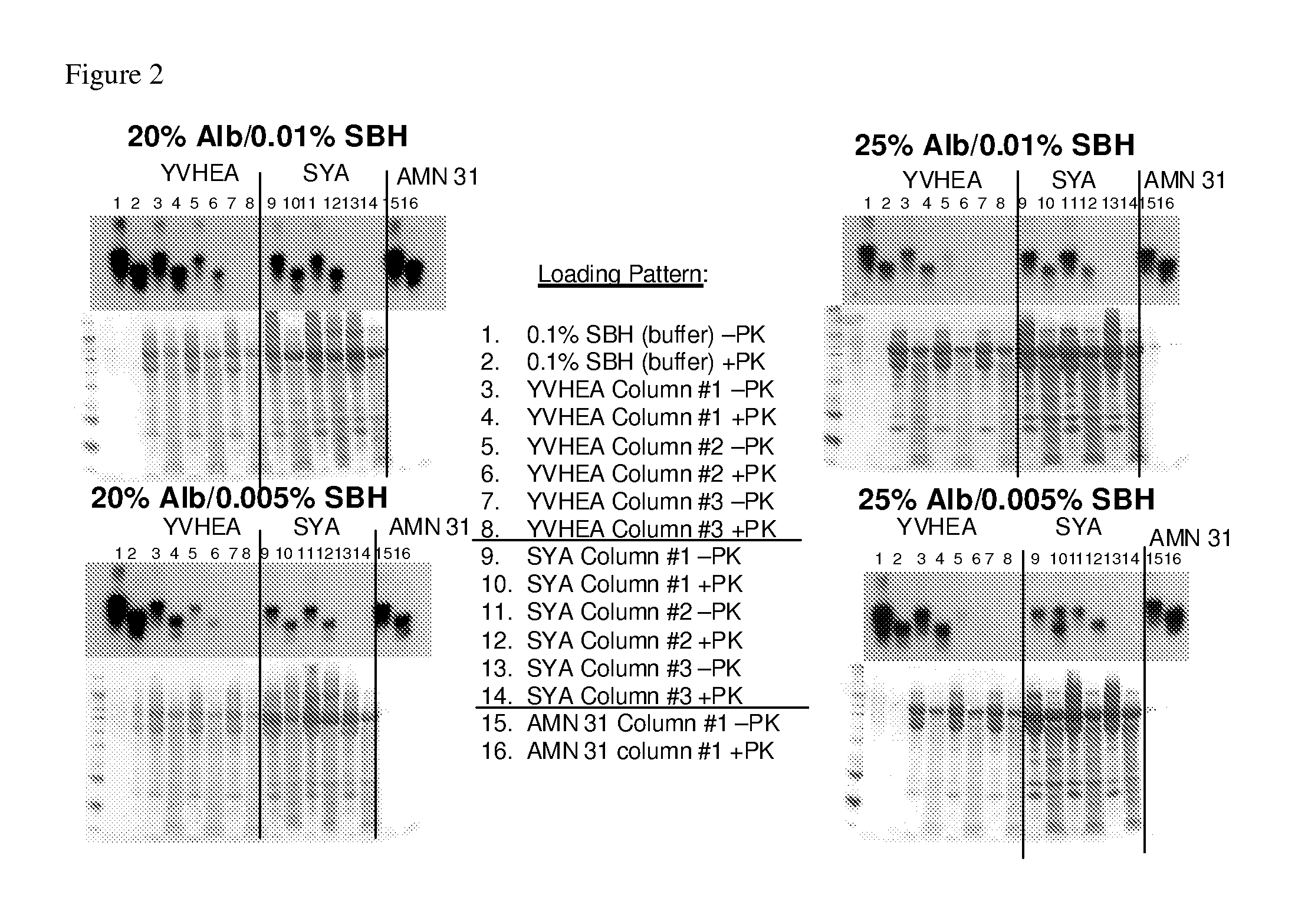
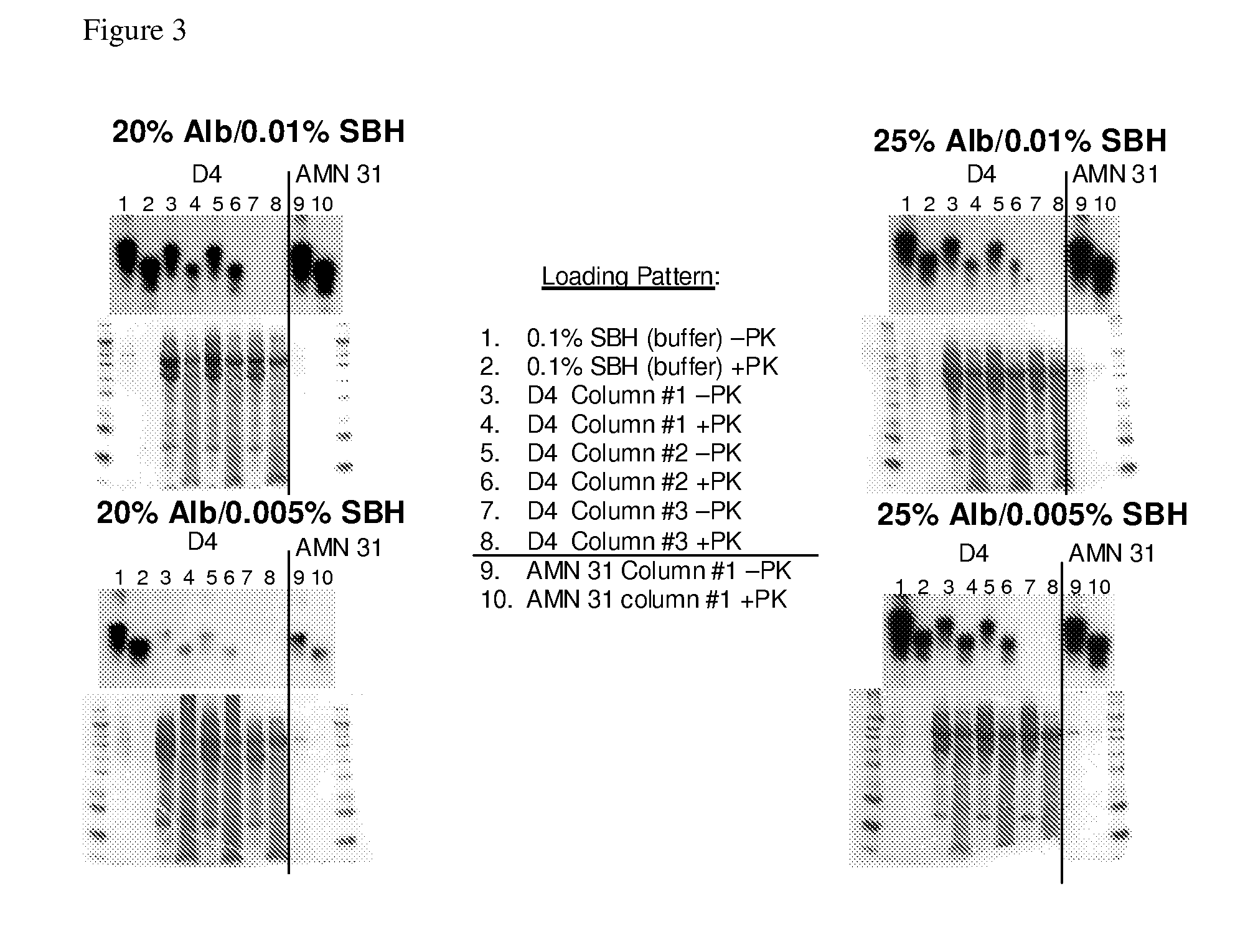
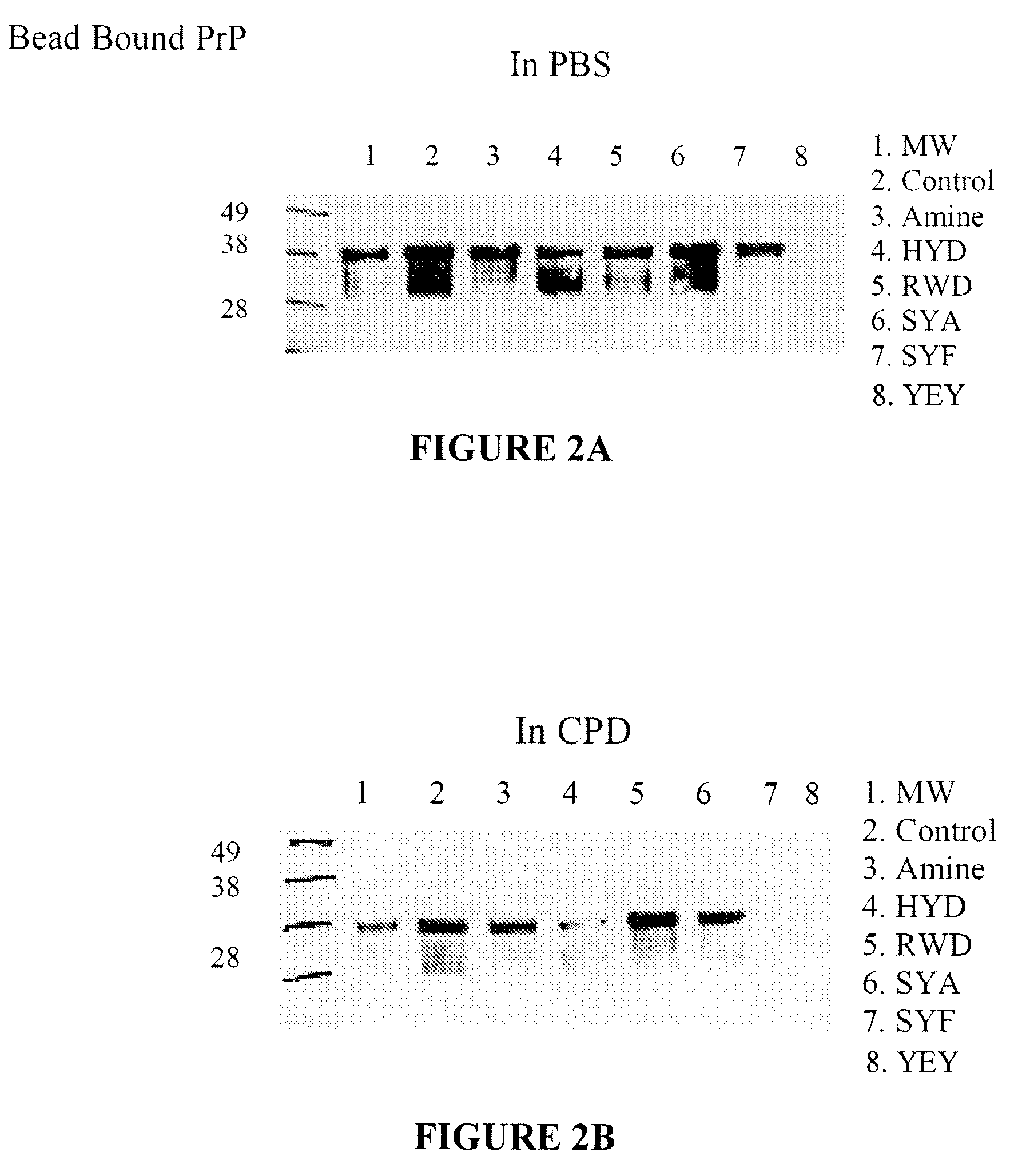
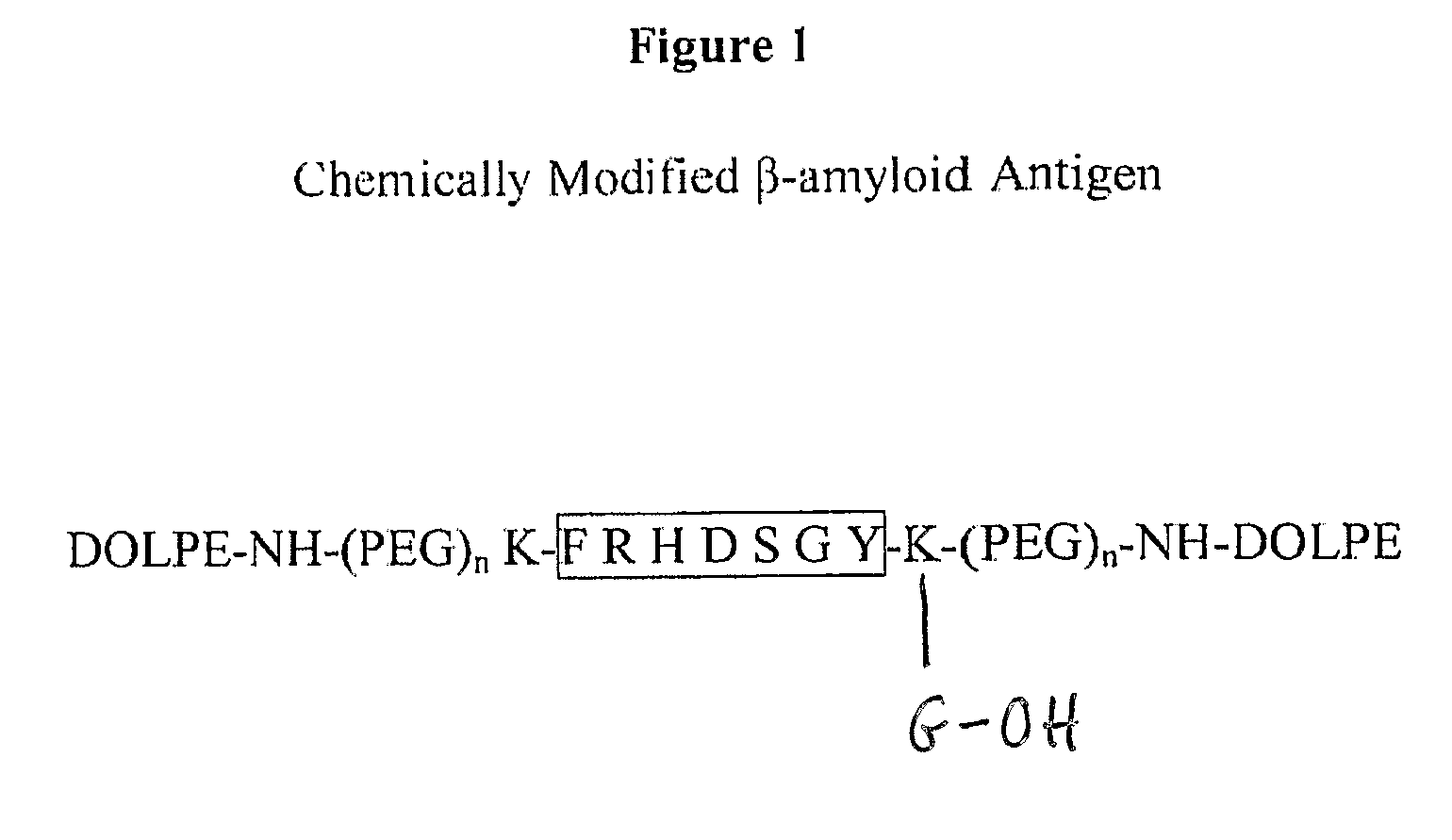Patents
Literature
184 results about "Prion Proteins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
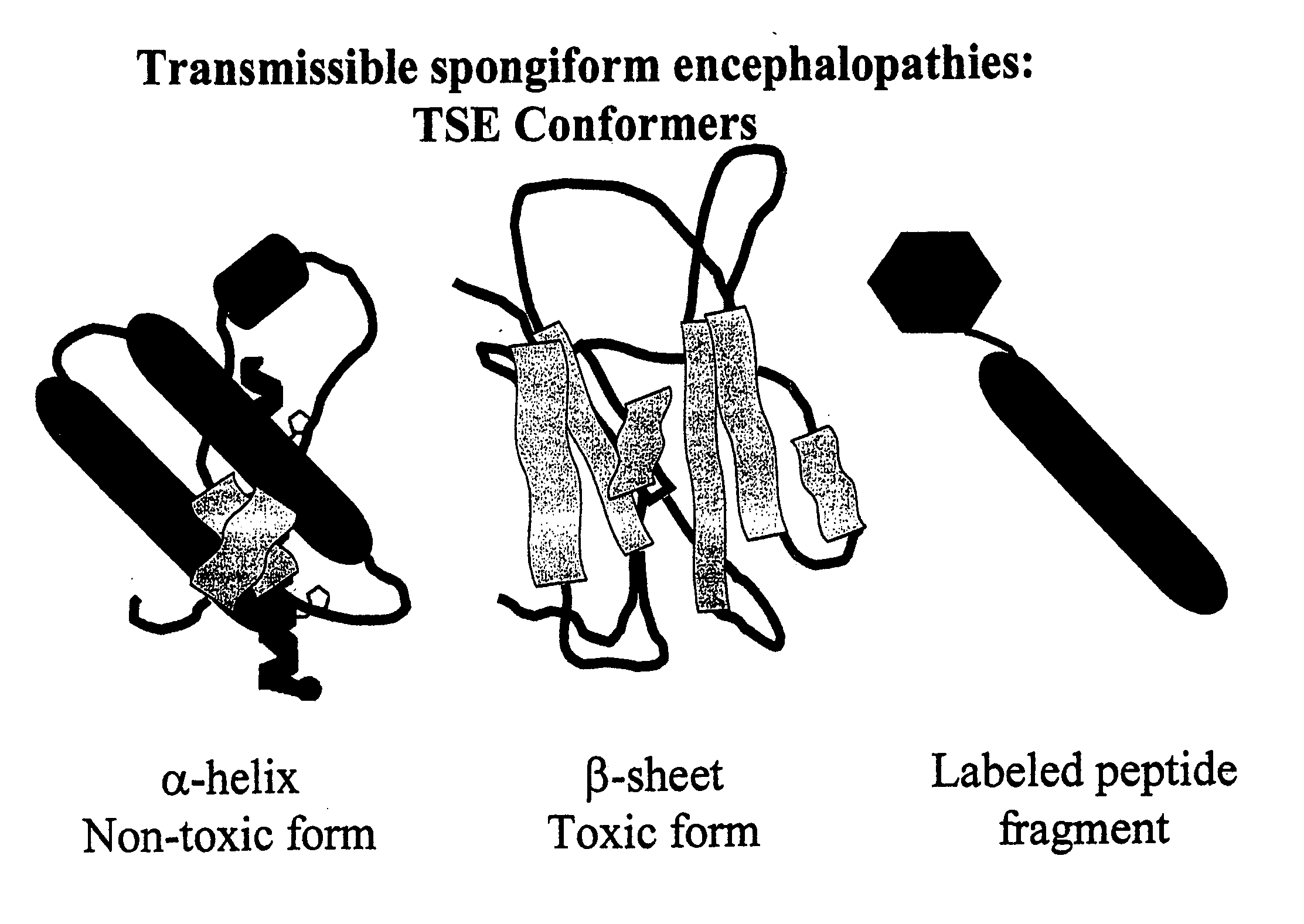
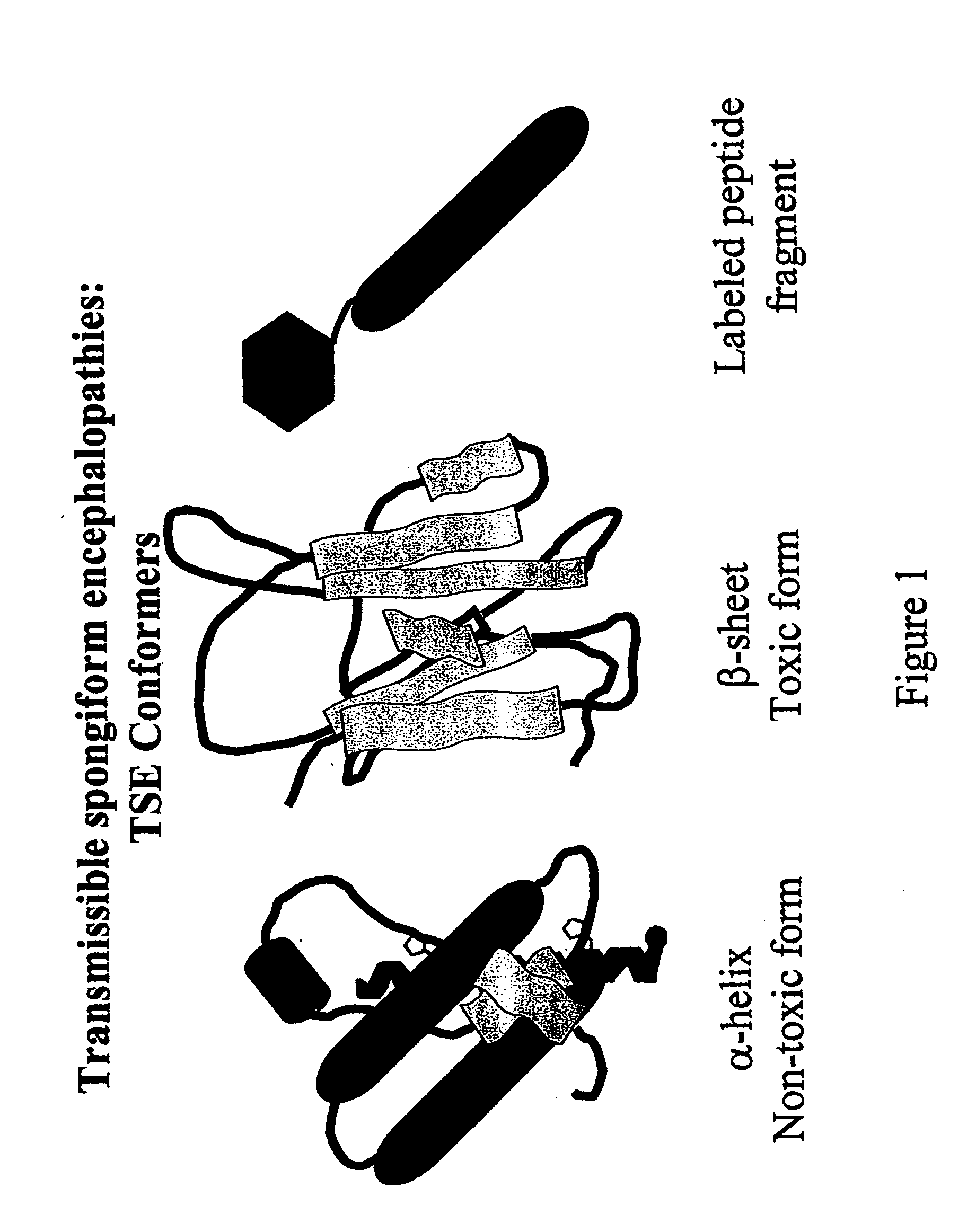
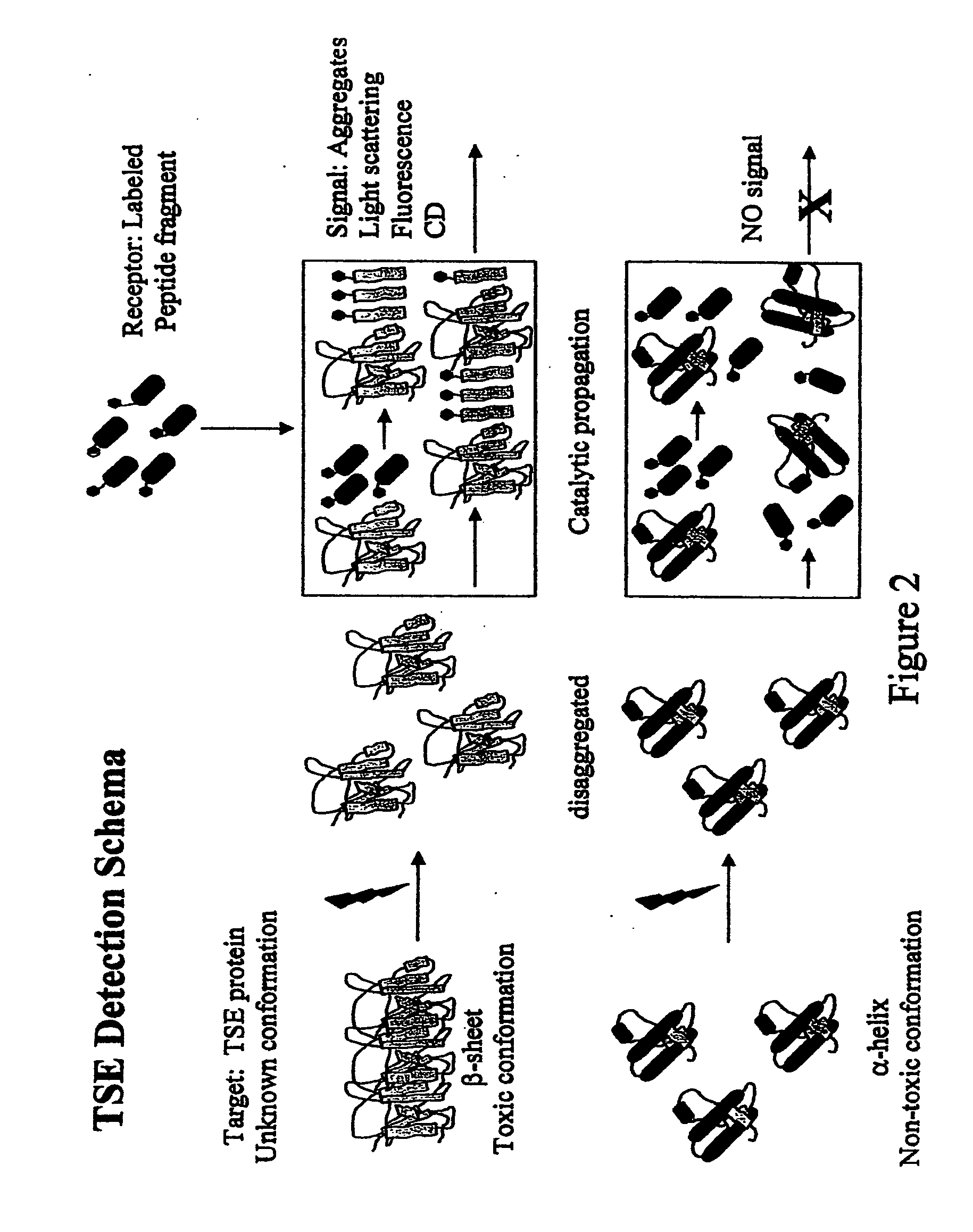
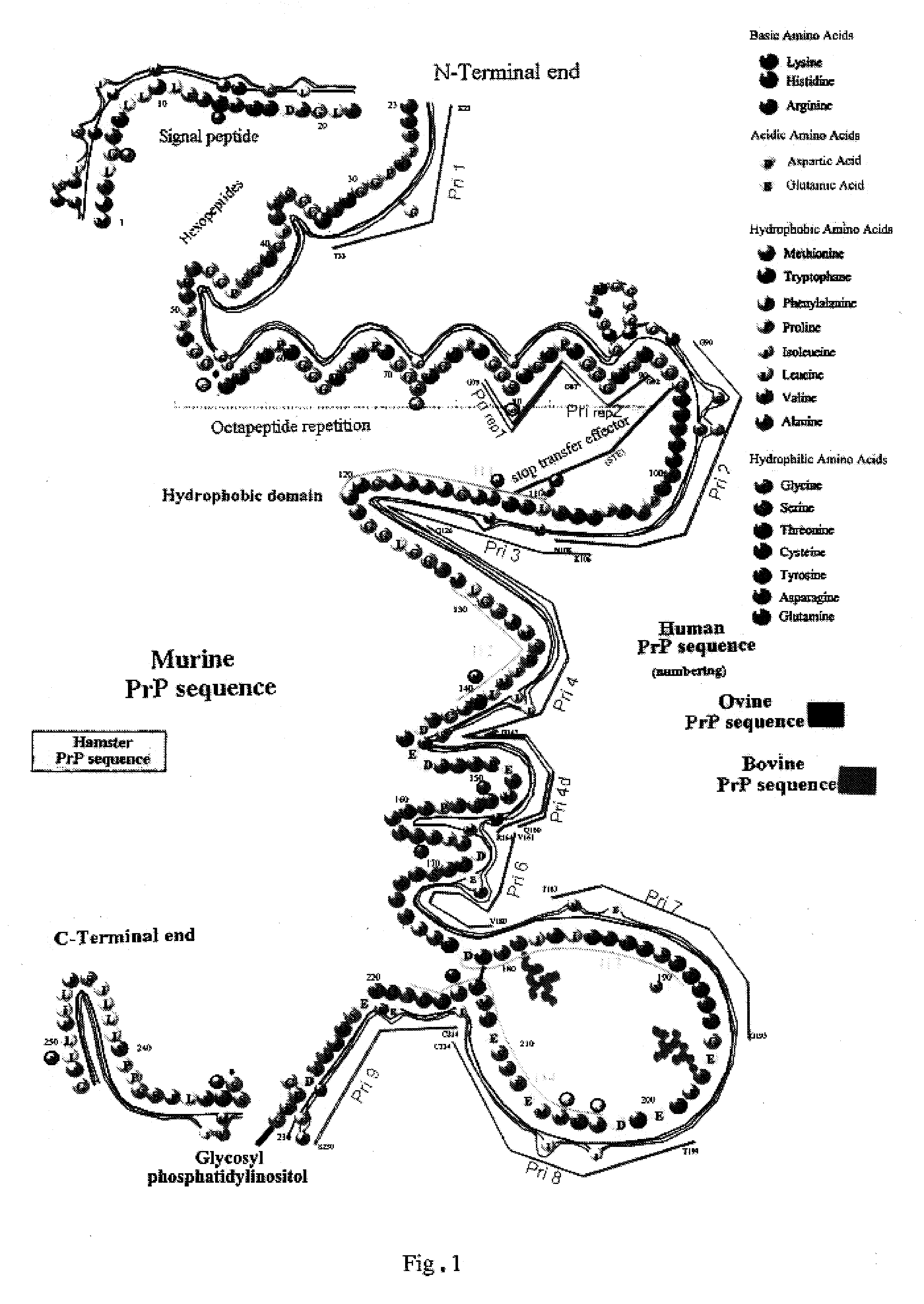
The term "prion" is derived from proteinacious infectious particle and refers to the pathogen that causes transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs). This small infectious particle is a disease-causing form of a protein called cellular prion protein (PrPc).
Optical sensor unit and procedure for the ultrasensitive detection of chemical or biochemical analytes
InactiveUS6346376B1High sensitivitySelective retentionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpecific detectionNon-covalent interactions
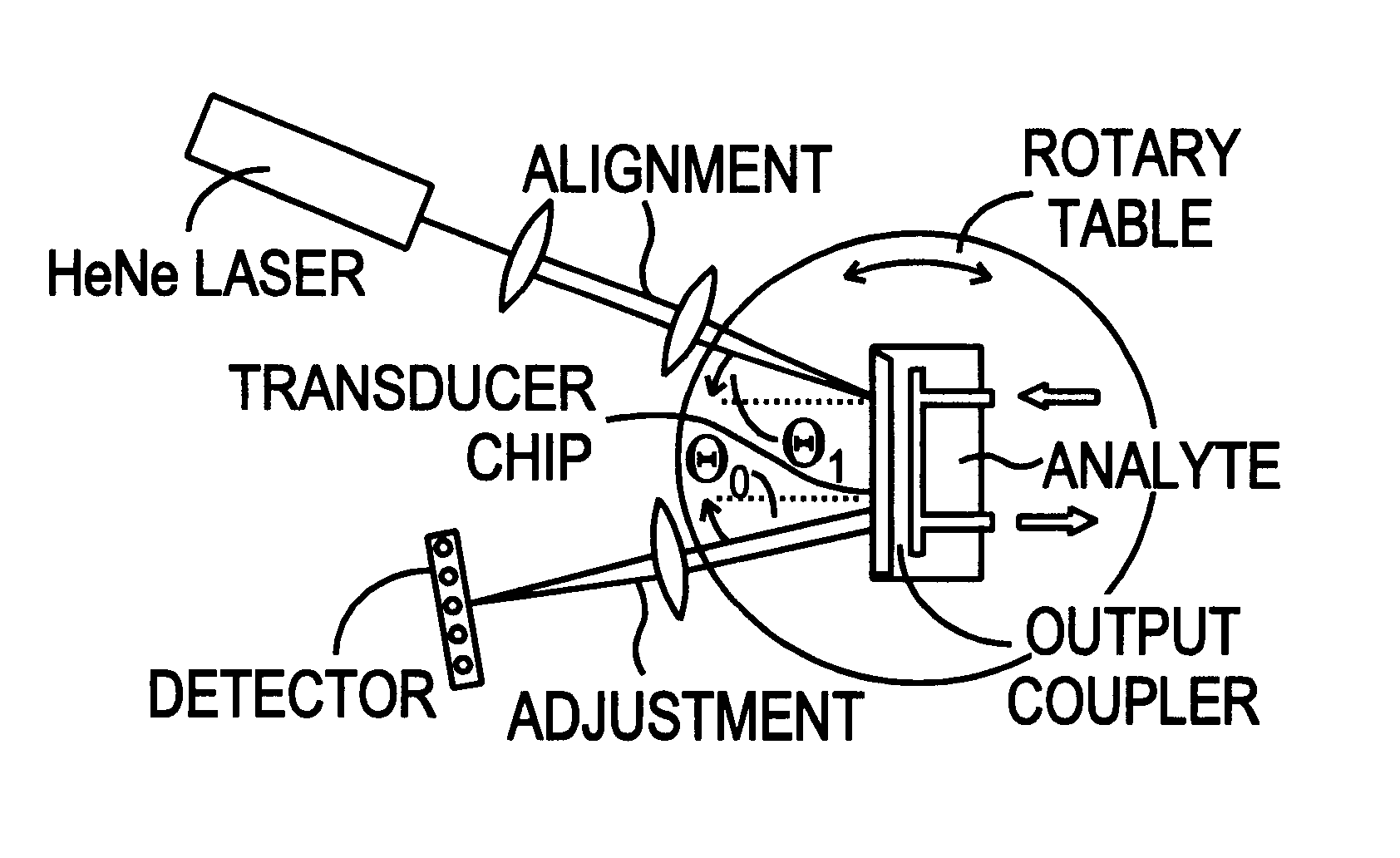
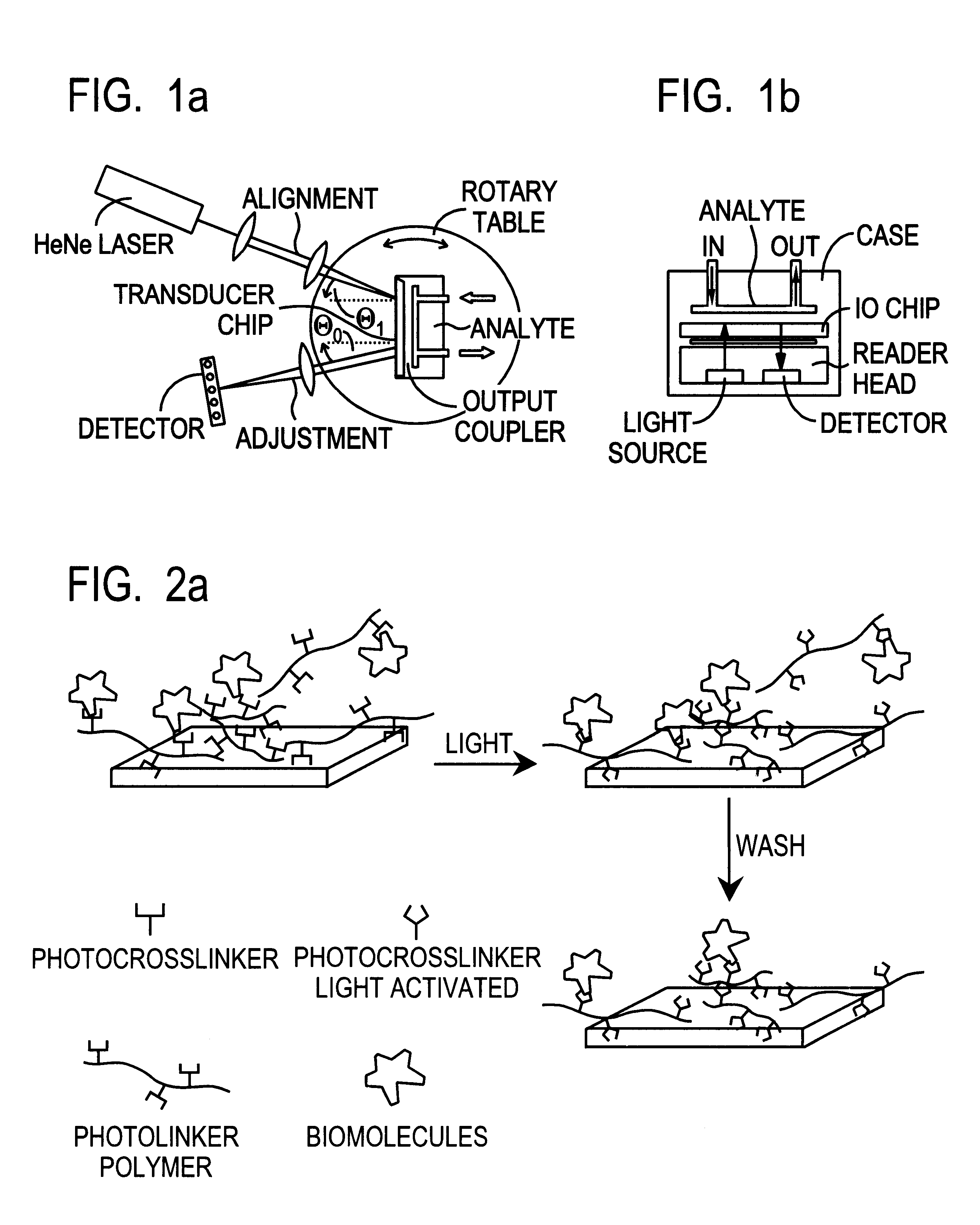
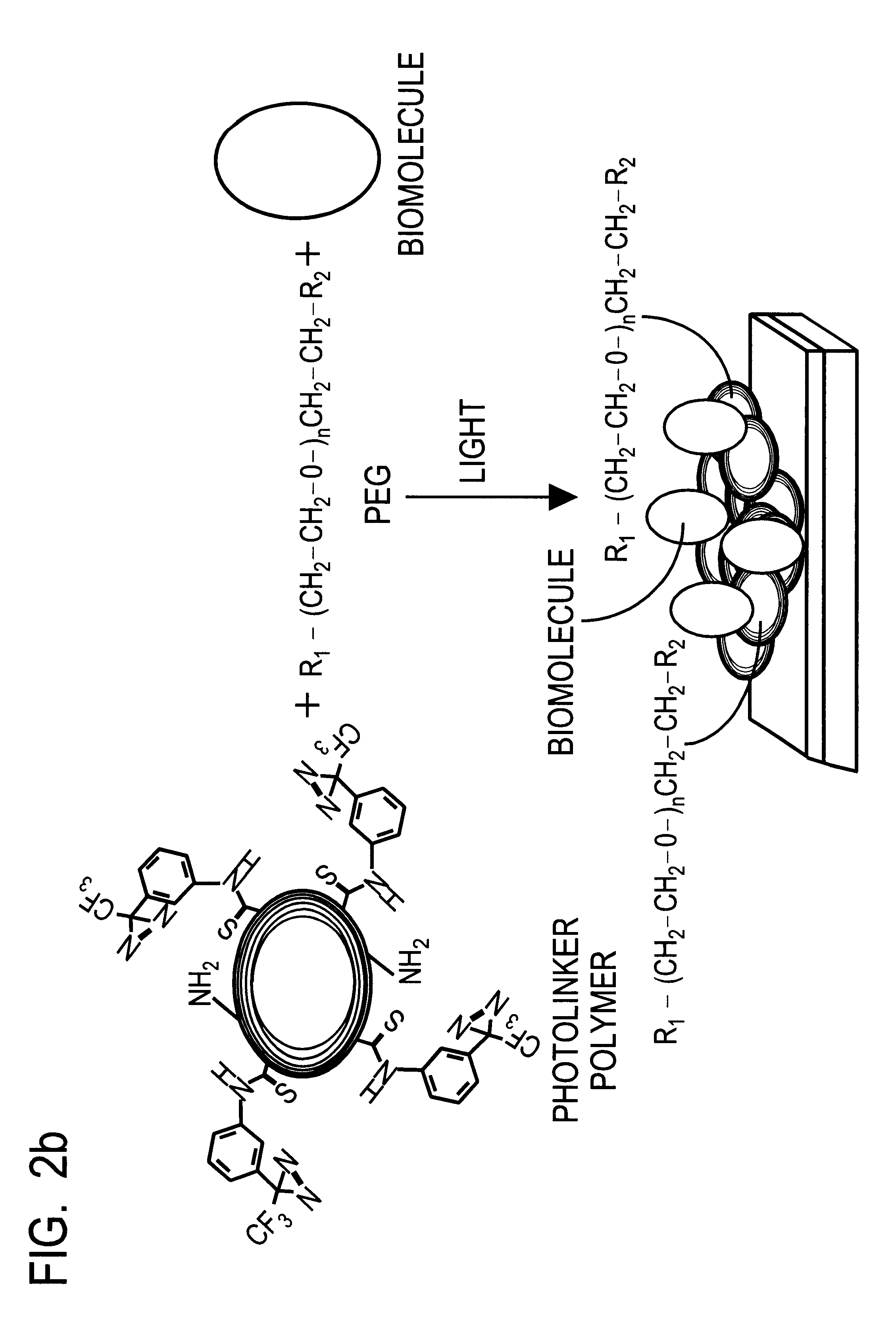
This document describes an optical sensor unit and a procedure for the specific detection and identification of biomolecules at high sensitivity in real fluids and tissue homogenates. High detection limits are reached by the combination of i) label-free integrated optical detection of molecular interactions, ii) the use of specific bioconstituents for sensitive detection and iii) planar optical transducer surfaces appropriately engineered for suppression of non-specific binding, internal referencing and calibration. Applications include the detection of prion proteins and identification of those biomolecules which non-covalently interact with surface immobilized prion proteins and are intrinsically involved in the cause of prion related disease.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
Method and kit for extracting prion protein
InactiveUS6150172AMethod is fastThe testing process is simplePeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesIonic strengthSheep brain
A method for extracting prion protein from a biological material, e.g., an animal tissue or product. In a specific example, abnormal prion protein is extracted from homogenized sheep brain with hexafluoro-2-propanol. The hexafluoro-2-propanol is separated from the aqueous brain preparation by increasing the ionic strength of the aqueous solution. Prion protein in the organic extract can be further purified, or the extract can be tested, e.g., by immunoassay, for the presence of prion protein, and more particularly abnormal prion protein. The extraction process permits testing for the presence of abnormal prior protein, e.g., for diagnosis of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSE).
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Diagnostic probes and remedies for diseases with accumulation of prion protein, and stains for prion protein
InactiveUS20050260126A1Strong binding specificityImprove blood-brain barrier permeabilityNervous disorderOrganic chemistry methodsChemistryPrion Proteins
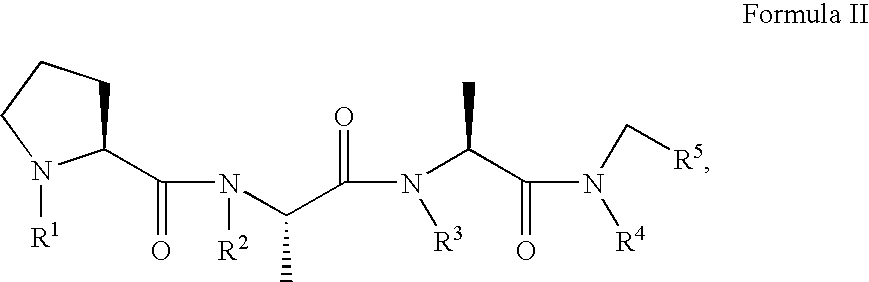
A compound, which is used for the diagnosis and the prophylaxis / treatment of diseases in which prion protein is accumulated, or specific staining of abnormal prion protein in samples, represented by the formula (I) or (II): or a salt or solvate thereof.
Owner:BF RES INST +1
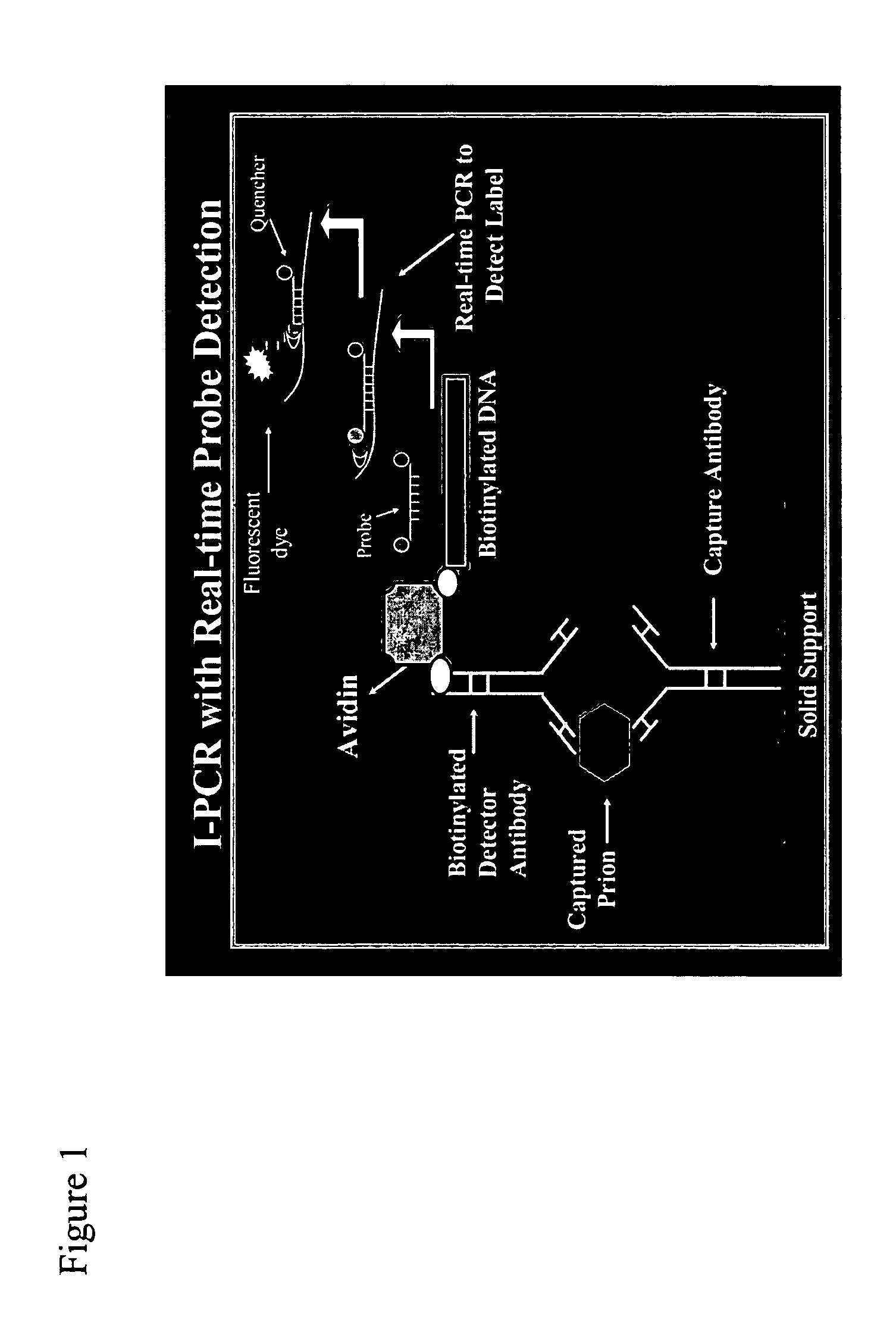
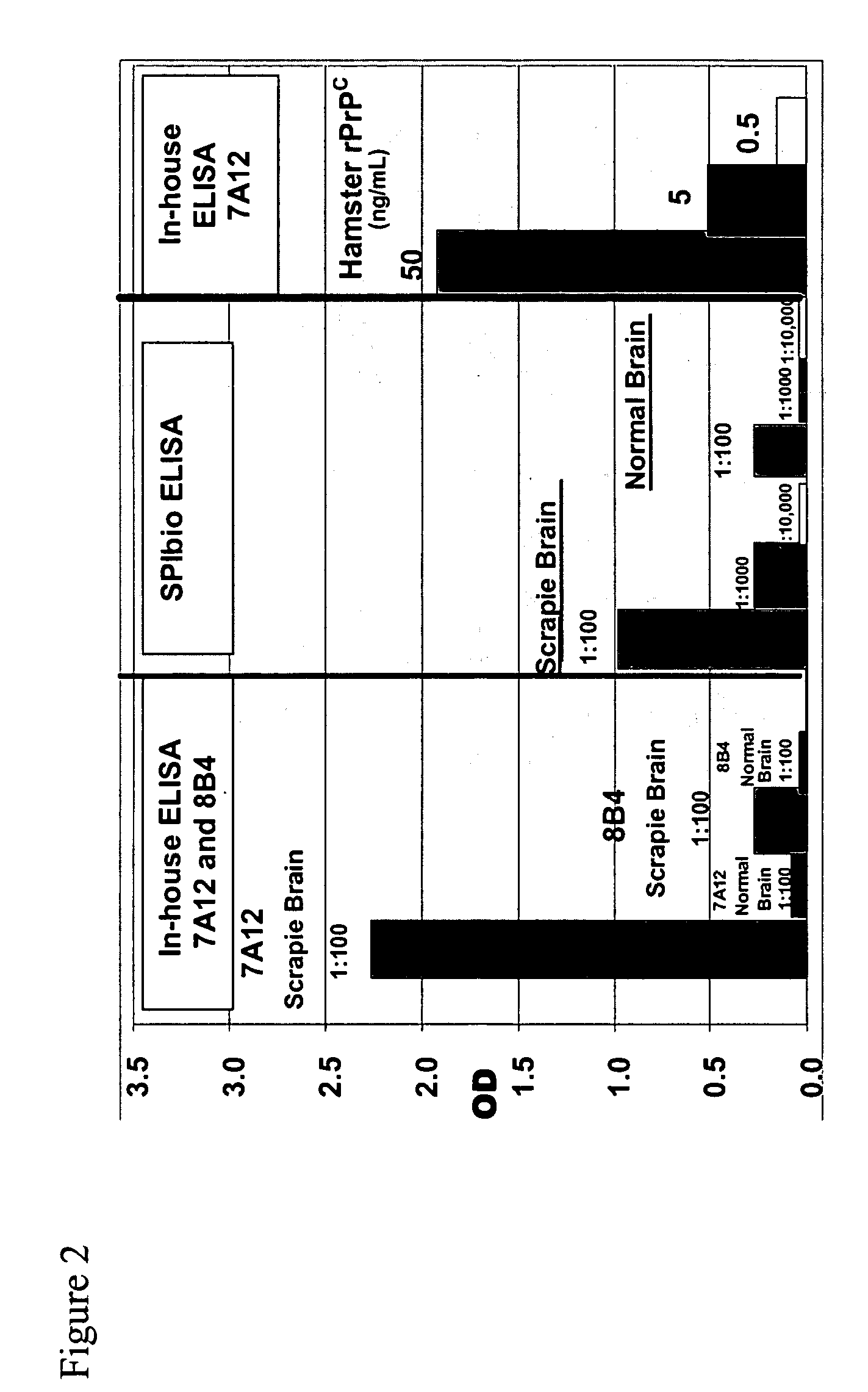
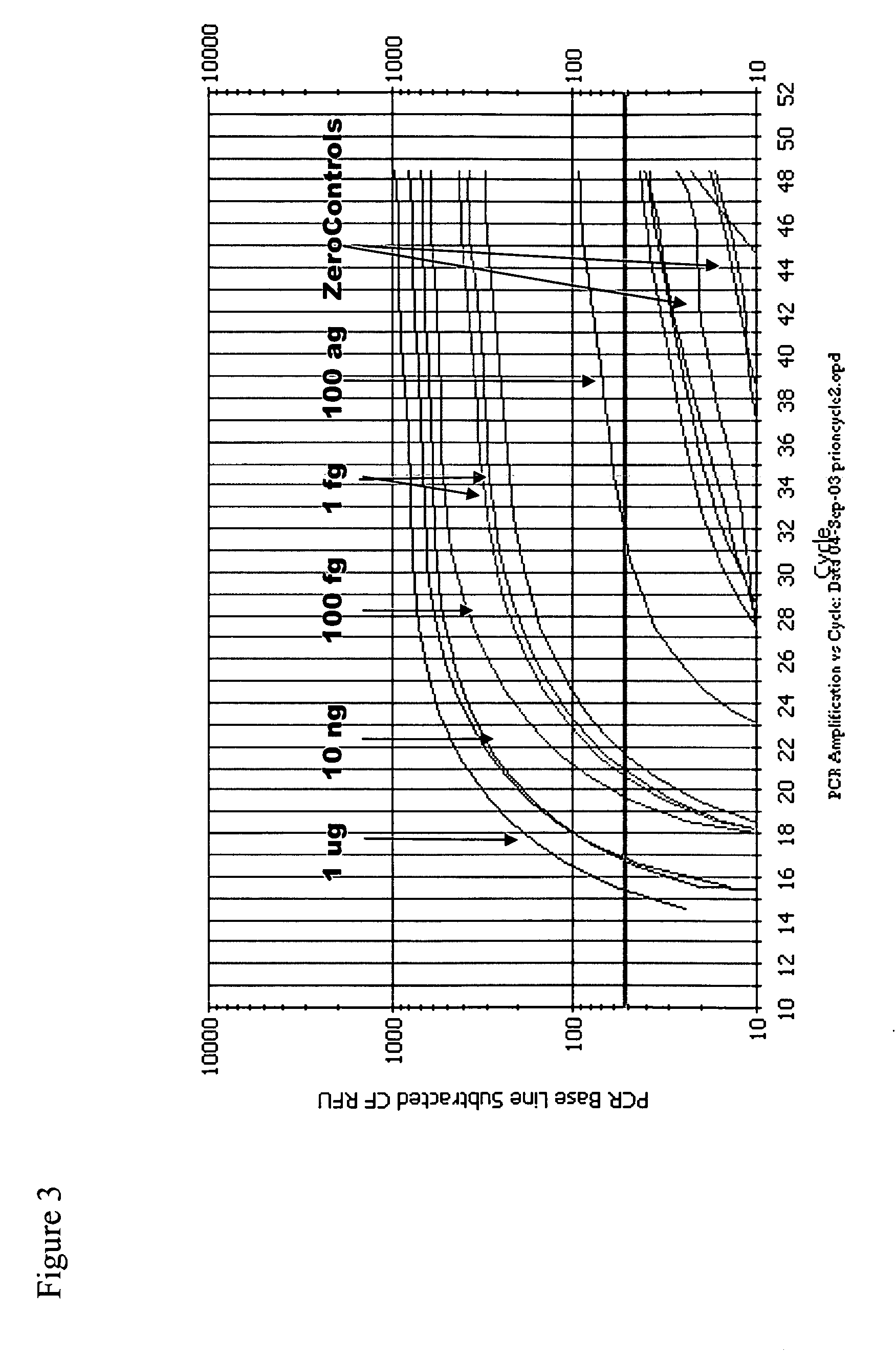
Immuno-PCR method for the detection of a biomolecule in a test sample
InactiveUS20050239108A1Simple and highly sensitiveSimple and highly methodMicrobiological testing/measurementAssay labelsHuman bodyNucleic acid amplification technique
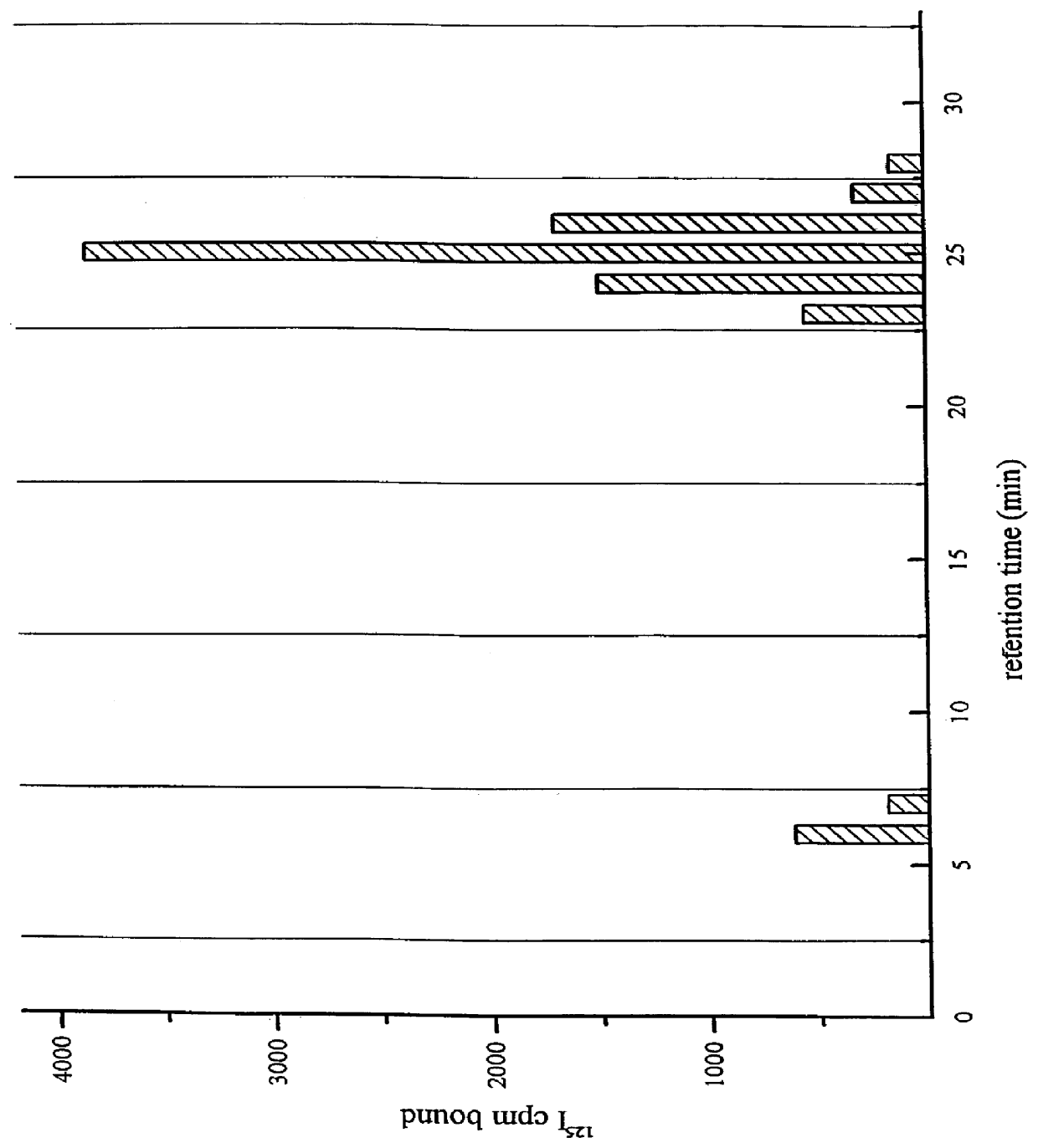
The invention relates to methods and kits for detecting and / or monitoring biological molecules in a test sample. For example, the invention relates to methods and kits for detecting and / or monitoring HIV p24 antigen in human body fluid, biological toxins such as ricin or botulism in an environmental or biological sample, and prion protein from human, deer or bovine, such as PrPSC, in a biological sample. The antigen detection signal is boosted by amplification of a polynucleotide linked to a detector molecule using methods for nucleic acid amplification technology.
Owner:UNIV OF MARLAND BALTIMORE +1
Method to measure and characterize microvesicles in the human body fluids
InactiveUS20090220944A1Low efficiencySimple yet reliableMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisHuman bodyNon invasive
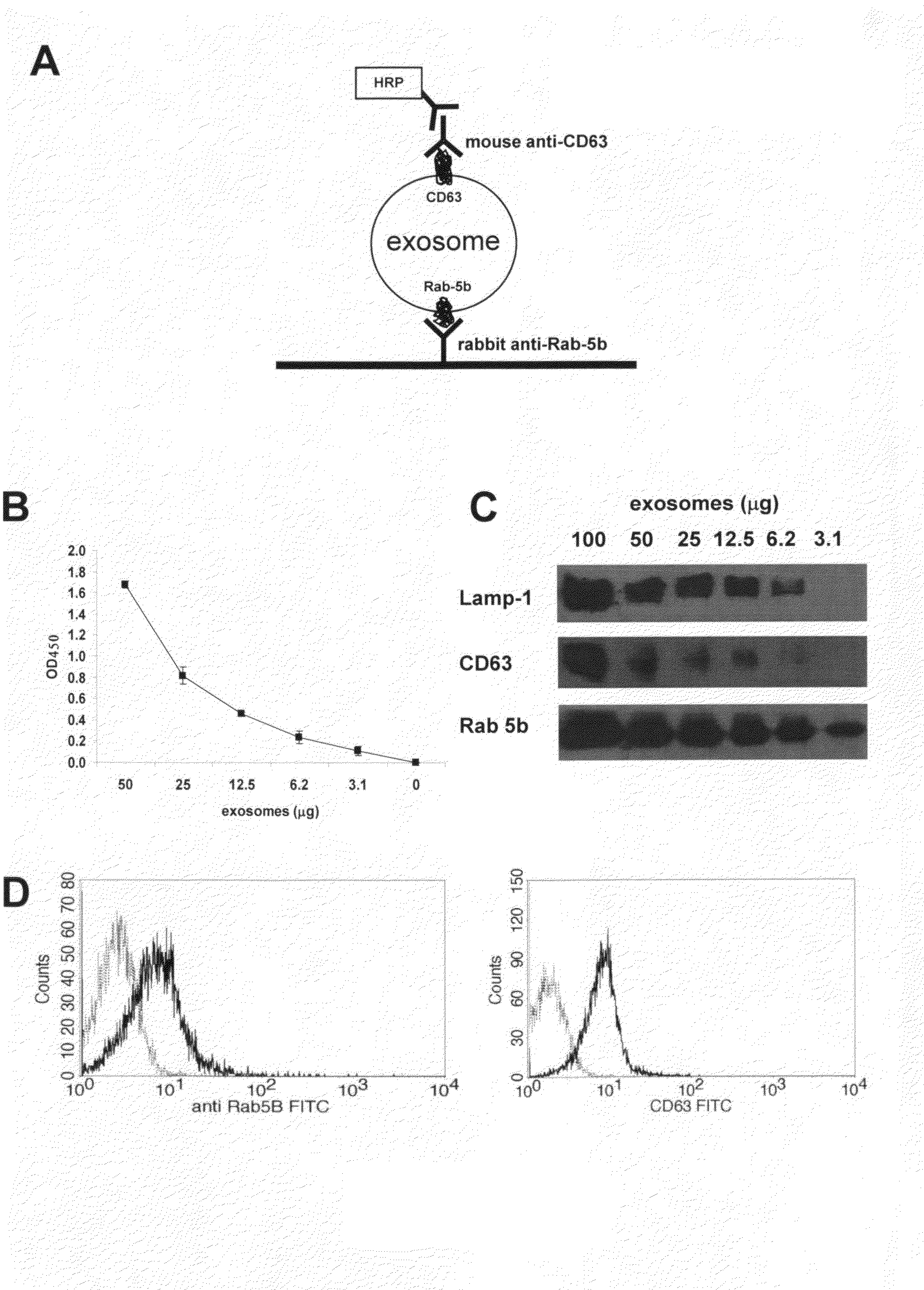
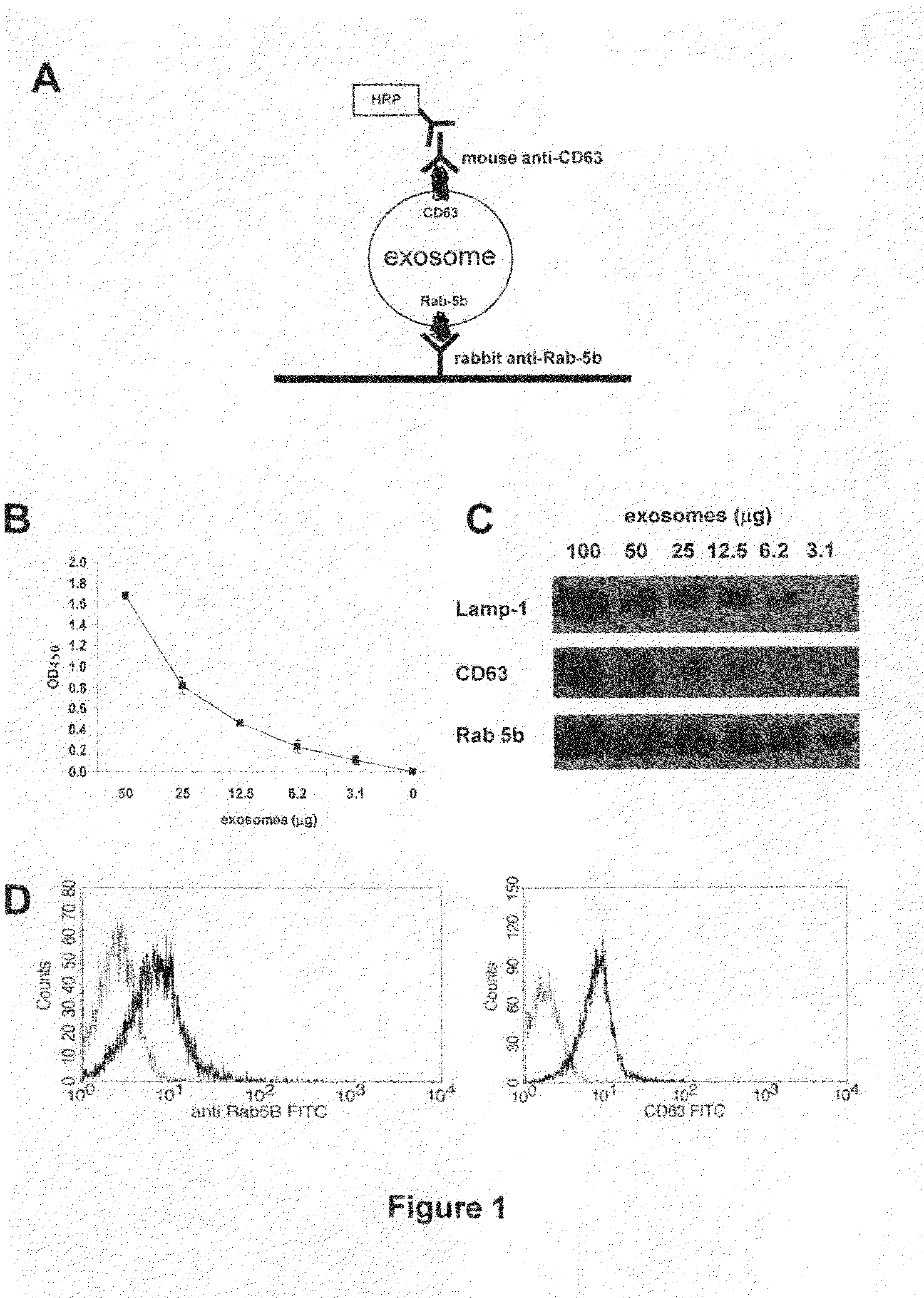
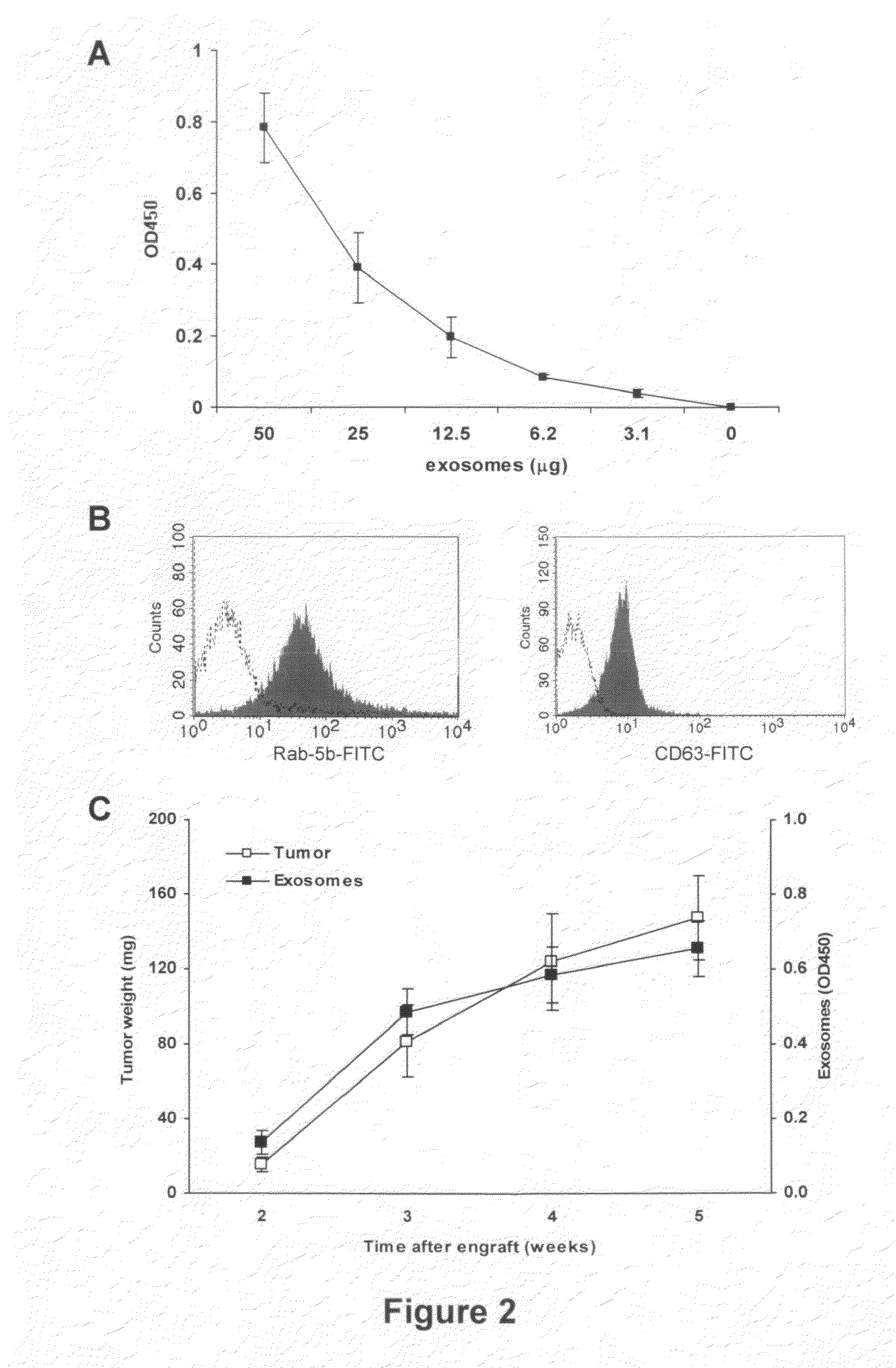
This disclosure provides a method to capture, detect, characterize and quantify human exosomes in small volumes of human body fluids by using a sandwich ELISA test. This method allows a full characterization of an exosome preparation, thus providing a tool to distinguish a disease-related condition from a healthy state, by the use of a non-invasive assay. In fact, this method may be useful in screening, diagnosis and prognosis of tumors, with a simple plasma sample. At the same time measurement of circulating exosomes may provide information on the level of tumor mass present in a patient. The method provided here is suitable to evaluate presence of some infectious and / or transmissible agents, such as viral proteins or prion proteins, within circulating exosomes.
Owner:EXOSOMICS SPA
Prion free nanoparticle compositions and methods of making thereof
InactiveUS20100297243A1Increase shearImprove conditionsPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsNanoparticleWater insoluble
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Transgenic animals and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060041945A1Increase opportunitiesDecreasing expression of endogenousTissue cultureImmunoglobulinsMammalUngulate
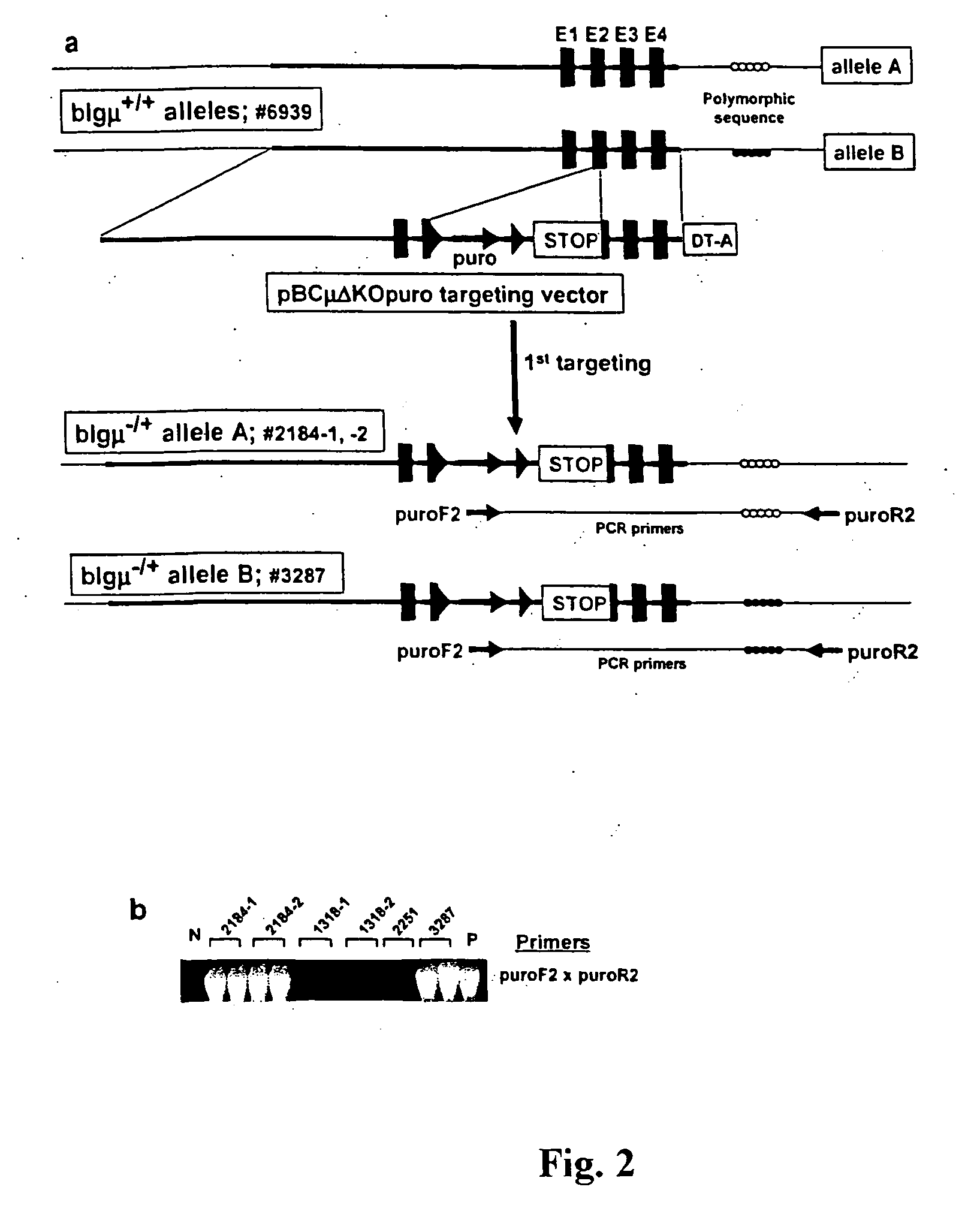
In general, the invention features genetically modified non-human mammals (e.g., bovines and other ungulates), and methods of making these mammals. In particular, the invention features transgenic ungulates having reduced levels of endogenous IgM heavy chain and / or prion protein.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Method of concentrating prion proteins in blood samples
A sample is prepared from blood in a manner which makes it possible to further analyze proteins in the sample, e.g. to detect prions in the sample. Blood is extracted, allowed to clot and subjected to separation processing (e.g. centrifugation) to obtain serum. The serum is treated with a complexing agent which agent binds prions in the sample forming an agent / protein complex which makes it possible to concentrate the complex. Concentration of the complex results in a sample which can be successfully analyzed, e.g. assayed using a range of different types of assay methodologies for detecting prions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Prion protein binding materials and methods of use
ActiveUS7393658B2Viral antigen ingredientsBiological testingHamsterProteinaceous infectious particle
Prion protein binding materials and methods for using the binding materials to detect or remove a prion protein from a sample, such as a biological fluid or an environmental sample. The binding materials are capable of binding to one or more forms of prion protein including cellular prion protein (PrPc), infectious prion protein (PrPsc), recombinant prion protein (PrPr), and proteinase resistant prion protein (PrPres). Prions from various species, including humans and hamsters, are bound by the binding materials.
Owner:PATHOGEN REMOVAL & DIAGNOSTIC TECH +1
Immobilized probes and methods of detecting conformationally altered prion proteins
InactiveUS20060057671A1Rapid diagnosisFacilitate prophylacticNervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementPrion ProteinsConformational change
Owner:ADLYFE INC
Synthetic immunogenic but non-deposit-forming polypeptides and peptides homologous to amyloid beta, prion protein, amylin, alpha-synuclein, or polyglutamine repeats for induction of an immune response thereto
InactiveUS7479482B2Reduce formationAvoid formingHormone peptidesNervous disorderPassive ImmunizationsAmyloid beta
The present invention relates to immunogenic but non-depositing-forming polypeptides or peptides homologous to amyloid β, prion, amylin or α-synuclein which can be used alone or conjugated to an immunostimulatory molecule in an immunizing composition for inducing an immune response to amyloid β peptides and amyloid deposits, to prion protein and prion deposits, to amylin and amylin deposits, to α-synuclein and deposits containing α-synuclein, or to polyglutamine repeats and deposits of proteins containing polyglutamine repeats. Described are also antibodies directed against such peptides, their generation, and their use in methods of passive immunization to such peptides and deposits.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Prion protein binding materials and methods of use
ActiveUS7510848B2Bacterial antigen ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsHamsterProteinaceous infectious particle
Prion protein binding materials and methods for using the binding materials to detect or remove a prion protein from a sample, such as a biological fluid or an environmental sample. The binding materials are capable of binding to one or more forms of prion protein including cellular prion protein (PrPc), infectious prion protein (PrPsc), recombinant prion protein (PrPr), and proteinase resistant prion protein (PrPres). Prions from various species, including humans and hamsters, are bound by the binding materials.
Owner:PATHOGEN REMOVAL & DIAGNOSTIC TECH +1
Prion-specific peptide reagents
InactiveUS20050118645A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsProteinaceous infectious particleAntibody
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Prion free nanoparticle compositions and methods of making thereof
The present invention provides prion-free compositions comprising nanoparticles comprising albumin and substantially water insoluble drugs. Also provided are methods of making prion-free compositions and methods of removing prion proteins from the nanoparticle compositions. Methods of using the compositions, as well as kits useful for carrying out the methods are also provided.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Prion protein ligands and methods of use
ActiveUS7863411B2Reduce developmentUseful in treatmentNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsHamsterProteinaceous infectious particle
Ligands that bind to prion proteins and methods for using the ligands for detecting or removing a prion protein from a sample, such as a biological fluid or an environmental sample. The ligands are capable of binding to one or more forms of prion protein including cellular prion protein (PrPc), infectious prion protein (PrPsc), and recombinant prion protein (PrPr). Prions from various species, including humans and hamsters, are bound by the ligands. Also provided is a method of treating or retarding the development of a prion-associated pathology in a subject.
Owner:PATHOGEN REMOVAL & DIAGNOSTIC TECH +1
Prion protein binding materials and methods of use
Prion protein binding materials and methods for using the binding materials to detect or remove a prion protein from a sample, such as a biological fluid or an environmental sample. The binding materials are capable of binding to one or more forms of prion protein including cellular prion protein (PrPc), infectious prion protein (PrPsc), recombinant prion protein (PrPr), and proteinase resistant prion protein (PrPres). Prions from various species, including humans and hamsters, are bound by the binding materials.
Owner:PATHOGEN REMOVAL & DIAGNOSTIC TECH +1
Methods for reducing levels of disease associated proteins
InactiveUS20060252775A1Reduction of dietary carbohydratesIncrease of dietary lipidsBiocideNervous disorderRegimenCell Aggregations
The subject invention concerns the reduction of protein aggregation in the neurons of a mammal through the use of a ketogenic treatment such as a ketogenic diet, a physical training regimen and / or administration of agents to increase fatty acid oxidation. Such ketogenic treatment can be useful in the reduction of certain aggregates including amyloid β peptide, polyglutamine containing huntintin protein, polyglutamine containing androgen receptor, polyglutamine containing atrophin-1, polyglutamine containing ataxins, α-synclein, prion protein, tau and superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1).
Owner:NEUERA PHARMA
Prion-specific peptide reagents
InactiveUS7439041B2Bacterial antigen ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseProteinaceous infectious particle
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
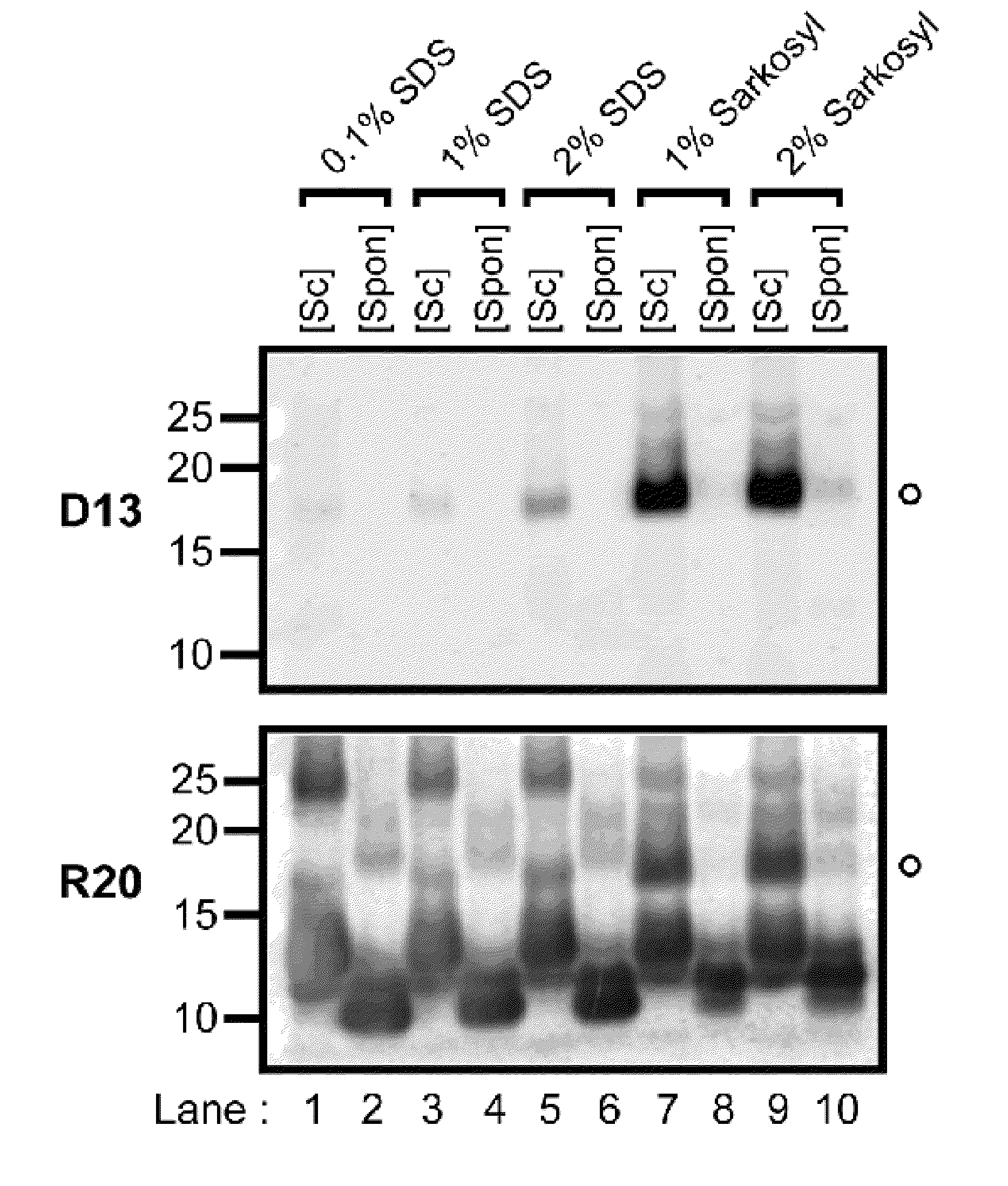
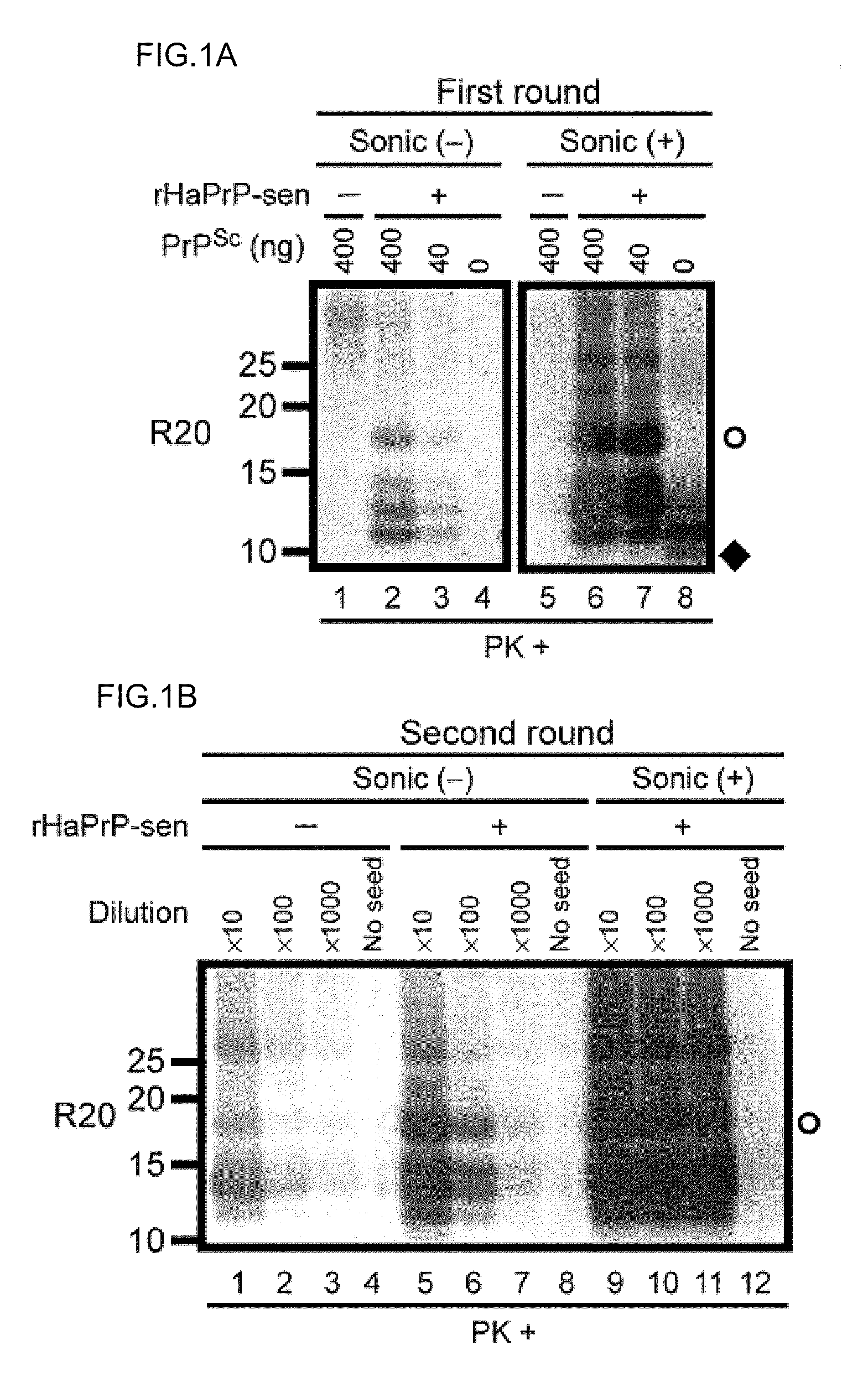
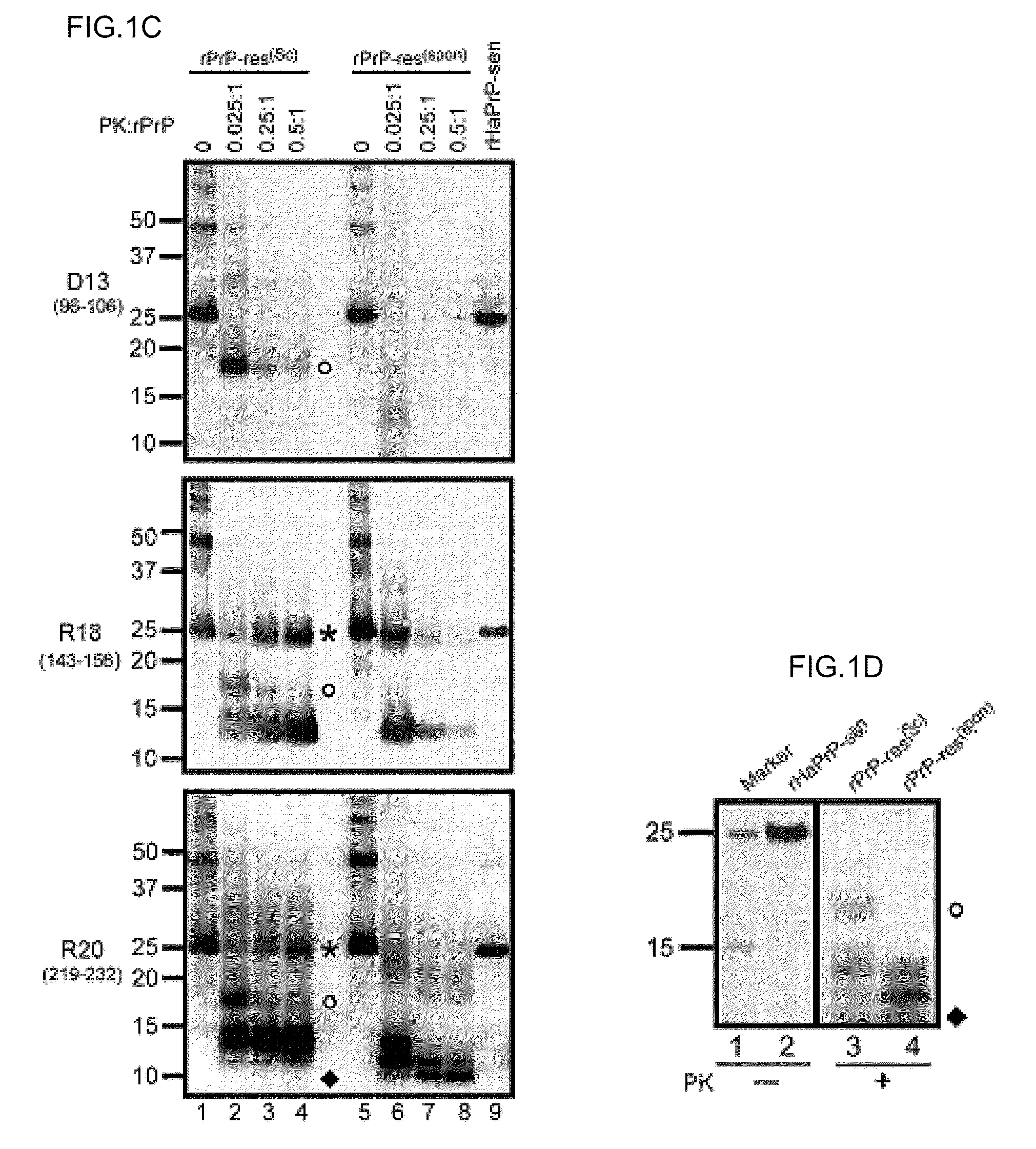
Detection of infectious prion protein by seeded conversion of recombinant prion protein
ActiveUS20090047696A1Transmission limitAddressing Insufficient SensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceRapid identificationFood supply
The present disclosure relates to methods and compositions for the detection of infectious proteins or prions in samples, including the diagnosis of prion related diseases. One embodiment is an ultrasensitive method for detecting PrP-res (PrPSc) that allows the use of recombinant PrP-sen (rPrP-sen) as a substrate for seeded polymerization. A sample is mixed with purified rPrP-sen to make a reaction mix which is incubated to permit aggregation of the rPrP-sen with the PrP-res that may be present in the sample. Any aggregates are intermittently disaggregated by agitation (for example by sonication) and the reaction allowed to proceed to amplify target substrate. Any rPrP-res(Sc) in the reaction mix is detected to indicate the presence of PrP-res in the original sample. This assay, which is called rPrP-PMCA, is surprisingly much faster than existing PMCA methods, yet it still retains sufficient sensitivity to detect extremely low levels of PrP-res. An alternative of rPrP-PMCA is the QUIC method in which shaking of the reaction mixture is substituted for sonication. The surprising speed and efficiency of the method permits the rapid identification and diagnosis of prion disease, which can limit the transmission of prion diseases, particularly through the food supply.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Smart contrast agent and method for detecting transition metal ions and treating related disorders
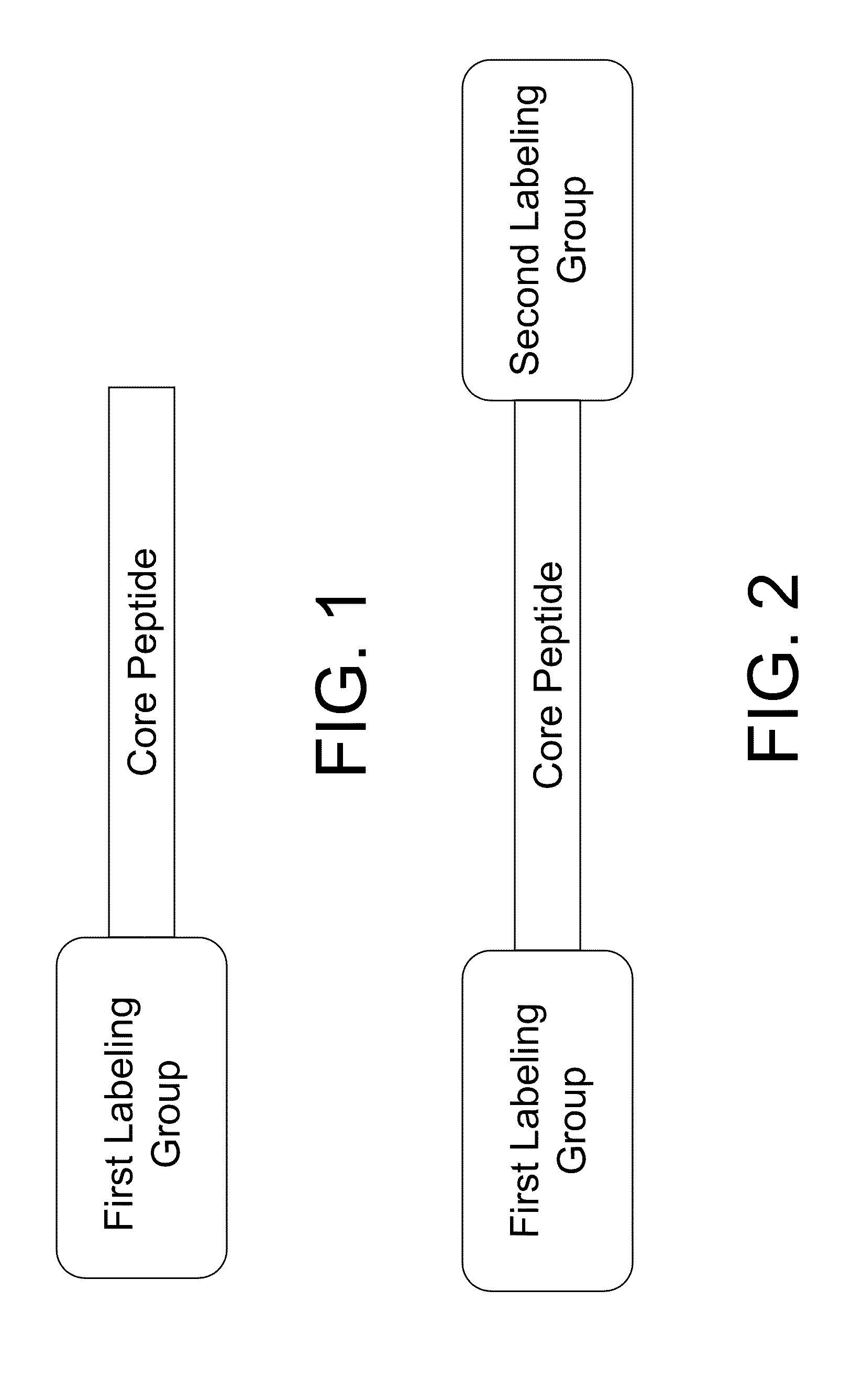
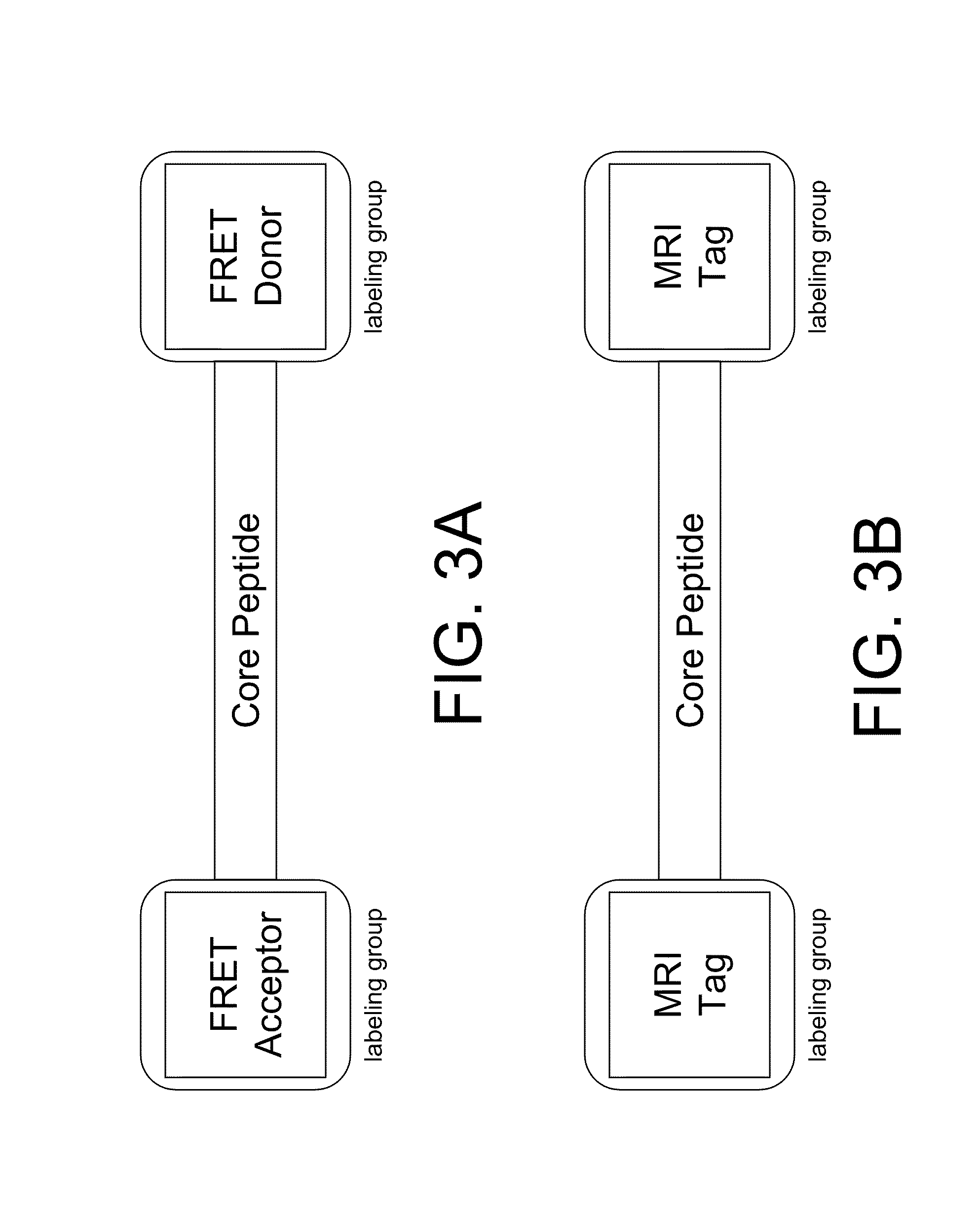
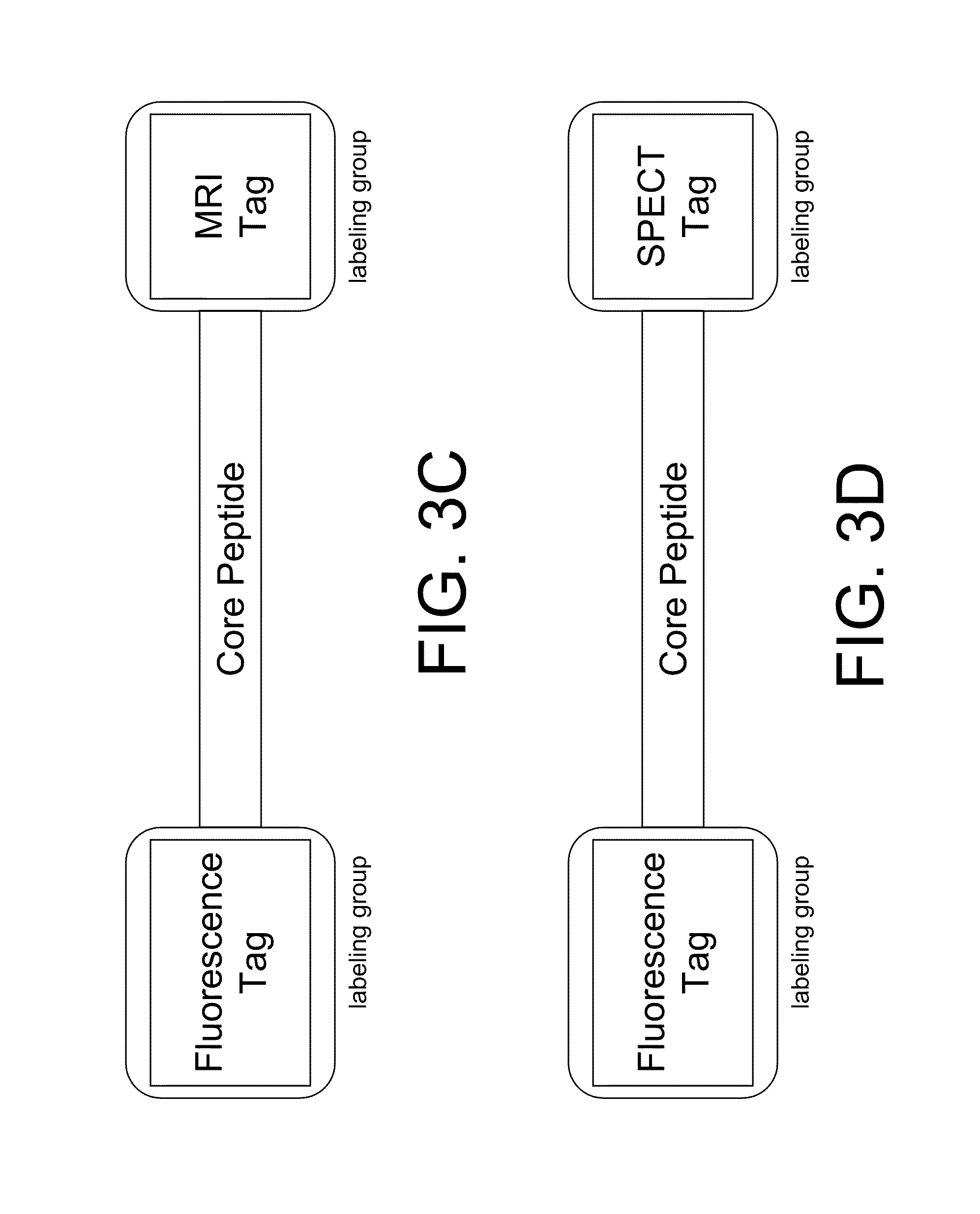
InactiveUS20100227794A1Reduce negative impactNervous disorderIn-vivo radioactive preparationsRelated disorderCore peptide
The present disclosure provides smart contrast agents for transition metals and a method of using the same. The smart contrast agents include a core peptide and a first labeling group attached to a first end of the core peptide. The smart contrast agents can also include a second labeling group attached to a second end of the core peptide. The core peptide can bind to transition metals, and can be homologous to a fragment selected from the extended octarepeat region of a prion protein.
Owner:I S T CORP
Method for diagnosing a transmissible spongiform subacute encephalyopathy caused by an unconventional transmissible agent strain in a biological sample
InactiveUS7097997B1High detection sensitivityHigh affinityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPrion ProteinsSheep prion
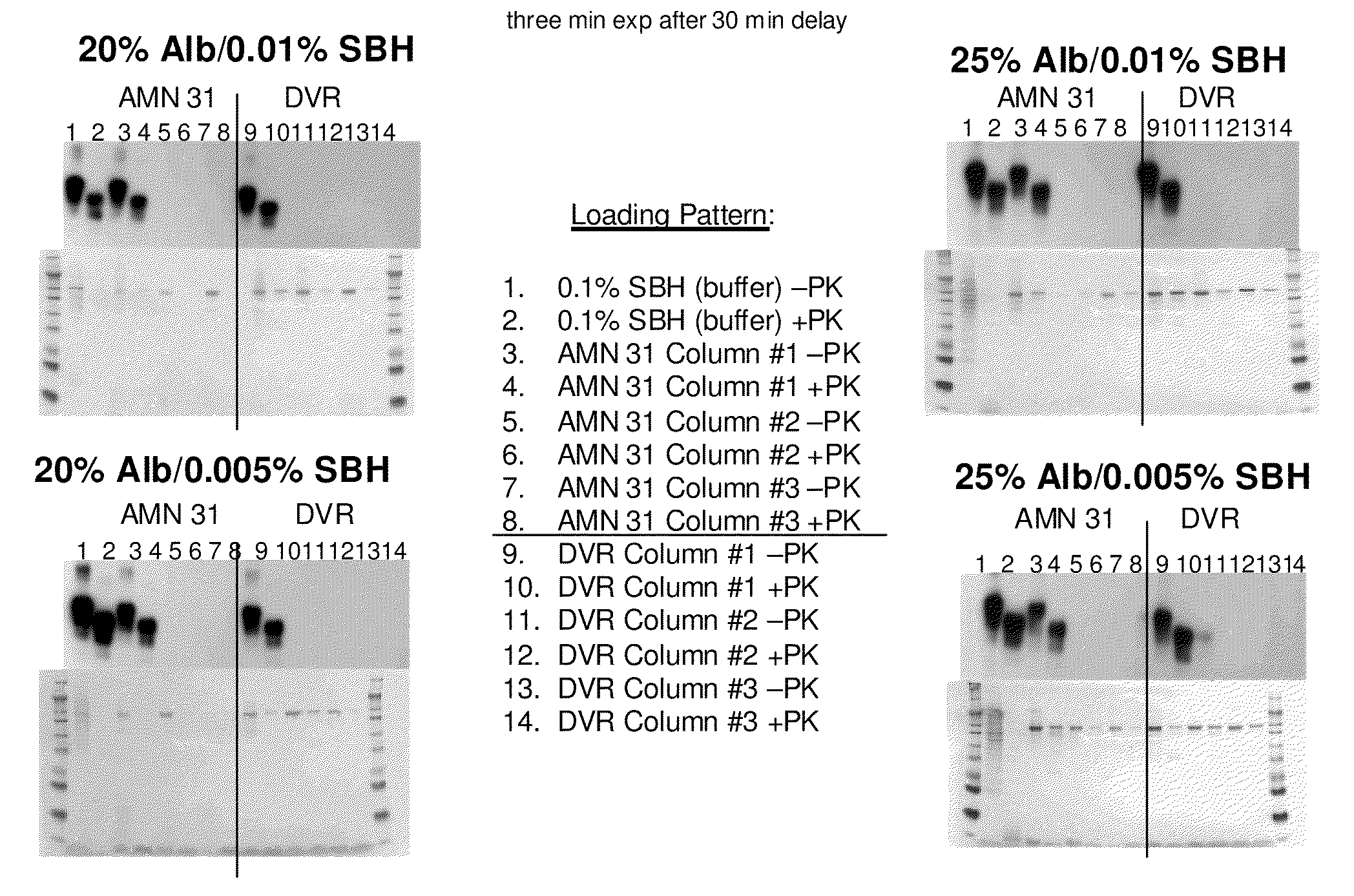
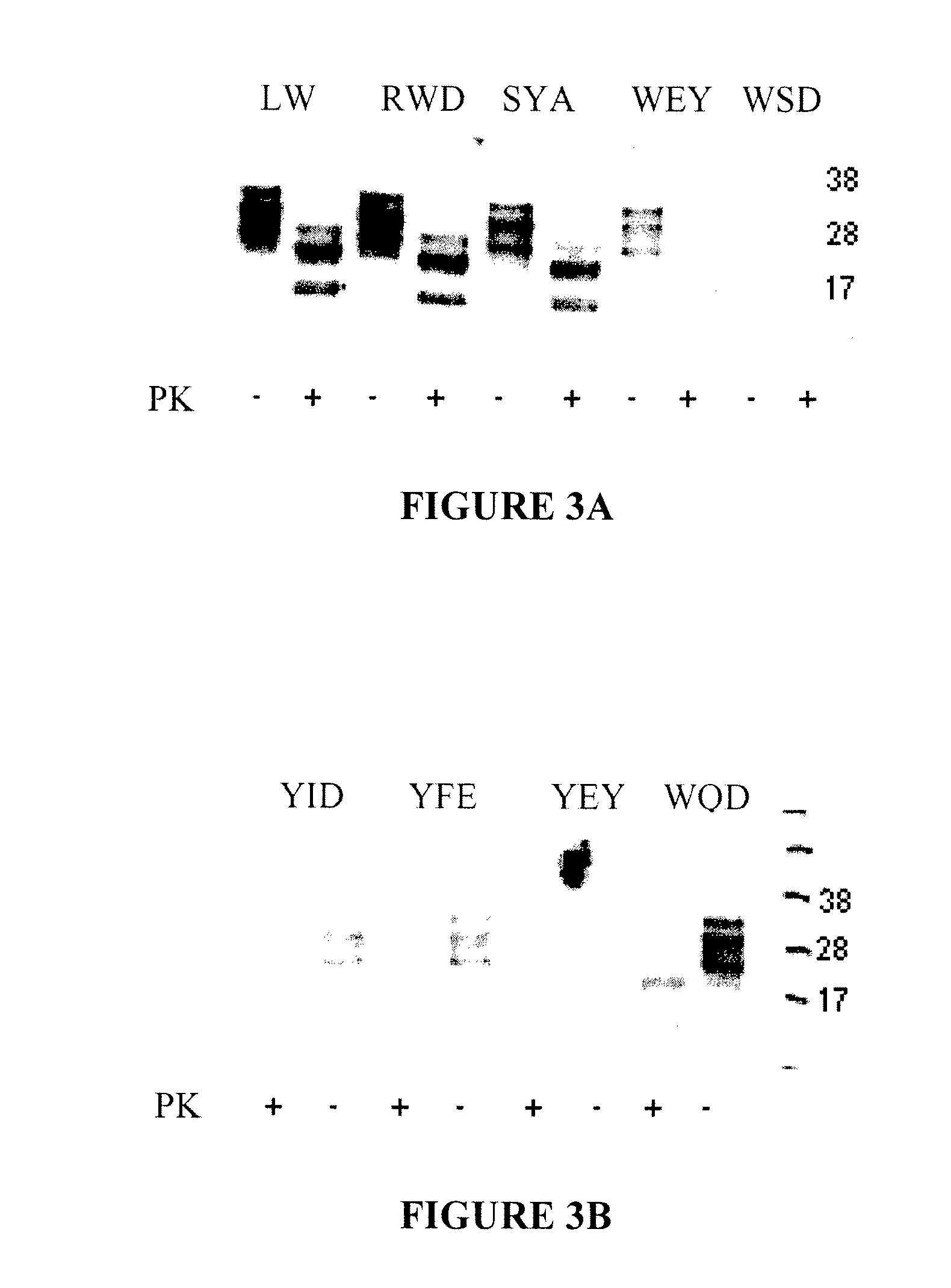
The invention relates to a method for diagnosing a transmissible spongiform subacute encephalopathy (TSSE) caused by an unconventional transmissible agent (UTA) or prion. The method involves treating a sample suspected of containing a prion with proteinase K for a time and under conditions that completely degrade normal prion protein (Prp-sen), but which only partially digest abnormal prion protein (PrP-res) so that all or some of the octapeptide motif repeats comprising P(H / Q)GGG(- / T)WGQ (SEQ ID NO: 1) in the abnormal prion protein (Prp-res) are retained.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Mucosal immunization to prevent prion infection
Vaccines against prion disease eliciting a humoral immune response when administered mucosally are described. The vaccines comprise a prion protein, a prion protein fragment, or a non-amyloidogenic prion protein homolog and an adjuvant suitable for inducing a humoral immune response after mucosal administration. Suitable adjuvants include cholera toxin subunit B, heat-labile enterotoxin and aluminum hydroxide. Alternatively, the vaccine comprises a vector encoding a prion protein, fragment, or homolog in an attenuated Salmonella host. The vaccines can be used to prevent or treat prion disease in humans and other mammals.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
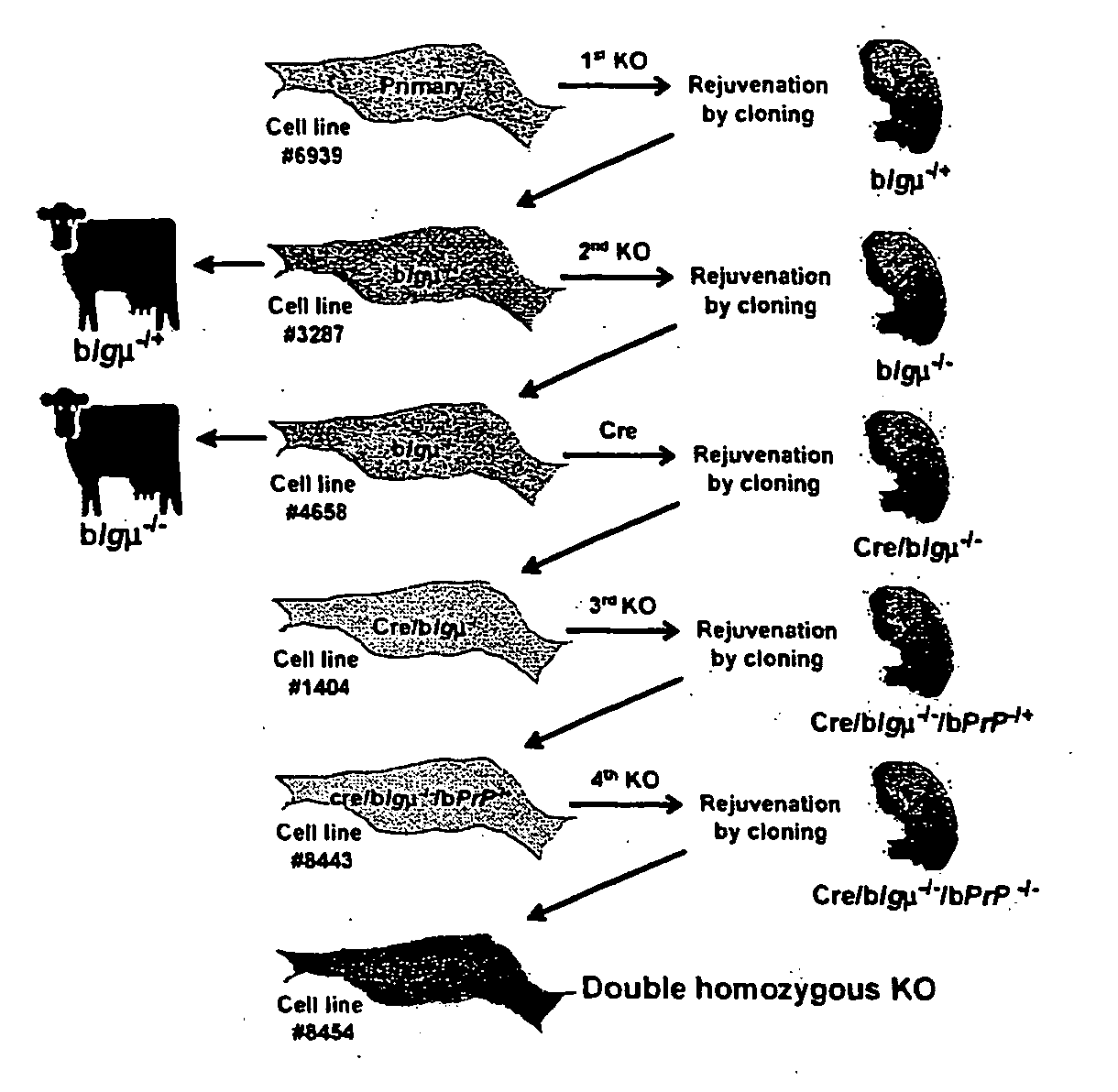
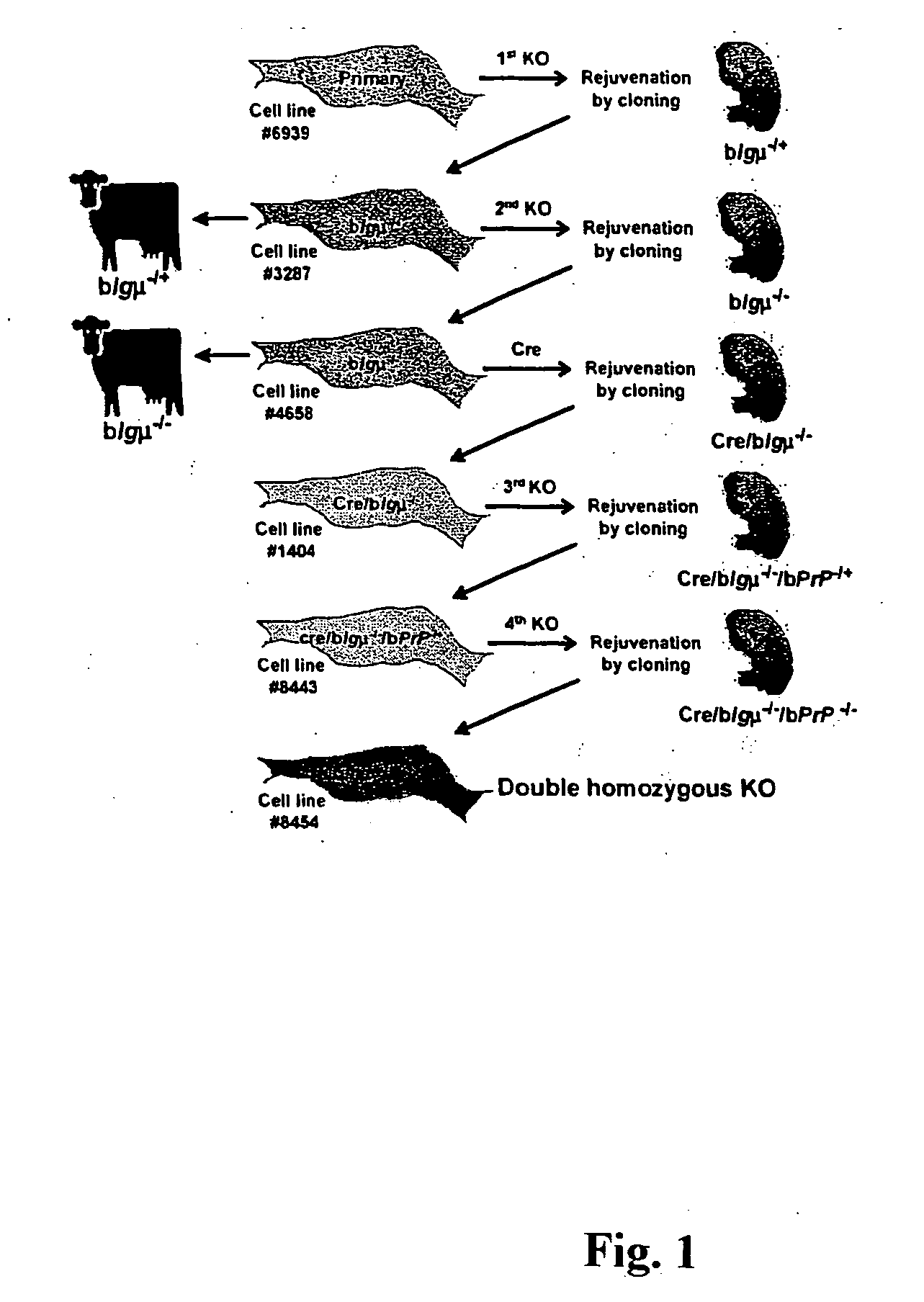
Transgenic ungulates having reduced prion protein activity and uses thereof
ActiveUS20050097627A1Animal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGenetically engineered
The invention provides cloned transgenic ungulates (e.g., bovines) in which prion protein activity is reduced by one or more genetically engineered mutations. Desirably, these transgenic bovines are also genetically modified to express xenogenous (e.g., human) antibodies. Because of their resistance to prion-related diseases such as bovine spongiform encephalopy (also known as mad cow disease), these bovines are a safer source of human antibodies for pharmaceutical uses and a safer source of agricultural products.
Owner:SAB LLC
Rapid prion-detection assay
Assays are provided for rapid detection, with high specificity of the pathogenic form of prion protein responsible for neurodegenerative diseases affecting humans and animals, such as transmissible spongiform encephalopathy in bovine, sheep, and cats. Also provided are assays for testing animal feedstock, such as animal feed, for the presence or concentration of pathogenic prion protein. Results are available in from about 0.5 to about 20 minutes and preferably within from about 5 to about 10 minutes. The assays employ proteinase-K to remove normal prion protein from a biological sample, so that the sample may be analyzed by immunochromatography to determine the presence and concentration of pathogenic prion protein. Because the proteinase-K is immobilized on a solid support for in situ removal of interfering components, the present invention obviates the need for subsequent extraction of the desired analyte. All aspects of the present invention are suitable for quantifying the minimal detectable amount of pathogenic prion protein in a biological sample. Moreover, the simplicity of sample preparation makes the present invention suitable for use in the field.
Owner:PRION DEVAL LAB
Method of removing abnormal prion protein from blood products
ActiveUS20100062412A1Easy and efficient removalLess hemolyzed cellNervous disorderOther blood circulation devicesWhole blood productWhite blood cell
Provided are a method of conveniently and efficiently removing abnormal prion protein from a blood product and a method of removing leukocyte simultaneously with abnormal prion protein. The method of removing an abnormal prion protein from a blood product includes filtering the blood product through a filter filled with a carrier coated with a polymer, which is composed of three units including 20 mol % or more and 40 mol % or less of a unit originating from a hydrophobic polymerizable monomer, 5 mol % or more and 13 mol % or less of a unit originating from a polymerizable monomer containing a basic nitrogen-containing part, and a unit originating from a polymerizable monomer containing a protonic neutral hydrophilic part as the balance, and then recovering the filtered blood product.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
Methods And Compositions Comprising Supramolecular Constructs
ActiveUS20070281006A1Increase exposureImprove accessibilityNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansEpitopePeptide sequence
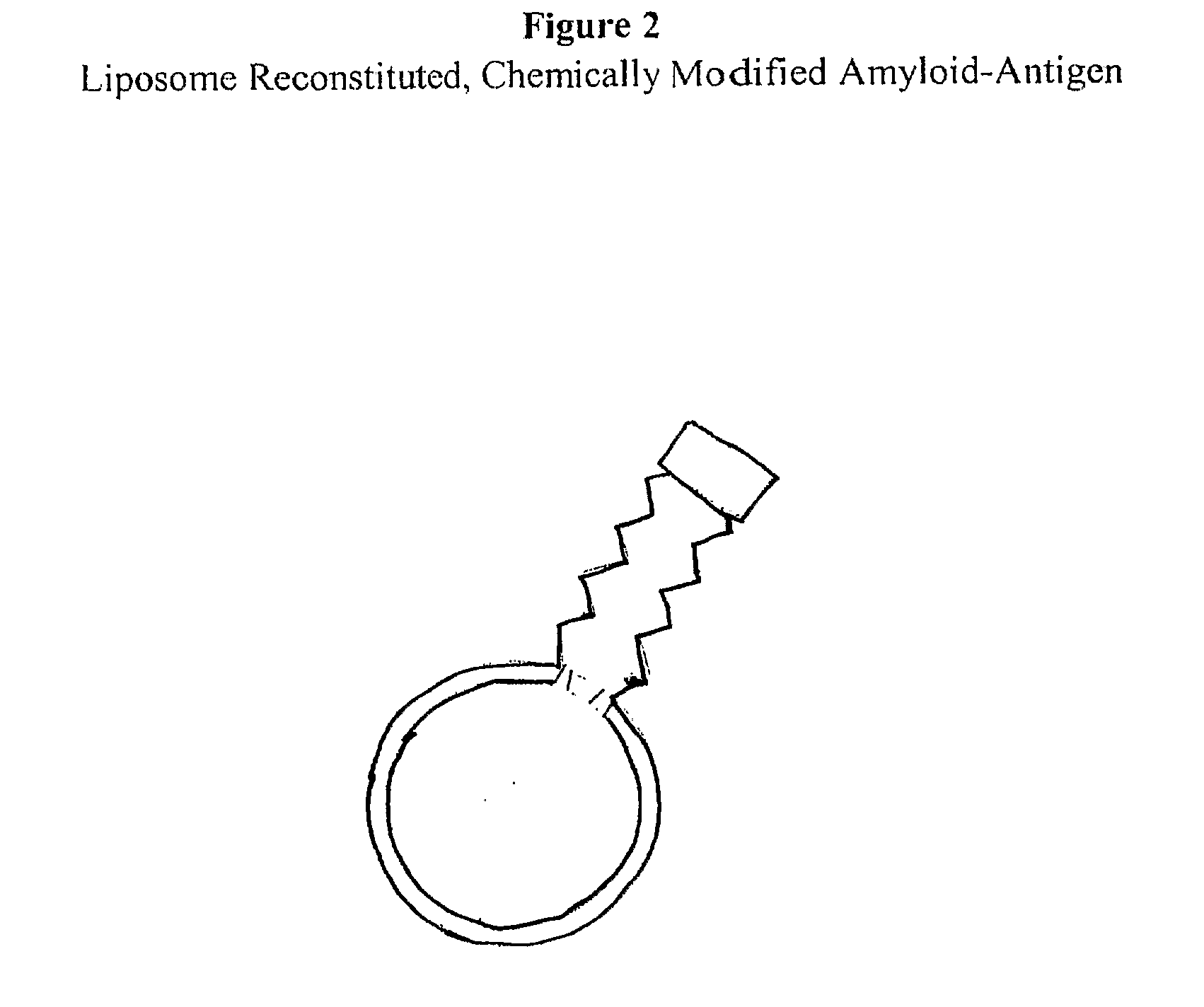
The present invention comprises novel compositions and methods for eliciting high immune responses, of great specifity yielding conformationally sensitive antibodies. These antibodies recognize specific epitopes on a wide variety of antigens including but not limited to, amyloid protein, prion protein, P170 glycoprotein. The novel compositions of the invention comprise supramolecular antigenic constructs generally comprising a peptide sequence, covalently attached to pegylated lysine resulting in modified and enhanced peptide presentation. The unique modification methodology of the present invention is applicable to a variety of peptides and can ultimately be employed in therapeutic formulations and vaccines for diseases and disorders such as Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:AC IMMUNE SA
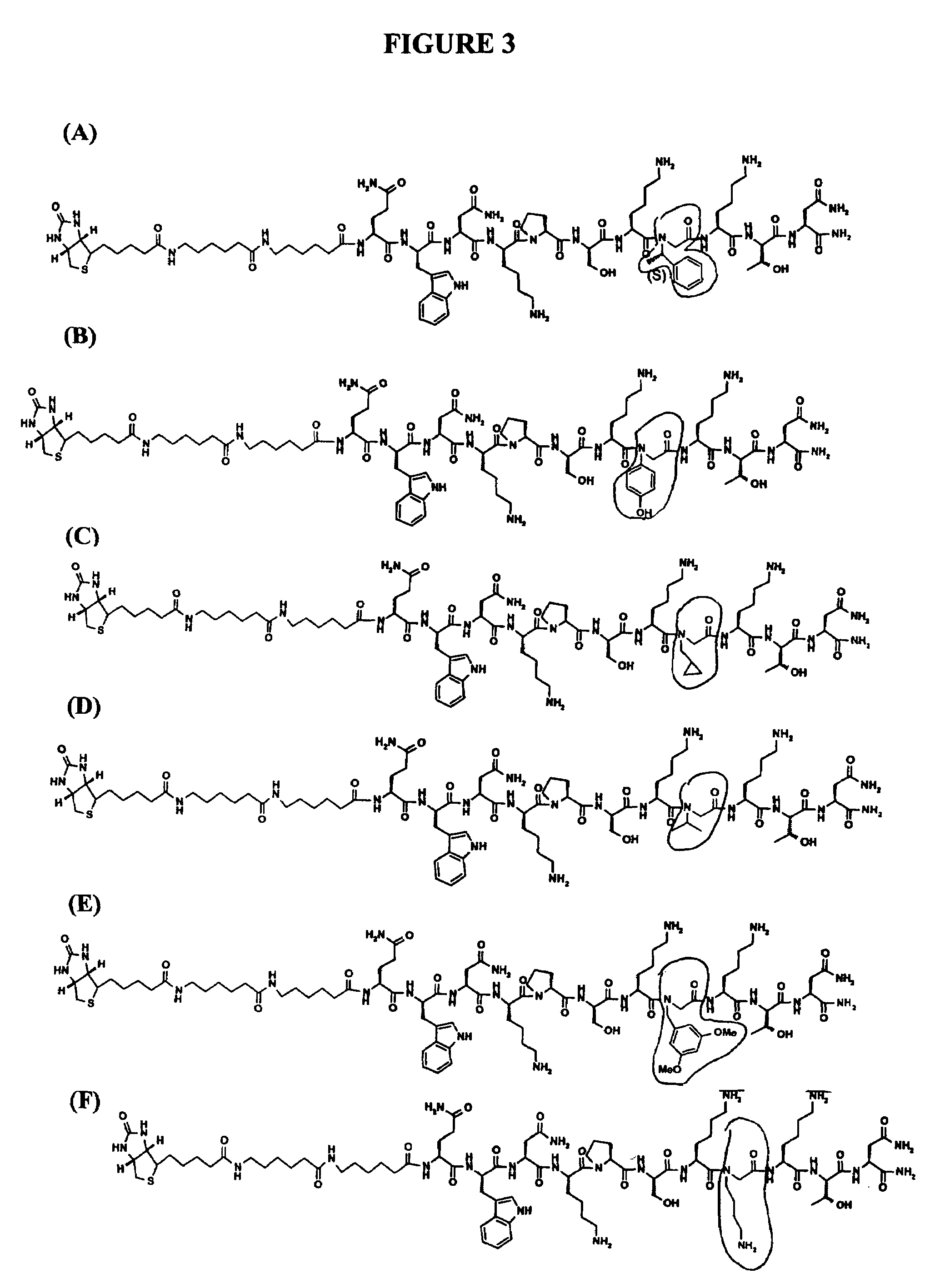
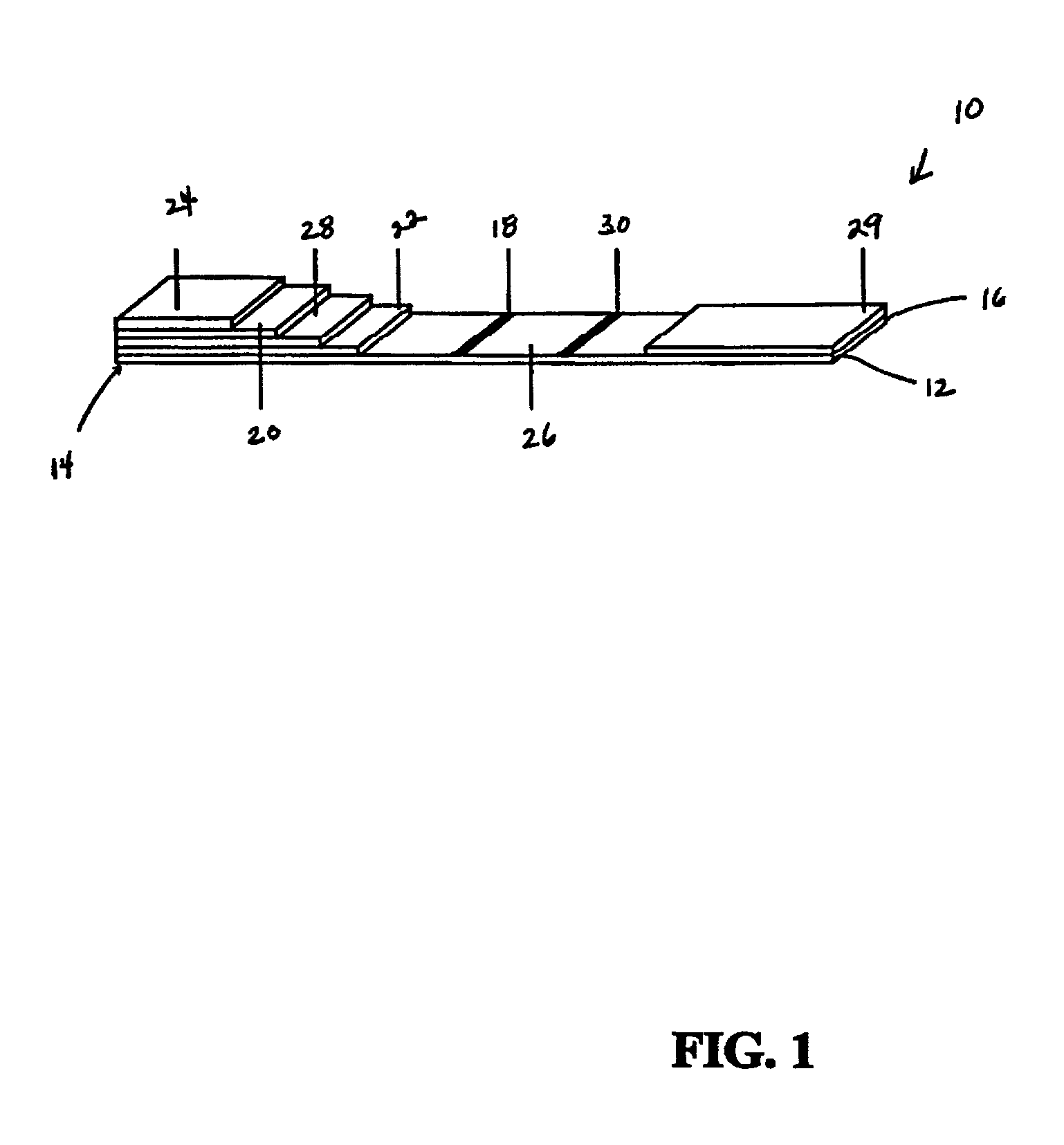
Composite peptide compounds for diagnosis and treatment of diseases caused by prion proteins
InactiveUS20060057636A1Low detection sensitivityAvoid detectionApolipeptidesImmunoglobulins against animals/humansTherapeutic treatmentDisease cause
The present invention relates to diseases caused by prion proteins, Novel composite peptide compounds are disclosed which comprise two or more peptides or peptide fragments optionally linked to a backbone and the peptides or peptide fragments are spatially positioned relative to each other so that they together form a non-linear sequence which mimics the tertiary structure of one or more PrPSc-specific epitopes as evidenced by the test described herein. The use of such conjugates as immunogens for the production of antibodies that specifically bind to the pathogenic form of a prion protein is revealed. Other uses of the composite peptide compounds are also disclosed, such as use in diagnostic assays, production of antibodies and uses as vaccine immunogens for the prophylactic protection and therapeutic treatment of subjects against transmissible prion disease.
Owner:COPENHAGEN BIOTECH ASSETAB
Rapid prion-detection assay
Owner:PRION DEVAL LAB
Prion inhibiting peptides and derivatives thereof
InactiveUS20050181998A1Nervous disorderTetrapeptide ingredientsTransmissible spongiform encephalopathyProteinaceous infectious particle
Short peptides and derivatives or analogs thereof for the treatment or prevention of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies, in particular CJD are herein described. These peptides and / or their derivatives have been designed to block the conformational changes that occur in the prion protein (PrP) and which are implicated in the pathogenesis of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies as well as to dissolve the fibrillar deposits already formed
Owner:LAB SERONO SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com