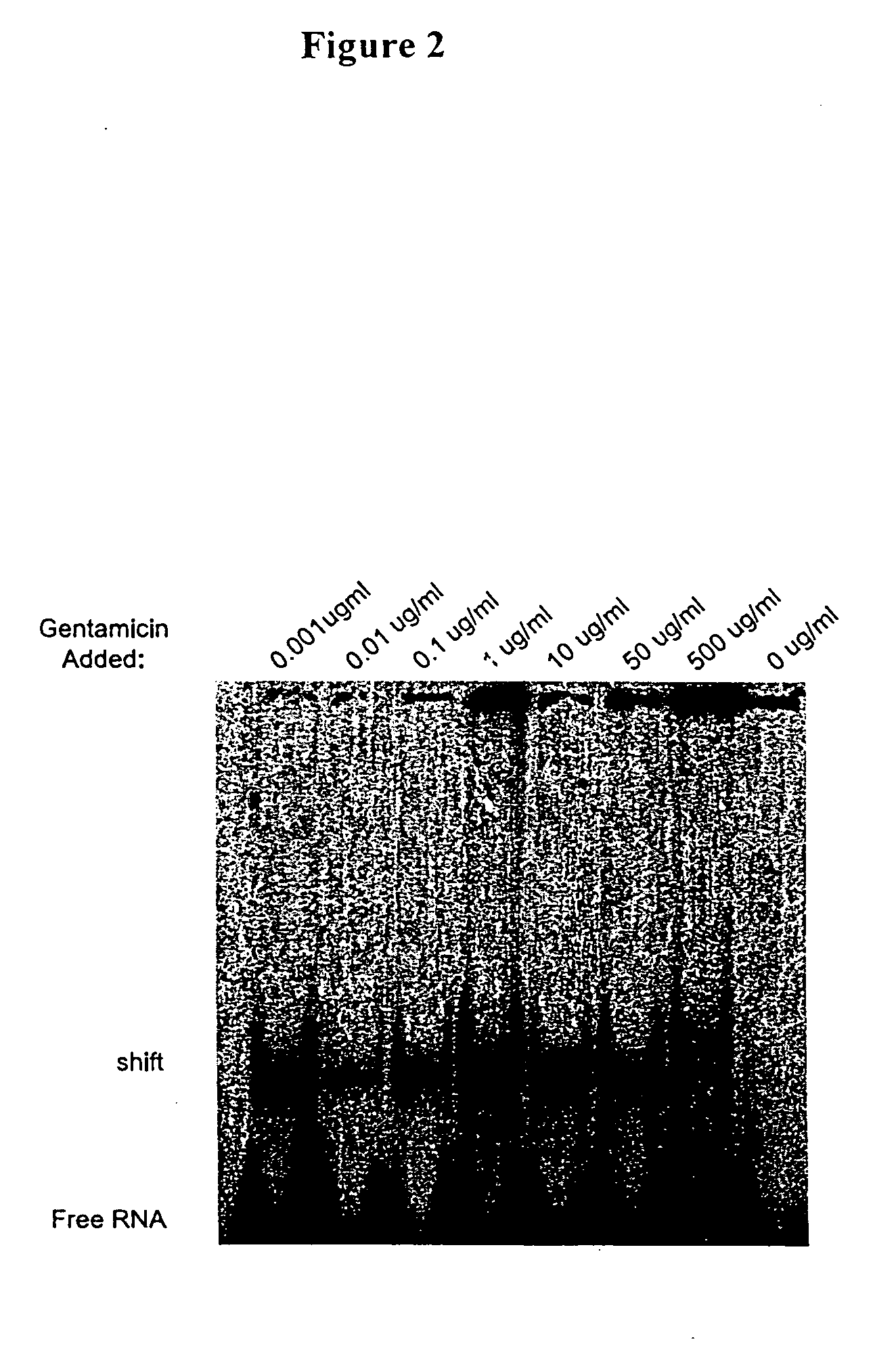
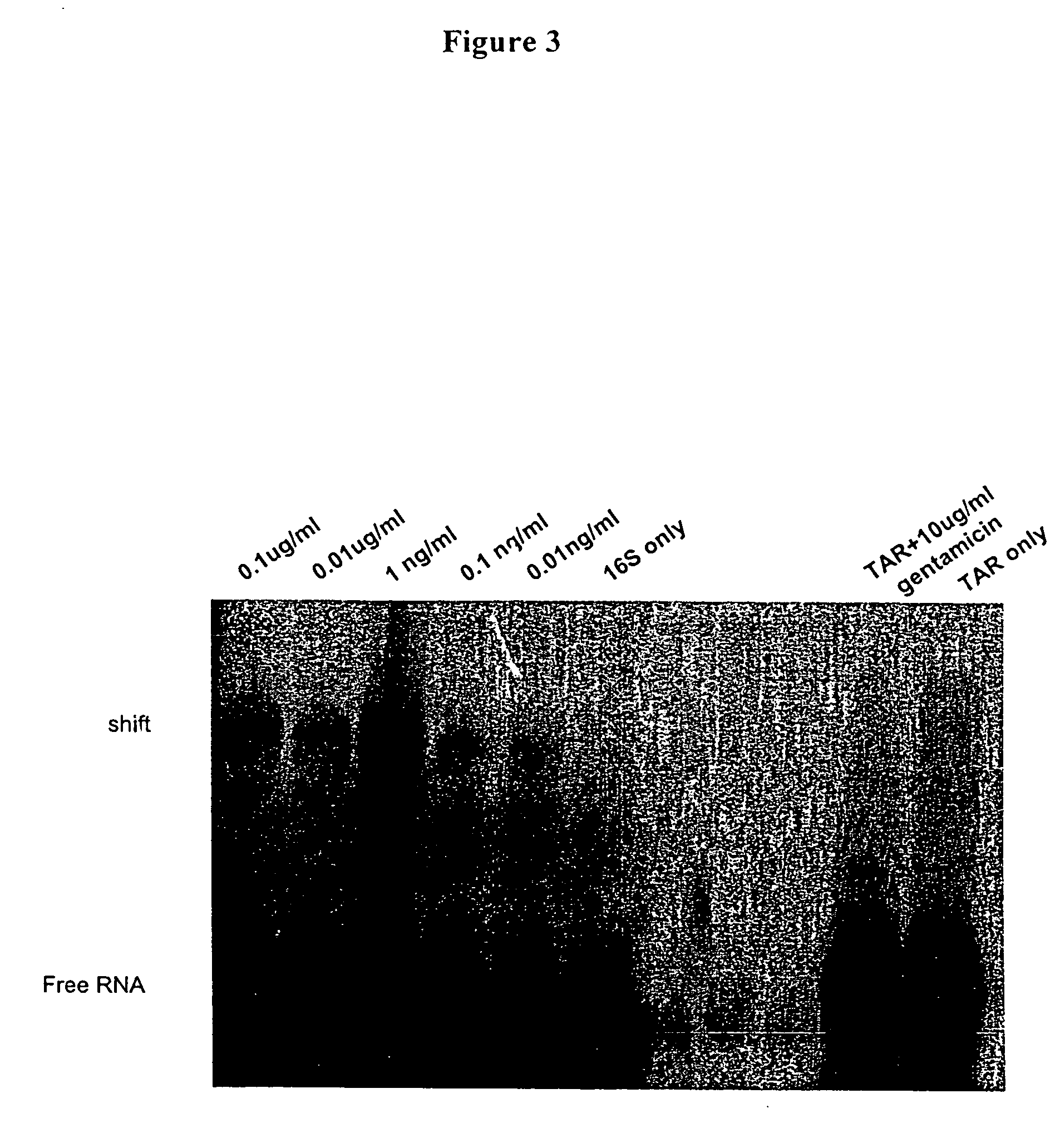
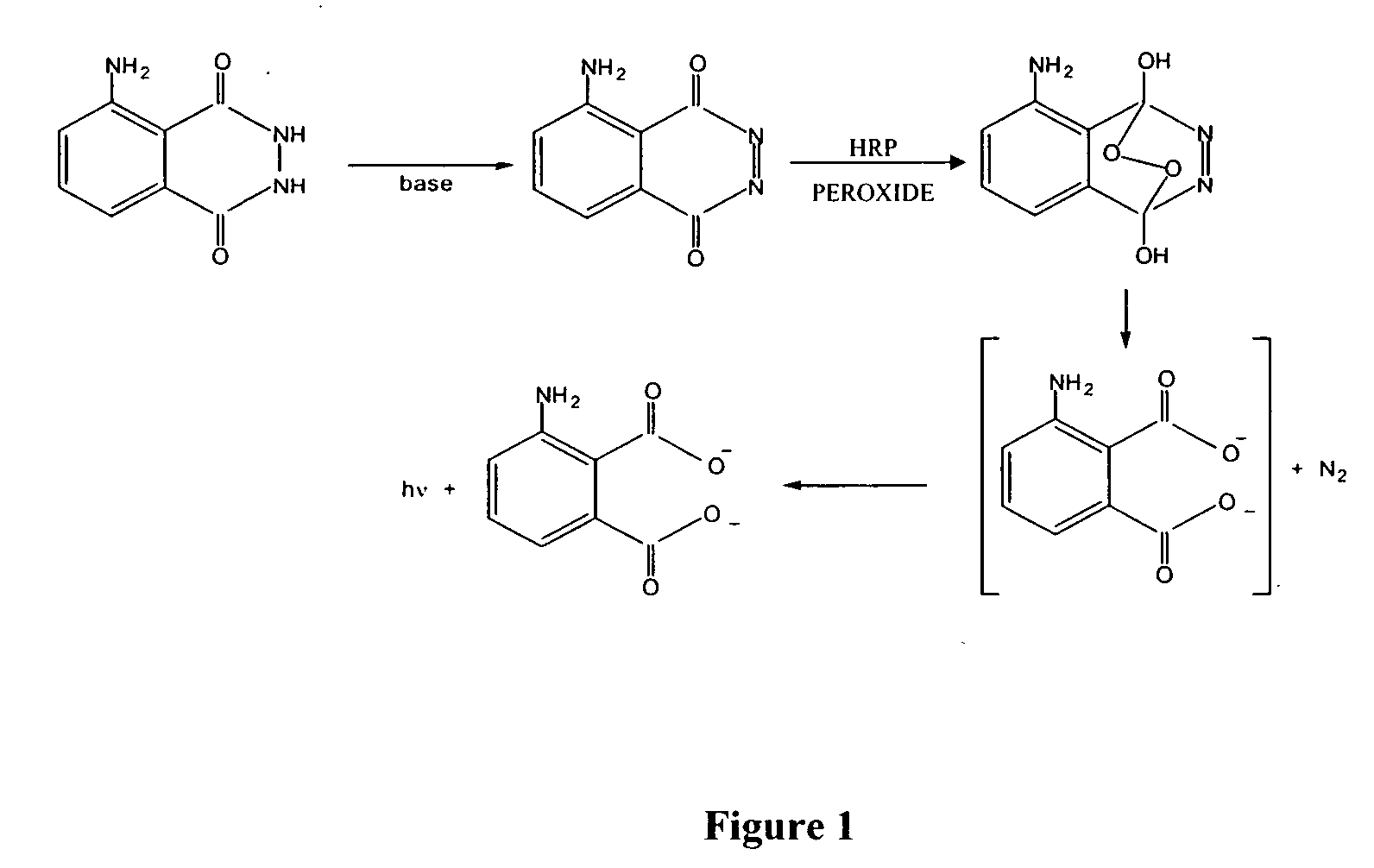
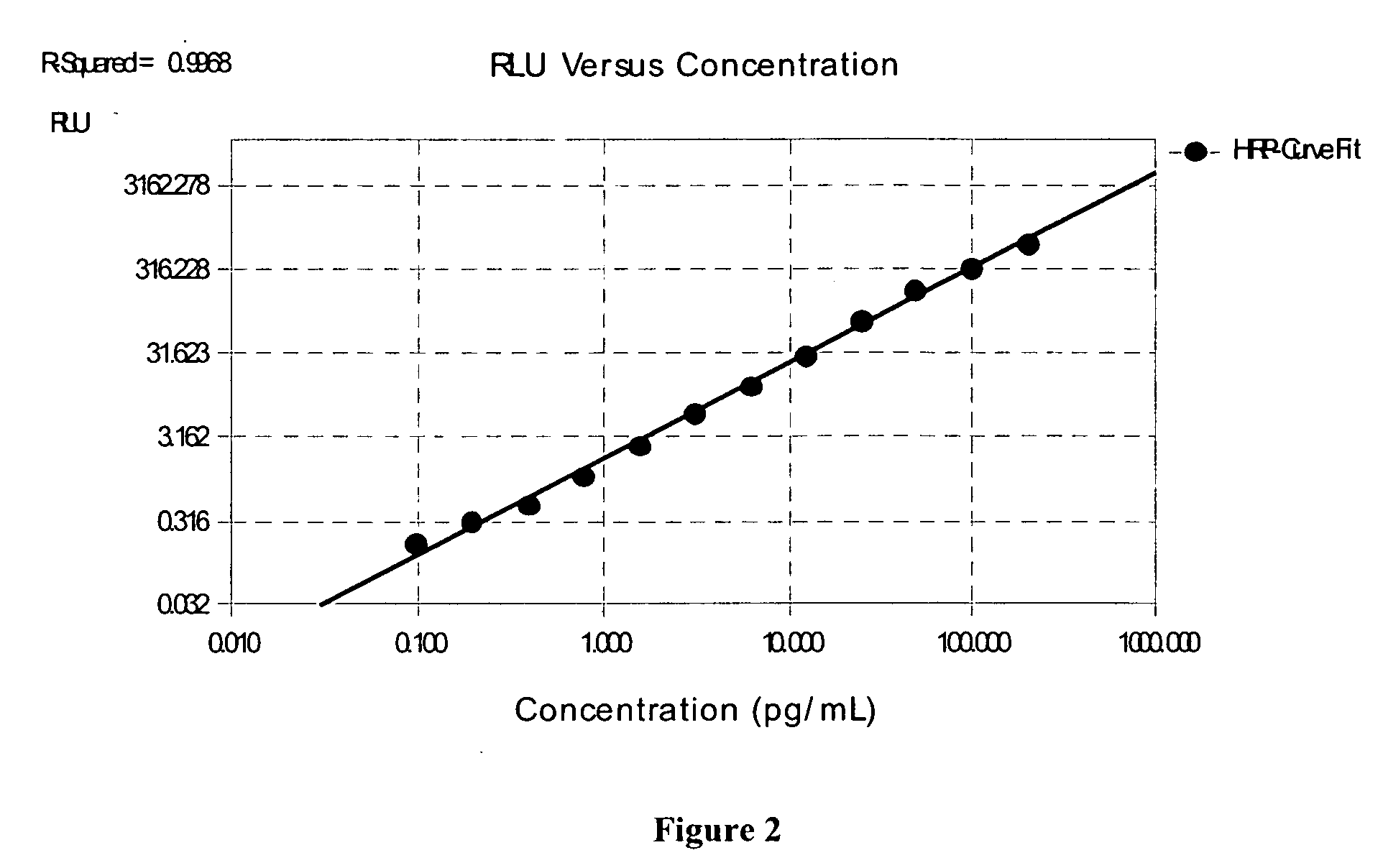
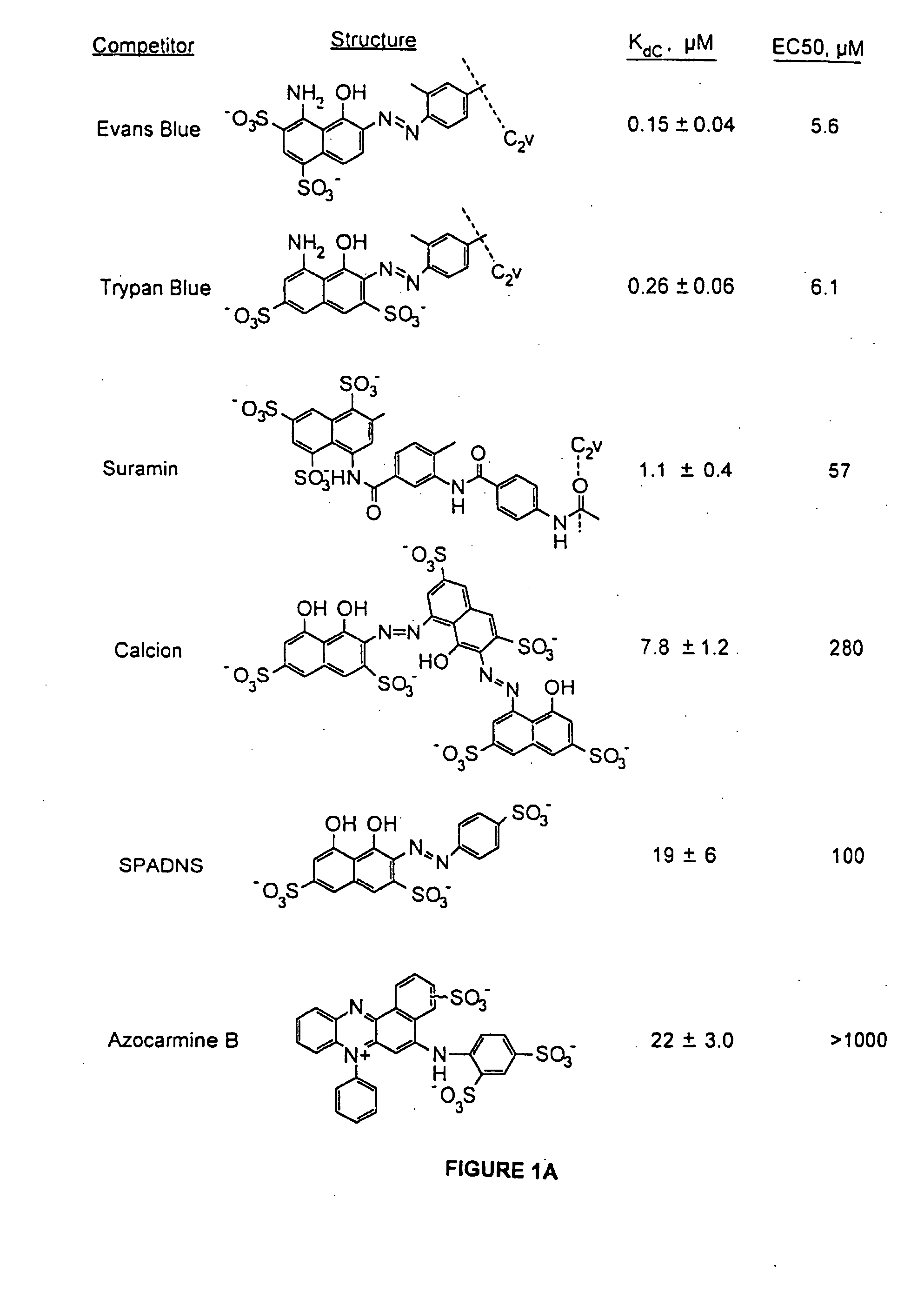
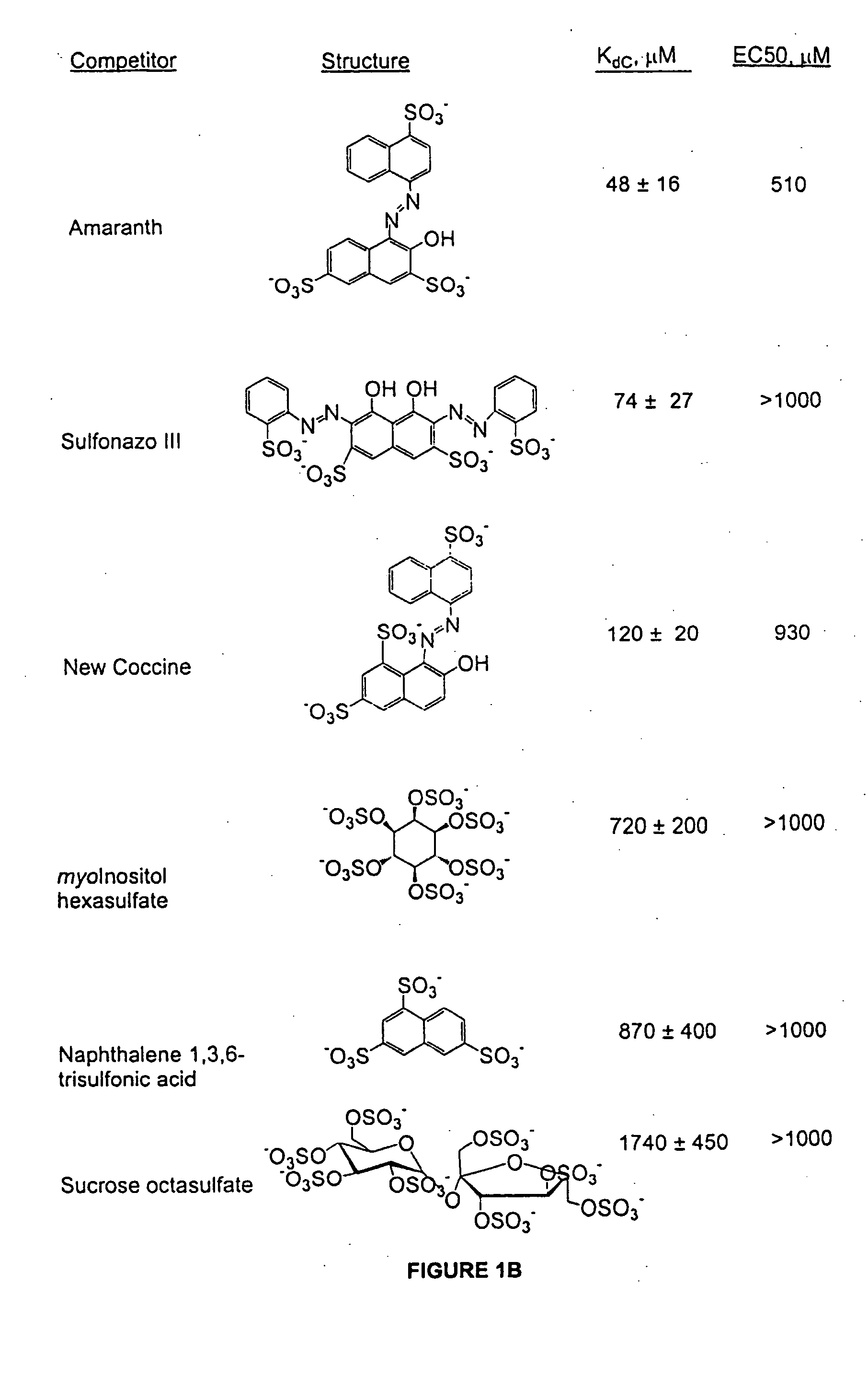
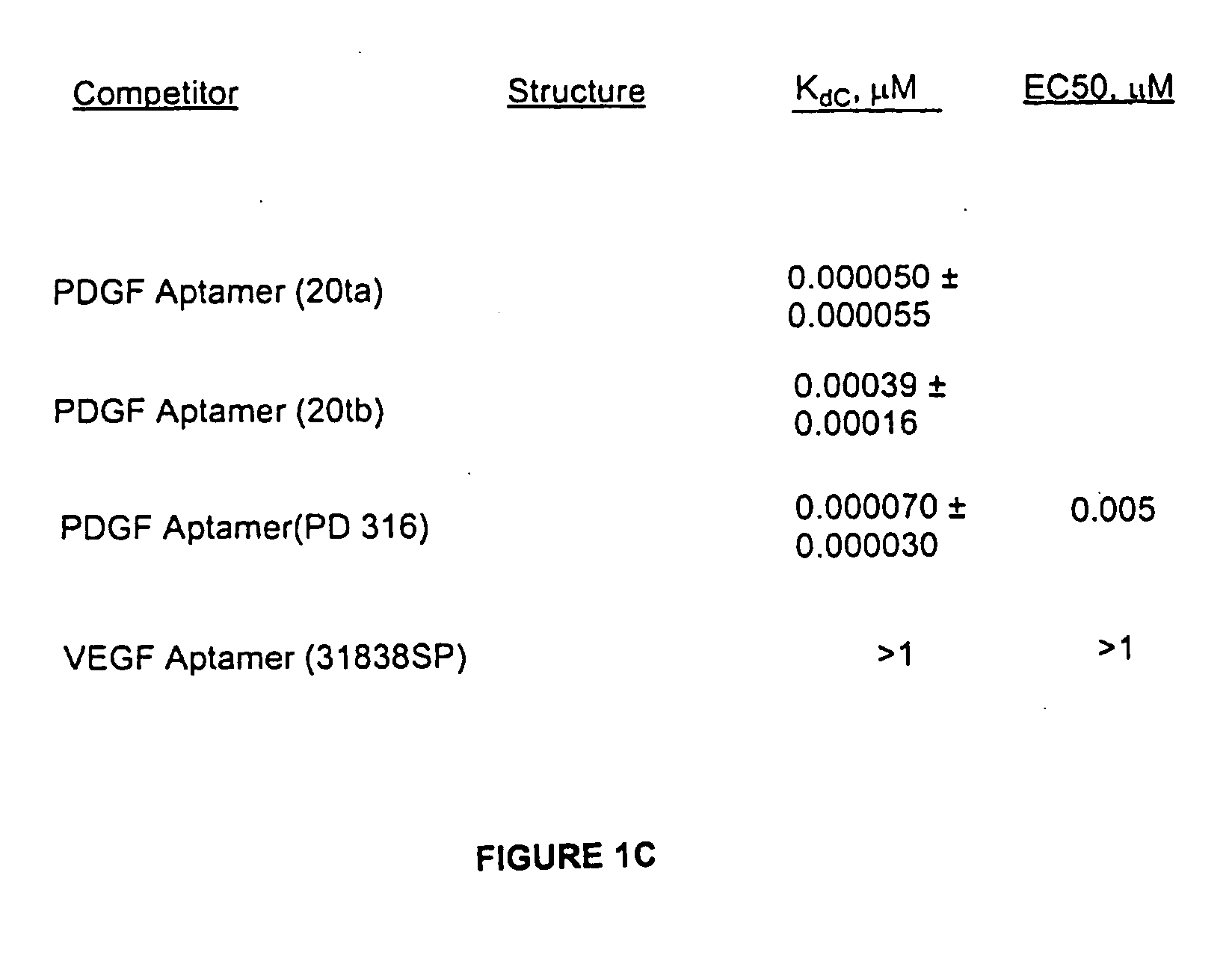
Patents
Literature
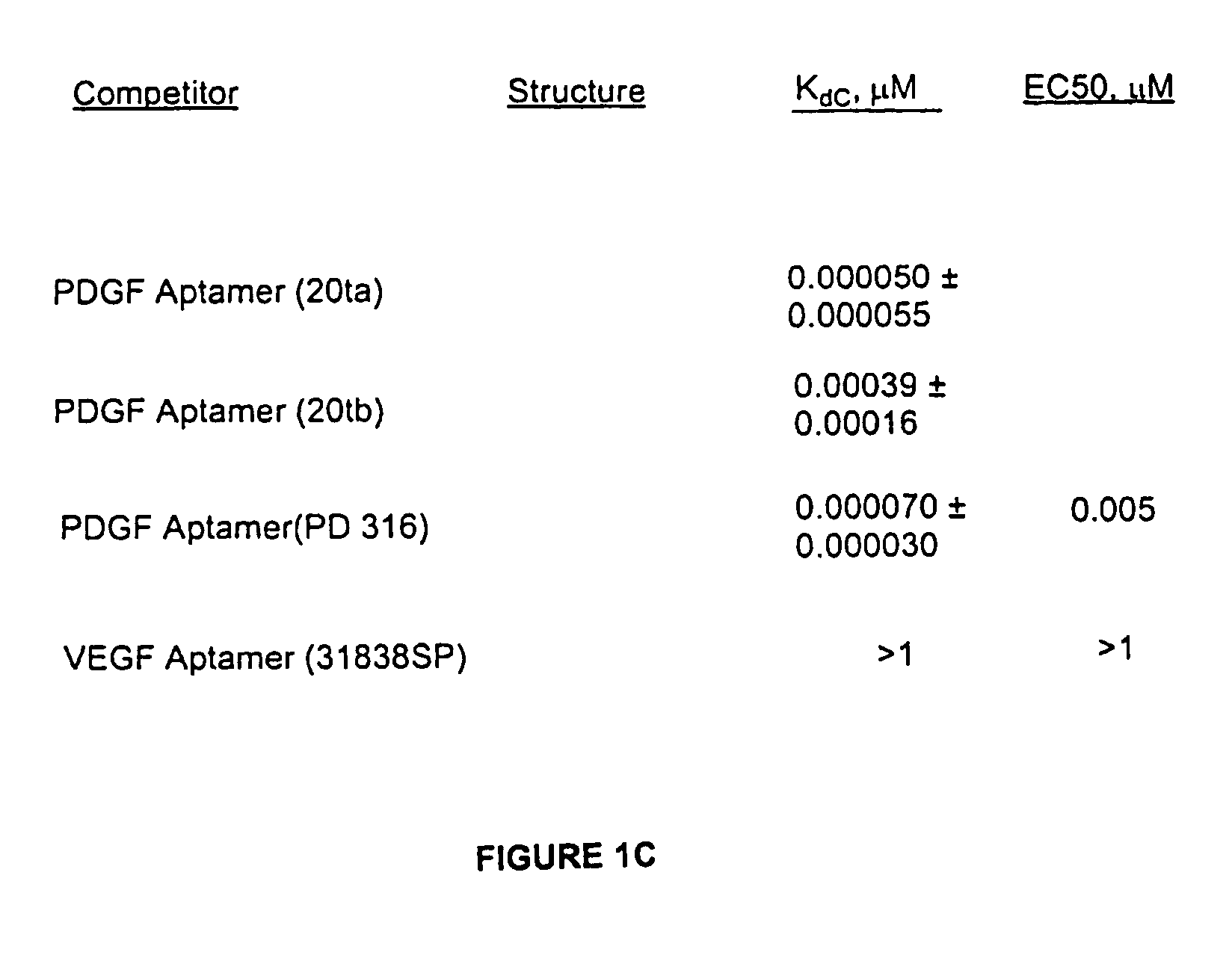
165 results about "Competitive binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
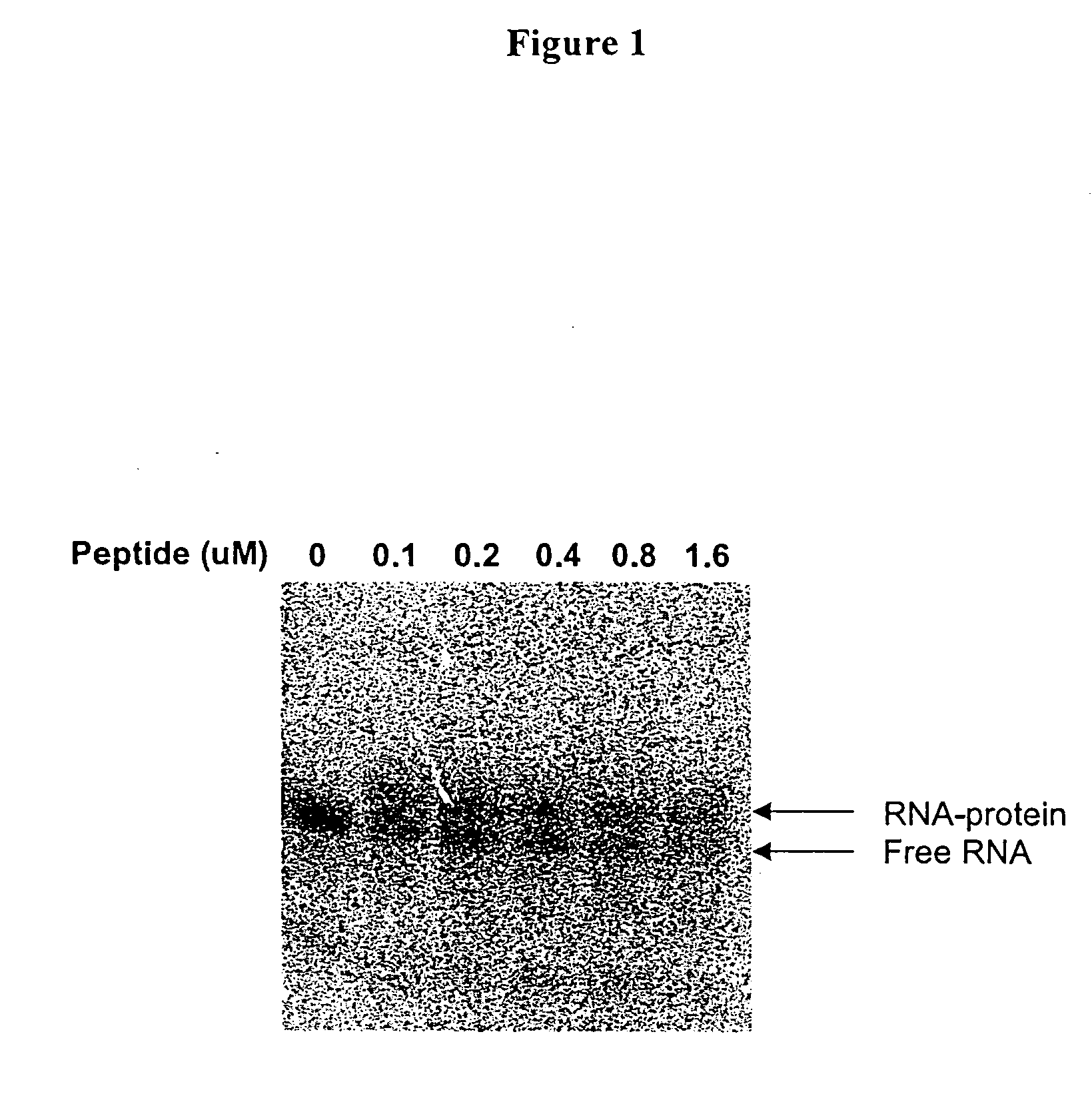
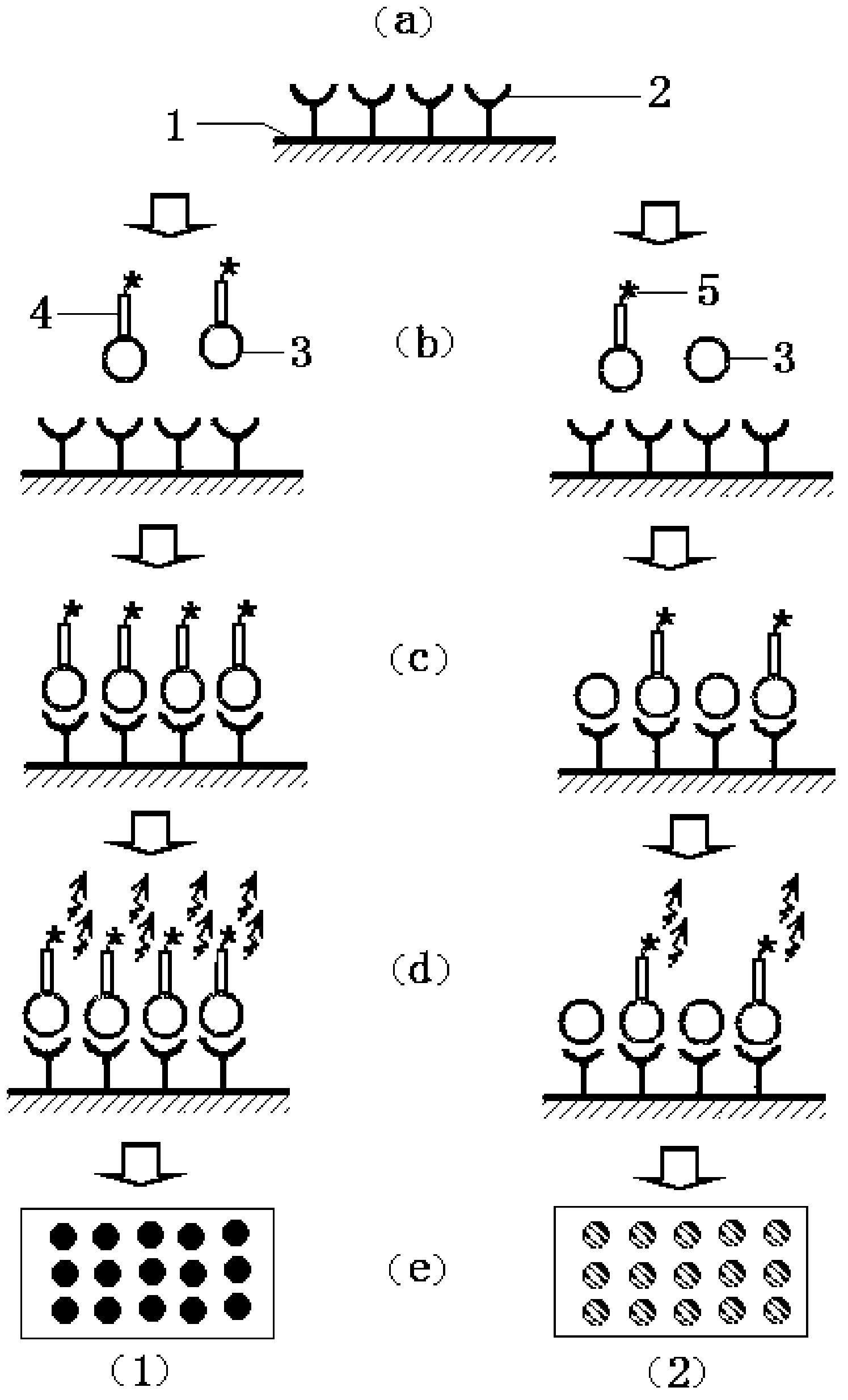
Competitive binding assay. n. An assay in which a biologically specific binding agent competes for radioactively labeled or unlabeled compounds, used especially to measure the concentration of hormone receptors in a sample by introducing a radioactively labeled hormone.
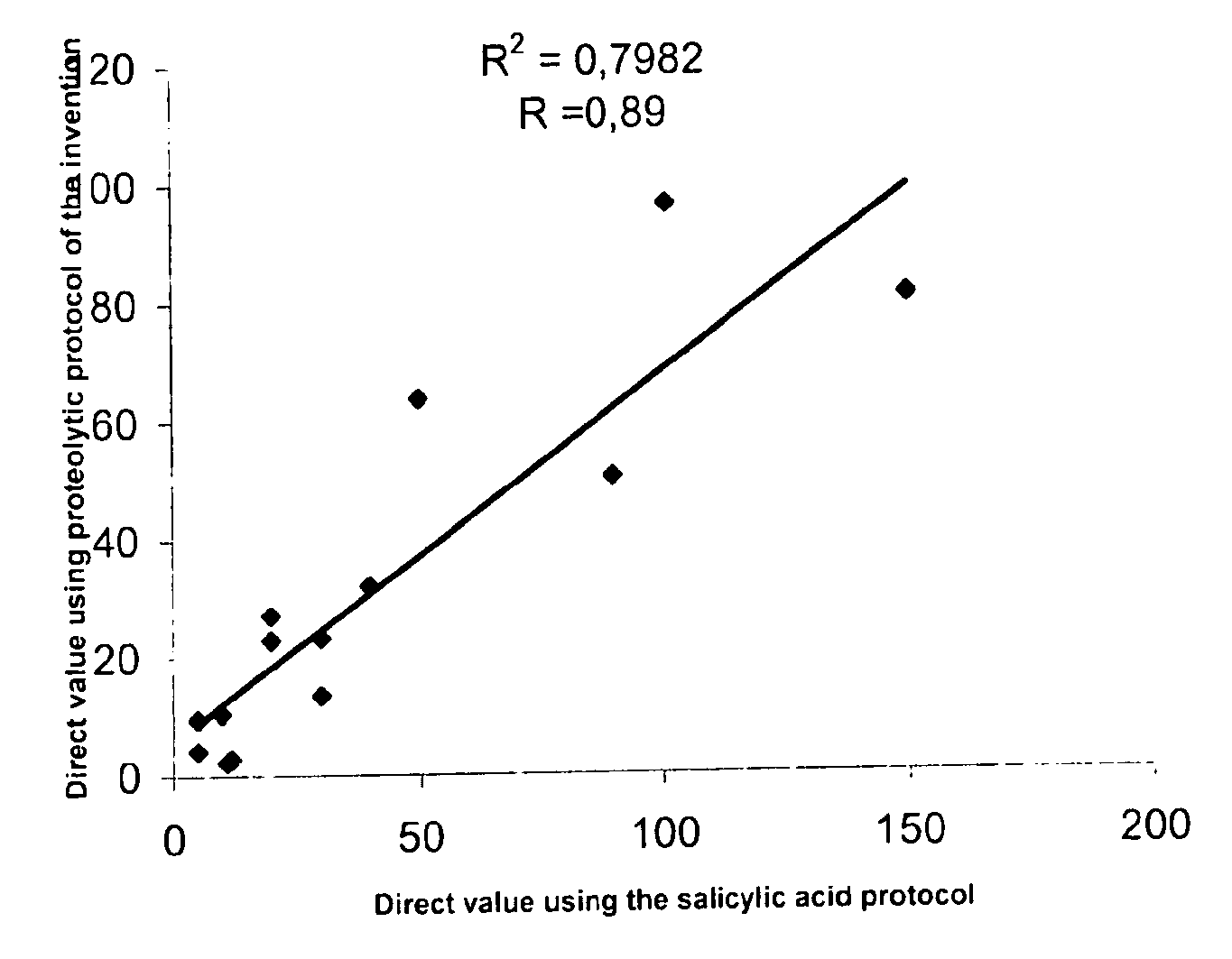
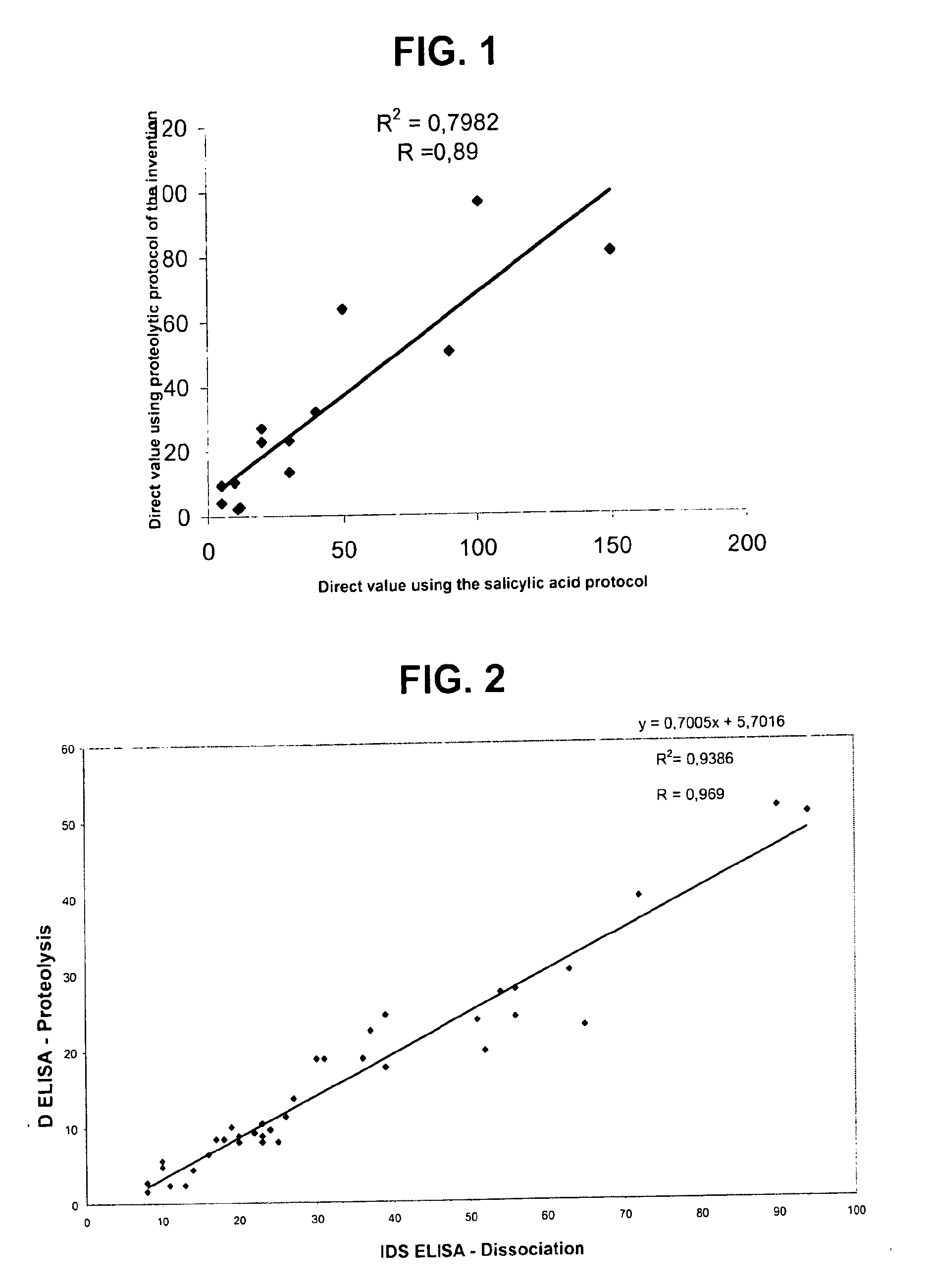
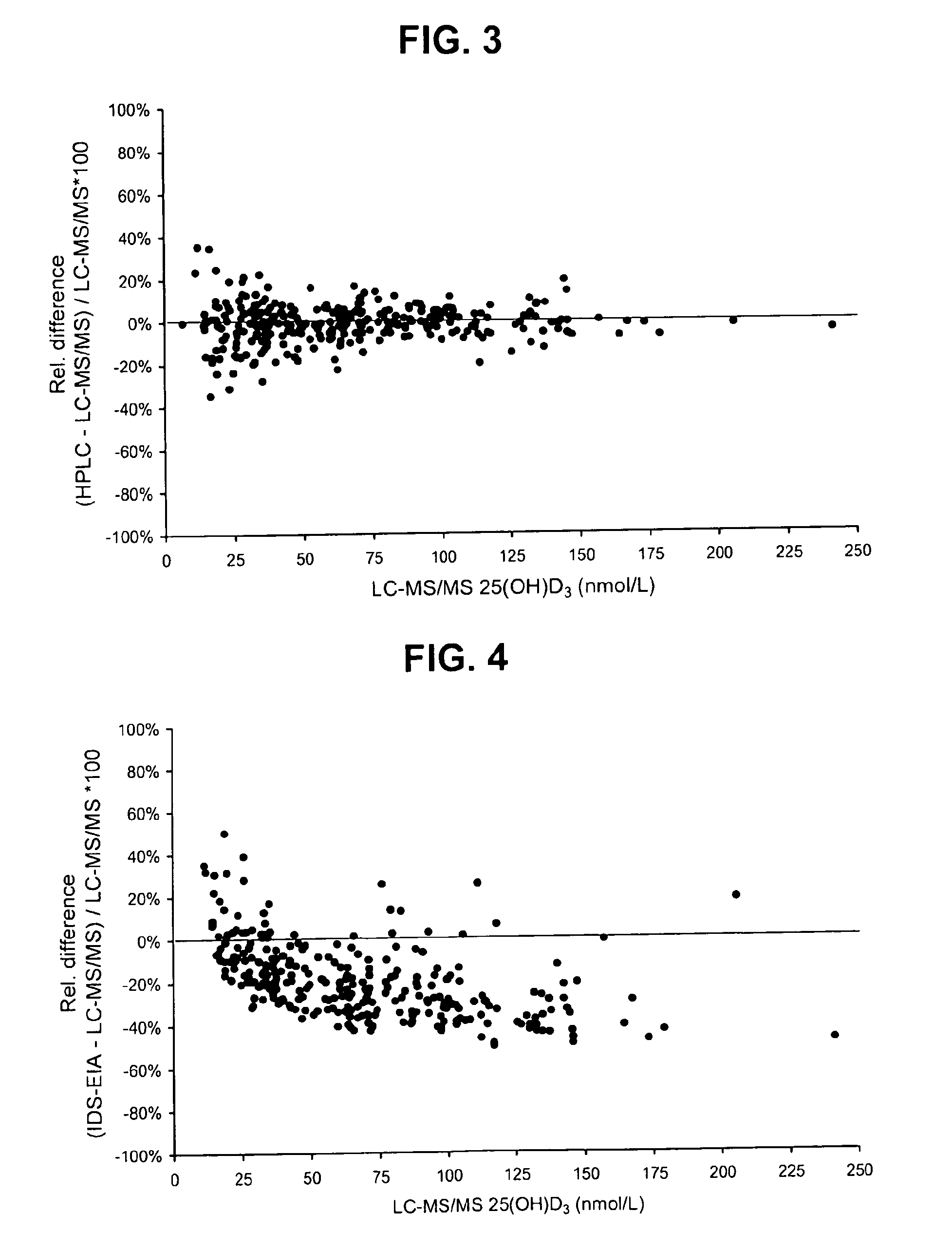
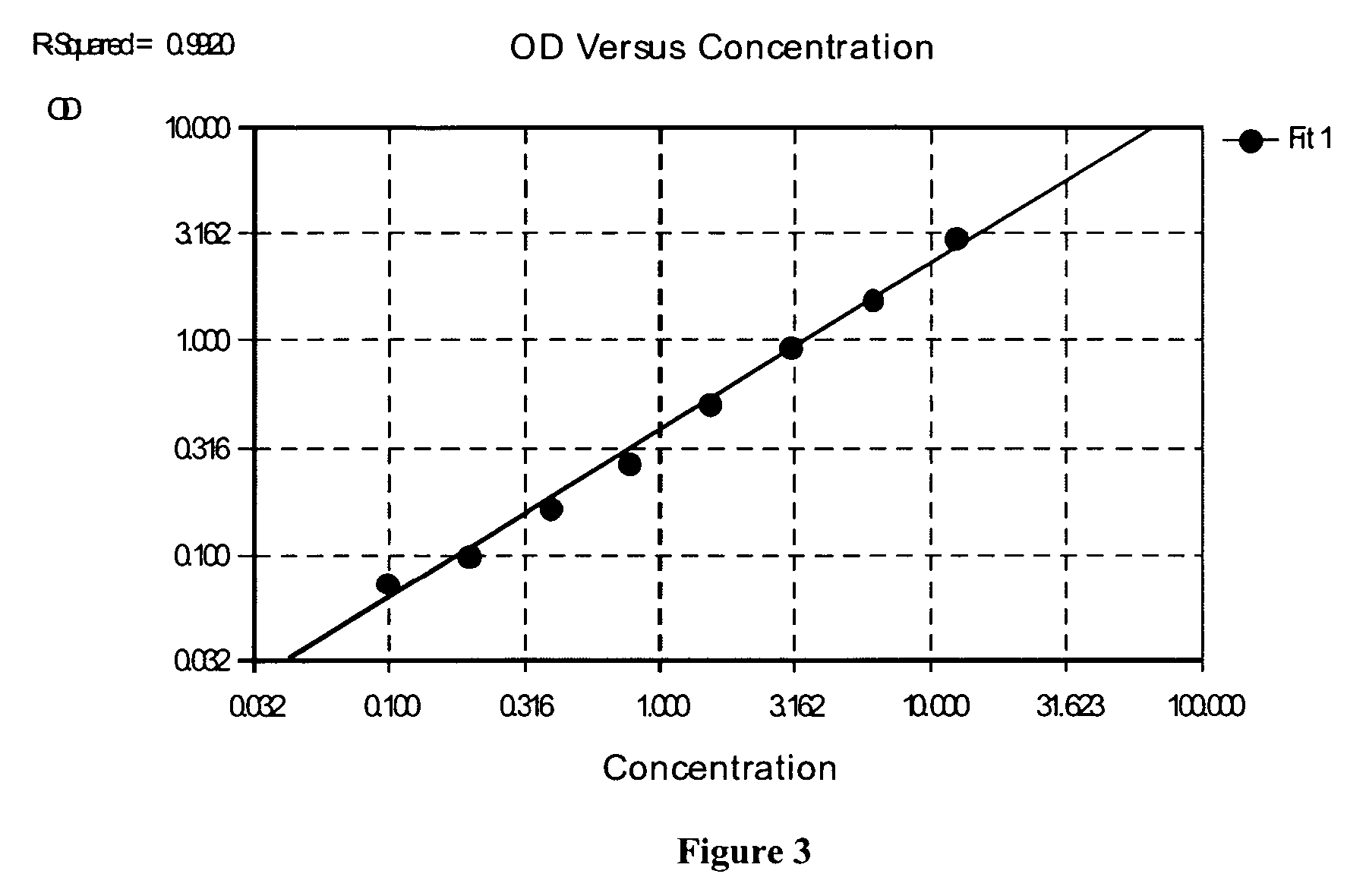
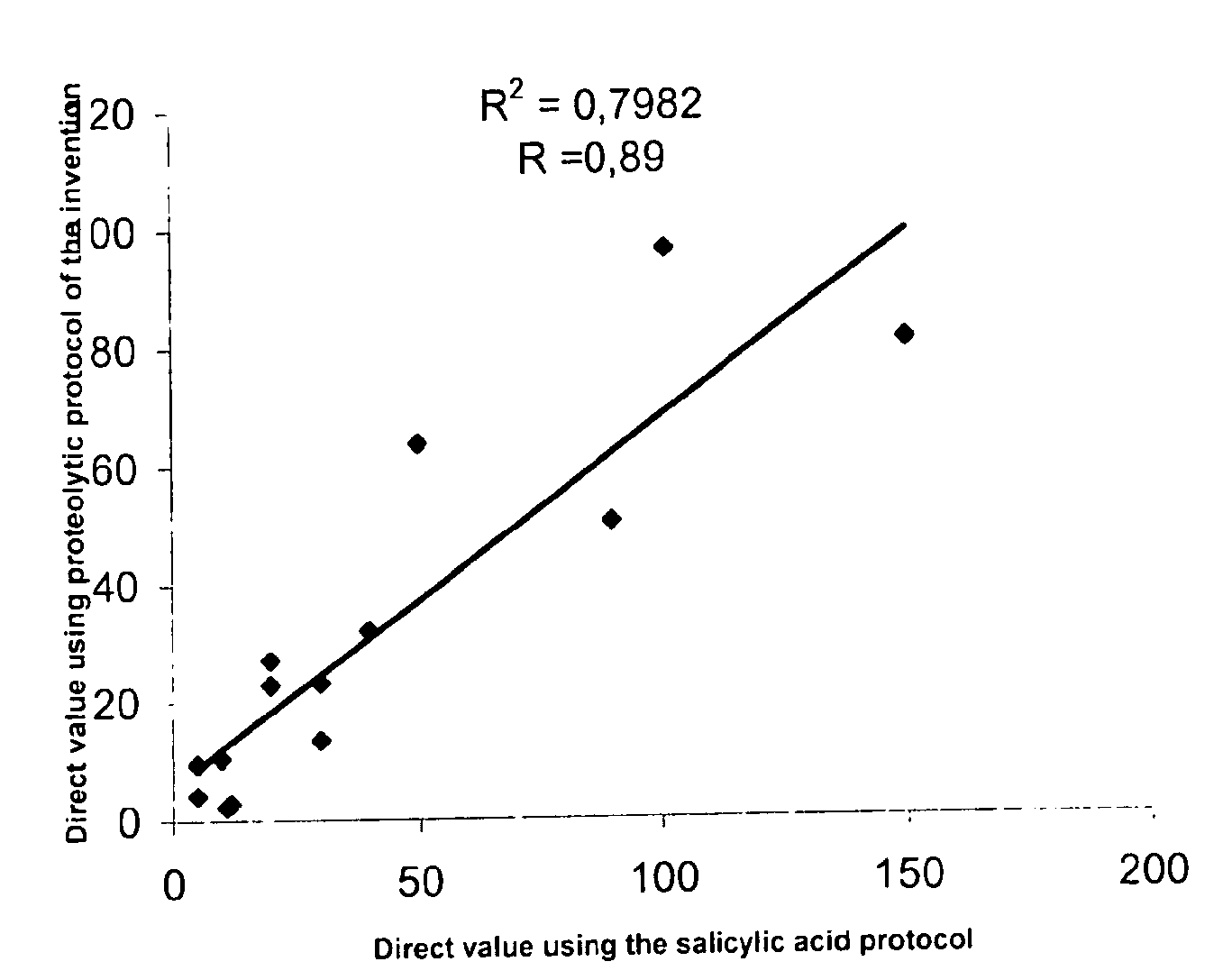
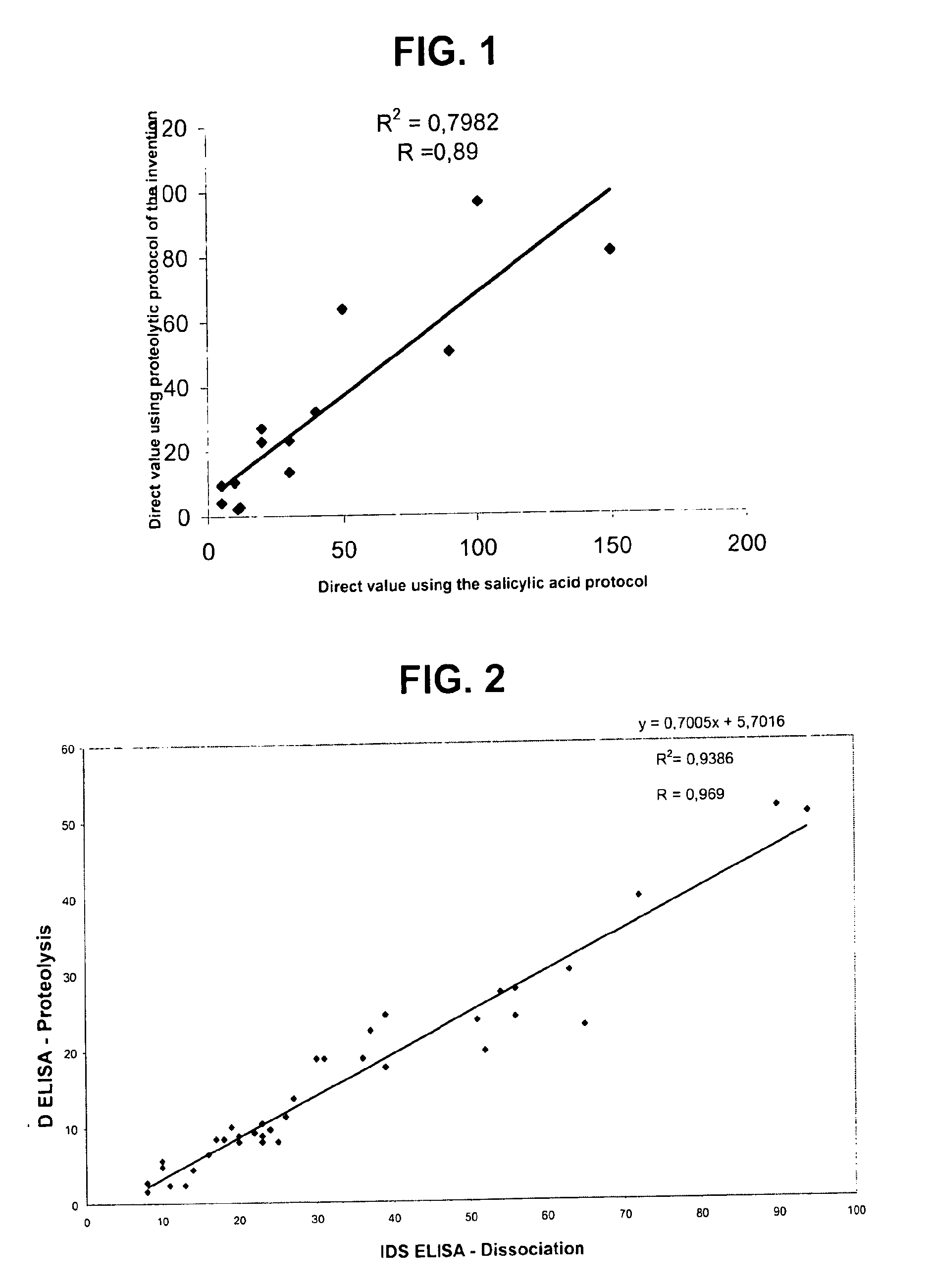
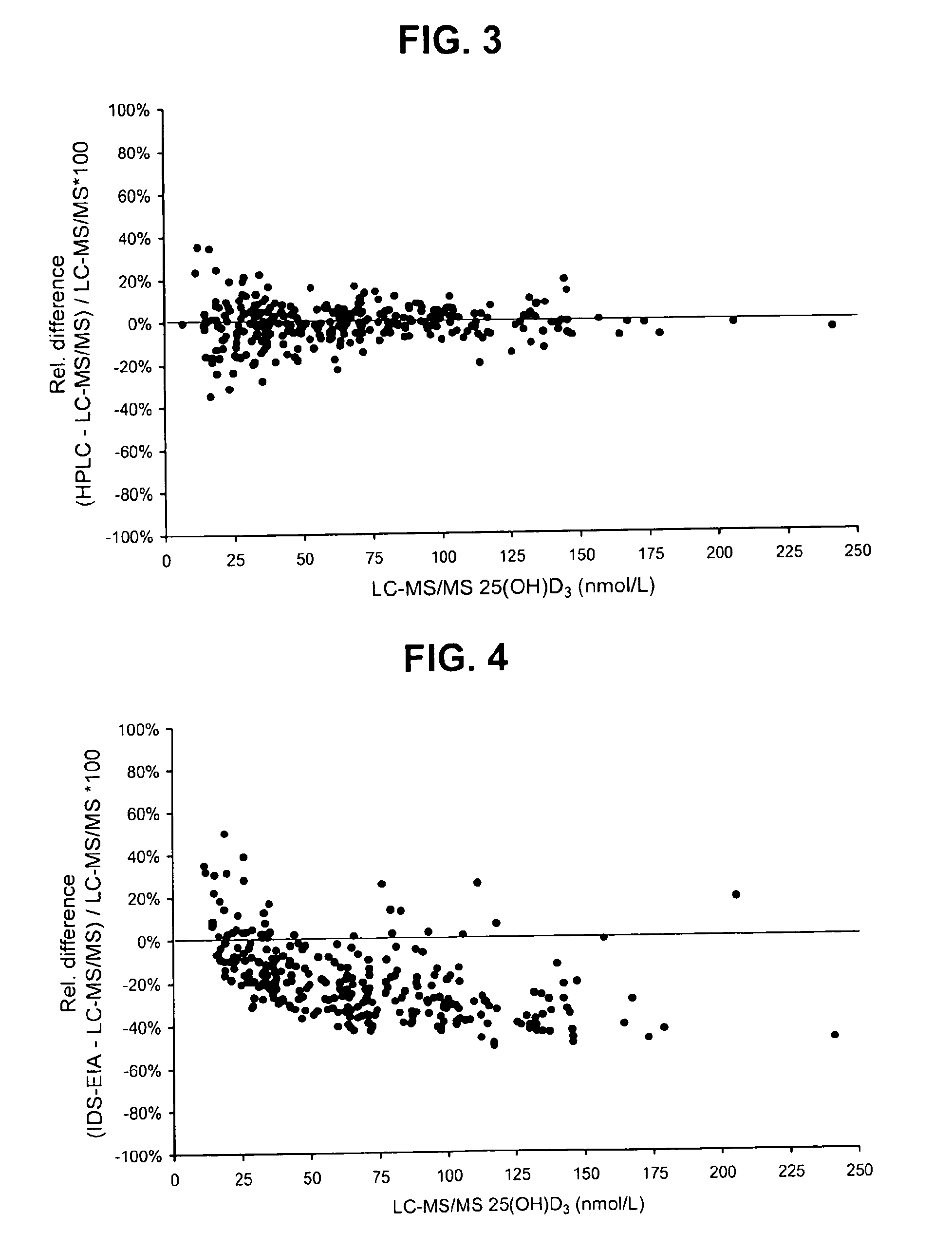
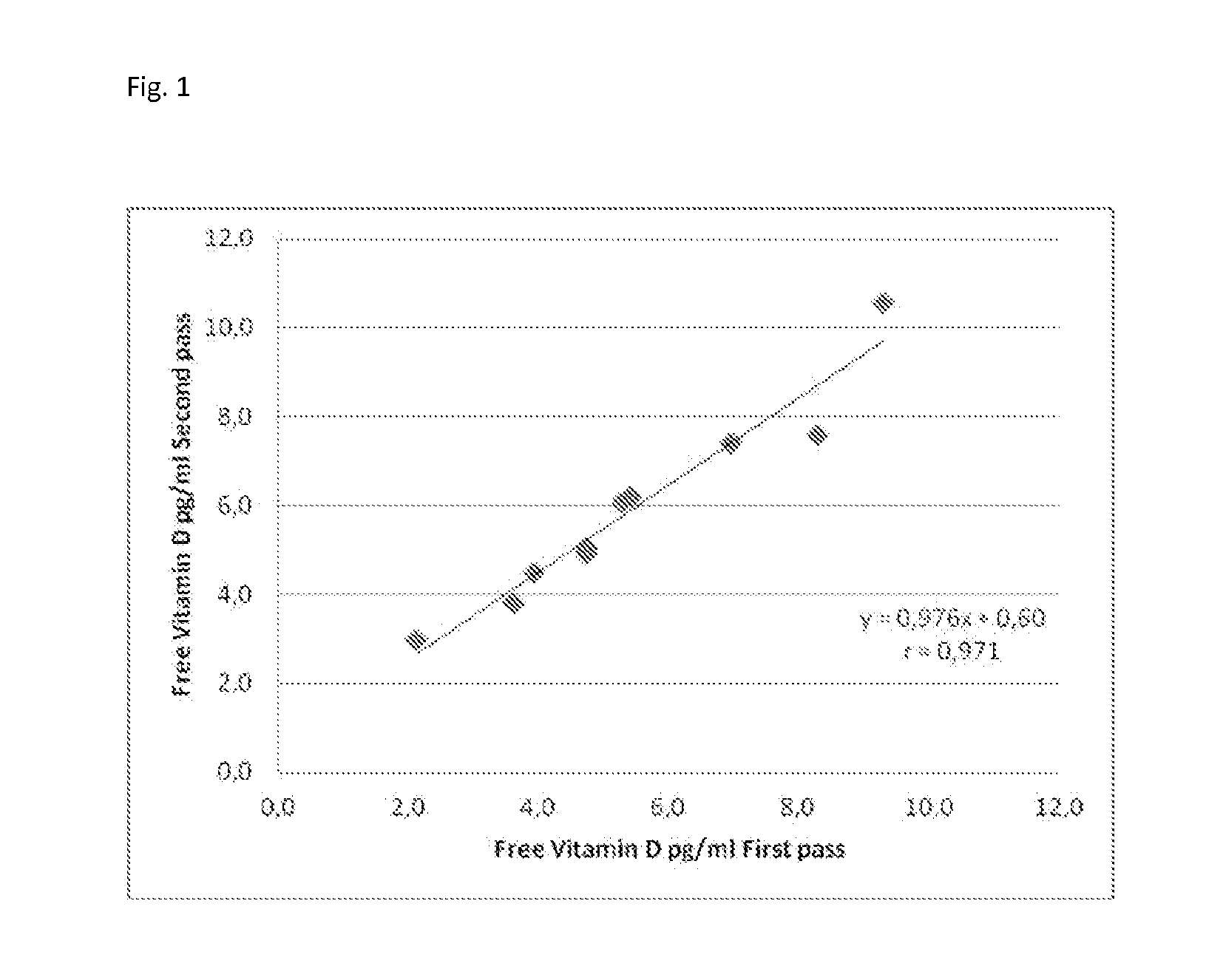
Direct determination of vitamin d in serum or plasma
ActiveUS20100068725A1Easy to controlPromote digestionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSerum igeCompetitive binding
A method for quantitating vitamin D metabolites directly in blood plasma or serum, without the need for prior purification of the vitamin D metabolites, comprising a digestion of the serum proteins with a serine protease such as proteinase K and sequence of steps for inhibiting the proteinase K activity in the competitive binding analysis. The advantages of this method are its high accuracy over the whole range of physiologically relevant values and that it can be easily adapted for a fully automated analysis of serum and plasma samples.
Owner:IMMUNDIAGNOSTIK
Microfluidic free interface diffusion techniques
InactiveUS20080182273A1Reduce concentrationFrom normal temperature solutionsFlow mixersFree interfaceCompetitive binding
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Quantum dot biolabeling and immunomagnetic separation for detection of contaminants
InactiveUS20080135490A1Rapid diagnosisImproved prognosisWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsAnalysis by material excitationChemical physicsCompetitive binding
Methods are provided for detecting, separating, isolating and quantifying contaminants in starting materials by separating the contaminant from the starting material using a bead coupled to an affinity moiety and quantum dot-labeling the contaminant. The contaminant is detected by the characteristic emission spectrum of the quantum dot. Also, competitive binding methods are provided wherein the starting material and a control material are contacted with a quantum dot coupled to an affinity moiety capable of binding the contaminant and a competitor complex. A decrease in the intensity of the characteristic emission spectrum of the quantum dot associated with the competitor complex from the starting material as compared to that of the control material is indicative of the presence of the contaminant in the starting material.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Latex enhanced immunoturbidimetry kit for detection of asymmetric dimethylarginine content
ActiveCN102628868AThe detection process is fastHigh detection specificityBiological testingCompetitive bindingLatex particle
The invention relates to a latex enhanced immunoturbidimetry kit for the detection of asymmetric dimethylarginine content. Specifically, the invention relates to a latex enhanced immunoturbidimetry kit for the detection of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) content in human blood samples. The kit comprises a mouse anti-human monoclonal antibody solution, an ADMA-human Serum albumin complex crosslinked latex particle expansion and an ADMA calibrator. According to the method, by the utilization of competitive binding of free ADMA in blood and ADMA crosslinked on the surface of latex particles to ADMA monoclonal antibody, turbidity formed by the reaction between the ADMA-crosslinked latex particles and ADMA monoclonal antibody is reduced. Therefore, the content of ADMA is detected through the reduction degree of turbidity. The kit provided by the invention can be applied in a biochemical analyzer commonly-used in clinic, is convenient and rapid to operate and has strong specificity. Both sensitivity and detection range of the kit can satisfy clinic application needs.
Owner:BEIJING STRONG BIOTECH INC
Microfluidic free interface diffusion techniques
InactiveUS7306672B2Reduce concentrationFrom normal temperature solutionsFlow mixersDiffusionFree interface
A static fluid and a second fluid are placed into contact along a microfluidic free interface and allowed to mix by diffusion without convective flow across the interface. In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, the fluids are static and initially positioned on either side of a closed valve structure in a microfluidic channel having a width that is tightly constrained in at least one dimension. The valve is then opened, and no-slip layers at the sides of the microfluidic channel suppress convective mixing between the two fluids along the resulting interface. Applications for microfluidic free interfaces in accordance with embodiments of the present invention include, but are not limited to, protein crystallization studies, protein solubility studies, determination of properties of fluidics systems, and a variety of biological assays such as diffusive immunoassays, substrate turnover assays, and competitive binding assays.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Methods for identifying small molecules that bind specific rna structural motifs
InactiveUS20040219545A1Easy to identifyEliminate biasMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsBiology
The present invention relates to a method for screening and identifying test compounds that bind to a preselected target ribonucleic acid ("RNA"). Direct, non-competitive binding assays are advantageously used to screen libraries of compounds for those that selectively bind to a preselected target RNA. Binding of target RNA molecules to a particular test compound is detected using any physical method that measures the altered physical property of the target RNA bound to a test compound. The structure of the test compound attached to the labeled RNA is also determined. The methods used will depend, in part, on the nature of the library screened. The methods of the present invention provide a simple, sensitive assay for high-throughput screening of libraries of compounds to identify pharmaceutical leads.
Owner:RANDO ROBERT F +1
Stabilized two component system for chemiluminescent assay in immunodiagnostics
The present invention provides stabilized chemiluminescent formulations for use in in vitro diagnostics, including competitive as well as sandwich-type immunological assays. The stabilized assay system may be composed of two components, where the first component may contain a chemiluminescent organic compound, an enhancer, a homogenizing agent, and a suitable buffer with formulations having a pH range from about 7.2 to about 12, and optionally a solubilizing agent. The chemiluminescent system of the present invention is useful in immunoenzymatic analytical procedures, such as immunometric, competitive binding and sandwich type assays. In such immunoassays employing the chemiluminescent system of the present invention, the detectable light signal shows a proportional decay with time in the test samples and standards, so that the decay of the light emitted does not effect the concentration of the analyte measured over the entire analyte measurement range of the immunoassay. This allows accurate measurement of analyte concentrations in a test sample over extended periods of time.
Owner:KALRA BHANU +1
Direct determination of vitamin D in serum or plasma
A method for quantitating vitamin D metabolites directly in blood plasma or serum, without the need for prior purification of the vitamin D metabolites, comprising a digestion of the serum proteins with a serine protease such as proteinase K and sequence of steps for inhibiting the proteinase K activity in the competitive binding analysis. The advantages of this method are its high accuracy over the whole range of physiologically relevant values and that it can be easily adapted for a fully automated analysis of serum and plasma samples.
Owner:IMMUNDIAGNOSTIK AG
Flexible Carbohydrate-Bearing Polymer
A sensor for the detection or measurement of a carbohydrate analyte in fluid comprises components of a competitive binding assay the readout of which is a detectable or measurable optical signal retained by a material that permits diffusion of the analyte but not the assay components, the assay components comprising: a carbohydrate binding molecule labelled with one of a proximity based signal generating / modulating moiety pair; and a carbohydrate analogue capable of competing with the analyte for binding to the carbohydrate binding molecule, the carbohydrate analogue being a flexible water-soluble polymer comprising: polymerized or co-polymerised residues of monomer units, the monomer unit residues bearing pendant carbohydrate or carbohydrate mimetic moieties and pendant moieties which are the other of the proximity based signal generating / modulating moiety pair.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Automatic lung parameter estimator for measuring oxygen and carbon dioxide gas exchange
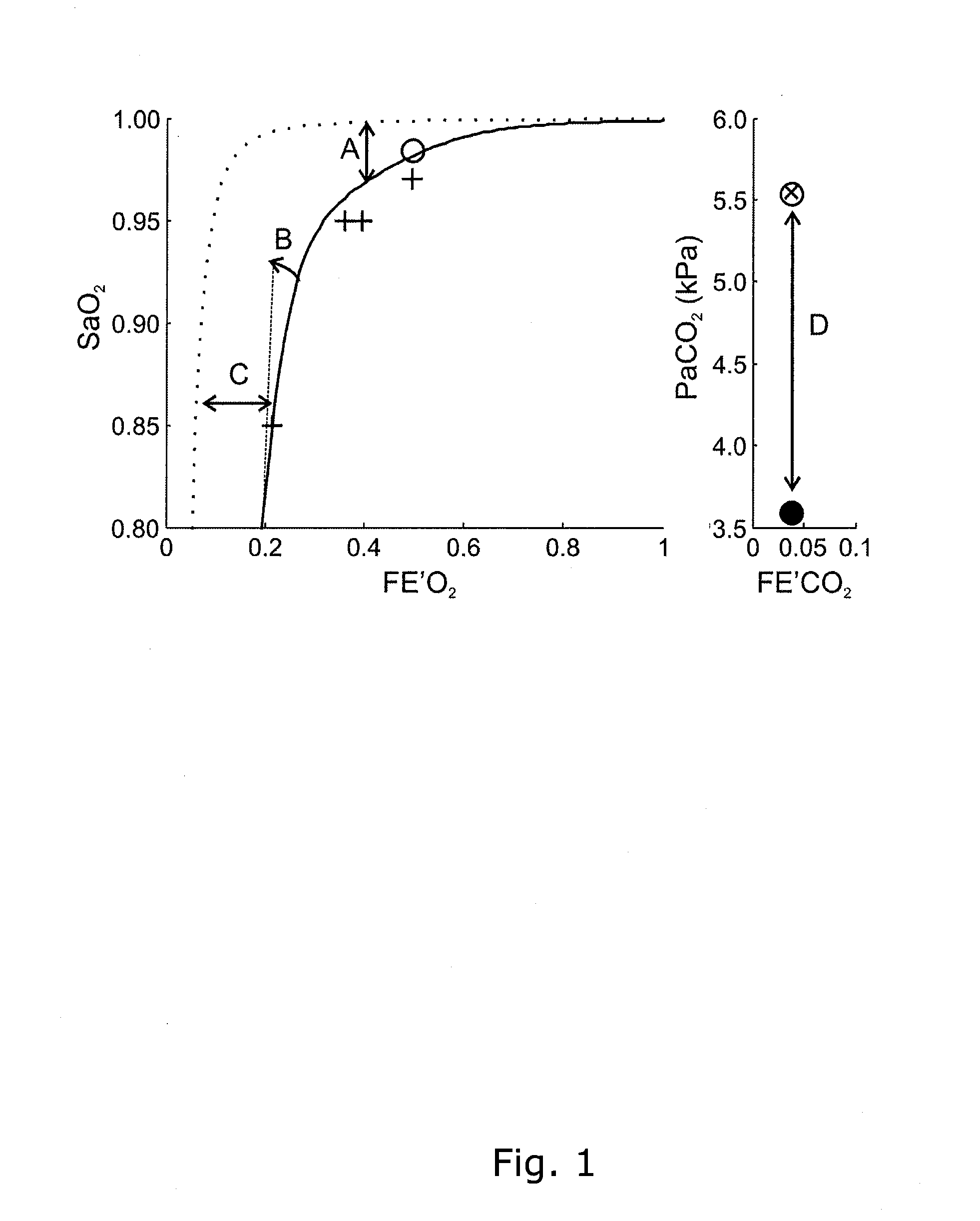
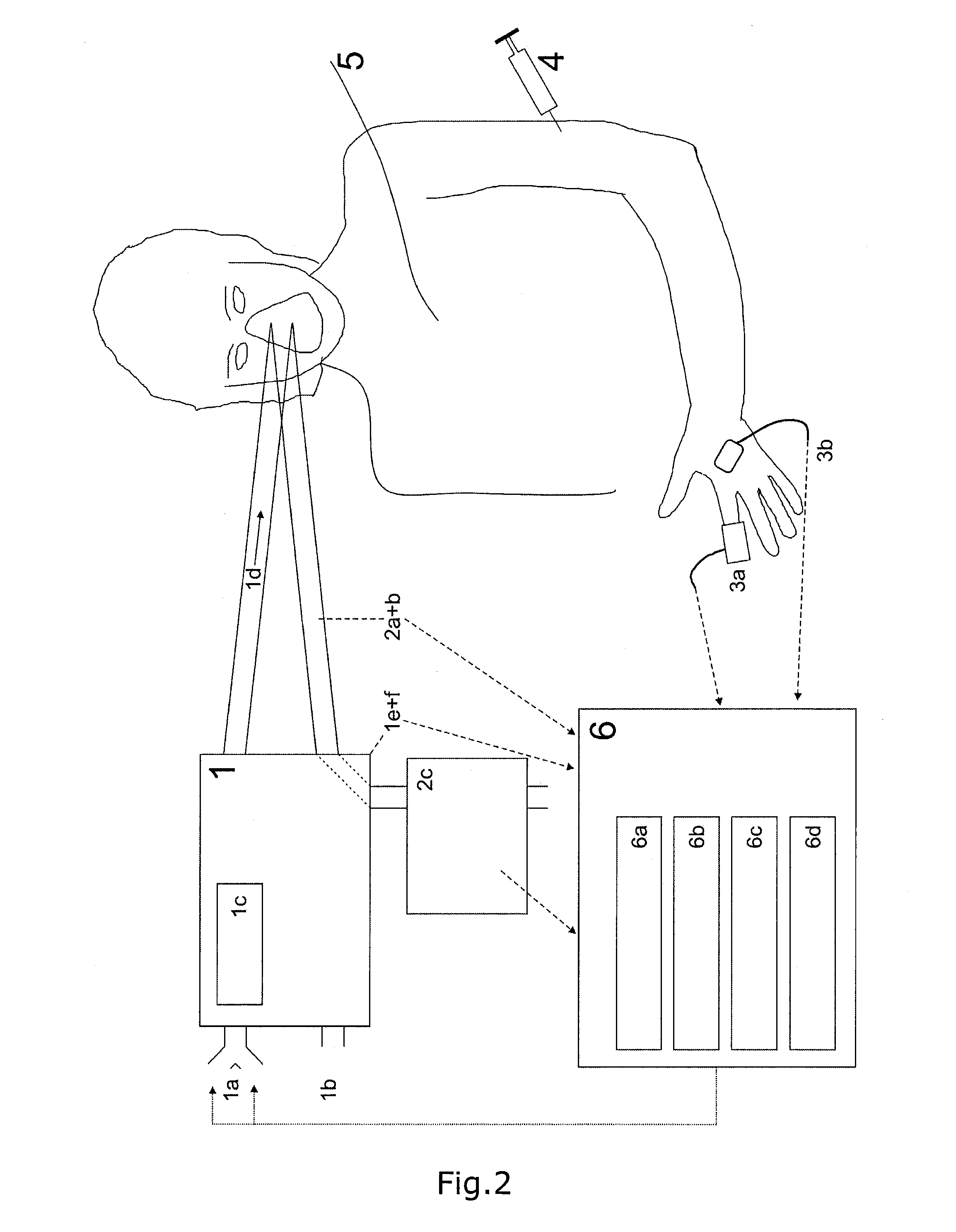
ActiveUS20130345572A1Fit closelyLow costRespiratorsMedical devicesCompetitive bindingObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
The invention relates to a device for determining two or more respiratory parameters relating to an individual and a method for determining two or more respiratory parameters relating to an individual by means of the device. The disclosed device and method may be used in an individual suffering from pulmonary gas exchange problems relating to gas exchange of oxygen and / or carbon dioxide, e.g. a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The device and method may also be used in a healthy individual or in an animal, e.g. for research experiments. The device has detection means for oxygen and carbon dioxide contents in inspired and expired gas and blood. The device is controlled by a computer with functionality for entering oxygenation, carbon dioxide and acid-base values from one or more blood samples from arterial, venous, central venous or mixed venous blood samples, and with the parameter estimation based on equations of gas exchange of both oxygen and carbon dioxide and equations describing the acid-base chemistry of blood potentially including the competitive binding of oxygen and carbon dioxide to hemoglobin.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Determining non-nucleic acid molecule binding to target by competition with nucleic acid ligands
InactiveUS7258980B2Easy to identifyQuick identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsCompetitive binding
A competitive binding assay is used to determine whether a non-nucleic acid molecule from a library of non-nucleic acid molecules binds to a target. The non-nucleic acid molecule competes with a labeled nucleic acid ligand for binding to the target which may be immobilized. Detecting displacement of labeled nucleic acid ligand from a complex of the labeled nucleic acid ligand and the target determines binding of the non-nucleic acid molecule to the target. The nucleic acid ligand may be immobilized and contacted with a labeled target to form a complex. Adding a non-nucleic acid molecule to the complex displaces labeled target from the complex, and detecting displacement of the labeled target determines binding of the non-nucleic acid molecule to the target. Labeled nucleic acid ligand or labeled target displaced from or remaining in the complex can be detected for detecting displacement. Nucleic acid ligands that bind to the target are identified by the SELEX method. The assay provides a high throughput screening method for determining whether a non-nucleic acid molecule binds to a target.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
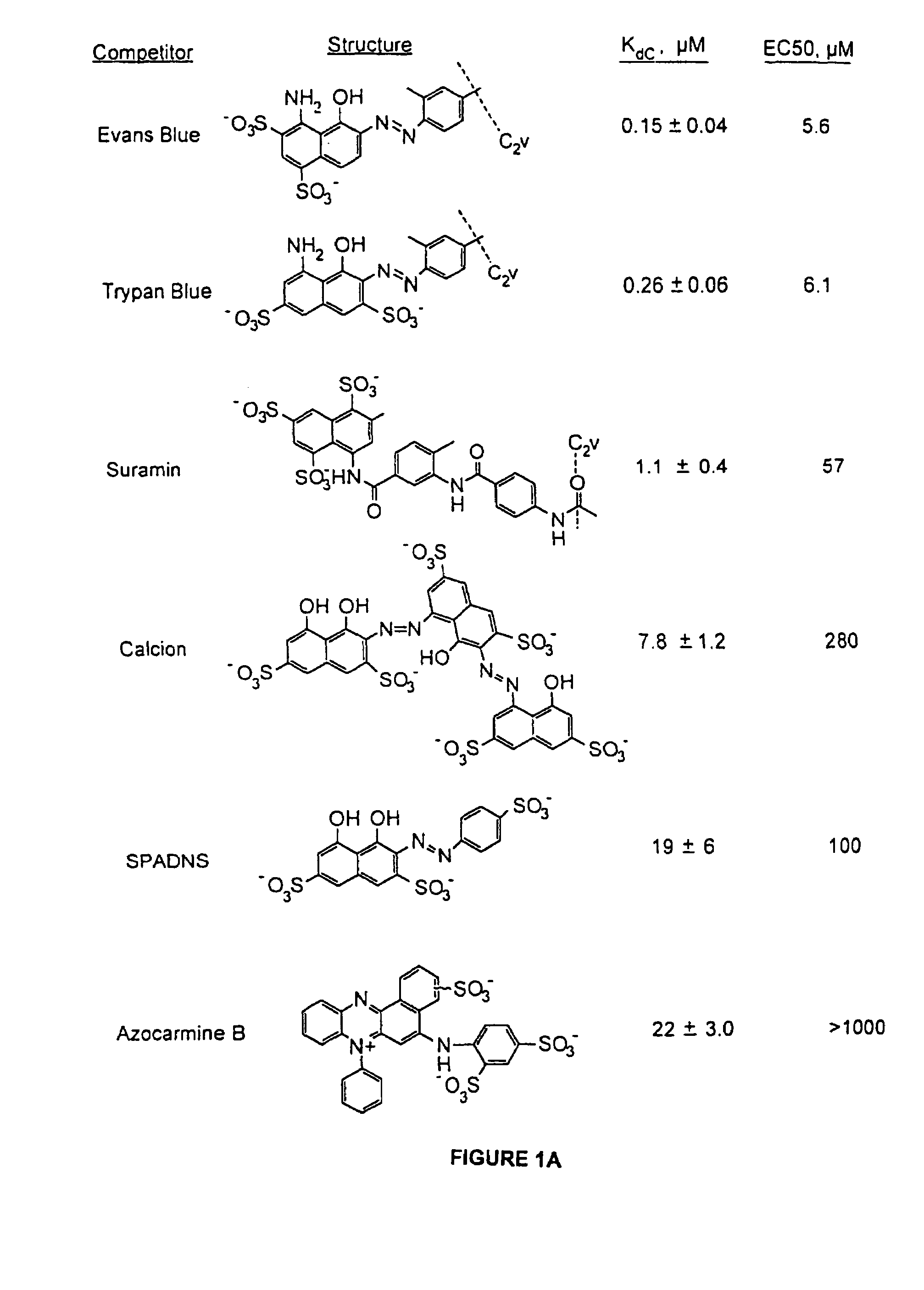
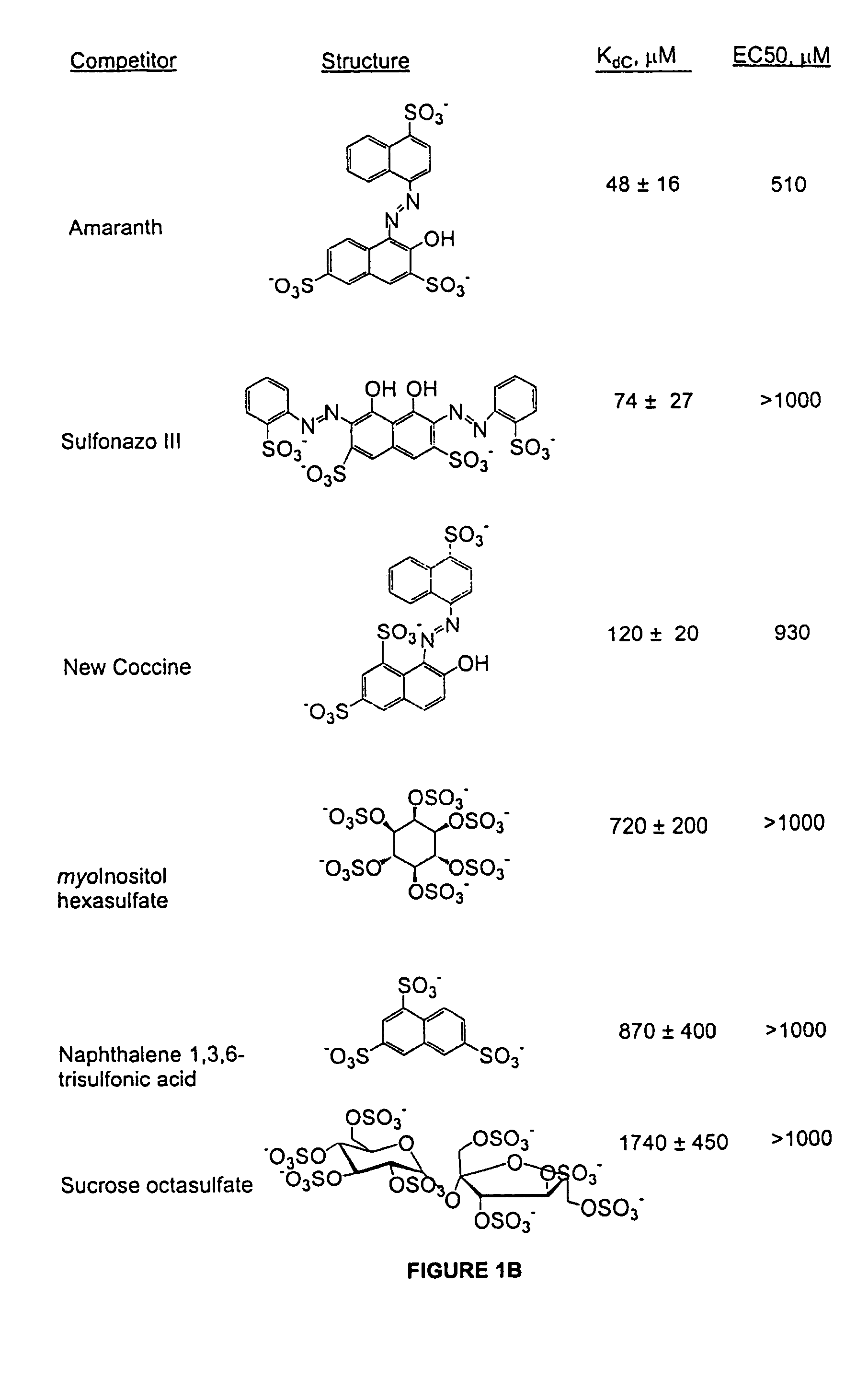
Thio/oxo-naphthalimide compound and application thereof
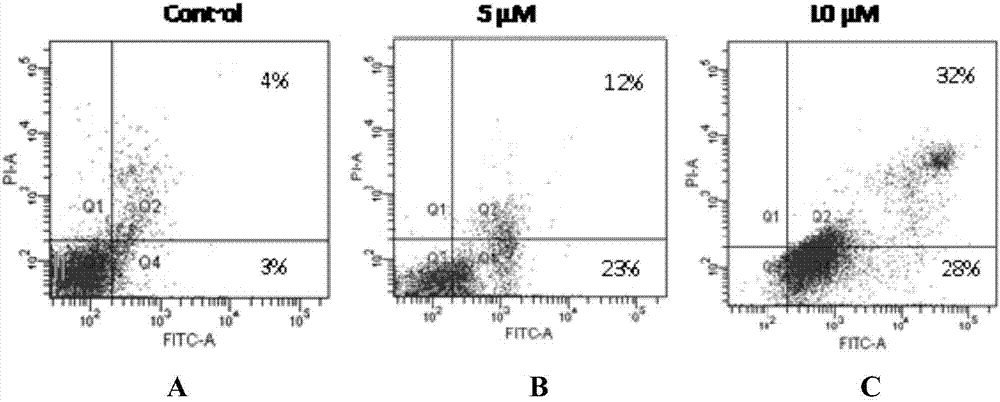
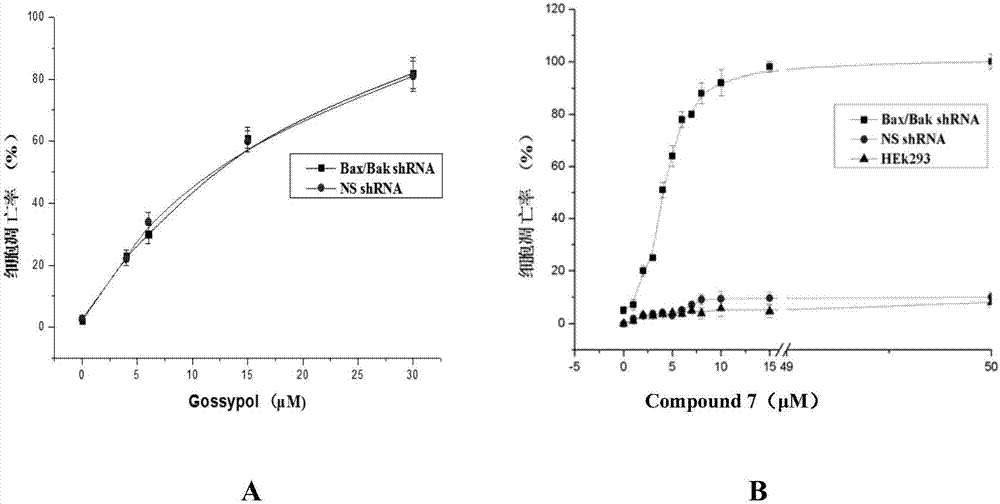
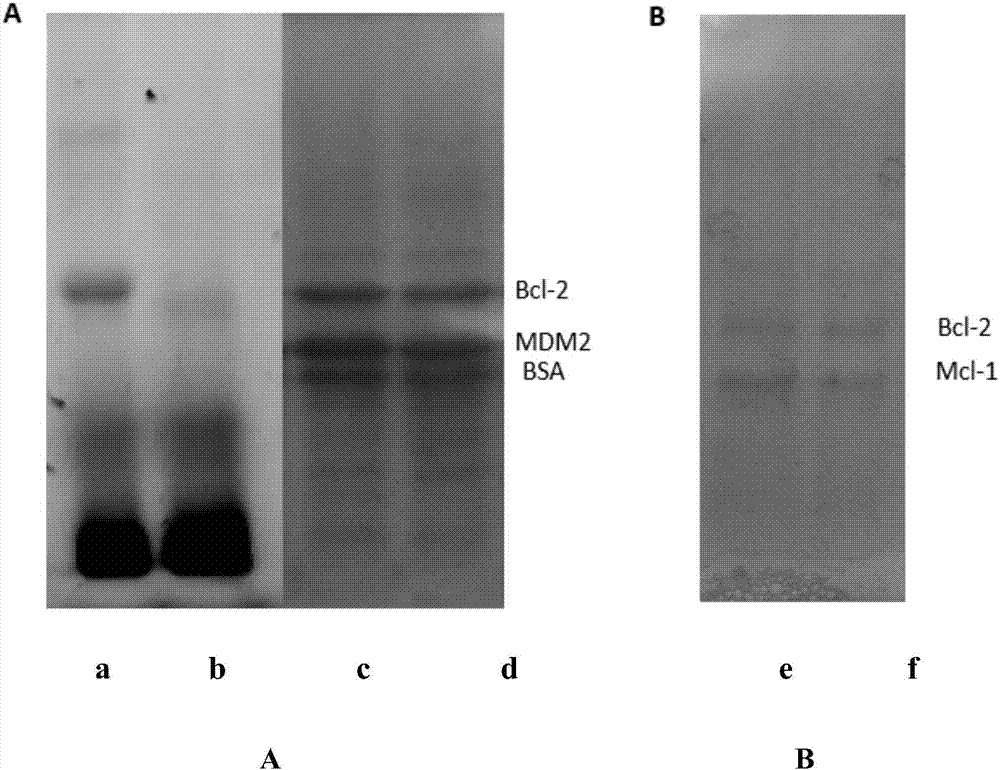
The invention provides a thio / oxo-naphthalimide compound and application thereof. The compound has a structure shown as a general formula I. The compounds are capable of realizing competitive binding and antagonism of Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 proteins in vitro and in cells so as to induce cell apoptosis, and refer to a type of apoptosis inducers and antitumor compounds with extremely high activities. In addition, the derivative designed based on the compound can serve as a bifunctional molecule and is capable of recognizing, separating, enriching and realizing fluorescence detection of Bcl-2 family proteins; or the derivative can serve as a PROTAC bifunctional complex for selectively degrading the Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 proteins in the cells, so that the level of the Bcl-2 family proteins in living cells is regulated. The structural formula is as shown in the specification.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
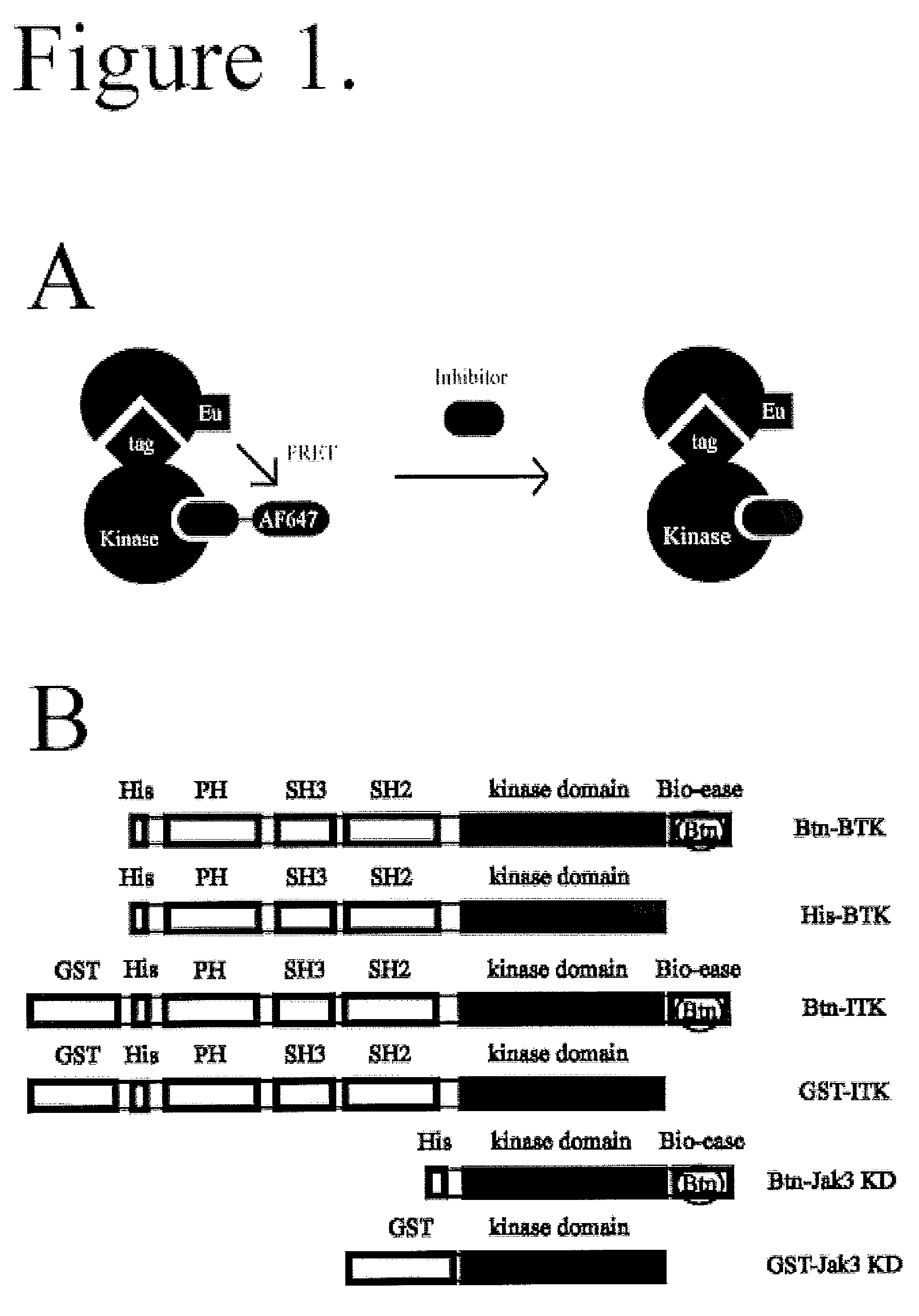
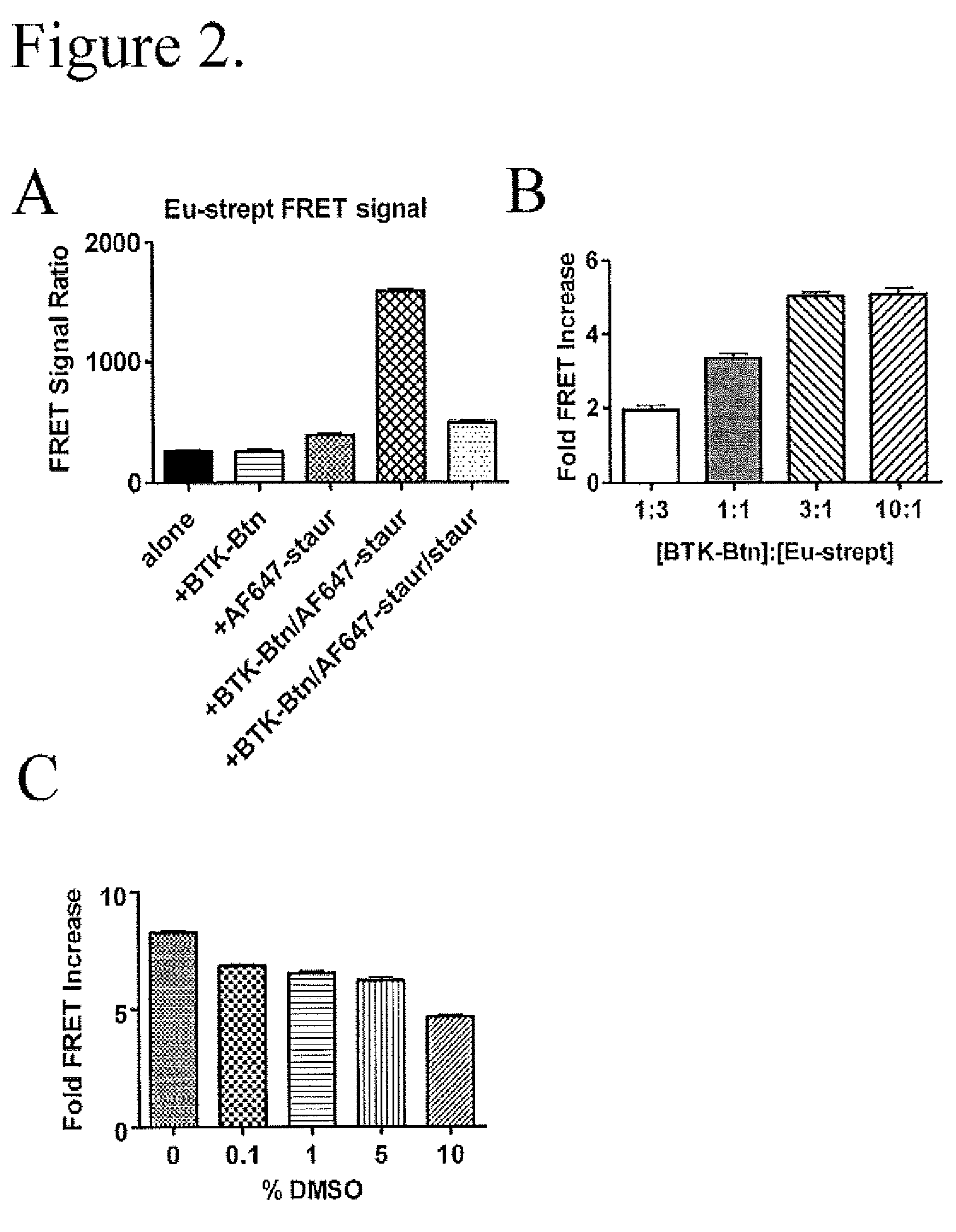
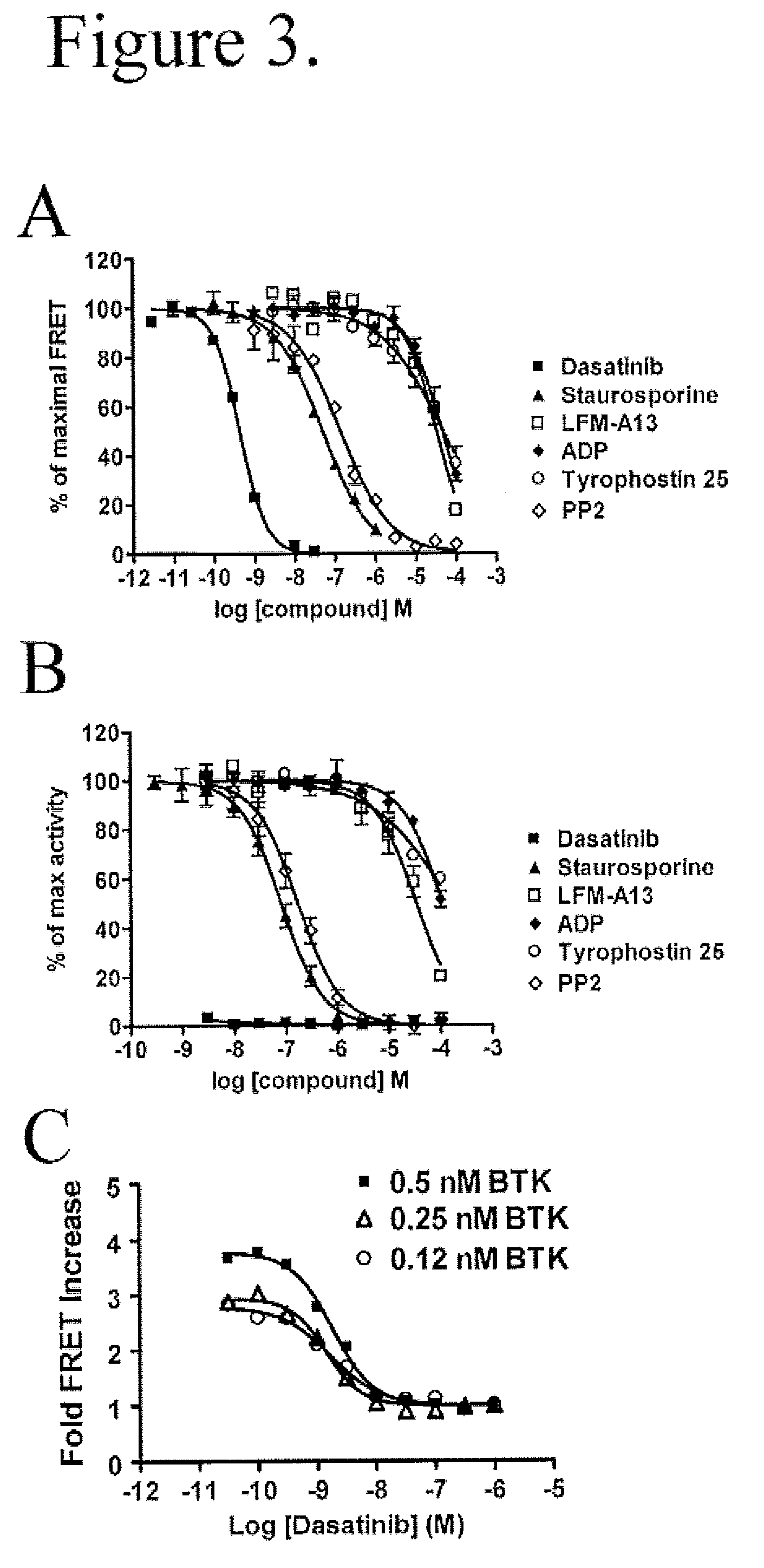
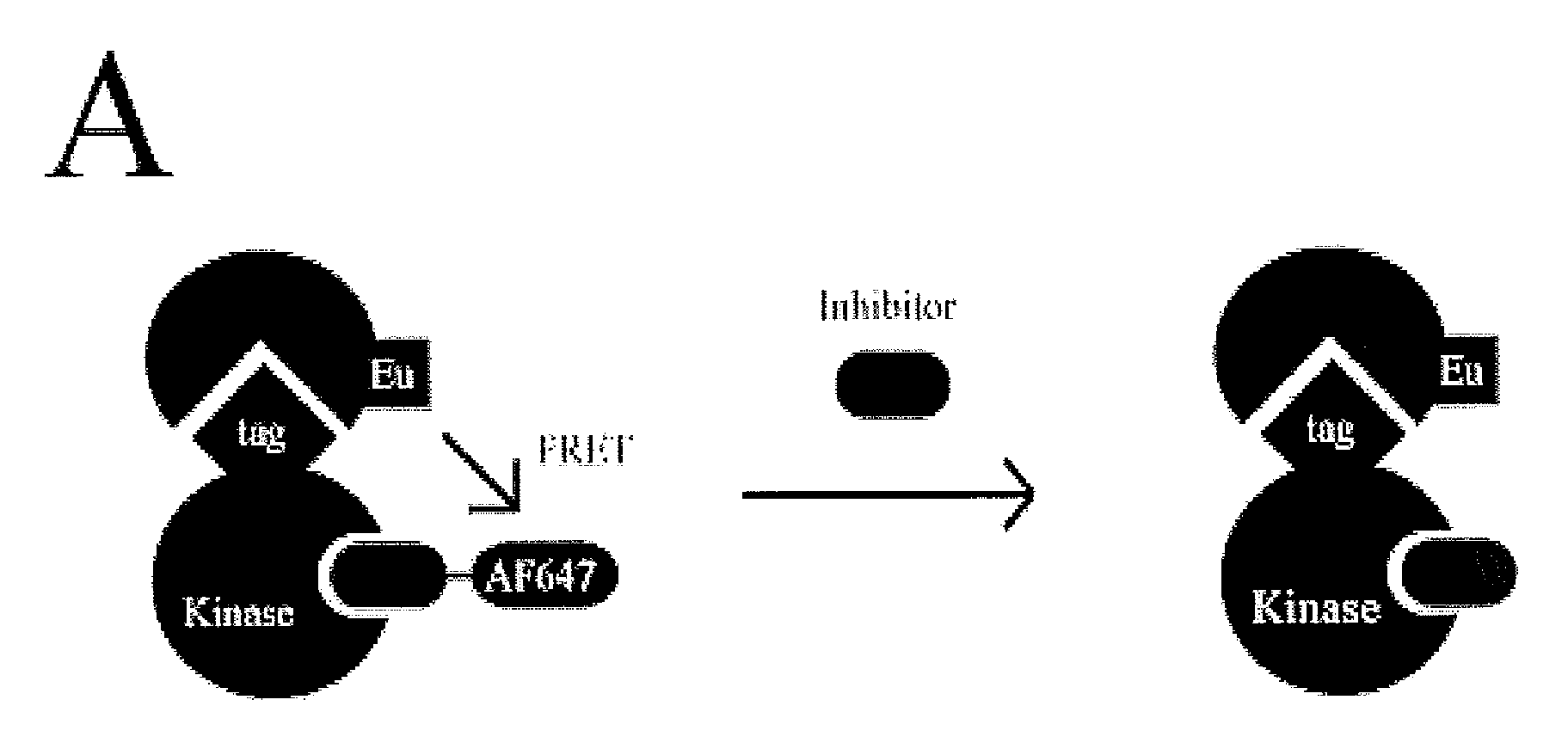
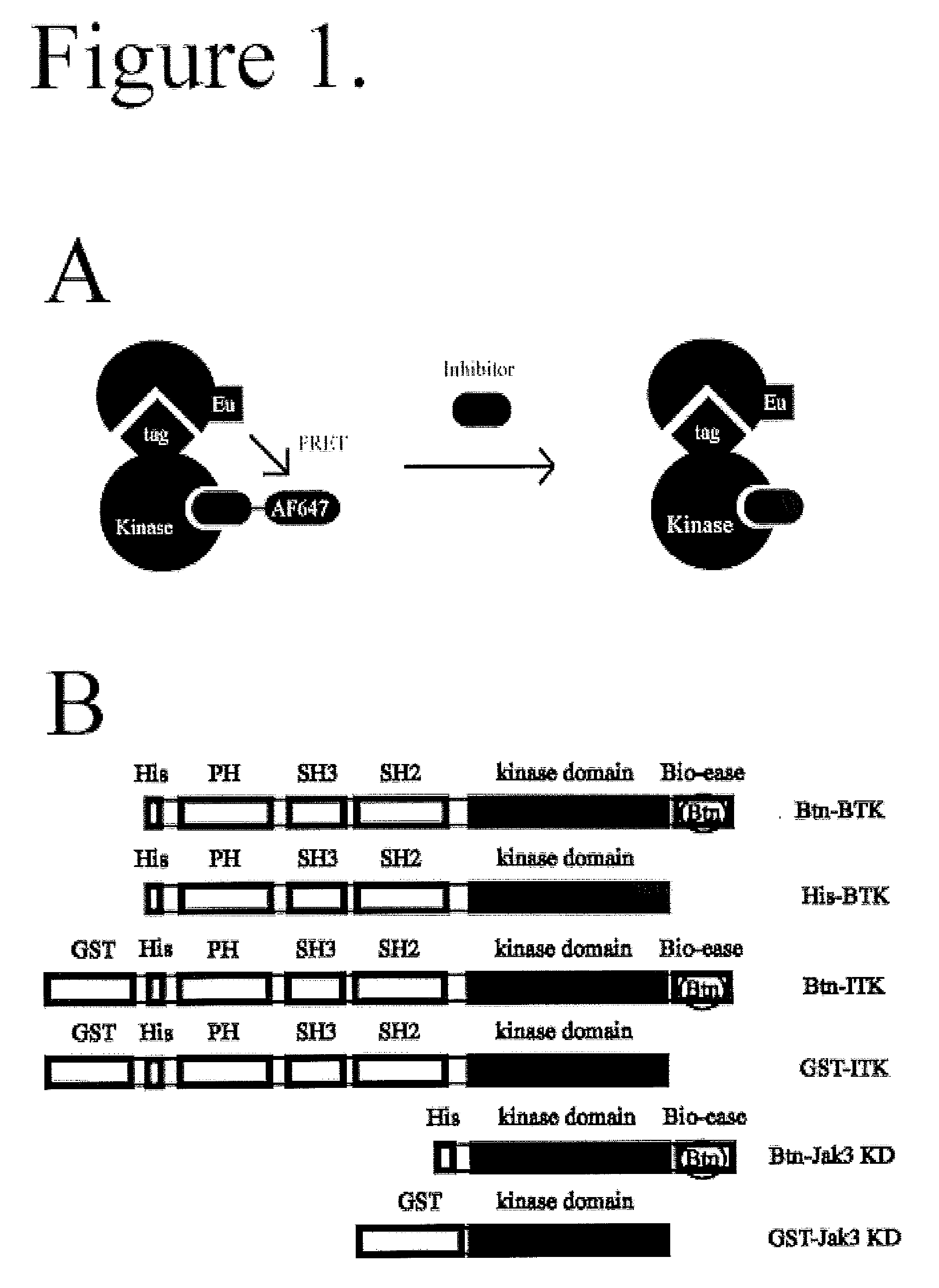
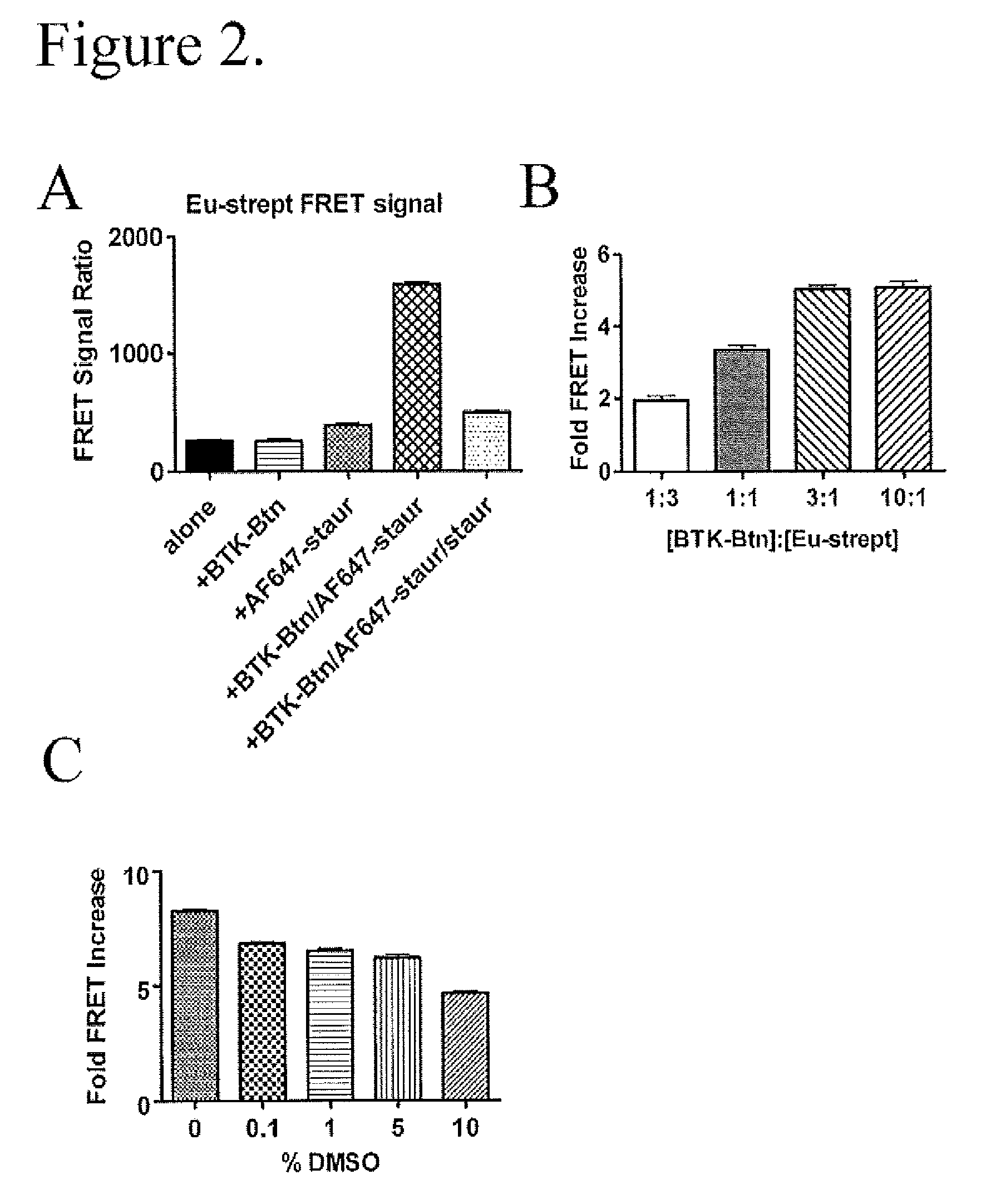
FRET-based binding assay
ActiveUS8153390B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingEnergy transferCompetitive binding
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC
Pesticide and veterinary drug multi-residue detection method based on microarray detection chip
ActiveCN103439514AImprove throughputStrong specificityBiological testingCompetitive bindingBovine serum albumin
The invention relates to a pesticide and veterinary drug multi-residue detection method based on a microarray detection chip. The method comprises the steps that a micromolecular pesticide and veterinary drug hapten is coupled with bovine serum albumin to prepare an immunizing antigen; a mouse is immunized by the immunizing antigen to prepare a corresponding pesticide and veterinary drug monoclonal antibody; a biochip sample application instrument for a monoclonal antibody acquisition probe performs sample application on an agarose modified slide solid phase carrier to prepare a multi-repeat monoclonal antibody acquisition probe microarray; the pesticide and veterinary drug hapten is coupled with ovalbumin to prepare a hapten-OVA (ovalbumin) couplet; a fluorescent molecule Cy3 is then used for labeling; sample liquid to be detected is incubated with the chip after mixed with a labeling detection antigen according to a certain concentration; a to-be-detected antigen in a sample and the corresponding labeling detection antigen are directly and competitively bound with the corresponding monoclonal antibody acquisition probe fixed on the chip; elution is performed under a certain condition; and a result is detected by a biochip scanner. The method can detect multiple pesticide and veterinary drug residues in the subsidiary agricultural product sample simultaneously, and is applicable to high-throughput, quick and accurate detection of drug residues in planting and culture production.
Owner:内蒙古敖敦食品股份有限公司
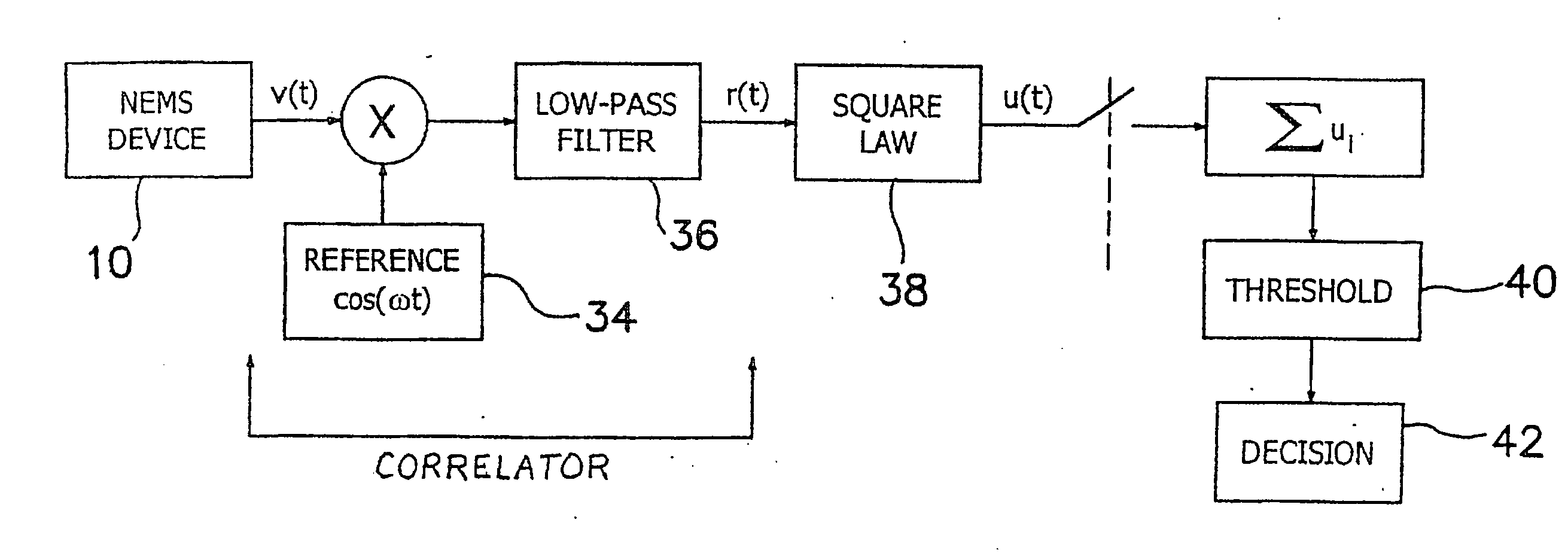
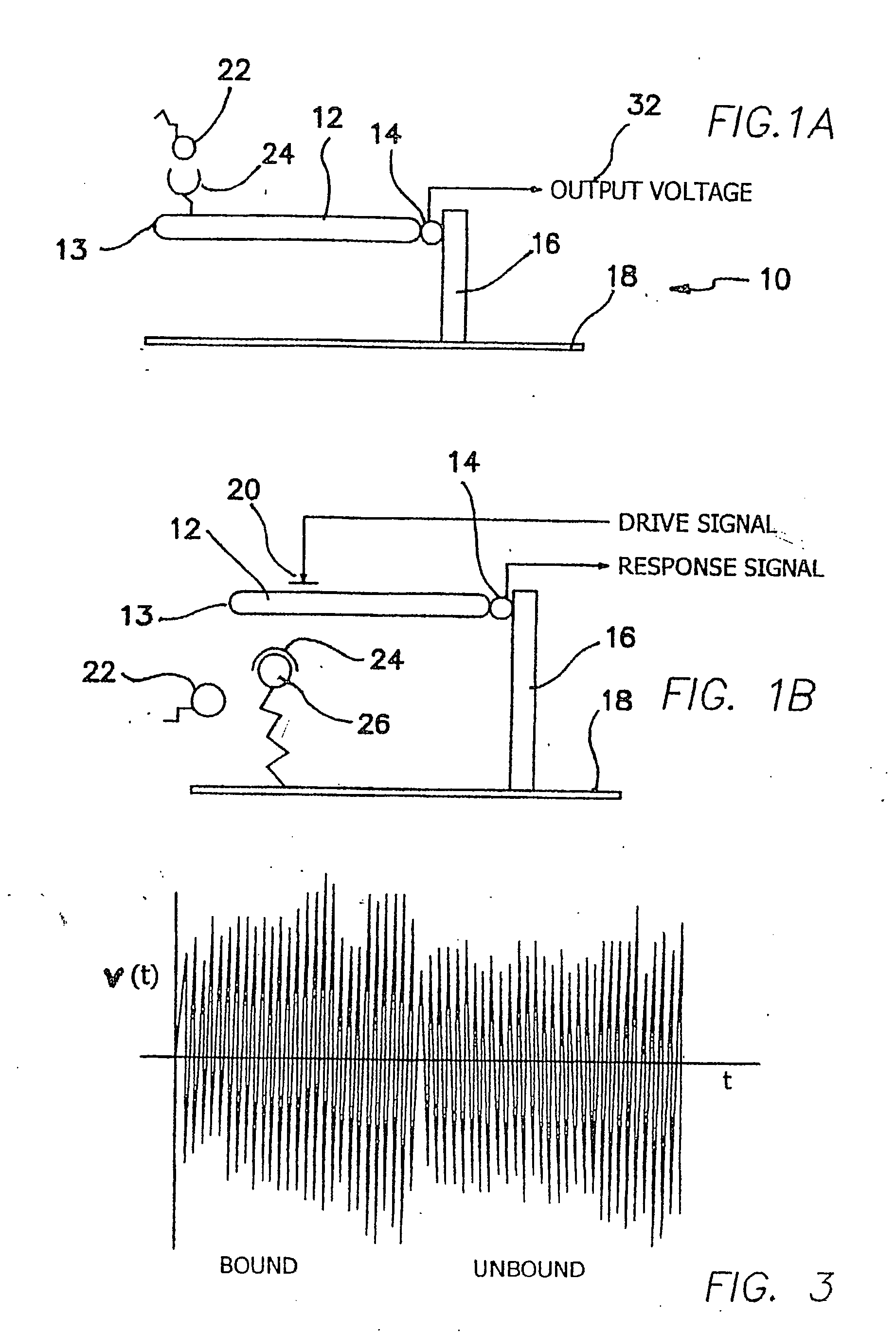
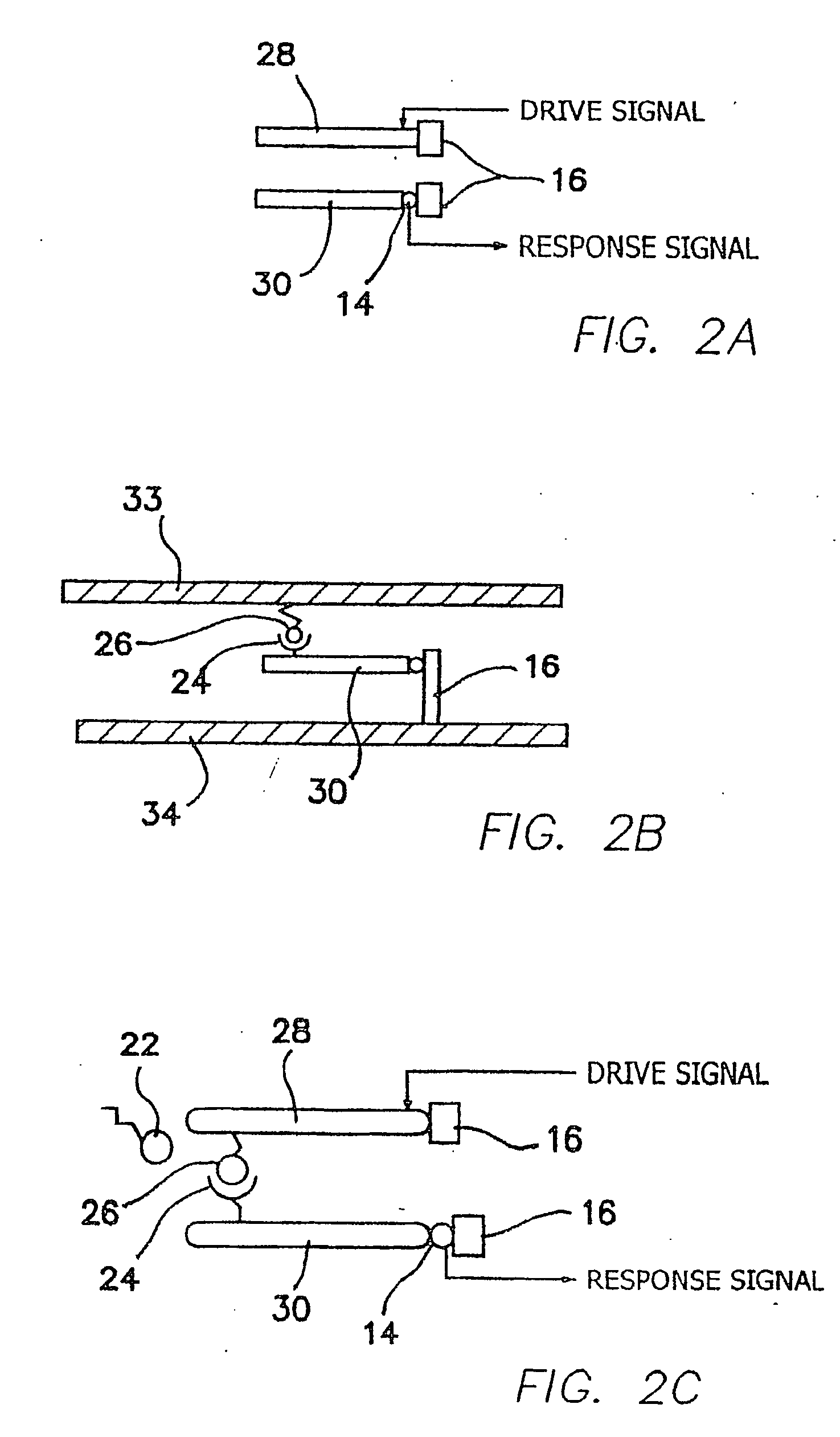
Method and apparatus for providing signal analysis of a BioNEMS resonator or transducer
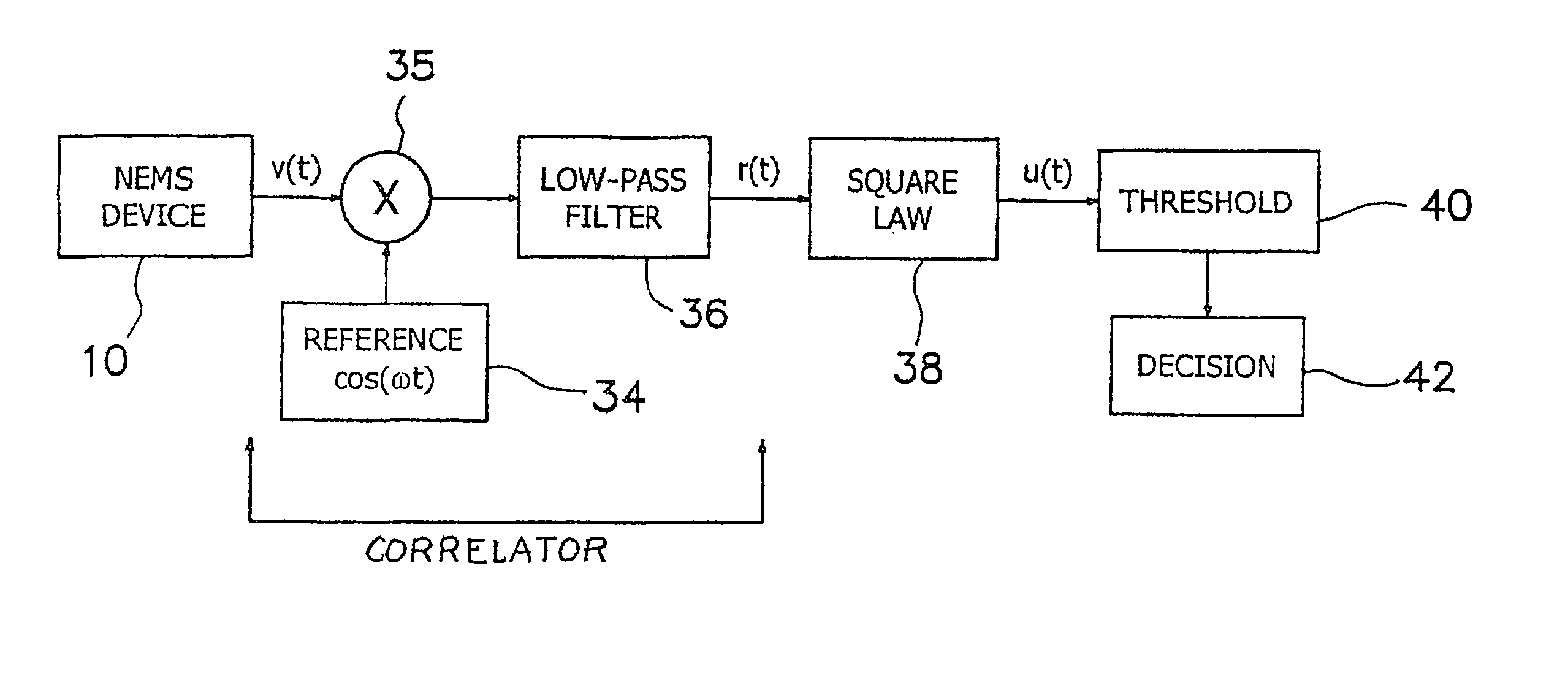
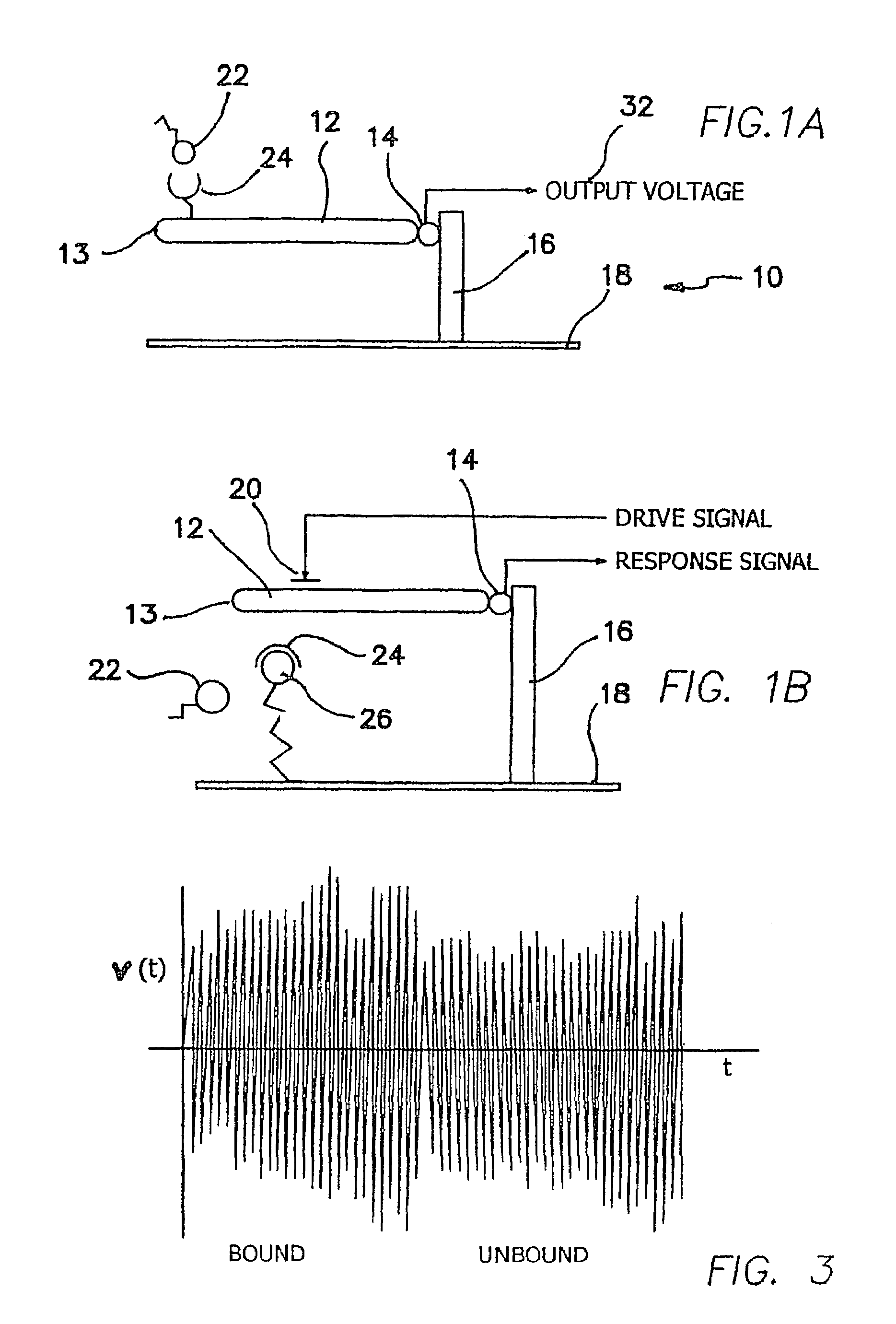
InactiveUS7330795B2Small sizeMore responsiveAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsCompetitive bindingTransducer
An outputs signal, v(t), is generated from a bioNEMs transducer and mixed with a reference signal and then filtered to generate a correlator output, r(t). The correlator output is detected to generate a signal u(t) and then determined whether the signal u(t) satisfies a predetermined threshold. If qualified, it is then decided whether the signal u(t) represents a predetermined type of interaction between a free ligand in a fluid in which the NEMS device is immersed and a receptor attached to the transducer. The threshold is the Neyman-Pearson criterion based on a predetermined probability of false detection, Pfa. The interaction may be binding of a free ligand to the receptor or releasing a bound ligand from the receptor by competitive binding with the free ligand. The step of detecting comprises detecting the envelope of the signal, r(t).
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Volume response sensors having analyte controlled reversible crosslinking
InactiveUS20160252505A1Improve stabilityAvoid leachingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCompetitive bindingGlucose sensors
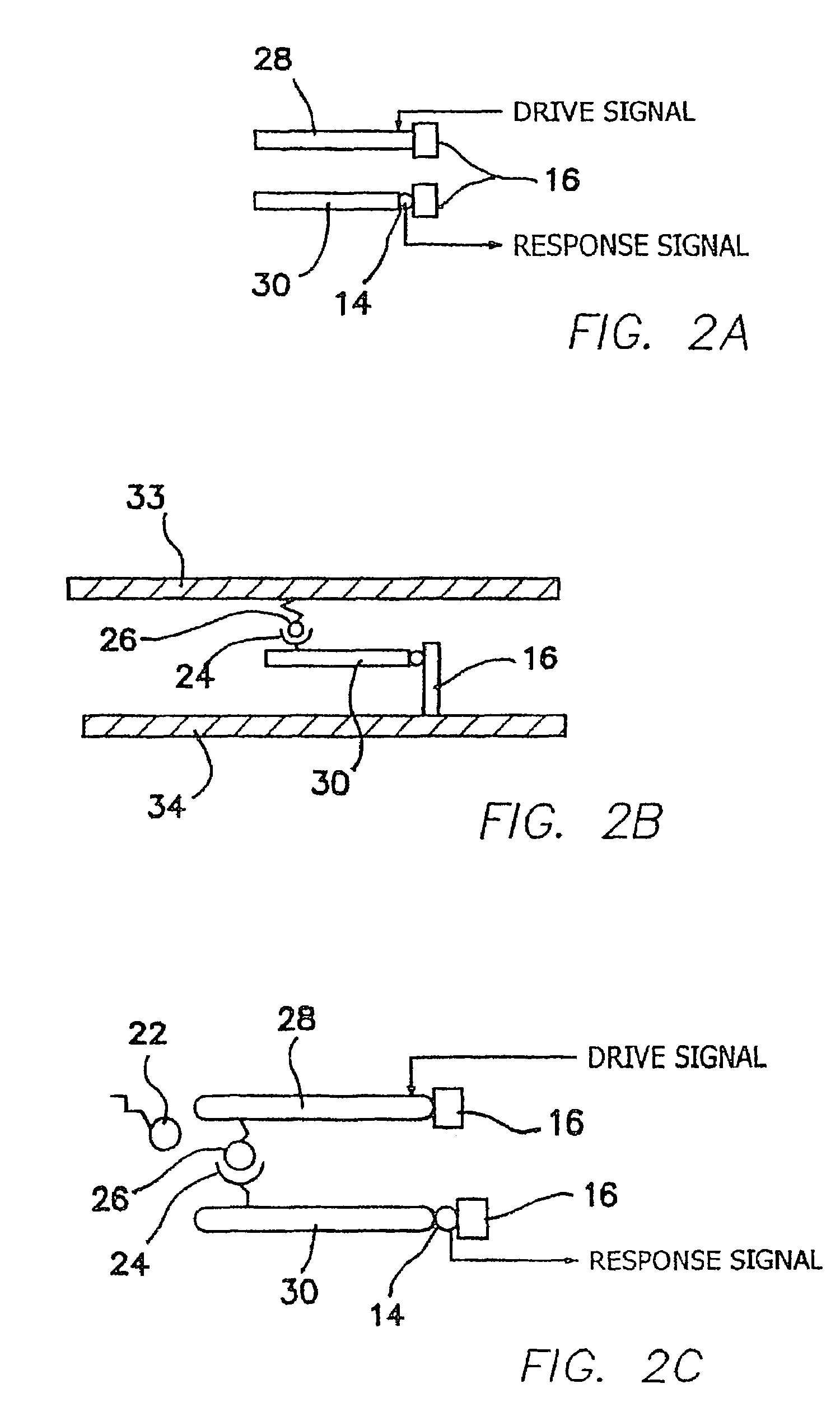
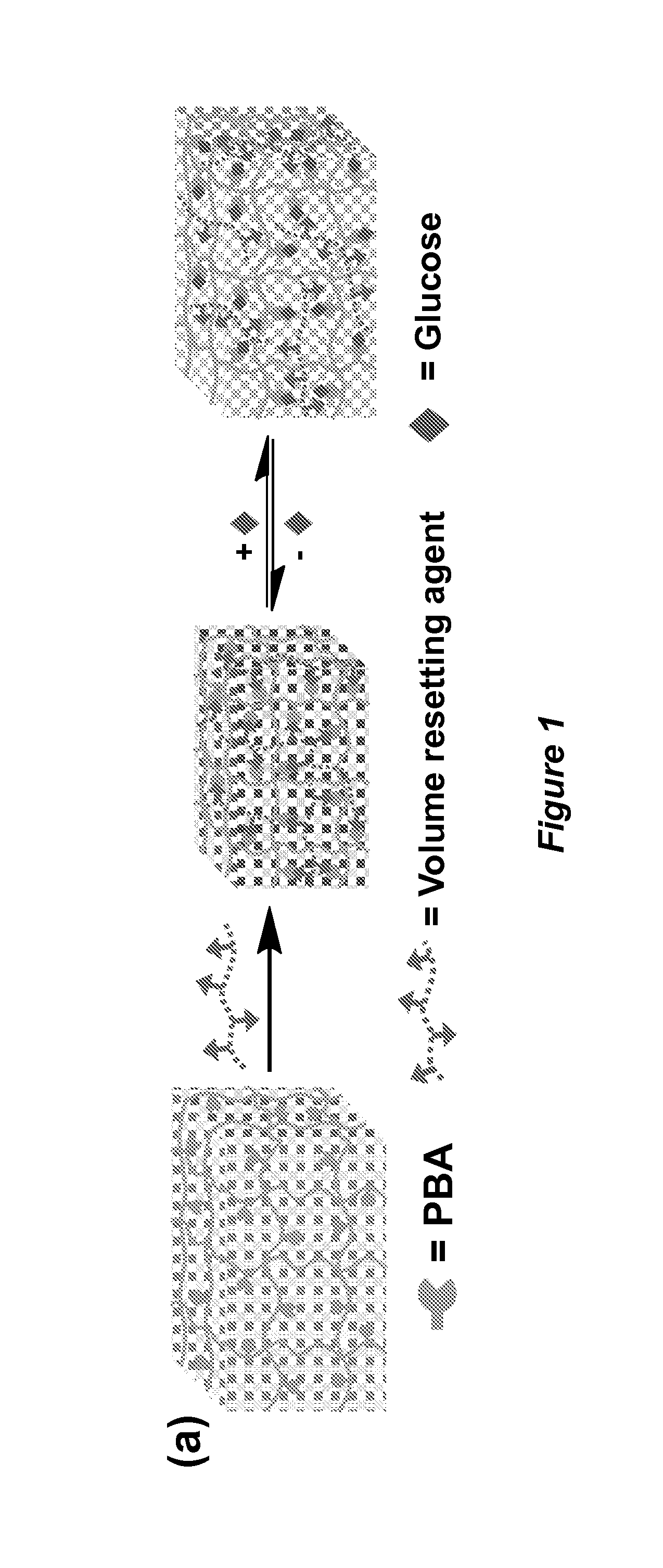
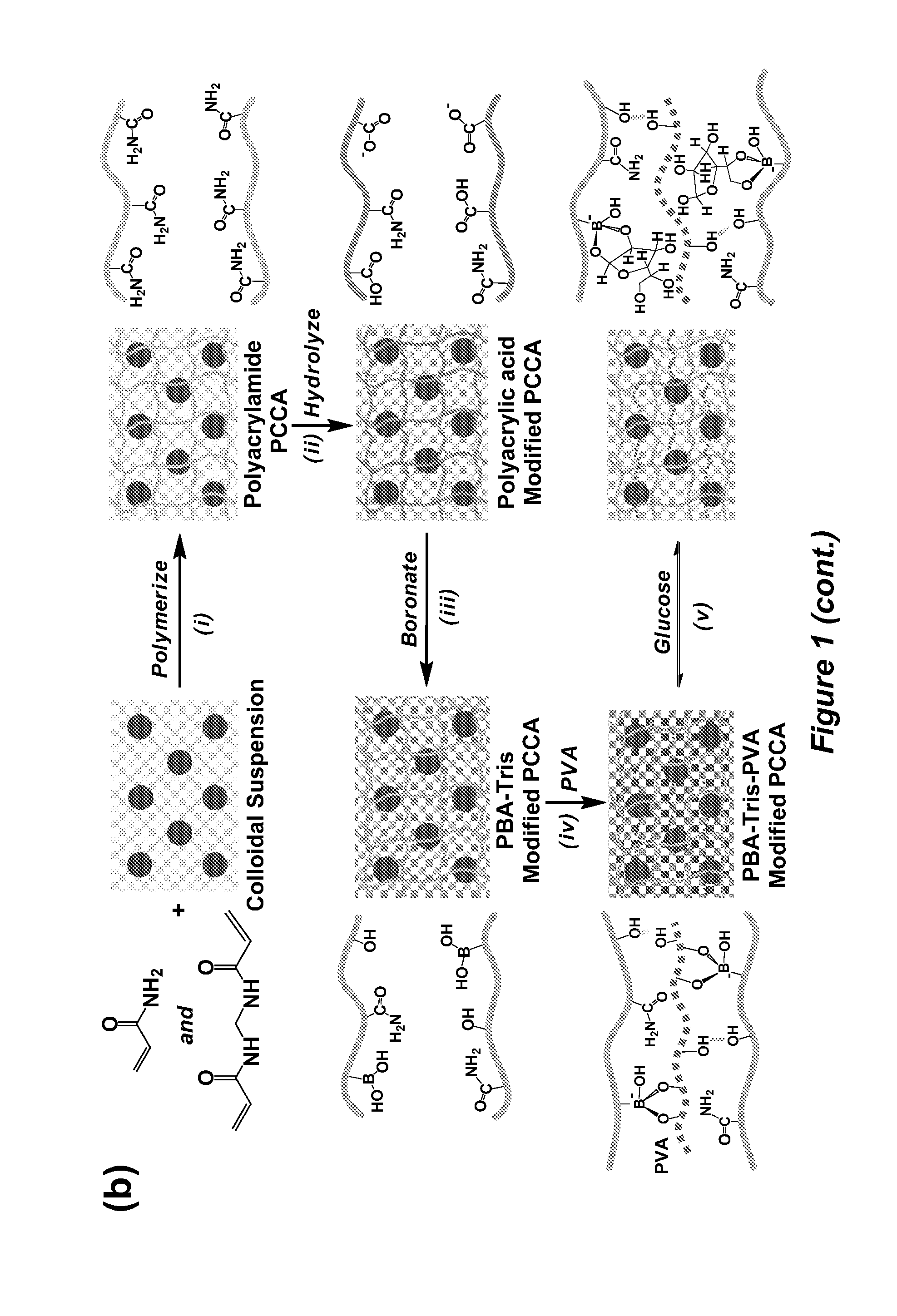
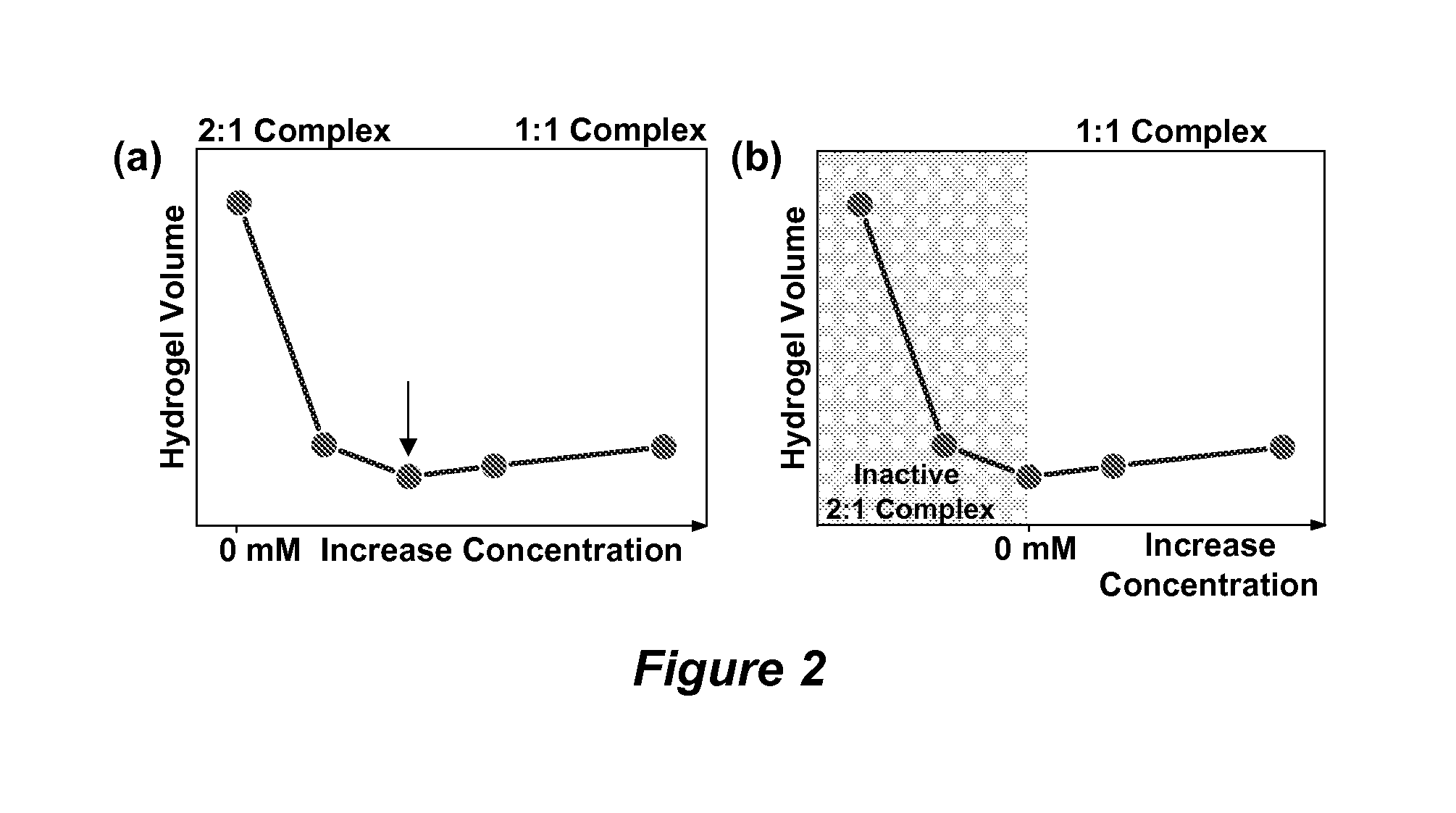
The invention relates to hydrogel and organogel sensors as well as their application to continuous analyte monitoring. The sensor can include a hydrogel or organogel matrix. Standard and inverse designed are provided. In one embodiment, the matrix can include a molecular recognition agent for an analyte (e.g., a glucose analyte), and a volume resetting agent that reversibly binds with the molecular recognition agent. Reversible crosslinks between the molecular recognition agent and volume resetting agent can change the volume of the matrix upon interacting with the analyte via a competitive binding process. In various embodiments, the invention provides a hydrogel-based glucose sensor and sensors for continuous glucose monitoring. The glucose sensor can be based on a glucose-responsive hydrogel with a volume linearly correlated with glucose concentrations, such as about 0.05-50 mM, under physiological conditions. The invention thus provides a blood glucose monitor suitable for use in clinical settings.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Immunoassay for free vitamin d
ActiveUS20130143241A1Preparing sample for investigationBiological testingSolubilityCompetitive binding
Disclosed is the invention to conduct immuno-adsorption of free 25(OH) vitamin D from blood or blood components, notably serum or plasma, after which the absorbed material is measured. A fluoro-alkyl surfactant is used to enhance the solubility of Vitamin D and allow the measurement of free Vitamin D. The invention thus employs a binding protein to absorb the free 25(OH) vitamin D. Thereafter the binding protein comprising the 25-OH vitamin D is subjected to a competitive binding assay with a labeled vitamin D compound, preferably radiolabeled, fluorescent labeled, luminescent labeled, biotin labeled, gold labeled or enzyme labeled. Alternatively the immunocaptured 25-OH vitamin D can be quantitated by mass spectrometry.
Owner:FUTURE DIAGNOSTICS
Method and apparatus for providing signal analysis of a bionems resonator or transducer
InactiveUS20060155478A1Small sizeMore responsiveAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsCompetitive bindingTransducer
An outputs signal, v(t), is generated from a bioNEMs transducer and mixed with a reference signal and then filtered to generate a correlator output, r(t). The correlator output is detected to generate a signal u(t) and then determined whether the signal u(t) satisfies a predetermined threshold. If qualified, it is then decided whether the signal u(t) represents a predetermined type of interaction between a free ligand in a fluid in which the NEMS device is immersed and a receptor attached to the transducer. The threshold is the Neyman-Pearson criterion based on a predetermined probability of false detection, Pfa. The interaction may be binding of a free ligand to the receptor or releasing a bound ligand from the receptor by competitive binding with the free ligand. The step of detecting comprises detecting the envelope of the signal, r(t).
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method of detecting surrogate markers in a serum sample
ActiveUS20130137598A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCompetitive bindingCholesterol
The invention provides a method of detecting surrogate markers for active tuberculosis in a serum sample. The surrogate markers are selected from serum mycolic acid antigen, serum anti-mycolic acid antibodies or both. The method includes the steps of combining the serum sample with a labelled monoclonal immunoglobulin antibody or fragment thereof to mycolic acids to produce a combined serum sample, the antibody or fragment thereof not substantially cross-reacting with cholesterol and the label being selected so that binding of the labelled antibody to immobilized mycolic acid antigen of mycobacterial origin produces a detectable signal and combining a blank sample with the labelled monoclonal immunoglobulin antibody or fragment thereof to mycolic acid to produce a combined blank sample. The method includes exposing both samples to immobilised mycolic acid antigen of mycobacterial origin or a synthetic analogue or analogues thereof so that the labelled immunoglobulin antibodies or fragments thereof in each sample bind to the immobilised antigen to produce detectable signals. If the surrogate markers are present, the signal produced by the blank sample will be stronger than that produced by the serum sample because of inhibition of binding of the labelled antibody in the serum sample arising from prior binding of the labelled antibody with the mycolic acid antigen in the serum sample or by competitive binding of serum anti-mycolic acid antibodies in the serum sample to the immobilised mycolic acid antigen or both.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA
Electrochemiluminescent assays for eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS6300143B1Microbiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceTherapeutic antibodyAffinity measurement
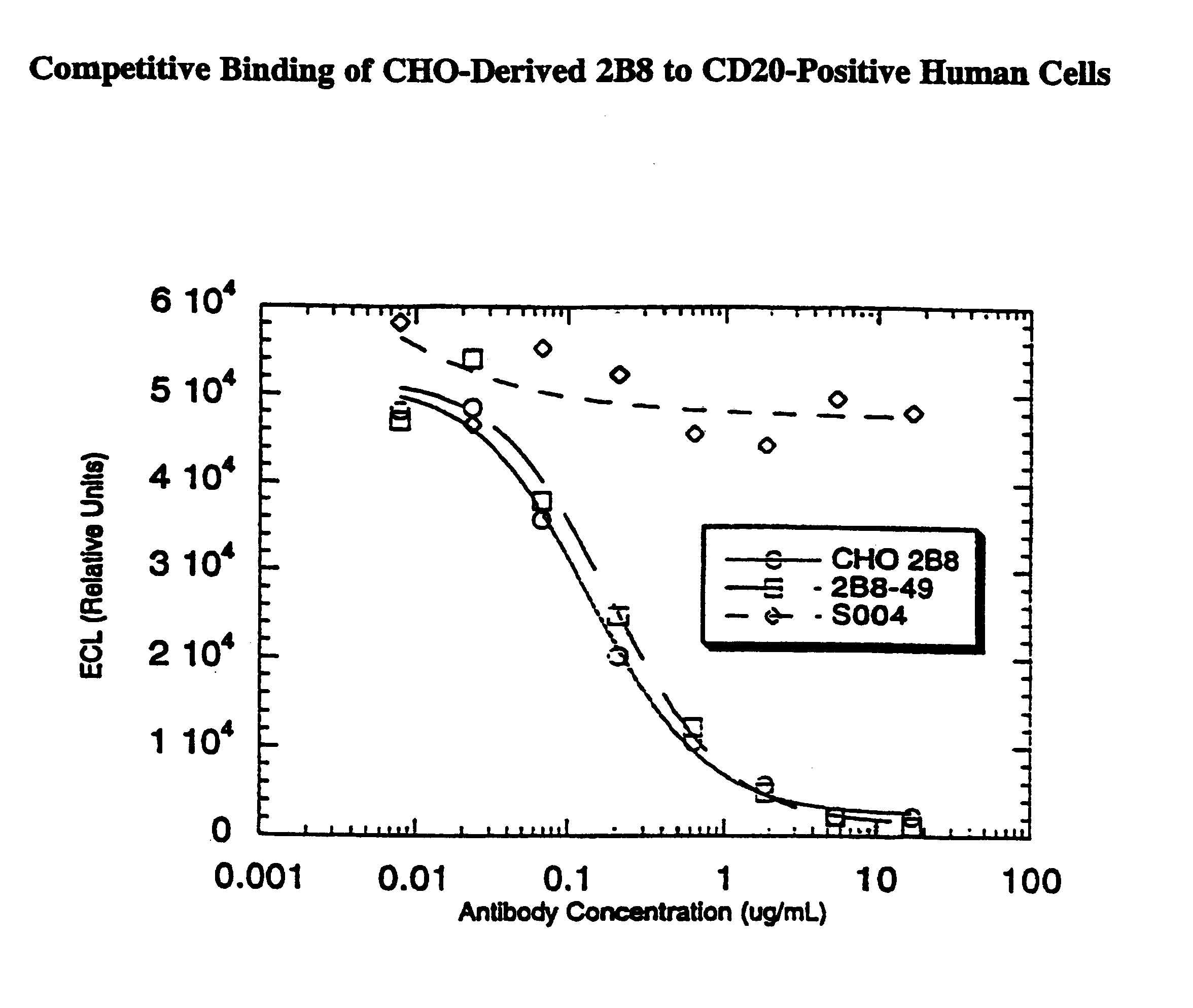
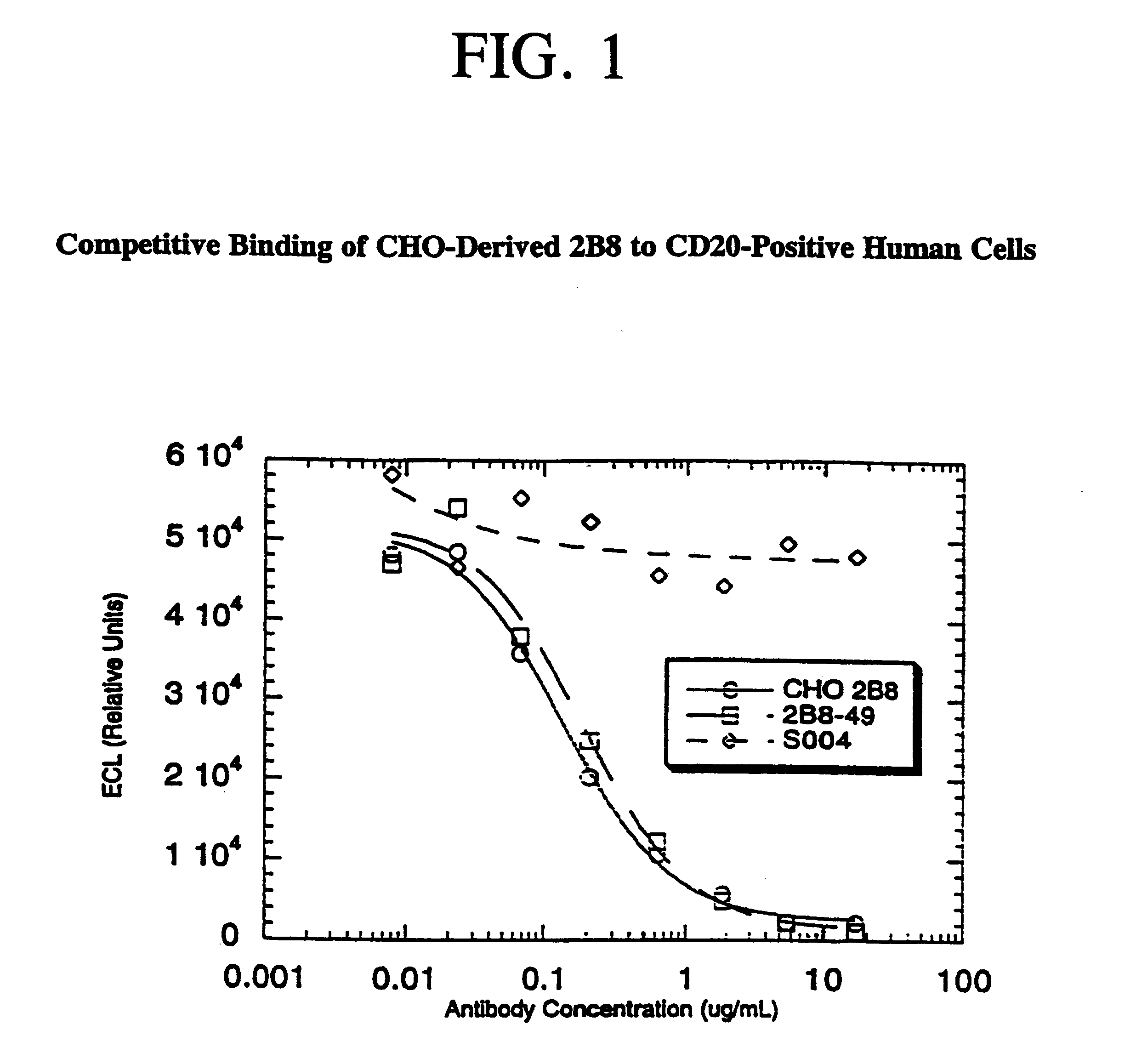
Disclosed are immunomagnetic electrochemiluminescence assays for eukaryotic cells, particularly human cells. A competitive binding assay is disclosed which enables affinity measurements of antibodies specific for eukaryotic cell membrane proteins. Such an assay is particularly useful for verifying or measuring the affinity of therapeutic antibodies following chelate conjugation.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
High-sensitivity chemiluminescence immunoassay kit, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108333344AAmplify the luminescent signalHigh sensitivityMaterial analysisTarget analysisBiotin-streptavidin complex
The invention provides a high-sensitivity chemiluminescence immunoassay kit, and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of clinical immunoassay. The high-sensitivity chemiluminescence immunoassay kit comprises a solid-phase vector directly coated with a capture molecule, a biotin-labeled marker molecule and luminescent substance-labeled streptavidin, whereinthe marker molecule is capable of binding to a target analyte in a to-be-detected sample, and the capture molecule is capable of specifically binding to the target analyte in the to-be-detected sample or is an analog of the target analyte in the to-be-detected sample; or the marker molecule is capable of competitively binding to the target analyte in the to-be-detected sample, and the capture molecule is capable of specifically binding to the target analyte in the to-be-detected sample. The kit provided by the invention is based on the structural characteristics of streptavidin; per mole of tetramer molecules can bind to four moles of biotin molecules, and strong affinity are formed between the tetramer molecules and the biotin molecules; and a cyclic amplification reaction process is constructed to realize signal amplification, so the sensitivity of the kit is improved.
Owner:南京仁迈生物科技有限公司
Method for detecting affinity of monoclonal antibodies of transmembrane proteins
ActiveCN106442967AEfficient determination of affinityReduce usageMaterial analysisCompetitive bindingIsotope
The invention discloses a method for detecting the affinity of monoclonal antibodies of transmembrane proteins. The method mainly includes steps of 1), constructing stable cell strains with membrane protein high expression to guarantee the maximum right shift of positive combination peaks in FACS (fluorescence-activated cell sorter) assay; 2), labeling antibodies by the aid of fluorecein; 3), carrying out saturation binding assay; 4), carrying out competitive binding assay; 5), processing data. The method has the advantages that the affinity of the monoclonal antibodies of the transmembrane proteins can be effectively measured; radioactive isotopes can be omitted, accordingly, the method is high in safety and sensitivity and good in repeatability, stable and reliable detection results can be obtained, and the like.
Owner:GMAX BIOPHARM +1
Sensor for detection of carbohydrate
A sensor for the detection or measurement of carbohydrate analyte (such as glucose) in fluid comprises components of a competitive binding assay the readout of which is a detectable or measurable optical signal (such as a FRET assay) retained by a material that permits diffusion of analyte but not the assay components, the assay components comprising: an animal lectin; and an analyte analogue capable of competing with analyte for binding to the lectin.
Owner:PRECISENSE AS
Method for improving structural stability of biological material and biological material
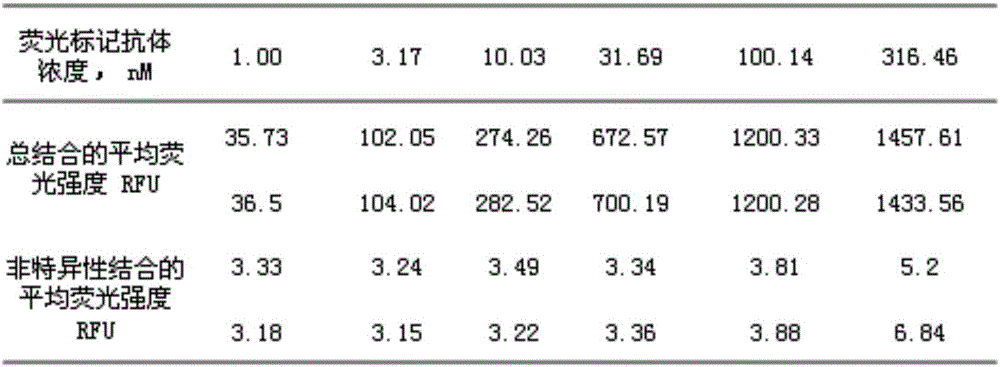
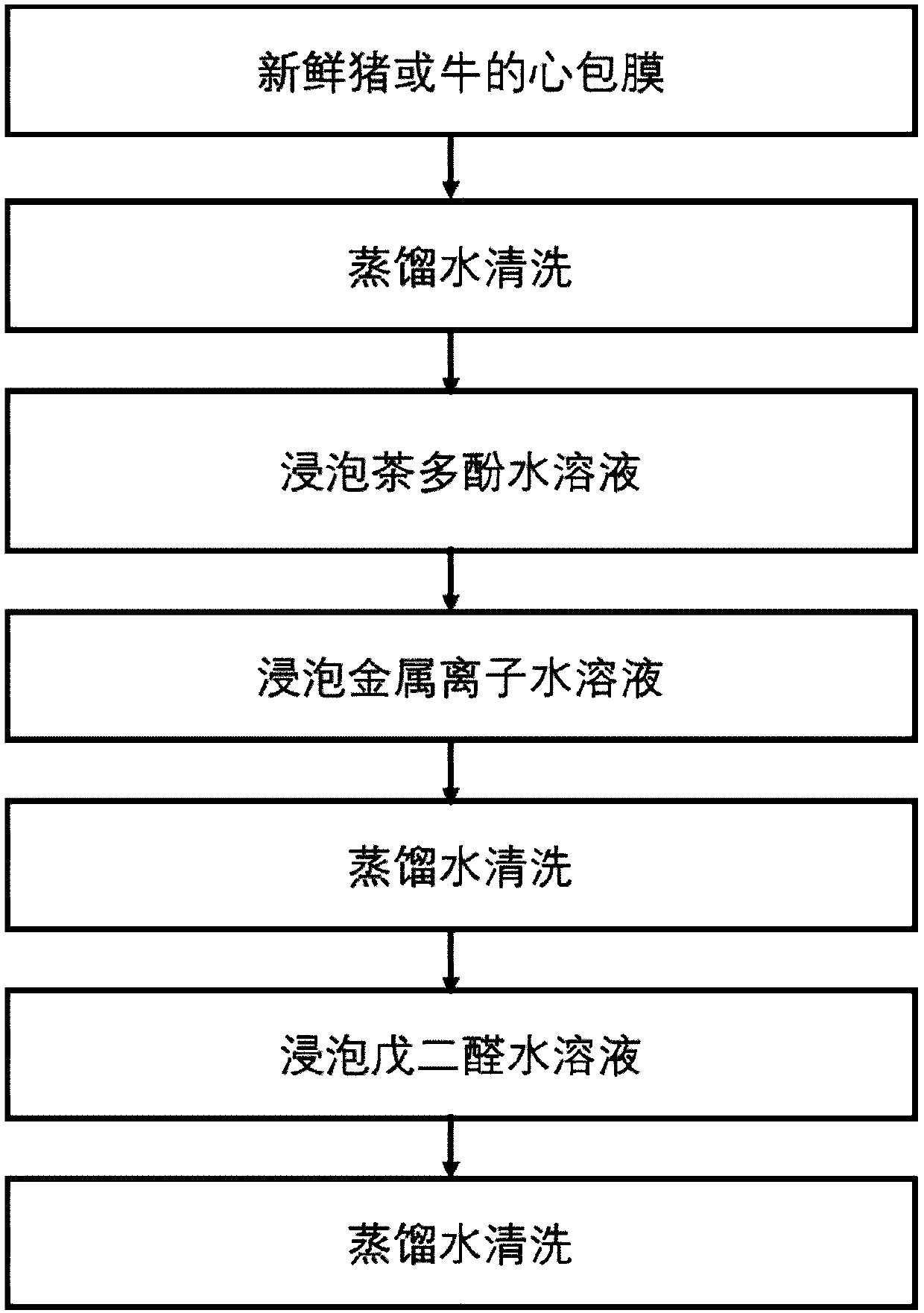
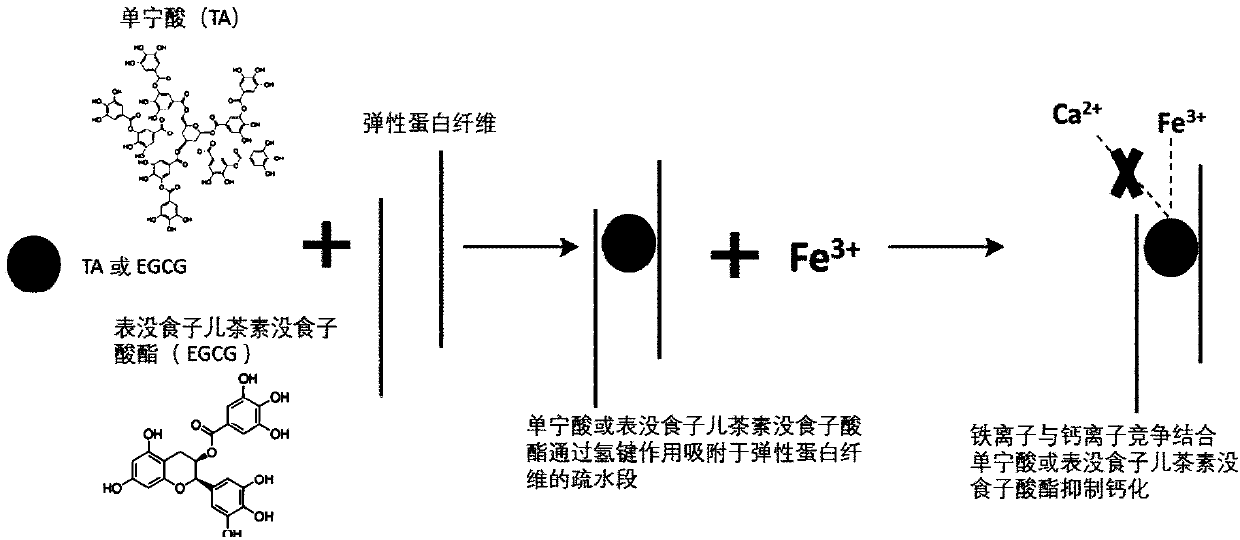
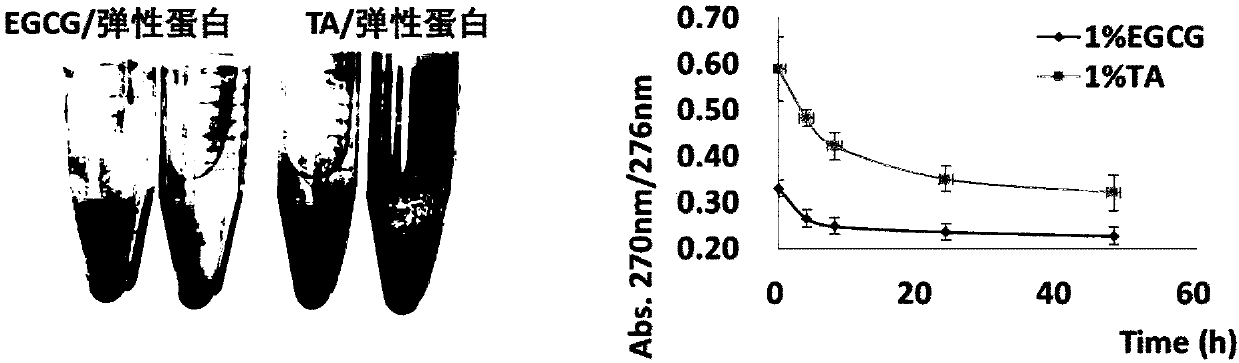
InactiveCN110152066AImprove anti-calcification propertiesImprove stabilityTissue regenerationProsthesisFiberCompetitive binding
The invention discloses a method for improving the structural stability of a biological material and the biological material. The method comprises the steps of soaking the biological material in an aqueous solution of tea polyphenol and metal ions, and adsorbing the tea polyphenol on hydrophobic sections of elastin fibers under the function of hydrogen bonds. In this way, the structural stabilityof elastin is improved, the metal ions and calcium ions conduct competitive binding to adsorb the tea polyphenol, and thus the calcification of the biological material is inhibited. By means of the method, the structural stability and anti-calcification performance of the biological material can be improved, and the service life of the biological material is potentially prolonged.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Release reagent for vitamin d
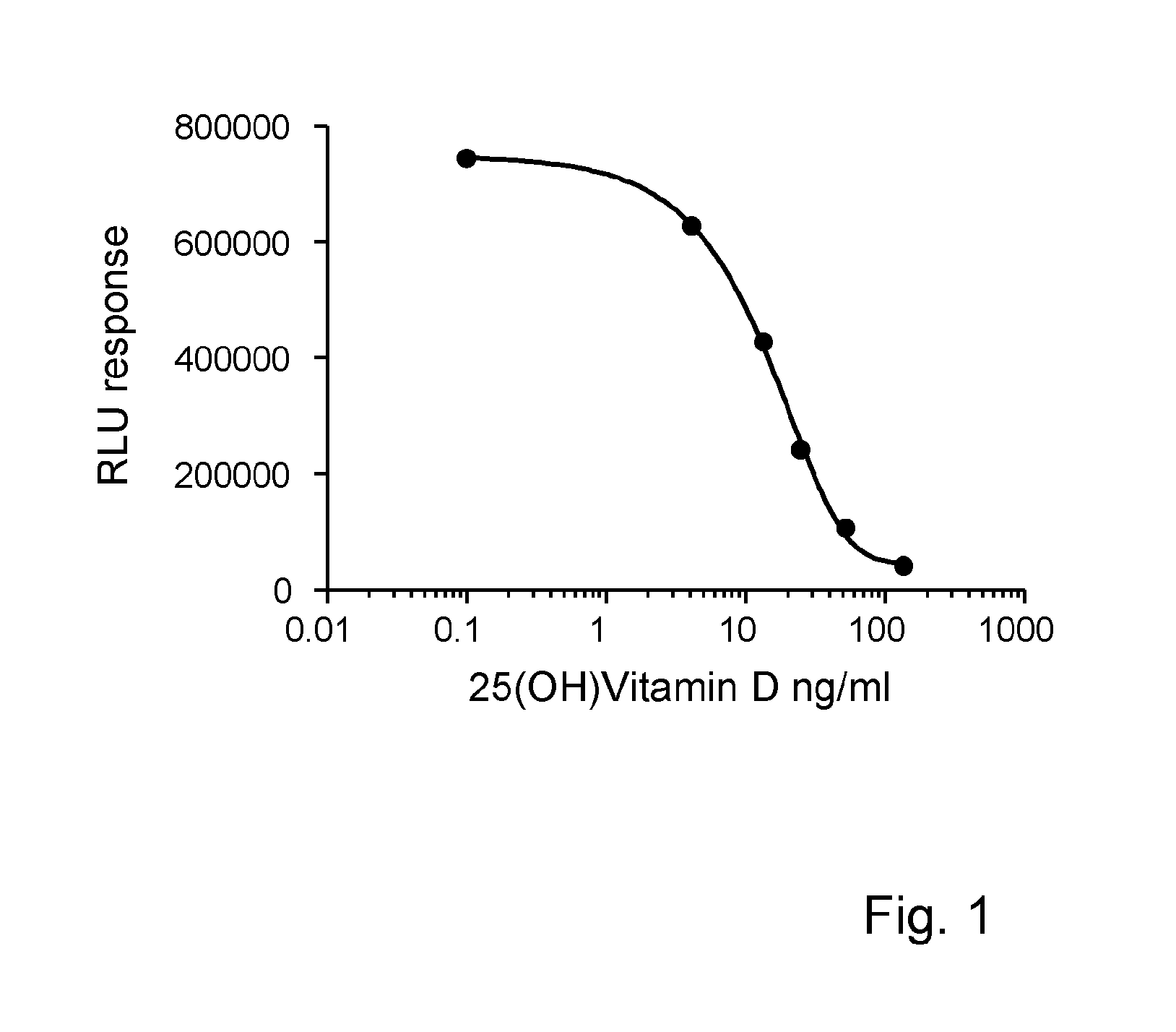
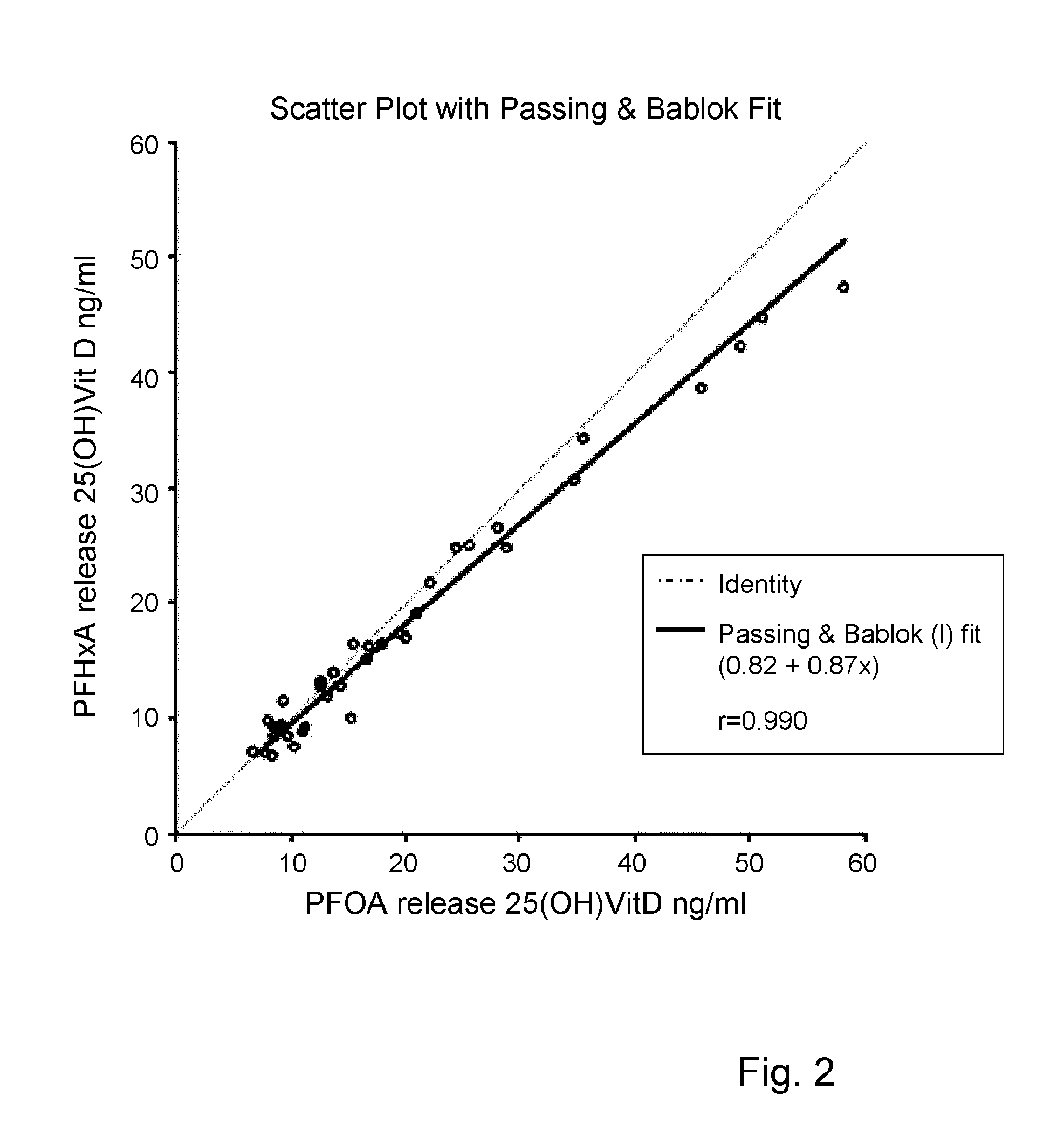
Disclosed is an invention in the field of conducting an immunoassay of 25(OH) vitamin D in blood or blood components, notably serum or plasma. The invention employs a perfluoro alkyl acid, or a salt thereof, to release 25(OH) vitamin D from vitamin D binding protein. Thereafter the binding protein comprising the 25-OH vitamin D is subjected to a competitive binding assay with a labeled vitamin D compound.
Owner:FUTURE DIAGNOSTICS
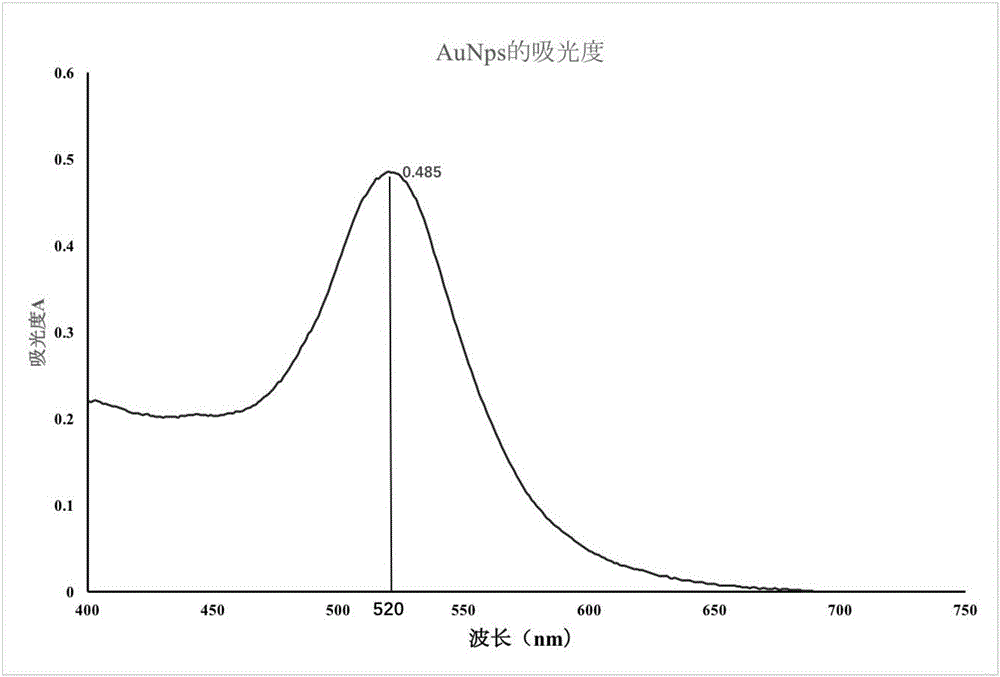
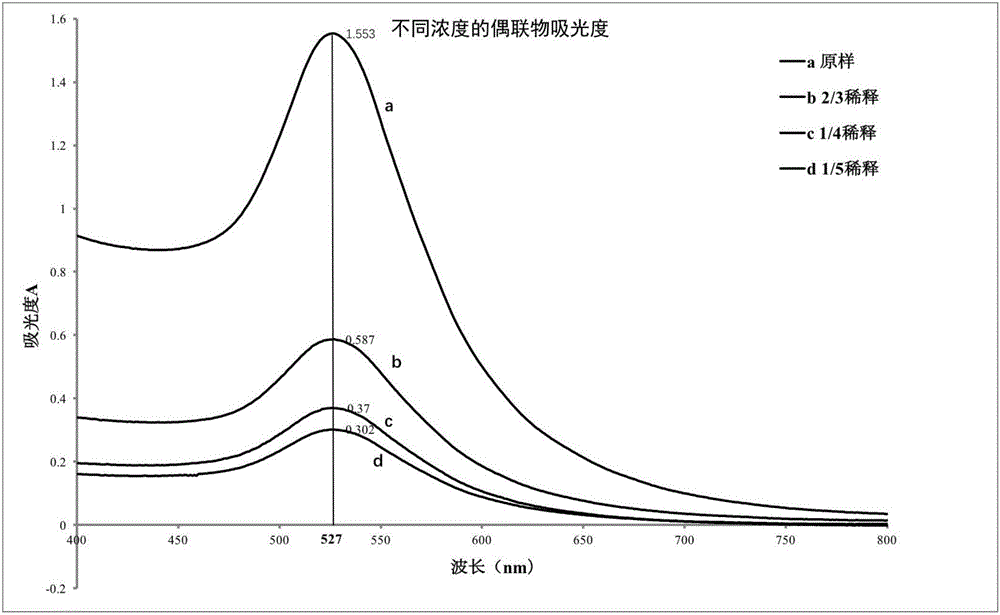
Method for detecting tetracycline (TET) based on colloidal gold (AuNPs) chromatography test strip of aptamer
InactiveCN106645679ASuitable for on-site screeningEfficient detection technologyBiological testingBiotin-streptavidin complexAptamer
The invention discloses a method for detecting tetracycline (TET) based on a colloidal gold (AuNPs) chromatography test strip of aptamer. The method uses specific binding between colloidal gold and the aptamer and competitive binding capacity strength between the tetracycline and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and the aptamer. The method comprises the following steps of synthesizing colloidal gold nanoparticles suitable for marking the aptamer; assembling and coupling the colloidal gold and the aptamer; assembling streptavidin with a DNA chain; preprocessing a sample pad and a gold pad; scribing lines on an NC membrane; assembling the test strip; detecting standard tetracycline; performing selectivity and specificity experiments; using the established colloidal gold test strip based on the aptamer to measure the tetracycline in a practical sample. The tetracycline detecting method provided by the invention has the advantages of having better selectivity and flexibility, being simple, economic and easy to operate and being more suitable for in-site quick detection.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
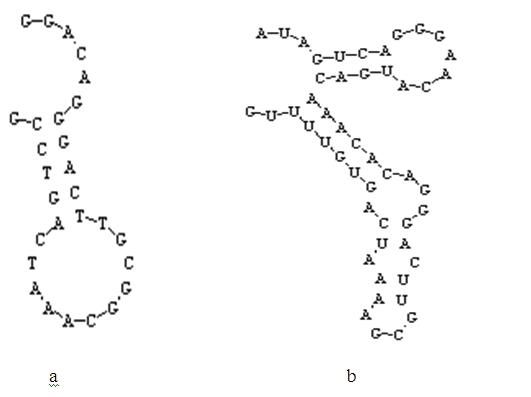
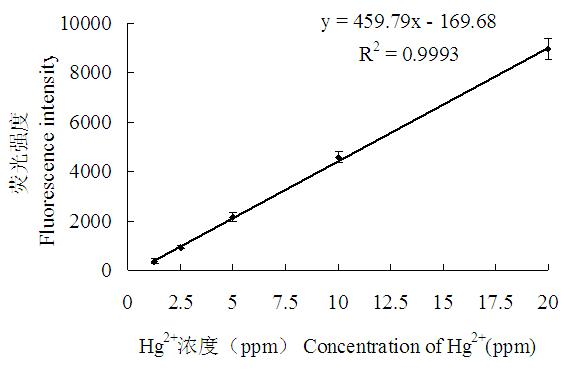
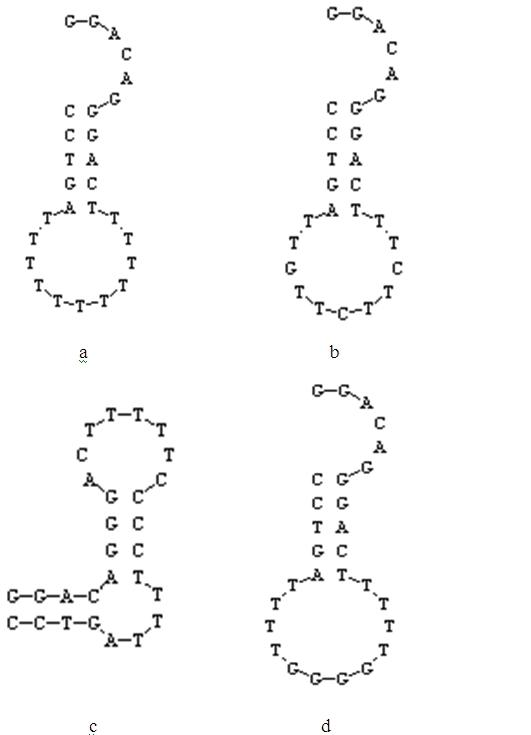
Method for detecting mercury ion residue of fluorescent signal conversion mechanism based on nucleic acid aptamer structure
InactiveCN102621120AHigh binding activityGood structure recognition functionFluorescence/phosphorescenceAptamerCompetitive binding
The invention relates to a method for detecting mercury ion residue of a fluorescent signal conversion mechanism based on a nucleic acid aptamer structure. In the method, a mercury ion nucleic acid aptamer marked with a fluorescein molecule, and a complementary sequence marked with a quenching element are utilized to form a fluorescent detection system, wherein the mercury ion nucleic acid aptamer is a stem loop structure composed of 27-28 bases and owns a stem formed by covalent binding of the bases GGAC and GTCC; and the base sequence of the complementary sequence Q2 is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The method for detecting the mercury ion residue by the fluorescent detection system comprises the following steps of: adding mercury ions with a serial concentration and a complementary sequence Q2 competitive binding nucleic acid aptamer; establishing a standard curve according to the change of fluorescent signals and determining the lowest detection limit and linear range; and then, carrying out marking detection on a sample to be detected and judging the content of the mercury ions in the sample according to the standard curve. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of rapidness, simplicity, high sensitivity and selectivity and less sample quantity demand, and is applicable to the detection of the mercury ions in the actual sample.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Fret-based binding assay
ActiveUS20100285503A1Great FRET signalEnhanced signalMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingEnergy transferCompetitive binding
The present invention provides for an assay that identifies kinase inhibitors by employing fluorescence resonance energy transfer in a competition binding approach.
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC
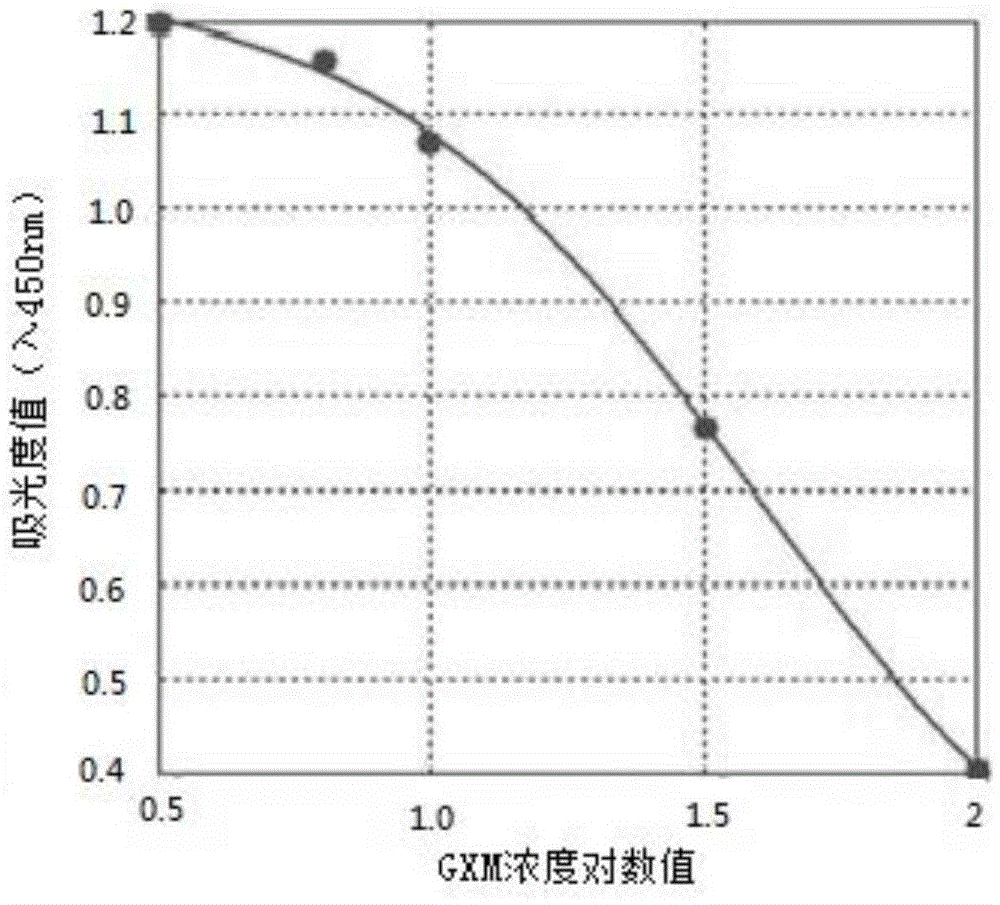
Novel crytococcus neoformans GXM (glucuronoxylomannan) antigen immunodetection kit as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105651996ASensitive detectionGood repeatabilityMaterial analysisAntigenCompetitive binding
The invention belongs to the technical field of immunodetection and relates to a novel crytococcus neoformans GXM (glucuronoxylomannan) antigen immunodetection kit. The kit comprises an enzyme-labelled carrier coated with GXM, an anti-GXM polyclonal enzyme-labelled antibody and a GXM standard substance, wherein GXM is obtained from a novel crytococcus neoformans culture solution through extraction and purification; according to the kit, an enzyme-labelled plate is coated with GXM firstly, then a to-be-detected sample or a standard antigen and a coating antigen are subjected to competitive binding with limited antibody binding sites, then an enzyme and a substrate have a chromogenic reaction, and the concentration value of a to-be-detected antigen is calculated according to the detection result. The detection kit has better sensitivity, specificity, repeatability and stability, is higher in recovery rate of target compounds, can provide more accurate and reliable detection results, is convenient and easy to use and operate and provides an effective tool for clinical detection of GXM.
Owner:DYNAMIKER BIOTECH TIANJIN
Determining non-nucleic acid molecule binding to target by competition with nucleic acid ligands
InactiveUS20050048521A1Easy to identifyQuick identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCompetitive bindingHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
A competitive binding assay is used to determine whether a non-nucleic acid molecule from a library of non-nucleic acid molecules binds to a target. The non-nucleic acid molecule competes with a labeled nucleic acid ligand for binding to the target which may be immobilized. Detecting displacement of labeled nucleic acid ligand from a complex of the labeled nucleic acid ligand and the target determines binding of the non-nucleic acid molecule to the target. The nucleic acid ligand may be immobilized and contacted with a labeled target to form a complex. Adding a non-nucleic acid molecule to the complex displaces labeled target from the complex, and detecting displacement of the labeled target determines binding of the non-nucleic acid molecule to the target. Labeled nucleic acid ligand or labeled target displaced from or remaining in the complex can be detected for detecting displacement. Nucleic acid ligands that bind to the target are identified by the SELEX method. The assay provides a high throughput screening method for determining whether a non-nucleic acid molecule binds to a target.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com