Patents
Literature
80 results about "Restriction fragment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
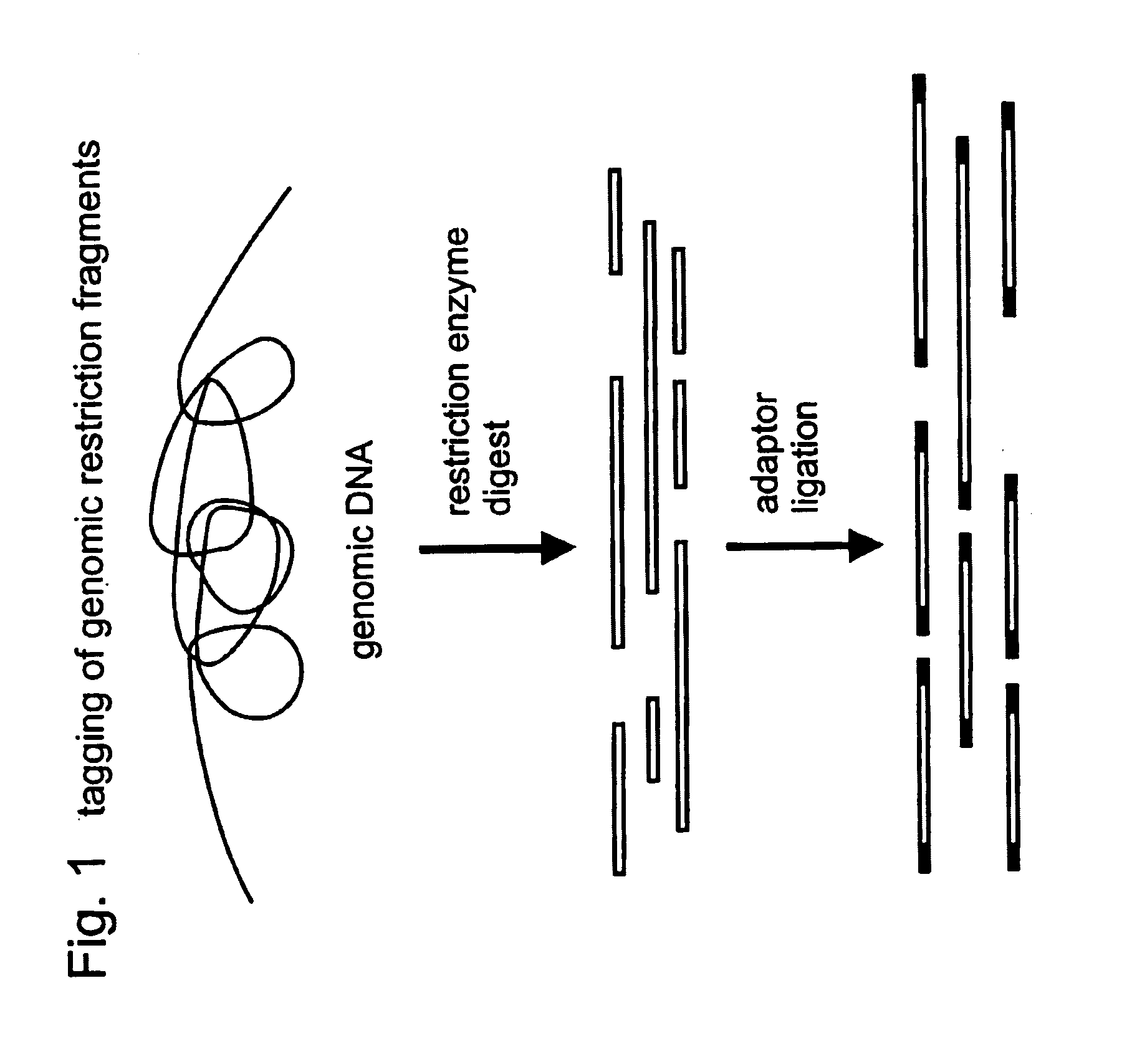
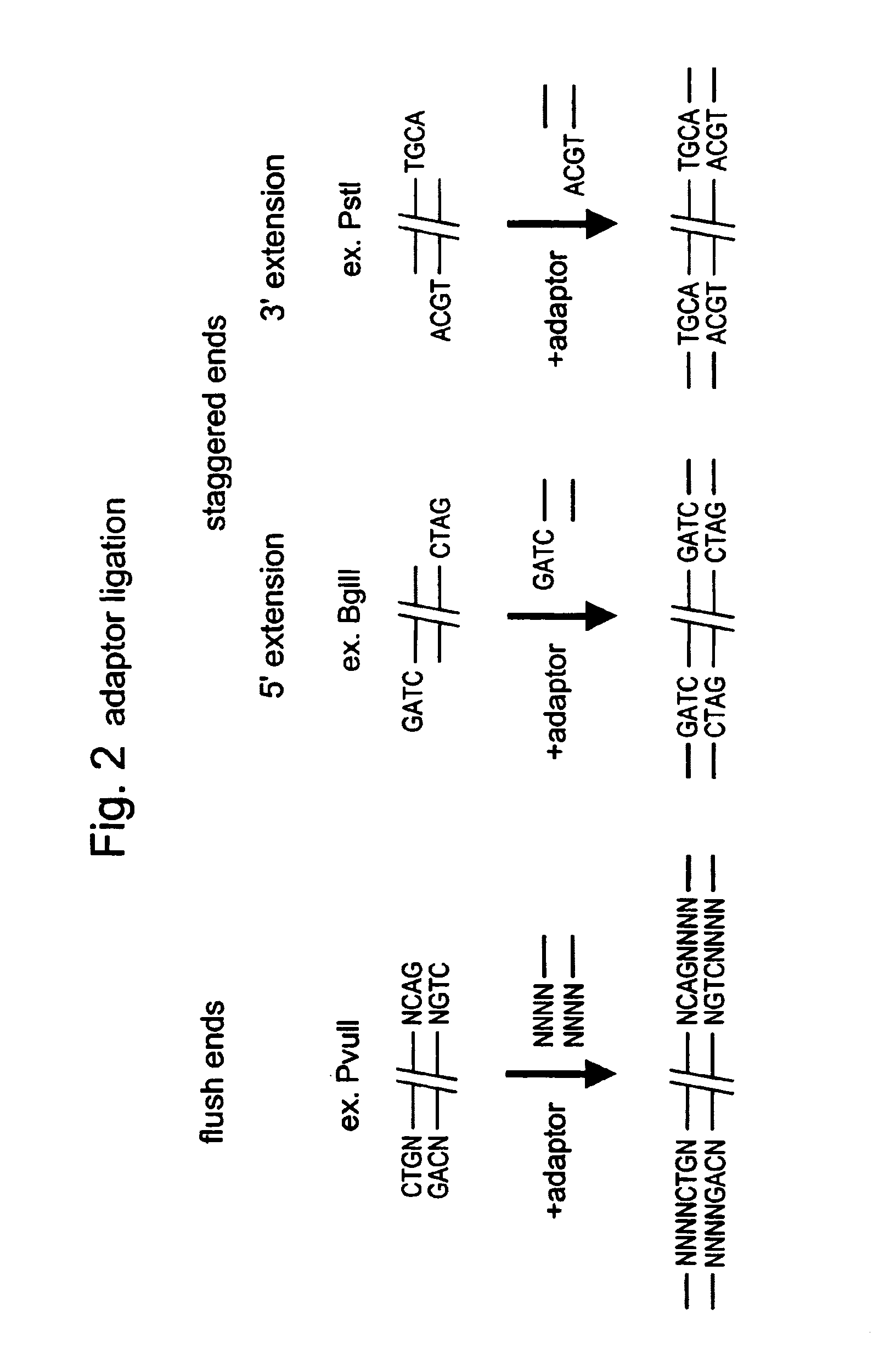
A restriction fragment is a DNA fragment resulting from the cutting of a DNA strand by a restriction enzyme (restriction endonucleases), a process called restriction. Each restriction enzyme is highly specific, recognising a particular short DNA sequence, or restriction site, and cutting both DNA strands at specific points within this site. Most restriction sites are palindromic, (the sequence of nucleotides is the same on both strands when read in the 5' to 3' direction of each strand), and are four to eight nucleotides long. Many cuts are made by one restriction enzyme because of the chance repetition of these sequences in a long DNA molecule, yielding a set of restriction fragments. A particular DNA molecule will always yield the same set of restriction fragments when exposed to the same restriction enzyme. Restriction fragments can be analyzed using techniques such as gel electrophoresis or used in recombinant DNA technology.
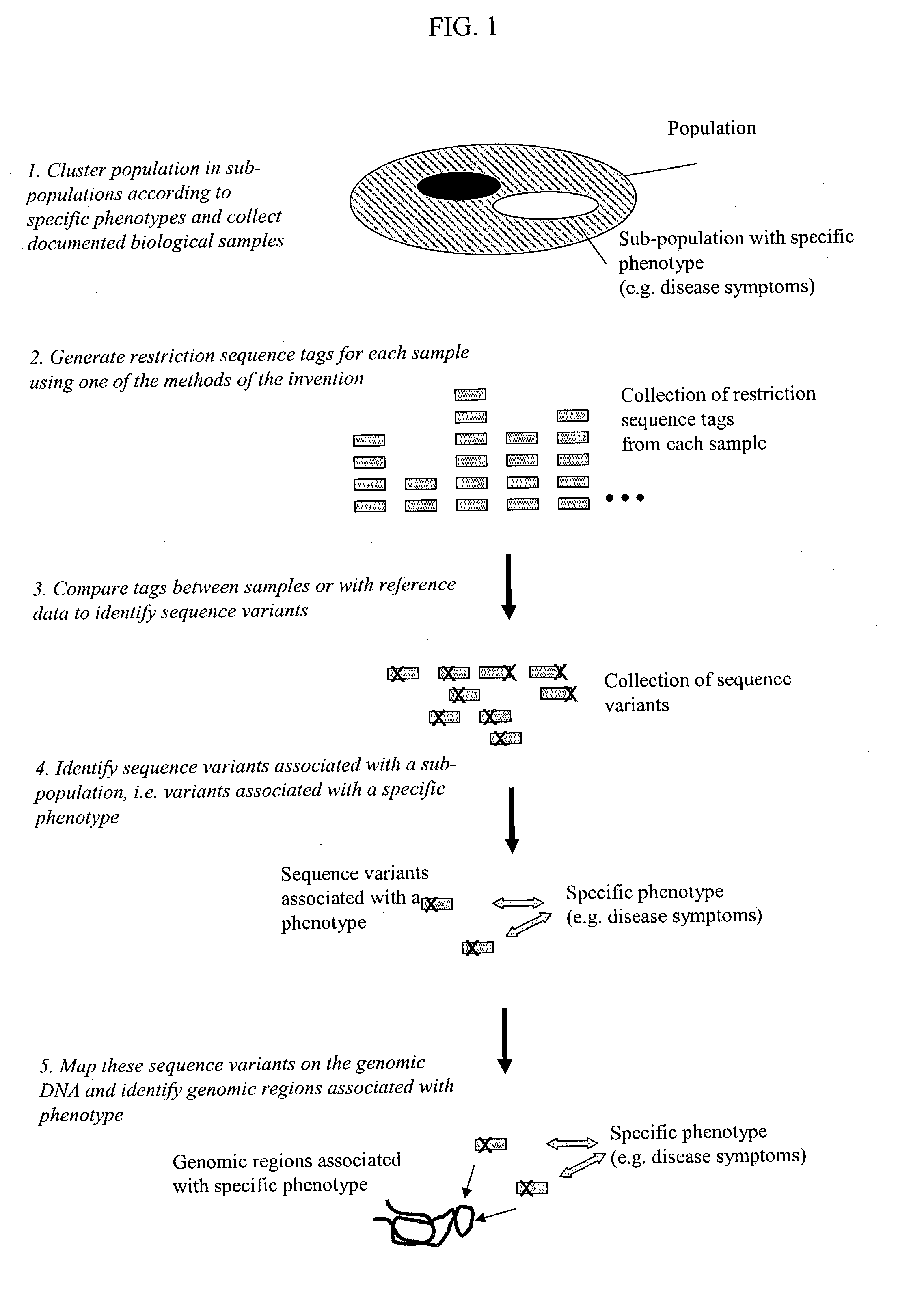
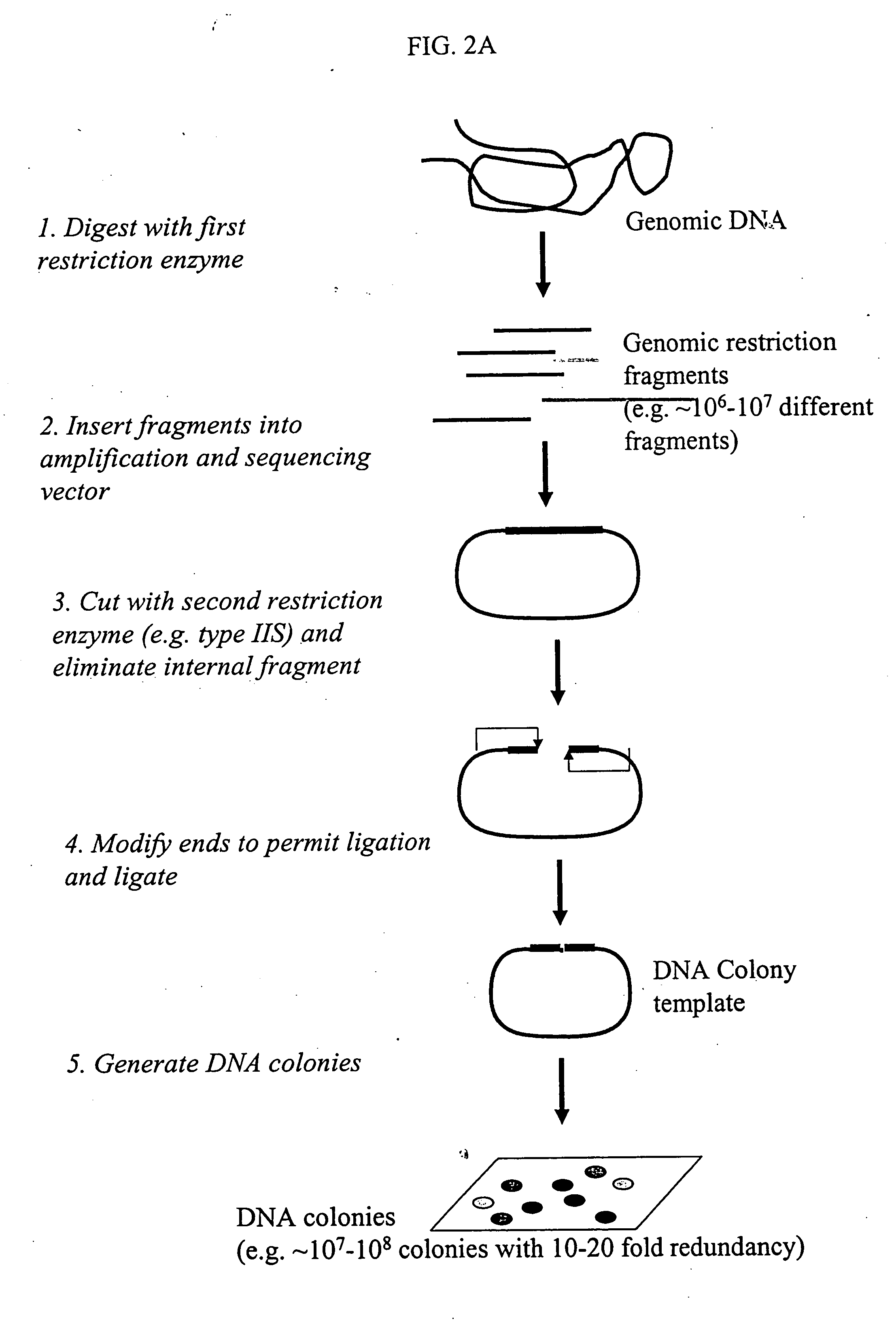
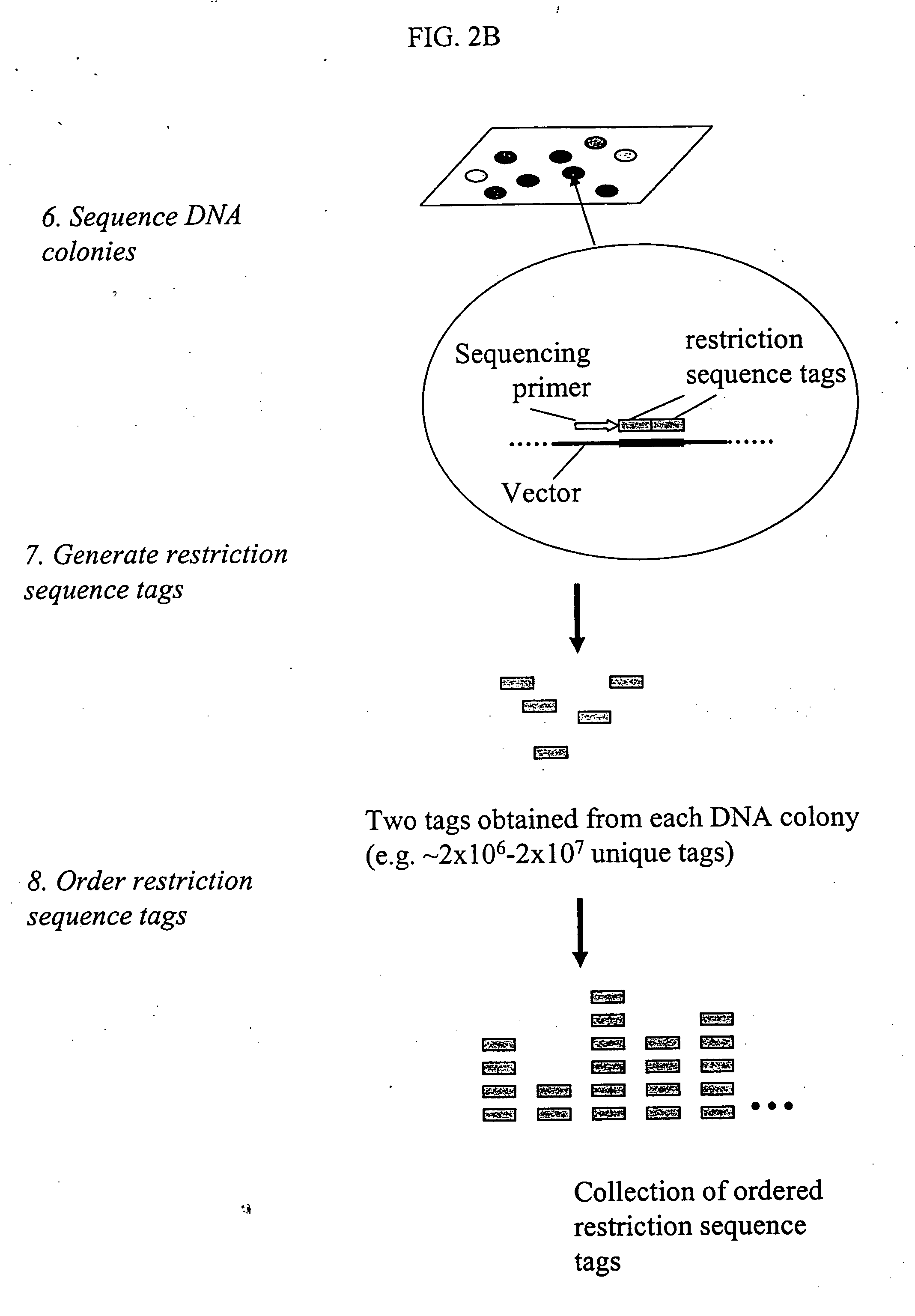
Methods for detecting genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype
InactiveUS20040002090A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationSub populationsGenetic risk factor
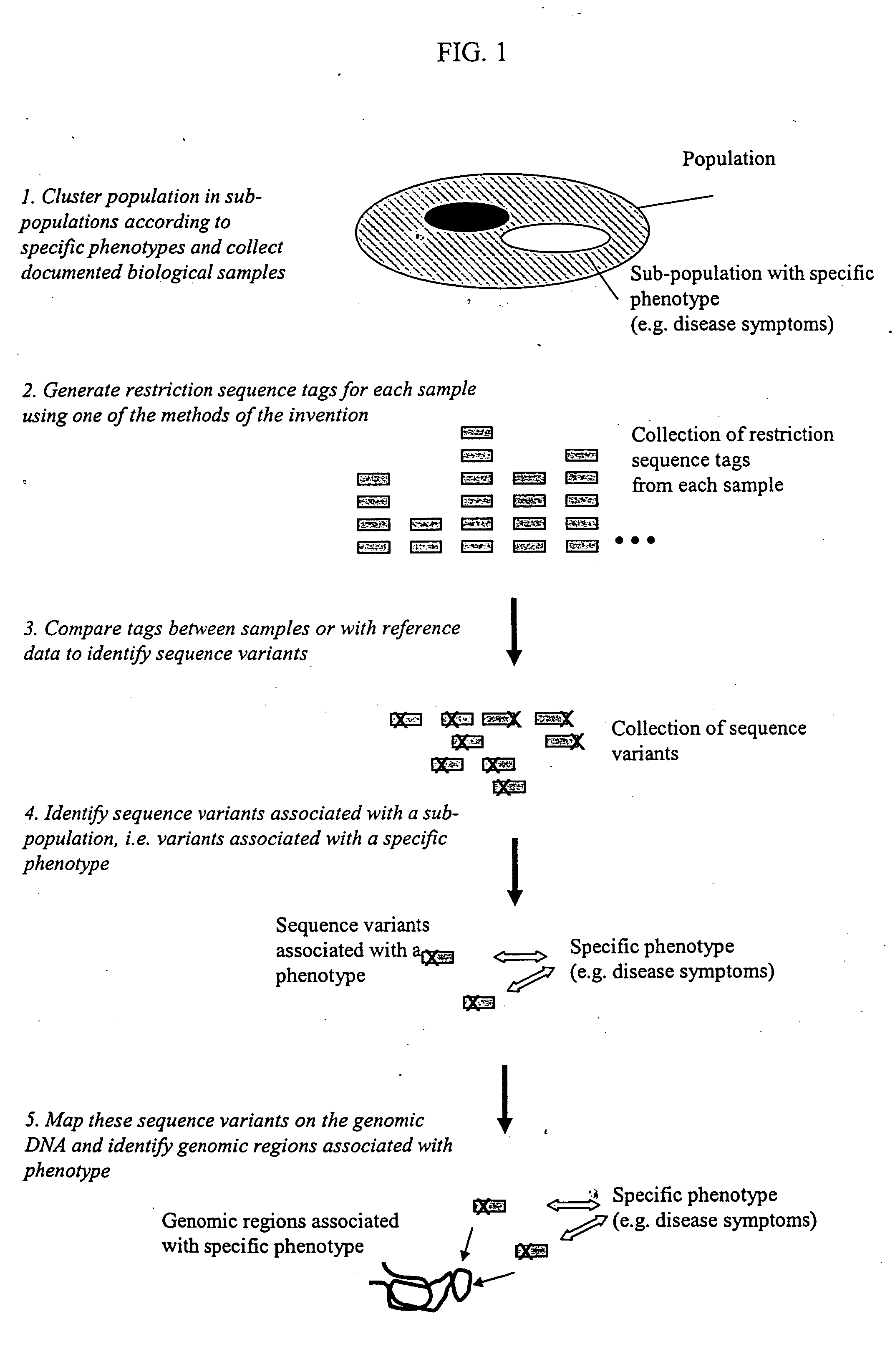
The invention provides methods for determining genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype of a species in a hypothesis-free manner. In the methods of the invention, a set of restriction fragments for each of a sub-population of individuals having the phenotype are generated by digesting nucleic acids from the individual using one or more different restriction enzymes. A set of restriction sequence tags for the individual is then determined from the set of restriction fragments. The restriction sequence tags for the sub-population of organisms are compared and grouped into one or more groups, each of which comprising restriction sequence tags that comprise homologous sequences. The obtained one or more groups of restriction sequence tags identify the sequence variations associated with the phenotype. The methods of the invention can be used for, e.g., analysis of large numbers of sequence variants in many patient samples to identify subtle genetic risk factors.
Owner:SOLEXA
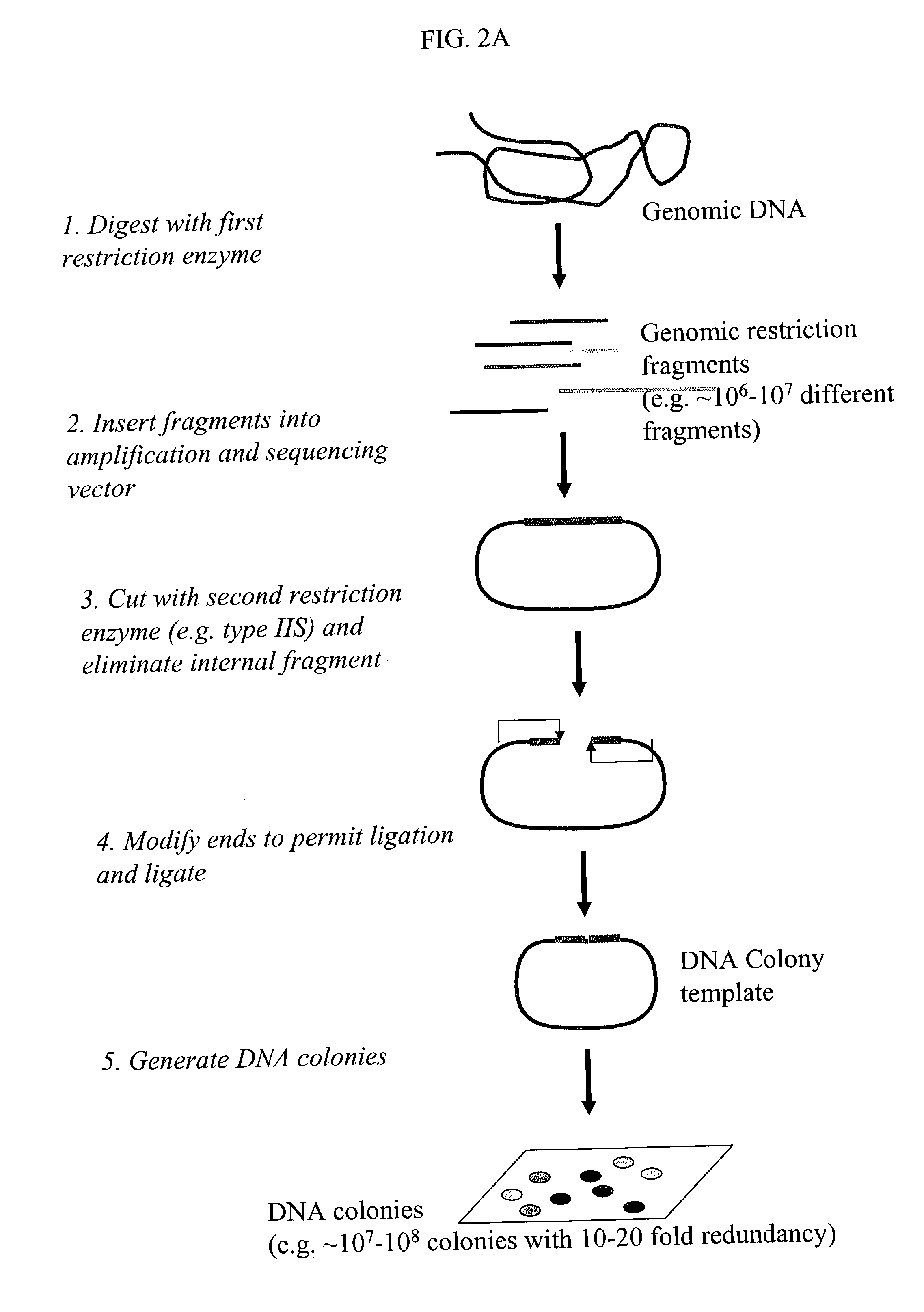
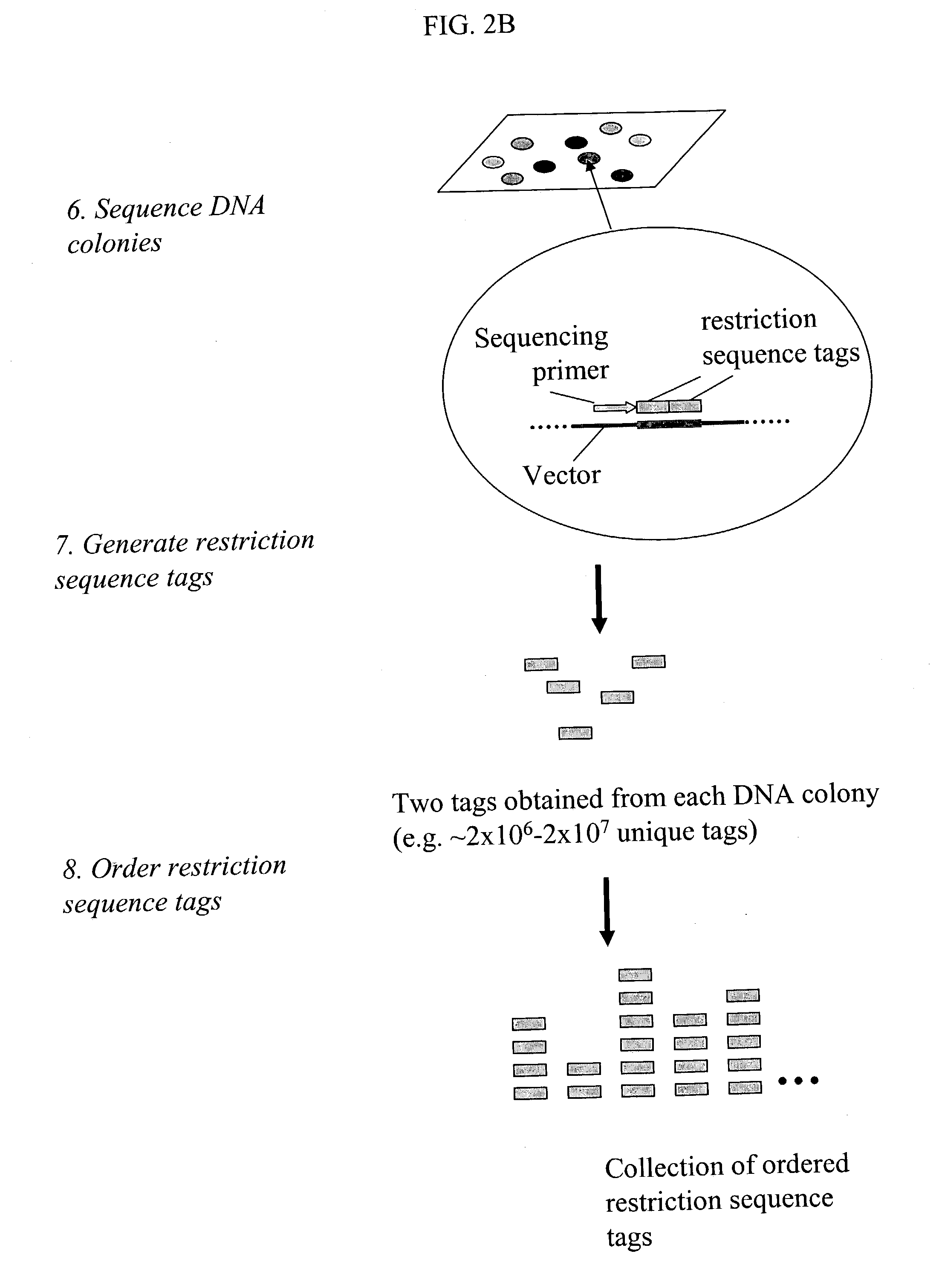
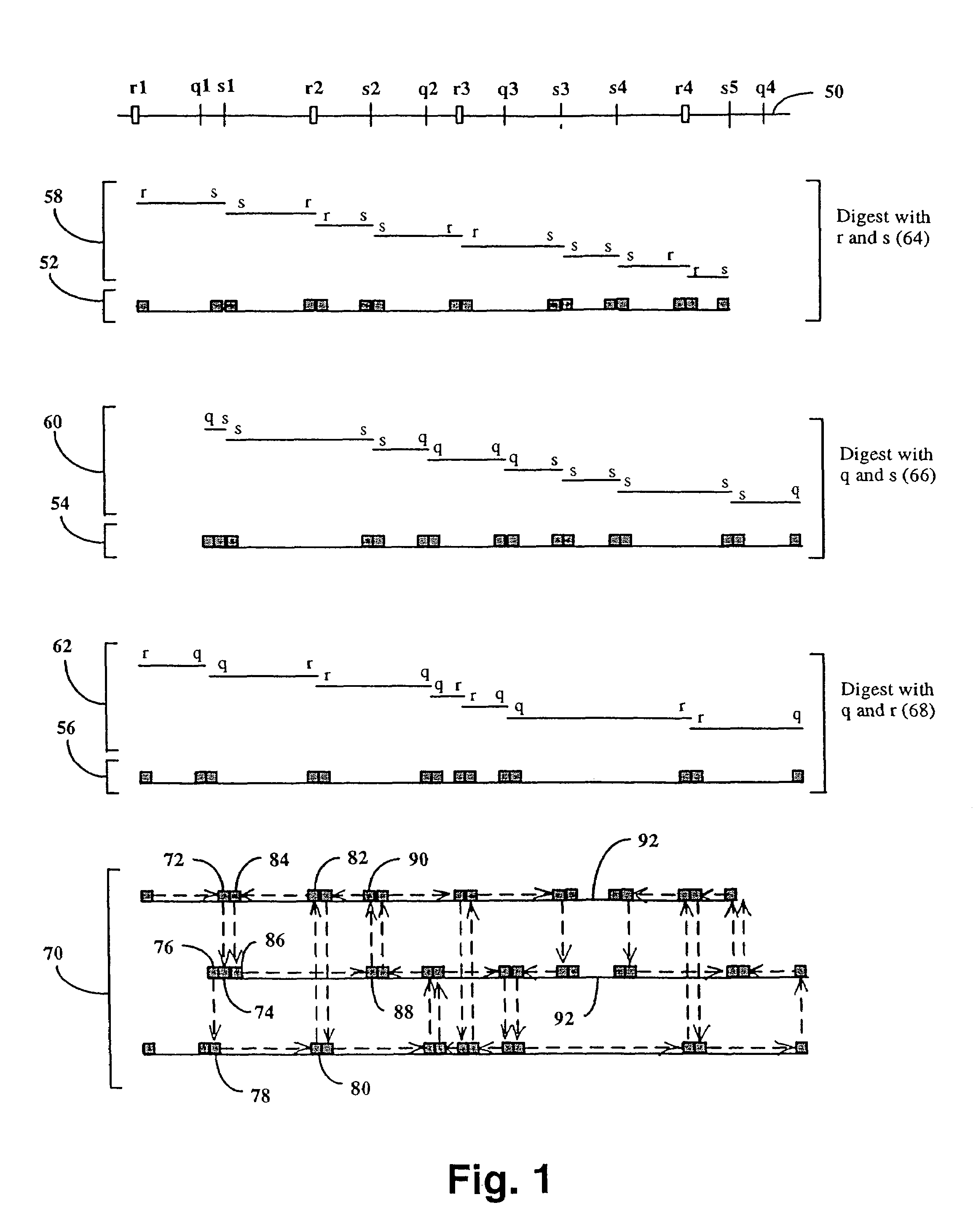
Method and compositions for ordering restriction fragments
InactiveUS7598035B2High density physicalPrecise positioningSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhysical MapsNucleotide sequencing
The invention provides a method for constructing a high resolution physical map of a polynucleotide. In accordance with the invention, nucleotide sequences are determined at the ends of restriction fragments produced by a plurality of digestions with a plurality of combinations of restriction endonucleases so that a pair of nucleotide sequences is obtained for each restriction fragment. A physical map of the polynucleotide is constructed by ordering the pairs of sequences by matching the identical sequences among the pairs.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Methods and apparatuses for characterization of single polymers
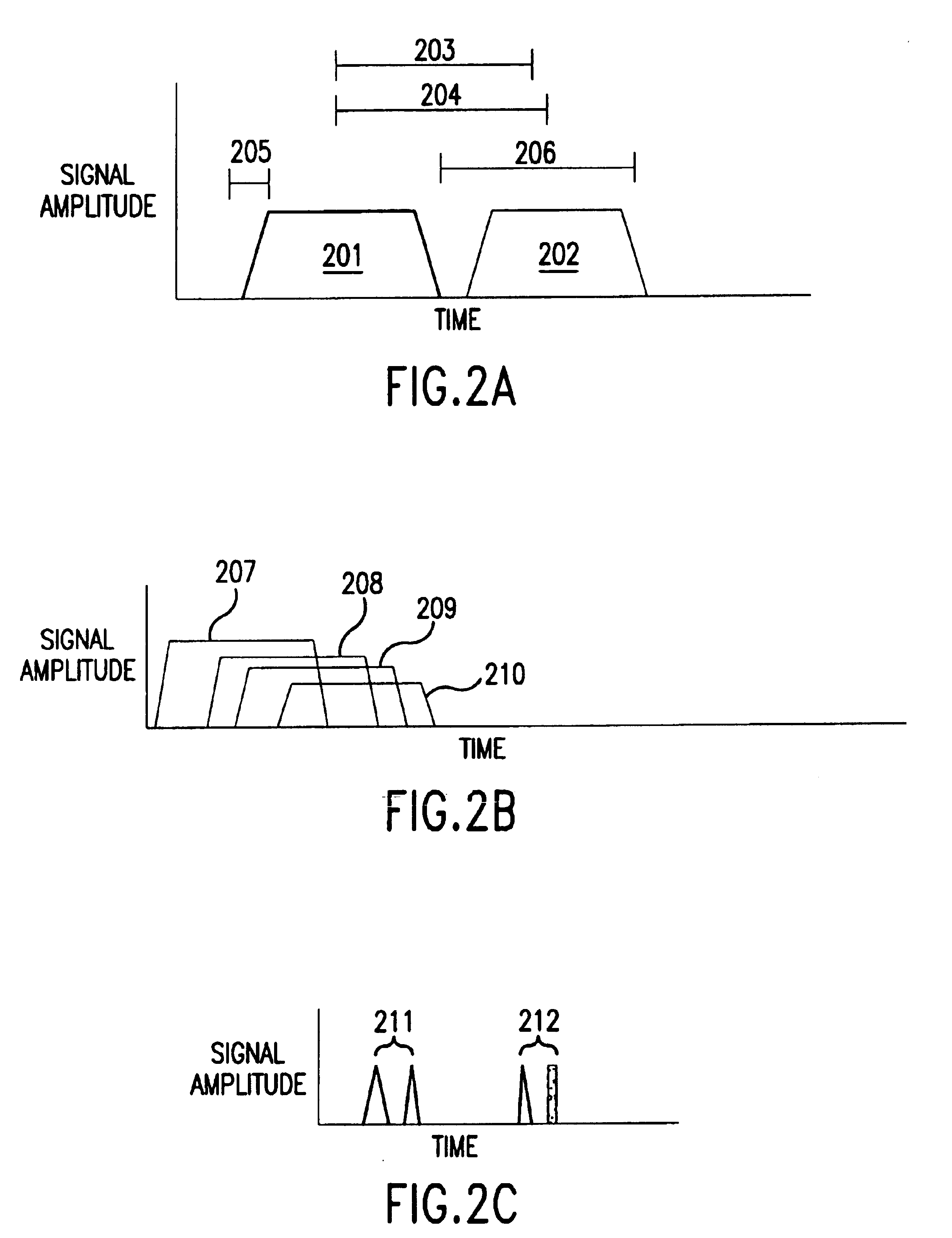
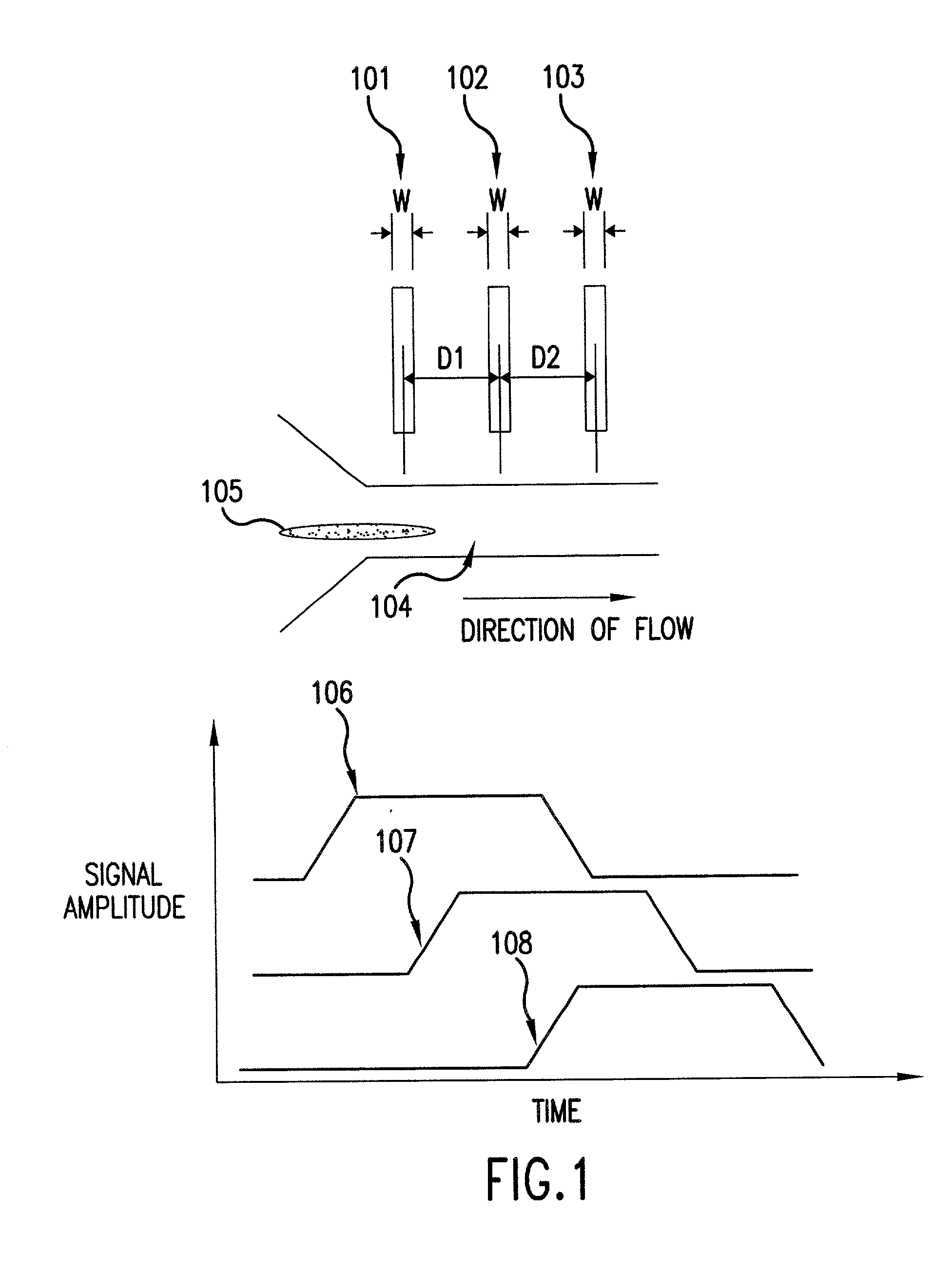
The present invention relates to methods and apparatuses for characterization of single polymers. In particular, the invention relates to methods and apparatuses for determination of the velocities of single elongated polymers. Center-of-mass velocity, center-to-center velocity, end-to-end velocity and rise-time velocity are determined using time-correlated measurements of single elongated polymers in two or more detection zones. The invention also relates to methods of determinating lengths and molecular masses of single polymers and to methods of determining the distance between landmarks on a single polymers based on their velocities. The invention further relates to methods of single-molecule DNA restriction fragment analysis.
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC
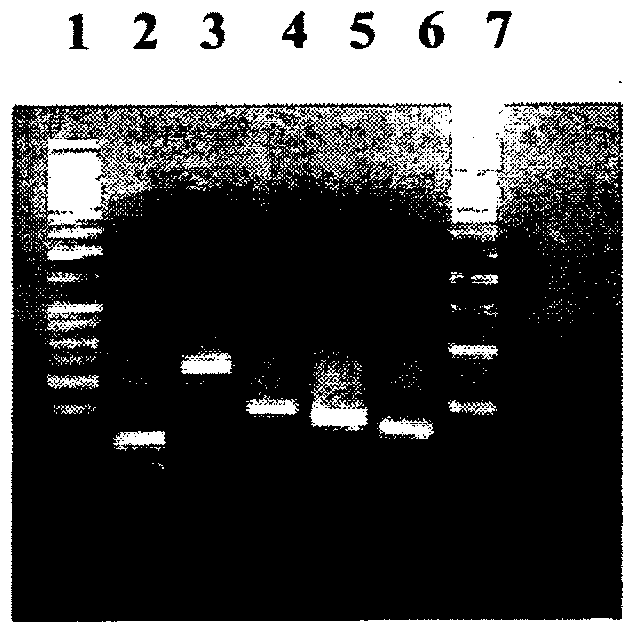
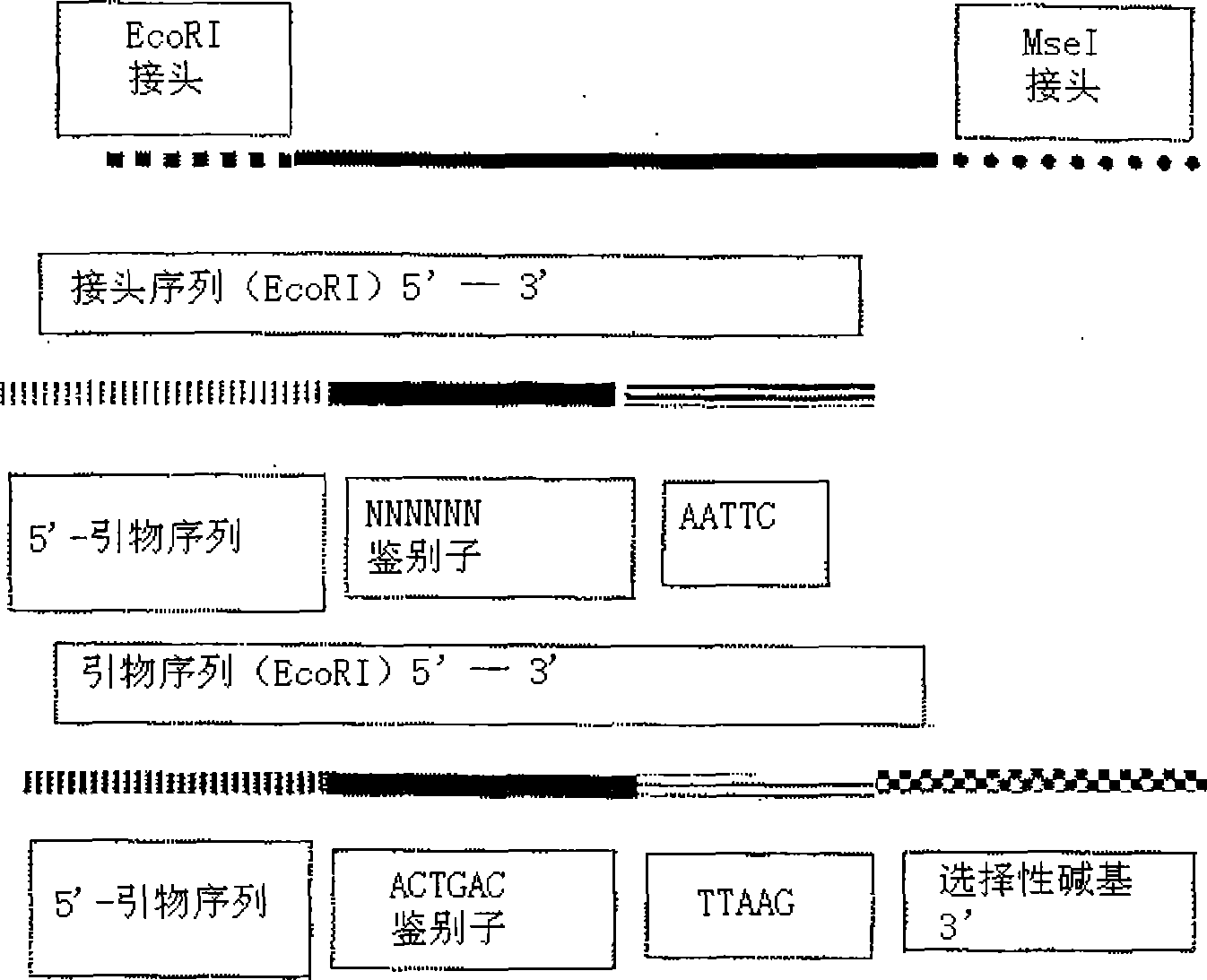
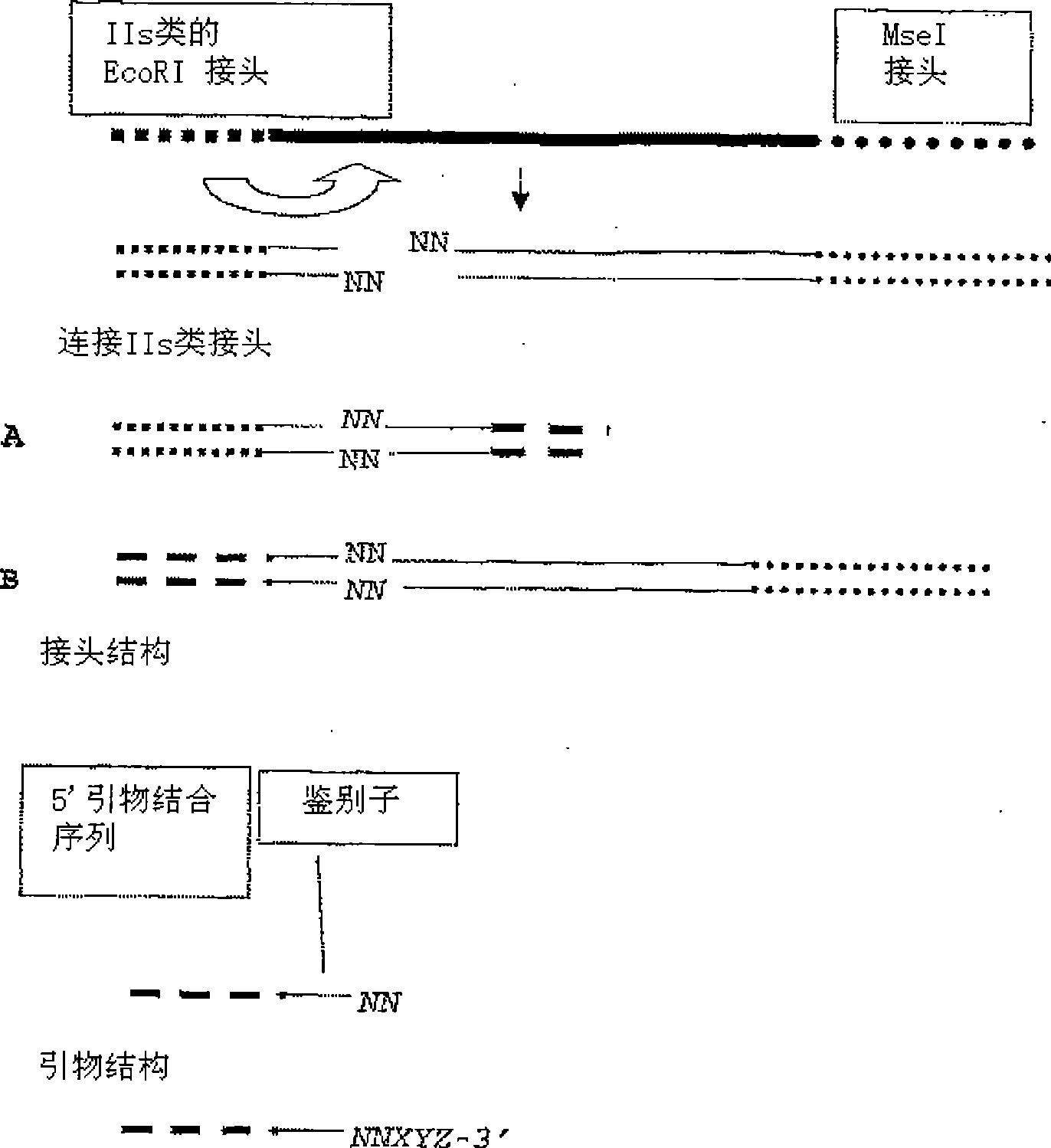
High Throughput Detection of Molecular Markers Based on AFLP and High Throughput Sequencing
InactiveUS20090253581A1Improve throughputOvercome problemsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsRestriction fragment
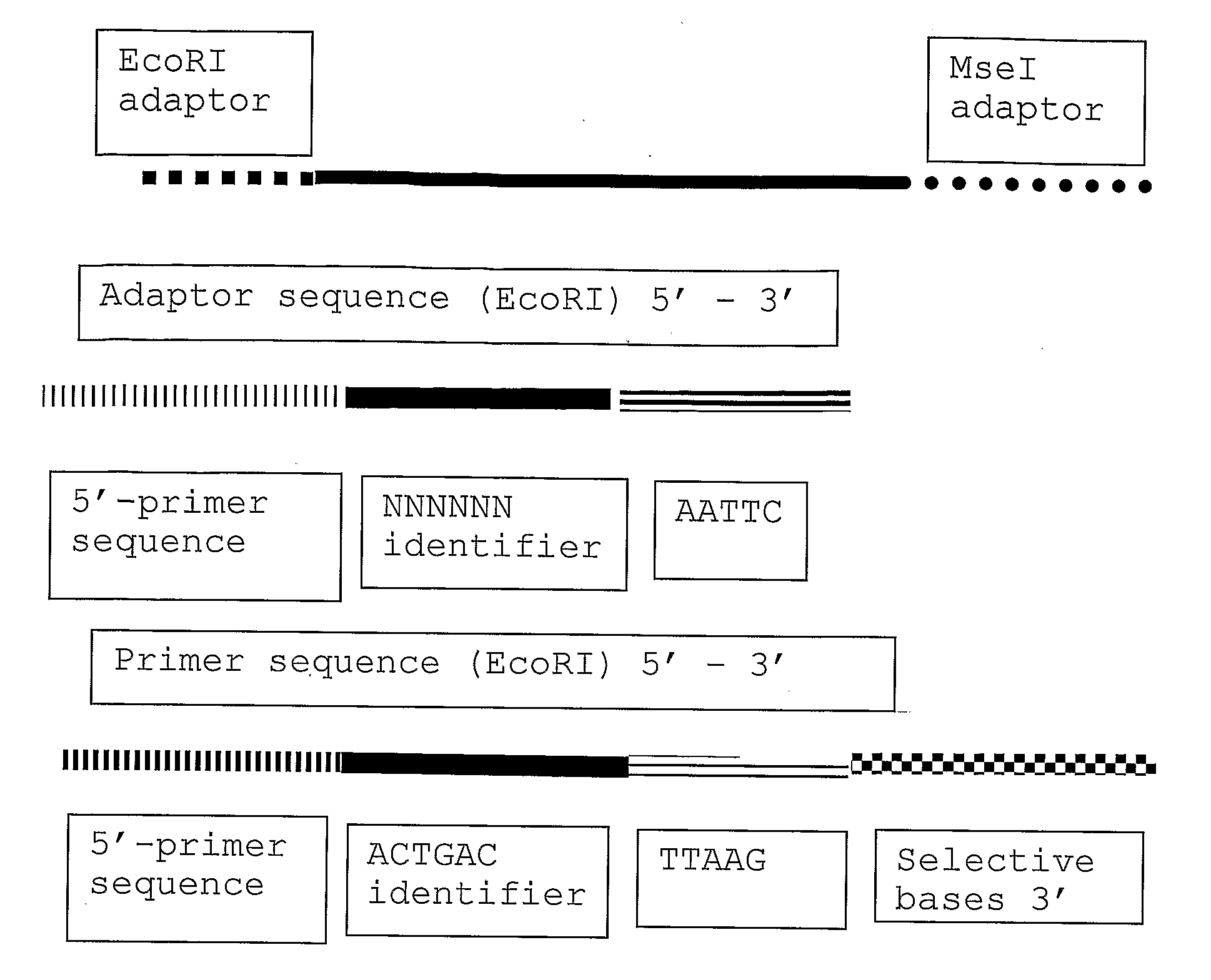
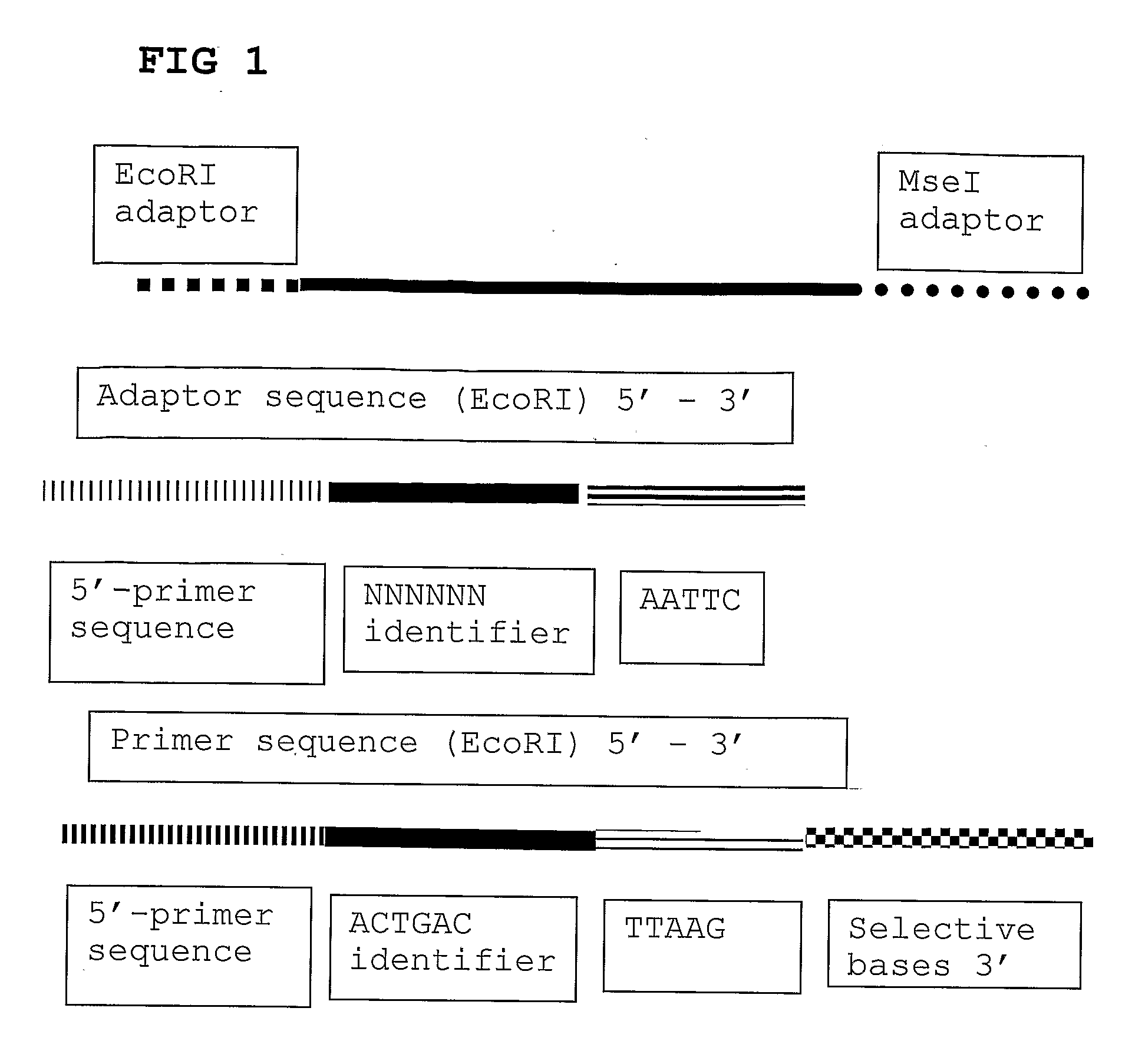
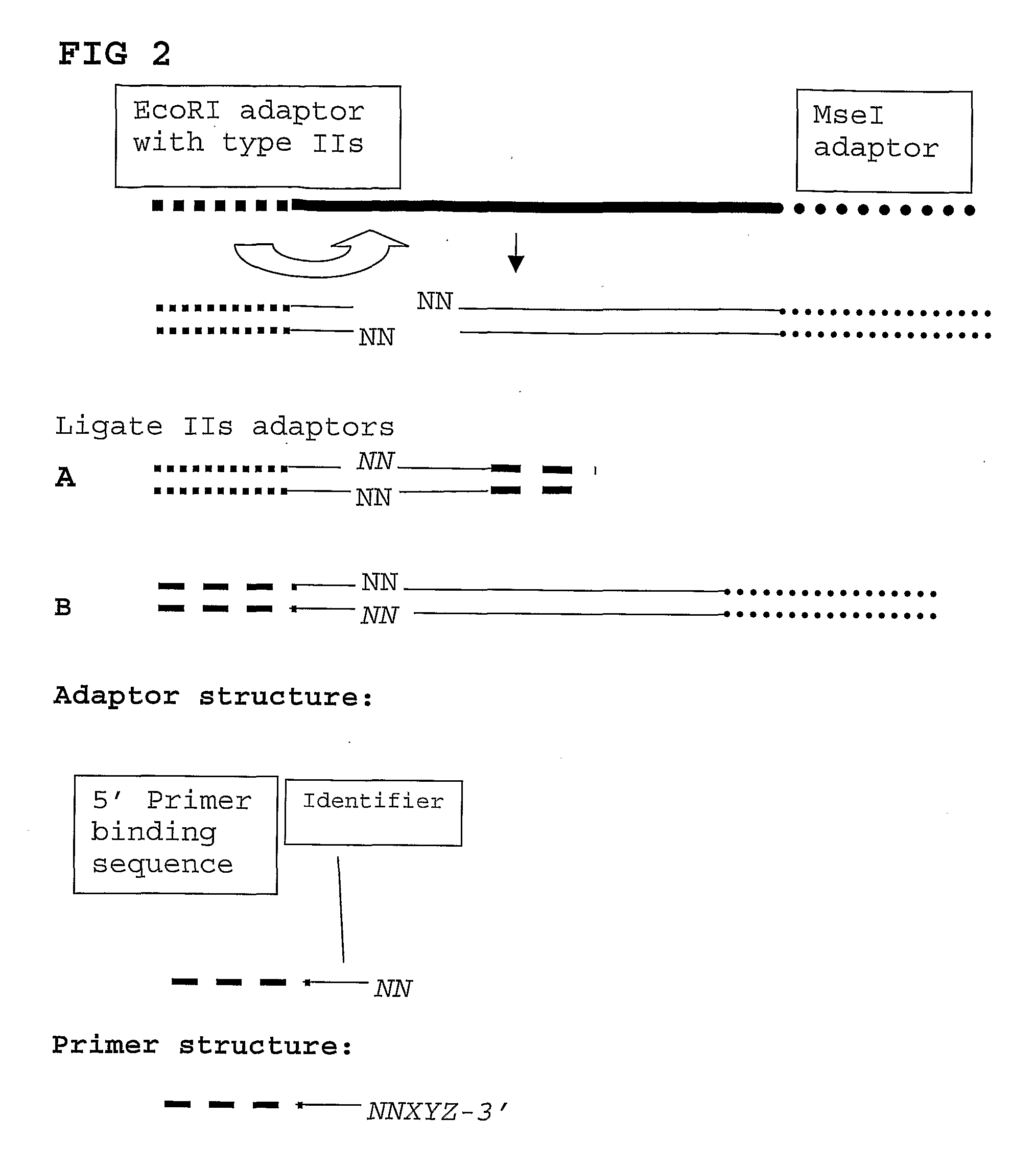
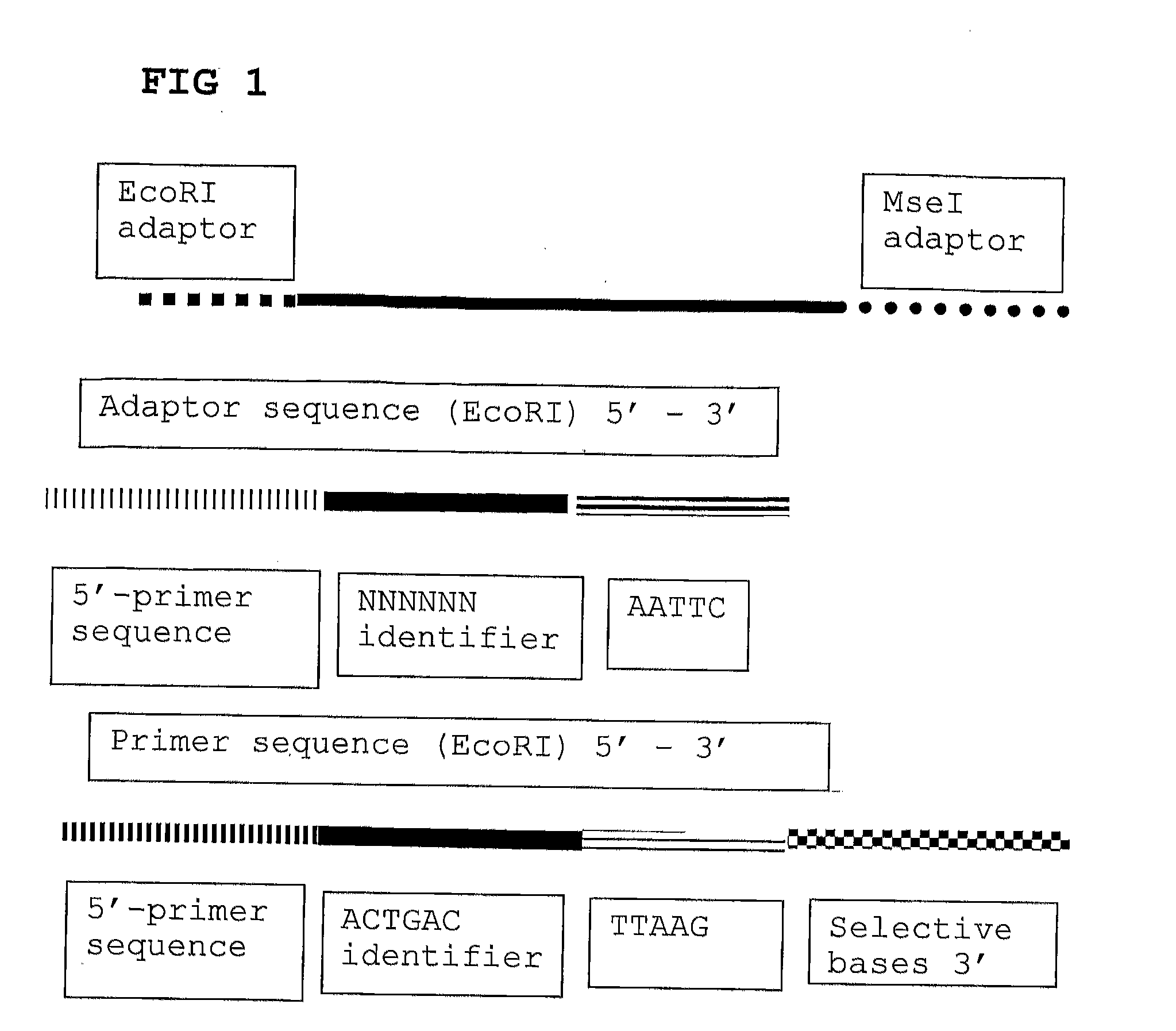
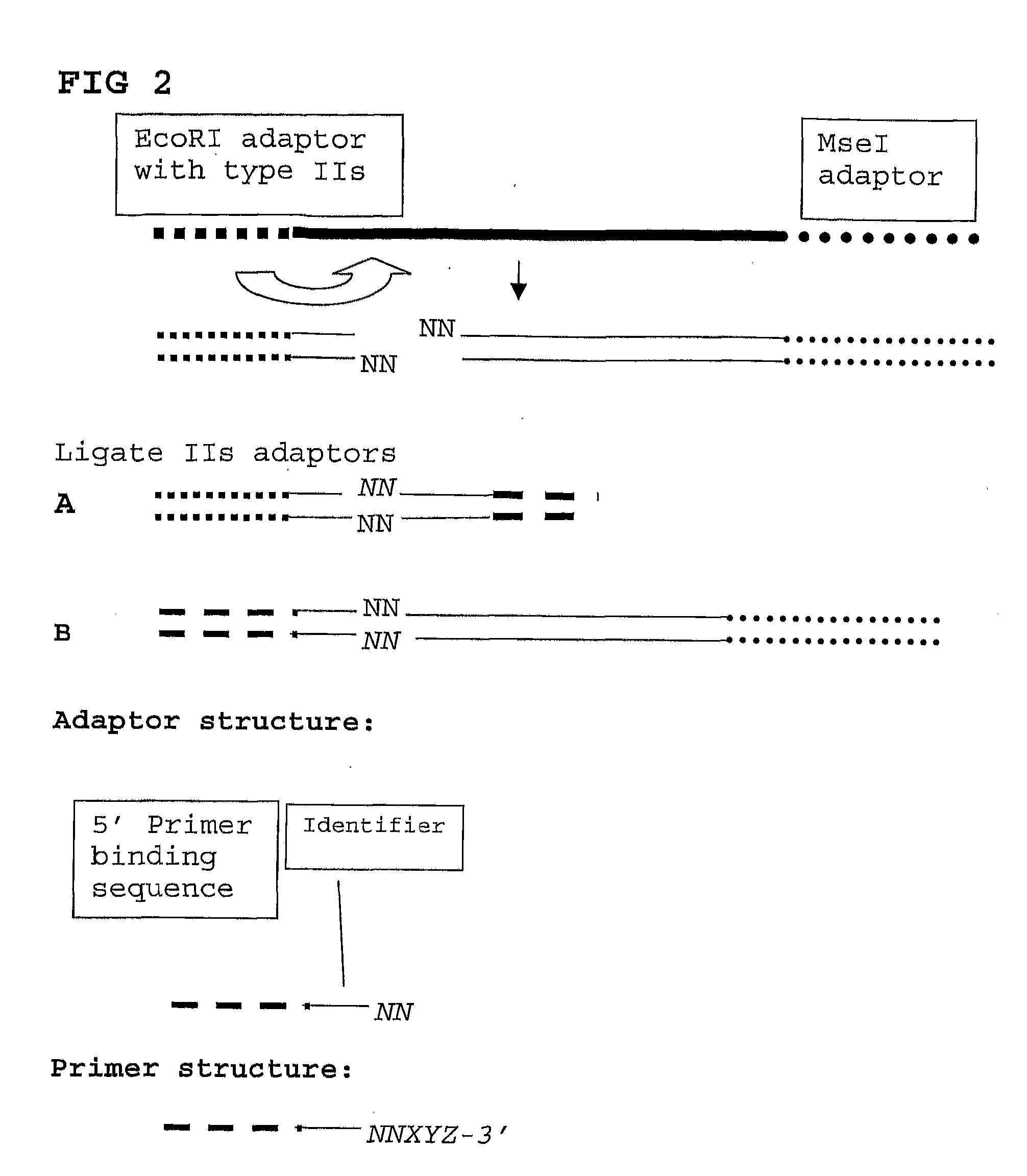
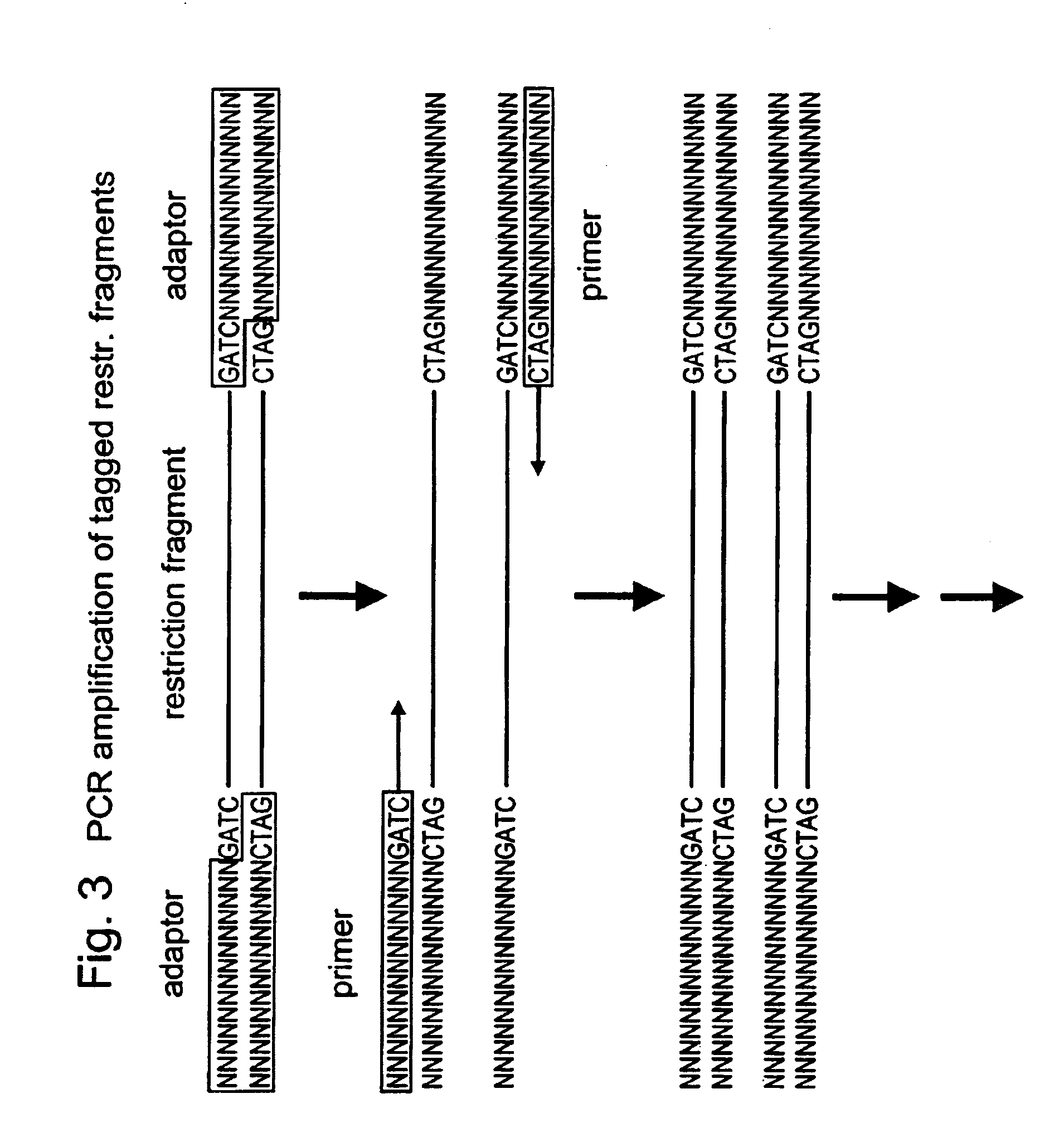
The present invention relates to a high throughput method for the identification and detection of molecular markers wherein restriction fragments are generated and suitable adaptors comprising (sample-specific) identifiers are ligated. The adapter-ligated restriction fragments may be selectively amplified with adaptor compatible primers carrying selective nucleotides at their 3′ end. The amplified adapter-ligated restriction fragments are, at least partly, sequenced using high throughput sequencing methods and the sequence parts of the restriction fragments together with the sample-specific identifiers serve as molecular markers.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Methods and apparatuses for characterization of single polymers
The present invention relates to methods and apparatuses for characterization of single polymers. In particular, the invention relates to methods and apparatuses for determination of the velocities of single elongated polymers. Center-of-mass velocity, center-to-center velocity, end-to-end velocity and rise-time velocity are determined using time-correlated measurements of single elongated polymers in two or more detection zones. The invention also relates to methods of determinating lengths and molecular masses of single polymers and to methods of determining the distance between landmarks on a single polymers based on their velocities. The invention further relates to methods of single-molecule DNA restriction fragment analysis.
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC
High throughput detection of molecular markers based on aflp and high through-put sequencing
InactiveUS20120135871A1Efficient and reliable improvementAdequate identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideGenetics
The present invention relates to a high throughput method for the identification and detection of molecular markers wherein restriction fragments are generated and suitable adaptors comprising (sample-specific) identifiers are ligated. The adapter-ligated restriction fragments may be selectively amplified with adaptor compatible primers carrying selective nucleotides at their 3′ end. The amplified adapter-ligated restriction fragments are, at least partly, sequenced using high throughput sequencing methods and the sequence parts of the restriction fragments together with the sample-specific identifiers serve as molecular marker.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
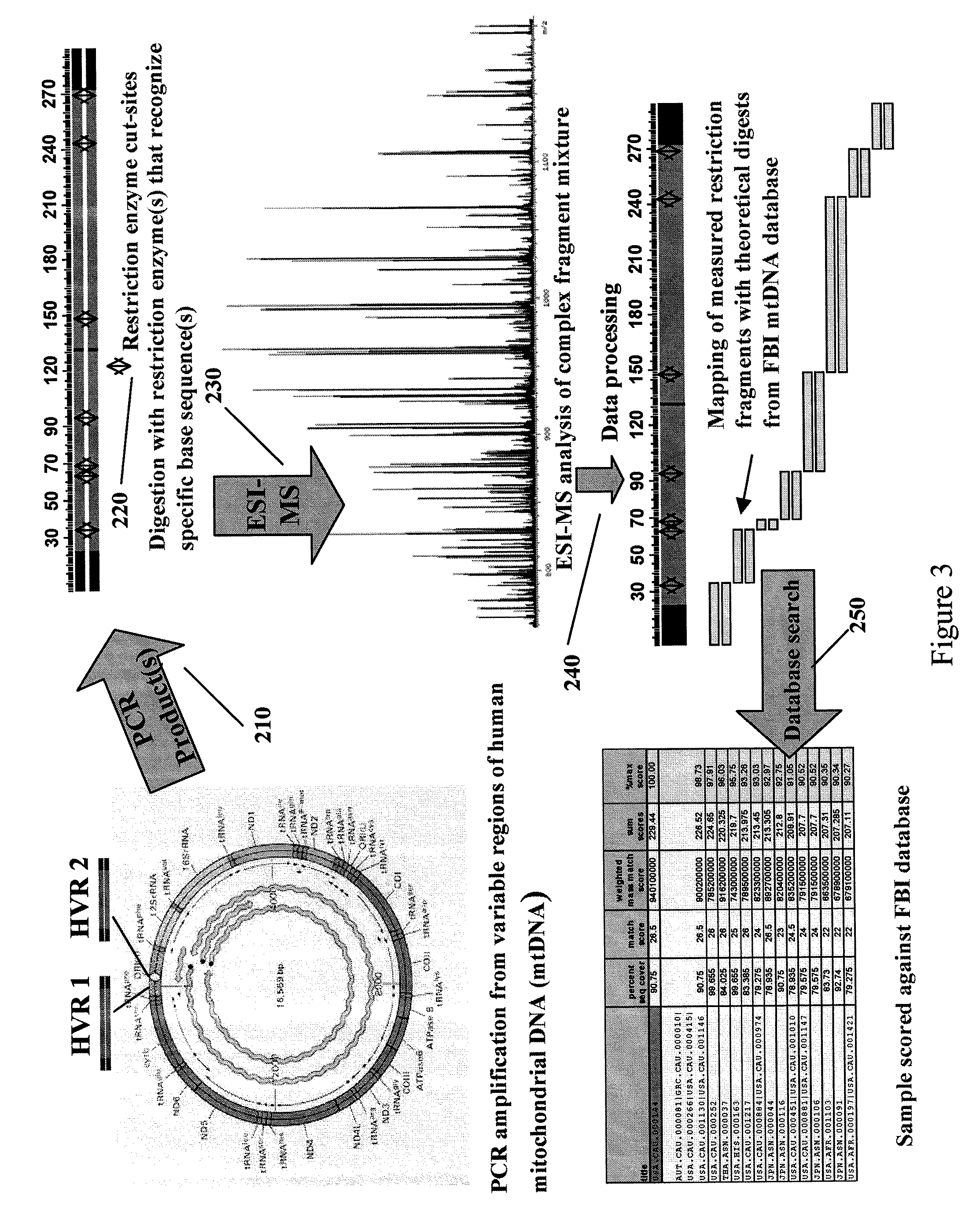
Methods for rapid forensic analysis of mitochondrial DNA
InactiveUS20050266411A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRestriction siteForensic science
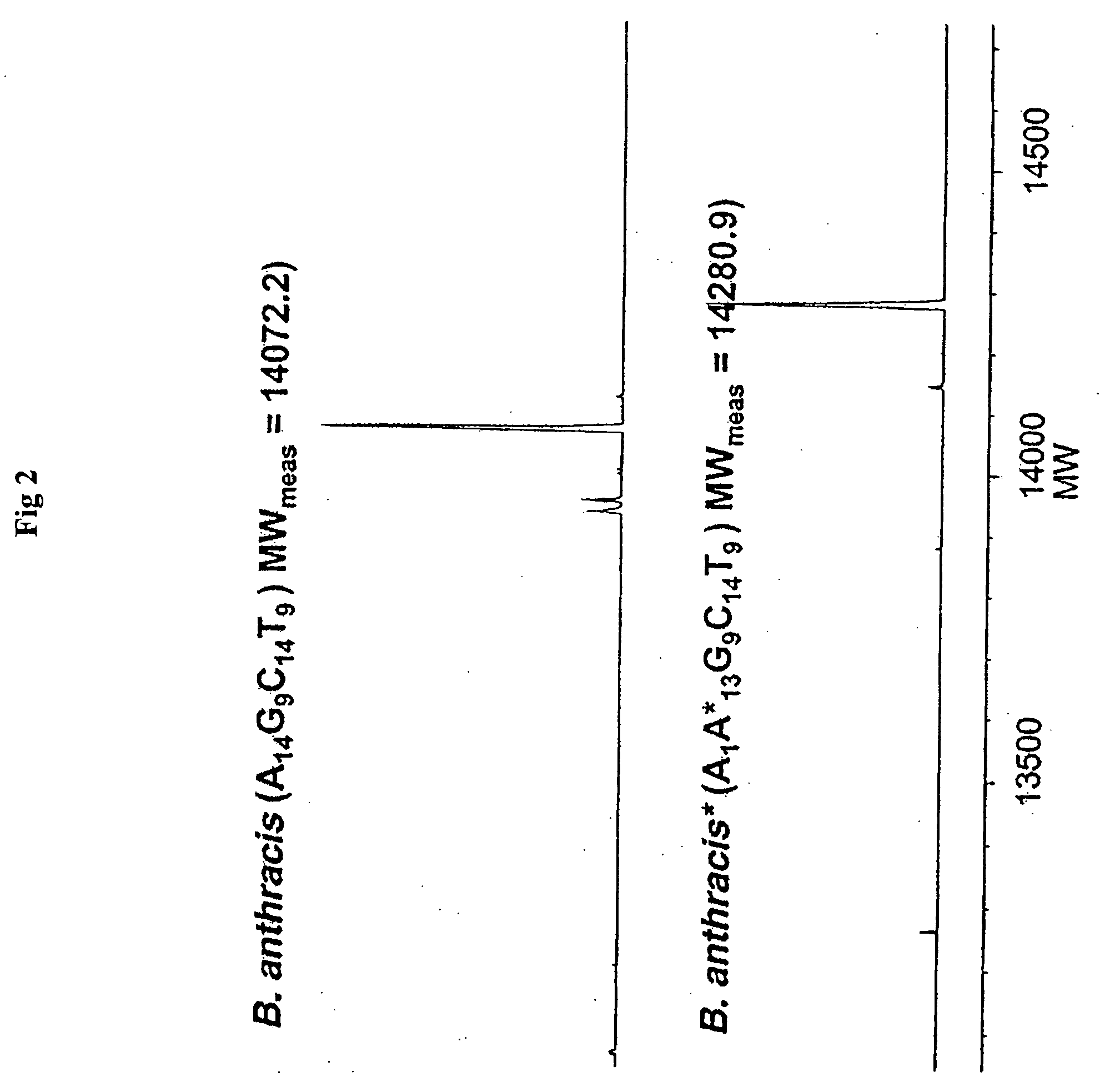
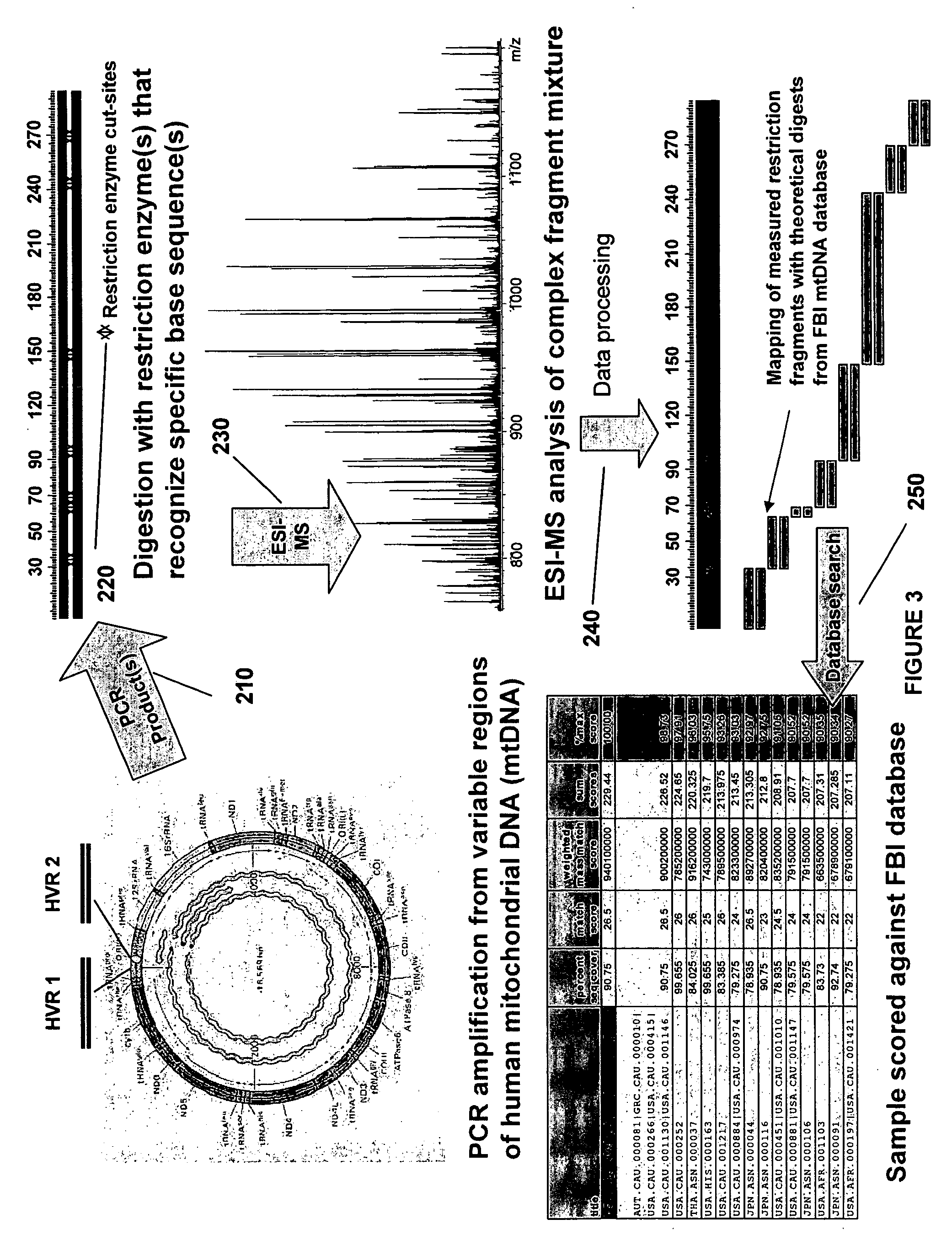
The present invention provides methods for rapid forensic analysis of mitochondrial DNA by amplification of a segment of mitochondrial DNA containing restriction sites, digesting the mitochondrial DNA segments with restriction enzymes, determining the molecular masses of the restriction fragments and comparing the molecular masses with the molecular masses of theoretical restriction digests of known mitochondrial DNA sequences stored in a database.
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI
Methods For Rapid Forensic Analysis Of Mitochondrial DNA
InactiveUS20090125245A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction enzyme digestionRestriction site
The present invention provides methods for rapid forensic analysis of mitochondrial DNA by amplification of a segment of mitochondrial DNA containing restriction sites, digesting the mitochondrial DNA segments with restriction enzymes, determining the molecular masses of the restriction fragments and comparing the molecular masses with the molecular masses of theoretical restriction digests of known mitochondrial DNA sequences stored in a database.
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI +1
Selective genome amplification
The invention provides methods and compositions for amplifying selected polynucleotides, especially selected subsets of restriction fragments. Generally, methods of the invention are implemented by ligating adaptors containing at least one promoter sequence to such fragments under conditions that promote the formation of closed single stranded or double stranded structures, which are capable of serving as cyclical templates for transcription.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
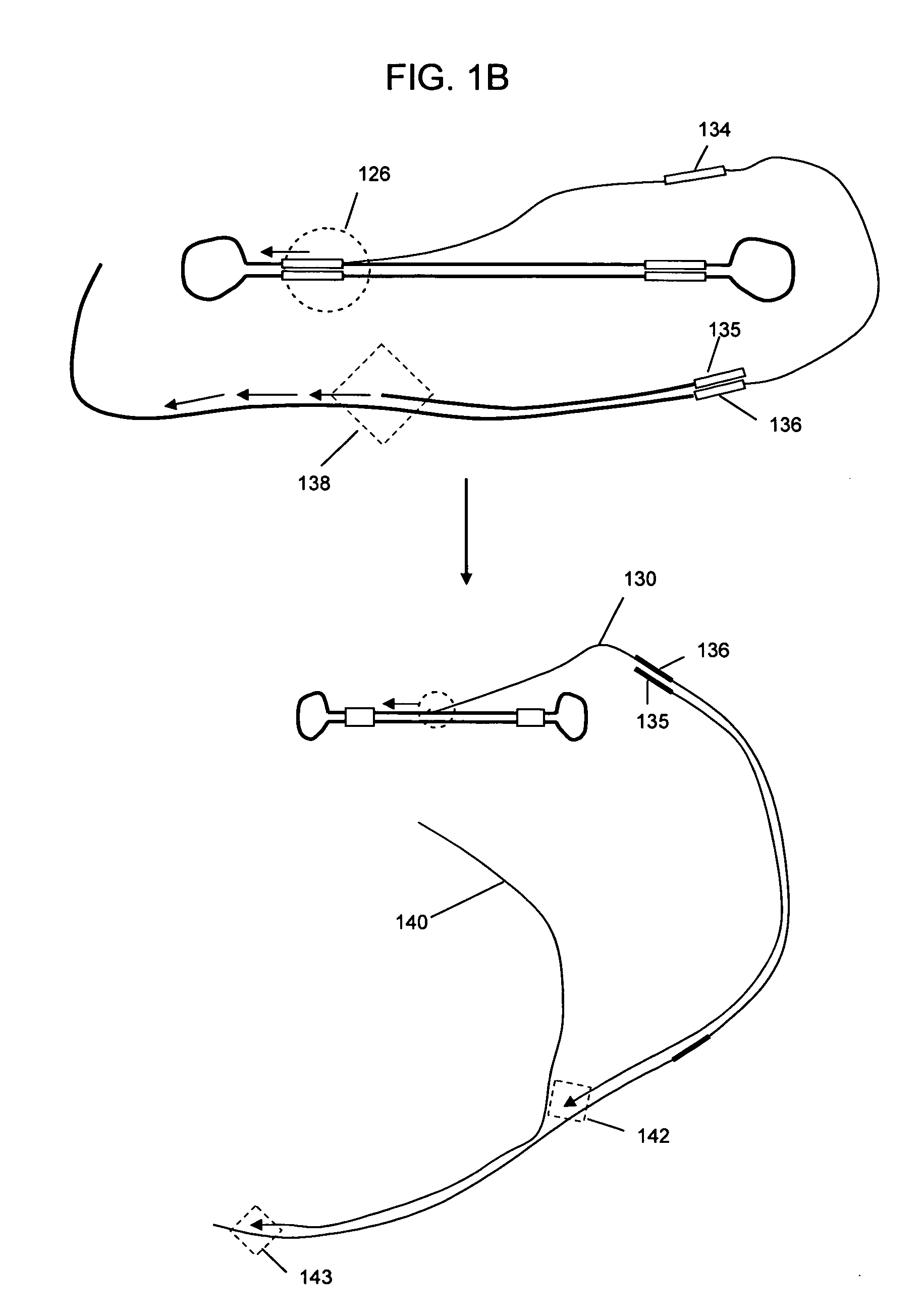
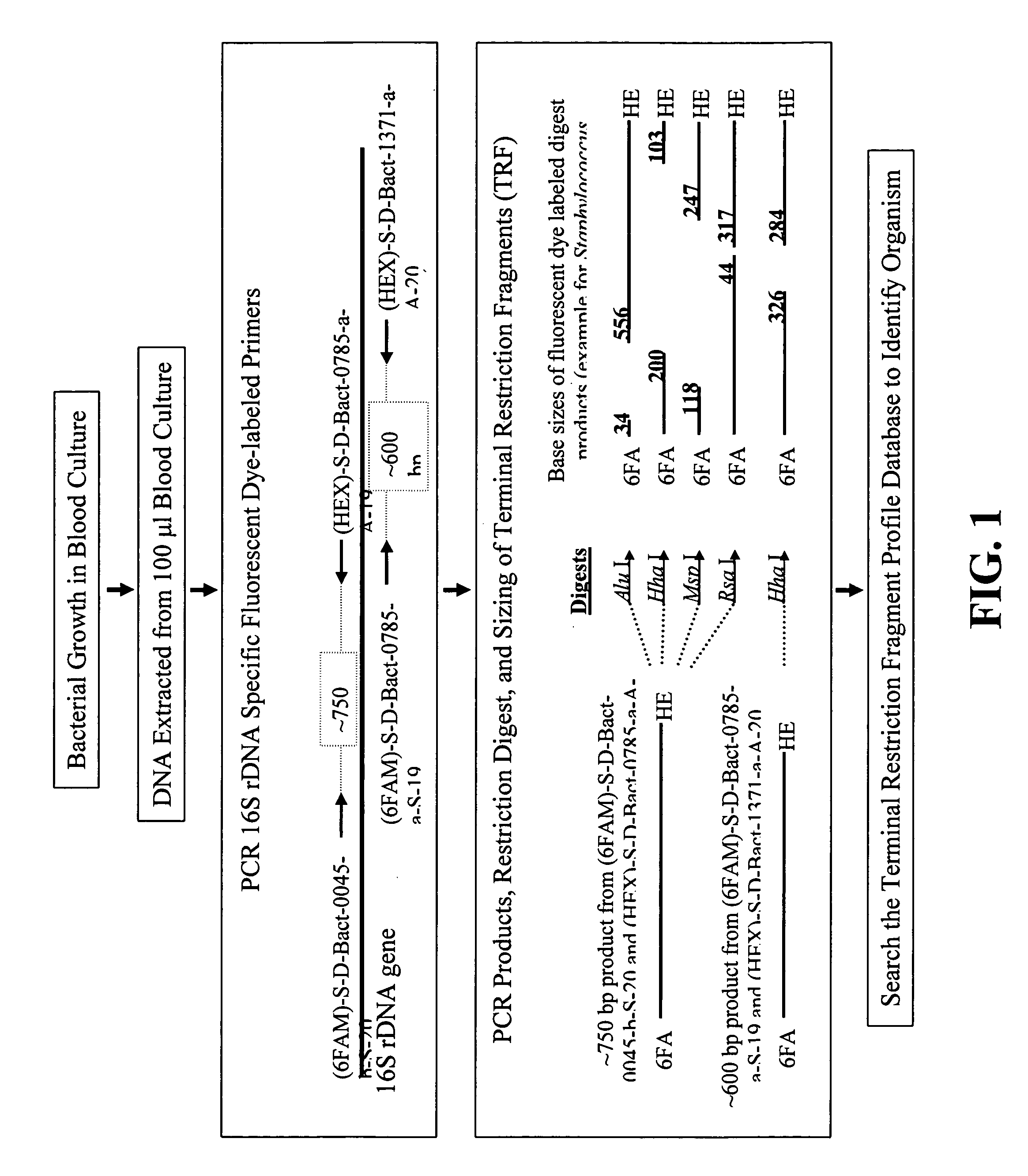
Rapid identification of bacteria from positive blood cultures
InactiveUS20050037408A1Reduce unnecessary useAvoid developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingRapid identificationPositive blood culture
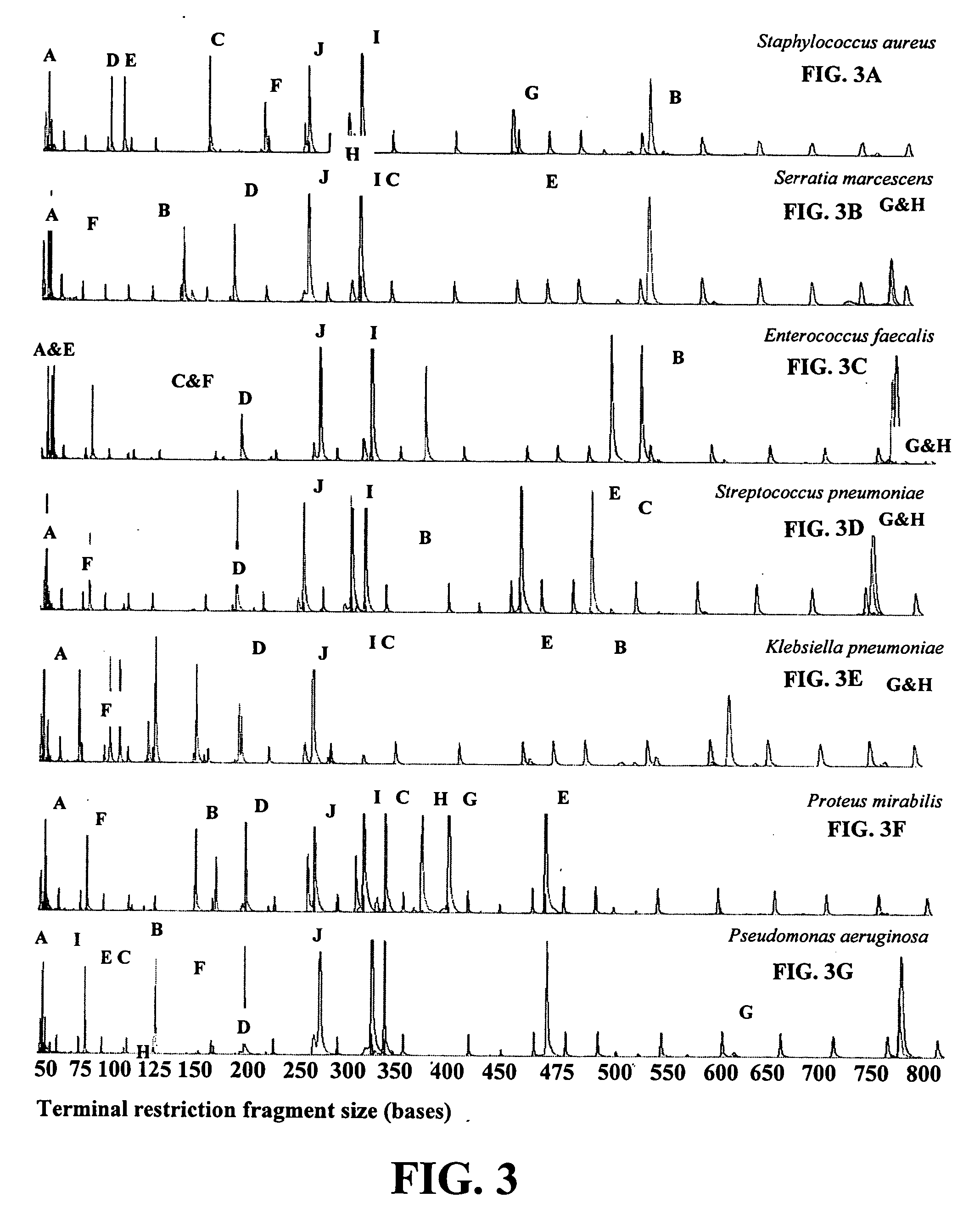
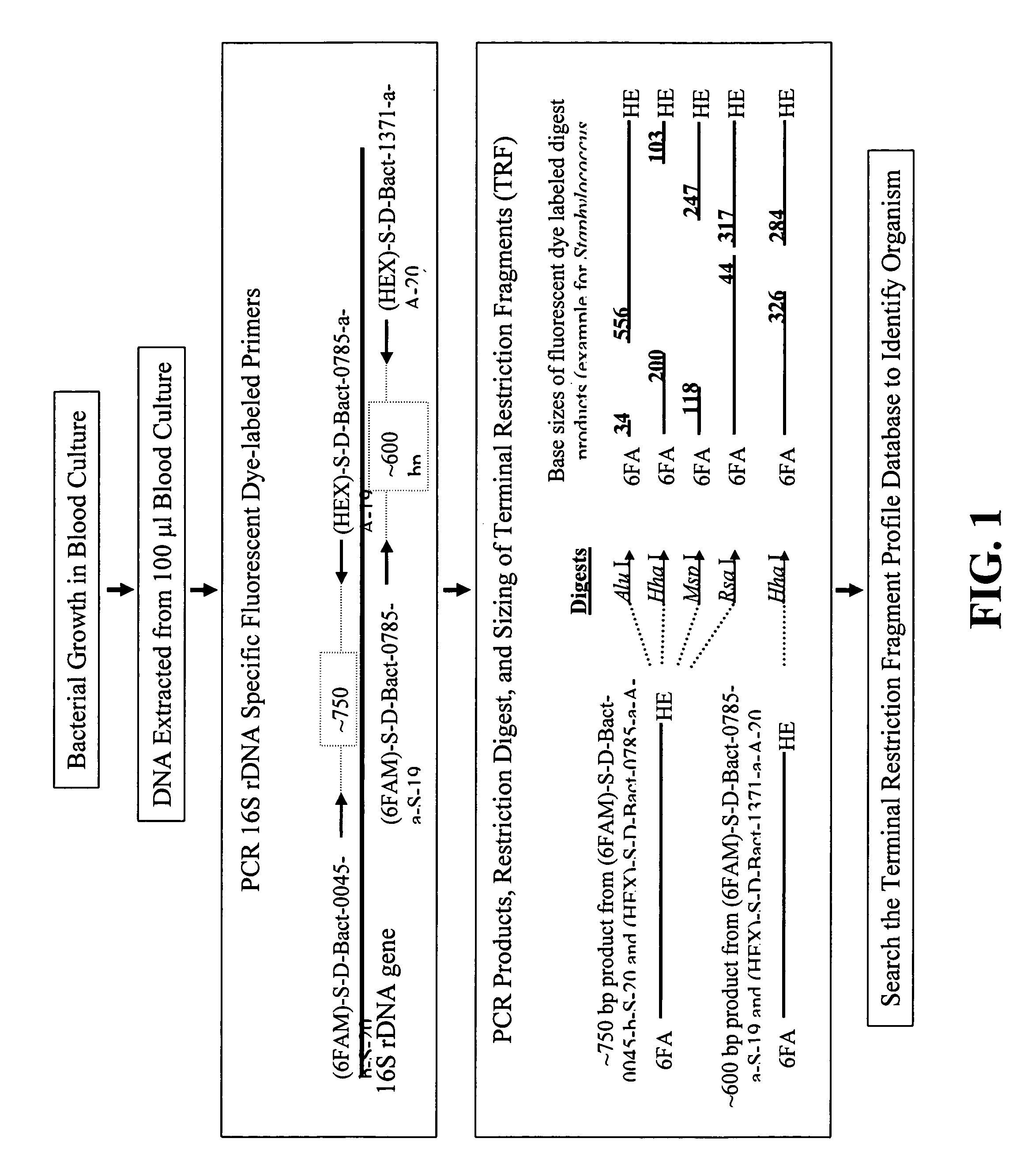
Disclosed is a method of detecting bacteria in a biological sample, especially a blood sample, without the need for extensive sub-culturing of the sample. Nucleic acid present within the sample is isolated and bacterial DNA specifically amplified using primers that uniquely prime the amplification of 16s rRNA-encoding nucleic acid. The amplicons are then digested with an endonuclease to yield a restriction fragment length profile for the biological sample. The restriction fragment length profile for the biological sample is then compare to a database of profiles made using cultures of known bacterial species. A match between the sample profile and the database quickly identifies the bacteria present in the sample.
Owner:MARSHFIELD CLINIC
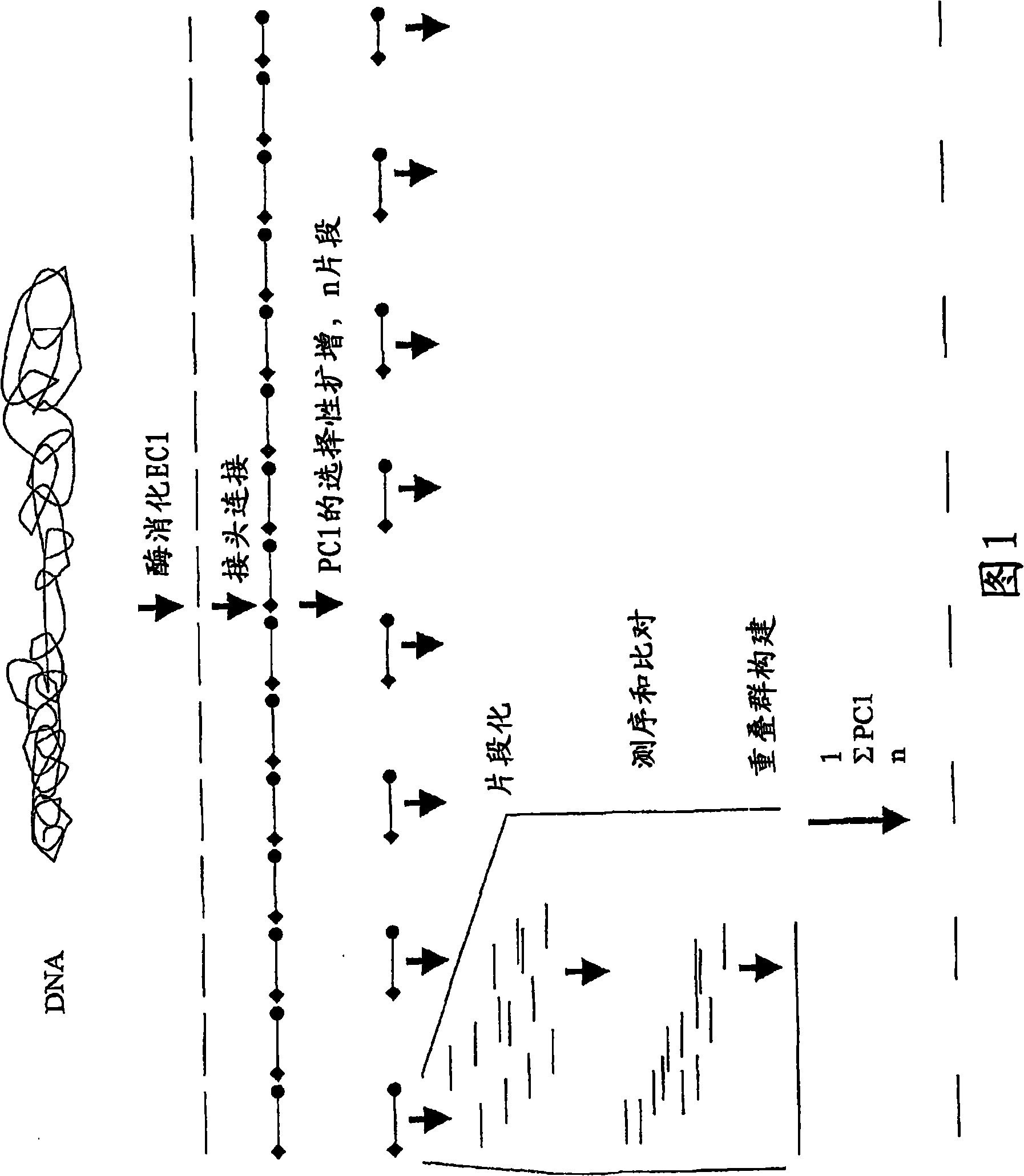
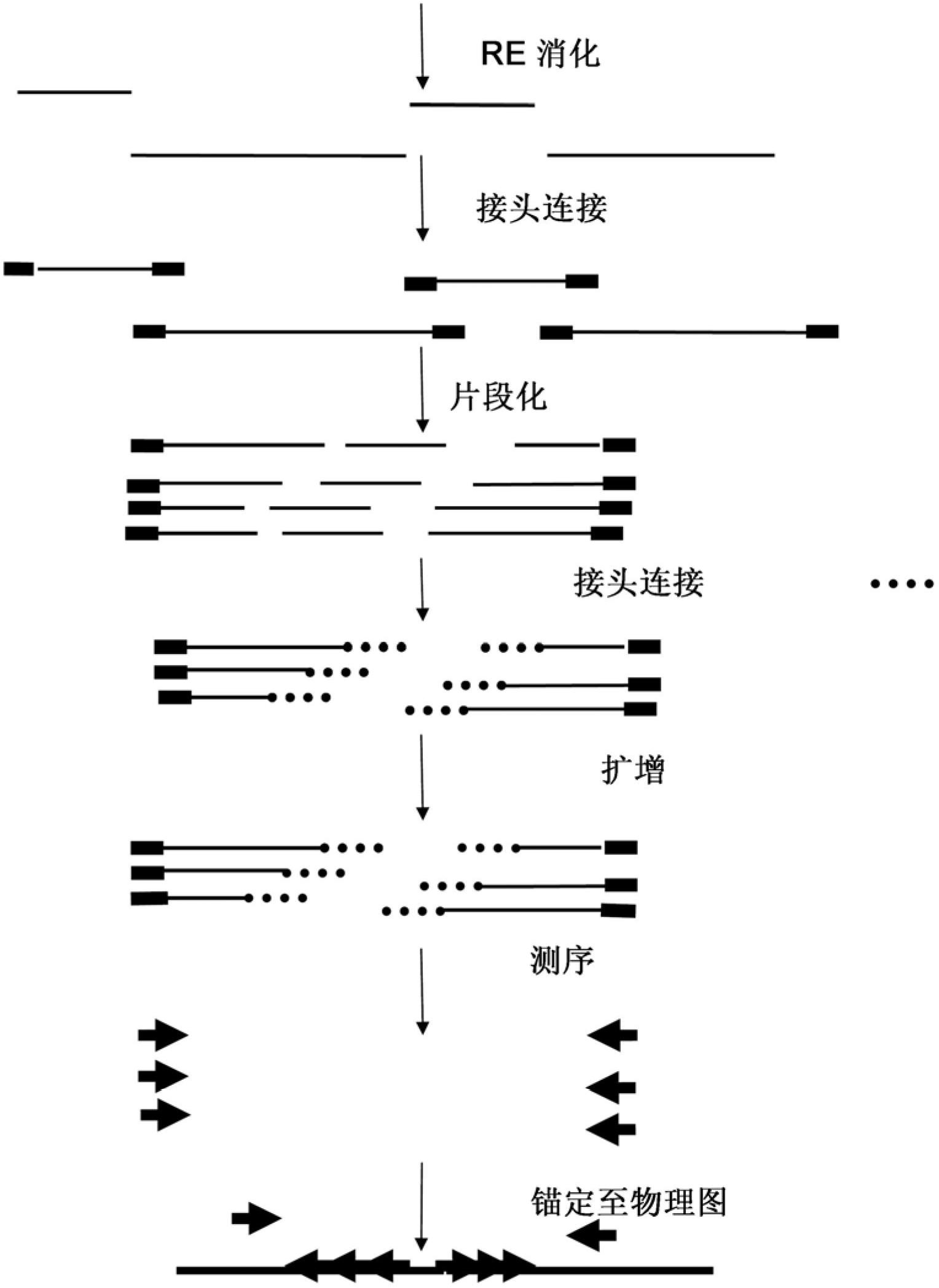
Strategies for sequencing complex genomes using high throughput sequencing technologies
InactiveUS20090142758A1Easy to useQuick sortingMicrobiological testing/measurementContigNucleotide sequencing
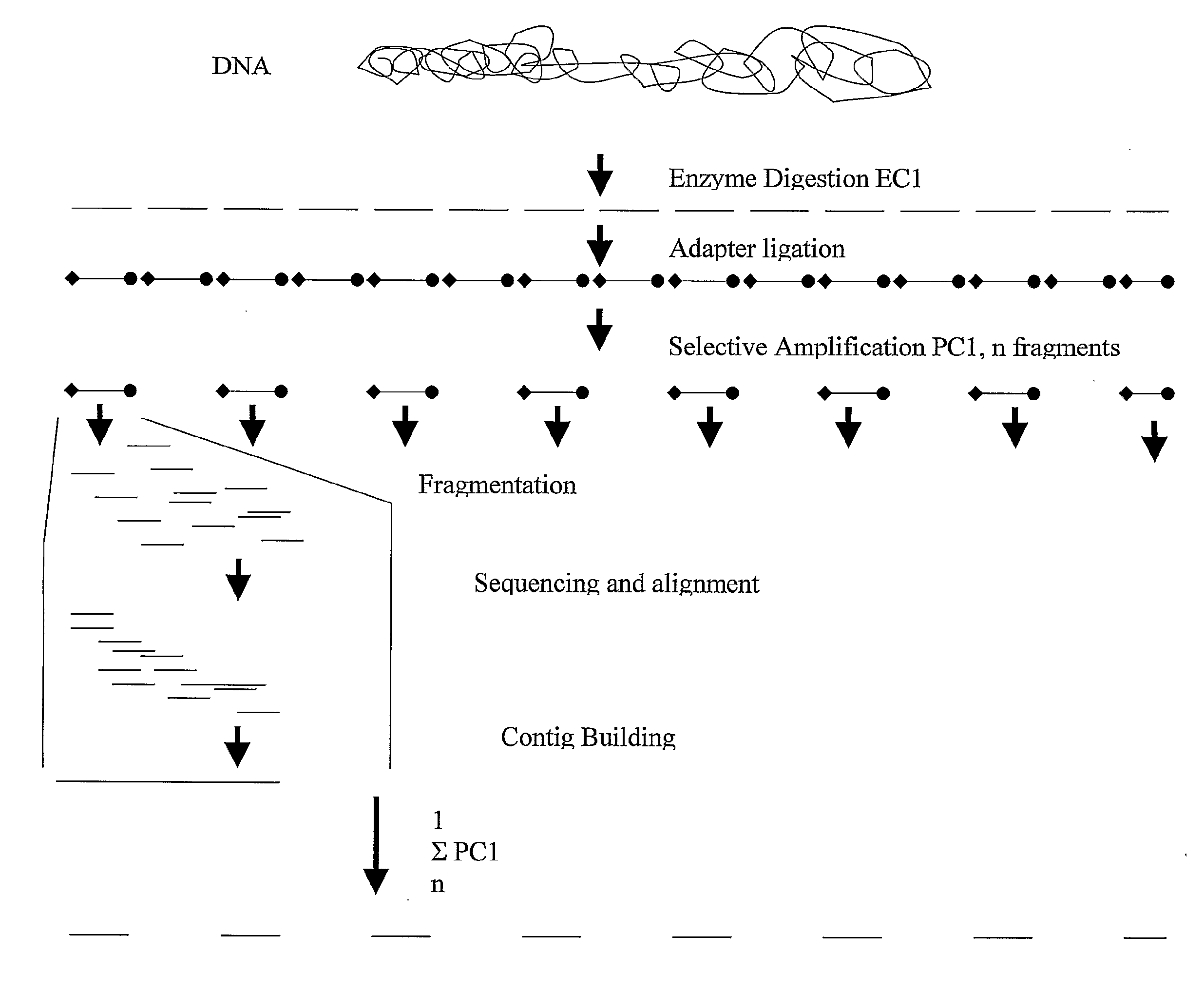
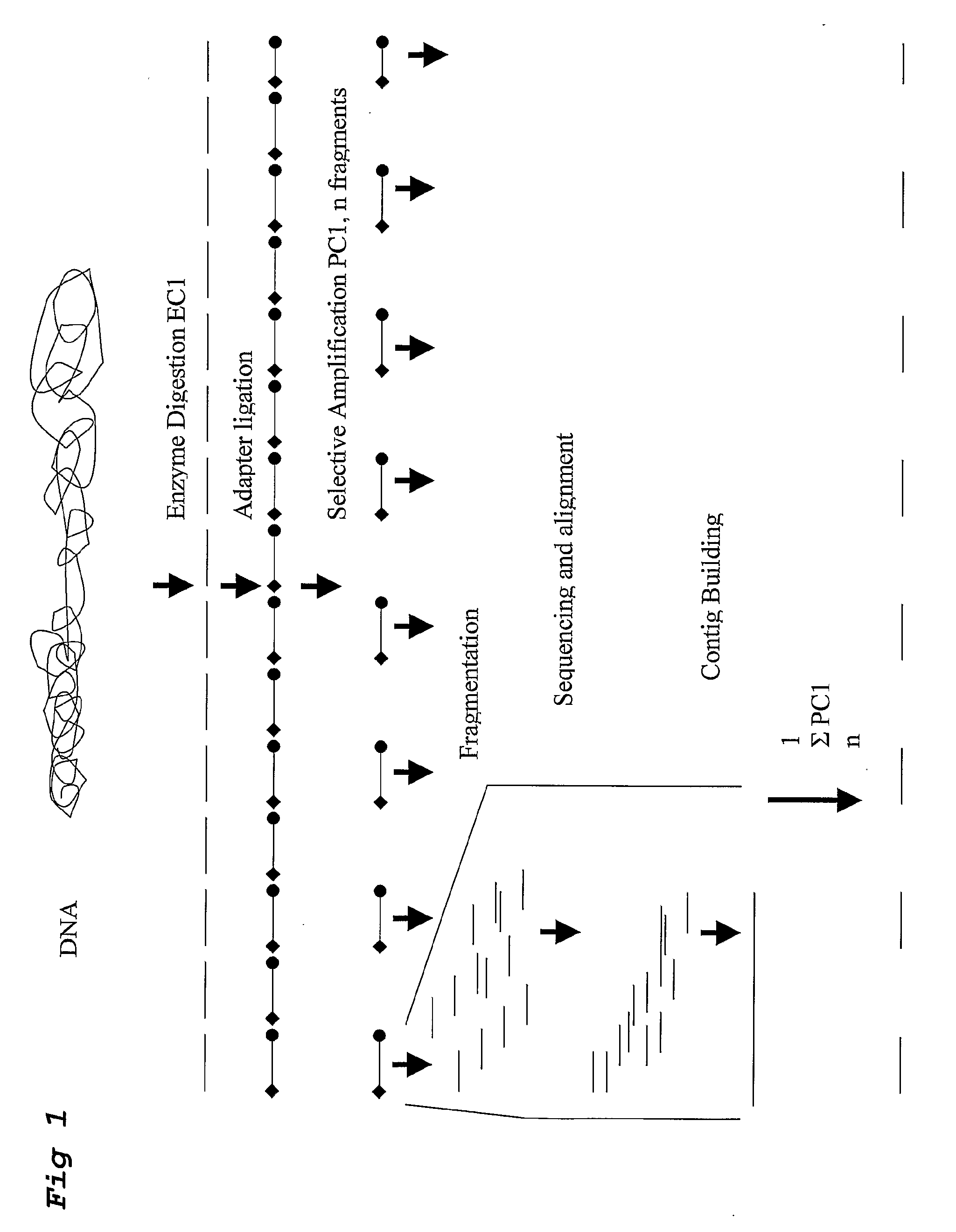
A method for determining a genome sequence comprising the steps of digesting the genome with at least one first restriction endonuclease, ligating at least one adaptor to the restriction fragments of the first subset, selectively amplifying the first set of adaptor-ligated restriction fragments using a first primer combination wherein at least a first primer contains a first selected sequence at the 3′ end of the primer sequence, comprising 1-10 selective nucleotides, repeating these steps with at least a second primer combinations wherein the primer contains a different second selected sequence, fragmenting each of the subsets of amplified adaptor-ligated restriction fragments to generate sequencing libraries, determine the nucleotide sequence of the fragments, aligning the sequence of the fragments in each of the libraries to generate contigs, repeating these steps for one second and / or further restriction endonucleases, aligning the contigs obtained for each of the second and / or further restriction endonucleases to provide for a sequence of the genome.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Rapid identification of bacteria from positive blood cultures
InactiveUS7205111B2Increase profitFast approachMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBacteroidesRapid identification
Disclosed is a method of detecting bacteria in a biological sample, especially a blood sample, without the need for extensive sub-culturing of the sample. Nucleic acid present within the sample is isolated and bacterial DNA specifically amplified using primers that uniquely prime the amplification of 16s rRNA-encoding nucleic acid. The amplicons are then digested with an endonuclease to yield a restriction fragment length profile for the biological sample. The restriction fragment length profile for the biological sample is then compare to a database of profiles made using cultures of known bacterial species. A match between the sample profile and the database identifies the bacteria present in the sample.
Owner:MARSHFIELD CLINIC
Molecule marking method for pig backfat thickness property
InactiveCN103497994ASolve the problems of high blindness and low selection accuracyShorten the generation intervalMicrobiological testing/measurementBOARAcyl coenzyme
The invention relates to a molecule marking method for pig backfat thickness property. The method comprises: extraction of pig genome DNA, design of a long-chain acyl-coenzyme Asynthetase 1 (ACSL1) gene seventh exon primer, amplification in vitro and genotype detection. For the first time, it is discovered that the polymorphism of the long-chain acyl-coenzyme Asynthetase 1 (ACSL1) gene seventeenth exon has significant correlation with the pig backfat thickness, and a method for detecting the restriction fragment polymorphism at mutation sites of the seventeenth exon is established. The molecule marking method is applicable to auxiliary selection on backfat thickness property during breeding of pigs, helps to realize early-stage breeding selection of boars, and even helps to accurately select breeding just when pigs are born, so that the generation interval is shortened, and the selection progress of the backfat thickness property is accelerated; and the method is simple in operation, condition requirements during a polymerase chain reaction are low, the length of amplified fragments is relatively short (292 bp), amplification is relatively easy, and the method helps to improve amplification efficiency and accuracy of genotype determining.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY MEDICINE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Array-based translocation and rearrangement assays
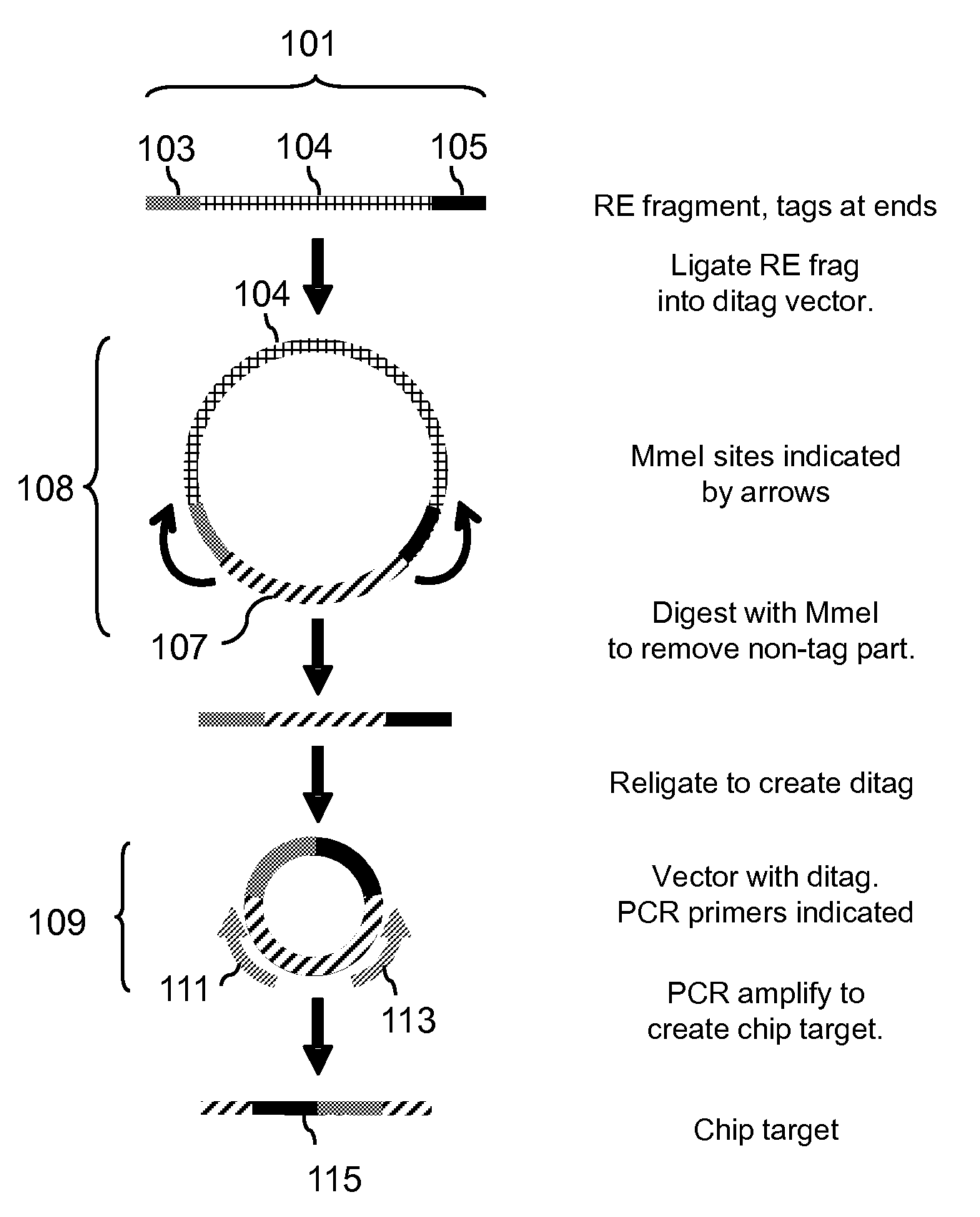
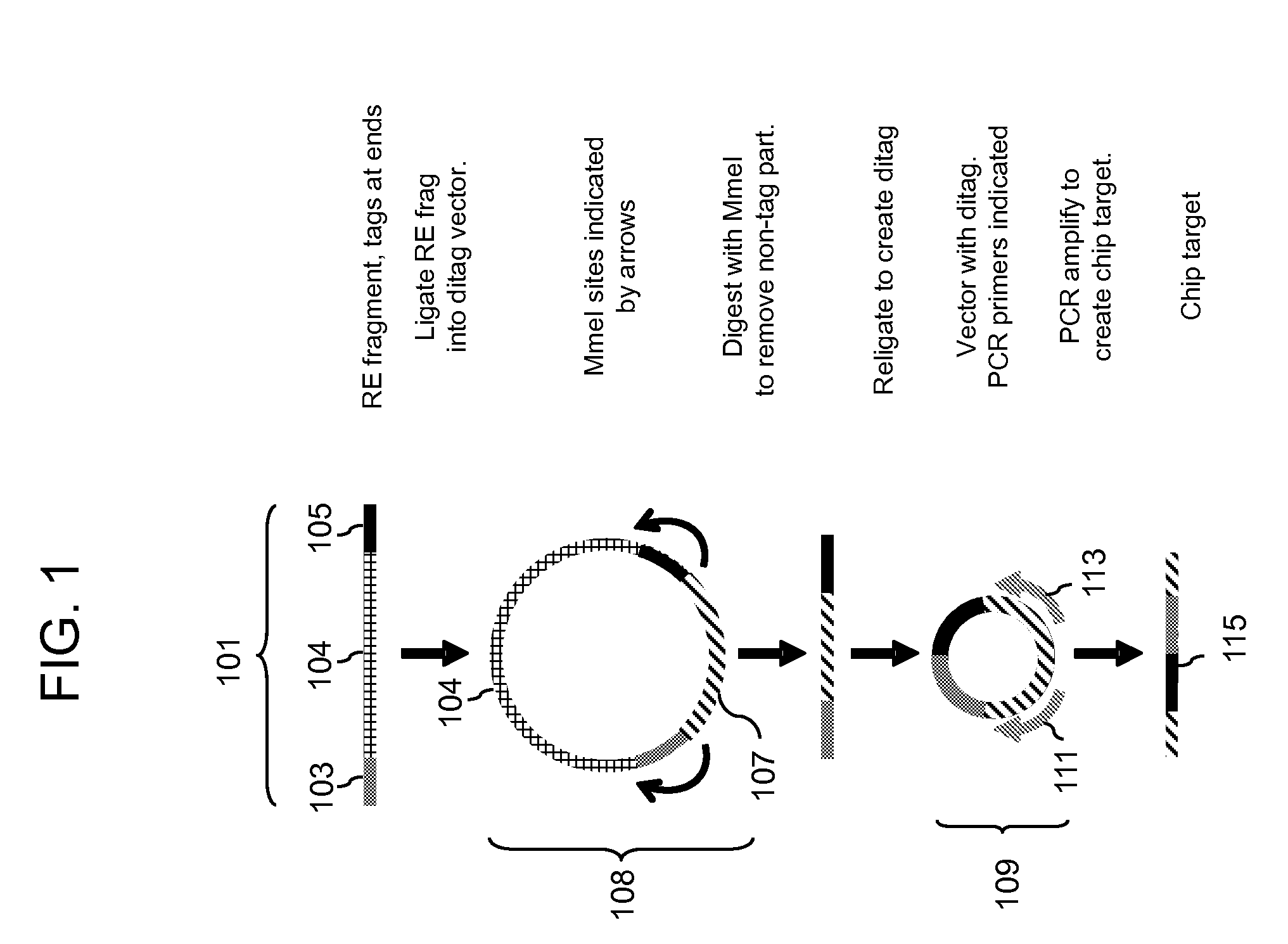
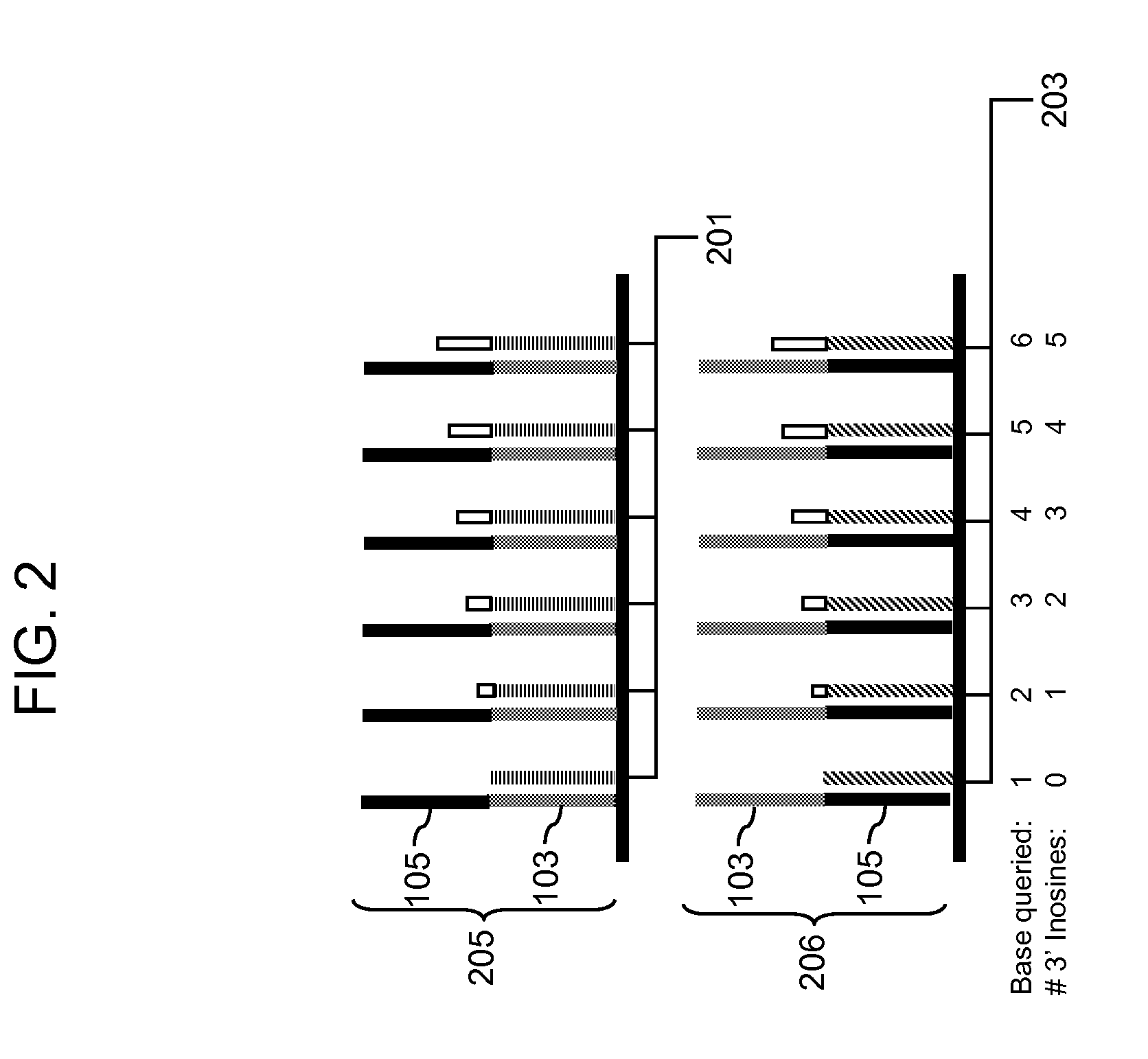
Methods for detecting genomic rearrangements are provided. In one embodiment, methods are provided for the use of paired end tags from restriction fragments to detect genomic rearrangements. Sequences from the ends of the fragments are brought together to form ditags and the ditags are detected. Combinations of ditags are detected by an on-chip sequencing strategy that is described herein, using inosine for de novo sequencing of short segments of DNA. In another aspect, translocations are identified by using target specific capture and analysis of the captured products on a tiling array.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Methods for detecting genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype
InactiveUS20070015200A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingSub populationsGenetic risk factor
The invention provides methods for determining genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype of a species in a hypothesis-free manner. In the methods of the invention, a set of restriction fragments for each of a sub-population of individuals having the phenotype are generated by digesting nucleic acids from the individual using one or more different restriction enzymes. A set of restriction sequence tags for the individual is then determined from the set of restriction fragments. The restriction sequence tags for the sub-population of organisms are compared and grouped into one or more groups, each of which comprising restriction sequence tags that comprise homologous sequences. The obtained one or more groups of restriction sequence tags identify the sequence variations associated with the phenotype. The methods of the invention can be used for, e.g., analysis of large numbers of sequence variants in many patient samples to identify subtle genetic risk factors.
Owner:SOLEXA
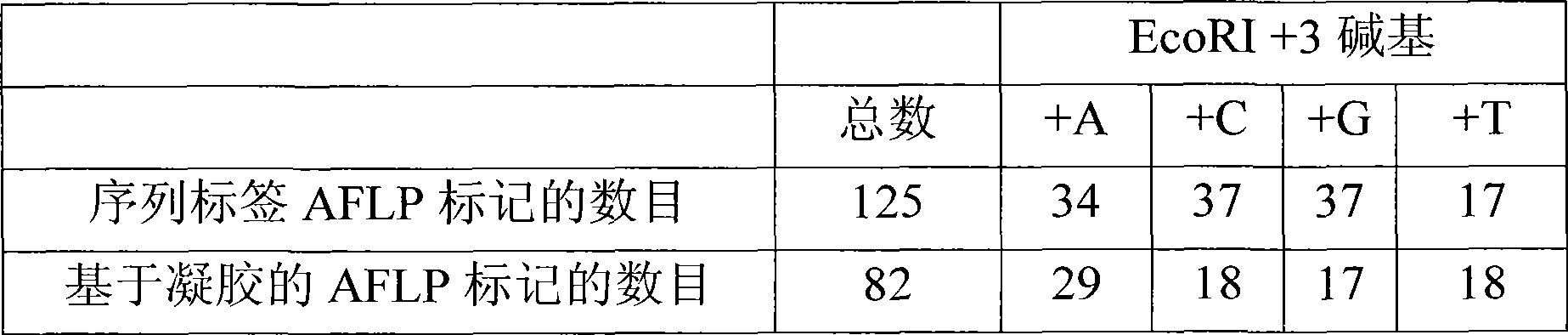
Method for acquiring chicken whole genome high-density SNP marker sites
ActiveCN105238859ALow costGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic sequencingGenetic engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and provides a method for acquiring chicken whole genome high-density SNP marker sites. The method comprises the following steps: (1) predicting distribution of restriction fragments acquired from double-restriction chicken genomes of EcoRI and MseI; (2) designing a universal joint, a barcode joint and a PCR amplification primer according to the distribution characteristics of the restriction fragments of EcoRI and MseI; (3) constructing a simplified genome sequencing library; (4) sequencing by virtue of the library constructed in the step (3) through a computer; and (5) according to a sequencing result, acquiring SNP marker sites. The method disclosed by the invention provides a universal strategy for the construction of a whole genome high-density SNP map by virtue of double-restriction GBS for different varieties of chickens, so that the cost on acquiring every SNP marker site is reduced by an order of magnitude compared with a conventional chip technology; and the method is stable in technology and high in repeatability.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Molecular marking method for pig litter size
InactiveCN101768642AShorten the generation intervalSpeed up the selection processMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionAnimal science
The present invention relates to a molecular marking method for pig litter size. The method comprises the steps of pig genome DNA extraction, exon 6 primer design of sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) genes, amplification in vitro and genotype detection. The present invention first discovers pig SHBG genes, discovers the obvious relationship between the polymorphism of exon 6 and pig litter size, and develops a restriction fragment enzyme digestion polymorphism detection method for detecting exon 6 mutational sites. The method can be used for the auxiliary selection of litter size during pig breeding, can realize the early selection of parent pigs and even can accurately select parent pigs when the pigs are born. Generation interval is largely shortened, and selection progress is accelerated. The method has the advantages of simple operation, low condition requirements in polymerase chain reaction processes, short amplification fragment length (217bp), easy amplification, high amplification efficiency and accurate genotype judgement.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY MEDICINE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Differentiation of avian infectious bronchitis virus serotypes
InactiveUS6214538B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSerotypeRestriction fragment length polymorphism
The present invention relates, in general, to the genetics of viruses. In particular, the present invention provides methods of distinguishing between serotypes of avian infectious bronchitis virus based on restriction fragment length polymorphisms derived from the region of the S1 gene of IBV, peptides derived from the restriction fragments, related primers for polymerase chain reaction, and certain restriction length polymorphism patterns.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Staphylococcus aureus multiple PCR-MIX rapid detection kit and detection method thereof
ActiveCN101613745AStrong specificityQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSmaIStaphylococcus aureus
The invention discloses a staphylococcus aureus multiple PCR-MIX rapid detection kit and a detection method thereof; the detection kit comprises PCR MIX; wherein, the PCR MIX contains 2*PCR buffer, 1.0-3.0mmol / L of MgCl2, 180-220mu mol / L of dNTP each, heat-resisting deoxyribonuclease nuc gene primer of which the base sequence is SEQ NO.1 and the concentration of SEQ NO.1 is 100-600nmol / L, plasma-coagulase clfA gene primer of which the base sequence is SEQ NO.3 and the concentration of SEQ NO.4 is 100-600nmol / L, SmaI restriction fragment specific sequence primer of which the base sequence is SEQ NO.5 and the concentration of SEQ NO.6 is 100-600nmol / L, 20-60U of Taq enzyme and bromophenyl blue dye. The multiple PCR-MIX rapid detection kit and the detection method provided by the invention have simple configuration, the detection kit and the detection method can be used in industrialized production; the detection method is sensitive and has short detection cycle and strong maneuverability, so that the method can be widely applied in the fields of food hygiene, environmental monitoring, etc.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM +1
Analysis of methylation using selective adaptor ligation
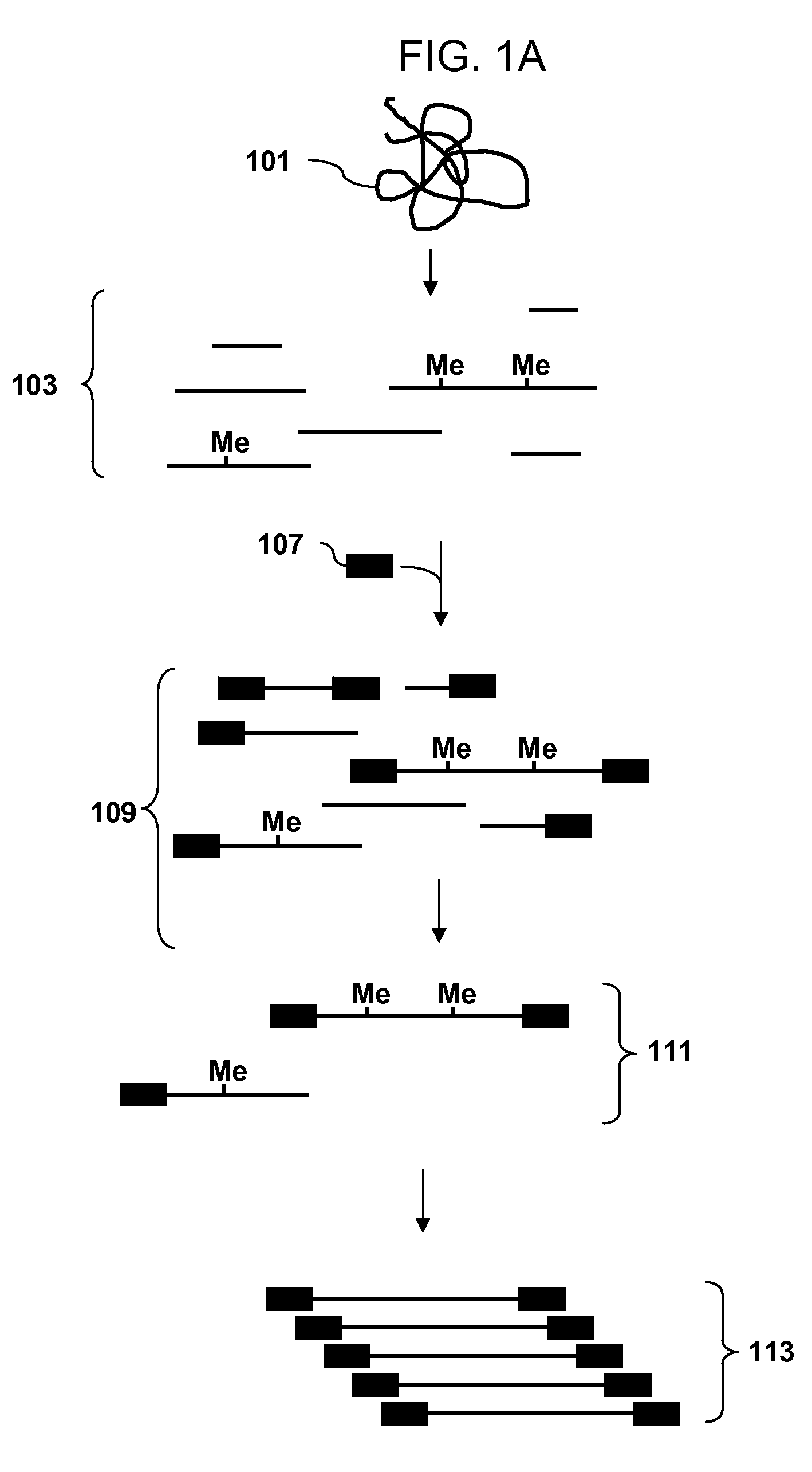
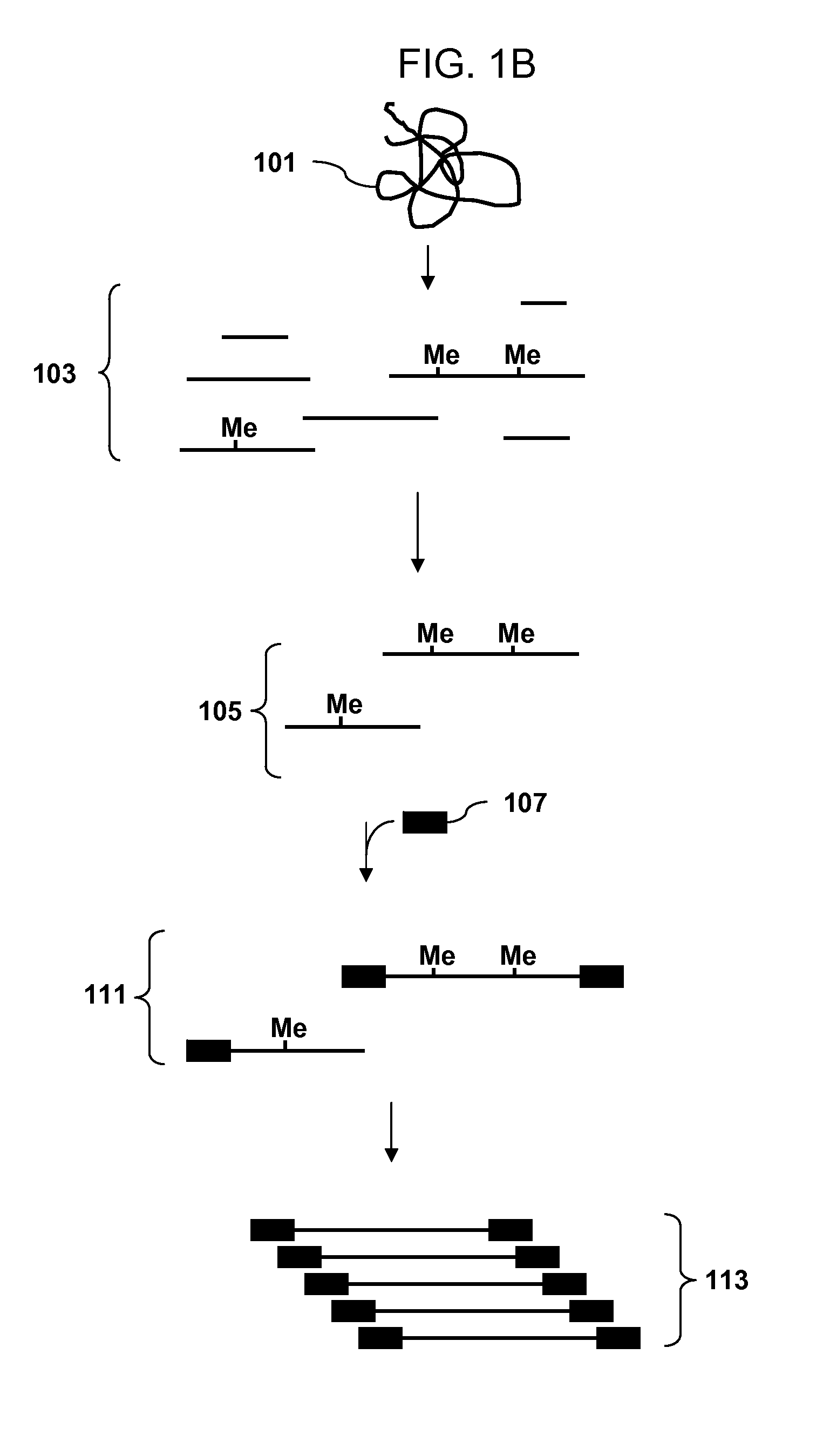
InactiveUS20080254453A1Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCytosineAnalysis dna
Methods of analyzing DNA to identify regions of the genome that are methylated in a genomic sample are disclosed. In one aspect genomic DNA is fragmented using a restriction enzyme with a degenerate recognition site, methylated restriction fragments are separated from unmethylated fragments by affinity purification. The complexity of the methylated fragments is reduced by amplification of a subset of the fragments using adaptors that ligate to a subset of the fragments. The amplified product is fragmented, labeled and hybridized to an array of probes. The hybridization pattern is analyzed to determine methylation status of cytosines.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Improved strategies for sequencing complex genomes using high throughput sequencing technologies
A method for determining a genome sequence comprising the steps of digesting the genome with at least one first restriction endonuclease, ligating at least one adaptor to the restriction fragments of the first subset, selectively amplifying the first set of adaptor-ligated restriction fragments using a first primer combination wherein at least a first primer contains a first selected sequence at the 3' end of the primer sequence, comprising 1-10 selective nucleotides, repeating these steps with at least a second primer combinations wherein the primer contains a different second selected sequence, fragmenting each of the subsets of amplified adaptor-ligated restriction fragments to generate sequencing libraries, determine the nucleotide sequence of the fragments, aligning the sequence of the fragments in each of the libraries to generate contigs, repeating these steps for one second and / or further restriction endonucleases, aligning the contigs obtained for each of the second and / or further restriction endonucleases to provide for a sequence of the genome.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Restriction enzyme based whole genome sequencing
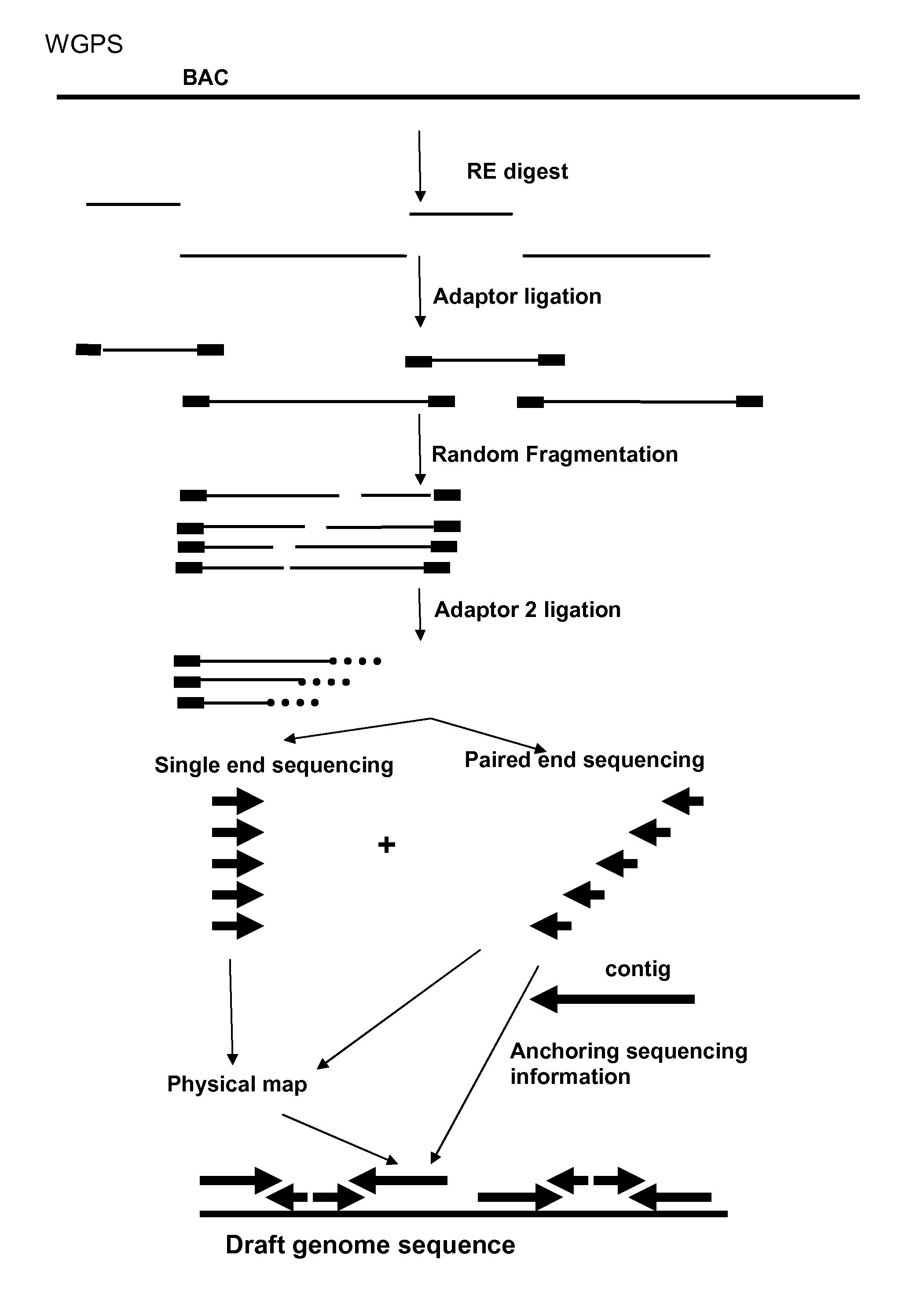
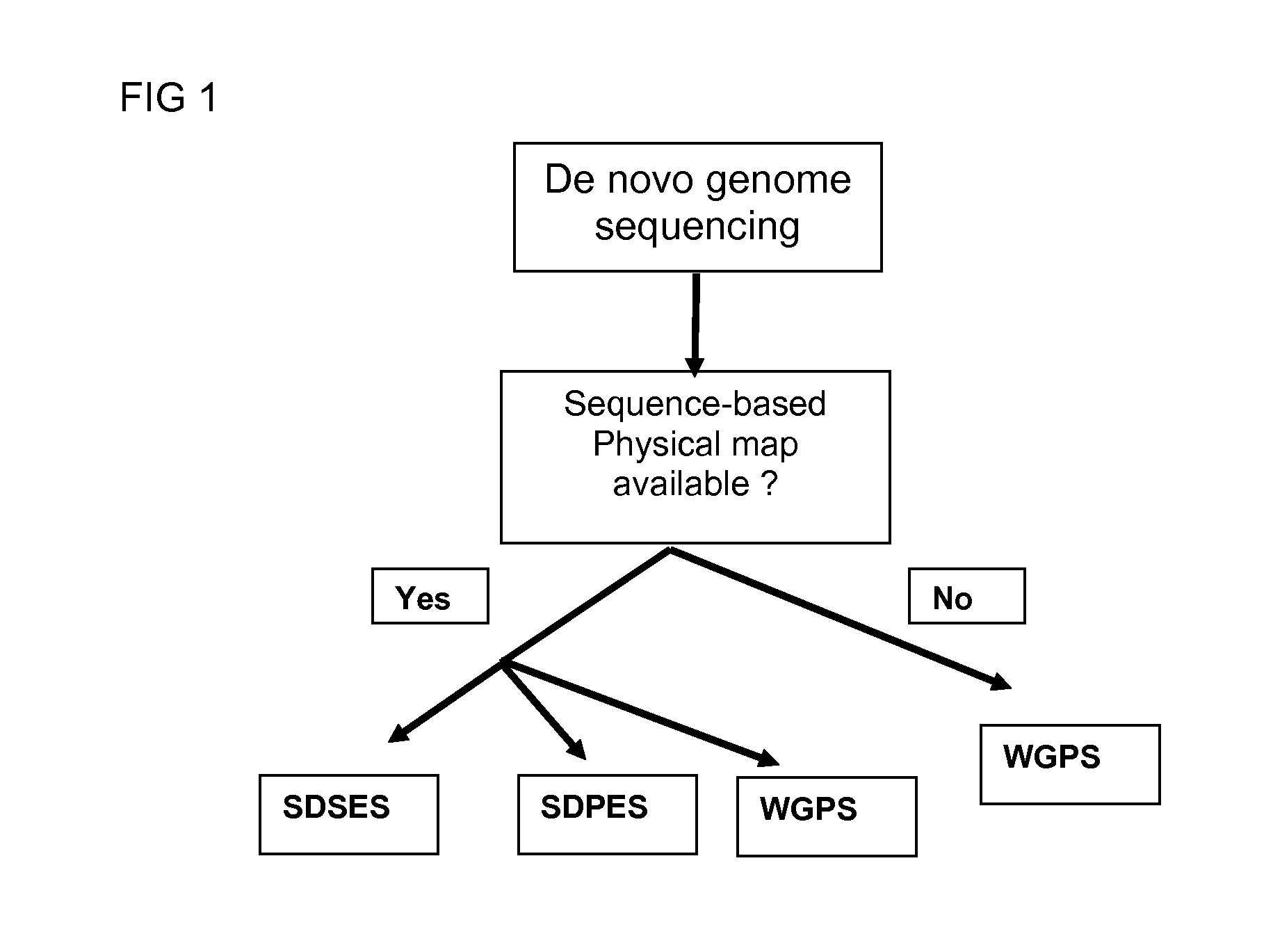
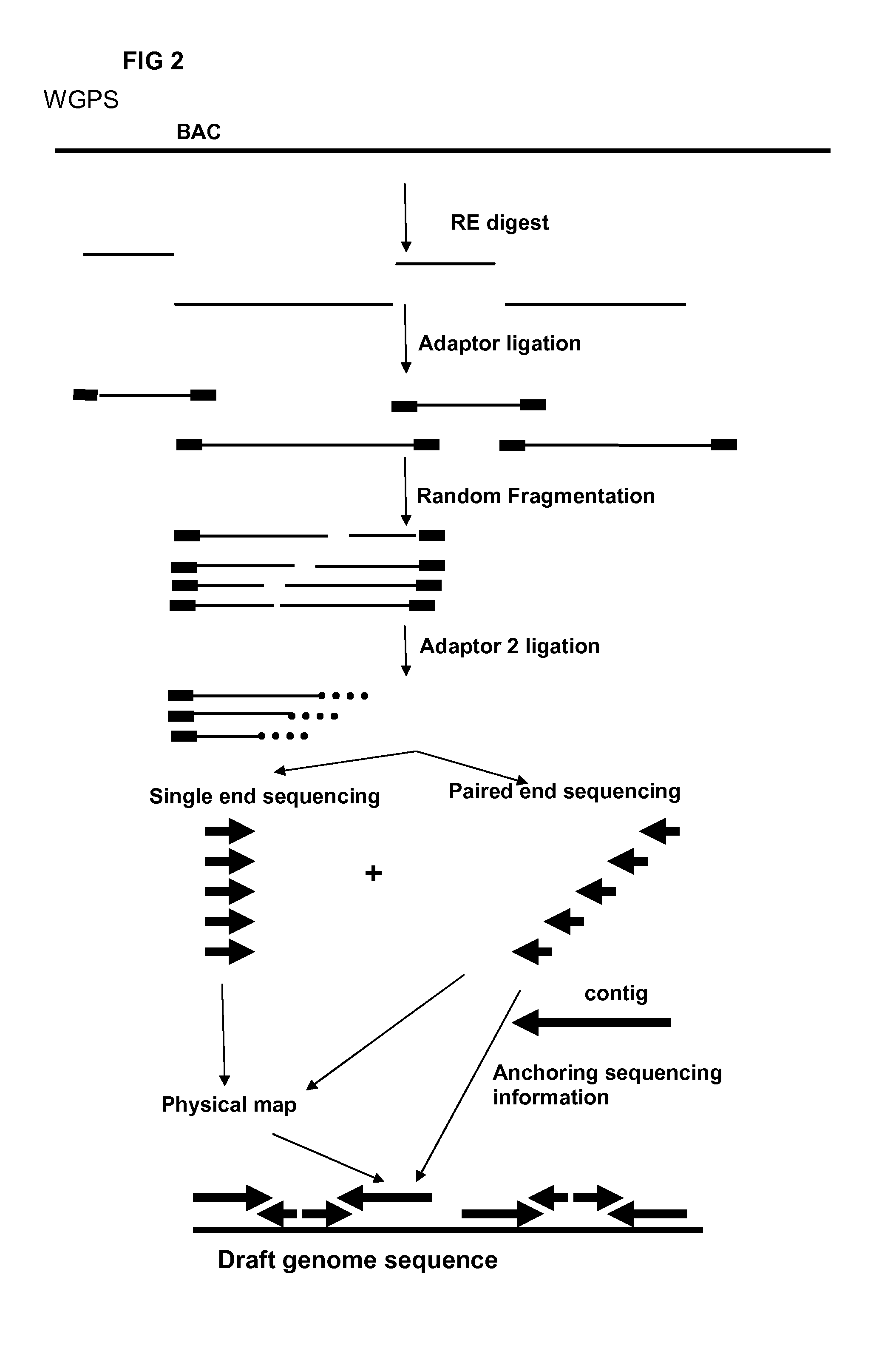
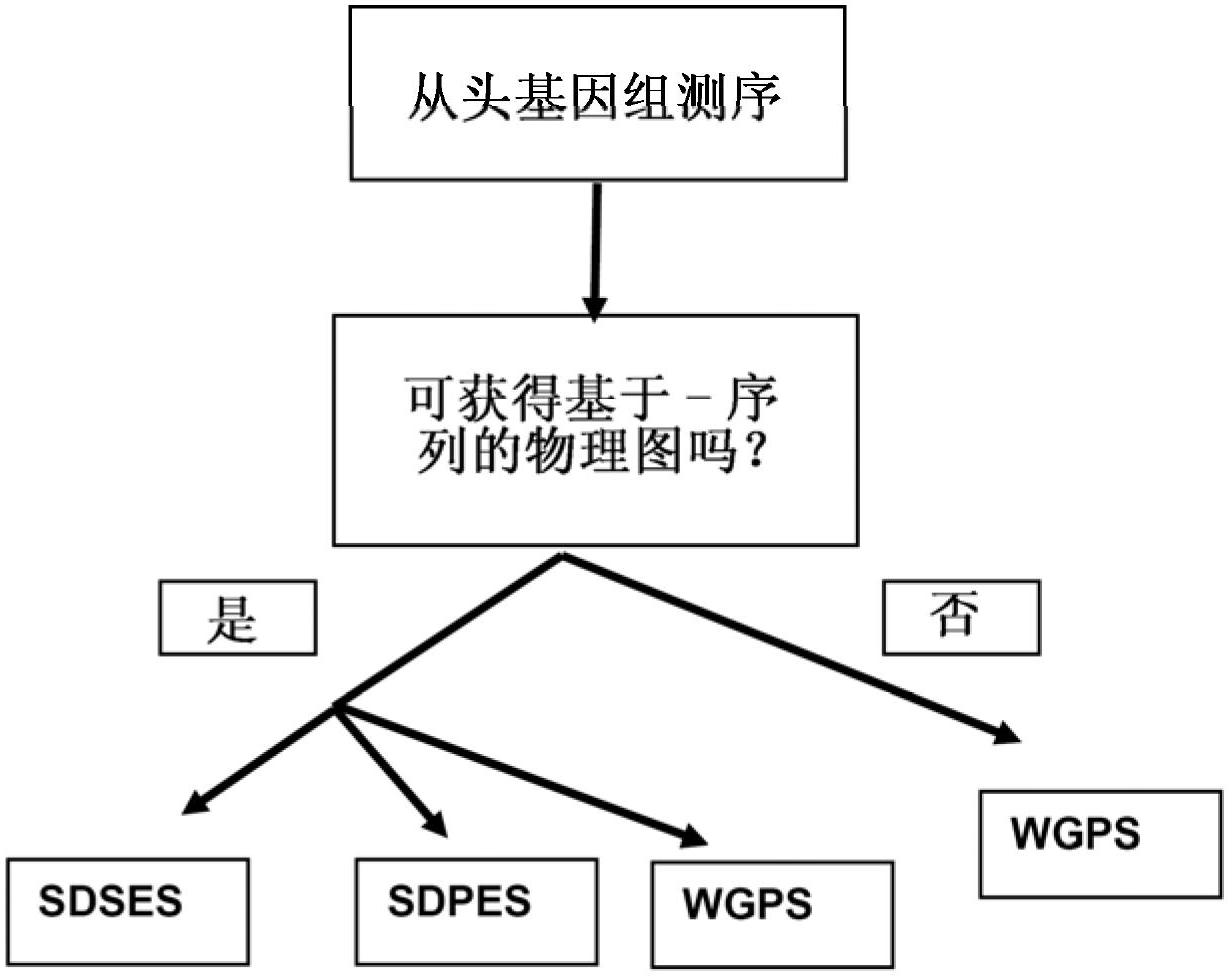
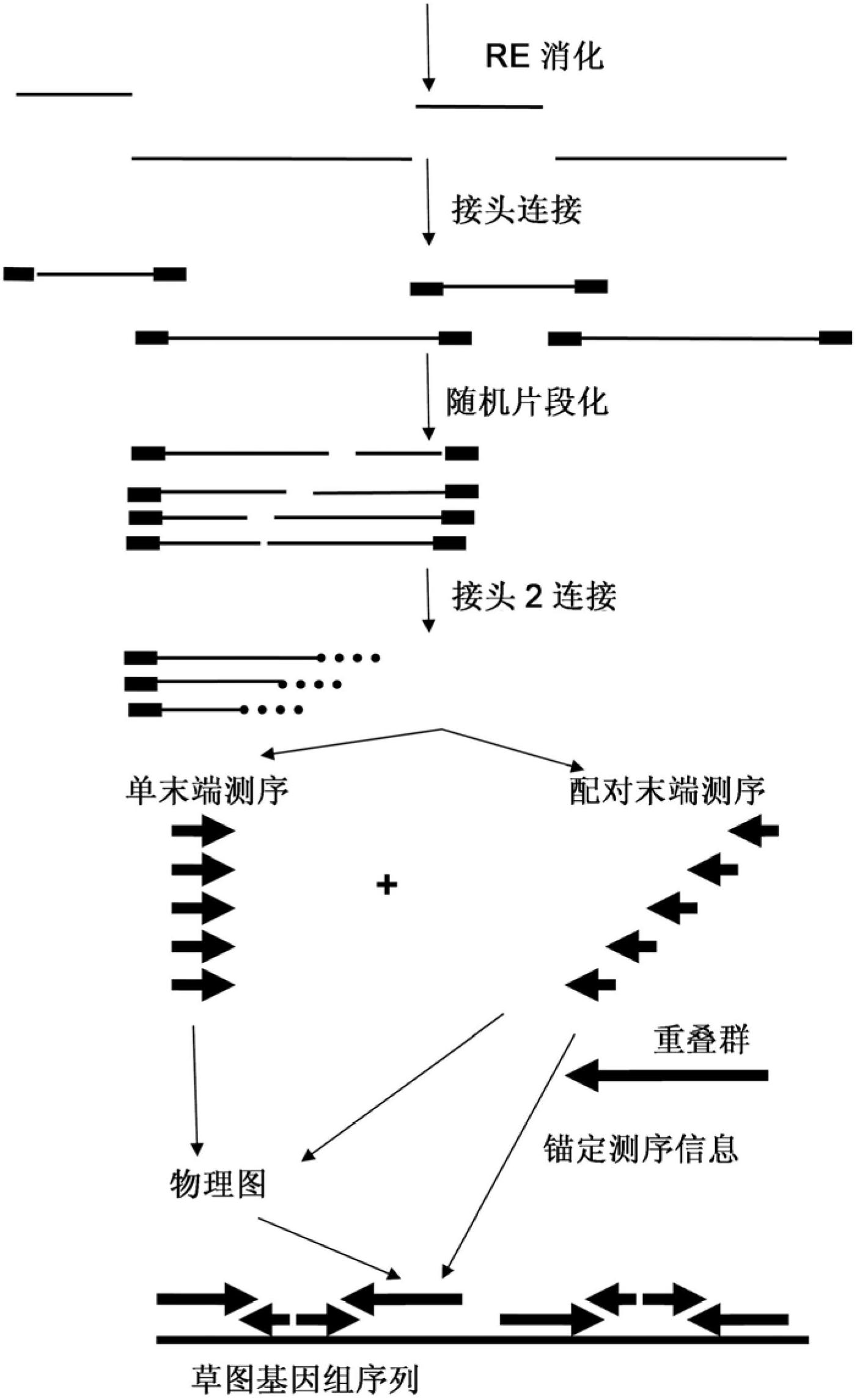
InactiveUS20120245037A1Maximize possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationWhole genome sequencingPhysical Maps
Method for de novo whole genome sequencing based on a (sequence-based) physical map of a DNA sample clone bank based on end-sequencing tagged adapter-ligated restriction fragments, in combination with sequencing adapter-ligated restriction fragments of the DNA sample wherein the recognition sequence of the restriction enzyme used in the generation of the physical map is identical to at least part of the recognition sequence of the restriction enzyme used in the generation of the DNA sample.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Selective genome amplification
The invention provides methods and compositions for amplifying selected polynucleotides, especially selected subsets of restriction fragments. Generally, methods of the invention are implemented by ligating adaptors containing at least one promoter sequence to such fragments under conditions that promote the formation of closed single stranded or double stranded structures, which are capable of serving as cyclical templates for transcription.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Selective restriction fragment amplification: fingerprinting
InactiveUS7026115B1Enable amplificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction siteRFLP - Restriction fragment length polymorphism
The invention relates to a process for the controlled amplification of at least one part of a starting DNA containing a plurality of restriction sites for a determined specific restriction endonuclease, and of which at least part or its nucleic acid is unknown.Application of this process to human, animal or plant DNA fingerprinting, to identification of restriction fragment length polymorphisms.Kit for the application of the process.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Methods for protein interaction determination
InactiveUS20050164214A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHybrid systemEukaryotic plasmids
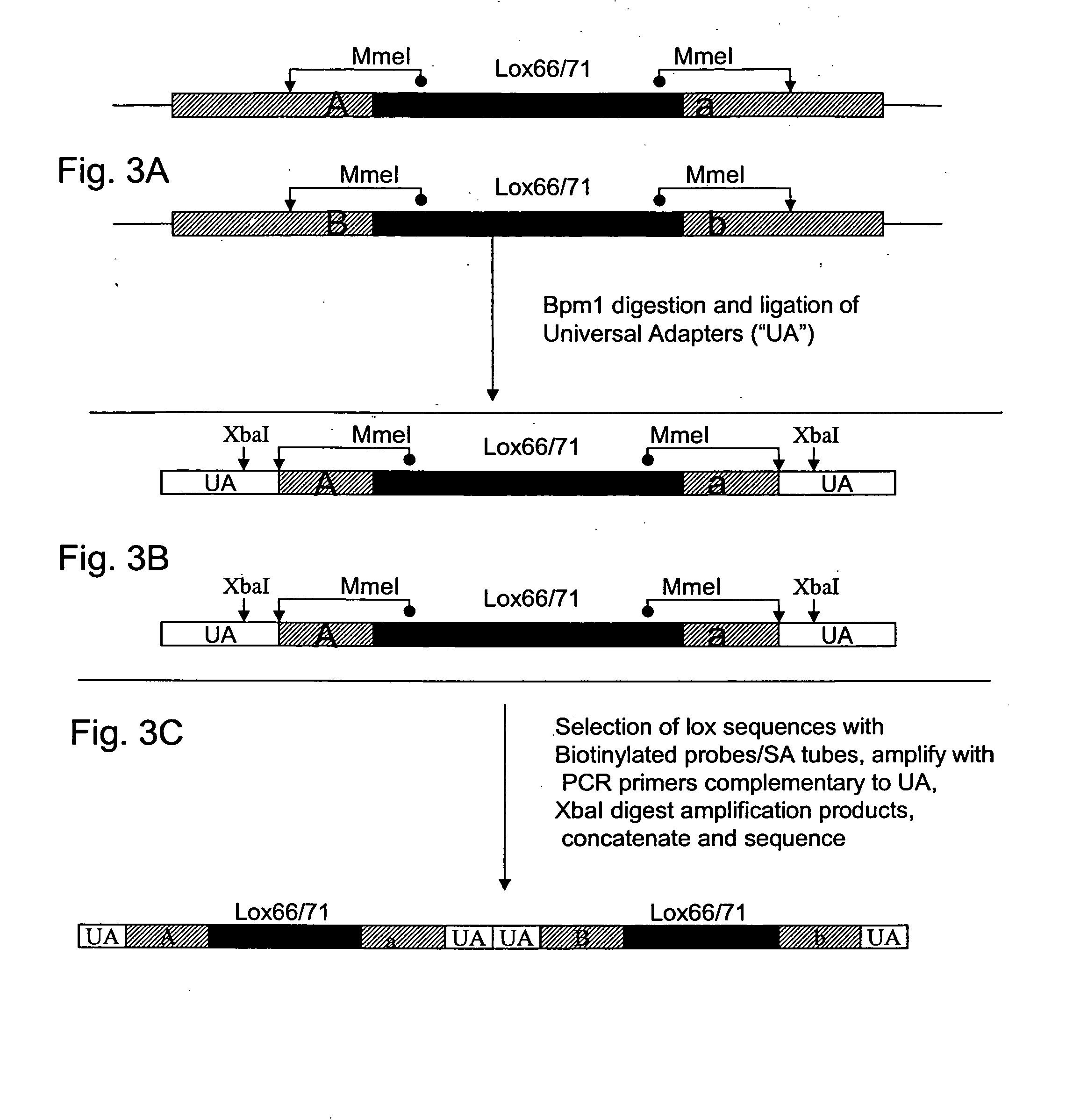
The present invention provides a method for identifying a plurality of pairs of interacting proteins and plasmids for use in the method. The pair of plasmids is adapted for use in a modified two hybrid system wherein wherein each plasmid comprises a recombinase recognition site. The method comprises the steps of providing cDNAs encoding test polypeptides, inserting the cDNAs into the first and second plasmids, recombining the first and second plasmids to obtain recombined plasmids, isolating and digesting the recombined plasmids, ligating the restriction fragments to a universal adapter to provide a pool of digested fragments flanked by a universal adapter, selecting and amplifying desired sequences, forming concatamers from the amplified sequences, and sequencing the concatamers to determine the nucleotide sequences encoding a plurality of pairs of interacting proteins.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
Restriction enzyme based whole genome sequencing
A method for de novo whole genome sequencing based on a (sequence-based) physical map of a DNA sample clone bank based on end-sequencing tagged adapter-ligated restriction fragments, in combination with sequencing adapter-ligated restriction fragments of the DNA sample wherein the recognition sequence of the restriction enzyme used in the generation of the physical map is identical to at least part of the recognition sequence of the restriction enzyme used in the generation of the DNA sample.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Method for detecting fungal pathogens
Early detection of pathogens during asymptotic stage can be useful for timely need based adoption of available methodologies to prevent establishment of the disease and associated yield loss. Beside this, it would be useful for predicting crop productivity and monitoring presence of pathogens in the samples being traded internationally by quarantine departments. Our innovation of designing universal primer to PCR amplify fungal rDNA sequences, restriction digestion of PCR products with HinFl enzyme and analysis of the restriction fragments through PathDec tool leads identification and detection of almost all the fungal pathogens of apple even before visual appearance of the disease symptoms in less than 6 hours.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
High throughput detection of molecular markers based on AFLP and high throughput sequencing
InactiveCN101432438AMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsAmplified fragment length polymorphism
The present invention relates to a high throughput method for the identification and detection of molecular markers wherein restriction fragments are generated and suitable adaptors comprising (sample-specific) identifiers are ligated. The adapter- ligated restriction fragments may be selectively amplified with adaptor compatible primers carrying selective nucleotides at their 3' end. The amplified adapter-ligated restriction fragments are, at least partly, sequenced using high throughput sequencing methods and the sequence parts of the restriction fragments together with the sample-specific identifiers serve as molecular markers.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Method for identifying traditional Chinese medical material corn cervi pantotrichum based on PCR-RFLP
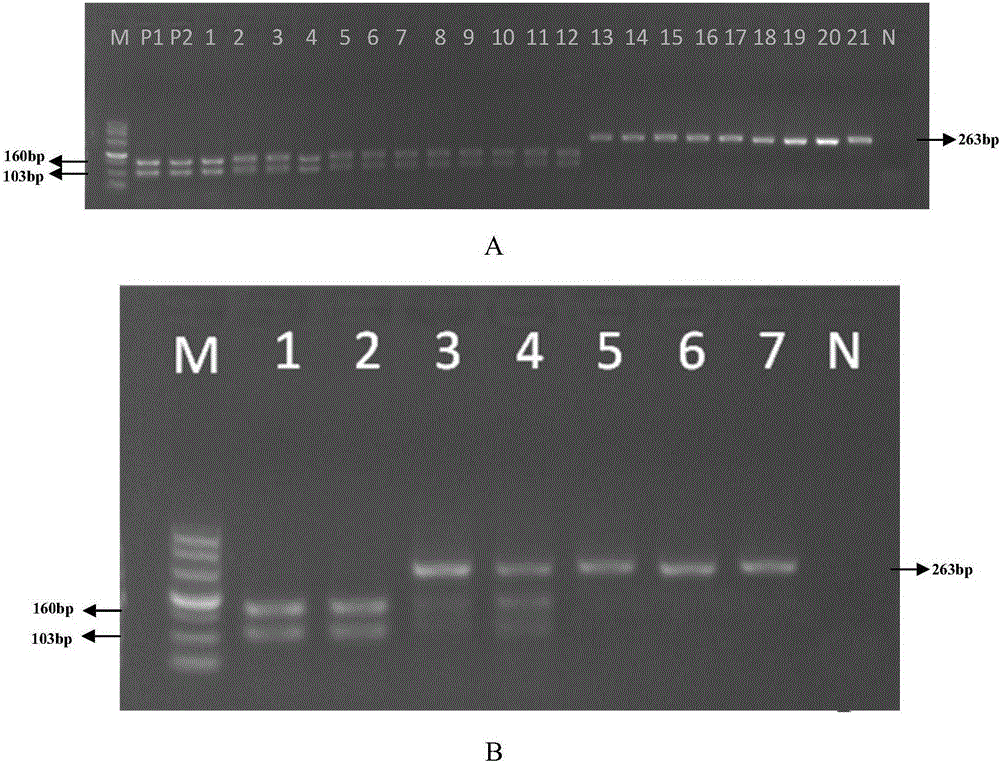
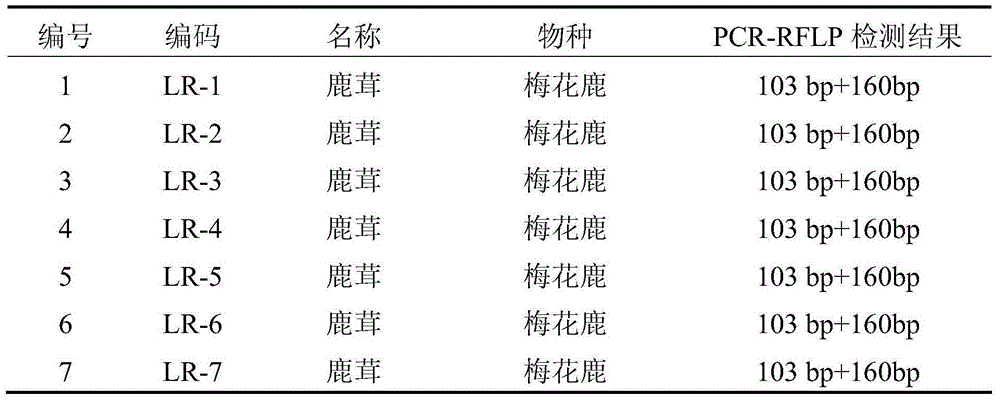
ActiveCN105176988AAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceSingle strand dna
The invention discloses a method for identifying the traditional Chinese medical material corn cervi pantotrichum based on PCR-RFLP. A reagent kit used for identifying the traditional Chinese medical material corn cervi pantotrichum comprises a primer pair shown in (a) or (b) and restriction enzyme DdeI or isoschizomers of the restriction enzyme DdeI, wherein (a) is the primer pair composed of two lines of single-stranded DNA molecules shown in a sequence 1 and a sequence 2 in a sequence table, (b) is the primer pair which is composed of two lines of single-stranded DNA molecules shown in the sequence obtained by replacing and / or deleting and / or adding one or several nucleotides shown in the sequence 1 and the sequence 2 in the sequence table and is identical with the primer pair in (a) in function. According to the method, cytochrome b gene sequences of the traditional Chinese medical material corn cervi pantotrichum and counterfeit drug of the traditional Chinese medical material corn cervi pantotrichum are analyzed, different SNP loci of the traditional Chinese medical material corn cervi pantotrichum and the counterfeit drug of the traditional Chinese medical material corn cervi pantotrichum are obtained, identification primers and the restriction enzyme are designed, and the traditional Chinese medical material corn cervi pantotrichum and the counterfeit drug of the traditional Chinese medical material corn cervi pantotrichum are accurately identified through the restriction fragment length polymorohism polymerase chain reaction technology.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
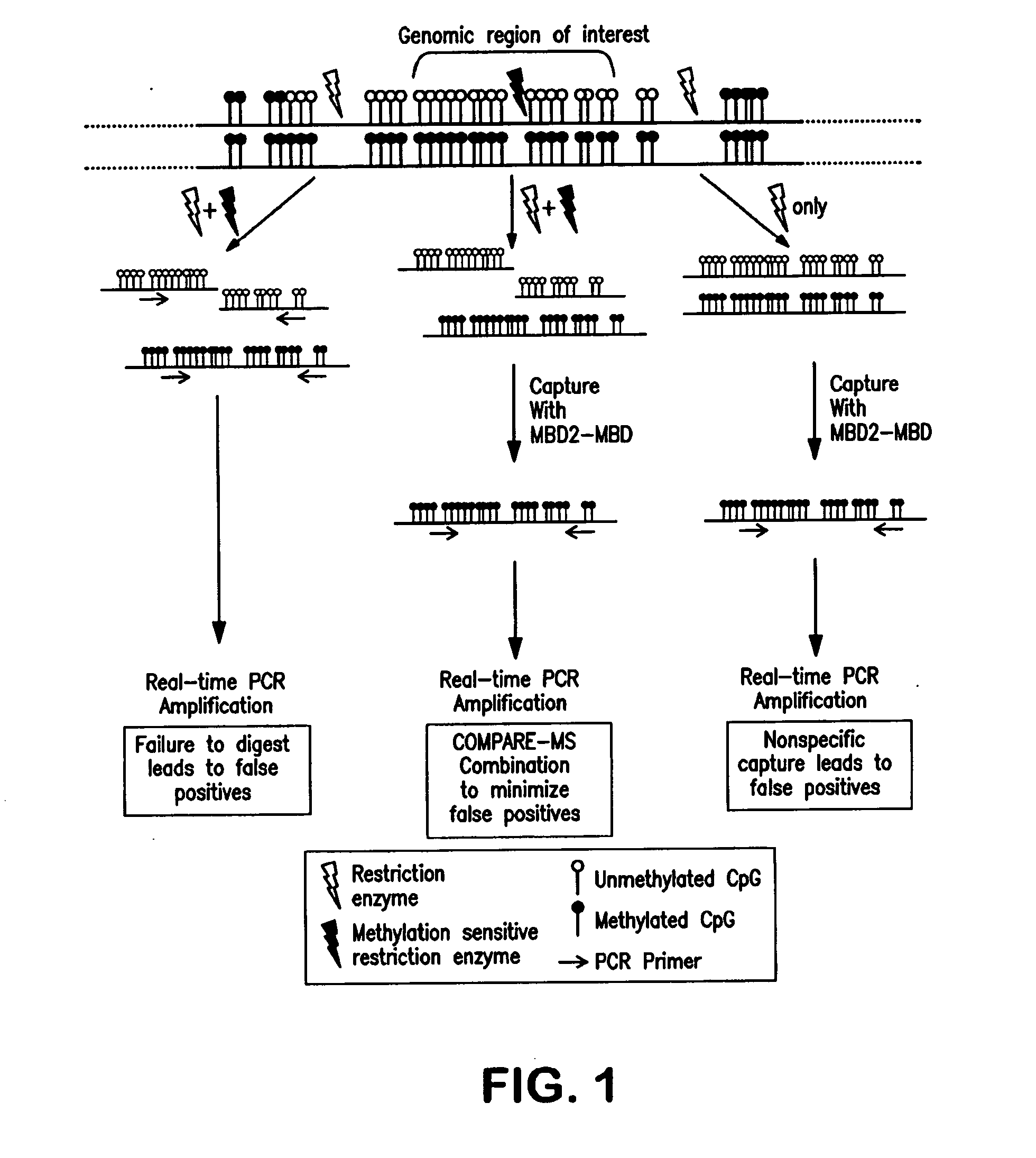
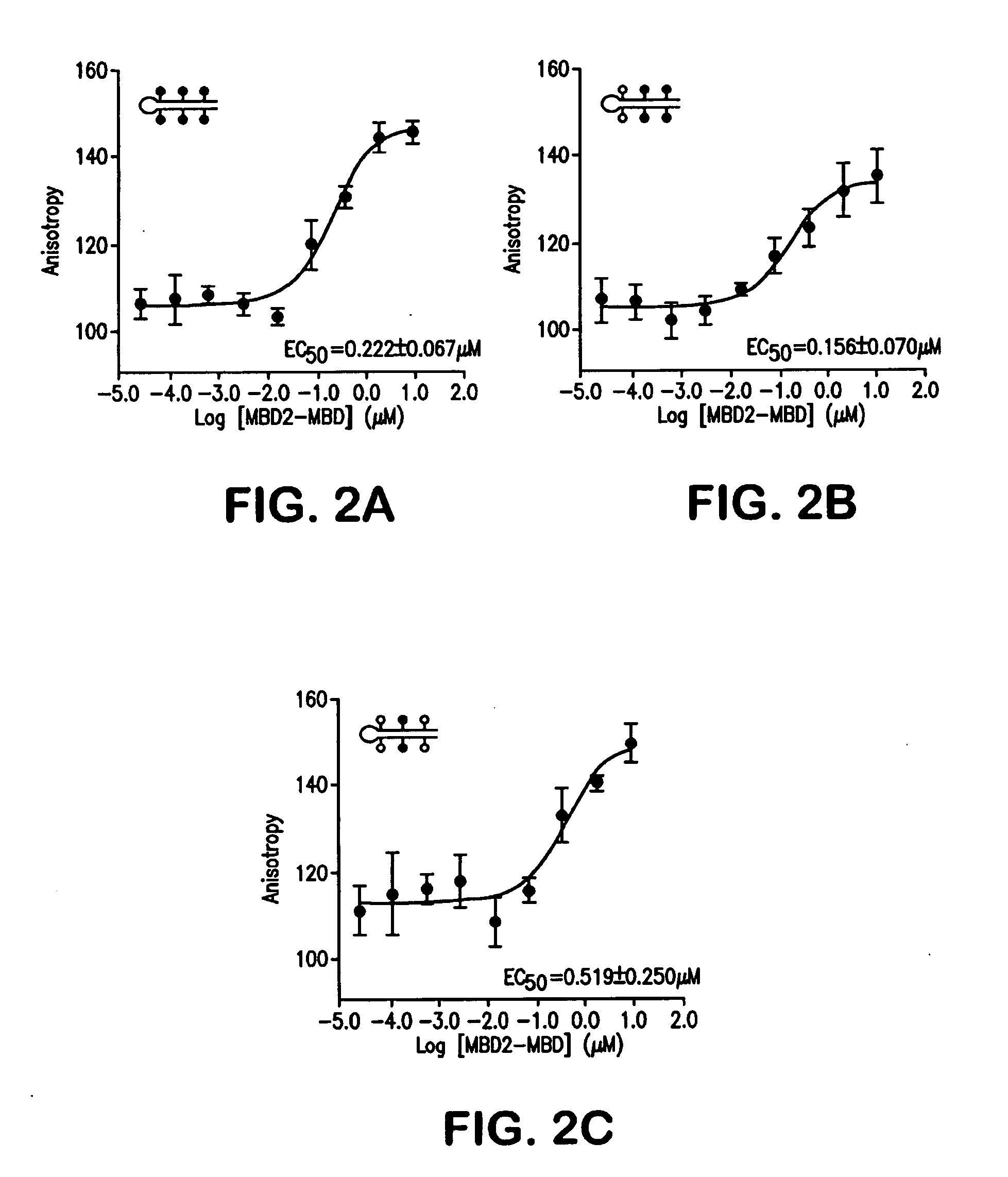
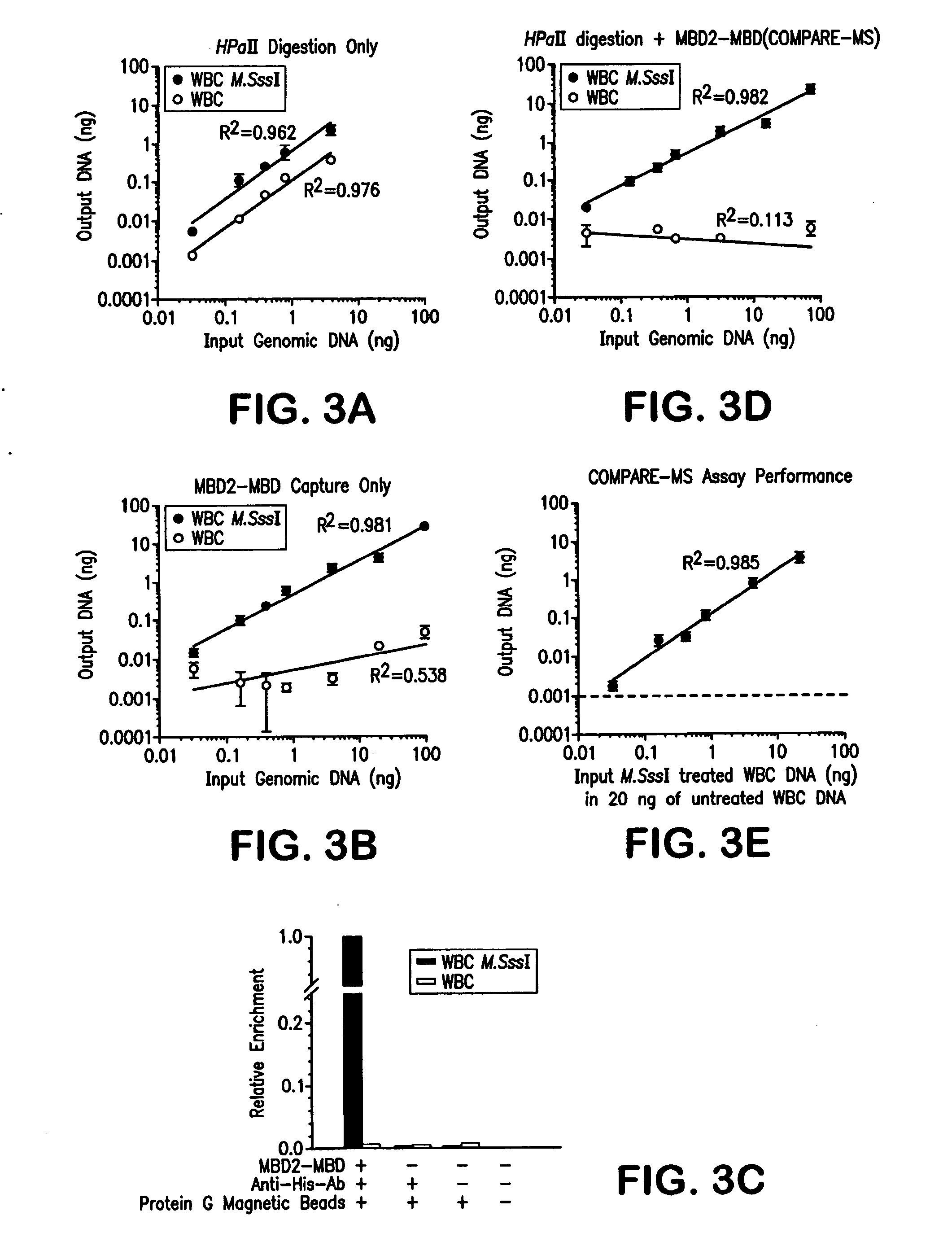
Compare-MS: Method Rapid, Sensitive and Accurate Detection of DNA Methylation
ActiveUS20090197263A1Reduce speedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationProstate cancer
The present invention provides methods and kits useful for enriching, identifying and quantifying methylated DNA3 particularly hypermethylated CpG islands by digesting a sample with a methylation-sensitive restriction endonuclease and capturing methylated restriction fragments with a methyl-binding capture reagent. The methods of the invention may be used in the detection of cancer, particularly detection of prostate cancer.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com