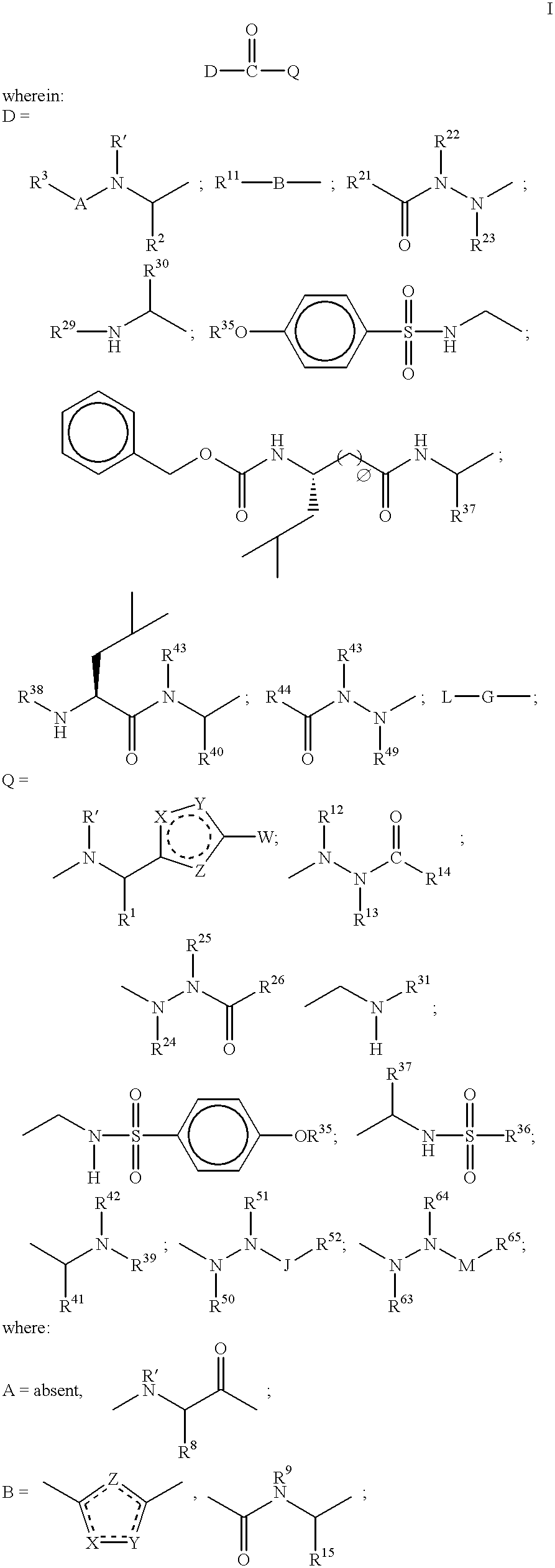
Patents
Literature
326 results about "Proteinase K" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In molecular biology Proteinase K (EC 3.4.21.64, protease K, endopeptidase K, Tritirachium alkaline proteinase, Tritirachium album serine proteinase, Tritirachium album proteinase K) is a broad-spectrum serine protease. The enzyme was discovered in 1974 in extracts of the fungus Engyodontium album (formerly Tritirachium album). Proteinase K is able to digest hair (keratin), hence, the name "Proteinase K". The predominant site of cleavage is the peptide bond adjacent to the carboxyl group of aliphatic and aromatic amino acids with blocked alpha amino groups. It is commonly used for its broad specificity. This enzyme belongs to Peptidase family S8 (subtilisin). The molecular weight of Proteinase K is 28,900 daltons (28.9 kDa).
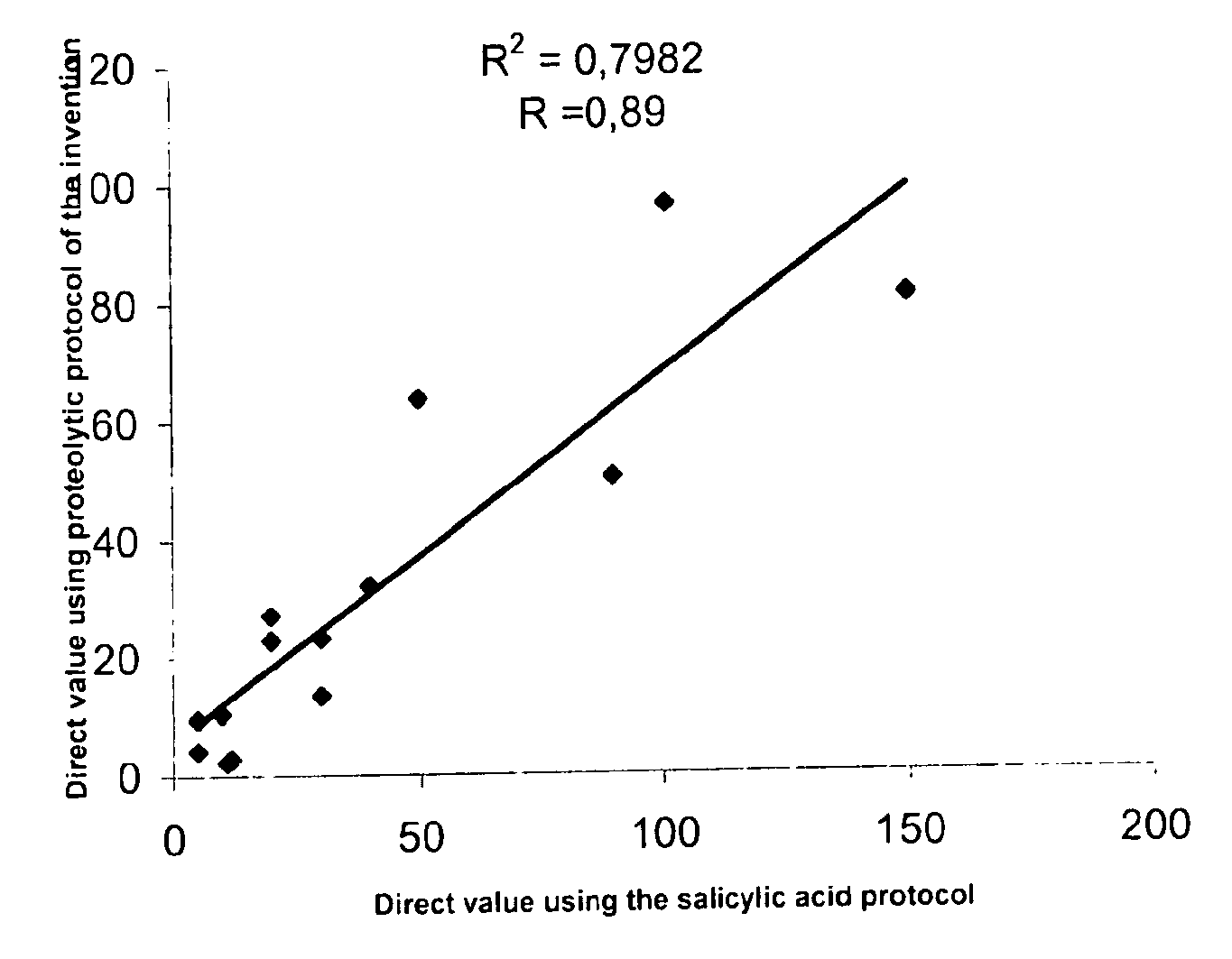
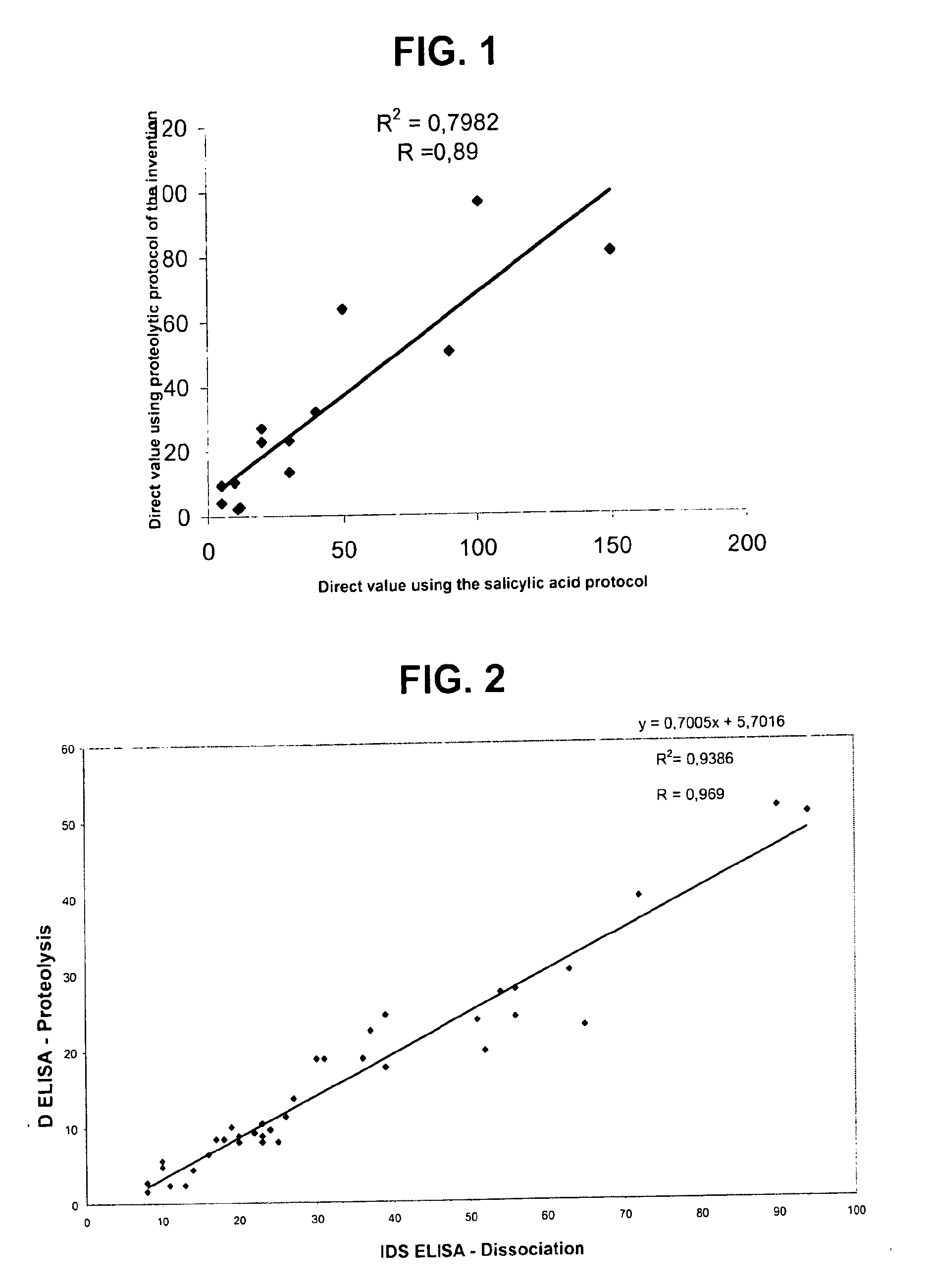
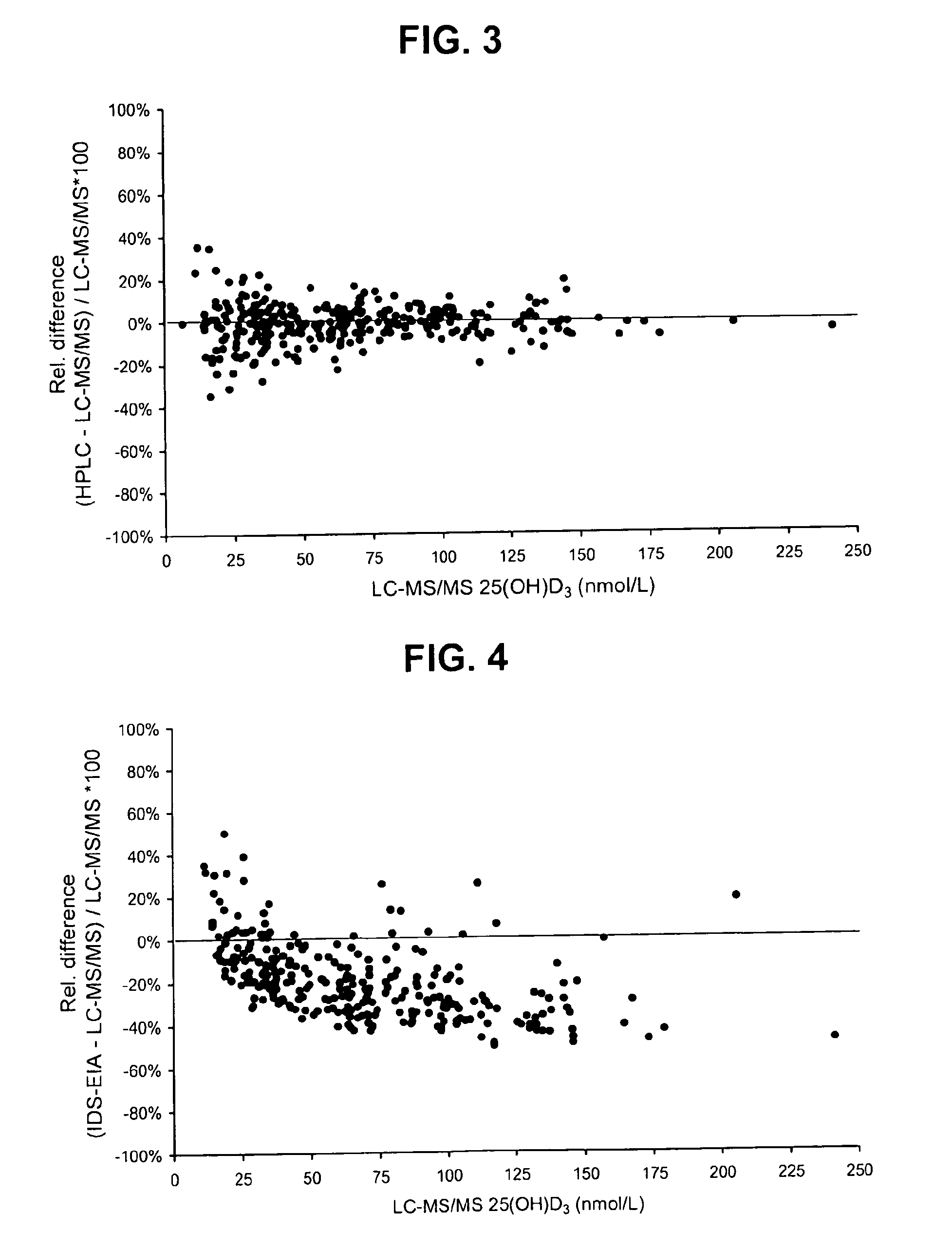
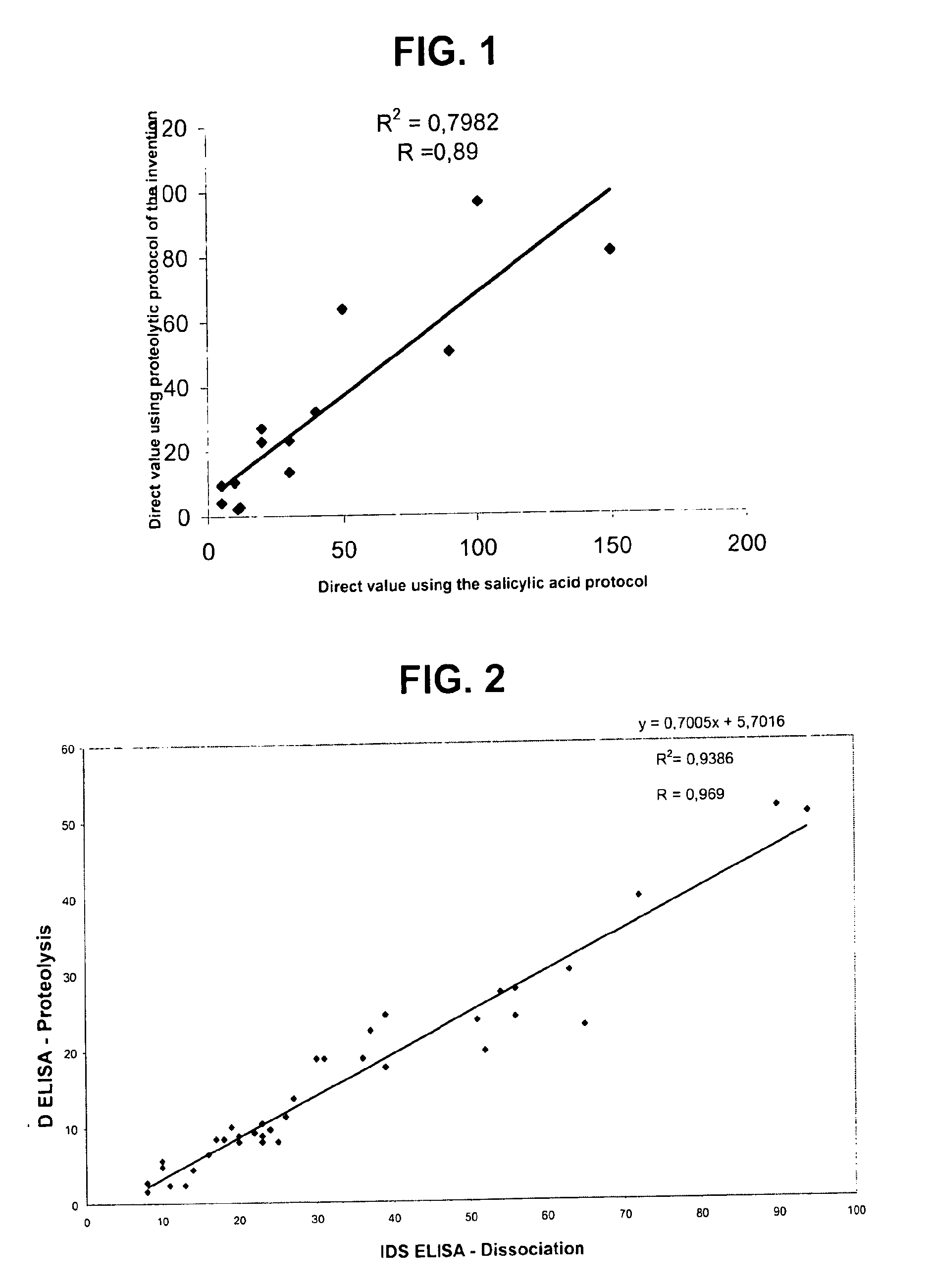
Direct determination of vitamin d in serum or plasma
ActiveUS20100068725A1Easy to controlPromote digestionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSerum igeCompetitive binding
A method for quantitating vitamin D metabolites directly in blood plasma or serum, without the need for prior purification of the vitamin D metabolites, comprising a digestion of the serum proteins with a serine protease such as proteinase K and sequence of steps for inhibiting the proteinase K activity in the competitive binding analysis. The advantages of this method are its high accuracy over the whole range of physiologically relevant values and that it can be easily adapted for a fully automated analysis of serum and plasma samples.
Owner:IMMUNDIAGNOSTIK
Hair analysis method
InactiveUS6949344B1Reliable solubilizationAccurate methodPre-tanning chemical treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementBetaineDigestion
A method the direct analysis of an analyte in keratinized structures, e.g., hair and fingernails, which comprises preparing a mixture containing a low redox potential activator compound such as dithiothreitol or dithioerythritol, an enzyme suitable for the digestion of the keratin structure, a sample of the keratin structure and a biological detergent that aids the digestion of the keratinized structure at a relatively low pH, e.g., between about 6.2 and 8; permitting the enzyme to at least substantially digest the sample of keratin structure, and subjecting the digest solution to analysis, preferably by radioimmunoassay, to determine the identity and amount of analyte in the keratin structure sample. To accelerate the method, cupric sulfate may be added to the mixture after degradation of the keratin sample. The enzyme may be a peptidase, endopeptidase or proteinase, with papain, chymopapain, and proteinase K being preferred for use in the invention. The preferred biological detergents include betaine, sulfo-betaine, alkylglucosides and bile acids.
Owner:PSYCHEMEDICS CORPORATION
Antibodies specific for native PrPSc
InactiveUS6372214B1Fast and efficient cost-effective assayFast and efficientImmunoglobulins against animals/humansHybrid cell preparationDiseaseMammal
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Method of inhibiting cathepsin K
InactiveUS6274336B1High specificity and stabilityInhibit synthesisHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsProteinase activityCathepsin K
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Exfoliated cell preservative fluid
InactiveCN101485303AHigh retention rateEvenly distributedDead animal preservationPh bufferingPreservative
The invention relates to a preservation solution for exfoliated cells, which is characterized by comprising a pH buffering agent, an osmotic pressure maintaining agent, an anti-corrosion antistaling agent, a fixative for maintaining cellular morphologies, an anticoagulant, a mucus softener, proteinase K and a component for destroying red blood cells. Compared with the prior art, the preservation solution has the advantages that the cell storage rate is high, the storage time at normal temperature is long, the mucus is sufficiently dissolved and the red blood cells are partially destroyed, the sheet-making effect comprises quite even cell distribution, the cellular morphologies are good, the cytolymph and the cell nucleus are divided clearly and are well arranged, the brightness of the cytolymph and the cell nucleus is quite good, and the karyoplasms, the morphological structures and the amount of the cells are quite clear.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HONGQI OPTICAL INSTR TECH
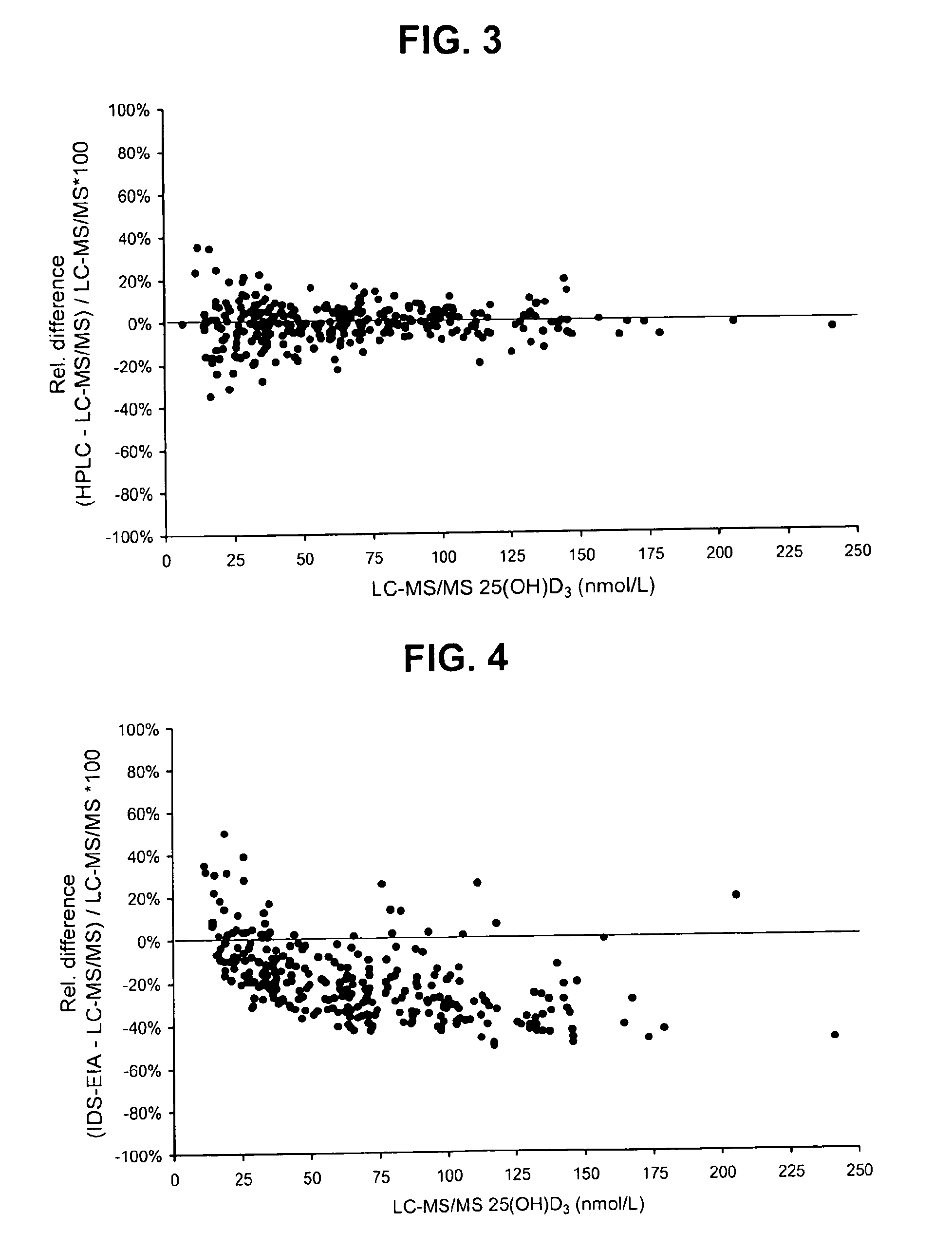
Direct determination of vitamin D in serum or plasma
A method for quantitating vitamin D metabolites directly in blood plasma or serum, without the need for prior purification of the vitamin D metabolites, comprising a digestion of the serum proteins with a serine protease such as proteinase K and sequence of steps for inhibiting the proteinase K activity in the competitive binding analysis. The advantages of this method are its high accuracy over the whole range of physiologically relevant values and that it can be easily adapted for a fully automated analysis of serum and plasma samples.
Owner:IMMUNDIAGNOSTIK AG
Proteinase K resistant surface protein of neisseria meningitidis
A highly conserved, immunologically accessible antigen at the surface of Neisseria meningitidis organisms. Immunotherapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic compositions and methods useful in the treatment, prevention an diagnosis of Neisseria meningitidis diseases. A proteinase K resistant Neisseria meningitidis surface protein having an apparent molecular weight of 22 kDa, the corresponding nucleotide and derived amino acid sequences (SEQ ID NO: 1, NO:3, NO:5 and NO:7: SEQ ID NO: 2, NO:4, NO:6, and NO:8), recombinant DNA methods for the production of the Neisseria meningitidis 22 kDA surface protein, and antibodies that bind to the Neisseria meningitidis 22 kDA surface protein.
Owner:ID BIOMEDICAL
Silica gel absorption column extraction kit and method for free DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of blood plasma or blood serum
InactiveCN108070584AGuaranteed unobstructedGuaranteed to dissolveMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationAbsorption columnBlood plasma
The invention discloses a silica gel absorption column extraction kit and method for free DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of blood plasma or blood serum and relates to the fieldof molecular biology. The kit comprises proteinase K, isopropyl alcohol, absolute ethyl alcohol and threefold-distilled water, and further comprises a lysis solution containing a nucleic acid separation accelerant, an adsorption solution containing a nucleic acid adsorption accelerant and a washing solution; the method is mainly carried out by utilizing the kit. By adopting the kit provided by the invention, the free DNA and RNA in the blood plasma or the blood serum can be rapidly and completely released, and denatured protein keeps a dissolved state; under the action of the adsorption solution, the free DNA and RNA are efficiently adsorbed on a silica gel absorption column; after the silica gel absorption column is washed by the washing solution, the free DNA and RNA with relatively high purity and concentration are obtained.
Owner:江苏然科生物技术有限公司
Kit for extracting RNA and application method
ActiveCN108949747AAvoid harmImprove integrityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationRNA extractionMagnetic bead
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and particularly relates to a kit for extracting ribonucleic acid (RNA) by virtue of a paramagnetic particle method and an extraction method. The kit contains tissue digestion fluid, lysate, proteinase K, DNase I, DNase IBuffer, nucleic acid, extraction magnetic beads, washing liquid I, washing liquid II and eluant. The invention further discloses a method for extracting the tissue RNA by virtue of the kit. According to the kit and the method, the extraction yield and purity of RNA are increased, the integrity of RNA is improved, meanwhile, the automatic extraction is realized, and the simultaneous parallel testing of multiple samples is realized, so that the labor cost and the time cost are saved.
Owner:广州奇辉生物科技有限公司
Preservative composition of blood DNA
The invention provides a preservative composition of blood DNA. The preservative composition of blood DNA comprises, by weight, 20 to 50 parts of a preservative, 5 to 15 parts of an anticoagulant, 0.5 to 5 parts of a nuclease inhibitor, 1 to 5 parts of a metabolic inhibitor and 40 to 70 parts of water, wherein the nuclease inhibitor comprises one or more of diatomite, bentonite, ethyl alcohol, formamide, vanadyl-ribonucleoside complex, dithioerythritol, diethyl pyrocarbonate, proteinase-K, heparin, beta-mercaptoethanol, hydroxylamine-O-copper ions, ammonium sulfate, dithiothreitol, cysteine, and 4-formylbenzoic acid and oxovanadium Schiff base complex.
Owner:上海迅伯生物科技有限公司 +1
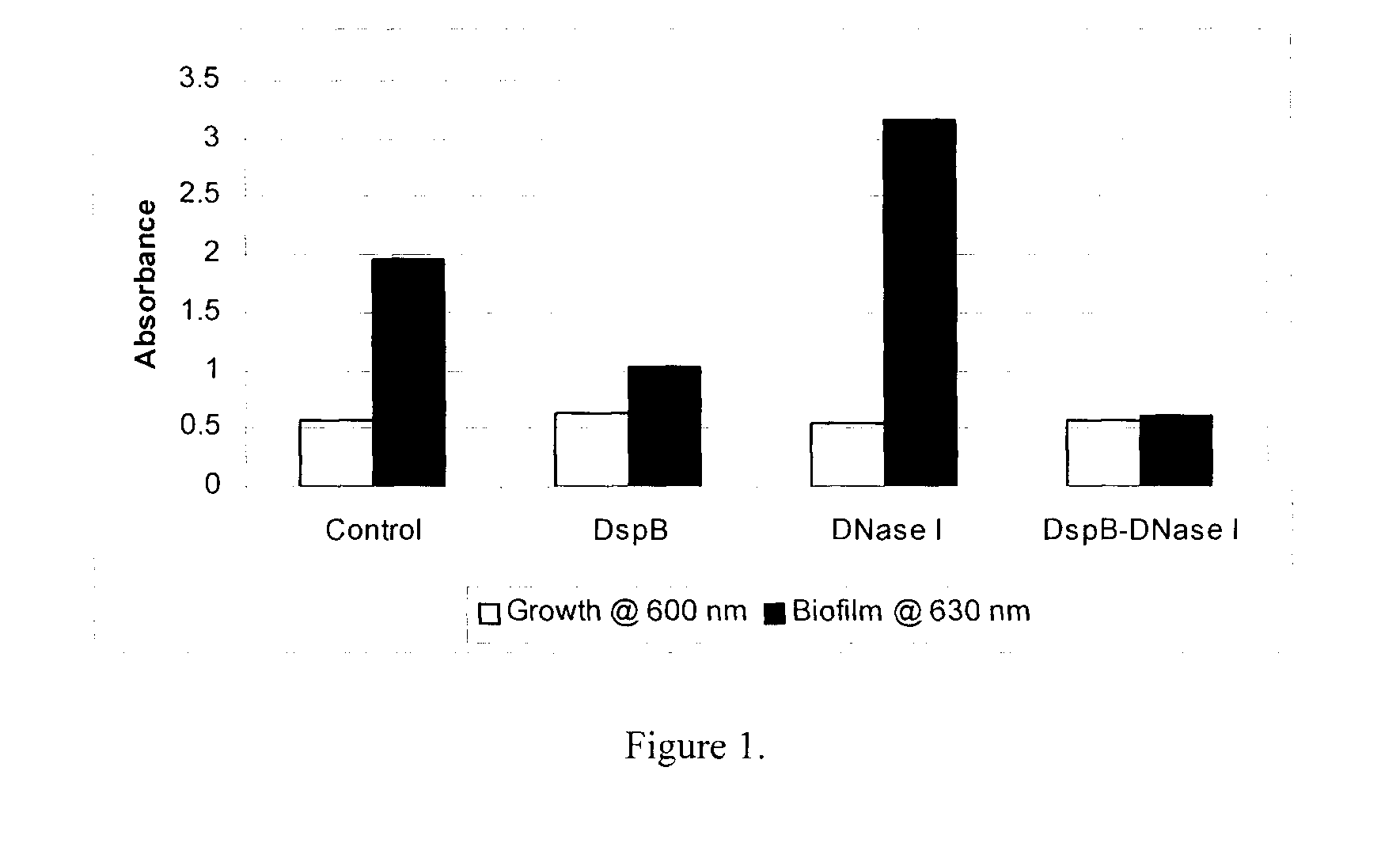
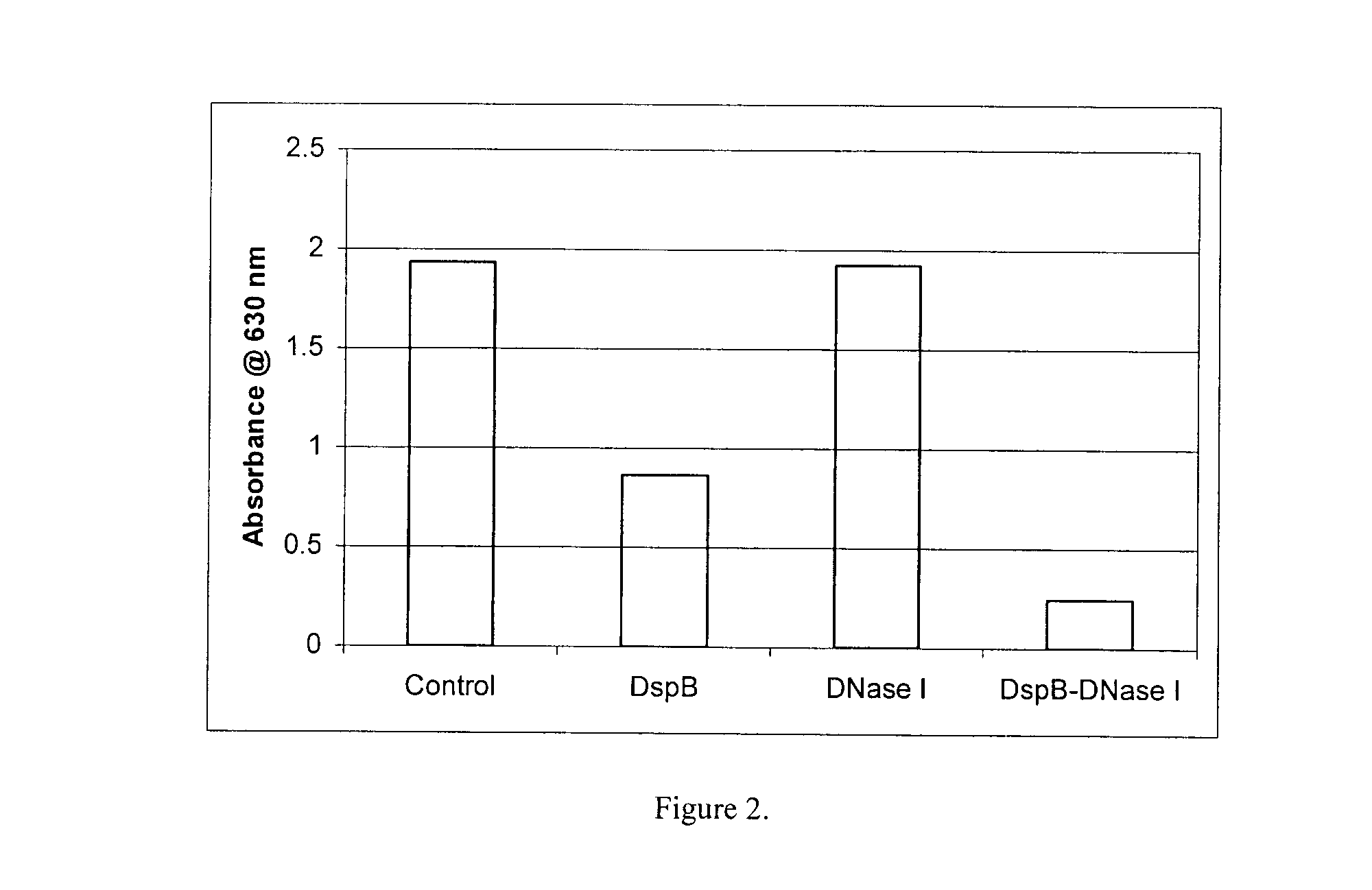
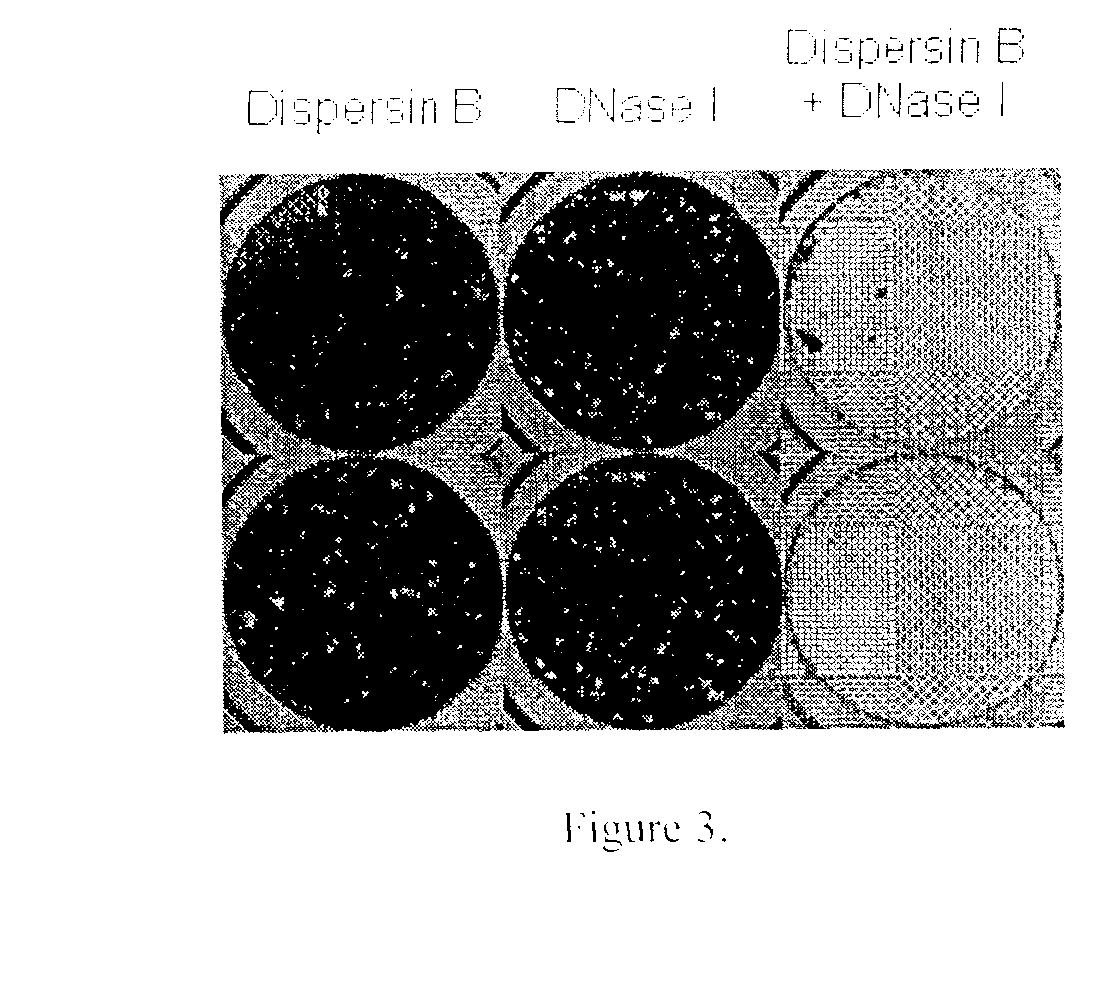
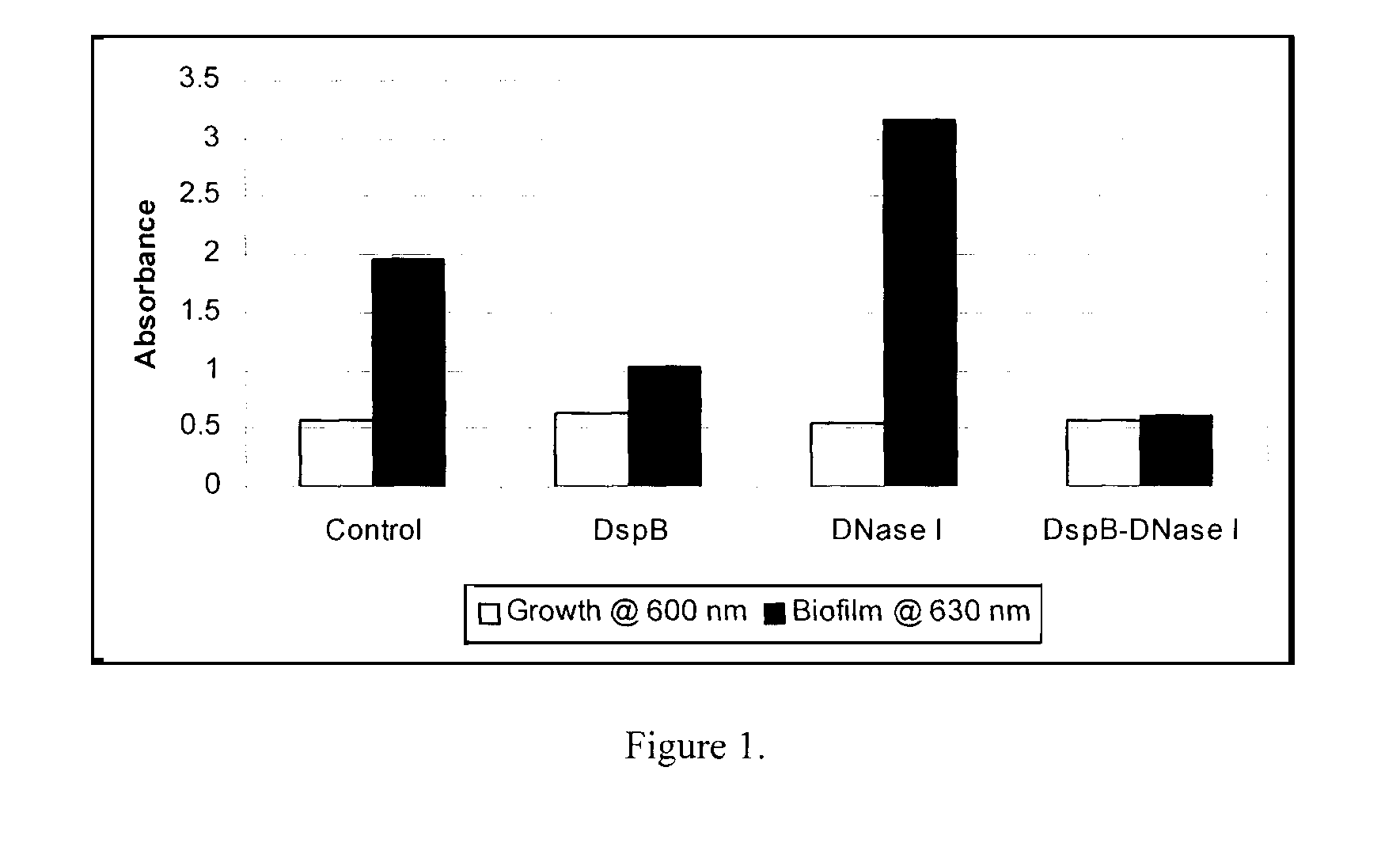
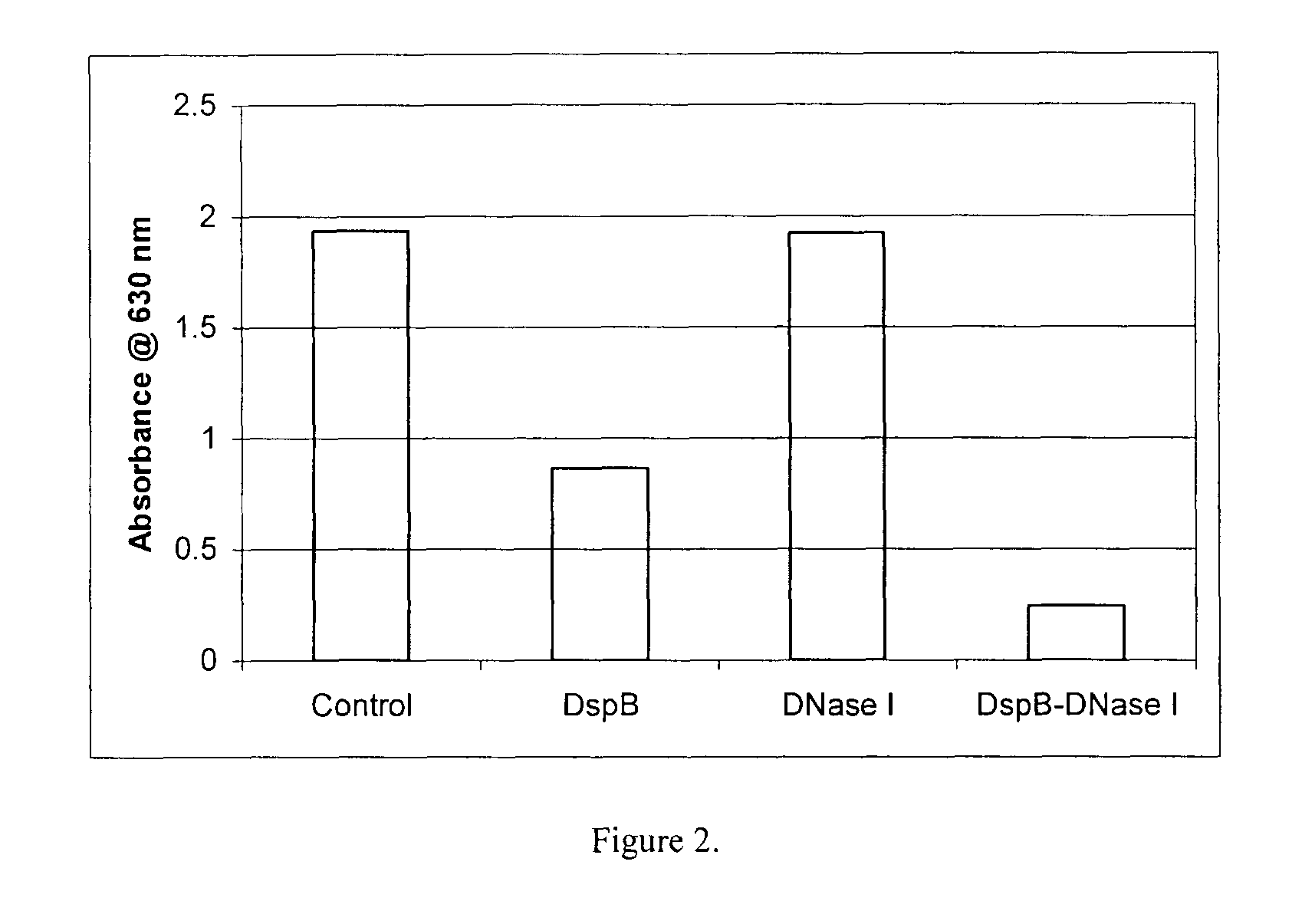
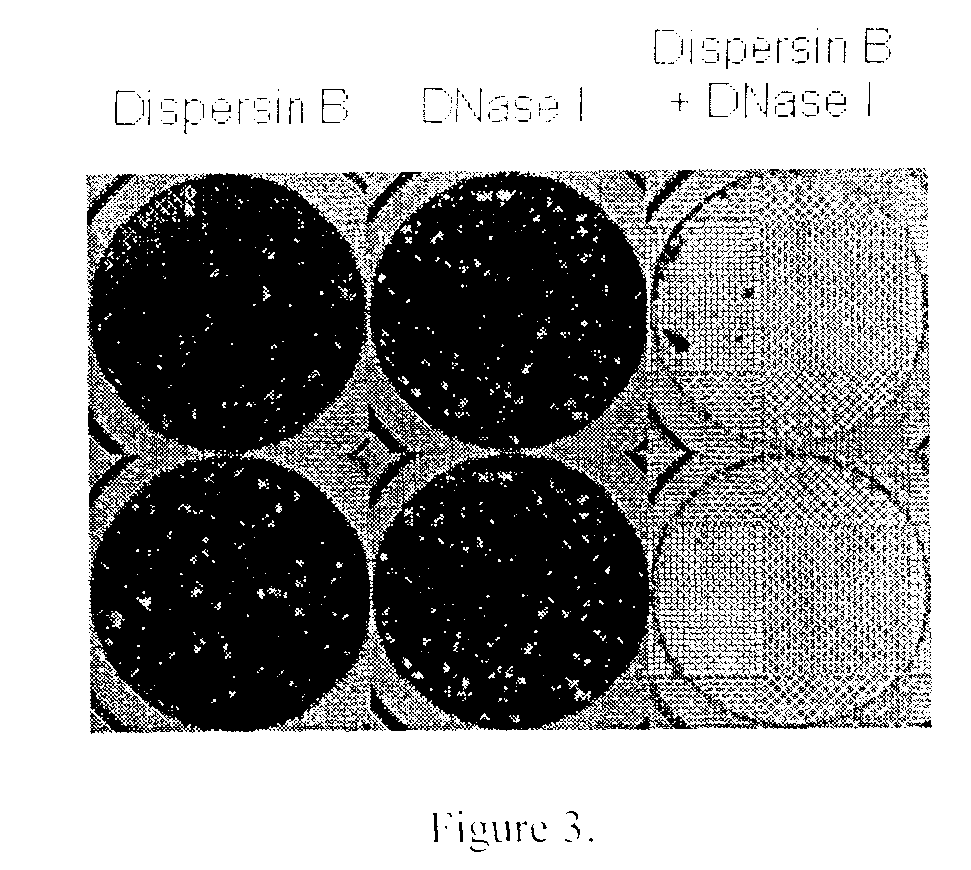
Dispersinb, 5-Fluorouracil, Deoxyribonuclease I and Proteinase K-Based Antibiofilm Compositions and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20110086101A1Avoid UTIsPrevents urinaryAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryMicroorganismProteinase K
The present invention provides antibiofilm composition comprising two or more agents selected from the group consisting of DispersinB™, 5-Fluorouracil, Deoxyribonuclease I and Proteinase K for preventing growth and proliferation of biofilm-embedded microorganisms in wound care, oral care, and disease-related infections and methods of treatment in mammals. The invention further provides methods for preparing medical devices, and wound care devices using an antibiofilm composition comprising two or more antimicrobial agents selected from the group consisting of DispersinB™, 5-Fluorouracil, Deoxyribonuclease I and Proteinase K.
Owner:KANE BIOTECH
Method for simultaneous extraction of nucleic acids from a biological sample
InactiveUS20070160999A1High extraction rateQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid reductionRNA - Ribonucleic acidPepsin
A new method of simultaneous and separate extraction of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) from a biological sample, indifferently from fresh, frozen, fixed or autoptic tissue with a weight no less than 5 mg. The main steps of the method are: 1 / sample lysis in a solution composed of a caotropic agent (urea or guanidine salt), a ionic detergent (SDS or SLS), a proteolytic enzyme (proteinase K, trypsin, chymotrypsin, pepsin or pronase), a reducing agent (β-mercaptoethanol or dithiothreitol); 2 / deproteination; 3 / precipitation of RNA from aqueous phase; 4 / precipitation of DNA from organic phase. The invention includes an extraction kit for nucleic acids, also of viral origin.
Owner:CALABRESE FIORELLA
Rapid prion-detection assay
Assays are provided for rapid detection, with high specificity of the pathogenic form of prion protein responsible for neurodegenerative diseases affecting humans and animals, such as transmissible spongiform encephalopathy in bovine, sheep, and cats. Also provided are assays for testing animal feedstock, such as animal feed, for the presence or concentration of pathogenic prion protein. Results are available in from about 0.5 to about 20 minutes and preferably within from about 5 to about 10 minutes. The assays employ proteinase-K to remove normal prion protein from a biological sample, so that the sample may be analyzed by immunochromatography to determine the presence and concentration of pathogenic prion protein. Because the proteinase-K is immobilized on a solid support for in situ removal of interfering components, the present invention obviates the need for subsequent extraction of the desired analyte. All aspects of the present invention are suitable for quantifying the minimal detectable amount of pathogenic prion protein in a biological sample. Moreover, the simplicity of sample preparation makes the present invention suitable for use in the field.
Owner:PRION DEVAL LAB
DNA extraction method suitable for structural analysis of microbial community in sediment
InactiveCN101696410AEfficient removalSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationTE bufferA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA extraction method suitable for structural analysis of microbial community in sediment, which comprises the following steps: washing a sediment sample with TENPbuffer, and suspending the washed sediment sample in PBS buffer; repeatedly freezing and melting the pretreated sediment sample, adding muramidase, adding proteinase K and sodium dodecyl sulfate into the sediment sample, centrifuging the sample at room temperature, taking supernate, adding mixed solution of phenol, chloroform and isoamylol in equal volume into the supernate, mixing evenly by oscillation, centrifuging the obtained sample at room temperature, taking a liquid phase, adding mixed solution of chloroform and isoamylol in equal volume into the liquid phase, centrifuging the obtained sample at room temperature, taking a liquid phase, and adding precooled isopropanol into the liquid phase; centrifuging the obtained sample to remove supernate, adding precooled ethanol into the sediment, washing the sediment for three times, and centrifuging to remove the ethanol; and naturally air-drying the sample, and dissolving DNA with TE buffer solution for preservation.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Lysate, nucleic acid extraction kit, and nucleic acid extraction method for nucleic acid extraction
ActiveCN110684764AReasonable ratioFully lysedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationLysisActive agent
The invention discloses a lysate, nucleic acid extraction kit, and nucleic acid extraction method for nucleic acid extraction. The lysate for the nucleic acid extraction is prepared from 0.5 to 2M ofsodium salt, 2 to 5M of guanidine salt, 1 to 5mM of a metal ion complexing agent, 0.25% to 1% of a nonionic surfactant, and 1% to 3% of PEG, and the molecular weight of the PEG is 6000 to 10000 Da, preferably 8000 Da. The lysate has a reasonable ratio, cells can be fully and effectively lysed, the lysis efficiency is high, so that the nucleic acids in the cells can be fully released, and the nucleic acids with higher concentration and purity can be obtained, and the quality and extraction efficiency of the nucleic acids are improved advantageously; and according to the lysate and the kit, digestion and removal of protein can be conducted without the aid of proteinase K during the entire nucleic acid extraction process, alcohols are not usedfor precipitate the nucleic acids,the obtained nucleic acids have high purity, and fragments are complete.
Owner:HANGZHOU BIGGER FISH BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
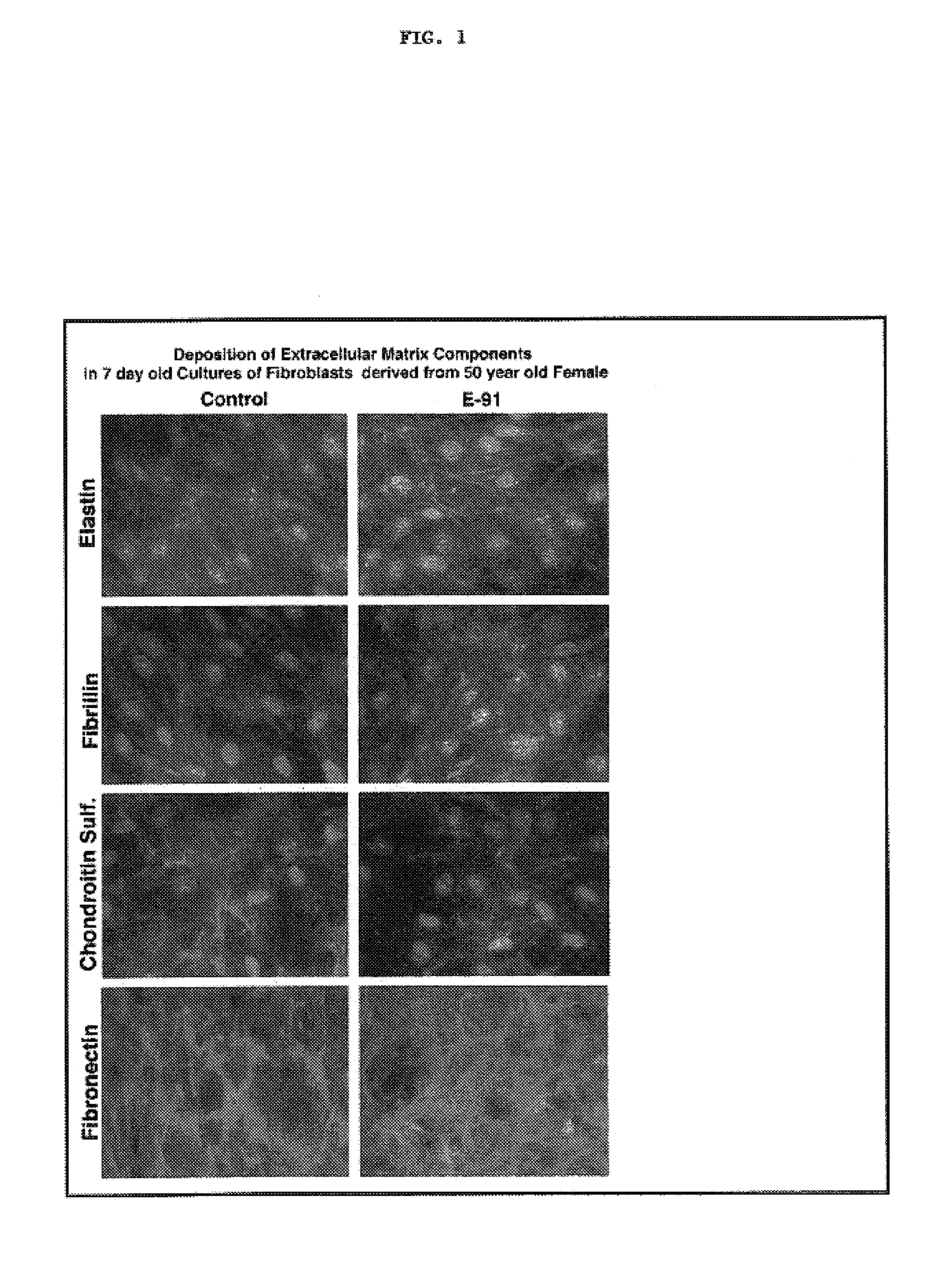
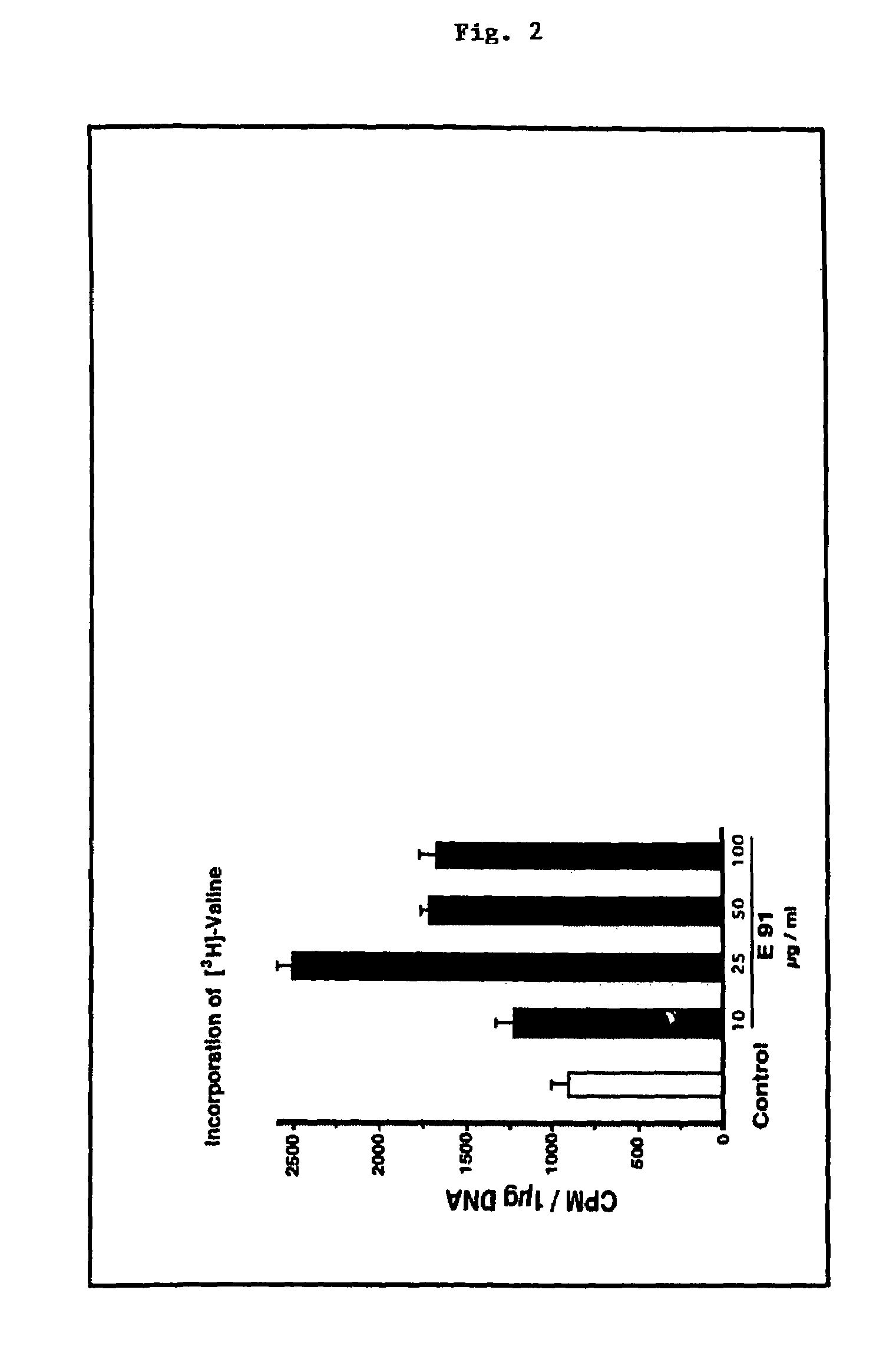
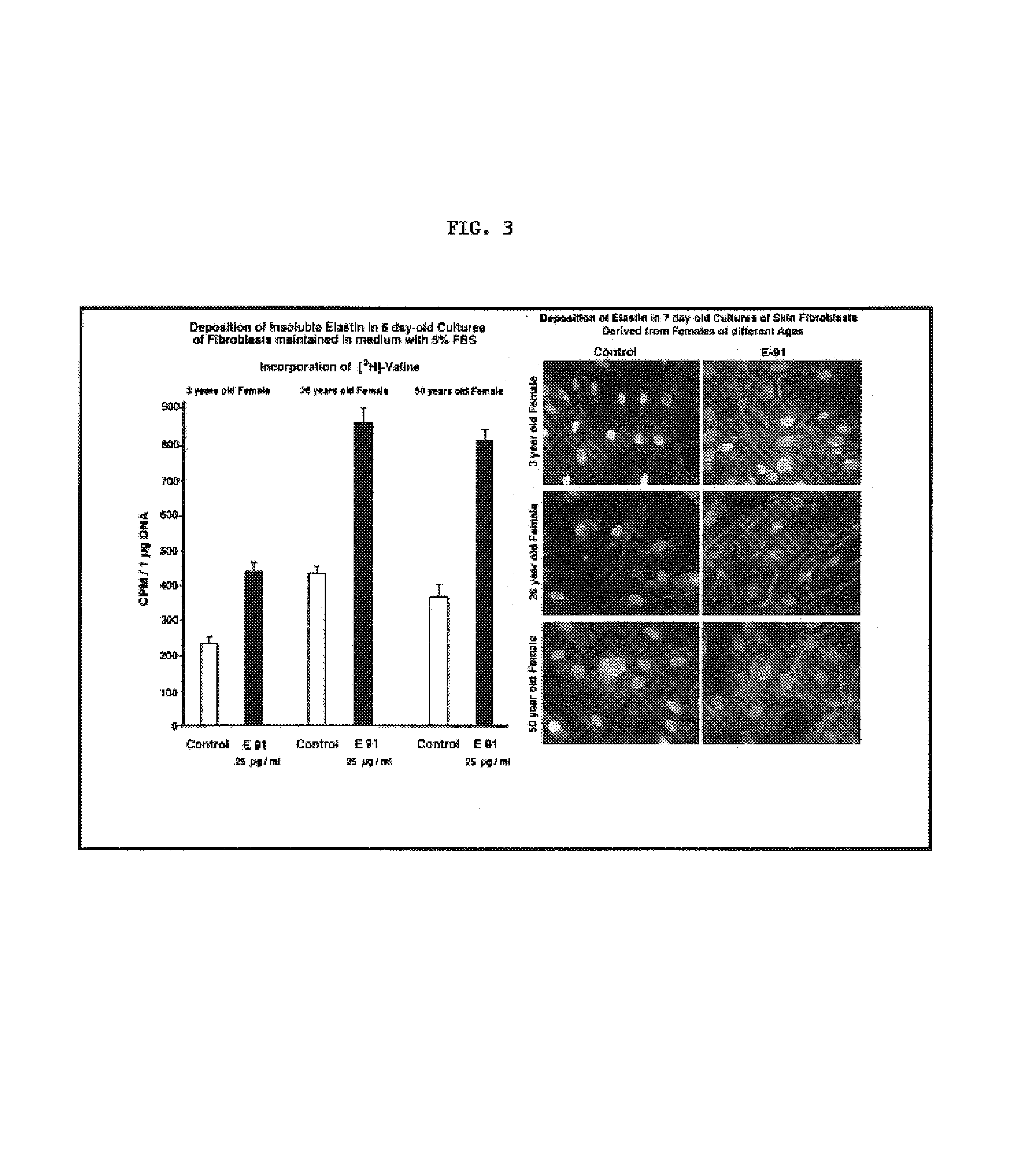
Elastin digest compositions and methods utilizing same
InactiveUS7560430B2Stimulate endogenous productionIncrease elasticityCosmetic preparationsDipeptide ingredientsLigament structureDigestion
The present invention provides compositions for the therapeutic and / or cosmetic treatment of Elastin comprising tissues. Therapeutic and cosmetic compositions comprising an elastin digest stimulate the endogenous production of Elastin and appear to enhance the elasticity of the skin and provide an external supply of peptide precursors of Elastin that penetrate into the tissue to which it is applied. The present invention describes compositions containing an elastin digest derived from proteolytic digestion of insoluble elastin derived from mammalian ligaments with a protein digesting composition, such as proteinase K. The elastin digest is a mixture of elastin peptides wherein the elastin peptide mixture comprises peptides of the sequence GXXPG, wherein X represents one of the natural amino acids. The elastin digest of the present invention may also comprise epitopes of cytokines, growth factors and di-peptides. Methods of using these elastin digest comprising compositions for treating tissues in need of increased elasticity and or Elastin are described.
Owner:ELASTOGENESIS LLC
Kit for extracting blood genome DNA based on magnetic bead method and use method for kit
The invention relates to a kit for extracting blood genome DNA based on a magnetic bead method. The kit comprises a cell lysis solution, a proteinase K solution, a magnetic bead dispersion solution, a first cleaning solution, a second cleaning solution and an elution solution, wherein the cell lysis solution comprises a guanidine compound, sodium chloride and a tween 20; a magnetic bead in the magnetic bead dispersion solution has the characteristics that a core is superparamagnetic ferroferric oxide, the surface is coated with silicon hydroxyl, and the particle size is 200-800nm; the first cleaning solution comprises Tris alkali, EDTA, isopropanol and water; the second cleaning solution is an ethanol solution; and the elution solution is Tris alkali or de-ionized water. The kit is simple to operate and can greatly improve working efficiency of blood genome DNA extraction; without pretreating erythrocytes, the cell lysis solution is directly adopted for pyrolyzing blood cells, and the magnetic bead dispersion solution can be added and combined with the genome DNA; and the kit is high in extraction volume and suitable for high-throughput experiments.
Owner:SUZHOU ENRICHING BIOTECH CO LTD
Salt-tolerant ethanol-tolerant protease-tolerant surfactant-tolerant exoinulinase, gene thereof, vector and strain
InactiveCN103981161APromote hydrolysisGood Salt Tolerance Ethanol Tolerance Tolerance To ProteaseBacteriaMicroorganism based processesExoinulinase activityBiofuel
The invention discloses a salt-tolerant ethanol-tolerant protease-tolerant surfactant-tolerant exoinulinase, a gene thereof, a vector and a strain. The exoinulinase InuAJB13 possesses the following properties: the optimum pH is 5.5, 50% or more of enzymatic activity is maintained in the pH scope of 4.0-7.0; the remnant enzyme activity reaches 90% or more after exoinulinase is processed by a buffer with a concentration of 0.1 M and pH of 4.0-7.0 for 1 h; the optimum temperature is 55 DEG C, and exoinulinase has the enzyme activity at 10-70 DEG C; a NaCl solution with a concentration of 0.6-4.5 M is capable of improving the enzyme activity by 0.2-0.6 times; 100% of the enzyme activity can be kept after exoinulinase is processed by a NaCl solution with a concentration of 0.2-4.5 M at 37 DEG C for 60 min; exoinulinase keeps the activity in 10% (V / V) of ethanol; exoinulinase keeps 88% or more of the activity after being processed in 3.0-15.0% (V / V) ethanol at 37 DEG C for 60 min; exoinulinase activity is not influenced or slightly influenced by trypsin, protease K, surfactants, most of metal ions, and commercial liquid laundry detergents; and exoinulinase is capable of hydrolyzing inulin, cane sugar, raffinose, stachyose, beta-2,6-fructan (levan) and soluble starch. The exoinulinase disclosed by the invention is applicable to industries such as feed, foodstuff, washing and biofuels.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Compositions and method for storage of nucleic acid from bodily fluids
The present invention provides an aqueous composition comprising SDS, Cyclohexanediamine tetraacetate, Tris-HCl and proteinase K for the extraction of nucleic acid from a sample of bodily fluid, such a saliva, wherein the extracted nucleic acid is stable for at least fourteen days at room temperature The composition permits direct use of the extracted and stored DNA in an amplification reaction without further processing.
Owner:DNA GENOTEK
Whole genome DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) extraction kit for blood and method thereof
ActiveCN104017800AReduce the chance of secondary pollutionImprove accuracyDNA preparationLiquid layerLithium chloride
The invention relates to a kit of extracting a whole genome DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) from blood and a using method thereof. The kit is characterized by comprising a red blood cell lysate, a white blood cell scrubbing solution, digestive juice, proteinase K, a purifying liquid, gDNA salting out liquid, a gDNA scrubbing solution, a gDNA eluant and the like. The using method of the whole genome DNA extraction kit for blood is characterized by comprising the following steps: washing the red blood cell split to obtain the white blood cell; splitting the white blood cell by the digestive juice containing the proteinase K; and further purifying by an improved lithium chloride purifying liquid, salting out the liquid layer, and carrying out chromatography to obtain the high purity whole genome DNA. When the kit provided by the invention is used to extract the whole genome DNA in blood, plasma and serum in blood are not separated in advance but fresh or frozen anti-freezing whole blood is taken, wherein the lowest blood volume required reaches 20 microliters or blood cakes are required. According t the kit provided by the invention, the whole genome DNA with high purity can be fully unlinked and the PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification is efficiently carried out, so that the kit is used for scientific research or clinical diagnostic analysis such as PCR amplification, gene expression, gene sequencing, whole genome sequencing, exome sequencing, gene mutation and single nucleotide polymorphism.
Owner:ZICHENG RUISHENGHUI BEIJING BIOTECH DEV CO LTD
DispersinB(TM), 5-fluorouracil, deoxyribonuclease I and proteinase K-based antibiofilm compositions and uses thereof
ActiveUS8617542B2Prevents urinary and vascular infectionAvoid infectionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseWound care
Owner:KANE BIOTECH
Method and reagent for extraction of viral/bacterial nucleic acid in animal sample
ActiveCN109385418AAvoid cloggingEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationSilica gelDigestion
The invention discloses a method and a reagent for extraction of viral / bacterial nucleic acid in an animal sample. The method comprises the following steps: taking the animal sample, and adding a lysate for lysis at a room temperature so as to obtain a lysis reaction solution; and adding an ethanol solution into the lysis reaction solution, transferring an obtained mixture into a silica gel containing adsorption membrane centrifugal column, carrying out adsorption with a manner of low-speed centrifugation, and carrying out washing and eluting. According to the invention, the bacterial nucleicacid extracted by using the method provided by the invention has high purity; no proteinase K for sample digestion is needed to be used in the process of extraction; reagent components and an operation flow are simplified; the cost of hardware equipment can be reduced through a manner of low-speed centrifugation in the process of extraction; a low-speed palm centrifuge can be adopted, is convenient to carry and is applicable to on-site operation; the components of the lysate are optimized; the binding ability of nucleic acid molecules to a silica-gel adsorption membrane is reinforced; and goodnucleic acid extraction efficiency is guaranteed.
Owner:USTAR BIOTECHNOLOGIES (HANGZHOU) CO LTD
Rapid prion-detection assay
Owner:PRION DEVAL LAB
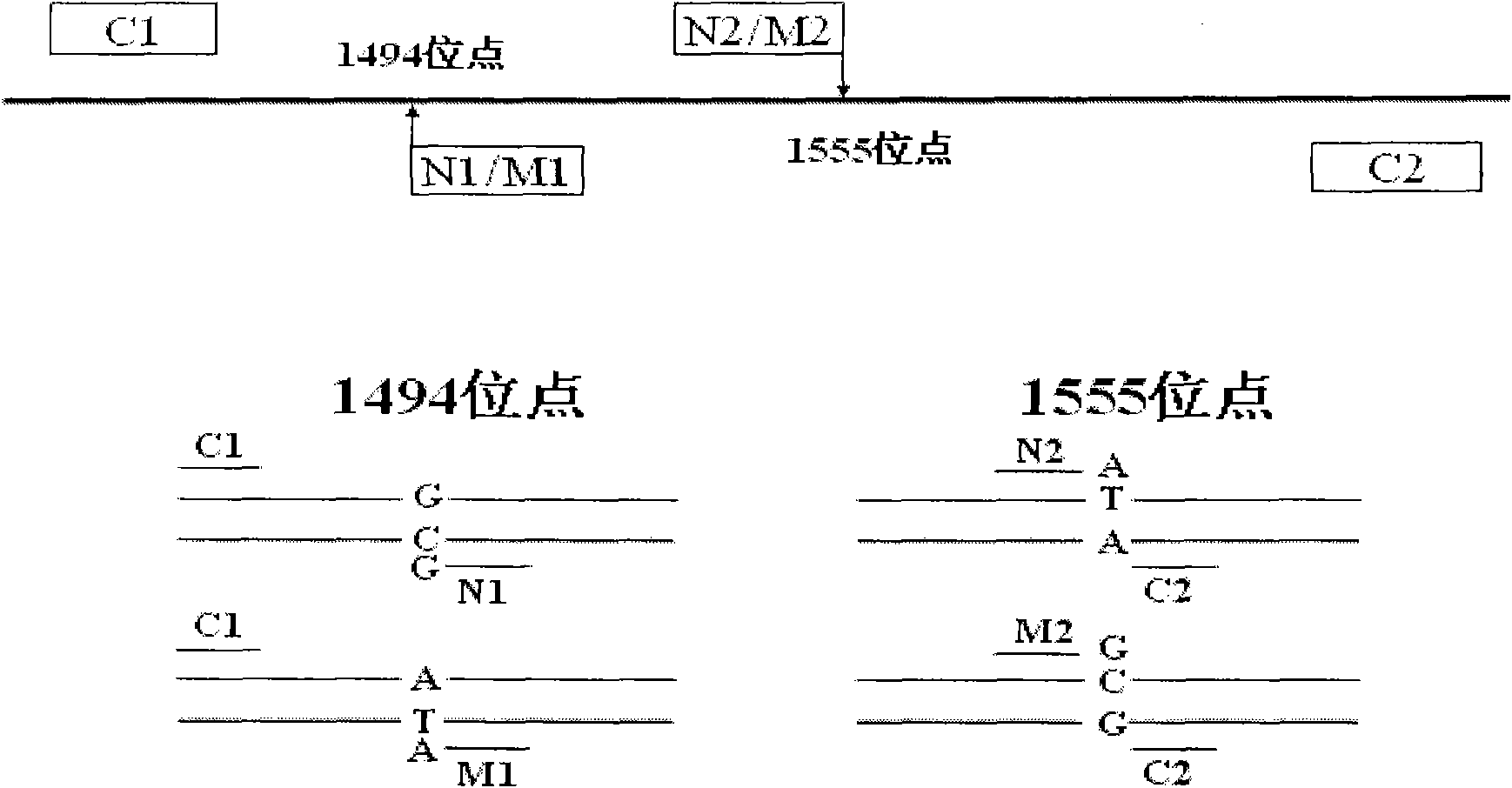
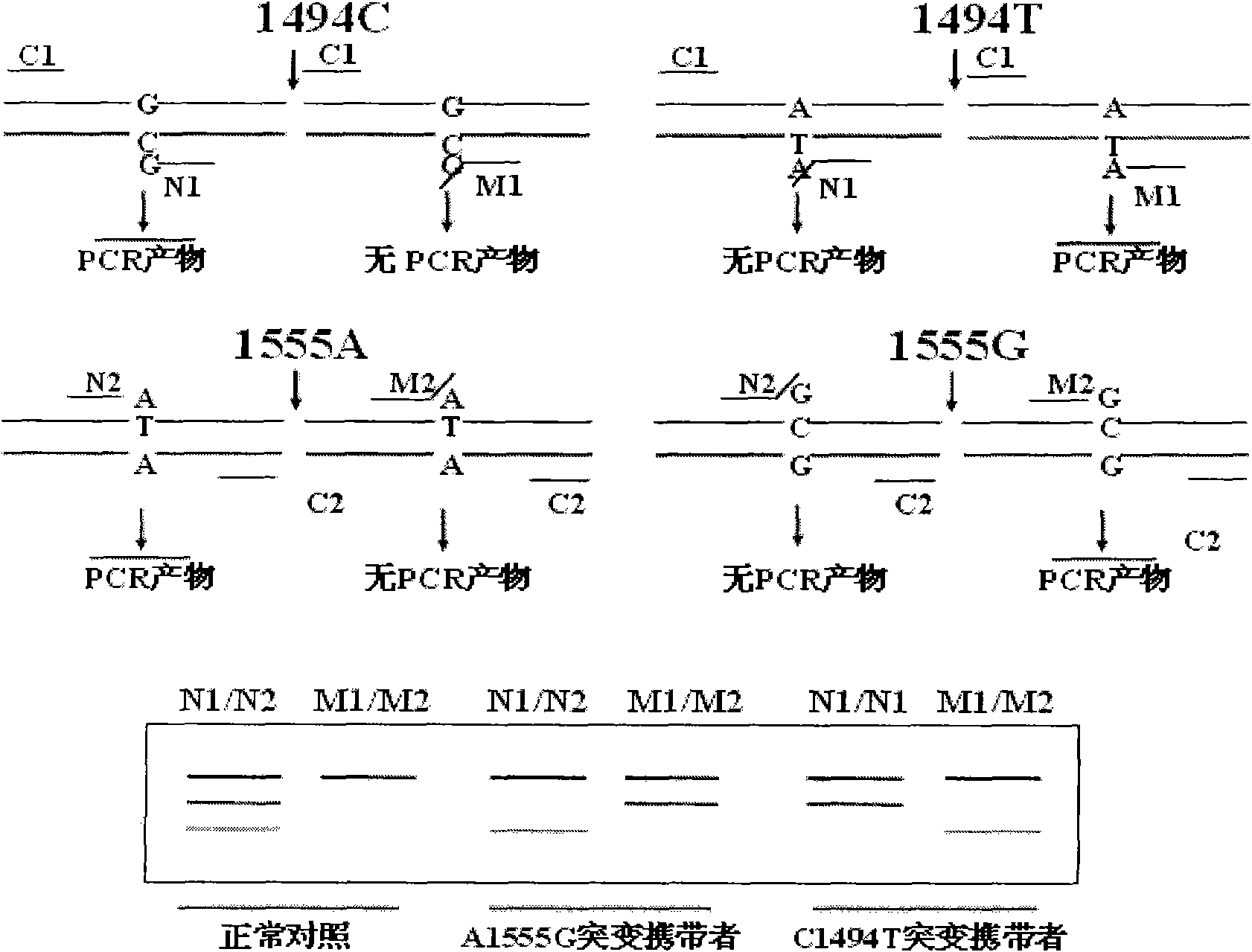
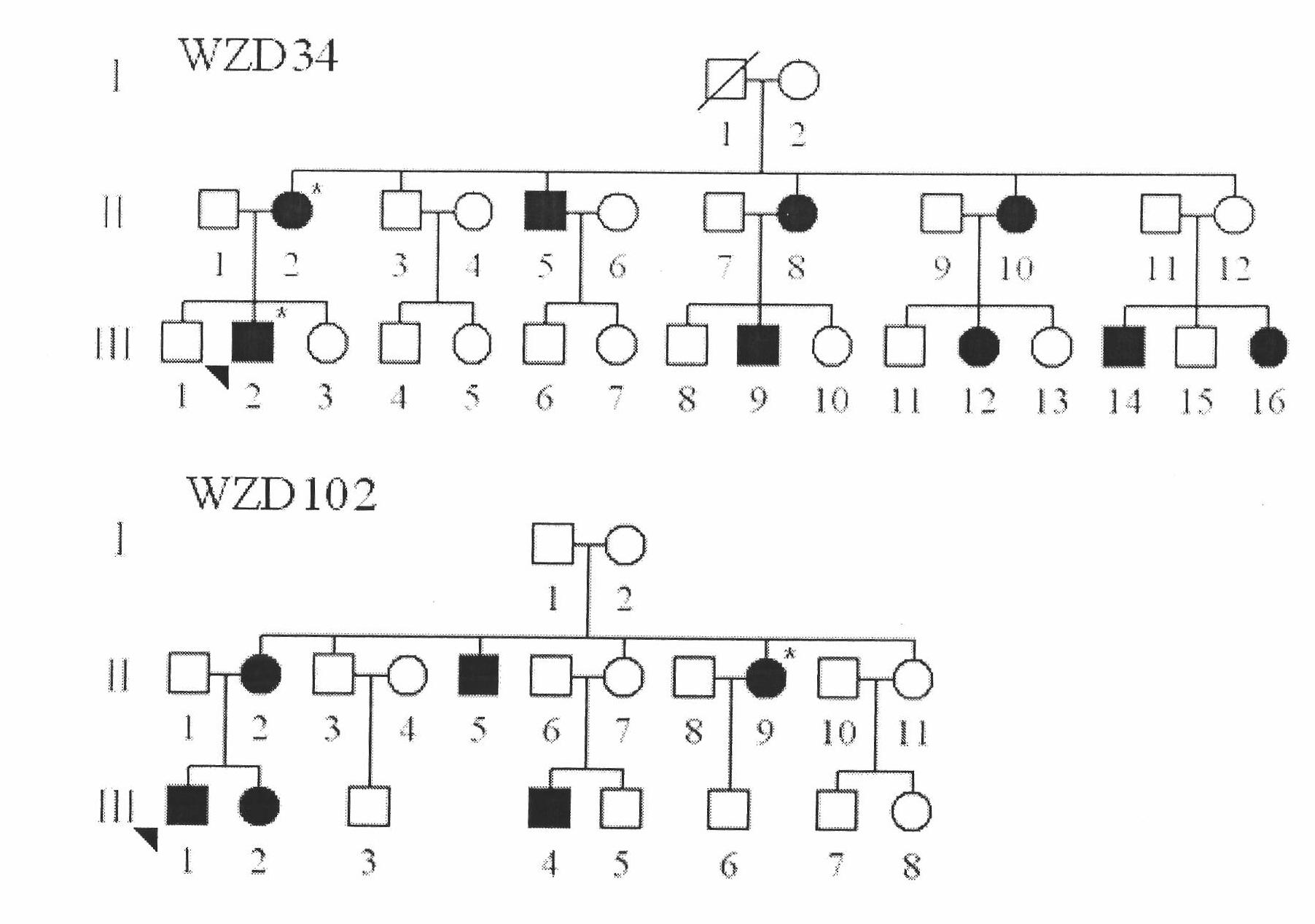
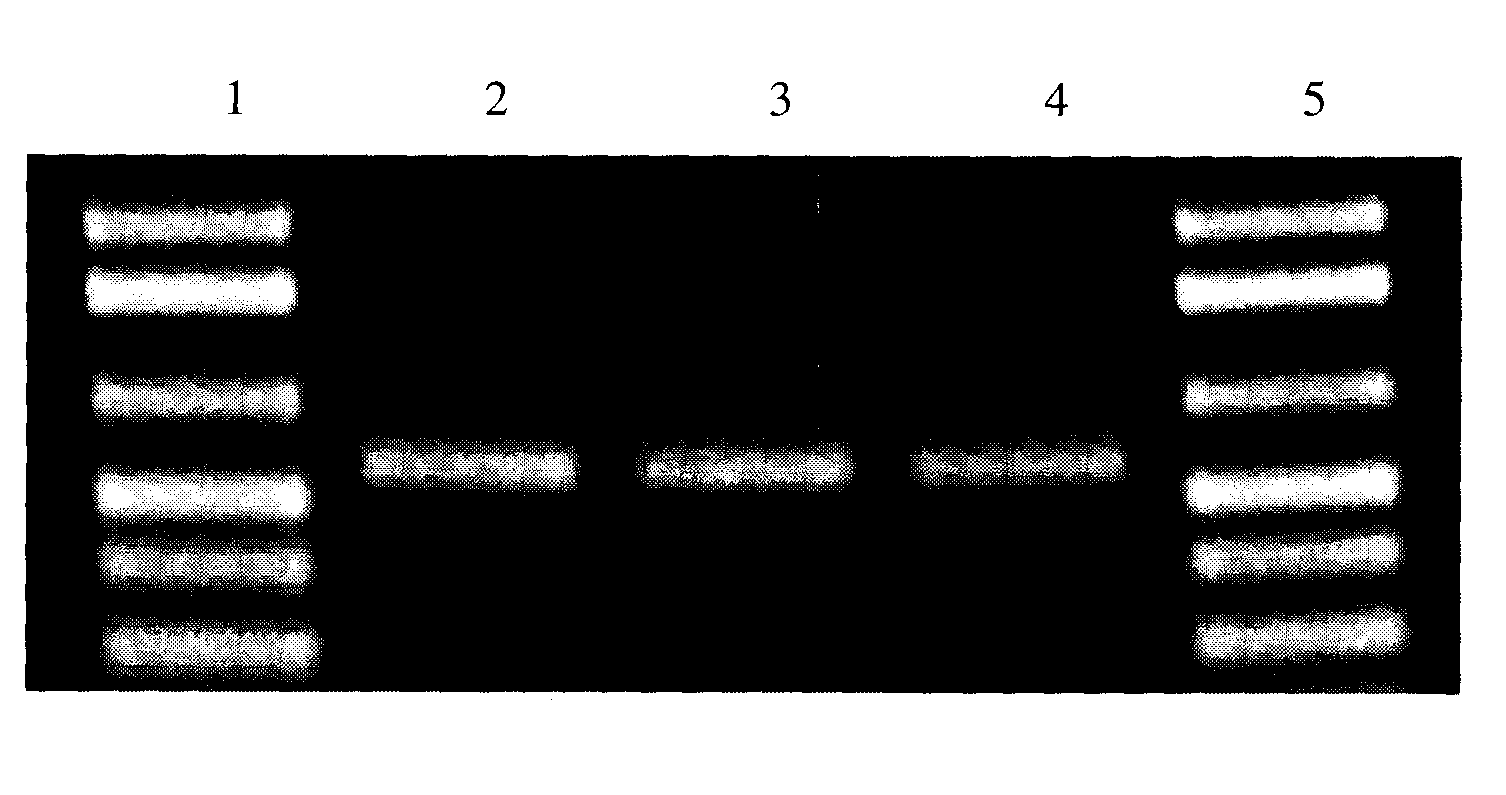
Kit for simultaneously detecting mutations in mitochondria DNA A1555G and C1494T and using method thereof
InactiveCN101768637ARelieve painSolve the problem of extracting DNAMicrobiological testing/measurementPositive controlGenomic DNA
The invention provides a kit for simultaneously detecting mutations in mitochondria DNA A1555G and C1494T related to maternally inherited drug-induced deafness and a using method thereof. The kit comprises a reagent for extracting sample genomic DNA, a PCR amplification reactive reagent, a primer mixed liquor, a positive control template and a negative control template. The using method of the kit mainly comprises the following steps: using blood, hair with follicle, oral mucosa doctor blade, saliva, and the like, as a sample; adopting a proteinase K digestion pyrolysis method to extract genomic DNA; and then simultaneously detecting mutations in A1555G and C1494T by multiple allele specific PCR. The kit is used for detecting the mutations in mitochondria DNA A1555G and C1494T related to maternally inherited drug-induced deafness and is more rapid, economical and simpler than the single detection for mutation in A1555G or C1494T, and the kit has low requirements for equipment and environment and is conducive to promotion and application.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Compositions and Method for Storage of Nucleic Acid From Bodily Fluids
ActiveUS20090123976A1Permit useHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementProteinase activityProteinase K
An aqueous composition comprising a denaturing agent, a chelator, a buffering agent and a protease for the extraction of nucleic acid from a sample of bodily fluid, such as saliva, such that the extracted nucleic acid is stable for at least fourteen days at room temperature and can be directly utilised in an amplification reaction without further processing. In particular, said composition comprises SDS, Cyclohexanediamine tetraacetate, Tris-HCl and proteinase K. A method and kit for the amplification of DNA directly from a bodily fluid, comprising said composition, is further provided.
Owner:DNA GENOTEK
Method for simply, conveniently and quickly extracting trace total deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of single roes and fries
InactiveCN102161988AEasy to collect and storeQuantity GuaranteeDNA preparationHigh concentrationGenomic DNA
The invention relates to a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) extraction technology, in particular to a method for simply, conveniently and quickly extracting trace total DNA of single roes and fries. The method comprises the following steps of: fixing and preserving collected roes or fries; washing to remove stationary liquid, adding DNA extraction buffer solution and lysis buffer solution, shearing the roes or the fries, adding proteinase K and ribonucleic acid (RNA) enzyme, incubating and digesting; and precipitating protein by using high-concentration NaCl solution, adding isopropanol to precipitate DNA, washing a precipitate by using 70 percent ethanol to remove salt ions, and adding ultrapure water or tris-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (TE) solution and dissolving after the ethanol is volatilized. The method solves the problem of the limitation of the application the conventional total DNA extraction method to samples with the low content of genomic DNA, such as roes or fries and thelike.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for extracting genomic DNA from giant salamander skin mucus
The invention discloses a method for extracting genomic DNA from giant salamander skin mucus. The method comprises the following steps: 1, saving a sample; 2, replacing ethanol; 3, splitting a cell; 4, precipitating protein; 5 precipiating DNA; 6, washing the DNA; and 7, obtaining DNA, wherein required pyrolysis liquid can be obtained by mixing 160 microliter 1 mol / L nacl aqueous solution, 40 microliter 1 mol / L TRIS-HCI aquenous solution with pH value of 8.0, and 2 microliter 100mmol / L EDTANa2 aqueous solution with pH value of 8.0 uniformly at normal temperature, and then adding 160 microliter 10% of SDS aqueous solution and 20 microliter 10 mg / ml proteinase K aqueous solution to the mixture and quickly mixing the mixture. The method provided by the invention adopts giant salamander skin mucus or skin as an extracting material of the genomic DNA, so that the giant salamander organism will be protected without damage.
Owner:YANGTZE RIVER FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Magnetic bead-based DNA extraction method, lysate and kit
ActiveCN109022420AReduce the steps of adding liquidImprove experiment safetyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMagnetic beadPolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a magnetic bead-based DNA extraction method, a lysate and a kit. The lysate is characterized in that a buffer solution with a sodium ion content of greater than or equal to 140mmol and a pH value of 7 to 9 contains a chaotropic agent with a concentration of 3 mol / L to 6 mol / L, 5 mmol to 20 mmol of a metal chelating agent and 5% to 15% by mass of polyethylene glycol. The extraction method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring a cleavage reaction system; (2) treating the cleavage reaction system; (3) adding nanometer magnetic beads; (4) acquiring magnetic beads binding to DNAs; (5) carrying out washing and then performing DNA elution. The kit comprises the lysate, a proteinase K solution, a magnetic bead dispersion liquid, a first washing solution, a second washing solution, a third washing solution and an eluent. Reagents used in the invention are non-toxic, so experimental safety is improved; and only one-step liquid adding operation is required, so labor cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:武汉纳磁生物科技有限公司
Method for extracting large numbers of DNA with magnetic particulate
The invention relates to the application field of nanometer and micrometer materials, in particular to a method for quickly extracting large numbers of genome DNA from biological samples with magnetic particulates. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) cracking biological samples: taking a certain amount of biological samples such as blood, tissue and like, adding proteinase K solution and guanidine hydrochloride cracking liquid with the concentration of 4 to 6 M, evenly mixing, and fully cracking in 56 DEG C water bath for 5 to 20 min; (2) adding combined solution into sample cracking liquid to form mixed solution containing magnetic particulates (DNA compound); (3) separating the magnetic particulates (DNA compound) from the mixed solution; (4) washing; (5) eluting: adding eluting liquid to enable DNA to be eluted from the magnetic particulates, separating the magnetic particulates and the eluted DNA under the action of an exterior magnetic field, and collecting supernatant liquid to obtain rarefied DNA. By using the invention, high purity DNA can be successfully extracted from large numbers of samples, large-scale instruments such as a centrifuge and like are not needed, the operation steps are simple and convenient and need short time.
Owner:SHANXI LIFEGEN
Quantitative detection kit for human immunodeficiency virus HIV-1
ActiveCN105087826AOperation time savingEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesHuman immunodeficiency virus HIV-1Fluorescence
The invention discloses a quantitative detection kit for human immunodeficiency virus HIV-1. The quantitative detection kit comprises sample treating agent, an upstream primer HIV-F used for target nucleotide amplification, a downstream primer HIV-R used for target nucleotide amplification, a Taqman probe HIV-P for detecting target nucleotide and RNA one-step reaction buffer, wherein the sample treating agent comprises guanidinium isothiocyanate, sodium citrate, dodecyl creatine sodium, beta-mercaptoethanol and proteinase K; a fluorescent group and fluorescence quencher are respectively combined to two ends of the Taqman probe HIV-P. When the quantitative detection kit is used for detecting, a to-be-detected sample is directly mixed with the sample treating agent and then is used for subsequent detection. Compared with a traditional quantitative detection kit for HIV virus, the quantitative detection kit has the advantages that the step of extracting and purifying nucleic acid molecules from the sample is omitted, and time-saving and simple operation is achieved.
Owner:FAPON BIOTECH INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com