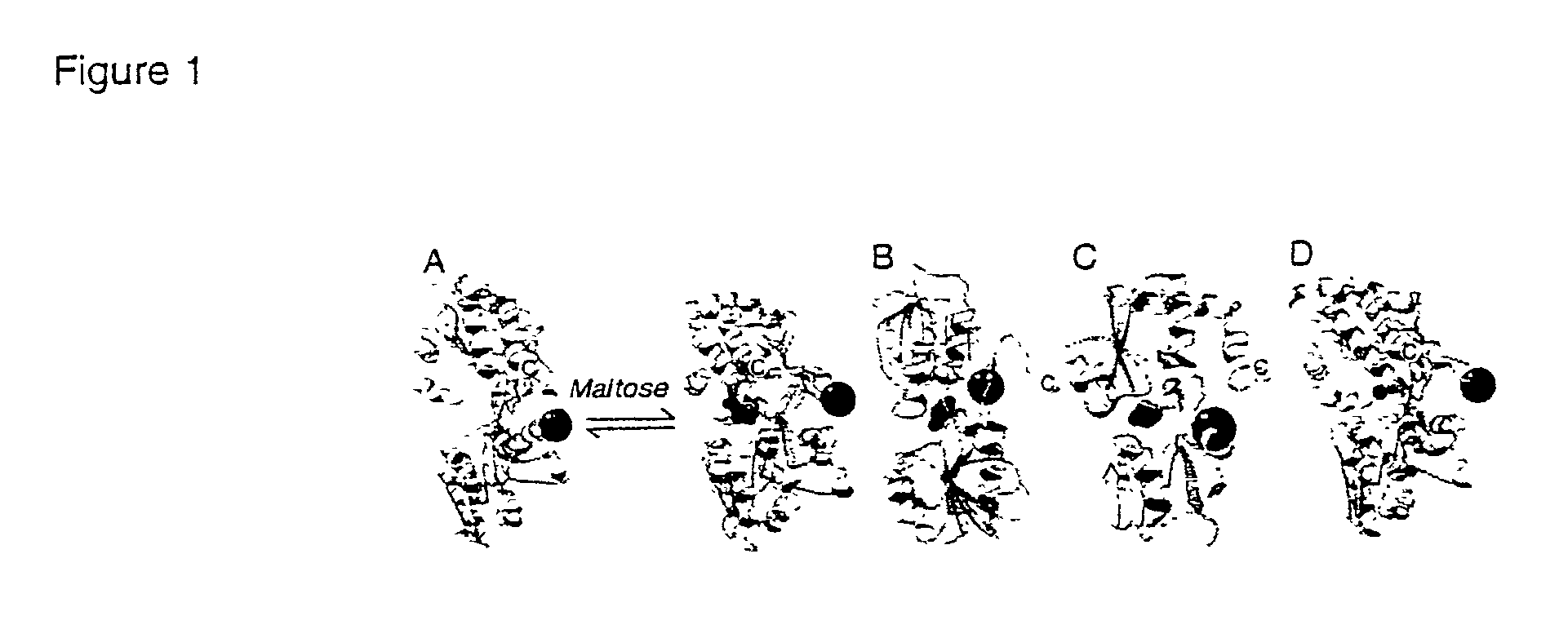Patents
Literature
214 results about "Conformational change" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
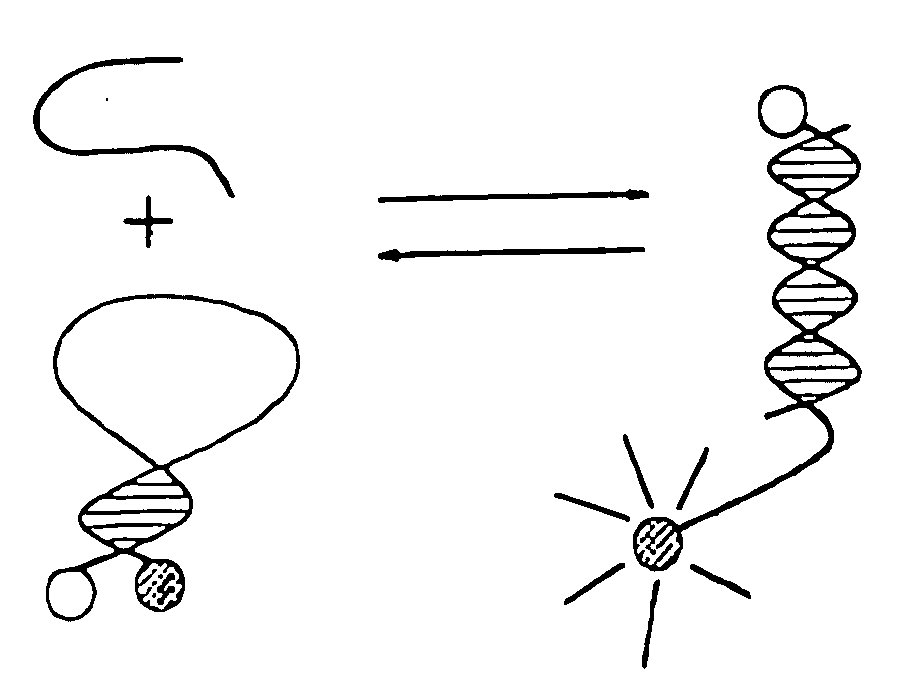
In biochemistry, a conformational change is a change in the shape of a macromolecule, often induced by environmental factors. A macromolecule is usually flexible and dynamic. It can change its shape in response to changes in its environment or other factors; each possible shape is called a conformation, and a transition between them is called a conformational change. Factors that may induce such changes include temperature, pH, voltage, light in chromophores, ion concentration, phosphorylation, or the binding of a ligand.Transitions between these states occur on a variety of length scales (tenths of Å to nm) and time scales (ns to s), and have been linked to functionally relevant phenomena such as allosteric signaling and enzyme catalysis.
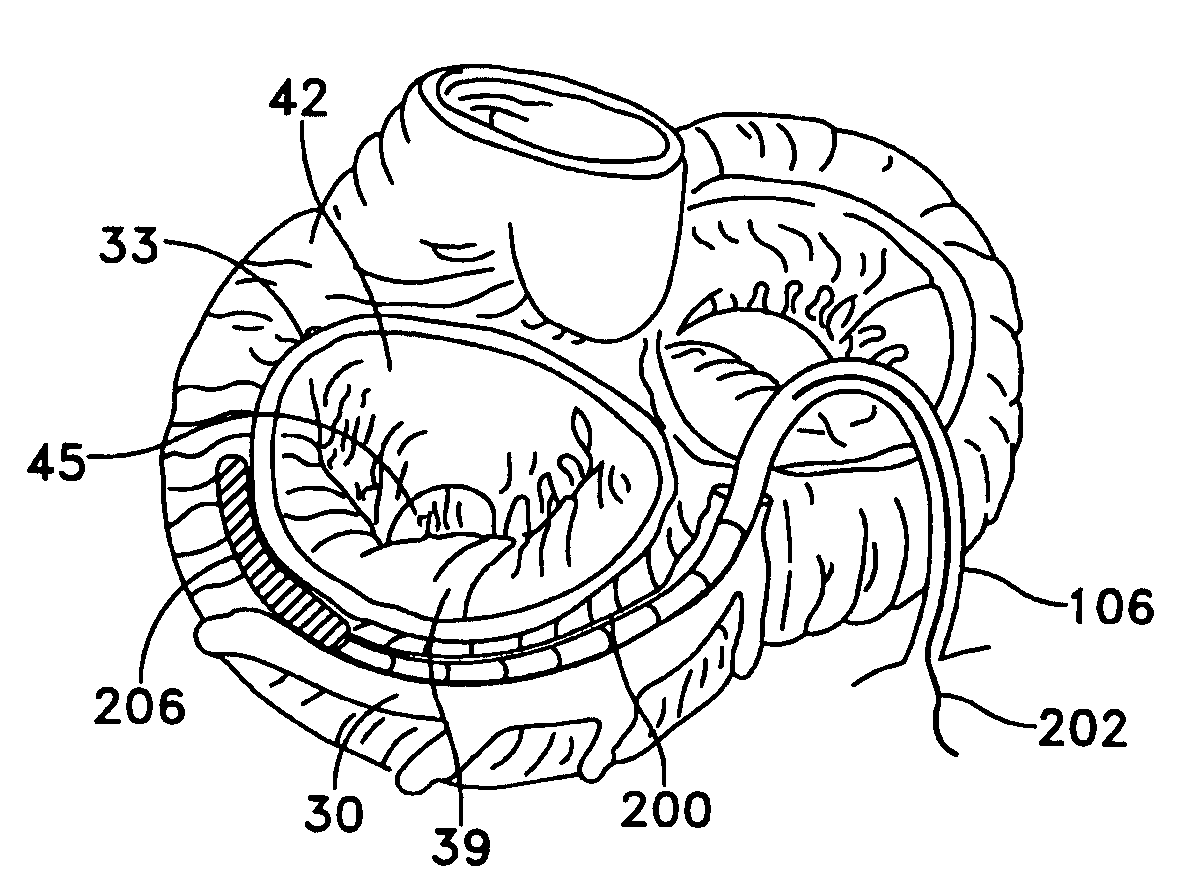
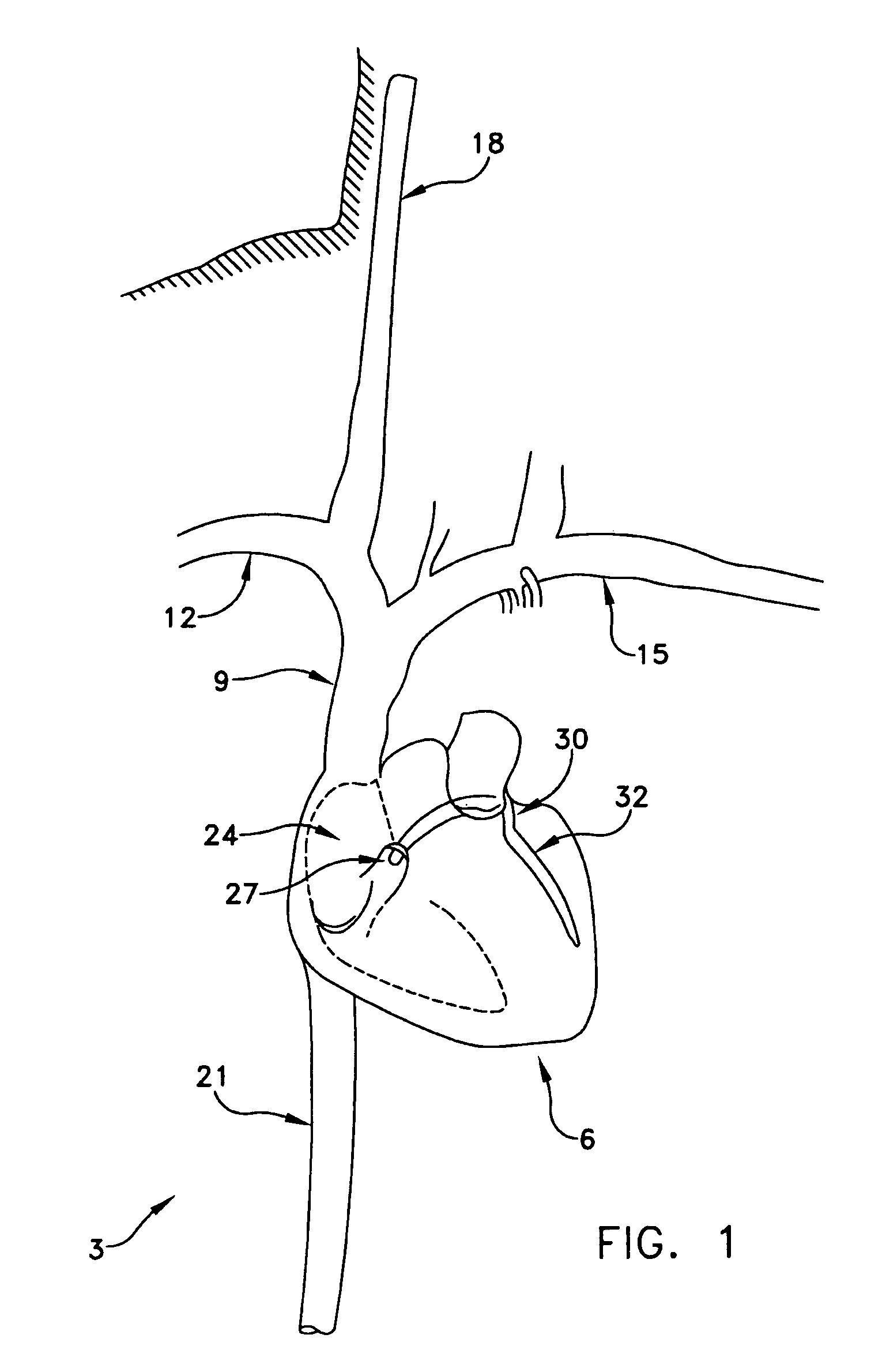
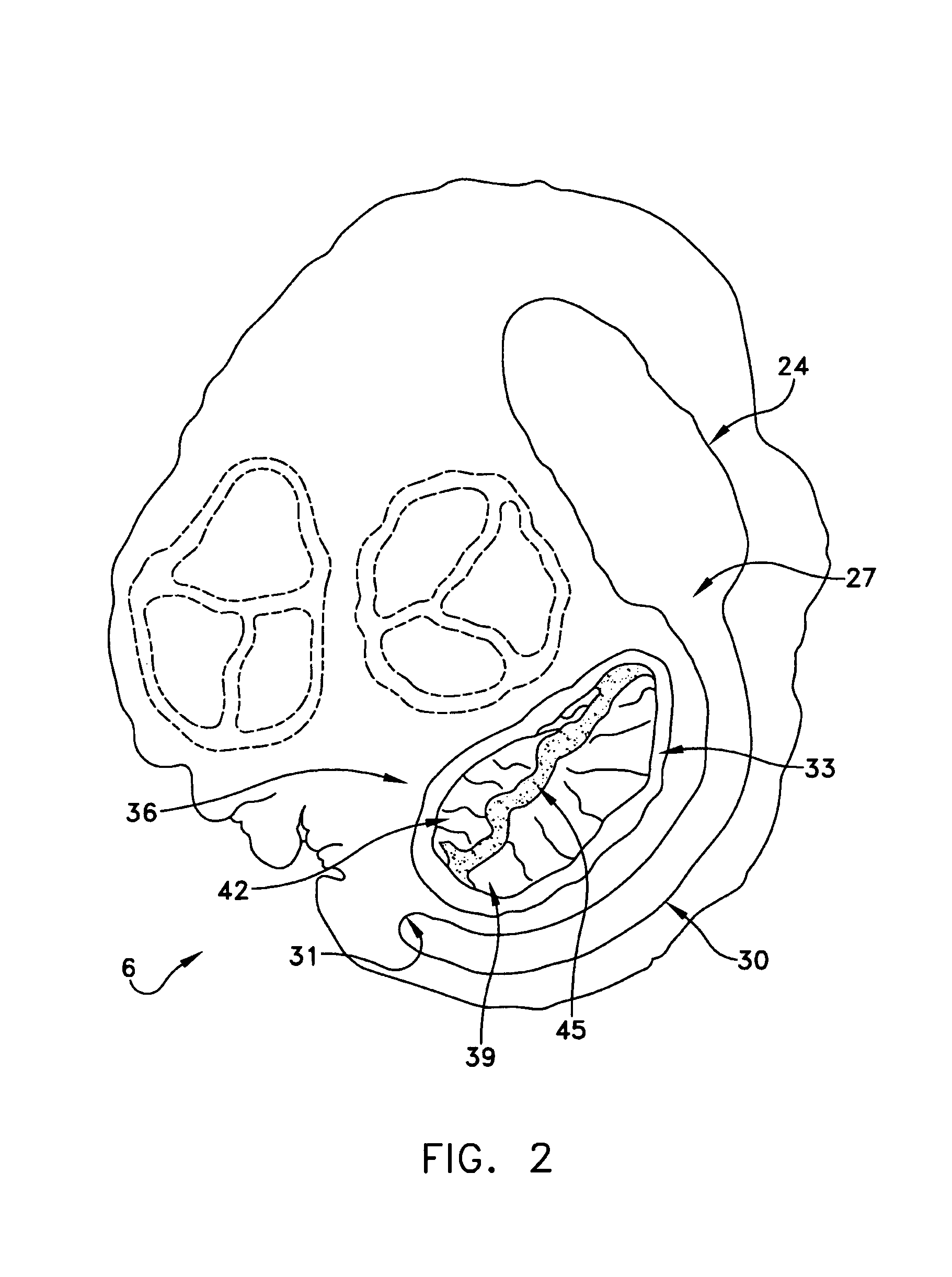
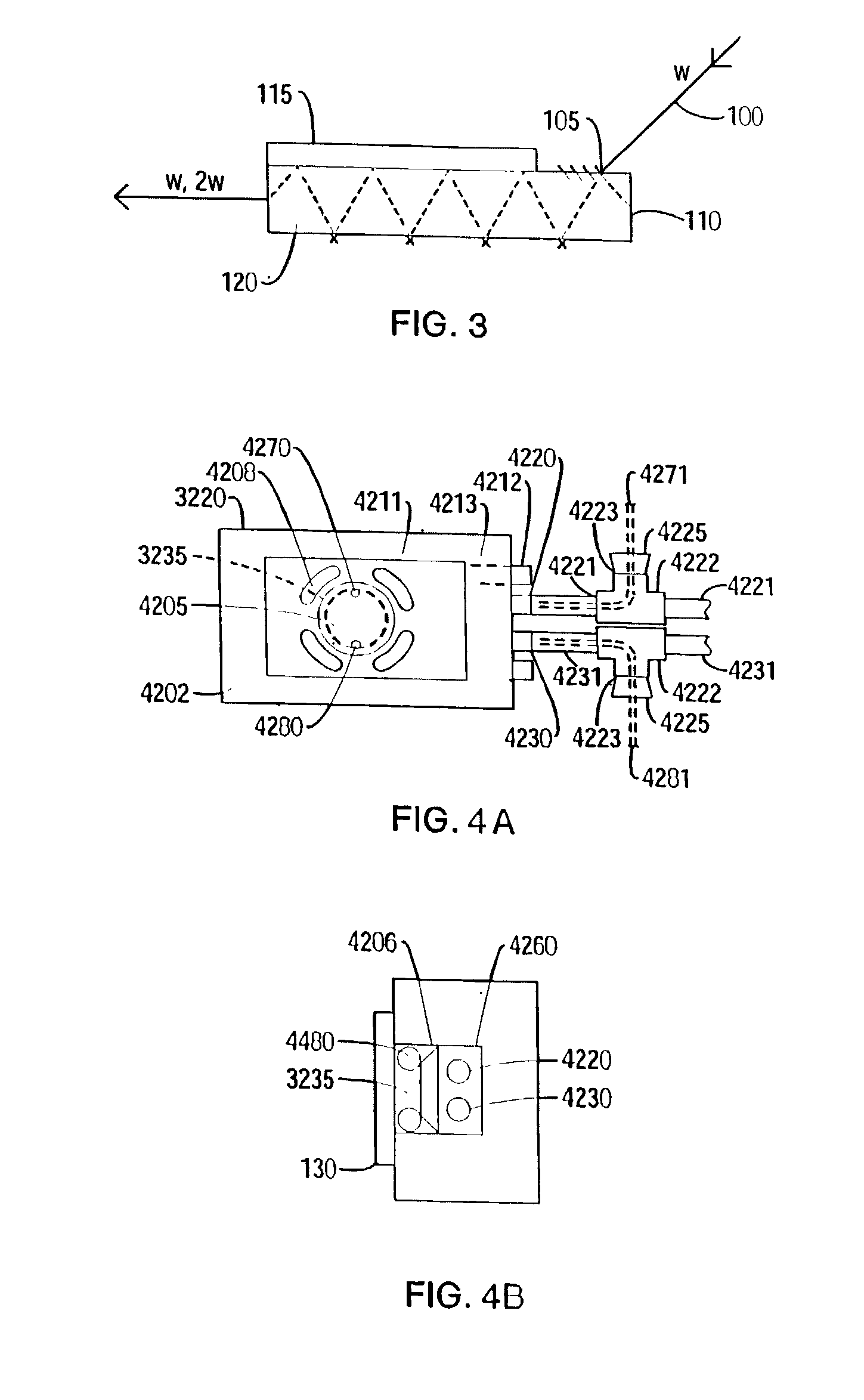
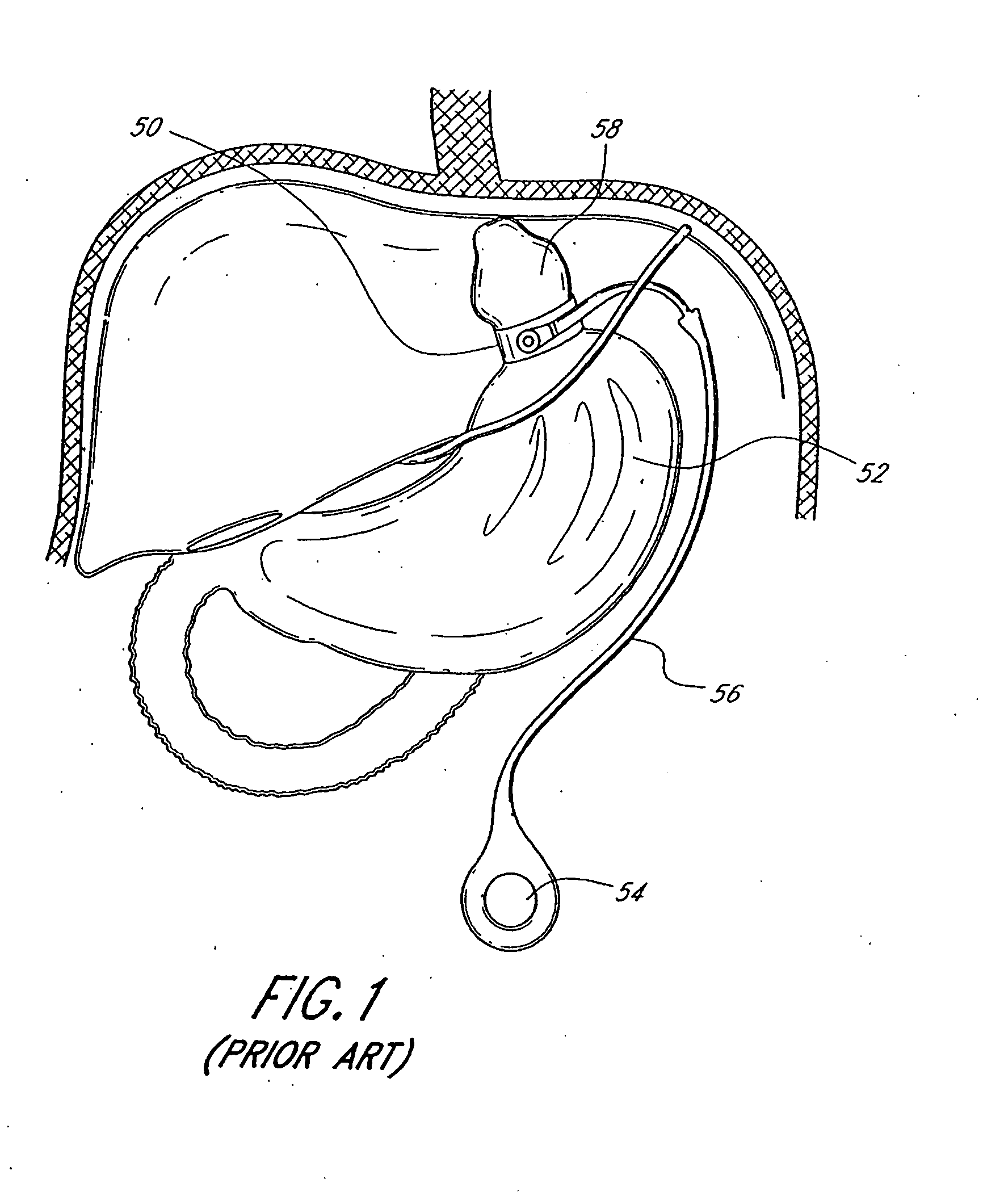
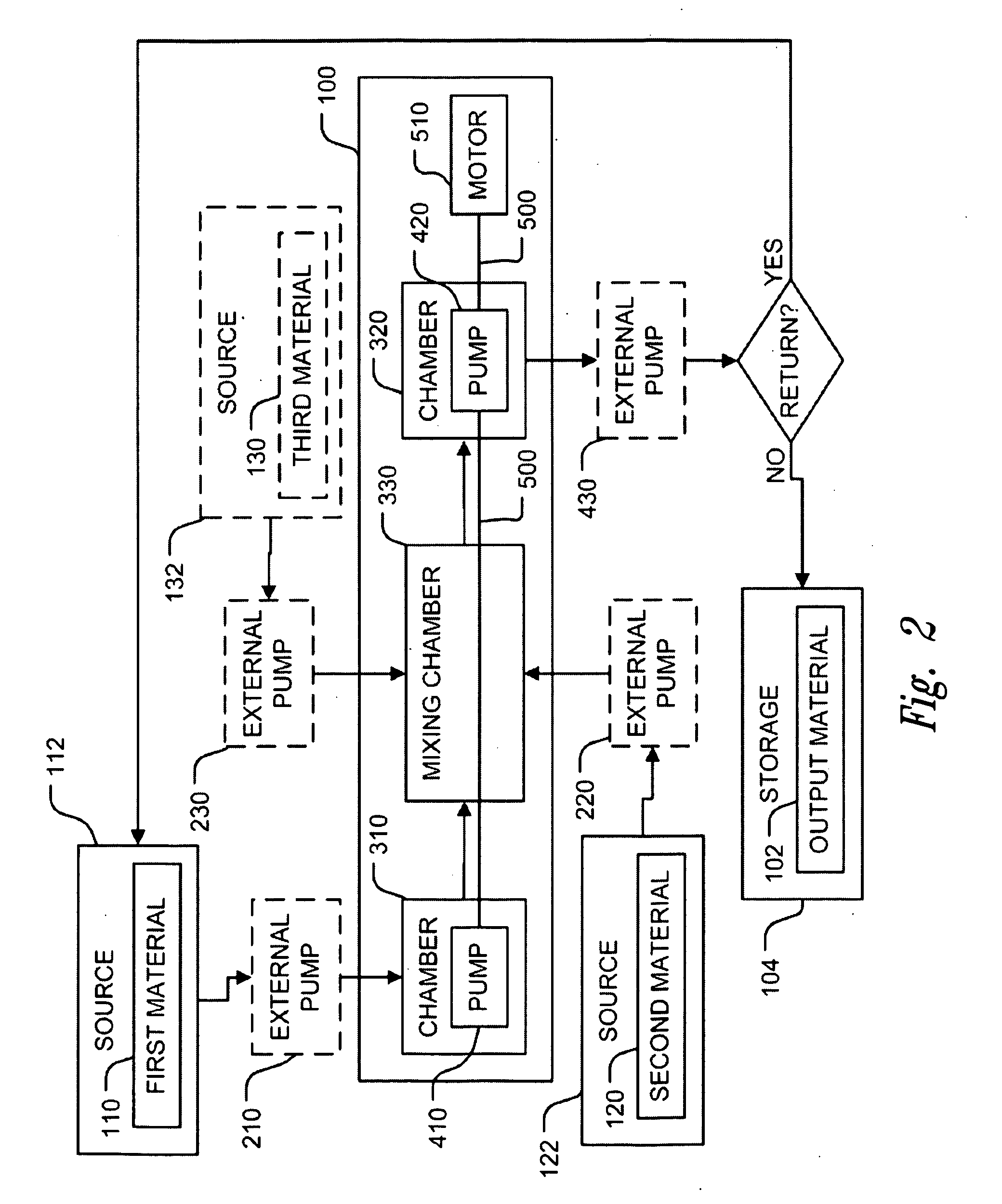
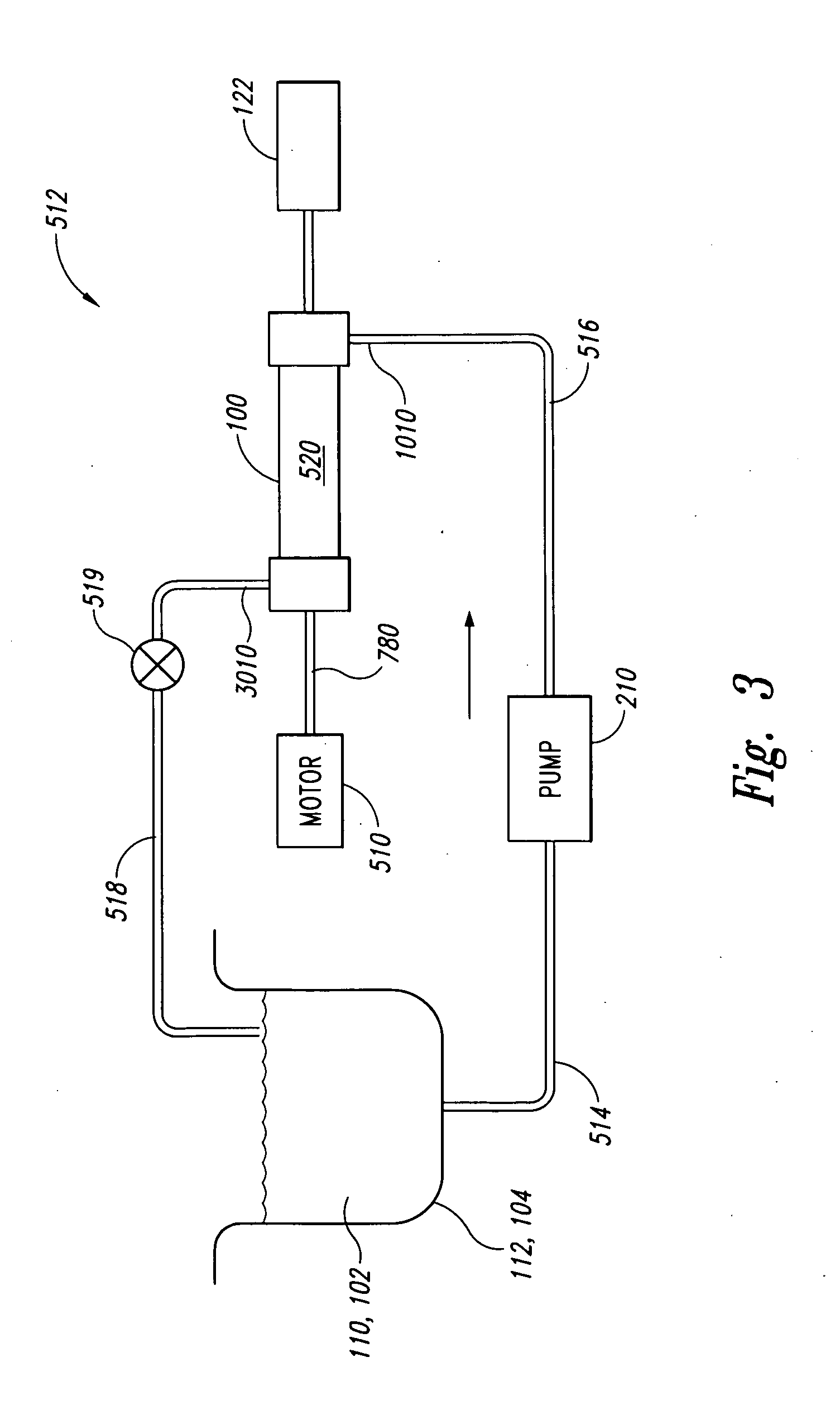
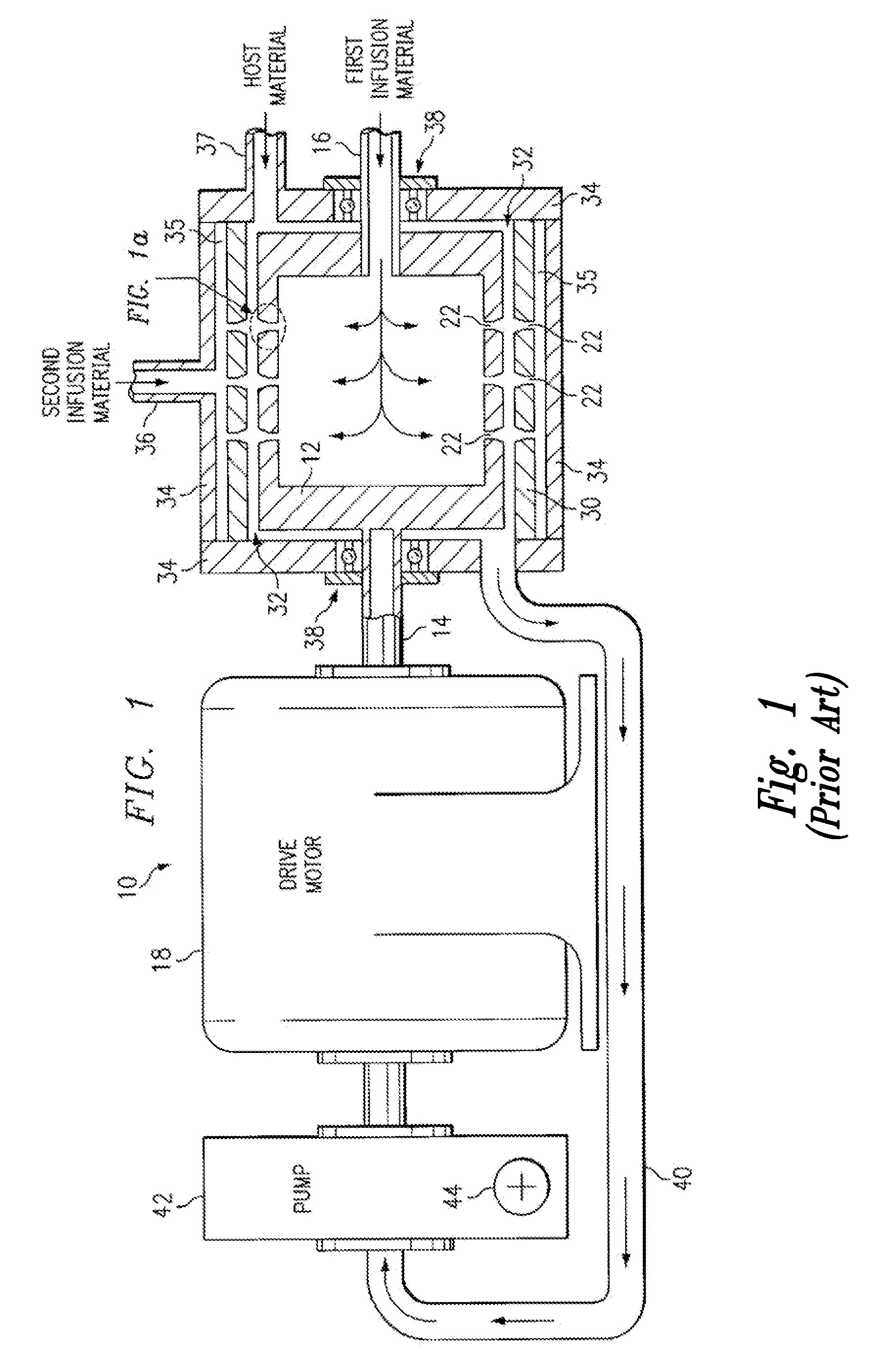
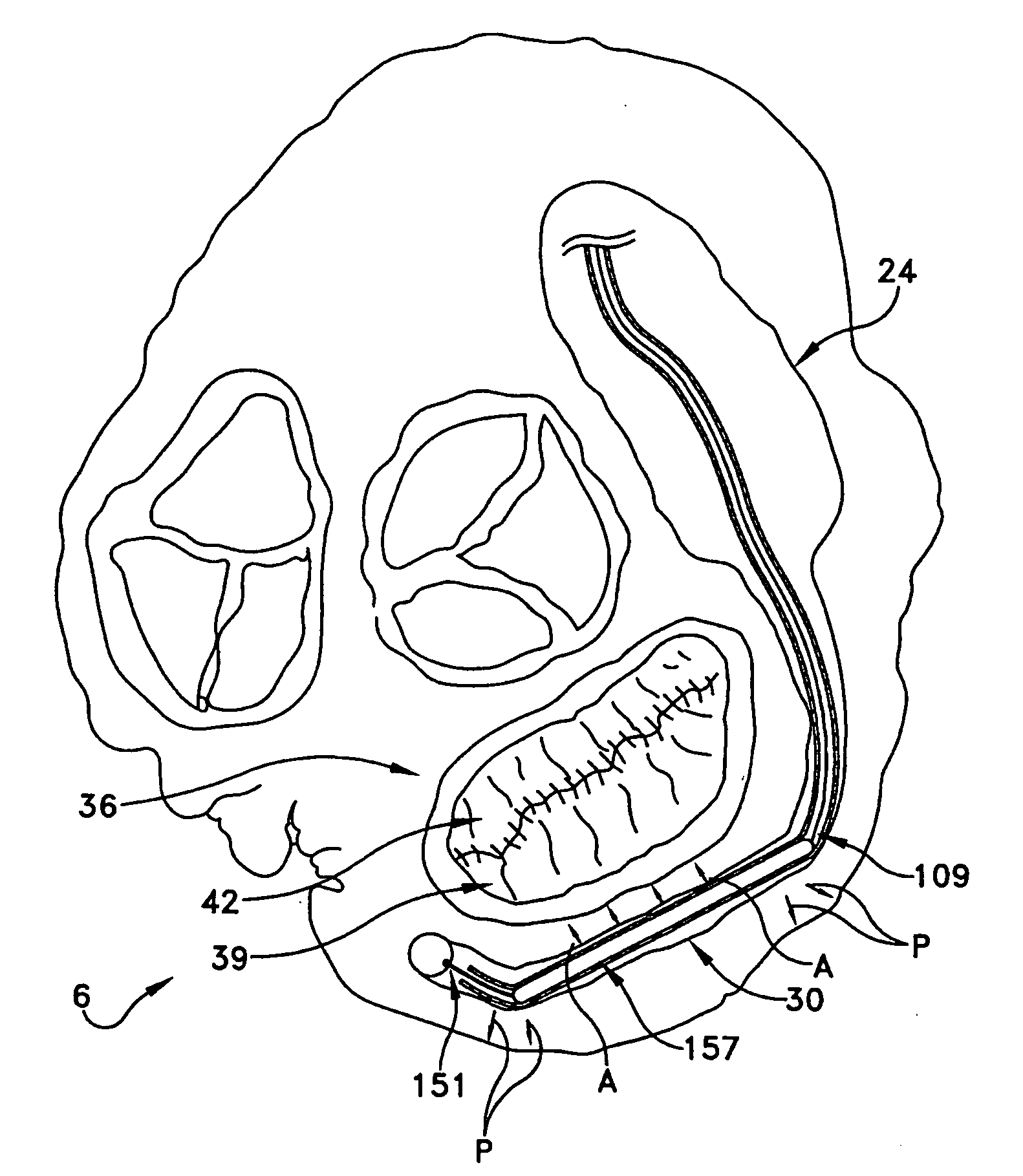
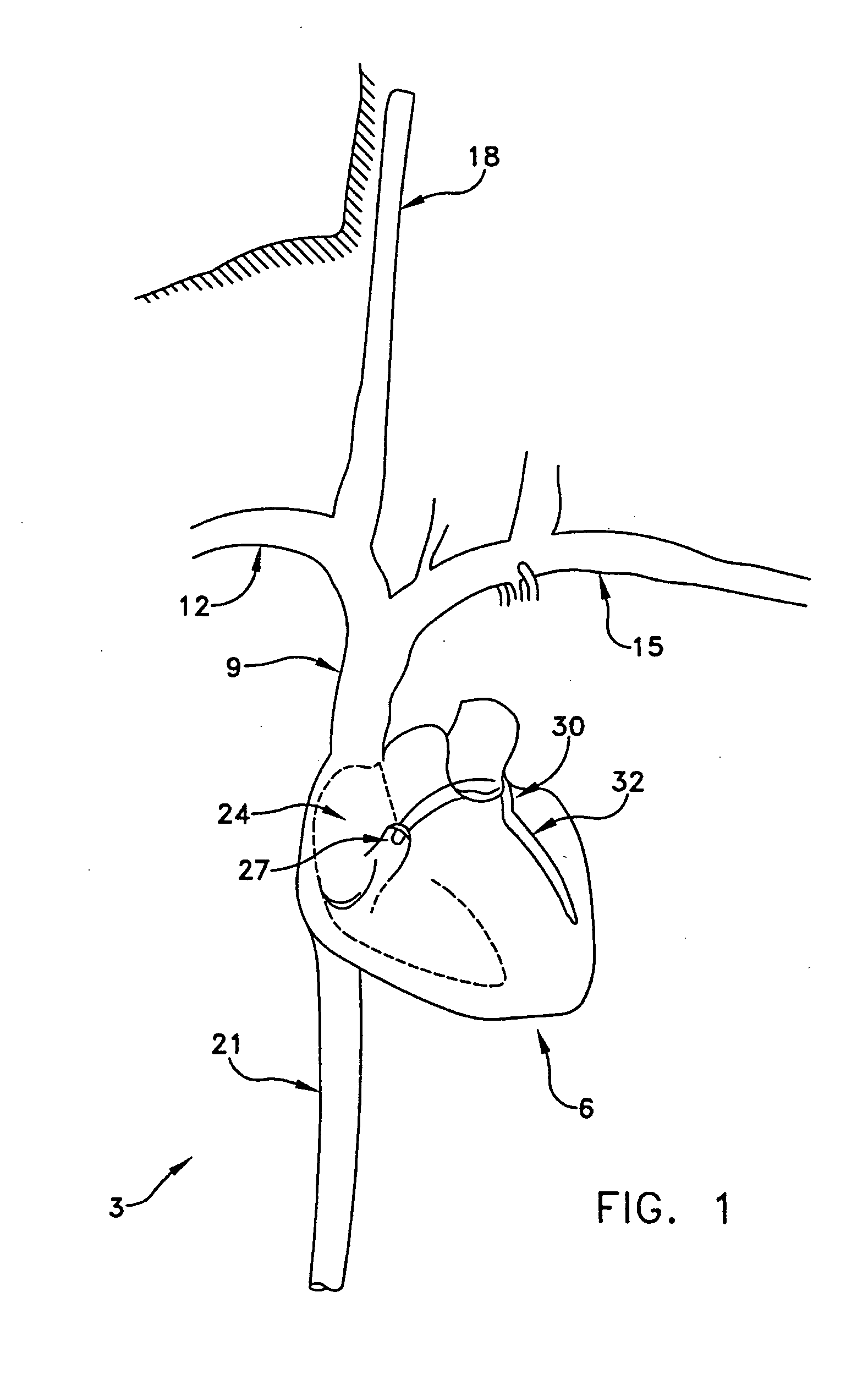
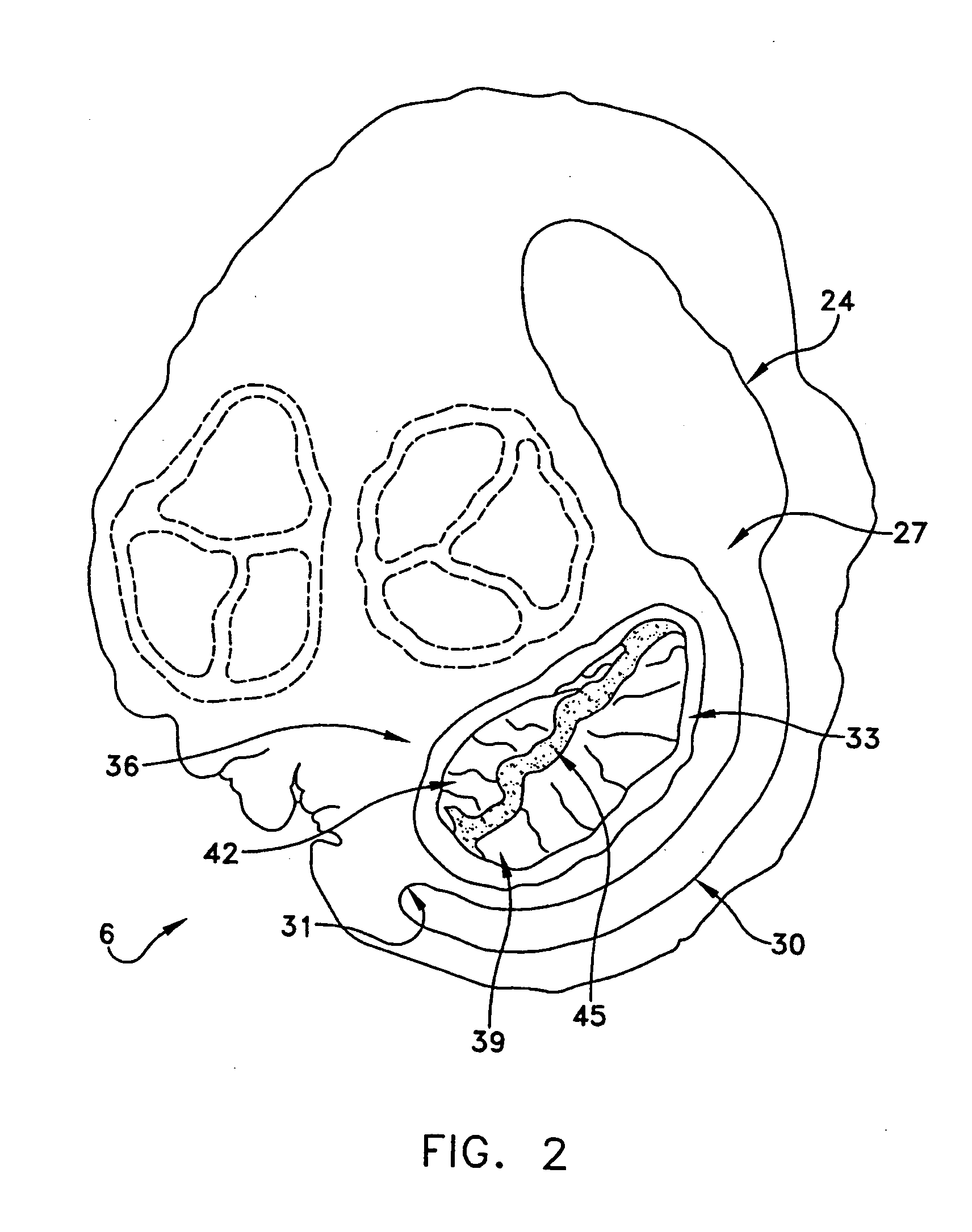
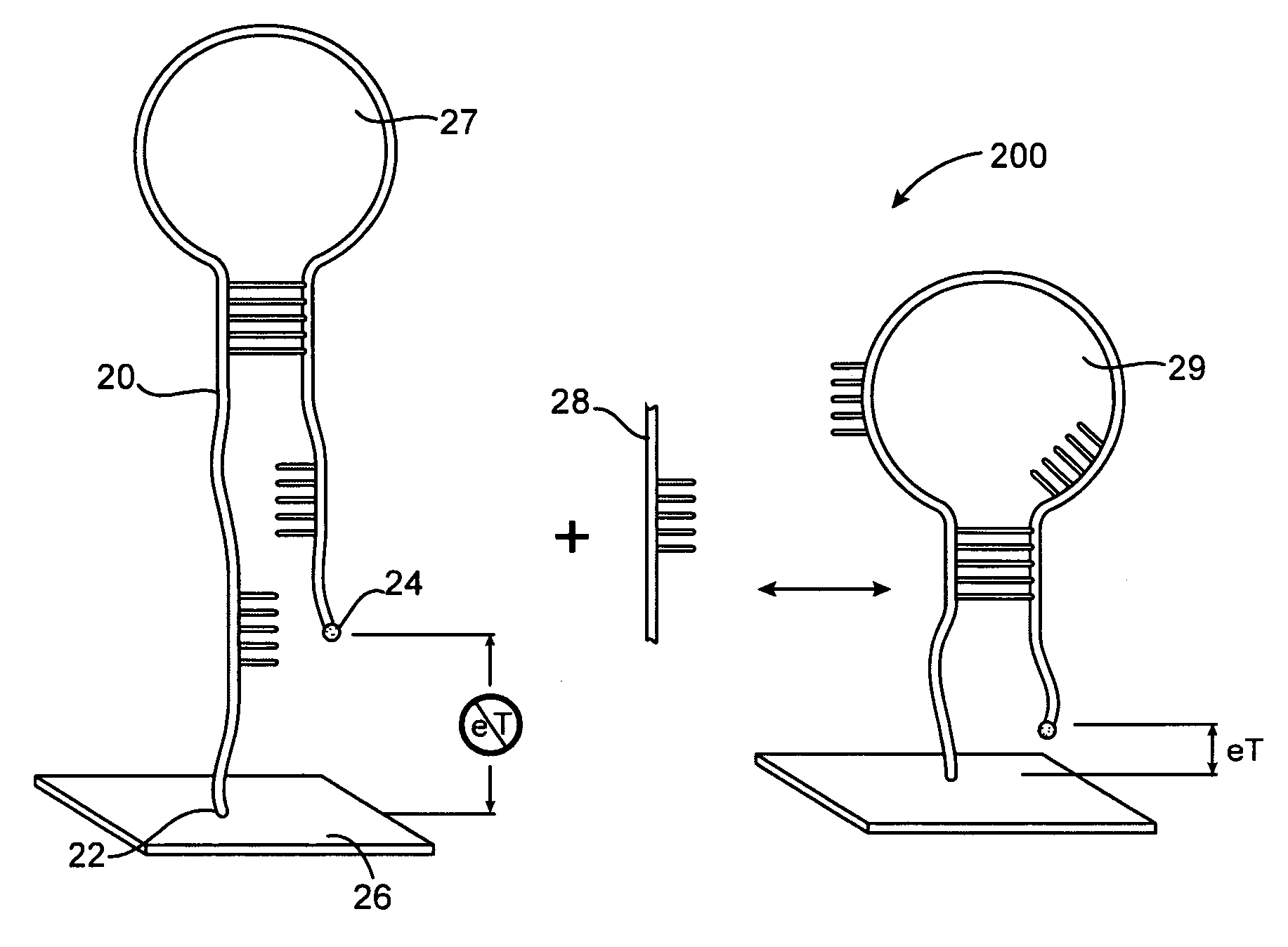
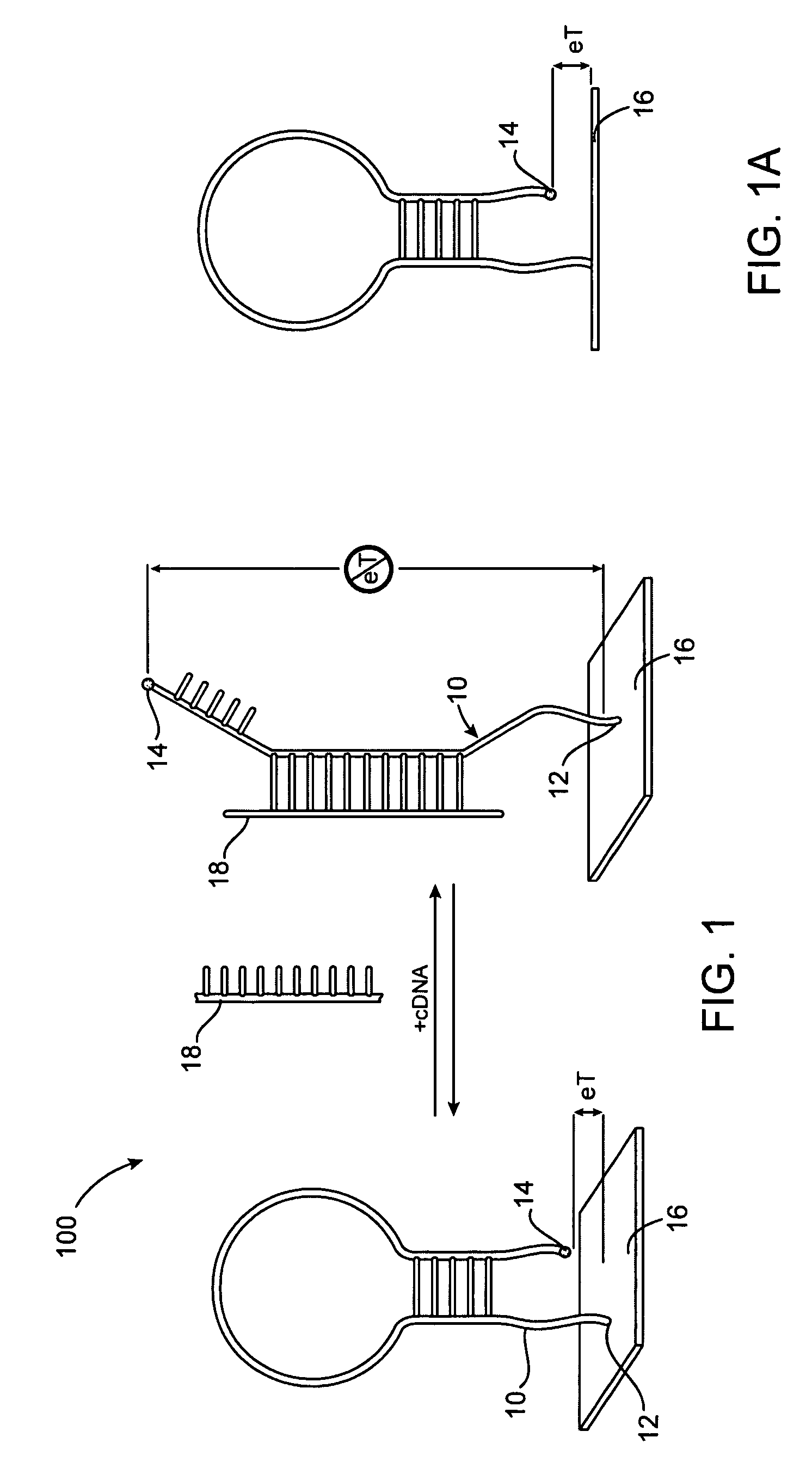
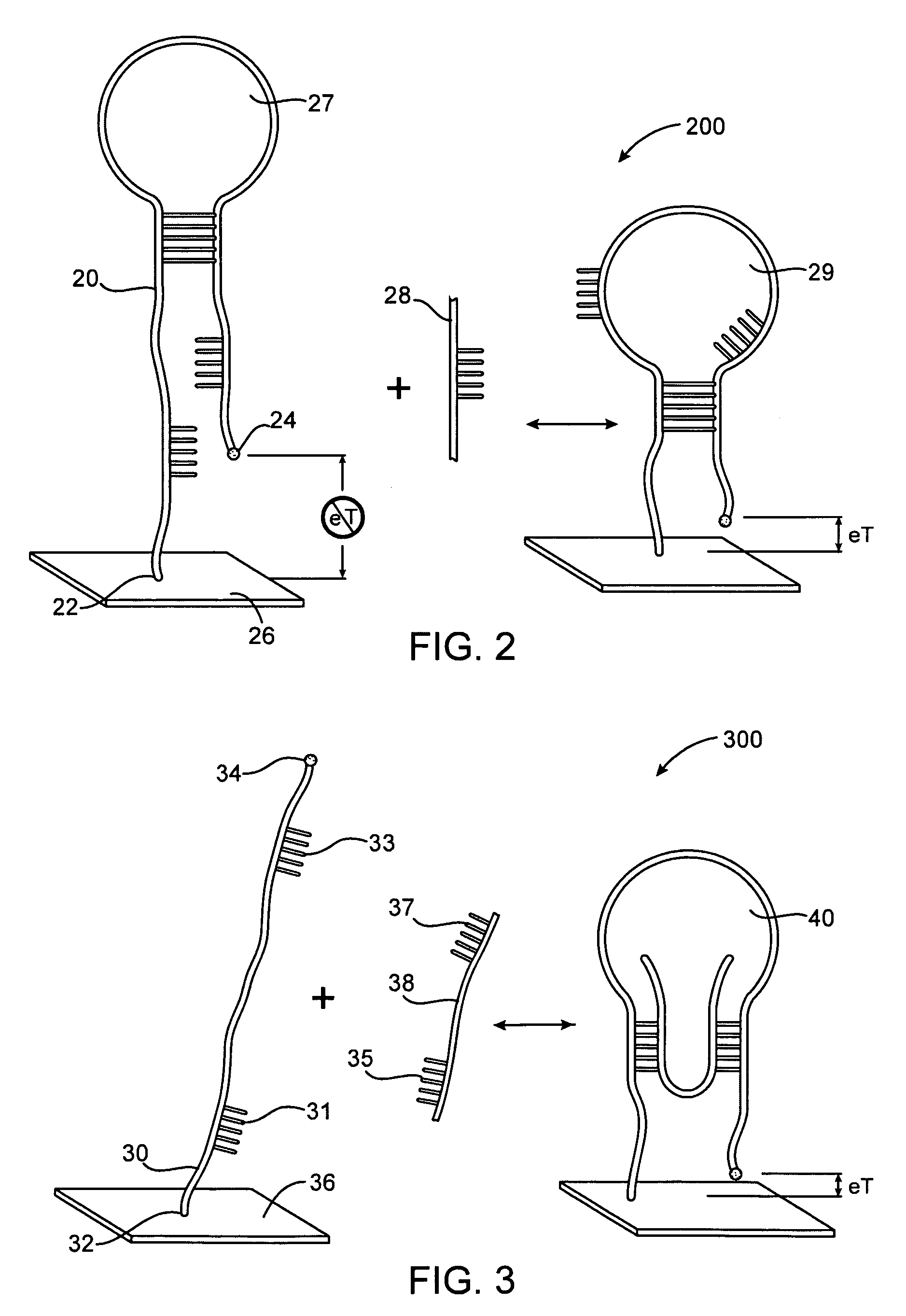
Method and apparatus for reducing mitral regurgitation
InactiveUS7052487B2Reducing mitral regurgitationReduce regurgitationHeart valvesSurgical needlesPosterior leafletMitral valve leaflet
A method for reducing mitral regurgitation includes deploying deforming matter into a selected one of (i) a mitral valve annulus adjacent a posterior leaflet, and (ii) tissue adjacent the mitral valve annulus and proximate the posterior leaflet, to cause conformational change in the mitral valve annulus to increase mitral valve leaflet coaptation.
Owner:ANCORA HEART INC
Nucleic acid-coupled colorimetric analyte detectors
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the direct detection of analytes and membrane conformational changes through the detection of color changes in biopolymeric materials. In particular, the present invention provide for the direct colorimetric detection of analytes using nucleic acid ligands at surfaces of polydiacetylene liposomes and related molecular layer systems.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method using a nonlinear optical technique for detection of interactions involving a conformational change
InactiveUS20030148391A1No need for labor and time-consuming washing stepLow backgroundCompound screeningMaterial nanotechnologyFrequency generationThird harmonic
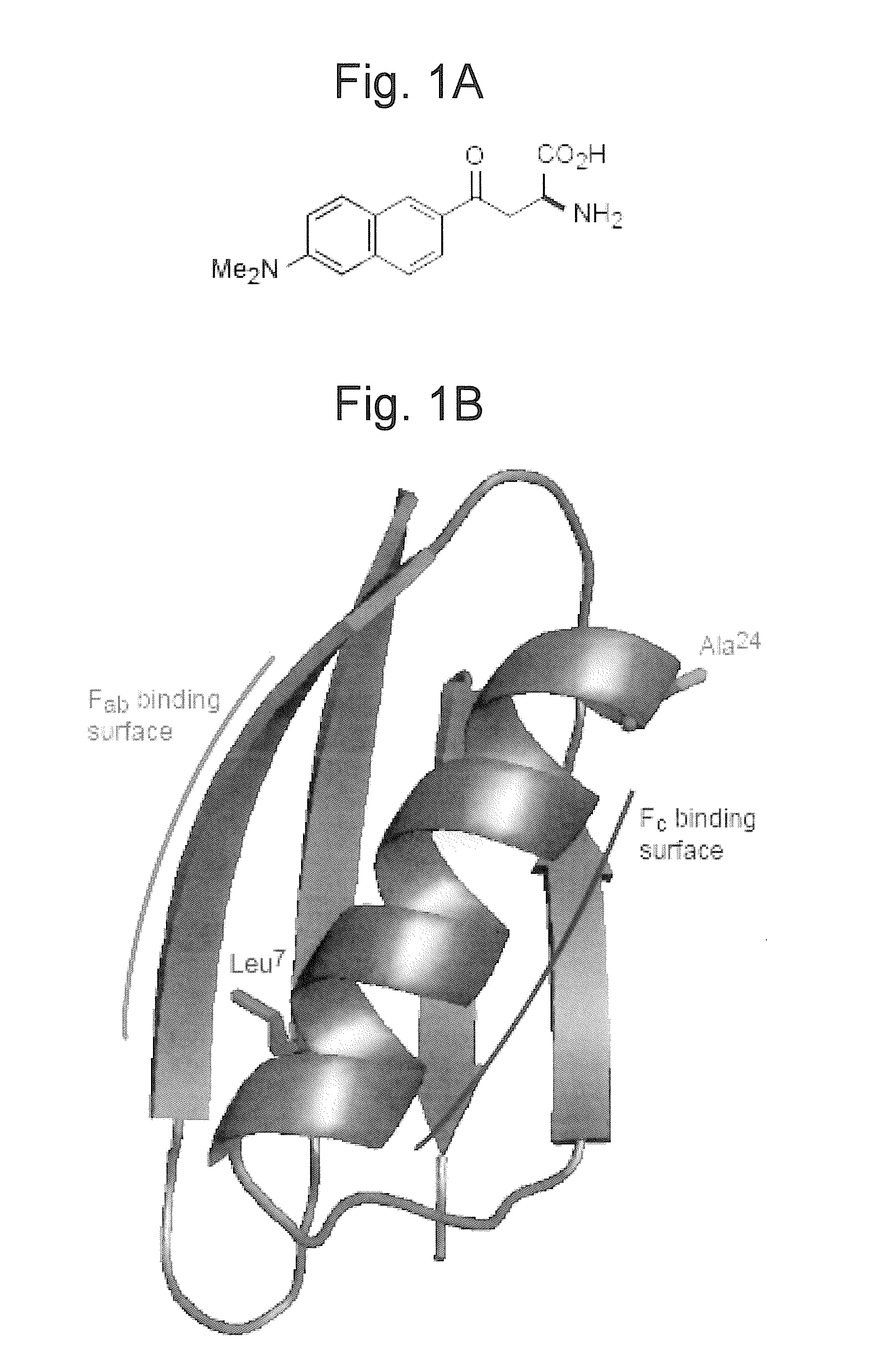
A nonlinear optical technique, such as second or third harmonic or sum or difference frequency generation, is used to detect binding interactions, or the degree or extent of binding, that comprise a conformational change. In one aspect of the present invention, the nonlinear optical technique detects a conformational change in a probe due to target binding. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate probes by detecting a conformational change due to a probe-target interaction. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate modulators of a probe-target interaction by detecting a conformational change in the presence of the modulator.
Owner:BIODESY
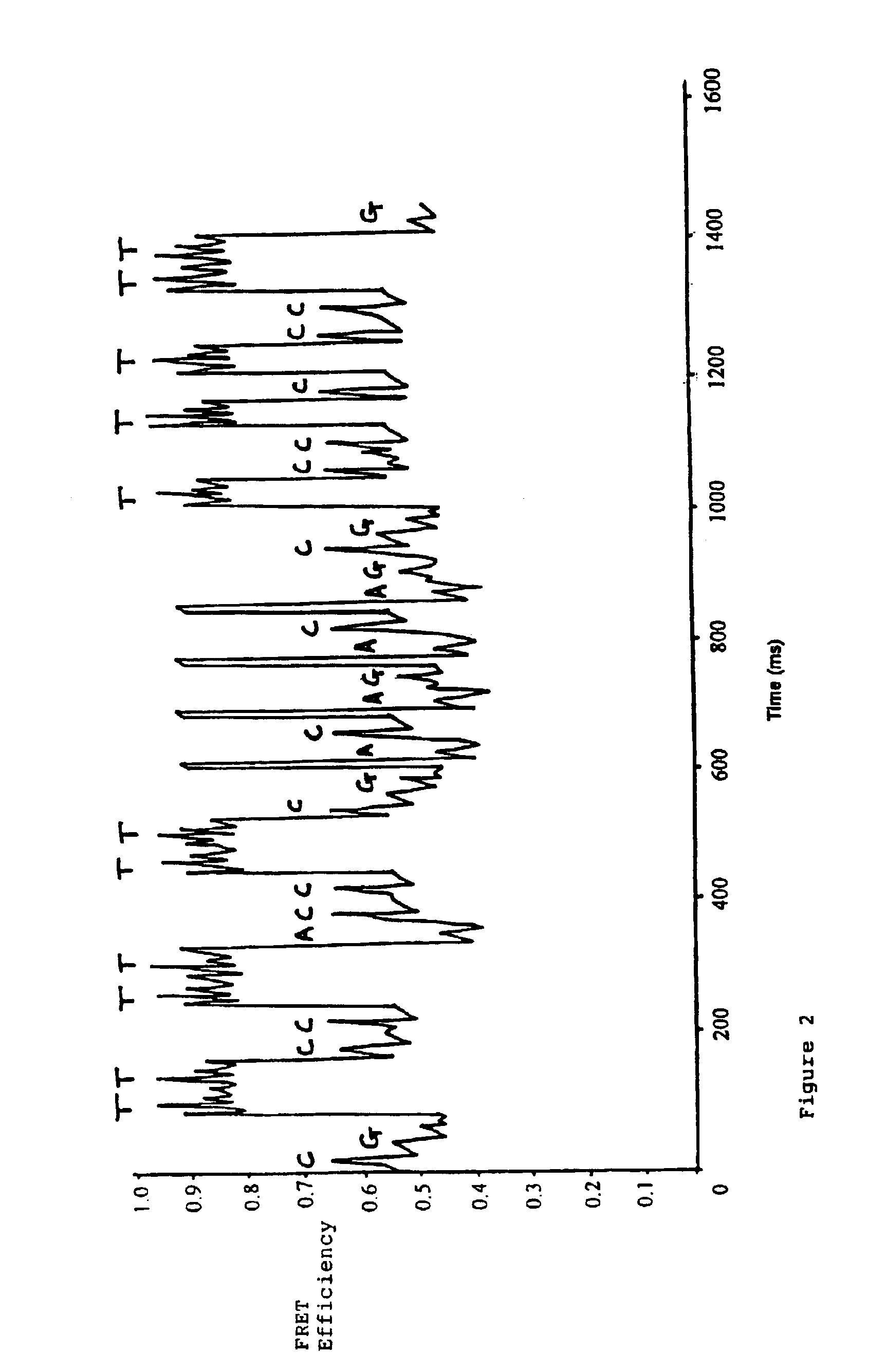
DNA sequencing method
InactiveUS6908736B1Reduce the amount requiredReduce the numberSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideFluorescence
The present invention pertains to a method for determining the sequence of a polynucleotide, the method relying on the detection of a conformational change in an enzyme that interacts with and processes along the polynucleotide. The detection of a conformational change may be carried out by measuring changes in a fluorophore bound to the enzyme.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Method using a nonlinear optical technique for detection of interactions involving a conformational change
InactiveUS20060228725A1No need for labor and time-consuming washing stepLow backgroundCompound screeningMaterial nanotechnologyThird harmonicFrequency generation
A nonlinear optical technique, such as second or third harmonic or sum or difference frequency generation, is used to detect binding interactions, or the degree or extent of binding, that comprise a conformational change. In one aspect of the present invention, the nonlinear optical technique detects a conformational change in a probe due to target binding. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate probes by detecting a conformational change due to a probe-target interaction. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate modulators of a probe-target interaction by detecting a conformational change in the presence of the modulator.
Owner:BIODESY
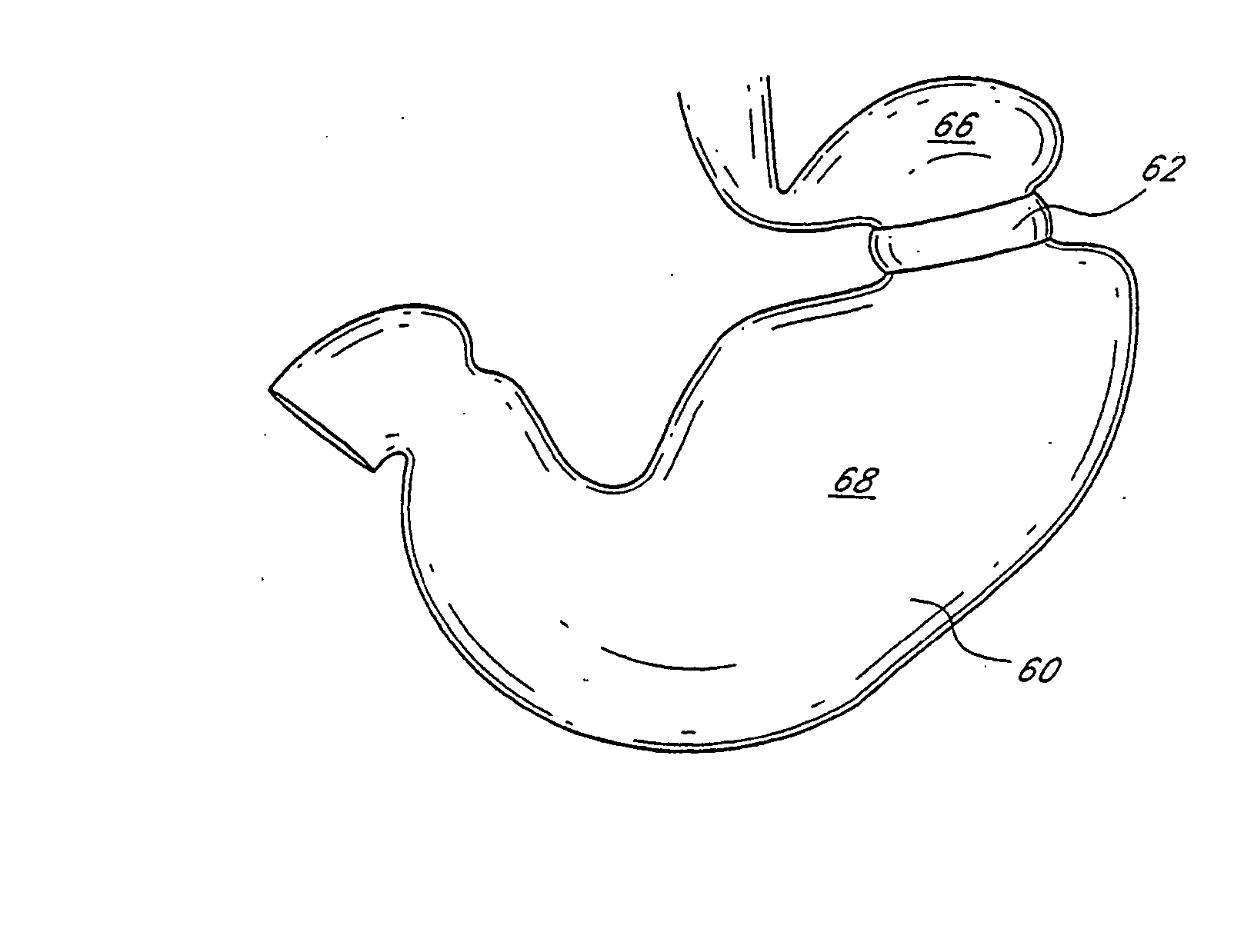
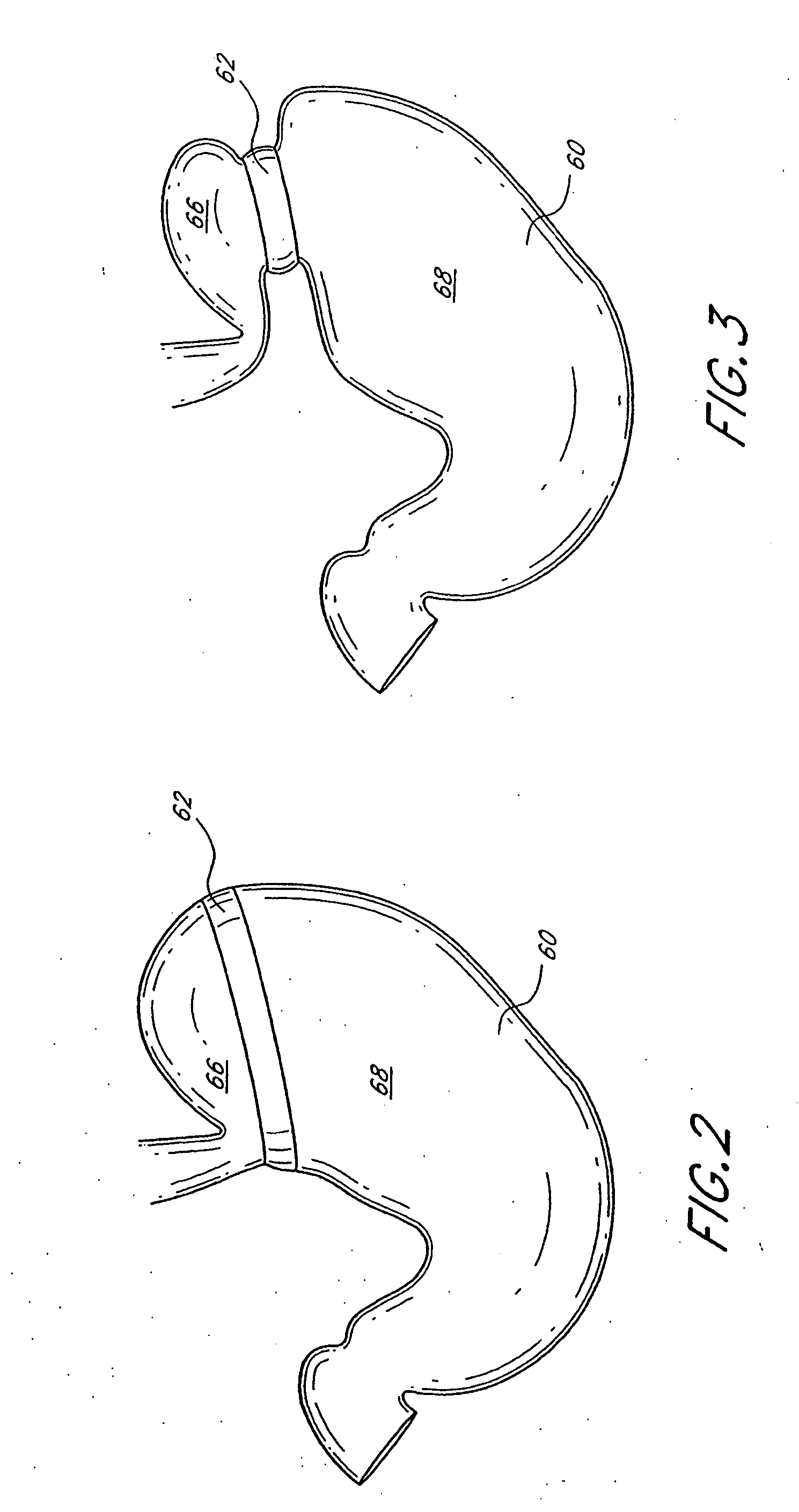
Dynamically adjustable gastric implants
InactiveUS20070265646A1Small sizeIncrease in sizeObesity treatmentWound clampsDevice implantGastric restriction
Gastric restriction device implants and their use in controlling body weight are described. In some embodiments, activation of a shape memory material drives an actuator coupled to an implant, resulting in a conformational change in the implant. In some embodiments latch and ratchet mechanisms operate incrementally to increase or decrease a size of a stomal opening produced by the gastric restriction device. Methods are described by which adjusting the size of the stomal opening is used to restrict the rate at which food passes through the stomach.
Owner:ELLIPSE TECH
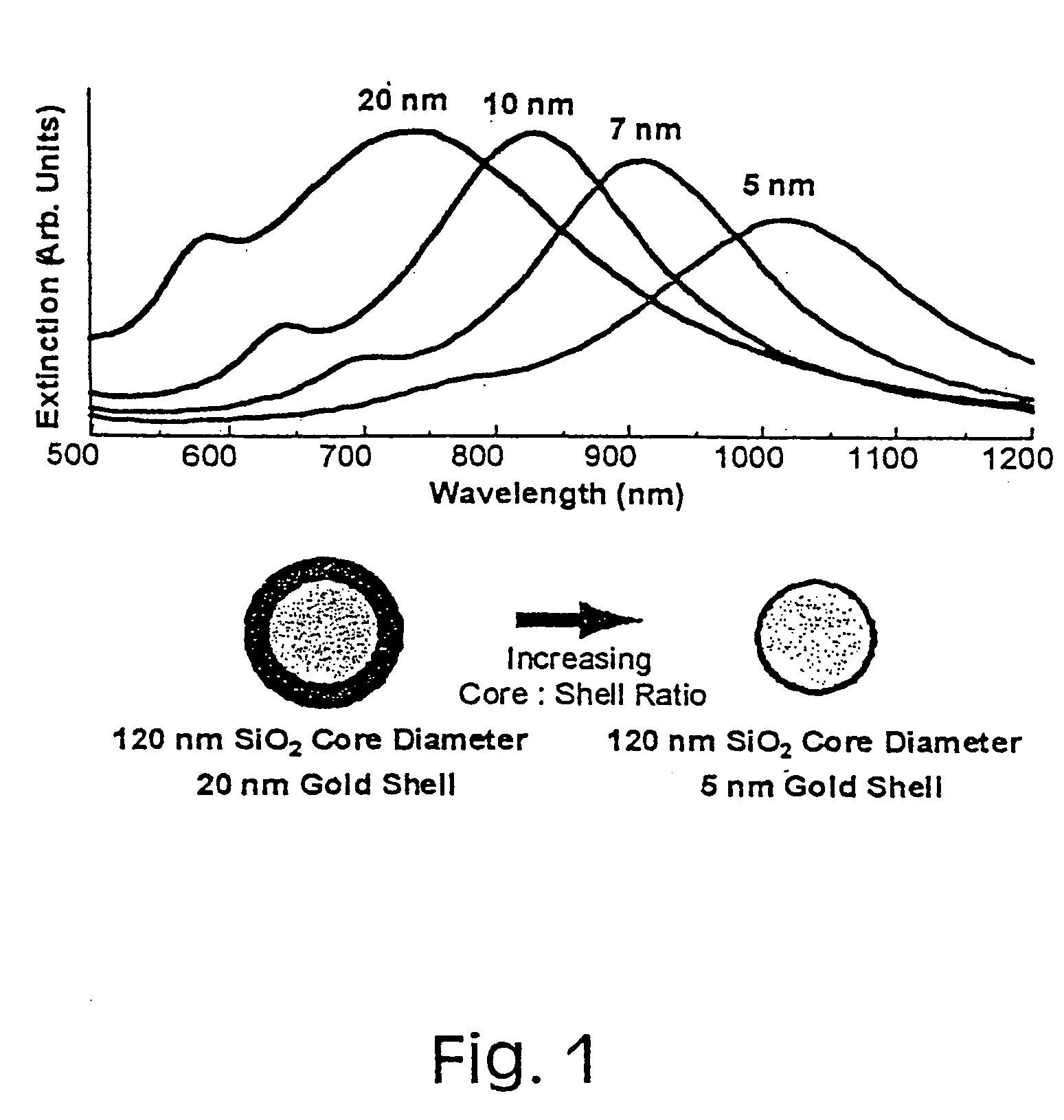
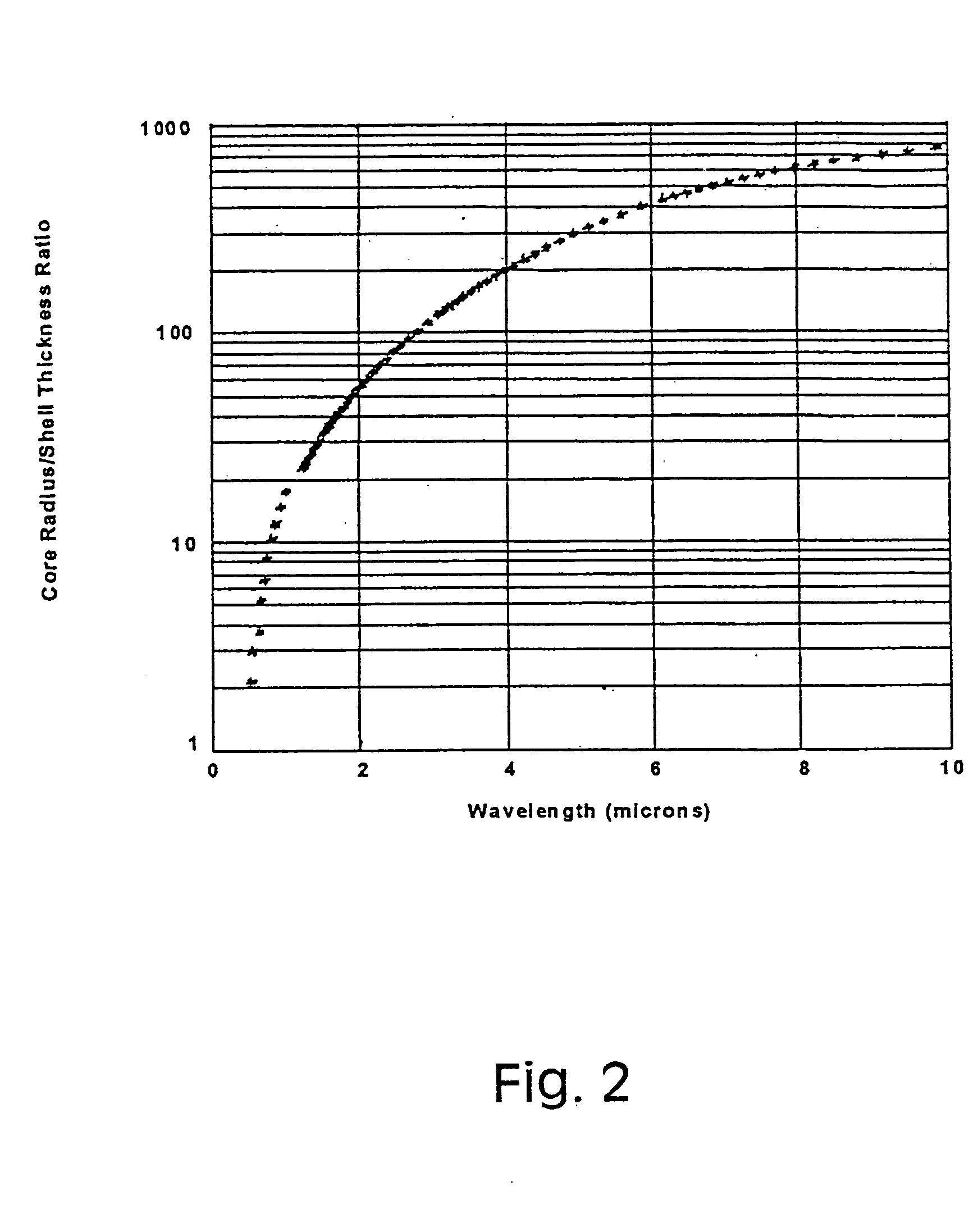
Metal nanoshells for biosensing applications
InactiveUS20050130324A1Eliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPigmenting treatmentUltravioletIn vivo
The present invention provides nanoshell particles (“nanoshells”) for use in biosensing applications, along with their manner of making and methods of using the nanoshells for in vitro and in vivo detection of chemical and biological analytes, preferably by surface enhanced Raman light scattering. The preferred particles have a non-conducting core and a metal shell surrounding the core. For given core and shell materials, the ratio of the thickness (i.e., radius) of the core to the thickness of the metal shell is determinative of the wavelength of maximum absorbance of the particle. By controlling the relative core and shell thicknesses, biosensing metal nanoshells are fabricated which absorb light at any desired wavelength across the ultraviolet to infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum. The surface of the particles are capable of inducing an enhanced SERS signal that is characteristic of an analyte of interest. In certain embodiments a biomolecule is conjugated to the metal shell and the SERS signal of a conformational change or a reaction product is detected.
Owner:RICE UNIV
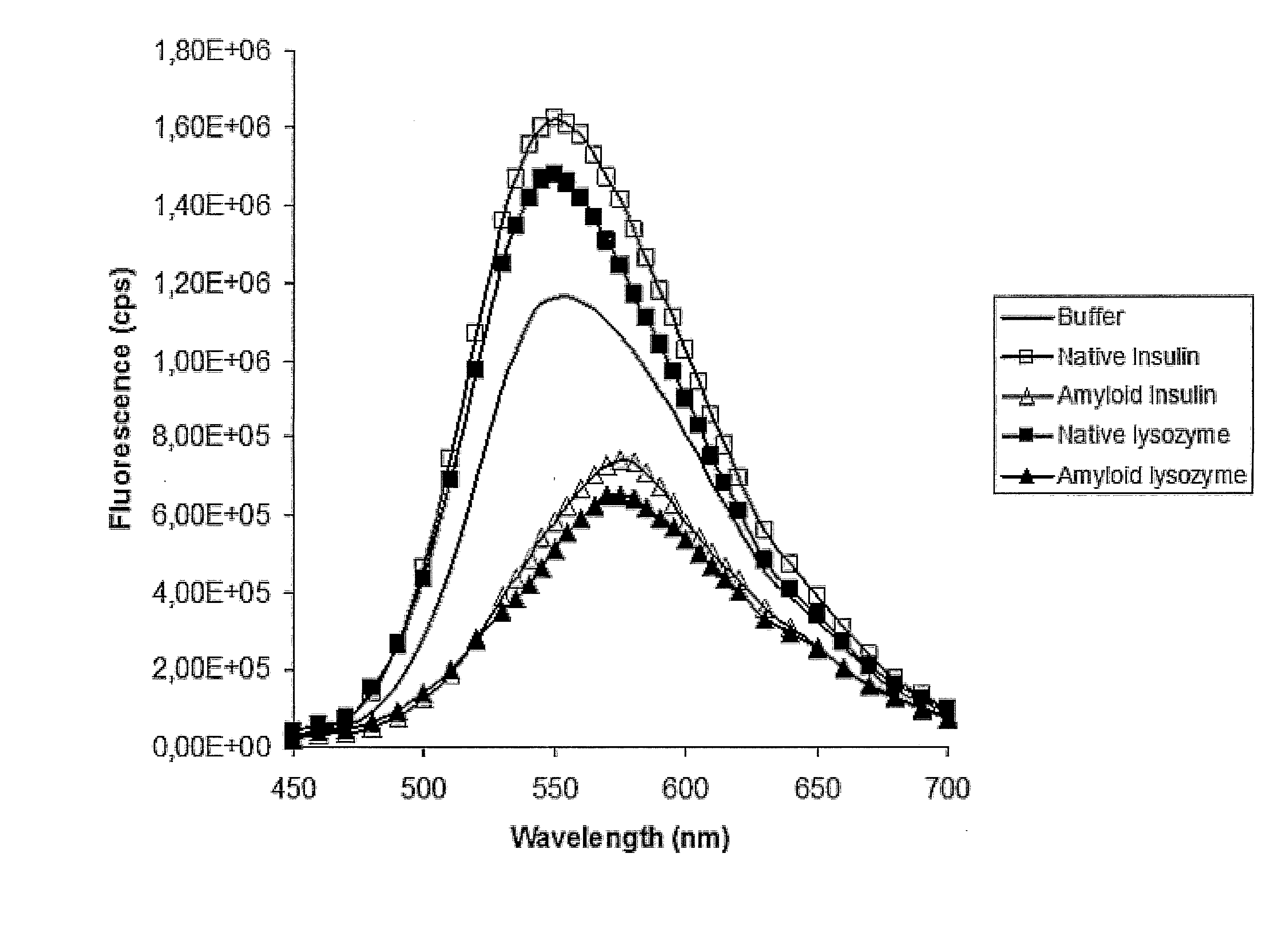
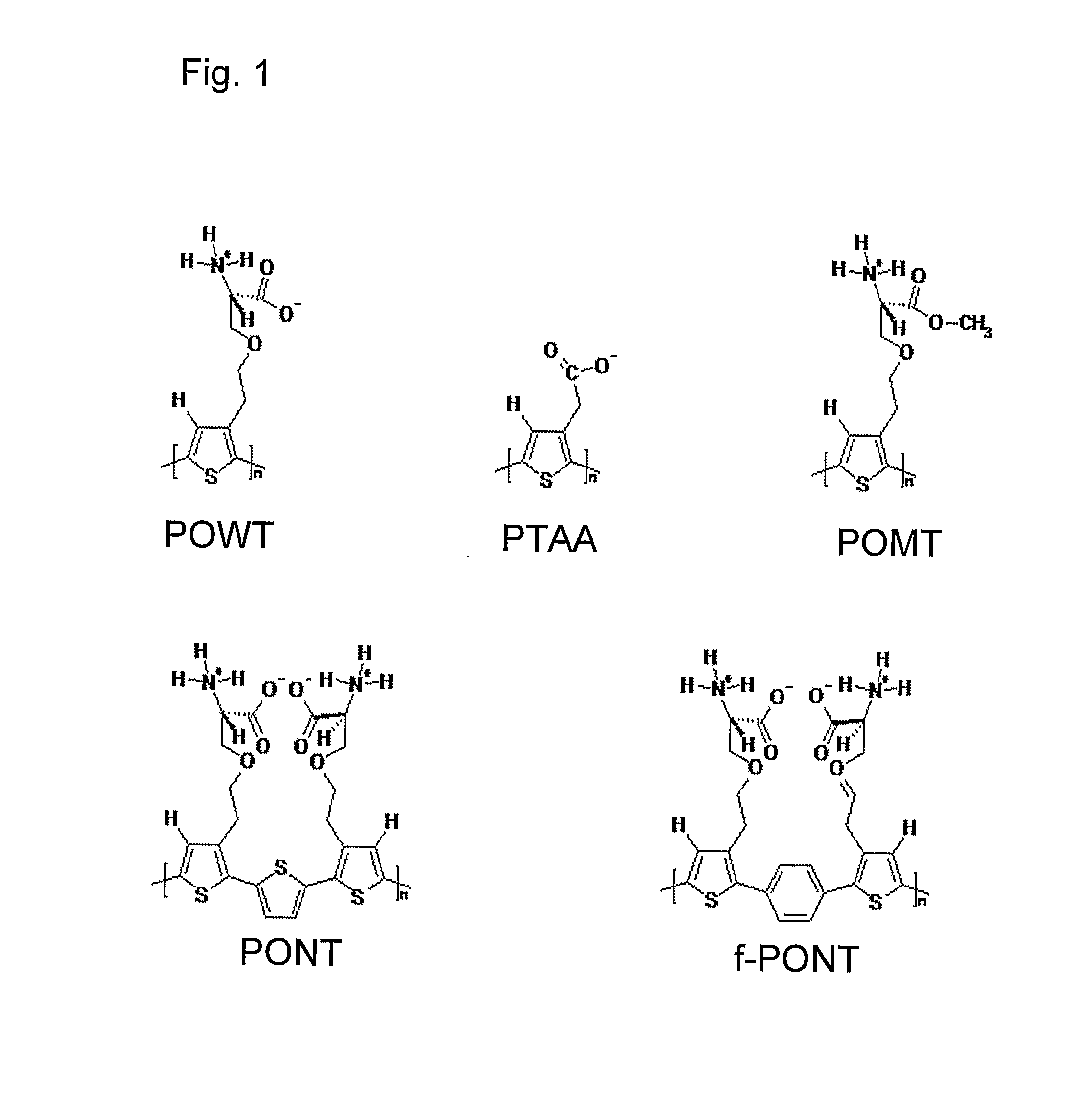
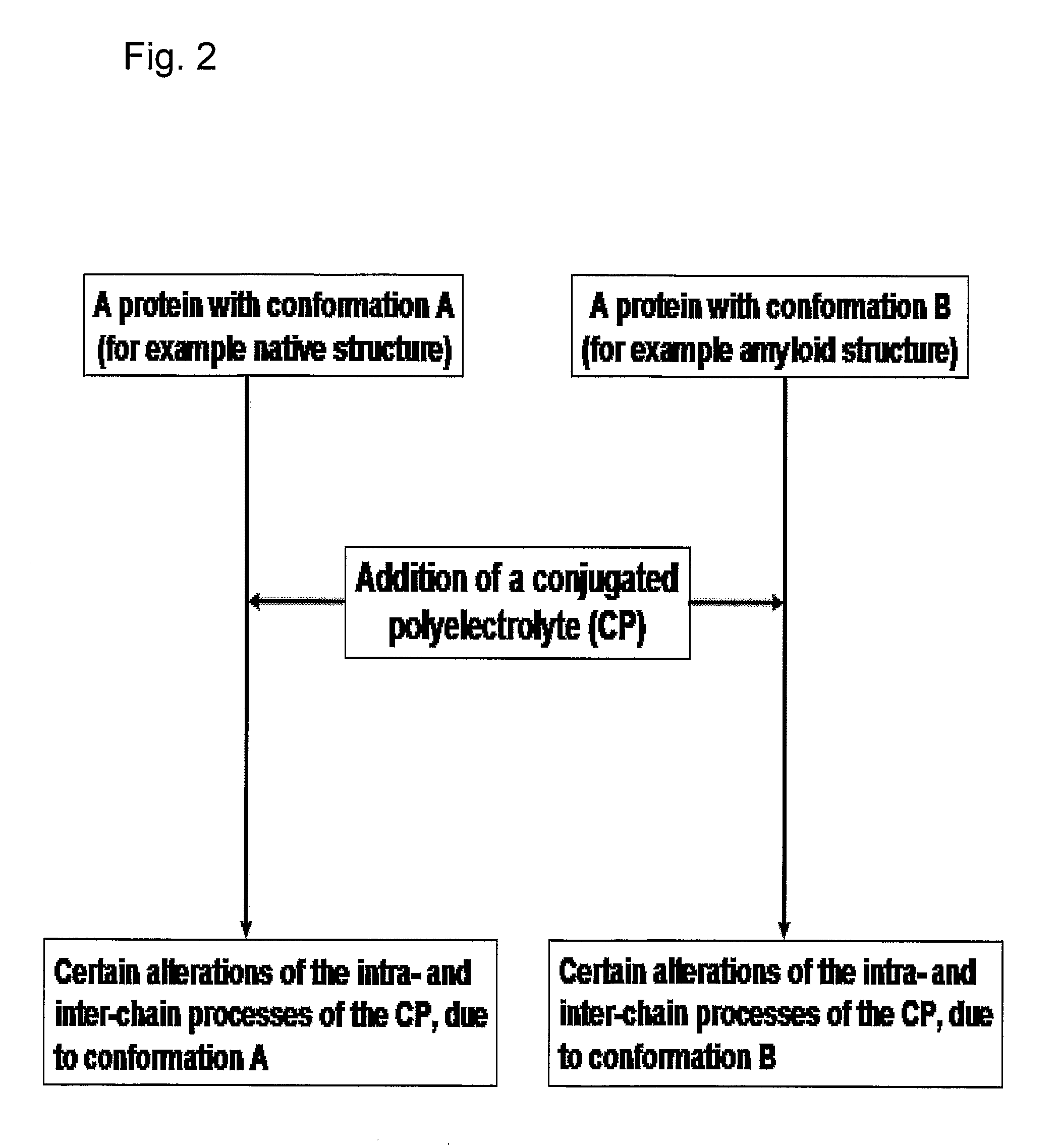
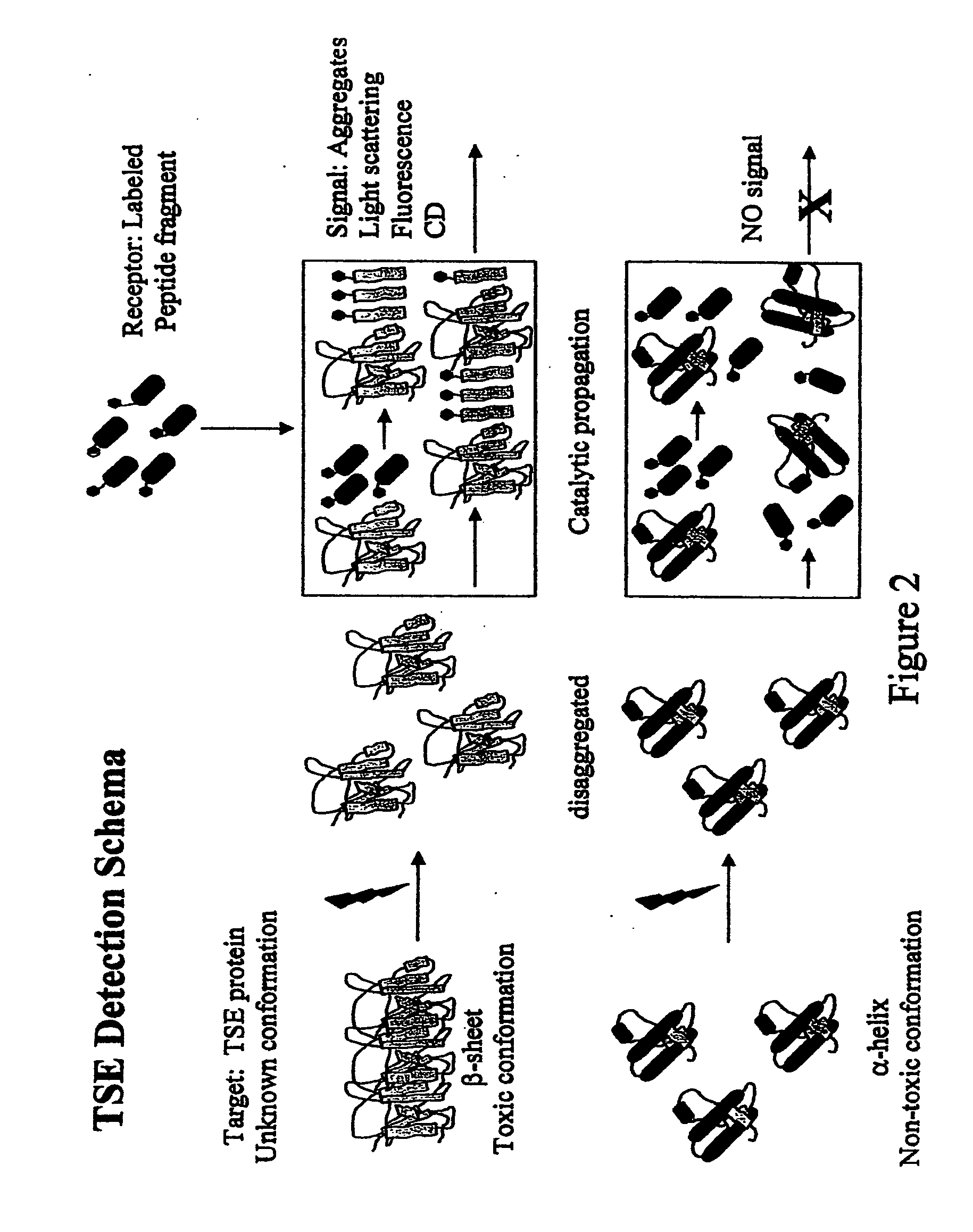
Methods for Determining Conformational Changes and Self-Assembly of Proteins
InactiveUS20080038751A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSelf-assemblyConjugated polyelectrolyte
The invention relates to methods for measuring conformational changes and self-assembly / aggregation of proteins, especially the formation of amyloid fibrils, using conjugated polyelectrolytes. The conjugate polyelectrolyte is exposed to the protein whereby the conjugated polyelectrolyte and the protein of interest interact, and a change of a property of the polyelectrolyte in response to conformational changes of the protein is observed. The detected change is used to determine different conformations of the protein, especially the formation of amyloid fibrils.
Owner:BIOCHROMIX
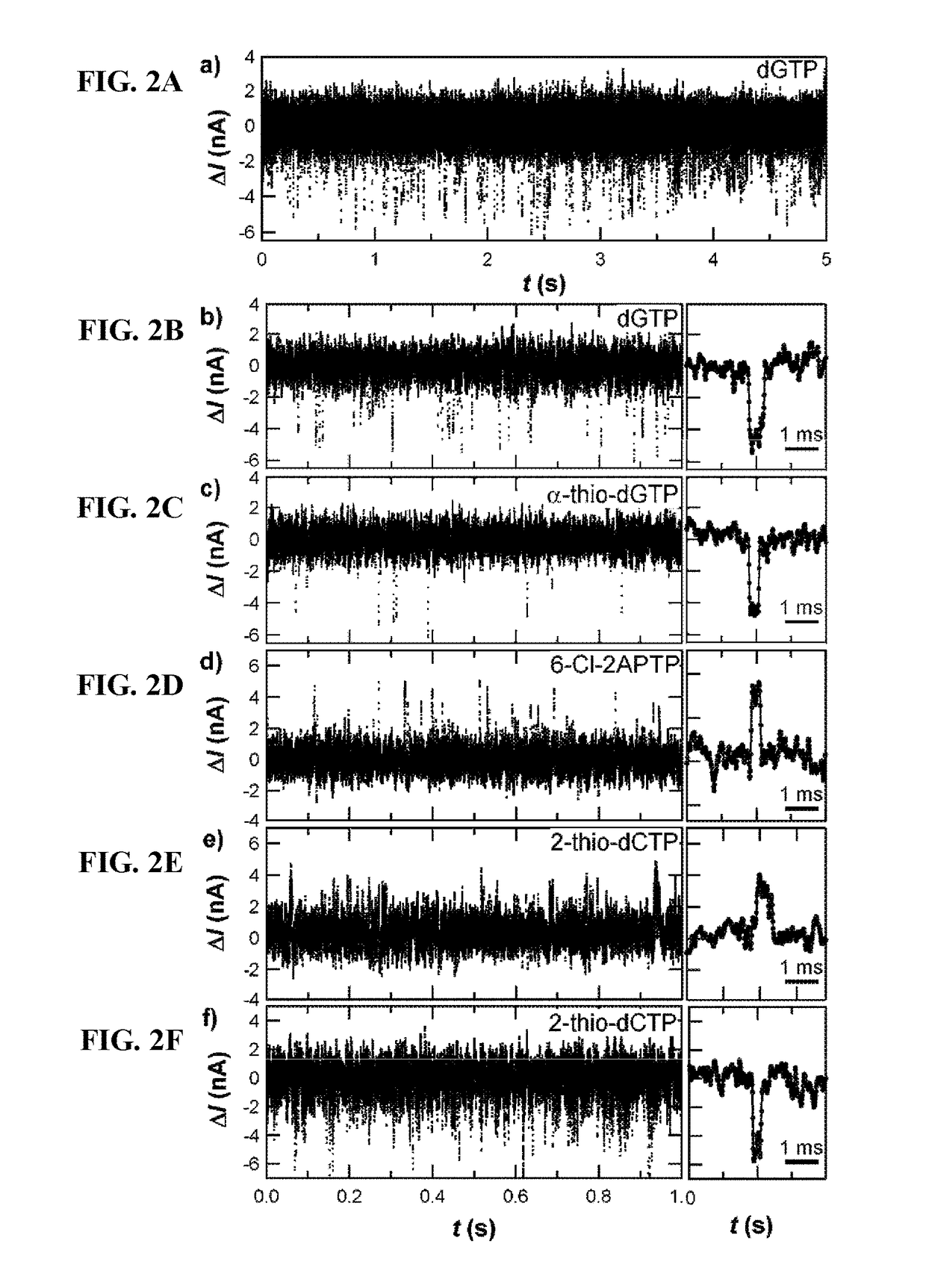
Dideoxynucleotide-triphosphate utilization by the hyper-thermophilic DNA polymerase from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus
InactiveUS6333183B1High sensitivityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesBinding site
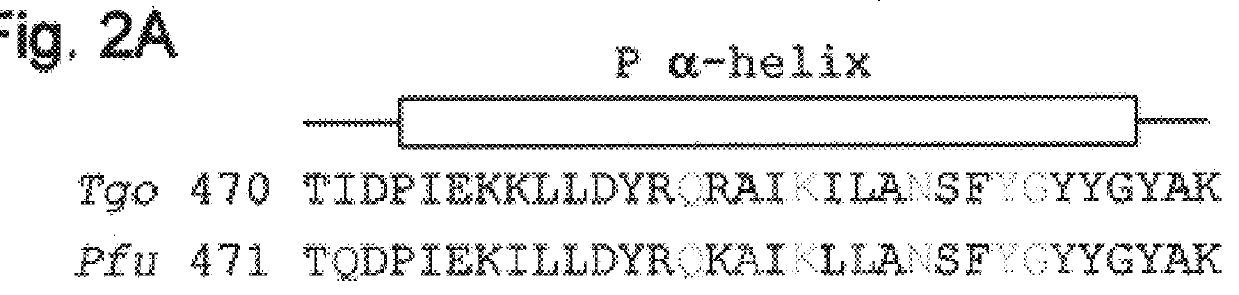
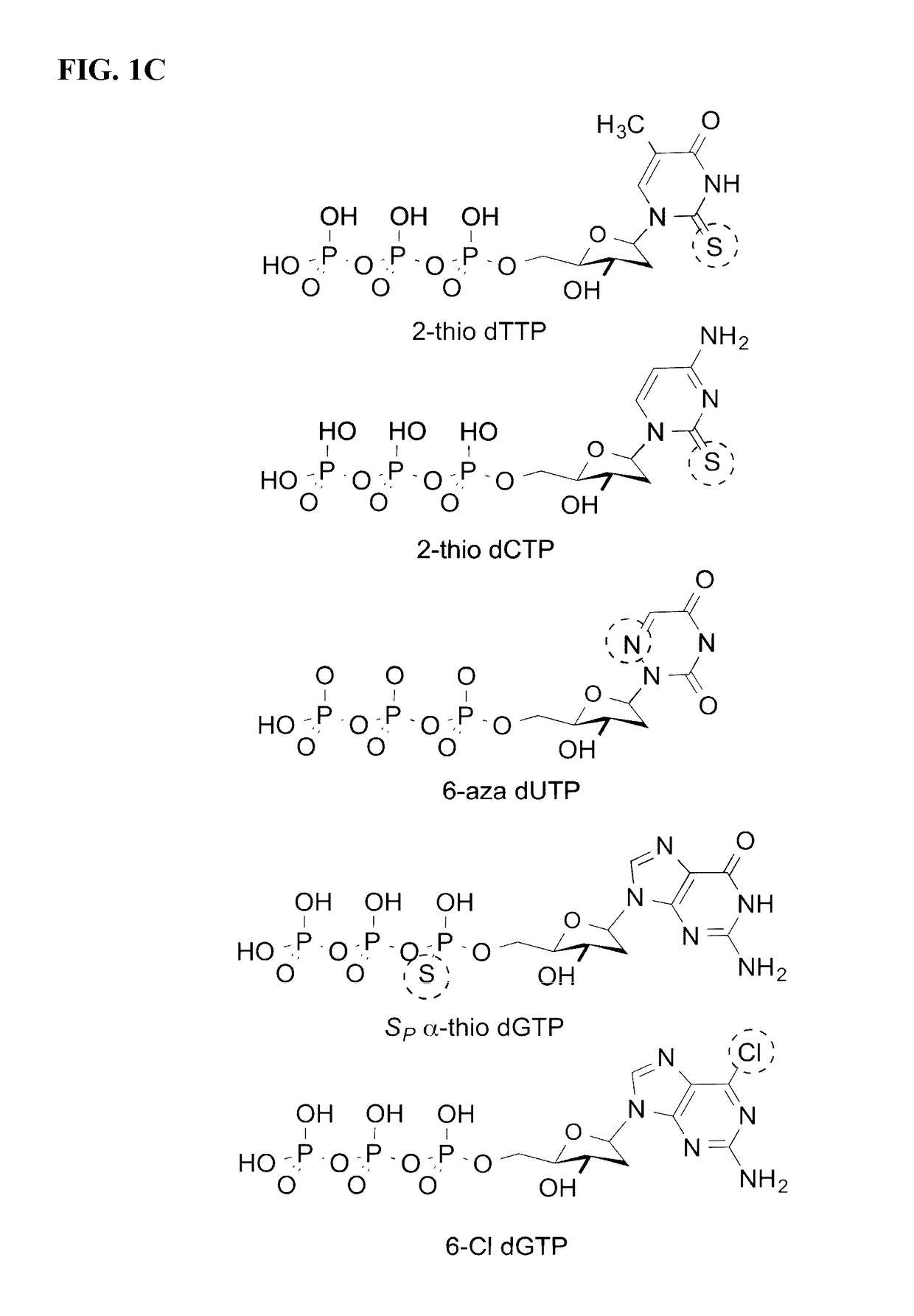
Polymerases from the Pol I family which are able to efficiently use ddNTPs have demonstrated a much improved performance when used to sequence DNA. A number of mutations have been made to the gene coding for the Pol II family DNA polymerase from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus with the aim of improving ddNTP utilisation. "Rational" alterations to amino acids likely to be near the dNTP binding site (based on sequence homologies and structural information) did not yield the desired level of selectivity for ddNTPs. However, alteration at four positions (Q472, A486, L490 and Y497) gave rise to variants which incorporated ddNTPs better than the wild type, allowing sequencing reactions to be carried out at lowered ddNTP:dNTP ratios. Wild type Pfu-Pol required a ddNTP:dNTP ratio of 30:1; values of 5:1 (Q472H), 1:3 (L490Y), 1:5 (A486Y) and 5:1 (Y497A) were found with the four mutants; A486Y representing a 150-fold improvement over the wild type. A486, L490 and Y407 are on an alpha-helix that lines the dNTP binding groove, but the side chains of the three amino acids point away from this groove; Q472 is in a loop that connects this alpha-helix to a second long helix. None of the four amino acids can contact the dNTP directly. Therefore, the increased selectivity for ddNTPs is likely to arise from two factors: 1) Small overall changes in conformation that subtly alter the nucleotide triphosphate binding site such that ddNTPs become favoured; 2) interference with a conformational change that may be critical both for the polymerisation step and discrimination between different nucleotide triphosphates.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Target sequences for synthetic molecules
The invention is based on the discovery that certain biarsenical molecules react with specified target sequences, thereby providing a facile means for labeling polypeptides containing the target sequence. The invention is useful in creating stable mammalian cell lines expressing a certain tetracysteine tagged polypeptides, thereby overcoming toxicity associated with native tetracysteine. In addition, the invention allows for orthogonal labeling of polypeptides, thereby allowing for the observation of protein-protein interactions and conformational changes in proteins, for example.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
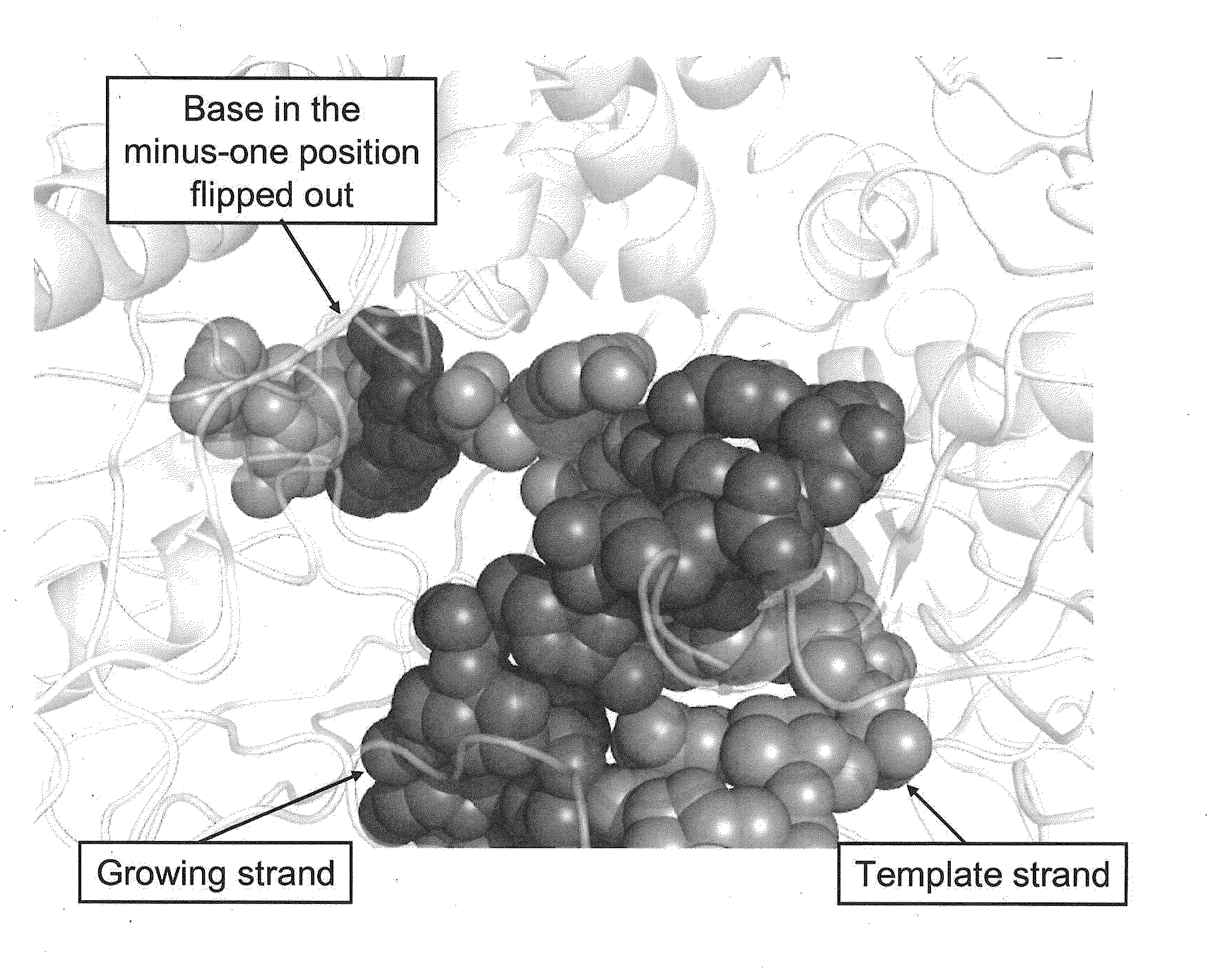
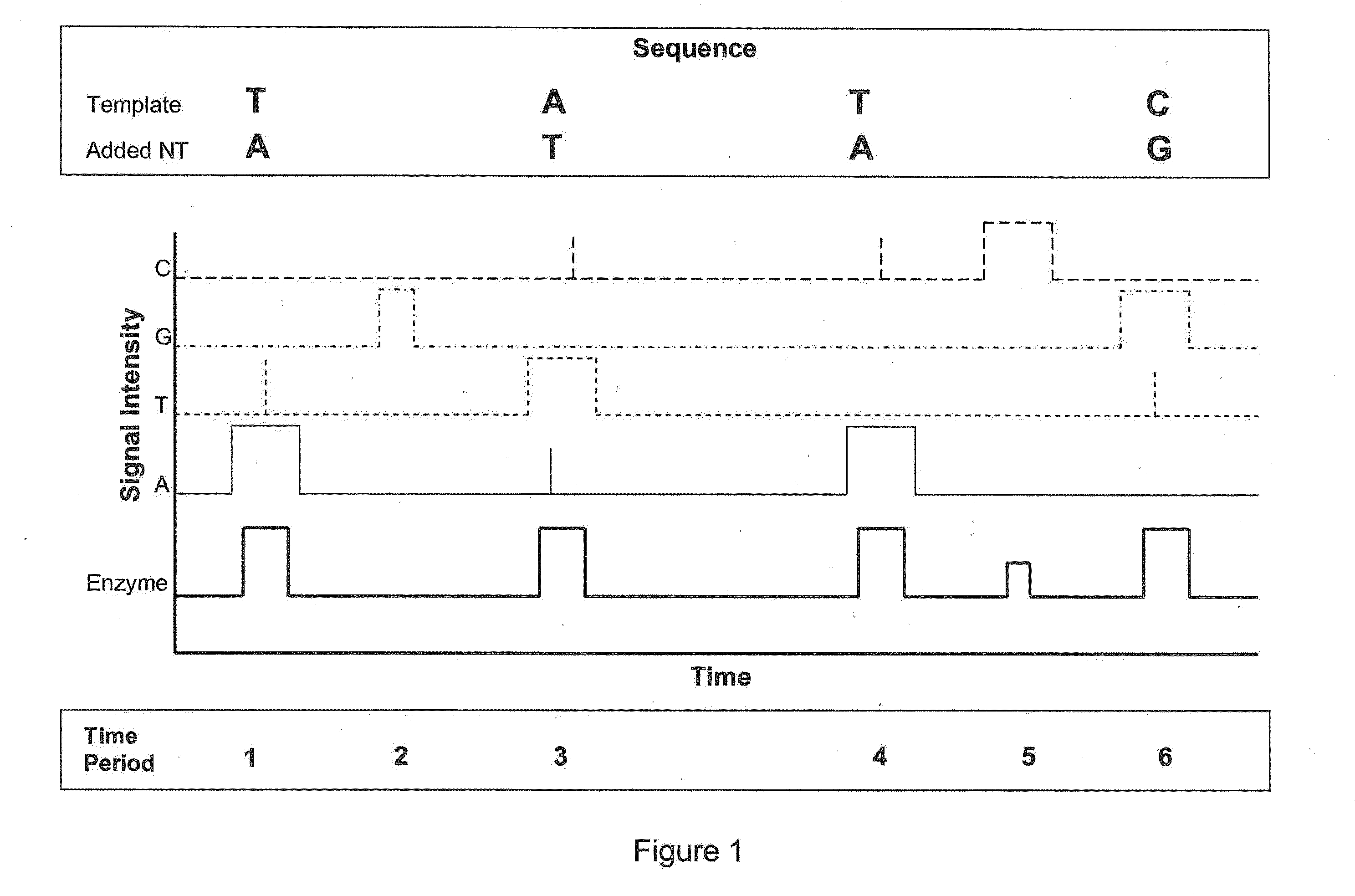
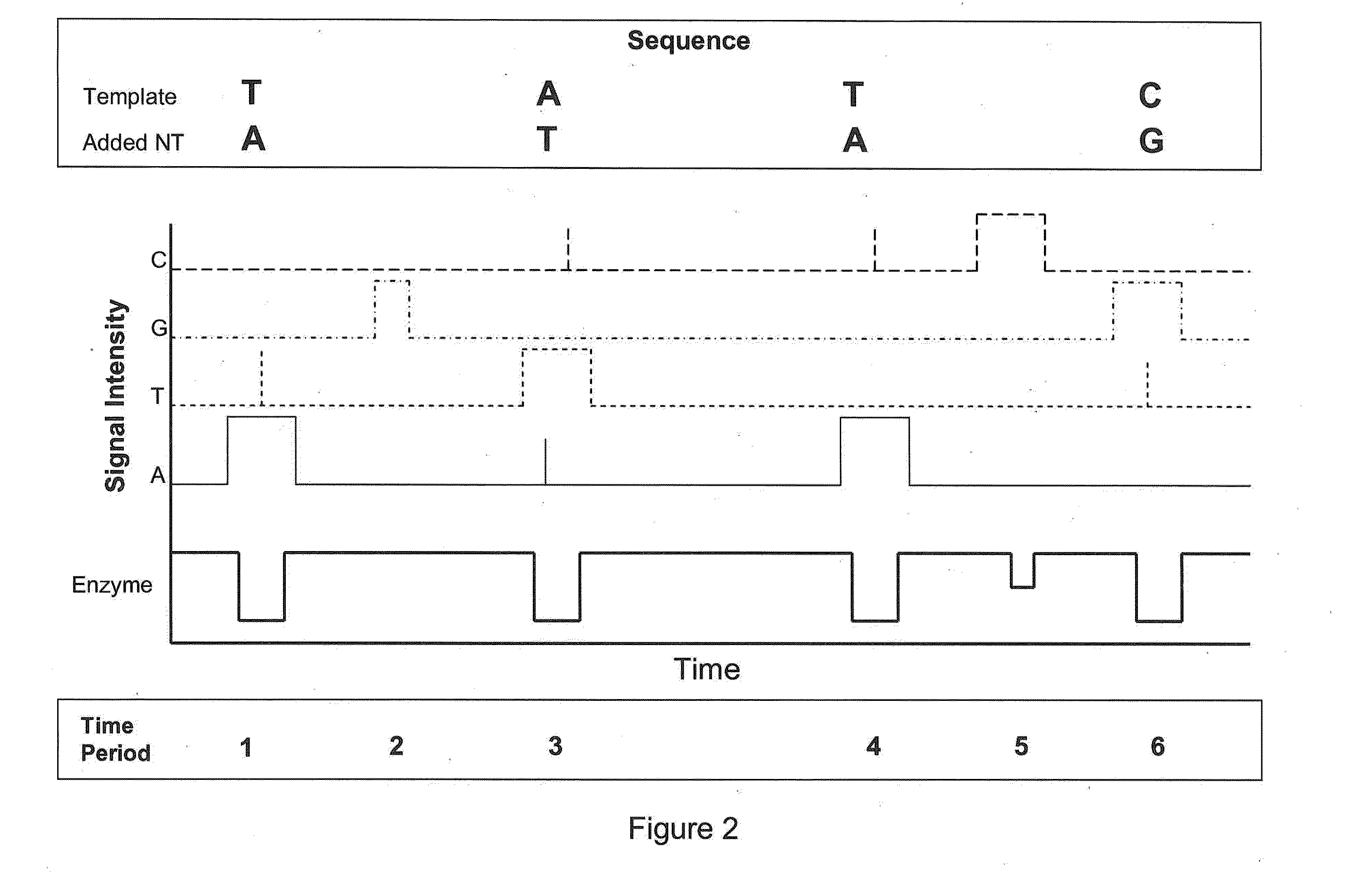
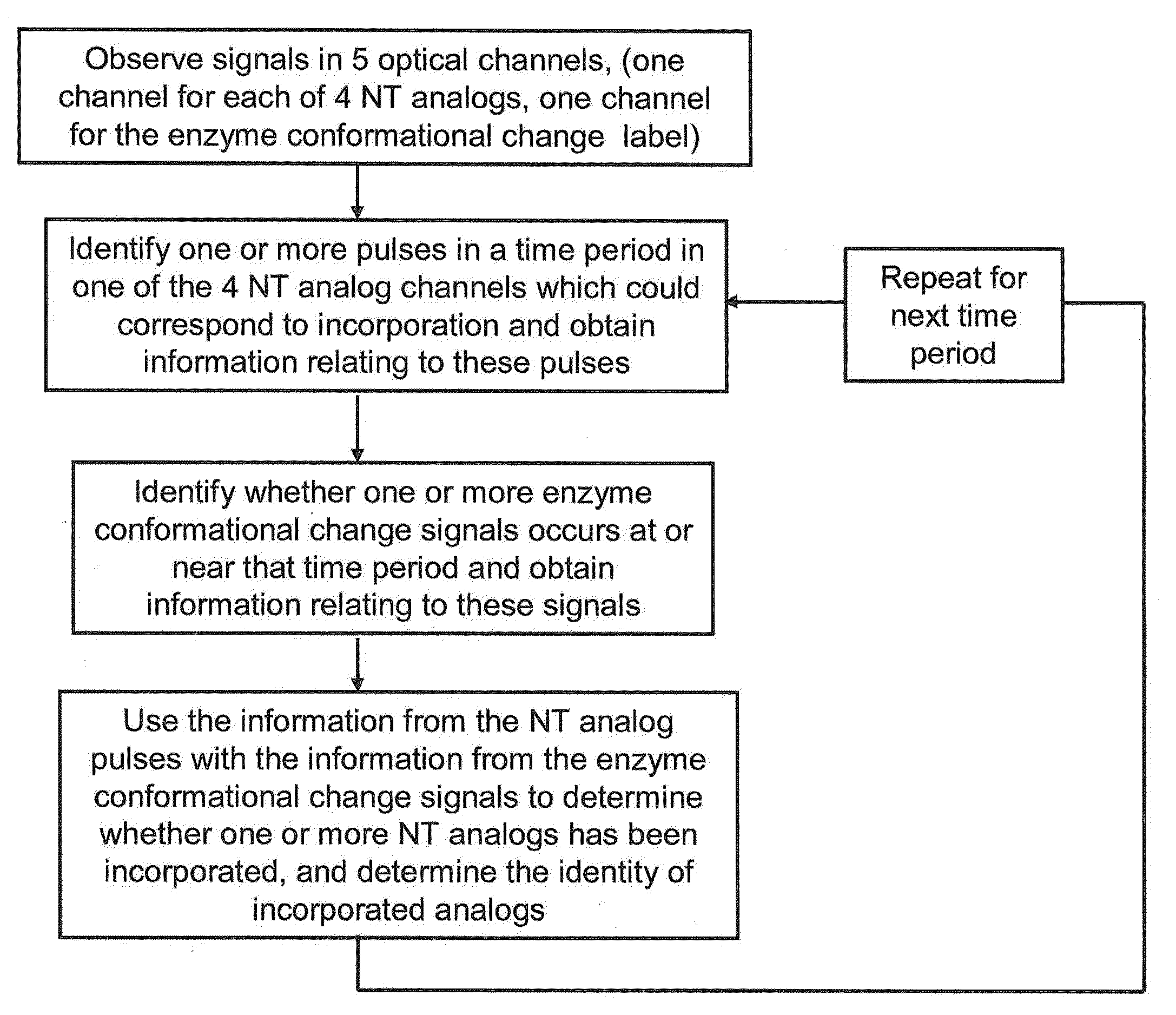
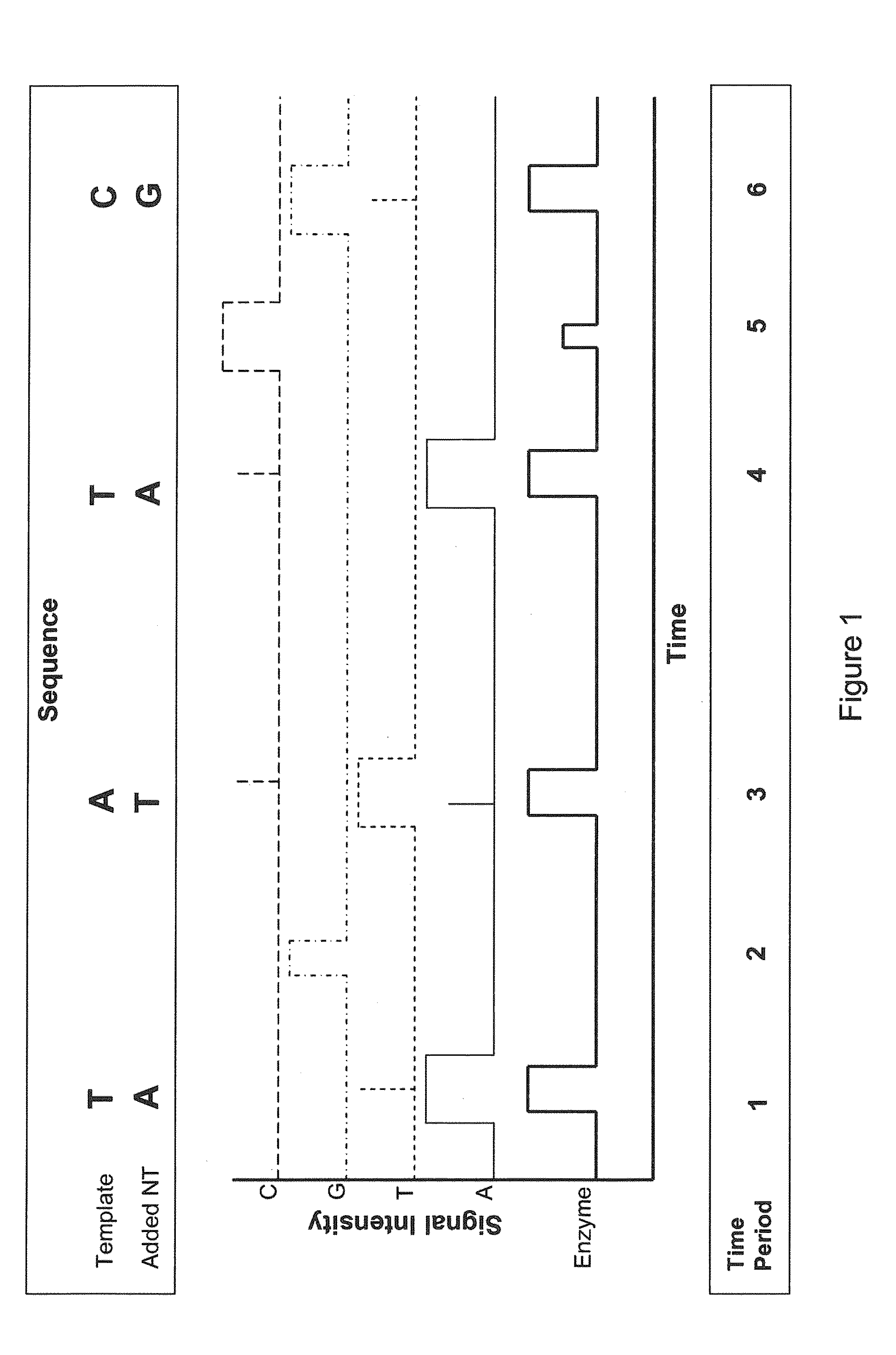
Sequencing methods using enzyme conformation
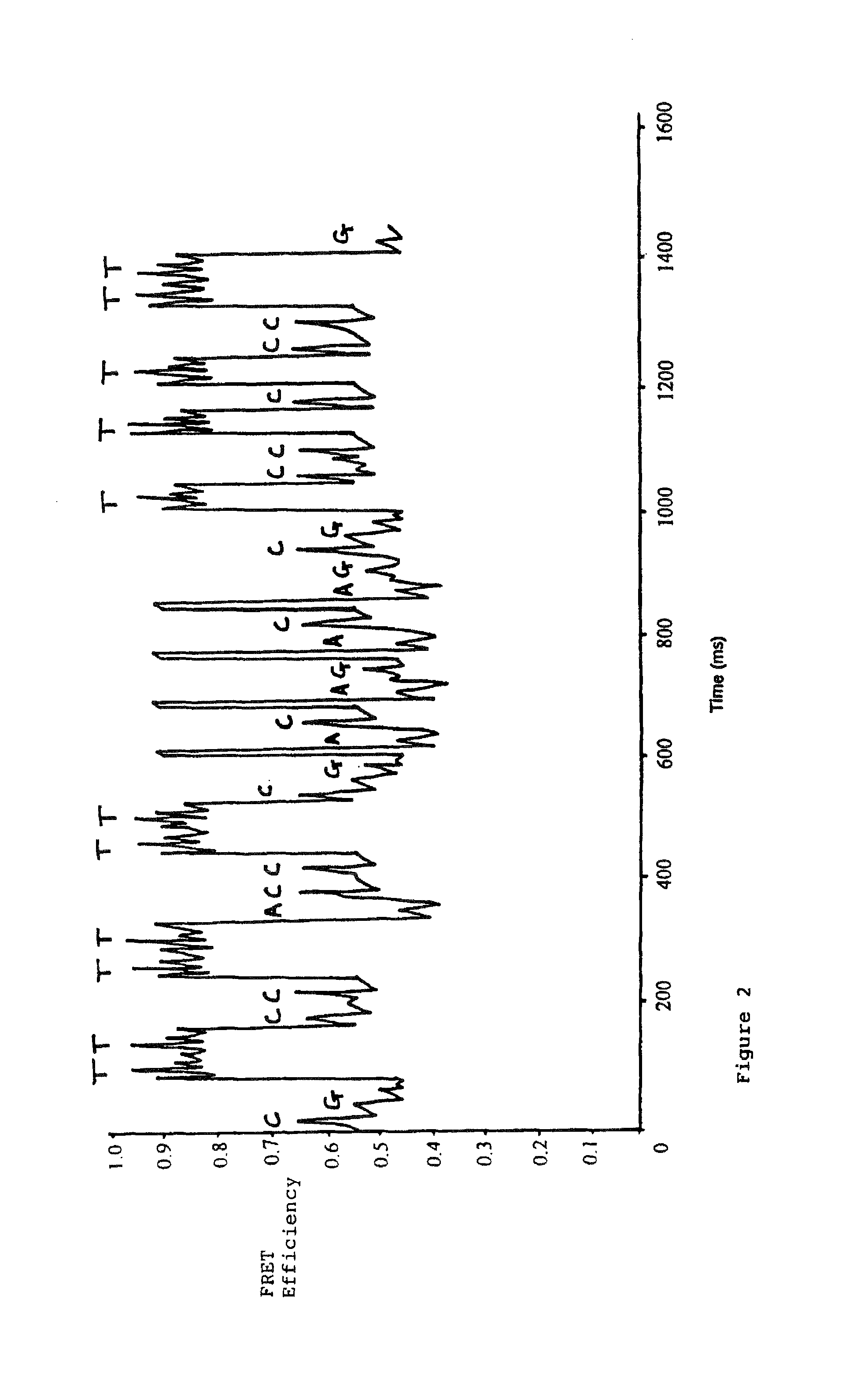
Systems and methods are provided for single-molecule sequencing of template nucleic acids in which the signal from a label attached to a polymerase enzyme is used to monitor conformational changes in the polymerase which occur while labeled nucleotides or nucleotide analogs are added to a growing nucleic acid chain which is complementary to the template nucleic acid. The signal indicative of the conformational state of the enzyme is used to determine with higher confidence when true nucleotide or nucleotide analog incorporation events occur, allowing for the improved quality of base calls and sequence determination.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Compositions and methods for modulating cellular membrane-mediated intracellular signal transduction
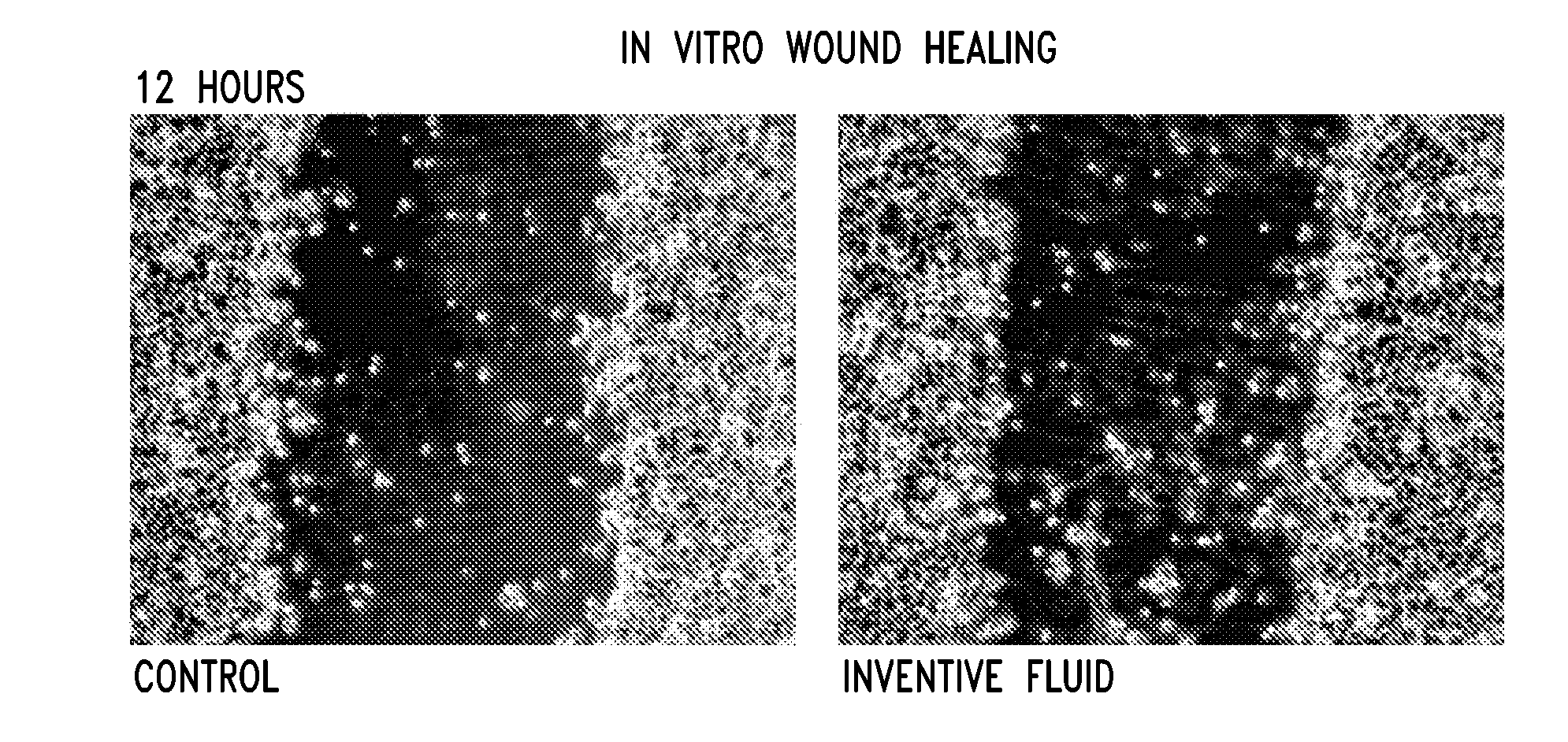
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., gas-enriched (e.g., oxygen-enriched) electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient to provide, upon contact with a cell, modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity. Particular aspects of the present invention provide compositions and methods suitable for modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity. Additional aspects provide compositions and methods suitable for modulating intracellular signal transduction, including modulation of at least one of membrane structure, membrane potential or membrane conductivity, membrane proteins or receptors, ion channels, and calcium dependant cellular messaging systems, comprising use of the inventive electrokinetically altered solutions to impart electrochemical and / or conformational changes in membranous structures (e.g., membrane proteins, receptors and / or other components) including G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), G-proteins, and / or intracellular junctions (e.g., tight junctions, gap junctions, zona adherins and desmasomes).
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Direct colorimetric detection of biocatalysts
InactiveUS6468759B1Rapid optical signalFast response timeMaterial nanotechnologyColor measuring devicesAnalyteColor changes
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the direct detection of membrane conformational changes through the detection of color changes in biopolymeric materials. In particular, the present invention allows for the direct colorimetric detection of membrane modifying reactions and analytes responsible for such modifications and for the screening of reaction inhibitors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Protein transistor device
ActiveUS20140048776A1Improve bindingGood reproducibilityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesProtein moleculesProtein insertion
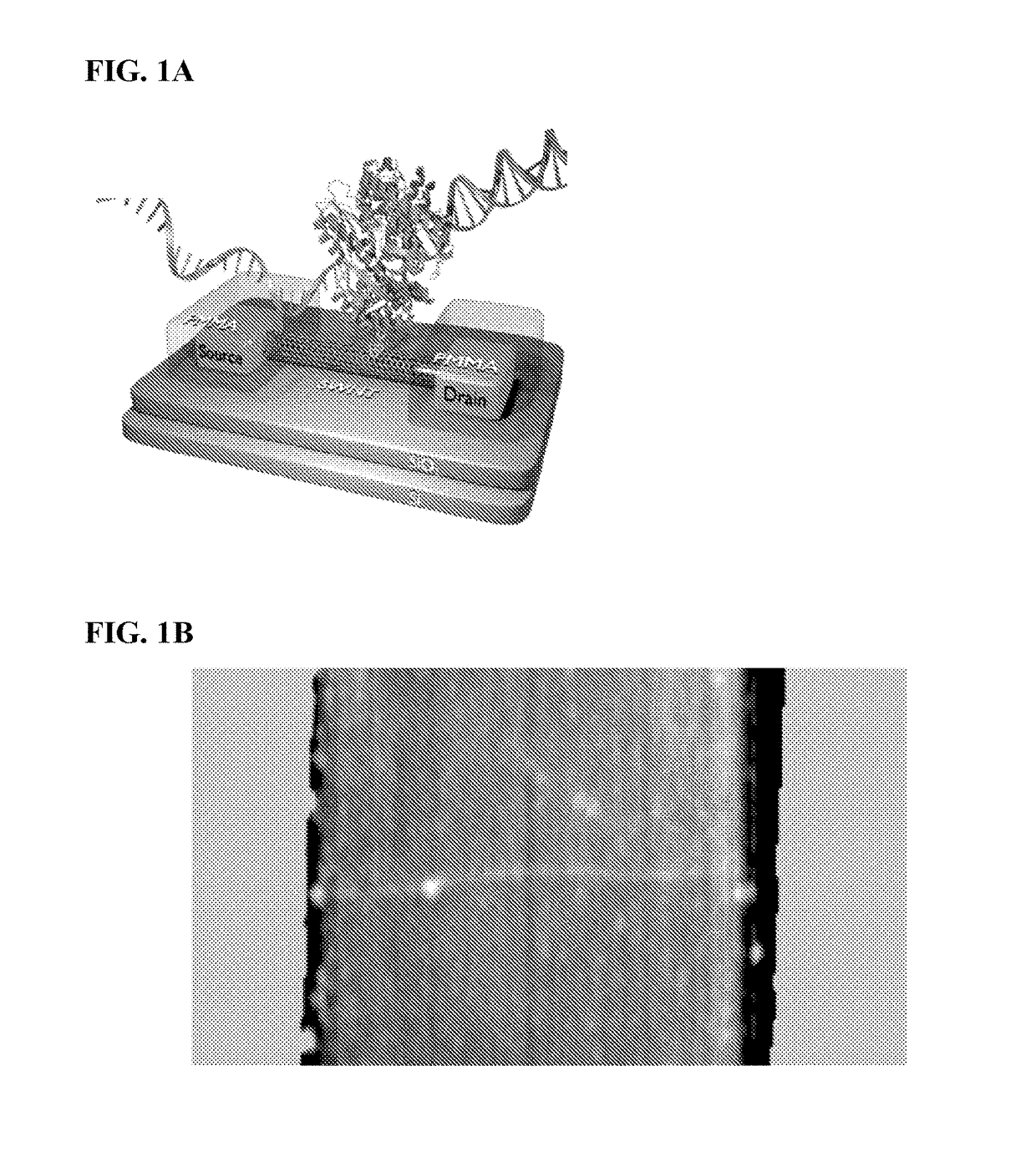
The present invention discloses a protein transistor device, wherein an antibody molecule (antibody-antigen) is bonded to at least two gold nanoparticles in a high reproducible self-assembly way to form molecular junctions, and wherein the two gold nanoparticles are respectively joined to a drain and a source. The protein transistor device can be controlled to regulate current via applying a bias to the gate. The conformational change of the protein molecule will cause the variation of the charge transport characteristics of the protein transistor device. The protein transistor device can be further controlled by different optical fields via conjugating a quantum dot to the molecular junctions. Therefore, the present invention has diversified applications.
Owner:ALLBIO LIFE CO LTD
Nonlinear optical detection of molecules comprising an unnatural amino acid possessing a hyperpolarizability
A system for making molecules, and proteins in particular, suitable for detection by a surface-selective nonlinear optical technique. A first use of the invention is for determining a protein's structure in real space and real time. A second use of the invention is to detect a protein or its activity (conformational change). A third use of the invention is for drug screening. A further aspect of the present invention is measuring probe tilt angle orientation in an oriented protein.
Owner:BLUELIGHT THERAPEUTICS INC
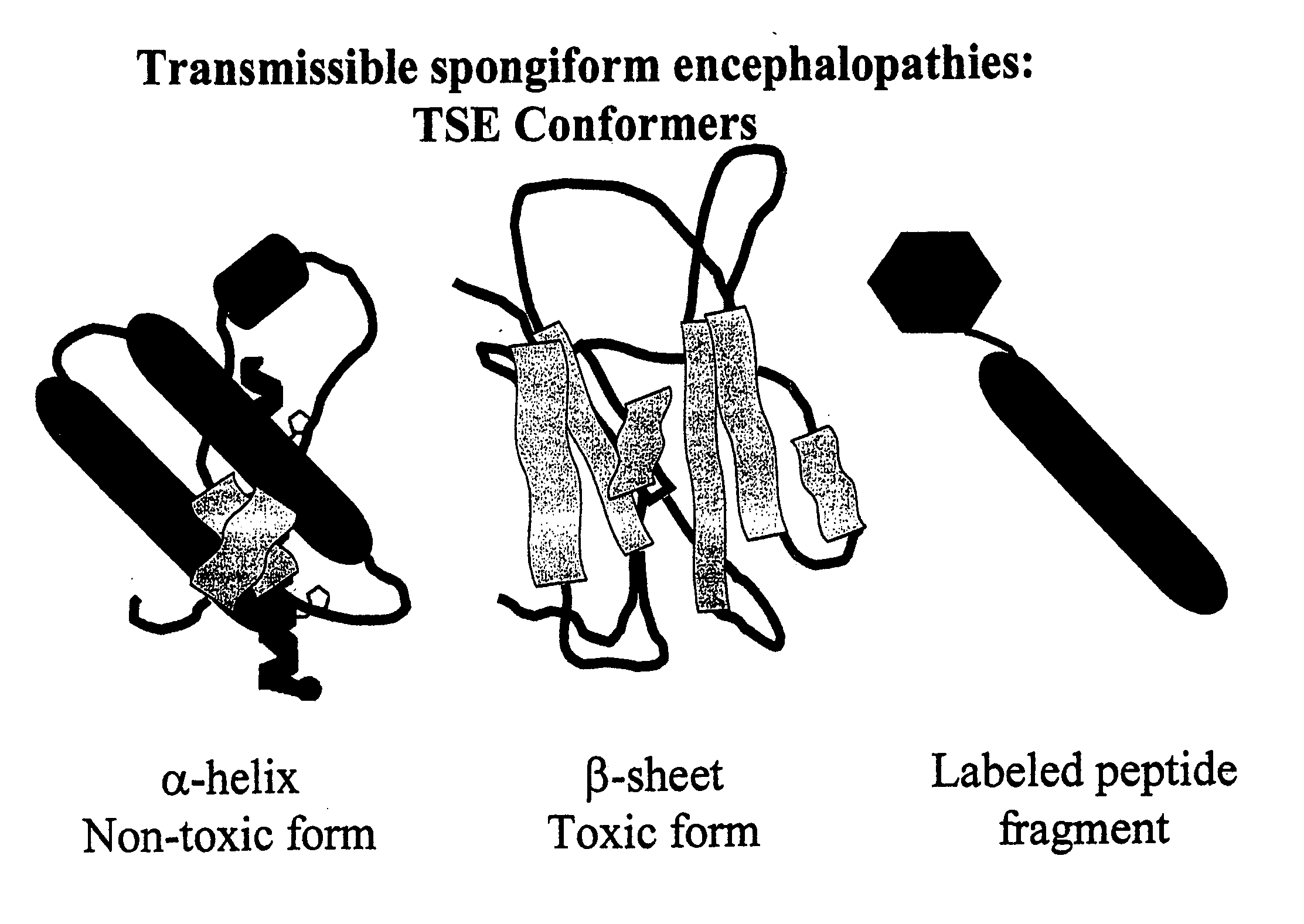
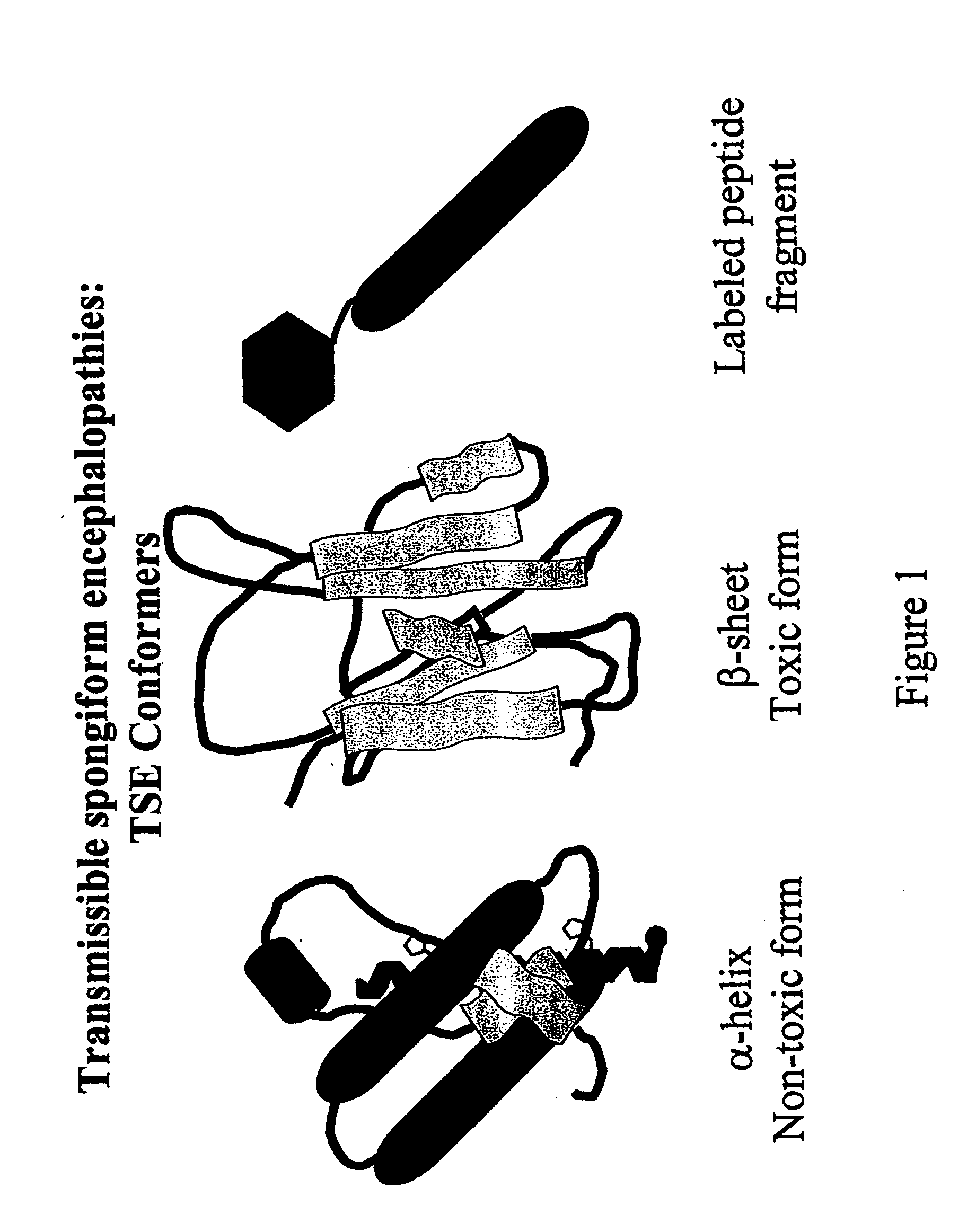
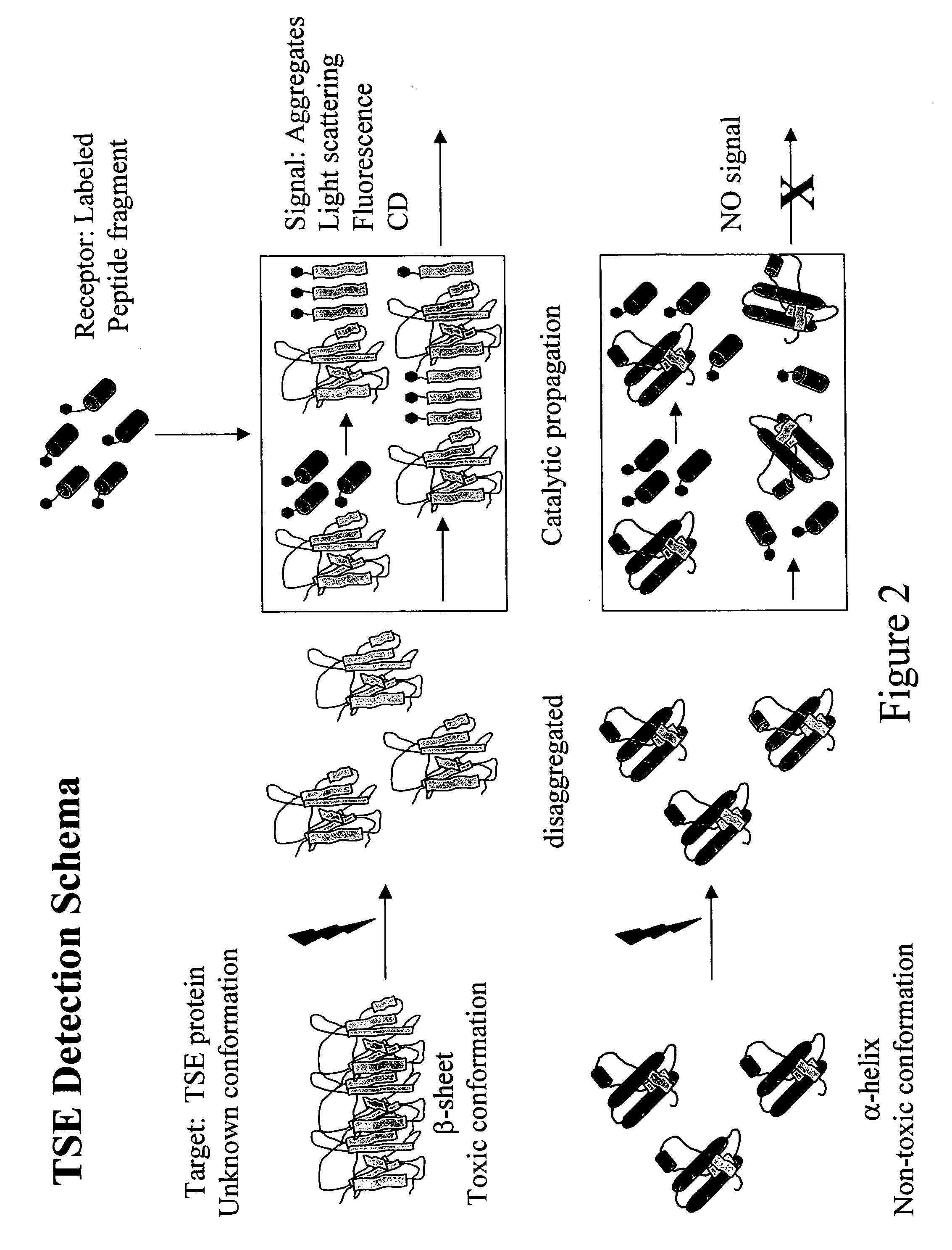
Immobilized probes and methods of detecting conformationally altered prion proteins
InactiveUS20060057671A1Rapid diagnosisFacilitate prophylacticNervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementPrion ProteinsConformational change
Owner:ADLYFE INC
Reagentless, reusable, bioelectronic detectors employing aptamers
ActiveUS20070020641A1Material nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectron transferBiology
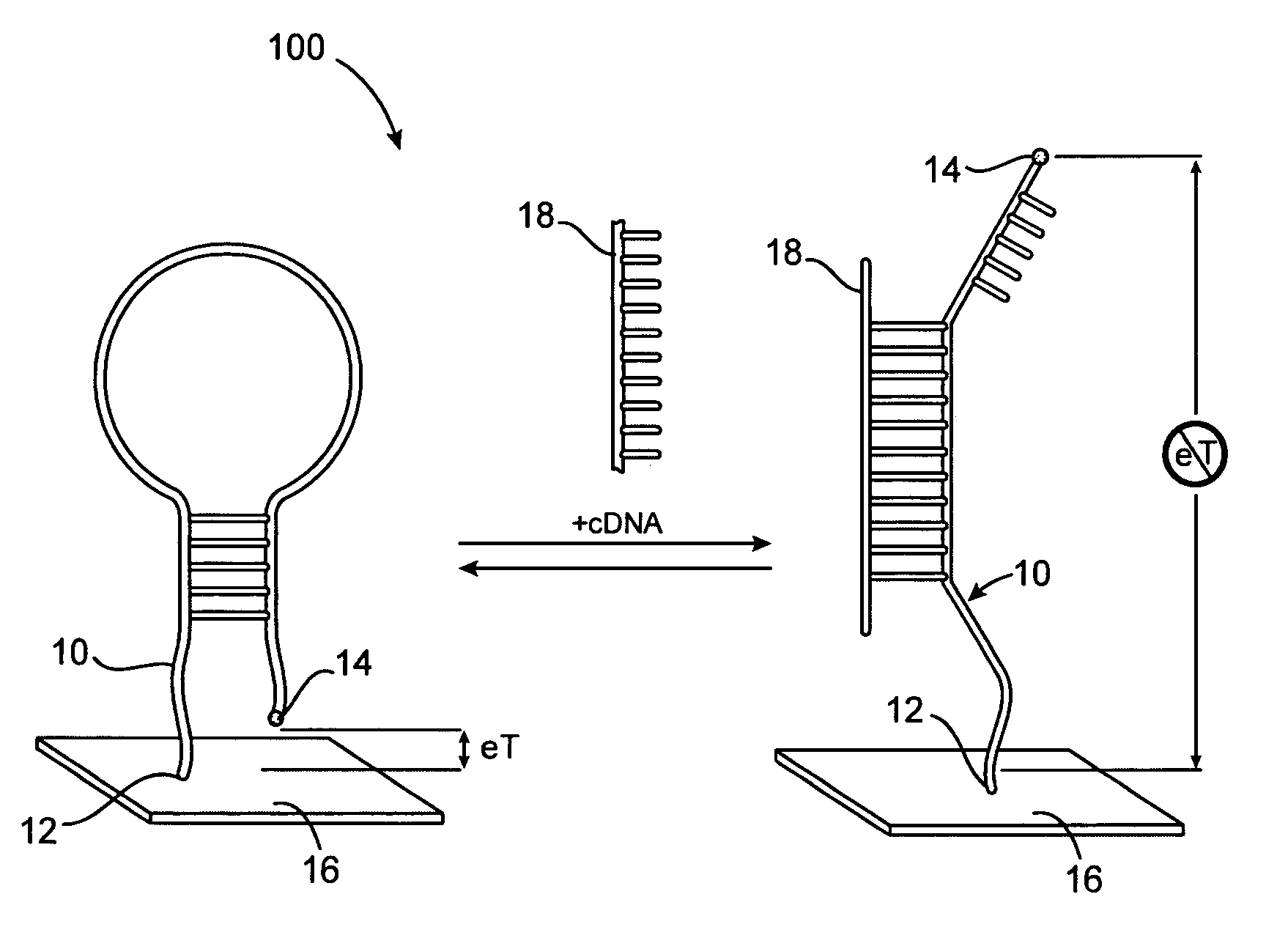
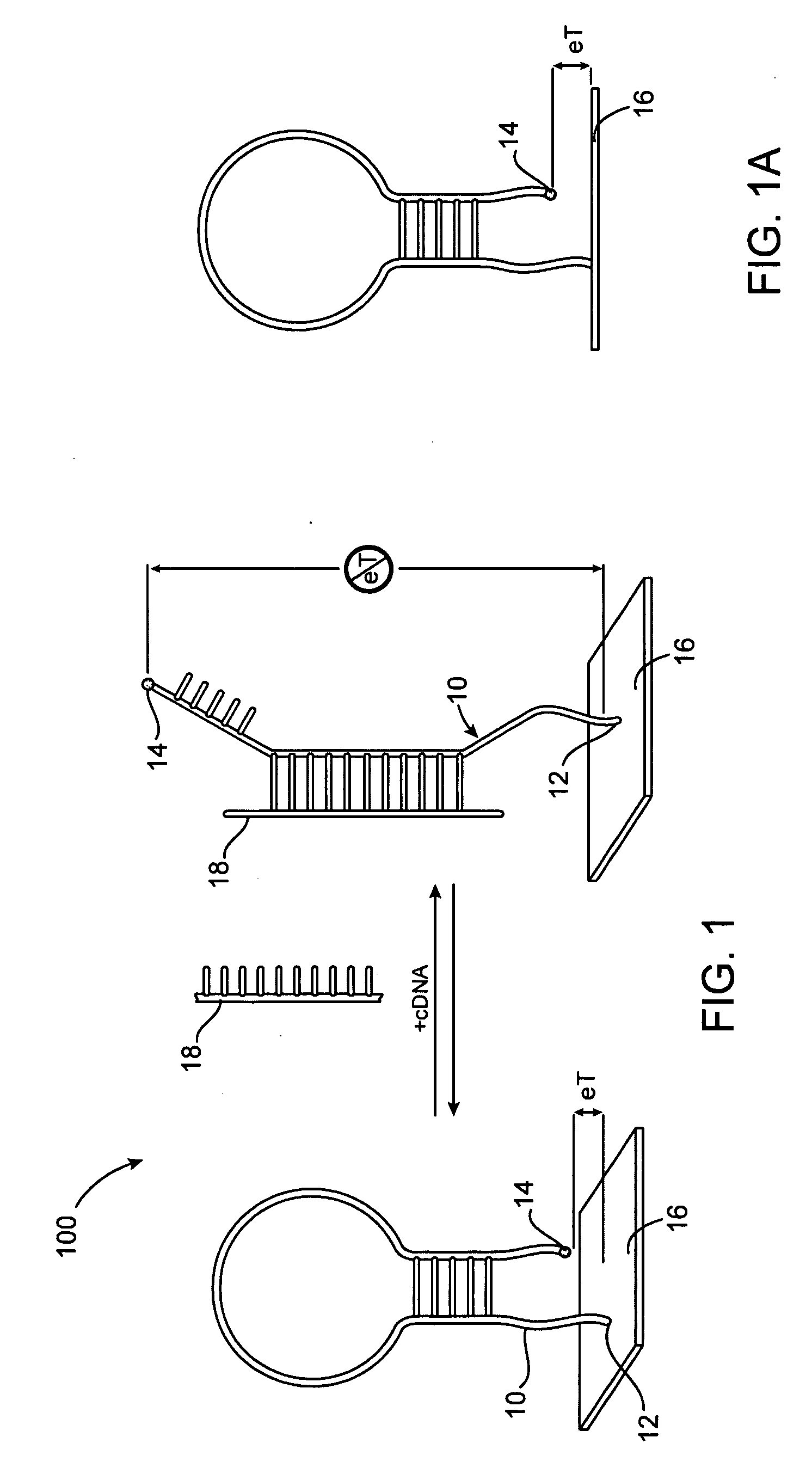
A reagentless, reusable bioelectronic DNA, or other oligonucleotide sequence sensor is disclosed. The sensor includes an oligonucleotide (aptamer) probe tagged with a electroactive, redoxable moiety, self-assembled on or near an electrode. This surface-confined oligonucleotide (aptamer) probe structure undergoes hybridization-induced conformational change in the presence of the target which changes the electron-transfer distance between the redoxable moiety and the electrode thereby providing a detectable signal change. In an alternative embodiment, the target can harbor the redoxable moiety.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Biosensor
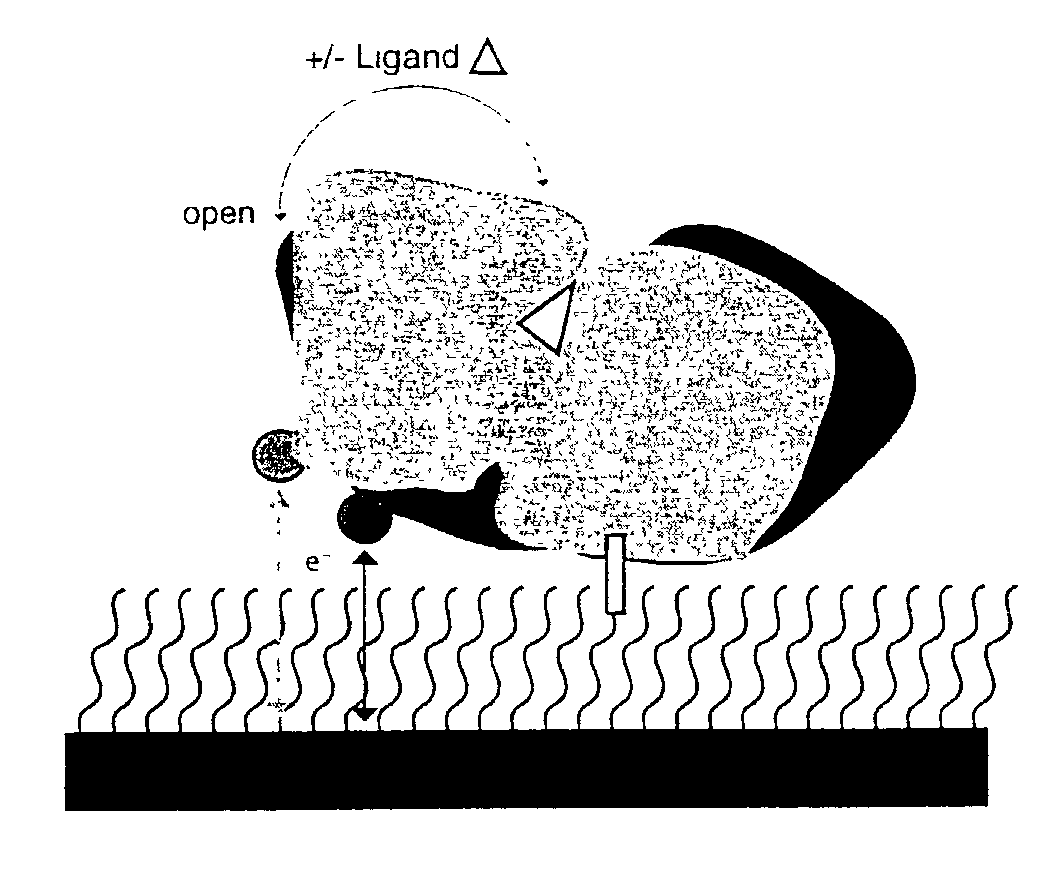
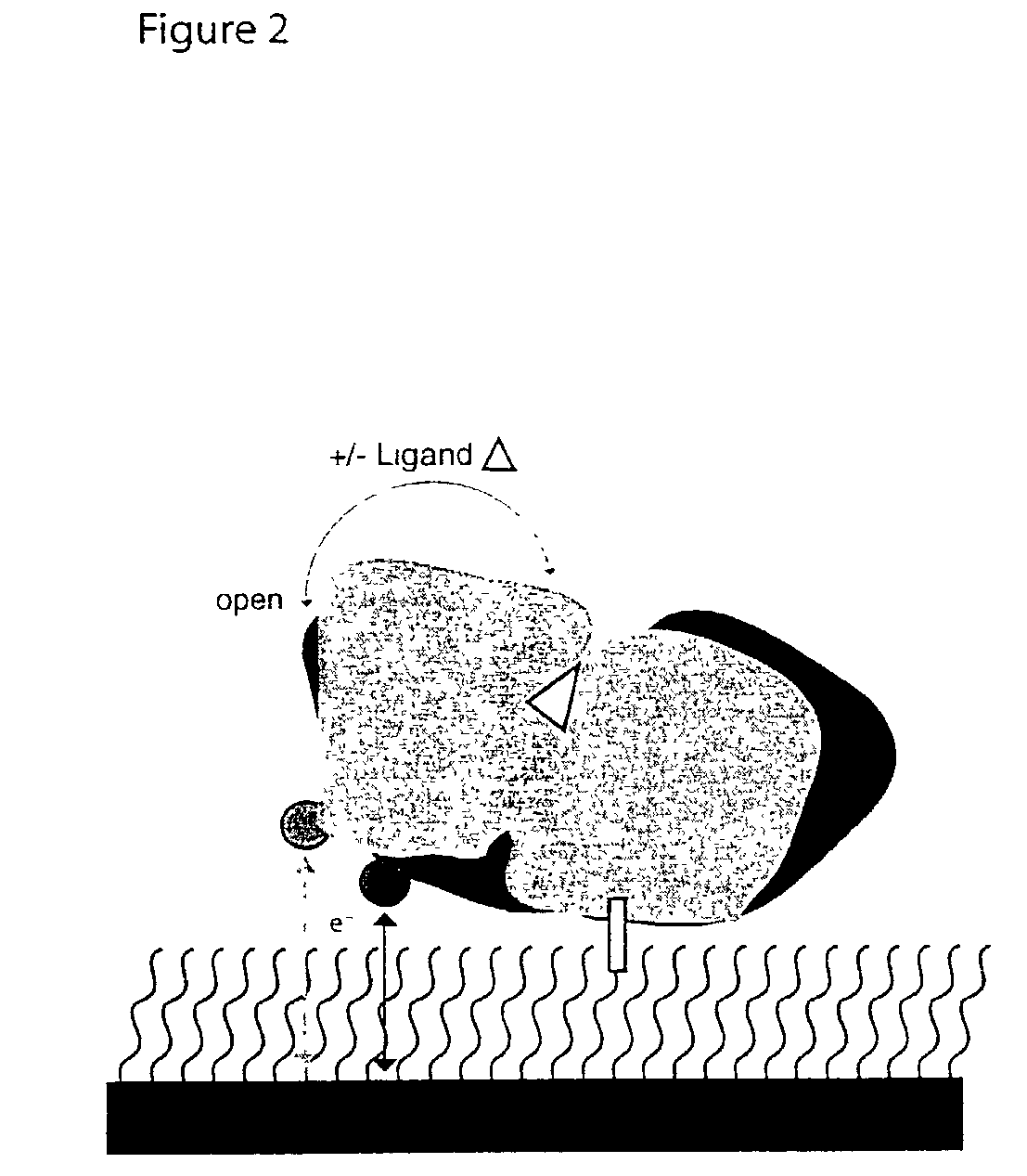
The present invention relates, in general, to biosensors and, in particular, to bioelectronic sensors comprising a macromolecule immobilized on an electrode surface so that a redox cofactor that is site-specifically attached to the surface of the macromolecule is between the macromolecule and electrode surface ligand-mediated conformational changes alter the geometry of interaction between the redox cofactor and the electrode surface resulting in a change in electronic coupling between the cofactor and electrode.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Compositions and methods for modulating cellular membrane-mediated intracellular signal transduction
InactiveUS20090227018A1Modulating gene expressionAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderCell membraneElectrochemistry
Particular aspects of the present invention provide compositions and methods for modulating intracellular signal transduction, including modulation of at least one of membrane structure, membrane potential or membrane conductivity, membrane proteins or receptors, ion channels, and calcium dependant cellular messaging systems, comprising use of the inventive electrokinetically generated solutions to impart electrochemical and / or conformational changes in membranous structures (e.g., membrane and / or membrane proteins, receptors or other components) including but not limited to G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) and / or G-proteins, and intracellular junctions. In particular embodiments, the electrokinetically generated solutions or compositions are gas-enriched and / or comprise other therapeutic agents. Other embodiments include particular therapeutic methods comprising administration or formulations of the therapeutic compositions, and in various combination treatments.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Detection of conformationally altered proteins and prions
InactiveUS20080171341A1Reliable and and safe methodRapid diagnosisPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesProteinaceous infectious particleDisease cause
Owner:ADLYFE INC
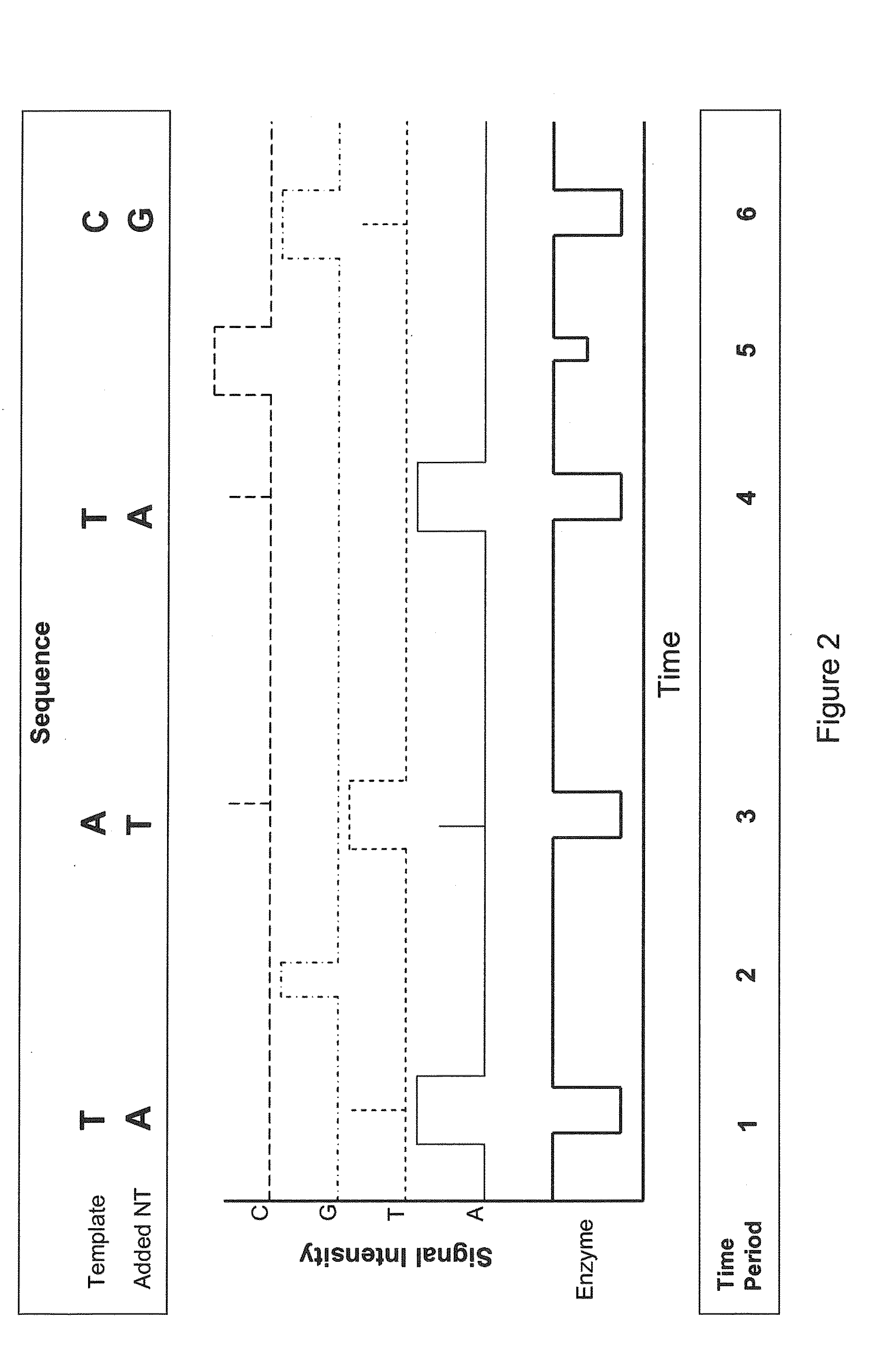
Sequencing methods using enzyme conformation
Systems and methods are provided for single-molecule sequencing of template nucleic acids in which the signal from a label attached to a polymerase enzyme is used to monitor conformational changes in the polymerase which occur while labeled nucleotides or nucleotide analogs are added to a growing nucleic acid chain which is complementary to the template nucleic acid. The signal indicative of the conformational state of the enzyme is used to determine with higher confidence when true nucleotide or nucleotide analog incorporation events occur, allowing for the improved quality of base calls and sequence determination.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Method and apparatus for reducing mitral regurgitation
InactiveUS20060229717A1Reduce regurgitationMinimally invasiveHeart valvesSurgical needlesPosterior leafletMitral valve leaflet
A method for reducing mitral regurgitation includes deploying deforming matter into a selected one of (i) a mitral valve annulus adjacent a posterior leaflet, and (ii) tissue adjacent the mitral valve annulus and proximate the posterior leaflet, to cause conformational change in the mitral valve annulus to increase mitral valve leaflet coaptation.
Owner:COHN WILLIAM E +4
DNA sequencing method
InactiveUS7939264B1Reduce the amount requiredReduce the numberMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyFluorescencePolynucleotide
The present invention pertains to a method for determining the sequence of a polynucleotide, the method relying on the detection of a conformational change in an enzyme that interacts with and processes along the polynucleotide. The detection of a conformational change may be carried out by measuring changes in a fluorophore bound to the enzyme.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Compositions and methods for modulating cellular membrane-mediated intracellular signal transduction
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., gas-enriched (e.g., oxygen-enriched) electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient to provide, upon contact with a cell, modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity. Particular aspects of the present invention provide compositions and methods suitable for modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity. Additional aspects provide compositions and methods suitable for modulating intracellular signal transduction, including modulation of at least one of membrane structure, membrane potential or membrane conductivity, membrane proteins or receptors, ion channels, and calcium dependant cellular messaging systems, comprising use of the inventive electrokinetically altered solutions to impart electrochemical and / or conformational changes in membranous structures (e.g., membrane proteins, receptors and / or other components) including G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), G-proteins, and / or intracellular junctions (e.g., tight junctions, gap junctions, zona adherins and desmasomes).
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Reagentless, reusable, bioelectronic detectors
A reagentless, reusable bioelectronic DNA, or other oligonucleotide sequence sensor is disclosed. The sensor includes an oligonucleotide (aptamer) probe tagged with a electroactive, redoxable moiety, self-assembled on or near an electrode. This surface-confined oligonucleotide (aptamer) probe structure undergoes hybridization-induced conformational change in the presence of the target which changes the electron-transfer distance between the redoxable moiety and the electrode thereby providing a detectable signal change. In an alternative embodiment, the target can harbor the redoxable moiety.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
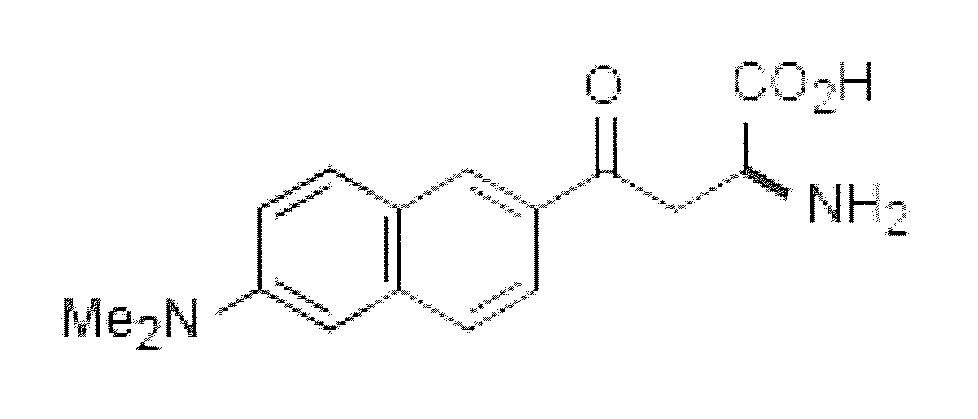
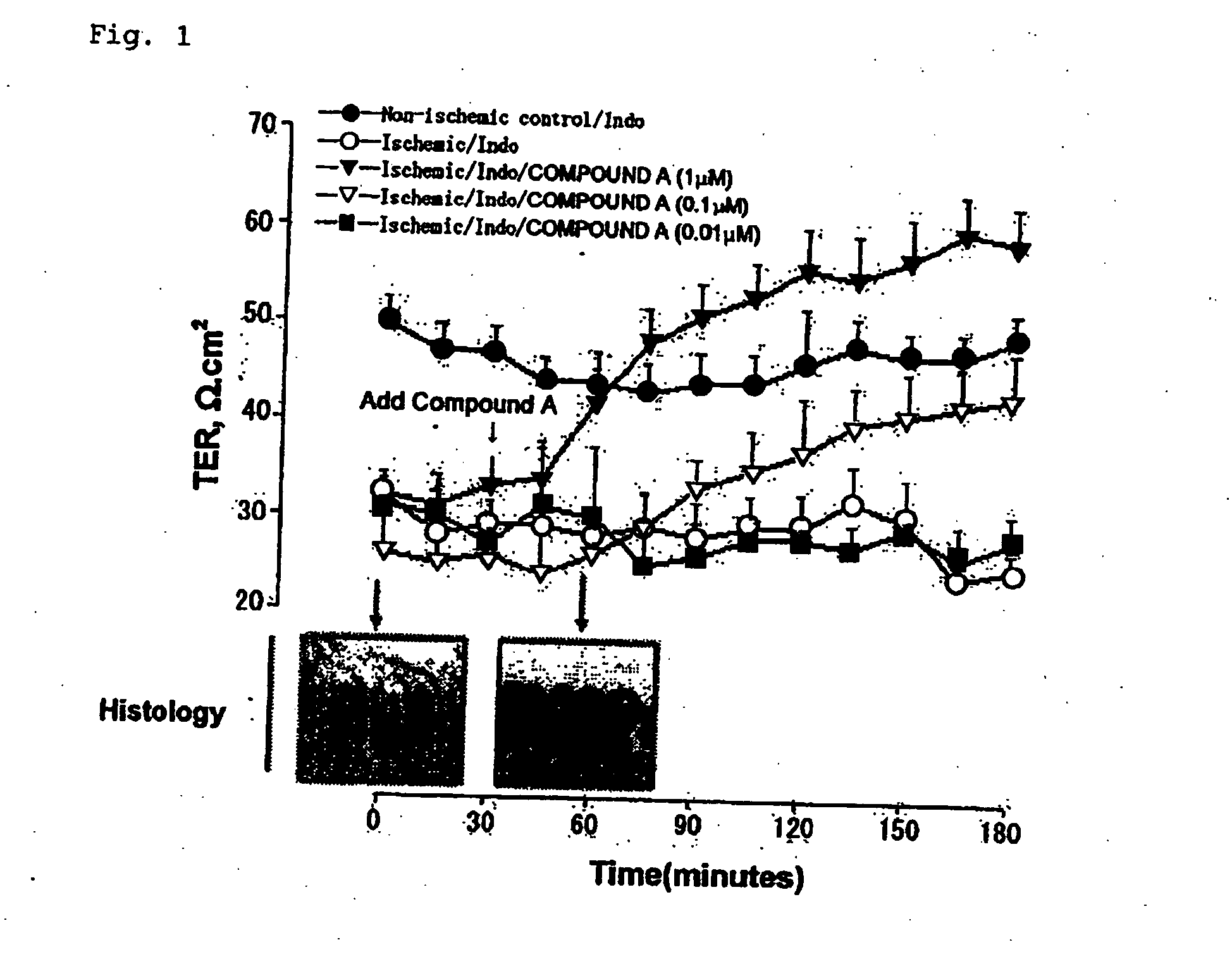
Method for treating mucosal disorders
Provided is a method for treating mucosal disorders using a specific prostaglandin compound. The prostaglandin compound induces a conformational change in the tight junction that results in recovery of mucosal barrier function. Accordingly, the prostaglandin compound used herein is useful for the treatment of mucosal disorders.
Owner:SUCAMPO +1
Detection of nucleic acid polymerase conformational changes using a nanotube
InactiveUS20180051316A1Low affinityIncrease concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesNucleotidePolynucleotide
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
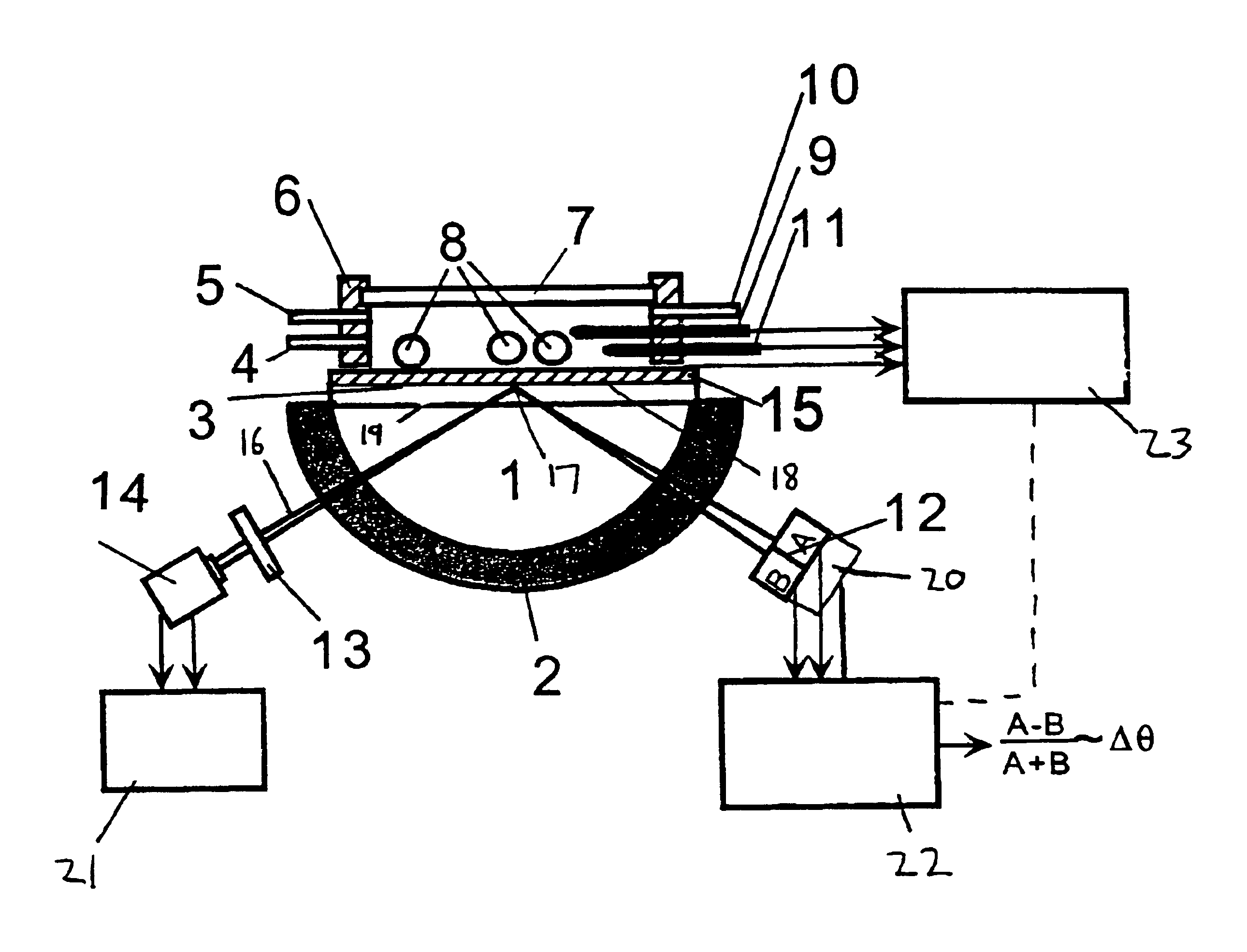
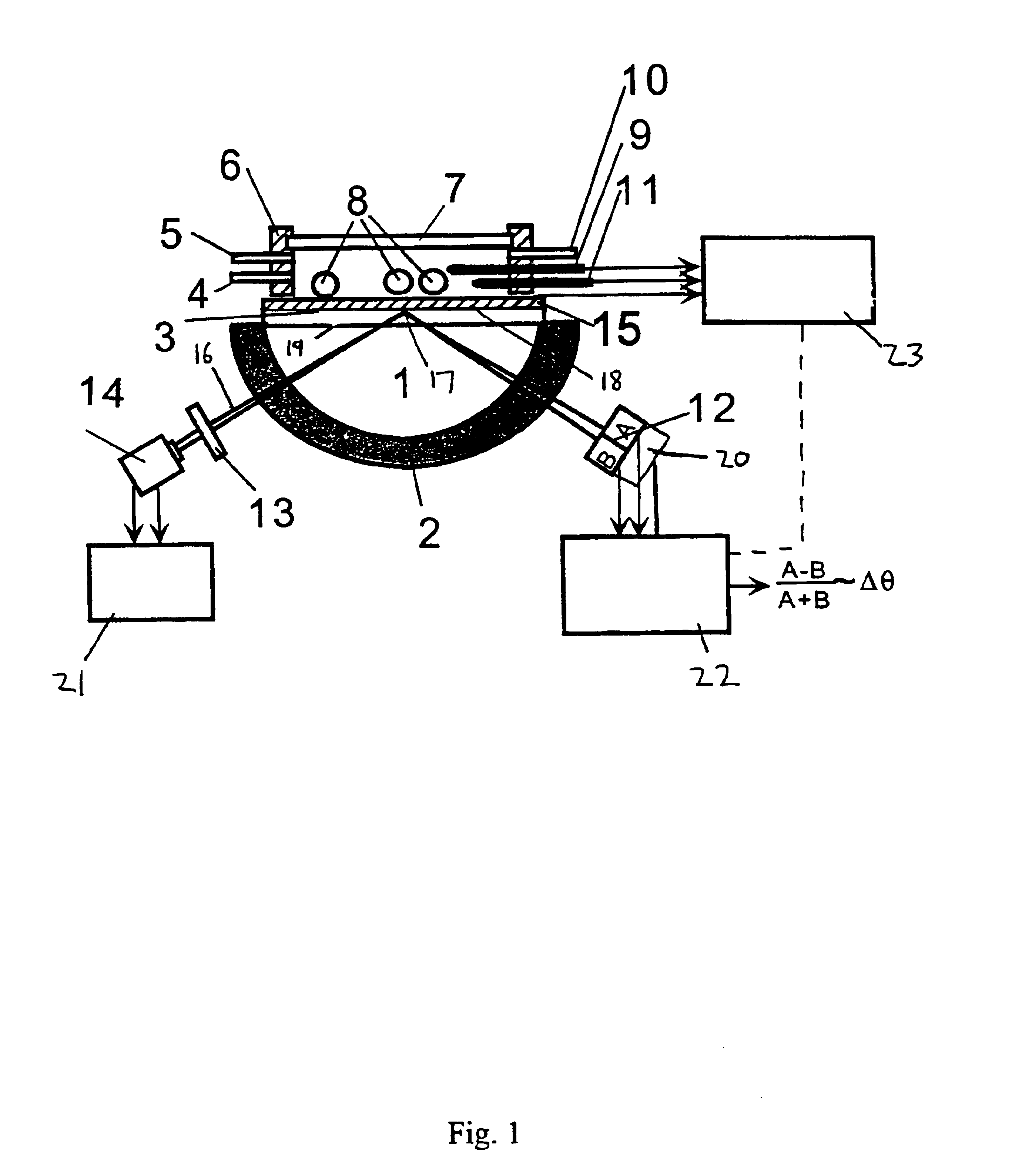
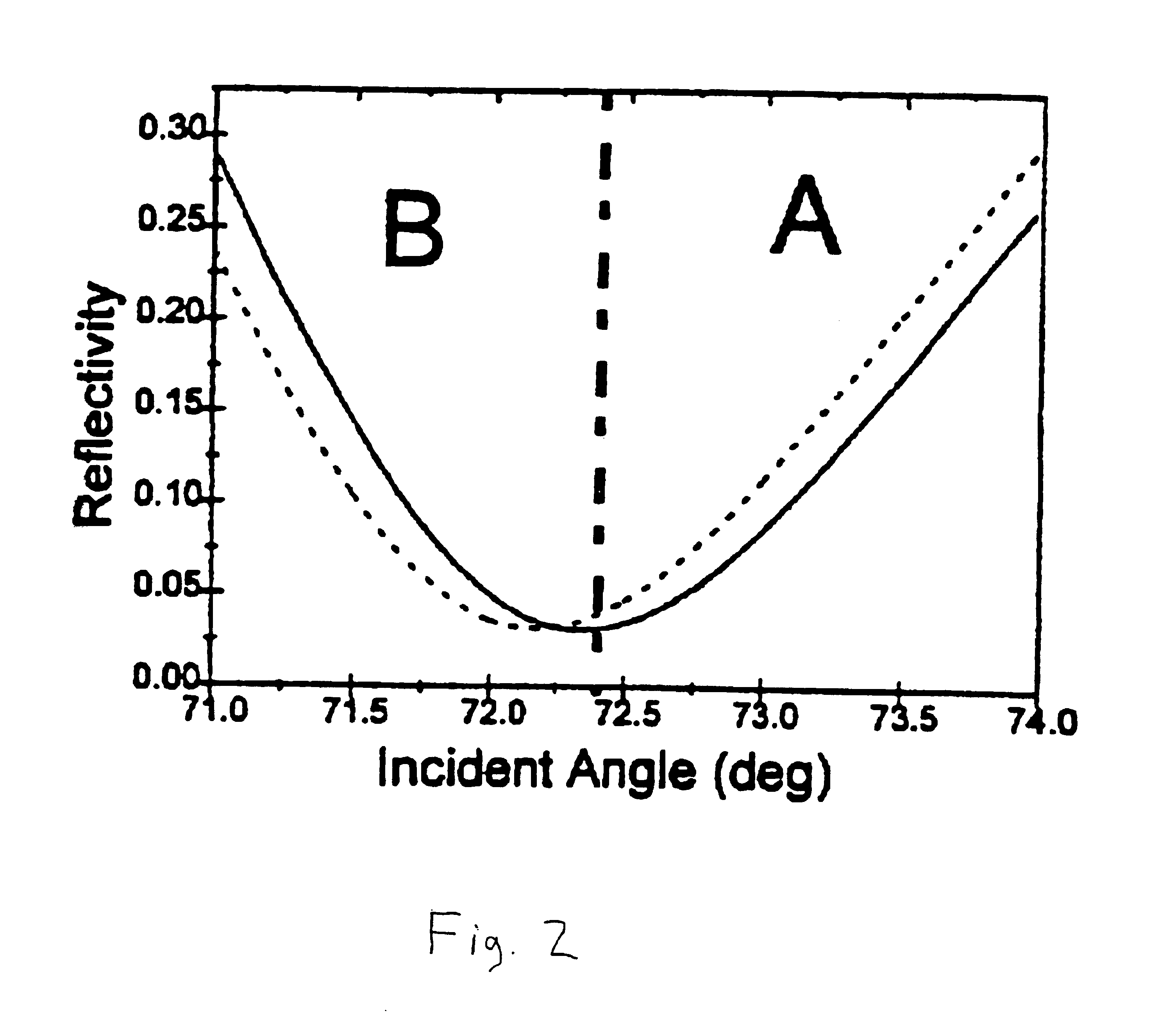
Surface plasmon resonance detection with high angular resolution and fast response time
InactiveUS6784999B1Scattering properties measurementsElectron transfer reactionsDifferential signaling
A device and method of detecting surface plasmon resonance for sensing molecules or conformational changes in molecules with high resolution and fast response time is disclosed. Light from a light source (14) is focused through a prism onto a metal thin film (15) on which sample molecules to be detected are adsorbed. The total internal reflection of the laser / incident light is collected with a differential position or intensity sensitive photo-detecting device instead of a single cell or an array of photo-detectors (12) that are widely used in previous works. The ratio of the differential signal to the sum signal of the differential position or intensity sensitive photo-detecting device (12) provides an accurate measurement of the shift in the surface plasmon resonance angle caused by the adsorption of molecules onto the metal films (15) or by conformational changes in the adsorbed molecules. The present invention requires no numerical fitting to determine the resonant angle and the setup is compact and immune to background light, The methods and sensors of this invention can be used in numerous biological, biochemical, and chemical applications such as measuring subtle conformational changes in molecules and electron transfer reactions can be studied.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
Measuringm ethod and device for fiber material transverse compression property
InactiveCN1587965ASolving precise measurementsAccurate Lateral Compression MeasurementOptical rangefindersPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryFiberObservational error
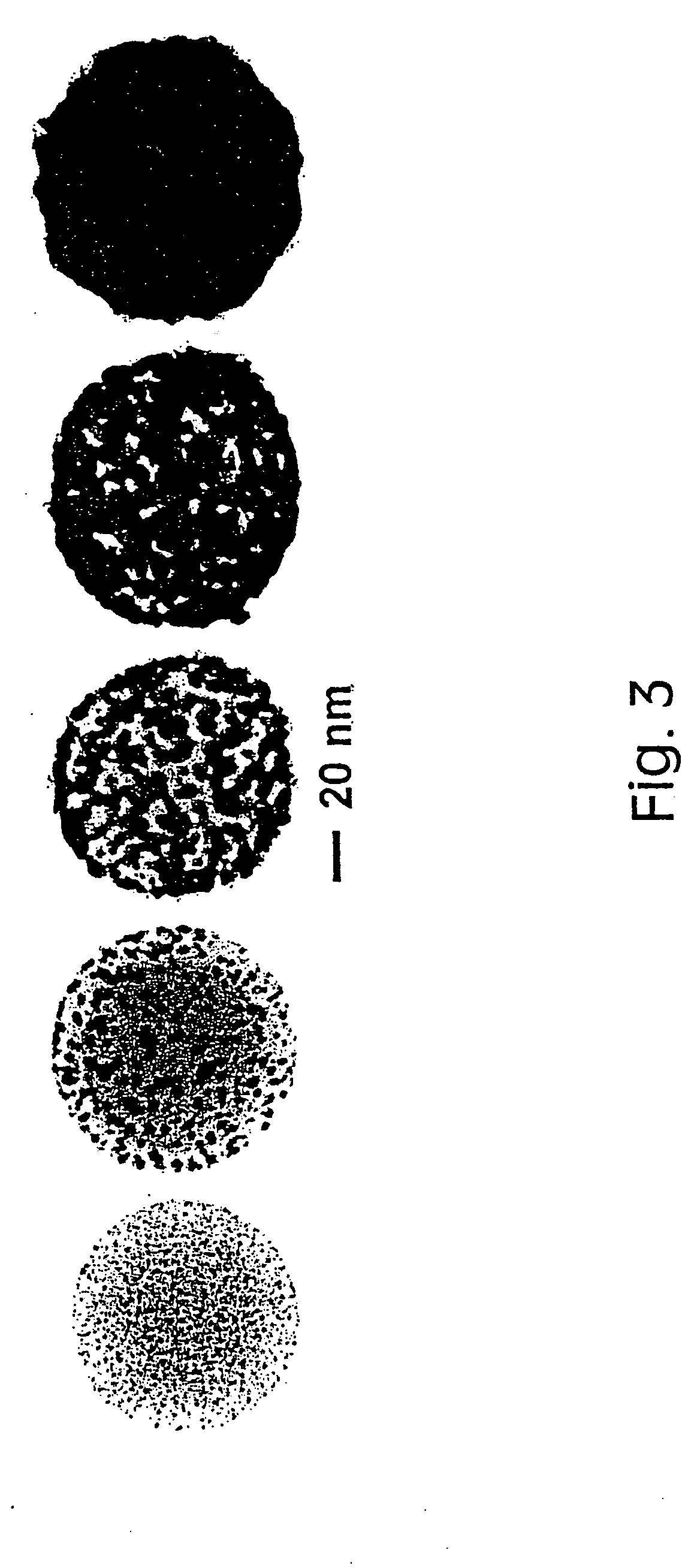
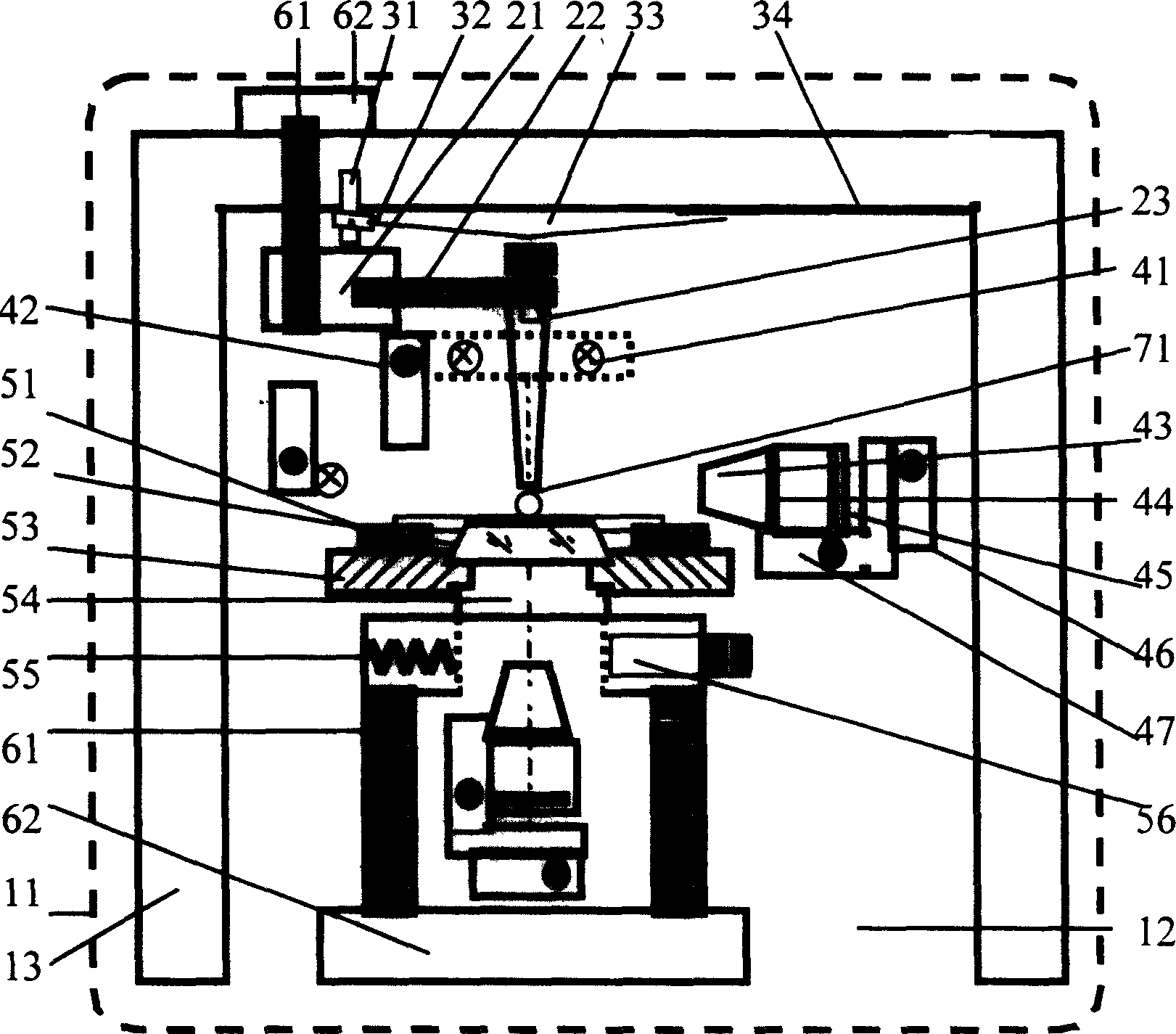
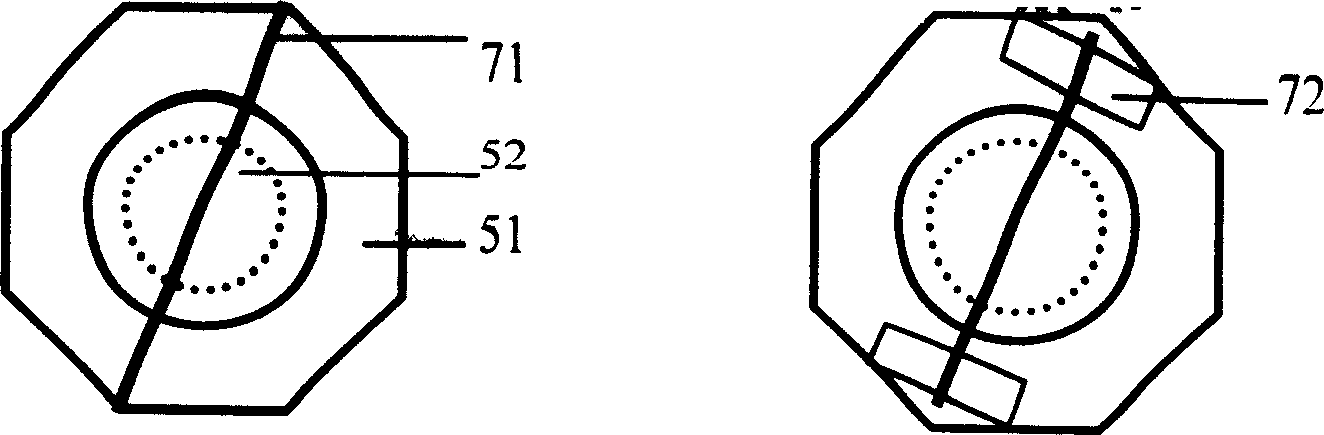
The invention relates to lateral compression performance measuring method and device of fibrous material, comprising the parts of fiber lateral cimpression element using pressure head on cantilever beam to lateral compress filament and overlapping fiber sample in multiangular tray, fiber deformation observing parts using two objectives with different direction finish stereo-observation and measurement to compressed fiber, compressive stress measuring elements with deflection correction to put in real time change of stress of pressure head in computer and the deflection correction is to correct vertical compressed displacement by small deflection deflection of cantilever beam when laser reflects measuring compression. By using multiple measurement of stress and conformational change and compact and novel design, lateral compression shape measurement is fast, accurate, overall, its measurement error has decreased greatly and the method is suitable for various kinds of fibrous material.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Electrochemical sensor for detecting kanamycin based on nucleic acid aptamer and preparation method of sensor
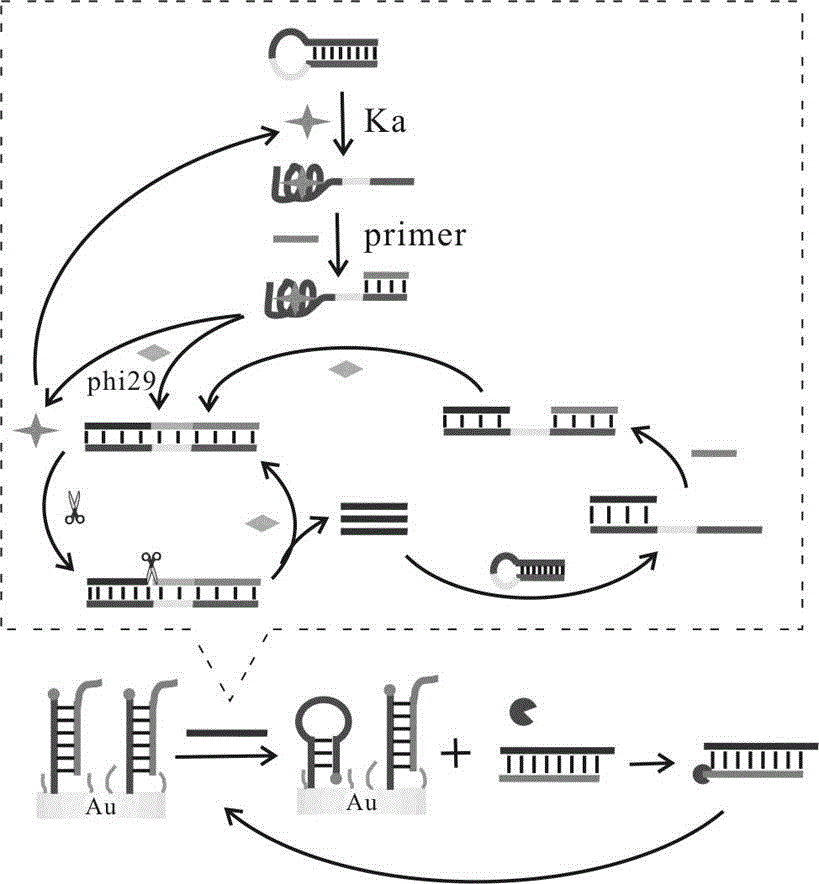
InactiveCN105158320AAchieve high specificity detectionAchieve recyclingMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerKanamycin
The invention relates to a biosensor for testing kanamycin based on conformational changes of a target-induced nucleic acid aptamer. The biosensor is prepared by sequentially modifying an HAP2 layer, a Helper layer and a homogeneous reaction mixed solution onto an electrode. The biosensor has the advantages that the specificity recognition function of the nucleic acid aptamer is adopted, and the aptamer of kanamycin is utilized as a recognition substance for high specificity detection of kanamycin in a target; through utilization of nucleic acid tool enzymes, the target is recycled and a signal amplification function is achieved, so that the detection sensitivity can be improved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com