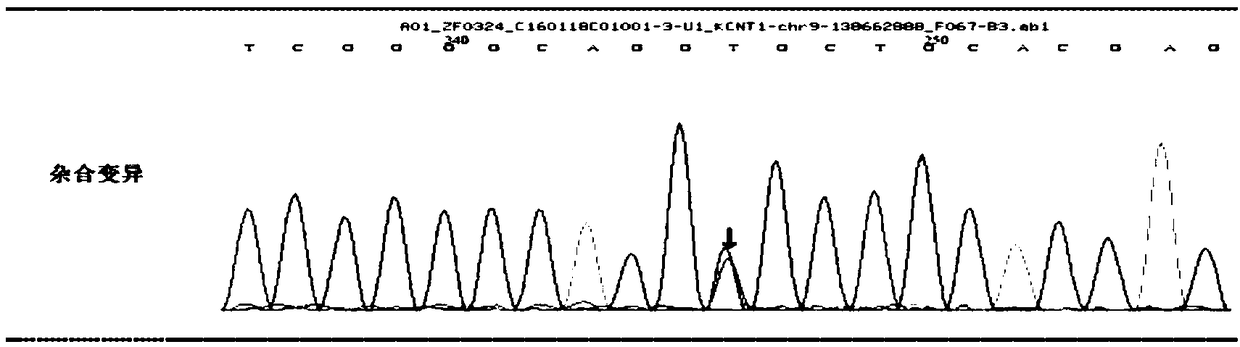
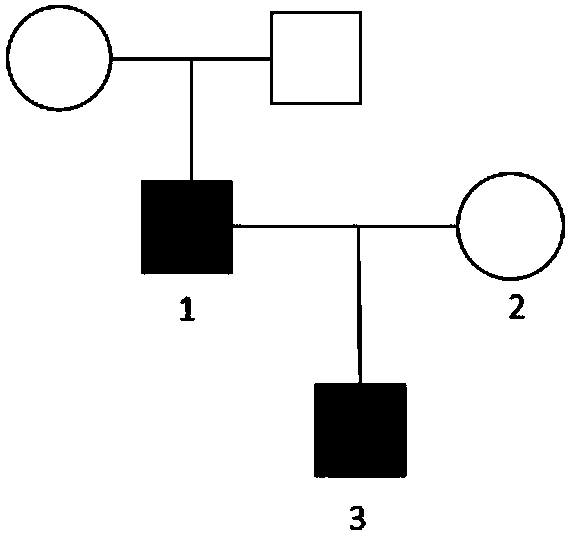
The invention discloses a marker assisting in epilepsy diagnosis and a detection kit thereof, and relates to the field of epilepsy diagnosis. According to the study of the marker assisting in epilepsydiagnosis and the detection kit thereof, by detecting KCNT1 genes of family members of an epilepsy patient, the KCNT1 gene of the epilepsy patient in the family has a mutational c.G1955T, and mutation of the gene causes that the amino acid in the 652 site of KCNT1 protein corresponding to the c.G1955T changes from glutamic acid (G) to valine (V), which is missense mutation. Both nucleic acid molecules containing c.G1955T mutation or protein containing mutational p.G652V can be used as a biomarker for epilepsy diagnosis, so that a fast and reliable detection assisting marker is provided for epilepsy diagnosis at the molecular level.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Marker for assisting epilepsy diagnosis and detection kit of marker
PendingCN108277272ANucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular levelGenes proteins
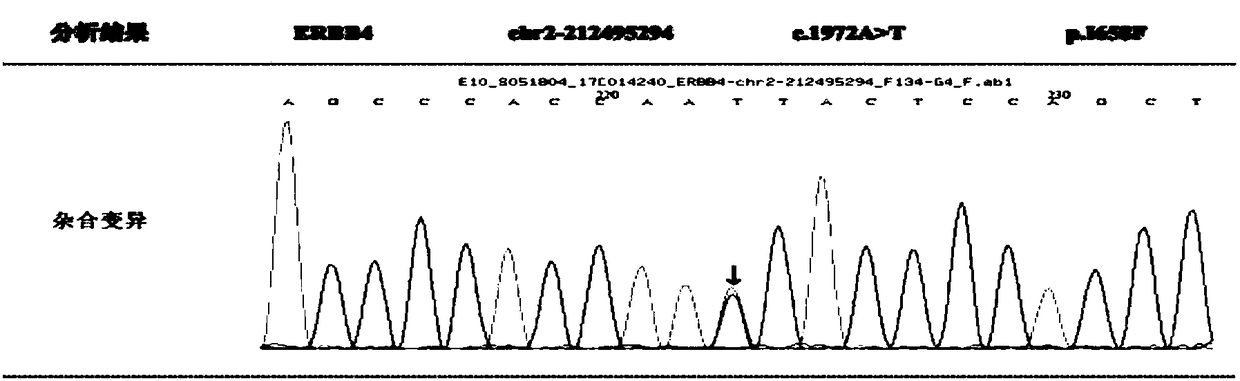
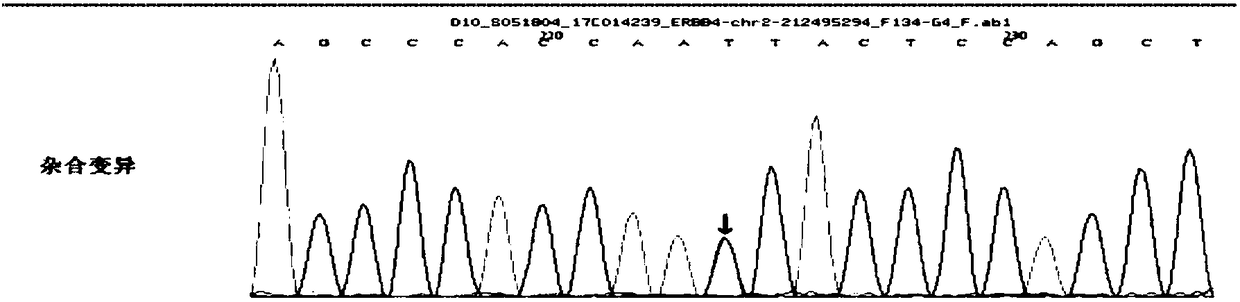
The invention discloses a marker for assisting epilepsy diagnosis and a detection kit of the marker, and relates to the field of the epilepsy diagnosis. Research for detecting an ERBB4 gene of membersof an epilepsy family discovers that the ERBB4 gene of the members suffering from epilepsy in the family has mutant c.A1972T; the gene mutation results in variation of 658th amino acid of the corresponding ERBB4 gene protein from isoleucine (I) to phenylalanine (F), and the variation is missense mutation; nucleic acid molecules containing the mutant c.A1972T or protein containing mutant p.I658F can be used as a biomarker for the epilepsy diagnosis, and a quick and reliable detection auxiliary marker is provided for the epilepsy diagnosis in molecular level.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Gene for identifying individuals with familial dysautonomia
InactiveUS20050204409A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAutonomic bladder dysfunctionProgenitor
This invention relates to methods and compositions useful for detecting mutations which cause Familial Dysautonomia. Familial dysautonomia (FD; Riley-Day syndrome), an Ashkenazi Jewish disorder, is the best known and most frequent of a group of congenital sensory neuropathies and is characterized by widespread sensory and variable autonomic dysfunction. Previously, we mapped the FD gene, DYS, to a 0.5 cM region of chromosome 9q31 and showed that the ethnic bias is due to a founder effect, with >99.5% of disease alleles sharing a common ancestral haplotype. To investigate the molecular basis of FD, we sequenced the minimal candidate region and cloned and characterized its 5 genes. One of these, IKBKAP, harbors two mutations that can cause FD. The major haplotype mutation is located in the donor splice site of intron 20. This mutation can result in skipping of exon 20 in the mRNA from FD patients, although they continue to express varying levels of wild-type message in a tissue-specific manner. RNA isolated from patient lymphoblasts is primarily wild-type, whereas only the deleted message is seen in RNA isolated from brain. The mutation associated with the minor haplotype in four patients is a missense (R696P) mutation in exon 19 that is predicted to disrupt a potential phosphorylation site. Our findings indicate that almost all cases of FD are caused by an unusual splice defect that displays tissue-specific expression; and they also provide the basis for rapid carrier screening in the Ashkenazi Jewish population.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
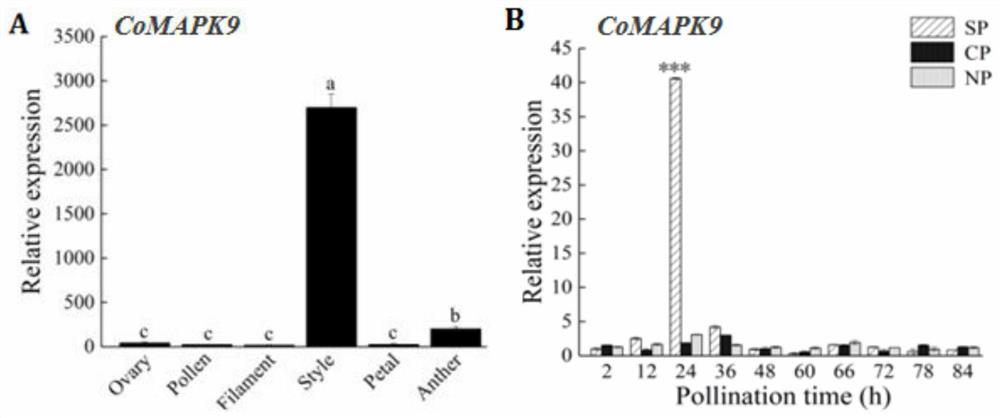
Camellia oleifera self-incompatibility associated gene, SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker and application
ActiveCN113502293AValid identificationGuaranteed efficient selectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyCamellia oleifera
The invention discloses a camellia oleifera self-incompatibility associated gene, an SNP marker and application. SNP missense mutation exists at the position of SNP071031 in OFR of the genome sequence of CoMAPK9, a basic group is changed from C to A, SNP missense mutation exists at the position of SNP181968, the basic group is changed from A to G, and the SNP mutations of the two sites have significant correlation with the self-incompatibility of camellia oleifera, which is shown in that the fruit setting rate of the SNP 071031 site genotype CC or CA after pollination is significantly higher than the fruit setting rate of the genotype AA; and after pollination, the fruit setting rate of the genotype AA or AG of the SNP181968 site is obviously higher than that of the genotype GG. The gene SNP combined molecular marker can be used for identifying the phenotypic seedling stage of the fruit setting rate of camellia oleifera, so that the variety configuration selection efficiency of a new camellia oleifera planting land and the yield of camellia oleifera per unit area are effectively improved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com