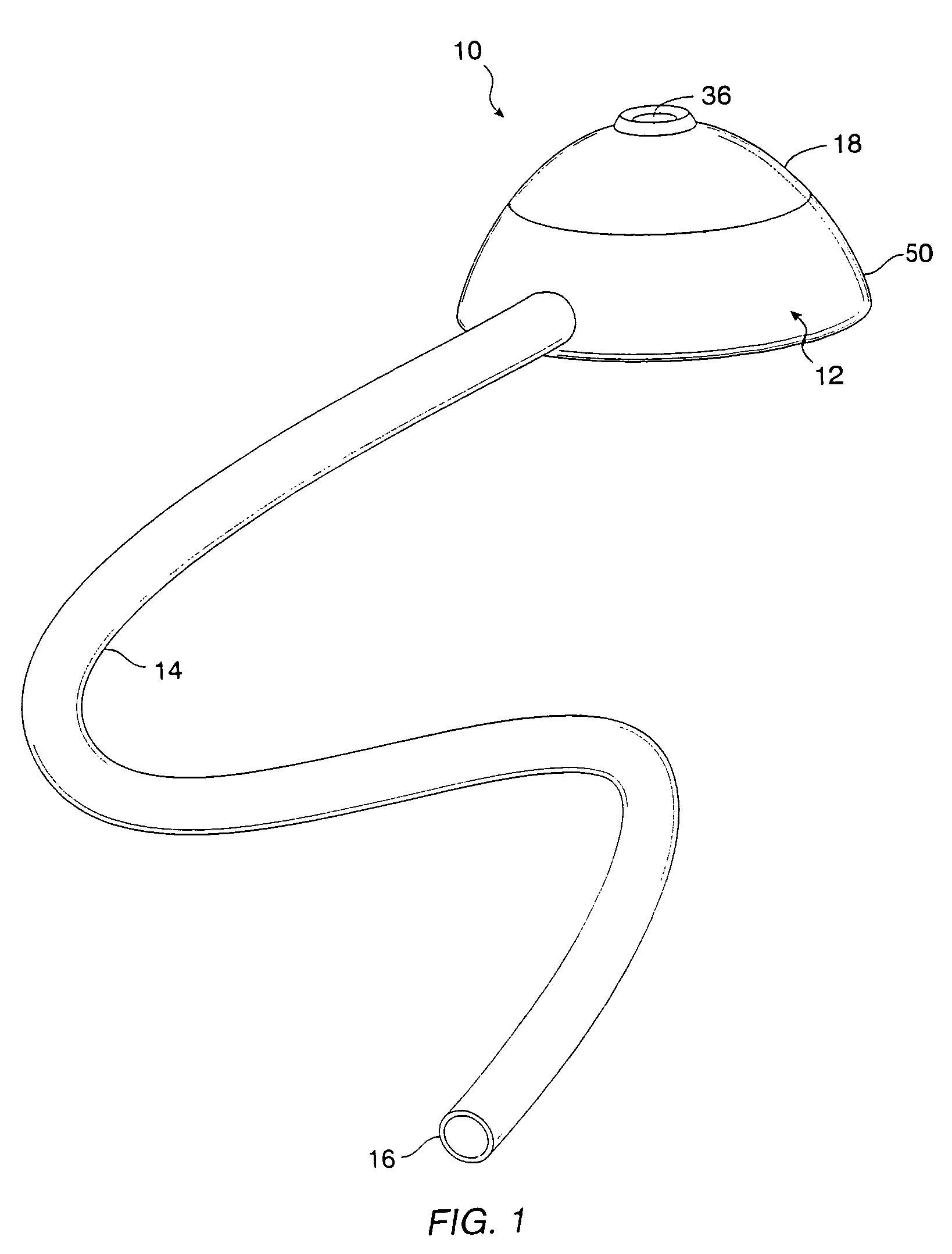
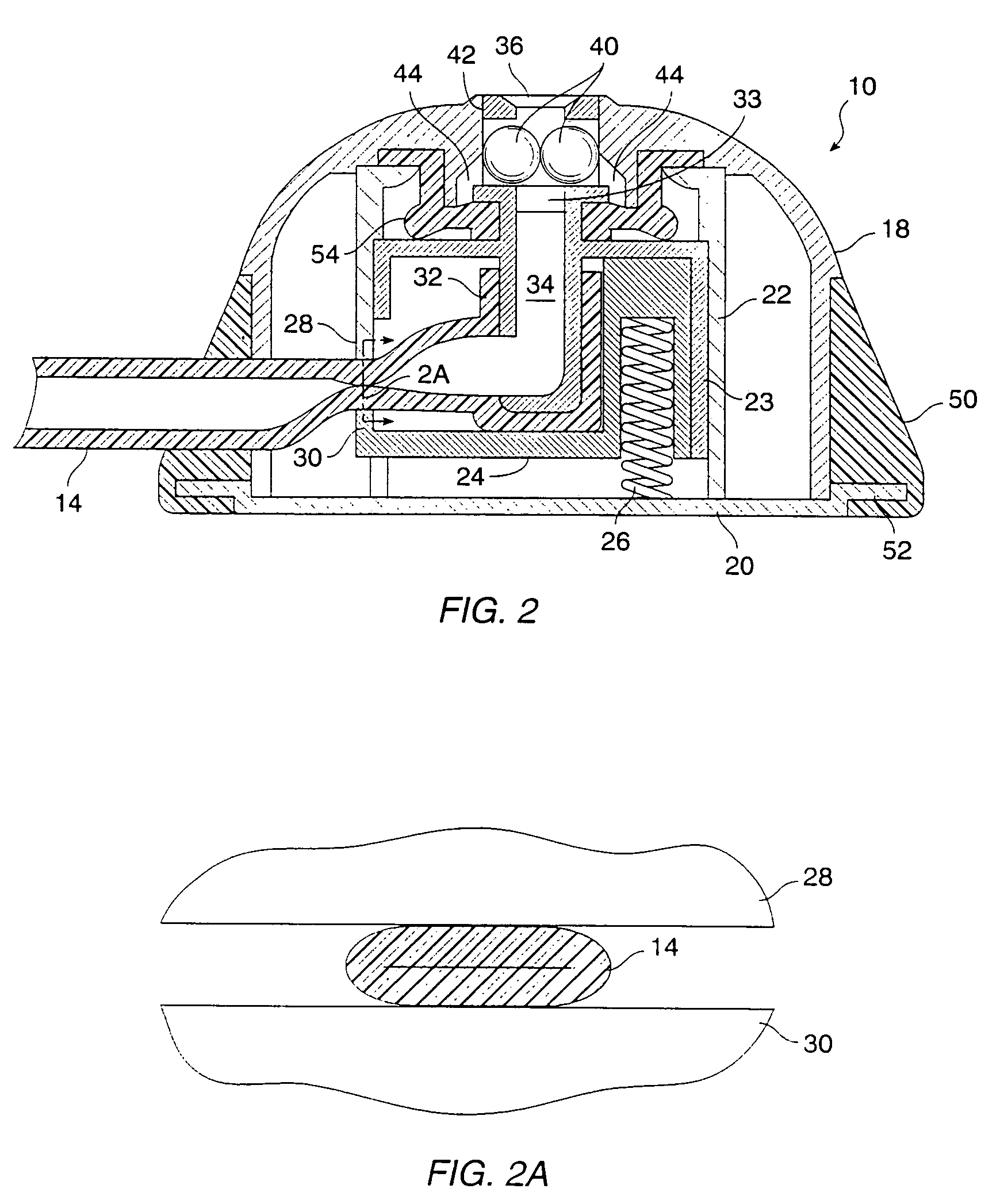
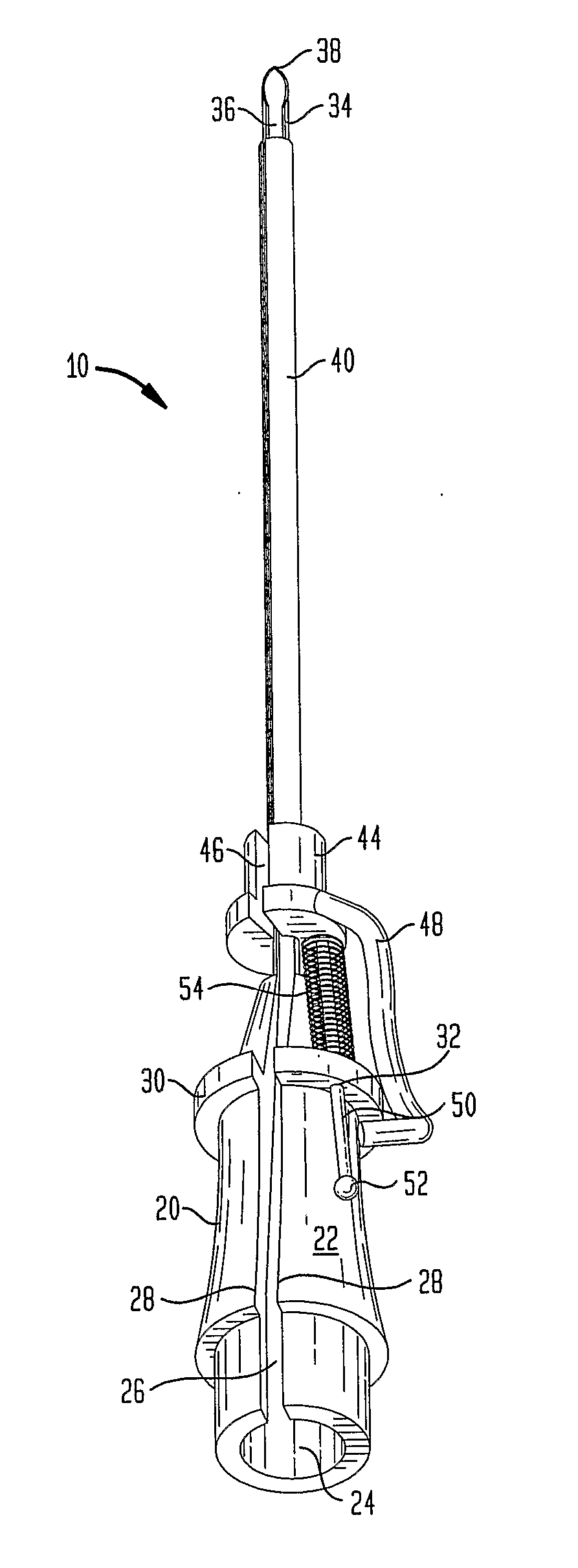
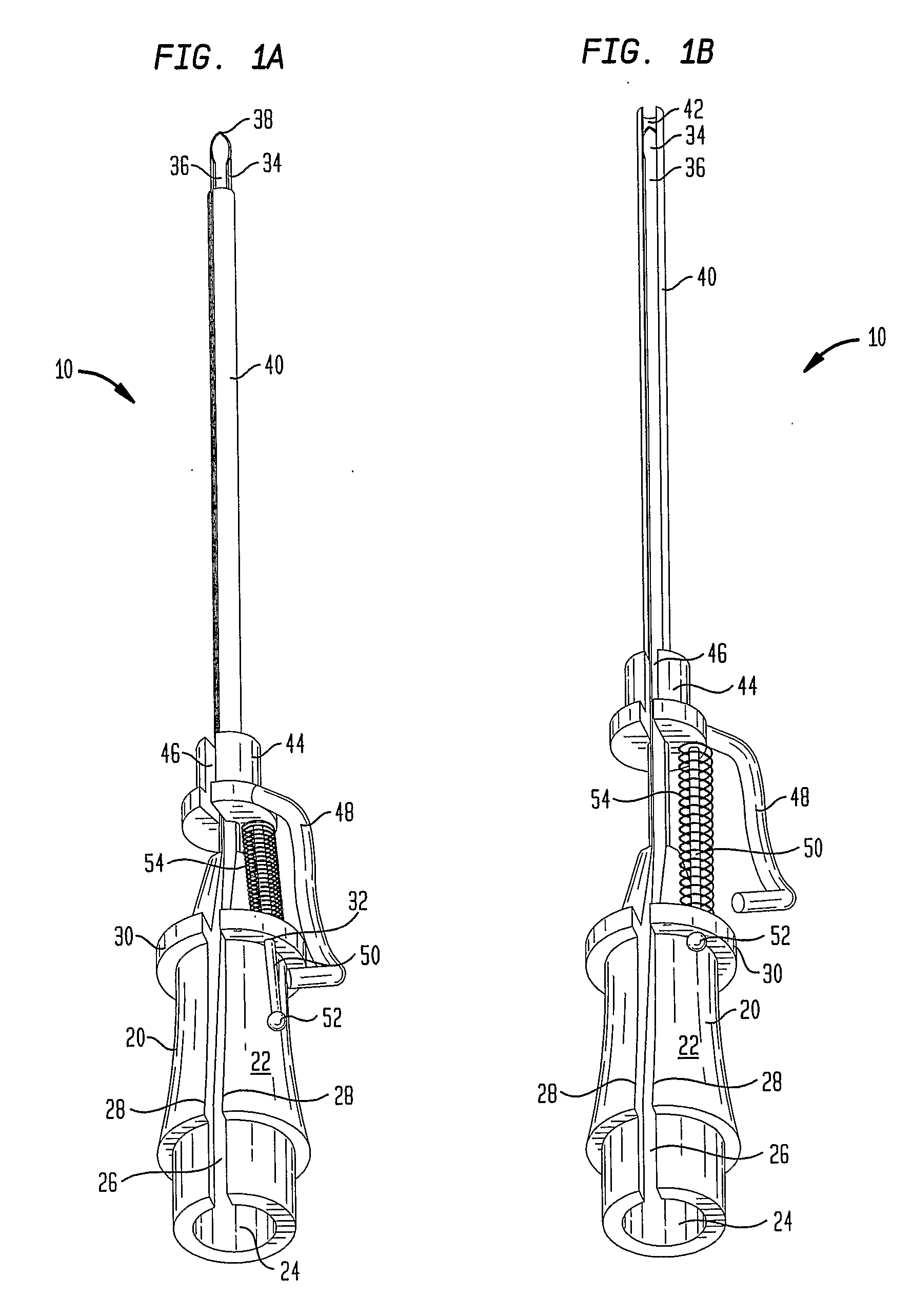
Patents
Literature
314 results about "Vascular access" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Vascular access refers to a rapid, direct method of introducing or removing devices or chemicals from the bloodstream. In hemodialysis, vascular access is used to remove the patient's blood so that it can be filtered through the dialyzer. Three primary methods are used to gain access to the blood: an intravenous catheter, an arteriovenous fistula (AV) or a synthetic graft. In the latter two, needles are used to puncture the graft or fistula each time dialysis is performed.
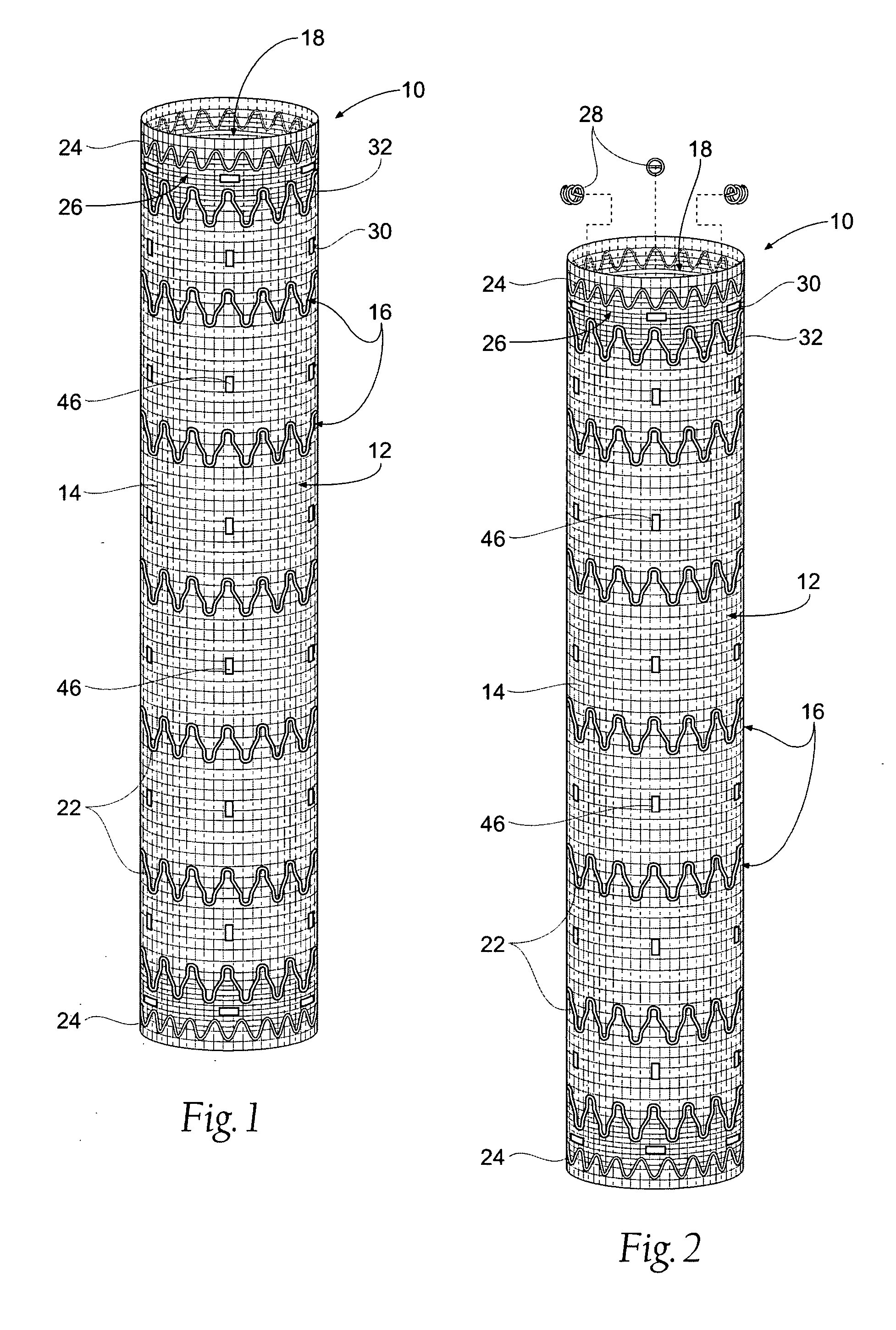
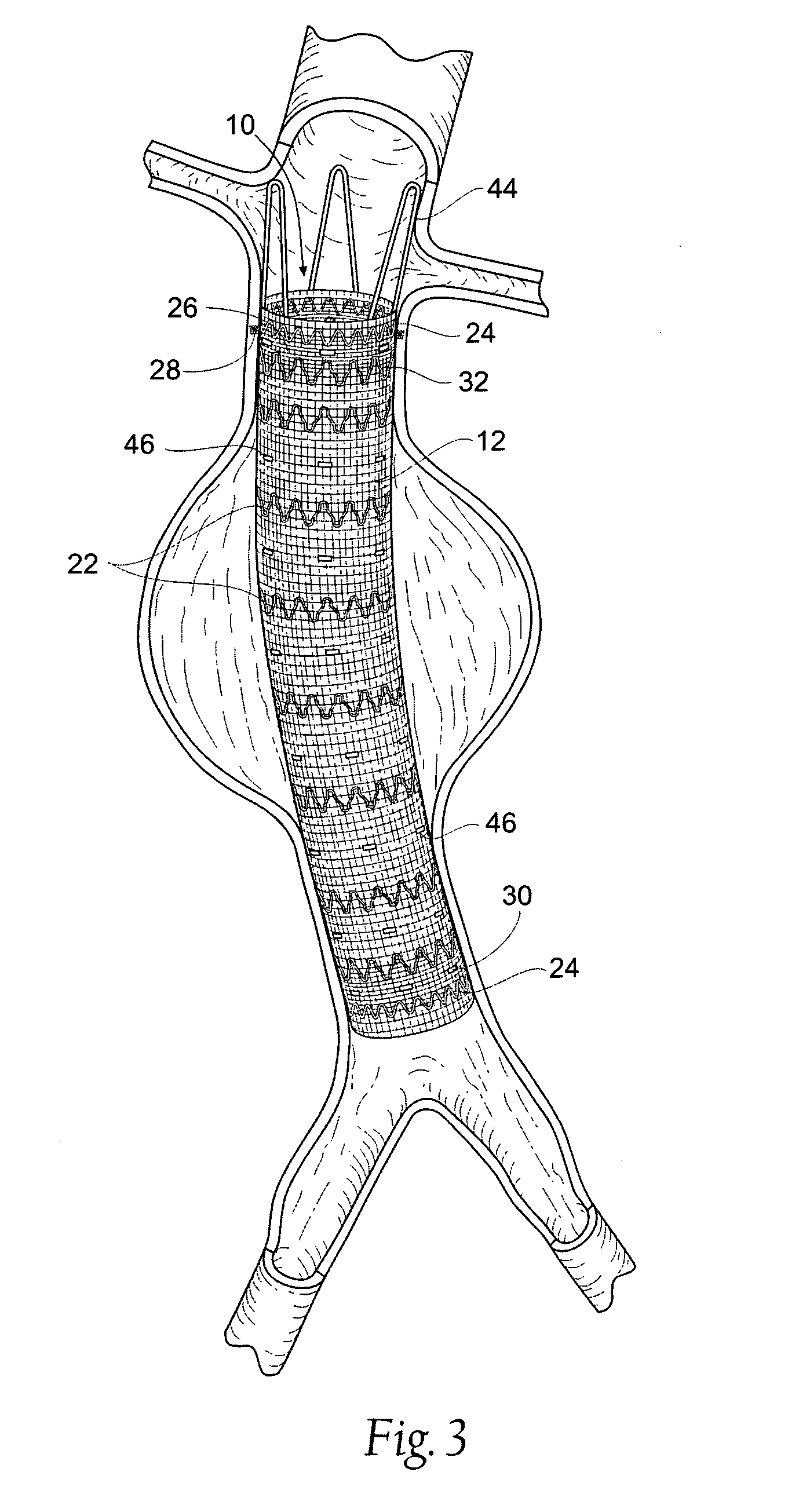
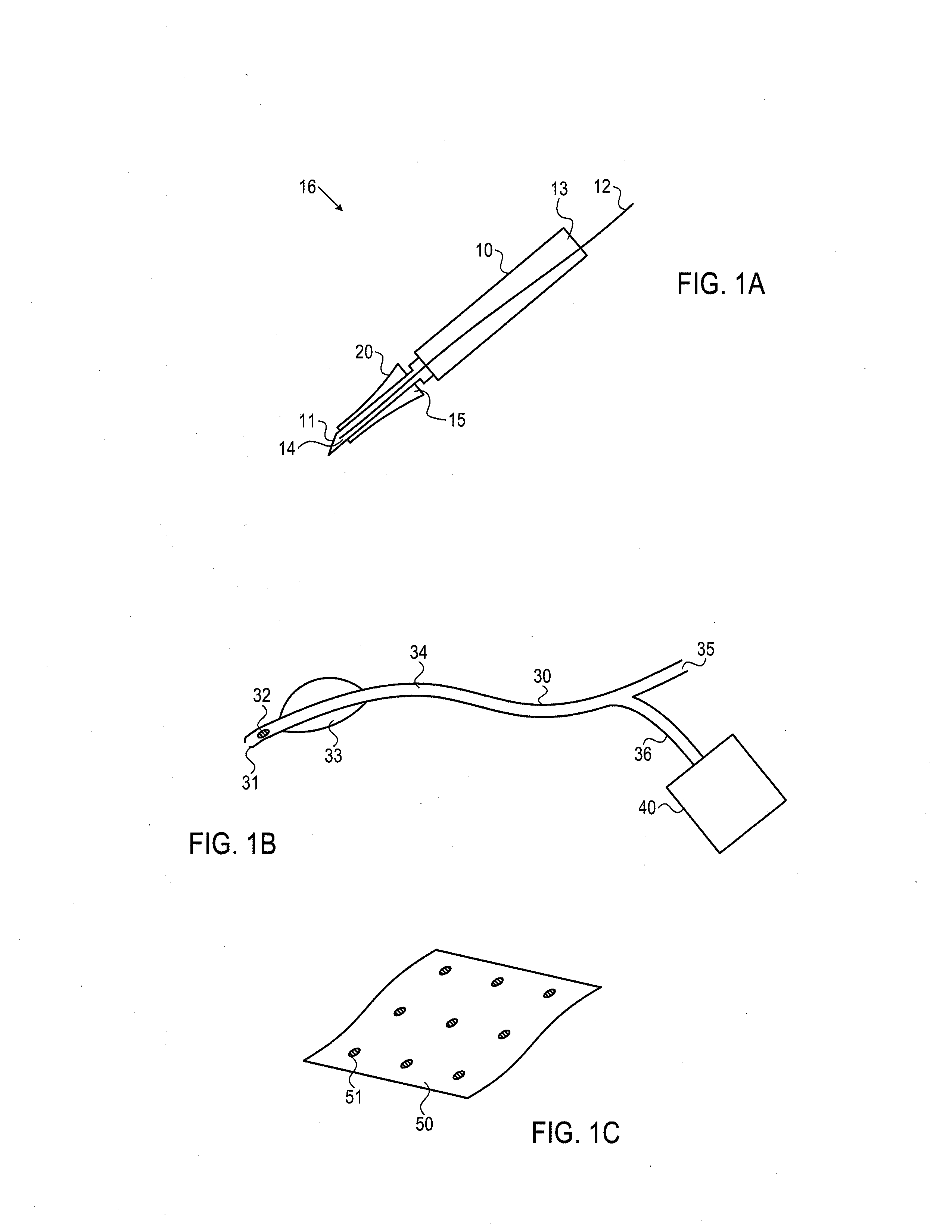
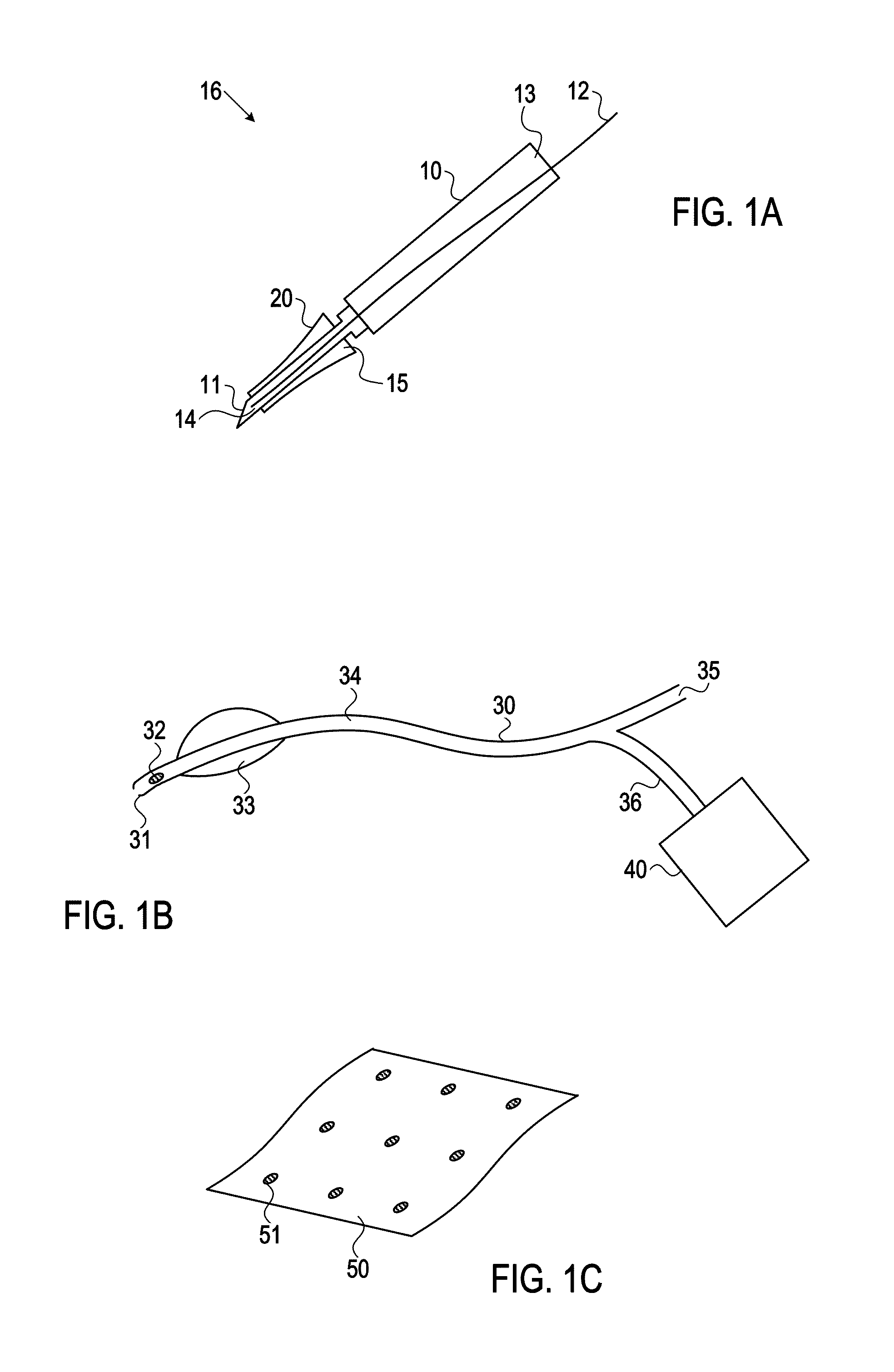
System and method for establishing vascular access
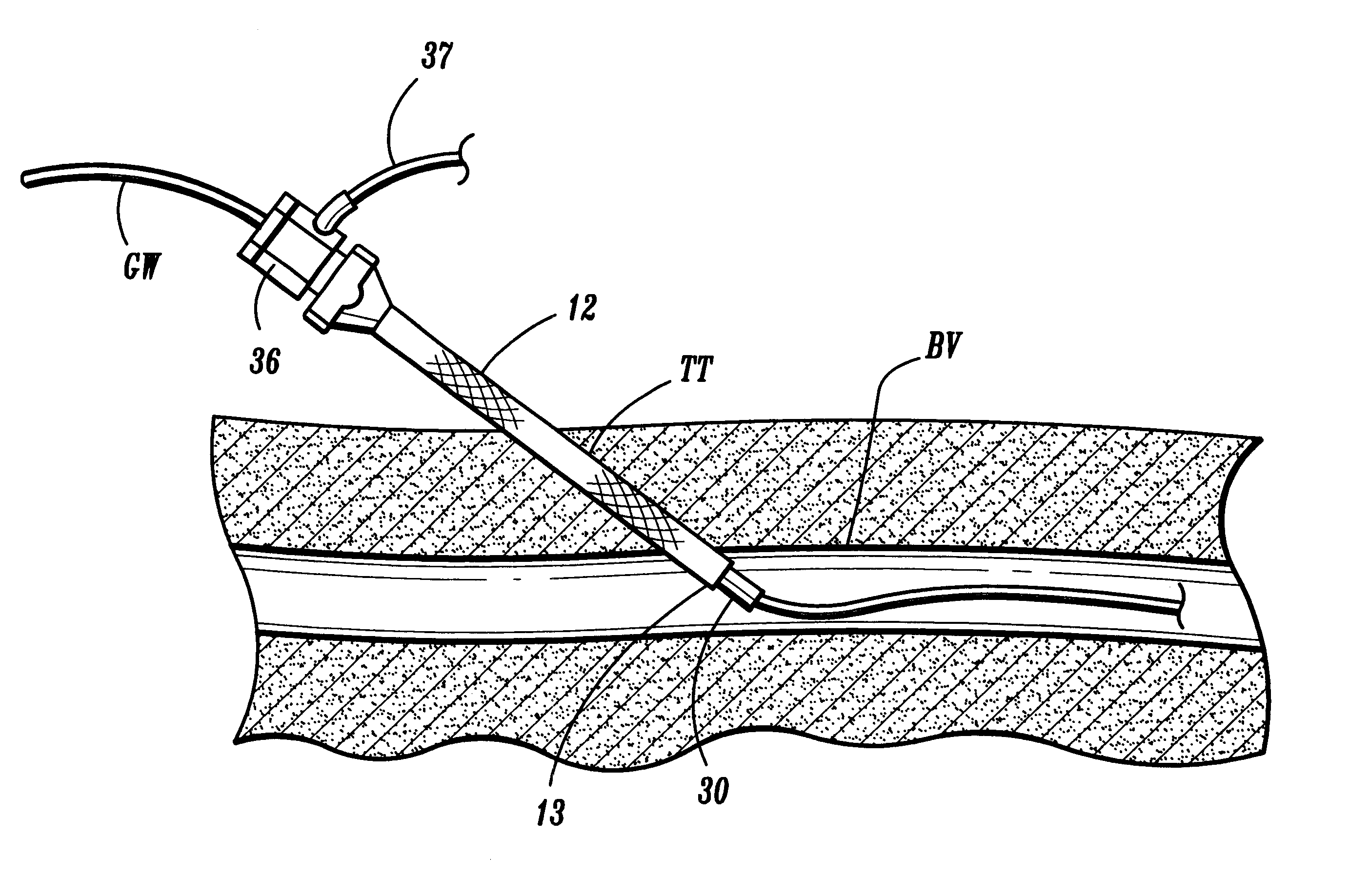
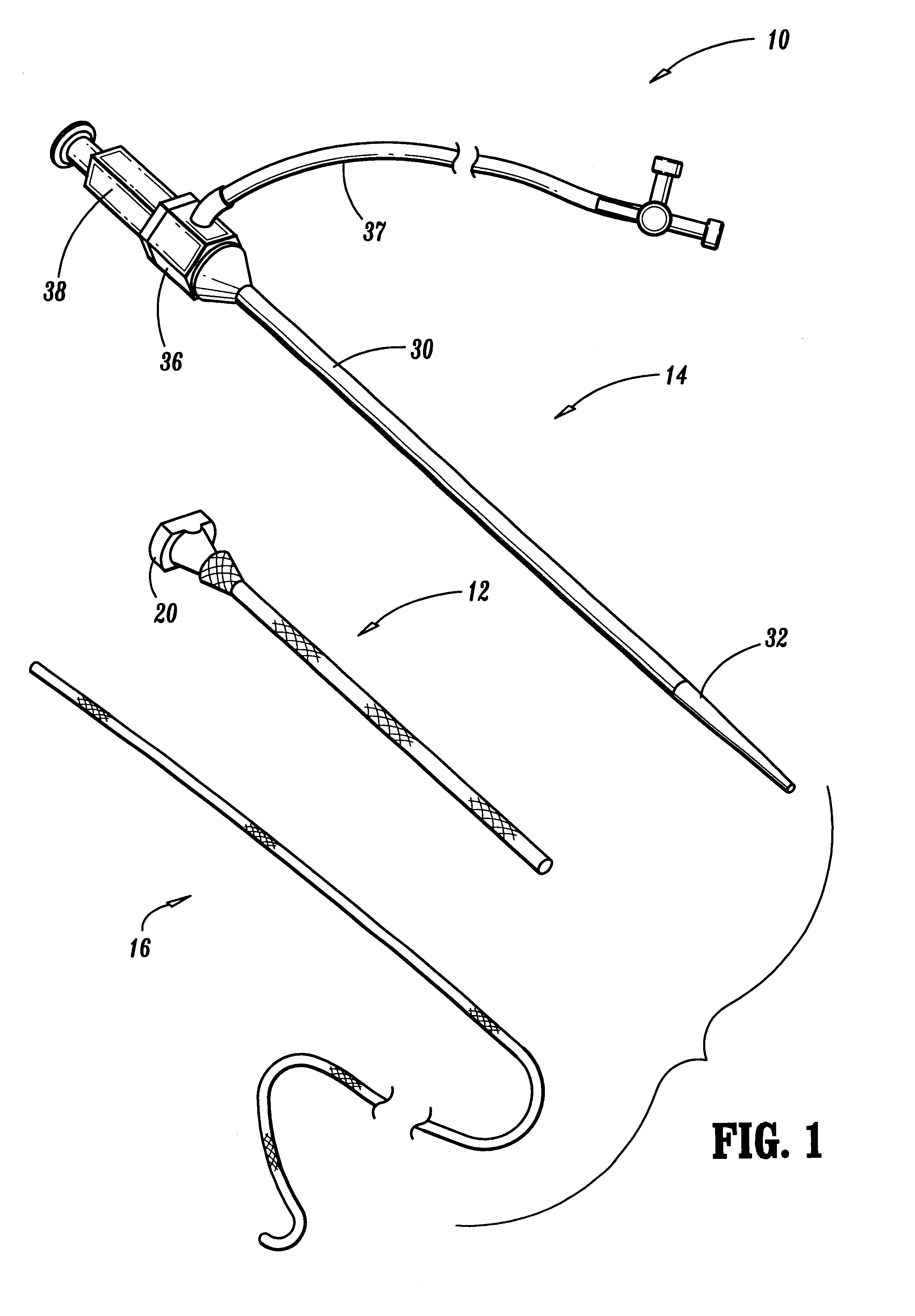
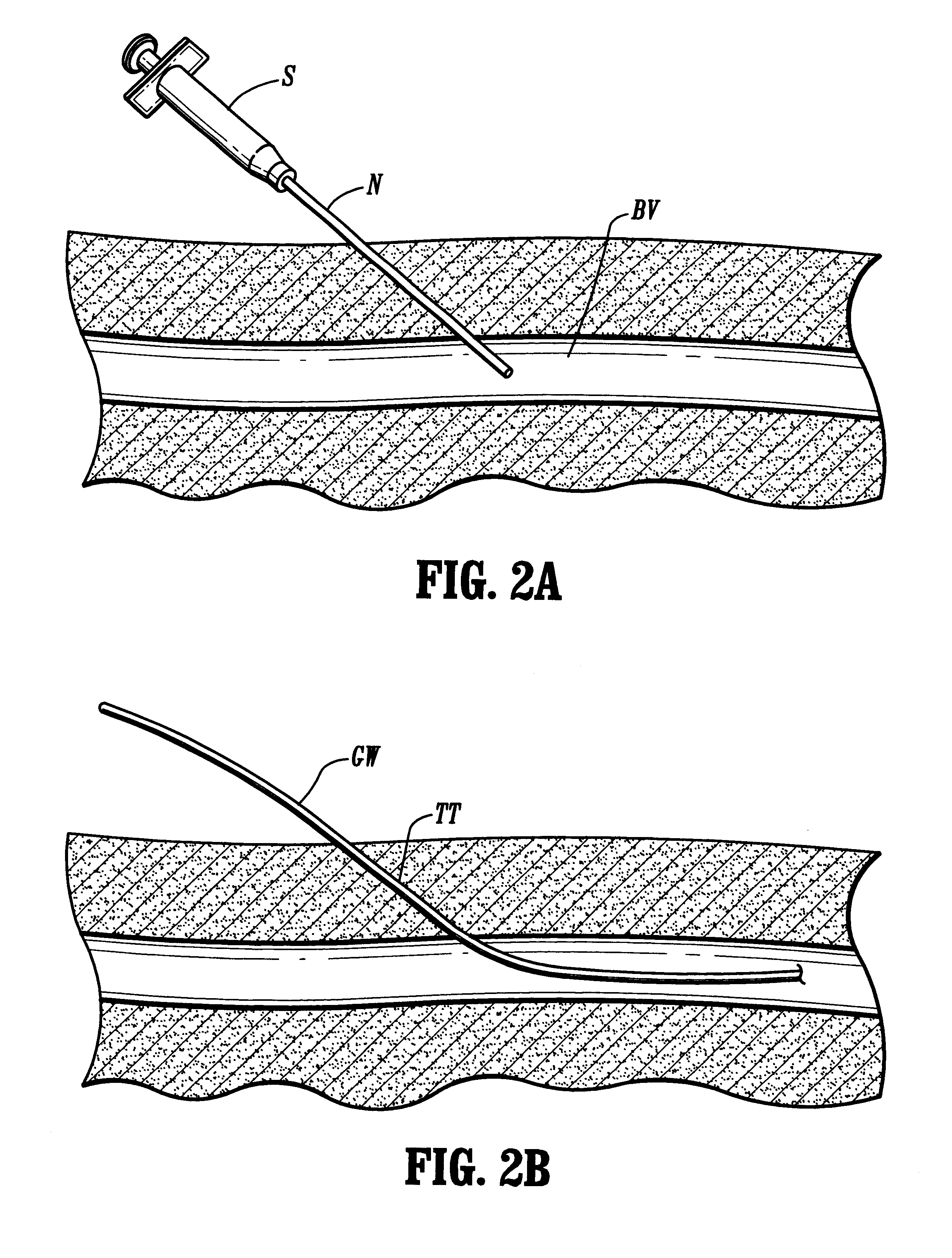
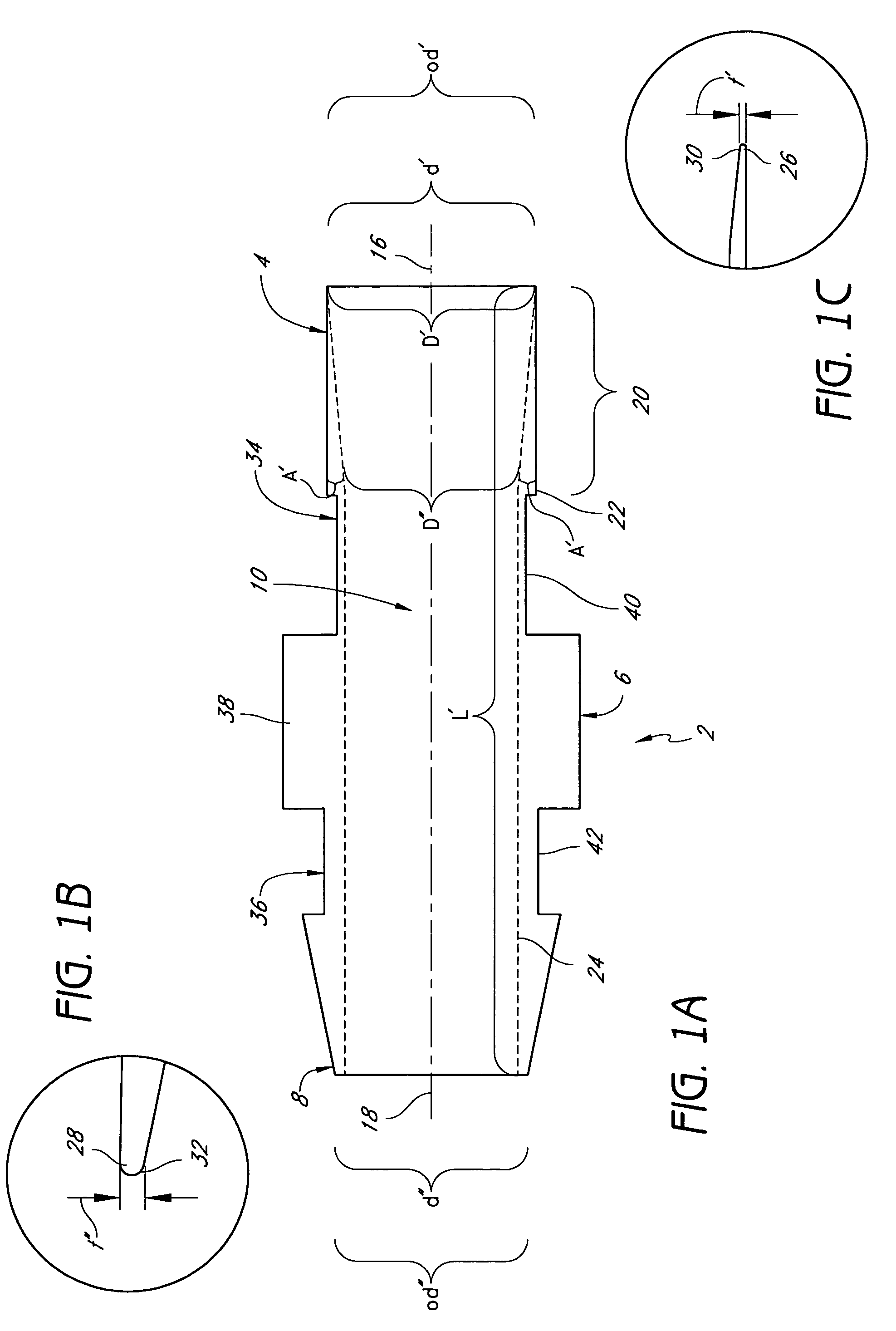
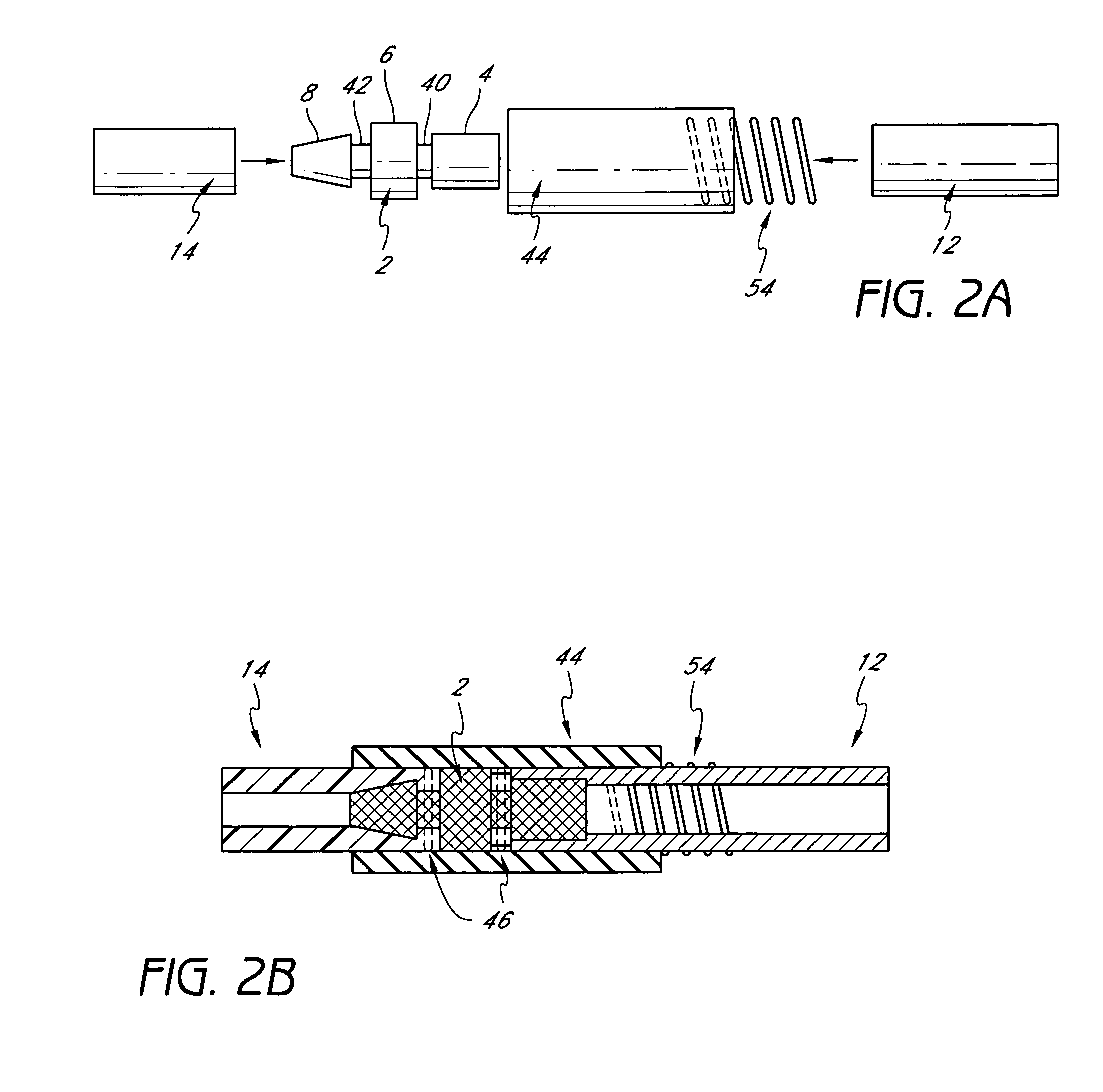
Systems, kits, and methods for establishing vascular access are described. A system may include a needle, a radially expandable sleeve and a dilator. The methods include creating an initial tissue tract to a target blood vessel with a radially expandable sleeve mounted on a needle. Upon removal of the needle, the dilator is then passed through the radially expandable sleeve to effect radial expansion of the sleeve. Use of the sleeve reduces the risk of injuring tissue surrounding the tissue tract by lessening the axial forces imparted to the tissue. Kits comprise at least the radially expandable sleeve together with instructions for use.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Apparatus and methods for preventing or treating failure of hemodialysis vascular access and other vascular grafts
InactiveUS6726923B2Reduce calcificationInhibiting smooth muscle cell proliferationBiocideOrganic chemistryVascular graftBlood vessel
Owner:VASCULAR THERAPIES INC
Intracardiovascular access (ICVATM) system
InactiveUS6890330B2Facilitate safe intravascular accessWithout excessive back bleedingCannulasSurgical needlesSurgeryBlood vessel
Apparatus is disclosed for providing access to a functioning vascular system of a patient, the apparatus comprising: a main body having sidewalls defining an interior region and an exterior region, a bottom end and a top end; a base being formed at the bottom end of the main body, securing means being configured on the base so as to allow attachment and formation of a seal between the base and the functioning vascular system of the patient, and the base being configurable to provide a passageway from the interior region of the main body to the functioning vascular system of the patient; and a cover being formed at the top end of the main body, wherein the cover provides a barrier between the interior region and the exterior region at the top end of the main body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
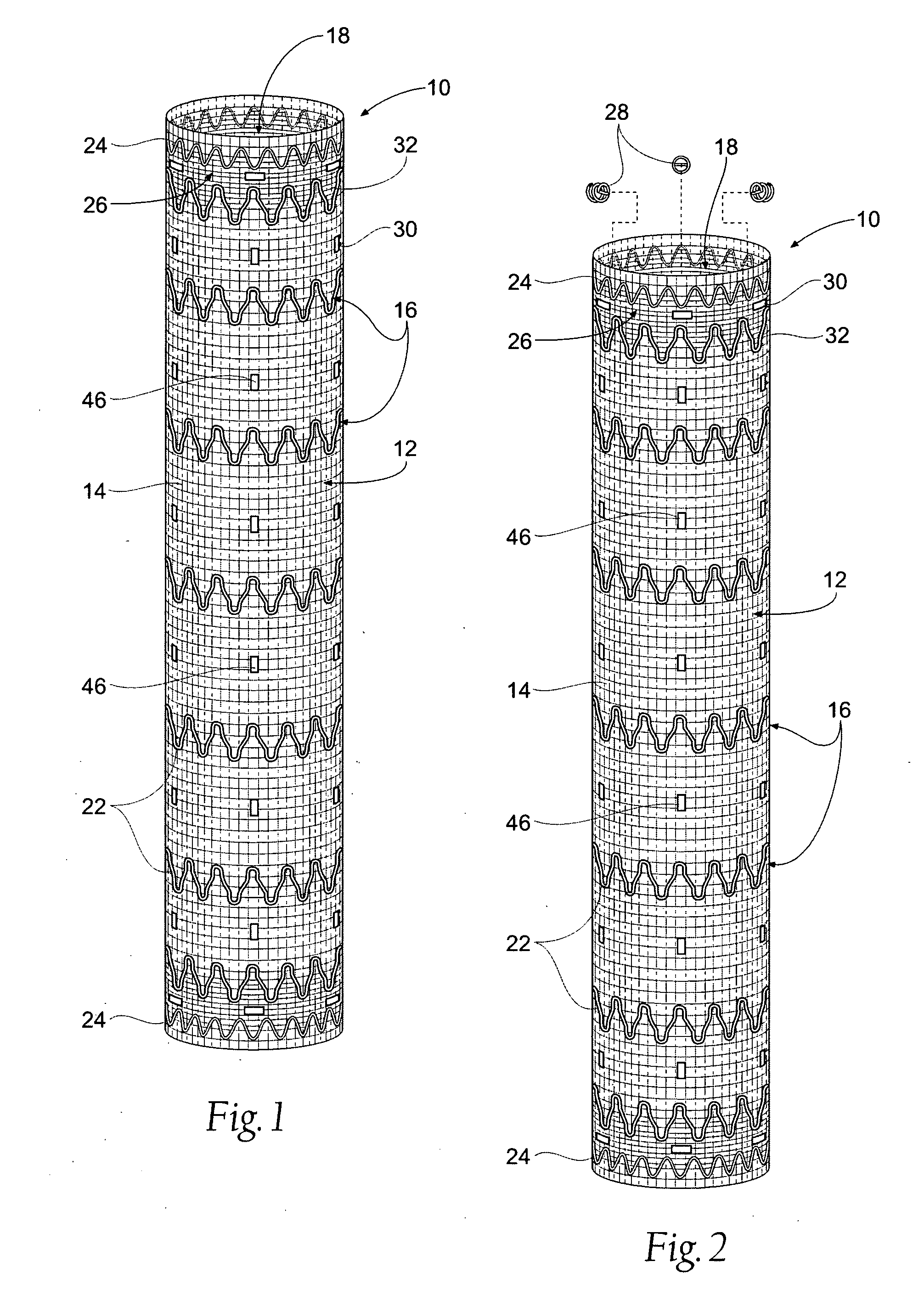
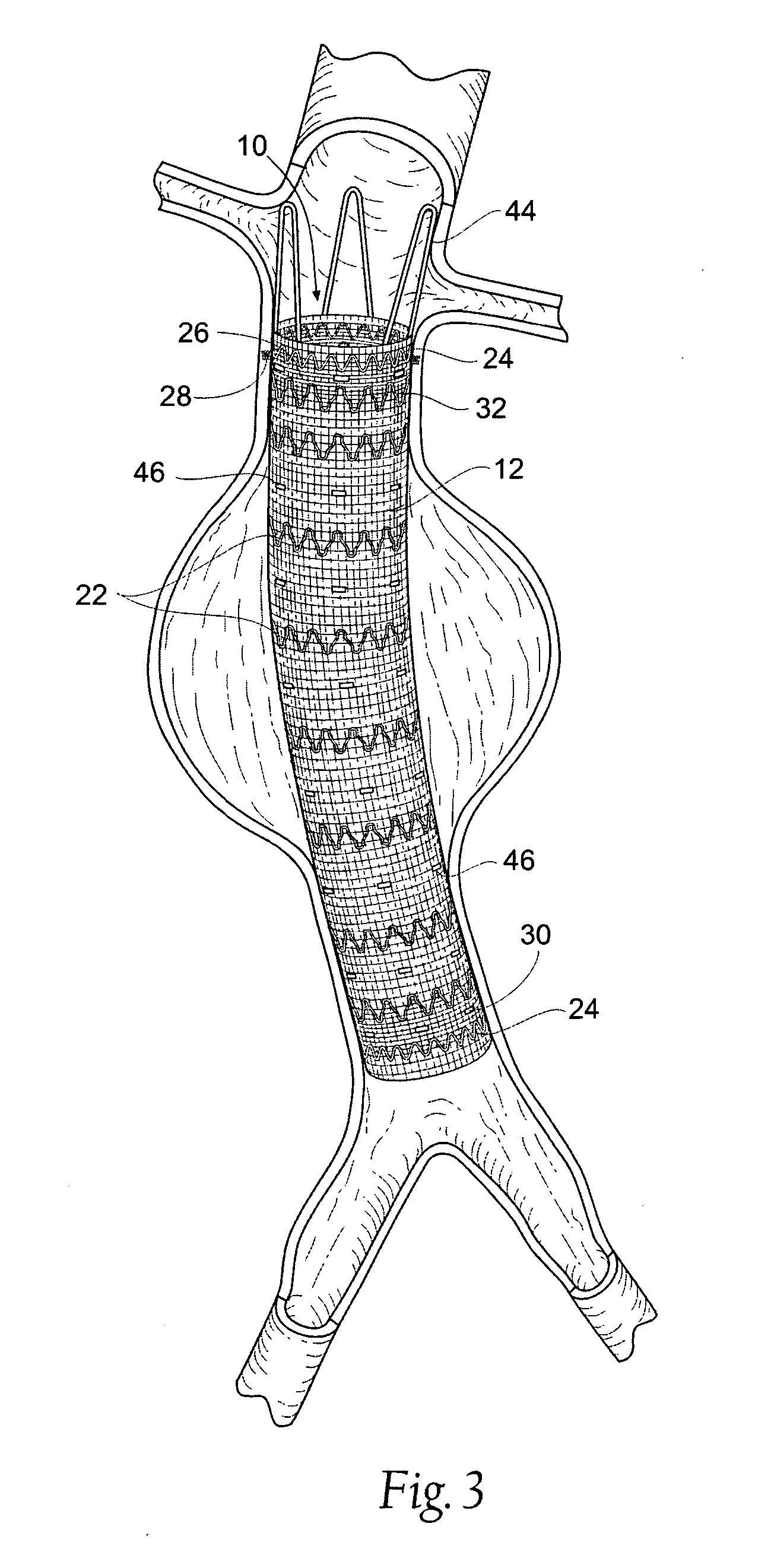
Systems and methods for attaching a prosthesis within a body lumen or hollow organ
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
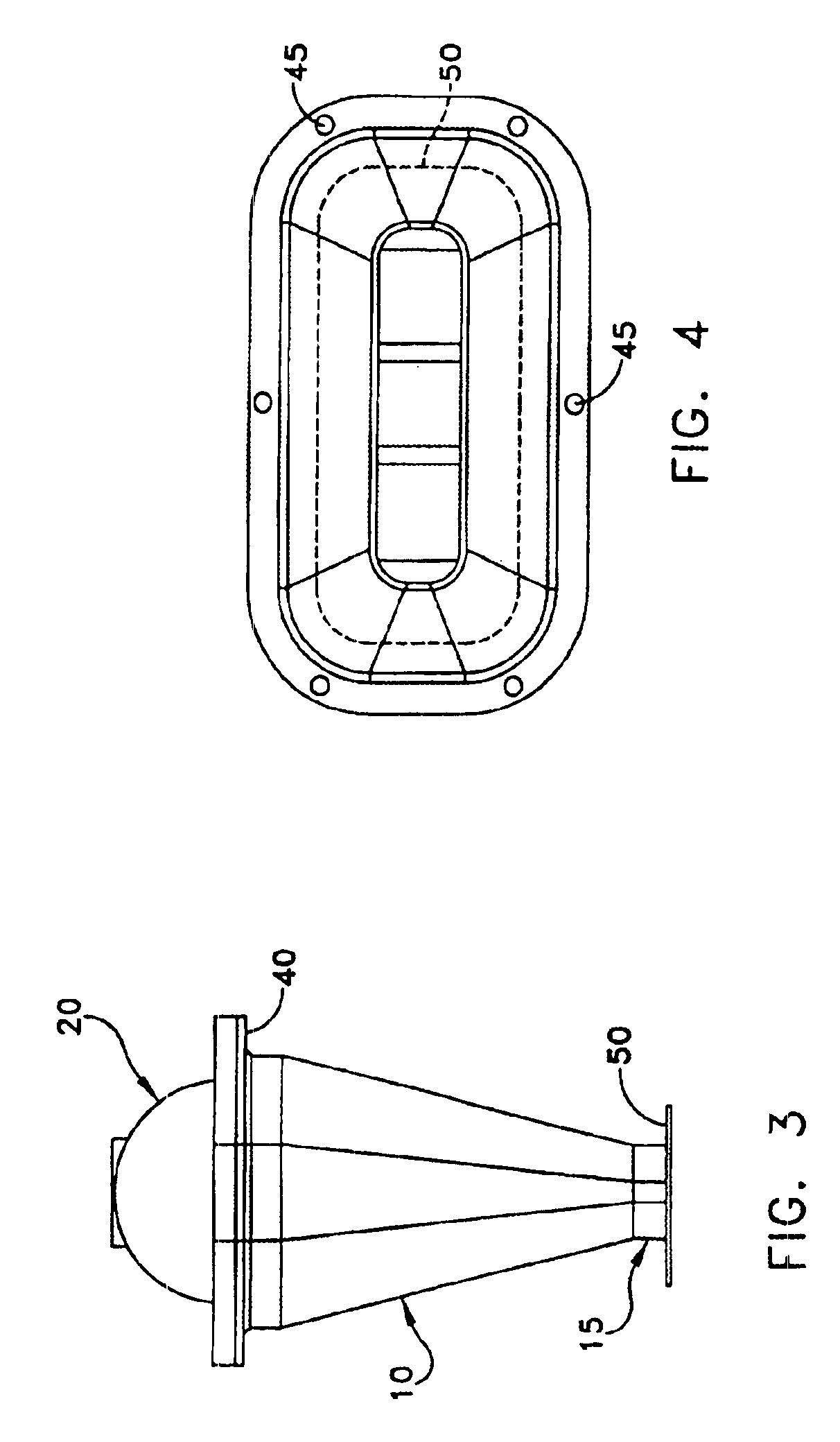
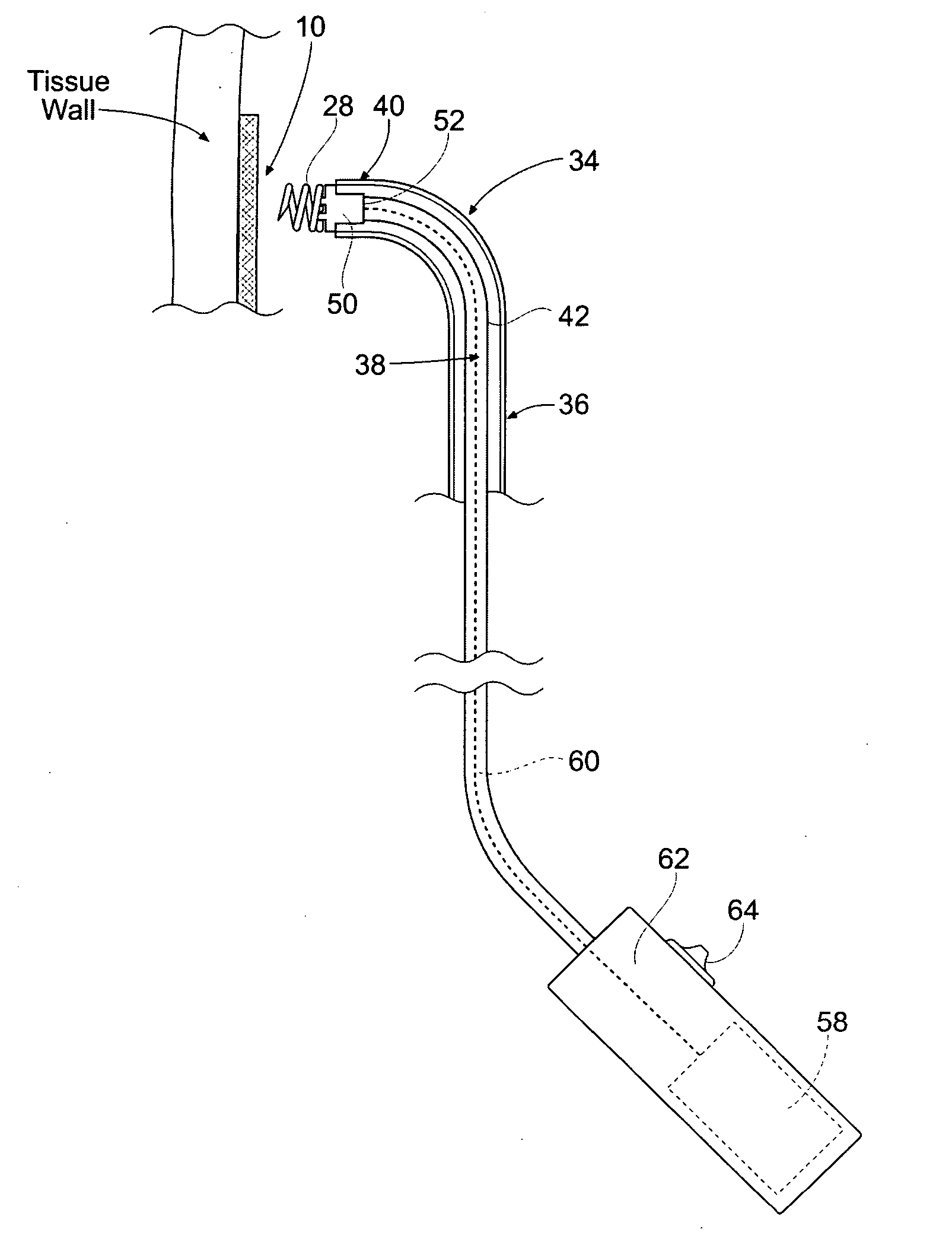
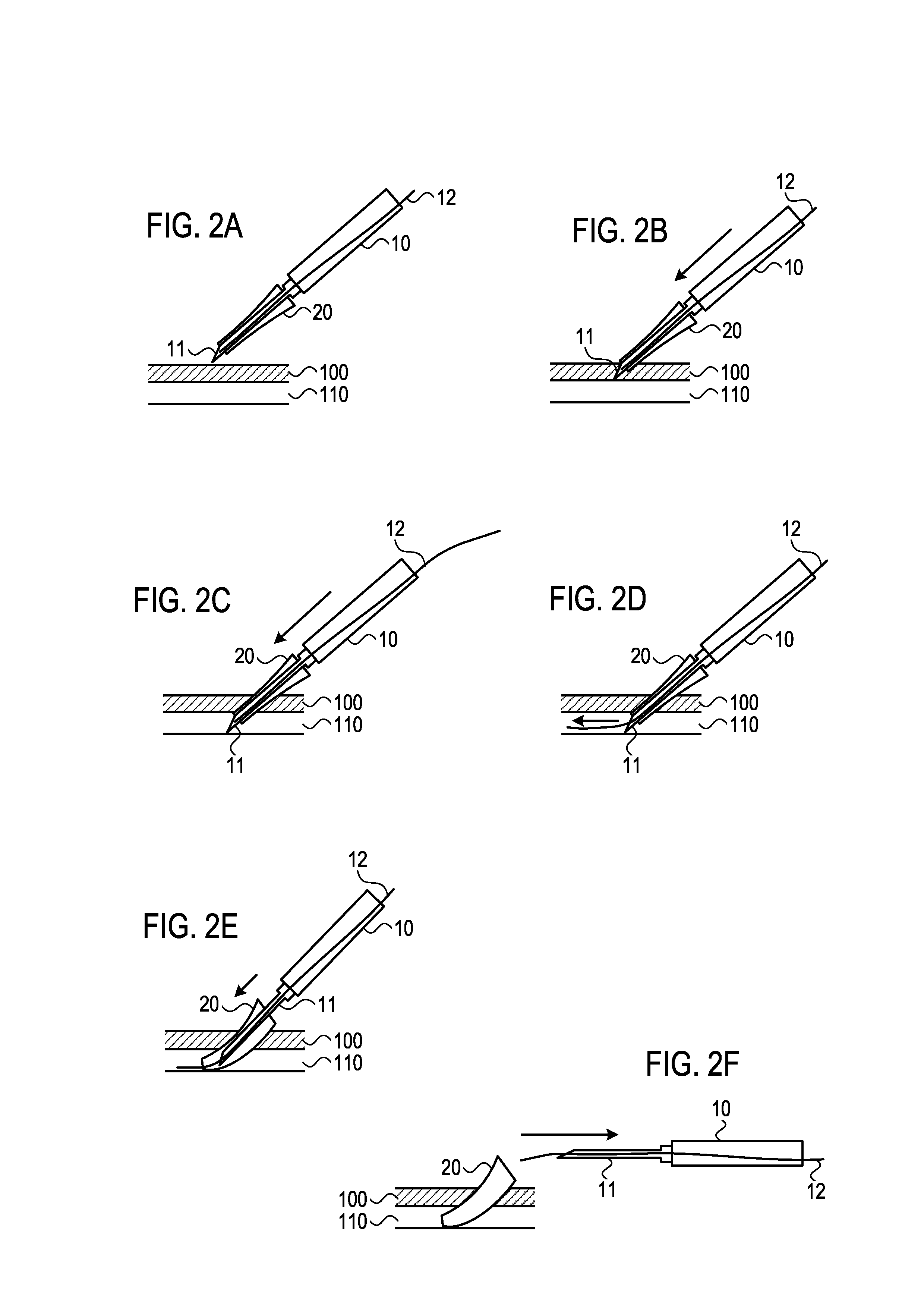
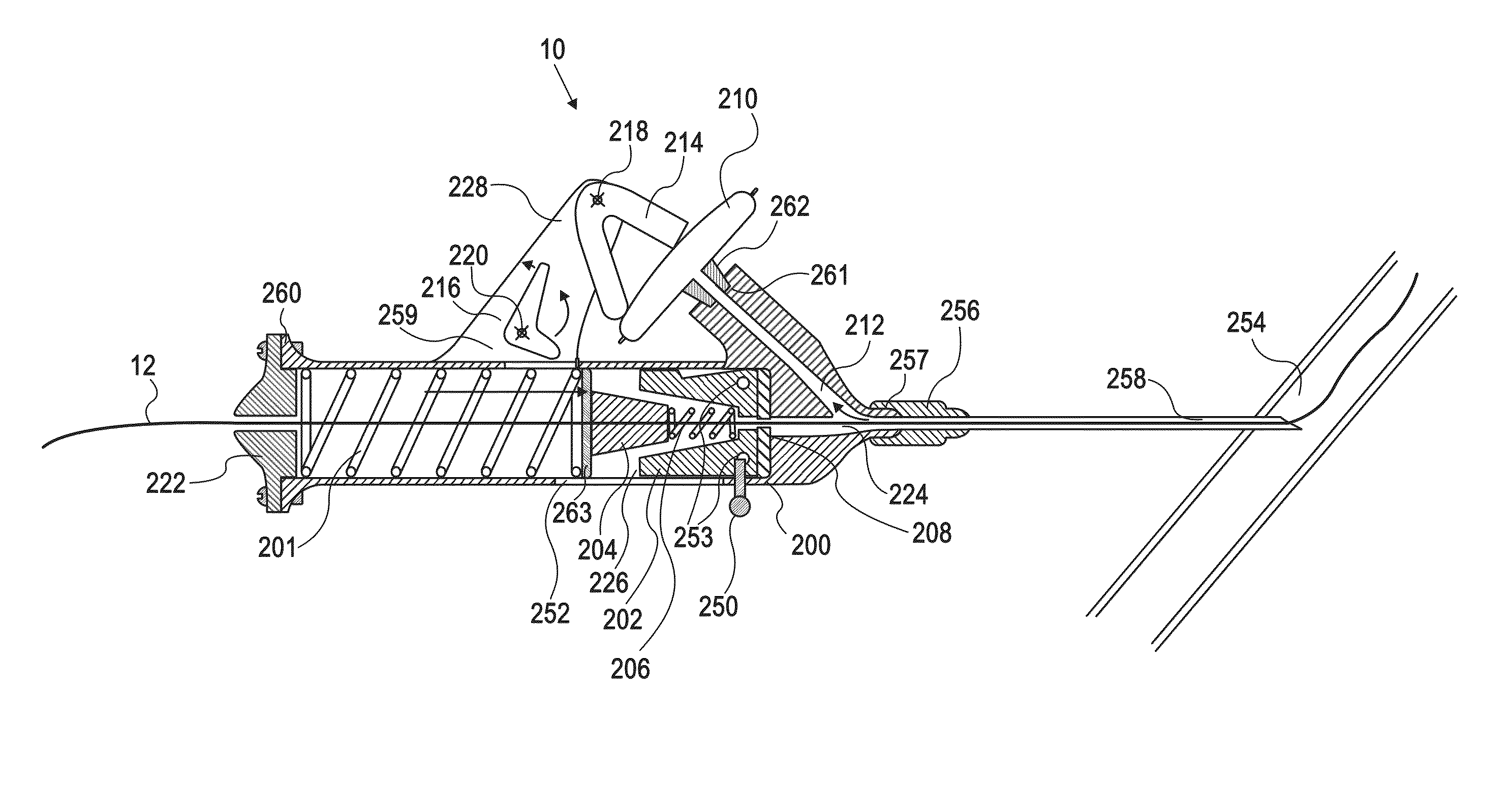
Device and method for vascular access
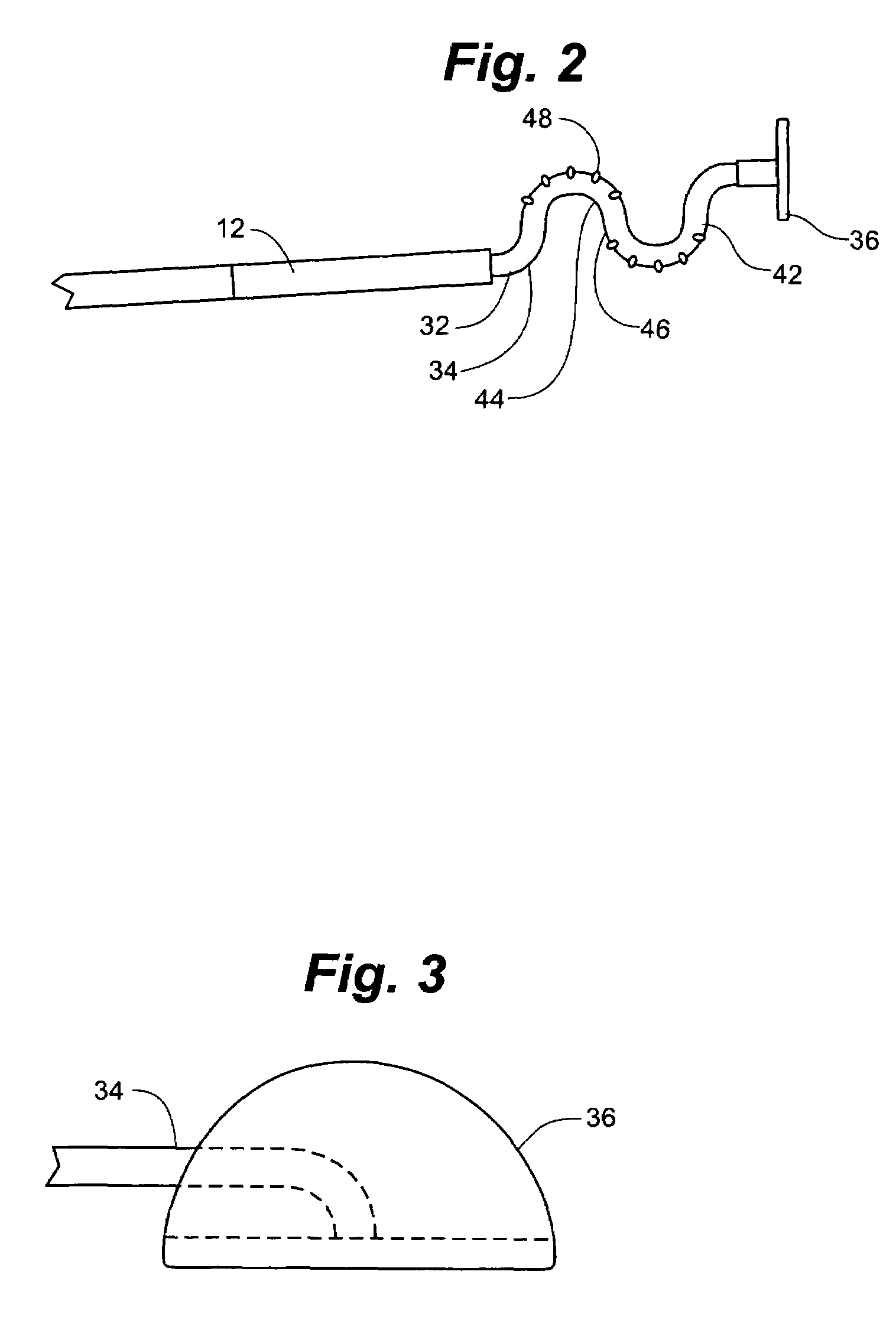
ActiveUS20060064159A1Reduce kinksReduce kinking in said catheter portionOther blood circulation devicesSurgeryVeinGraft portion
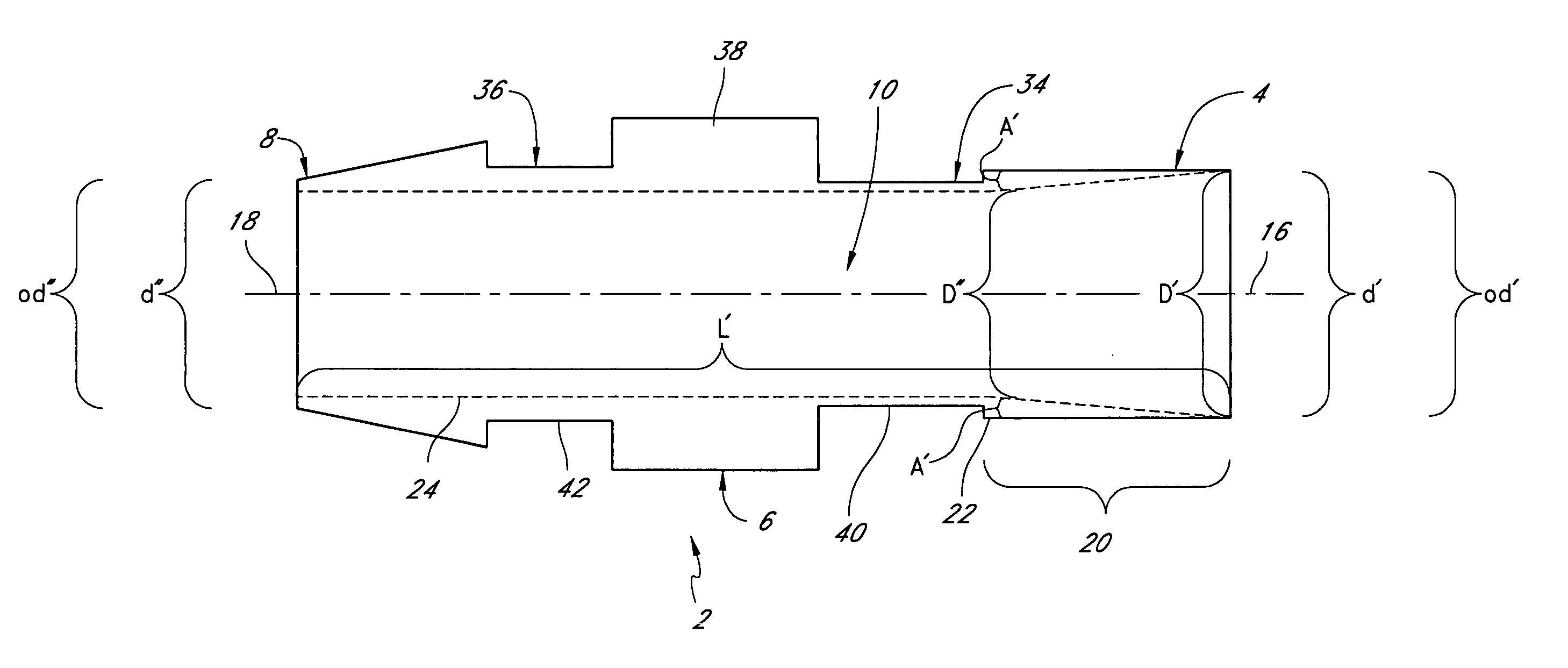
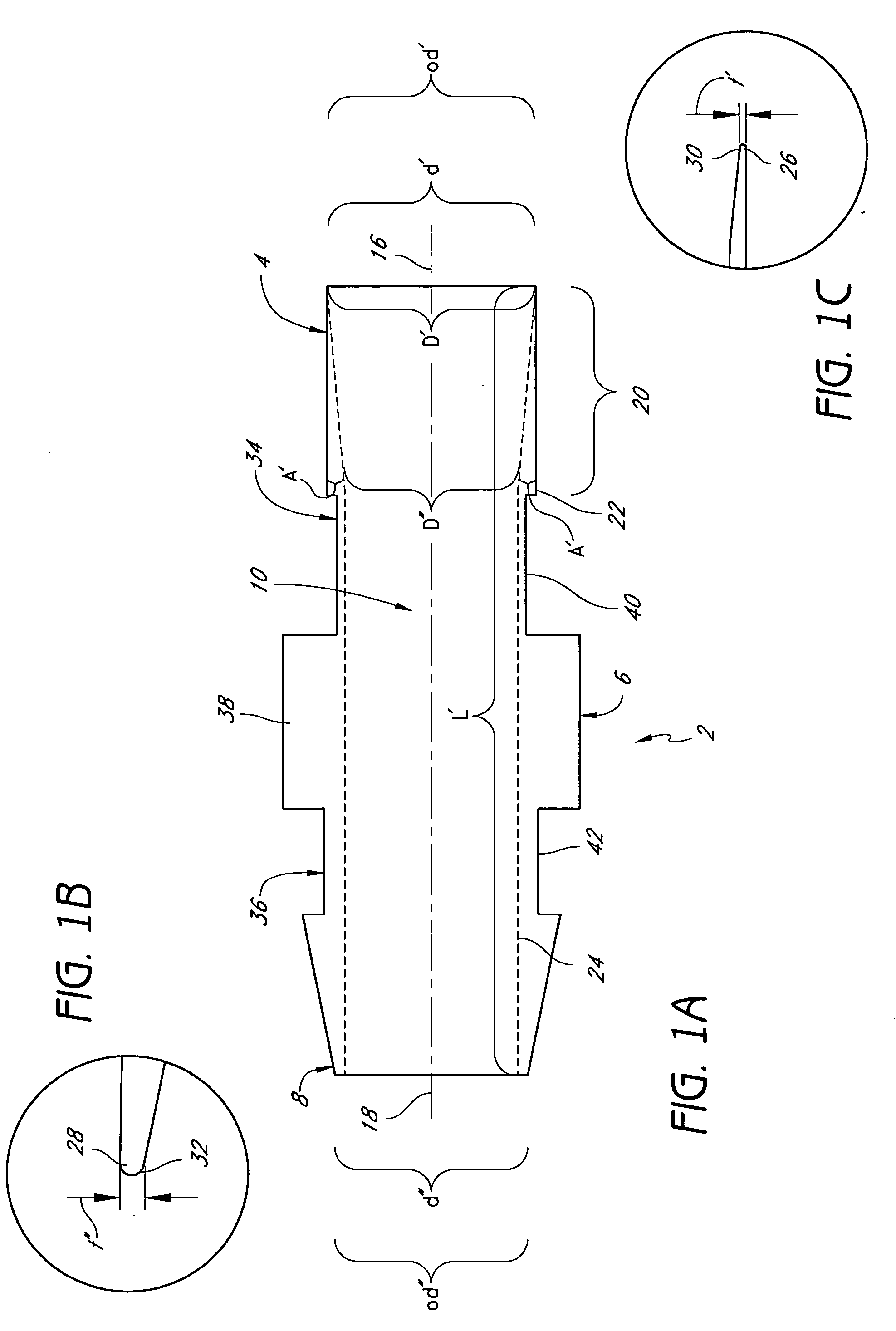
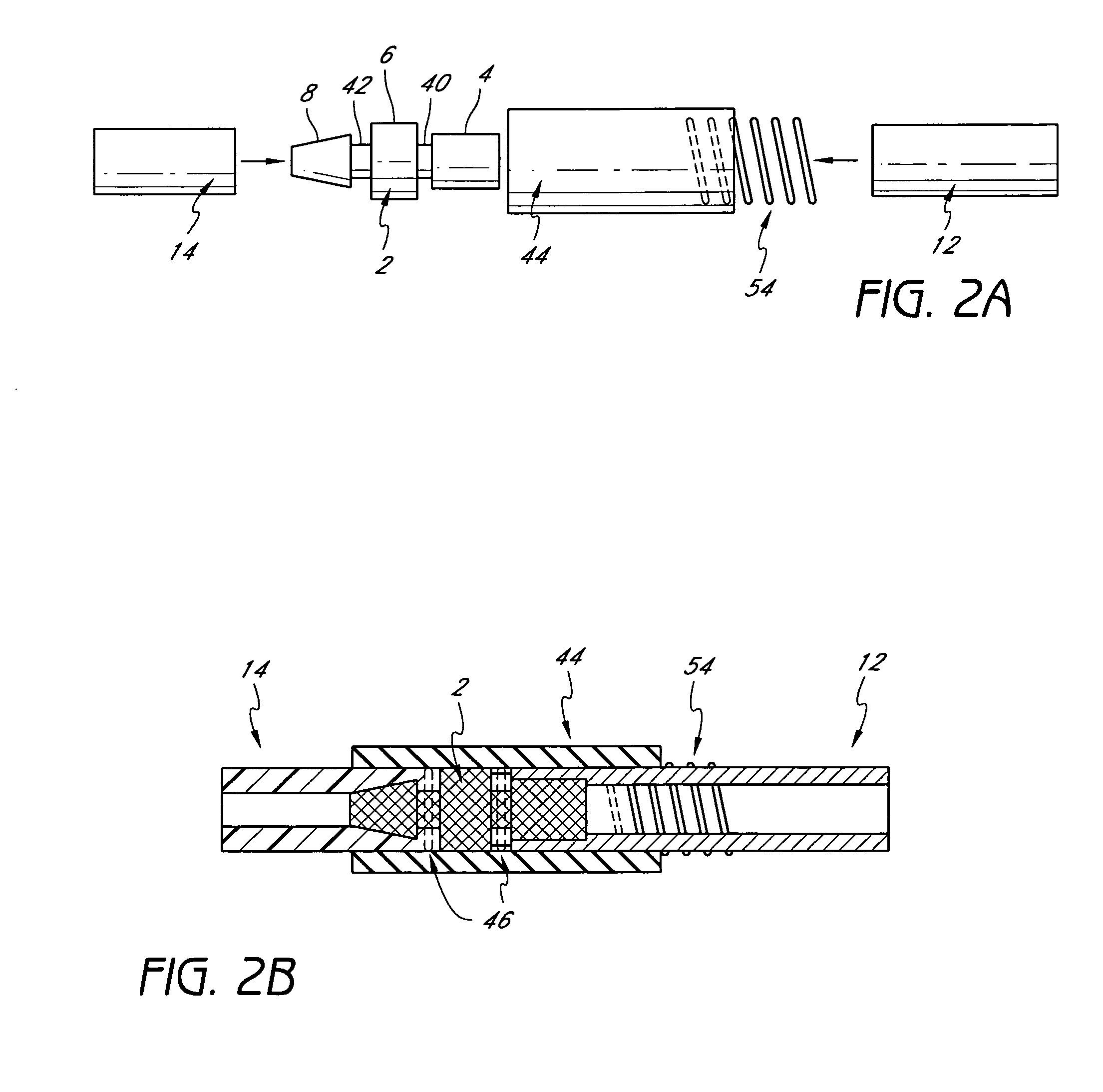
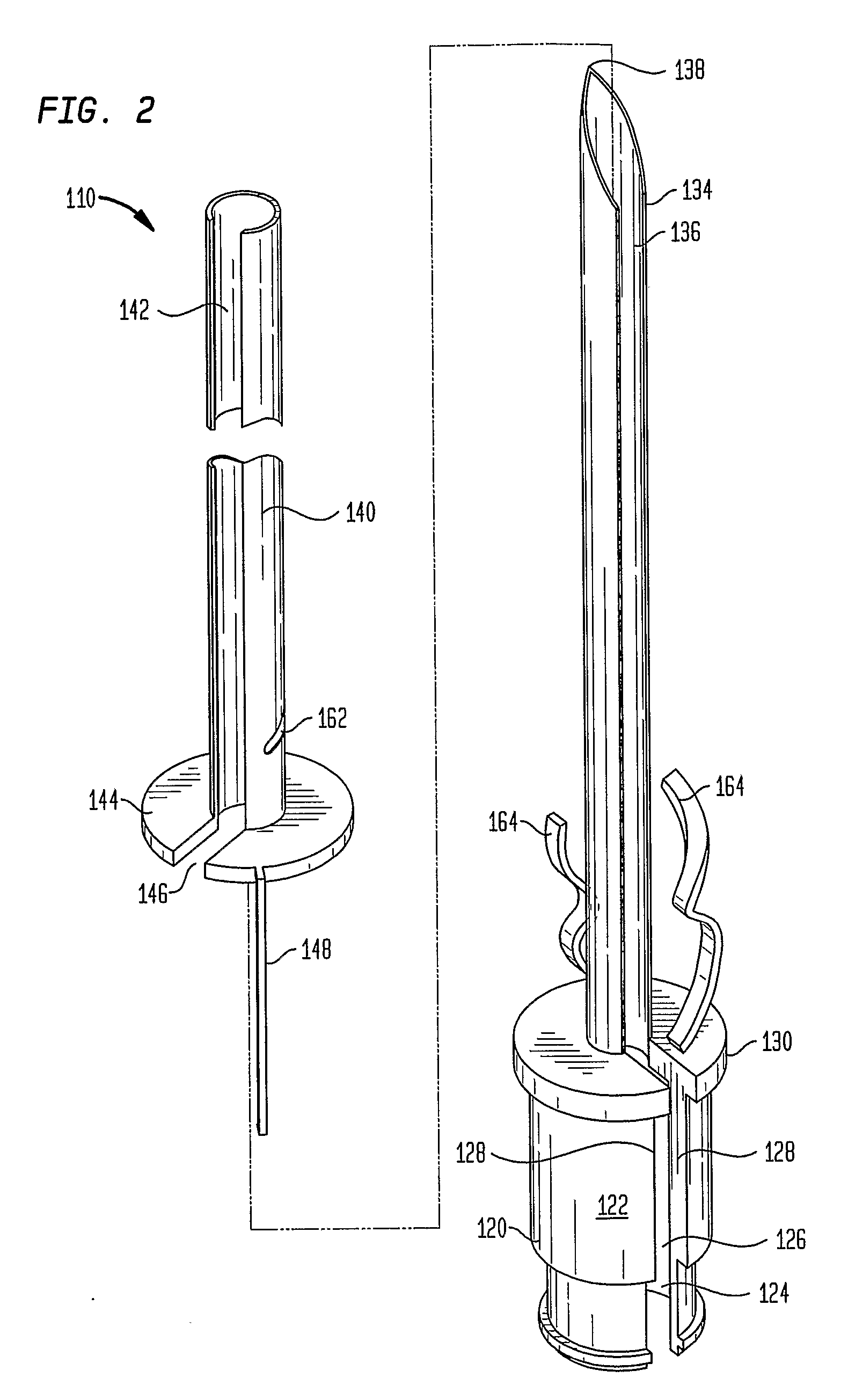
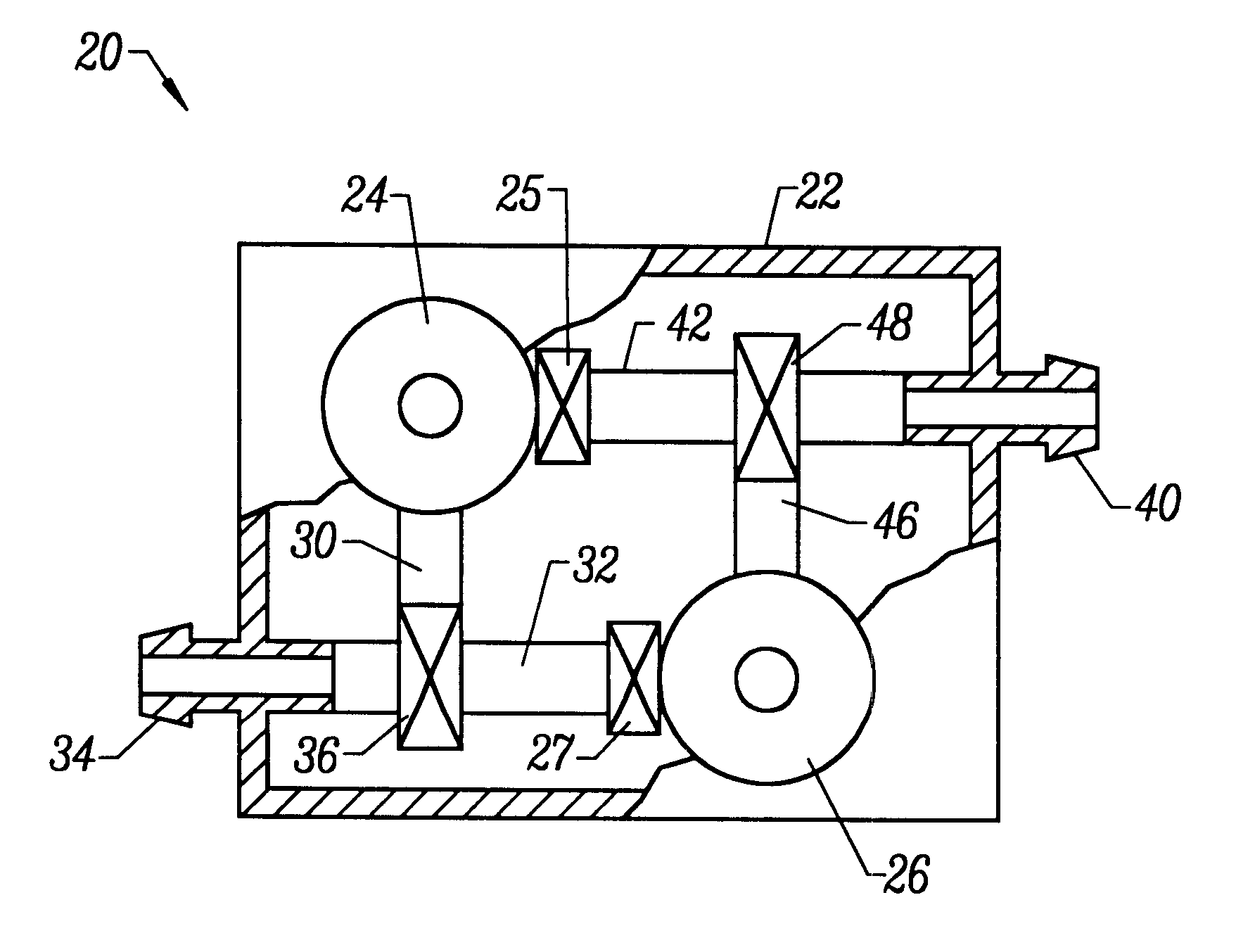
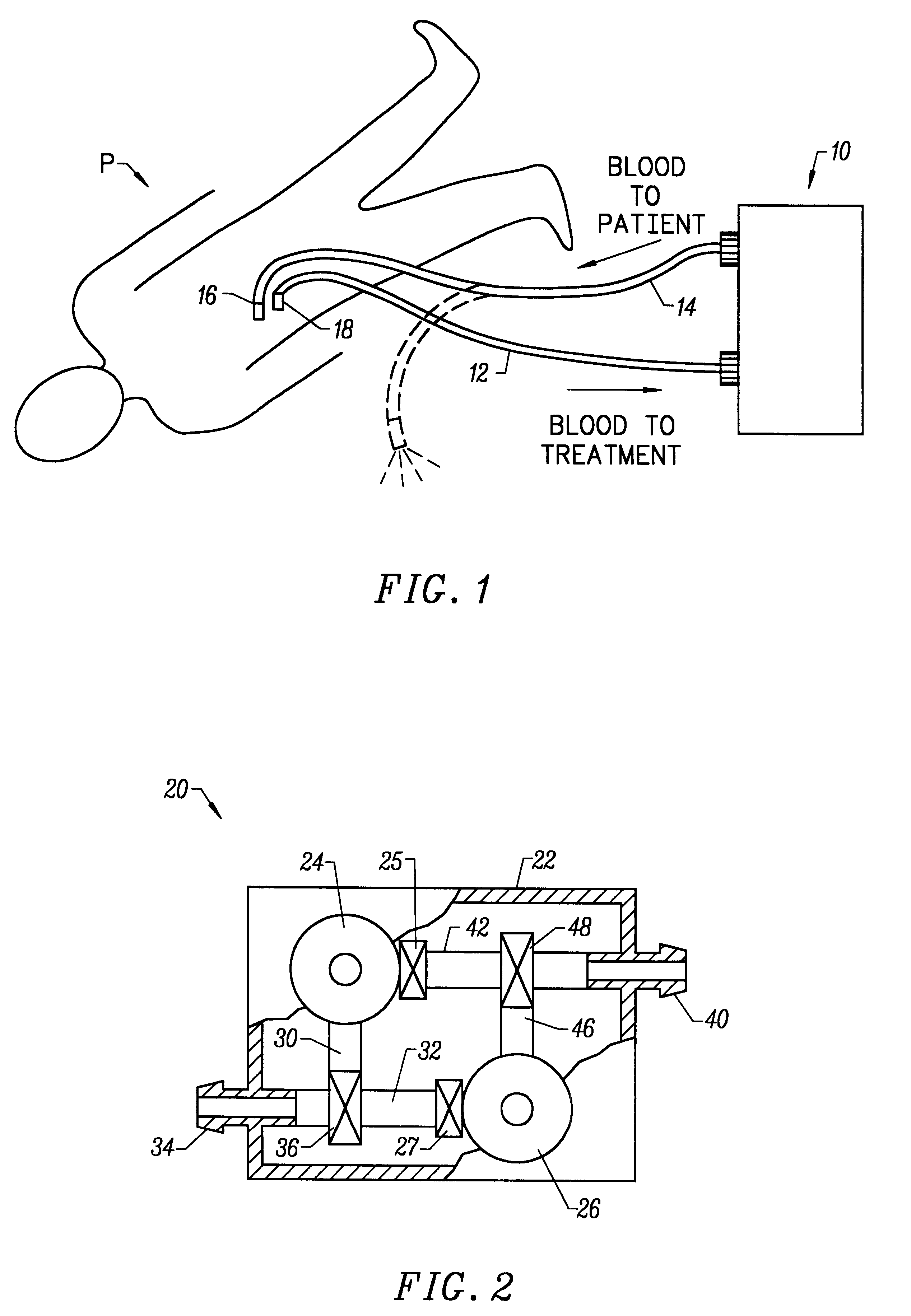
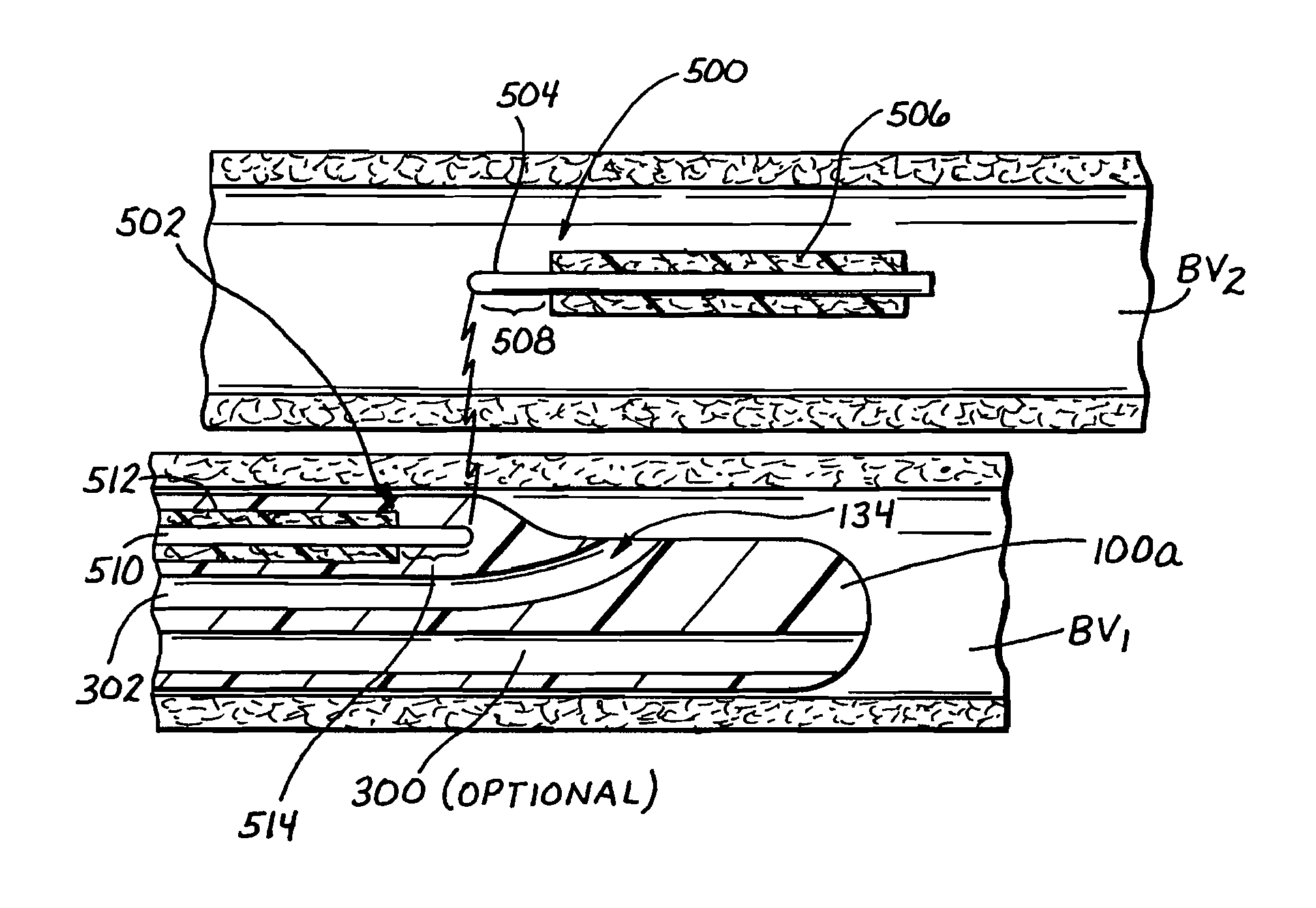
Vascular access systems for performing hemodialysis are disclosed. The vascular access system contemplates a catheter section adapted for insertion into a vein and a graft section adapted for attachment to an artery. The catheter section may have metal or polymer wall reinforcements that allow the use of thin-walled, small outer diameter conduits for the vascular access system. One or more of the adhered, embedded or bonded conduit reinforcement structures may be removable without significant damage to the conduit sections to facilitate attachment of the sections, or to a connector between the sections. Various self-sealing materials are provided for use in the vascular access system, as well as temporary access sites and flow control / sensor systems.
Owner:MERIT MEDICAL SYST INC
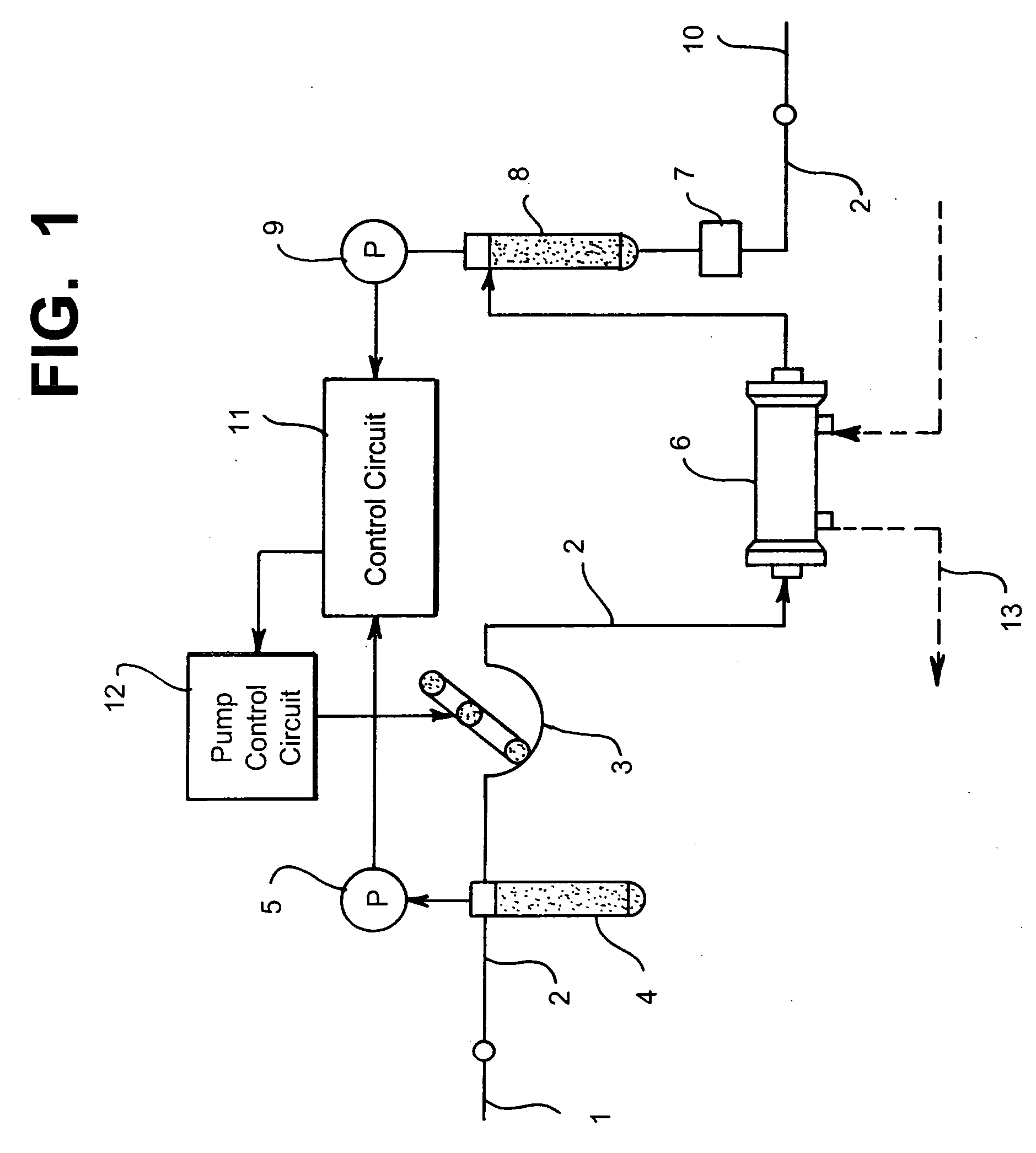
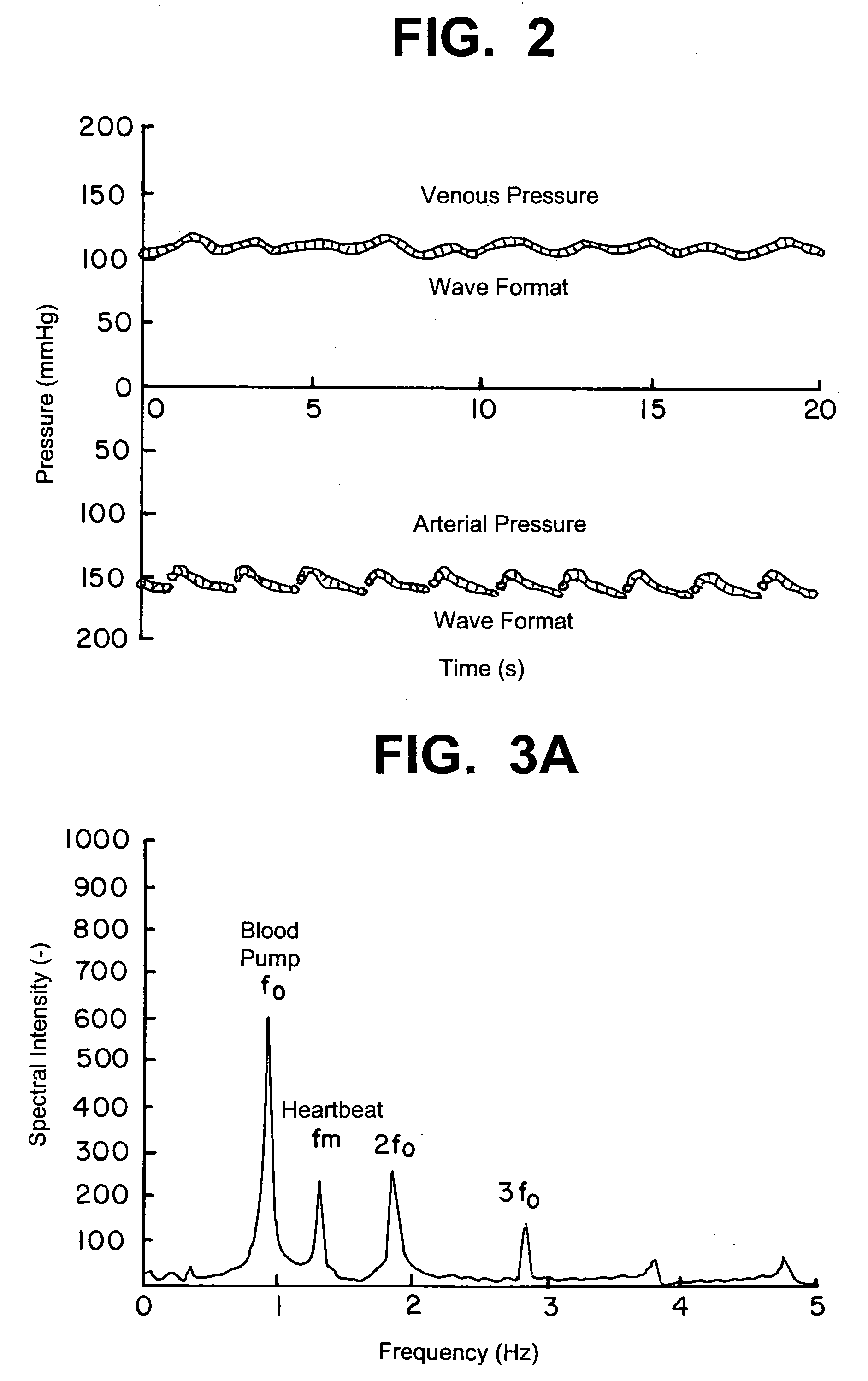
Method and device for measuring pulse rate, blood pressure, and monitoring blood vessel access
A method and device for measuring a patient's pulse rate and blood pressure and also the condition of the blood vessel access can be accurately monitored by identifying a frequency component of the pressure wave caused by the patient's heartbeat among other pressure waves in a fluid by frequency analysis. The method and device are used when a medical device is connected to the patient's blood vessel via a blood vessel access and has a mechanical device for applying pressure to a fluid to transport it to said blood vessel.
Owner:NIKKISO COMPANY
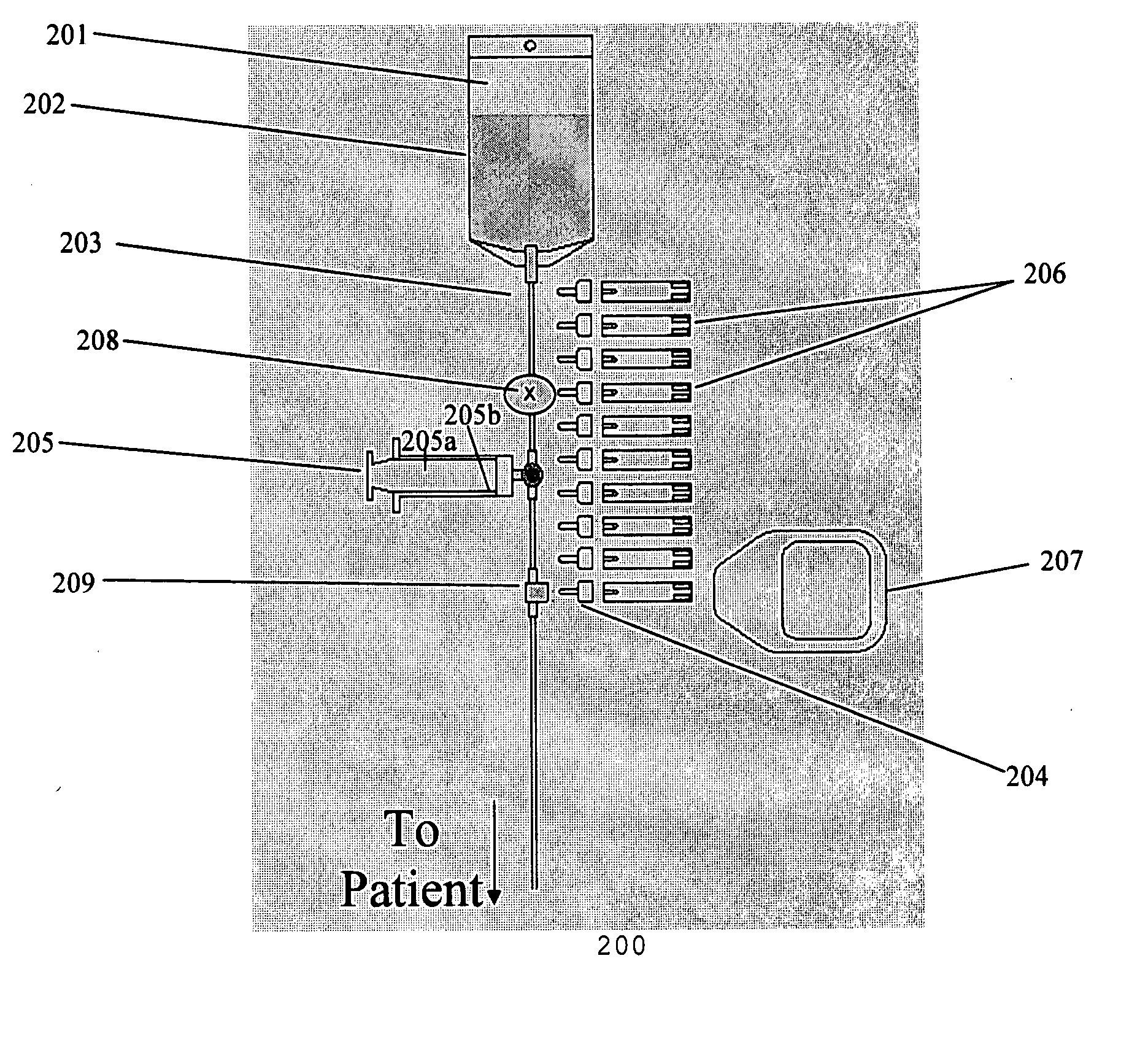
Blood parameter testing system
InactiveUS20070129618A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalyteAccess line
A substantially automatic blood parameter testing apparatus for obtaining a blood sample and determining the concentration of at least one analyte is connected to a venous or arterial access line and further comprises a pump fixedly attached to a tube originating from the vascular access point; a valve fixedly attached to the tube and located above the pump mechanism; at least one measurement element; a needleless port; and an electronic meter. In addition, the automated blood parameter testing apparatus may be integrated into a complete system, further including a monitor and a central monitoring station.
Owner:GLUCON
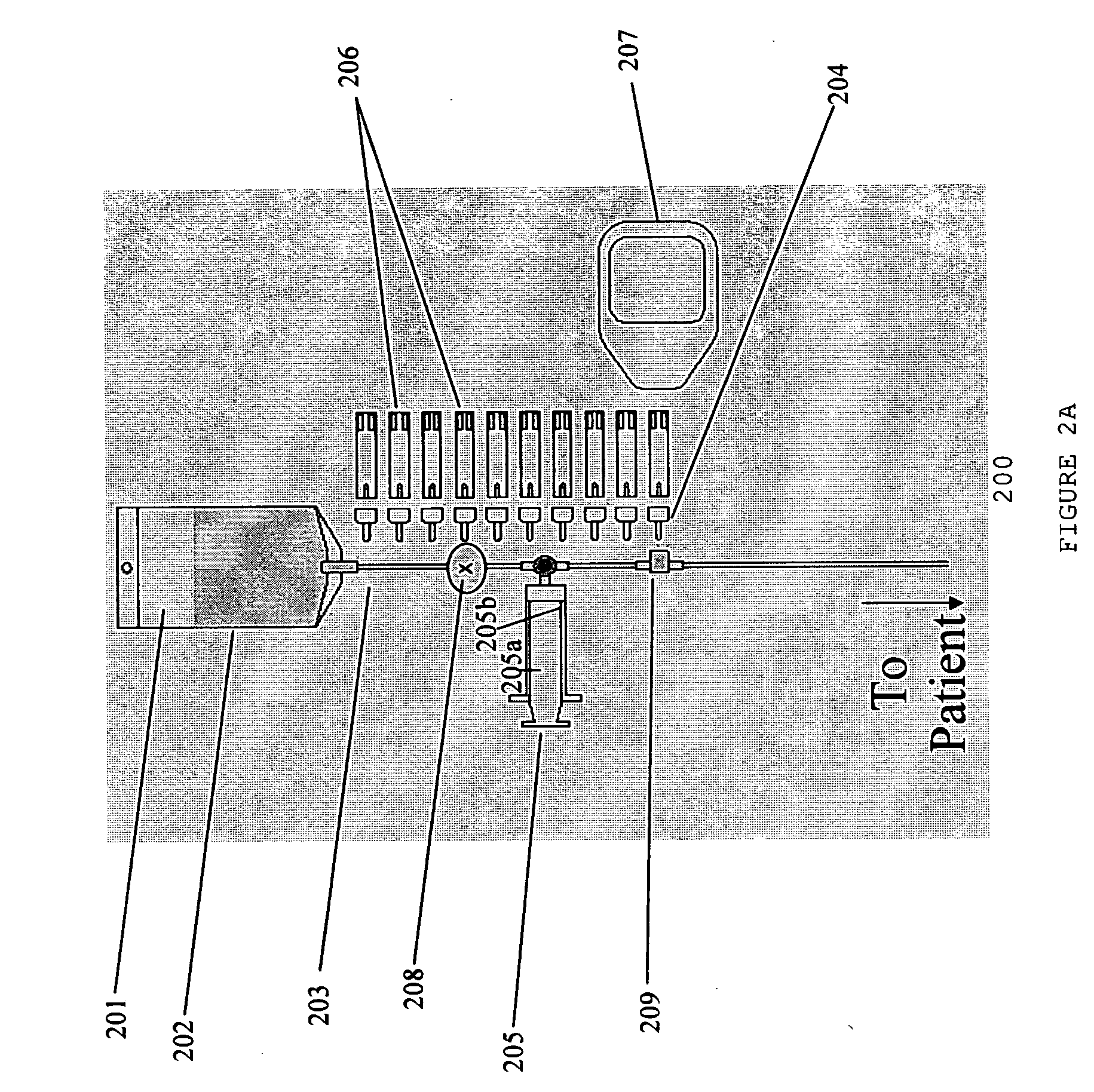
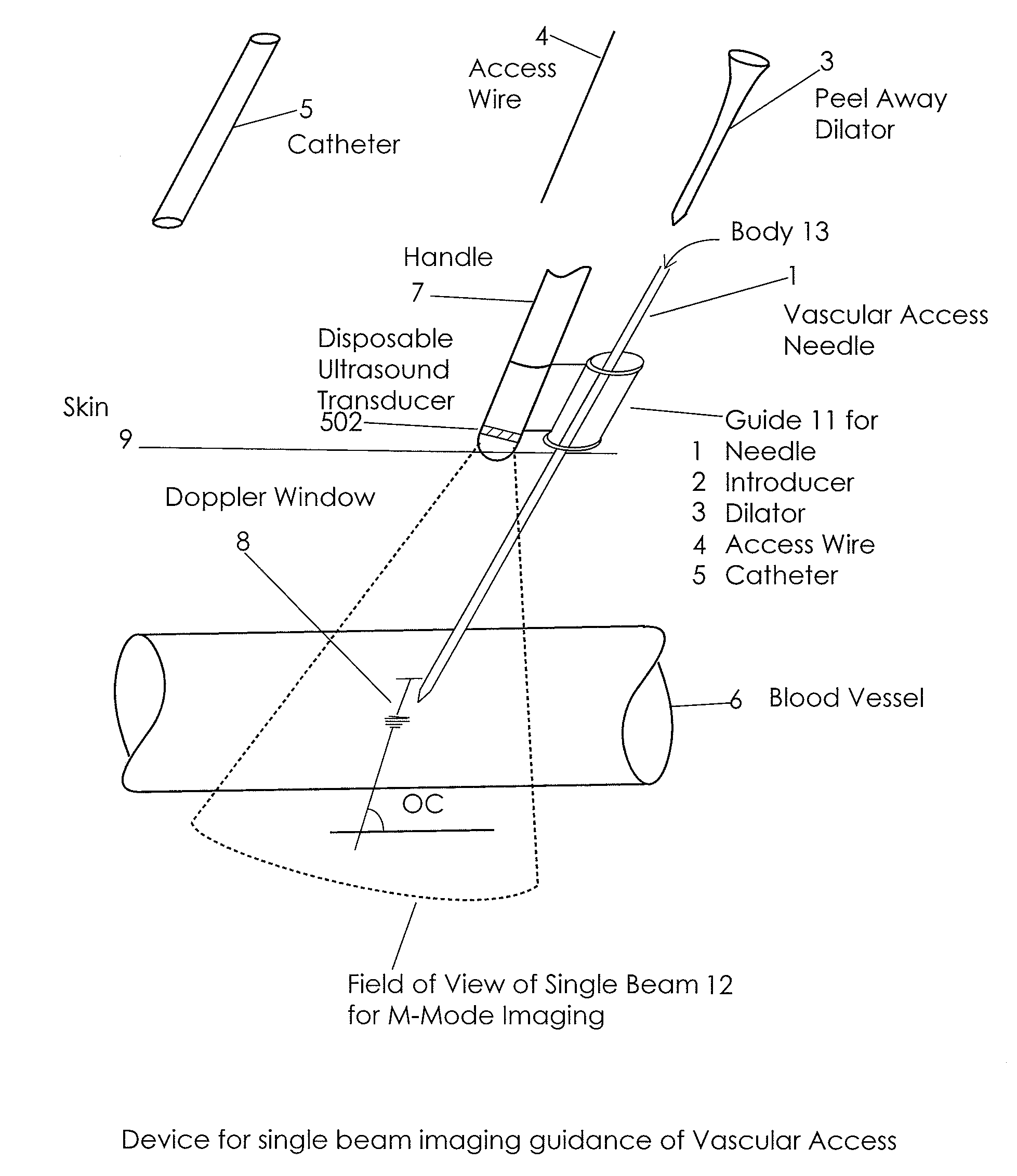
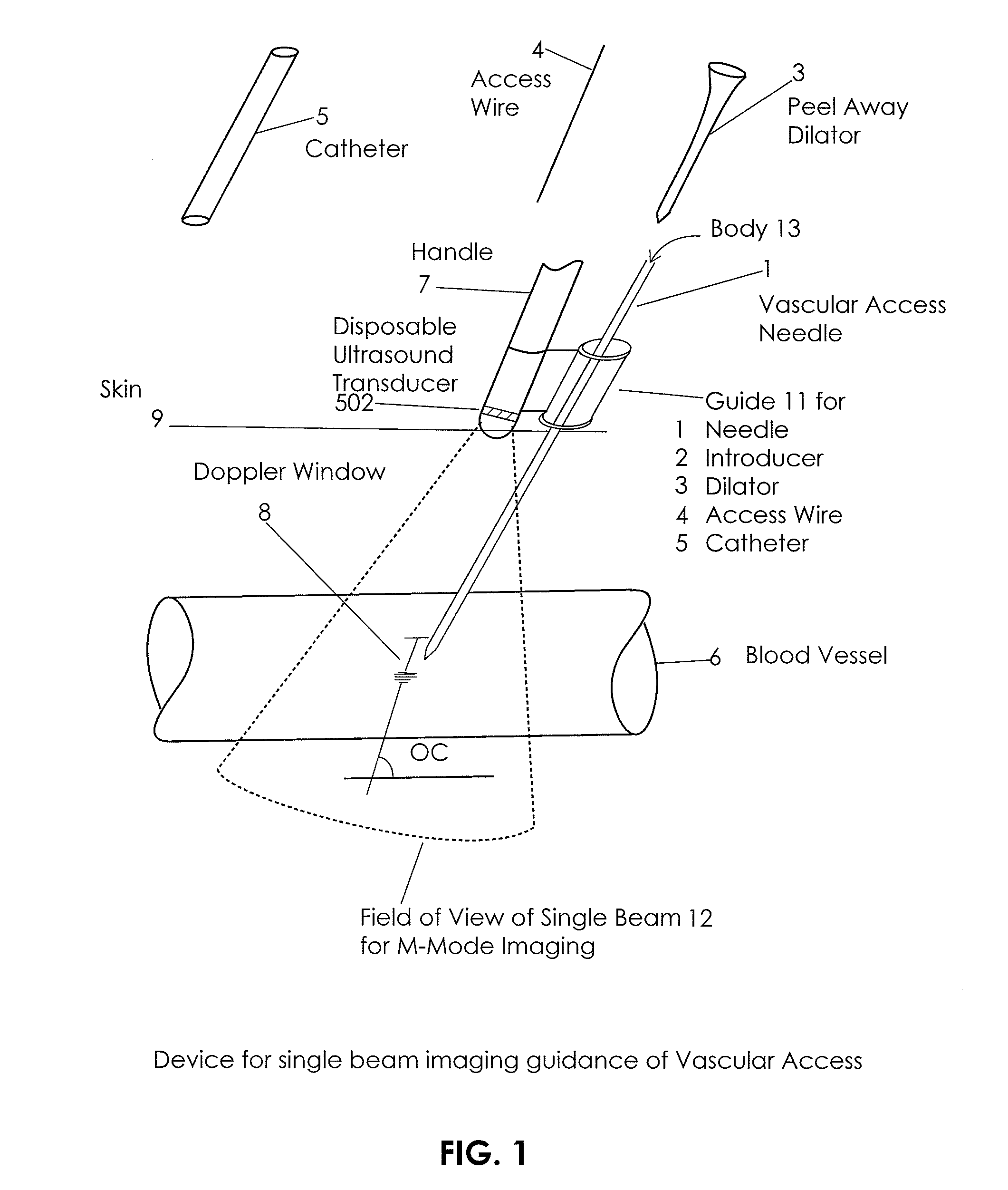
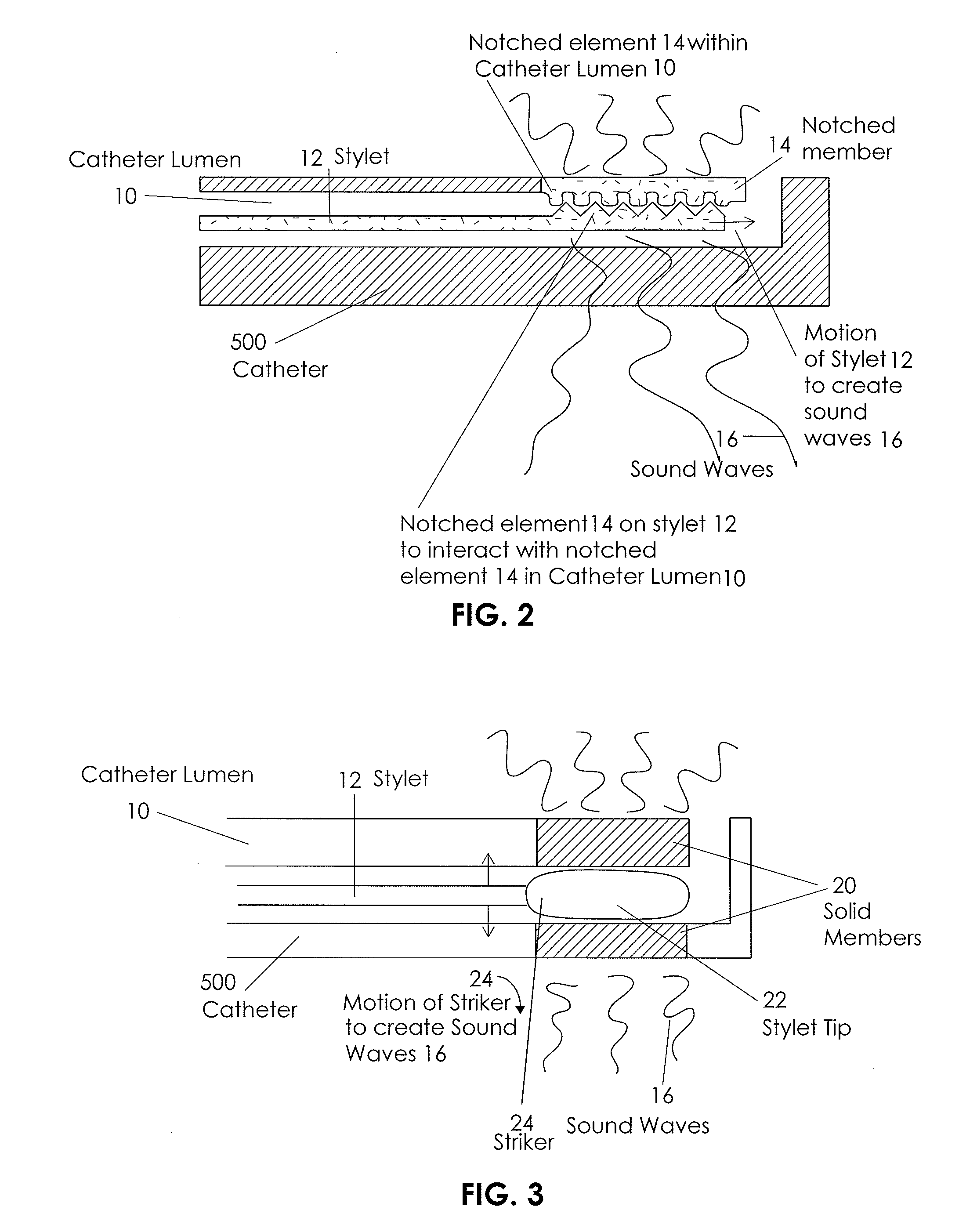
Apparatus and Method for Vascular Access
InactiveUS20090118612A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce needData processing applicationsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesVeinX-ray
In an aspect, embodiments of the invention relate to the effective and accurate placement of intravascular devices such as central venous catheters, in particular such as peripherally inserted central catheters or PICC. One aspect of the present invention relates to vascular access. It describes devices and methods for imaging guided vascular access and more effective sterile packaging and handling of such devices. A second aspect of the present invention relates to the guidance, positioning and placement confirmation of intravascular devices without the help of X-ray imaging. A third aspect of the present invention relates to devices and methods for the skin securement of intravascular devices and post-placement verification of location of such devices. A forth aspect of the present invention relates to improvement of the workflow required for the placement of intravascular devices.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Systems and methods for attaching a prosthesis within a body lumen or hollow organ
Systems and methods introduce and deploy prosthesis into a blood vessel or hollow body organ by intra-vascular access. The prosthesis is secured in place by fasteners which are implanted by an applier that is also deployed by intra-vascular access. The applier is configured to permit controlled, selective release of the fastener in a step that is independent of the step of implantation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Valve port and method for vascular access
InactiveUS7056316B1Reduce accessReduce riskPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedical devicesLocking mechanismBiomedical engineering
Owner:VASCA
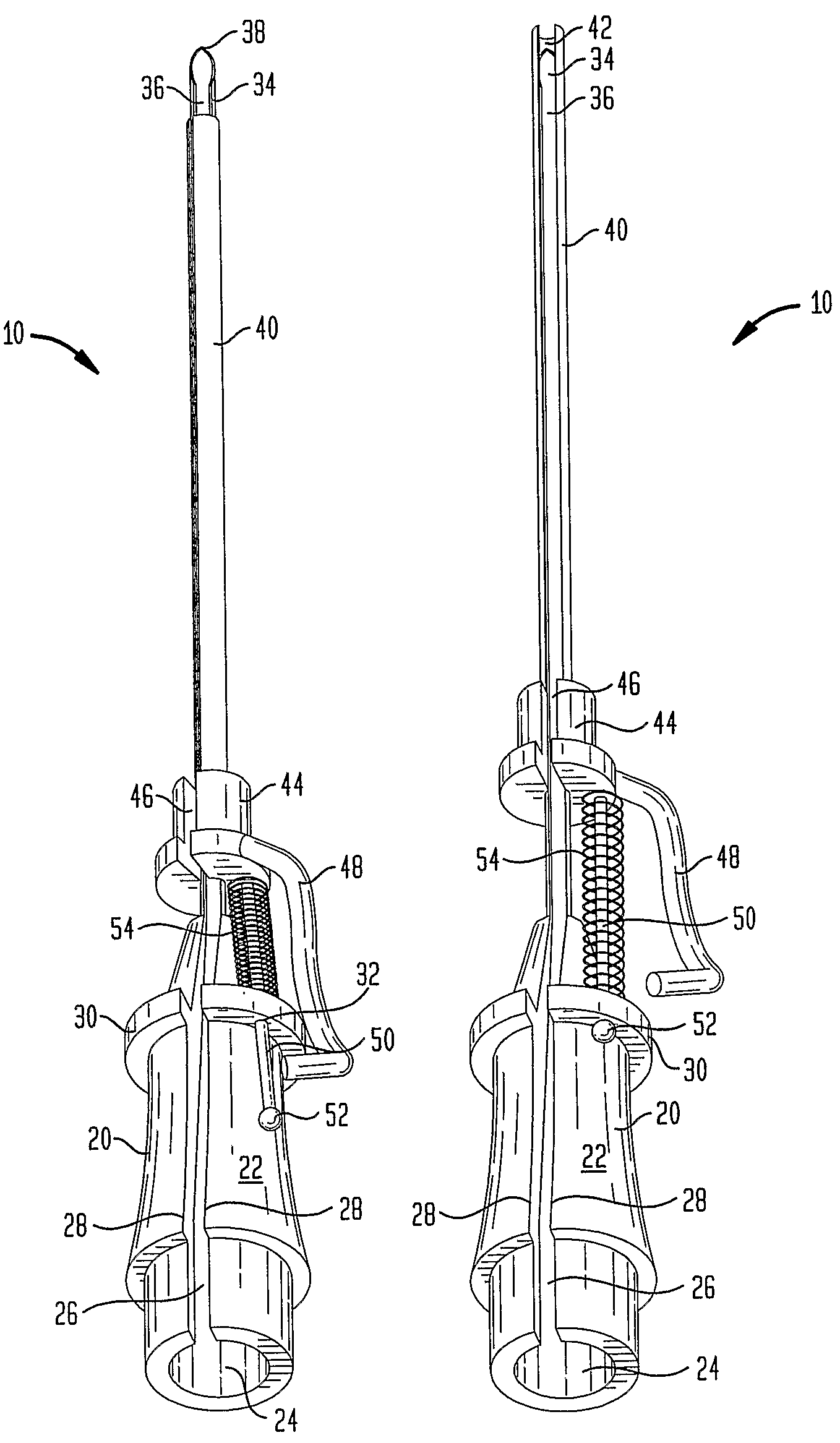
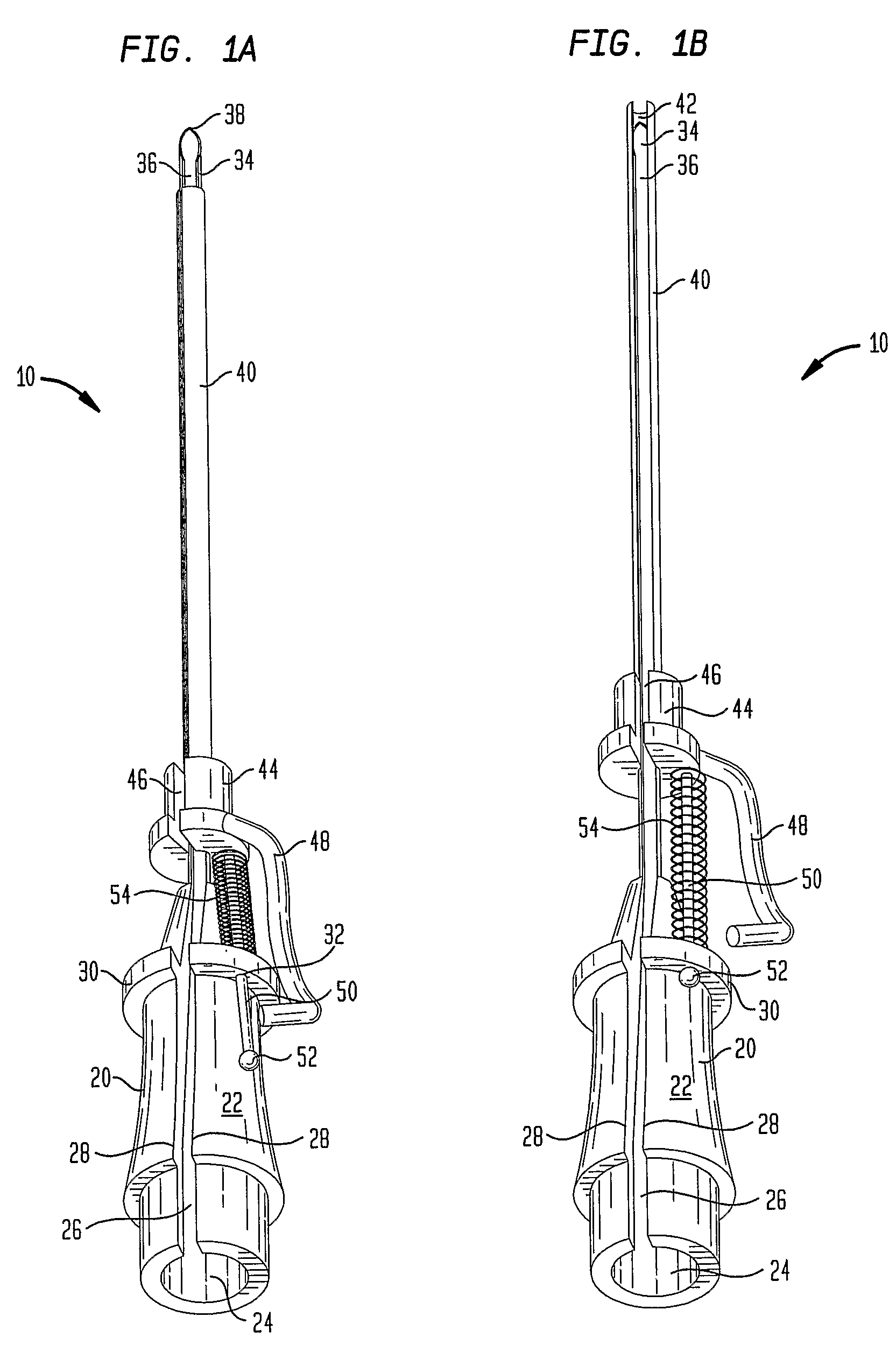
Vascular Access Needle
A vascular access needle assembly is provided. The needle assembly includes a housing interconnected with a needle. The housing and the needle have slots along their lengths which are aligned to form a slot extending along the entire needle assembly. A sheath interconnected with the needle extends partially about the needle and includes a slot. The vascular access needle, with the needle point exposed and needle slot closed, can be inserted into the blood vessel of a subject and a guide wire can be inserted into the blood vessel through the needle assembly. The sheath is then moved to cover the needle point and to expose the needle slot so that the guide wire can be lifted through the needle, sheath and housing slots and the vascular access needle assembly removed, leaving the guide wire in the subject. The device can also be used as a wire introducer for catheters. The vascular needle assembly can also be used as a biopsy needle for obtaining biopsy tissue wherein the edges of one or both of the needle slot and sheath slot are sharpened for cutting tissue.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Biodegradable and/or bioabsorbable member for vascular sealing
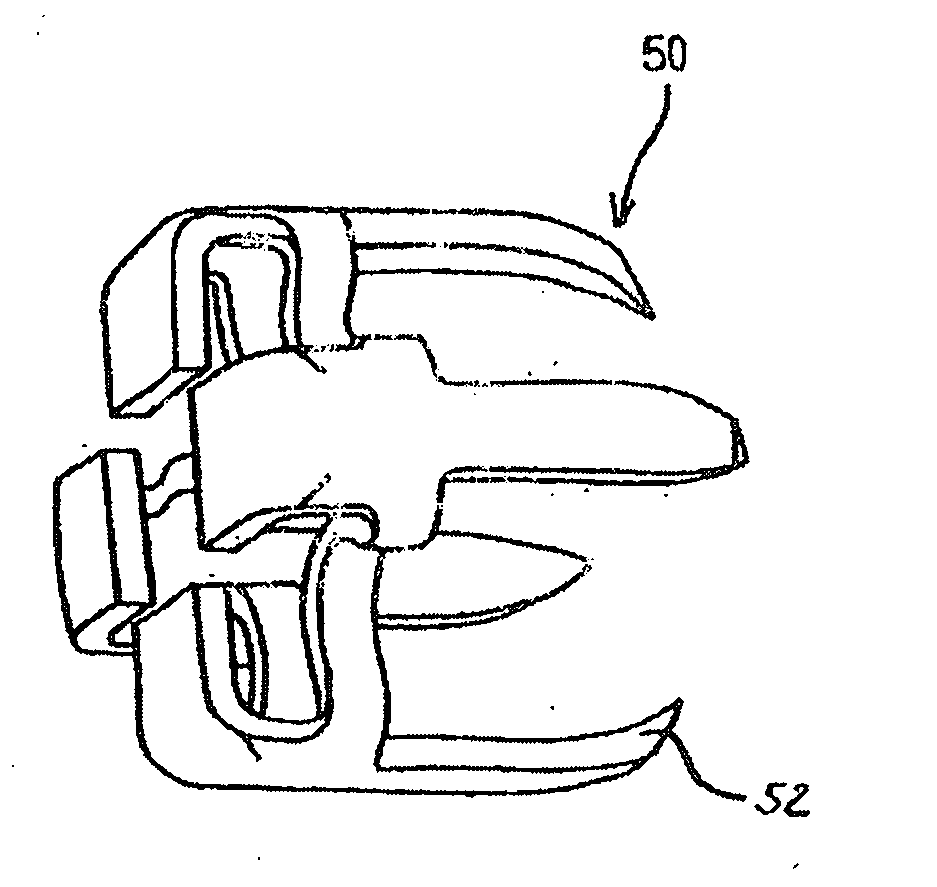
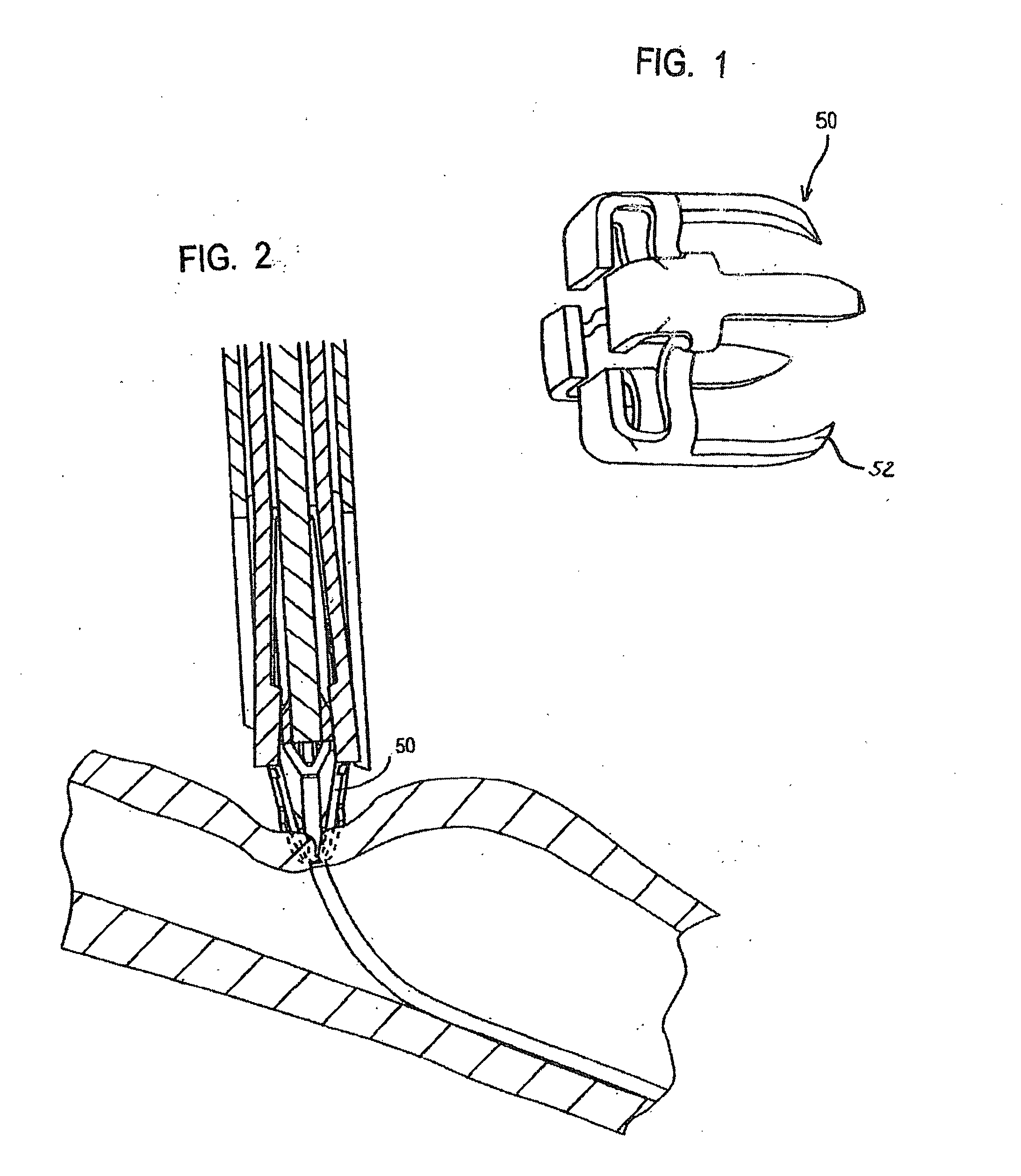
An implantable, bioresorbable and / or biodegradable sealing member, such as a staple, clip, snap or rivet, is used for clamping vessels, vessel side-branches, aneurysms, or any other tube like body-parts or for sealing vascular access sites and wound site management. The implantable, bioresorbable and / or biodegradable member comprises a combination of materials which dissolve or degrade in the human body without any harmful effects on the person that wears the member.
Owner:BIOTRONIK VI PATENT
Leadless Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator
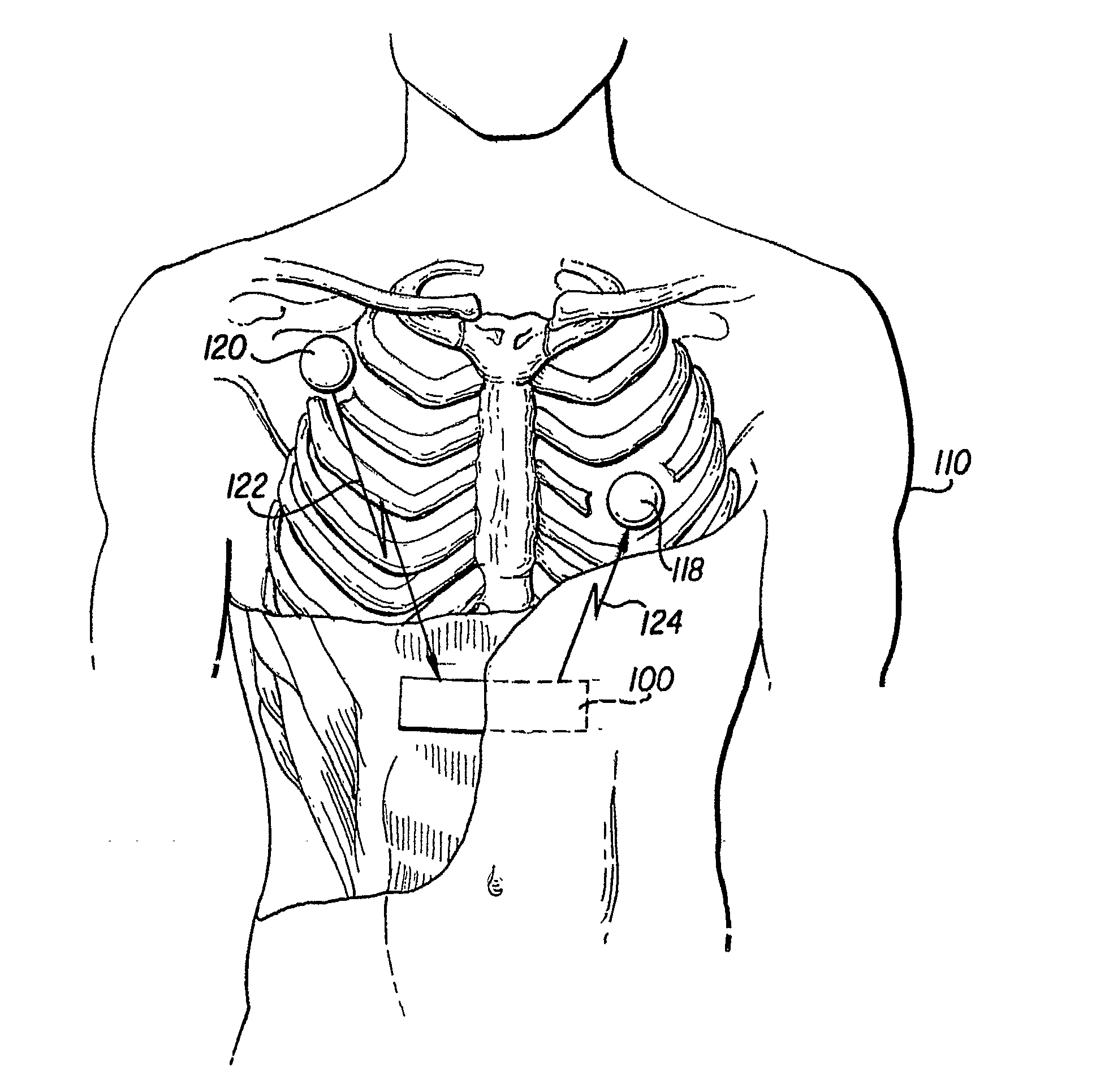
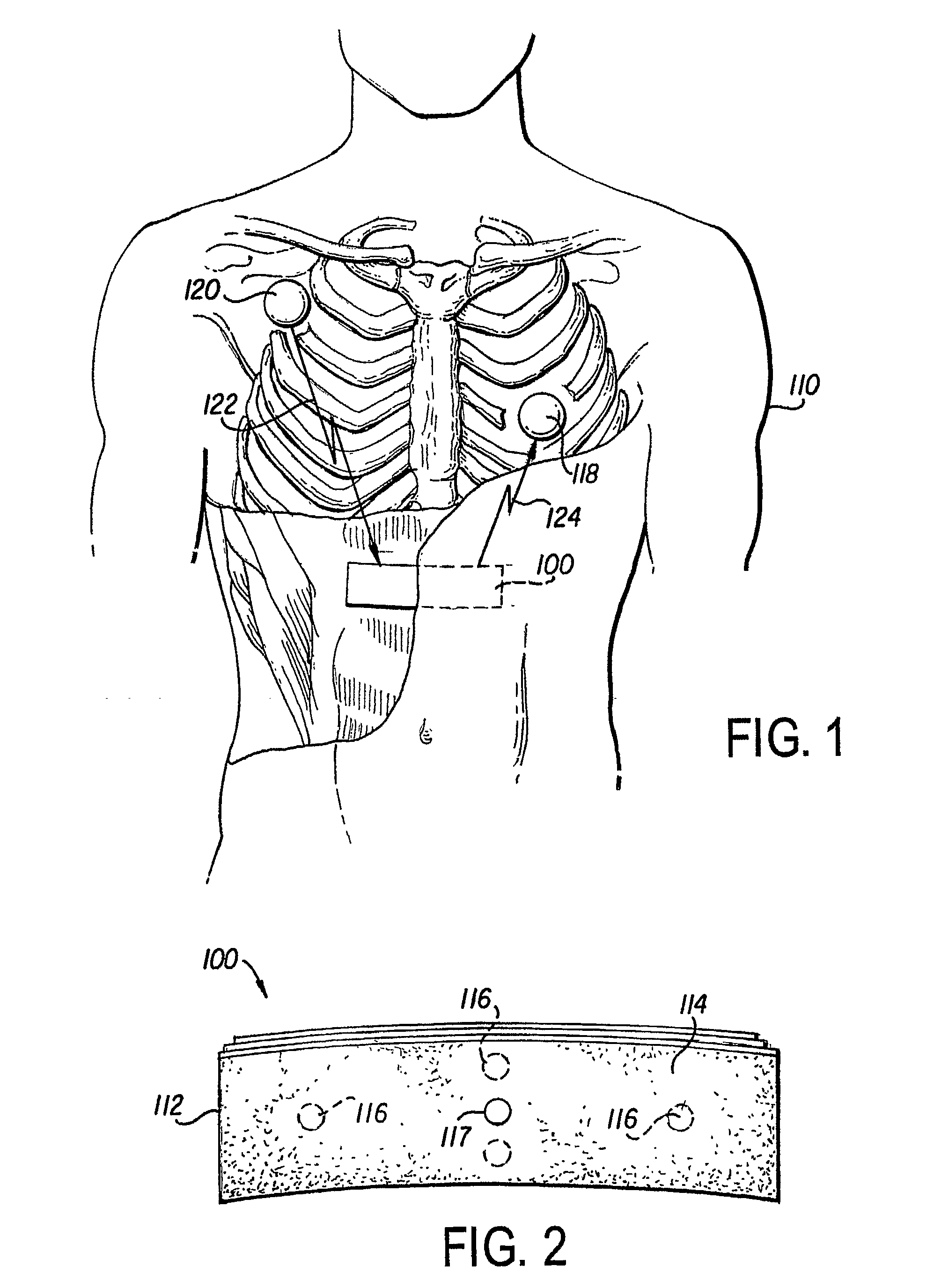
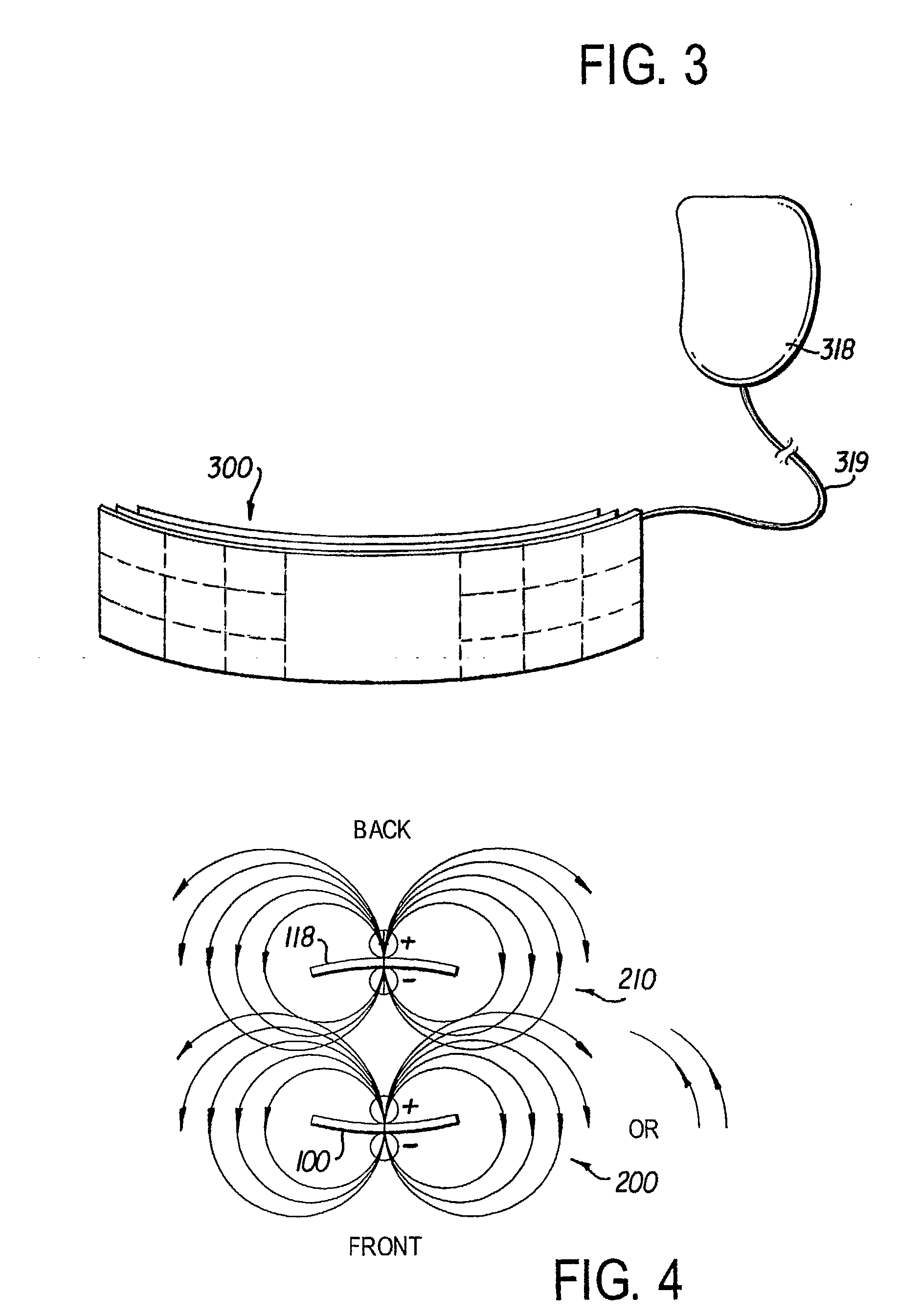
A leadless implantable cardioverter defibrillator (5) for treatment of sudden cardiac death includes a controller and at least one remote module. The defibrillator does not require transvenous / vascular access for intracardiac lead placement. The controller is leadless and uses subcutaneous tissue in proximity of the chest and abdomen for both sensing and defibrillation. The controller and one or more remote sensors sense a need for defibrillation and wireless communicate with the controller. The controller and one of the sensors discharge a synchronized defibrillation pulse to the surrounding subcutaneous tissue in proximity to the heart.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
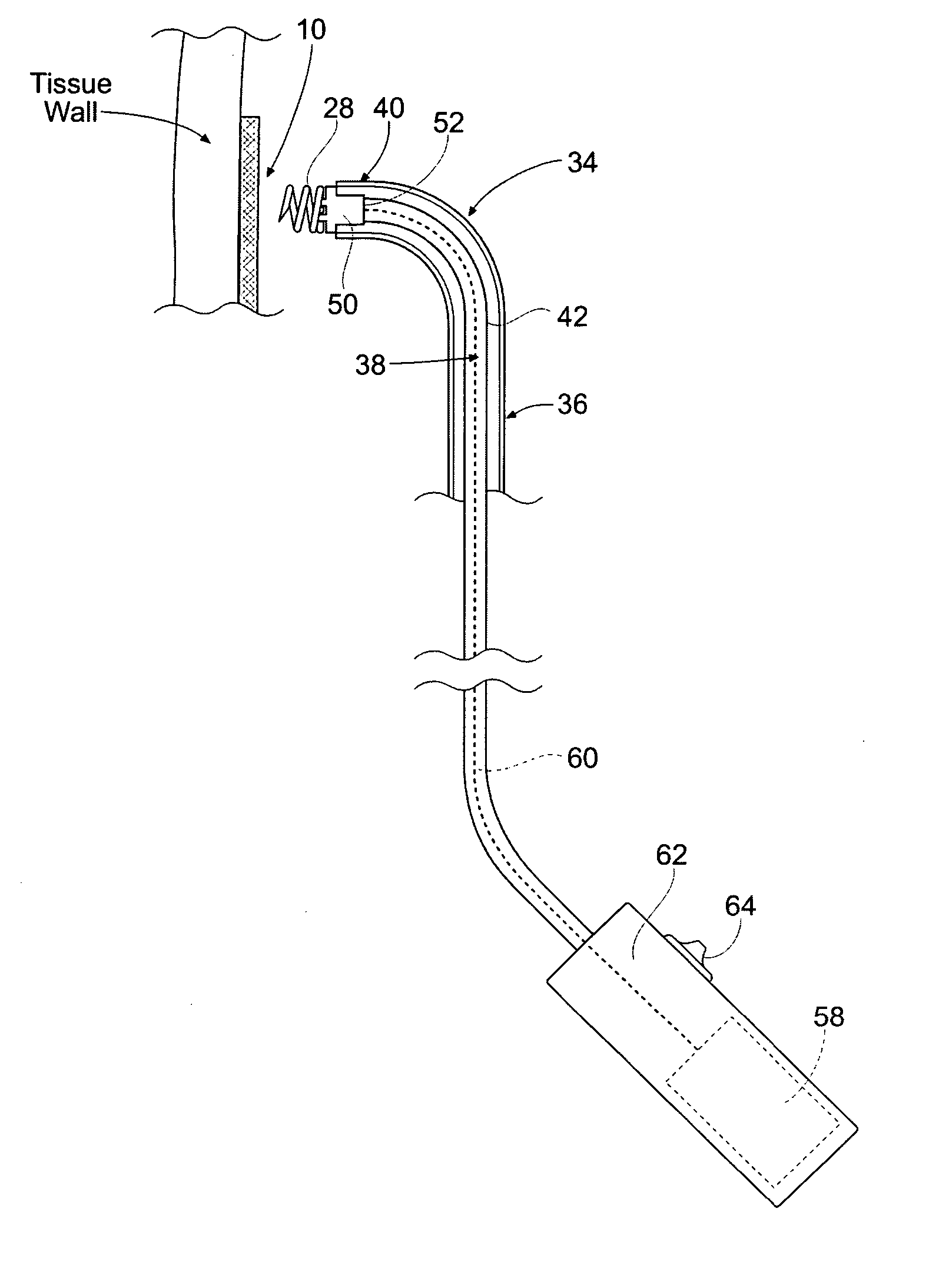
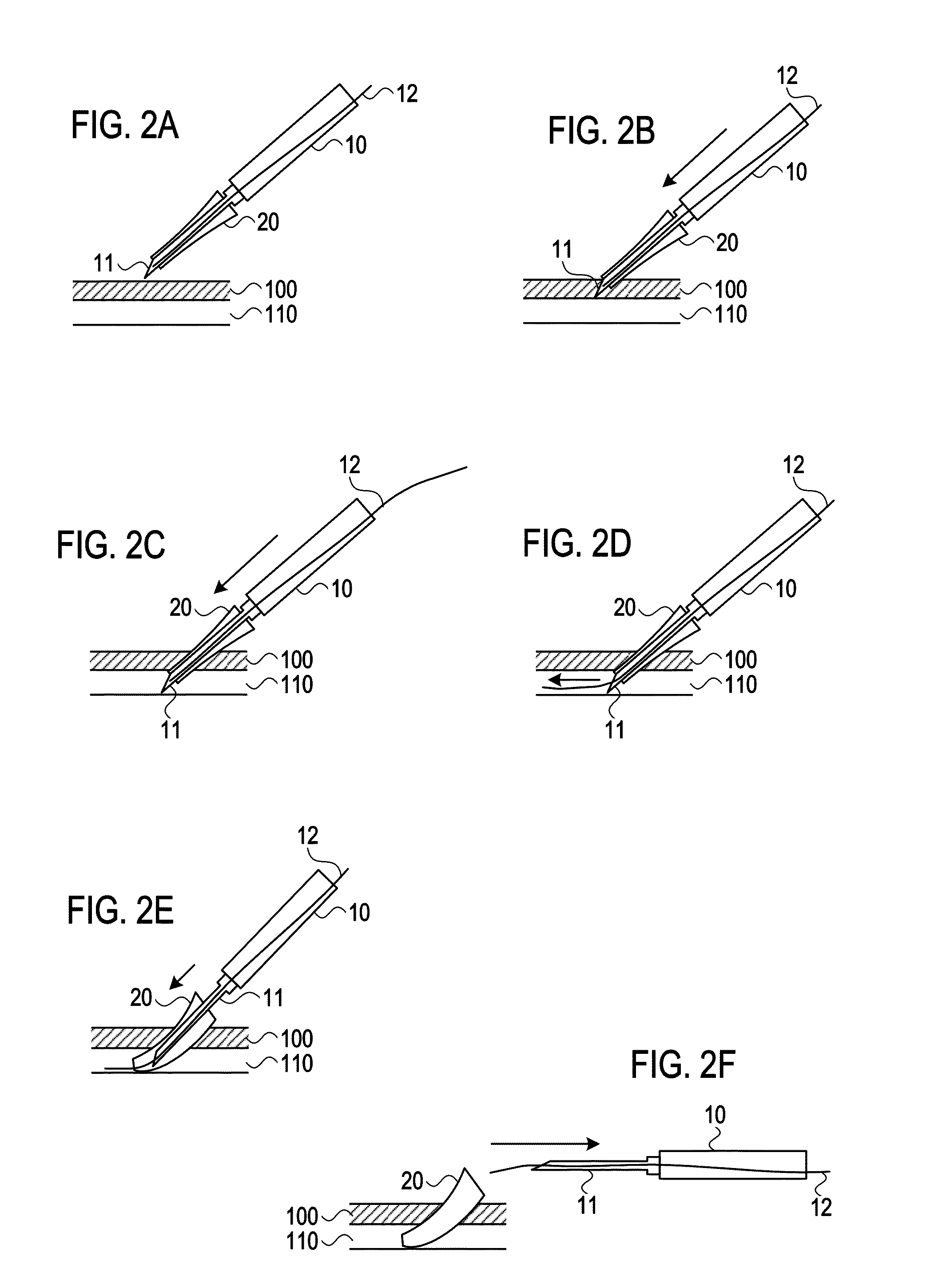
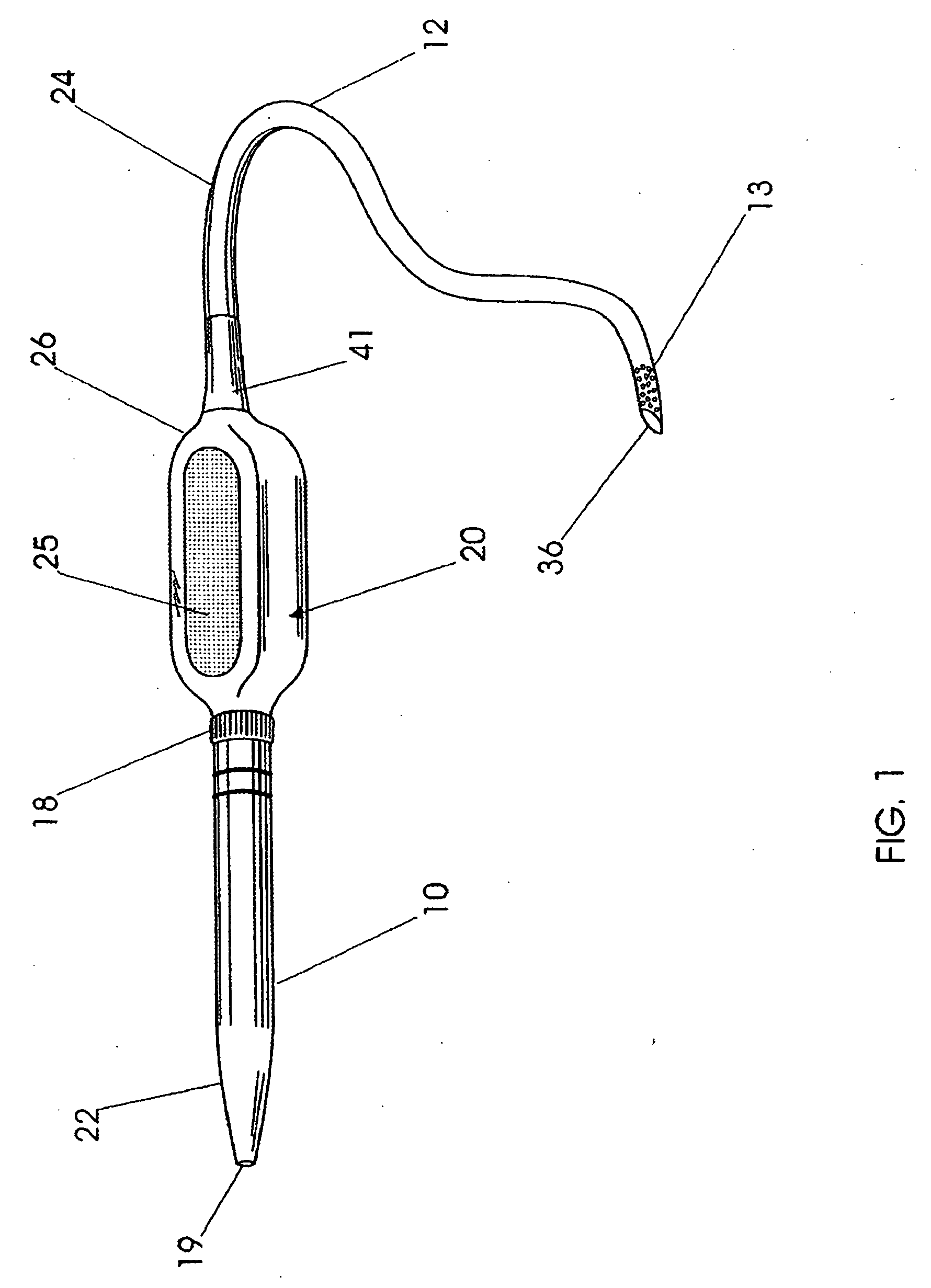
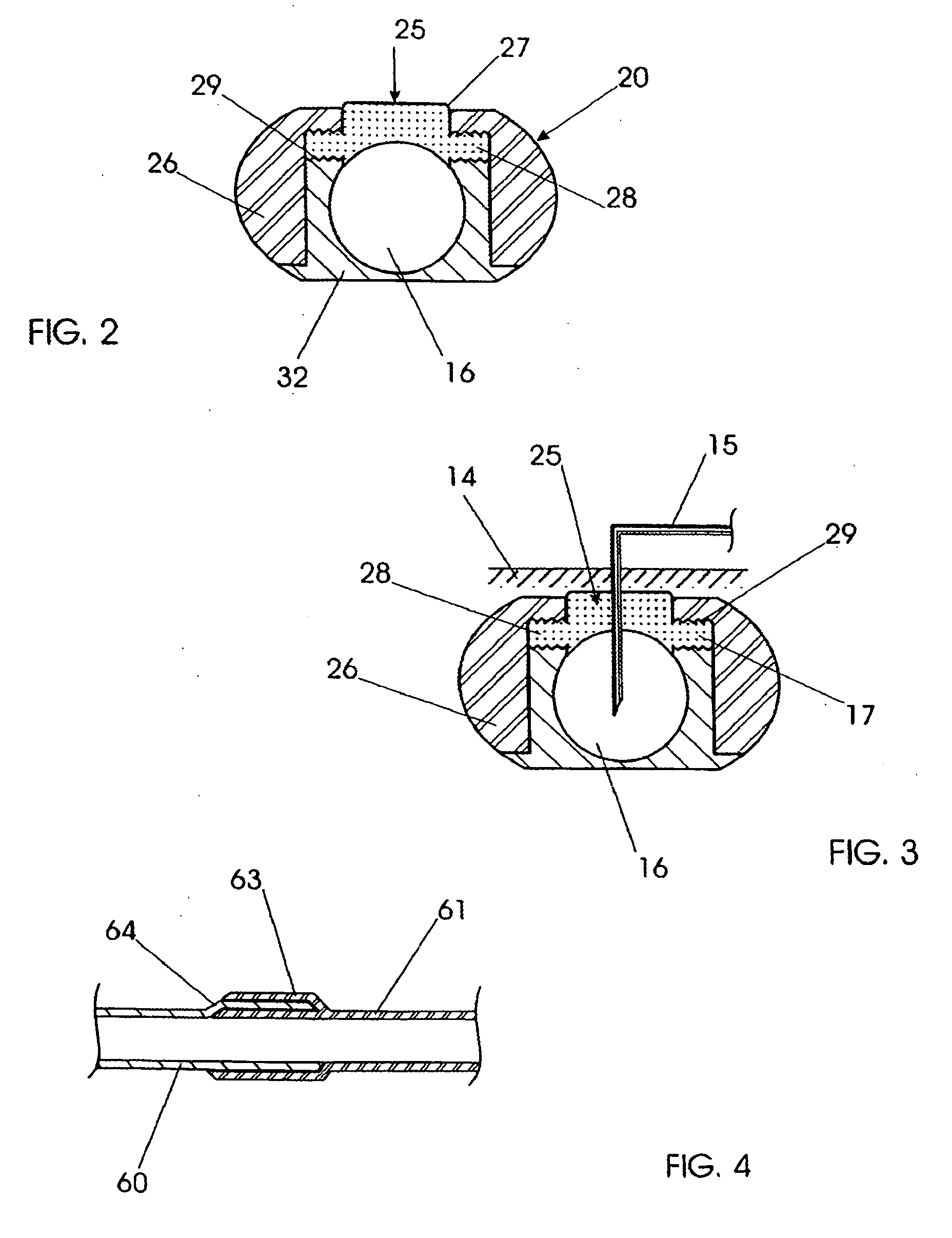
Vascular access closure system
InactiveUS7488340B2Easy to operateEasy to installSuture equipmentsSurgical veterinaryHand heldEngineering
A sealing device for sealing punctures in blood vessel walls including a flange connected to a flexible stem having an expansion portion in it. The flexible stem is adapted to be accommodated inside a delivery tube. The delivery tube further includes a hand-hold for ease of handling. The sealing device may further include a loader and a cutter. The flange and flexible stem are preferably constructed of a biodegradable material that has a tensile strength, rigidity, memory and other physical qualities similar to medical grade silicone. The resilient transverse expansion portion expands when deployed beyond the delivery tube in the tissue tract to create a frictional interface with the interior surface of the tissue tract to resist displacement of the flexible stem from a desired location in the tissue tract. The flexible stem also includes a flange at the distal end of the flexible stem to seal the puncture when the flexible stem is deployed.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
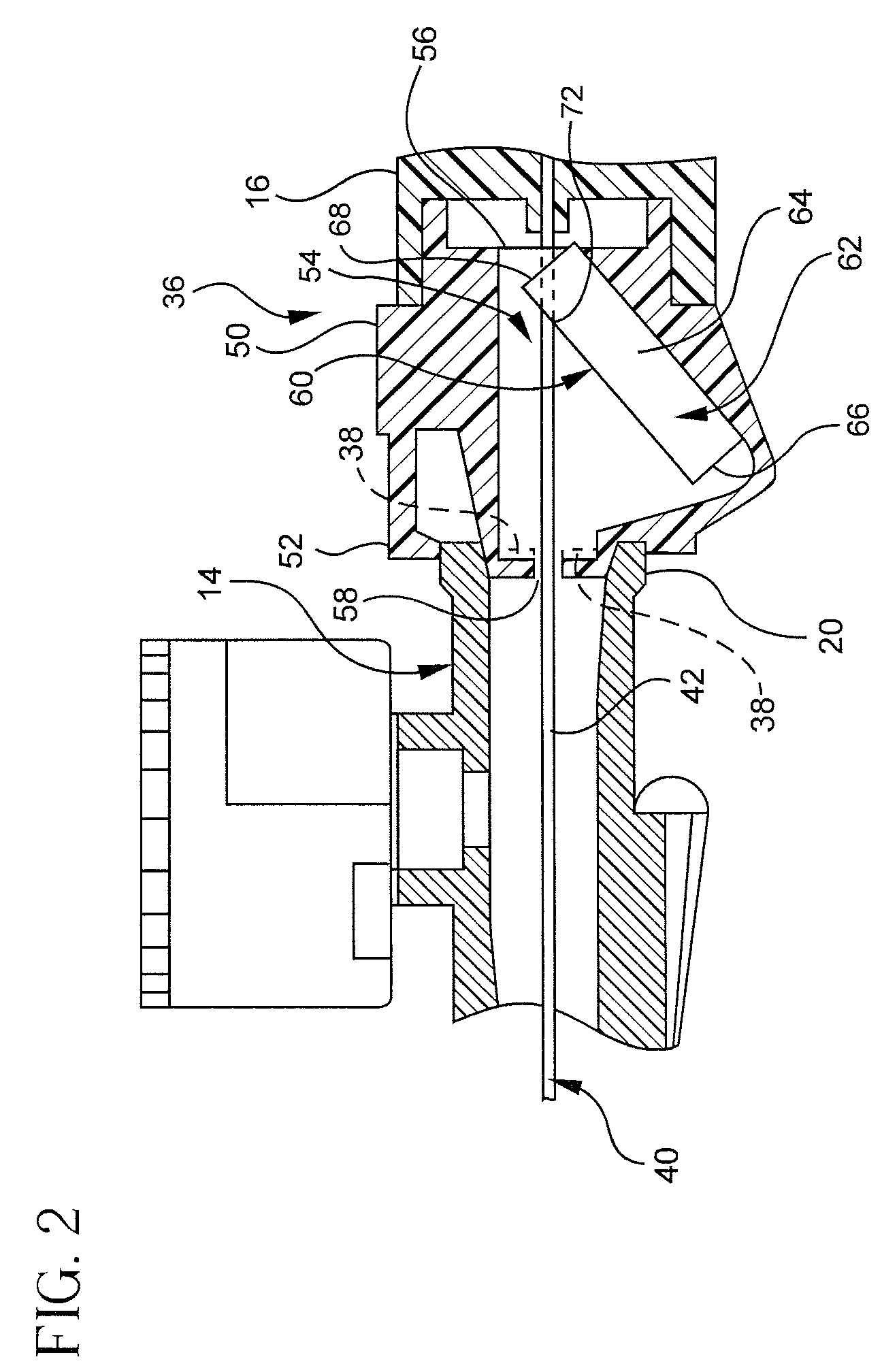
Device and method for vascular access
ActiveUS7762977B2Reduce kinksReduce kinking in said catheter portionOther blood circulation devicesSurgeryVeinHaemodialysis machine
Vascular access systems for performing hemodialysis are disclosed. The vascular access system contemplates a catheter section adapted for insertion into a vein and a graft section adapted for attachment to an artery. The catheter section may have metal or polymer wall reinforcements that allow the use of thin-walled, small outer diameter conduits for the vascular access system. One or more of the adhered, embedded or bonded conduit reinforcement structures may be removable without significant damage to the conduit sections to facilitate attachment of the sections, or to a connector between the sections. Various self-sealing materials are provided for use in the vascular access system, as well as temporary access sites and flow control / sensor systems.
Owner:MERIT MEDICAL SYST INC
Valve port assembly with interlock
InactiveUS6565525B1Semi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesBiomedical engineeringBlood vessel
A dual port vascular access assembly comprises a first access port and a second access port. The linkage is coupled between the first access port to close the second access port in the absence of an access tube in the first access port. Such port assemblies are particularly useful for implantation in patients receiving hemodialysis. By connecting the first access port to the blood withdrawal side of the system, blood withdrawal will be automatically terminated upon cessation of blood returned to due loss of the return access tube in the port assembly.
Owner:VASCA
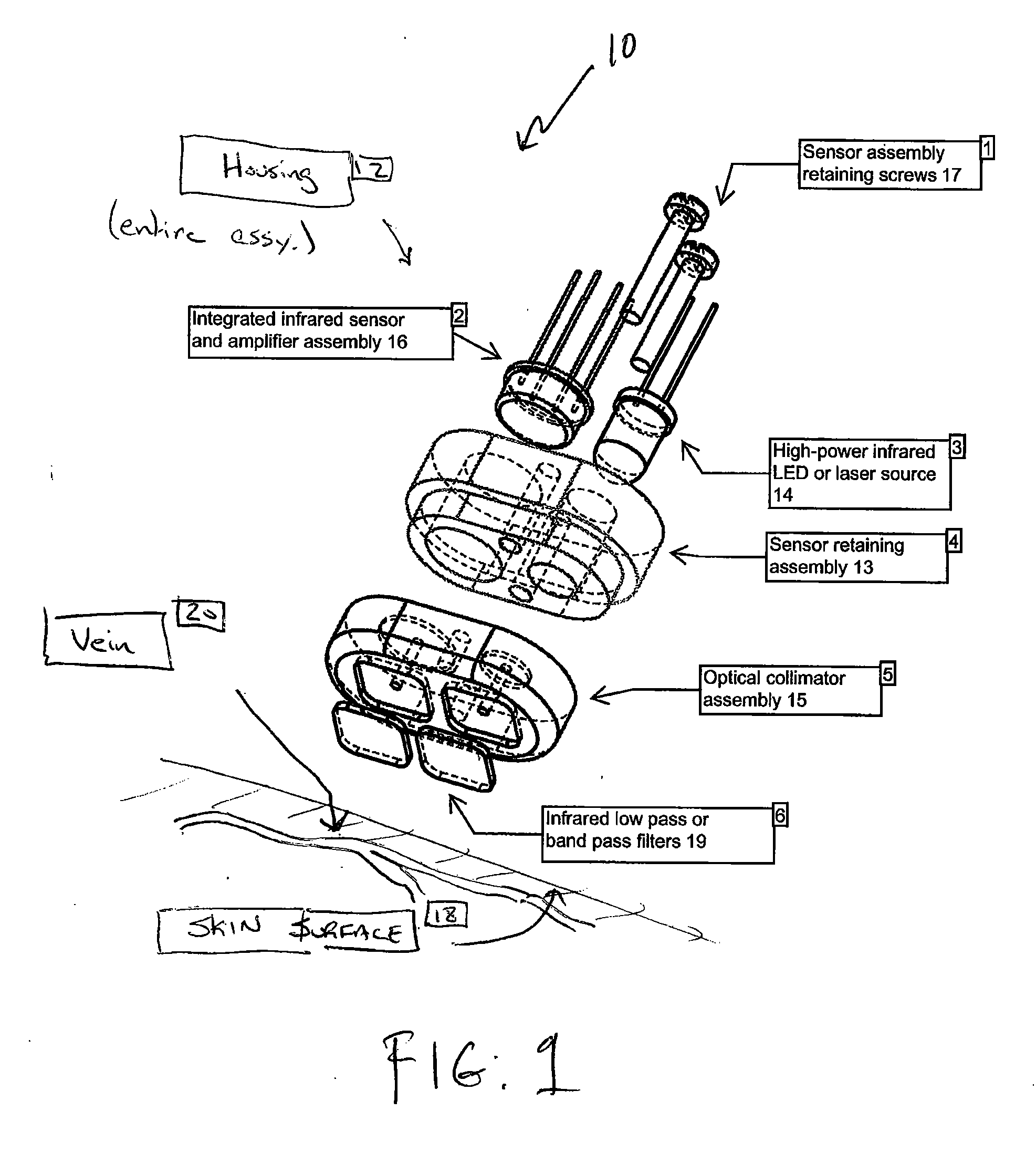
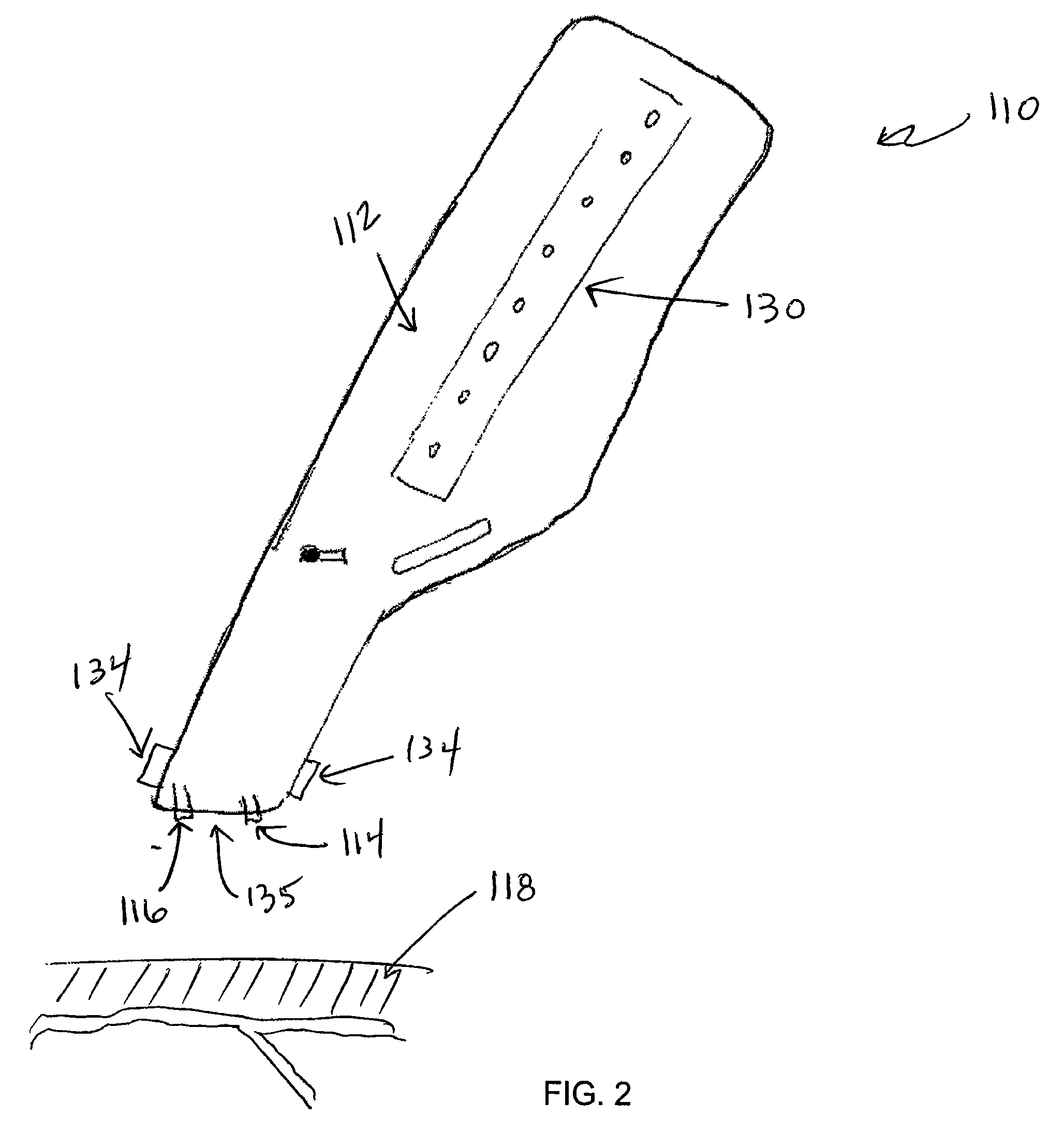
Vein locating device for vascular access procedures
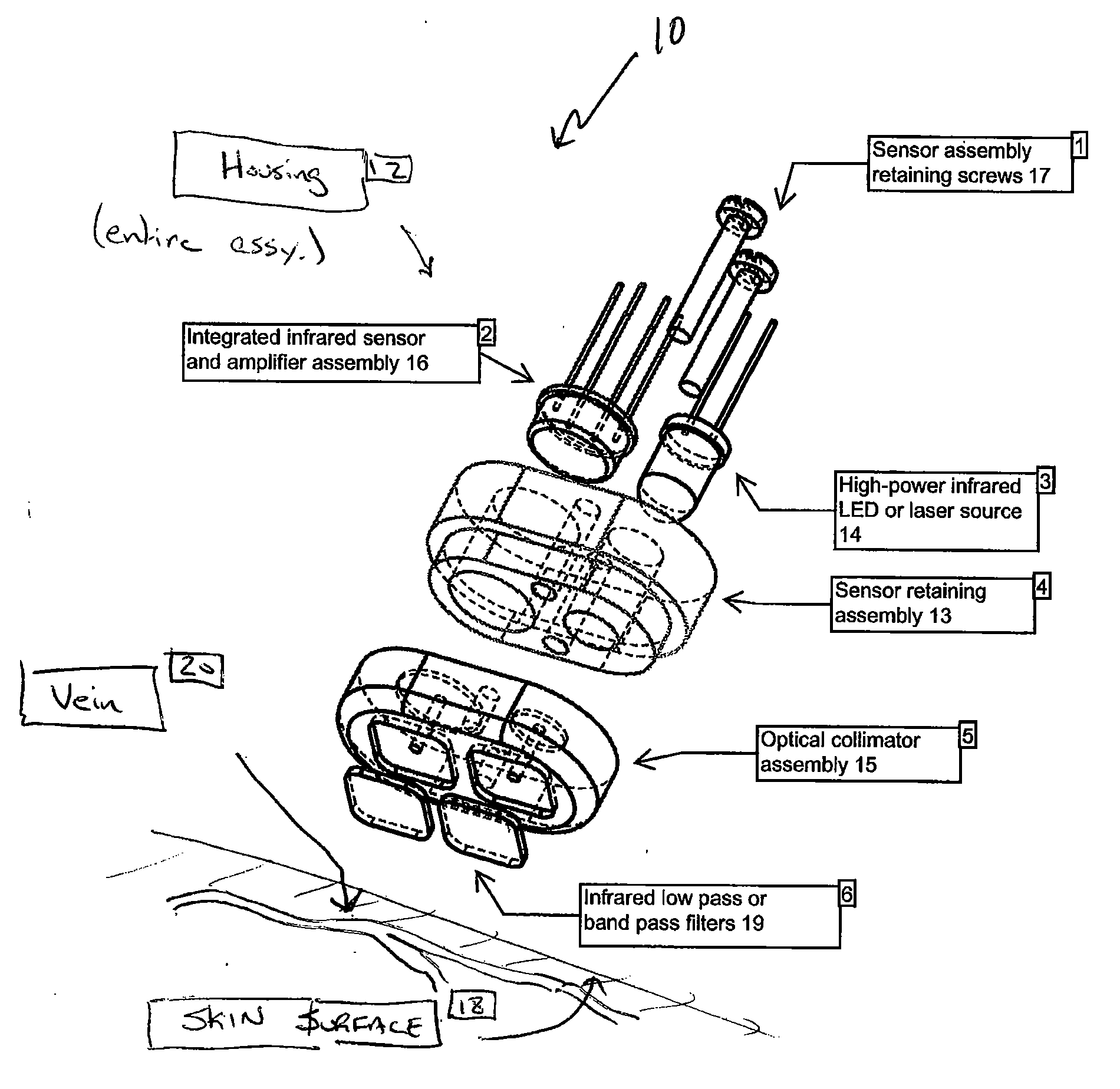
InactiveUS20080147147A1Improve abilitiesLocation can be detectedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using lightMedicineOptical energy
A device for detecting a venous structure or vessels in a patient or animal. The device includes an optical source for transmitting optical energy into the tissue of the patient, an optical detector for detecting at least a portion of the optical energy that is transmitted into and reflected by the tissue, and an indicator operably associated with the optical source and the optical detector. The indicator is adapted to indicate relative changes in the detected reflection or scattering of the optical energy transmitted into the tissue of the patient.
Owner:MEDRAD INC.
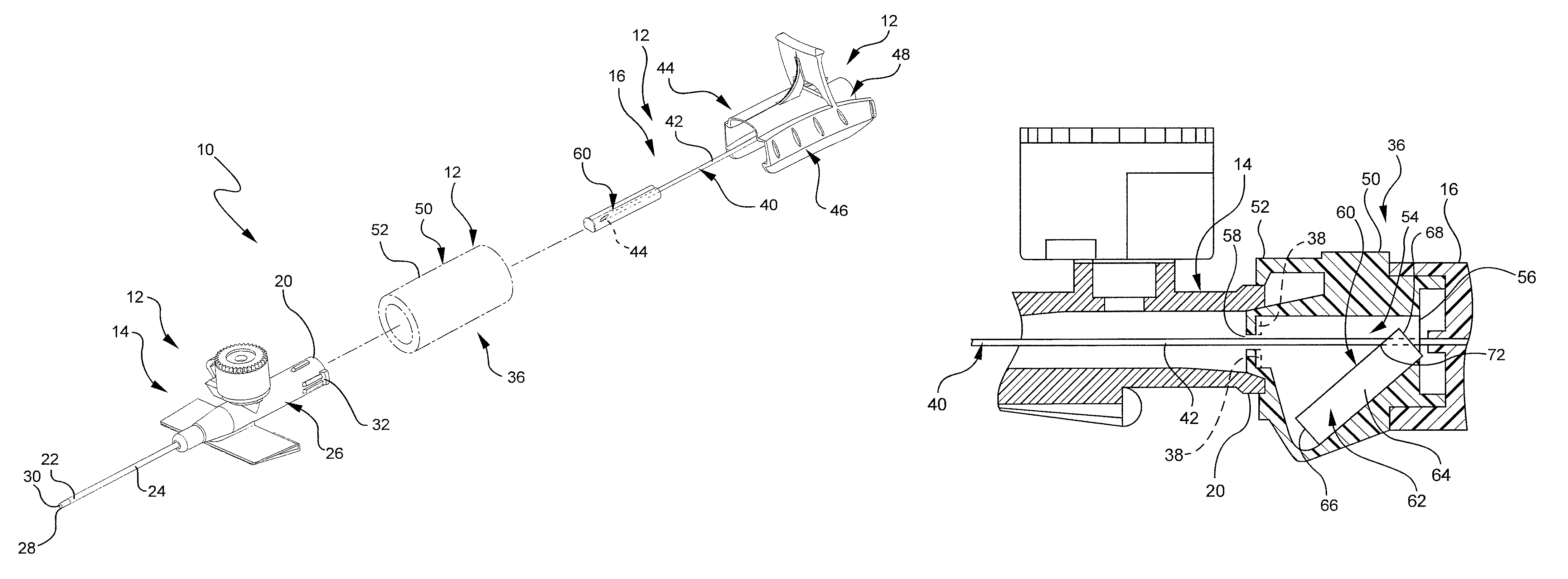
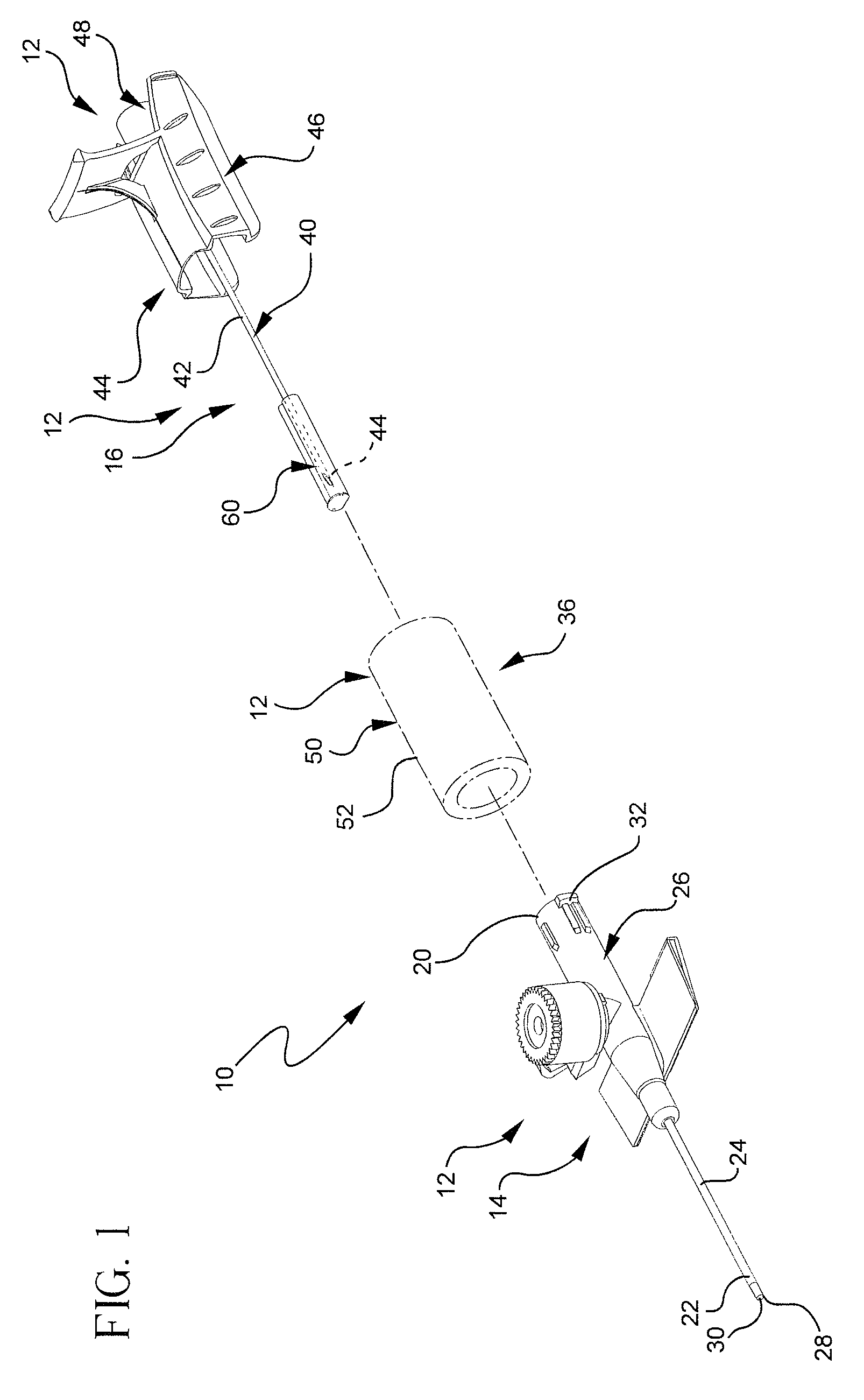
Interface device and method for interfacing instruments to vascular access simulation systems
InactiveUS7308831B2Improve realismSimulate the realCosmonautic condition simulationsData processing applicationsControl signalSkin traction
An interface device and method for interfacing instruments to a vascular access simulation system serve to interface peripherals in the form of mock or actual medical instruments to the simulation system to enable simulation of medical procedures. The interface device includes a catheter unit assembly for receiving a catheter needle assembly, and a skin traction mechanism to simulate placing skin in traction or manipulating other anatomical sites for performing a medical procedure. The catheter needle assembly and skin traction mechanism are manipulated by a user during a medical procedure. The catheter unit assembly includes a base, a housing, a bearing assembly and a shaft that receives the catheter needle assembly. The bearing assembly enables translation of the catheter needle assembly, and includes bearings that enable the shaft to translate in accordance with manipulation of the catheter needle assembly. The shaft typically includes an encoder to measure translational motion of a needle of the catheter needle assembly, while the interface device further includes encoders to measure manipulation of the catheter needle assembly in various degrees of freedom (e.g., translation, pitch and yaw) and the skin traction mechanism. Alternatively, the shaft may include an additional encoder to measure translational motion of an instrument inserted through the catheter needle assembly. The simulation system receives measurements from the interface device encoders and updates the simulation and display, while providing control signals to the force feedback device to enable application of force feedback to the catheter needle assembly.
Owner:IMMERSION MEDICAL
Composite structures and methods for ablating tissue to form complex lesion patterns in the treatment of cardiac conditions and the like
InactiveUS7115122B1Avoiding costly and intrusiveElectrotherapyDiagnosticsFibrillationElectrical impulse
A method of ablating tissue in the heart to treat atrial fibrillation introduces into a selected atrium an energy emitting element. The method exposes the element to a region of the atrial wall and applies ablating energy to the element to thermally destroy tissue. The method forms a convoluted lesion pattern comprising elongated straight lesions and elongated curvilinear lesions. The lesion pattern directs electrical impulses within the atrial myocardium along a path that activates the atrial myocardium while interrupting reentry circuits that, if not interrupted, would cause fibrillation. The method emulates the surgical maze procedure, but lends itself to catheter-based procedures that do not require open heart surgical techniques. A composite structure for performing the method is formed using a template that displays in planar view a desired lesion pattern for the tissue. An array of spaced apart element is laid on the template. Guided by the template, energy emitting and non-energy emitting zones are formed on the elements. By overlaying the elements, the composite structure is formed, which can be introduced into the body to ablate tissue using catheter-based, vascular access techniques.
Owner:EP TECH
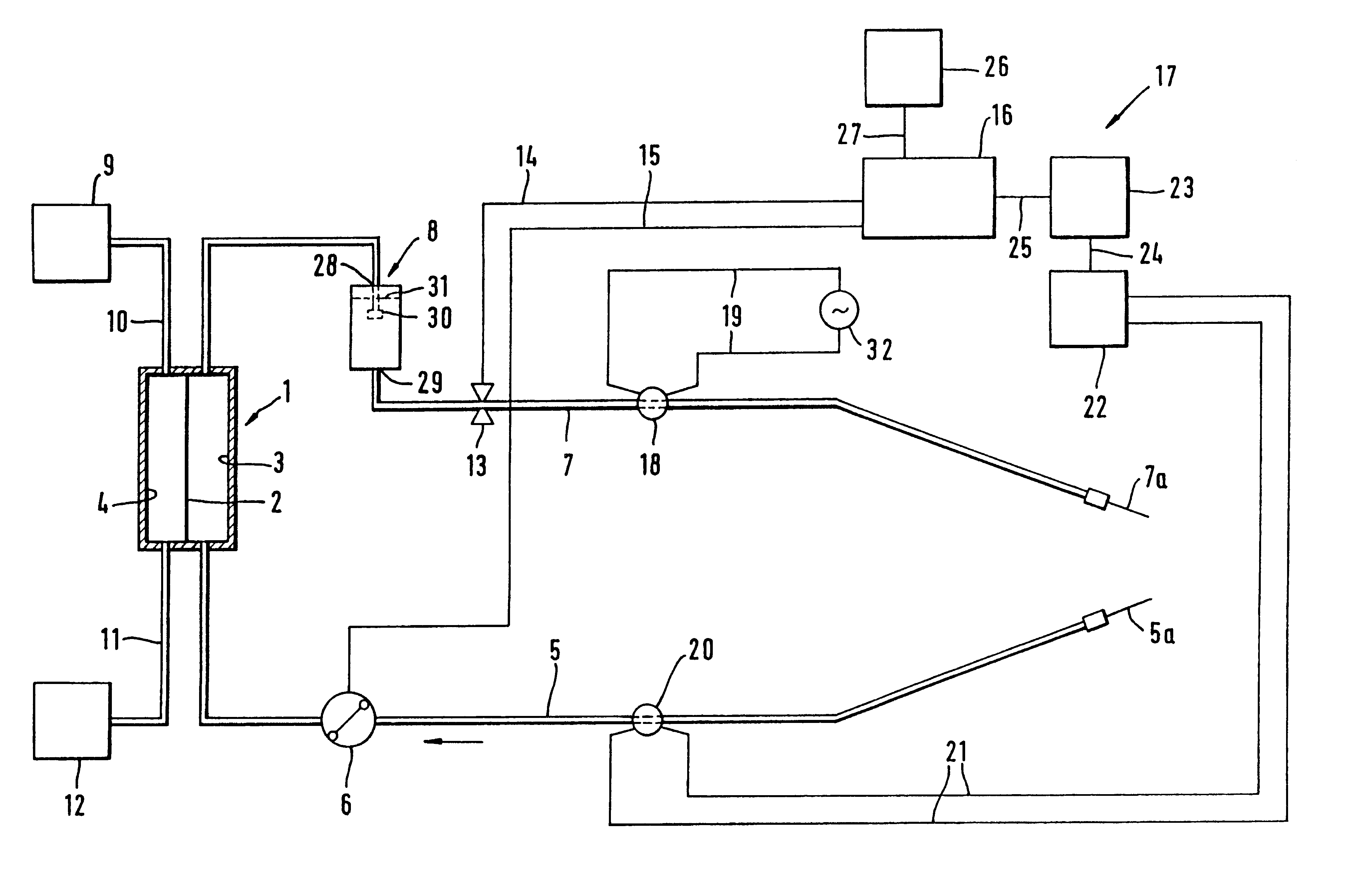
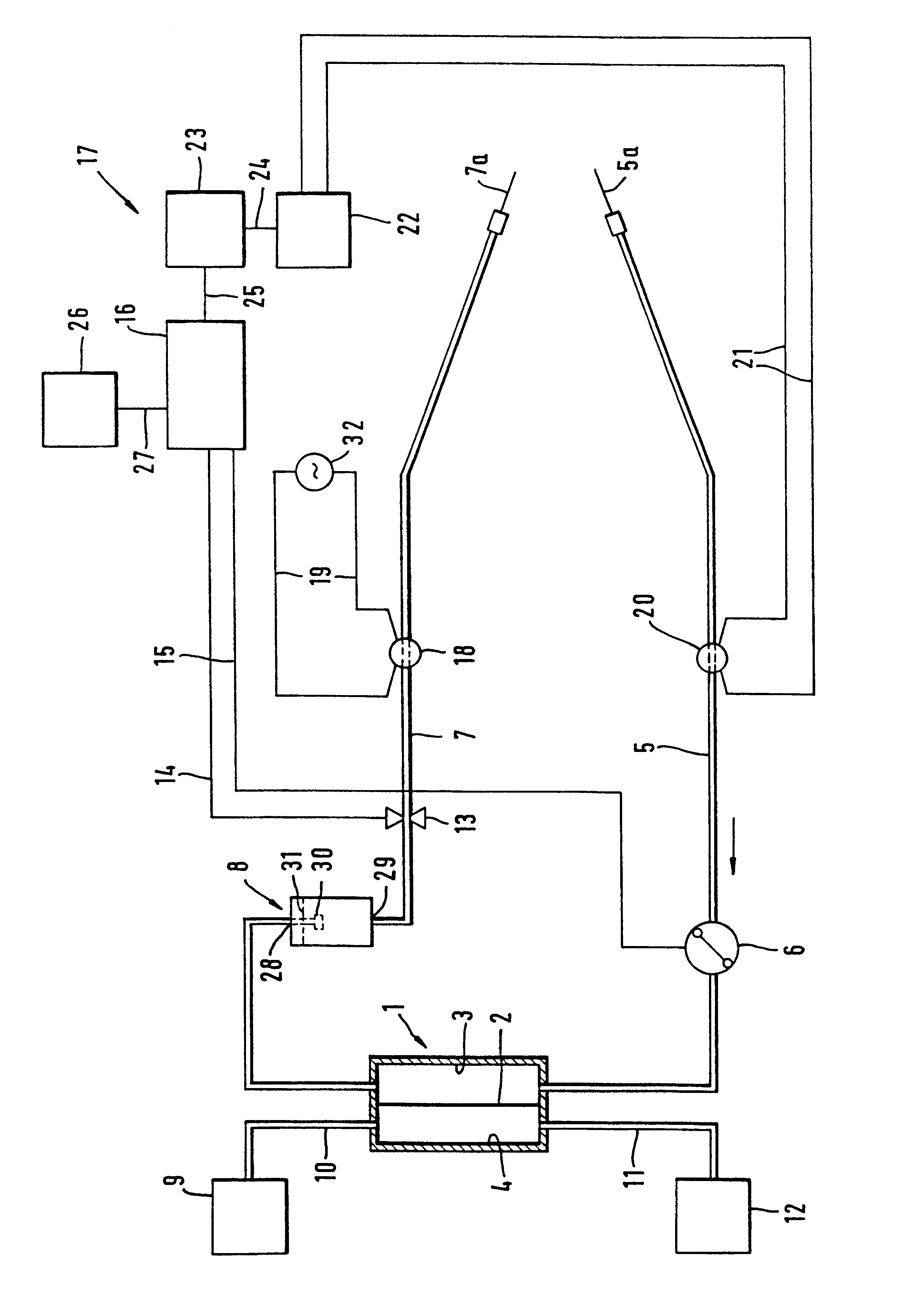
Method and device for monitoring vessel access during extracorporeal blood treatment
InactiveUS6663585B1Improve reliabilitySimple technical meanSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionExtracorporeal circulationBlood treatments
A method and device for monitoring vascular access is described. A field coil is placed at a location on an extracorporeal circulation loop connected to the vascular system of a patient, and an induction coil is placed at another different location. A voltage is supplied to the field coil, inducing an electric current in the blood. The current induces a voltage in the induction coil. Monitoring the voltage in the induction coil reveals if vascular access is defective.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Tip shield for needle stick prevention
A vascular access system for preventing needle sticks includes a needle, a tip shield, and a housing. The needle may be a hypodermic needle or other conventional needle having a needle shaft terminating at a needle tip. The tip shield provides an enclosure defining a chamber. The enclosure includes a closed distal end and a proximal end that slidably engages the needle shaft. The enclosure further includes at least one side wall configured to slidably engage the needle shaft. The housing defines a passageway with respective proximal and distal openings through which the needle extends. The tip shield is also disposed in the passageway and is releasably retained therein. The needle and / or the tip shield is adapted to prevent the needle shaft from being completely withdrawn from the tip shield. The tip shield further secures the needle tip in the chamber upon withdrawal of the needle tip into the chamber.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Vascular access needle
A vascular access needle assembly is provided. The needle assembly includes a housing interconnected with a needle. The housing and the needle have slots along their lengths which are aligned to form a slot extending along the entire needle assembly. A sheath interconnected with the needle extends partially about the needle and includes a slot. The vascular access needle, with the needle point exposed and needle slot closed, can be inserted into the blood vessel of a subject and a guide wire can be inserted into the blood vessel through the needle assembly. The sheath is then moved to cover the needle point and to expose the needle slot so that the guide wire can be lifted through the needle, sheath and housing slots and the vascular access needle assembly removed, leaving the guide wire in the subject. The device can also be used as a wire introducer for catheters. The vascular needle assembly can also be used as a biopsy needle for obtaining biopsy tissue wherein the edges of one or both of the needle slot and sheath slot are sharpened for cutting tissue.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Pressure activated safety valve with improved flow characteristics and durability
A valve assembly for vascular access, comprising a body defining a lumen adapted for flowing blood, the body including a luer housing for connection with a first blood conduit and a barb housing for connection with a second blood conduit and a plurality of slitted membranes disposed within the body portion, each of the slitted membranes generating a partial pressure drop for flow therethrough, each of the partial pressure drops being smaller than a total pressure drop for flow through the body portion.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Devices and methods for endovascular access and therapy
ActiveUS20130178711A1Short response timeQuick and safe and easy deploymentBalloon catheterDiagnosticsOcclusion catheterEndovascular therapy
The present invention provides for devices and methods for providing endovascular therapy, including facilitating establishment of vascular access, placement of endovascular sheaths, catheter tip localization, and administration of vascular occlusion. The inventions includes a vessel cannulation device, an expandable sheath, an occlusion catheter, and a localizer each of which may be provided separately or used as part of a system.
Owner:TRAUMATEK SOLUTIONS
Devices and methods for endovascular access and therapy
ActiveUS20130281787A1Quick and safe and easy deploymentStop hemorrhageBalloon catheterDiagnosticsOcclusion catheterEndovascular therapy
The present invention provides for devices and methods for providing endovascular therapy, including facilitating establishment of vascular access, placement of endovascular sheaths, catheter tip localization, and administration of vascular occlusion. The invention includes a vessel cannulation device, an expandable sheath, an occlusion catheter, and a localizer each of which may be provided separately or used as part of a system. One embodiment of the invention is a vessel cannulation device including: a housing having a distal end with a distal tip and a proximal end; a guidewire lumen passing through the housing and at least the distal tip; a sensor coupled to the guidewire lumen; and an advancing member, which is configured for advancing at least one of a guidewire or a sheath and which is operably coupled to the sensor.
Owner:TRAUMATEK SOLUTIONS
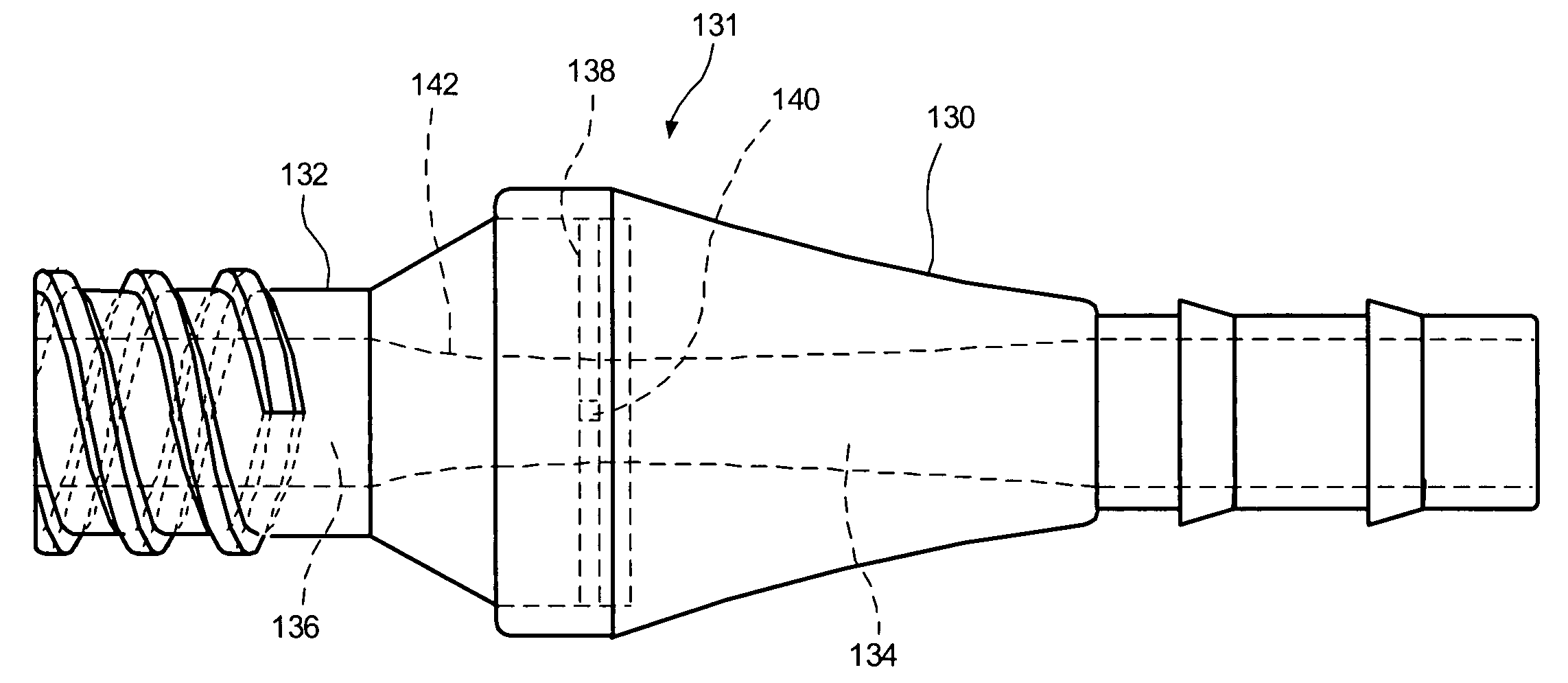
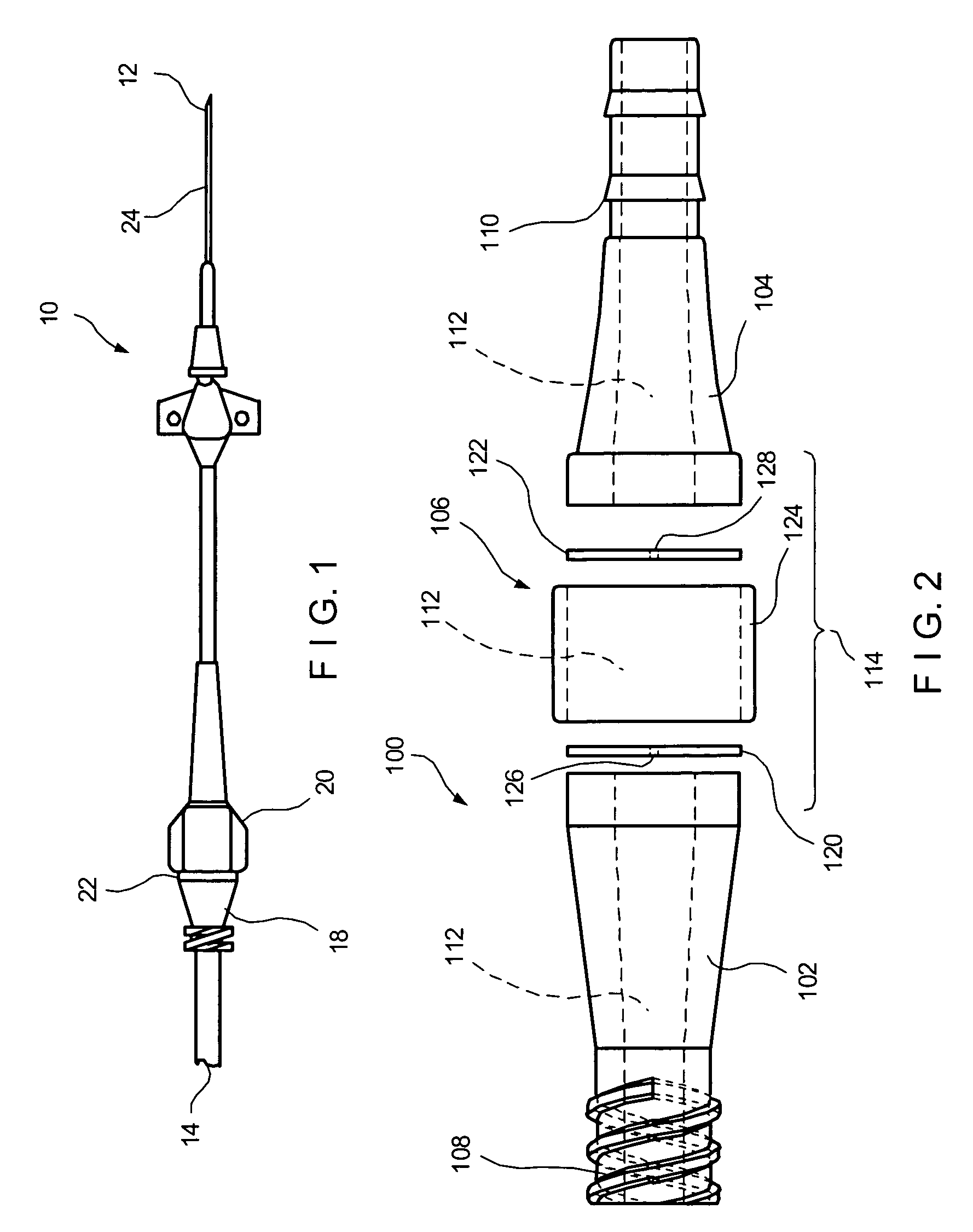
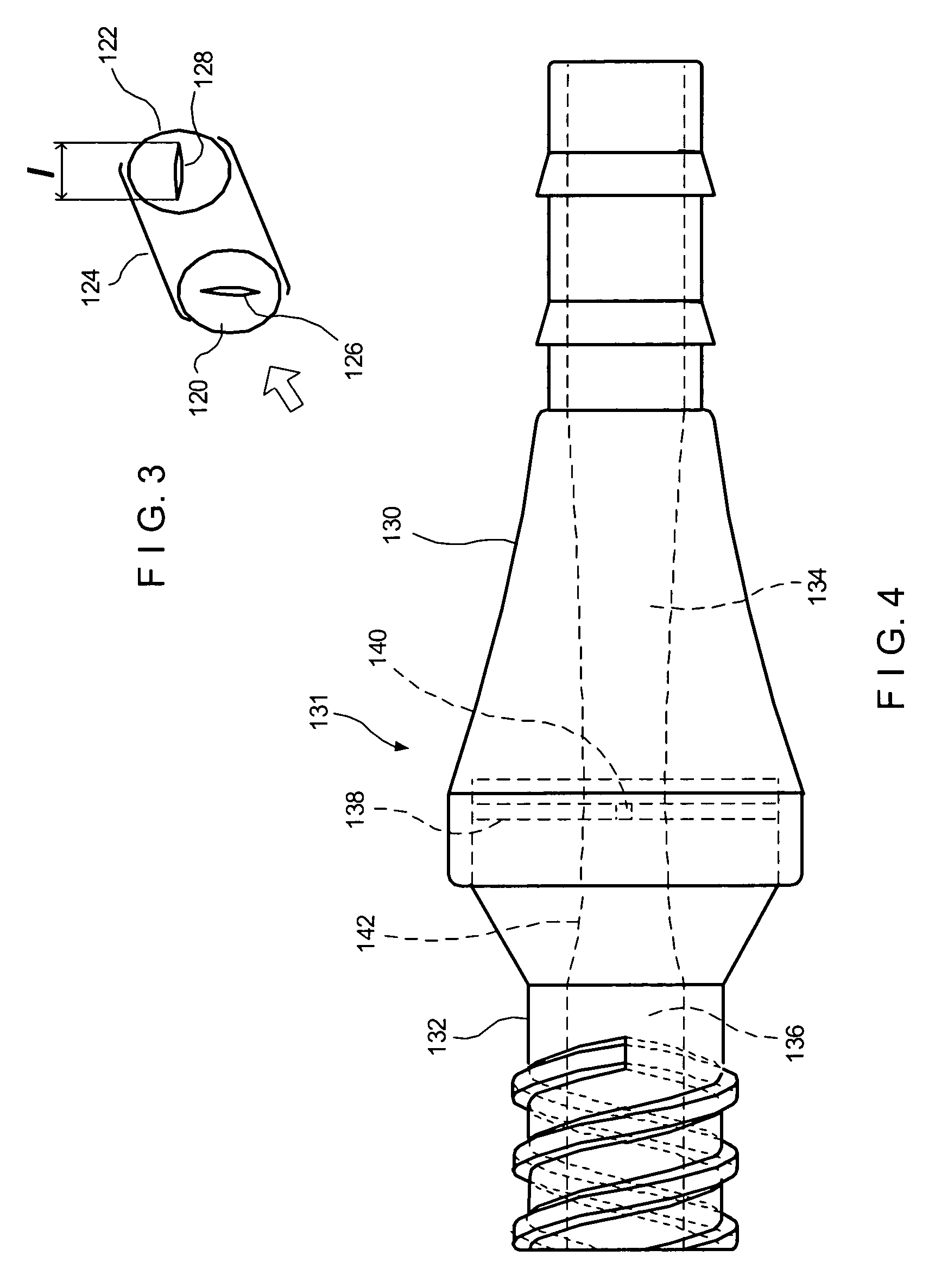
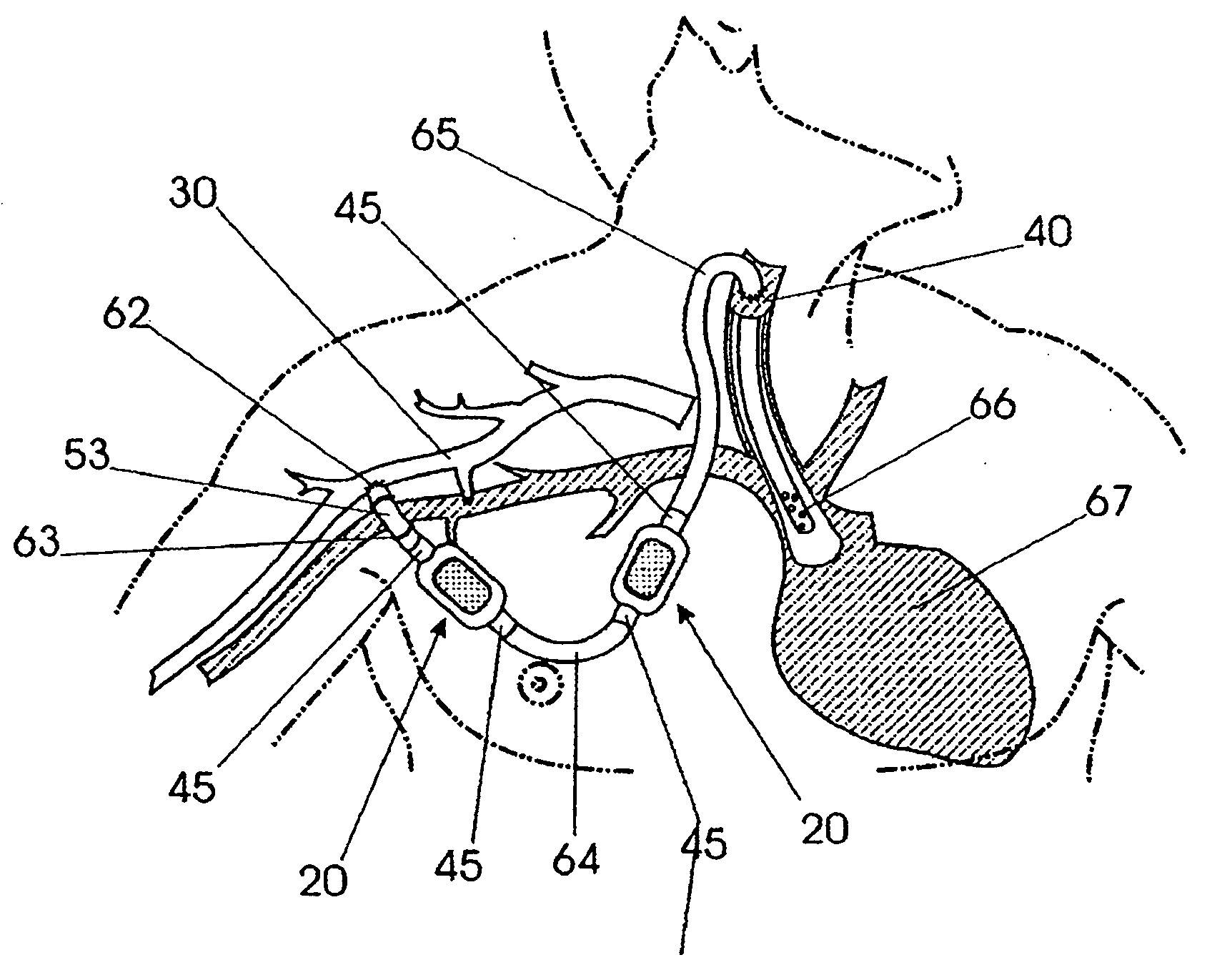
Squitieri hemodialysis and vascular access systems
InactiveUS20070123811A1Increased longevityImprove performanceOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsVenous accessHaemodialysis machine
A hemodialysis and vascular access system comprises a subcutaneous composite PTFE silastic arteriovenous fistula having an indwelling silastic venous end which is inserted percutaneously into a vein and a PTFE arterial end which is anastomosed to an artery. Access to a blood stream within the system is gained by direct puncture of needle(s) into a needle receiving site having a tubular passage within a metal or plastic frame and a silicone upper surface through which needle(s) are inserted. In an alternate embodiment of the invention, percutaneous access to a blood stream may be gained by placing needles directly into the system (i.e. into the PTFE arterial end). The invention also proposes an additional embodiment having an arterialized indwelling venous catheter where blood flows from an artery through a tube and a port into an arterial reservoir and is returned to a vein via a port and a venous outlet tube distinct and distant from the area where the blood from the artery enters the arterial reservoir. The site where blood is returned to the vein is not directly fixed to the venous wall but is free floating within the vein. This system provides a hemodialysis and venous access graft which has superior longevity and performance, is easier to implant and is much more user friendly.
Owner:HEMOSPHERE
Catheters and related devices for forming passageways between blood vessels or other anatomical structures
InactiveUS8753366B2Precise rotation controlPrecise positioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasAnatomical structuresDistal portion
The inventions described in this patent application include i) a torqueable introducer sheath which is useable in conjunction with a transvascular passageway forming catheter to effect precise rotational control of the catheter; ii) an anchorable guide catheter which is useable in conjunction with an intravascular imaging catheter and a transvascular passageway-forming catheter to effect precise positioning and aiming of the passageway-forming catheter; iii) a passageway forming catheter having a torqueable proximal portion to facilitate precise rotational positioning of the distal portion of the catheter; iv) a deflectable-tipped passageway forming catheter, v) various markers and other apparatus useable in conjunction with any of the passageway-forming catheters to facilitate precise positioning and aiming of the catheter, and vi) an apparatus which may be formed within a catheter to prevent a member, apparatus of flow of material from being inadvertently advanced through a lumen of the catheter.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
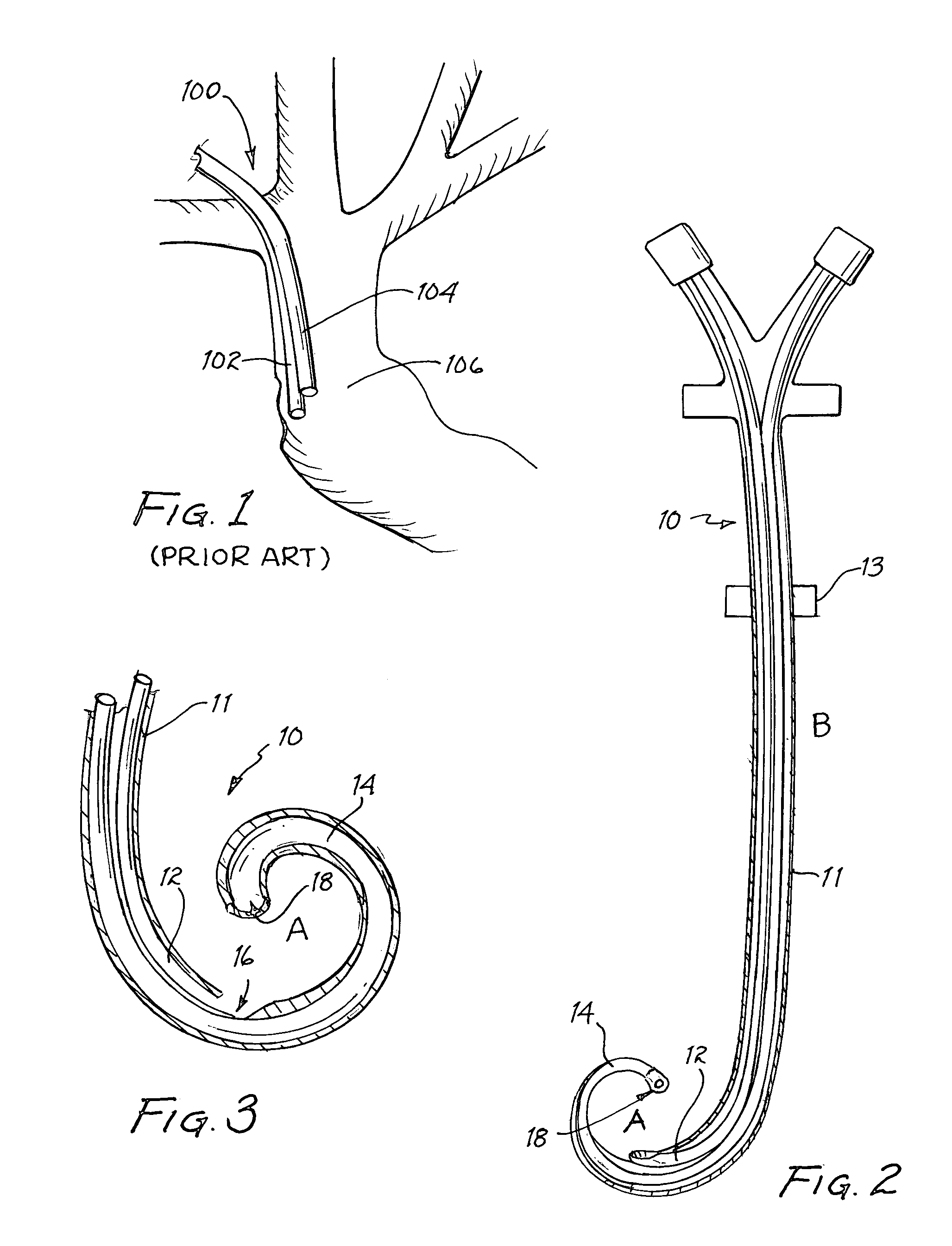
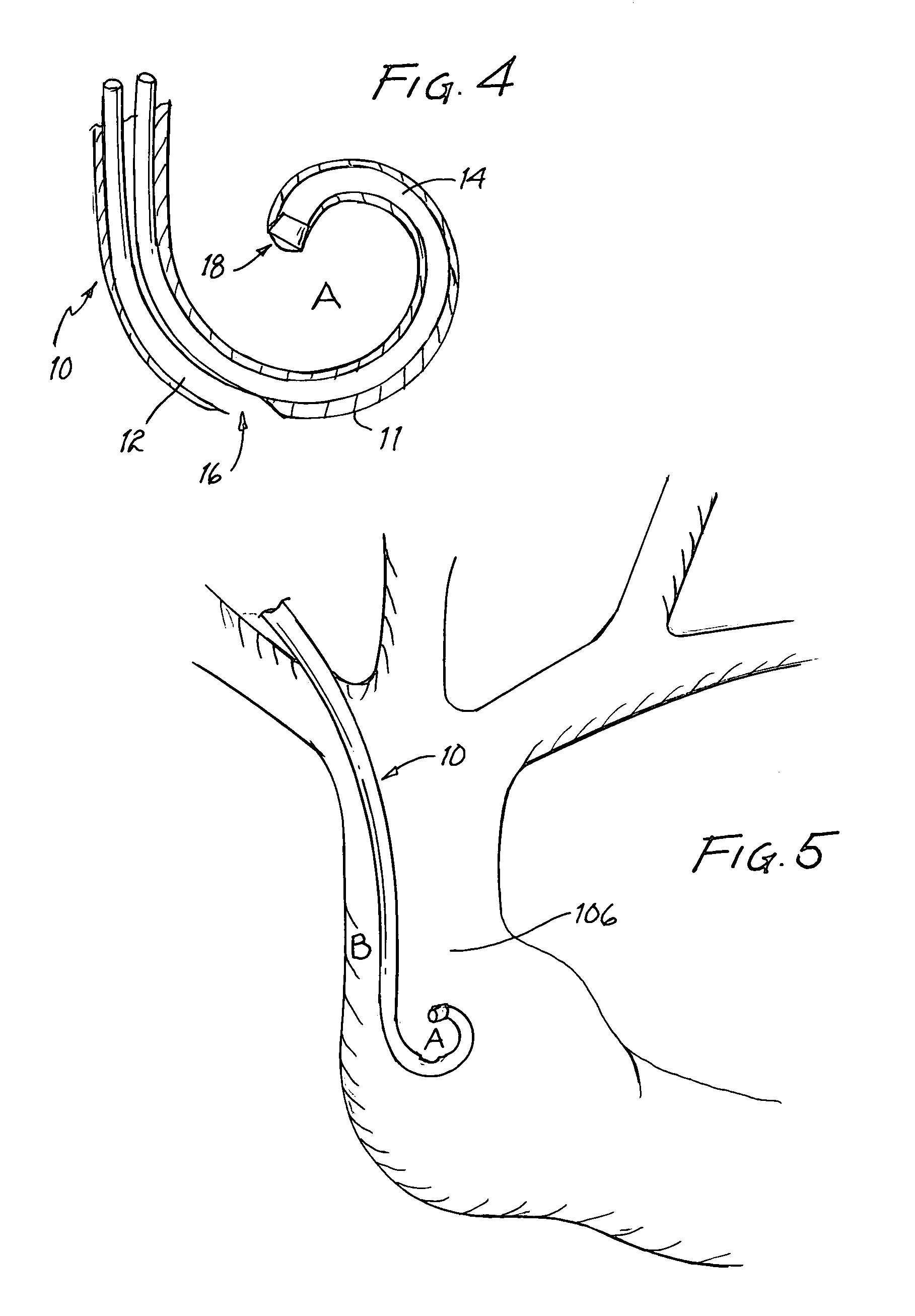
Vascular access catheter having a curved tip and method
InactiveUS6997894B2Reduces risk of occlusionReduce riskMulti-lumen catheterOther blood circulation devicesVeinThree vessels
A vascular access catheter having a curved tip. Preferably, the curved tip is formed into a substantially pig-tail shape. Where the catheter is of the double lumen variety, the terminus of the draw lumen is at the end of the curved tip, and thus is shielded from direct contact with a side wall of the blood vessel into which the catheter is inserted. This configuration lessens risks associated with prior art vascular access catheters, including occlusion of the catheter and damage to the vein wall.
Owner:CARESIO JOSEPH F
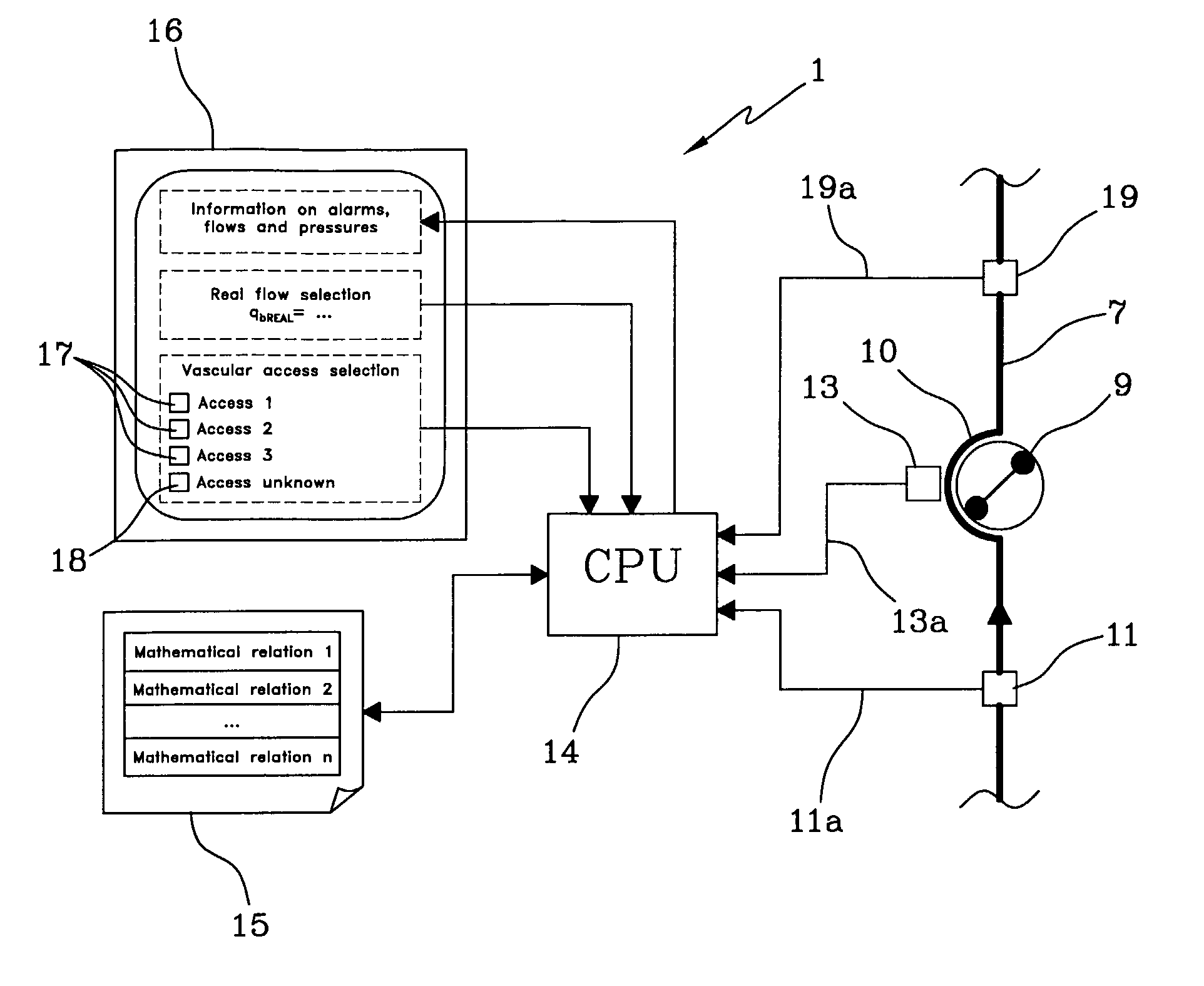
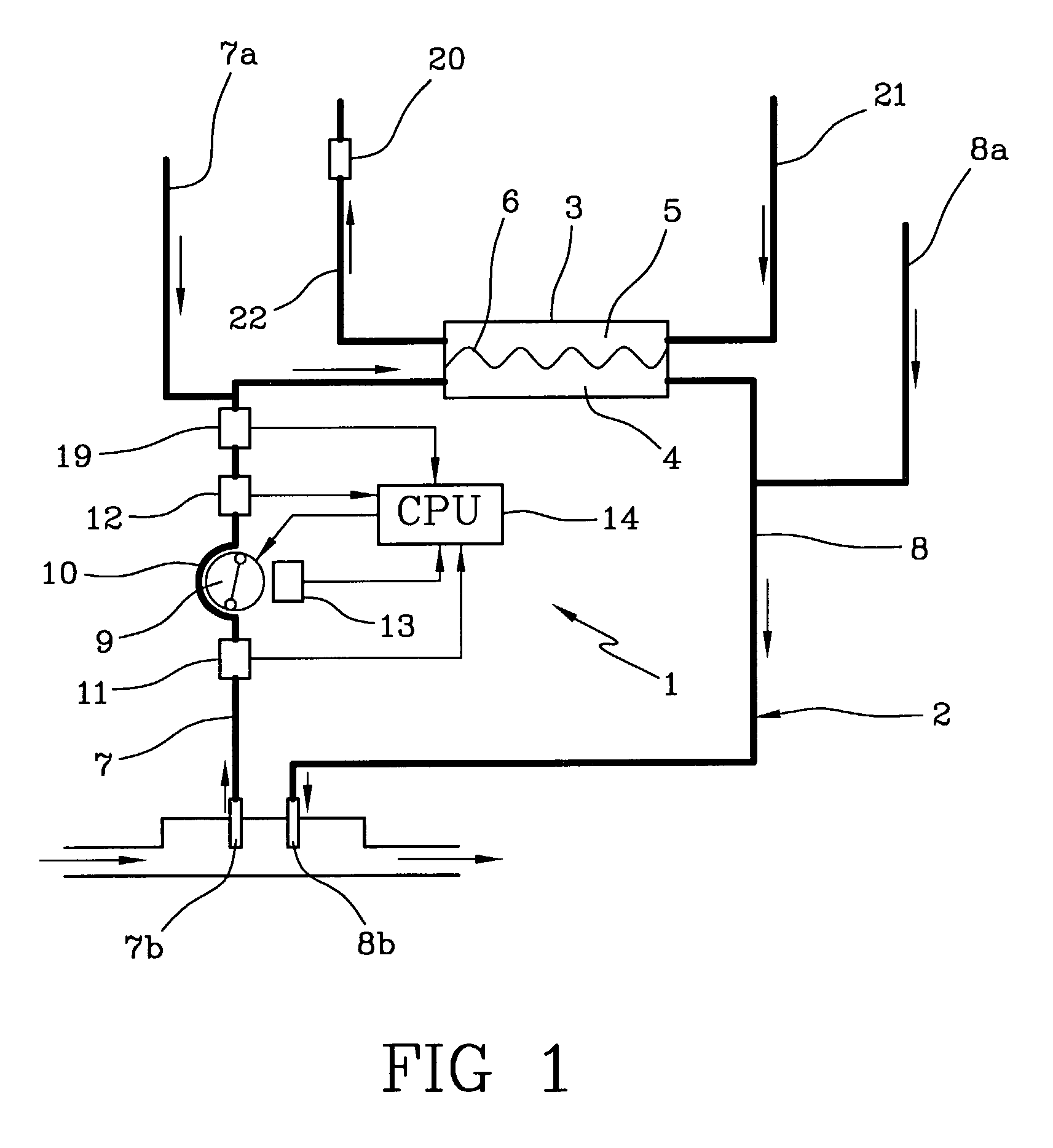
Apparatus for controlling blood flow in an extracorporeal circuit
ActiveUS7794419B2Semi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionExtracorporeal circulationAngular velocity
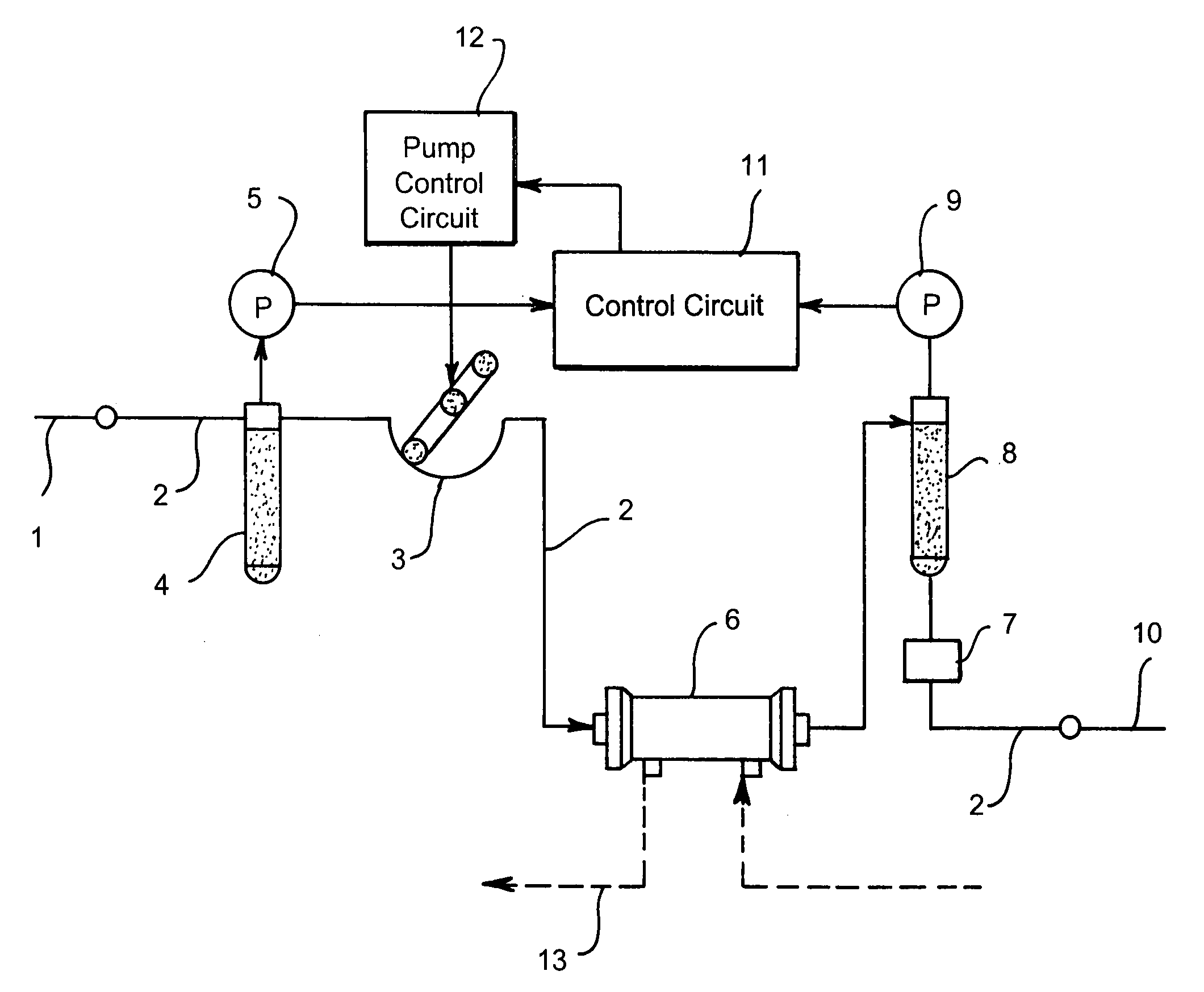
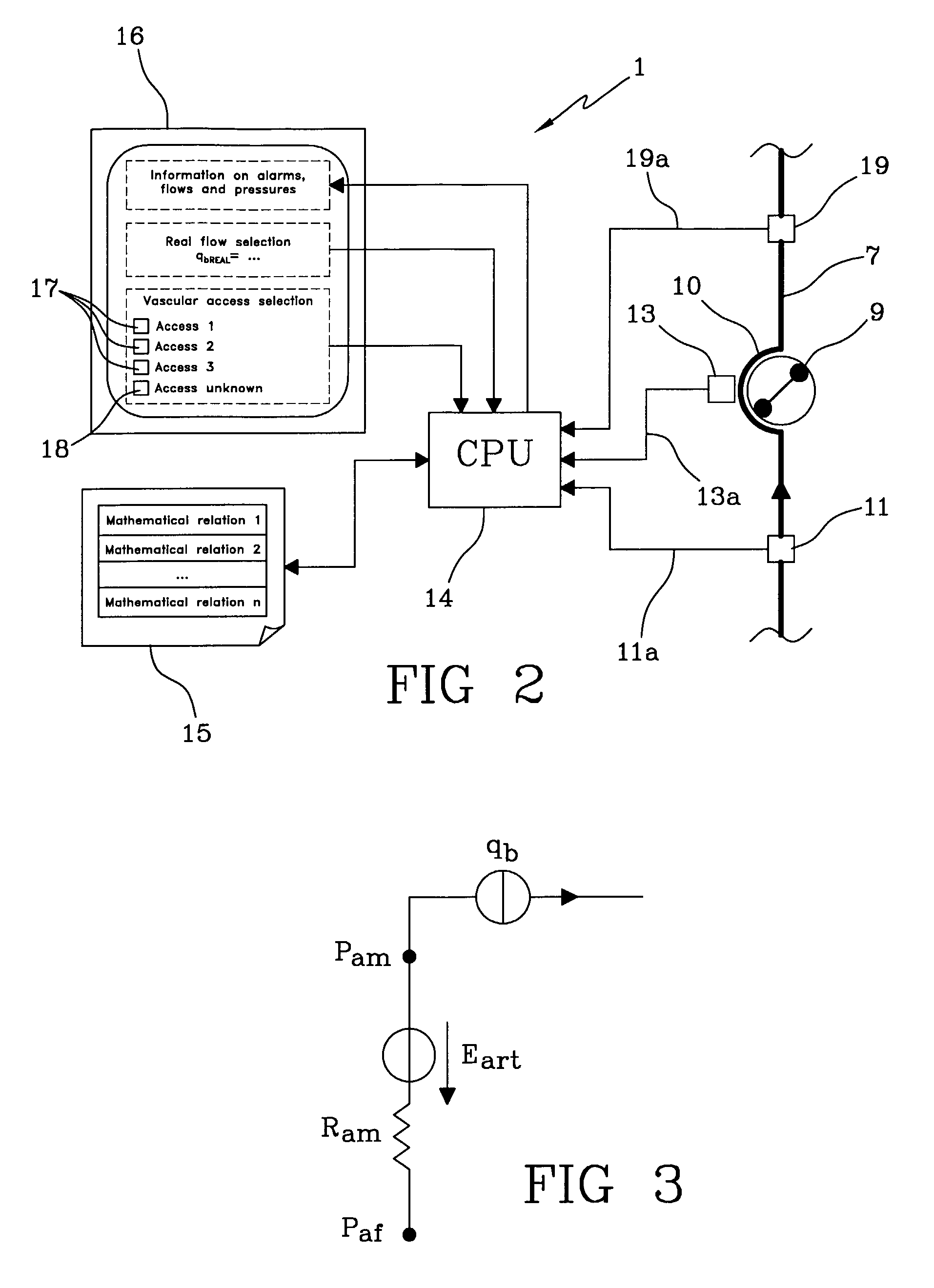
The apparatus for blood flow control in an extracorporeal circuit comprises: a user interface for setting a desired blood flow value (qbREAL) and a datum relating to the vascular access, a memory for recording a plurality of mathematical relations having mathematical expressions relating to the vascular access organ to be used, and a control unit. The control unit identifies the vascular access, selects, from among the plurality of mathematical relations present in the memory, a relation which corresponds to the vascular access identified, and calculates, as a mathematical function of the set value for the desired flow (qbREAL), a value at which to set the angular velocity of the pump associated to the extracorporeal circuit and / or a theoretical value of the arterial pressure upstream of the pump.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Total vascular occlusion treatment system and method
InactiveUS20080033423A1Avoid resistanceSufficient torqueElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingActuatorConductor Coil
Owner:EMERGE MEDSYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com