Patents
Literature
891 results about "Venous blood" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
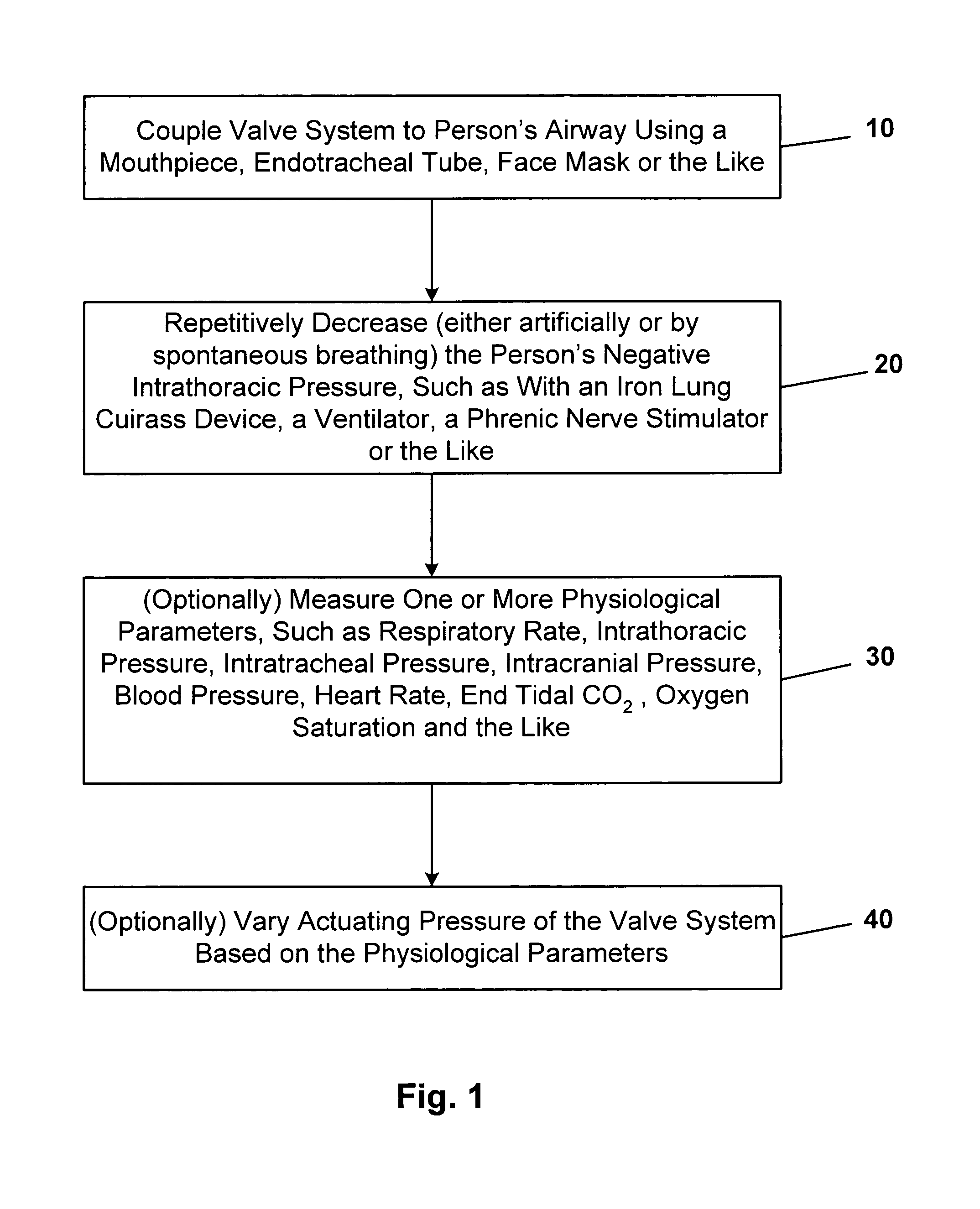
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
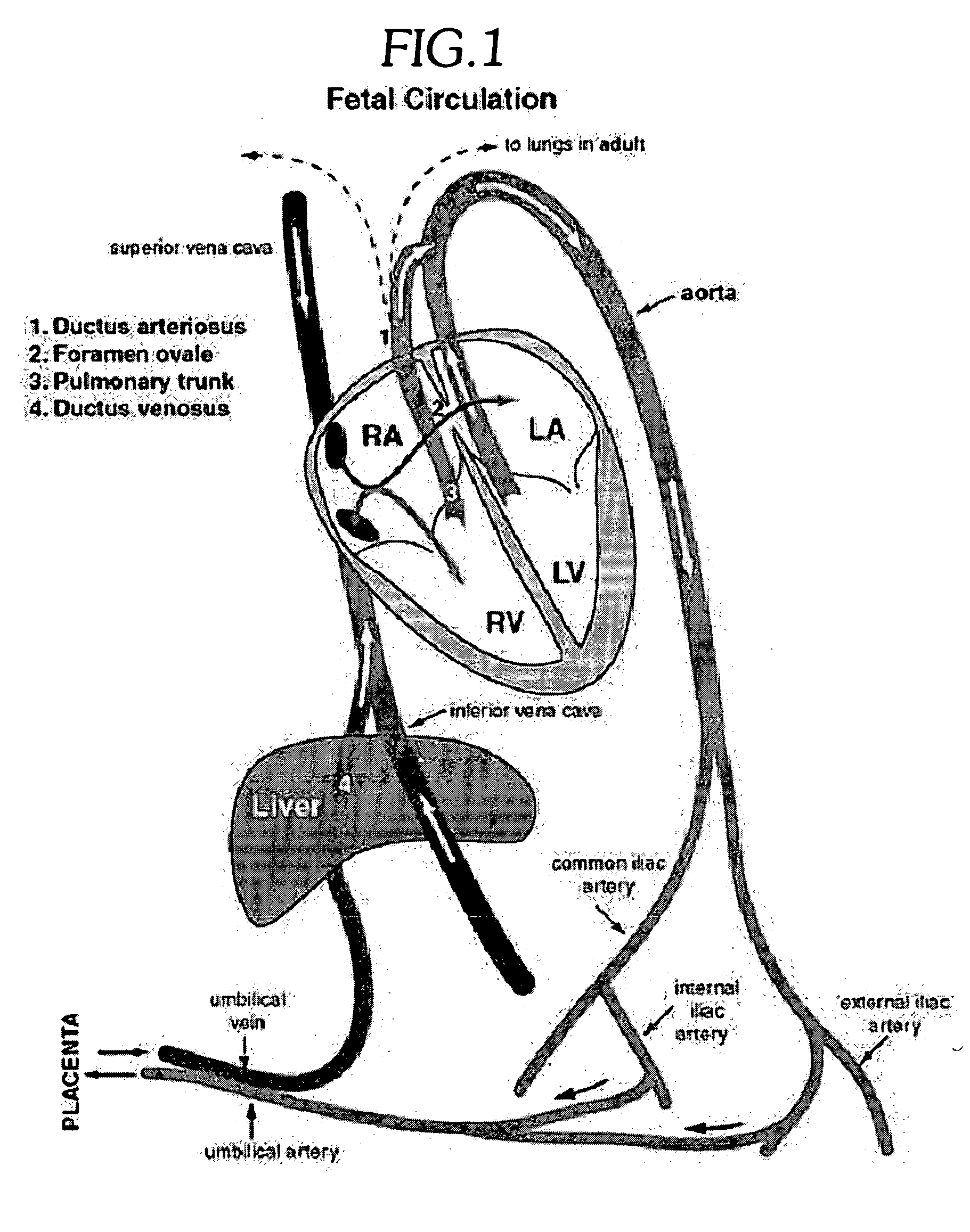
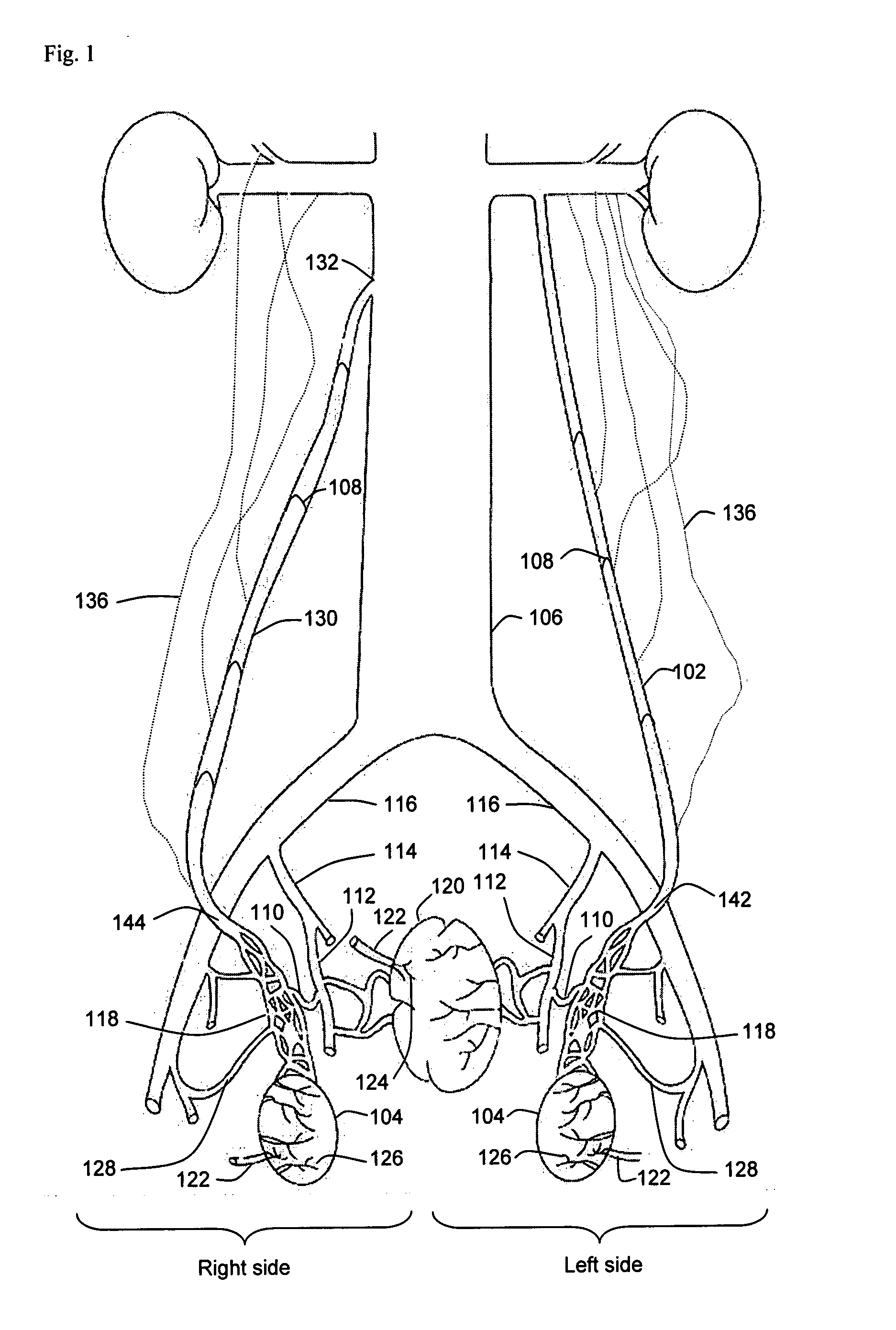
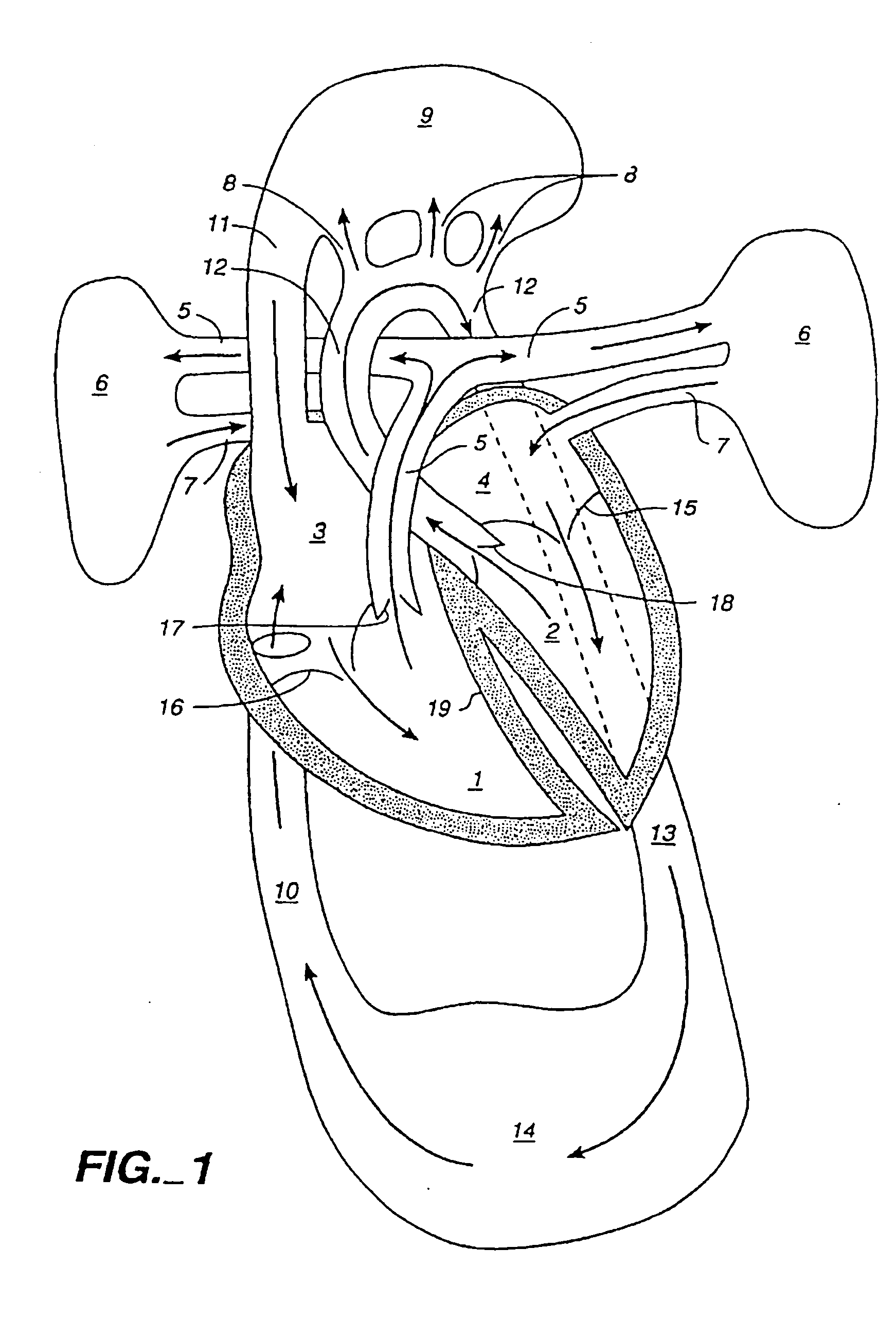
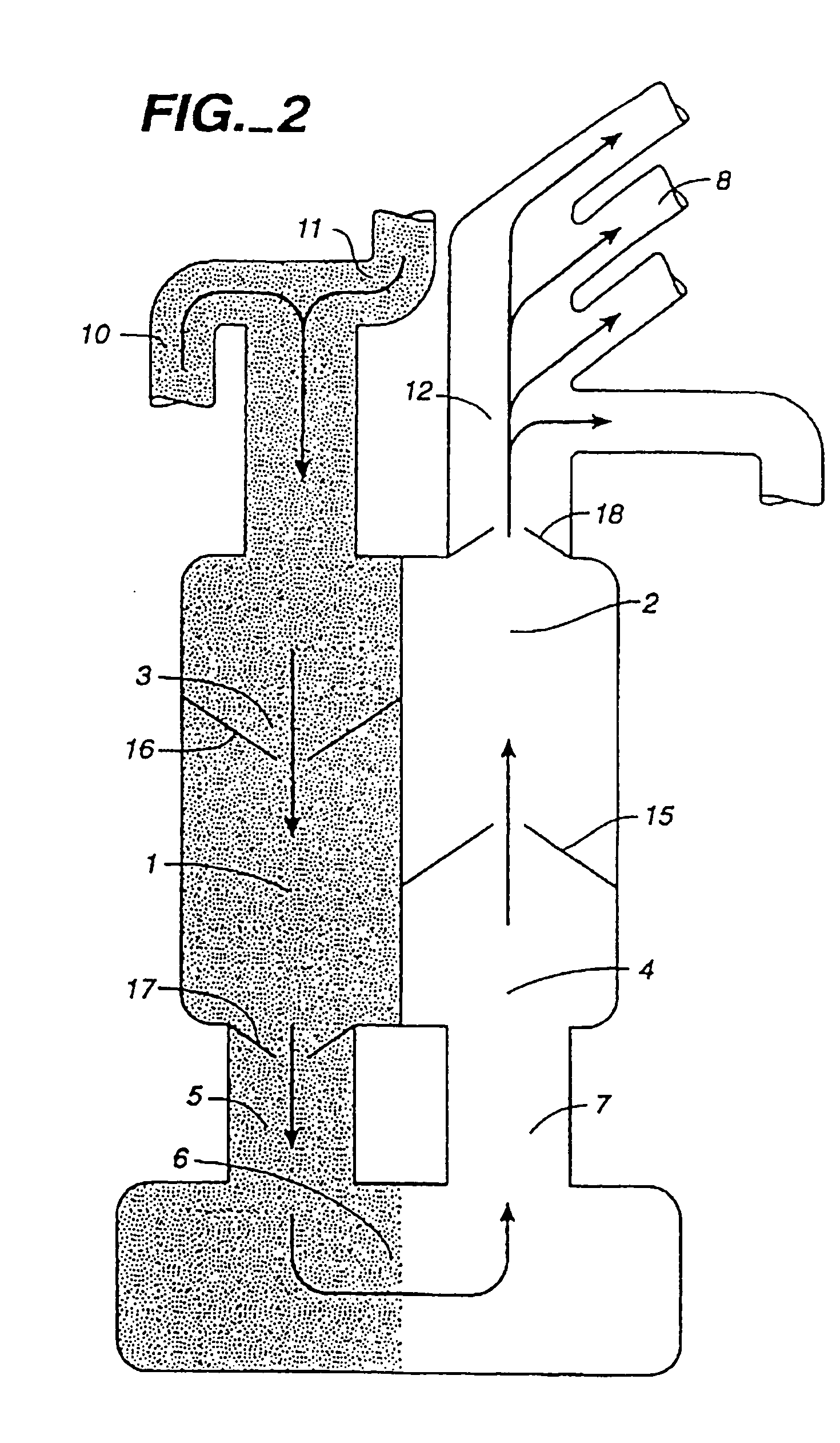
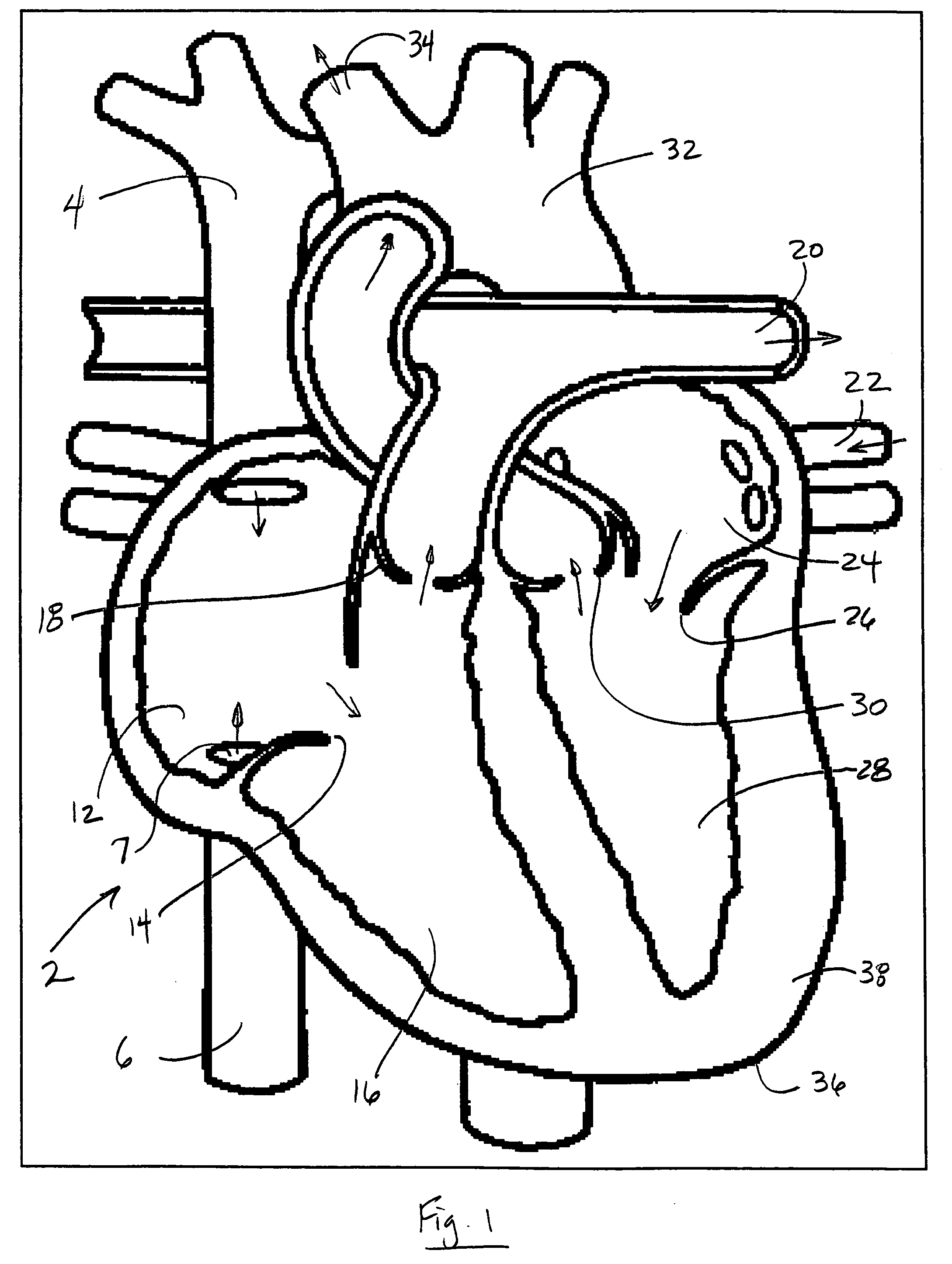
Venous blood is deoxygenated blood which travels from the peripheral vessels, through the venous system into the right atrium of the heart. Deoxygenated blood is then pumped by the right ventricle to the lungs via the pulmonary artery which is divided in two branches, left and right to the left and right lungs respectively. Blood is oxygenated in the lungs and returns to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
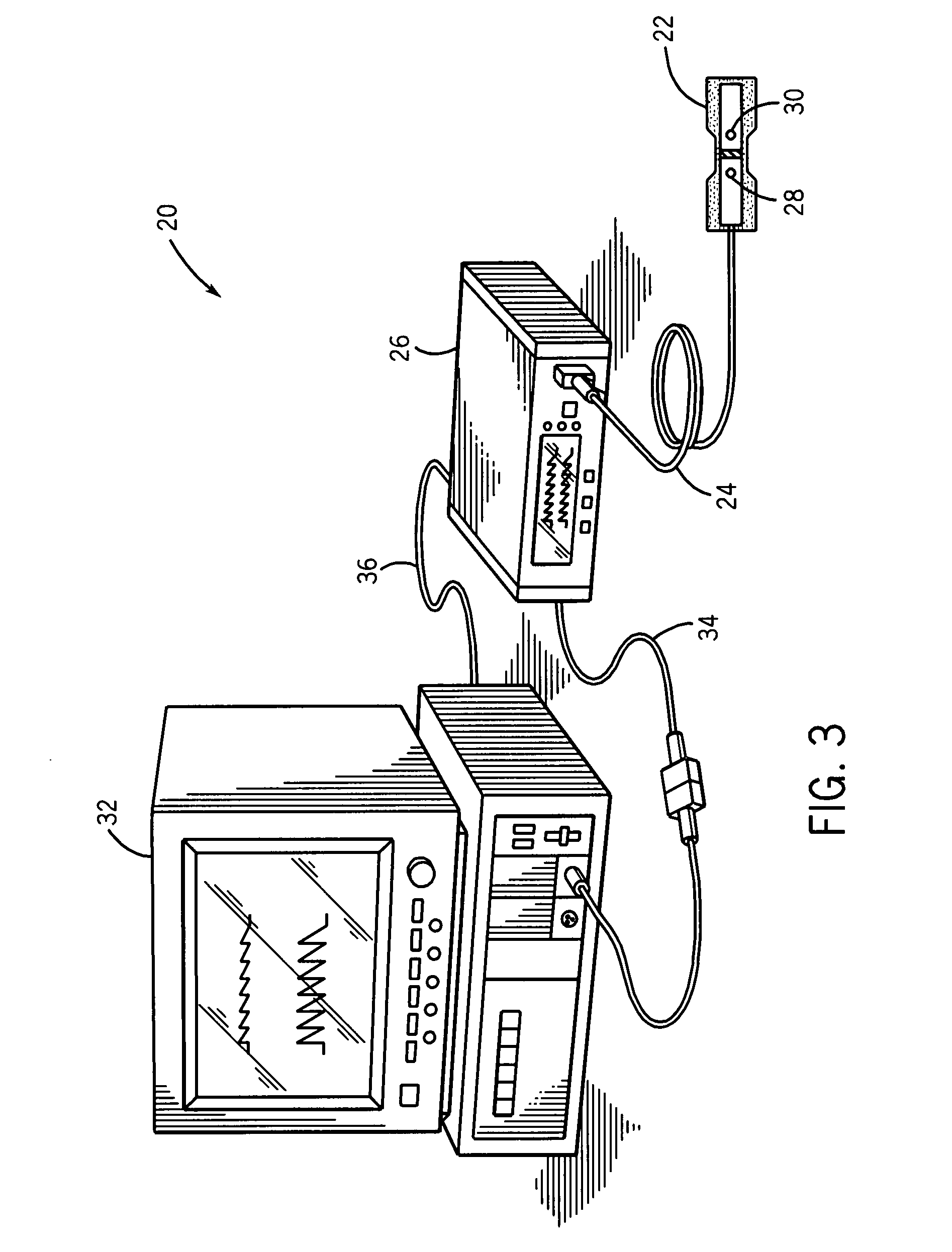
Stereo pulse oximeter
InactiveUS6898452B2Exact reproductionAccurate measurementRespiratorsMedical devicesVenous blood specimenVenous blood
An improved pulse oximeter provides for simultaneous, noninvasive oxygen status and photoplethysmograph measurements at both single and multiple sites. In particular, this multiple-site, multiple-parameter pulse oximeter, or “stereo pulse oximeter” simultaneously measures both arterial and venous oxygen saturation at any specific site and generates a corresponding plethysmograph waveform. A corresponding computation of arterial minus venous oxygen saturation is particularly advantageous for oxygen therapy management. An active pulse-inducing mechanism having a scattering-limited drive generates a consistent pulsatile venous signal utilized for the venous blood measurements. The stereo pulse oximeter also measures arterial oxygen saturation and plethysmograph shape parameters across multiple sites. A corresponding calculation of delta arterial saturation and comparison of plethysmograph shape parameters between multiple sites is particularly advantageous for the detection and management of persistent pulmonary hypertension in neonates (PPHN), a patent ductus arteriosis (PDA), and aortic coarctation.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Method and apparatus for improving the accuracy of noninvasive hematocrit measurements
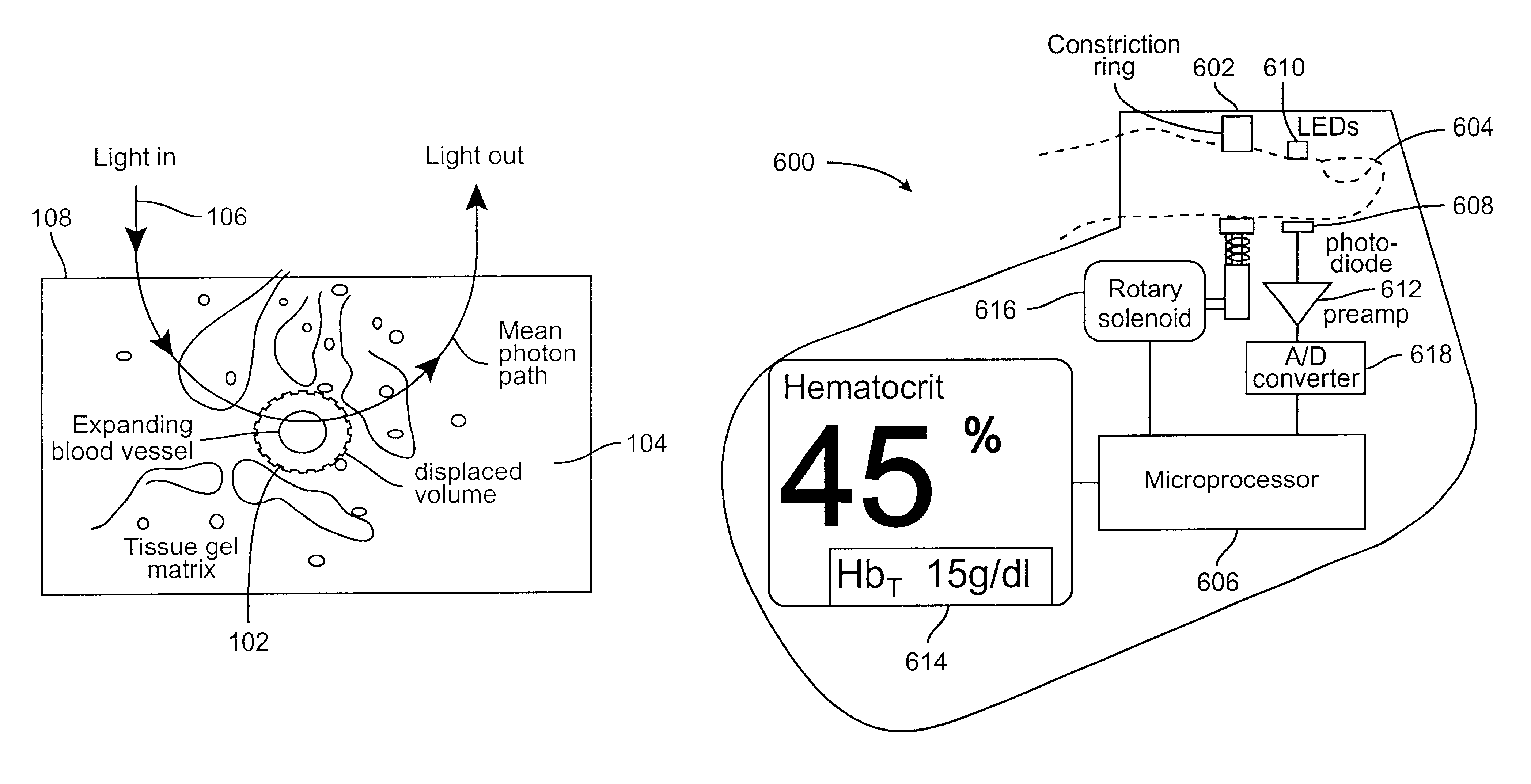
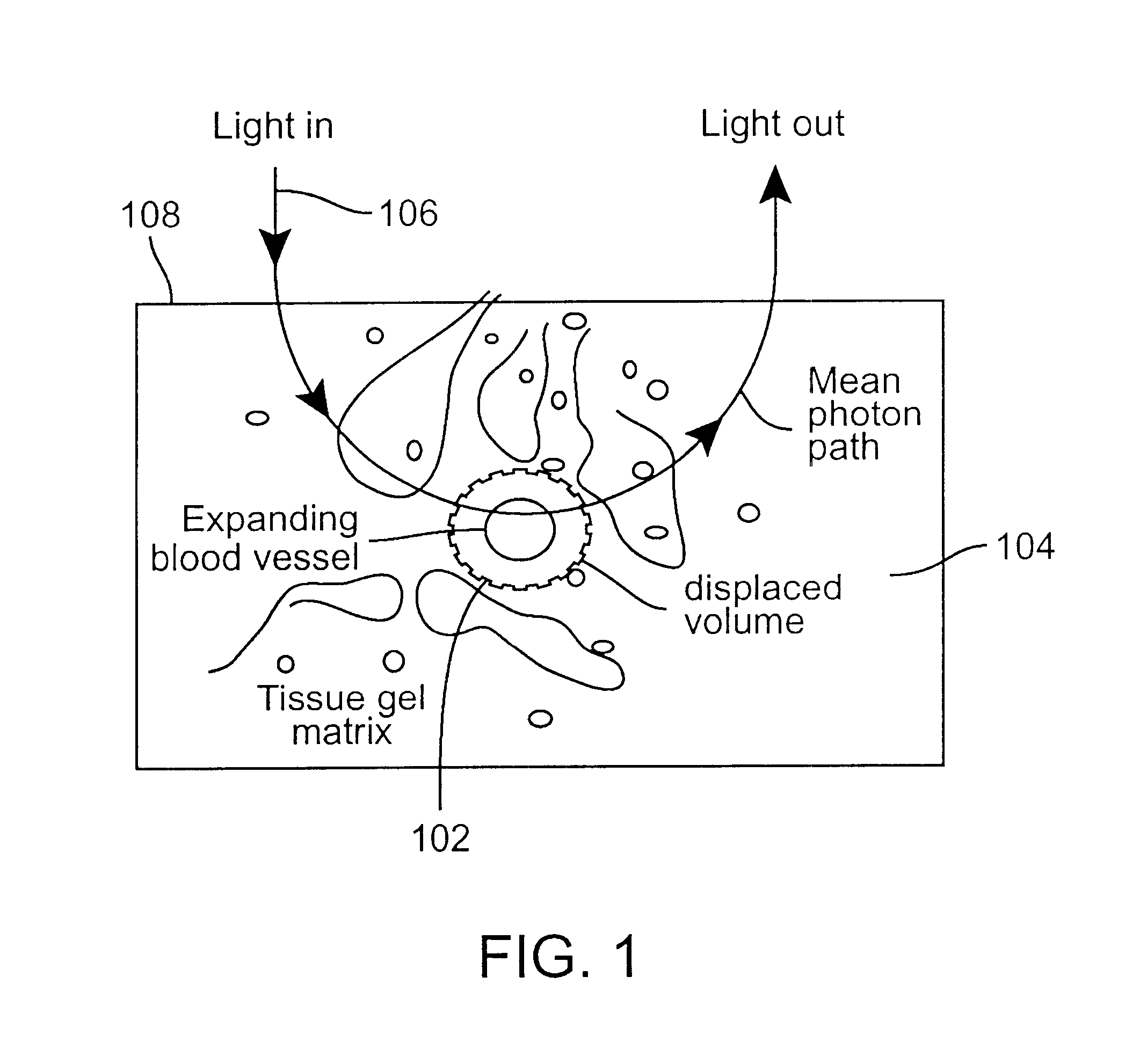
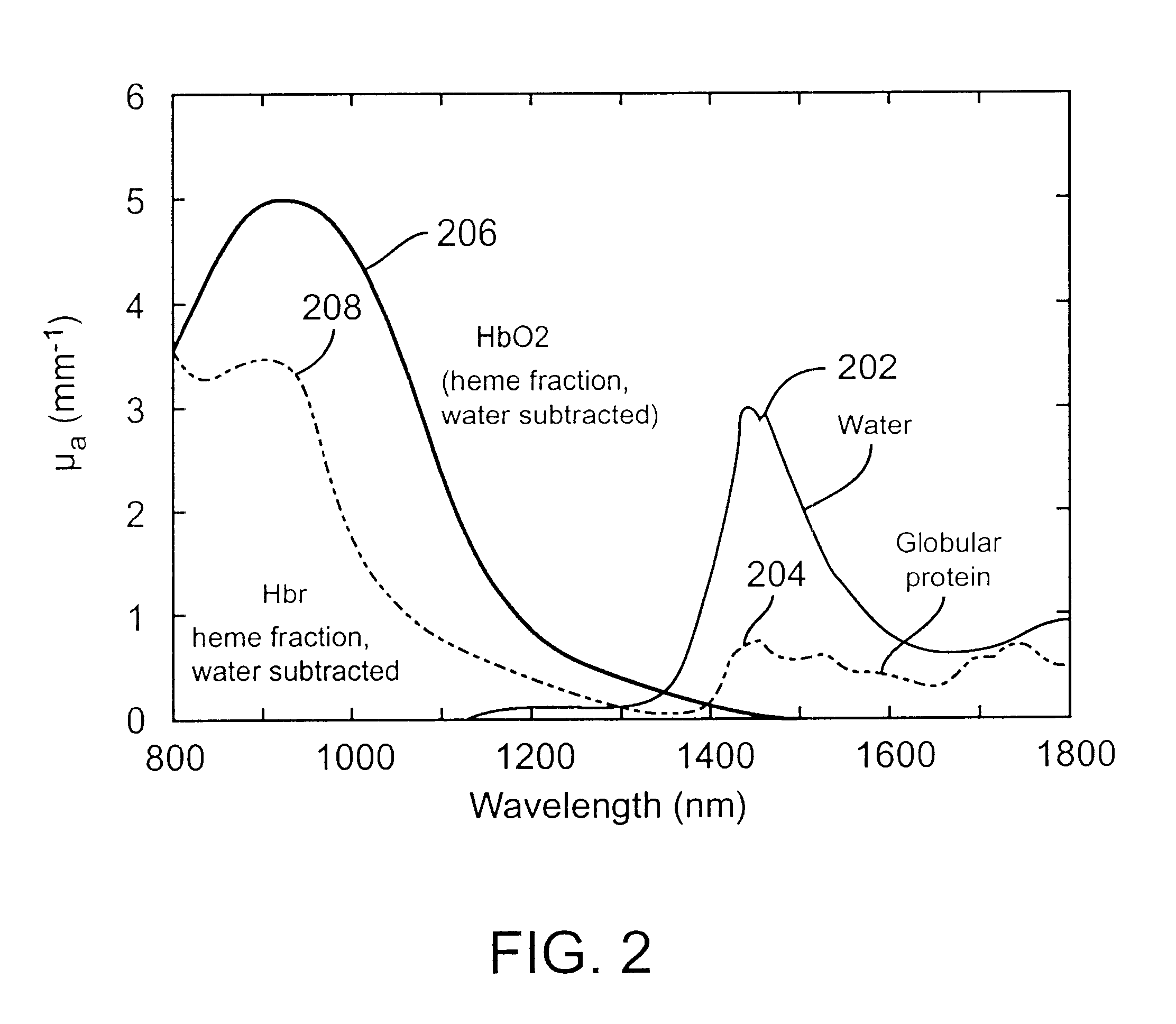
A device and a method to provide a more reliable and accurate measurement of hematocrit (Hct) by noninvasive means. The changes in the intensities of light of multiple wavelengths transmitted through or reflected light from the tissue location are recorded immediately before and after occluding the flow of venous blood from the tissue location with an occlusion device positioned near the tissue location. As the venous return stops and the incoming arterial blood expands the blood vessels, the light intensities measured within a particular band of near-infrared wavelengths decrease in proportion to the volume of hemoglobin in the tissue location; those intensities measured within a separate band of wavelengths in which water absorbs respond to the difference between the water fractions within the blood and the displaced tissue volume. A mathematical algorithm applied to the time-varying intensities yields a quantitative estimate of the absolute concentration of hemoglobin in the blood. To compensate for the effect of the unknown fraction of water in the extravascular tissue on the Hct measurement, the tissue water fraction is determined before the occlusion cycle begins by measuring the diffuse transmittance or reflectance spectra of the tissue at selected wavelengths.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Convertible blood clot filter
A vena cava blood clot filter is described that is attached to the walls of the vena cava by barbed anchors. In its filtering state, the filter is cone shaped which causes the blood to be filtered. The cone shape is formed by an appropriate restraining mechanism. When it is desired to stop filtering, the restraining mechanism is released and the filter takes a cylindrical shape. The cylindrical shaped filter will then line the vena cava wall and cease filtration of the blood.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Smart disposable plastic lab-on-a-chip for point-of-care testing
InactiveUS20050130292A1None of measures has been particularly successfulRelieve painBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCombination devicesVenous bloodLab-on-a-chip
Disclosed herein is a fully-integrated, disposable biochip for point-of-care testing of clinically relevant parameters. Specifically, in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, the biochip is designed for POCT (point-of-care-testing) of an array of metabolic parameters including partial pressure of oxygen, Glucose, and Lactate concentration from venous blood samples. The biochip is fabricated on a low-cost plastic substrate using mass manufacturing compatible fabrication processes. Furthermore, the biochip contains a fully-integrated metallic micro-needle for blood sampling. The biochip also uses smart passive microfluidics in conjunction with low-power functional on-chip pressure generators for microfluidic sequencing. The design, configuration, assembly and operation of the biochip are ideally suited for a disposable biochip specifically targeted towards POCT applications.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Mechanical tissue device and method
InactiveUS20080119886A1Rigid enoughLength of device being increasedDilatorsOcculdersVeinVenous blood
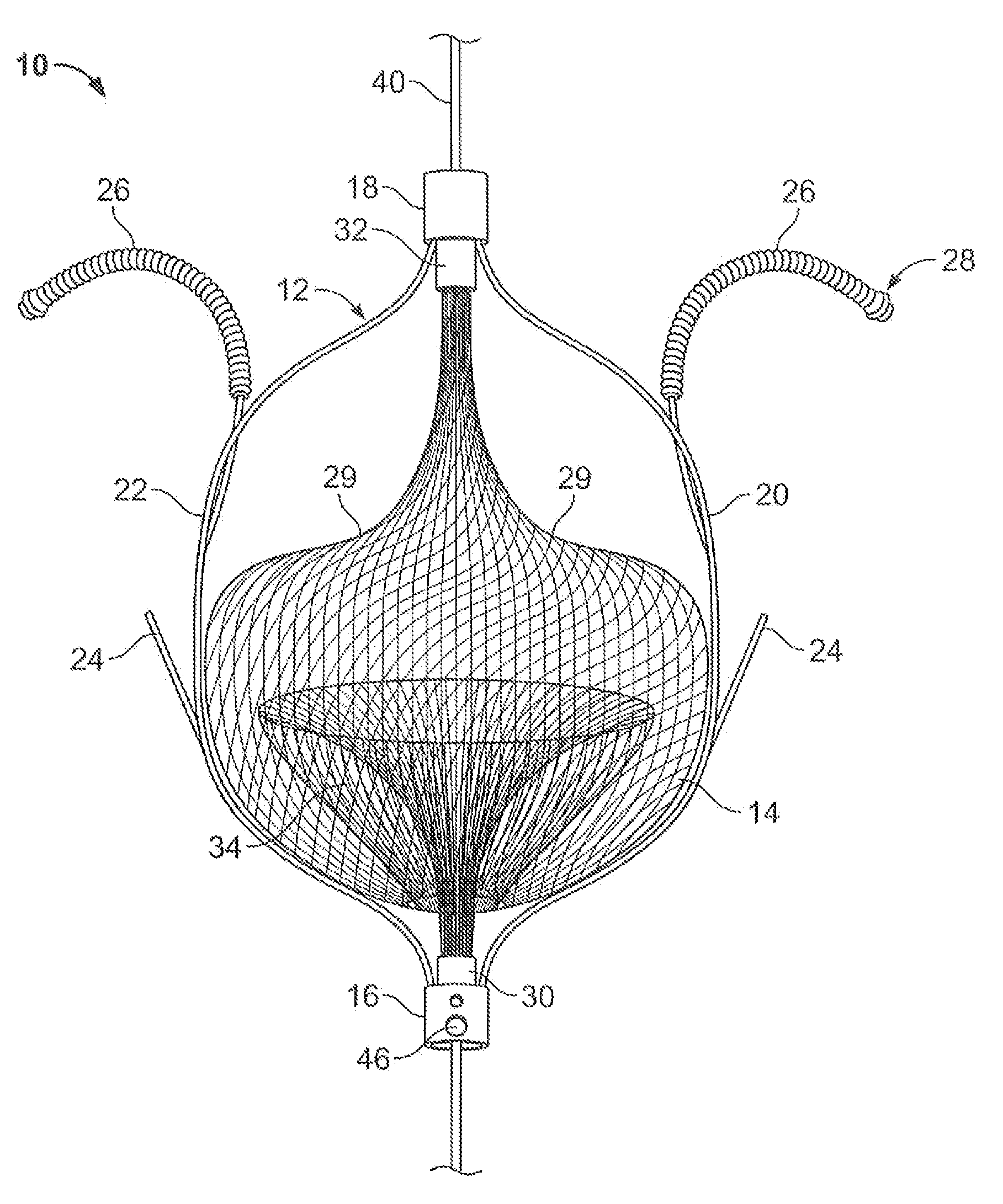
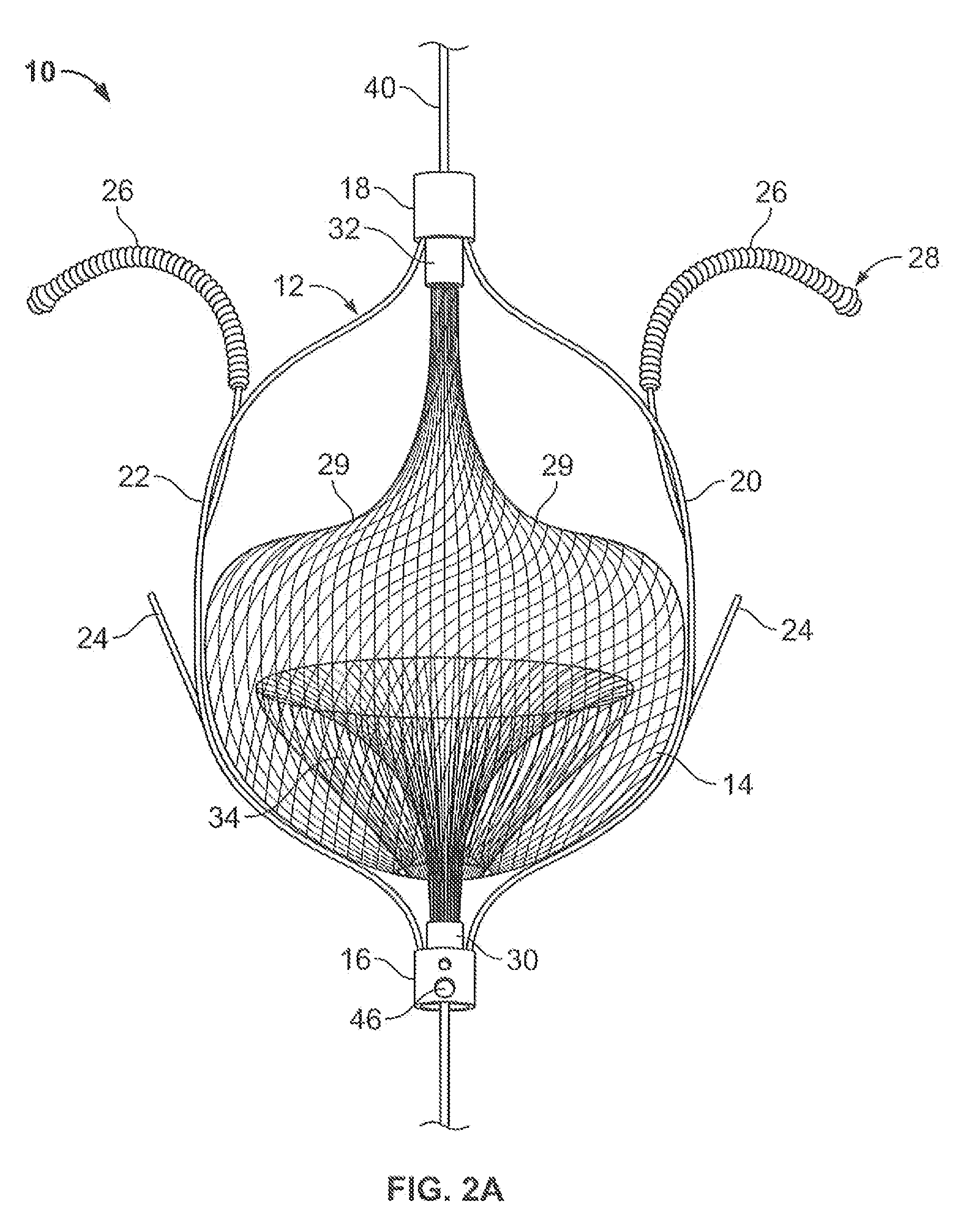
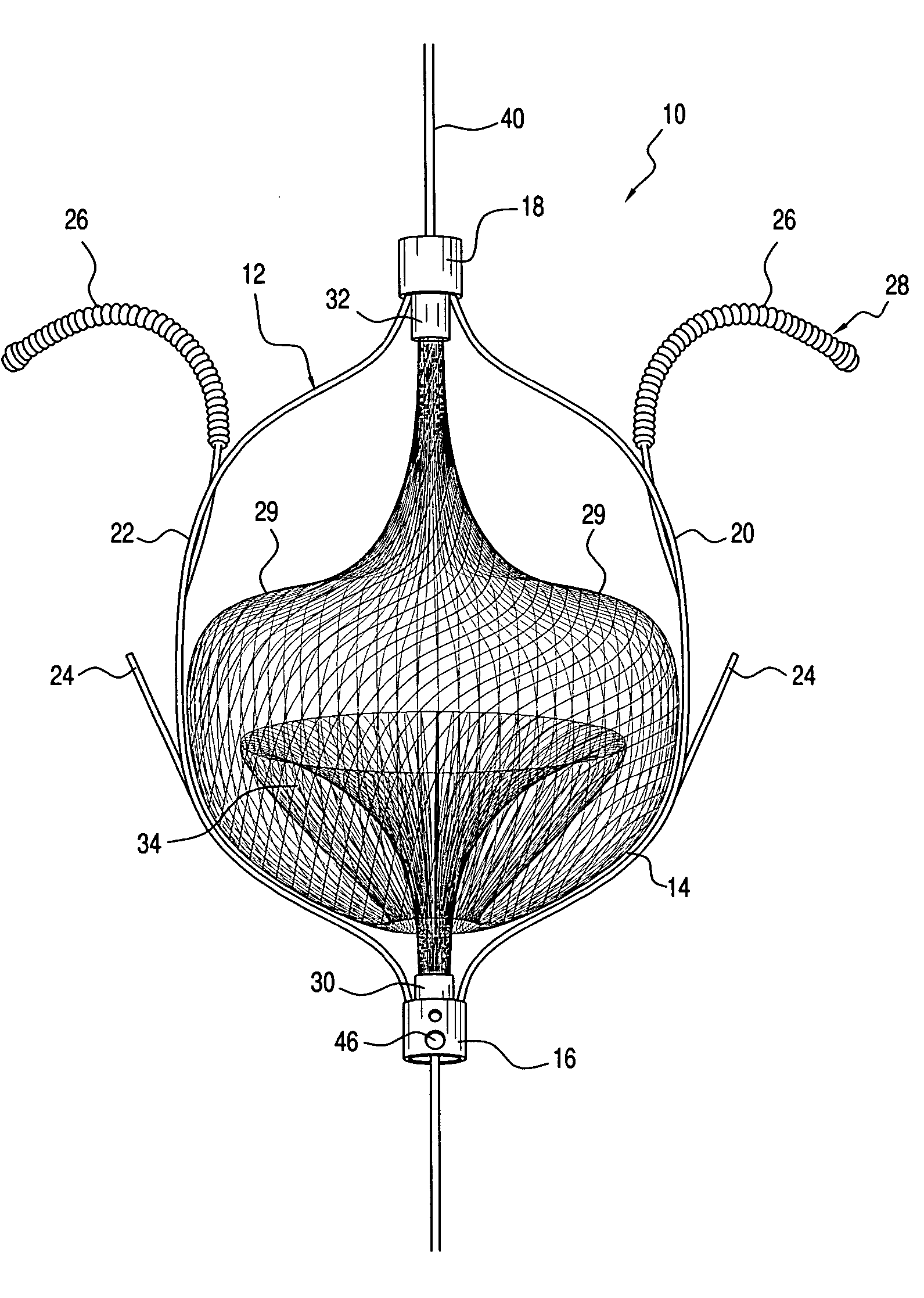
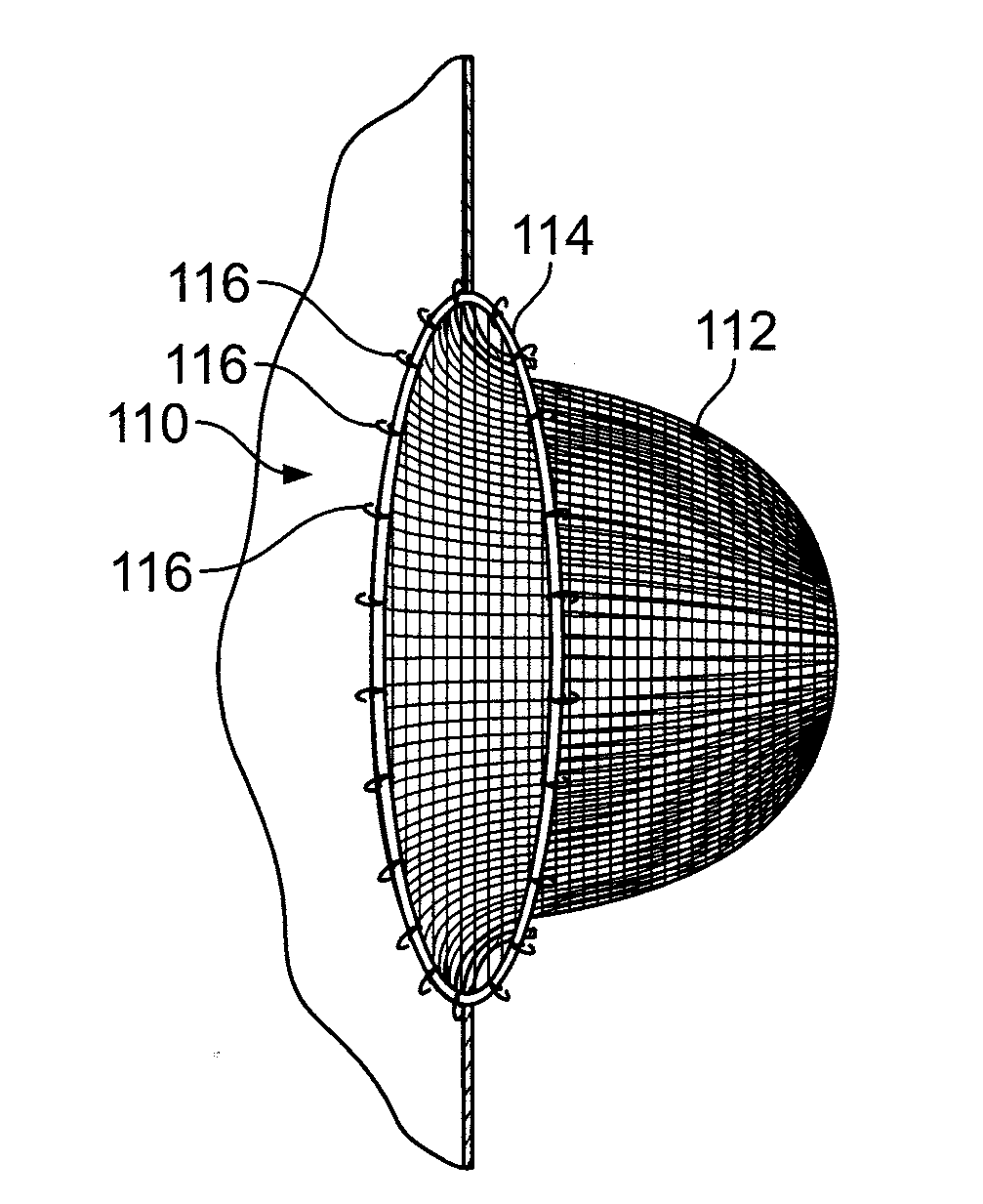
The present invention relates generally to a device and method for preventing the undesired passage of emboli from a venous blood pool to an arterial blood pool. The invention relates especially to a device and method for treating certain cardiac defects, especially patent foramen ovales and other septal defects, through the use of an embolic filtering device capable of instantaneously deterring the passage of emboli from the moment of implantation. The device consists of a frame, and a braided mesh of sufficient dimensions to prevent passage of emboli through the mesh. The device is preferably composed of shape memory allow, such as Nitinol, which conforms to the shape and dimension of the defect to be treated.
Owner:SEPTRX
Embolic filtering method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060009799A1Obstruct passageEncourage and facilitate growth of tissueAnnuloplasty ringsDilatorsVenous bloodCardiac defects
The present invention relates generally to a device and method for preventing the undesired passage of emboli from a venous blood pool to an arterial blood pool. The invention relates especially to a device and method for treating certain cardiac defects, especially patent foramen ovales and other septal defects, through the use of an embolic filtering device capable of instantaneously deterring the passage of emboli from the moment of implantation. The device consists of a frame, and a braided mesh of sufficient dimensions to prevent passage of emboli through the mesh. The device is preferably composed of shape memory allow, such as nitinol, which conforms to the shape and dimension of the defect to be treated.
Owner:SEPTRX
Composition and method for the repair and regeneration of cartilage and other tissues
InactiveUS7148209B2Add supportImprove coagulation/solidificationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthRepair tissue
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Composition and method for the repair and regeneration of cartilage and other tissues
InactiveUS20060029578A1Add supportImprove coagulation/solidificationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthRepair tissue
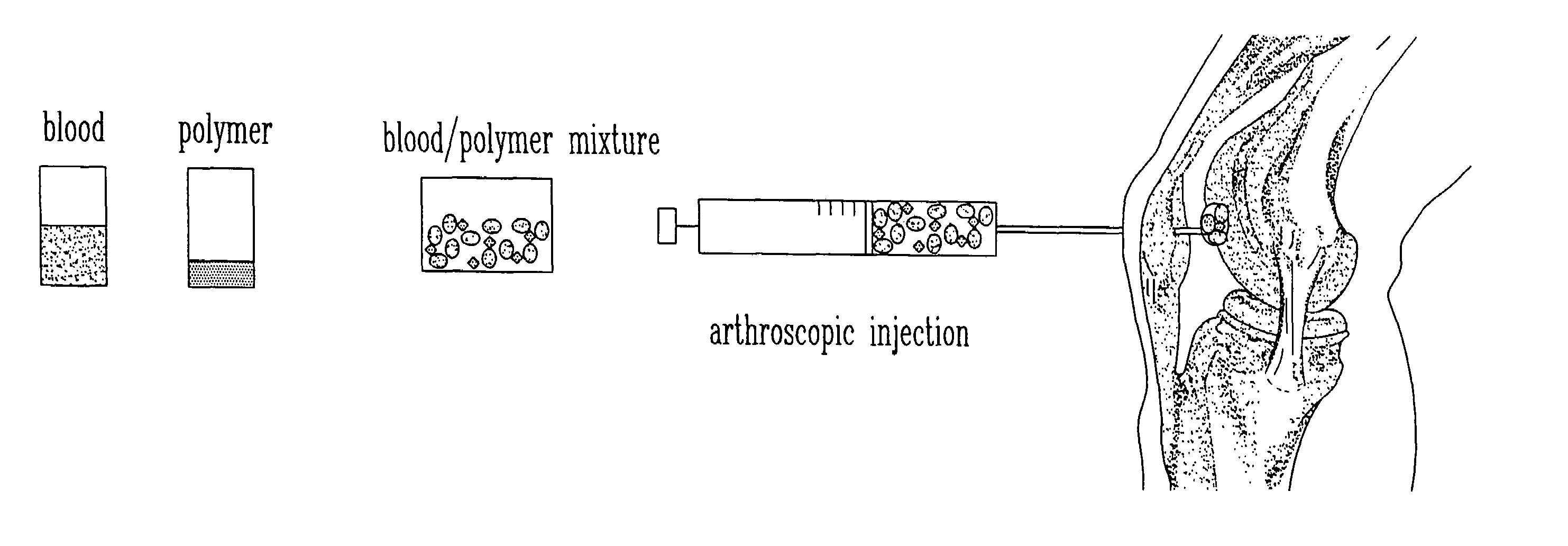
The present invention relates to a new method for repairing human or animal tissues such as cartilage, meniscus, ligament, tendon, bone, skin, cornea, periodontal tissues, abscesses, resected tumors, and ulcers. The method comprises the step of introducing into the tissue a temperature-dependent polymer gel composition such that the composition adhere to the tissue and promote support for cell proliferation for repairing the tissue. Other than a polymer, the composition preferably comprises a blood component such as whole blood, processed blood, venous blood, arterial blood, blood from bone, blood from bone-marrow, bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, placenta blood, erythrocytes, leukocytes, monocytes, platelets, fibrinogen, thrombin and platelet rich plasma. The present invention also relates to a new composition to be used with the method of the present invention.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Blood perfusion system
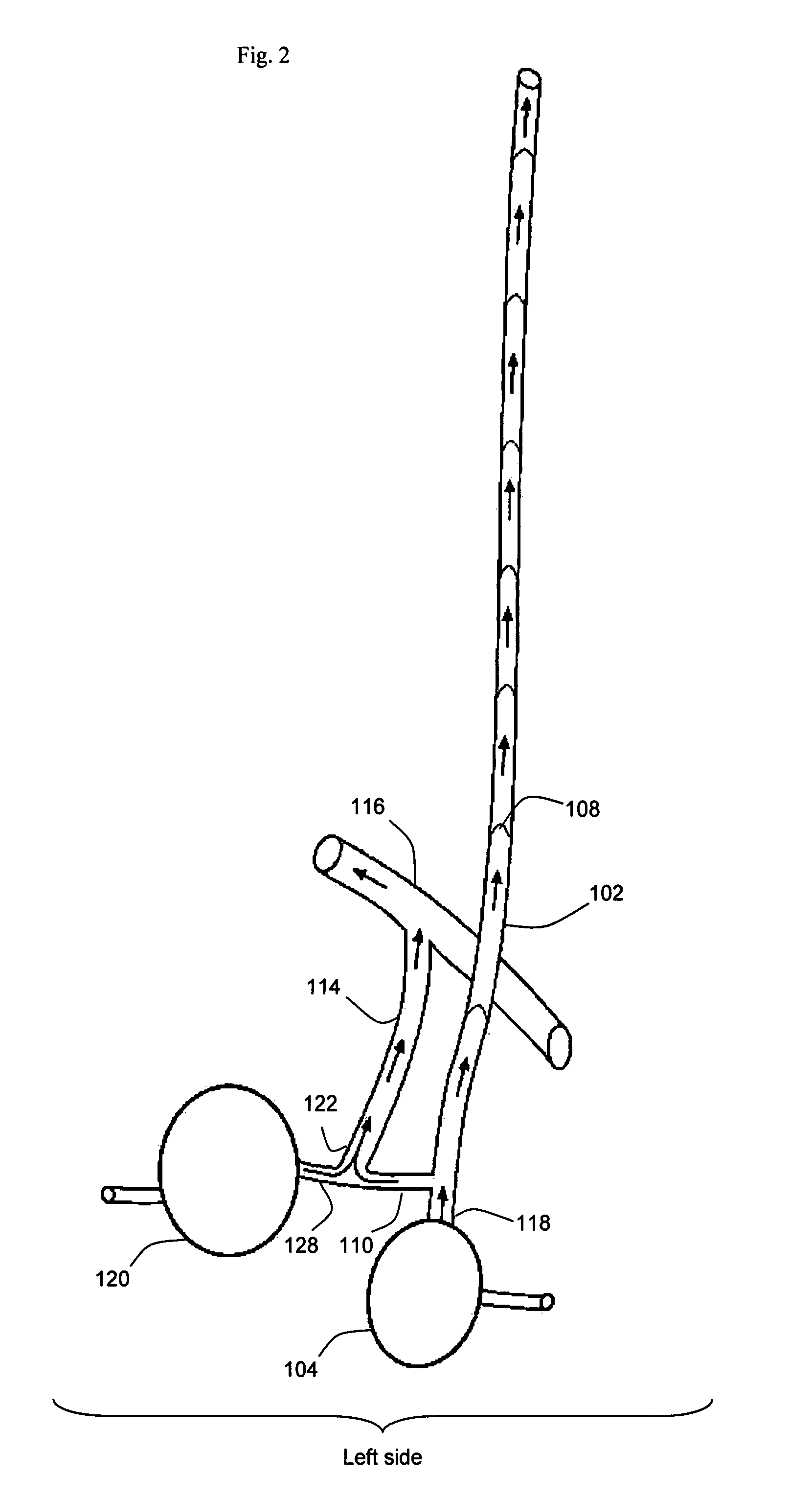
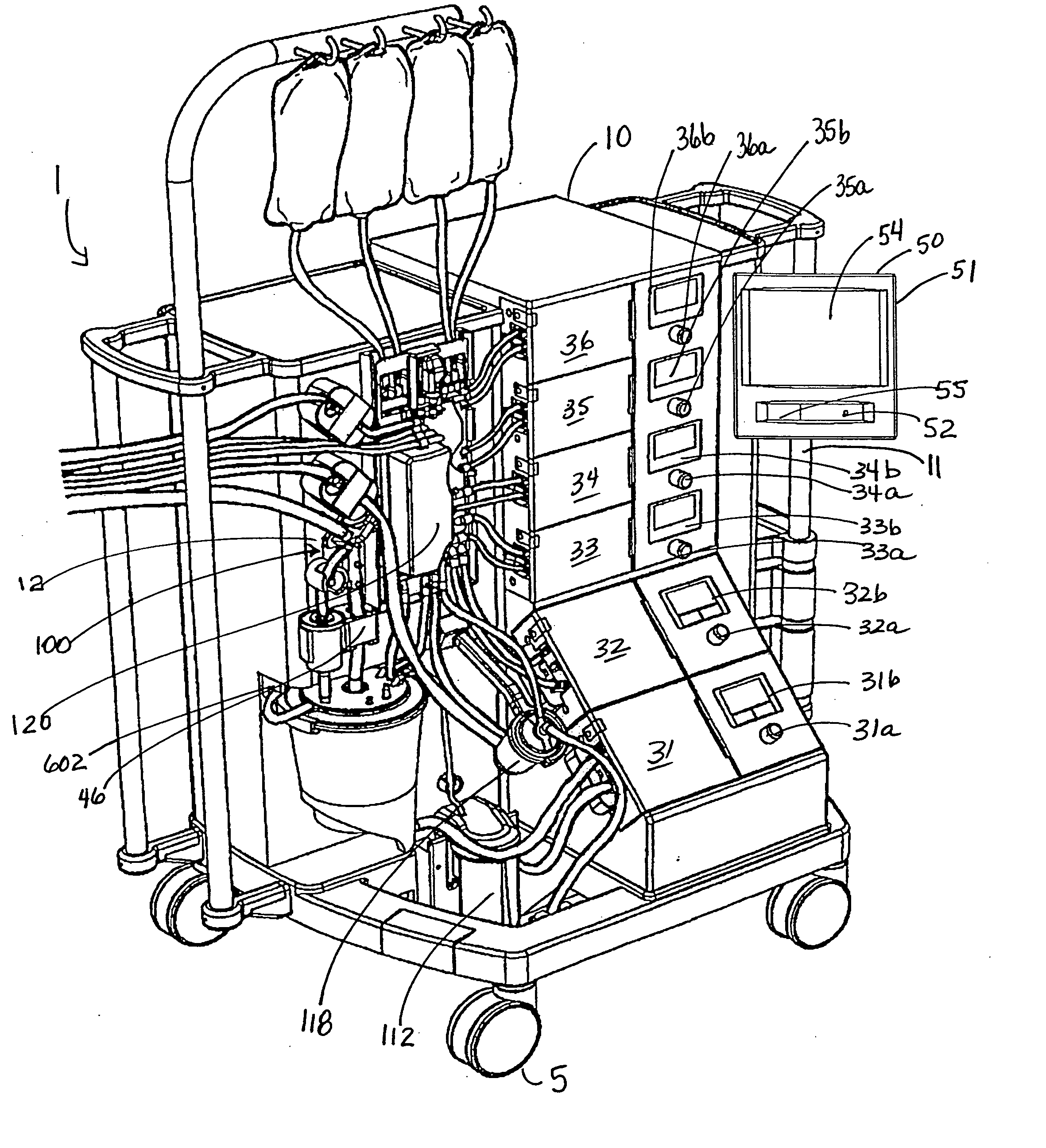
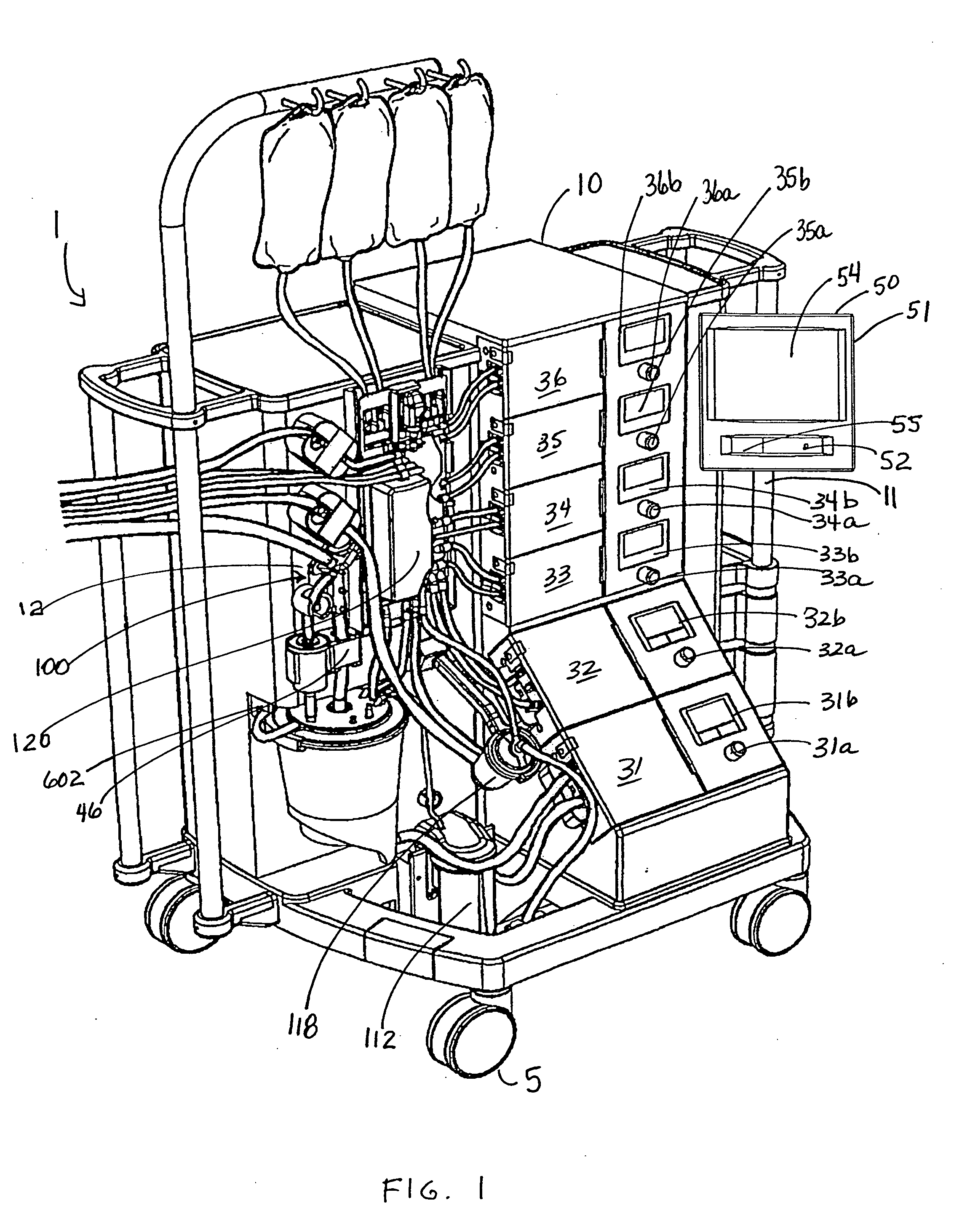
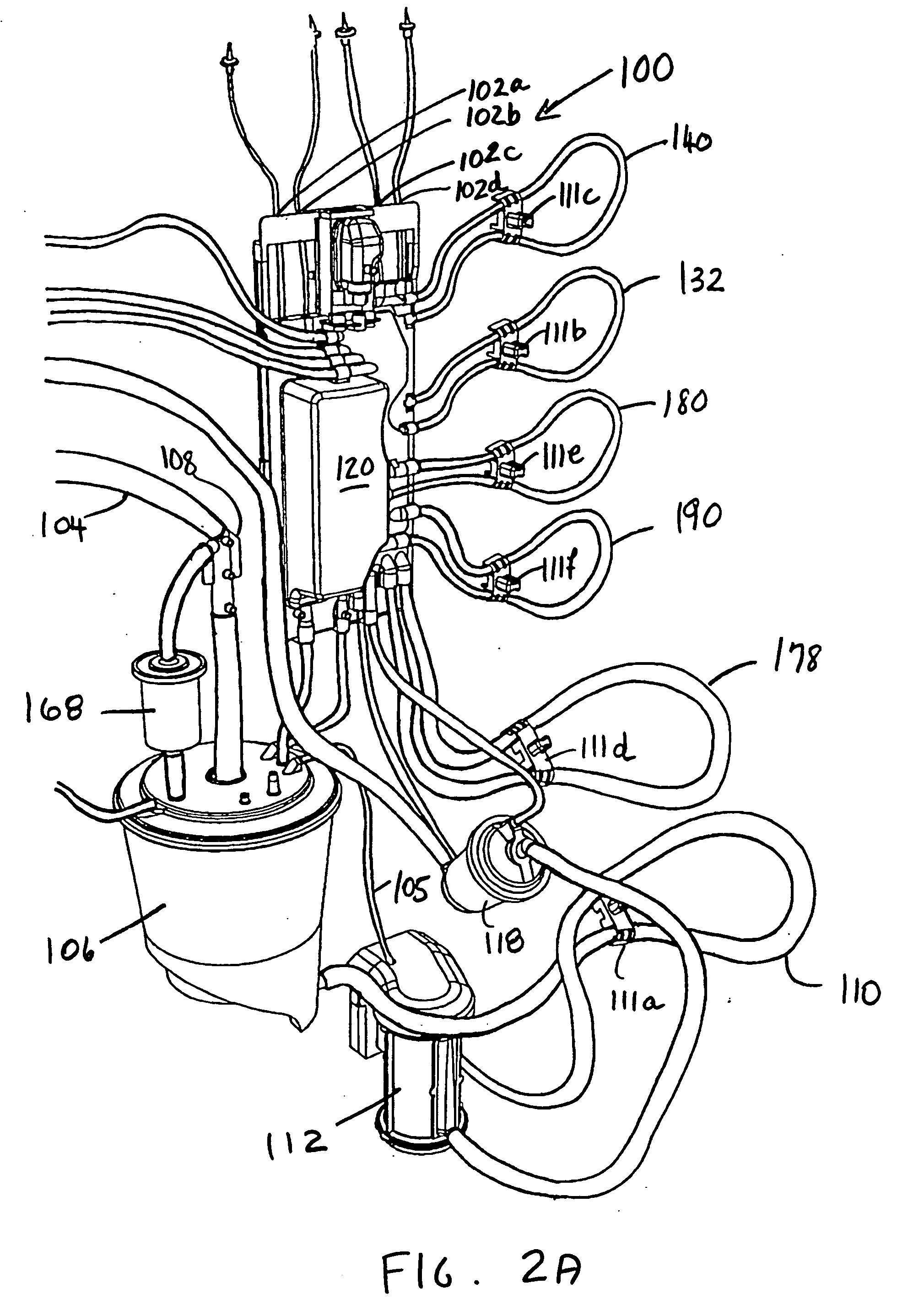
ActiveUS20060167400A1Simplified interconnection/disconnectionSimple setupOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesVenous bloodDisplay device
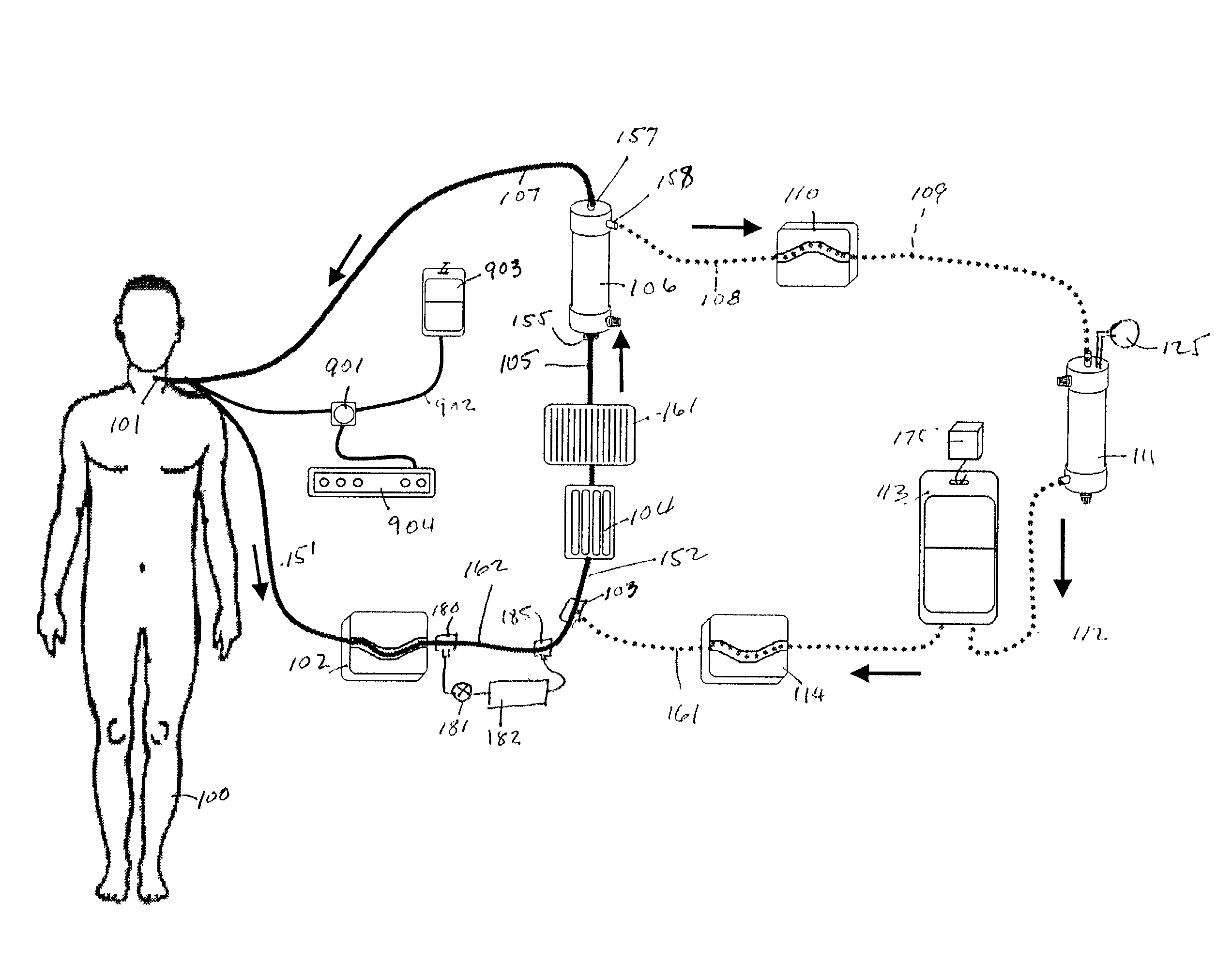
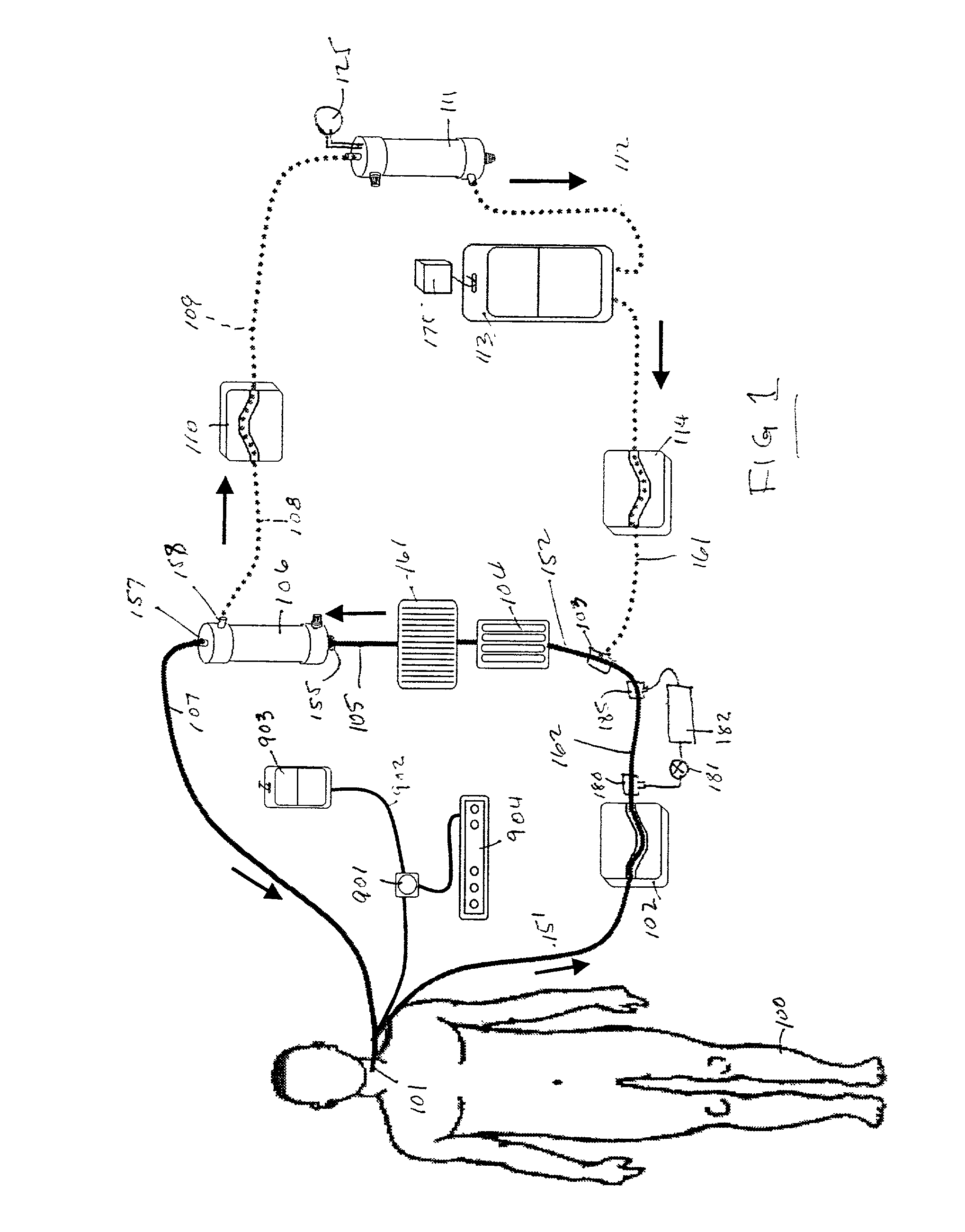
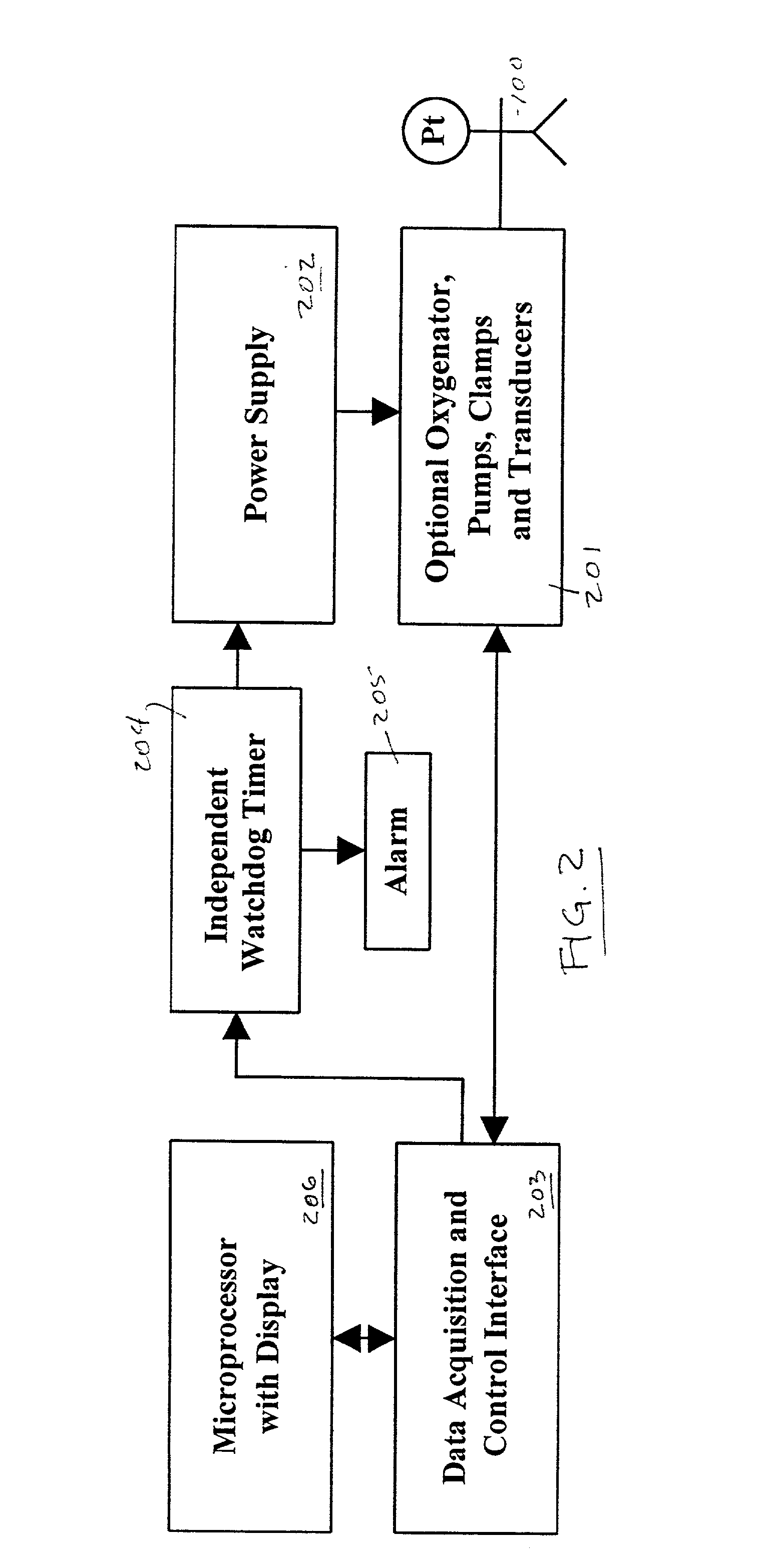
An extracorporeal blood perfusion system includes a disposable assembly and a control unit having a control interface region. The interface region includes pump assemblies for selective pumping of venous blood, arterial blood, cardioplegia solution, suctioned blood and blood removed from the left ventricle. Valve assemblies control the flow of fluids through the assembly and to / from the patient and sensors monitor various fluid parameters including temperature and pressure within the various fluid circuits. The user interface is a functional screen interface for effecting the operation of the control unit and valve assemblies. The screen interface may be a touch screen having objects that corresponds to the component interface region. The display may be selectively controlled to provide graphic depictions of disposable assembly components with corresponding narrative instructions.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
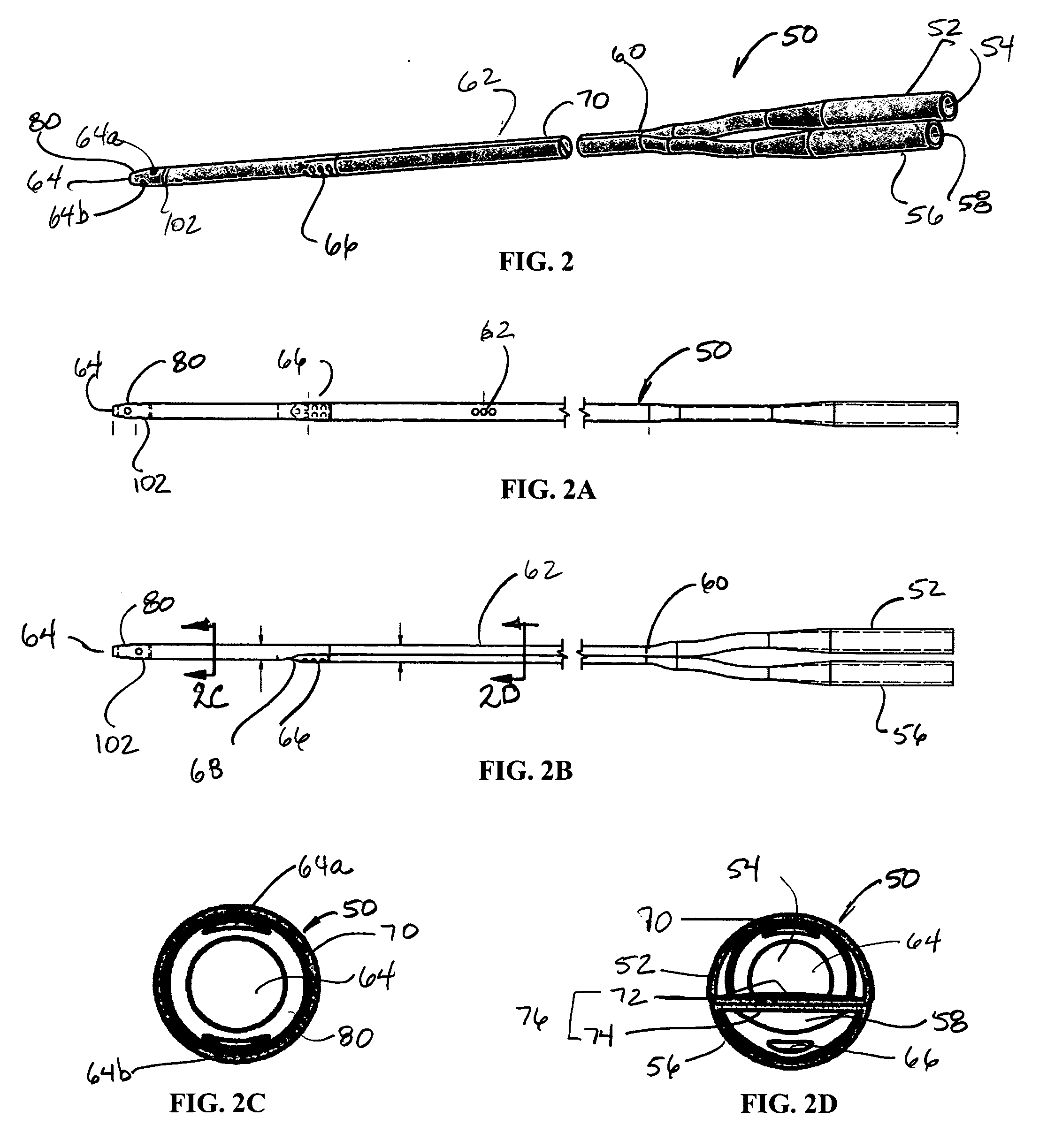
Venous cannula and cardiopulmonary bypass system
InactiveUS20050222532A1Improve efficiencyEasy to useStentsBalloon catheterExtracorporeal circulationVenous blood
This invention relates to a venous cannula for use in conjunction with cardiovascular examinations, treatments and surgery. The venous cannula is configured for two-stage drainage of oxygen-depleted venous blood from a central venous location via a peripheral venous insertion site, such as a femoral vein. The venous cannula is optimized for use in a cardiopulmonary bypass system that includes a multichannel arterial perfusion catheter. The cardiopulmonary bypass system is advantageous for use in performing standard open chest or least invasive cardiac surgical procedures.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
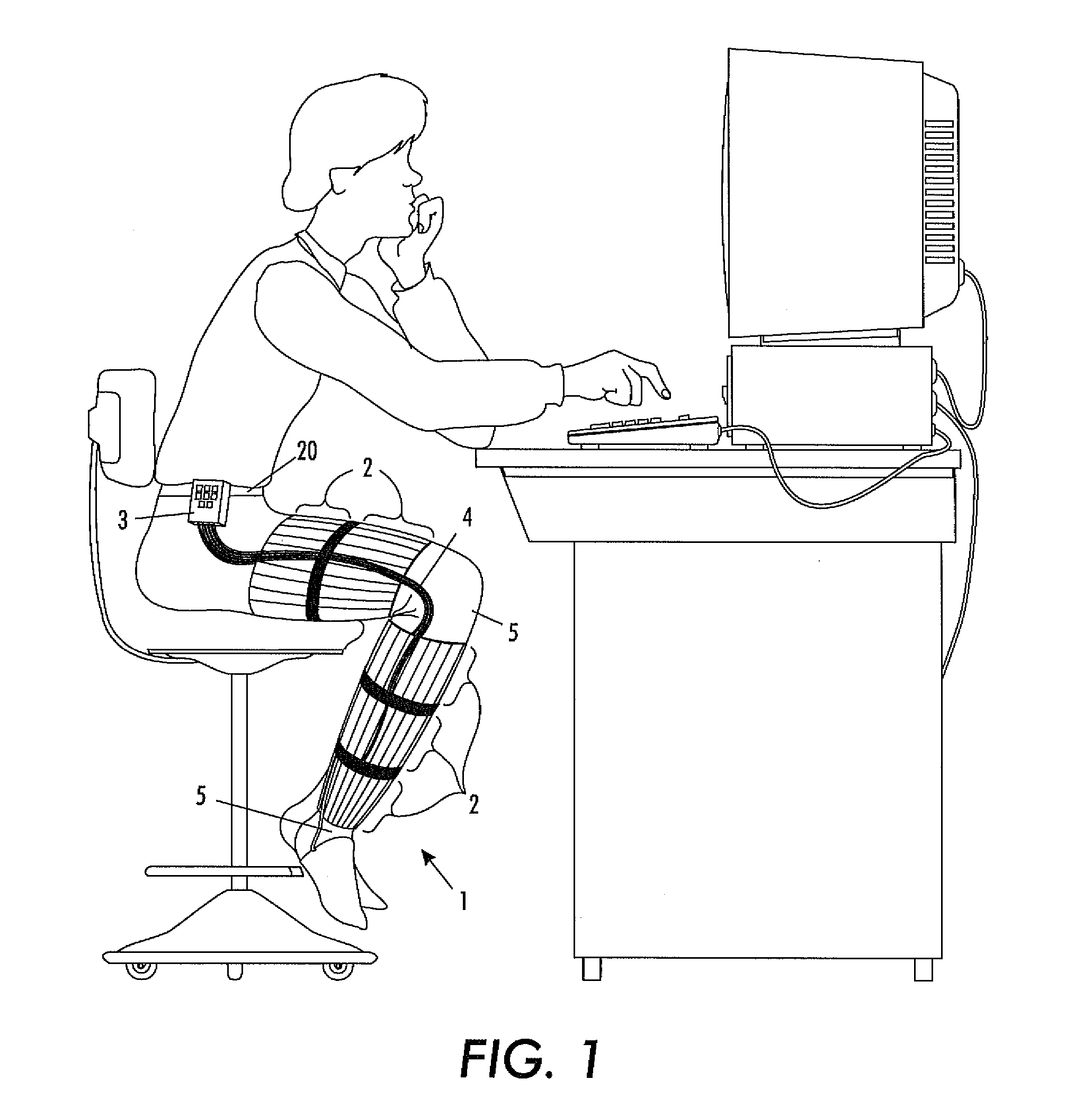
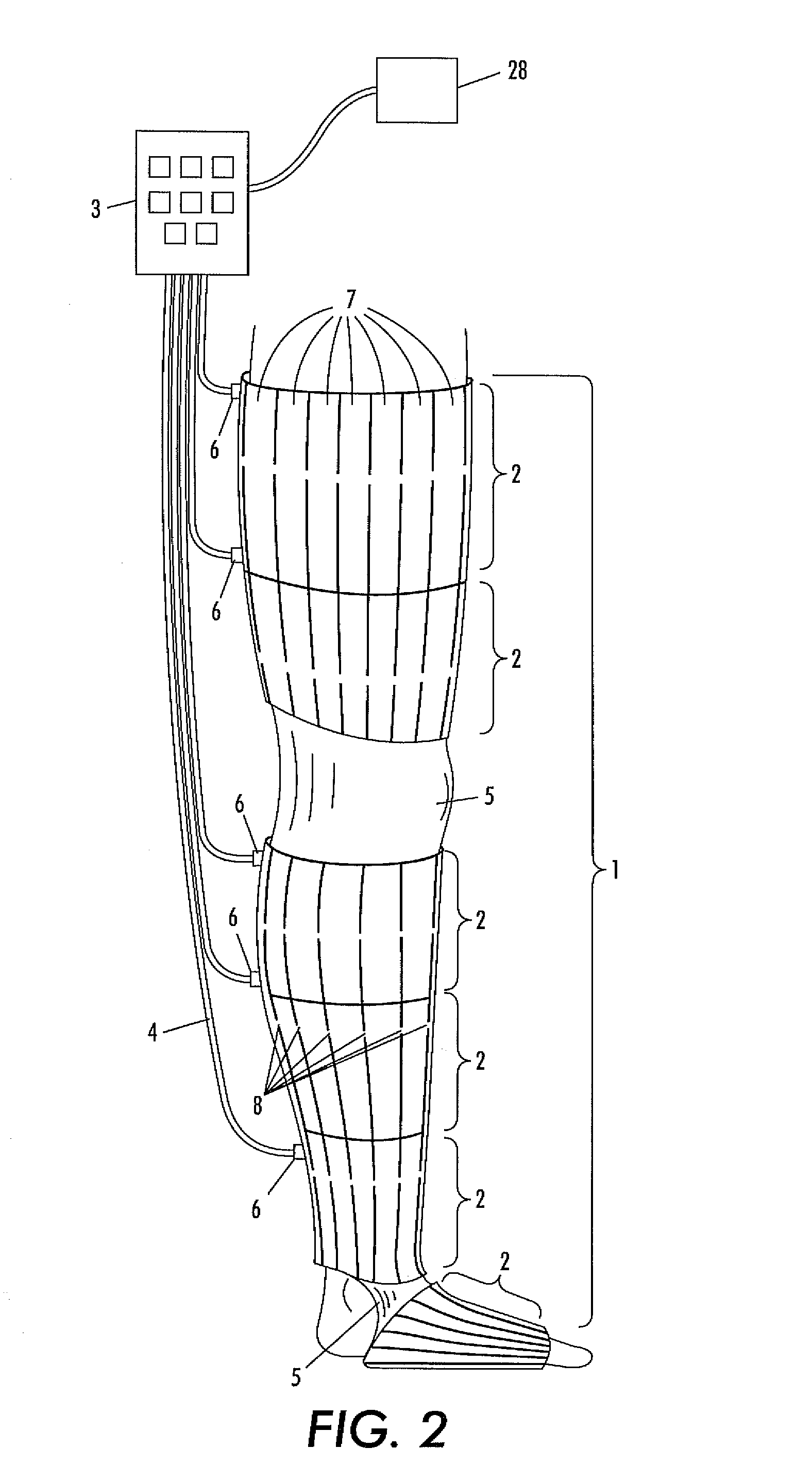
Method and apparatus for assisting vascular flow through external compression synchronized with venous phasic flow
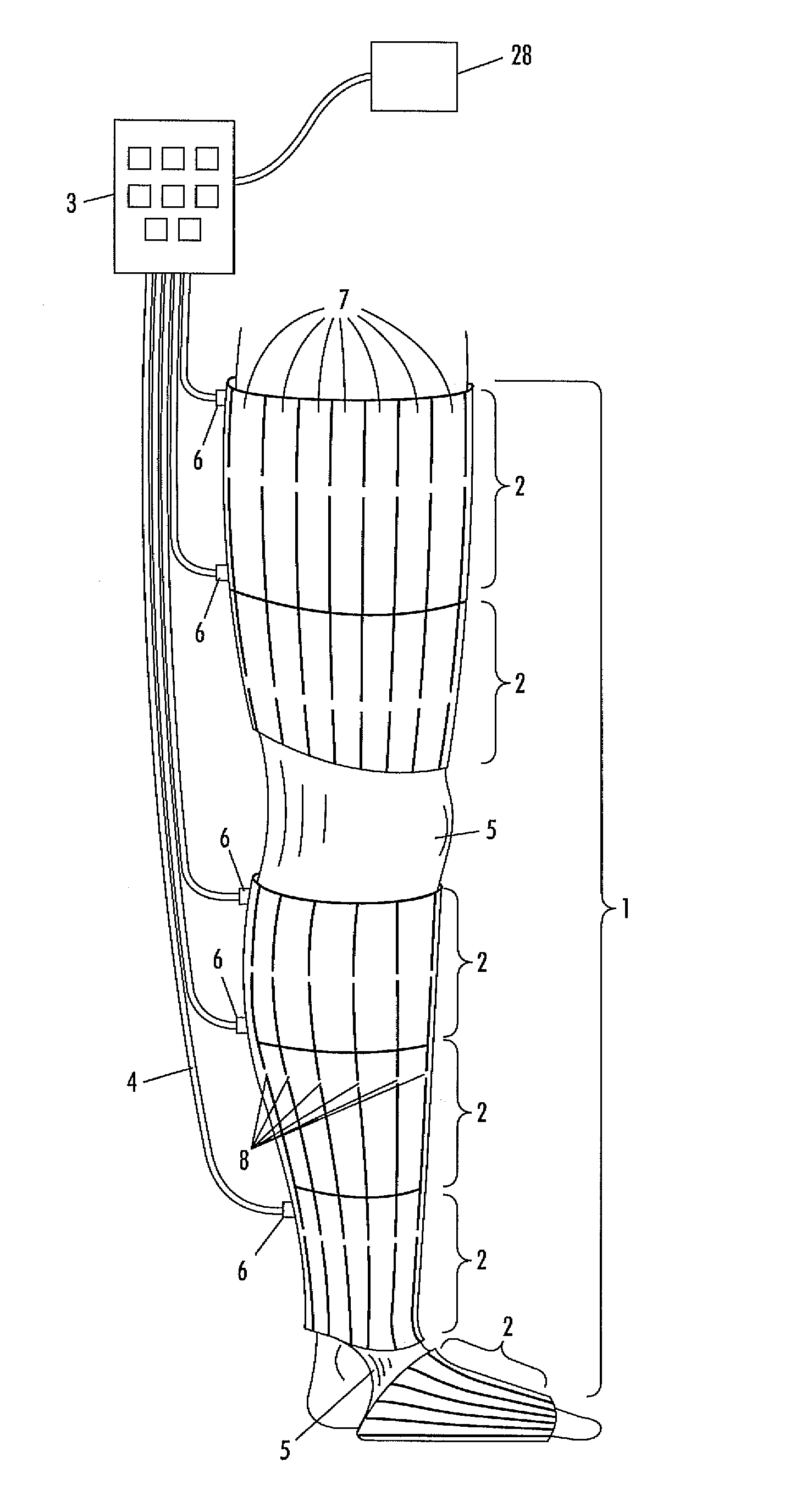
An automatic portable ambulant miniaturized system for applying pneumatic pressure to a body limb including a portable ambulant hand-held fluid source unit, a conduit for delivering fluid generated by the unit, and a pressure sleeve coupled to the conduit and adapted to envelop a body limb. The pressure sleeve contains individually inflatable cells, each cell being subdivided into longitudinally extending confluent intra-cell compartments along the axis of the body limb. The intra-cell compartments are inflated and deflated essentially simultaneously by the portable fluid source unit. To increase the peak venous velocity generated by any kind of external compressive force on a limb with any kind of tempo-spatial regime, the venous phasic flow is monitored to determine so that the venous flow generated by the external compressive force can be synchronized with the in-phasic natural venous flow.
Owner:ZIMMER SURGICAL
Single expandable double lumen cannula assembly for veno-venous ECMO
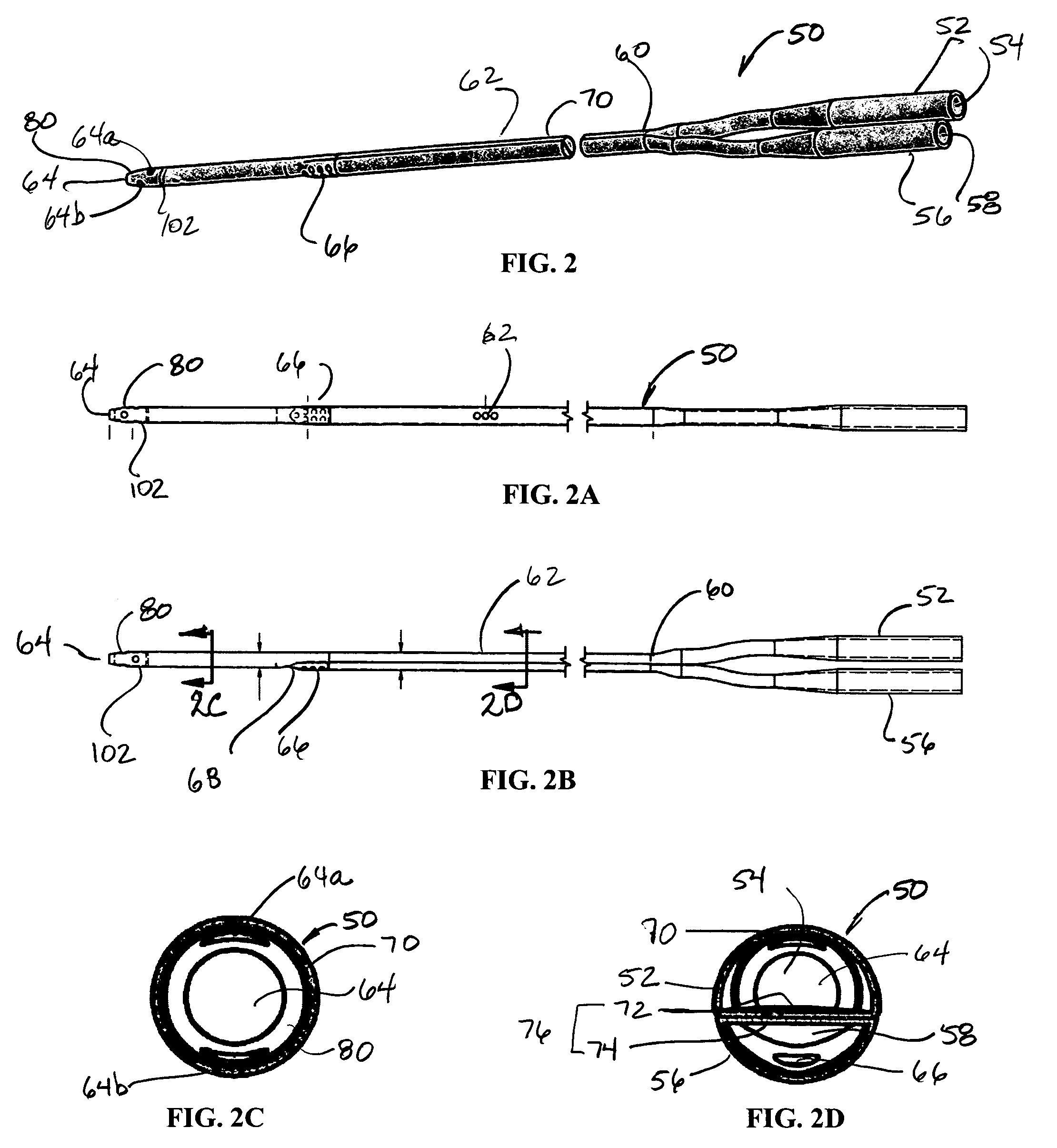
ActiveUS20050085761A1Insufficient gas exchangeDecreased surgical and blood traumaMulti-lumen catheterOther blood circulation devicesVeinVenous blood
The present invention provides an apparatus, system, and method of use of a simple, less invasive, self-expandable percutaneous double lumen cannula assembly for VV ECMO that overcomes the limitations and obstacles of the techniques described above. The present invention achieves near theoretical total venous blood drainage, total extracorporeal gas exchange, and prevents recirculation and multiple cannulation, thereby simplifying VV ECMO, decreasing surgical and blood trauma, and expanding its application.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
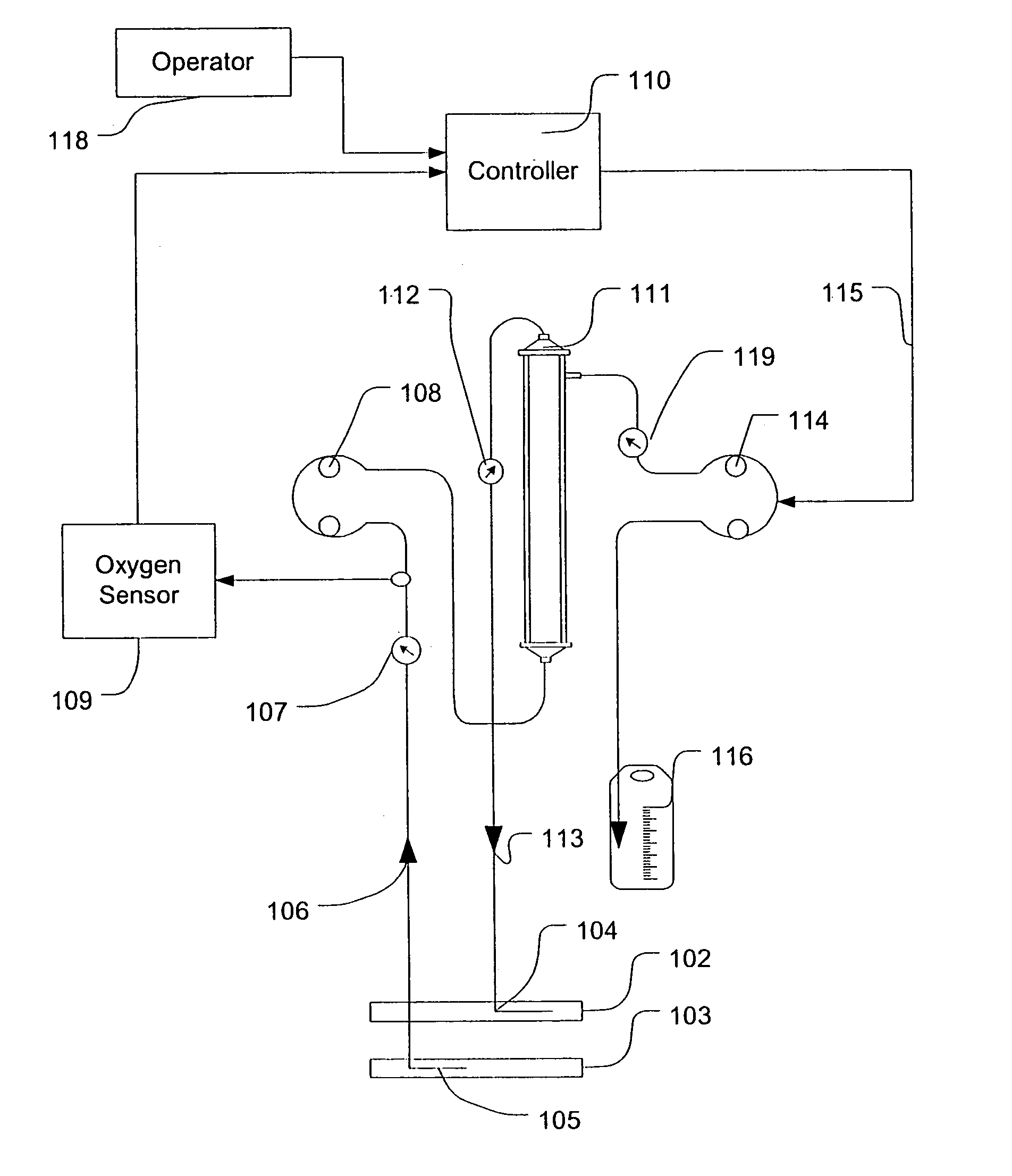
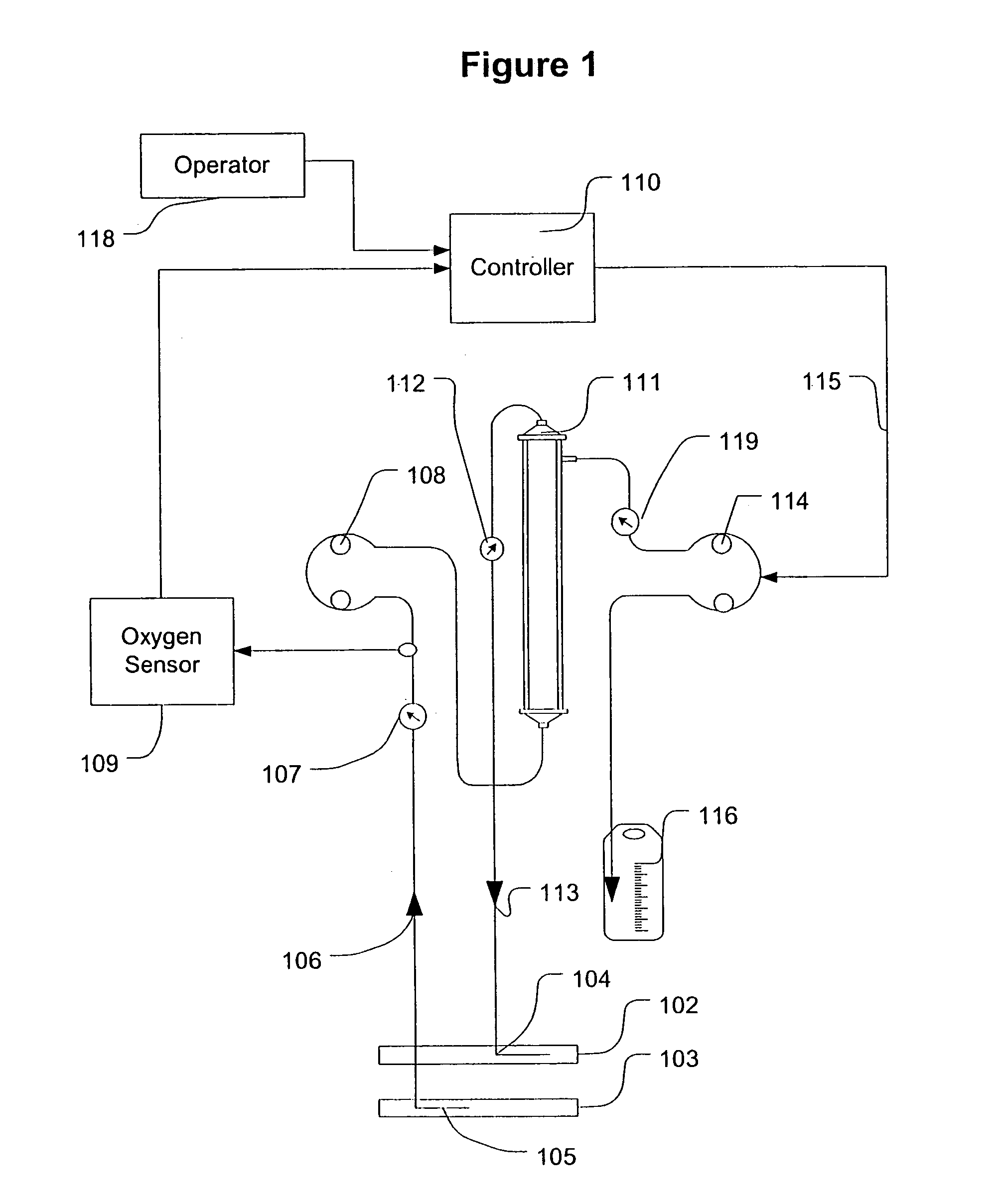
Feedback control of ultrafiltration to prevent hypotension
InactiveUS7175809B2Easy to adaptAvoid hypotensionSemi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesBlood levelVein
A method and system for the extracorporeal treatment of blood to remove fluid from the fluid overloaded patient is disclosed that non-invasively measures an oxygen level in the venous blood. The oxygen blood level is used to detect when hypotension is about to occur in a patient. The oxygen level measurements are used as feedback signals. These feedback signals are applied to automatically control the rate of fluid extraction to achieve the desired clinical outcome and avoid precipitating a hypotensive crisis in the patient.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Method and apparatus for treating acute myocardial infarction with hypothermic perfusion
InactiveUS20050004503A1Optimal myocardial salvageRapid coolingStentsBalloon catheterVenous bloodCatheter device
An apparatus and method are described for quickly inducing therapeutic hypothermia of the heart by perfusing the myocardium with hypothermic fluid in alternatingly antegrade and retrograde directions. The apparatus and method provide rapid cooling of the affected myocardium to achieve optimal myocardial salvage in a patient experiencing acute myocardial infarction. The therapeutic hypothermia system includes one or more coronary artery perfusion catheters, a coronary sinus perfusion catheter and a fluid source for delivering a hypothermically-cooled physiologically-acceptable fluid, such as saline solution, oxygenated venous blood, autologously-oxygenated arterial blood and / or an oxygenated blood substitute. The system may also include one or more guidewires, subselective catheters and / or interventional catheters introduced through a lumen in one or more of the perfusion catheters.
Owner:CARDEON
Method and device for monitoring the supply of substitution fluid during an extracorporeal blood treatment
ActiveUS20050065459A1Increase amplitudePossible to monitorOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationBlood treatmentsMedicine
The invention relates to a method for monitoring the supply of substitution liquid during an extracorporeal blood treatment and to an extracorporeal blood treatment unit equipped with a device for monitoring the supply of substitution liquid. The monitoring of the supply of substitution liquid is based on the measurement of pressure waves, which are generated by the substitution liquid pump, in the extracorporeal blood circulation system. A disturbance in the supply of substitution liquid is inferred when the amplitude of the pressure waves exceeds a predetermined limit value. The amplitude of the pressure waves is preferably monitored in the venous blood line.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
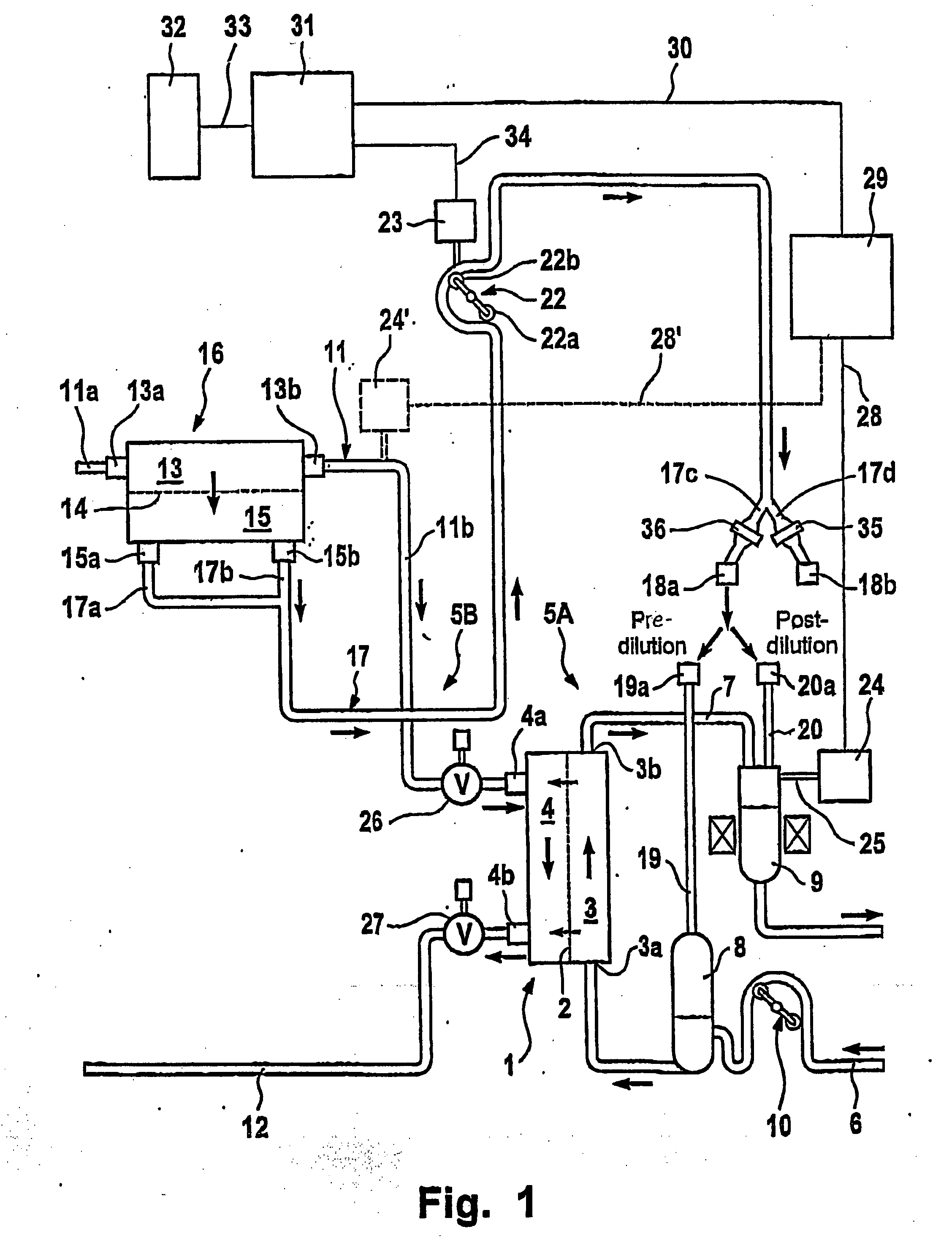
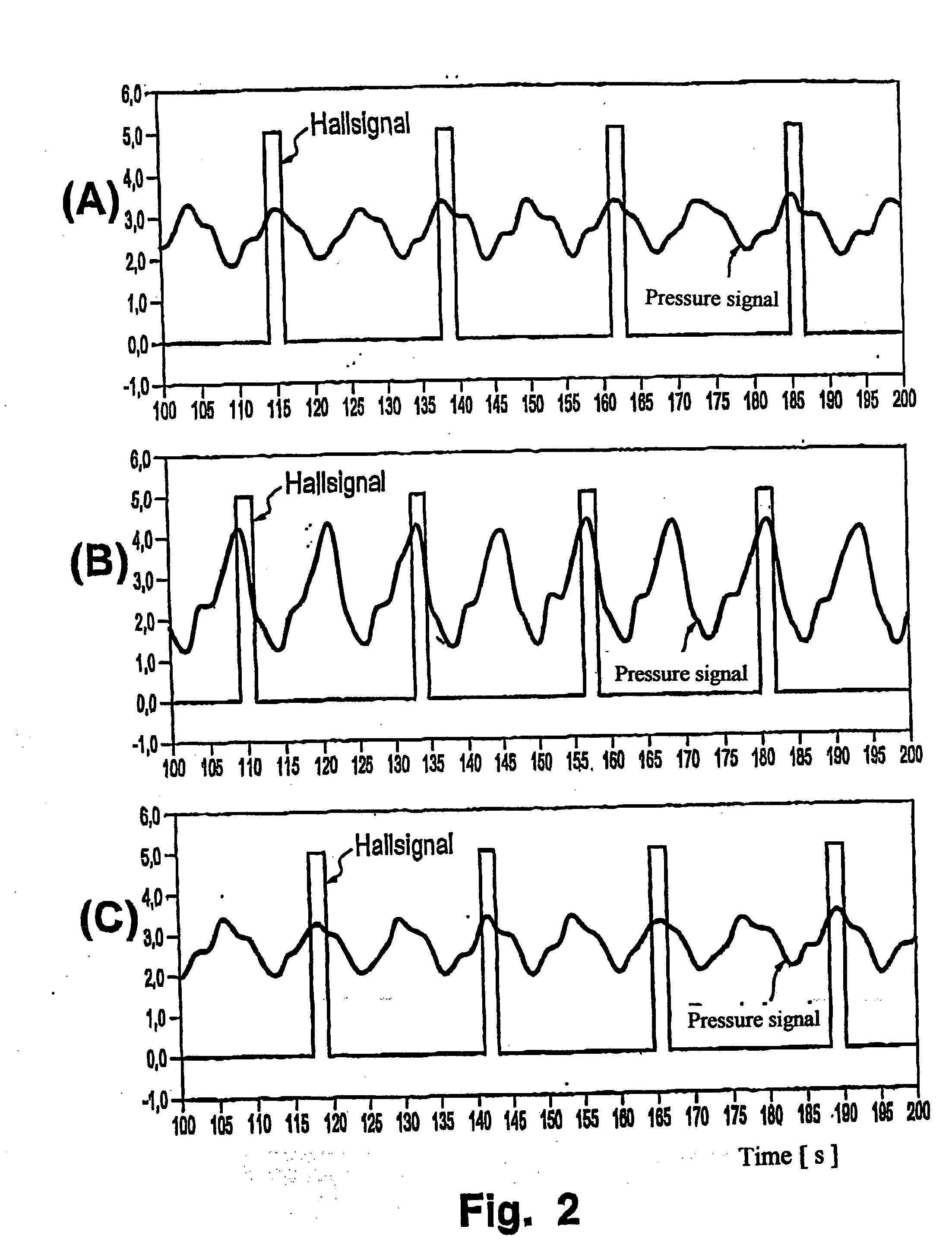
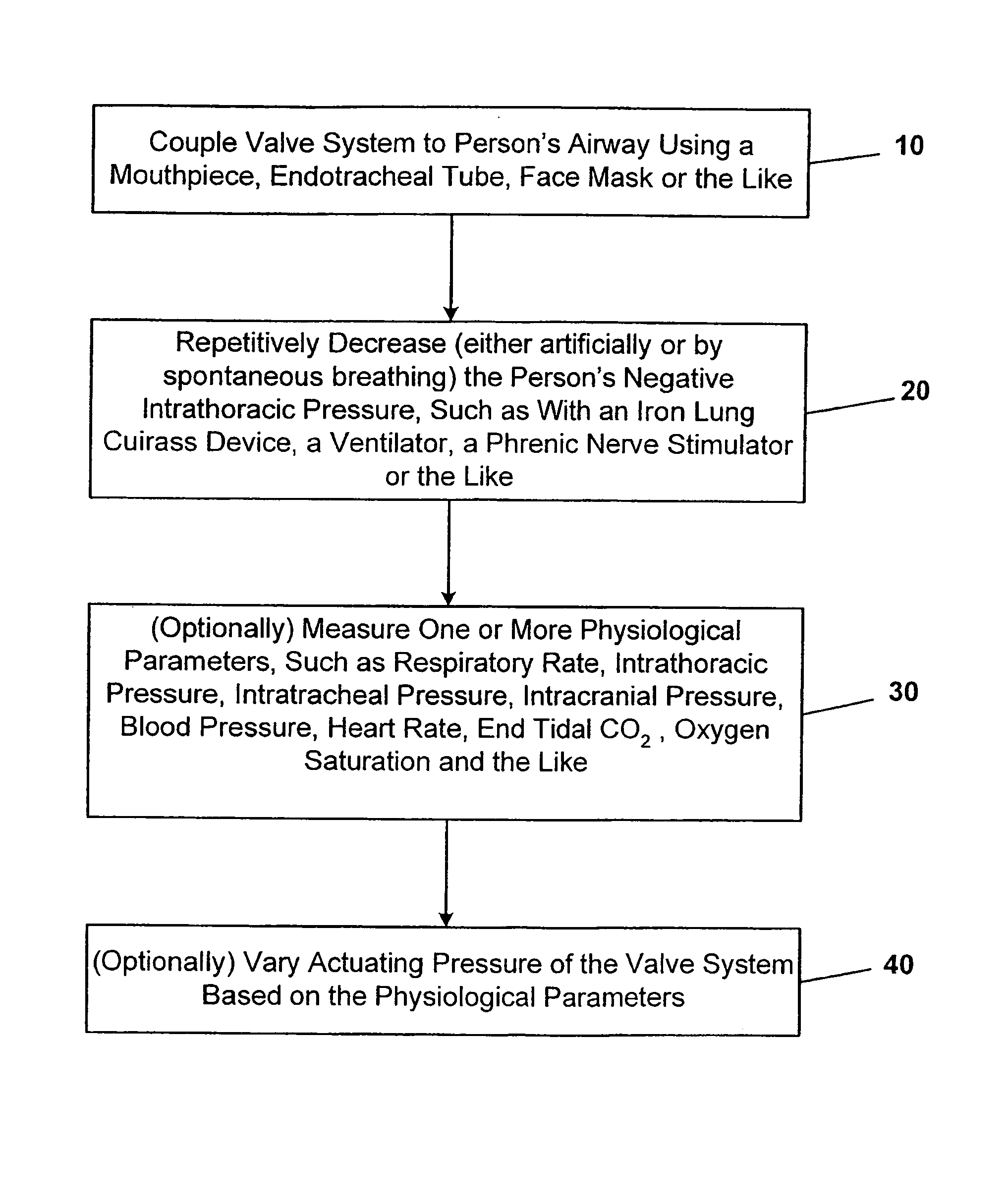
Systems and methods for reducing intracranial pressure
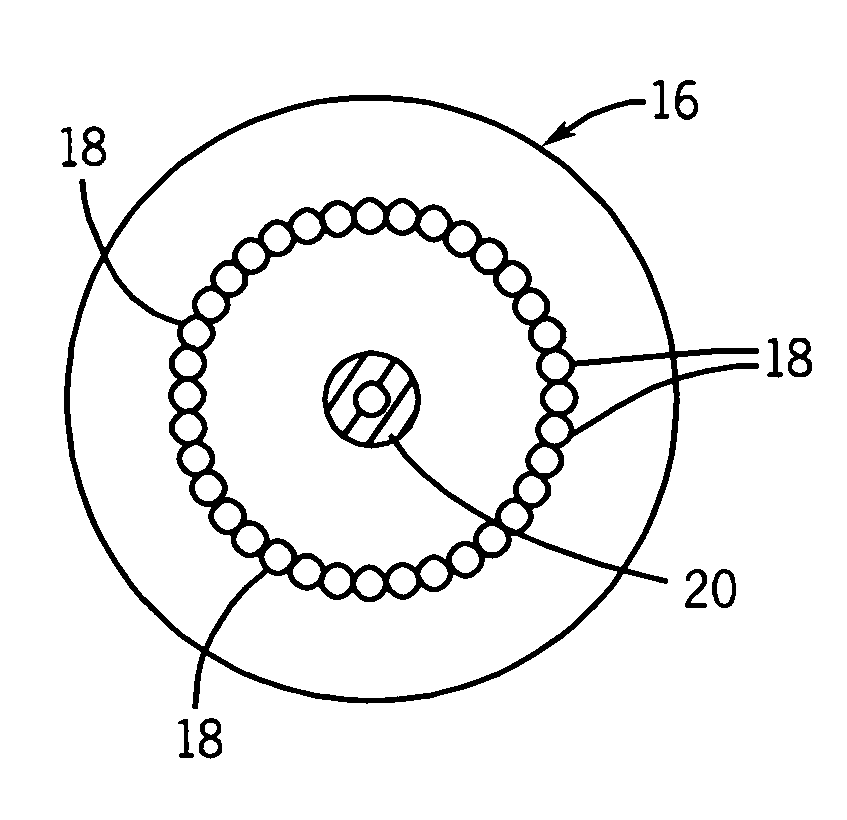
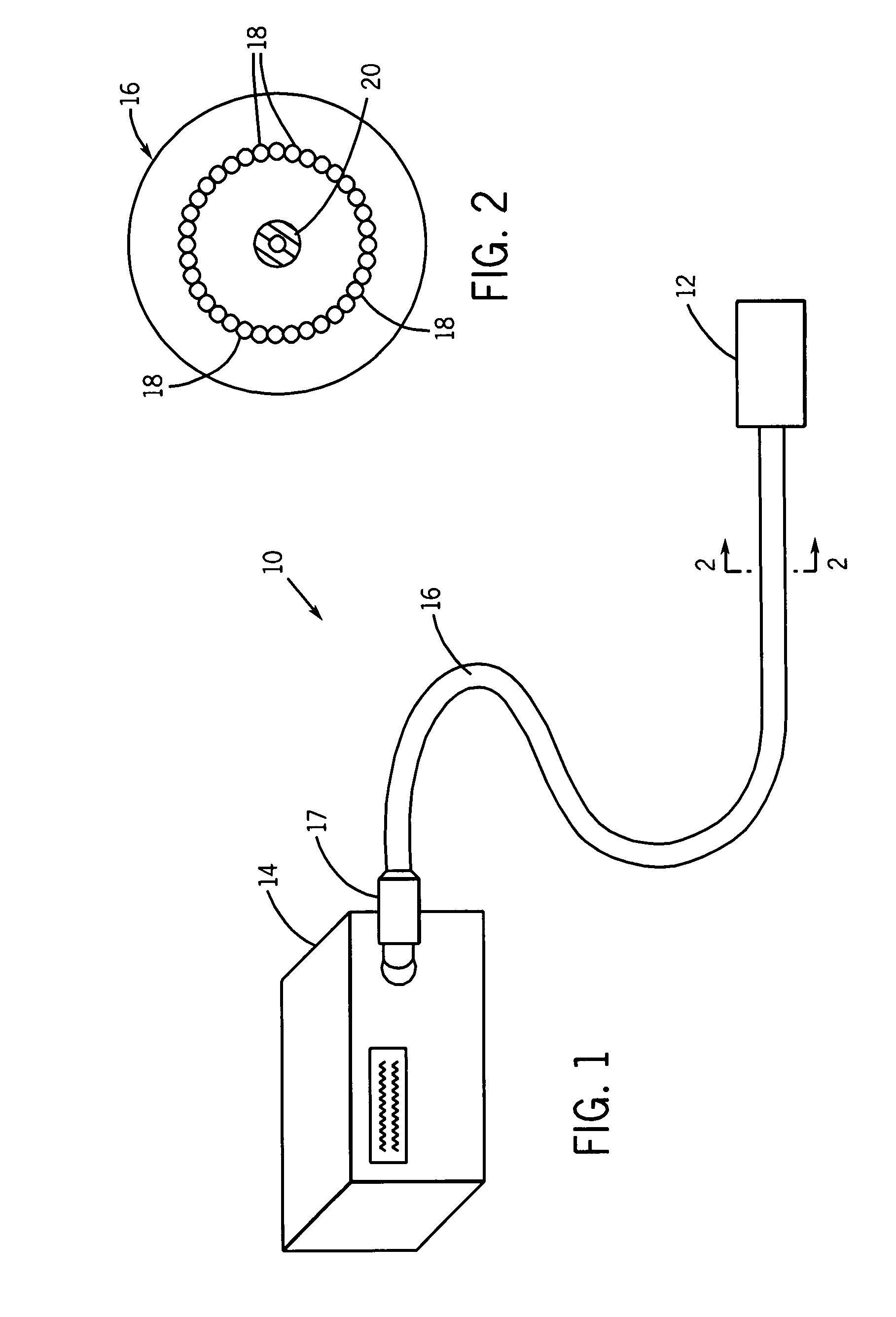
ActiveUS7195012B2Decreasing intracranial and intraocular pressureReduce pressureElectrocardiographyBreathing filtersVeinHuman airway
In one embodiment, the invention provides a device for decreasing intracranial or intraocular pressures. The device comprises a housing having an inlet opening and an outlet opening that is adapted to be interfaced with a person's airway. The device further includes a valve system that is operable to regulate respiratory gas flows through the housing and into the person's lungs during spontaneous or artificial inspiration. The valve system assists in lowering intrathoracic pressures during each inspiration to repetitively lower pressures in the venous blood vessels that transport blood out of the head to thereby reduce intracranial or intraocular pressures.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
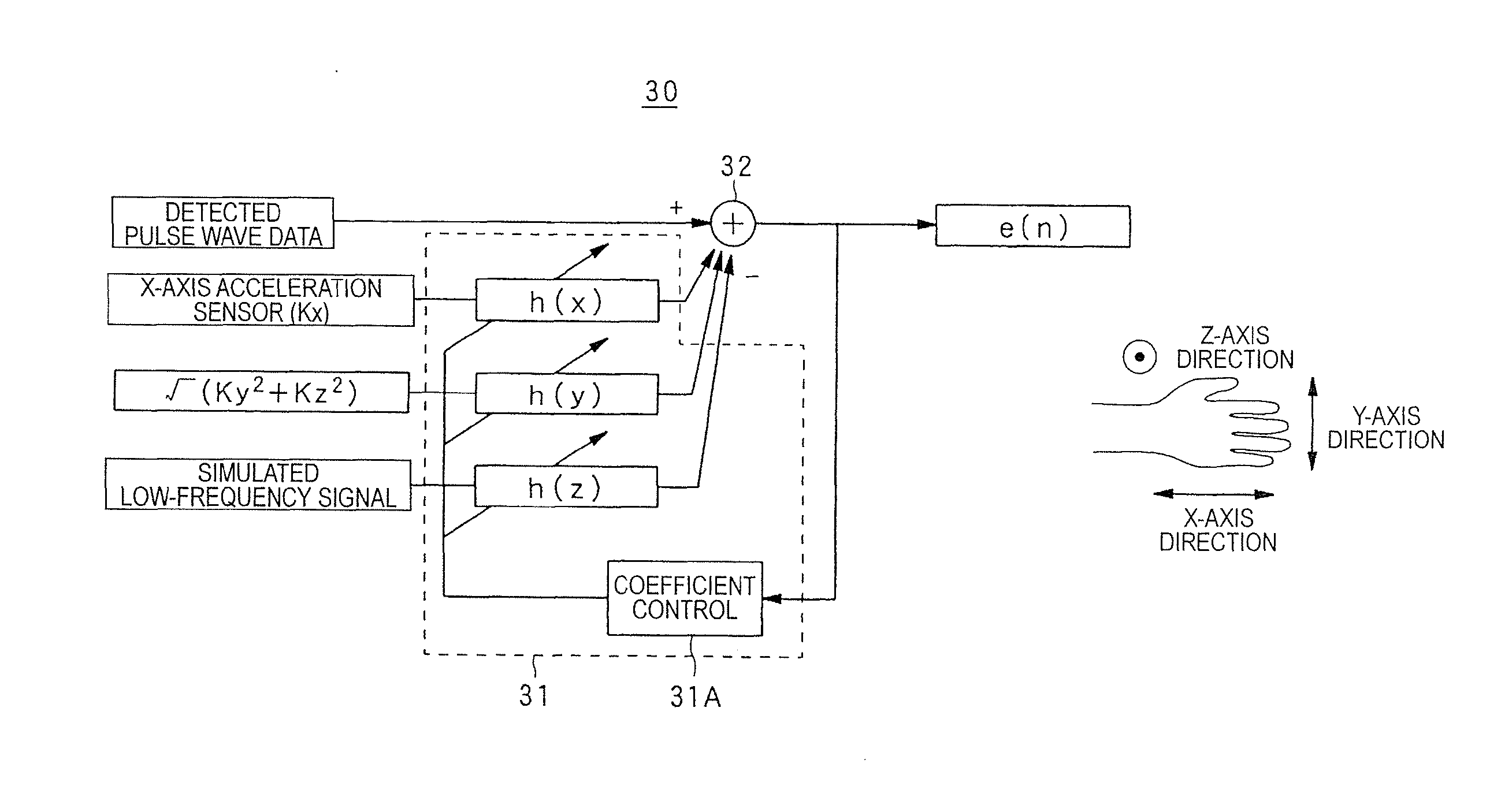
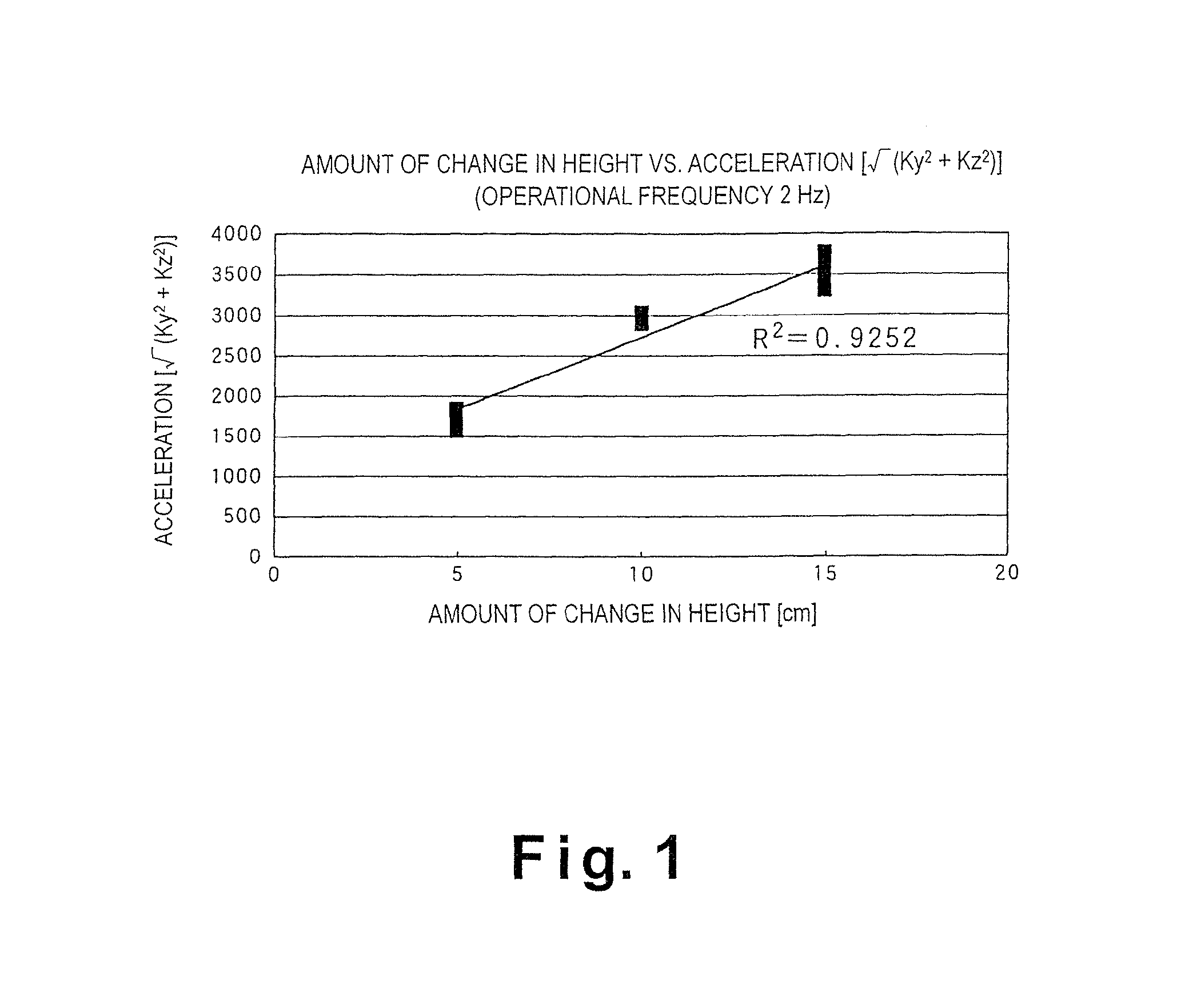
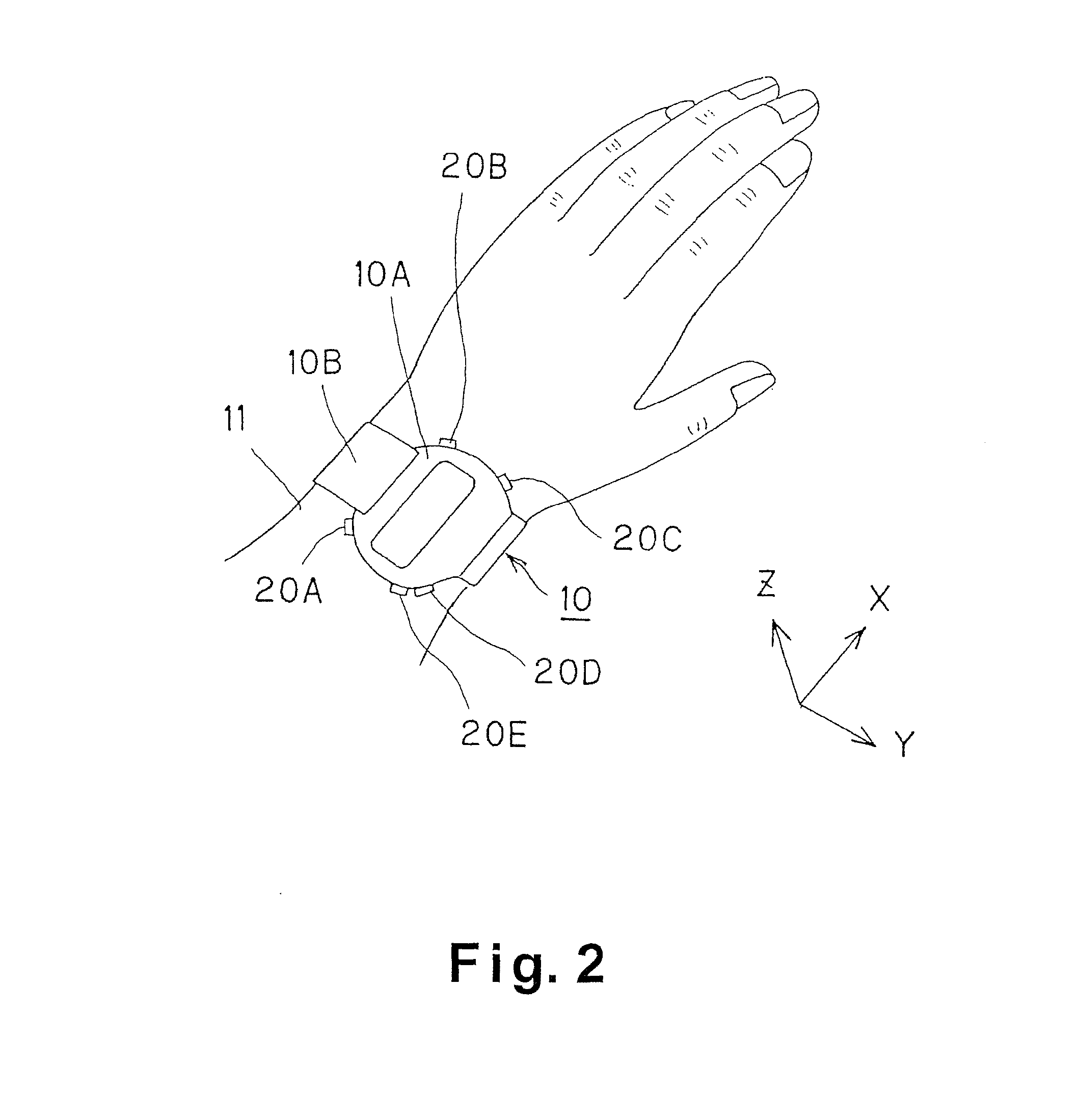
Pulse meter, method for controlling pulse meter, wristwatch-type information device, control program, storage medium, blood vessel simulation sensor, and living organism information measurement device
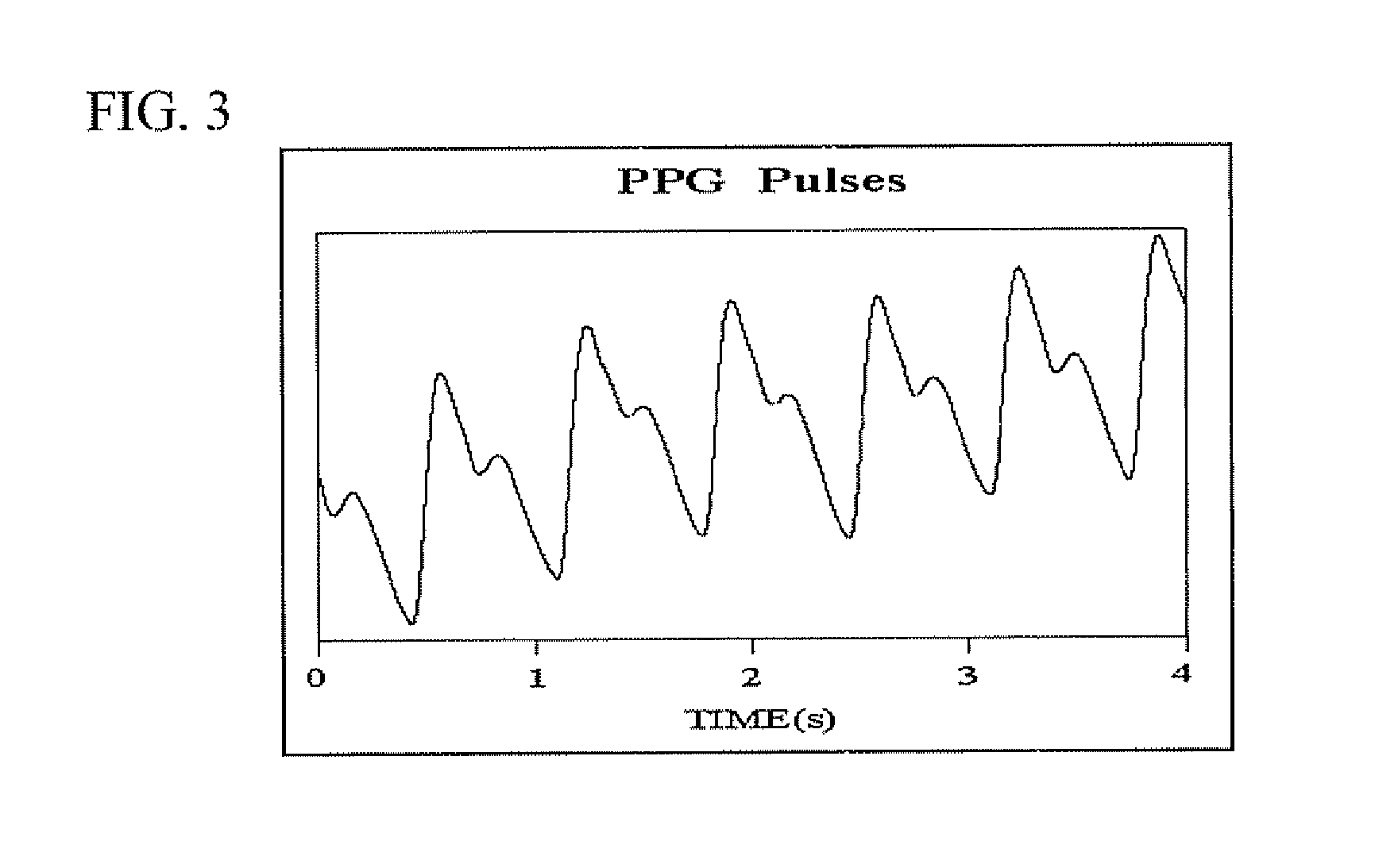
ActiveUS8303512B2Component can be removedAcceleration measurement using interia forcesPerson identificationMeasurement deviceVenous blood
The present invention realizes calculating a pulse rate accurately, even when a body movement component has no periodical characteristics, by surely removing the body movement component generated in a living organism from a pulse wave component. A pulse wave detecting section includes a pulse wave sensor and outputs a pulse wave detection signal to an MPU functioning as a body motion component removing section. A body motion sensor outputs a body motion detection signal corresponding to a body motion that affects the behavior of venous blood to the MPU. As a result, to the MPU removes the body motion component from the pulse wave detection signal based on the body motion detection signal. A pulse rate calculating section calculates the pulse rate based on the pulse wave detection signal from which the body motion component has been removed. The pulse rate is displayed on a liquid crystal display device.
Owner:138 EAST LCD ADVANCEMENTS LTD
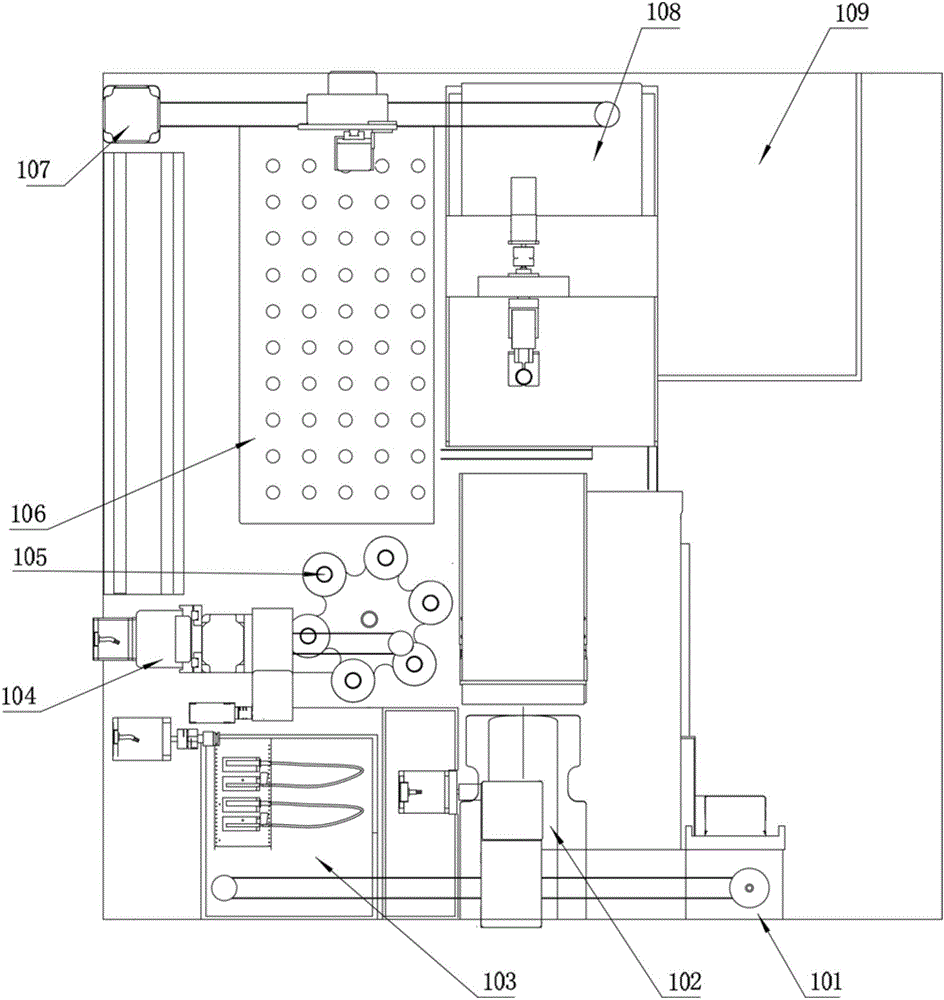
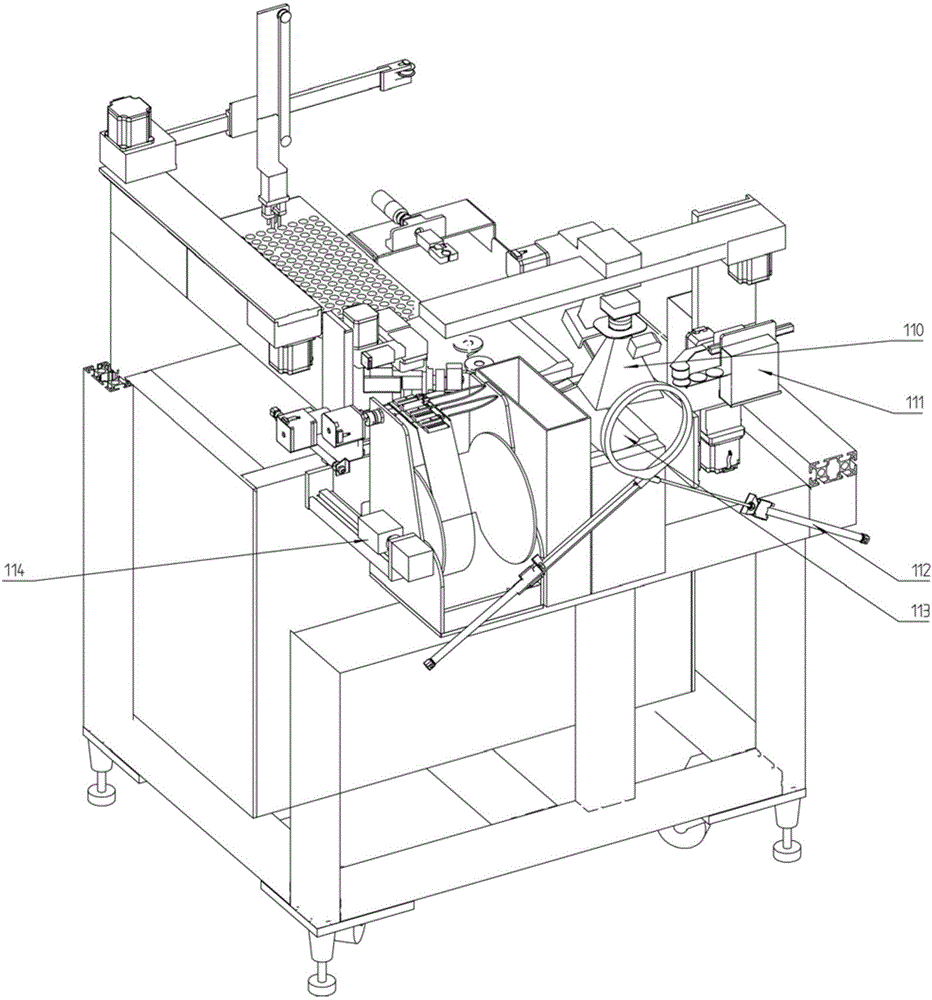
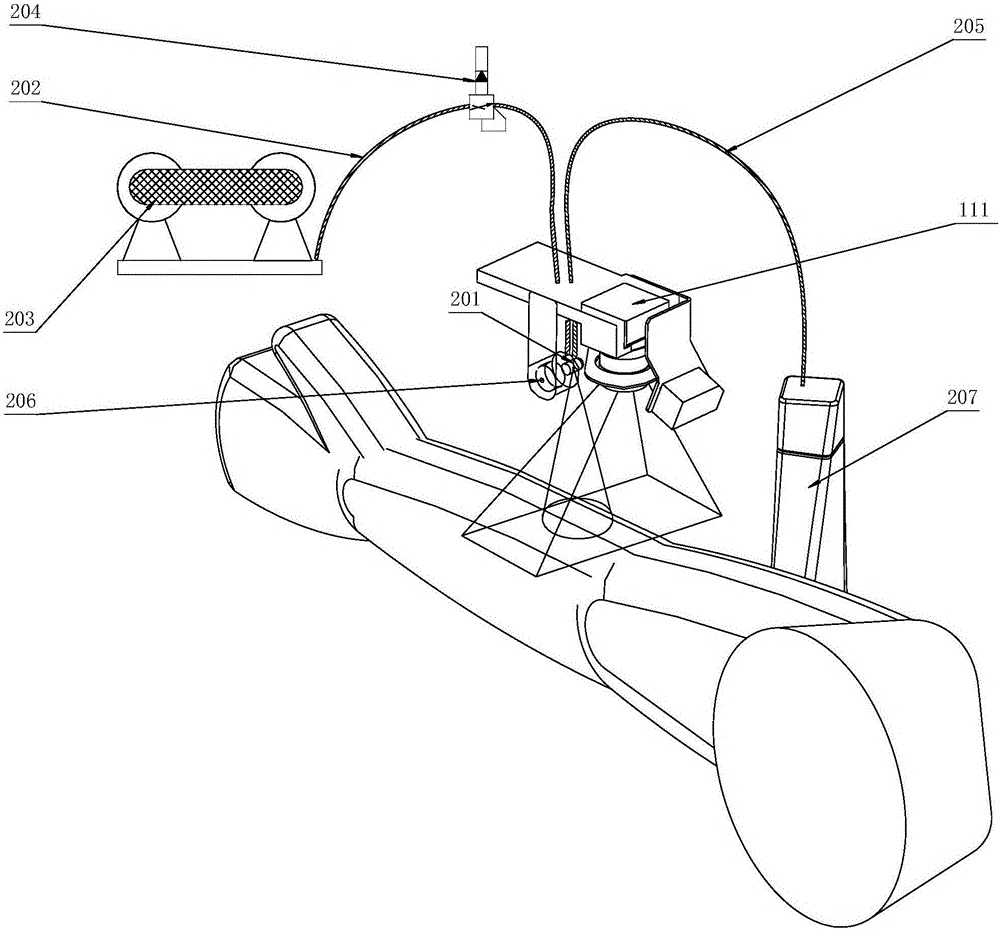
Venous blood collection robot and venous blood collection method employing same
ActiveCN106580344AHigh positioning accuracyRelieve painDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsVeinBlood collection
The invention relates to a venous blood collection robot, comprising an arm rest; a full-automatic recognition positioning device and a mechanical drive mechanism connected with a clamping device that clamps a blood collection needle are arranged above the arm reset, the lateral side of the arm rest is provided with an intelligent navigation vessel-recognizing device, and the front of the arm rest is provided with an automatic vein presser. The venous blood collection robot is capable of preventing operational errors due to manual operation, reducing blood collection difficulty and relieving the pain of a person under blood collection.
Owner:BEIJING MAGICNURSE SURGICAL ROBOT TECH CO LTD
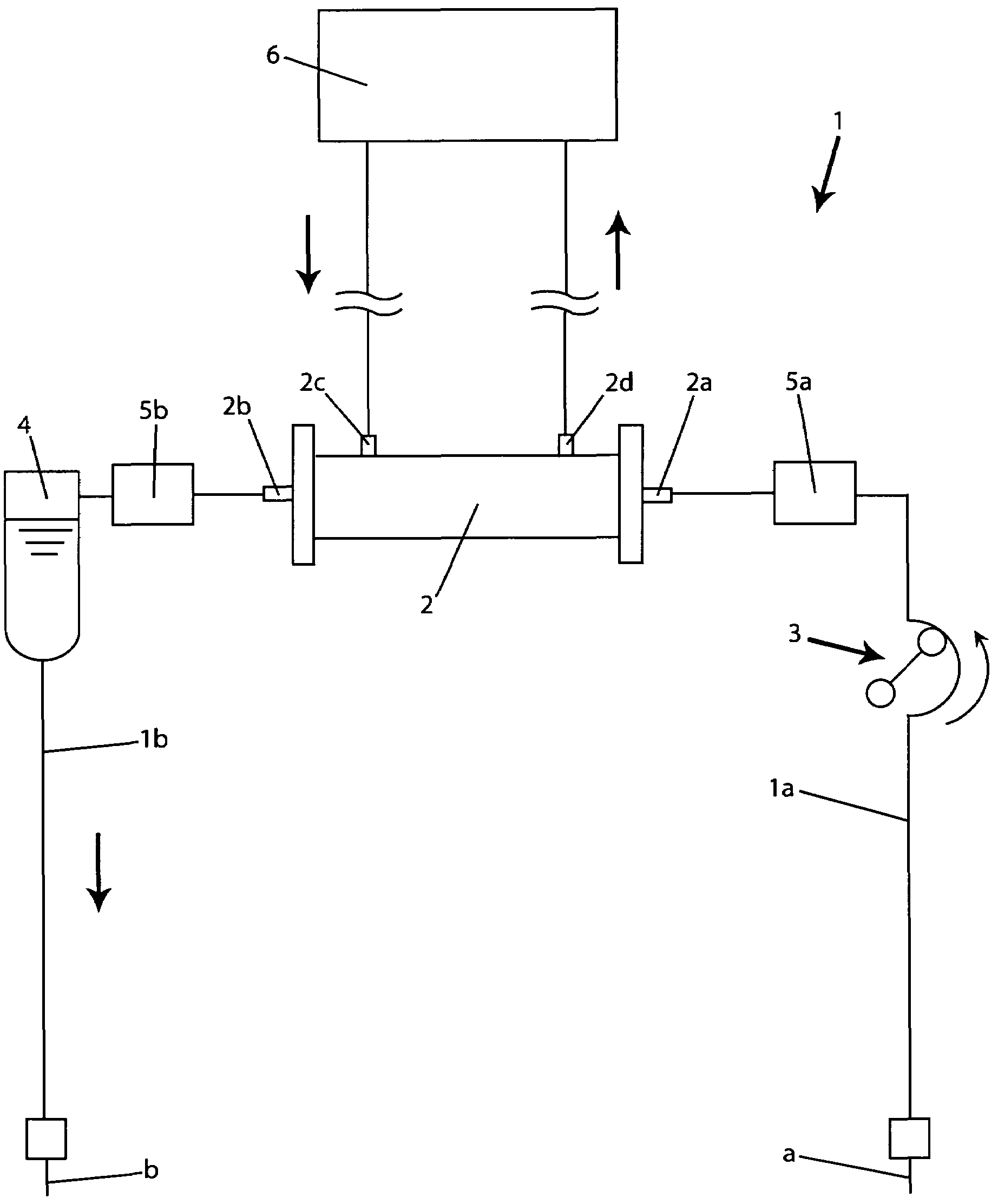
Blood purification device
ActiveUS7537688B2Reduce parameterAccurate detectionHaemofiltrationDialysis systemsBlood concentrationUltrafiltration
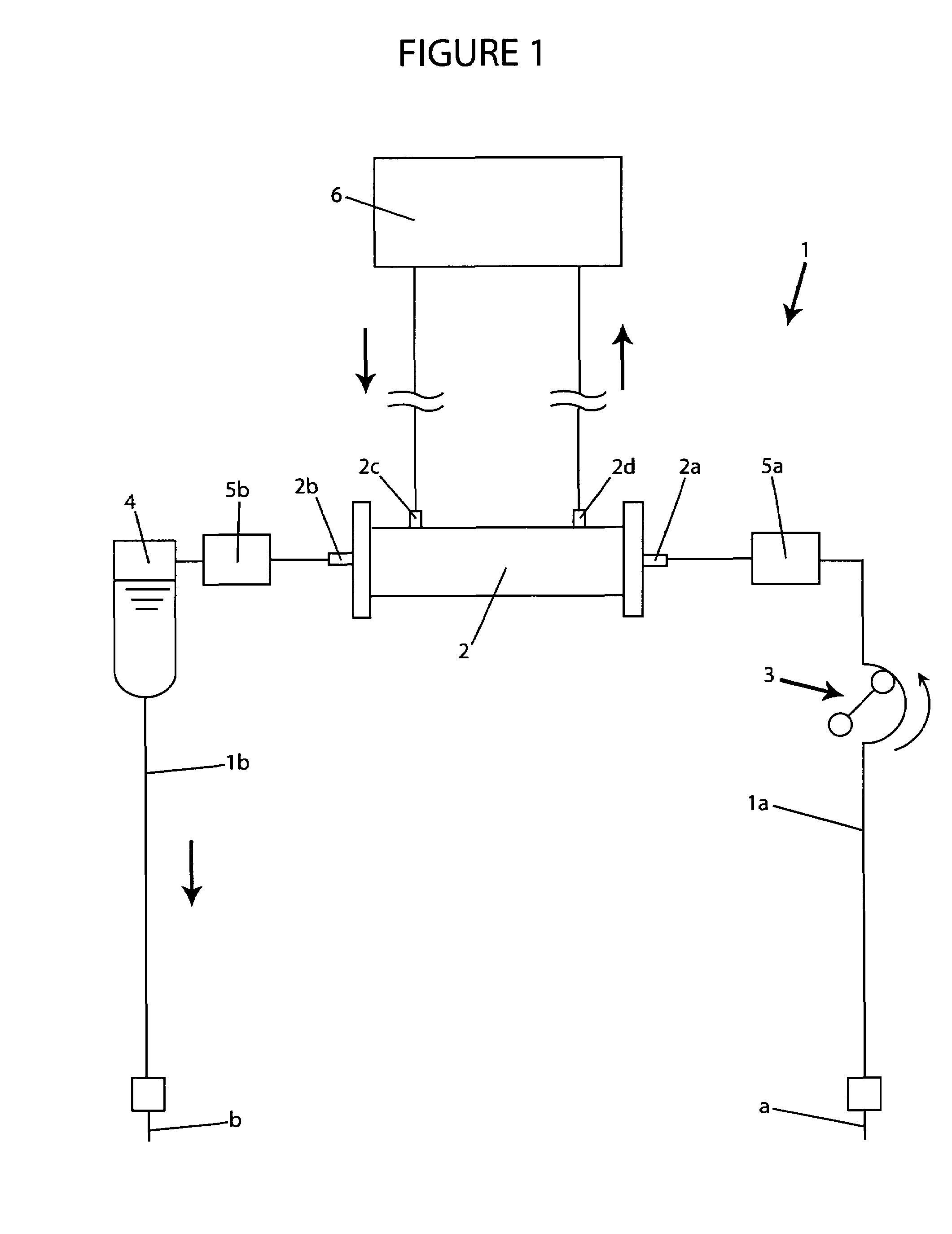
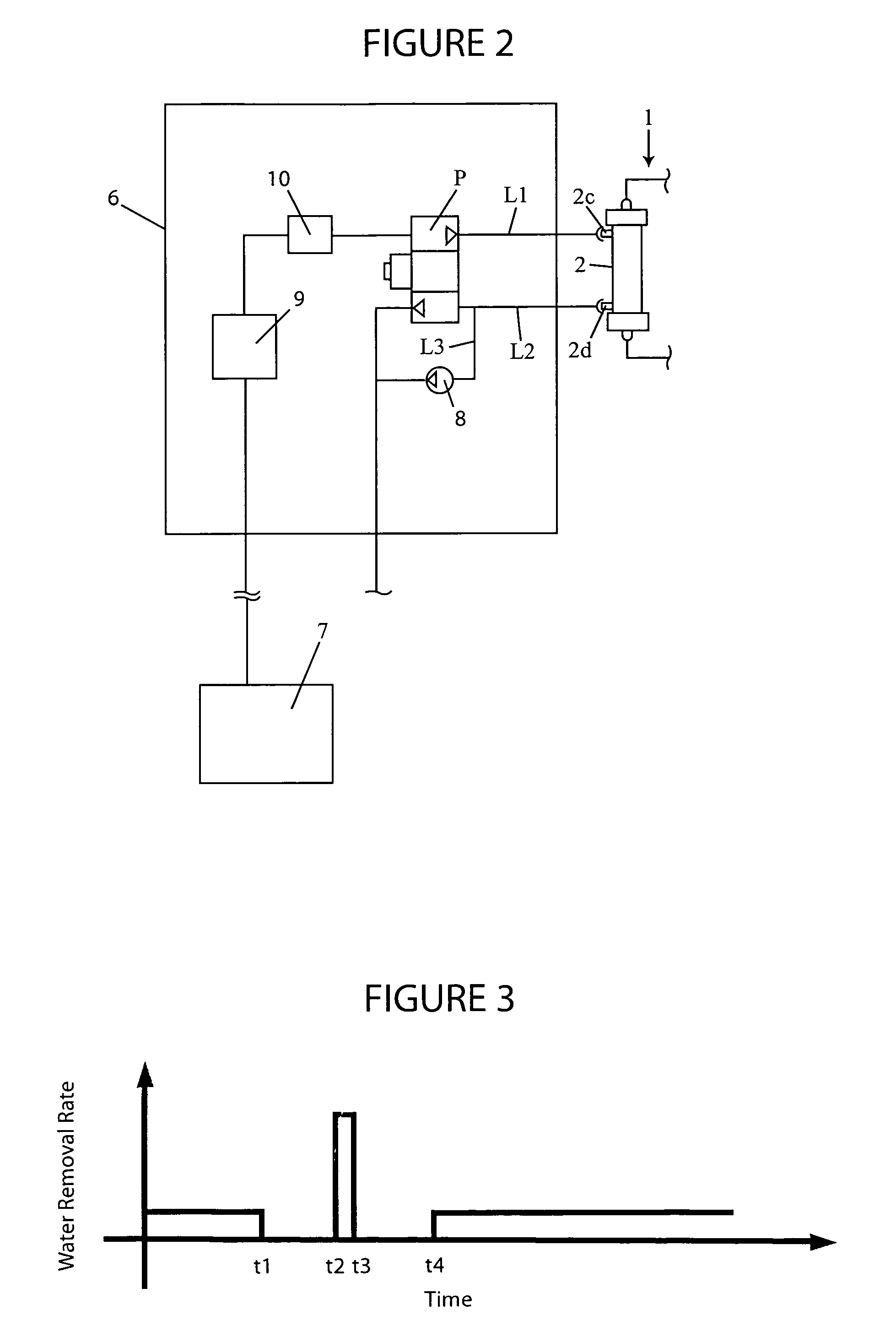
A blood purification device confirms whether a specific peak is provided by e.g. an ultrafiltration pump, to concentrate the blood or not and also accurately measures a blood re-circulation with a minimum of parameters providing a ratio of re-circulating blood. The blood purification device composed of arterial blood circuit route 1a and venous blood circuit route 1b, blood pump 3, dialyzer 2, water removal pump 8 providing the specific peak in the variation of blood concentration by removing water rapidly, and a detector detecting the specific peak, can measure the blood re-circulation thereby. The re-circulating blood flowing is the blood which was introduced again to arterial blood circuit route 1a after it had been returned to a patient from venous blood circuit route 1b. A first detector 5a installed in the arterial blood circuit route 1a and a second detector 5b installed in venous blood circuit route detector.
Owner:NIKKISO COMPANY
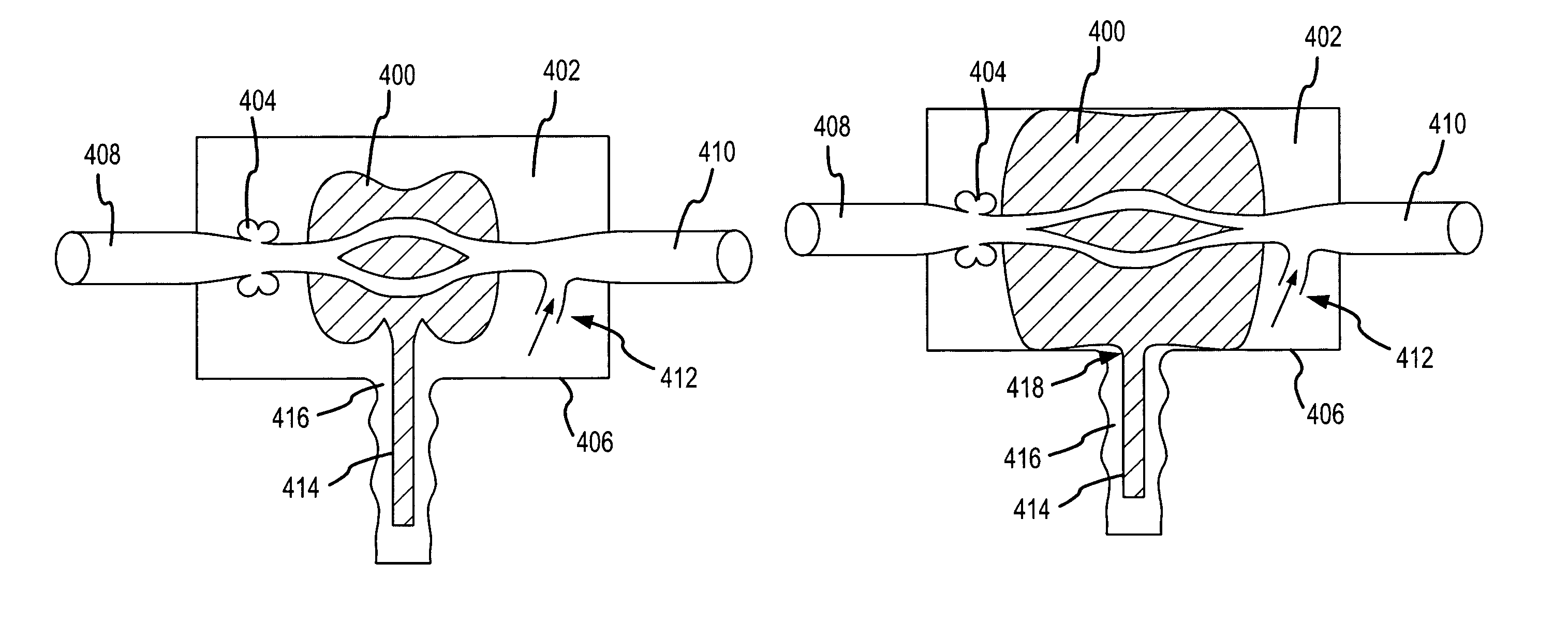
Multi-lumen vascular catheter and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050288623A1Avoid recyclingMinimize adhesionMulti-lumen catheterMedical syringesVeinVenous blood
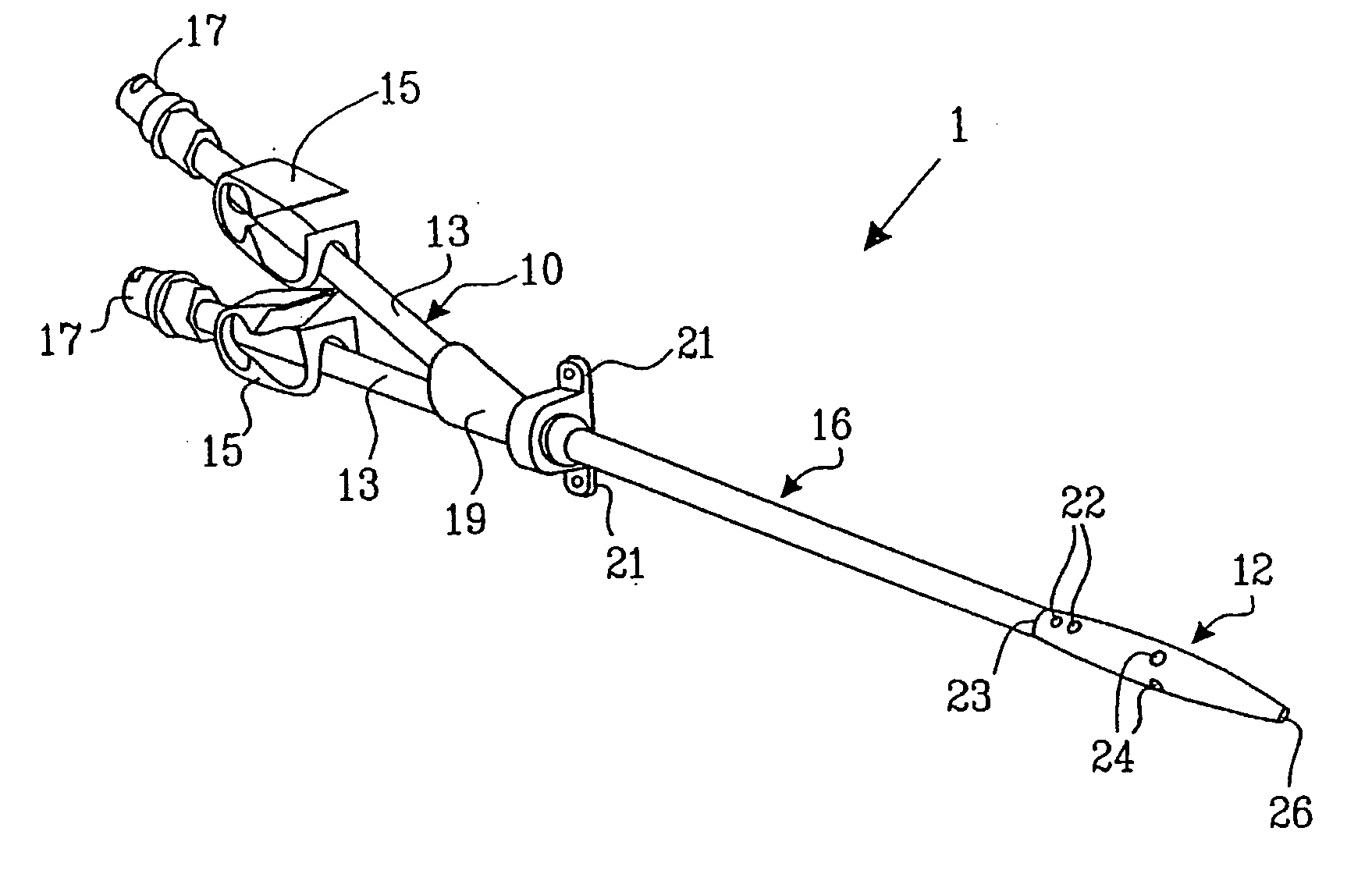
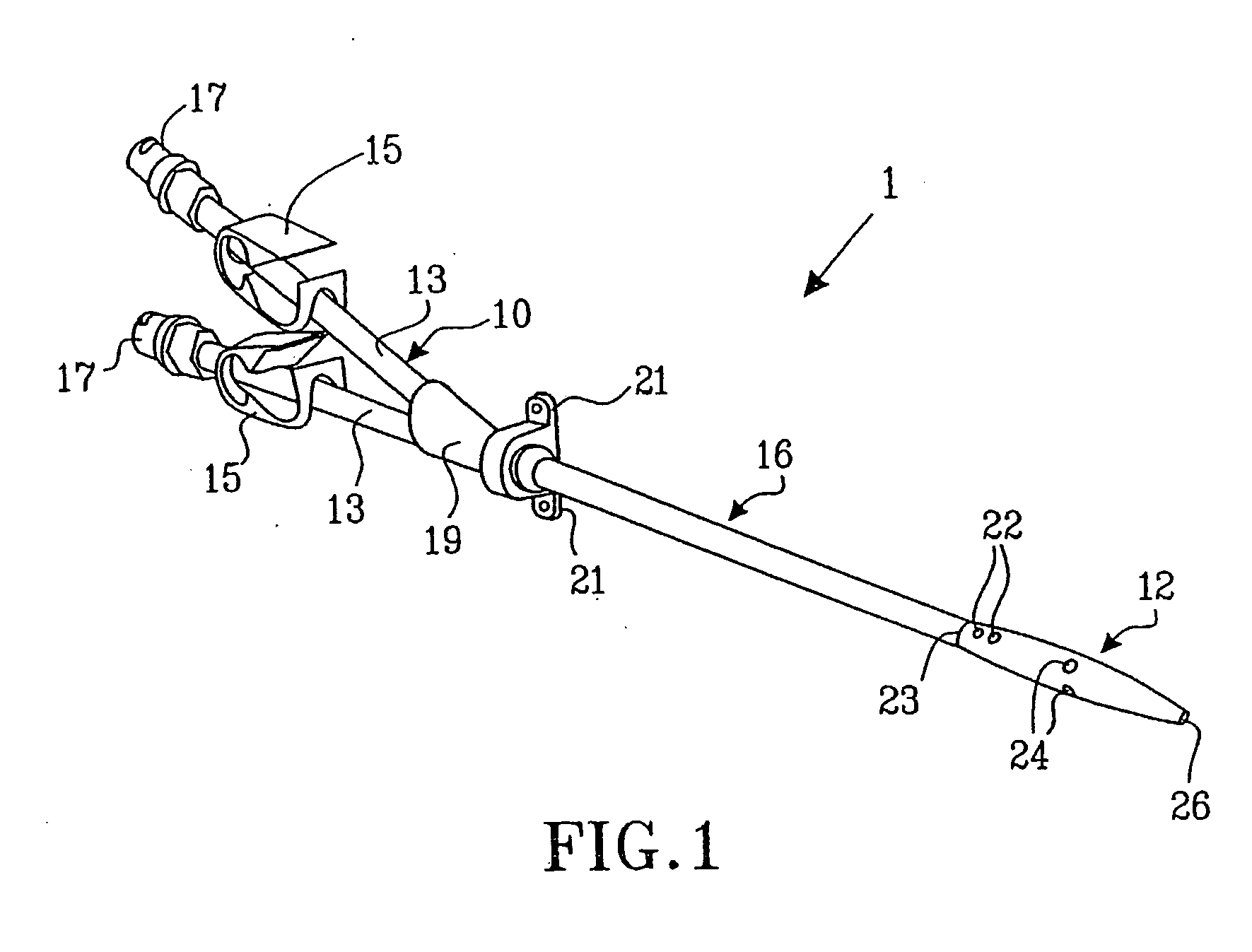
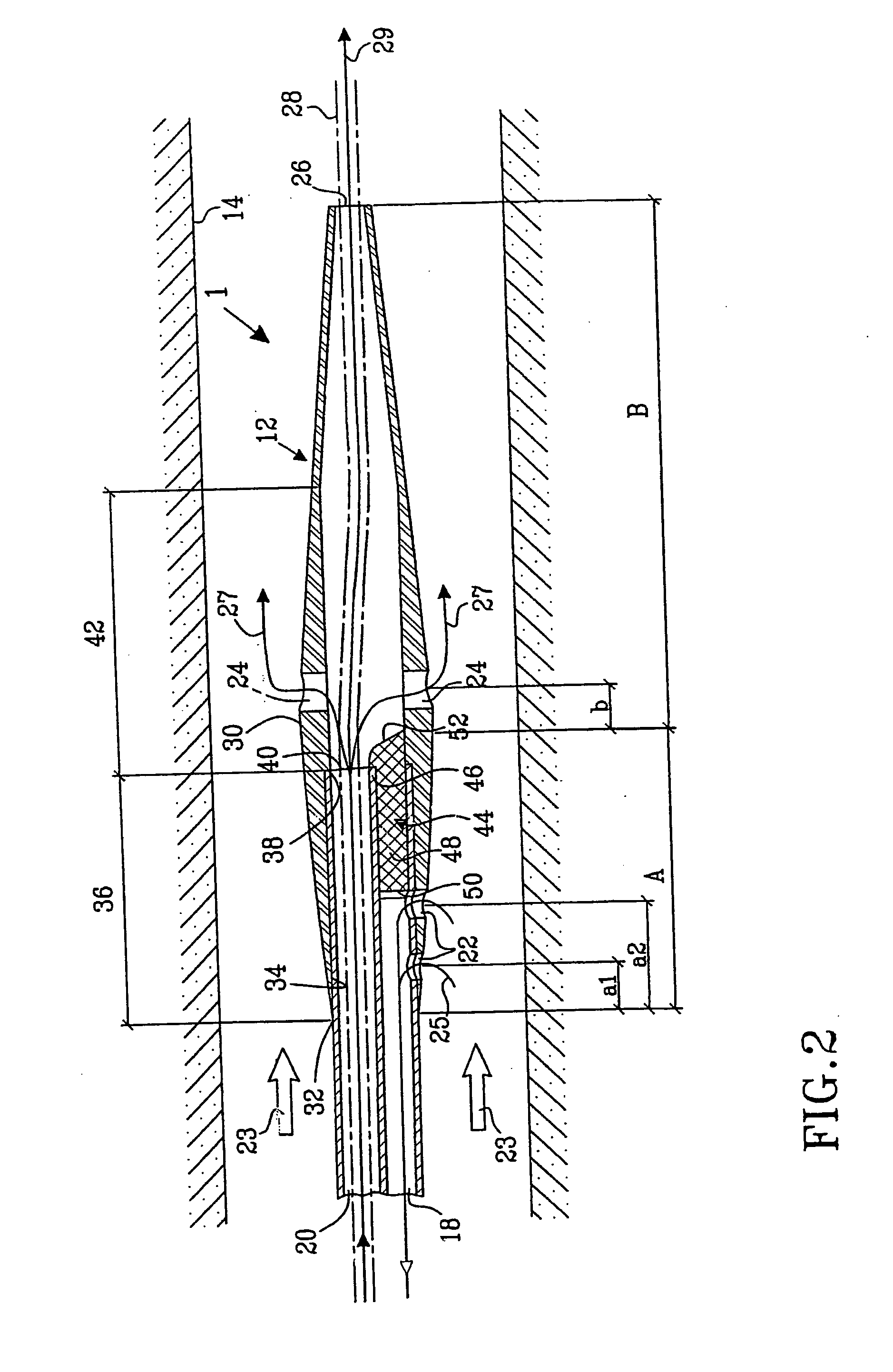
A multilumen vascular catheter (1) for treatment of patients by insertion of the vascular catheter in a venous blood vessel (14) by means of a guide-wire (28), the vascular catheter having a proximal connection point (10), a distal end-portion (12) which is terminated within a guide-wire opening (26), and a flexible catheter tube (16) arranged between the proximal connection portion (10) and the distal end-portion (12). The catheter tube (16) has a first lumen (18) for extraction of fluid such as untreated blood from the vessel (1) and a second lumen (20) for introducing fluid such as treated blood to the blood vessel (14). One or more suction openings (22) communicate with the first lumen (18) and are located upstream of one or more outlet openings (24), which in turn communicate with the second lumen (20), the suction openings (22) and the outlet openings (24) being located at the distal end-portion (12). The distal end-portion (12) is permanently bulbous and has a first, widening section (A) starting from the catheter tube (16) with a gradually increasing external cross-section in the direction toward the guide-wire opening (26). The first section (A) transits downstream via a shoulder (30) with a maximum external diameter into a second, narrowing section (B) having a gradually decreasing external cross-section in the direction toward the guide-wire opening (26). One or more of the suction openings (22) are located in the first, widening section (A) of the distal end-portion (12) while one or more of the outlet openings (24) are located in the second, narrowing section (B).
Owner:NORDIC MED COM
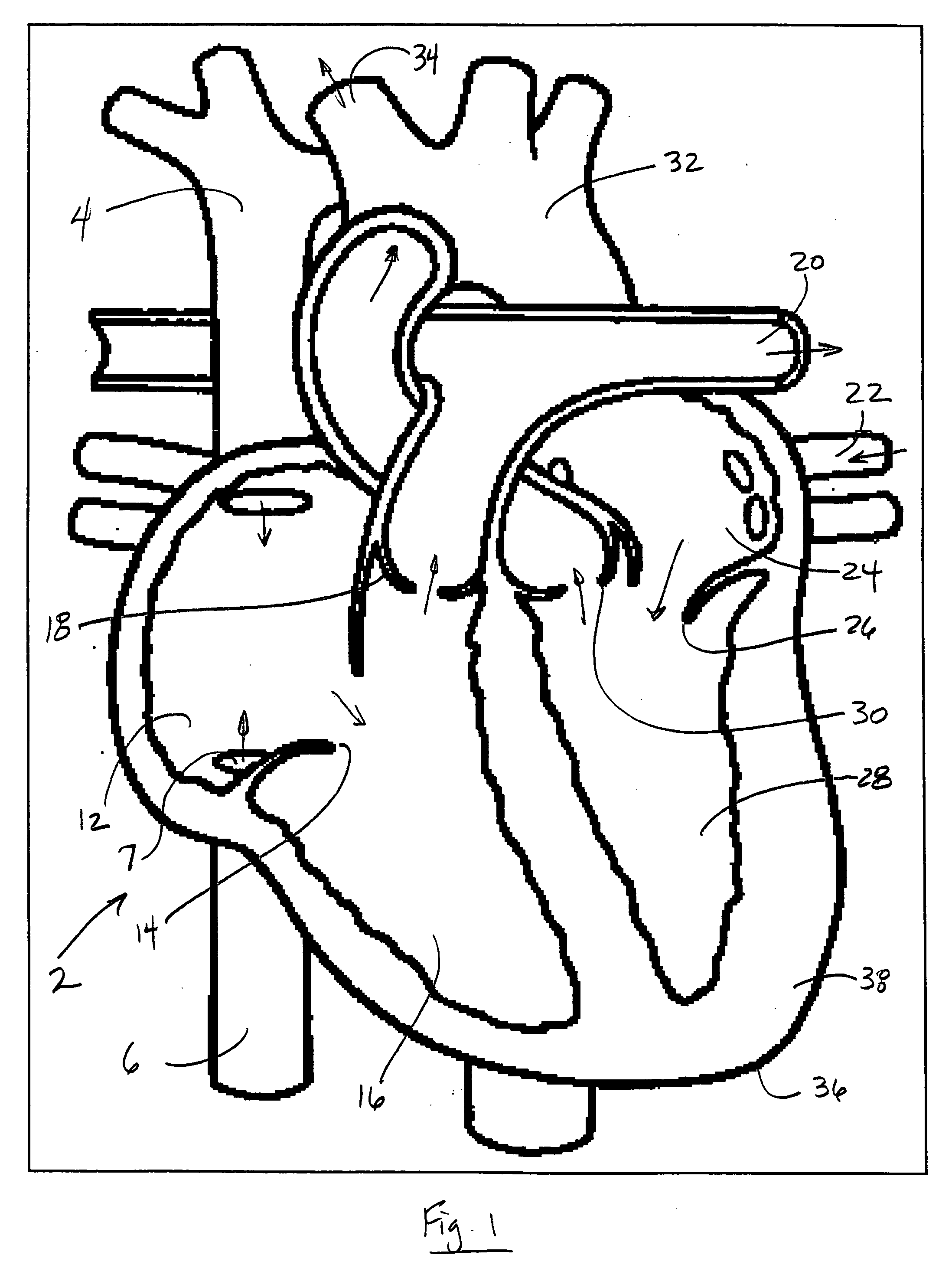
Simplified cerebral retroperfusion apparatus and method
InactiveUS20020077581A1Extended time windowReduce reperfusion injuryGuide needlesBalloon catheterSuperior sagittal sinusVenous blood
A method and apparatus for retroperfusing cerebral venous vasculature with autologous venous blood through a percutaneous entry site which incorporates a double-lumen catheter, a self-inflating pressure-regulated balloon mounted on the catheter and a perfusion outflow region either distal to the balloon for direct perfusion into the superior sagittal sinus, or proximal to the balloon for perfusion into the transverse sinus near the junction of the superior sagittal sinus.
Owner:DAVIDNER ALAN +1
Forearm transaxial compression band
A device adapted to be circumferentially fitted around the forearm to alleviate symptoms of overuse injuries, such as tennis elbow. The device is an elongate band composed of two elongate arcuate compression plates detachably and adjustably linked end to end by flexible straps. Each of the compression plates has an inwardly concave skin contacting surface which, in operation, are in circumferent opposition on the forearm to compress the skin overlying the radial extensor and flexor muscles within the forearm transaxially disposed therebetween. When the band is circumferentially tensioned and fastened to encircle the forearm, only the discrete, anatomically opposed skin contacting surfaces of the compression plates press against the skin. The skin contacting surfaces of the two compression plates are positioned by the user to immediately overlie the extensor and flexor muscle mass respectively. Only the skin underlying the skin-contacting surface of the compression plates and the intervening tissue transaxially disposed therebetween is compressed. Other circumferential portions of the forearm underlying the band are not compressed and the venous blood return is substantially unimpaired by the band.
Owner:FAREED DONALD O
Systems and methods for increasing cerebral spinal fluid flow
InactiveUS7185649B2Decreasing intracranial and intraocular pressureReduce pressureElectrocardiographyBreathing filtersVeinCerebrospinal fluid
In one embodiment, the invention provides a device for decreasing intracranial or intraocular pressures. The device comprises a housing having an inlet opening and an outlet opening that is adapted to be interfaced with a person's airway. The device further includes a valve system that is operable to regulate respiratory gas flows through the housing and into the person's lungs during spontaneous or artificial inspiration. The valve system assists in lowering intrathoracic pressures during each inspiration to repetitively lower pressures in the venous blood vessels that transport blood out of the head to thereby reduce intracranial or intraocular pressures.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Method for identification of sensor site by local skin spectrum data
A method is provided for determining the location of the sensor. The method comprises determining a physiological parameter based on detected light and determining the location of the sensor based on the physiological parameter. In addition, a method is provided for operating a sensor that includes calibrating a sensor based on a patient-specific physiological parameter, in which the patient-specific physiological parameter is skin color, age, gender, pooled blood, venous blood pulsation, or abnormal tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
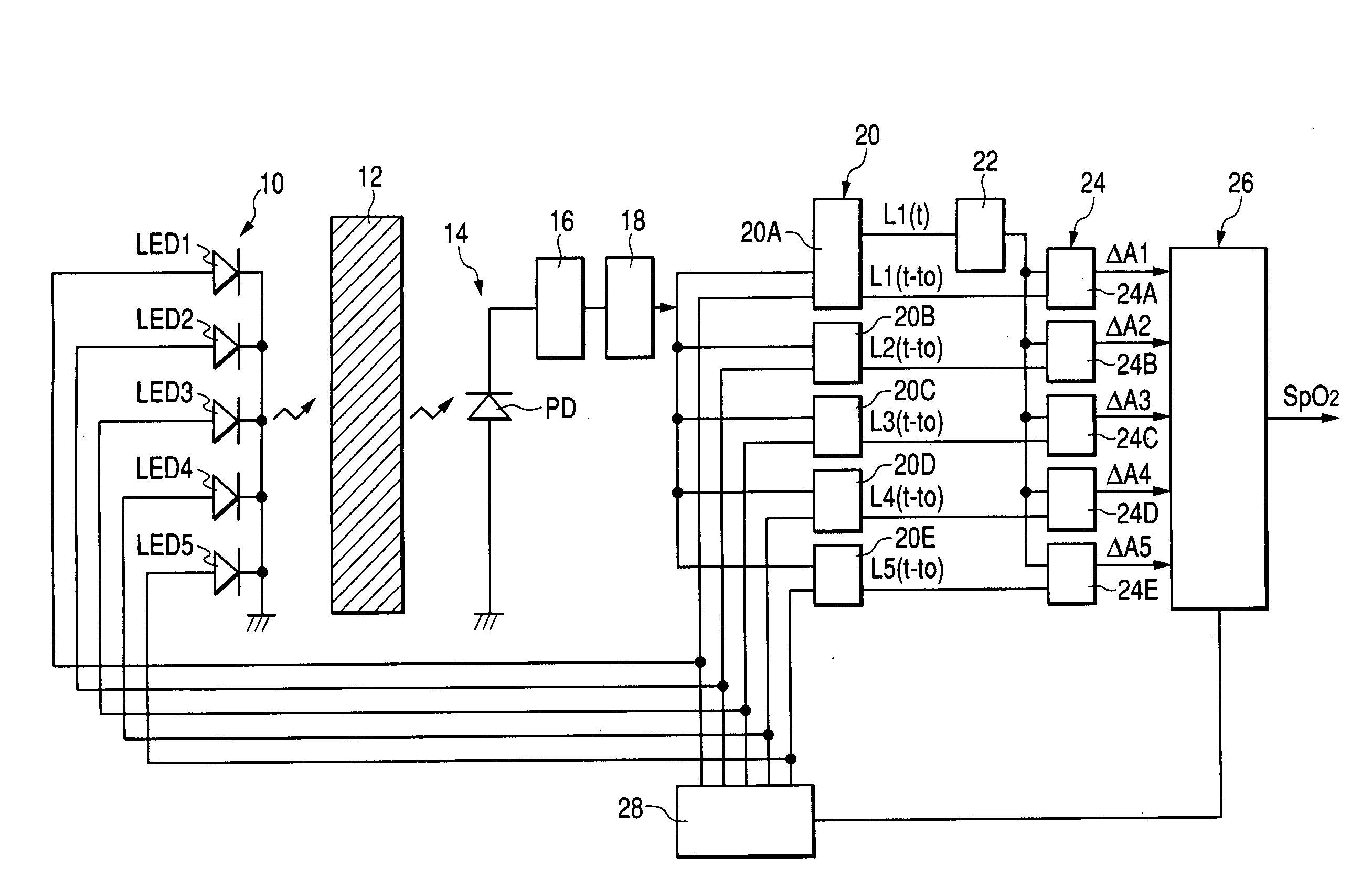
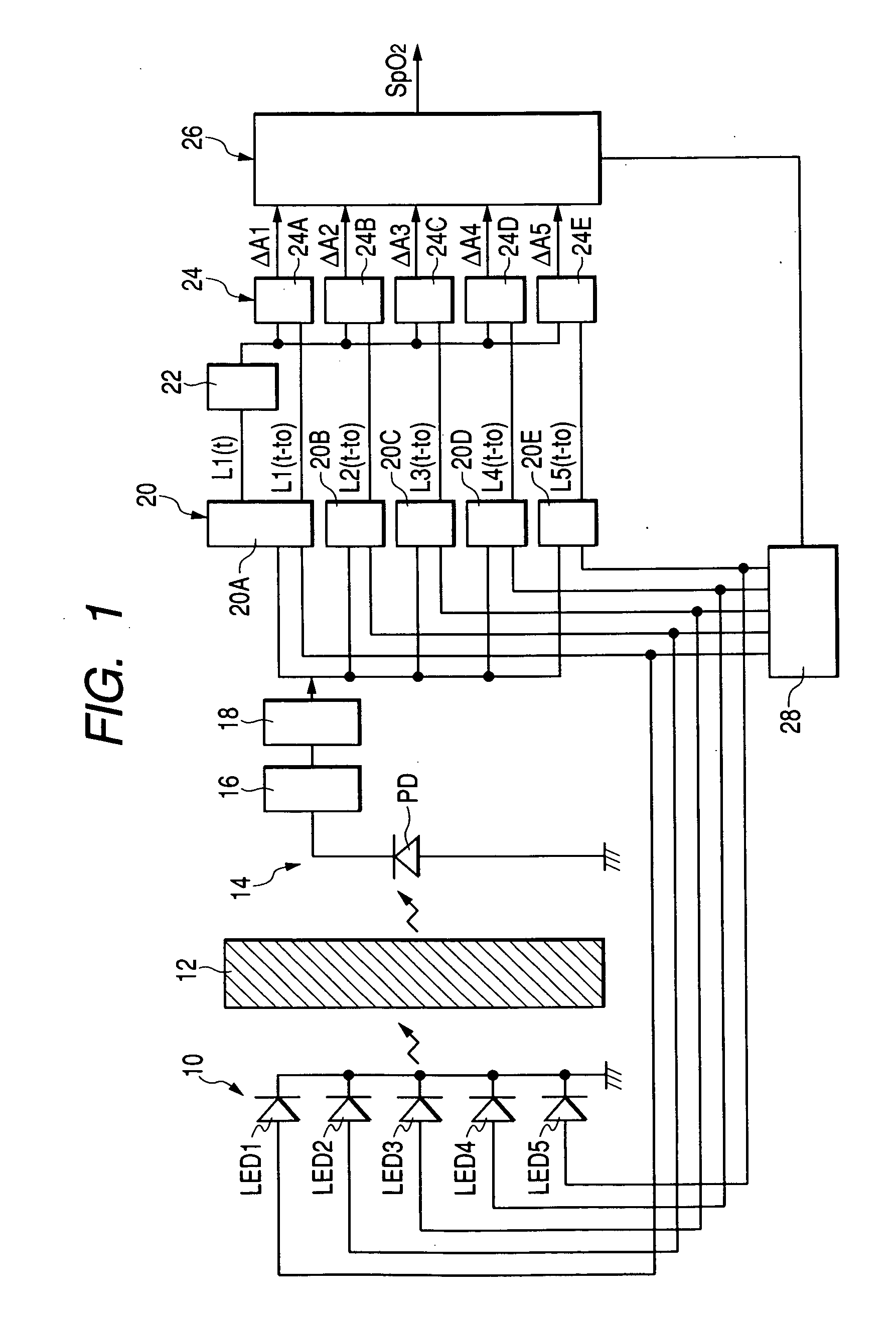
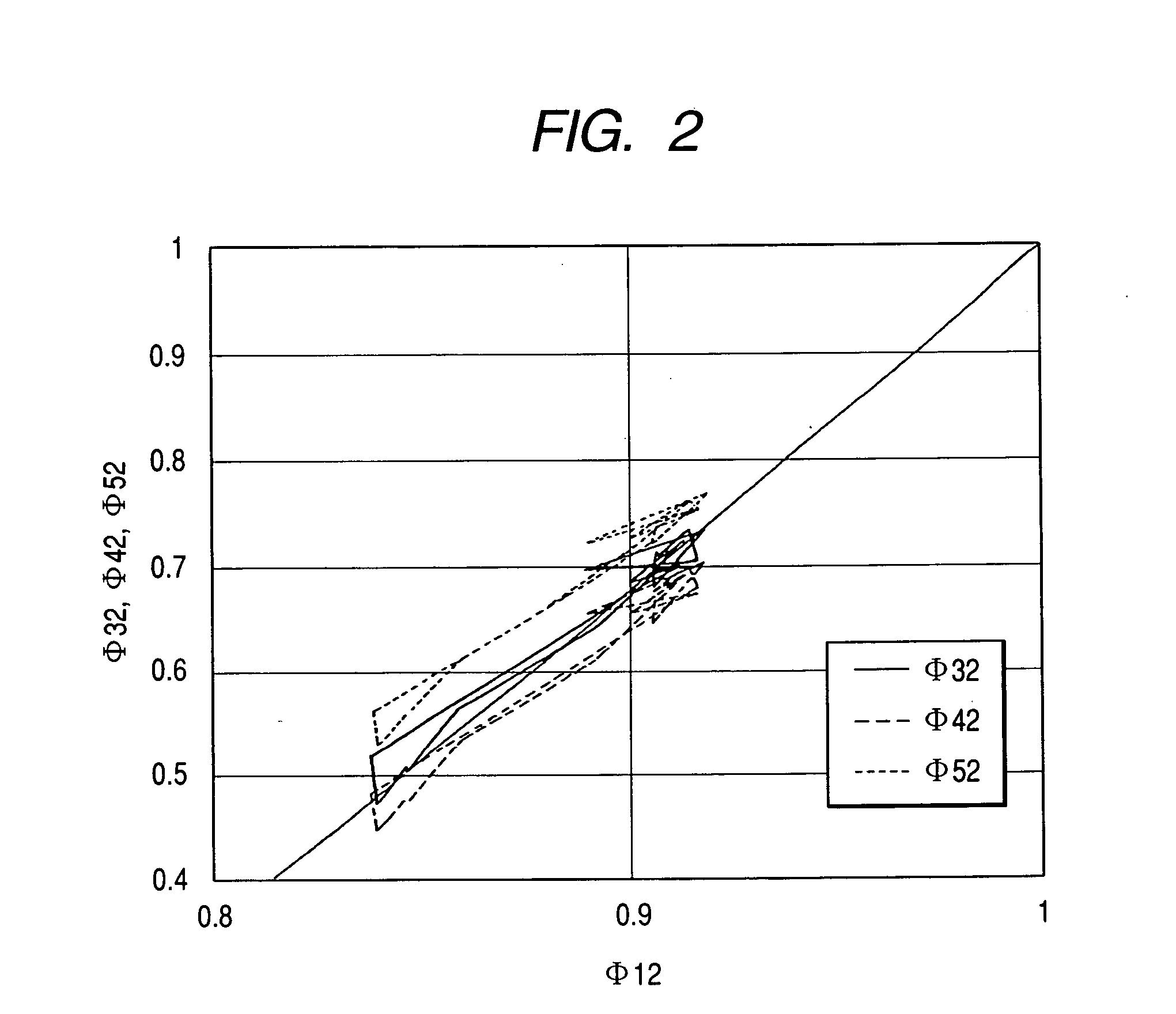
Pulse oximeter
ActiveUS20050049469A1Accurate SpO valueEasy to breatheDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsVenous bloodPulse oximetry
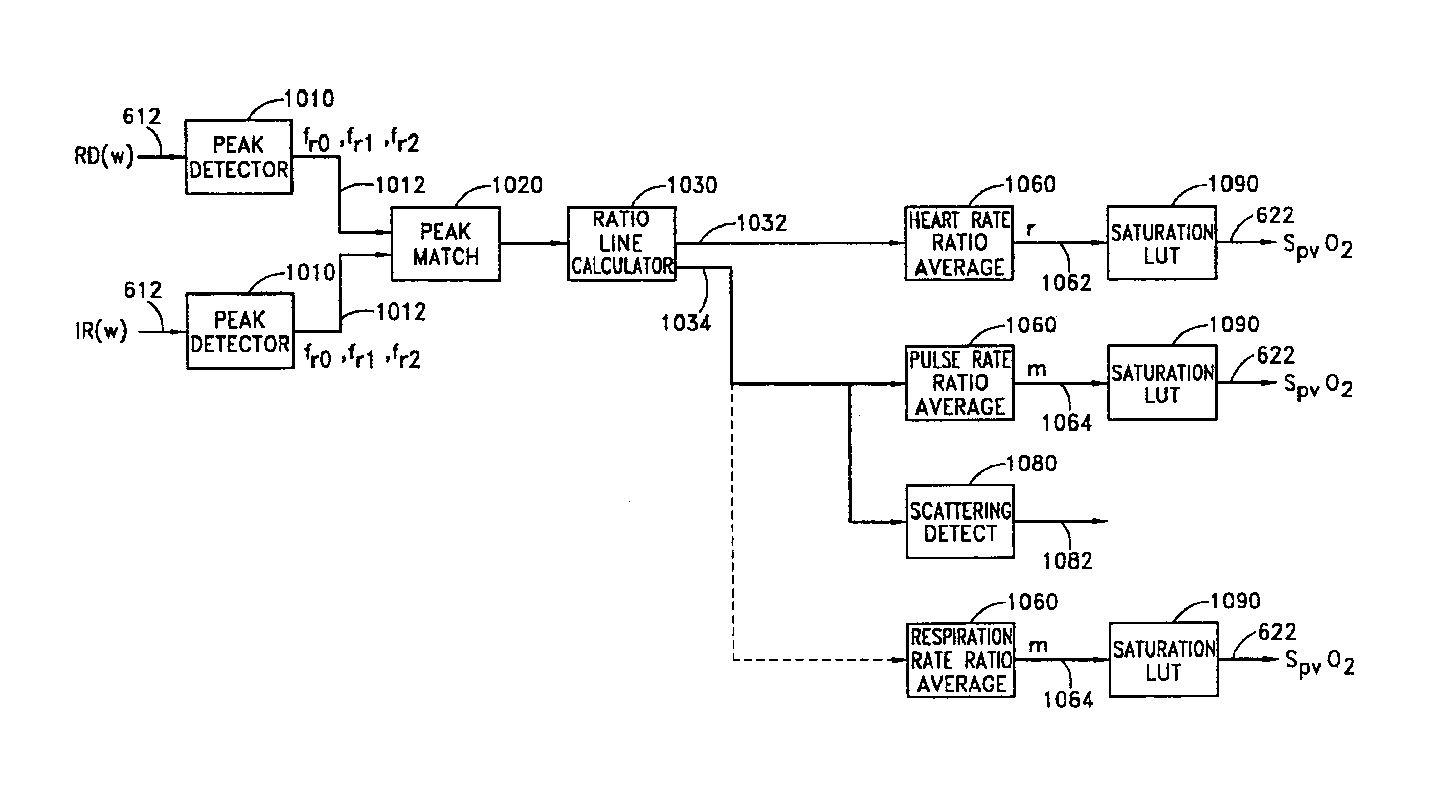
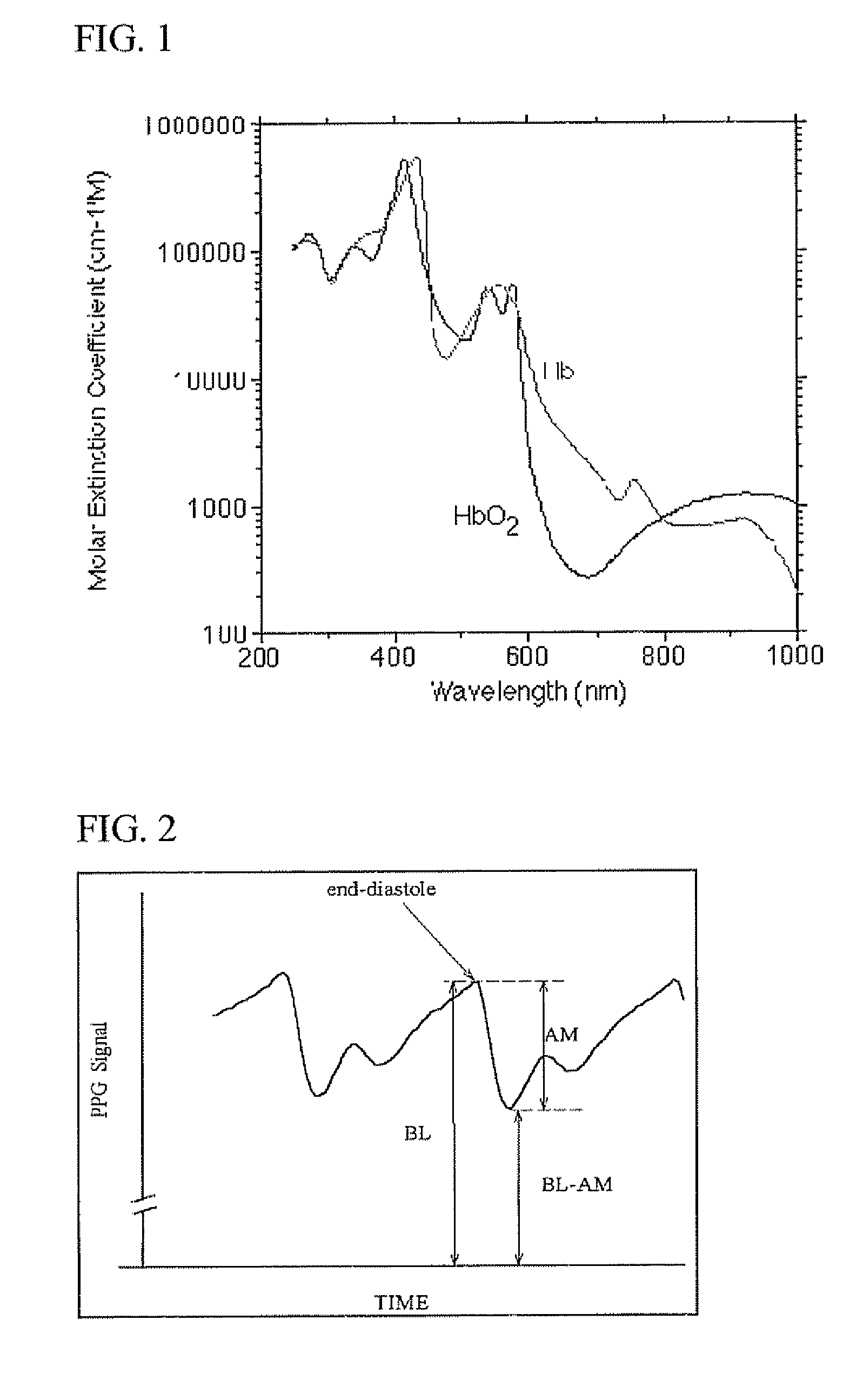
In a pulse oximeter for obtaining an oxygen saturation in a blood, a light emitter irradiates a living tissue with light beams having five different wavelengths. A light receiver receives respective light beams reflected from or transmitted through the living tissue, and converts the received light beams to electric signals. A first calculator calculates five attenuation changes of the living tissue based on fluctuations of the respective electric signals. A second calculator calculates at least four attenuation change ratios from the five attenuation changes. Each of the attenuation change ratios is defined by a ratio between any two of the five attenuation changes. A third calculator calculates the oxygen saturation based on the attenuation change ratios, while taking an oxygen saturation of arterial blood, an oxygen saturation of venous blood, a ratio between changes in arterial blood and venous blood, and a tissue term as four unknown values.
Owner:NIHON KOHDEN CORP
Mechanical Tissue Device and Method
The present invention relates generally to a device and method for preventing the undesired passage of emboli from a venous blood pool to an arterial blood pool. The invention relates especially to a device and method for treating certain cardiac defects, especially patent foramen ovales and other septal defects, through the use of an embolic filtering device capable of instantaneously deterring the passage of emboli from the moment of implantation. The device consists of a frame, and a braided mesh of sufficient dimensions to prevent passage of emboli through the mesh. The device is preferably composed of shape memory alloy, such as Nitinol, which conforms to the shape and dimension of the defect to be treated.
Owner:SEPTRX
Single expandable double lumen cannula assembly for veno-venous ECMO
ActiveUS7473239B2Decreased surgical and blood traumaLess invasiveMulti-lumen catheterOther blood circulation devicesVeinVenous blood
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Modified Pulse Oximetry Technique For Measurement Of Oxygen Saturation In Arterial And Venous Blood
A method for the measurement of oxygen saturation in arterial blood SaO2 by means of pulse oximetry without calibration is described. Photoplethysmography (PPG) is measured in three wavelengths in the infrared and for each PPG curve the relative change in light transmission is obtained. Two equations, each relating SaO2 to the ratio of the relative changes in light transmission for two wavelengths, using the values of the extinction coefficients of oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin for the three wavelengths, enable the determination of SaO2, assuming linear dependence of the optical path-length on the wavelength, for the three wavelengths in the infrared. Similar technique for the determination of oxygen saturation in venous blood from changes in light transmission due to changes in venous blood volume is suggested
Owner:JERUSALEM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOG
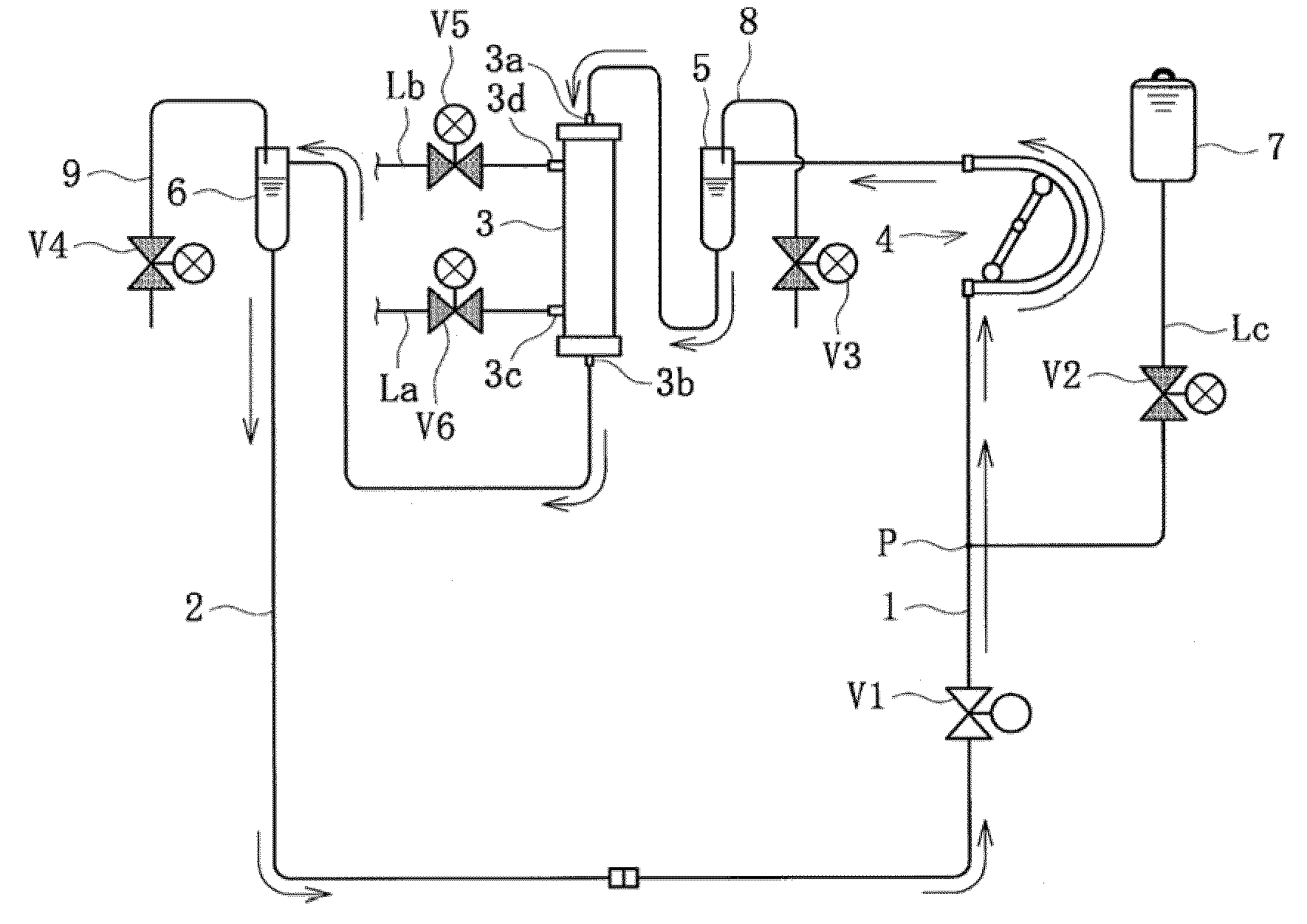
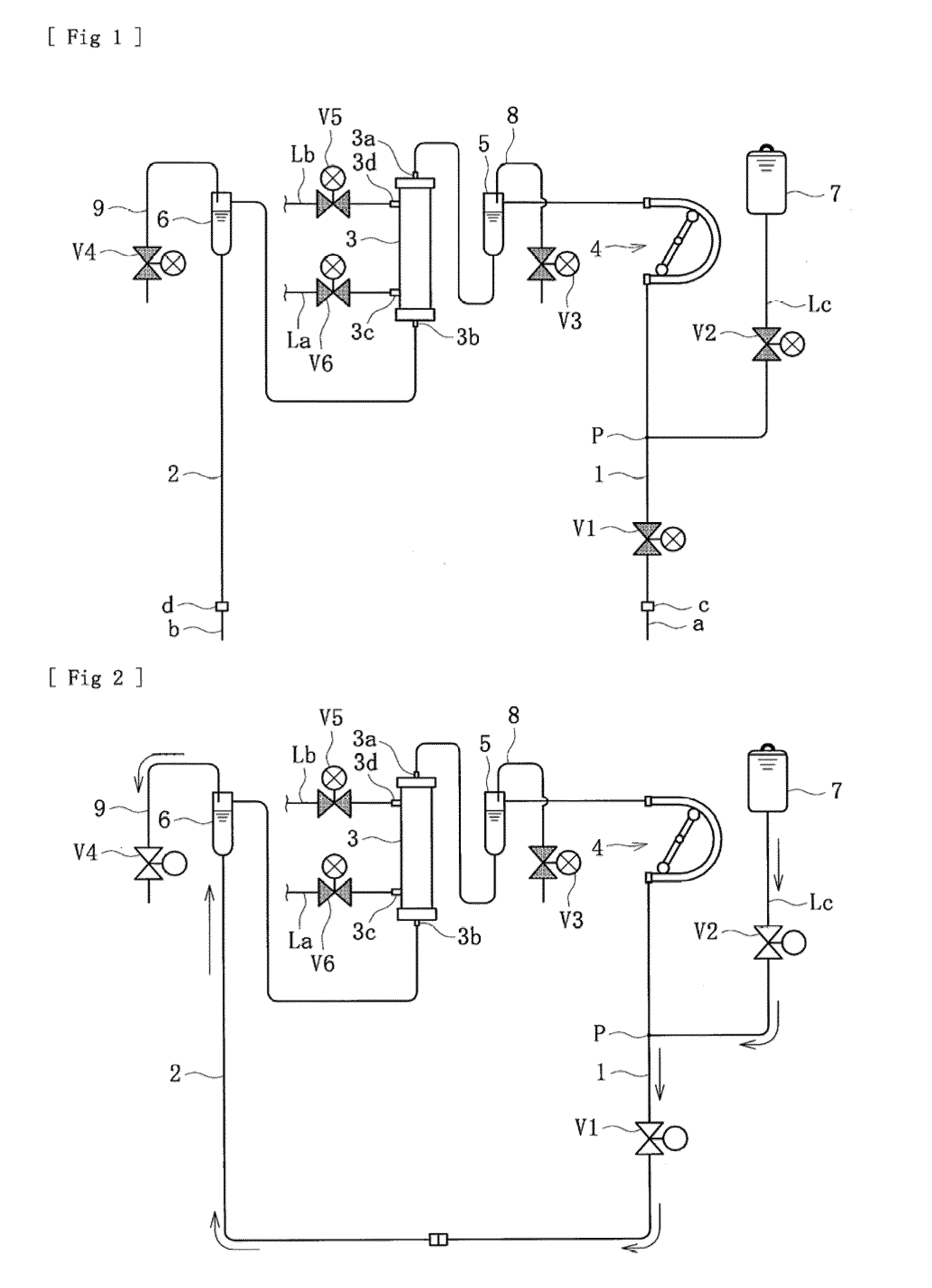
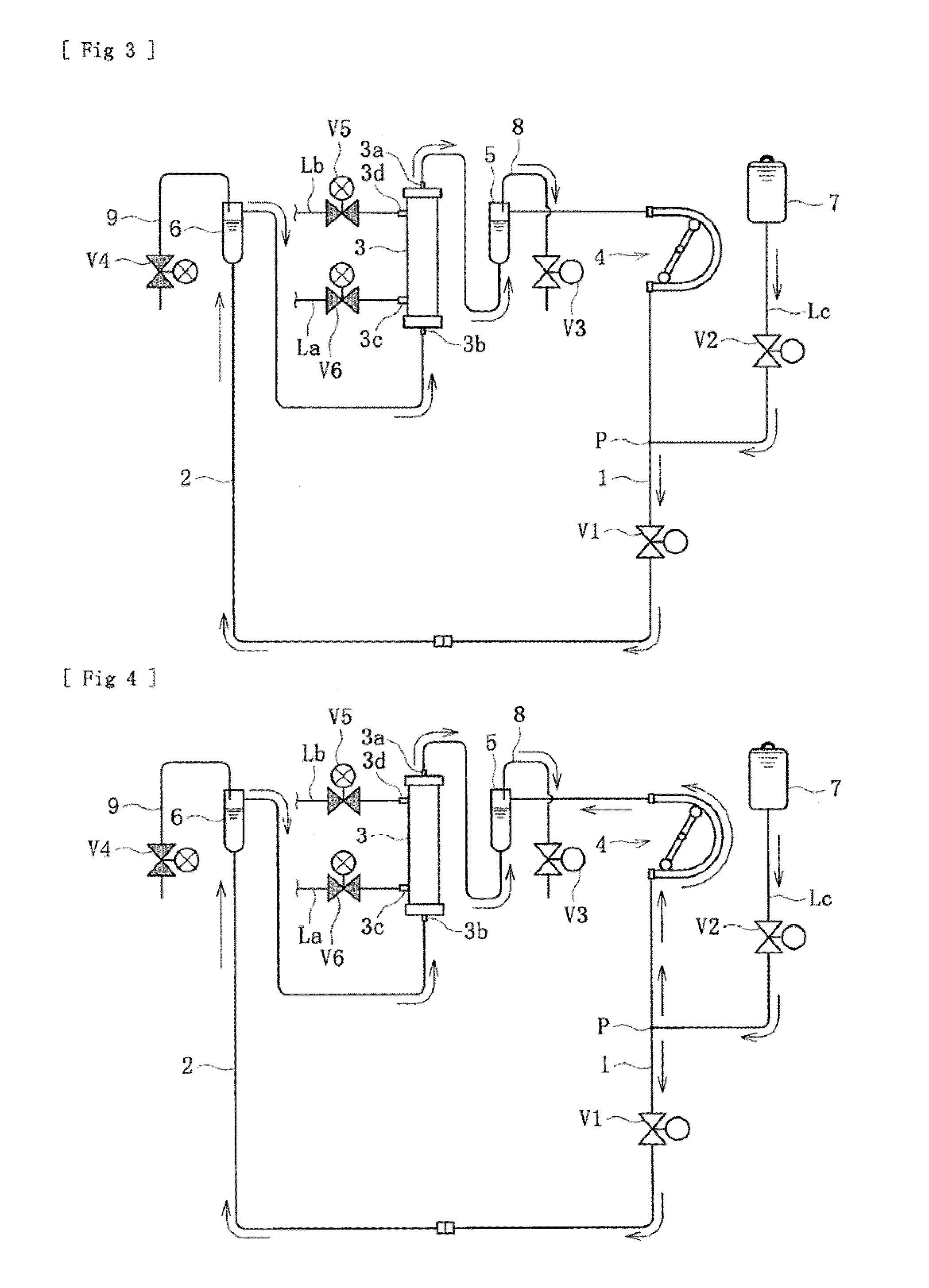
Blood purification apparatus and priming method thereof
InactiveUS20090312686A1Firmly expelFirmly and smoothly performDialysis systemsMedical devicesVenous bloodBlood arterial
An object of the present invention is to provide a blood purification apparatus and a priming method thereof which can firmly perform the bubble purging smoothly and in a short time during priming operation. According to the blood purification apparatus of the present invention, the tip of the arterial blood circuit can be connected to and communicated with the tip of the venous blood circuit during priming of the blood purification apparatus before dialysis, and the blood purification apparatus can perform a priming solution charging step for supplying and charging the blood circuits with priming solution under a condition in which the tip of the arterial blood circuit and the tip of the venous blood circuit are connected to and communicated with each other; and a priming solution circulating step for forcing the charged priming solution to be flowed and circulated through the blood circuits by successively changing the driving speed of the blood pump after the priming solution charging step.
Owner:NIKKISO COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com