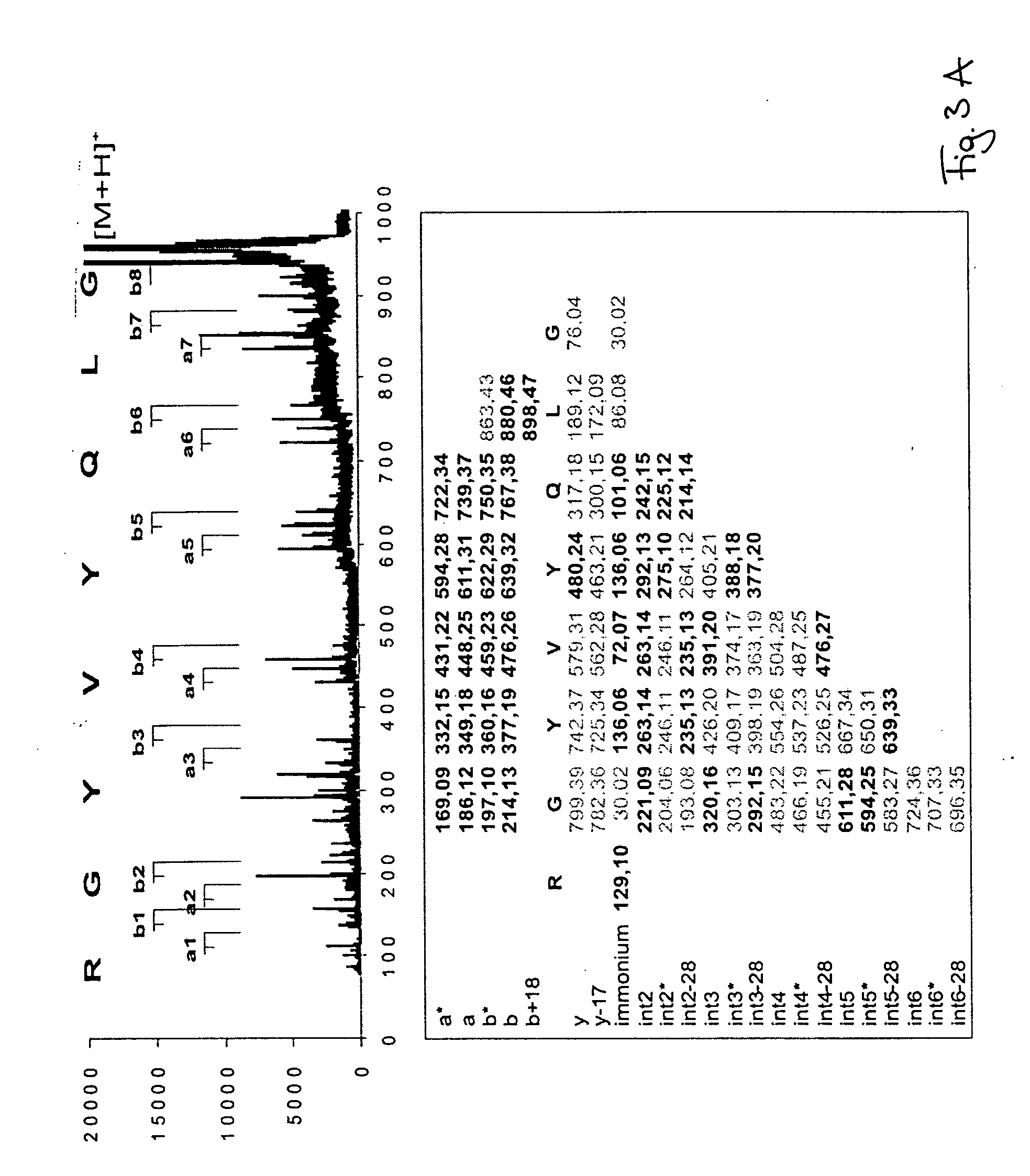
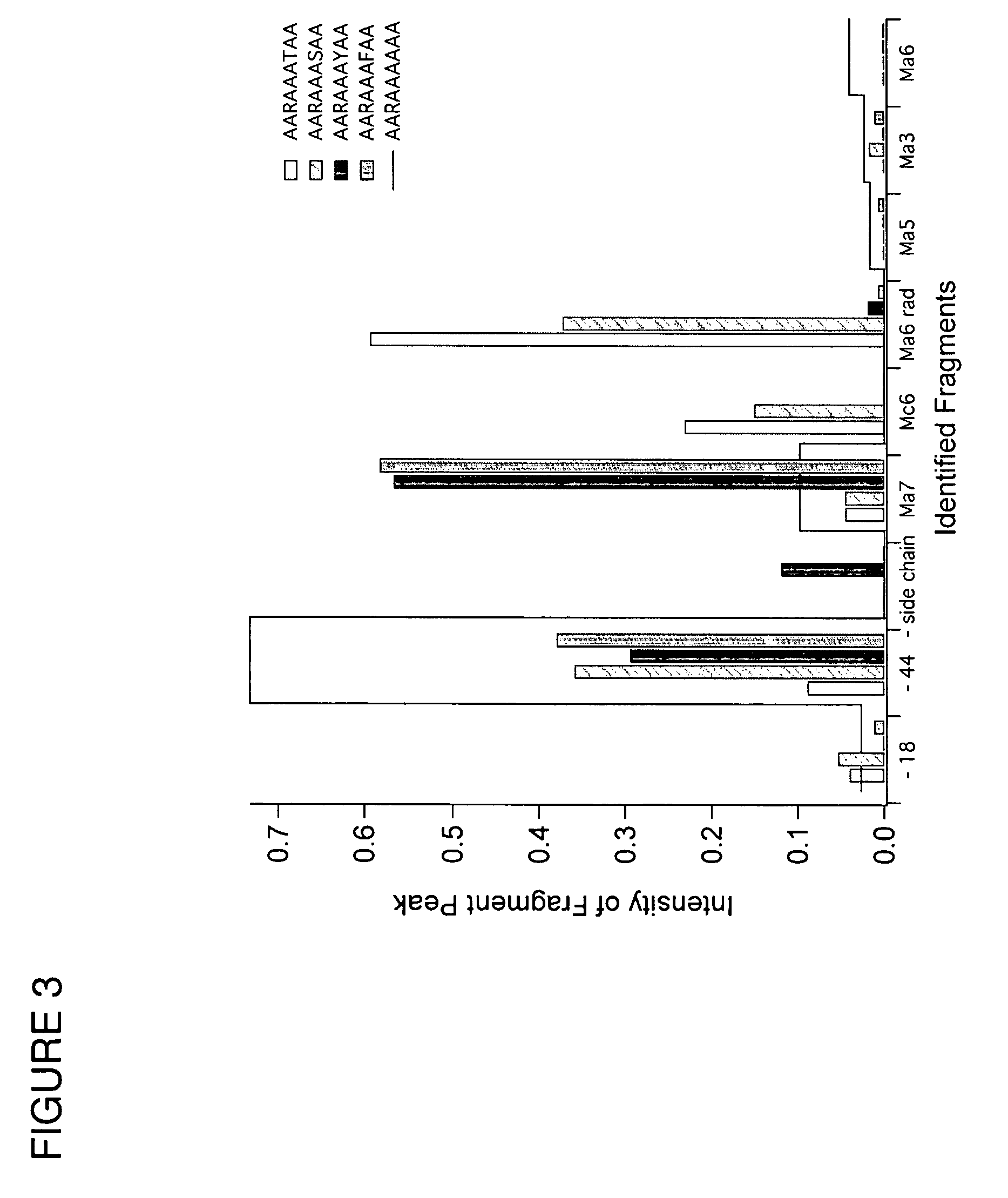
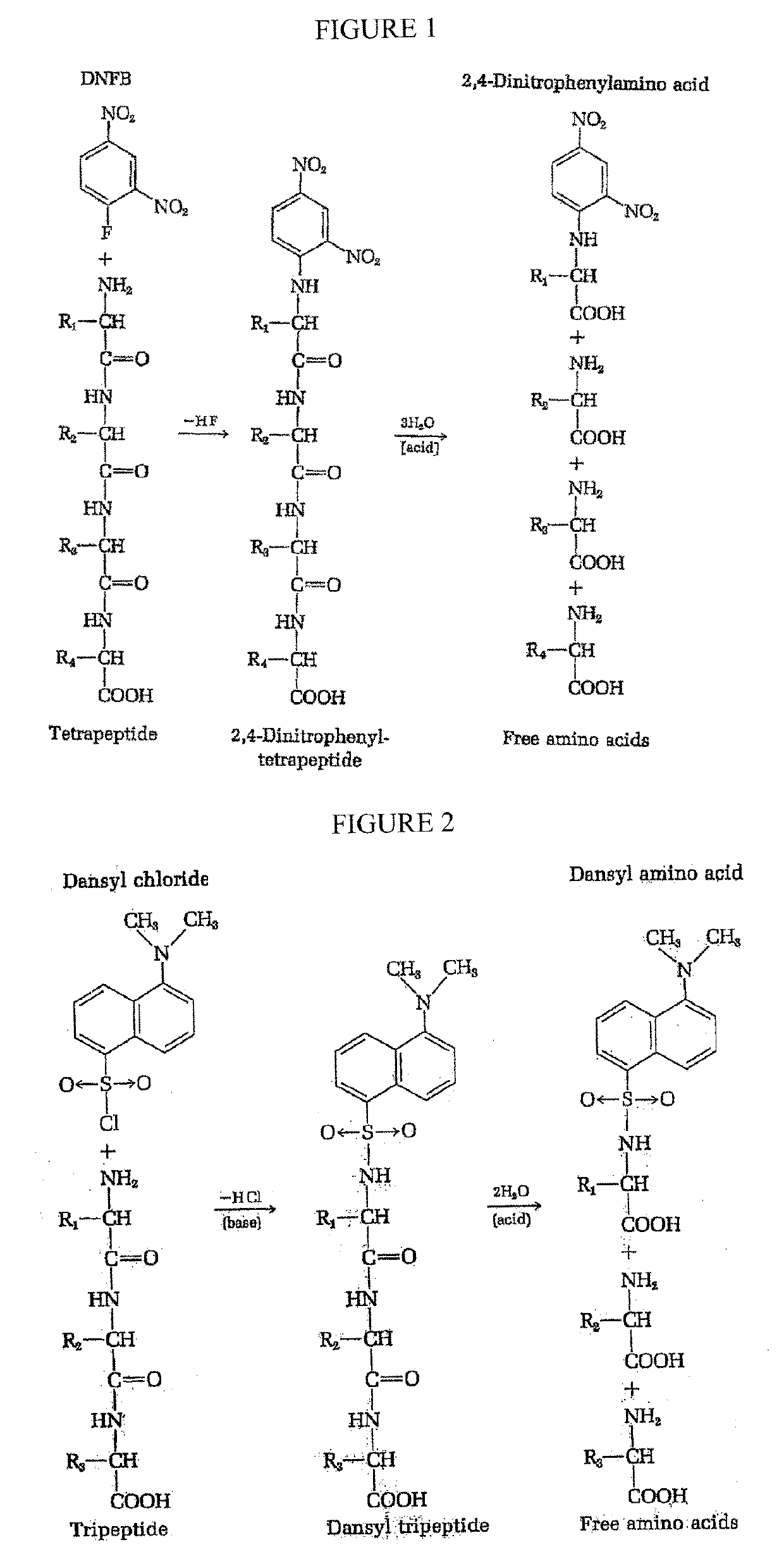
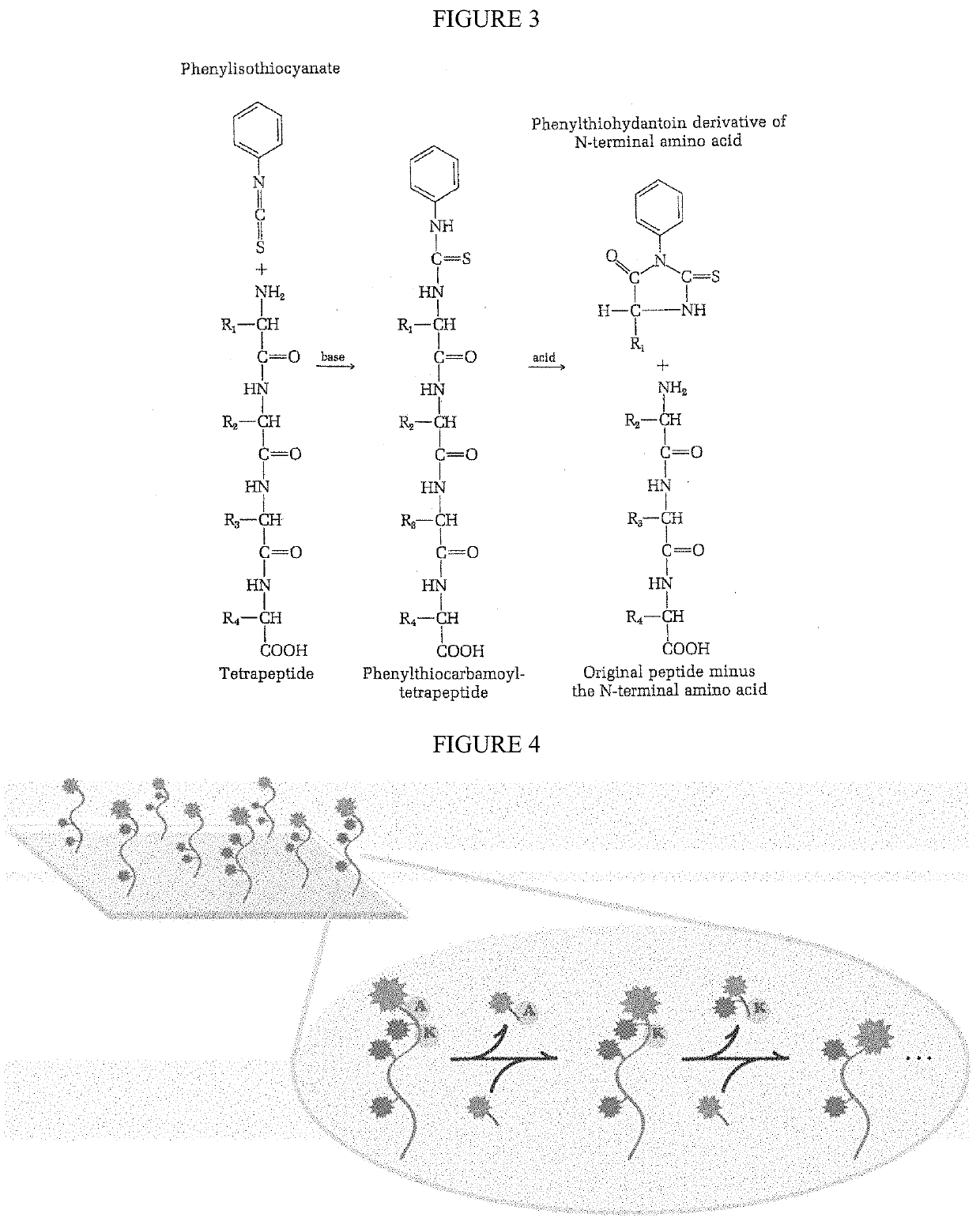
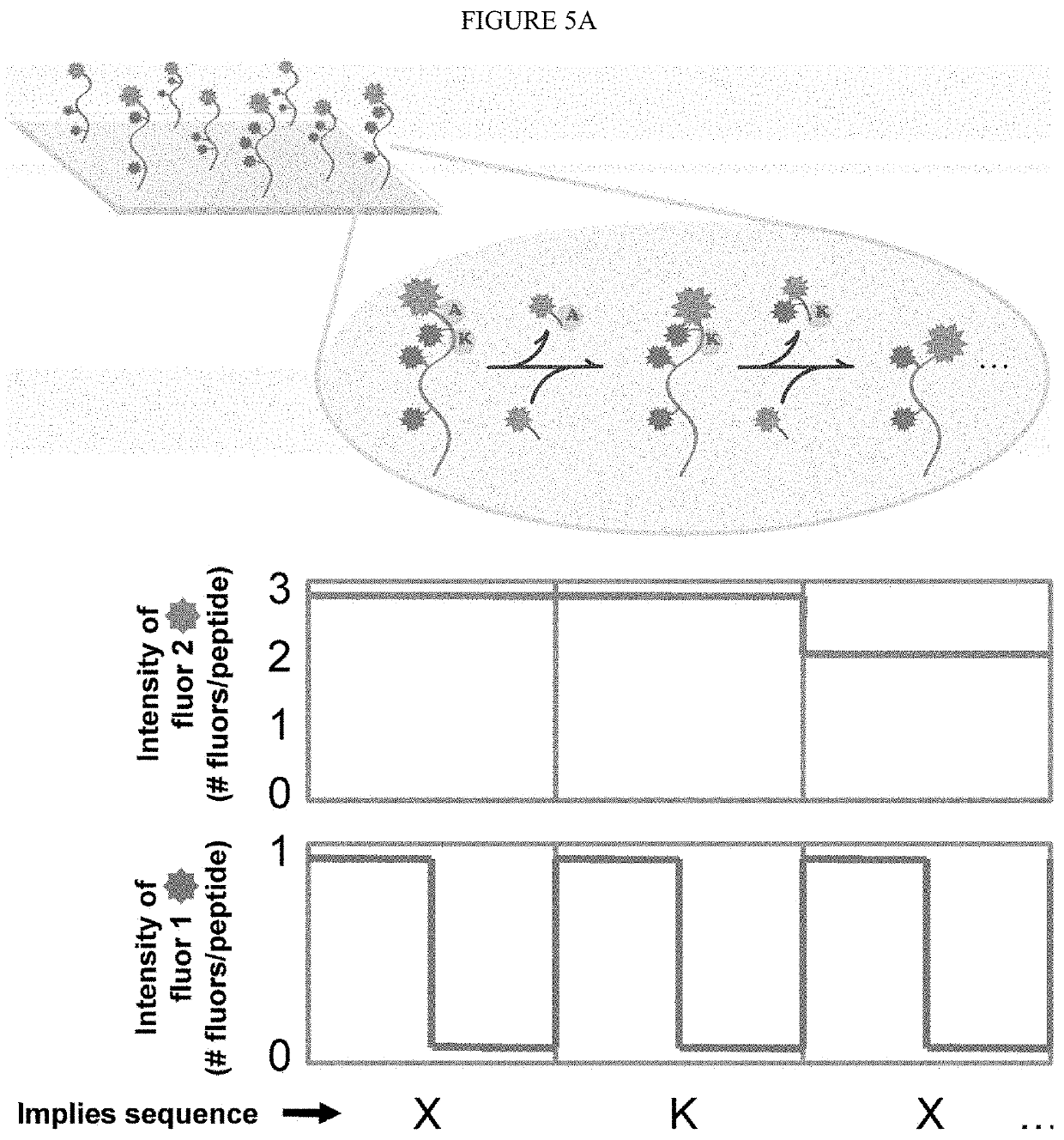
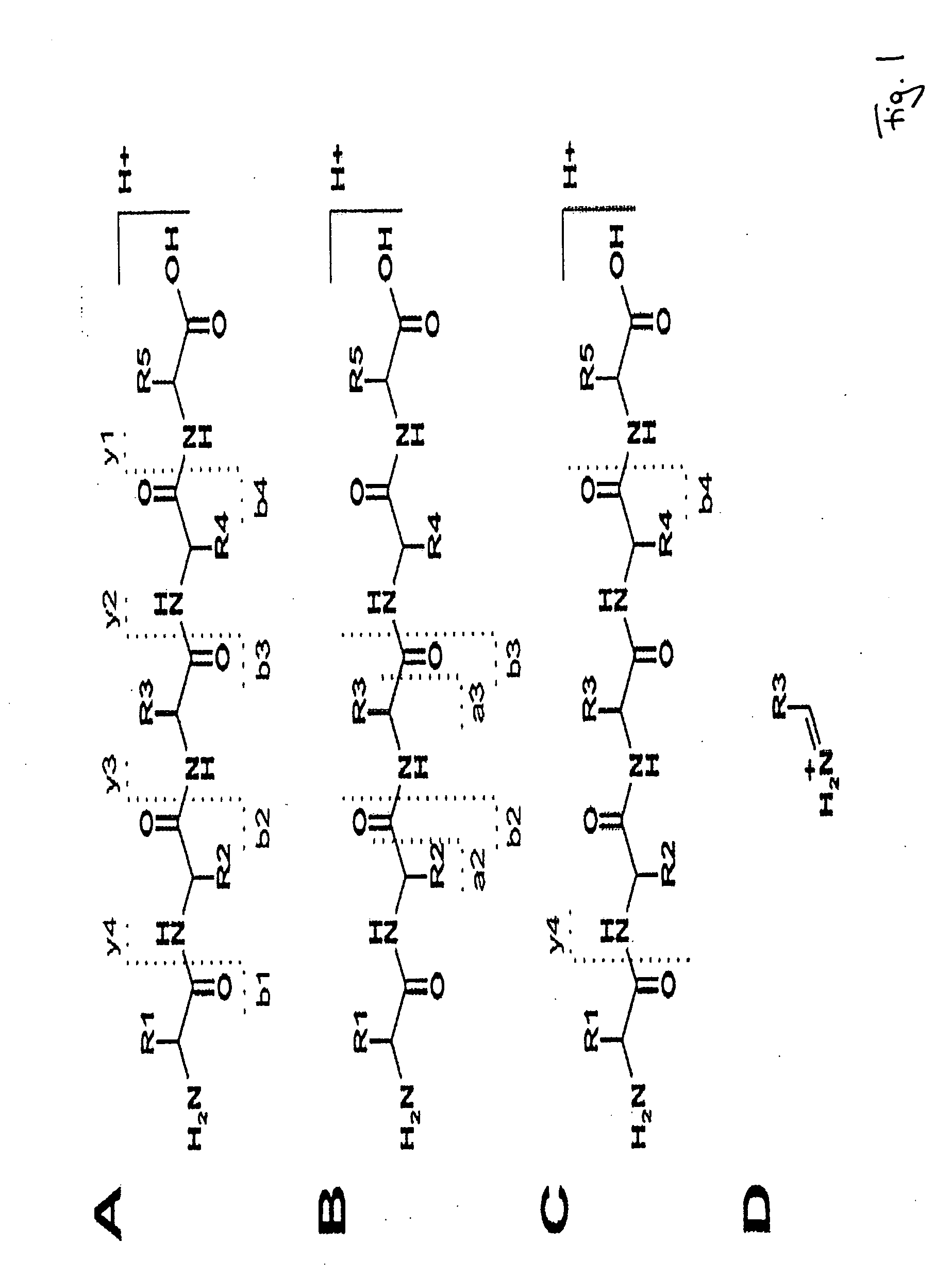Patents
Literature
34 results about "Peptide sequencing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
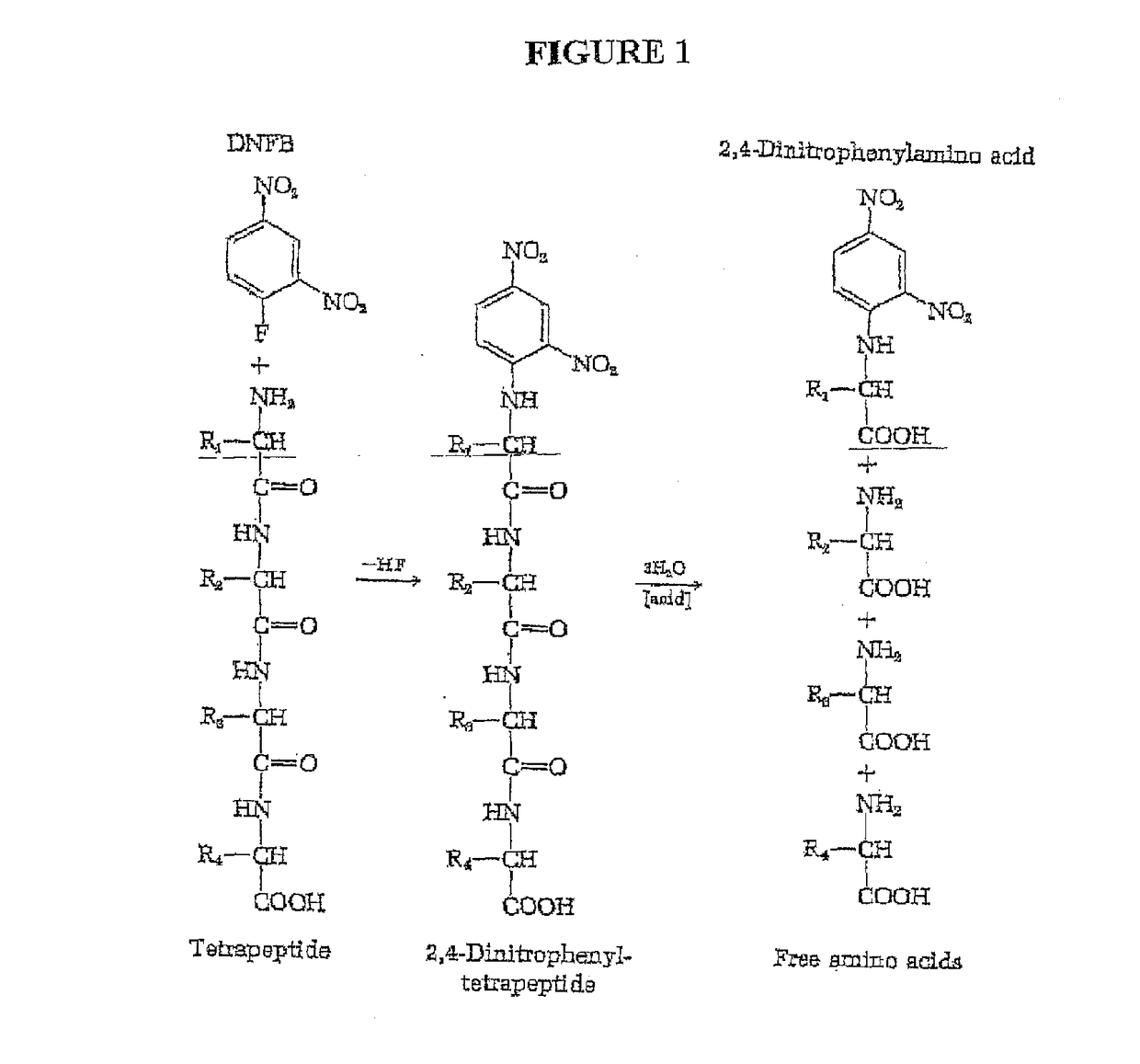
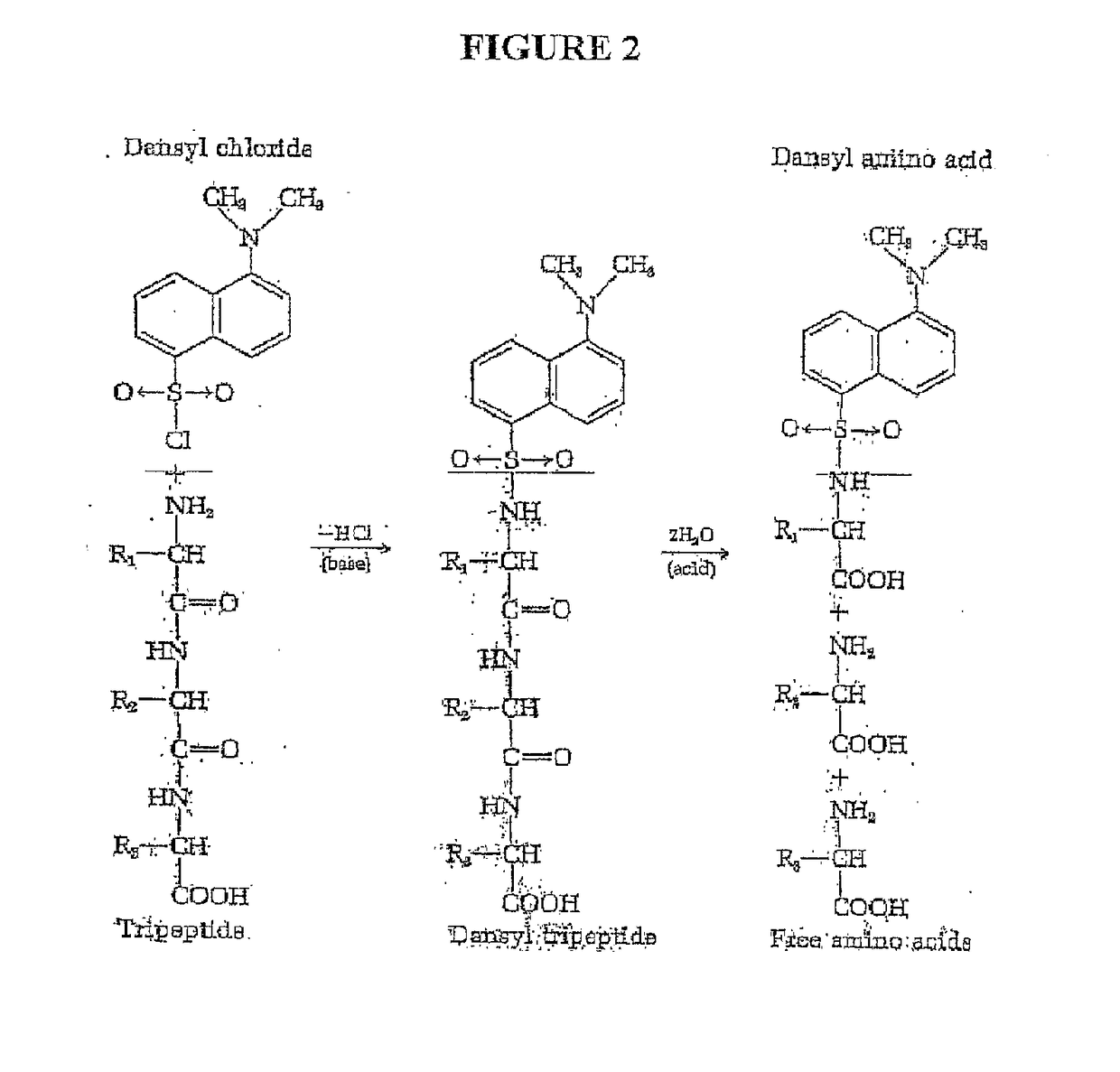
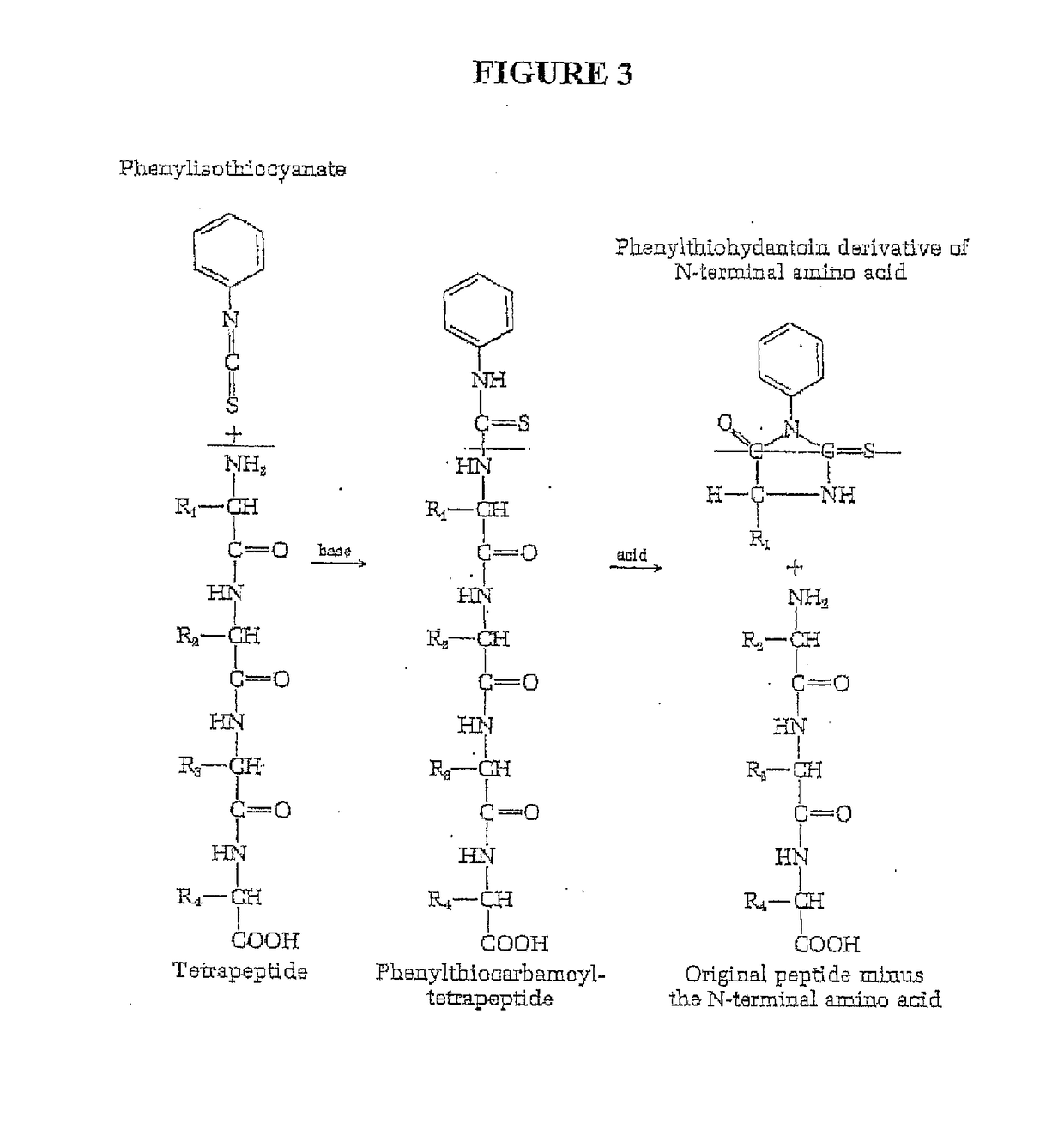
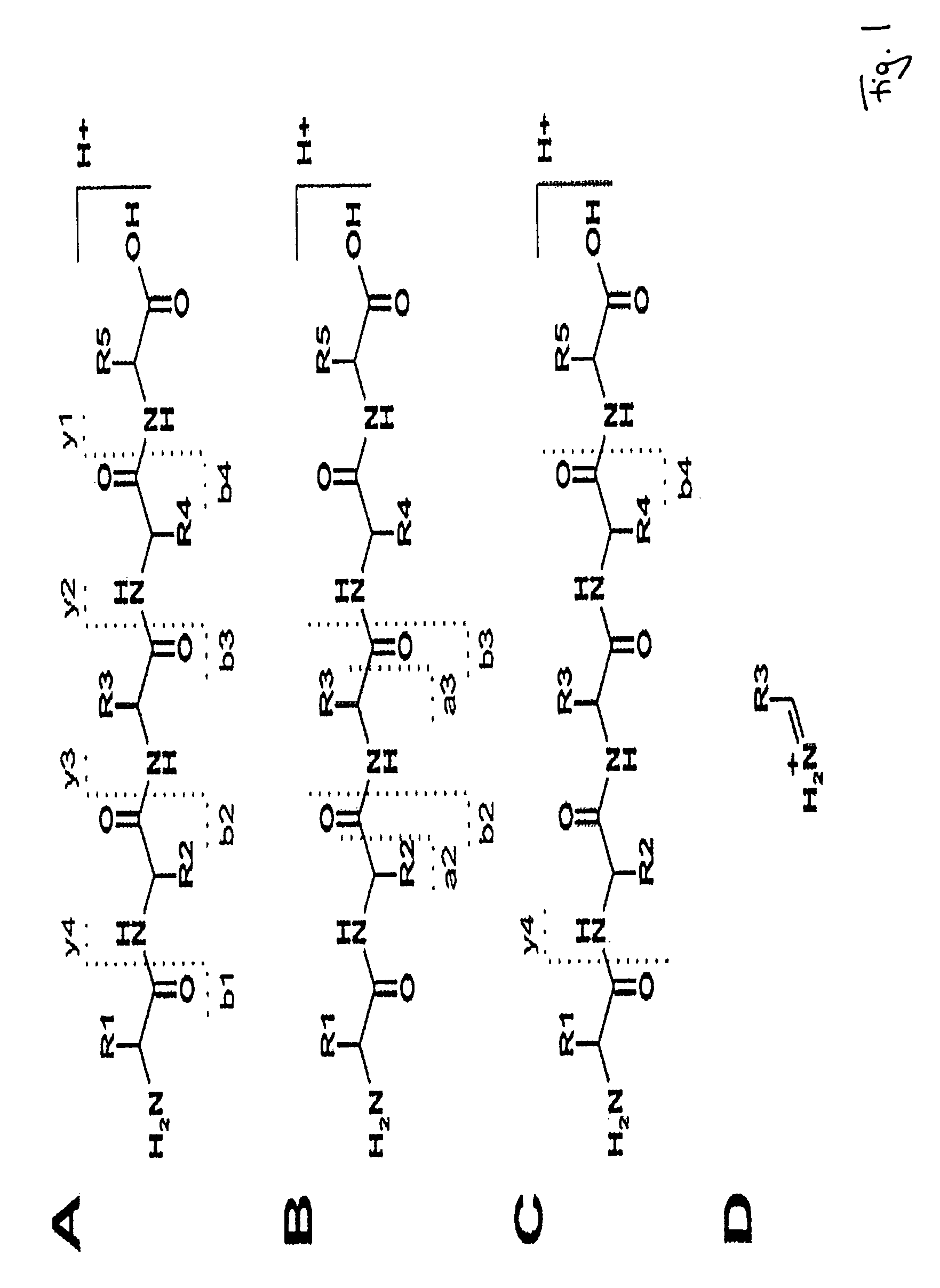
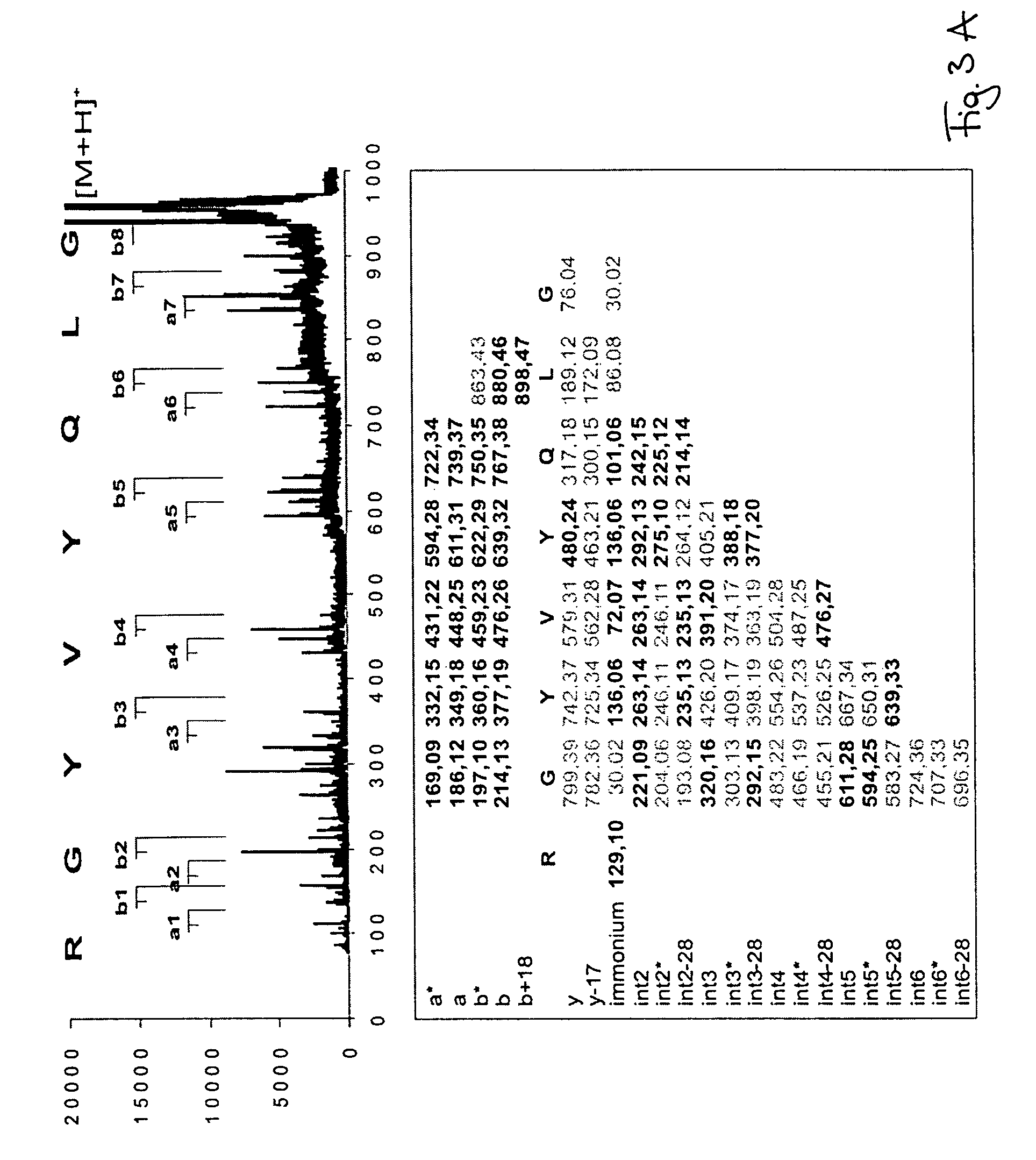
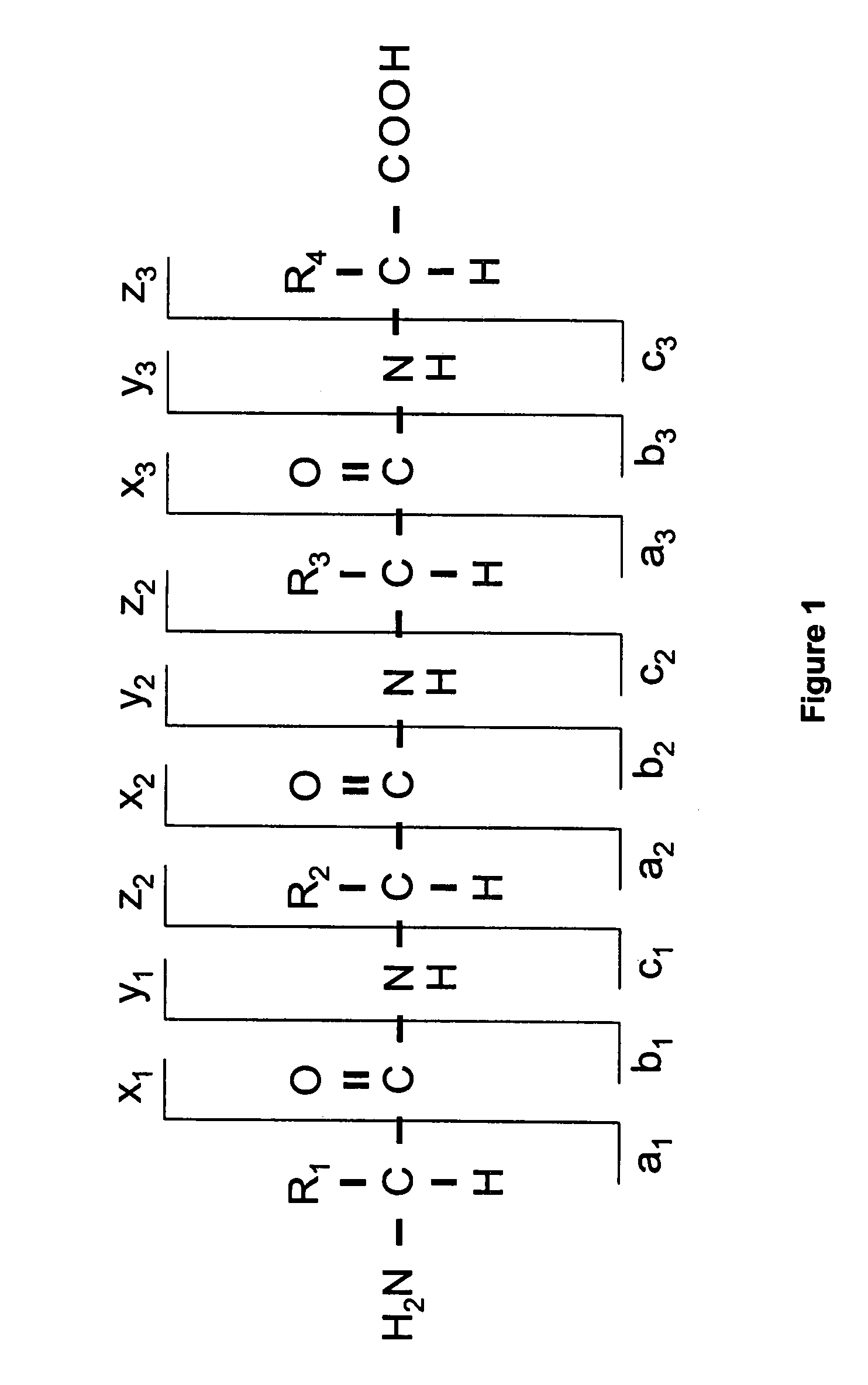
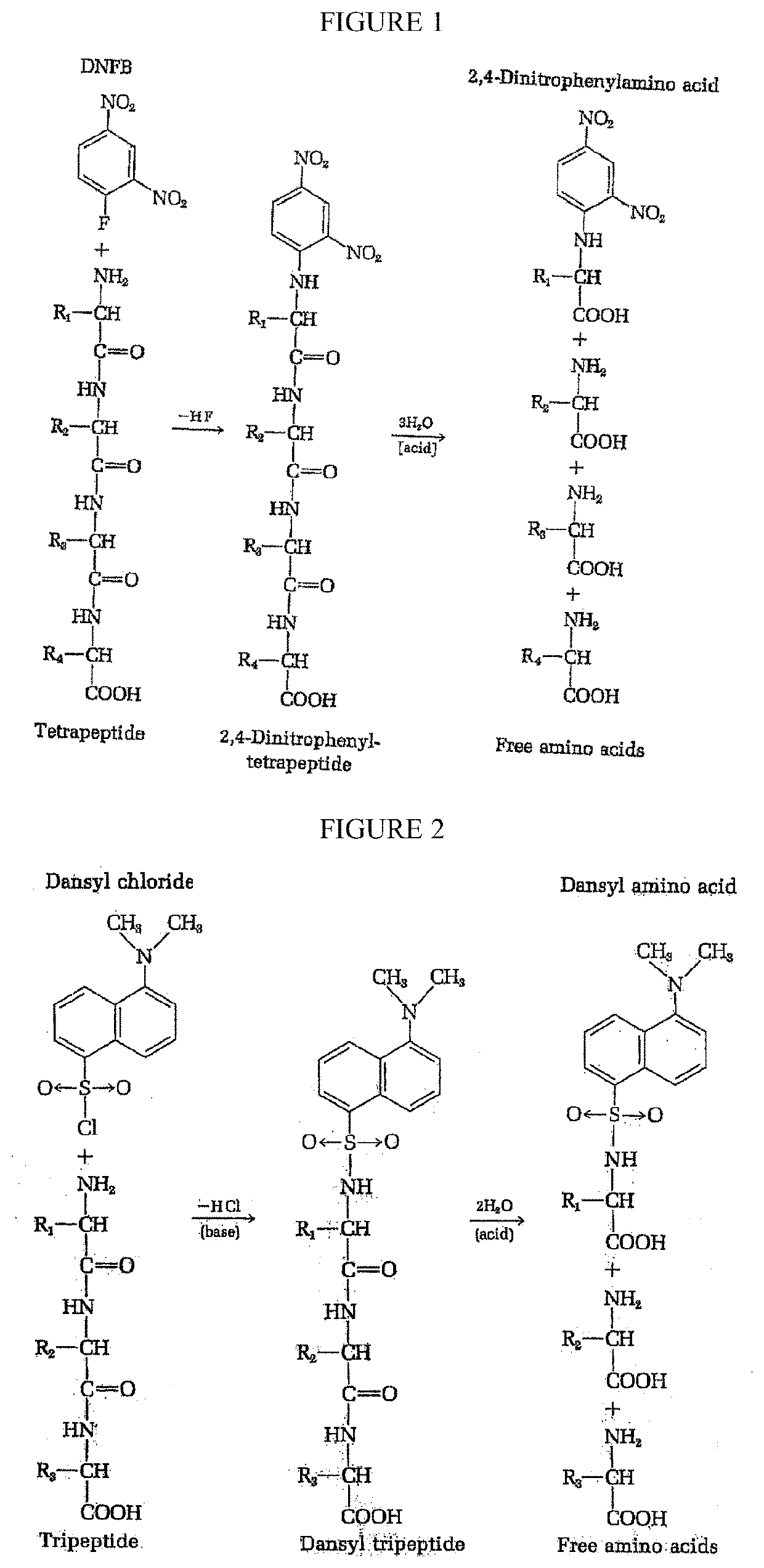
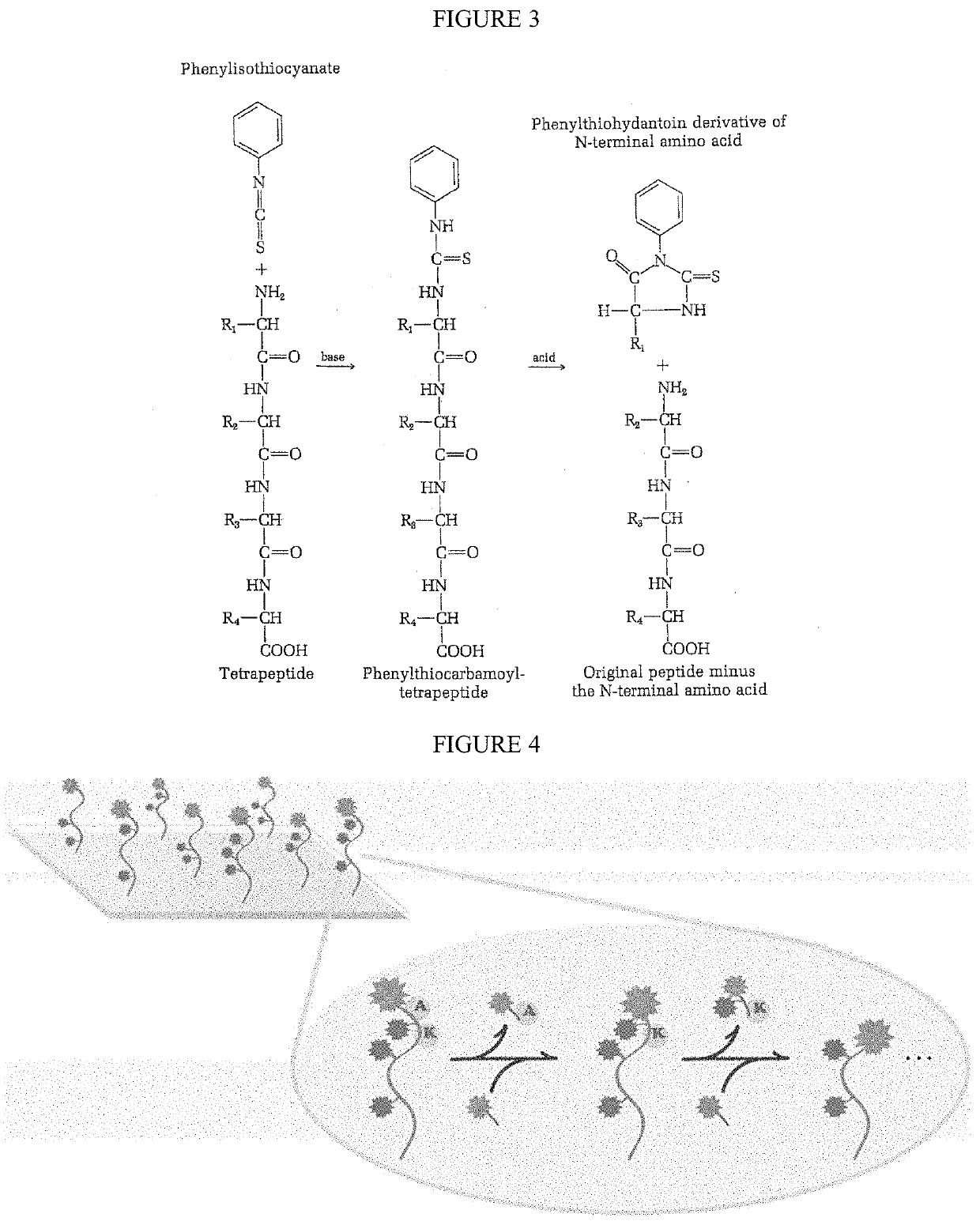
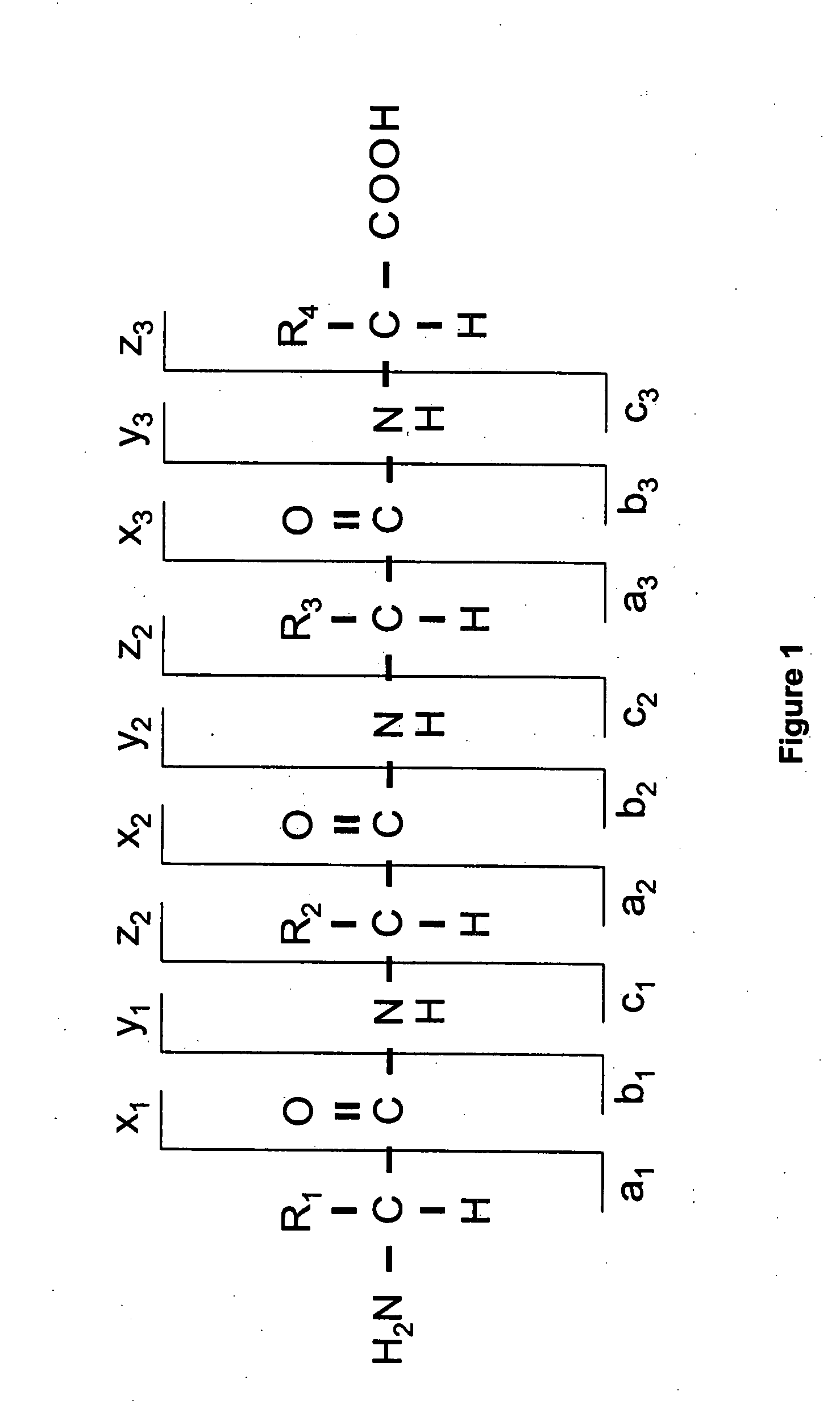
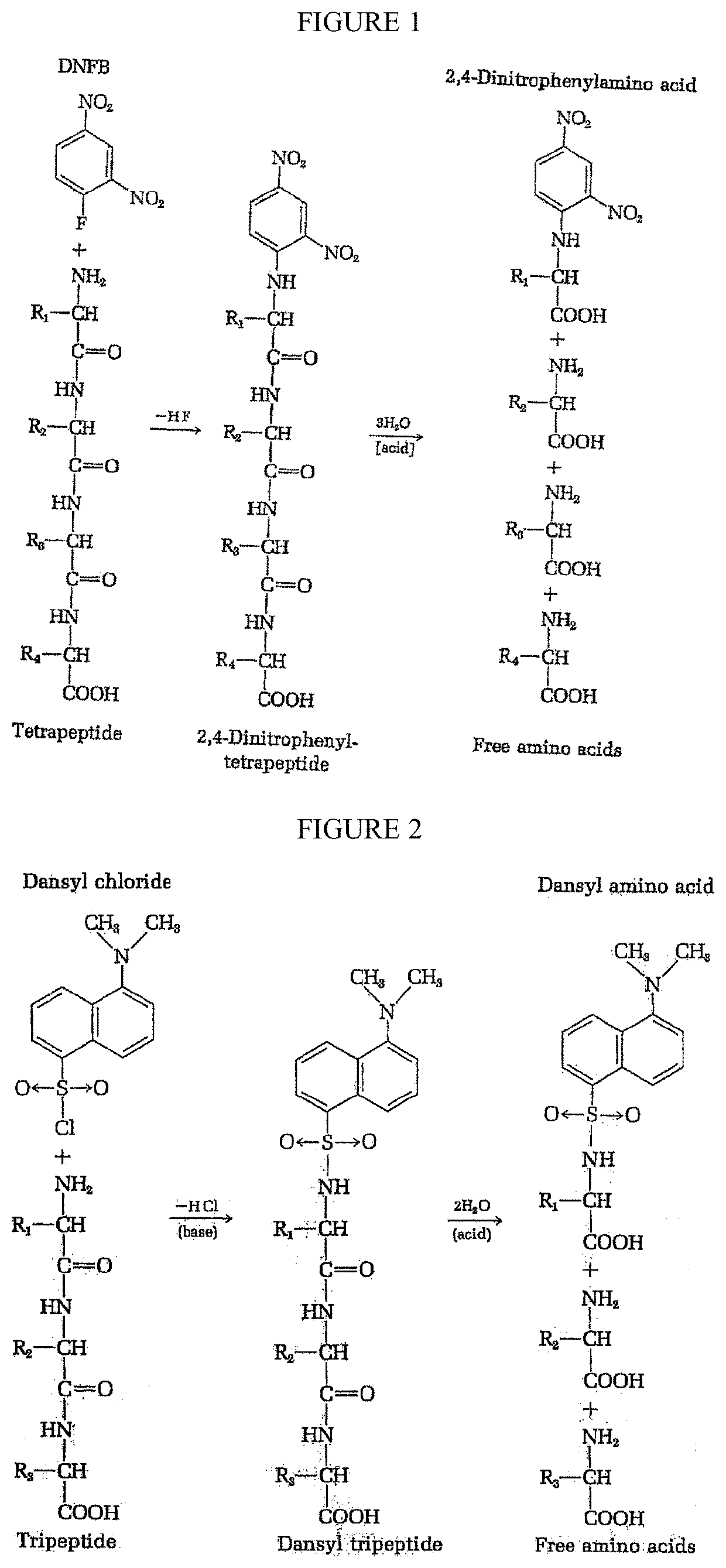
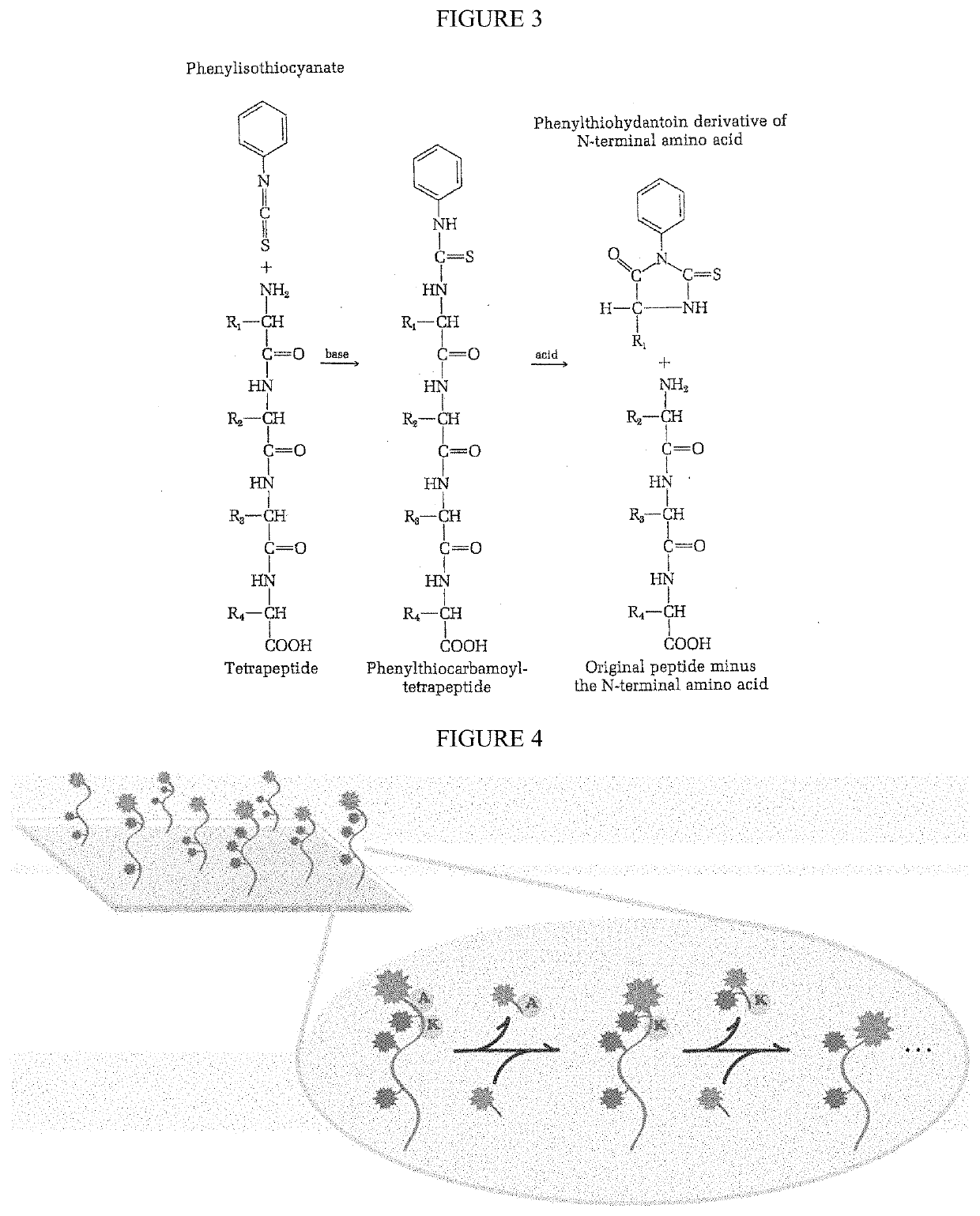
Peptide sequence and amino acid sequence is the order in which amino acid residues, connected by peptide bonds, lie in the chain in peptides and proteins. The sequence is generally reported from the N-terminal end containing free amino group to the C-terminal end containing free carboxyl group.
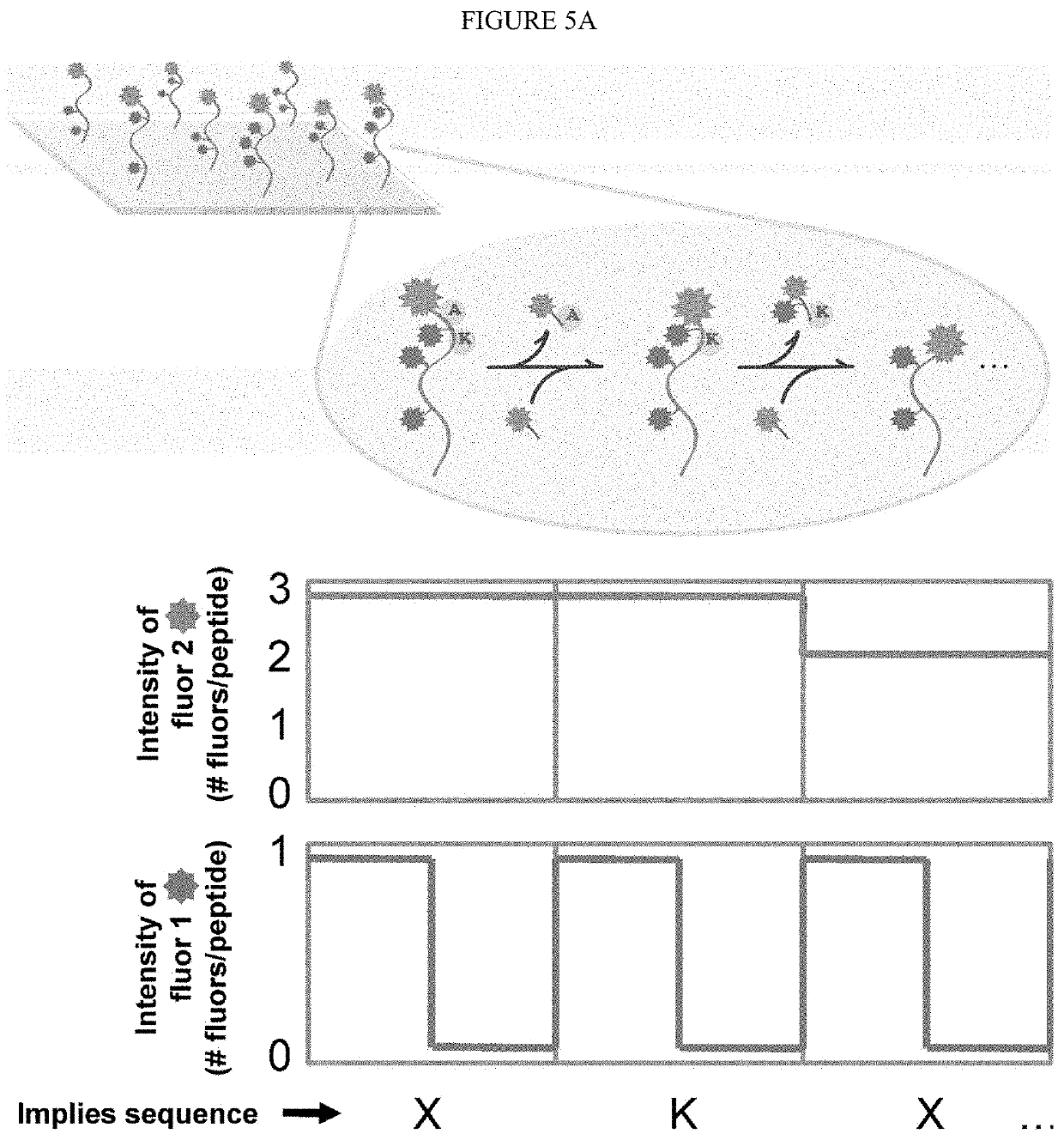
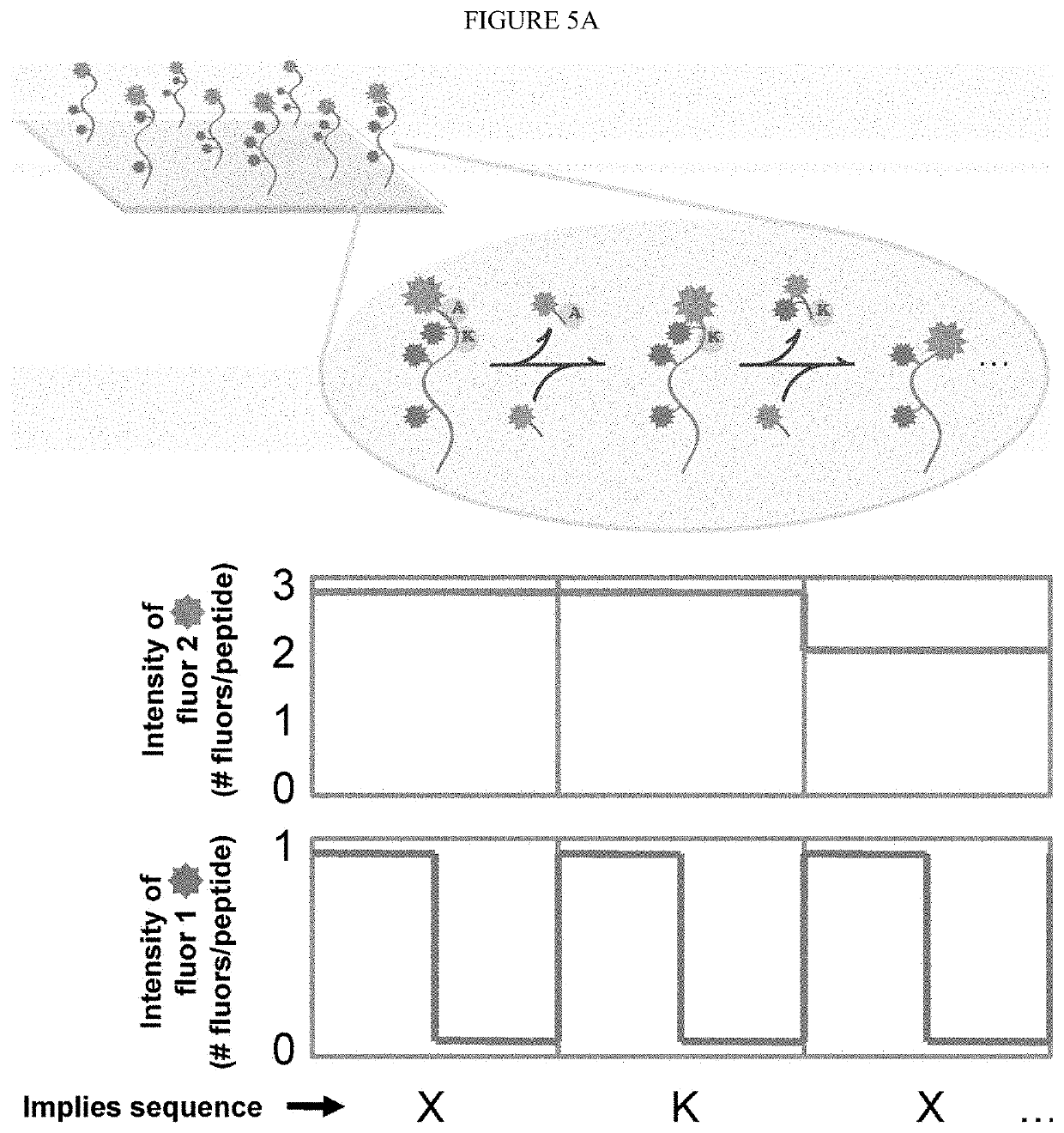
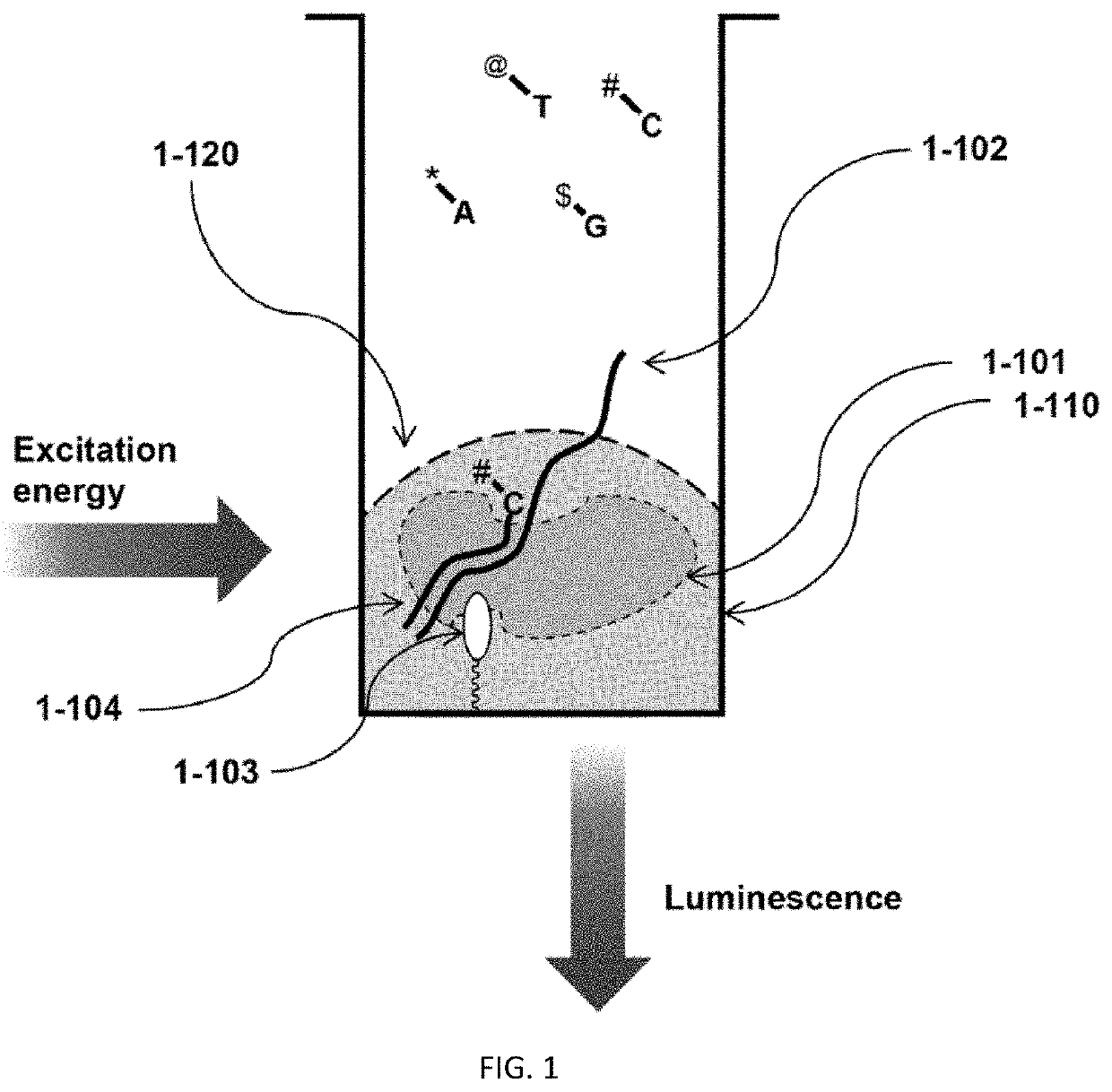
Single molecule peptide sequencing
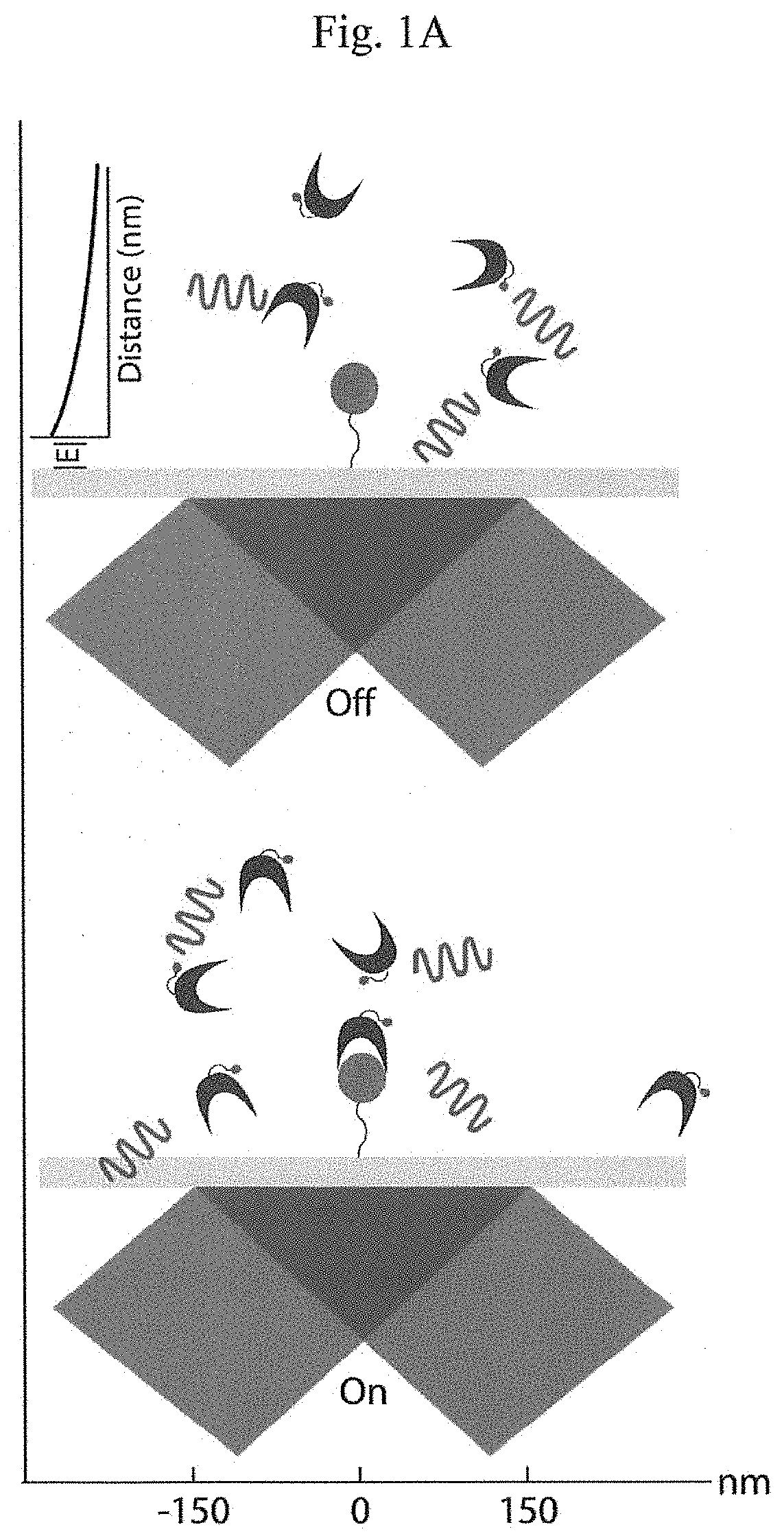
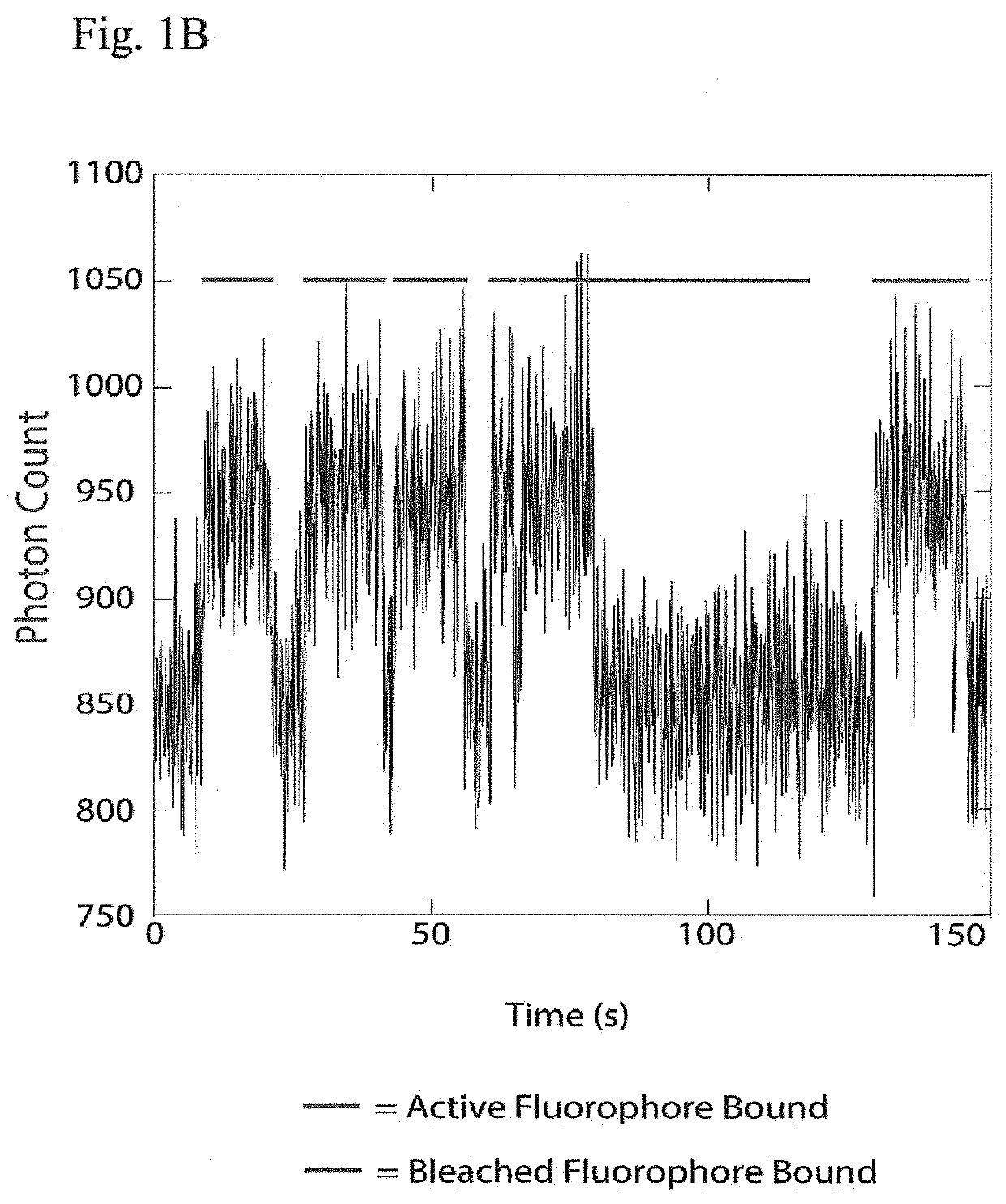
The present invention relates to the field of identifying proteins and peptides, and more specifically large-scale sequencing of single peptides in a mixture of diverse peptides at the single molecule level. The present invention also relates to methods for identifying amino acids in peptides, including peptides comprising unnatural amino acids. In one embodiment, the present invention contemplates labeling the N-terminal amino acid with a first label and labeling an internal amino acid with a second label. In some embodiments, the labels are fluorescent labels. In other embodiments, the internal amino acid is Lysine. In other embodiments, amino acids in peptides are identified based on the fluorescent signature for each peptide at the single molecule level.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
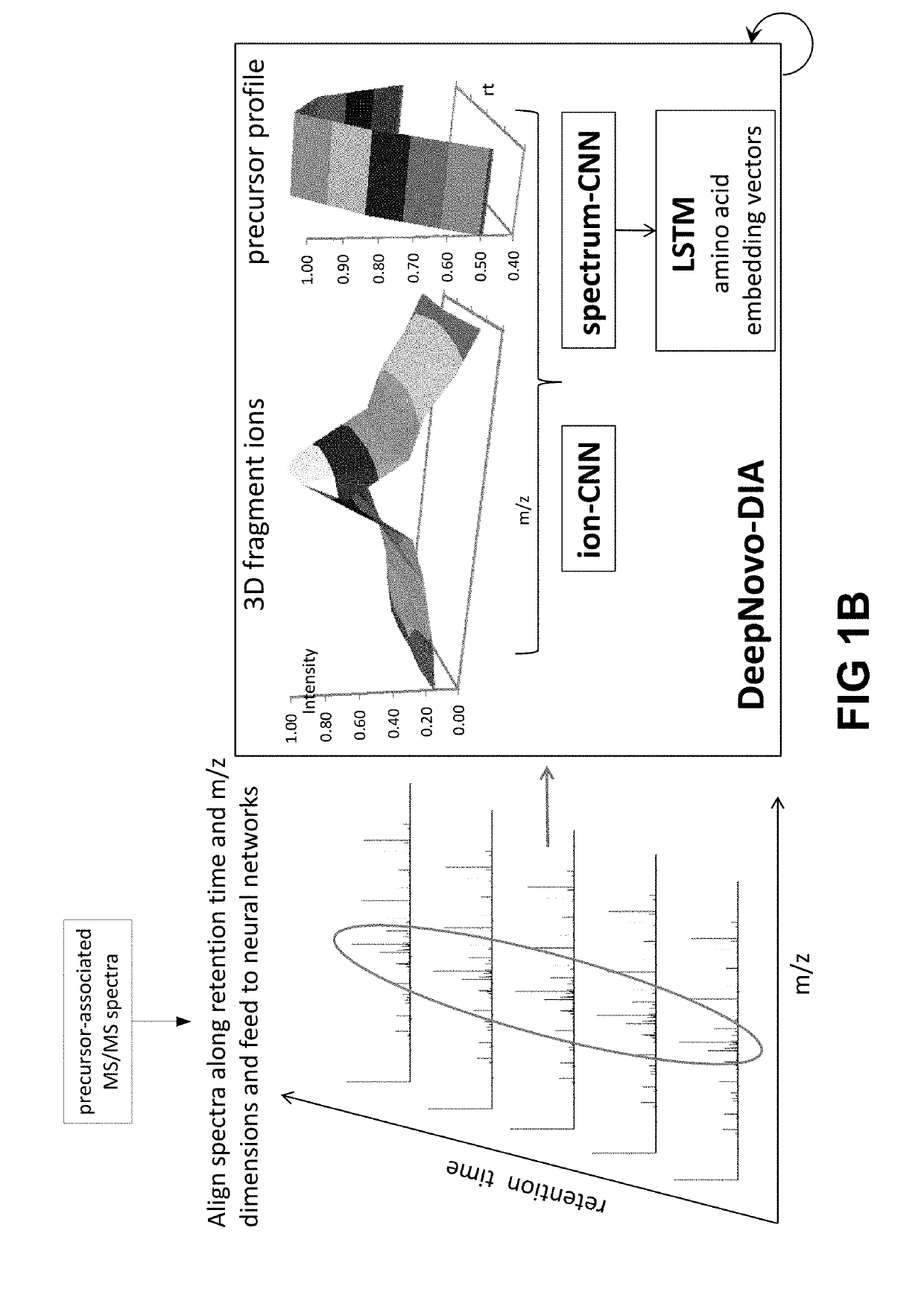
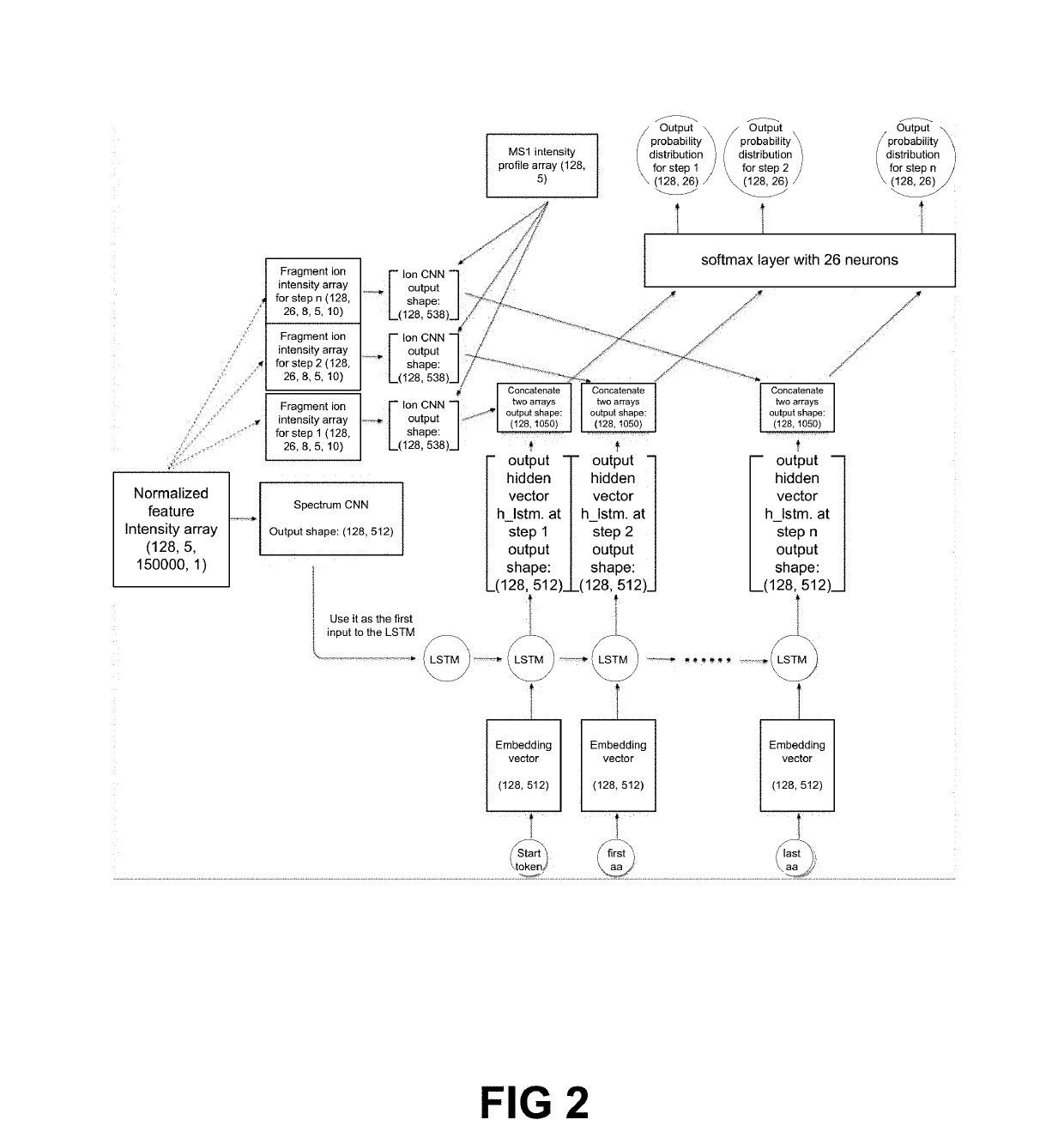
Systems and methods for de novo peptide sequencing from data-independent acquisition using deep learning
ActiveUS20190147983A1High sensitivityImproved identification and determinationParticle separator tubesBiological neural network modelsRetention timeMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
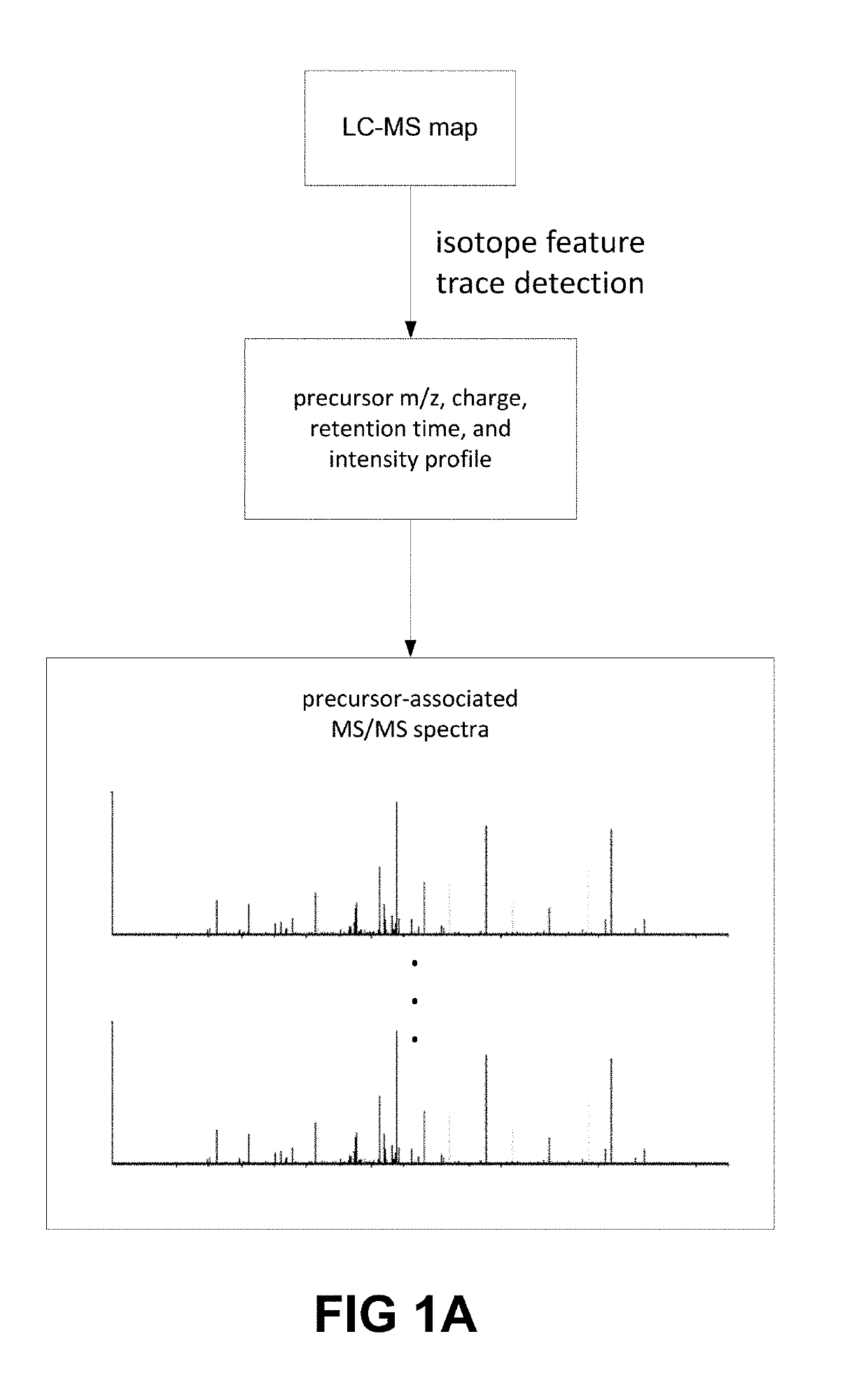
The present systems and methods introduce deep learning to de novo peptide sequencing from tandem mass spectrometry data, and in particular mass spectrometry data obtained by data-independent acquisition. The systems and methods achieve improvements in sequencing accuracy over existing systems and methods and enables complete assembly of novel protein sequences without assisting databases. To sequence peptides from mass spectrometry data obtained by data-independent acquisition, precursor profiles representing intensities of one or more precursor ion signals associated with a precursor retention time and fragment ion spectra representing signals from fragment ions and fragment retention times are fed into a neural network.
Owner:BIOINFORMATICS SOLUTIONS
Peptide sequencing from peptide fragmentation mass spectra
The invention relates to a method of peptide sequencing from peptide fragment mass data, wherein a plurality of candidate peptide sequences are determined comprises the steps of: calculating peptide fragment masses, searching a plurality of peak data for masses matching said calculated peptide fragment masses, annotating all permutations of said peak data with amino acid sequences that correspond to the calculated peptide fragment masses, extending said potential sequences to resulting masses with additional matching masses, extending stepwise additions until the resulting masses correspond to parental peptide masses or said parental peptide masses minus the mass of water, and identifying at least one peptide sequence by deleting sequences that can not be extended to endpoints of said parental peptide masses, and deleting identical sequences generated.
Owner:CHARITE UNIVS MEDIZIN BERLIN
Constrained de novo sequencing of peptides
InactiveUS20130144540A1Low costBiostatisticsBiological testingDe novo peptide sequencingPeptide sequencing
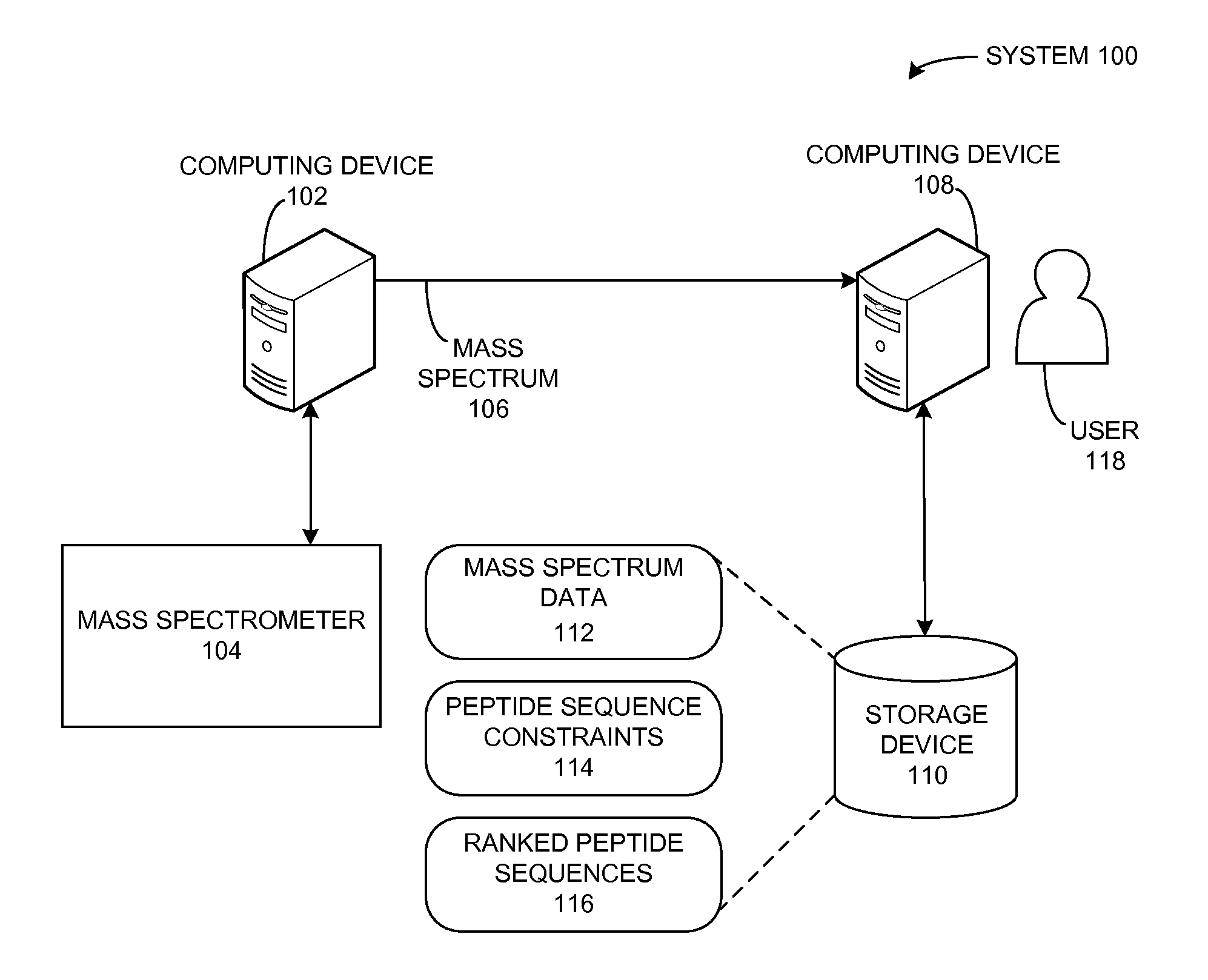
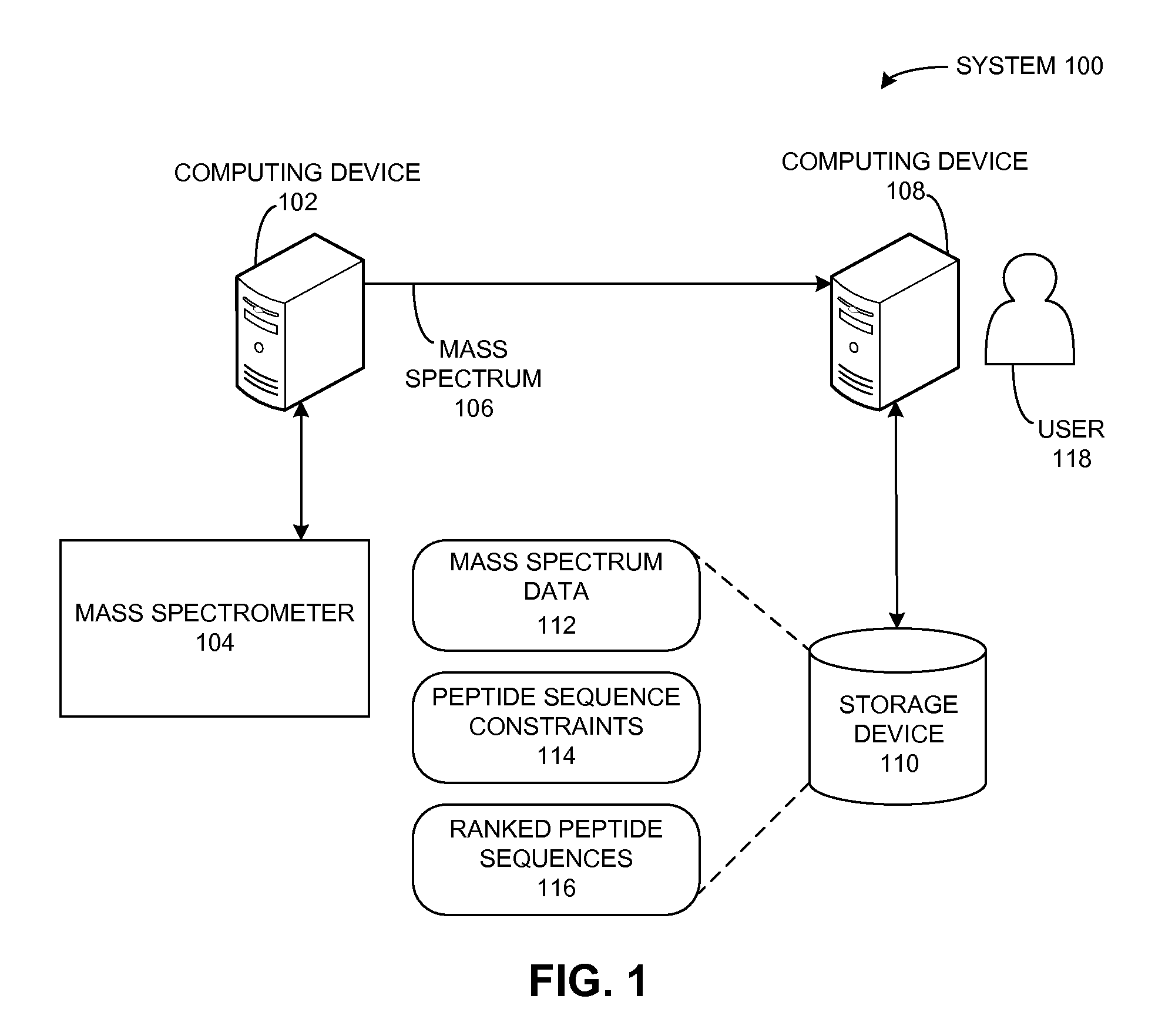
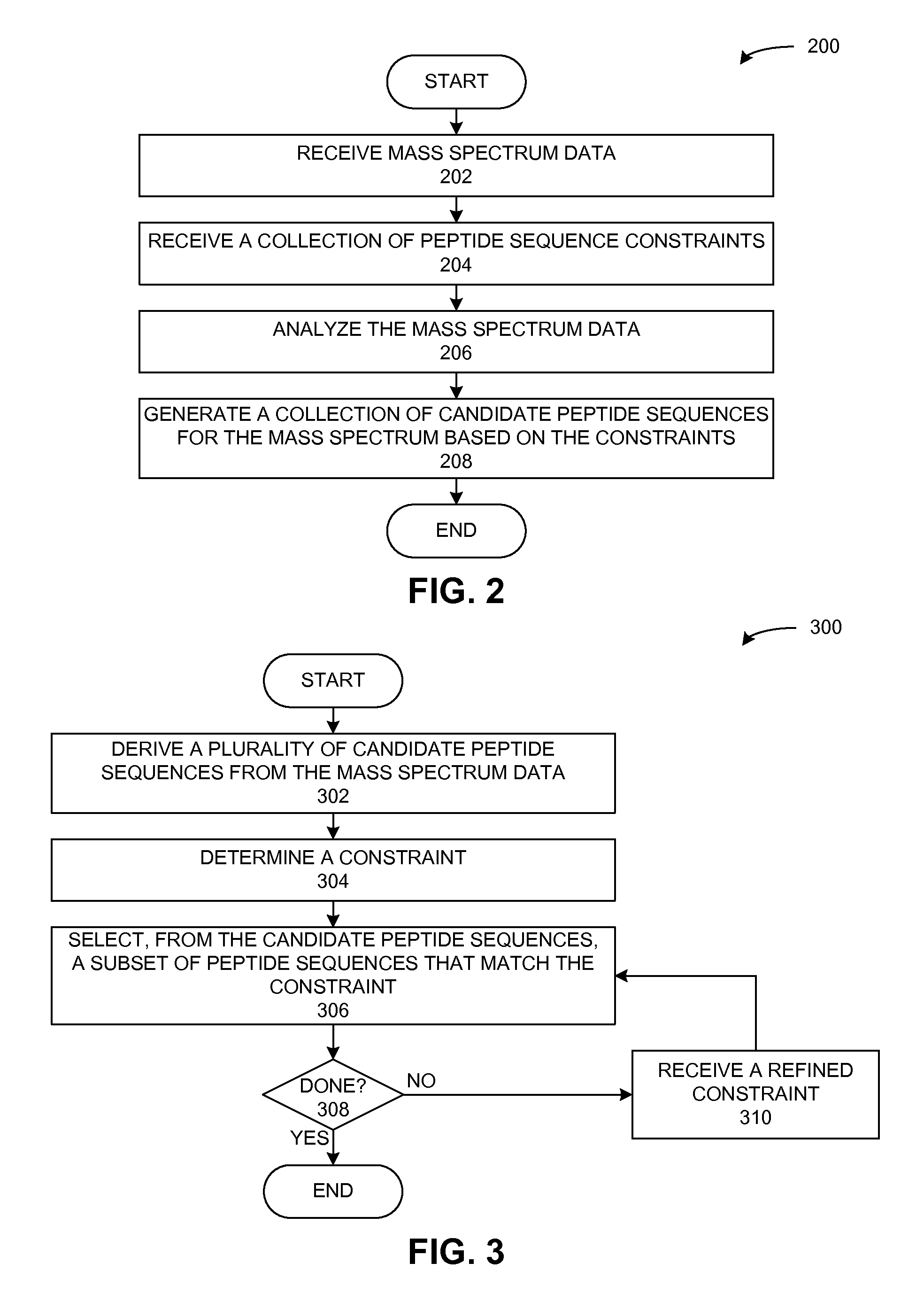
A peptide sequencing system derives a peptide sequence from a mass spectrum. The system can receive a description for a peptide sequence constraint, such that the constraint indicates a symbol pattern that is to be present in a peptide sequence derived from the mass spectrum. Then, the system generates a peptide sequence based on the mass spectrum and the constraint, such that the peptide sequence matches the constraint and has a mass that matches the total mass of the peptide as determined from the mass spectrum.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
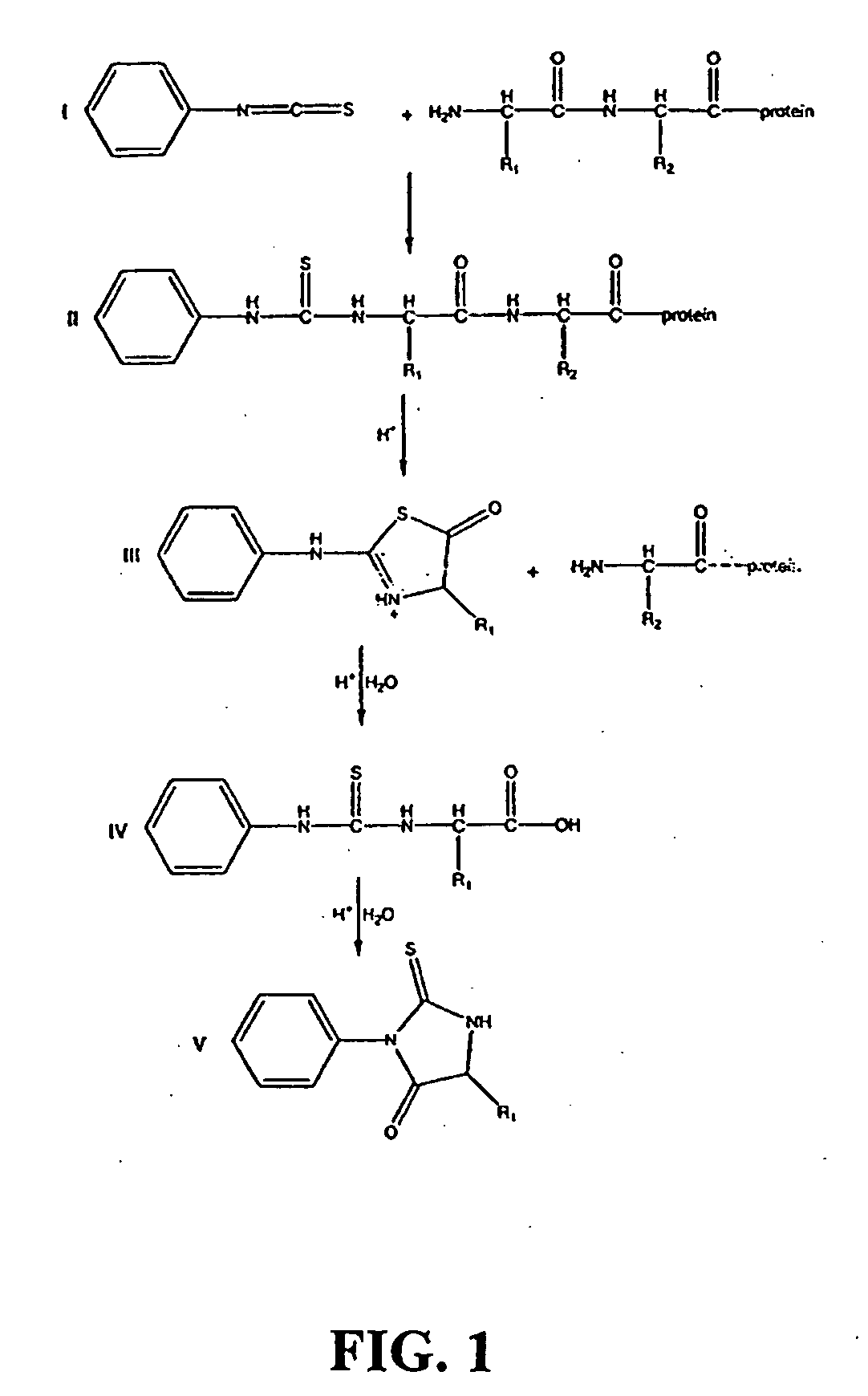
Protein/Peptide Sequencing By Chemical Degradation in the Gas Phase
ActiveUS20080248585A1The parameters are accurate and reliableHigh performance resultIsotope separationRadio frequency spectrometersGas phaseMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A fast and sensitive method and device for protein sequencing are disclosed. The method uses a combination of Edman degradation chemistry and mass spectrometry to sequence proteins and polypeptides. A peptide degradation reaction is performed on a polypeptide or protein ion reactant in the gas phase. The reaction yields a first ion product corresponding to a first amino acid residue of the polypeptide or protein reactant and a polypeptide or protein fragment ion. The mass-to-charge ratio for the first ion product, or the polypeptide or protein fragment ion, or both, is then determined. The first amino acid residue of the polypeptide or protein reactant is then identified from the mass-to-charge ratio so determined.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
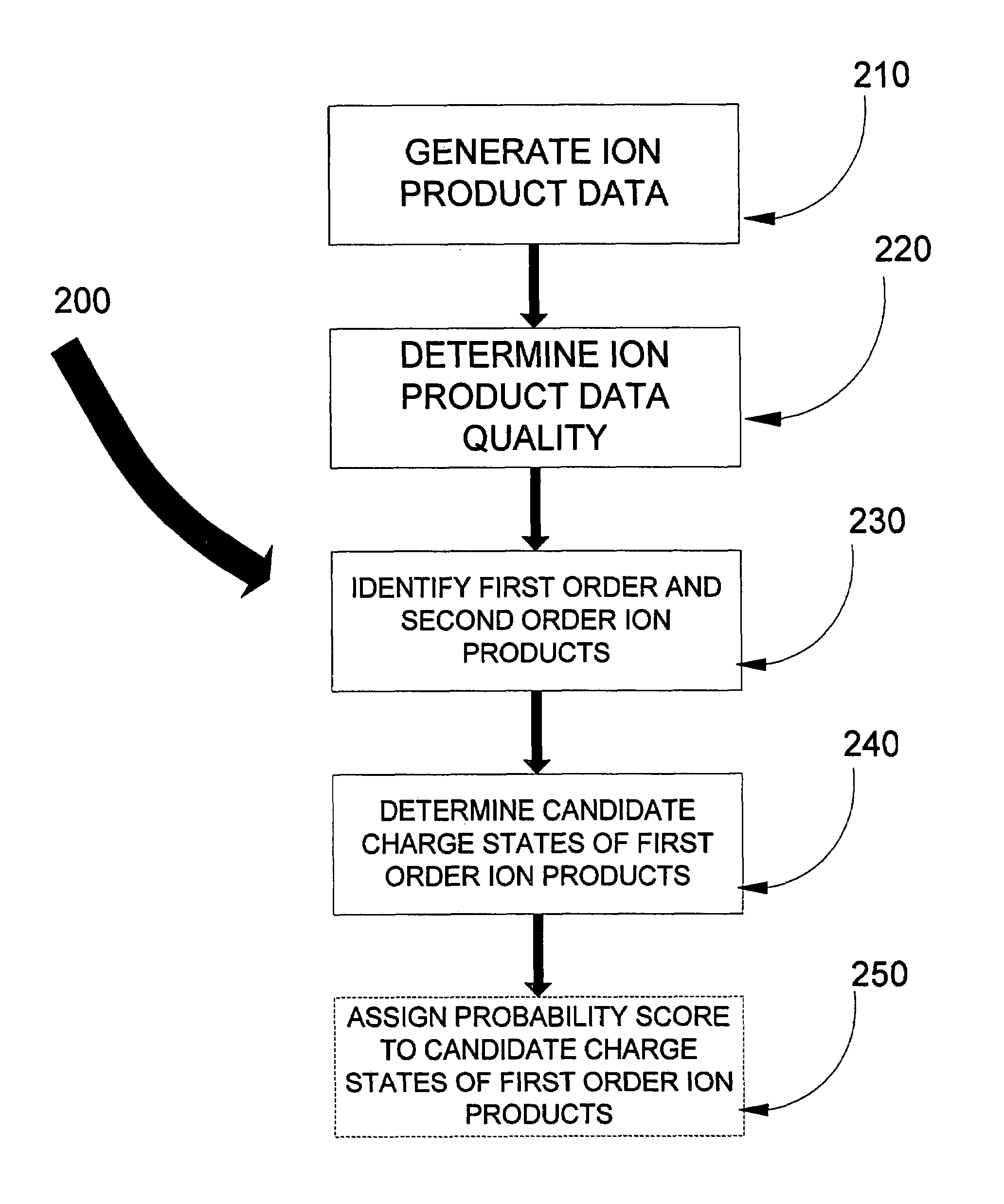
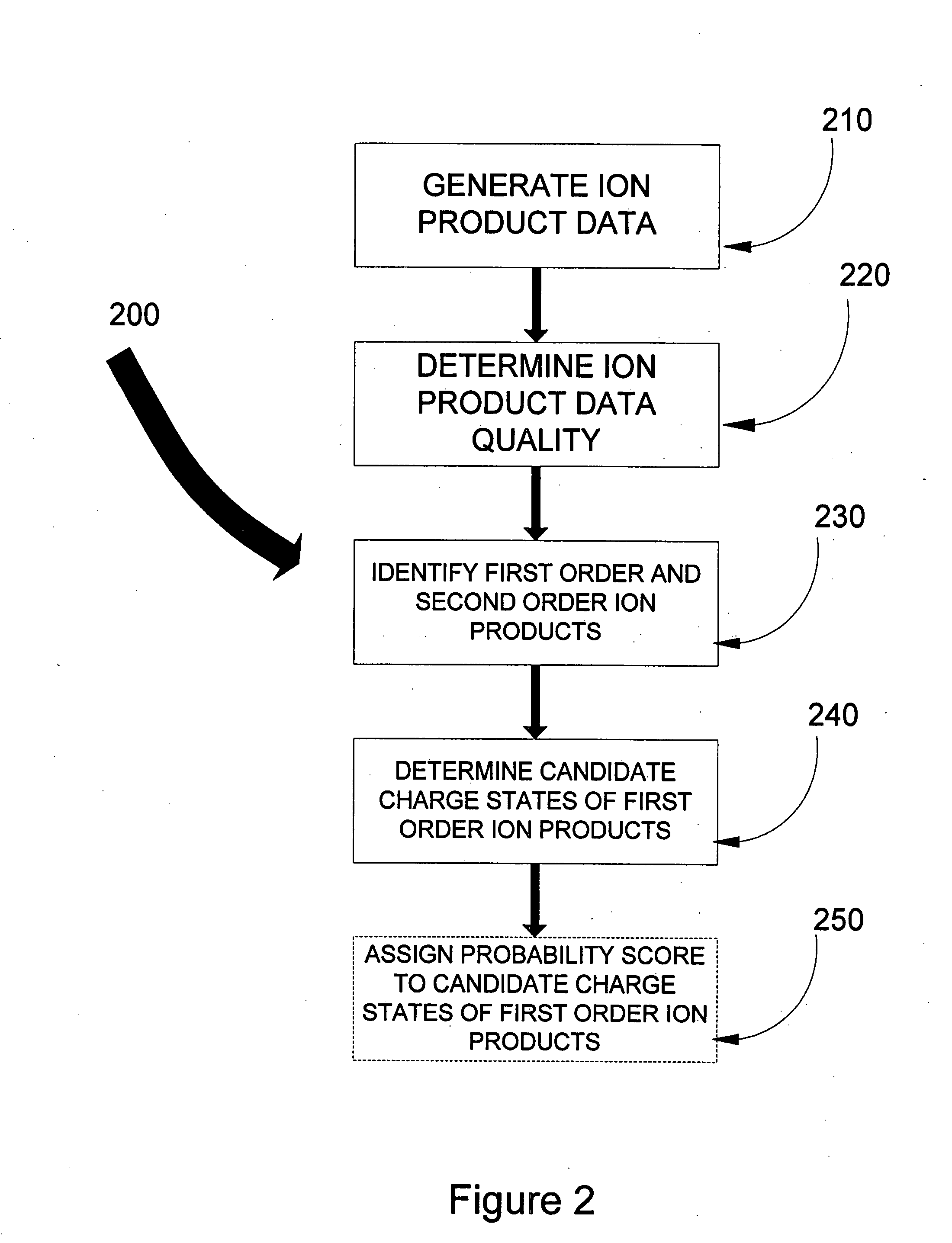
Data analysis to provide a revised data set for use in peptide sequencing determination
ActiveUS7595485B1ConfidenceLess timeParticle separator tubesMicrobiological testing/measurementData setPeptide sequence
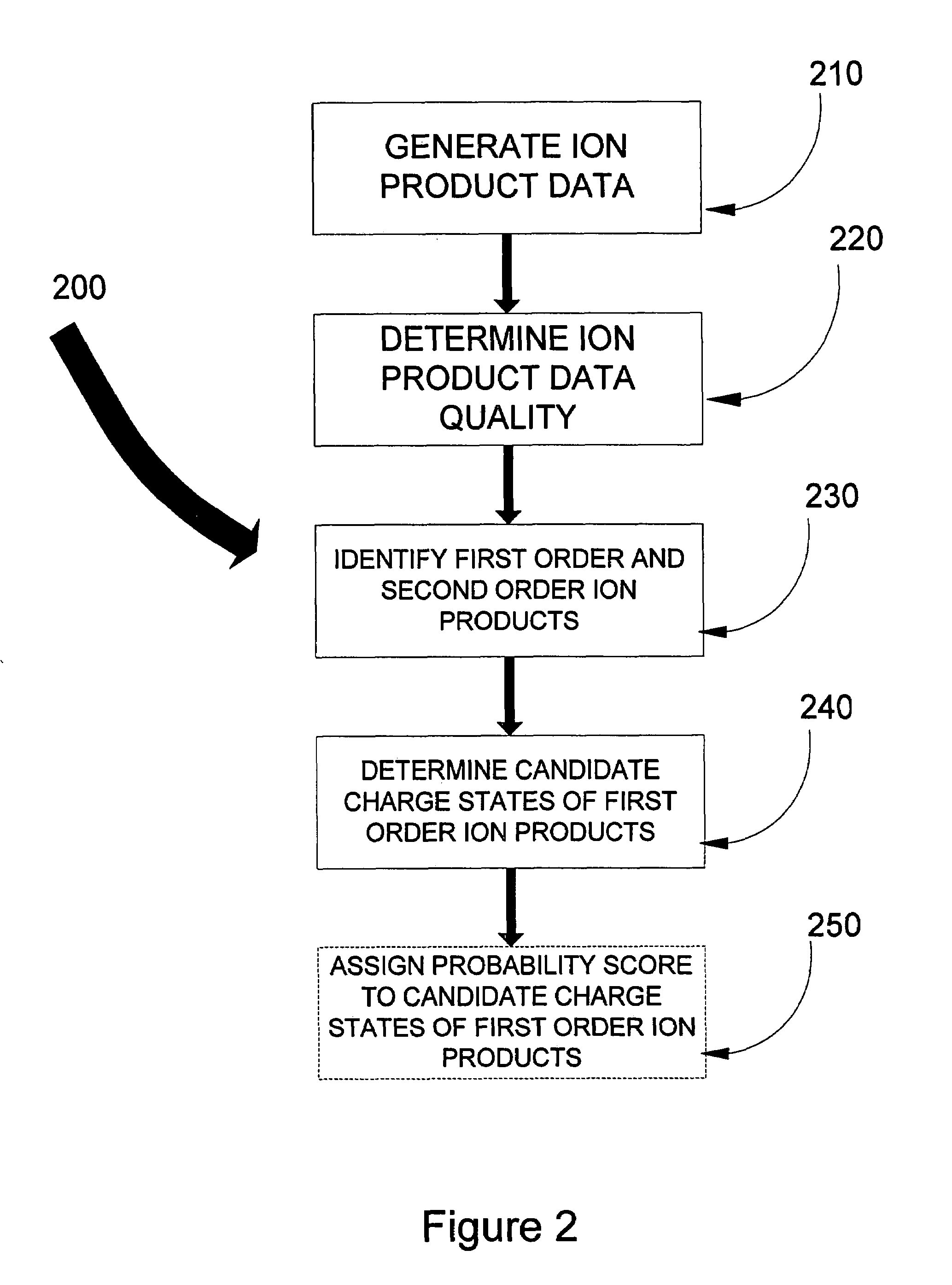
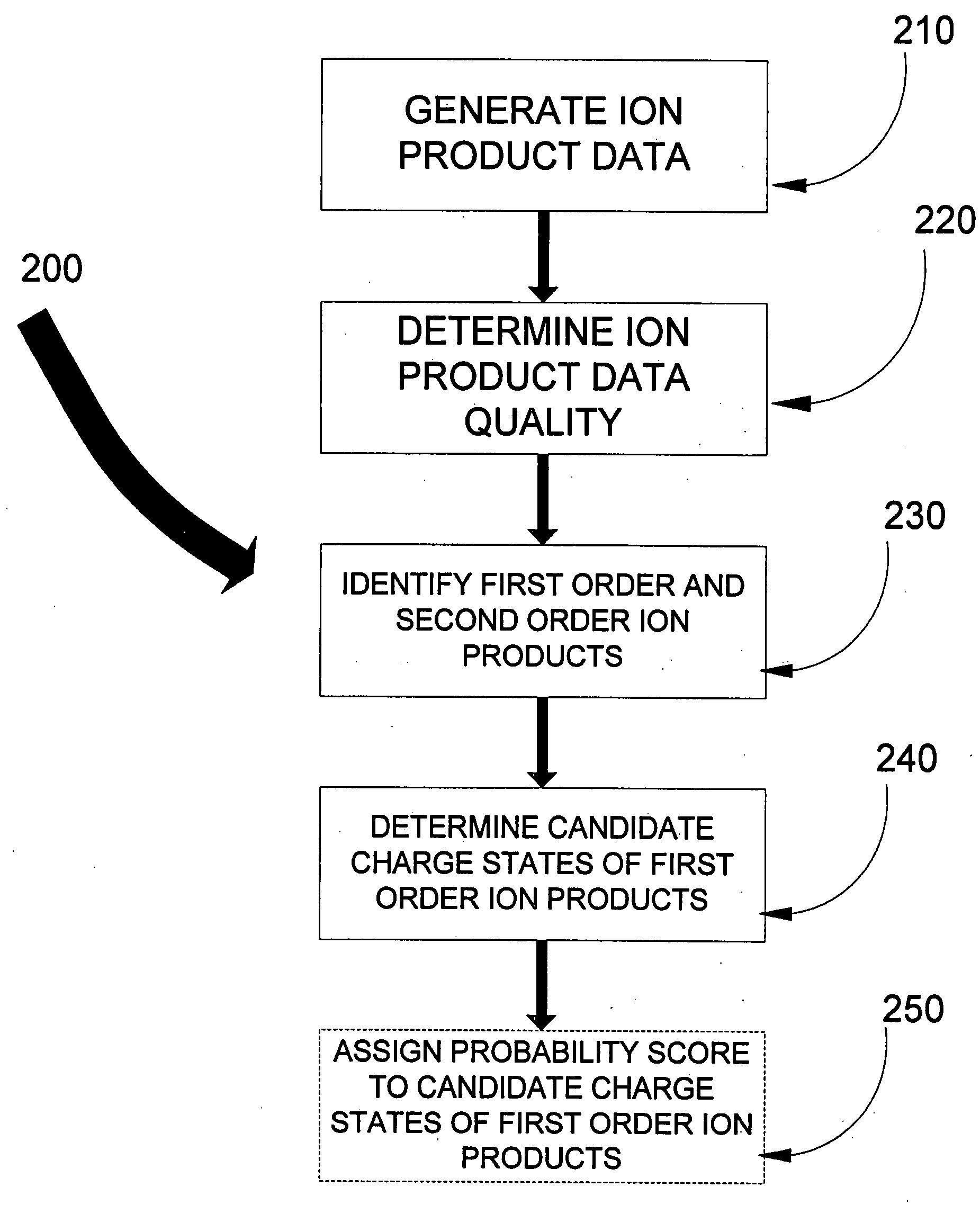
In one aspect of the present invention, the less “useful” spectral data is disregarded from the spectral data resulting from the fragmentation by ETD and candidate charge states for the “useful” data assigned. Knowledge of the first order ion product charge state reduces the subset of comparison data hence aiding in the eventual identification of the precursor ion, and thus aiding in peptide sequence database searching capabilities. Such capabilities include, but are not limited to, computational requirements for database search and data storage, CPU time, the volume taken up on the hard disk to store results, visualization and dissemination of data, and overall improvement in the confidence in the precursor identification. Thus determination of the peptide sequence can be resolved in less time, costing less money, and requiring less computer power.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Systems and methods for patient-specific identification of neoantigens by de novo peptide sequencing for personalized immunotherapy
PendingUS20200243164A1High sensitivityImprove accuracyBiostatisticsProteomicsDe novo peptide sequencingPeptide sequencing
The present systems and workflows identify neoantigens for cancer immunotherapy by introducing deep learning to de novo peptide sequencing from tandem mass spectrometry data. The systems and workflow allows for patient specific identification of neoantigens for personalized immunotherapy.
Owner:BIOINFORMATICS SOLUTIONS
Peptide sequencing from peptide fragmentation mass spectra
The invention relates to a method of peptide sequencing from peptide fragment mass data, wherein a step of deriving a plurality of candidate peptide sequences comprises the following steps: calculating peptide fragment masses by adding to masses of a proton, hydronium ion, b1 ion or y1 ion masses of one amino acid or more amino acids; searching a plurality of peak data for masses matching said calculated peptide fragment masses; annotating in all permutations said peak data with amino acid sequences that correspond to said calculated peptide fragment masses, thereby creating one or more potential sequences; extending said potential sequences to resulting masses with additional matching masses by stepwise adding masses of one or more amino acids and searching for masses in said plurality of peak data that match said resulting masses; extending said stepwise additions until said resulting masses correspond to parental peptide masses or said parental peptide masses minus the mass of water, depending on whether the b or y ion series sequences are calculated; and providing at least one identified peptide sequence by deleting sequences from said potential sequences that can not be extended to endpoints of said parental peptide masses, and deleting from said potential sequences identical sequences generated in at least one of the foregoing steps.
Owner:CHARITE UNIVS MEDIZIN BERLIN
Blind extraction of pure component mass spectra from overlapping mass spectrometric peaks
InactiveUS7804062B2Increasing the instrumental duty cycleComponent separationIsotope separationConfocalHigh pressure
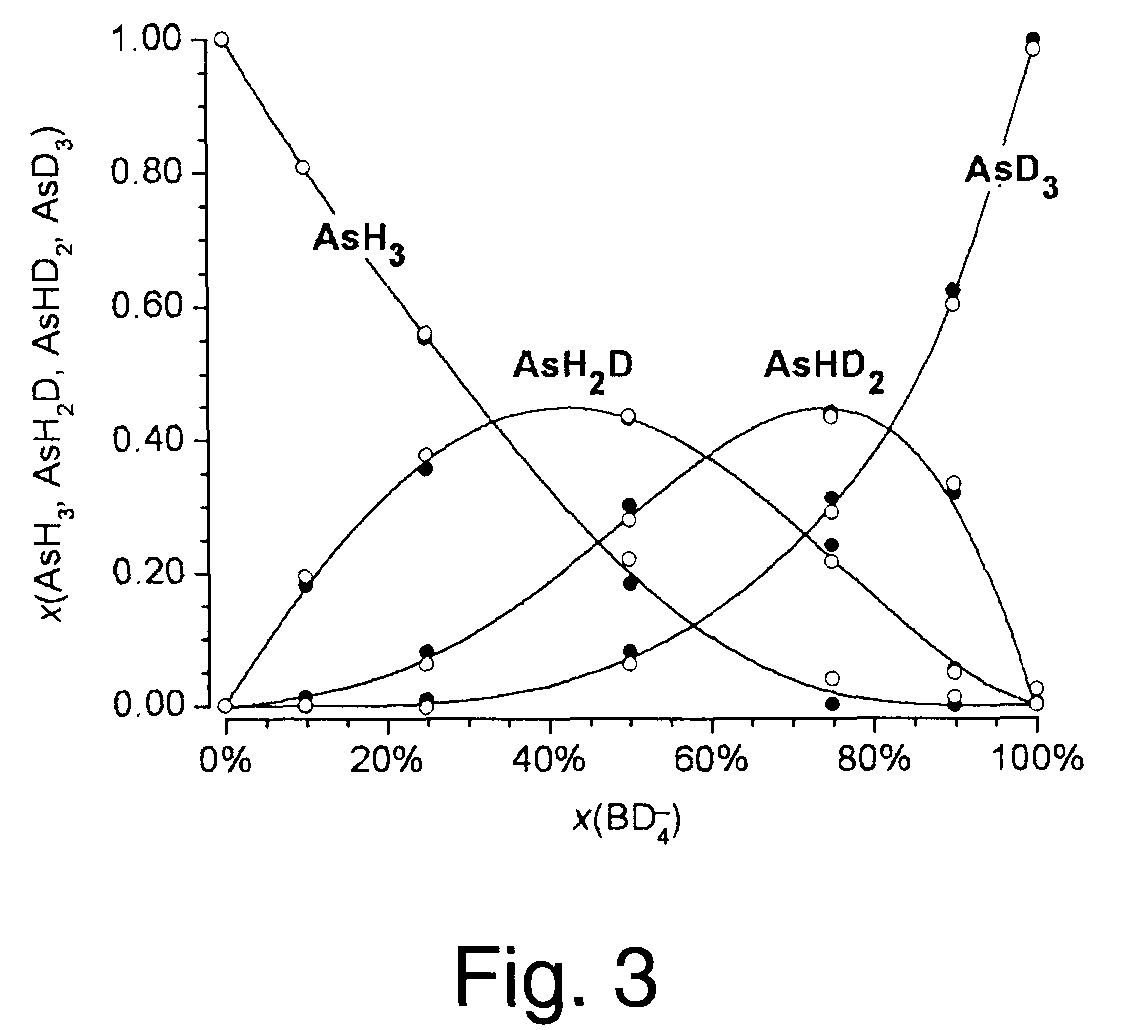
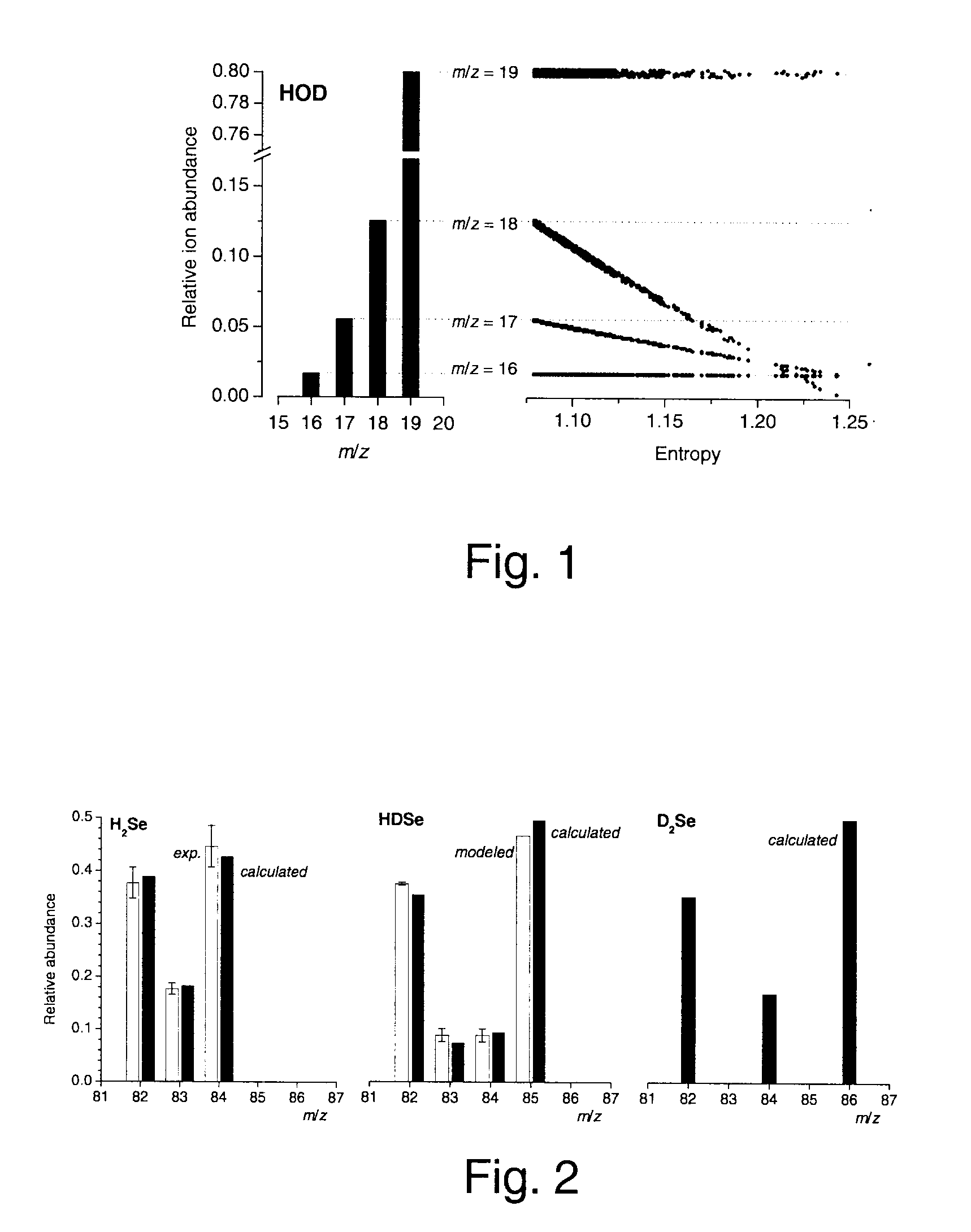
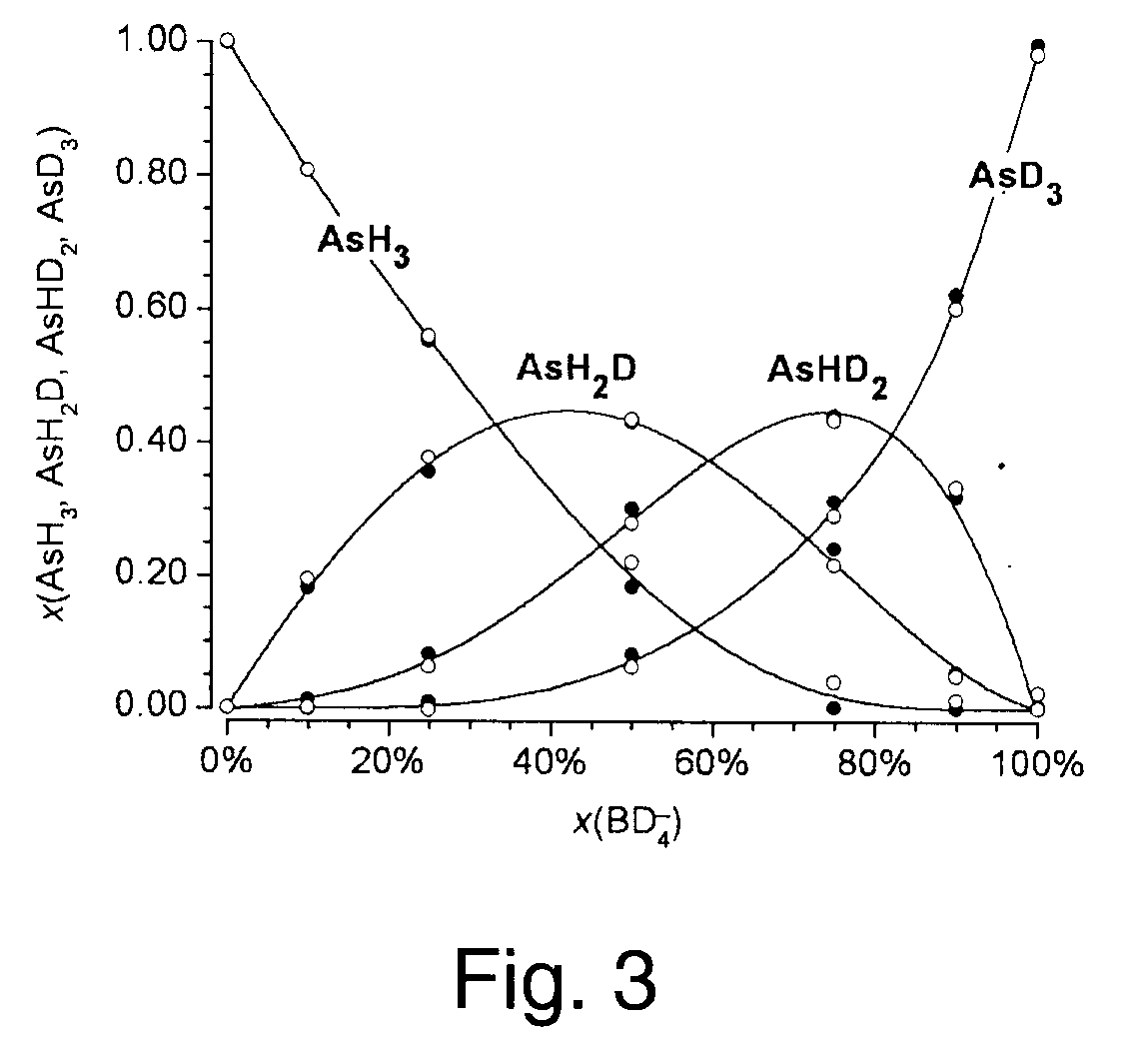
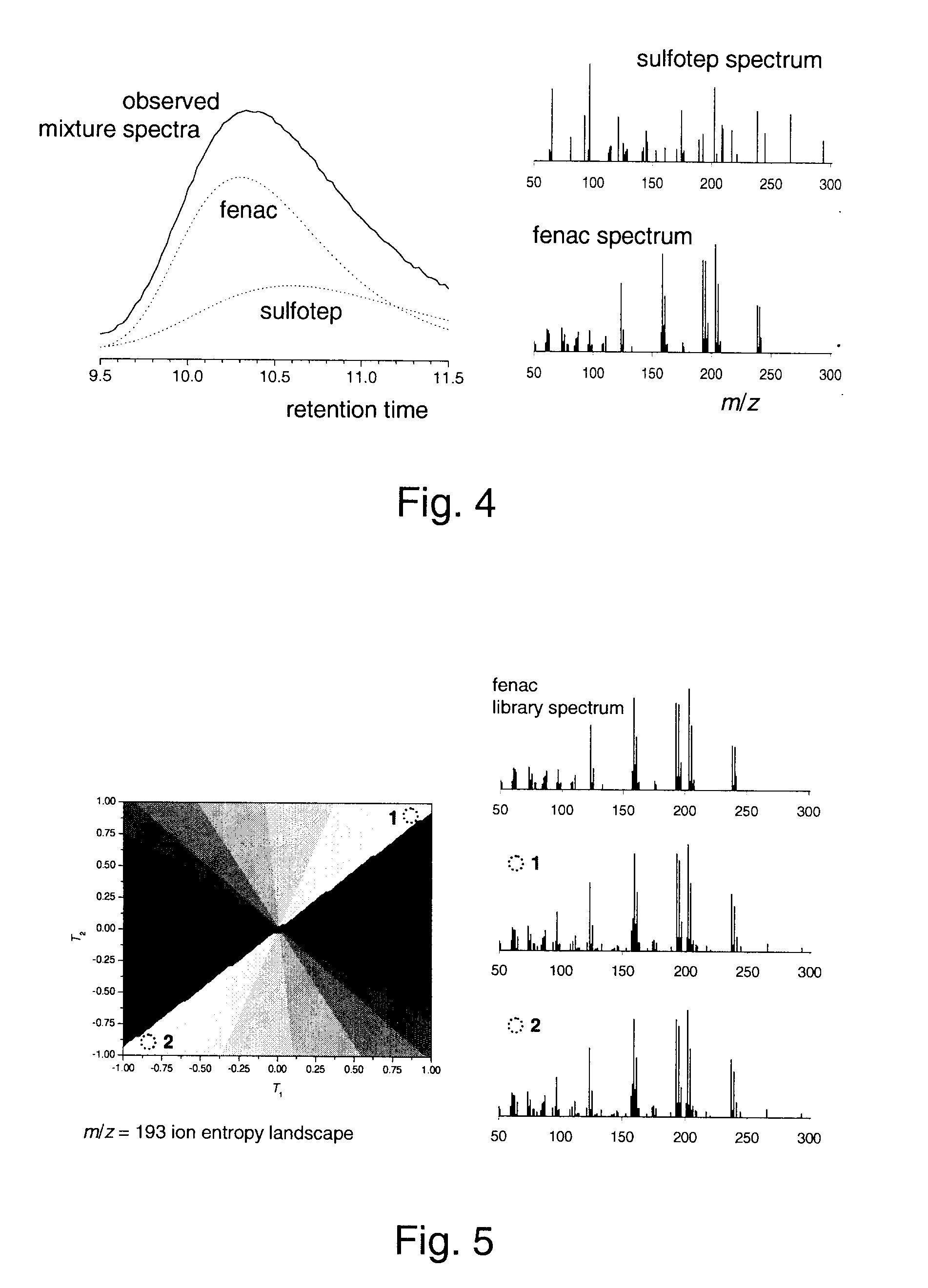
A method of obtaining pure component mass spectra or pure peak elution profiles from mass spectra of a mixture of components involves estimating number of components in the mixture, filtering noise, and extracting individual component mass spectra or pure peak elution profiles using blind entropy minimization with direct optimization (e.g. downhill simplex minimization). The method may be applied to deconvolution of pure GC / MS spectra of overlapping or partially overlapping isotopologues or other compounds, separation of overlapping or partially overlapping compounds in proteomics or metabolomics mass spectrometry applications, peptide sequencing using high voltage fragmentation followed by deconvolution of the obtained mixture mass spectra, deconvolution of MALDI mass spectra in the separation of multiple components present in a single solution, and specific compound monitoring in security and / or environmentally sensitive areas.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Blind Extraction of Pure Component Mass Spectra from Overlapping Mass Spectrometric Peaks
InactiveUS20090121125A1Increasing the instrumental duty cycleParticle separator tubesComponent separationIsotopeHigh pressure
A method of obtaining pure component mass spectra or pure peak elution profiles from mass spectra of a mixture of components involves estimating number of components in the mixture, filtering noise, and extracting individual component mass spectra or pure peak elution profiles using blind entropy minimization with direct optimization (e.g. downhill simplex minimization). The method may be applied to deconvolution of pure GC / MS spectra of overlapping or partially overlapping isotopologues or other compounds, separation of overlapping or partially overlapping compounds in proteomics or metabolomics mass spectrometry applications, peptide sequencing using high voltage fragmentation followed by deconvolution of the obtained mixture mass spectra, deconvolution of MALDI mass spectra in the separation of multiple components present in a single solution, and specific compound monitoring in security and / or environmentally sensitive areas.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
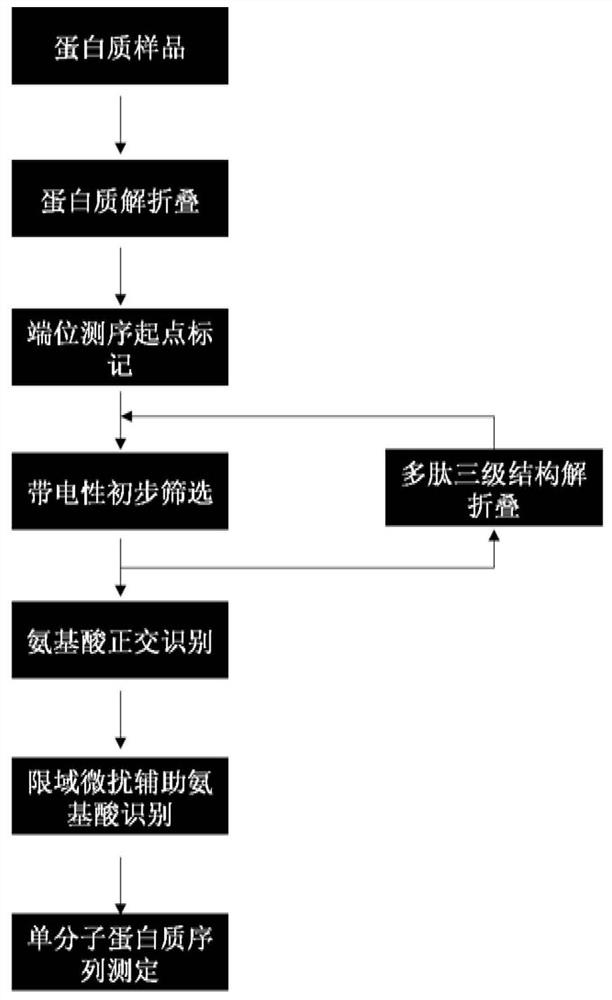
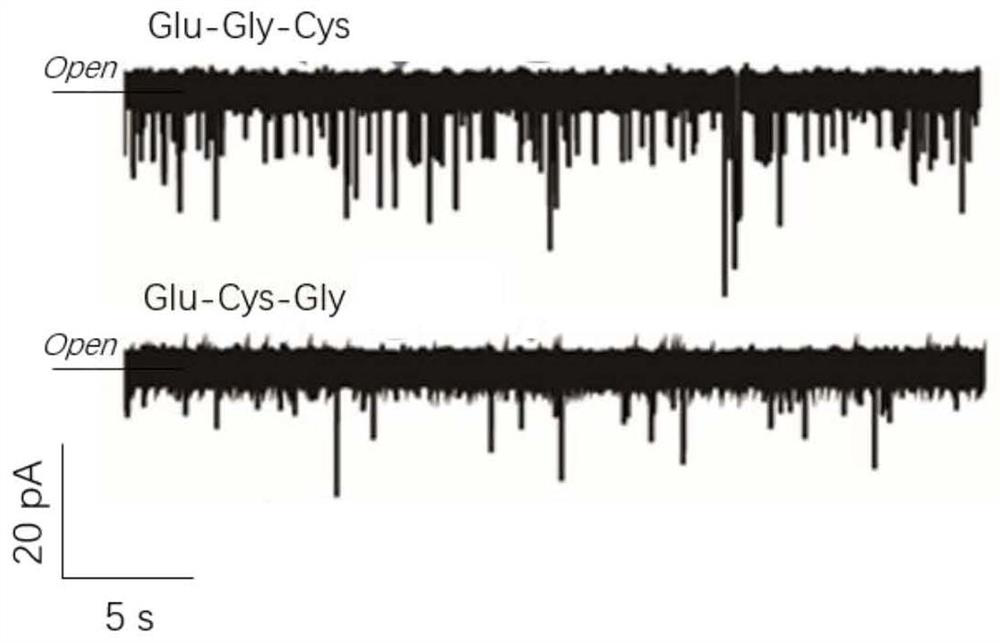
Protein/polypeptide sequencing method adopting Aerolysin nanopores
PendingCN112480204AEasy to identifyAccurately obtain single-molecule sequence informationPeptide preparation methodsMaterial analysisAerolysinProtein molecules
The invention provides a method for protein / polypeptide sequencing based on Aerolysin nanopores. The method realizes specific resolution of natural amino acid and post-translational modification thereof and accurate acquisition of a single-molecule protein sequence, and comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out protein unfolding; (2) marking an end position sequencing starting point; (3) carrying out electrified preliminary screening; (4) unfolding a polypeptide tertiary structure; (5) carrying out amino acid orthogonal recognition; (6) carrying out limited range perturbation assisted amino acid recognition; and (7) carrying out single molecule protein sequence determination. According to the method, an innovative method for accurate measurement of single protein molecule amino acidsequence and post-translational modification is established for sensitive detection of information of 20 amino acid sequences.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
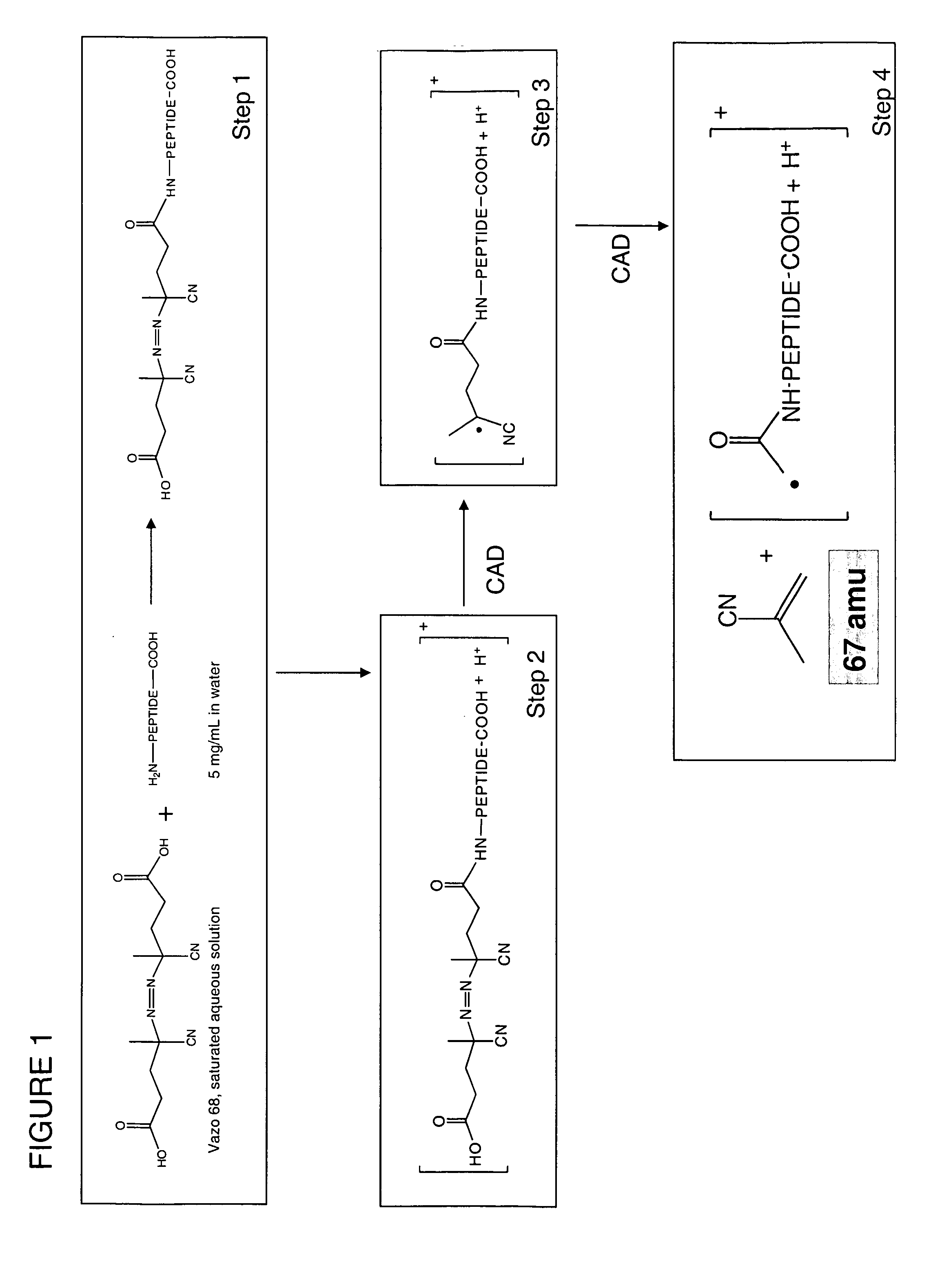
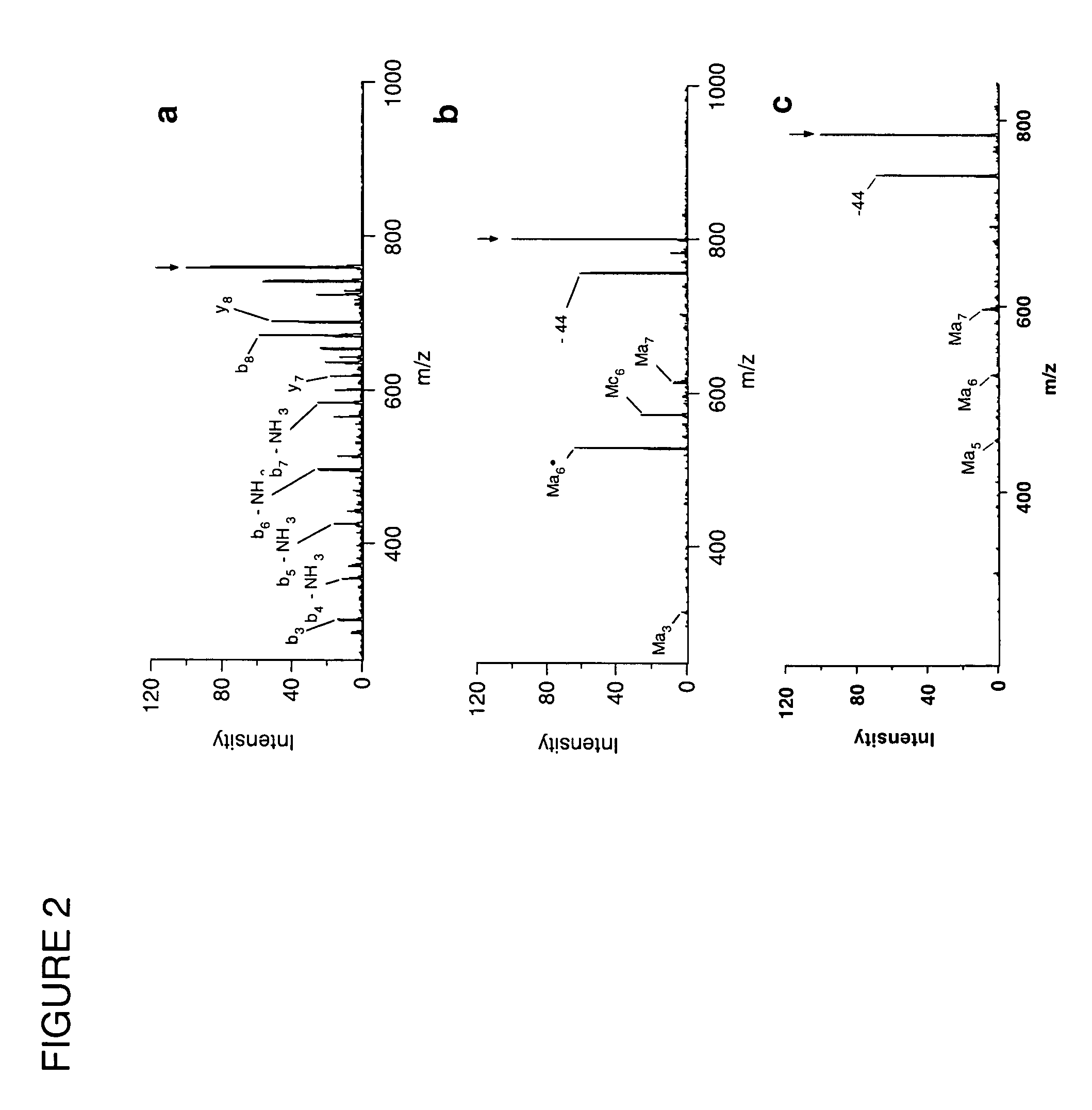
System and method of free radical initiated protein sequencing
A method for the selective fragmentation of peptides using free radical initiator-peptide conjugates is provided. Free radical initiated peptide sequencing, or FRIPS, consists of covalently attaching a free radical initiator to a peptide and collisionally activating this conjugate. This results in fragment formation. Subsequent collision-activated dissociation further dissociates the fragments, producing a group of ions based on the interaction of the free radical initiator and the target molecule. The methodology is applied to the fundamental study of biologically relevant reactions of free radicals with peptides and proteins in the gas phase, as well as to a completely gas-phase approach to protein sequencing.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Single molecule peptide sequencing
ActiveUS20200018768A1OmicsCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesLarge-Scale SequencingProtein Sequence Determination
Identifying proteins and peptides, and more specifically large-scale sequencing of single peptides in a mixture of diverse peptides at the single molecule level is an unmet challenge in the field of protein sequencing. Herein are methods for identifying amino acids in peptides, including peptides comprising unnatural amino acids. In one embodiment, the N-terminal amino acid is labeled with a first label and an internal amino acid is labeled with a second label. In some embodiments, the labels are fluorescent labels. In other embodiments, the internal amino acid is Lysine. In other embodiments, amino acids in peptides are identified based on the fluorescent signature for each peptide at the single molecule level.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Single molecule peptide sequencing
ActiveUS20220091130A1OmicsCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesLarge-Scale SequencingProtein Sequence Determination
Identifying proteins and peptides, and more specifically large-scale sequencing of single peptides in a mixture of diverse peptides at the single molecule level is an unmet challenge in the field of protein sequencing. Herein are methods for identifying amino acids in peptides, including peptides comprising unnatural amino acids. In one embodiment, the N-terminal amino acid is labeled with a first label and an internal amino acid is labeled with a second label. In some embodiments, the labels are fluorescent labels. In other embodiments, the internal amino acid is Lysine. In other embodiments, amino acids in peptides are identified based on the fluorescent signature for each peptide at the single molecule level.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
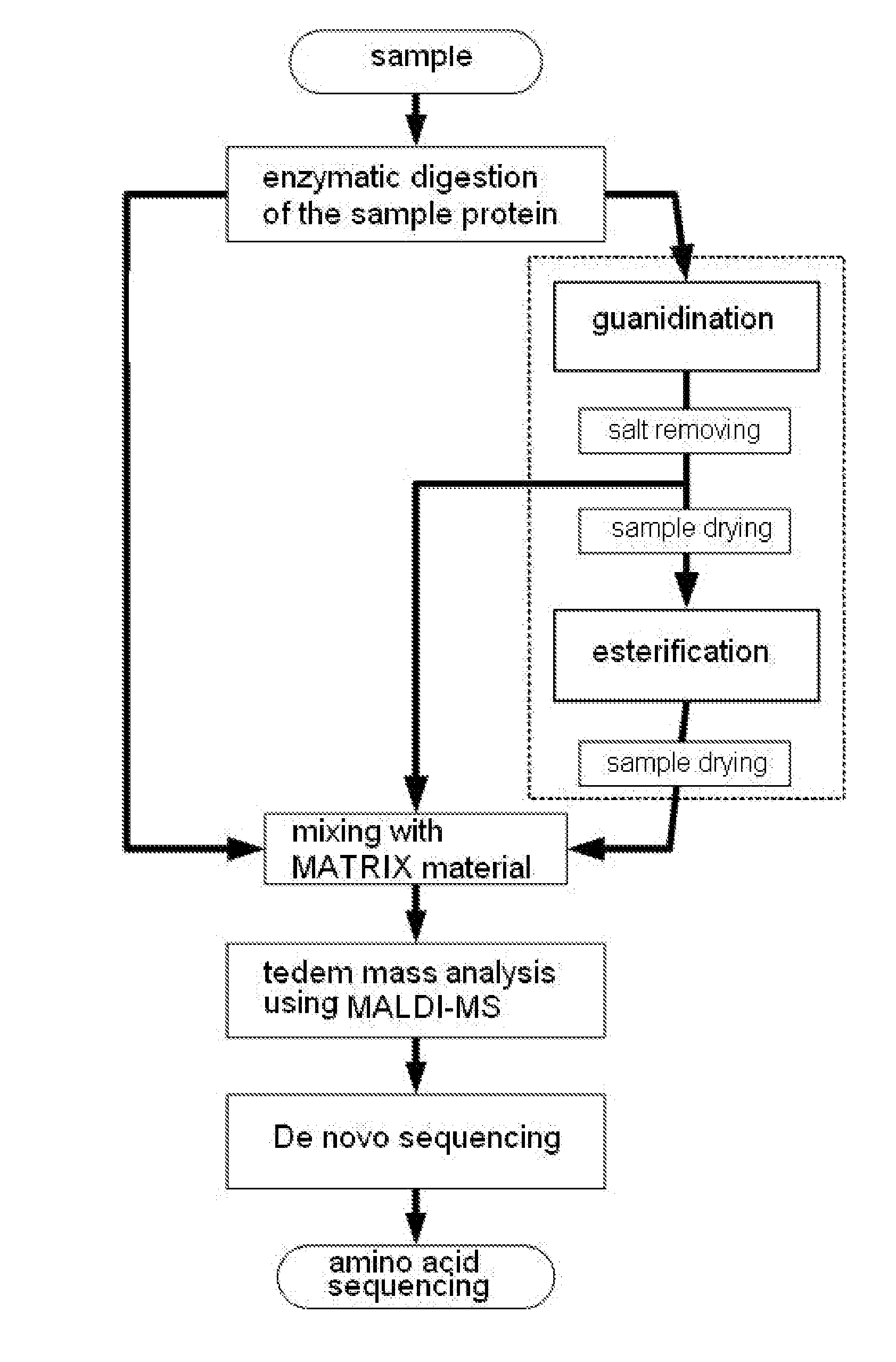
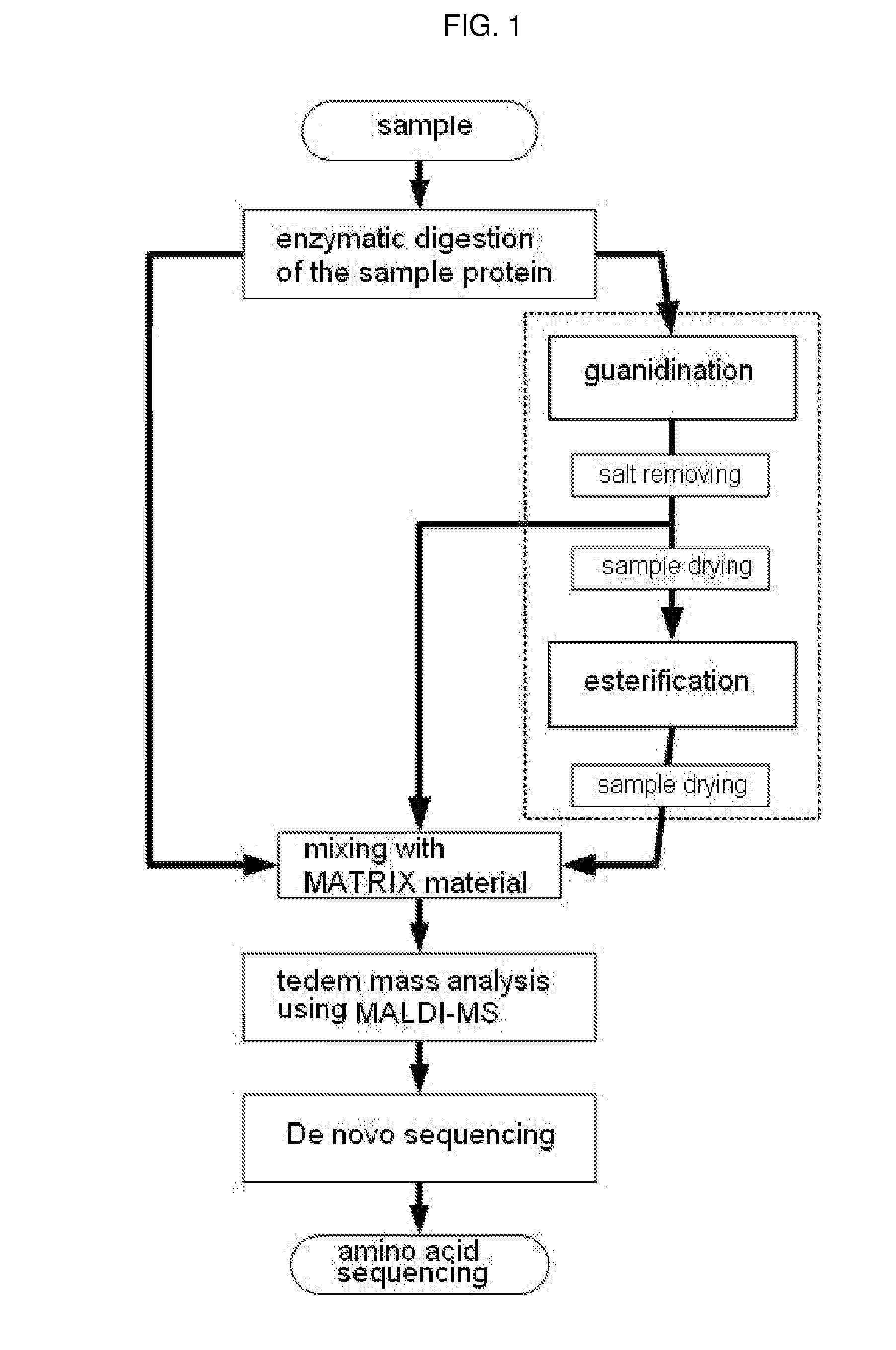
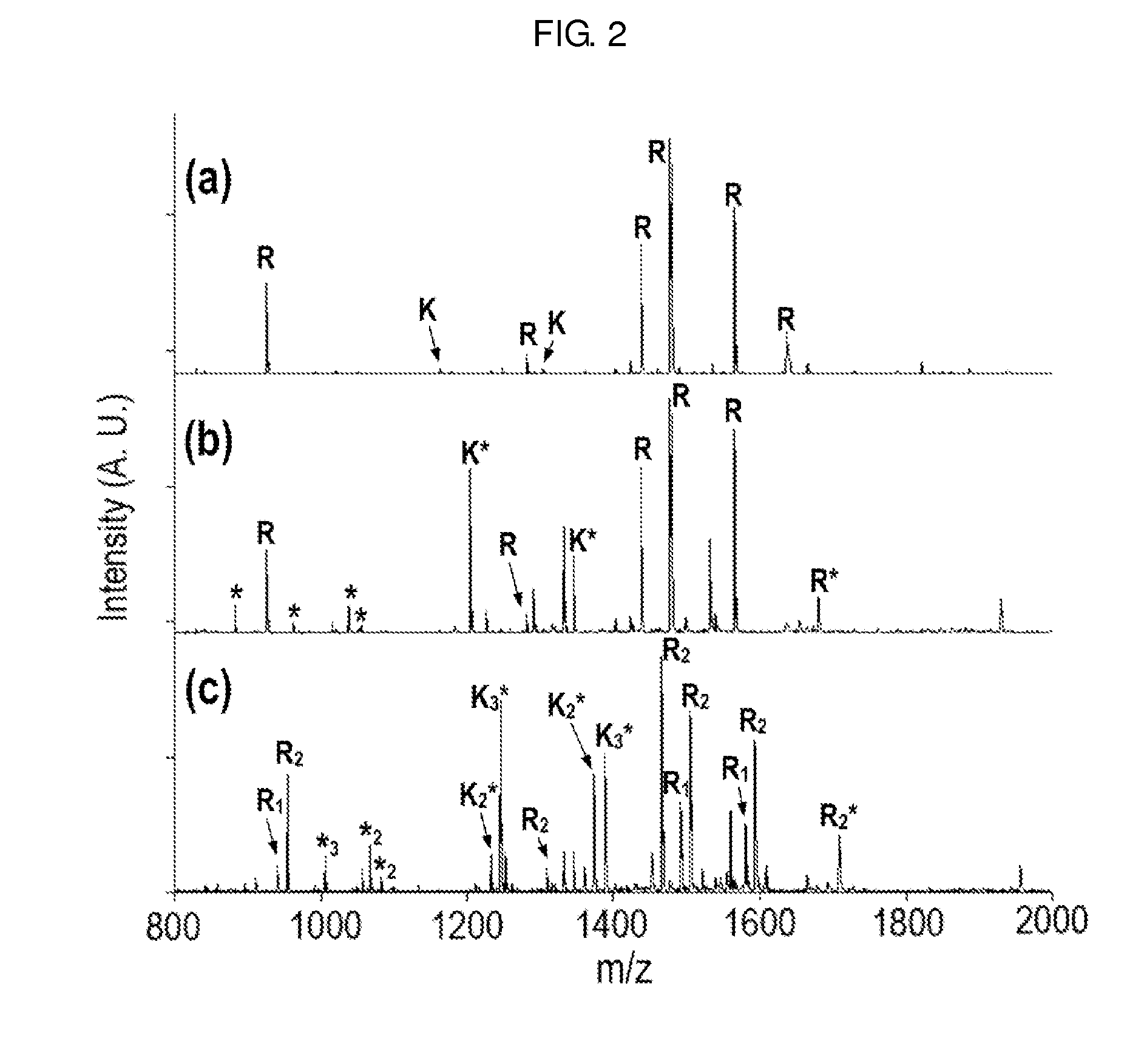
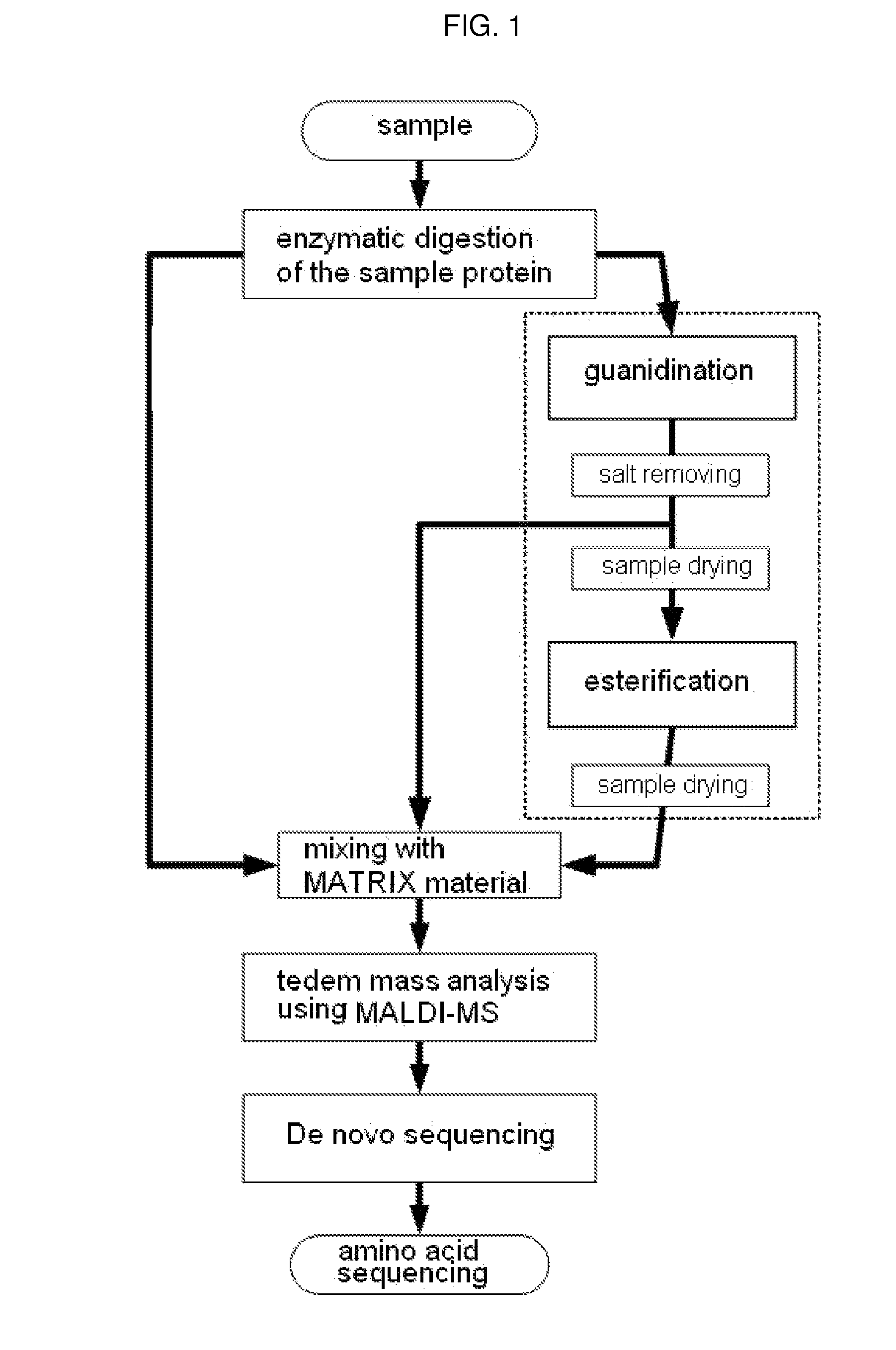
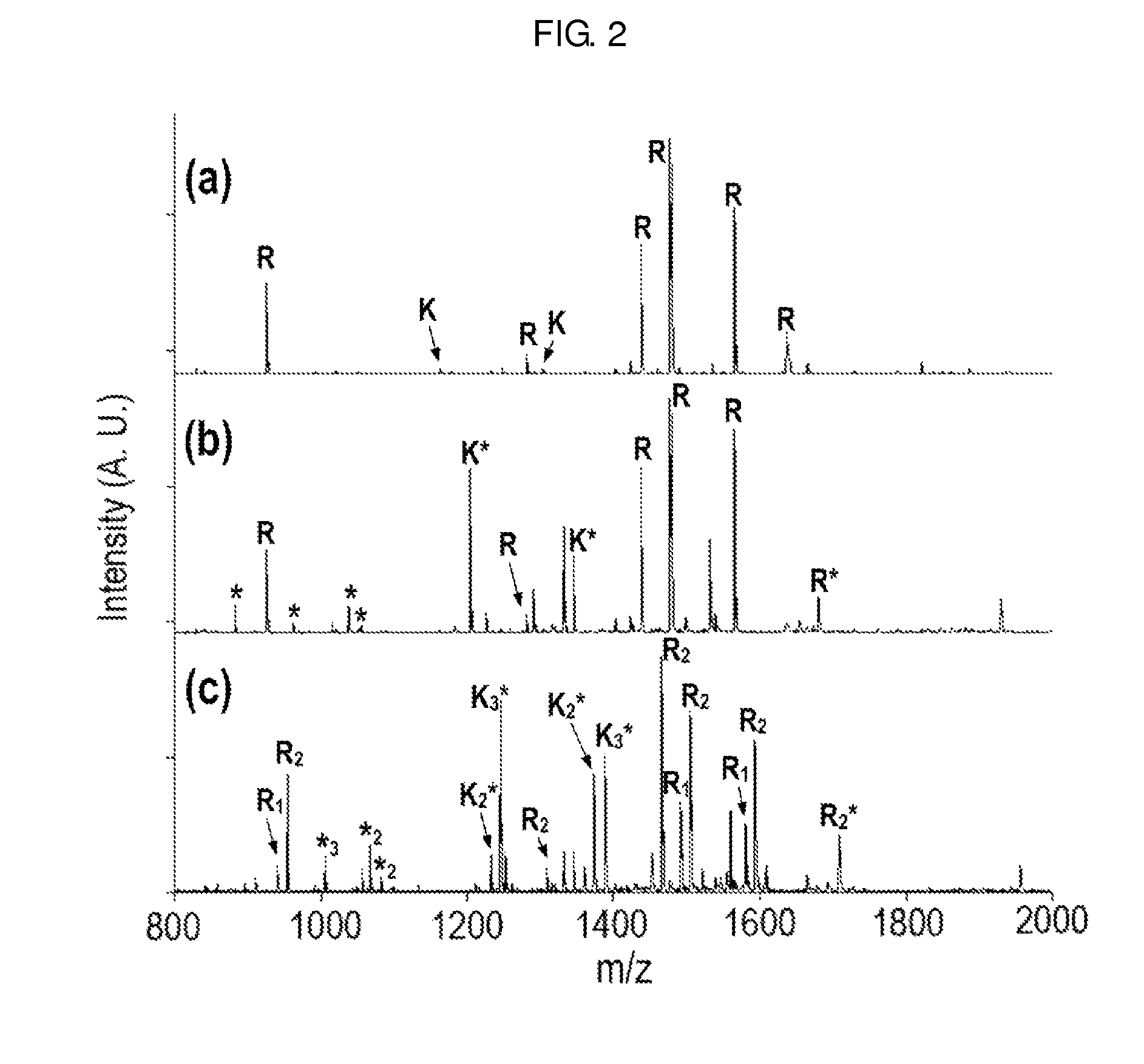
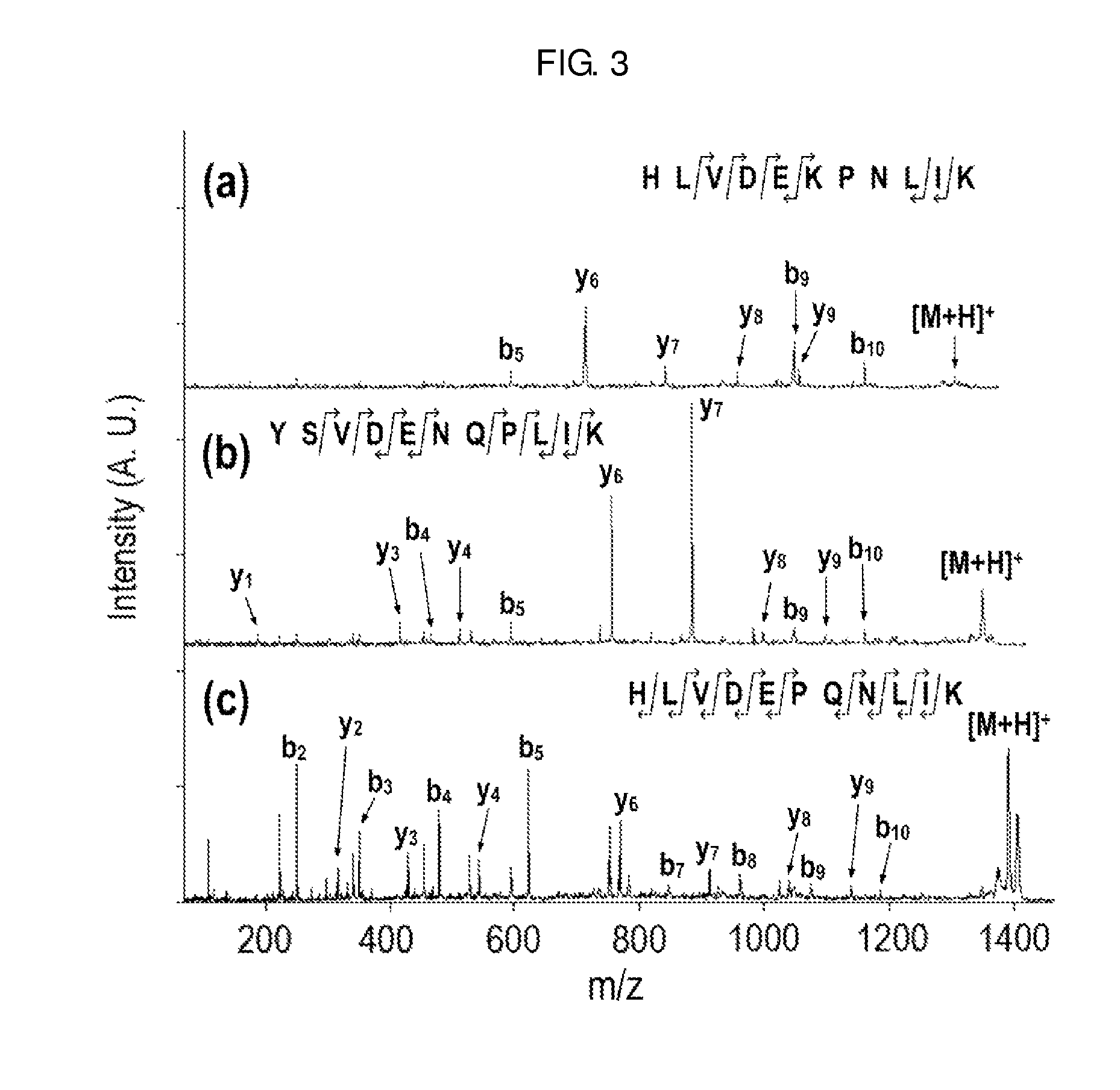
Method of De Novo Sequencing of Peptide Using the Maldi Mass Spectrometry, Method and Apparatus for Preparing Sample for Maldi Mass Spectrometry
ActiveUS20080138845A1Wide variation of detection sensitivityHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementElectron/ion optical arrangementsPeptide sequencingMass spectrometric
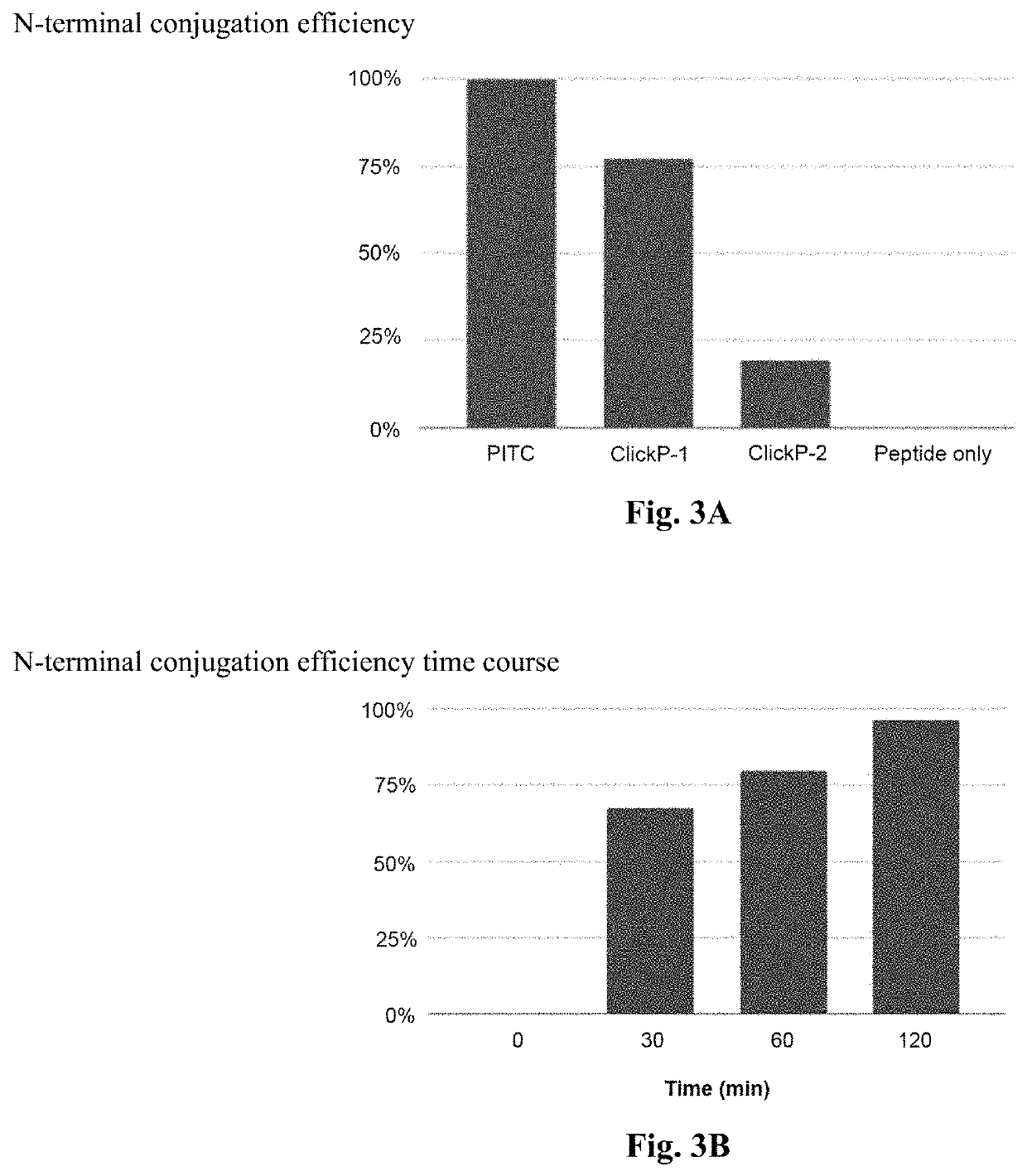
The present invention relates to a method of peptide sequencing by MALDI (matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization) tandem mass spectrometry, which comprises the steps of chemically modifying a sample peptide with at least one chemical modification method selected from the group consisting of guanidination and esterification in order to change the ionization status of the peptide and performing mass spectrometry using a MALDI tandem mass spectrometer and programmed MALDI tandem mass spectrometry. The peptide sequencing method of the present invention is advantageous in that detection sensitivity of the peptide improves significantly and various daughter ions are detected uniformly, thereby enabling perfect de novo sequencing with tandem mass spectrometry only, without database search.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND +1
Single-molecule protein and peptide sequencing
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method of de novo sequencing of peptide using the MALDI mass spectrometry, method and apparatus for preparing sample for MALDI mass spectrometry
ActiveUS7723917B2Wide detection rangeHigh detection sensitivitySolid cathode detailsMaterial analysisMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryDe novo peptide sequencing
The present invention relates to a method of peptide sequencing by MALDI (matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization) tandem mass spectrometry, which comprises the steps of chemically modifying a sample peptide with at least one chemical modification method selected from the group consisting of guanidination and esterification in order to change the ionization status of the peptide and performing mass spectrometry using a MALDI tandem mass spectrometer and programmed MALDI tandem mass spectrometry. The peptide sequencing method of the present invention is advantageous in that detection sensitivity of the peptide improves significantly and various daughter ions are detected uniformly, thereby enabling perfect de novo sequencing with tandem mass spectrometry only, without database search.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND +1
Single molecule peptide sequencing methods
ActiveUS20200400677A1Microbiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceProtein Sequence DeterminationPeptide sequencing
The invention, in part, includes methods of single molecule protein sequencing that include using weak binding spectra in the amino acid identification.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Data analysis to provide a revised data set for use in peptide sequencing determination
ActiveUS20090254285A1ConfidenceLess timeParticle separator tubesMicrobiological testing/measurementData setData profiling
In one aspect of the present invention, the less “useful” spectral data is disregarded from the spectral data resulting from the fragmentation by ETD and candidate charge states for the “useful” data assigned. Knowledge of the first order ion product charge state reduces the subset of comparison data hence aiding in the eventual identification of the precursor ion, and thus aiding in peptide sequence database searching capabilities. Such capabilities include, but are not limited to, computational requirements for database search and data storage, CPU time, the volume taken up on the hard disk to store results, visualization and dissemination of data, and overall improvement in the confidence in the precursor identification. Thus determination of the peptide sequence can be resolved in less time, costing less money, and requiring less computer power.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Method for Identification of Enzymes
InactiveUS20070264632A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesNucleic acid hybridisation
The present invention provides a method of identifying an enzyme, the method generally involving contacting a sample containing an enzyme with a selected enzyme substrate, where the contacting provides for covalent binding of the substrate to an amino acid of the enzyme to form a covalently modified enzyme; and determining the amino acid sequence of at least a portion of the covalently modified enzyme, using any available peptide sequencing technology, such as tandem mass spectrometry. The present invention further provides methods of identifying a nucleic acid encoding an enzyme, the methods generally involving identifying an enzyme; and, based on the amino acid sequence of at least a portion of the enzyme, designing nucleic acid probes or primers that hybridize to the nucleic acid encoding the enzyme.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Single molecule peptide sequencing methods
ActiveUS20220291226A1Microbiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceProtein Sequence DeterminationPeptide sequencing
The invention, in part, includes methods of single molecule protein sequencing that include using weak binding spectra in the amino acid identification.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
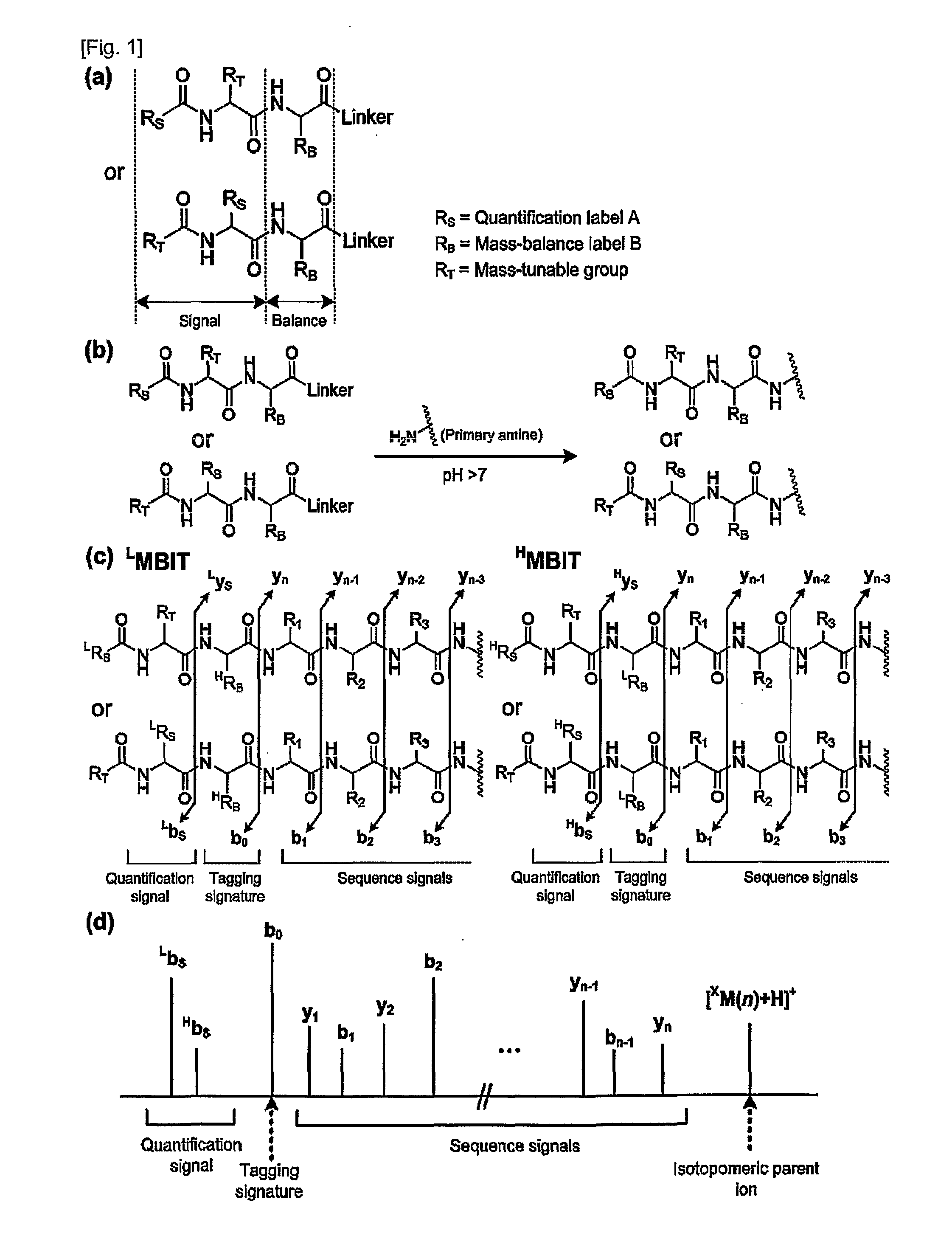
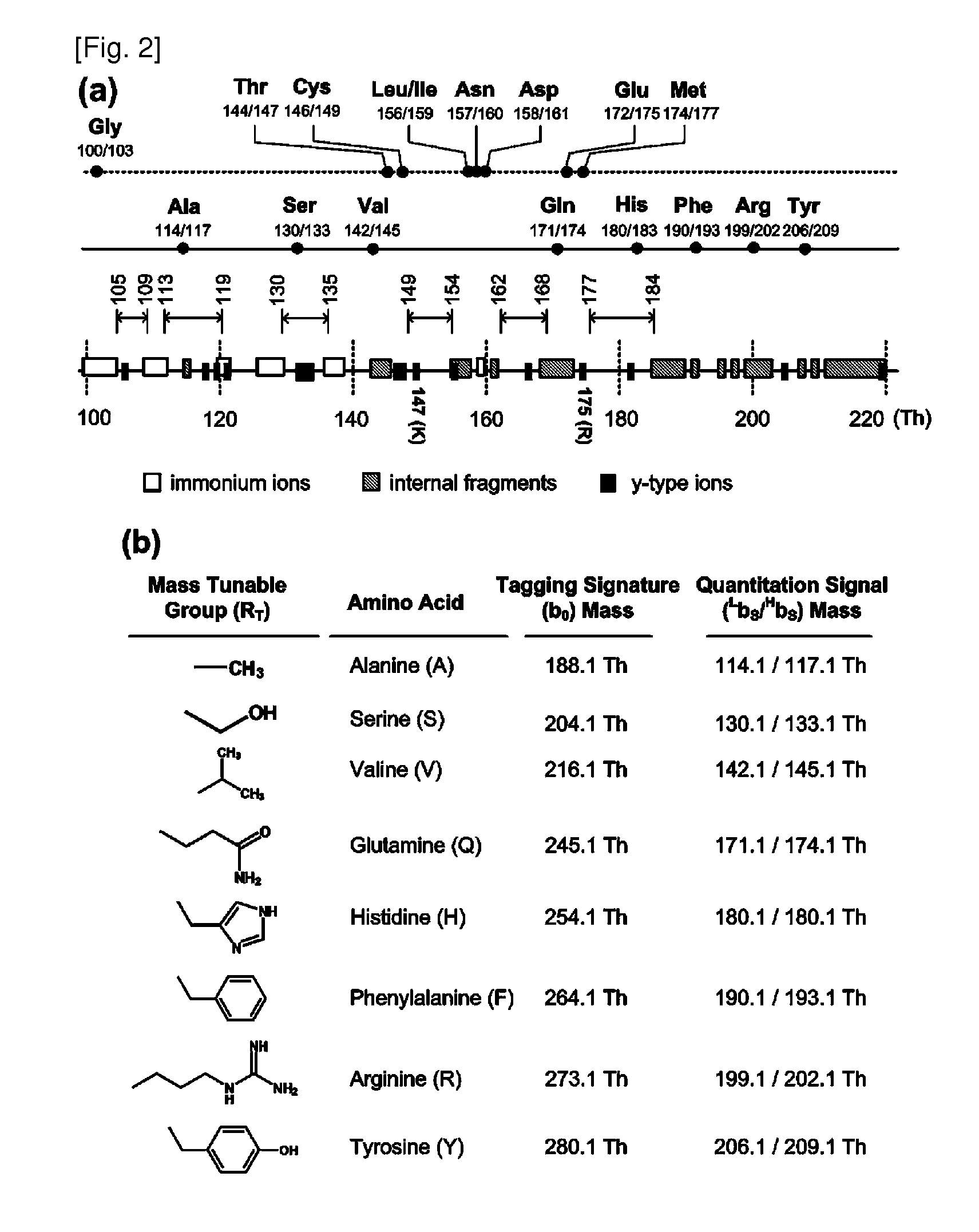
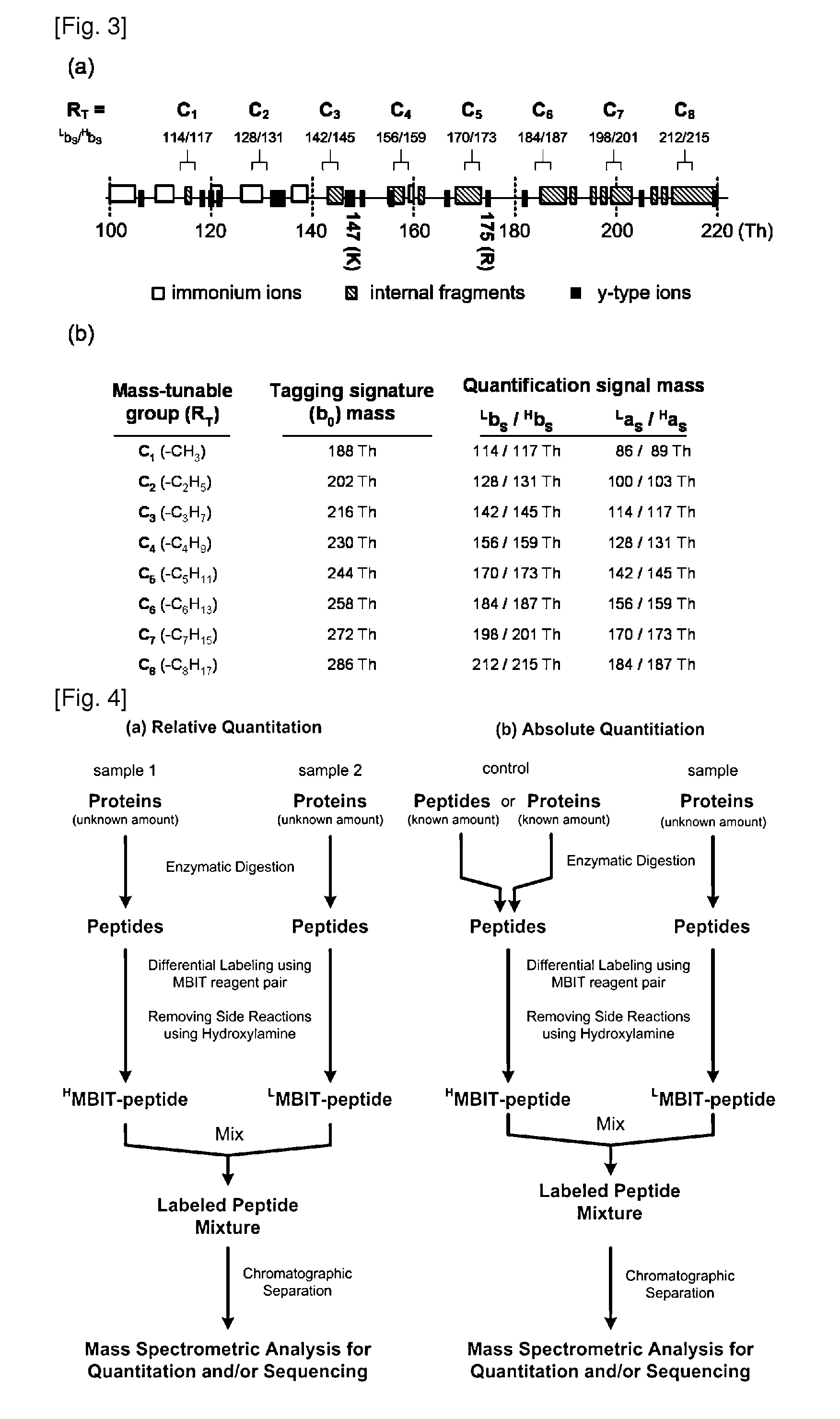
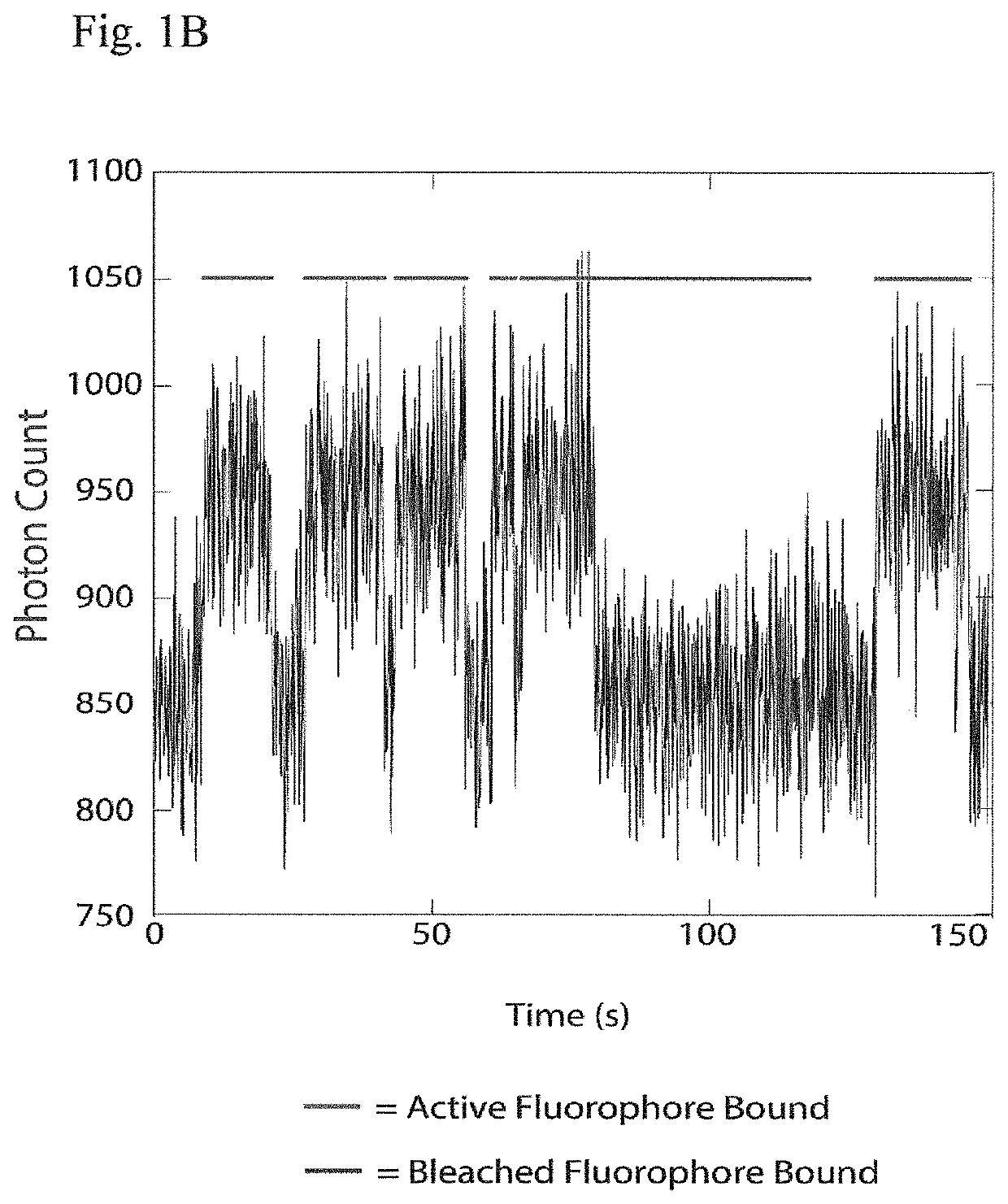
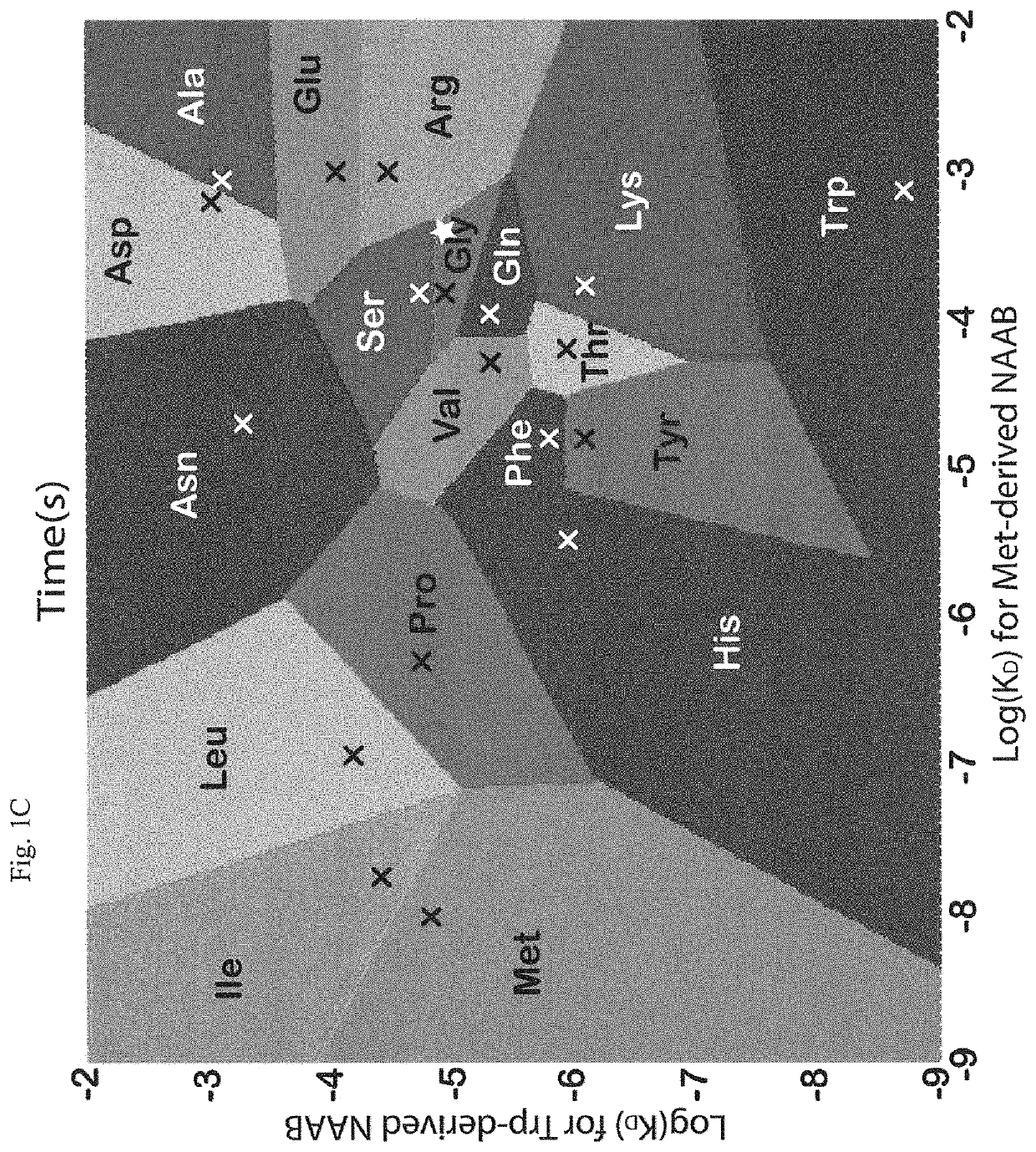
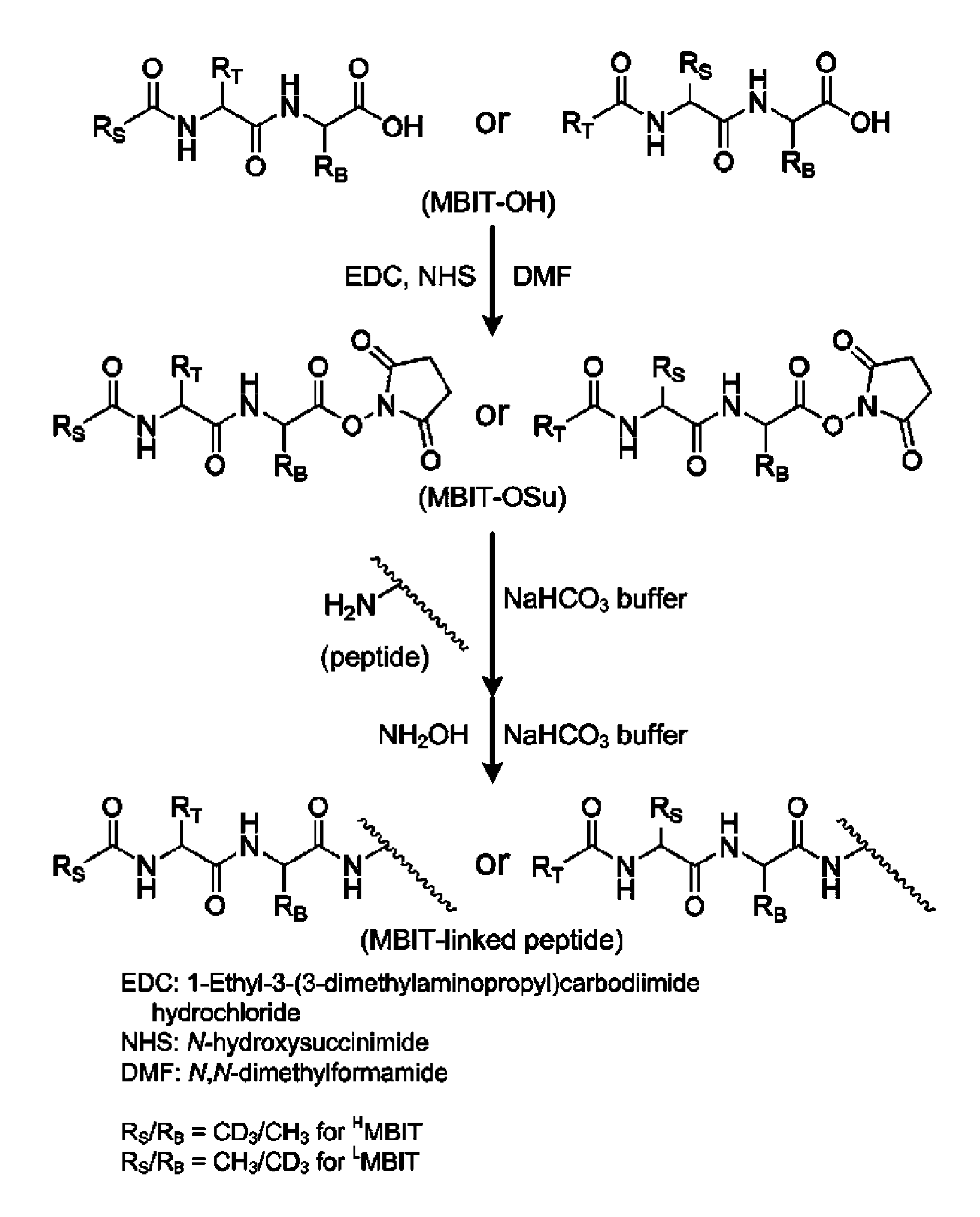
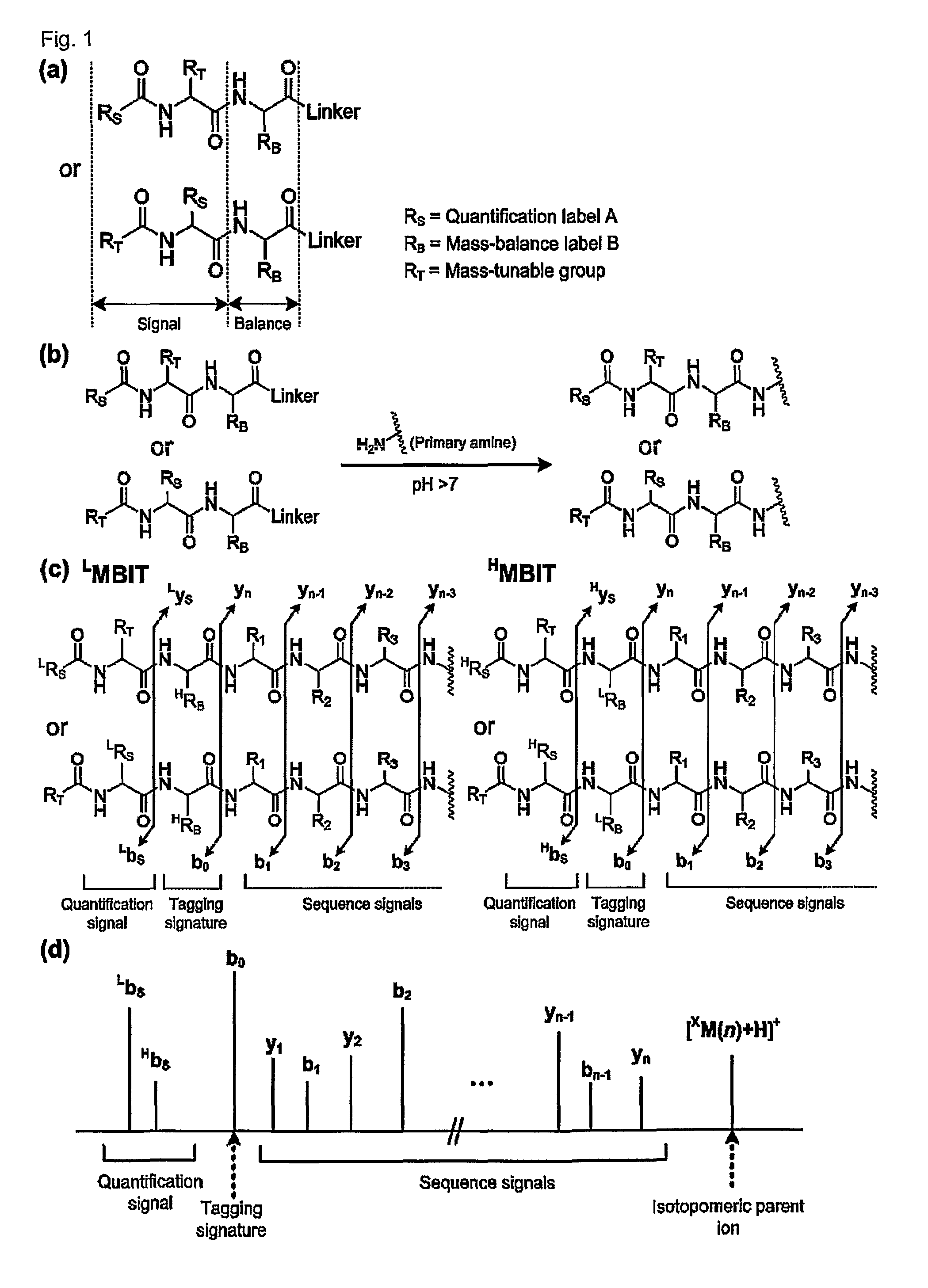
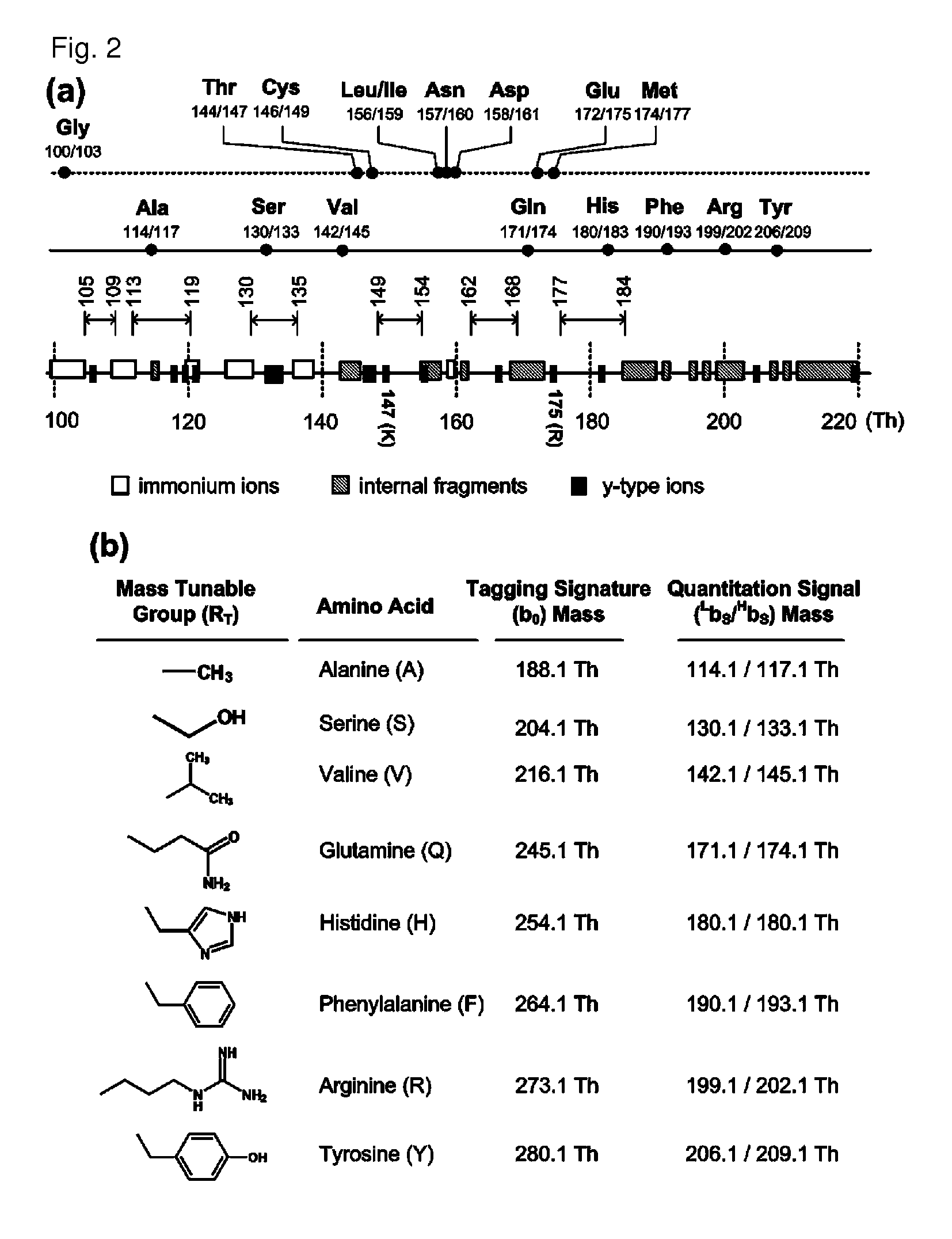
Mass- and property-tuned variable mass labeling reagents and analytical methods for simultaneous peptide sequencing and multiplexed protein quantification using thereof
InactiveUS20110071040A1Tunability is providedPeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsAnalysis methodComputational chemistry
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Single molecule peptide sequencing
ActiveUS11435358B2OmicsCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesLarge-Scale SequencingProtein Sequence Determination
Identifying proteins and peptides, and more specifically large-scale sequencing of single peptides in a mixture of diverse peptides at the single molecule level is an unmet challenge in the field of protein sequencing. Herein are methods for identifying amino acids in peptides, including peptides with unnatural amino acids. In one embodiment, the N-terminal amino acid is labeled with a first label and an internal amino acid is labeled with a second label. In some embodiments, the labels are fluorescent labels. In other embodiments, the internal amino acid is Lysine. In other embodiments, amino acids in peptides are identified based on the fluorescent signature for each peptide at the single molecule level.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
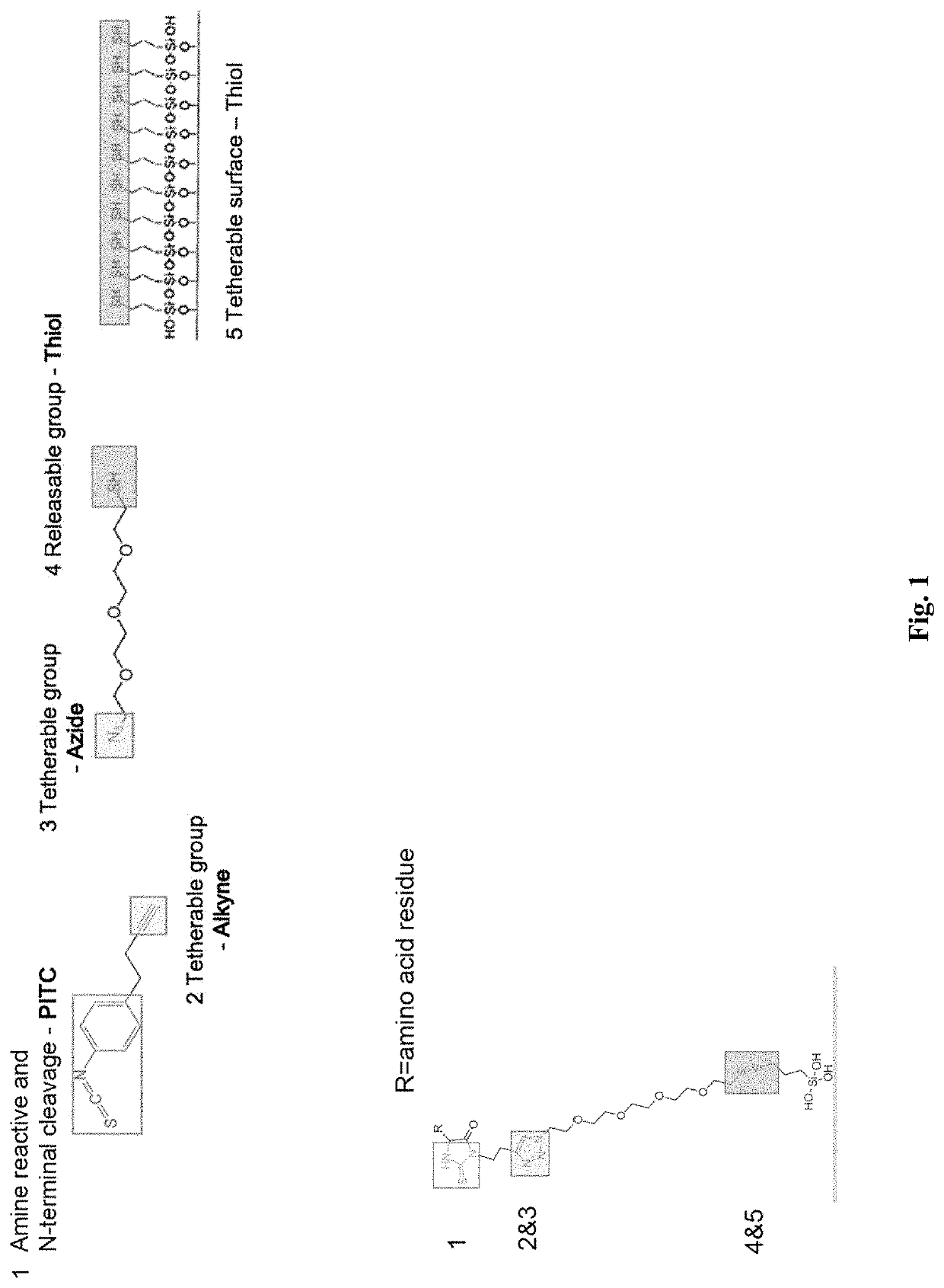
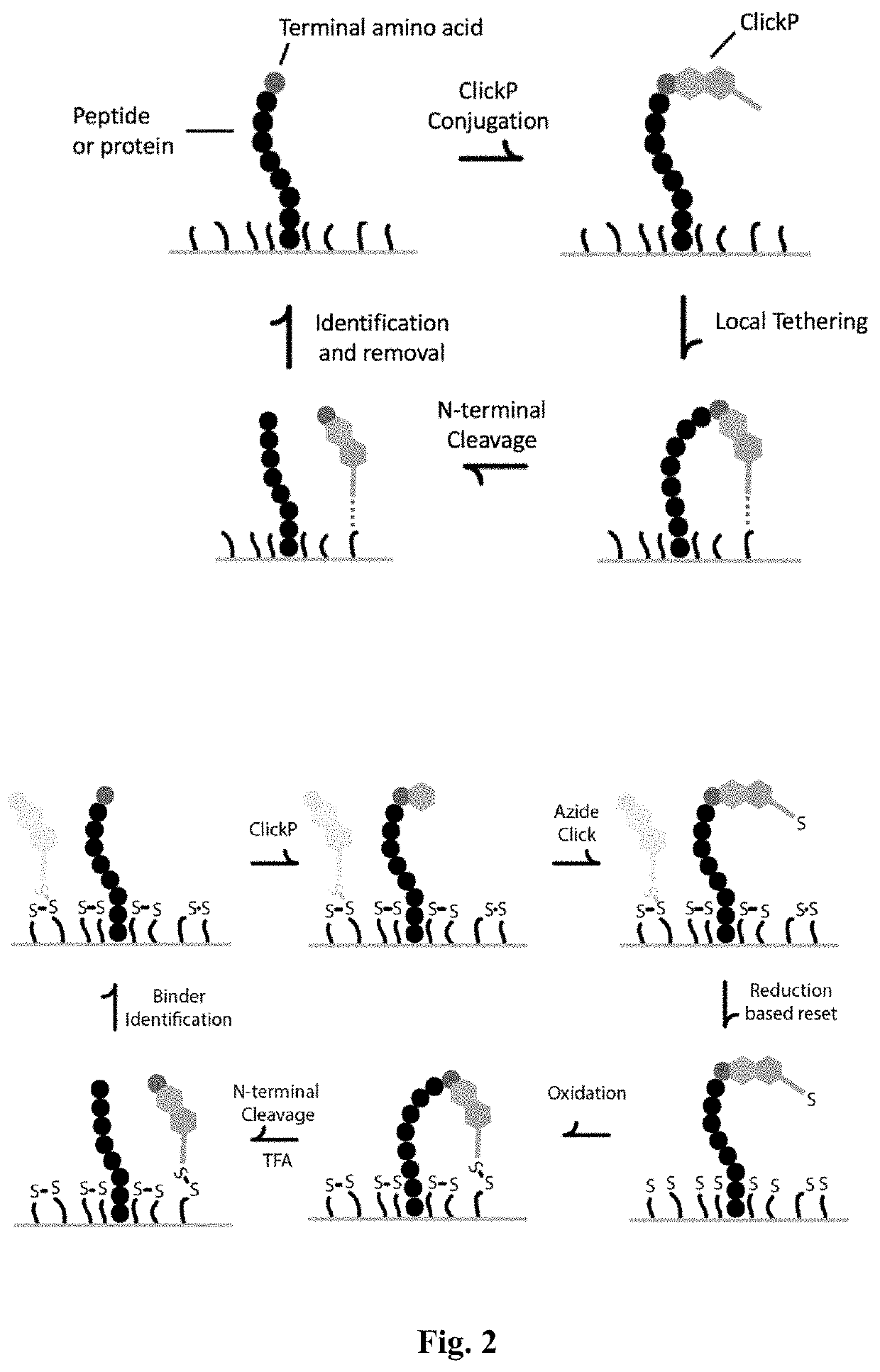
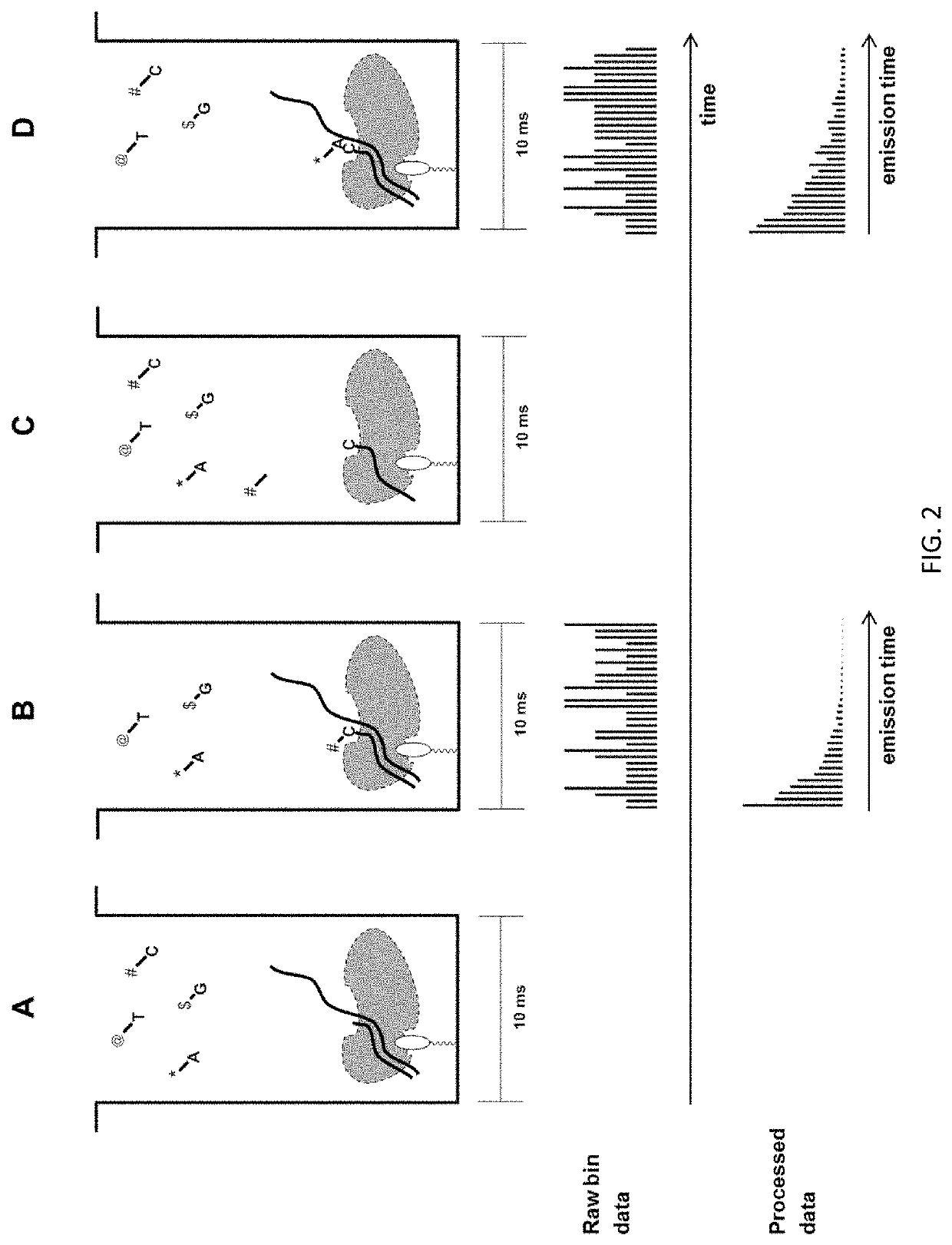
Methods to minimize photodamage during nucleic acid and peptide sequencing
PendingUS20220098658A1Minimize extentReduce deliveryMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical MoietyClick chemistry
Provided herein are methods and integrated devices for improved sequencing of nucleic acid and peptide biomolecules. The present disclosure relates to improved mechanisms for protecting a luminescent label from photo-induced damage through the use of quenching moieties. Further provided herein are methods for improved immobilization of quenching moieties and other molecules of interest through functionalization with chemical moieties, such as click chemistry handles, capable of participating in cross-linking reactions. Quenching moieties may be immobilized to the surface of a sample well in a sequencing substrate or apparatus in a manner that minimizes or eliminates photobleaching of the labeled molecule. The disclosed methods provide for minimized photodamage, increased sensitivity, accuracy and length of reads during nucleic acid and polypeptide sequencing.
Owner:QUANTUM SI
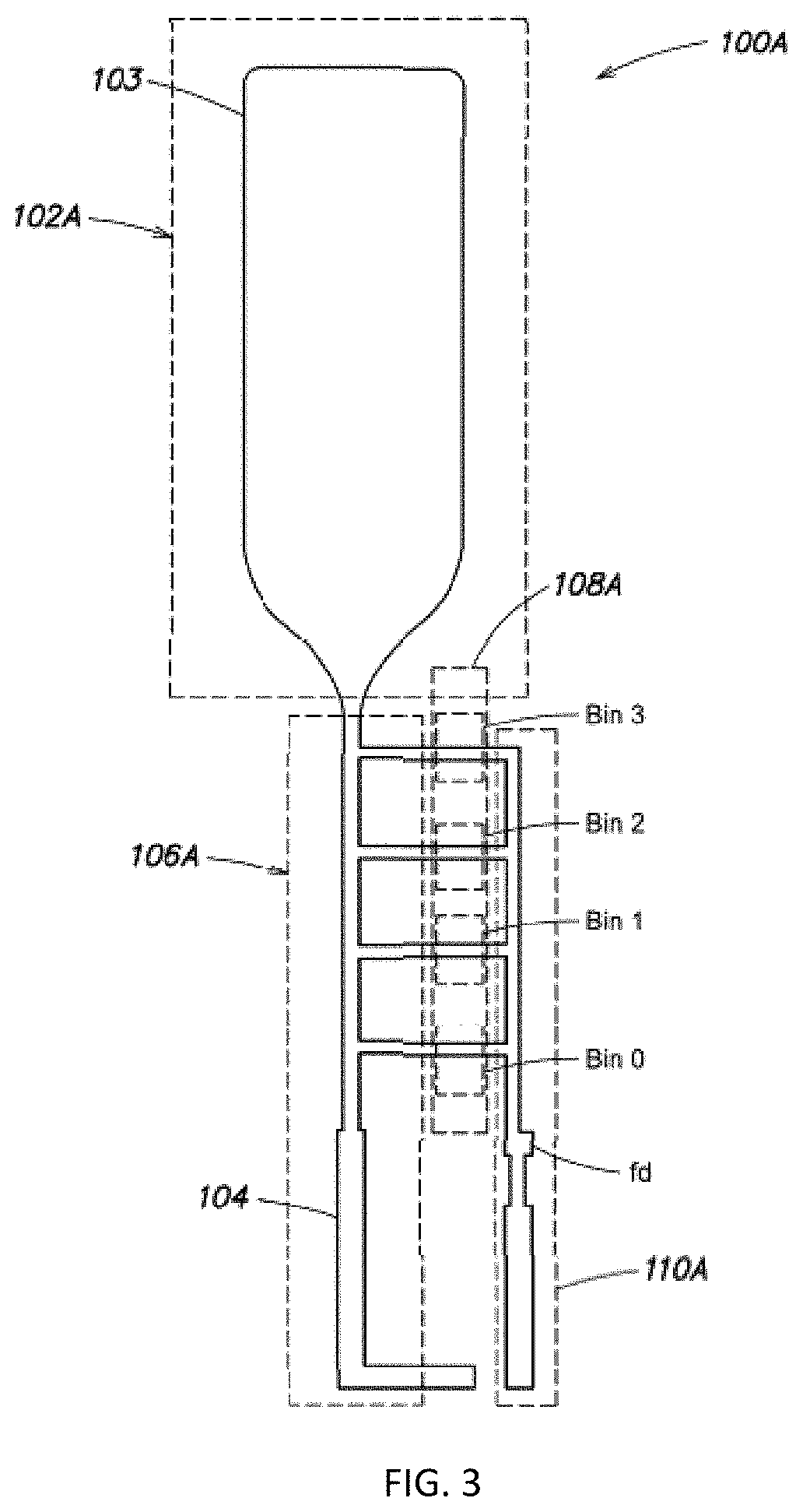
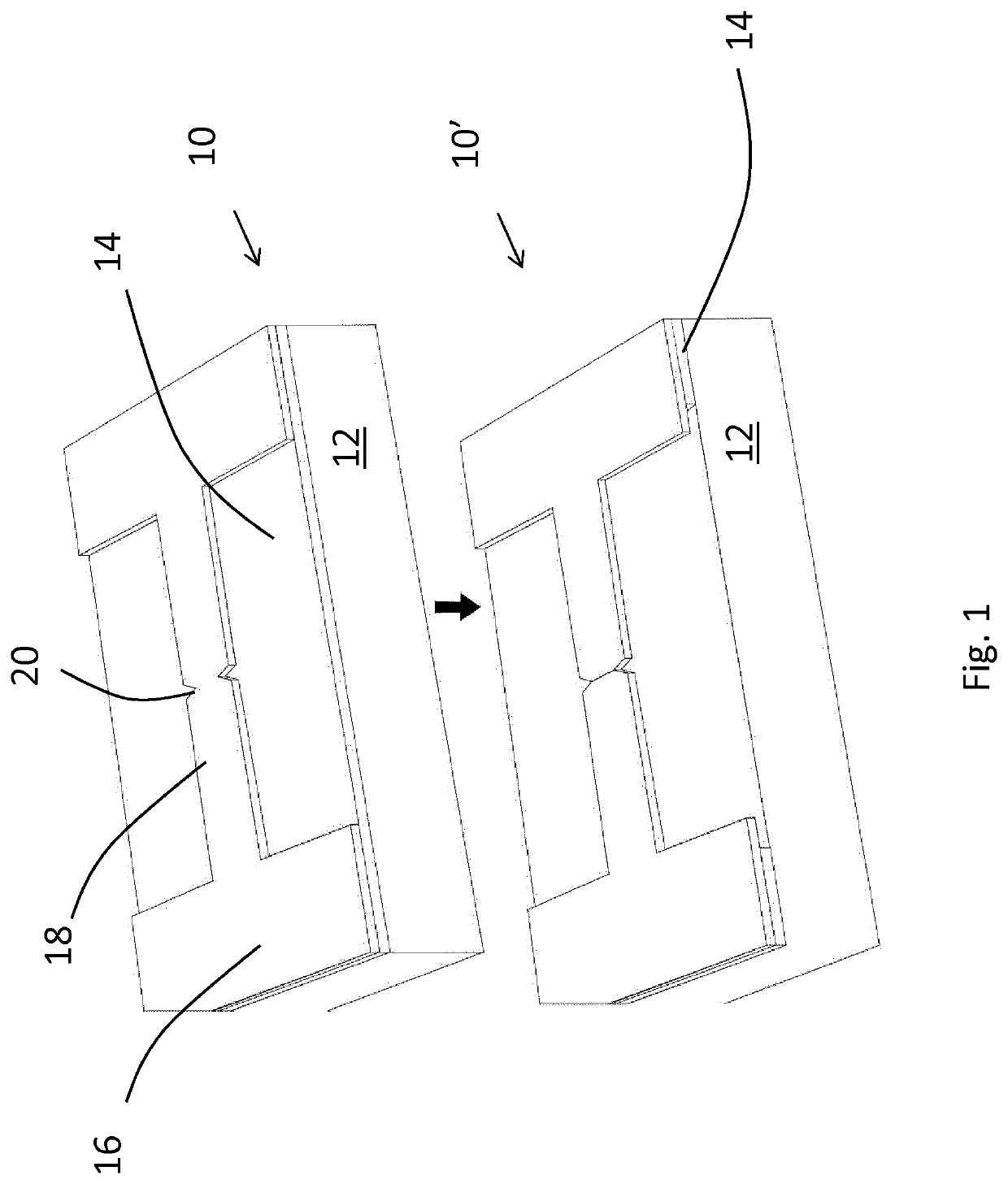
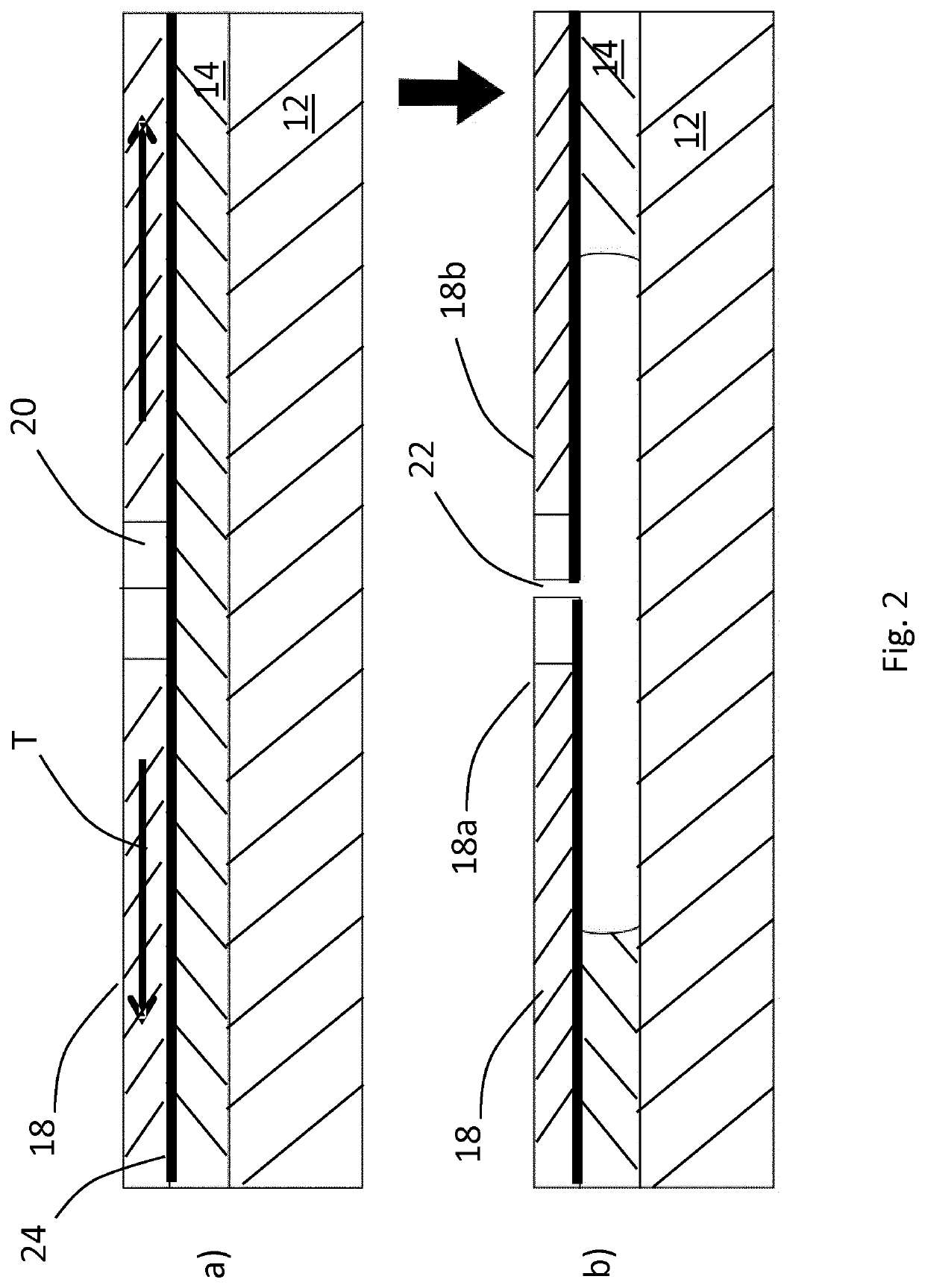
Crack structures, tunneling junctions using crack structures and methods of making same
ActiveUS10782249B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide sequenceBiology
Disclosed is a method of making a crack structure on a substrate, the crack structure being usable as a tunneling junction structure in a nanogap device, including the controlled fracture or release of a patterned layer under built-in stress, thereby forming elements separated by nanogaps or crack-junctions. The width of the crack-defined nanogap is controlled by locally release-etching the film at a notched bridge patterned in the film. The built-in stress contributes to forming the crack and defining of the width of the crack-defined nanogap. Further, by design of the length of the bridge in a range between sub-μπι to >25μαι, the separation between the elements, defined by the width of the crack-defined nanogaps, can be controlled for each individual crack structure from <2 nm to >100 nm. The nanogaps can be used for tunneling devices in combination with nanopores for DNA, RNA or peptides sequencing.
Owner:ZEDNA AB
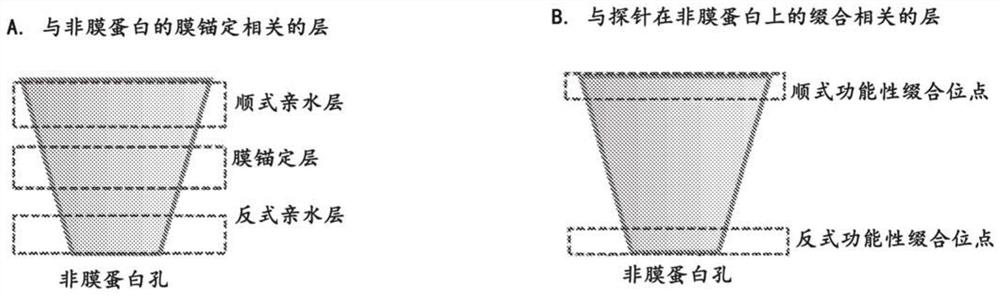
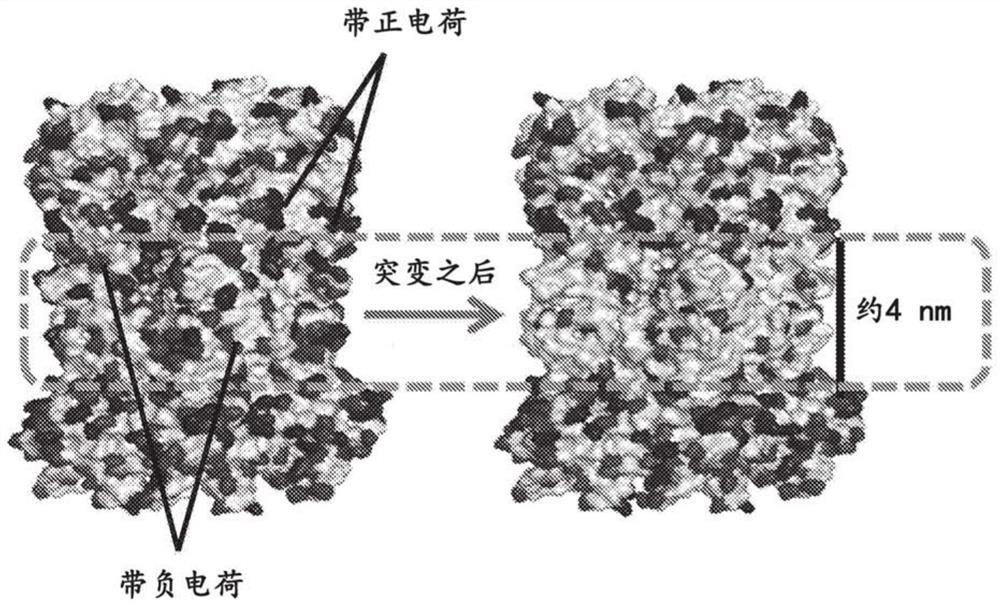
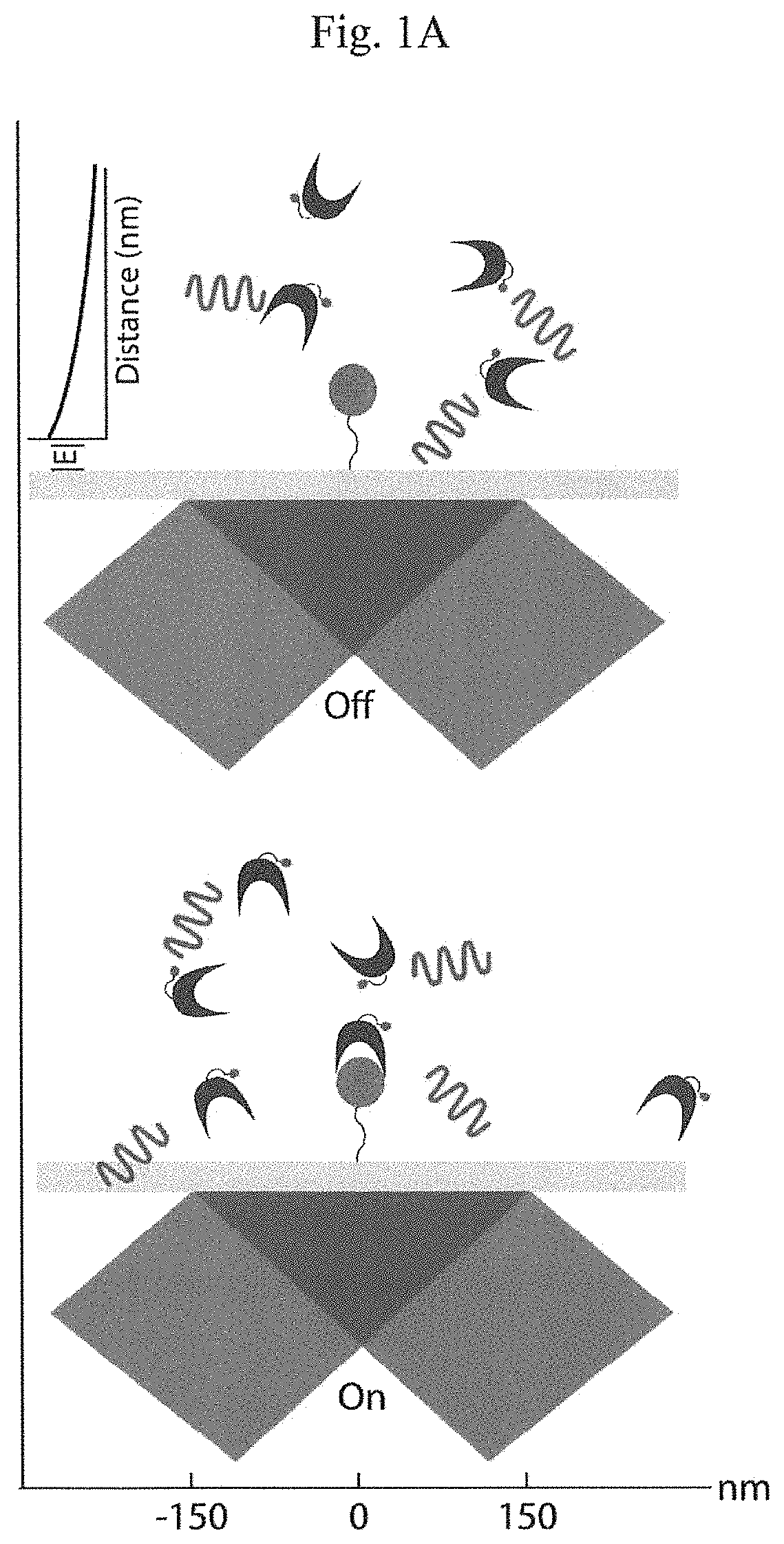
Nanopore assemblies and uses thereof
PendingCN112423878ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiseaseAnalyte
The disclosure provides a nanopore system assembled with non-membrane proteins for detecting analytes. Also disclosed are the methods, kits, and detection devices employing the disclosed nanopore system. The nanopore system has a wide variety of applications, including single molecule detection, DNA / RNA / peptide sequencing, sensing of chemicals, biological reagents, and polymers, and disease diagnosis.
Owner:OXFORD NANOPORE TECH LTD
Single molecule peptide sequencing methods
ActiveUS11346842B2Microbiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceProtein Sequence DeterminationPeptide sequencing
The invention, in part, includes methods of single molecule protein sequencing that include using weak binding spectra in the amino acid identification.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Mass- and property-tuned variable mass labeling reagents and analytical methods for simultaneous peptide sequencing and multiplexed protein quantification using thereof
InactiveUS8945940B2Tunability is providedPeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsAnalysis methodComputational chemistry
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
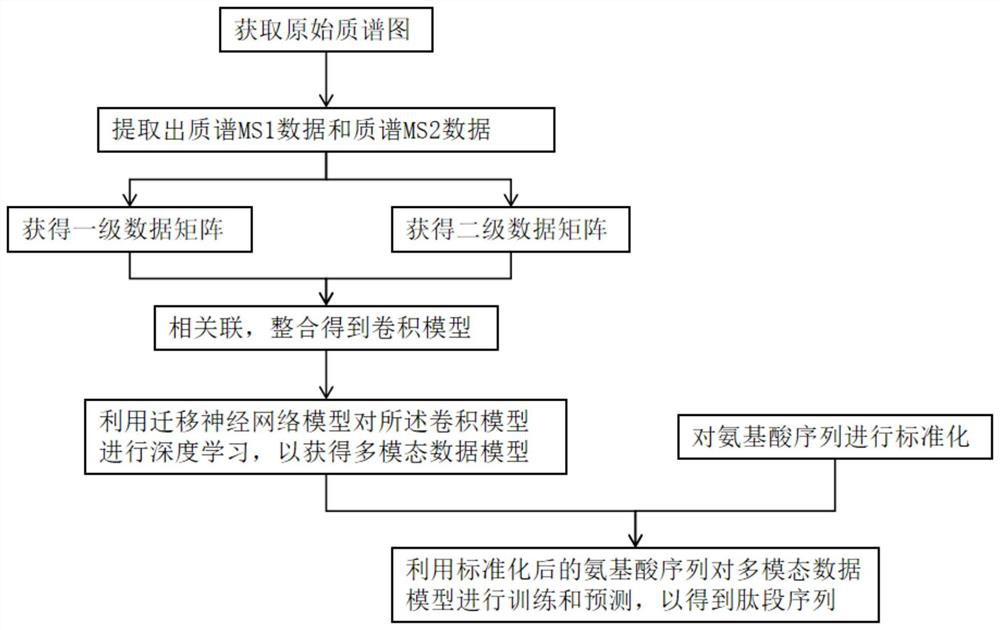
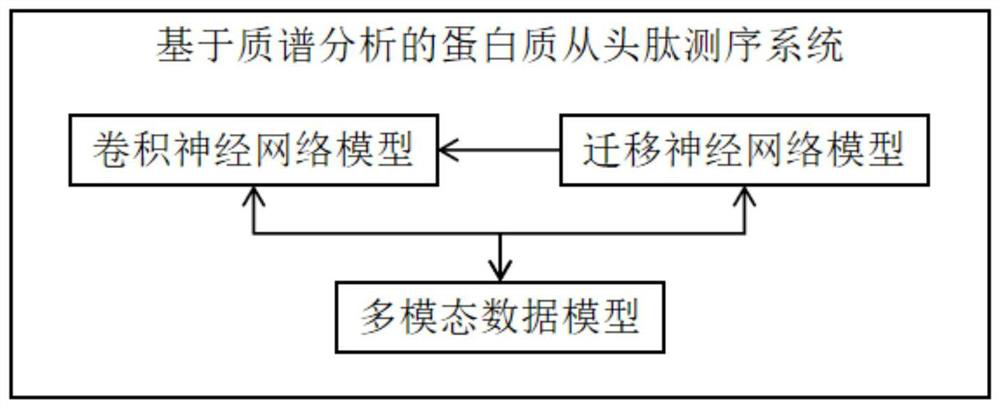
Mass spectrometry-based protein de novo peptide sequencing method and system
PendingCN113921086AAddressing the Accuracy of No-Reference SequencingNovel methodBiostatisticsBiological testingNetwork modelDe novo peptide sequencing
The invention provides a mass spectrometry-based protein de novo peptide sequencing method and a system. The system comprises a convolutional neural network model, a migration neural network model and a multi-modal data model; the convolutional neural network model extracts mass spectrum MS1 data and mass spectrum MS2 data from the original mass spectrum, and performs feature extraction and processing; the migration neural network model is migrated to perform deep learning on the convolutional neural network model; and the multi-modal data model trains and predicts the convolutional neural network model and the migration neural network model by using the amino acid sequence to obtain a peptide fragment sequence. According to the method, the mass spectrum MS2 data is filtered and screened through the ion retention time of the mass spectrum MS1 data, and deep learning is performed on the convolution model by using the migration neural network model, so that the peptide fragment sequence of the original map can be accurately predicted finally, and the problem of how to improve the accuracy of no reference sequencing in protein de novo peptide sequencing is solved.
Owner:上海中科新生命生物科技有限公司
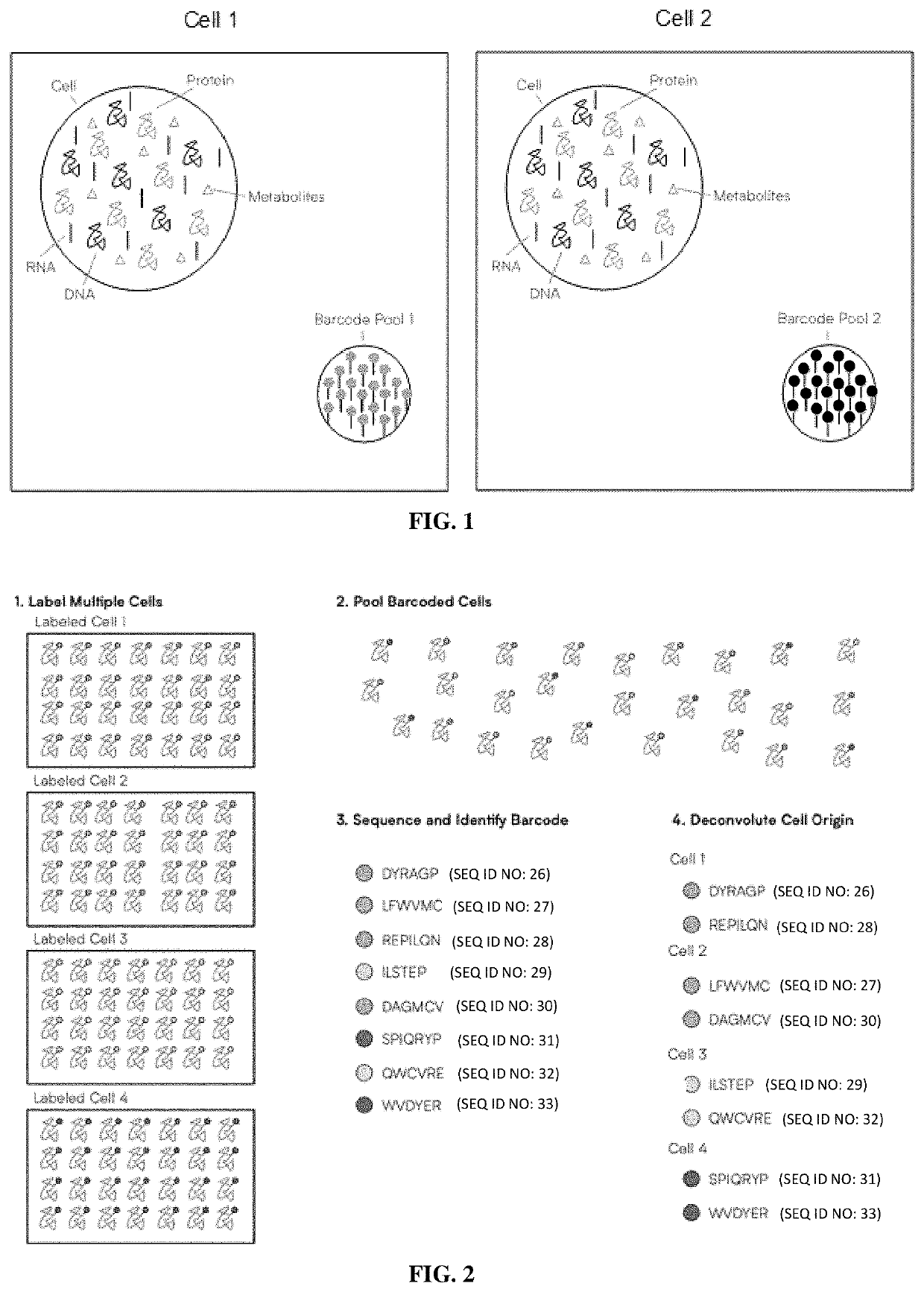
Methods of single-cell polypeptide sequencing
PendingUS20210139973A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisDirect sequencingPeptide sequencing
Provided herein are methods of single-cell polypeptide and / or polynucleic acid sequencing, which facilitate the direct sequencing of a single cell without amplification. Also provided herein are compositions, kits and devices useful for the same.
Owner:QUANTUM SI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com