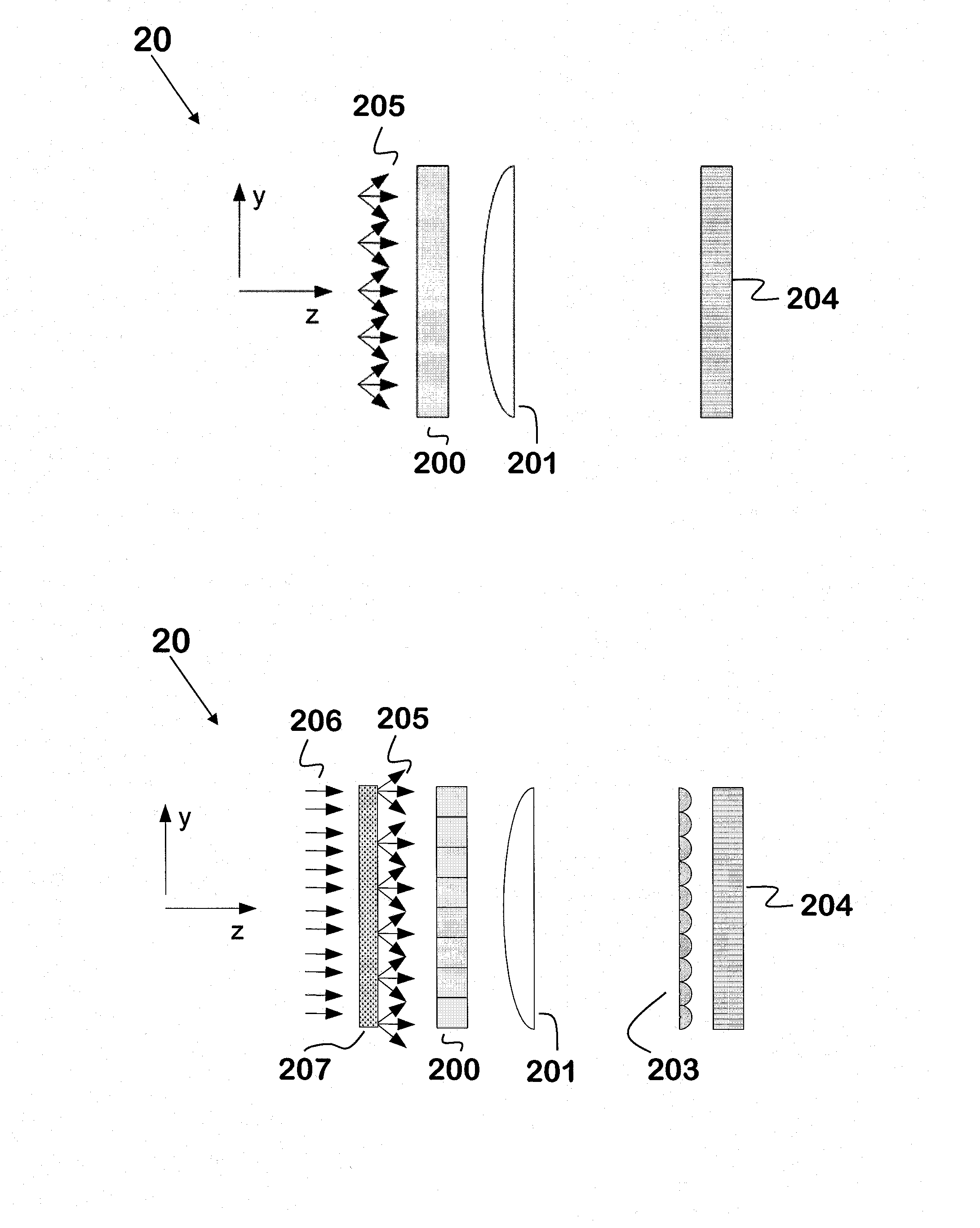
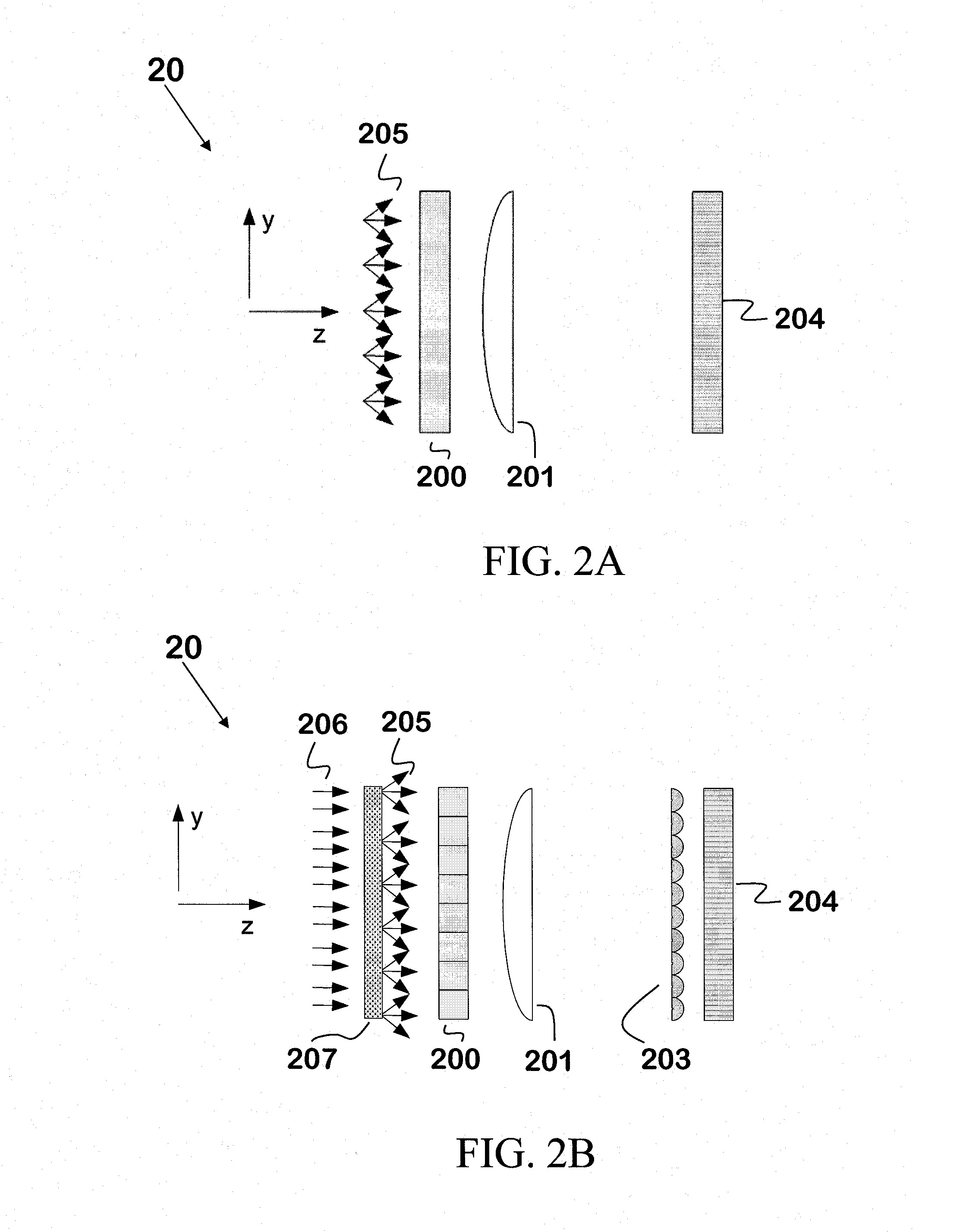
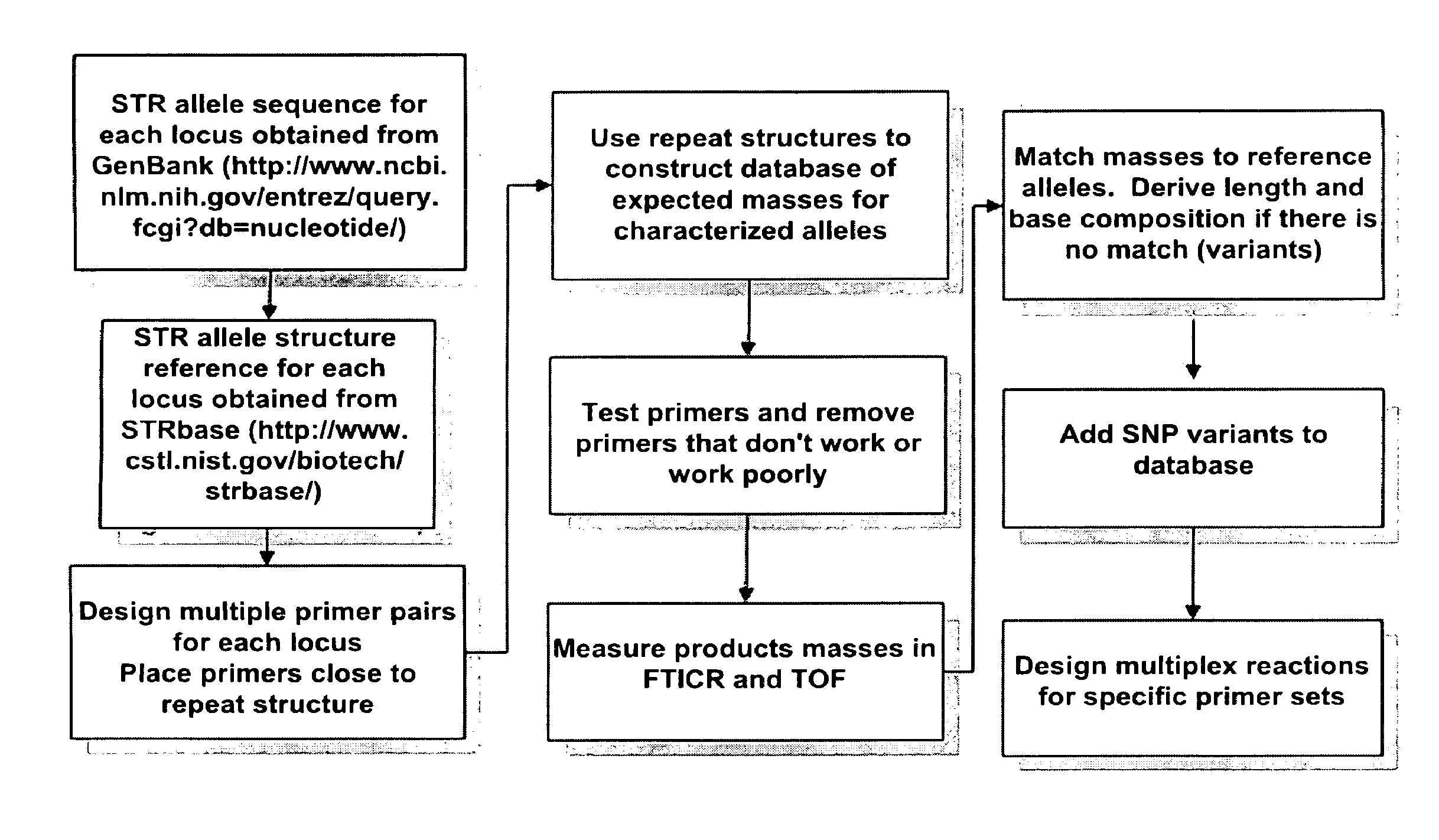
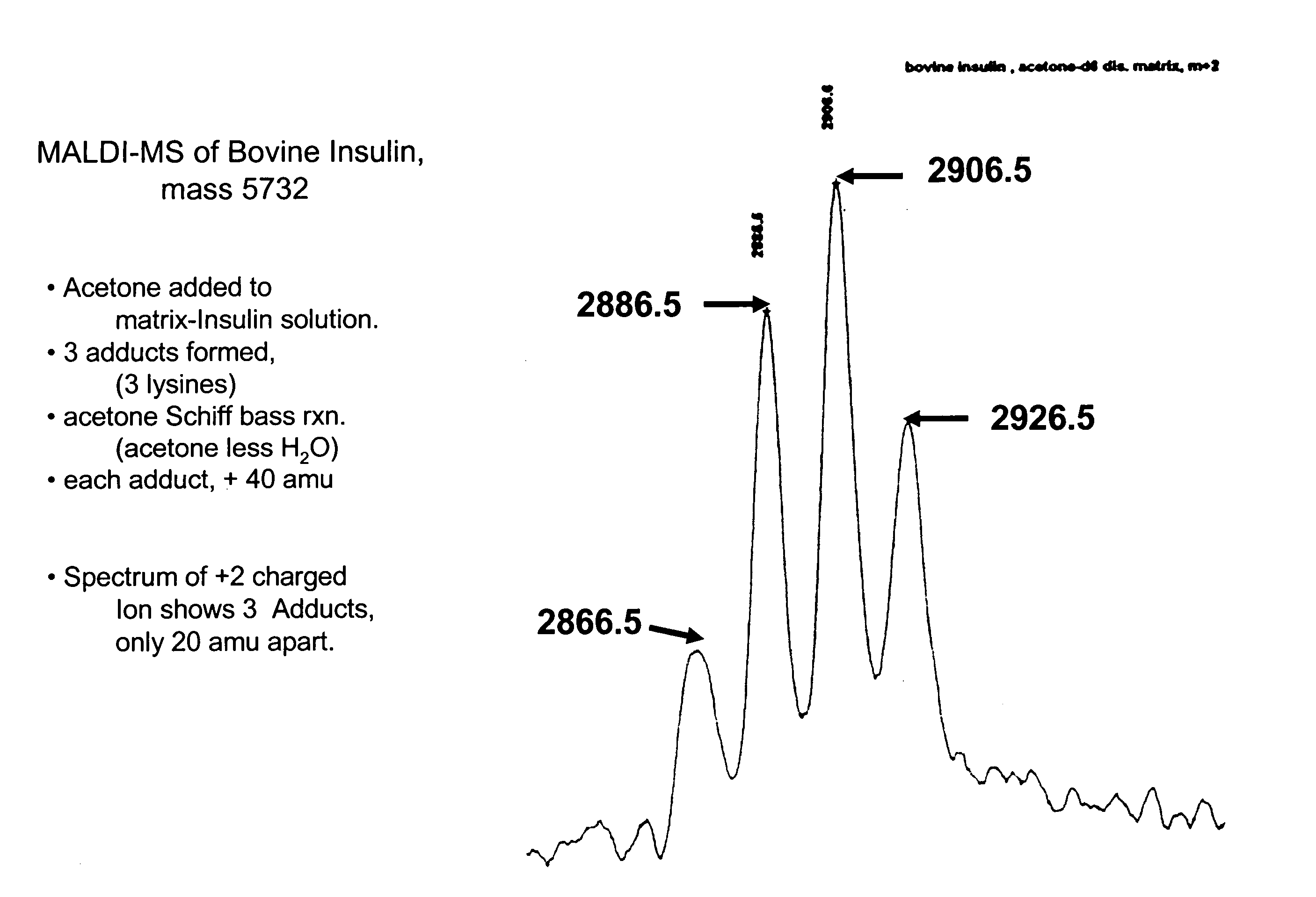
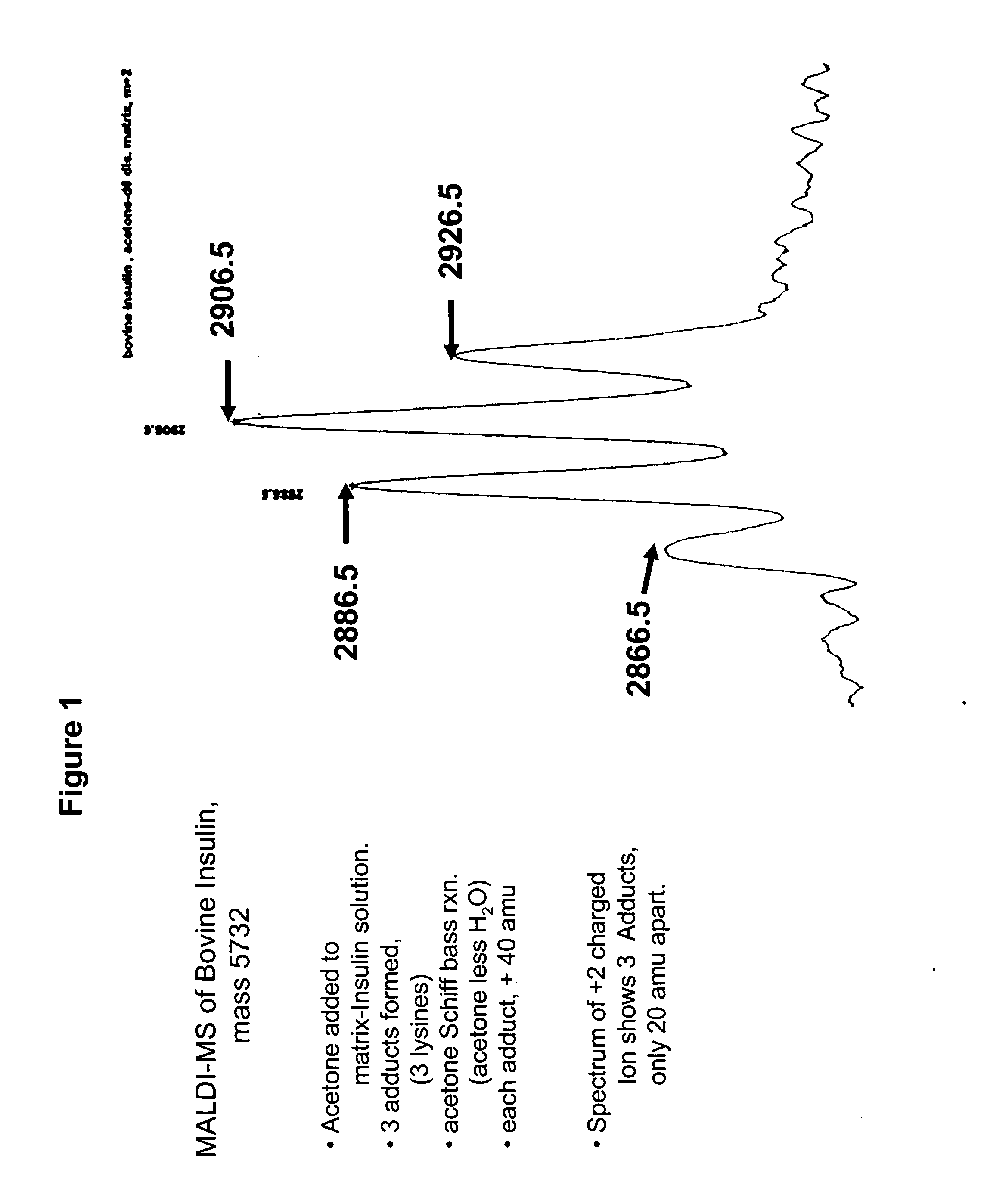
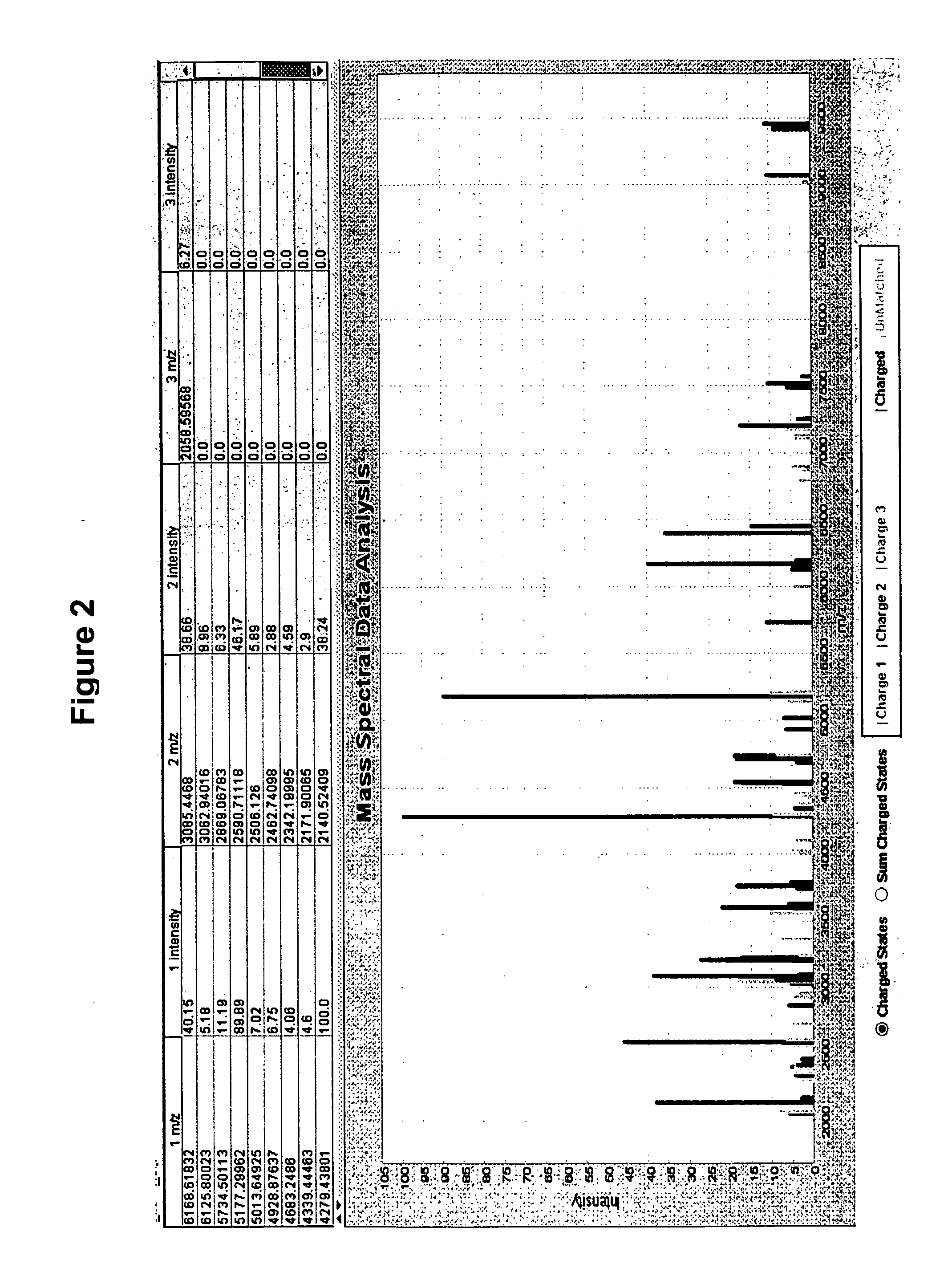
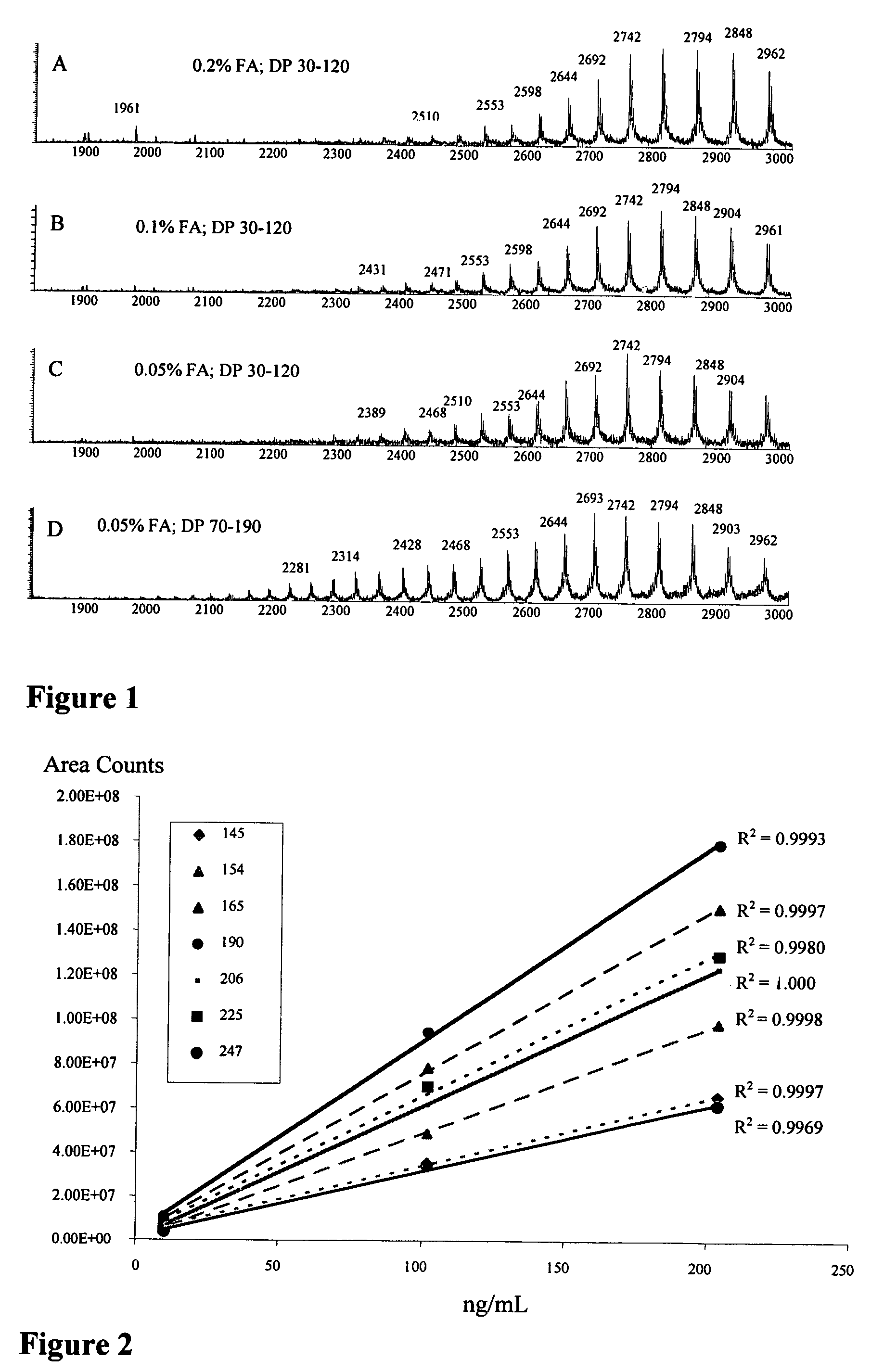
Patents
Literature
1692 results about "Mass spectrometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
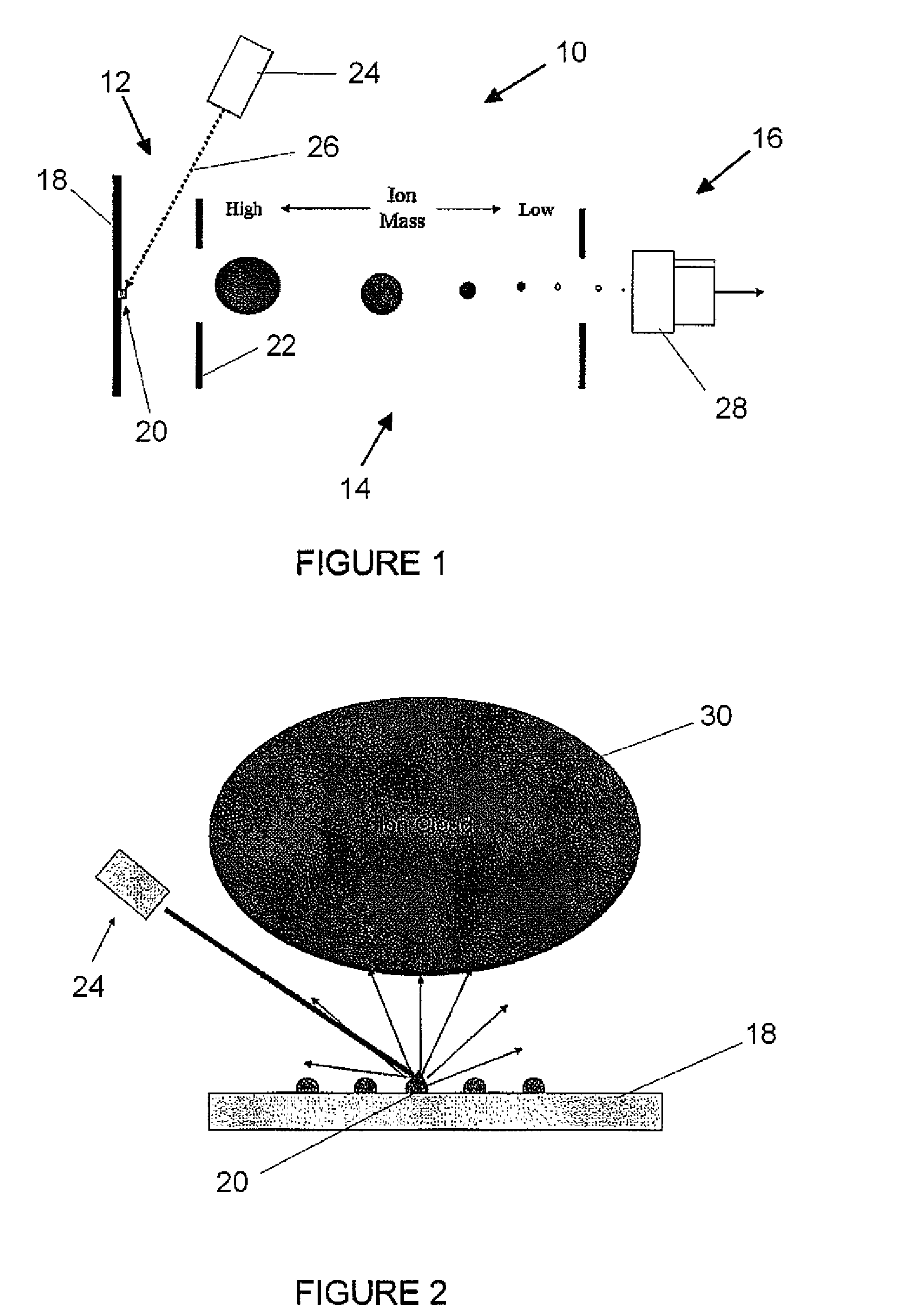
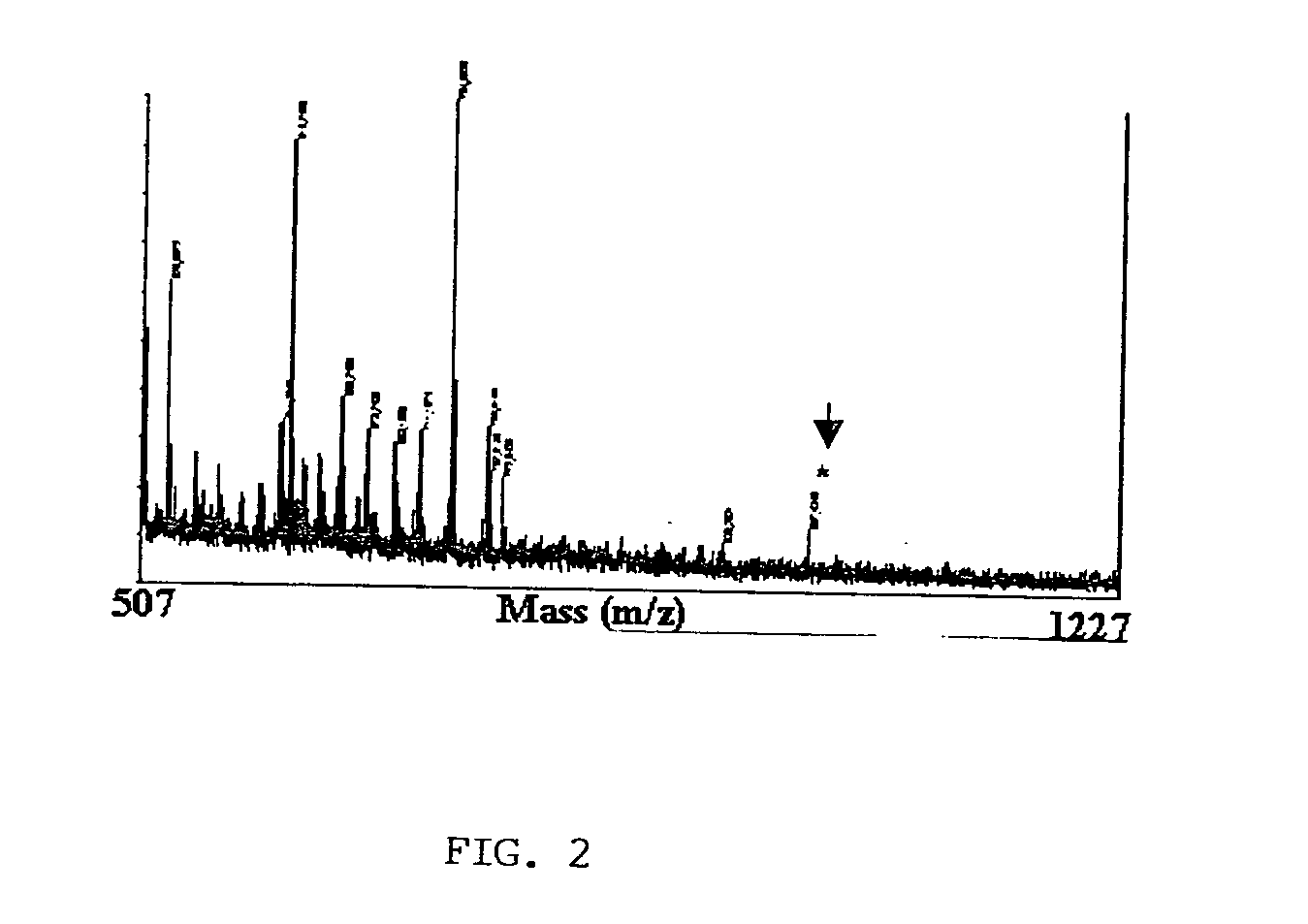
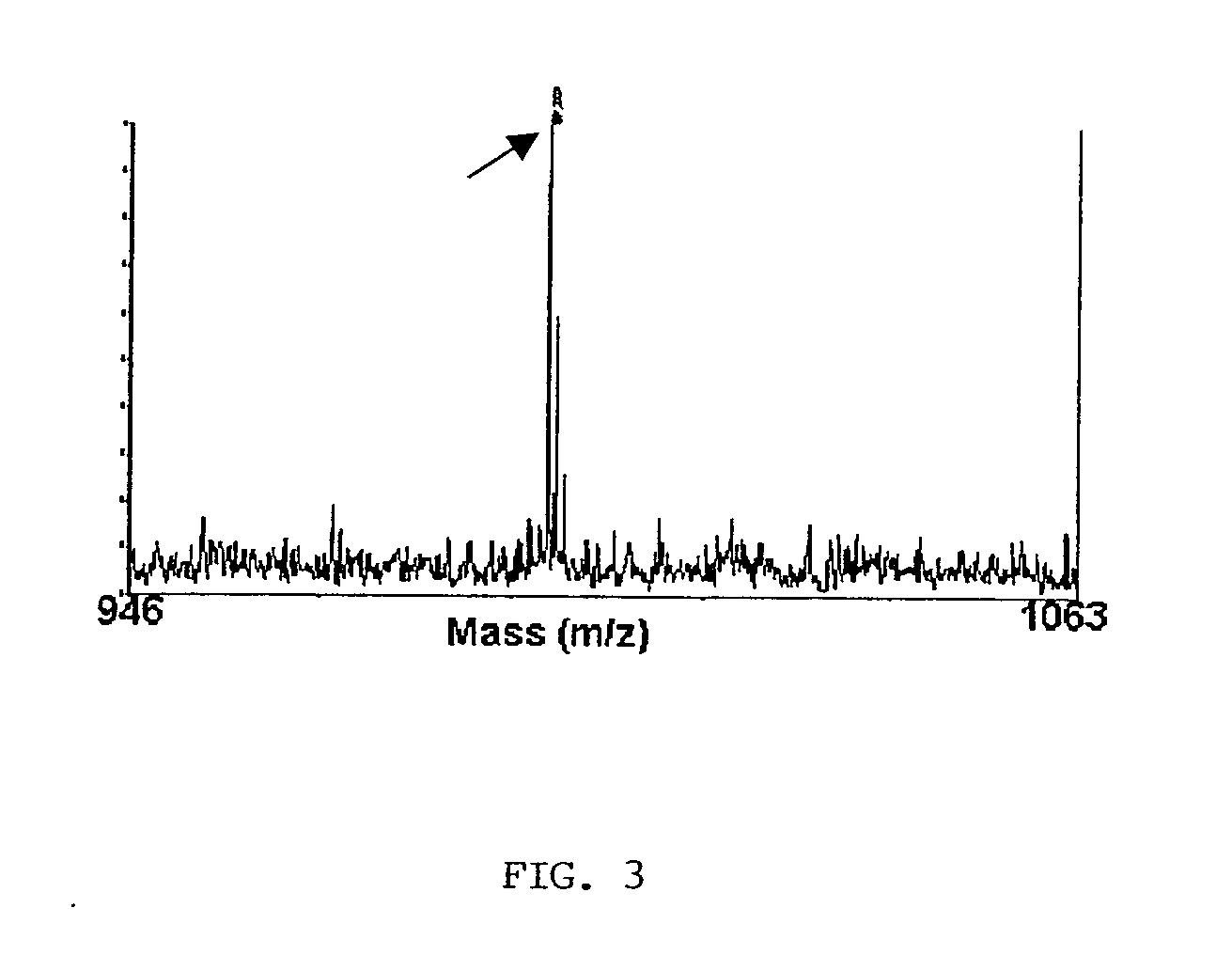
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are typically presented as a mass spectrum, a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures.
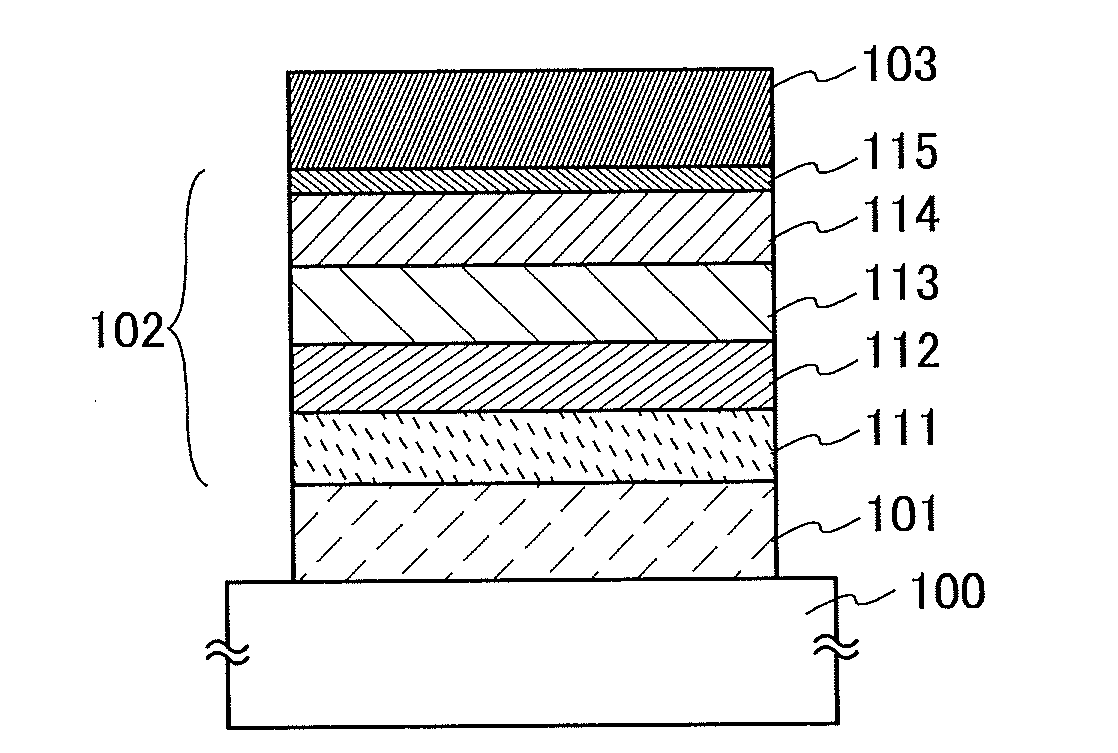
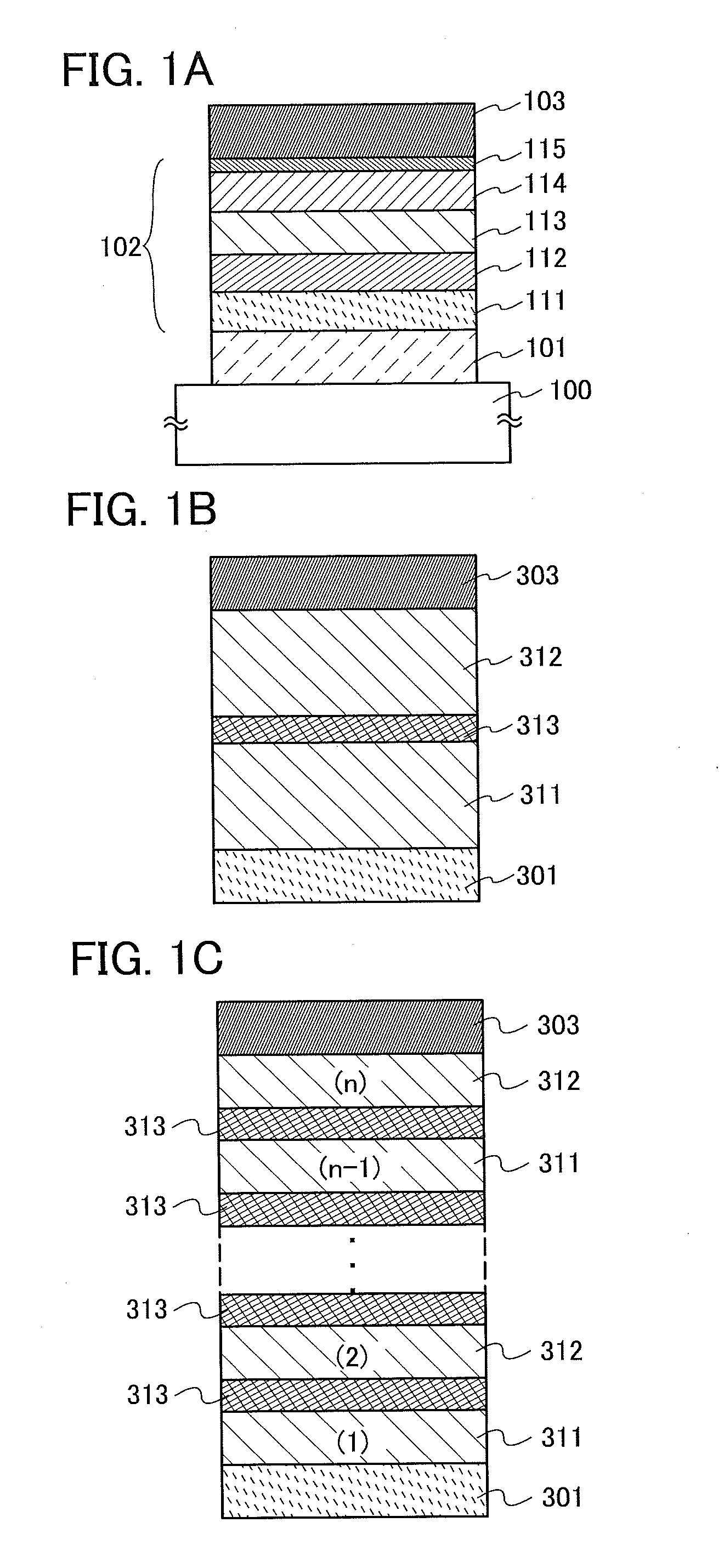
Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, Electronic Appliance, and Lighting Device
InactiveUS20140183503A1Reduce the driving voltageImprove current efficiencyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesLow voltageQuinoline
Disclosed is a light-emitting element having high emission efficiency, capable of driving at low voltage, and showing a long lifetime. The light-emitting element contains a compound between a pair of electrodes, and the compound is configured to give a first peak of m / z around 202 and a second peak of m / z around 227 in a mass spectrum. The first and second peaks are product ions of the compound and possess compositions of C16H9 and C17H10N, respectively, which are derived from a dibenzo[f,h]quinoline unit.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
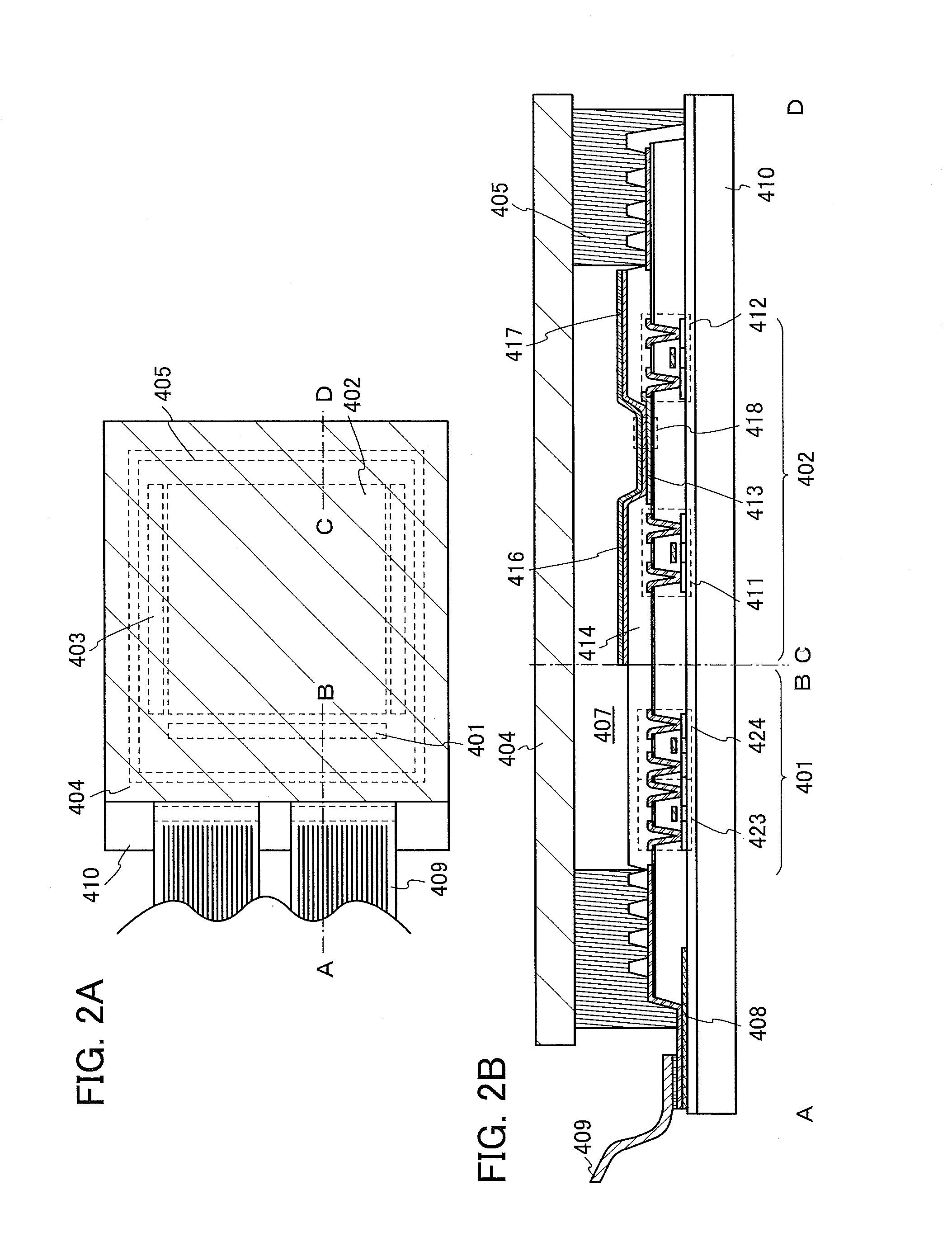
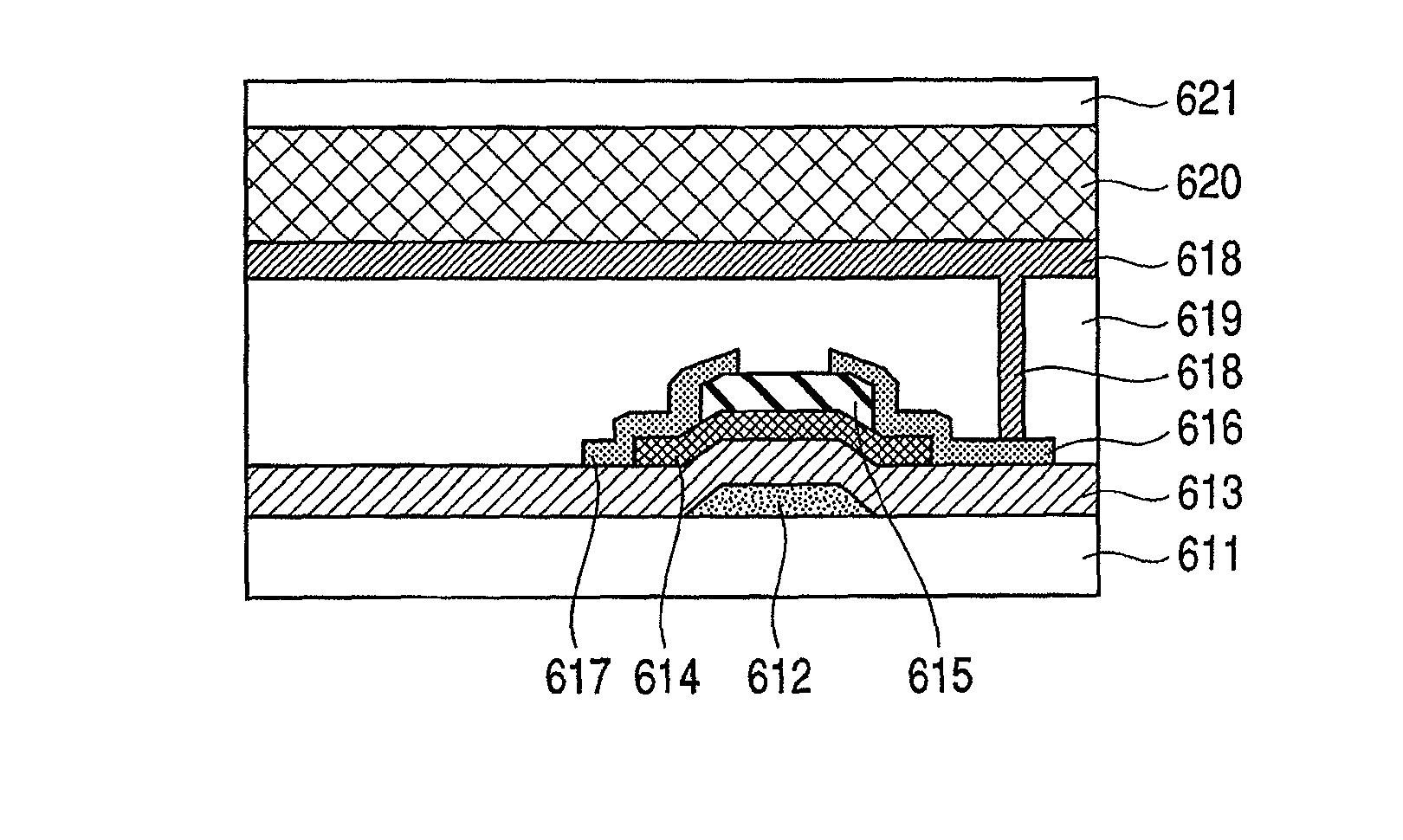
Bottom gate type thin film transistor, method of manufacturing the same, and display apparatus
InactiveUS8148721B2Optimise total massImprove batch productivityTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesDesorptionBottom gate
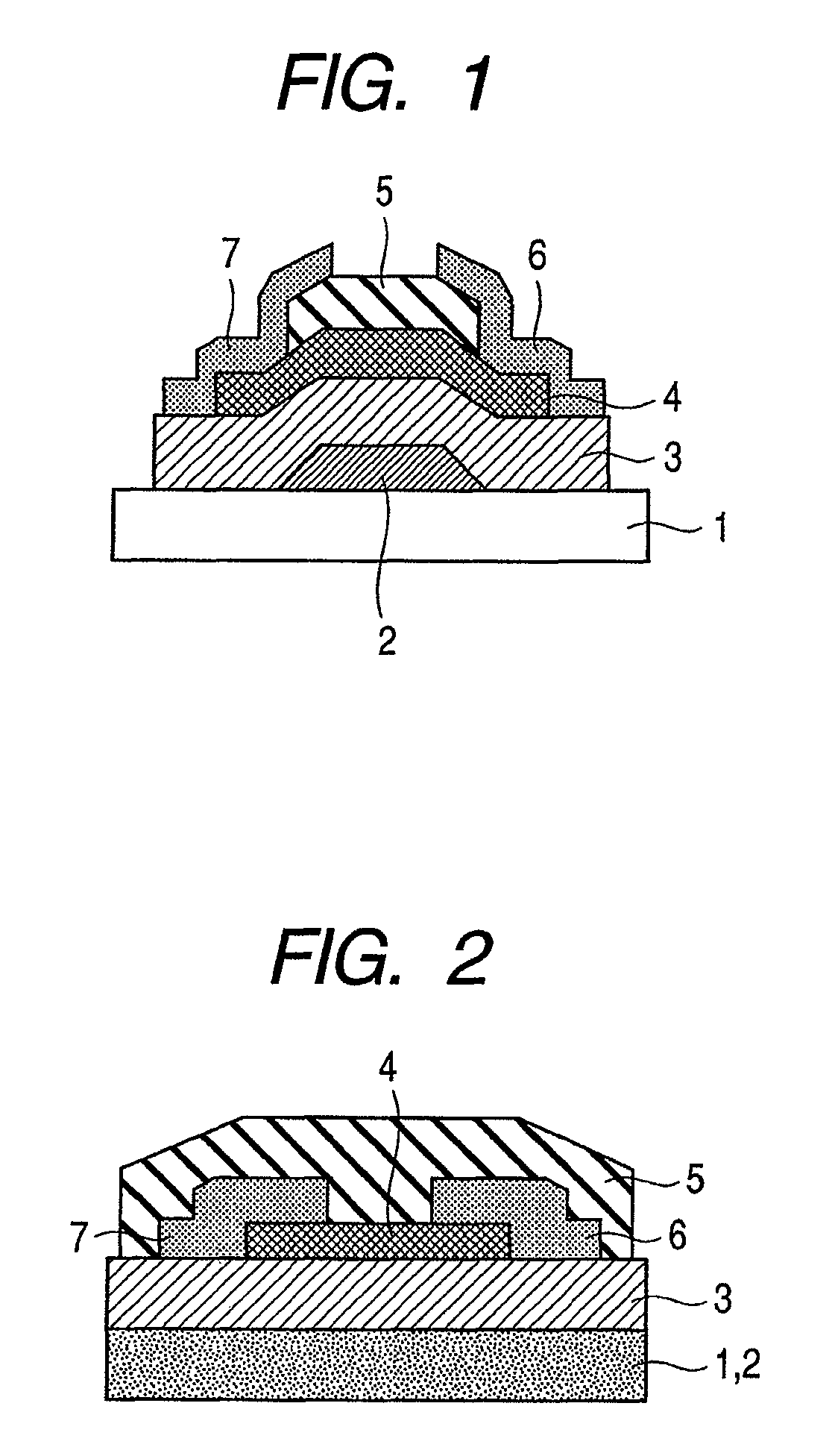
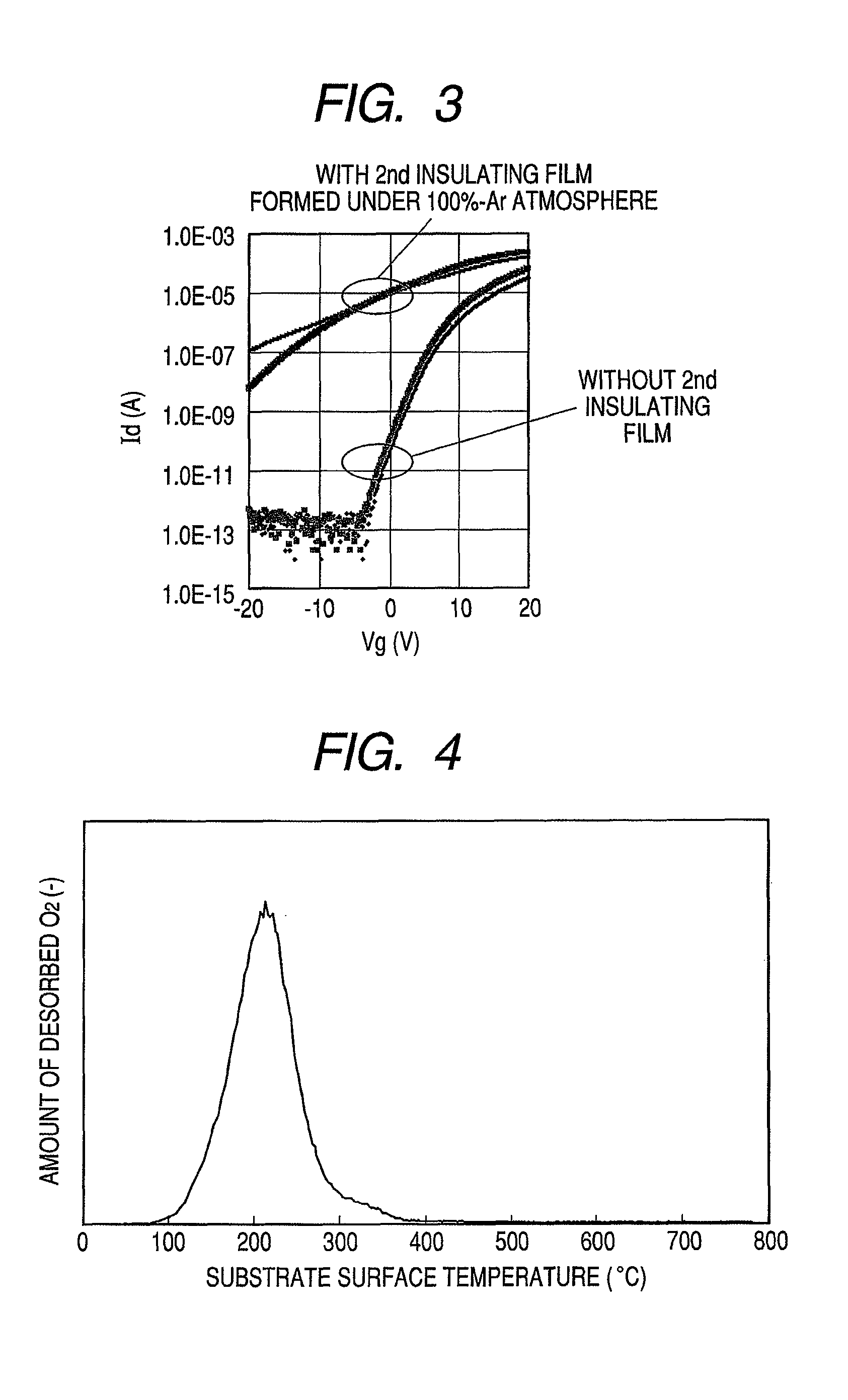
Provided is a bottom gate type thin film transistor including on a substrate (1) a gate electrode (2), a first insulating film (3) as a gate insulating film, an oxide semiconductor layer (4) as a channel layer, a second insulating film (5) as a protective layer, a source electrode (6), and a drain electrode (7), in which the oxide semiconductor layer (4) includes an oxide including at least one selected from the group consisting of In, Zn, and Sn, and the second insulating film (5) includes an amorphous oxide insulator formed so as to be in contact with the oxide semiconductor layer (4) and contains therein 3.8×1019 molecules / cm3 or more of a desorbed gas observed as oxygen by temperature programmed desorption mass spectrometry.
Owner:CANON KK
Microfluidic sample delivery devices, systems, and methods
ActiveUS7303727B1Improve throughputResidue reductionParticle separator tubesComponent separationSpray nozzleMass spectrometry
Methods and apparatus for delivering fluidic materials to sample destinations, including mass spectrometers for analysis are provided. In preferred embodiments, sample aliquots are electrosprayed from tapered spray tips of capillary elements into the orifices of mass spectrometric inlet systems. In certain embodiments, fluidic samples are orthogonally sprayed from capillary elements or other fluid conduits, whereas in other embodiments samples are sprayed after devices are rotated or otherwise translocated from sample sources to sample destinations. In still other embodiments, samples are sprayed from flexed or deflected capillary elements at selected sample destinations.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
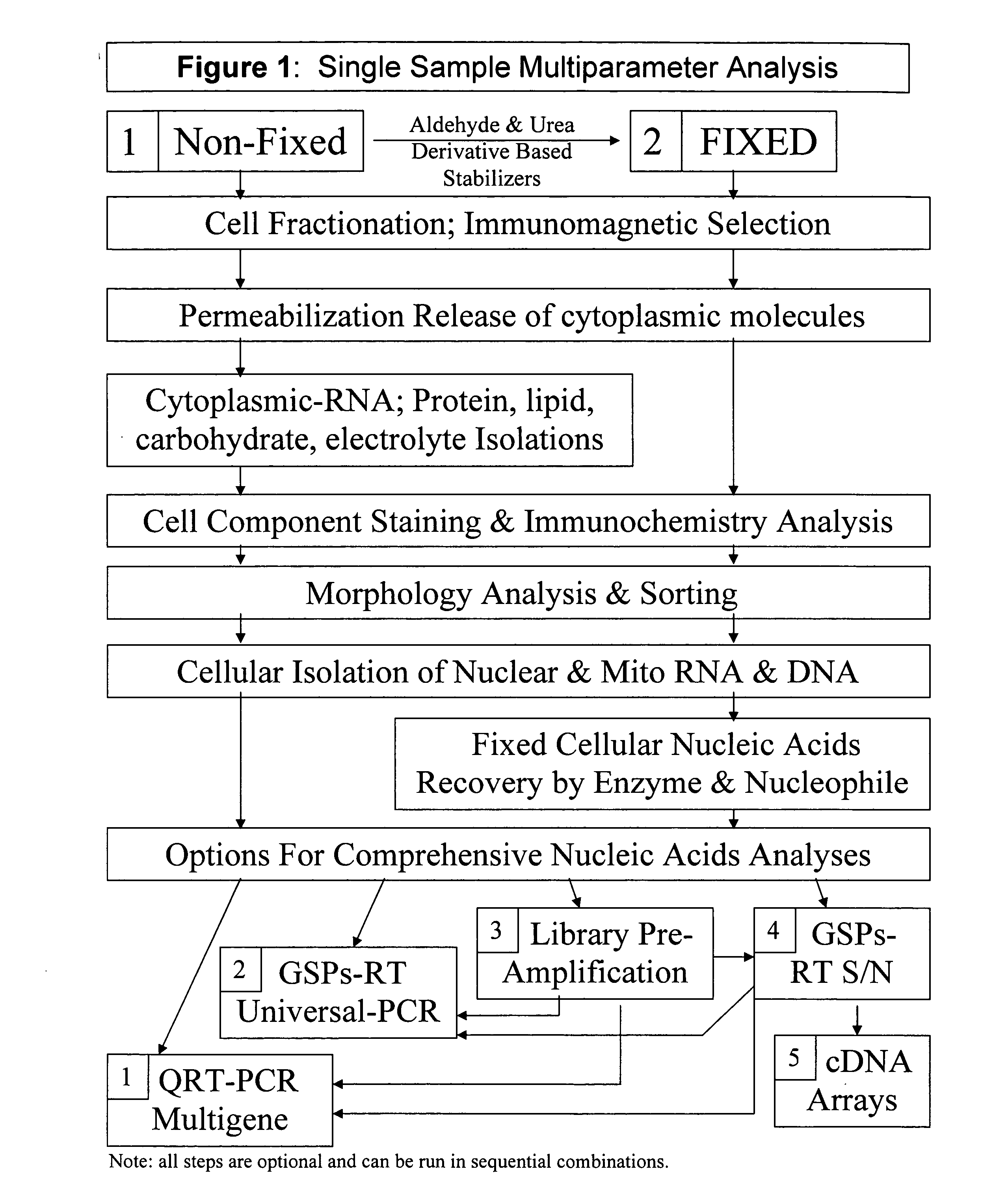
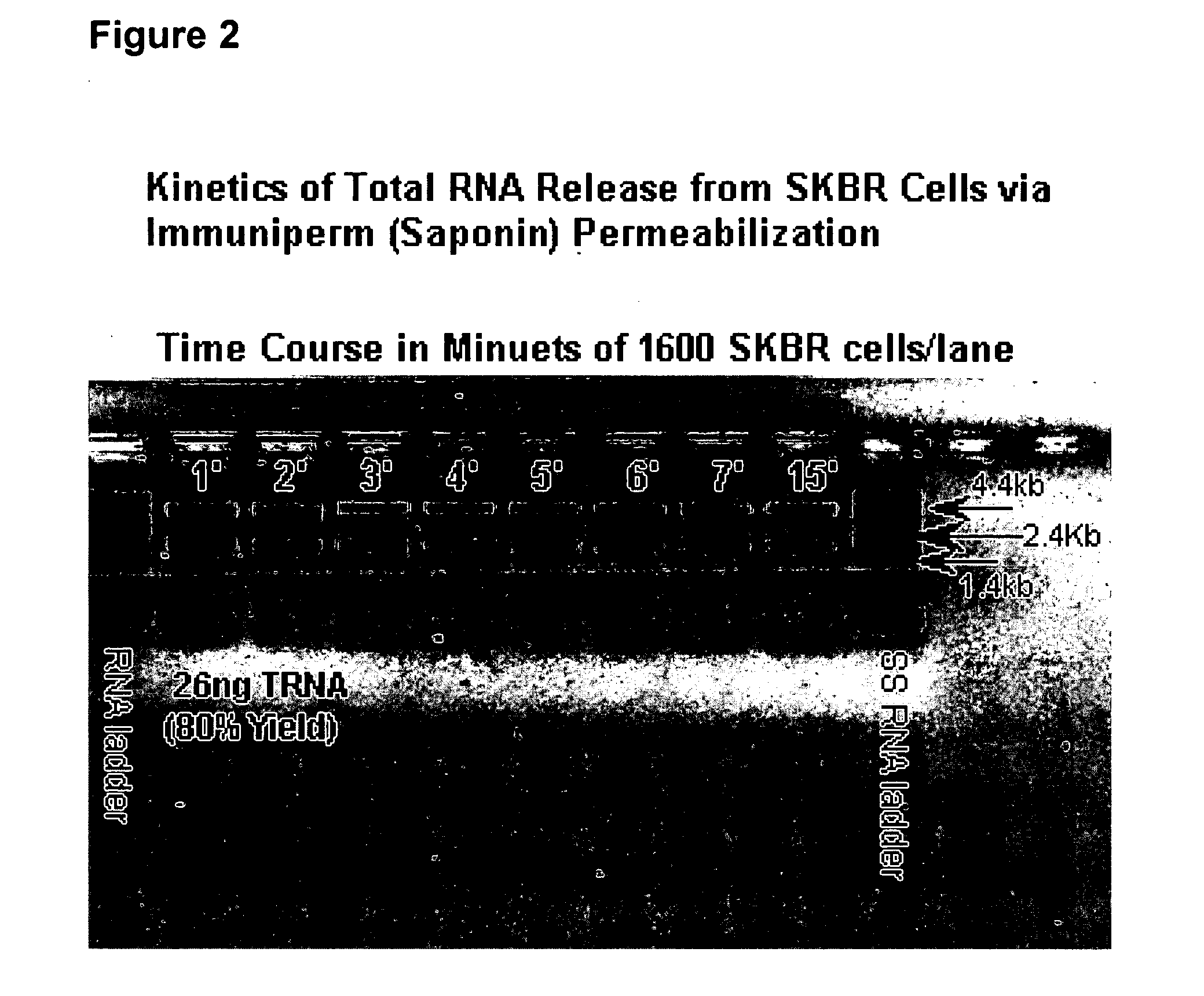
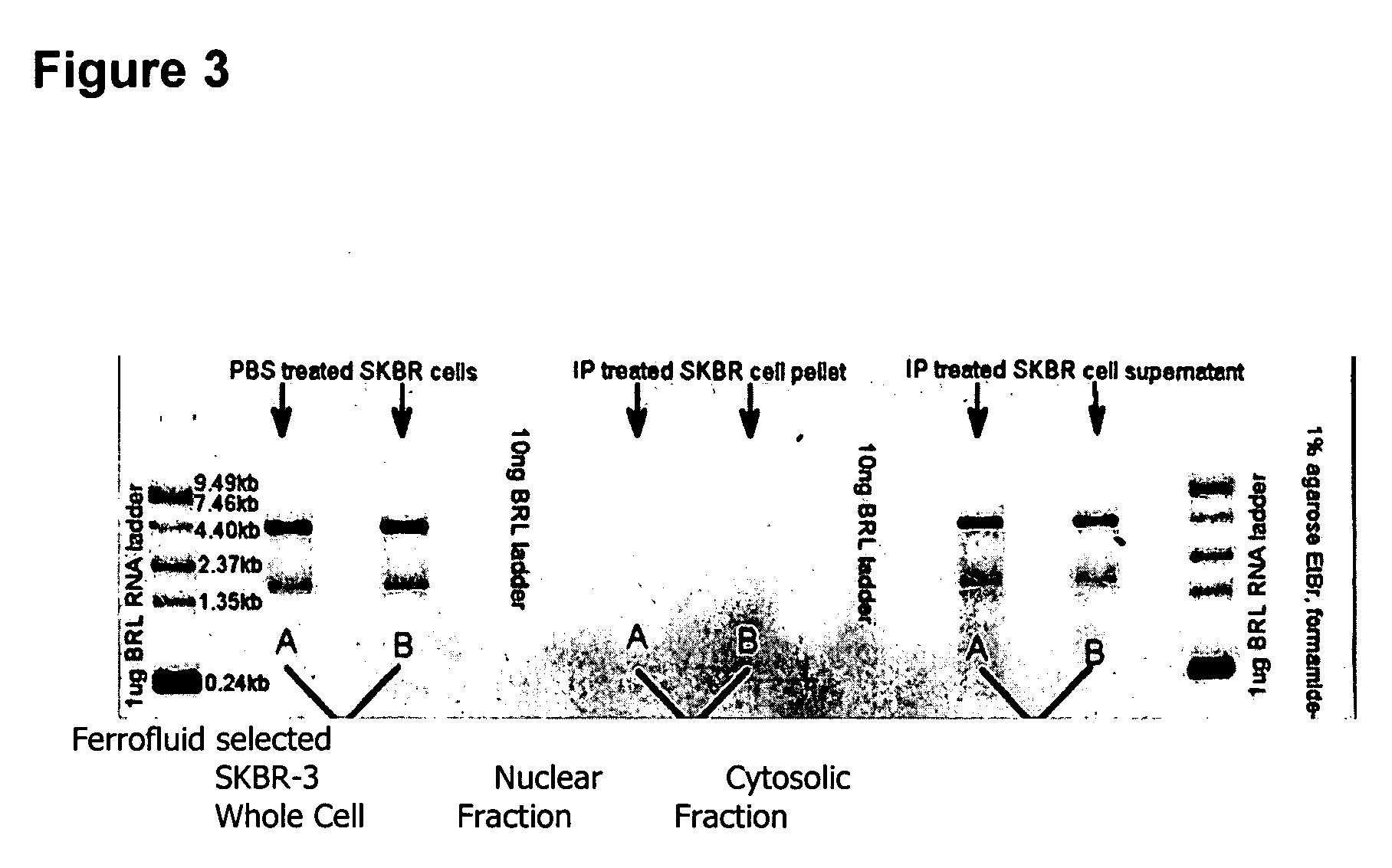
Multiparameter analysis of comprehensive nucleic acids and morphological features on the same sample
InactiveUS20060008807A1Microbiological testing/measurementMicroorganism lysisProtein profilingMass spectrometry
A highly sensitive assay is disclosed which utilizes a method for gene specific primed amplification of mRNA libraries from rare cells and rare transcripts found in blood. The assay allows detection of rare mRNA (10 copies / cell) found in 1 to 10 cells isolated through immunomagnetic enrichment. The assay is an improvement over multiplex PCR and allows efficient detection of rare coding sequences for circulating carcinoma cells in the blood. The methods are useful in profiling of cells isolated from tissues or body fluids and serves as an adjunct to clinical diagnosis of diverse carcinomas including early stage detection and classification of circulating tumor cells. Monitoring of nucleic acid and protein profiles of cells either in conventional or microarray formats, facilitates management of therapeutic intervention including staging, monitoring response to therapy, confirmation of remission and detection of regression.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
Mass label linked hybridisation probes
InactiveUS20050042625A1Increase the number ofEasy to separateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHybridization probeMass spectrometry
An array of hybridization probes, each of which comprises a mass label linked to a known base sequence of predetermined length, wherein each mass label of the array, optionally together with the known base sequence, is relatable to that base sequence by mass spectrometry.
Owner:XZILLION
Microrna as ligands and target molecules
InactiveUS20050142581A1Improve bindingIncreased binding affinityMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processMicroRNAMass spectrometry
The present invention provides methods for the identification of target molecules that bind to ligands, particularly microRNA ligands and mimics thereof and / or microRNA target molecules and mimics thereof, with as little as millimolar (mM) affinity using mass spectrometry. The methods may be used to determine the mode of binding interaction between two or more of these target molecules to the ligand as well as their relative affinities. Also provided are methods for designing compounds having greater affinity to a ligand by identifying two or more target molecules using mass spectrometry methods of the invention and linking the target molecules together to form a novel compound.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
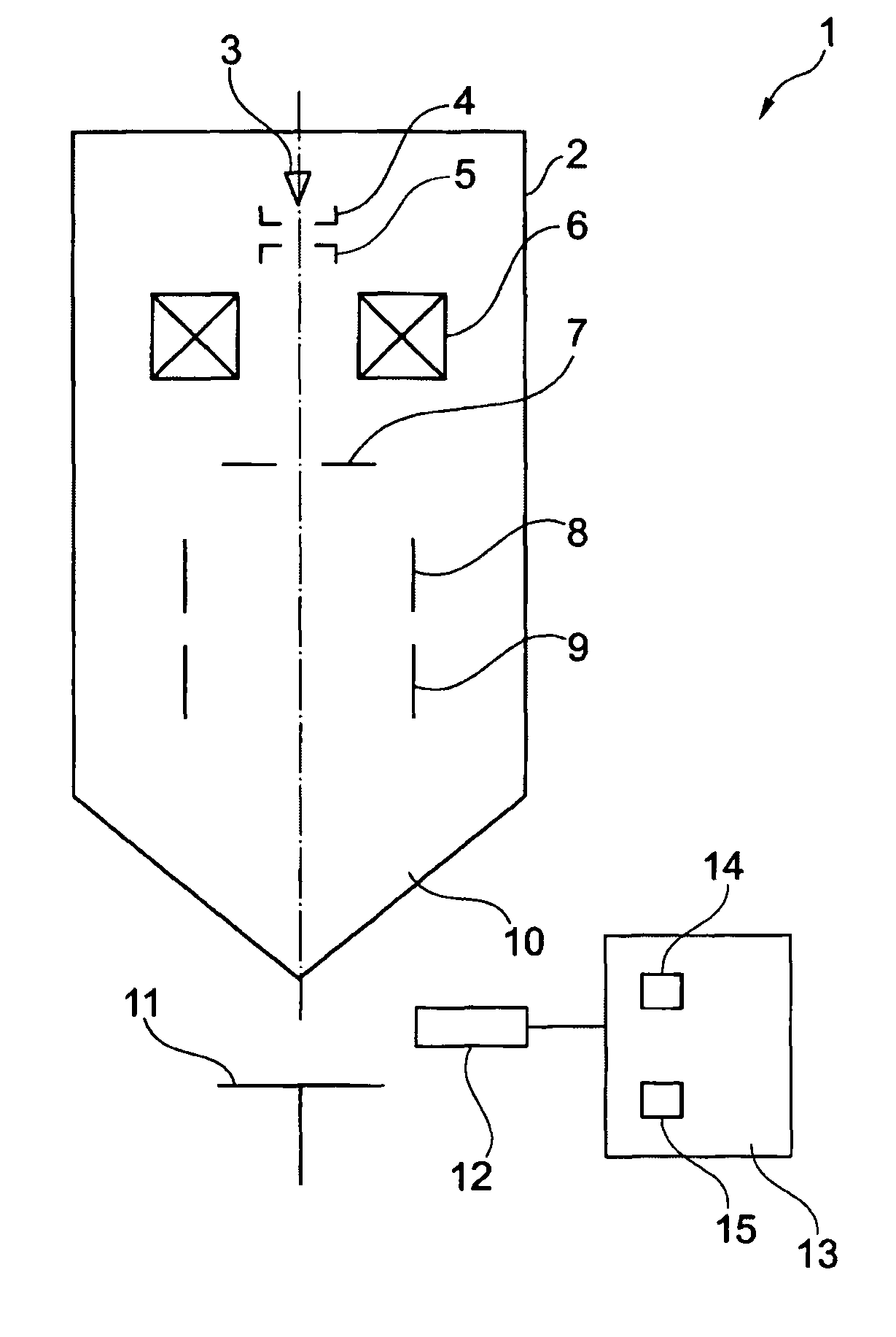
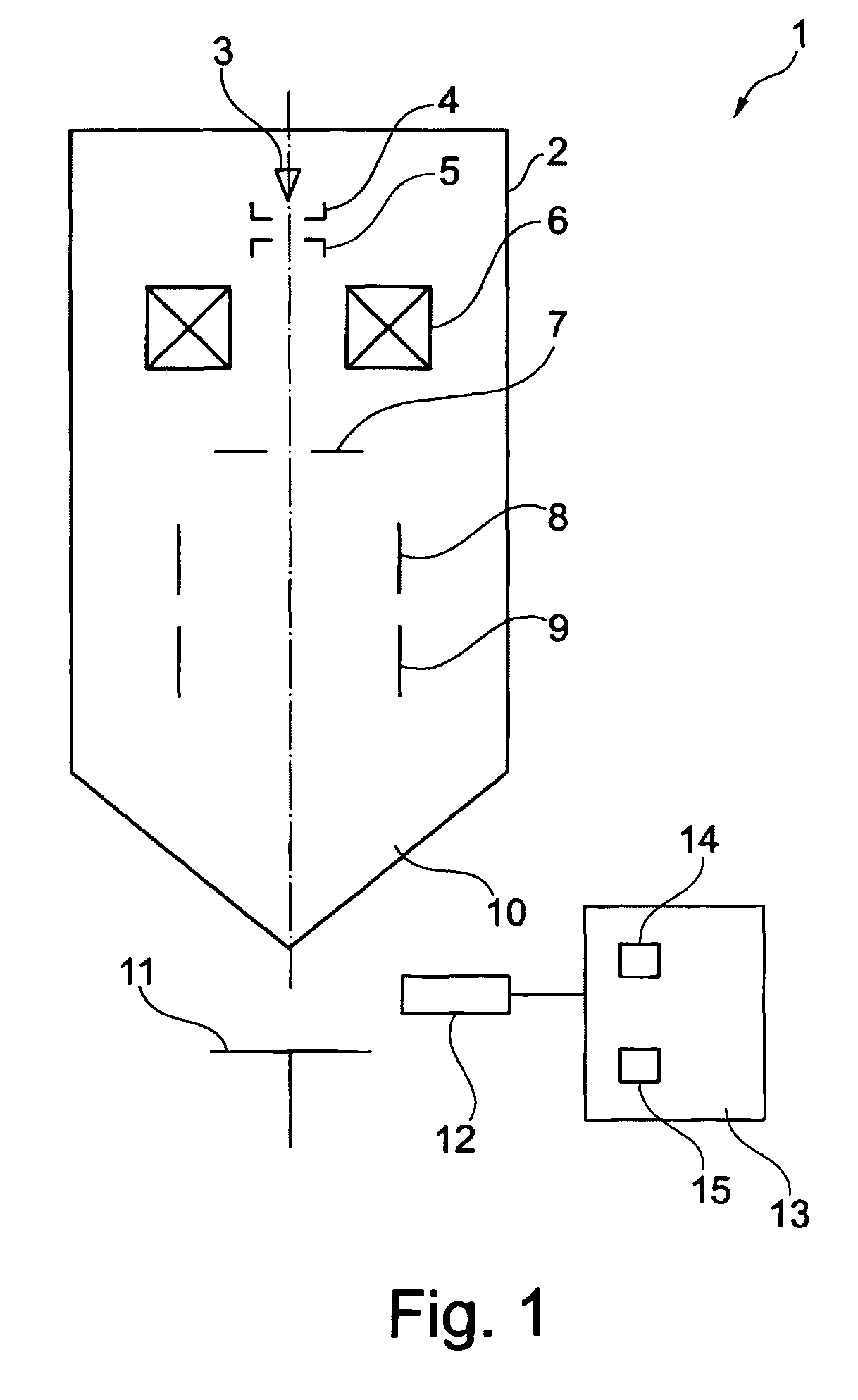
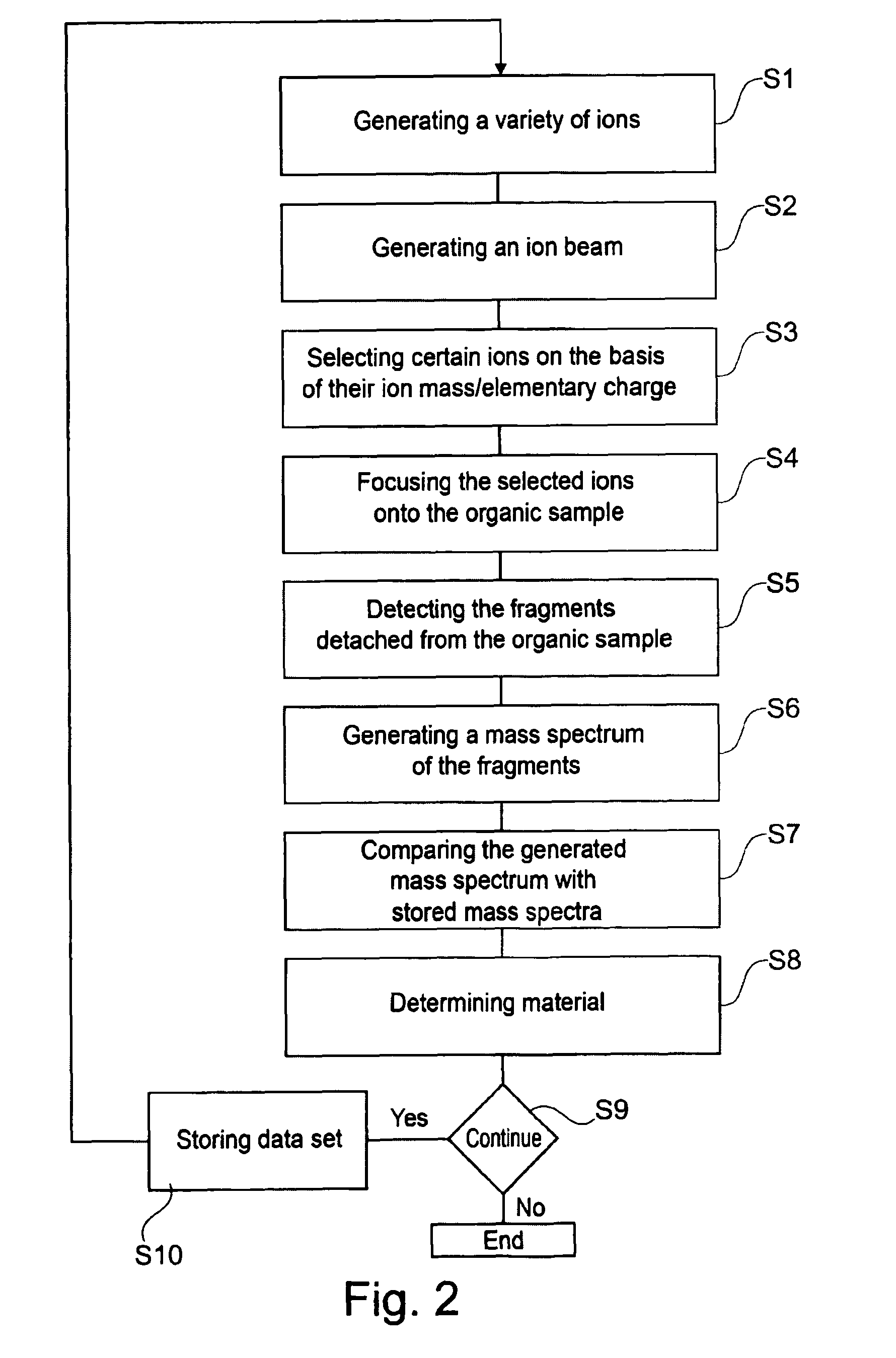
Device and method for analyzing an organic sample
ActiveUS8263933B2Easy to analyzeHigh resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
A device and method for analyzing an organic sample provide high spatial resolution. A focused ion beam is directed onto the organic sample. Fragments detached from the sample are examined using mass spectroscopy.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Laser ablation feedback spectroscopy
InactiveUS20050061779A1Precise depth controlReduce the amount requiredWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusMass spectrometryAblation plasma
Methods, for use with a laser ablation or drilling process, which achieve depth-controlled removal of composite-layered work-piece material by real-time feedback of ablation plasma spectral features. The methods employ the use of electric, magnetic or combined fields in the region of the laser ablation plume to direct the ablated material. Specifically, the electric, magnetic or combined fields cause the ablated material to be widely dispersed, concentrated in a target region, or accelerated along a selected axis for optical or physical sampling, analysis and laser feedback control. The methods may be used with any laser drilling, welding or marking process and are particularly applicable to laser micro-machining. The described methods may be effectively used with ferrous and non-ferrous metals and non-metallic work-pieces. The two primary benefits of these methods are the ability to drill or ablate to a controlled depth, and to provide controlled removal of ablation debris from the ablation site. An ancillary benefit of the described methods is that they facilitate ablated materials analysis and characterization by optical and / or mass spectroscopy.
Owner:BLUMENFELD WALTER +2
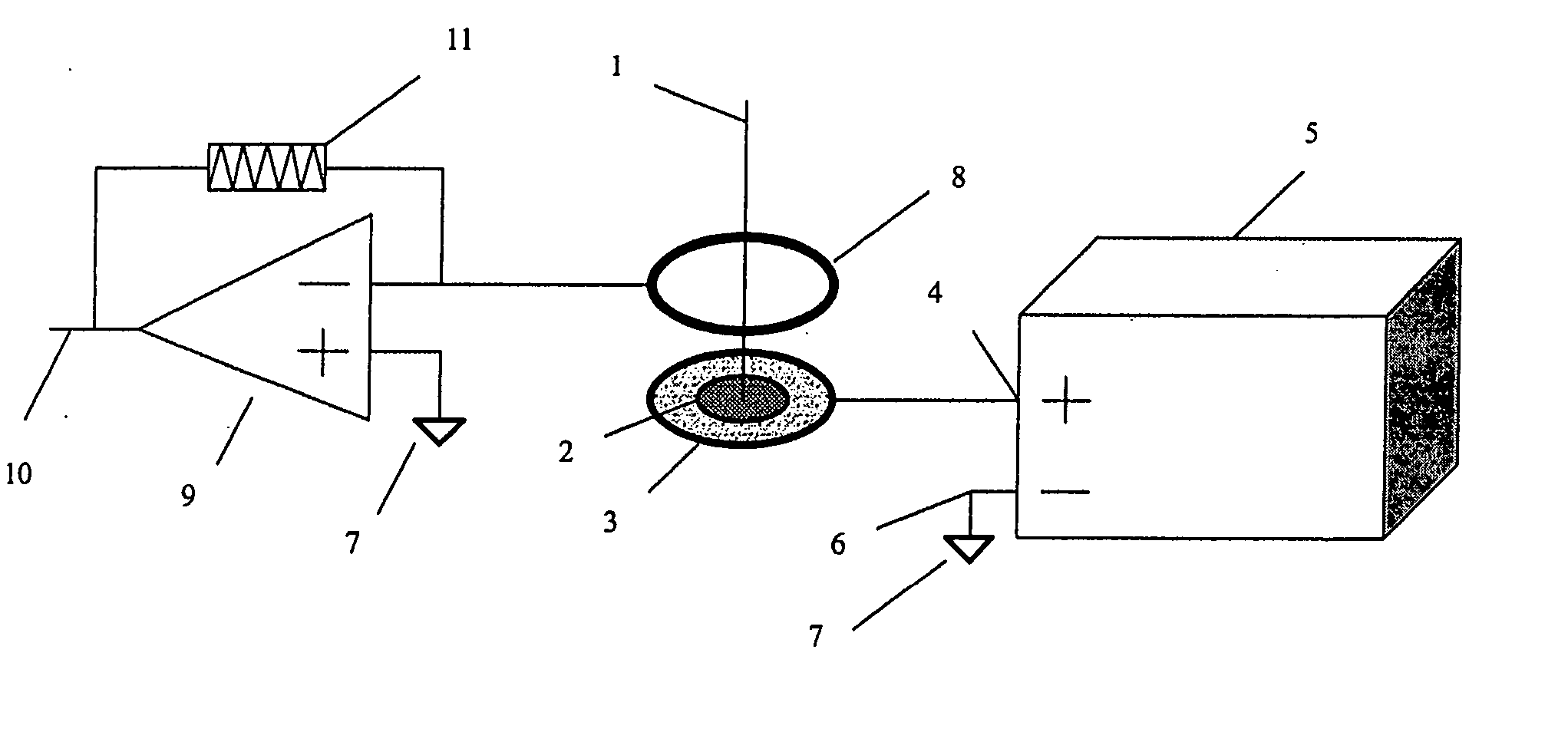
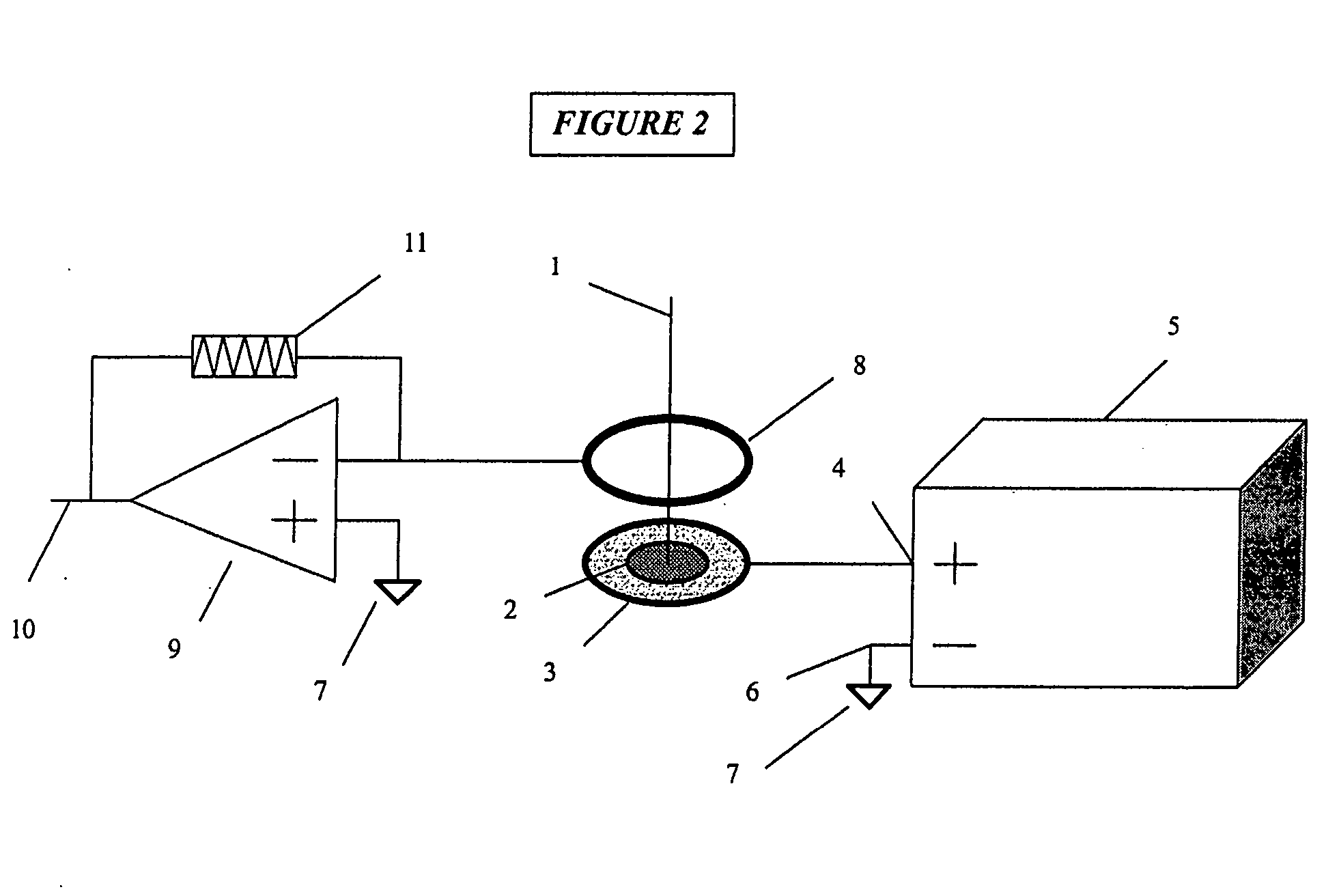
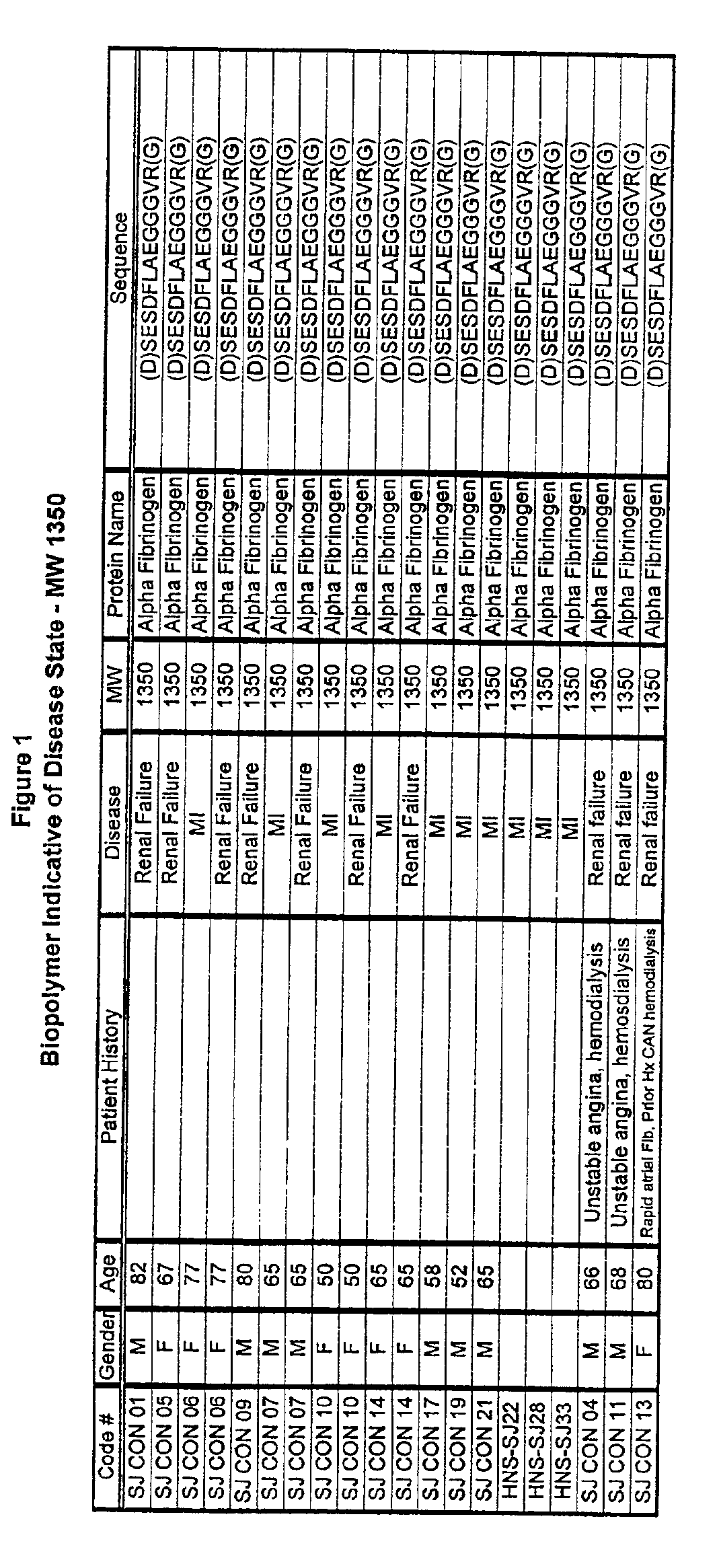
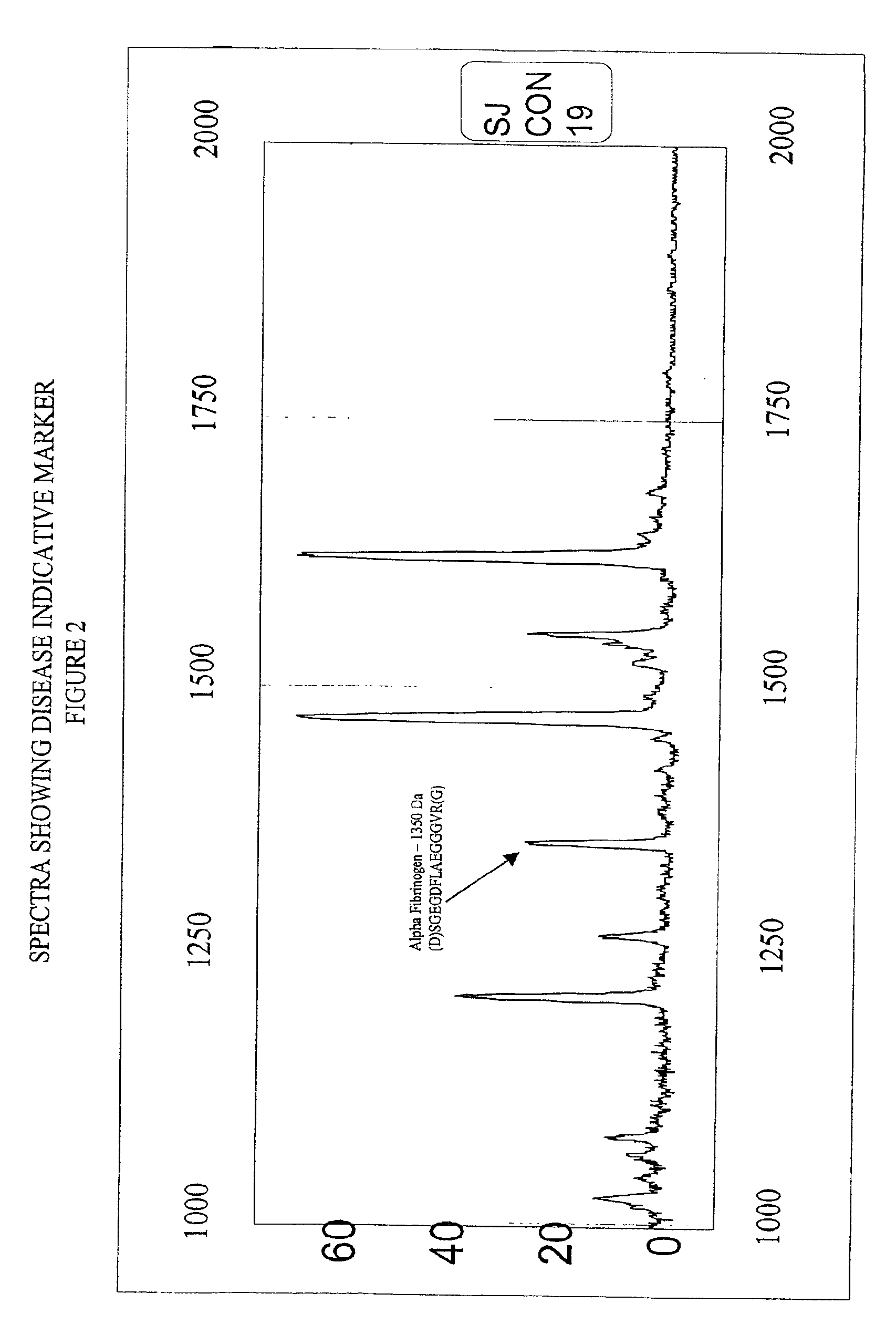
Biopolymer marker indicative of disease state having a molecular weight of 1350 daltons
InactiveUS6890763B2Maximize diversityThwart these maladiesAnalysis using chemical indicatorsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseBiopolymer
The instant invention involves the use of a combination of preparatory steps in conjunction with mass spectroscopy and time-of-flight detection procedures to maximize the diversity of biopolymers which are verifiable within a particular sample. The cohort of biopolymers verified within such a sample is then viewed with reference to their ability to evidence at least particular disease state; thereby enabling a diagnostician to gain the ability to characterize either the presence or absence of at least one disease state relative to recognition of the presence and / or the absence of the biopolymer.
Owner:NANOGEN INC
Technique for detecting microorganisms
A technique for detecting the presence of microorganisms in a simple, rapid, and efficient manner is provided. More specifically, the technique involves identifying one or more volatile compounds associated with a particular microorganism of interest. The volatile compounds may be identified, for instance, using solid phase microextraction in conjunction with gas chromatography / mass spectroscopy (“GC / MS”) analysis methods. Once identified, an indicator may then be selected that is configured to undergo a detectable color change in the presence of the identified volatile compound(s). If desired, the indicator may be provided on a substrate to form an indicator strip for use in a wide variety of applications. In this manner, the presence of the microorganism may be rapidly detected by simply observing a color change of the indicator strip.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
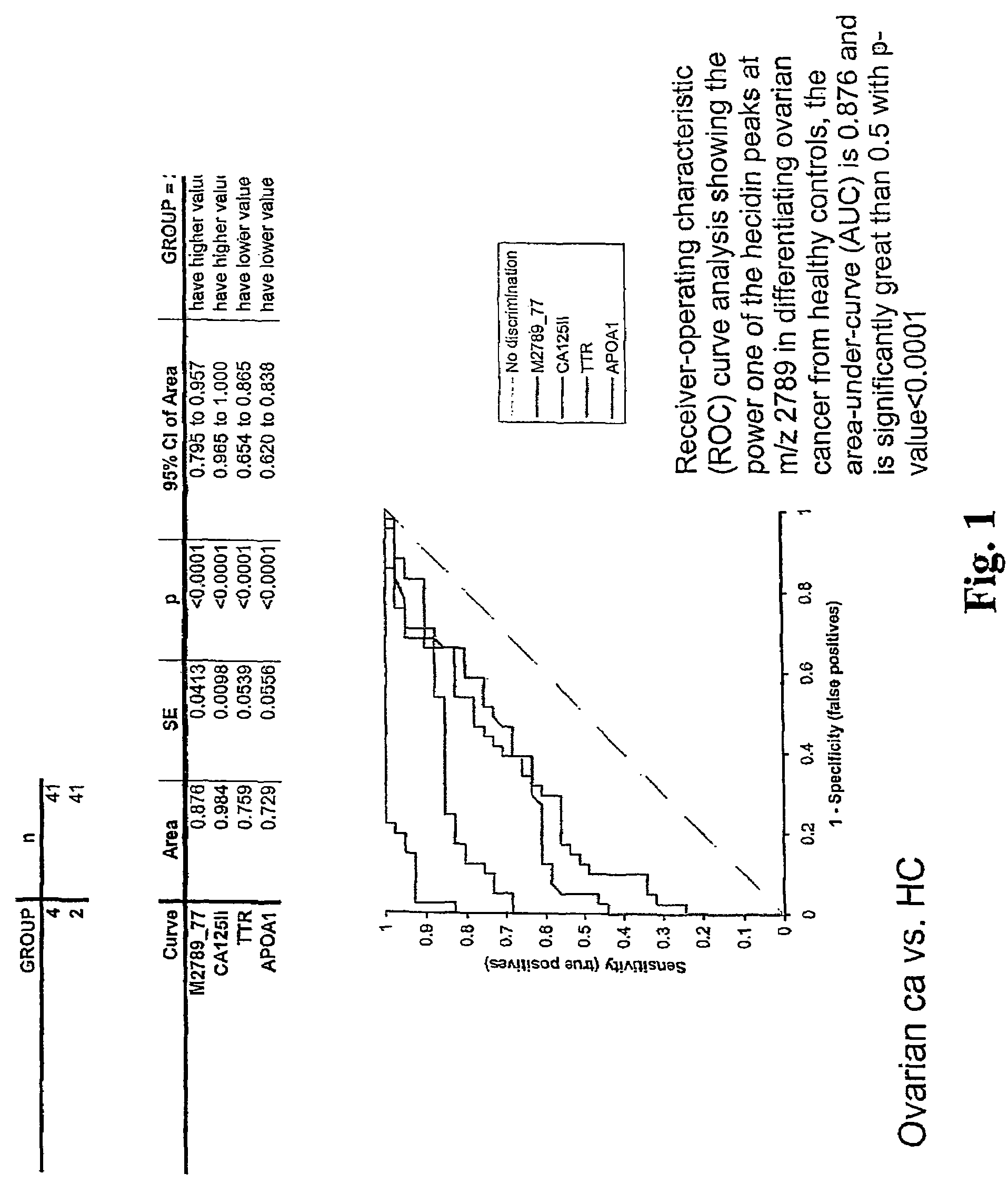
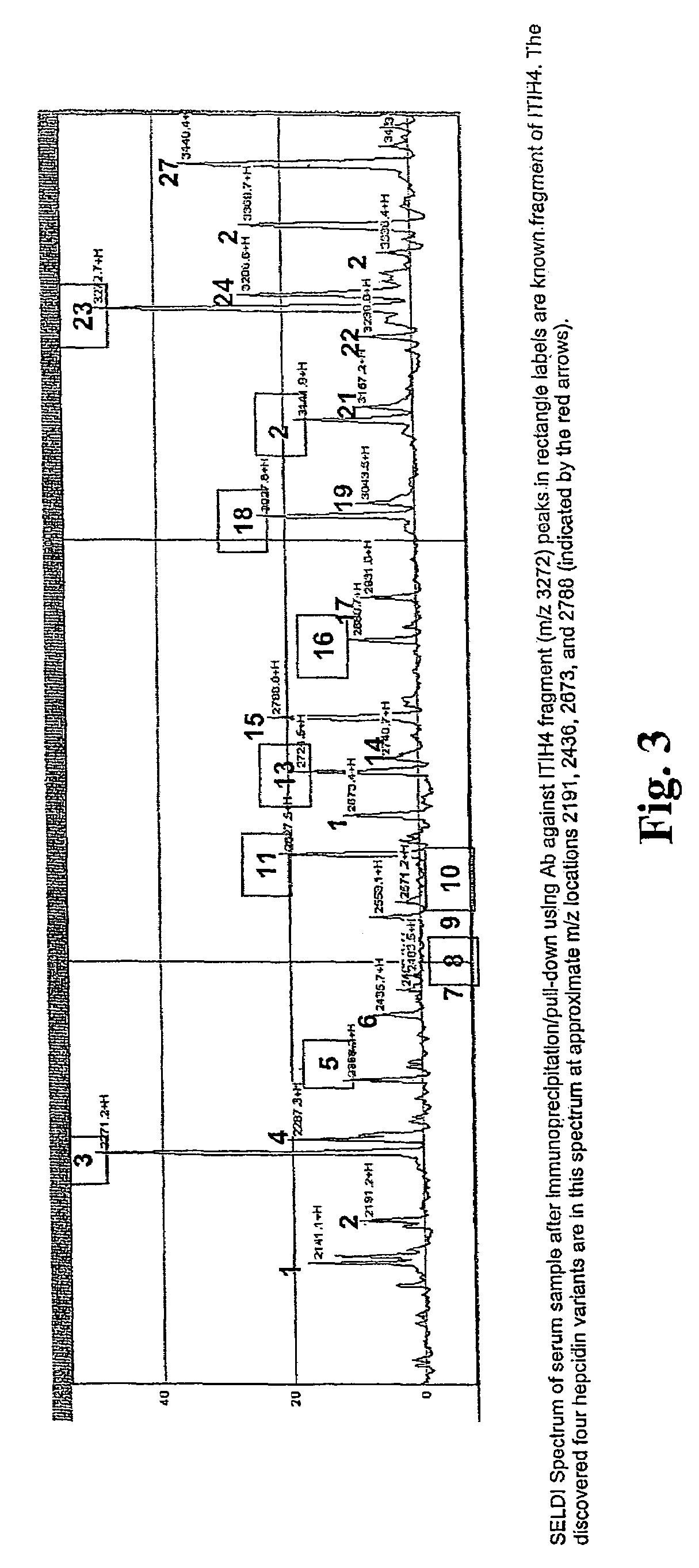
Biomarker for ovarian and endometrial cancer: hepcidin
ActiveUS7510842B2Improve diagnostic capabilitiesImprove the level ofBiocideCompound screeningThyroxine measurementMass spectrometry
The present invention provides protein-based biomarkers and biomarker combinations that are useful in qualifying ovarian cancer status as well as endometrical cancer status in a patient. In particular, it has been found that hepcidin is a biomarker for both ovarian cancer and endometrial cancer and that a panel of biomarkers, including hepcidin, transthyretin and optionally other markers are useful to classify a subject sample as ovarian cancer or non-ovarian cancer. The biomarkers can be detected by SELDI mass spectrometry.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +2
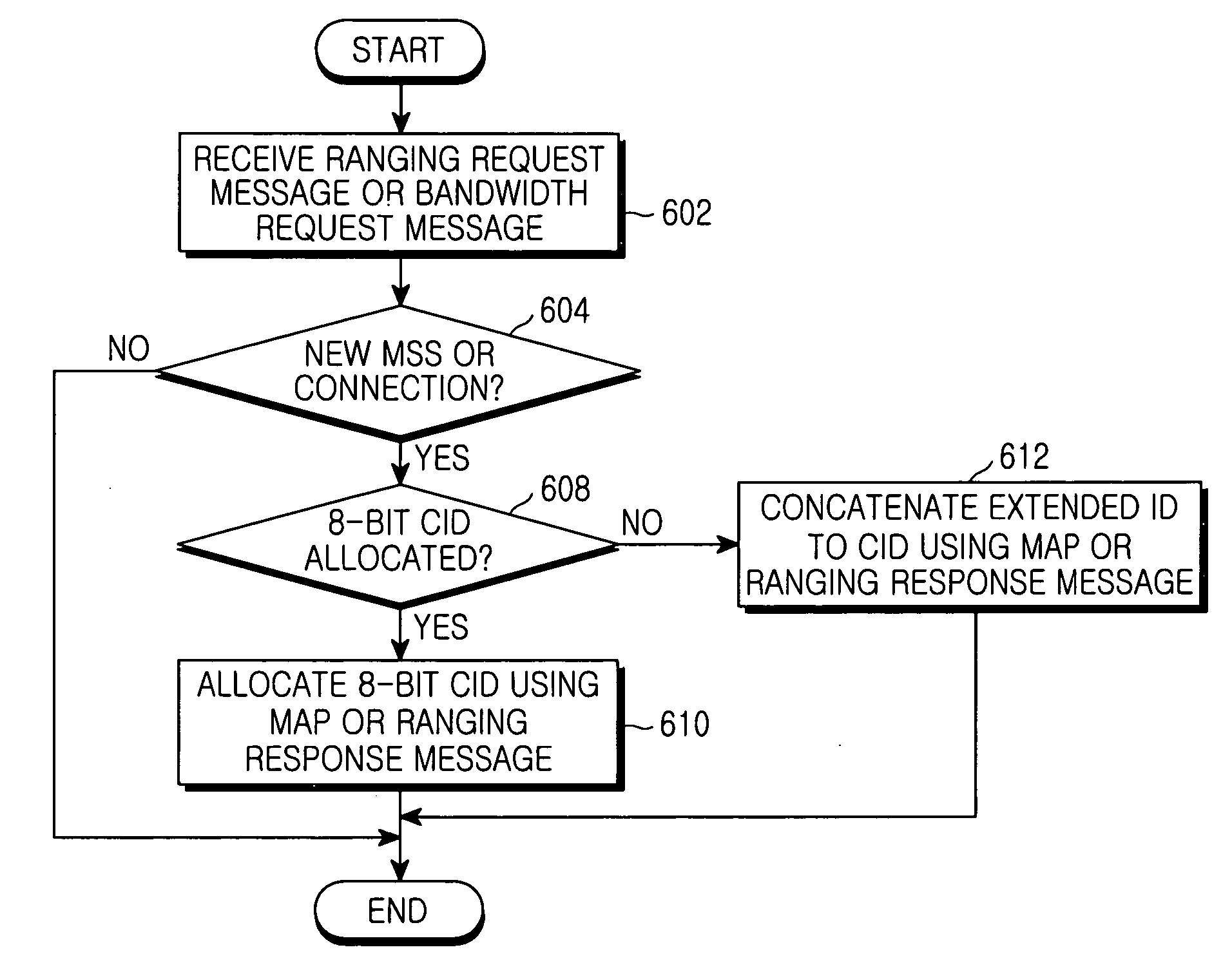
Connection identification allocating system and method in a broadband wireless access communication system
ActiveUS20050286451A1Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexCommunications systemBroadband
Provided is a connection identification (CID) allocating method in a Broadband Wireless Access (BWA) communication system having a medium access control protocol data unit (MAC PDU) format with a header field including control information and a payload field including user data. The header field has a first CID field of a first length indicating a CID of a mobile subscriber station (MSS), a second CID field of a second length and indicating the CID of the MSS by being concatenated with a CID of the first CID field, and a type field indicating whether the second CID field is used. The method includes determining a CID to be allocated to a particular MSS; and if the length of the determined CID is equal to the first length, including the determined CID in the first CID field, including, in the type field, information indicating that the second CID field is not used, and transmitting the MAC PDU to the MSS.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of making Group III nitrides
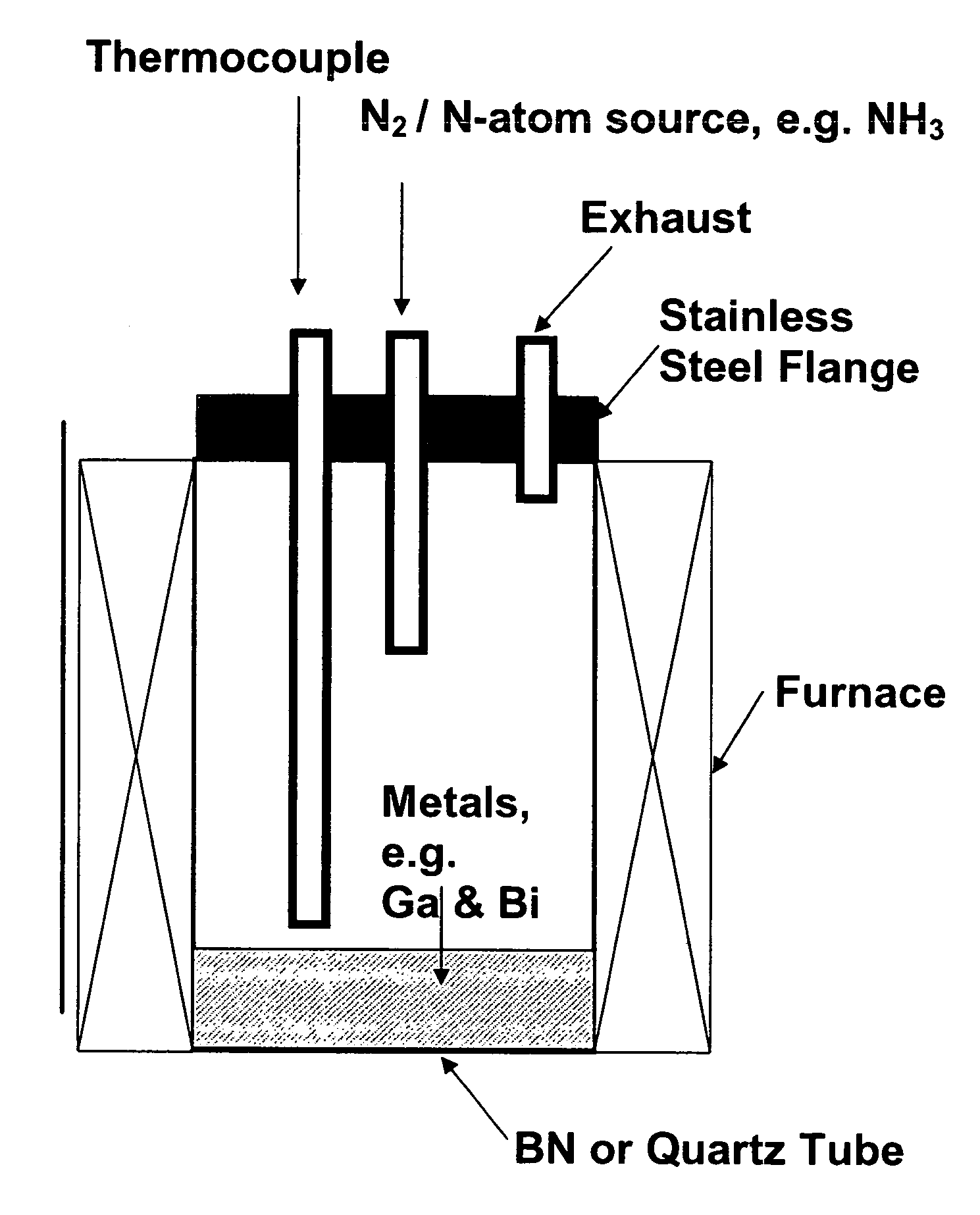
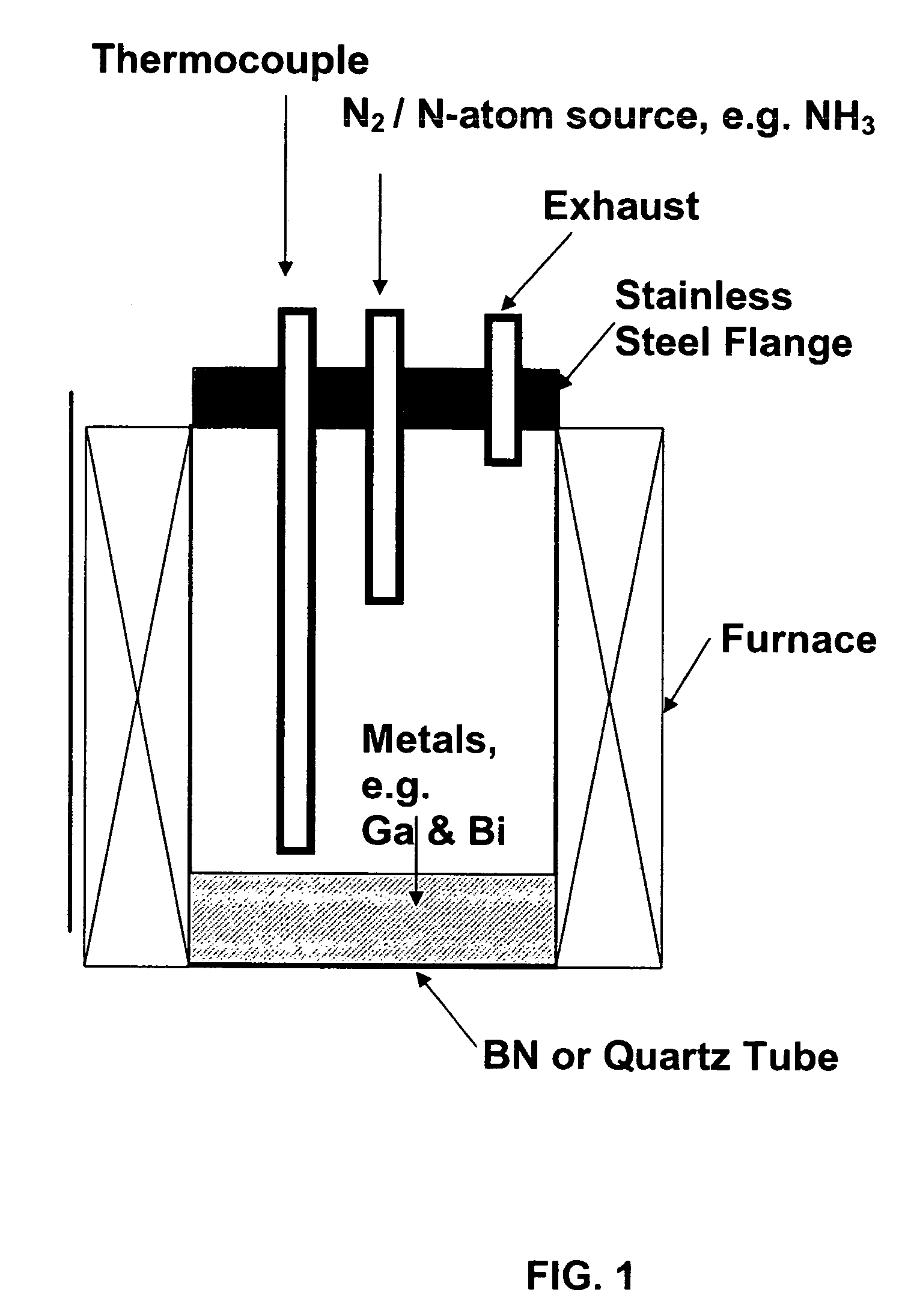
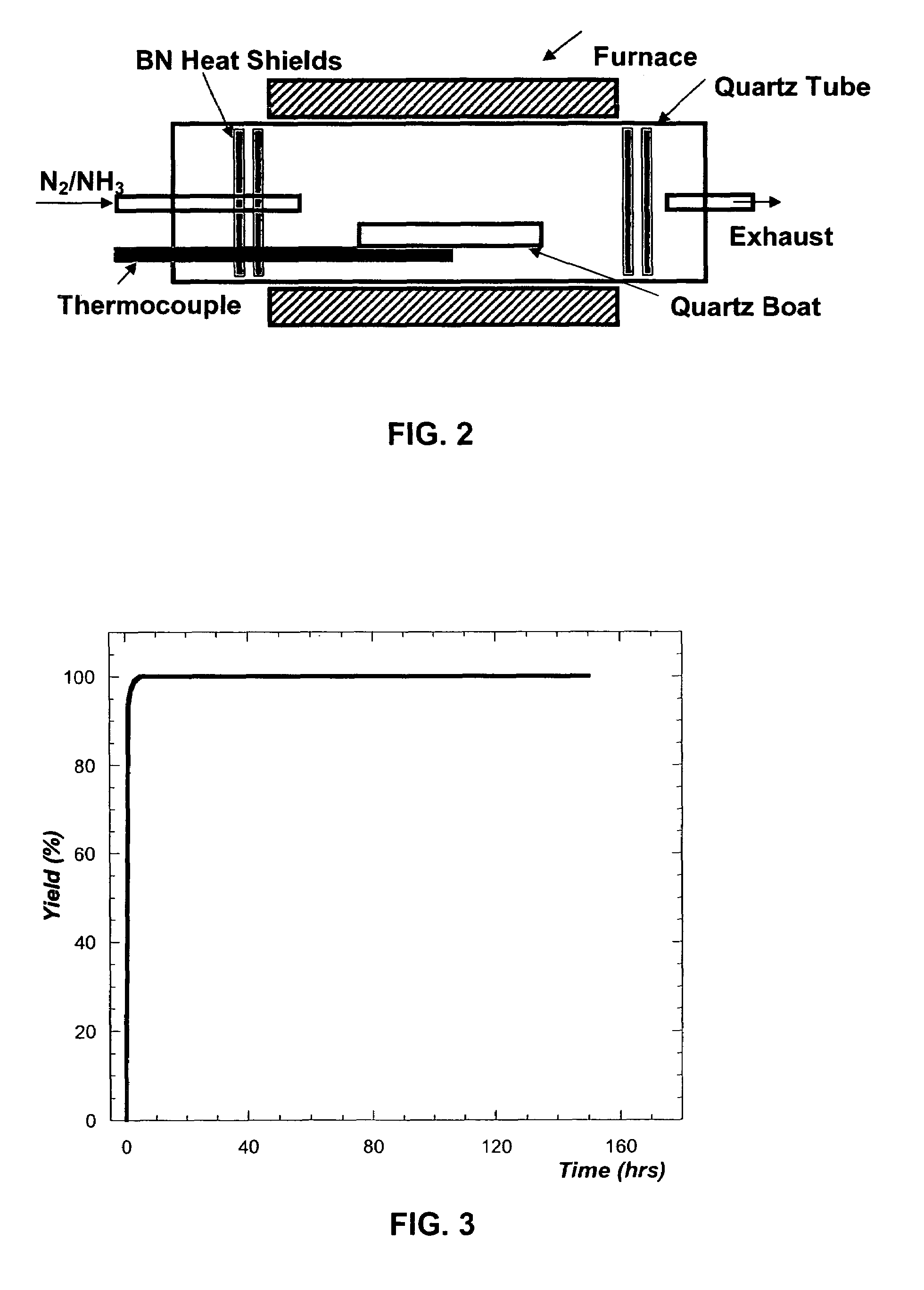
InactiveUS7381391B2High purityShort reaction timePolycrystalline material growthNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsOptical propertyGlow Discharge Mass Spectrometry
The present invention provides compositions and a novel high-yielding process for preparing high purity Group III nitrides. The process involves heating a Group III metal and a catalytic amount of a metal wetting agent in the presence of a nitrogen source. Group III metals can be stoichiometrically converted into high purity Group III nitride powders in a short period of time. The process can provide multi-gram quantities of high purity Group III nitrides in relatively short reaction times. Detailed characterizations of GaN powder were preformed and are reported herein, including morphology and structure by SEM and XRD, optical properties by cathodoluminescence (CL), and Raman spectra to determine the quality of the GaN particles. The purity of GaN powder was found to be greater than 99.9% pure, as analyzed by Glow Discharge Mass Spectrometry (GDMS). Green, yellow, and red light emission can be obtained from doped GaN powders.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
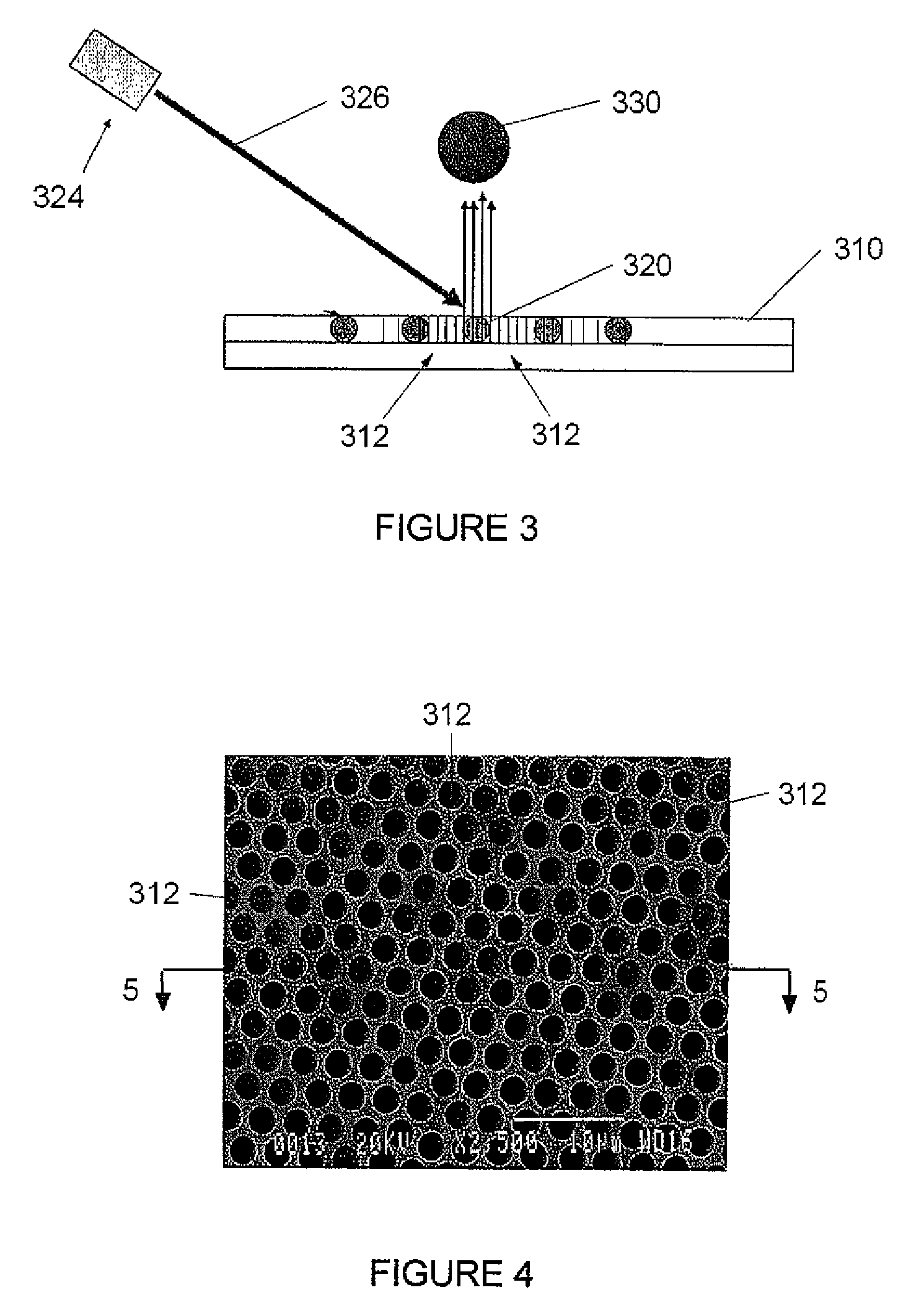
MALDI target plate utilizing micro-wells
ActiveUS7695978B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGlass fiberSpectroscopy
An arrangement for a MALDI sample plate for ion mass spectroscopy is disclosed. The sample is configured to shape the hypersonic explosion which creates the ions generated in a MALDI-type time-of-flight mass spectrometer. The MALDI sample plate includes a glass wafer formed from a plurality of clad glass fibers and has a first planar surface. The plate also has a plurality of micro-wells formed in the glass wafer. The micro-wells extend to a depth that is less than the thickness of the glass wafer and act to hold a spot sample in a manner that prevents spreading, maximizes the formation of ions, and shapes the resulting ion cloud to improve ion migration.
Owner:PHOTONIS SCI INC
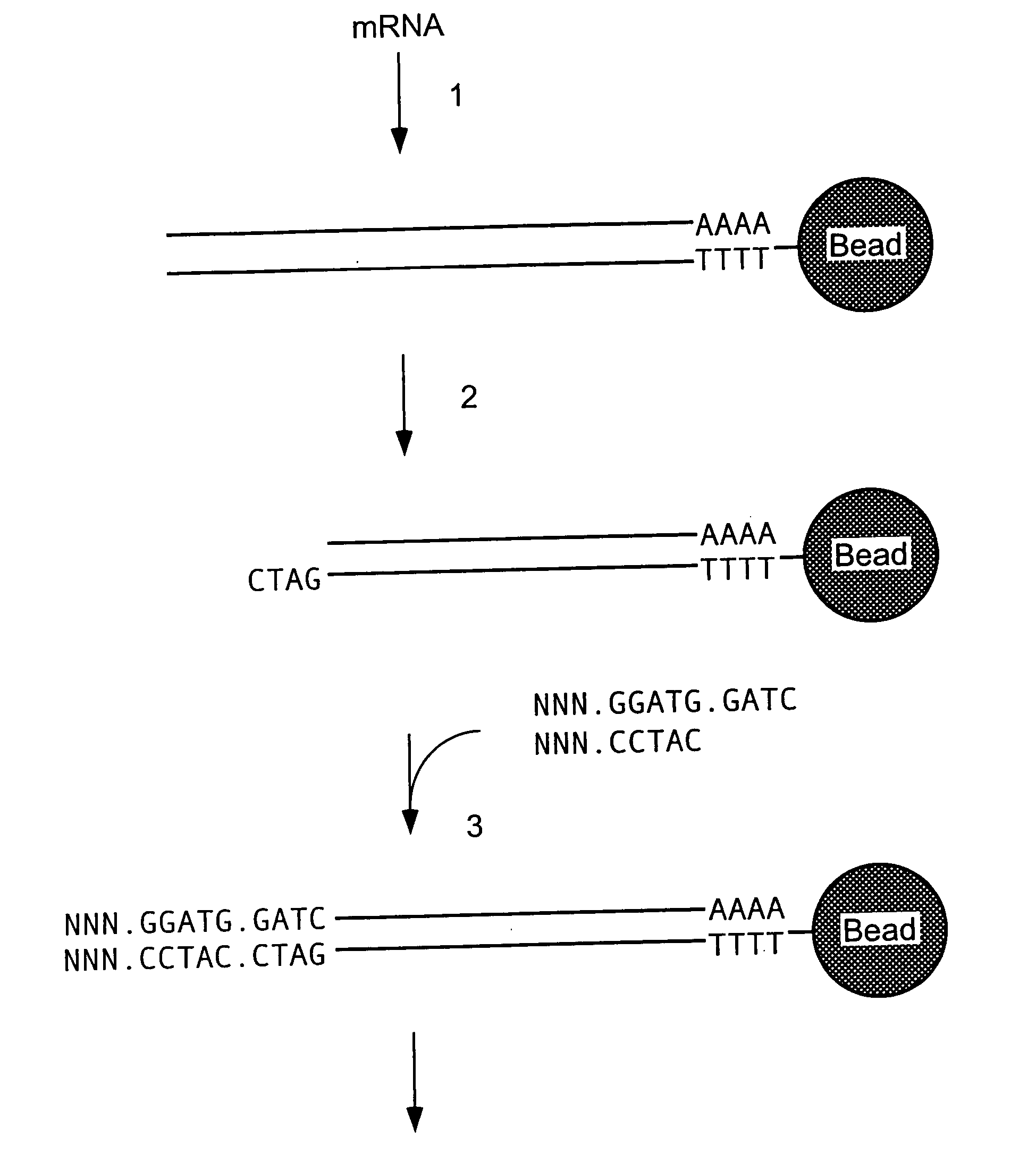
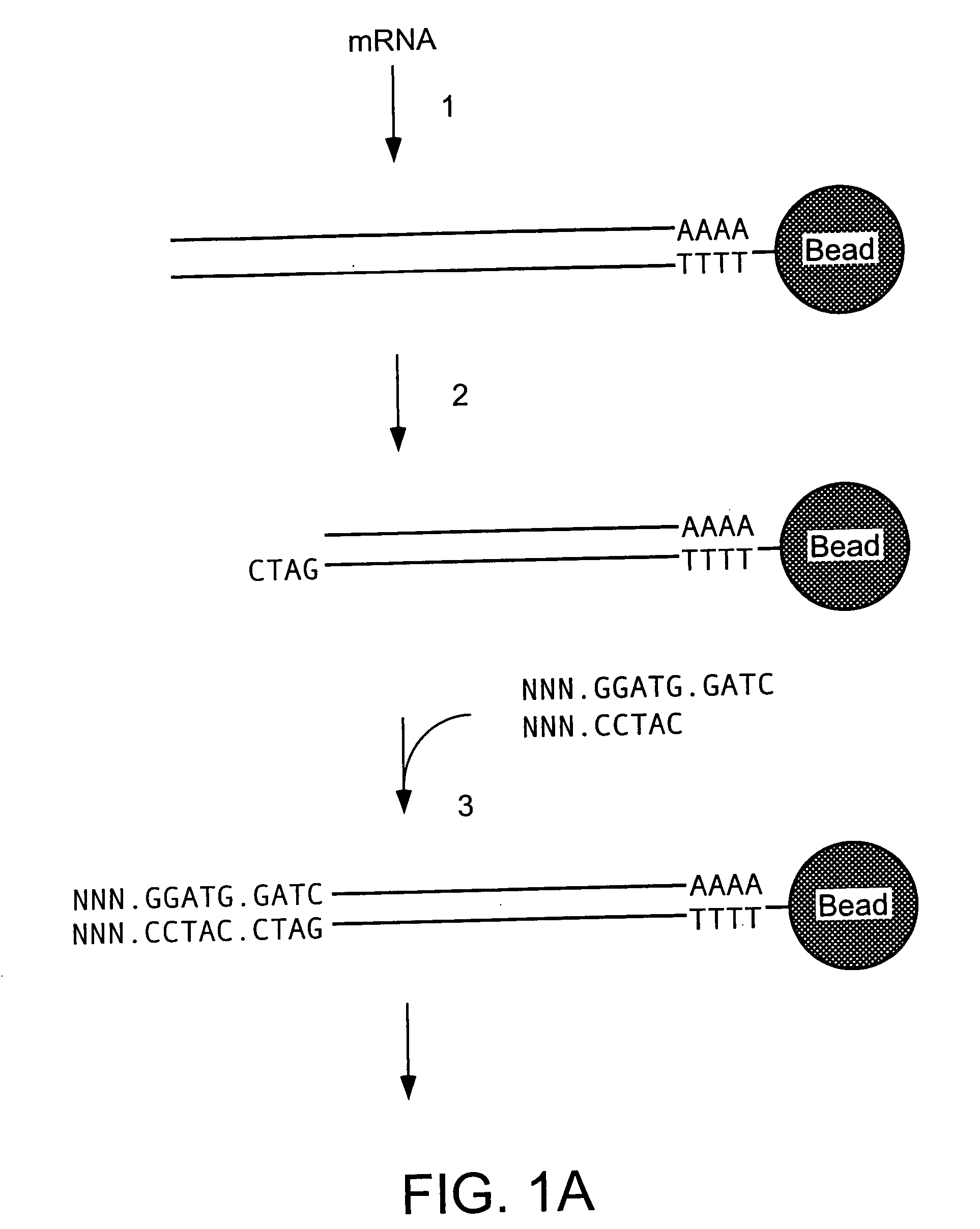
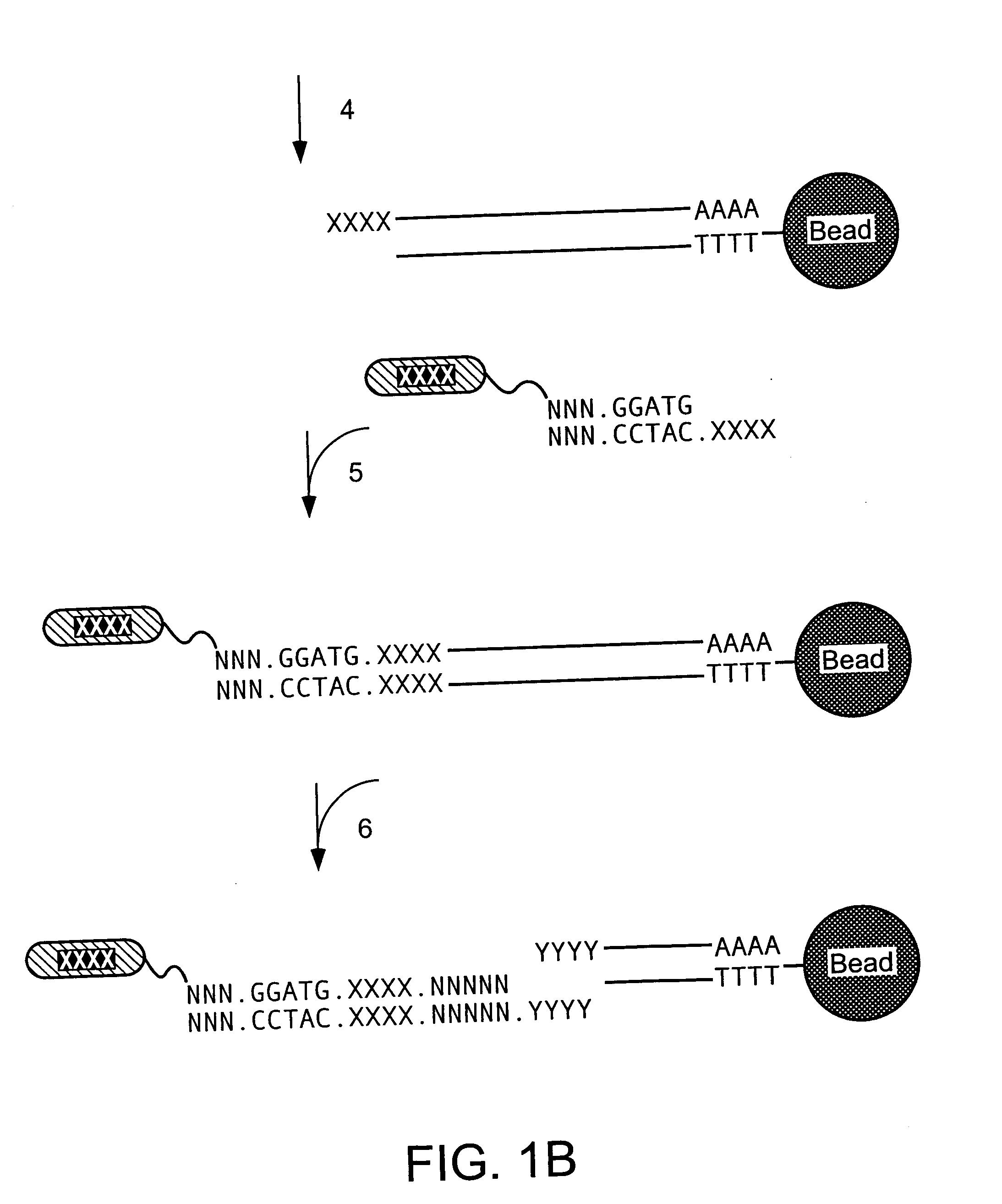
Characterization of mRNA molecules
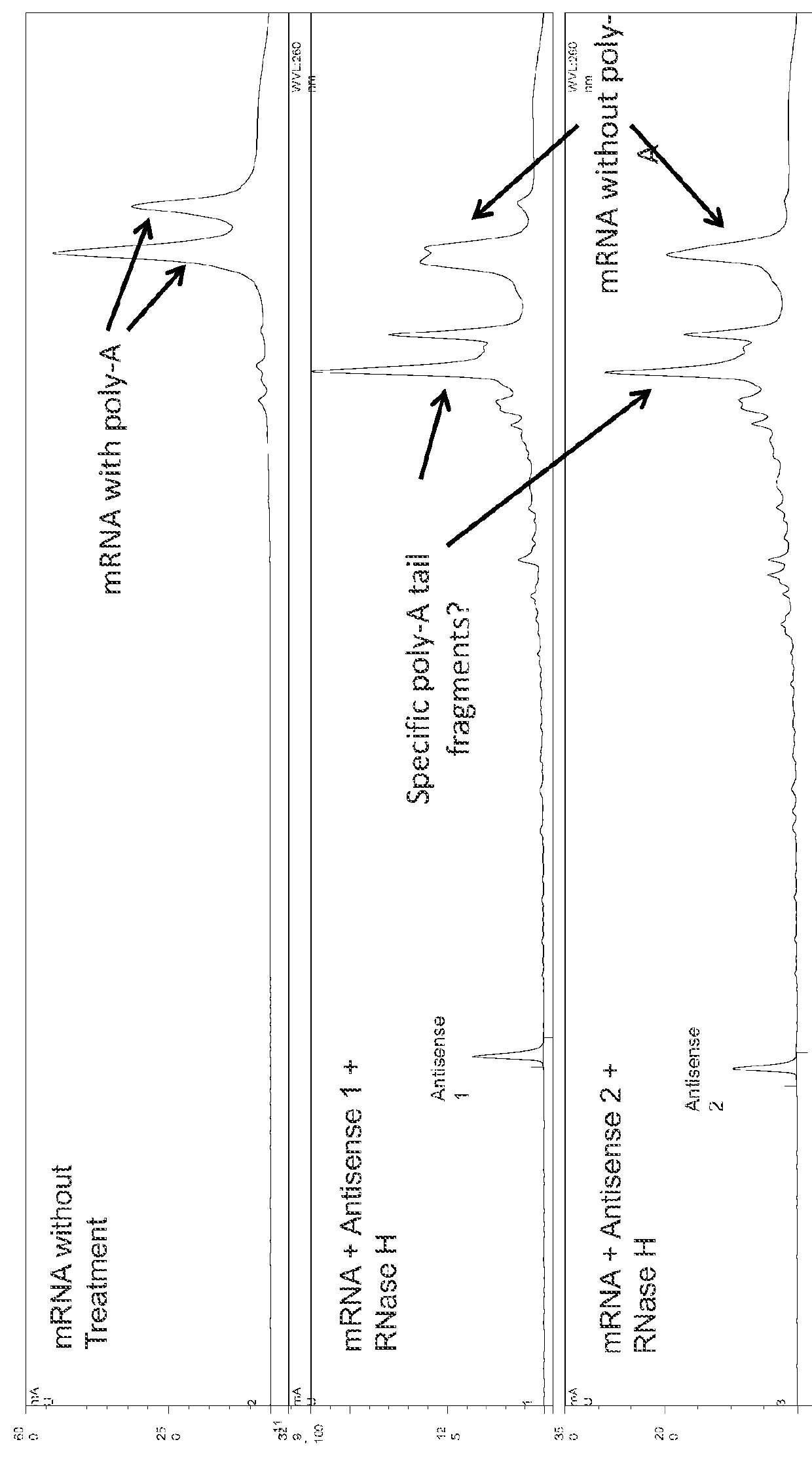
InactiveUS20160032273A1Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisReverse transcriptase
The present invention describes methods for the characterization of mRNA molecules during mRNA production. Characterizing mRNA includes processes such as oligonucleotide mapping, reverse transcriptase sequencing, charge distribution analysis, and detection of RNA impurities. Oligonucleotide mapping includes using an RNase to digest antisense duplexes from an RNA transcript, and then subjecting the digested RNA to reverse phase HPLC, anion exchange HPLC, and / or mass spectrometry analysis. Reverse transcriptase sequencing involves reverse transcription of an RNA transcript followed by DNA sequencing. Charge distribution analysis can comprise procedures such as anion exchange HPLC, or capillary electrophoresis. Detection of impurities includes detecting short mRNA transcripts, RNA-RNA hybrids, and RNA-DNA hybrids.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
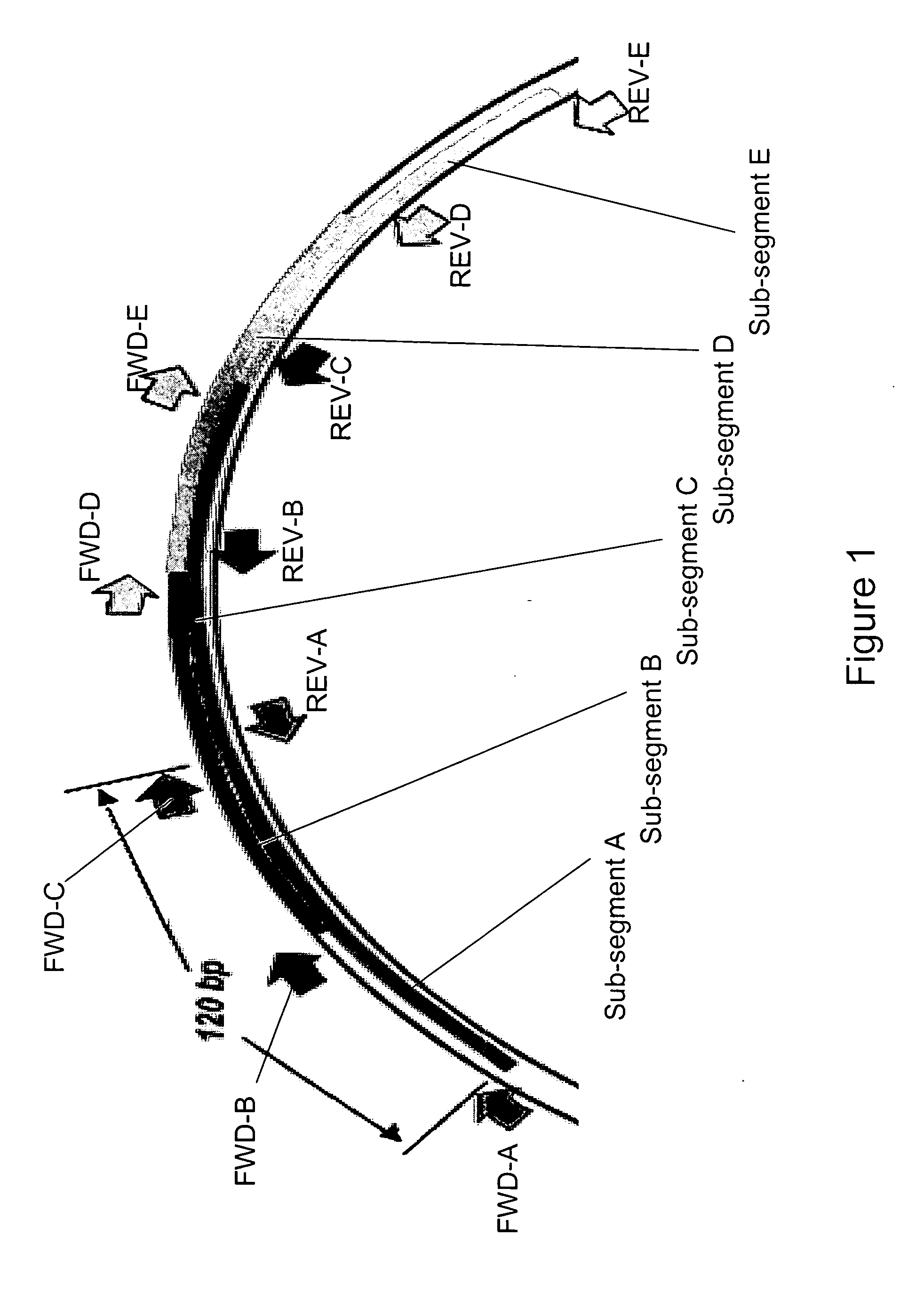
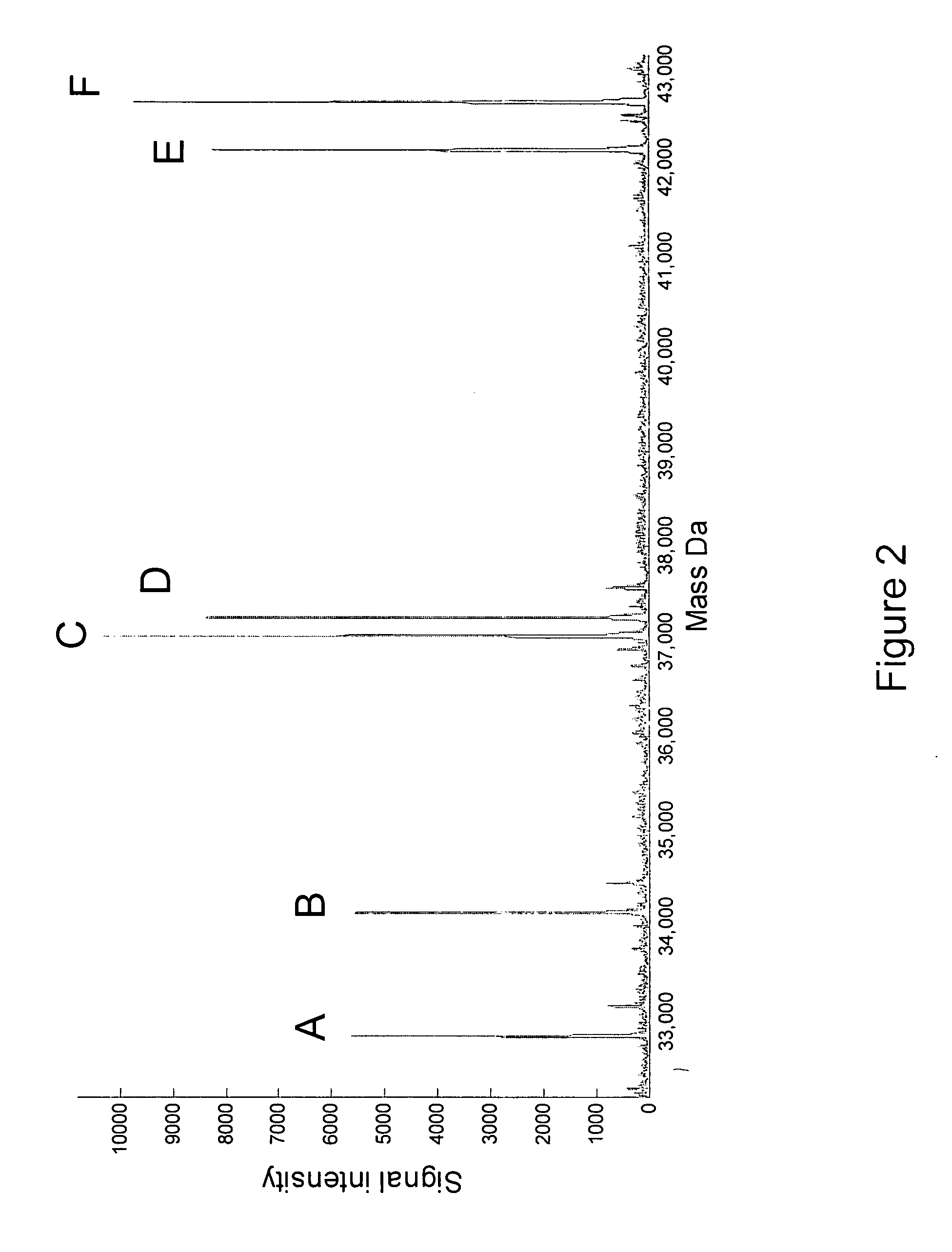
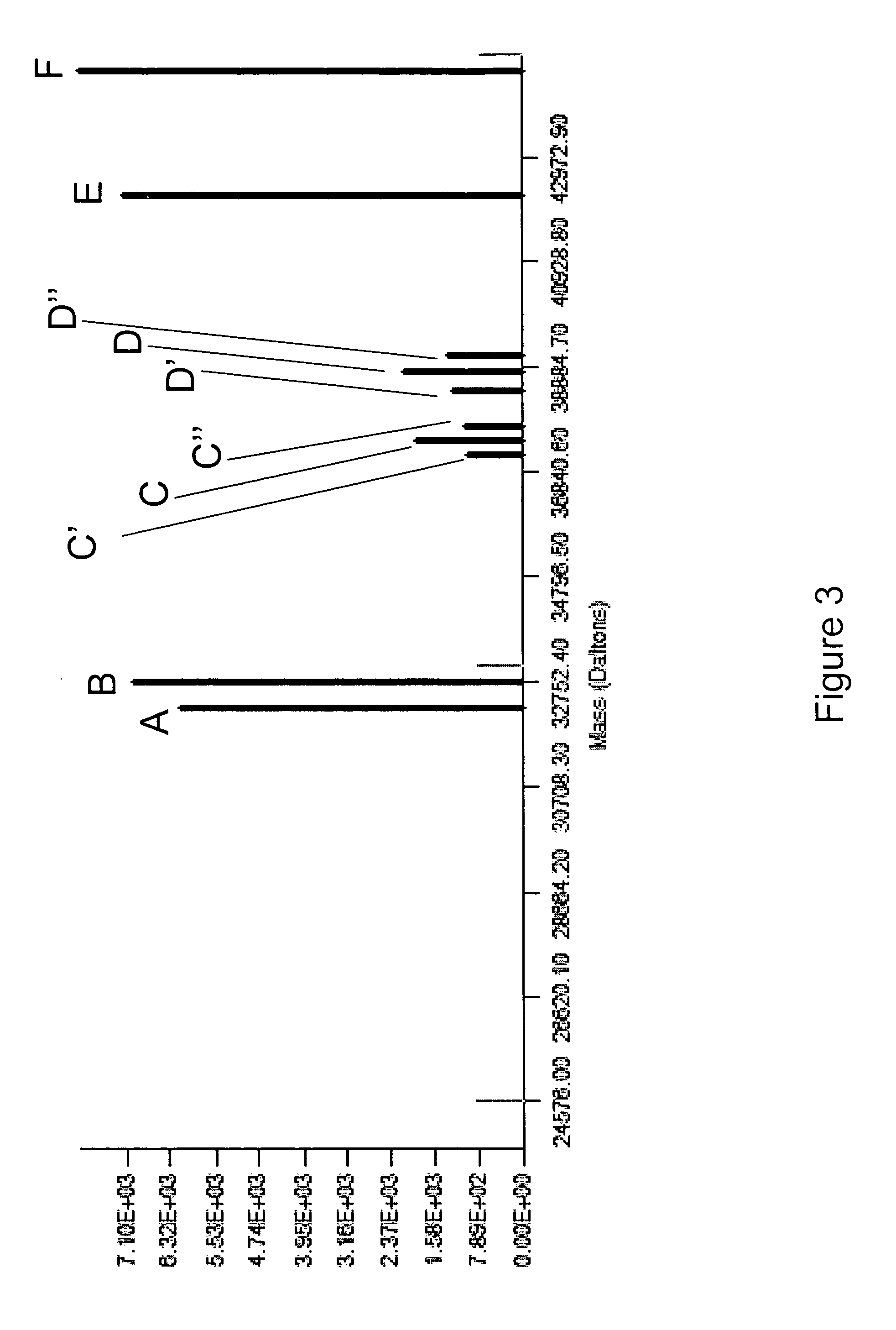
Methods for rapid identification and quantitation of nucleic acid variants
InactiveUS20070218467A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationRapid identificationMass spectrometry
There is a need for nucleic acid analysis which is both specific and rapid, and in which no nucleic acid sequencing is required. The present invention addresses this need, among others by providing a method of nucleic acid amplification of overlapping sub-segments of a nucleic acid followed by molecular mass measurement of resulting amplification products by mass spectrometry, and determination of the base compositions of the amplification products.
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI
Microbial identification based on the overall composition of characteristic oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20050142584A1Create accuracyCreate speedMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismBiological body
Identification of microorganisms based on the sequences of their 5S, 23S and particularly 16S ribosomal RNAs is growing in utility as the database of known ribosomal RNA sequences expands. Experimental identification is usually based on matching the experimentally-determined sequence of an organisms rRNA to a previously-determined sequence in the databank, or hybridization of the organisms rRNA or encoding rDNA to an oligonucleotide probe specific for an organism anticipated to be present in the sample. Here we propose the identification of microorganisms based on the overall composition (not sequence or hybridization propensity) of characteristic molecules derived from their rRNA or rDNA sequences by enzymatic cleavage or localized amplification. Ribonuclease T1 fragments of rRNA composition determination by mass spectrometry are especially favored. The characteristic molecules used can be chosen to be “compositional signatures” whose presence / absence is known to be associated with particular groups of organisms.
Owner:JACKSON GEORGE W
Multiplex spatial profiling of gene expression
The present invention provides mass tag complexes that permit simultaneously obtaining information of a plurality of biological molecules. The biological molecules may be RNA or protein, and the information includes both level of expression as well as spatial disposition within a cell or tissue. The mass tag comprise a core structure, a target binding structure (e.g., nucleic acid or peptide binding structure), a cleavable linker and a mass tag that exhibits a unique mass spectroscopy signal.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Aptamer-based methods for identifying cellular biomarkers
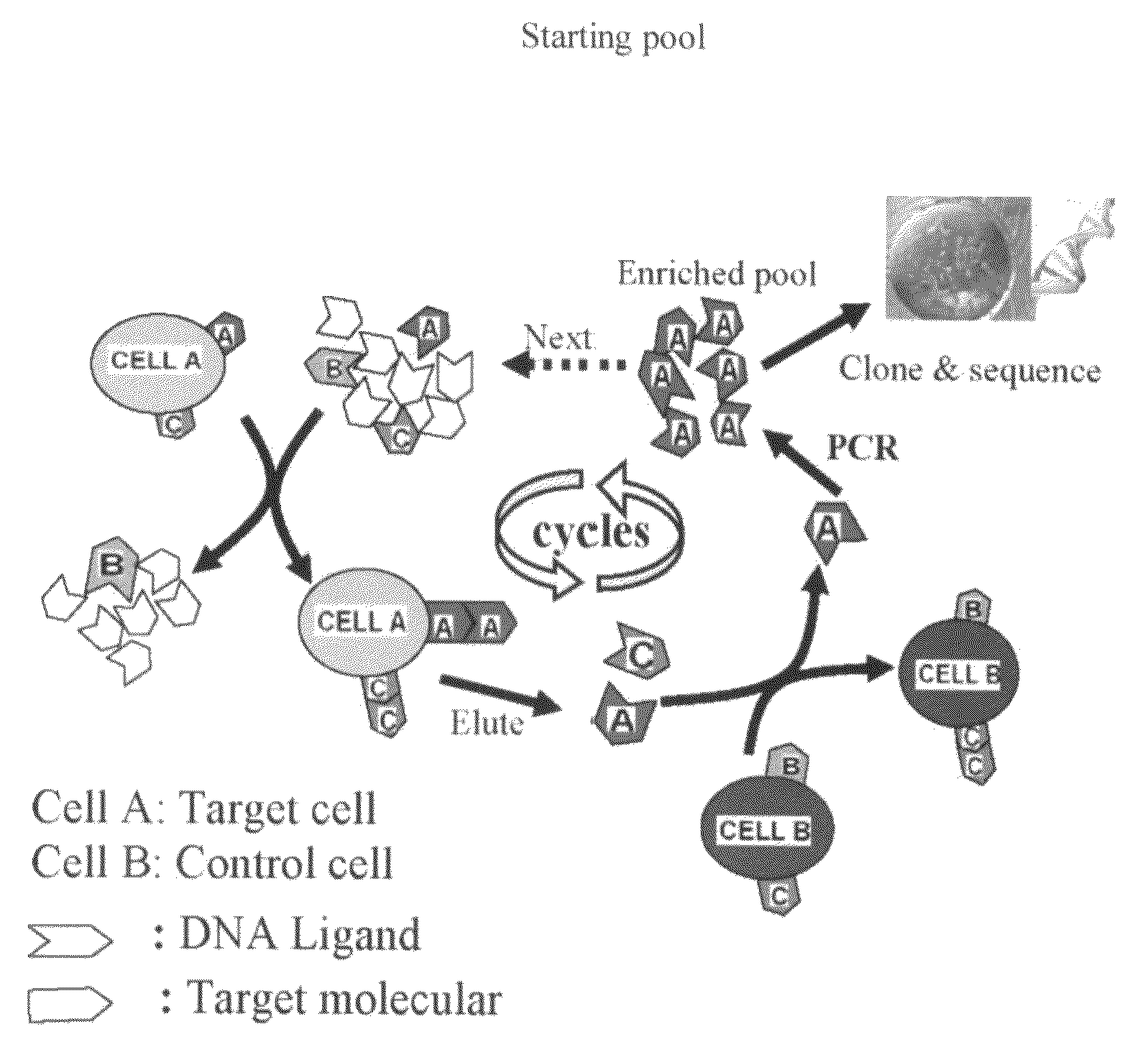
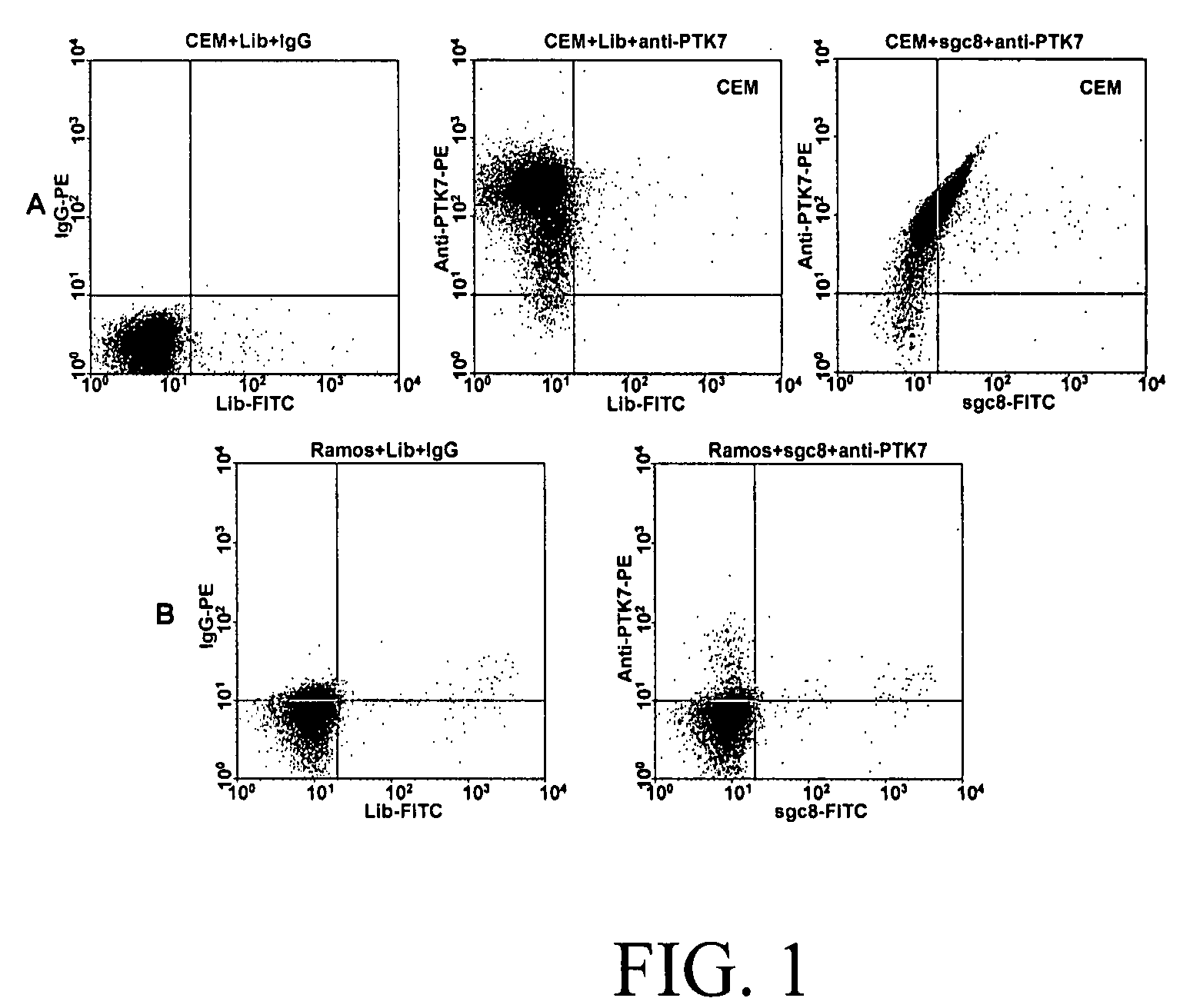
InactiveUS20090117549A1Easy to fixEasy to synthesizeElectrolysis componentsParticle separator tubesBiotin-streptavidin complexCancer cell
In this invention, a biomarker discovery method has been developed using specific biotin-labeled oligonucleotide ligands and magnetic streptavidin beads. In one embodiment, the oligonucleotide ligands are firstly generated by whole-cell based SELEX technique. Such ligands can recognize target cells with high affinity and specificity and can distinguish cells that are closely related to target cells even in patient samples. The targets of these oligonucleotide ligands are significant biomarkers for certain cells. These important biomarkers can be captured by forming complexes with biotin-labeled oligonucleotide ligands and collecting the complexes using magnetic streptavidin beads, whereupon the captured biomarkers are analyzed to identify the biomarkers. Analysis of biomarkers include HPLC-Mass Spectroscopy analysis, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, flow cytometry, and the like. The identified biomarkers can be used for pathological diagnosis and therapeutic applications. Using the disclosed methods, highly specific biomarkers of any kinds of cells, in particular cancer cells, can easily be identified without prior knowledge of the existence of such biomarkers.
Owner:TAN WEIHONG +1
Method for the analysis of tissue sections
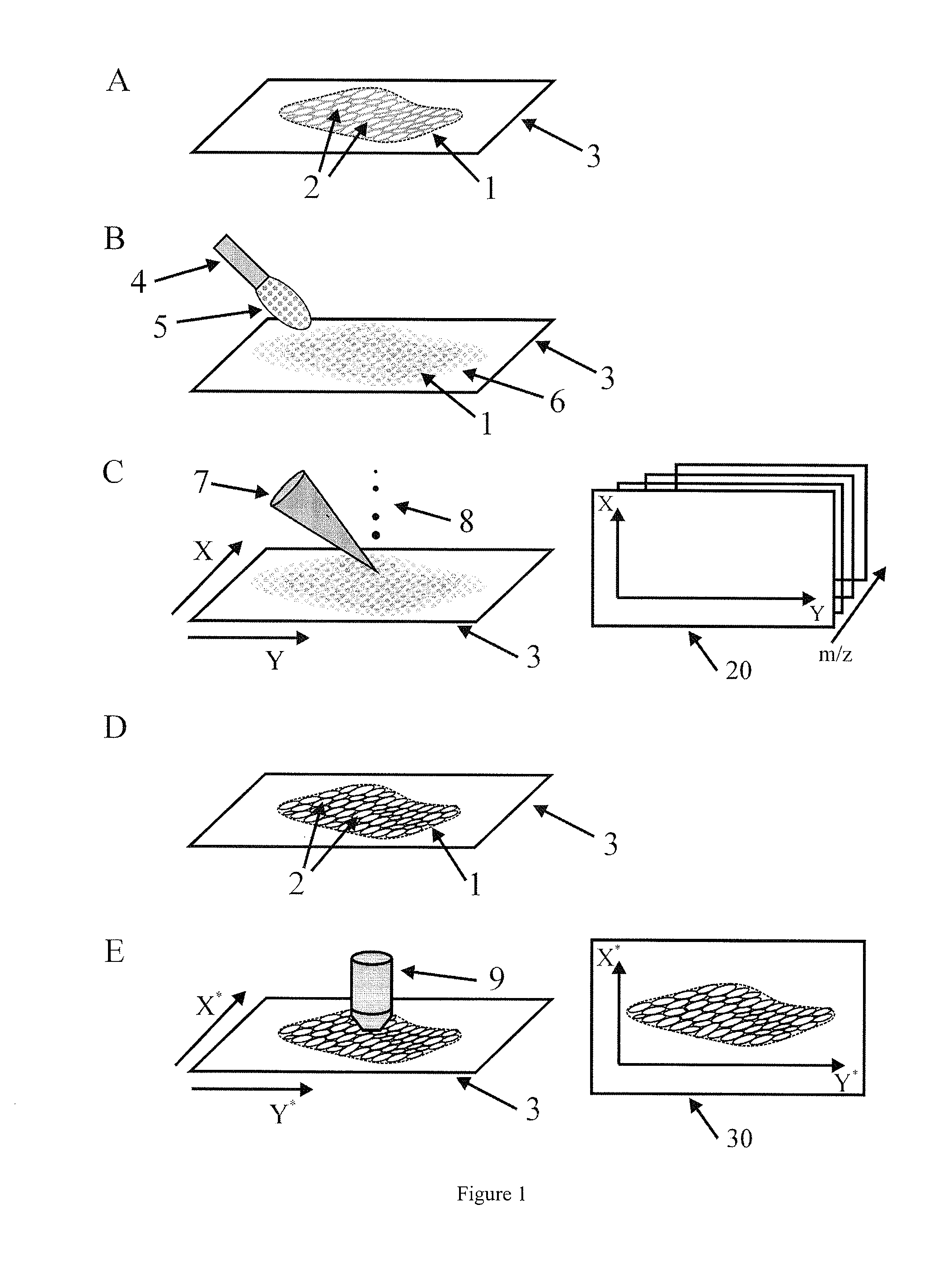
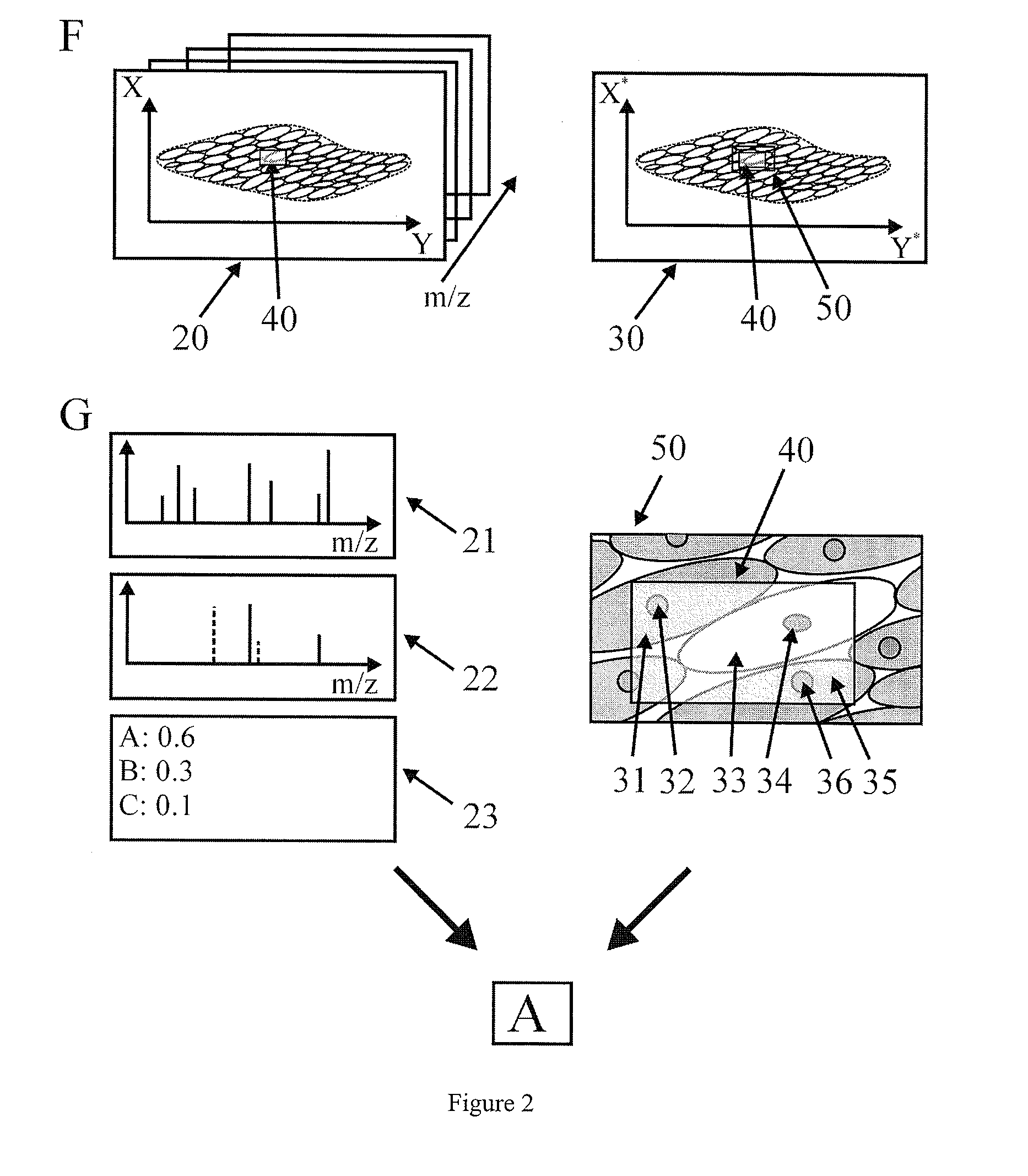
InactiveUS20090289184A1Reduce spatial resolutionIncrease contentImage enhancementImage analysisSpatially resolvedImage resolution
The present invention relates to a method for the histologic classification of a tissue section. The method includes acquiring a mass spectrometric image and a light-optical image of the same tissue section (the optical image having a higher spatial resolution than the mass spectrometric image) and combining optical information on the structures of a subarea of the tissue section with mass spectrometric information on the subarea (the structures not being spatially resolved in the mass spectrometric image).
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Low-cost spectrometry system for end-user food analysis
ActiveUS20140320858A1Addressing Insufficient SensitivitySolve the lack of resolutionSpectrum investigationSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionFourier transform on finite groupsMass spectrometry
A compact spectrometer is disclosed that is suitable for use in mobile devices such as cellular telephones. In preferred embodiments, the spectrometer comprises a filter, at least one Fourier transform focusing element, a micro-lens array, and a detector, but does not use any dispersive elements. Methods for using the spectrometer as an end-user device for performing on-site determinations of food quality, in particular, by comparison with an updatable database accessible by all users of the device, are also disclosed.
Owner:VERIFOOD
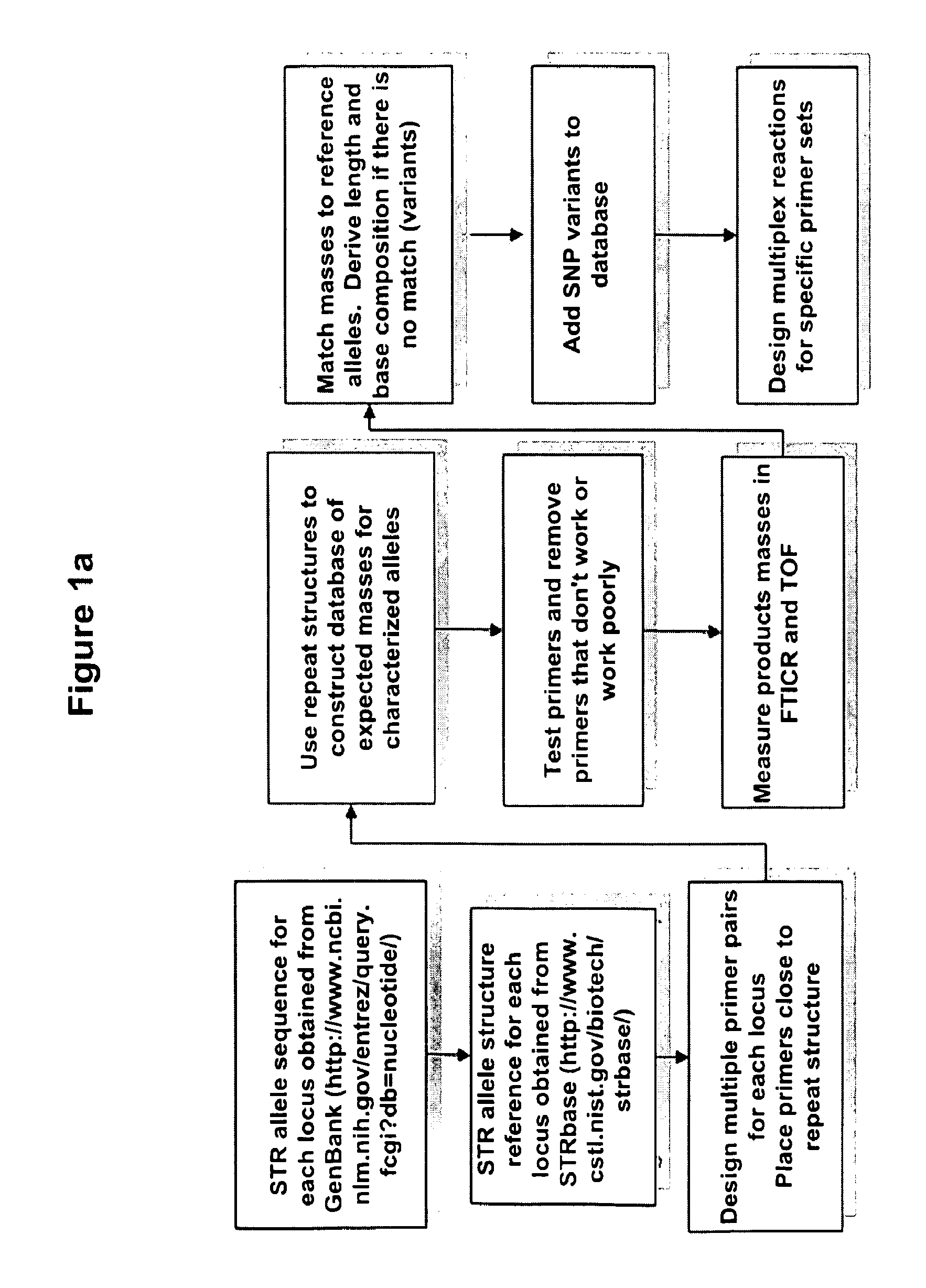
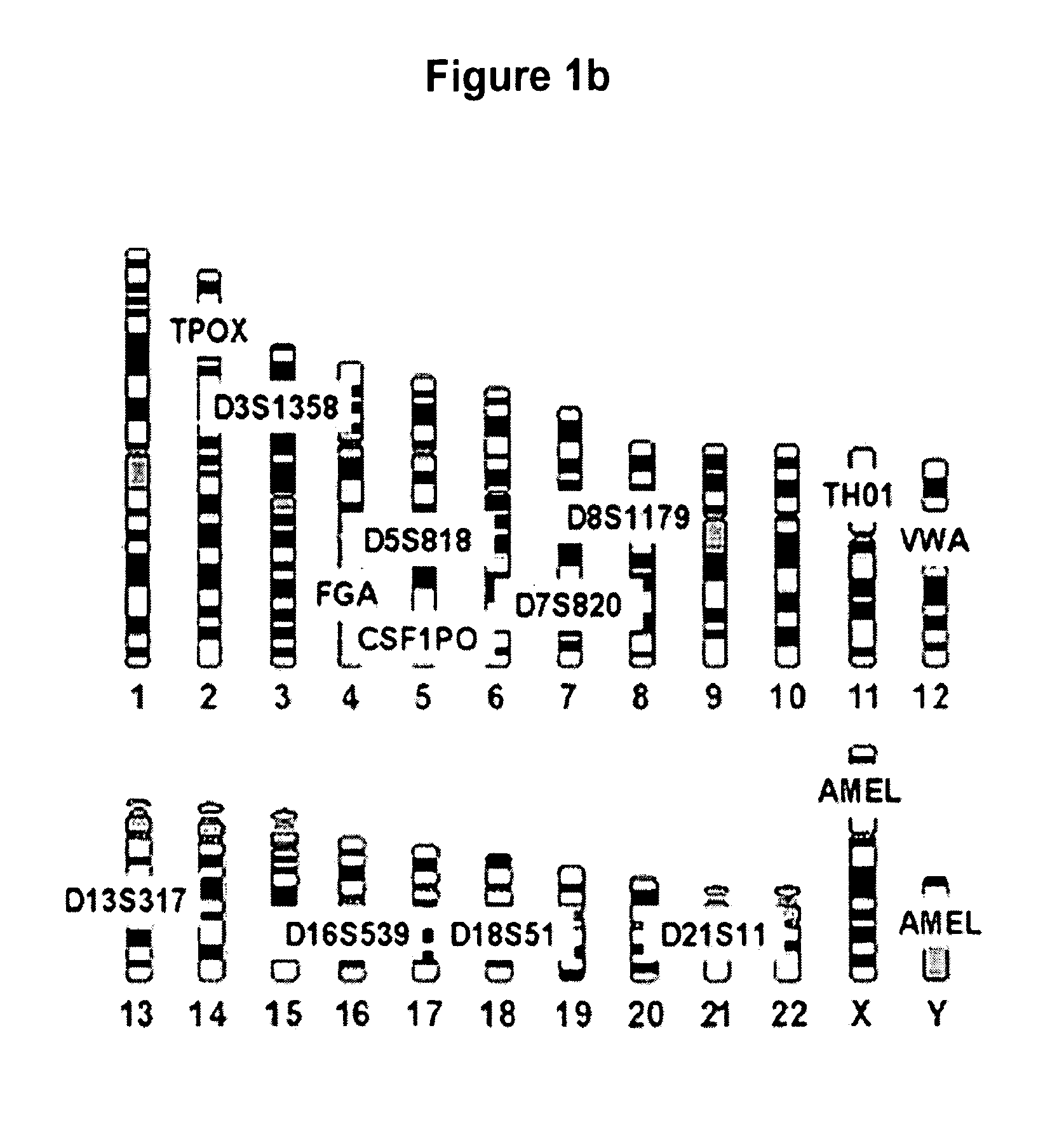
Methods for rapid forensic DNA analysis
The present invention provides methods and primer pairs for rapid, high-resolution forensic analysis of DNA and STR-typing by using amplification and mass spectrometry, determining the molecular masses and calculating base compositions of amplification products and comparing the molecular masses with the molecular masses of theoretical amplicons indexed in a database.
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI
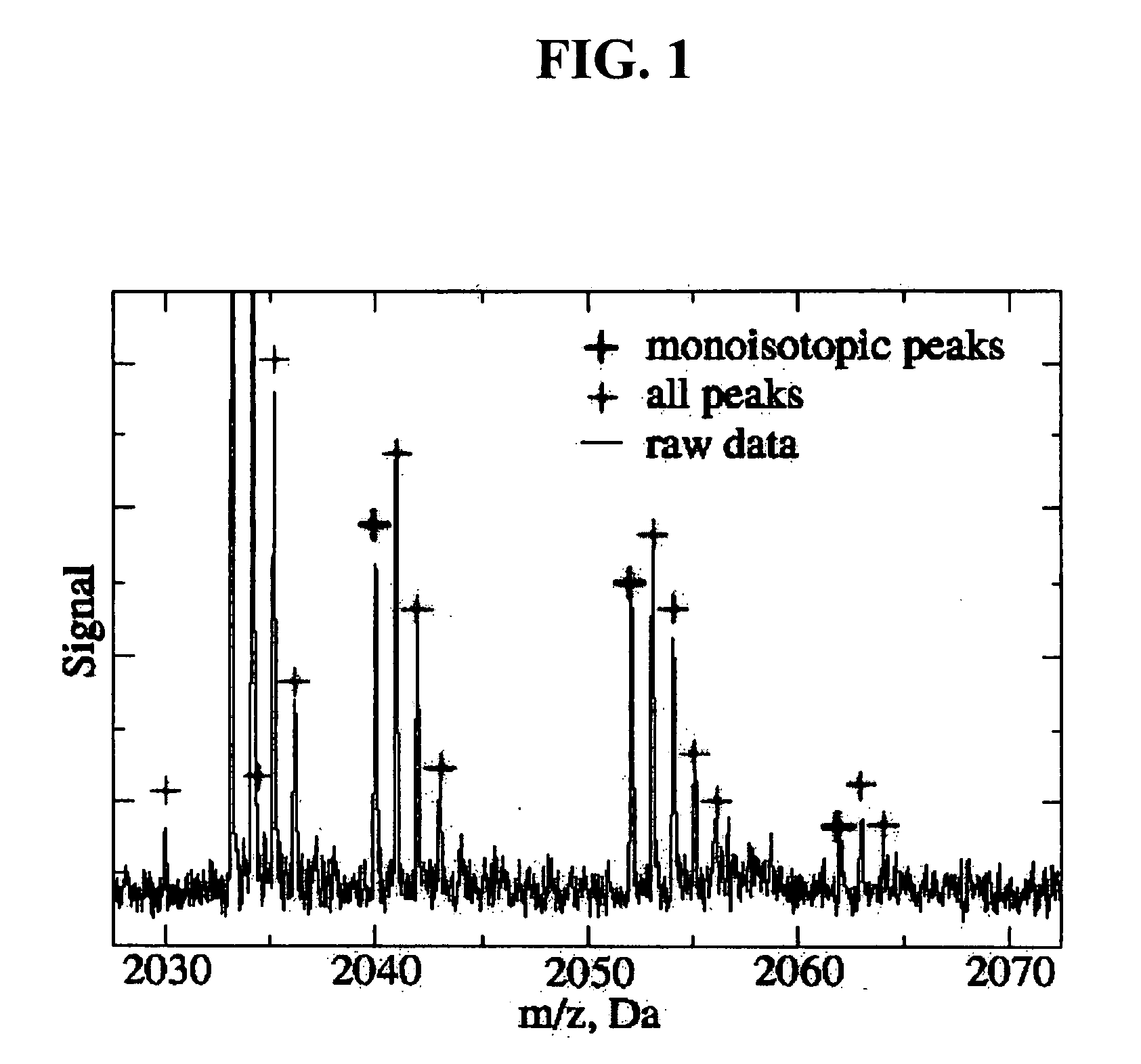
Method to automatically identify peak and monoisotopic peaks in mass spectral data for biomolecular applications
InactiveUS20050267689A1Improve reliabilityHigh sensitivityComponent separationBiological testingMass spectrometryComputer science
A method for identifying peaks in mass spectral data includes: eliminating non-constant levels of background noise; detecting all peaks above a user-identified signal-to-noise ration threshold; and compiling a list of all detected peaks.
Owner:BIODESIX
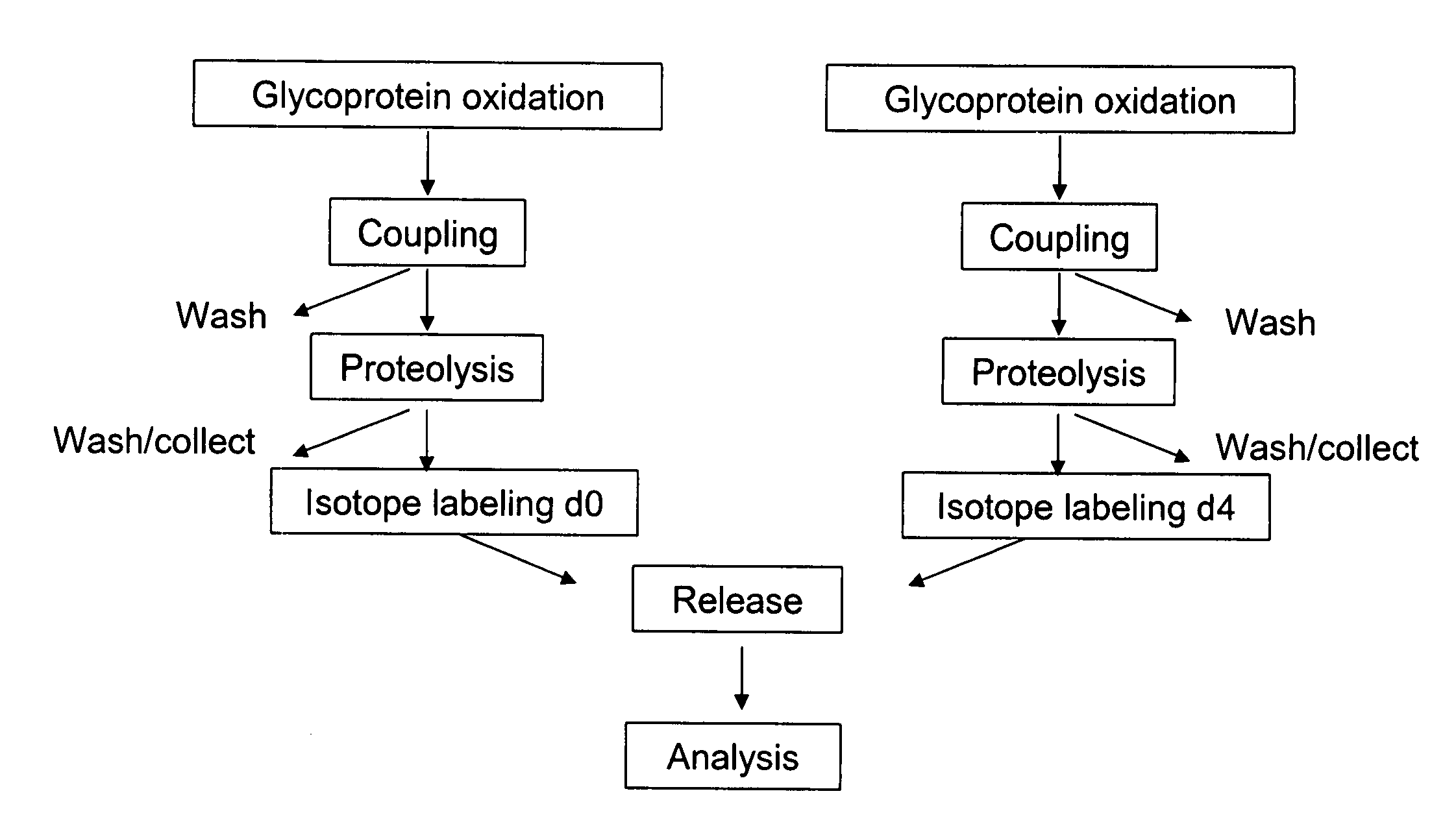
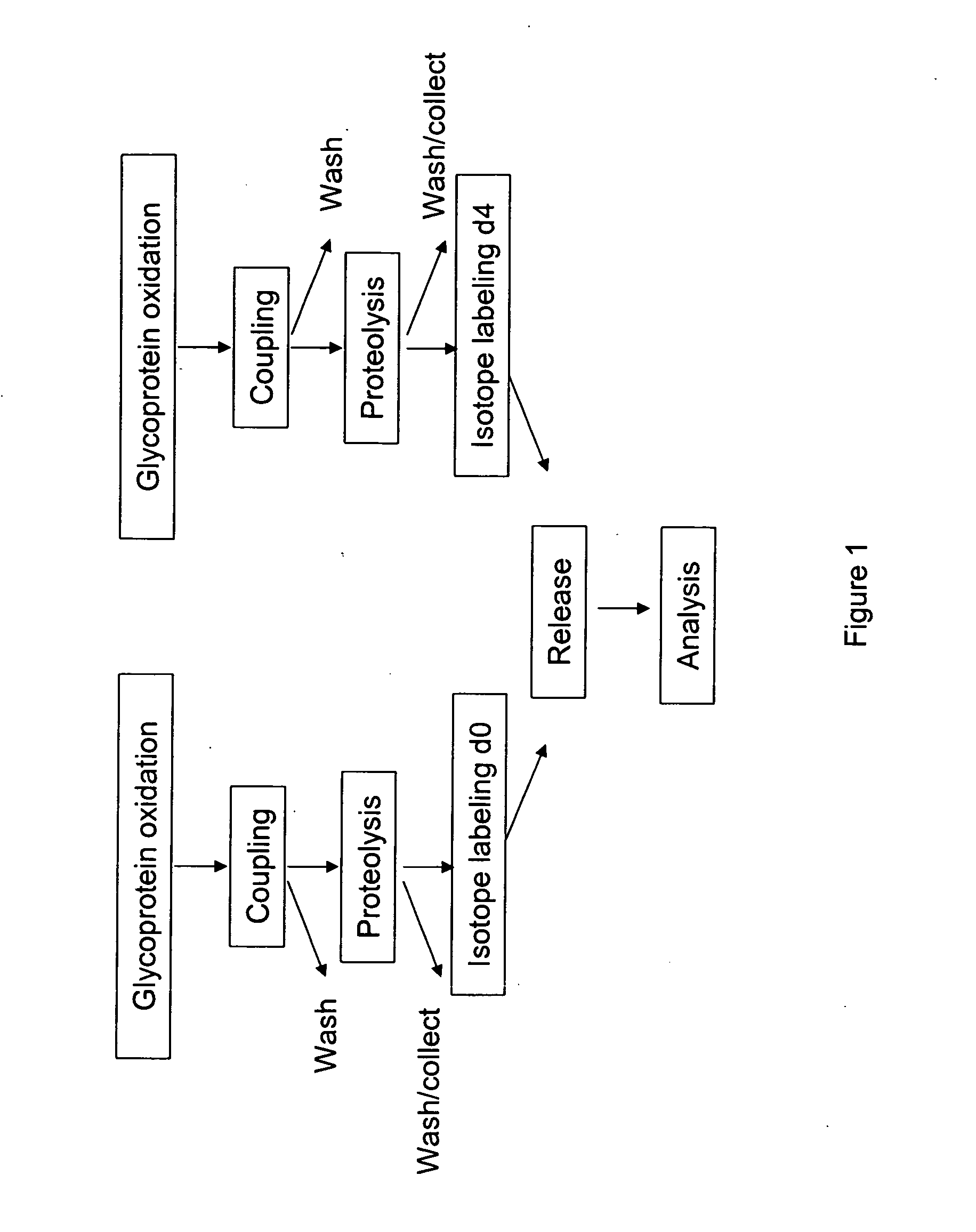
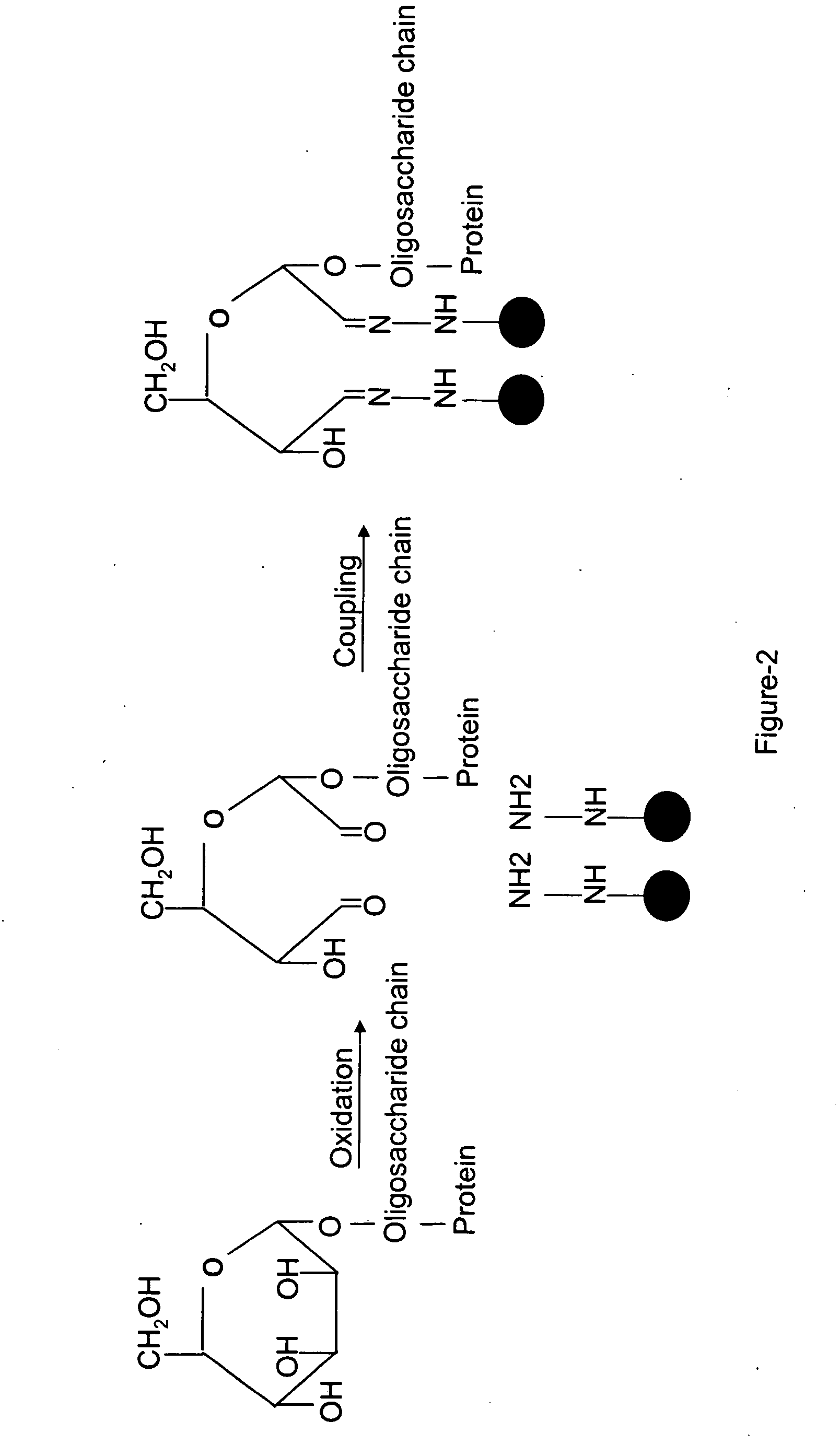
Methods for quantitative proteome analysis of glycoproteins
InactiveUS20070269895A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingGlycopeptideGlycoprotein i
The invention provides a method for identifying and quantifying polyglycopeptides in a sample. The method can include the steps of immobilizing glycopolypeptides to a solid support; cleaving the immobilized glycopolypeptides, thereby releasing non-glycosylated peptides and retaining immobilized glycopeptides; releasing the glycopeptides from the solid support; and analyzing the released glycopeptides. The method can further include the step of identifying one or more glycopeptides, for example, using mass spectrometry.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY
Enhanced resolution matrix-laser desorption and ionization TOF-MS sample surface
InactiveUS6071610AInhibit aggregationEfficient substrateParticle separator tubesSamplingImage resolutionEvaporation
A thin layer for sample analysis by matrix-assisted laser desorption mass spectrometry, comprising a matrix material in a supported dispersion wherein the support is a solid or is formed from a solid. The invention is also directed to a method of making a thin layer for sample analysis by matrix-assisted laser desorption mass spectrometry, the layer comprising a matrix-solid composition disposed upon a substrate, comprising the step of depositing a solution containing matrix, solid and solvent upon a spinning substrate at a deposition rate sufficient to allow evaporation of the solvent, thereby interspersing the matrix and support on the substrate in a thin layer. Enhanced mass resolution is described.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Pattern recognition of whole cell mass spectra
ActiveUS20050061967A1Improve accuracyIncrease speedSamples introduction/extractionIsotope separationMass spectrometryAdduct
A method for reproducibly analyzing mass spectra from different sample sources is provided. The method deconvolutes the complex spectra by collapsing multiple peaks of different molecular mass that originate from the same molecular fragment into a single peak. The differences in molecular mass are apparent differences caused by different charge states of the fragment and / or different metal ion adducts and / or reactant products of one or more of the charge states. The deconvoluted spectrum is compared to a library of mass spectra acquired from samples of known identity to unambiguously determine the identity of one or more components of the sample undergoing analysis.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
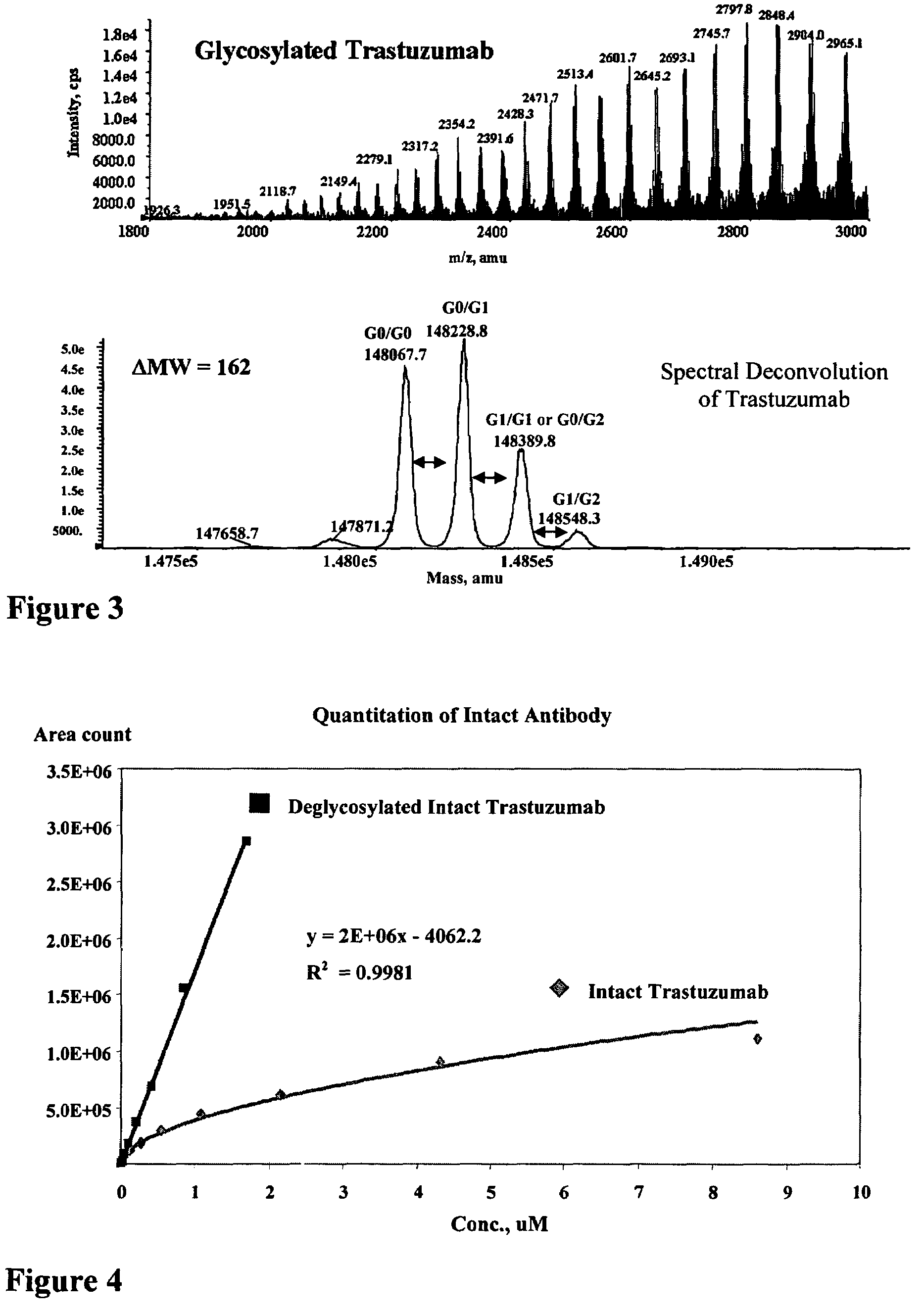
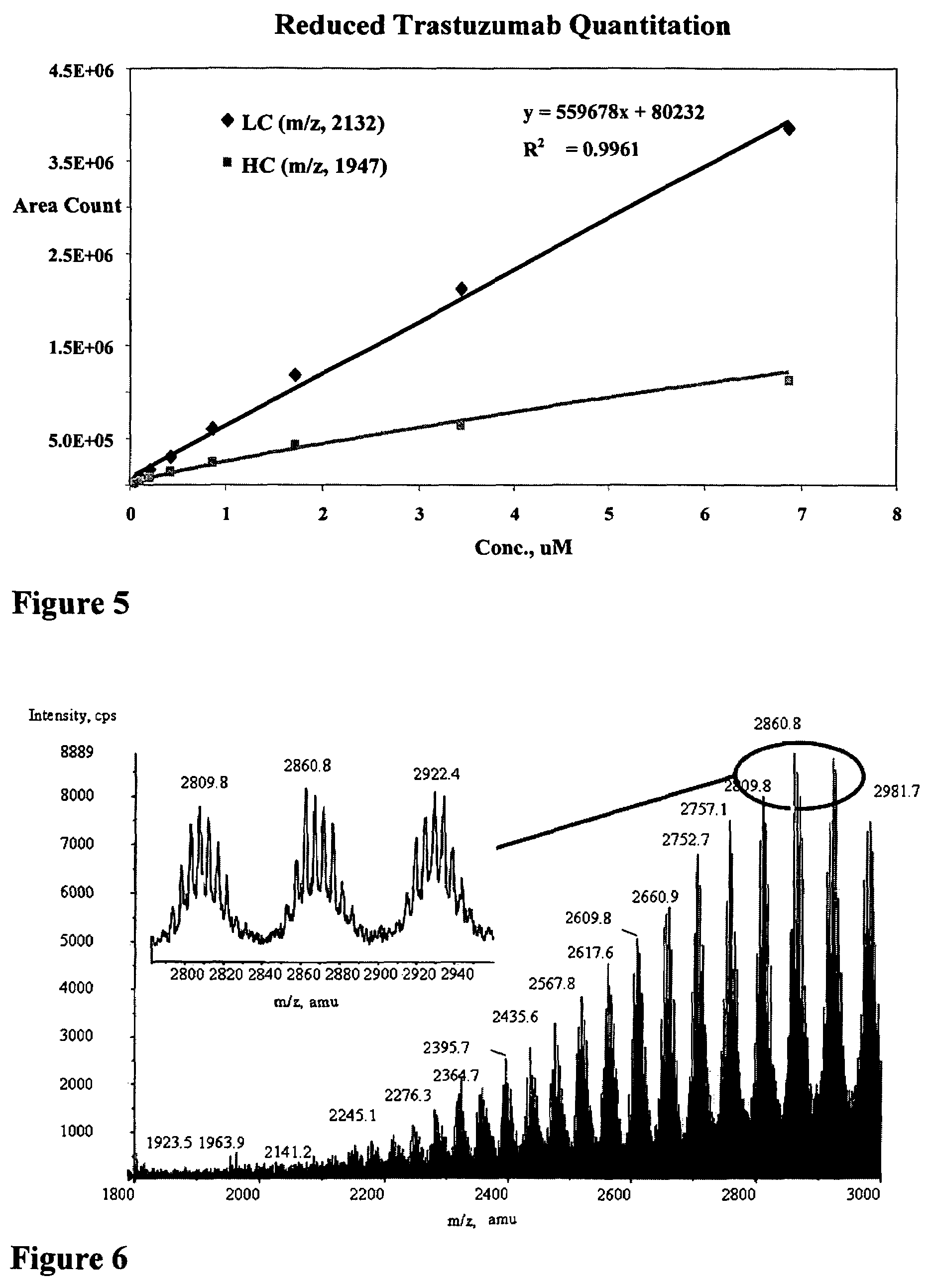
Mass spectrometry of antibody conjugates
ActiveUS7662936B2High resolutionHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMetaboliteAntibody conjugate
Methods to detect, screen, and quantitate biological samples after administration of antibody conjugates, antibody-drug conjugates of Formula I, antibodies, and fragments and metabolites thereof, by affinity separation, chromatography, and mass spectrometry are disclosed.Ab-(L-D)p IwhereinAb is an antibody;D is a drug moiety;L is a linker covalently attached to Ab, and covalently attached to D; andp is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, or 8.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Biomarkers for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
ActiveUS20050148026A1Microbiological testing/measurementMuscular disorderAmyotrophic lateral sclerosisPharmaceutical drug
The invention provides a method for diagnosing amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) in a subject, a method for assessing the effectiveness of a drug in treating ALS, and a method for determining the site of onset of ALS in a subject. Each method comprises (a) obtaining a sample from the subject, (b) analyzing the proteins in the sample by mass spectroscopy, and (c) determining a mass spectral profile for the sample. In some embodiments, the method comprises comparing the mass spectral profile of the sample to the mass spectral profile of a positive or a negative standard.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Methods for predicting the biological, chemical, and physical properties of molecules from their spectral properties
InactiveUS6898533B1Advantageously computer implementedParticle separator tubesColor/spectral properties measurementsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMass spectrometry
Methods are disclosed for establishing a quantitative relationship between spectral properties of molecules and a biological, chemical, or physical endpoint of the molecules. Spectral data including data from nuclear magnetic resonance, mass spectrometric, infrared, and ultraviolet-visible techniques are used along with endpoint data to train a pattern-recognition program. The training yields a spectral data-activity relationship that may be used to predict the endpoint value of a molecule from its spectral data alone. Methods for rapidly screening isolated compounds or mixtures of compounds based upon their spectral data are included.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Photocrosslinked hydrogel surface coatings
InactiveUS20070082019A1Fast curing timeHigh binding capacityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteMass spectrometry
A hydrogel layer is applied to a substrate advantageously when the layer is formed in situ, using a polymeric or copolymeric precursor that includes, respectively, monomer subunits that have a photocrosslinkable functionality and monomer subunits that have a chemically selective functionality for binding a biomolecular analyte, such as a protein. A hydrogel-coated substrate thus obtained is particularly useful as a probe for mass spectroscopic analysis, including SELDI analysis. Hydrogel particles also can be used for SELDI analysis.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com