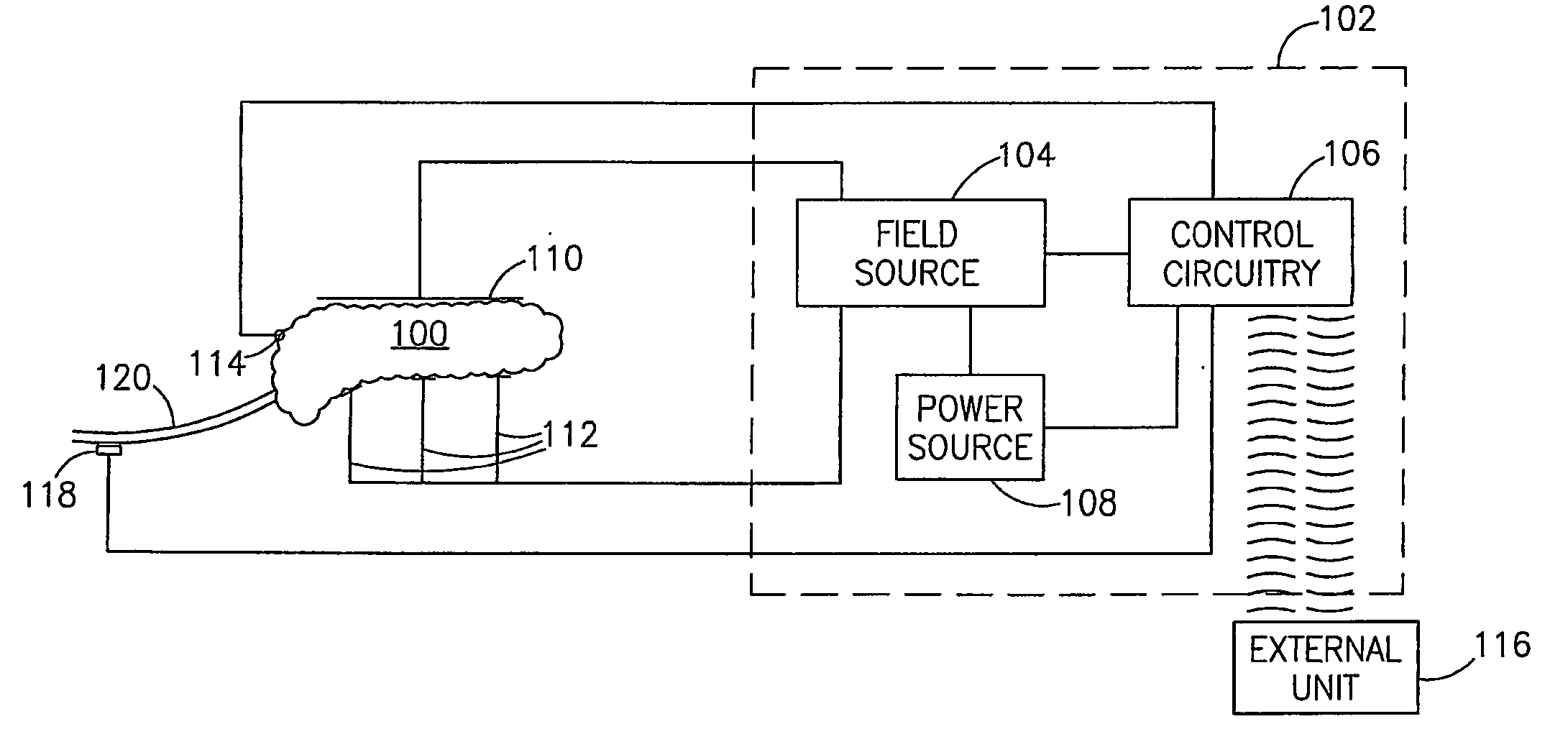
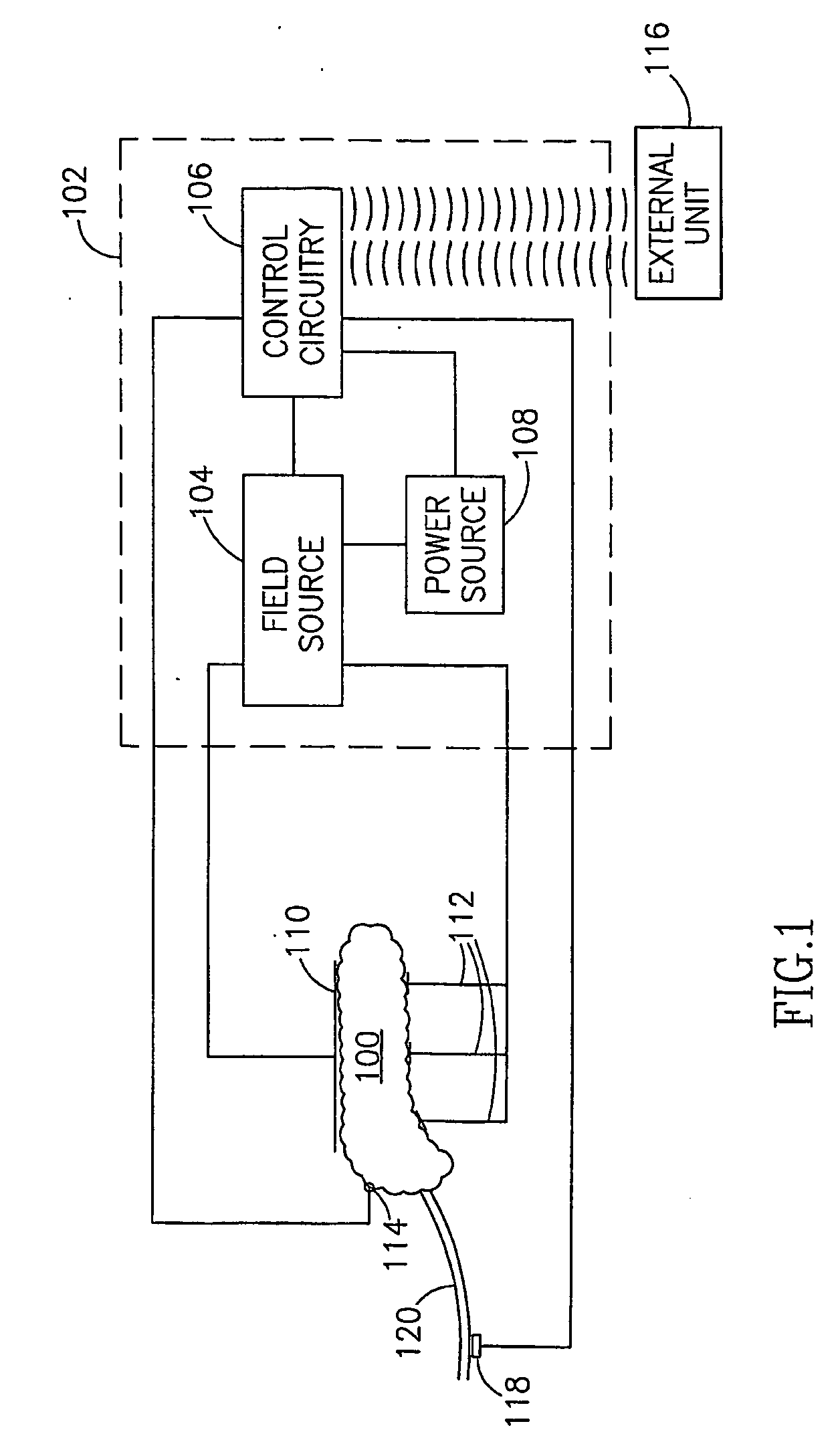
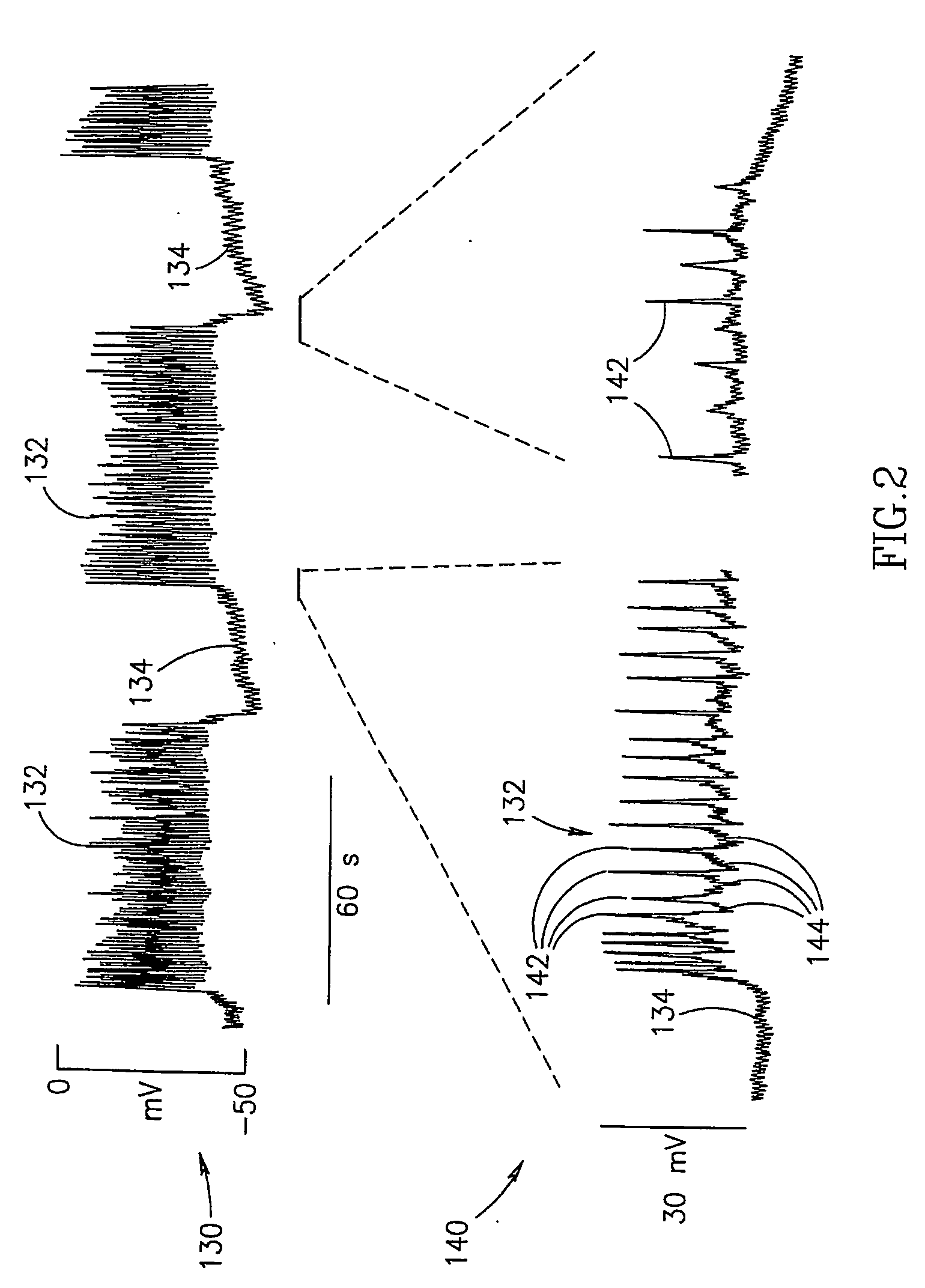
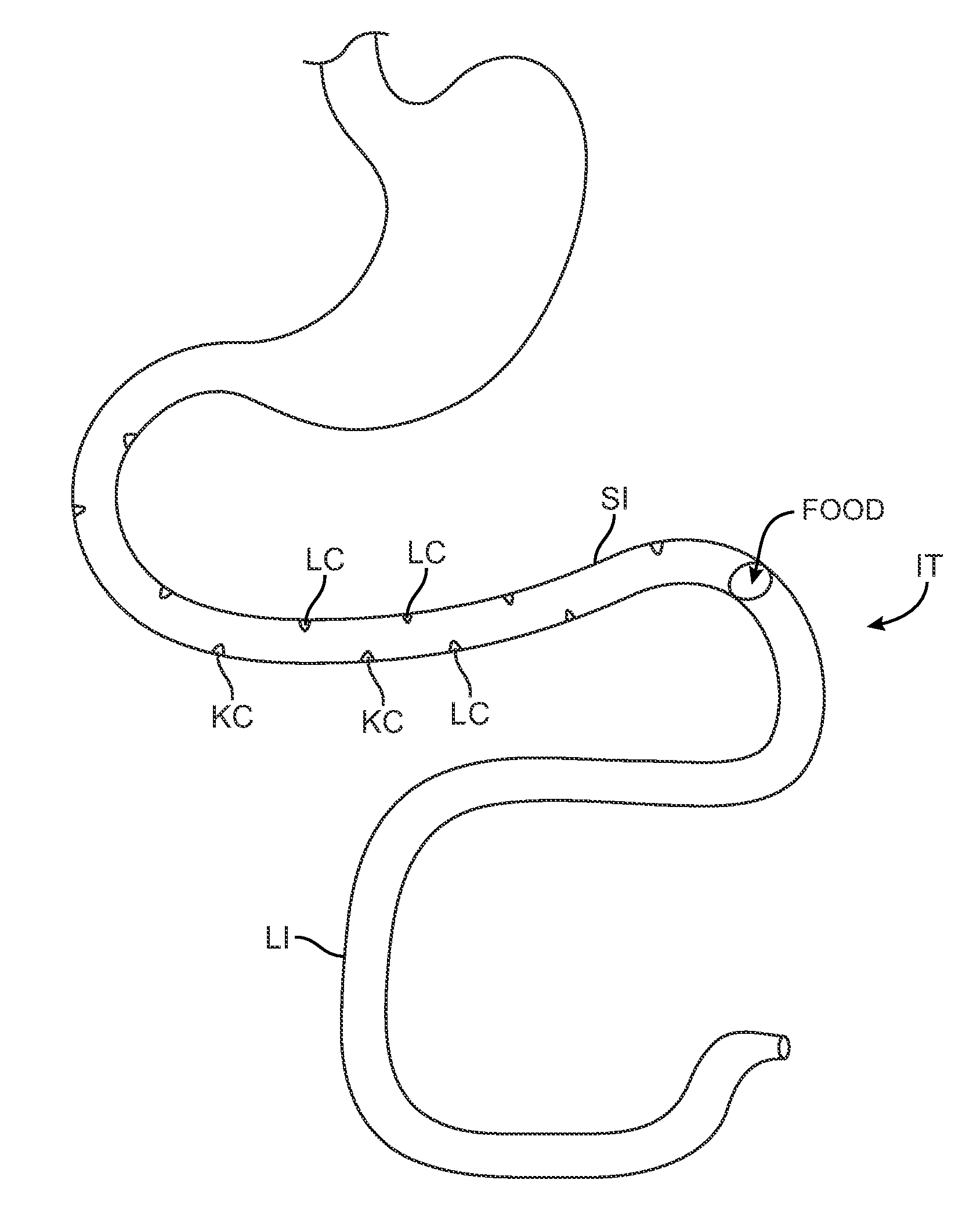
Patents
Literature
297results about "Digestive electrodes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
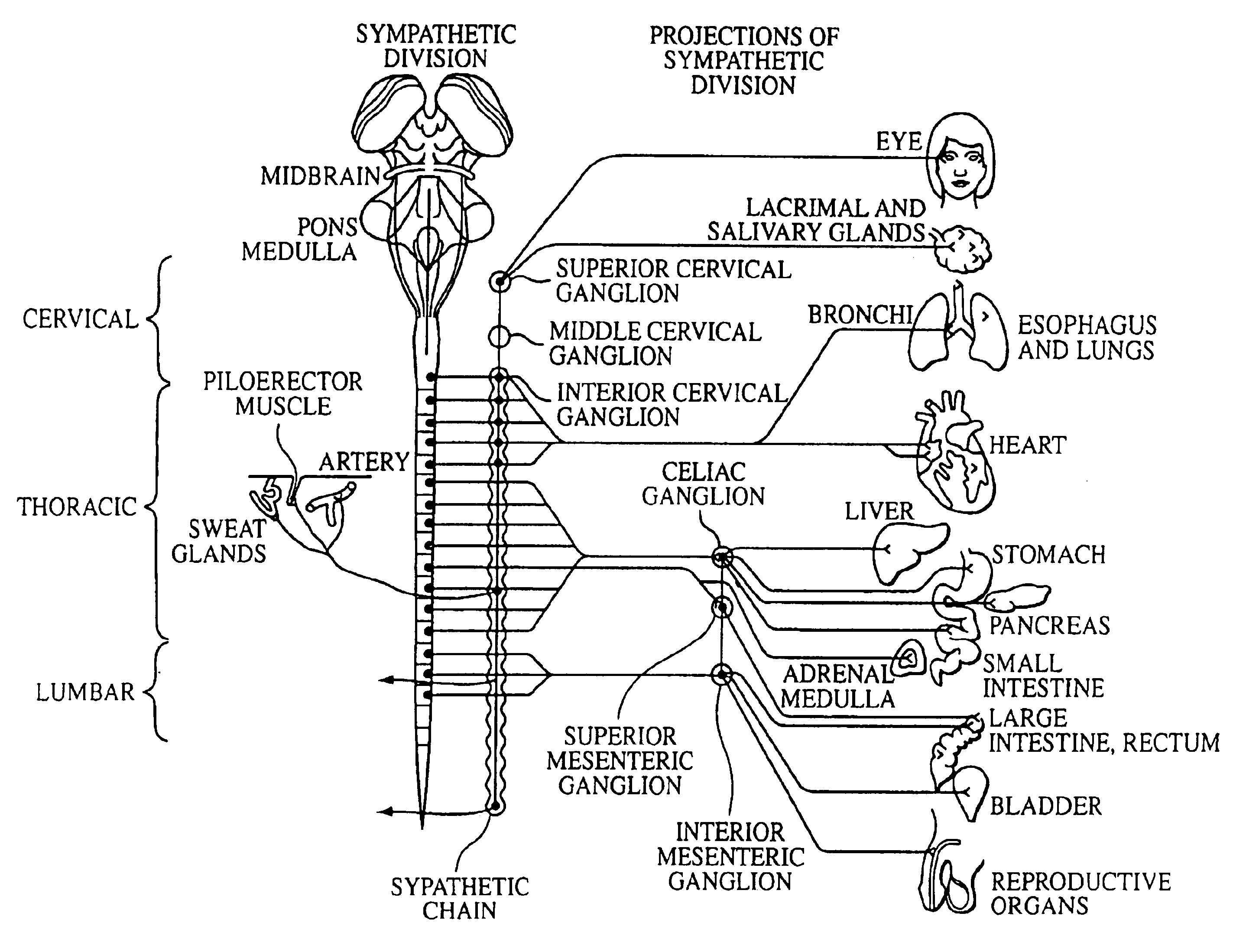
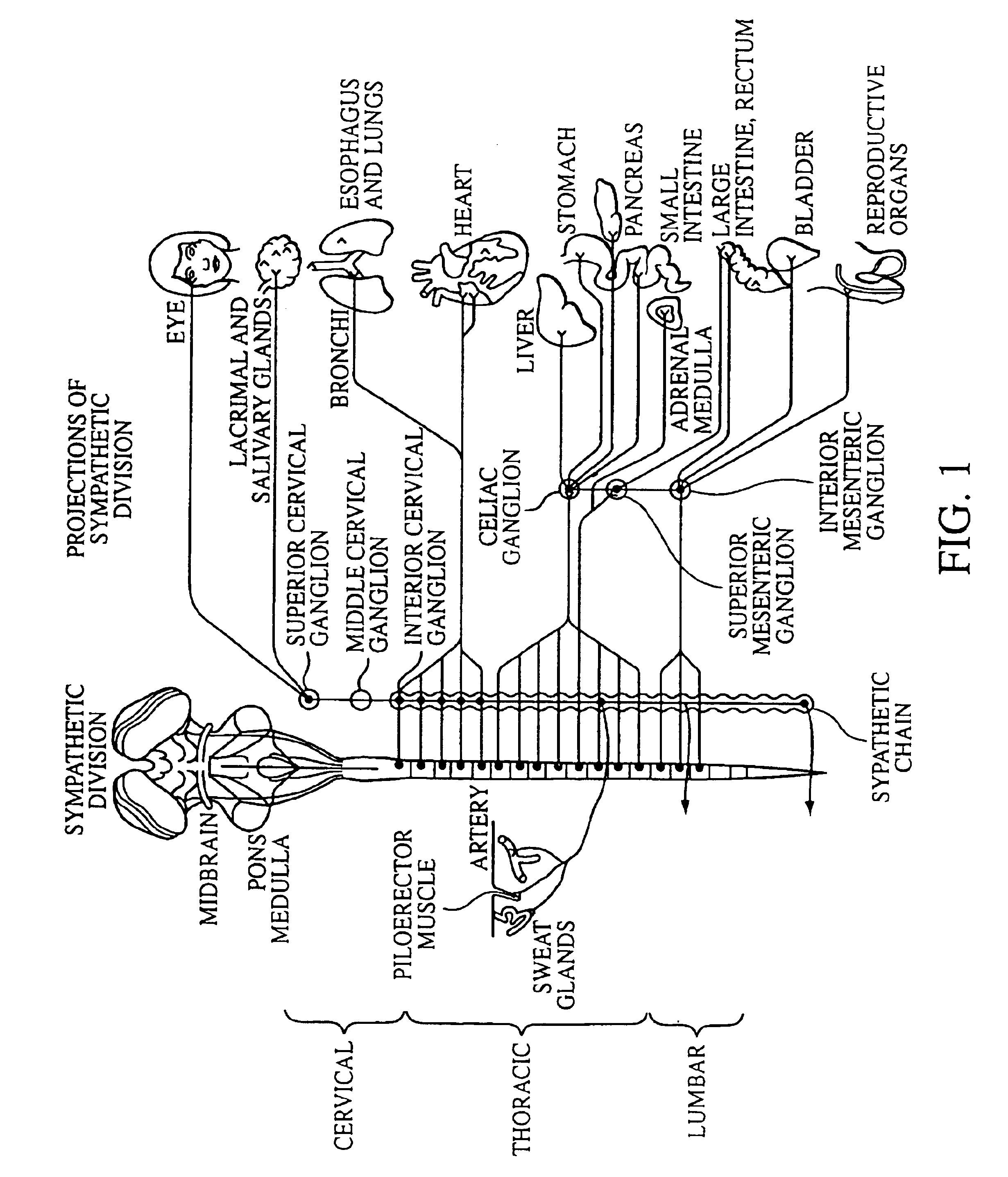
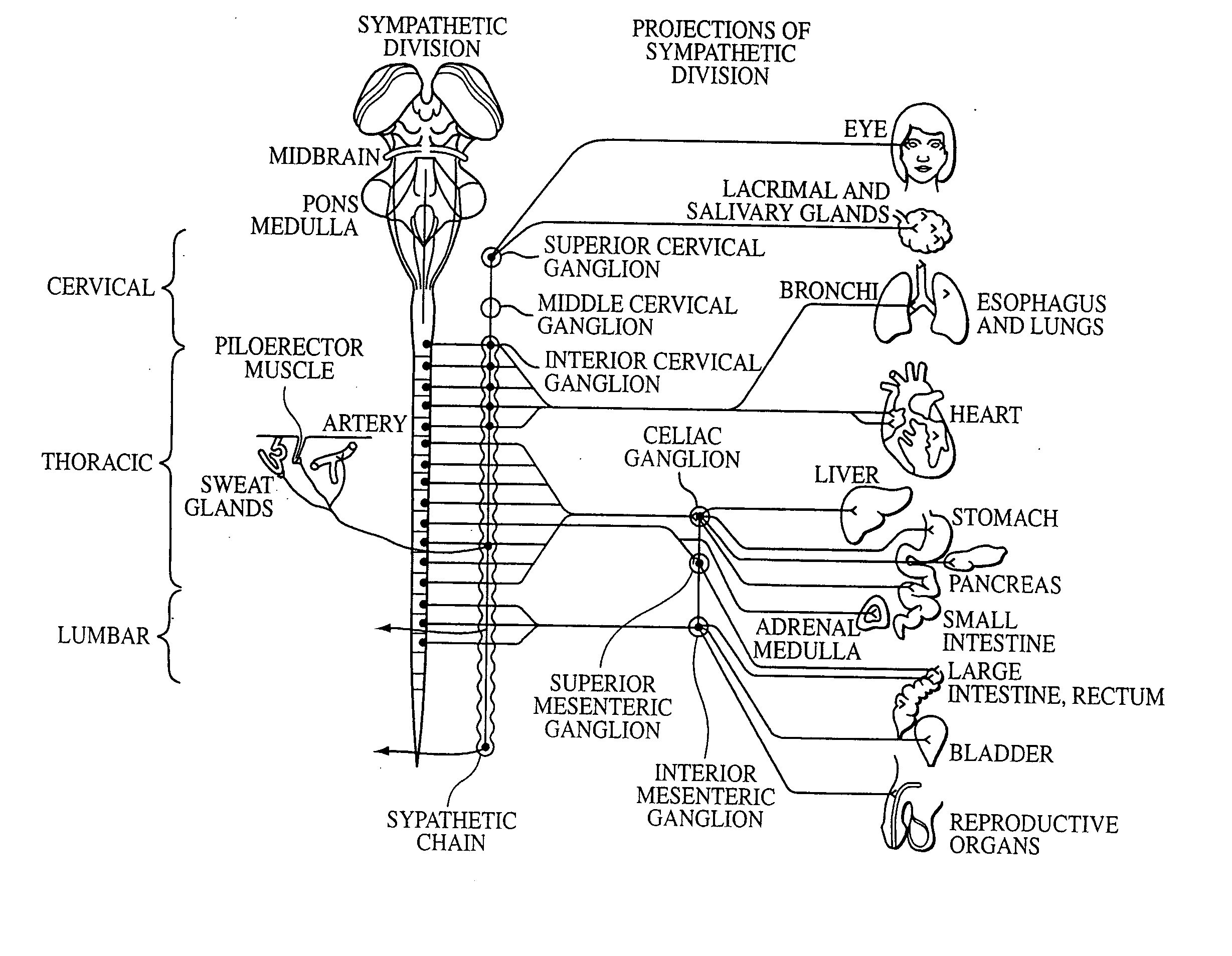
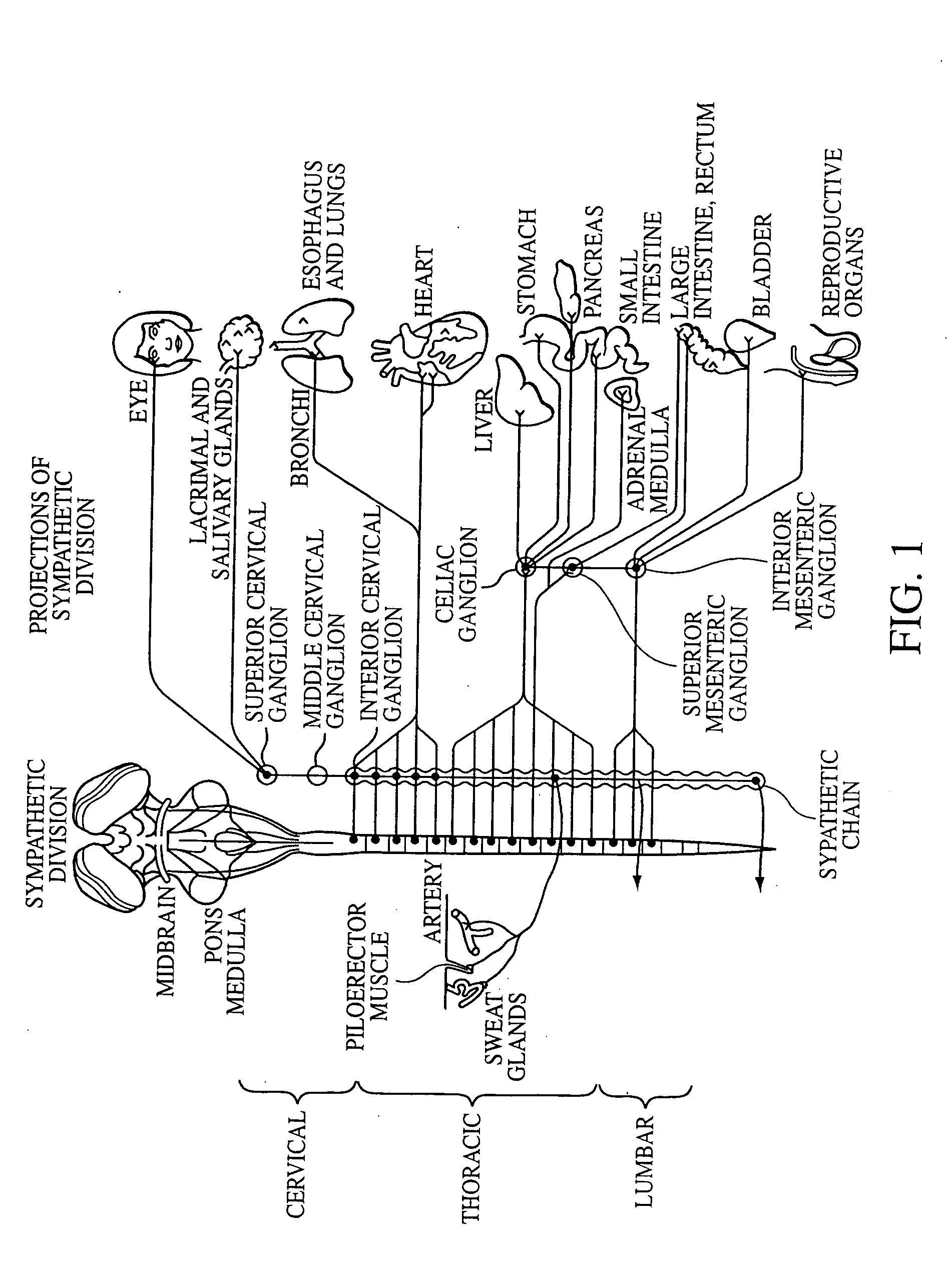
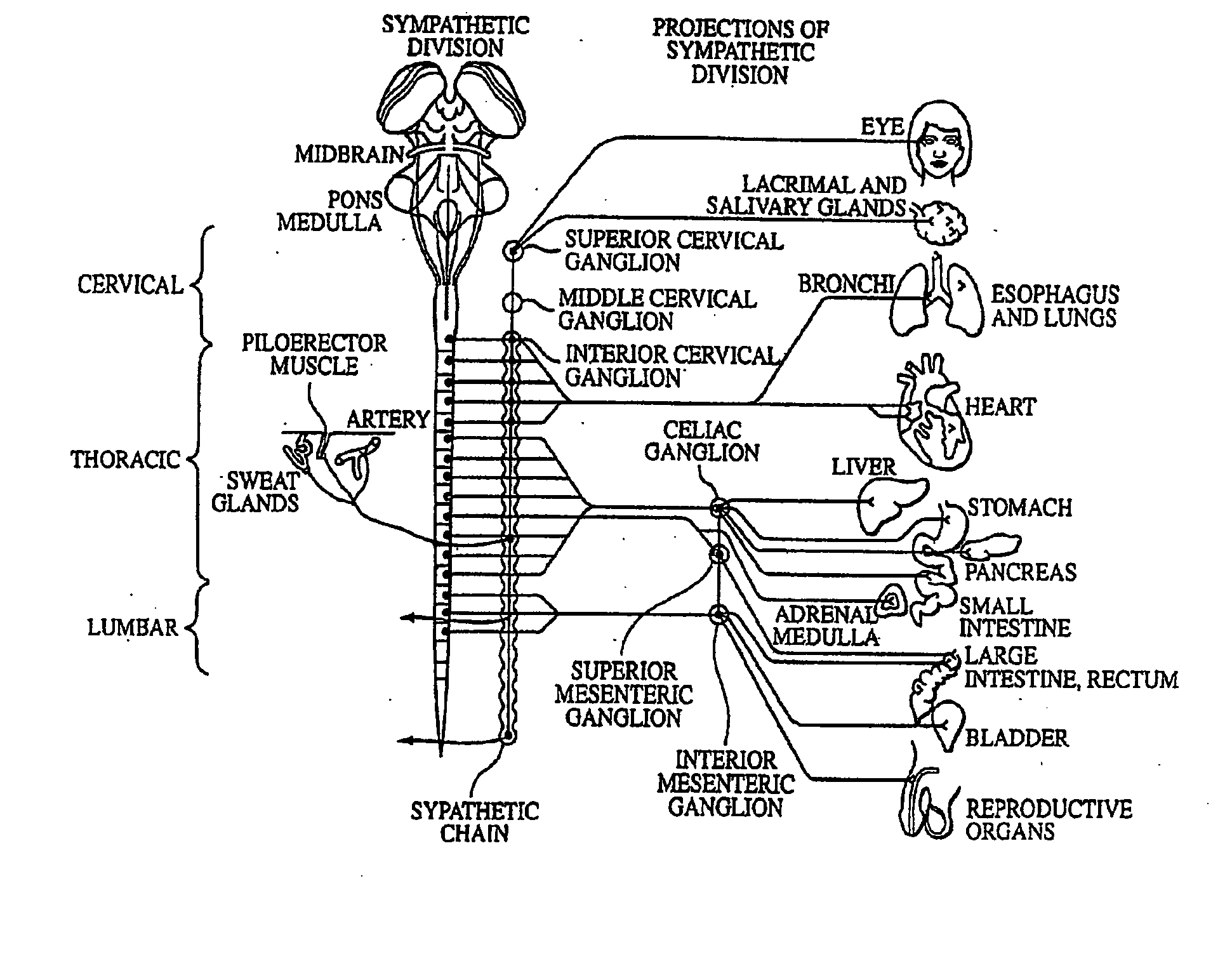
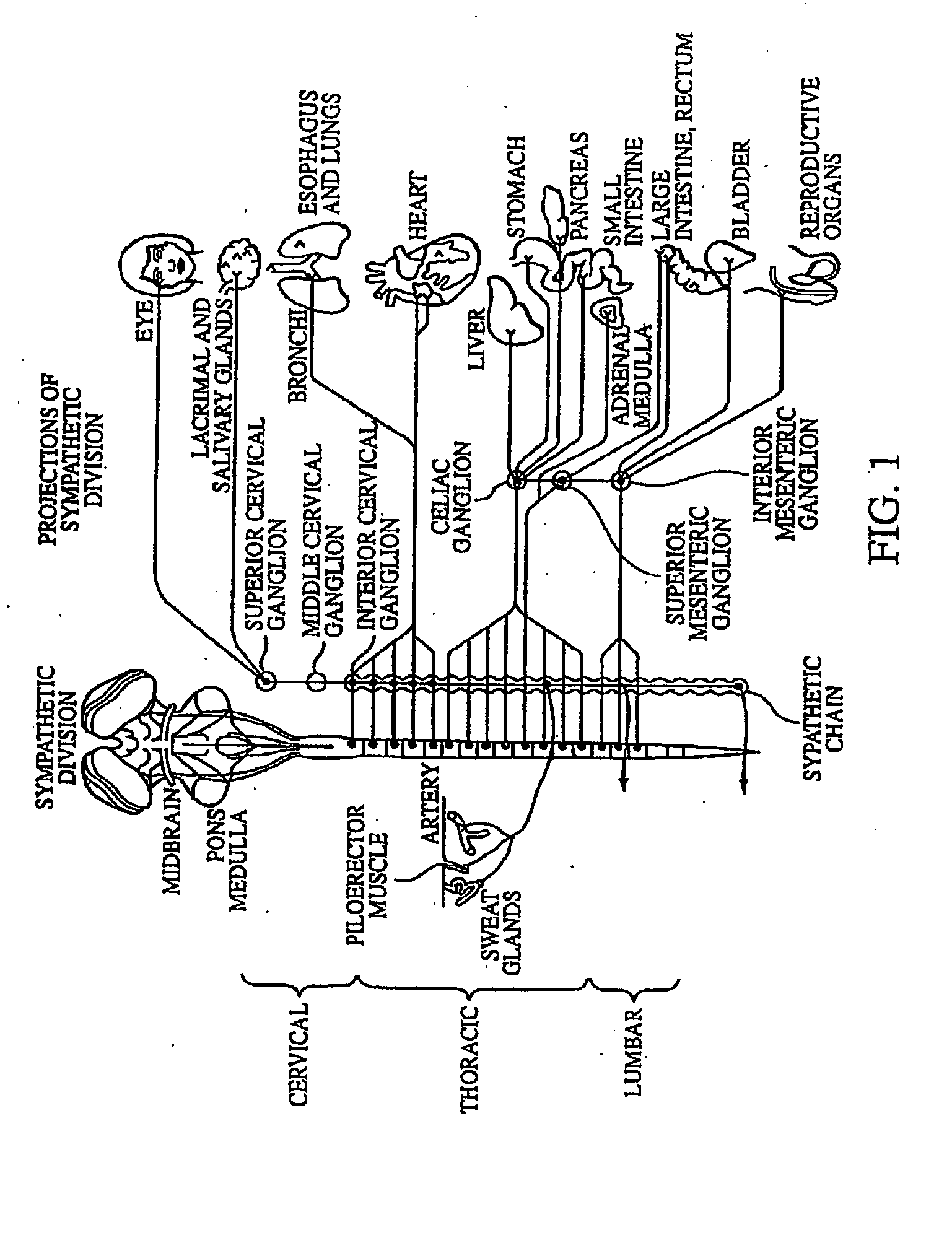
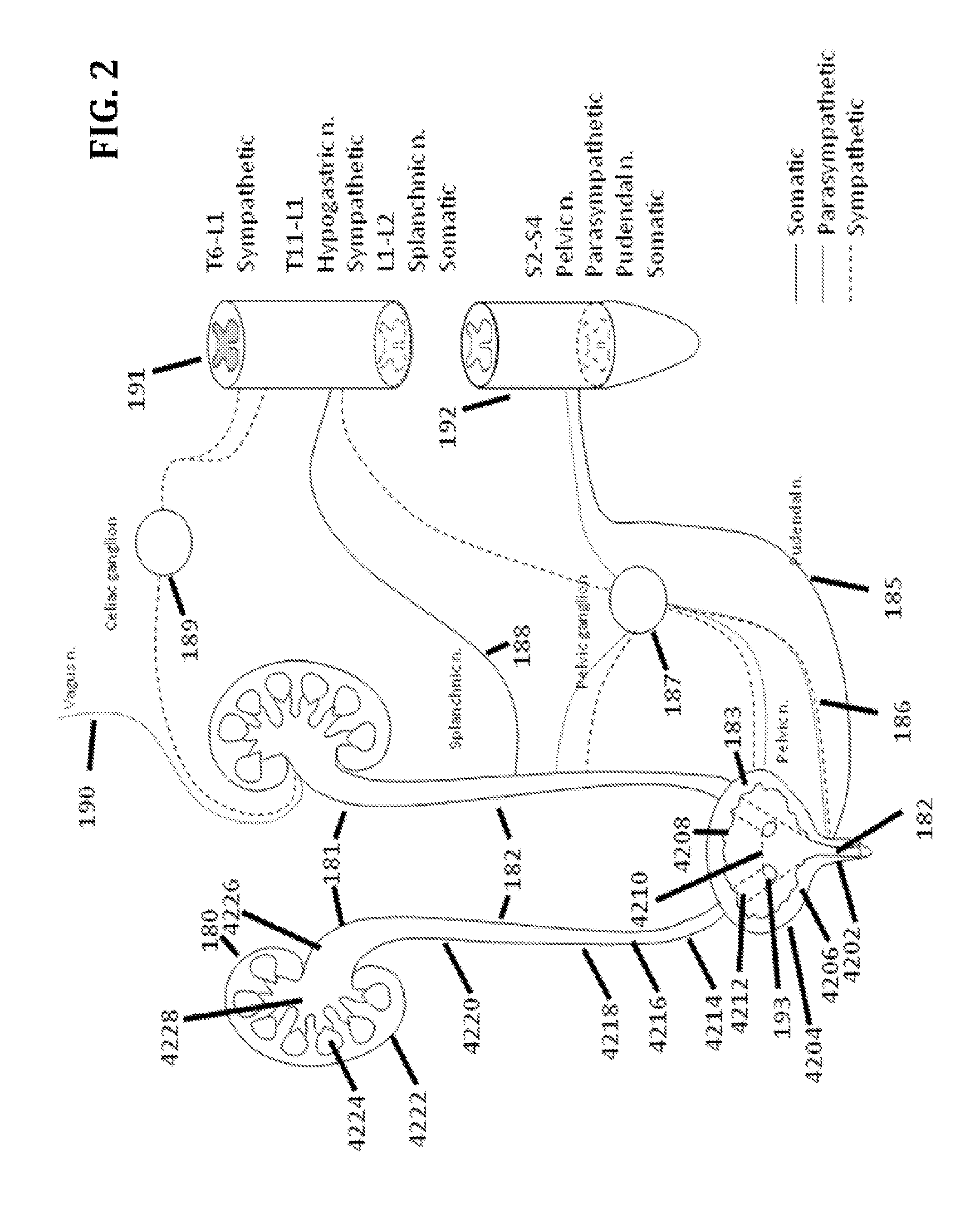
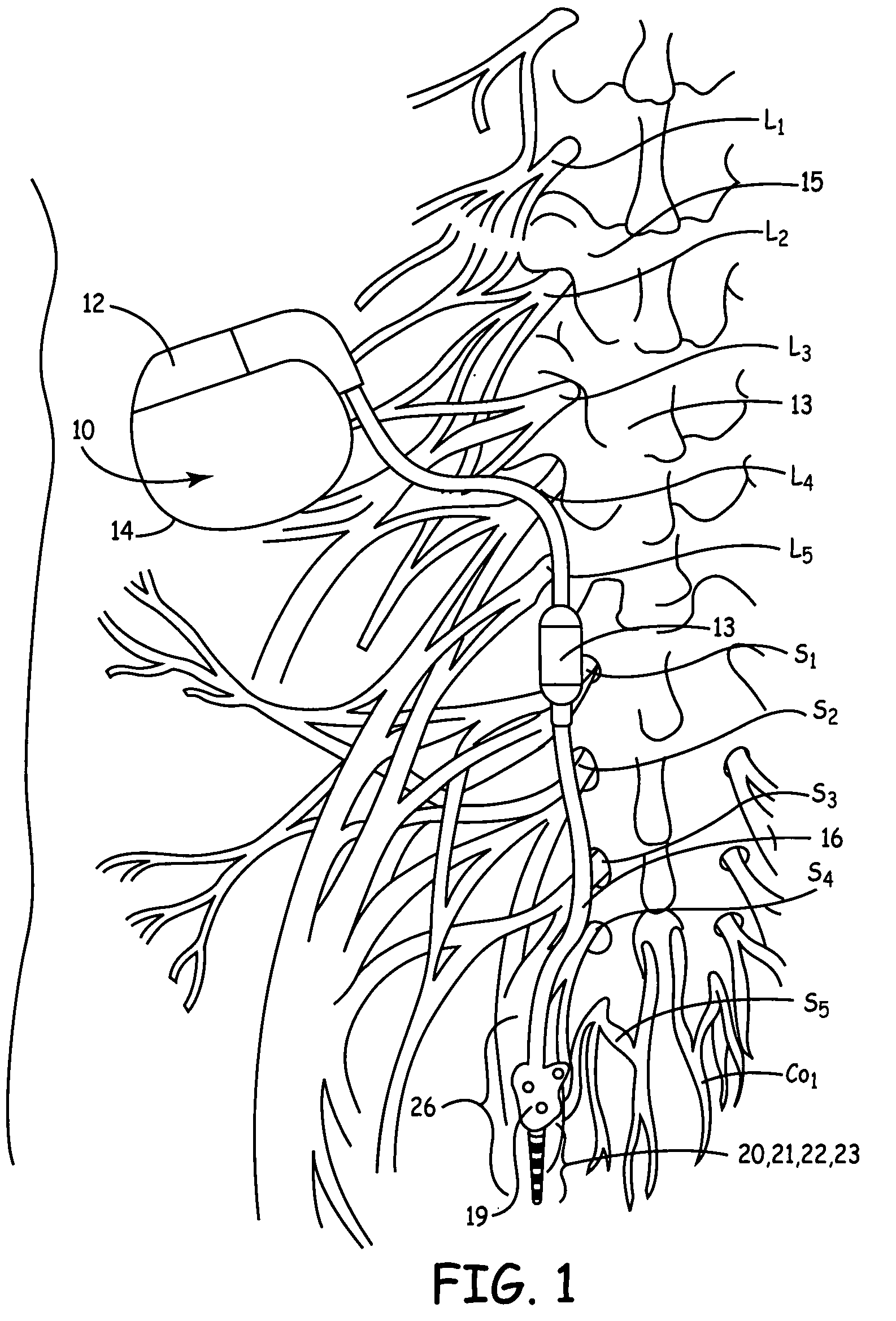
Electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve chain
InactiveUS6885888B2Minimizing stimulationMinimize complicationsSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSympathetic nerveSacral sympathetic chain
The present invention provides a method of affecting physiological disorders by stimulating a specific location along the sympathetic nerve chain. Preferably, the present invention provides a method of affecting a variety of physiological disorders or pathological conditions by placing an electrode adjacent to or in communication with at least one ganglion along the sympathetic nerve chain and stimulating the at least one ganglion until the physiological disorder or pathological condition has been affected.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve chain
InactiveUS20050065573A1Minimizing stimulationMinimize complicationsSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSympathetic nerveSacral sympathetic chain
The present invention provides a method of affecting physiological disorders by stimulating a specific location along the sympathetic nerve chain. Preferably, the present invention provides a method of affecting a variety of physiological disorders or pathological conditions by placing an electrode adjacent to or in communication with at least one ganglion along the sympathetic nerve chain and stimulating the at least one ganglion until the physiological disorder or pathological condition has been affected.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve chain
InactiveUS20050065562A1Convenient treatmentModulating levelSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSympathetic nerveSacral sympathetic chain
The present invention provides a method of affecting physiological disorders by stimulating a specific location along the sympathetic nerve chain. Preferably, the present invention provides a method of affecting a variety of physiological disorders or pathological conditions by placing an electrode adjacent to or in communication with at least one ganglion along the sympathetic nerve chain and stimulating the at least one ganglion until the physiological disorder or pathological condition has been affected.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
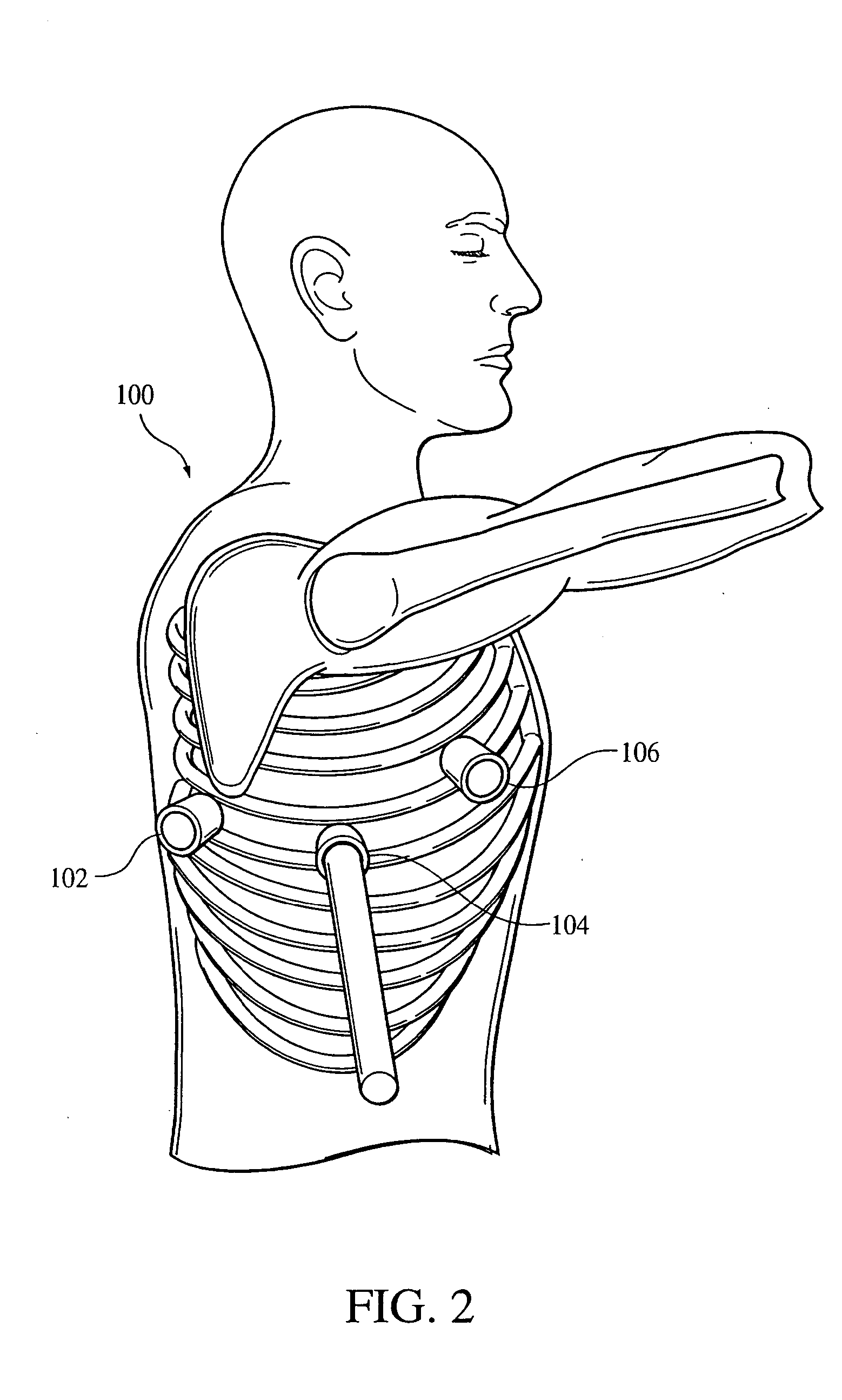
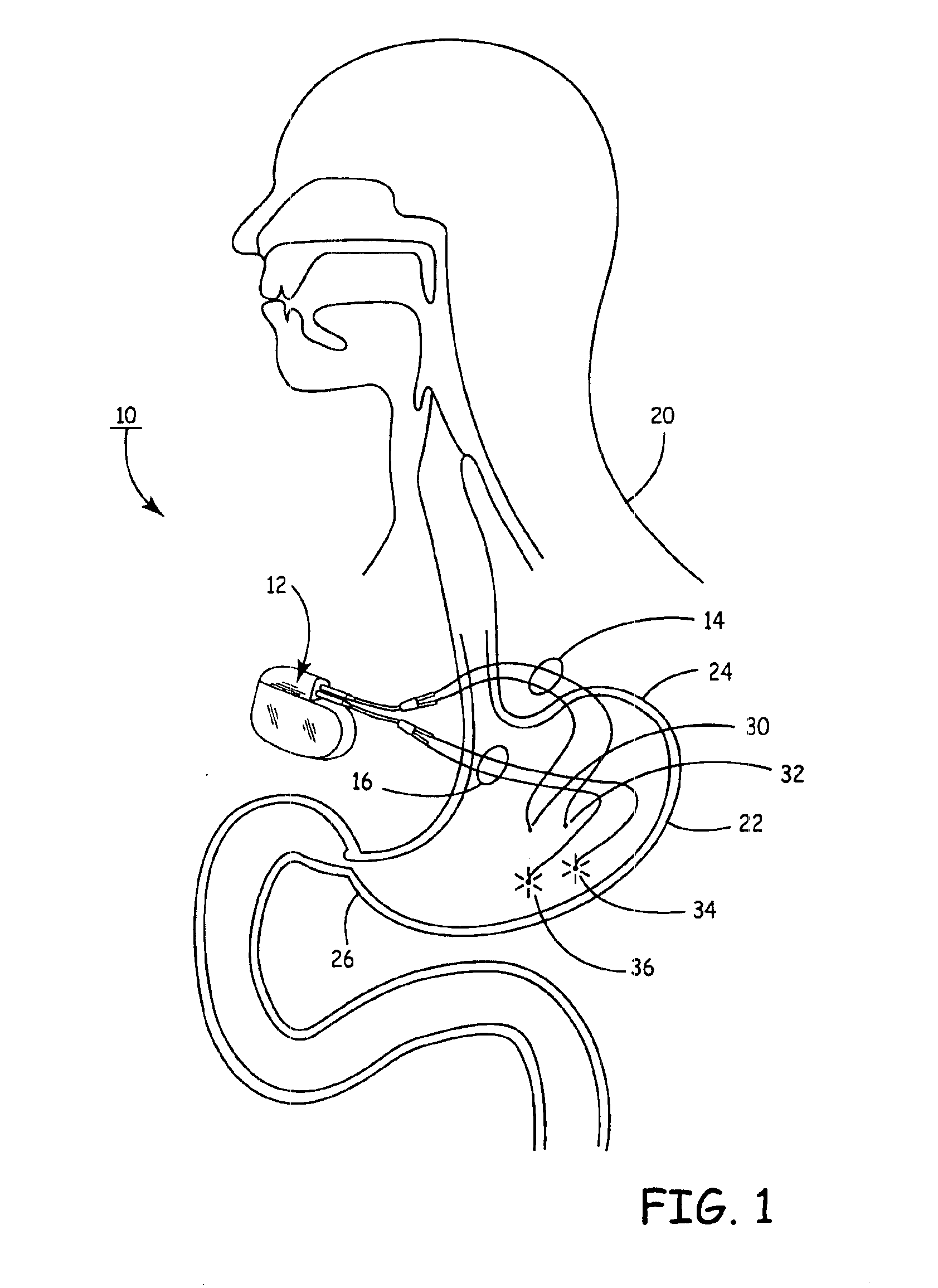
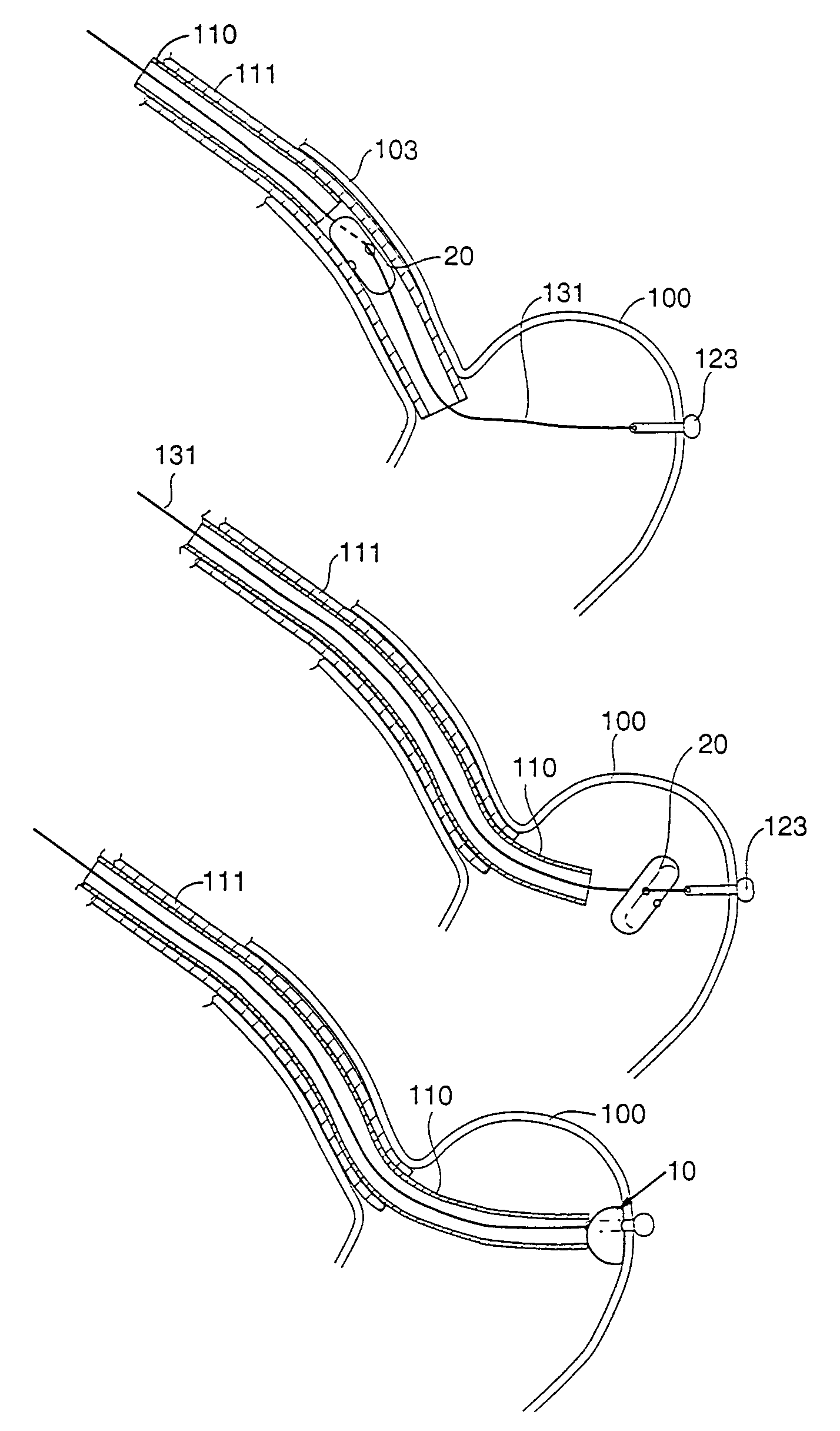
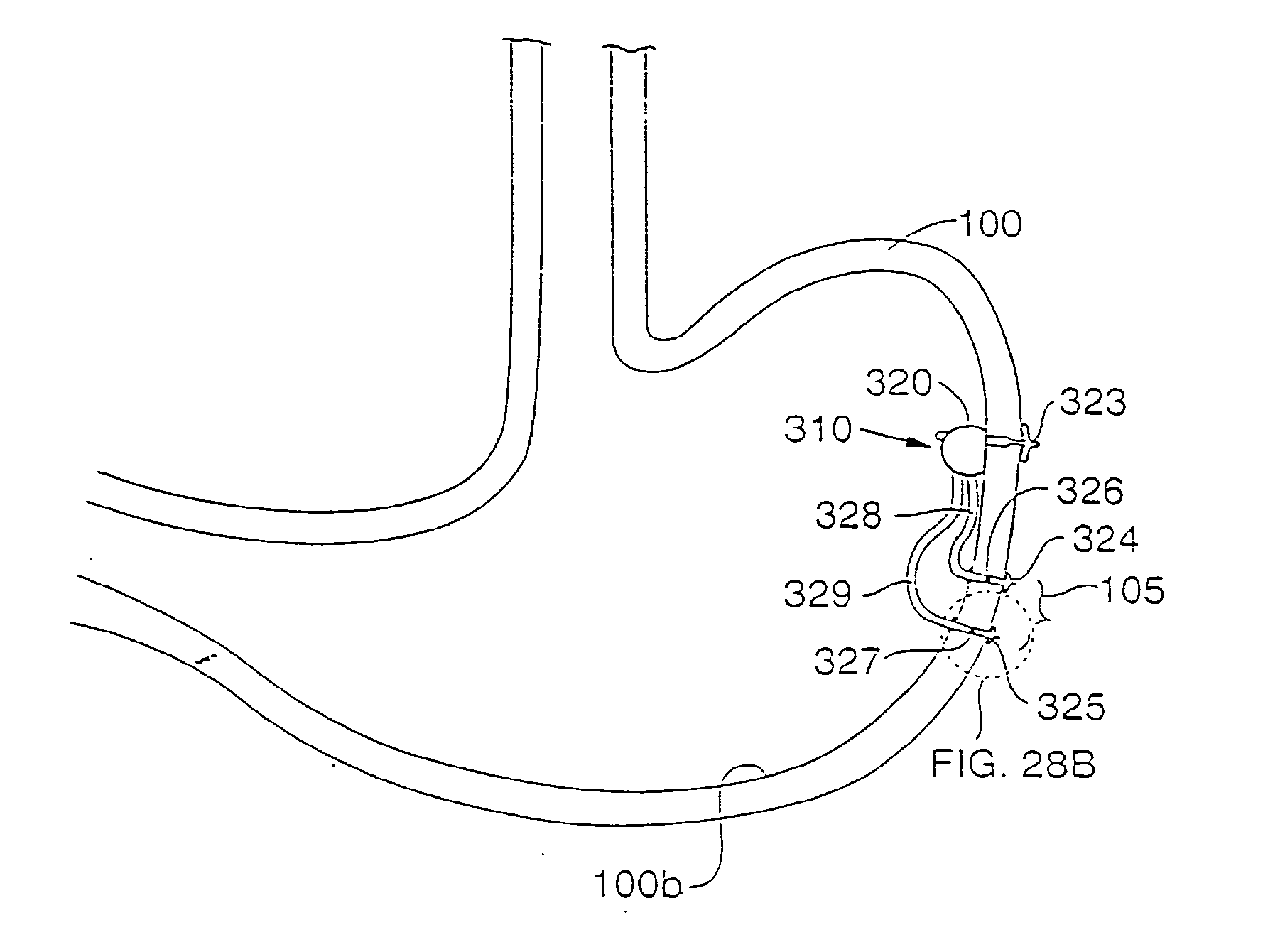
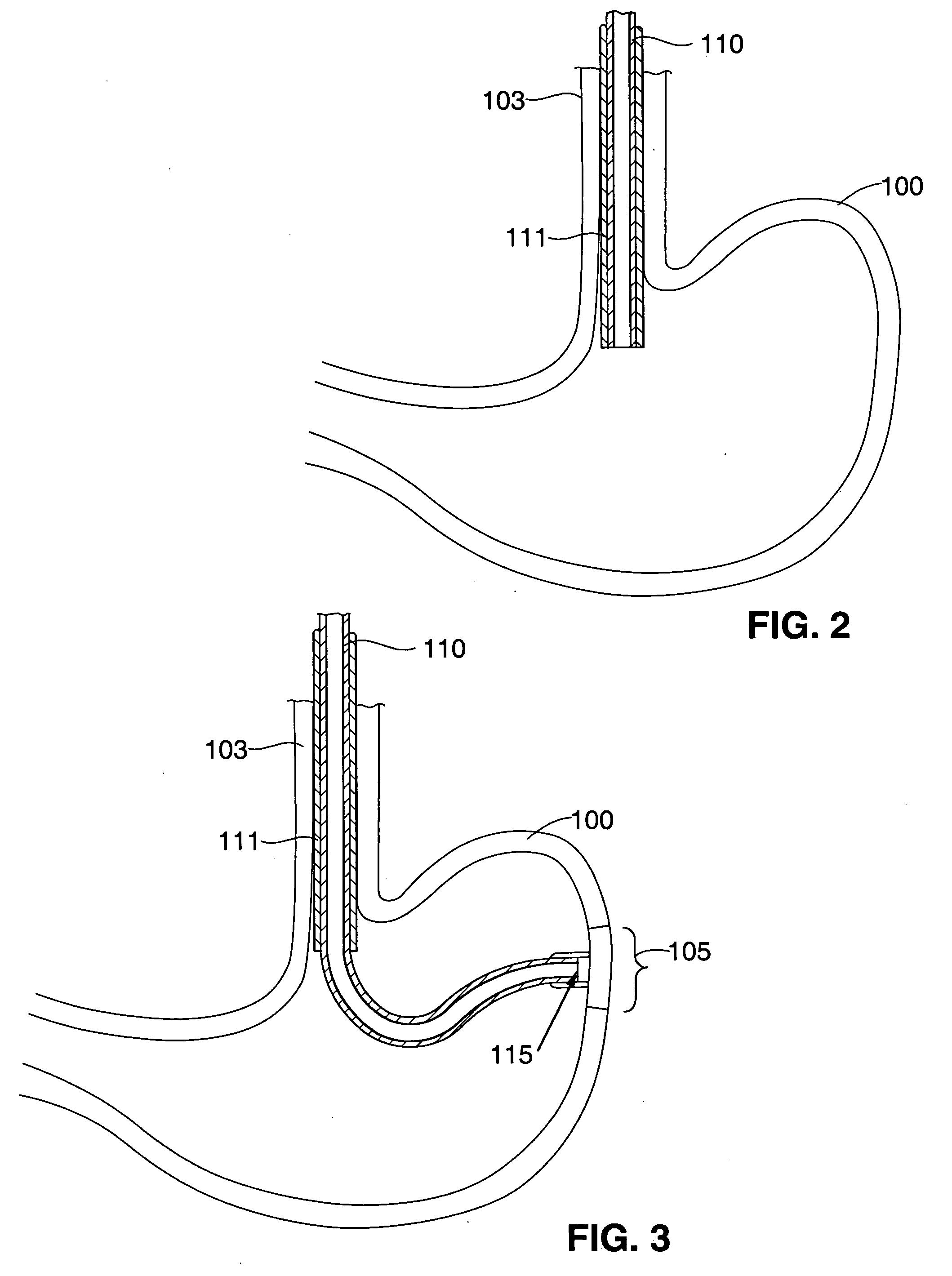
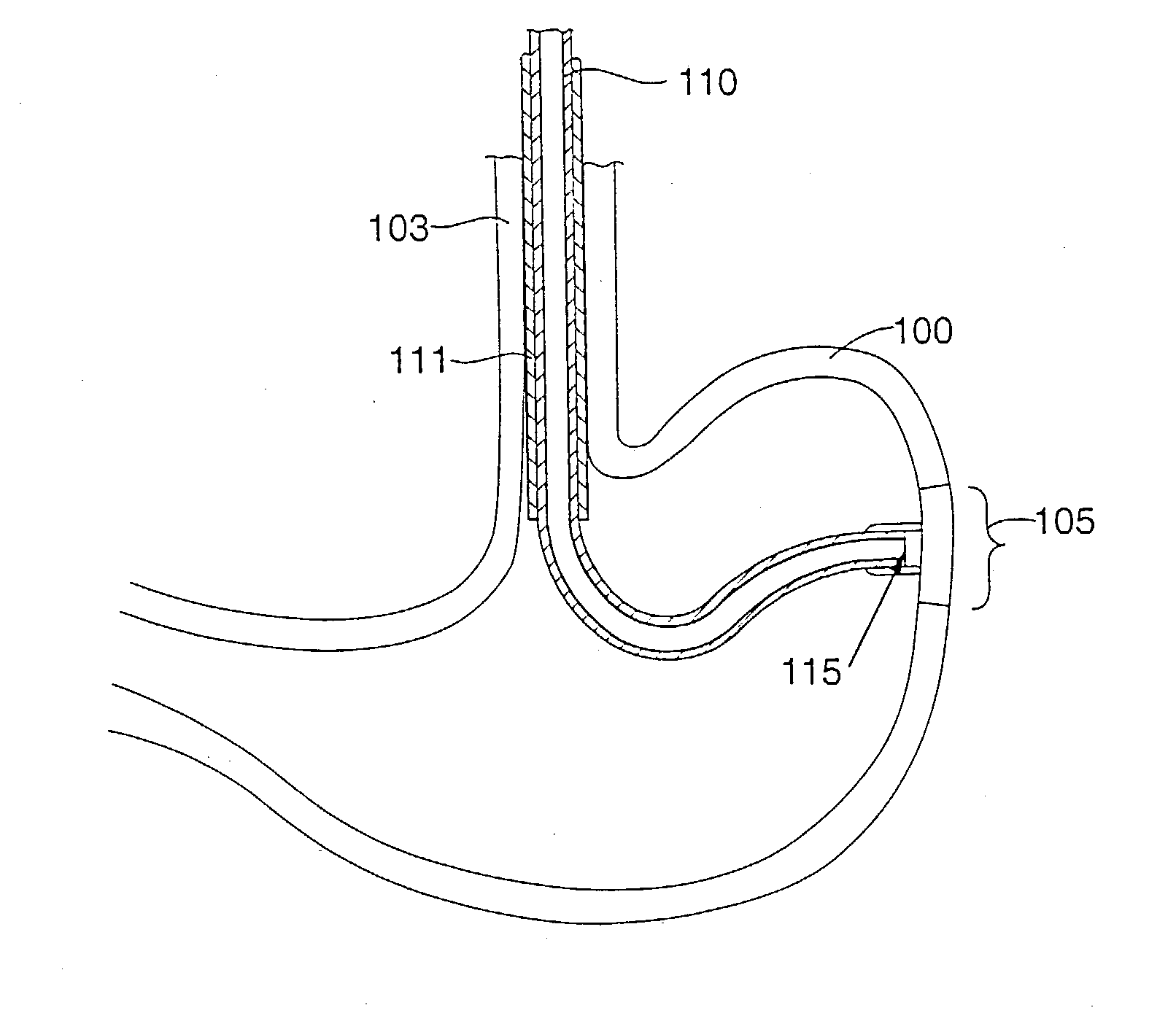
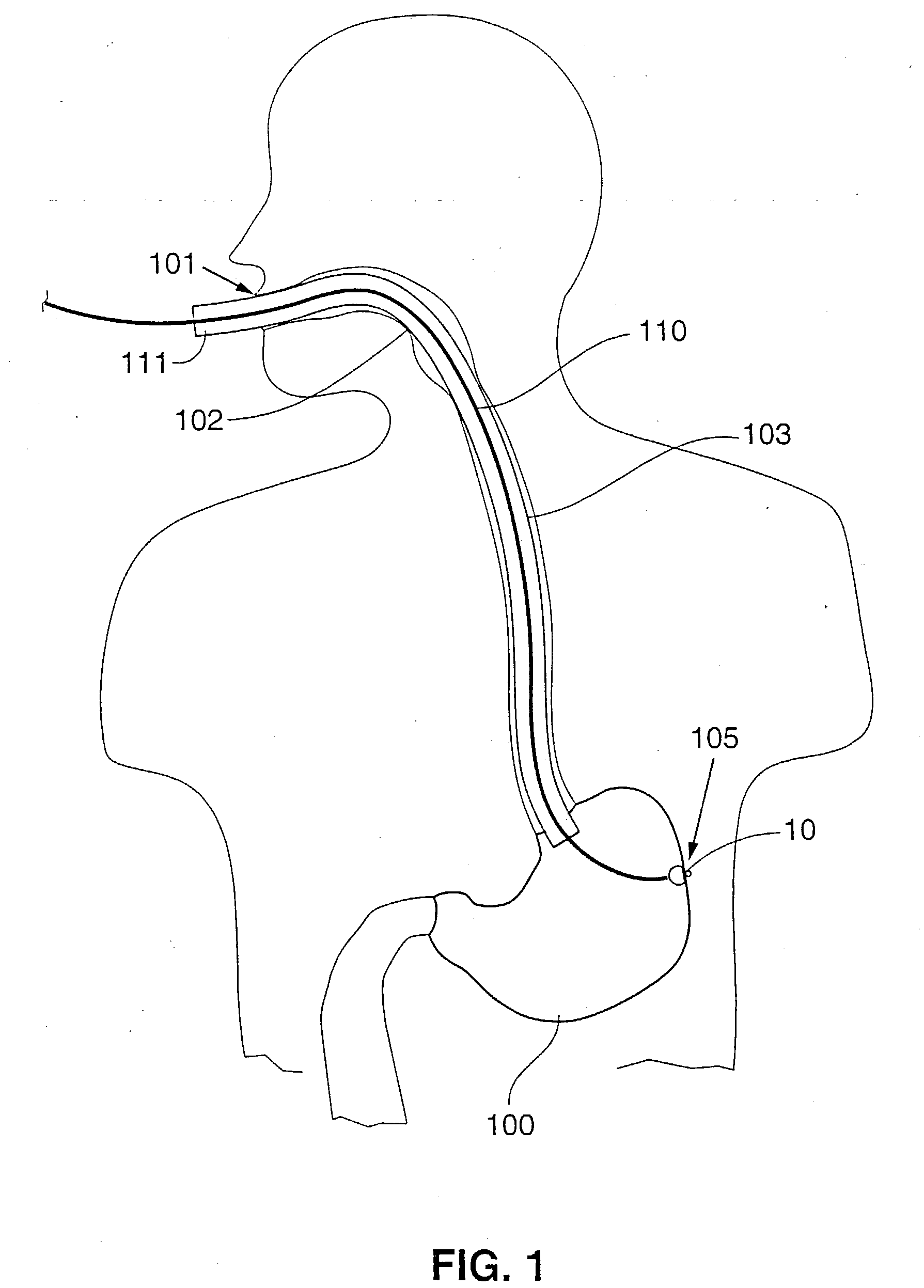
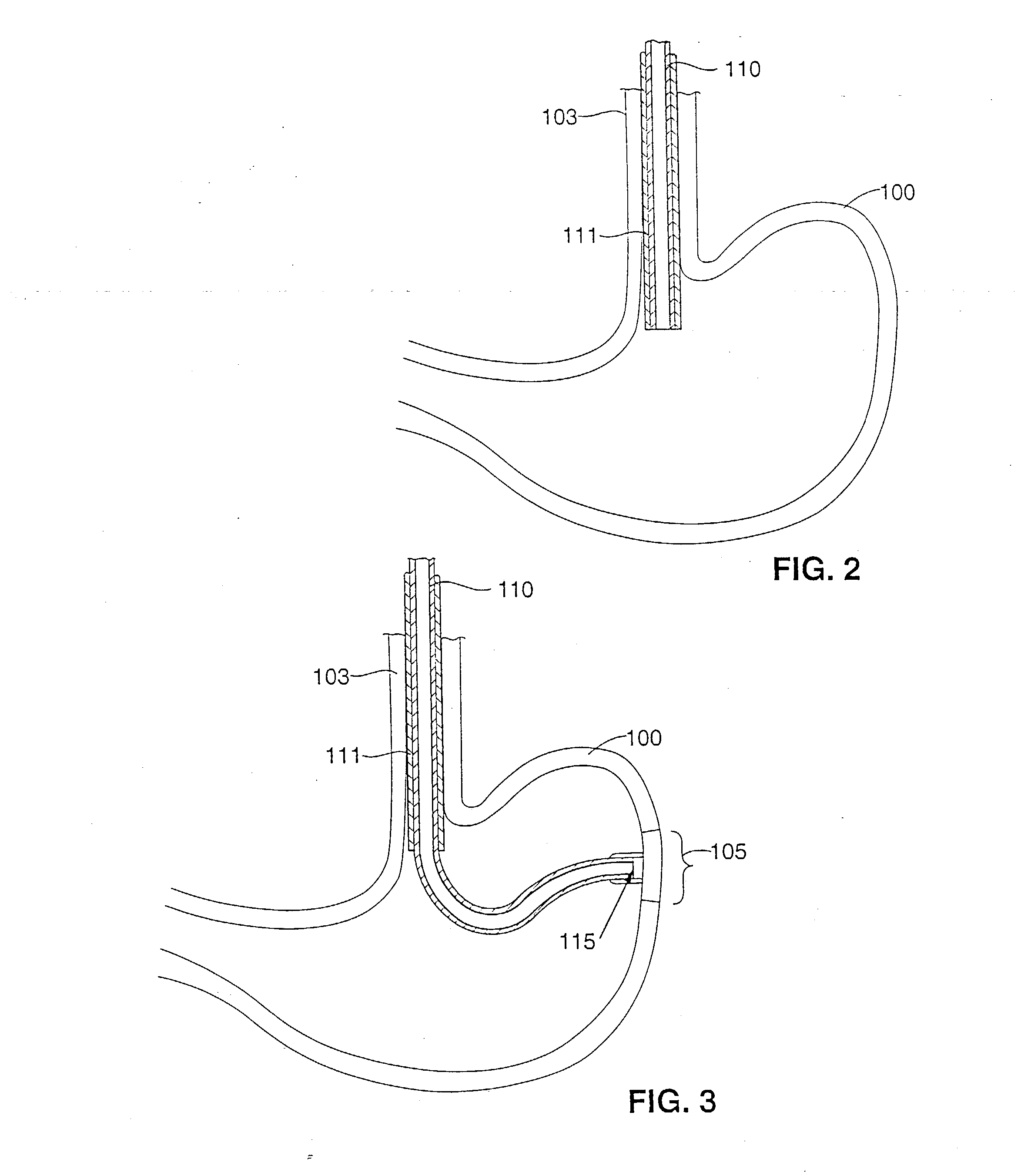
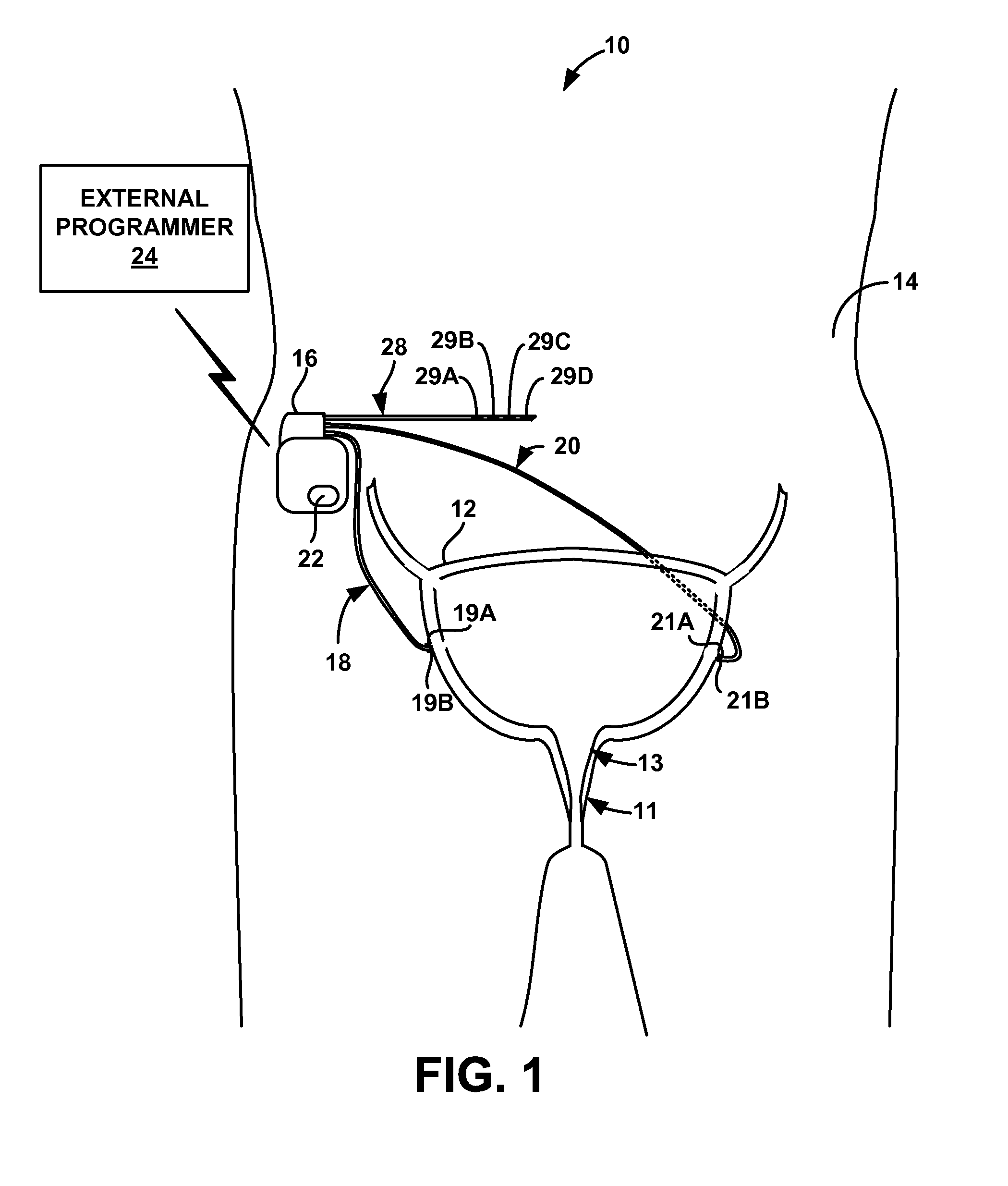
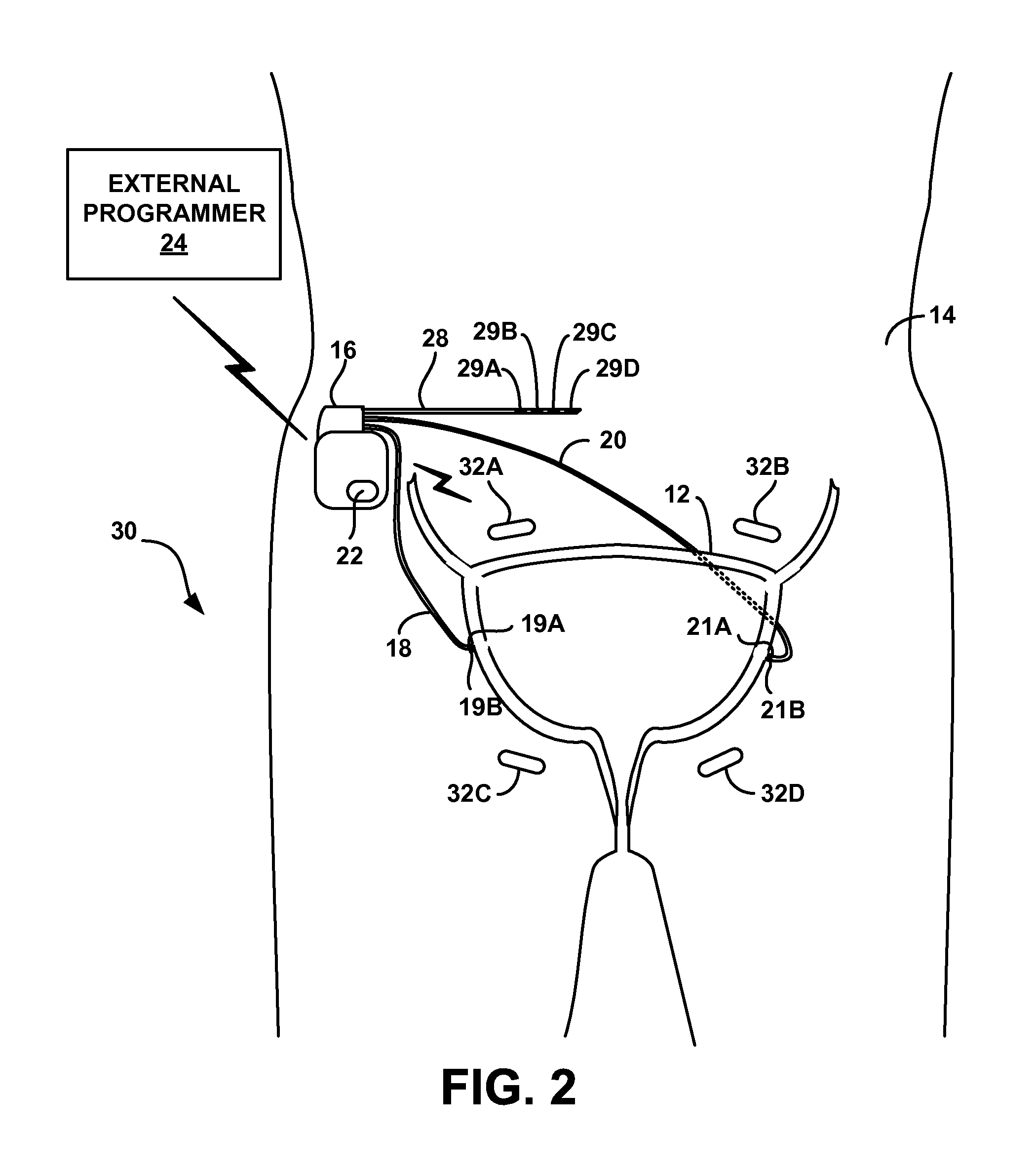
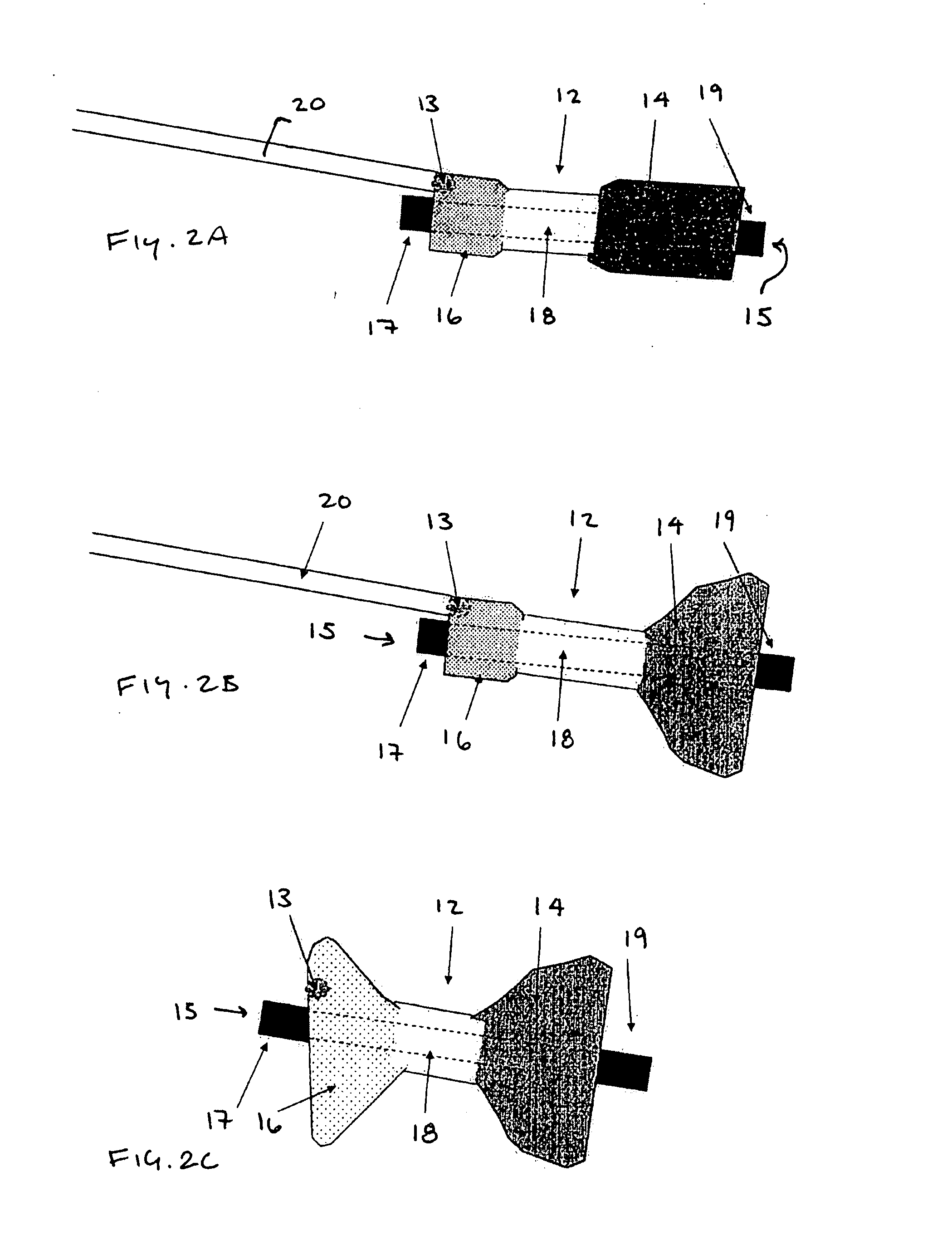
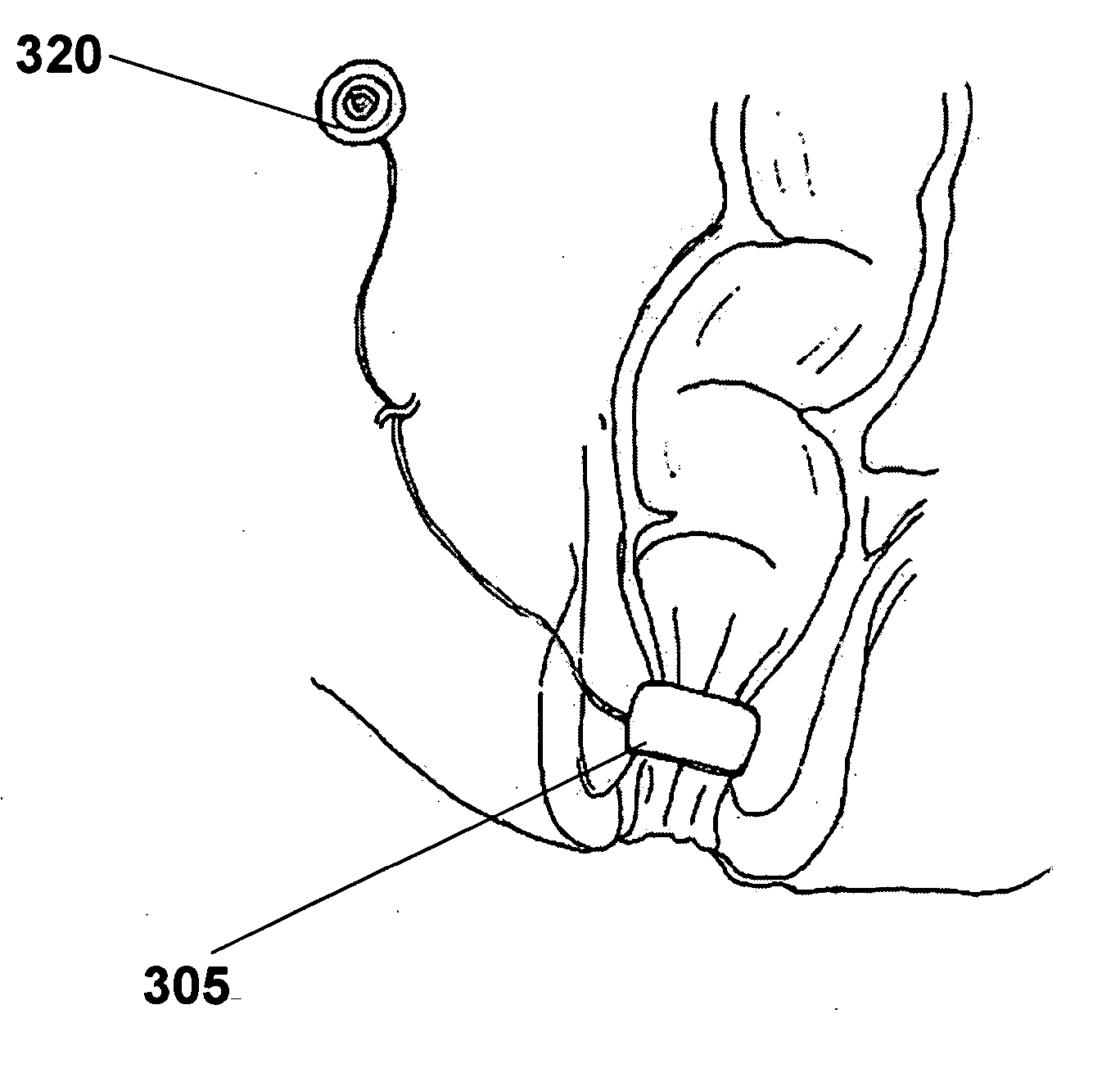
Implantable bifurcated gastrointestinal lead with active fixation
InactiveUS6876885B2Maximizing numberSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesTherapeutic DevicesActive fixation
Bifurcated, active fixation, gastrointestinal leads adapted to be implanted within the body at a site of the GI tract to conduct electrical stimulation and electrical signals of the GI tract between the gastrointestinal stimulator and the site are disclosed. The GI tract lead has a lead body comprising a common lead body trunk extending from a lead body trunk proximal end to a junction with a first plurality of lead body legs that extend from the junction to a like first plurality of lead body leg distal ends. An electrode head is formed at each lead body leg distal end having a plate and supporting at least one stimulation / sense electrode and an active fixation mechanism, whereby a plurality of active fixation attachment mechanisms are supported by a like plurality of electrode heads. The plurality of electrode heads can be affixed by the fixation mechanism at a plurality of spaced apart locations of the GI tract. The plurality of electrode heads can be affixed spaced apart an optimal distance for efficacious sensing and / or stimulation accommodating the physiology and any defects or surgical interventions of the physiology or other therapeutic equipment or IMDs that restrict full access to the GI tract.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
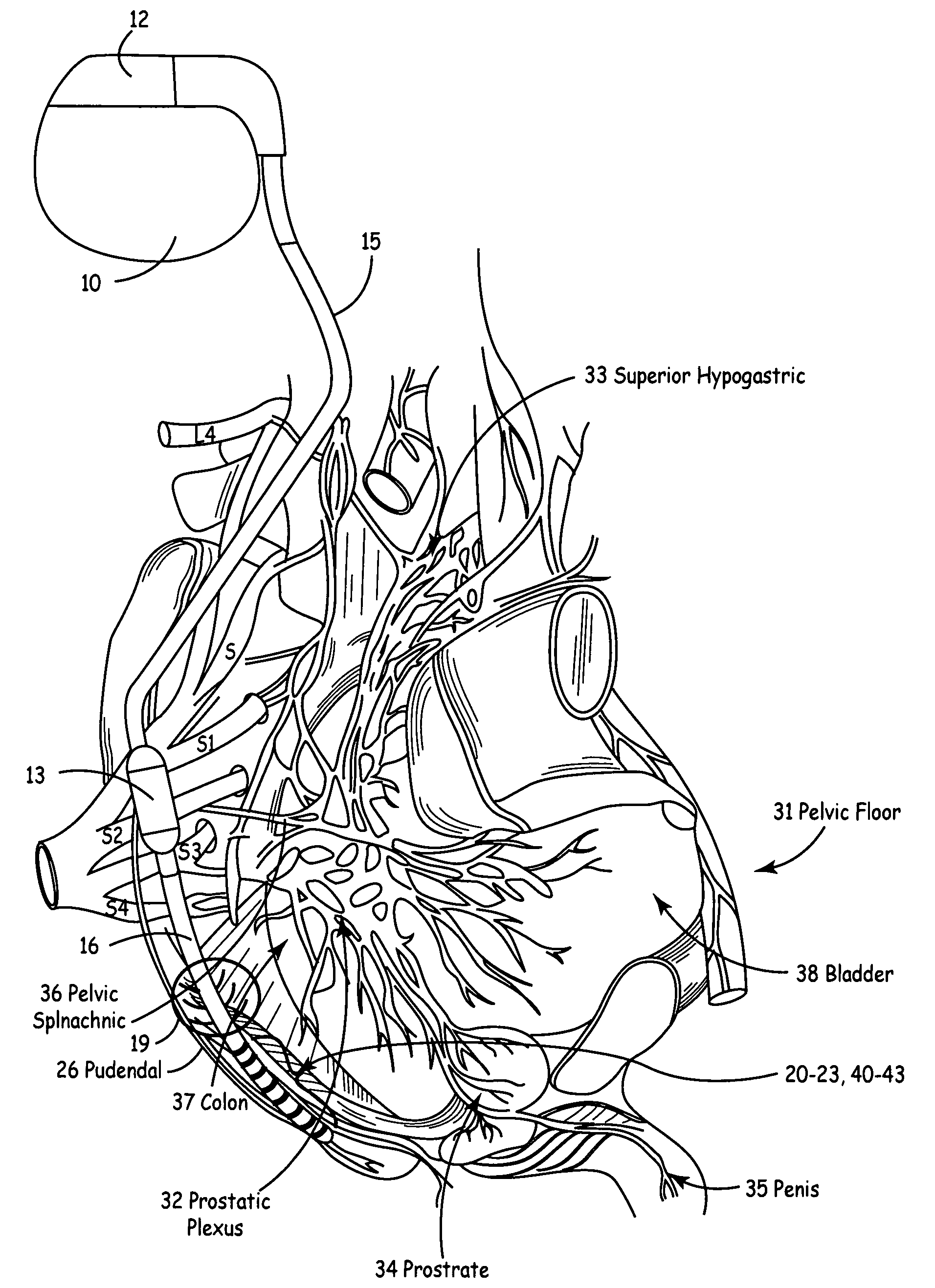
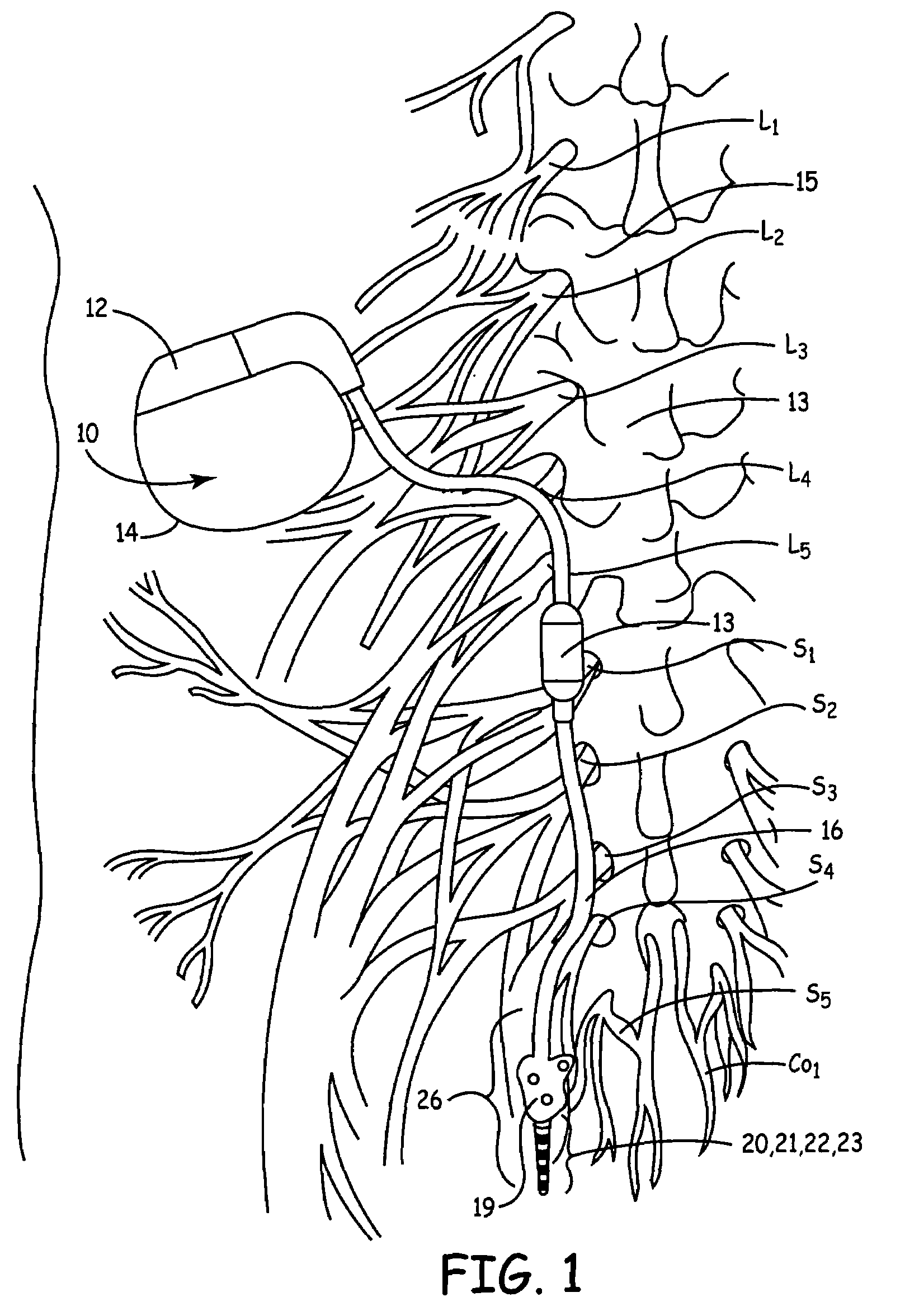
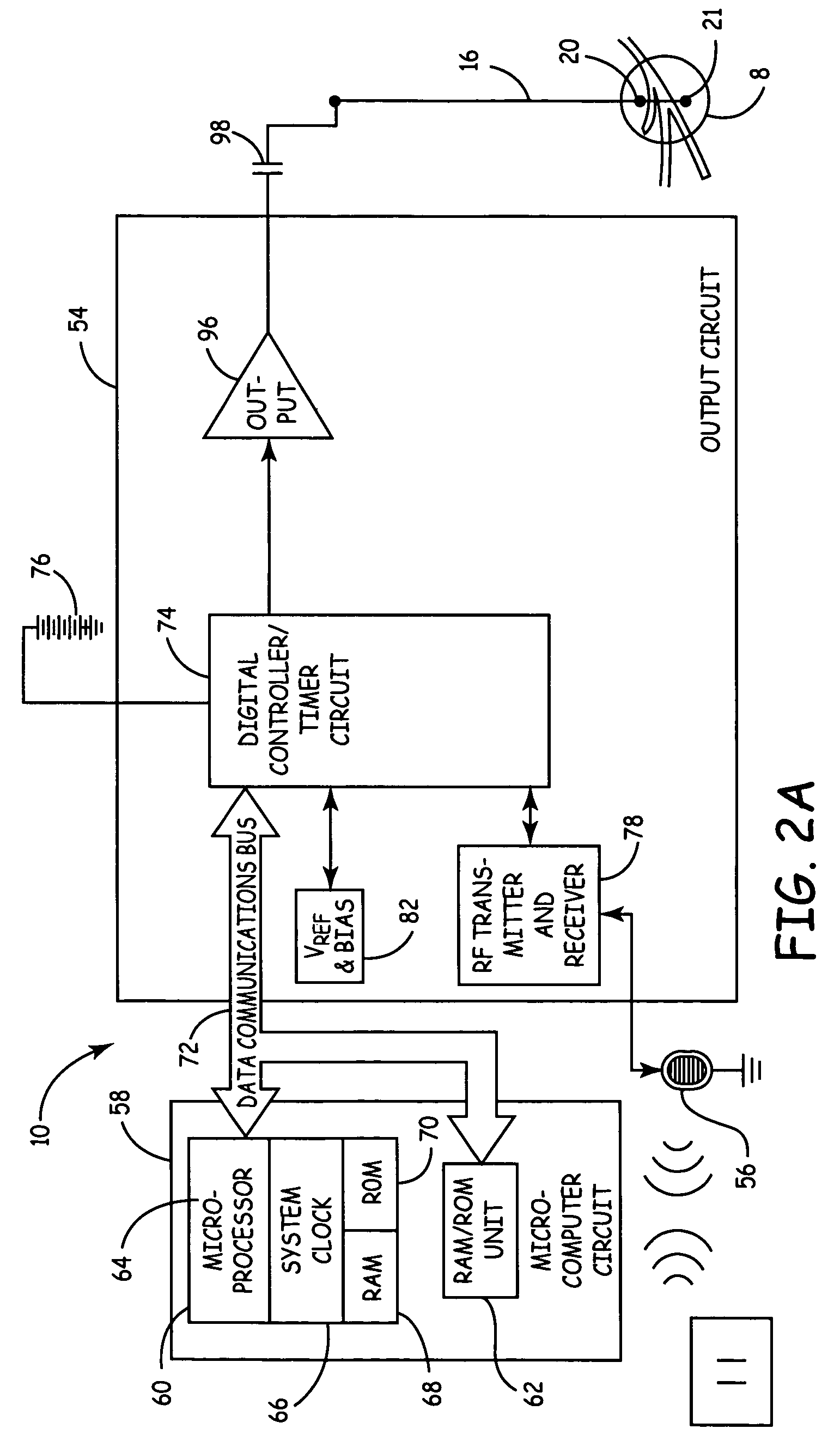
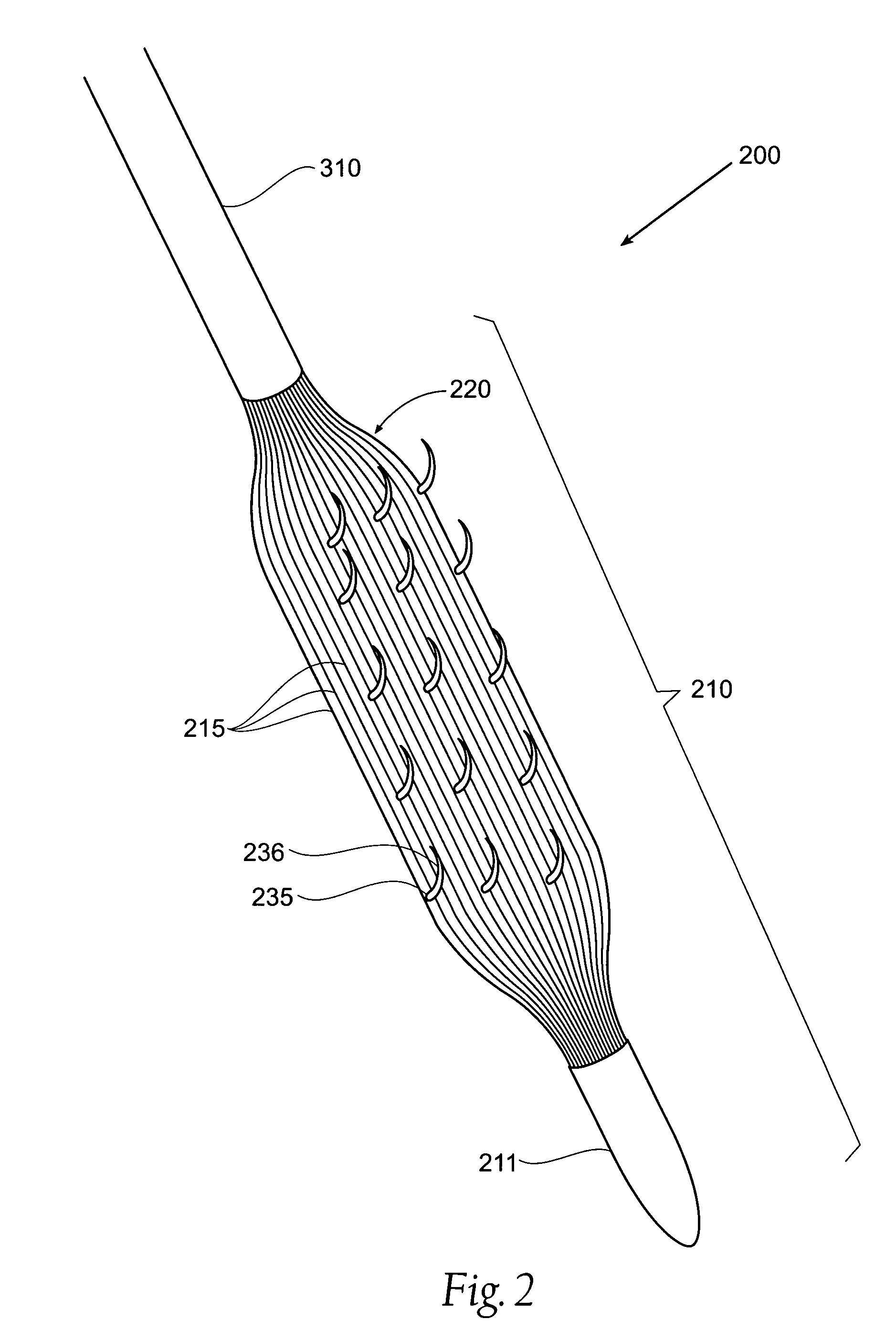
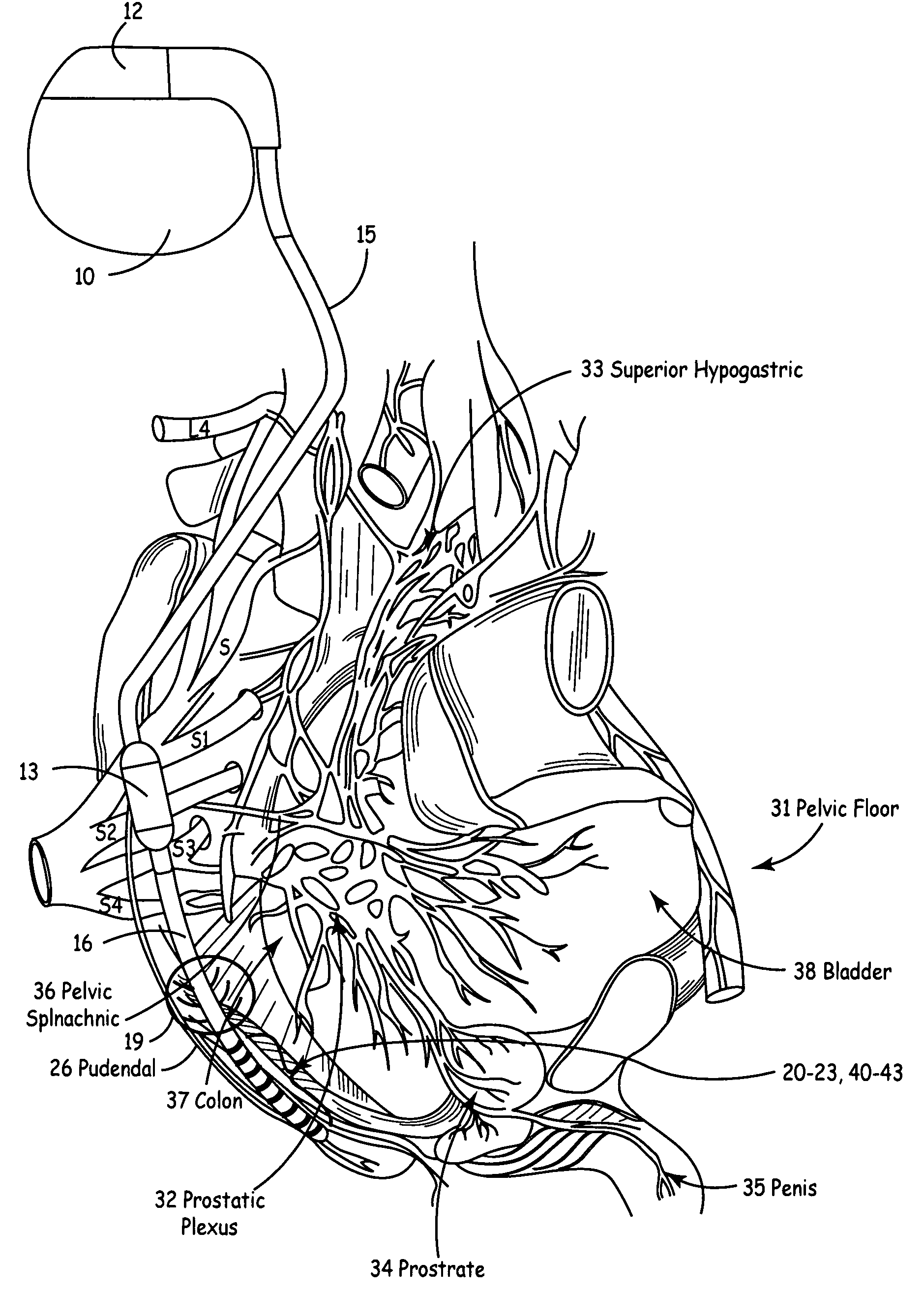
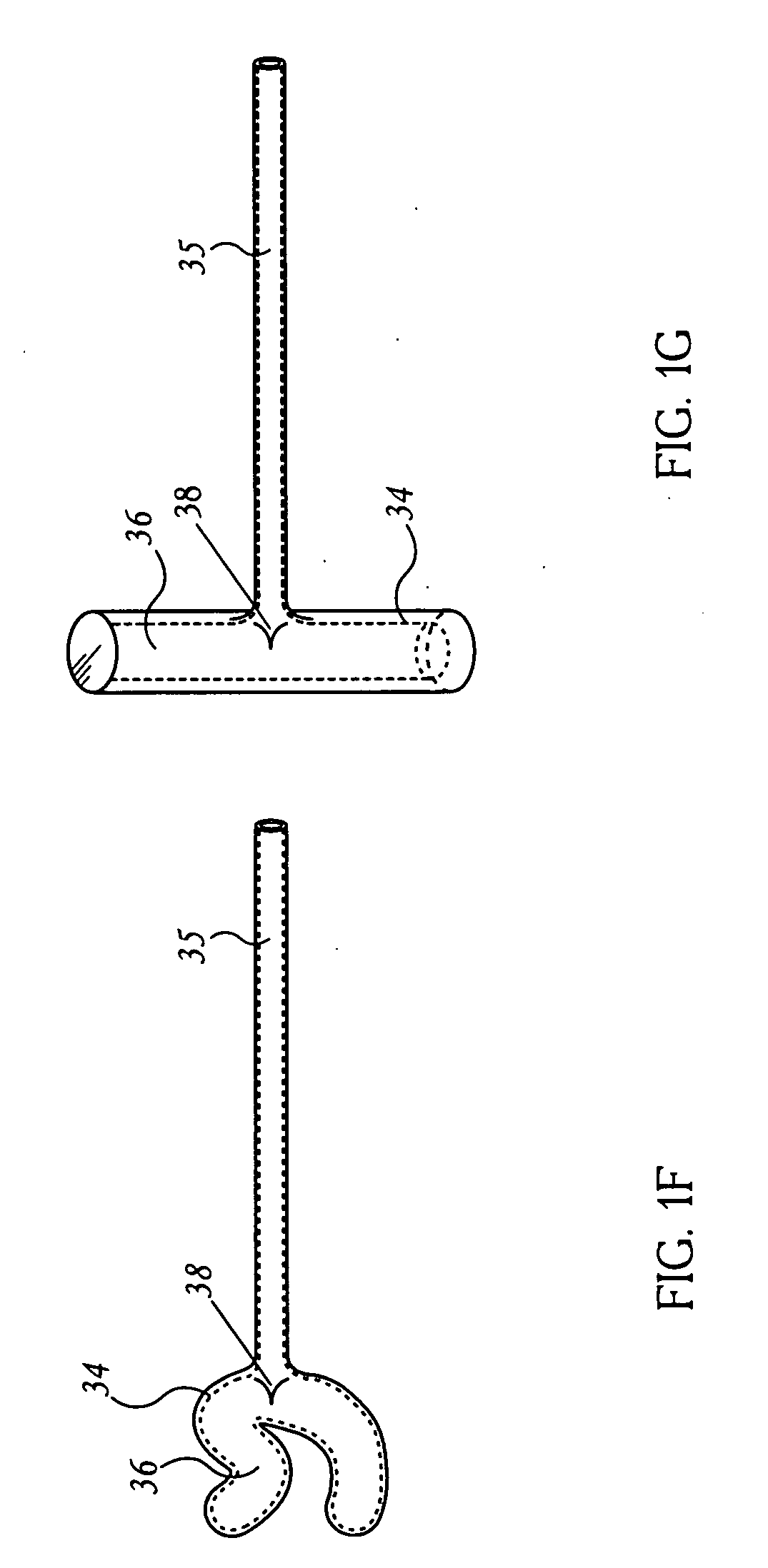
Method, system and device for treating disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudendal and associated nerves, and the optional delivery of drugs in association therewith
ActiveUS7328068B2Undesirable side effects of sacral nerve stimulation may be avoided or minimizedUndesirable side-effectDigestive electrodesGenital electrodesDiseaseProstatalgia
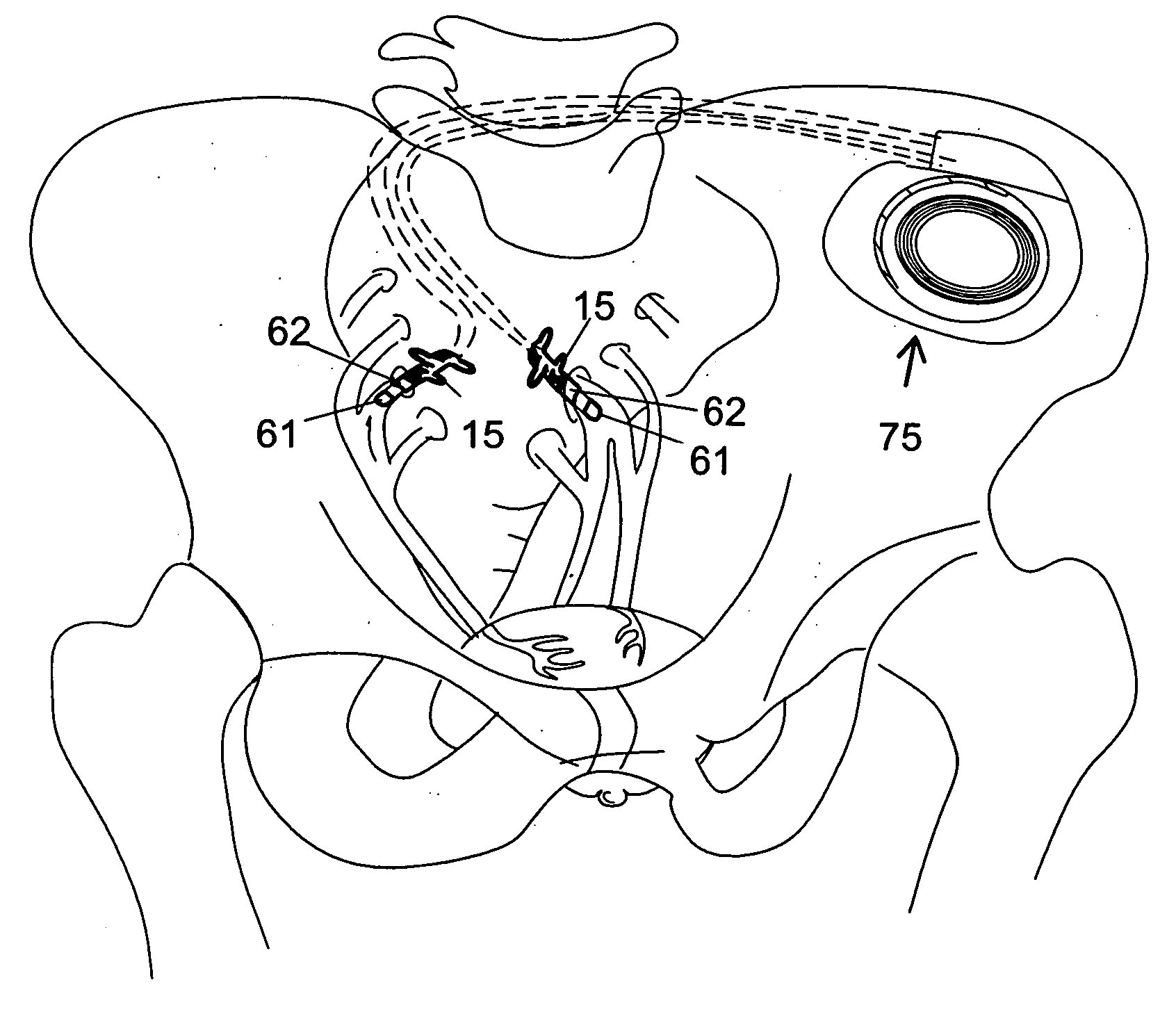
Described are implantable devices and methods for treating various disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudendal or other nerves, and optional means for delivering drugs in association therewith. A method of precisely positioning and implanting a medical electrical lead so as to provide optimal stimulation of the pudendal nerve or a portion thereof is also described. Placement of a stimulation lead next to or on the pudendal nerve may be performed using conventional prior art techniques through gross anatomical positioning, but usually does not result in truly optimal lead placement. One method of the present invention utilizes neurophysiological monitoring to assess the evoked responses of the pudendal nerve, and thereby provide a method for determining the optimal stimulation site. Additionally, one or more electrical stimulation signals are applied, and optionally one or more drugs are infused, injected or otherwise administered, to appropriate portions of a patient's pelvic floor and pudendal nerve or portions thereof in an amount and manner effective to treat a number of disorders, including, but not limited to, urinary and / or fecal voiding dysfunctions such as constipation, incontinence disorders such as urge frequency and urinary retention disorders, sexual dysfunctions such as orgasmic and erectile dysfunction, pelvic pain, prostatitis, prostatalgia and prostatodynia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
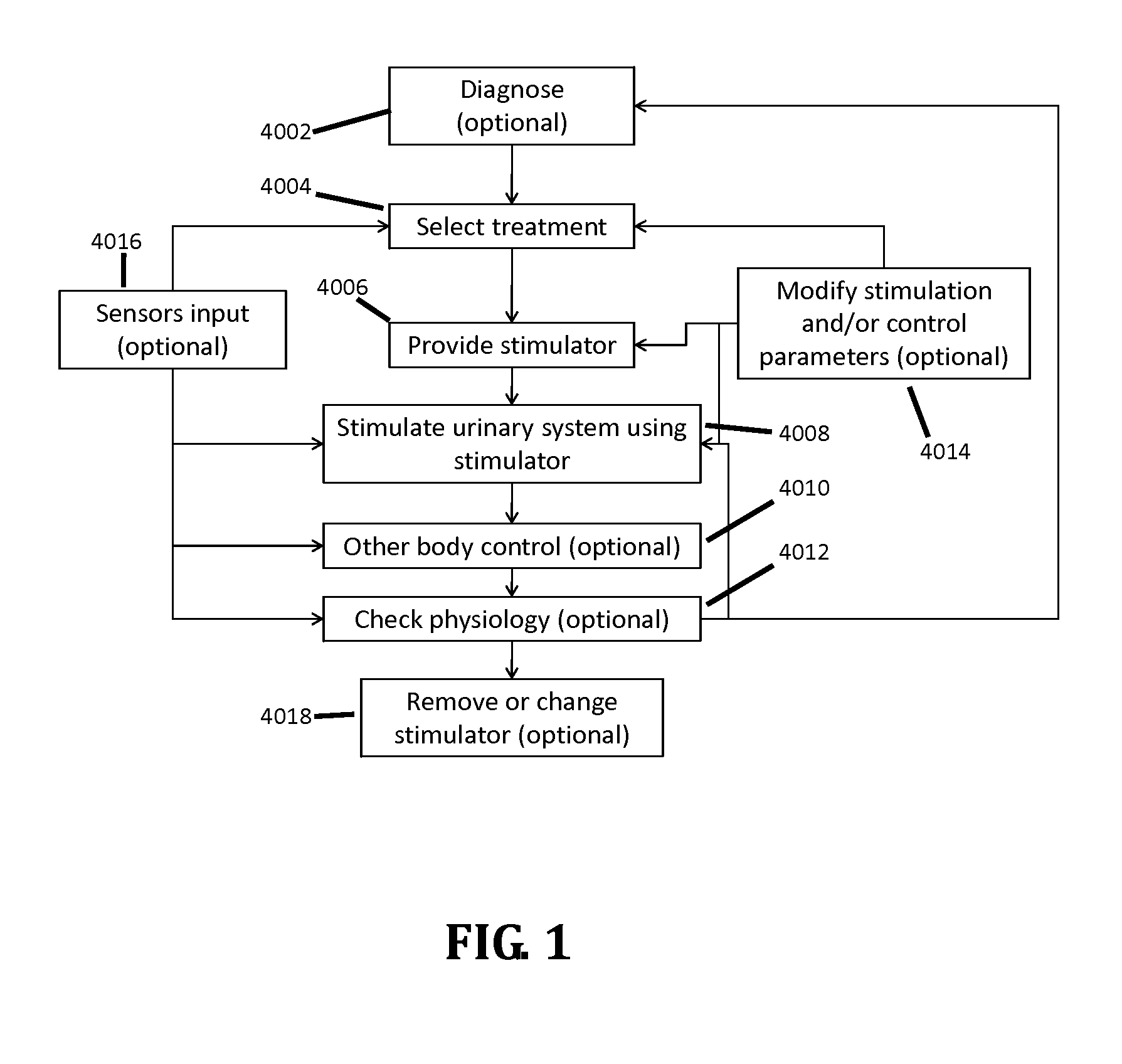
Stimulation of the urinary system
InactiveUS20110301662A1Prevent rotationNot interfere with mobilitySpinal electrodesDigestive electrodesUrethraShort urethra
Apparatus and methods are provided, including a bladder stimulator that includes an elongate element adapted to pass through a urethra or adapted to pass through another opening in the bladder, an expandable body coupled to said elongate element, and an array of one or more stimulator contacts coupled to the expandable body, the array including at least one contact adapted to contact a portion of a bladder of a subject when the expandable body is inserted in the bladder and expanded. A controller stimulates the portion of the bladder by driving a pulse into the bladder via the contact, the pulse having a frequency of 5 Hz-1 kHz. Other applications are also described.
Owner:NEPHERA LTD
Surgical weight control device
InactiveUS7326207B2Optimize quantityEasy to eatStentsBalloon catheterCurative treatmentPhysical therapy
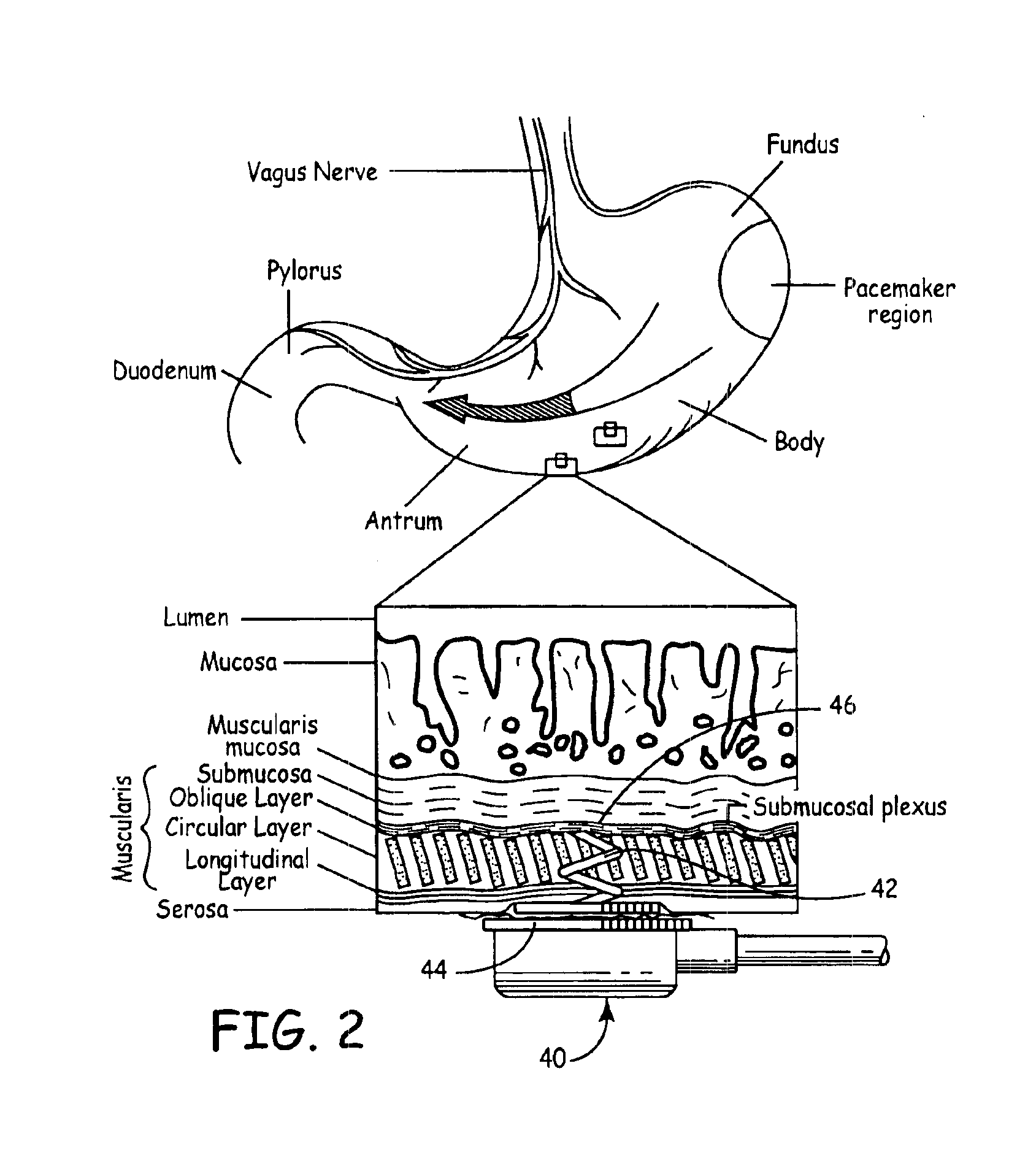
This invention provides a method and system for the curative treatment of obesity. A first aspect of this invention is that it enables identification of the nerves responsible for the relaxation of the stomach muscles that occurs prior to and during eating. A second aspect of the invention is that it allows the physician to identify focal nerve sites in the stomach and upper duodenum that are associated with producing sensations of hunger and satiety. Nervous transmission from these sites can be modulated or blocked all together so as to minimize the sensation of hunger. A third aspect of this invention is that allows a physician to shrink selected portions of the innermost oblique muscle and middle circular muscle layers of the stomach. This can be performed in a physician's office using local anesthesia. Shrinkage of these muscles produces a feeling of satiety that enhances the patient's efforts to restrict his caloric intake.
Owner:MEDERI RF LLC
Method, system and device for treating disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudenal and associated nerves, and the optional delivery of drugs in association therewith
ActiveUS20050113877A1Reduce traumaAvoid damageDigestive electrodesArtificial respirationDiseaseProstatalgia
Described are implantable devices and methods for treating various disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudendal or other nerves, and optional means for delivering drugs in association therewith. A method of precisely positioning and implanting a medical electrical lead so as to provide optimal stimulation of the pudendal nerve or a portion thereof is also described. Placement of a stimulation lead next to or on the pudendal nerve may be performed using conventional prior art techniques through gross anatomical positioning, but usually does not result in truly optimal lead placement. One method of the present invention utilizes neurophysiological monitoring to assess the evoked responses of the pudendal nerve, and thereby provide a method for determining the optimal stimulation site. Additionally, one or more electrical stimulation signals are applied, and optionally one or more drugs are infused, injected or otherwise administered, to appropriate portions of a patient's pelvic floor and pudendal nerve or portions thereof in an amount and manner effective to treat a number of disorders, including, but not limited to, urinary and / or fecal voiding dysfunctions such as constipation, incontinence disorders such as urge frequency and urinary retention disorders, sexual dysfunctions such as orgasmic and erectile dysfunction, pelvic pain, prostatitis, prostatalgia and prostatodynia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
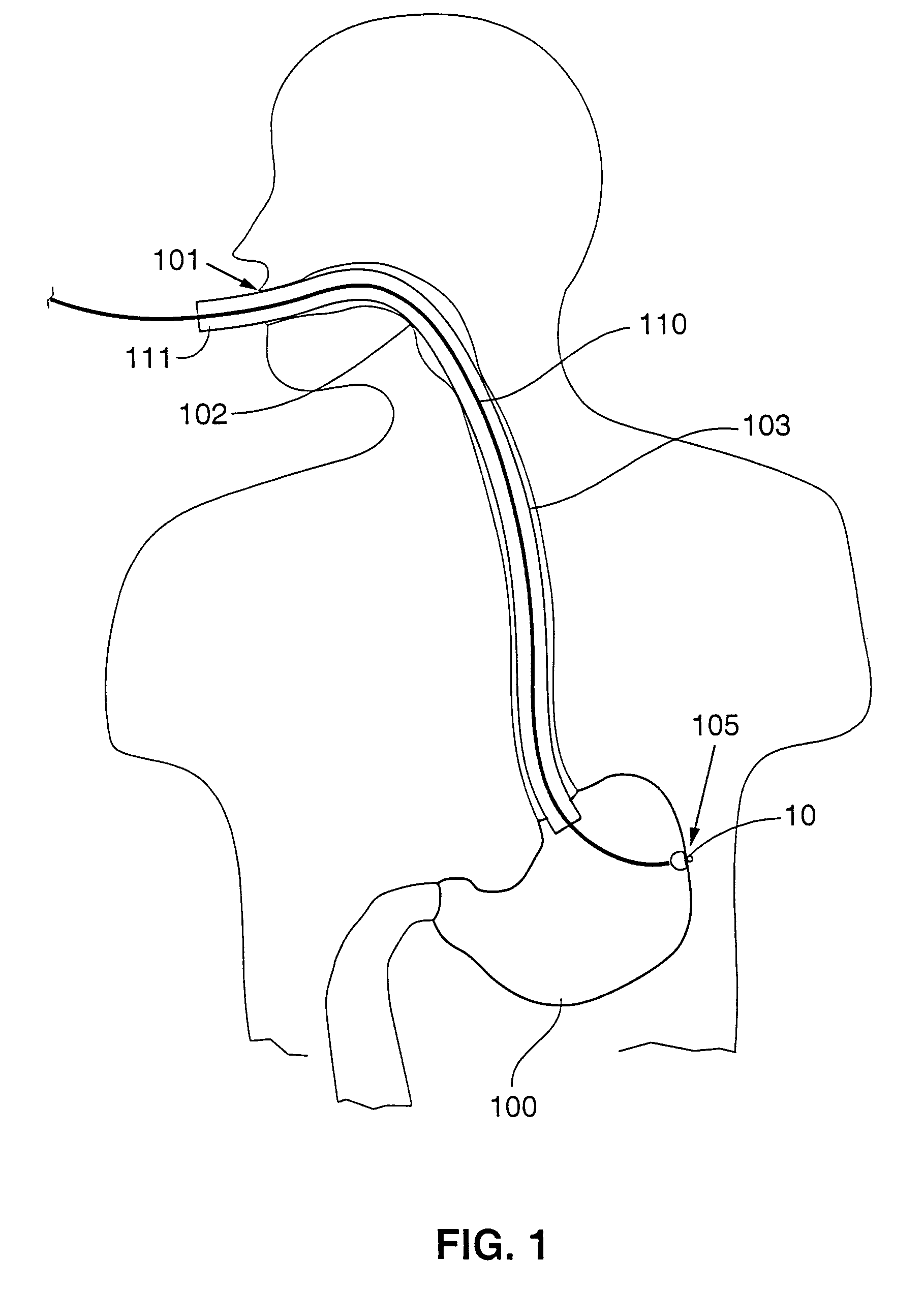
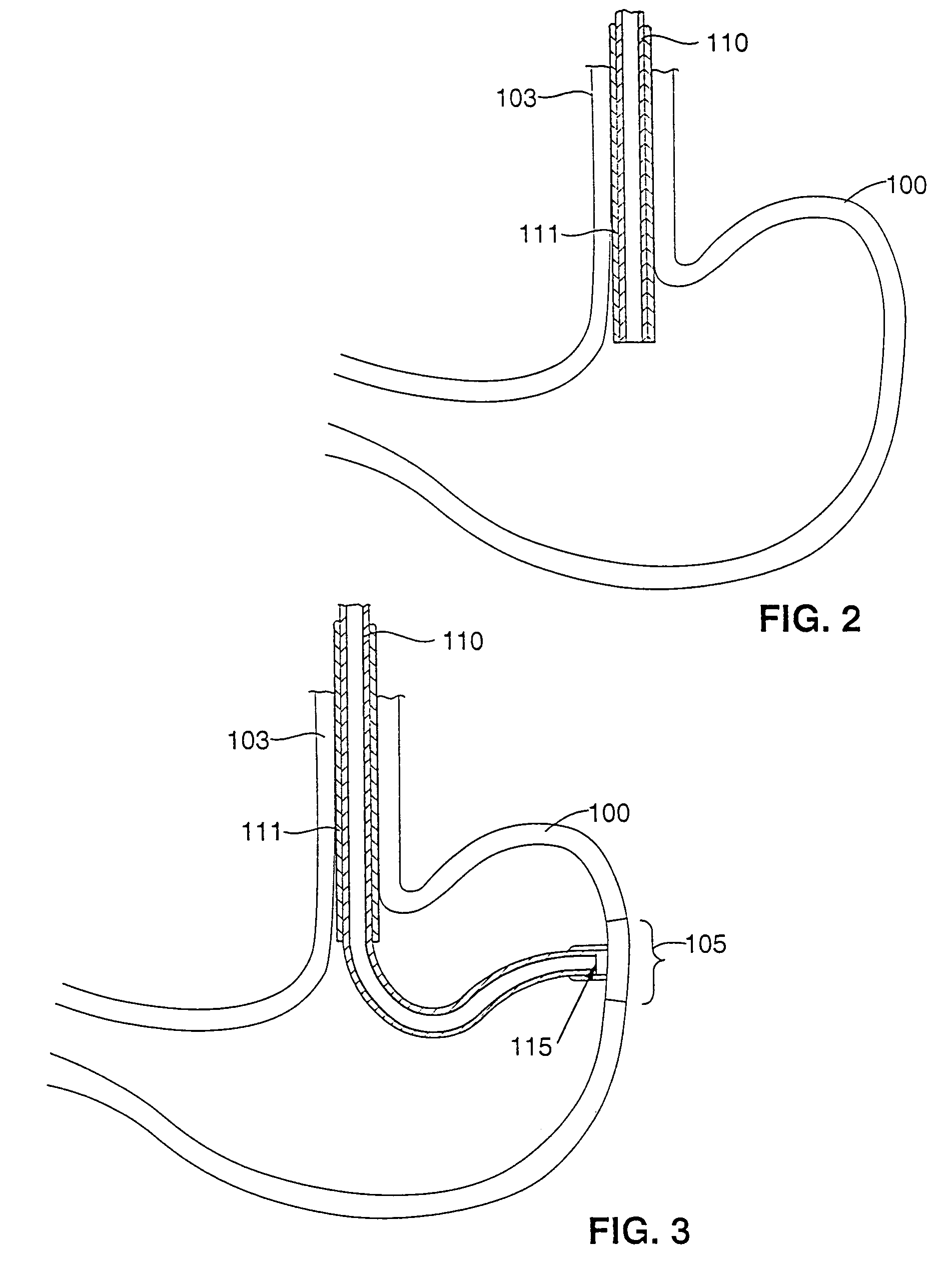
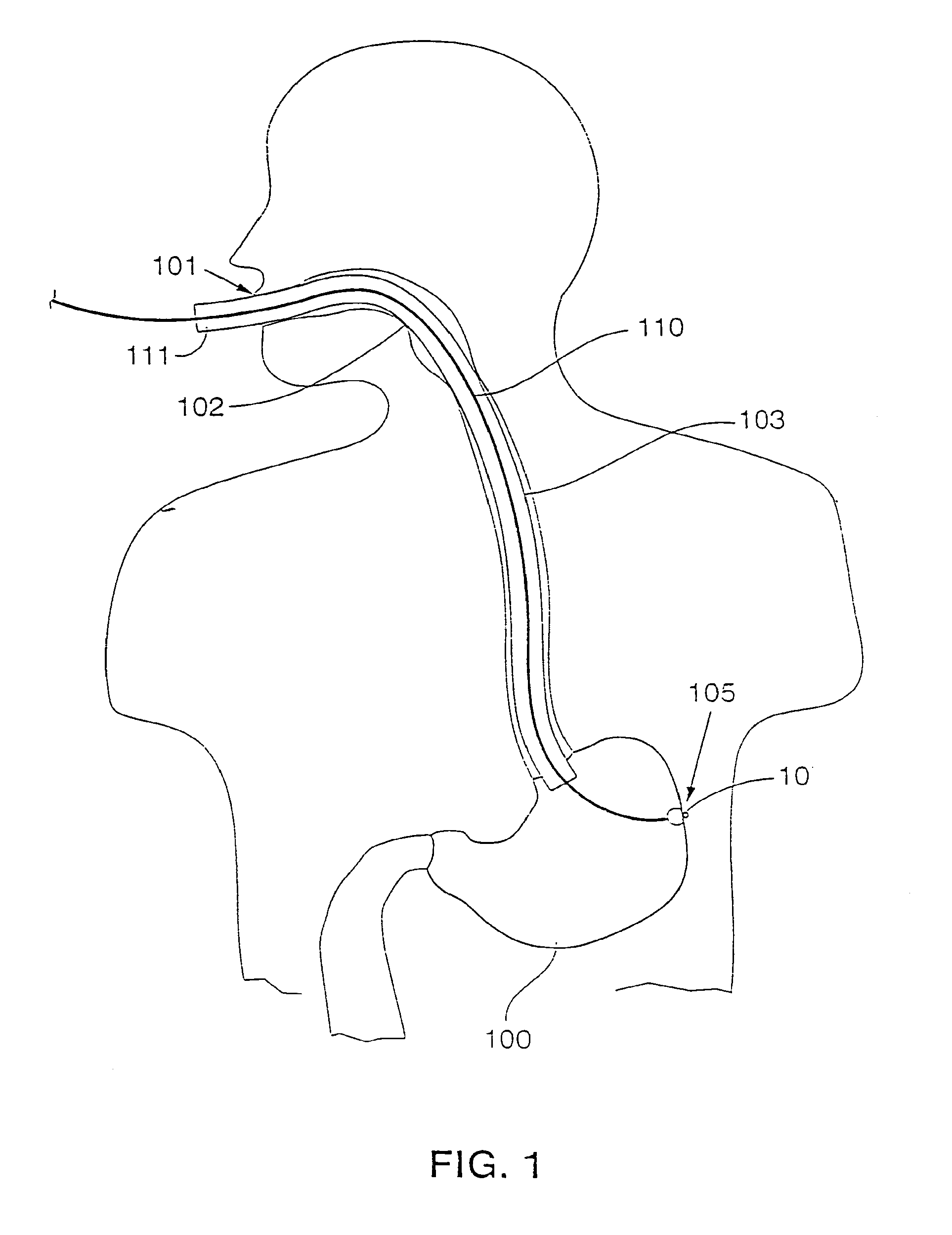
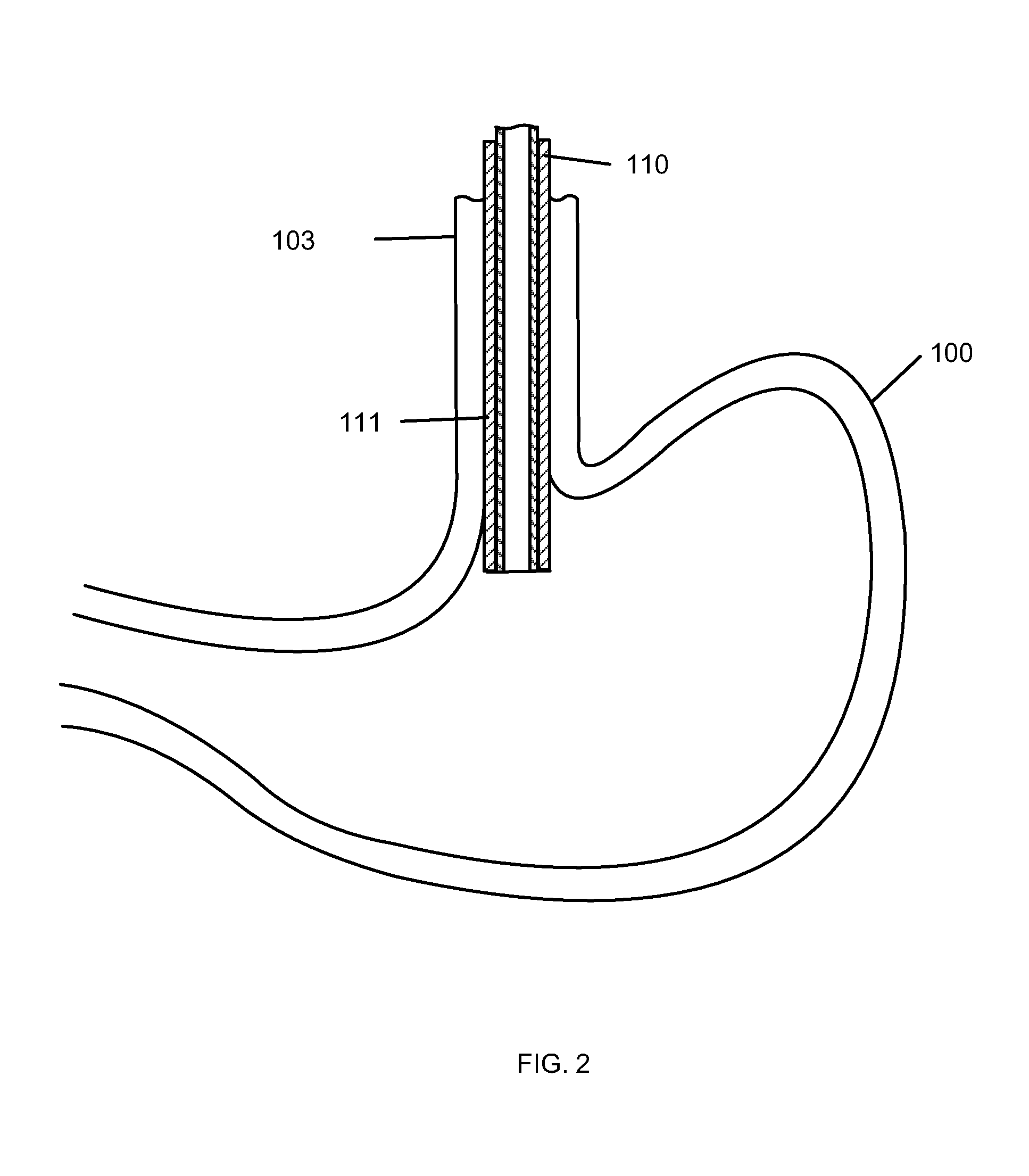
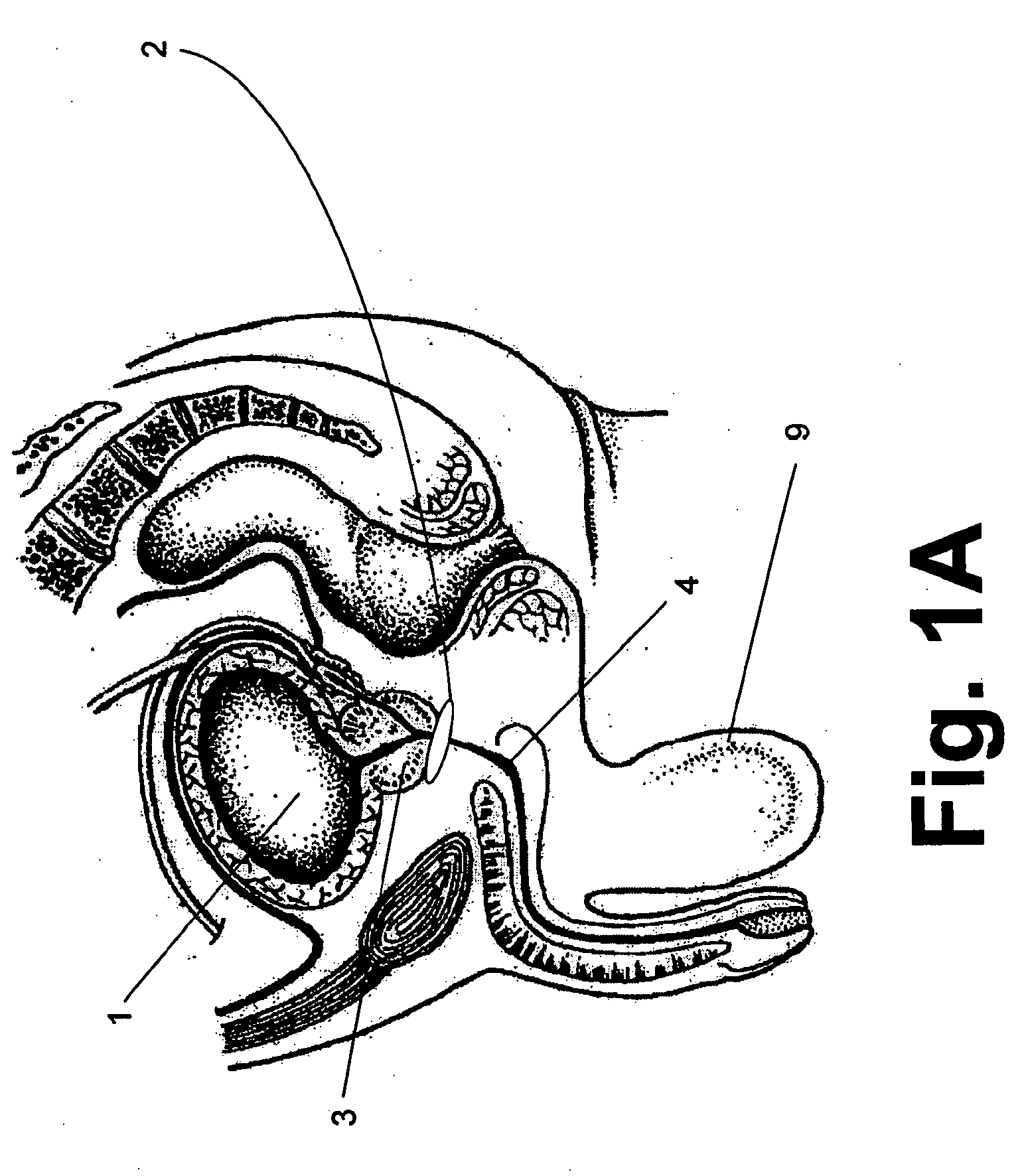
Gastric treatment and diagnosis device and method
InactiveUS20040088023A1Minimize stressReduce potential tissue damageCannulasSurgical needlesStomach wallsGastric Disorders
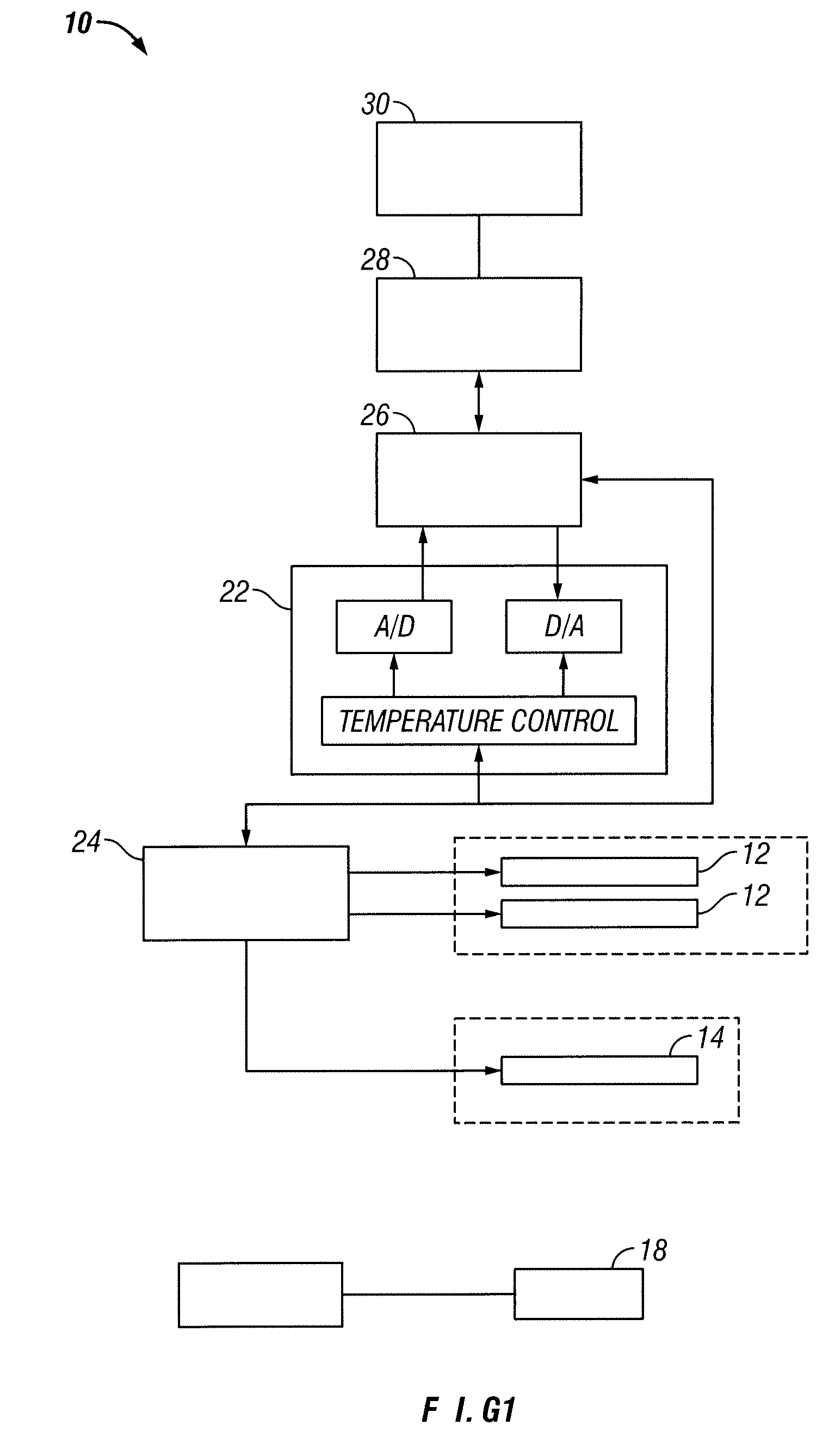
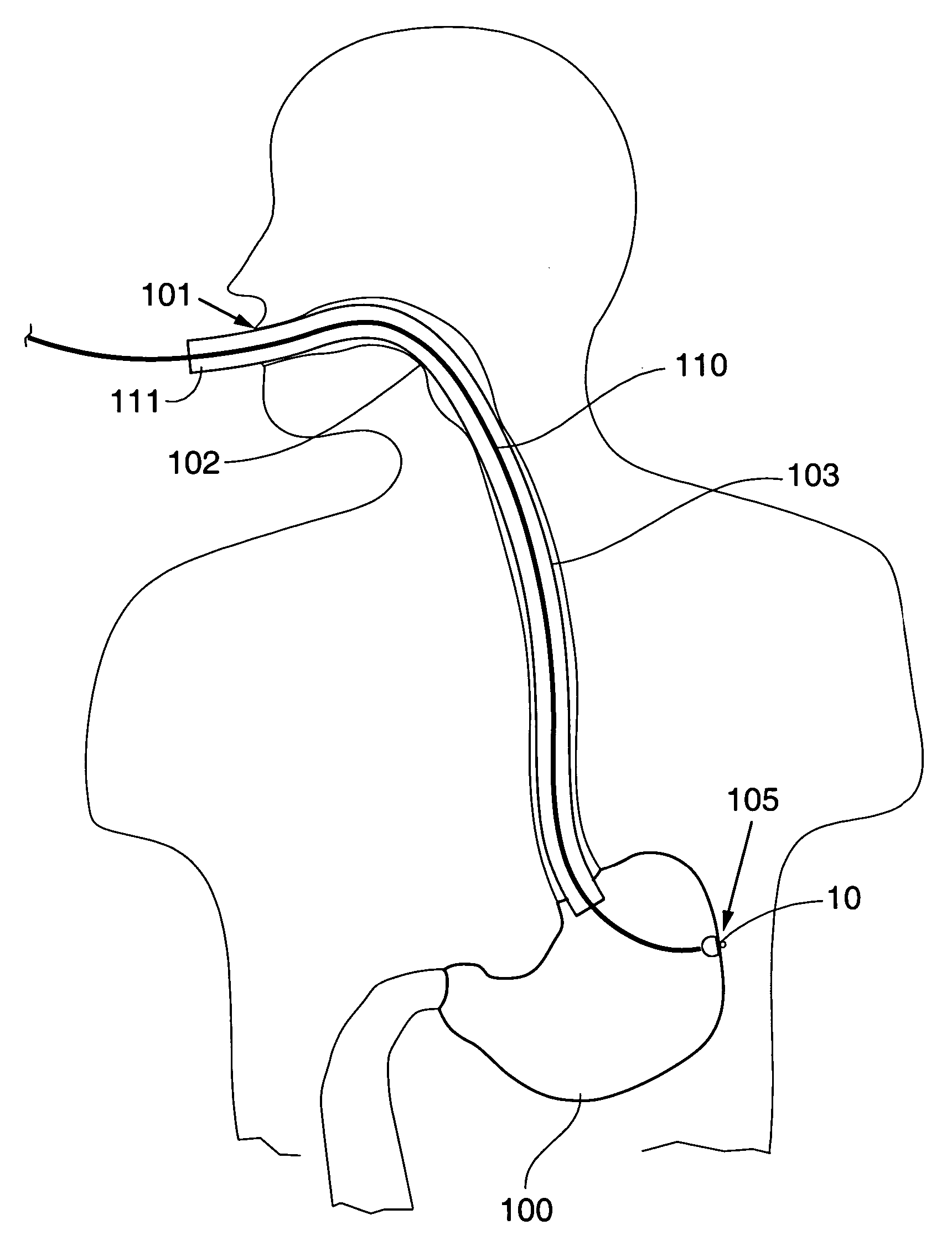
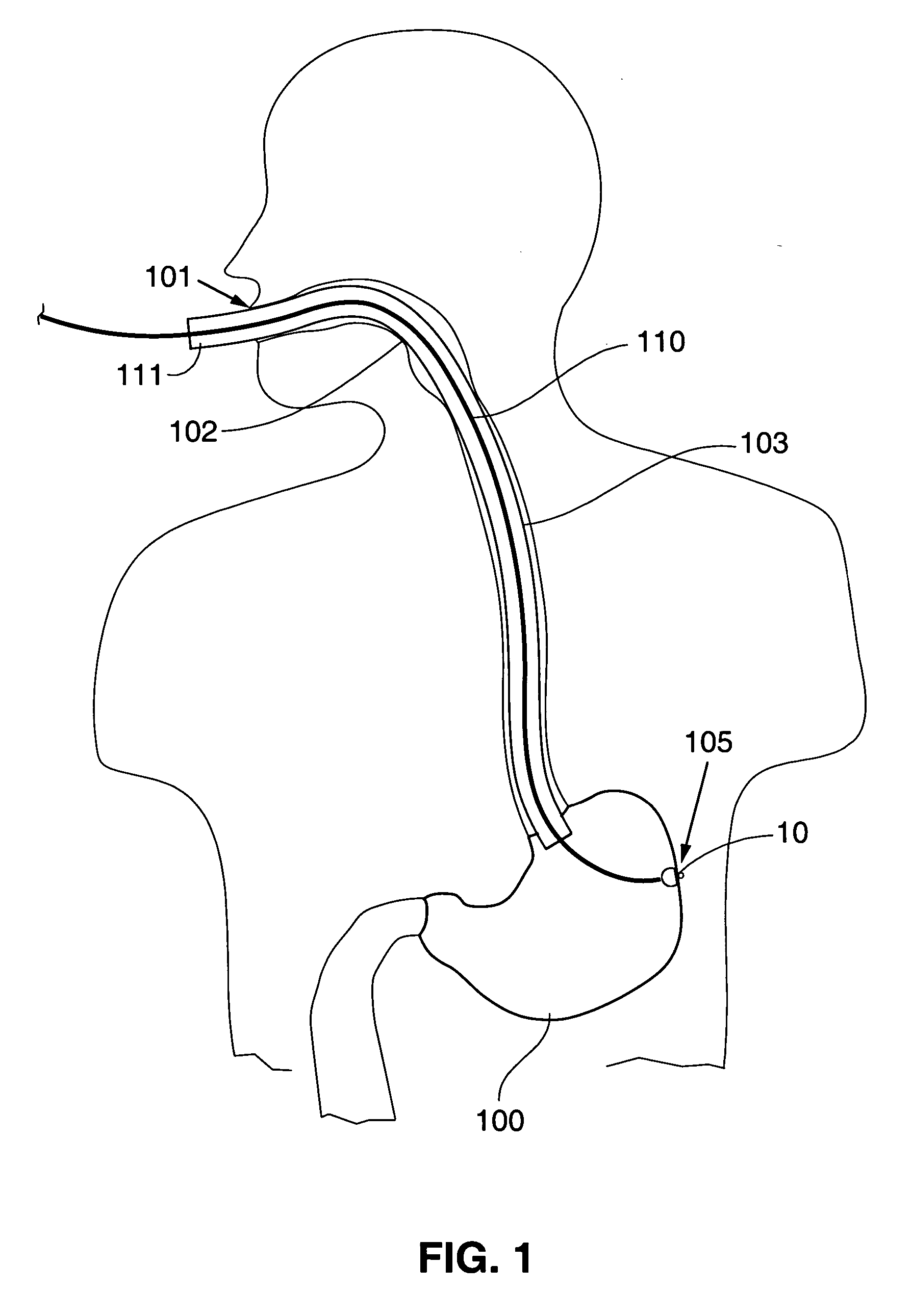
A device, system and method for diagnosing and treating gastric disorders is provided. A functional device resides within the patient's stomach and is secured to the stomach wall by an attachment device. The functional device may be a sensor for sensing various parameters of the stomach or stomach environment, or may be a therapeutic delivery device. The functional device in one embodiment provides a device, system and method for gastric electrical stimulation where stimulating electrodes are secured to the wall of the stomach by the attachment device or otherwise. A preferred device includes: at least one stimulating electrode in electrical contact with the stomach wall; an electronics unit containing the electronic circuitry of the device; and an attachment mechanism for attaching the device to the stomach wall. The functional devices may be programmed to respond to sensed information or signals. An endoscopic delivery system delivers the functional device through the esophagus and into the stomach where it is attached the stomach wall. The endoscopic instruments attach or remove the attachment devices and functional devices from the stomach and may be used to assist in determining the optimal attachment location.
Owner:INTRAPACE
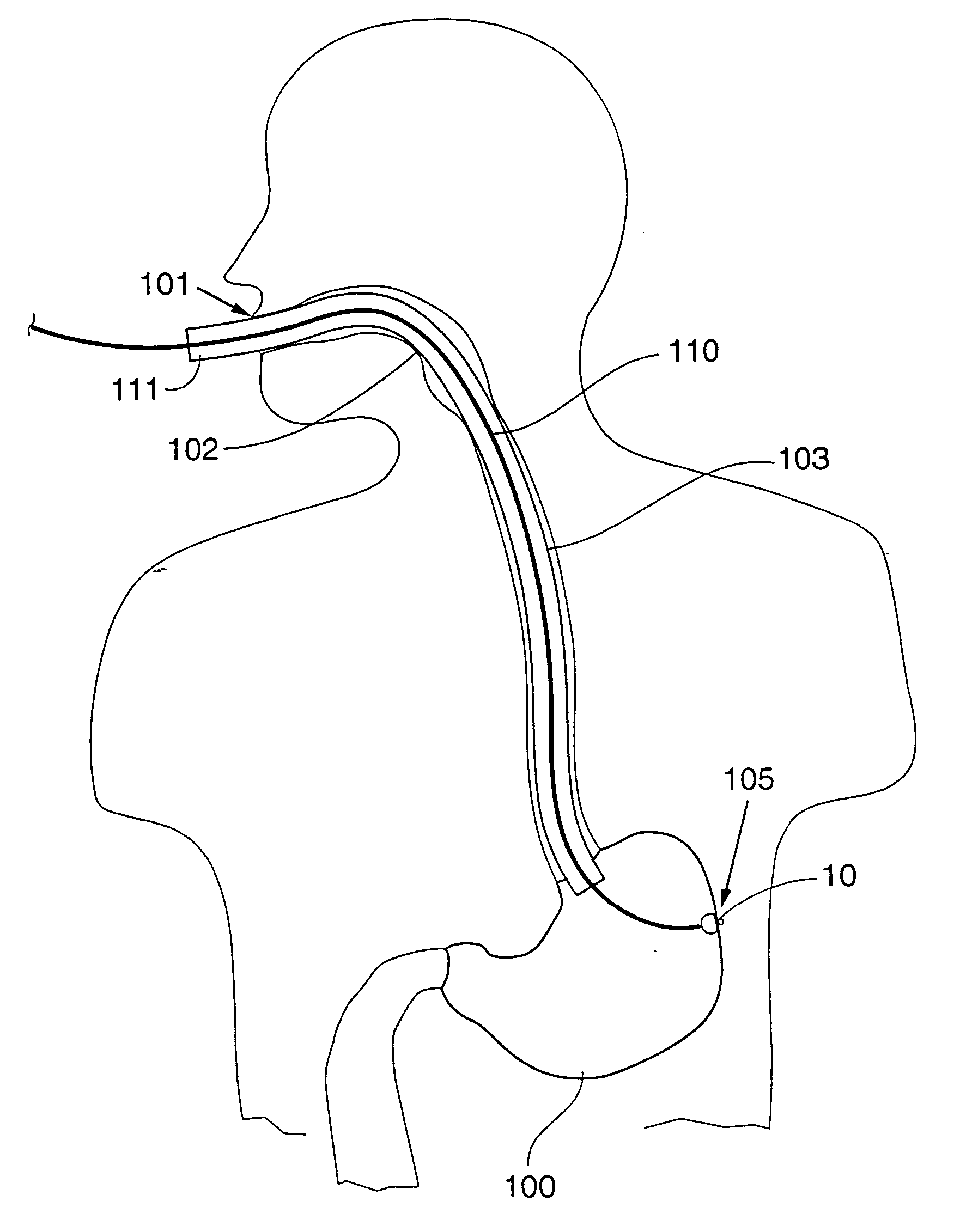
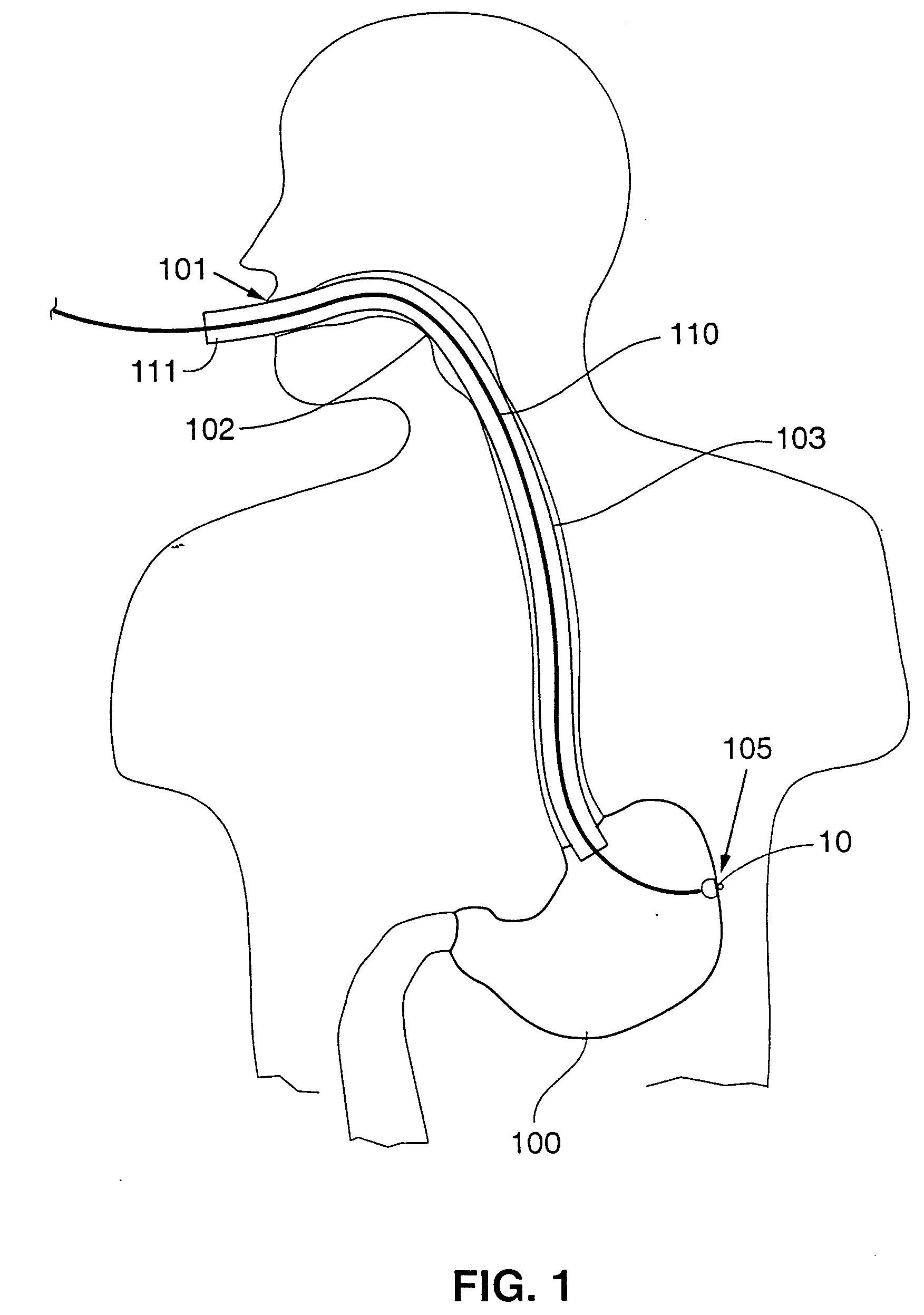
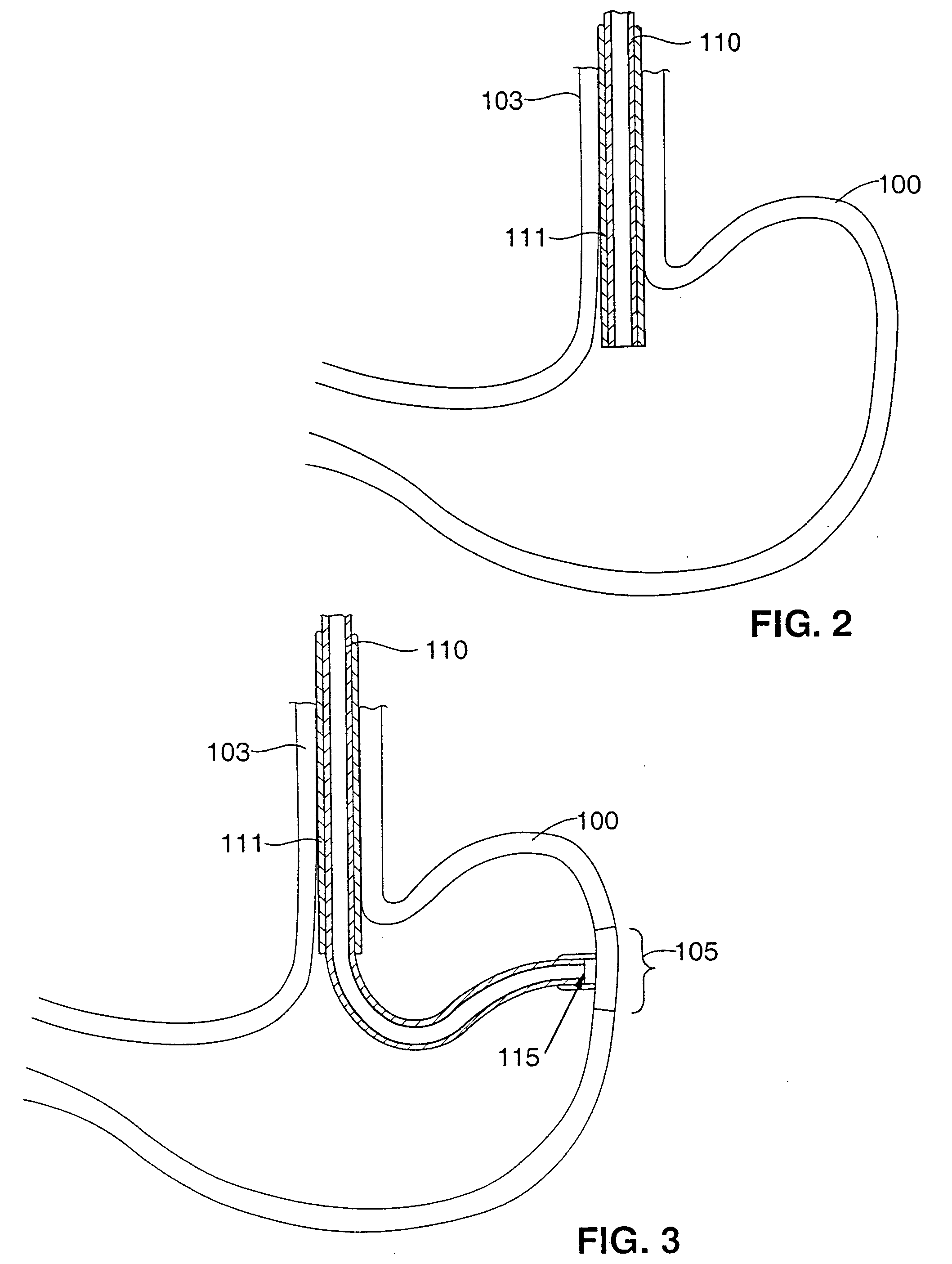
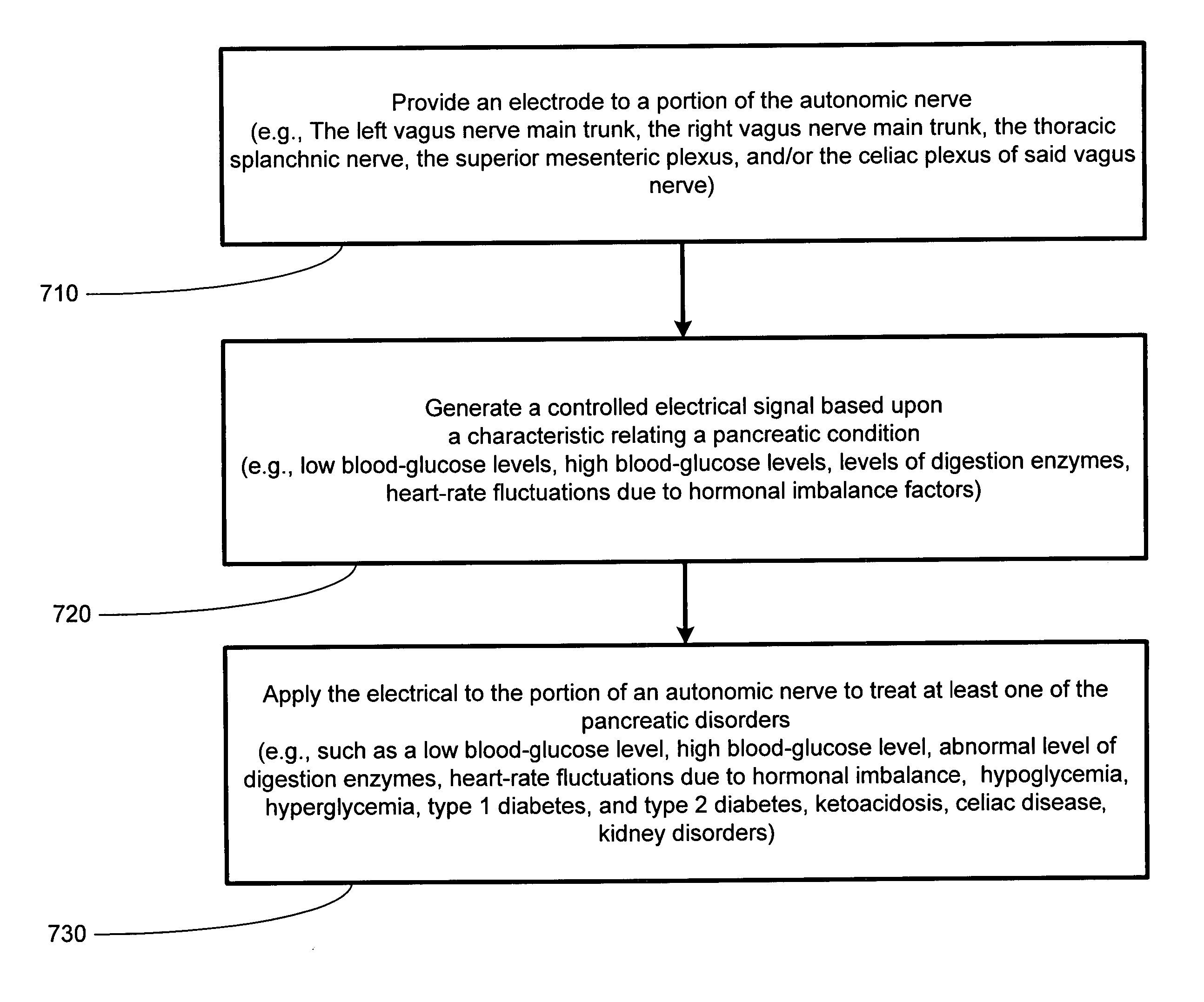
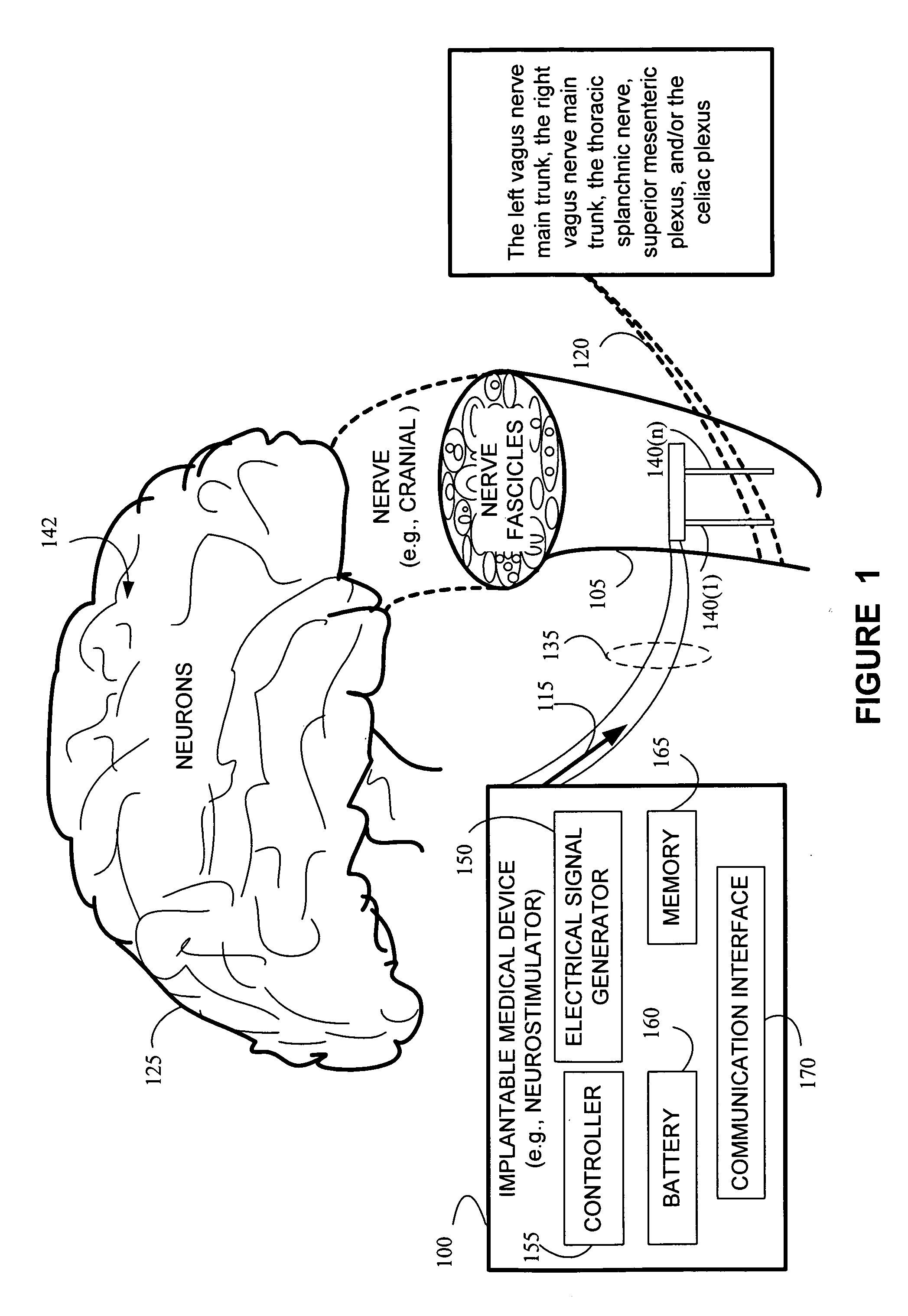
Autonomic nerve stimulation to treat a pancreatic disorder
A method for stimulating a portion of a vagus nerve of a patient to treat a pancreatic disorder is provided. At least one electrode is coupled to at least one portion of an autonomic nerve of the patient. The portion may include a celiac plexus, a superior mesenteric plexus, and a thoracic splanchnic. An electrical signal is applied to the portion of the vagus nerve using the electrode to treat the pancreatic disorder.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Implantable gastrointestinal lead with active fixation
InactiveUS6952613B2Avoid displacementReduce polarizationSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesActive fixationCatheter
Active fixation, gastrointestinal leads adapted to be implanted within the body at a site of the GI tract to conduct electrical stimulation from an implantable or external gastrointestinal stimulator to the site and to conduct electrical signals of the GI tract from the site to the implantable or external gastrointestinal stimulator are disclosed. Disclosed active fixation mechanisms include one or more of hooks, and helixes extending from stops, e.g. plates, of an electrode head and functioning as stimulation / sense electrodes in unipolar and bipolar configurations or simply as fixation mechanisms. The active fixation mechanisms are coated to reduce inflammation and polarization effects.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
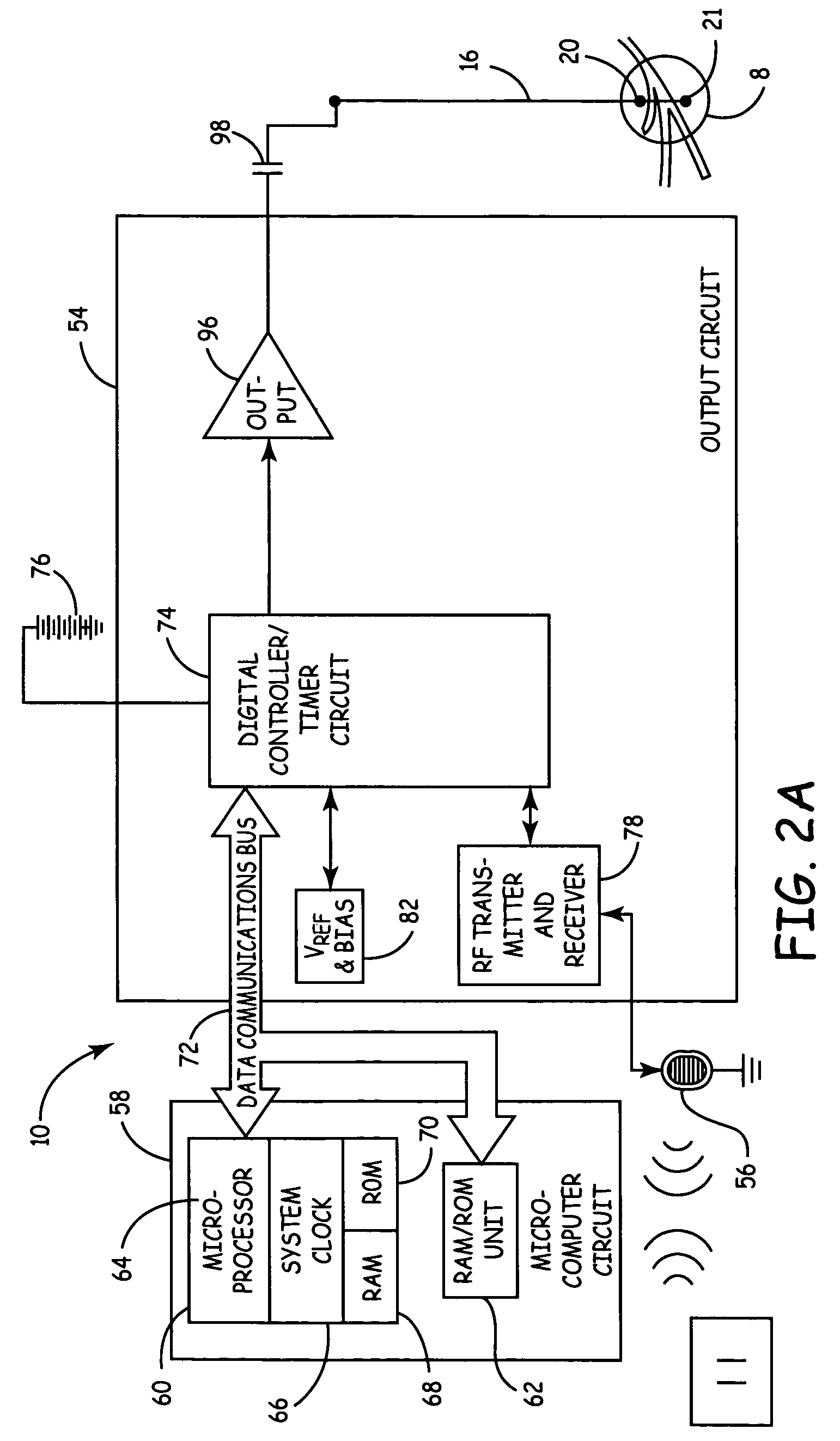
Method and system for modulating sacral nerves and/or its branches in a patient to provide therapy for urological disorders and/or fecal incontinence, using rectangular and/or complex electrical pulses
A method and system for providing pulsed electrical stimulation to sacral nerves and / or its branches, to provide therapy for urinary / fecal incontinence and other urological disorders. The stimulation system comprising implanted and external components. The pulsed electrical stimulation may be provided using a system which is one from a group comprising: a) an implanted stimulus-receiver with an external stimulator; b) an implanted stimulus-receiver comprising a high value capacitor for storing charge, used in conjunction with an external stimulator; c) a programmer-less implantable pulse generator (IPG) which is operable with an external magnet; d) a programmable implantable pulse generator; e) a combination implantable device comprising both a stimulus-receiver and a programmable IPG; and f) an implantable pulse generator (IPG) comprising a rechargeable battery. In one embodiment, the external components such as the programmer or external stimulator may comprise telemetry means for interrogation or programming of the implanted device from a remote location, over a wide area network.
Owner:BOVEJA BIRINDER R +1
Gastric anchor and method
Owner:INTRAPACE
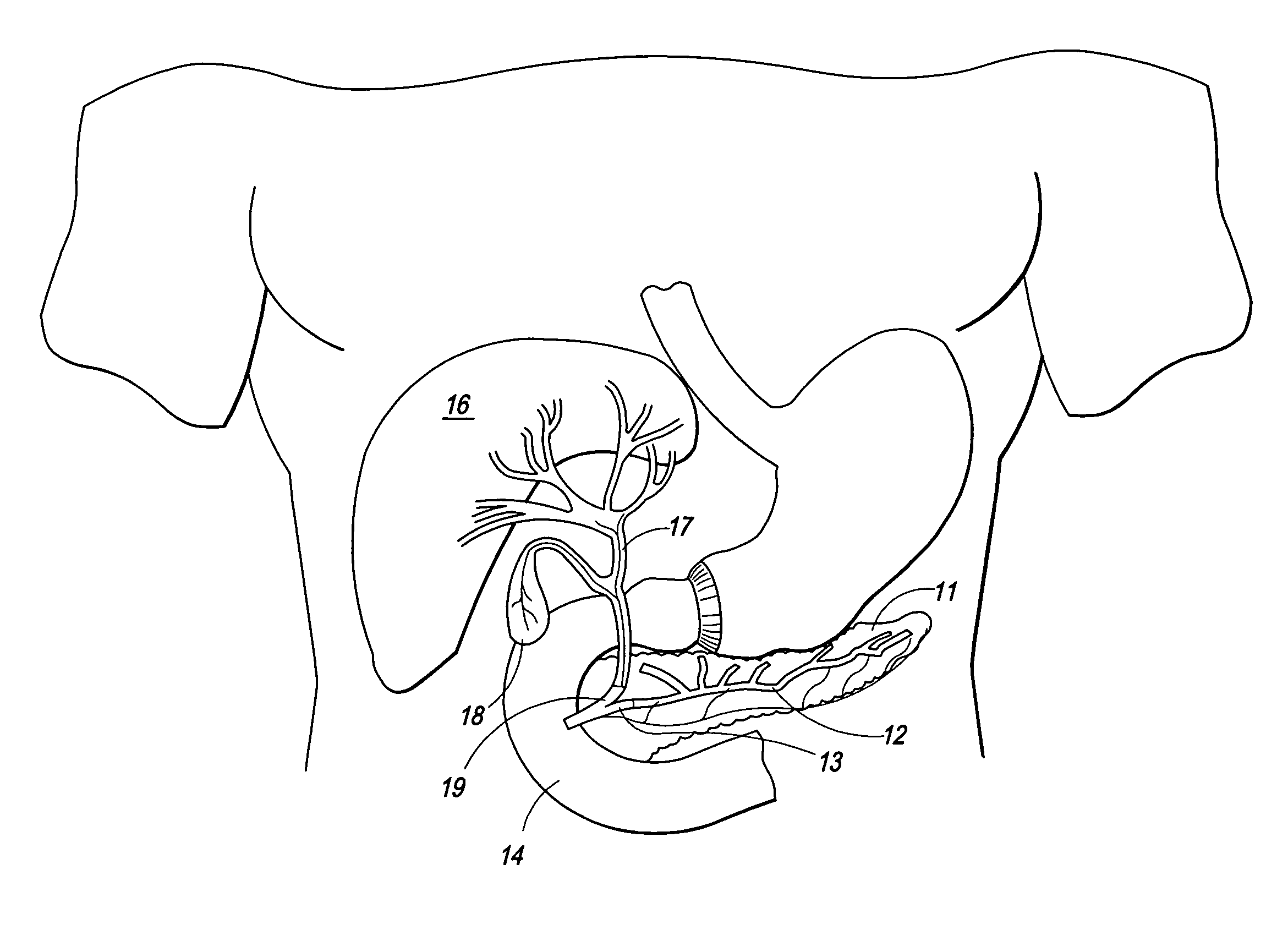
Method and Apparatus for Electrical Stimulation of the Pancreatico-Biliary System
ActiveUS20080195171A1Efficient secretionInhibition of relaxationExternal electrodesDigestive electrodesTreatment effectDigestion
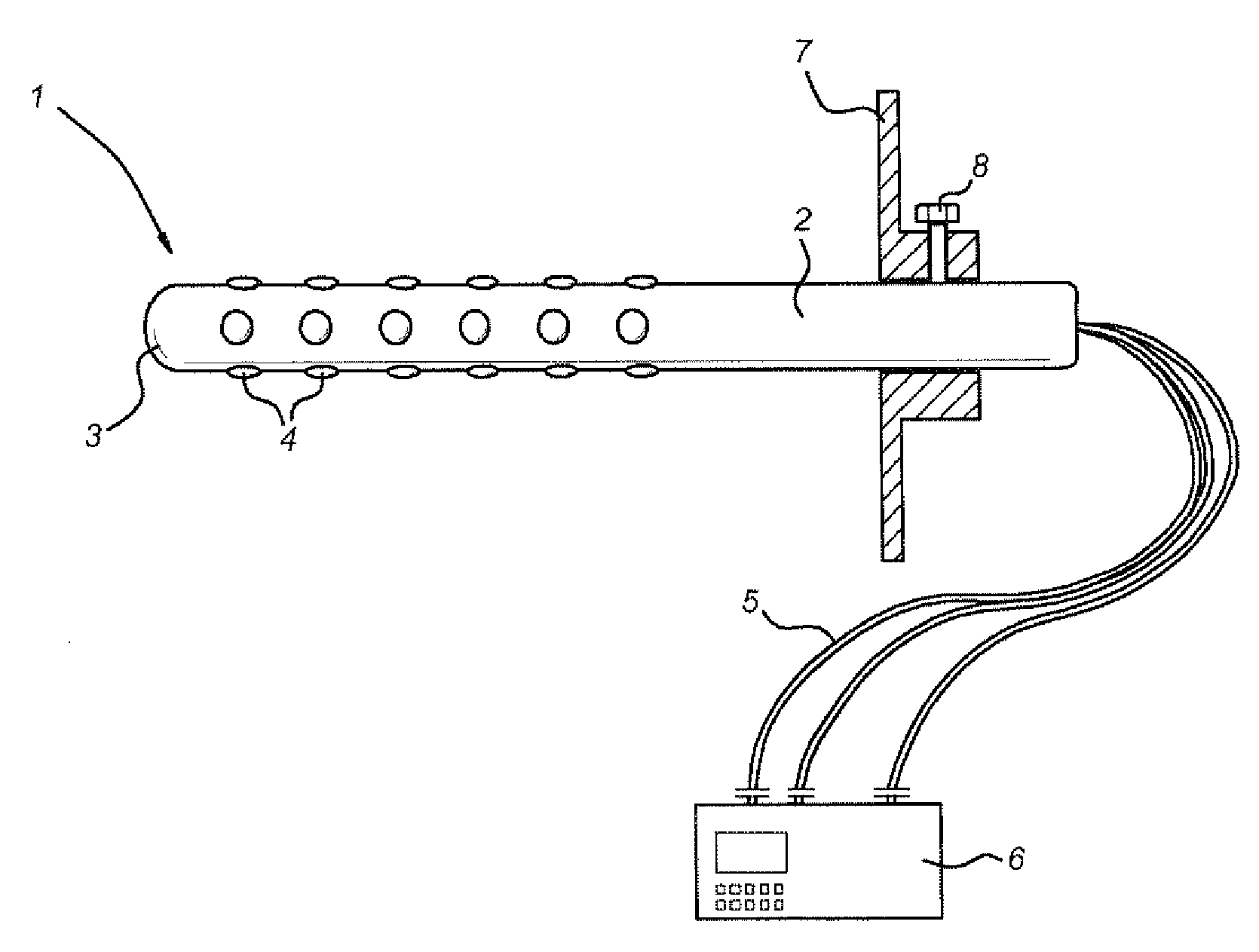
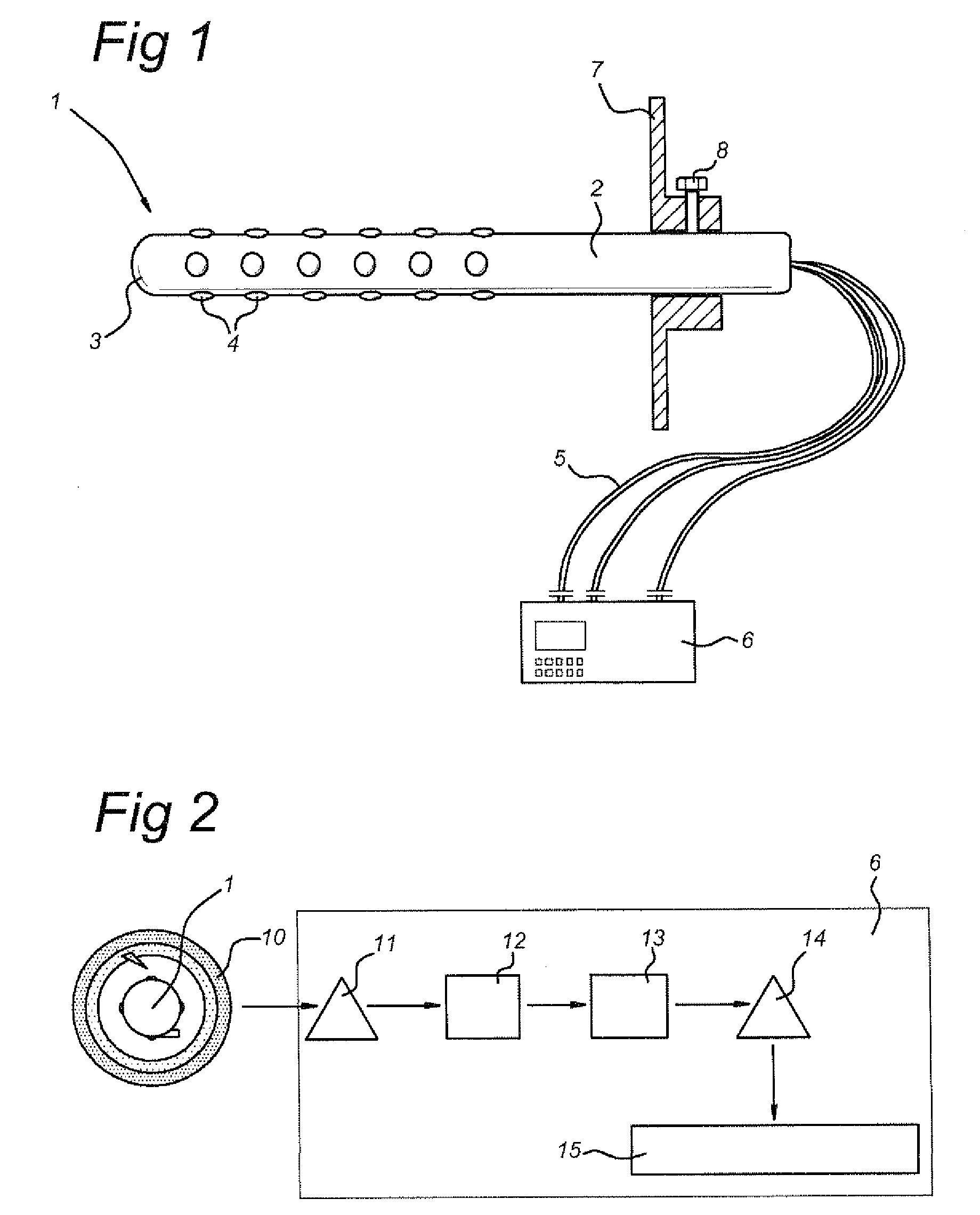
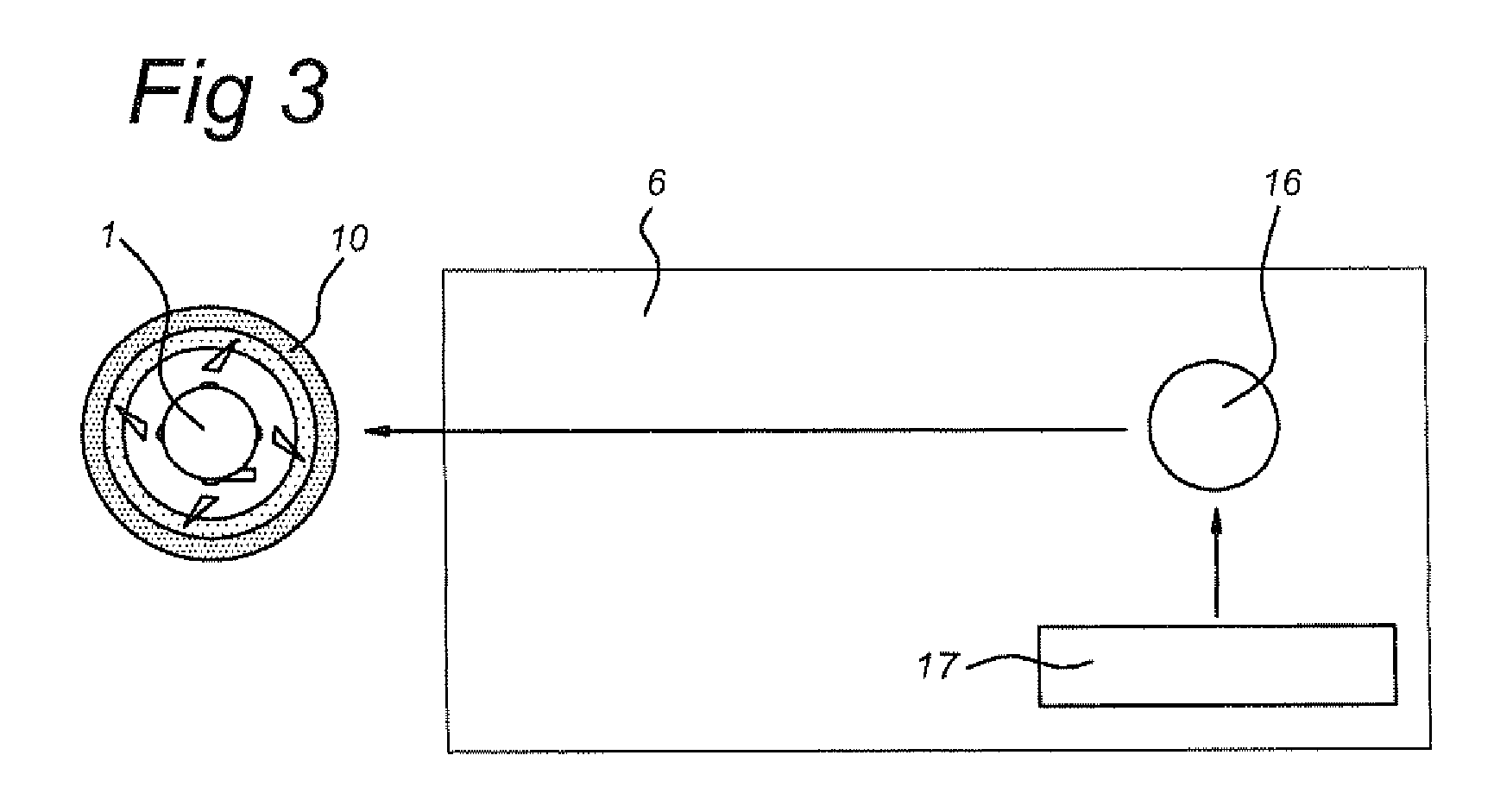
The present invention is directed to a method and apparatus for electrical stimulation of the pancreatico-biliary system. Electrode sets are placed in the pancreatico-biliary system in an arrangement that induce contractions or relaxation of the portion or whole of the pancreatico-biliary system by electrical stimulation of the surrounding tissue, muscles and nerves. The electrical stimulus is applied for periods of varying duration and varying frequency so as to produce the desired therapeutic effect, including inhibiting fat digestion or fat absorption by a patient and inducing satiety in the patient.
Owner:SHARMA VIRENDER K
Extragastric minimally invasive methods and devices to treat obesity
InactiveUS20060264699A1Increase heightLonger-term implantationSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesObesityAbdominal trocar
Methods and devices to externally create a restriction on the stomach are described. In some embodiments, the devices are contoured to fit the stomach and can be further anchored to the stomach. In further embodiments, the degree of deployment of the extragastric restriction device is controllable after implantation. In other embodiments, specialized wires, catheters, ports, and trocars specific for placement of extragastric restriction devices are presented. In still further embodiments, systems are described in which adjustability of the devices is provided along with sensing and actuating ability.
Owner:GERTNER MICHAEL
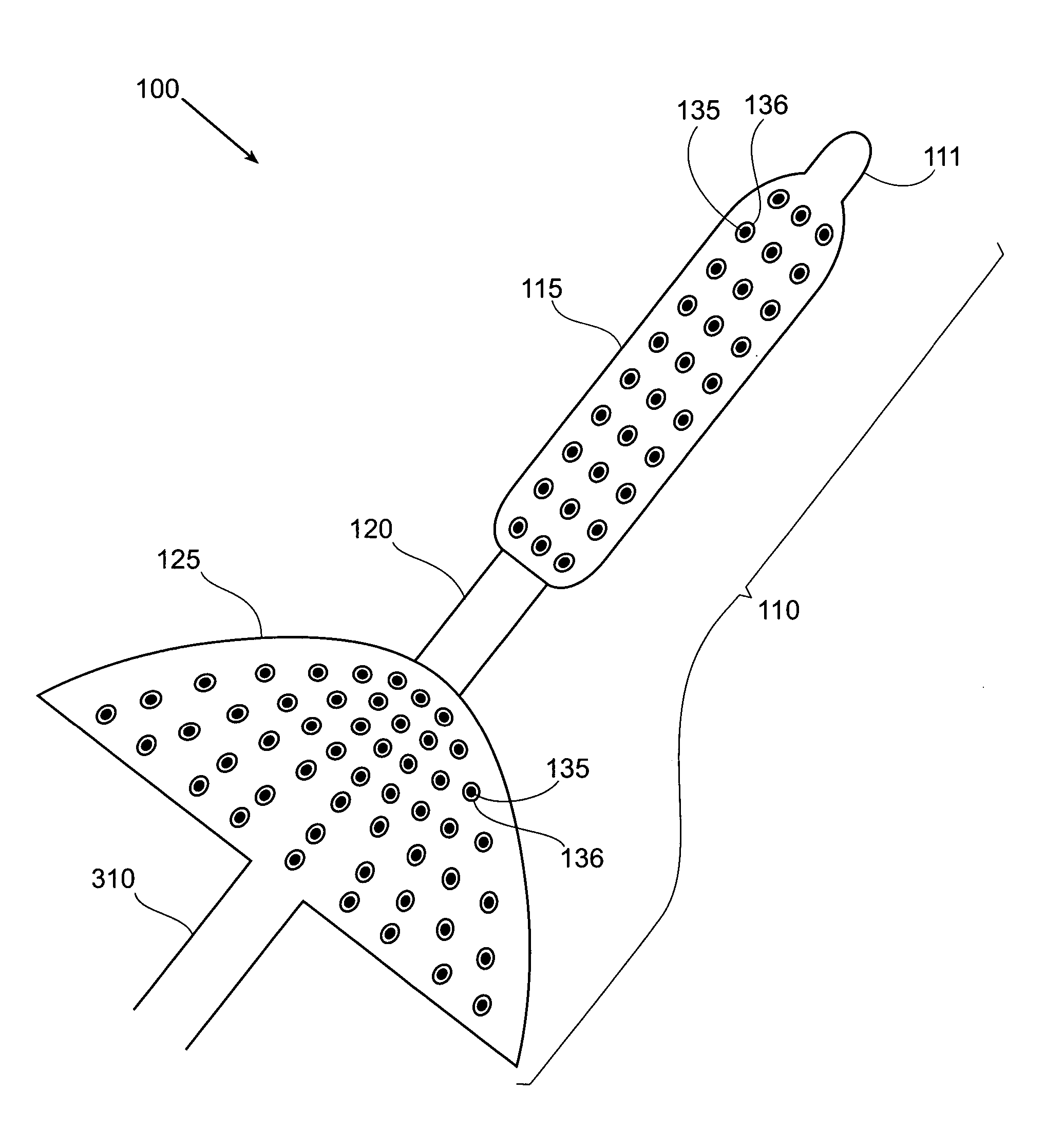
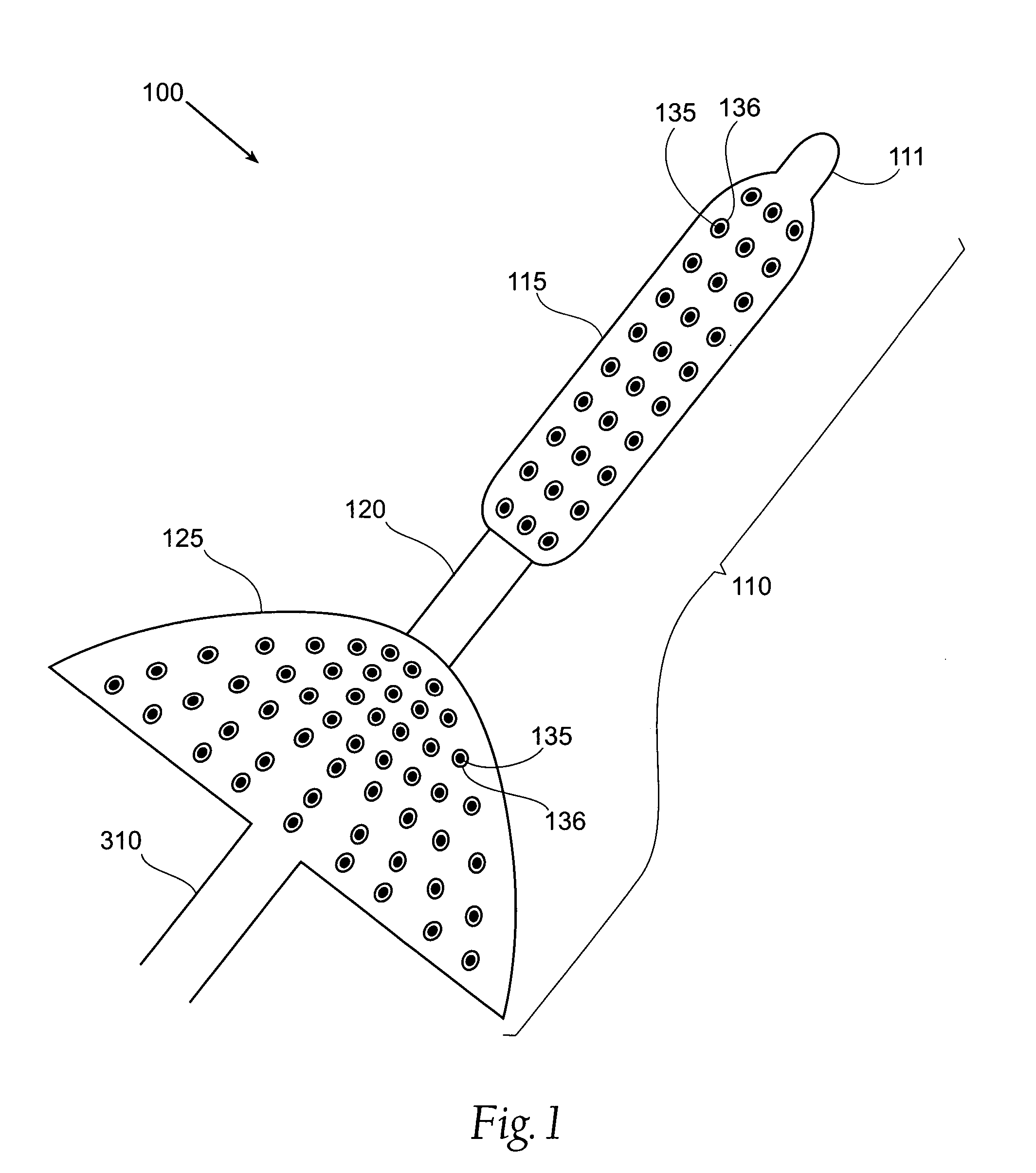
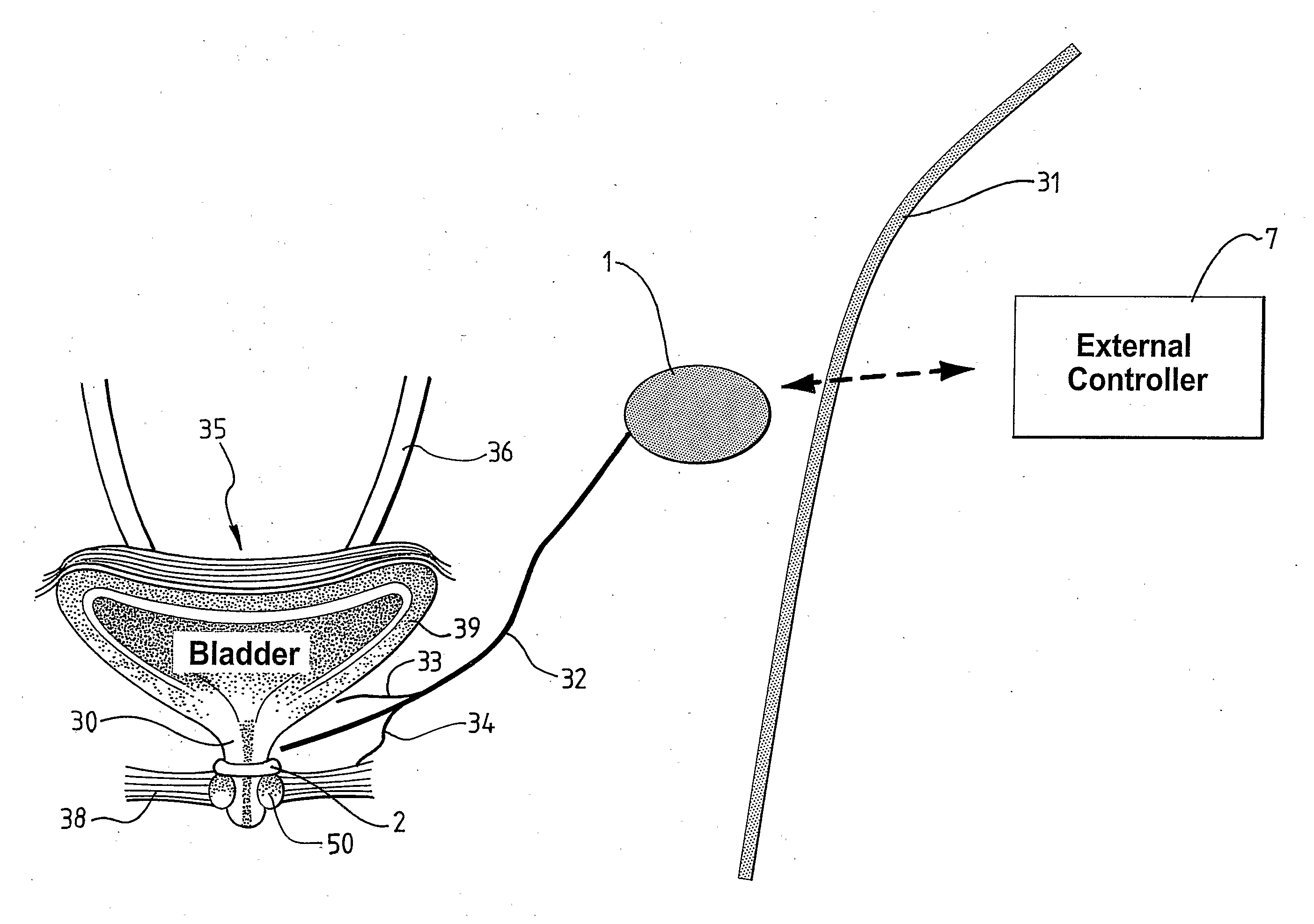
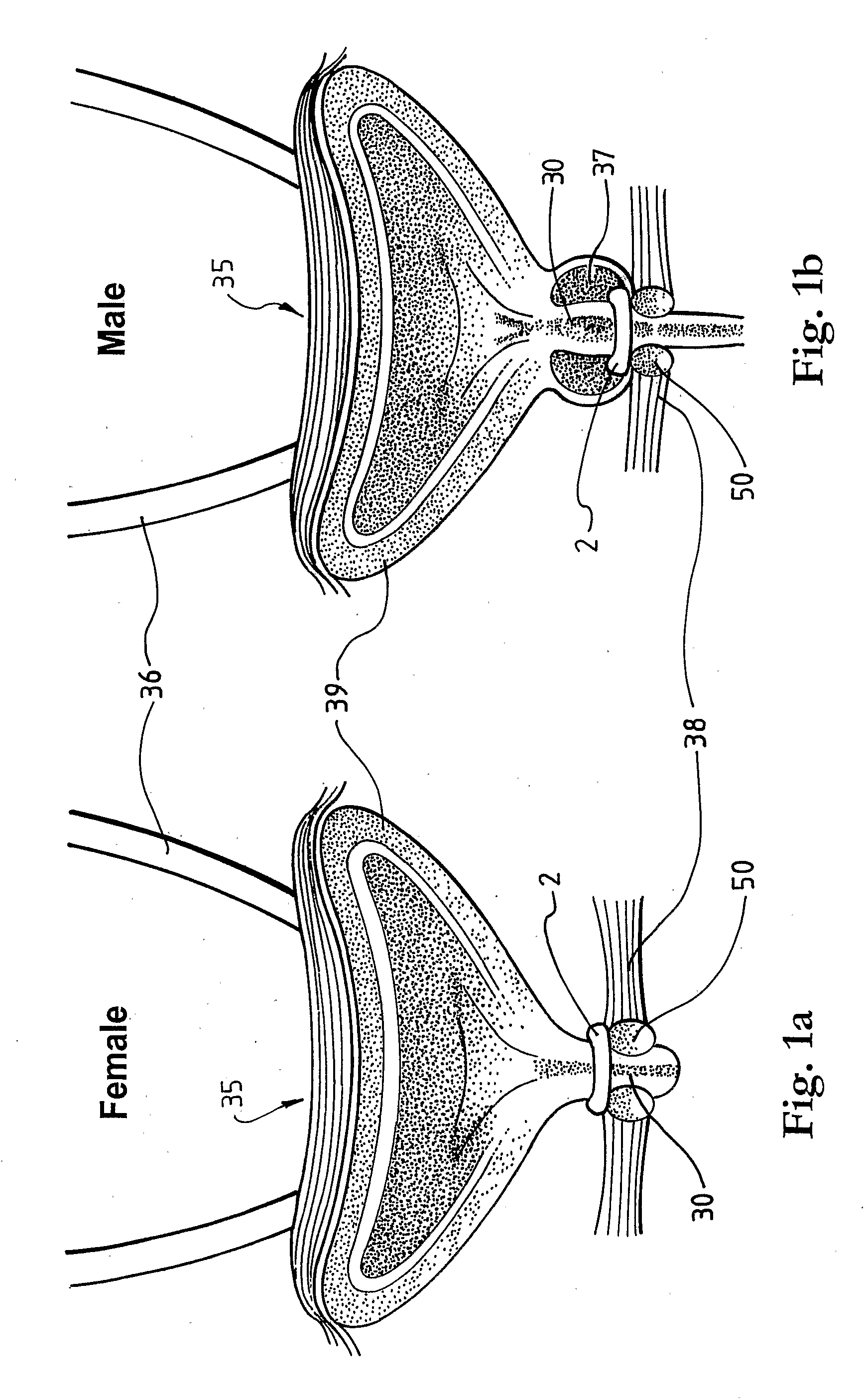
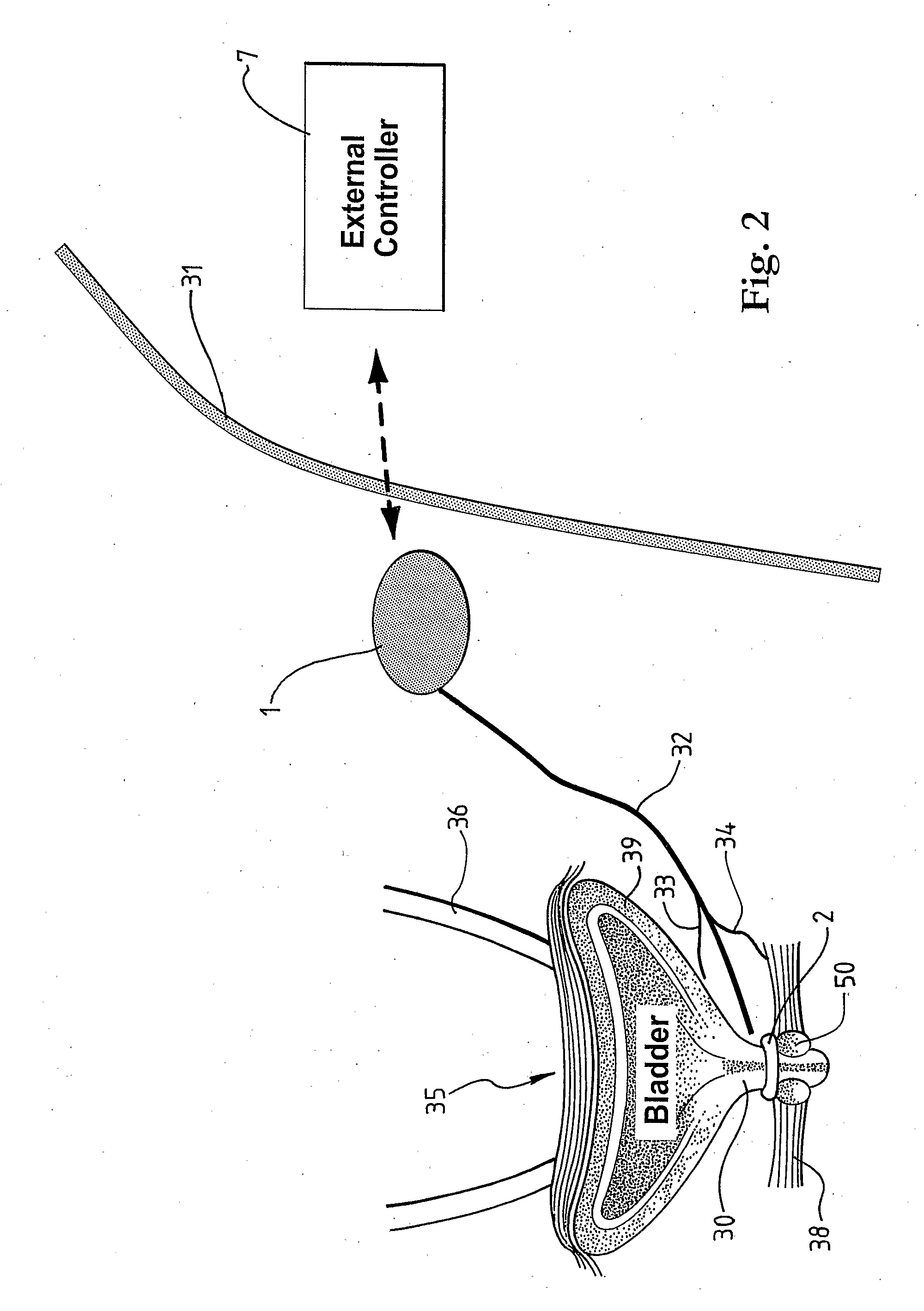
Method and Apparatus for Treating Incontinence
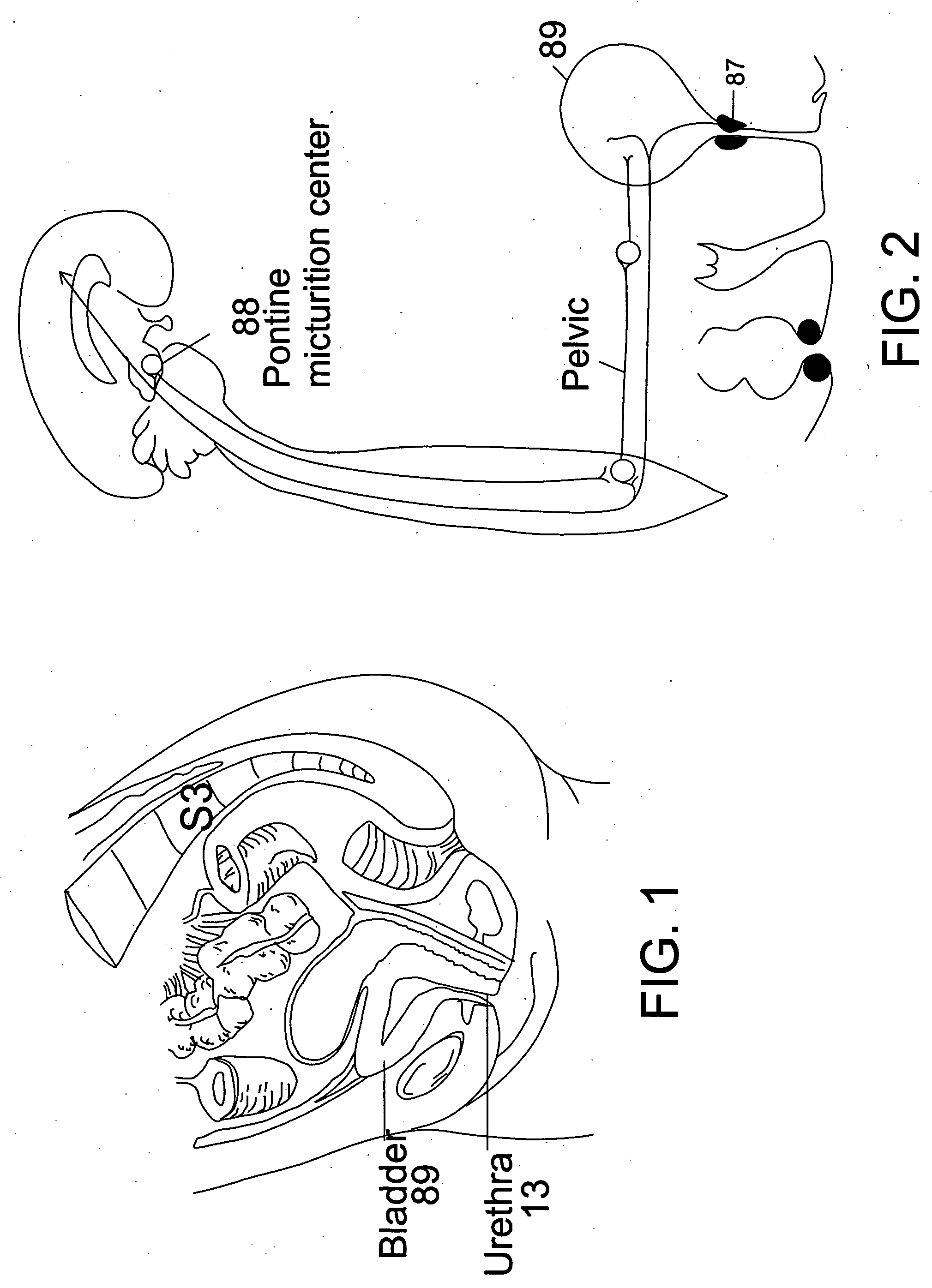
InactiveUS20090054950A1Alleviate and avoid symptomDigestive electrodesProsthesisSmooth muscleUrethra
A medical condition is treated using electrical stimulation of contractile tissue, such as a sphineter, as well as electrical stimulation of afferent nerves to illicite a neuron-modulation response. The device (1) and method is particular useful for treating urge incontinence where the tissue is a smooth muscle neo-sphineter (2) about the urethra and the nerves are in the pelvic region.
Owner:CONTINENCE CONTROL SYST INT
Gastric Simulation Anchor and Method
InactiveUS20100305656A1Minimize stressAvoid foldingCannulasSurgical needlesStomach wallsGeneral surgery
Owner:INTRAPACE
Methods for treating tissue sites using electroporation
InactiveUS20080132885A1Create insufficiencySurgical needlesDiagnostic recording/measuringControl mannerElectroporation
Methods for treating a tissue site. Introducing at least first and second mono-polar electrodes to a tissue site of the patient. Positioning the at least first and second mono-polar electrodes at or near the tissue site. Applying an electric field in a controlled manner to the tissue site in an amount sufficient to produce electroporation of cells at the tissue site and below an amount that causes thermal damage to a majority of the tissue site.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Gastrointestinal anchor with optimal surface area
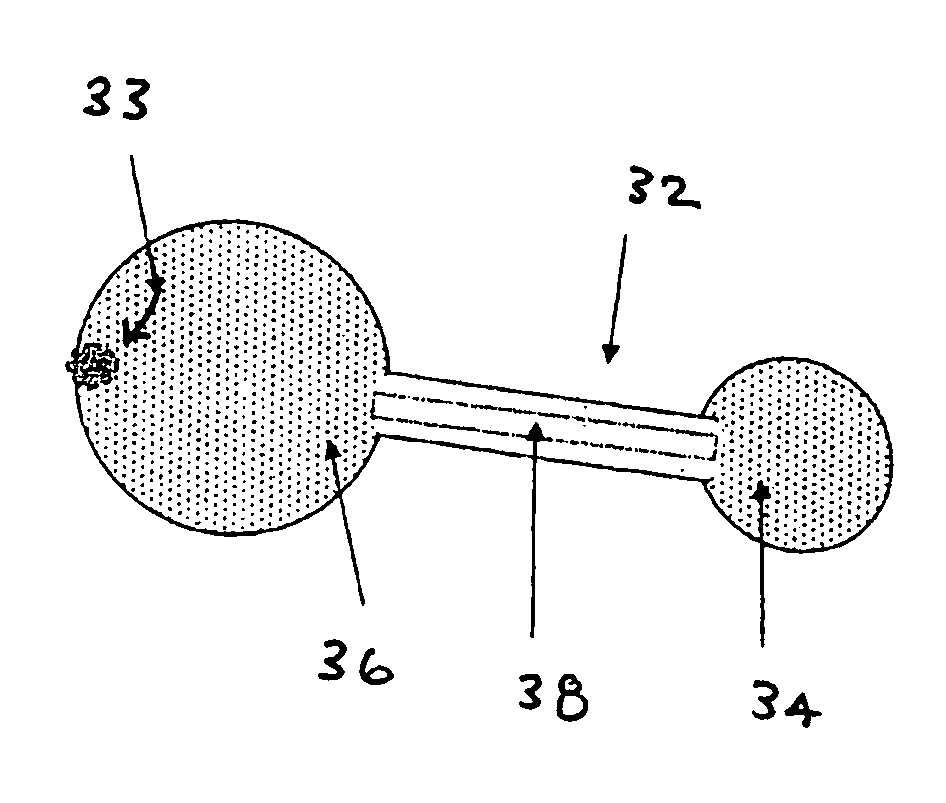
InactiveUS20050143784A1Equally distributedUneven distributionCannulasSurgical needlesOptimal weightArea ratio
A device, system and method for anchoring a device to a stomach is provided. The device may be, among other things, a sensor for sensing various parameters of the stomach or stomach environment, or may be a therapeutic delivery device. The anchor of the device is constructed to resist pull out forces. An anchor has an optimal weight to surface area ratio.
Owner:INTRAPACE
Aendoscopic instrument system@
InactiveUS20050236277A9Minimize stressAvoid foldingCannulasSurgical needlesStomach wallsGastric Disorders
A device, system and method for diagnosing and treating gastric disorders is provided. A functional device resides within the patient's stomach and is secured to the stomach wall by an attachment device. The functional device may be a sensor for sensing various parameters of the stomach or stomach environment, or may be a therapeutic delivery device. The functional device in one embodiment provides a device, system and method for gastric electrical stimulation where stimulating electrodes are secured to the wall of the stomach by the attachment device or otherwise. A preferred device includes: at least one stimulating electrode in electrical contact with the stomach wall; an electronics unit containing the electronic circuitry of the device; and an attachment mechanism for attaching the device to the stomach wall. The functional devices may be programmed to respond to sensed information or signals. An endoscopic delivery system delivers the functional device through the esophagus and into the stomach where it is attached the stomach wall. The endoscopic instruments attach or remove the attachment devices and functional devices from the stomach and may be used to assist in determining the optimal attachment location.
Owner:INTRAPACE
Endoscopic Instrument for Engaging a Device
A device, system and method for diagnosing and treating a patient is provided where a functional device is attached to a stomach wall. The device in one embodiment provides electrical stimulation of the stomach wall. The device may also have other functional aspects such as a sensor for sensing various parameters of the stomach or stomach environment, or a substance delivery device. The implant may be programmed to respond to sensed information or signals. The device may be modular with a portion of the device accessible for removal and replacement. In one embodiment, an endoscopic delivery system delivers the functional device through the esophagus and into the stomach where it is attached the stomach wall with the assistance of a suction used to stabilize the tissue of the stomach wall. The device includes a chamber for receiving tissue of the stomach wall for attachment where a vacuum pressure is applied through the chamber to draw the tissue into the chamber.
Owner:INTRAPACE
Stimulation therapy for bladder dysfunction
ActiveUS8989861B2Reduce stimulus intensityDecrease in frequency of bladder contractionElectromyographySensorsPhysical therapyElectrical stimulations
A medical system may include a control module and a therapy delivery module configured to generate and deliver electrical stimulation therapy to a patient. The control module may be configured to control the therapy delivery module to deliver electrical stimulation at a first stimulation intensity for a first time period, to deliver electrical stimulation at a second stimulation intensity for a second time period immediately following the first time period, and to deliver electrical stimulation at the first stimulation intensity for a third time period immediately following the second time period. The second stimulation intensity may be less than the first stimulation intensity. The electrical stimulation may elicit a first inhibitory physiological response during the first time period and a second inhibitory physiological response during the second time period. The second inhibitory physiological response may be greater than the first inhibitory physiological response.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Devices and methods for gastrointestinal stimulation
ActiveUS20070250132A1Eliminate needFacilitate and enhance performanceObesity treatmentDigestive electrodesGastrointestinal wallEnergy delivery
Devices and methods for applying gastrointestinal stimulation include implanting a stimulation device including a body with at least one expandable portion and a bridging portion and at least one stimulation member in the gastrointestinal tract. The at least one stimulation member includes one or more energy delivery members, one or more sensors, or a combination of both. The body maintains the device within the gastrointestinal space, and preferentially within the pyloric portion of the patient's stomach, and prevents passage of the device from the gastrointestinal space, but is not rigidly anchored or affixed to the gastrointestinal wall tissue.
Owner:BARONOVA
Method and apparatus for programming of autonomic neuromodulation for the treatment of obesity
InactiveUS20090187230A1Reduce or prevent conditionReducing and preventing symptomSensorsDigestive electrodesAfferent NeuronsDisease
The present invention teaches methods and apparatus for user control and operation of physiological modulation, including neural and gastrointestinal modulation, for the purposes of treating several disorders, including obesity. This includes programming of neuromodulatory signal for the modulation of autonomic neural and neuromuscular modulators, used to modulate tissues, including the afferent neurons of the sympathetic nervous system to induce satiety and efferent neurons to modulate metabolism.
Owner:DILORENZO DANIEL J
Blood glucose level control
InactiveUS20060085045A1Reduced glucose levelIncrease insulin levelsDigestive electrodesBlood insulinLevel insulin
A method of glucose level control, comprising providing at least one electrode adapted to apply an electric field to a pancreas; and applying an electric field to the pancreas using said at least one electrode such that blood glucose levels are significantly reduced and blood insulin levels are not significantly increased.
Owner:TYLERTON INT INC
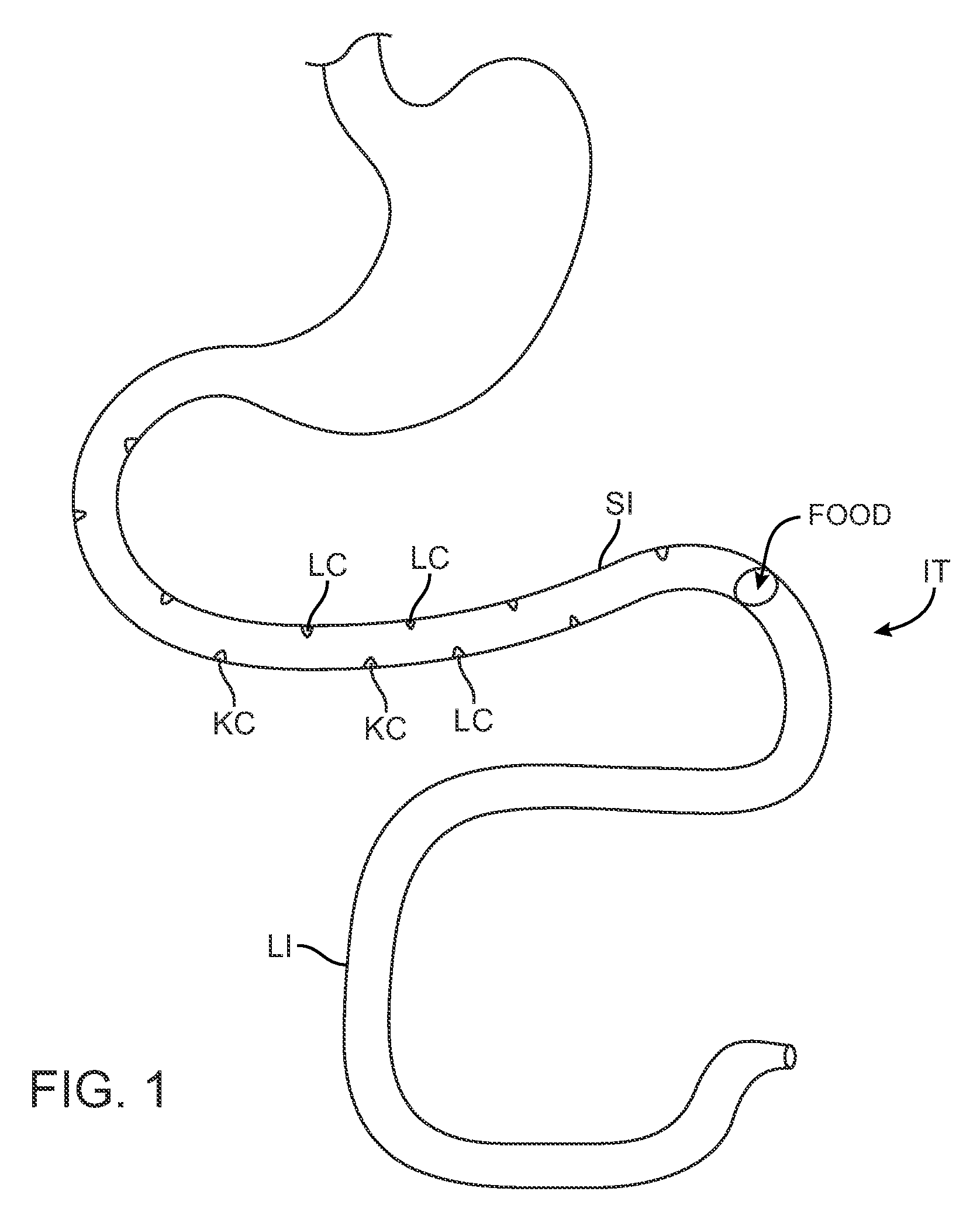
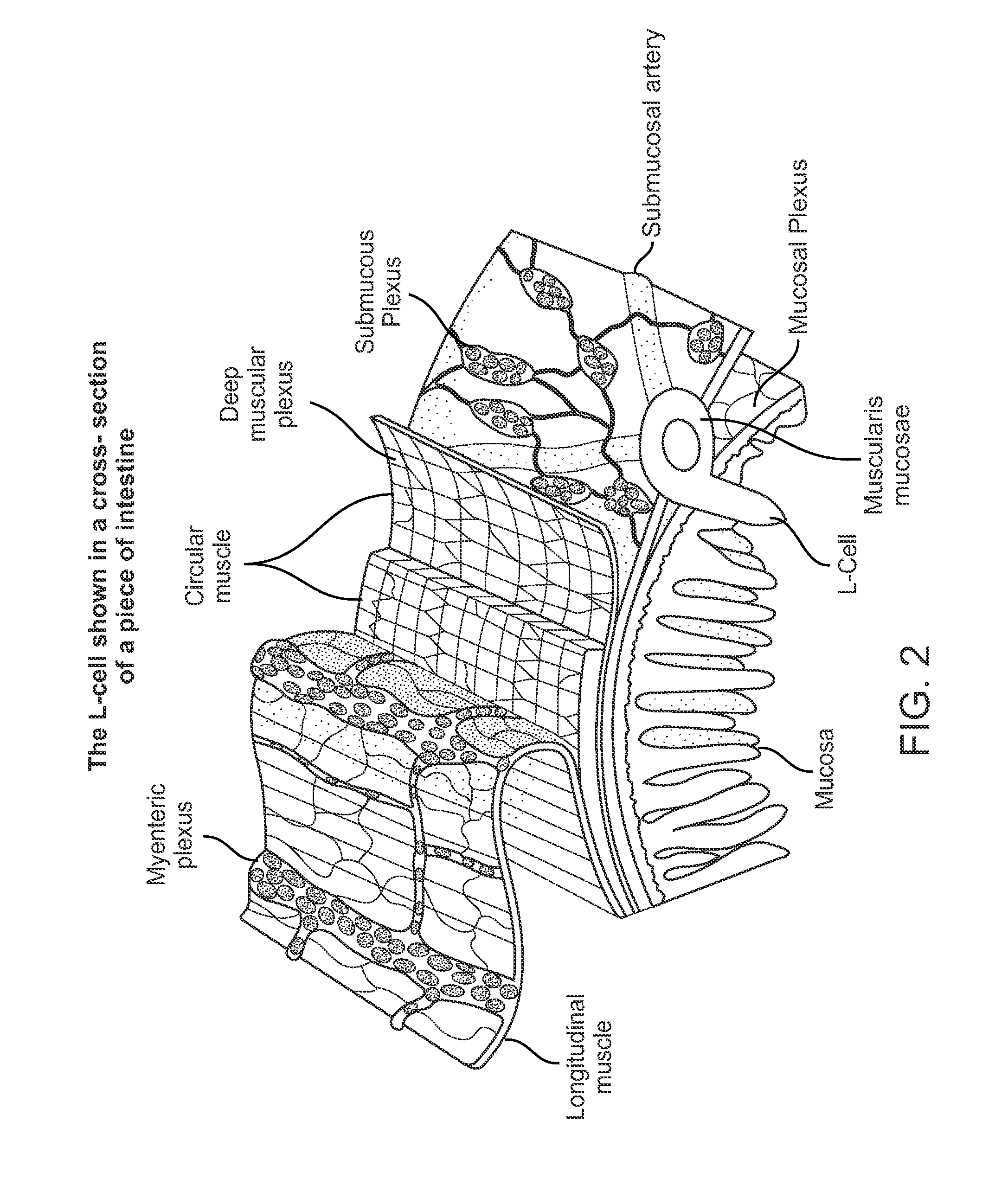
Swallowable capsule and method for stimulating incretin production within the intestinal tract
ActiveUS8682440B2Improve accuracyHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiabetes mellitusGlucose polymers
Embodiments of the invention provide apparatus and methods for stimulating L cells in the intestinal tract to produce incretins for the treatment of conditions including diabetes and obesity. Many embodiments provide a method and apparatus for the treatment of diabetes by electrically stimulating L-cells to secrete incretins to stimulate or otherwise modulate the production of insulin. Particular embodiments provide a swallowable capsule for stimulating L-cells in the intestinal tract as the capsule moves through the tract. The capsule can include two or more electrodes for providing electrical stimulation to L-cells, a power source for powering one or more components of the capsule, a sensor for sensing the location of the capsule in the intestinal tract; a controller and a waveform generator for generating the electrical signals emitted by the electrodes to stimulate the L-cells to secrete incretins such as GLP-1 to stimulate insulin production for glucose regulation of diabetic conditions.
Owner:INCUBE LABS
Artificial sphincter
A biologically implantable artificial sphincter system and methods of using the same is disclosed. The artificial sphincter system disclosed herein comprises a support and an electroactive polymer element, both of which are adapted and configured to open and / or close a body cavity. The artificial sphincter systems are useful in the treatment of urinary incontinence, fecal incontinence, and reflux disorders. The implanted artificial sphincter can also provide a signal to the recipient to urinate or defecate.
Owner:PAVAD MEDICAL
GI Lead Implantation
InactiveUS20090204063A1Reduce the possibilityReduced activityGastroscopesSurgical needlesTransluminal approachTransabdominal approach
A method is provided, including physically contacting a gastric implantation site of a stomach via a transluminal approach, physically contacting the site via a transabdominal approach, stabilizing the site, and implanting an electrode at the site based on the physical contact provided by the transluminal and transabdominal approach. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:TYLERTON INT INC
Medical probe
A probe system for electro-stimulation and bio-feedback training of muscles in the pelvic floor region, in particular for pelvic floor physiotherapy and diagnosis, includes a probe having a probe body which is insertable into a vagina or a rectum, and a plurality of electrodes which are positioned at several locations along the length and around the circumference on the outer surface of the probe, the probe system further includes a control unit, operationally coupled to the probe, adapted for receiving EMG signals from each of the electrodes and for processing each of the signals for mapping the response of the muscles in the pelvic floor region.
Owner:NOVUQARE PELVIC HEALTH BV
Method for controlling flow of intestinal contents in a patient's intestines
ActiveUS20090240100A1Eliminate the problemAnti-incontinence devicesSurgical needlesSurgeryBlood circulating
There is provided a method for controlling a flow of intestinal contents in the intestinal passageway of a patient's intestines. The method comprises gently constricting (i.e., without substantially hampering the blood circulation in the intestinal tissue wall) at least one portion of the intestinal tissue wall to influence the flow in the intestinal passageway, and stimulating the constricted wall portion to cause contraction of the wall portion to further influence the flow in the intestinal passageway. The method can be used for restricting or stopping the flow in the intestinal passageway, or for actively moving the fluid in the intestinal passageway, with a low risk of injuring the intestines.
Owner:FORSELL PETER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com