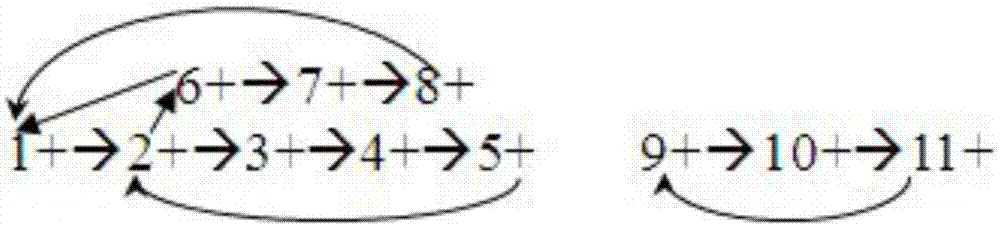Patents
Literature
47 results about "De novo sequencing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
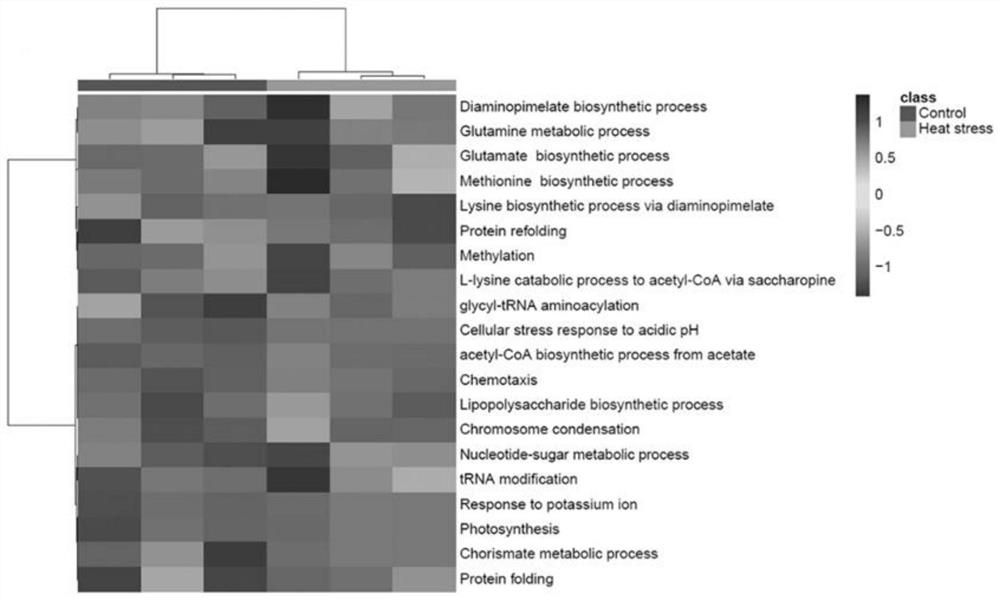
De Novo Sequencing. What Is De Novo Sequencing? De novo sequencing refers to sequencing a novel genome where there is no reference sequence available for alignment. Sequence reads are assembled as contigs, and the coverage quality of de novo sequence data depends on the size and continuity of the contigs (ie, the number of gaps in the data).
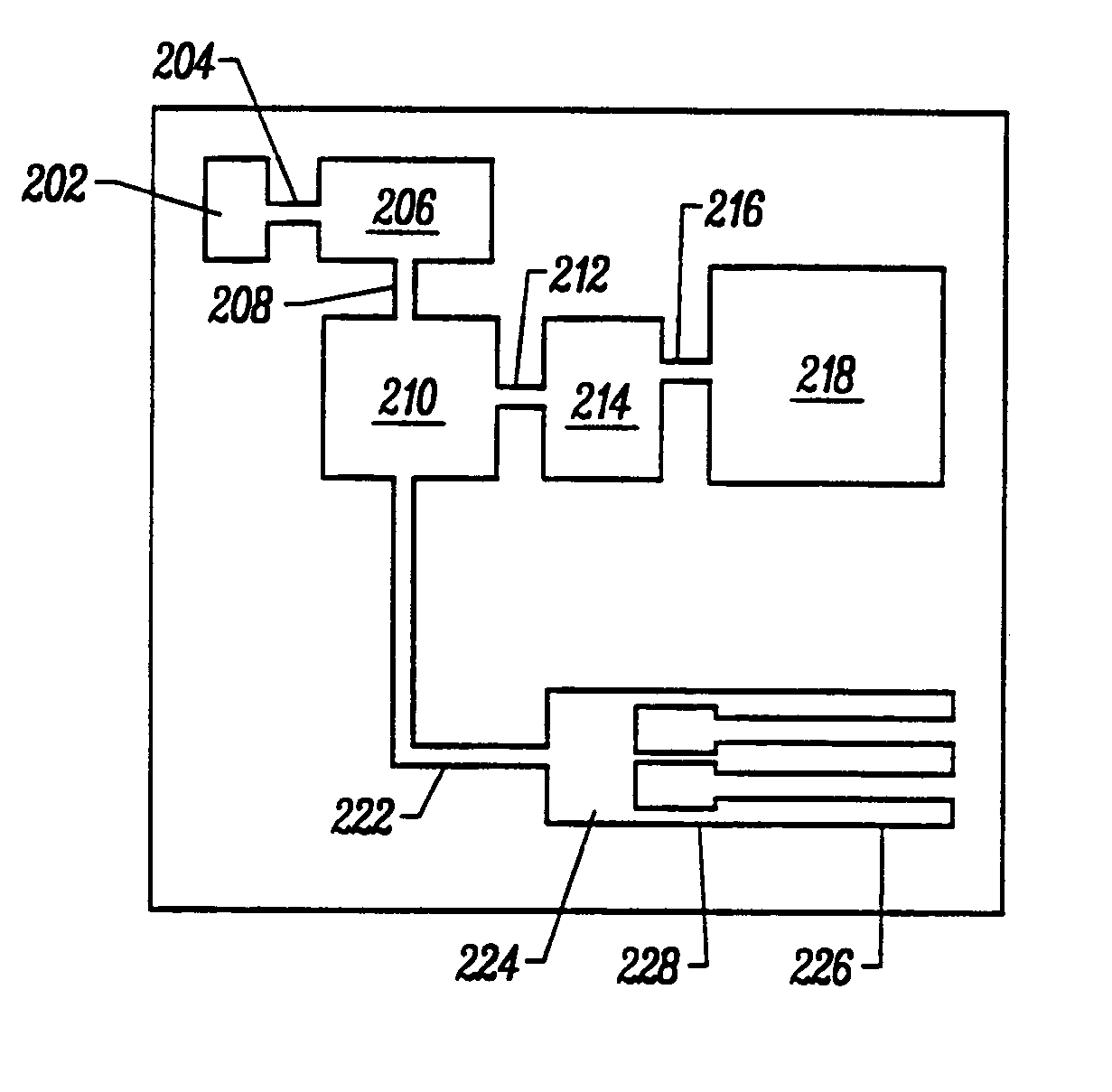
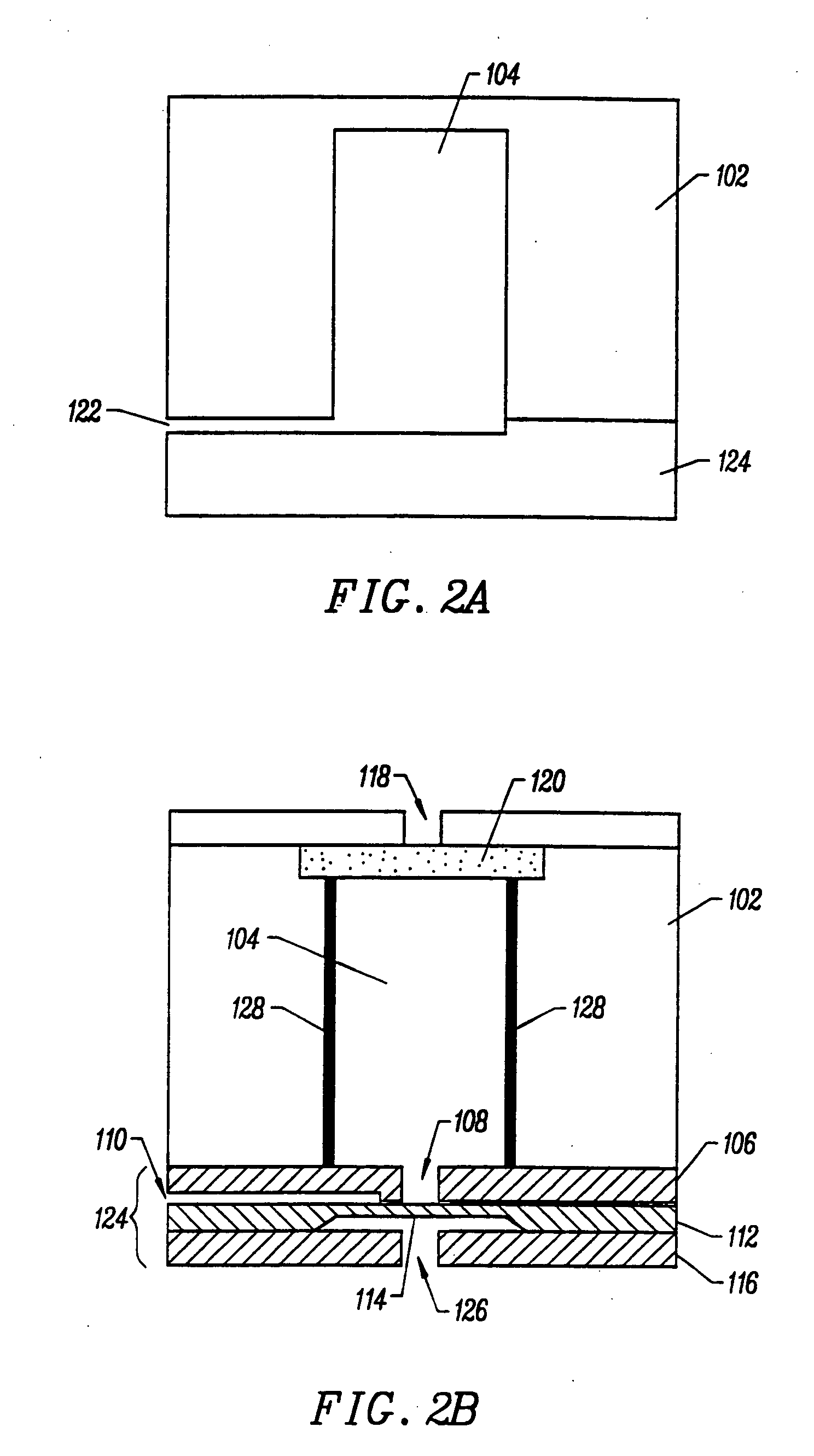
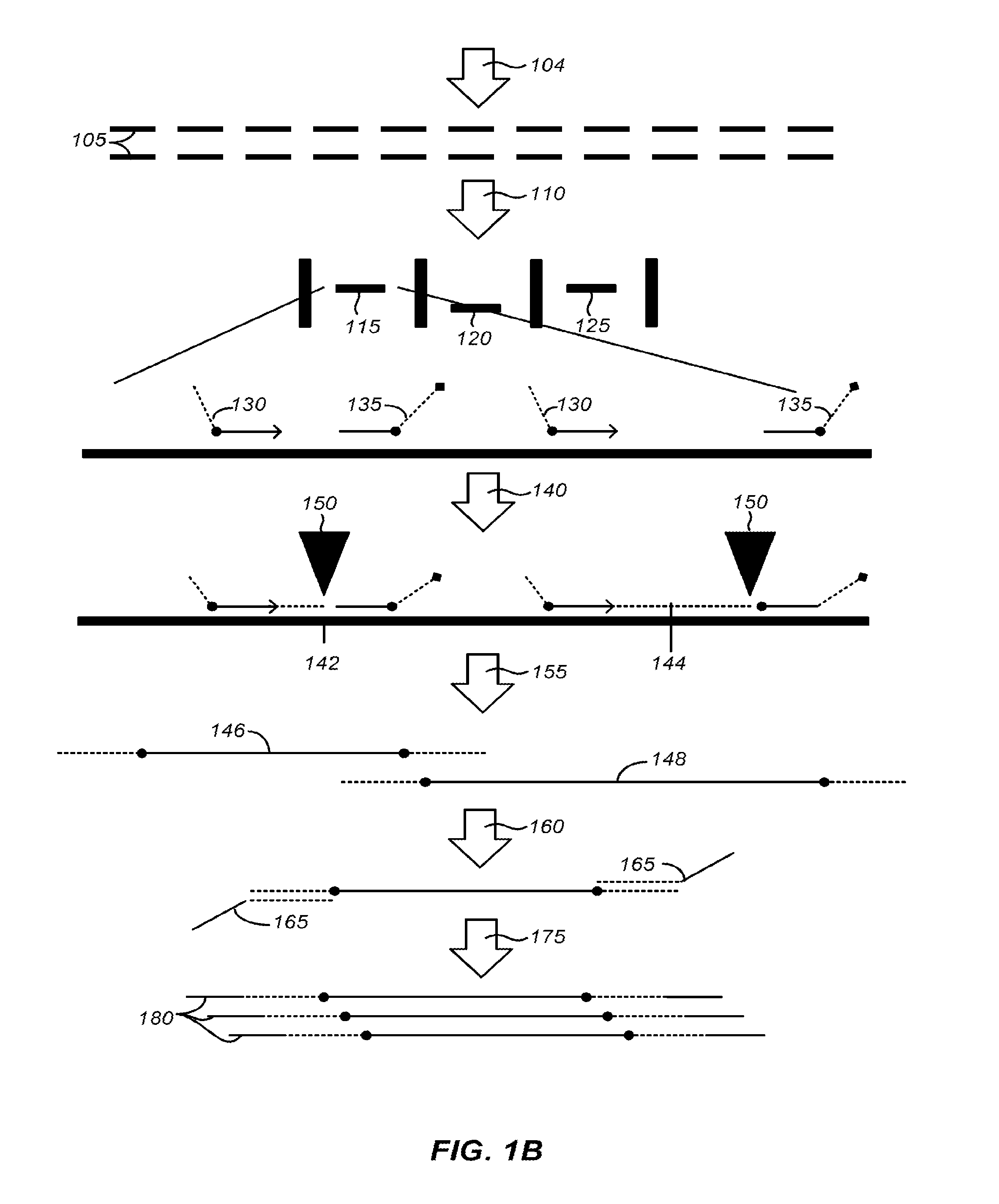
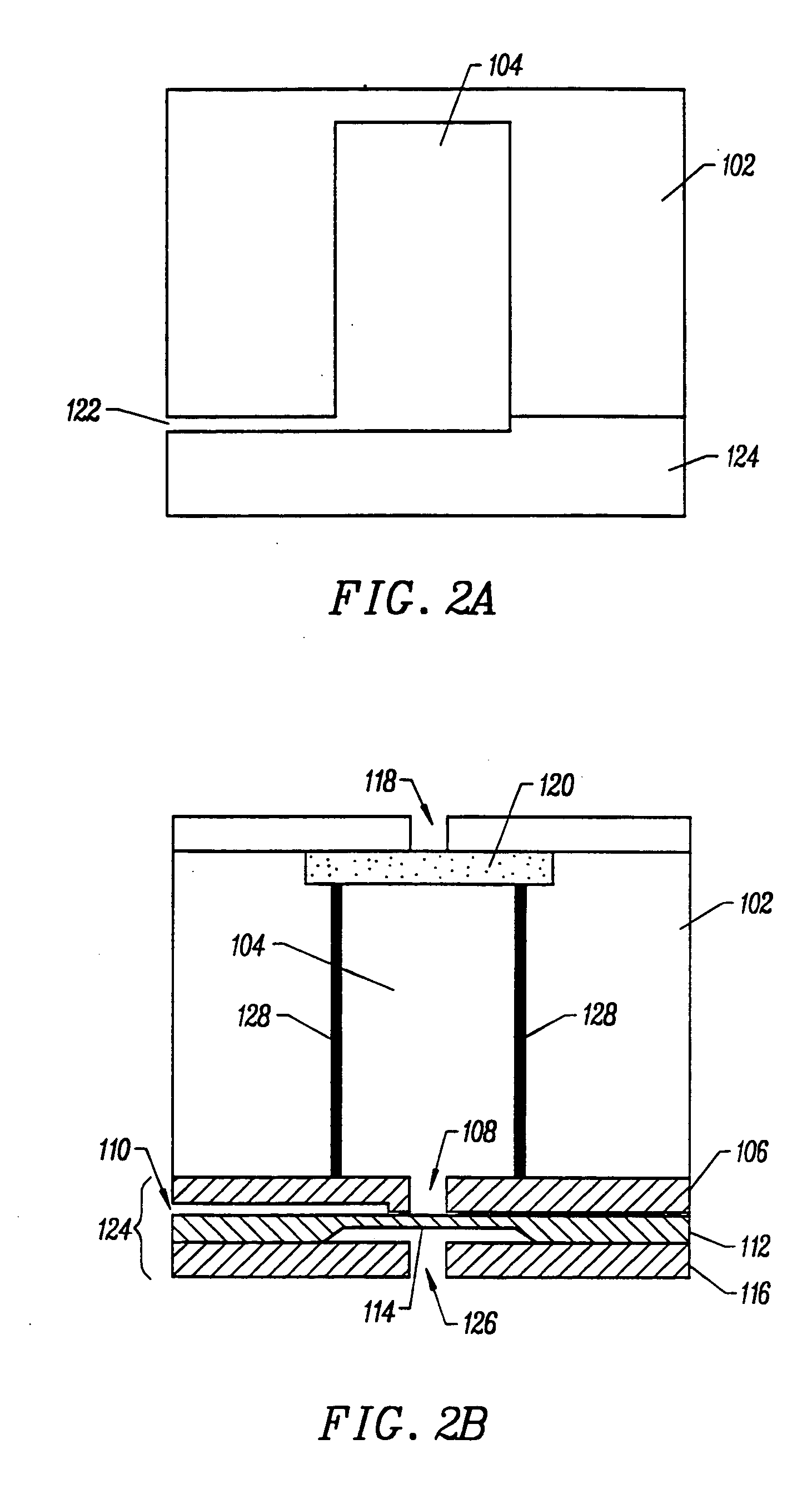
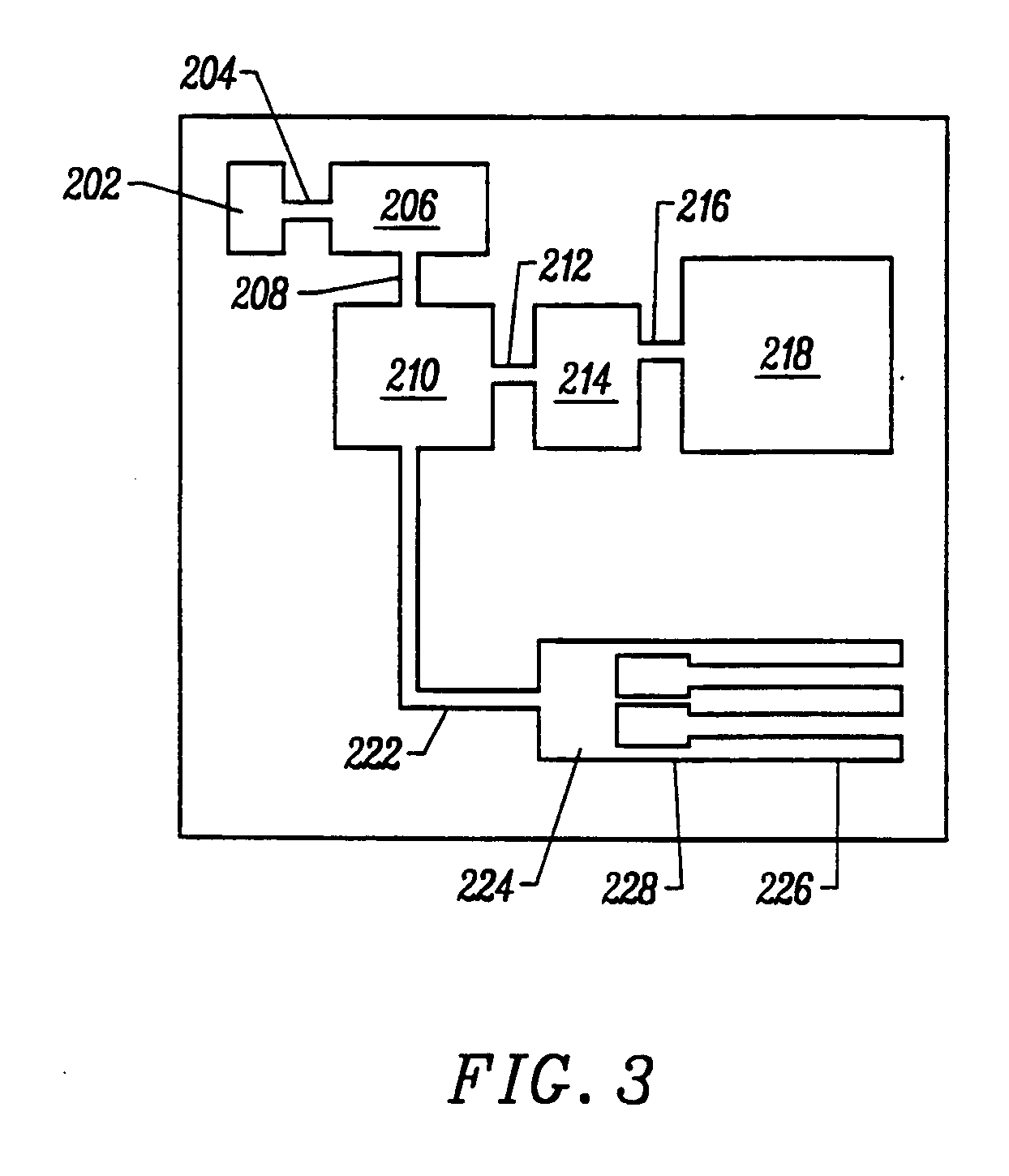
Integrated nucleic acid diagnostic device
InactiveUS20050250199A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMiniaturizationNucleic acid
The present invention provides a miniaturized integrated nucleic acid diagnostic device and system. The device of the invention is generally capable of performing one or more sample acquisition and preparation operations, in combination with one or more sample analysis operations. For example, the device can integrate several or all of the operations involved in sample acquisition and storage, sample preparation and sample analysis, within a single integrated unit. The device is useful in a variety of applications, and most notably, nucleic acid based diagnostic applications and de novo sequencing applications.
Owner:ANDERSON ROLFE C +3
Methods of sample preparation
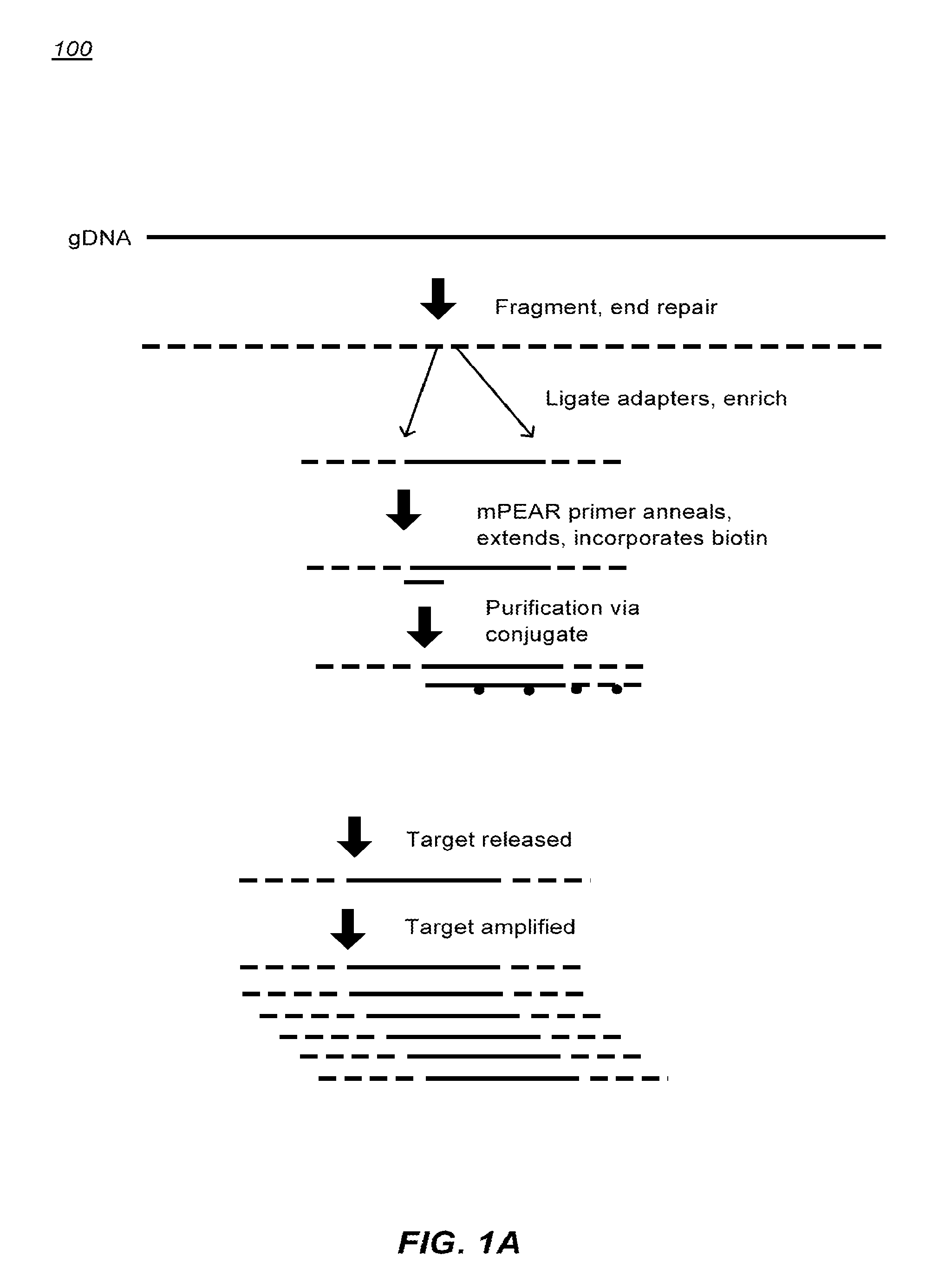
ActiveUS20150265995A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsNucleotide librariesHigh throughput sequenceComputational biology
The present disclosure provides methods, compositions, and kits for methods that can improve techniques nucleic acid analysis, and can allow for more reliable and accurate targeted, multiplexed, high throughput sequencing. The methods, compositions, and kits can be used for sequencing target loci of nucleic acid. The methods, compositions, and kits disclosed herein can be used for assisted de novo targeted sequencing. The methods, compositions, and kits disclosed herein can also be used for library labeling for de novo sequencing and phasing.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Integrated nucleic acid diagnostic device and method for in-situ confocal microscopy
InactiveUS20050100946A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMiniaturizationConfocal microscopy
The present invention provides a miniaturized integrated nucleic acid diagnostic device and system. The device of the invention is generally capable of performing one or more sample acquisition and preparation operations, in combination with one or more sample analysis operations. For example, the device can integrate several or all of the operations involved in sample acquisition and storage, sample preparation and sample analysis, within a single integrated unit. The device is useful in a variety of applications, and most notably, nucleic acid based diagnostic applications and de novo sequencing applications.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Array-based translocation and rearrangement assays
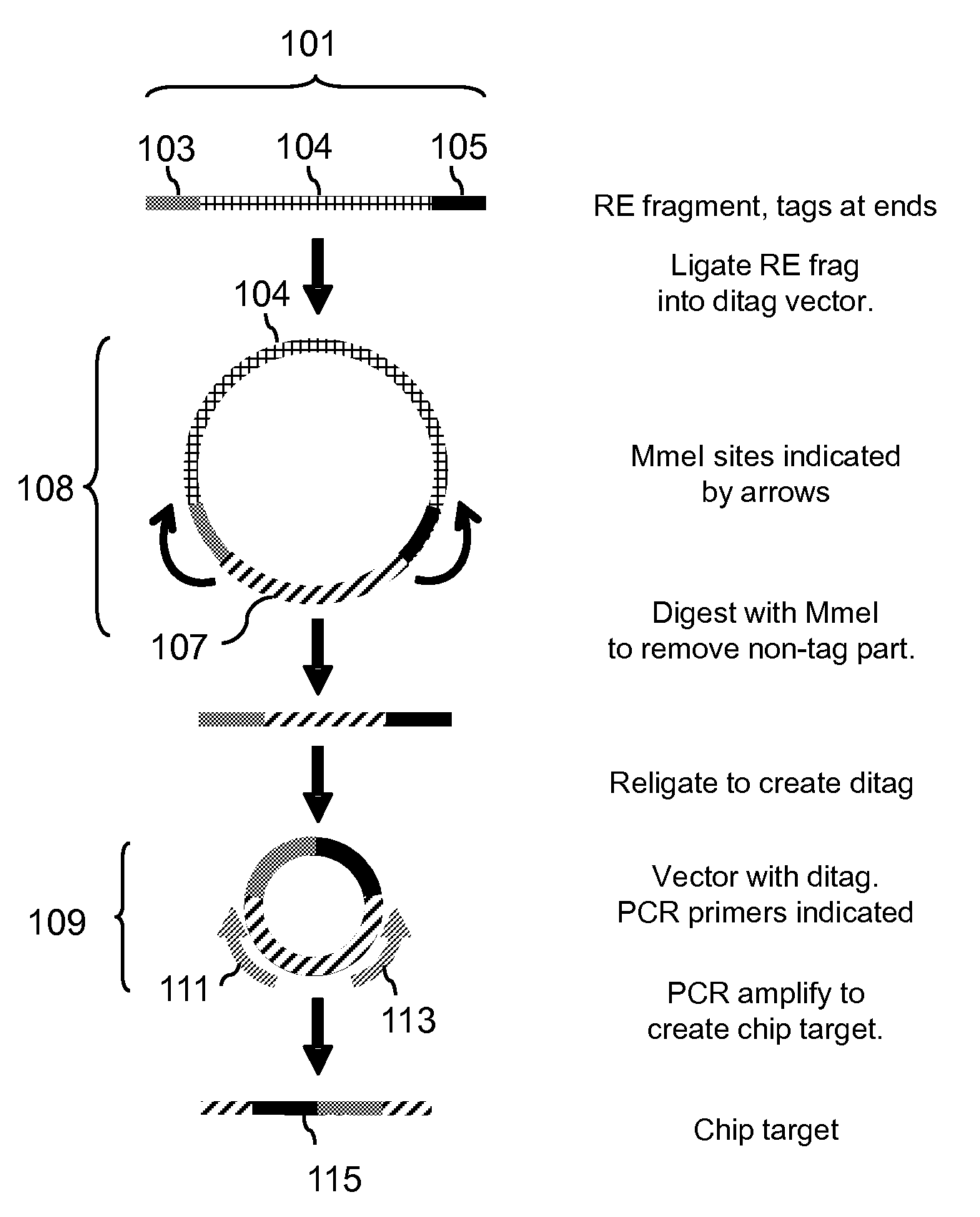
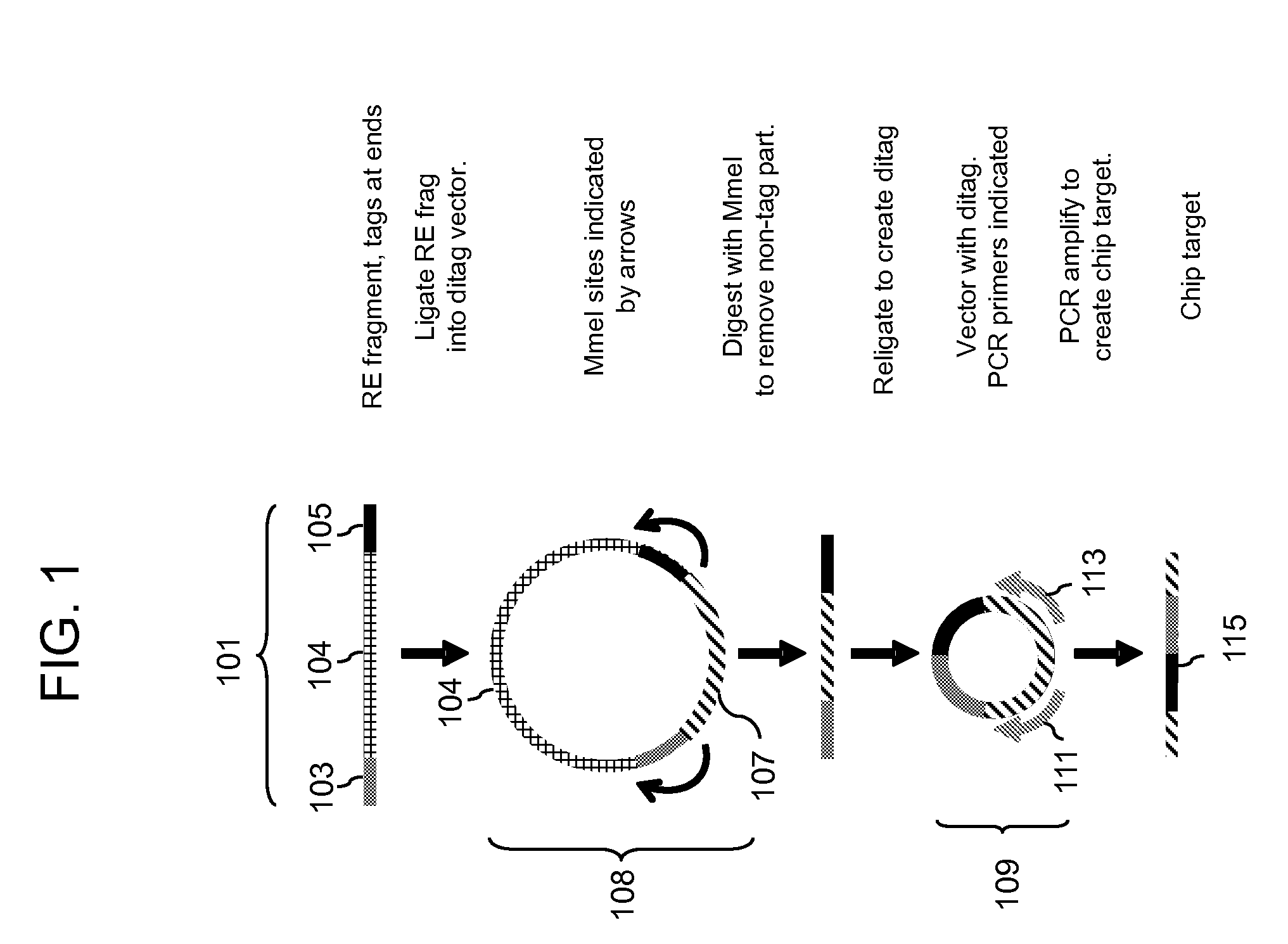
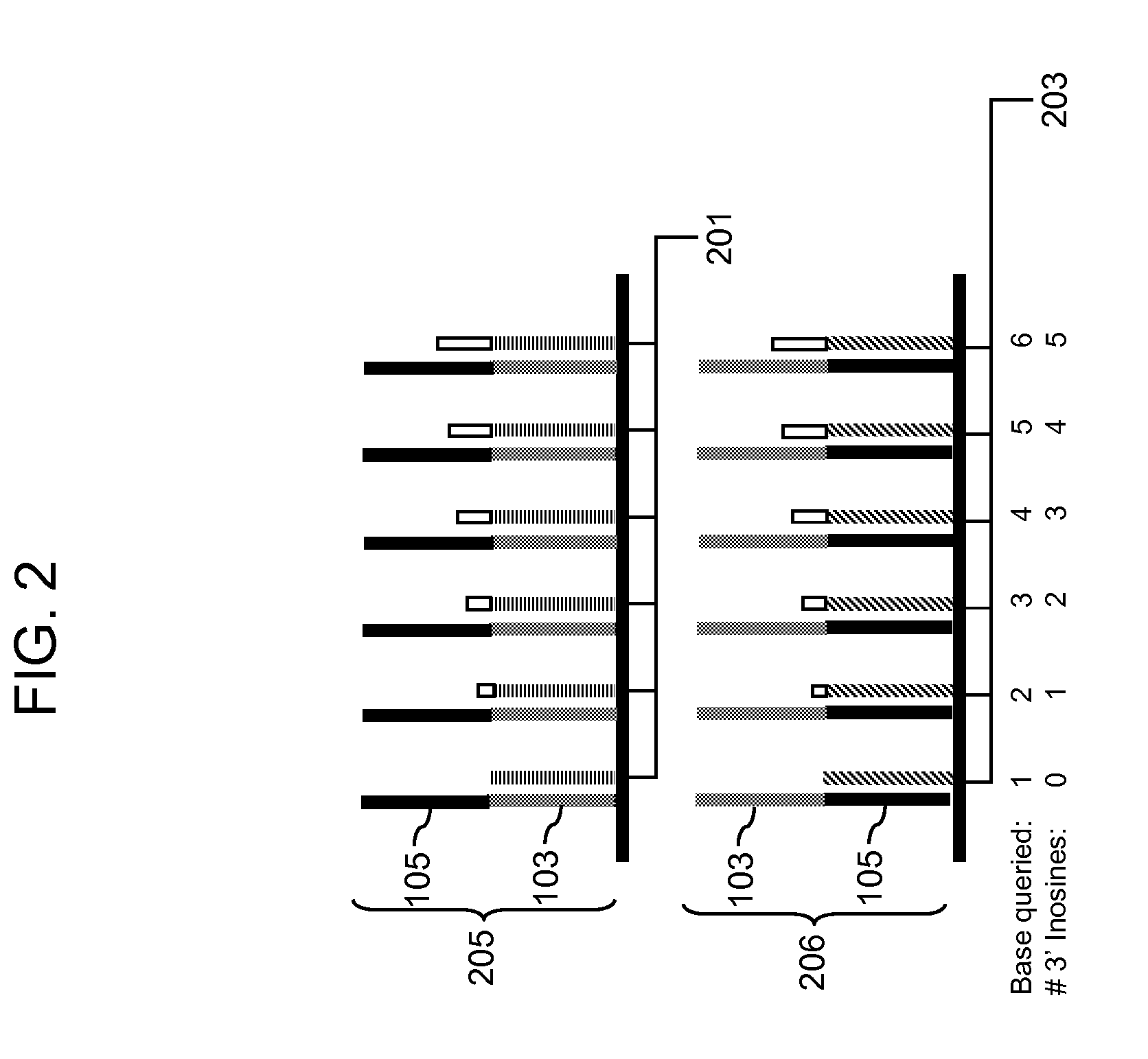
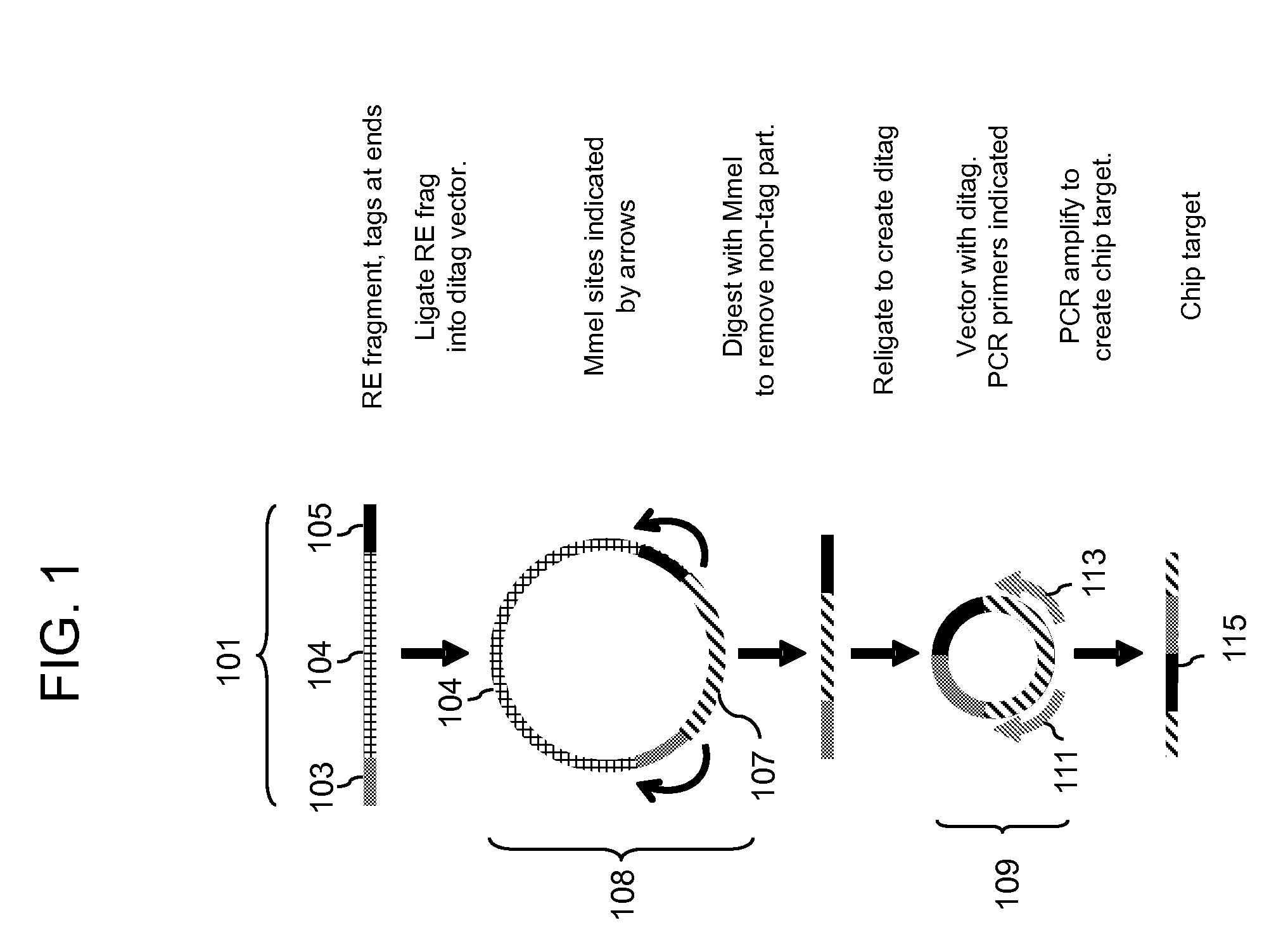
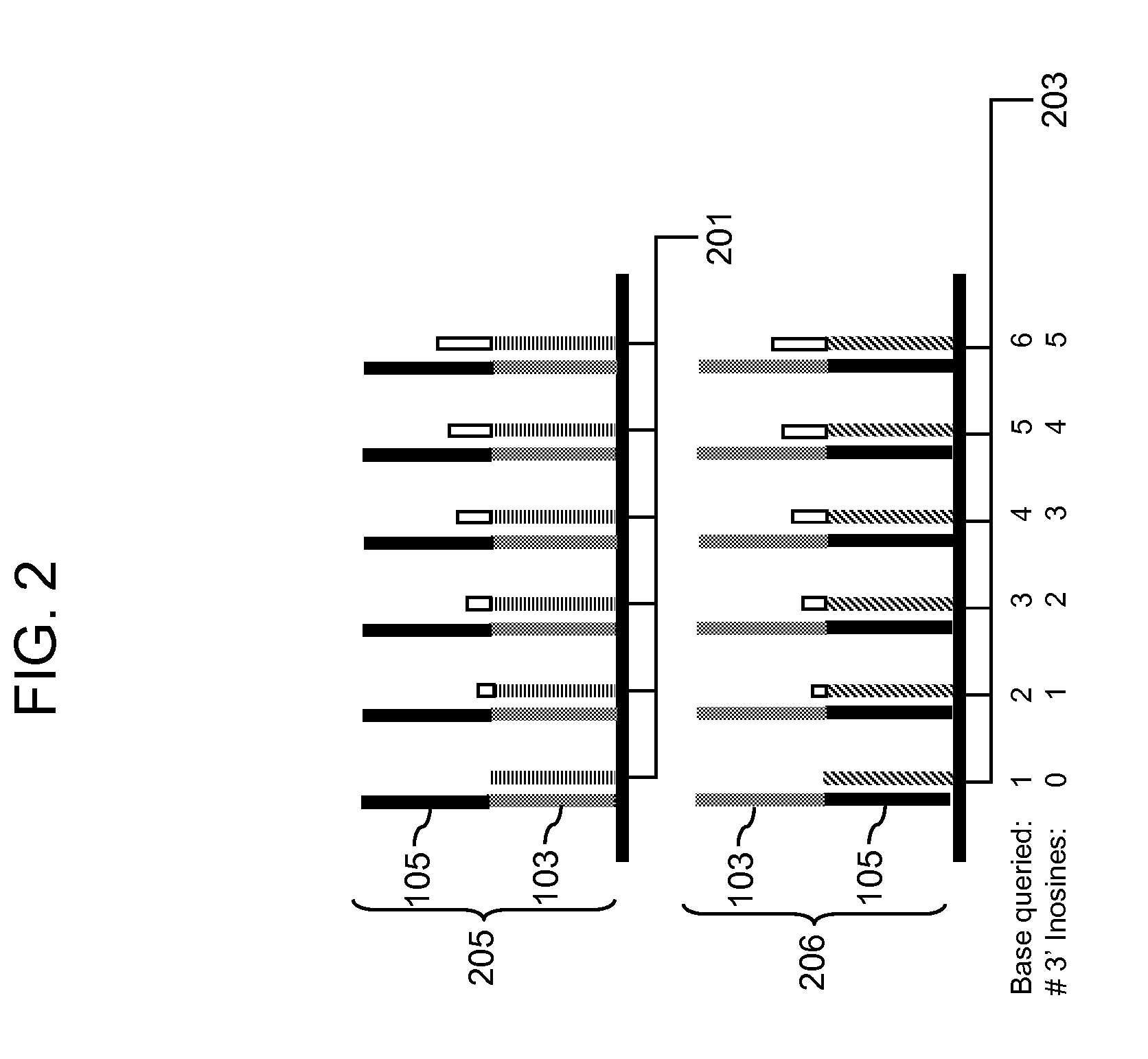
Methods for detecting genomic rearrangements are provided. In one embodiment, methods are provided for the use of paired end tags from restriction fragments to detect genomic rearrangements. Sequences from the ends of the fragments are brought together to form ditags and the ditags are detected. Combinations of ditags are detected by an on-chip sequencing strategy that is described herein, using inosine for de novo sequencing of short segments of DNA. In another aspect, translocations are identified by using target specific capture and analysis of the captured products on a tiling array.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Array-based translocation and rearrangement assays
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Method and reagent kit for enriching and sequencing peptide fragment containing histidine
InactiveCN101042377AGreat practicabilityIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationProtein insertionAminoacidemia
This invention provides one new method and agent case for collecting and testing group aminoacidemia peptides, which comprises the following steps: protein restores alkyl base and tryptone protein enzyme cut, peptides section N end amidogen decoration and group aminoacidemia peptides color spectrum collection and mass spectrum testing sequence; identifying the protein with peptides sections in mixture objects.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Building method of long fragment nucleic acid library
InactiveCN104711250ARead longSolve assembly problemsMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGenome resequencingGenome
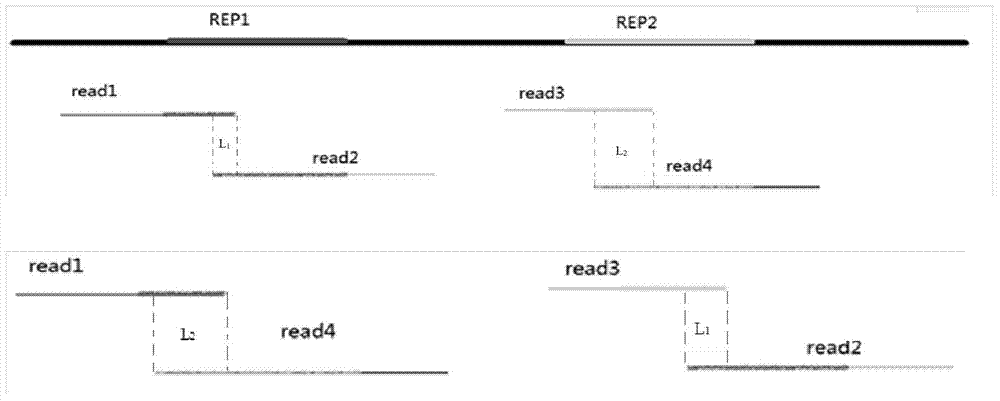
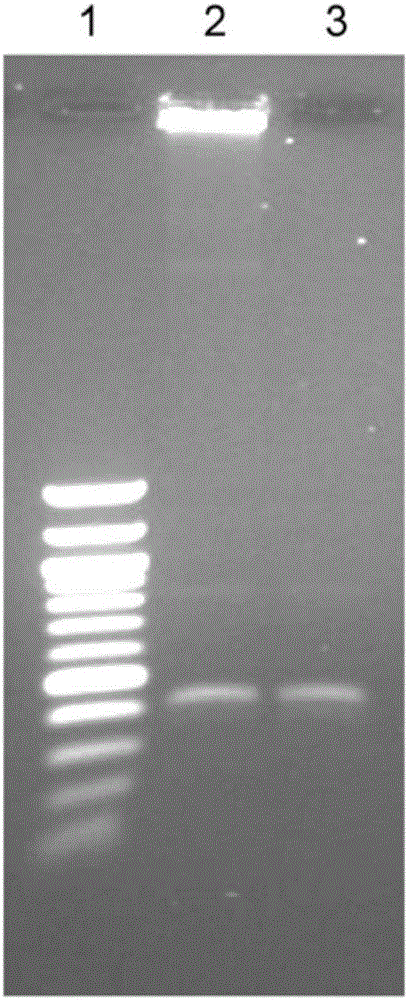
The invention provides a building method of a long fragment nucleic acid library. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a batch of Index label clusters, marking long fragment nucleic acid molecules in batch, using whole genome resequencing library building to build long fragment libraries suitable for illumine sequencing platforms, allowing all fragments to have connectors suitable for the illumine sequencing platforms under the action of transposase, carrying out PCR amplification, and screening the well build library. The method effectively solves the problem of influences of polyploid and repeated sequence in a genome de novo sequencing technology on the assembling accuracy, and can be used for assembling complex genomes and assisting de novo sequencing assembling to improve the assembling accuracy and shorten the assembling time.
Owner:BIOMARKER TECH
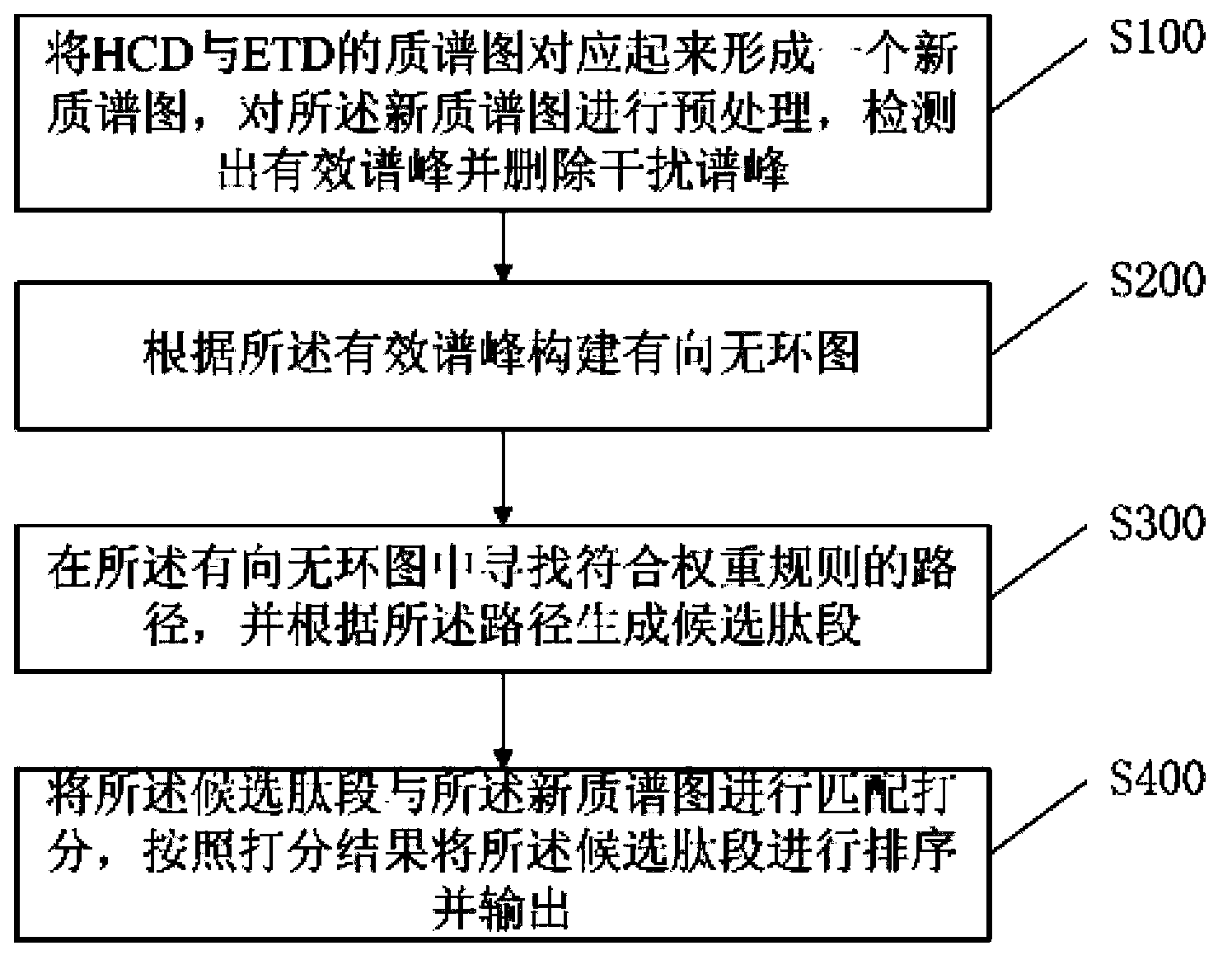
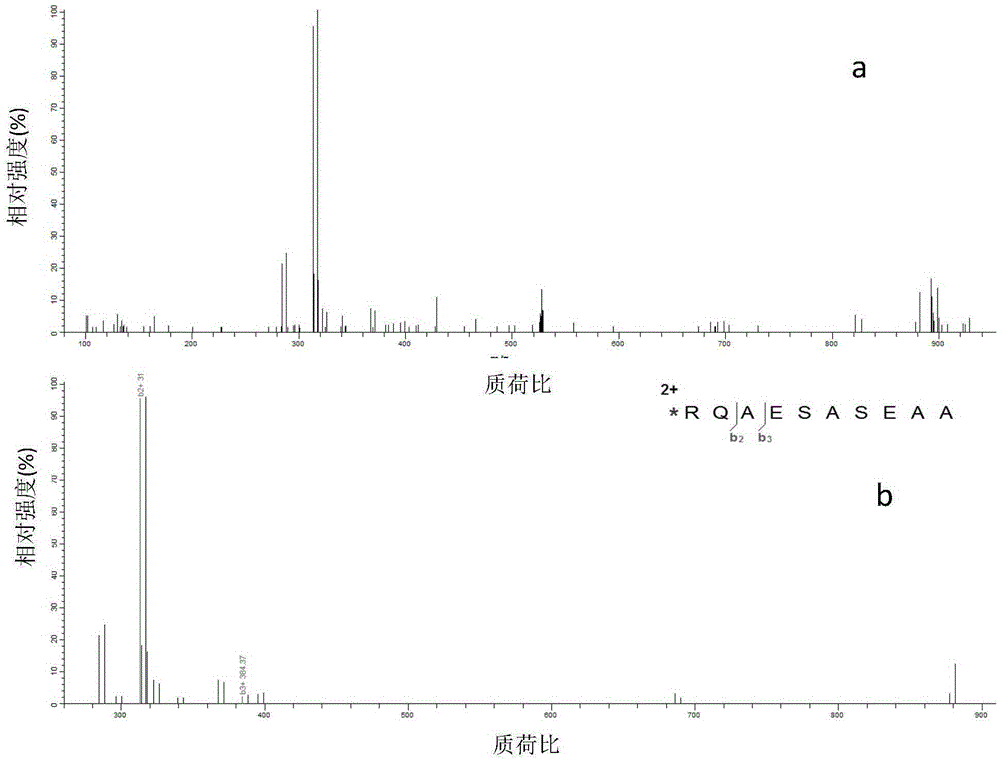
Method and system based on HCD mass spectrogram and ETD mass spectrogram for peptide fragment de novo sequencing
ActiveCN103852513AMake up for the shortcomings of incomplete peaksImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPath generationIsotope
The invention provides a method and a system based on an HCD mass spectrogram and an ETD mass spectrogram for peptide fragment de novo sequencing. The method includes steps of: (1) homologizing the HCD mass spectrogram and the ETD mass spectrogram to form a new mass spectrum, pretreating the new mass spectrum, detecting effective spectral peaks and deleting interference peaks; (2) constructing a directed acyclic graph according to the effective spectral peaks; (3) searching a route conforming the weight roles in the directed acyclic graph, and generating candidate peptide fragments according to the route; and (4) matching the candidate peptide fragments and the new mass spectrum, grading, sequencing the candidate peptide fragments according to the grading results, and outputting. The method and the system overcome disadvantages of defective spectral peaks caused by single fracture types, combine advantages of the HCD mass spectrogram and the ETD mass spectrogram, and increase the accuracy of the de novo sequencing. Pretreatment is performed before de novo sequencing to remove many isotope spectral peaks and noise spectral peaks, thus preventing the isotope spectral peaks and the noise spectral peaks from interfering the de novo sequencing algorithm. A grading algorithm with a high distinction degree is adopted, thus improving the performance of the de novo sequencing.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
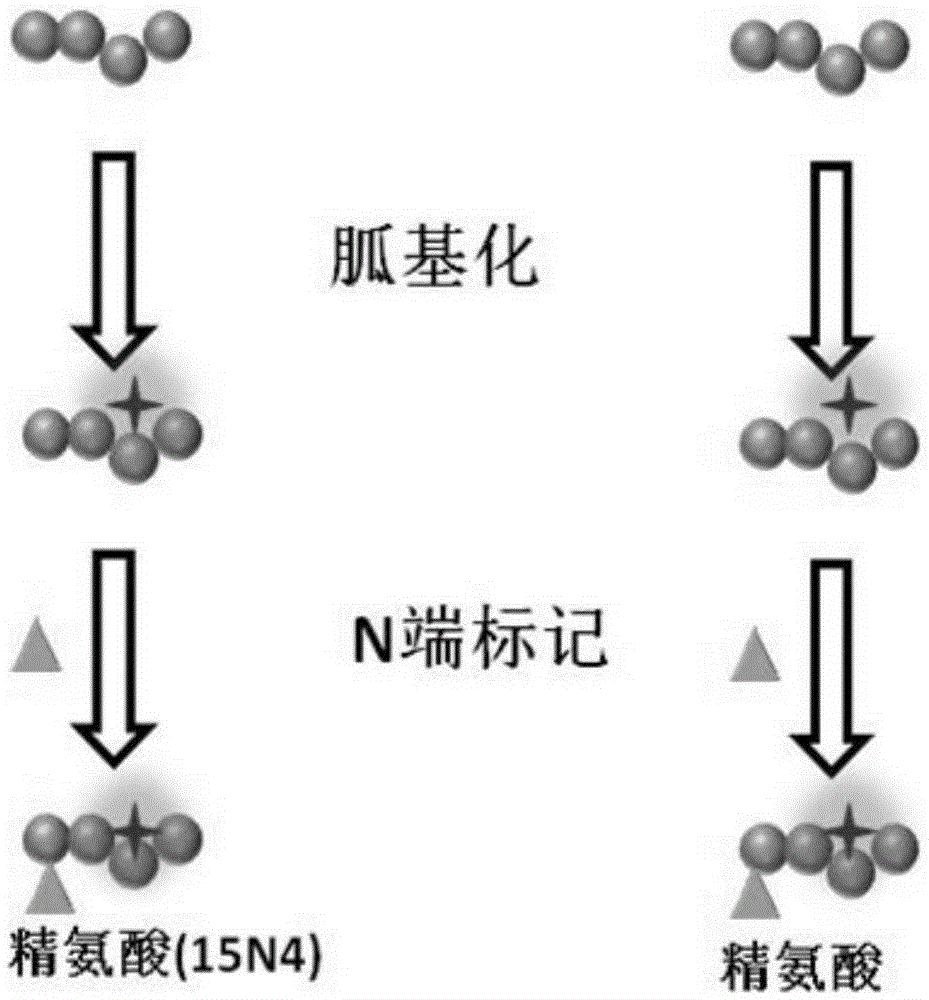
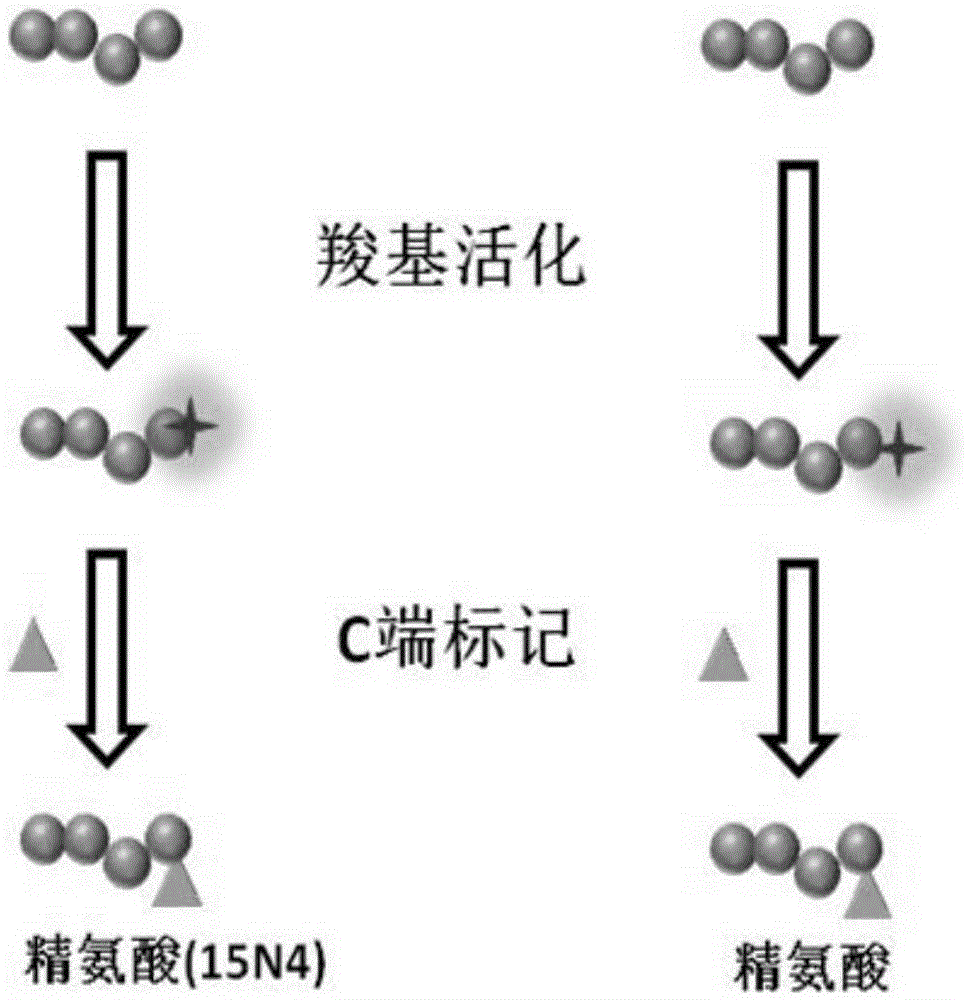
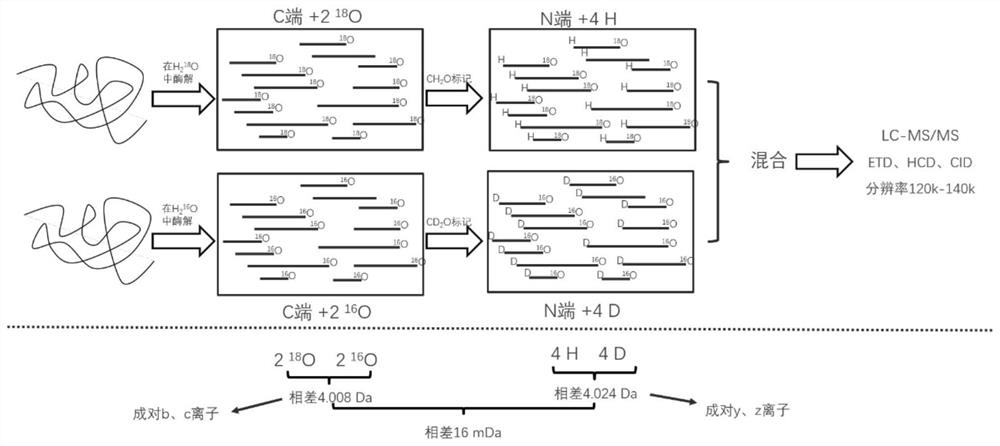
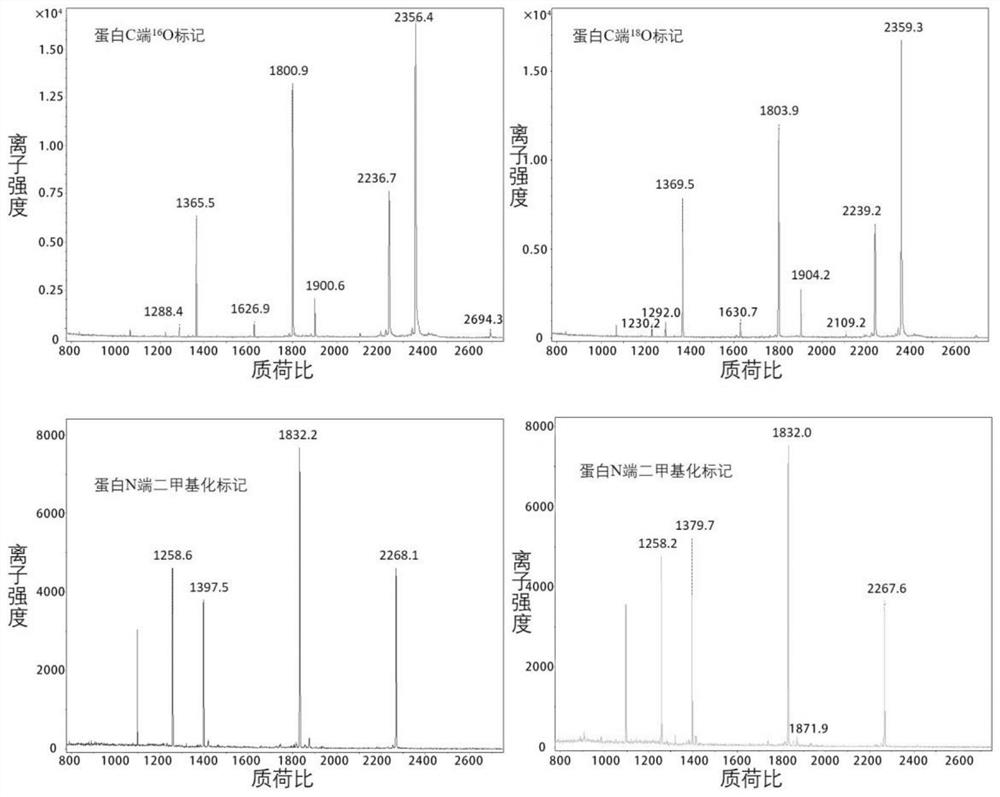
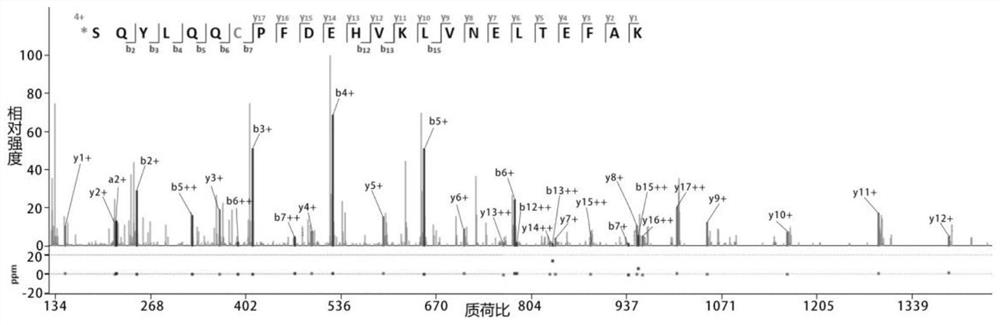
Polypeptide amino acid sequence De novo sequencing method based on chemical modification and isotope labeling
ActiveCN106645437AAccurate and fast sequencingStrong specificityComponent separationRetention timeMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present invention relates to a polypeptide amino acid sequence De novo sequencing method based on chemical modification and isotope labeling, wherein the MS / MS maps of the same polypeptides having different labels are subjected to correlation by using the correlation between the N-terminal labeling and C-terminal labeling polypeptide molecule quality and the retention time, the polypeptides in different labeled samples form N-terminal fragment ion pair and the C-terminal fragment ion pair during a mass spectrometry fragmentation process, and the polypeptide amino acid sequence is subjected to De novo sequencing. According to the present invention, the polypeptide is modified with the positively charged reagent so as to make the polypeptide easily form the rich fragment ions in the mass spectrometry during fragmentation, and by using the reagents containing different light and weight isotopes to label, the polypeptide form the paired fragment ions in the mass spectrometry during fragmentation so as to be easily distinguished, such that the influence of the interfering signal is reduced, and the fragment ion selection specificity and the De novo sequencing speed can be improved; and by using the complementarity of the N-terminal fragment ions and the C-terminal fragments, the accuracy and the efficiency of the polypeptide sequencing can be improved.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
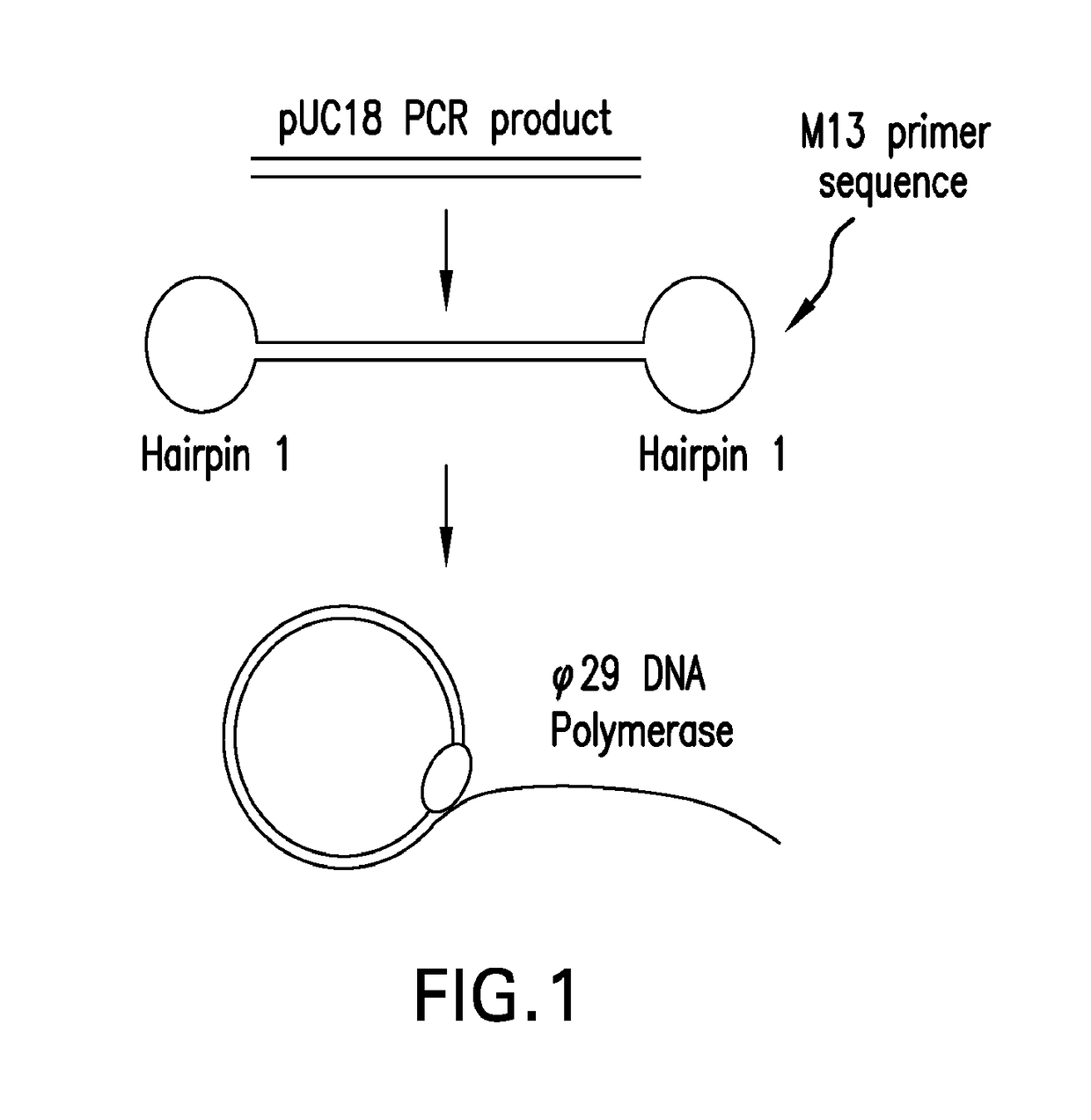
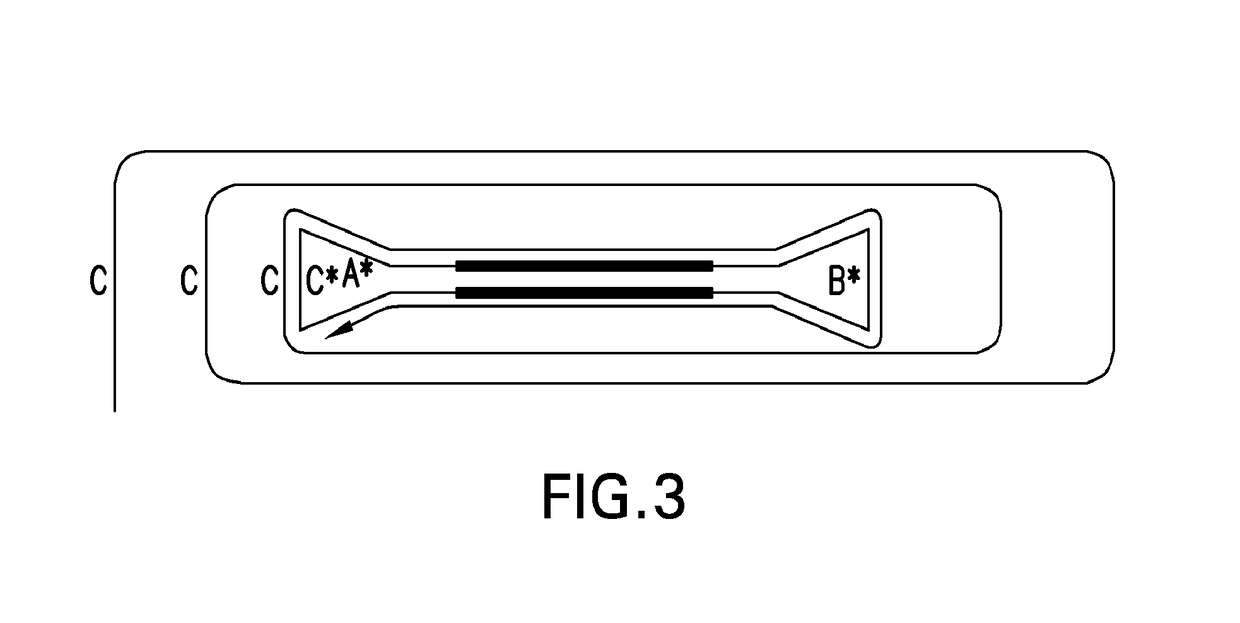
Systems and methods for clonal replication and amplification of nucleic acid molecules for genomic and therapeutic applications
PendingUS20170067097A1Efficient productionCreate efficientlyMicrobiological testing/measurementChromosomal regionHaplotype
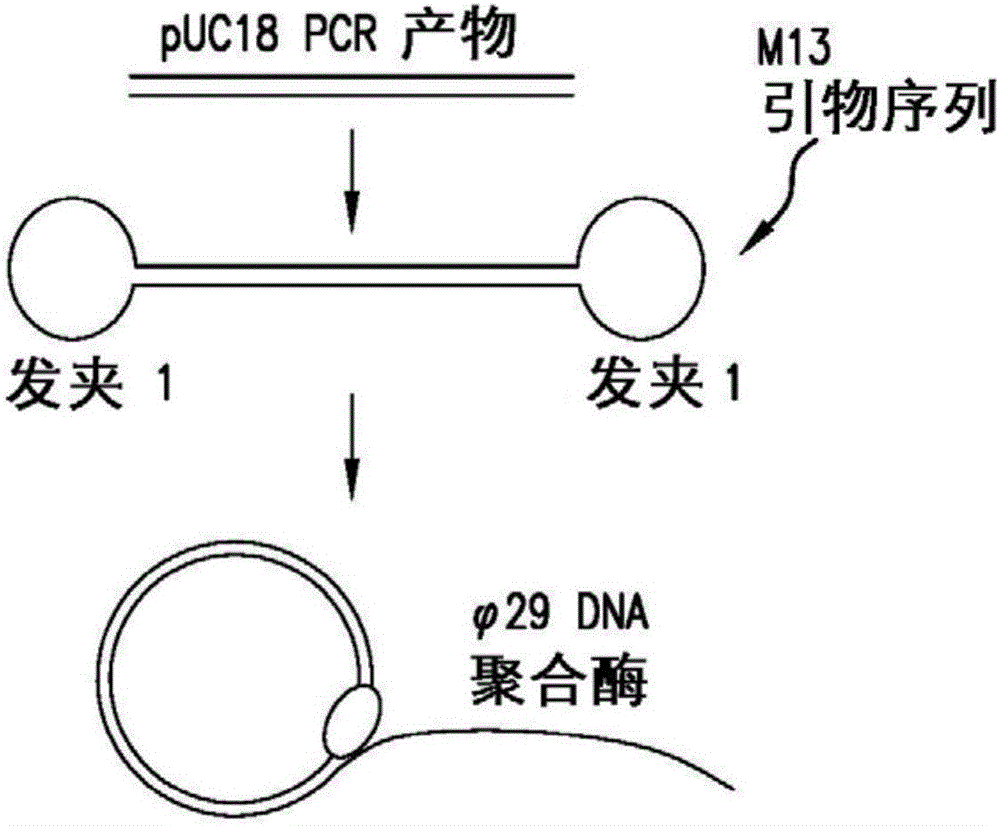
The present invention provides for methods, reagents, apparatuses, and systems for the replication or amplification of nucleic acid molecules from biological samples. In one embodiment of the invention, the nucleic molecules are isolated from the sample, and subjected to fragmenting and joining using ligating agents of one or more hairpin structures to each end of the fragmented nucleic molecules to form one or more dumbbell templates. The one or more dumbbell templates are contacted with at least one substantially complementary primer attached to a substrate, and subjected to rolling circle replication or rolling circle amplification. The resulting replicated dumbbell templates or amplified dumbbell templates are used in numerous genomic applications, including whole genome de novo sequencing; sequence variant detection, structural variant detection, determining the phase of molecular haplotypes, molecular counting for aneuploidy detection; targeted sequencing of gene panels, whole exome, or chromosomal regions for sequence variant detection, structural variant detection, determining the phase of molecular haplotypes and / or molecular counting for aneuploidy detection; study of nucleic acid-nucleic acid binding interactions, nucleic acid-protein binding interactions, and nucleic acid molecule expression arrays; and testing of the effects of small molecule inhibitors or activators or nucleic acid therapeutics.
Owner:REDVAULT BIOSCI
Genome sequencing data sequence assembling method
ActiveCN104750765AThe result is accurate and effectiveSpecial data processing applicationsGenomic sequencingGenetics
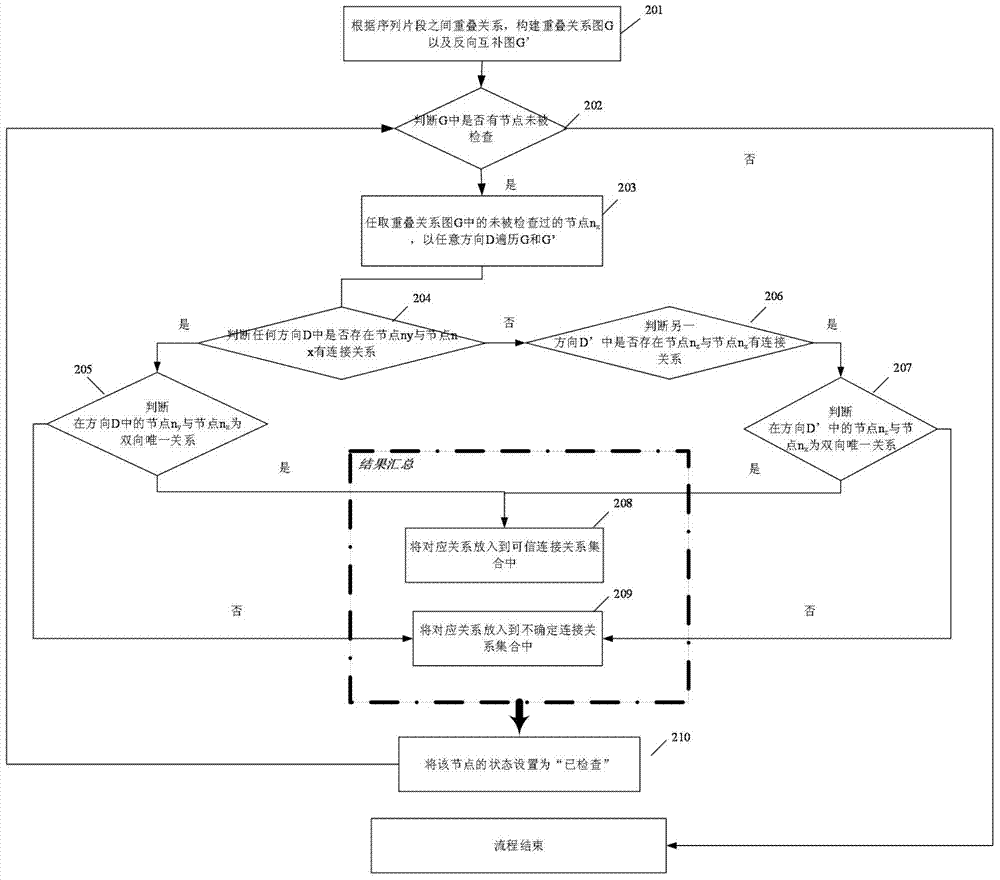
The embodiment of the invention provides a genome sequencing data sequence assembling method. By means of the method, the advantages of denovo sequencing and the advantages of re-sequencing can be integrated, and genome sequencing data sequences are effectively assembled. A drafted sequence traversal path of the genome sequencing sequences obtained based on a reference sequence and generated after sequencing data are mapped to the reference sequence in a comparing mode and an overlapping relation set of the genome sequencing data are known. The set comprises a determined relation subset and an undetermined relation subset. The method includes the steps that after the sequencing data sequences are mapped to an affinis reference genome in a comparing mode, the drafted data traversal path of the genome sequencing sequences is obtained based on the reference sequence, all nodes in the drafted sequence traversal path are checked one by one; iterated revision is conducted on the drafted sequence traversal path according to the connection relation of the determined relation subset and / or the undetermined relation subset in the overlapping relation set, and the overlapping relation set is updated; the next node is checked based on the updated drafted sequence traversal path and the updated overlapping relation set till the last node is checked.
Owner:天工生物科技(天津)有限公司
Systems and methods for clonal replication and amplification of nucleic acid molecules for genomic and therapeutic applications
The present invention provides for methods, reagents, apparatuses, and systems for the replication or amplification of nucleic acid molecules from biological samples. In one embodiment of the invention, the nucleic molecules are isolated from the sample, and subjected to fragmenting and joining using ligating agents of one or more hairpin structures to each end of the fragmented nucleic molecules to form one or more dumbbell templates. The one or more dumbbell templates are contacted with at least one substantially complementary primer attached to a substrate, and subjected to rolling circle replication or rolling circle amplification. The resulting replicated dumbbell templates or amplified dumbbell templates are used in numerous genomic applications, including whole genome de novo sequencing; sequence variant detection, structural variant detection, determining the phase of molecular haplotypes, molecular counting for aneuploidy detection; targeted sequencing of gene panels, whole exome, or chromosomal regions for sequence variant detection, structural variant detection, determining the phase of molecular haplotypes and / or molecular counting for aneuploidy detection; study of nucleic acid - nucleic acid binding interactions, nucleic acid - protein binding interactions, and nucleic acid molecule expression arrays; and testing of the effects of small molecule inhibitors or activators or nucleic acid therapeutics.
Owner:REDVAULT BIOSCI
Assembling method for de novo sequencing data based on optics map platform Irys
ActiveCN106021978AImprove gene assembly effectSpeed up the calculation processProteomicsGenomicsContigAccessory genome
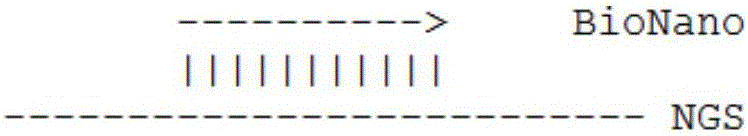
The invention relates to an assembling method for de novo sequencing data based on an optics map platform Irys. The method comprises: using the optics map platform Irys to obtain a gene assembly file; getting a scaffold file: fai file of NGS; preprocessing data: through setting a threshold value, filtering a comparison result whose confidence level is low, combining cmap files, sorting, calculating N50; counting assembling effects: counting comparison results of BioNano and NGS, including the contig of the BioNano, and the length, number, and total quantity of scaffold of NGS; according to the contig of the BioNano and network topological relations among the scaffold of the NGS, analyzing length of the assembled new contig and length of scaffold in a classified manner. The method can assist genome assembly, and obviously improves gene assembly effects of species.
Owner:GENERGY BIO TECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
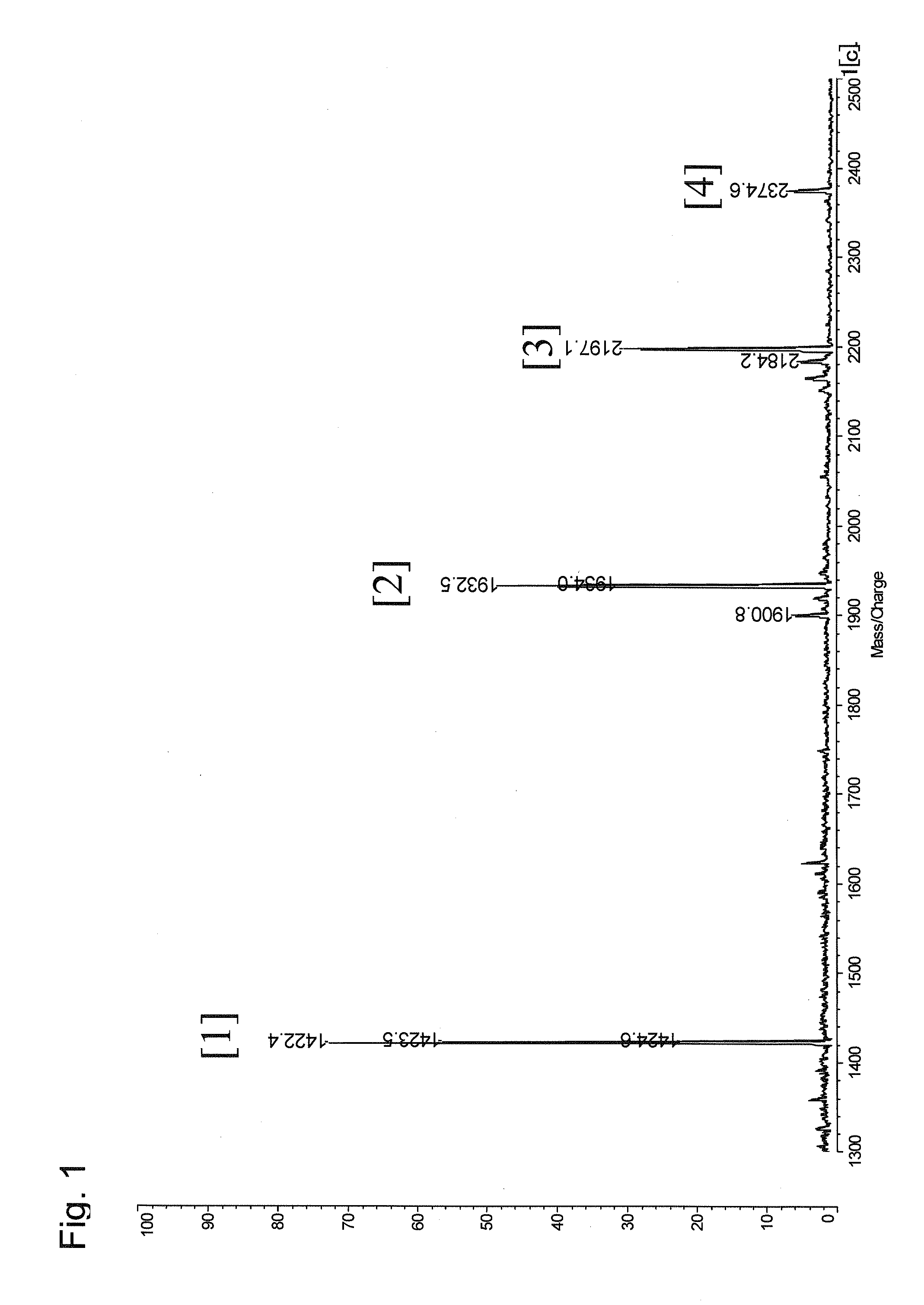
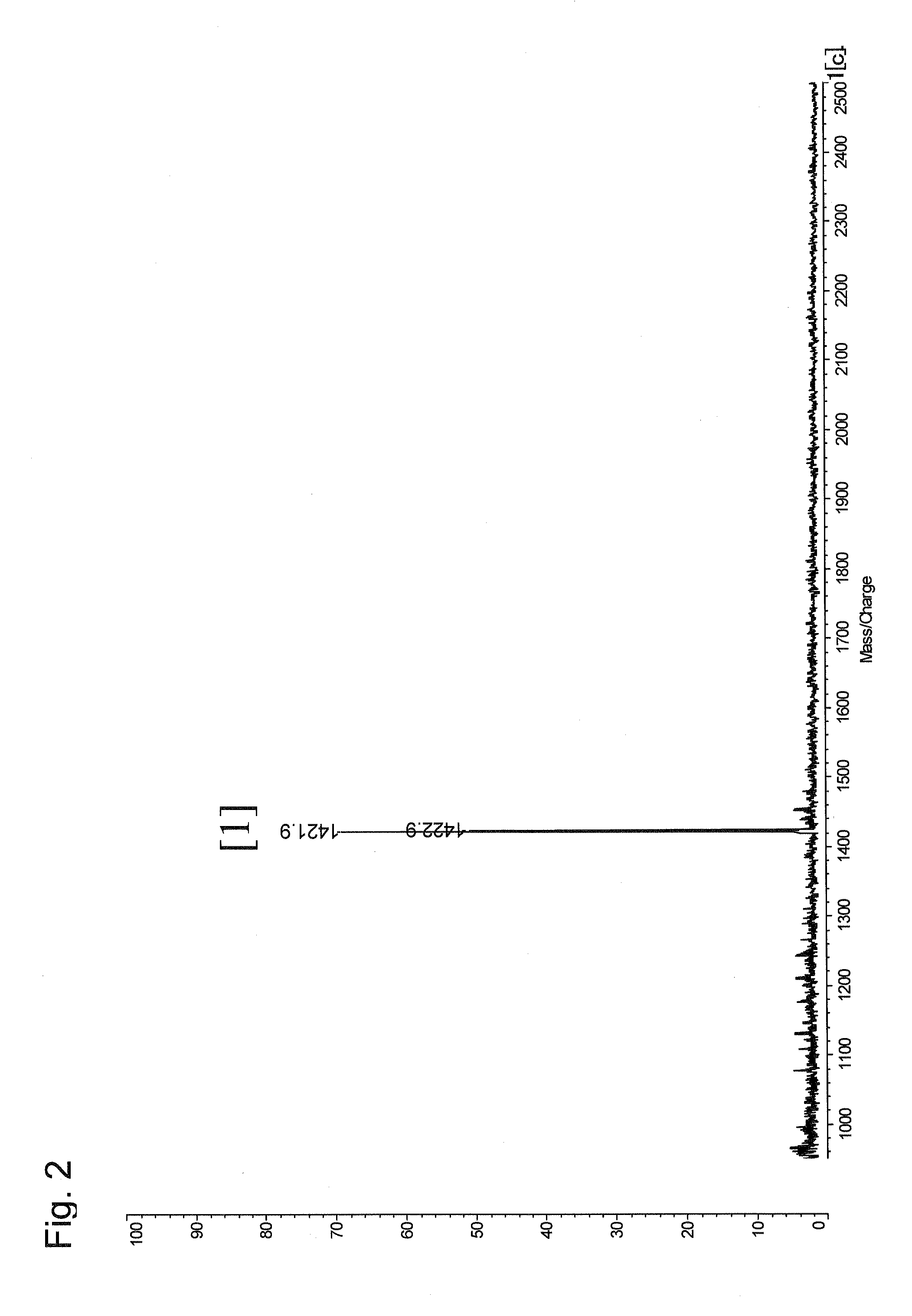
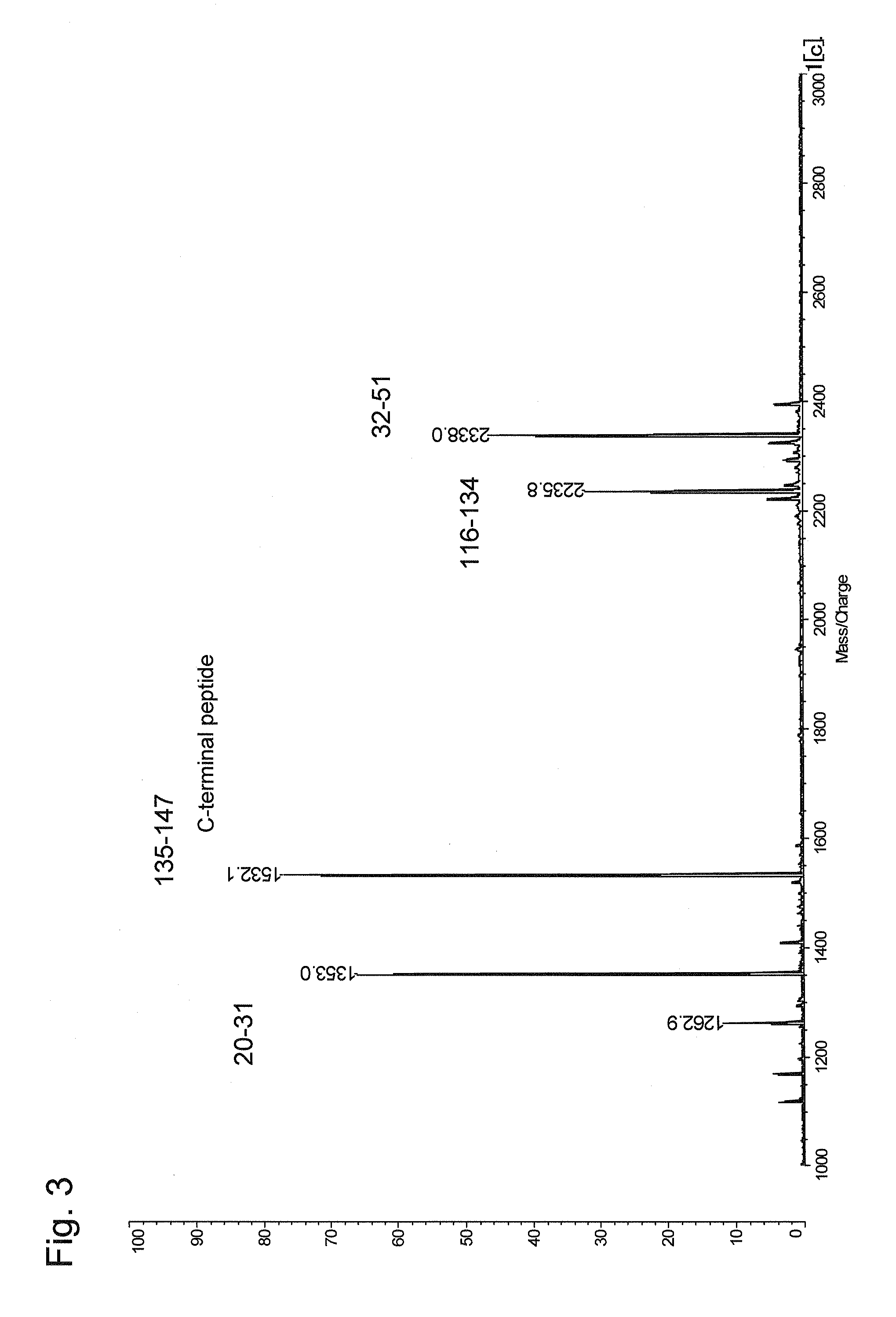
Method for selectively recovering c-terminal peptide of protein and method for determining amino acid sequence of c-terminal peptide of protein using the same
InactiveUS20090142851A1Sure easyHigh detection sensitivityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsMass spectrometry measurementPeptide fragment
The present invention provides a method for specifically recovering a C-terminal peptide fragment, and a method for easily determining the sequence of a C-terminal peptide fragment, which is difficult to be determined by a conventional method, with the use of a mass spectrometer, in particular a method capable of de novo sequencing of a C-terminal peptide fragment. A method for selectively recovering a C-terminal peptide of a protein, comprising the steps of: in a cleavage product of a protein containing a C-terminal peptide fragment (A) having an α-amino group but not having an ε-amino group and the other peptide fragments (B) having an α-amino group and an ε-amino group, selectively modifying the α-amino groups to obtain a C-terminal peptide fragment modified (A′) and the other peptide fragments modified (B′); and separating the C-terminal peptide fragment modified (A′) from the modified cleavage product by allowing a carrier to hold the other peptide fragments modified (B′) via the ε-amino group. A method for determining the amino acid sequence of a C-terminal peptide of a protein, comprising the steps of: selectively recovering a C-terminal peptide of a protein by the above method; and determining the amino acid sequence by subjecting a recovered C-terminal peptide fragment to mass spectrometry measurement.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Methods of sample preparation
ActiveUS9968901B2Sequential/parallel process reactionsNucleotide librariesComputational biologyThroughput
The present disclosure provides methods, compositions, and kits for methods that can improve techniques nucleic acid analysis, and can allow for more reliable and accurate targeted, multiplexed, high throughput sequencing. The methods, compositions, and kits can be used for sequencing target loci of nucleic acid. The methods, compositions, and kits disclosed herein can be used for assisted de novo targeted sequencing. The methods, compositions, and kits disclosed herein can also be used for library labeling for de novo sequencing and phasing.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Amino acid sequence determination method based on quasi-isobaric double labeling at two ends of polypeptide
ActiveCN112986570AImprove reaction efficiencyHigh selectivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingStable Isotope LabelingEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to an amino acid sequence de novo sequencing method of protein based on quasi-isobaric stable isotope labeling at two ends of polypeptide. According to the de novo sequencing method, trypsin is used for carrying out enzyme digestion on protein subjected to denaturation, reduction and alkylation, and a peptide fragment containing N-terminal alpha-amino and C-terminal alpha-carboxyl is formed. The method comprises the following steps: dividing a sample into two parts, carrying out derivative reaction on one part in 18O water by using trypsin, and then carrying out N-terminal dimethylation by using formaldehyde; directly carrying out N-terminal dimethylation labeling of the peptide fragment on the other part by using deuterated formaldehyde; and finally, mixing the two labeled samples, and separating and identifying peptide fragments by using high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. According to the method, the window of a mass spectrum is reduced, the influence of interference signals can be effectively reduced, and the selection specificity of fragment ions and the accuracy of polypeptide sequencing are improved. Meanwhile, b and y ions do not need to be distinguished, a de novo sequencing algorithm of the protein amino acid sequence is simplified, and the de novo sequencing speed is increased.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
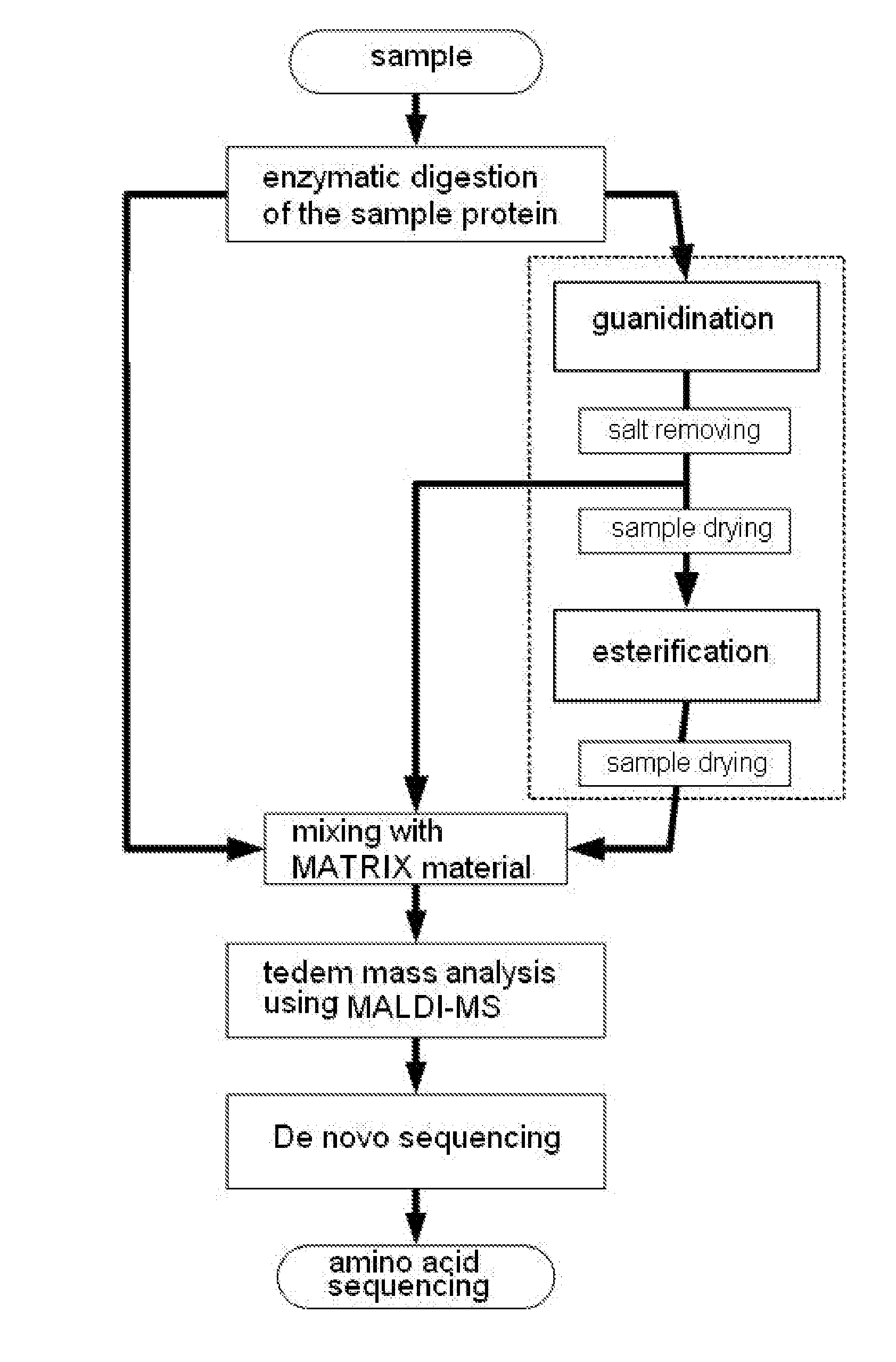
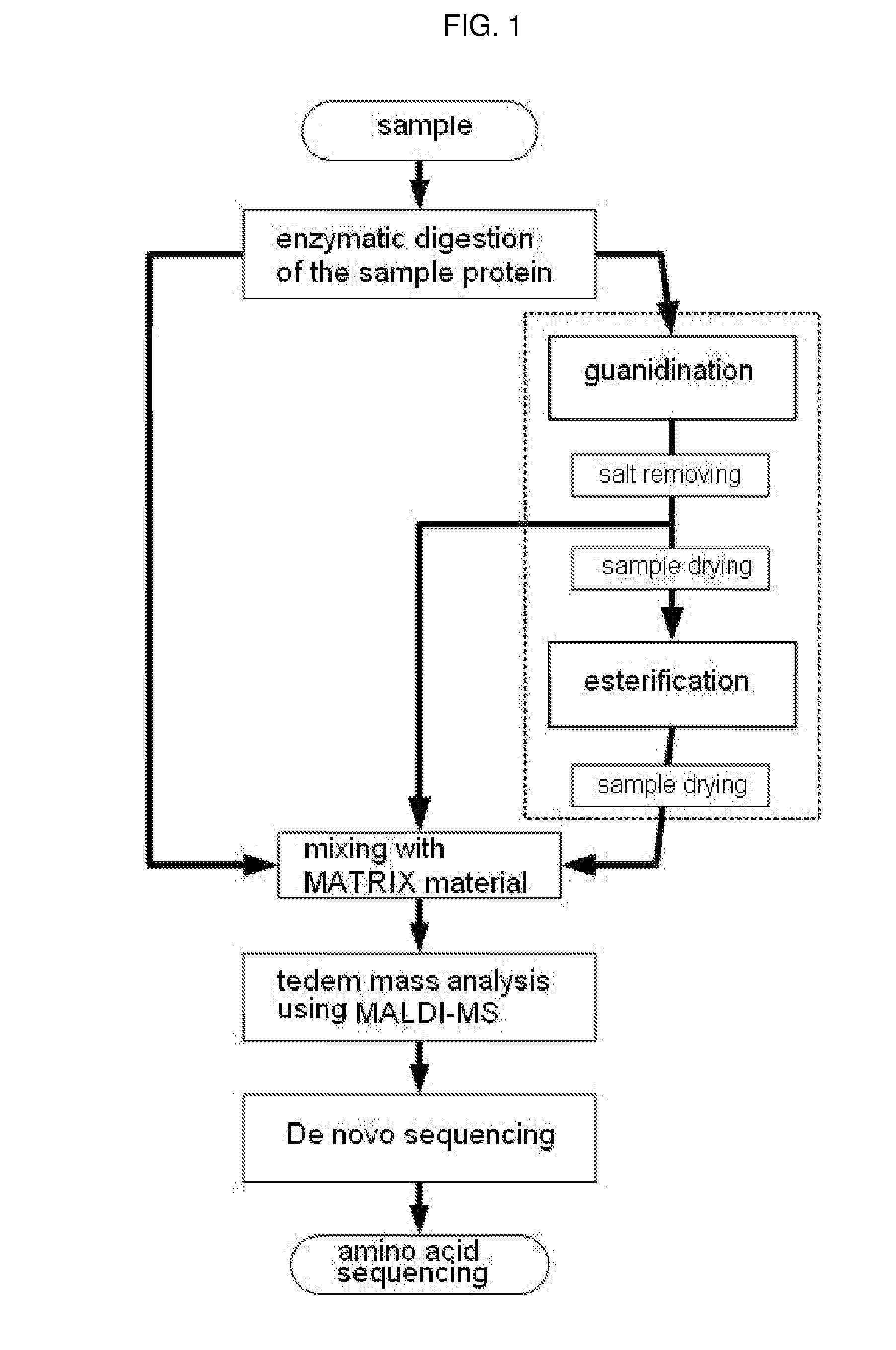
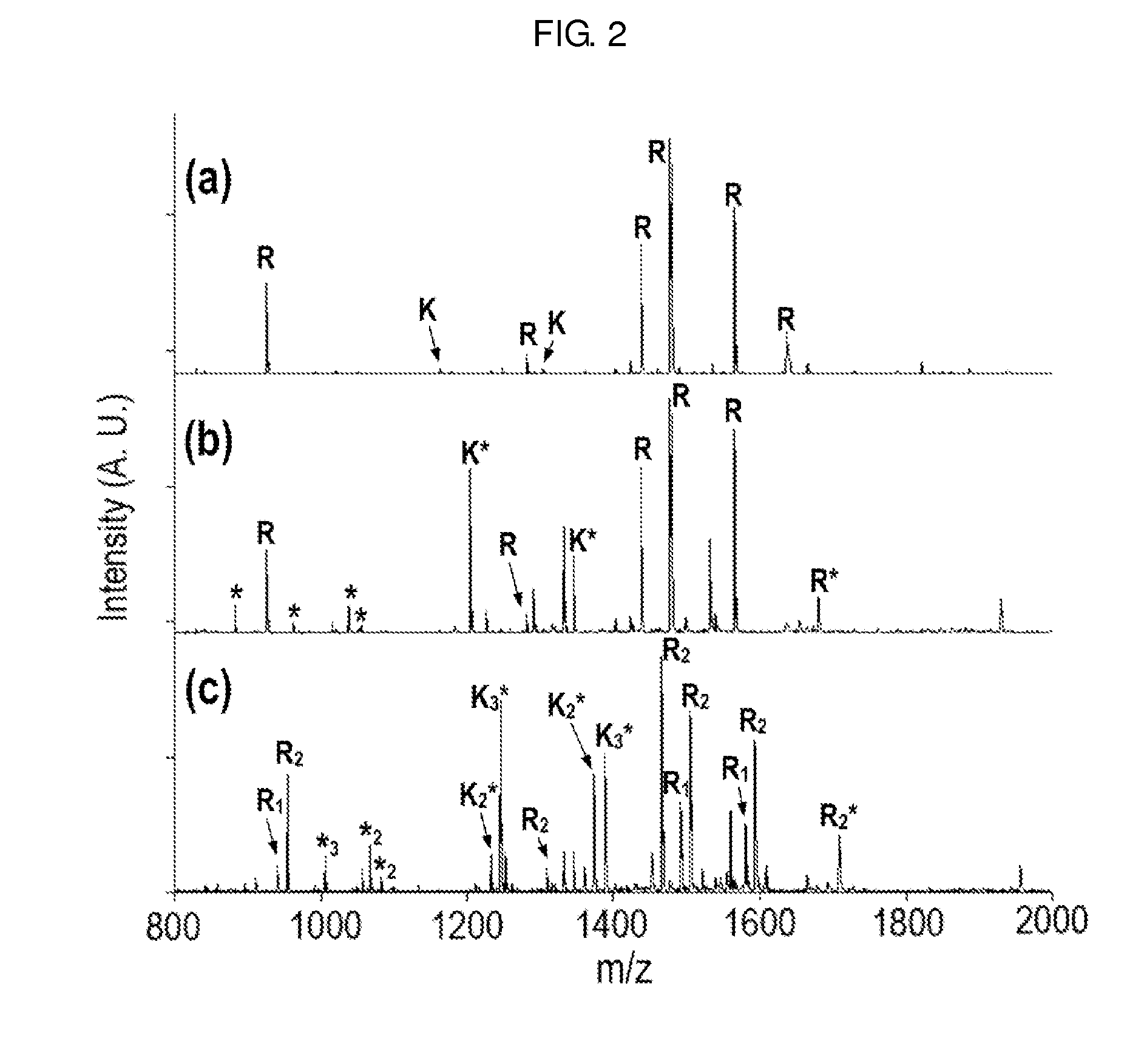
Method of De Novo Sequencing of Peptide Using the Maldi Mass Spectrometry, Method and Apparatus for Preparing Sample for Maldi Mass Spectrometry
ActiveUS20080138845A1Wide variation of detection sensitivityHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementElectron/ion optical arrangementsPeptide sequencingMass spectrometric
The present invention relates to a method of peptide sequencing by MALDI (matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization) tandem mass spectrometry, which comprises the steps of chemically modifying a sample peptide with at least one chemical modification method selected from the group consisting of guanidination and esterification in order to change the ionization status of the peptide and performing mass spectrometry using a MALDI tandem mass spectrometer and programmed MALDI tandem mass spectrometry. The peptide sequencing method of the present invention is advantageous in that detection sensitivity of the peptide improves significantly and various daughter ions are detected uniformly, thereby enabling perfect de novo sequencing with tandem mass spectrometry only, without database search.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND +1
Silico iterations correlating mass spectrometer outputs with peptides in databases and success of same
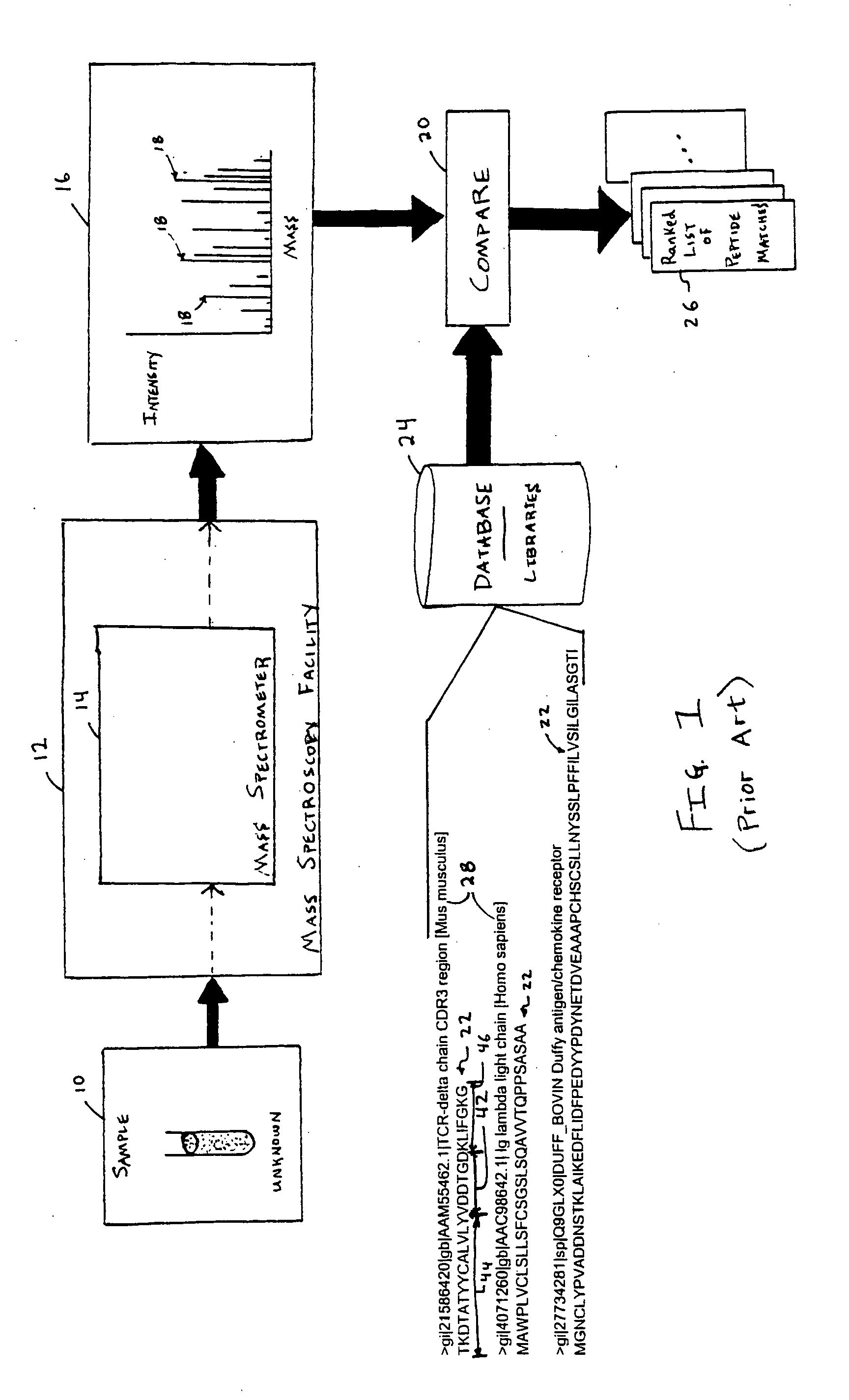
InactiveUS20050283316A1Minimal human interventionFaster processing timeIon sources/gunsBiological testingFrequency spectrumScoring algorithm
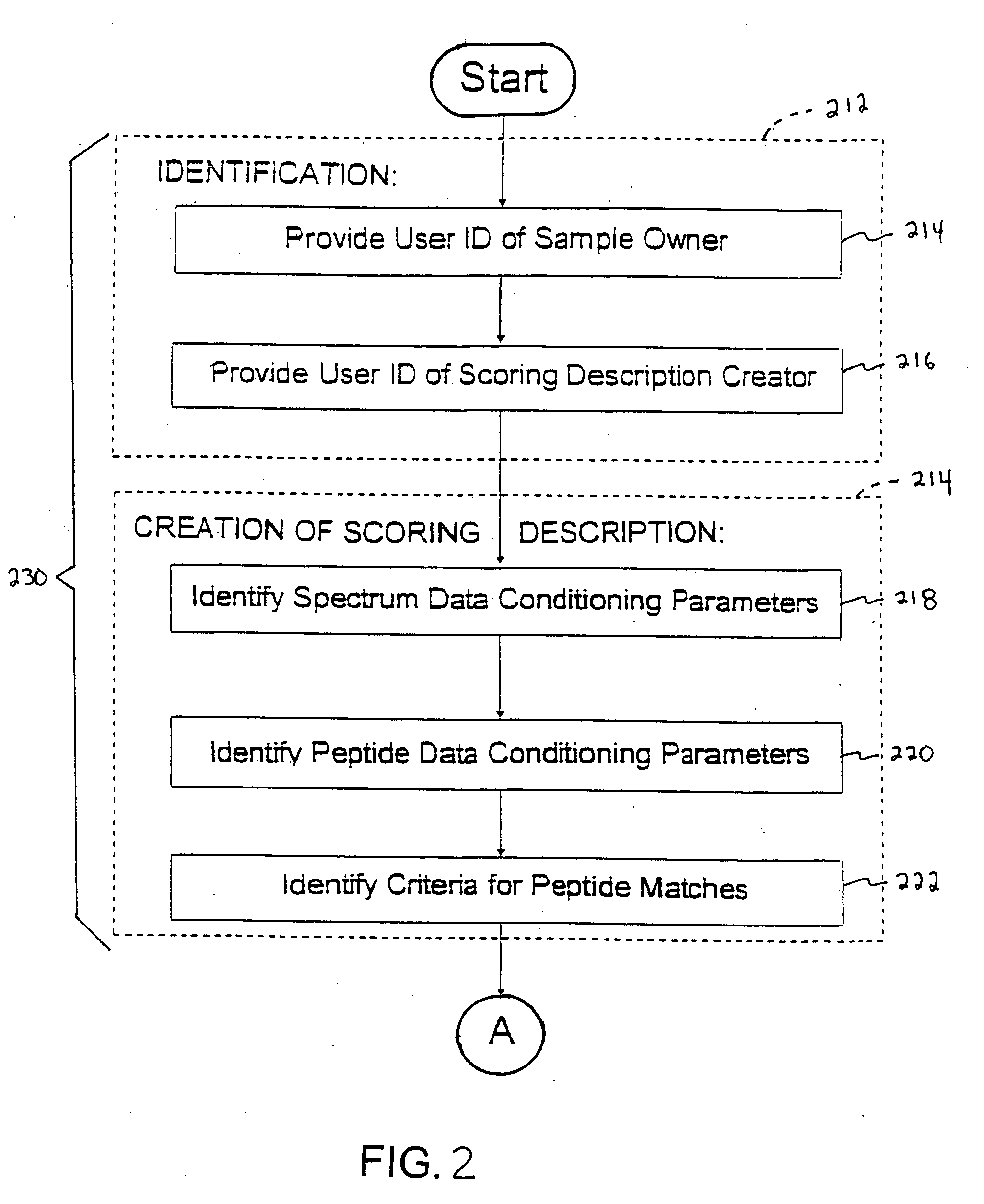
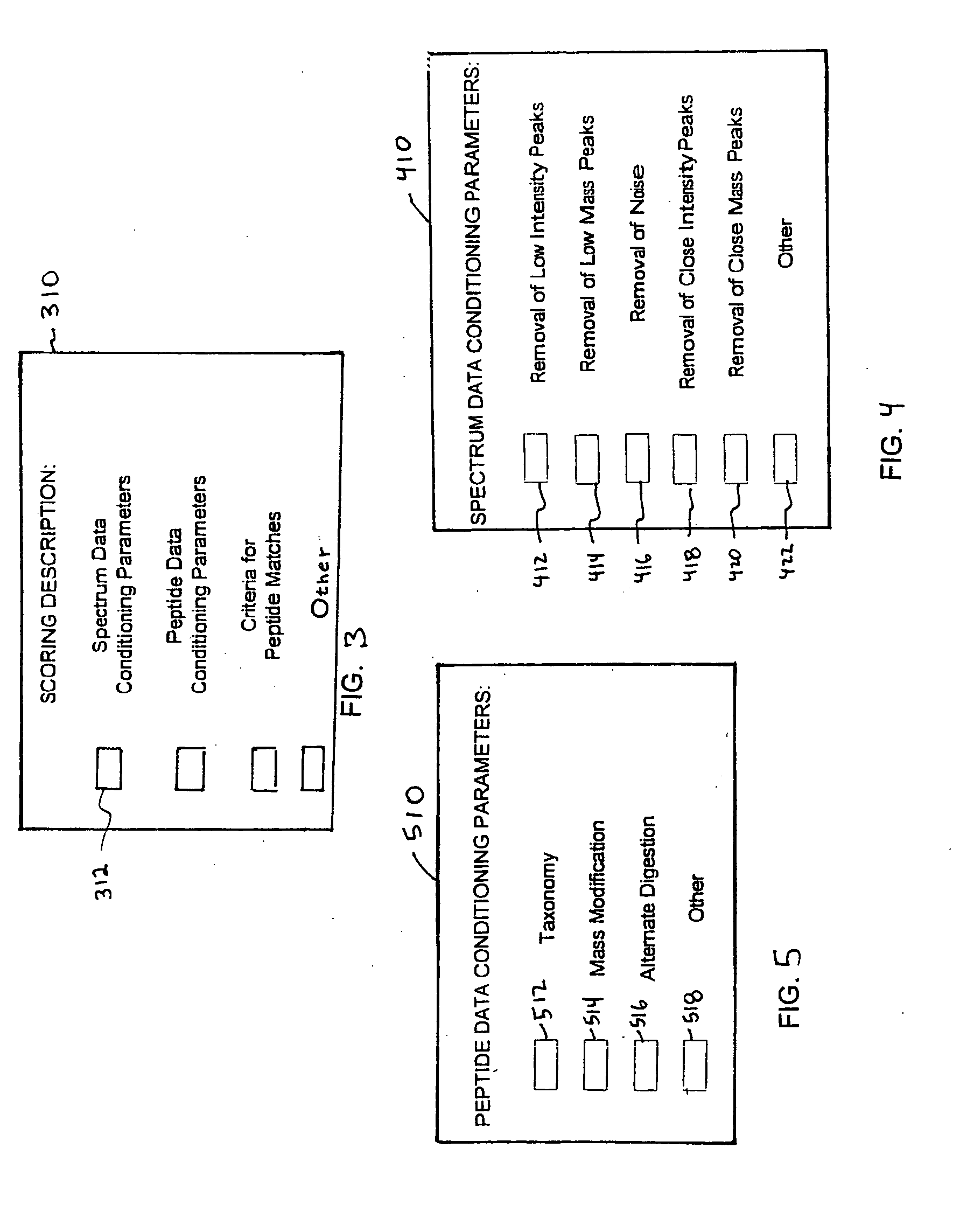
Independent of scoring algorithm for matching or correlating mass spectrometer outputs to peptides in database(s), methods for identifying when a scoring algorithm has achieved a successful correlation include identifying criteria indicative of the successful correlation, conducting a plurality of scoring algorithm runs or analyses, and making an in silico determination as to whether the criteria is met. A first analysis occurs with initial parameters while subsequent analyses occur with modified parameters and / or other scoring algorithms. Parameters include spectrum data conditioning parameters applicable to mass spectrometer outputs and / or peptide data conditioning parameters applicable to peptides or their database. Preferred criteria indicating successful correlation include meeting a threshold algorithm score, obtaining a desired peptide coverage percentage or obtaining an amount of spectrum coverage used in matching. De novo sequencing information may also be used. Computer readable media and computing system environments are some embodiments for performing the invention.
Owner:HANDS ISAAC J
Massively parallel 2-dimensional capillary electrophoresis
ActiveUS8828209B2Ensure adequate heatingInhibit evaporation and contaminationSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesFluorescence
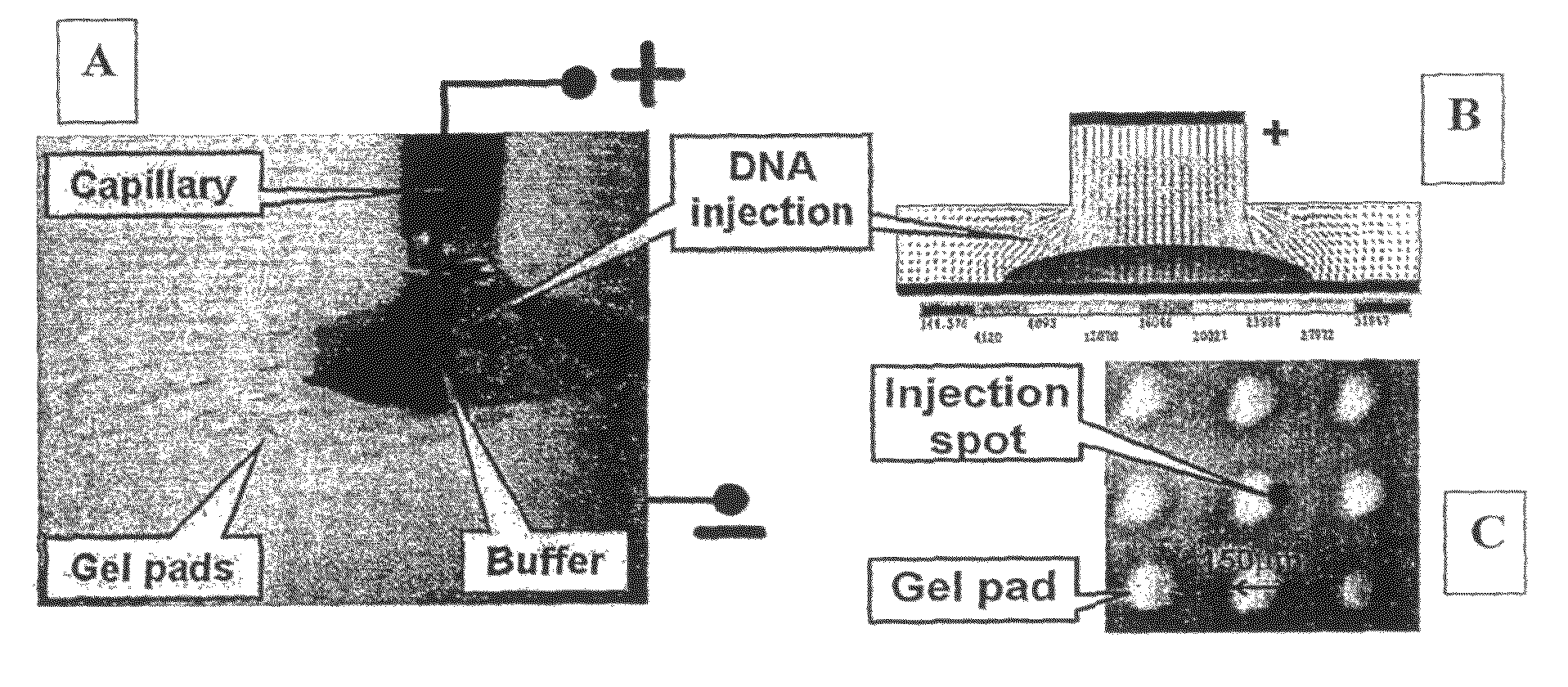
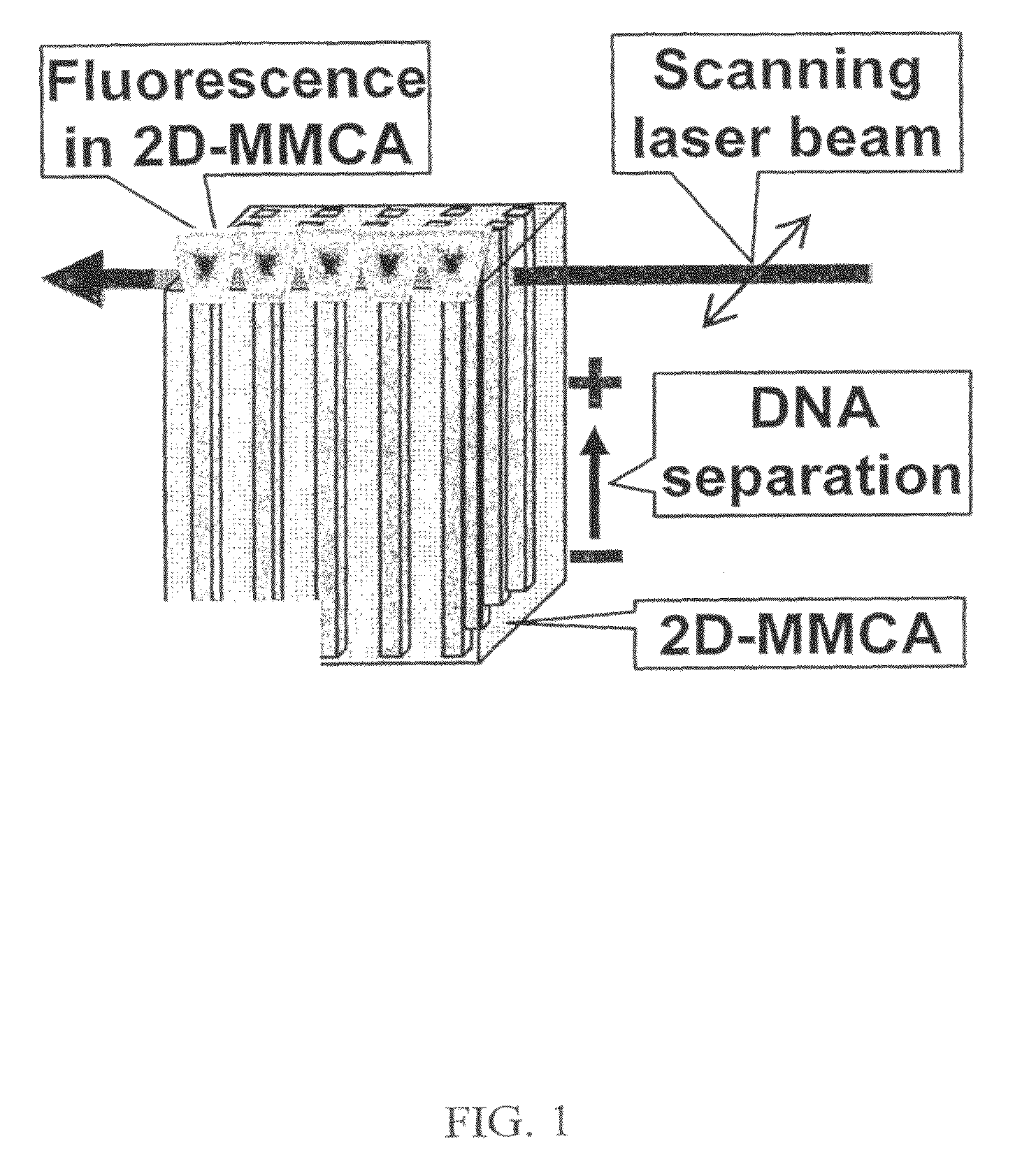
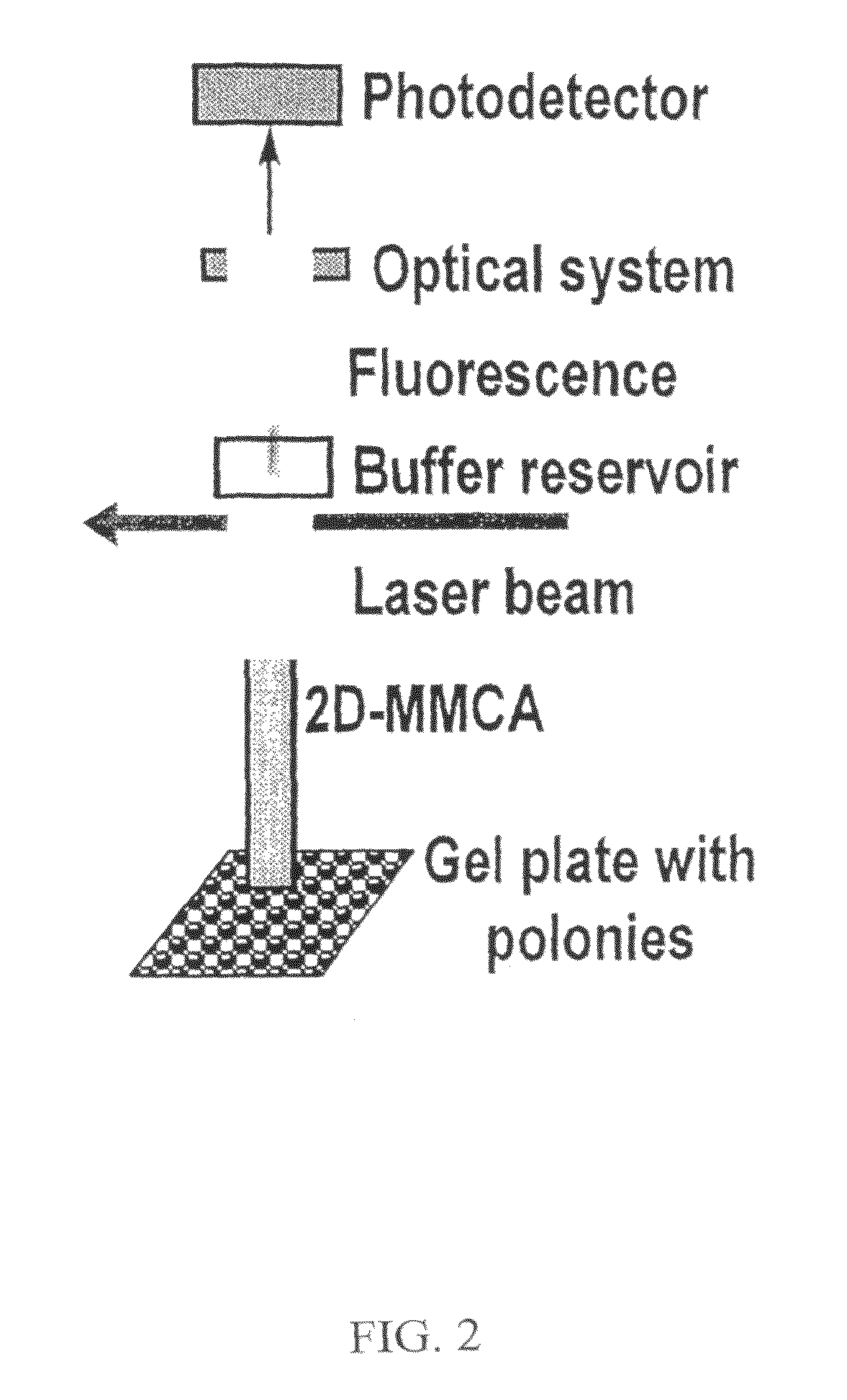
This invention discloses a highly efficient method, system and apparatus for nucleic acid analysis, including sequencing (both automated re-sequencing and de-novo sequencing). The system is capable of sequencing DNA sizes ranging from fragments to mammalian size genomes having mouse draft quality at a much reduced cost. The system comprises a massive parallel capillary electrophoretic separation using two-dimensional monolith multi-capillary arrays (2D-MMCA). Sequence identification can be performed using fluorescent or otherwise labeled dideoxynucleotide-terminated DNA extension product generated by gel matrix-, or beads-, or substrate tethered-, or otherwise immobilized colonies of single template molecules. Cost reduction is a significant advantage over currently known methods because of: (i) using massively parallel sub-nanoliter volume reactions; and (ii) employing 2D-MMCAs that increase the throughput of the CE separation and detection by at least two orders of magnitude compared to the commercial high-throughput DNA machines.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Automatic analysis method and system for sequencing data of whole genome of bacteria
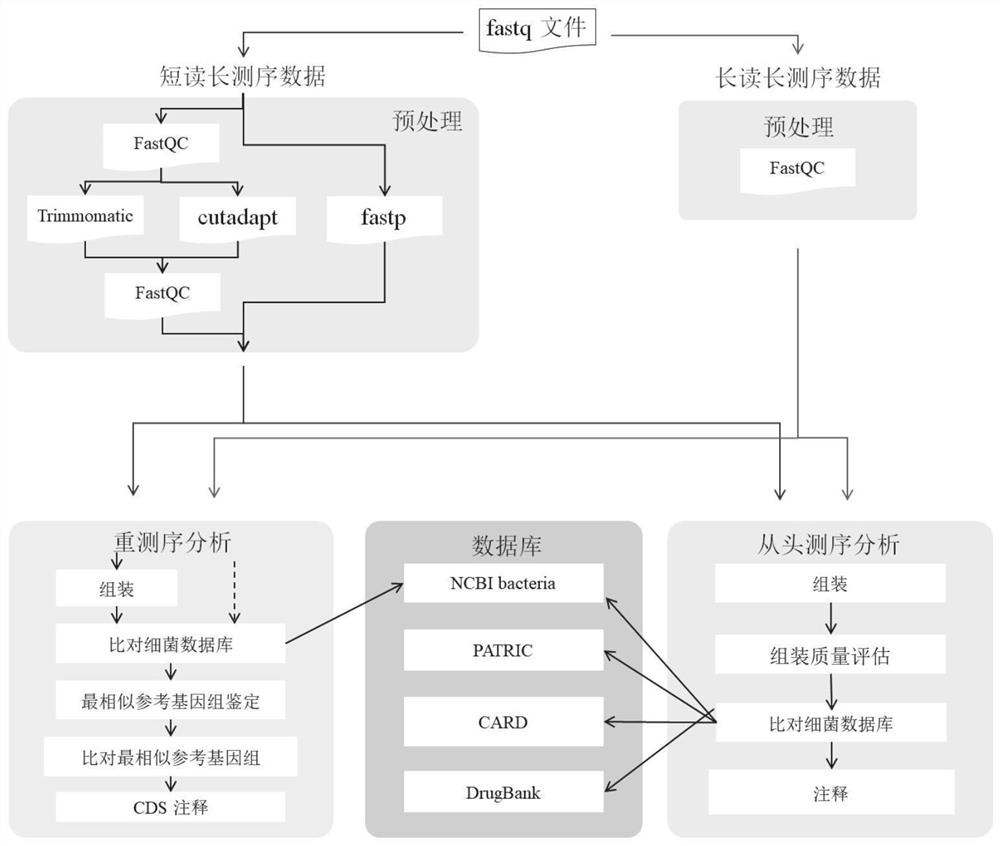
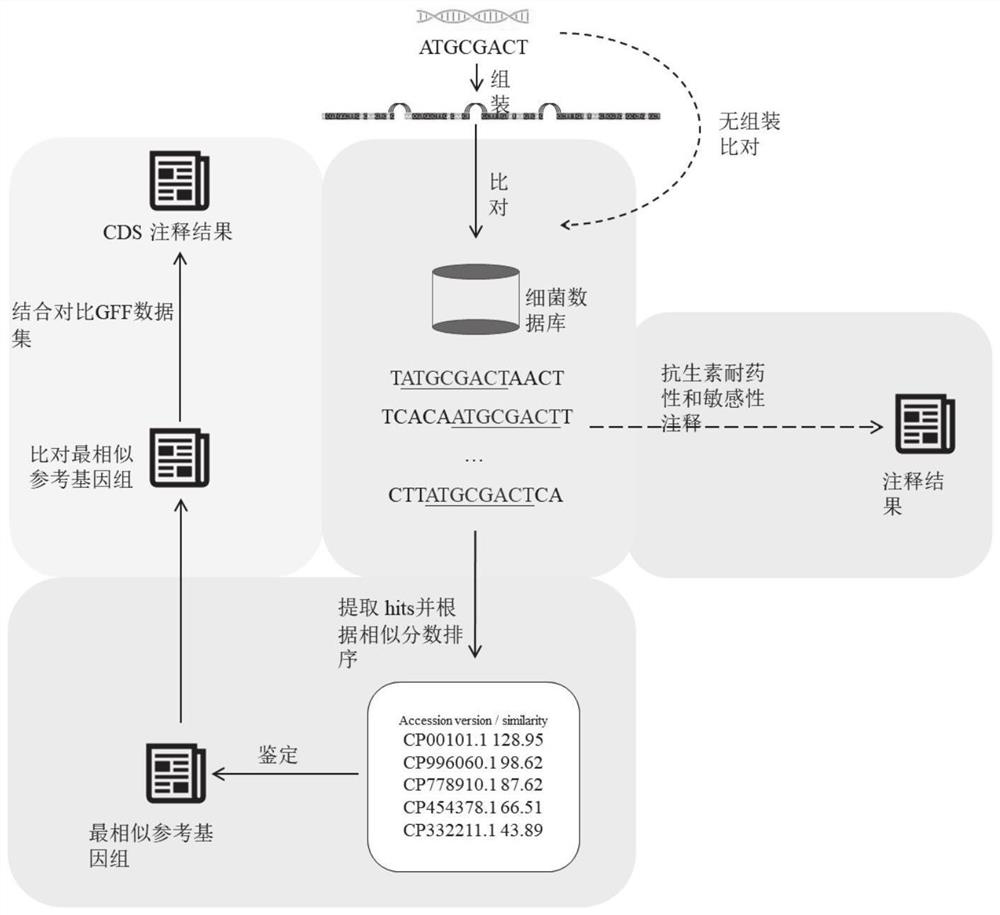
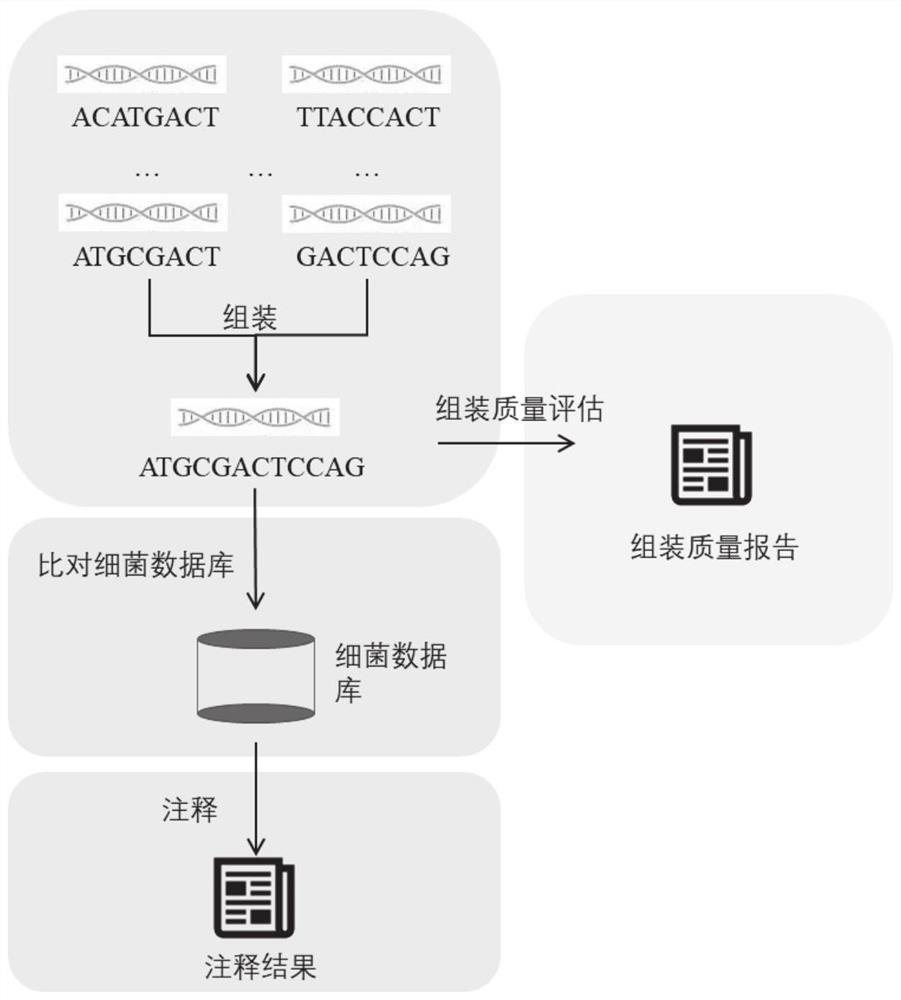
PendingCN112863603AAchieve freedom of choiceImplement custom settingsSequence analysisInstrumentsSequence analysisGenomic sequencing
The invention provides an automatic analysis method for bacterial whole genome sequencing data, which comprises the following steps: acquiring bacterial genome sequencing data, and judging the type of the sequencing data; respectively carrying out corresponding preprocessing according to the type of the sequencing data; performing re-sequencing analysis and de novo sequencing analysis on the preprocessed sequencing data according to an analysis type selected by a user and preset tool software and software parameters; and realizing the identification and annotation of the whole genome of the bacteria. The scheme provides a user-friendly automated analysis method, for researchers and clinicians without professional bioinformatics knowledge, automated bioinformatics analysis steps including sequencing quality control, re-sequencing and de novo assembly, similar bacterial reference genome identification, bacterial genome annotation, and at the same time, researchers and clinicians without professional bioinformatics knowledge; meanwhile, customized bioinformatics analysis can be carried out according to short-read-length and long-read-length sequencing data generated by different platforms, and an accurate analysis result is obtained.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Amino acid sequence analyzing method and system
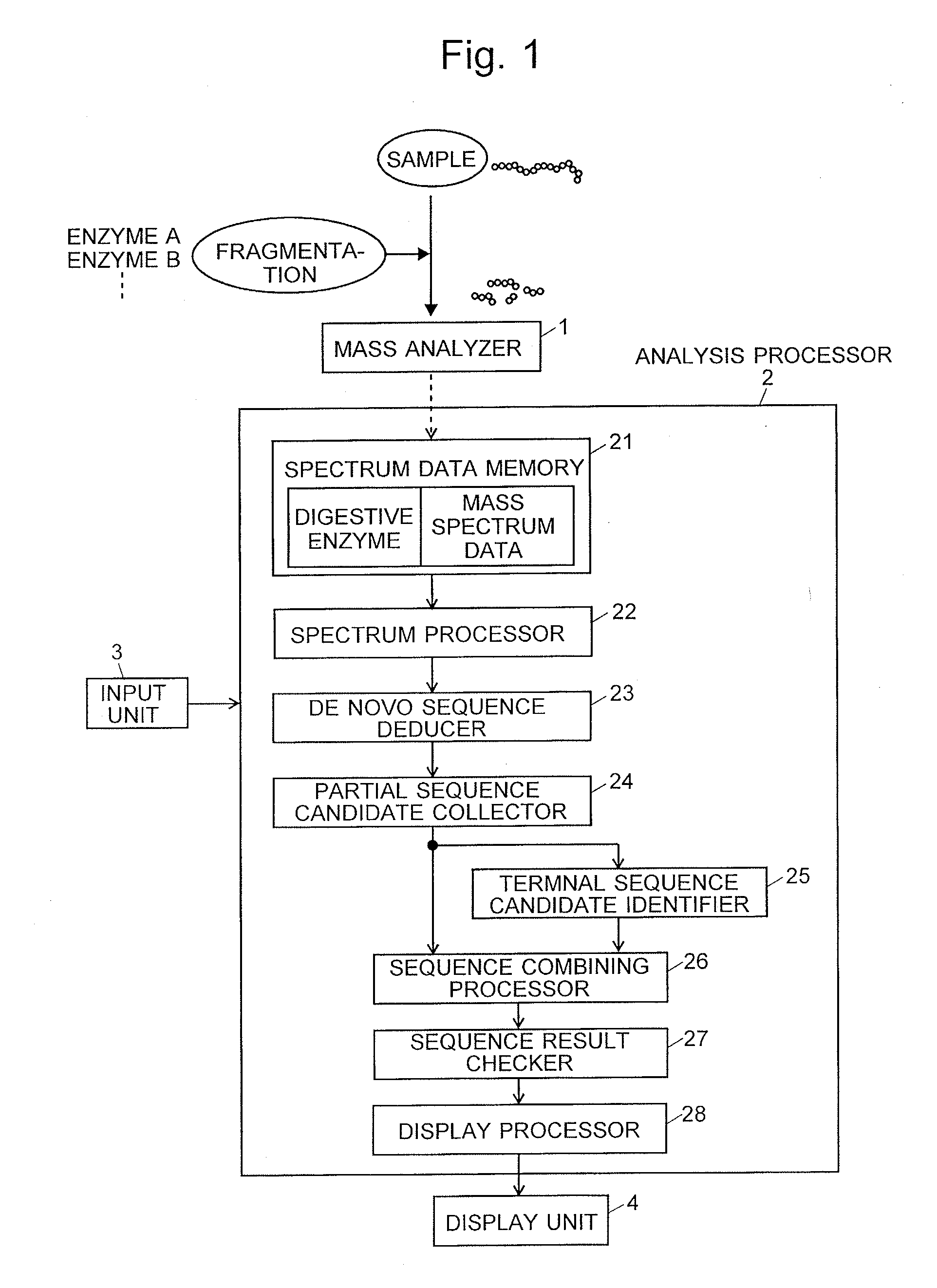
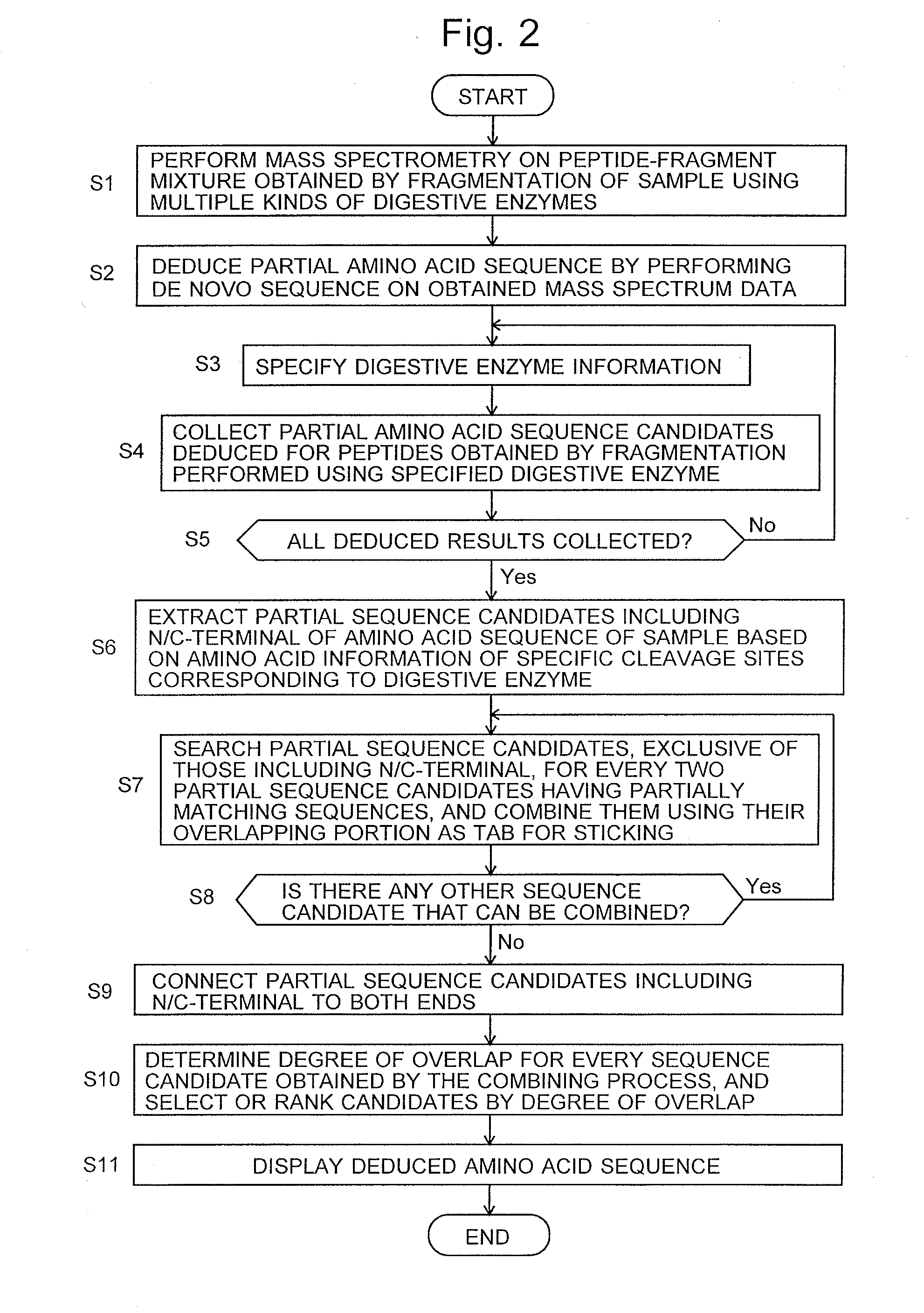
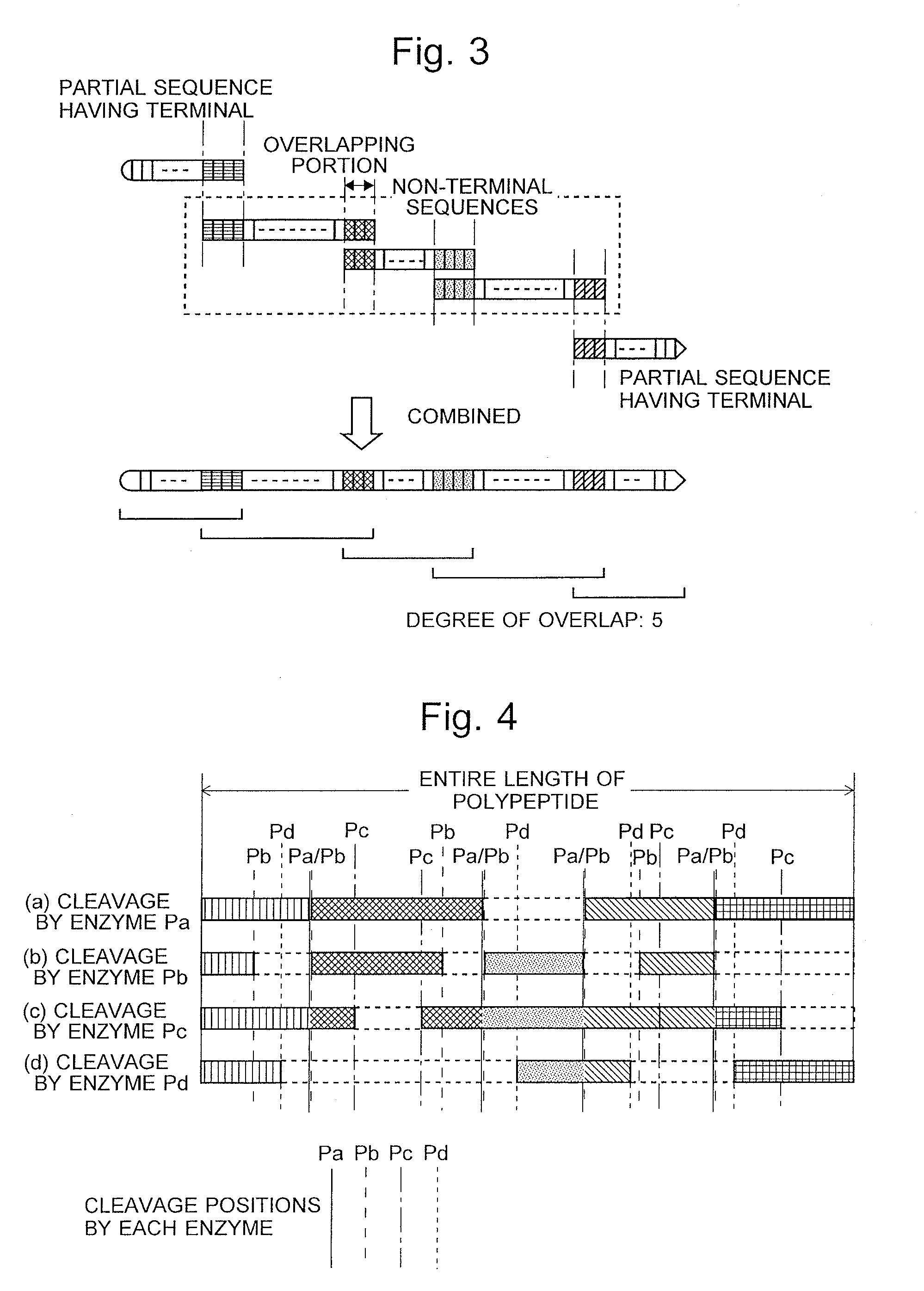
InactiveUS20160275237A1Deduction accuracy of the amino acid sequence of a protein or peptide can be improvedImprove accuracyParticle separator tubesSequence analysisRepetitive taskMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Peptide-fragment mixtures obtained by fragmenting a sample with each of multiple enzymes which cause cleavage at different sites are subjected to mass spectrometry. De novo sequencing is performed on the obtained results to deduce partial sequence candidates for various kinds of fragments (S1 and S2). Using the fact that a specific amino acid residue should appear at the cleavage site depending on the enzyme, a partial sequence candidate including the terminal of the original amino acid sequence is extracted from a number of candidates (S6). The task of searching for and combining non-terminal partial sequence candidates including an overlapping portion is repeated (S7 and S8). The sequence candidates including the terminal are subsequently connected to the ends of the sequence obtained through the repetitive task (S9). The eventually obtained amino acid sequence is highly likely to be the correct solution (S10 and S11).
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
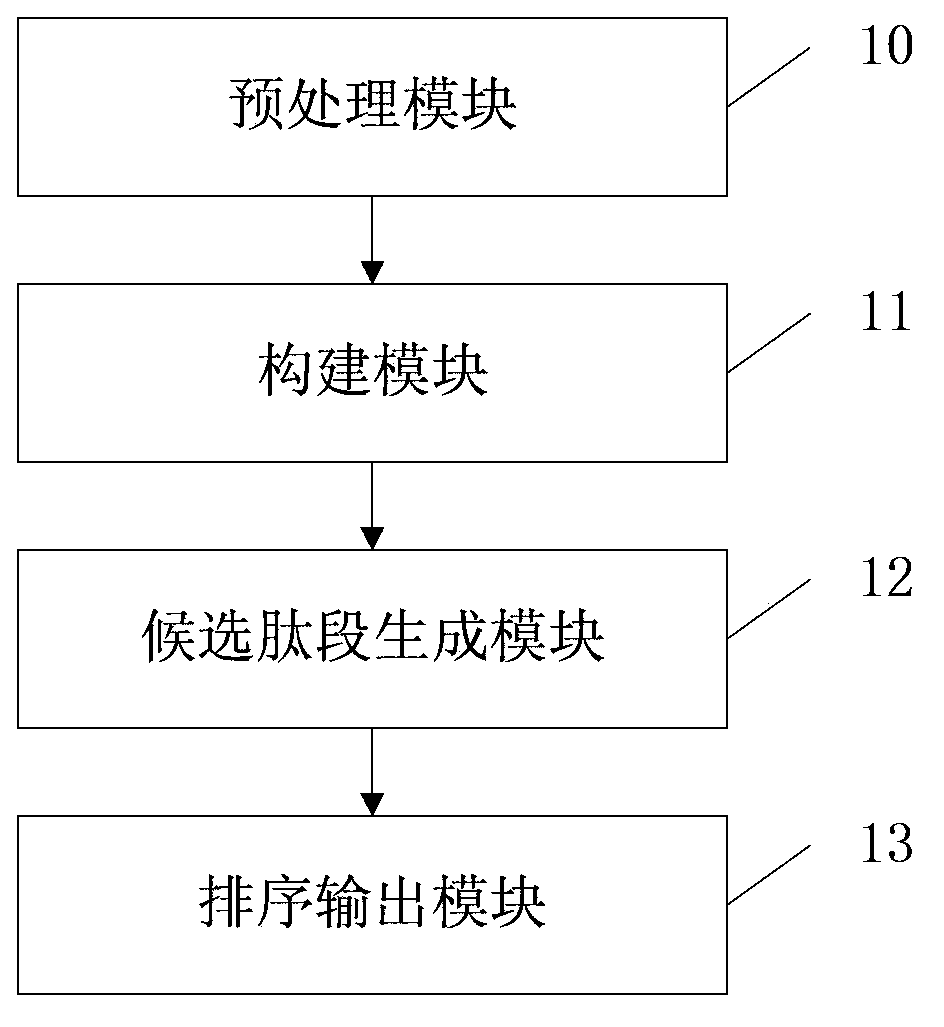
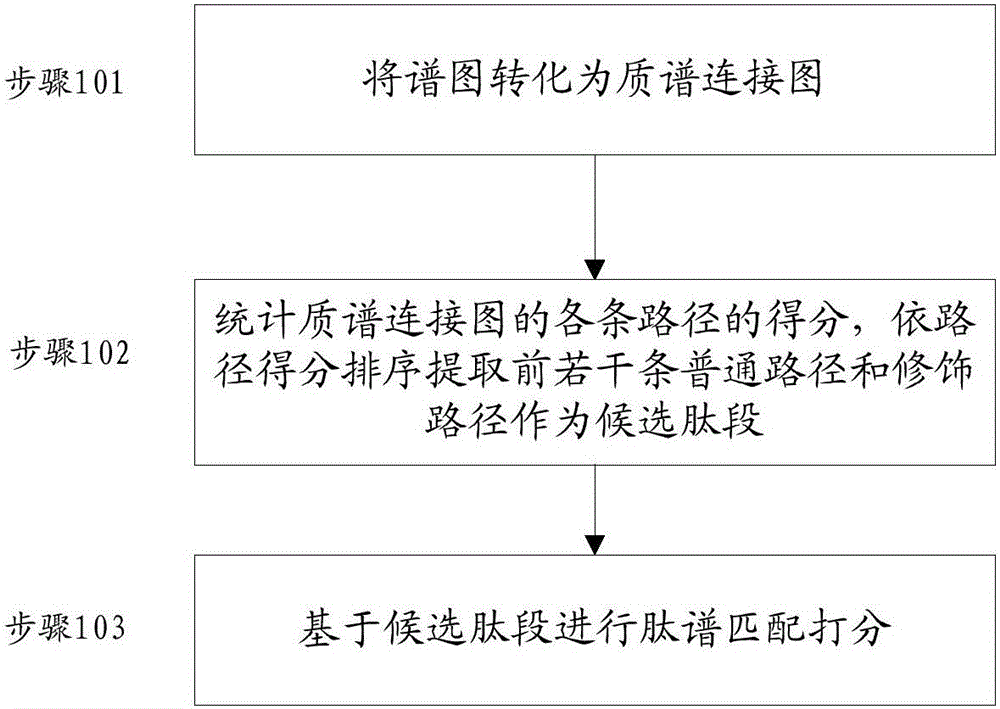
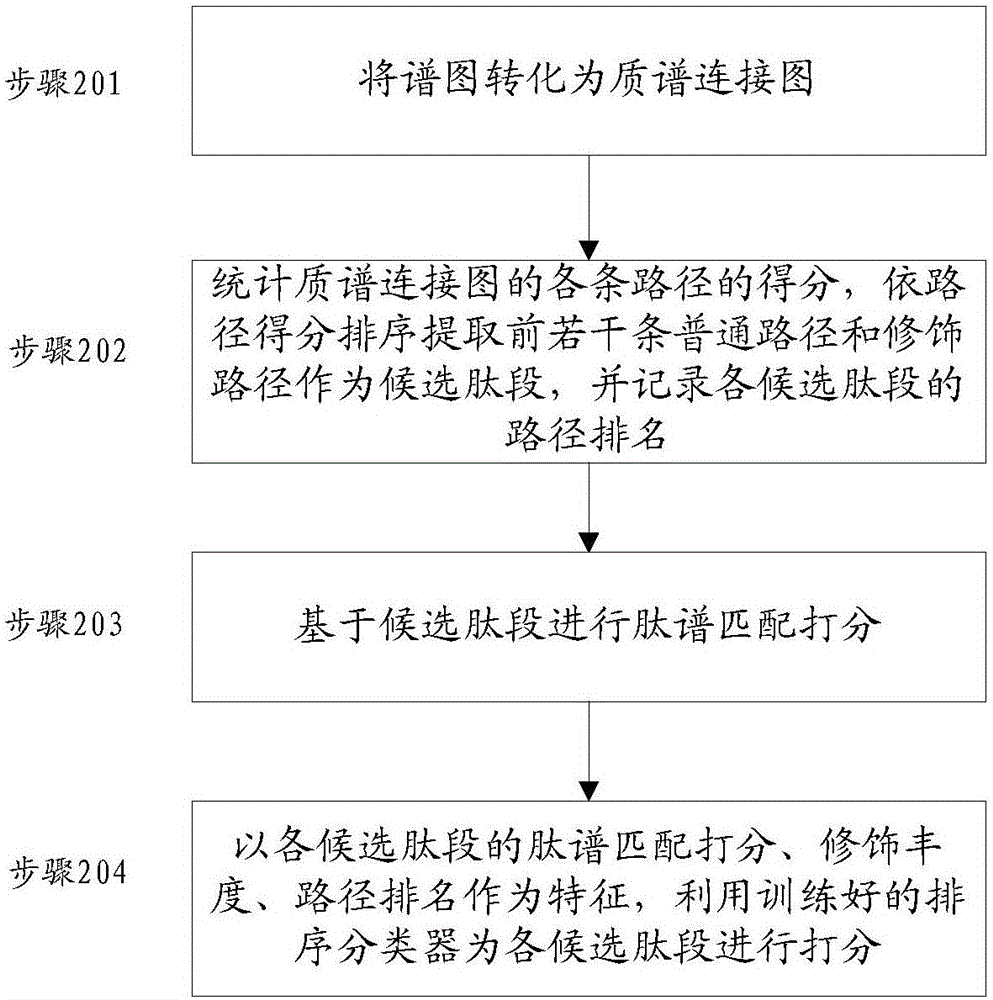
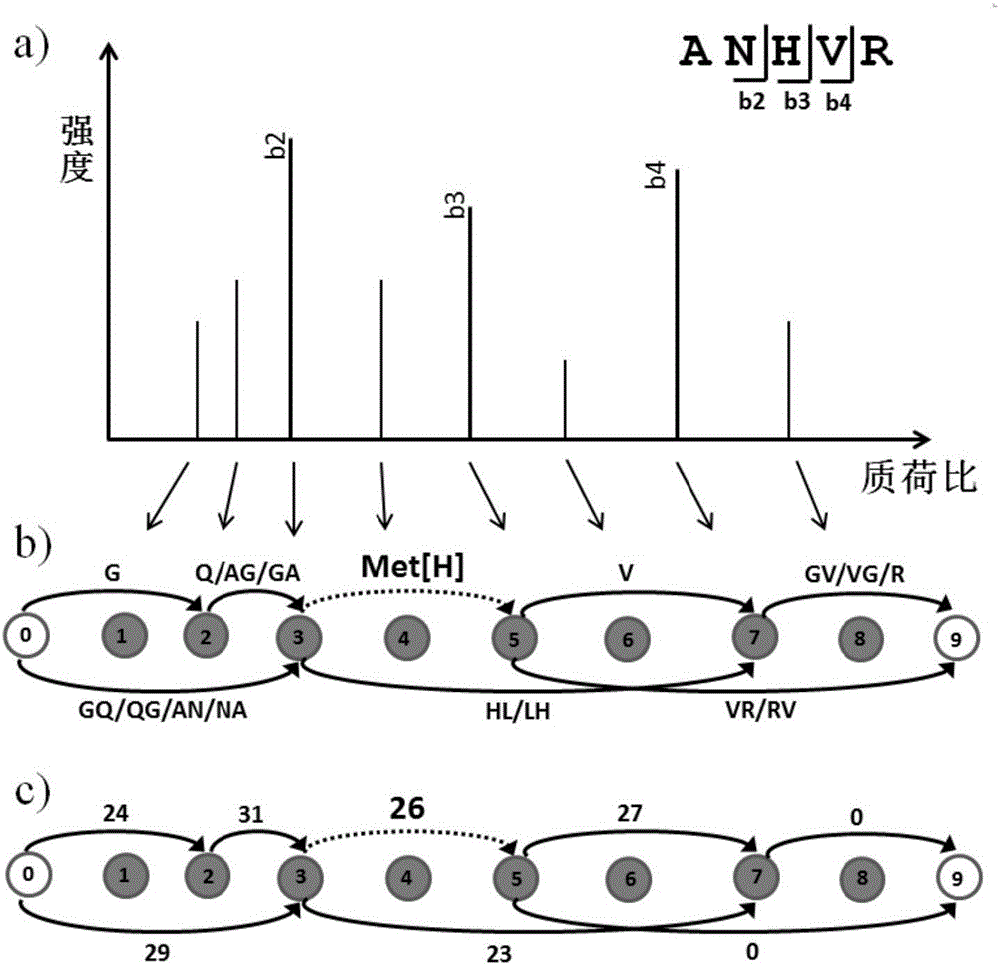
Denovo sequencing method and device
ActiveCN106770605ASpeed effectImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGranularityPeptide fragment
The invention provides a denovo sequencing method. The method comprises the following steps: transforming a to-be-analyzed spectrogram into a mass spectrum connection diagram, counting the score of each path in the mass spectrum connection diagram, extracting a plurality of front normal paths with high path score and a modification path as a candidate peptide fragment, wherein the normal path is the path only formed by normal sides, and the modification path is the path formed by the normal side and a modification side, and only contains one modification side; performing peptide spectrum matching scoring on each candidate peptide fragments, and taking the candidate peptide fragment with the highest peptide spectrum matching scoring as the peptide fragment corresponding to the spectrogram. By use of the method disclosed by the invention, the discovery of thousands of accident modificaitons can be supported without greatly influencing the peptide fragment identification speed; furthermore, the similar peptide fragment sequences can be distinguished in finer granularity, and the accuracy rate of the peptide identification is improved.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
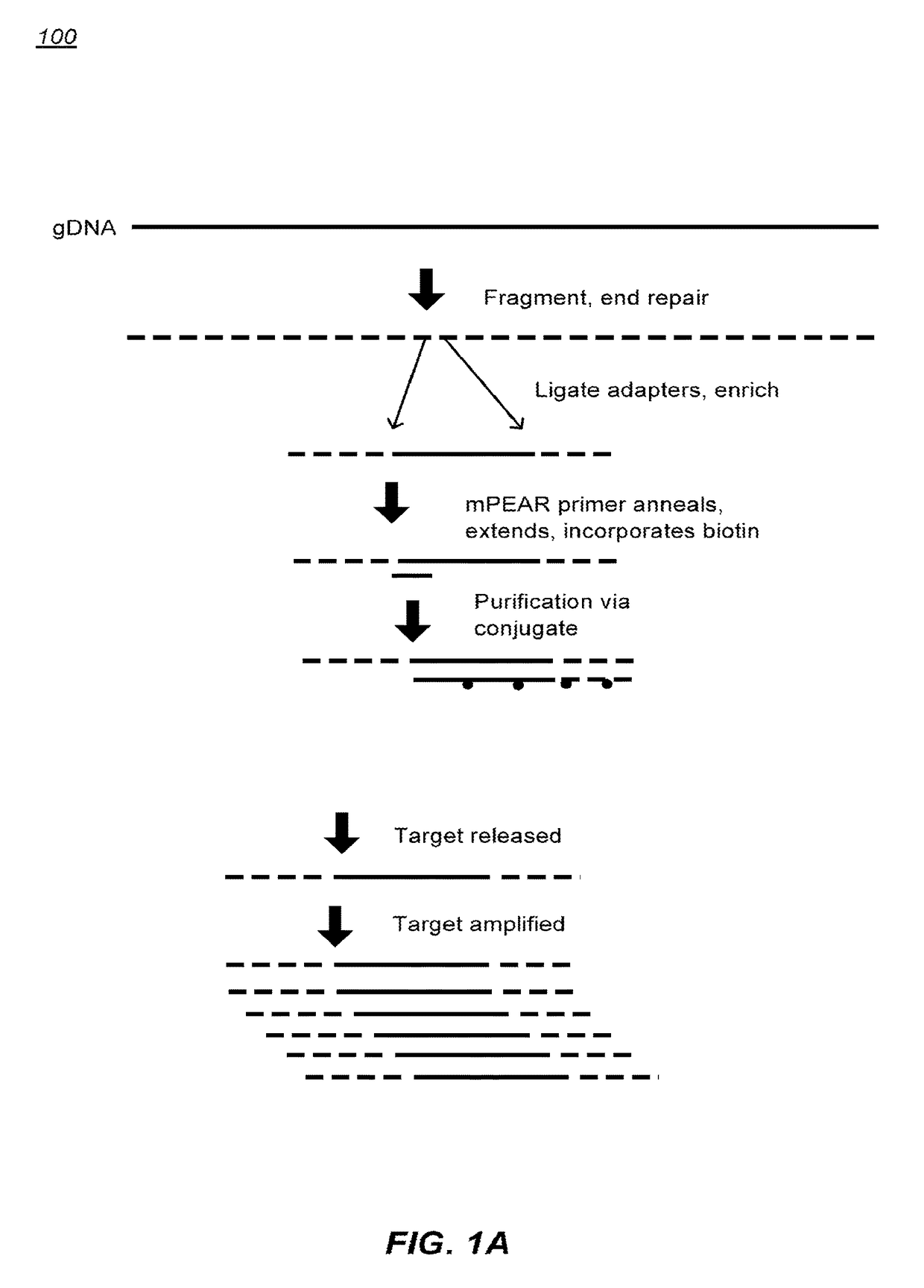
Methods for genome assembly, haplotype phasing, and target independent nucleic acid detection
ActiveCN108368542AMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisGenomicsNucleic acid detection
The disclosure provides methods to assemble genomes of eukaryotic or prokaryotic organisms. The disclosure provides methods for haplotype phasing and meta-genomics assemblies. The disclosure providesa streamlined method for accomplishing these tasks, such that intermediates need not be labeled by an affinity label to facilitate binding to a solid surface. The disclosure also provides methods andcompositions for the de novo generation of scaffold information, linkage information, and genome information for unknown organisms in heterogeneous metagenomic samples or samples obtained from multiple individuals. Practice of the methods can allow de novo sequencing of entire genomes of uncultured or unidentified organisms in heterogeneous samples, or the determination of linkage information fornucleic acid molecules in samples comprising nucleic acids obtained from multiple individuals.
Owner:DOVETAIL GENOMICS
Thermally-tolerant pectin methylesterase
InactiveUS20090130722A1Improve processing and appearanceLow viscositySugar derivativesBacteriaMolecular communicationPlant cell
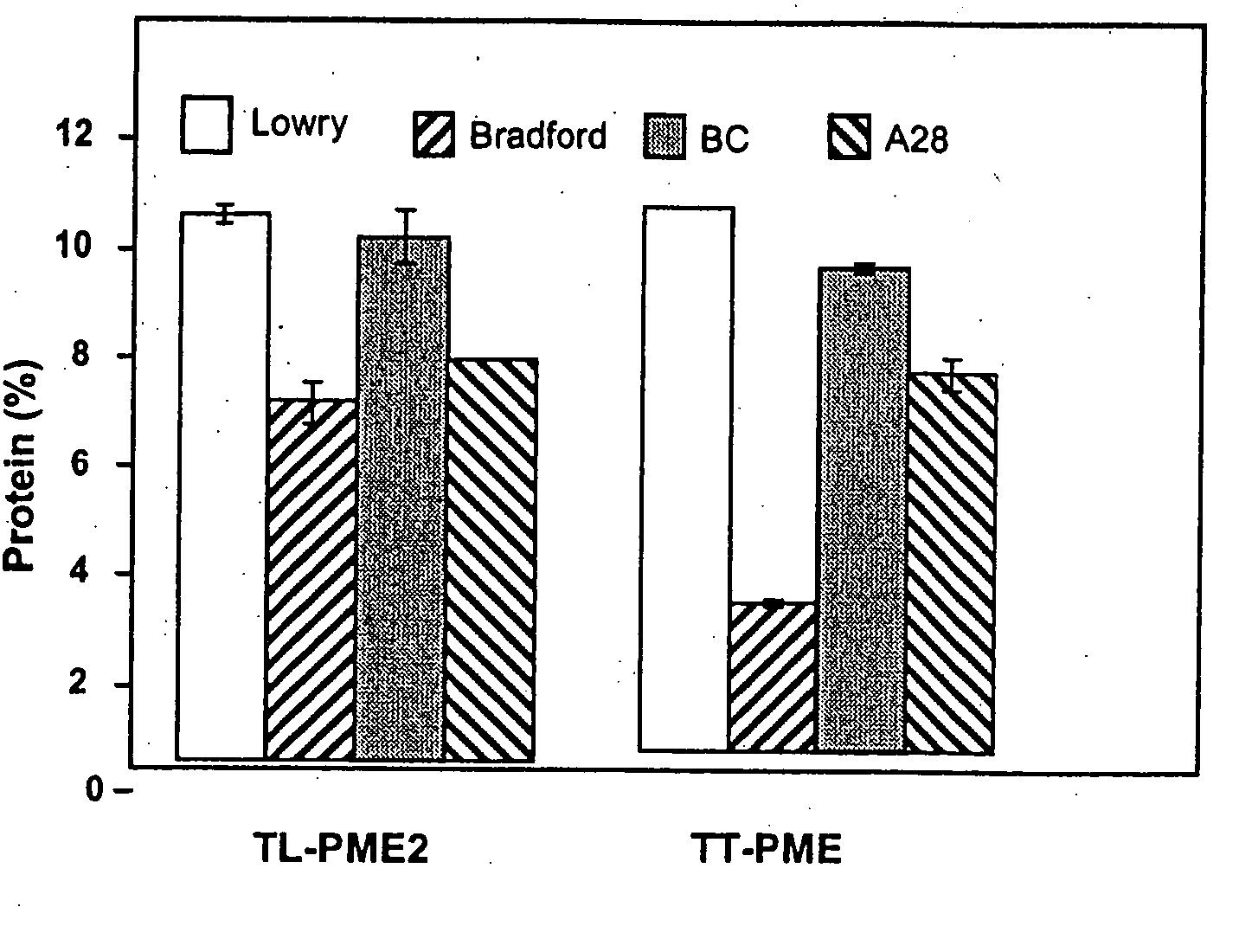
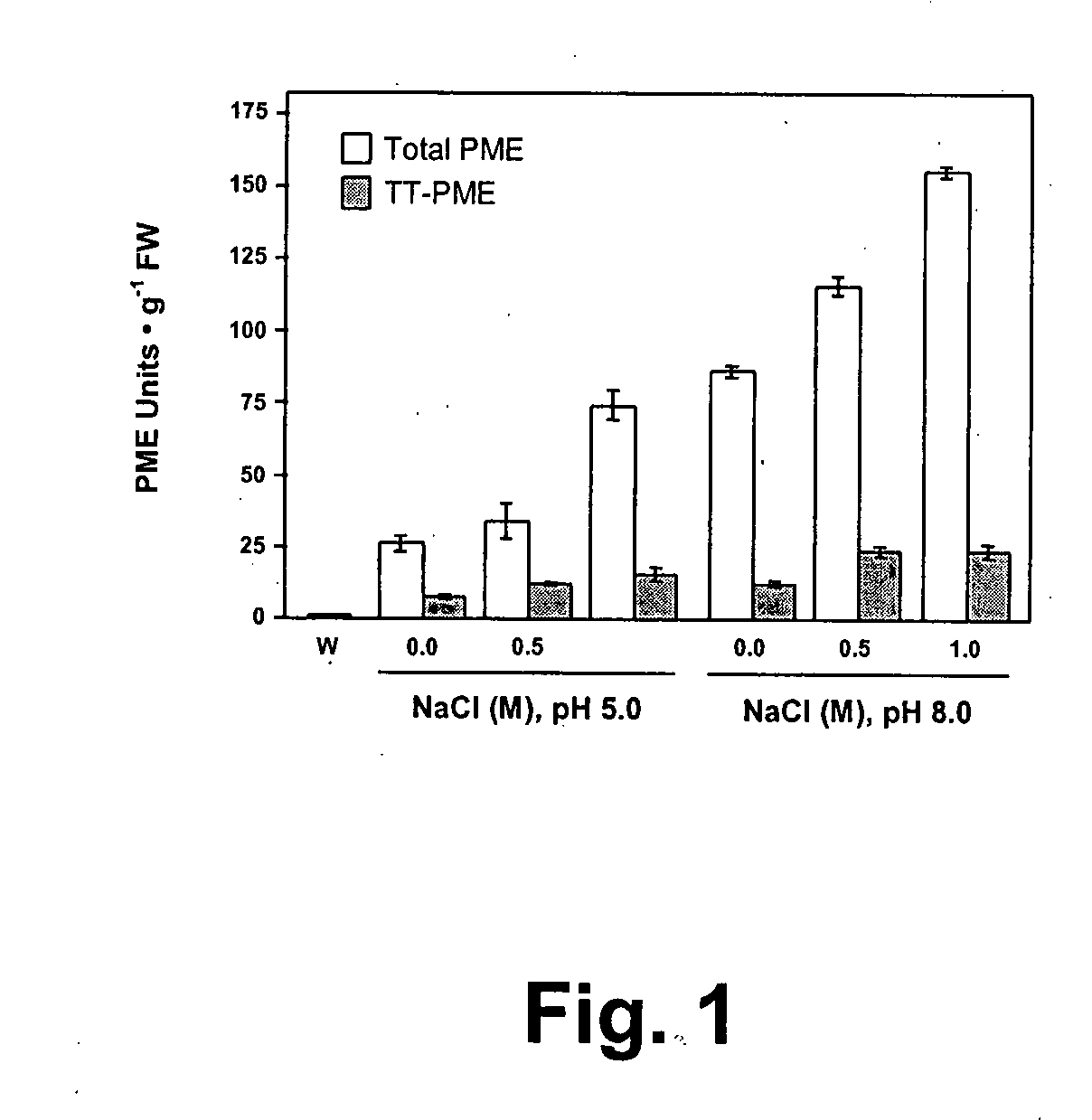
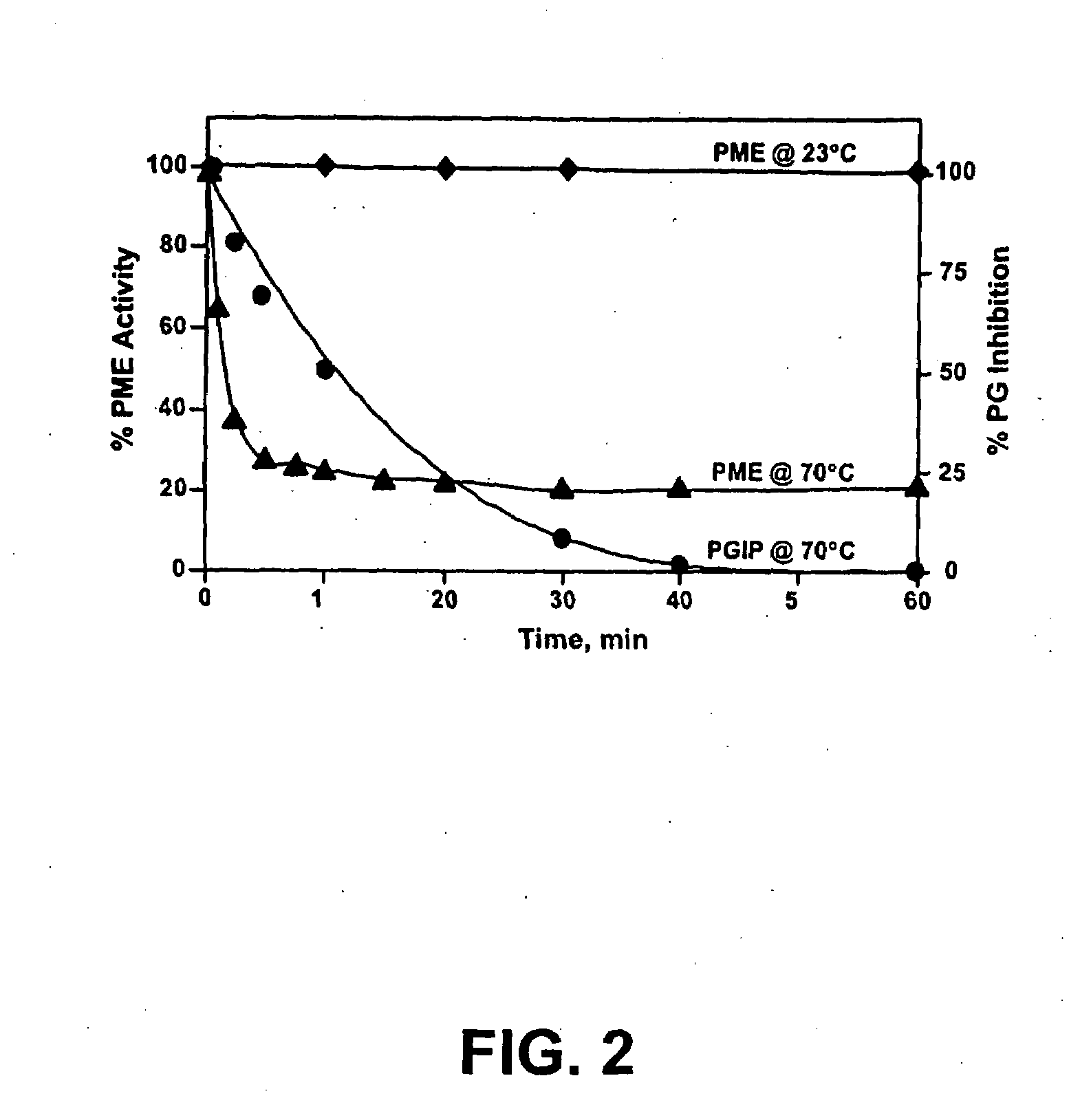
Enzymes accumulated in plant cell walls serve diverse physiological functions including metabolism, polysaccharide structure modification, and molecular communication in interactions with other organisms. Pectin methylesterases are economically important enzymes for their impact on quality and processing properties of fruit and vegetable food products. We have now purified TT-PME to homogeneity from sweet orange finisher pulp and determined the complete corresponding nucleic acid sequence. Purified TT-PME was observed by SDS-PAGE as two doublet bands with molecular masses of approximately 46,000 Da and 56,000 Da. Direct Edman sequencing from these proteins showed a common N-terminal peptide. De novo sequencing of eight TT-PME tryptic peptides determined by MALDI-TOF / TOF mass spectrometry provided additional internal sequences. TT-PME did not correspond to any previously reported Citrus spp. PME sequence. Our results show Citrus TT-PME is a distinctive new isoform with phylogenetic relationship closer to PME isoforms in other species rather than to previously described Citrus PME genes.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
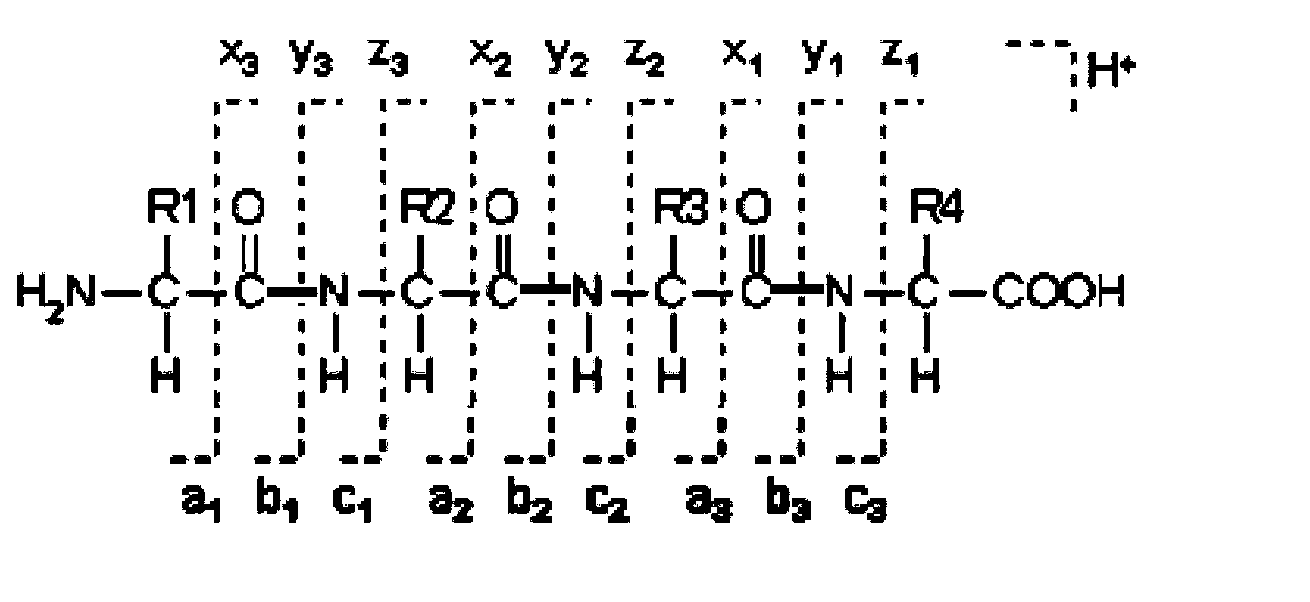
Methods for de novo protein sequencing
ActiveUS11047863B2Serum immunoglobulinsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPeptide ionsArginine
A method for determining an amino acid sequence of a polypeptide, including comprising: contacting a first sample containing the polypeptide with a first protease(e.g., Trypsin) to produce a first set of digested peptide fragments; fragmenting the first set of digested peptide fragments to produce a first set of fragmented peptide ions; determining masses of the first set of fragmented peptide ions; contacting a second sample containing the polypeptide with a second protease (e.g., Tryp-N); fragmenting the second set of digested peptide fragments to produce a second set of fragmented peptide ions; selecting pairs of peptide ions from the first and the second set of fragmented peptide ions that differ in mass by a mass of an arginine amino acid residue or a lysine amino acid residue; assigning an ion type (either N-terminal peptide ion or C-terminal peptide ion) to the selected pairs of the peptide ions from two sets of fragmented peptide ions;selecting a mass ladder of the same-type peptide ions in either set of fragmented peptide ions with incremental mass by the mass of amino acid residue(s), and assembling the identified amino acid residues from the mass ladder to determine the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide of interest.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Development method and application of siniperca chuatsi sex specific marker
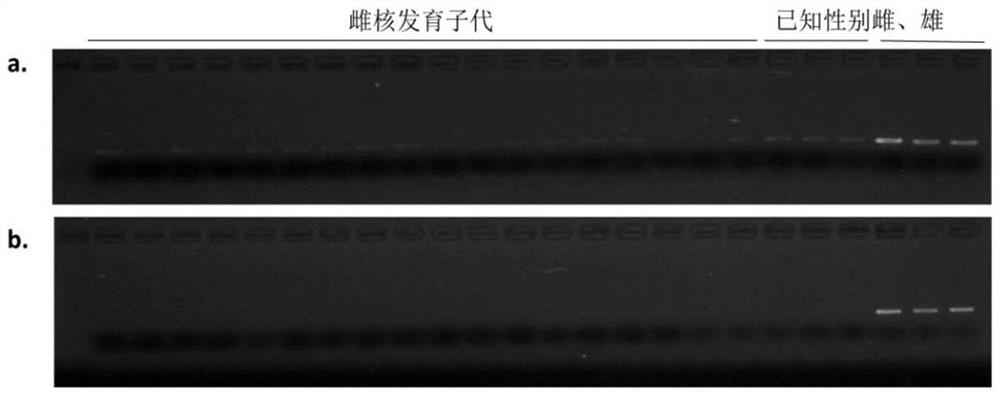
PendingCN112359104ASimple and fast operationSave time and costMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsMolecular identificationMedicine
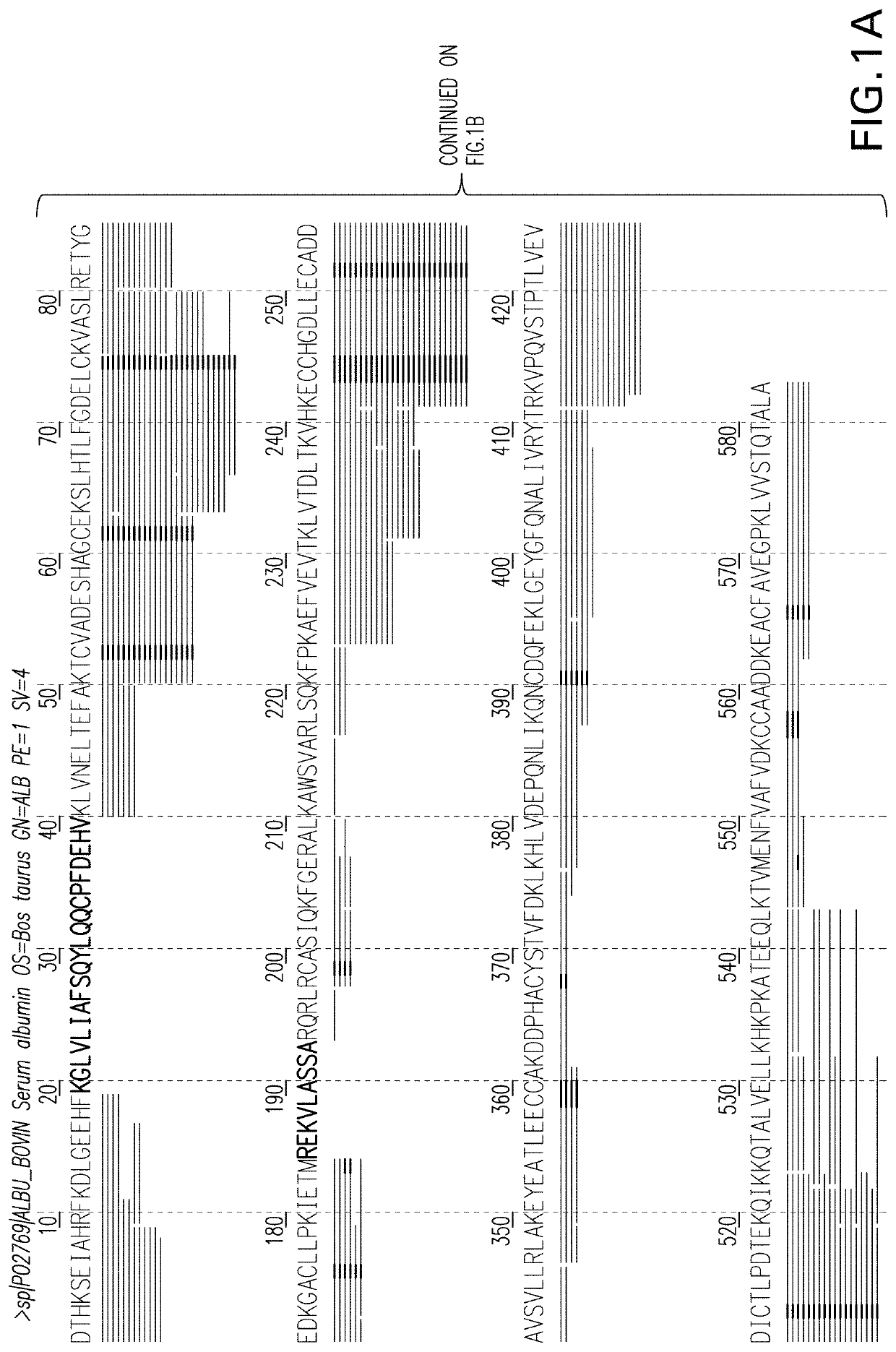
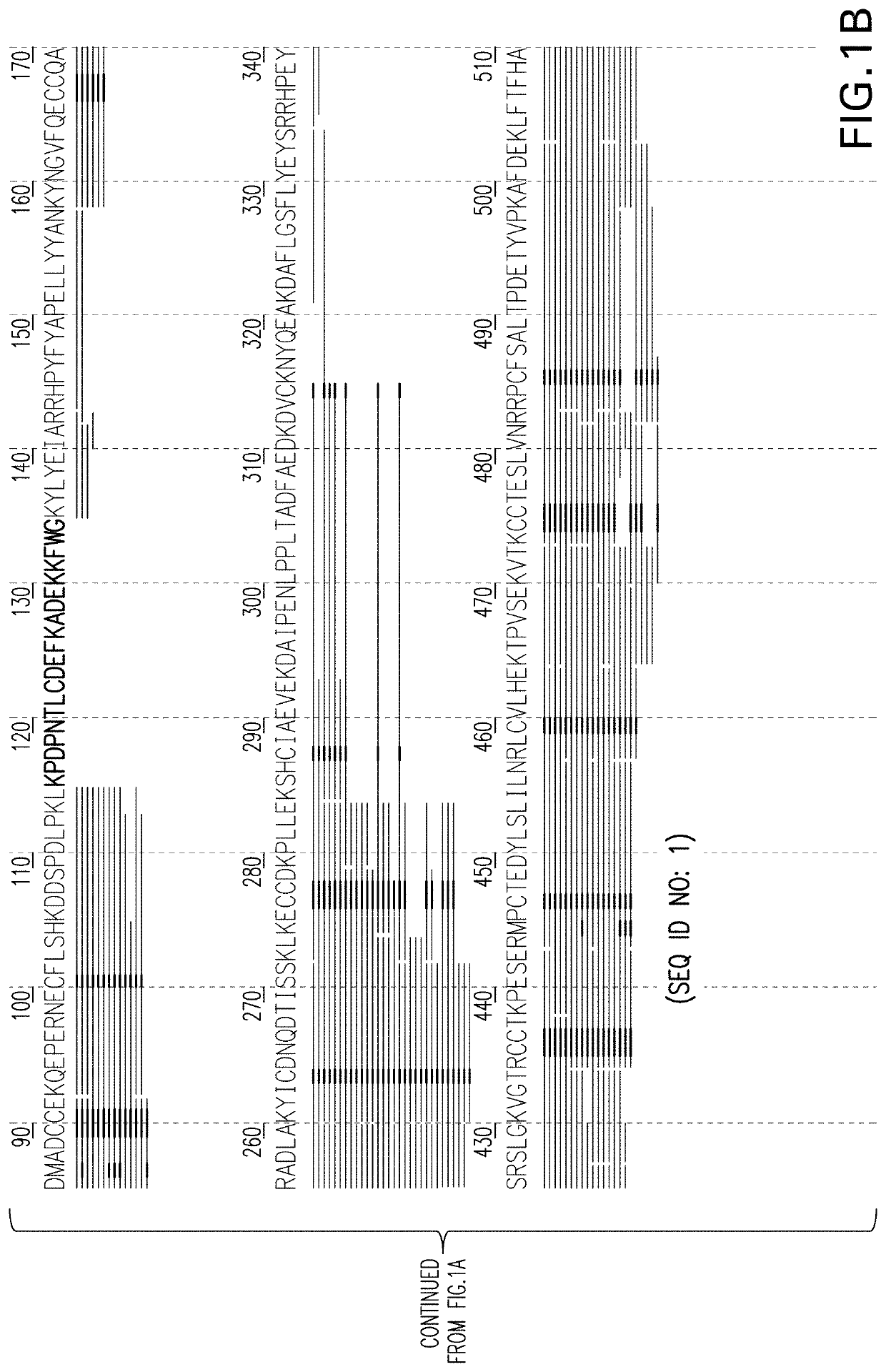
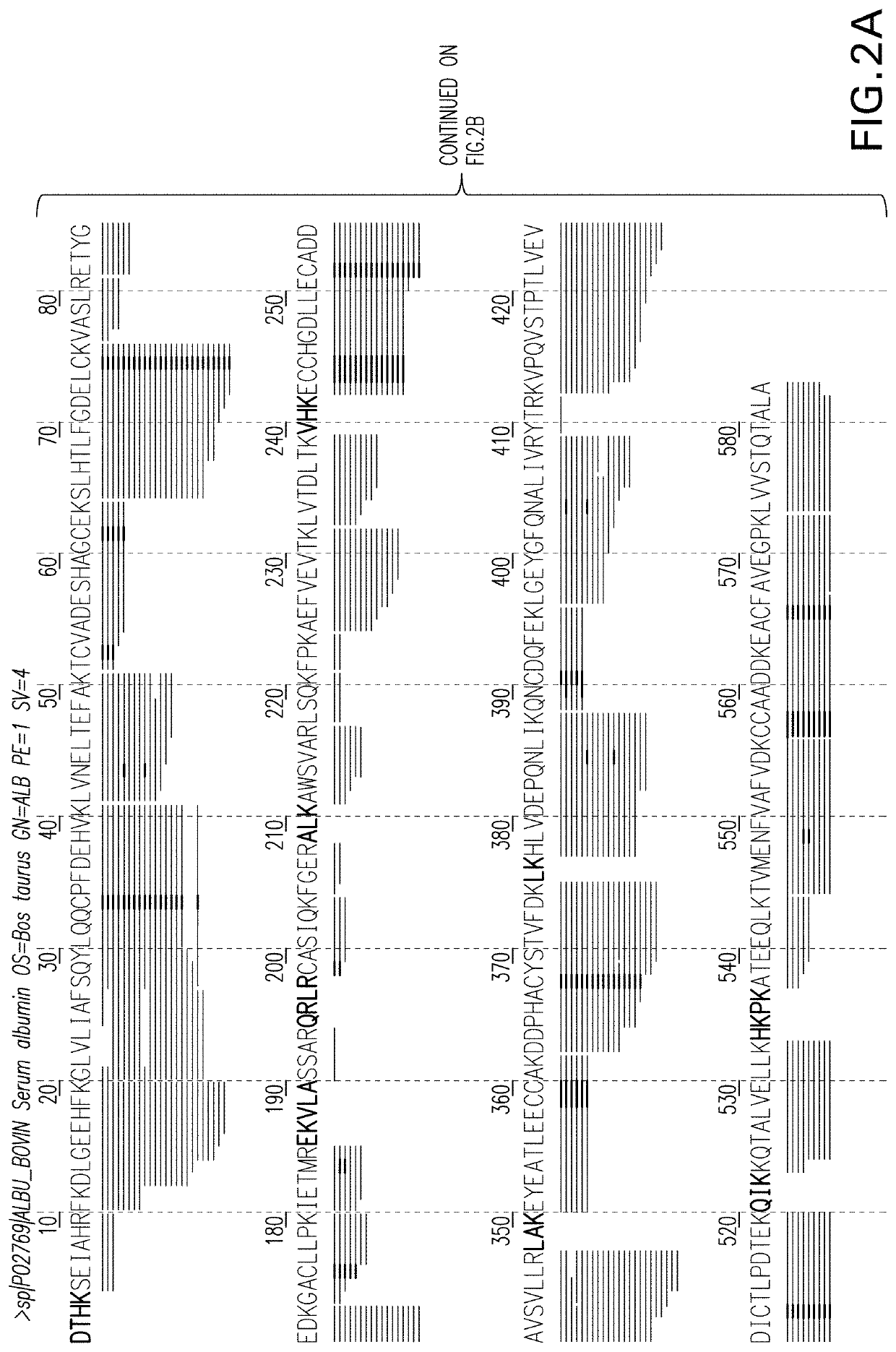
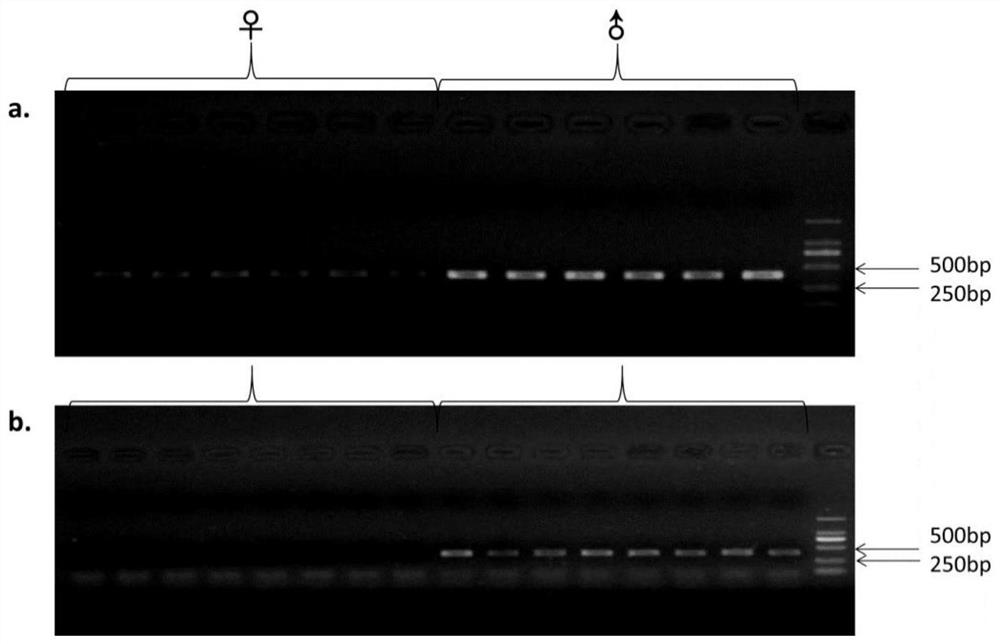
The invention provides a development method and the application of a siniperca chuatsi sex specific marker. The development method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining male and female siniperca chuatsi specific short sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 by utilizing a high-throughput sequencing method based on a 2b RAD technology; (2) obtaining a male siniperca chuatsi whole genome sequence by using a high-throughput de novo sequencing method; and (3) searching the male siniperca chuatsi specific short sequence obtained in the step (1) in the male siniperca chuatsi whole genome sequence obtained in the step (2) to obtain a longer male siniperca chuatsi specific sequence, namely SEQ ID NO.2, and performing later primer design to be applied to genetic sex identification of siniperca chuatsi. The method has the advantages of quickness, directness, simplicity, convenience and the like, and sex molecular identification can be performed on a large number of samples.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
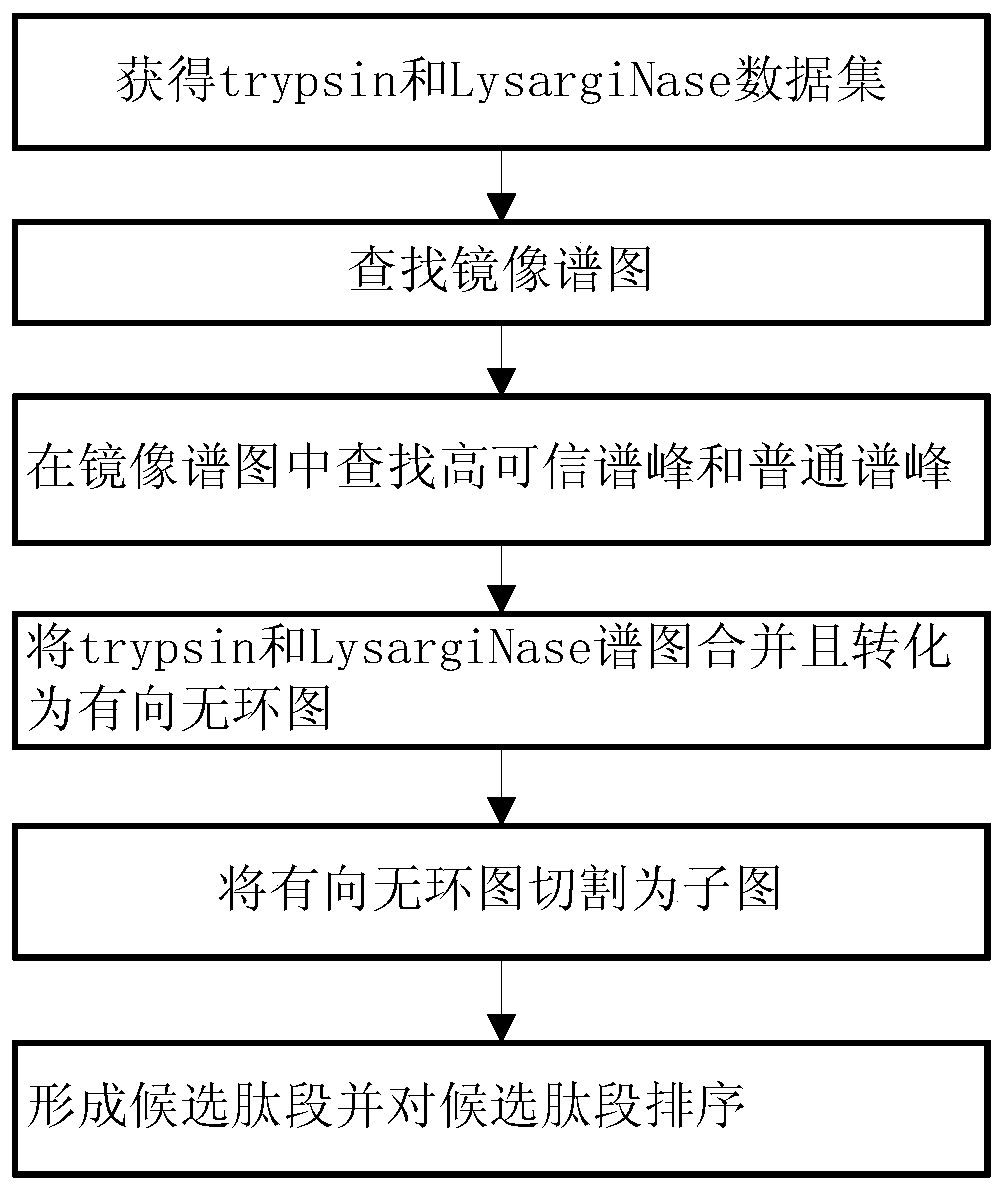
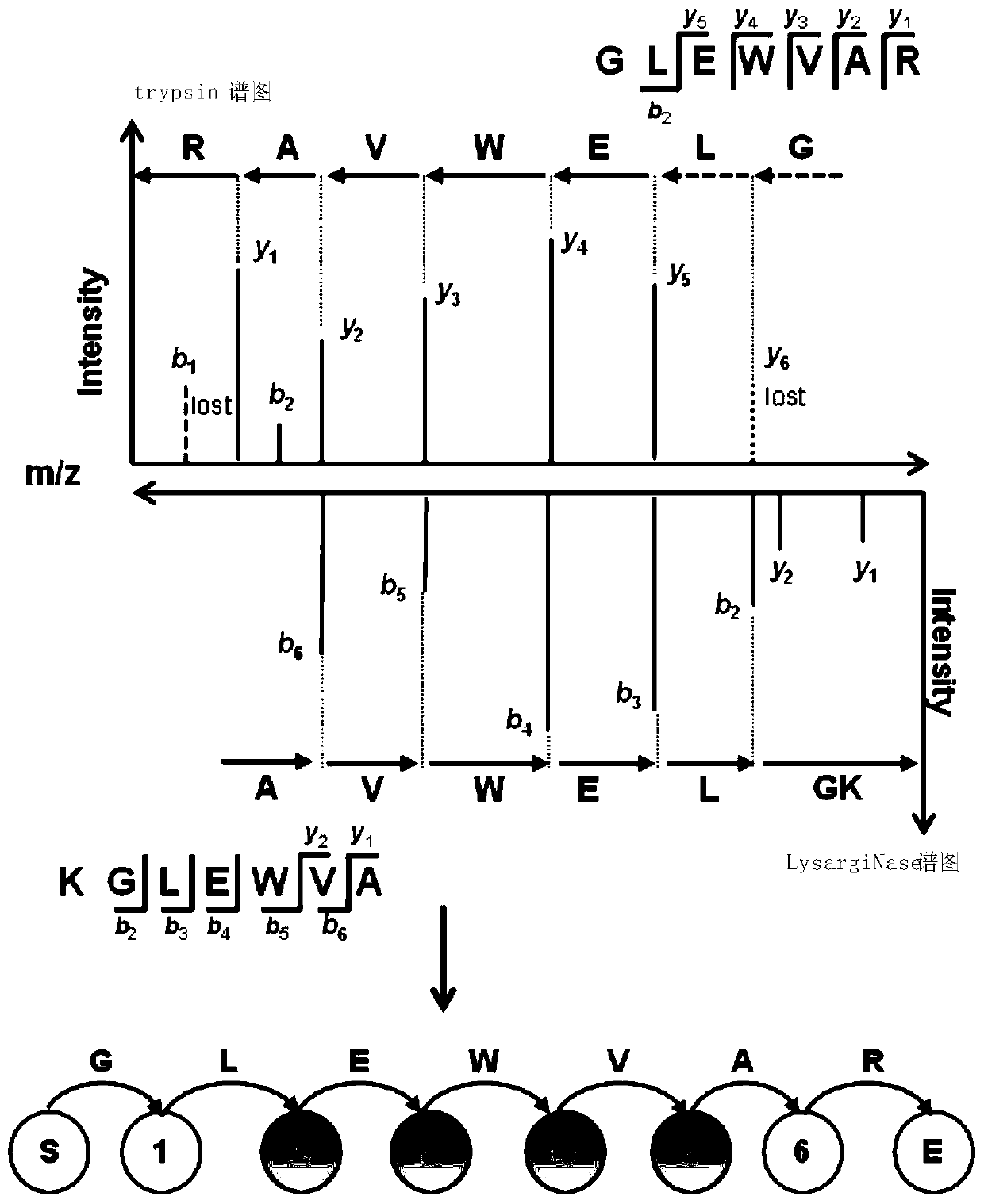
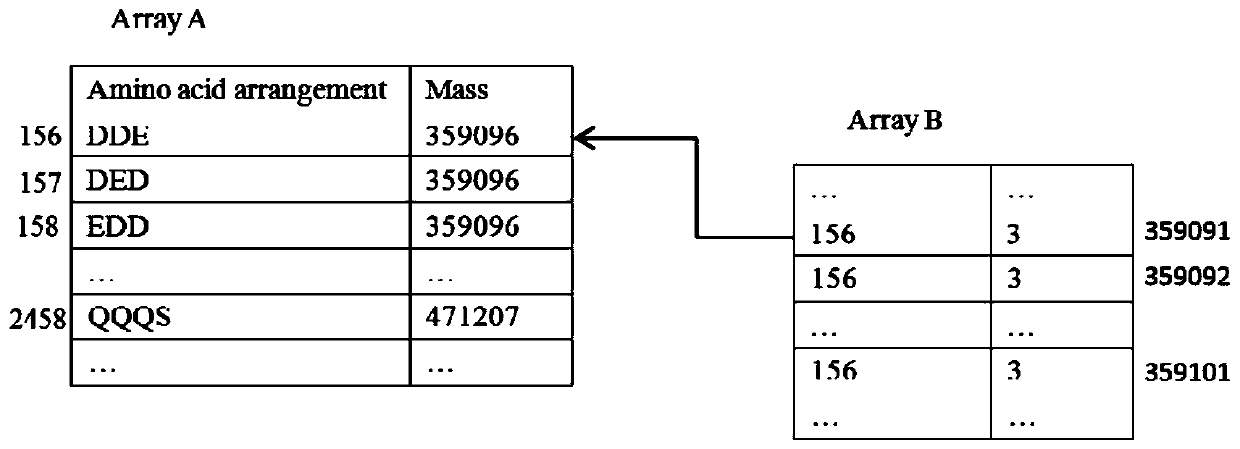
A de novo sequencing method
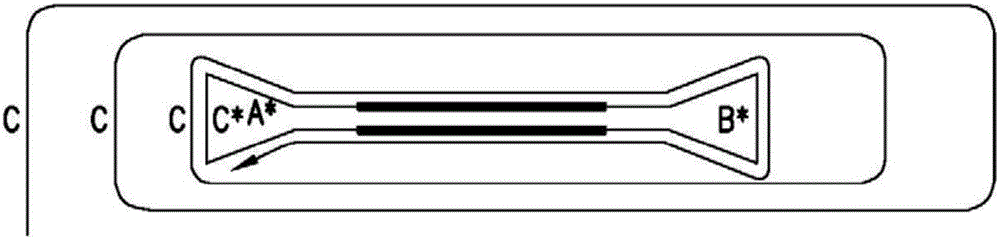
ActiveCN107729719BIntact fragment ionEffectively determine the ion typeData visualisationHybridisationEnzyme digestionData set
The invention provides a de novo sequencing method which includes the steps: seeking a mirror image spectrogram corresponding to a mirror image peptide fragment in two data sets generated by enzyme digestion; detecting a high-reliability spectrum peak and a common spectrum peak from the mirror image spectrogram; building a directed acyclic graph according to the high-reliability spectrum peak andthe common spectrum peak; generating a candidate peptide fragment based on the built directed acyclic graph. A node corresponding to the high-reliability spectrum peak is a high-reliability node, anda node corresponding to the common spectrum peak is a common node. According to the method, mutual evidence is achieved by the aid of the mirror image spectrogram, and de novo sequencing accuracy of the peptide fragment can be improved.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A Mass Spectrometry De novo Sequencing Method Based on Peptide C-terminus Selective Enzyme Labeling
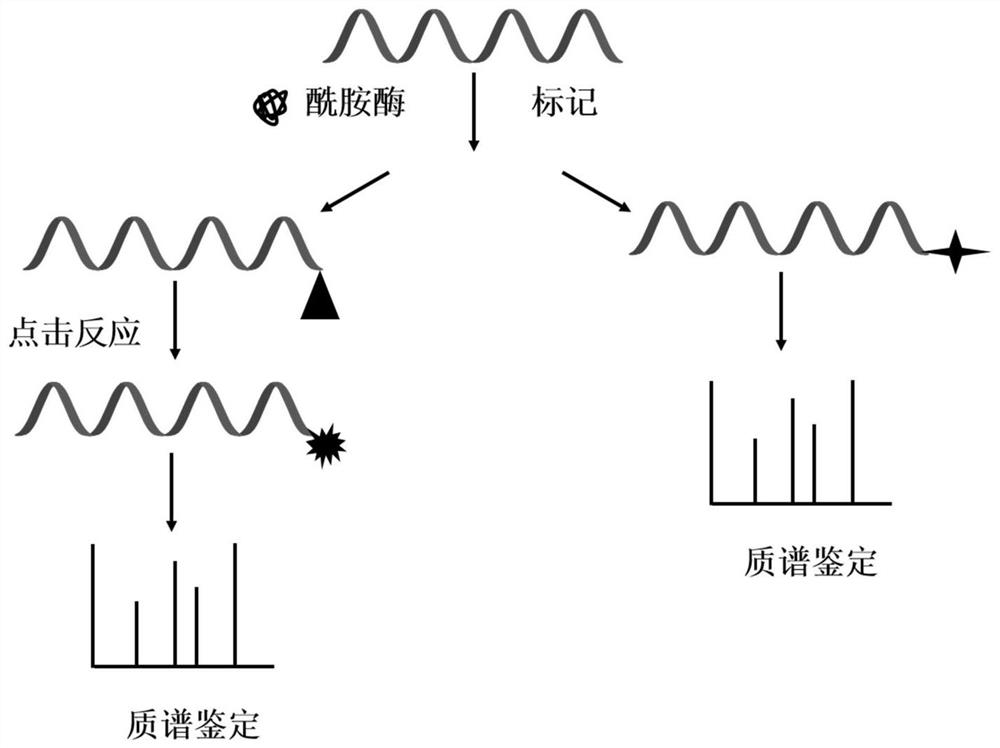
ActiveCN109900834BGood terminal selectivityAvoid reactionComponent separationUnsaturated hydrocarbonClick chemistry
The invention relates to a mass spectrometry de novo sequencing method based on peptide C-terminal selective enzyme labeling and its application. The method is that under the catalysis of amidase at the C-terminus of the peptide, the carboxyl group at the C-terminus of the peptide is directly labeled with a small molecule with a basic group through an amidation reaction or is first labeled with an amino group with an amino group through an amidation reaction. Saturated hydrocarbons are further linked to basic functional molecules through the click chemical reaction of azide-alkynyl or mercapto-ene. The basic molecule on the C-terminal label of the peptide increases the number of y ions in the secondary mass spectrometry, and improves the response and fragmentation efficiency of the peptide in the mass spectrometer, thereby realizing peptide sequencing.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for de novo protein sequencing
PendingUS20210278414A1Serum immunoglobulinsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPeptide ionsArginine
A method for determining an amino acid sequence of a polypeptide, including comprising: contacting a first sample containing the polypeptide with a first protease (e.g., Trypsin) to produce a first set of digested peptide fragments; fragmenting the first set of digested peptide fragments to produce a first set of fragmented peptide ions; determining masses of the first set of fragmented peptide ions; contacting a second sample containing the polypeptide with a second protease (e.g., Tryp-N); fragmenting the second set of digested peptide fragments to produce a second set of fragmented peptide ions; selecting pairs of peptide ions from the first and the second set of fragmented peptide ions that differ in mass by a mass of an arginine amino acid residue or a lysine amino acid residue; assigning an ion type (either N-terminal peptide ion or C-terminal peptide ion) to the selected pairs of the peptide ions from two sets of fragmented peptide ions; selecting a mass ladder of the same-type peptide ions in either set of fragmented peptide ions with incremental mass by the mass of amino acid residue(s), and assembling the identified amino acid residues from the mass ladder to determine the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide of interest.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Macro-proteome mining method and application of macro-proteome mining method in obtaining hydrolysis characteristics of intestinal microbial proteins
PendingCN112786105ALower confidenceReduce false positive identificationsProteomicsGenomicsEscherichia coliProtein Databases
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and discloses a semi-trypsin polypeptide-centered metaproteome data mining method, which comprises the steps of two-step library searching, de novo sequencing, open retrieval and matching of various library searching software, and large-scale semi-trypsin polypeptide-centered metaproteome information mining is carried out aiming at high-resolution mass spectrum data. These strategies can reduce the false positive rate resulting from database incompleteness and post-translational modification. When the method is used for analyzing the escherichia coli proteome, 93.4% of peptide fragments identified from a huge macro protein database are consistent with peptide fragments identified from a traditional escherichia coli reference database.
Owner:THE FIFTH AFFILIATED HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com