Patents
Literature
76 results about "Lead Placement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
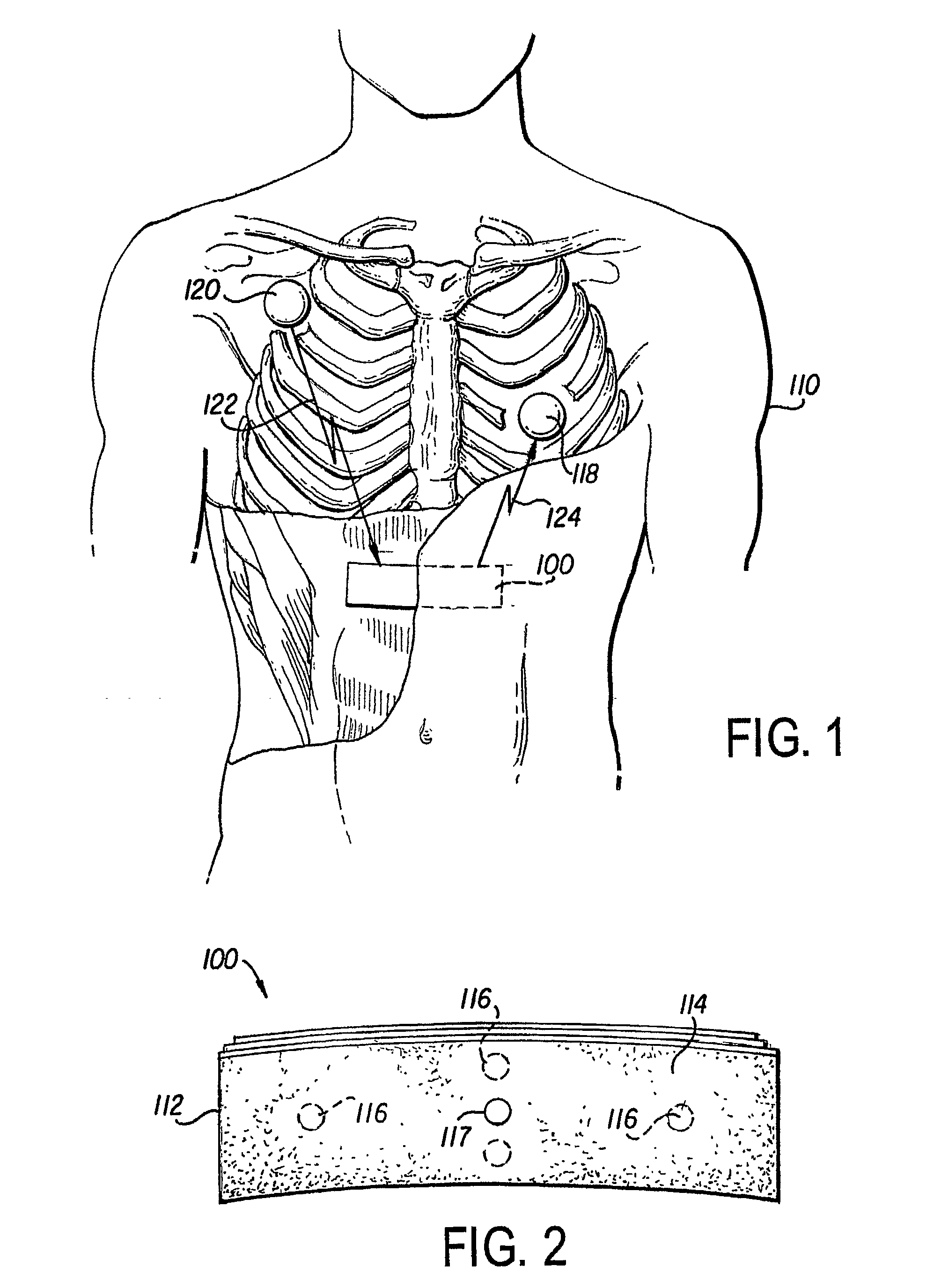
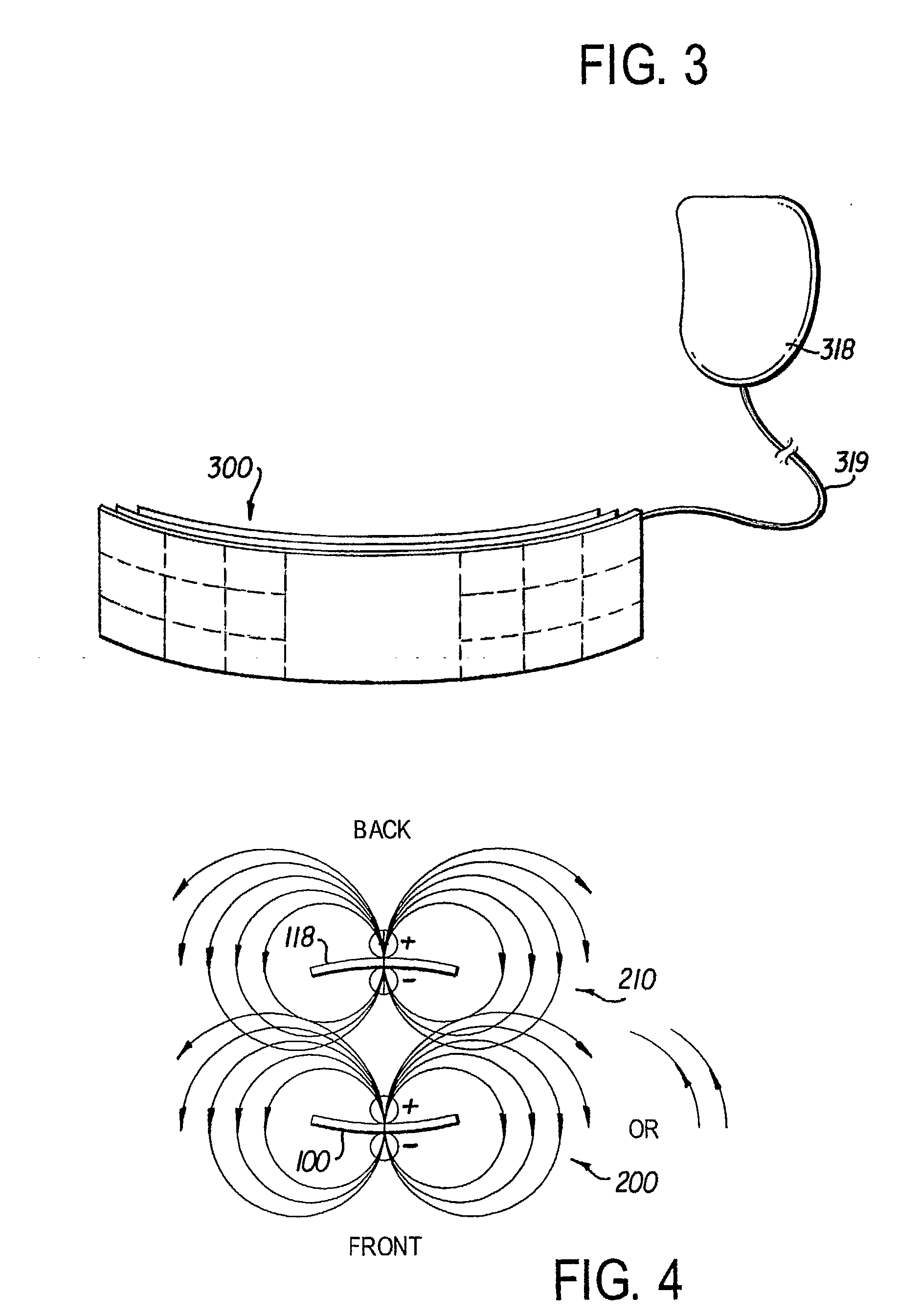
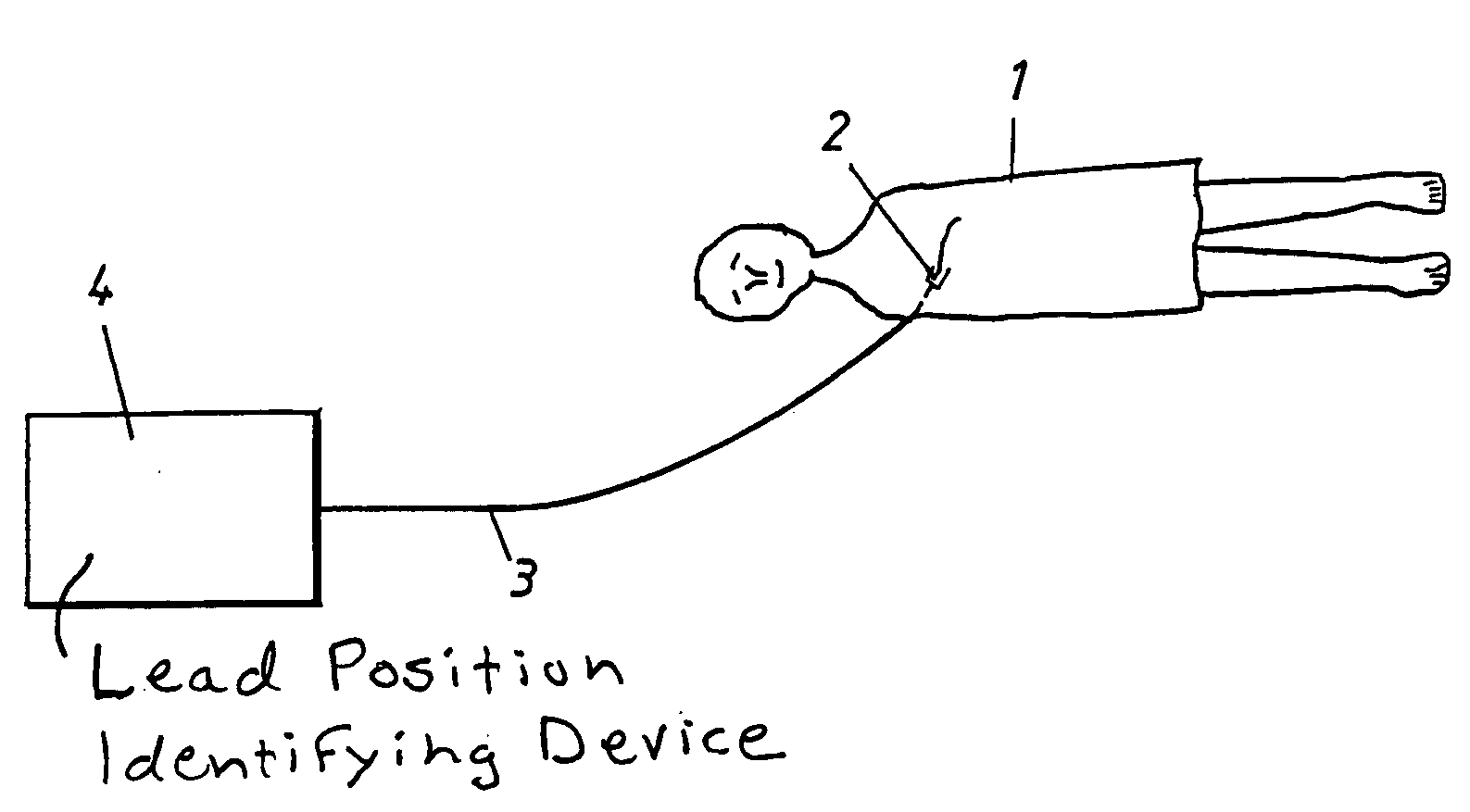
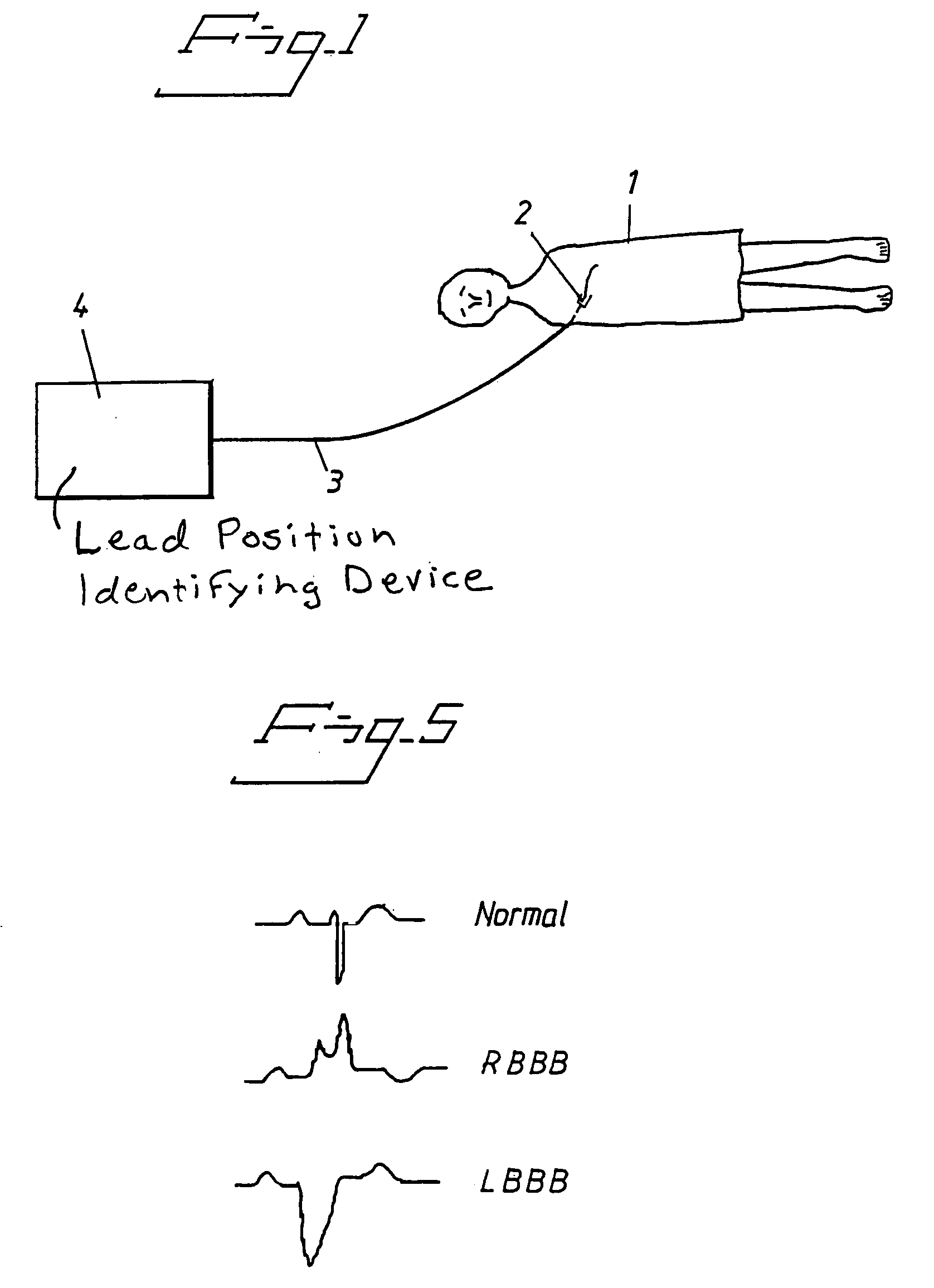
The spatial property of the way in which an electrocardiogram lead is placed on the body.
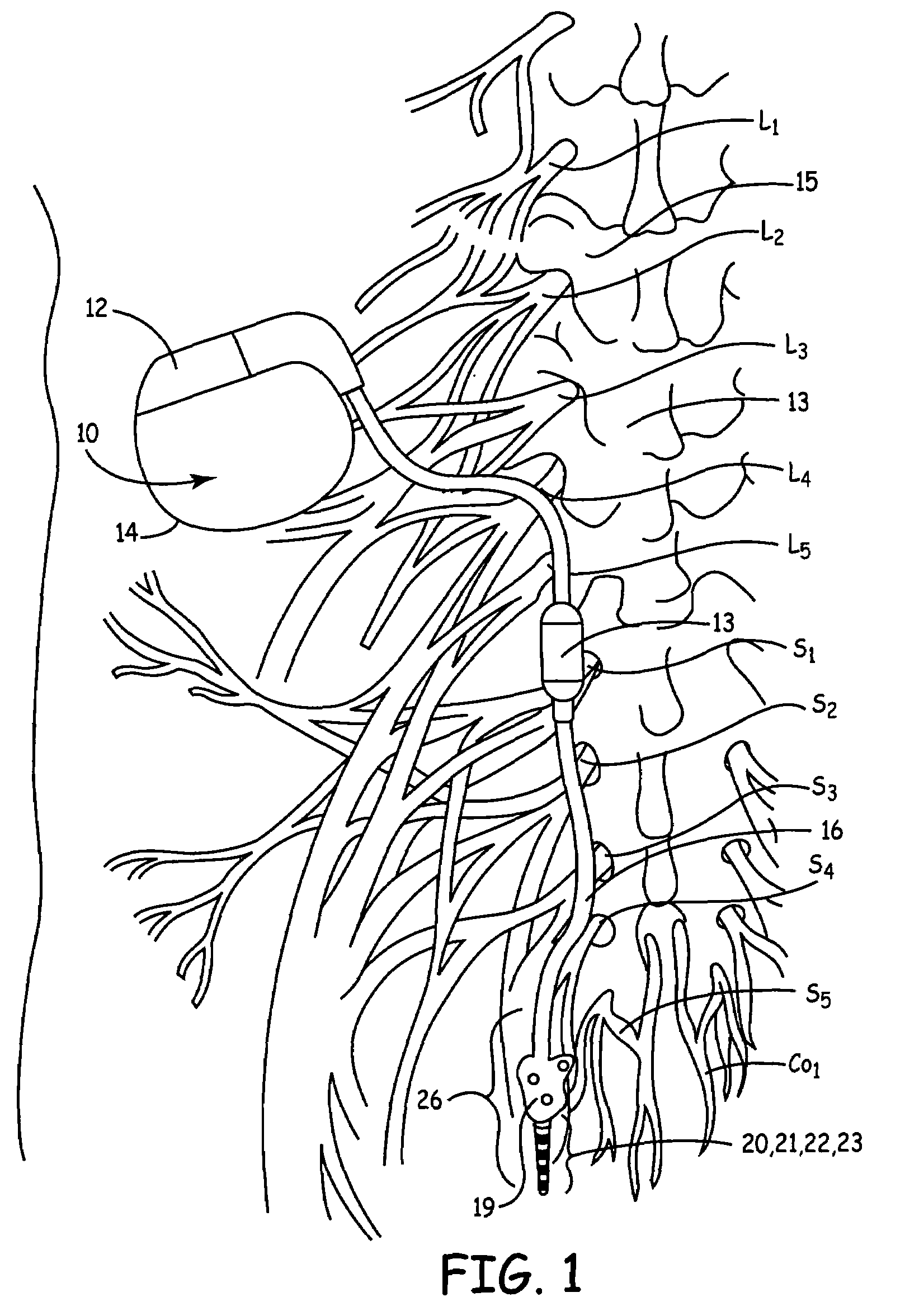
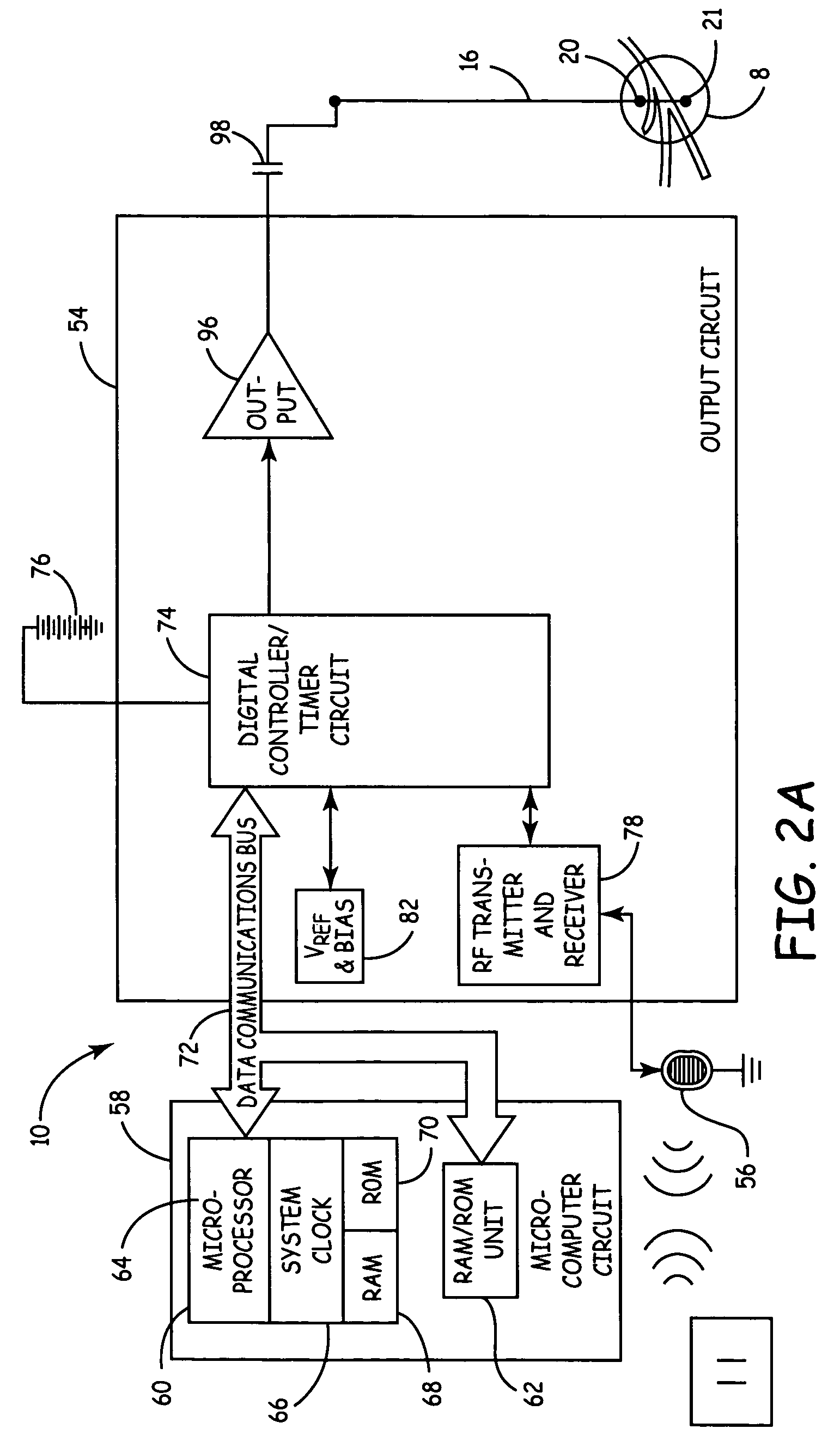
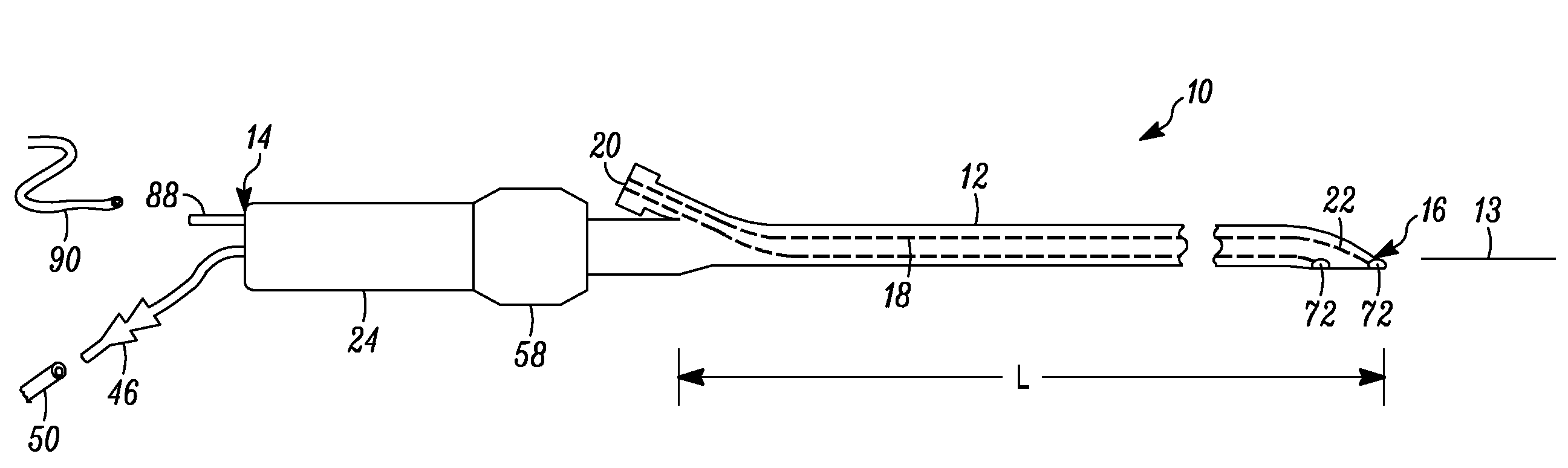
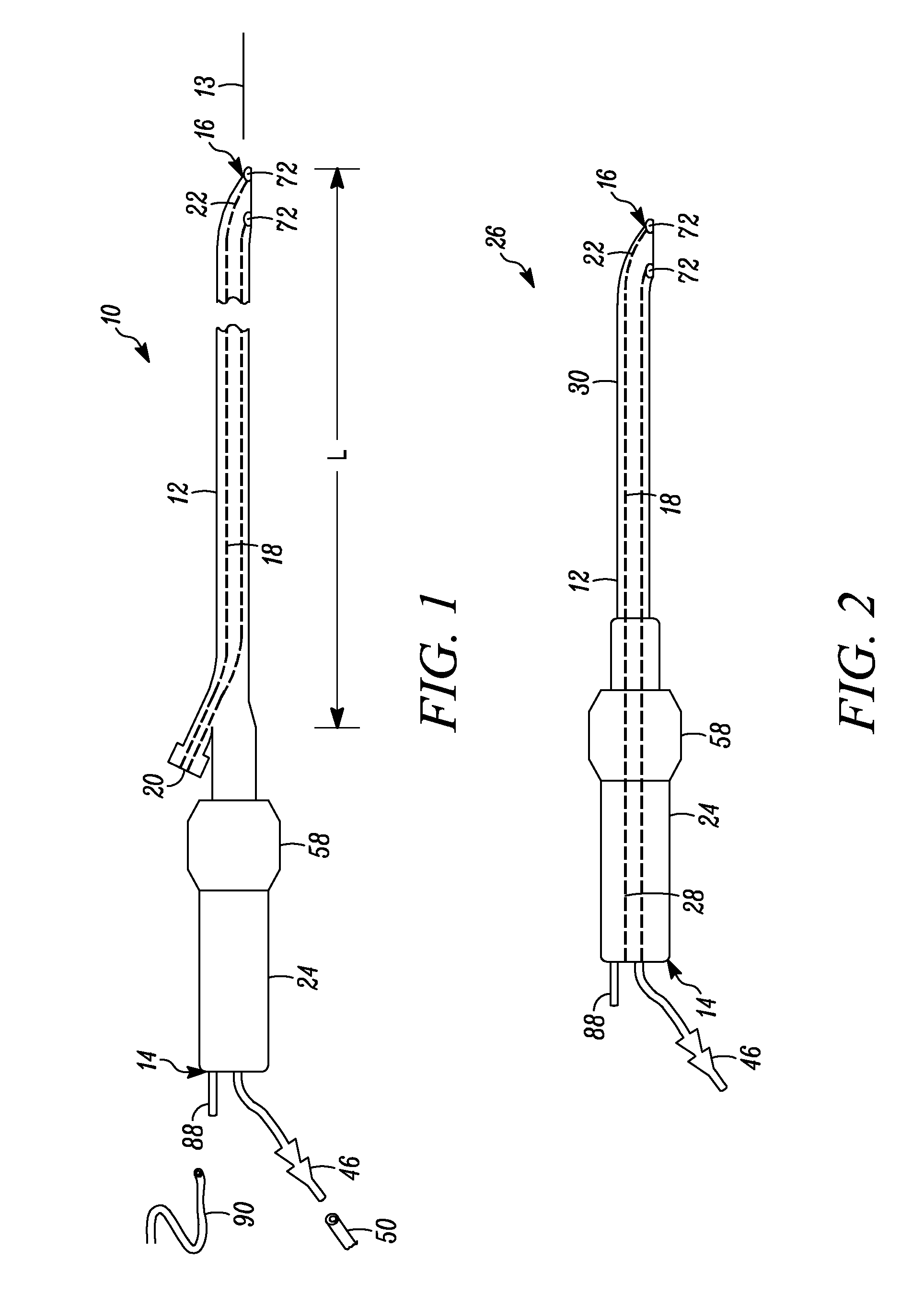
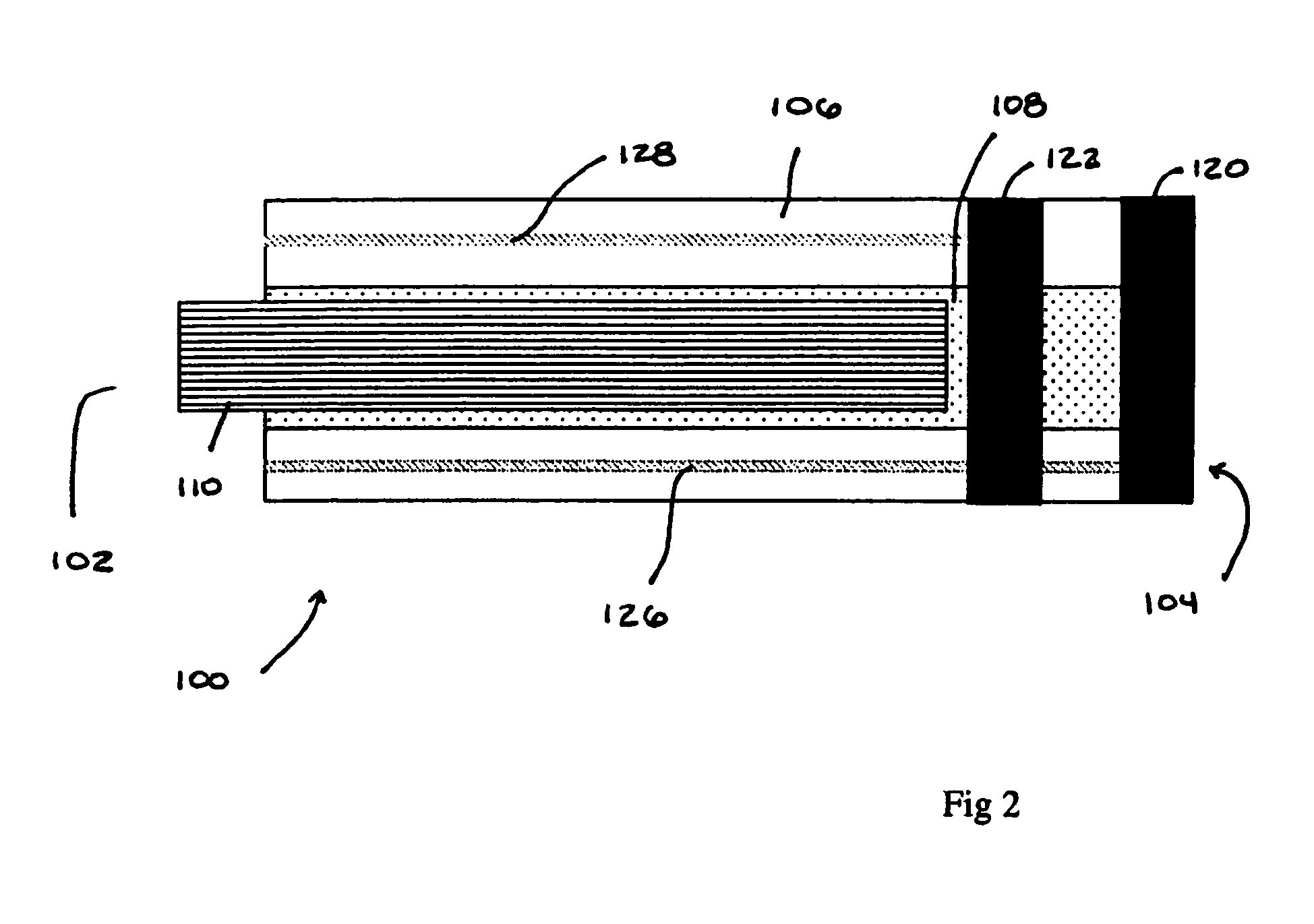
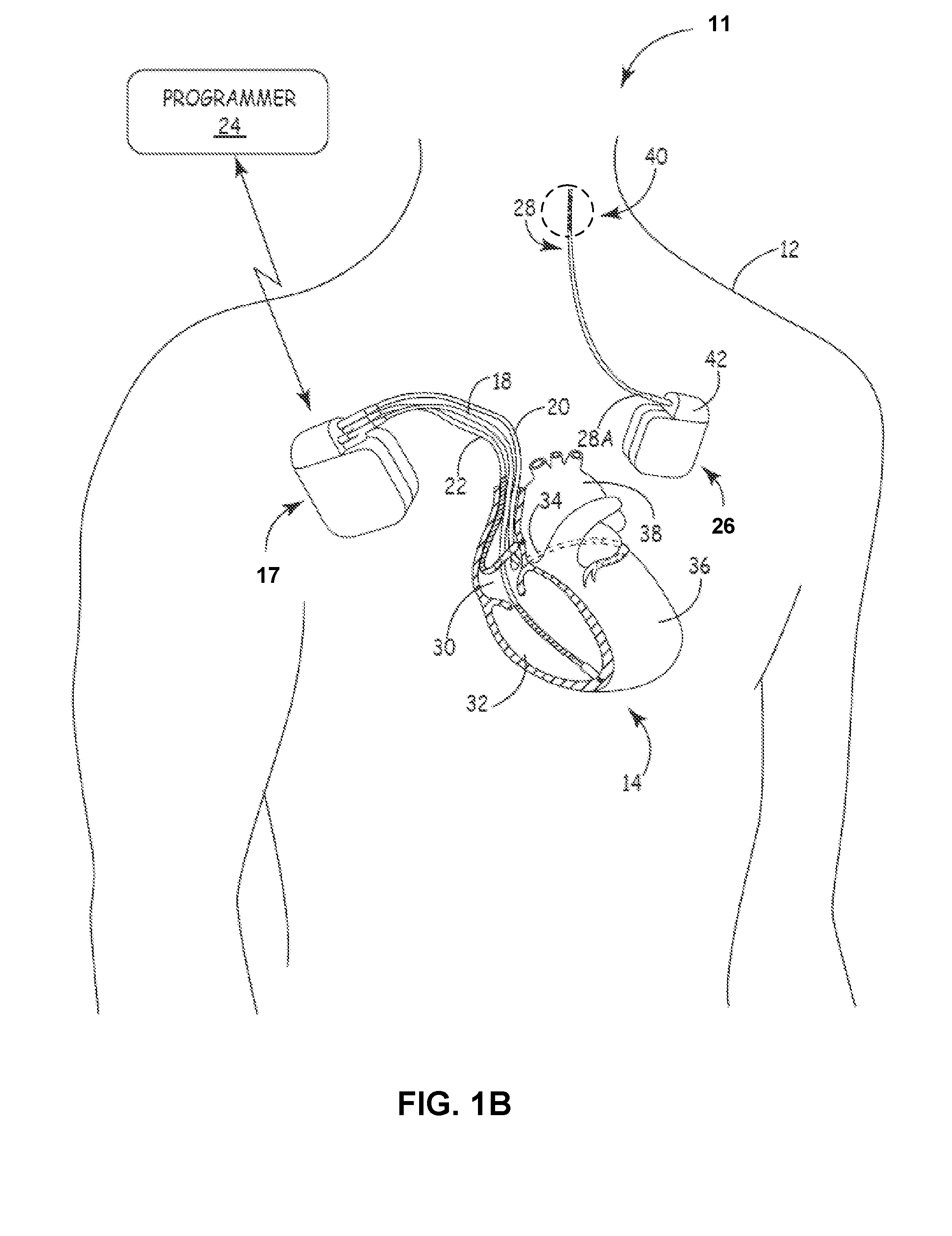
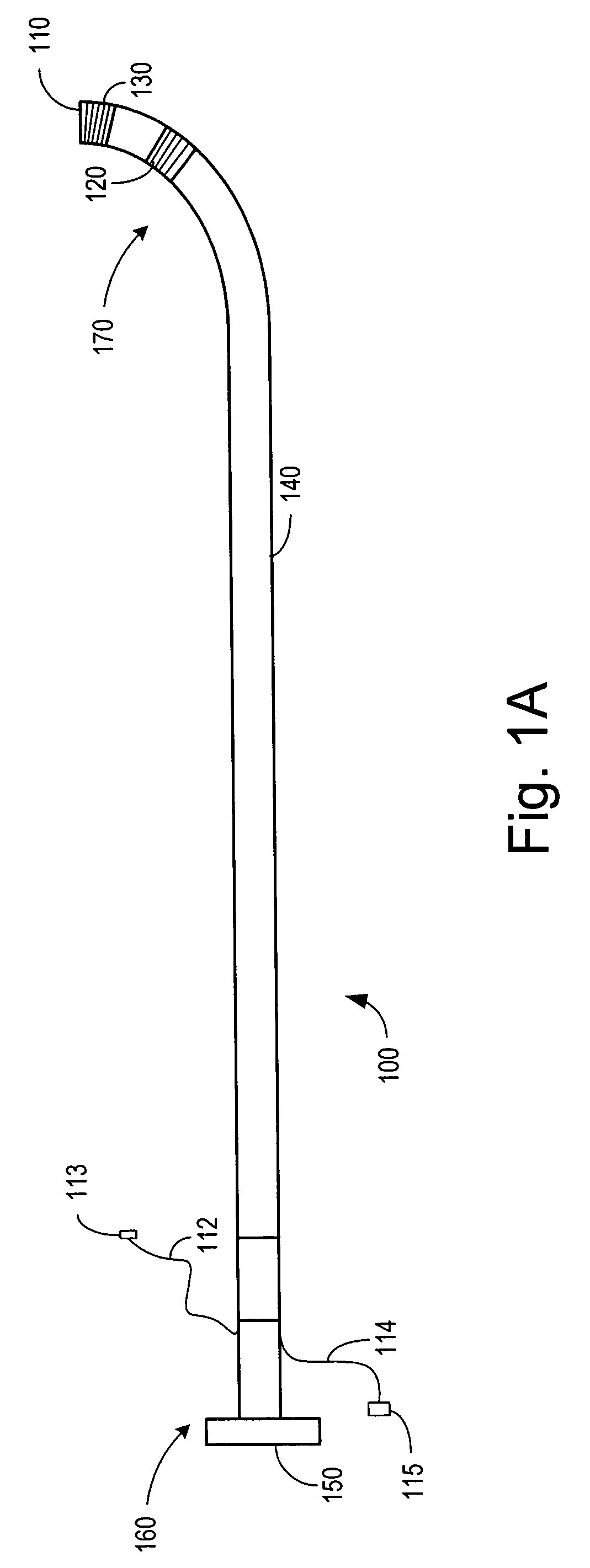
Neurostimulating lead
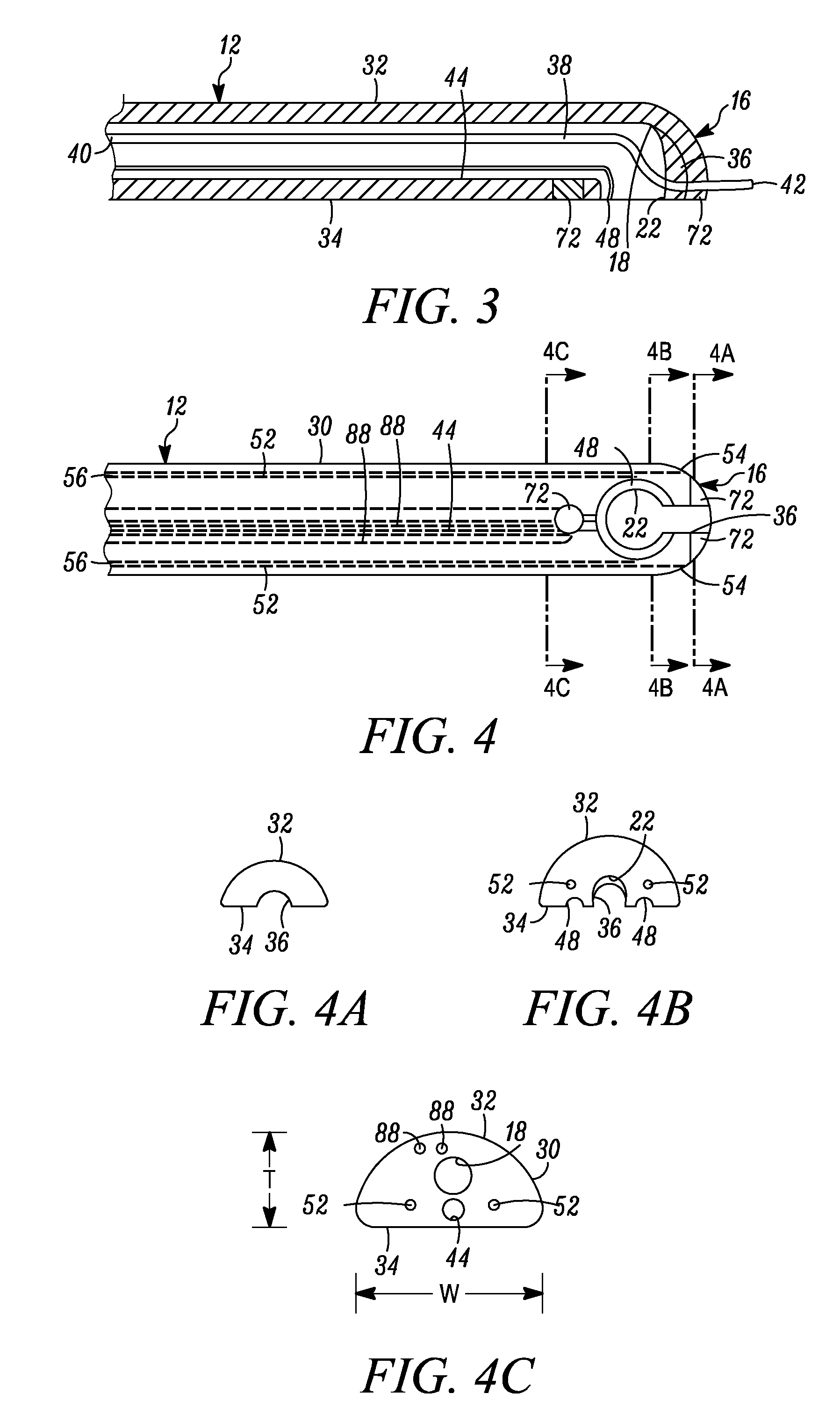
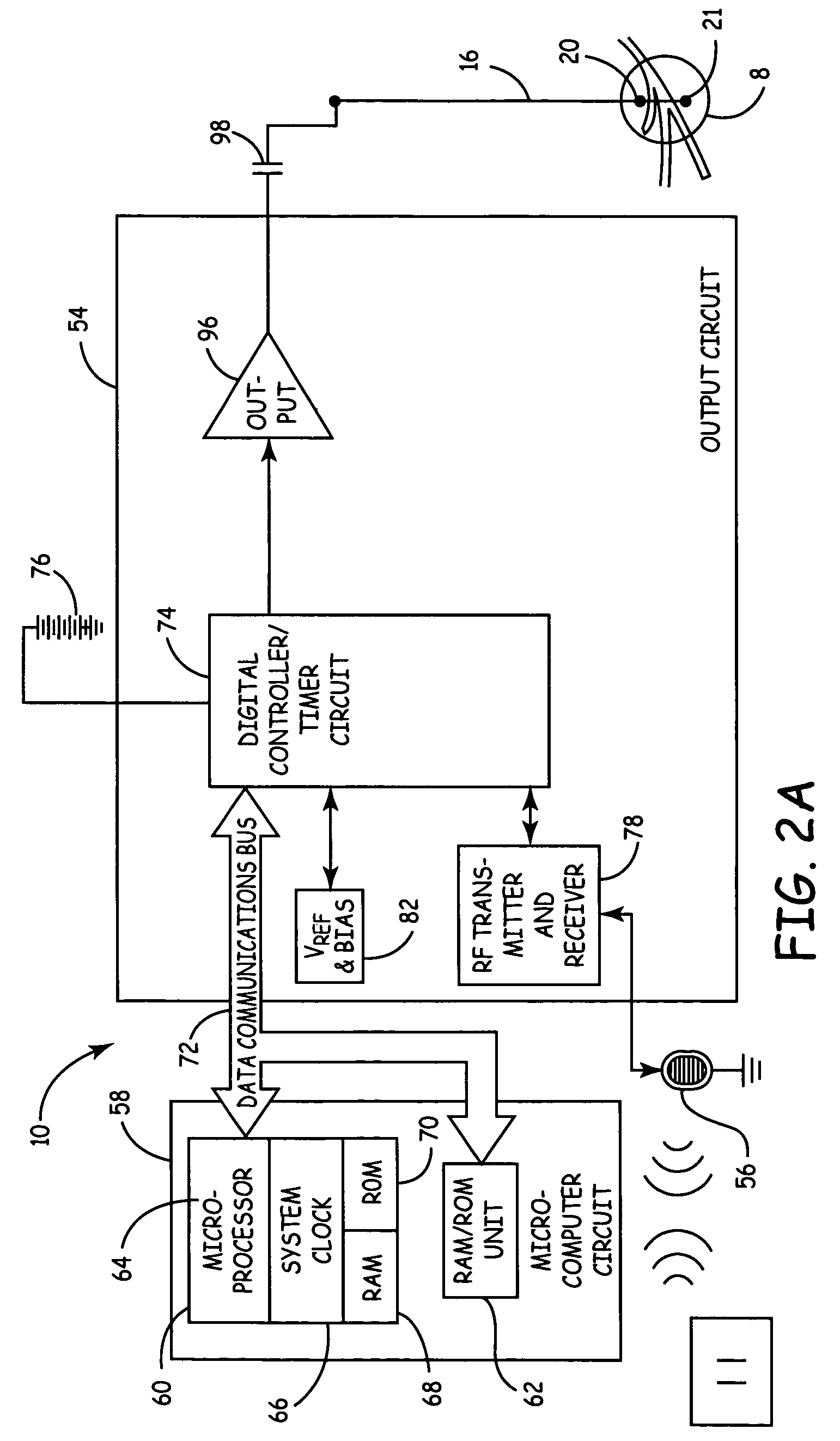
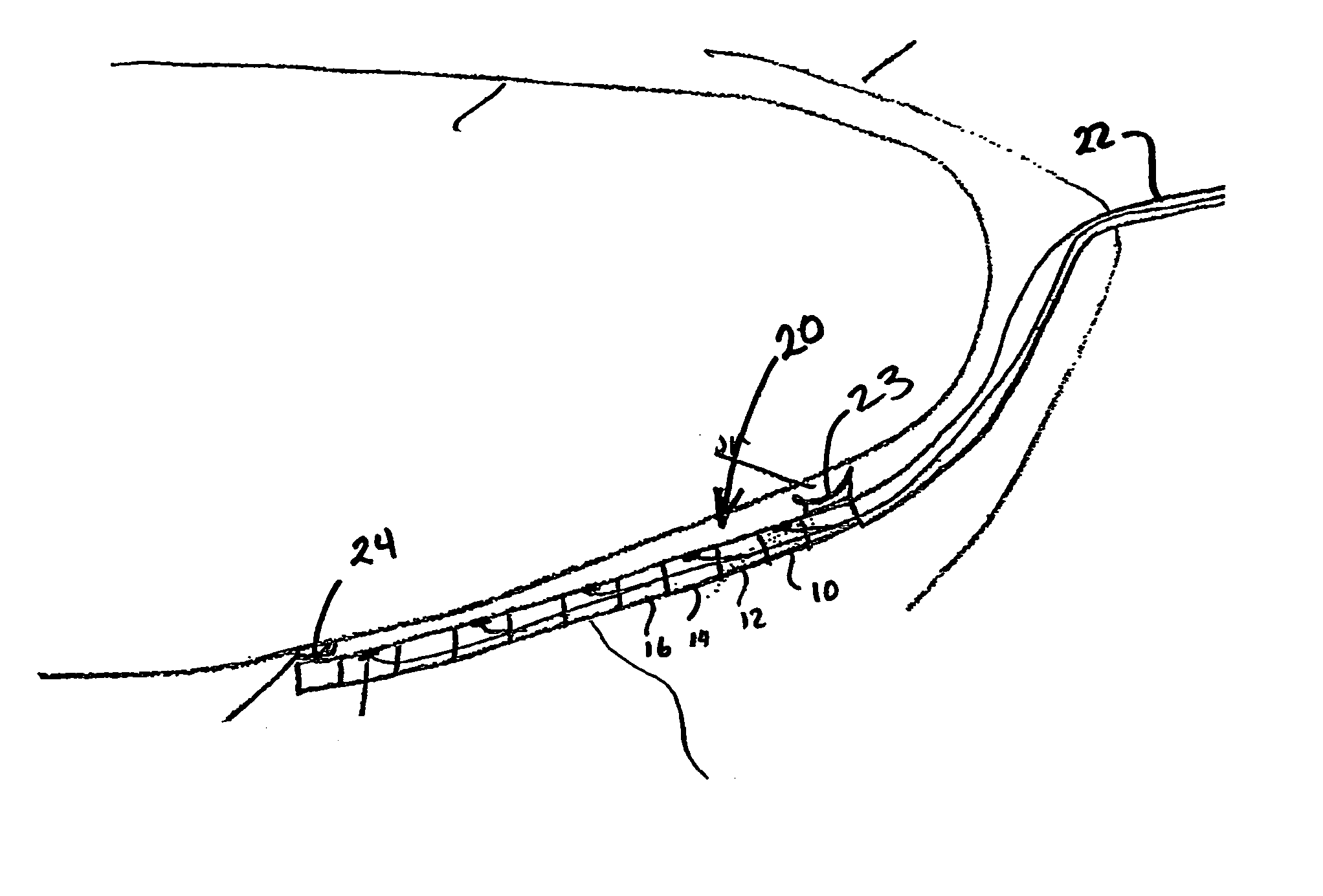
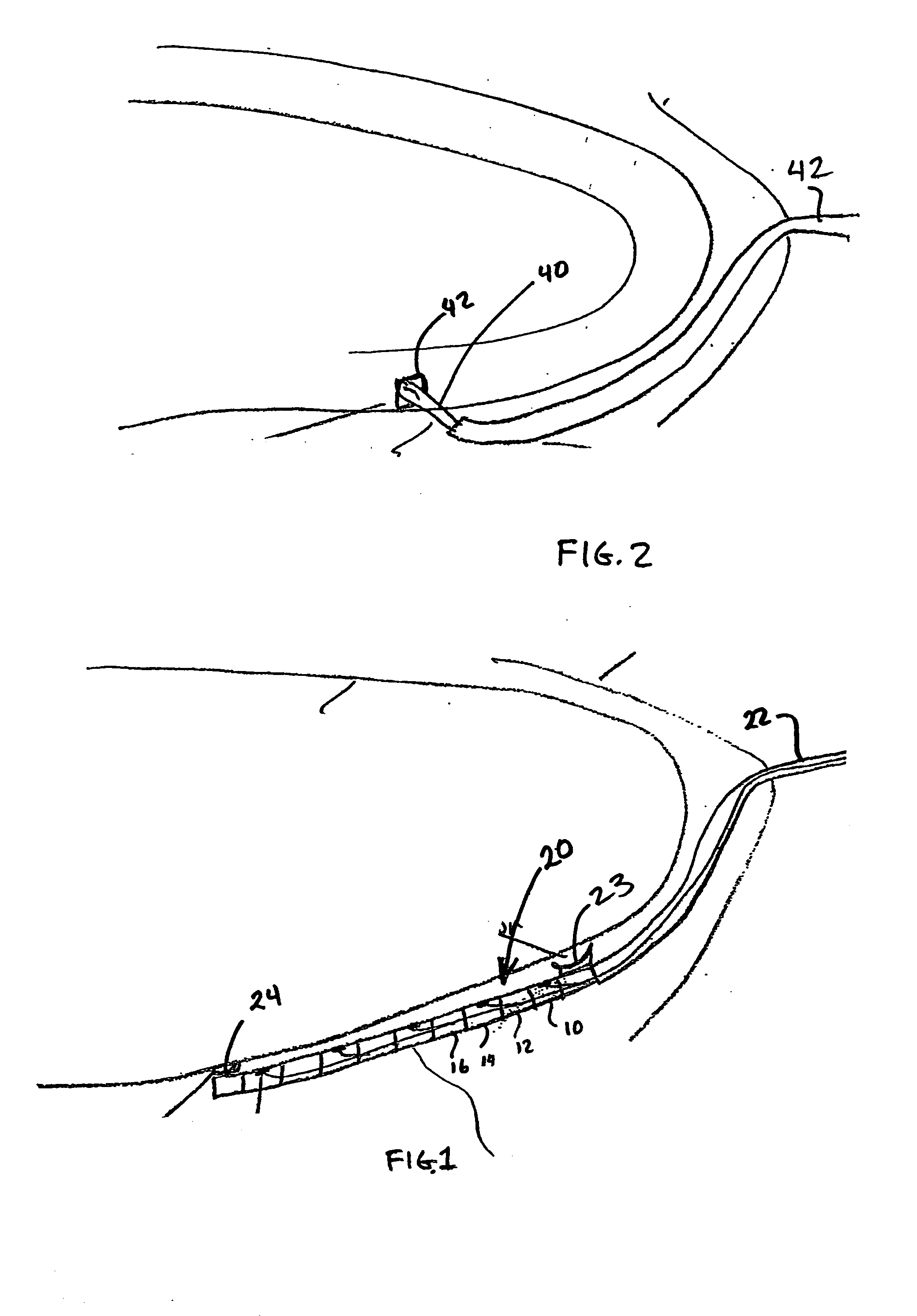
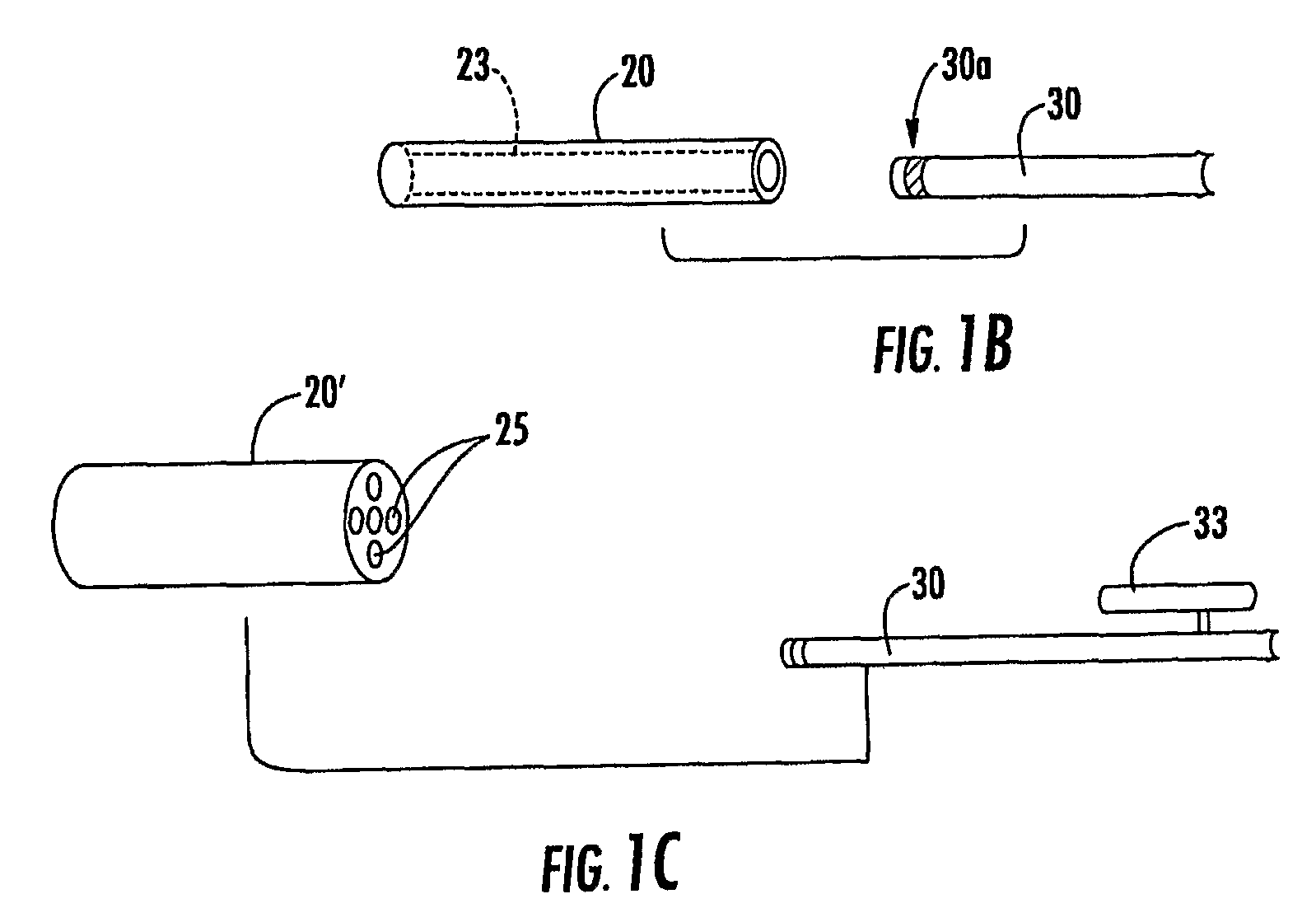
A neurostimulating lead is provided for use in stimulating the spinal chord, spinal nerves, or peripheral nerves or for use in deep brain stimulation that comprises an elongated, flexible lead having improved steerability properties. The lead includes a plurality of thin-film metal electrodes connected by conductors embedded within the wall of the lead to electrical contacts at the proximal end of the lead. The lead is further designed to include an internal lumen for use with a guidewire in an over-the-wire lead placement.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
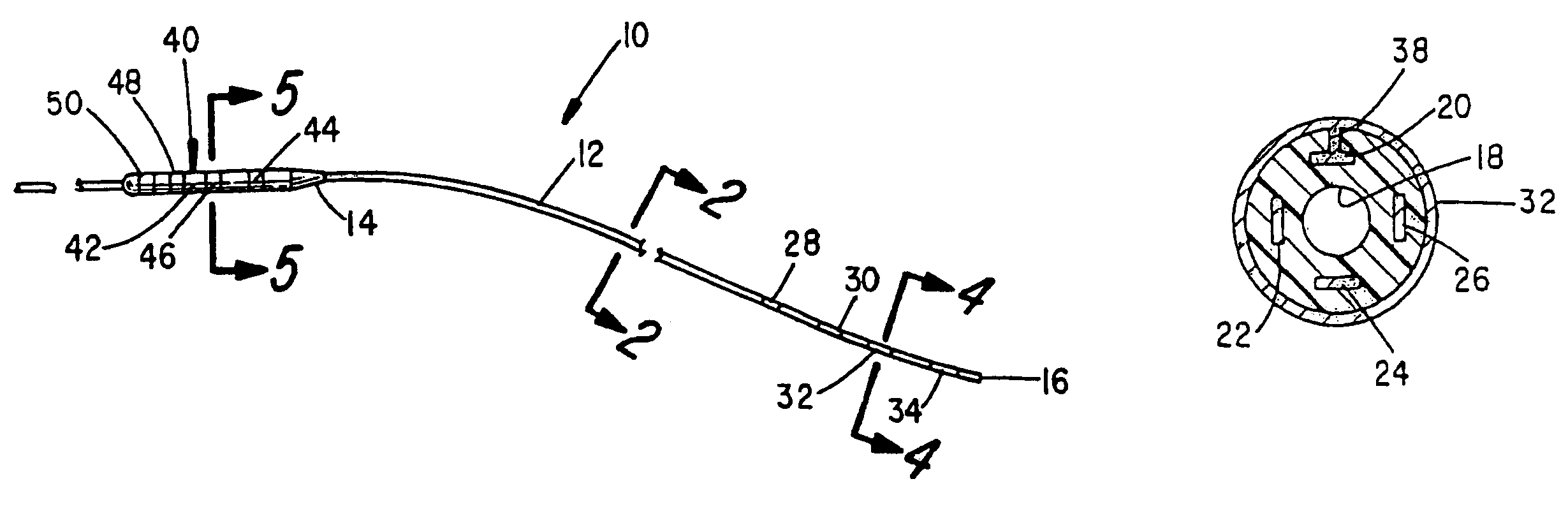
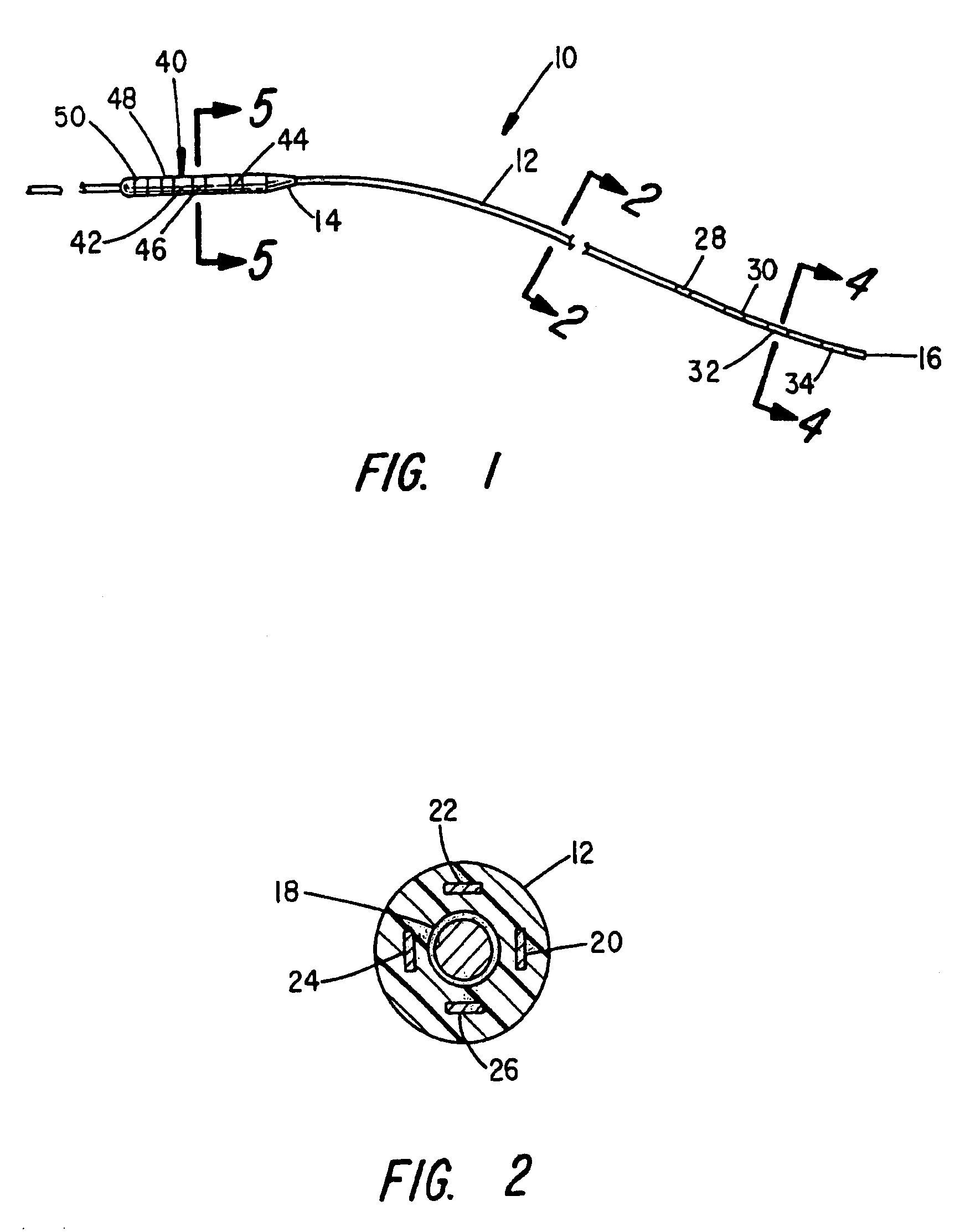
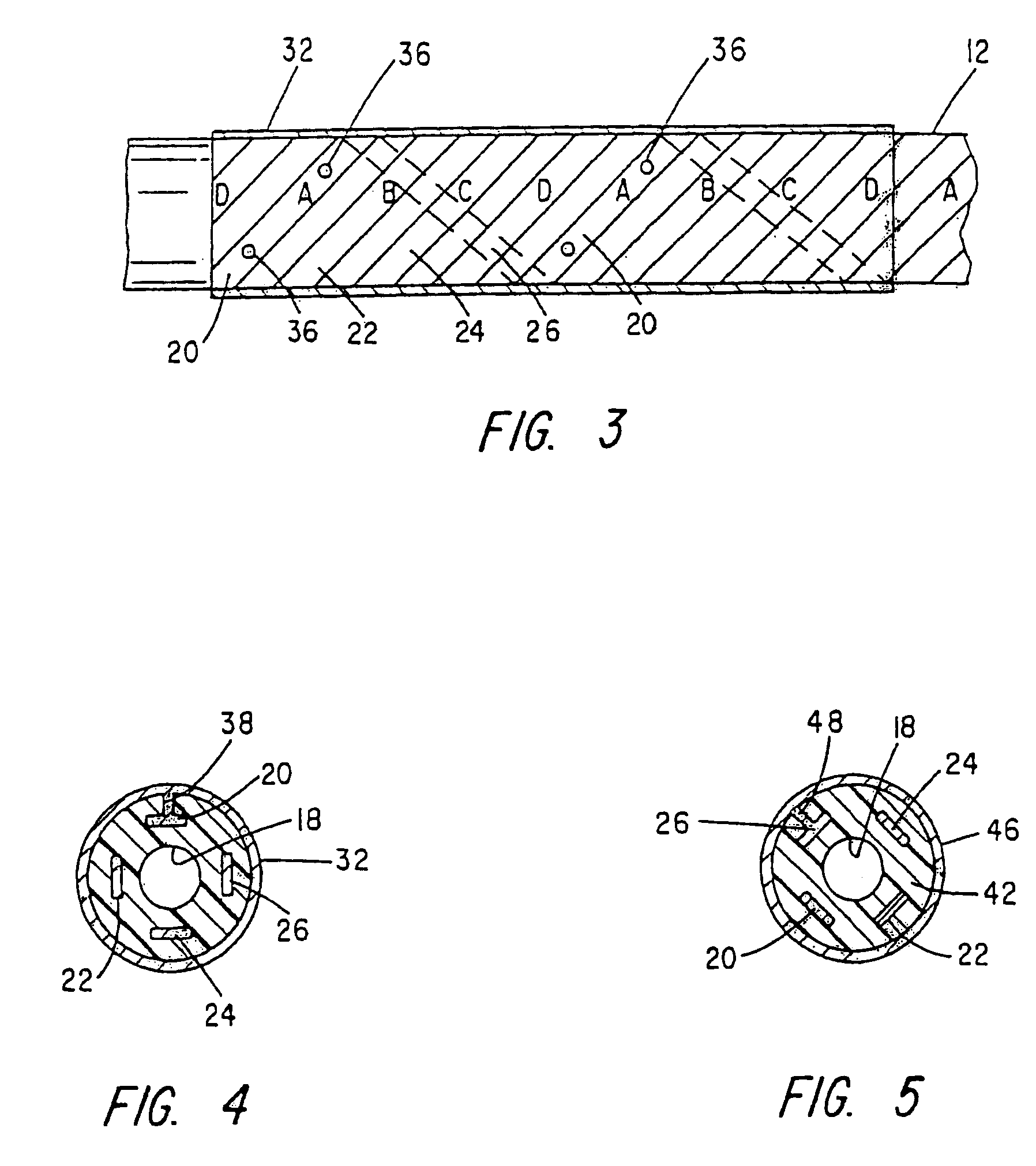
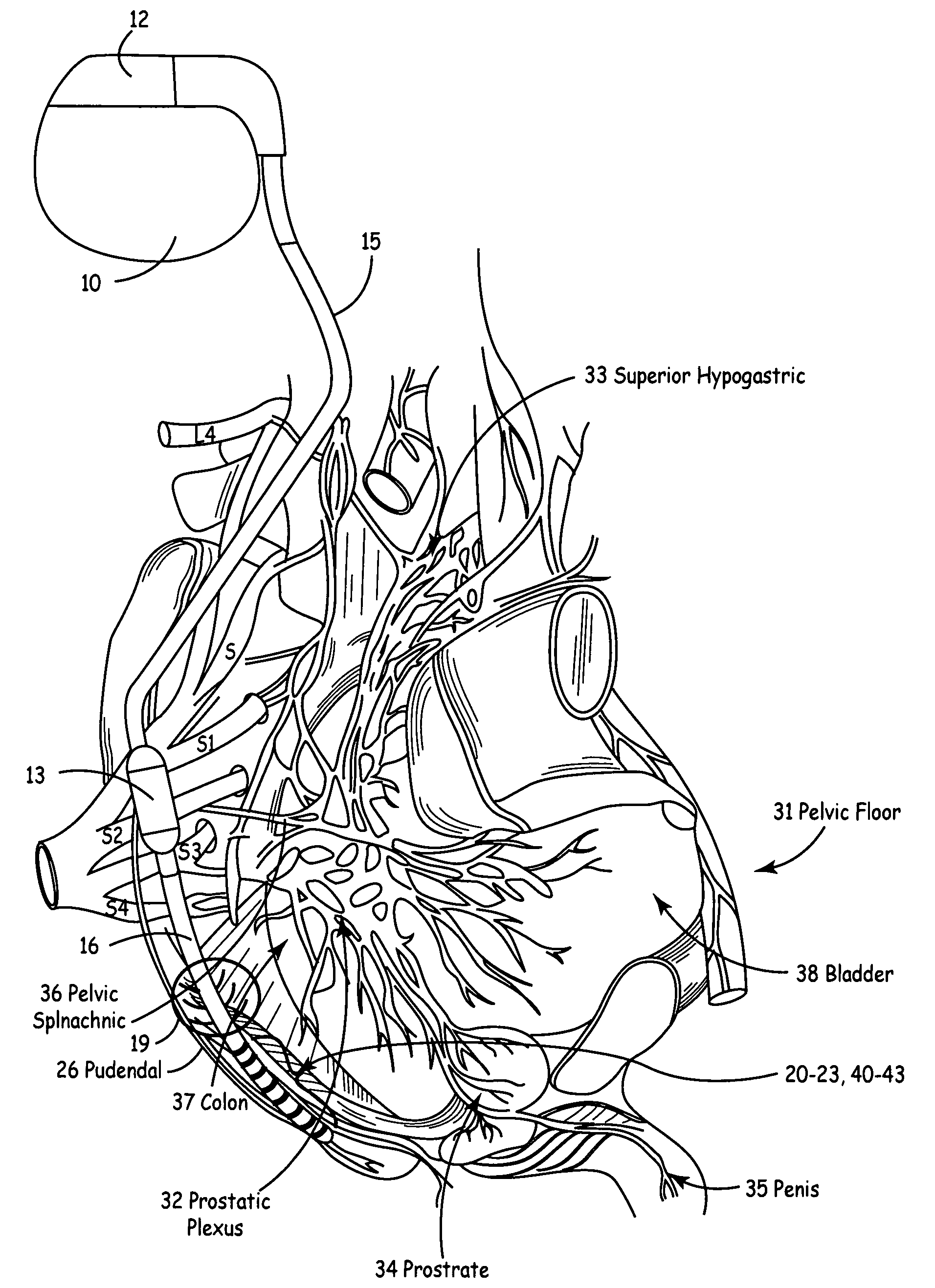
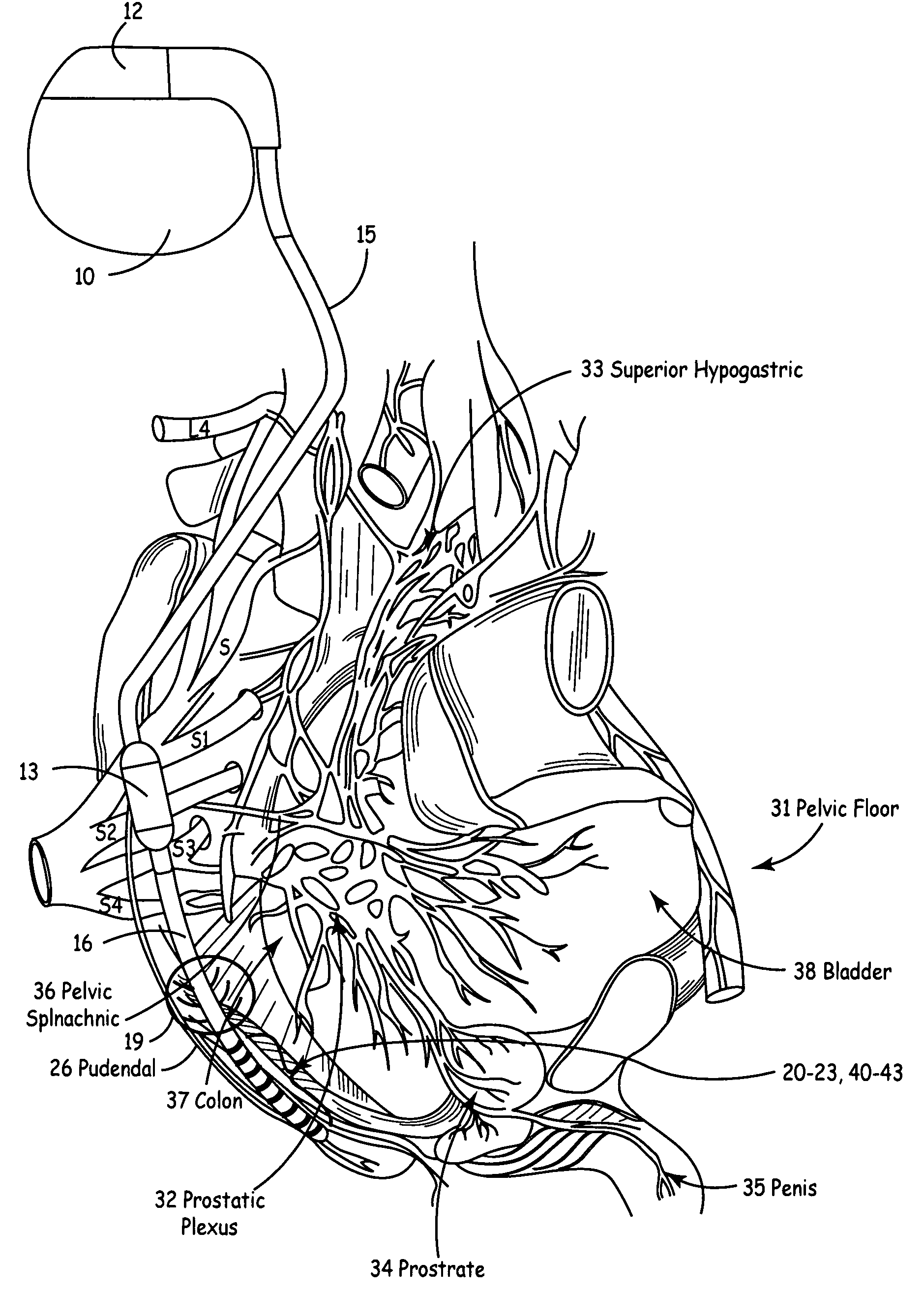
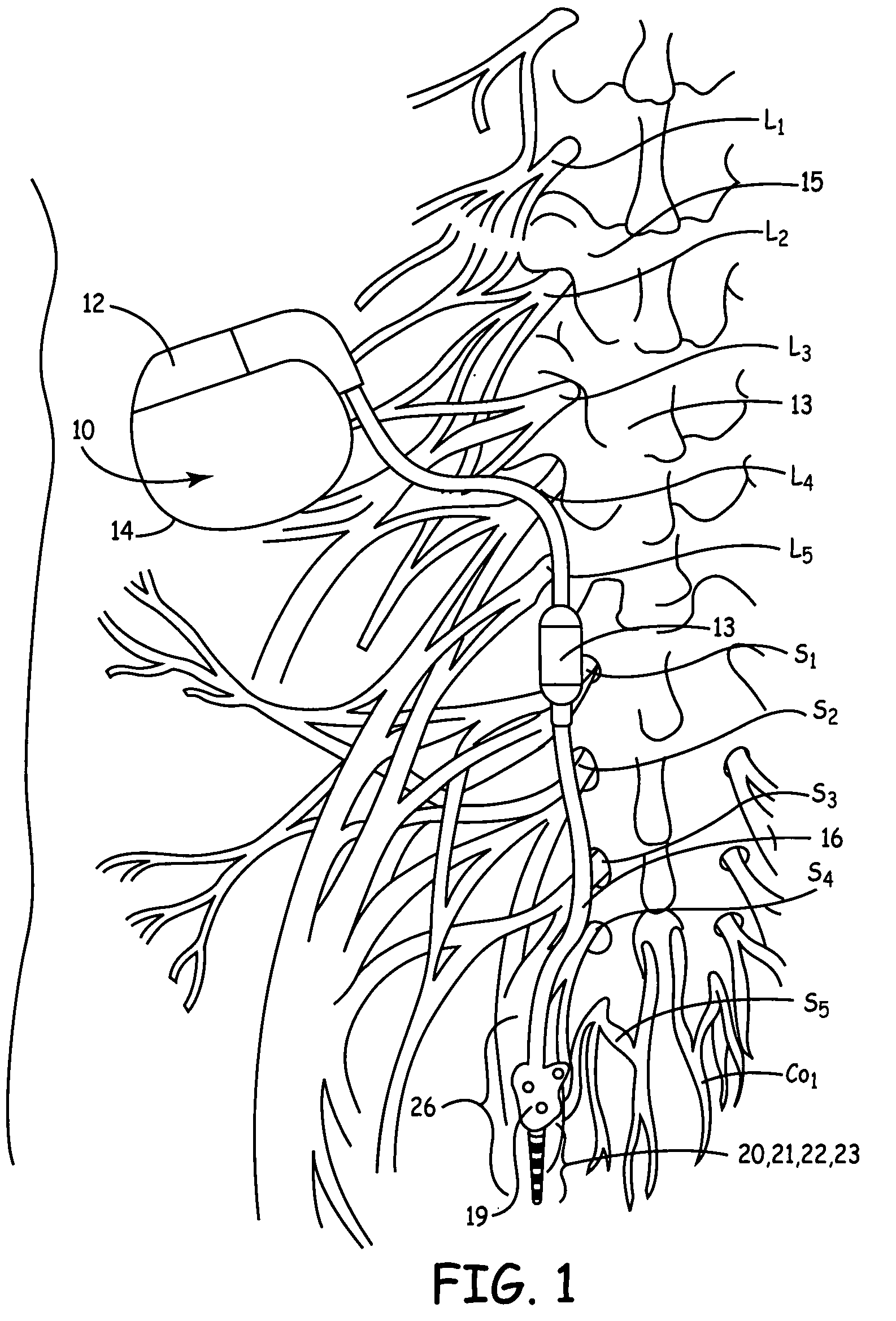
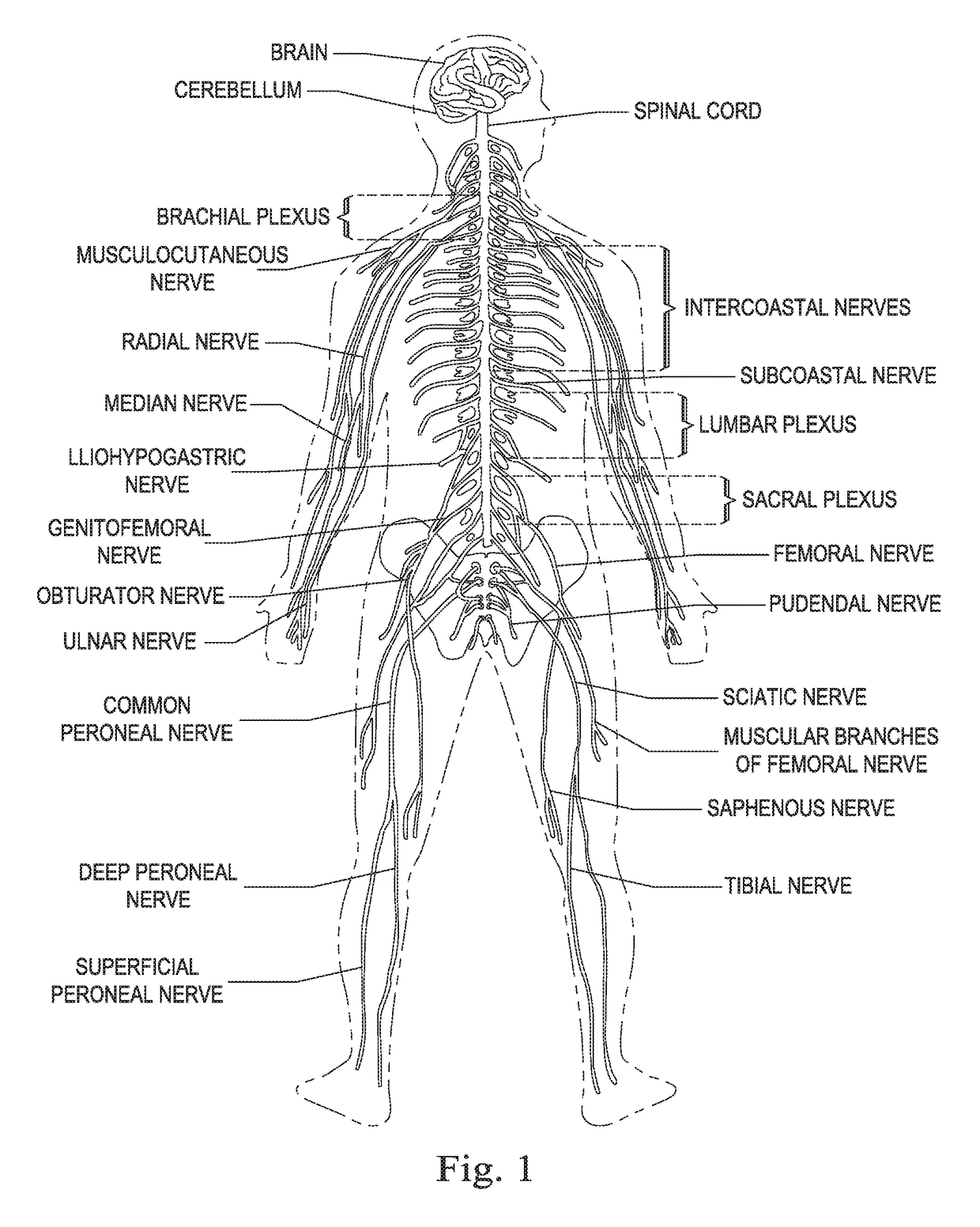
Method, system and device for treating disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudendal and associated nerves, and the optional delivery of drugs in association therewith
ActiveUS7328068B2Undesirable side effects of sacral nerve stimulation may be avoided or minimizedUndesirable side-effectDigestive electrodesGenital electrodesDiseaseProstatalgia
Described are implantable devices and methods for treating various disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudendal or other nerves, and optional means for delivering drugs in association therewith. A method of precisely positioning and implanting a medical electrical lead so as to provide optimal stimulation of the pudendal nerve or a portion thereof is also described. Placement of a stimulation lead next to or on the pudendal nerve may be performed using conventional prior art techniques through gross anatomical positioning, but usually does not result in truly optimal lead placement. One method of the present invention utilizes neurophysiological monitoring to assess the evoked responses of the pudendal nerve, and thereby provide a method for determining the optimal stimulation site. Additionally, one or more electrical stimulation signals are applied, and optionally one or more drugs are infused, injected or otherwise administered, to appropriate portions of a patient's pelvic floor and pudendal nerve or portions thereof in an amount and manner effective to treat a number of disorders, including, but not limited to, urinary and / or fecal voiding dysfunctions such as constipation, incontinence disorders such as urge frequency and urinary retention disorders, sexual dysfunctions such as orgasmic and erectile dysfunction, pelvic pain, prostatitis, prostatalgia and prostatodynia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
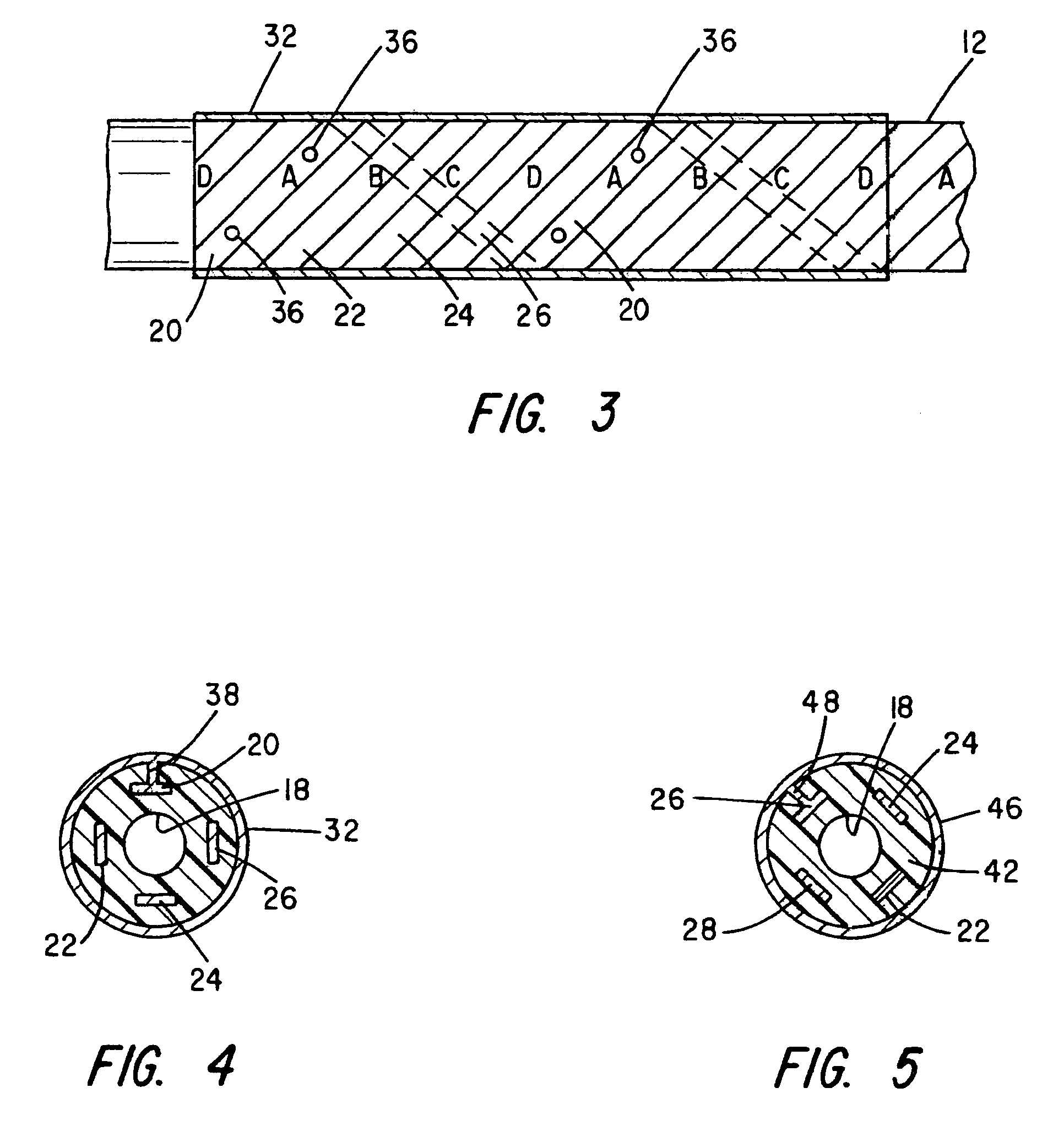
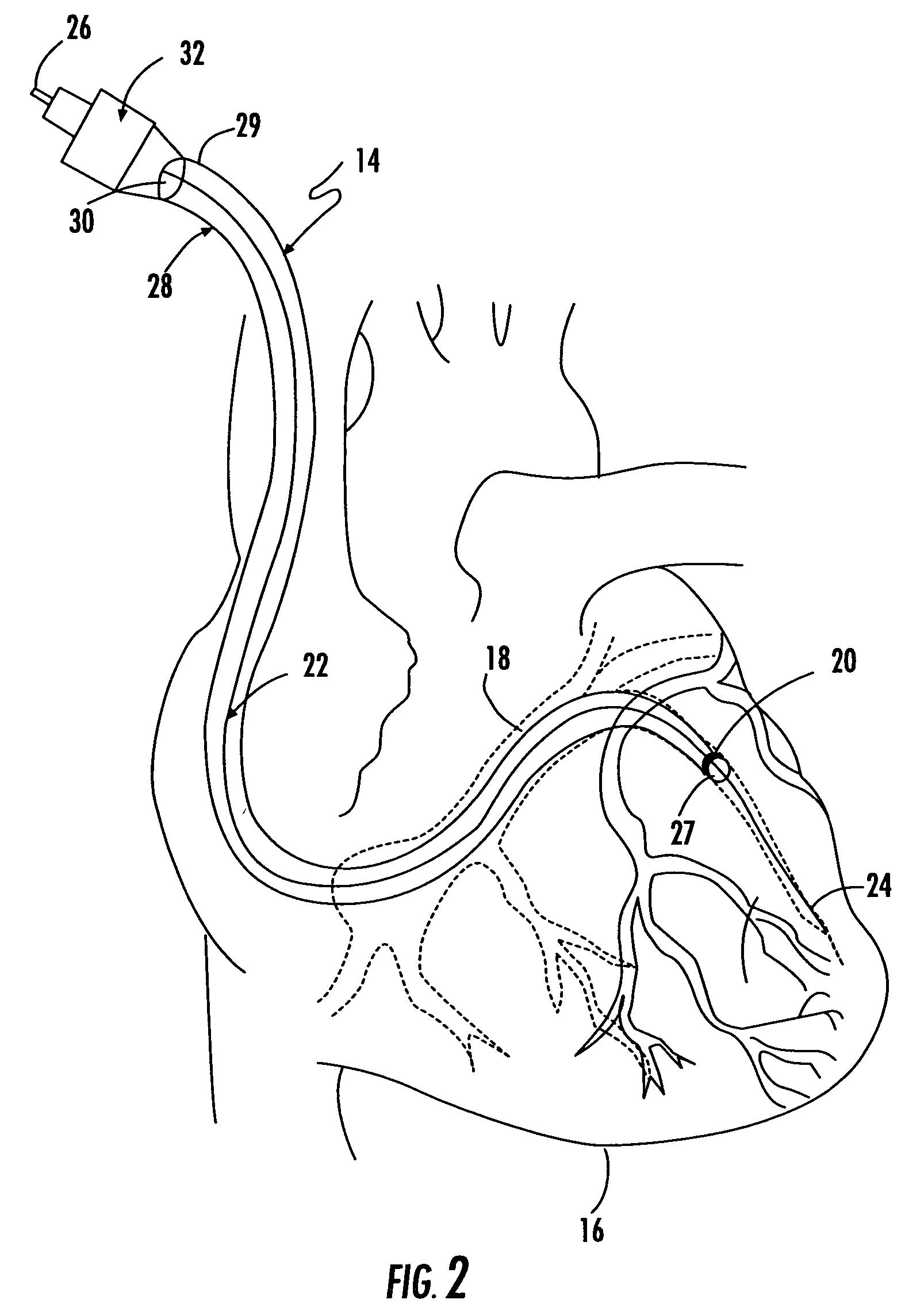
Methods and apparatus for lead placement on a surface of the heart
ActiveUS7610104B2Easy constructionEasy to placeEpicardial electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesCardiac surfacePericardium
The methods and apparatus for lead placement on a surface of the heart are employed using an elongated body having proximal and distal end portions. The body defines a lead receiving passageway extending between a proximal inlet and a distal outlet for receiving a lead therethrough for contact with the heart surface. The elongated body is adapted for insertion between a pericardium and an epicardial surface. At least a portion of the body may have a non-circular cross-sectional shape adapted to retain the body orientation between the pericardium and the epicardial surface.
Owner:SENTREHEART LLC
Method, system and device for treating disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudenal and associated nerves, and the optional delivery of drugs in association therewith
ActiveUS20050113877A1Reduce traumaAvoid damageDigestive electrodesArtificial respirationDiseaseProstatalgia
Described are implantable devices and methods for treating various disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudendal or other nerves, and optional means for delivering drugs in association therewith. A method of precisely positioning and implanting a medical electrical lead so as to provide optimal stimulation of the pudendal nerve or a portion thereof is also described. Placement of a stimulation lead next to or on the pudendal nerve may be performed using conventional prior art techniques through gross anatomical positioning, but usually does not result in truly optimal lead placement. One method of the present invention utilizes neurophysiological monitoring to assess the evoked responses of the pudendal nerve, and thereby provide a method for determining the optimal stimulation site. Additionally, one or more electrical stimulation signals are applied, and optionally one or more drugs are infused, injected or otherwise administered, to appropriate portions of a patient's pelvic floor and pudendal nerve or portions thereof in an amount and manner effective to treat a number of disorders, including, but not limited to, urinary and / or fecal voiding dysfunctions such as constipation, incontinence disorders such as urge frequency and urinary retention disorders, sexual dysfunctions such as orgasmic and erectile dysfunction, pelvic pain, prostatitis, prostatalgia and prostatodynia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
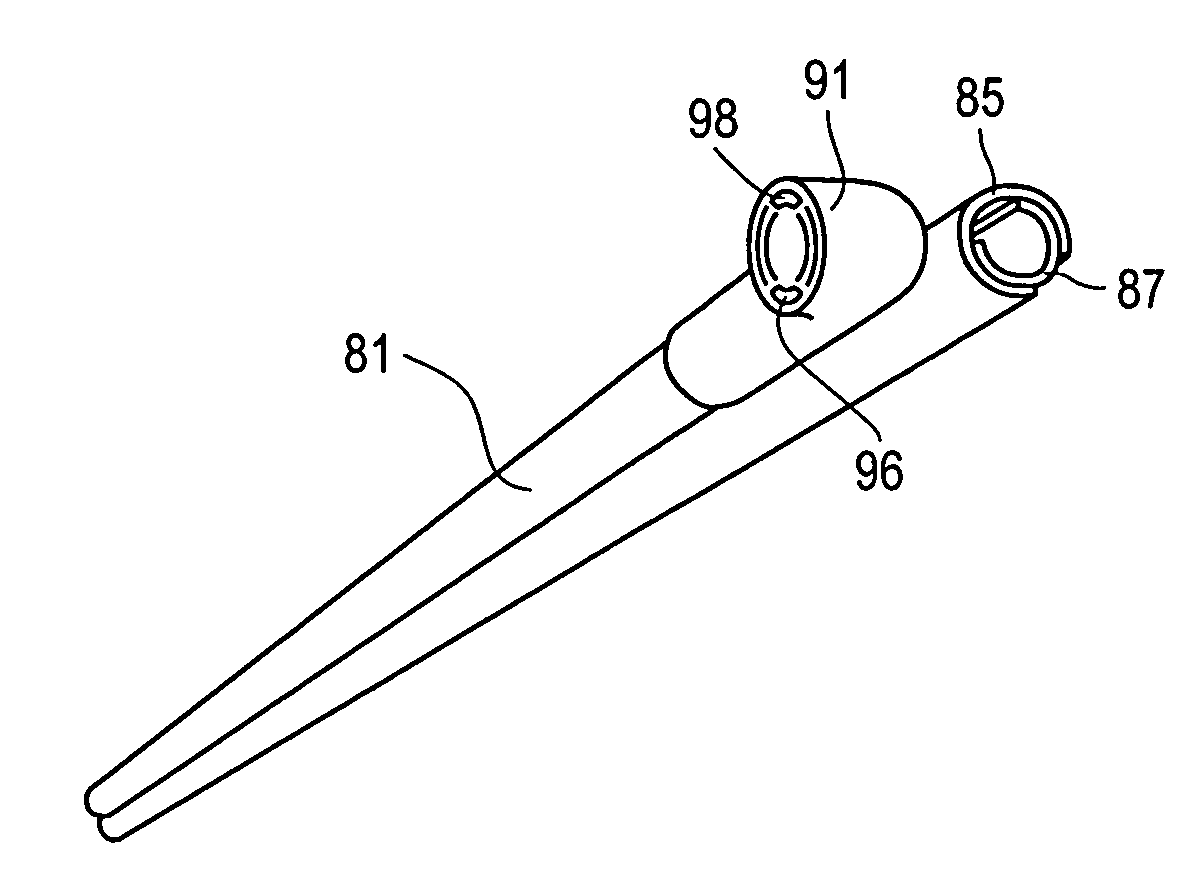
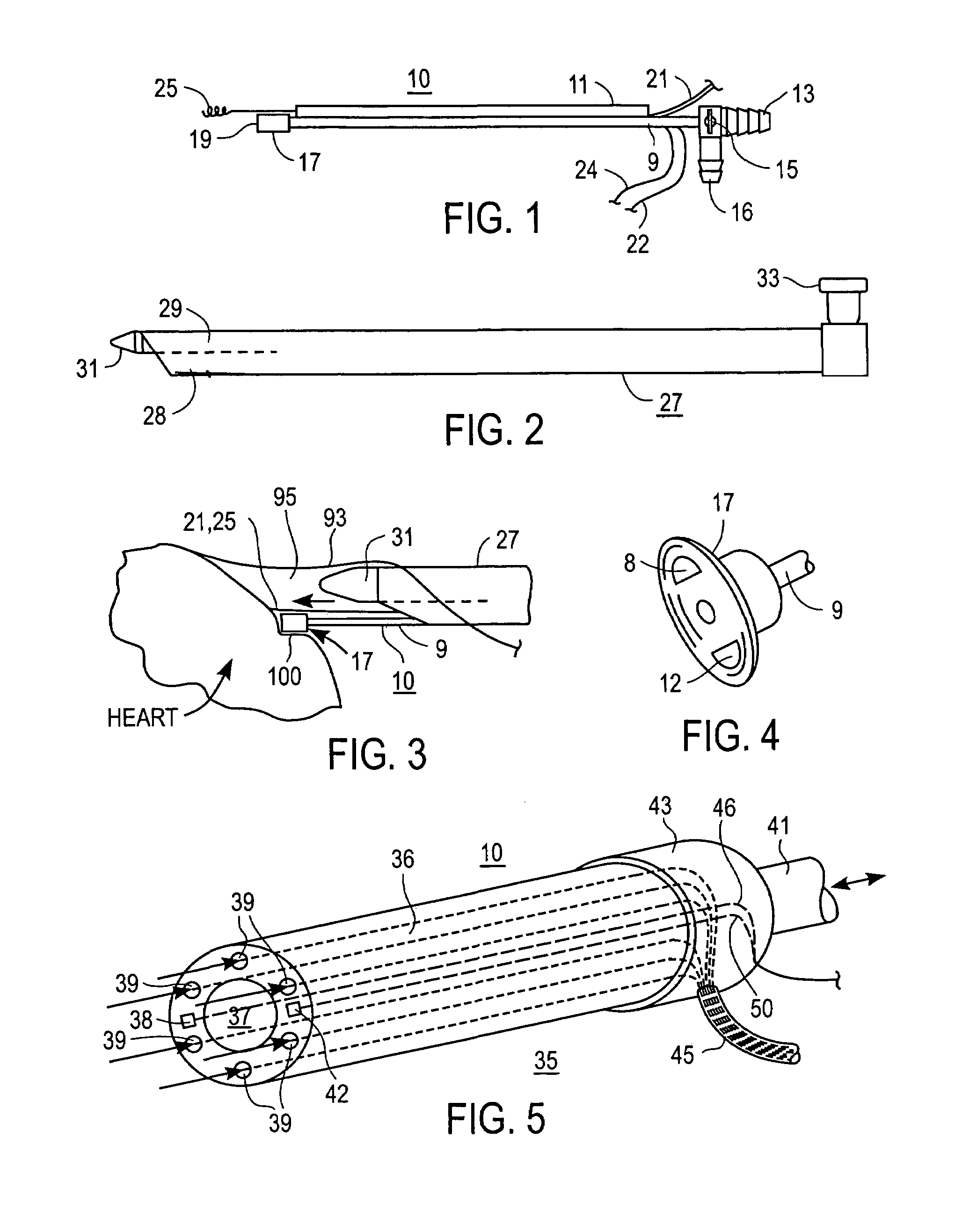
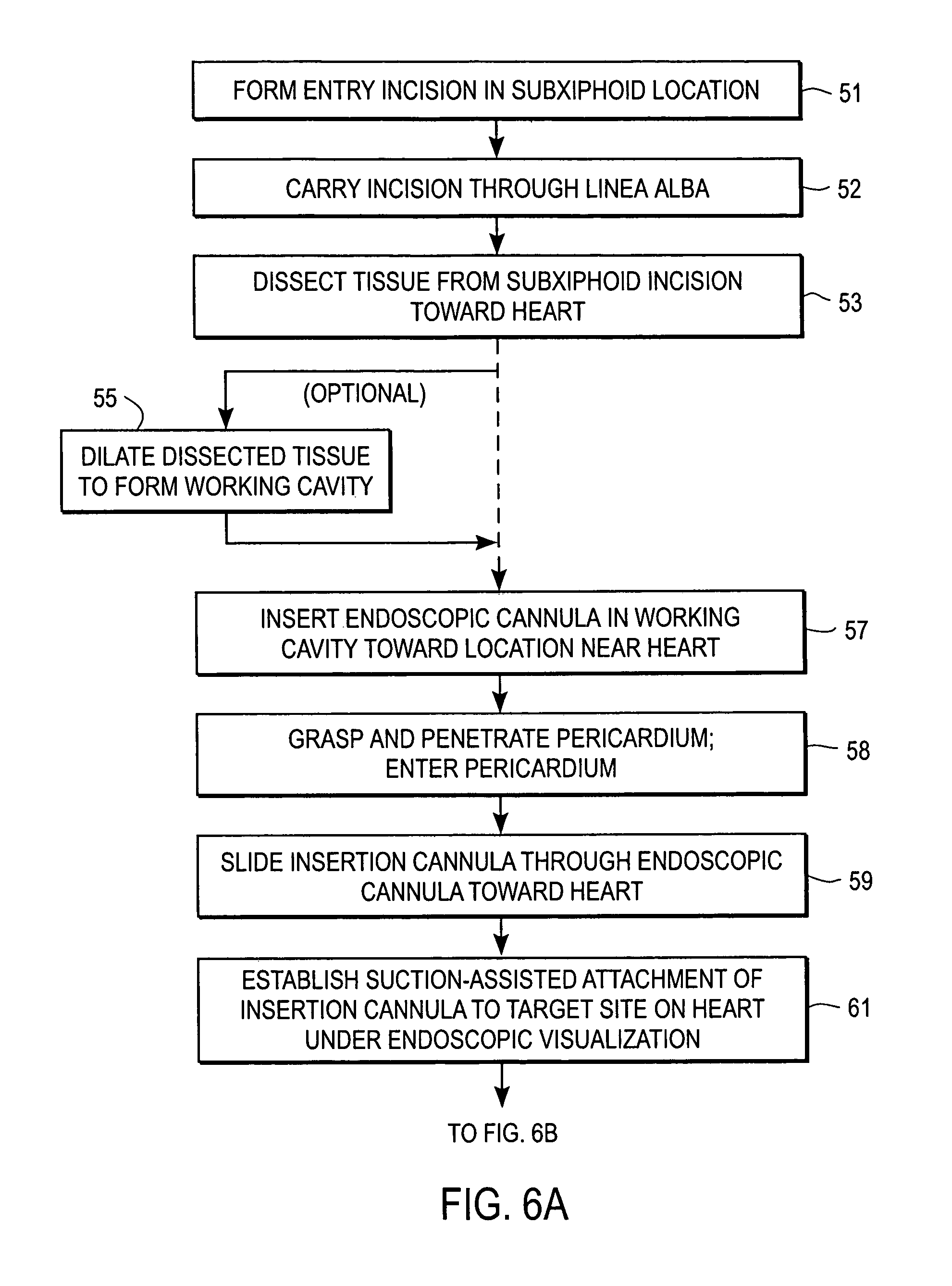
Apparatus for endoscopic cardiac mapping and lead placement
InactiveUS7526342B2Easy to installPenetration becomes shallowSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyEpicardial mappingHemodynamics
Apparatus and surgical methods establish temporary suction attachment to a target site on the surface of a beating heart for analyzing electrical signals or hemodynamic responses to applied signals at the target sites for enhancing the accuracy of placement of cardiac electrodes at selected sites and for enhancing accurate placement of a surgical instrument maintained in alignment with the suction attachment. A suction port on the distal end of a supporting cannula carries surface-contacting electrodes and provides suction attachment to facilitate temporary positioning of the electrodes in contact with tissue at the target site, and a clamping and release mechanism to facilitate anchoring a cardiac electrode on the moving surface of a beating heart at a selected site. Analyses of sensed signals or responses to applied signals at target sites promote epicardial mapping of a patient's heart for determining optimum sites at which to attach cardiac electrodes.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
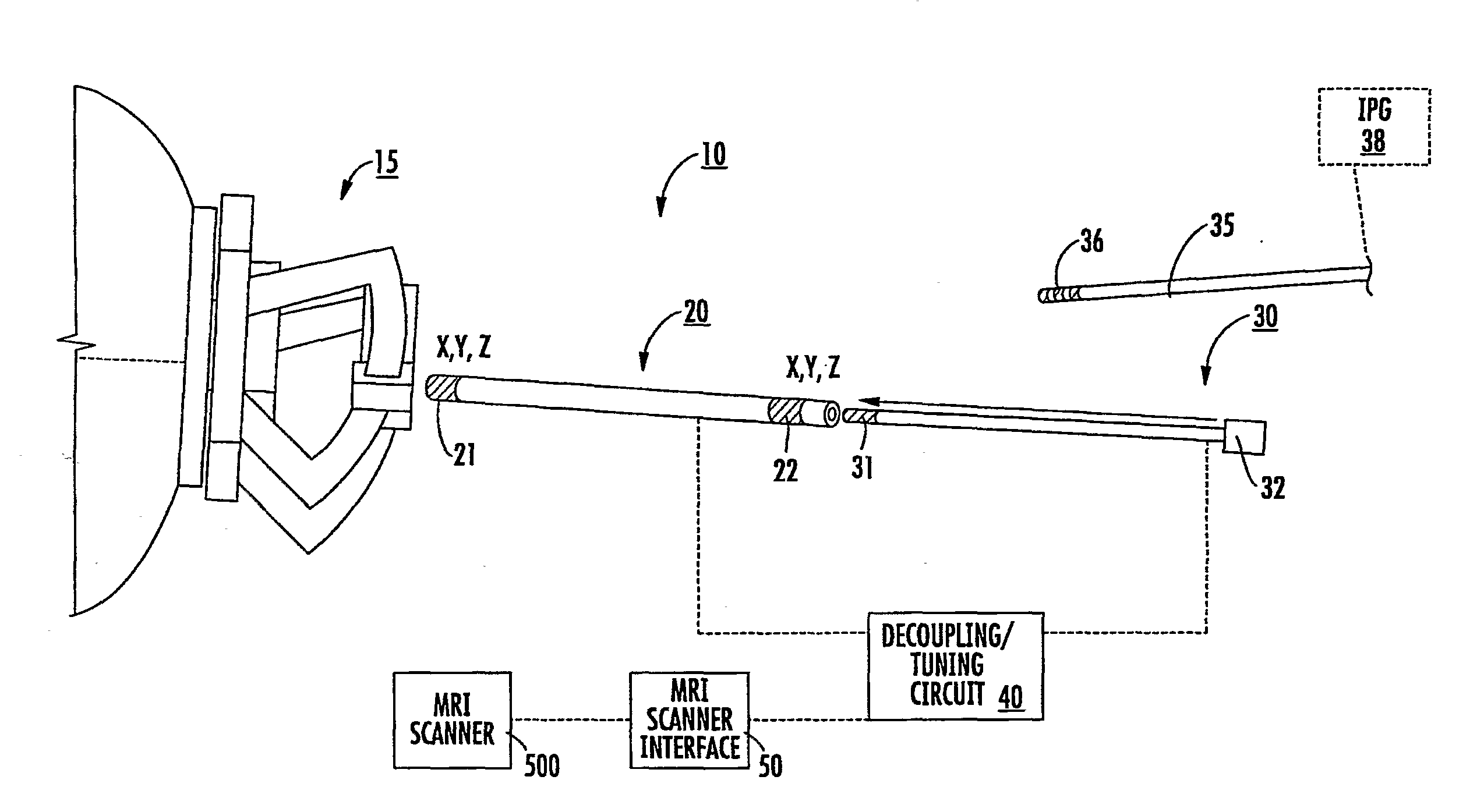
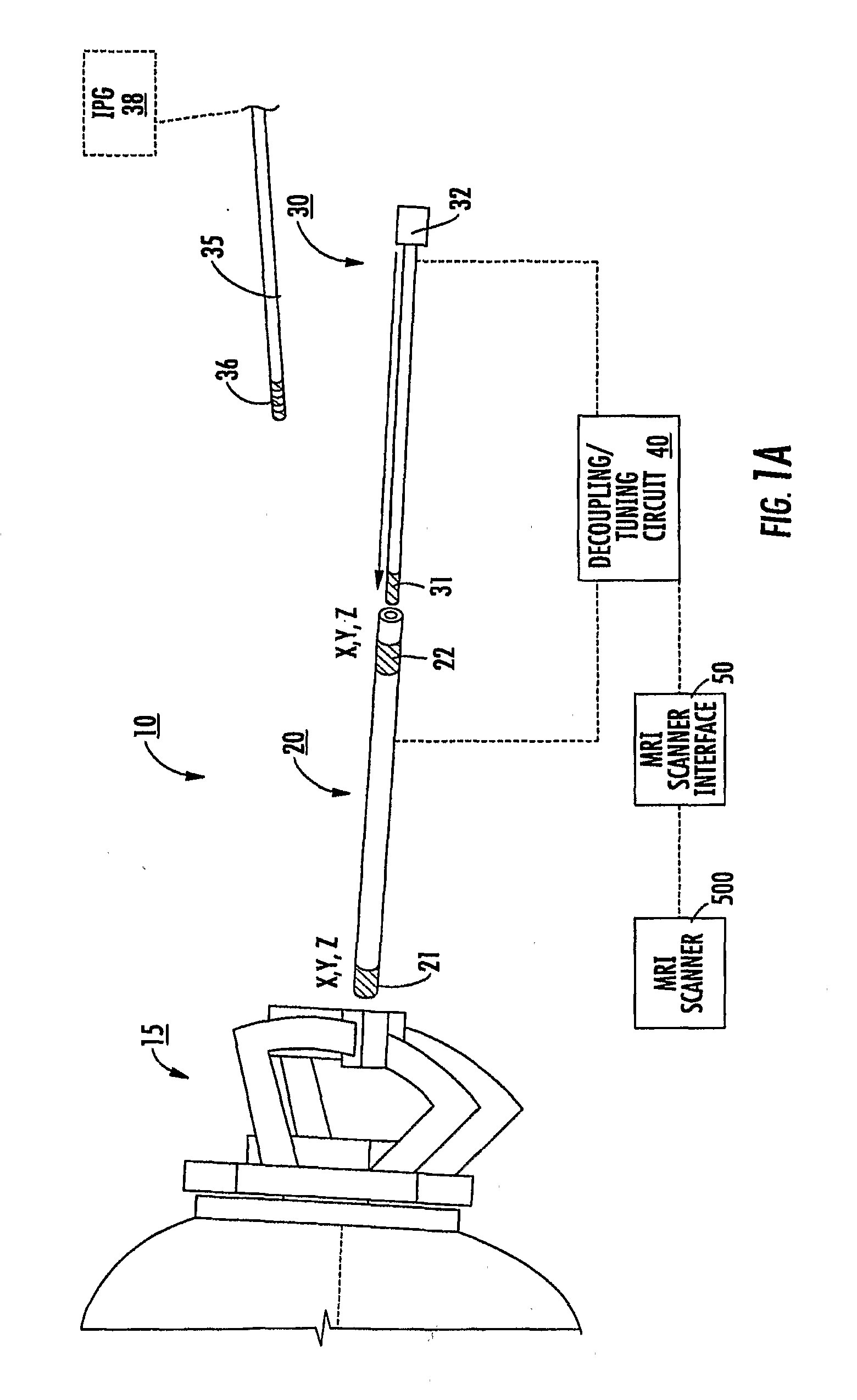
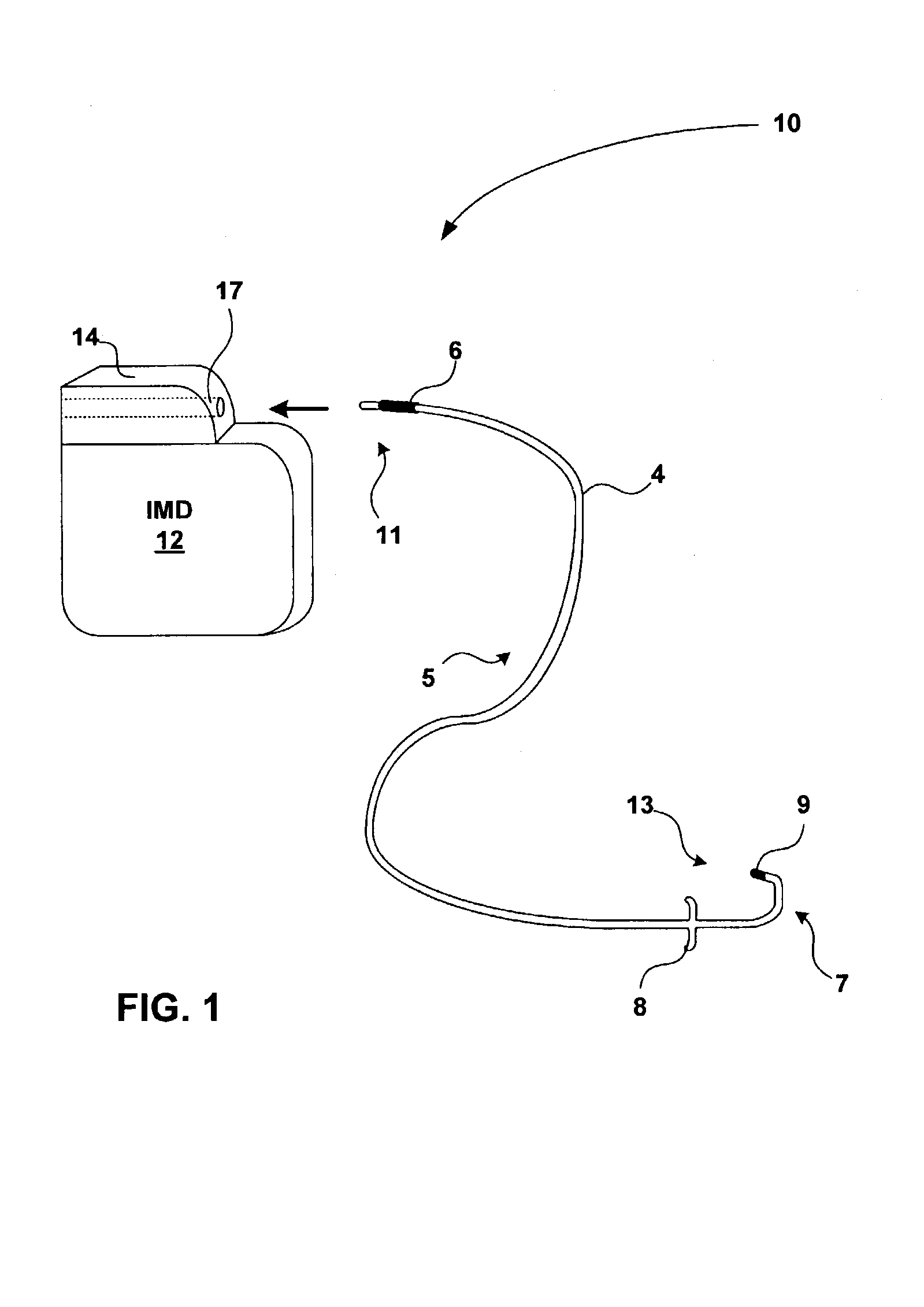
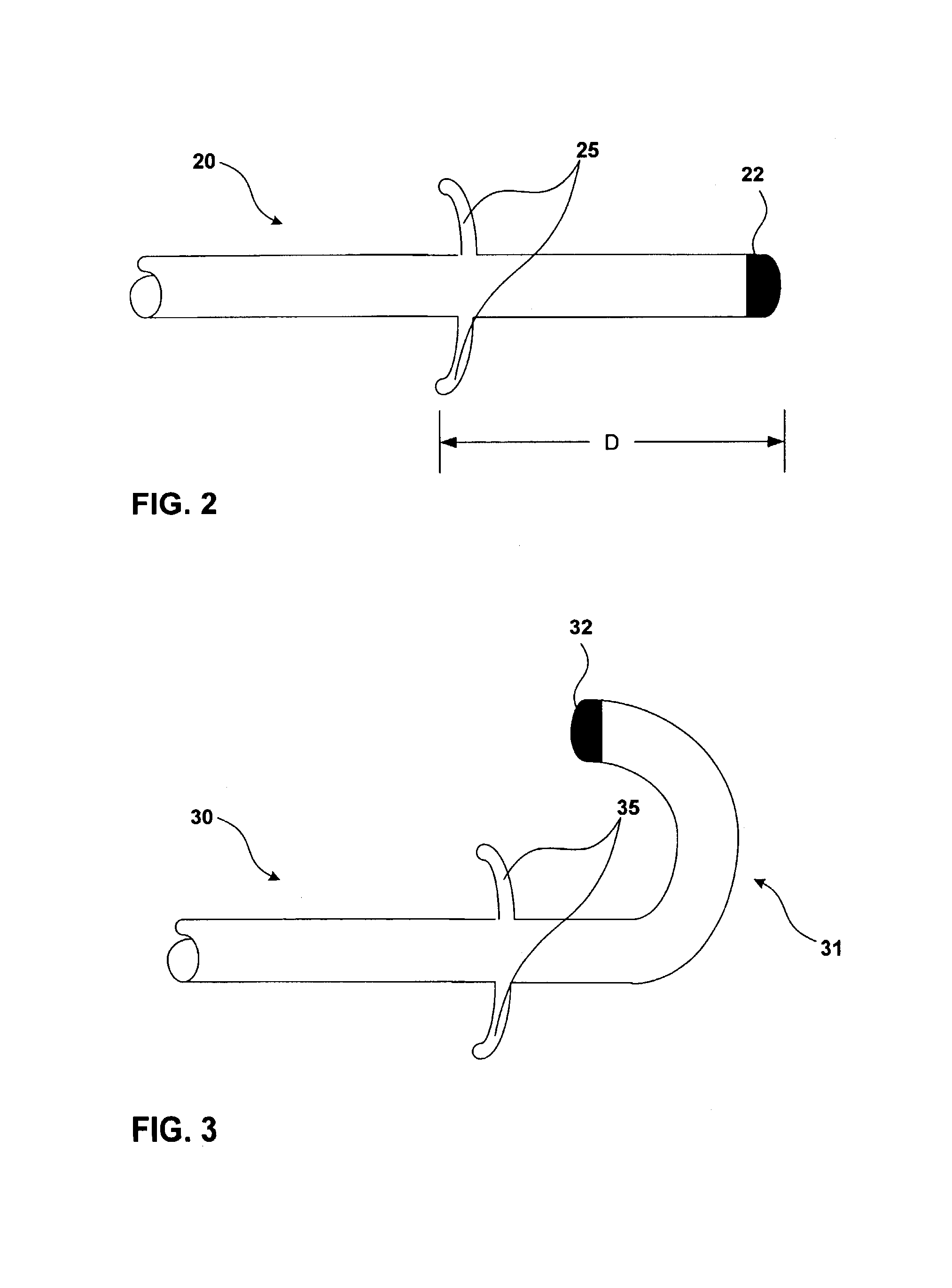
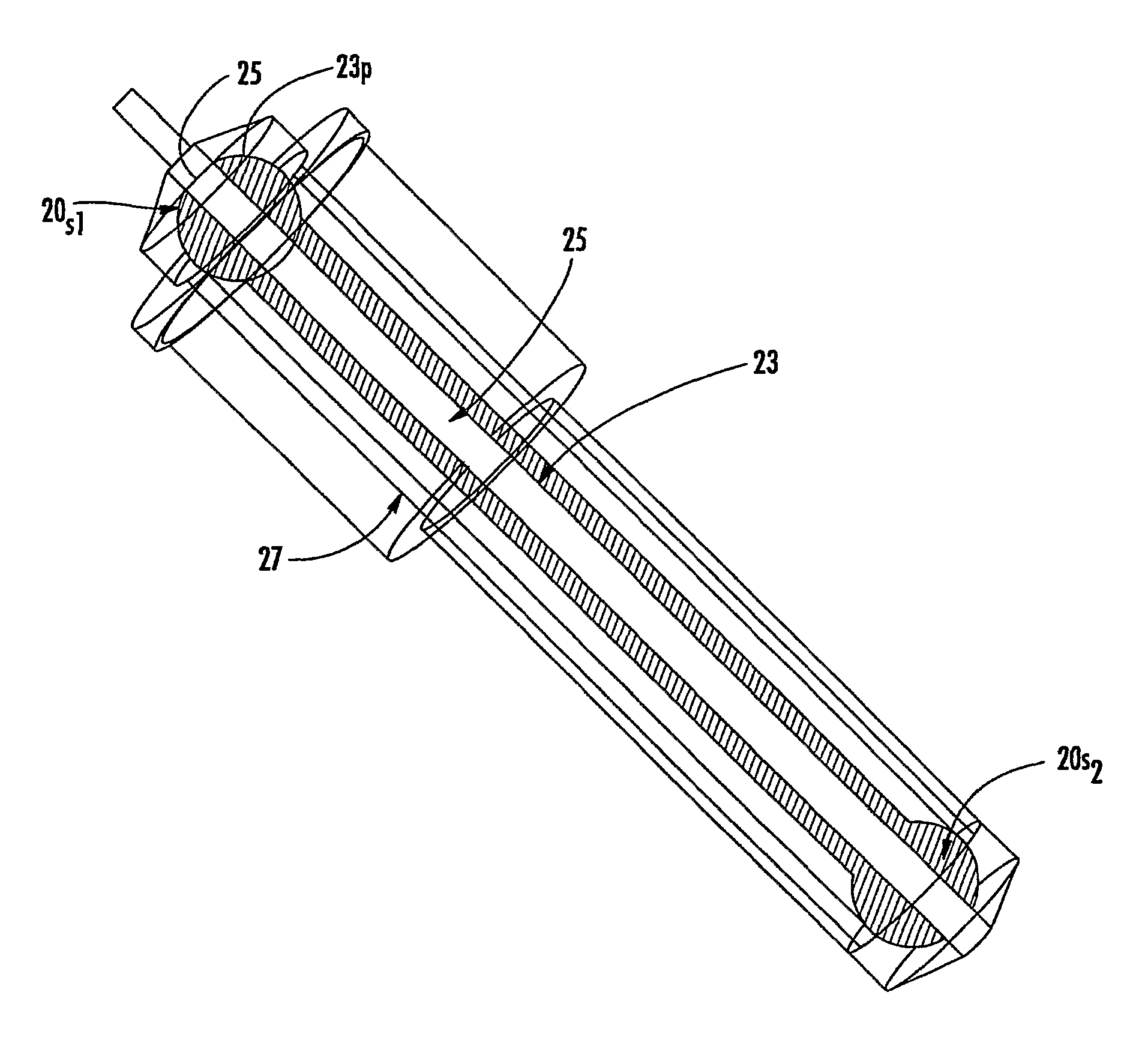
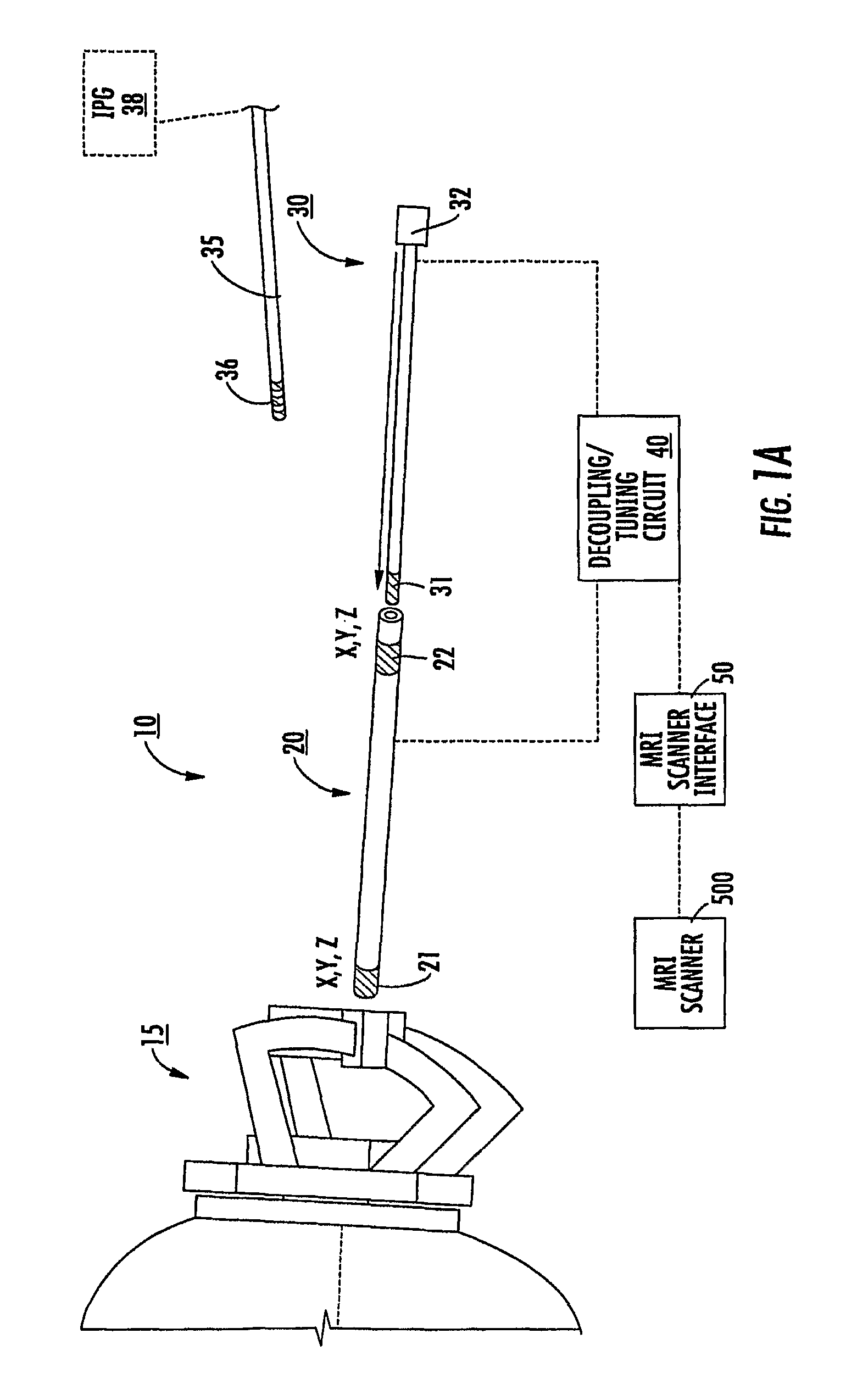
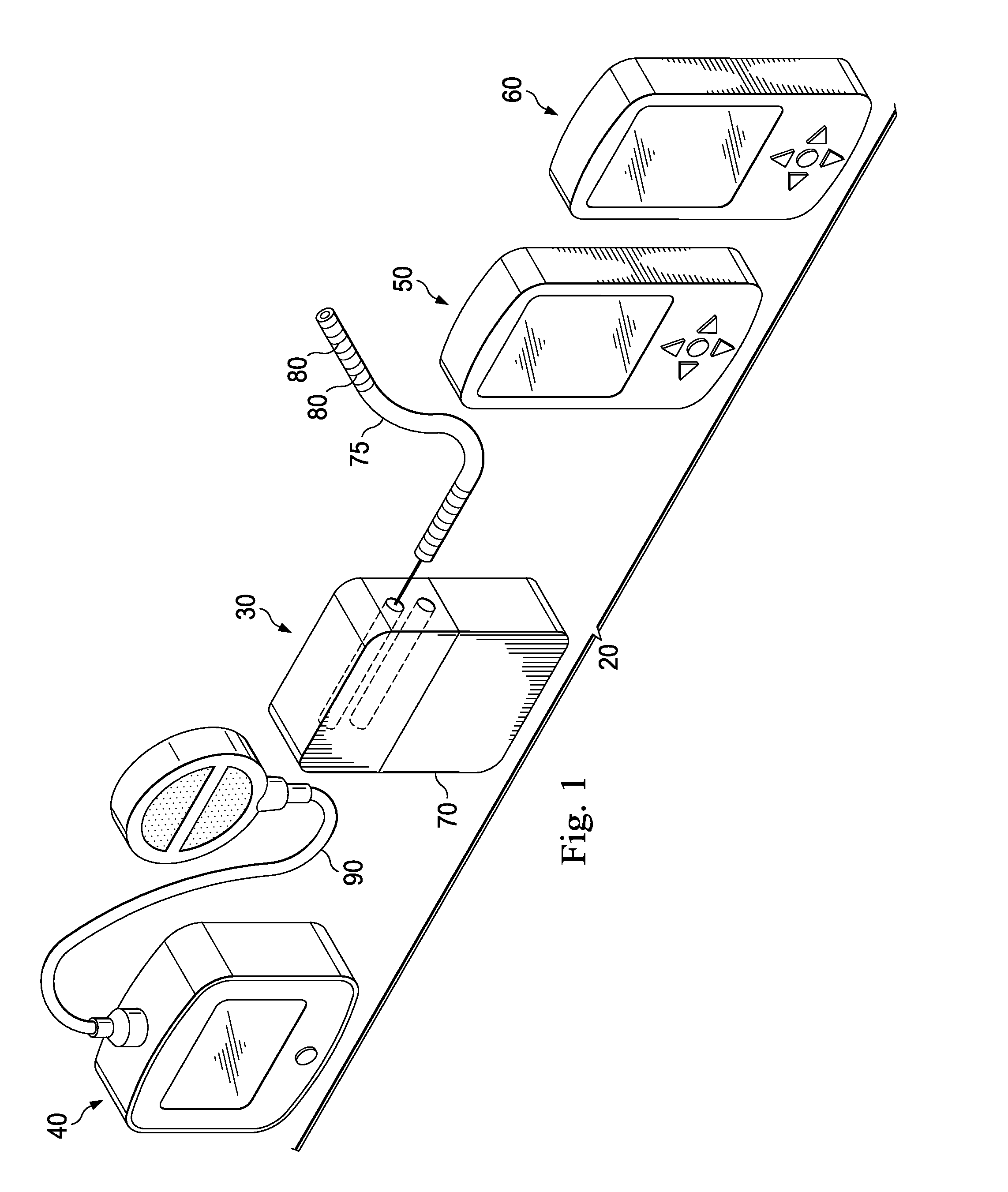
Mri-guided localization and/or lead placement systems, related methods, devices and computer program products
MRI compatible localization and / or guidance systems for facilitating placement of an interventional therapy and / or device in vivo include: (a) a mount adapted for fixation to a patient; (b) a targeting cannula with a lumen configured to attach to the mount so as to be able to controllably translate in at least three dimensions; and (c) an elongate probe configured to snugly slidably advance and retract in the targeting cannula lumen, the elongate probe comprising at least one of a stimulation or recording electrode. In operation, the targeting cannula can be aligned with a first trajectory and positionally adjusted to provide a desired internal access path to a target location with a corresponding trajectory for the elongate probe. Automated systems for determining an MR scan plane associated with a trajectory and for determining mount adjustments are also described.
Owner:CLEARPOINT NEURO INC
Neurostimulating lead
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
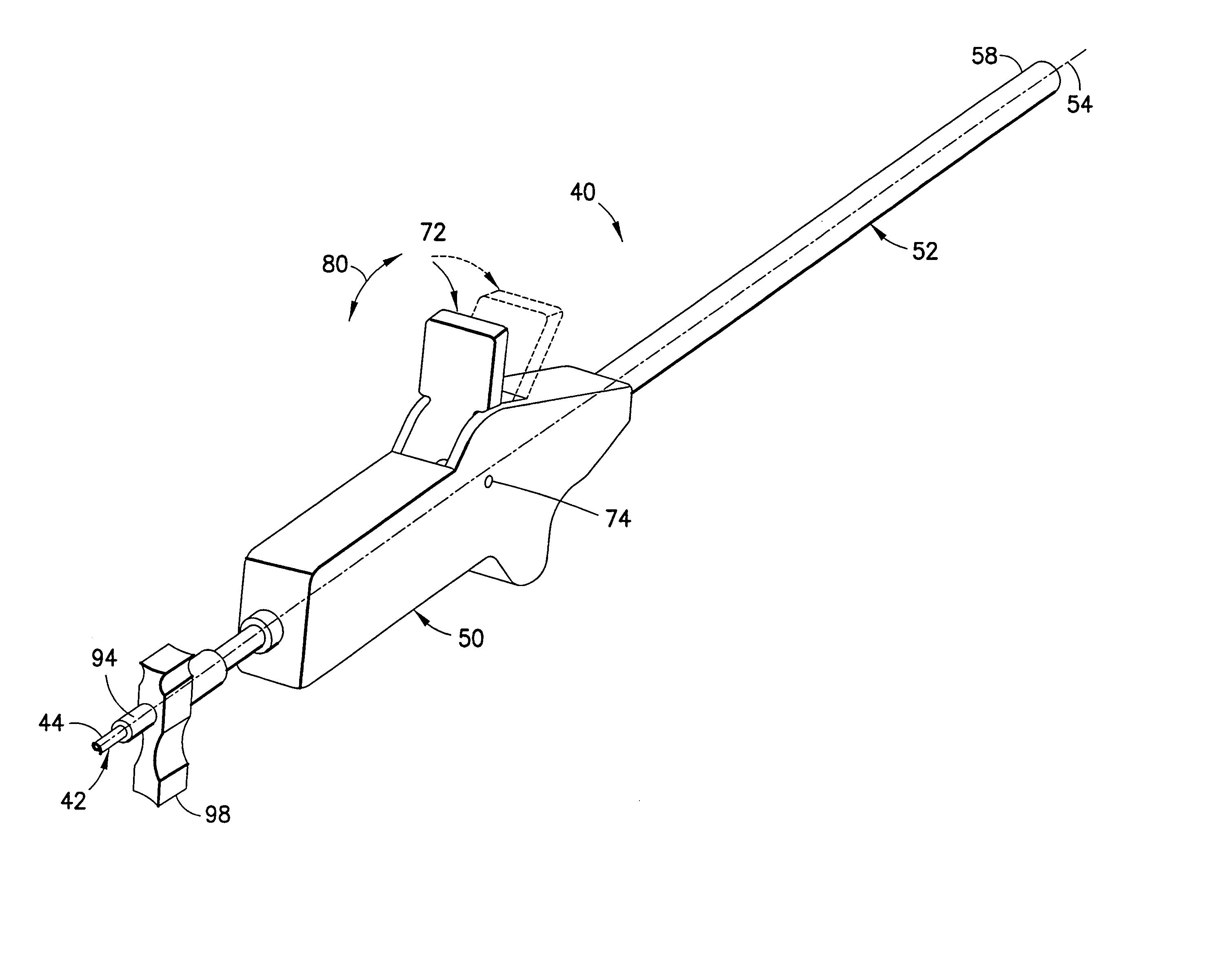
Lead placement device
Lead placement apparatus to transmit electrical signals to stimulate selected body tissue includes an introducer handle supporting a tubular outer sheath of flexible resilient material including a rigid section and a deflectable section adjacent the distal end, enabling the deflectable section to deflect among a plurality of positions in orientations transverse of a longitudinal axis. An operative member on the introducer handle connected to the distal end of the outer sheath serves to move that distal end. An inner tubular sheath of flexible resilient material slidably received within the outer sheath includes a driving socket fixed to its distal end whereby, with a lead slidably received within the inner tubular sheath and including a driven socket fixed to its distal end for releasable mating engagement by the driving socket, an electrode at the distal tip of the lead can be advanced and directed to the selected body tissue for stimulation.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method and system for optimizing left-heart lead placement
InactiveUS20070055124A1Easy to placePredict successUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyCardiac wallBlood flow
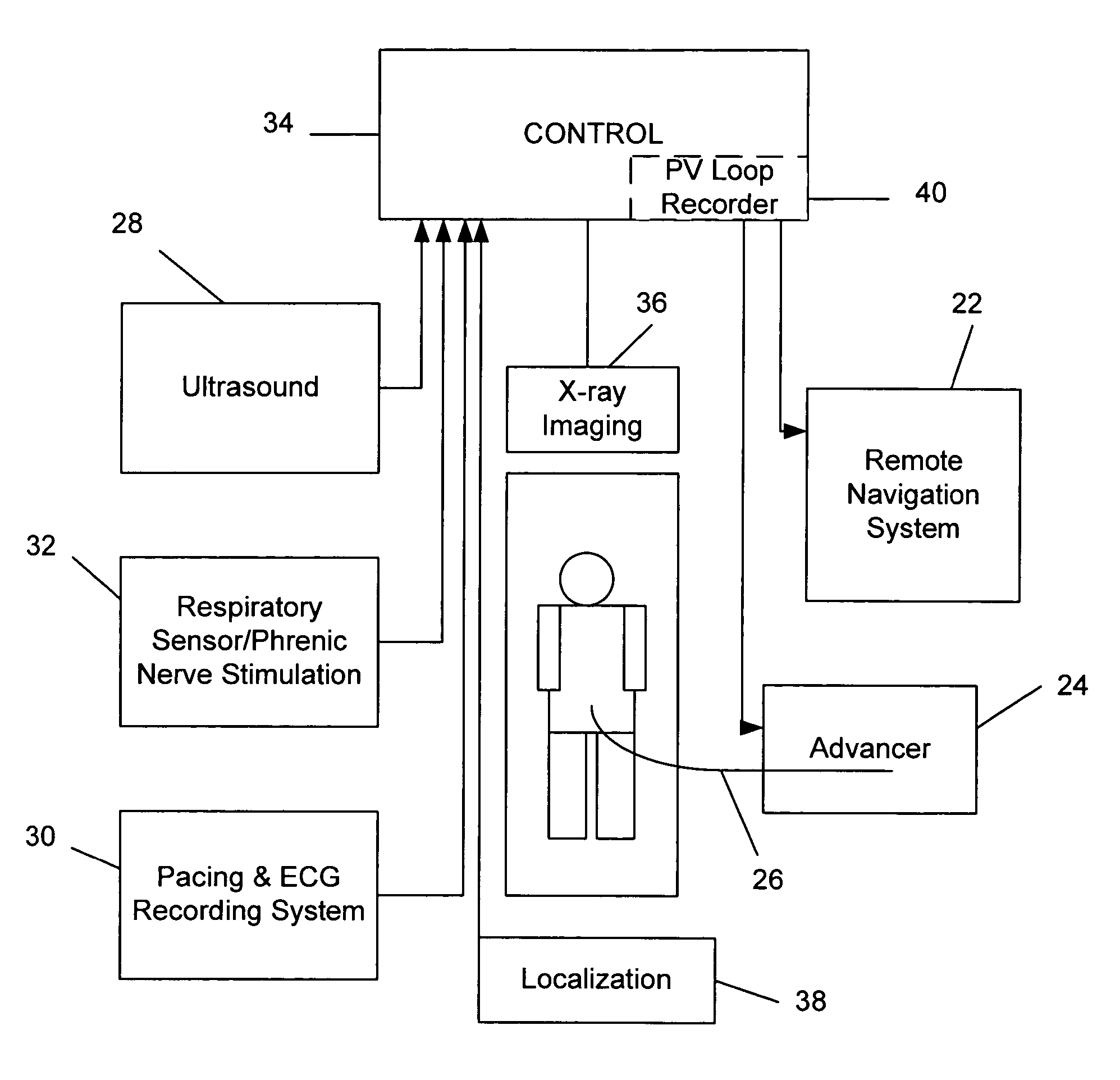
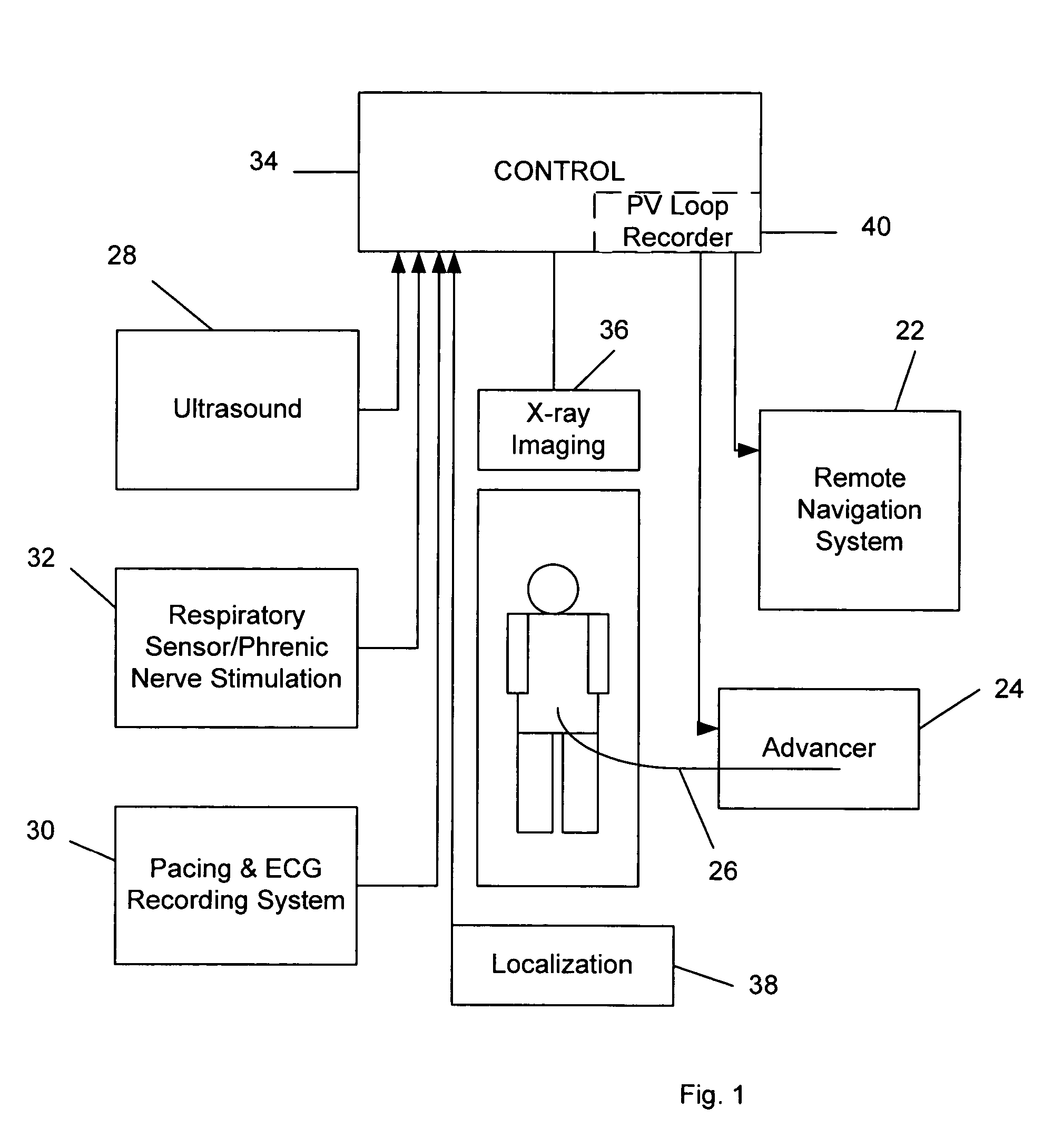
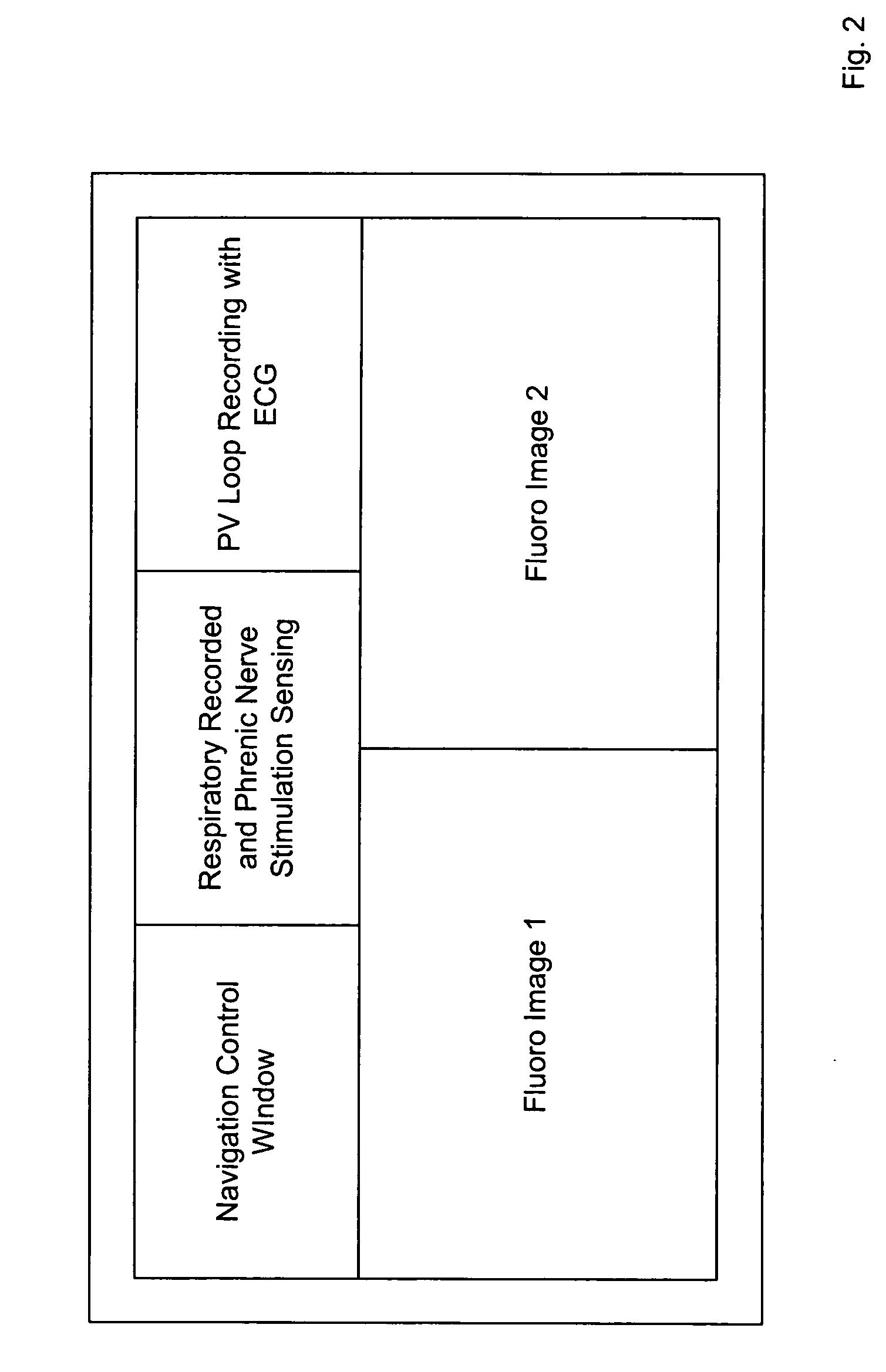
A system for identifying locations for pacing the heart, the system comprising a pacing electrode, a remote navigation system for positioning the pacing electrode at each of a plurality of locations; a system for determining Pressure-Volume loop data resulting from pacing at each location; an ECG system, a phrenic nerve stimulation detection system, and a means of identifying at least one preferred location based upon at least the Pressure-Volume loop, ECG, and phrenic nerve stimulation data at each location. A method of identifying locations for pacing the heart, the method comprising: navigating a pacing electrode to each of a plurality of locations in the heart; pacing the heart at each of the plurality of locations; and assessing the effectiveness of the pacing at each location by measuring cardiac blood flow and cardiac wall strain.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
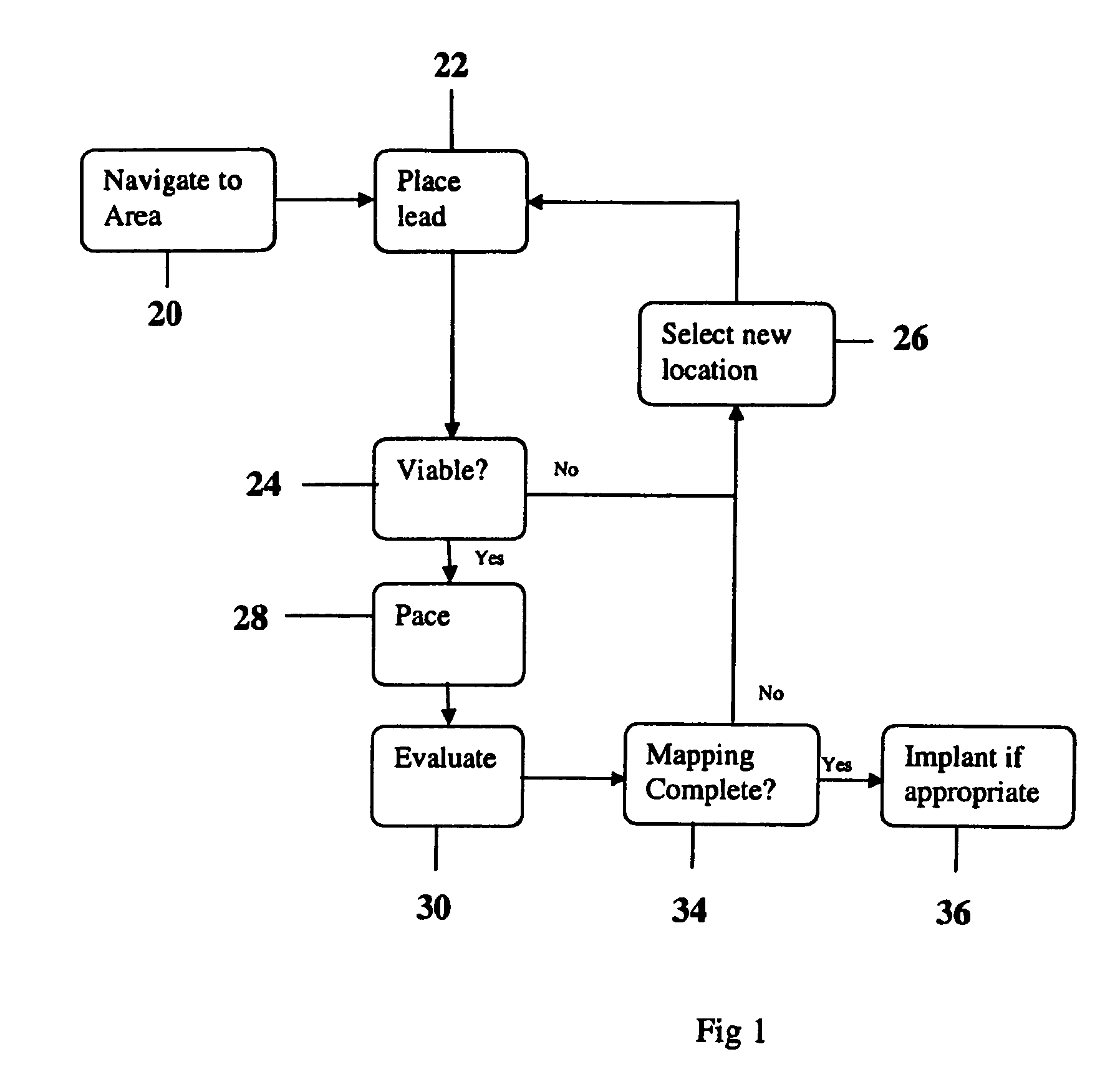
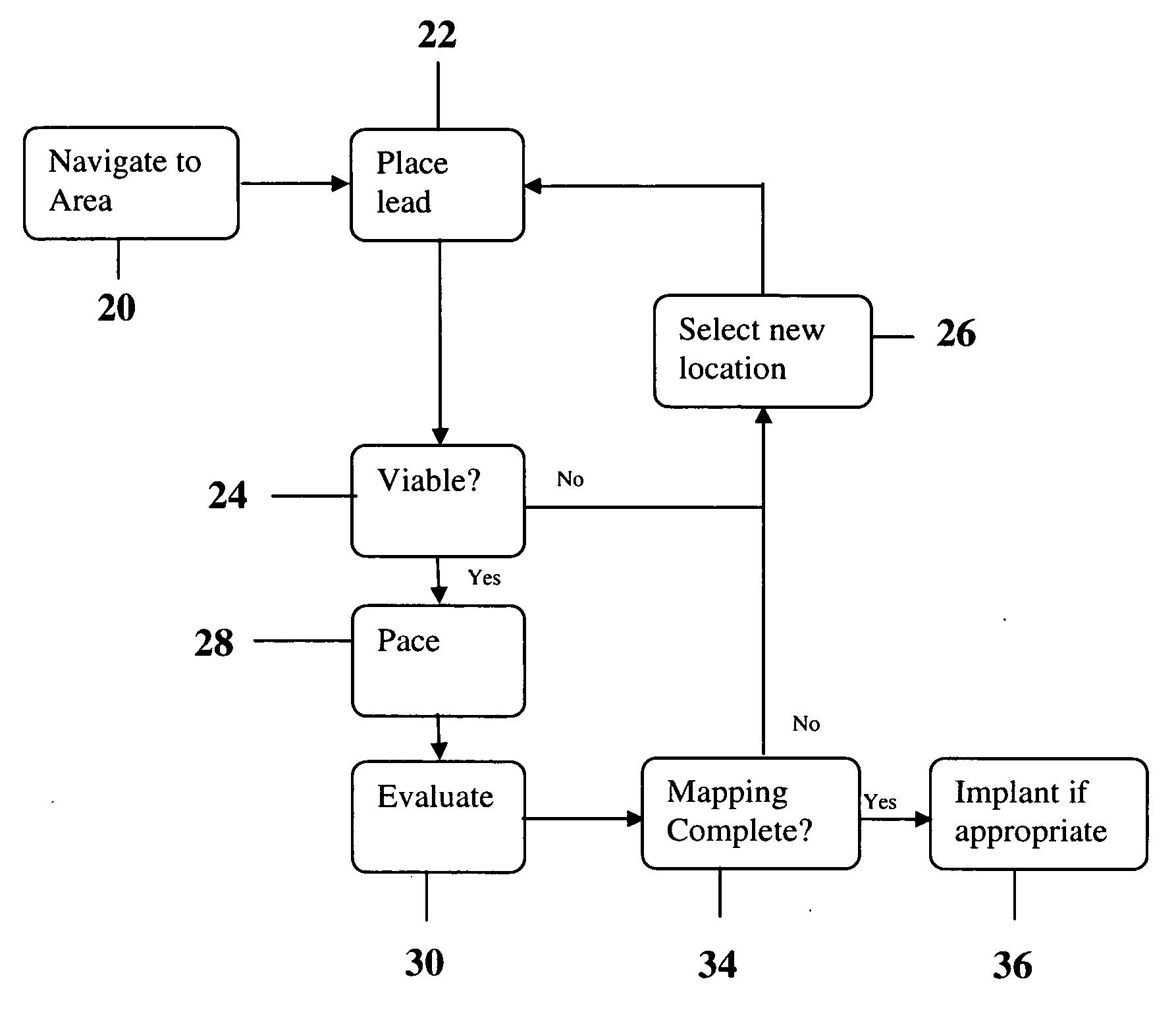
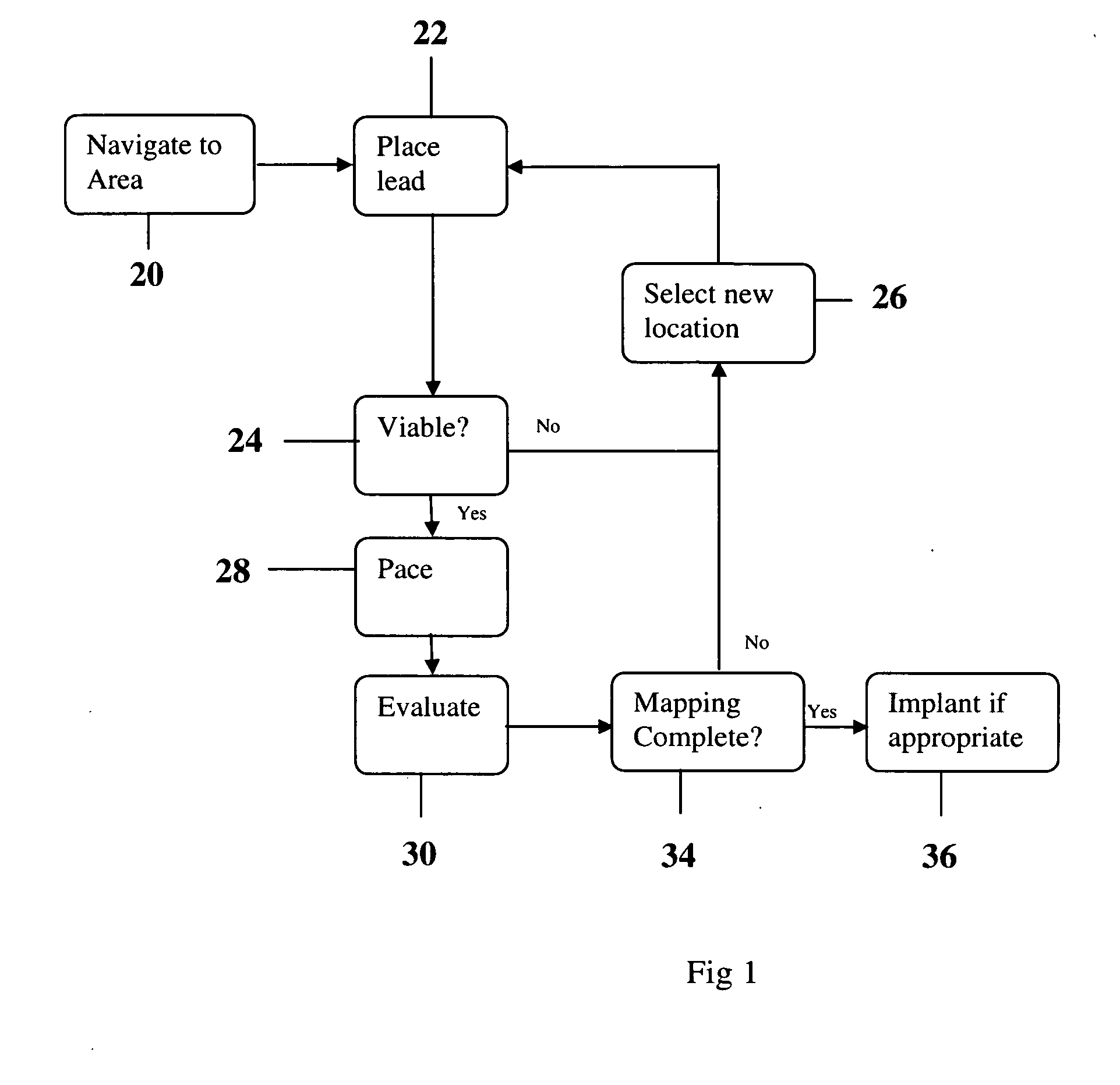
Methods and devices for mapping the ventricle for pacing lead placement and therapy delivery
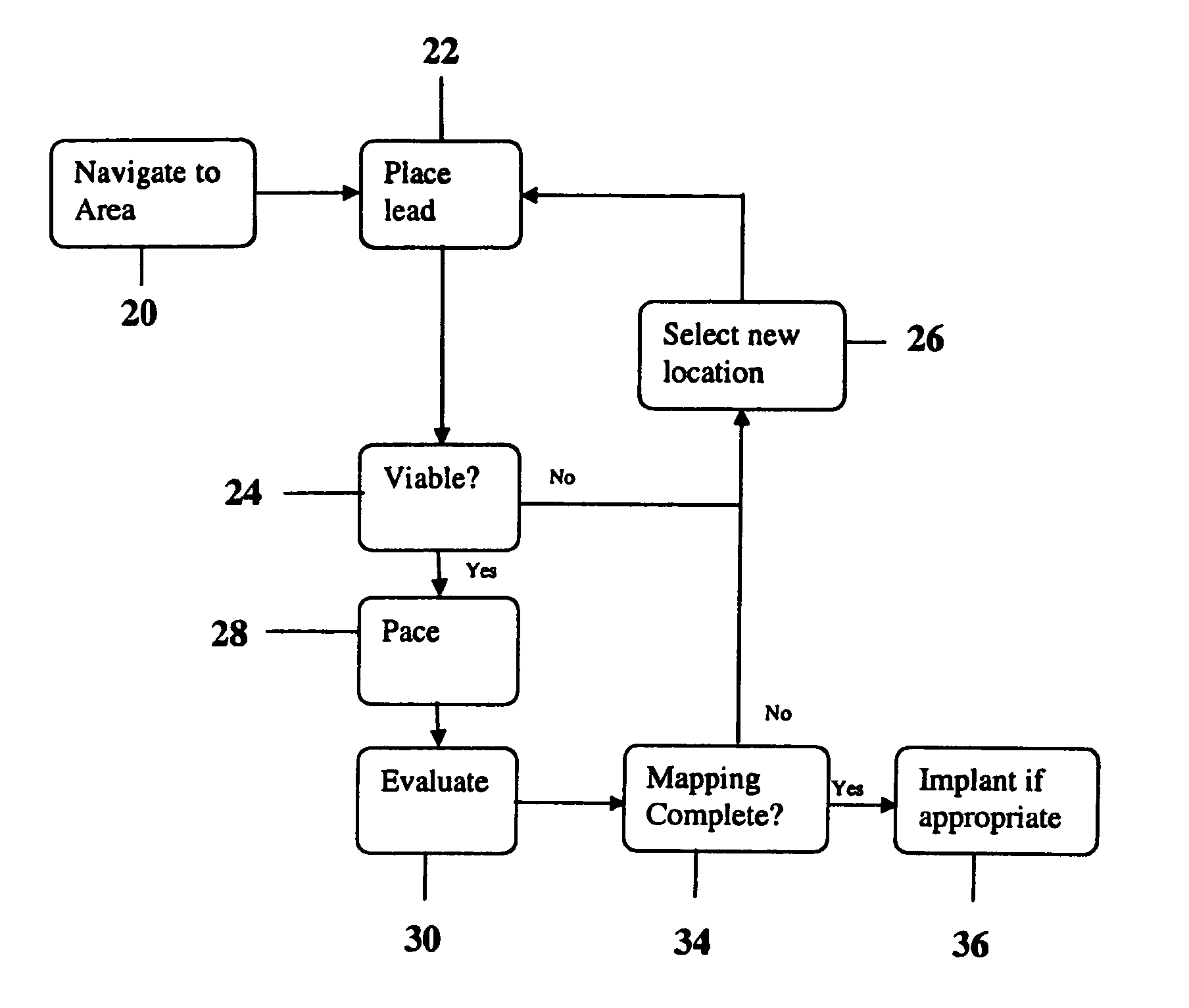
InactiveUS20070060992A1Easy to placeImprove heart functionInternal electrodesSurgical instrument detailsLead PlacementCatheter device
A method of placing a pacing lead in the heart includes moving an electrode catheter successively to a plurality of possible placement sites. The viability of the tissue at each site is determined. If the tissue at the site is viable, a pacing signal is applied to the tissue at the site, and the effectiveness of the pacing from the site is measured. After the area has been mapped in this fashion, at least one pacing lead is placed from at least one of the sites which exceeded a predetermined level of pacing effectiveness.
Owner:PAPPONE CARLO
Techniques for placing medical leads for electrical stimulation of nerve tissue
ActiveUS9572982B2Spinal electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesAnesthesiaElectrical stimulations
This disclosure is directed to extra, intra, and transvascular medical lead placement techniques for arranging medical leads and electrical stimulation and / or sensing electrodes proximate nerve tissue within a patient.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
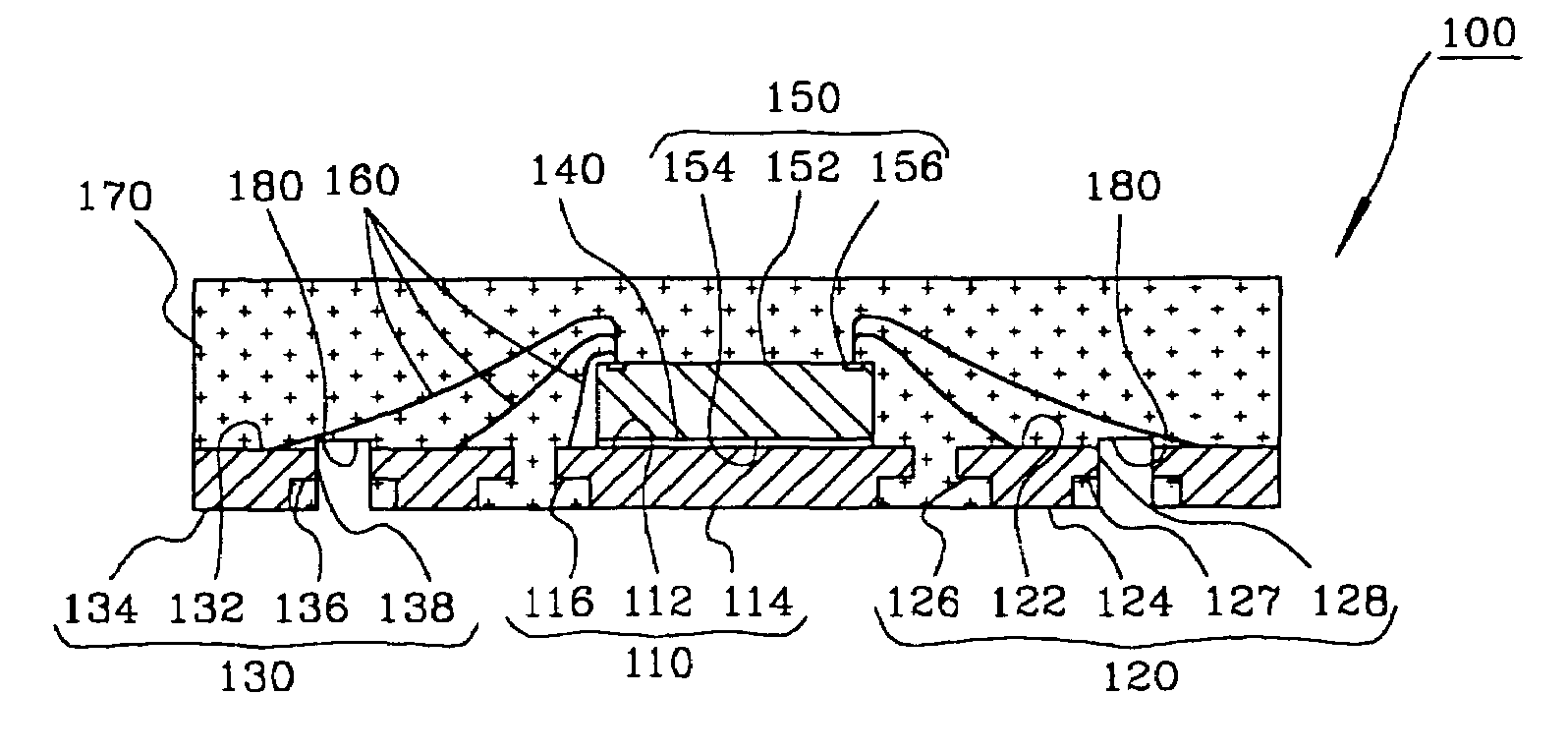
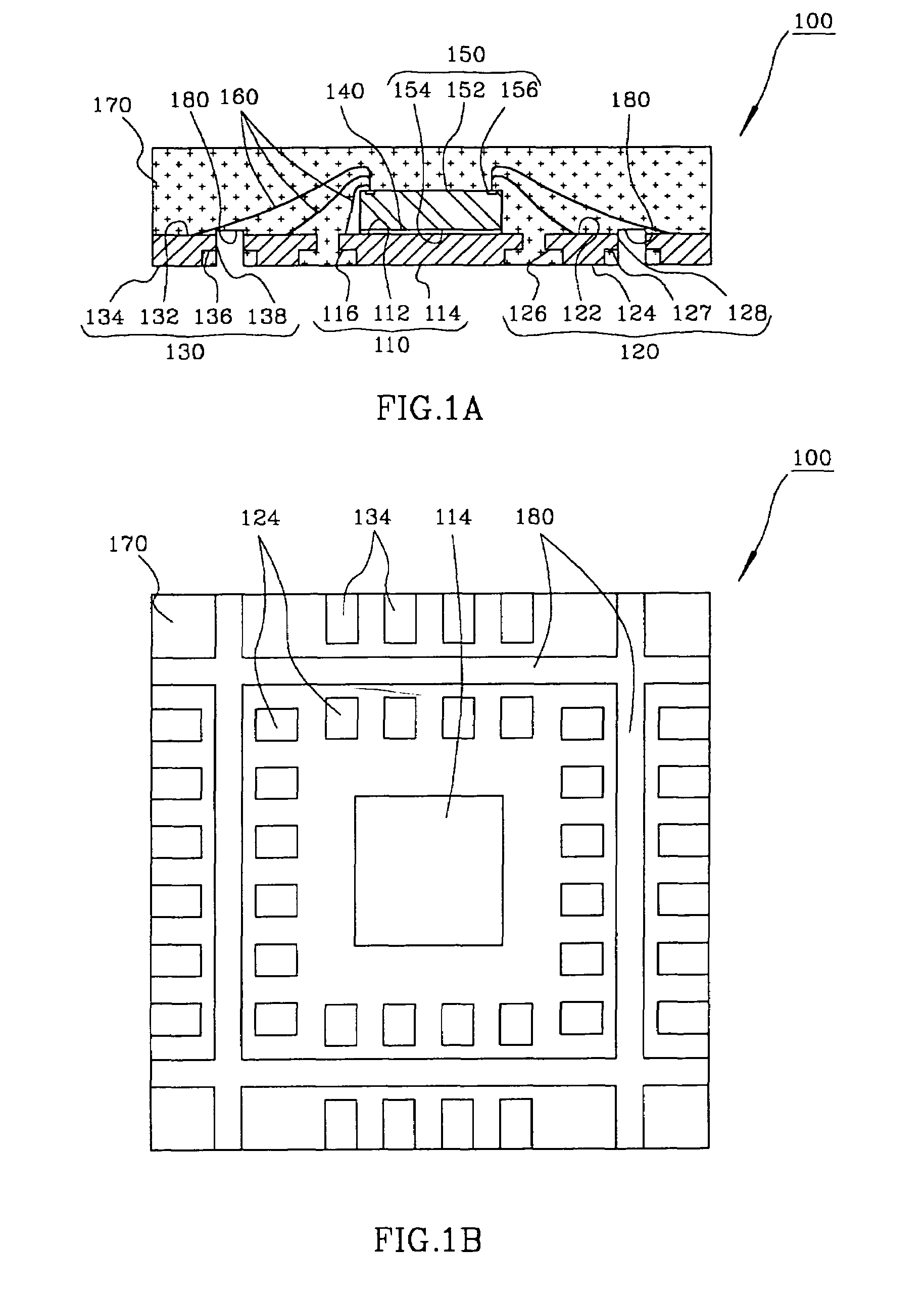
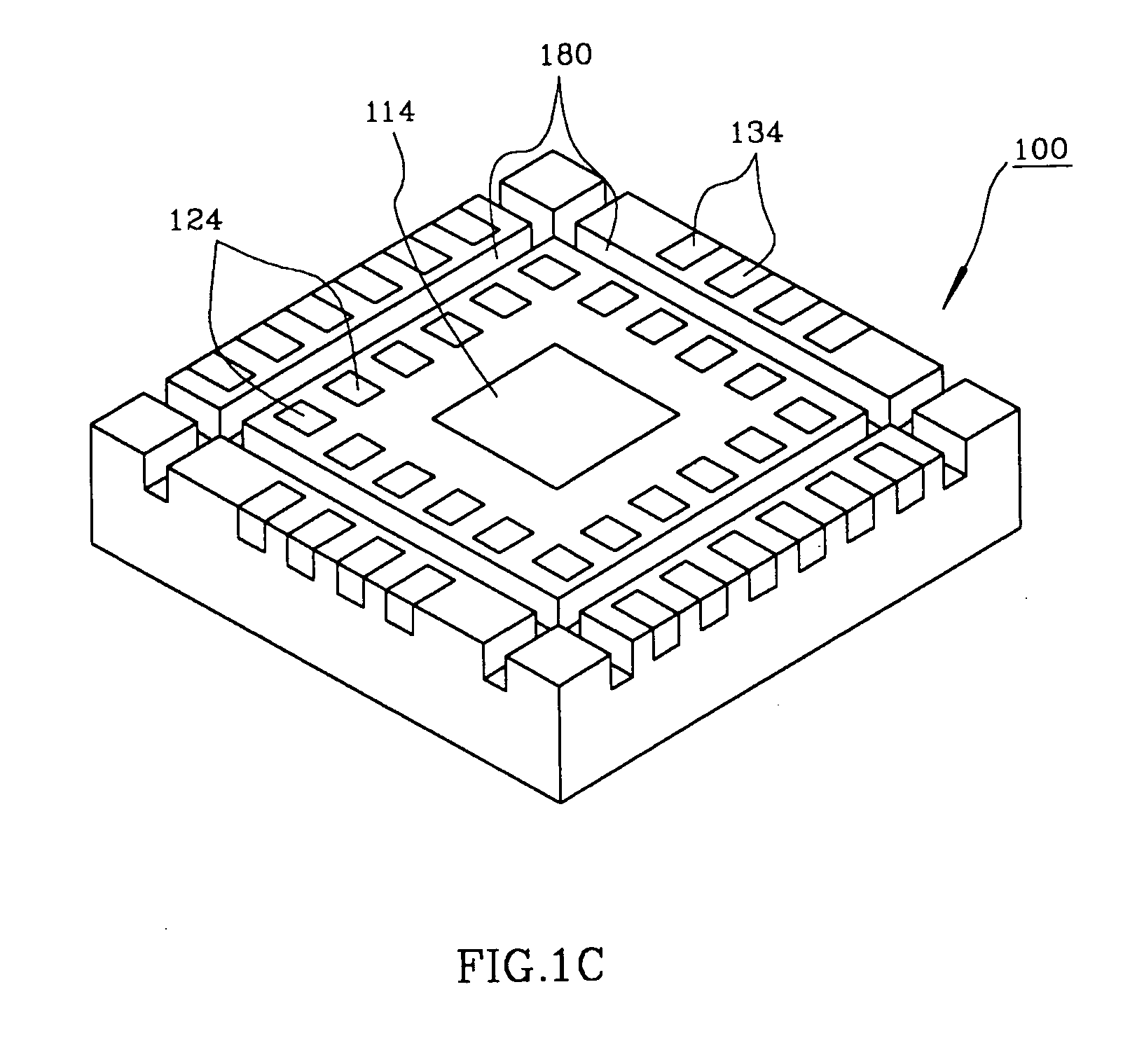
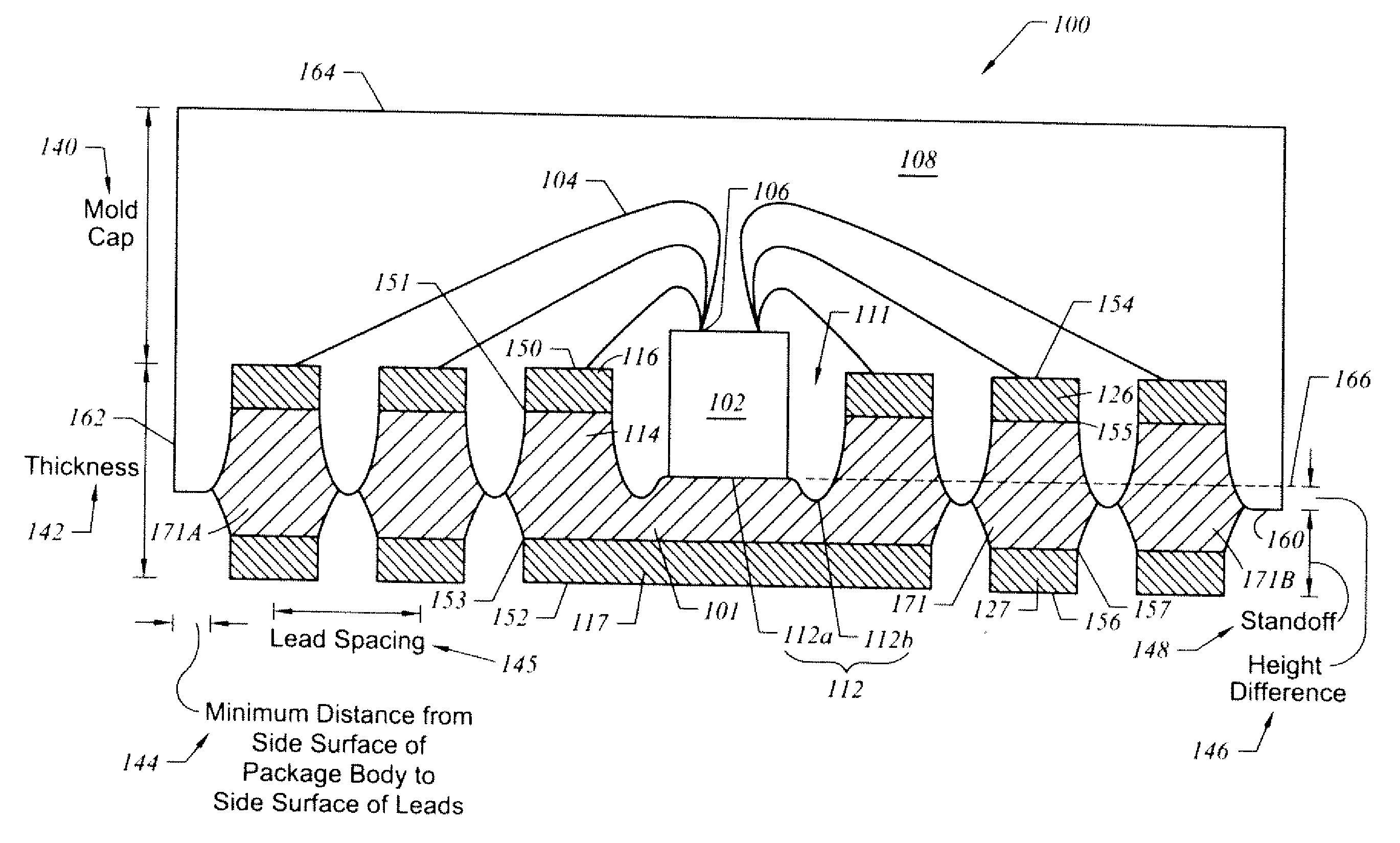
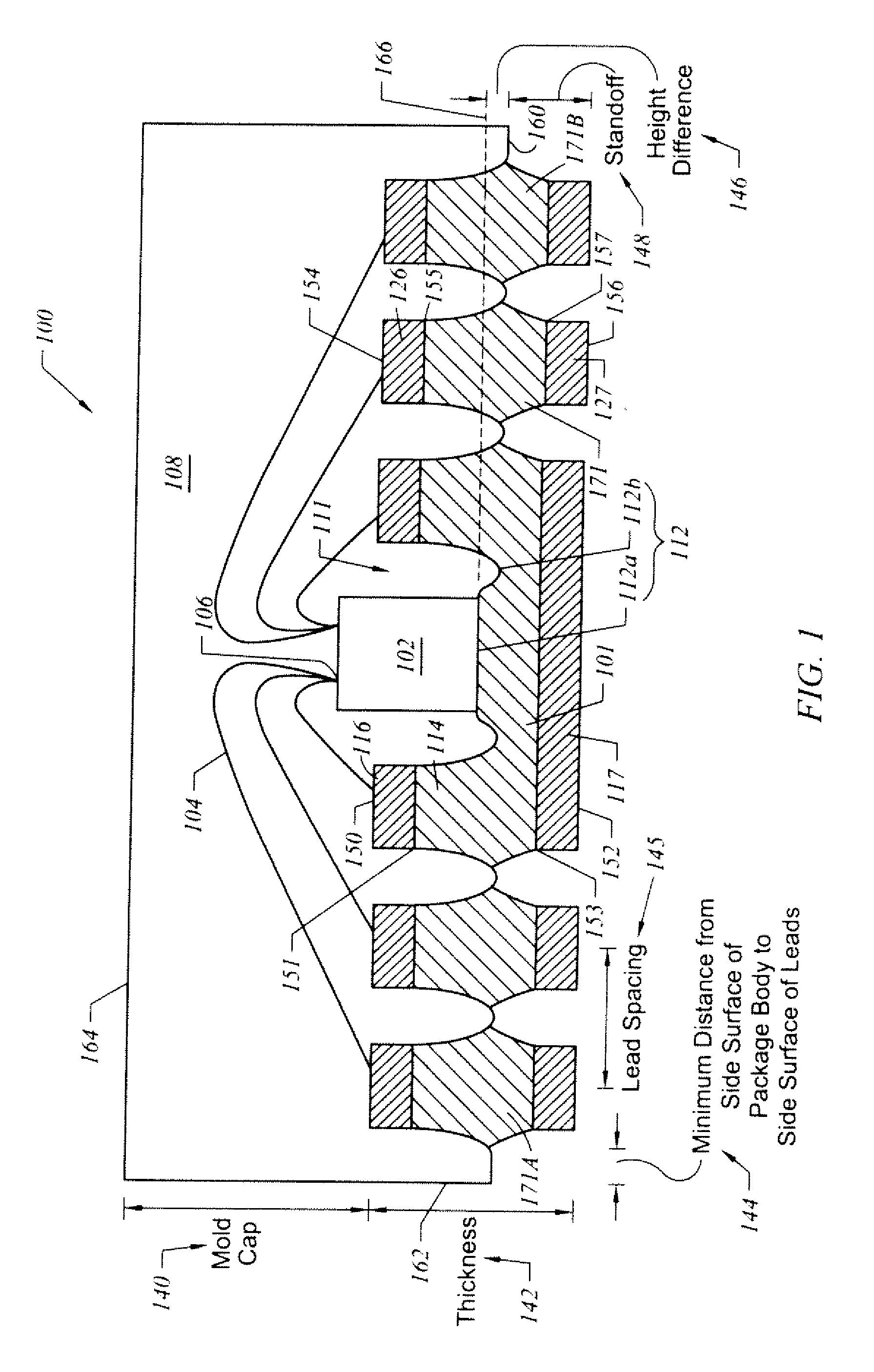
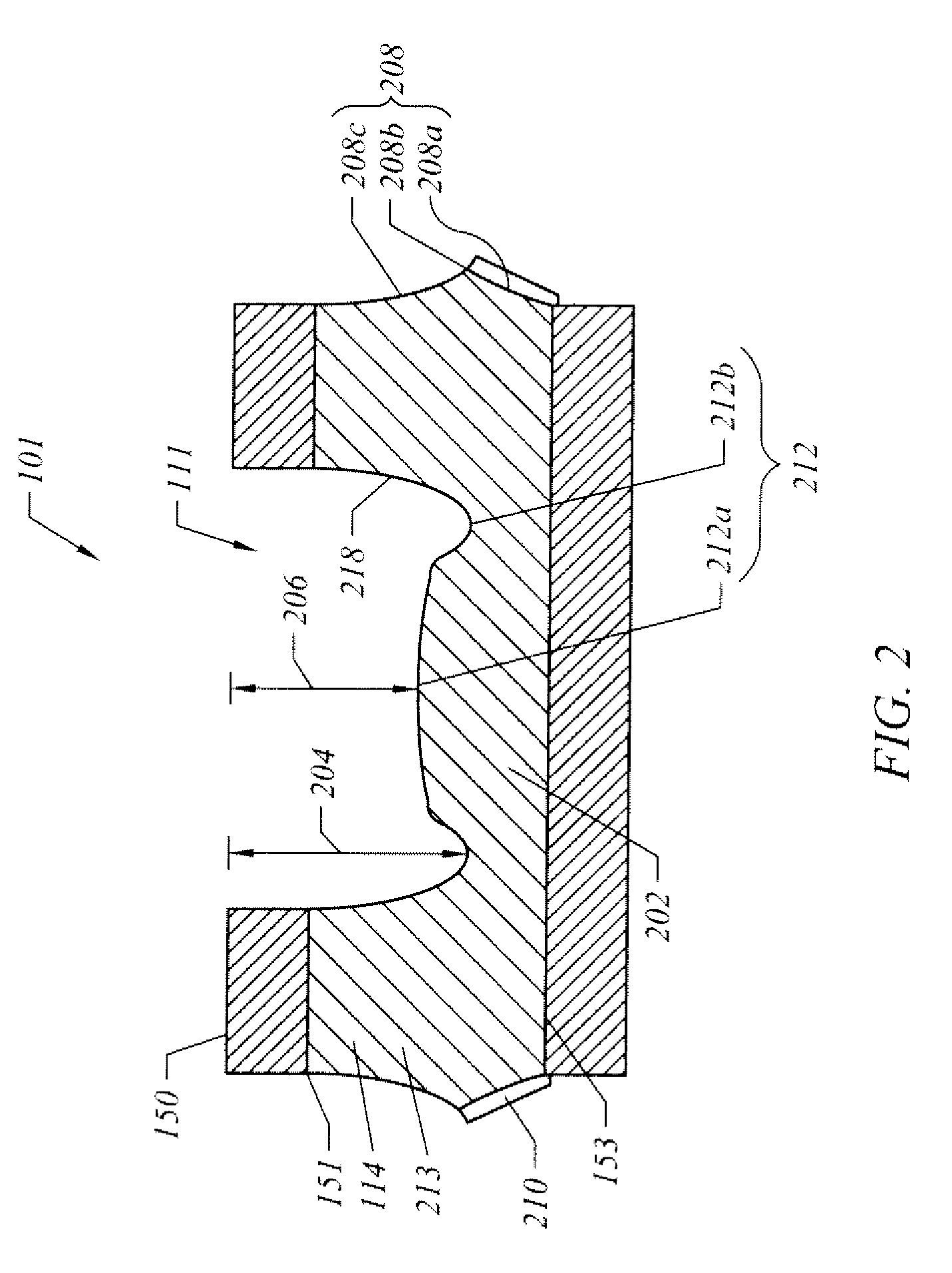
Semiconductor package exhibiting efficient lead placement
InactiveUS6927483B1Effective placementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageLead frame
A semiconductor package exhibiting efficient placement of semiconductor leads in a micro lead frame design is provided. An integrated circuit die is bonded to the top surfaces of leads, thereby allowing the leads to partially reside under the die. As a result, surface area on the bottom surface of the semiconductor package is recaptured. The die can be further bonded a die paddle if so desired. One or more channels can be cut into the bottom surface of the package in order to separate first and second leads. Such channels allow separate leads to be fabricated from a single lead member which is subsequently cut.
Owner:AMKOR TECH SINGAPORE HLDG PTE LTD
Optimization method for cardiac resynchronization therapy
ActiveUS6978184B1Shortening of pre-ejection periodIncrease in rate of contractionInternal electrodesHeart stimulatorsAccelerometerLeft ventricular size
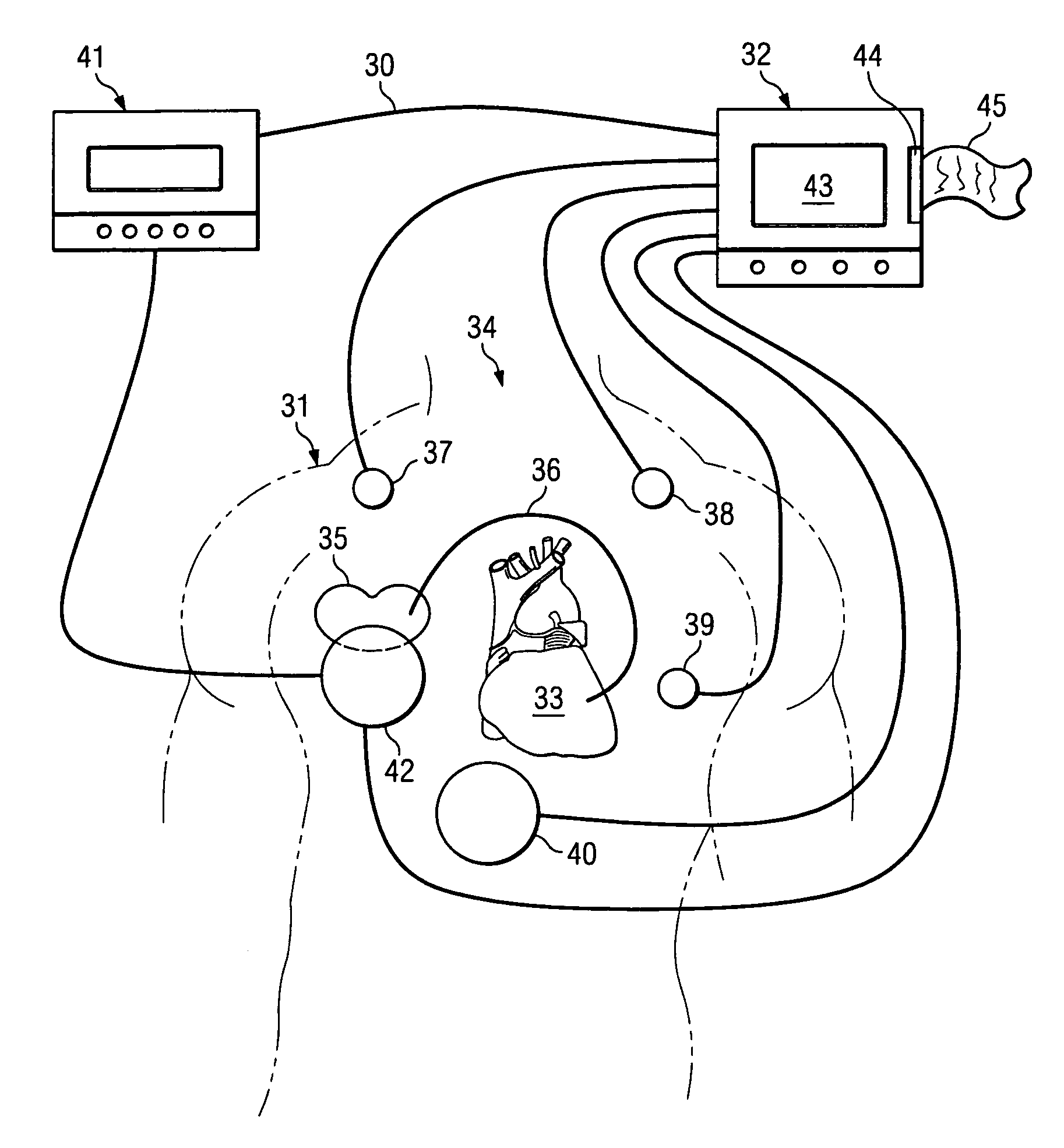
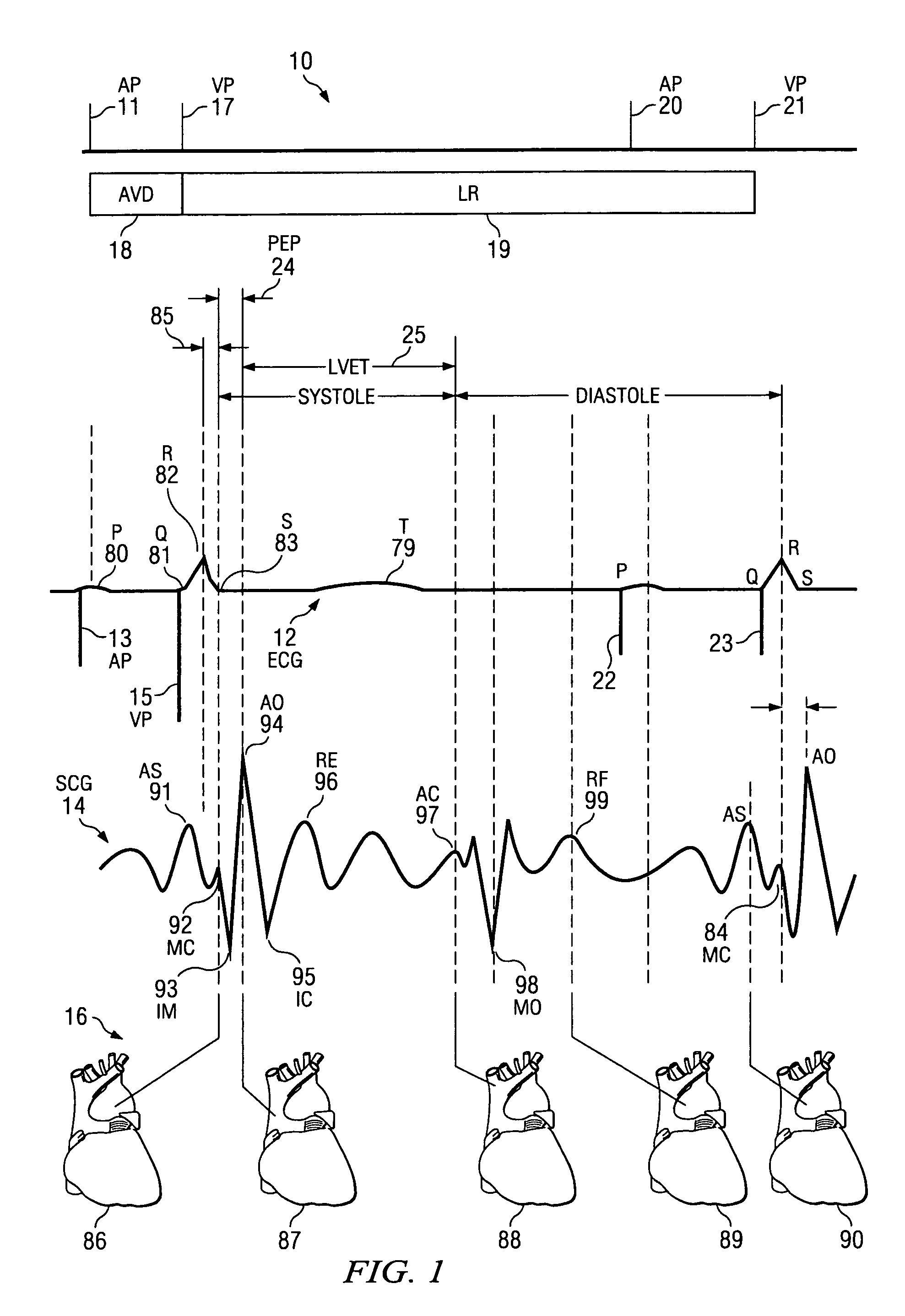
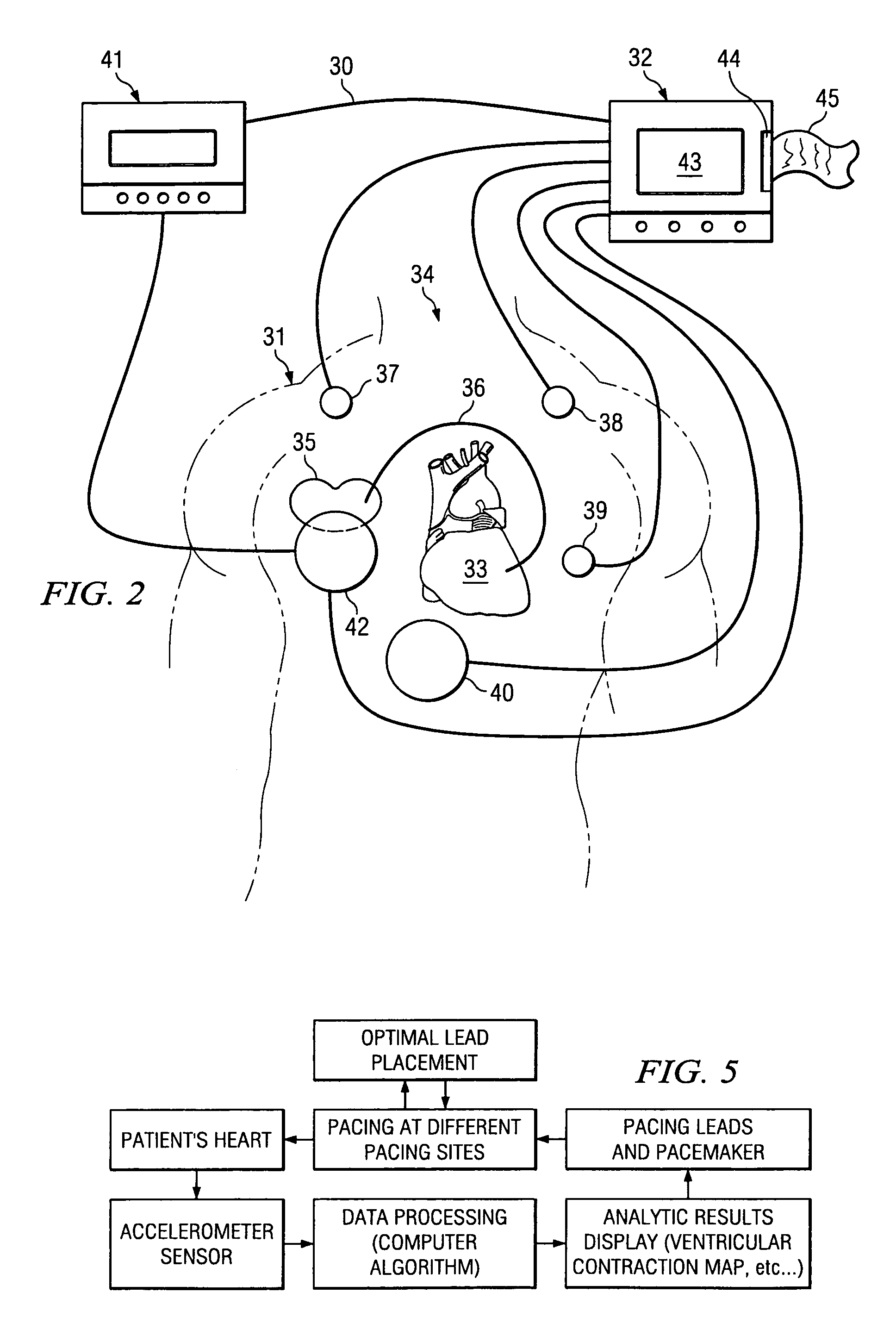
The patterns of contraction and relaxation of the heart before and during left ventricular or biventricular pacing are analyzed and displayed in real time mode to assist physicians to screen patients for cardiac resynchronization therapy, to set the optimal A-V or right ventricle to left ventricle interval delay, and to select the site(s) of pacing that result in optimal cardiac performance. The system includes an accelerometer sensor; a programmable pace maker, a computer data analysis module, and may also include a 2D and 3D visual graphic display of analytic results, i.e. a Ventricular Contraction Map. A feedback network provides direction for optimal pacing leads placement. The method includes selecting a location to place the leads of a cardiac pacing device, collecting seismocardiographic (SCG) data corresponding to heart motion during paced beats of a patient's heart, determining hemodynamic and electrophysiological parameters based on the SCG data, repeating the preceding steps for another lead placement location, and selecting a lead placement location that provides the best cardiac performance by comparing the calculated hemodynamic and electrophysiological parameters for each different lead placement location.
Owner:HEART FORCE MEDICAL +1
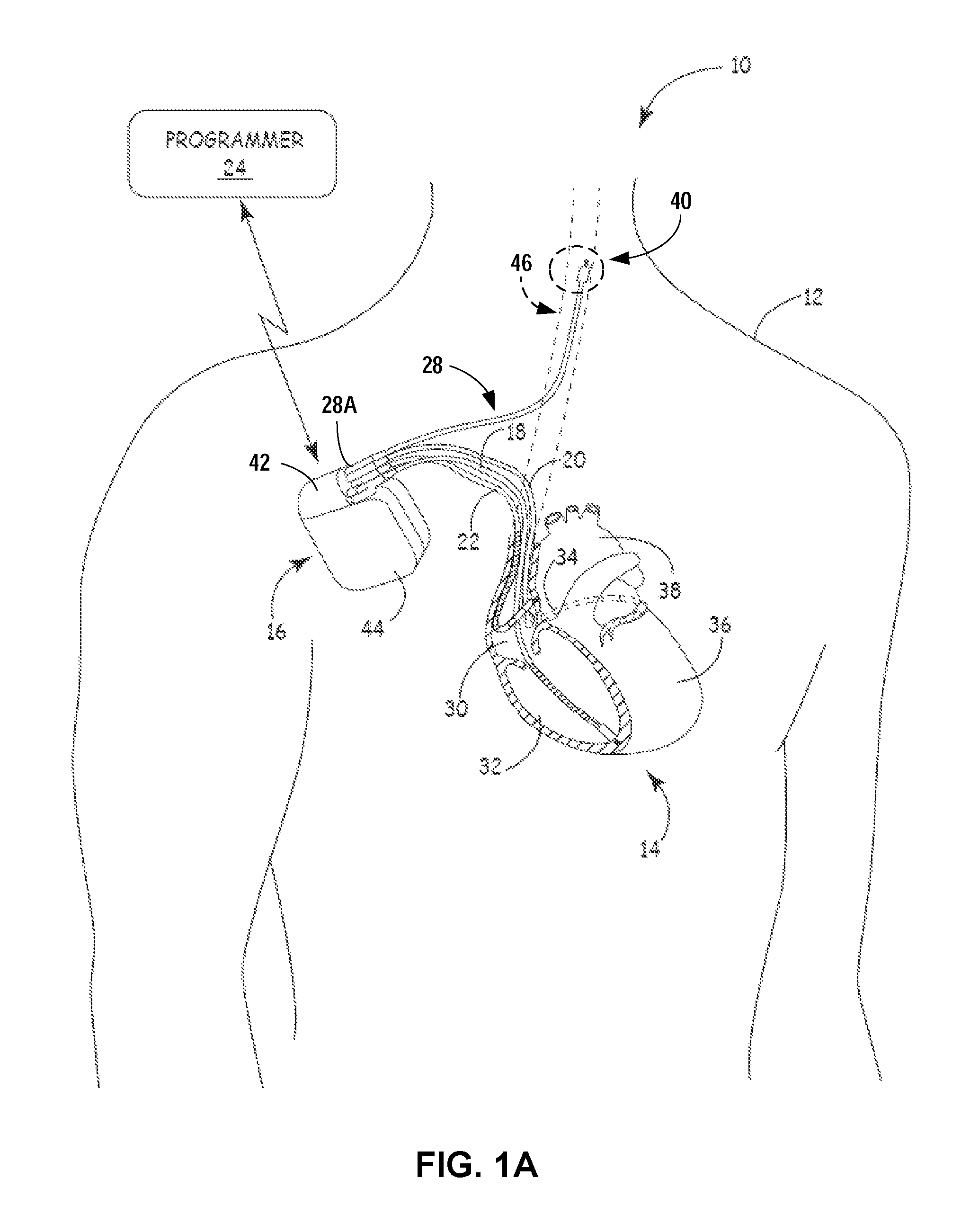
Leadless Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator
A leadless implantable cardioverter defibrillator (5) for treatment of sudden cardiac death includes a controller and at least one remote module. The defibrillator does not require transvenous / vascular access for intracardiac lead placement. The controller is leadless and uses subcutaneous tissue in proximity of the chest and abdomen for both sensing and defibrillation. The controller and one or more remote sensors sense a need for defibrillation and wireless communicate with the controller. The controller and one of the sensors discharge a synchronized defibrillation pulse to the surrounding subcutaneous tissue in proximity to the heart.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
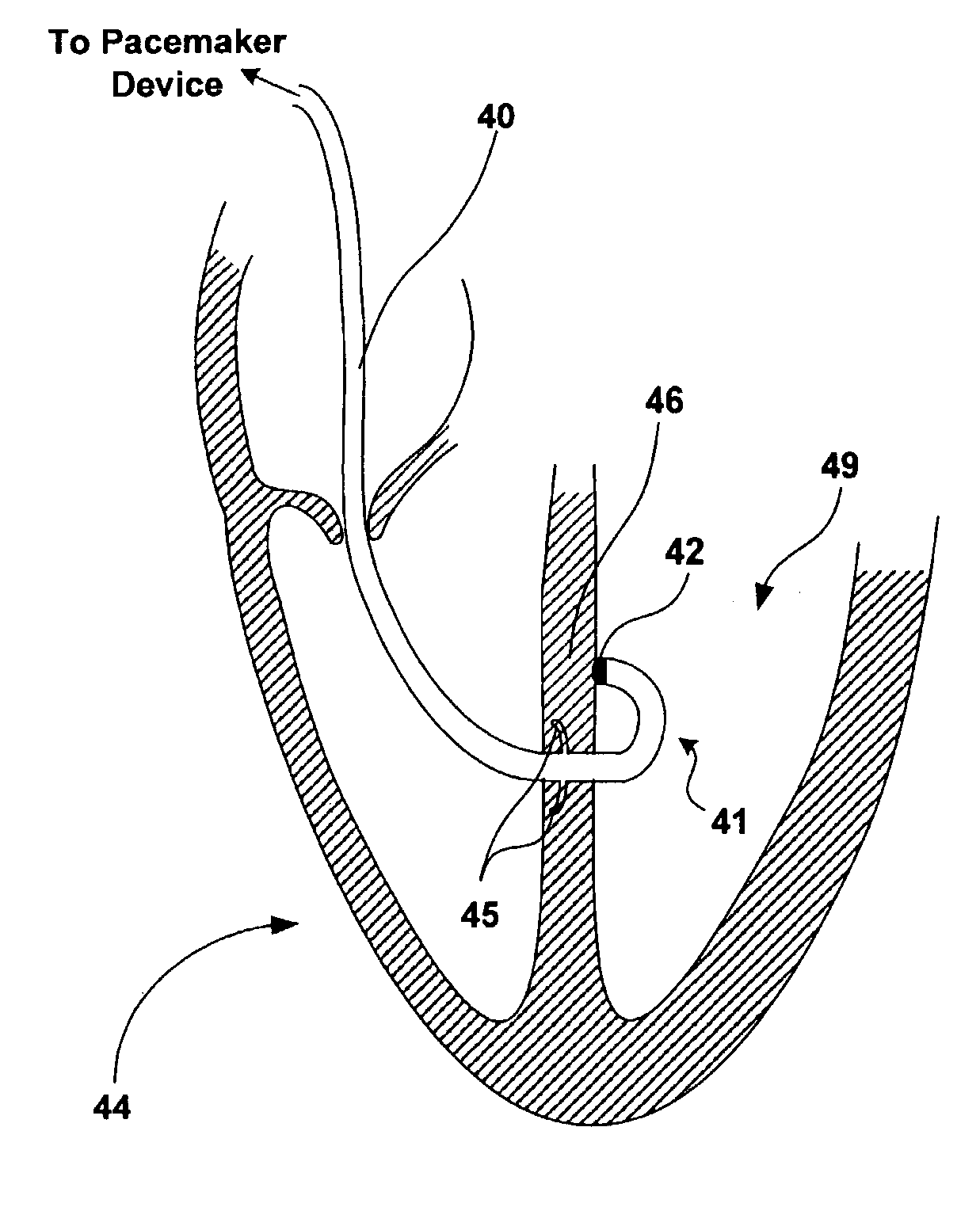
Perficardial pacing lead placement device and method
InactiveUS20050102003A1Heart stimulatorsSurgical instruments for heatingPericardial spaceLead Placement
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for pacing the ventricle of a patient's heart through the pericardial space, including an epicardial lead and a method for placement of the lead.
Owner:GRABEK JAMES R +1
Advanced quad flat no lead chip package having marking and corner lead features and manufacturing methods thereof
ActiveUS20090230525A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipSemiconductor package
A semiconductor package and related methods are described. In one embodiment, the package includes a die pad, a first plurality of leads disposed in a lead placement area around the die pad, a second plurality of leads disposed in corner regions of the lead placement area, a semiconductor chip on the die pad and coupled to each lead, and a package body. Each lead includes an upper sloped portion and a lower sloped portion. An average of surface areas of lower surfaces of each of the second plurality of leads is at least twice as large as an average of surface areas of lower surfaces of each of the first plurality of leads. The package body substantially covers the upper sloped portions of the leads. The lower sloped portions of the leads at least partially extend outwardly from a lower surface of the package body.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
Methods and devices for mapping the ventricle for pacing lead placement and therapy delivery
InactiveUS20060276867A1Easy to placeImprove heart functionDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsLead PlacementCatheter device
A method of placing a pacing lead in the heart includes moving an electrode catheter successively to a plurality of possible placement sites. The viability of the tissue at each site is determined. If the tissue at the site is viable, a pacing signal is applied to the tissue at the site, and the effectiveness of the pacing from the site is measured. After the area has been mapped in this fashion, at least one pacing lead is placed from at least one of the sites which exceeded a predetermined level of pacing effectiveness.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
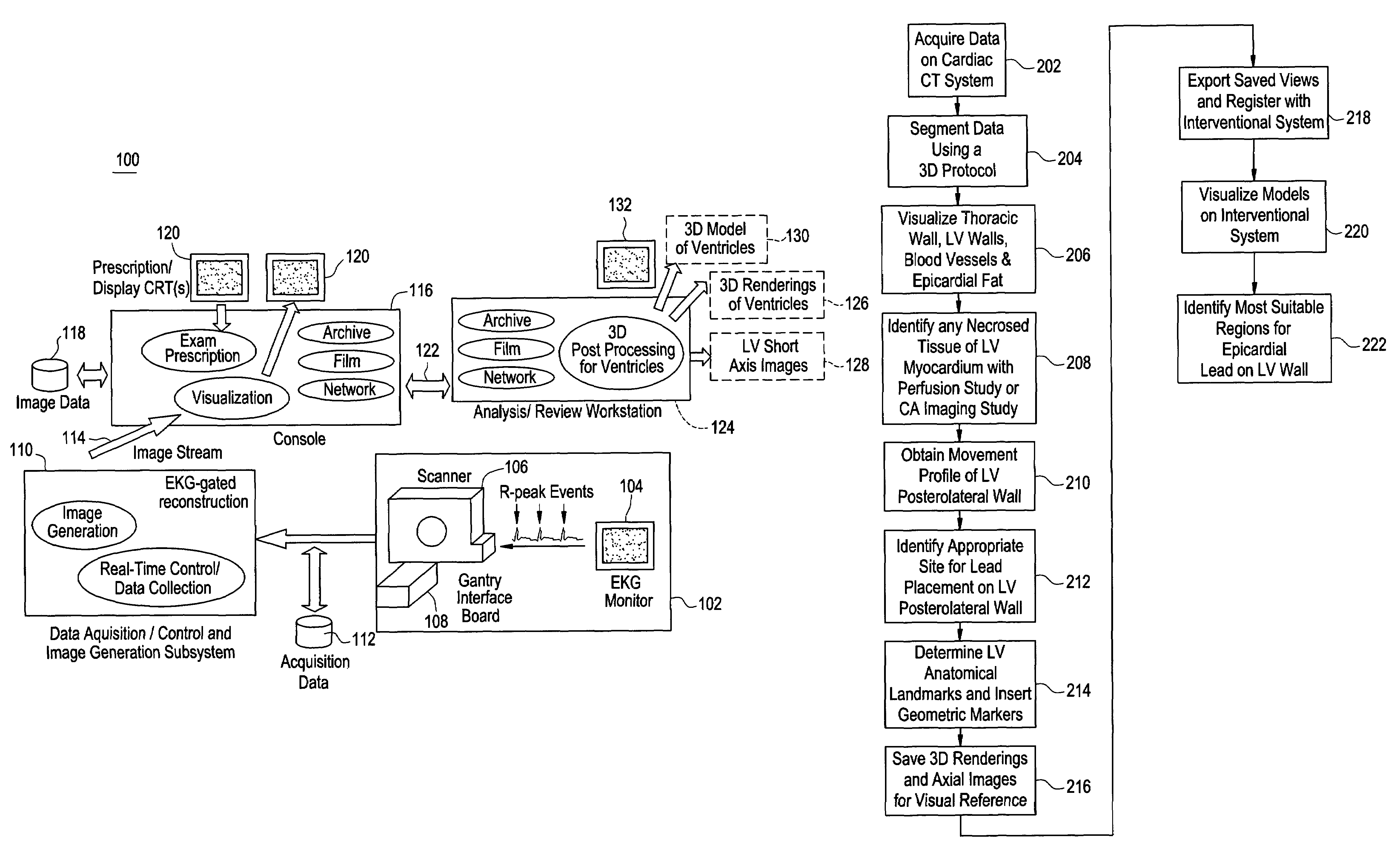
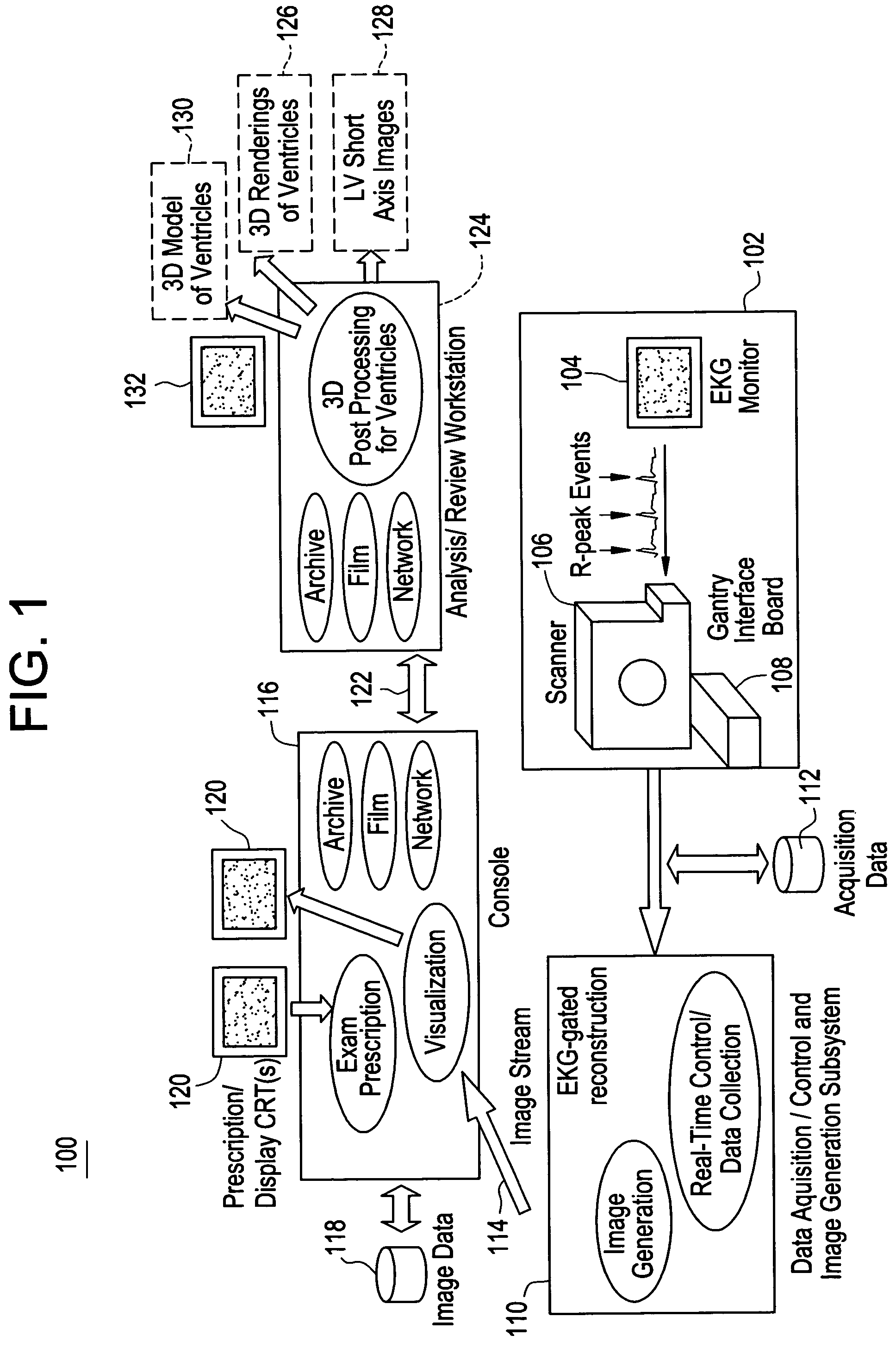
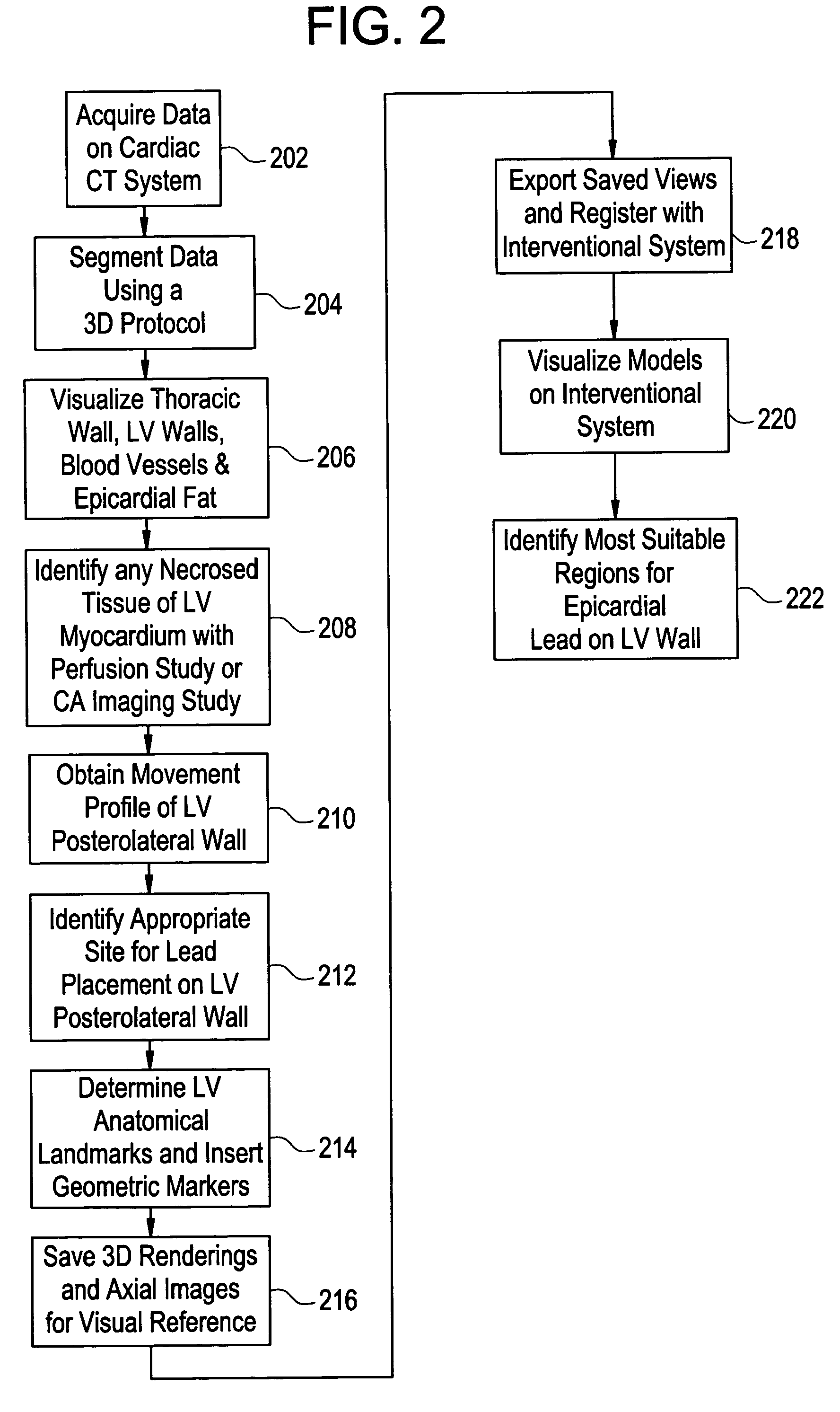
Cardiac CT system and method for planning and treatment of biventricular pacing using epicardial lead
ActiveUS7343196B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyAnatomical landmarkThoracic wall
A method for planning biventricular pacing lead placement for a patient includes obtaining acquisition data from a medical imaging system and generating a 3D model of the left ventricle and thoracic wall of the patient. One or more left ventricle anatomical landmarks are identified on the 3D model, and saved views of the 3D model are registered on an interventional system. One or more of the registered saved views are visualized with the interventional system, and at least one suitable region on the left ventricle wall is identified for epicardial lead placement.
Owner:APN HEALTH +1
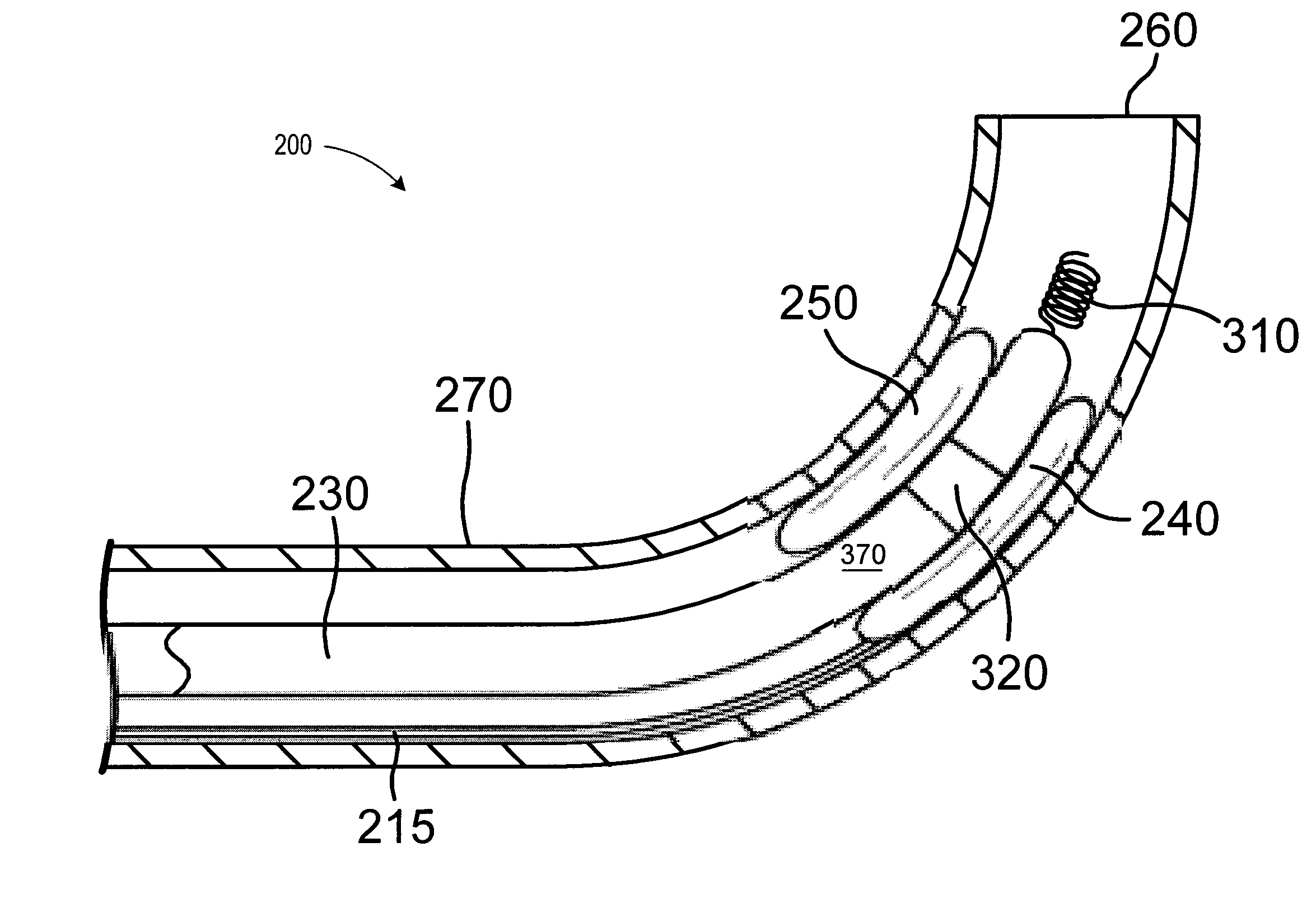
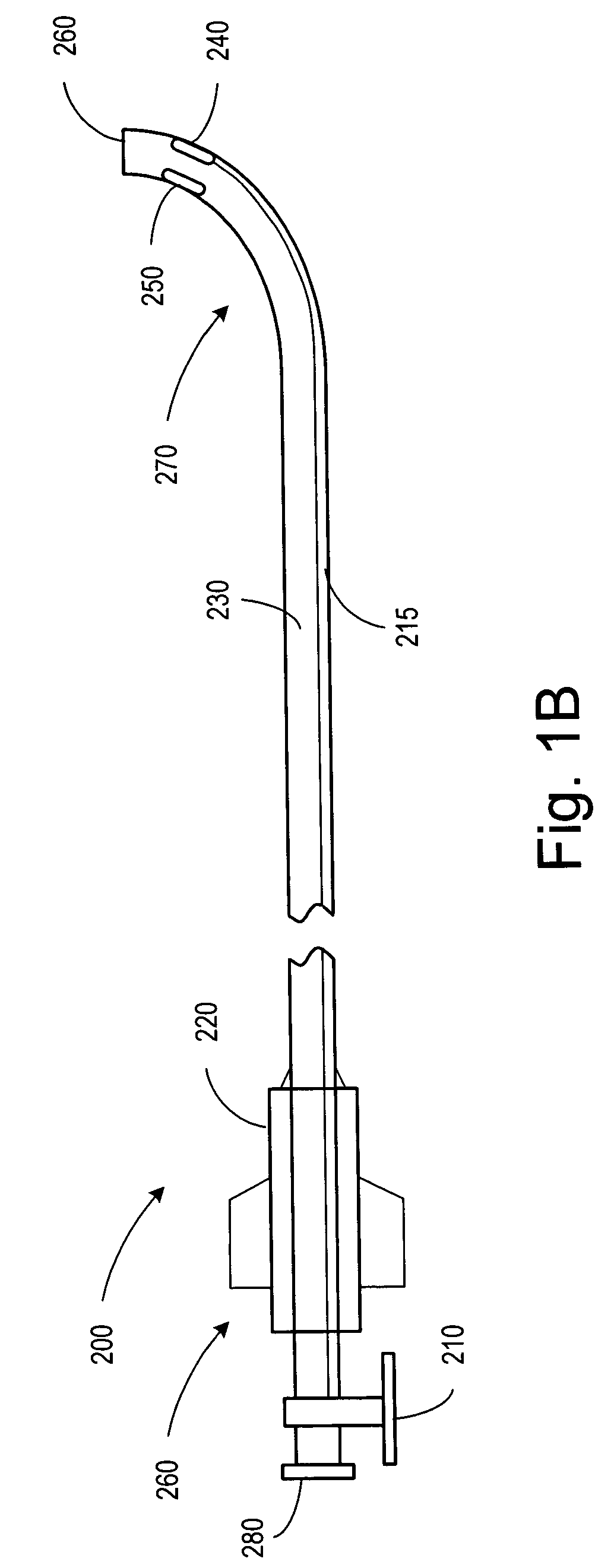
Catheter lead placement system and method
InactiveUS7035680B2Facilitate grasping and releasePrevent movementElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesBalloon catheterLead Placement
A catheter system includes a mapping catheter having an open lumen and a mapping arrangement provided at a distal end of the mapping catheter. A balloon catheter is movably disposed within the open lumen of the mapping catheter. The balloon catheter has an open lumen dimensioned to receive a lead. A balloon arrangement is provided at a distal end of the balloon catheter and inflatable with an inflation mechanism provided at a proximal end of the balloon catheter. The balloon arrangement is dimensioned to prevent movement of the lead upon inflation of the balloon arrangement, and to permit movement of the lead within the open lumen of the balloon catheter upon deflation of the balloon arrangement.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System and method for planning LV lead placement for cardiac resynchronization therapy
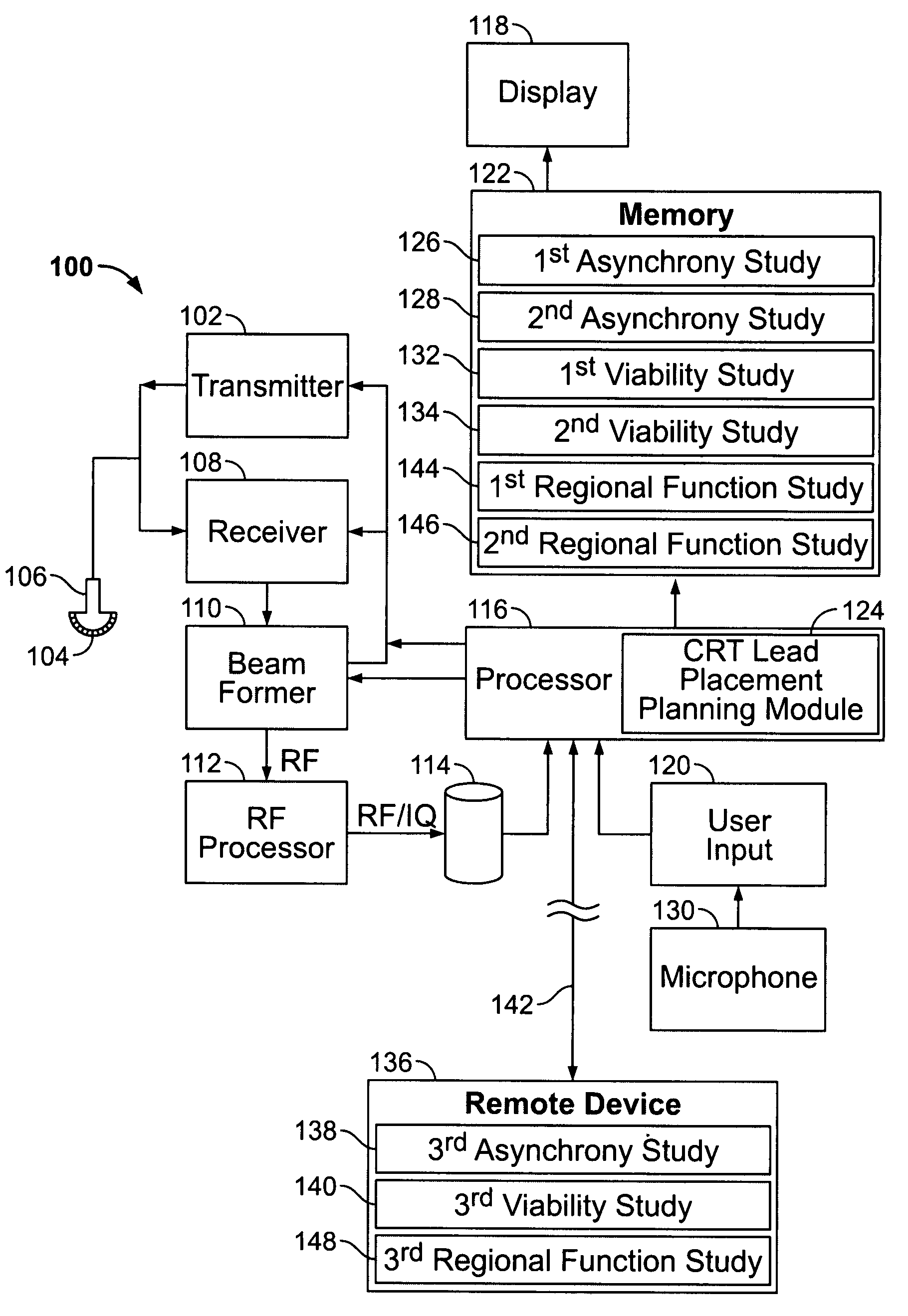
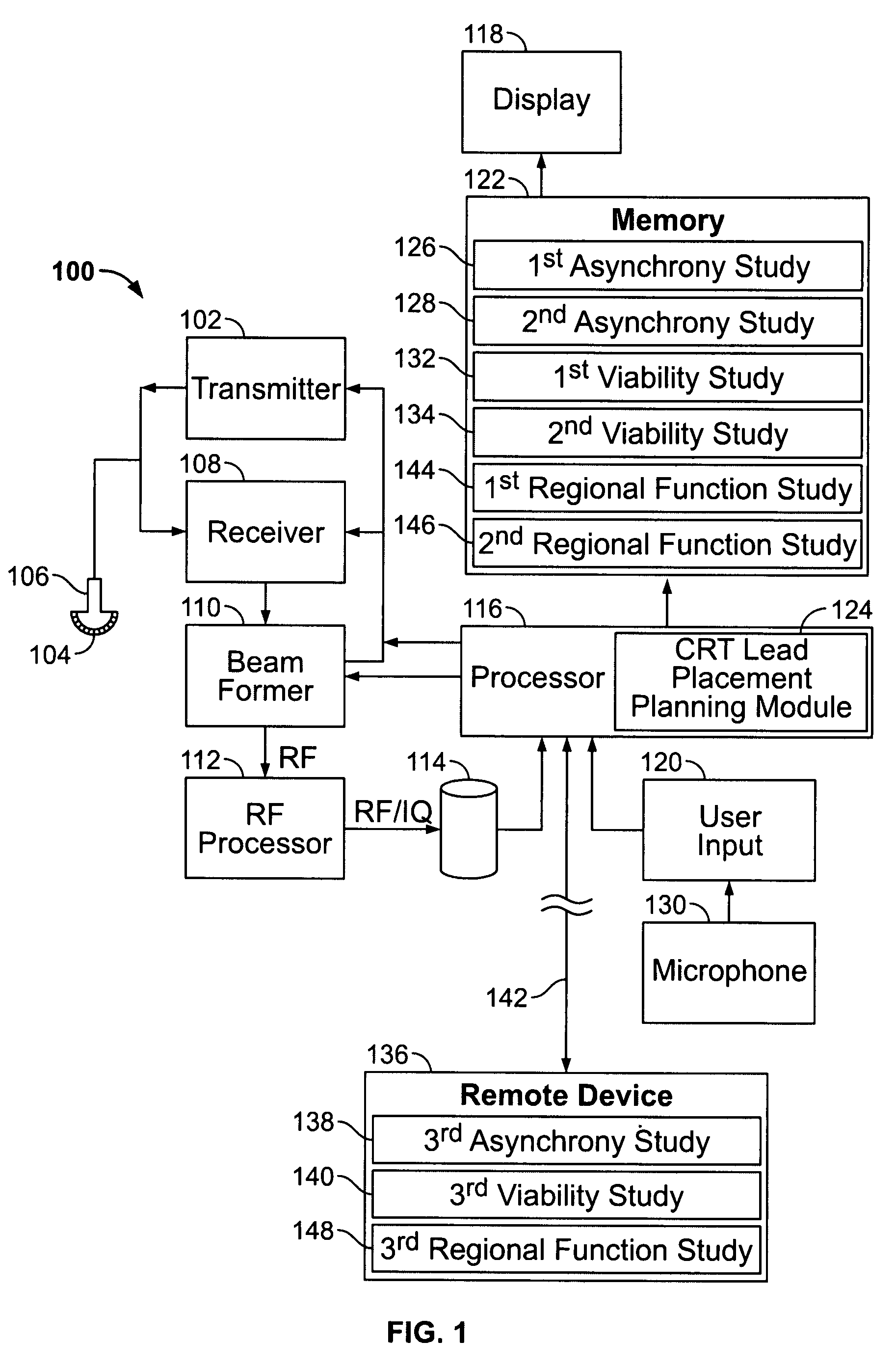
An ultrasound system comprises a memory for storing patient study data associated with segments of a patient's left ventricle (LV). The patient study data comprises at least a first asynchrony study and at least one of a first viability study and a first regional function study. A cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) lead placement planning module compares at least a portion of the patient study data for each of the segments. An output device indicates at least one location for placement of an LV lead within one of the segments of the patient's LV during a CRT procedure based on the comparison of the at least a portion of the patient study data for each of the segments.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
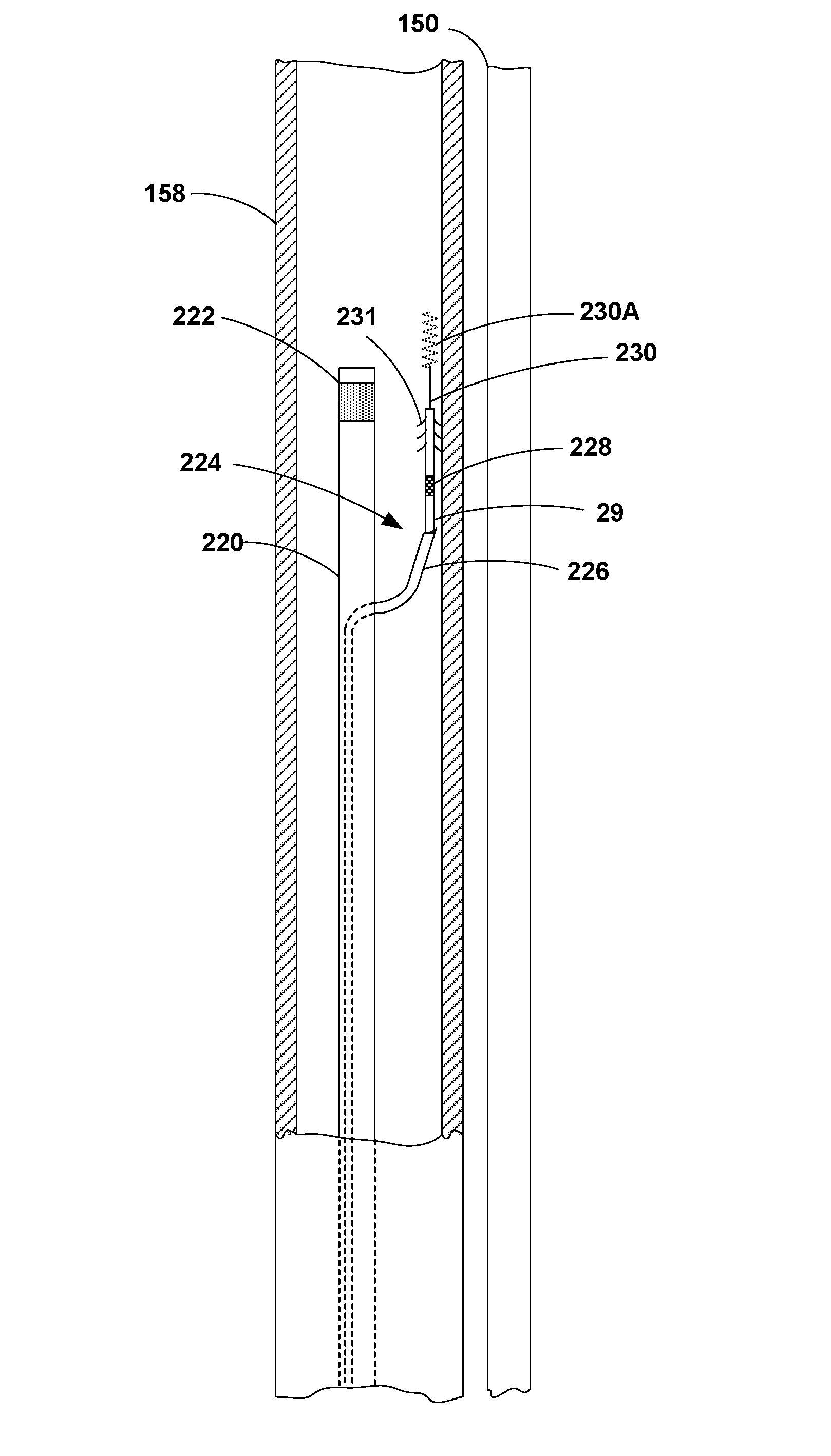
Medical lead designs for lead placement through tissue
InactiveUS7546166B2Easy to implantEasy to fixTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesLead PlacementMedical treatment
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
MRI-guided localization and/or lead placement systems, related methods, devices and computer program products
MRI compatible localization and / or guidance systems for facilitating placement of an interventional therapy and / or device in vivo include: (a) a mount adapted for fixation to a patient; (b) a targeting cannula with a lumen configured to attach to the mount so as to be able to controllably translate in at least three dimensions; and (c) an elongate probe configured to snugly slidably advance and retract in the targeting cannula lumen, the elongate probe comprising at least one of a stimulation or recording electrode. In operation, the targeting cannula can be aligned with a first trajectory and positionally adjusted to provide a desired internal access path to a target location with a corresponding trajectory for the elongate probe. Automated systems for determining an MR scan plane associated with a trajectory and for determining mount adjustments are also described.
Owner:CLEARPOINT NEURO INC
The ECG shirt
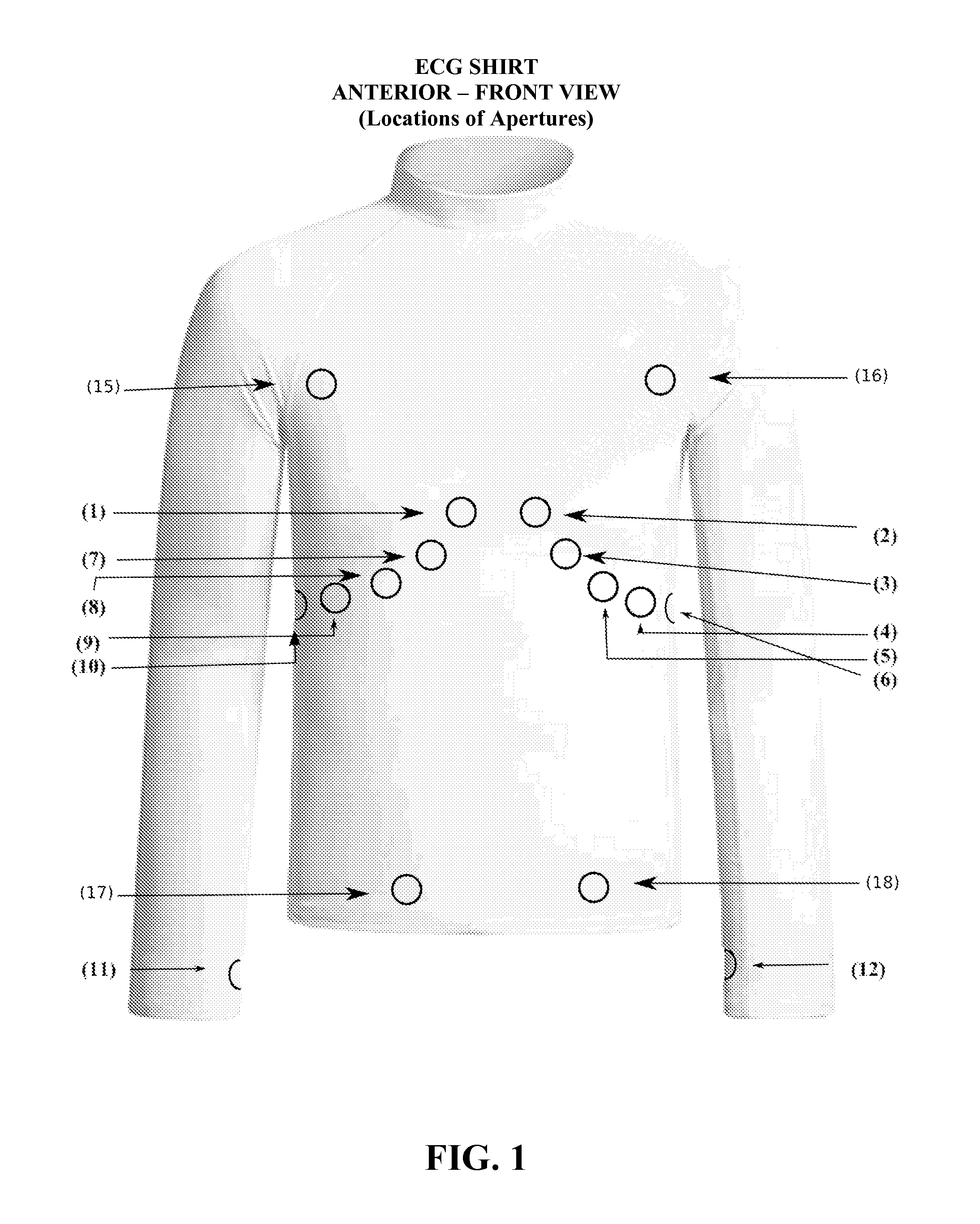
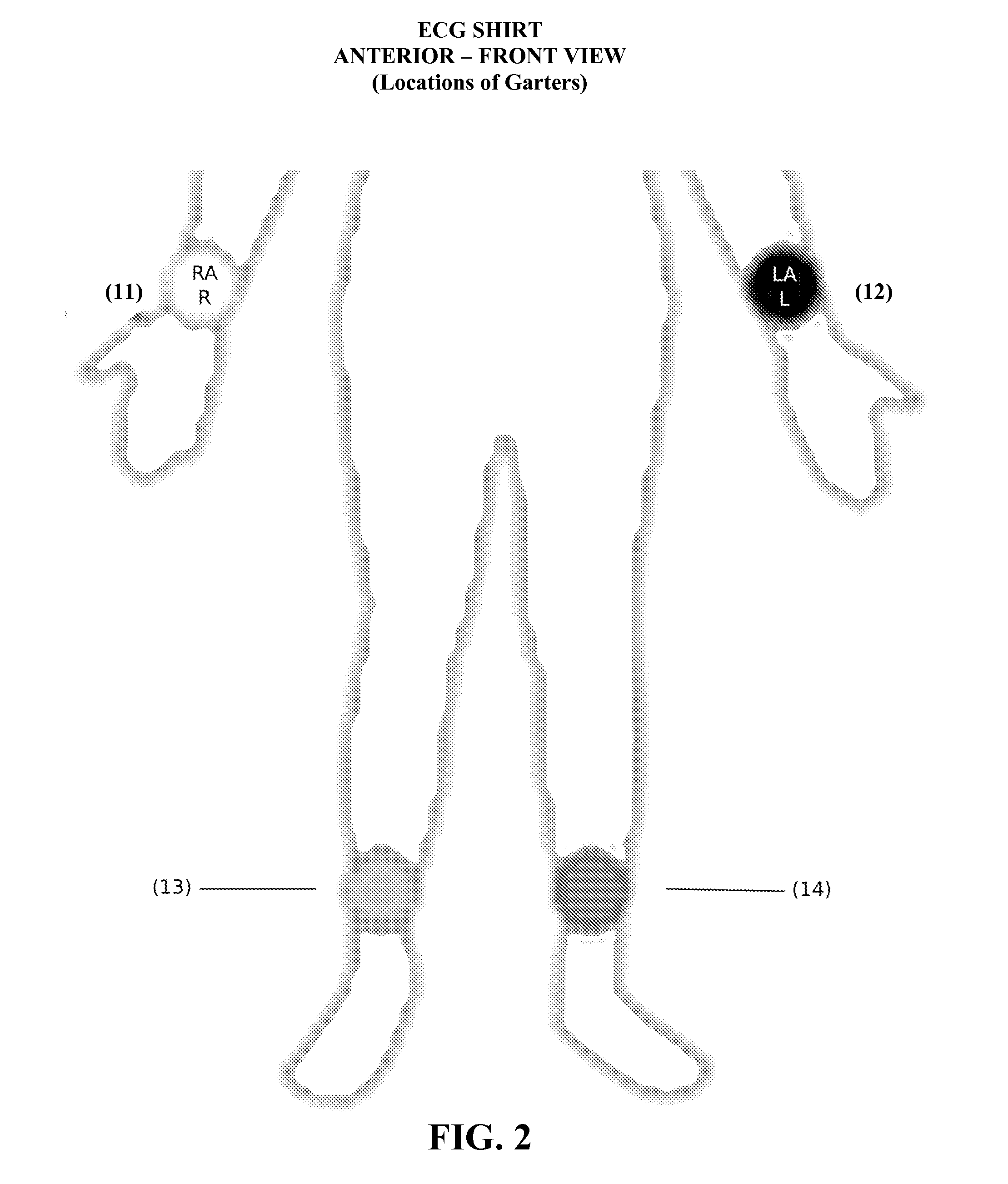
InactiveUS20110004088A1Less timeWide variationElectrocardiographySensorsExercise testingsLead Placement
The electrocardiograph (ECG) Shirt is an extremely elastic non-electric and non-mechanical method that creates a more secure bond to the skin and more accurate and standardized ECG electrode lead placement for men, women, and children. The ECG Shirt reduces unexpected movement or dislocation. Contrasted with much prior art that analyzes errors after the fact the ECG Shirt eliminates the potential for errors to occur. The ECG Shirt is capable of using most ECG devices with different types of electrode lead connectors or pads. The ECG Shirt facilitates not only twelve lead resting ECG testing but also exercise testing, monitoring, fifteen lead, and two different types of eighteen lead ECG testing. The ECG Shirt is a tool for teaching expert ECG electrode lead placement.
Owner:GROSSMAN KURT PAUL
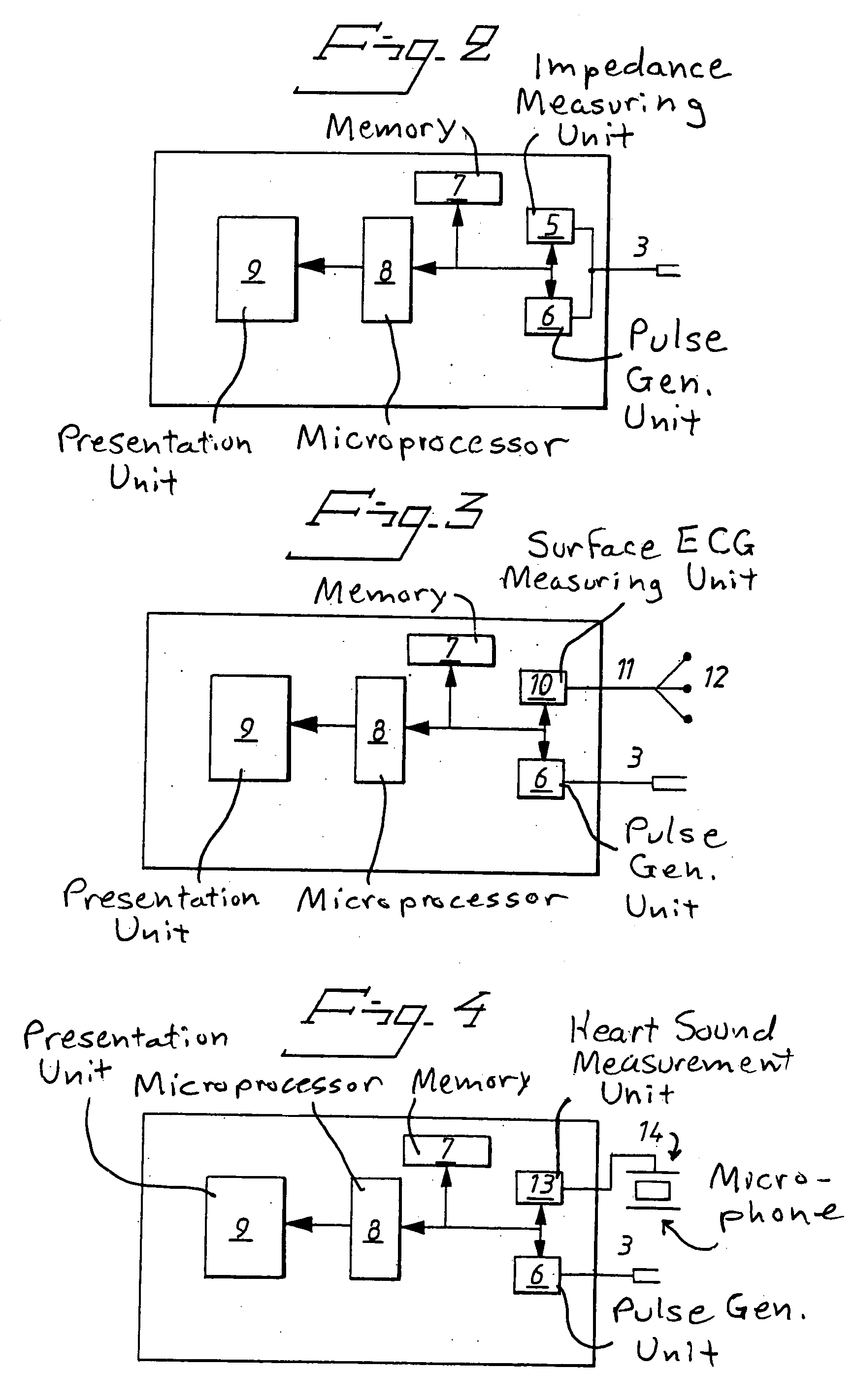
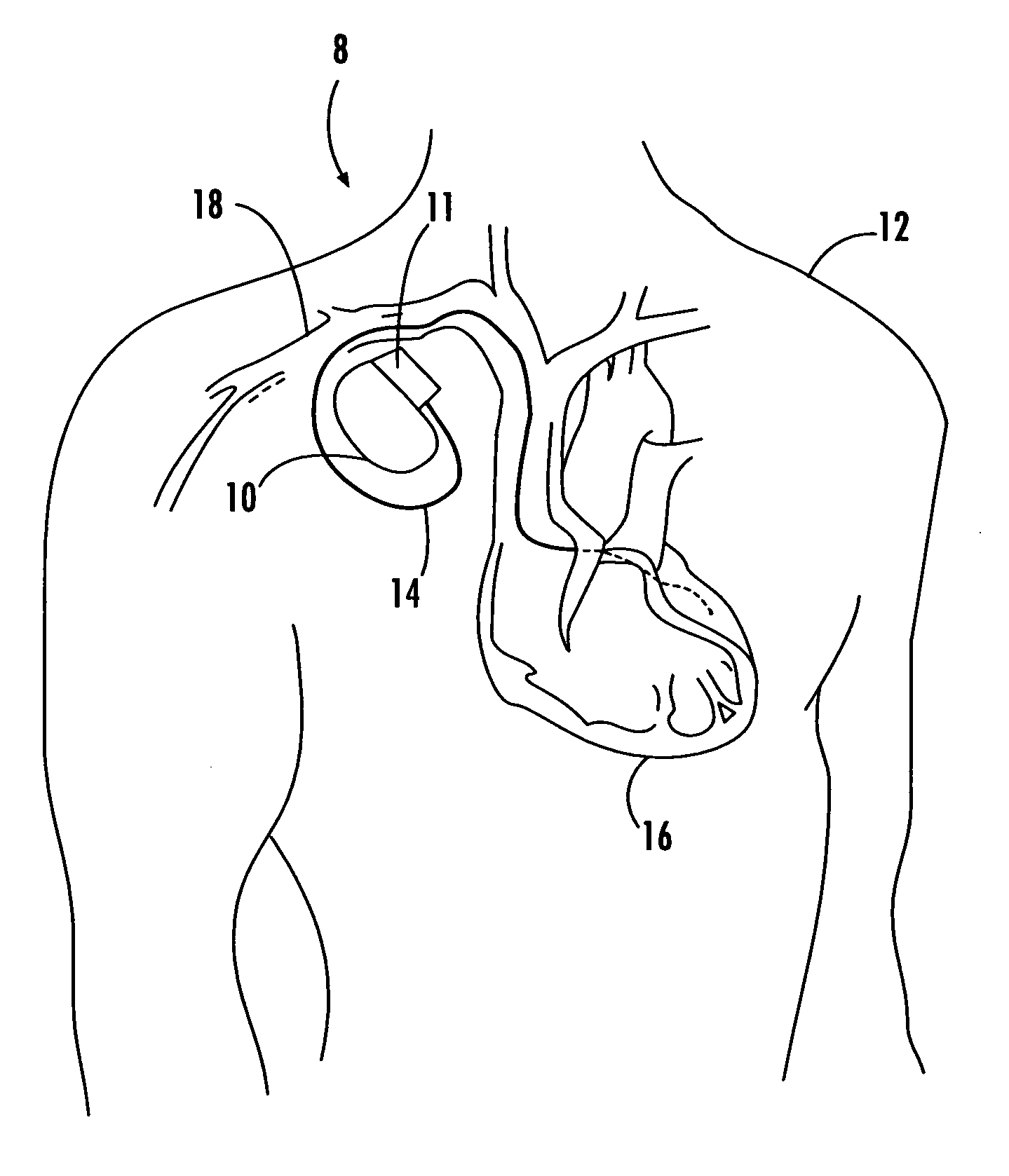
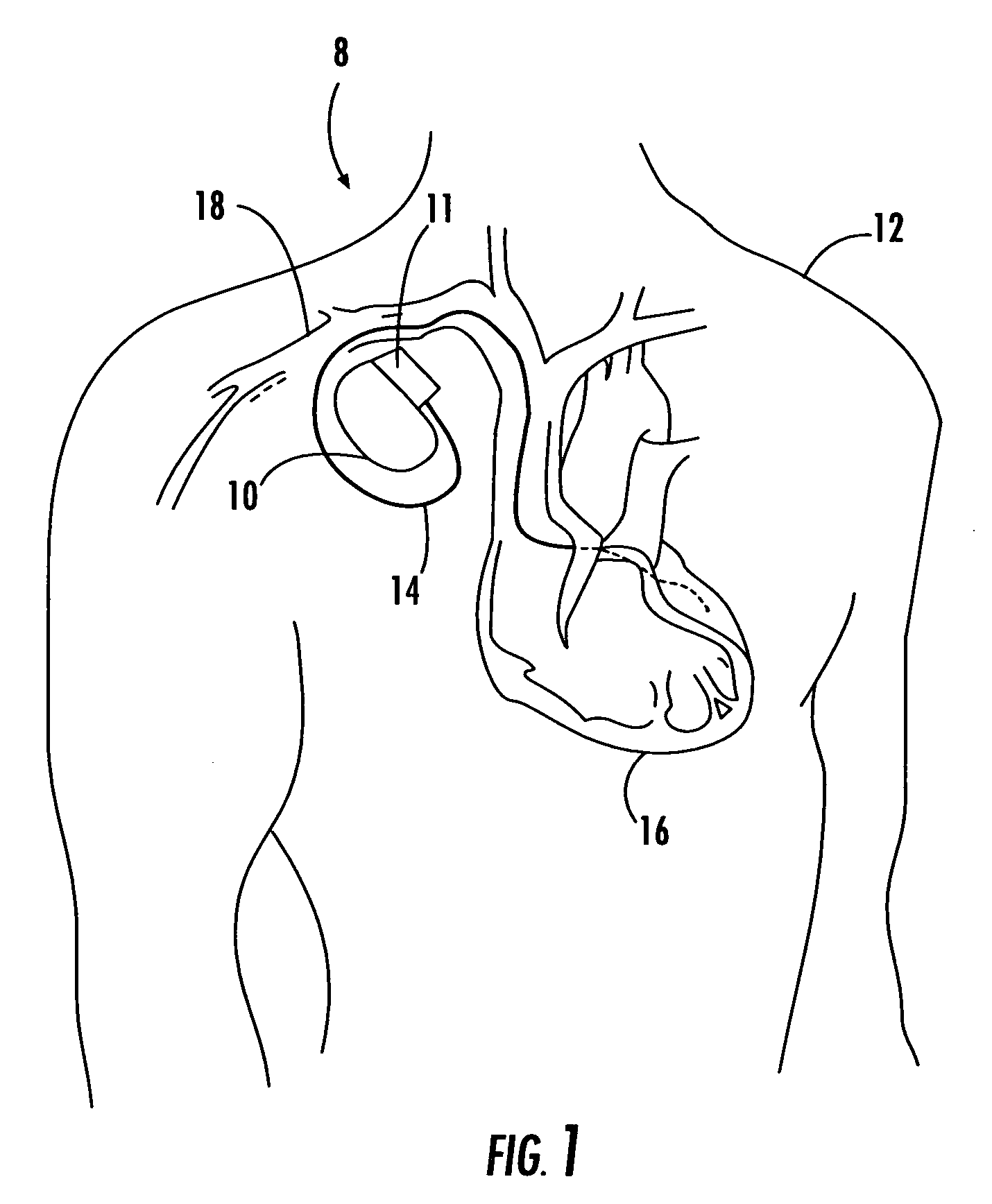
Arrangement and Method for Evaluating Operational Effectiveness of Implantable Medical Electrode Leads for Different Lead Placements
InactiveUS20080249375A1Improved and simplifiedElevated PSAElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyEcg signalOperational effectiveness
In a method and an arrangement for evaluating operational effectiveness of an implantable medical device for different lead placements associated with the medical device, a measuring unit records signals that are characteristic of cardiac activity at respectively different lead positions, and these signals are stored. A processor accesses the stored signals and, from the stored signals, determines a measure of cardiac activity at each of the lead positions. The recorded signals may be intracardiac ECG signals, surface ECG signals, heart sound signals obtained from a microphone, or impedance signals. The lead position at which the best hemodynamic behavior of the heart is identified from the analysis of the stored signals, and is determined as being the optimum site for placement of the electrode leads.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
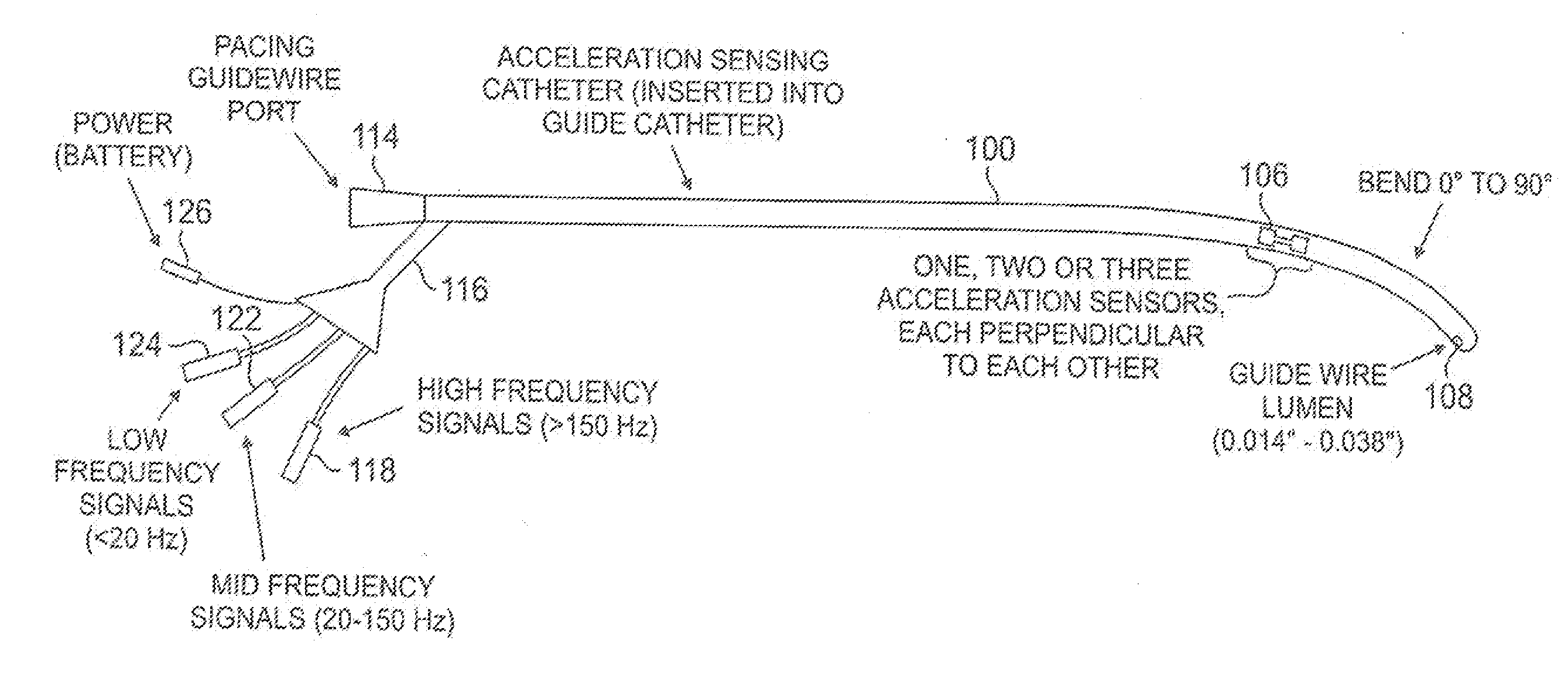
Method and apparatus for reliably placing and adjusting a left ventricular pacemaker lead
InactiveUS20060106445A1Easy to anchorImprove positionTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesLocking mechanismLeft ventricular size
A left ventricular stimulation lead construction and a technique for lead placement that provides for improved anchoring and positioning of the electrode located on the distal end of the lead, while also including a method for readjusting the positioning of the lead as necessary. The lead includes a small diameter guide wire wherein the distal end of the guide wire serves as an anchor for the pacing lead. The lead structure includes a central hollow lumen to allow passage of the guide wire and a locking mechanism positioned on the proximal end of the pacing lead to fix the ends of the guide wire and pacing lead relative to one another. The method provides for advancing the guide wire until it is anchored, positioning the pacing lead along the guide wire into the desired position relative to the cardiac tissue, releasably fixing the lead relative to the guide wire, wherein the guide wire is permanently retained to serve as an anchor.
Owner:WOOLLETT IAN
System and method of image guided pericardial procedures including pericardioscopy, pericardial ablation, pericardial material delivery, pericardial tissue grasping and manipulation, pericardial lead placement, and pericardial surgical fastener placement
InactiveUS20150305770A1Minimize the possibilitySurgical needlesSurgical instrument detailsDisplay deviceMethod of images
A system and method of performing percutaneous image guided pericardial procedures is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of: providing a tool tracking system having a display for visualization of virtual representations of tracked tools which is configured to have a field of operation encompassing percutaneous pericardial space access and procedures; providing a patient specific three dimensional model of the patient for use in percutaneous pericardial space procedures that is registered with the tool tracking system for simultaneous display of the model and the virtual representation of the tracked tools on the system display; percutaneously inserting at least one tracked tool for the tool tracking system into the pericardial space; and simultaneously visualizing the virtual representation of the tracked tool and the patient specific model on the system display at least through a portion of a pericardial procedure.
Owner:EPICARDIAL FRONTIERS
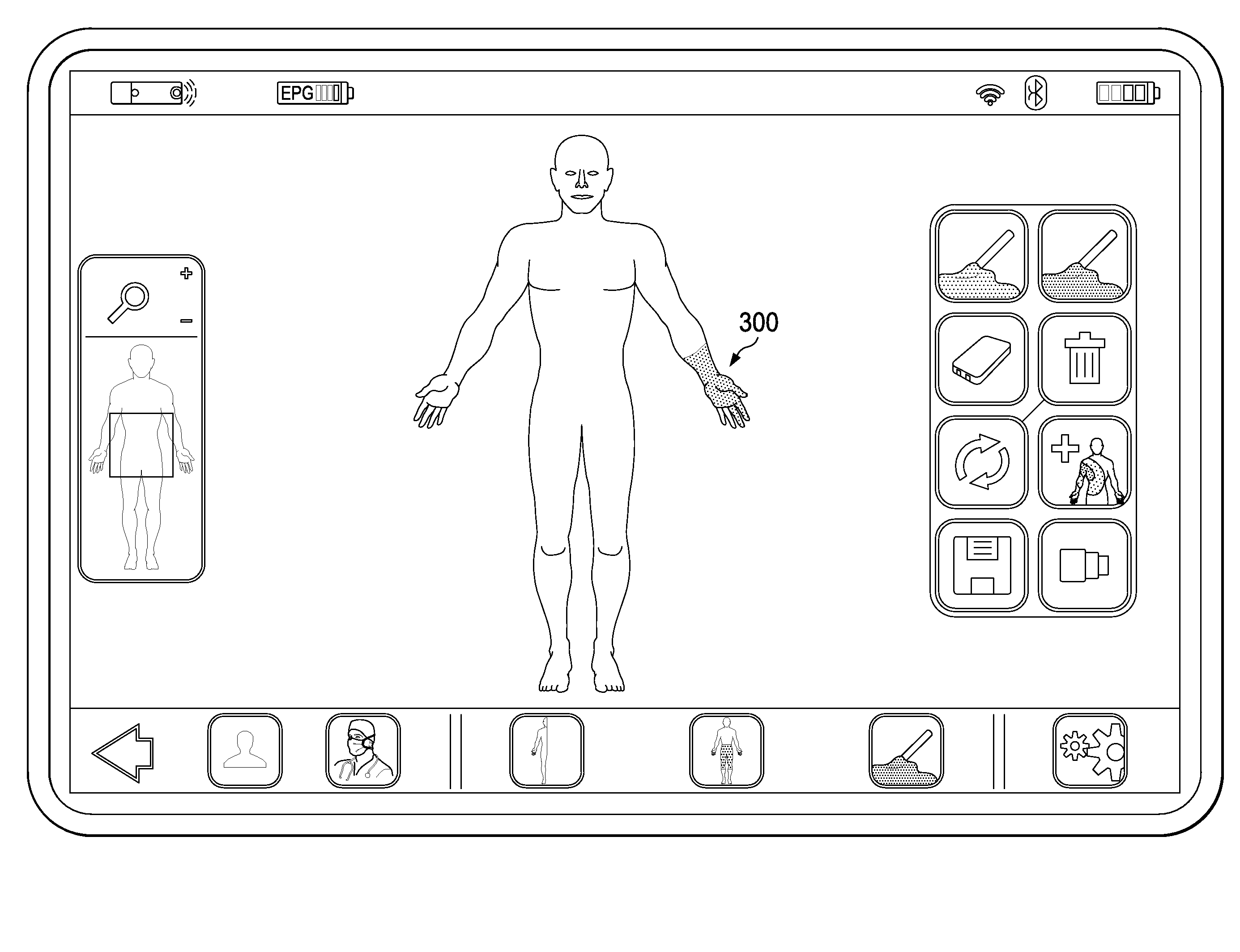
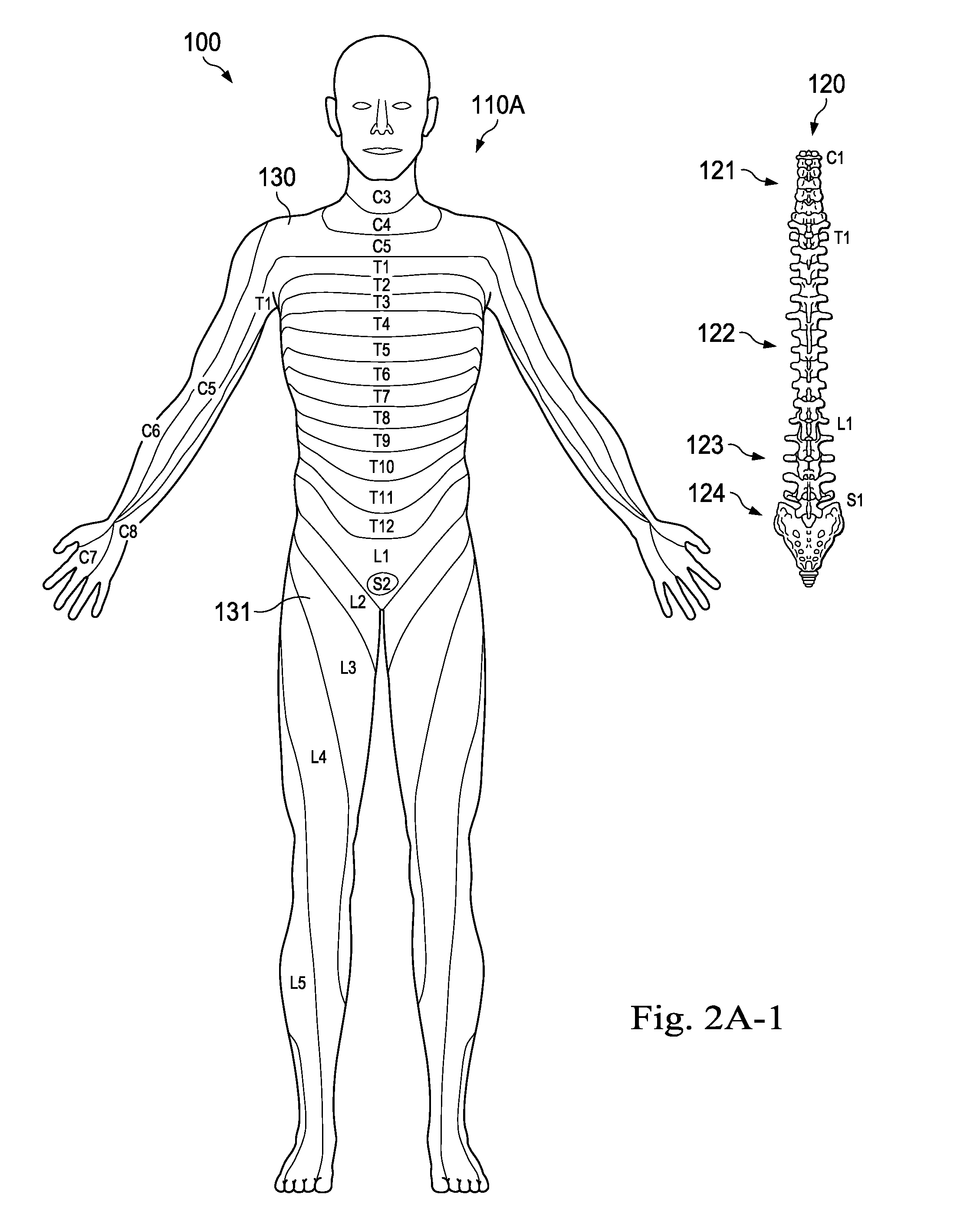
Method and System of Suggesting Spinal Cord Stimulation Region Based on Pain and Stimulation Maps with a Clinician Programmer
InactiveUS20140067354A1Physical therapies and activitiesMedical simulationUser inputPhysical therapy
The present disclosure involves a method of determining stimulation lead placements for a healthcare professional with respect to an implant of a neurostimulator device in a target patient. A human body model is provided. A pain map is generated over the human body model in response to user input. The pain map visually represents body regions of the target patient that are experiencing pain. A dermatome map is provided. The dermatome map includes a visual correlation between regions of a human body and segments of a spinal cord. The pain map is compared with the dermatome map. Recommendations regarding the implant of the neurostimulator device are displayed in response to the comparing.
Owner:NUVECTRA
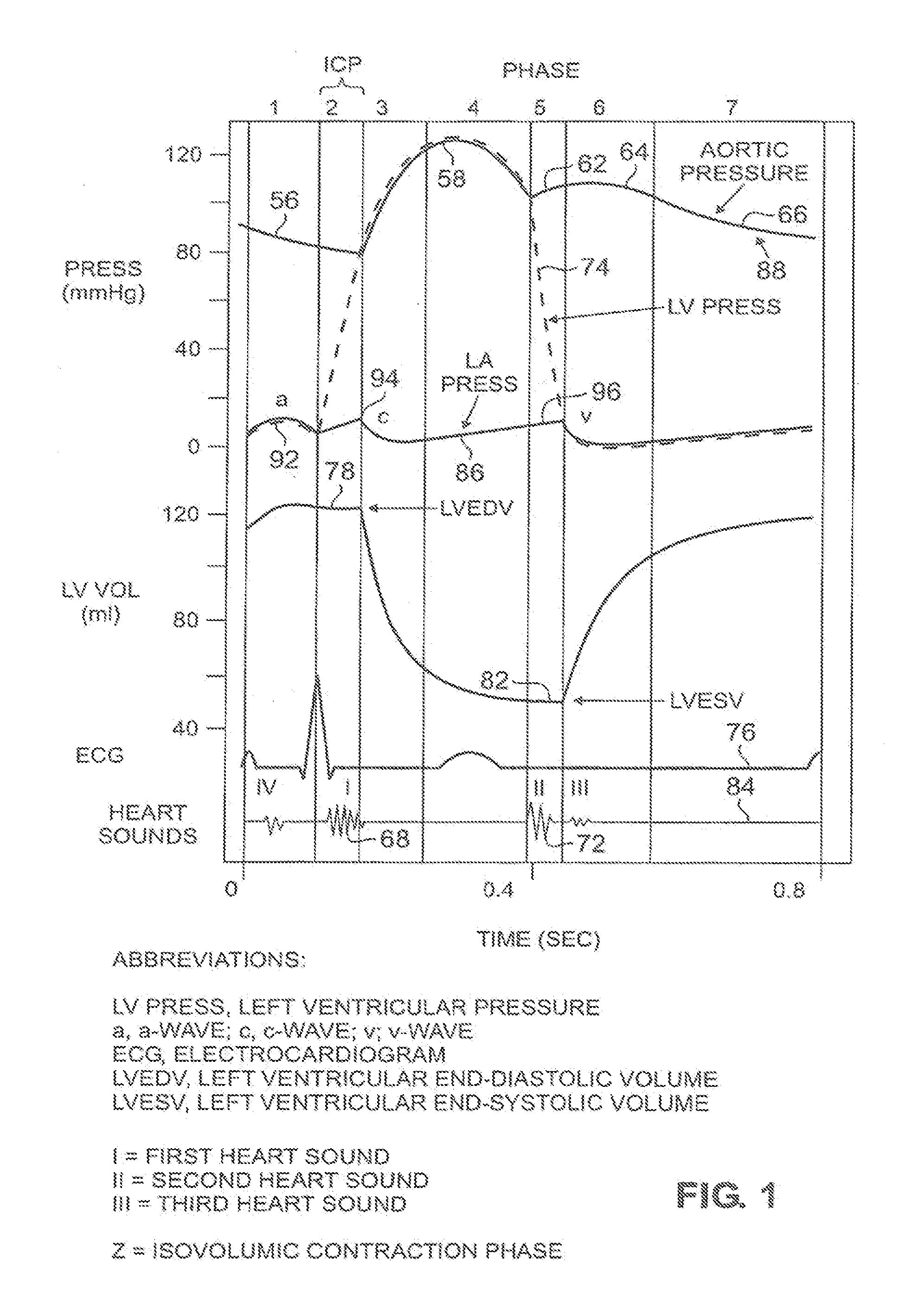
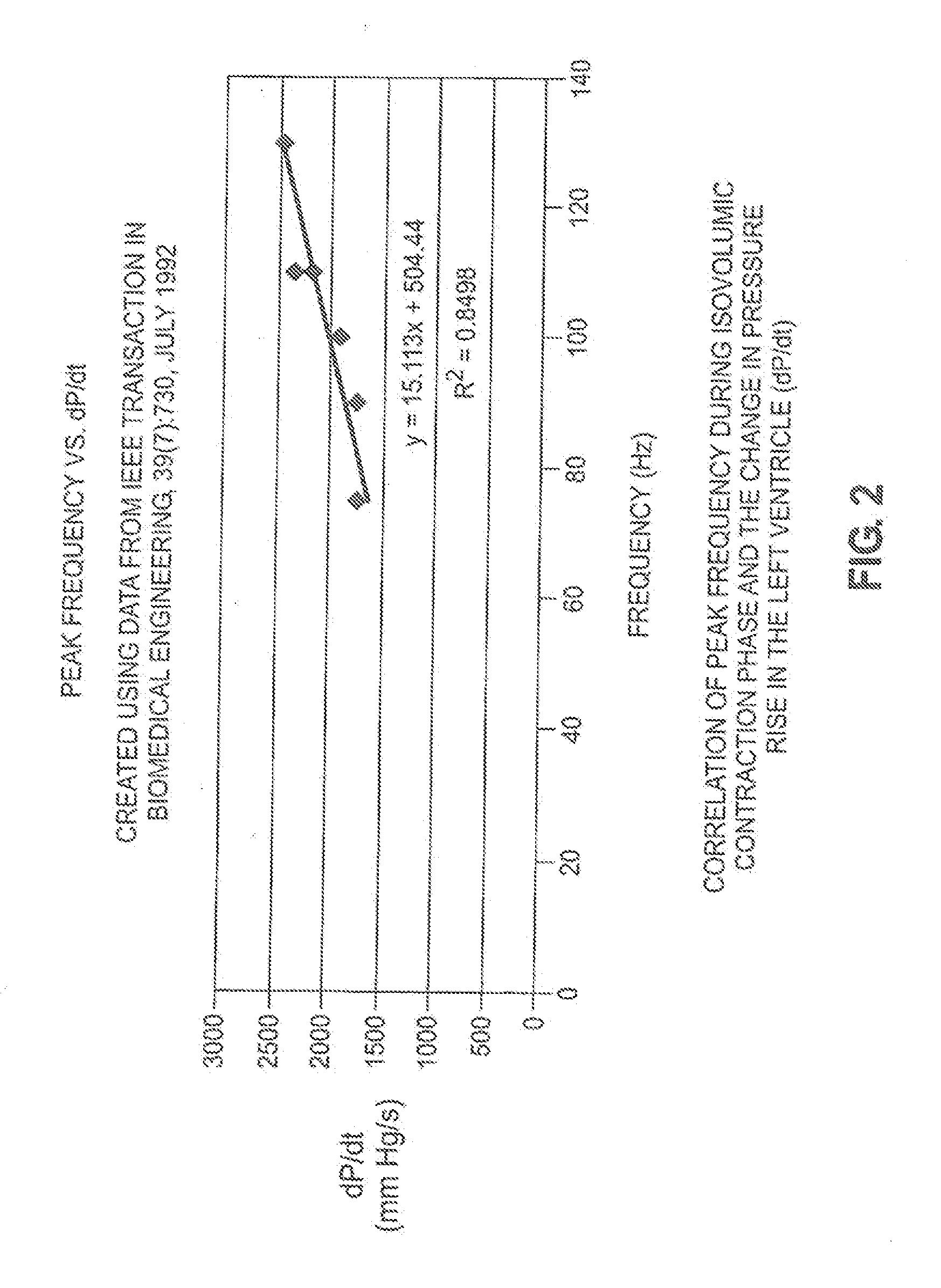
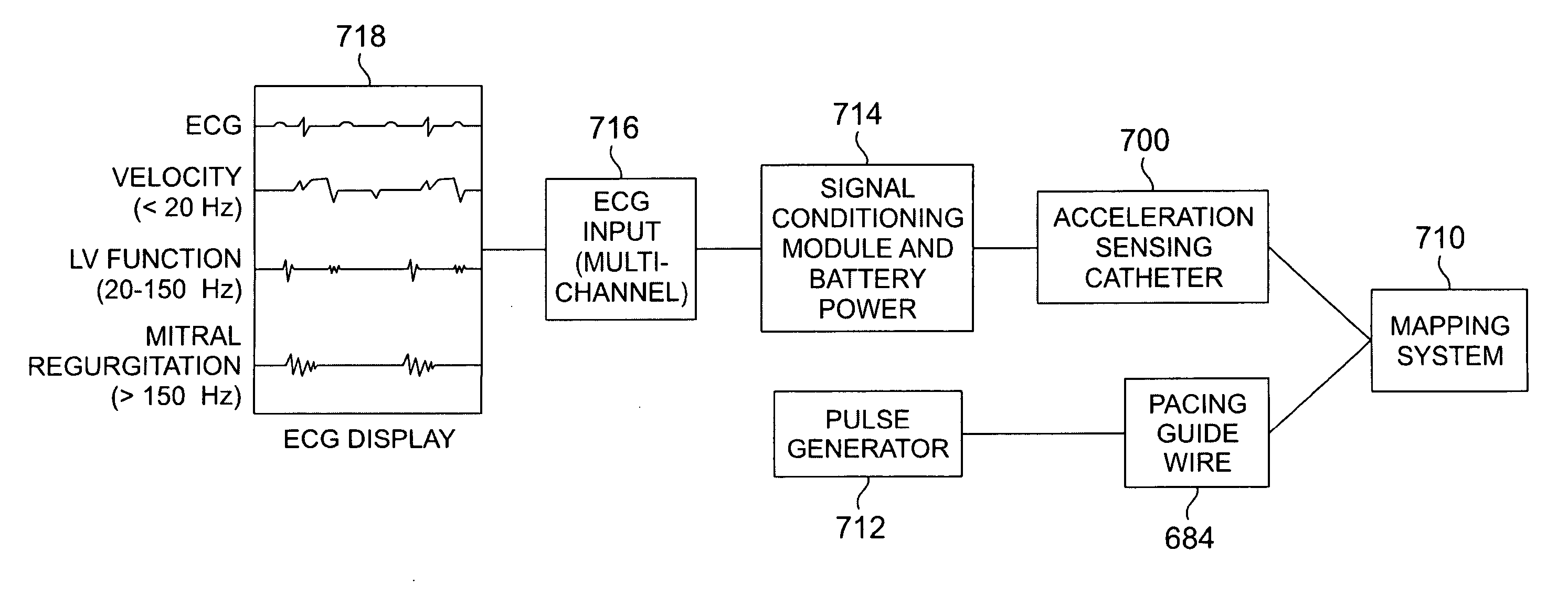
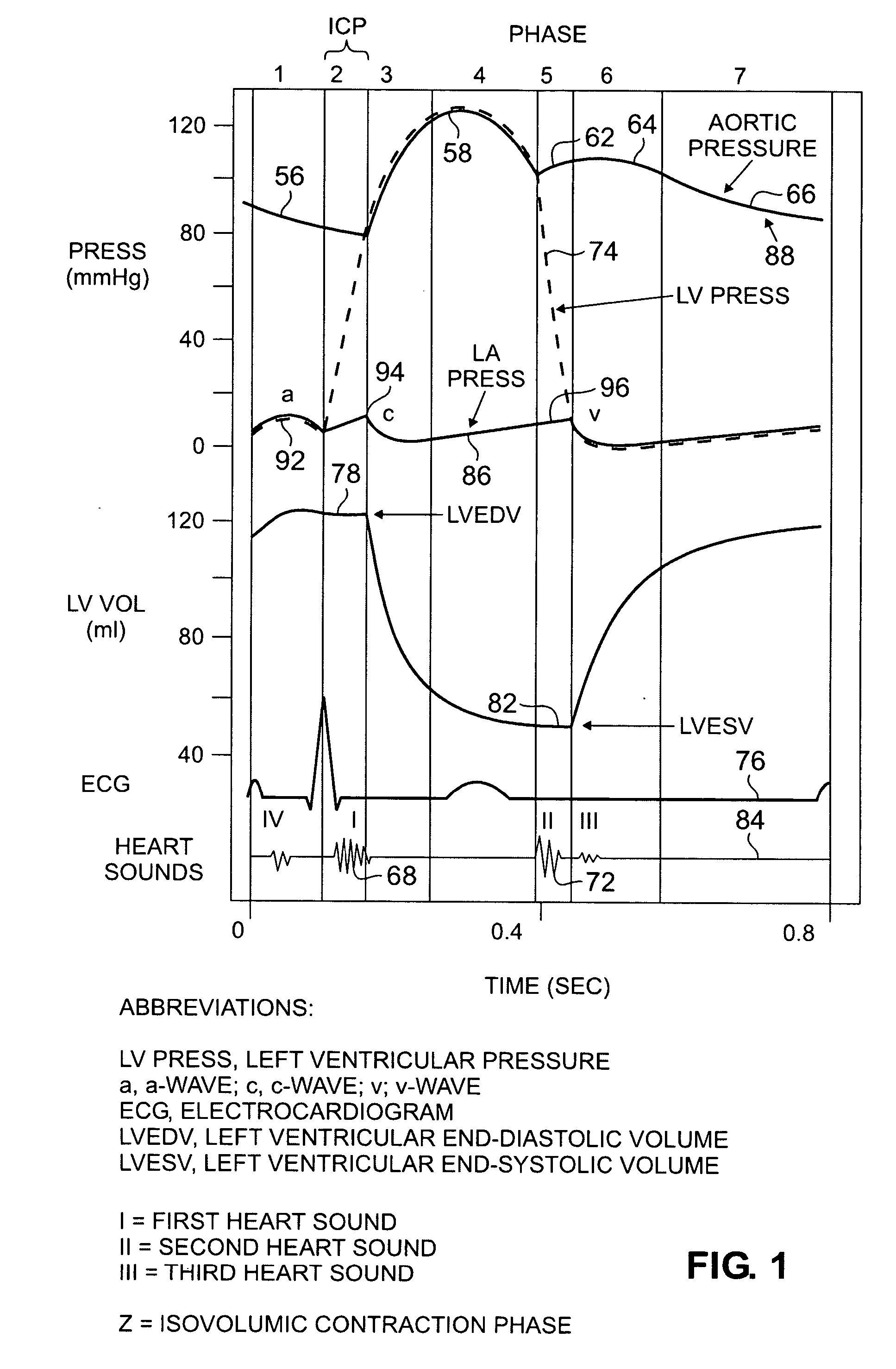
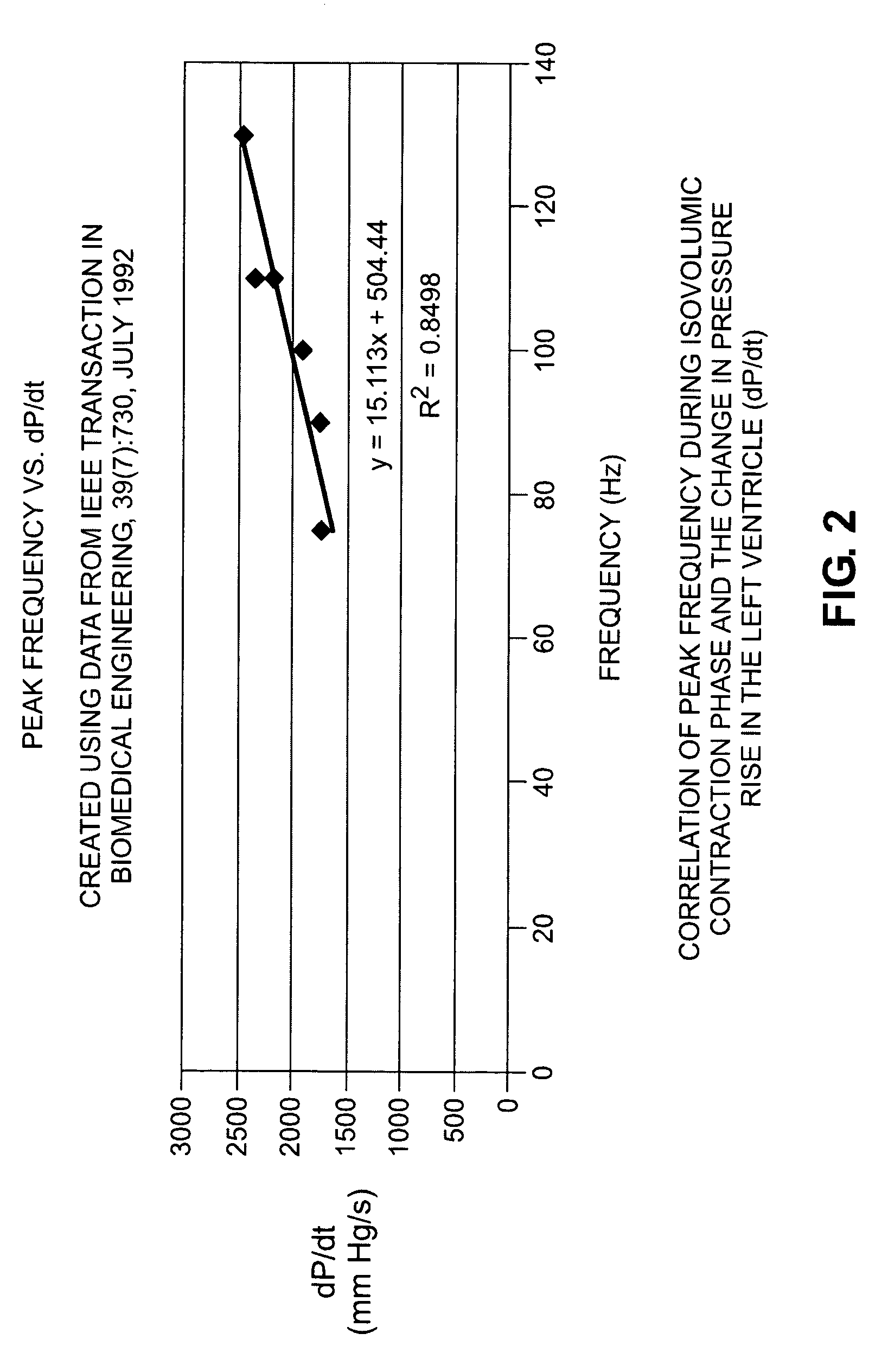
Accelerometer-based monitoring of the frequency dynamics of the isovolumic contraction phase and pathologic cardiac vibrations
InactiveUS20090306736A1Reduce sensitivityMore practicalElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesAccelerometerPacing interval
Methods and systems are disclosed that characterize cardiac function using an acceleration sensor to acquire and analyze the frequency dynamics associated with the isovolumic contraction phase (“ICP”). This information can be used to characterize heart function; optimize therapy for cardiomyopathy, including CRT therapy (including pacing intervals and required pharmacologic therapy); and to optimize CCM therapy. In addition, this information can be used to identify target pacing regions for CRT lead placement. Further, analyzing the frequency dynamics can be used to characterize pathologic heart vibrational motion, such as mitral regurgitation and the third or fourth heart sound, and the response of this motion to therapy for cardiomyopathy.
Owner:DOBAK III JOHN D
Accelerometer-based monitoring of the frequency dynamics of the isovolumic contraction phase and pathologic cardiac vibrations
InactiveUS20060178589A1Reduce sensitivityMore practicalElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesAccelerometerSystole
Methods and systems are disclosed that characterize cardiac function using an acceleration sensor to acquire and analyze the frequency dynamics associated with the isovolumic contraction phase (“ICP”). This information can be used to characterize heart function; optimize therapy for cardiomyopathy, including CRT therapy (including pacing intervals and required pharmacologic therapy); and to optimize CCM therapy. In addition, this information can be used to identify target pacing regions for CRT lead placement. Further, analyzing the frequency dynamics can be used to characterize pathologic heart vibrational motion, such as mitral regurgitation and the third or fourth heart sound, and the response of this motion to therapy for cardiomyopathy.
Owner:CARDIOSYNC
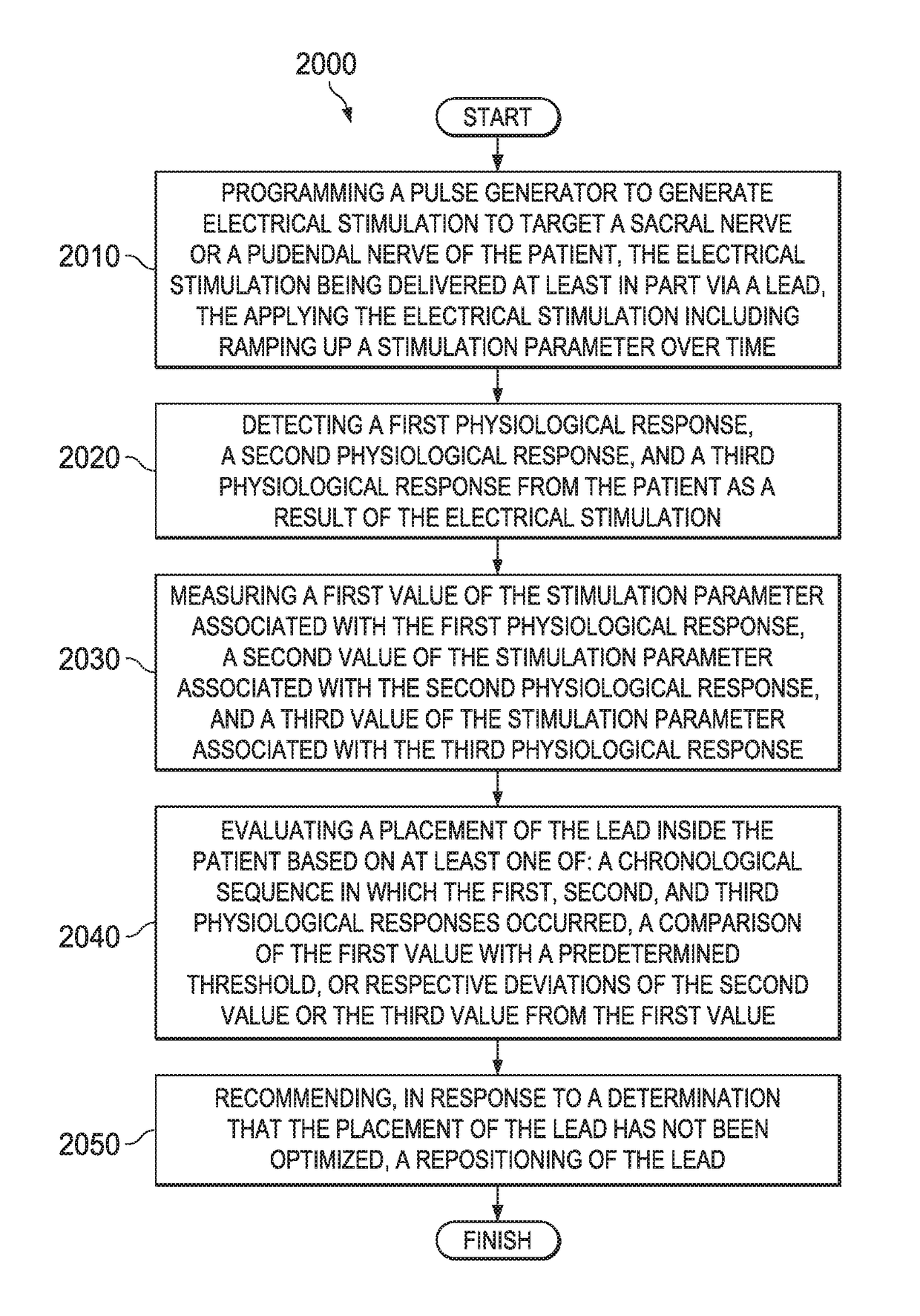
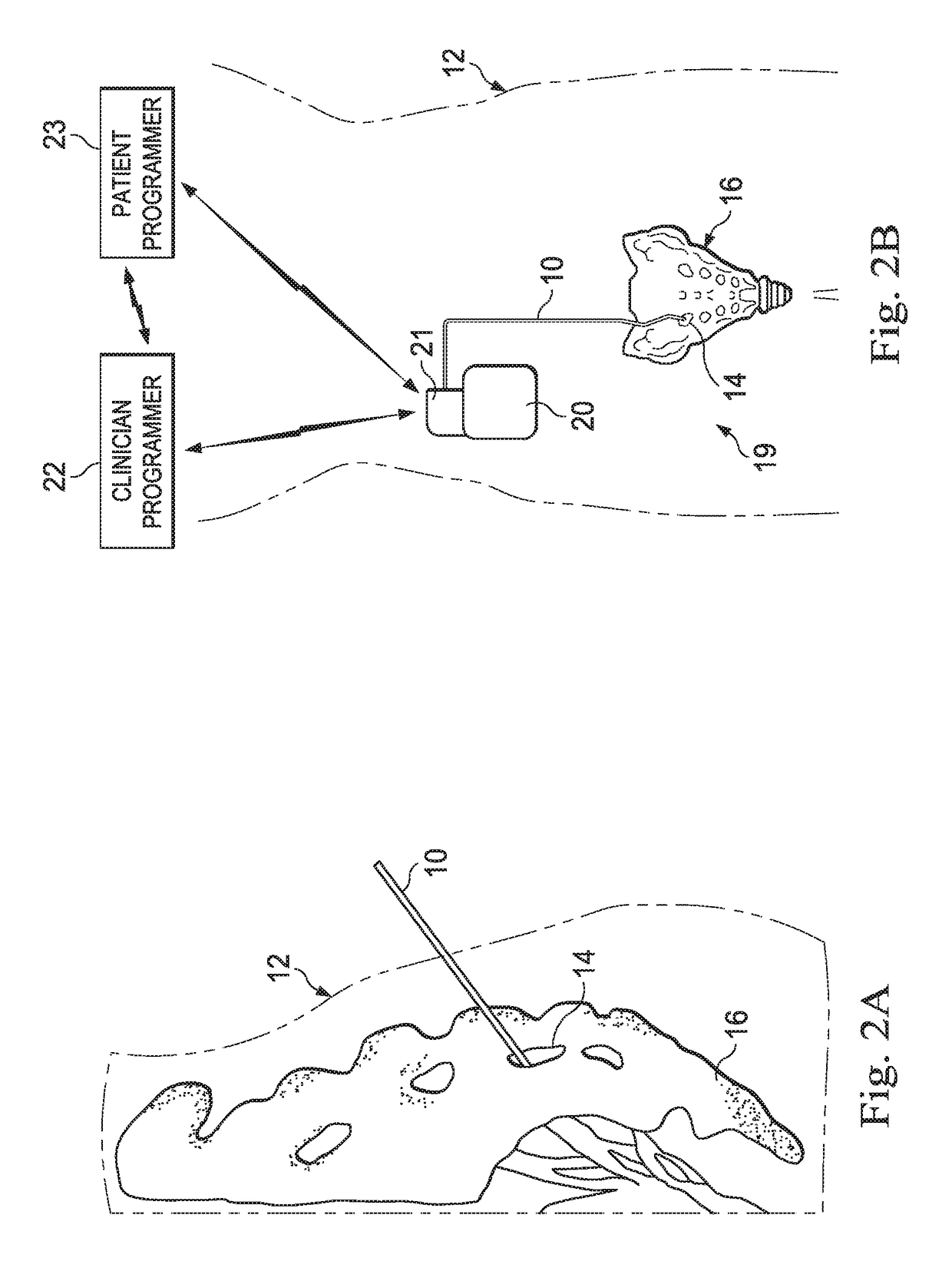
Systems, methods, and devices for evaluating lead placement based on patient physiological responses
A pulse generator is programmed to generate electrical stimulation to target a sacral nerve or a pudendal nerve of the patient. The electrical stimulation being delivered at least in part via a lead. The electrical stimulation is applied by ramping up a stimulation parameter over time. A first, a second, and a third physiological response are detected from the patient as a result of the electrical stimulation. A first value, a second value, and a third value of the stimulation parameter associated with the first, second, and third physiological response are measured, respectively. A placement of the lead inside the patient is evaluated based on at least one of: a chronological sequence in which the first, second, and third physiological responses occurred, a comparison of the first value with a predetermined threshold, or respective deviations of the second value or the third value from the first value.
Owner:CIRTEC MEDICAL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com