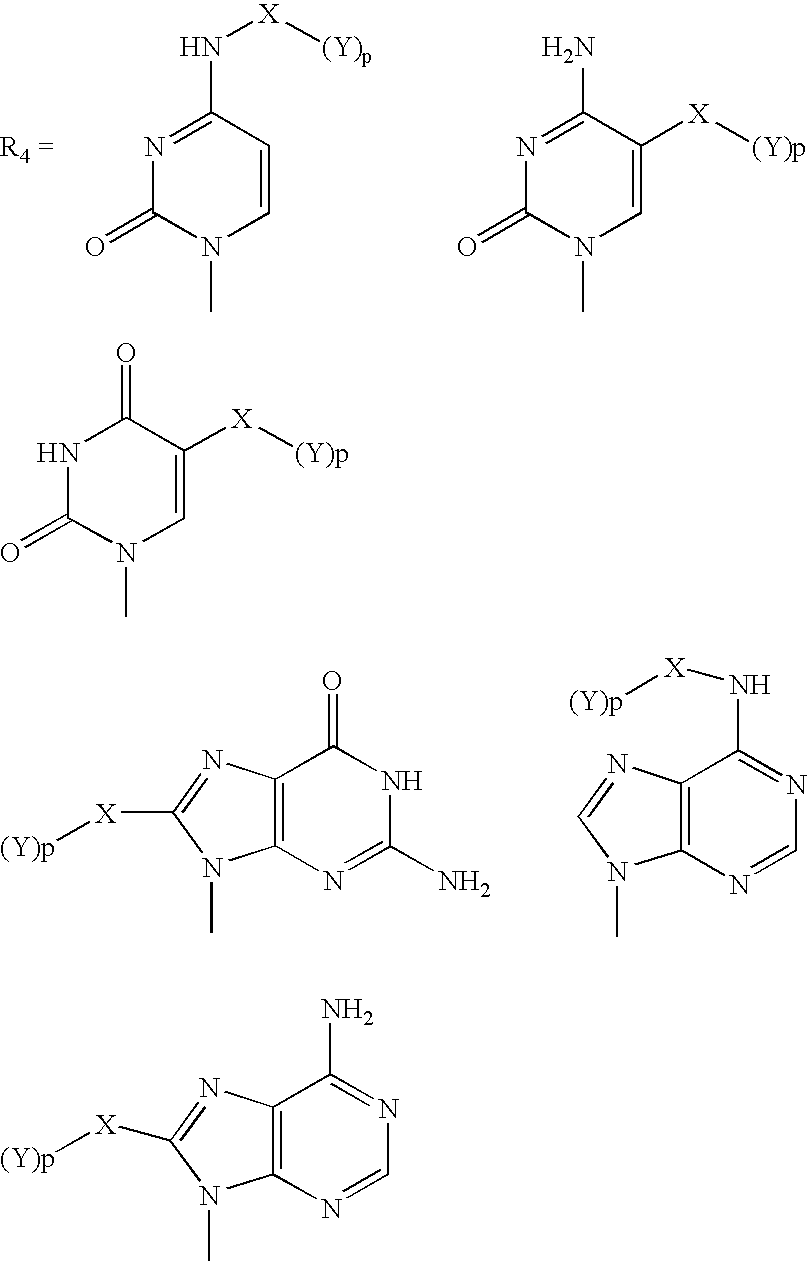
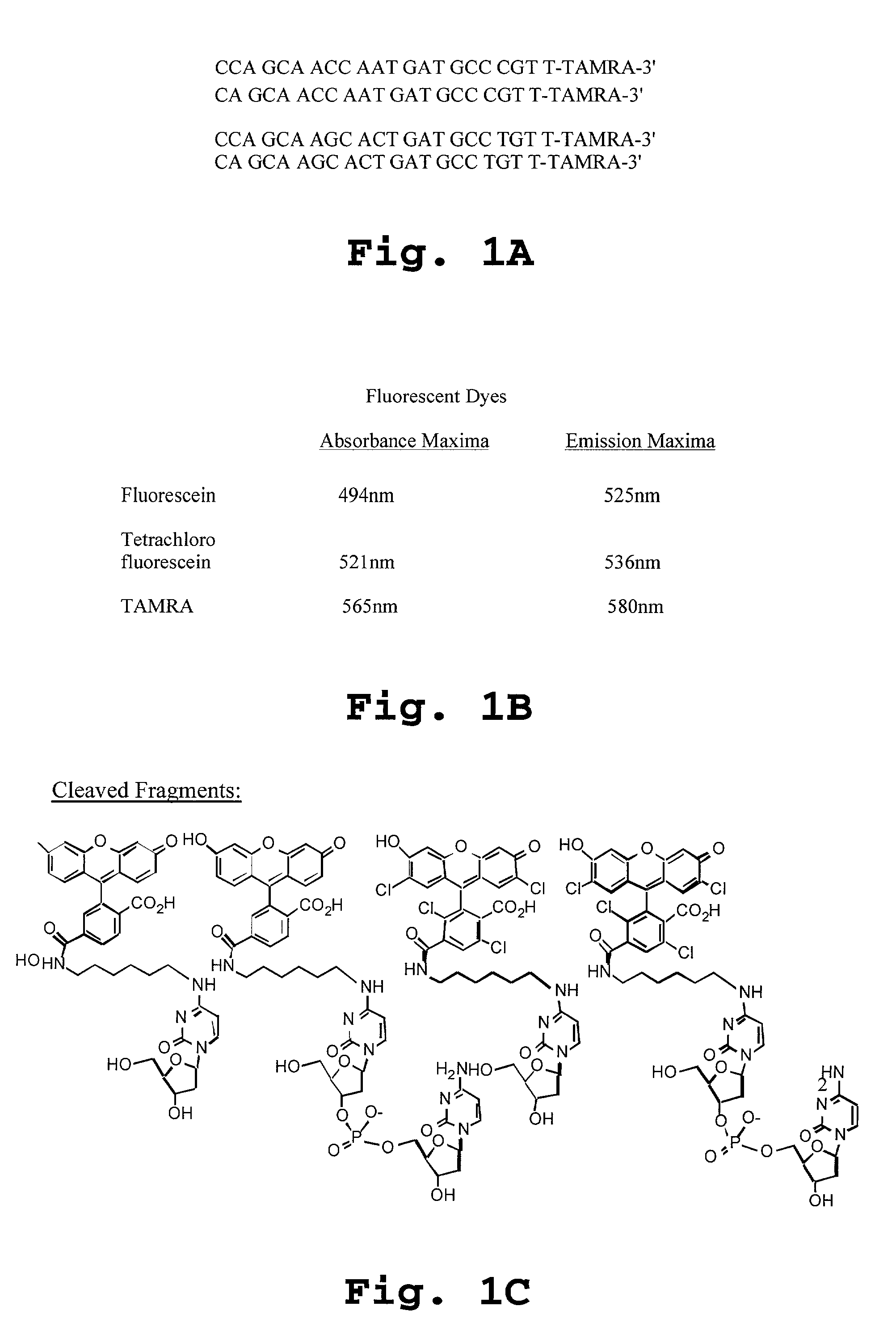
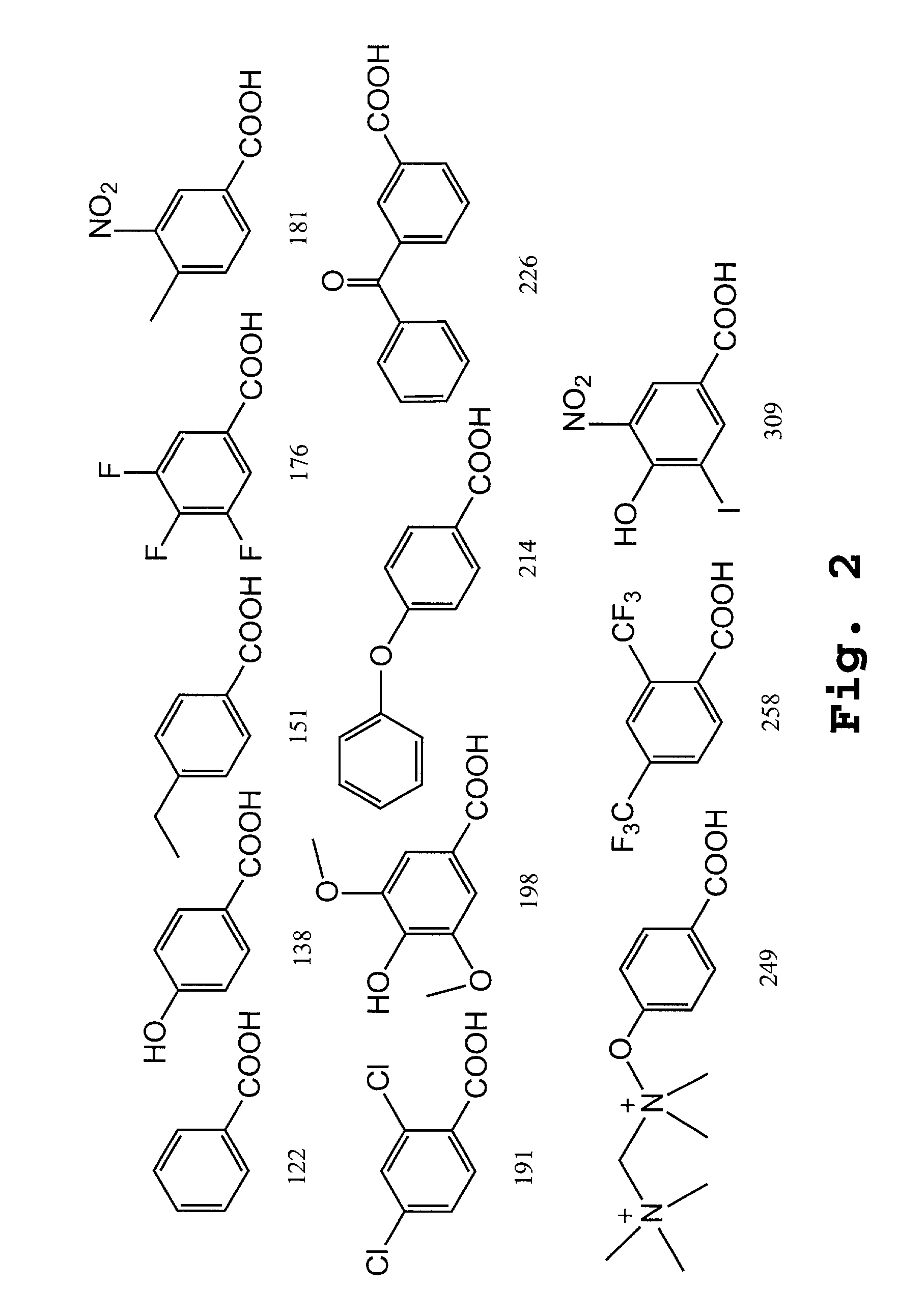
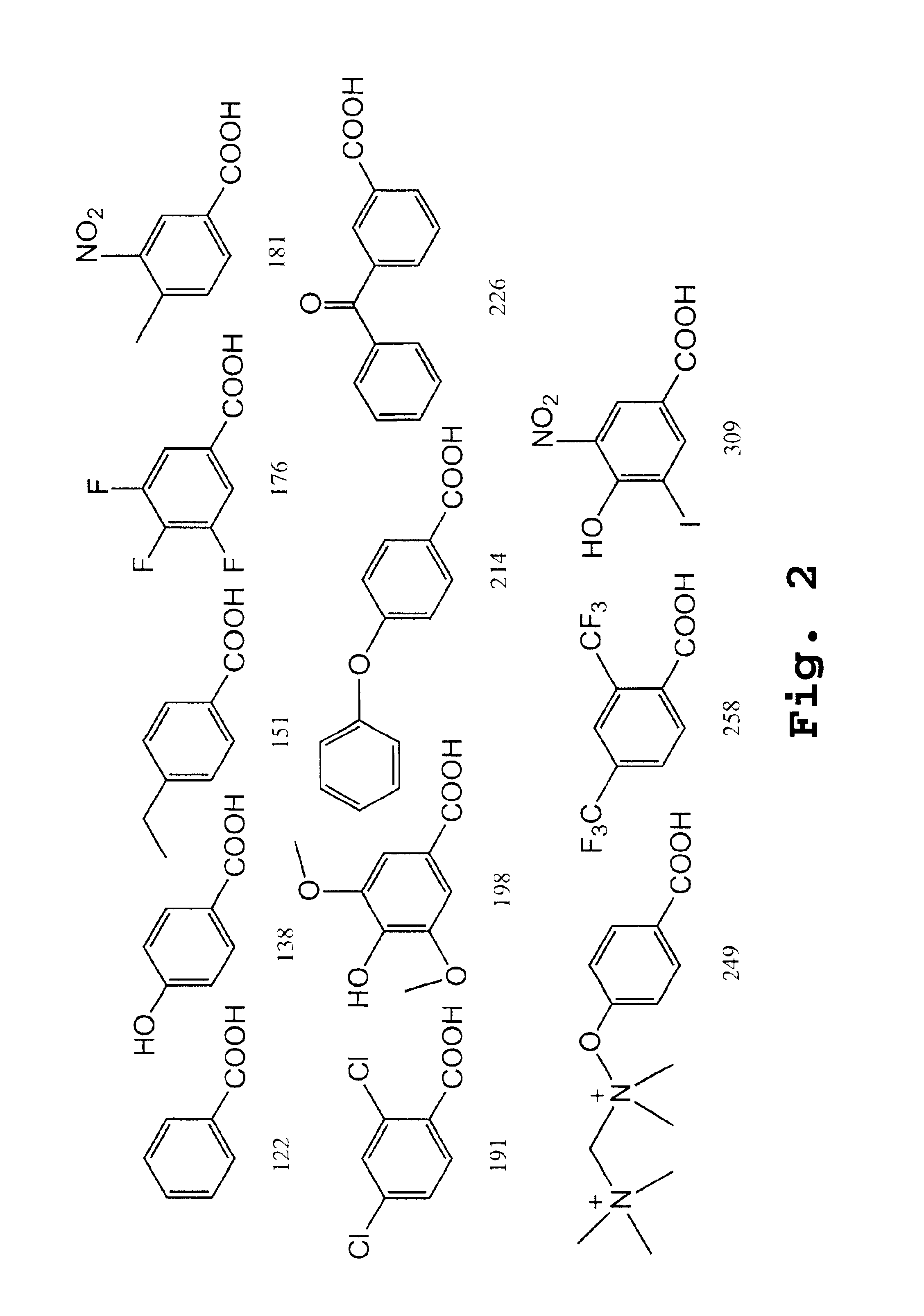
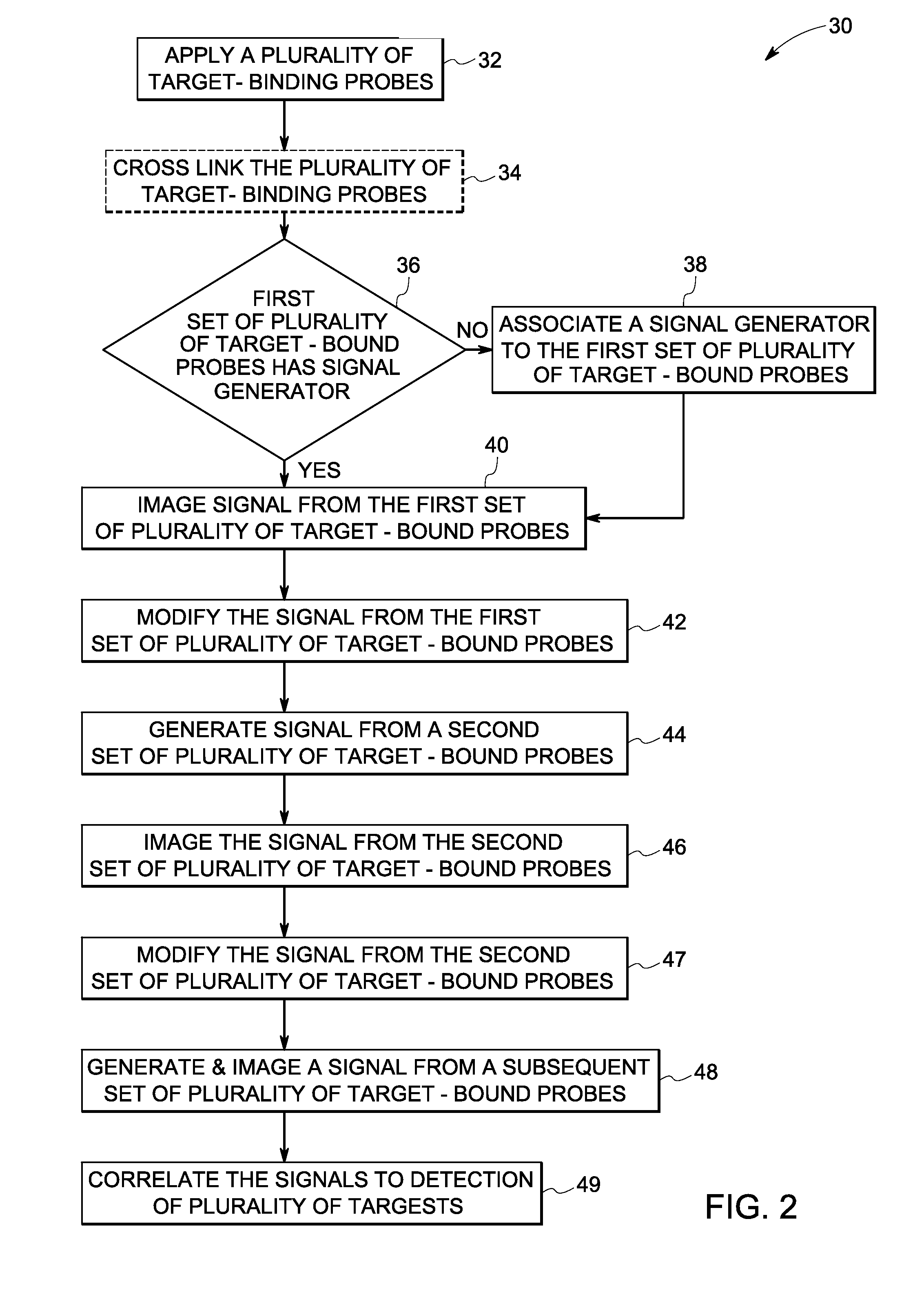
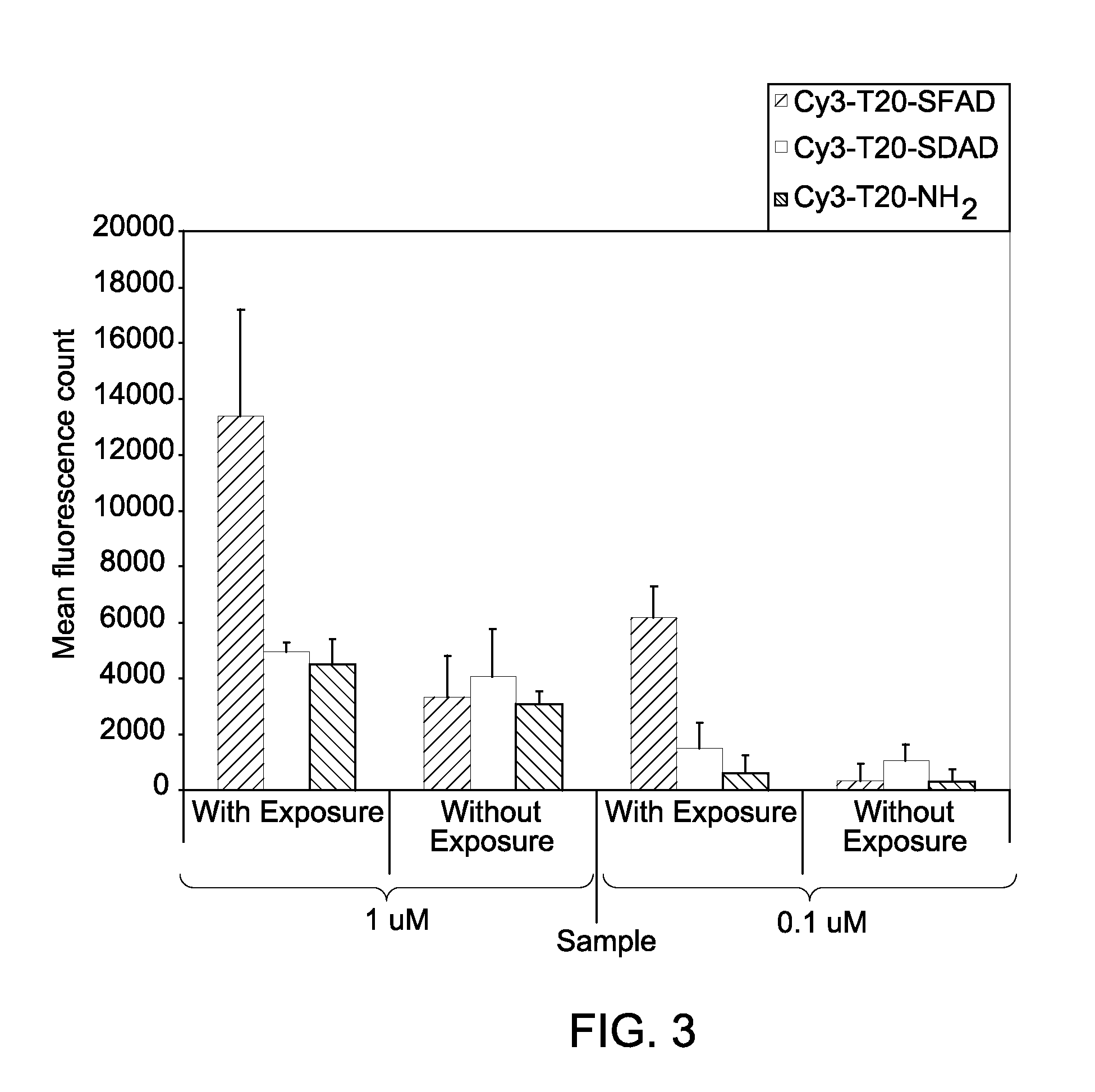
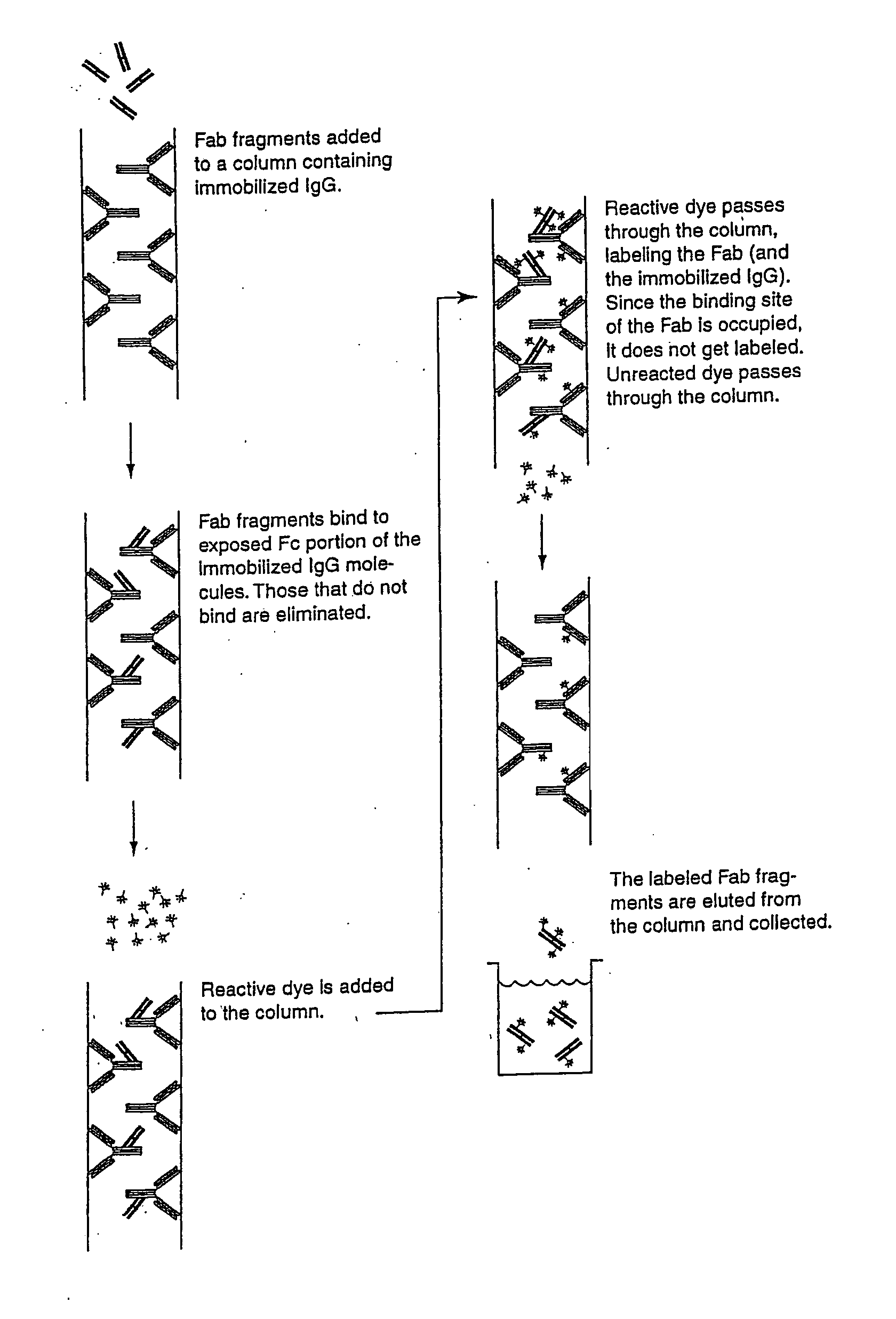
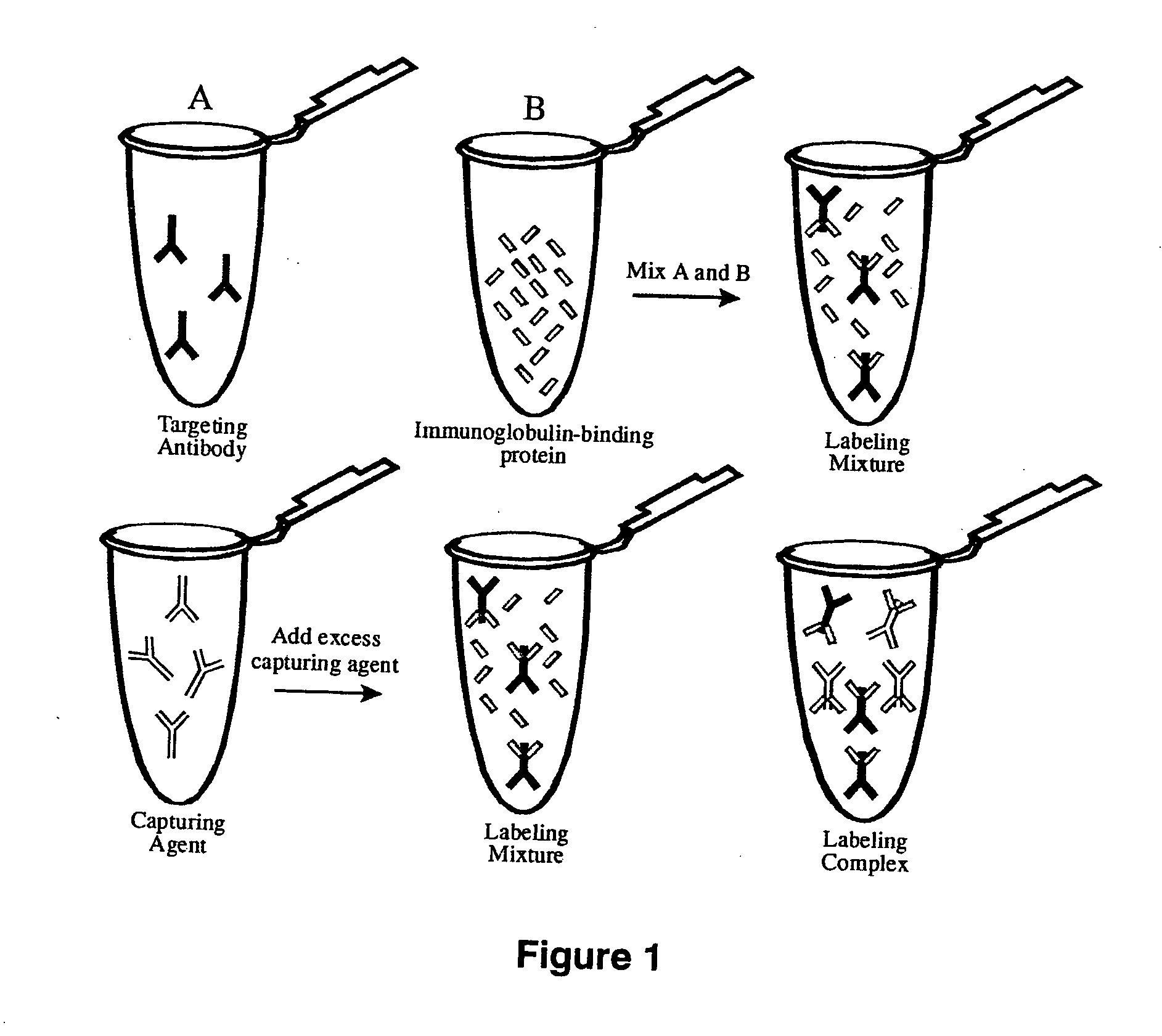
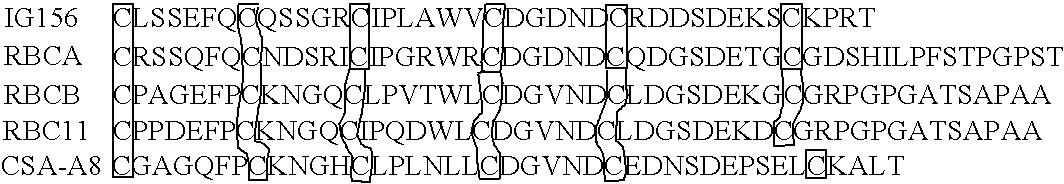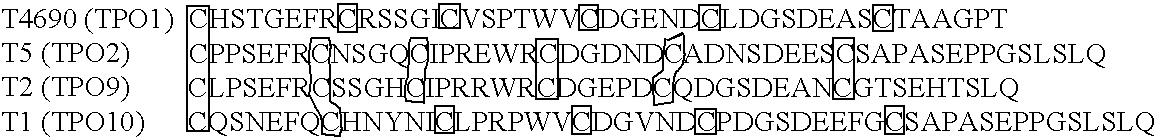Patents
Literature
410 results about "Target binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Novel proteins with targeted binding
InactiveUS20050089932A1Stimulate and inhibit activityEasy screeningPeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsMonomerComputational biology
Methods for identifying discrete monomer domains and immuno-domains with a desired property are provided. Methods for generating multimers from two or more selected discrete monomer domains are also provided, along with methods for identifying multimers possessing a desired property. Presentation systems are also provided which present the discrete monomer and / or immuno-domains, selected monomer and / or immuno-domains, multimers and / or selected multimers to allow their selection. Compositions, libraries and cells that express one or more library member, along with kits and integrated systems, are also included in the present invention.
Owner:AMGEN MOUNTAIN VIEW
Single-molecule selection methods and compositions therefrom
InactiveUS20020034757A1Highly specific controlImprove complianceNanotechSugar derivativesNucleotideAdhesive
Single-molecule selection methods are provided for identifying target-binding molecules from diverse sequence and shape libraries. Complexes and imprints of selected target-binding molecules are also provided. The subject selection methods are used to identify oligonucleotide and nonnucleotide molecules with desirable properties for use in pharmaceuticals, drug discovery, drug delivery, diagnostics, medical devices, cosmetics, agriculture, environmental remediation, smart materials, packaging, microelectronics and nanofabrication. Single oligonucleotide molecules with desirable binding properties are selected from diverse sequence libraries and identified by amplification and sequencing. Alternatively, selected oligonucleotide molecules are identified by sequencing without amplification. Nonnucleotide molecules with desirable properties are identified by single-molecule selection from libraries of conjugated molecules or nucleotide-encoded nonnucleotide molecules. Alternatively, target-specific nonnucleotide molecules are prepared by imprinting selected oligonucleotide molecules into nonnucleotide molecular media. Complexes and imprints of molecules identified by single-molecule selection are shown to have broad utility as drugs, prodrugs, drug delivery systems, willfully reversible cosmetics, diagnostic reagents, sensors, transducers, actuators, adhesives, adherents and novel multimolecular devices.
Owner:MOLECULAR MACHINES
Pseudo-antibody constructs
InactiveUS20030211078A1Reduce productionInhibit synthesisOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHalf-lifeIn vivo
This invention relates to novel pharmaceutically useful compositions that bind to a biological molecule, having improved circulatory half-life, increased avidity, increased affinity, or multifunctionality, and methods of use thereof. The present invention provides a pseudo-antibody comprising an organic moiety covalenty coupled to at least two target-binding moieties, wherein the target-binding moieties are selected from the group consisting of a protein, a peptide, a peptidomimetic, and a non-peptide molecule that binds to a specific targeted biological molecule. The pseudo-antibody of the present invention may affect a specific ligand in vitro, in situ and / or in vivo. The pseudo-antibodies of the present invention can be used to measure or effect in an cell, tissue, organ or animal (including humans), to diagnose, monitor, modulate, treat, alleviate, help prevent the incidence of, or reduce the symptoms of, at least one condition.
Owner:CENTOCOR
Multifunctional and multispectral biosensor devices and methods of use
InactiveUS6743581B1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectromagnetic radiationBiology
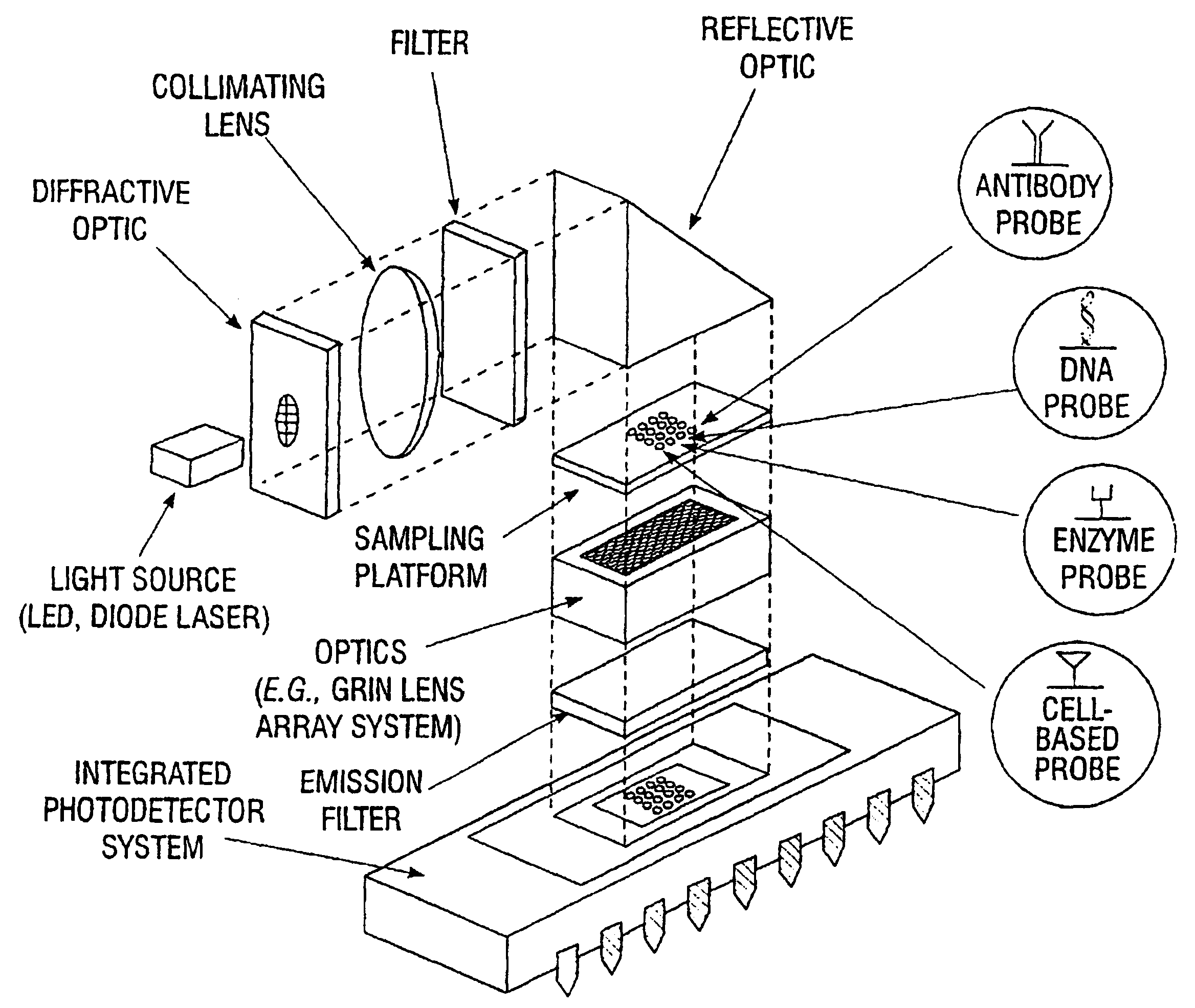
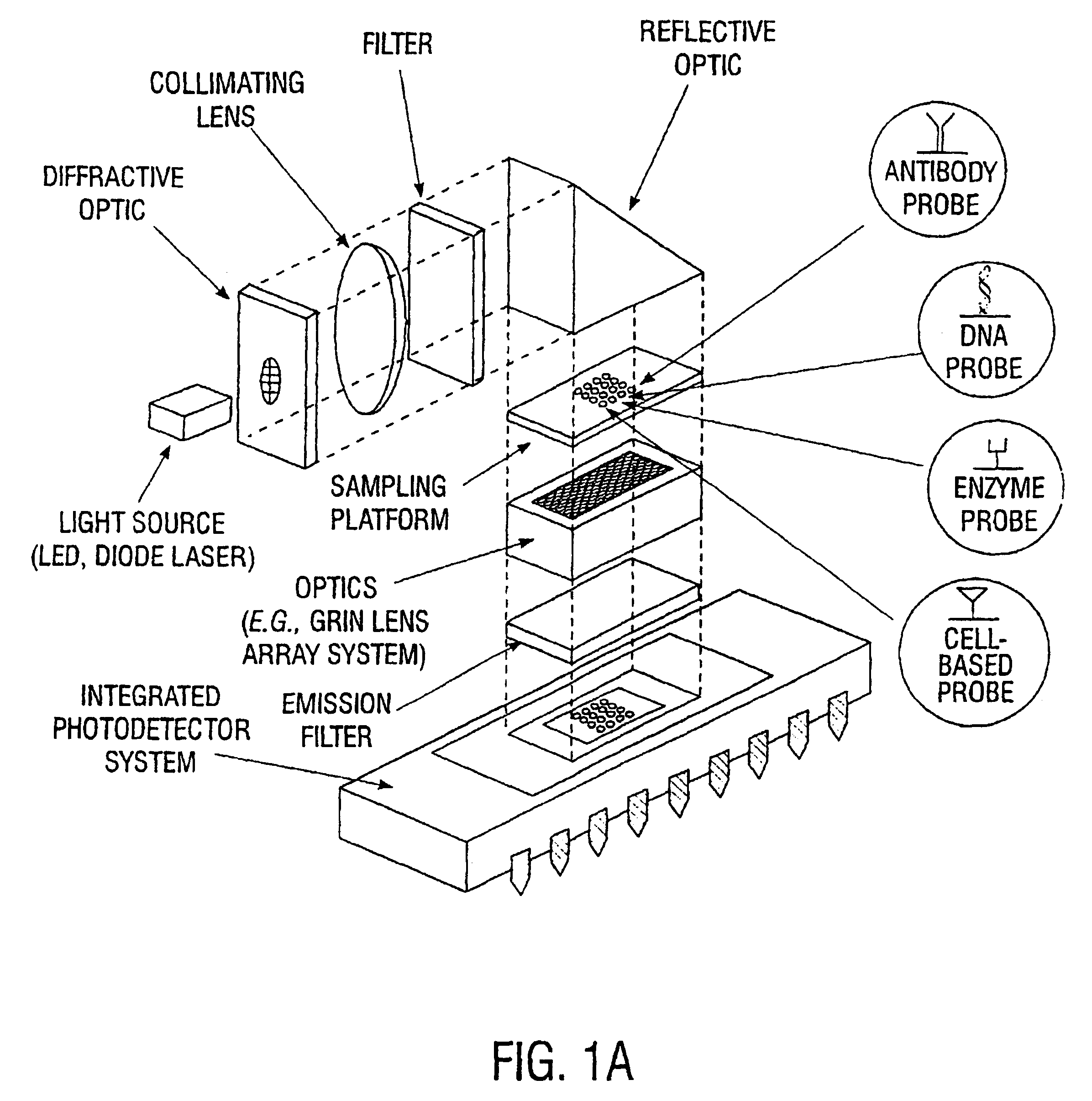
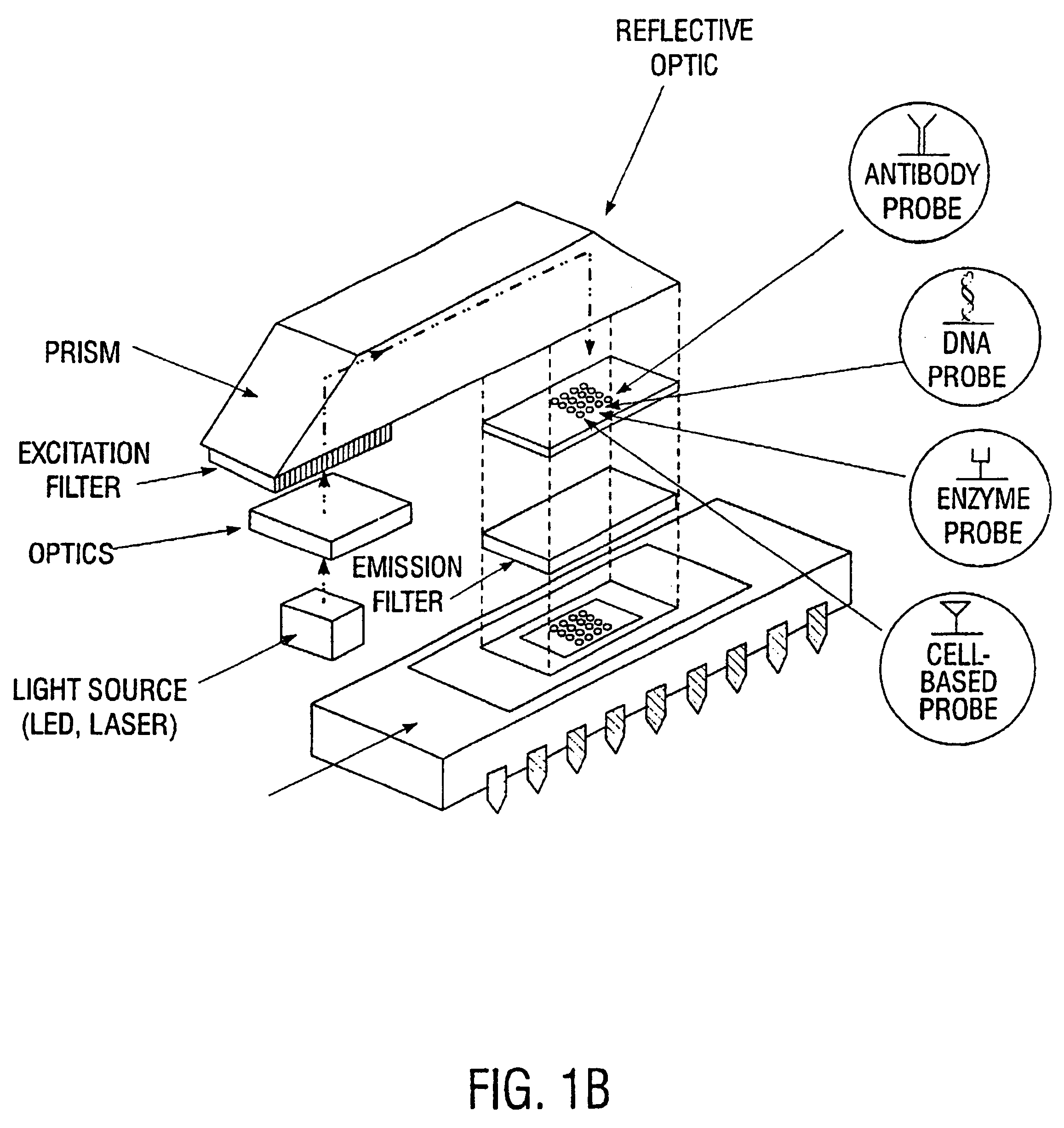
An integrated biosensor system for the simultaneously detection of a plurality of different types of targets includes at least one sampling platform, the sampling platform including a plurality of receptors for binding to the targets. The plurality of receptors include at least one protein receptor and at least one nucleic acid receptor. At least one excitation source of electromagnetic radiation at a first frequency is provided for irradiating the receptors, wherein electromagnetic radiation at a second frequency different from the first frequency is emitted in response to irradiating when at least one of the different types of targets are bound to the receptor probes. An integrated circuit detector system having a plurality of detection channels is also provided for detecting electromagnetic radiation at said second frequency, the detection channels each including at least one detector.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Detection of nucleic acids and nucleic acid units
InactiveUS6127120AReduce riskReducing operator timeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideBiology
PCT No. PCT / GB96 / 01830 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 21, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 21, 1998 PCT Filed Jul. 25, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 05280 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 13, 1997The invention relates to the detection of target nucleic acids or nucleic acid units in a sample, by obtaining a SER(R)S spectrum for a SER(R)S-active complex containing, or derived directly from, the target. The complex includes at least a SER(R)S-active label, and optionally a target binding species containing a nucleic acid or nucleic acid unit. In this detection method, the concentration of the target present in the SER(R)S-active complex, or of the nucleic acid or unit contained in the target binding species in the SER(R)S-active complex, is no higher than 10-10 moles per liter. Additionally or alternatively, one or more of the following features may be used with the method: i) the introduction of a polyamine; ii) modification of the target, and / or of the nucleic acid or nucleic acid unit contained in the target binding species, in a manner that promotes or facilitates its chemi-sorption onto a SER(R)S-active surface; iii) inclusion of a chemi-sorptive functional group in the SER(R)S-active label. The invention also provides SER(R)S-active complexes for use in such a method, a kit for use in carrying out the method or preparing the complexes and a method for sequencing a nucleic acid which comprises the use of the detection method to detect at least one target nucleotide or sequence of nucleotides within the acid.
Owner:RENISHAW DIAGNOSTICS
Variant target binding agents and uses thereof
ActiveUS8455622B2In-vivo radioactive preparationsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseCytotoxicity
The present invention provides variant target binding agents and methods relating to the use of such binding agents for the prophylaxis or treatment of cancers and immunological disorders. The variant target binding agent is conjugated to a therapeutic agent that exerts a cytotoxic, cytostatic, or immunomodulatory effect on target cells.
Owner:SEAGEN INC
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation of Bcl-2
InactiveUS7622453B2Comparable and enhanced biological effectInteresting biological propertiesBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseOligomer
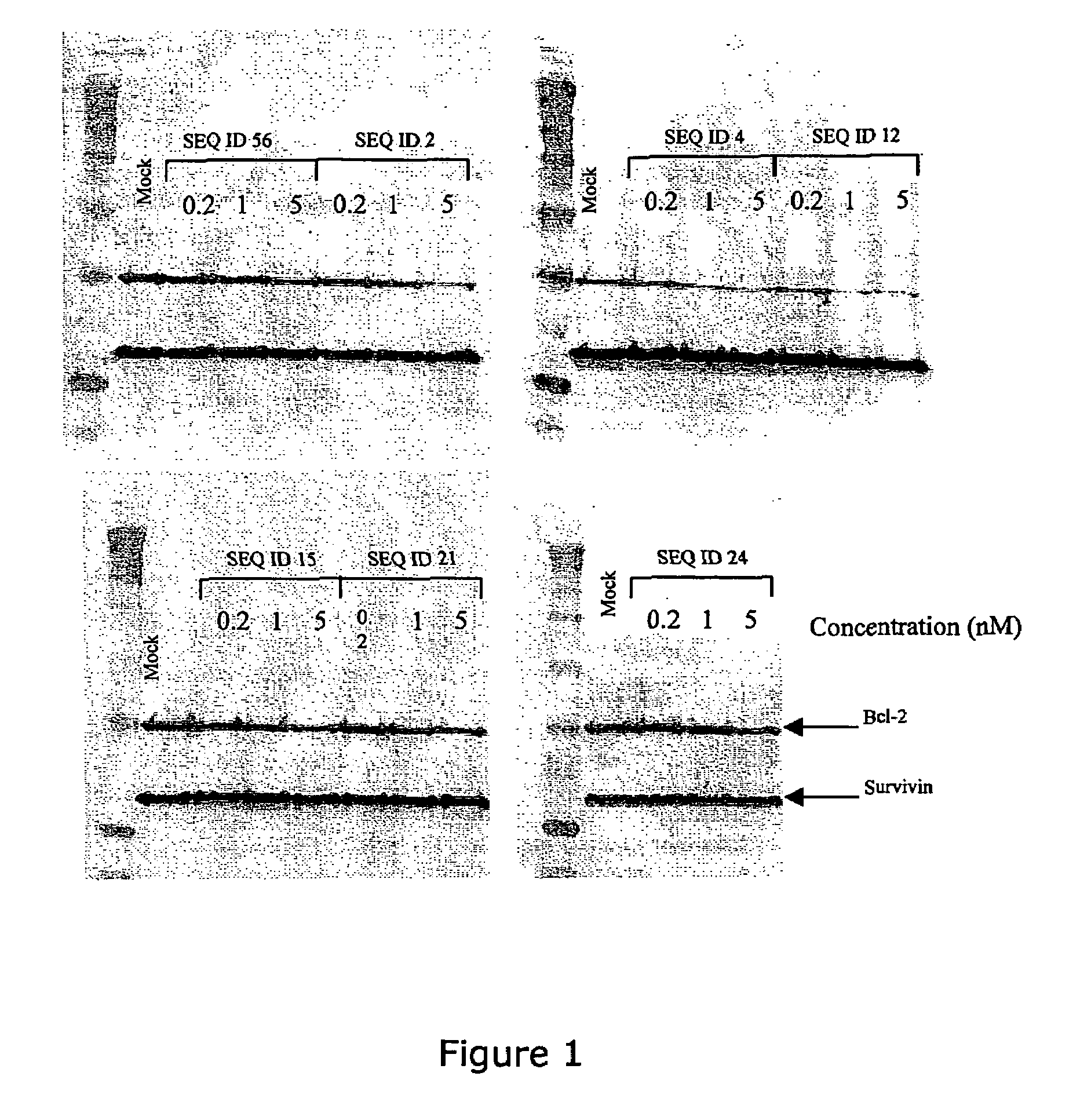
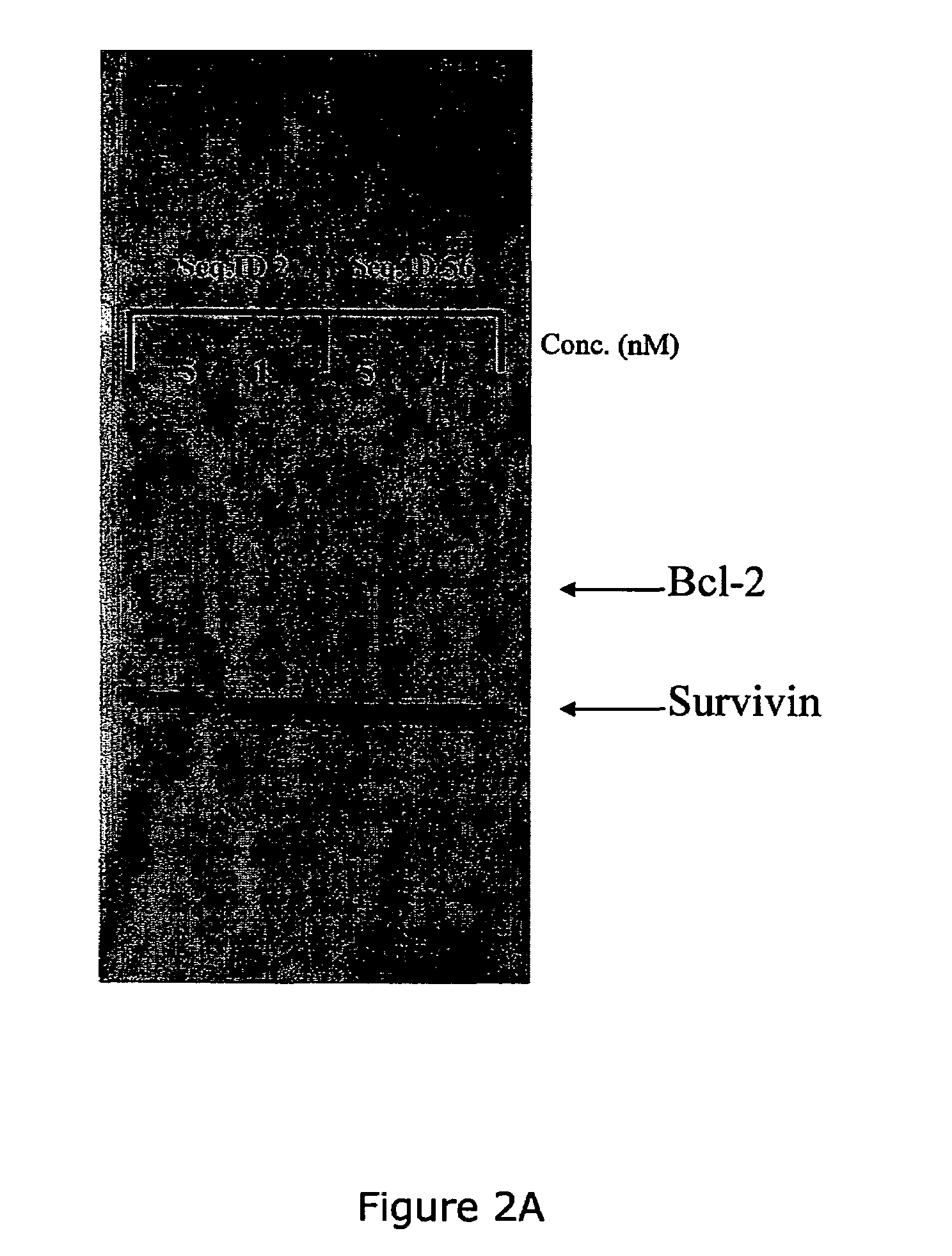
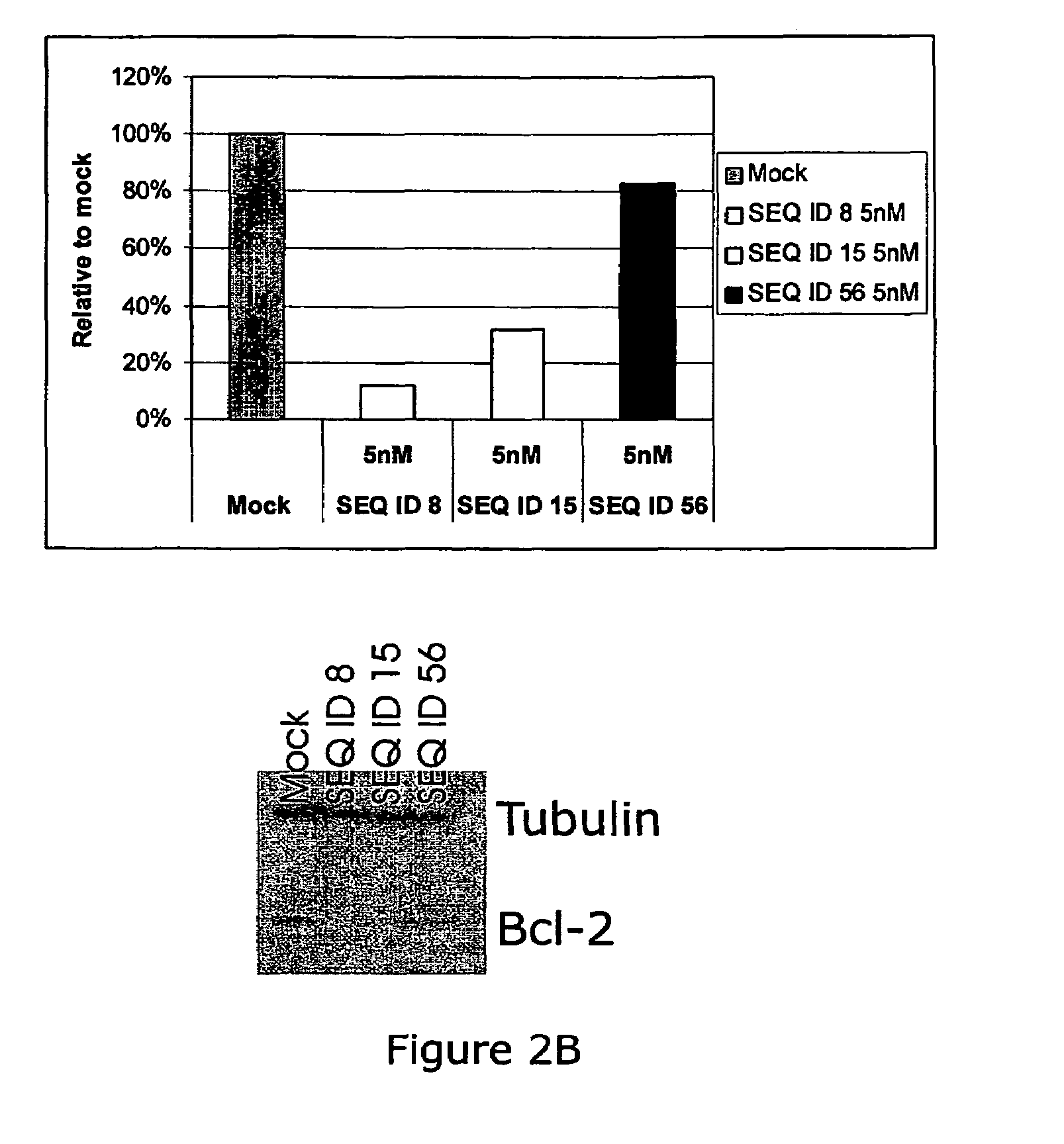
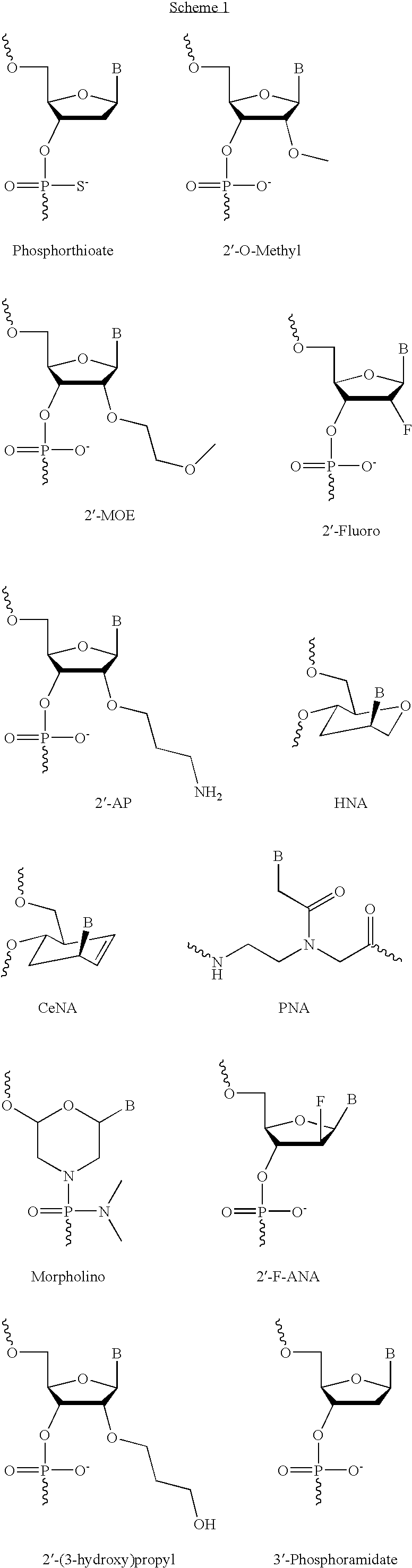
The present invention provides improved oligomeric compound, in particular oligonucleotide compounds, and methods for modulating the expression of the Bcl-2 gene in humans. In particular, this invention relates to oligomeric compounds of 10-30 nucleobases in length which comprise a target binding domain that is specifically hybridizable to a region ranging from base position No. 1459 (5′) to No. 1476 (3′) of the human Bcl-2 mRNA, said target binding domain having the formula: 5′-[(DNA / RNA)0-1-(LNA / LNA*)2-7-(DNA / RNA / LNA*)4-14-(LNA / LNA*)2-7-(DNA / RNA)0-1]-3′ and said target binding domain comprising at least two LNA nucleotides or LNA analogue nucleotides linked by a phosphorothioate group (—O—P(O,S)—O—). In particular the oligo is predominantly or fully thiolated. The invention also provides the use of such oligomers or conjugates or chimera for the treatment of various diseases associated with the expression of the Bcl-2 gene, such as cancer.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
Aptamers and antiaptamers
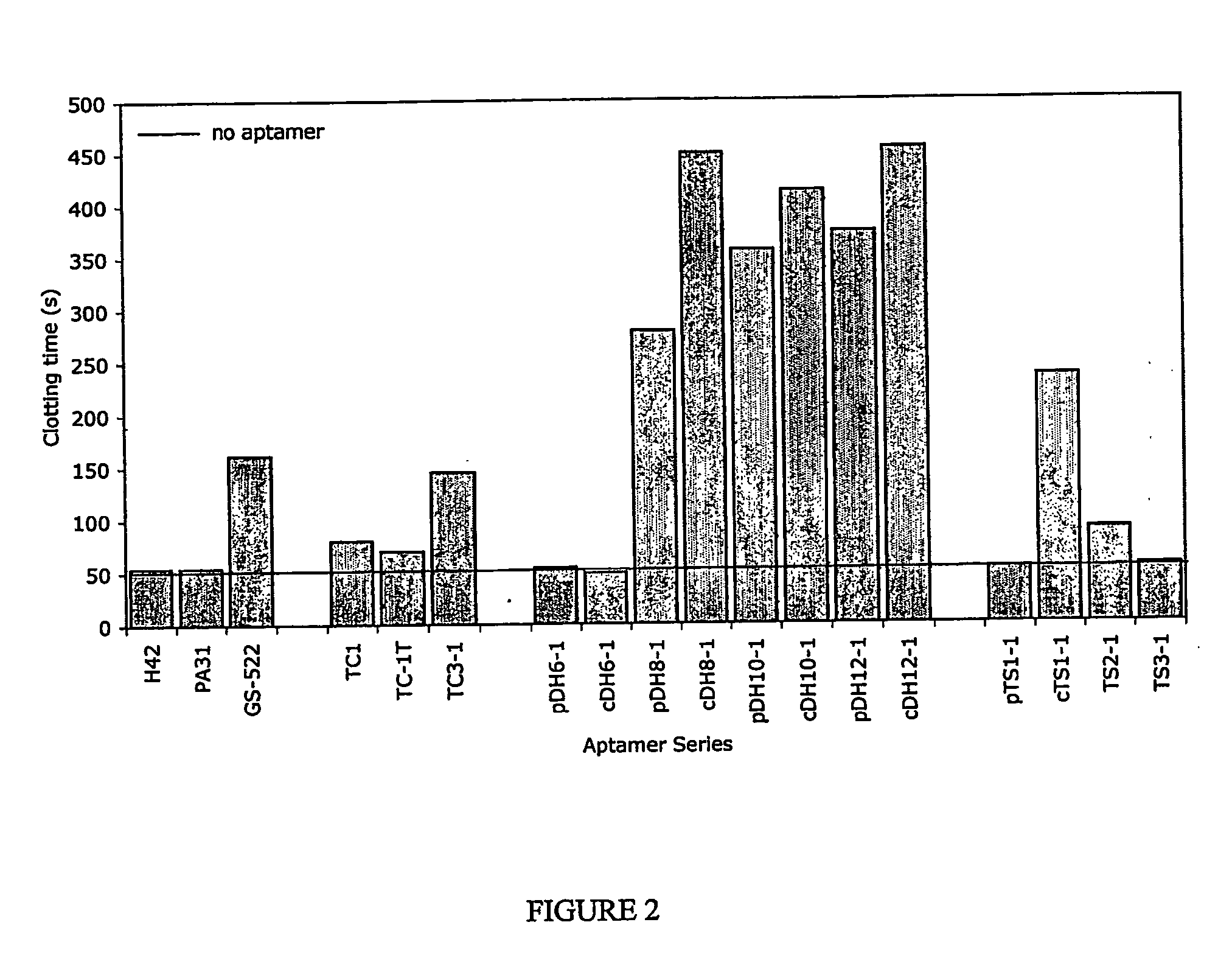
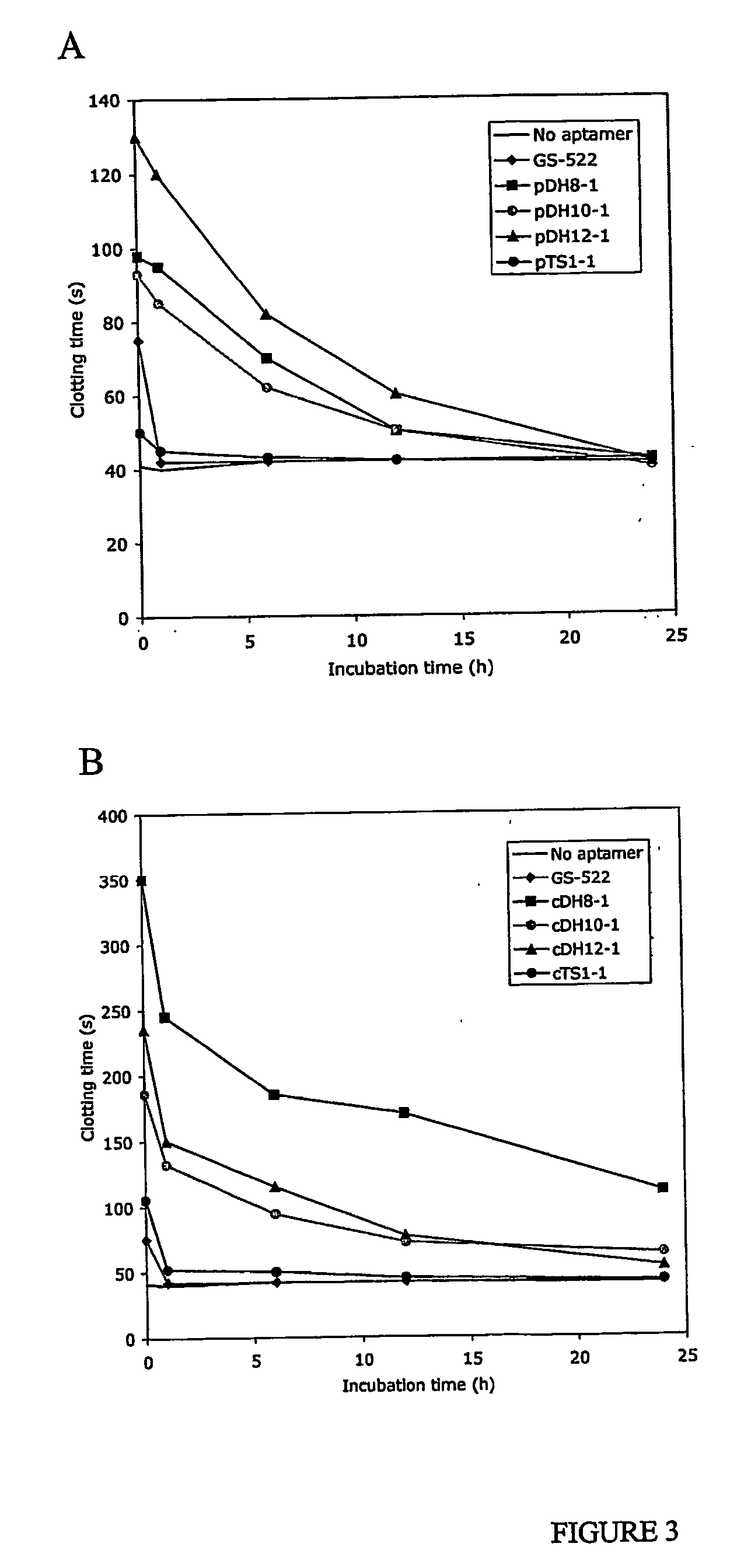
InactiveUS20050176940A1Preventing and reducing coagulation of bloodOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNucleotideThrombin activity
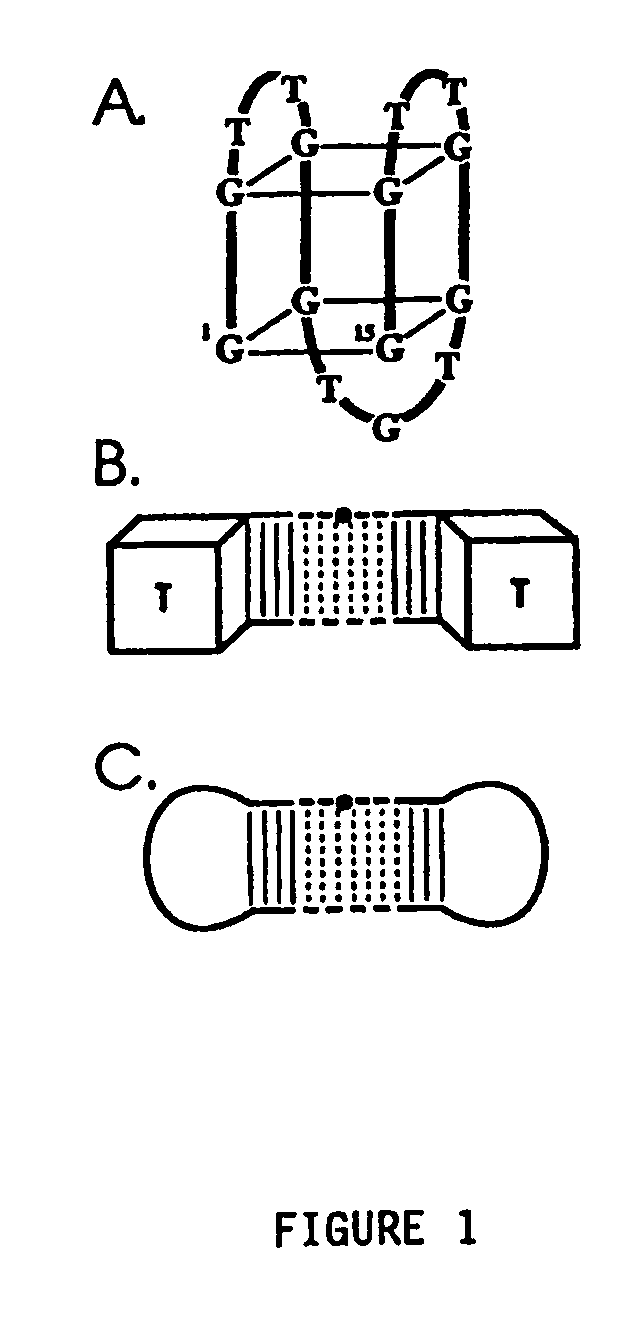
The present invention relates to: An aptamer comprising a circular oligonucleotide defining one to four target binding regions; An aptamer comprising an oligonucleotide defining two, three or four thrombin binding quadruplex regions separated by at least partially duplex regions, wherein the quadruplex regions comprise a GGTMGGXGGTTGG sequence wherein M represents A or T and X represents a sequence of two to five nucleotides and / or nucleotide analogues; An aptamer represented by formula (I): 5′D1, wQxD1D2yQzD2,3′—the variables are as defined in the specification; and Aptamers selected from specific sequences.
Owner:UNISEARCH LTD
Sequential analysis of biological samples
ActiveUS20100120043A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiophysicsTarget binding
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Method using a nonlinear optical technique for detection of interactions involving a conformational change
InactiveUS20030148391A1No need for labor and time-consuming washing stepLow backgroundCompound screeningMaterial nanotechnologyFrequency generationThird harmonic
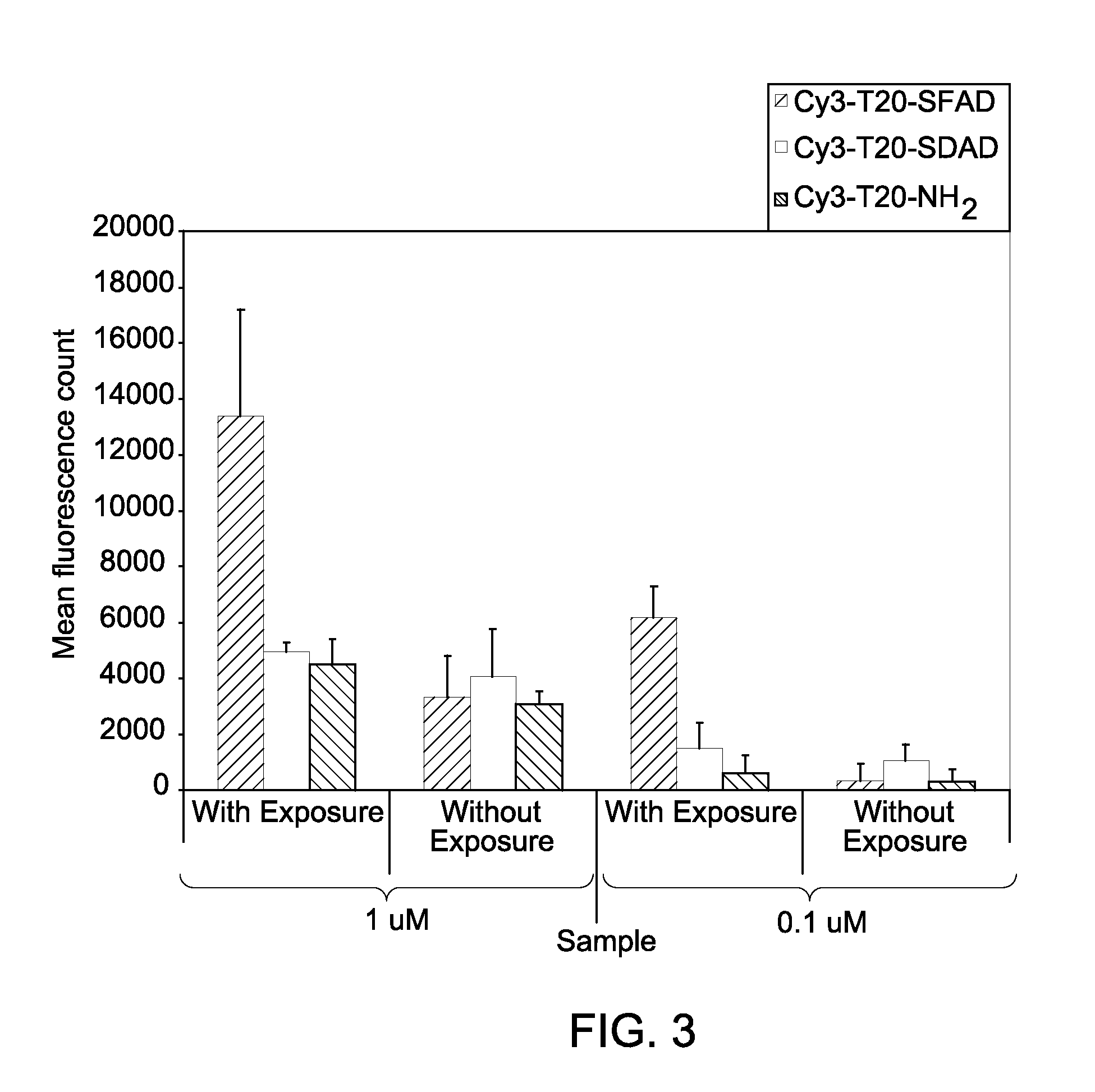
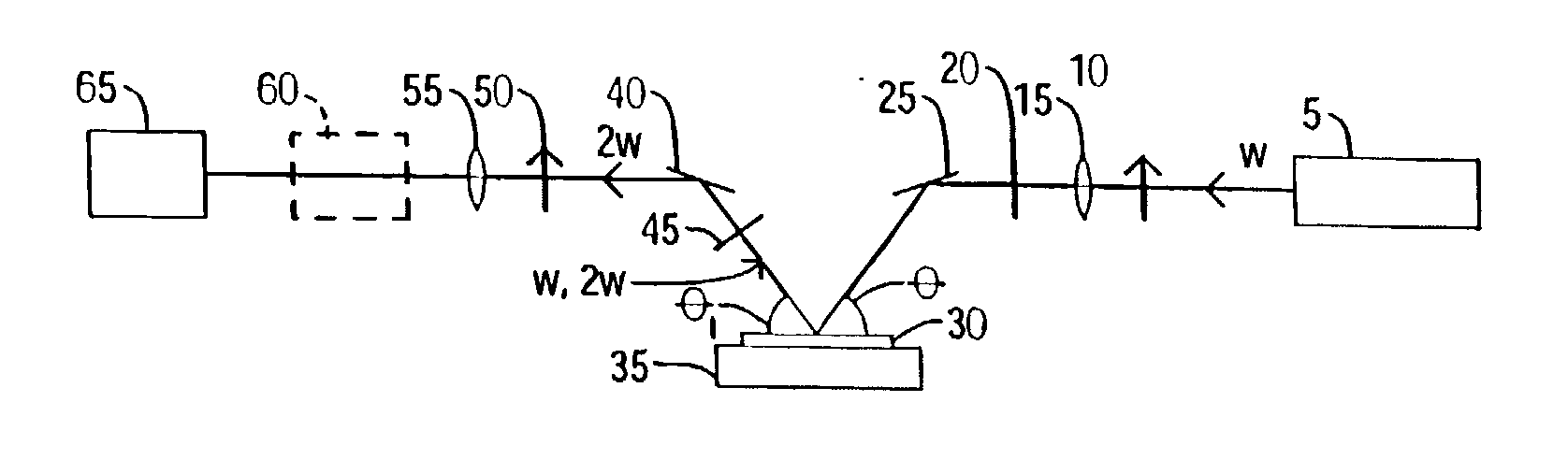
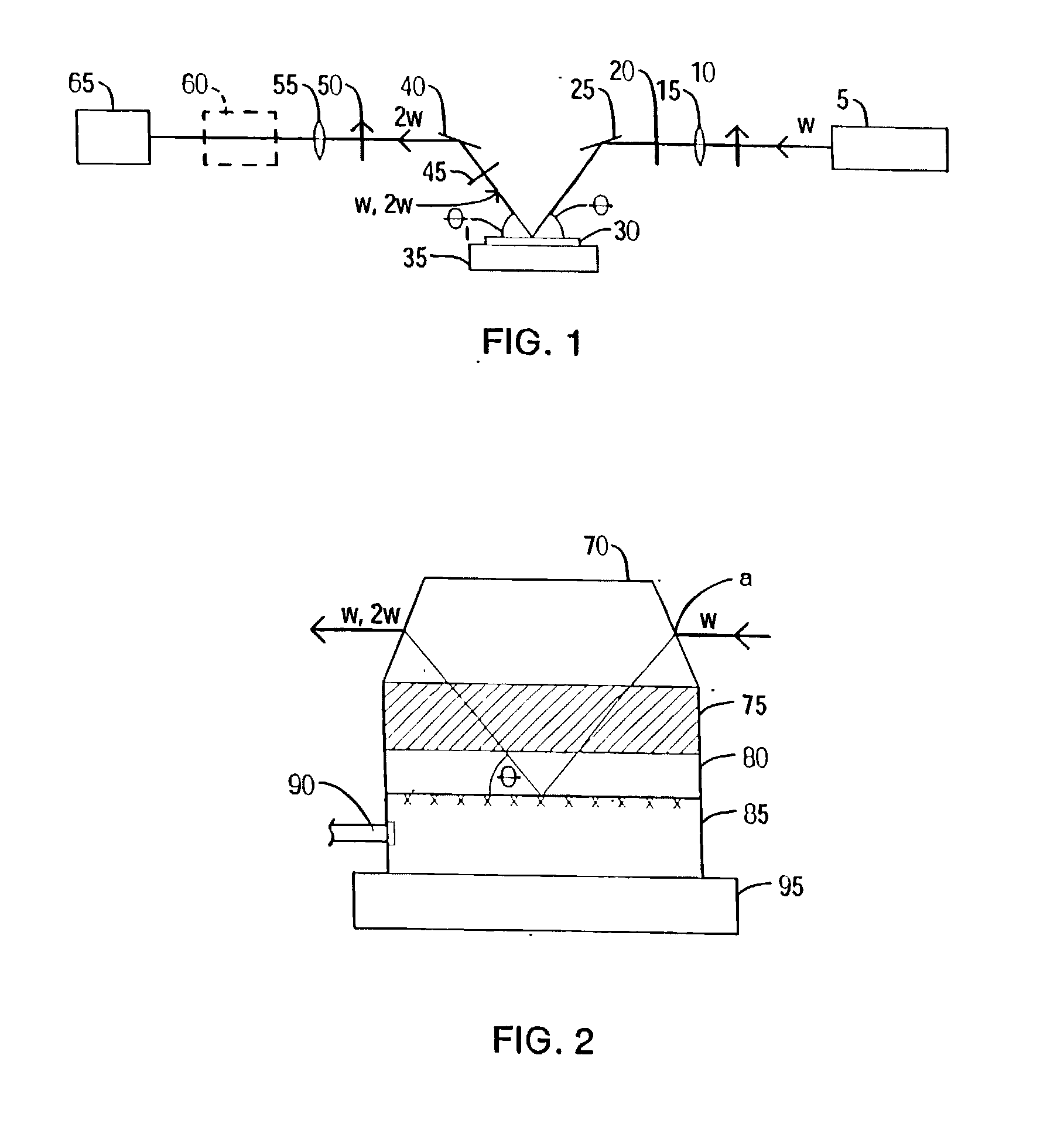
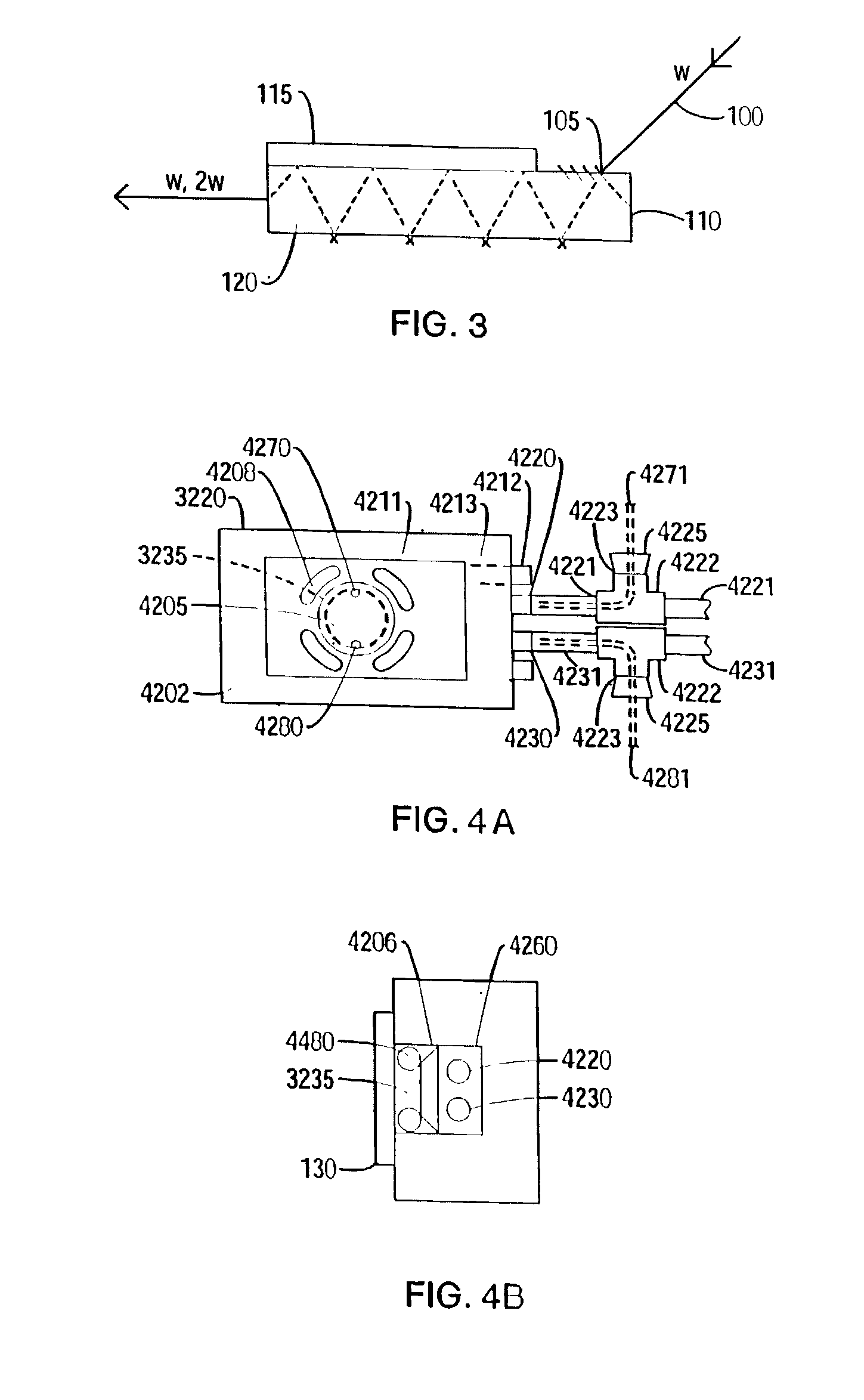
A nonlinear optical technique, such as second or third harmonic or sum or difference frequency generation, is used to detect binding interactions, or the degree or extent of binding, that comprise a conformational change. In one aspect of the present invention, the nonlinear optical technique detects a conformational change in a probe due to target binding. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate probes by detecting a conformational change due to a probe-target interaction. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate modulators of a probe-target interaction by detecting a conformational change in the presence of the modulator.
Owner:BIODESY
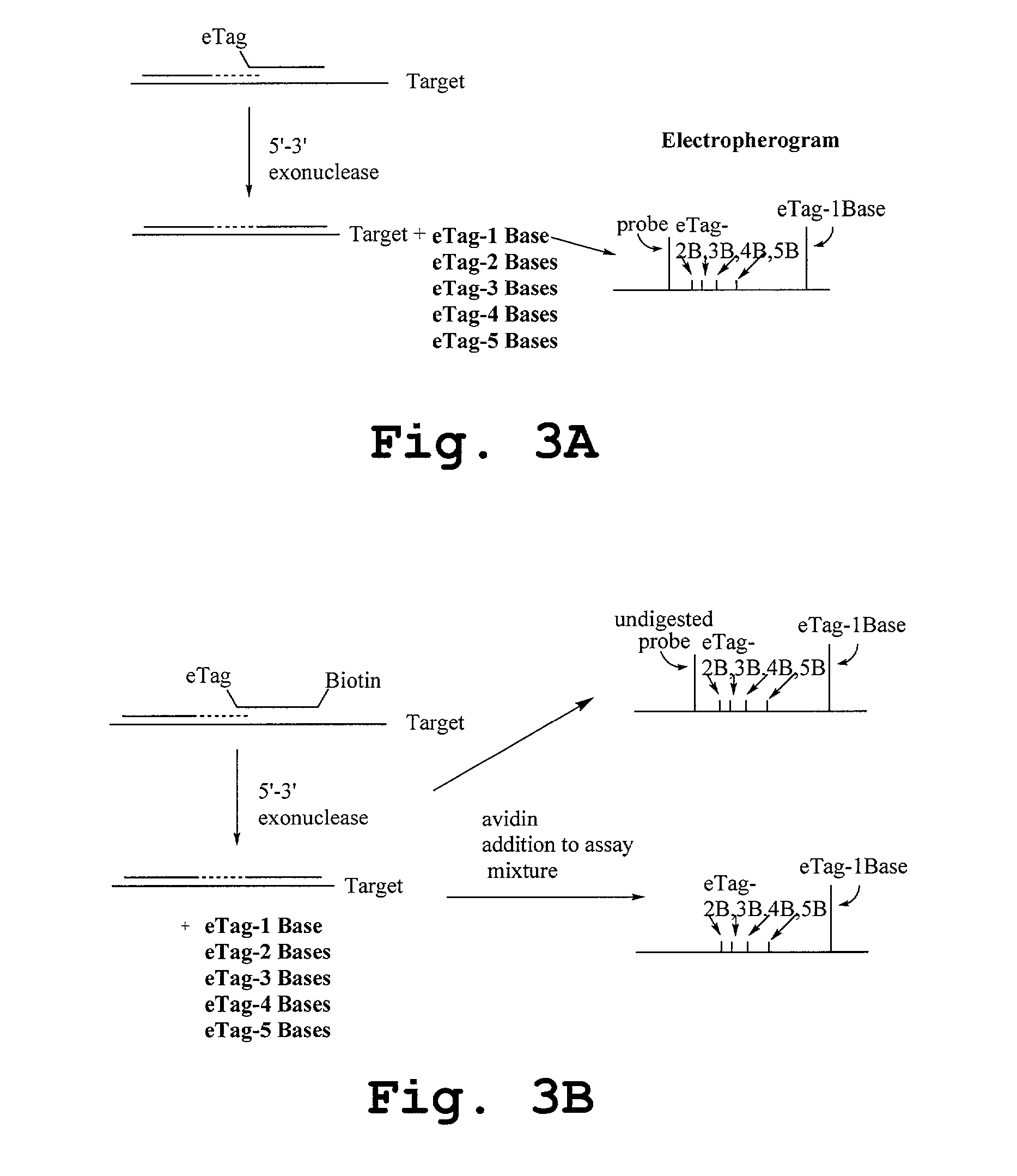
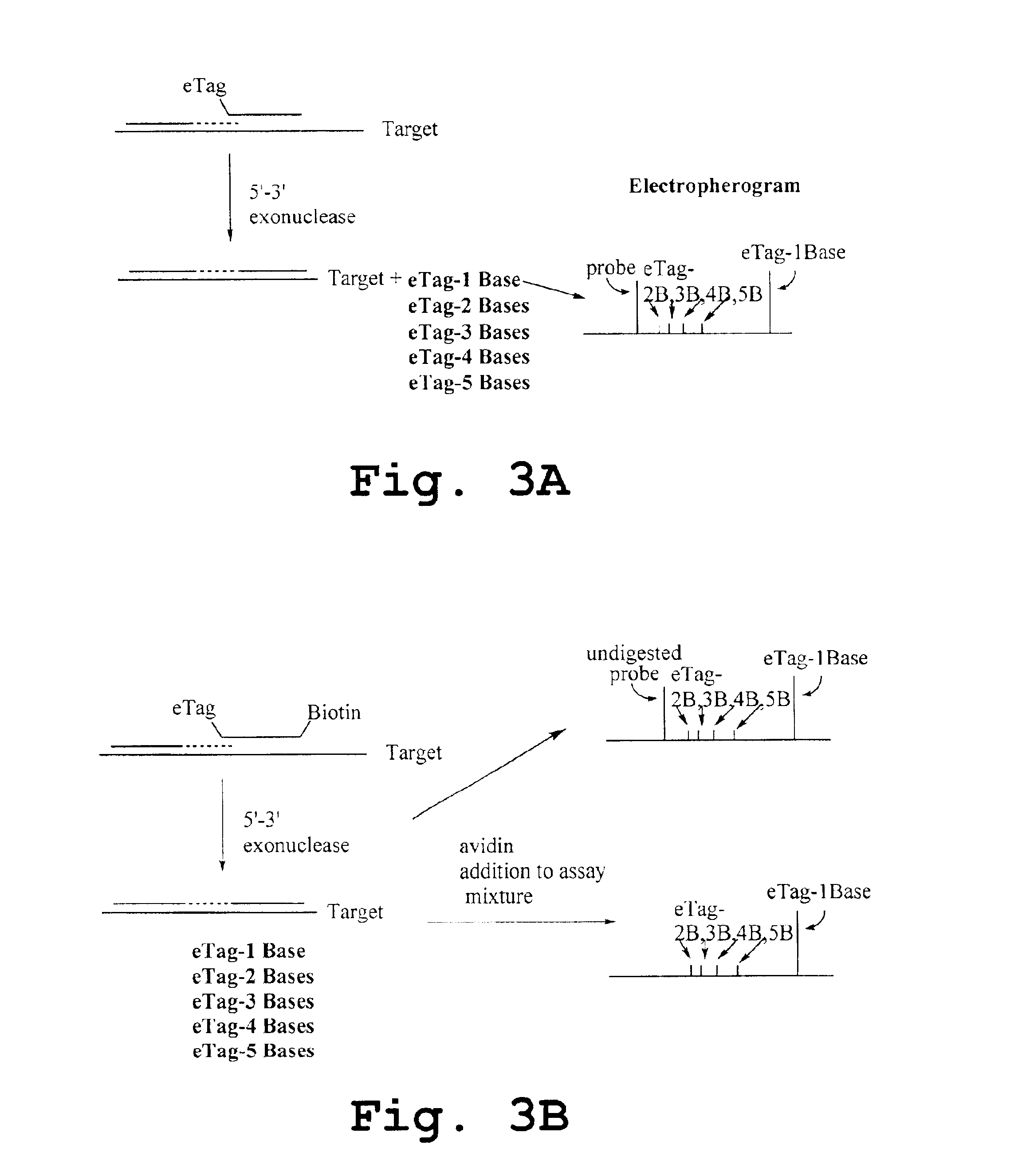
Nucleic acid detection using degradation of a tagged sequence
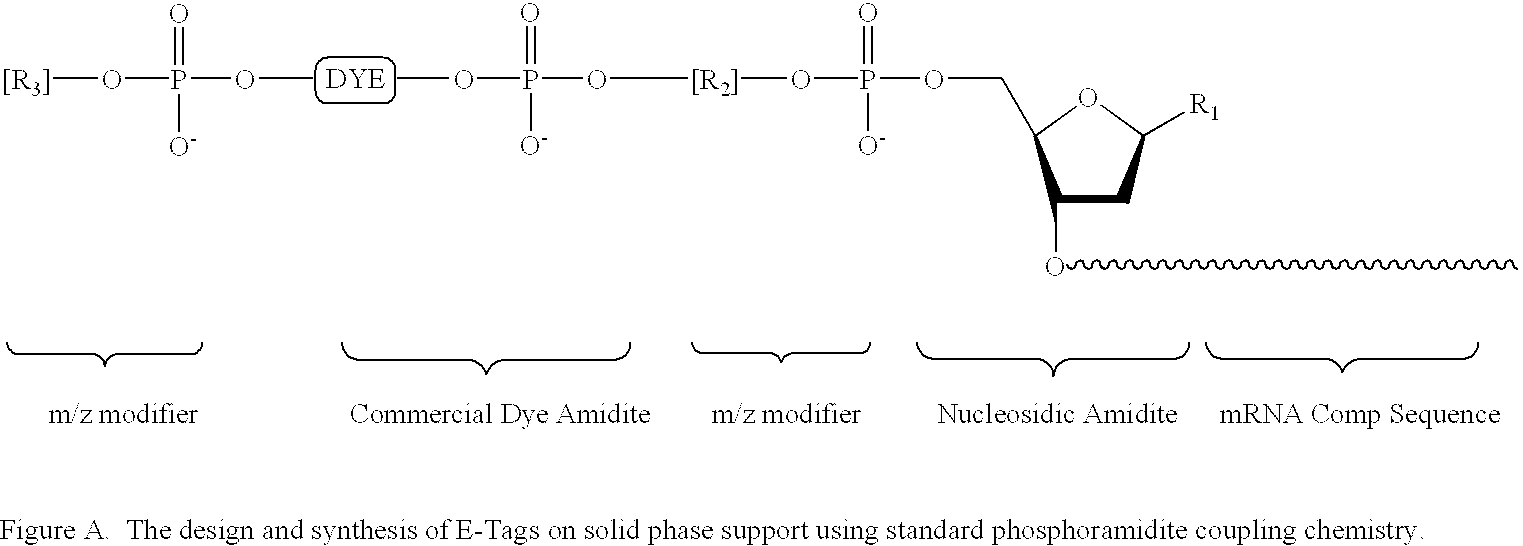
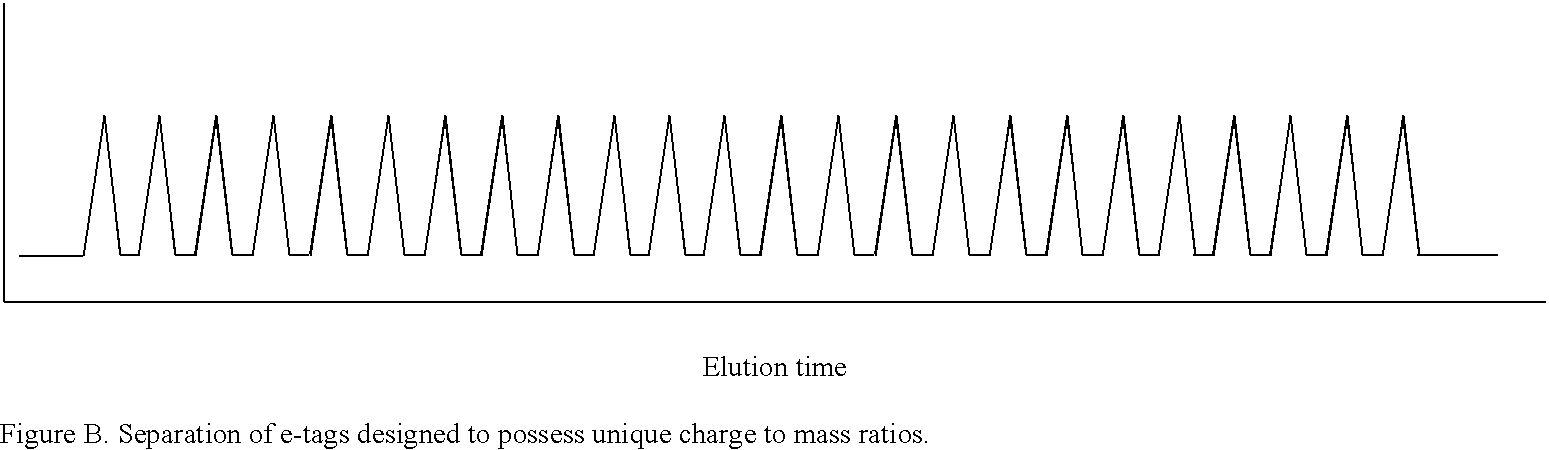
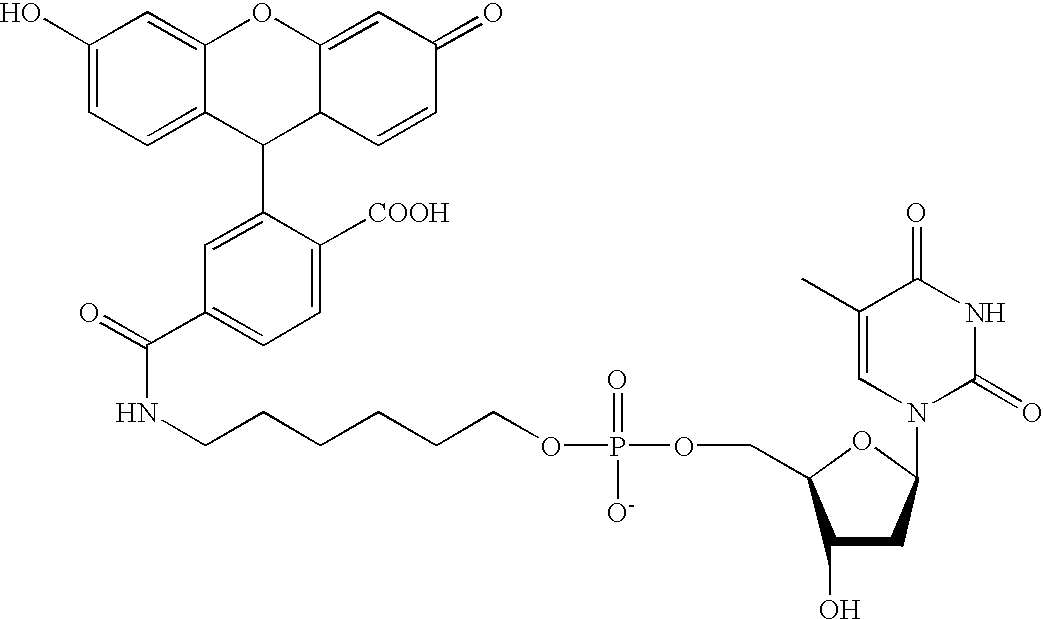
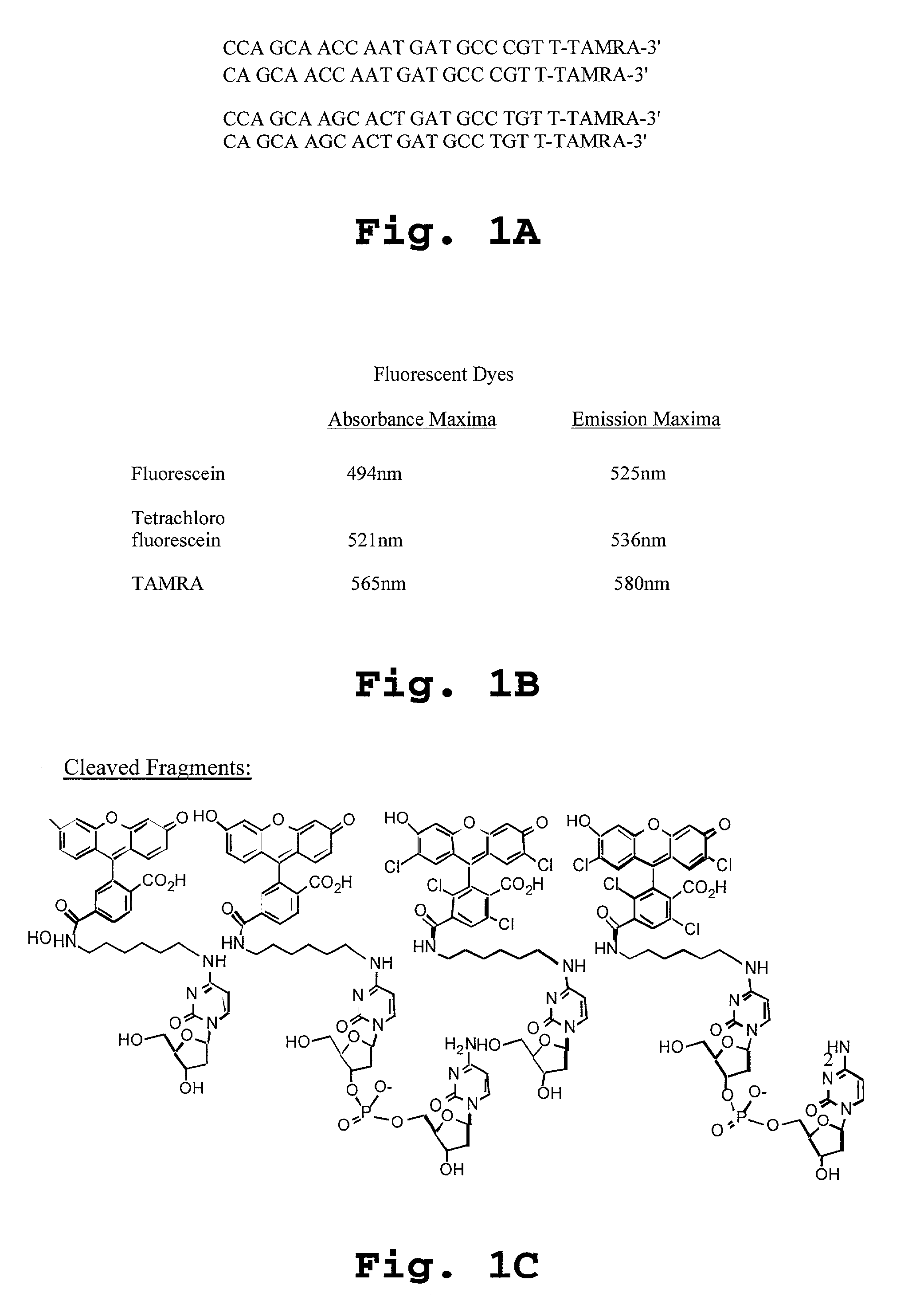
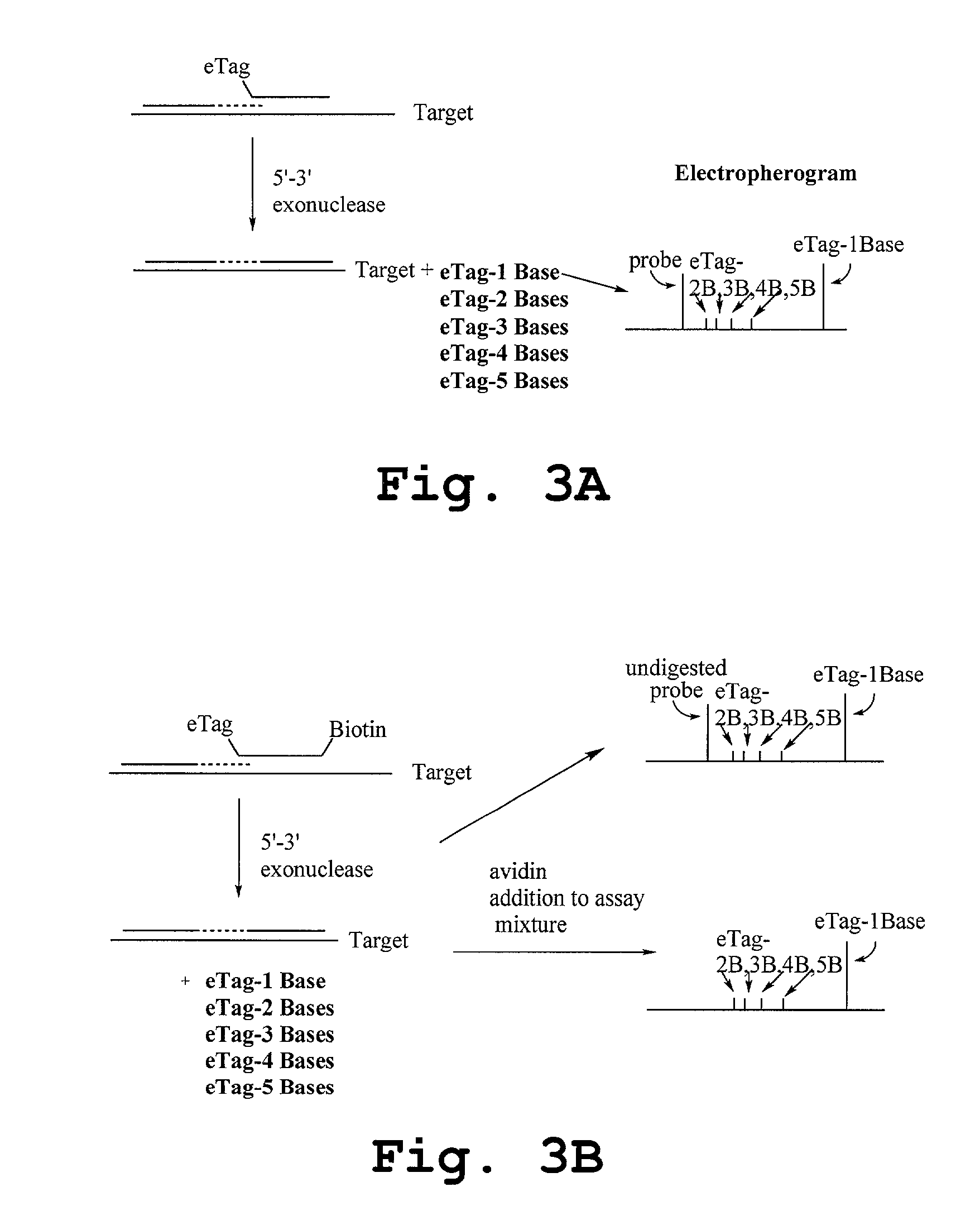
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting target molecules, e.g. DNA sequences, particularly single nucleotide polymorphisms, using a pair of nucleotide sequences, a primer and a snp detection sequence, where the snp detection sequence binds downstream from the primer to the target DNA in the direction of primer extension, or ligands and receptors. The methods employ e-tags comprising a mobility-identifying region joined to a detectable label and a target-binding region. The result of the binding of the target-binding region to the target is to have a bond cleaved in the starting material with the production of a detectable product with a different mobility from the starting material, where the different e-tags can be separated and detected.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Methods and compositions for enhancing detection in determinations employing cleavable electrophoretic tag reagents
InactiveUS20040096825A1Accurate detectionDifferent massPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsElectrophoresisBiology
Probe sets for the multiplexed detection of the binding of, or interaction between, one or more ligands and target antiligands are provided. Detection involves the release of identifying tags as a consequence of target recognition. The probe sets include electrophoretic tag probes or e-tag probes, comprising a detection region and a mobility-defining region called the mobility modifier, both linked to a target-binding moiety. The probes comprise interactive functionalities adjacent the cleaved portion positioned in the probes such that the interactive functionality does not form part of the e-tag reporters. Target antiligands are contacted with a set of e-tag probes and the contacted antiligands are treated with a selected cleaving agent resulting in a mixture of e-tag reporters and uncleaved and / or partially cleaved e-tag probes. The mixture is exposed to a capture agent effective to bind to uncleaved or partially cleaved e-tag probes, followed by electrophoretic separation. In a multiplexed assay, different released e-tag reporters may be separated and detected providing for target identification.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Methods employing generalized target-binding e-tag probes
Methods for the multiplexed detection of the binding of, or interaction between, one or more ligands and target antiligands are provided. Detection involves the release of identifying tags as a consequence of target recognition. The methods include the use of electrophoretic tag probes or e-tag probes, comprising a detection region and a mobility-defining region called the mobility modifier, both linked to a target-binding moiety. In practicing the methods, target antiligands are contacted with a set of e-tag probes and the contacted antiligands are treated with a selected cleaving agent resulting in a mixture of e-tag reporters and uncleaved and / or partially cleaved e-tag probes. The mixture is exposed to a capture agent effective to bind to uncleaved or partially cleaved e-tag probes, followed by electrophoretic separation. In a multiplexed assay, different released e-tag reporters may be separated and detected providing for target identification.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Single-molecule selection methods and compositions therefrom
InactiveUS6762025B2Highly specific controlImprove complianceNanotechSugar derivativesNucleotideOligonucleotide
Single-molecule selection methods are provided for identifying target-binding molecules from diverse sequence and shape libraries. Complexes and imprints of selected target-binding molecules are also provided. The subject selection methods are used to identify oligonucleotide and nonnucleotide molecules with desirable properties for use in pharmaceuticals, drug discovery, drug delivery, diagnostics, medical devices, cosmetics, agriculture, environmental remediation, smart materials, packaging, microelectronics and nanofabrication. Single oligonucleotide molecules with desirable binding properties are selected from diverse sequence libraries and identified by amplification and sequencing. Alternatively, selected oligonucleotide molecules are identified by sequencing without amplification. Nonnucleotide molecules with desirable properties are identified by single-molecule selection from libraries of conjugated molecules or nucleotide-encoded nonnucleotide molecules. Alternatively, target-specific nonnucleotide molecules are prepared by imprinting selected oligonucleotide molecules into nonnucleotide molecular media. Complexes and imprints of molecules identified by single-molecule selection are shown to have broad utility as drugs, prodrugs, drug delivery systems, willfully reversible cosmetics, diagnostic reagents, sensors, transducers, actuators, adhesives, adherents and novel multimolecular devices.
Owner:MOLECULAR MACHINES
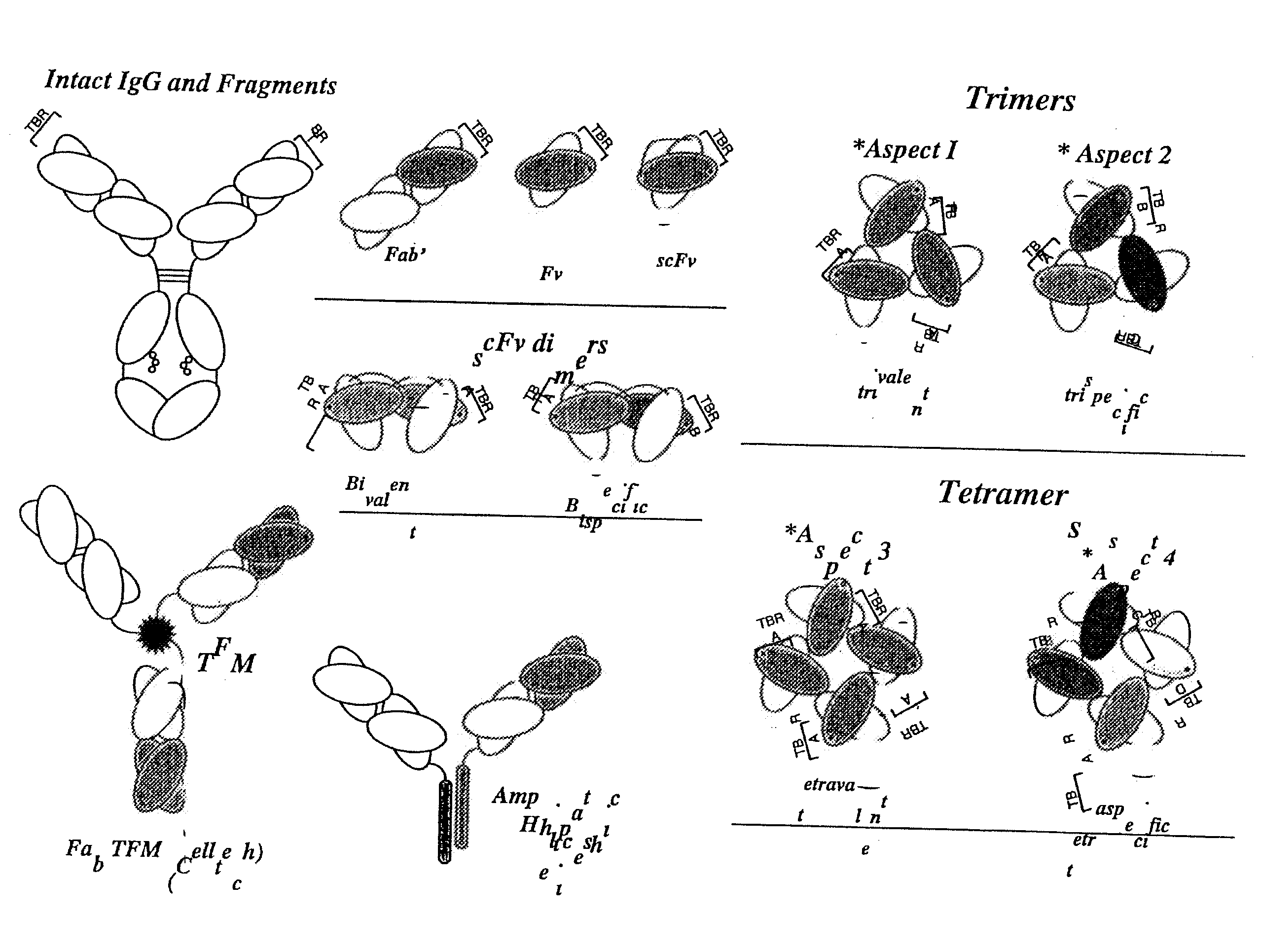
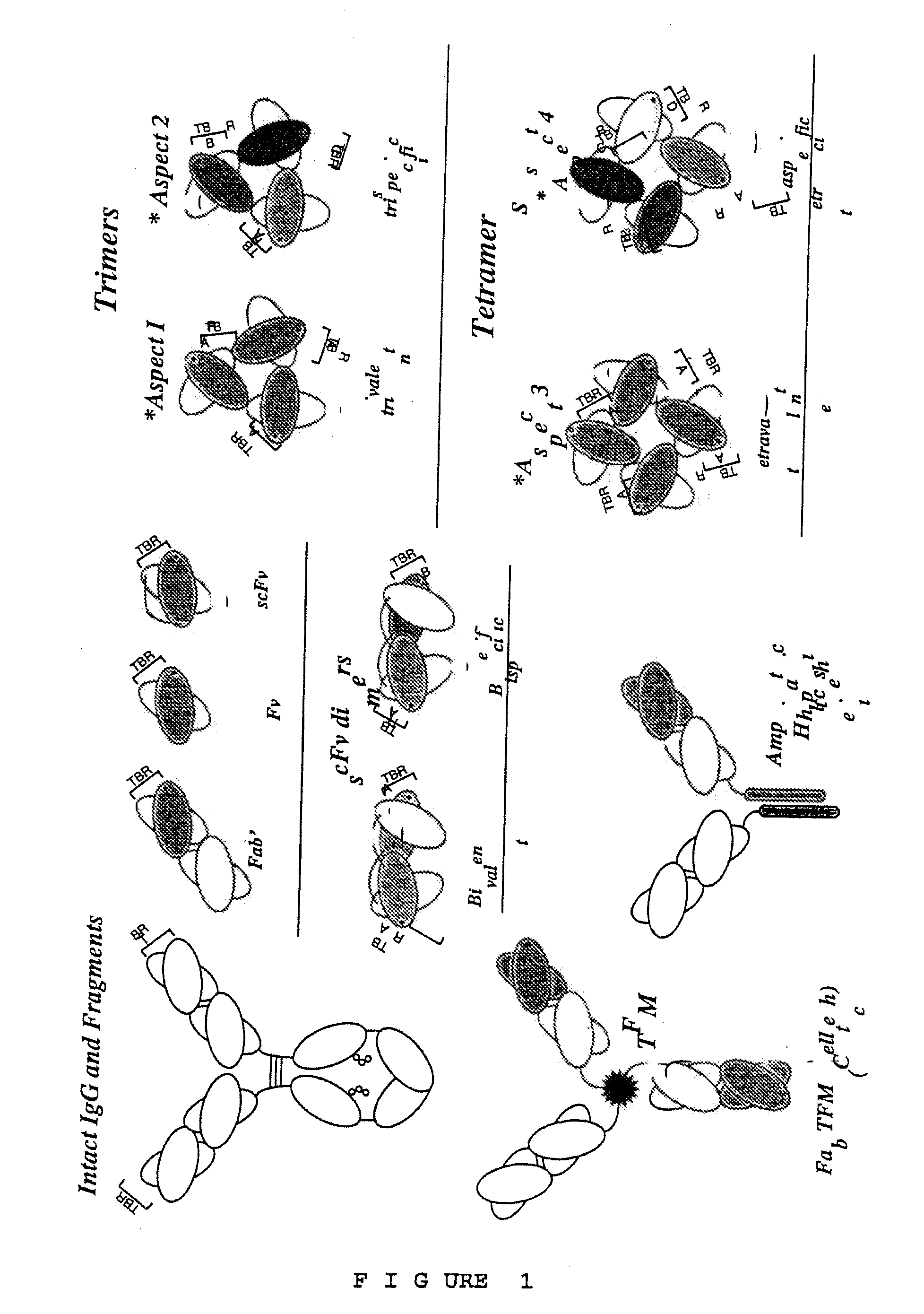
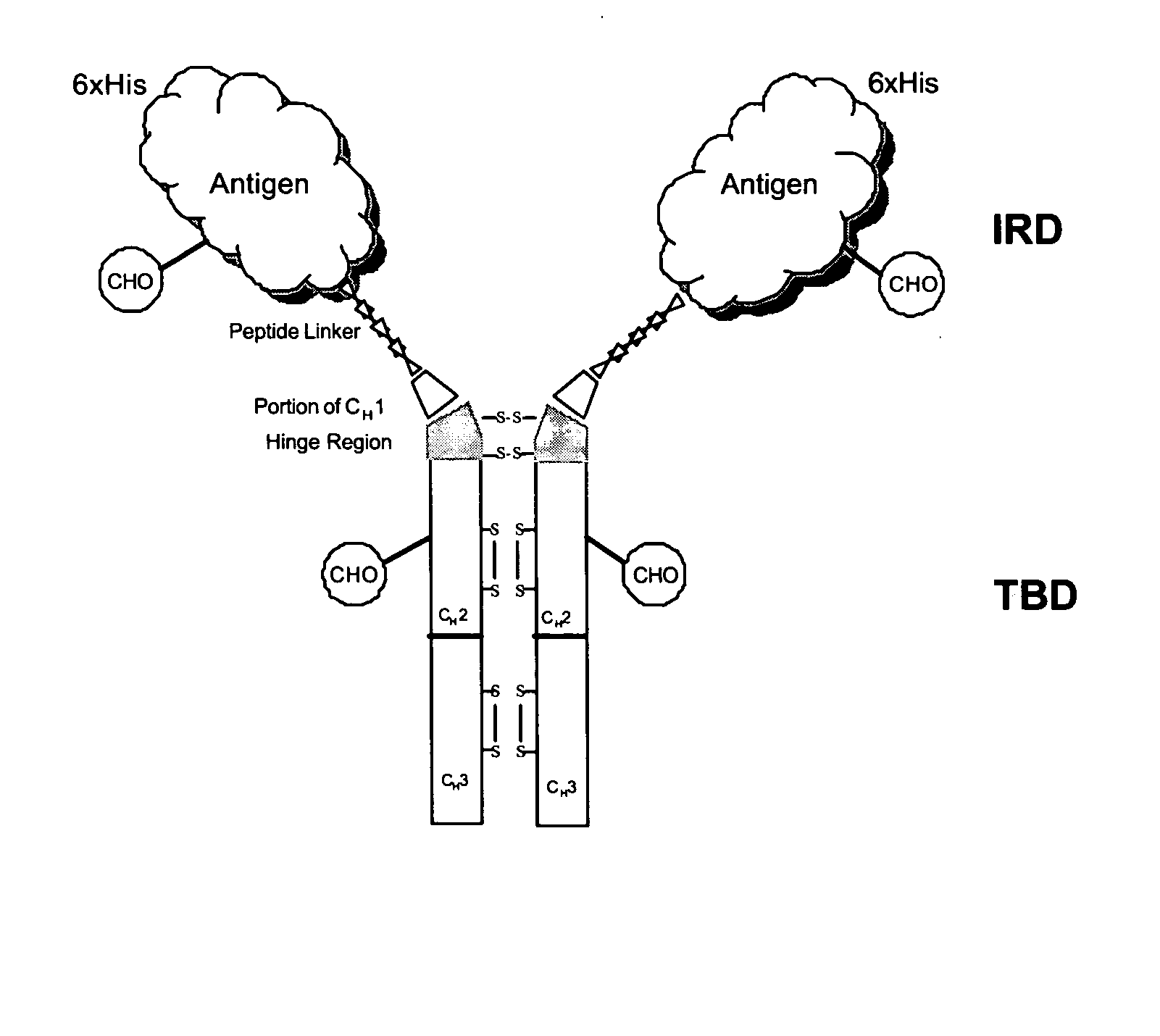
High avidity polyvalent and polyspecific reagents
InactiveUS20080152586A1In-vivo radioactive preparationsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansEGF-like domainImaging agent
This invention provides polyvalent or polyspecific protein complexes, comprising three or more polypeptides which associate to form three or more functional target-binding regions (TBRs), and in which each individual polypeptide comprises two or more immunoglobulin-like domains which are covalently joined together, such that two Ig-like domains in a single polypeptide do not associate with each other to form a TBR. By using a linker peptide of fewer than three amino acid residues the immunoglobulin-like domains of the individual polypeptides are prevented from associating, so that complex formation between polypeptides is favoured. Preferably the polyvalent or polyspecific protein is a trimer or tetramer. The proteins of the invention have specificities which may be the same or different, and are suitable for use as therapeutic, diagnostic or imaging agents.
Owner:AVIPEP
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation of Bcl-2
InactiveUS20050203042A1Comparable and enhanced biological effectInteresting biological propertiesBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseNucleobase
The present invention provides improved oligomeric compound, in particular oligonucleotide compounds, and methods for modulating the expression of the Bcl-2 gene in humans. In particular, this invention relates to oligomeric compounds of 10-30 nucleobases in length which comprise a target binding domain that is specifically hybridizable to a region ranging from base position No. 1459 (5′) to No. 1476 (3′) of the human Bcl-2 mRNA, said target binding domain having the formula: 5′-[(DNA / RNA)0-1-(LNA / LNA*)2-7-(DNA / RNA / LNA*)4-14-(LNA / LNA*)2-7-(DNA / RNA)0-1]-3 and said target binding domain comprising at least two LNA nucleotides or LNA analogue nucleotides linked by a phosphorothioate group (—O—P(O,S)—O—). In particular the oligo is predominantly or fully thiolated. The invention also provides the use of such oligomers or conjugates or chimera for the treatment of various diseases associated with the expression of the Bcl-2 gene, such as cancer.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
Method using a nonlinear optical technique for detection of interactions involving a conformational change
InactiveUS20060228725A1No need for labor and time-consuming washing stepLow backgroundCompound screeningMaterial nanotechnologyThird harmonicFrequency generation
A nonlinear optical technique, such as second or third harmonic or sum or difference frequency generation, is used to detect binding interactions, or the degree or extent of binding, that comprise a conformational change. In one aspect of the present invention, the nonlinear optical technique detects a conformational change in a probe due to target binding. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate probes by detecting a conformational change due to a probe-target interaction. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate modulators of a probe-target interaction by detecting a conformational change in the presence of the modulator.
Owner:BIODESY
Multiplex spatial profiling of gene expression
The present invention provides mass tag complexes that permit simultaneously obtaining information of a plurality of biological molecules. The biological molecules may be RNA or protein, and the information includes both level of expression as well as spatial disposition within a cell or tissue. The mass tag comprise a core structure, a target binding structure (e.g., nucleic acid or peptide binding structure), a cleavable linker and a mass tag that exhibits a unique mass spectroscopy signal.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Methods for Amplifying a Complete Genome or Transcriptome
InactiveUS20140274811A1Eliminates misprimingReduces misprimingLibrary creationDNA preparationNucleotidePolymerase L
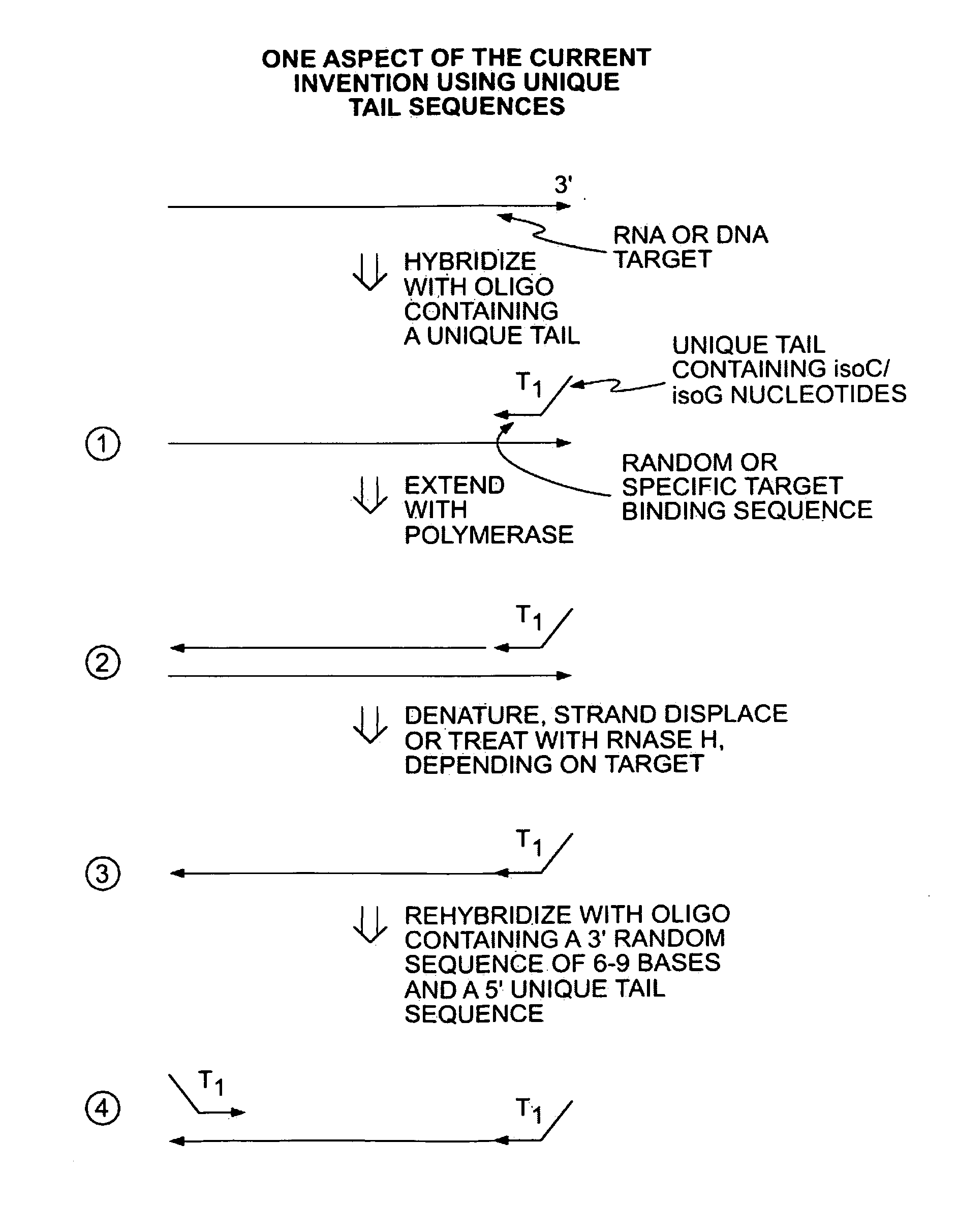
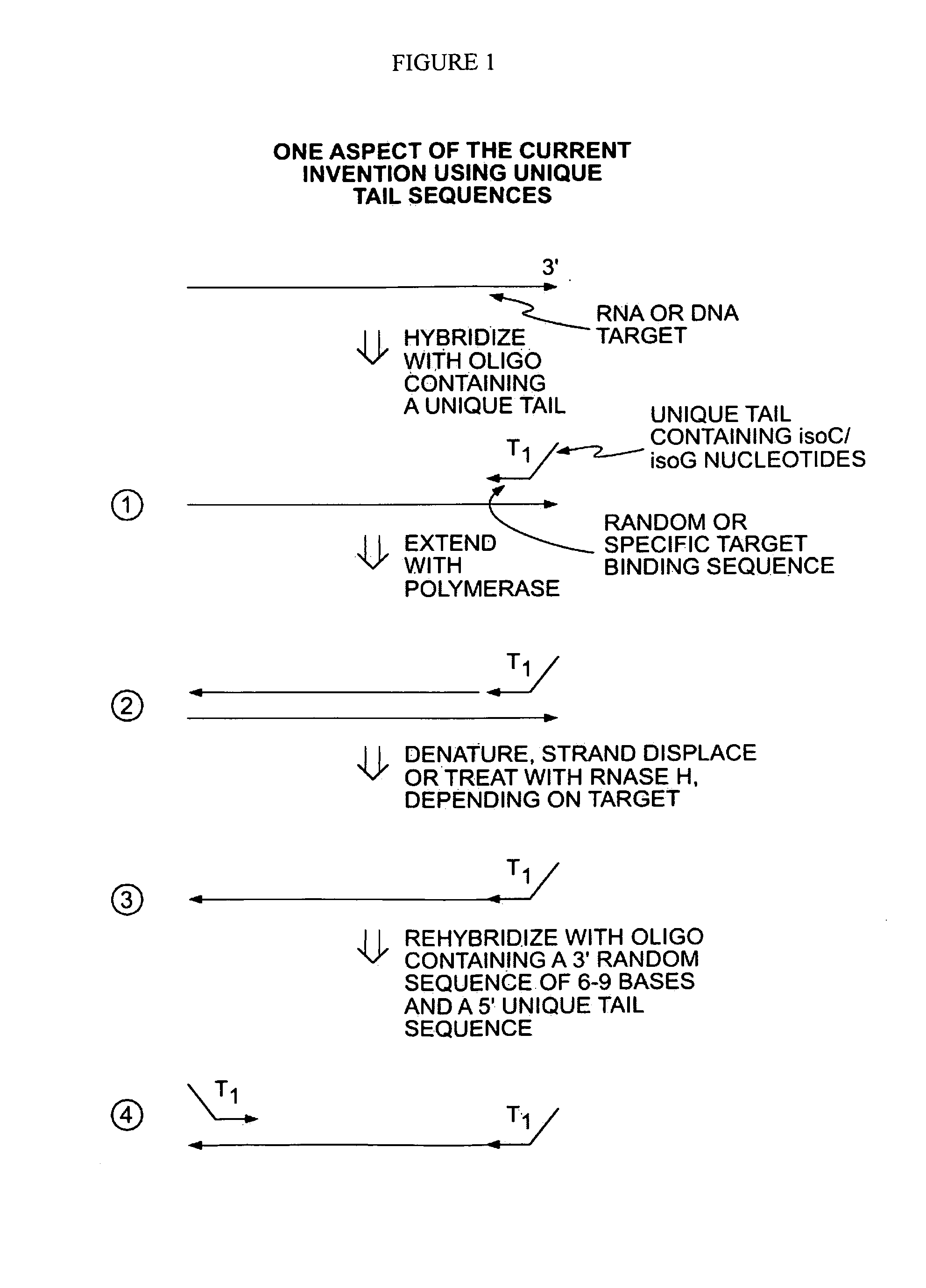
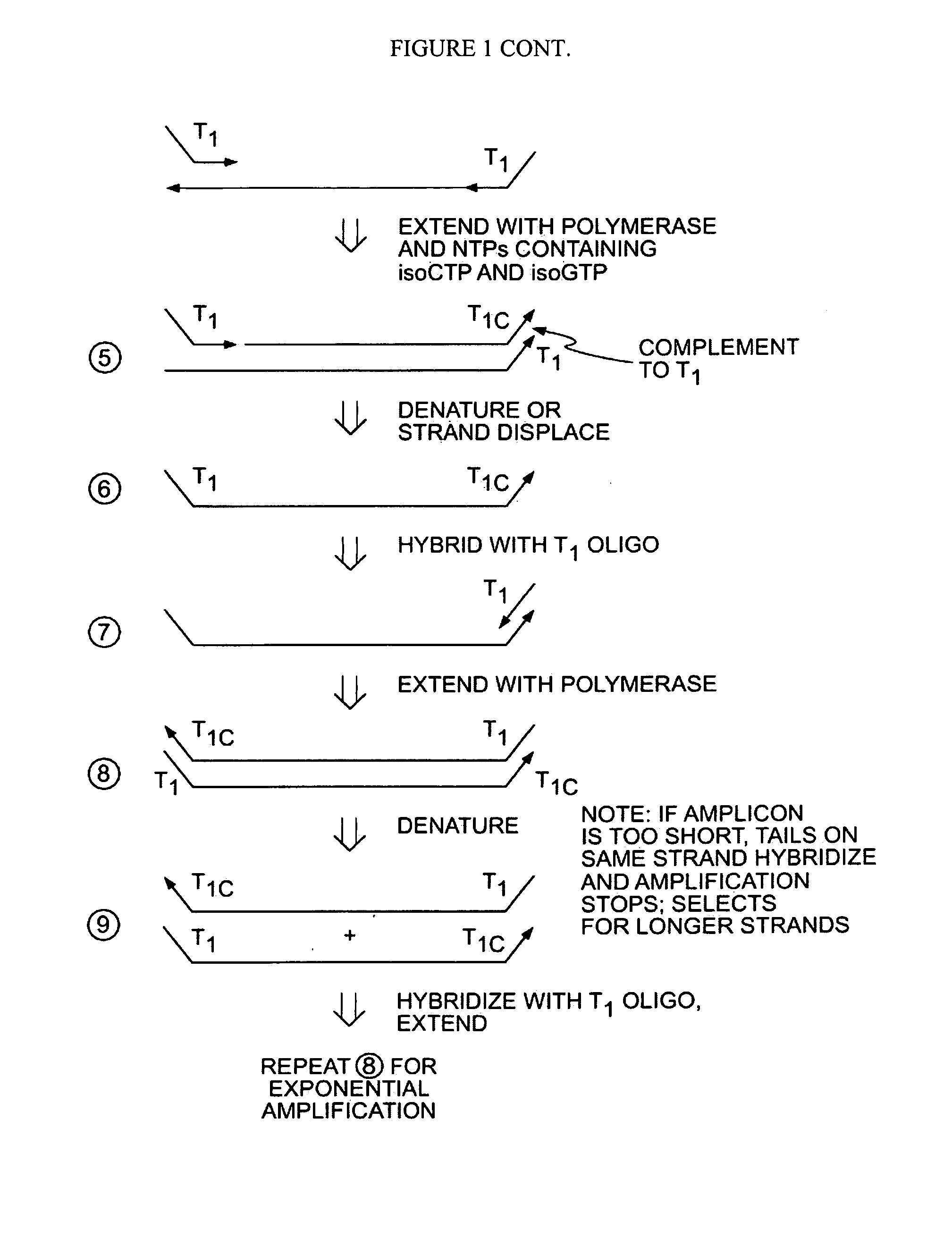
The present invention provides methods for amplifying a complete genome or transcriptome. The genome or transcriptome is prepared as a set of target nucleic acids and mixed with a first primer. The first primer comprises a target-binding region having a first random sequence of about 6 to about 9 nucleotides and a tag sequence that contains one or more non-natural nucleotides. The first primer is annealed to the target nucleic acids and extended by polymerase to produce a first duplex nucleic acid. The target nucleic acid is removed from the first nucleic acid. A second primer is annealed to the first nucleic acid having a second random sequence of about 6 to about 9 nucleotides and a tag sequence that contains one or more non-natural nucleotides. The second primer is extended by polymerase to produce a second duplex nucleic acid. The second nucleic acid contains a tag sequence on one terminus and a complement of the tag sequence on the other. The first nucleic acid is removed from the second nucleic acid. A third primer is annealed to the second nucleic acid having the same sequence as the tag sequence or a portion thereof and at least one of the non-natural nucleotides of the tag sequence. The third primer is extended by polymerase to produce a third duplex nucleic acid. The second nucleic acid is removed from the third nucleic acid. The third primer is annealed to the second nucleic acid and the third nucleic acid. The third primer is extended by polymerase. Repeating these last three steps thereby results in amplification of the genome or transcriptome.
Owner:AEGEA BIOTECH
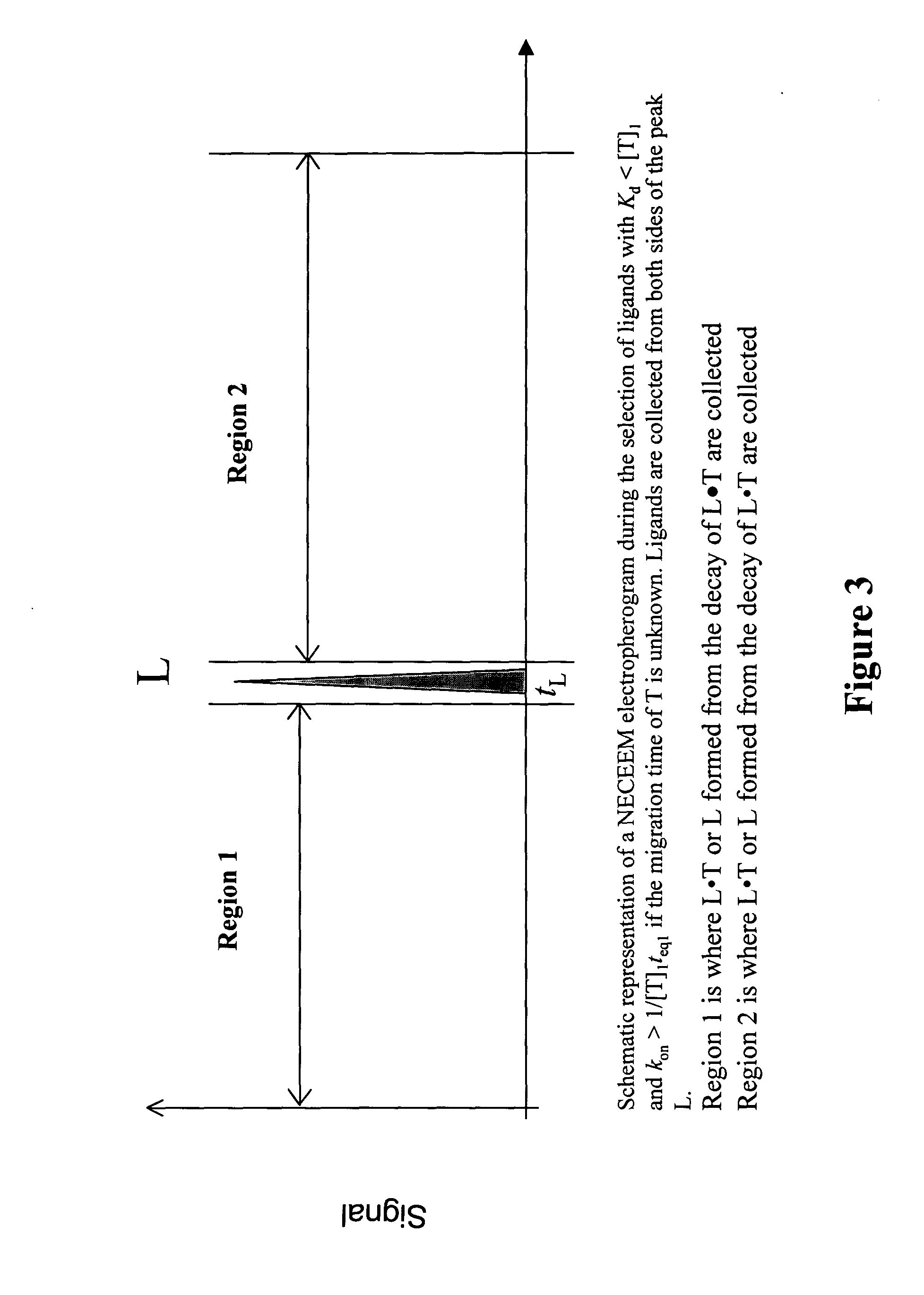
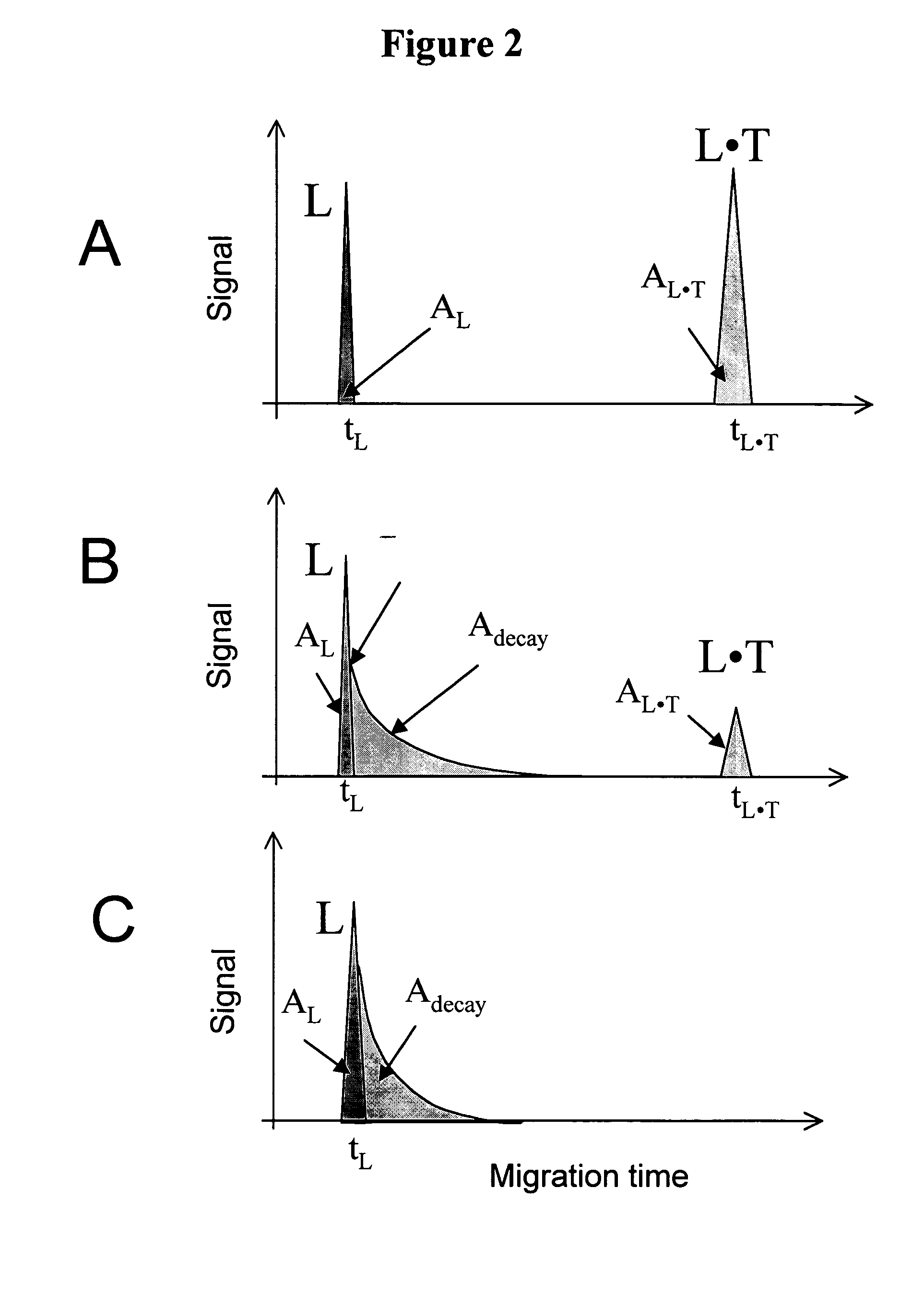
Non-equilibrium capillary electrophoresis of equilibrium mixtures (NECEEM) - based methods for drug and diagnostic development
ActiveUS20050003362A1Enhances electrophoretic separationEasy to separateCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSolid substrateNucleotide Aptamers
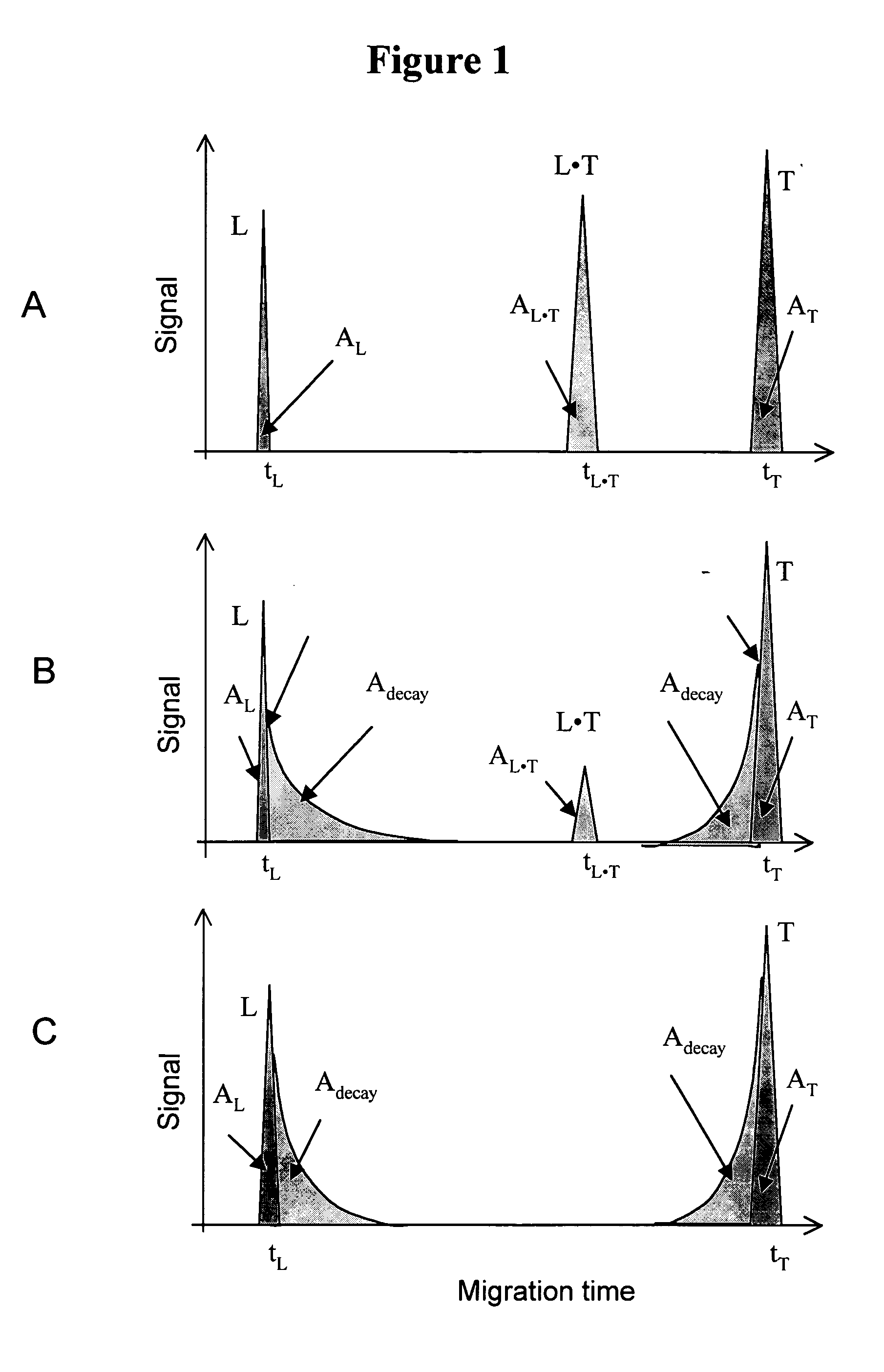
The invention discloses a Non-Equilibrium Capillary Electrophoresis of Equilibrium Mixtures (NECEEM) method and NECEEM-based practical applications. The NECEEM method is a homogeneous technique, which, in contrast to heterogeneous methods, does not require affixing molecules to a solid substrate. The method of the invention facilitates 3 practical applications. In the first application, the method allows the finding of kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of complex formation. It advantageously allows for revealing two parameters, the equilibrium dissociation constant, Kd, and the monomolecular rate constant of complex decay, koff, in a single experiment. In the second practical application, the method of this invention provides an approach for quantitative affinity analysis of target molecules. It advantageously allows for the use of affinity probes with relatively high values of koff. In the third practical application, the method of this invention presents a new and powerful approach to select target-binding molecules (ligands) from complex mixtures. Unique capabilities of the method in its third application include but not limited to: (a) the selection of ligands with pre-determined ranges of kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of target-ligand interactions, (b) the selection of ligands present in minute amounts in complex mixtures of biological or synthetic compounds such as combinatorial libraries of oligonucleotides, and (c) the selection of ligands for targets available in very low amounts. In particular, the method of this invention provides a novel approach for the selection of oligonucleotide aptamers. The NECEEM-based method can be used for discovery and characterization of drug candidates and the development of new diagnostic methods.
Owner:KRYLOV SERGEY
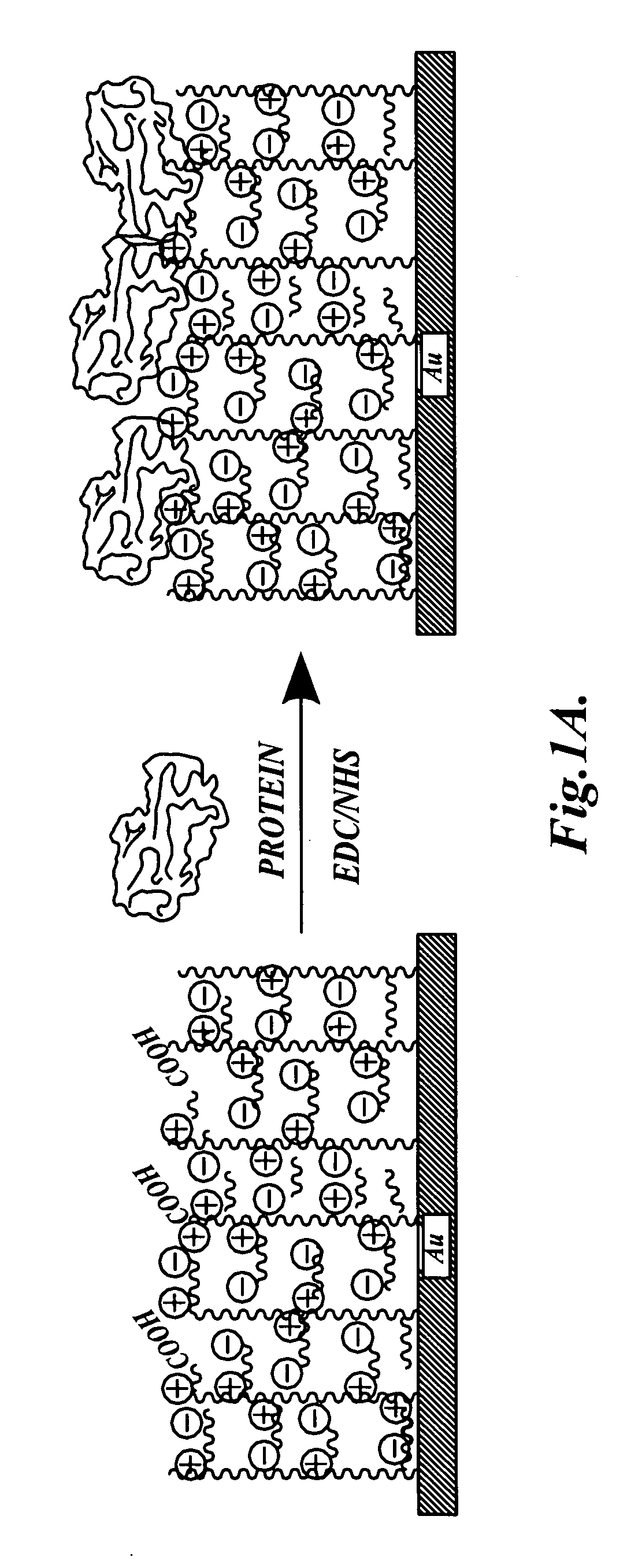
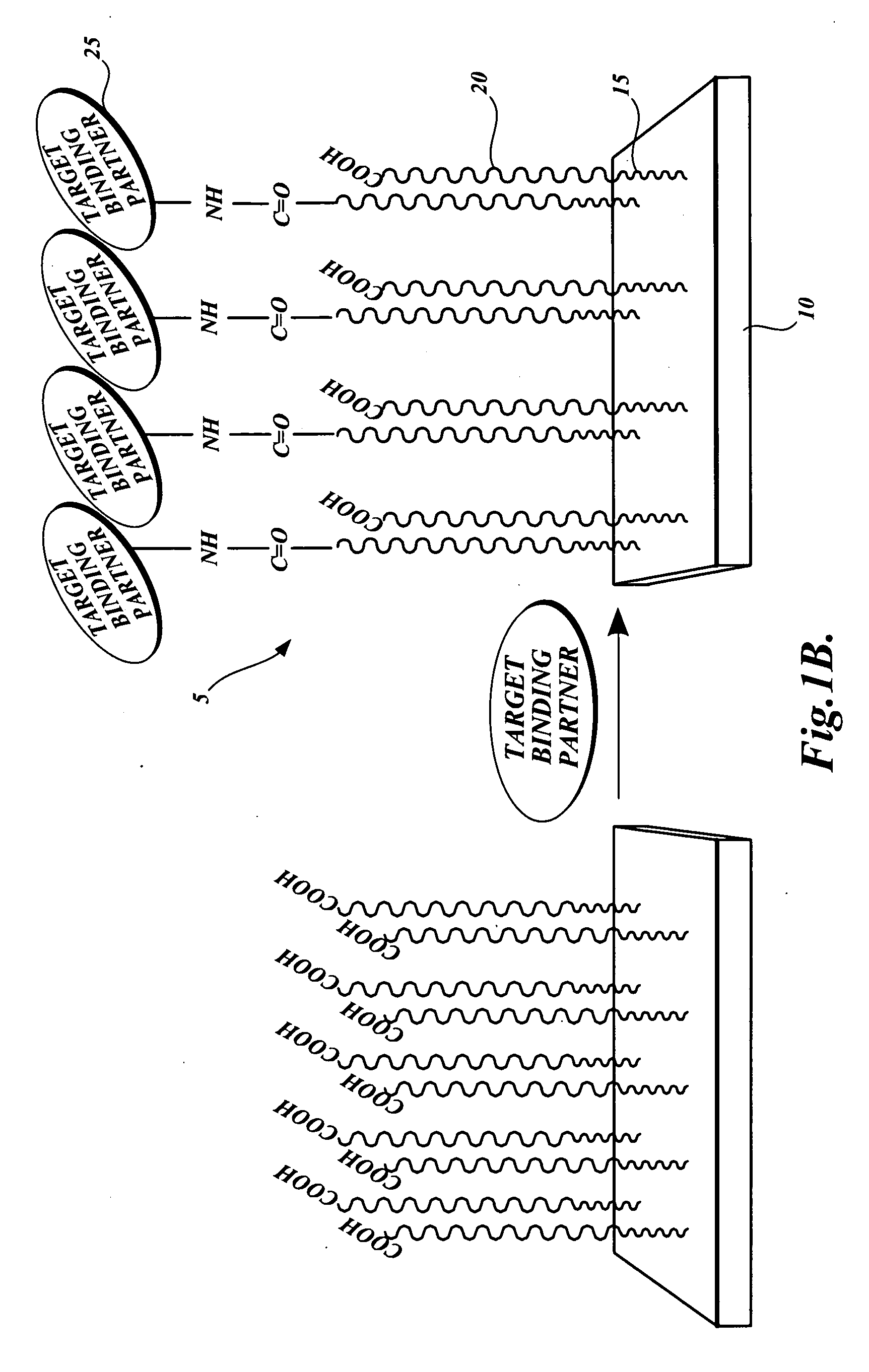
Dual-functional nonfouling surfaces and materials
ActiveUS20100099160A1Vegetable proteins working-upOn/in organic carrierCell adhesionBiological materials
Dual-functional nonfouling surfaces and materials, methods for making dual-functional nonfouling surfaces and materials, and devices that include dual-functional nonfouling surfaces and materials. The dual-functional surfaces are nonfouling surfaces that resist non-specific protein adsorption and cell adhesion. The dual-functional surfaces and materials include covalently coupled biomolecules (e.g., target binding partners) that impart specific biological activity thereto. The surfaces and materials are useful in medical diagnostics, biomaterials and bioprocessing, tissue engineering, and drug delivery.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Kits employing generalized target-binding e-tag probes
InactiveUS7001725B2Easy to analyzeIncrease the number ofElectrolysis componentsOrganic chemistry methodsElectrophoresisBiology
Kits for the multiplexed detection of the binding of, or interaction between, one or more ligands and target antiligands are provided. Detection involves the release of identifying tags as a consequence of target recognition. The kits include sets of electrophoretic tag probes or e-tag probes, a capture agent and optionally a cleaving agent. The e-tag probes comprise a detection region and a mobility-defining region called the mobility modifier, both linked to a target-binding moiety. In using the kits, target antiligands are contacted with a set of e-tag probes and the contacted antiligands are treated with a selected cleaving agent resulting in a mixture of e-tag reporters and uncleaved and / or partially cleaved e-tag probes. The mixture is exposed to a capture agent effective to bind to uncleaved or partially cleaved e-tag probes, followed by electrophoretic separation. In a multiplexed assay, different released e-tag reporters may be separated and detected providing for target identification.
Owner:VIROLOGIC INC
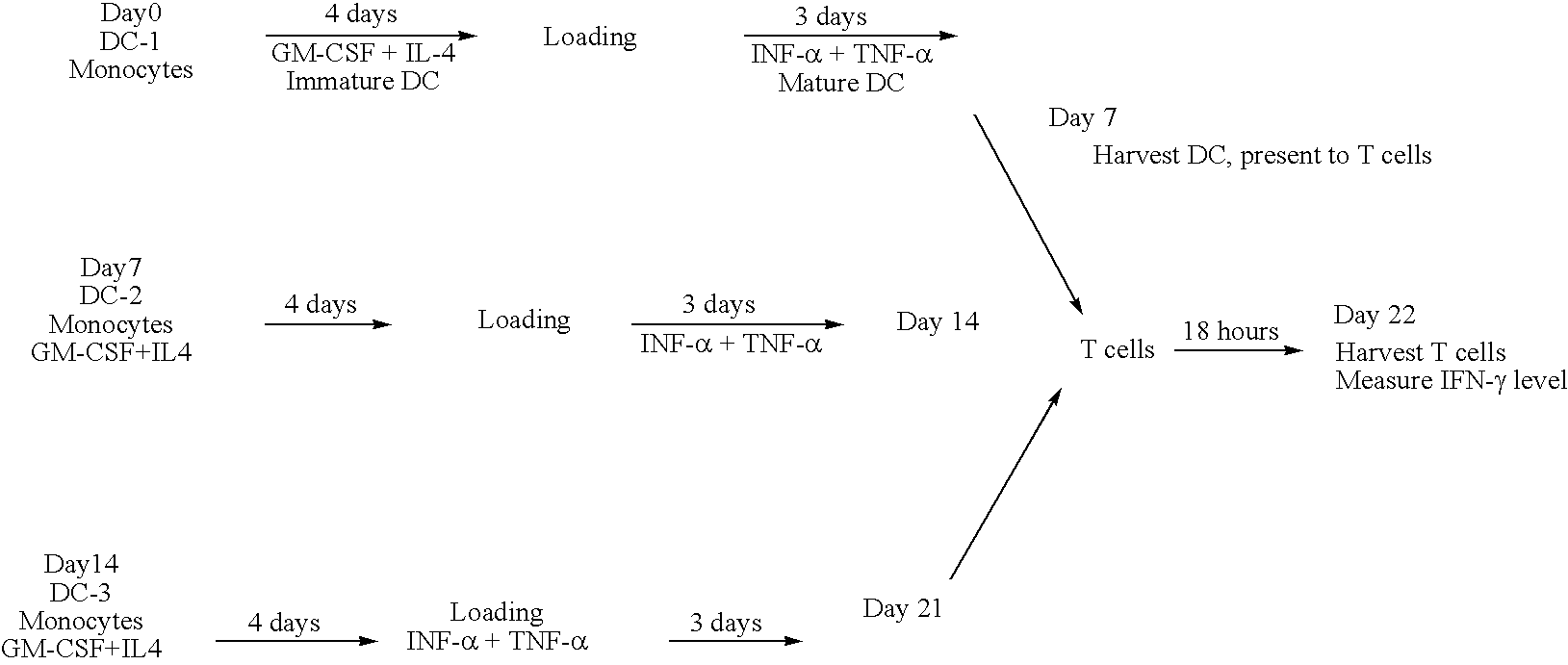
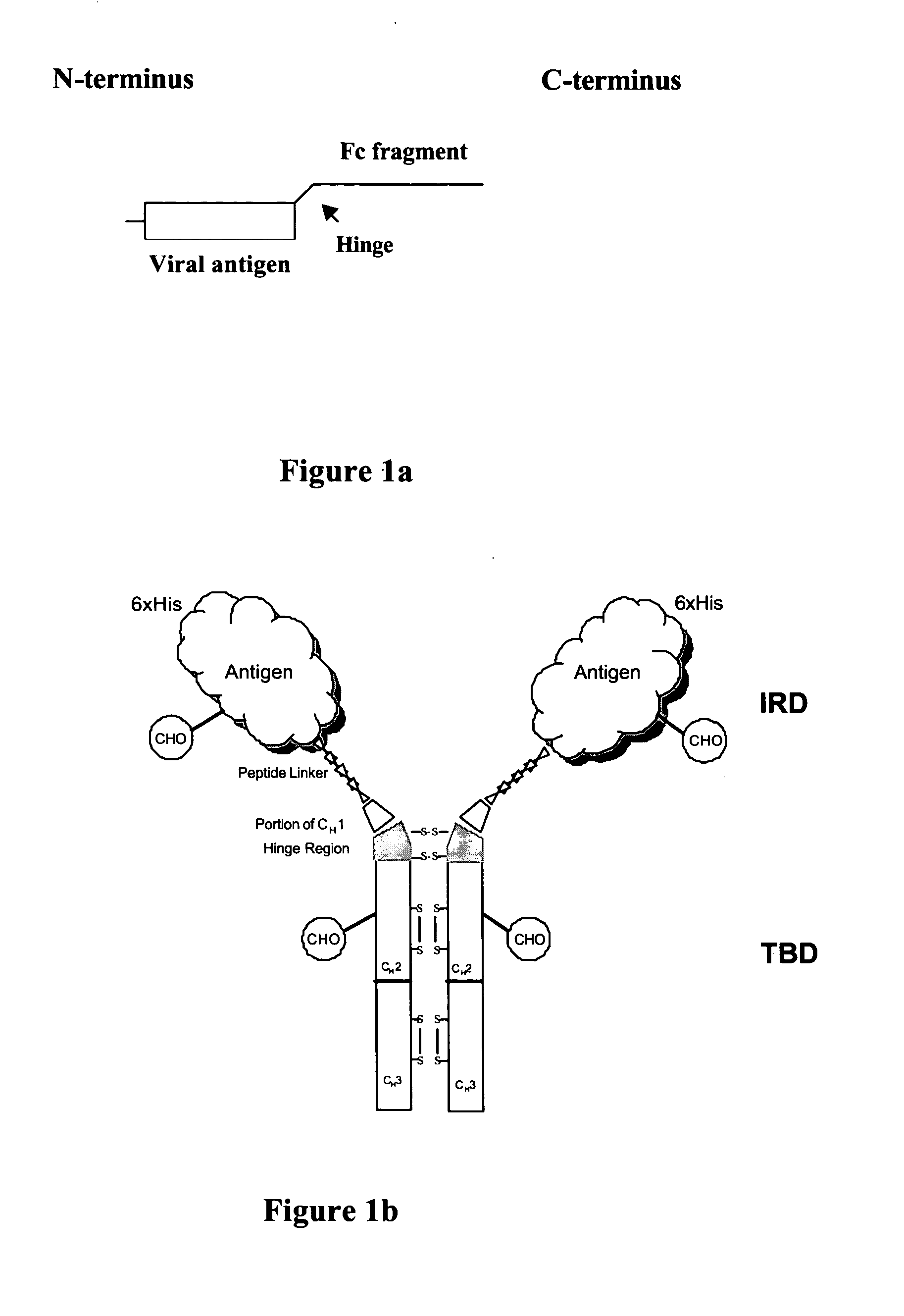
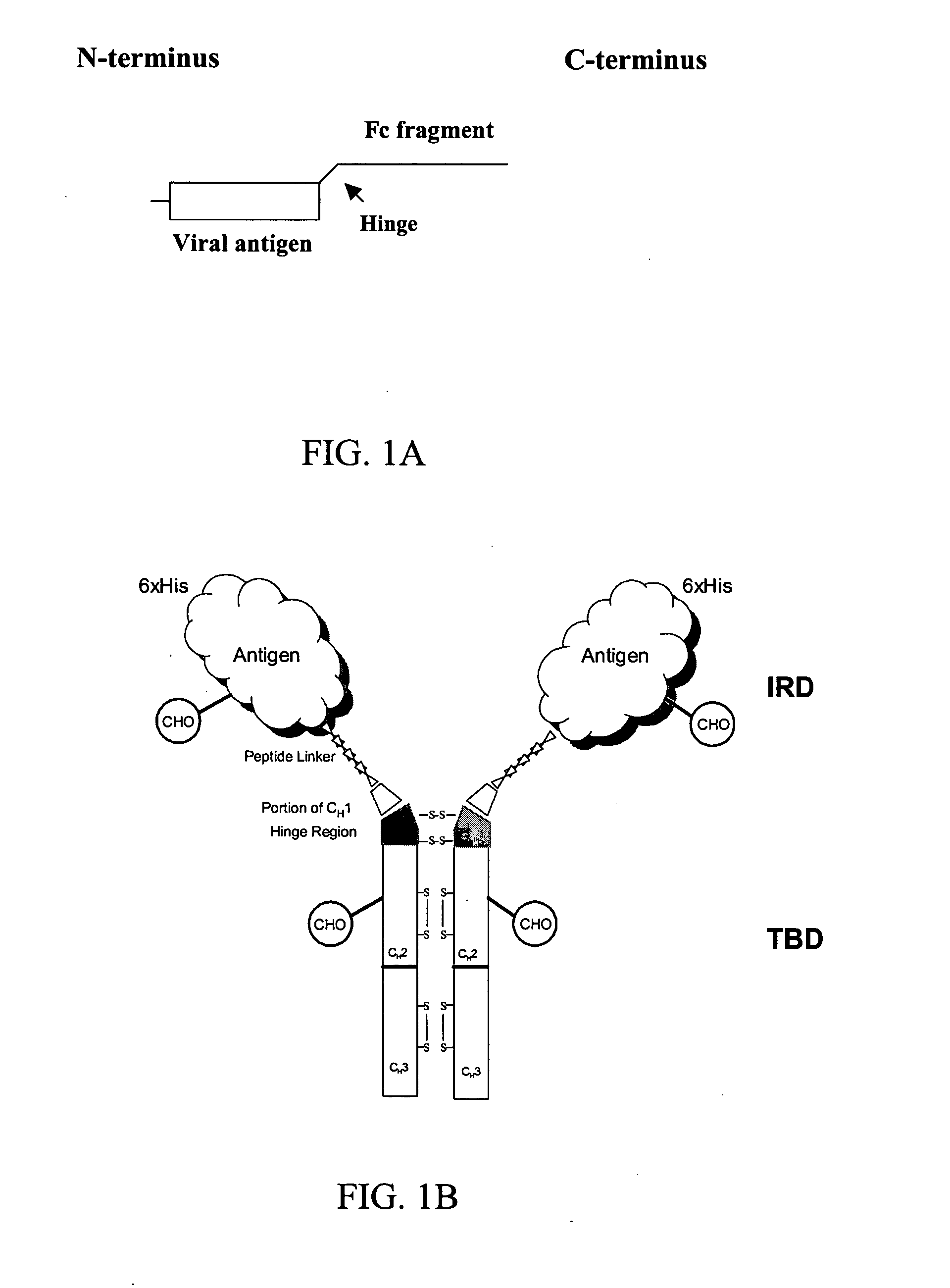
Chimeric antigens for eliciting an immune response
ActiveUS20050013828A1Effective presentationImprove efficiencyBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseHost immunityAntibody fragments
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods for eliciting immune responses against antigens. In particular embodiments, the compounds and methods elicit immune responses against antigens that are otherwise recognized by the host as “self” antigens. The immune response is enhanced by presenting the host immune system with a chimeric antigen comprising an immune response domain and a target binding domain, wherein the target binding domain comprises a xenotypic antibody fragment. By virtue of the target binding domain, antigen presenting cells take up, process, and present the chimeric antigen, eliciting both a humoral and cellular immune response.
Owner:KAIMI BIOMEDICINE (CHENGDU) CO LTD
Methods and compositions for enhancing detection in determinations employing cleavable electrophoretic tag reagents
InactiveUS7037654B2Effective isolationPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsElectrophoresisBiology
Probe sets for the multiplexed detection of the binding of, or interaction between, one or more ligands and target antiligands are provided. Detection involves the release of identifying tags as a consequence of target recognition. The probe sets include electrophoretic tag probes or e-tag probes, comprising a detection region and a mobility-defining region called the mobility modifier, both linked to a target-binding moiety. The probes comprise interactive functionalities adjacent the cleaved portion positioned in the probes such that the interactive functionality does not form part of the e-tag reporters. Target antiligands are contacted with a set of e-tag probes and the contacted antiligands are treated with a selected cleaving agent resulting in a mixture of e-tag reporters and uncleaved and / or partially cleaved e-tag probes. The mixture is exposed to a capture agent effective to bind to uncleaved or partially cleaved e-tag probes, followed by electrophoretic separation. In a multiplexed assay, different released e-tag reporters may be separated and detected providing for target identification.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Kits employing generalized target-binding e-tag probes
Owner:VIROLOGIC INCORPORATED
Sequential analysis of biological samples
ActiveUS9201063B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTarget bindingBiophysics
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Antibody complexes and methods for immunolabeling
InactiveUS20070269902A1Eliminate needTime requiredMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceAntibody fragments
The present invention provides labeling reagents and methods for labeling primary antibodies and for detecting a target in a sample using an immuno-labeled complex that comprises a target-binding antibody and one or more labeling reagents. The labeling reagents comprise monovalent antibody fragments or non-antibody monomeric proteins whereby the labeling reagents have affinity for a specific region of the target-binding antibody and are covalently attached to a label. Typically, the labeling reagent is an anti-Fc Fab or Fab′ fragment that was generated by immunizing a goat or rabbit with the Fc fragment of an antibody. The present invention provides for discrete subsets of labeling reagent and immuno-labeled complexes that facilitate the simultaneous detection of multiple targets in a sample wherein the immuno-labeled complexes are distinguished by i) a ratio of label to labeling reagent, or ii) a physical property of said label, or iii) a ratio of labeling reagent to said target-binding antibody, or iv) by said target-binding antibody. This is particularly useful for fluorophore labels that can be attached to labeling reagents and subsequently immuno-labeled complexes in ratios for the detection of multiple targets.
Owner:MOLECULAR PROBES
Probe composition and method
InactiveUS20050112608A1Electrolysis componentsComponent separationChromatographic separationNucleotide
Method and composition for detecting one or more selected polynucleotide regions in a target polynucleotide. In one embodiment of the invention, a plurality of different-sequence probe pairs are added to a target polynucleotide, where each probe pair includes two polynucleotide probe elements which are complementary in sequence to adjacent portions of a selected one of the target sequences in the target polynucleotide. In each probe pair, one of the probe elements contains a non-polynucleotide polymer chain which imparts a distinctive mobility to the associated probe pair, when the elements in the pair are ligated. The other element in the pair contains a detectable reporter label. After the probe pairs have been allowed to hybridize with the target polynucleotide, the hybridized polynucleotides are treated under conditions effective to ligate the end subunits of target-bound probe elements when their end subunits are base-paired with adjacent target bases. The ligated probe pairs are then released from the target polynucleotide and separated electrophoretically in a sieving matrix, or chromatographically.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Tunable genetic switch for regulating gene expression
ActiveUS20100175141A1Eliminating background expressionInhibit expressionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseBinding site
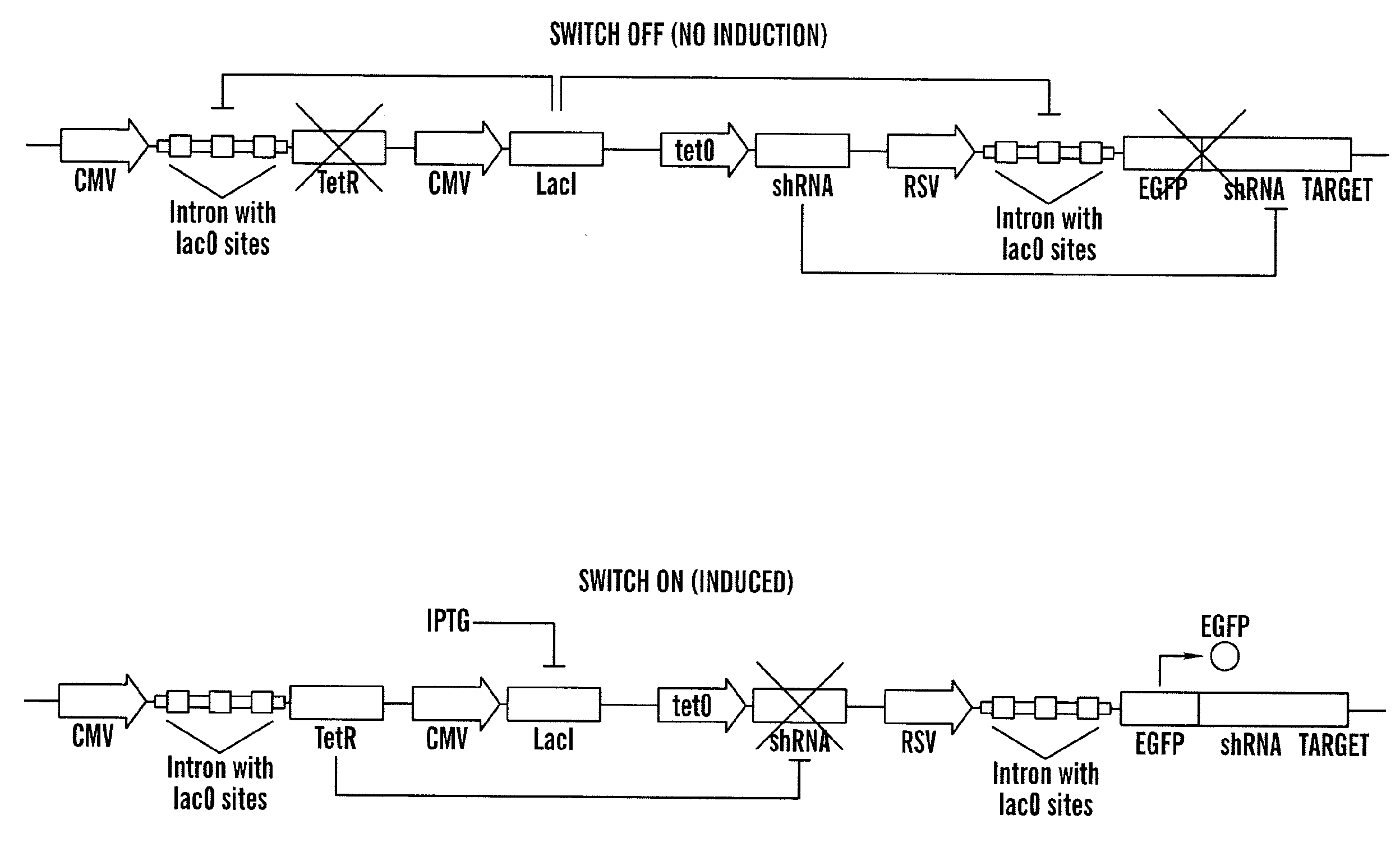
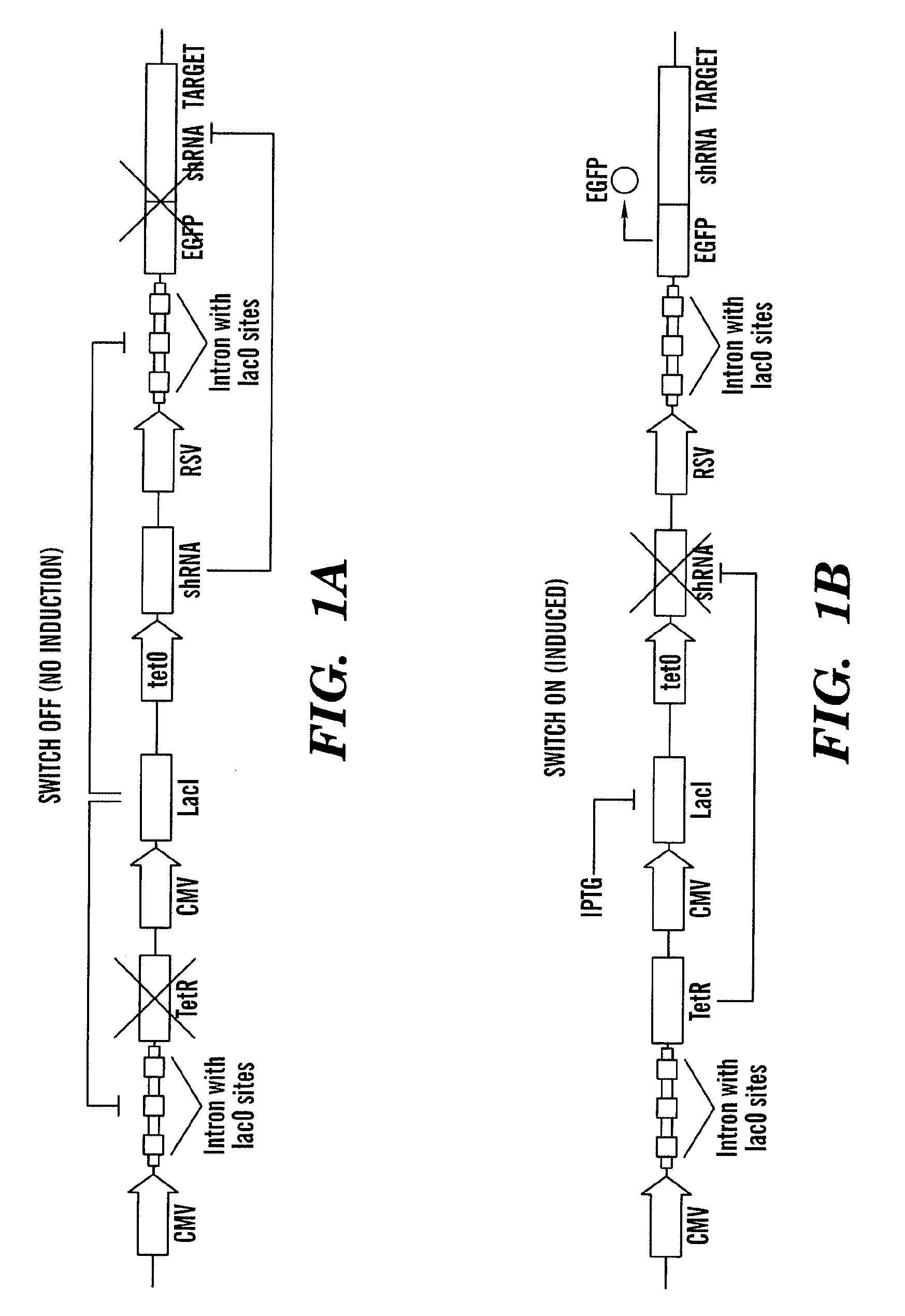
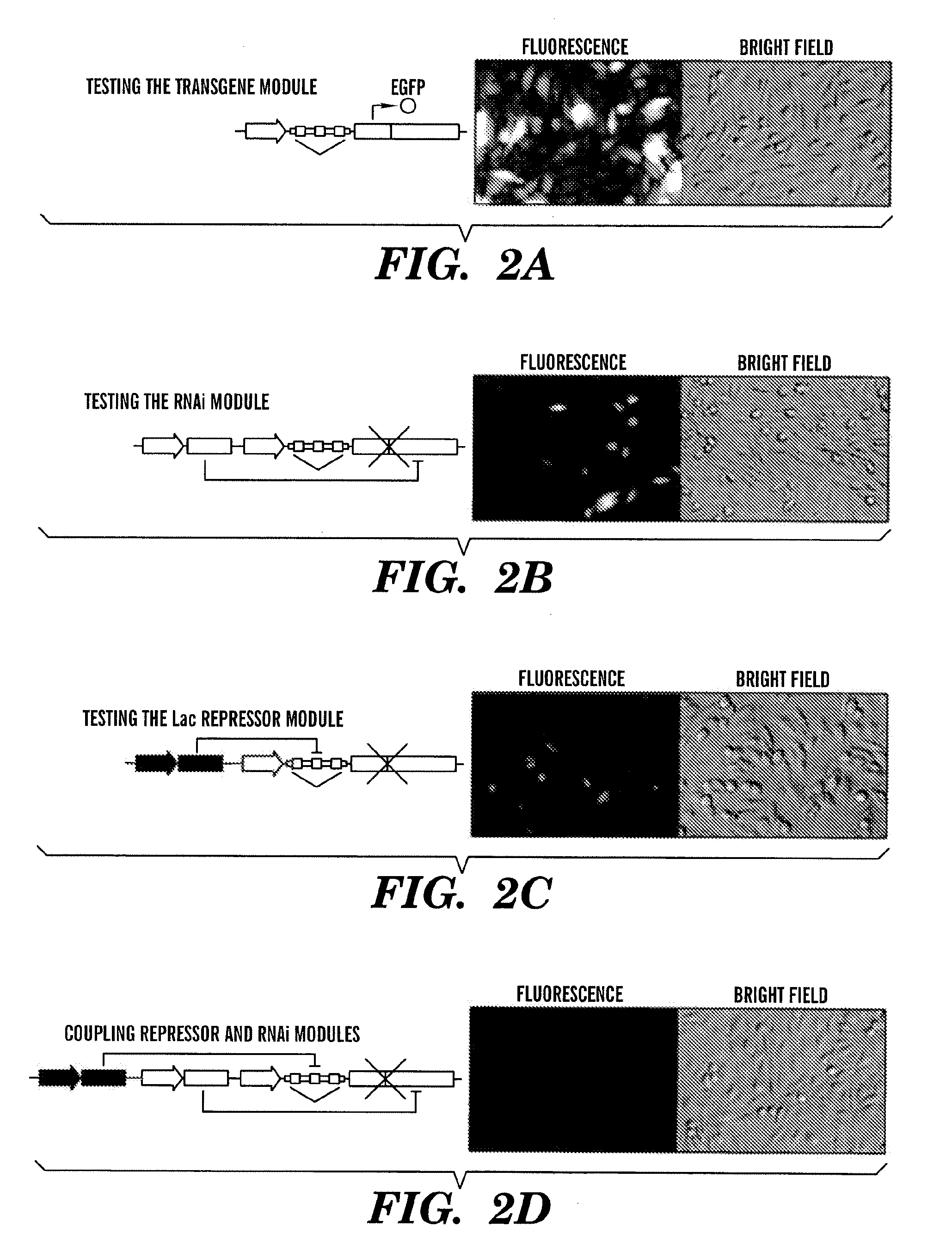
The present invention relates generally the field of genetics, in particular methods, compositions and systems for controlling the inducible expression of transgenes, while eliminating background expression of transgene expression. The present invention relates to methods of use of the compositions and systems as disclosed herein for controlling the inducible expression of transgenes while eliminating background expression of transgene expression, such as use in, for example, the in generation of transgenic animals, use in therapeutic application and use in assays. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to a system of controlled expression of RNAi molecules which target binding sites in the untranslated regions of transgene, thereby the expression of the transgene is modulated and leakiness is reduced. The compositions and methods of the present invention can be used to for therapy, prophylaxis, research and diagnostics in diseases and disorders which afflict mammalian species, generation of transgenic animals, in the study of biological processes as well as for enhance performance of agricultural crops.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Chimeric antigens for breaking host tolerance to foreign antigens
ActiveUS20050031628A1Enhance immune responseAvoid infectionAntibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses positive-senseHost immunityAntibody fragments
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods for eliciting immune responses against antigens. In particular, the compounds and methods elicit immune responses against foreign antigens that are otherwise recognized by the host as "self" antigens, thus breaking host tolerance to those antigens. Presenting the host immune system with a chimeric antigen comprising an immune response domain and a target binding domain, wherein the target binding domain comprises an antibody fragment, enhances the immune response against the foreign or tolerated antigen. Antigen presenting cells take up, process, and present the chimeric antigen, eliciting both a humoral and cellular immune response against the desired antigen.
Owner:KAIMI BIOMEDICINE (CHENGDU) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com