Patents
Literature
84 results about "Afferent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
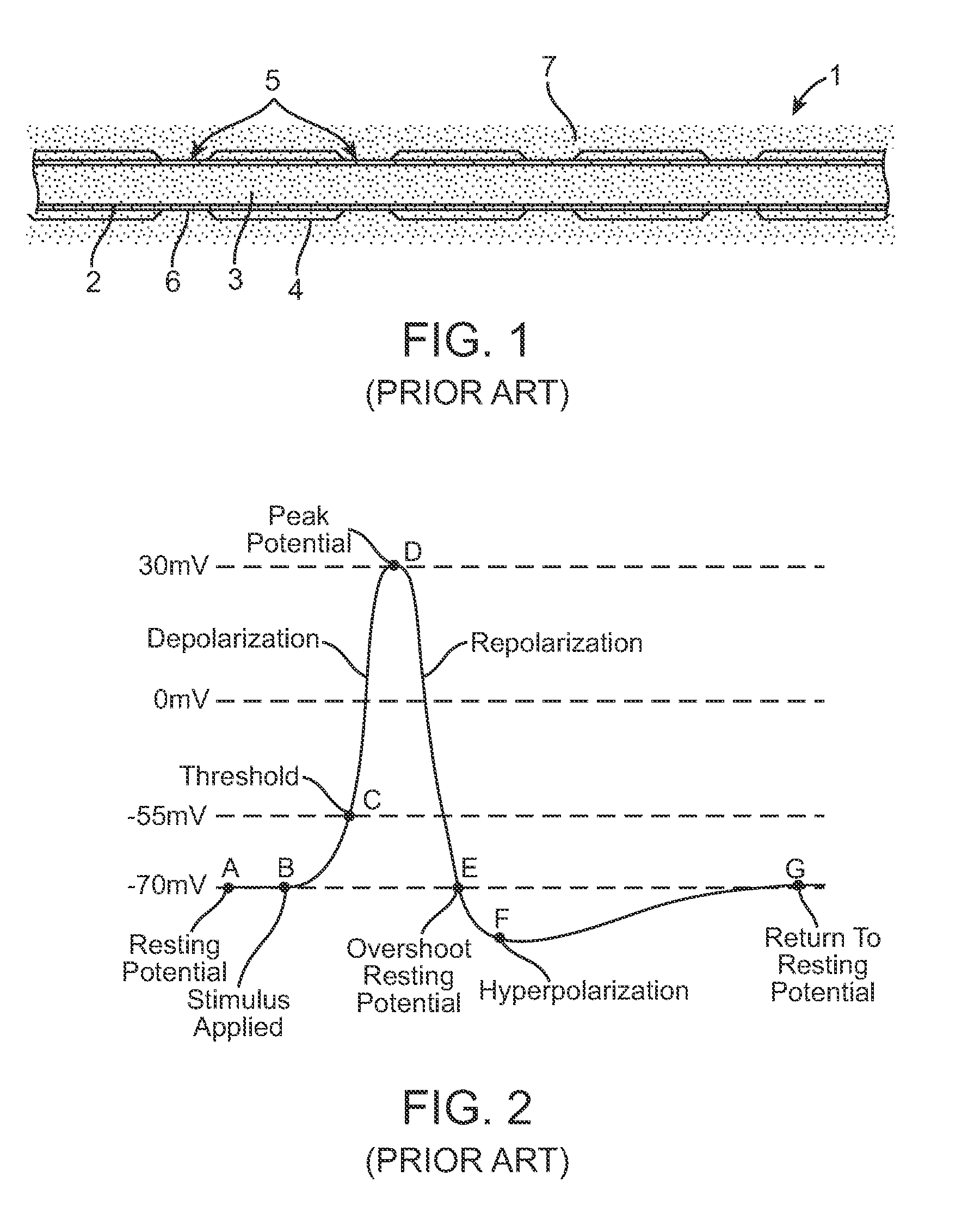
Afferent is an anatomical term with the following meanings: Conveying towards a center, for example the afferent arterioles conveying blood towards the Bowman's capsule in the kidney Something that so conducts, see Afferent nerve fiber Afferent lymphatic vessels
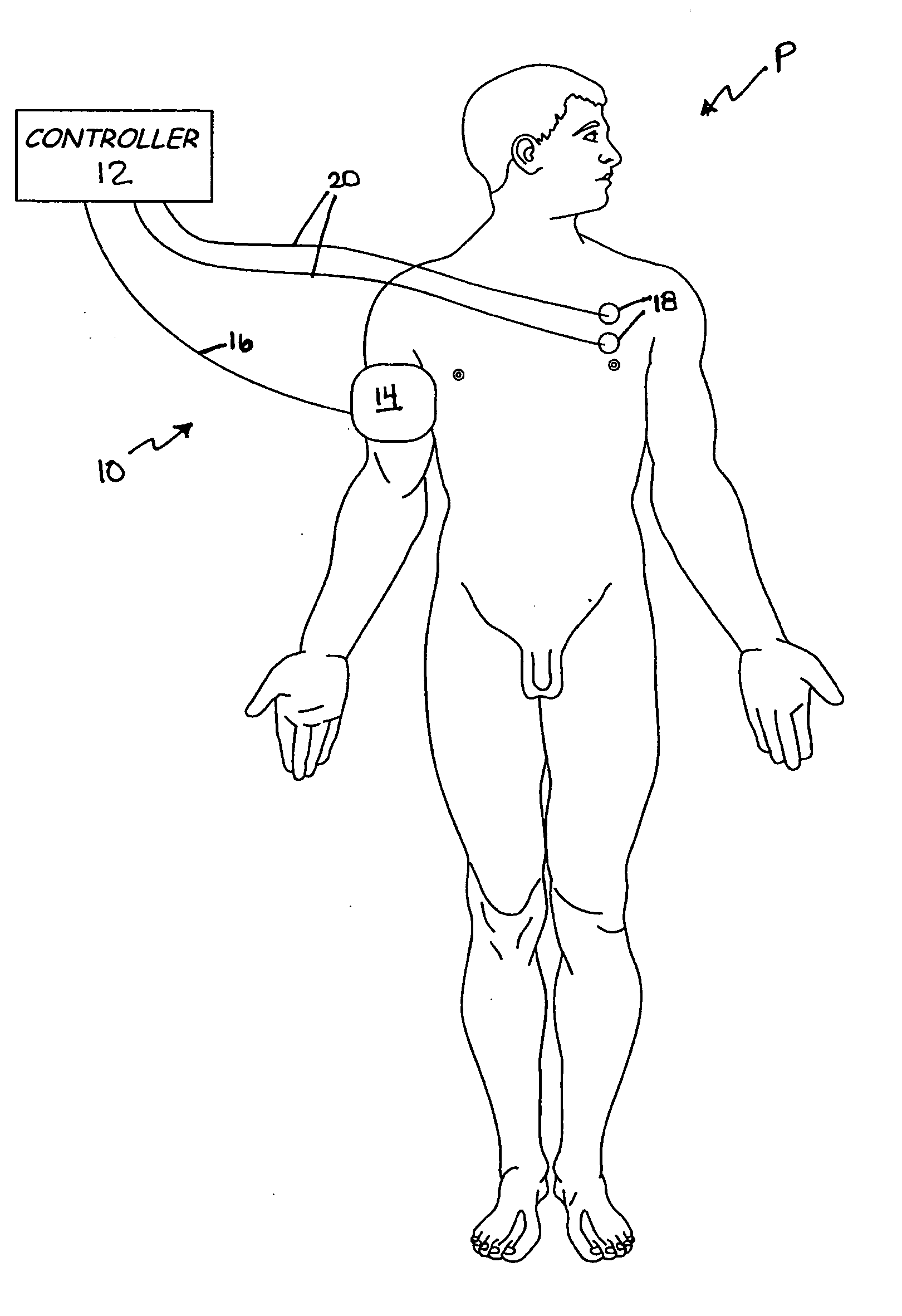
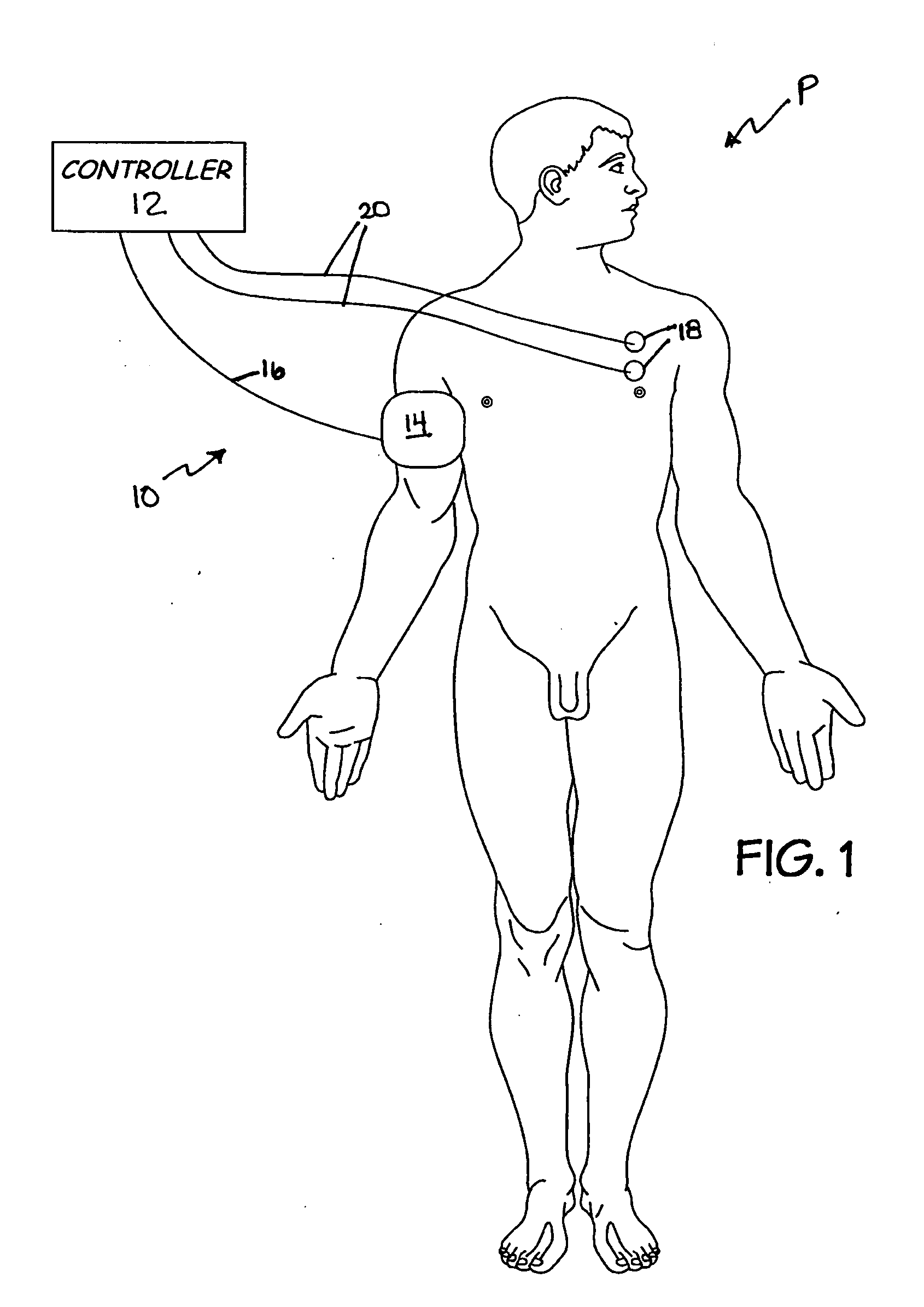
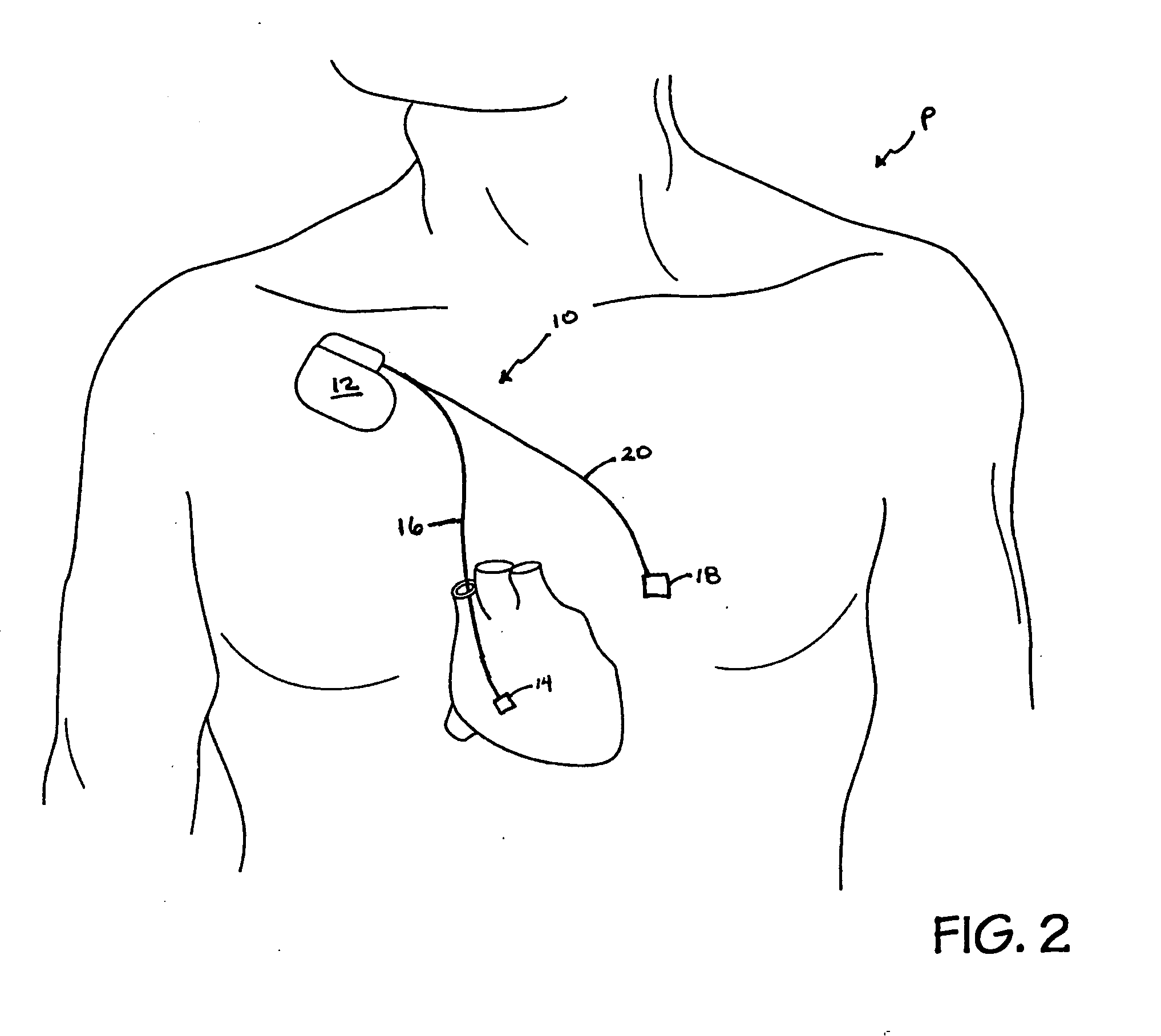
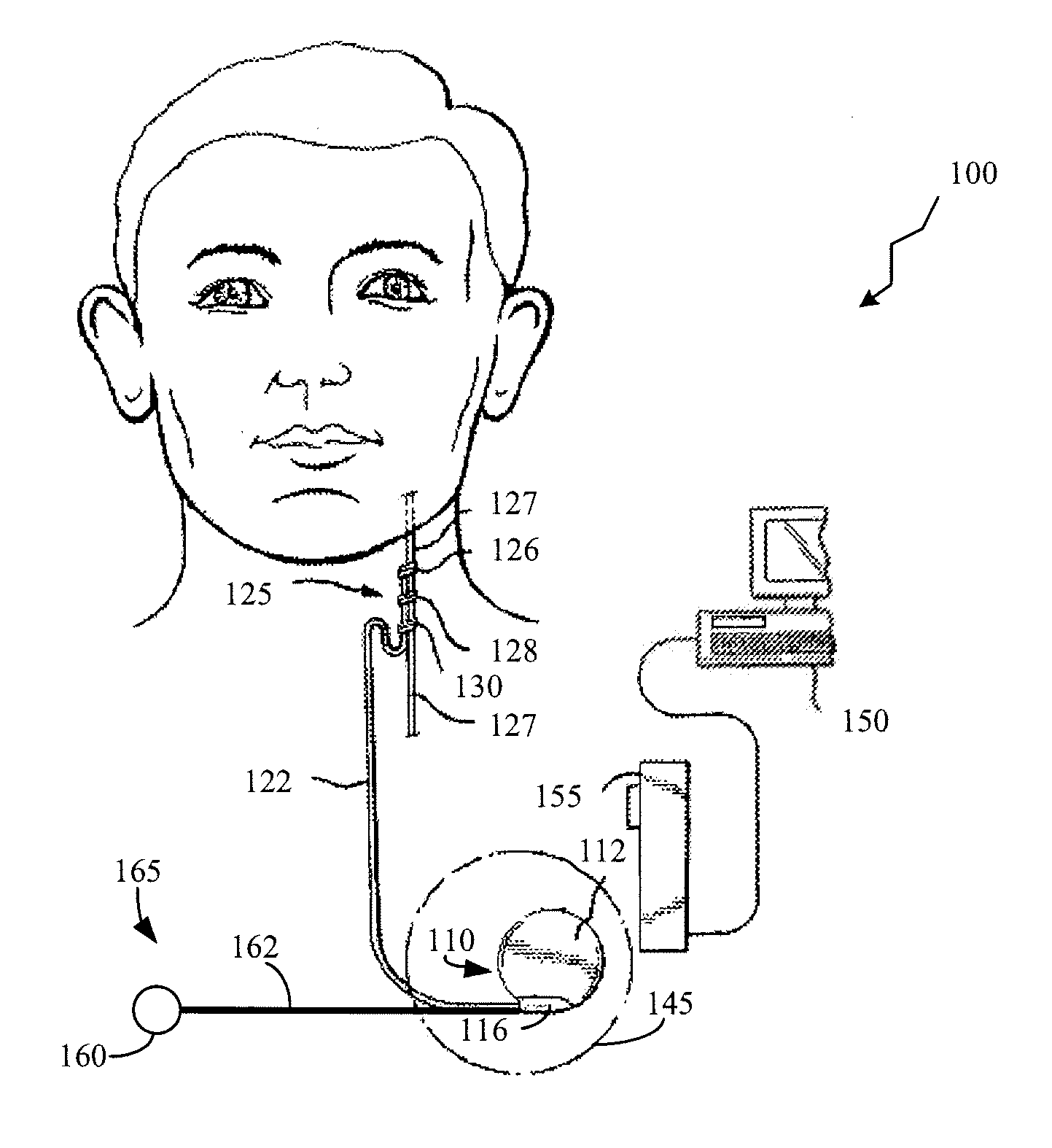
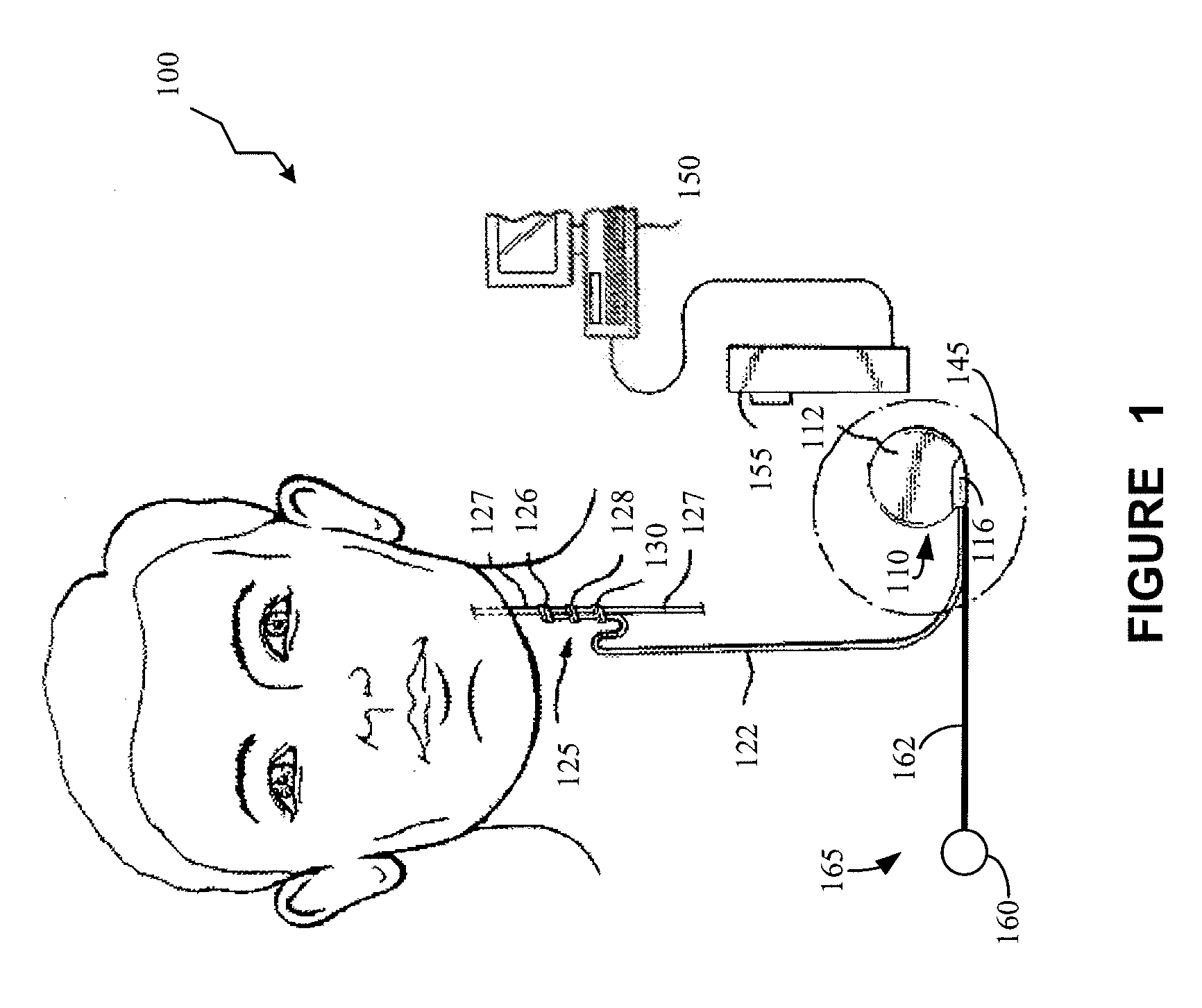
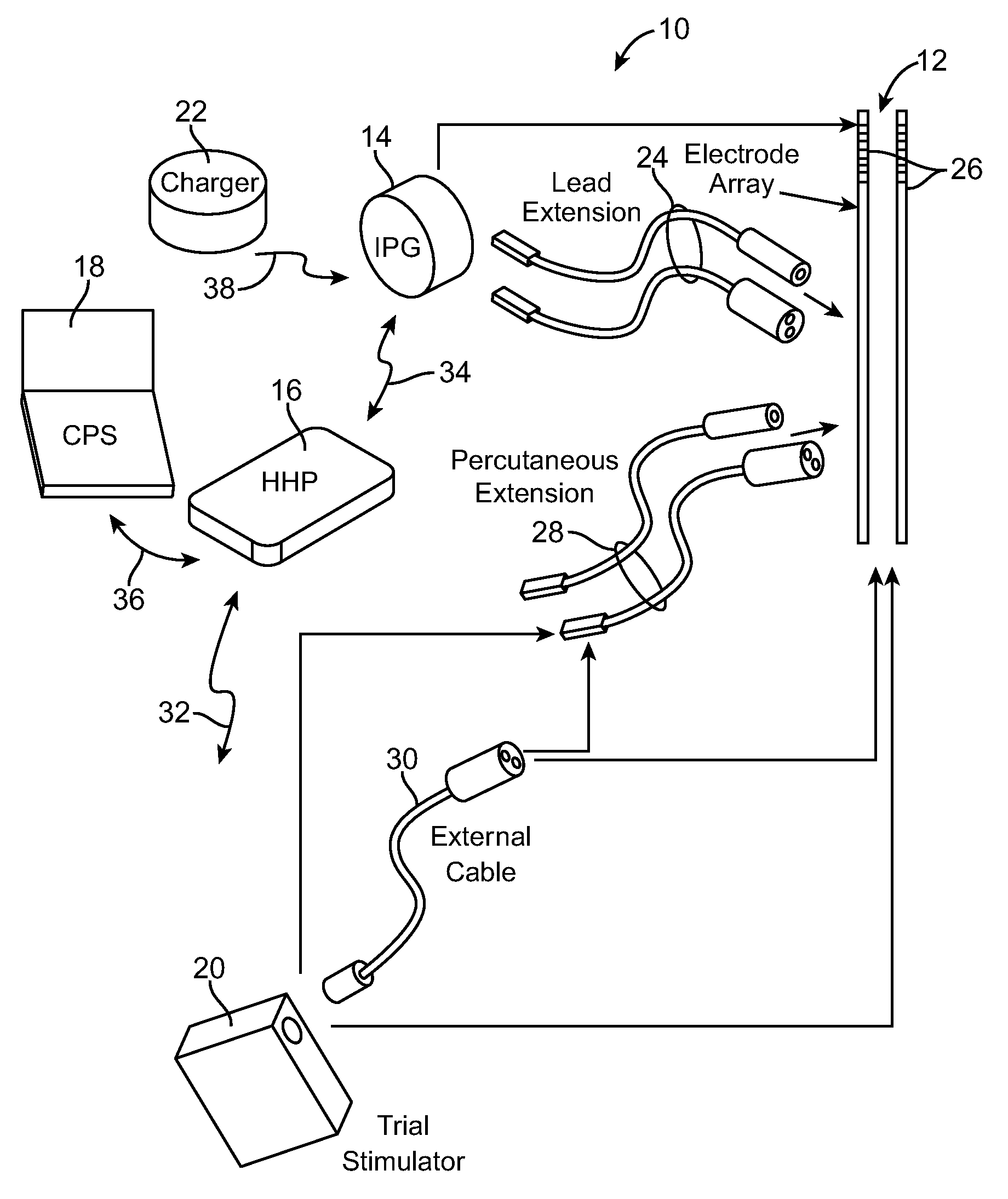
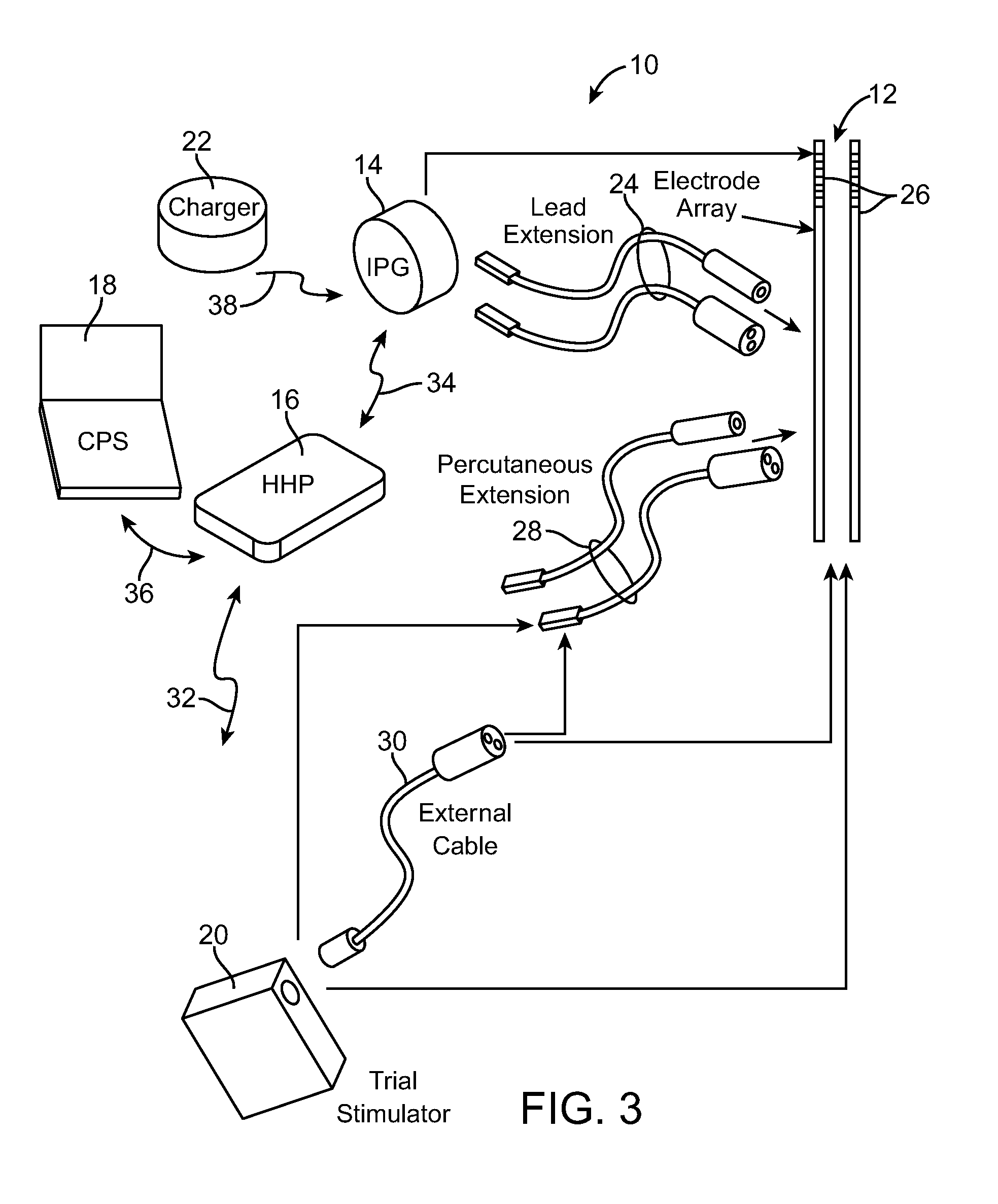
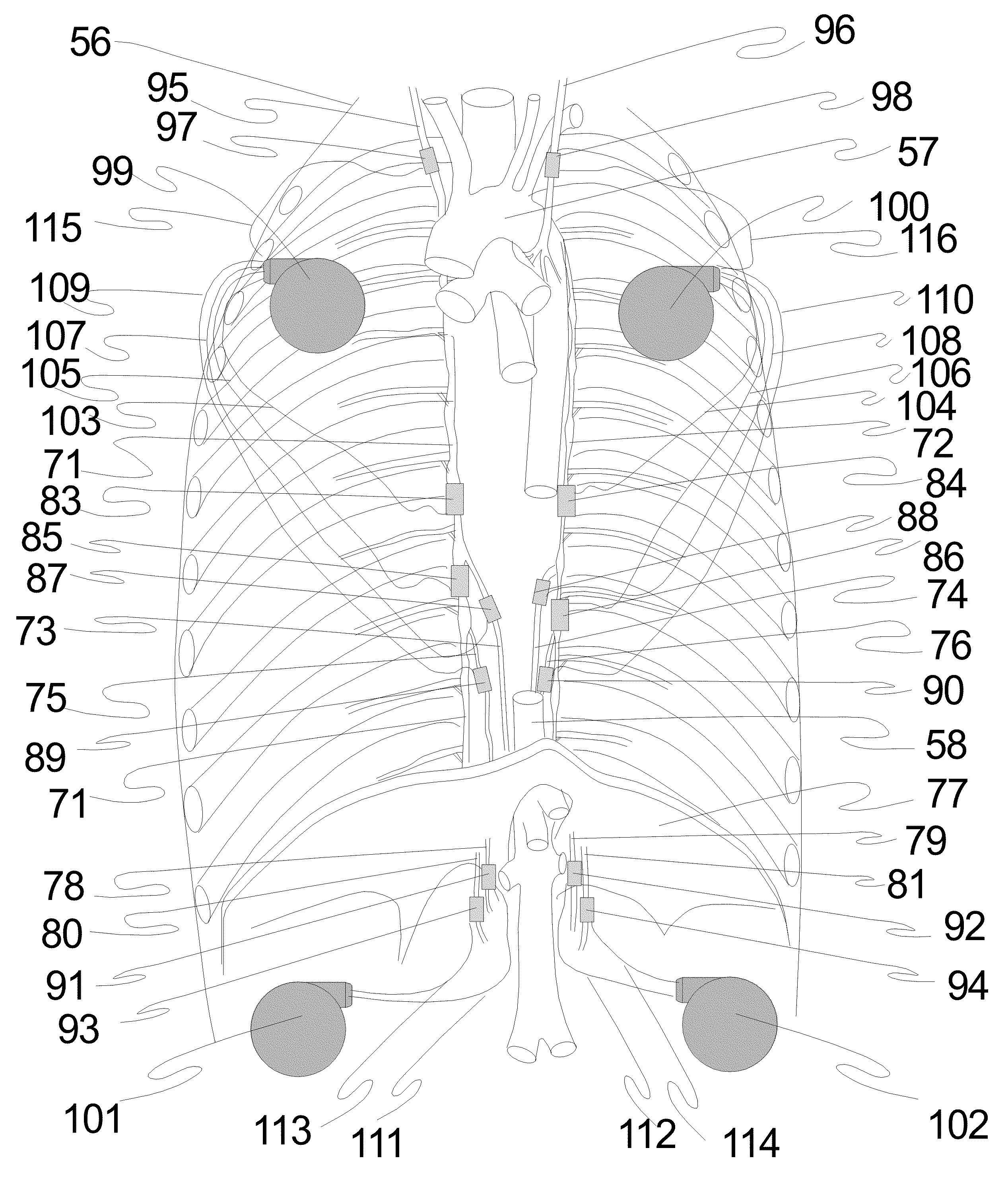
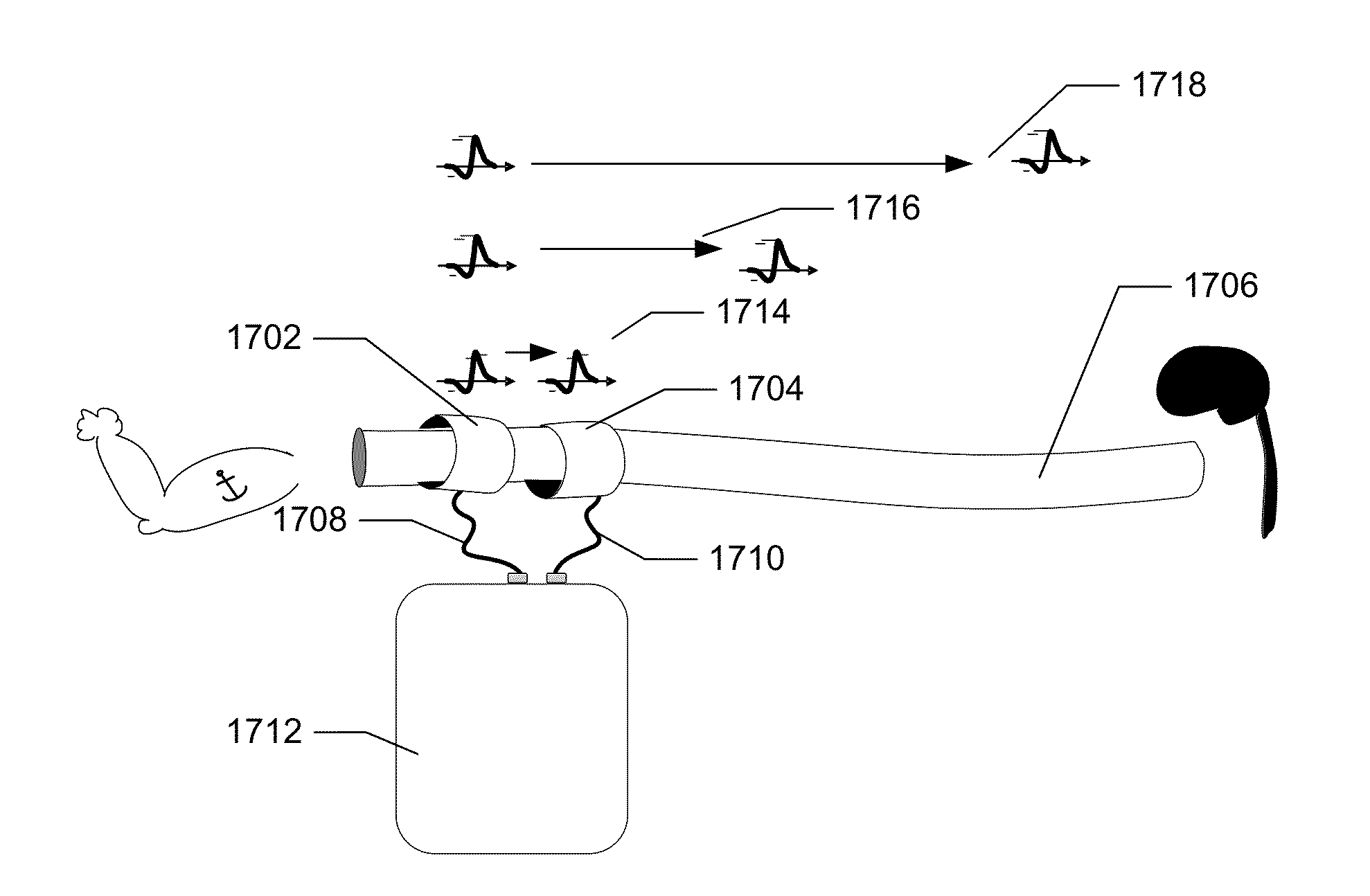
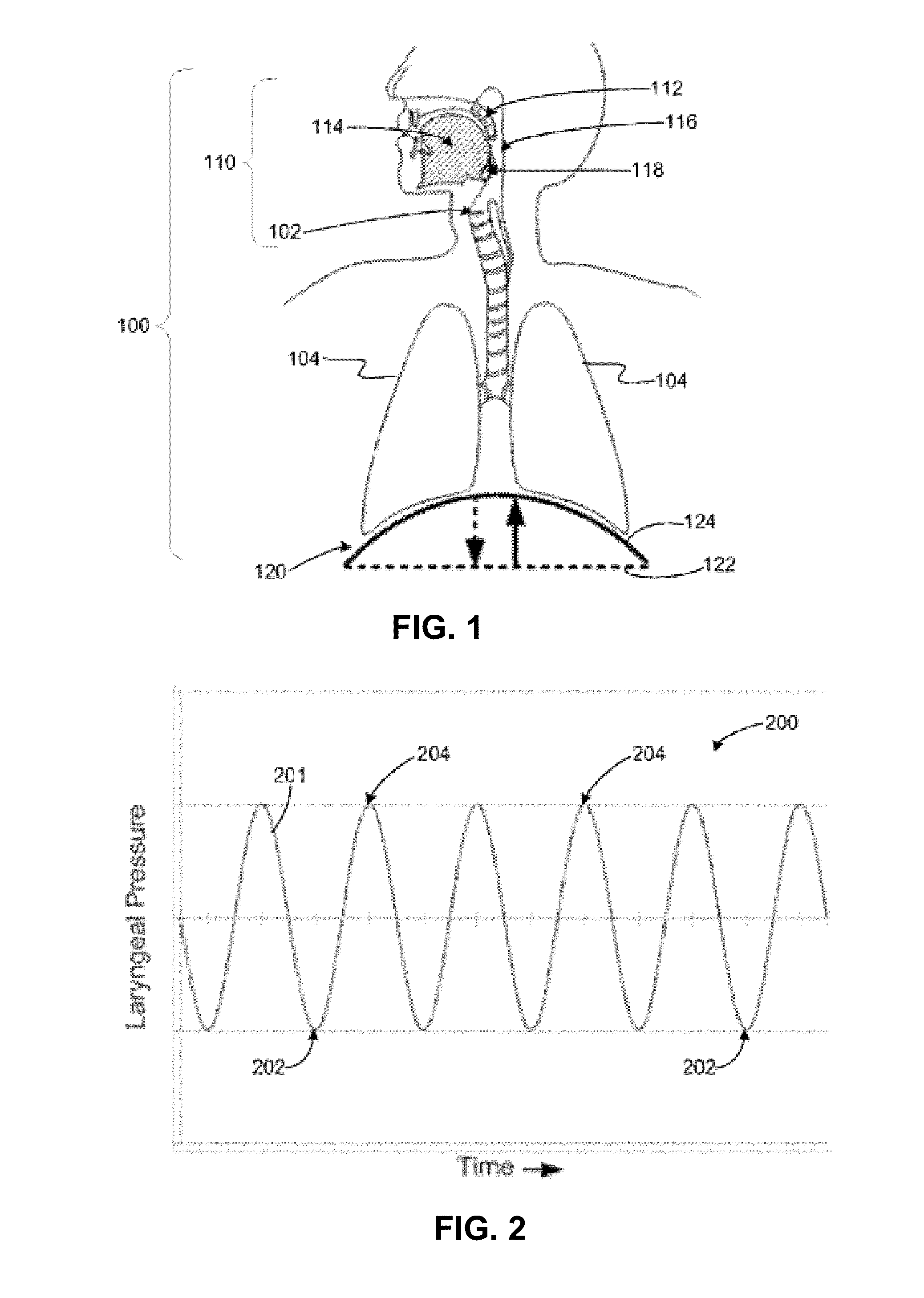
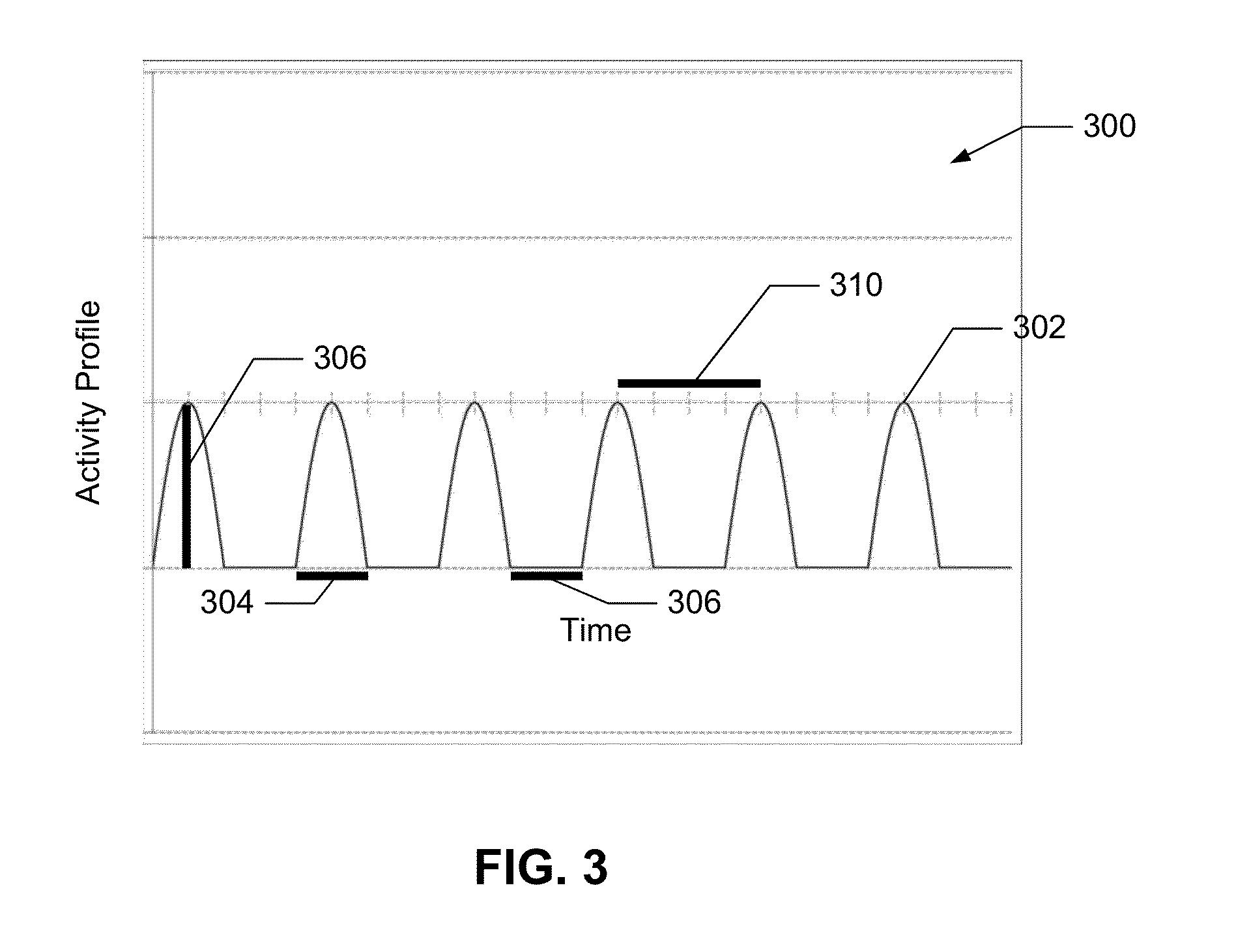
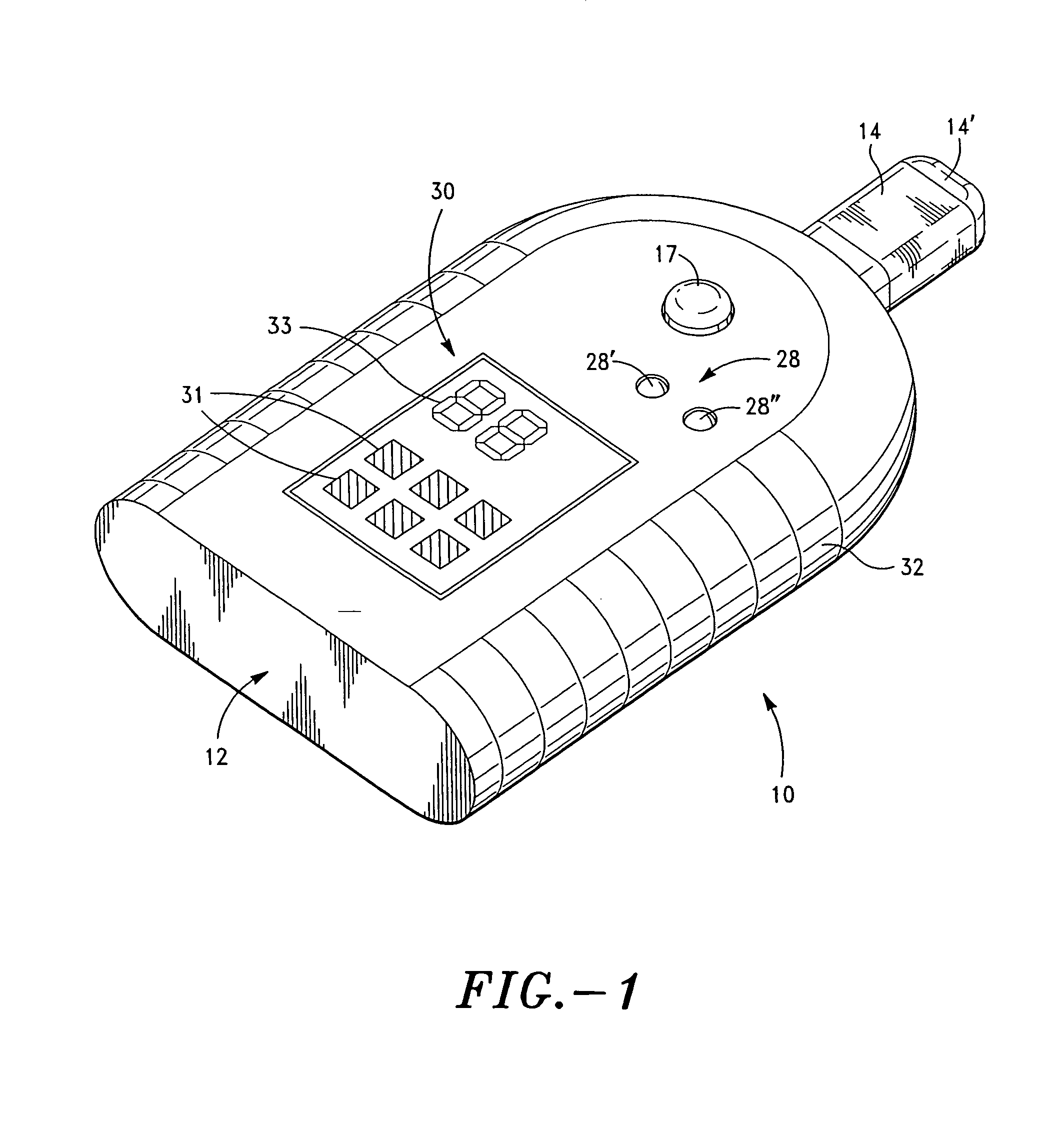
Method and system for vagal blocking and/or vagal stimulation to provide therapy for obesity and other gastrointestinal disorders
InactiveUS20050137644A1Eliminates repeated surgeryOvercomes shortcomingElectrotherapyArtificial respirationDiseaseDisease irritable bowel
Method and system to provide therapy for obesity and gastrointestinal disorders such as FGIDs, gastroparesis, gastro-esophageal reflex disease (GERD), pancreatitis and ileus comprises vagal blocking and / or vagal stimulation. Vagal blocking may be in the afferent or efferent direction, and may be with or without stimulation pulses. Blocking may be provided by one of a number of different electrical blocking techniques. Electrical signals may be provided with an external stimulator in conjunction with an implanted stimulus-receiver, or an implanted stimulus-receiver comprising a high value capacitor for temporary power source. In one embodiment, the external stimulator may comprise an optional telemetry unit. The addition of the telemetry unit to the external stimulator provides the ability to remotely interrogate and change stimulation programs over a wide area network, as well as other networking capabilities,
Owner:NEURO & CARDIAC TECH
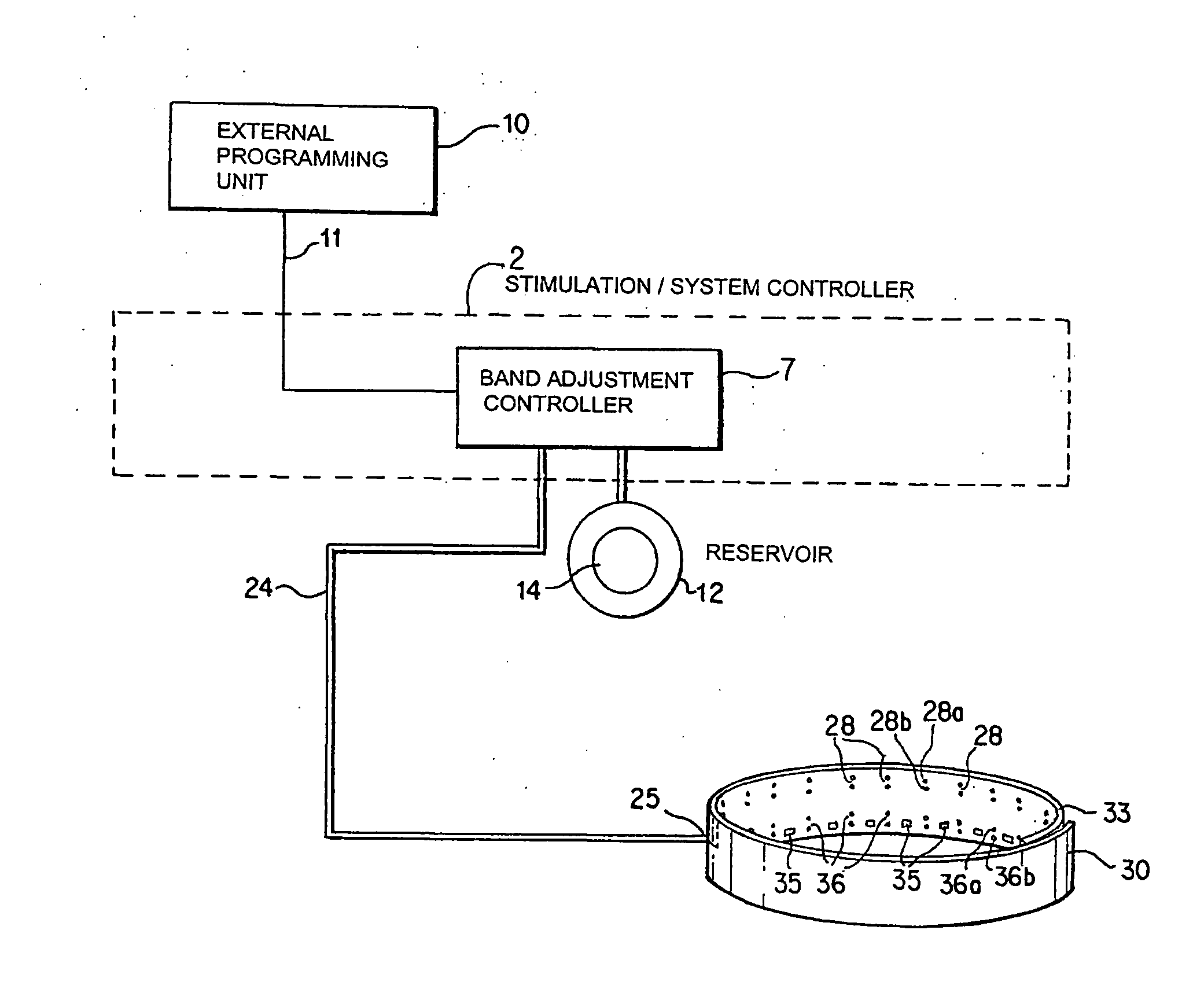
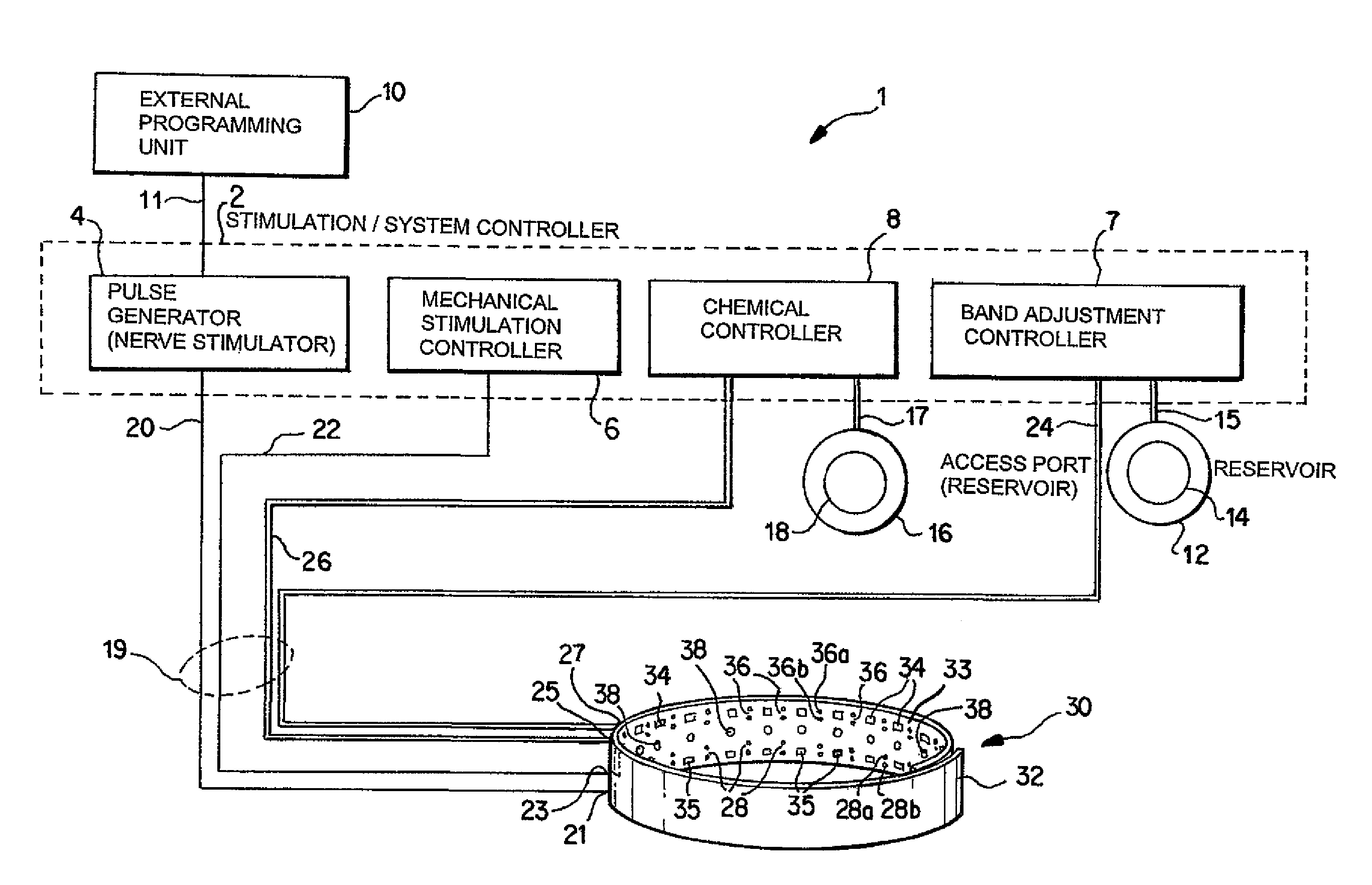
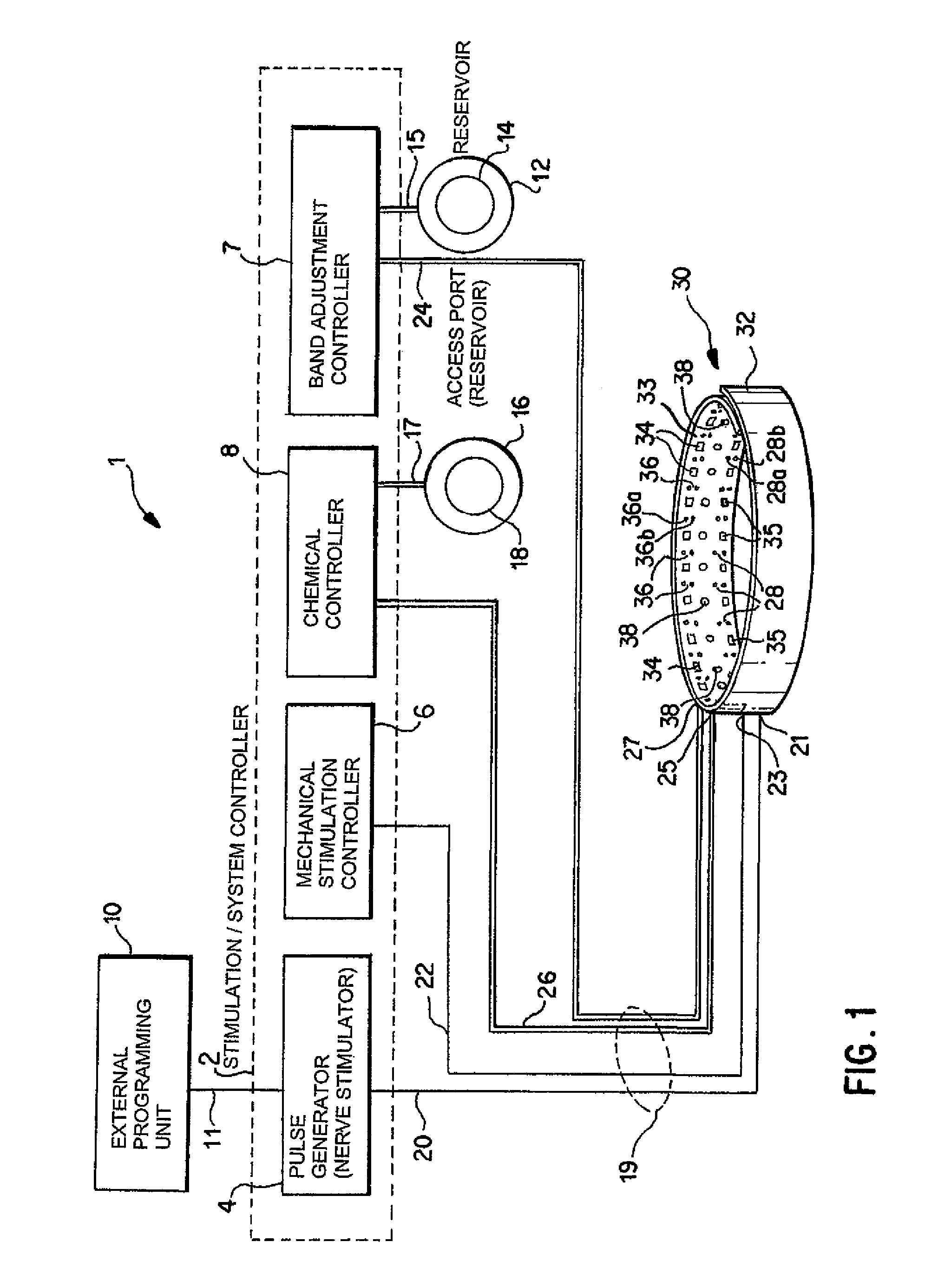
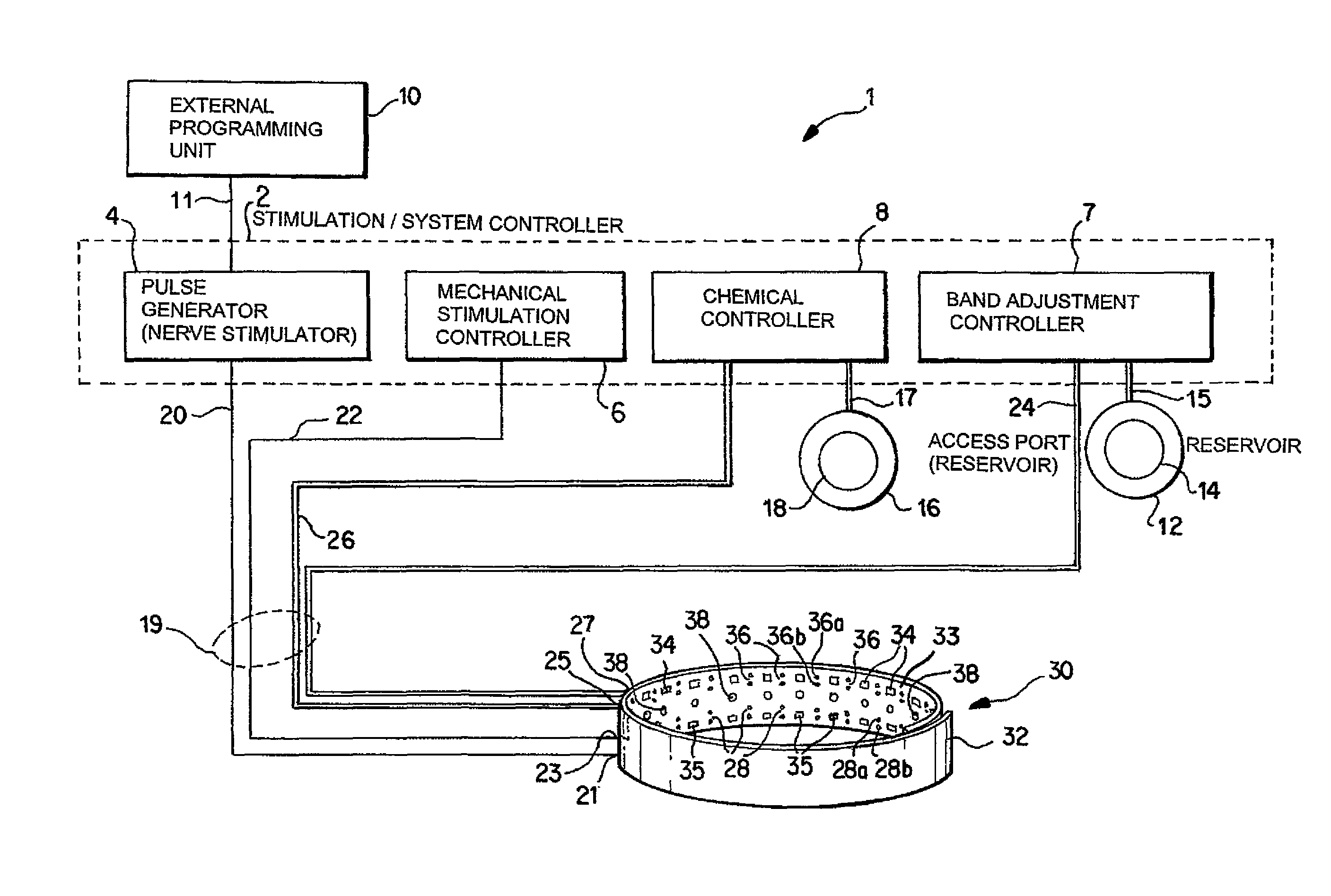
Noninvasively adjustable gastric band
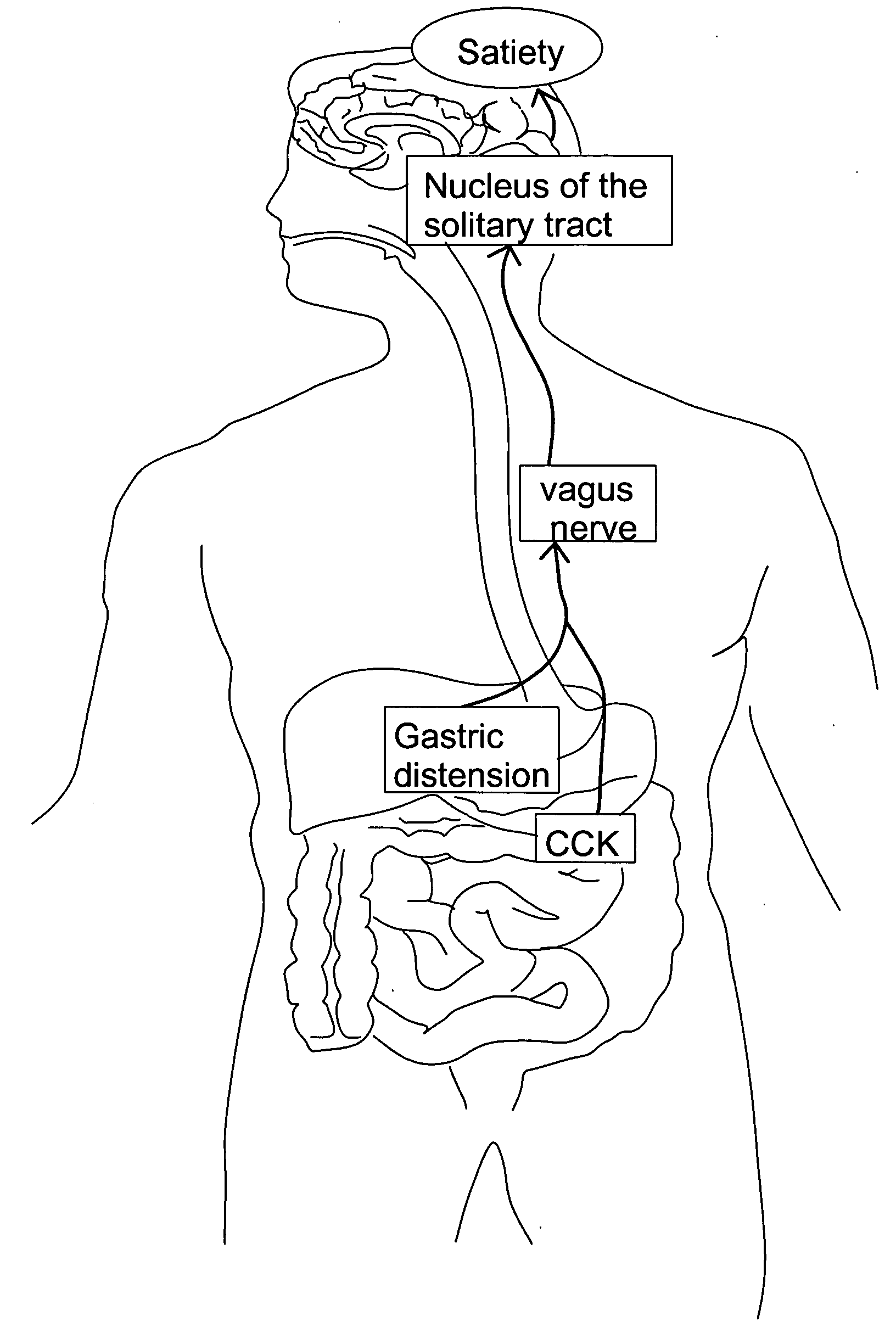
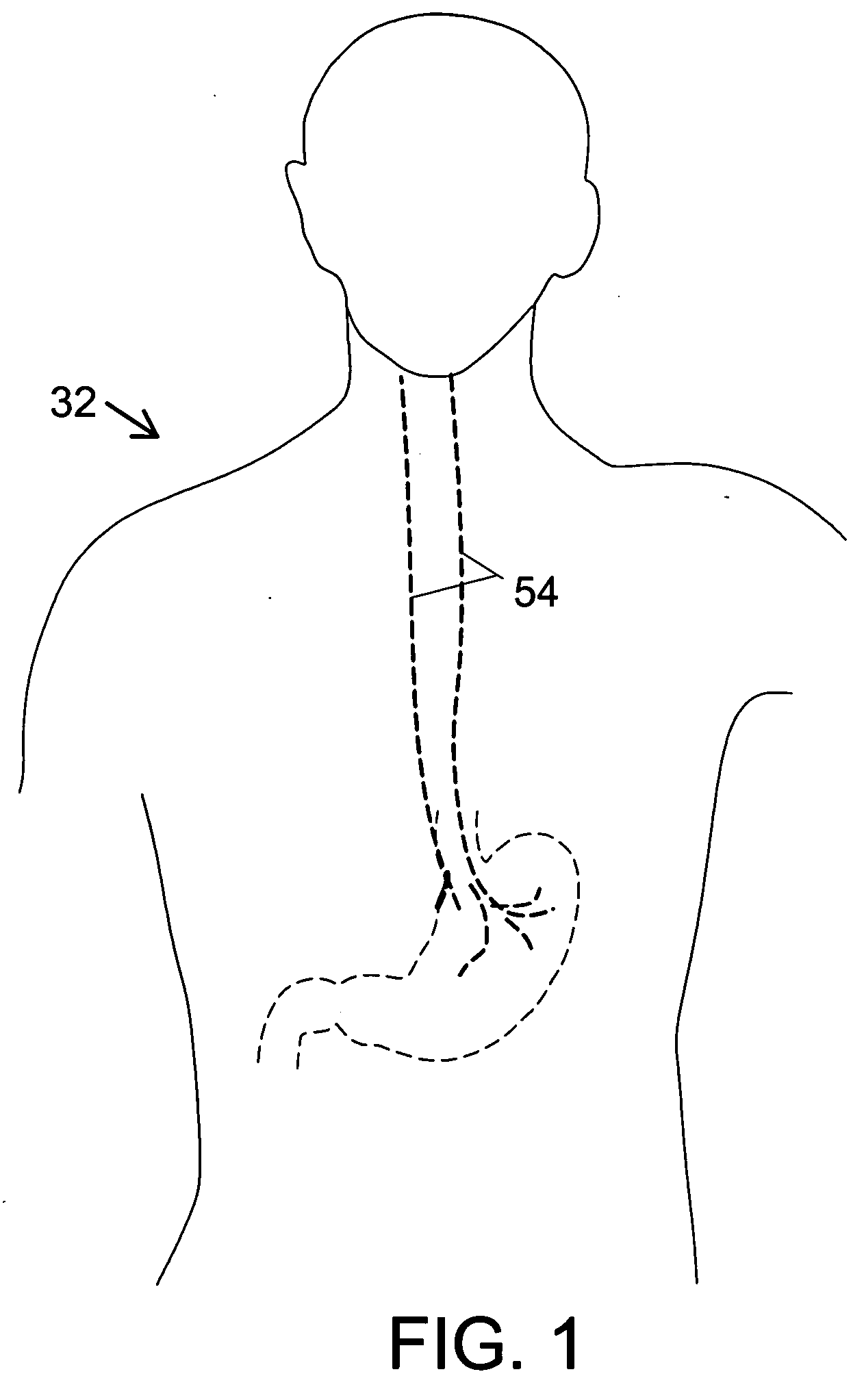
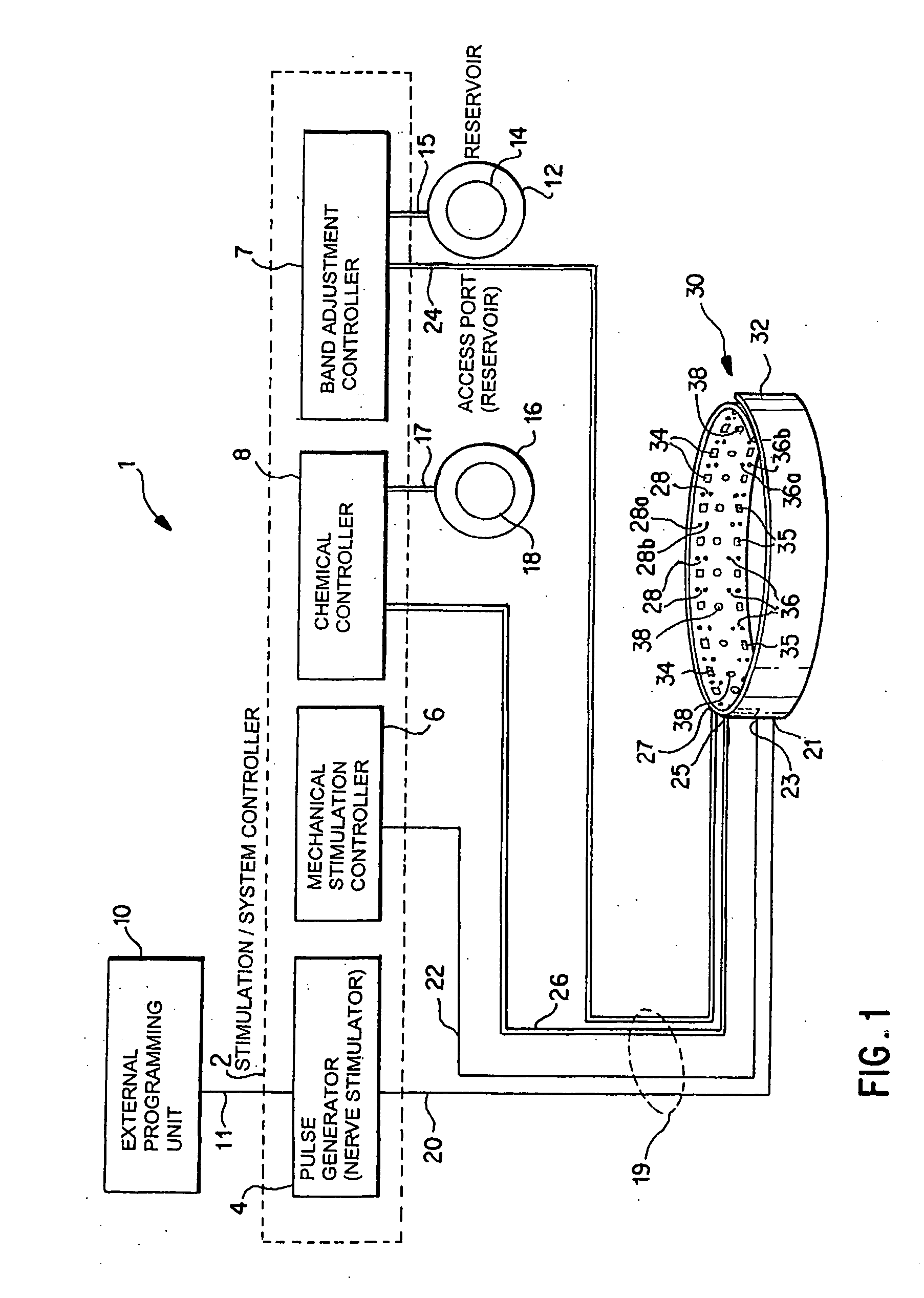
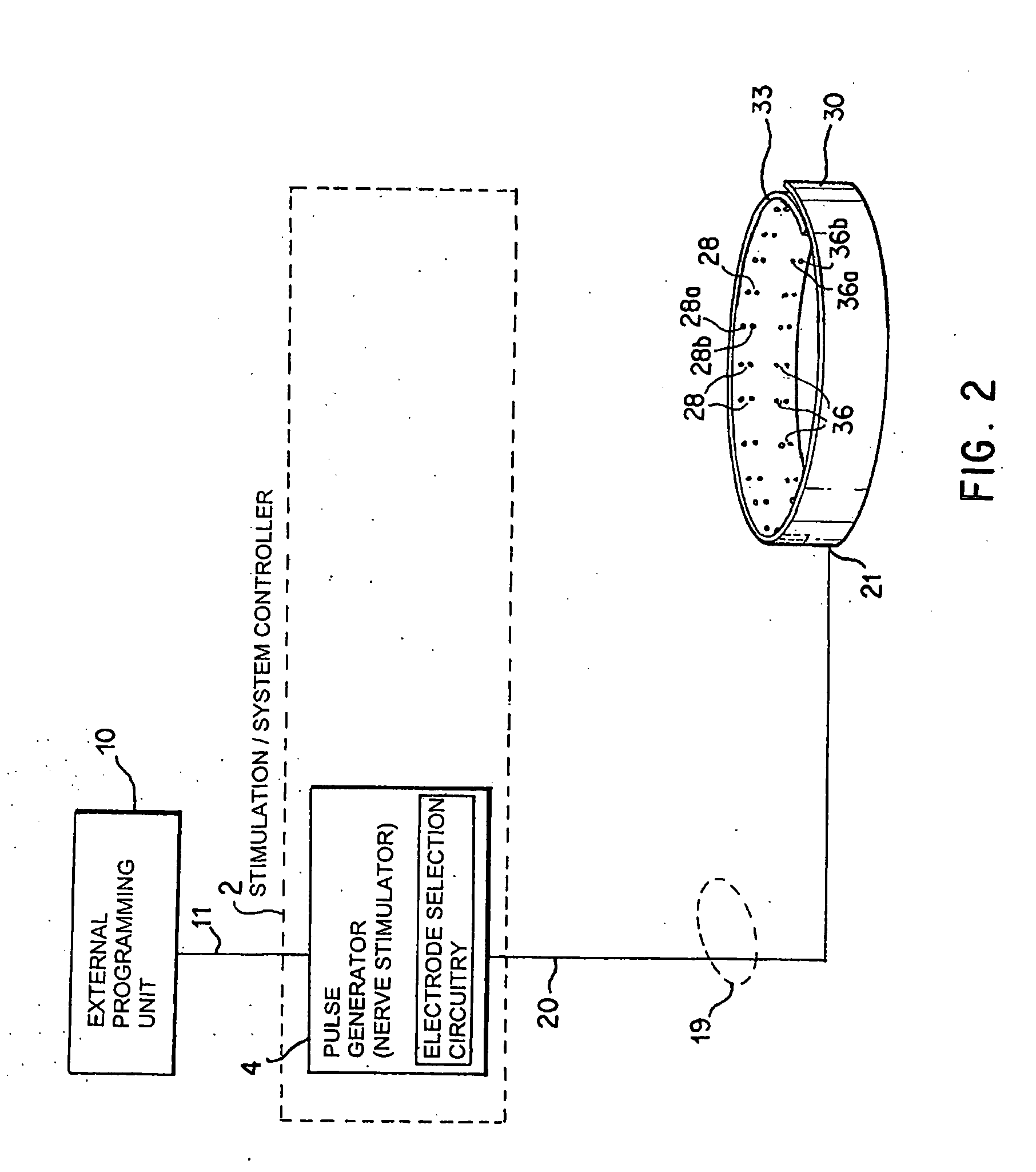
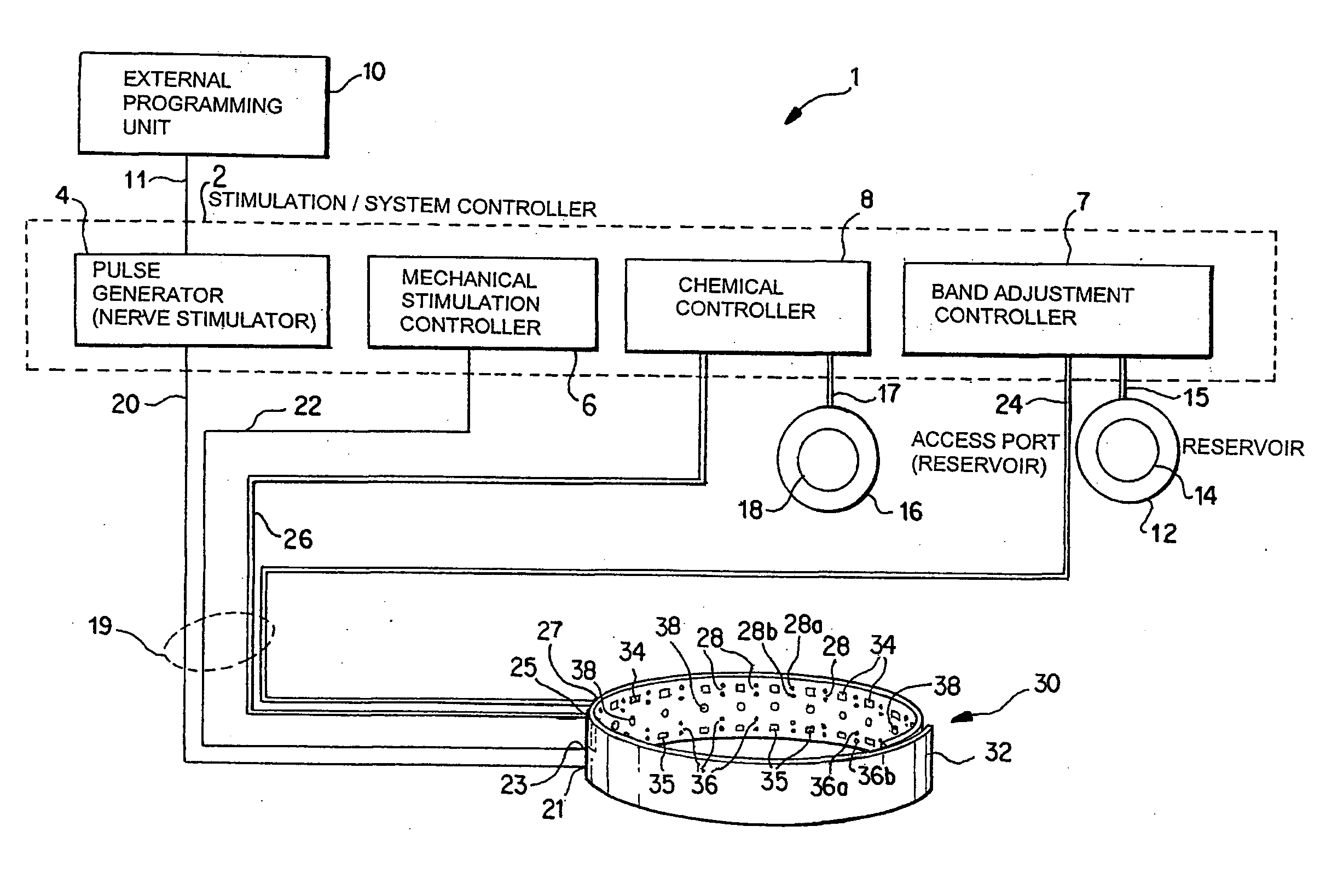
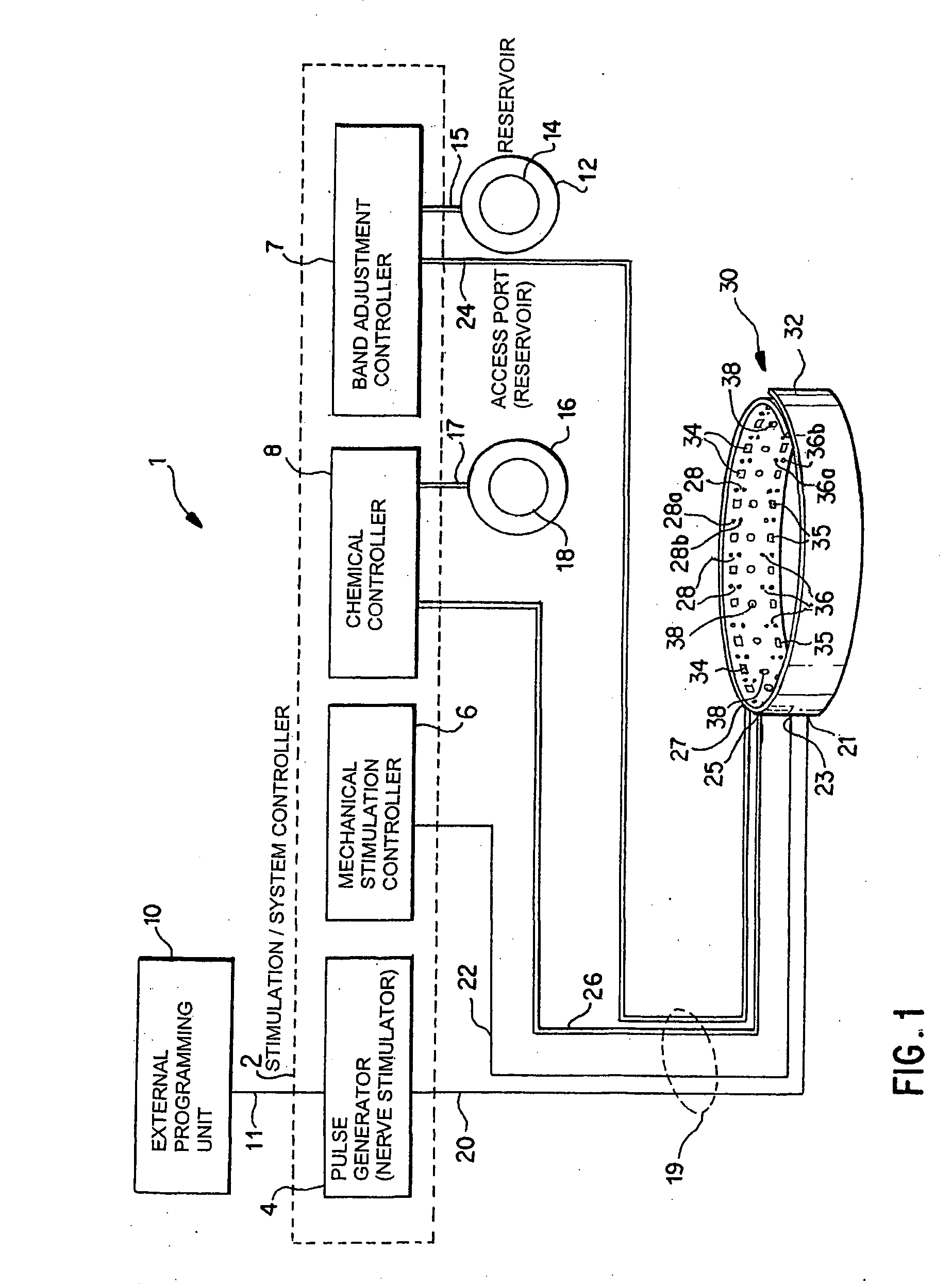
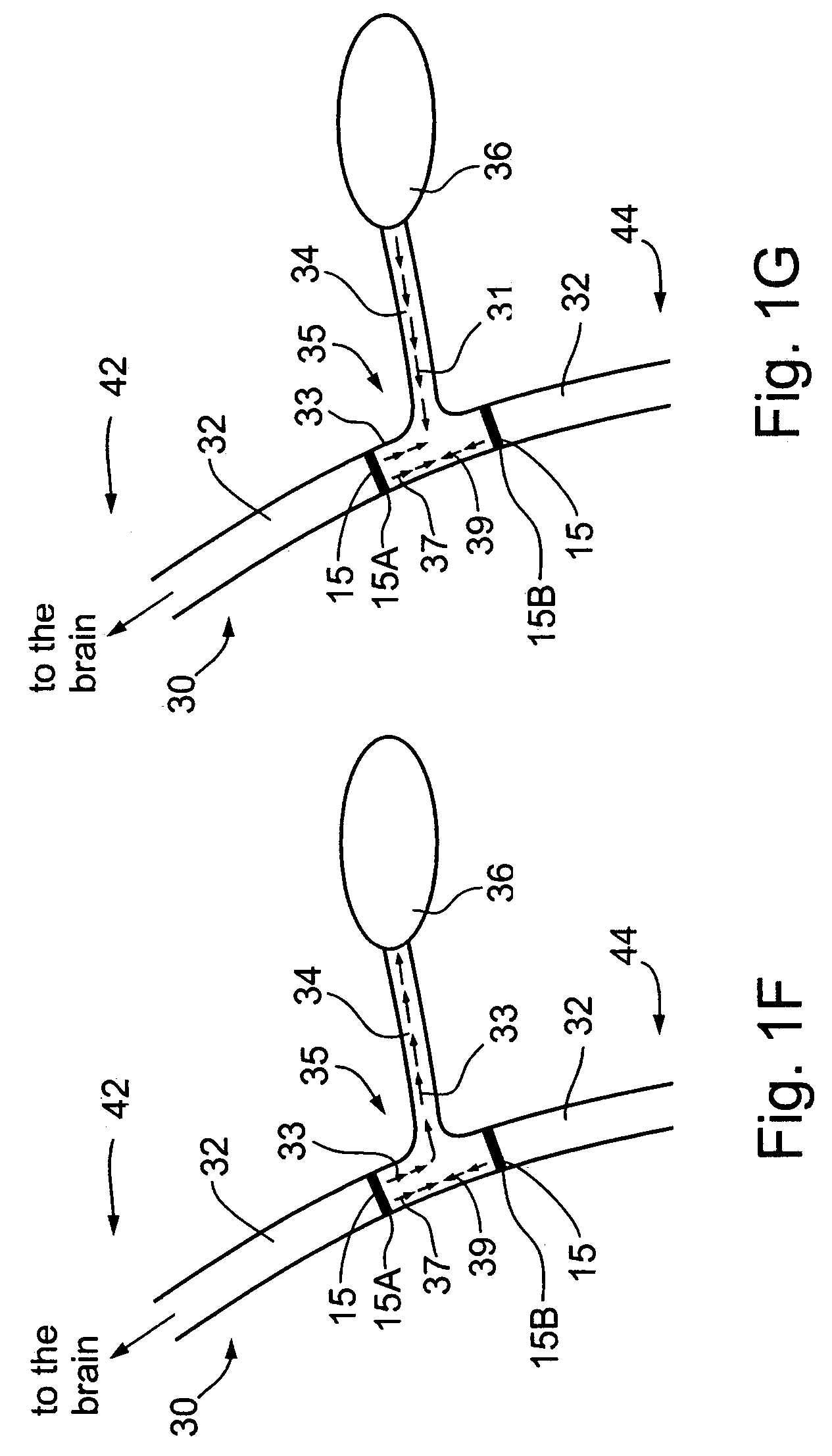
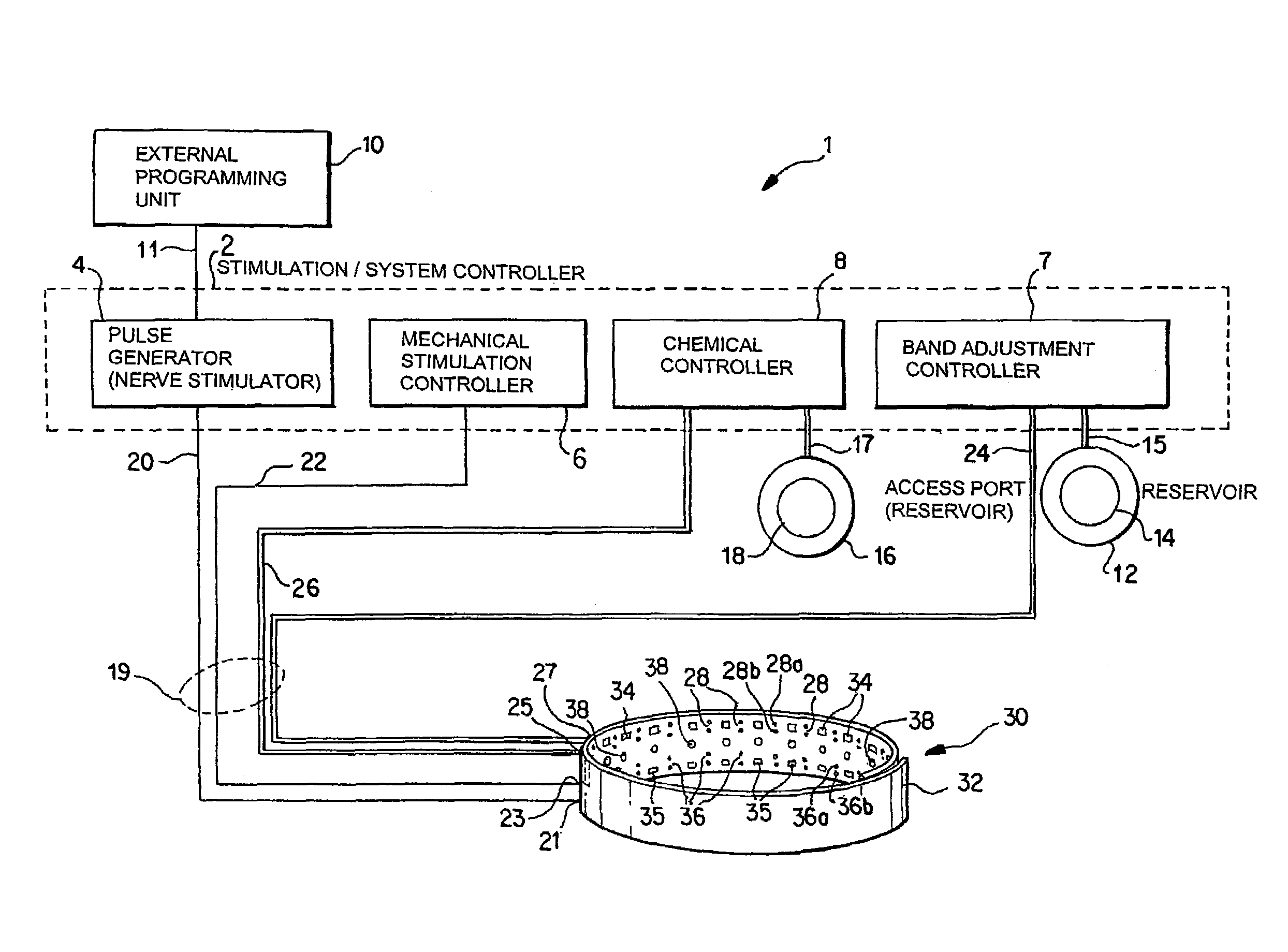
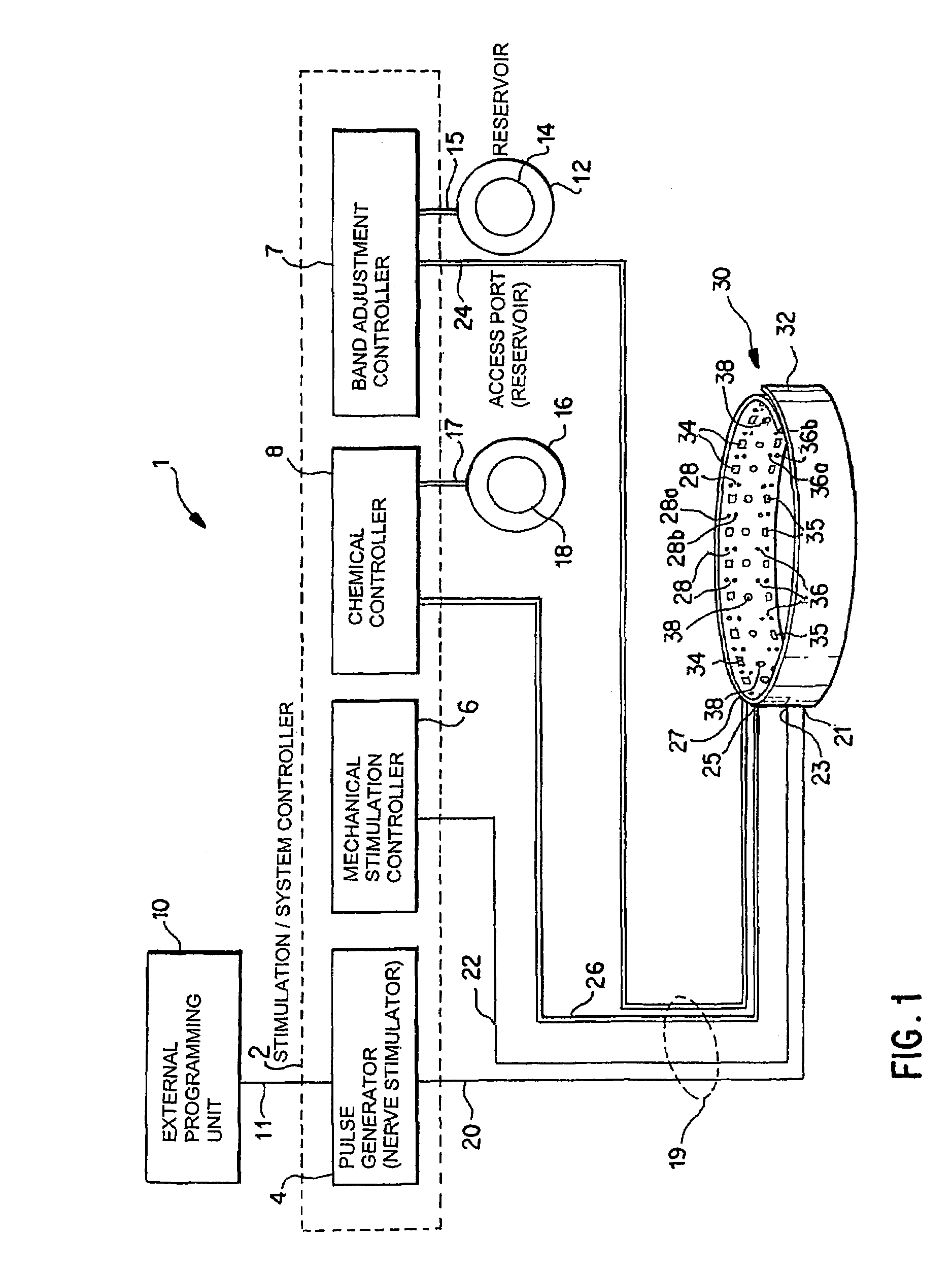
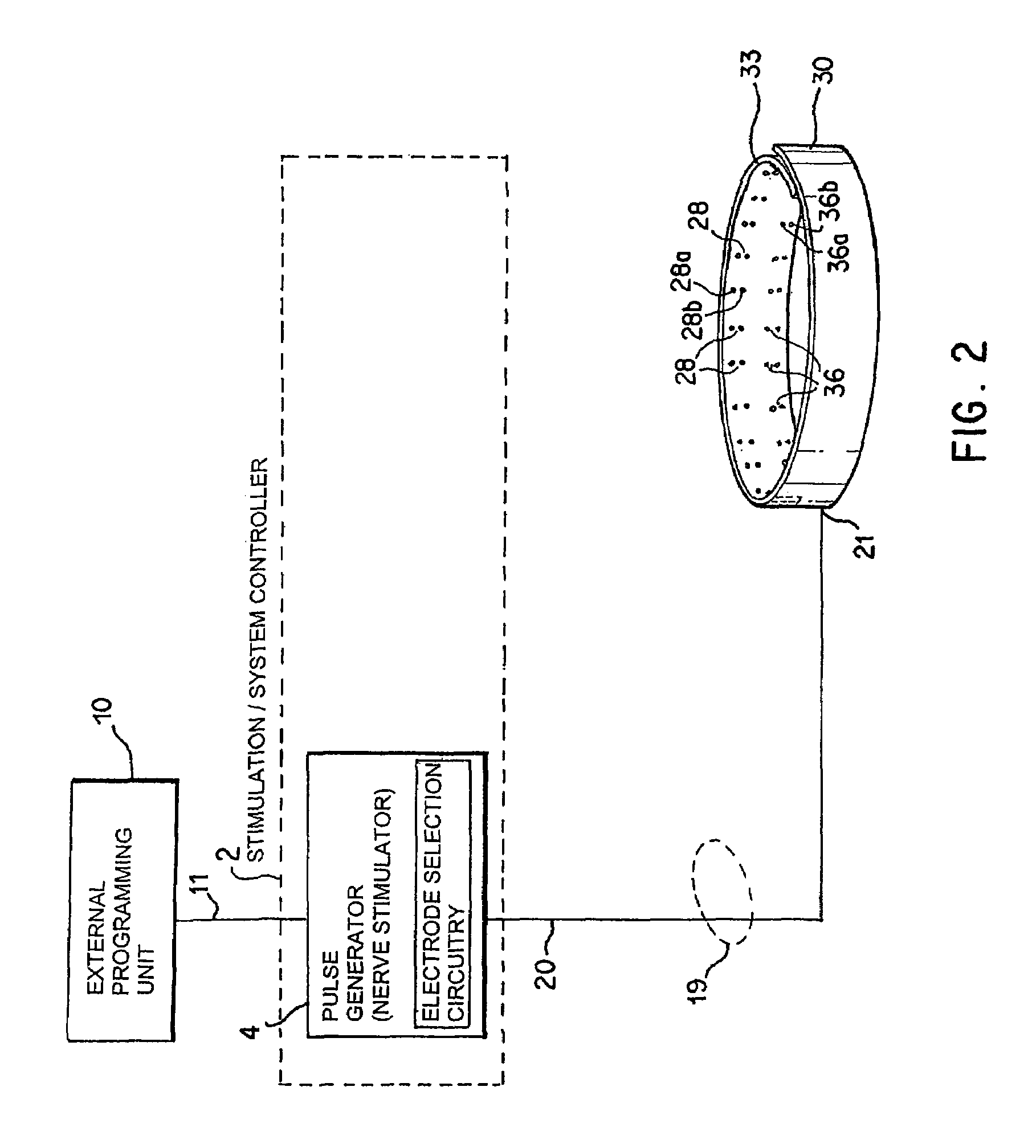
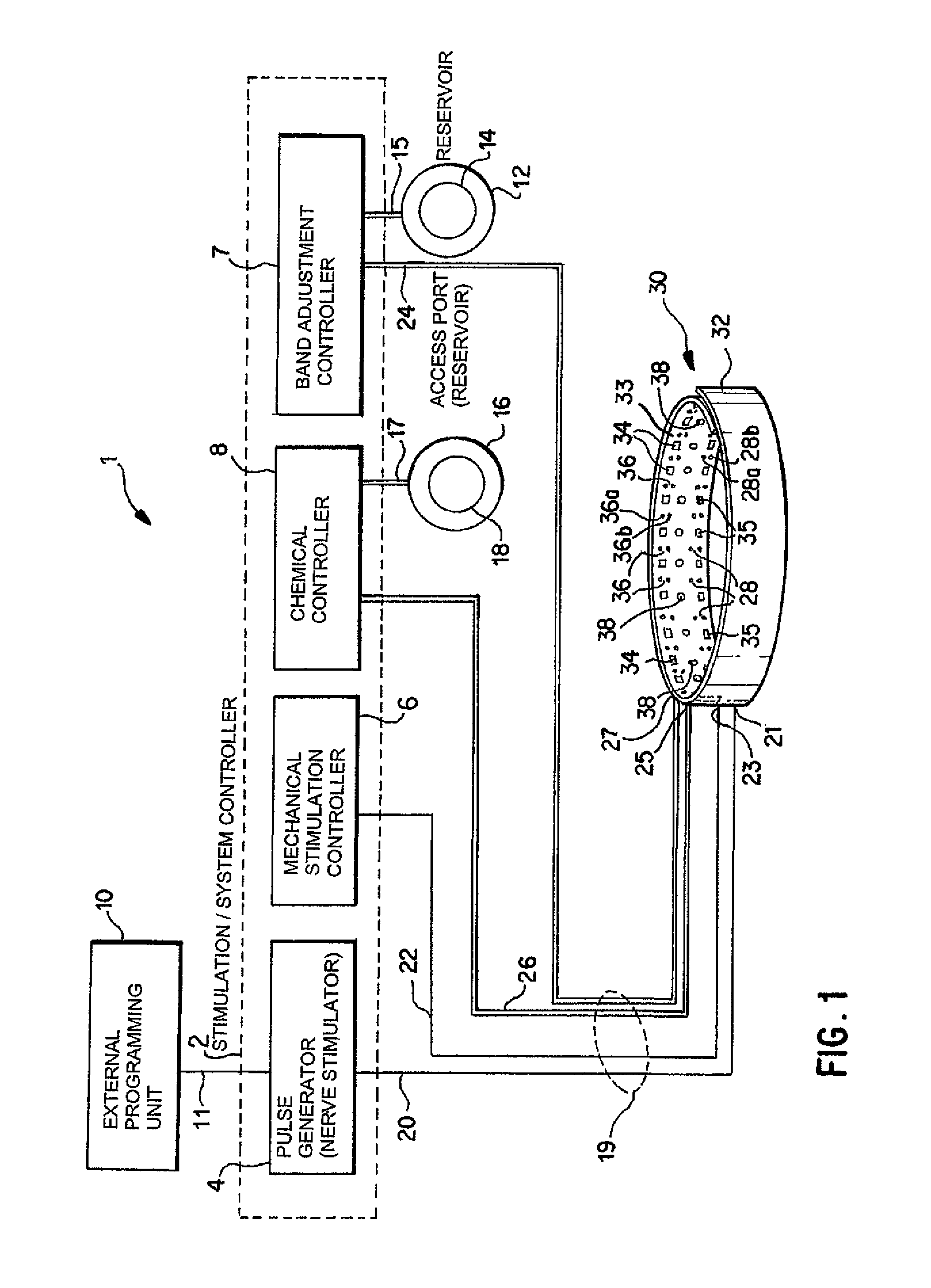
A method and apparatus for treatment of an eating disorder includes electrically, mechanically and / or pharmaceutically / chemically stimulating a of the vagus nerve of the lower esophagus, cardia, esophageal / cardia junction, cardia / fundus junction or upper stomach so as to induce afferent action potentials on the vagus nerve. The device may be noninvasively adjusted after implantation to provide increased or decreased restriction on the patient's gastrointestinal tract. Each stimulus may be administered as a series of programmed pulses of defined amplitude, duration and period, to evoke a responsive signal to the brain by the target nerve, effective for producing a temporary feeling of satiety in the person. An implantable stimulus generator may be operatively coupled to a nerve electrode, pressure device or chemical outlet to apply a defined signal to a selected nerve branch. The implantable stimulus generator is programmable to allow clinician programming of defined signal parameters effective to treat the eating disorder of the patient. Methods are also provided to identify electrodes nearest to a branch of the vagus nerve to apply an electrical stimulation signal with improved efficiency.
Owner:CYBERONICS INC
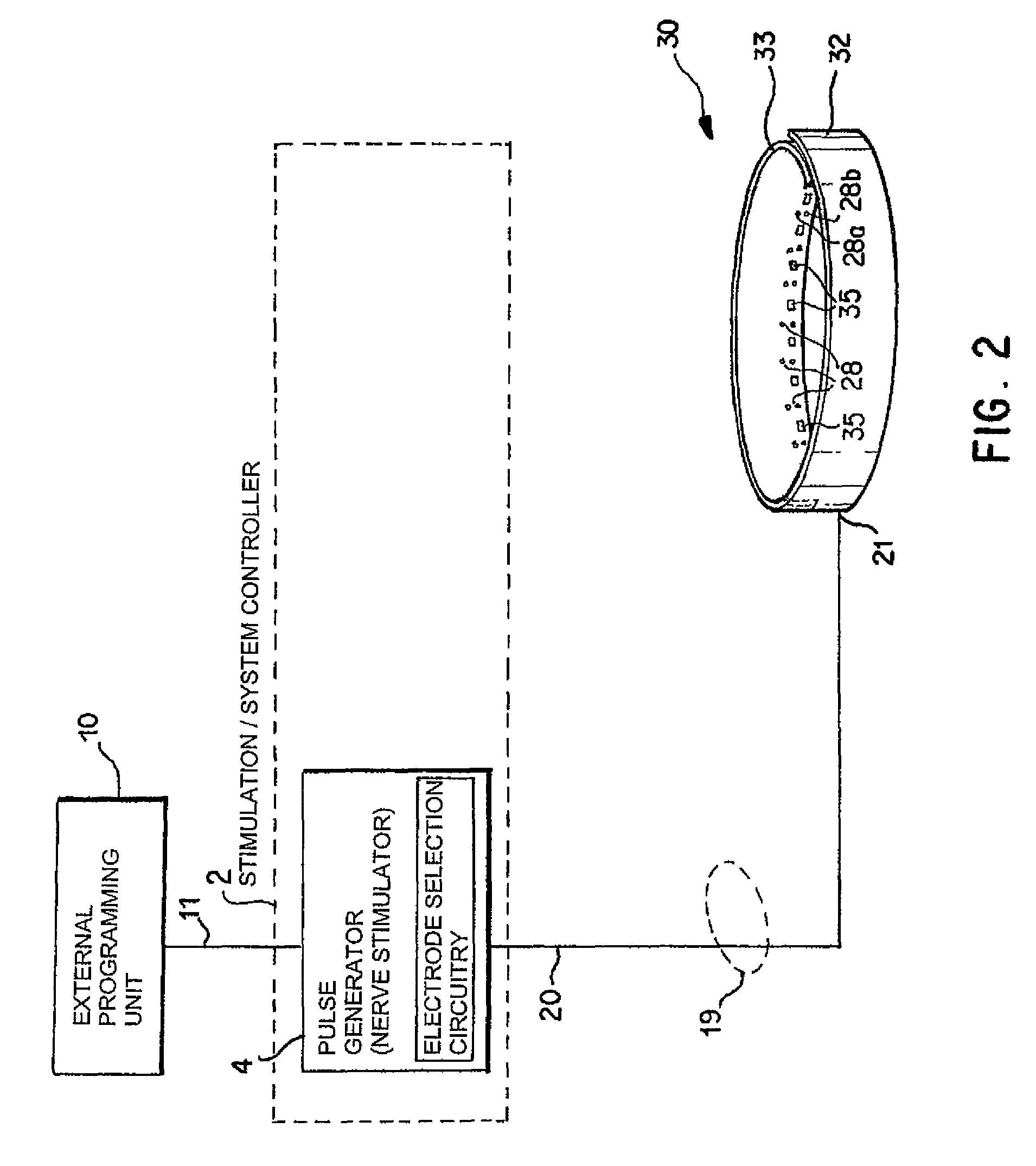
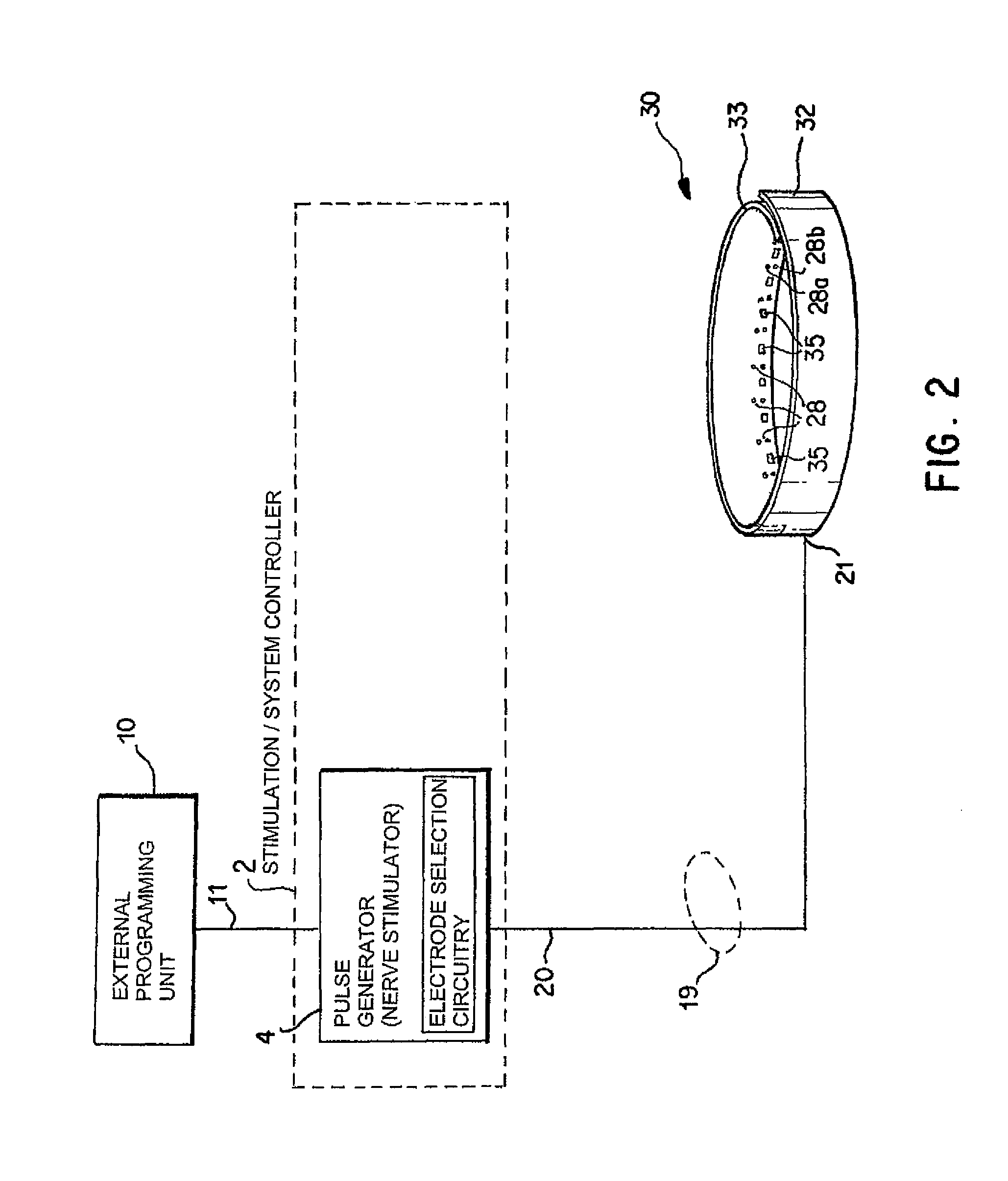
Identification of electrodes for nerve stimulation in the treatment of eating disorders
A method and apparatus for treatment of an eating disorder includes electrically, mechanically and / or pharmaceutically / chemically stimulating a of the vagus nerve of the lower esophagus, cardia, esophageal / cardia junction, cardia / fundus junction or upper stomach so as to induce afferent action potentials on the vagus nerve. The device may be noninvasively adjusted after implantation to provide increased or decreased restriction on the patient's gastrointestinal tract. Each stimulus may be administered as a series of programmed pulses of defined amplitude, duration and period, to evoke a responsive signal to the brain by the target nerve, effective for producing a temporary feeling of satiety in the person. An implantable stimulus generator may be operatively coupled to a nerve electrode, pressure device or chemical outlet to apply a defined signal to a selected nerve branch. The implantable stimulus generator is programmable to allow clinician programming of defined signal parameters effective to treat the eating disorder of the patient. Methods are also provided to identify electrodes nearest to a branch of the vagus nerve to apply an electrical stimulation signal with improved efficiency.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
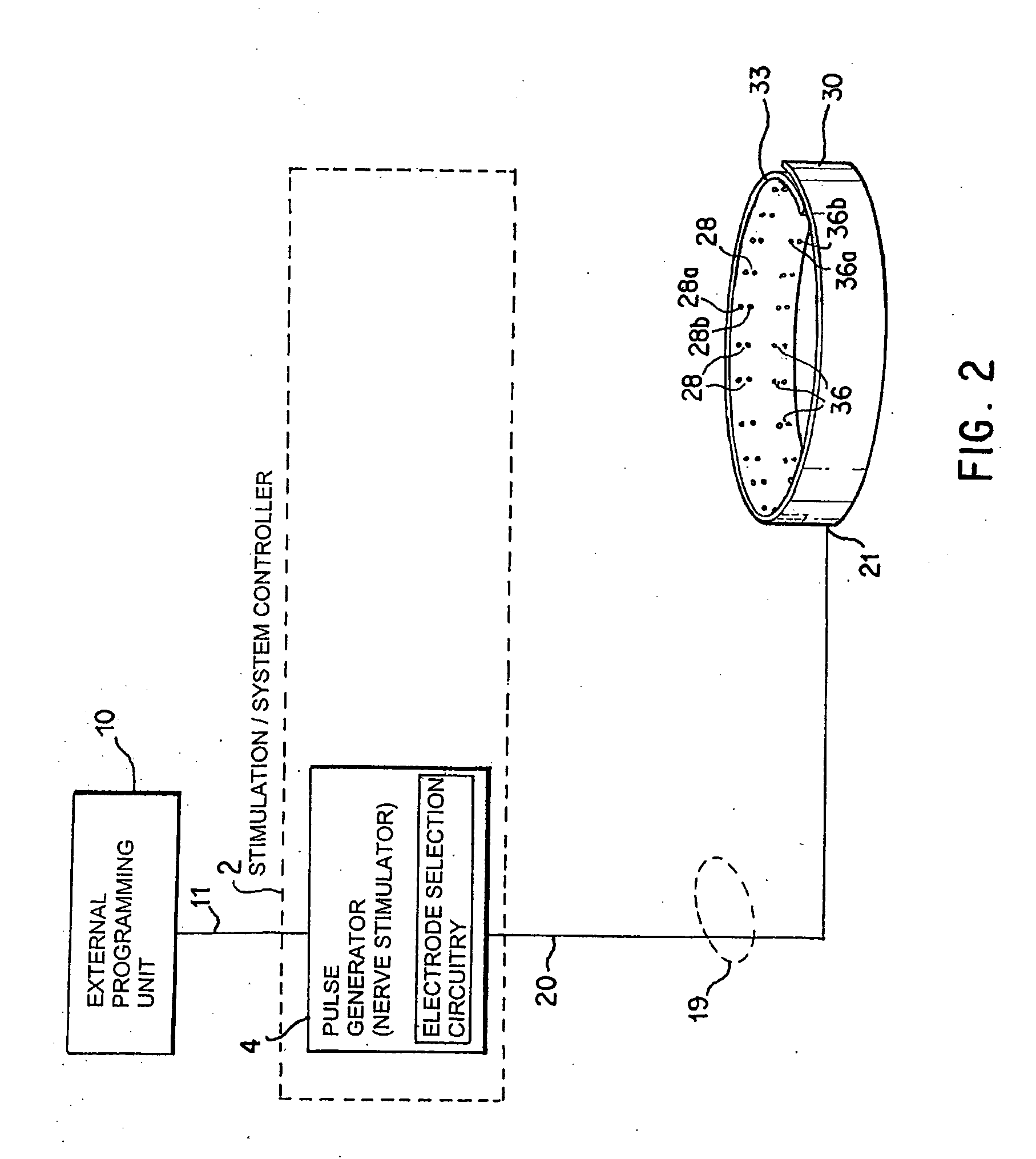
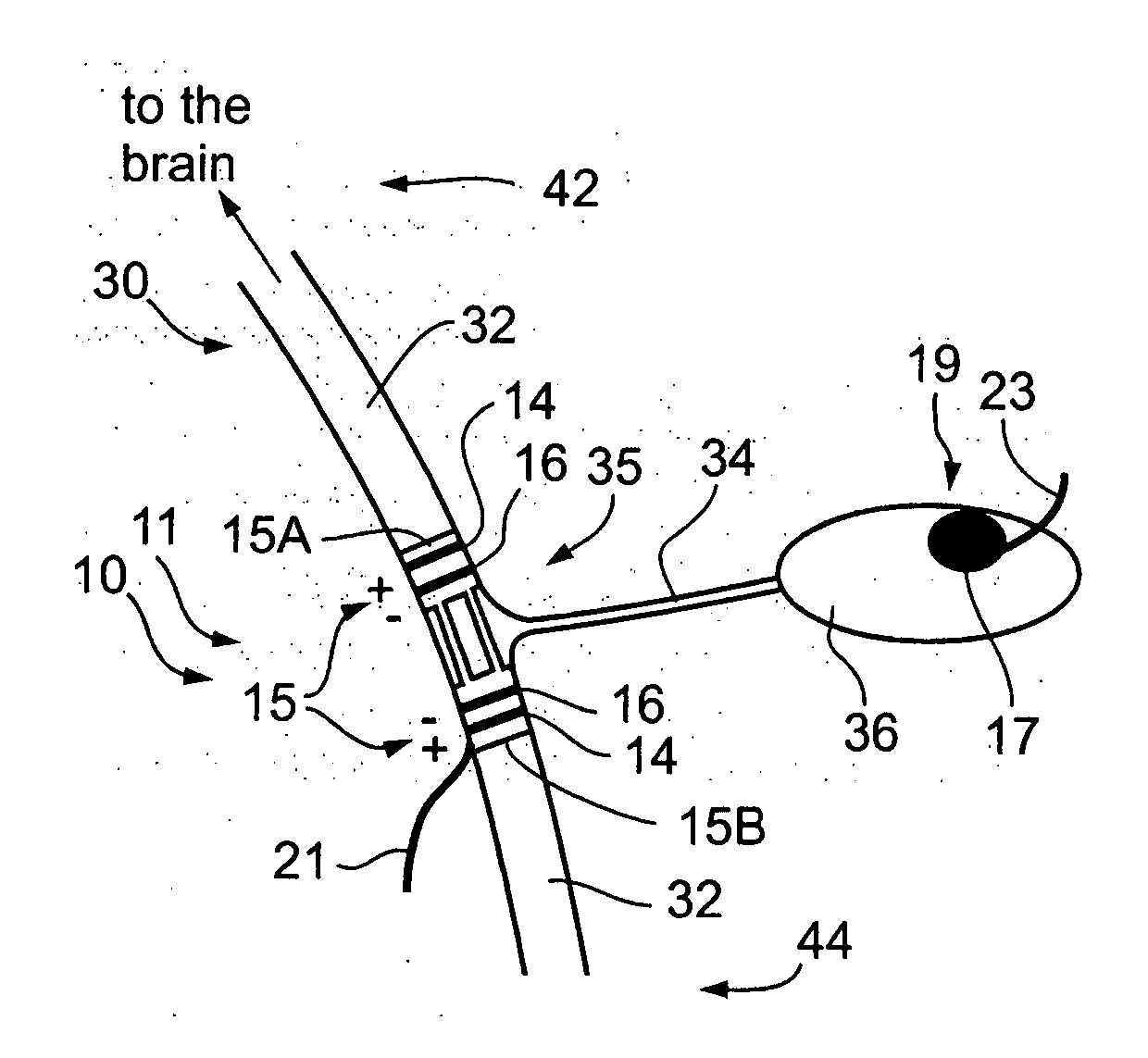
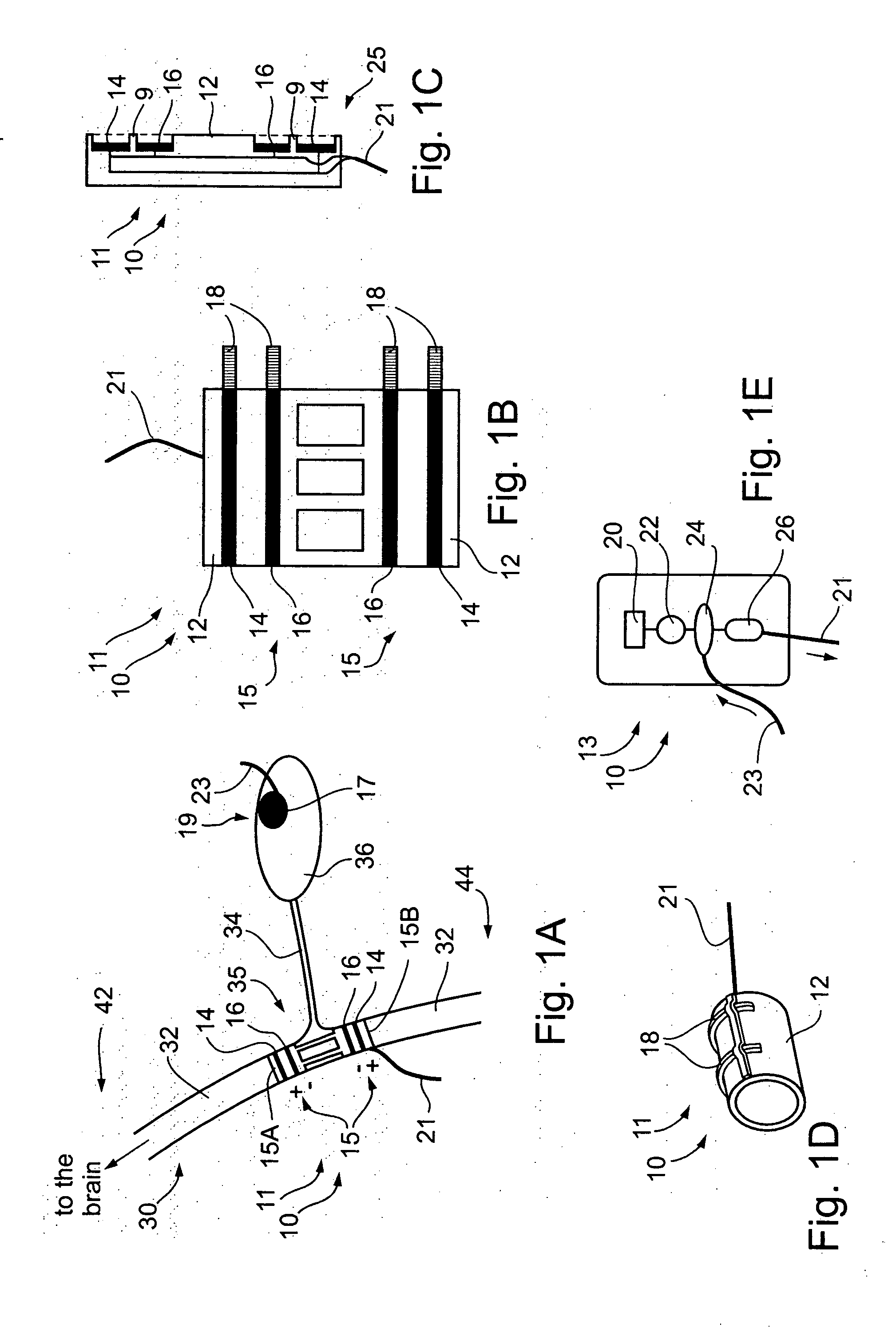
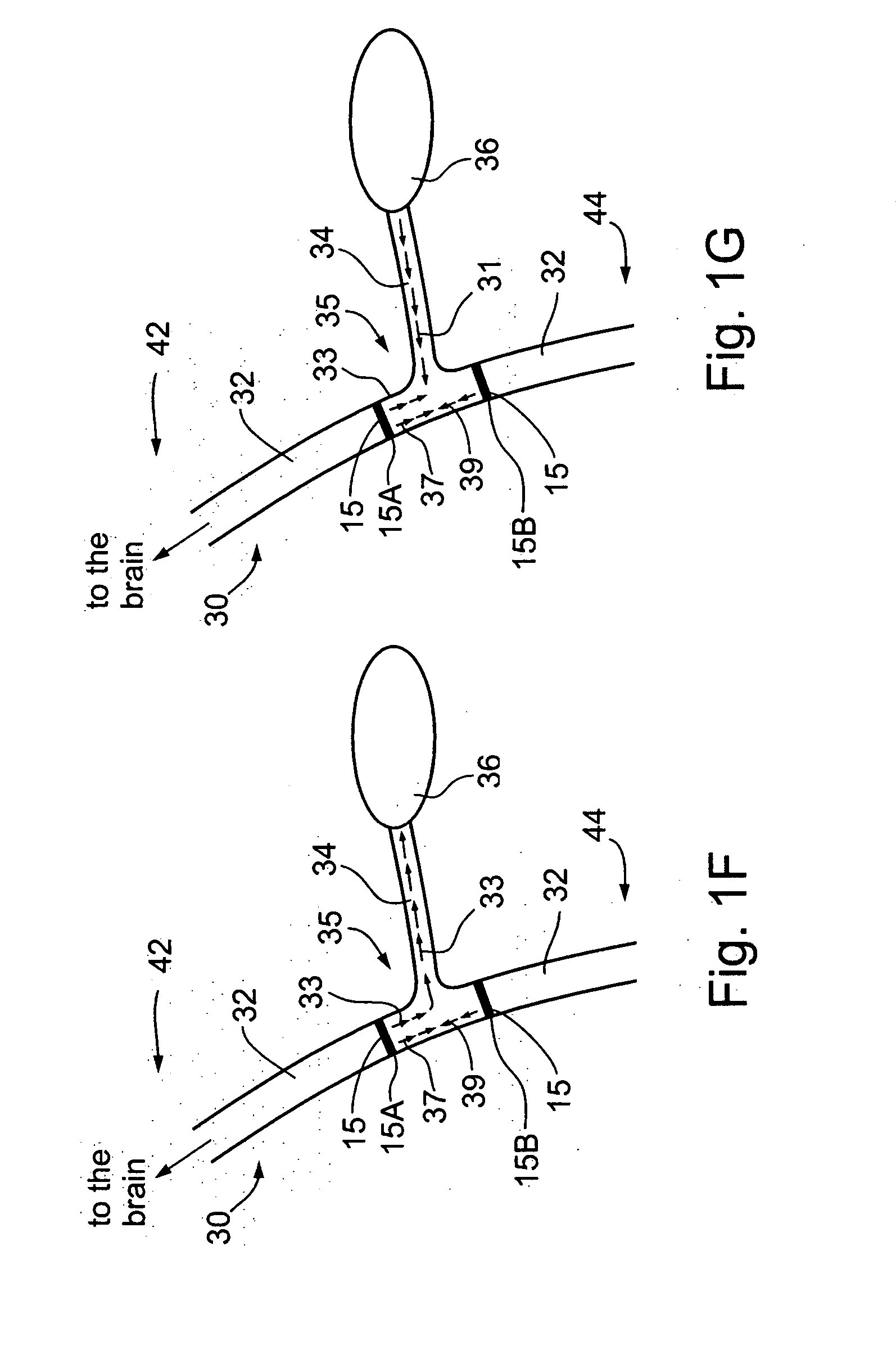
Nerve-branch-specific action-potential activation,inhibition, and monitoring
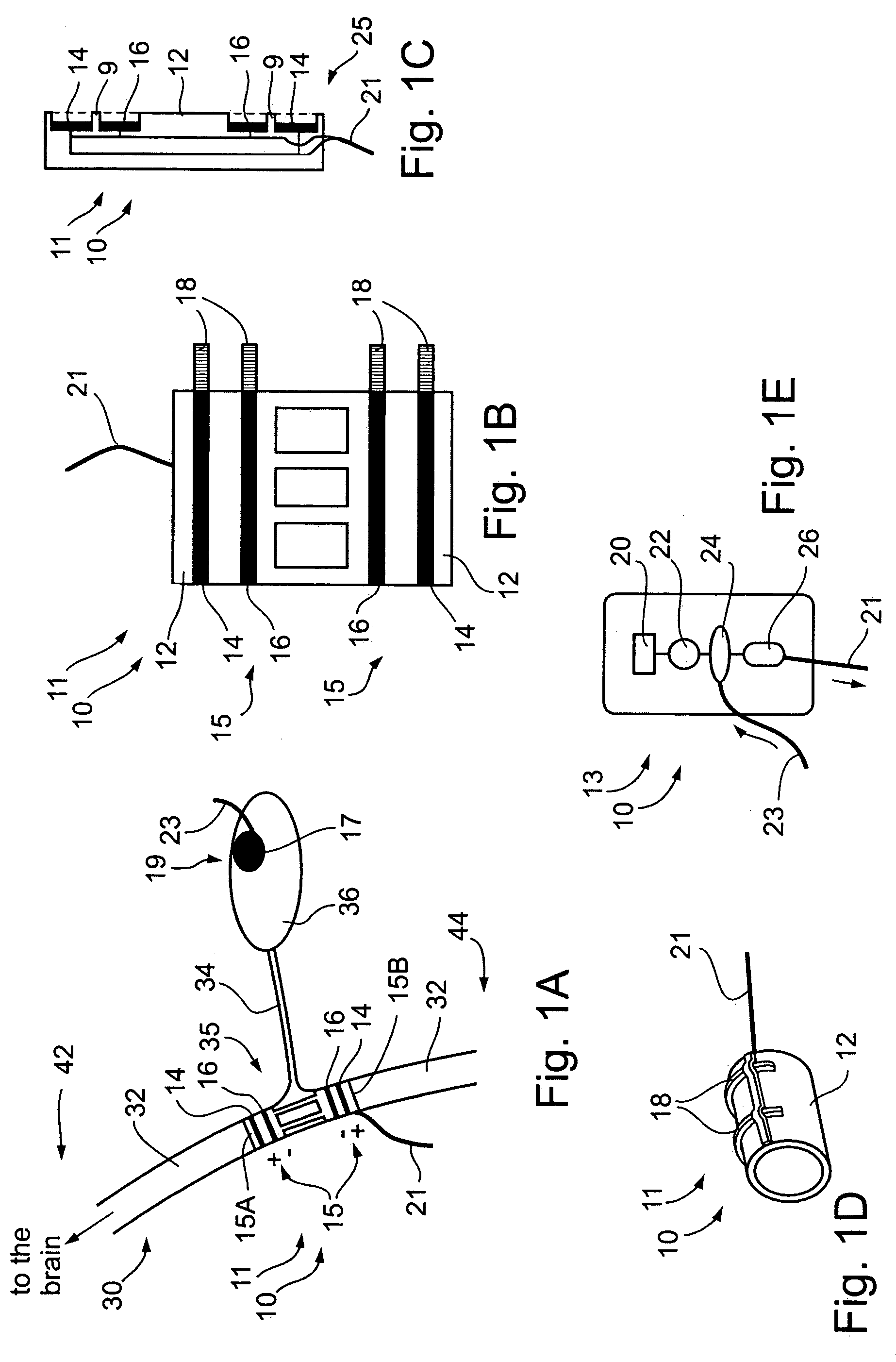
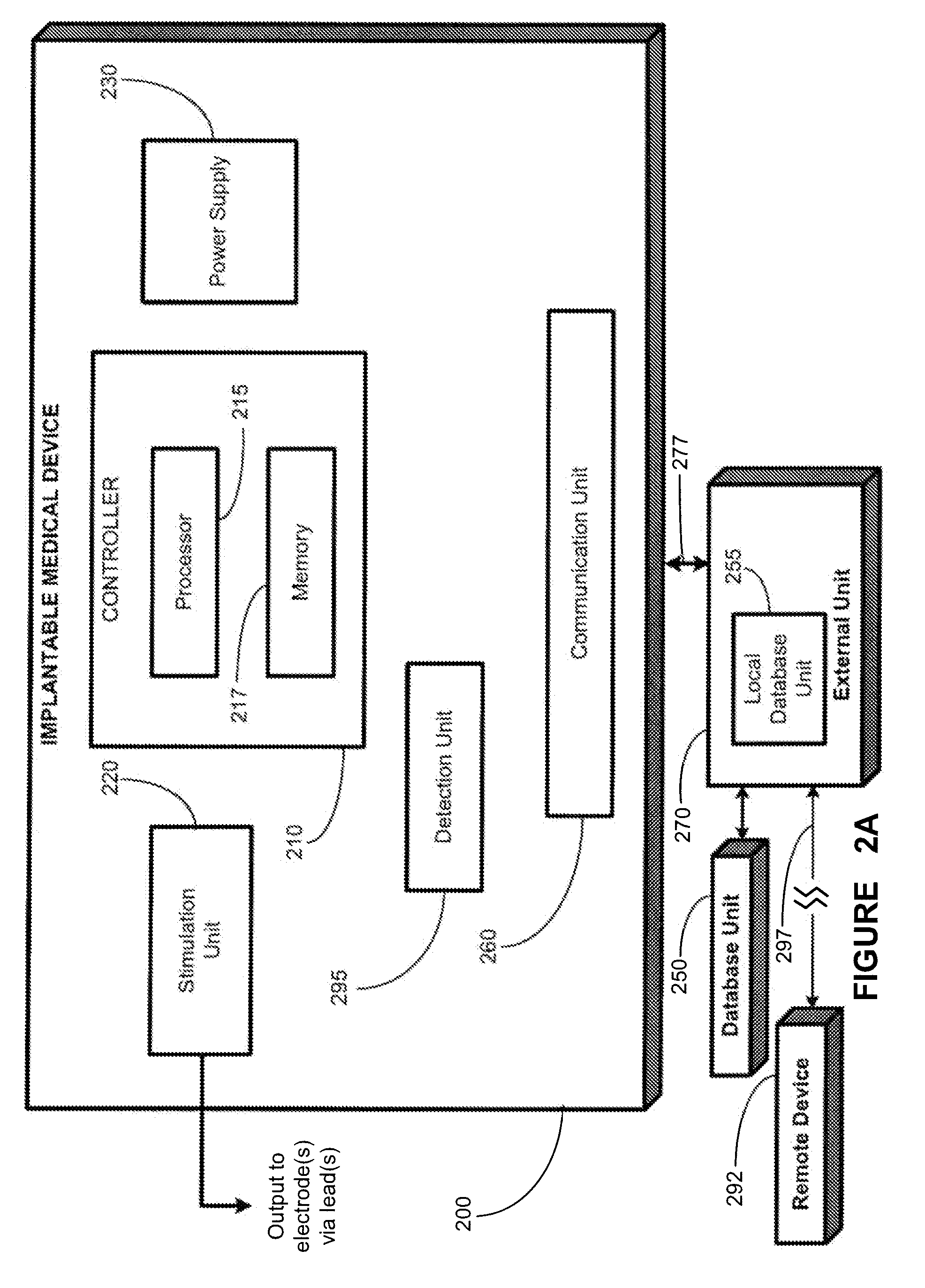
A dual electrode arrangement, is provided, wherein two, preferably unidirectional, electrode configurations flank a nerve junction from which a preselected nerve branch issues, proximally and distally to the junction, with respect to the brain. The arrangement is conducive to the following: generating efferent action-potential propagations, substantially restricted to the preselected nerve branch, inhibiting afferent action-potential propagations, from the preselected nerve branch, selectively generating action-potential propagations, in a subset of nerve fibers of a predetermined diameter range, substantially restricted to the preselected nerve branch, and selectively inhibiting action-potential propagations, in a subset of nerve fibers of a predetermined diameter range, substantially restricted to the preselected nerve branch. The dual electrode arrangement is further conducive to monitoring naturally-occurring, efferent action-potential propagations, heading towards the preselected nerve branch, and monitoring naturally-occurring, afferent action-potential propagations, from the preselected nerve branch. The unidirectional electrode configurations may be monopolar, bipolar, tripolar, or multipolar. Communication with extracorporeal stations, and closed loop operations are also provided.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
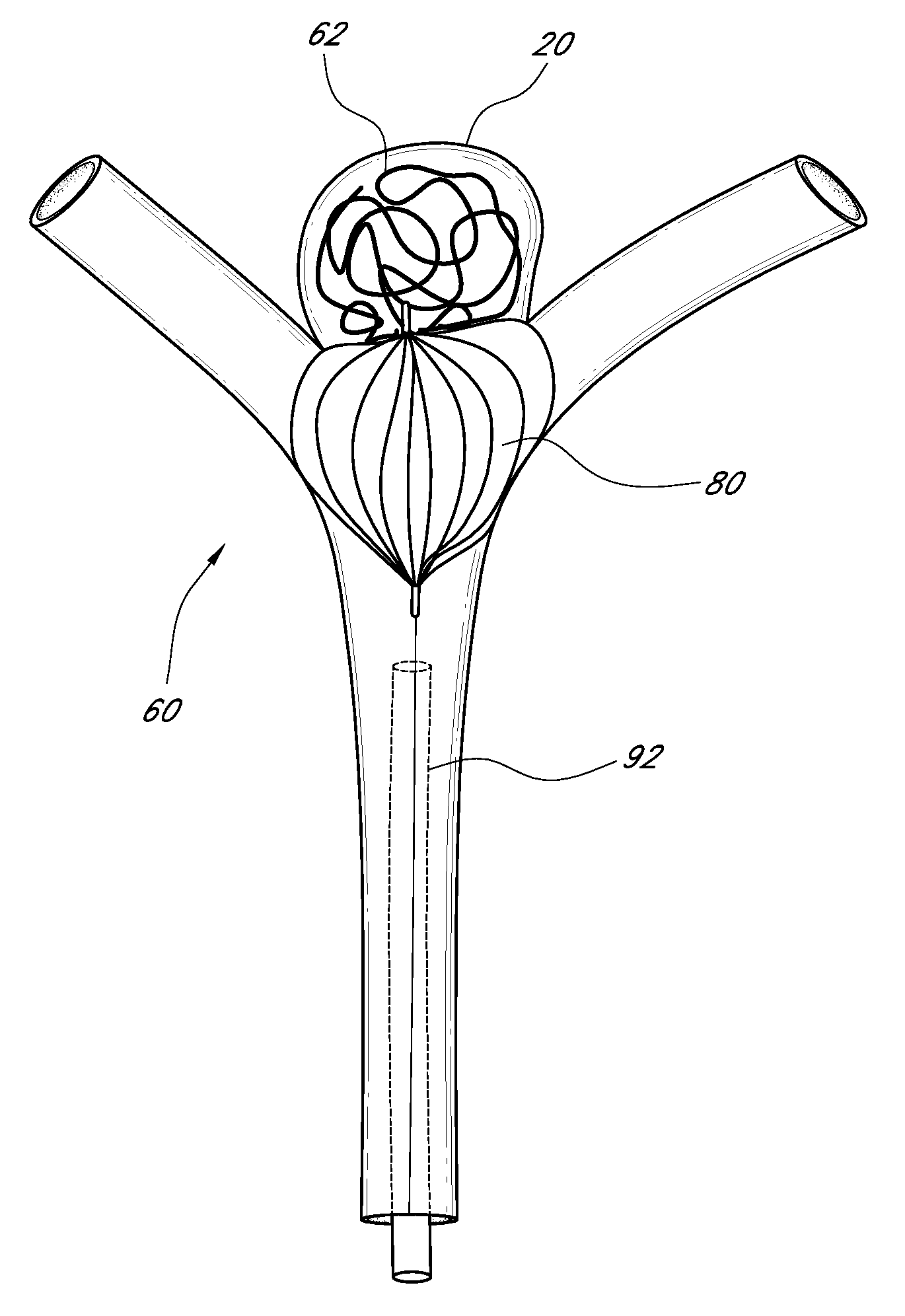
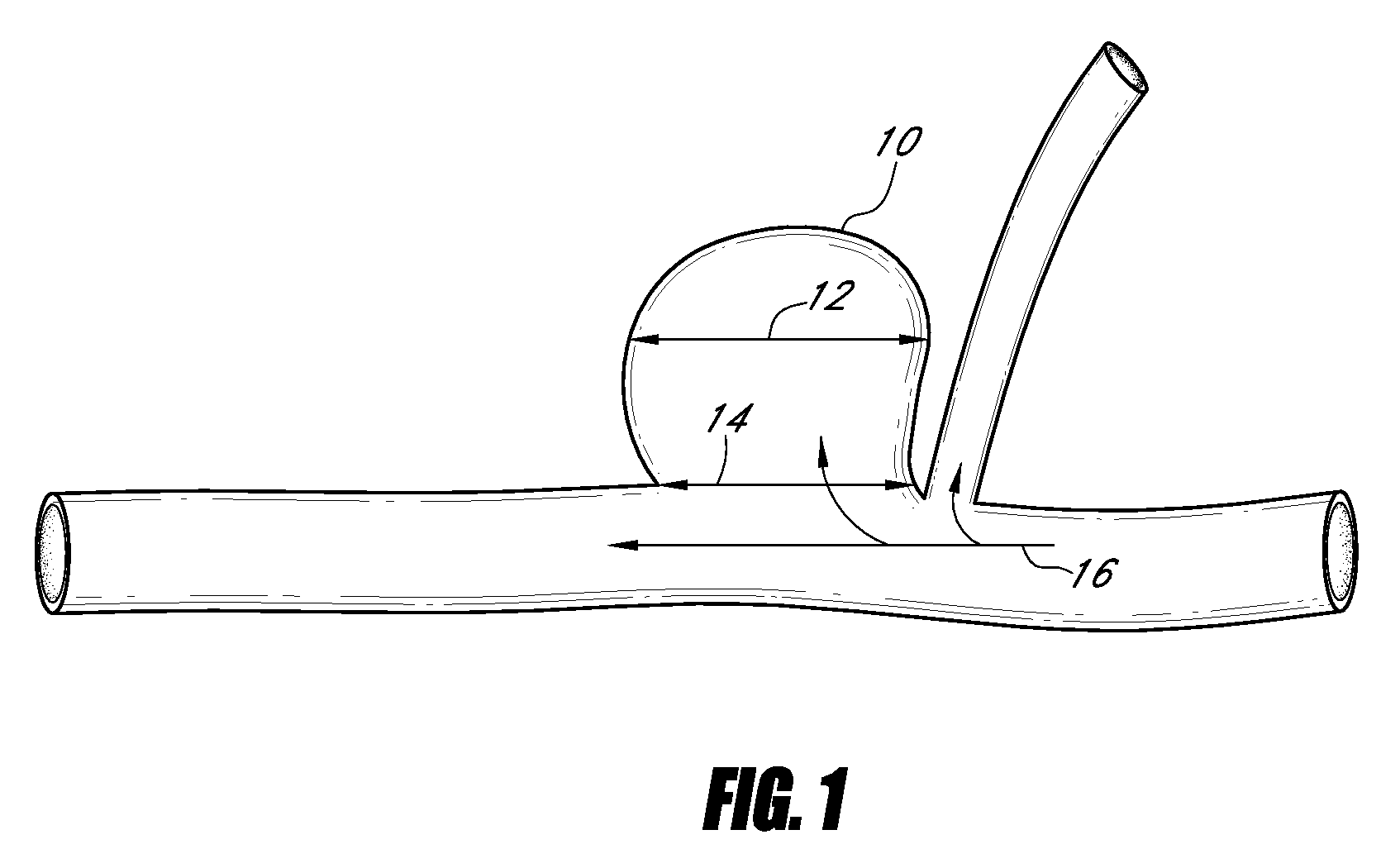
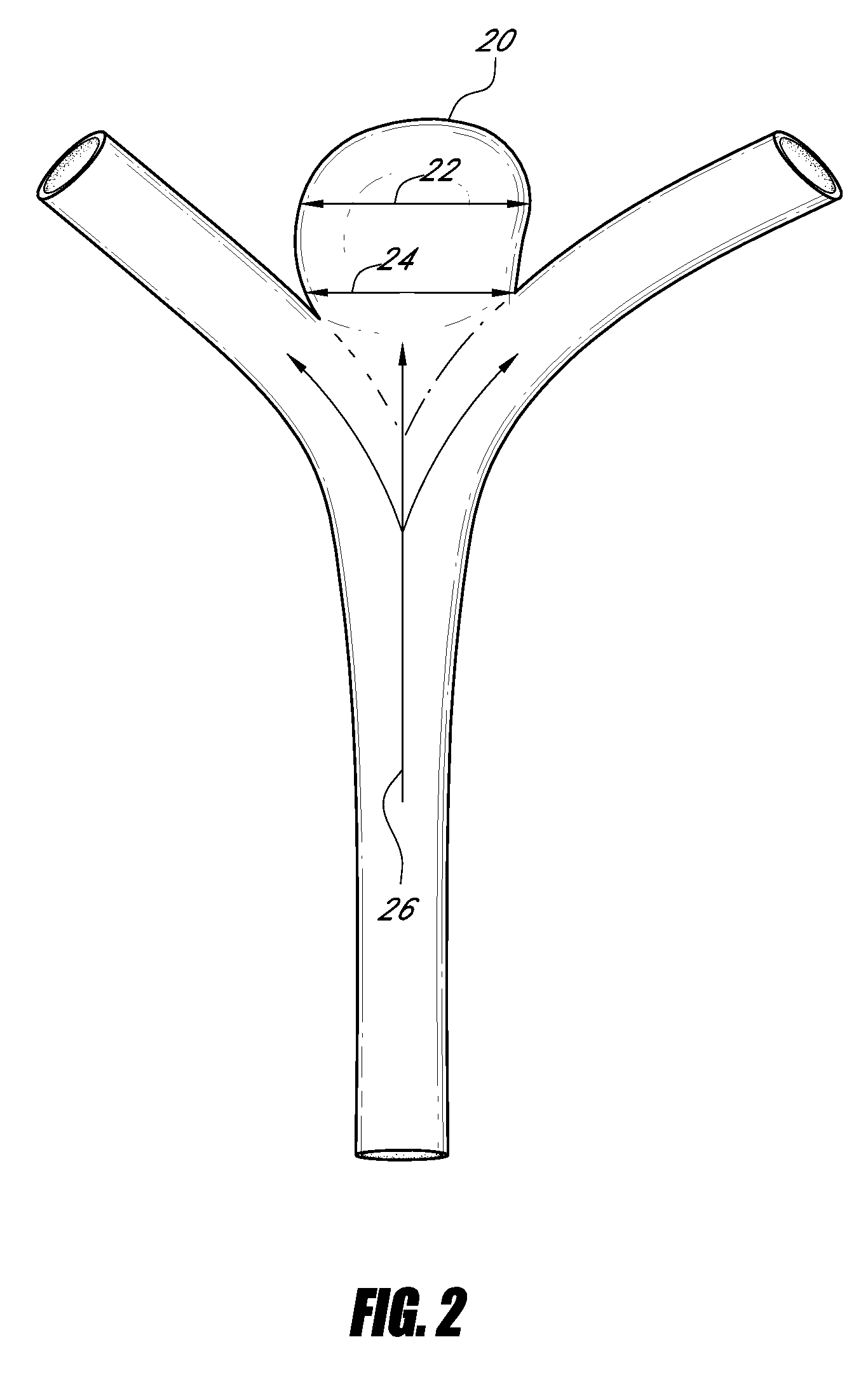
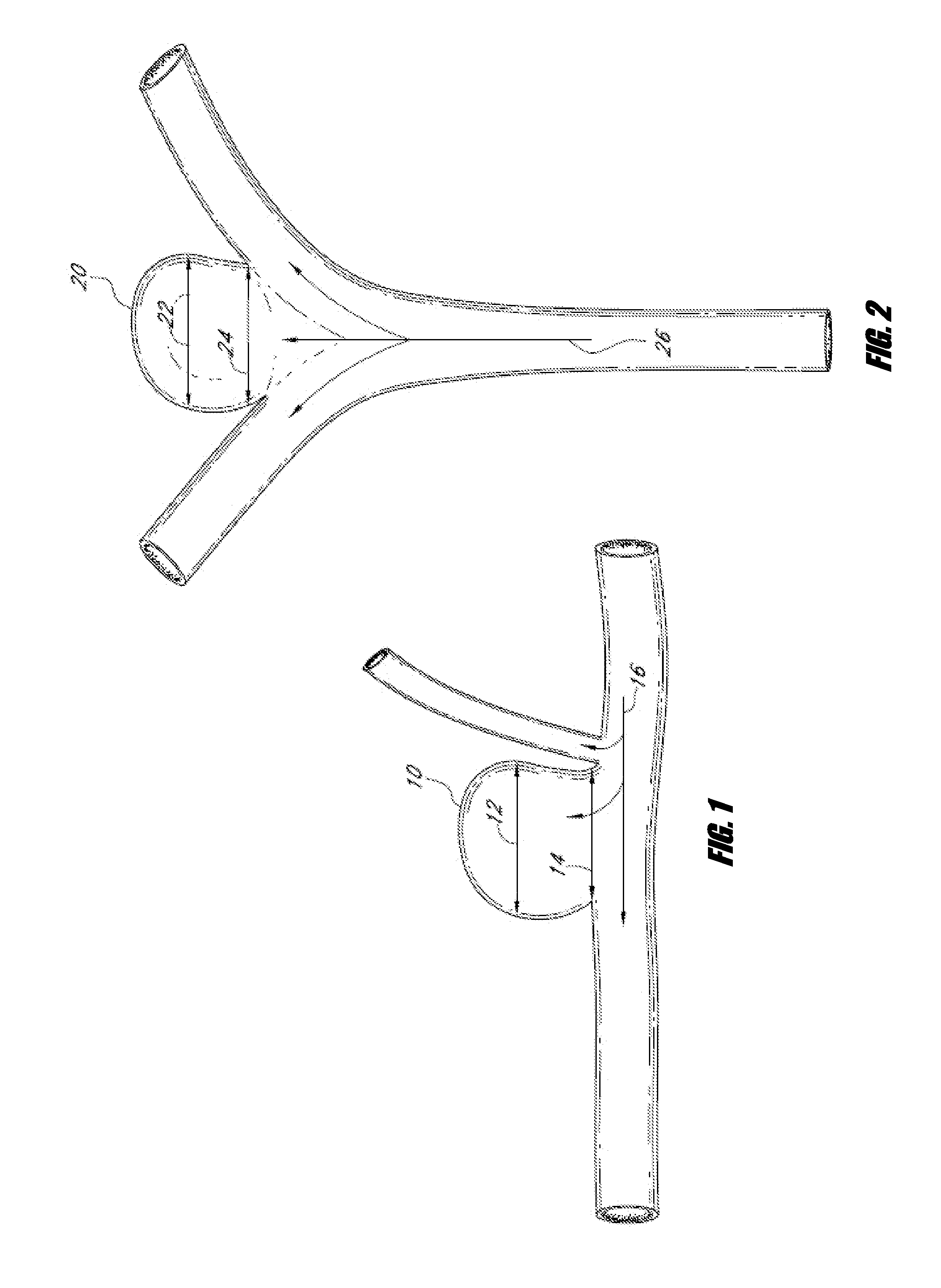
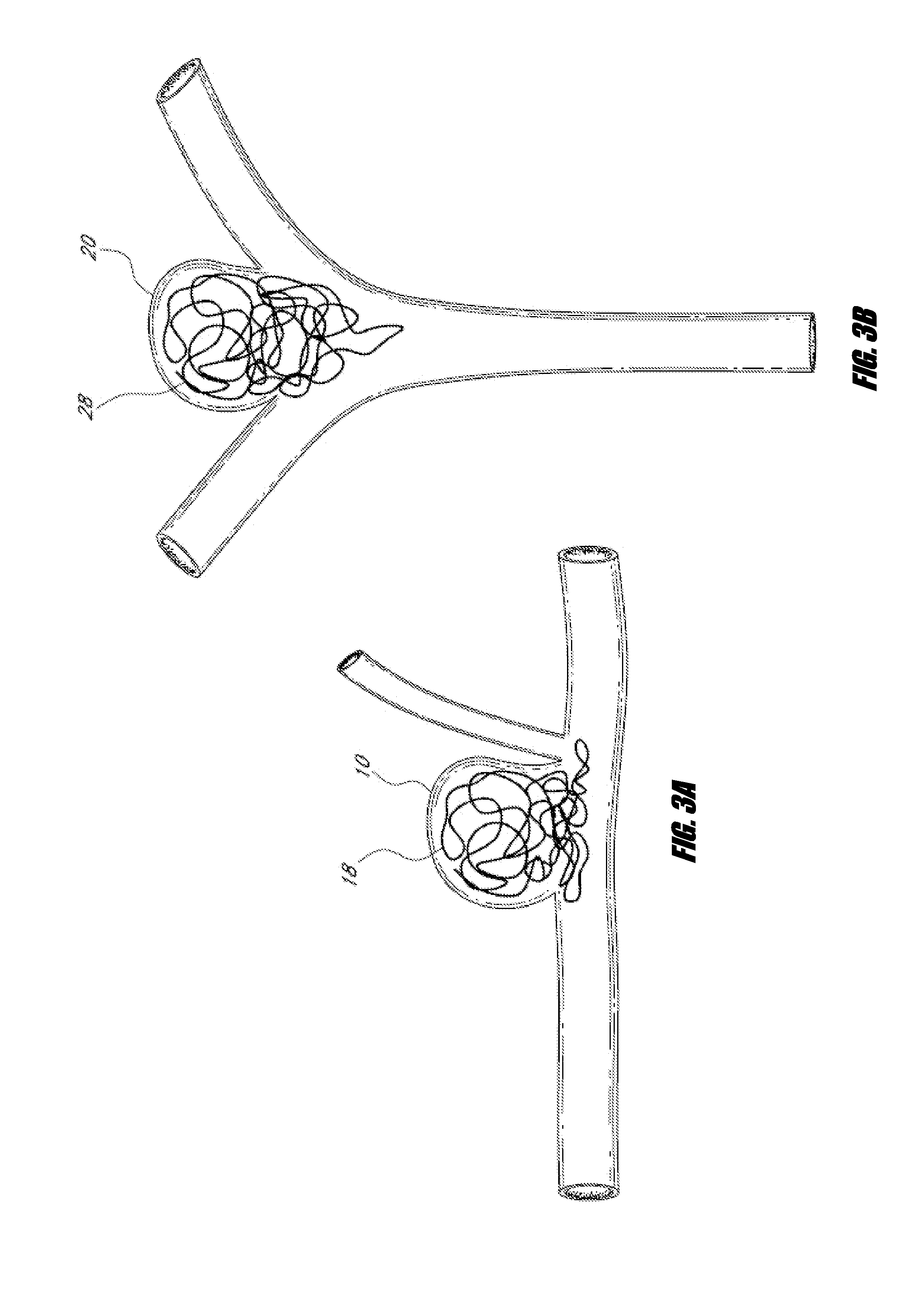
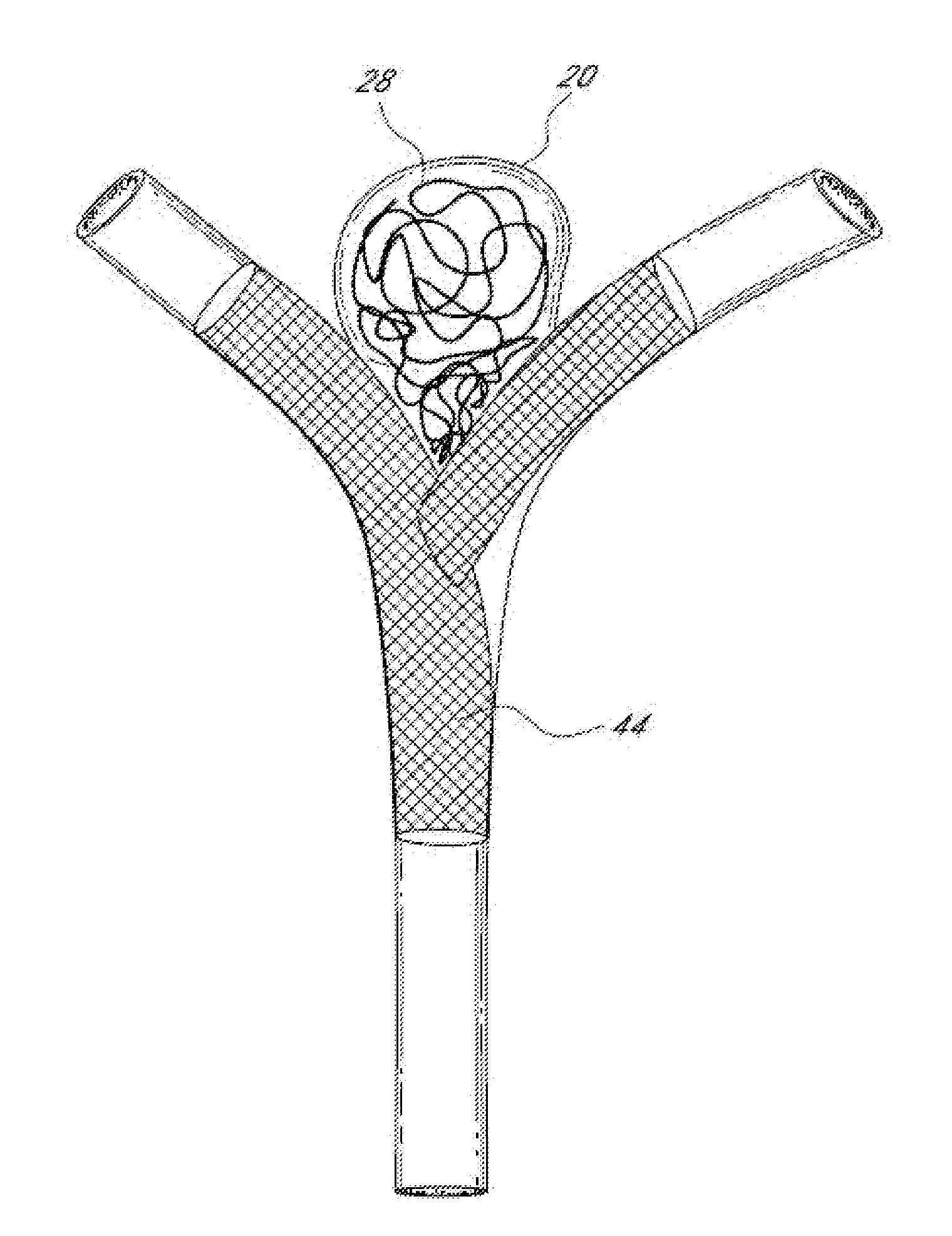
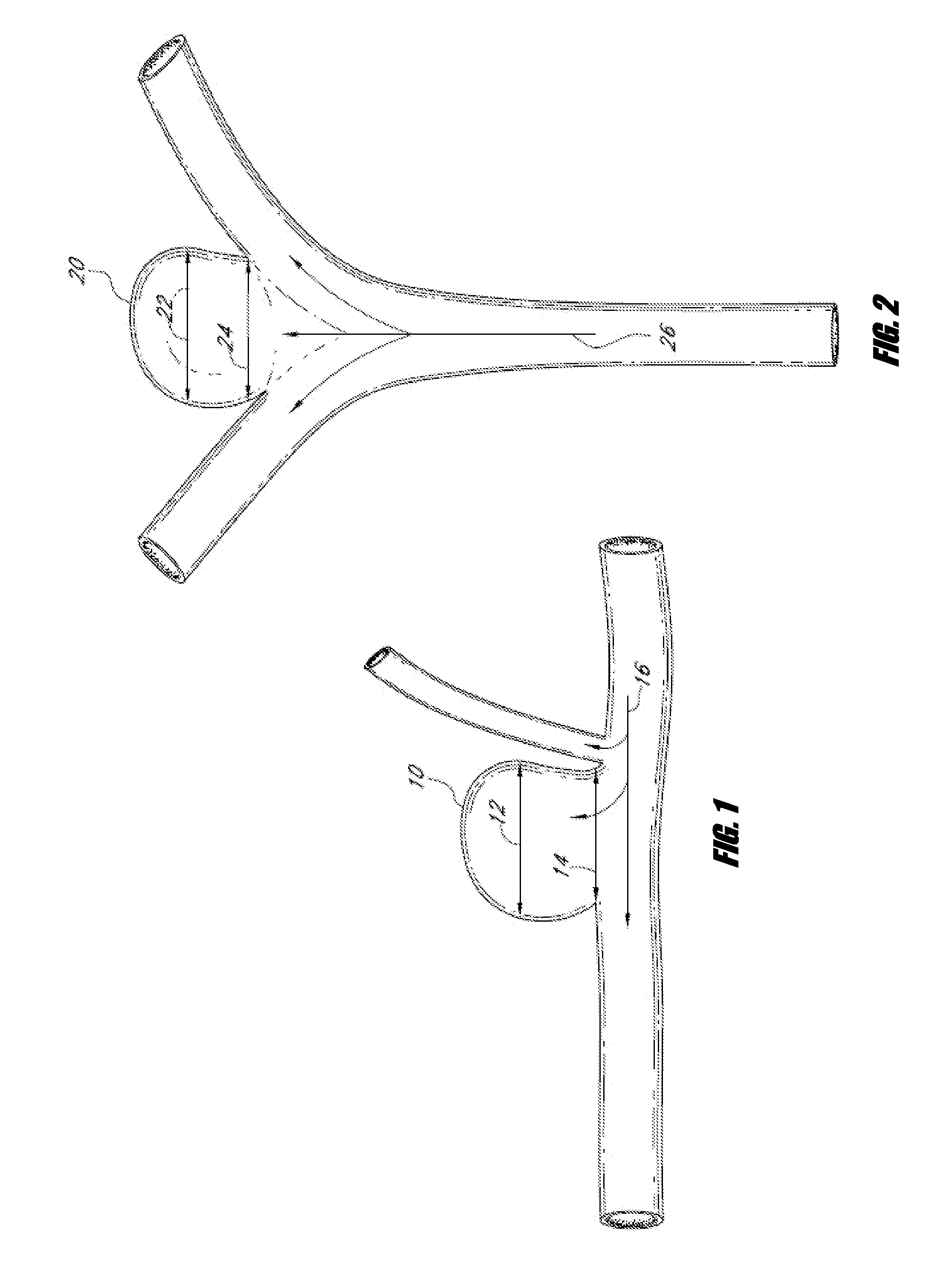
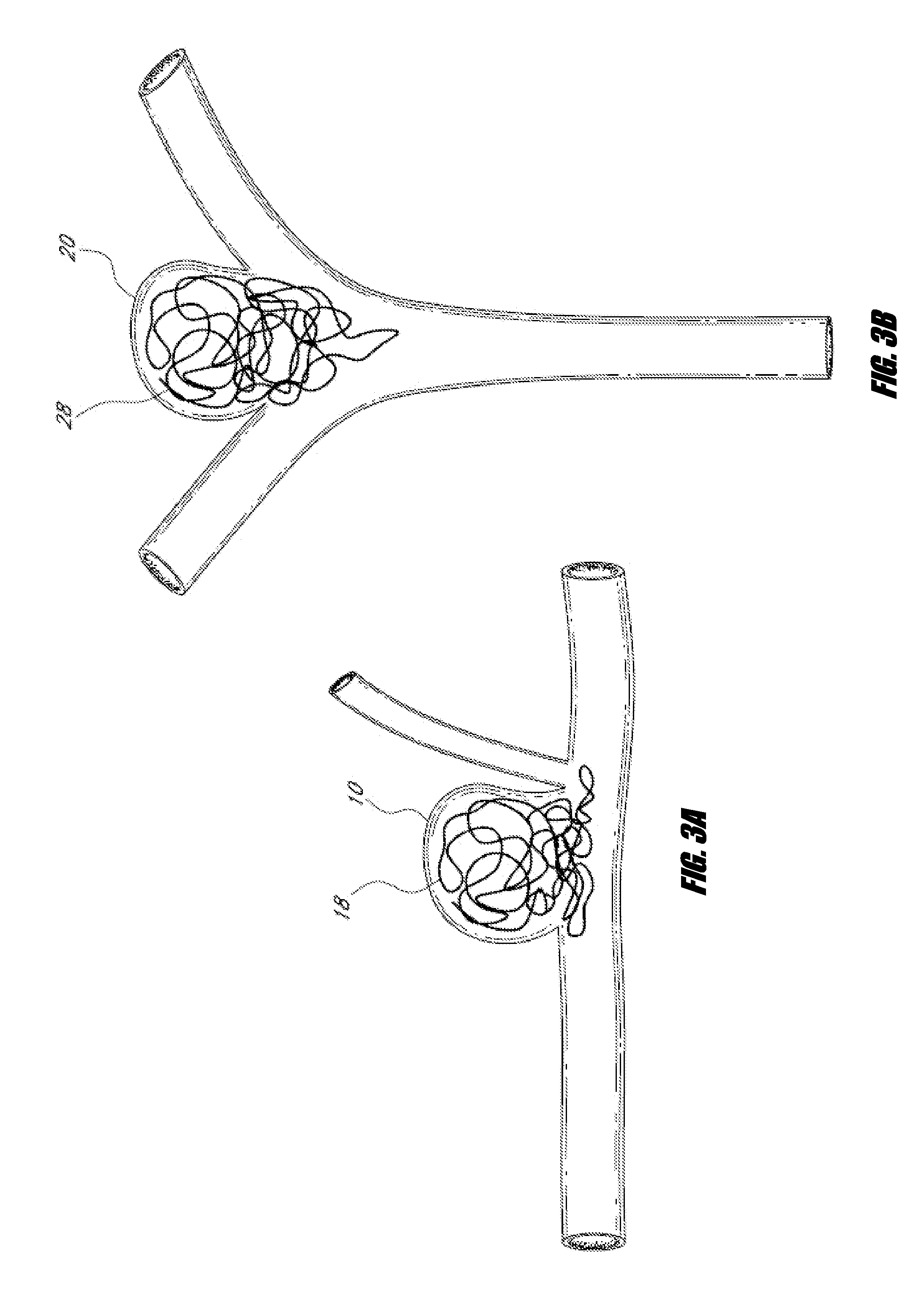
Vascular remodeling device
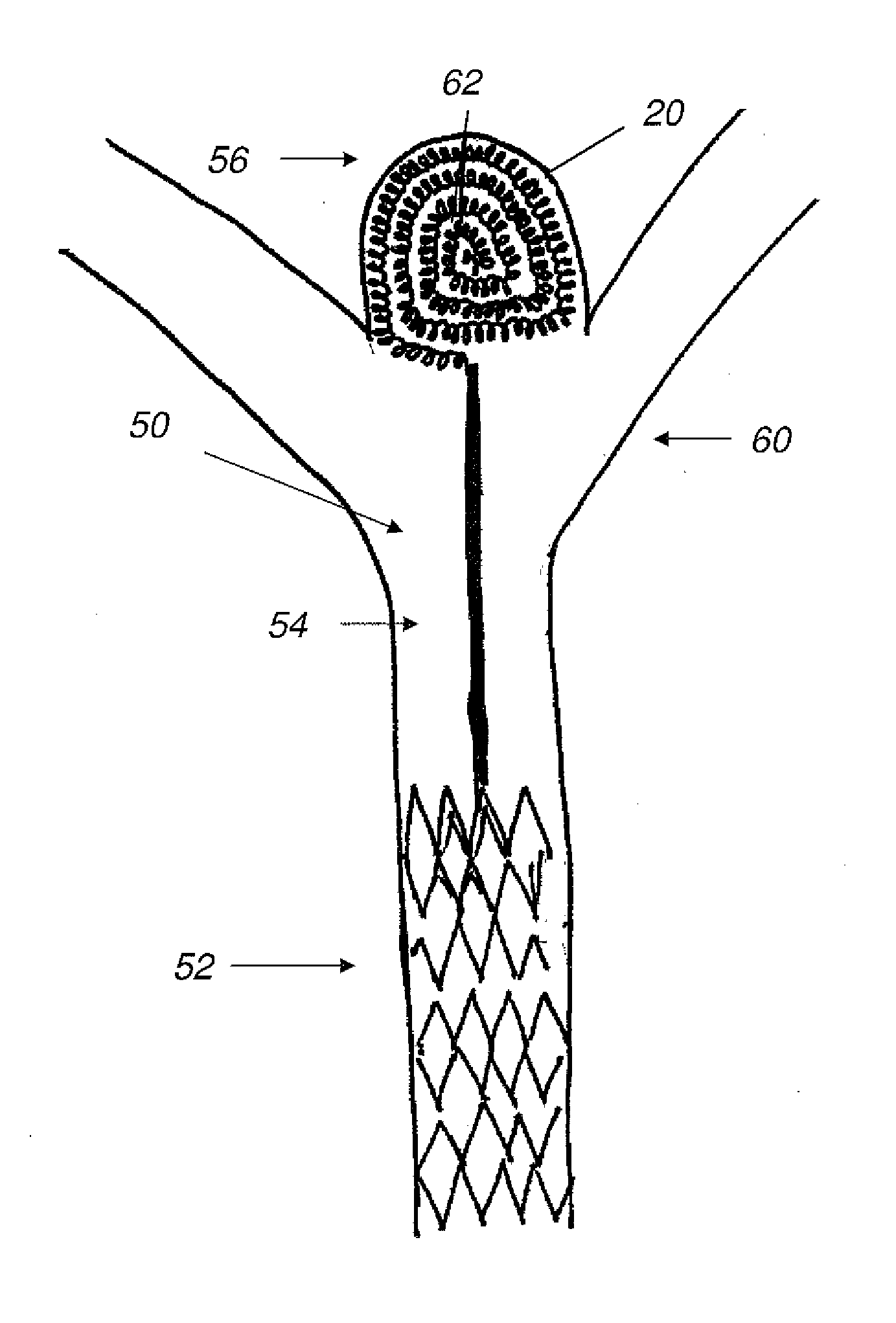
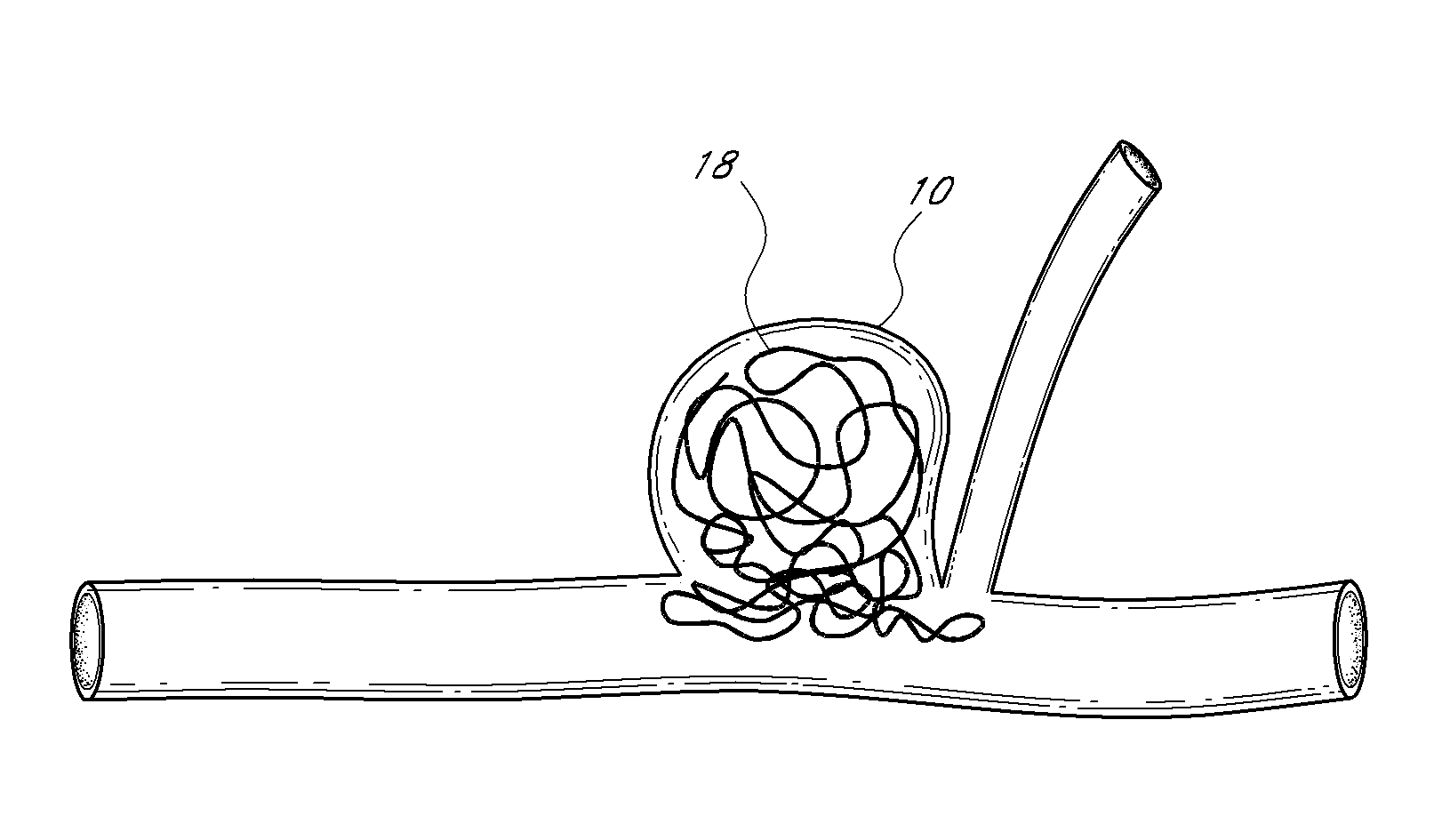
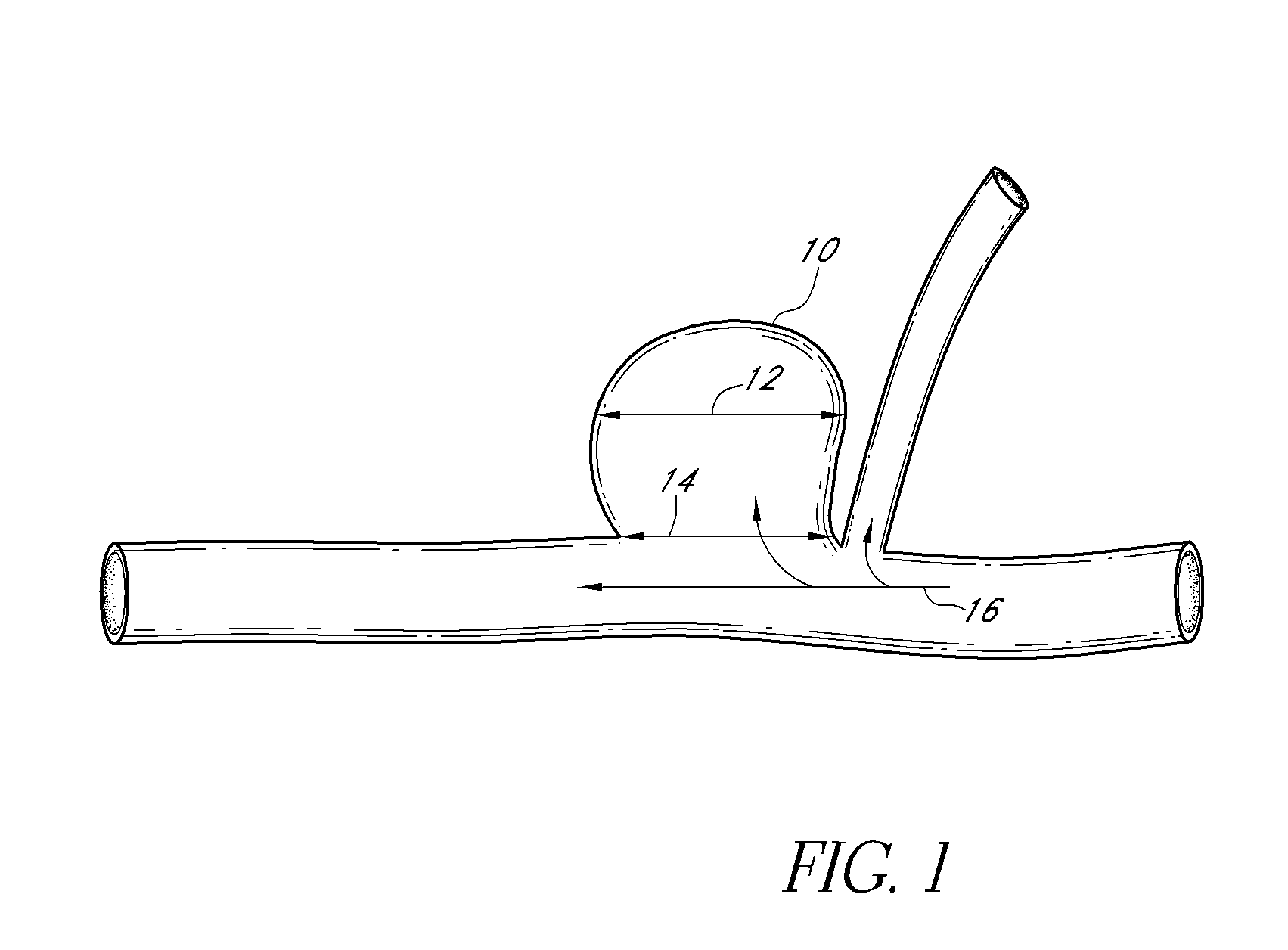
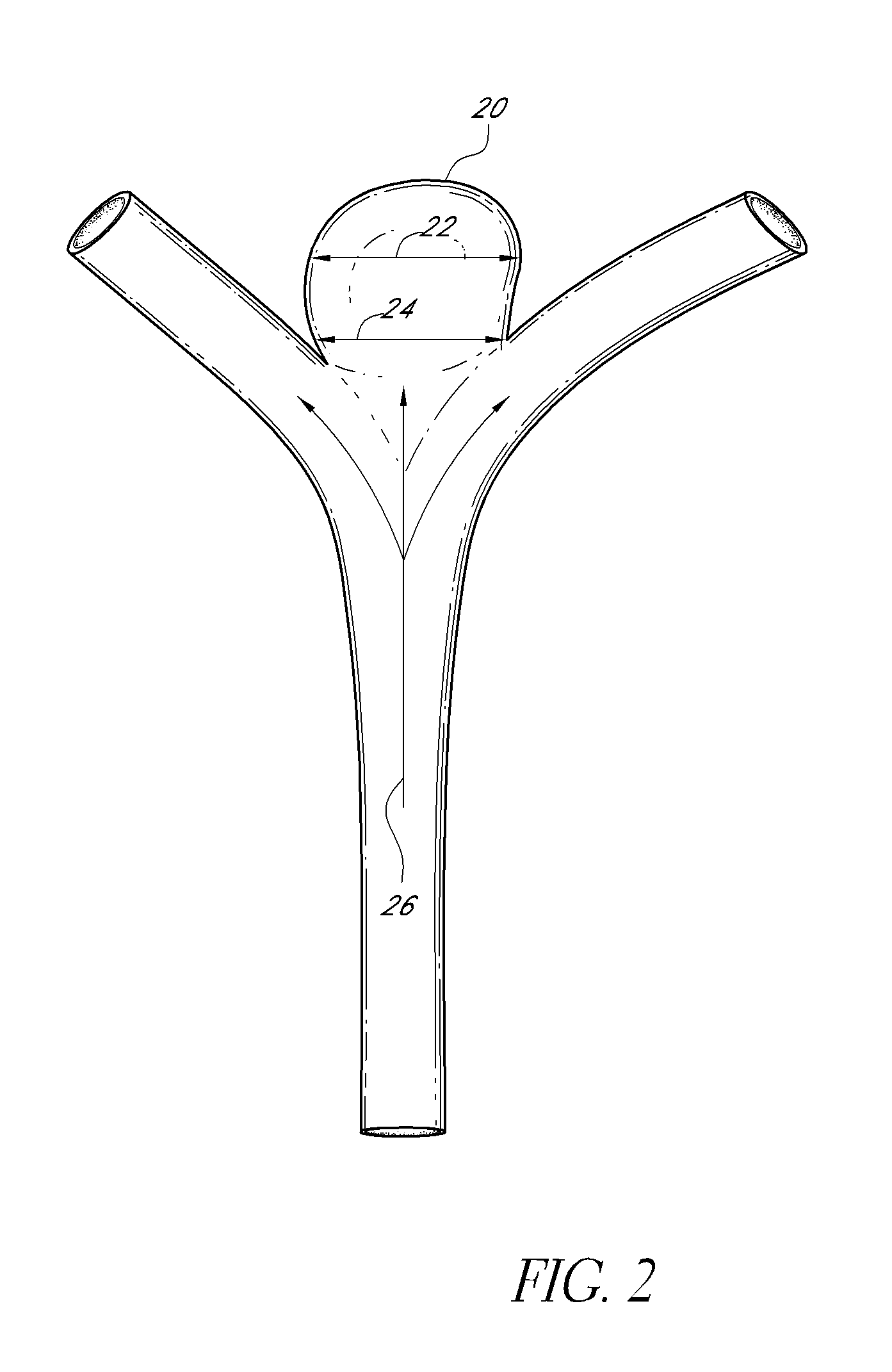
A generally spherical vascular remodeling device is permanently positionable at a junction of afferent and efferent vessels of a bifurcation having an aneurysm. After positioning the device at the junction to substantially conform the device to the shape of the junction, the device acts as a scaffolding to inhibit herniation of objects out of the aneurysm and the device permits perfusion to the efferent vessels. Positioning the device may include deployment and mechanical or electrolytic release from a catheter. Embolic material may be inserted in the aneurysm before or after positioning the device. The device may have a first end, a second end substantially opposite to the first end, and a plurality of filaments extending between and coupled at the first end and the second end. Such devices may be football shaped, pumpkin shaped, or twisted. The device may include a plurality of loops forming a generally spherical shape.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method and apparatus for preventing obstructive sleep apnea
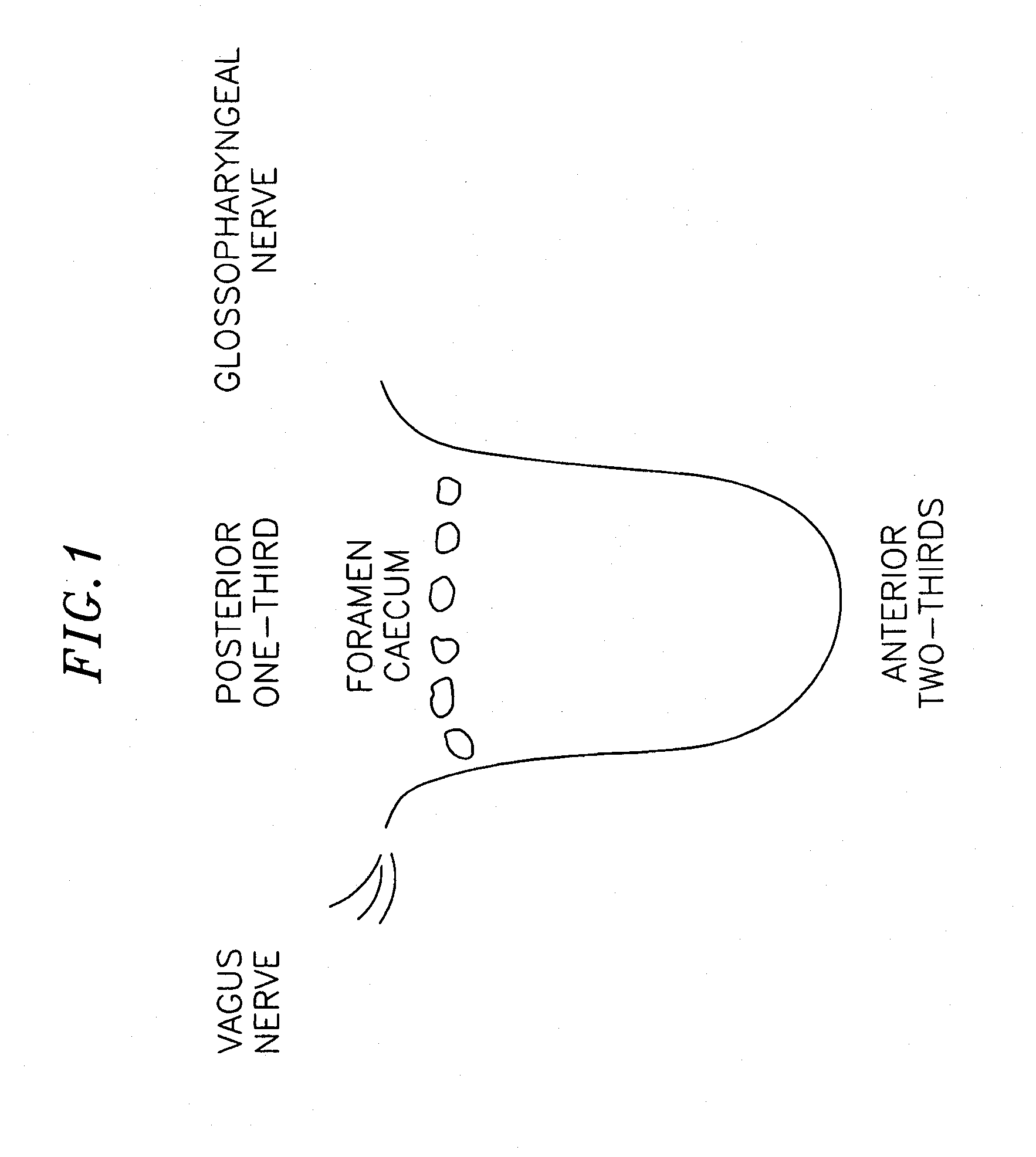
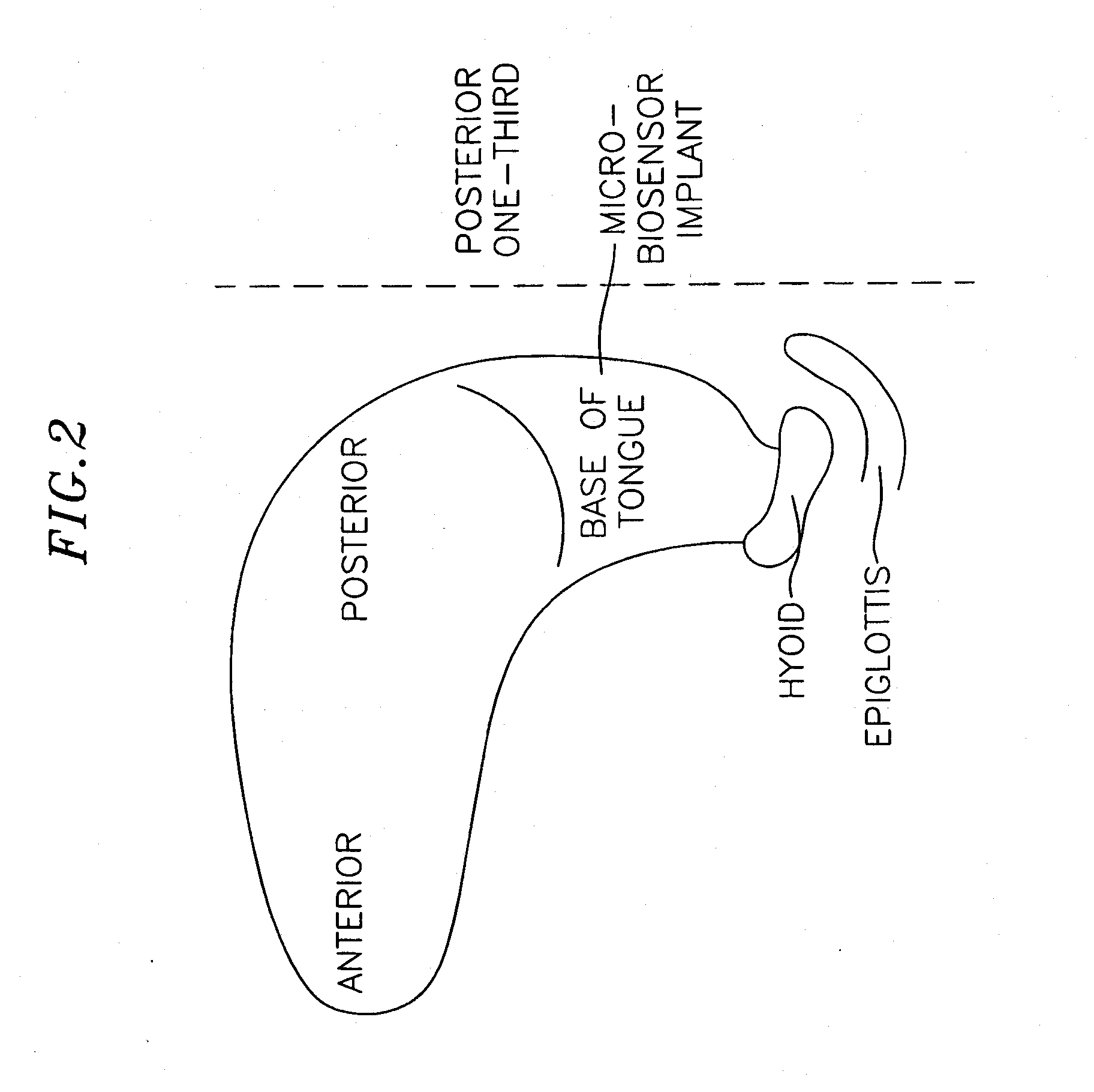
InactiveUS20070173893A1Patient compliance is goodRelieve symptomsElectrotherapyArtificial respirationMuscle toneGenioglossus muscle
A method and device for creating an afferent stimulus for preventing obstructive sleep apnea are disclosed. The device includes at least one electrode and a stimulator, of which at least one electrode stimulates the genioglossus muscle of a patient having obstructive sleep apnea. The electrode is capable of conducting selected electrical stimulation generated by the stimulator, and the system is capable of delivering the selected electrical stimulation during a selected time of day. The electrical stimulation is selected to maintain sufficient muscle tone of the genioglossus muscle to prevent it from obstructing the airway during sleep, preferably at a stimulus intensity low enough to avoid awakening the patient during sleep. A removable mouthpiece having a battery, at least one electrode, and a controller, and optionally a sensor, can be used for providing the stimulation.
Owner:PITTS WALTER C
Identification of electrodes for nerve stimulation in the treatment of eating disorders
A method and apparatus for treatment of an eating disorder includes electrically, mechanically and / or pharmaceutically / chemically stimulating a of the vagus nerve of the lower esophagus, cardia, esophageal / cardia junction, cardia / fundus junction or upper stomach so as to induce afferent action potentials on the vagus nerve. The device may be noninvasively adjusted after implantation to provide increased or decreased restriction on the patient's gastrointestinal tract. Each stimulus may be administered as a series of programmed pulses of defined amplitude, duration and period, to evoke a responsive signal to the brain by the target nerve, effective for producing a temporary feeling of satiety in the person. An implantable stimulus generator may be operatively coupled to a nerve electrode, pressure device or chemical outlet to apply a defined signal to a selected nerve branch. The implantable stimulus generator is programmable to allow clinician programming of defined signal parameters effective to treat the eating disorder of the patient. Methods are also provided to identify electrodes nearest to a branch of the vagus nerve to apply an electrical stimulation signal with improved efficiency.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
System and method for regulating blood pressure and electrolyte balance
The present invention is an apparatus and method for controlling blood pressure by stimulating the cardiac afferent sympathetic nerves. The invention may be implemented in a medical device having a pressure sensor for sensing blood pressure, an electrode for providing electrical signals to the cardiac afferent sympathetic nerves, and a controller for providing signals to the electrode as a function of blood pressure signals received from the pressure sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Vascular remodeling device
ActiveUS20120143237A1Good flexibilityGood wall appositionStentsDilatorsIliac AneurysmEmbolization material
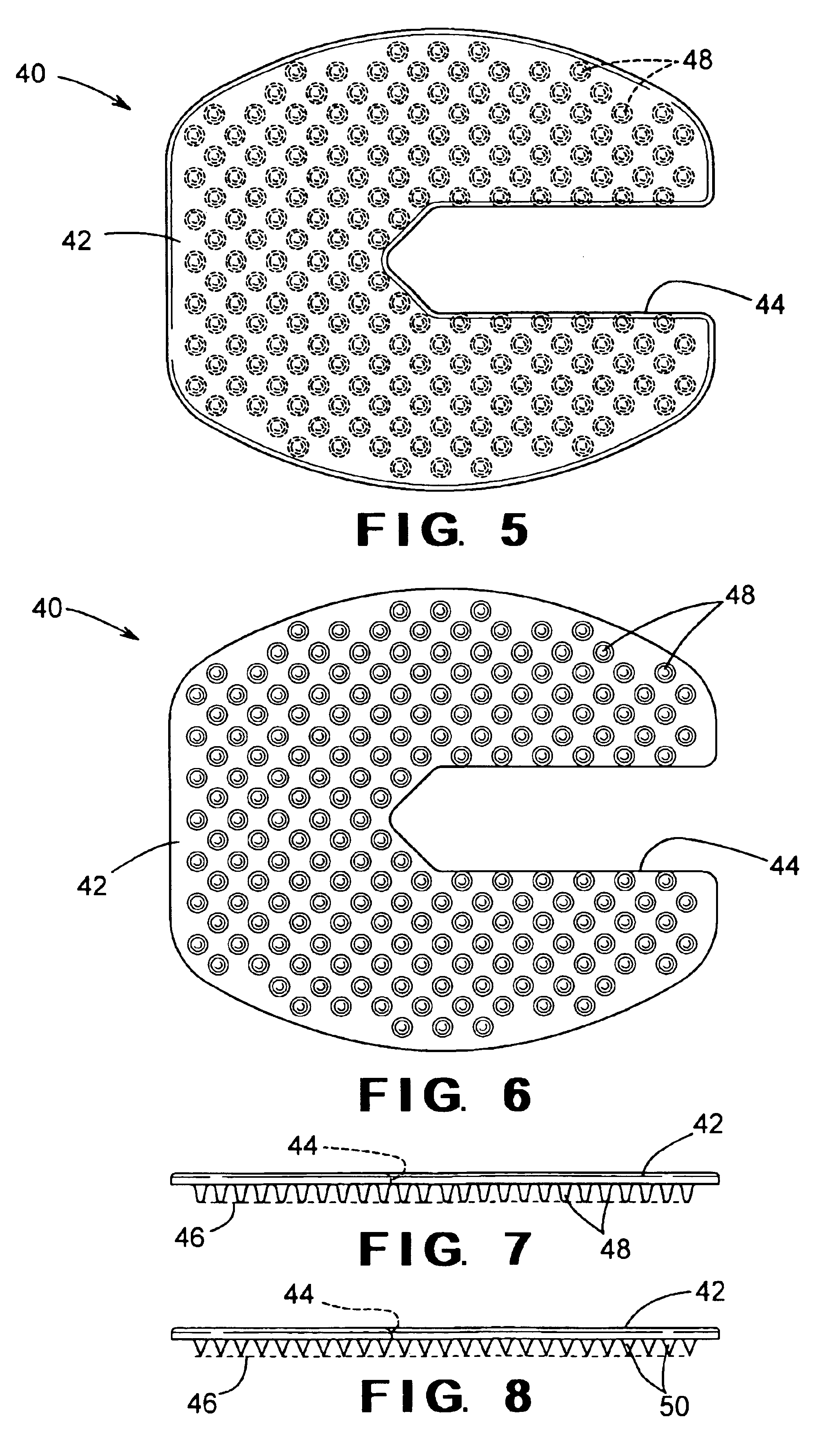
Described herein are vascular remodeling devices that include a proximal section, an intermediate section, and a distal section. During deployment, the proximal section can expand from a compressed delivery state to an expanded state and anchors the device in an afferent vessel of a bifurcation. The distal section expands from the compressed delivery state to an expanded state that may be substantially planar, approximately semi-spherical, umbrella shaped, or reverse umbrella shaped. The distal section is positioned in a bifurcation junction across the neck of an aneurysm or within an aneurysm. The intermediate section allows perfusion to efferent vessels. Before or after the device is in position, embolic material may be used to treat the aneurysm. The distal section can act as a scaffolding to prevent herniation of the embolic material. The device can be used for clot retrieval with integral distal embolic protection.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
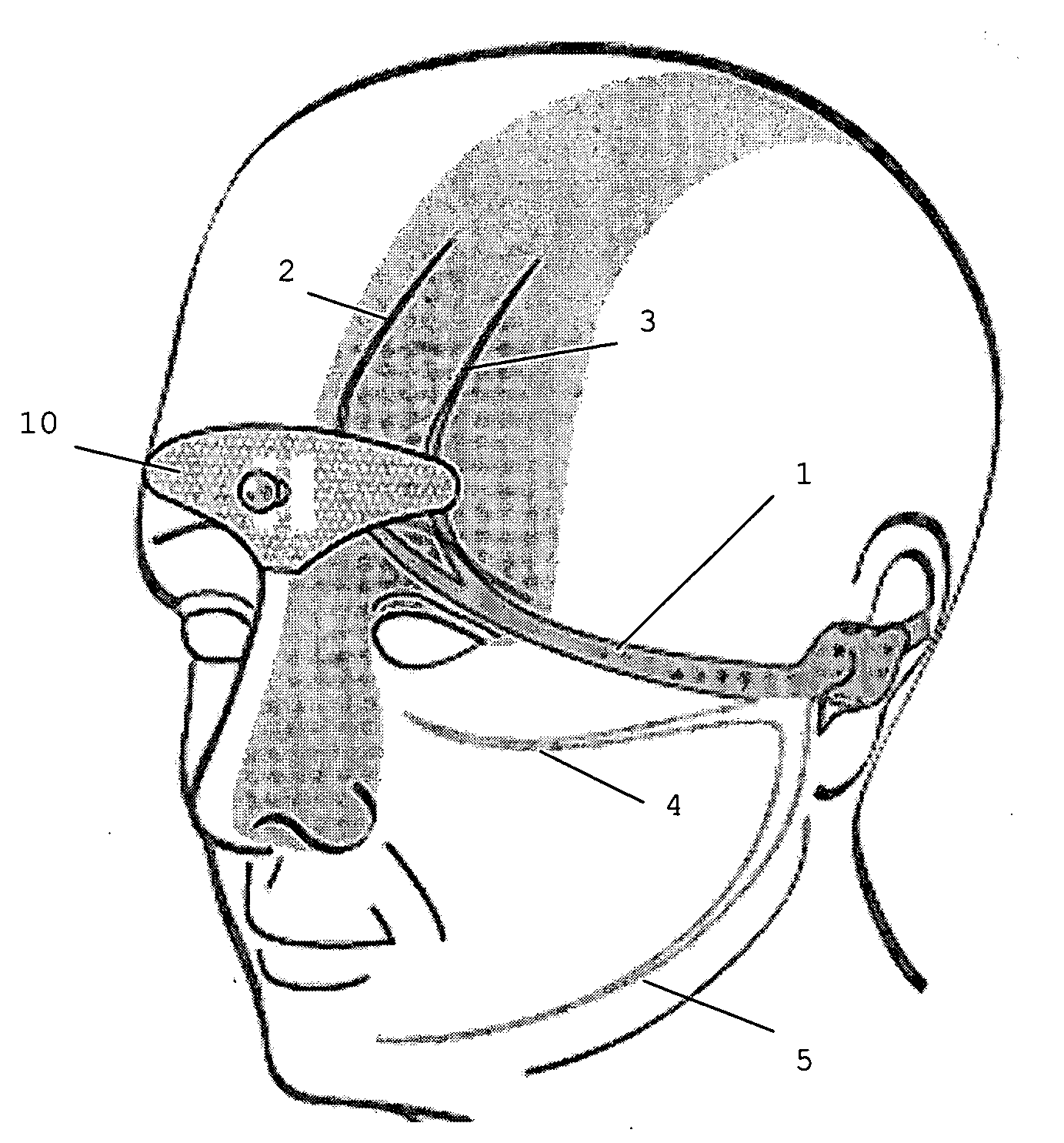
Device for the electrotherapeutic treatment of tension headaches
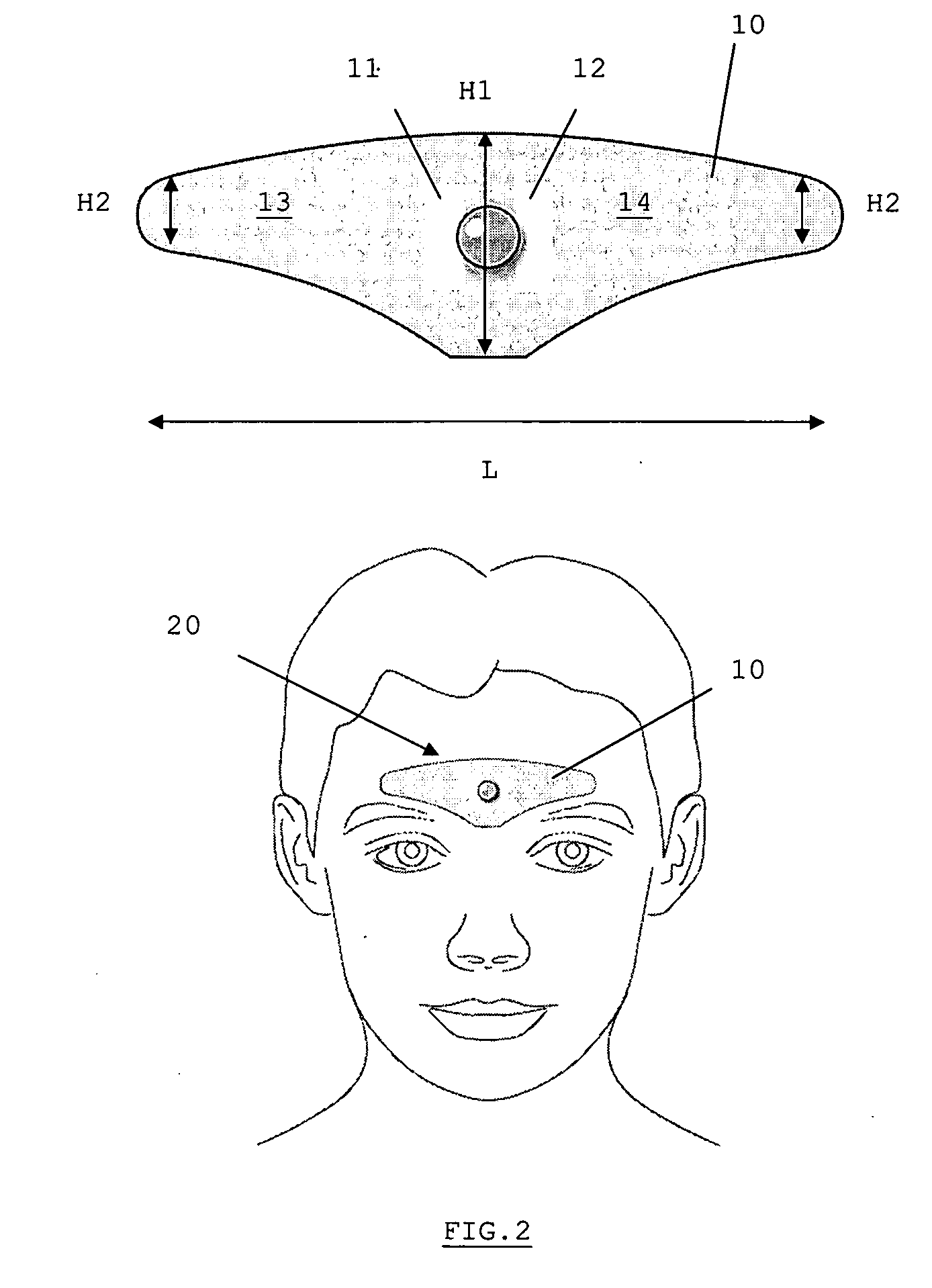
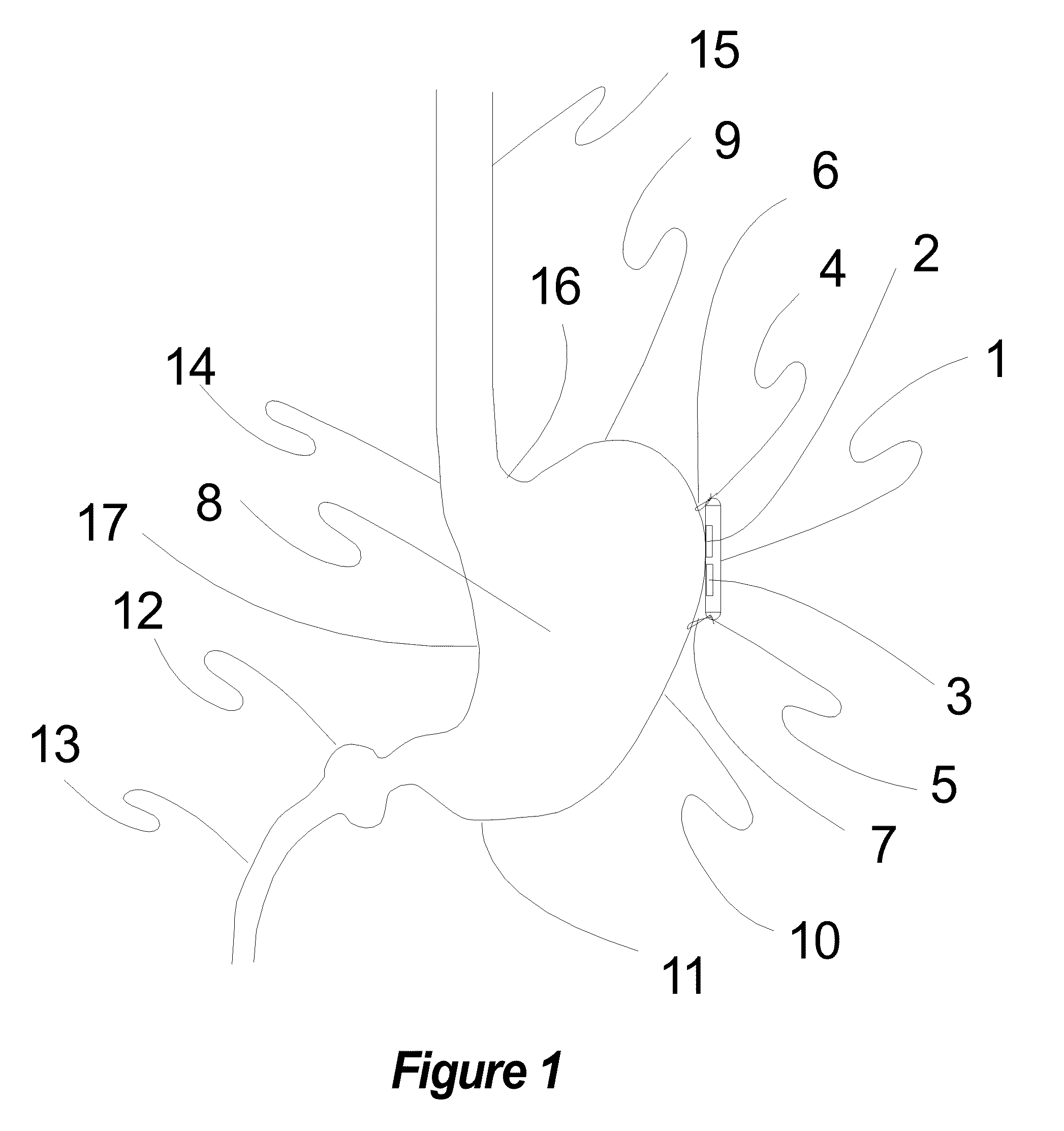
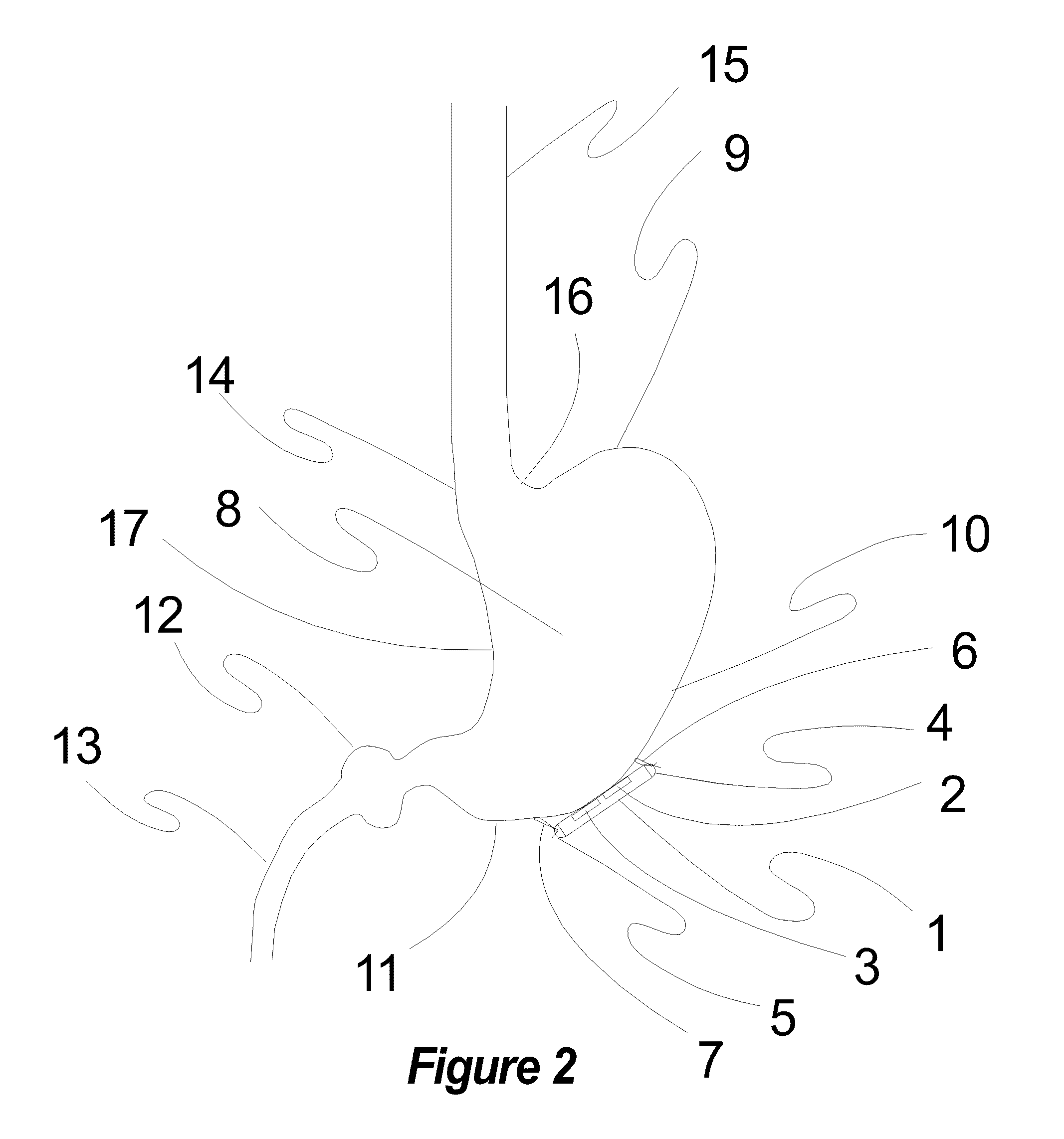
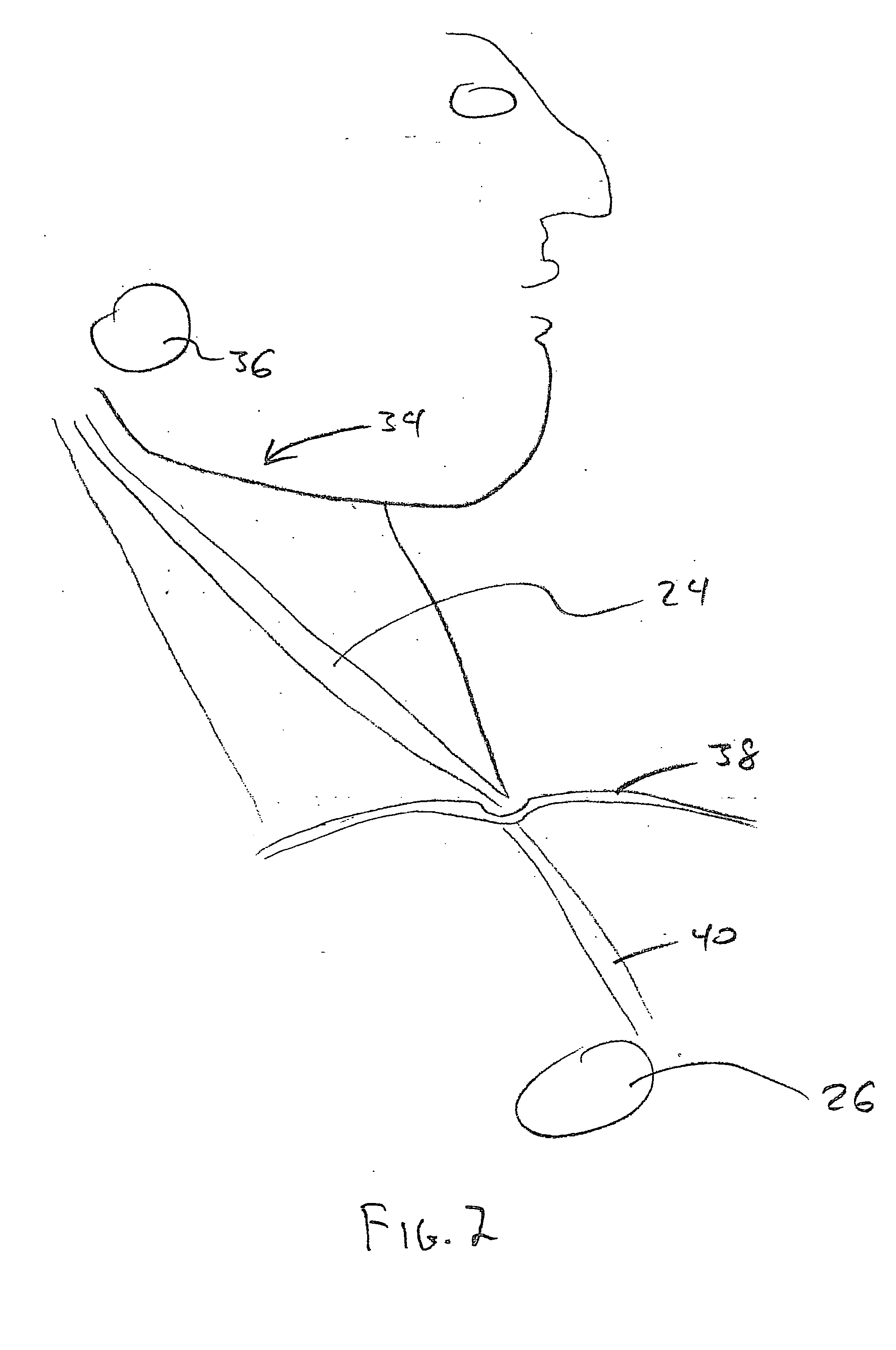
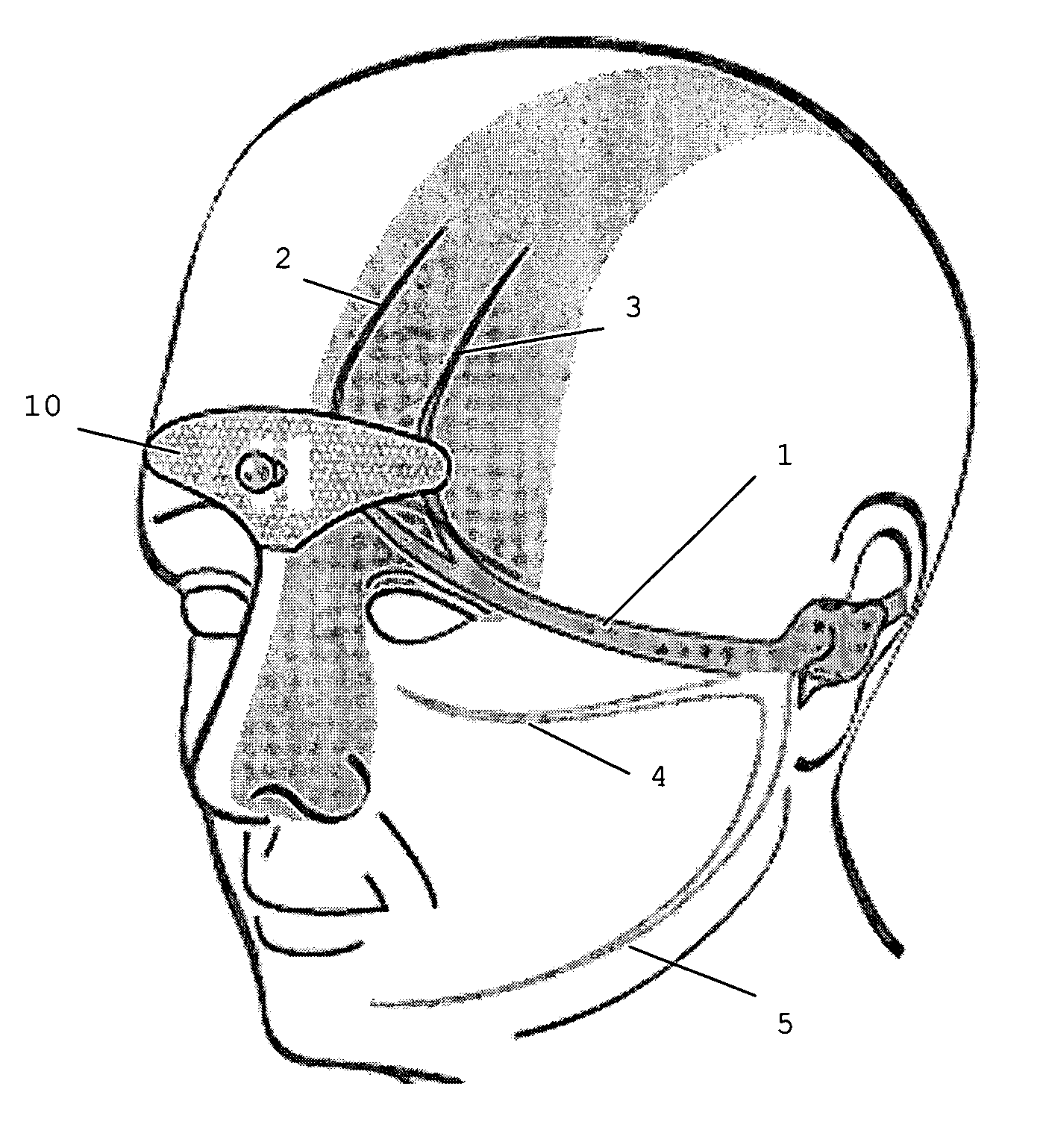
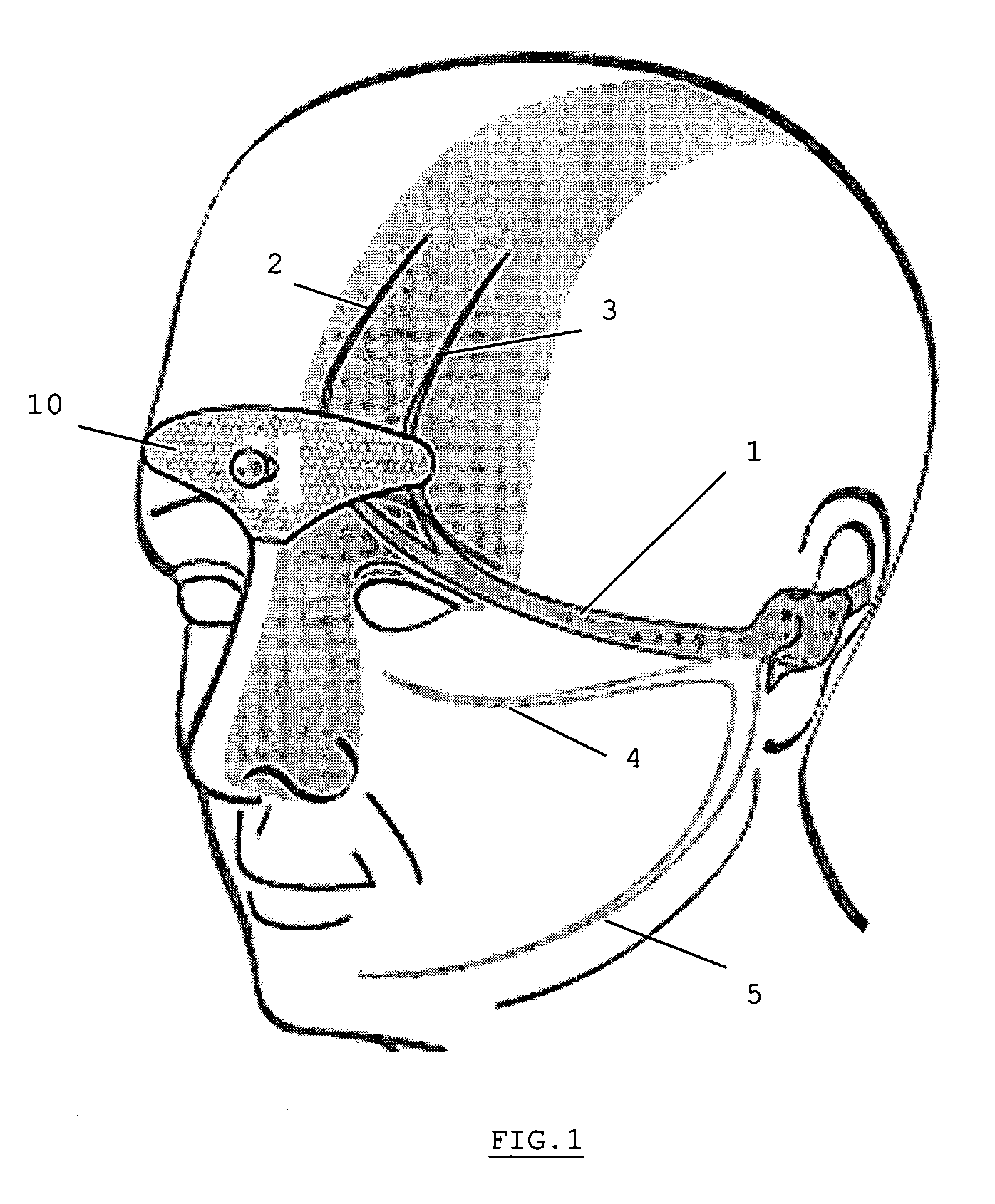
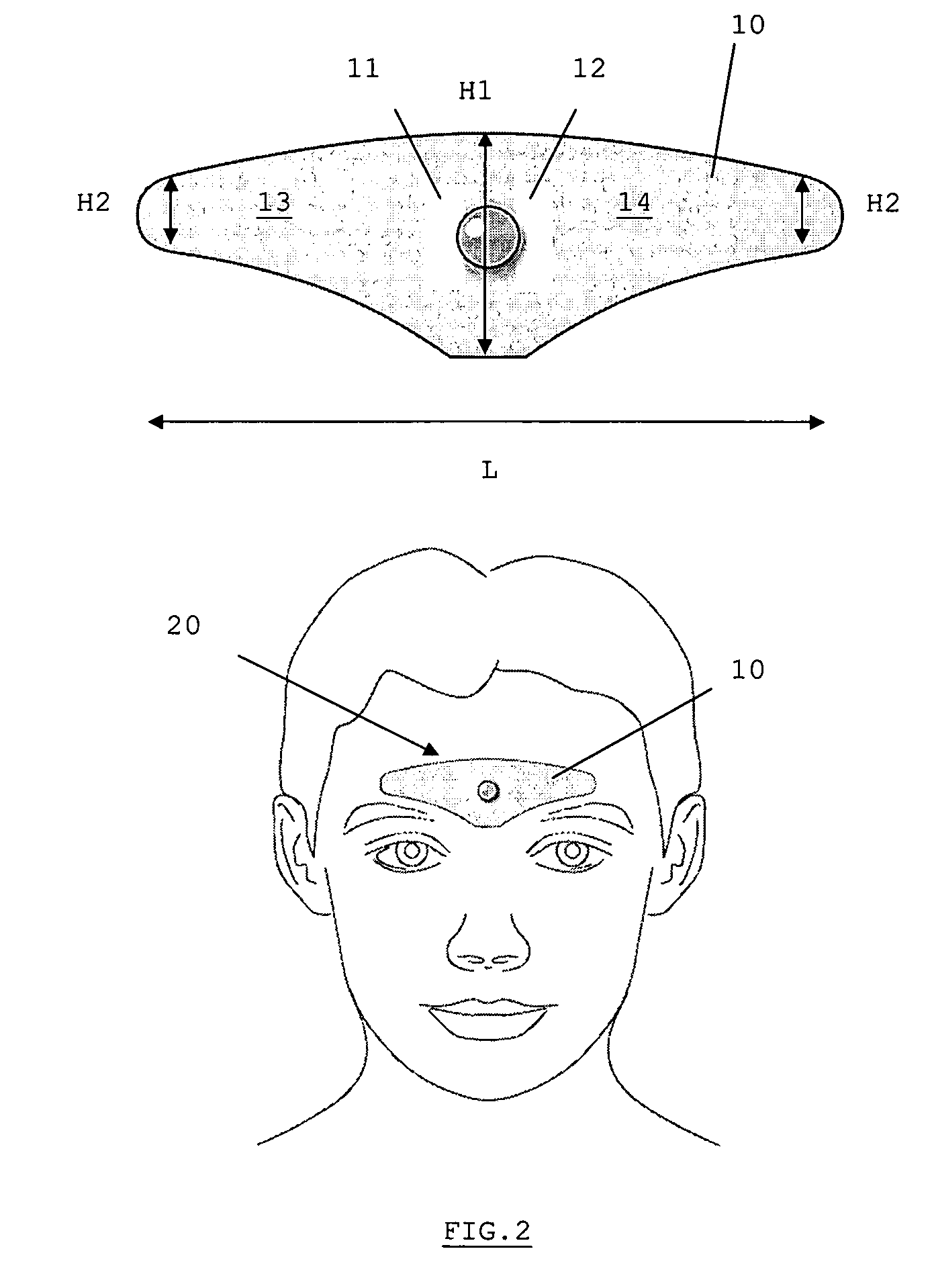
A device is for the electrotherapeutic treatment of headaches such as tension headaches and migraines. An electrode support (10) has a shape and is size selected so as to allow, independently from the subject, the excitation of the afferent paths of the supratrochlear (2) and supraorbital (3) nerves of the ophthalmic branch (1) of the trigeminal nerve. An electrical circuit includes a programmable signal generator suitable for creating pulses of a duration of between 150 and 450 microseconds with a maximum increase in intensity of 0 to 20 milliamperes at a rate of less than or equal to 40 microamperes per second and with a step up in intensity not exceeding 50 microamperes.
Owner:ORSAN MEDICAL TECH
Synchronization of vagus nerve stimulation with the cardiac cycle of a patient
ActiveUS20070233194A1Facilitate conductionIncrease variabilityElectroencephalographySpinal electrodesIncreased heart rateRR interval
Disclosed herein are methods, systems, and apparatus for treating a medical condition of a patient, involving detecting a physiological cycle or cycles of the patient and applying an electrical signal to a portion of the patient's vagus nerve through an electrode at a selected point in the physiological cycle(s). The physiological cycle can be the cardiac and / or respiratory cycle. The selected point can be a point in the cardiac cycle correlated with increased afferent conduction on the vagus nerve, such as a point from about 10 msec to about 800 msec after an R-wave of the patient's ECG, optionally during inspiration by the patient. The selected point can be a point in the cardiac cycle when said applying increases heart rate variability, such as a point from about 10 msec to about 800 msec after an R-wave of the patient's ECG, optionally during expiration by the patient.
Owner:CATHOLIC HEALTHCARE WEST ST JOSEPHS HOSPITAL
Method to enhance afferent and efferent transmission using noise resonance
ActiveUS20110009919A1Reduces neuroplasticityReduces and prevents neuroplasticitySpinal electrodesHead electrodesElectricitySub threshold
Methods of providing therapy to a patient are provided. In one method, the patient has a neuron to which a sub-threshold biological electrical stimulus is applied. The method comprises applying electrical noise energy to the neuron, wherein resonance between the biological electrical stimulus and the electrical noise energy is created, such that an action potential is propagated along the axon of the neuron. In another method, the patient has a neuron to which a supra-threshold biological electrical stimulus is applied. This method comprises applying supra-threshold electrical noise energy to the neuron, thereby preventing an action potential from being propagated along the axon of the neuron. Still another method comprises applying an electrical stimulus to a neuron, and applying supra-threshold electrical noise energy to the neuron, thereby preventing or reversing any neurological accommodation of the neuron that may occur in response to the electrical stimulus.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Conjugates of galactose-binding lectins and clostridial neurotoxins as analgesics
InactiveUS7052702B1Pain reliefReduce and preferably prevent transmissionNervous disorderBacteriaGalactose binding lectinProtein translocation
A class of novel agents that are able to modify nociceptive afferent function is provided. The agents may inhibit the release of neurotransmitters from discrete populations of neurones and thereby reduce or preferably prevent the transmission of afferent pain signals from peripheral to central pain fibers. They comprise a galactose-binding lectin linked to a derivative of a clostridial neurotoxin. The derivative of the clostridial neurotoxin comprises the L-chain, or a fragment thereof, which includes the active proteolytic enzyme domain of the light (L) chain, linked to a molecule or domain with membrane translocating activity. The agents may be used in or as pharmaceuticals for the treatment of pain, particularly chronic pain.
Owner:HEALTH PROTECTION AGENCY +1
Method for controlling the pain from injections or minor surgical procedures and apparatus for use therewith
InactiveUS6902554B2Reducing and eliminating painReduce and eliminate painSurgeryMedical devicesFiberNerve fiber bundle
The pain associated with an injection or minor surgical procedure at a site on the skin of a patient is reduced by urging a skin engaging surface of a pressure member against the skin proximate the site, thereby stimulating the large diameter afferent sensory nerve fibers in the skin proximate the site and at least partially blocking pain signals from the small diameter afferent pain nerve fibers in the skin proximate the site. An apparatus for use in this method comprises a pressure member having a skin engaging surface adapted to be pressed against the skin of a patient proximate the site to stimulate the large diameter afferent sensory nerve fibers in the skin proximate the site. In certain embodiments, the skin engaging surface is comprised of a plurality of projections extending from the pressure member. Various embodiments include a syringe retainer adapted to be secured to a syringe, and a least one resilient member, such as a spring, resiliently securing the pressure member to the syringe retainer.
Owner:BIONIX DEVMENT
Vascular remodeling device
A vascular remodeling device is provided that can comprise a proximal section, an intermediate section, and a distal section. During deployment, the proximal section can expand from a compressed delivery state to an expanded state and anchor the device in the afferent vessel of a bifurcation. The distal section can comprise at least one embolization coil that can be positioned within an aneurysm to treat the aneurysm and expand from the compressed delivery state to an expanded state upon deployment. The intermediate section can allow perfusion to efferent vessels. Before, during, and / or after the device is positioned, additional embolic material can be used to treat the aneurysm.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Apparatus for autonomic neuromodulation for the treatment of systemic disease
InactiveUS20100241183A1Delay is slowPreserving and prolonging effect of modulationSpinal electrodesUltrasound therapyNervous systemEfferent
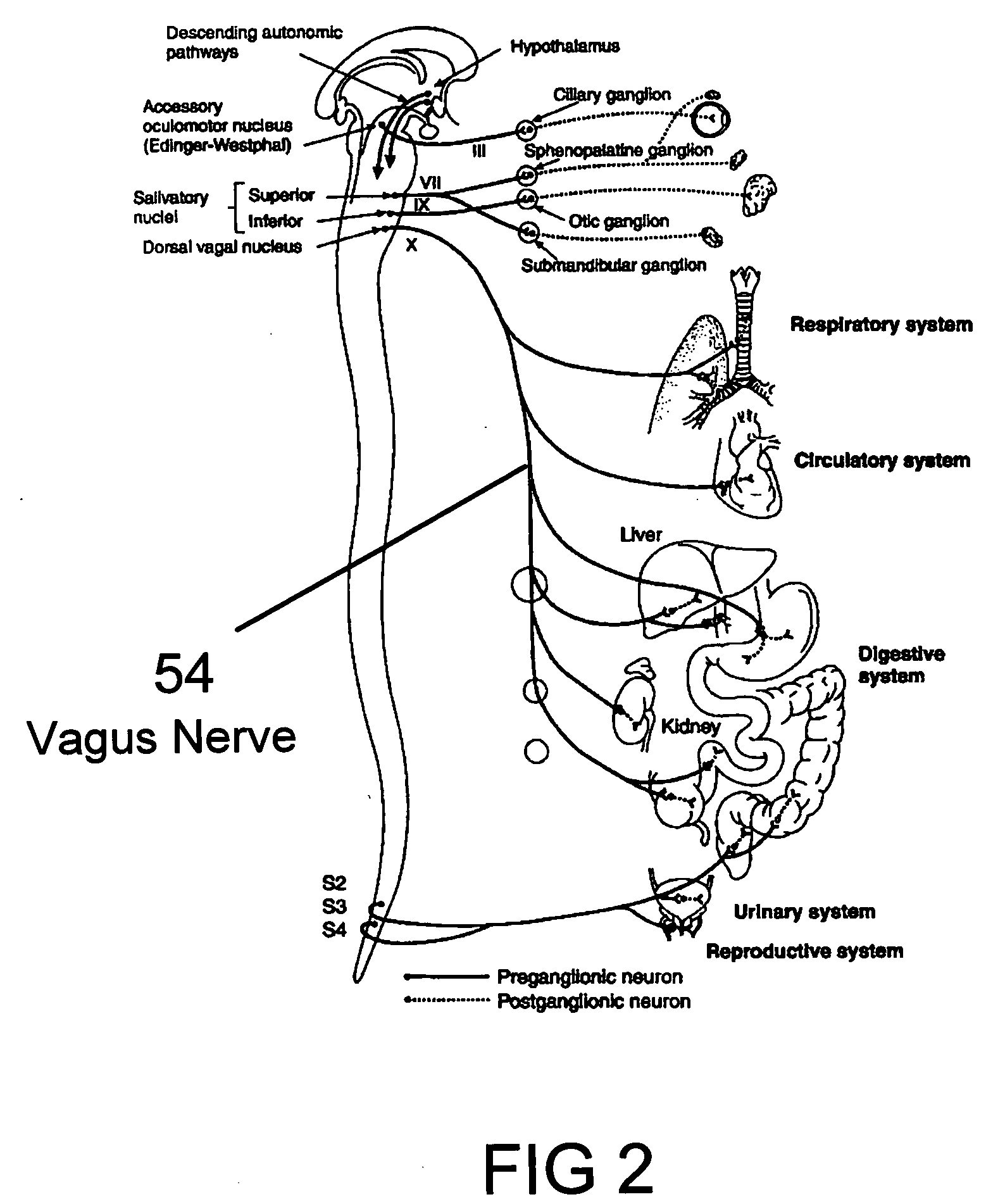
A method, apparatus, and surgical technique for the modulation of autonomic function, for the purpose of treating any of several conditions and diseases, including obesity, metabolic disorders, endocrine disorders, diabetes, respiratory disease, asthma, inflammatory disease, immunological disease, infection, cancer, cardiac disease, cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, stroke, vasospasm, vascular disease, psychiatric disease, depression, affective disorders, anxiety disorders, and other conditions. This includes neural and tissue modulators, including implanted devices, used to modulate efferent and afferent autonomic neurons to influence or control autonomic or other neural function, including modulation of sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system components as well as their combination.
Owner:DILORENZO BIOMEDICAL
Vascular remodeling device
ActiveUS20120143317A1Good flexibilityGood wall appositionStentsOcculdersIliac AneurysmEmbolization material
Described herein are vascular remodeling devices that include a proximal section, an intermediate section, and a distal section. During deployment, the proximal section can expand from a compressed delivery state to an expanded state and anchors the device in an afferent vessel of a bifurcation. The distal section expands from the compressed delivery state to an expanded state that may be substantially planar, approximately semi-spherical, umbrella shaped, or reverse umbrella shaped. The distal section is positioned in a bifurcation junction across the neck of an aneurysm or within an aneurysm. The intermediate section allows perfusion to efferent vessels. Before or after the device is in position, embolic material may be used to treat the aneurysm. The distal section can act as a scaffolding to prevent herniation of the embolic material. The device can be used for clot retrieval with integral distal embolic protection.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
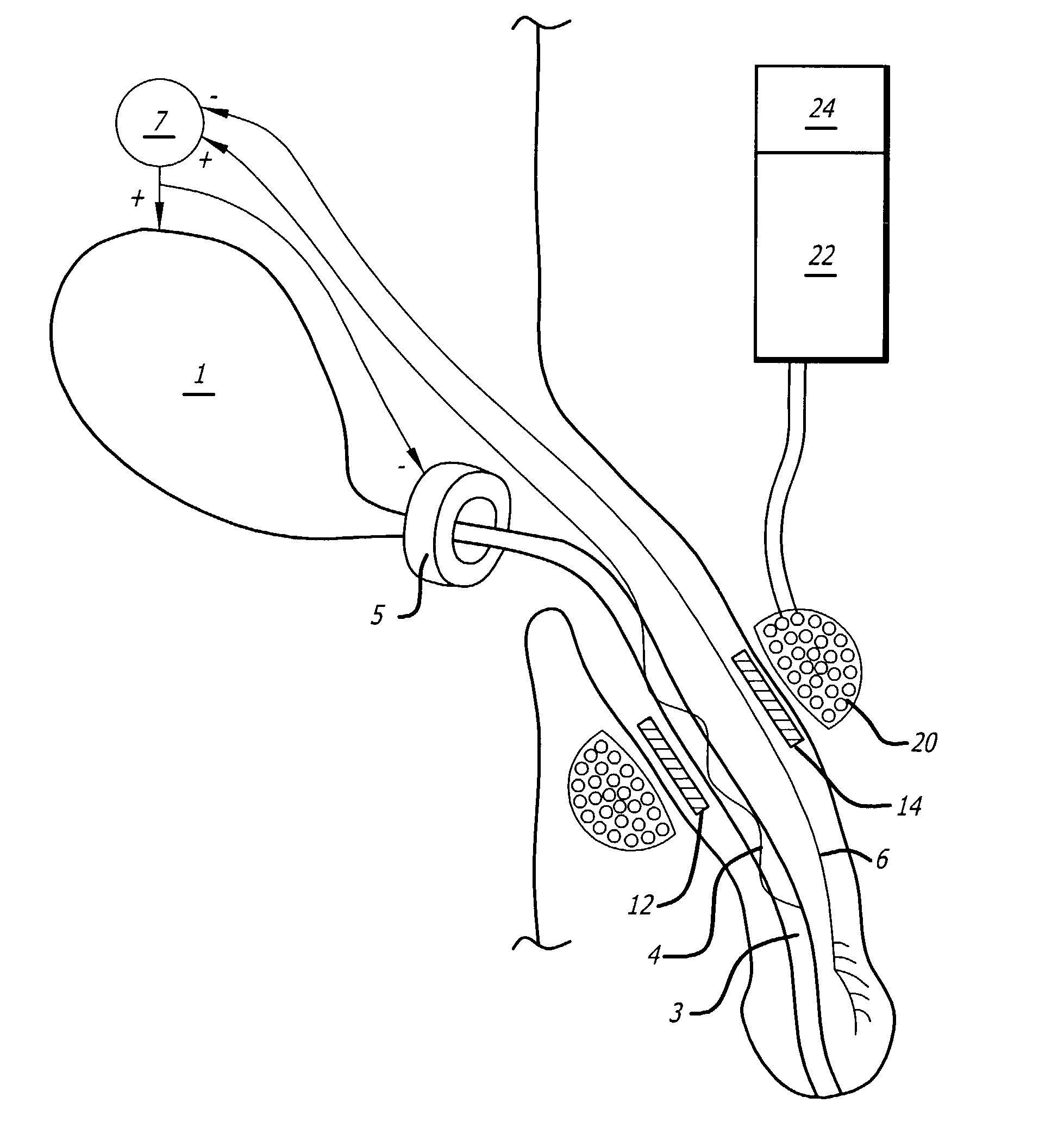
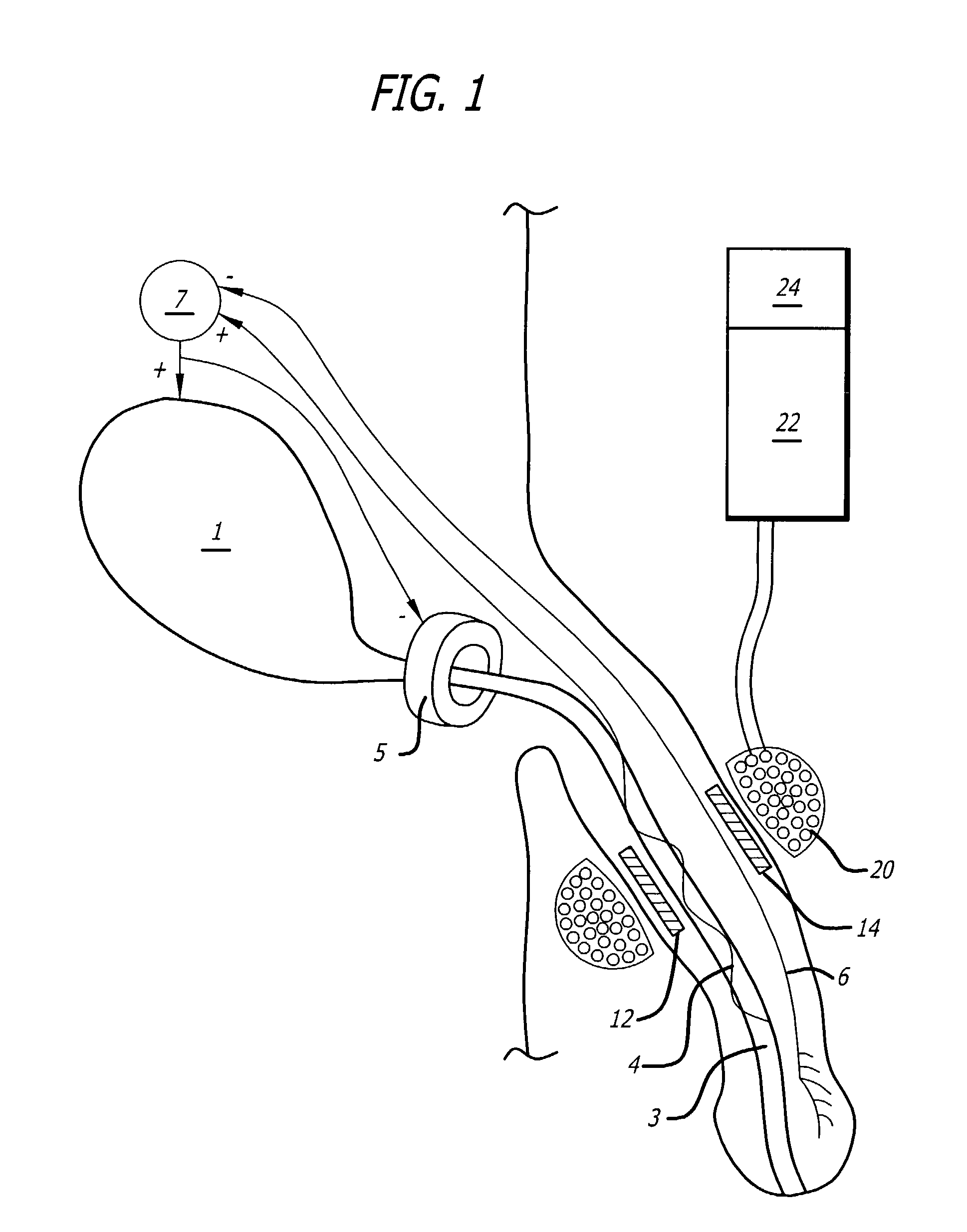
Method and apparatus for the treatment of urinary tract dysfunction
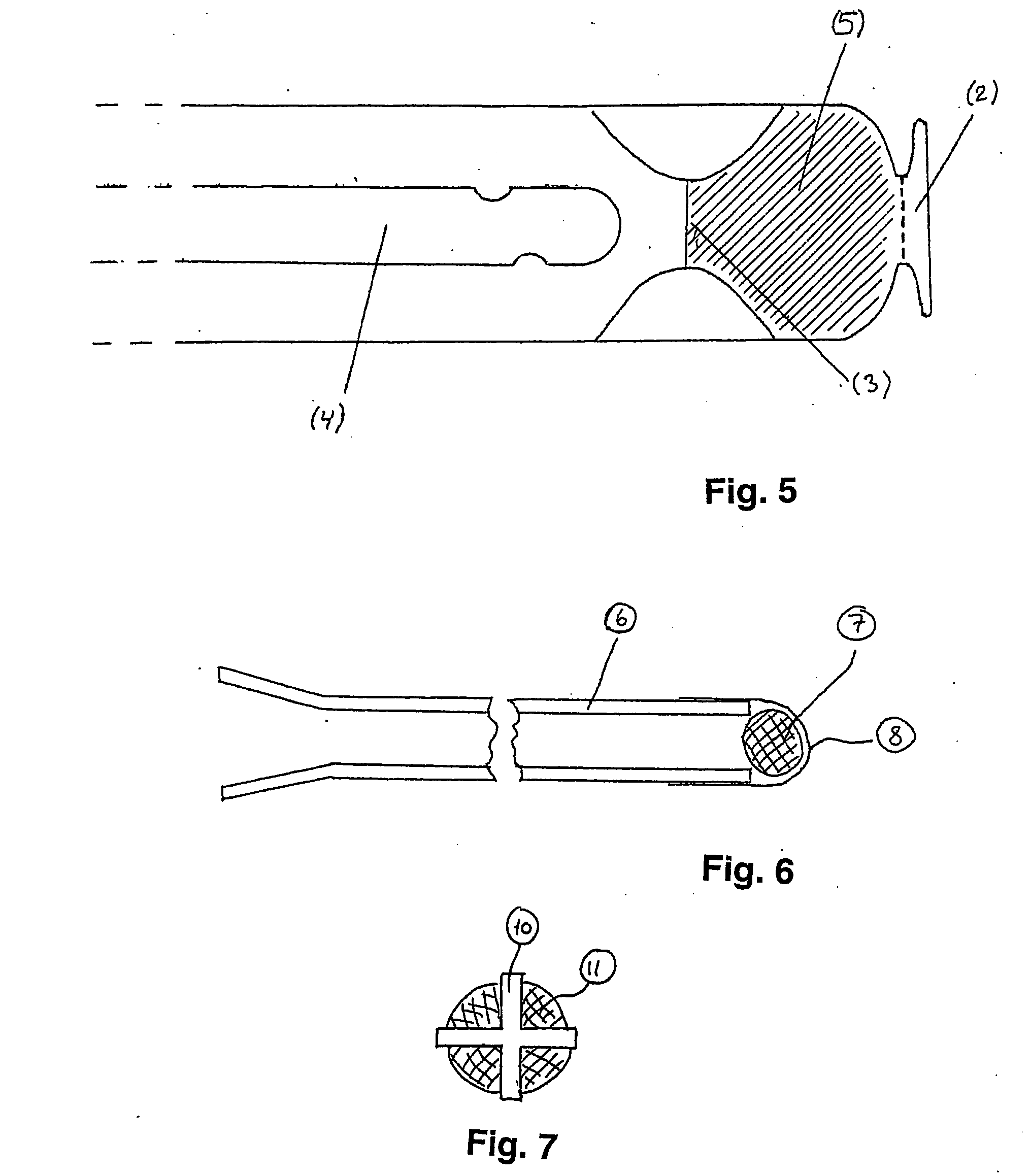
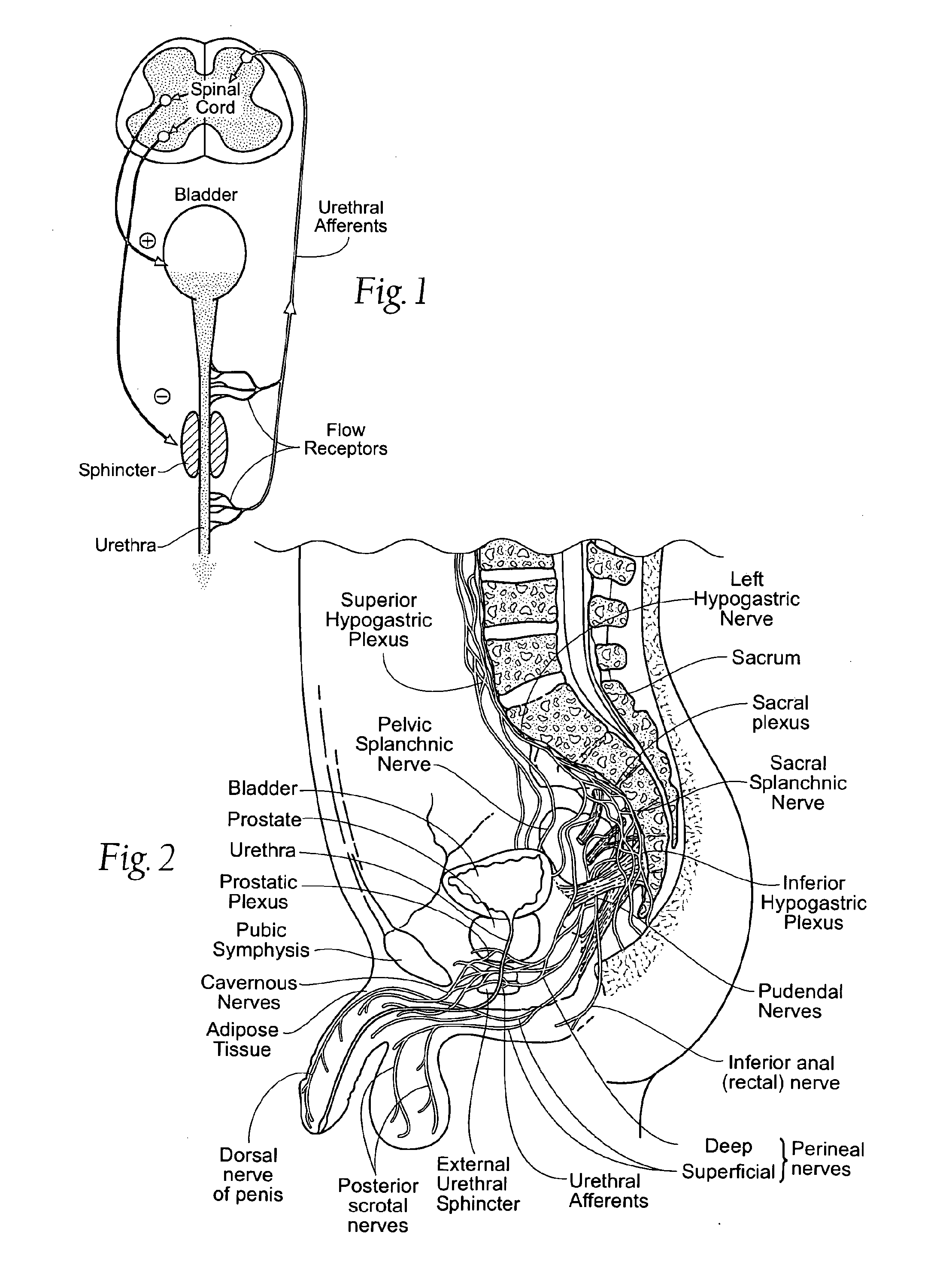
Electrical stimulation of specific sensory nerves to control the filling and / or emptying of the urinary bladder. A wireless, injectable microstimulator is implanted into the soft tissues through which the sensory nerves pass, but where they are not normally accessible by conventional open surgical implantation of conventional electrical stimulators or electrodes with leads. In males, the dorsal penile nerves 6 are stimulated by a microstimulator injected into the dorsal quadrant of the penis. The activity induced in these nerves cause the spinal cord to generate reflex responses that result in relaxation of the detrusor muscle, increasing bladder capacity and preventing incontinence as a result of inappropriate bladder contractions. The sensory nerves, such as urethral afferents 4, supplying the urethra are stimulated by a microstimulator implanted into the corpus of the penis, adjacent to the urethra. The activity induced in the urethral afferents 4 cause the spinal cord to generate reflex responses that result in contractions of the detrusor muscle and relaxation of the sphincter 5, emptying the bladder.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN INST FOR BIOMEDICAL ENG AT THE UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
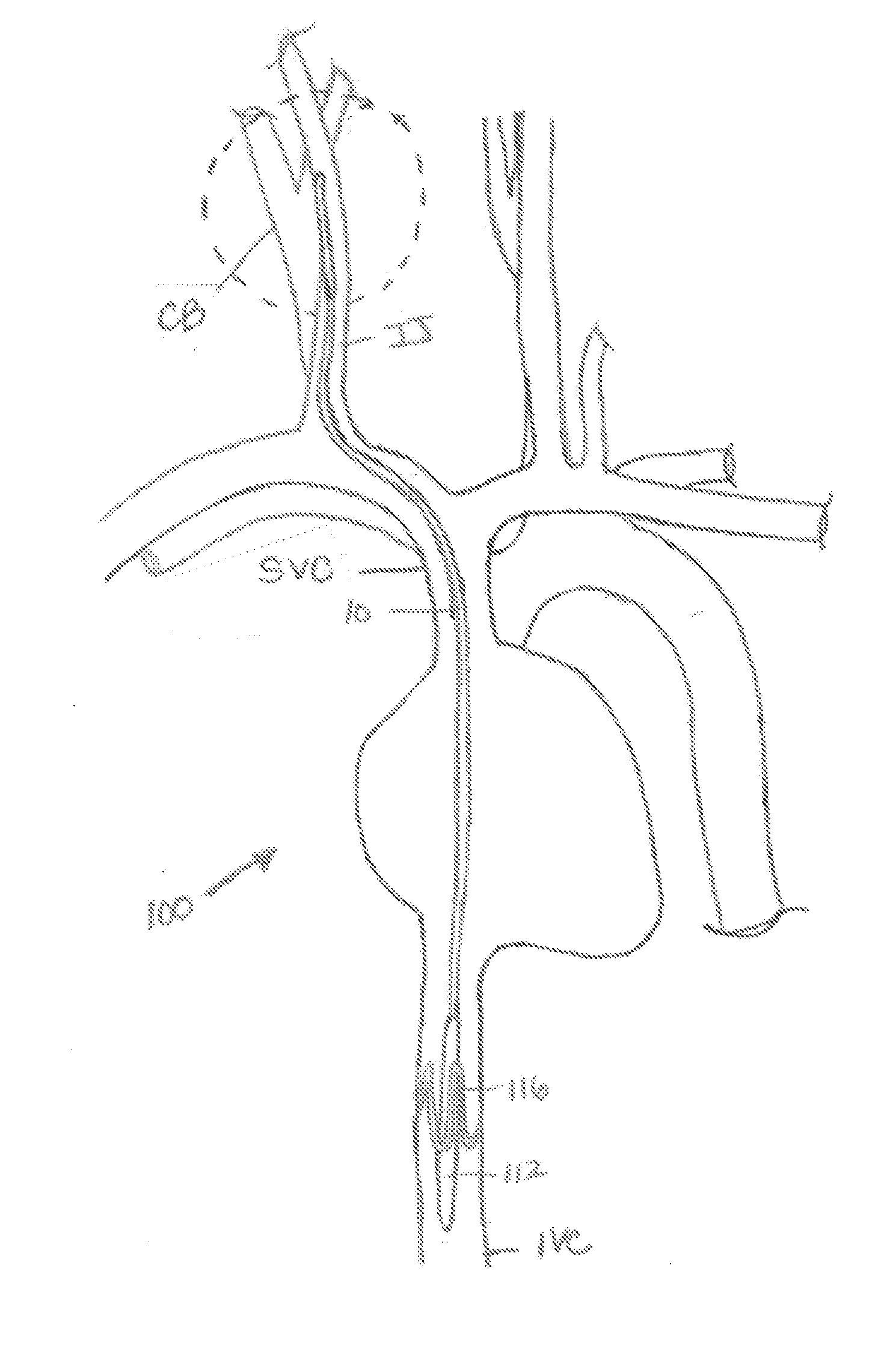
Intravascular system and method for blood pressure control
InactiveUS20100211131A1Spinal electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesNervous systemBlood vessel
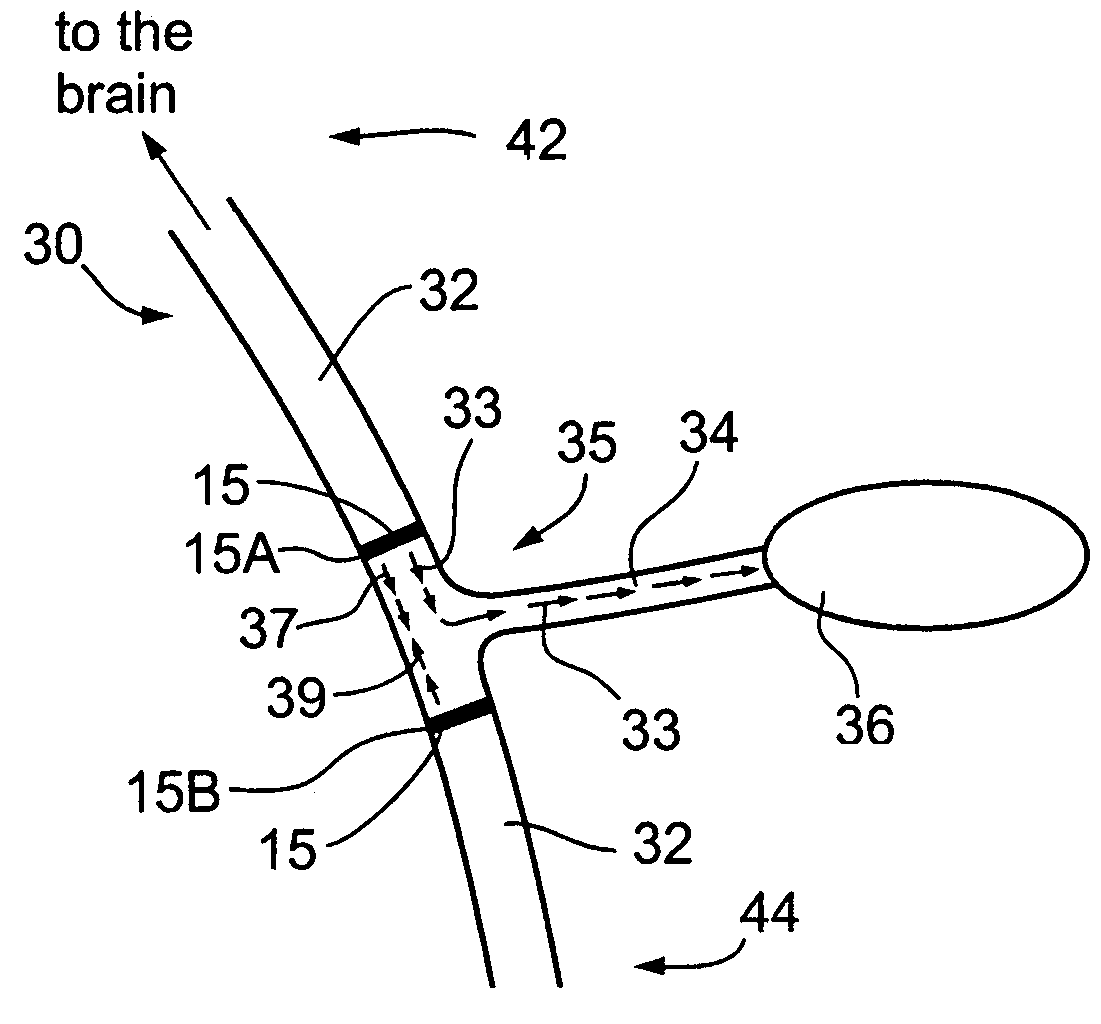
An intravascular lead is used to deliver energy for stimulating nervous system targets using energy delivery elements (e.g. electrodes) that are in direct contact with the nervous system targets. The lead may be positioned within the internal jugular vein and the nervous system targets may include the carotid artery / carotid sinus bulb and / or associated baroreceptor afferents, and / or surrounding nervous system targets in the region of the internal jugular vein, such as the carotid sinus nerve and / or associated nerve branches and / or the vagus nerve and / or associated nerve branches. Stimulation energy travels along a conductive bridge that extends from the intravascular lead to the nervous system target, or is relayed from the intravascular lead to another device disposed within or surrounding the target structure.
Owner:INTERVENTIONAL AUTONOMICS
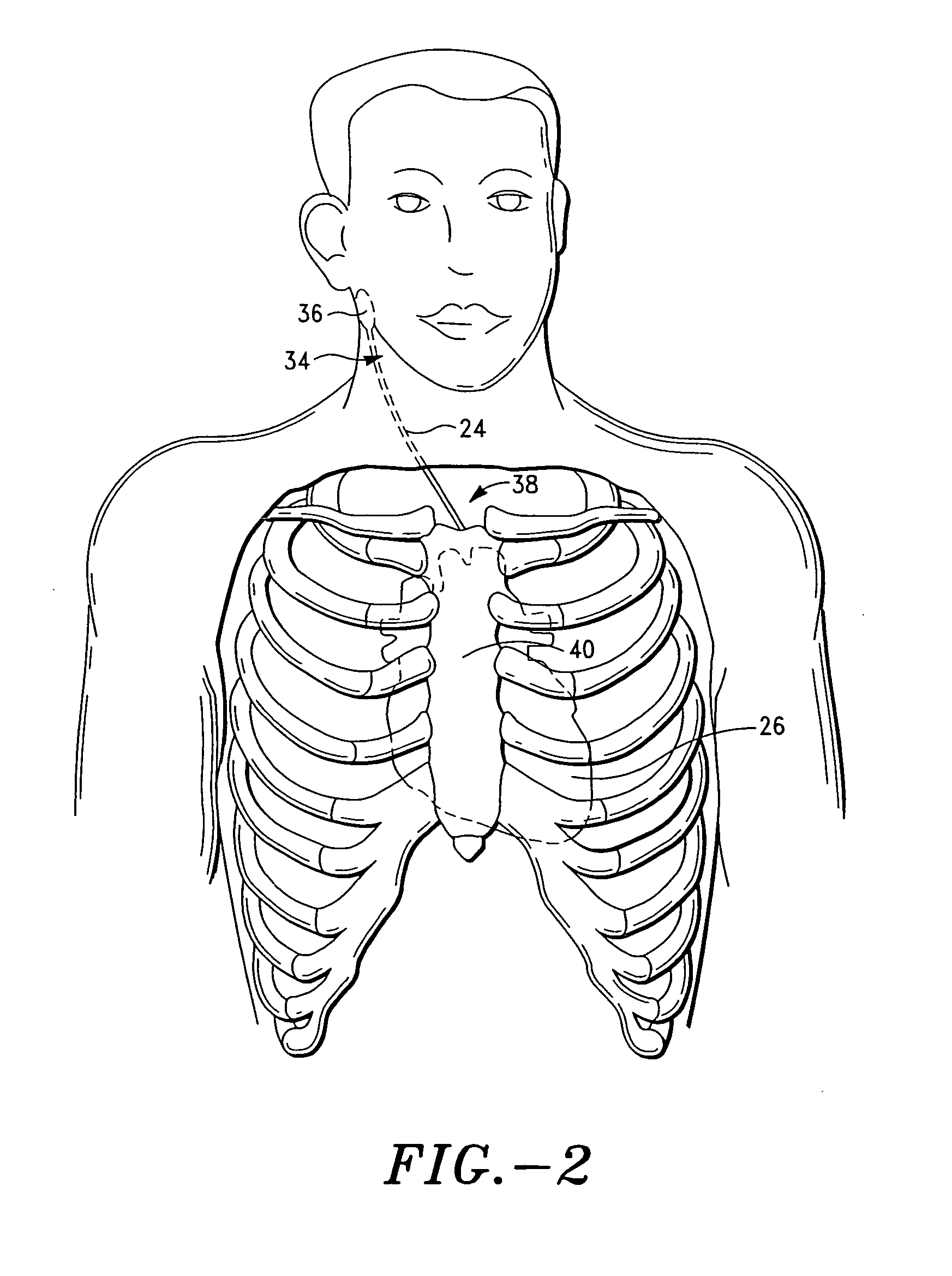
Device and procedure to treat cardiac atrial arrhythmias
A non-invasive vagal stimulation device and method. The device comprises a body having a vibration member. The stimulation is created by the vibration member which has a vibratory rate that can be adjusted from being off to a preferred operating range. The non-invasive stimulation method consists of placing the non-invasive stimulation device in the vicinity of the carotid artery bifrication where arises a carotid sinus and body which contain afferent sensory nerves that travel to medulla oblongata of brain, and either applying pressure in place, or moving the device along the target arm. The method can be accomplished either with the vibration feature of the device turned on or off.
Owner:NEUROSIGNAL TECH
Vascular remodeling device
An intraluminal apparatus including a catheter and device is positionable at a junction of afferent and efferent vessels of a bifurcation having an aneurysm. After positioning the device to substantially conform the device to the shape of the junction, the device acts as a scaffolding to inhibit herniation of objects out of the aneurysm and the device permits perfusion to the efferent vessels. Positioning the device may include deployment and optional release from a catheter. Embolic material may be inserted in the aneurysm before or after positioning the device. The device may have a proximal end, a distal end, and a plurality of filaments extending between and coupled at the proximal end and the distal end. The device may include a central filament configured to reshape the device. The distal end of the device may include a covering. The device may be football shaped, pumpkin shaped, or acorn shaped.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Neural monitoring methods and systems for treating upper airway disorders
Methods and systems for monitoring, preventing and / or treating upper airway disorders such as apnea, dysphagia, reflux and / or snoring are described. The methods and systems monitor the upper airway disorders by processing one or more neural signals obtained from one or more upper airway afferents. Upper airway disorders are prevented and / or treated by delivering one or more stimulations to one or more reflex-related afferents, efferents, muscles, and sensory receptors to manipulate the threshold and / or trigger an upper airway reflex including, but not limited to a swallow reflex and / or a negative-pressure reflex.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Device and procedure to treat cardiac atrial arrhythmias
A non-invasive vagal stimulation device and method. The device comprises a body having a vibration member. The stimulation is created by the vibration member which has a vibratory rate that can be adjusted from being off to a preferred operating range. The non-invasive stimulation method consists of placing the non-invasive stimulation device in the vicinity of the carotid artery bifrication where arises a carotid sinus and body which contain afferent sensory nerves that travel to medulla oblongata of brain, and either applying pressure in place, or moving the device along the target arm. The method can be accomplished either with the vibration feature of the device turned on or off.
Owner:ORTIZ & LOPEZ PLLC
Conjugates of galactose-binding lectins and clostridial neurotoxins as analgesics
InactiveUS7452543B2Pain reliefReduce and preferably prevent transmissionNervous disorderBacteriaGalactose binding lectinProtein translocation
A class of novel agents that are able to modify nociceptive afferent function is provided. The agents may inhibit the release of neurotransmitters from discrete populations of neurones and thereby reduce or preferably prevent the transmission of afferent pain signals from peripheral to central pain fibers. They comprise a galactose-binding lectin linked to a derivative of a clostridial neurotoxin. The derivative of the clostridial neurotoxin comprises the L-chain, or a fragment thereof, which includes the active proteolytic enzyme domain of the light (L) chain, linked to a molecule or domain with membrane translocating activity. The agents may be used in or as pharmaceuticals for the treatment of pain, particular chronic pain.
Owner:HEALTH PROTECTION AGENCY
Noninvasively adjustable gastric band
A method and apparatus for treatment of an eating disorder includes electrically stimulating the vagus nerve of the lower esophagus, cardia, esophageal / cardia junction, cardia / fundus junction or upper stomach so as to induce afferent action potentials on the vagus nerve. A device comprising a gastric band including stimulation electrodes may be noninvasively adjusted after implantation to provide increased or decreased restriction on the patient's gastrointestinal tract. Each stimulus may be administered as a series of programmed pulses of defined amplitude, duration and period, to evoke a responsive signal to the brain by the target nerve, effective for producing a temporary feeling of satiety in the person. A programmable implantable stimulus generator may be operatively coupled to a nerve electrode. Methods are also provided to identify electrodes nearest to a branch of the vagus nerve to apply an electrical stimulation signal with improved efficiency.
Owner:CYBERONICS INC
Weight loss method and device
A method and apparatus for treatment of an eating disorder includes electrically, mechanically and / or pharmaceutically / chemically stimulating a of the vagus nerve of the lower esophagus, cardia, esophageal / cardia junction, cardia / fundus junction or upper stomach so as to induce afferent action potentials on the vagus nerve. The device may be noninvasively adjusted after implantation to provide increased or decreased restriction on the patient's gastrointestinal tract. Each stimulus may be administered as a series of programmed pulses of defined amplitude, duration and period, to evoke a responsive signal to the brain by the target nerve, effective for producing a temporary feeling of satiety in the person. An implantable stimulus generator may be operatively coupled to a nerve electrode, pressure device or chemical outlet to apply a defined signal to a selected nerve branch. The implantable stimulus generator is programmable to allow clinician programming of defined signal parameters effective to treat the eating disorder of the patient. Methods are also provided to identify electrodes nearest to a branch of the vagus nerve to apply an electrical stimulation signal with improved efficiency.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Urinary catheter device with a pharmaceutically active composition
The invention relates to a device for urinary catheterisation comprising a catheter element and a pharmaceutically active composition containing a hormone, an efferent blocking agent, an afferent blocking agent and / or a sympathomimetic agent, the catheter element being adapted to deliver the pharmaceutically active composition in the lower urinary tract system during catheterisation. The invention also relates to the use of said pharmaceutically active composition for the manufacture of a device for the treatment, alleviation or prophylaxis of incontinence in a human and to a method of treating a human suffering from or being susceptible to incontinence. The invention further relates to a device for urinary catheterisation comprising a discrete unit dose comprising a pharmaceutically active composition and a catheter element adapted to shed said pharmaceutically active composition in the lower urinary tract system during catheterisation.
Owner:COLOPLAST AS
Systems and methods for the treatment of bladder dysfunctions using neuromodulation
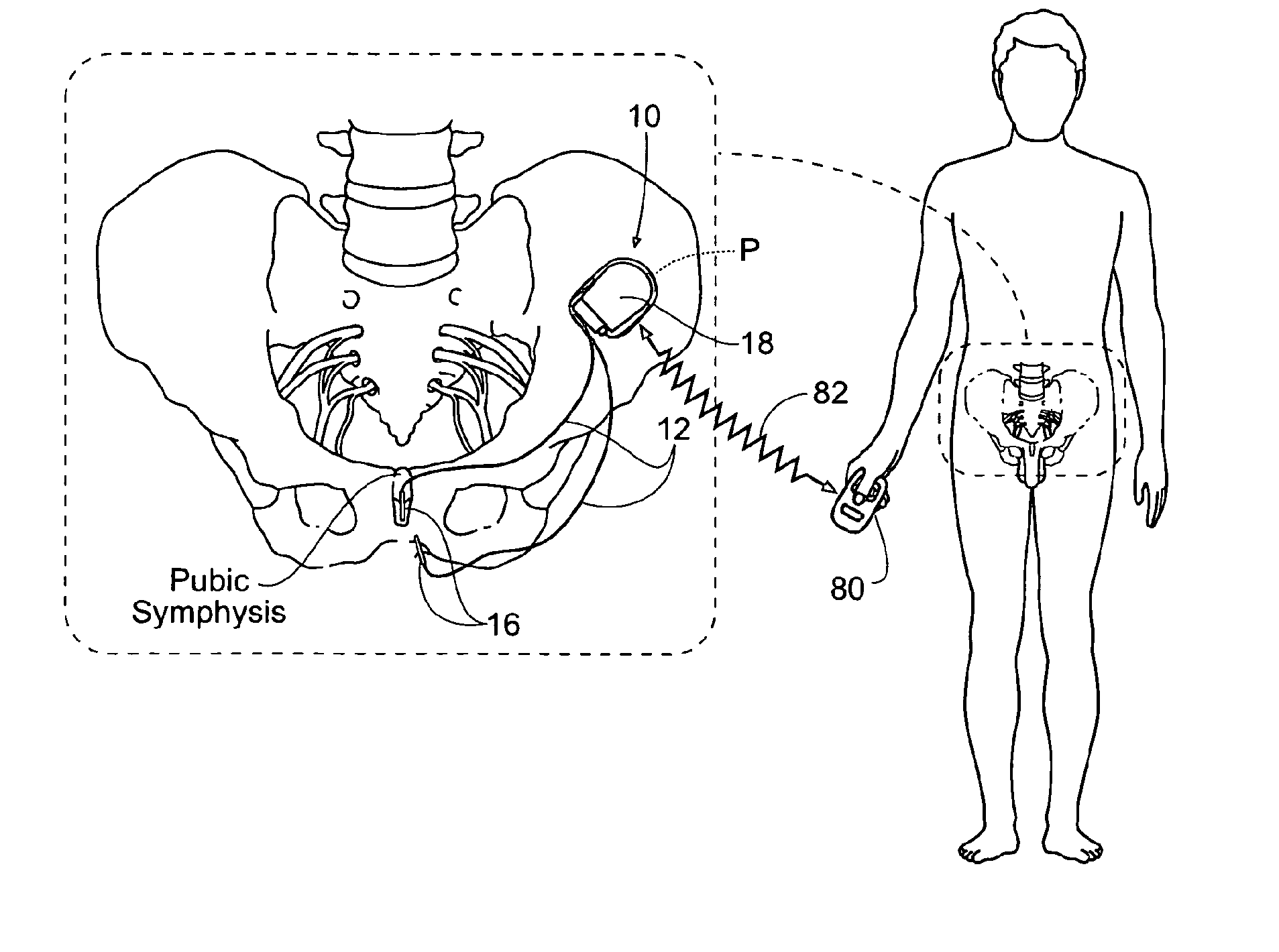
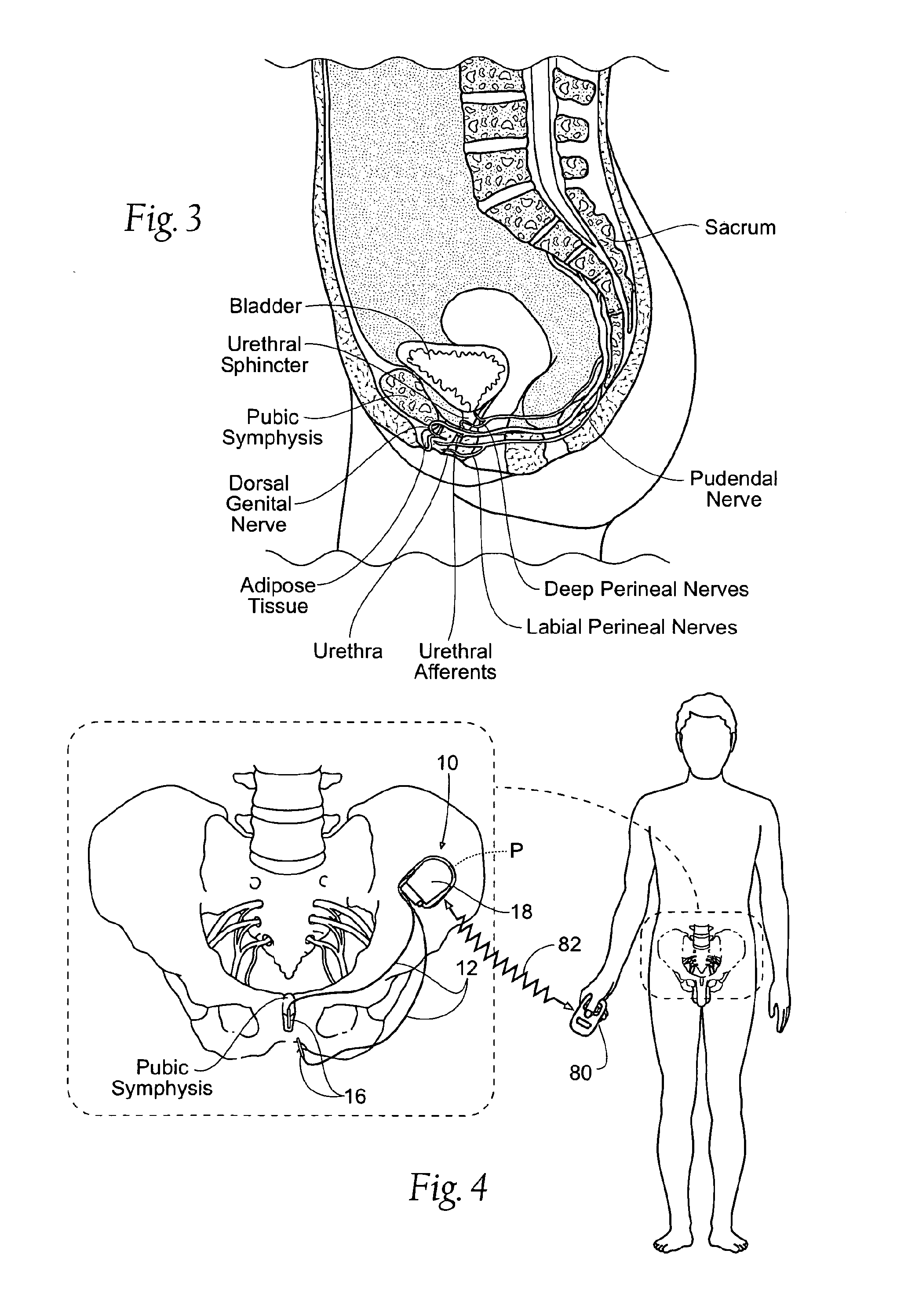
Systems and Methods treat bladder dysfunctions using neuromodulation stimulation. Bladder emptying through stimulation of urethral afferents, and continence through stimulation of the dorsal genital nerve, is provided with one or more implanted pulse generators and one or more leads. A simple surgical procedure preserves all existing functions. A stimulating catheter is provided to be used as a clinical screening tool. The stimulating catheter is used to measure bladder pressures and stimulate the urethra at the same time.
Owner:MEDTRONIC URINARY SOLUTIONS
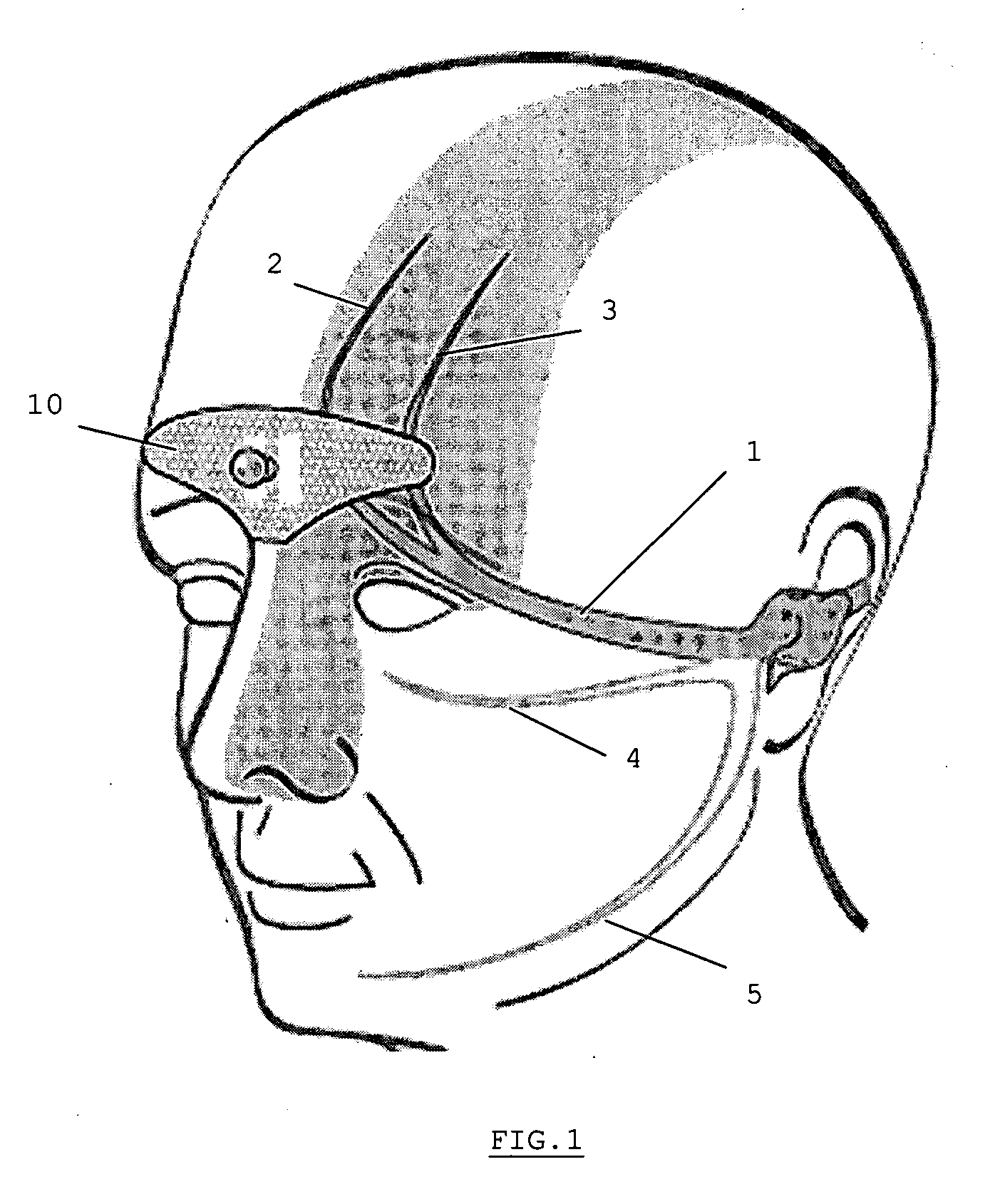
Device for the electrotherapeutic treatment of tension headaches
A device is for the electrotherapeutic treatment of headaches such as tension headaches and migraines. An electrode support (10) has a shape and is size selected so as to allow, independently from the subject, the excitation of the afferent paths of the supratrochlear (2) and supraorbital (3) nerves of the ophthalmic branch (1) of the trigeminal nerve. An electrical circuit includes a programmable signal generator suitable for creating pulses of a duration of between 150 and 450 microseconds with a maximum increase in intensity of 0 to 20 milliamperes at a rate of less than or equal to 40 microamperes per second and with a step up in intensity not exceeding 50 microamperes.
Owner:ORSAN MEDICAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com