Patents
Literature
115 results about "Vascular catheter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
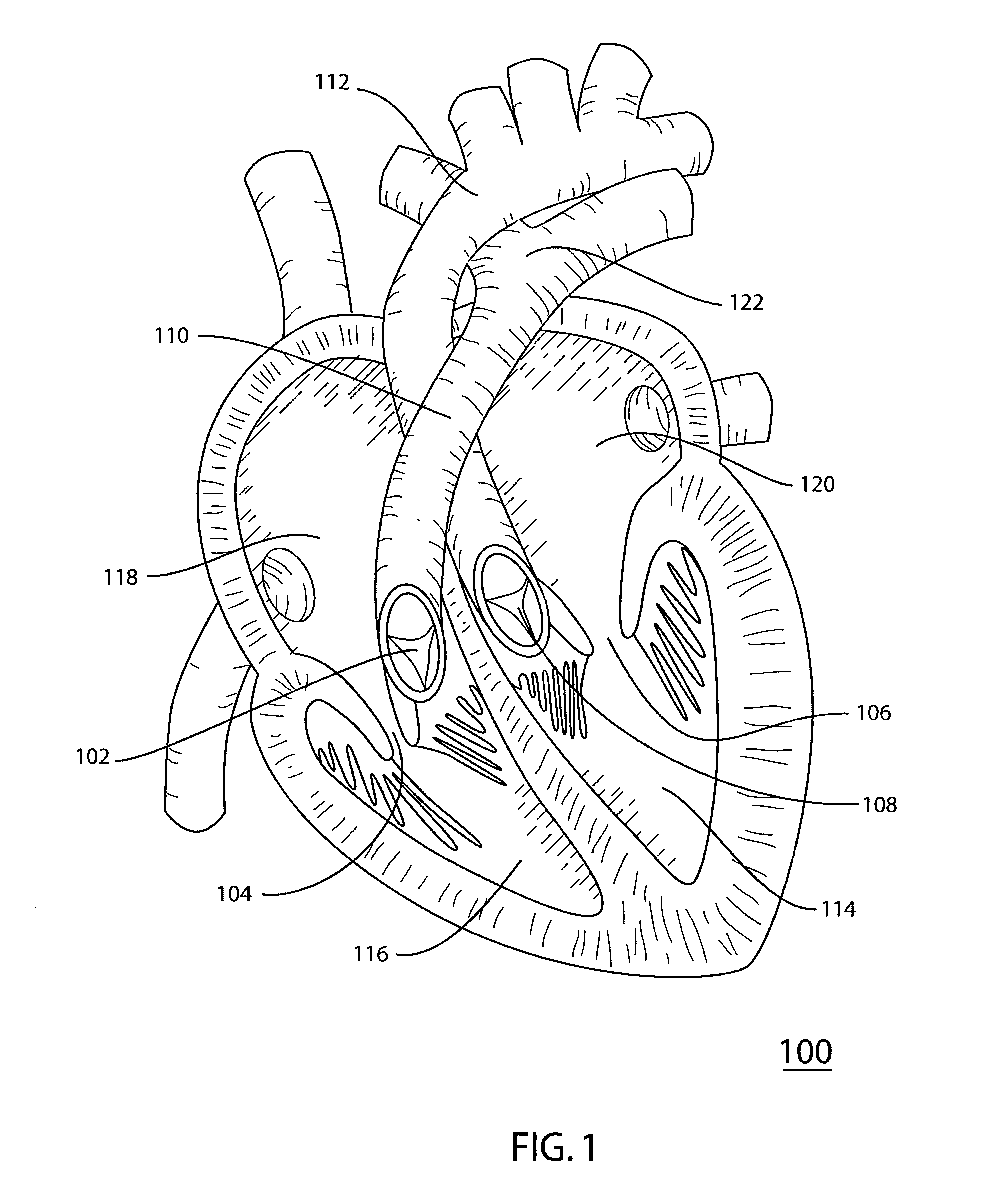
A vascular catheter, or venous catheter, is a thin flexible plastic tube that is inserted into a patient’s vein and remains there for repeated access to the vein. The catheter allows easy access to a patient’s bloodstream for medical uses, such as periodic blood draws and intravenous (IV) drug administration.
Staple and staple applicator for use in skin fixation of catheters
An inexpensive surgical stapler, such as for use in securing vascular catheters, has a plastic applicator made for use with a single staple. The applicator has a backbone and two identical arms. The inside face of the backbone has a retaining channel that secures the crown portion of the staple against movement. The inside faces of the arms have guidance grooves that direct the movement of the staple as the applicator arms are squeezed with finger pressure. The outside faces of the arms are configured to permit gripping by the operator's fingers. The stapler can be used in lieu of suturing. Other staple and applicator assemblies can include two or more of such assemblies.
Owner:DEAN ALLGEYER M D
Complaint implantable medical devices and methods of making same
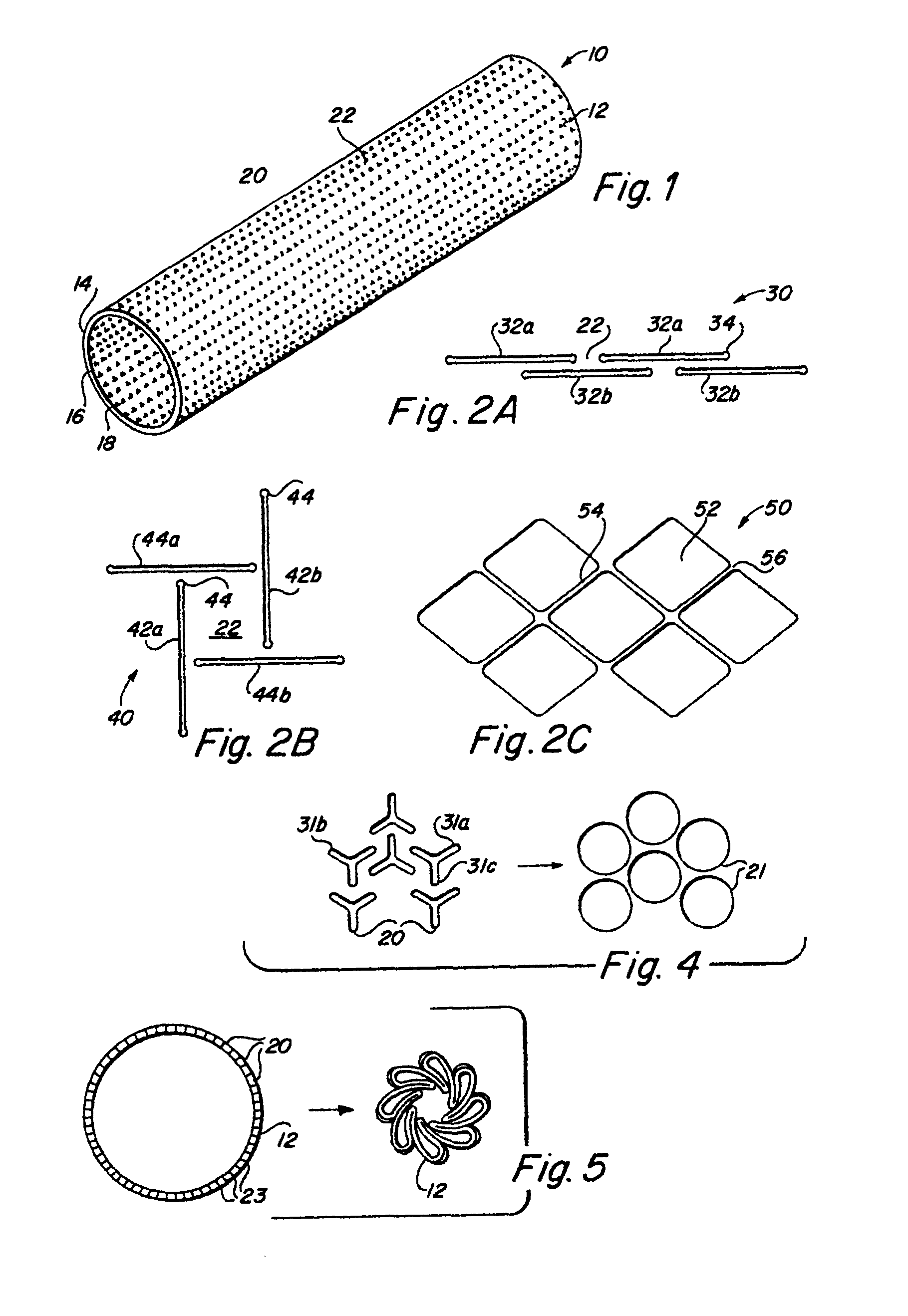
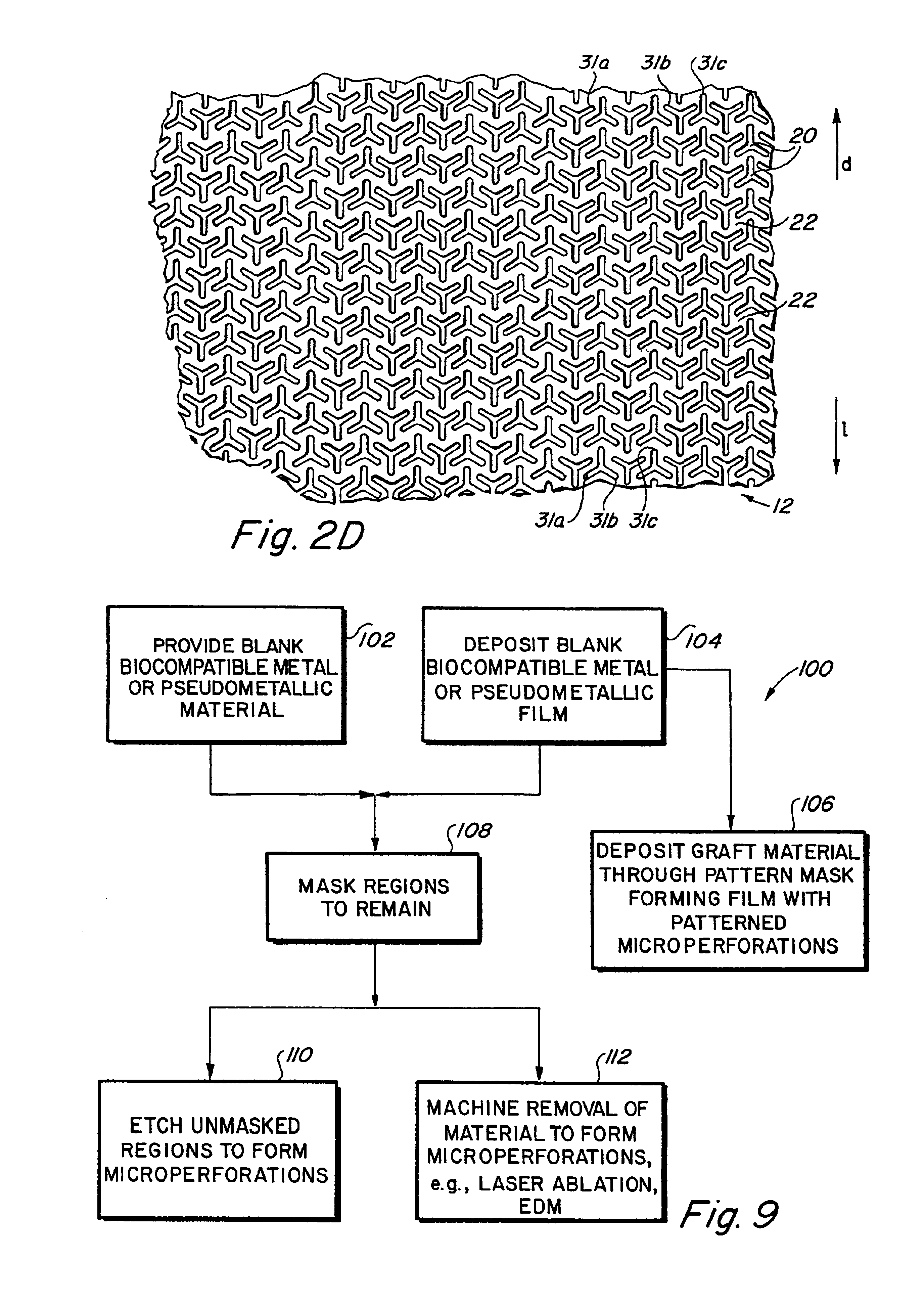
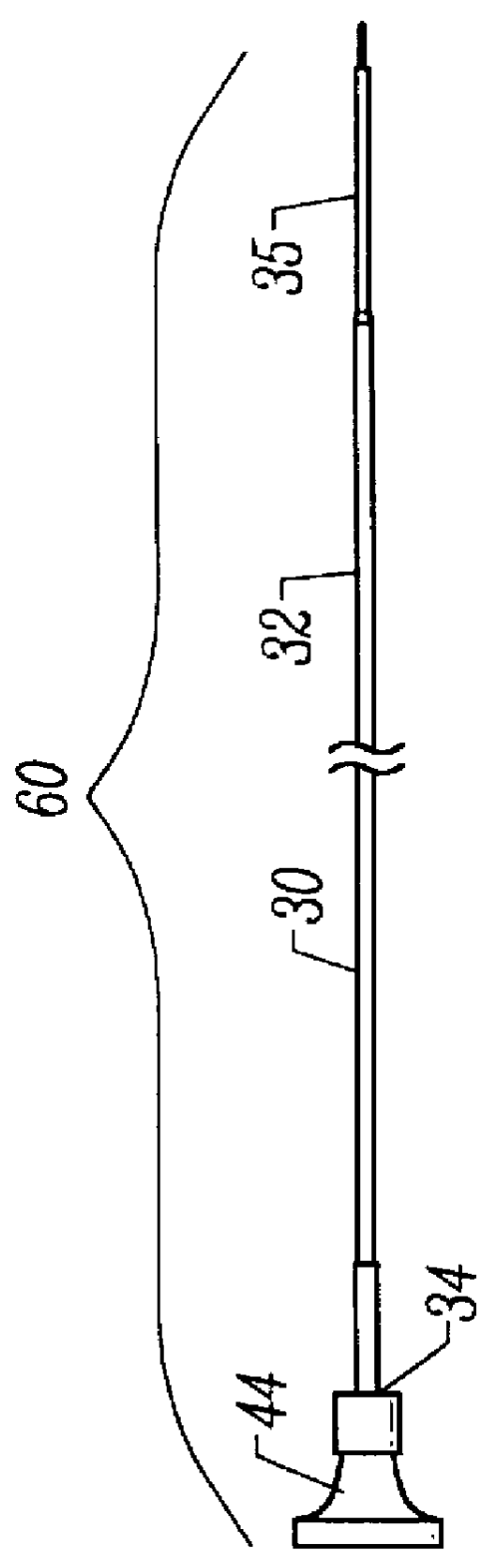
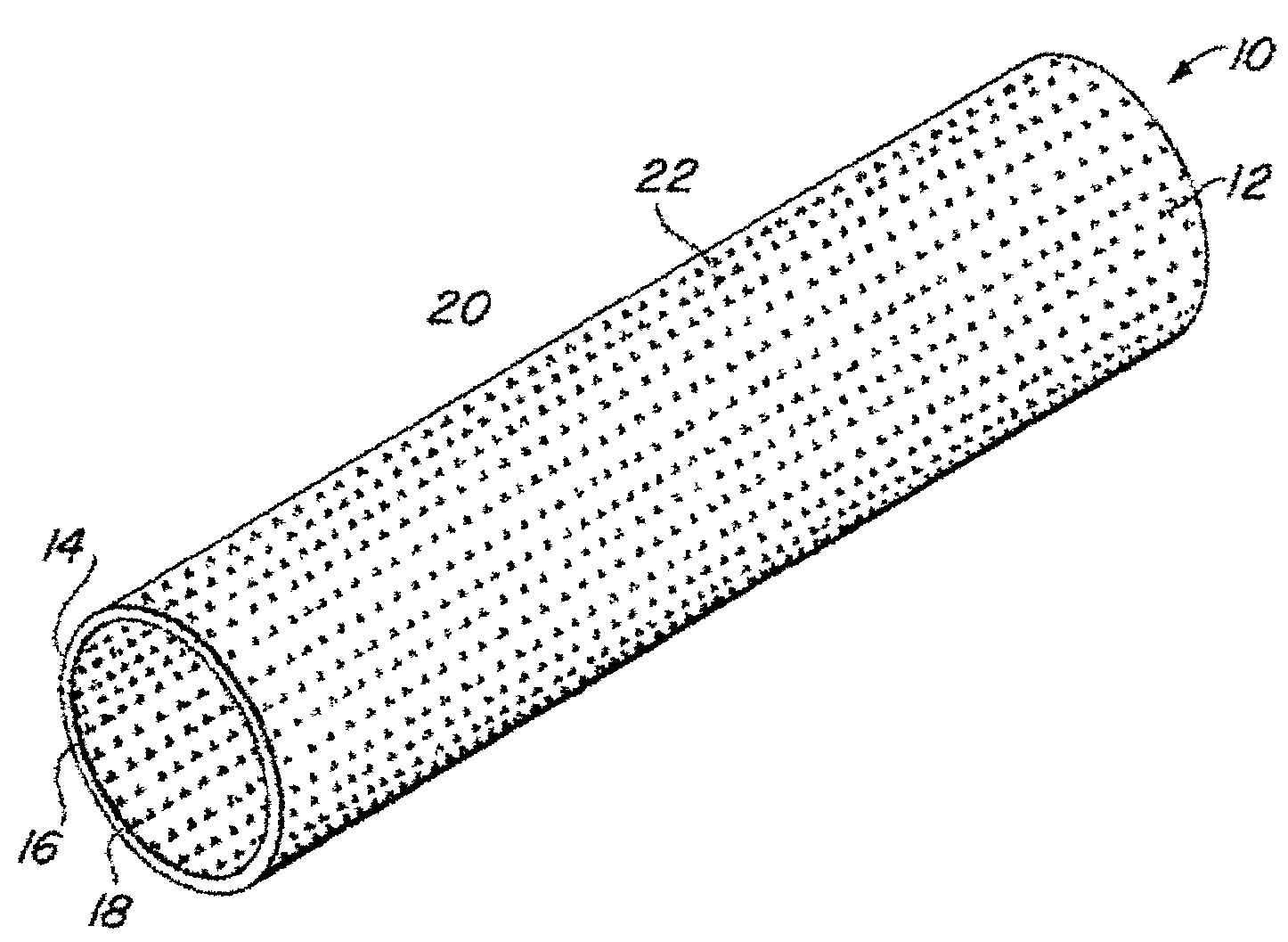
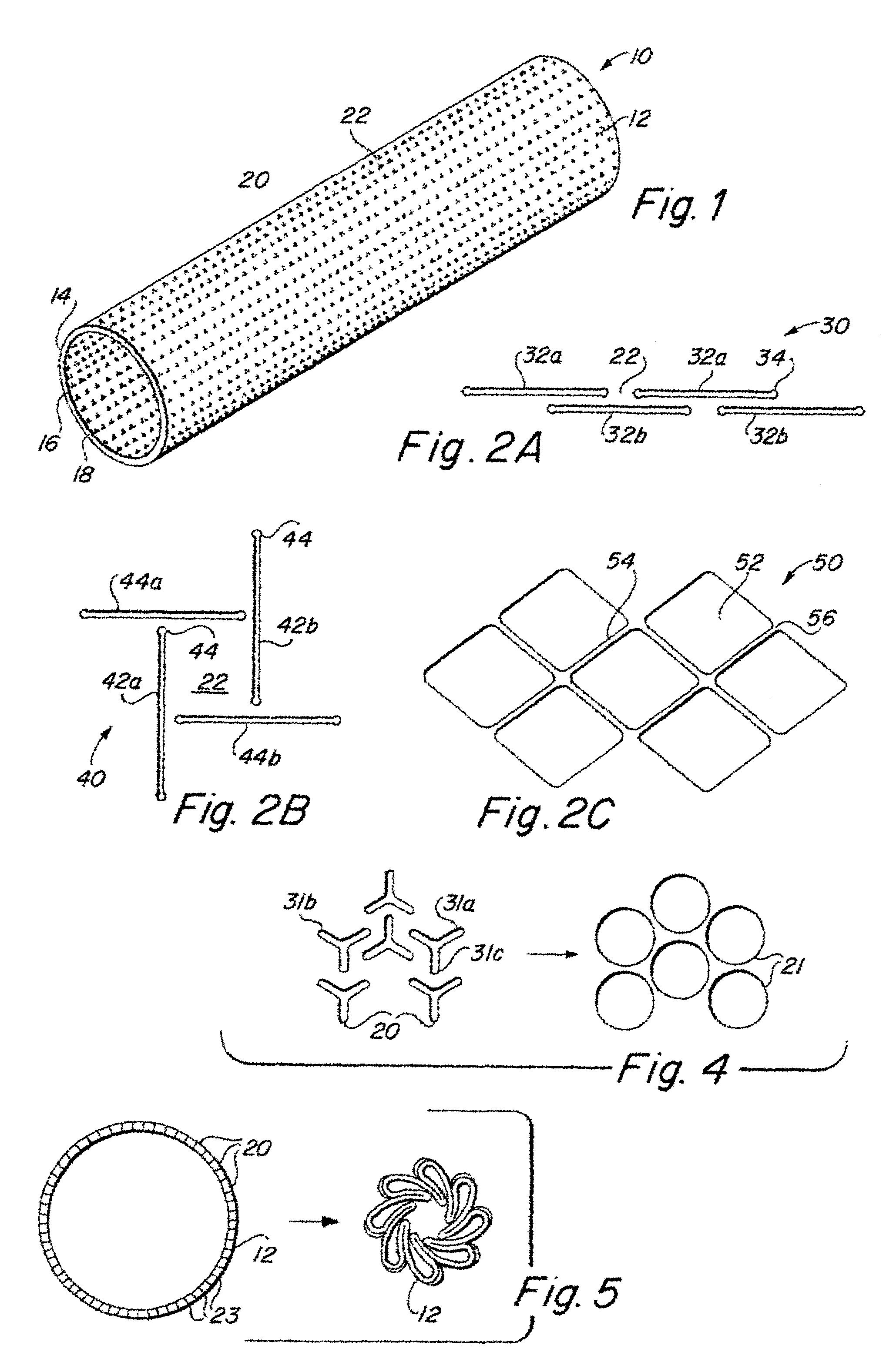
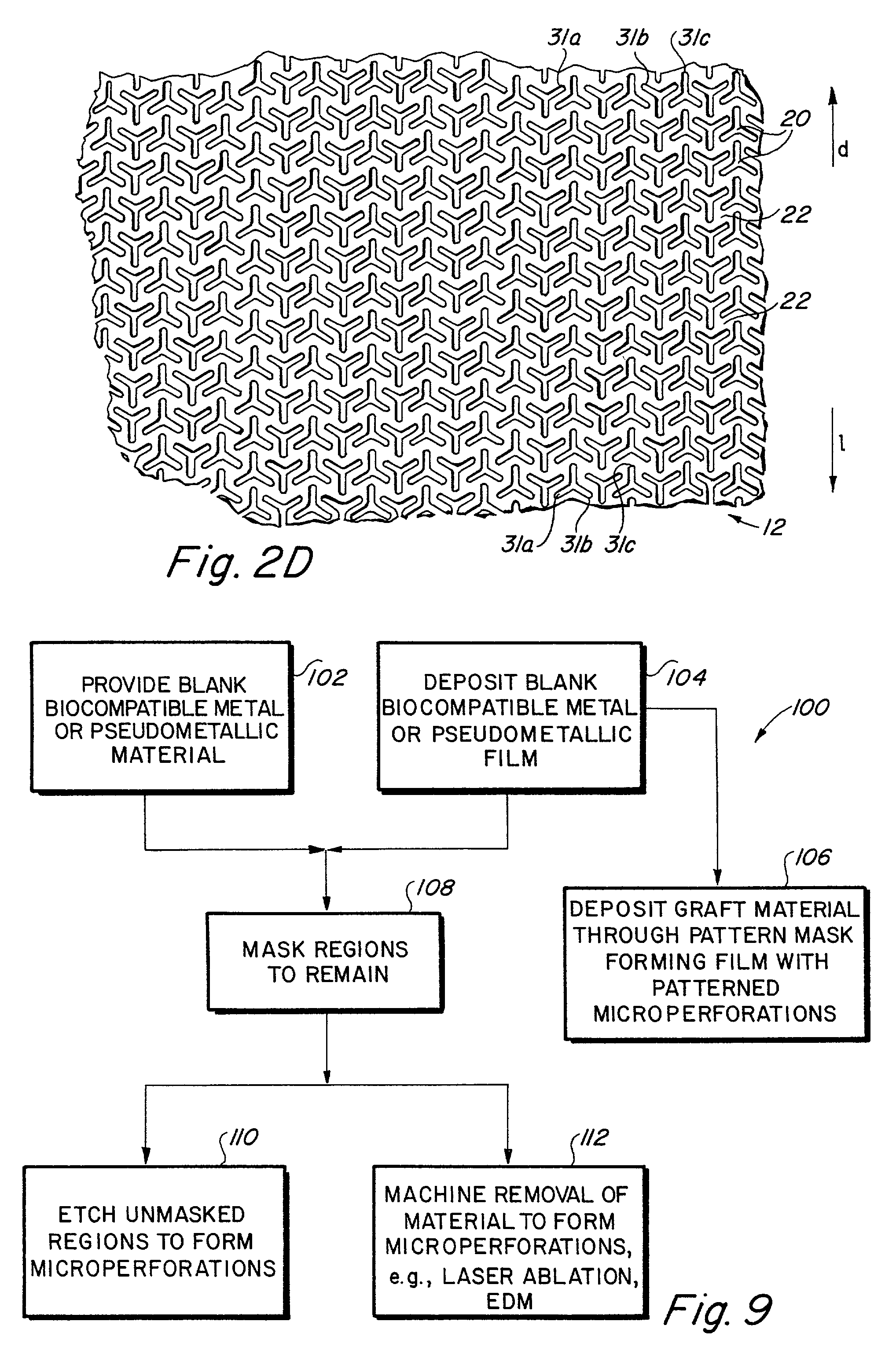
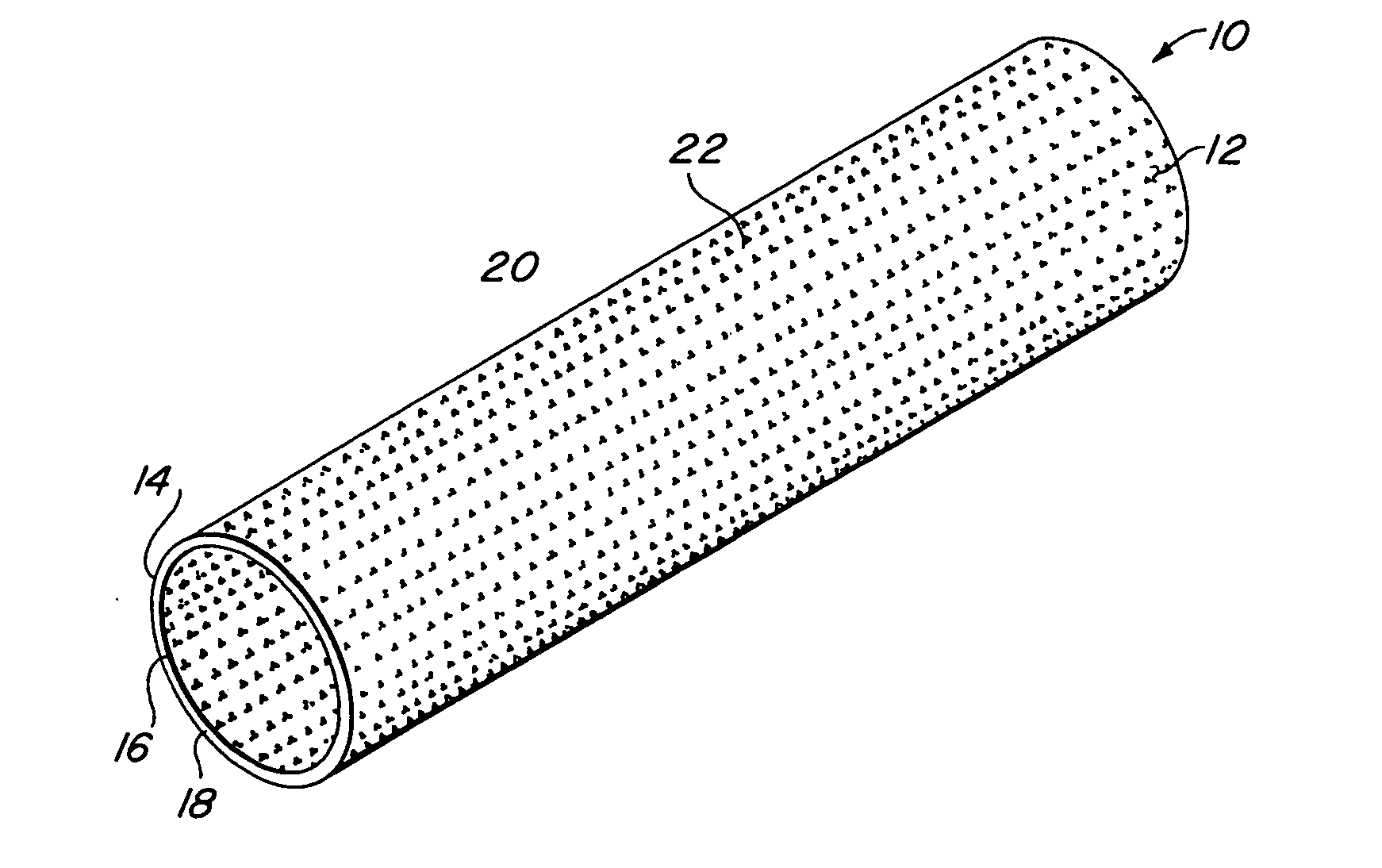
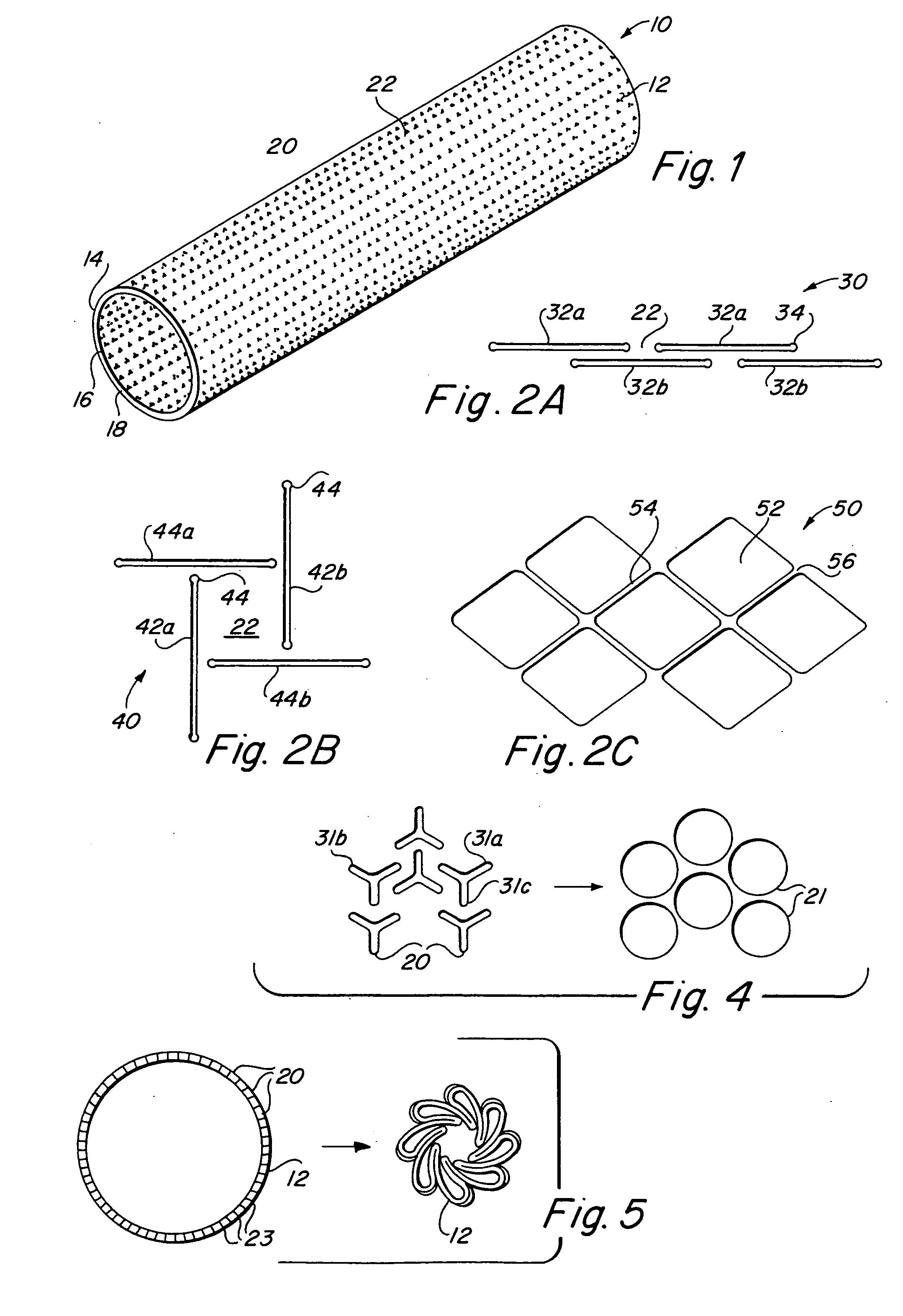
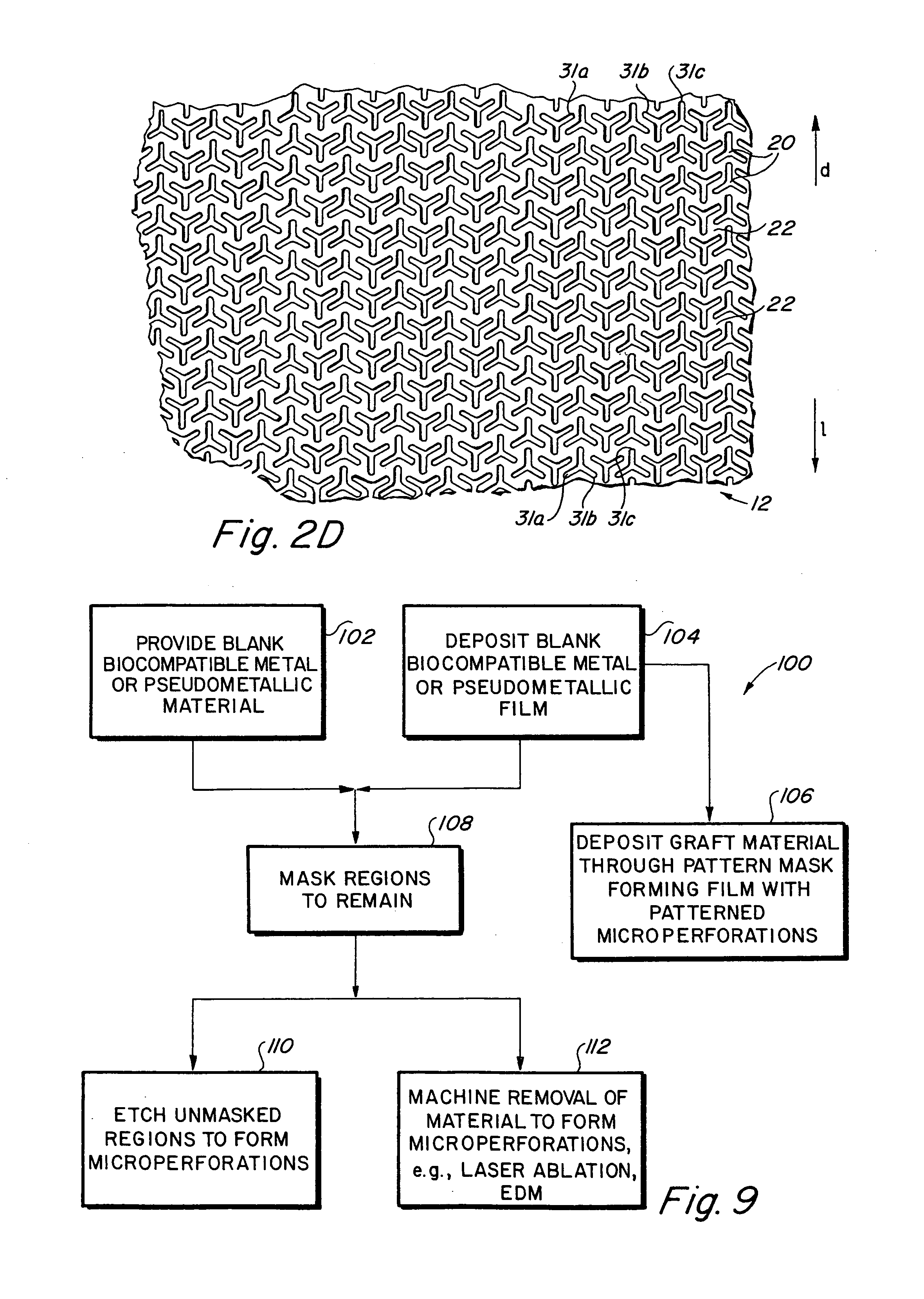
InactiveUS6936066B2Give flexibilityFacilitating transmural endothelializationStentsHeart valvesSurgical GraftMetallic materials
Implantable medical grafts fabricated of metallic or pseudometallic films of biocompatible materials having a plurality of microperforations passing through the film in a pattern that imparts fabric-like qualities to the graft or permits the geometric deformation of the graft. The implantable graft is preferably fabricated by vacuum deposition of metallic and / or pseudometallic materials into either single or multi-layered structures with the plurality of microperforations either being formed during deposition or after deposition by selective removal of sections of the deposited film. The implantable medical grafts are suitable for use as endoluminal or surgical grafts and may be used as vascular grafts, stent-grafts, skin grafts, shunts, bone grafts, surgical patches, non-vascular conduits, valvular leaflets, filters, occlusion membranes, artificial sphincters, tendons and ligaments.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
Catheher system having connectable distal and proximal portions
InactiveUS6050949AEnhanced hoop strengthBending stiffnessUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryPlastic materialsUltrasonic imaging
A vascular catheter system comprises a catheter body having a proximal and distal portion and a single common lumen therebetween. The catheter body includes a first connector secured to the distal end of the proximal portion and a second connector secured to the proximal end of the distal portion. The connectors can be selectively connected to each other to join the lumens of the proximal and distal portions together in a continuous, axially fixed relationship. Disposed within the lumens, when the proximal and distal portions are joined together, is a drive cable. The drive cable may be movably, rotatable about its own longitudinal axis and carries at its distal end, a work element, which is typically an ultrasonic imaging transducer or interventional device. The lumen carrying the cable will be sufficiently large along a proximal portion to permit preferential collapse of the cable should rotation of the distal end become impeded. The catheter body may be made of a polymer or plastic material, such as polyetheretherketone (PEEK), which provides adequate bonding stiffness and resistance to kinking from large hoop stresses.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Self-supporting metallic implantable grafts, compliant implantable medical devices and methods of making same
Implantable medical grafts fabricated of metallic or pseudometallic films of biocompatible materials having a plurality of microperforations passing through the film in a pattern that imparts fabric-like qualities to the graft or permits the geometric deformation of the graft. The implantable graft is preferably fabricated by vacuum deposition of metallic and / or pseudometallic materials into either single or multi-layered structures with the plurality of microperforations either being formed during deposition or after deposition by selective removal of sections of the deposited film. The implantable medical grafts are suitable for use as endoluminal or surgical grafts and may be used as vascular grafts, stent-grafts, skin grafts, shunts, bone grafts, surgical patches, non-vascular conduits, valvular leaflets, filters, occlusion membranes, artificial sphincters, tendons and ligaments.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
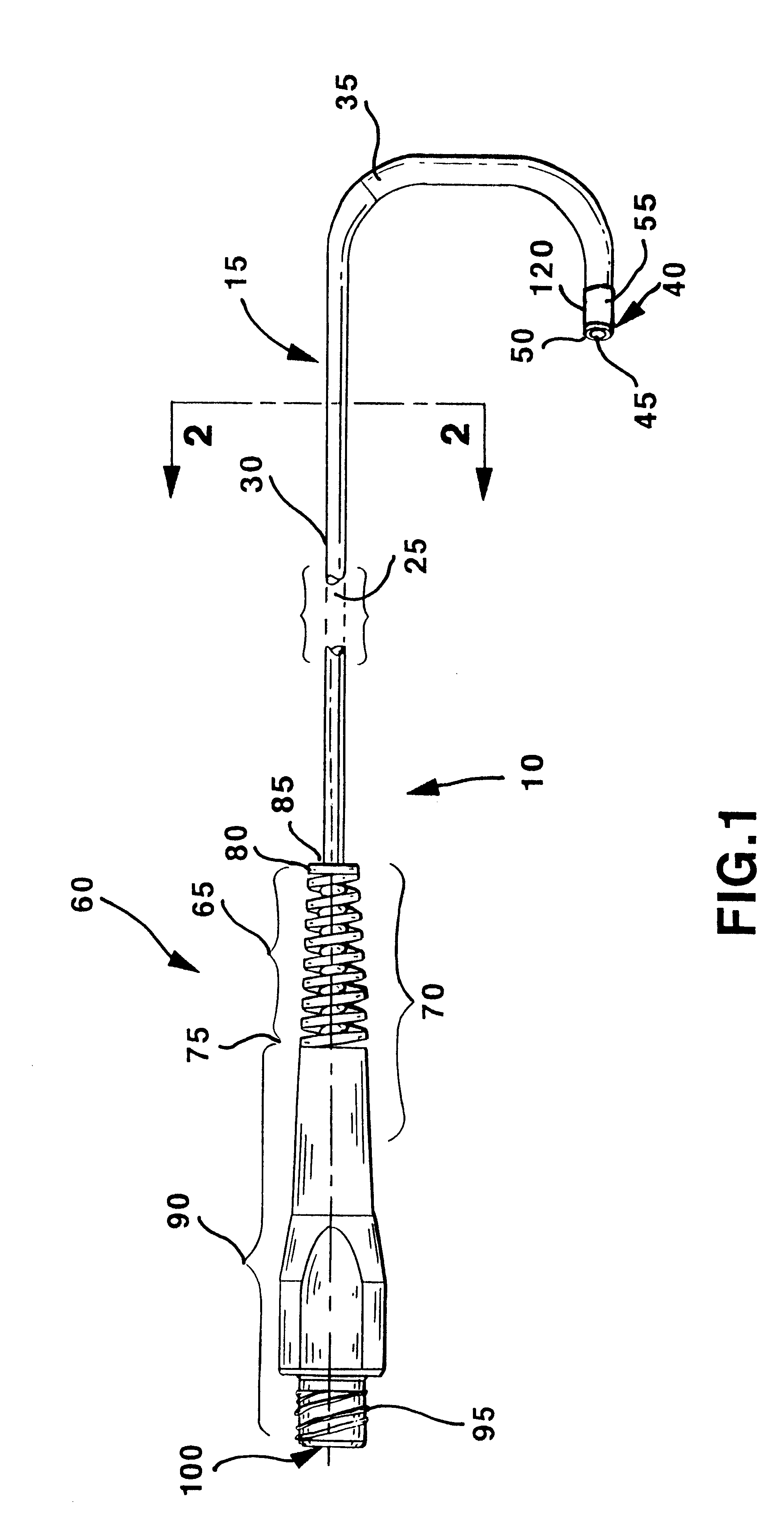
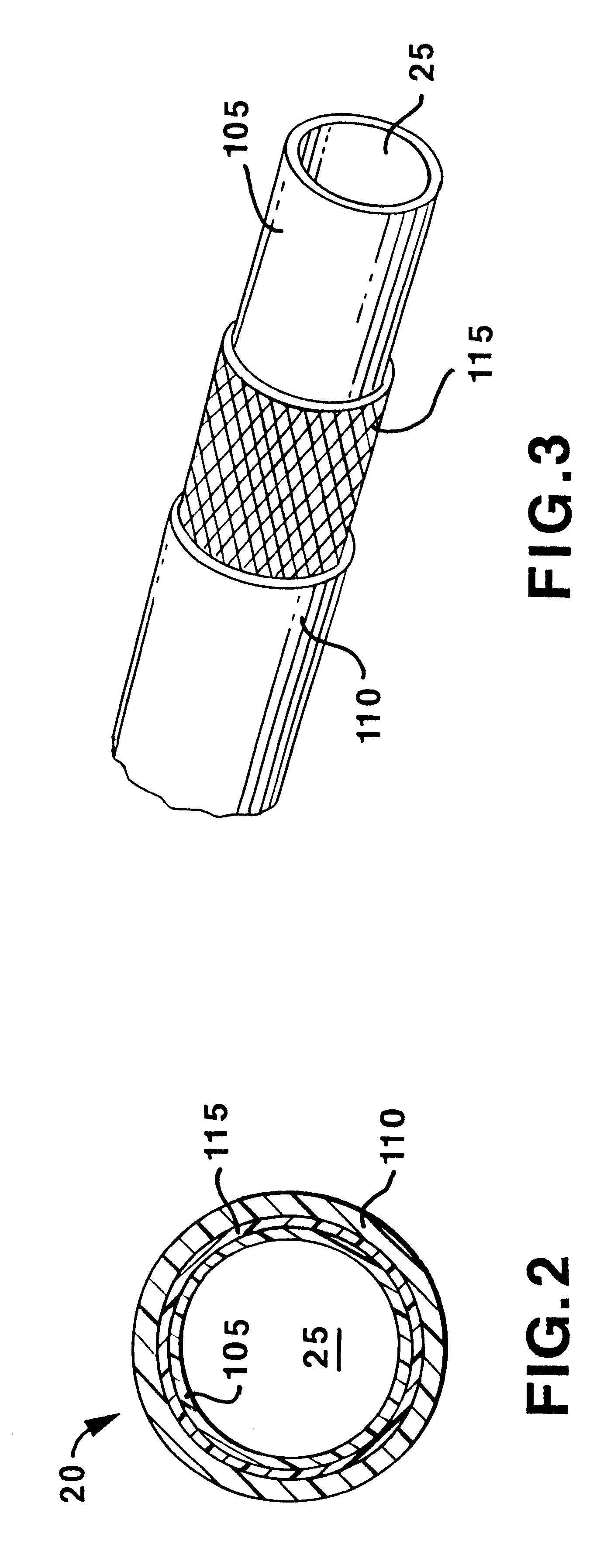
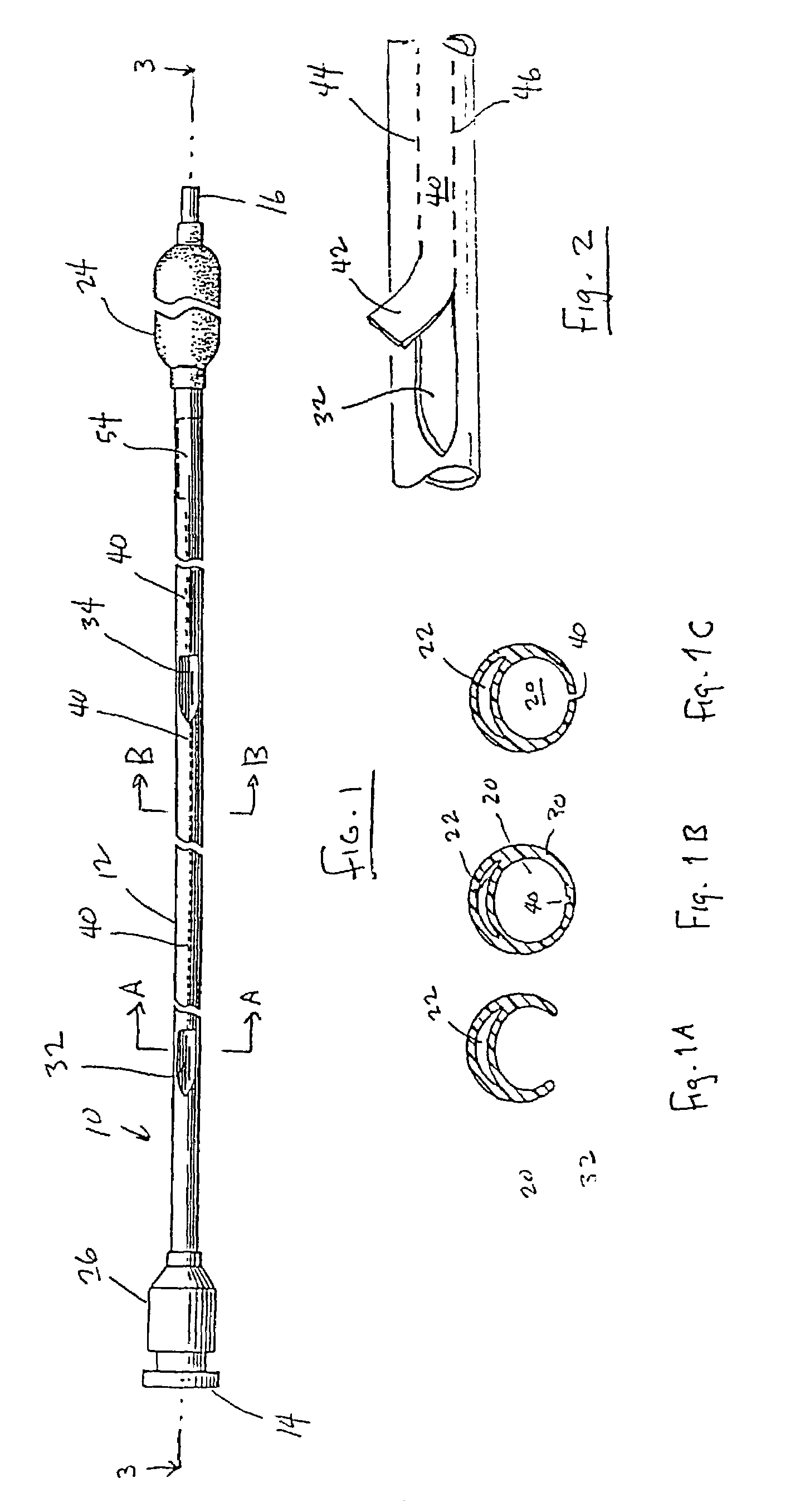
Multiple segment catheter and method of fabrication
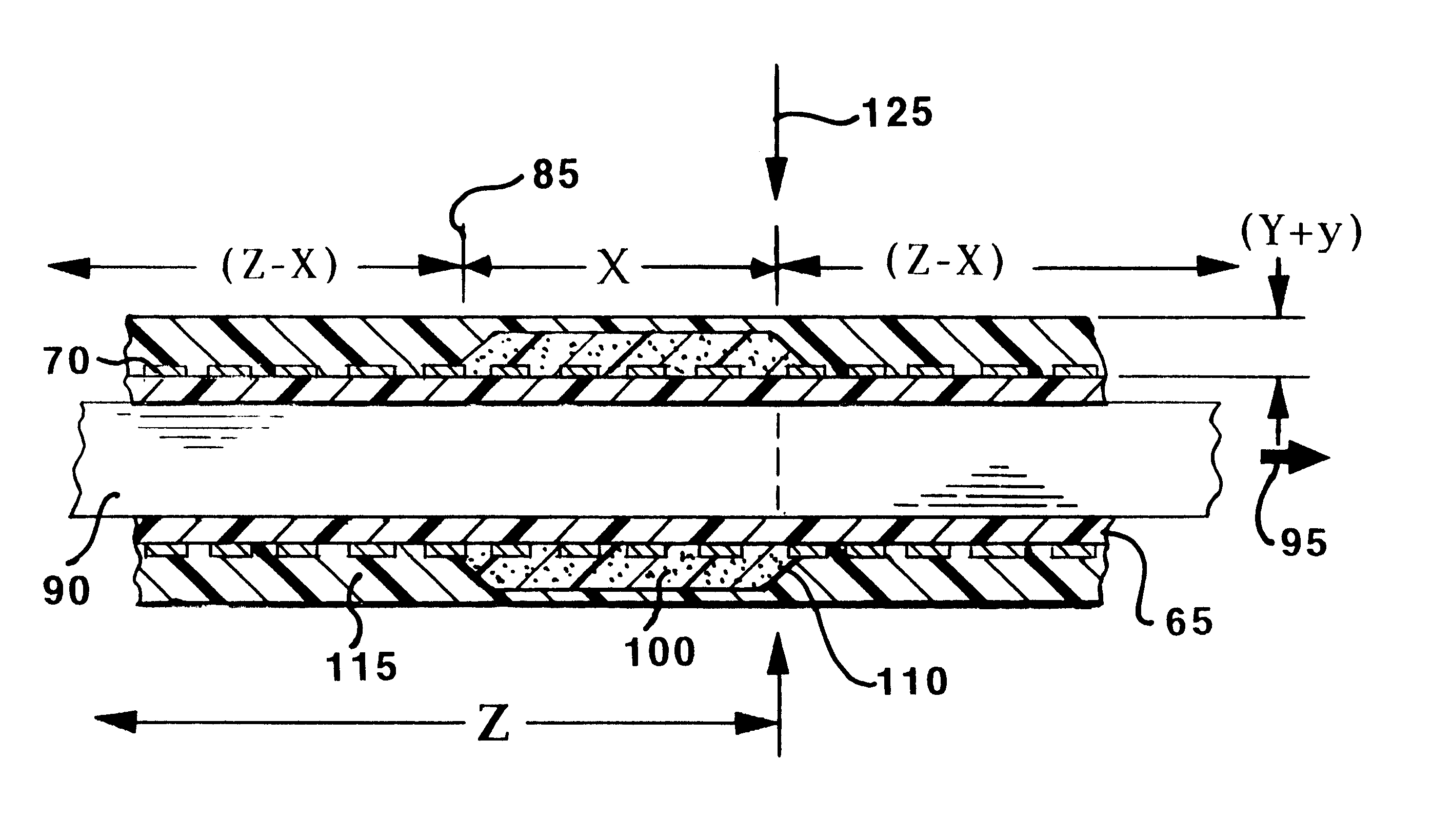
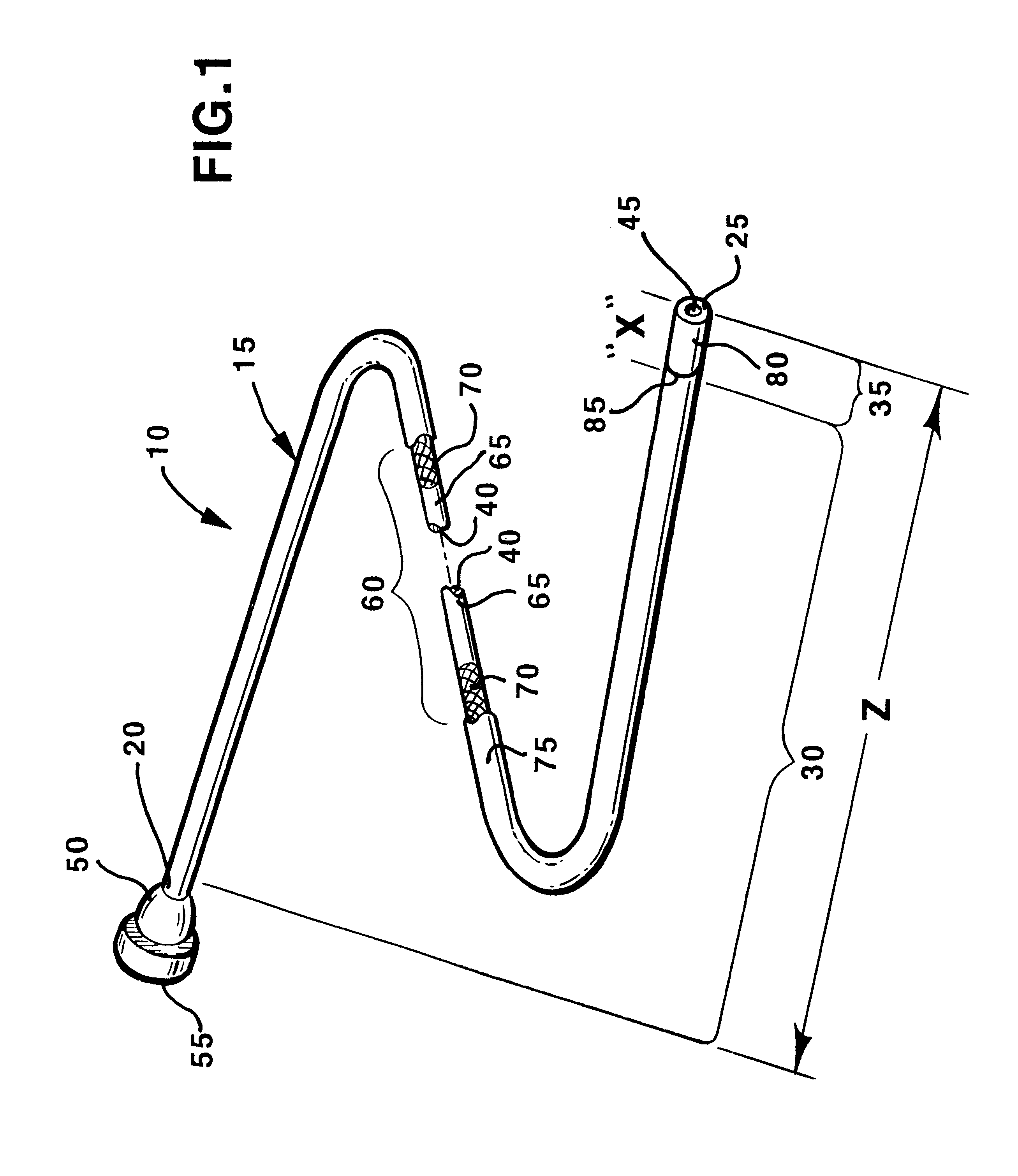
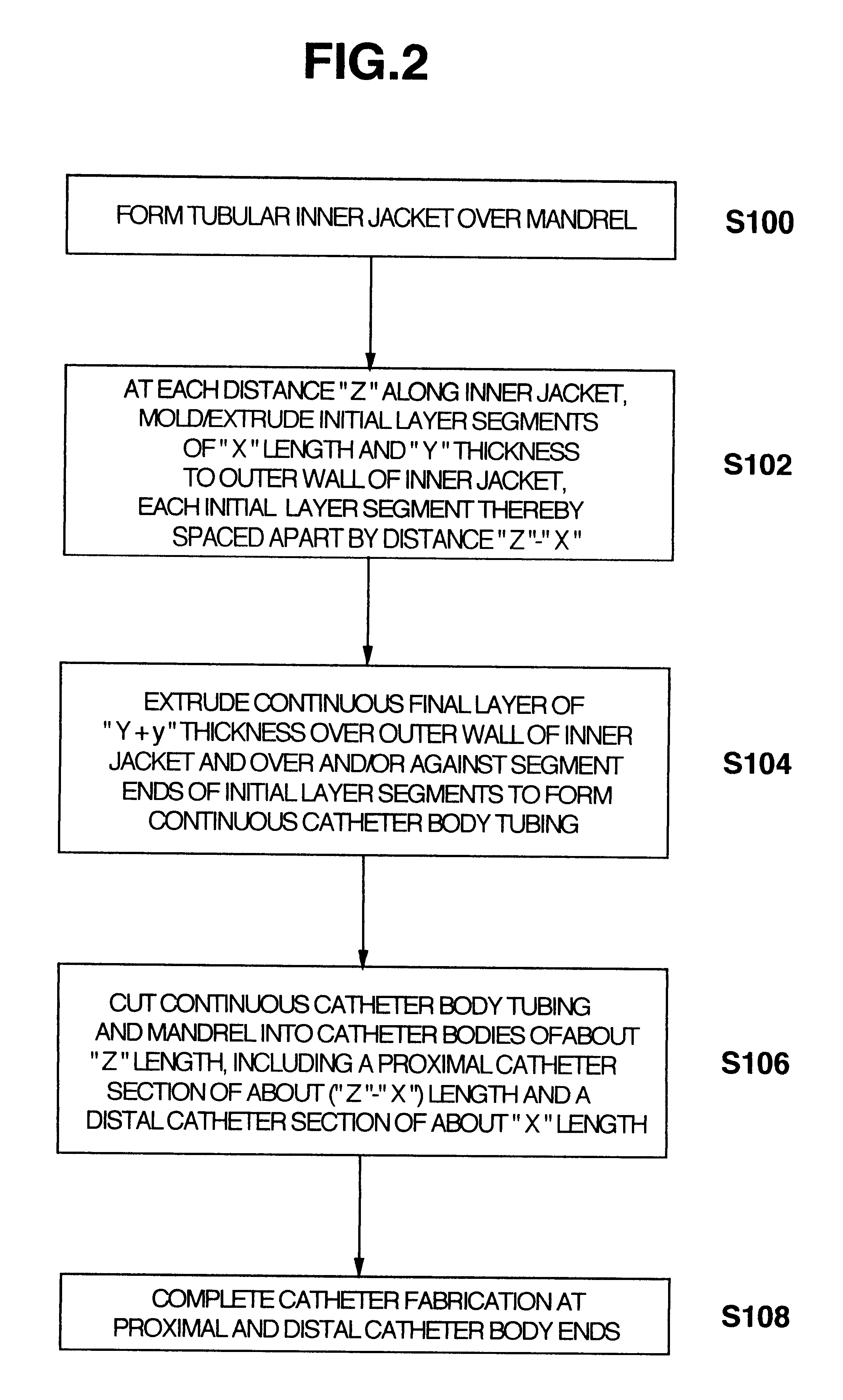
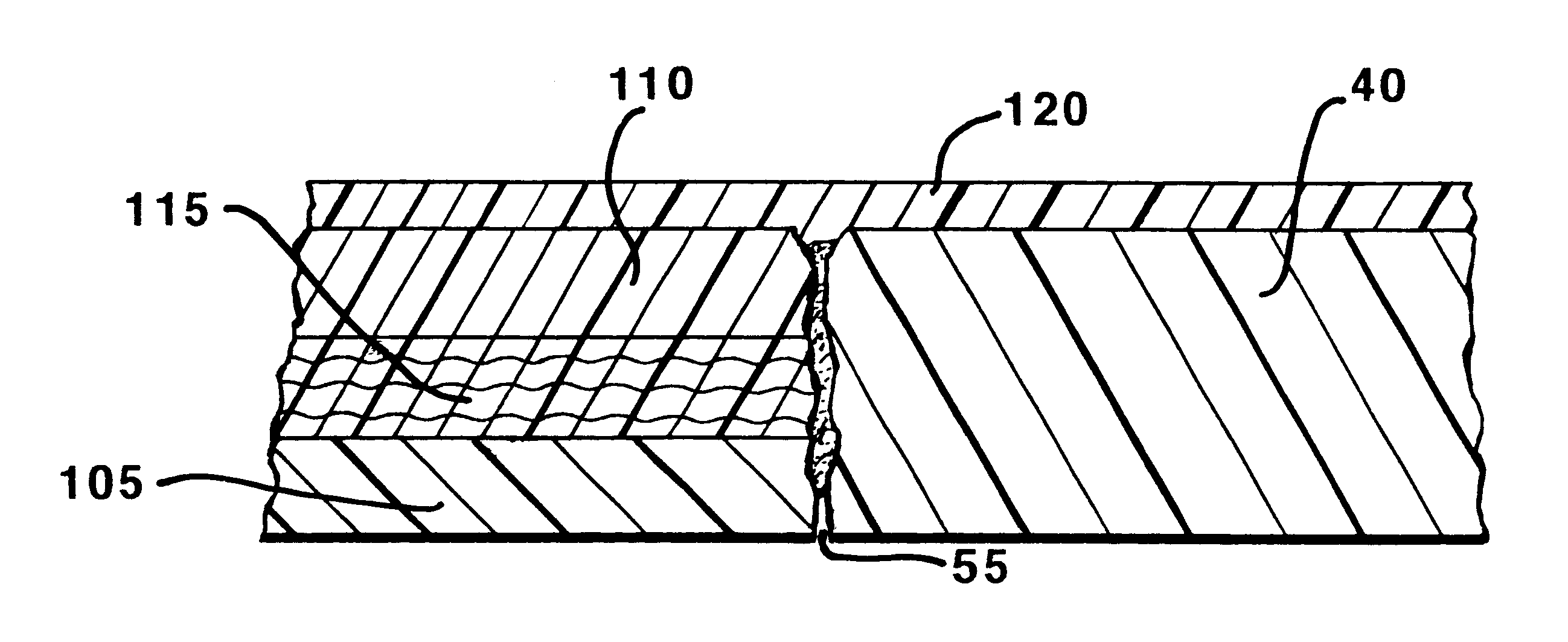
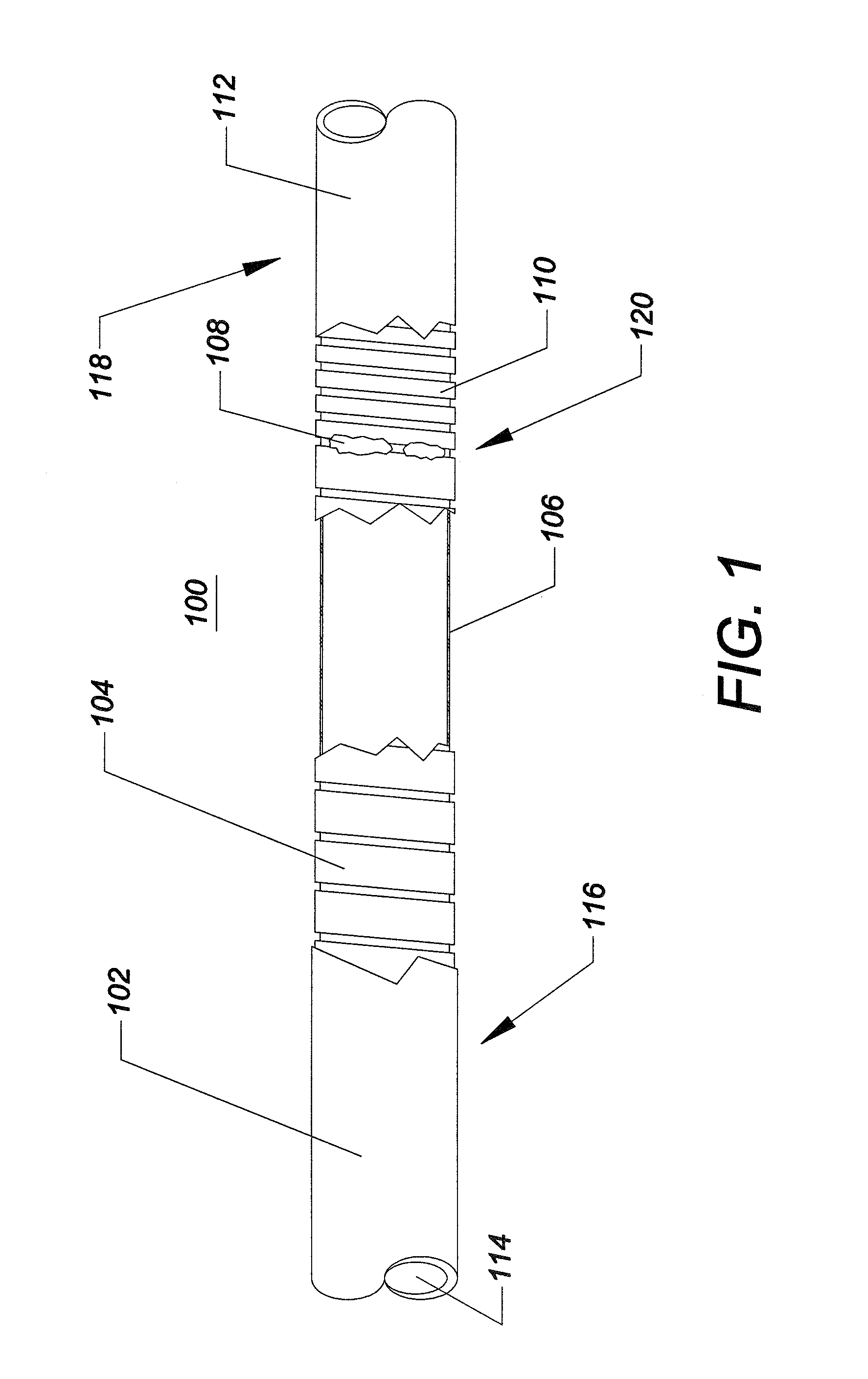
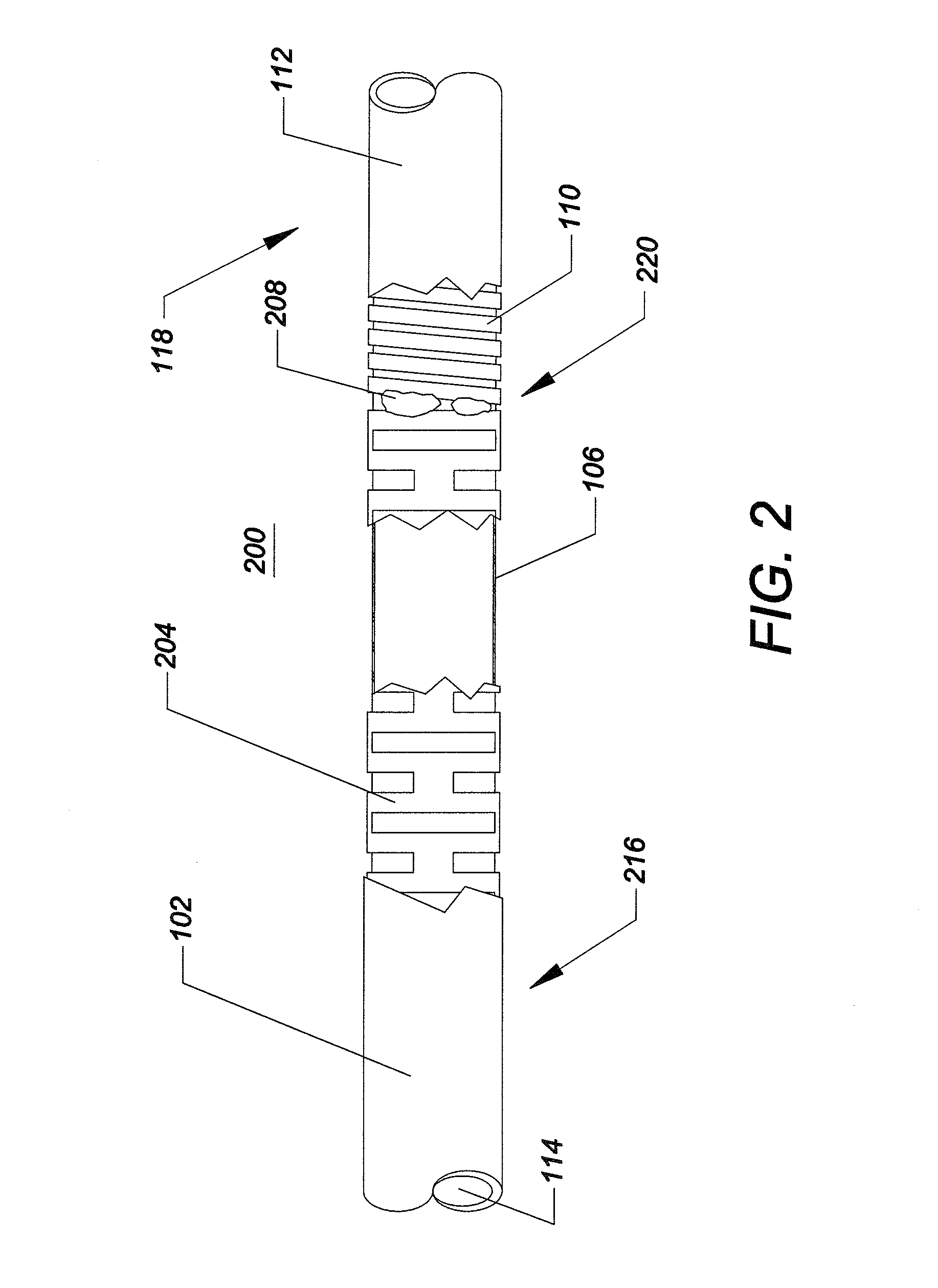
Methods of fabricating medical vascular catheters adapted to be inserted into a blood vessel from an incision through the skin of a patient for introducing other devices or fluids for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes and particularly methods for fabricating such catheters with catheter bodies having catheter sections of differing flexibility are disclosed. Such catheter bodies having a proximal catheter body end and a distal catheter body end and formed of a proximal section and at least one distal section that have differing flexibilities are formed in a process comprising the steps of: (1) forming a continuous tubular inner jacket preferably of an inner liner and a reinforcement layer; (2) forming initial layer segments having an initial layer thickness along the length of the inner jacket from a material of first durometer hardness, whereby each initial layer segment is separated by a separation distance: (3) forming a final layer of a material of second durometer hardness with a second layer thickness over the tubular inner jacket along the separation distances and over and / or against the proximal and distal initial layer ends of the initial layer segments to form a continuous catheter body tubing; (4) severing the continuous catheter body tubing into catheter body lengths including a proximal catheter section formed of the material of second hardness and a distal catheter section of the material of first hardness; and (5) completing the catheter fabrication at the proximal catheter body end and the distal catheter body end. Centerless grinding of the catheter body or body tubing, formation of Intermediate catheter body sections, distal soft tips, and discontinuities in the reinforcement layer formed prior to step (2) are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
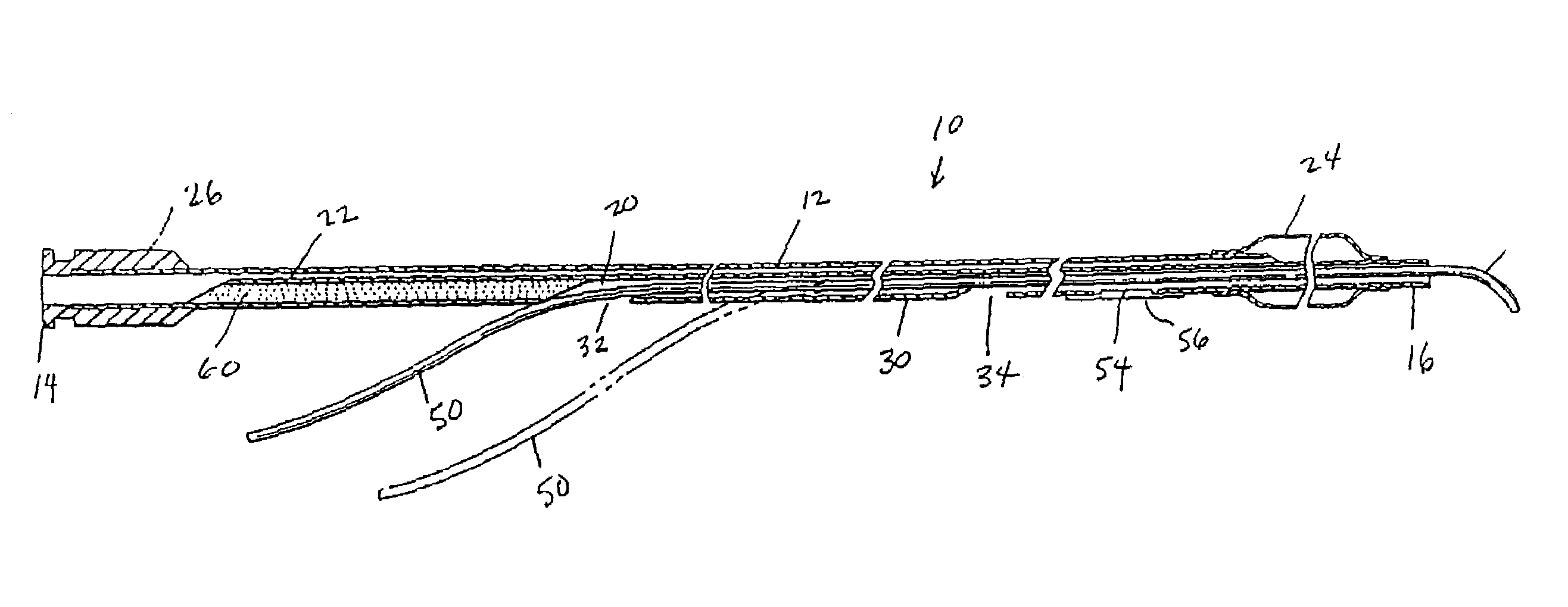
Soft tip guiding catheter and method of fabrication
The present invention relates to medical vascular catheters adapted to be inserted into a blood vessel from an incision through the skin of a patient for introducing ther devices or fluids for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes, and particularly to an improved distal soft tip or segment attachment with a relatively stiff proximal catheter shaft. A tubular sleeve is bonded through the application of pressure and heat to a distal portion of the catheter shaft and a proximal portion of the distal segment of soft distal tip bridging the attachment junction. In the preferred method, the catheter shaft distal end is aligned with the distal segment or soft tip proximal end and the sleeve is fitted over the attachment junction. A heat shrink tube is fitted over the sleeve and adjoining portions of the catheter shaft and the distal segment or distal soft tip and heat is applied. The shrinkage force of the heat shrink tube over the assembly of the tubular sleeve overlying and bridging the attachment junction and the applied heat melts and force the materials of the tubular sleeve and the catheter shaft and the distal segment or distal soft tip together to fill interstitial spaces of the attachment junction and reduces the outer diameter of the sleeve. The heat shrink tube is removed after the assembly cools and solidifies. Preferably, the catheter shaft distal end and the soft tip or intermediate segment proximal end are each formed with a like plurality of ungular cut sections that are complementary in shape to one another, whereby the ungular cut sections are aligned with and mated together along the attachment junction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
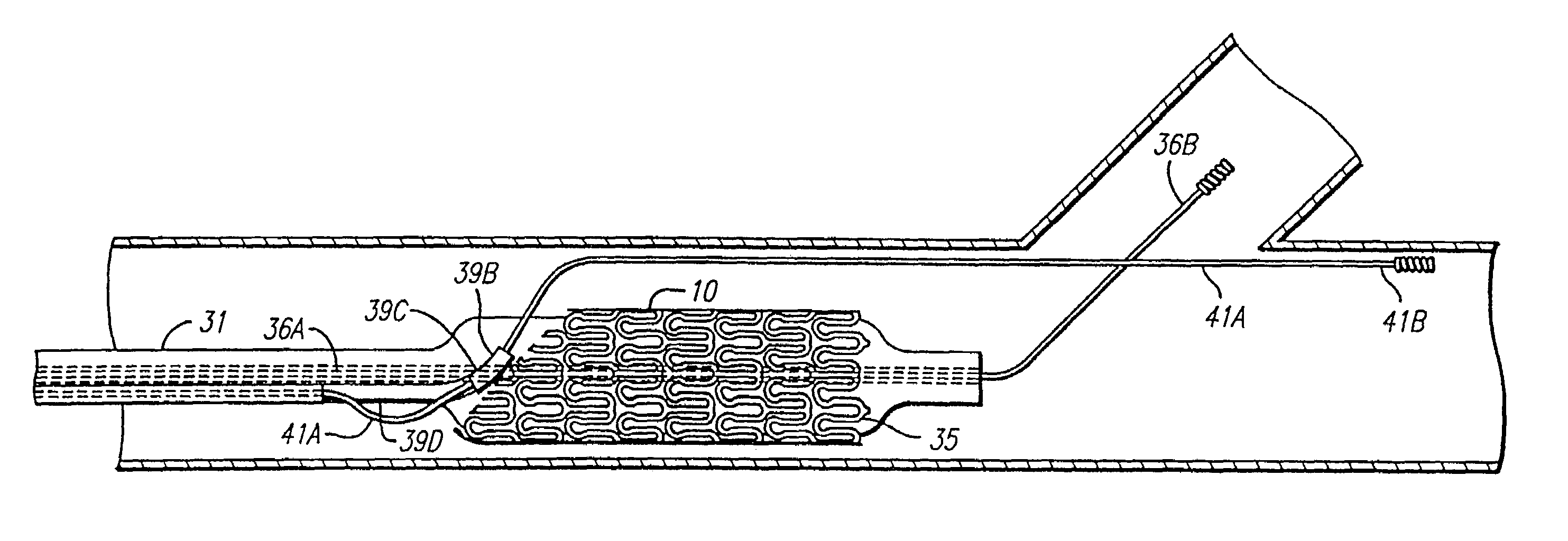
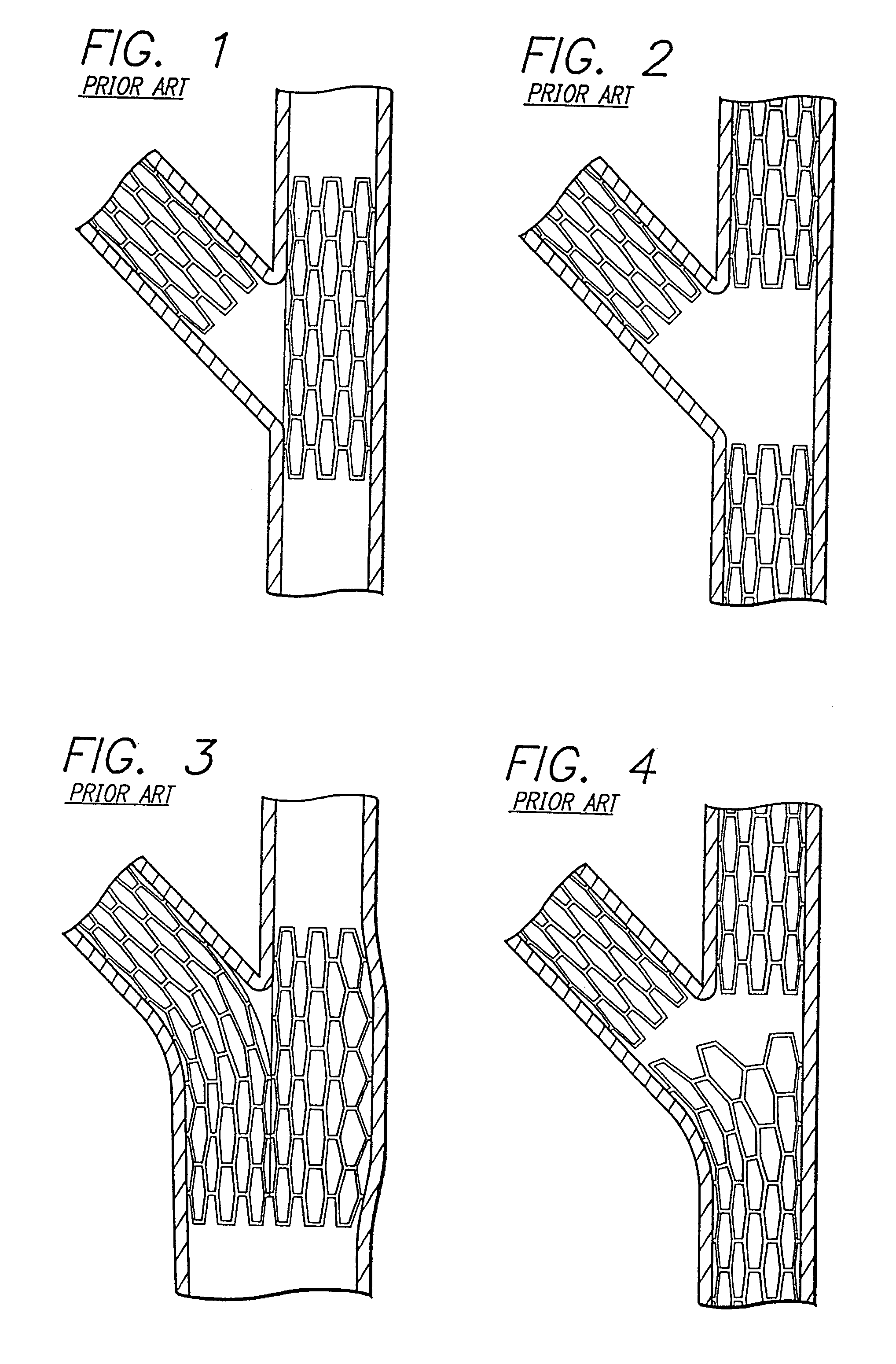
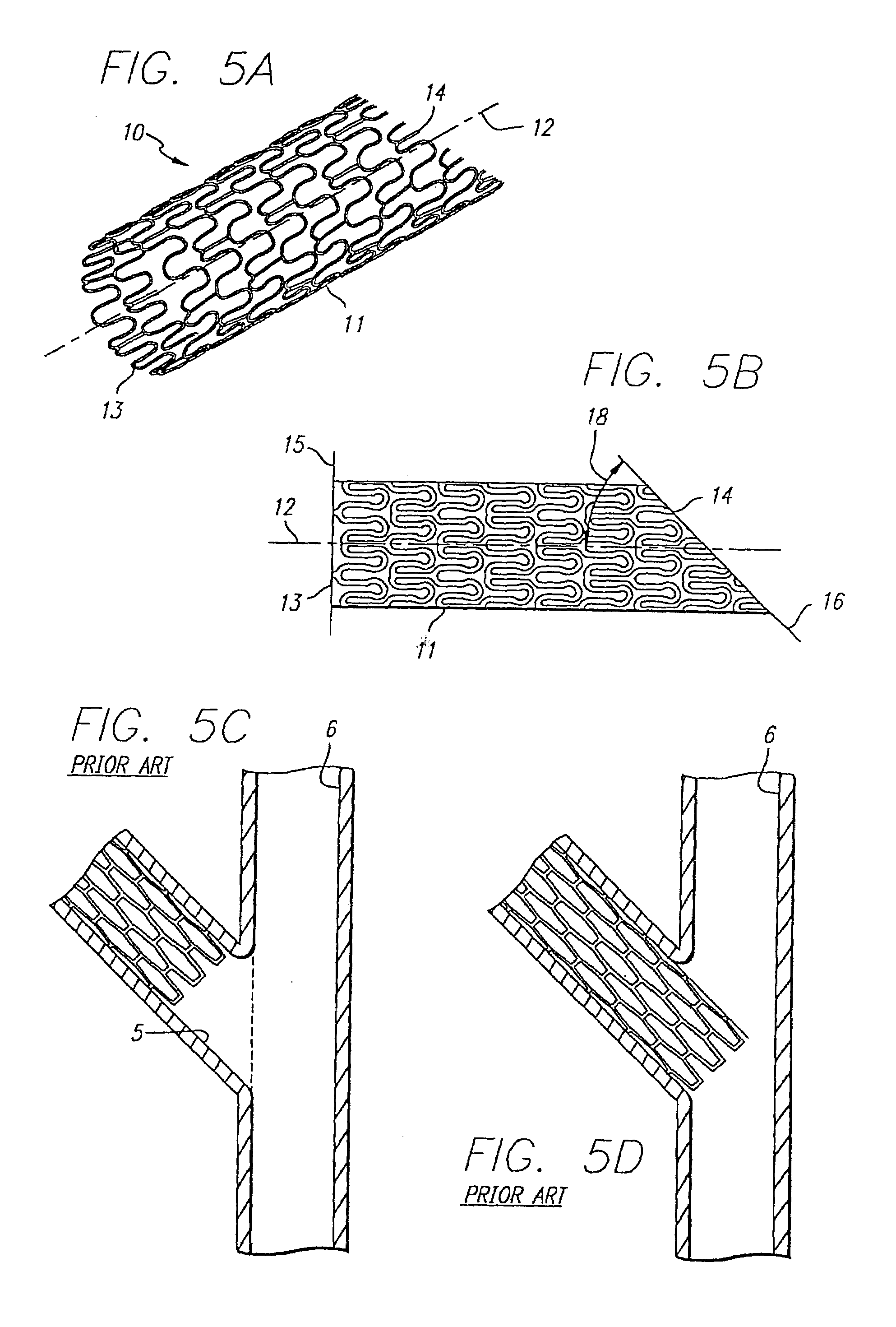
Stent and catheter assembly and method for treating bifurcations
An apparatus and method is provided for stenting bifurcated vessels. A proximal angled stent is configured for implanting in a side-branch vessel wherein the proximal angled stent has an angulated portion that corresponds to the angle formed by the intersection of the side-branch vessel and the main vessel so that all portions of the side-branch vessel at the bifurcation are covered by the proximal angled stent. A main-vessel stent is provided for implanting in the main vessel, wherein the main-vessel stent has an aperture or stent cell that aligns with the opening to the side-branch vessel to permit unobstructed blood flow between the main vessel and the side-branch vessel. Side-branch and main-vessel catheter assemblies are advanced over a pair of guide wires for delivering, appropriately orienting, and implanting the proximal angled stent and the apertured stent.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
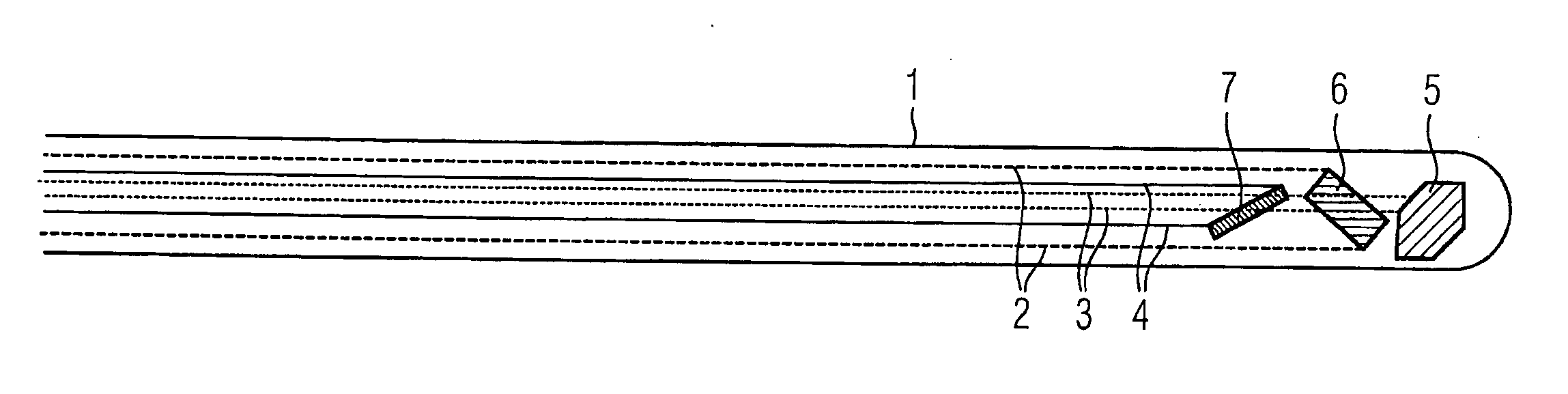
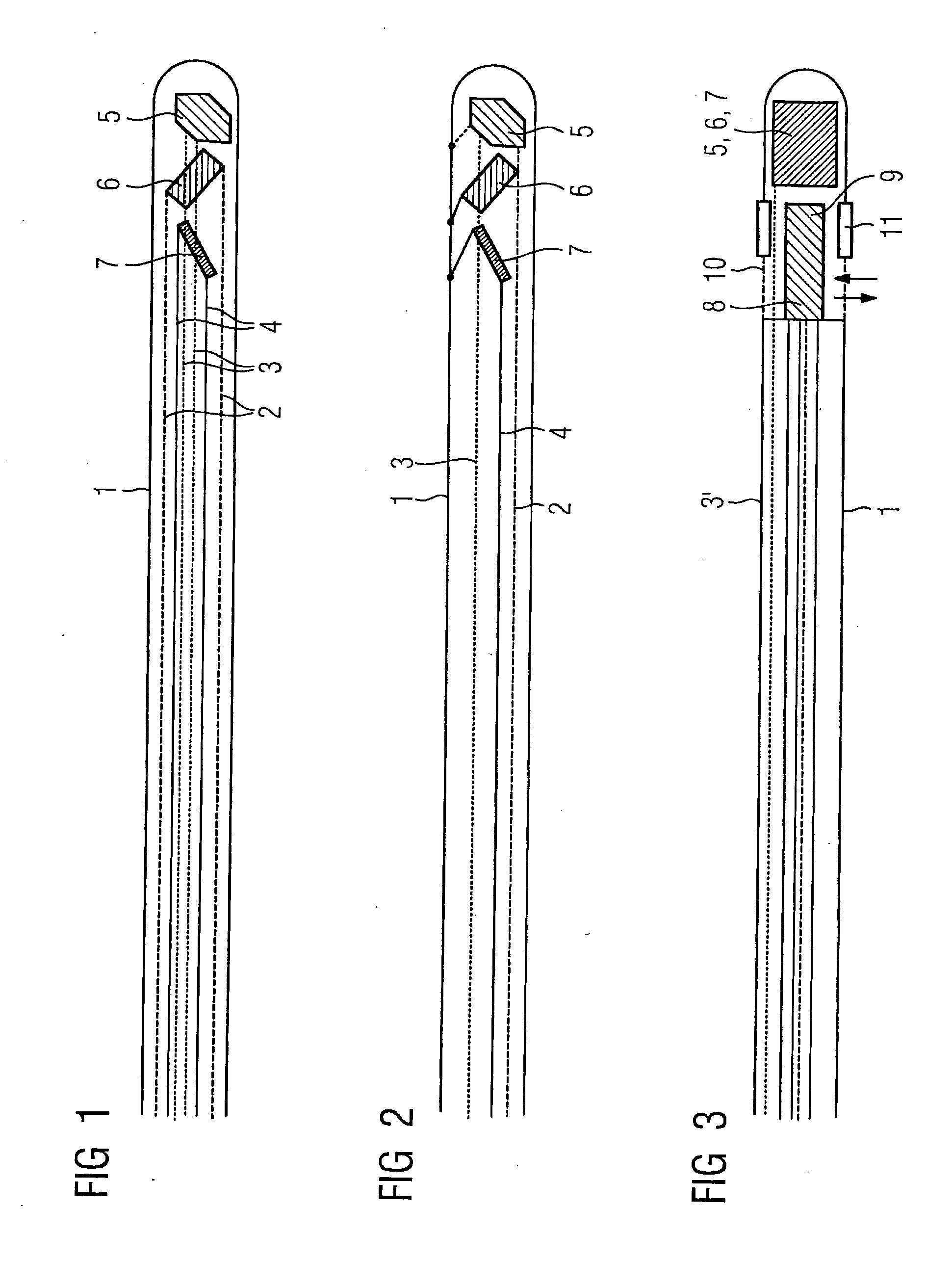
Guidewire for vascular catheters
InactiveUS20060116571A1Precise positioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsGuide wiresBlood vesselBiomedical engineering
Guidewire for catheters which can be inserted into cavities, preferably coronary vessels of humans or animals, said guidewire being provided with electromagnetic receive or transmit locate to position its position in conjunction with corresponding external electromagnetic transmit or receive antennas, as well as with signal lines guiding the processing unit controlling the transmit antennas or transmit coils.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Stent and catheter assembly and method for treating bifurcations
An apparatus and method is provided for stenting bifurcated vessels. A proximal angled stent is configured for implanting in a side-branch vessel wherein the proximal angled stent has an angulated portion that corresponds to the angle formed by the intersection of the side-branch vessel and the main vessel so that all portions of the side-branch vessel at the bifurcation are covered by the proximal angled stent. A main-vessel stent is provided for implanting in the main vessel, wherein the main-vessel stent has an aperture or stent cell that aligns with the opening to the side-branch vessel to permit unobstructed blood flow between the main vessel and the side-branch vessel. Side-branch and main-vessel catheter assemblies are advanced over a pair of guide wires for delivering, appropriately orienting, and implanting the proximal angled stent and the apertured stent.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Translation dilator and stand alone vascular guide catheter
Systems and methods for delivering implantable devices, catheters, or substances in or near and / or restoring flow through body lumens, such as blood vessel lumens are described. A catheter having a proximal portion of a first diameter and a distal portion of a second diameter (smaller than the first diameter) is advanced into a body lumen. The distal portion of the catheter is caused to expand to a diameter that is larger than the second diameter but no larger than the first diameter. A working device is then advanced out of the distal end of the catheter and used to remove obstructive matter, deliver an implantable device or substance and / or restore flow. The distal portion can be reduced in diameter prior to removal from the body. A stand alone, guide catheter is also disclosed possessing high resistance to kinking even with a very thin wall.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Medical devices having superhydrophobic surfaces, superhydrophilic surfaces, or both
InactiveUS20070005024A1Reduce frictionLower resistanceMedical devicesCatheterUrinary catheterLeft ventricular size
According to an aspect of the invention, medical devices are provided, which have the following (a) one or more superhydrophobic surface regions, (b) one or more superhydrophilic surface regions having a durometer of at least 40 A, or (c) a combination of one or more superhydrophobic surface regions and one or more superhydrophilic surface regions having a durometer of at least 40 A. Such surfaces are created, for example, to provide reduced resistance to the movement of adjacent materials, including adjacent fluids and solids. Examples of medical device surface regions benefiting from the present invention include, for example, outside and / or inside (luminal) surfaces of the following: vascular catheters, urinary catheters, hydrolyser catheters, guide wires, pullback sheaths, left ventricular assist devices, endoscopes, airway tubes and injection needles, among many other devices.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Clip applier configured to prevent clip fallout
ActiveUS20110224696A1Facilitate advancementFacilitate formationDiagnosticsSurgical staplesEngineeringSurgical Clips
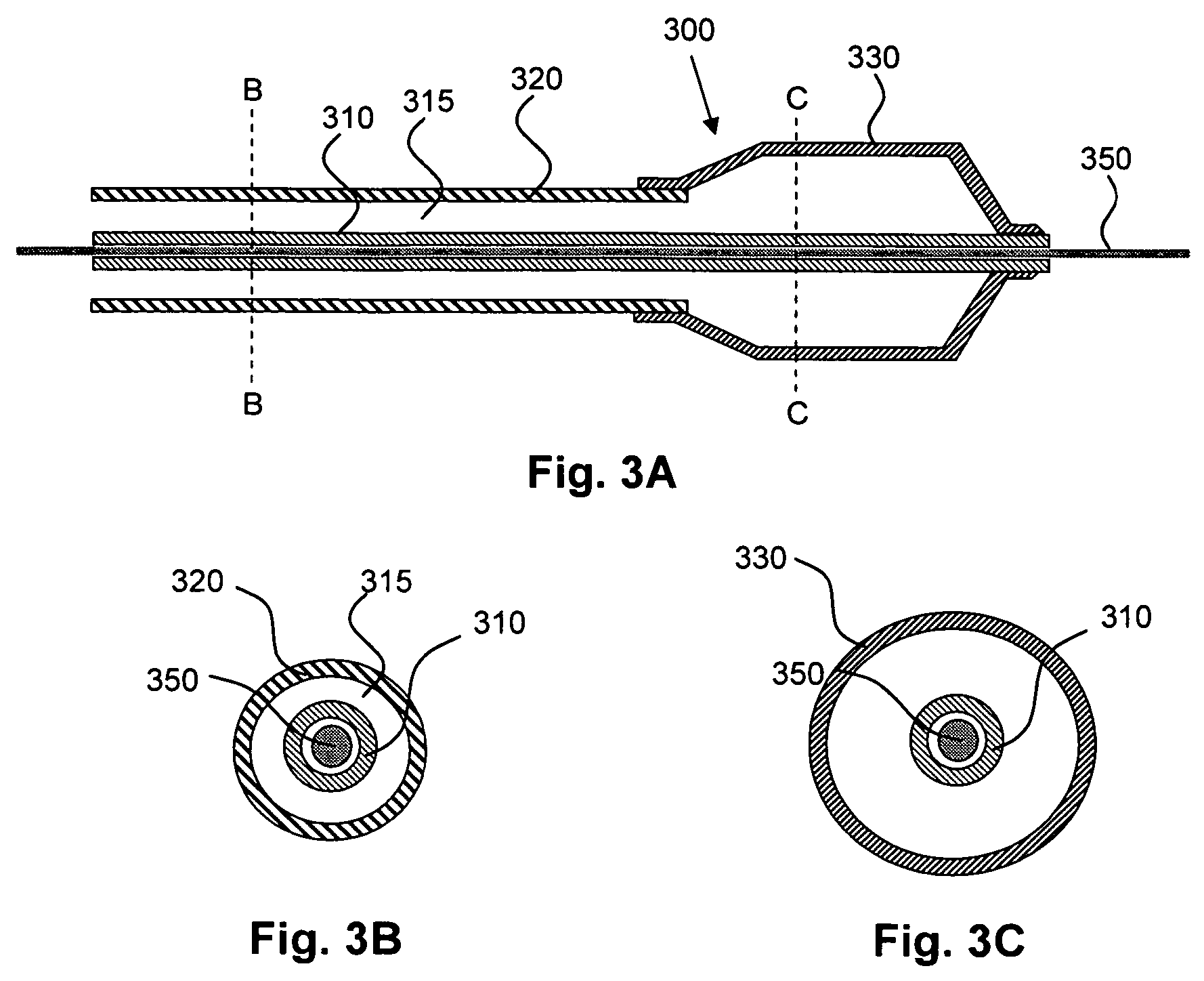
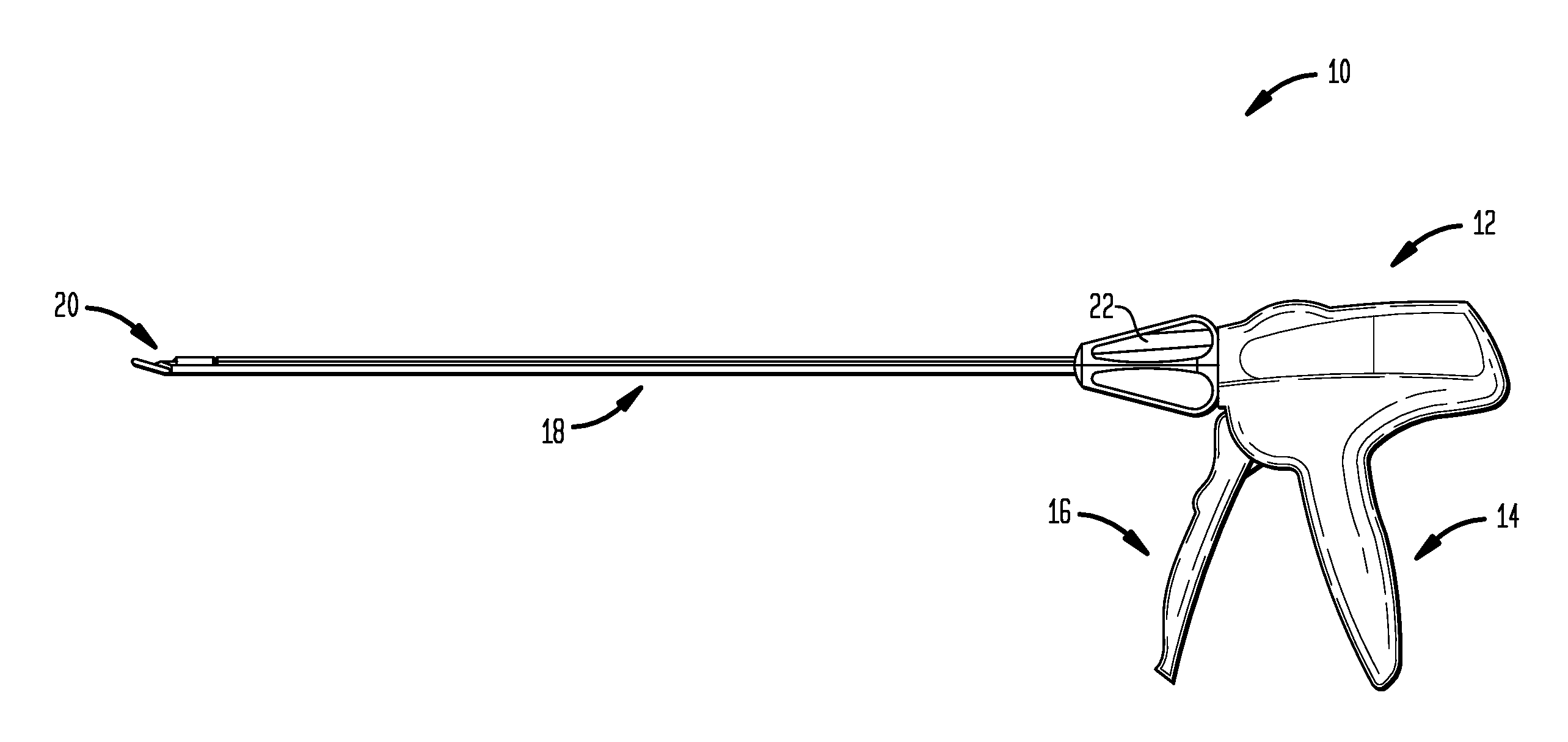
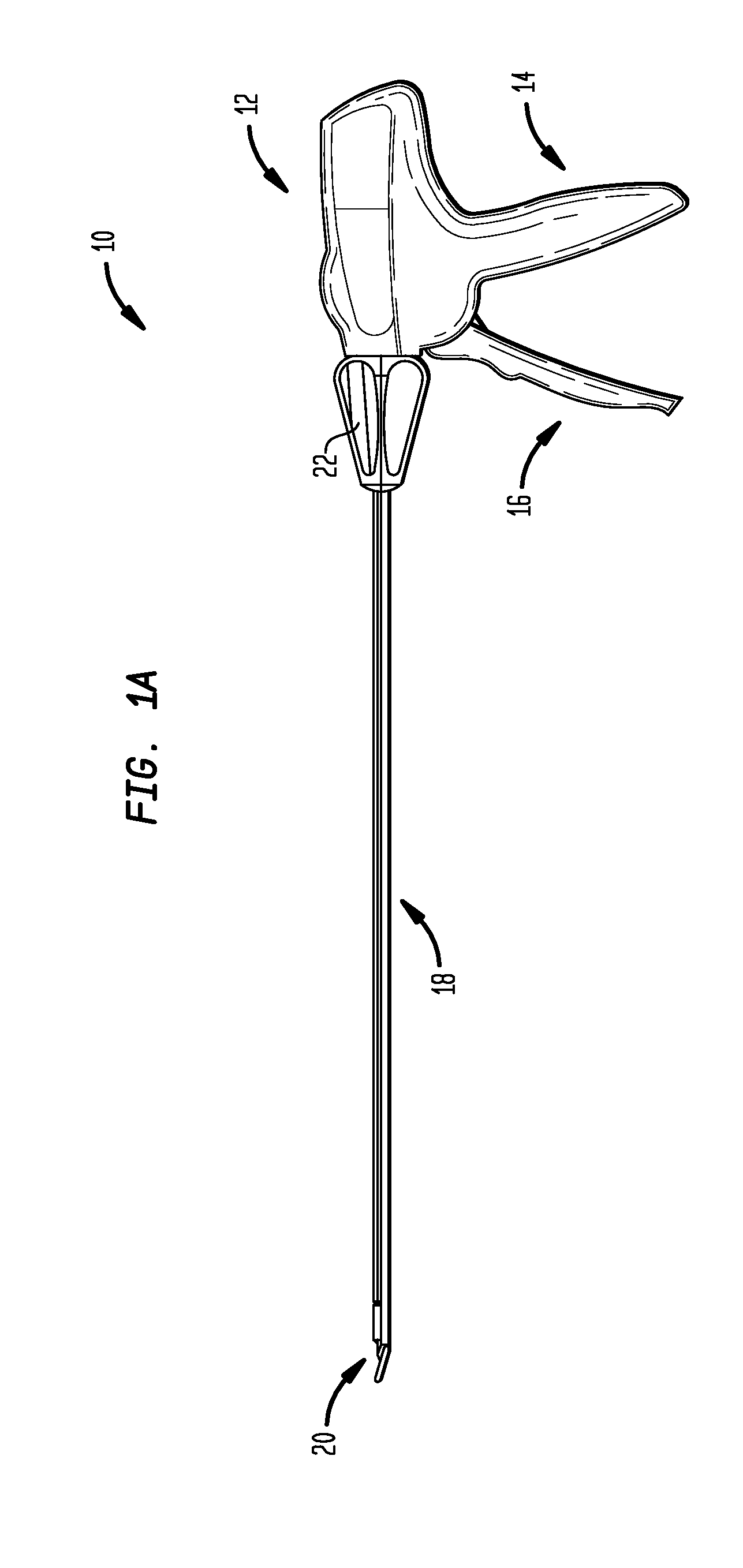
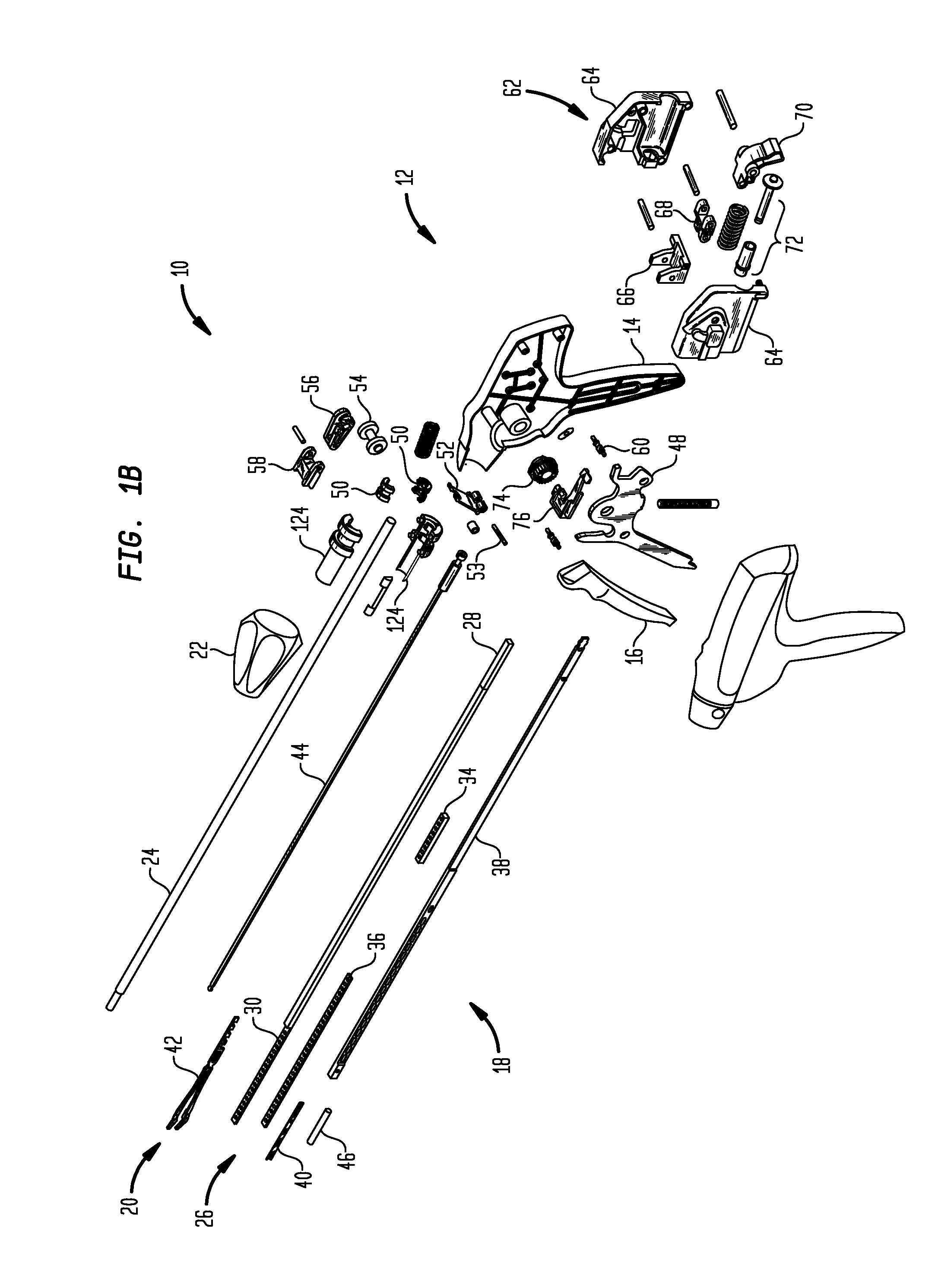
A surgical clip applier and methods for applying surgical clips to a vessel, duct, shunt, etc., during a surgical procedure are provided. In one exemplary embodiment, a surgical clip applier is provided having a housing with a trigger movably coupled thereto and a shaft extending therefrom with opposed jaws formed on a distal end thereof. The trigger is adapted to advance a clip to position the clip between the jaws, and to move the jaws from an open position to a closed position to crimp the clip positioned therebetween. The surgical clip applier can include a variety of features to facilitate use of the device, including features to align a clip with the jaws, features to prevent unintentional migration of a clip, and features to prevent clip fallout during formation.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Sleeved clip safety
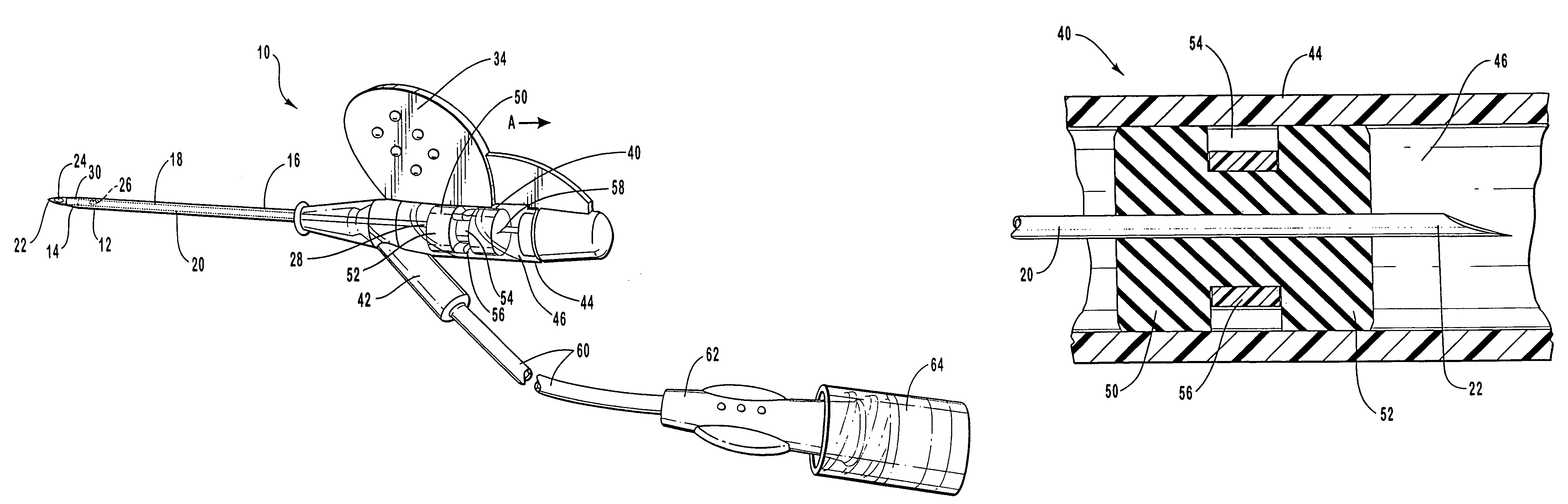
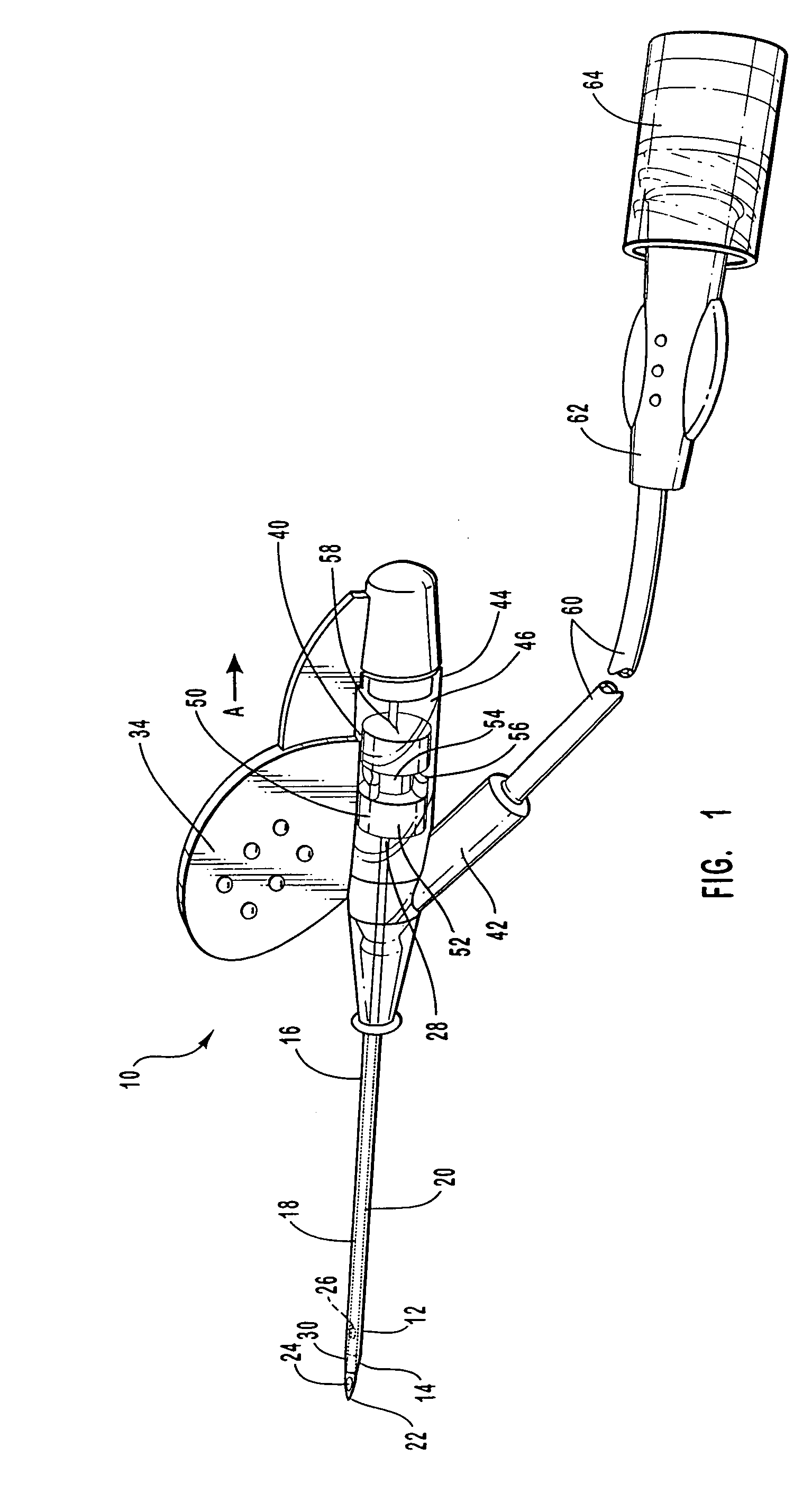
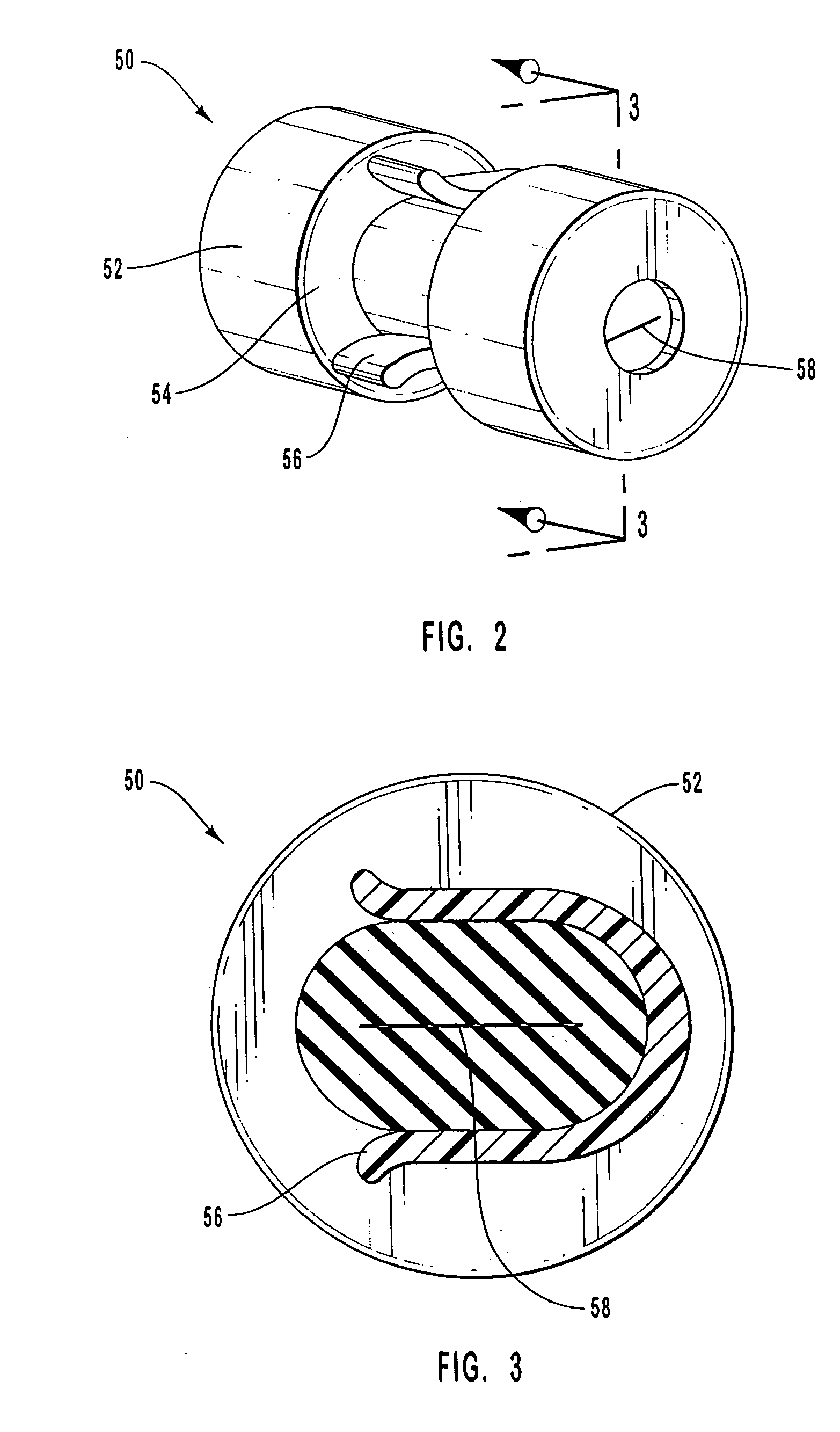
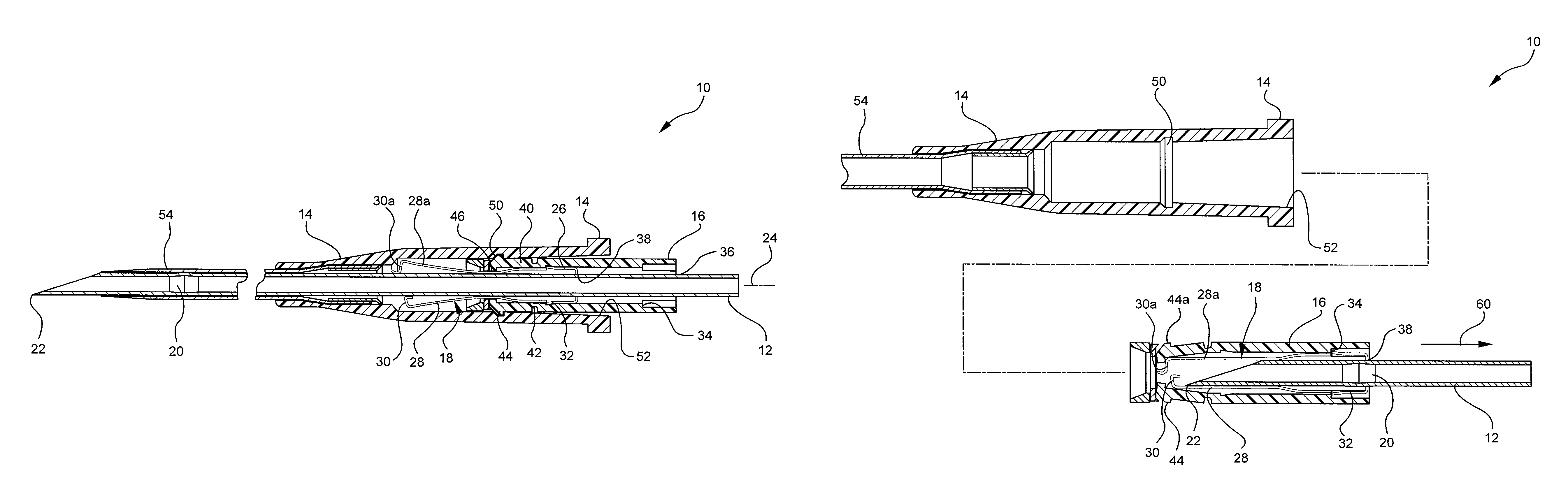
ActiveUS20090281499A1Reduce blood exposureReduce exposureInfusion syringesCatheterCATHETER ADAPTERBiomedical engineering
The present invention relates to a safety clip device for shielding and retaining a tip of an introducer needle following insertion of a vascular catheter. The safety clip device includes a sleeve having an interlock system for locking together the sleeve and the catheter adapter. The sleeve houses a safety clip wherein a portion of the introducer needle extends through the safety clip and is pinched between arm portions of the safety clip. As the tip of the introducer needle is withdrawn from the catheter adapter, the tip of the introducer needle is retained in the safety clip, whereafter the safety clip is retained within the sleeve and the sleeve is released from the catheter adapter for safe disposal.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
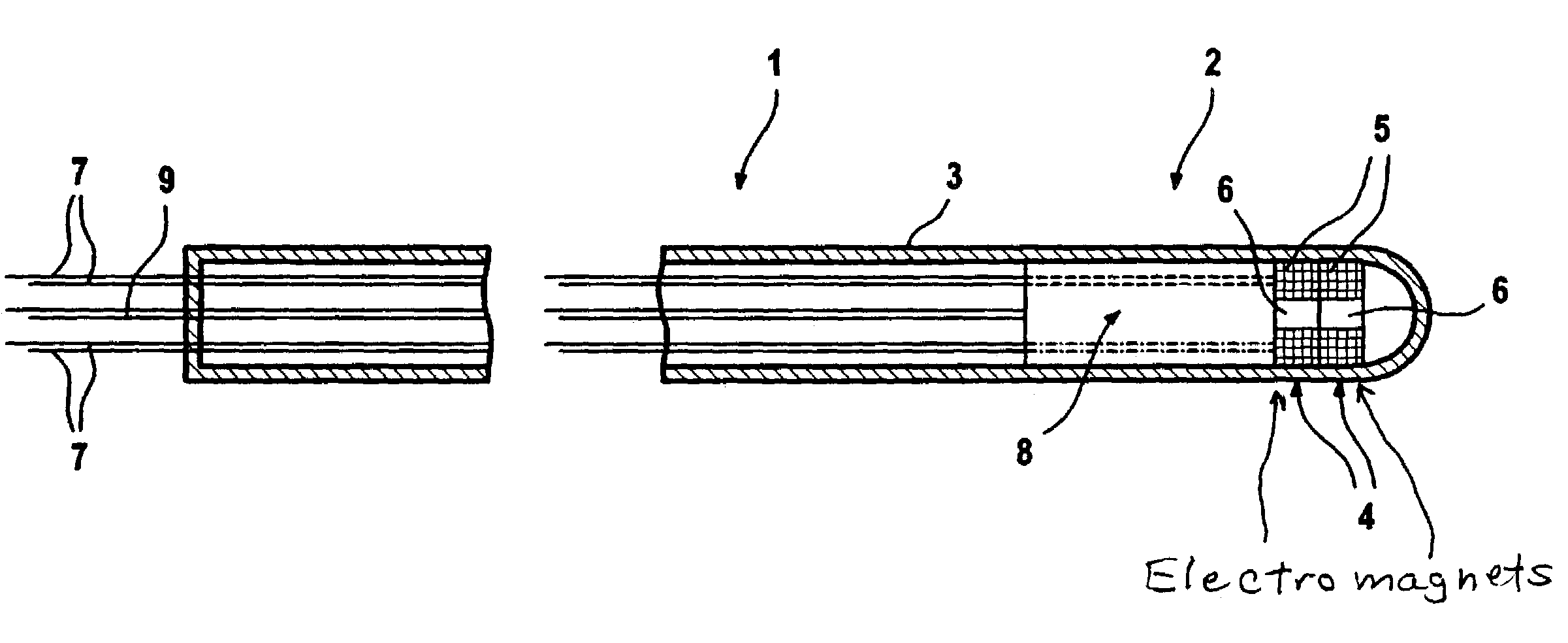
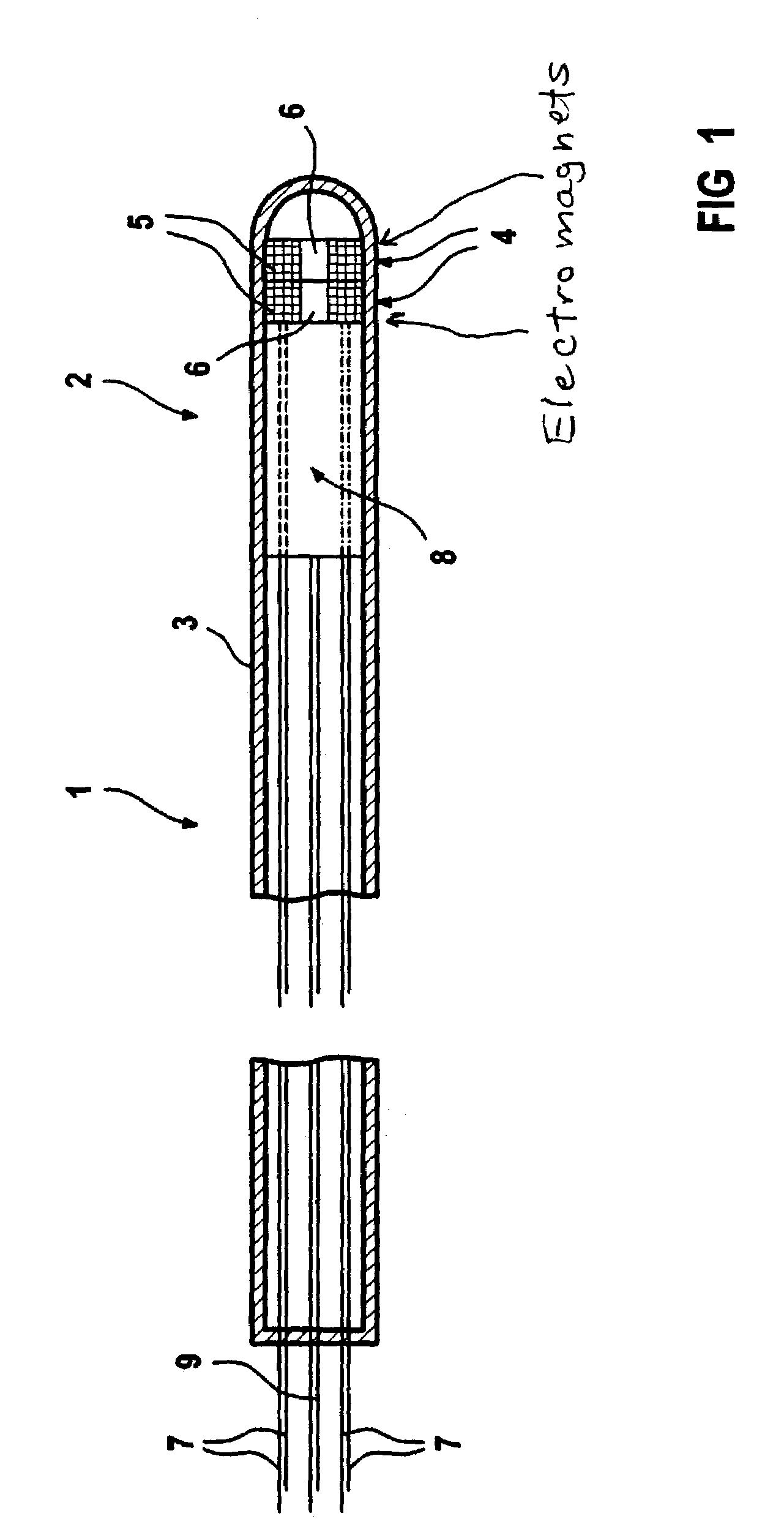
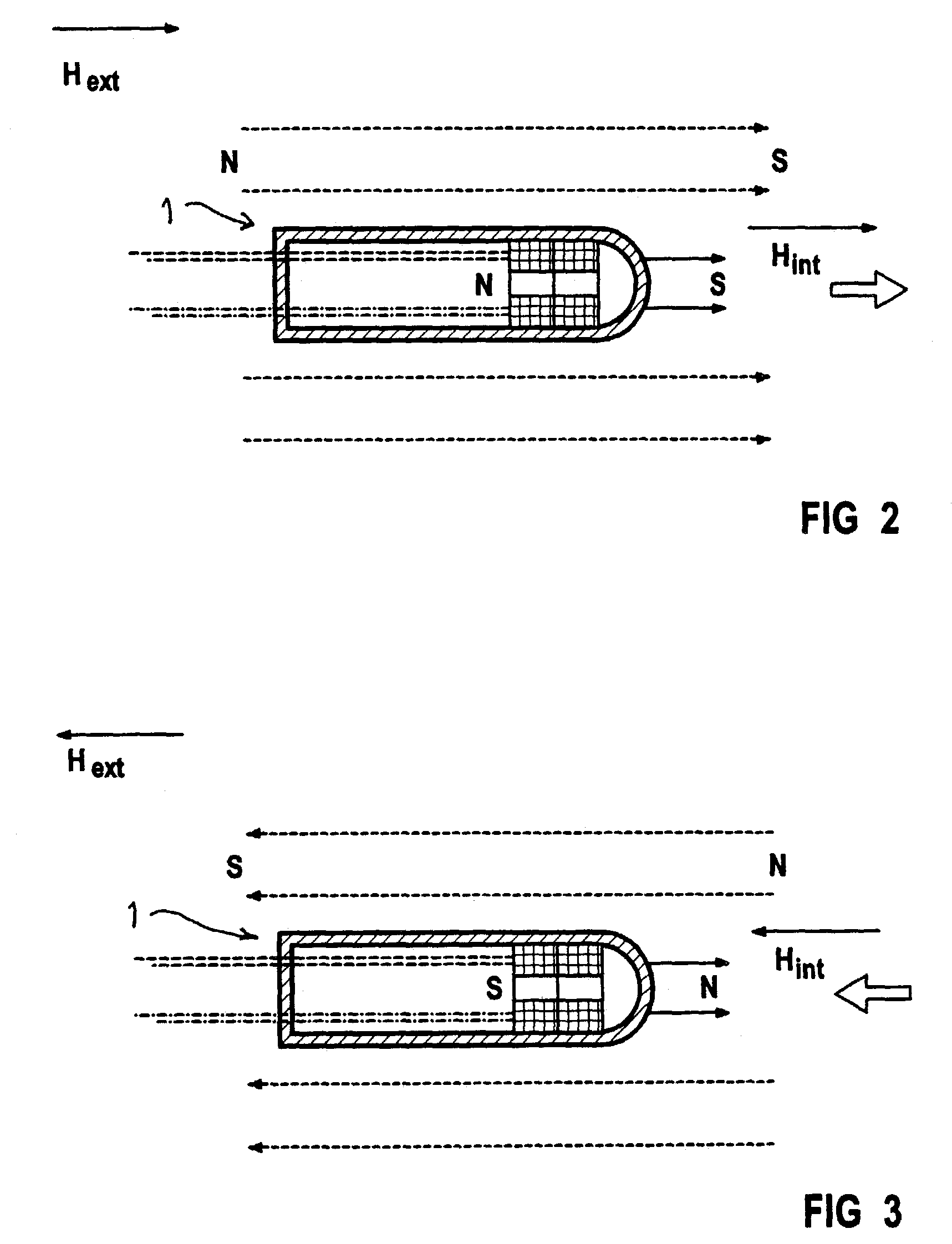
Catheter with variable magnetic field generator for catheter guidance in a subject
InactiveUS7686767B2Reduce decreaseSimpler navigation and movementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterIntravascular catheterBlood vessel
A catheter, particularly an intra-vascular catheter, has at least one magnetic field-generating element arranged in the catheter envelope in the region of the catheter tip, characterized in that the magnetic field of which is variable while the catheter is inserted into a patient.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Transvascular catheter for extravascular delivery
ActiveUS20140121641A1Reduce or eliminate patient discomfort and painReduces potential traumaBalloon catheterSurgical needlesHuman bodyPerfusion
An intravascular catheter for peri-vascular and / or peri-urethral tissue ablation includes multiple needles advanced through guide tubes which may be supported by an expandable balloon. The guide tubes expand with open ends around a central axis to engage the interior surface of the wall of the renal artery or other vessel of a human body allowing the injection an ablative fluid for ablating tissue, and / or nerve fibers in the outer layer or deep to the outer layer of the vessel, or in prostatic tissue. The diameter of the inflated balloon is less than the inside diameter of the vessel, allowing perfusion across the inflated balloon and guide tubes.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
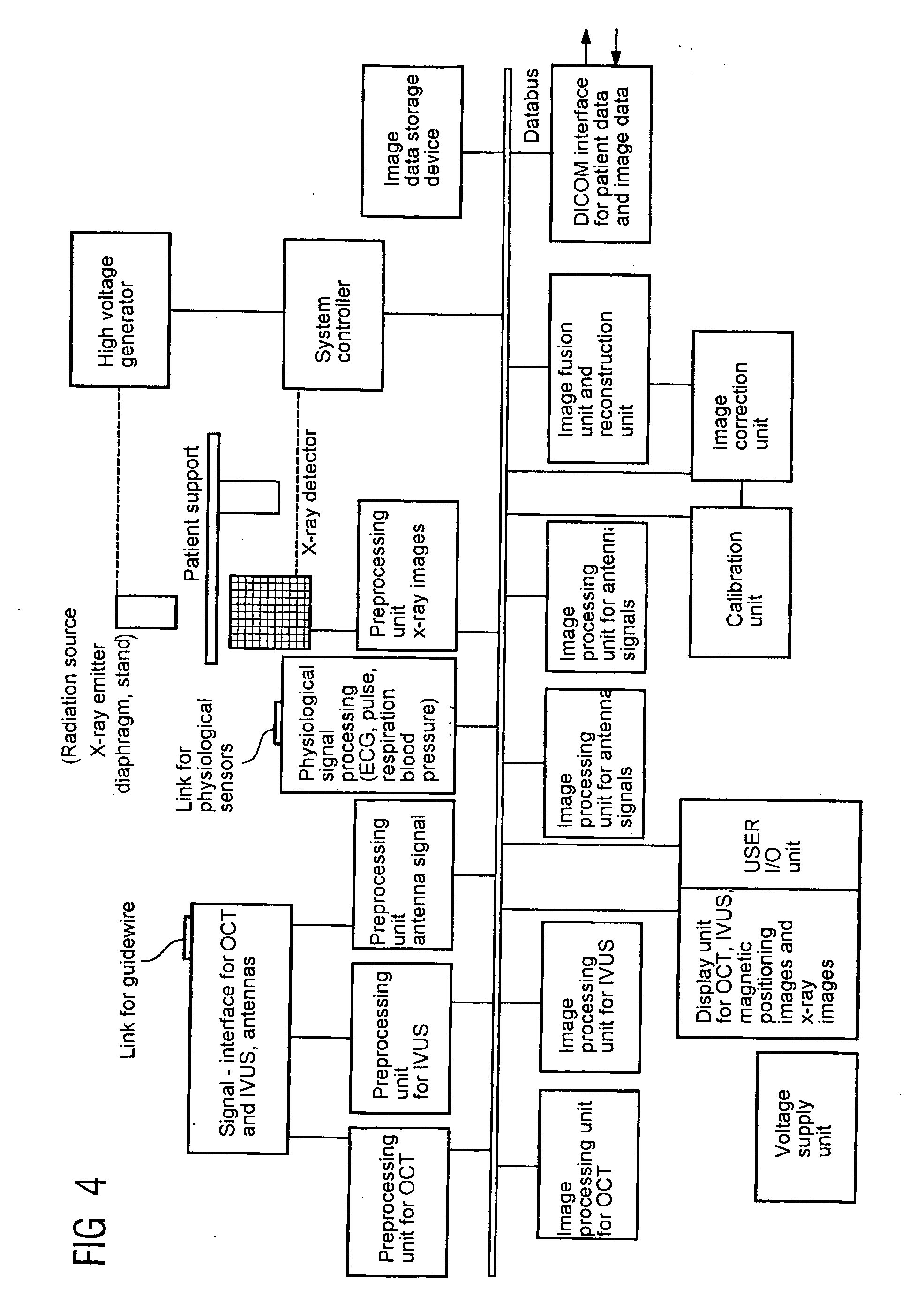
System and method for intraluminal imaging
InactiveUS6364841B1Enhanced hoop strengthBending stiffnessUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasonic imagingPlastic materials
A vascular catheter system comprises a catheter body having a proximal and distal portion and a single common lumen therebetween. The catheter body includes a first connector secured to the distal end of the proximal portion and a second connector secured to the proximal end of the distal portion. The connectors can be selectively connected to each other to join the lumens of the proximal and distal portions together in a continuous, axially fixed relationship. Disposed within the lumens, when the proximal and distal portions are joined together, is a drive cable. The drive cable may be movably, rotatable about its own longitudinal axis and carries at its distal end, a work element, which is typically an ultrasonic imaging transducer or interventional device. The lumen carrying the cable will be sufficiently large along a proximal portion to permit preferential collapse of the cable should rotation of the distal end become impeded. The catheter body may be made of a polymer or plastic material, such as polyetheretherketone (PEEK), which provides adequate bonding stiffness and resistance to kinking from large hoop stresses.
Owner:BOSTON SCI LTD +1
Compliant implantable medical devices and methods of making same
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
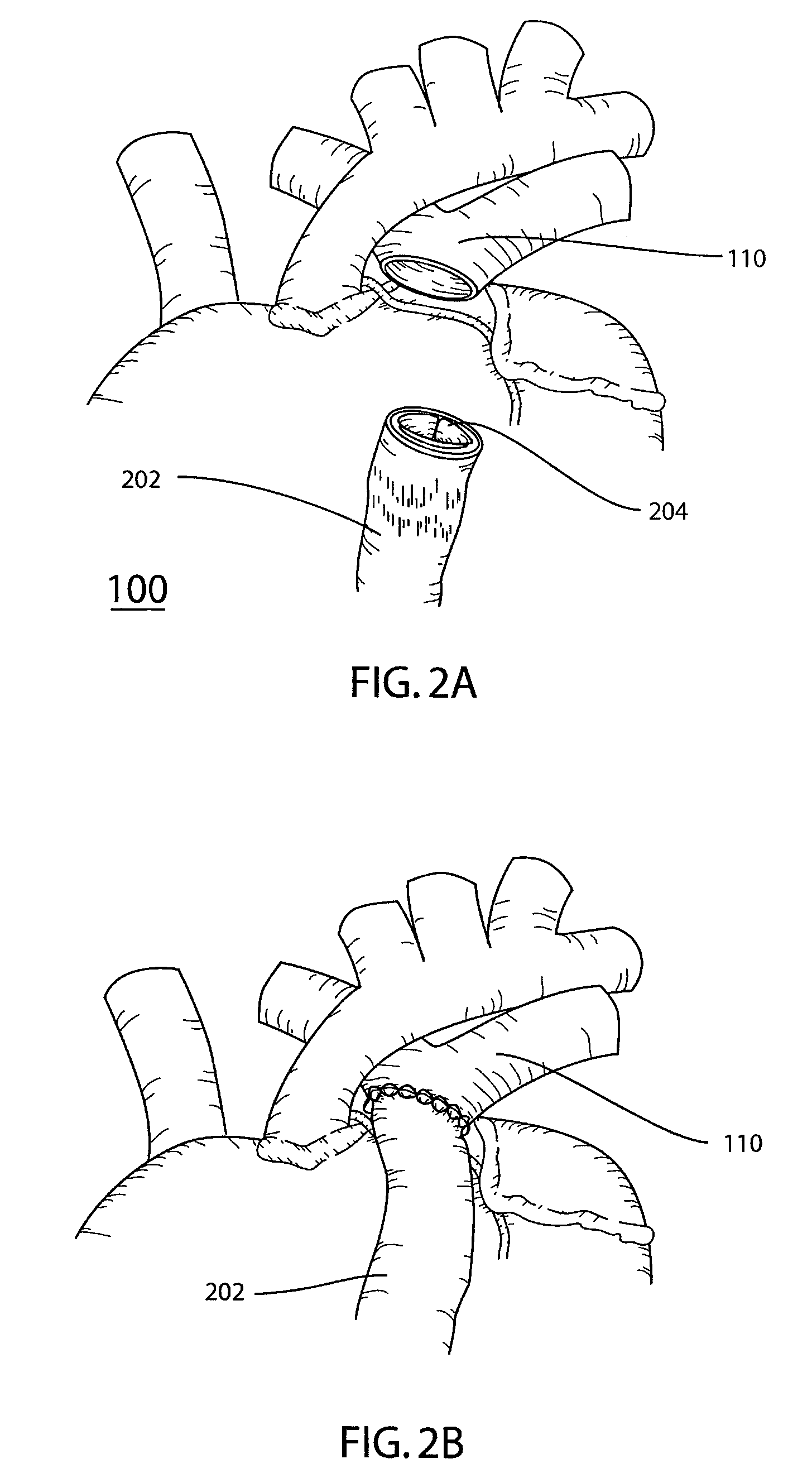
Vascular conduit device and system for implanting
The present invention provides a vascular conduit device including a deformable flange and complementary securing ring in cooperation for securing the device within an aperture defined in a tissue wall. The present invention further provides a system for implanting such a vascular conduit device in a tissue wall. More specifically, the present invention provides a system including a coring device for defining an aperture in a tissue wall (such as a ventricle and / or a blood vessel) and securely implanting a vascular conduit device therein so as to provide fluid communication between a first and second surface of the tissue wall via the vascular conduit device.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
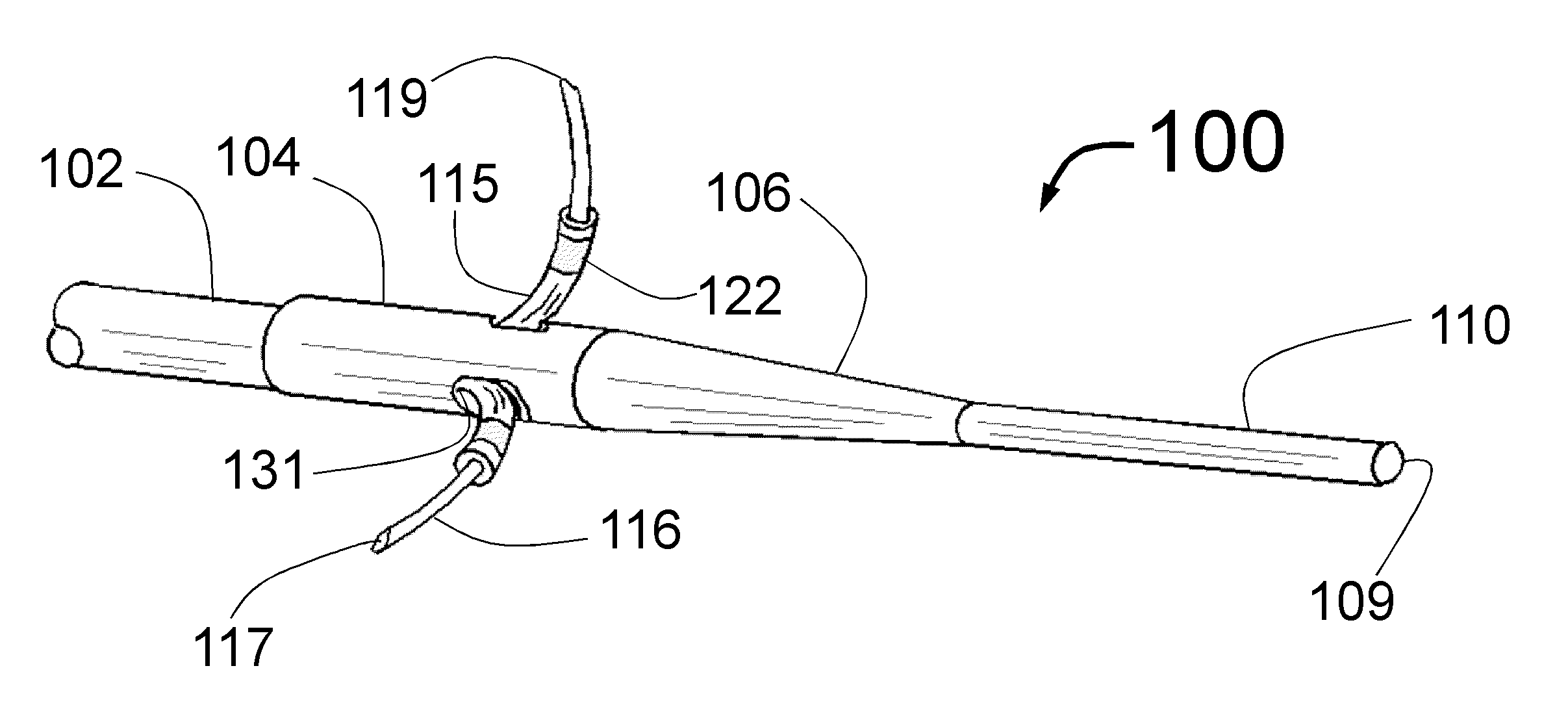
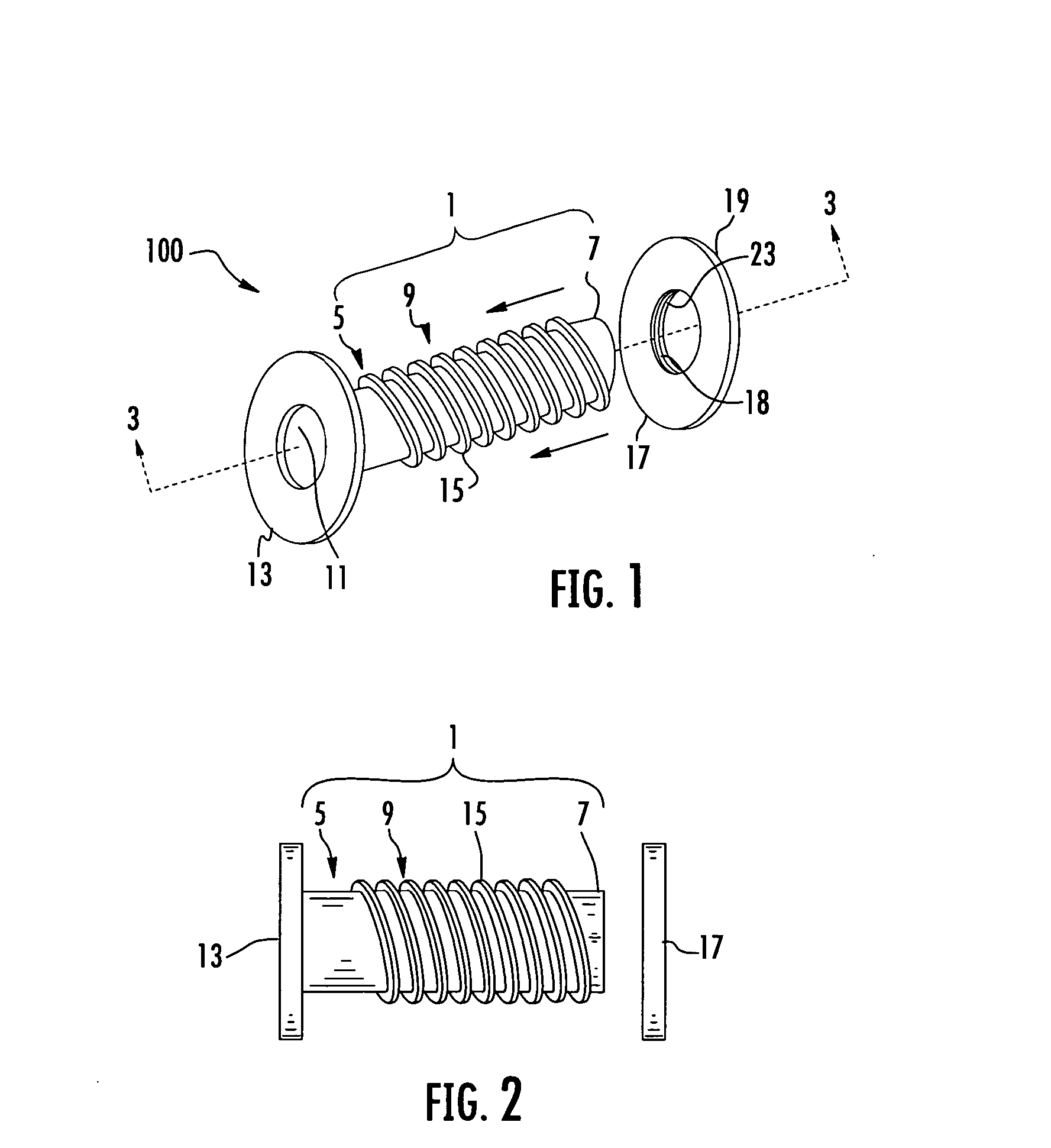
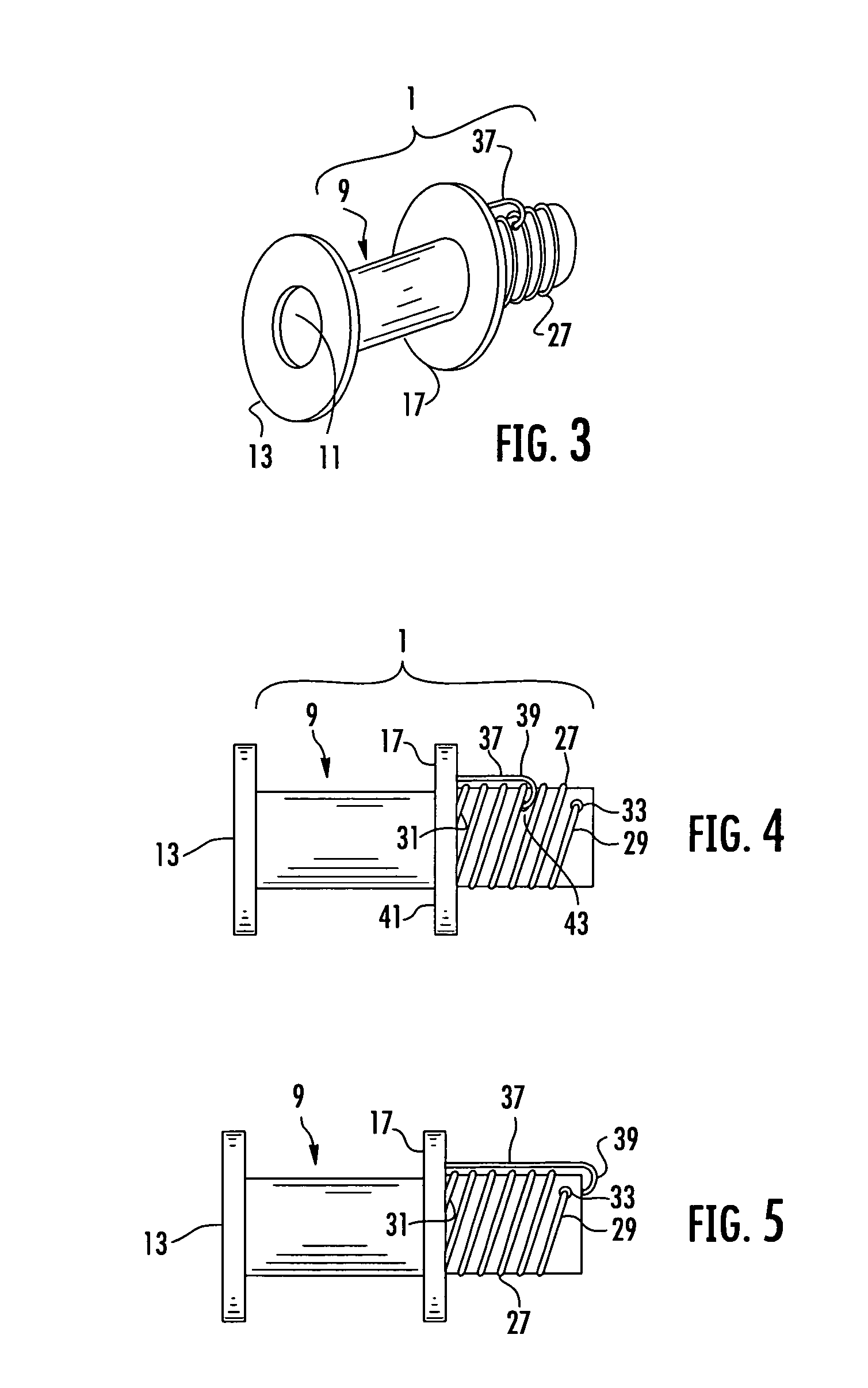
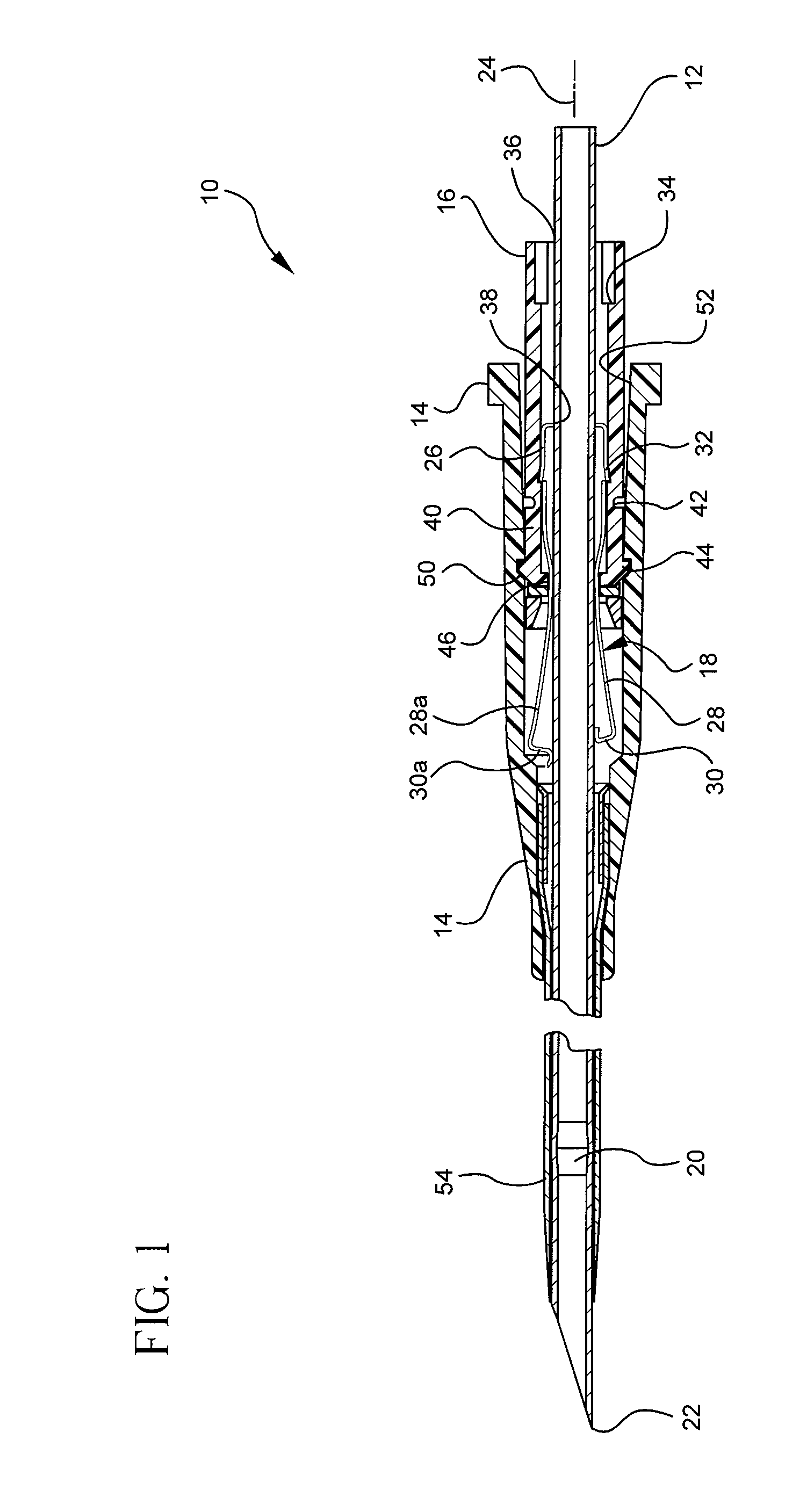
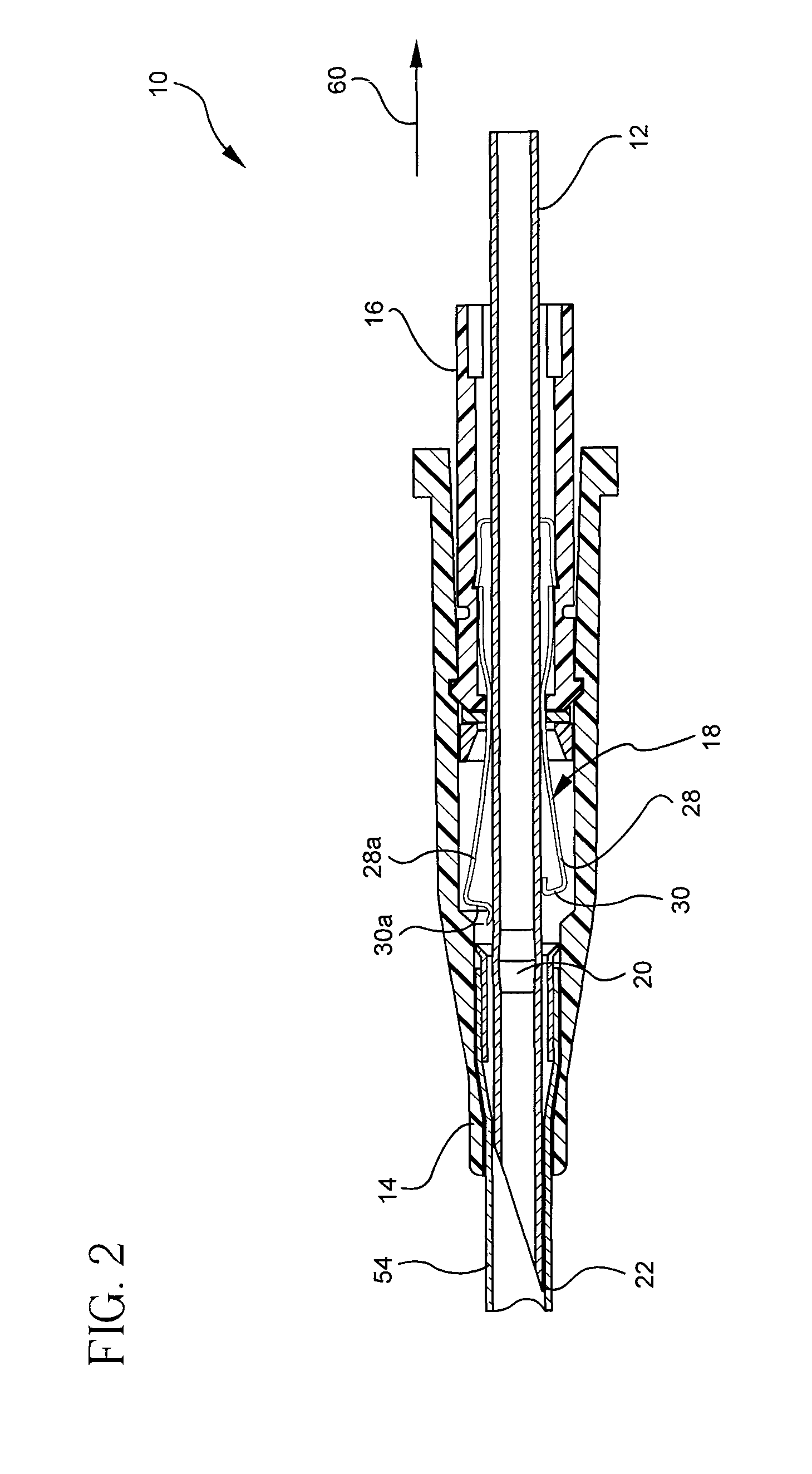
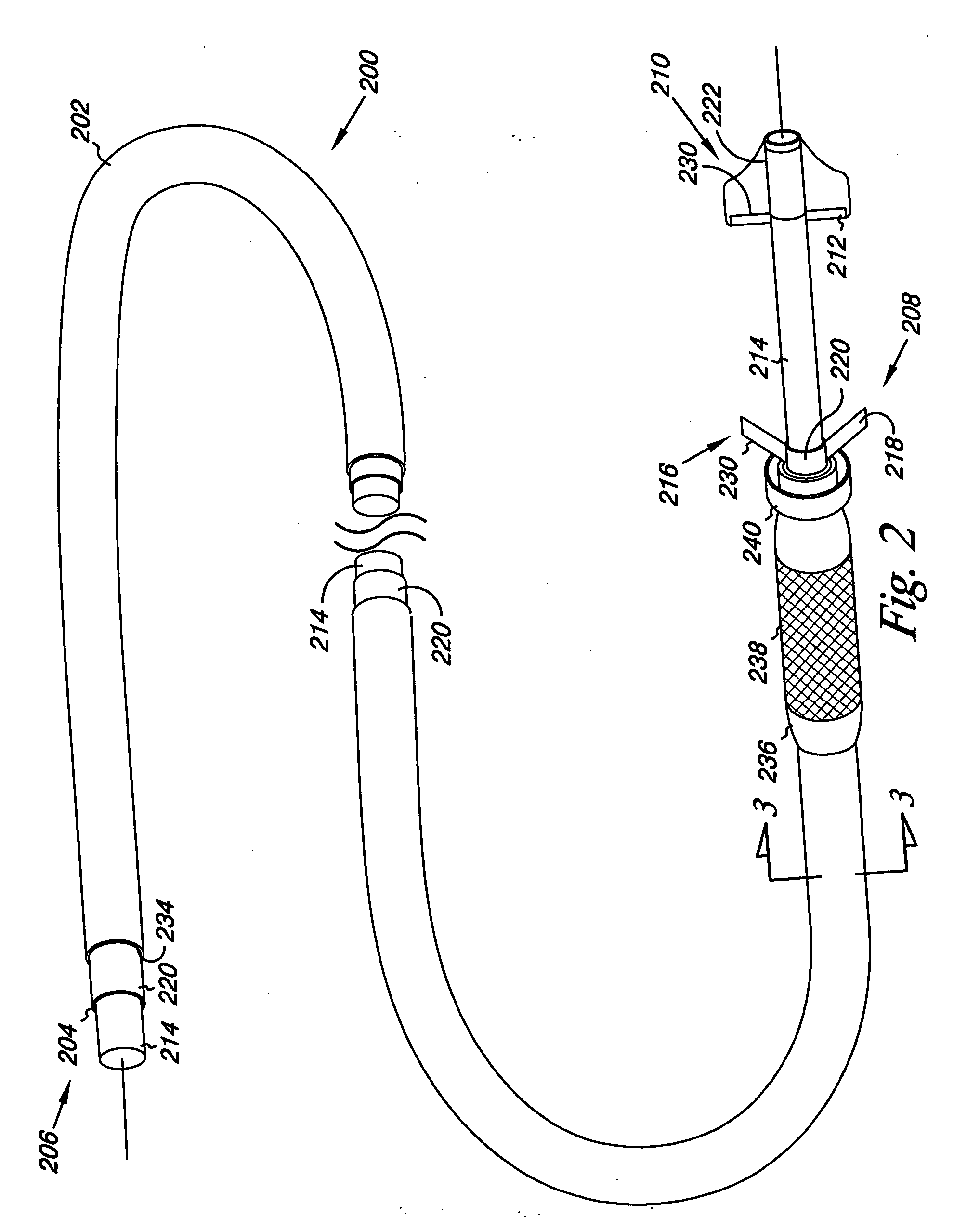
Security tip for vascular catheter and method of using same
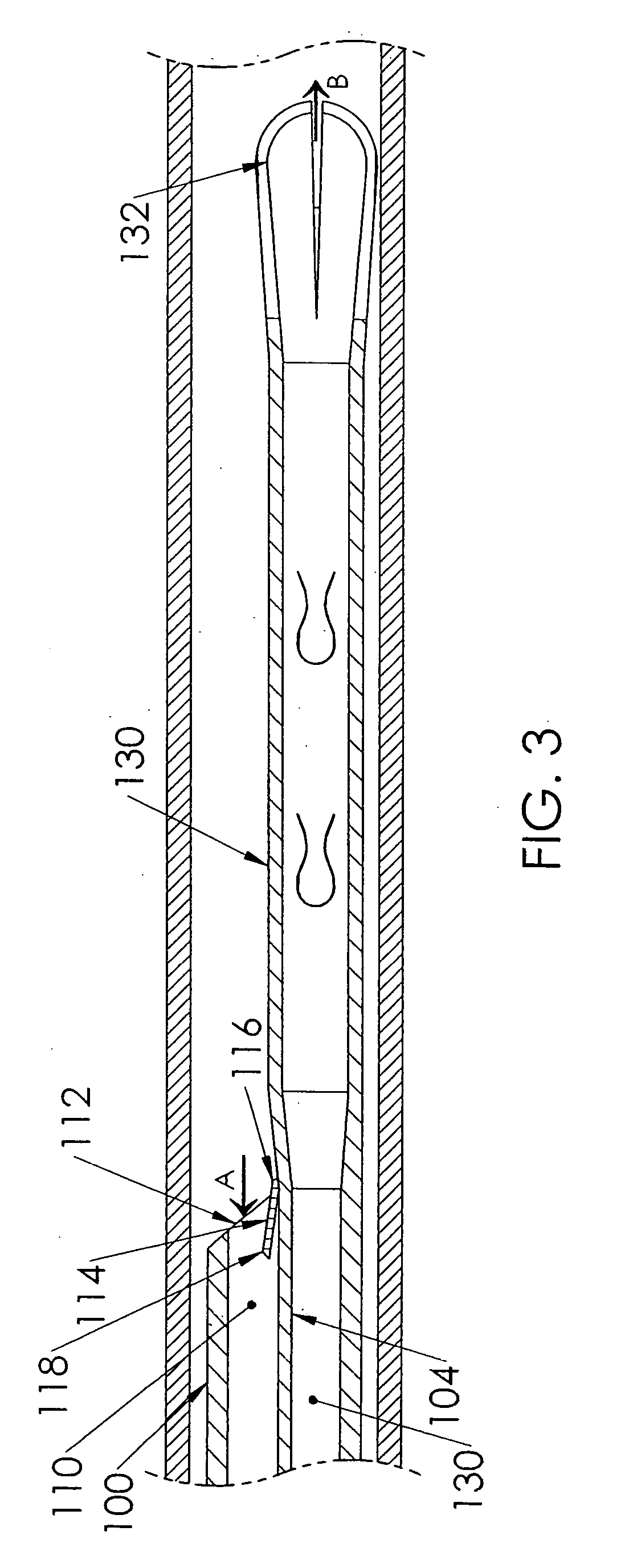
A catheter (100) having a first lumen (110) having a first distal tip (112) and a second lumen (130) having a second distal tip (132). The first and second distal tips (112,132) include openable portions that are normally closed when undeflected by lumen fluid pressure imbalance relative to the blood pressure of the patient. The first lumen (110) has an openable portion, flap (114) that opens proximally into the first lumen when the first lumen is under negative pressure to withdraw blood from the vessel through the first lumen to be dialysed (but that can open distally into the vessel under positive lumen pressure to permit blood flow into the vessel). The second lumen (130) extends distally beyond the first distal tip (112) to its second distal tip (132), and its openable portion is several lip sections (135) that are normally closed against each other when undeflected but that open outwardly when the second lumen is positively pressurized during hemodialysis, permitting blood to return to the patient's vessel.
Owner:MEDICAL COMPONENTS INC
Soft tip guiding catheter and method of fabrication
The present invention relates to medical vascular catheters adapted to be inserted into a blood vessel from an incision through the skin of a patient for introducing other devices or fluids for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes, and particularly to an improved distal soft tip or segment attachment with a relatively stiff proximal catheter shaft. A tubular sleeve is bonded through the application of pressure and heat to a distal portion of the catheter shaft and a proximal portion of the distal segment of soft distal tip bridging the attachment junction. In the preferred method, the catheter shaft distal end is aligned with the distal segment or soft tip proximal end and the sleeve is fitted over the attachment junction. A heat shrink tube is fitted over the sleeve and adjoining portions of the catheter shaft and the distal segment or distal soft tip and heat is applied. The shrinkage force of the heat shrink tube over the assembly of the tubular sleeve overlying and bridging the attachment junction and the applied heat melts and force the materials of the tubular sleeve and the catheter shaft and the distal segment or distal soft tip together to fill interstitial spaces of the attachment junction and reduces the outer diameter of the sleeve. The heat shrink tube is removed after the assembly cools and solidifies. Preferably, the catheter shaft distal end and the soft tip or intermediate segment proximal end are each formed with a like plurality of ungular cut sections that are complementary in shape to one another, whereby the ungular cut sections are aligned with and mated together along the attachment junction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Vascular access device
InactiveUS7691088B2Avoid blood leakagePrevent leakageEngine diaphragmsCheck valvesVascular Access DevicesGuide tube
A vascular access device having a spring-biased septum is provided for preventing the leakage of blood during the placement and use of vascular catheters and similar devices. The structure of the device includes a housing with an internal channel. A spring-biased septum is placed securely within the channel such that it substantially blocks blood flow through the channel. The spring-biased septum includes an elastic plug having a pre-slit or pre-molded hole and a biasing element disposed about the elastic plug. A needle or other object may be withdrawn through the slit or hole, after which the biasing element forces the hole closed, preventing blood leakage.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Sleeved clip safety
The present invention relates to a safety clip device for shielding and retaining a tip of an introducer needle following insertion of a vascular catheter. The safety clip device includes a sleeve having an interlock system for locking together the sleeve and the catheter adapter. The sleeve houses a safety clip wherein a portion of the introducer needle extends through the safety clip and is pinched between arm portions of the safety clip. As the tip of the introducer needle is withdrawn from the catheter adapter, the tip of the introducer needle is retained in the safety clip, whereafter the safety clip is retained within the sleeve and the sleeve is released from the catheter adapter for safe disposal.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
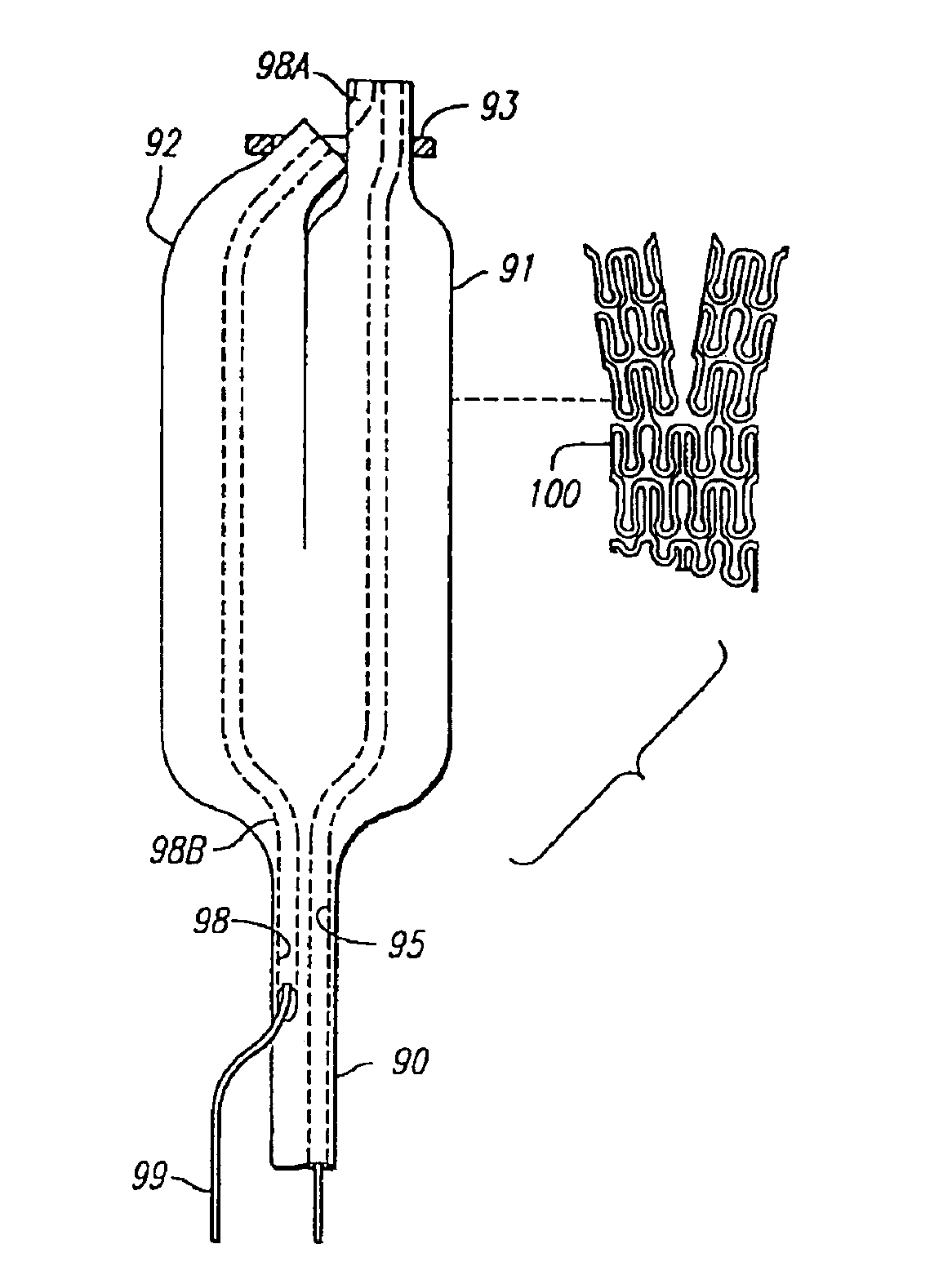
Vascular catheter, system, and method
A catheter including an elongate body, a first cutting head and a second cutting head both having a blade, where the blades moves relative each other to provide a shearing action for cardiac tissue. The catheter can further include a stent positioned over an inflatable balloon, where the inflatable balloon can deploy the expandable stent over sheared cardiac tissue. The catheter can further be included in a system having a sheath, where at least a part of the catheter resides in the lumen of the sheath. The sheath further includes a cardiac valve and an expandable filter. The sheath can move relative the cardiac valve and the expandable filter to deploy the cardiac valve and at least a portion of the expandable filter proximal the inflatable balloon and the expandable stent.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
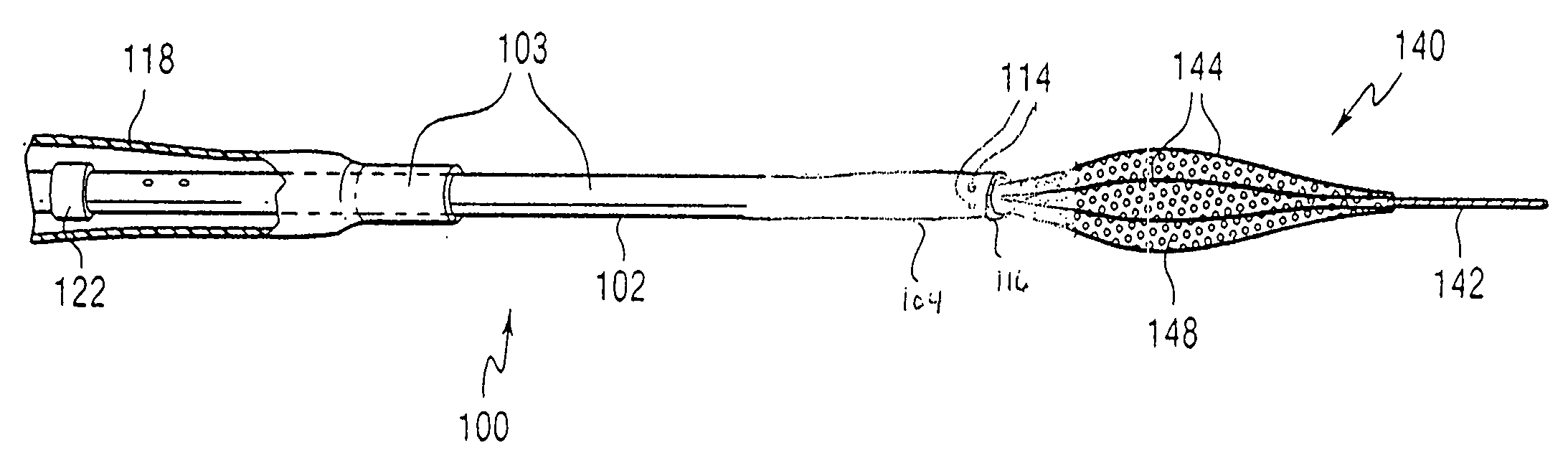
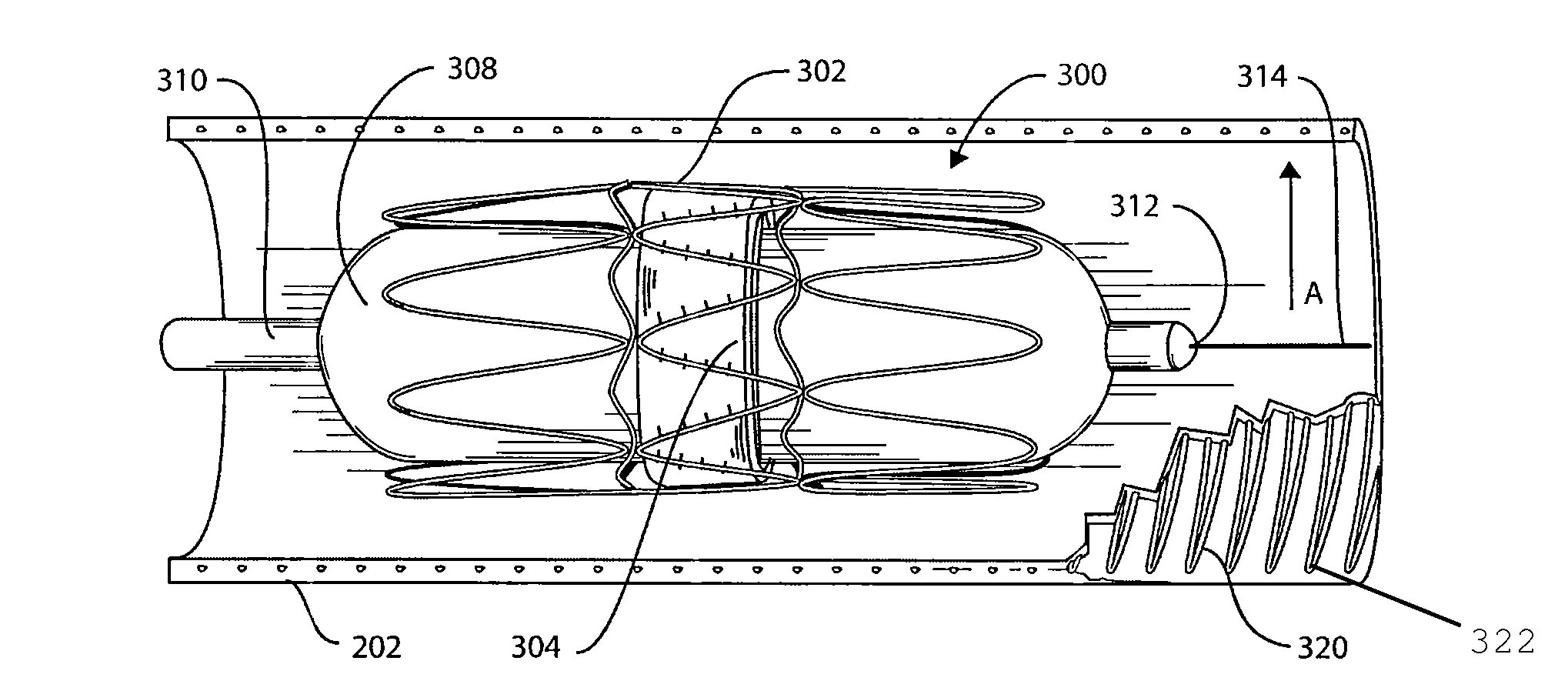
Vascular catheter with an expandable section and a distal tip for delivering a thromboembolic protection device and method of use
A vascular catheter including a radially expandable initial dilation segment, such as an inflatable balloon and an expanded distal tip for releasably housing at least a portion of a thromboembolic protection device is disclosed. A vascular catheter including a shaft structured and arranged to at least partially house a thromboembolic protection device, a radially expandable initial dilation segment disposed on the shaft, and a radially expandable stent expanding segment disposed on the shaft, is also disclosed.
Owner:WHOLEY MARK H +1
Reinforced surgical conduit for implantation of a stented valve therein
A pulmonary valve replacement system having a vascular conduit and a prosthetic valve device including a valve operably connected to a support structure. The prosthetic valve device is positioned within the vascular conduit. A conduit support includes a substantially circular cross-section. The conduit support is positioned adjacent to and reinforces the vascular conduit. In one embodiment, the pulmonary valve replacement system includes a catheter and an inflatable member operably attached to the catheter. The prosthetic valve device is disposed on the inflatable member. The invention provides a method for replacing a pulmonary valve including providing a vascular conduit positioned at a treatment site. The vascular conduit includes a conduit support positioned adjacent the vascular conduit. A prosthetic valve device is deployed within the vascular conduit via catheter. The prosthetic valve device includes a valve operably connected to a support structure. The vascular conduit is supported with the conduit support.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
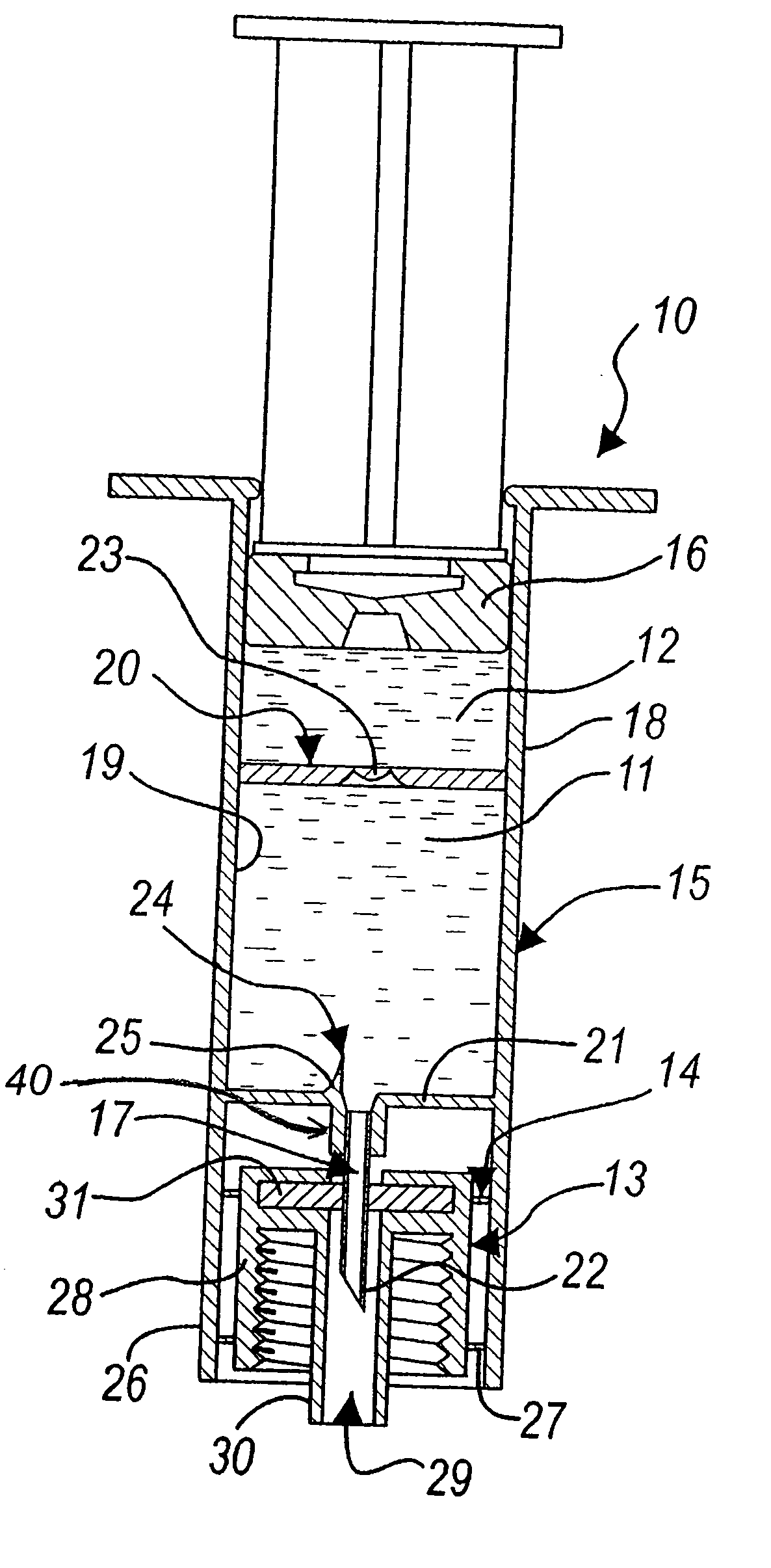
Syringe for sequential expression of different liquids and method of using same
A device (10,110,210) for the expression of liquids, such as for the maintenance treatment of vascular catheters. A syringe (16;116a,116b;216) has a support structure (15,215) and includes at least two separate compartments (11,12;111,112;211,212) in which liquids for treating the lumen (L,283) of a catheter (C,280) with which the device is associated. The syringe further includes a closure plug (13,213) to be associated with the lumen being treated, which is coupled, by virtue of a releasable securement arrangement, to support structure (15,215). At least one plunger (16;116a,116b;216) is also included for infusing, in preset order, the different treatment liquids into the lumen to be treated, and the syringe further includes a duct (17,217) which is in fluid communication with the two compartments and is arranged through a through hole through the closure plug (13,213) in order to allow access of the treatment liquid to the interior of the lumen (L,283) upon activation of the plunger.
Owner:MEDICAL COMPONENTS INC
Convertible mode vascular catheter system
An angioplasty catheter comprising a catheter shaft having a proximal portion and a distal end, an angioplasty balloon attached to the shaft at the distal end, a balloon inflation lumen extending through the shaft and communicating with the interior of the balloon, a guidewire lumen extending through the shaft and through the balloon for receiving a steerable guidewire, the guidewire lumen having an outside wall, wherein the guidewire lumen has a proximal opening located at a point normally outside of the patient during use of the catheter for insertion of a guidewire into the lumen, and a side port adapted to permit passage of a guidewire into the lumen through the outside wall of the guidewire lumen, the side port located distally of the proximal opening and at a point normally inside of the patient during use, and guidewire removing means in the outside wall of the guidewire lumen extending from the proximal opening to the side port for permitting a guidewire in the guidewire lumen to be moved laterally from the guidewire lumen through the outside wall of the guidewire lumen. Also disclosed are a removable “Y” connector and methods for using the catheter and for exchanging catheters and guidewires during vascular catheterization procedures.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
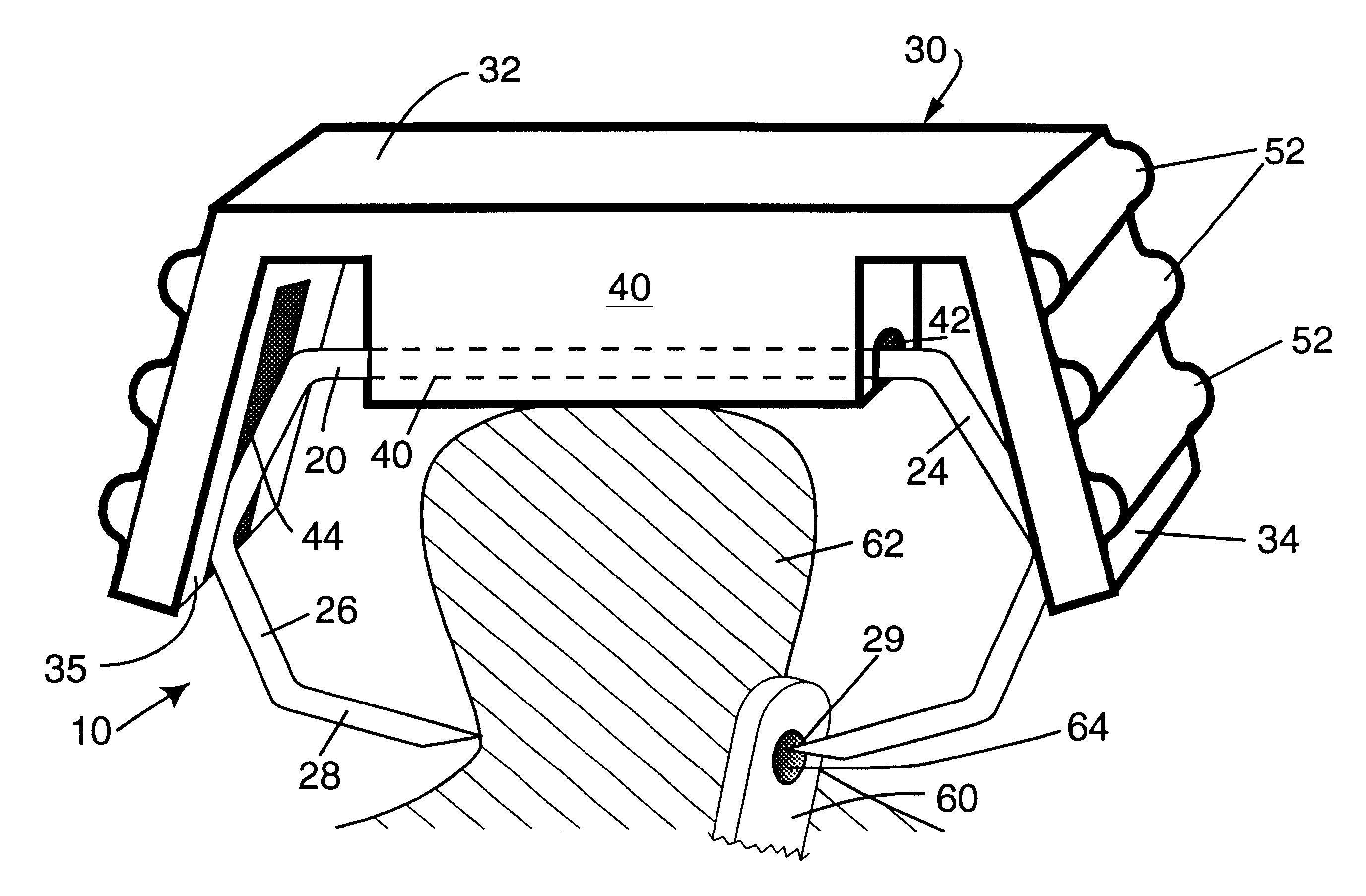
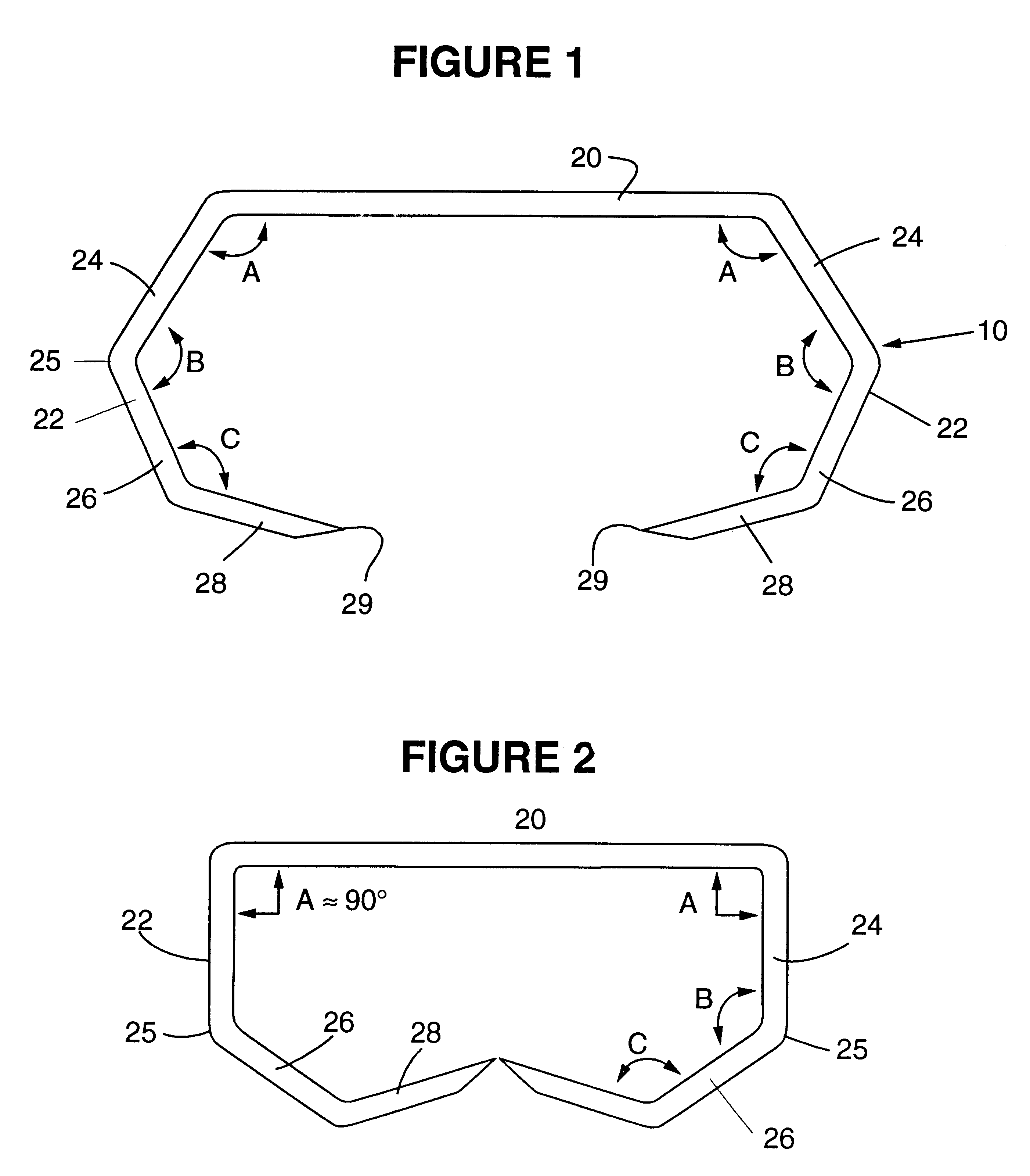
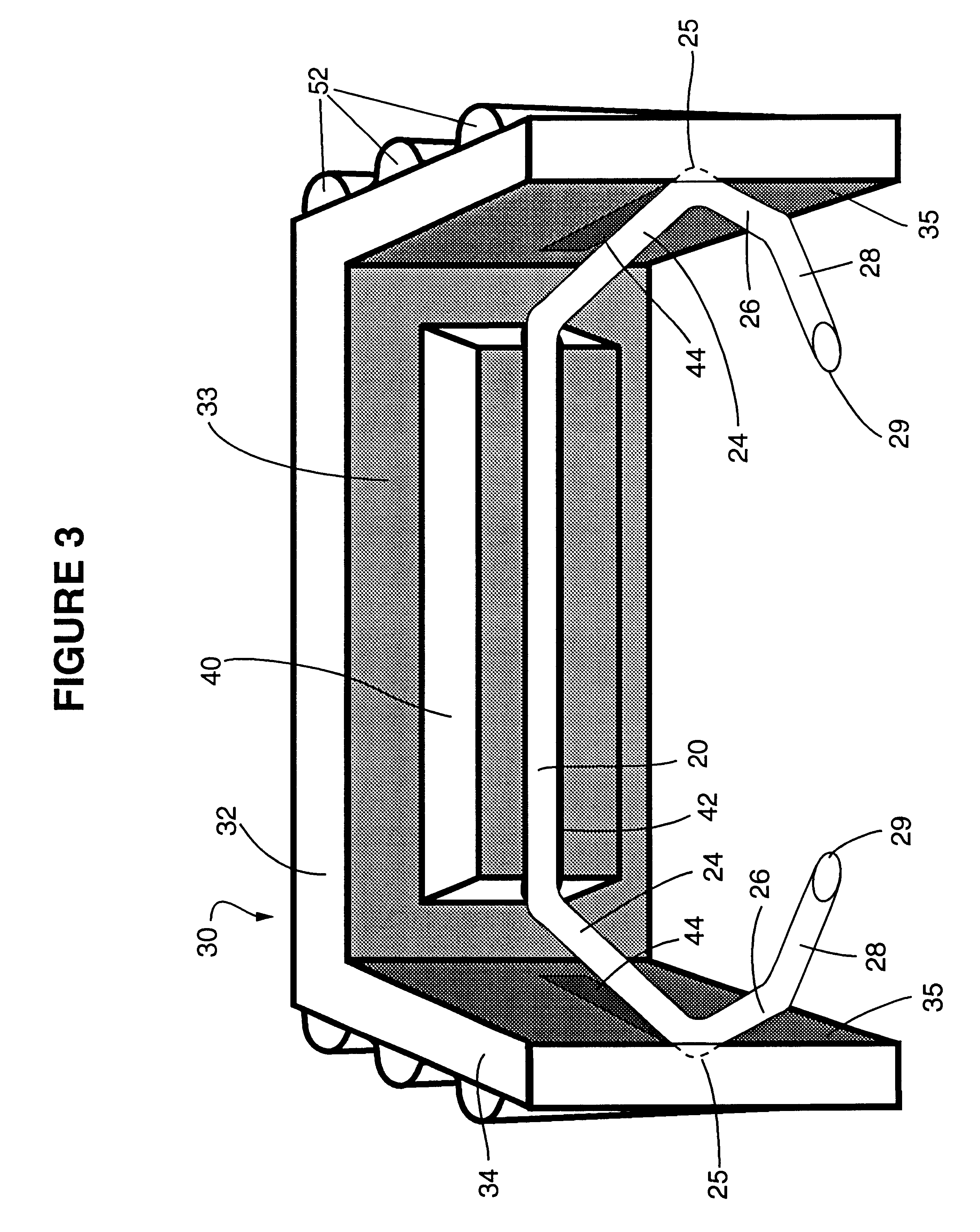
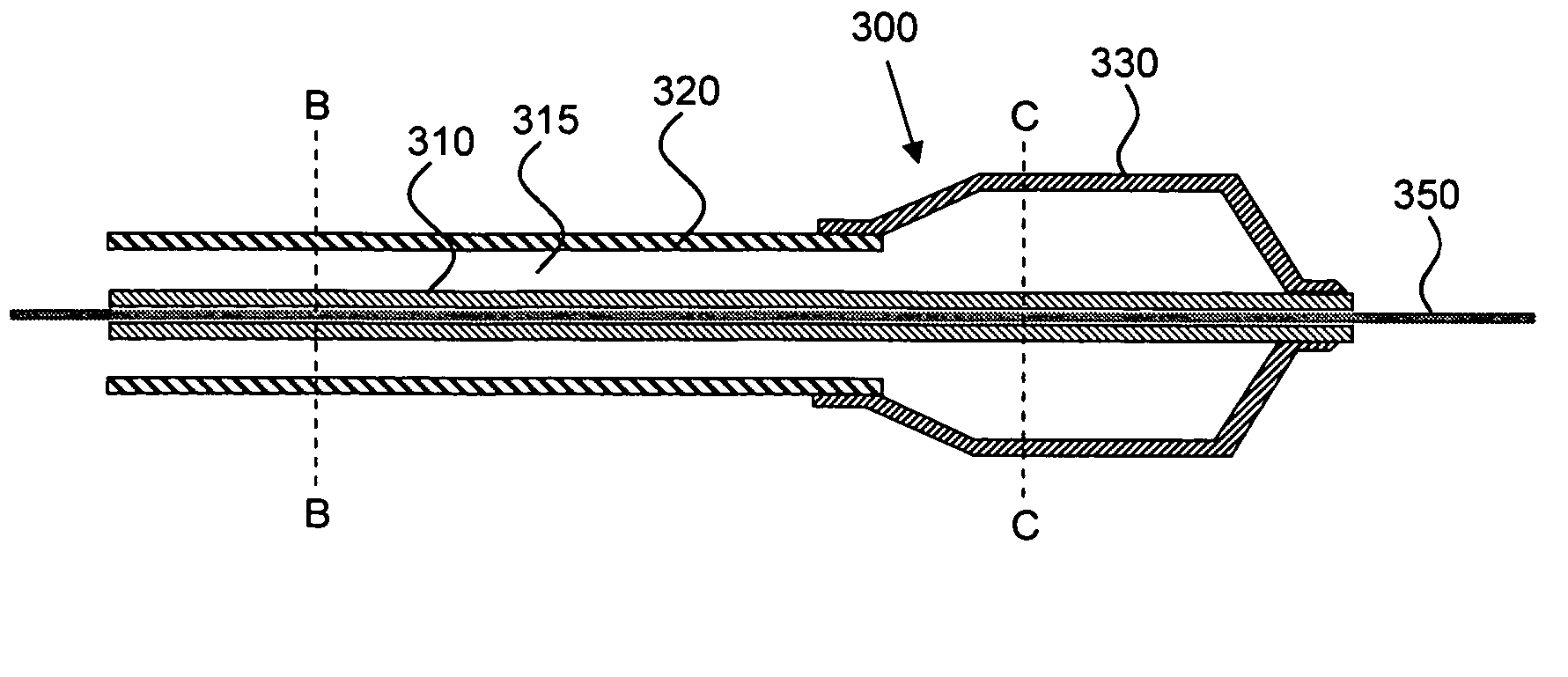
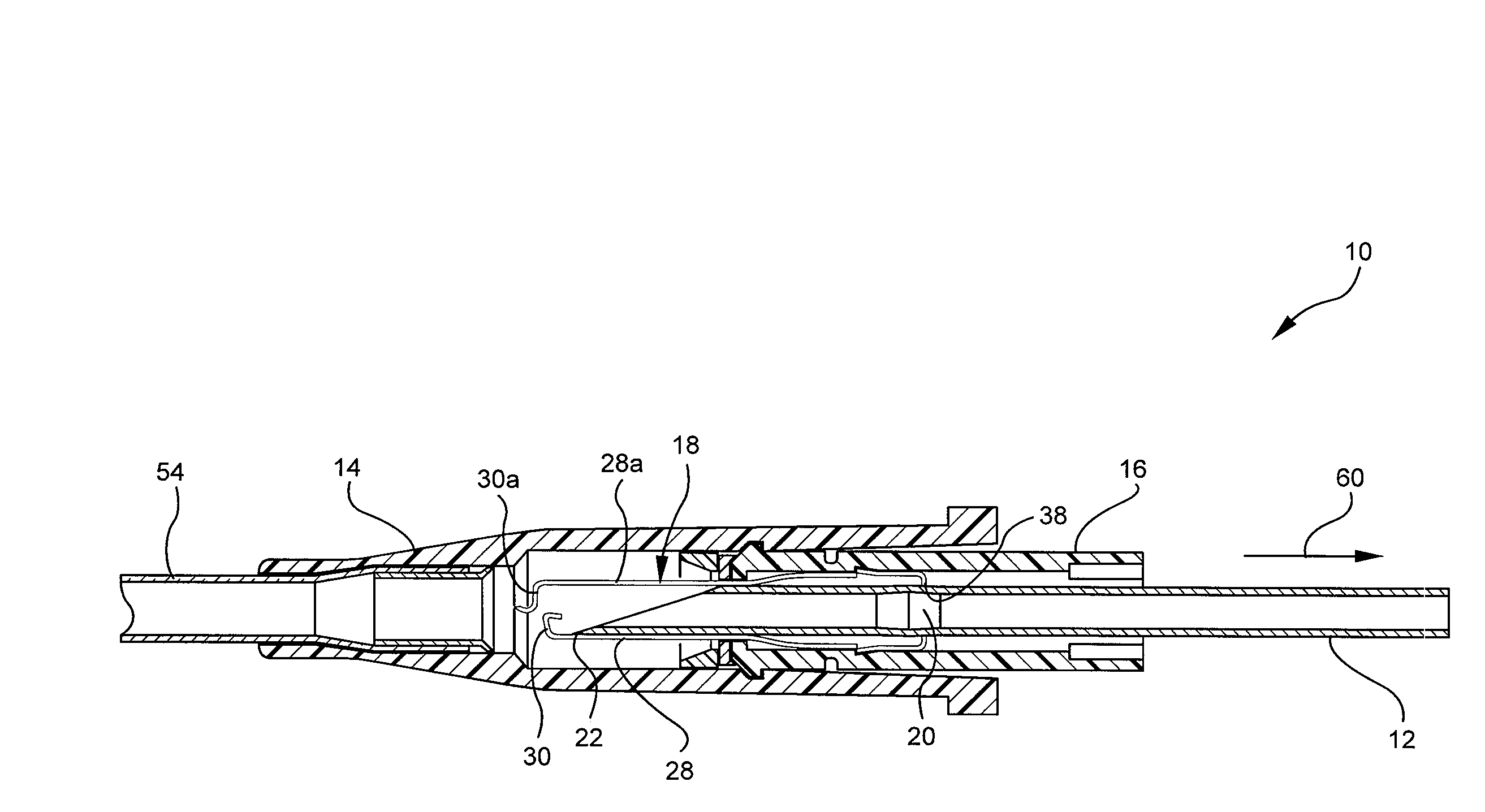
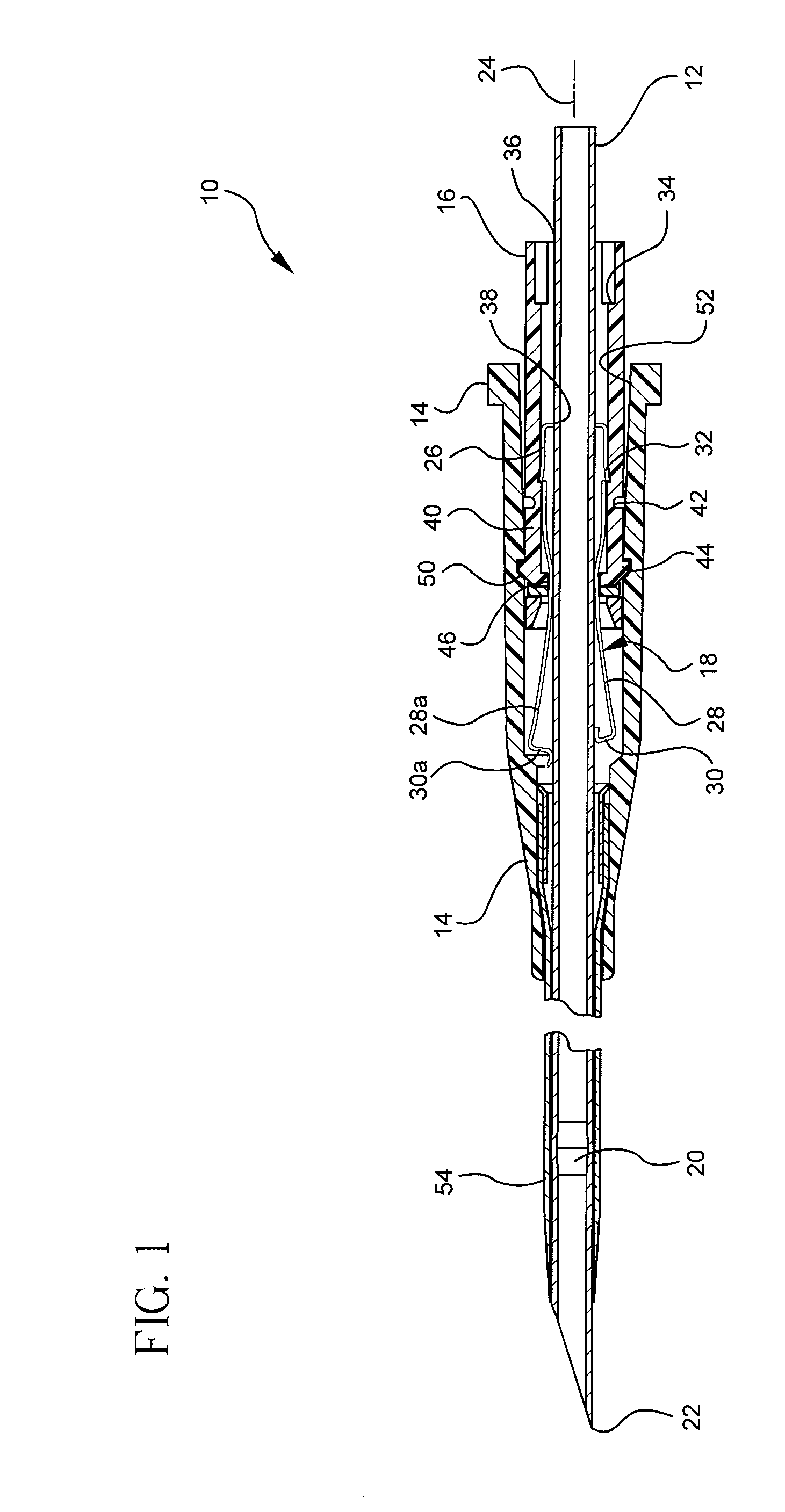
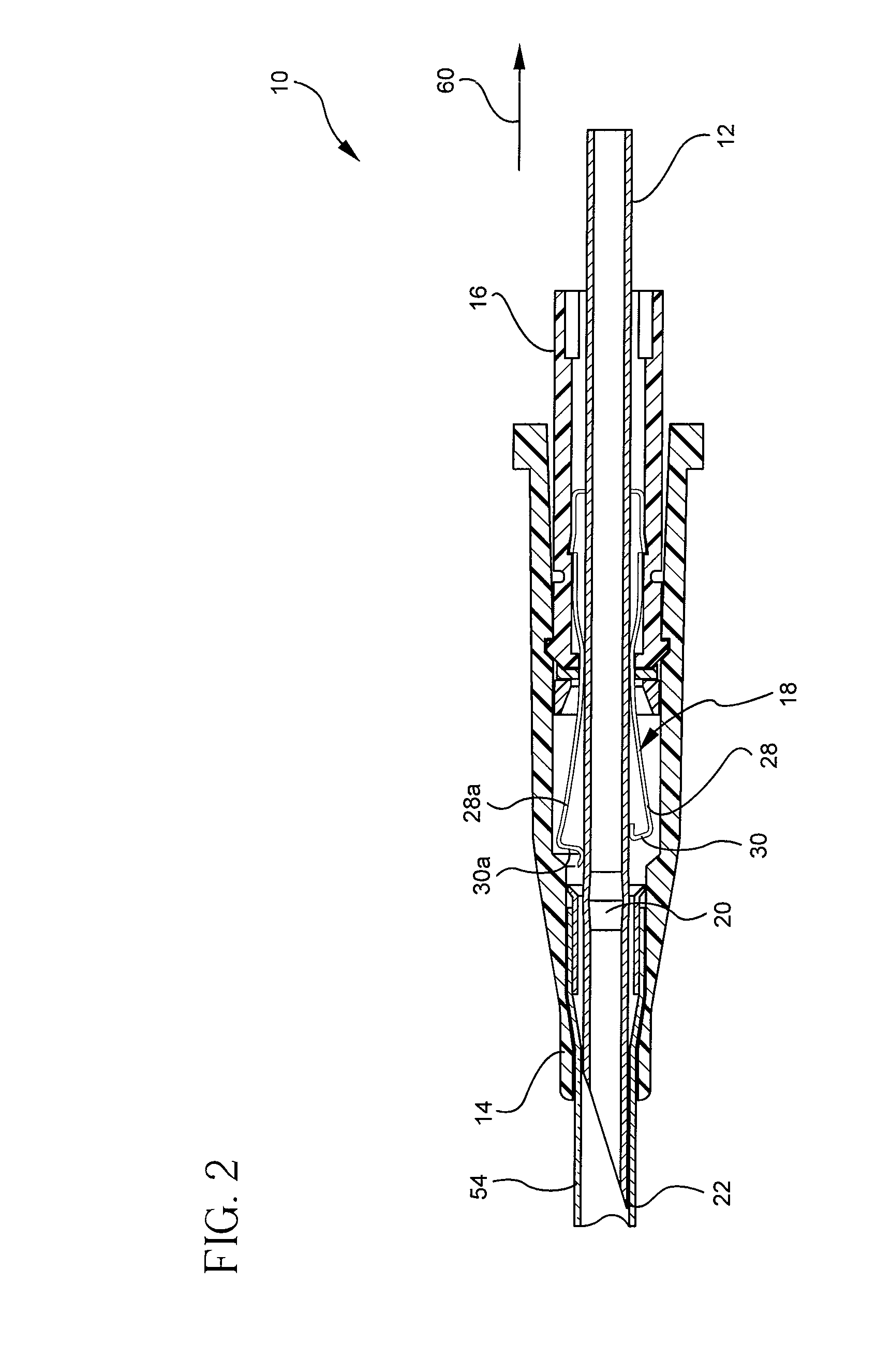
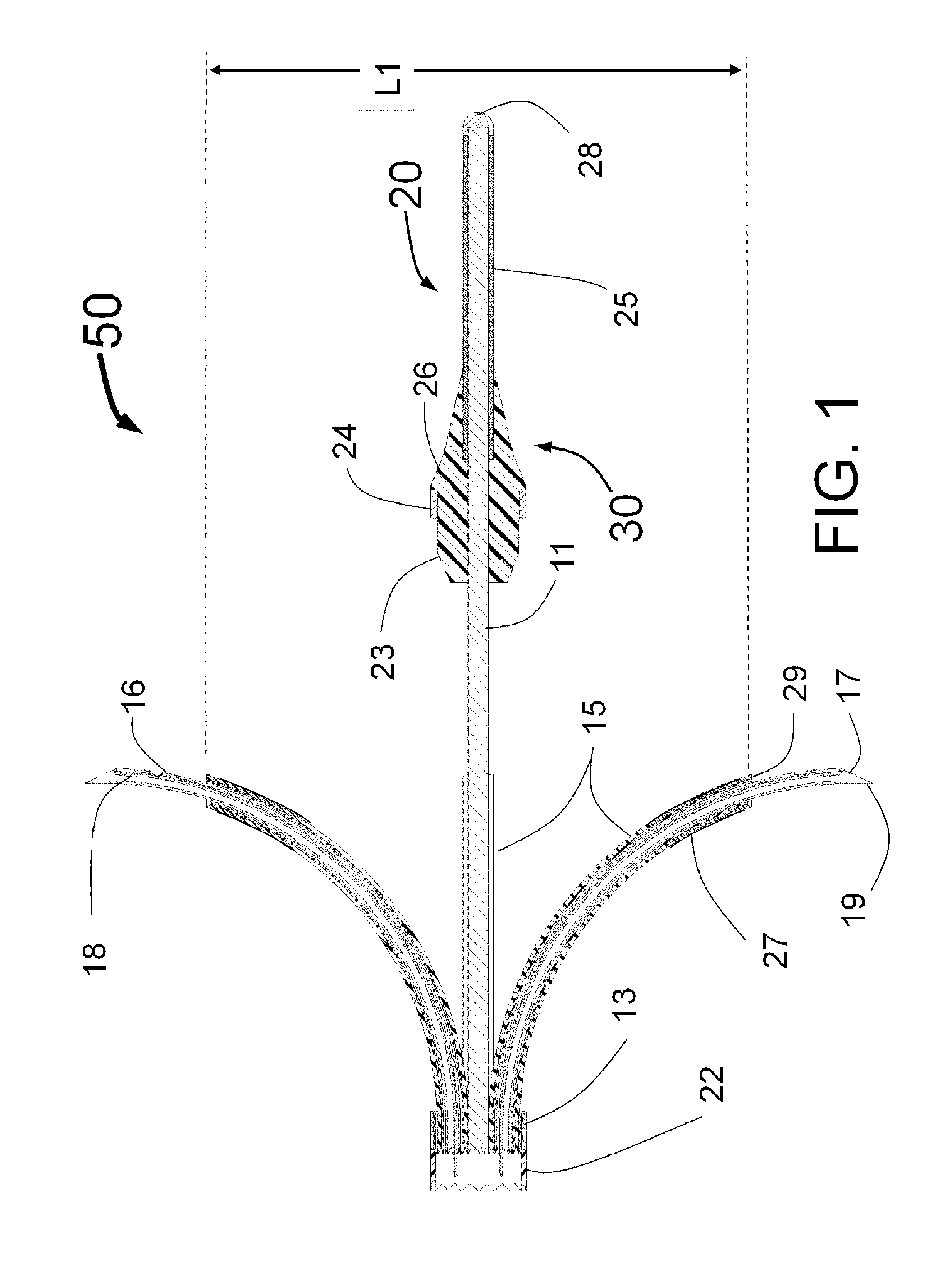
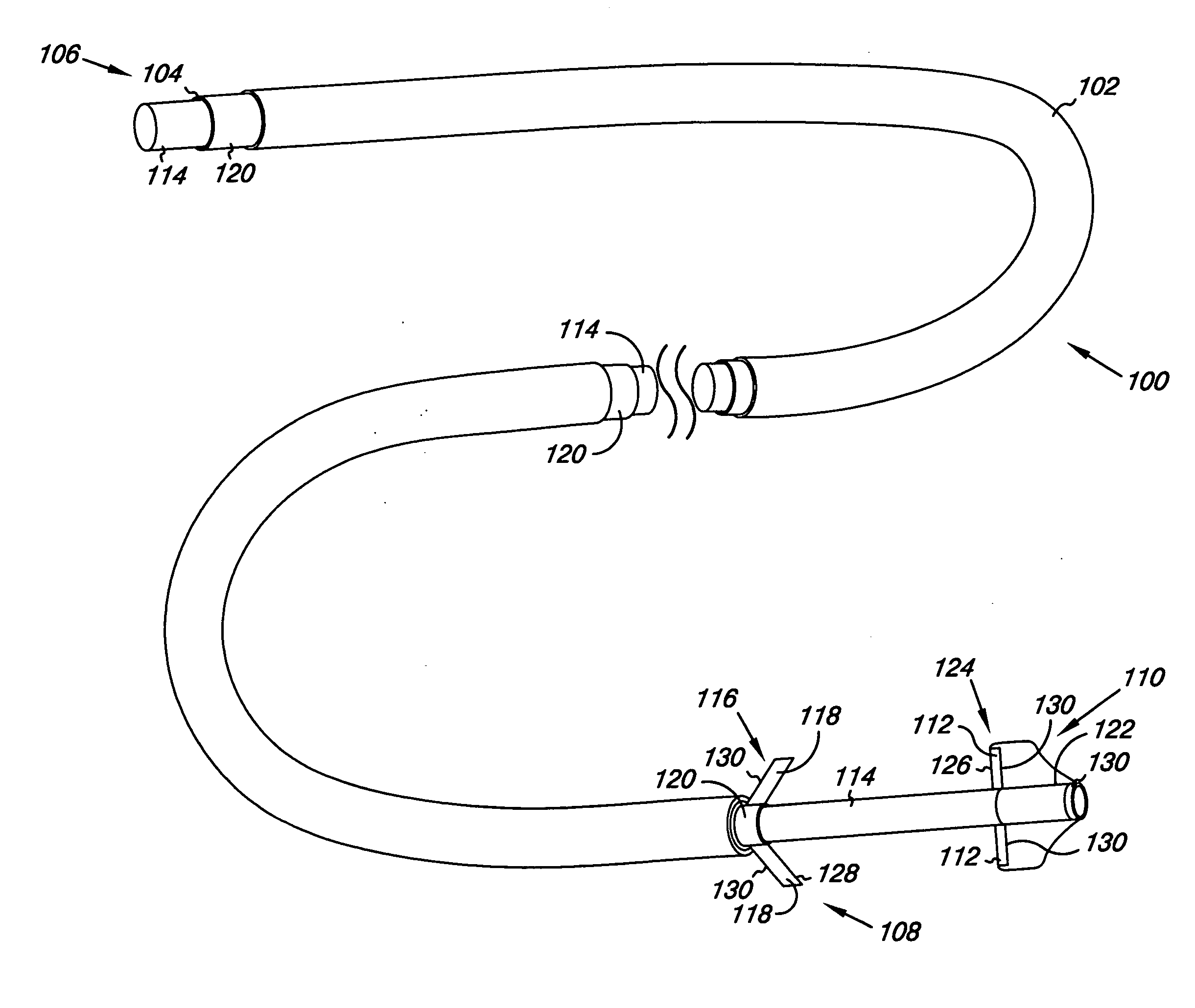
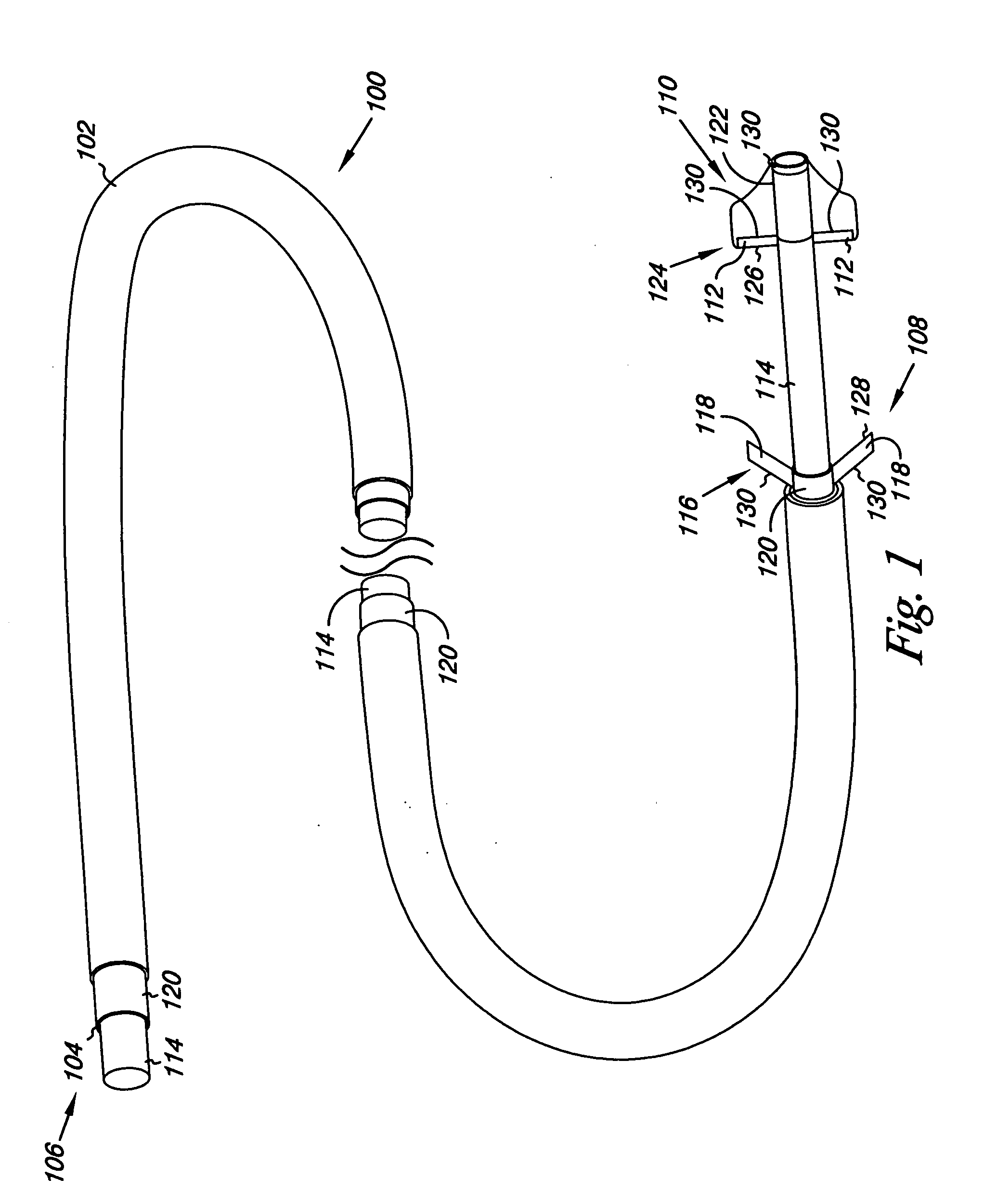
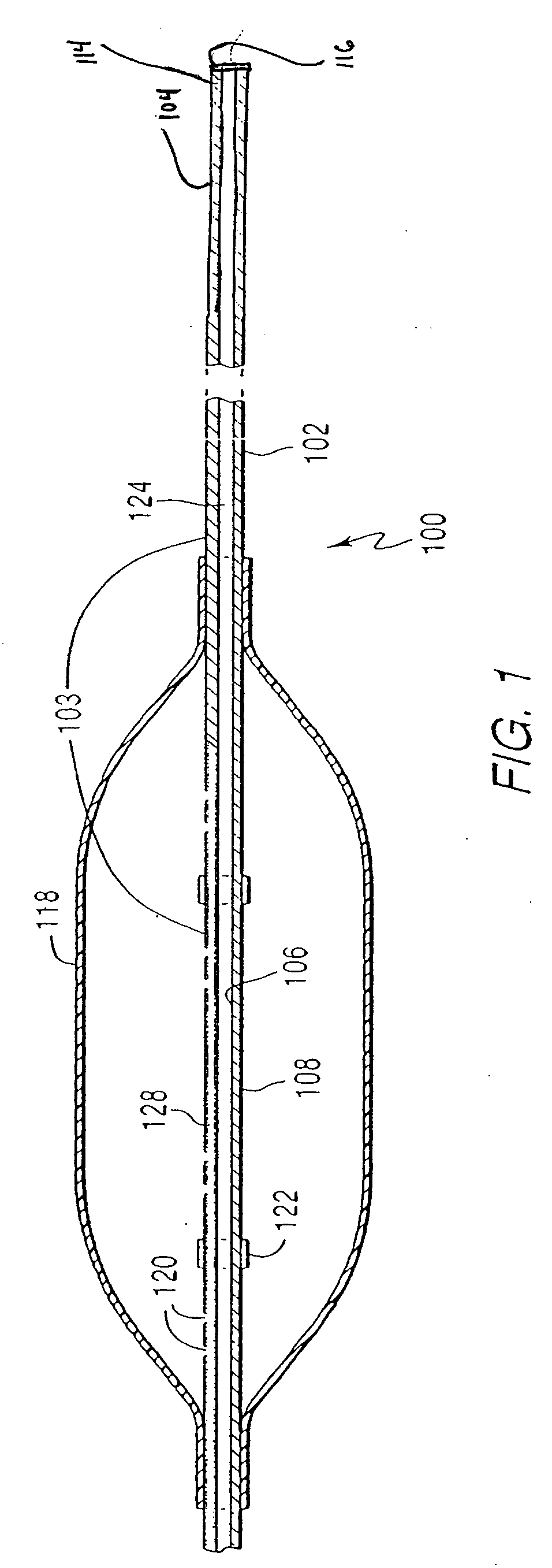
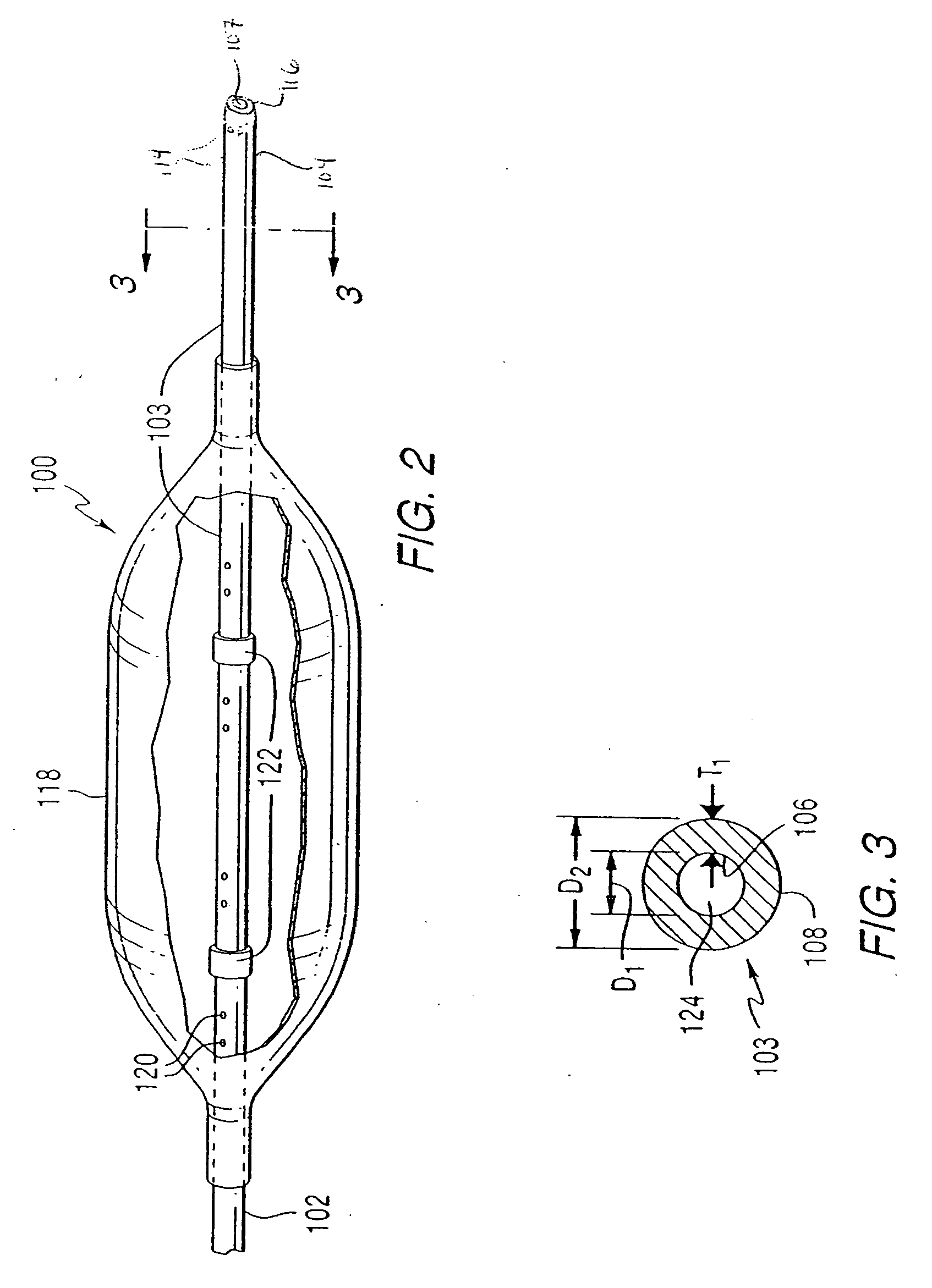
Multi-lumen vascular catheter and method for manufacturing the same
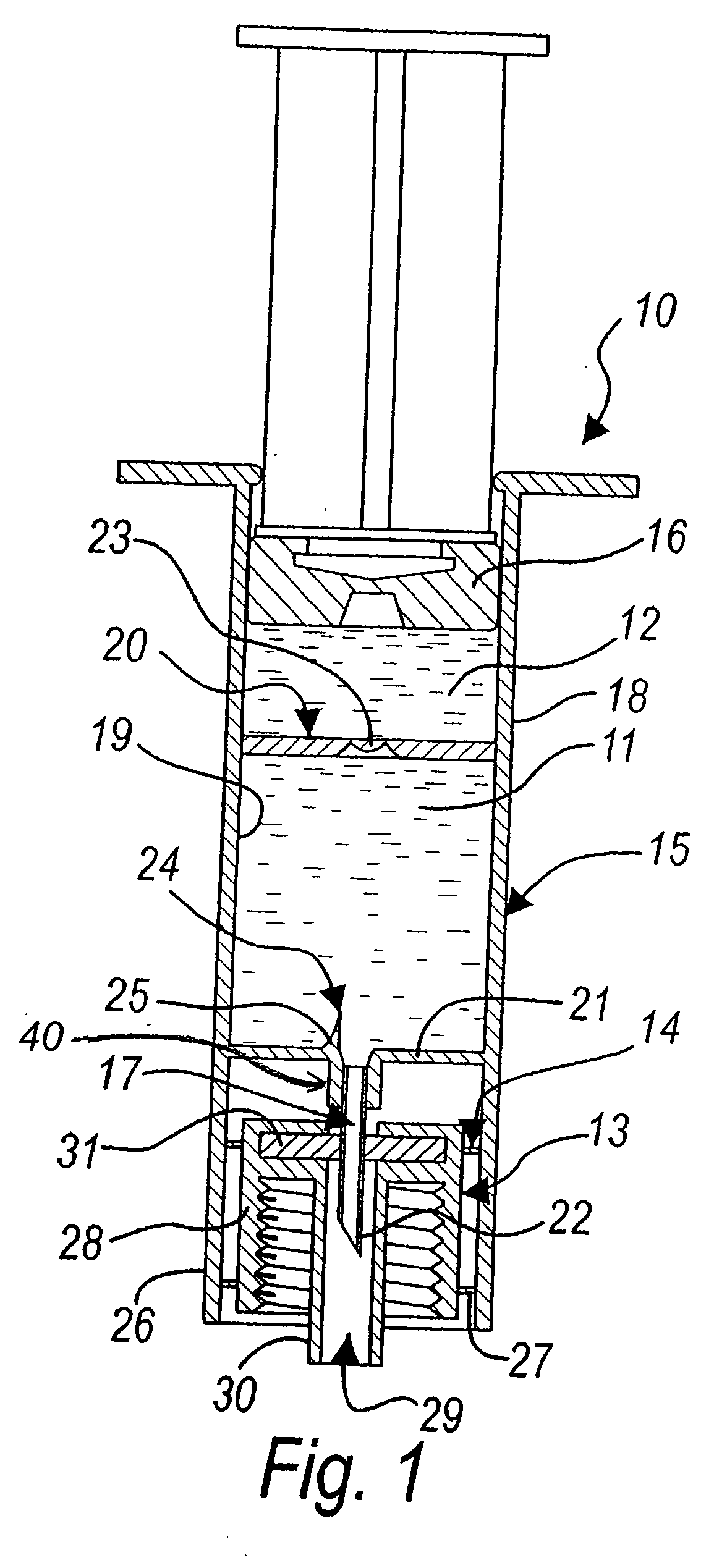
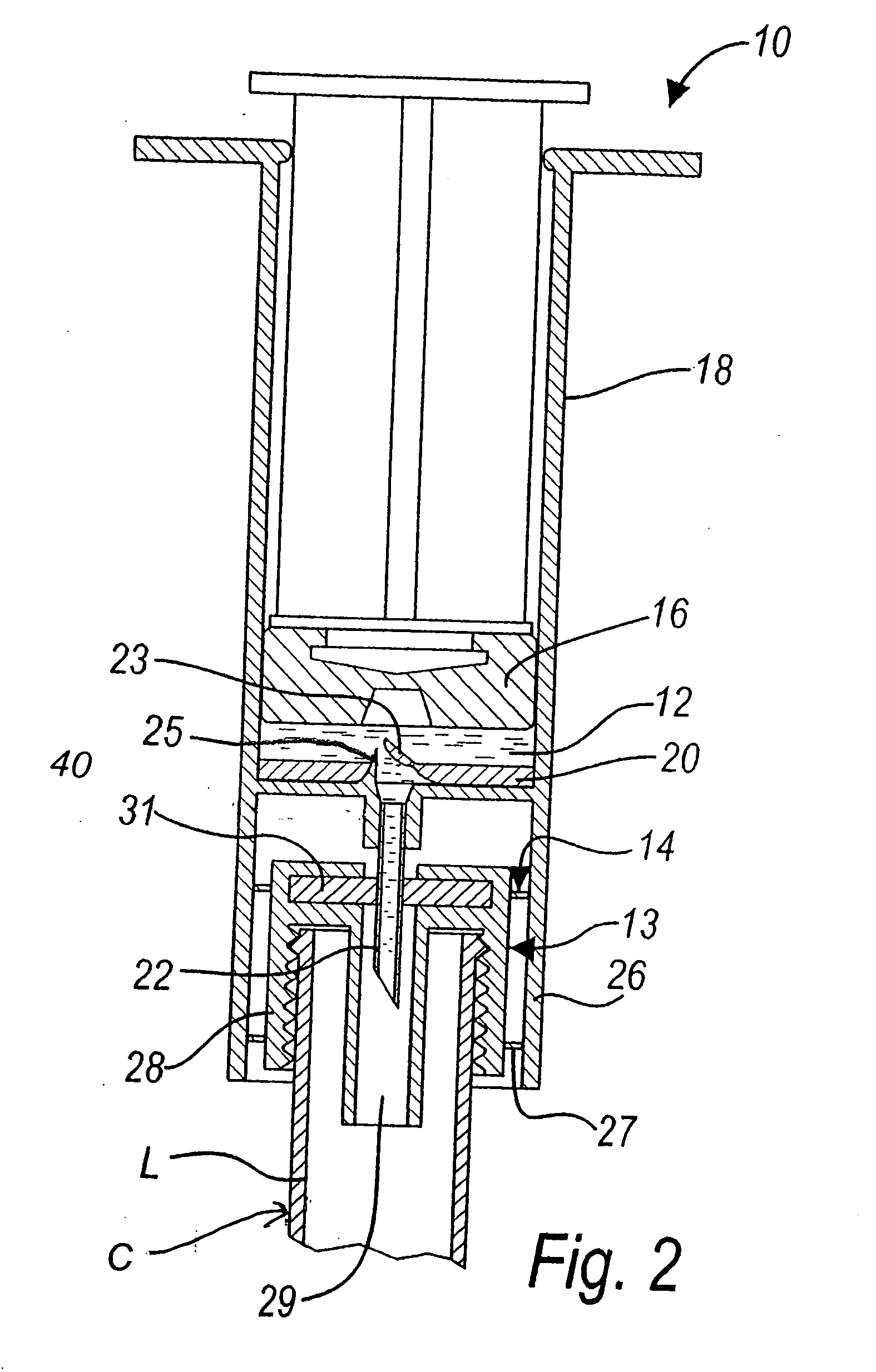
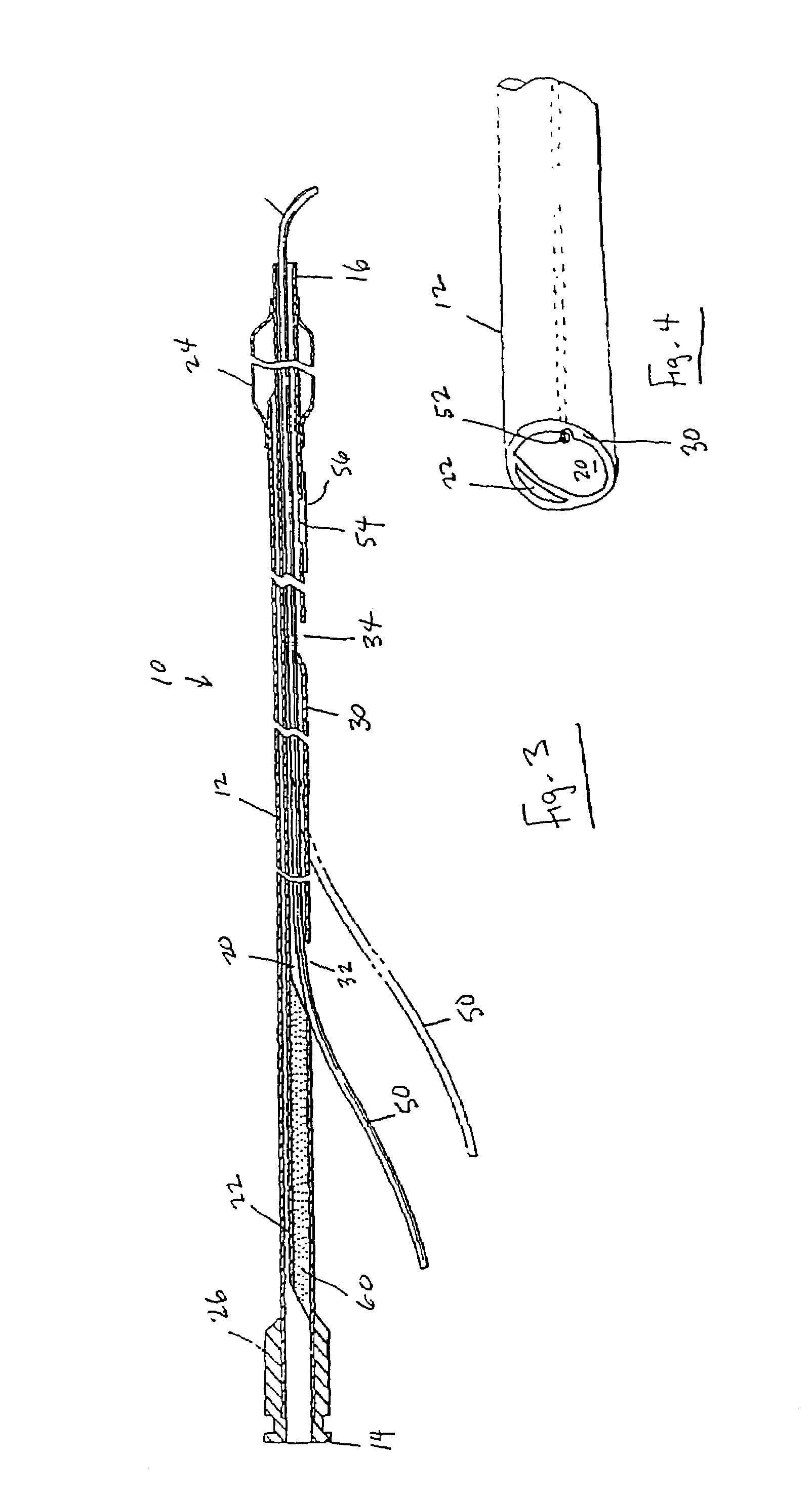
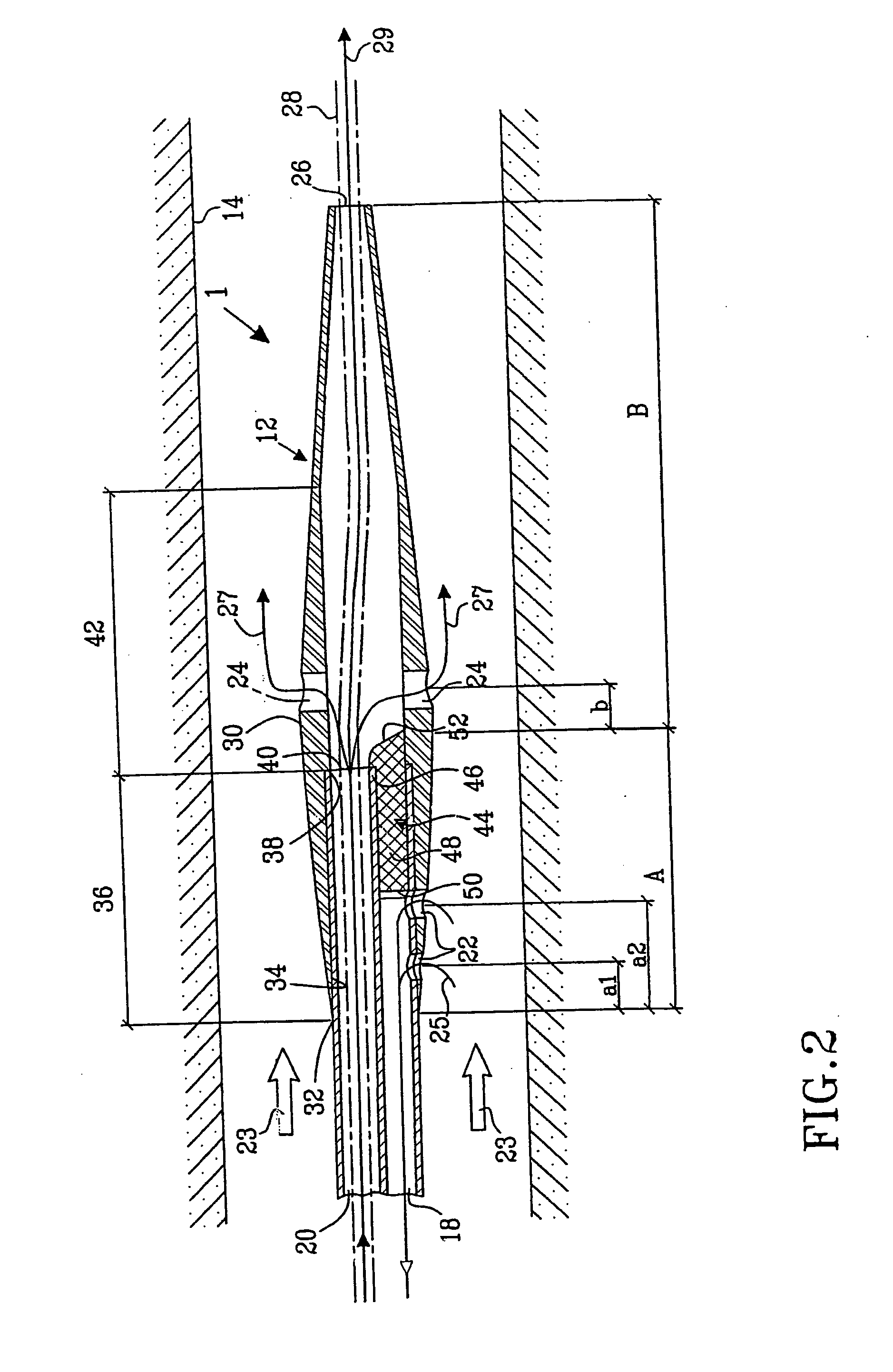
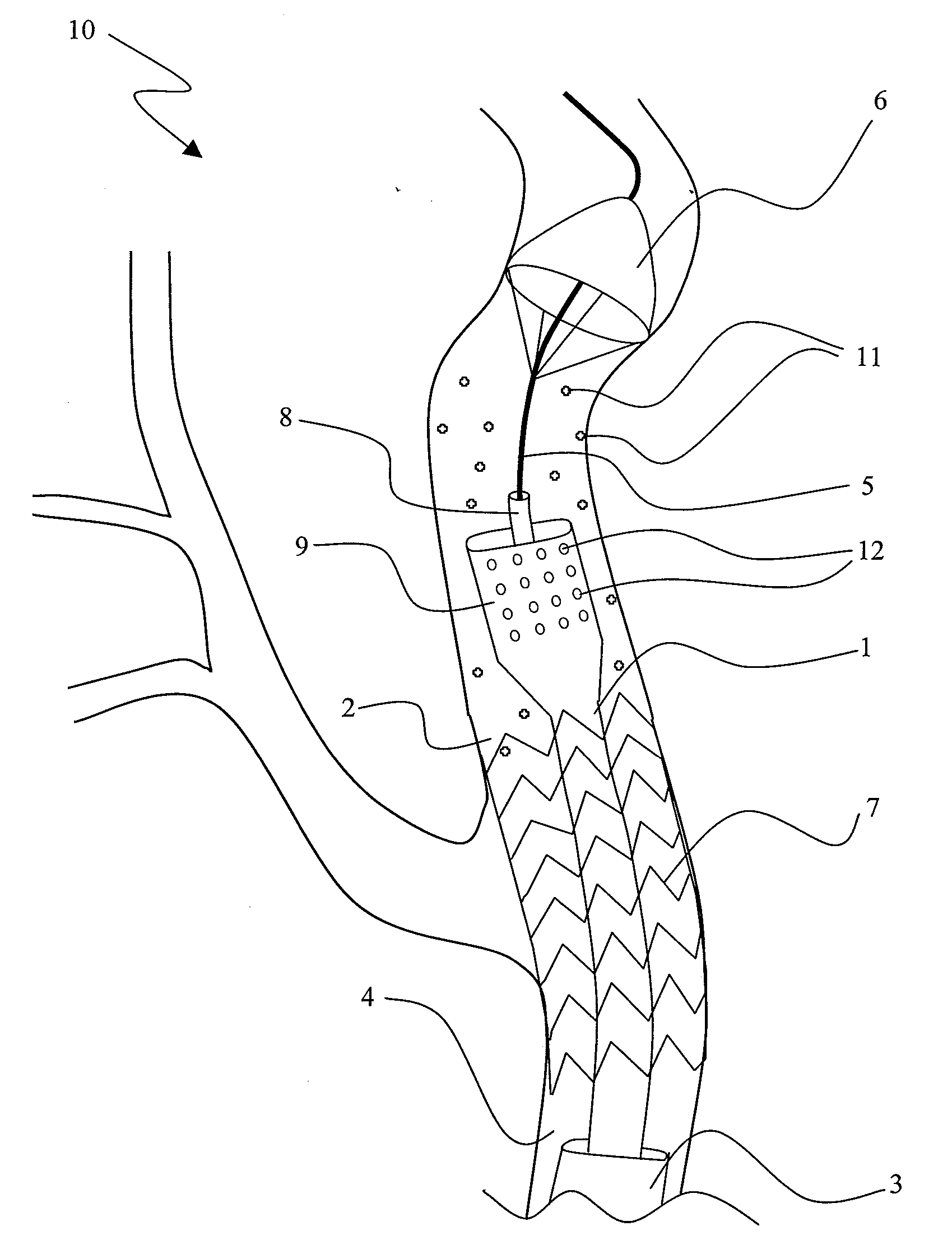
ActiveUS20050288623A1Avoid recyclingMinimize adhesionMulti-lumen catheterMedical syringesVeinVenous blood
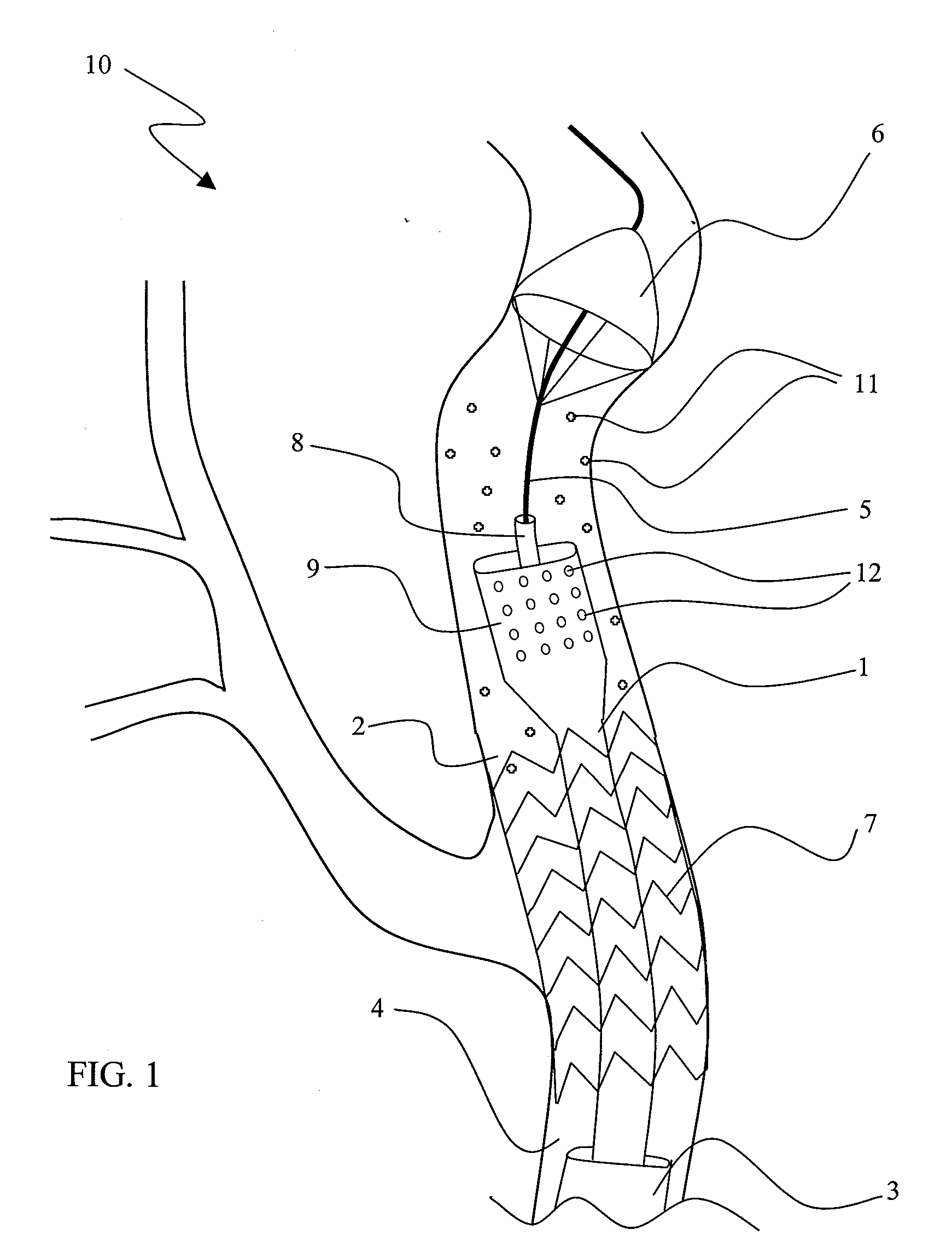
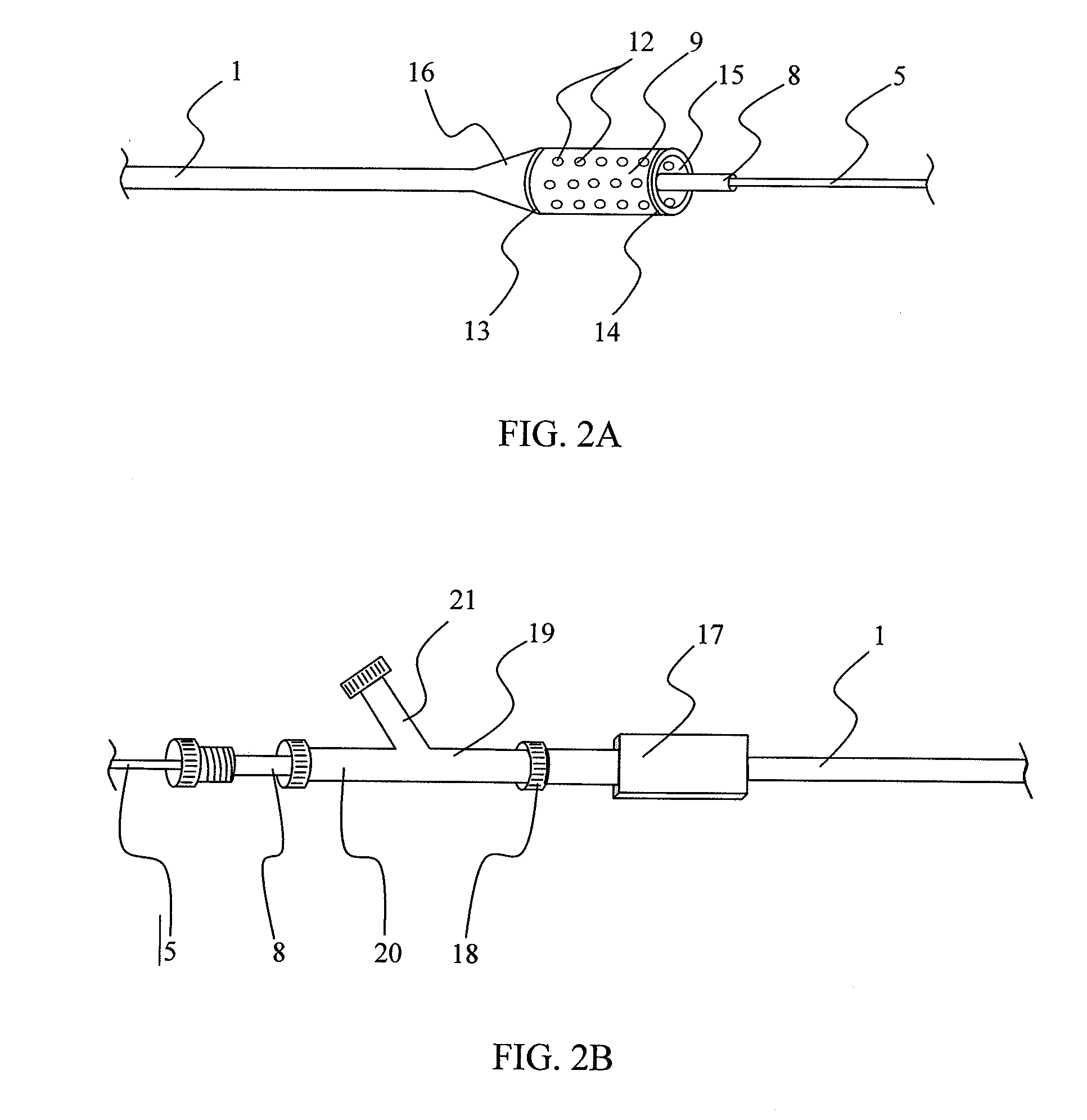
A multilumen vascular catheter (1) for treatment of patients by insertion of the vascular catheter in a venous blood vessel (14) by means of a guide-wire (28), the vascular catheter having a proximal connection point (10), a distal end-portion (12) which is terminated within a guide-wire opening (26), and a flexible catheter tube (16) arranged between the proximal connection portion (10) and the distal end-portion (12). The catheter tube (16) has a first lumen (18) for extraction of fluid such as untreated blood from the vessel (1) and a second lumen (20) for introducing fluid such as treated blood to the blood vessel (14). One or more suction openings (22) communicate with the first lumen (18) and are located upstream of one or more outlet openings (24), which in turn communicate with the second lumen (20), the suction openings (22) and the outlet openings (24) being located at the distal end-portion (12). The distal end-portion (12) is permanently bulbous and has a first, widening section (A) starting from the catheter tube (16) with a gradually increasing external cross-section in the direction toward the guide-wire opening (26). The first section (A) transits downstream via a shoulder (30) with a maximum external diameter into a second, narrowing section (B) having a gradually decreasing external cross-section in the direction toward the guide-wire opening (26). One or more of the suction openings (22) are located in the first, widening section (A) of the distal end-portion (12) while one or more of the outlet openings (24) are located in the second, narrowing section (B).
Owner:NORDIC MED COM
Optimal radiopaque catheter
InactiveUS20090287189A1Efficient procedureIncrease awarenessCatheterTube connectorsBlood vesselOpen wounds
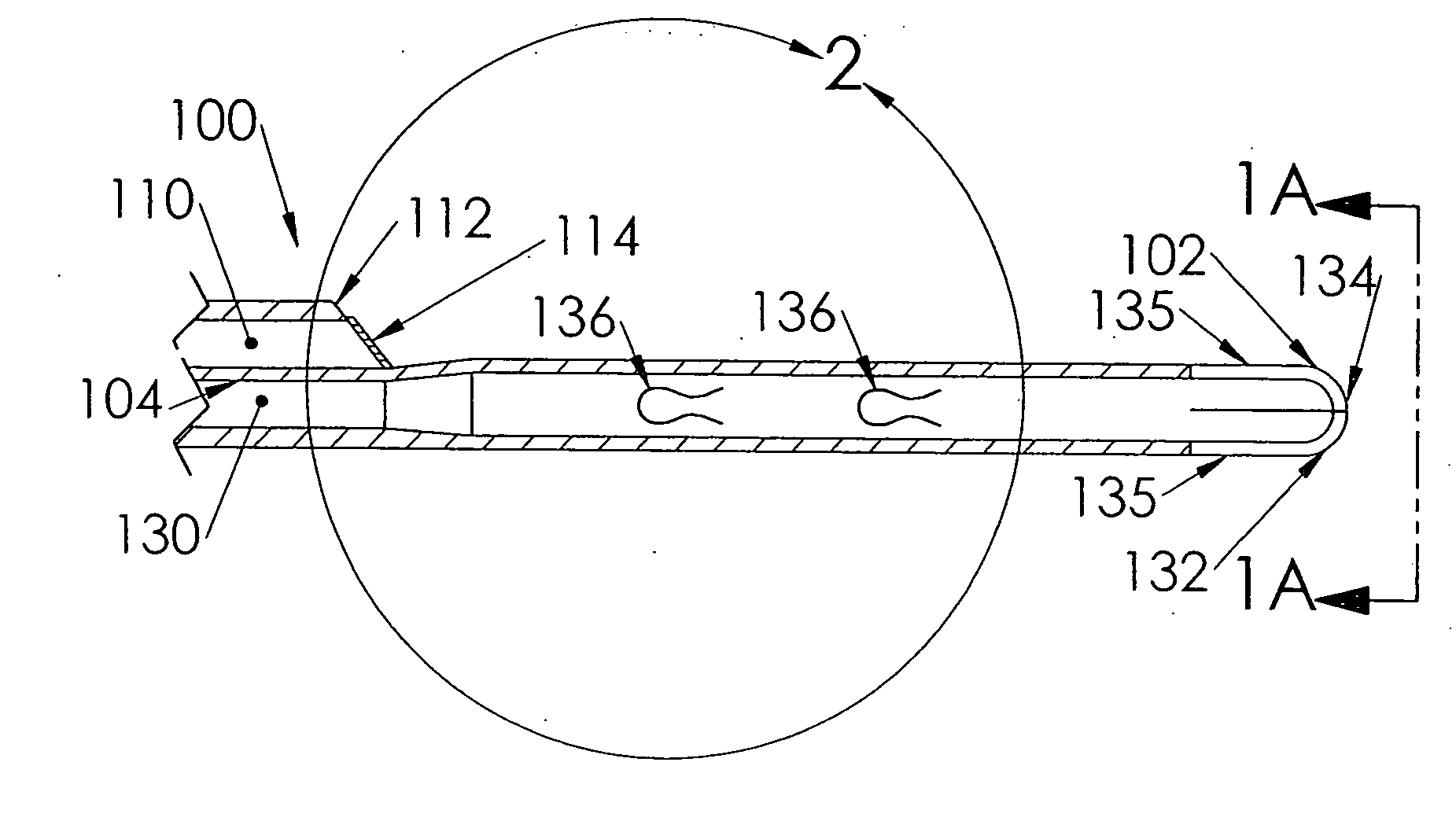
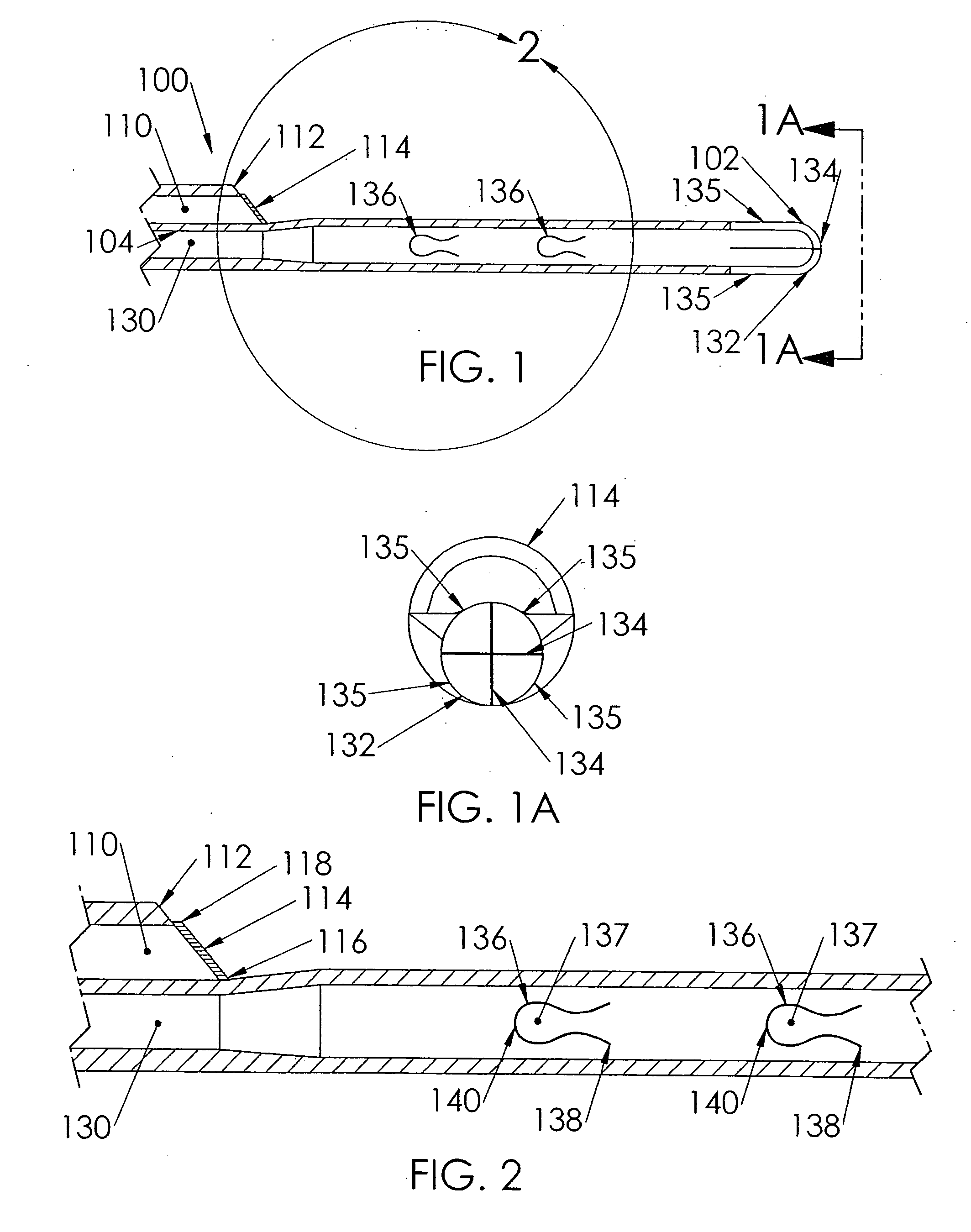
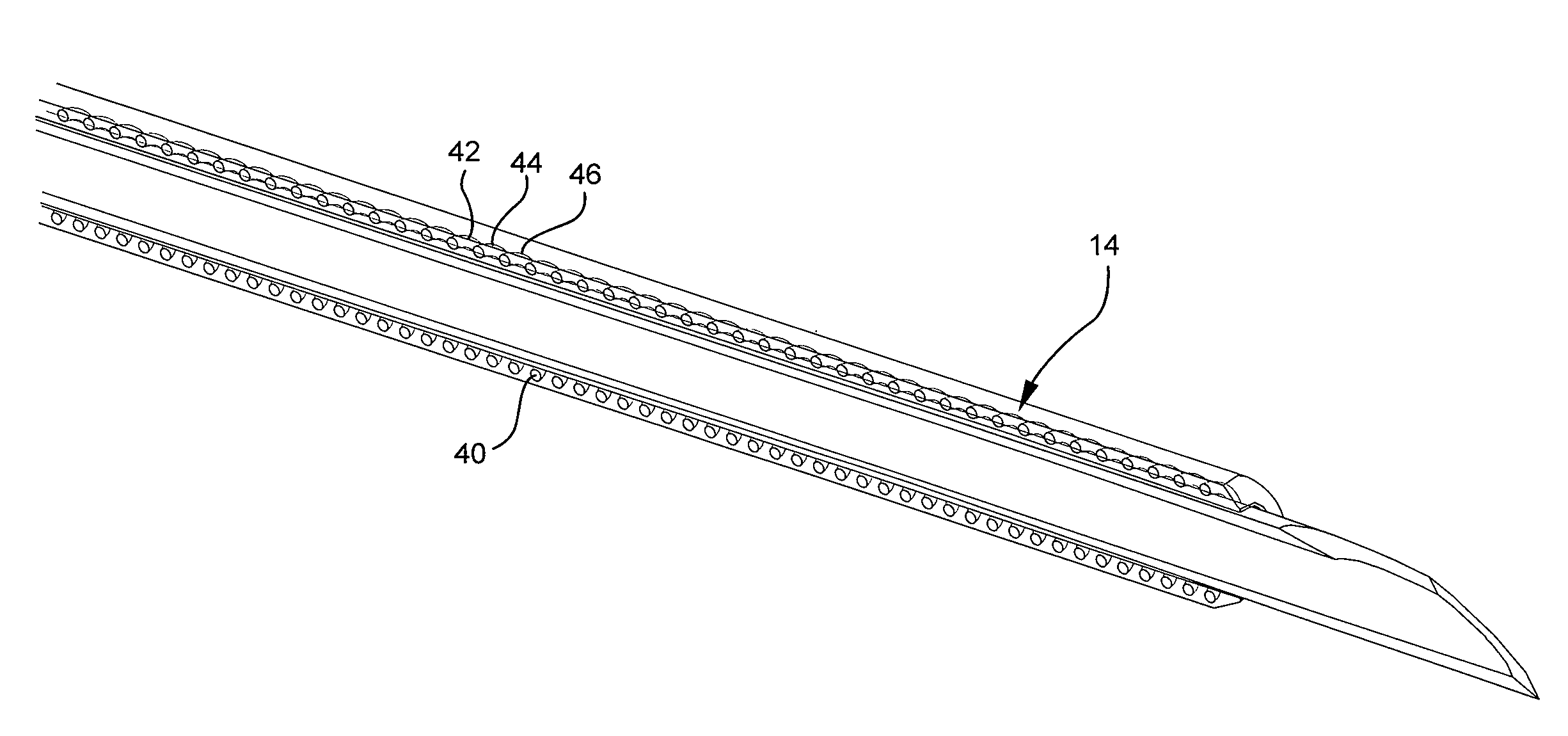
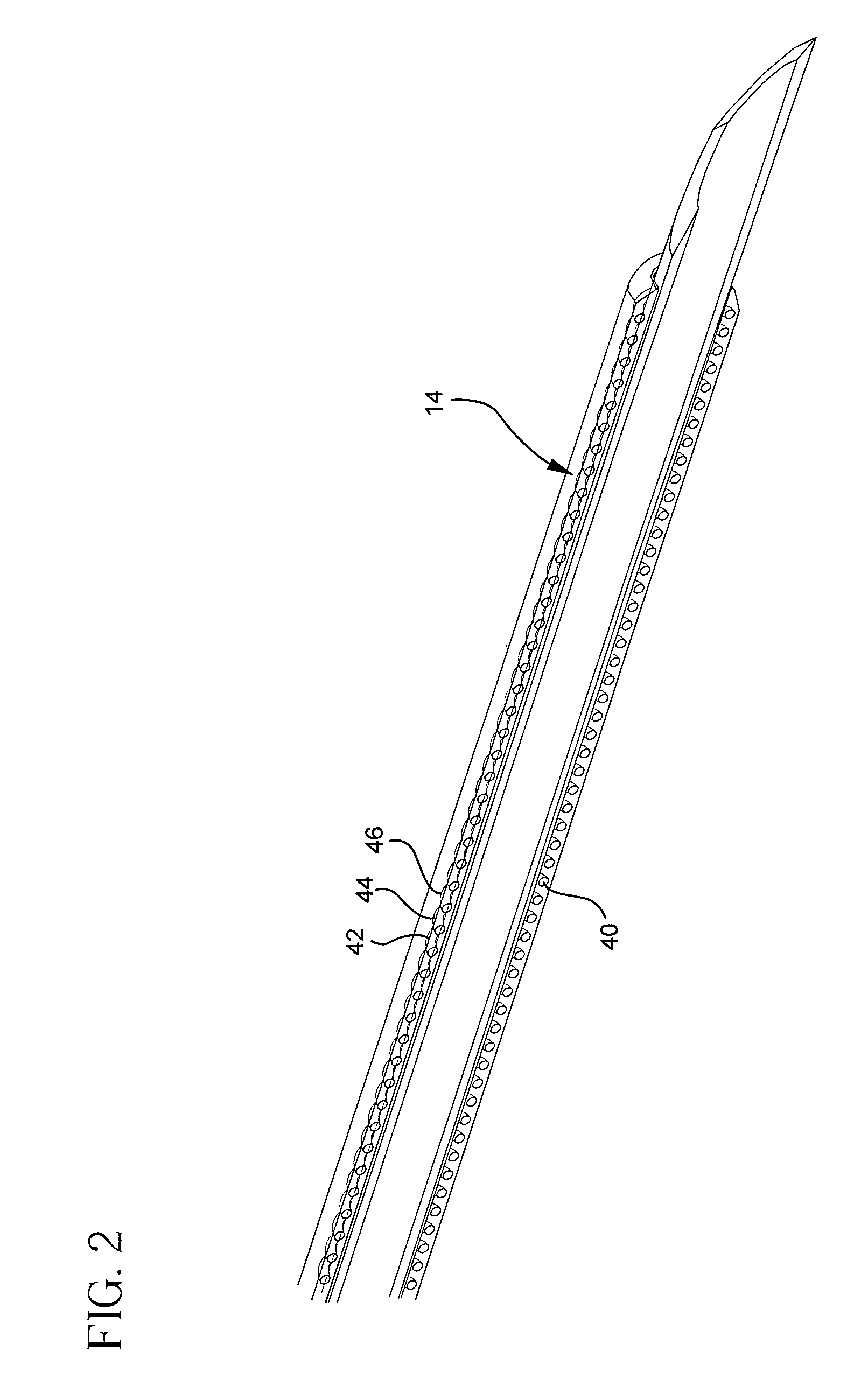
A vascular catheter embedded with a radiopaque material providing a distinct, non-physiological pattern that may be easily detected on a radiograph. The radiopaque material may be embedded within the wall of the catheter in an open wound, helical formation. Detection of the catheter by x-ray is increased due to the non-physiological radiograph pattern and due to the increased presence of the radiopaque material. The non-physiological formation increases the radiopacity of the catheter, yet requires less radiopaque material than traditional radiopaque catheters. The non-physiological formation and decreased amount of radiopaque material provides for a more detectible and less rigid catheter that is resistant to kinks and occlusions.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Vascular catheter with aspiration capabilities and expanded distal tip
A vascular catheter and method of use of the catheter for aiding in balloon angioplasty and stent placement procedures are disclosed. The vascular catheter has a retrieval catheter with an expanded distal portion. The expanded distal portion has aspiration holes which allow aspiration of embolic debris during recovery of the embolic filter. A guide sheath may be used to guide the retrieval catheter past a stent and into position for aspiration and retrieval of the filter after stent placement.
Owner:WHOLEY MICHAEL H +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com