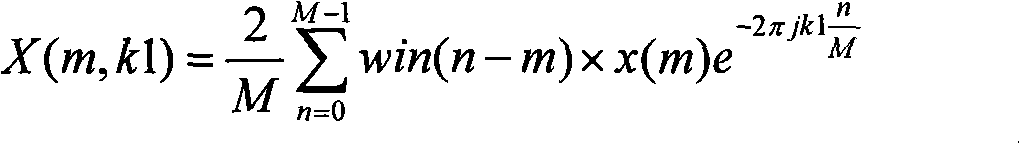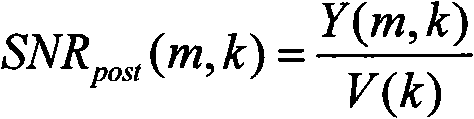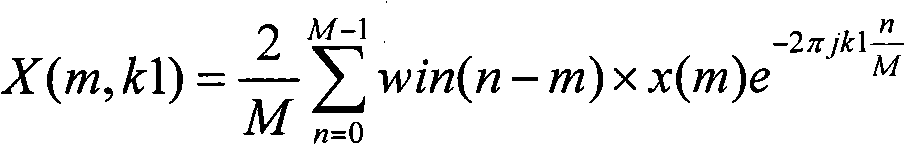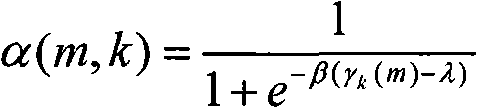Patents
Literature
448 results about "Noise energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Noise is unwanted electrical or electromagnetic energy that degrades the quality of signals and data. Noise occurs in digital and analog systems, and can affect files and communications of all types, including text, programs, images, audio, and telemetry.
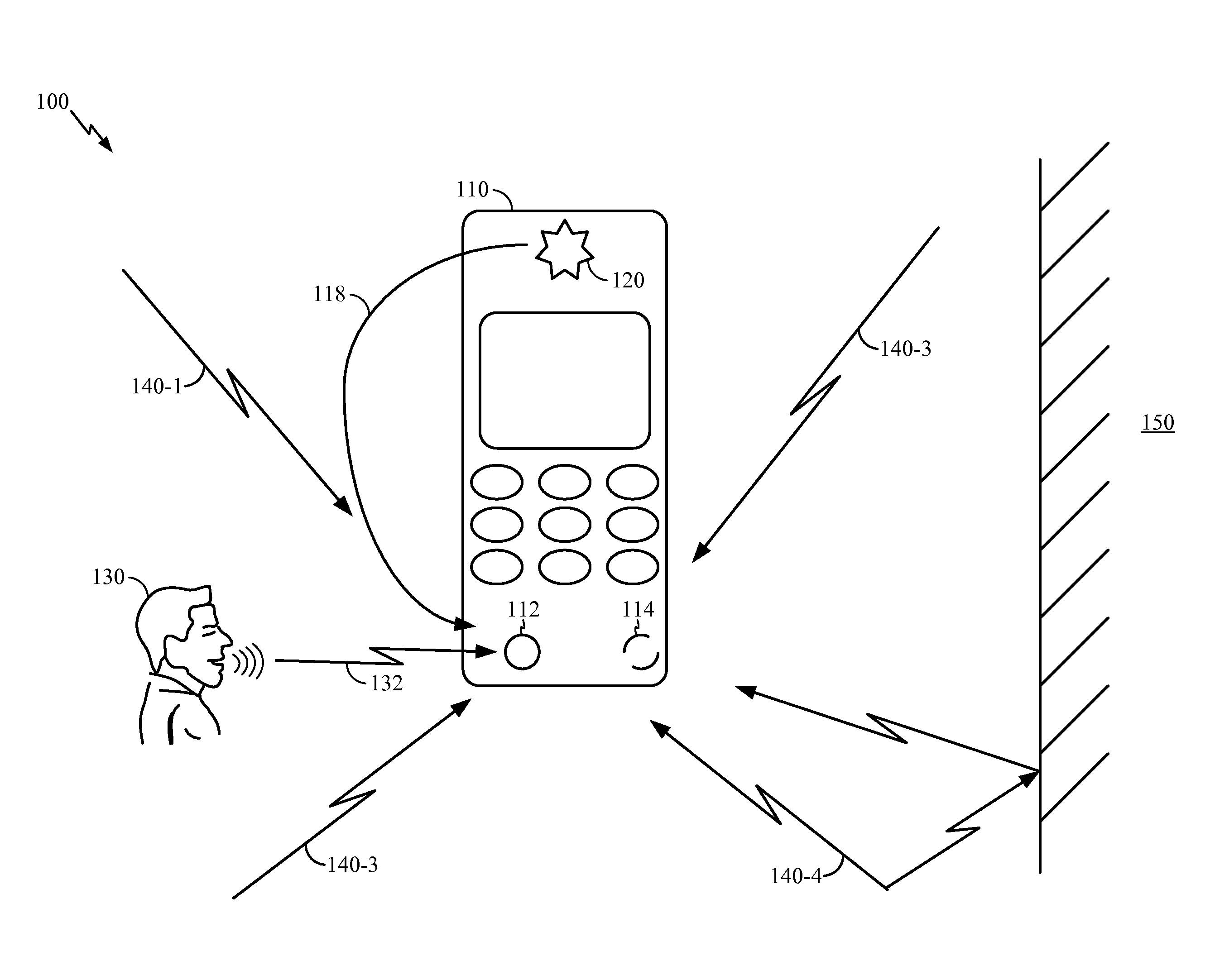
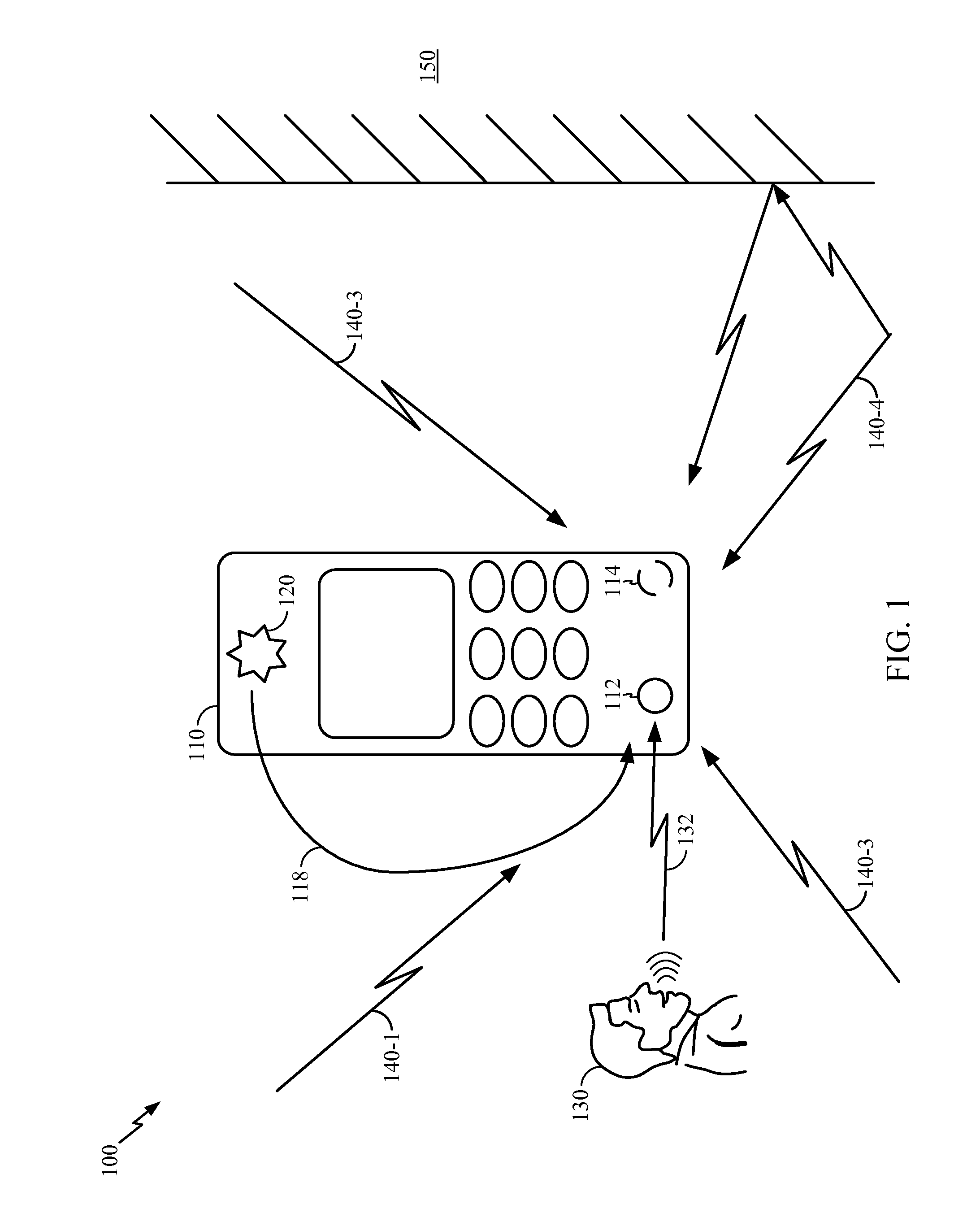
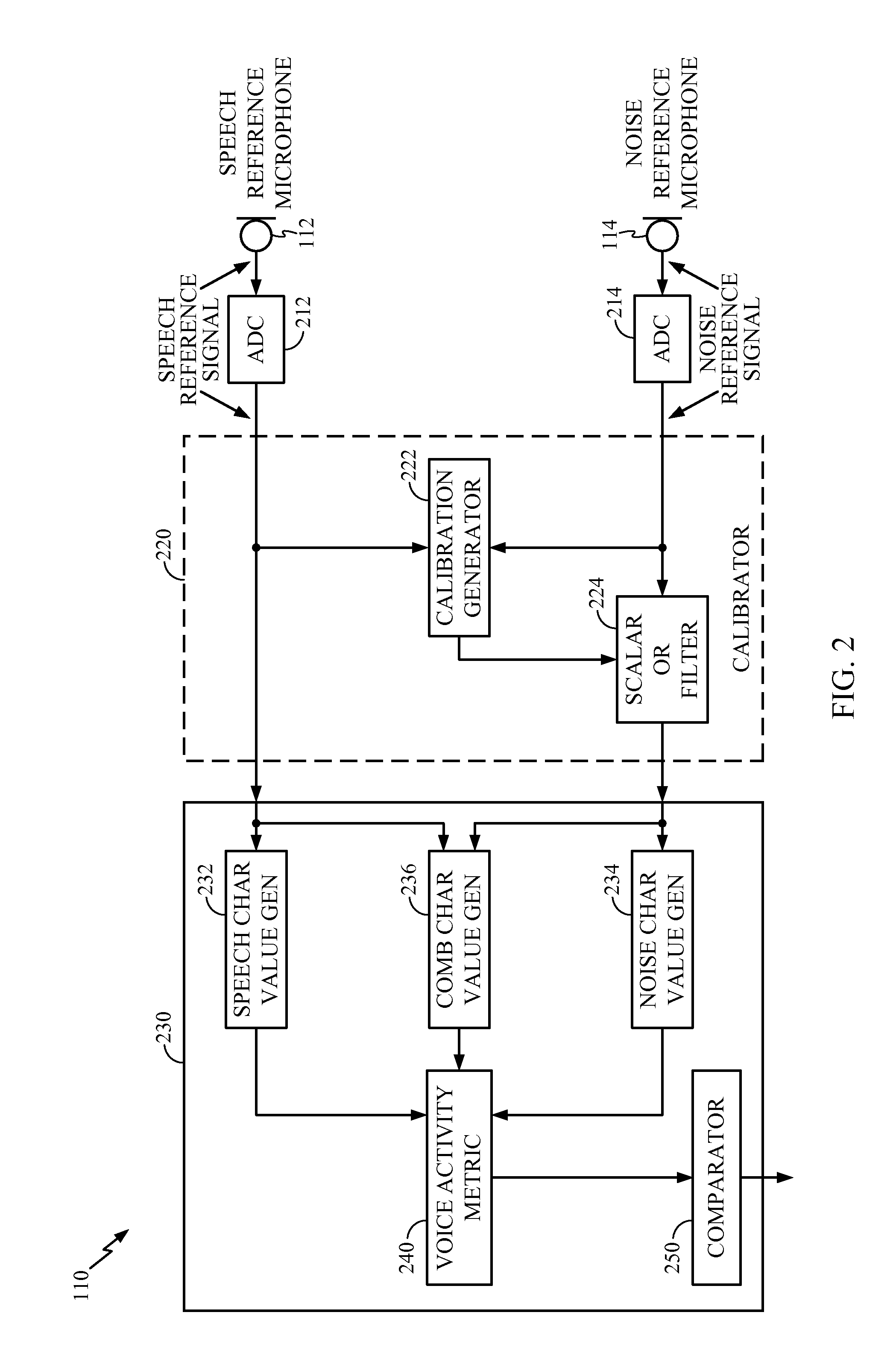
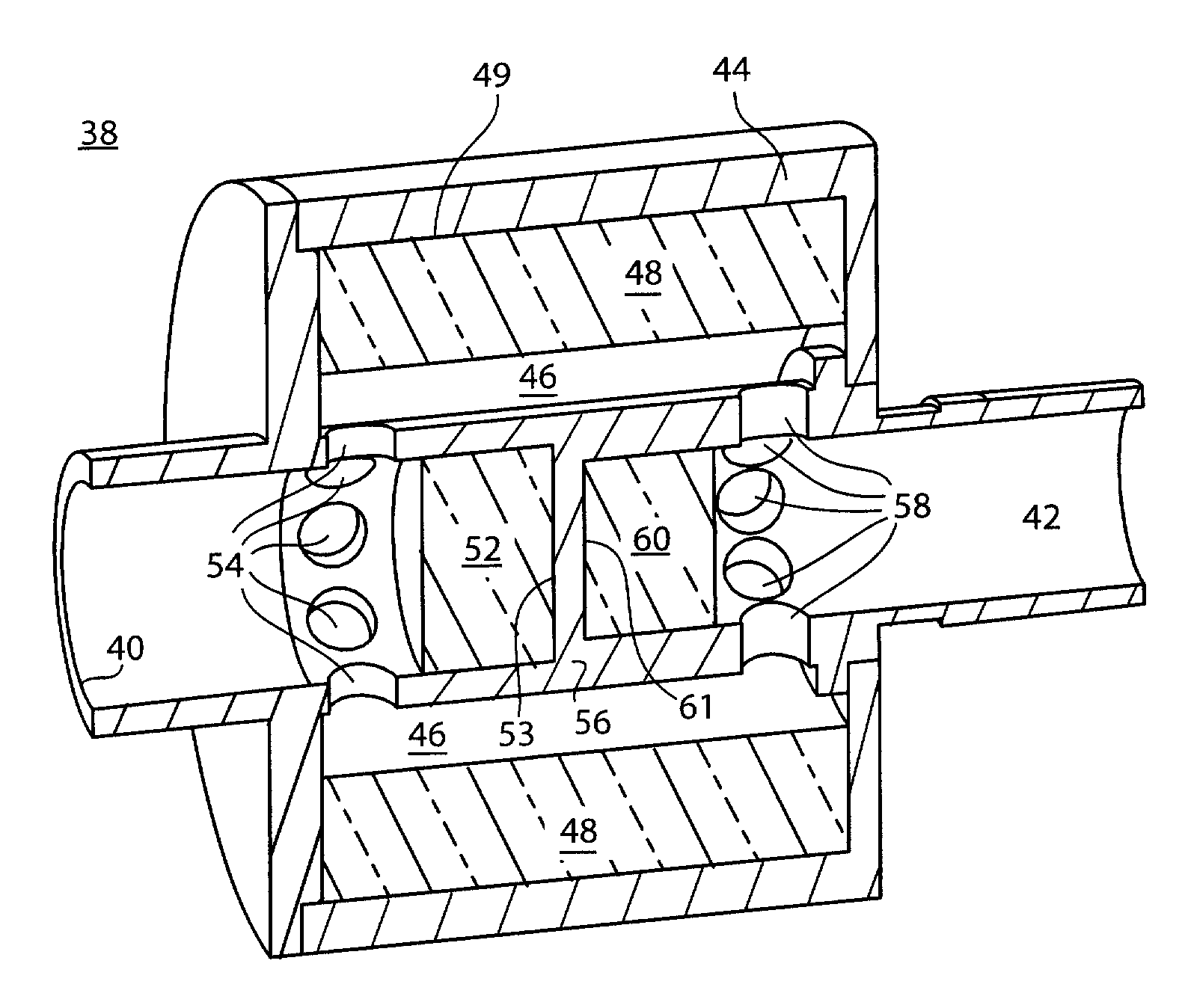
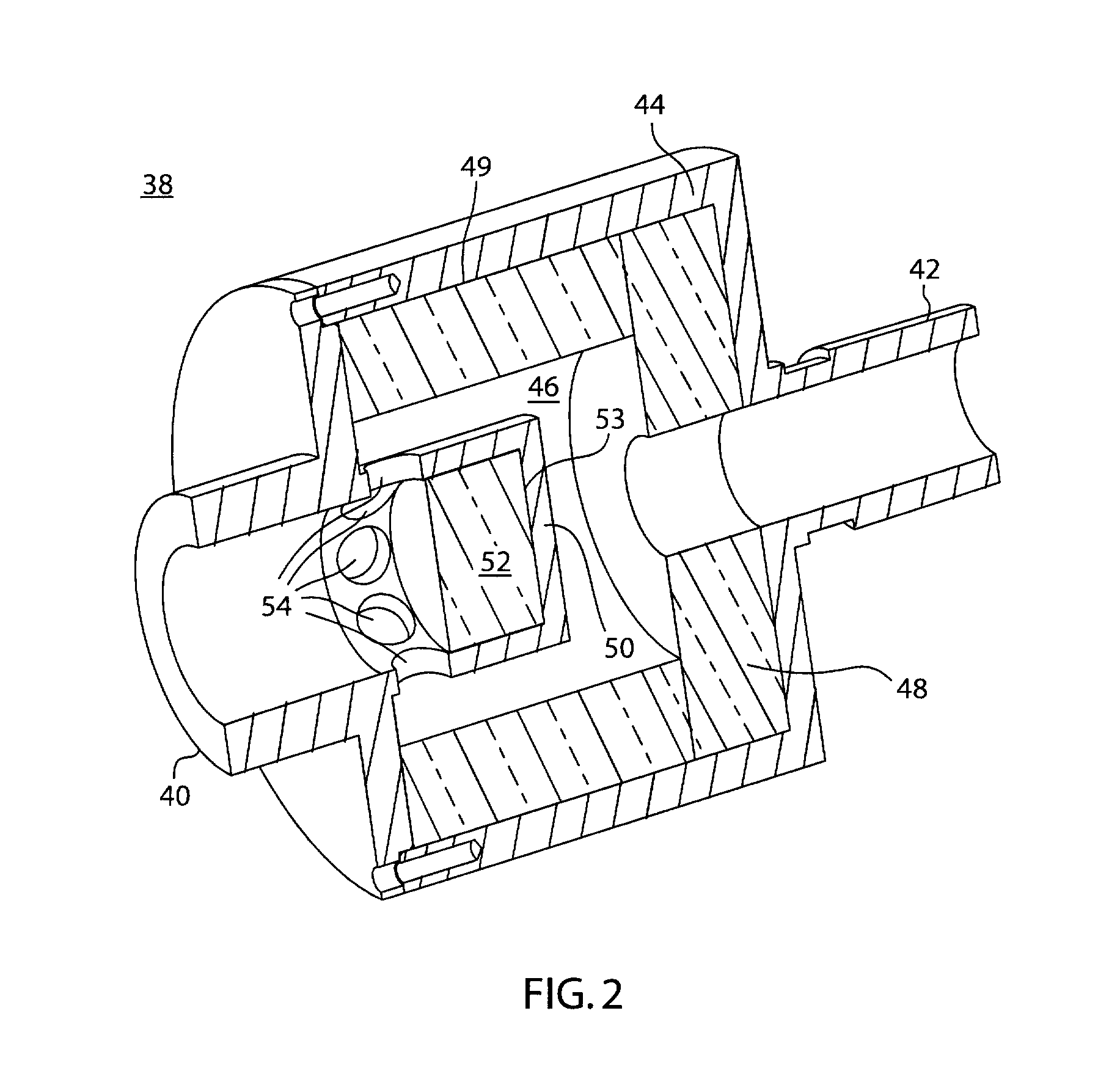
Multiple microphone voice activity detector
Voice activity detection using multiple microphones can be based on a relationship between an energy at each of a speech reference microphone and a noise reference microphone. The energy output from each of the speech reference microphone and the noise reference microphone can be determined. A speech to noise energy ratio can be determined and compared to a predetermined voice activity threshold. In another embodiment, the absolute value of the autocorrelation of the speech and noise reference signals are determined and a ratio based on autocorrelation values is determined. Ratios that exceed the predetermined threshold can indicate the presence of a voice signal. The speech and noise energies or autocorrelations can be determined using a weighted average or over a discrete frame size.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
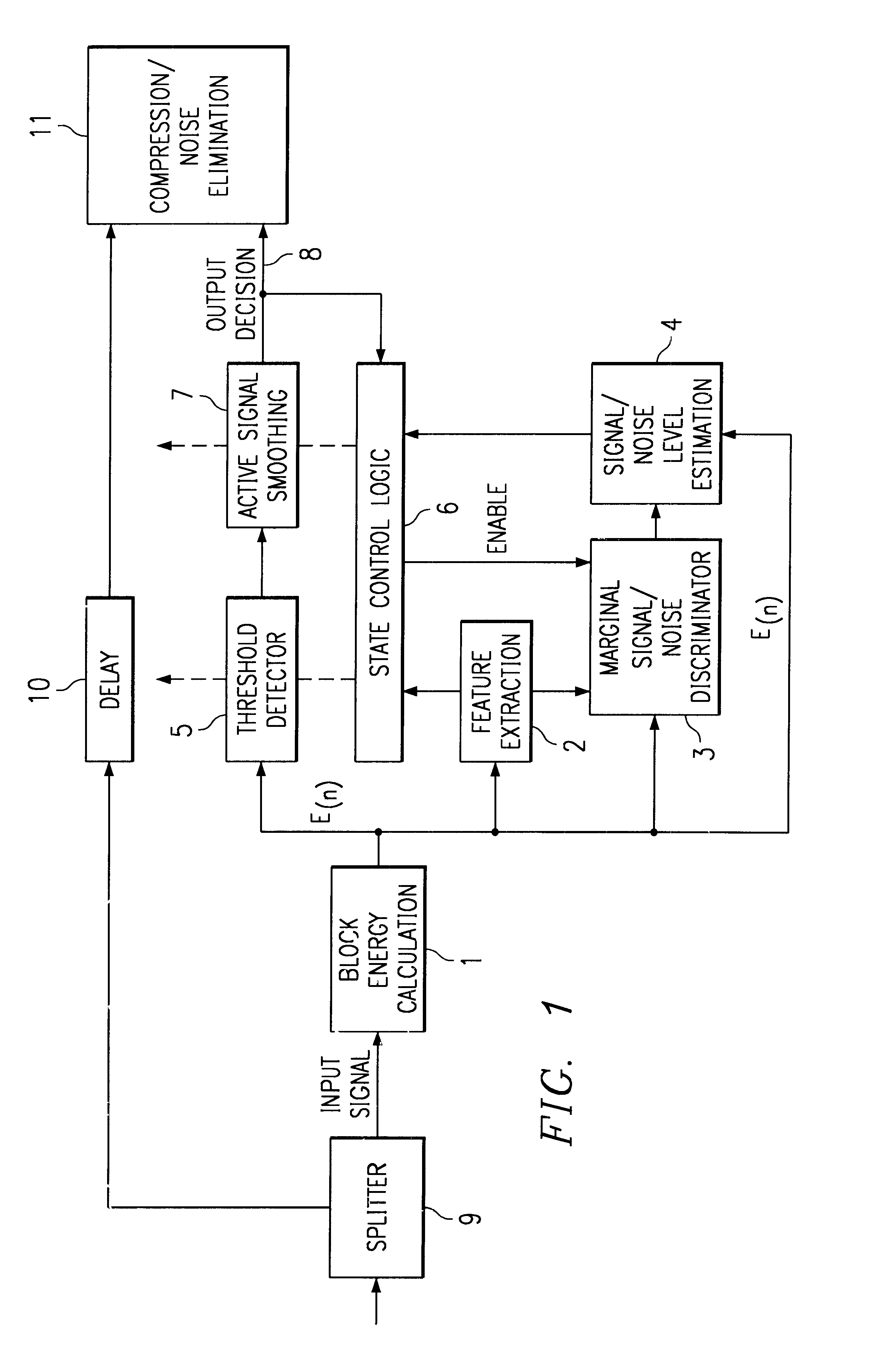
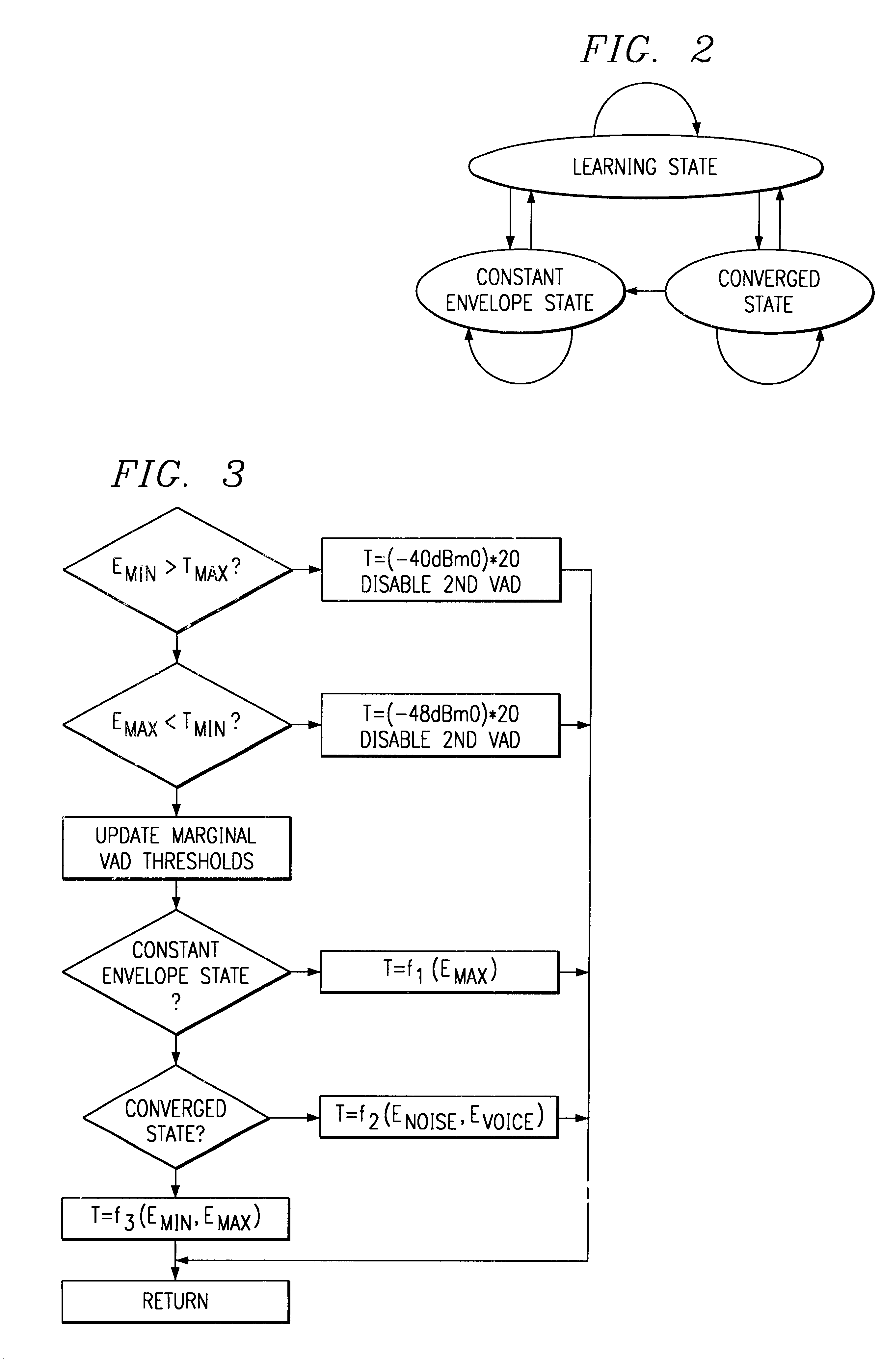
Adaptive two-threshold method for discriminating noise from speech in a communication signal
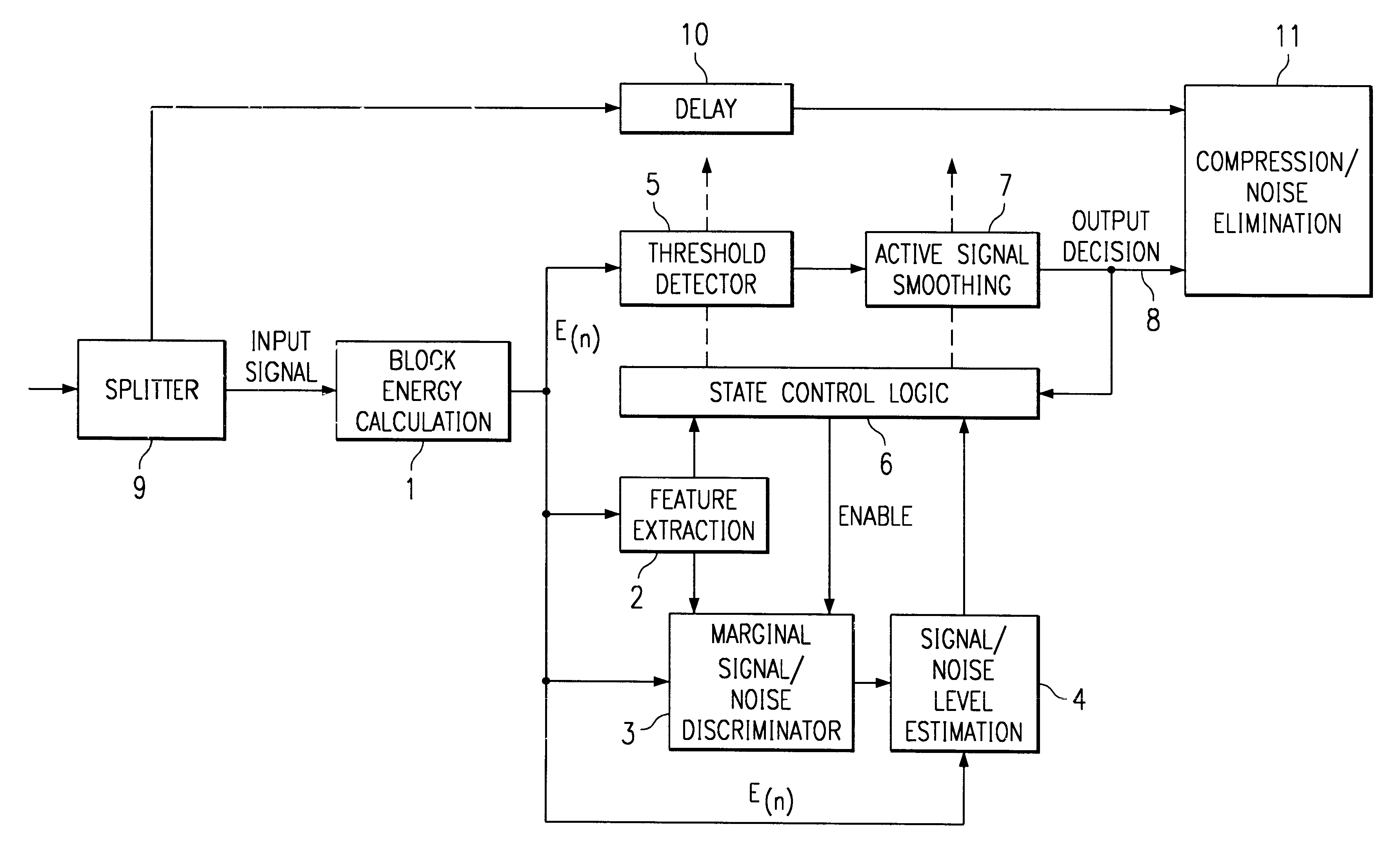
A method of discriminating noise and voice energy in a communication signal. A signal is measured in a plurality of block periods, which are sampled to obtain a measurement of the block energy value for the signal. The blocks are compared to a noise threshold and to a voice threshold to discriminate between noise and voice. The thresholds for noise and voice are periodically updated based on the minimum and maximum energy levels measured for block energies. In a preferred embodiment, the voice energy threshold and noise energy threshold values are updated according to a formula where the revised thresholds are based upon a factor of the minimum and maximum energy levels of the current block and the most recent past block and the average energy of the previous blocks. Updating of threshold levels allows for more accurate estimation of noise and voice during changes in either noise, voice or both to avoid missclassification of noise and / or voice.
Owner:TELOGY NETWORKS
Method to enhance afferent and efferent transmission using noise resonance
ActiveUS20110009919A1Reduces neuroplasticityReduces and prevents neuroplasticitySpinal electrodesHead electrodesElectricitySub threshold
Methods of providing therapy to a patient are provided. In one method, the patient has a neuron to which a sub-threshold biological electrical stimulus is applied. The method comprises applying electrical noise energy to the neuron, wherein resonance between the biological electrical stimulus and the electrical noise energy is created, such that an action potential is propagated along the axon of the neuron. In another method, the patient has a neuron to which a supra-threshold biological electrical stimulus is applied. This method comprises applying supra-threshold electrical noise energy to the neuron, thereby preventing an action potential from being propagated along the axon of the neuron. Still another method comprises applying an electrical stimulus to a neuron, and applying supra-threshold electrical noise energy to the neuron, thereby preventing or reversing any neurological accommodation of the neuron that may occur in response to the electrical stimulus.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Reducing acoustic noise in wireless and landline based telephony
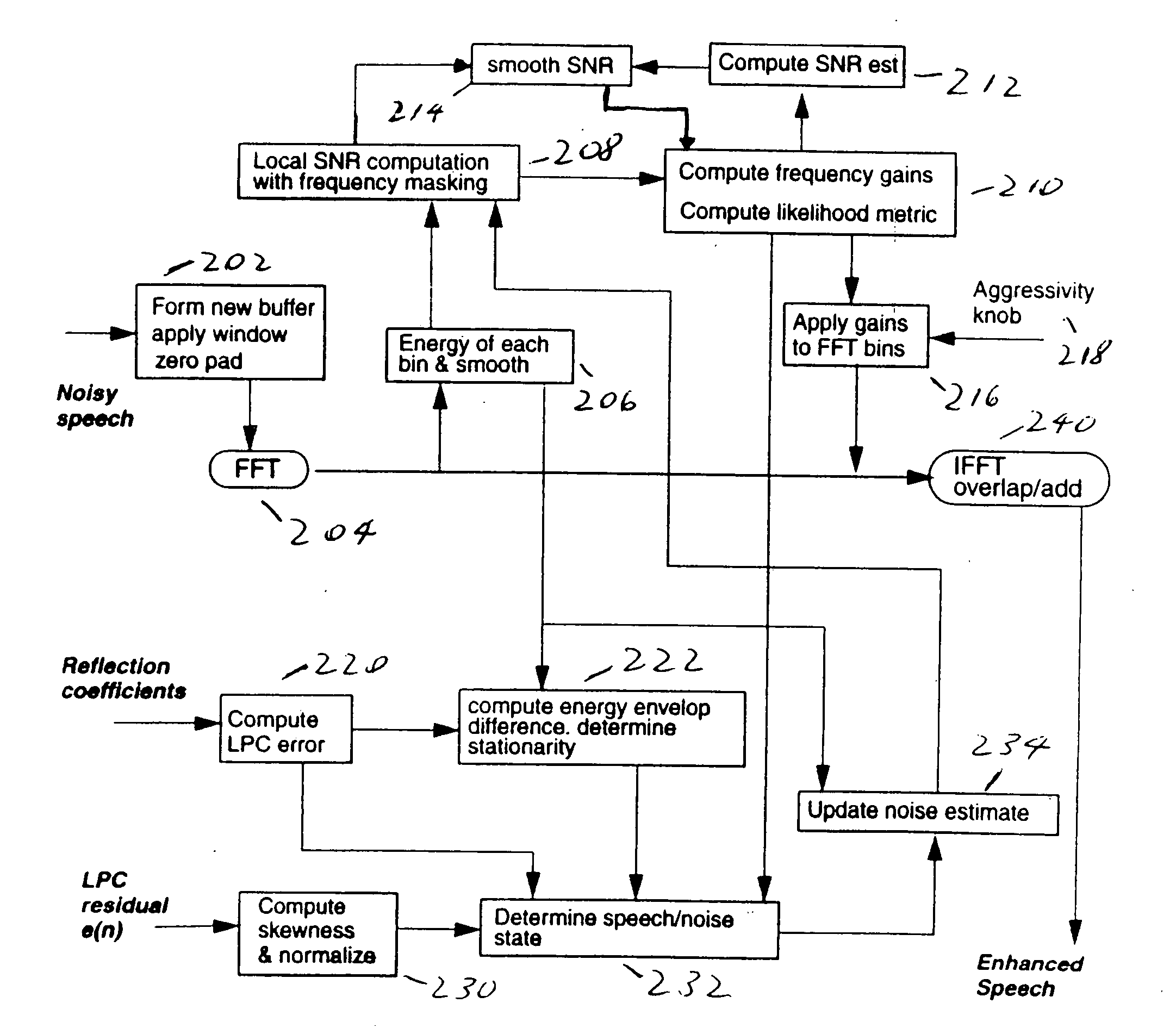
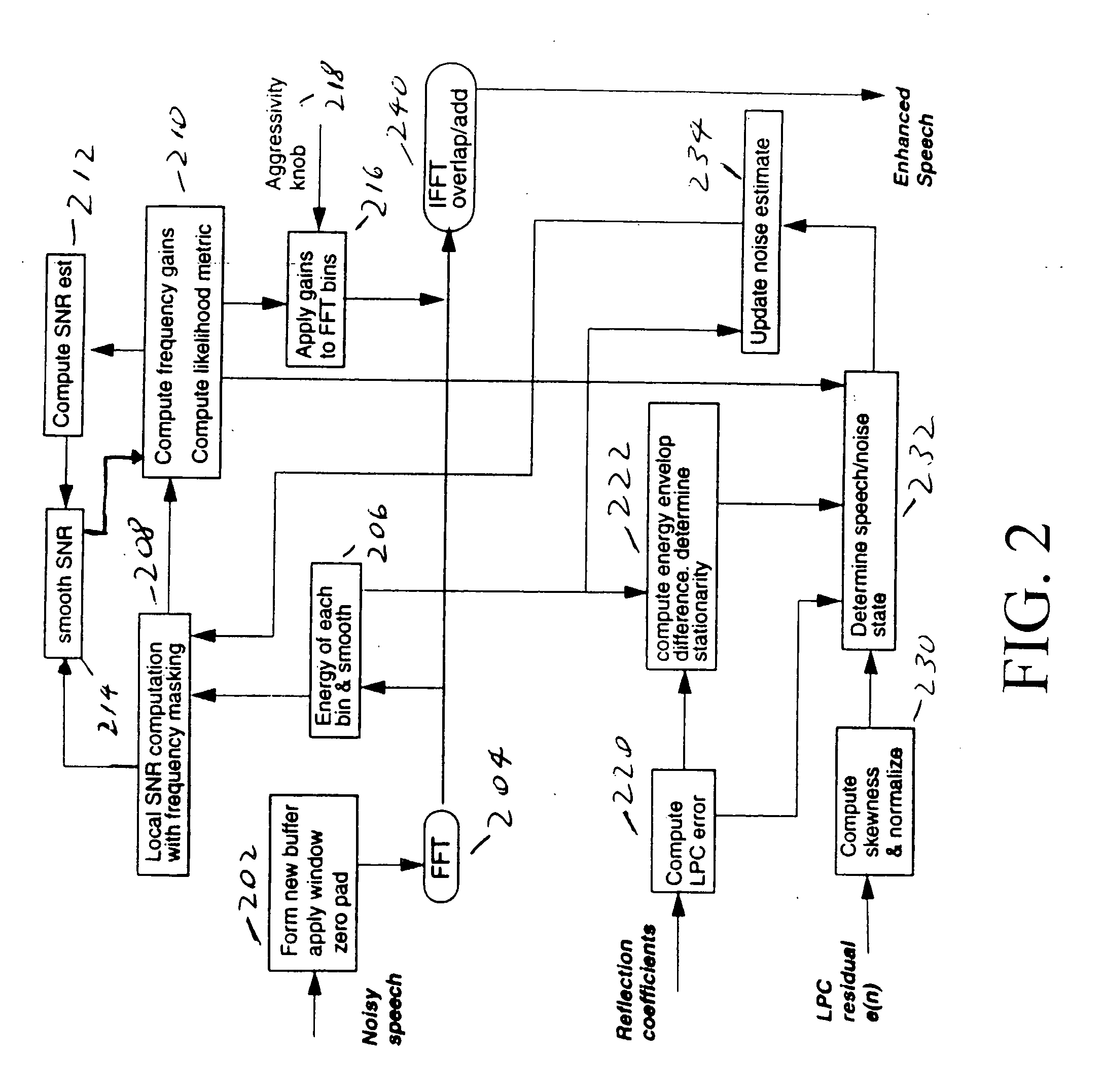
Acoustic noise for wireless or landline telephony is reduced through optimal filtering in which each frequency band of every time frame is filtered as a function of the estimated signal-to-noise ratio and the estimated total noise energy for the frame. Non-speech bands and other special frames are further attenuated by one or more predetermined multiplier values. Noise in a transmitted signal formed of frames each formed of frequency bands is reduced. A respective total signal energy and a respective current estimate of the noise energy for at least one of the frequency bands is determined. A respective local signal-to-noise ratio for at least one of the frequency bands is determined as a function of the respective signal energy and the respective current estimate of the noise energy. A respective smoothed signal-to-noise ratio is determined from the respective local signal-to-noise ratio and another respective signal-to-noise ratio estimated for a previous frame. A respective filter gain value is calculated for the frequency band from the respective smoothed signal-to-noise ratio. Also, it is determined whether at least a respective one as a plurality of frames is a non-speech frame. When the frame is a non-speech frame, a noise energy level of at least one of the frequency bands of the frame is estimated. The band is filtered as a function of the estimated noise energy level.
Owner:APPLE INC
Apparatus and system for reducing mechanical ventilator noise
InactiveUS20080127976A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMechanical ventilatorsEngineering
A sound dampening apparatus to be disposed in pneumatic connection with a respiratory support system. The respiratory support system may comprise a source of medical gas, a plurality of pneumatic connections and a patient interface. The sound dampening apparatus comprises an inlet, an outlet, and an outer case which forms a sound dampening chamber. As the medical gas flows through the sound dampening apparatus, the noise energy associated with the flow of medical gas is reduced.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
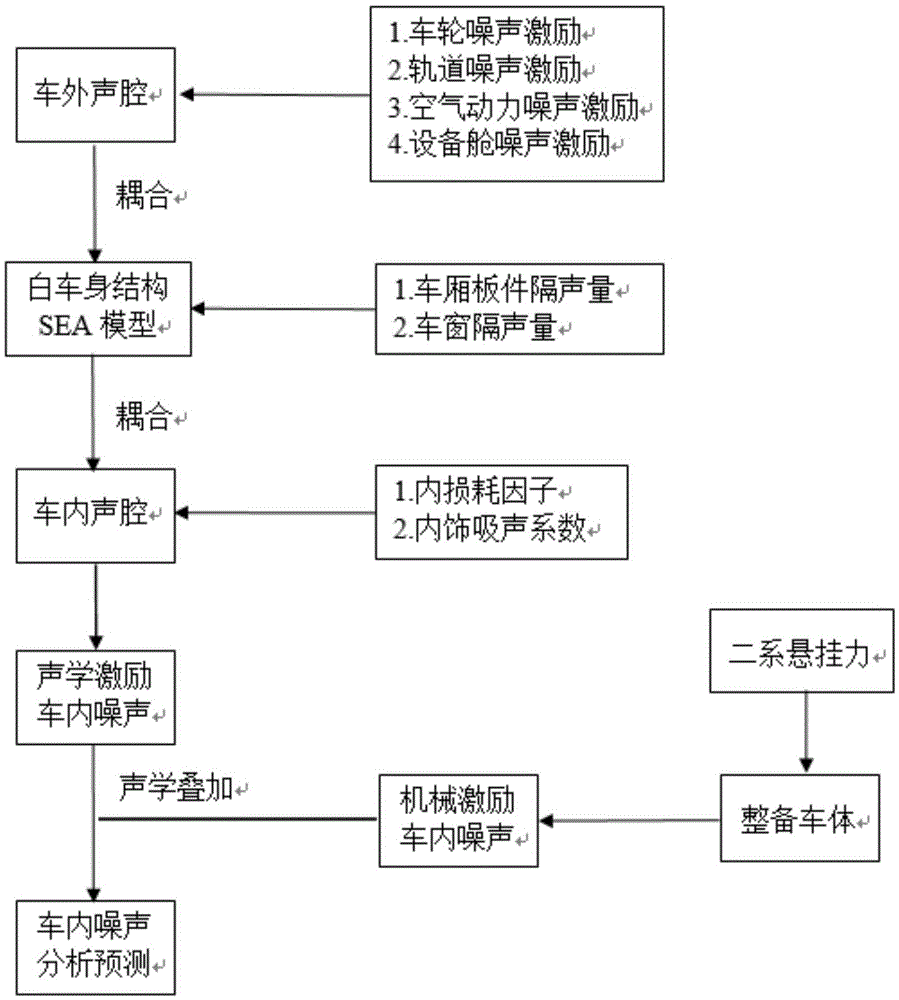
Interior noise analysis and prediction method of high speed train
InactiveCN105590003AShorten the development cycleAccuracy impactGeometric CADSustainable transportationEngineeringInterior noise
The invention discloses an interior noise analysis and prediction method of a high speed train. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a train reconditioning train body model, a statistical energy analysis model of a body in white structure and an interior and exterior vocal cavity statistical energy analysis model, and carrying out simplification and subsystem division; obtaining the statistical energy analysis parameters of the train body structure and an interior vocal cavity model, and loading the statistical energy analysis parameters onto a train body structure model plate subsystem and a vocal cavity model subsystem; and obtaining exterior vocal excitation source energy borne on the train body, applying the exterior vocal excitation source energy onto the exterior vocal cavity statistical energy analysis model, causing the exterior vocal excitation source energy to reach an interior vocal cavity after the exterior vocal excitation source energy is attenuated by the sound insulation property of a structural plate in a body in white structure model so as to obtain structural noise energy radiated into the train by the reconditioning train body under the function of the two-line suspension force of a compartment, and then, carrying out interior noise analysis and prediction. The problem that the interior noise of the train is difficult in prediction and the problems of the upper limit boundedness of a frequency domain, complex calculation flow, incomplete motivation consideration in the traditional method are overcome, calculation efficiency and prediction accuracy are improved, and development and test cost is lowered.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and apparatus for reducing noise in speech and audio signals
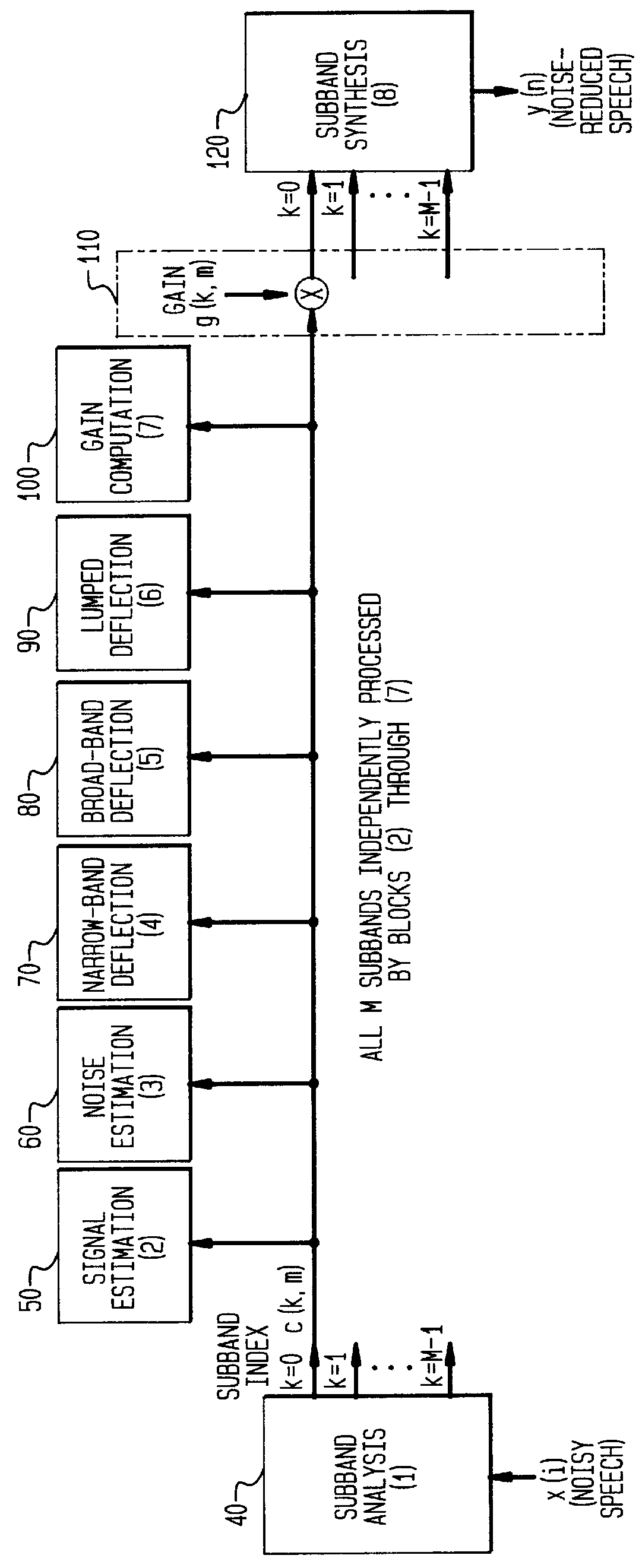
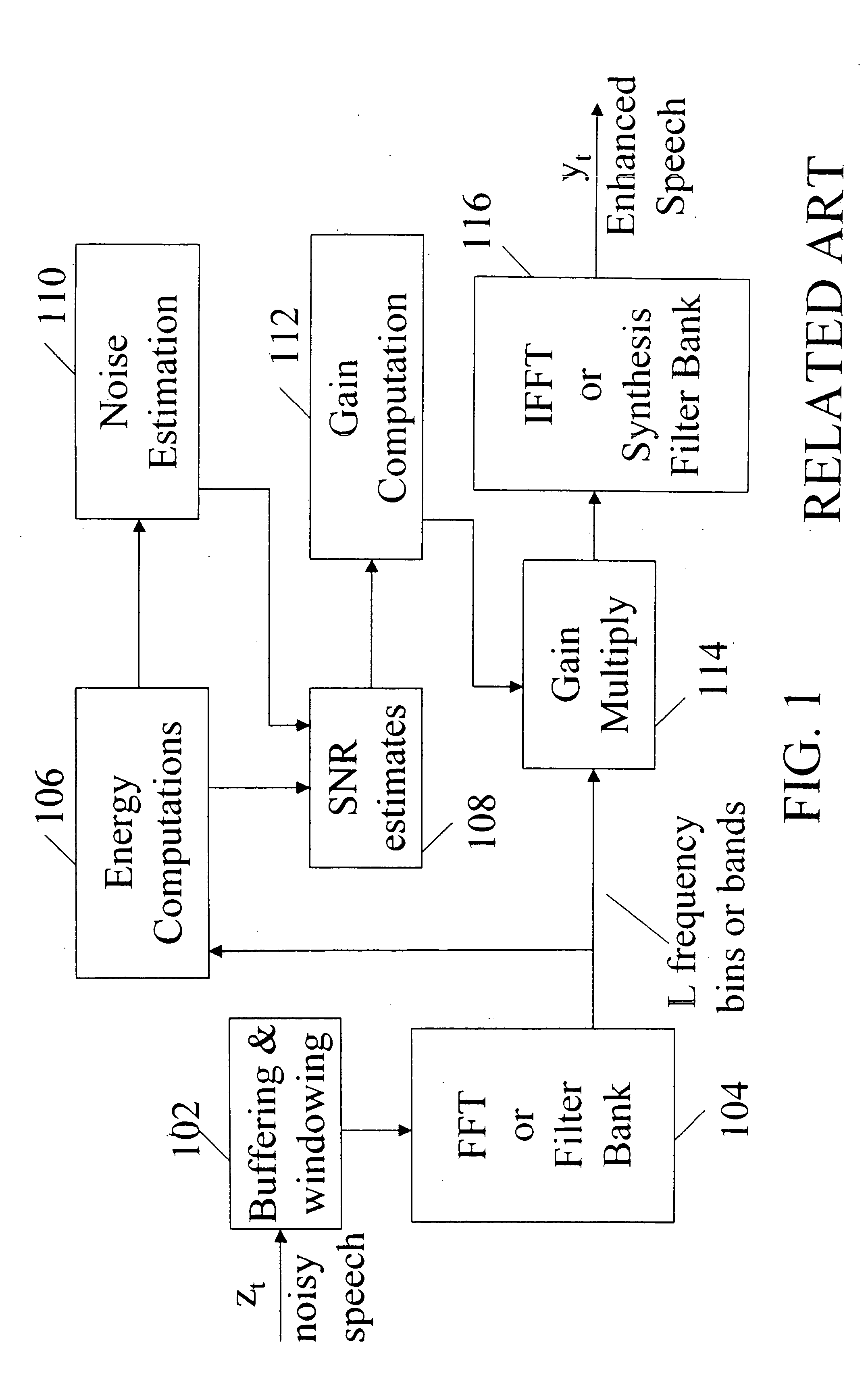
A method and apparatus are disclosed for enhancing, within a signal bandwidth, a corrupted audio-frequency signal. The signal which is to be enhanced is analyzed into plural sub-band signals, each occupying a frequency sub-band smaller than the signal bandwidth. A respective signal gain function is applied to each sub-band signal, and the respective sub-band signals are then synthesized into an enhanced signal of the signal bandwidth. The signal gain function is derived, in part, by measuring speech energy and noise energy, and from these determining a relative amount of speech energy, within the corresponding sub-band. In certain embodiments of the invention, the signal gain function is also derived, in part, by determining a relative amount of speech energy within a frequency range greater than, but centered on, the corresponding sub-band. In other embodiments of the invention, the sub-band noise energy is determined from a noise estimate that is updated at periodic intervals, but is not updated if the newest sample of the signal to be enhanced exceeds the current noise estimate by a multiplicative threshold (i.e., a threshold expressible in decibels). In still other embodiments of the invention, the value of the noise estimate is limited by an upper bound that is matched to the dynamic range of the signal to be enhanced.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and system for judging double-end conversation and method and system for eliminating echo
ActiveCN101719969AEliminate high frequency effectsAccurate judgmentTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsCommunications systemMicrophone signal
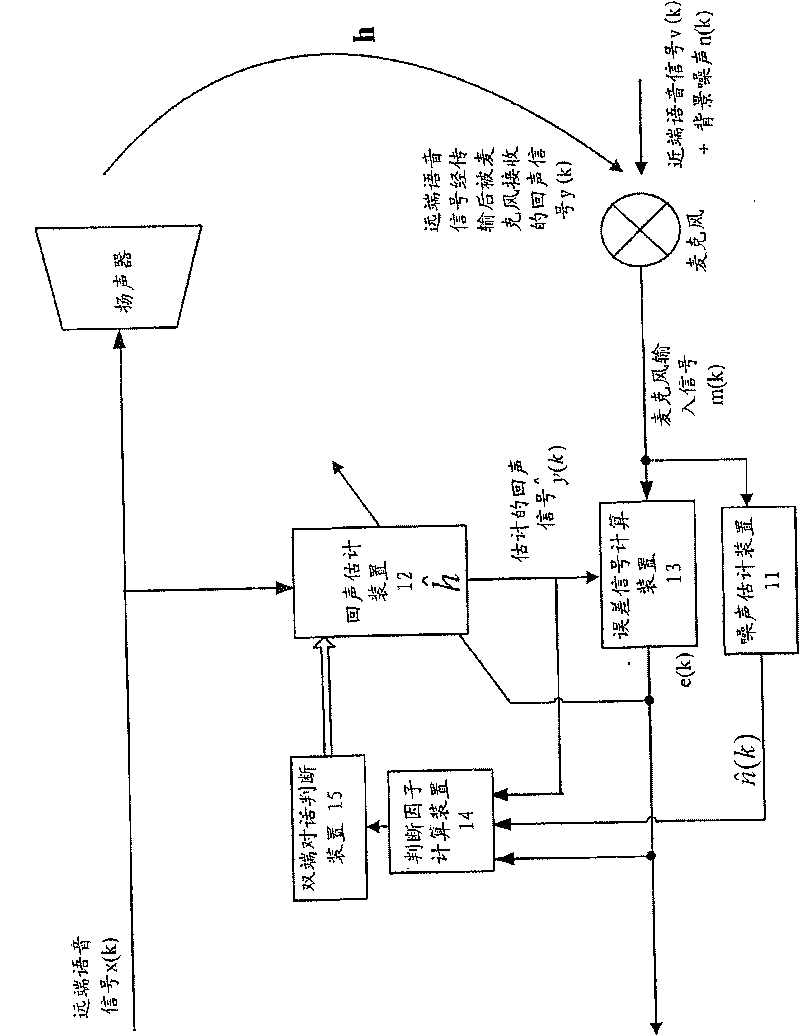
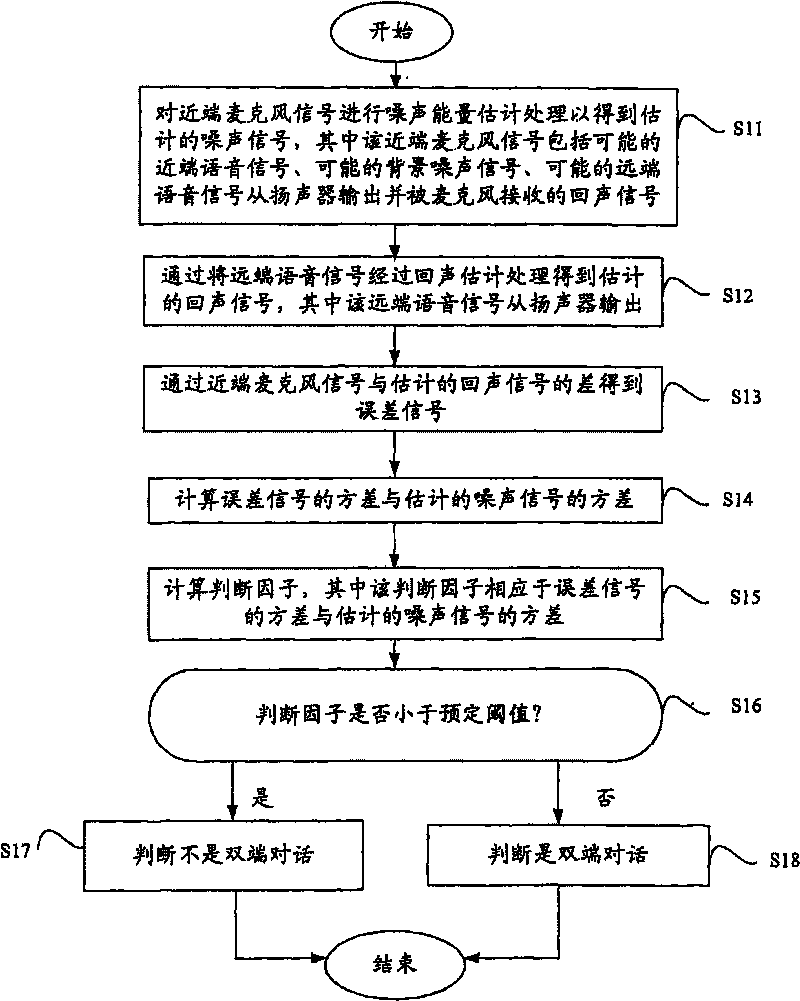
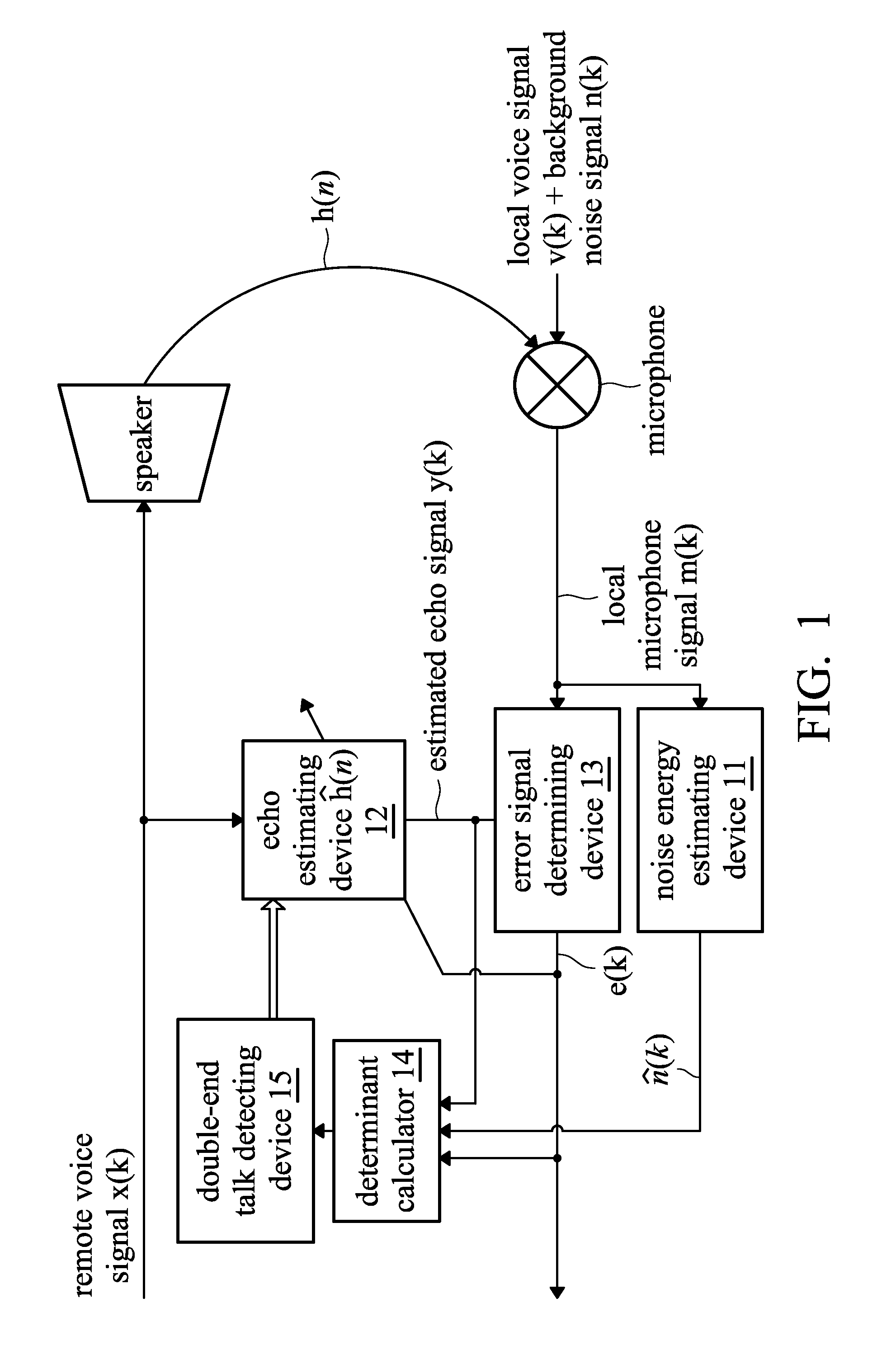
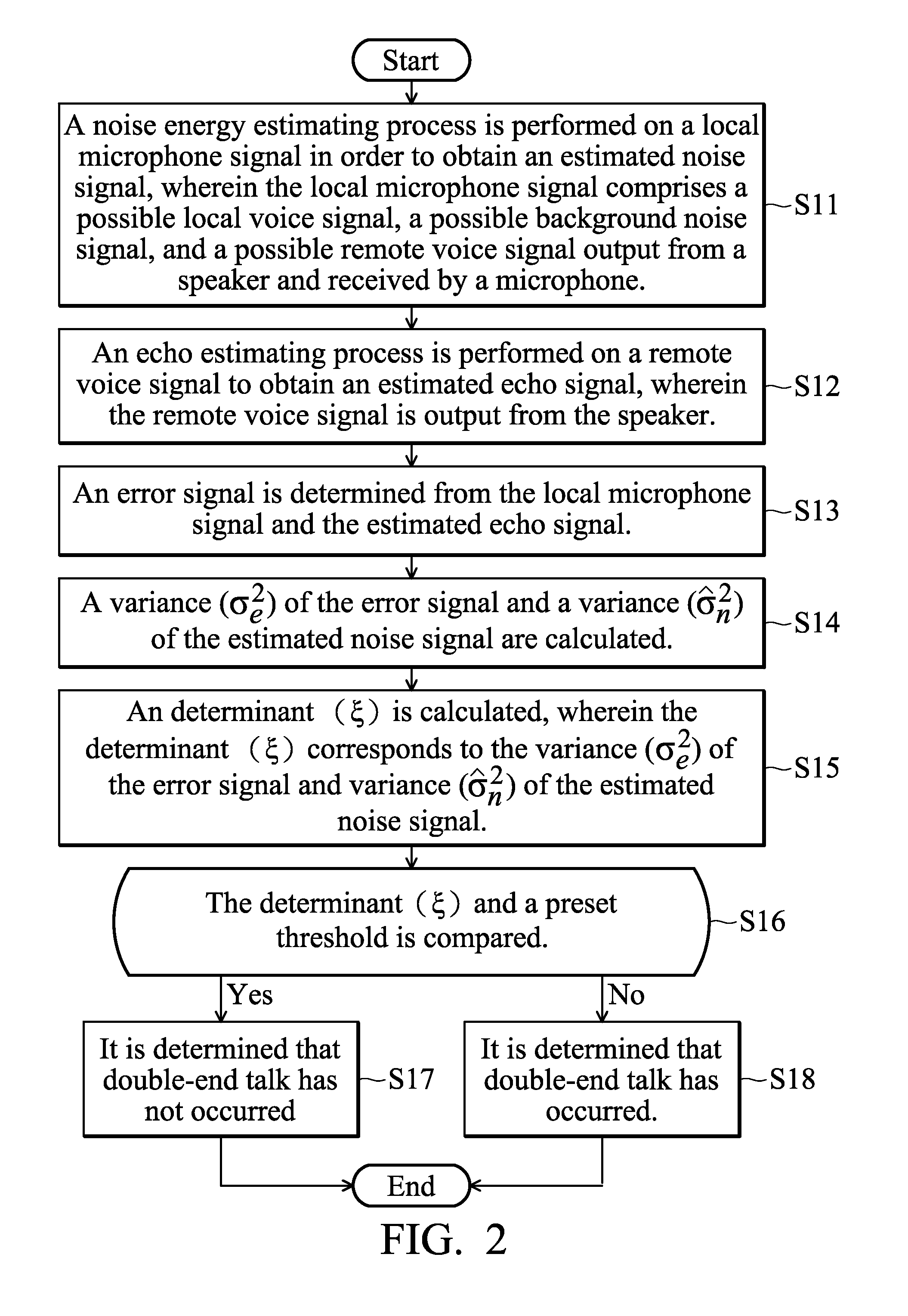
The invention provides a method and a system for eliminating echo in a communication system with a loudspeaker and a microphone, the method comprises the following steps: carry out the noise energy estimation processing to a near-end microphone signal to obtain an estimated noise signal, wherein, the near-end microphone signal comprises a possible near-end speech signal, a possible background noise signal, an echo signal which is formed by outputting a possible far-end speech signal from the loudspeaker and being received by the microphone; carry out the echo estimation processing to the far-end speech signal to obtain an estimated echo signal, wherein, the far-end speech signal is output from the loudspeaker; obtain an error signal by the difference of the near-end microphone signal and the estimated echo signal; calculate the variance of the error signal and the variance of the estimated noise signal; calculate an judging factor, wherein, the judging factor corresponds to the variance of the error signal and the variance of the estimated noise signal; compare the judging factor and a predetermined threshold value, when the judging factor is less than the predetermined threshold value, judge a conversation which is not a double-end conversation, otherwise, judge the conversation which is the double-end conversation.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method of and apparatus for reducing acoustic noise in wireless and landline based telephony
Acoustic noise for wireless or landline telephony is reduced using frequency domain of optimal filtering in which each frequency band of every time frame is filtered as a function of the estimated signal-two-noise ratio and the estimated total noise energy for the frame. Non-speech, non-speech frames and other special frames are further attenuated by one or more predetermined multiplier values. Noise in a transmitted signal comprised of frames each comprised of frequency bands is reduced. A respective total signal energy and a respective current estimate of the noise energy for at least one of the frequency bands is determined. A respective local signal-to-noise ratio-for at least one of the frequency bands is determined as a function of the respective signal energy and the respective current estimate of the noise energy. A respective smoothed signal-to-noise ratio is determined from the respective local signal-to-noise ratio and another respective signal-to-noise ratio estimated for a previous frame. A respective filter gain value is calculated for the frequency band from the respective smoothed signal-to-noise ratio. Also, it is determined whether at least a respective one as a plurality of frames is a non-speech frame. When the frame is a non-speech frame, a noise energy level of at least one of the frequency bands of the frame is estimated. The band is filtered as a function of the estimated noise energy level.
Owner:APPLE INC
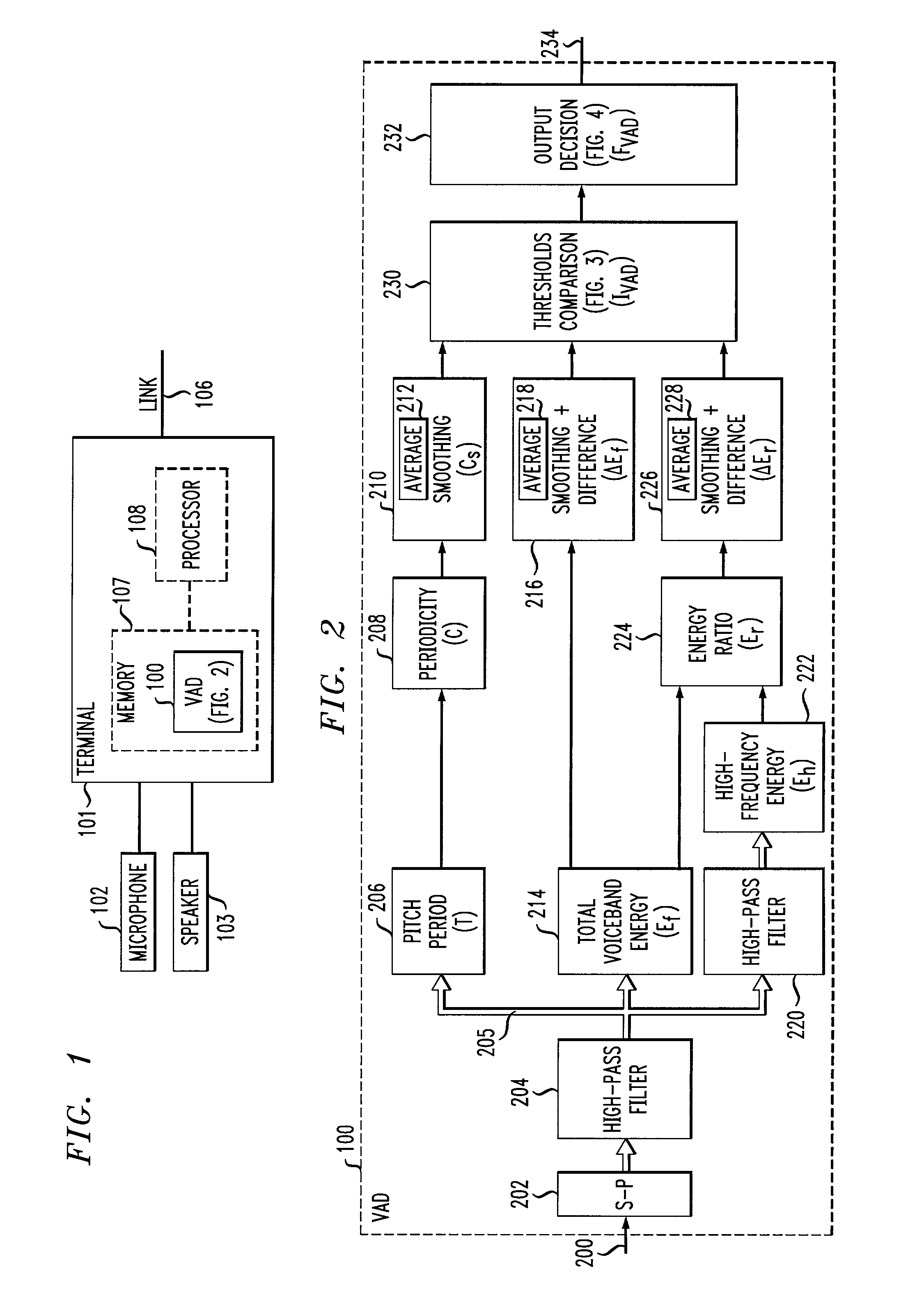
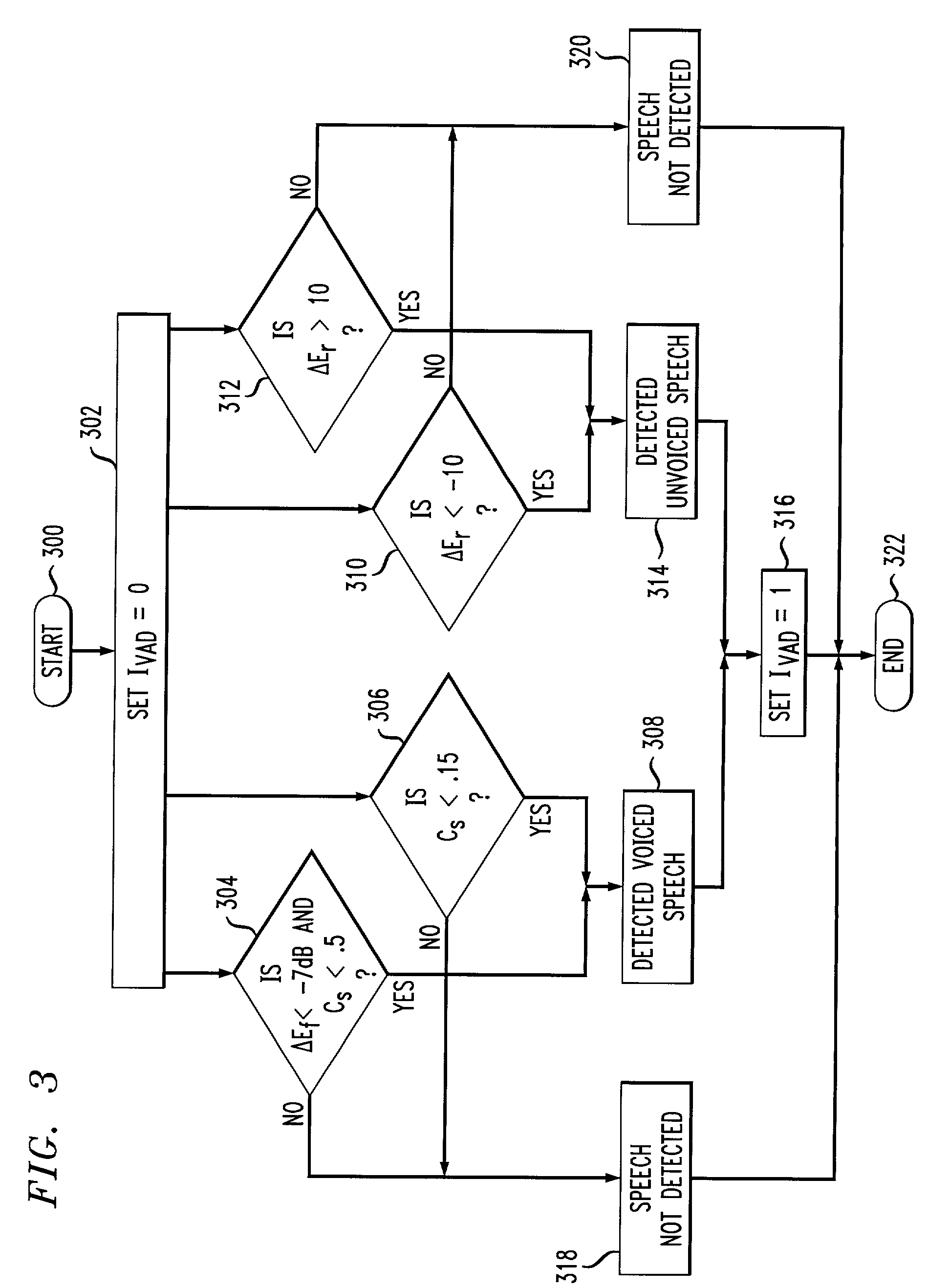
Voice-activity detection using energy ratios and periodicity
A voice activity detector (100) filters (204) out noise energy and then computes a high-frequency (2400 Hz to 4000 Hz) versus low-frequency (100 Hz to 2400 Hz) signal energy ratio (224), total voiceband (100 Hz to 4000 Hz) signal energy (214), and signal periodicity (208) on successive frames of signal samples. Signal periodicity is determined by estimating the pitch period (206) of the signal, determining a gain value of the signal over the pitch period as a function of the estimated pitch period, and estimating a periodicity of the signal over the pitch period as a function of the estimated pitch period and the gain value. Voice is detected (230–232) in a segment if either (a) the difference between the average high-frequency versus low-frequency signal energy ratio and the present segment's high-frequency versus low-frequency energy ratio either exceeds (310) a high threshold value or is exceeded (312) by a low threshold value, or (b) the average periodicity of the signal is lower (306) than a low threshold value, or (c) the difference between the average total signal energy and the present segment's total energy exceeds (304) a threshold value and the average periodicity of the signal is lower (304) than a high threshold value, or (d) the average total signal energy exceeds (412) a minimum average total signal energy by a threshold value and voice has been detected (410) in the preceding segment.
Owner:AVAYA INC
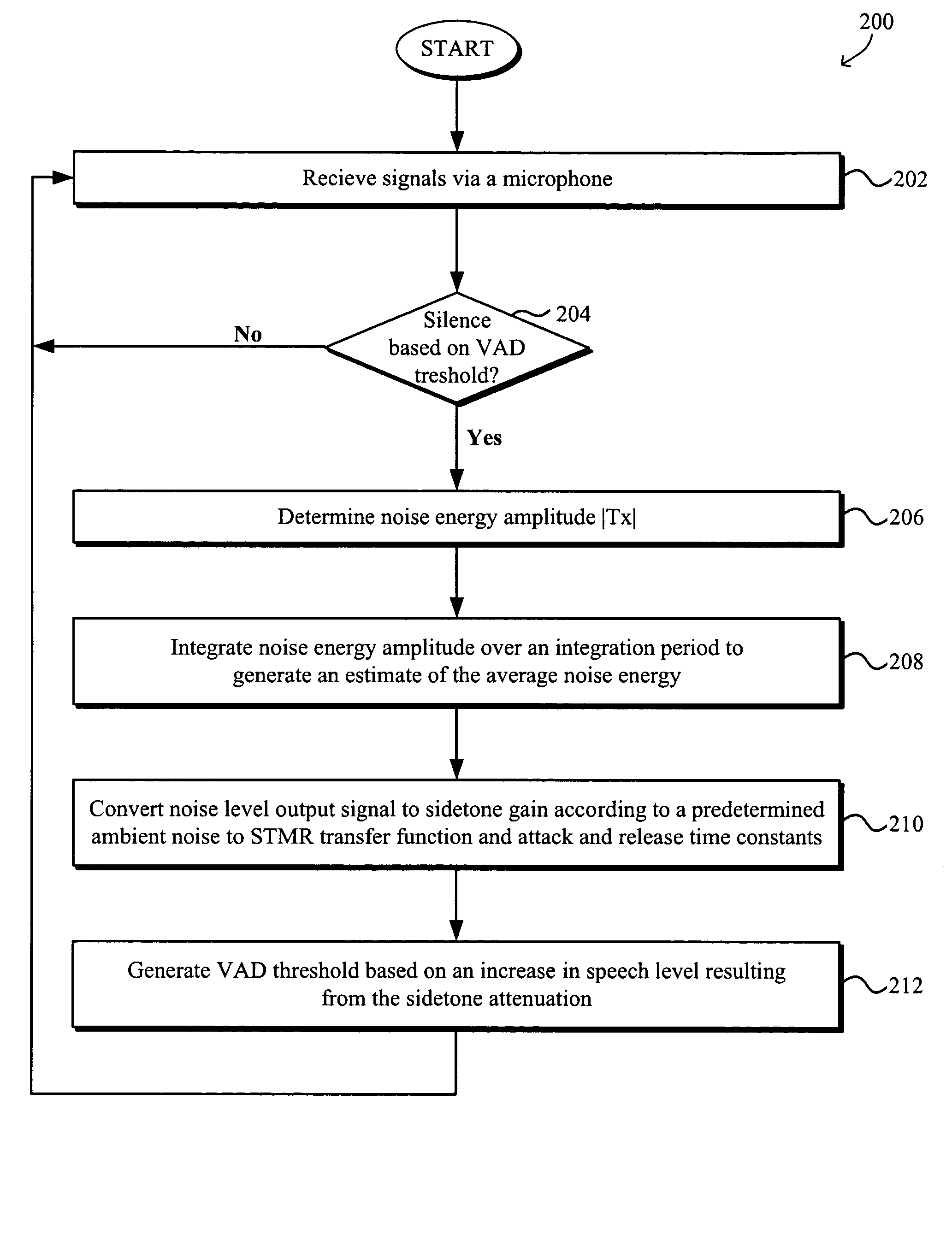
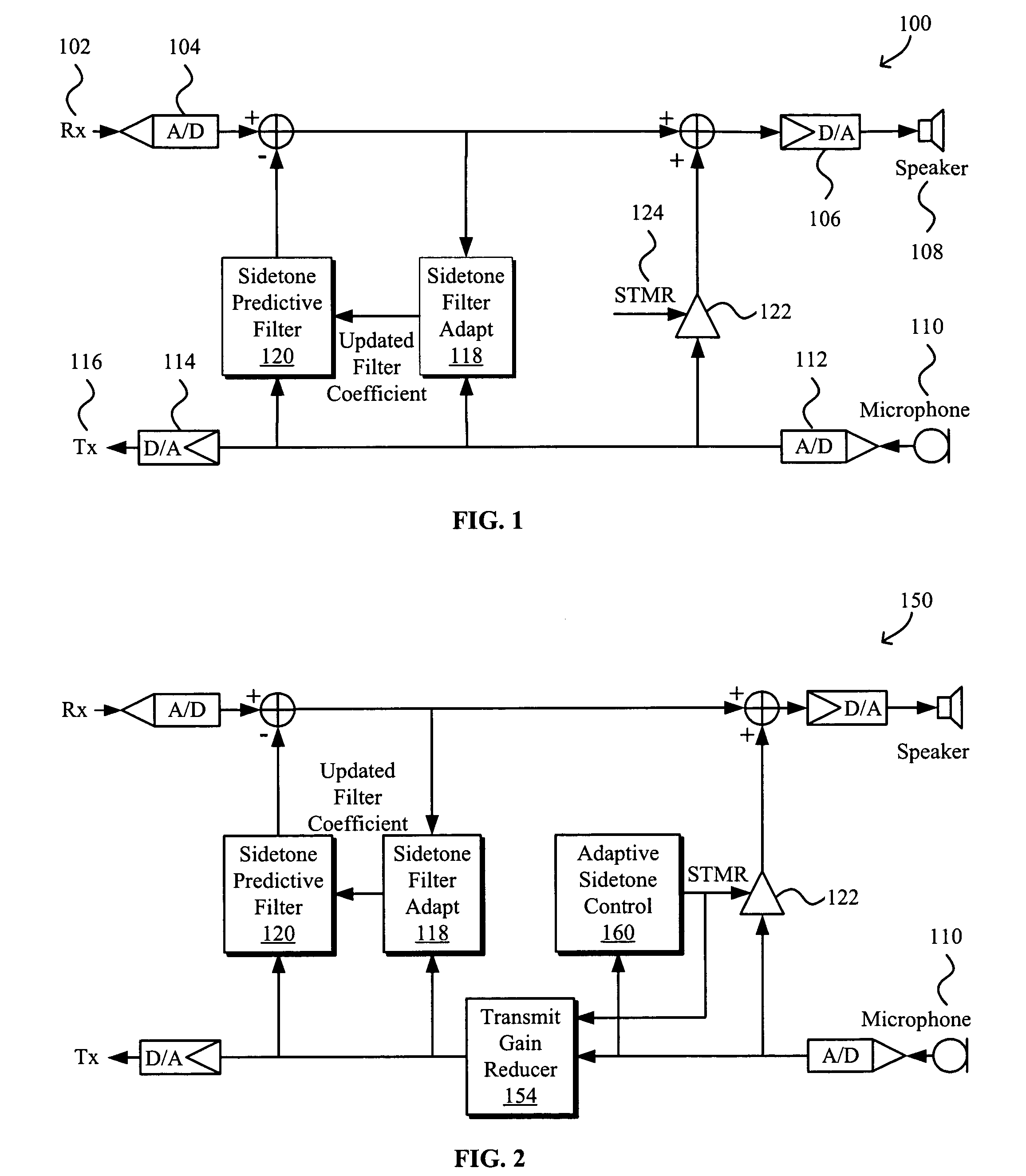
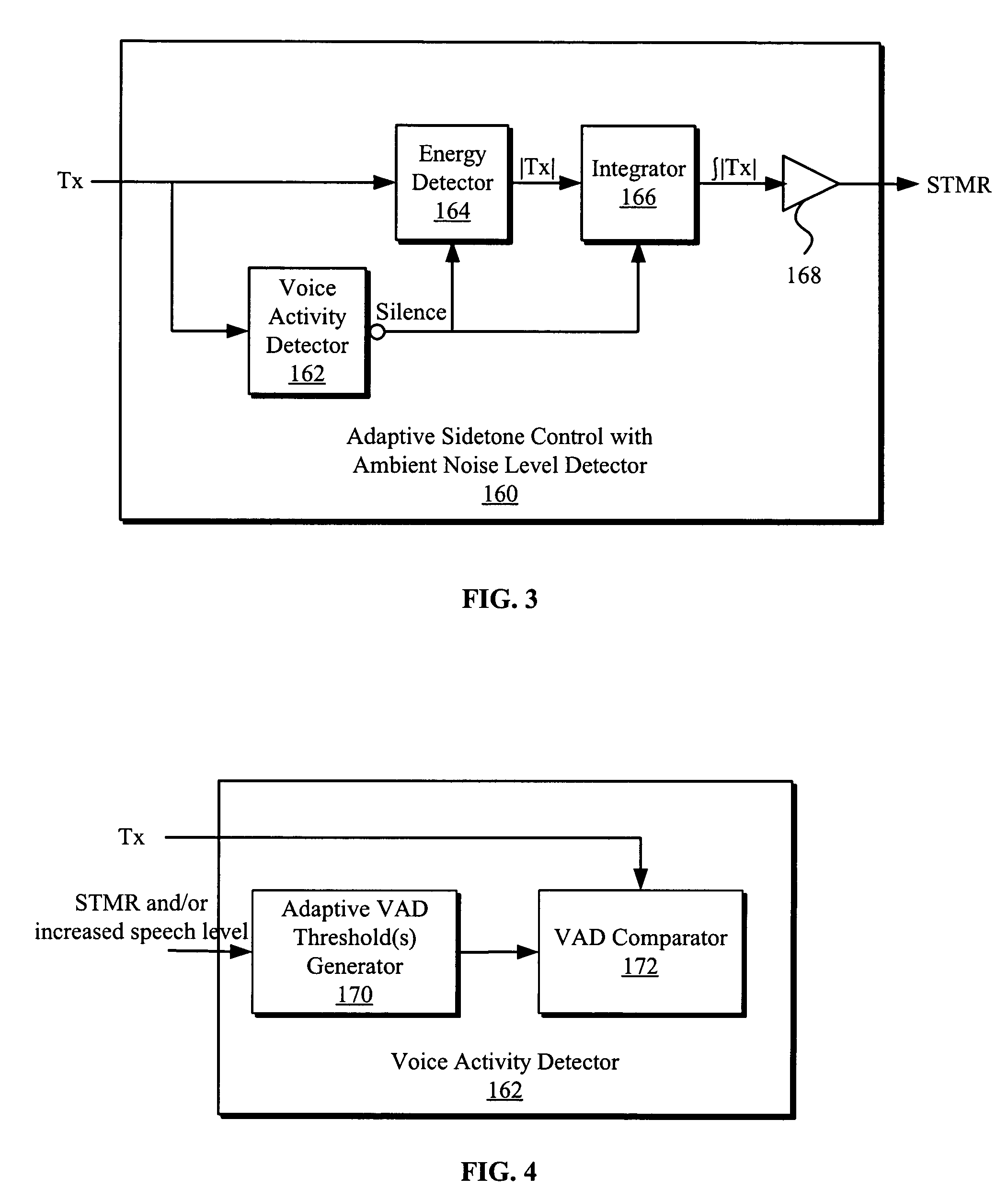
Adaptive sidetone and adaptive voice activity detect (VAD) threshold for speech processing
ActiveUS7881927B1Increase volumeEnhanced signalInterconnection arrangementsSpeech analysisUltrasound attenuationSidetone
Systems and methods for adaptive sidetone and adaptive voice activity detect (VAD) threshold for speech processing are disclosed. The VAD system generally includes an adaptive VAD threshold generator configured to generate a VAD threshold based on an increase in voice level resulting from sidetone attenuation and a comparator for comparing received signals to the adaptive VAD threshold to determine the existence of voice activity. The sidetone attenuation is based on an average ambient noise energy level determined from a noise energy amplitude during periods of no voice activity and a comparator for comparing received signals to the adaptive VAD threshold to determine existence of voice activity.
Owner:PLANTRONICS
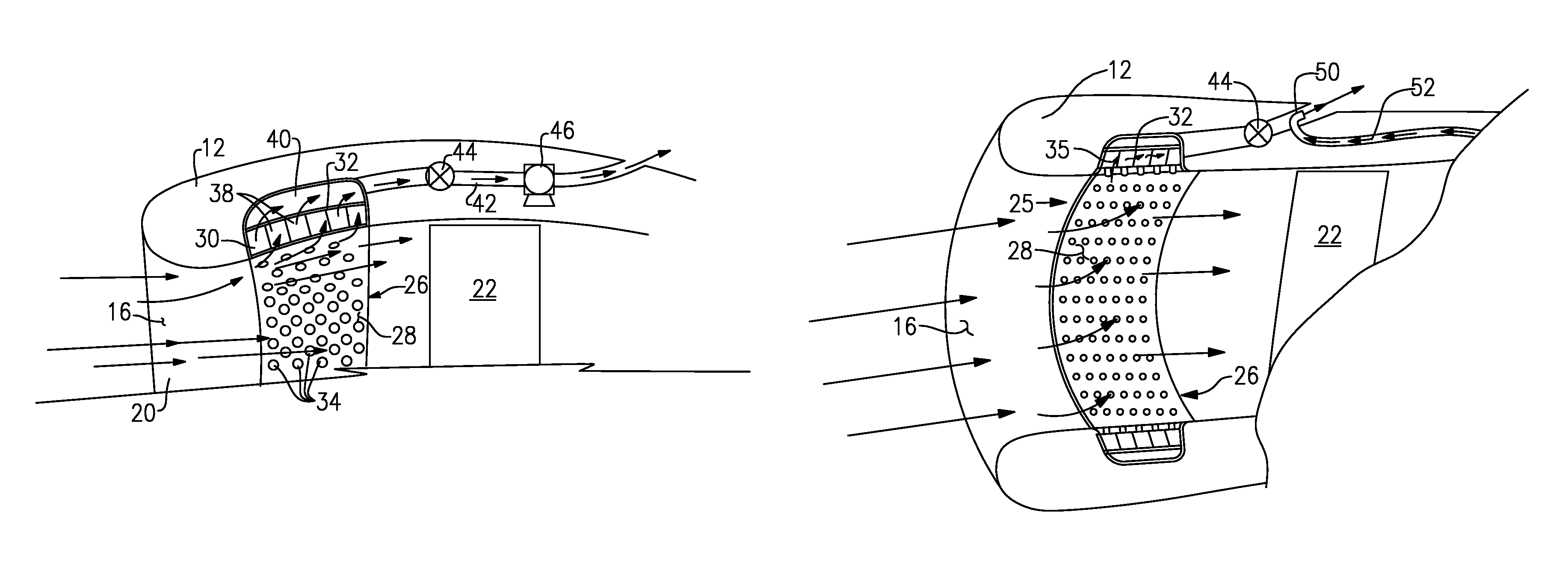
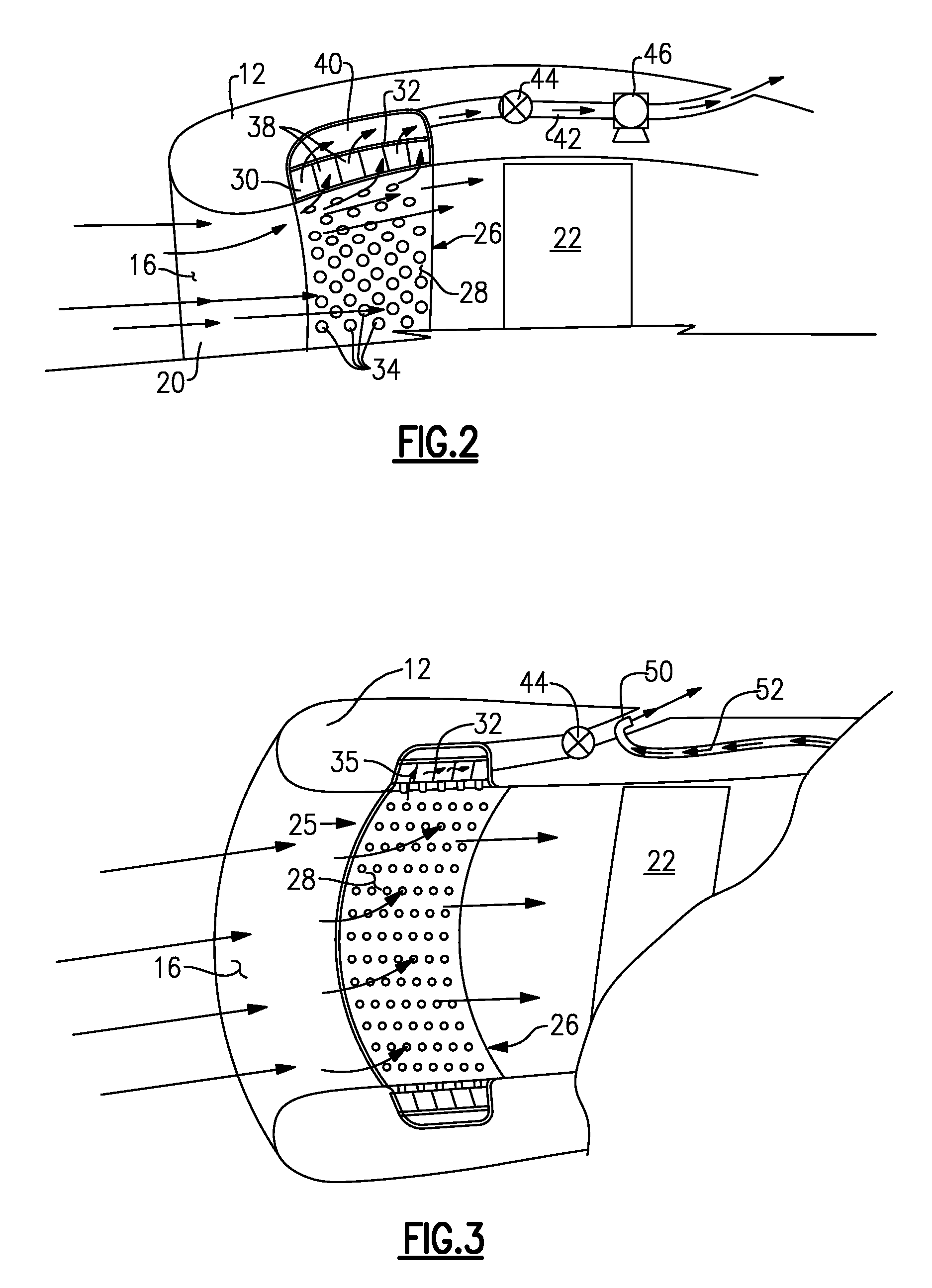
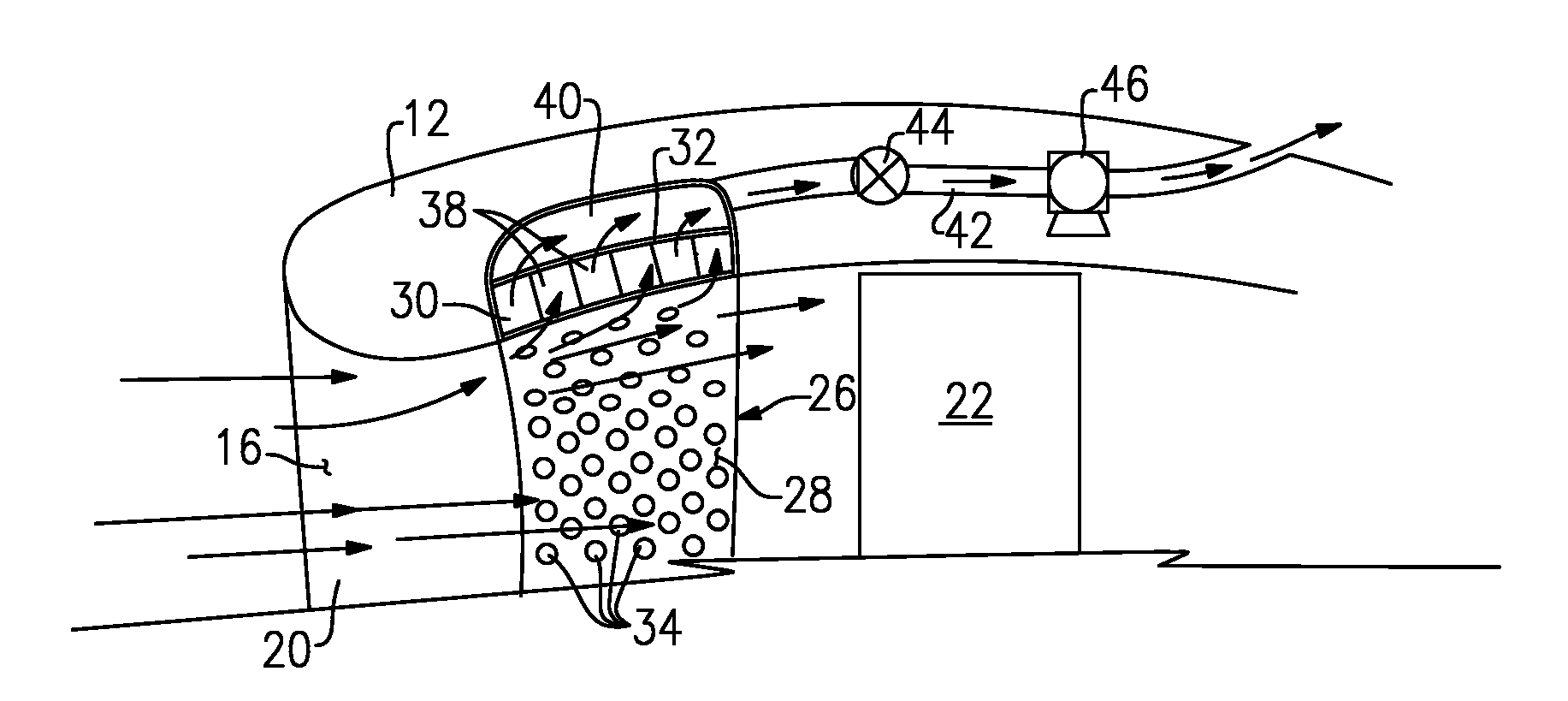
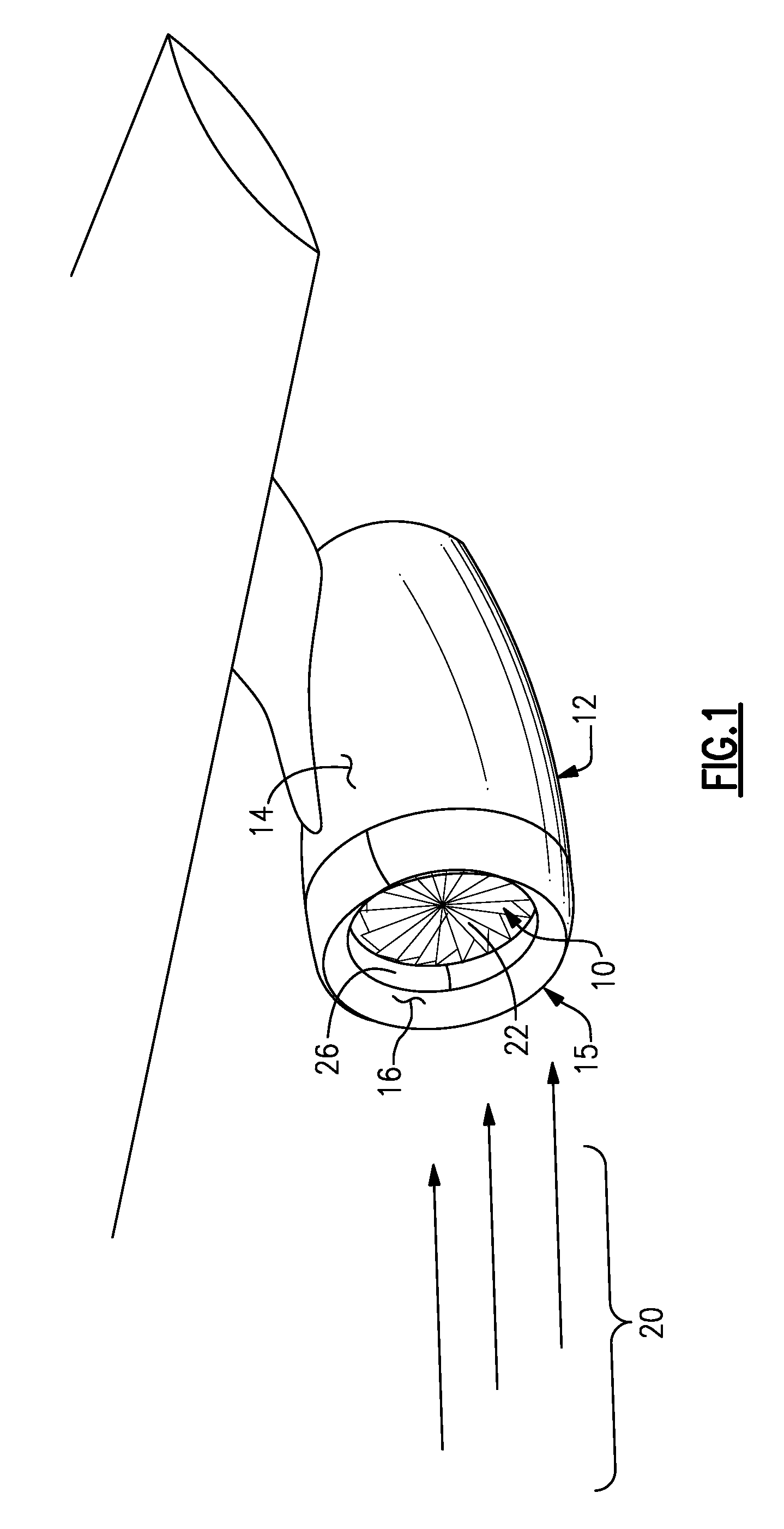
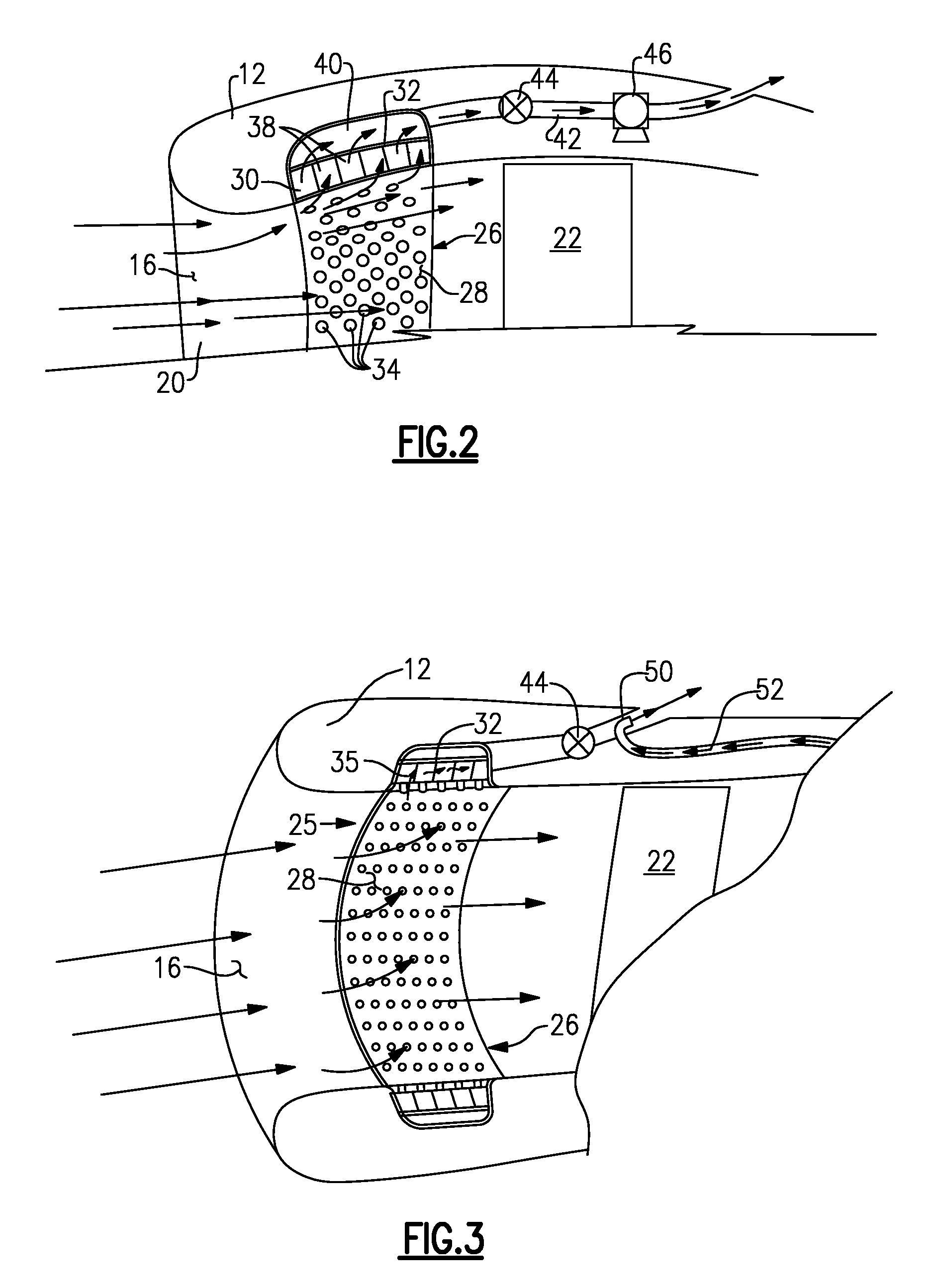
Integral suction device with acoustic panel
InactiveUS7766280B2Avoid separationLower performance requirementsEngine fuctionsWingsNacelleControl system
An inlet flow control system disposed within a nacelle includes a panel on an inner surface of that nacelle. The panel includes a noise attenuation layer that dissipates noise energy. A vacuum source generates a pressure differential across the noise attenuation layer for drawing airflow through the panel and away from an inner surface of the nacelle.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
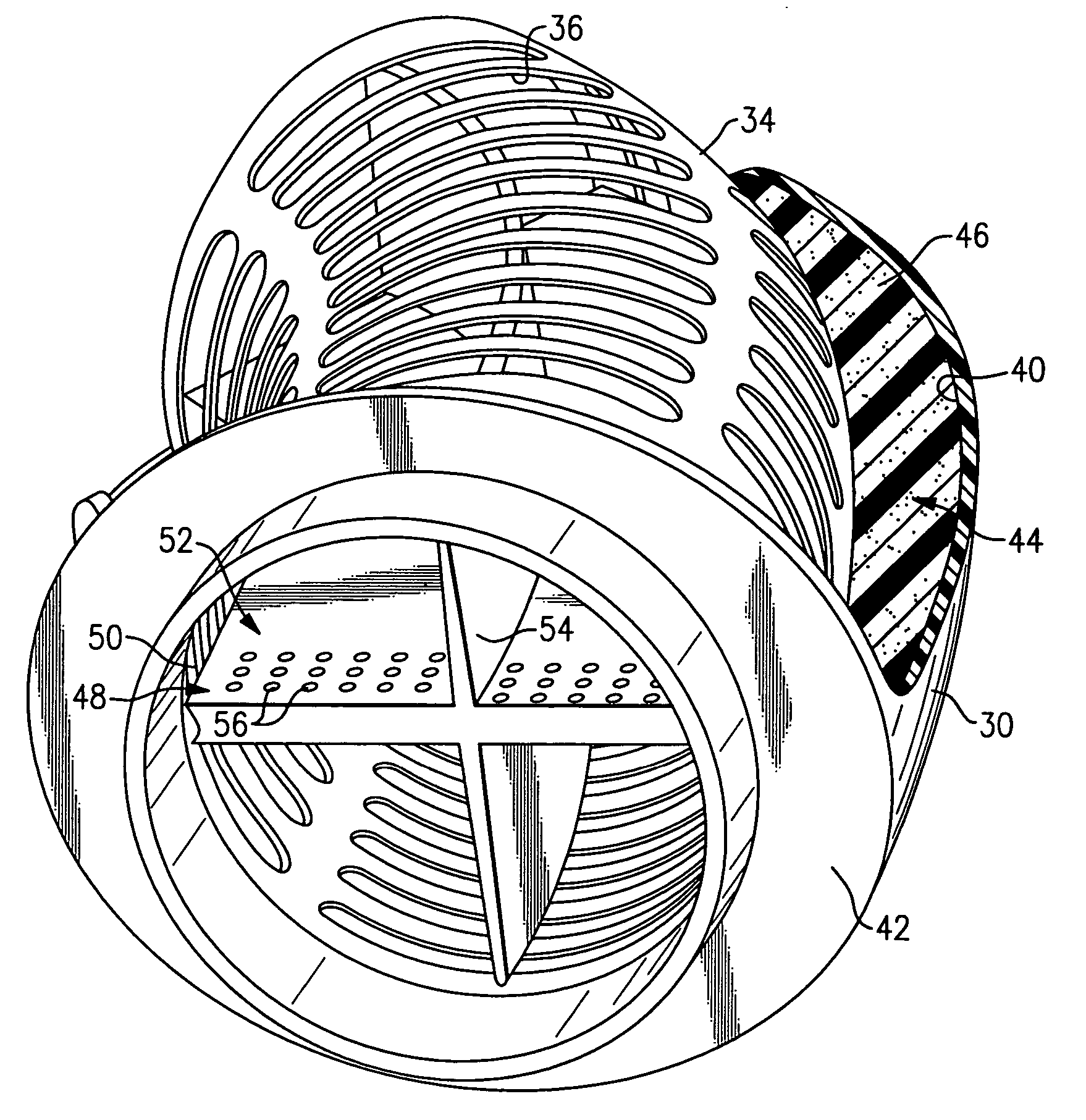
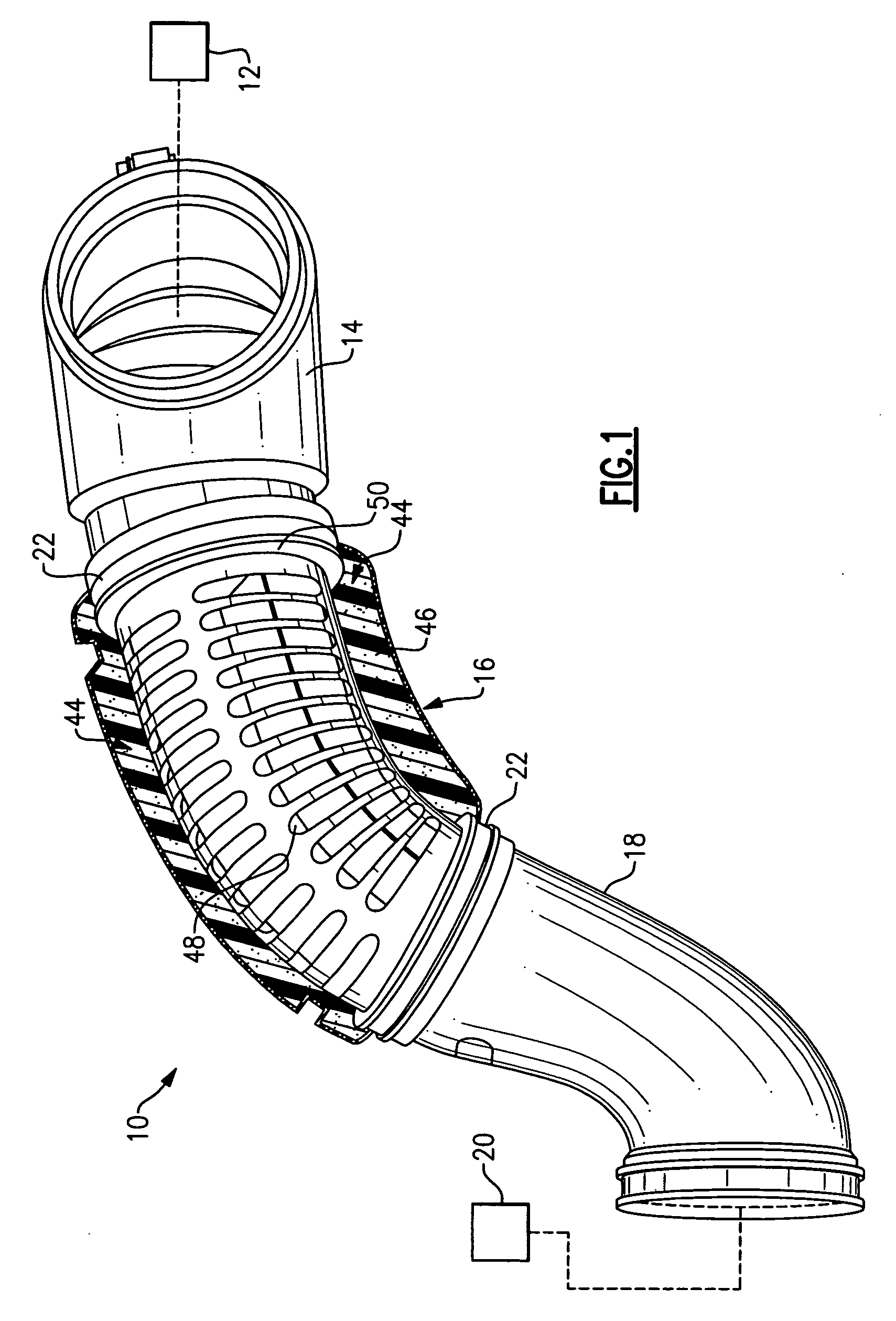
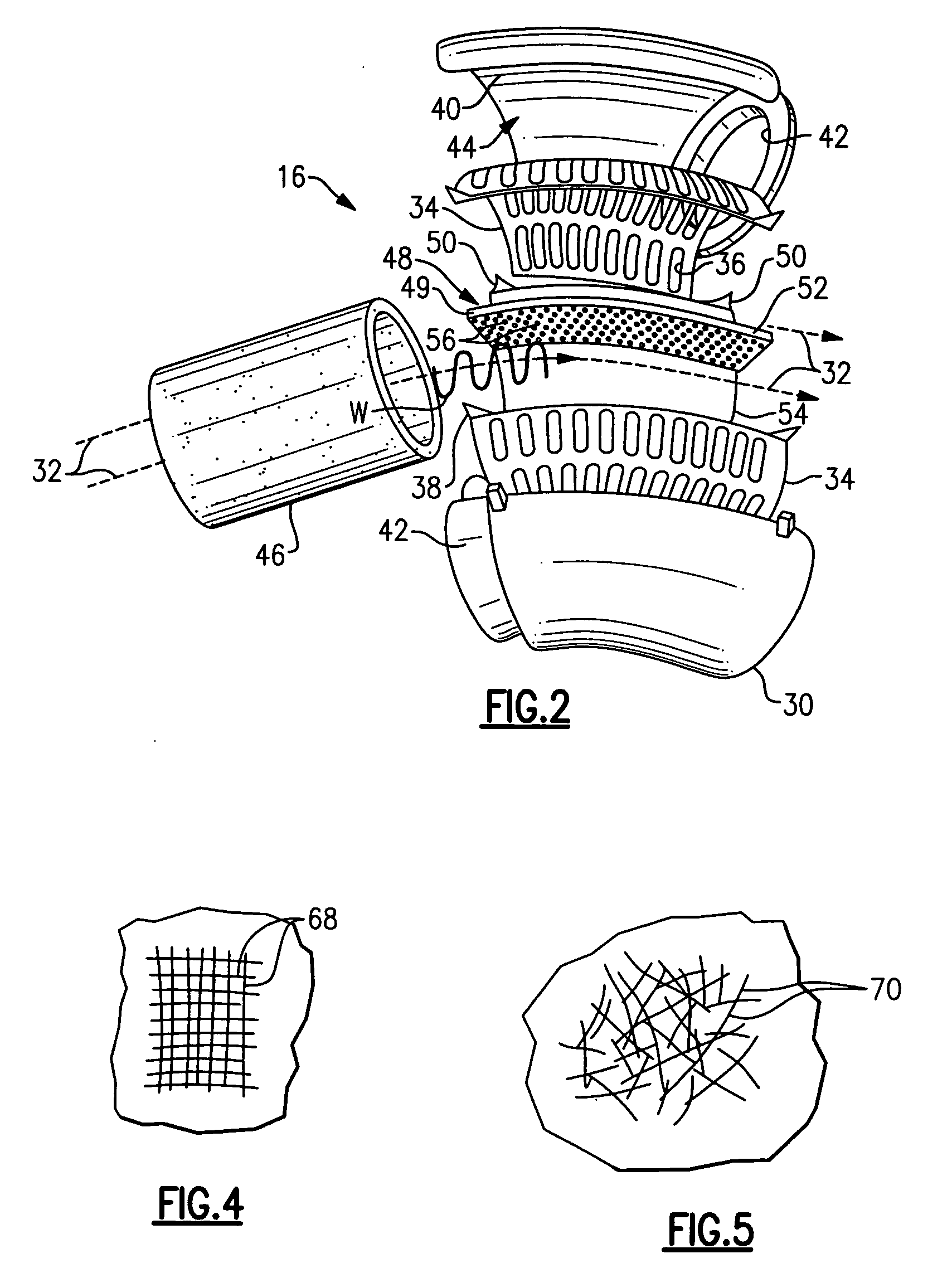
Silencer for air induction system and high flow articulated coupling
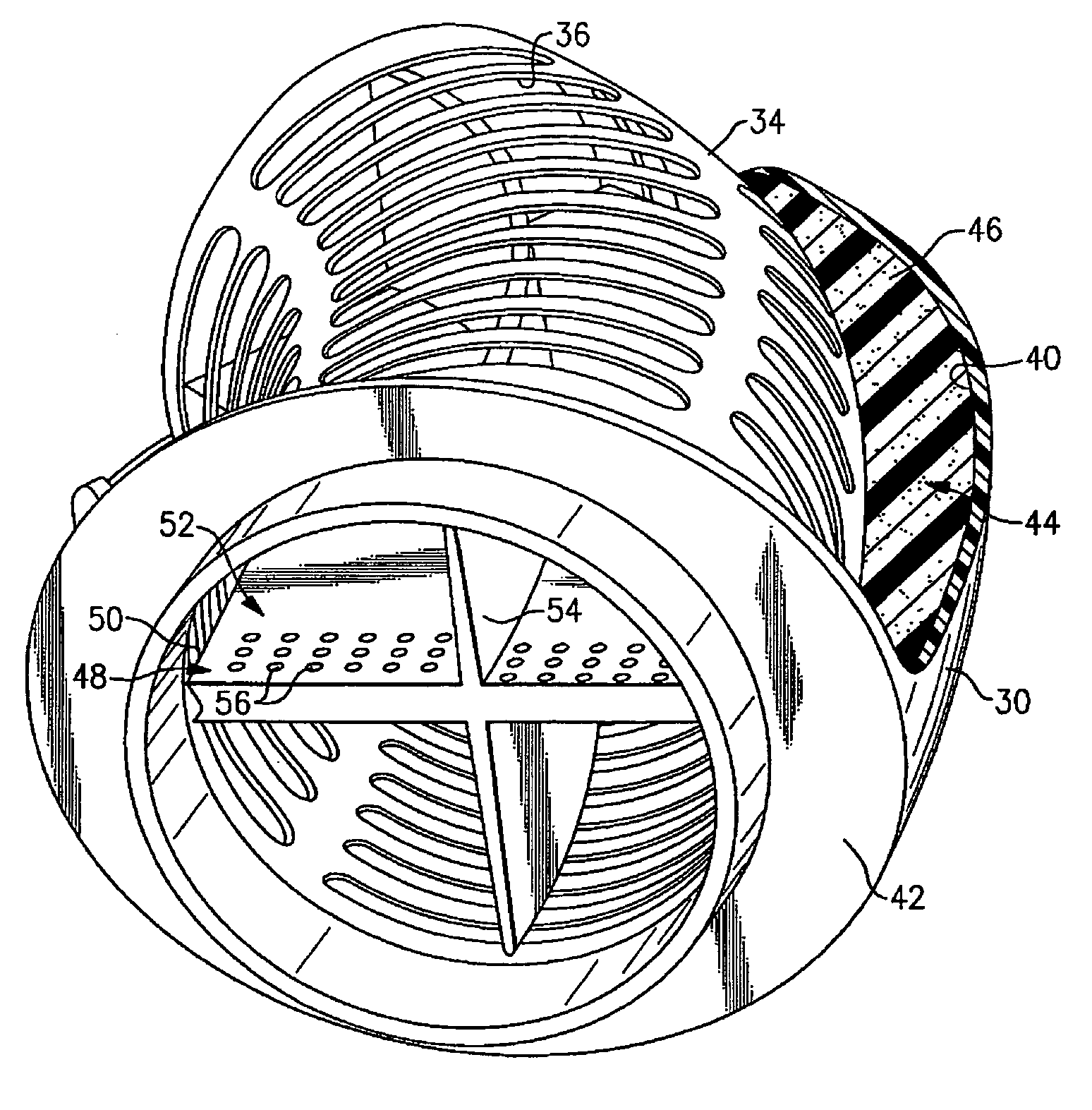
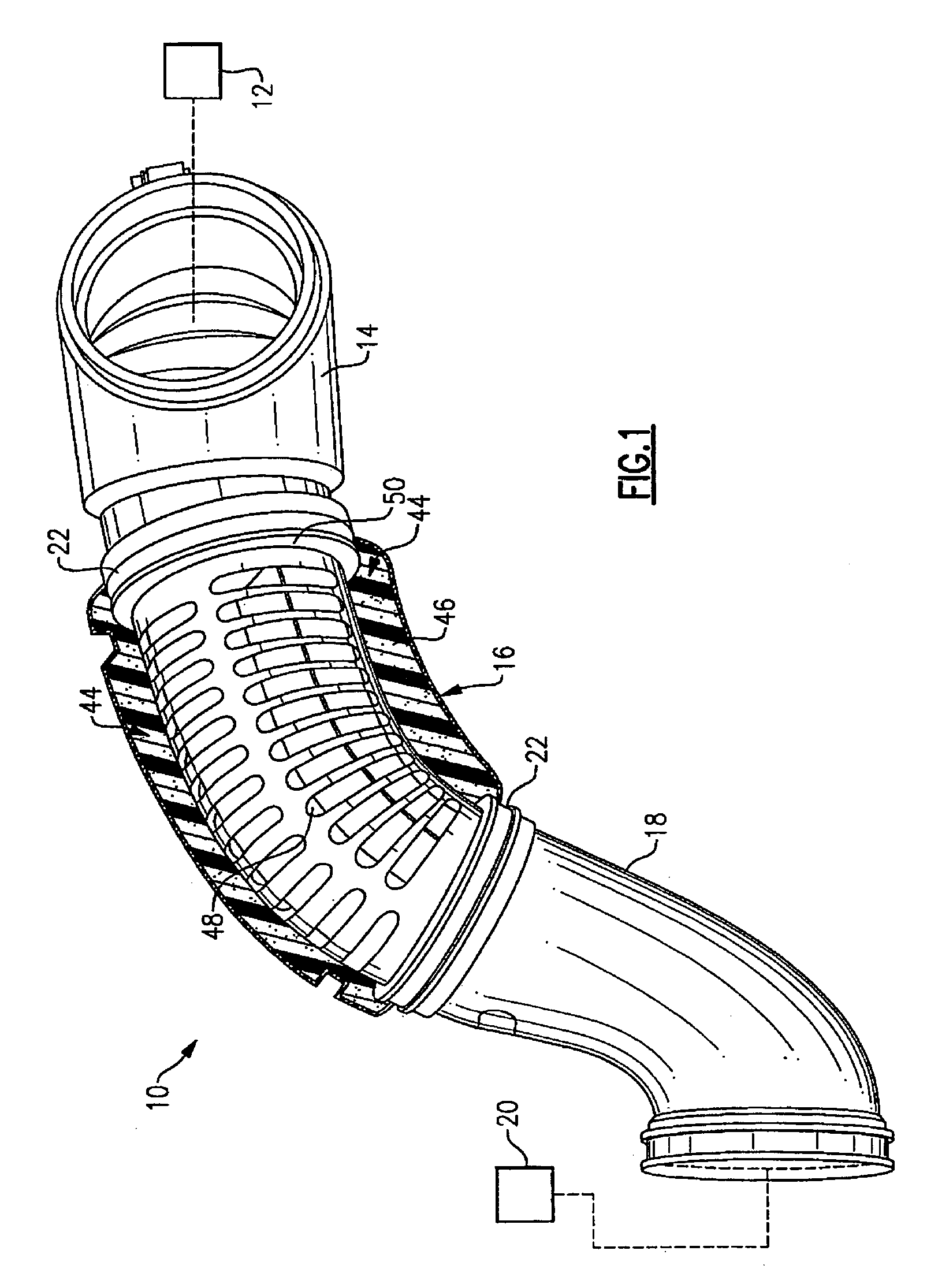
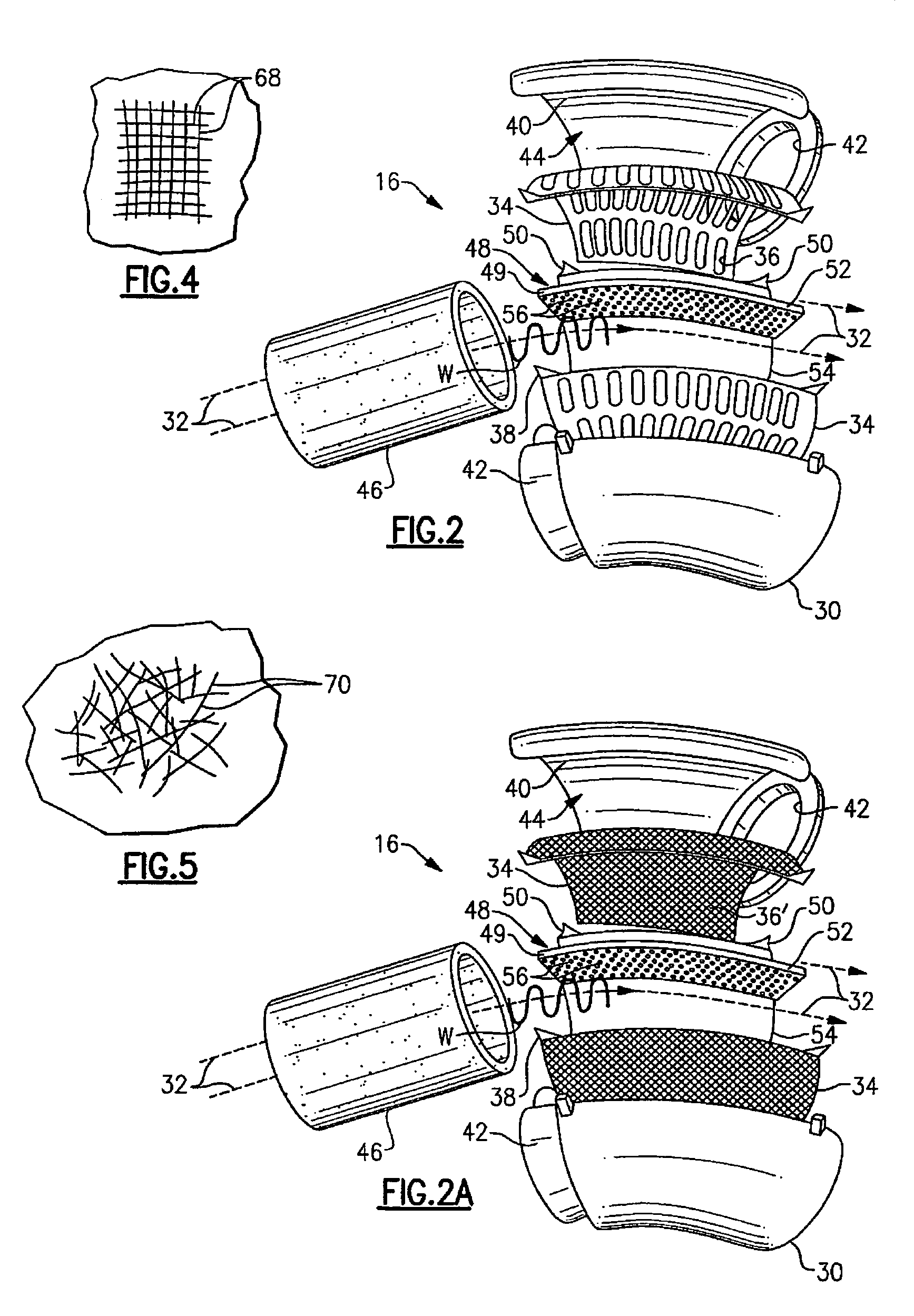
InactiveUS7631726B2Reduce flowReduce noise energySilencing apparatusMachines/enginesCouplingEngineering
An air induction silencer assembly includes an acoustic interference member disposed within a conduit. The acoustic interference member is tuned to acoustically cancel a selected noise energy frequency. An acoustic absorbing member is also disposed within the conduit. The acoustic absorbing member converts noise energy within the conduit into heat energy to attenuate noise energy within the air induction silencer assembly. The air induction silencer assembly connects to a flexible conduit that includes an inlet portion, an outlet portion, and a flexible joint that connects the inlet portion and the outlet portion together. The flexible joint includes a rolling lobe and a rolling surface. The rolling lobe moves along the rolling surface when the inlet portion moves relative to the outlet portion.
Owner:SIEMENS VDO AUTOMOTIVE INC
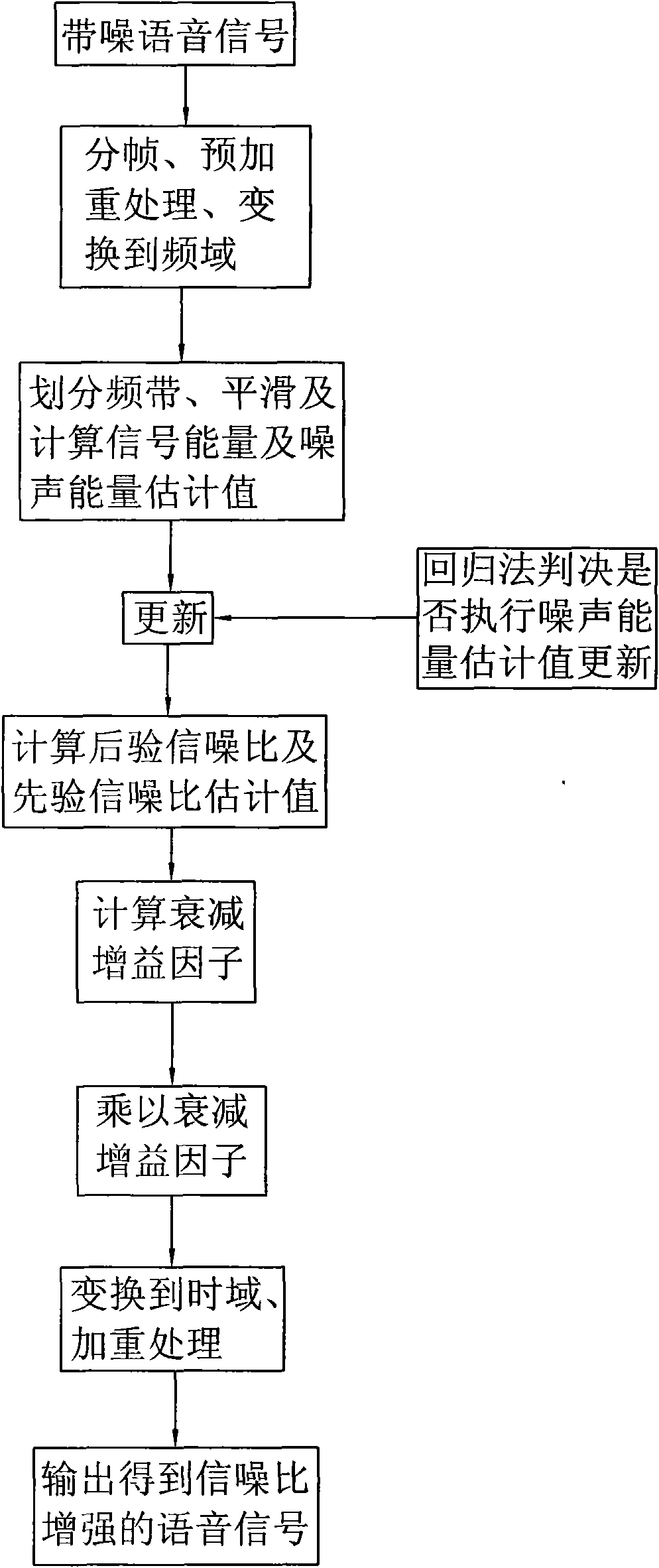
Method and voice collecting system for speech enhancement
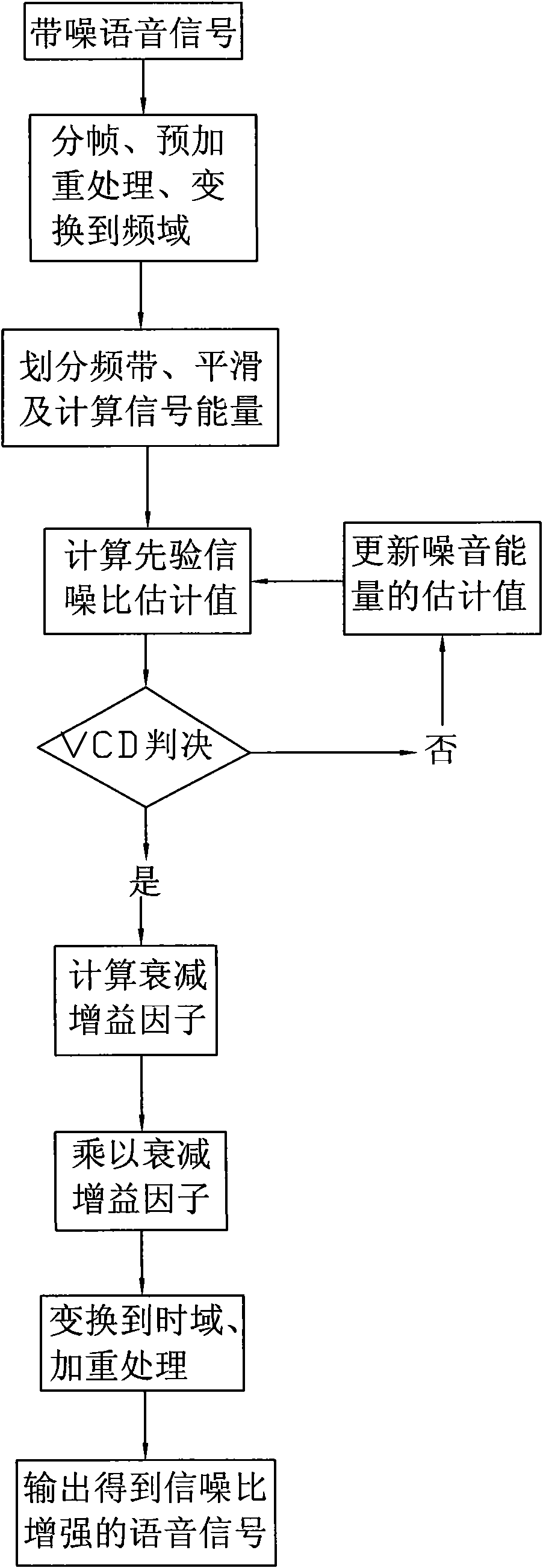
InactiveCN101582264AFast decayGuaranteed intelligibilitySpeech analysisTime domainSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention provides a method and a voice collecting system for speech enhancement. The system comprises a microphone collecting device and a chip which integrates the method for the speech enhancement. The method for speech enhancement comprises the following steps of: carrying out frame division and pre-emphasis treatment on the noise-contained speech signal so as to be converted to frequency domains; dividing into a plurality of frequency bands; calculating the signal energies of each channel; calculating the estimation value of the posterior signal-to-noise-ratio and the prior signal-to-noise ratio of the current frame; judging whether updating the estimation value of the noise energy; calculating and processing the attenuation factor of each frequency band so as to obtain the speech signal with enhanced signal-to-noise ratio; and converting the processed speech signal into the time domain and outputting the speech signal.
Owner:AAC ACOUSTIC TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
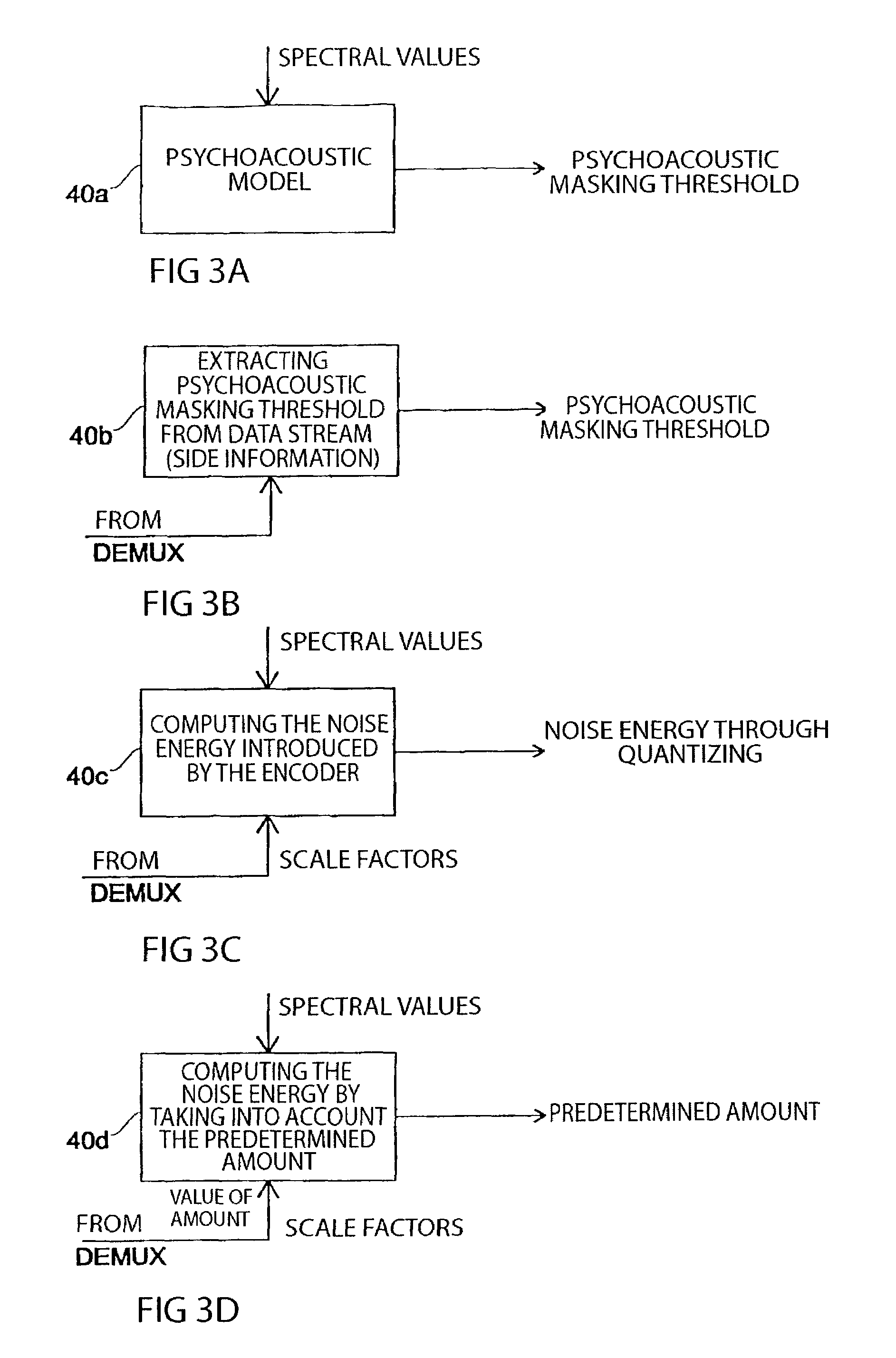
Method and apparatus for introducing information into a data stream and method and apparatus for encoding an audio signal
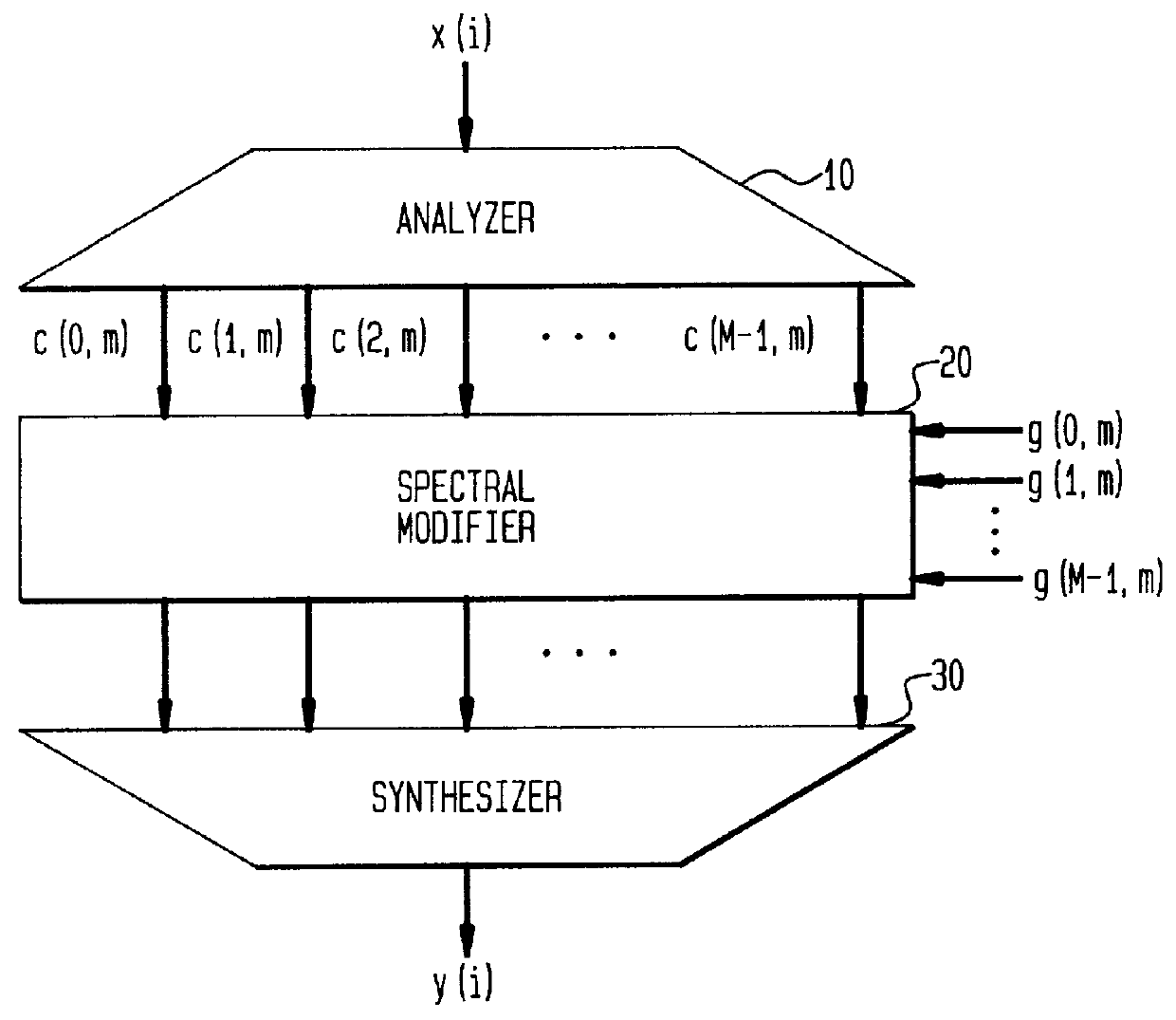
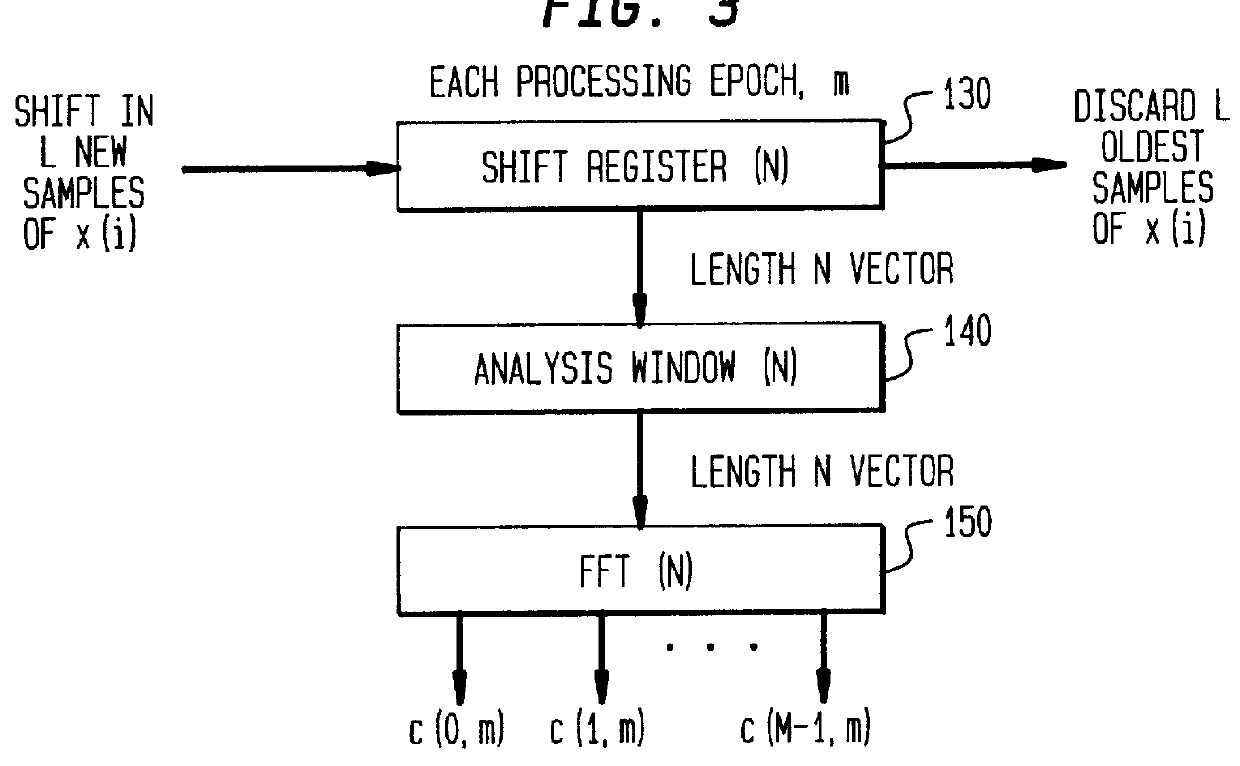
InactiveUS7454327B1Improve interoperabilityEasy to implementSpeech analysisPlural information simultaneous broadcastTime domainFrequency spectrum
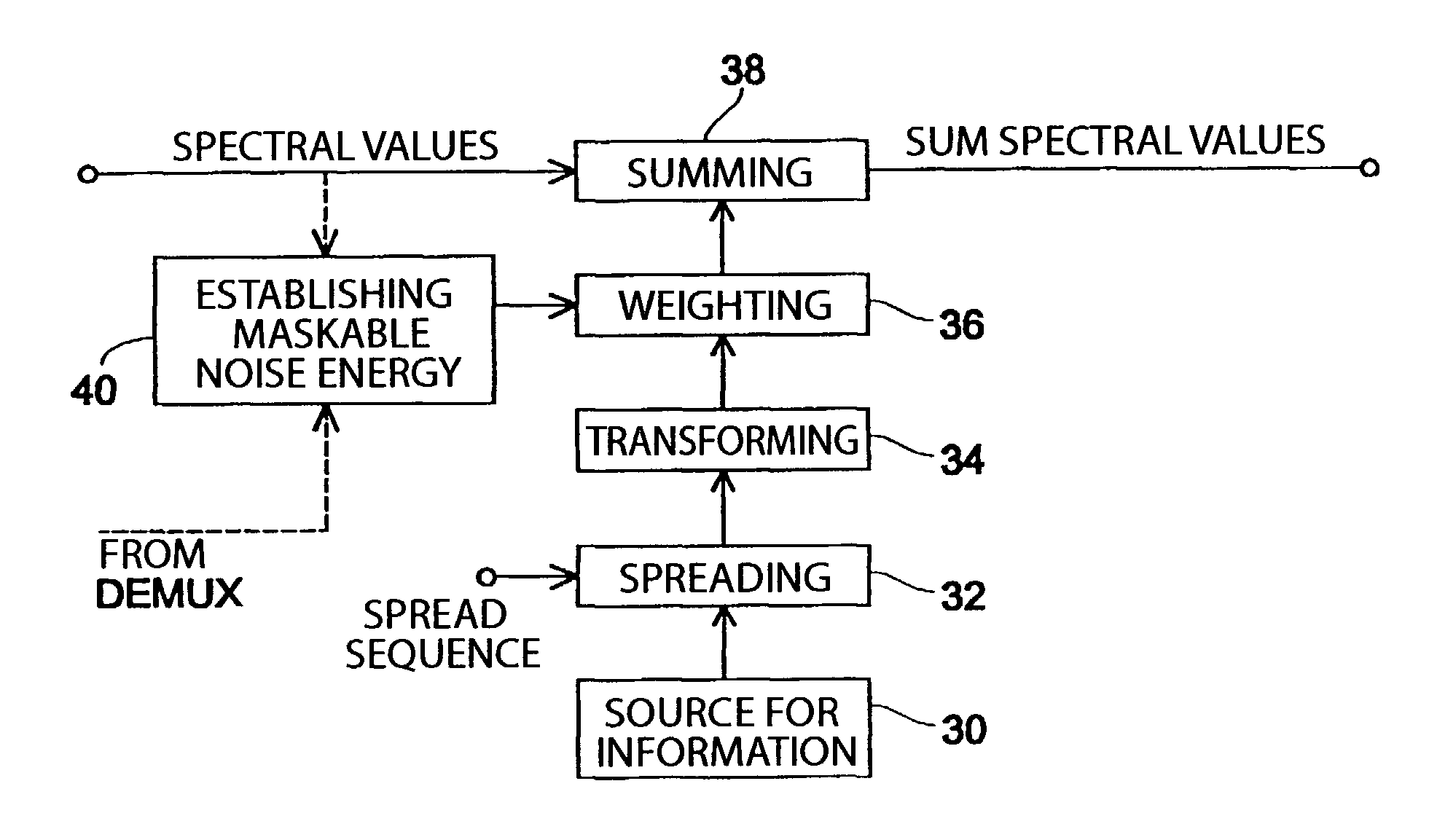
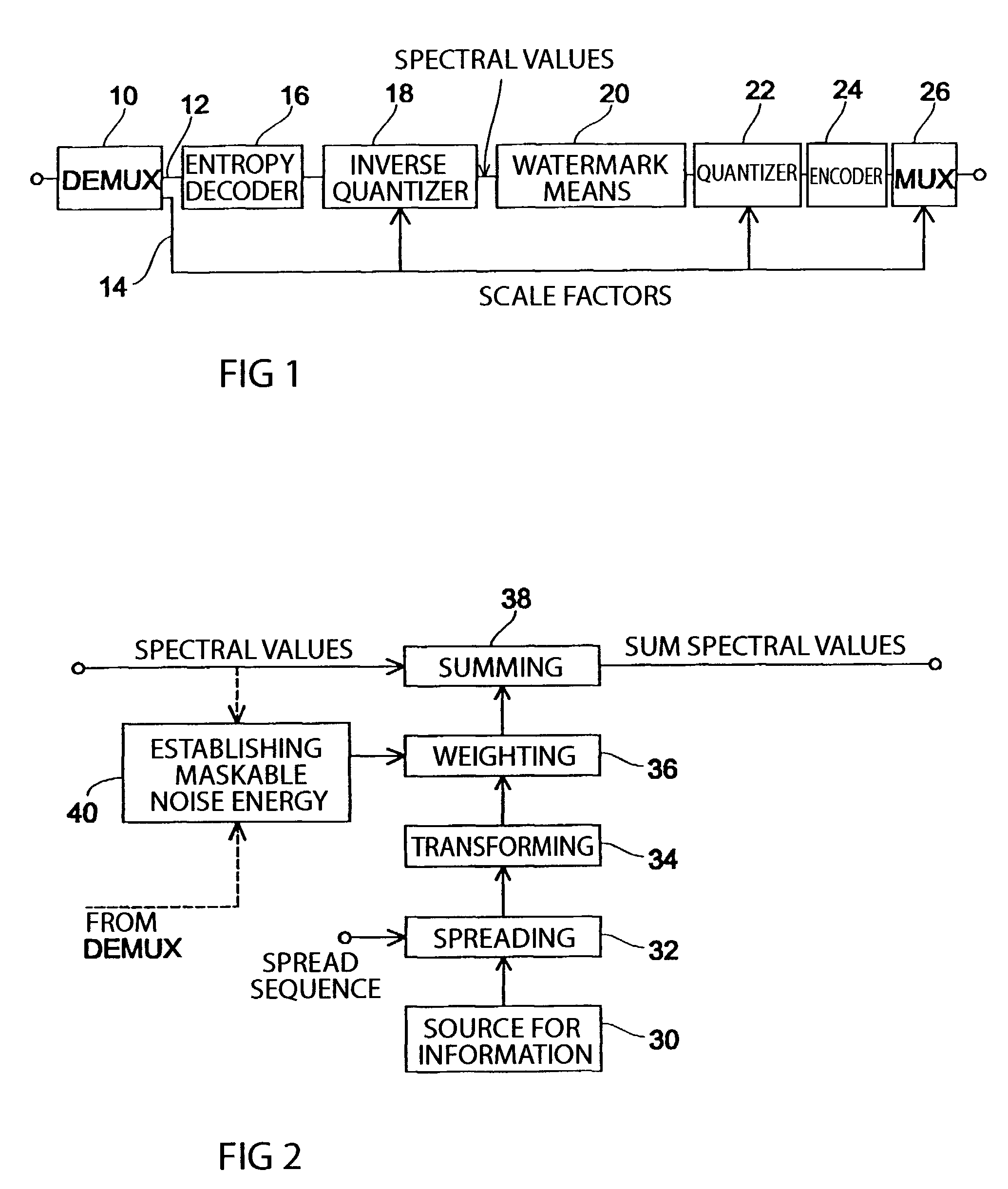
An inventive method for introducing information into a data stream including data about spectral values representing a short-term spectrum of an audio signal first performs a processing of the data stream to obtain the spectral values of the short-term spectrum of the audio signal. Apart from that, the information to be introduced are combined with a spread sequence to obtain a spread information signal, whereupon a spectral representation of the spread information is generated which will then be weighted with an established psychoacoustic maskable noise energy to generate a weighted information signal, wherein the energy of the introduced information is substantially equal to or below the psychoacoustic masking threshold. The weighted information signal and the spectral values of the short-term spectrum of the audio signal will then be summed and afterwards processed again to obtain a processed data stream including both audio information and information to be introduced. By the fact that the information to be introduced are introduced into the data stream without changing to the time domain, the block rastering underlying the short-term spectrum will not be touched, so that introducing a watermark will not lead to tandem encoding effects.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Self-adaptive denoising method and system based on sub-band noise analysis
ActiveCN103871421ASignificant Gain DifferenceImprove signal-to-noise ratioSpeech analysisTarget signalAdaptive denoising
The invention relates to the field of voice technologies, in particular to a self-adaptive denoising method based on sub-band noise analysis. The method includes the steps that firstly, framing and short time frequency domain transformation are conducted on input time domain audio signals with noise, and then frequency domain audio signals with noise are generated; secondly, a noise energy spectrum of the frequency domain audio signals with noise is estimated through a minimum value tracking method; thirdly, the posterior signal to noise ratio and the prior signal to noise ratio of the noise energy spectrum are calculated; fourthly, through a nonlinear gain extension method, denoising gains of all time frequency units are calculated through the posterior signal to noise ratio and the prior signal to noise ratio; fifthly, smoothing filtering is conducted on the denoising gains of all the time frequency units to reduce tone quality distortion; sixthly, the denoising gains act on all the time frequency units of the audio signals with noise in the first step, and then denoised frequency domain audio signals are acquired; seventhly, short time frequency domain inverse transformation is conducted, and then the final denoised time frequency audio signals are acquired and output. According to the method and system, stable noise in target signals can be greatly lowered.
Owner:厦门莱亚特医疗器械有限公司
Silencer for air induction system and high flow articulated coupling
InactiveUS20050284692A1Effective attenuationReduce flow of turbulent airSilencing apparatusMachines/enginesCouplingEngineering
An air induction silencer assembly includes an acoustic interference member disposed within a conduit. The acoustic interference member is tuned to acoustically cancel a selected noise energy frequency. An acoustic absorbing member is also disposed within the conduit. The acoustic absorbing member converts noise energy within the conduit into heat energy to attenuate noise energy within the air induction silencer assembly. The air induction silencer assembly connects to a flexible conduit that includes an inlet portion, an outlet portion, and a flexible joint that connects the inlet portion and the outlet portion together. The flexible joint includes a rolling lobe and a rolling surface. The rolling lobe moves along the rolling surface when the inlet portion moves relative to the outlet portion.
Owner:SIEMENS VDO AUTOMOTIVE CORP
Method for speech enhancement
ActiveCN101599274AGuaranteed intelligibilityDecay fastSpeech analysisTime domainSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention provides a method for achieving speech enhancement, which comprises the following steps: performing frame separation and pre-emphasis processing on a noisy speech signal, and transforming the noisy speech signal into a frequency domain; dividing the noisy speech signal into a plurality of frequency bands, calculating the signal energy of each frequency channel, and updating the estimated value of the noise energy; calculating the posteriori signal-to-noise ratio of the current frame, and the estimated value of the priori signal-to-noise ratio; calculating the attenuation factor of each frequency band, and processing the attenuation factor to obtain a speech signal with increased signal-to-noise ratio; and transforming the speech signal after the processing into a time domain, and outputting the speech signal.
Owner:AAC TECH PTE LTD +1
Noise spectrum tracking in noisy acoustical signals
ActiveUS20100067710A1Accurate estimateReduce computational complexityElectrical apparatusSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumNoise power spectrum
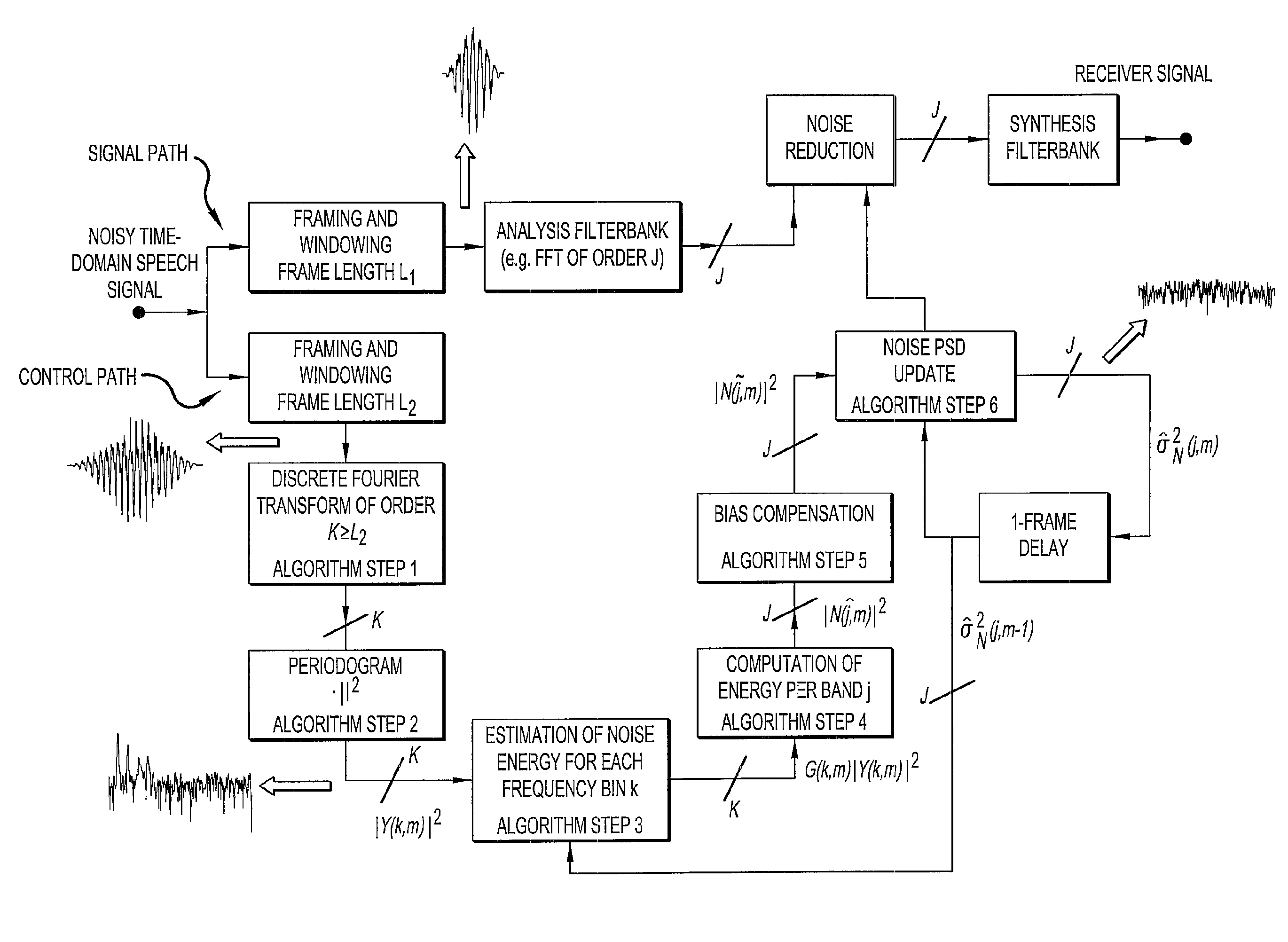
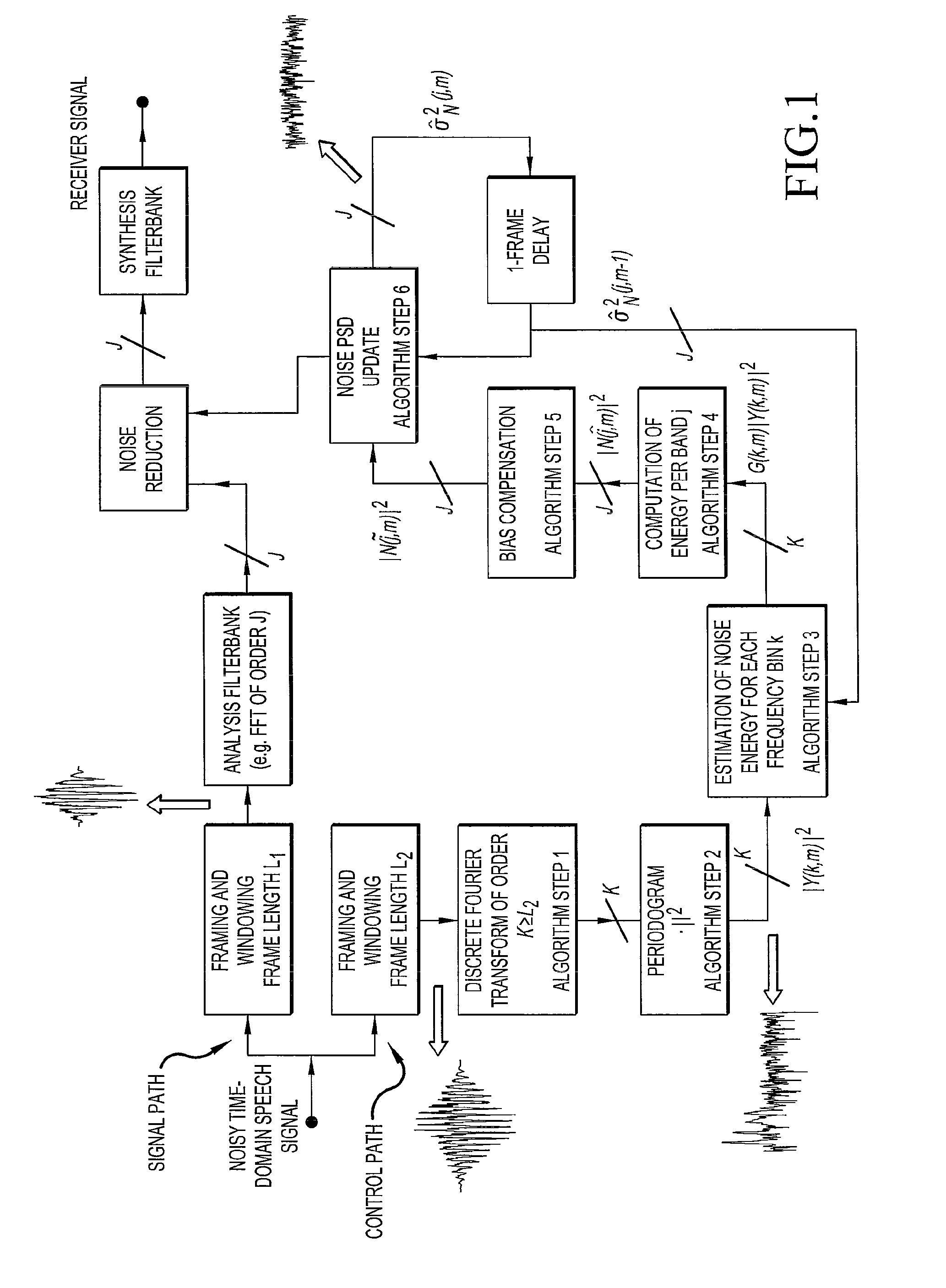
The invention relates to a method of estimating noise power spectral density PSD in an input sound signal comprising a noise signal part and a target signal part. The invention further relates to a system to its use. The object of the present invention is to provide a scheme for estimating the noise PSD in an acoustic signal consisting of a target signal contaminated by acoustic noise. The problem is solved by a method comprising the steps of d) providing a digitized electrical input signal to a control path and performing; d1) storing a number of time frames of the input signal each comprising a predefined number N2 of digital time samples xn (n=1, 2, . . . , N2), corresponding to a frame length in time of L2=N2 / fs; d2) performing a time to frequency transformation of the stored time frames on a frame by frame basis to provide corresponding spectra Y of frequency samples; d3) deriving a periodogram comprising the energy content |Y|2 for each frequency sample in a spectrum, the energy content being the energy of the sum of the noise and target signal; d4) applying a gain function G to each frequency sample of a spectrum, thereby estimating the noise energy level |Ŵ|2 in each frequency sample, |Ŵ|2=G·|Y|2; d5) dividing the spectra into a number Nsb2 of sub-bands, each sub-band comprising a predetermined number nsb2 of frequency samples, and assuming that the noise PSD level is constant across a sub-band; d6) providing a first estimate |{circumflex over (N)}|2 of the noise PSD level in a sub-band based on the non-zero noise energy levels of the frequency samples in the sub-band; d7) providing a second, improved estimate |Ñ|2 of the noise PSD level in a sub-band by applying a bias compensation factor B to the first estimate, |Ñ|2=B·|{circumflex over (N)}|2. The invention may e.g. be used in listening devices, e.g. hearing aids, mobile telephones, headsets, active earplugs, etc.
Owner:OTICON
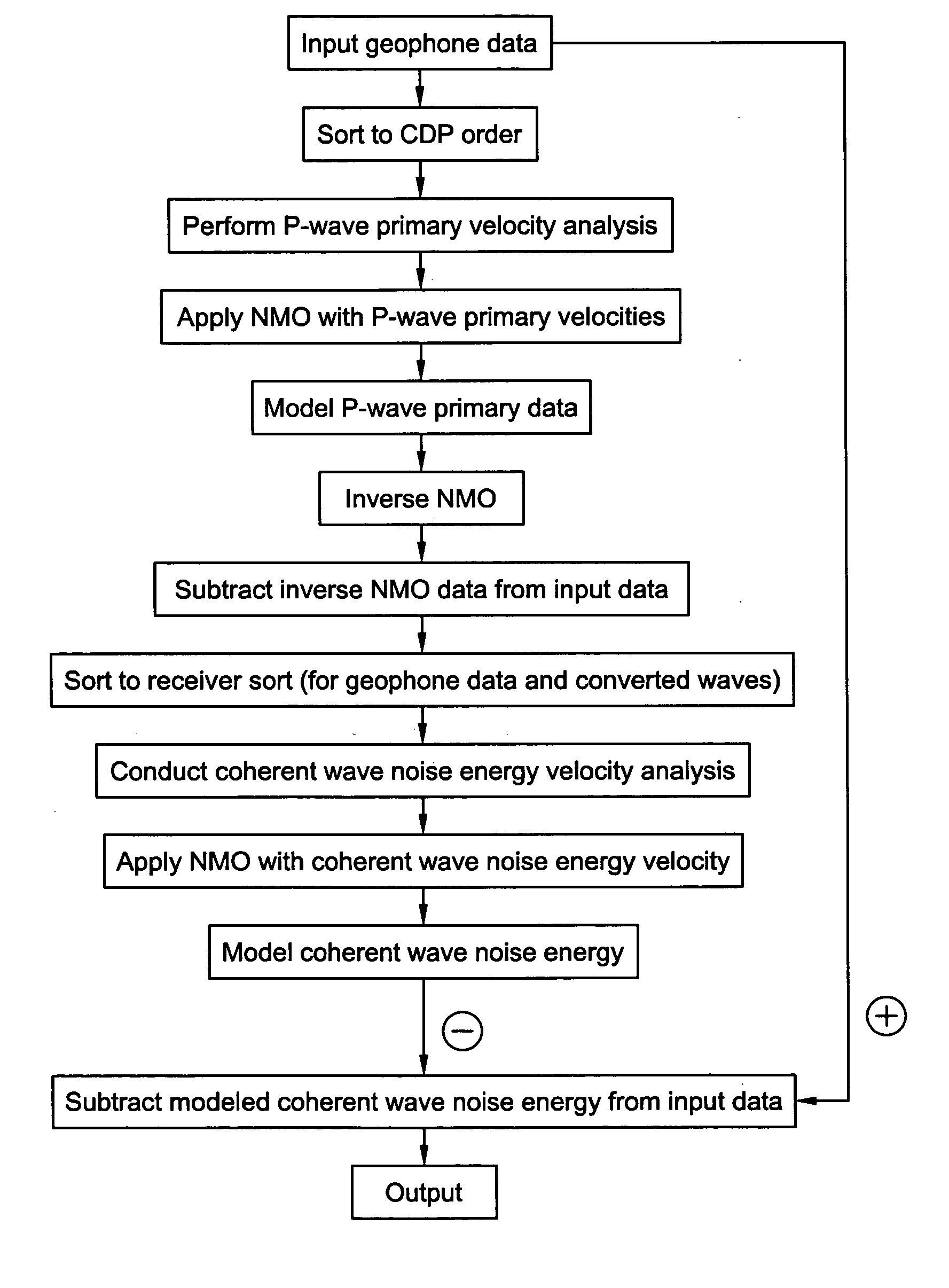
Coherent wave energy removal from seismic data
ActiveUS20070076525A1Efficient modelingRemove coherent wave noise energySeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsData setCoherent wave
Coherent wave noise energy is removed from seismic data by modeling both the P-wave primary energy and the coherent wave noise energy. The P-wave primary energy is modeled first and then subtracted from the input data. The data with the P-wave primary energy removed is used as the input for coherent wave energy removal. The coherent wave energy is modeled and subtracted from the original input data, i.e. the data input into P-wave primary removal. This leaves a dataset with P-wave primary energy and noise energy not related to coherent waves. This method can be utilized to remove all types of coherent noise with a velocity difference to the desired P-wave primary energy or with a different type of moveout (change of time of arrival with source-receiver distance) such as, for example, linear moveout.
Owner:FAIRFIELD INDUSTRIES INC
Voice wake-up method and apparatus
InactiveCN105261368AReduce power consumptionReduce the number of VADsSpeech analysisPower supply for data processingActivation detectionComputer science
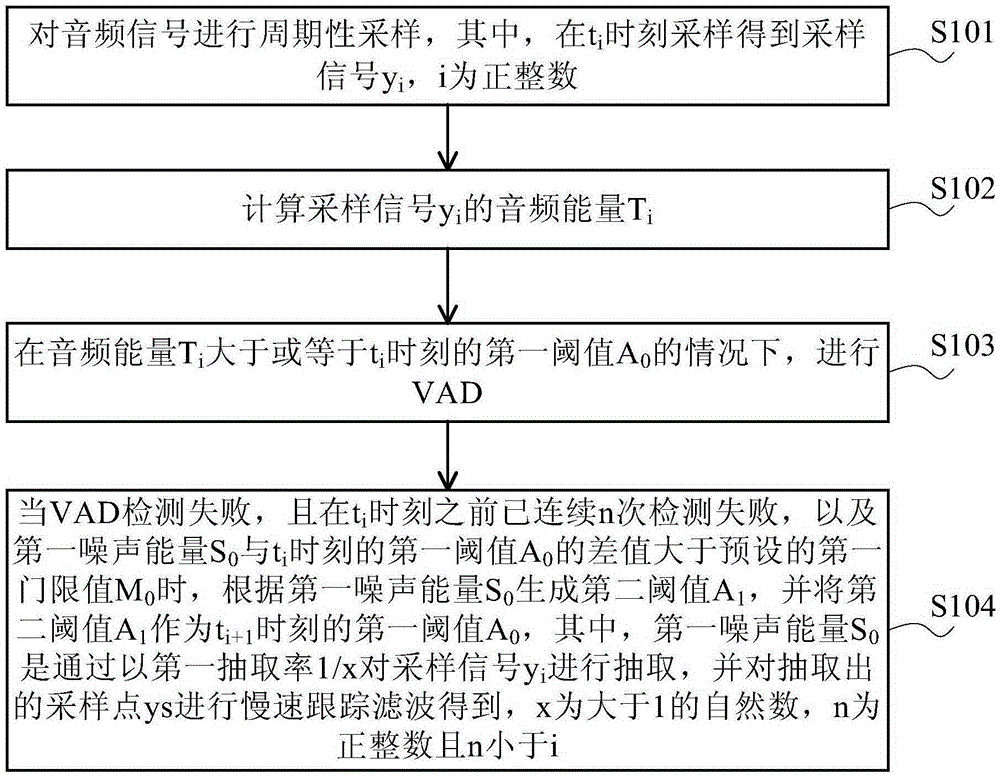
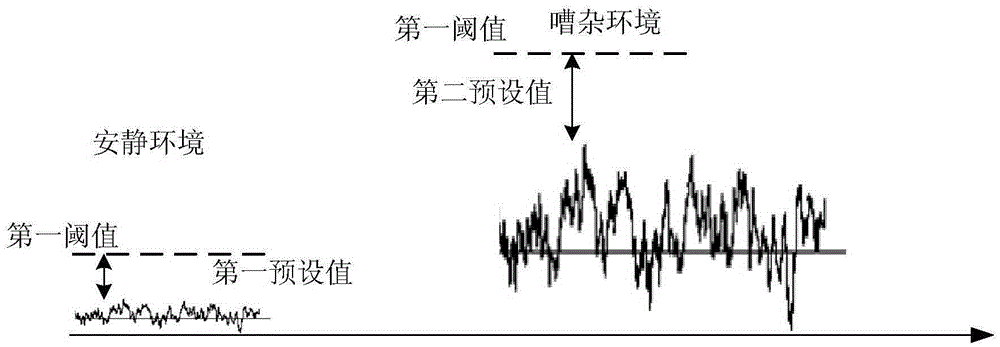
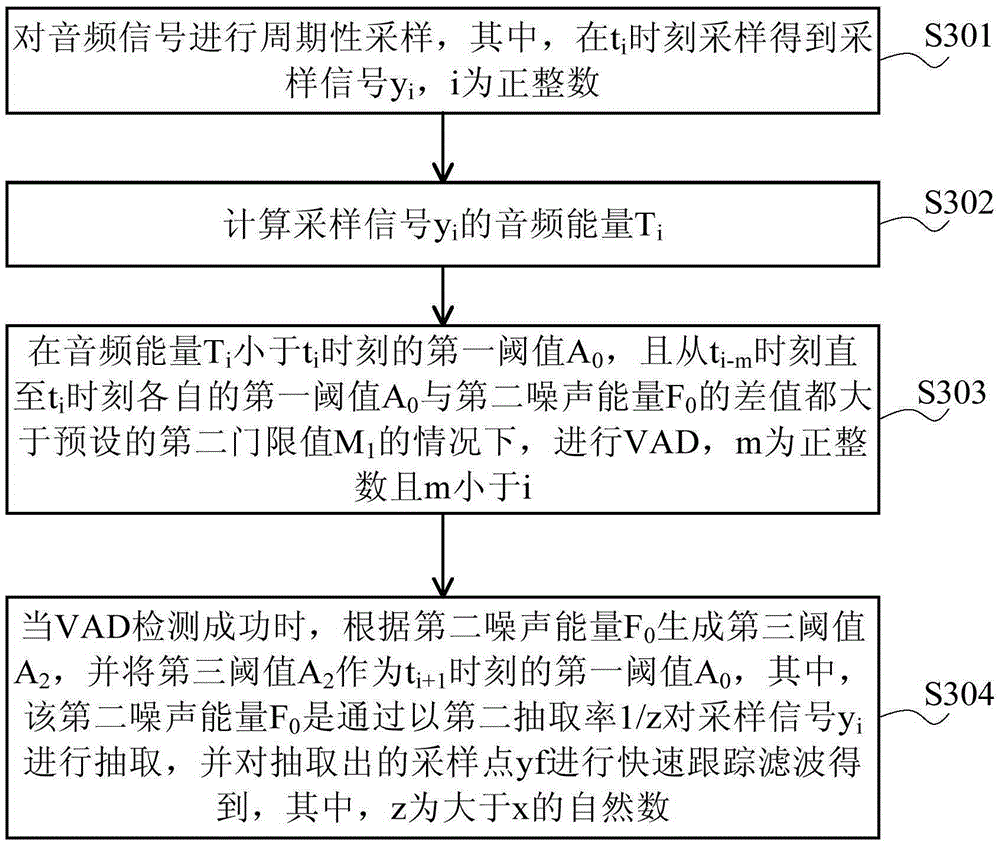
The embodiment of the invention provides a voice wake-up method and apparatus. The method comprises: periodic sampling is carried out on an audio signal, wherein sampling is carried out at ti time to obtain a sampling signal; audio energy of the sampling signal is calculated; when the audio energy is larger than or equal to a first threshold value at the ti time, a digital signal processor (DSP) is waken up to carry out voice activation detection (VAD); when the VAD fails, detection fails n times continuously before the ti time, and a difference value between first noise energy and a first threshold value at the ti time is larger than a preset first threshold value, a second threshold value is generated according to the first noise energy and is used as a first threshold value at ti+1 time, wherein the first noise energy is obtained by extracting the sampling signal by a first extraction rate 1 / x and carrying out slow-speed tracking filtering on the extracted sampling point. According to the embodiment of the invention, the number of times of VAD is reduced and reduction of power consumption of the terminal in a noisy environment is realized.
Owner:NANJING ADVANCED BIOLOGICAL MATERIALS & PROCESS EQUIP INST CO LTD
Apparatuses, systems and methods for detecting corona
ActiveUS20140270205A1Testing using acoustic measurementsTesting circuitsElectrical conductorHarmonic
Apparatuses, systems and methods for detecting corona using audio data are disclosed. A method of processing audio data to detect corona includes determining an indicator of energy at a substantially fundamental frequency in the audio data, determining an indicator of the energy at a plurality of harmonic frequencies in the audio data, determining an indicator of the noise energy in the audio data, determining a comparison indicator of the noise energy relative to the energy at the harmonic frequencies, determining a masking indicator having thresholds for each of the harmonics relative to the fundamental frequency, and determining a corona detection indicator. An apparatus for detecting corona includes a memory, an audio detector configured to obtain the audio data near an electrical conductor in an AC system, and a processor to process the audio data, fundamental and harmonic frequencies of the audio data and their corresponding thresholds to detect corona.
Owner:HUBBELL INC
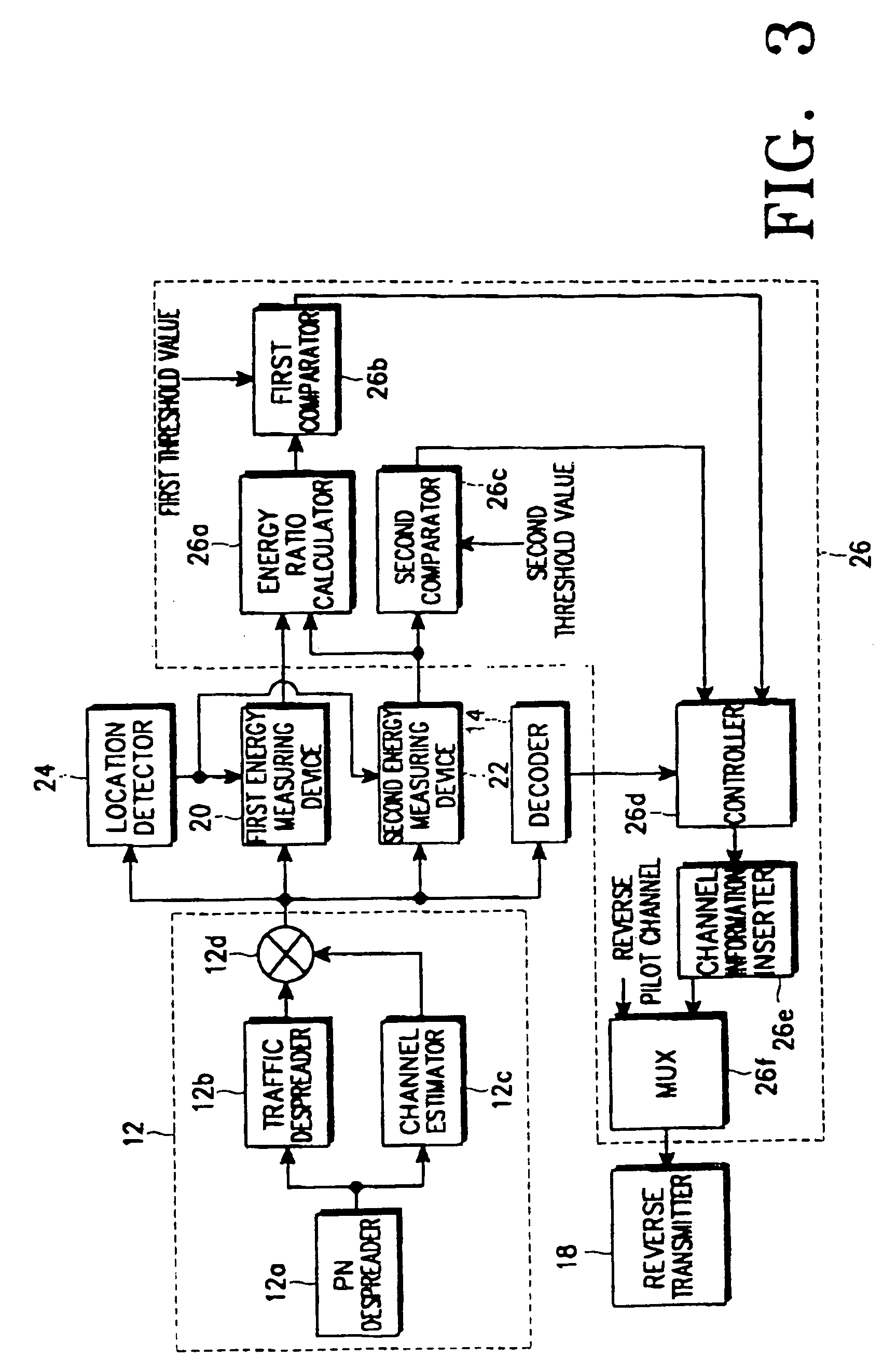
Apparatus and method of controlling forward link power when in discontinuous transmission mode in a mobile communication system
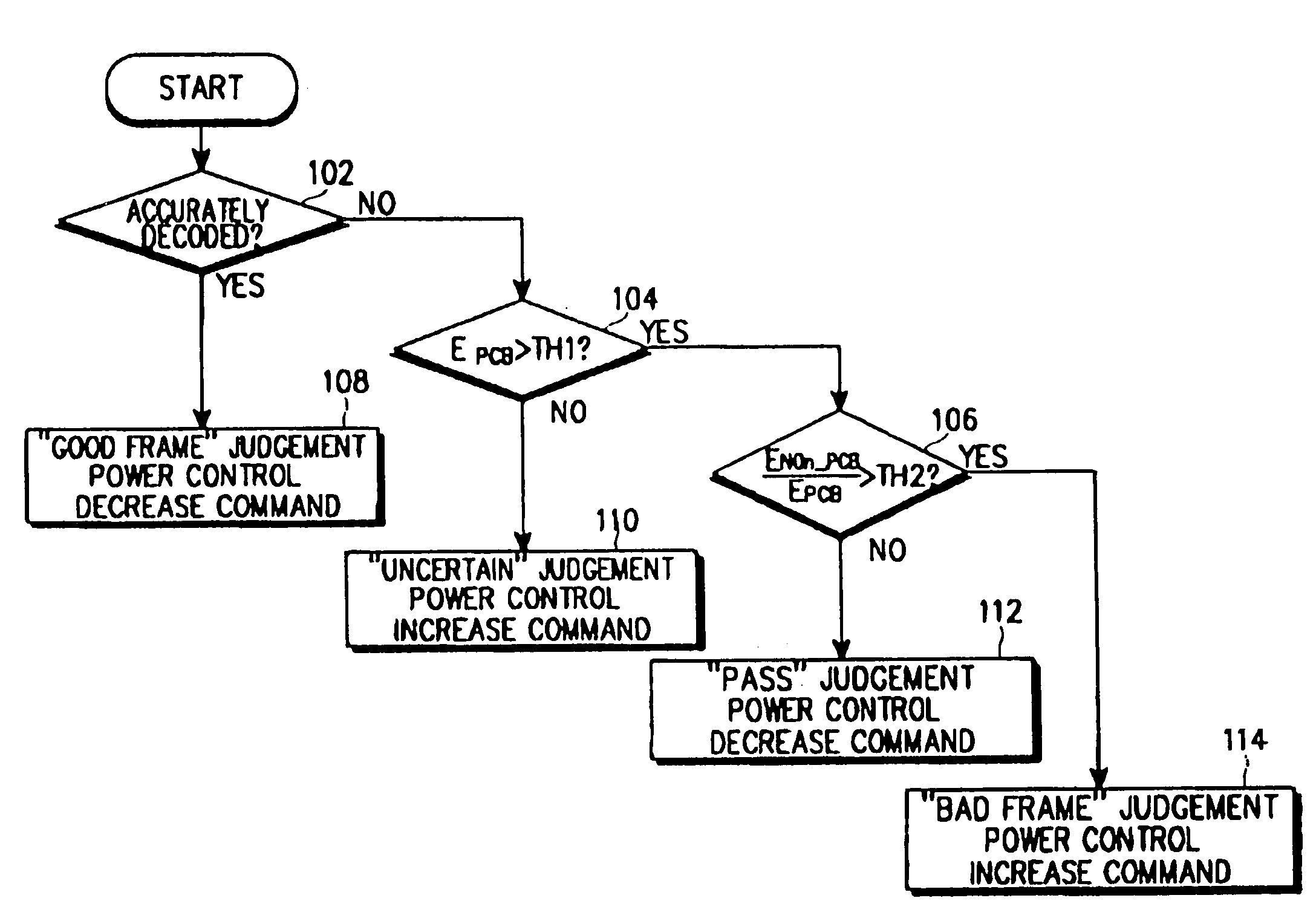
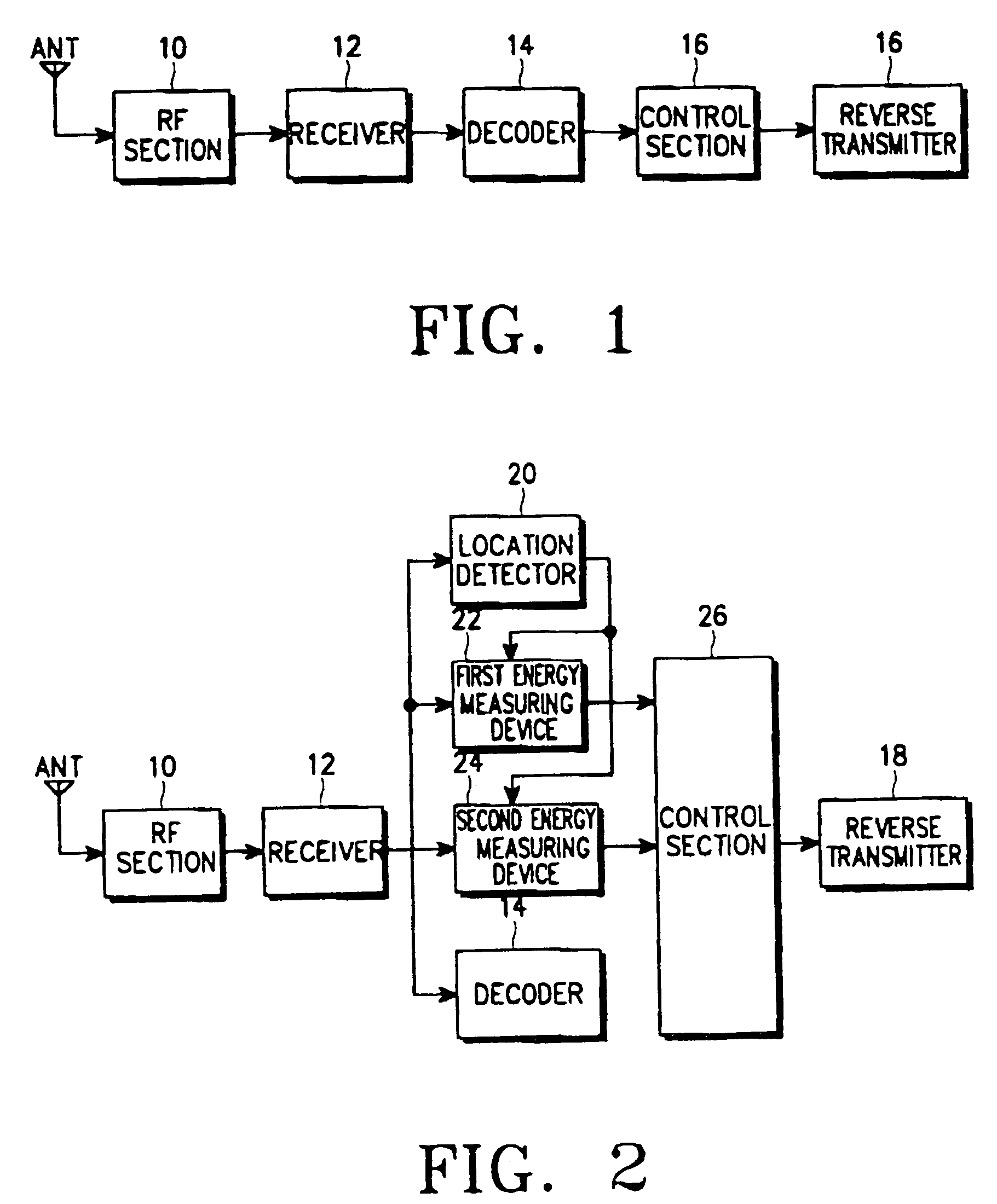
InactiveUS7283836B2Accurate judgmentRaise the ratioEnergy efficient ICTPower managementTransfer modeMobile communication systems
An apparatus and method of detecting whether data exists in a received signal while a mobile communication terminal is in discontinuous transmission mode. The apparatus and method comprises generating and transmitting a forward power control command for providing the forward power control, and performing forward power control in a mobile communication system. According to the forward power control method, a power control command is generated based on a received frame including a plurality of slots each of which includes power control bits. The ratio of the power control bit energy to noise energy, which is given by a ratio of the accumulated energy of the power control bits in the slots of the received frame to an accumulated energy value of noise in the slots of the received frame, is provided, and the power control command based on a ratio of the accumulated energy value of traffic symbol bits in the slots to the accumulated energy value of the power control bits is generated when the provided ratio of the power control bits to noise is acceptable.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Integral suction device with acoustic panel
InactiveUS20080296439A1Avoid separationLower performance requirementsEngine fuctionsWingsNacelleControl system
An inlet flow control system disposed within a nacelle includes a panel on an inner surface of that nacelle. The panel includes a noise attenuation layer that dissipates noise energy. A vacuum source generates a pressure differential across the noise attenuation layer for drawing airflow through the panel and away from an inner surface of the nacelle.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
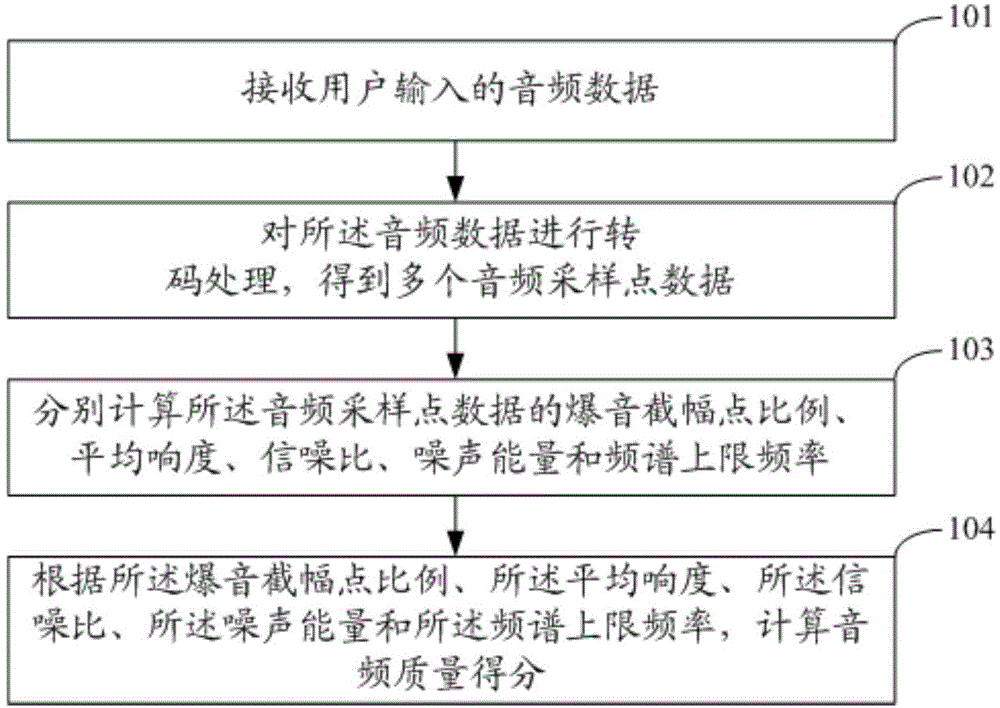
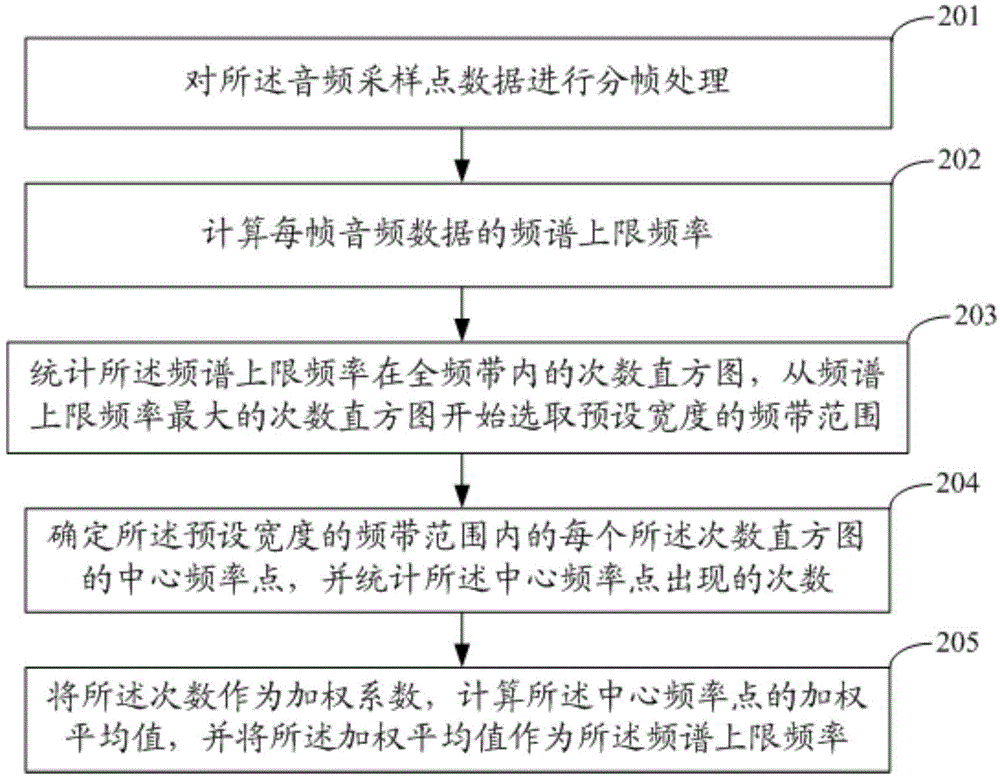
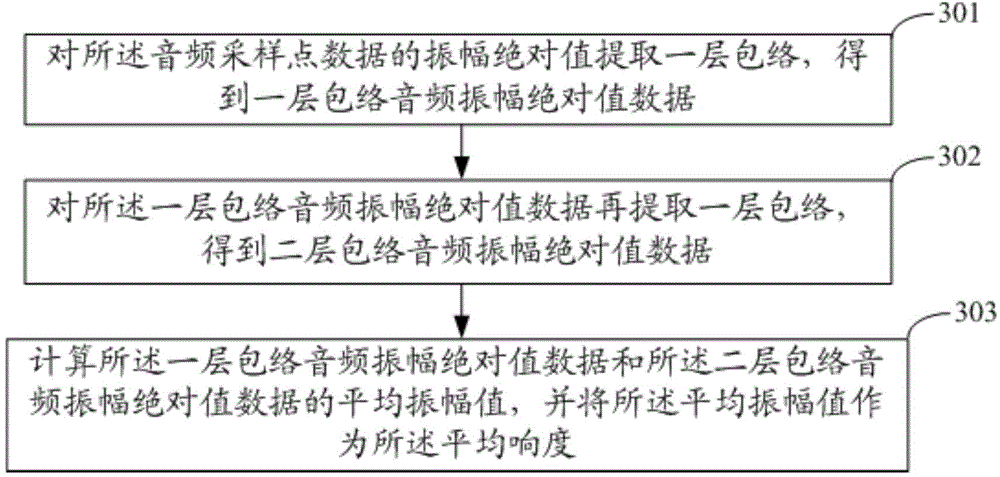
Audio quality evaluation method and system
ActiveCN105989853AUniversalMeet the needs of the applicationSpeech analysisShock waveFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses an audio quality evaluation method and an audio quality evaluation system, which belong to the technical field of speech signal processing. The audio quality evaluation method comprises the steps of: receiving audio data input by a user; carrying out transcoding treatment on the audio data to obtain a plurality of pieces of audio sampling point data; calculating shock-wave noise sever amplitude point ratios, mean loudness, signal-to-noise ratios, noise energy and spectrum upper-limit frequencies of the plurality of pieces of audio sampling point data separately; and calculating an audio quality score according to the shock-wave noise sever amplitude point ratios, the mean loudness, the signal-to-noise ratios, the noise energy and the spectrum upper-limit frequencies. The audio quality evaluation method is used for evaluating audio quality through integrating multiple audio quality parameters, is high in general applicability of evaluation results, and can meet the needs of most application occasions.
Owner:IFLYTEK CO LTD
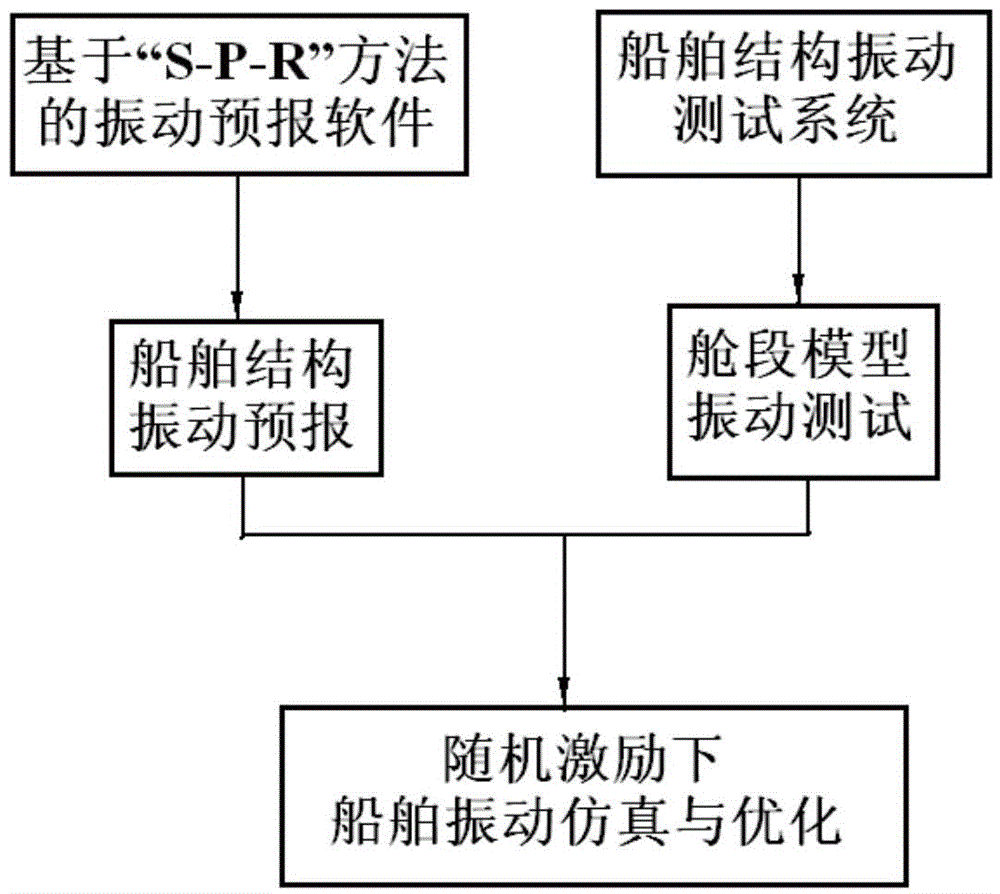
Ship structure vibration and noise forecasting system based on S-P-R
InactiveCN105021363AReduce vibrationLow costSpecial data processing applicationsVibration testingNoise levelEngineering
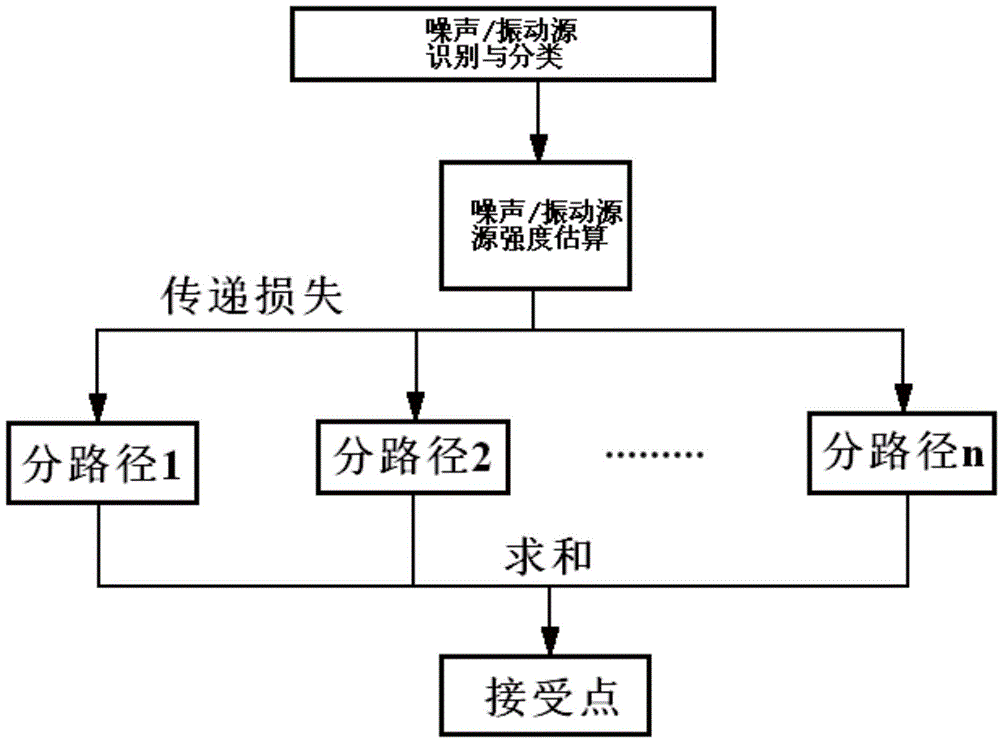
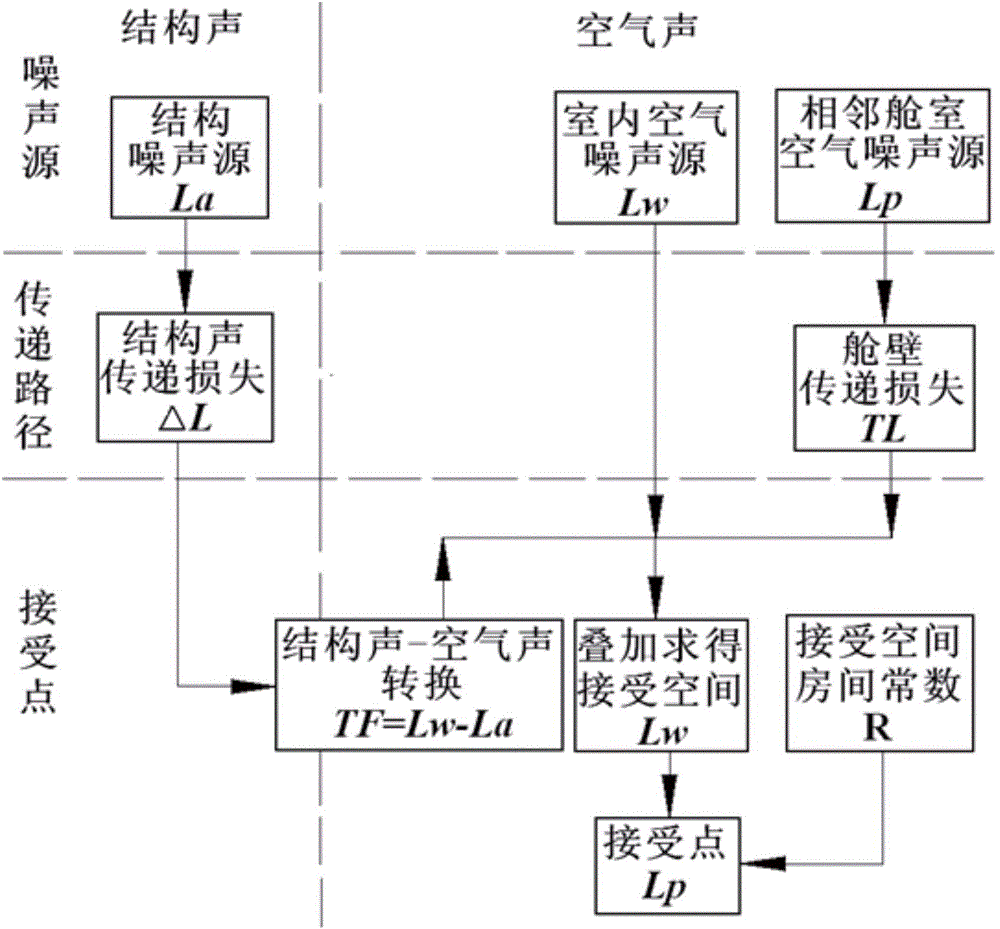
The invention provides a ship structure vibration and noise forecasting system based on S-P-R, comprising a database module, a modeling and calculating module, and a result processing module. The database module stores the vibration intensity data of various kinds of vibration sources in each cabin of a ship, and the noise intensity data of various kinds of noise sources; the modeling and calculating module comprises a ship modeling submodule, a key excitation source recognition submodule, a transmission path determination submodule, and a receiving station energy calculating module, and is used for defining transmission paths, calculating the transmission loss of the vibration / noise energy generated by each excitation source by the transmission to a receiving station along a transmission path, and then calculating the vibration / noise total energy of the receiving station. The system of the invention combines an analysis method, a numerical method and an experimental method to analyze ship structure vibration source and transmission path characteristics, calculates cabin air noise levels according to the analysis procedure of an S-P-R method, and overcomes the problem that corresponding remedial measures can not be taken according to vibration and noise measurement results until a ship is completed.
Owner:SHANGHAI GUANTU ELECTRICAL TECH CO LTD
End-point detecting method, apparatus and speech recognition system based on sliding window
The invention discloses an end detection method and device, which comprises the following steps: applying a window to the input phonetic signal; selecting certain frame quantity as window dimension; affirming the background noise starting point in the input phonetic signal; calculating the background noise energy; calculating the present frame phonetic energy and window energy; comparing the widow total phonetic energy whether more than the product of background noise energy multiplied by phonetic starting point signal-to-noise ratio; sliding the window to the next frame and returning to calculate the present frame phonetic energy if not; judging the present frame as phonetic starting point if yes. The invention improves the detection accuracy, robustness and total discrimination of phonetic identification system, which is used in the phonetic identification system.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
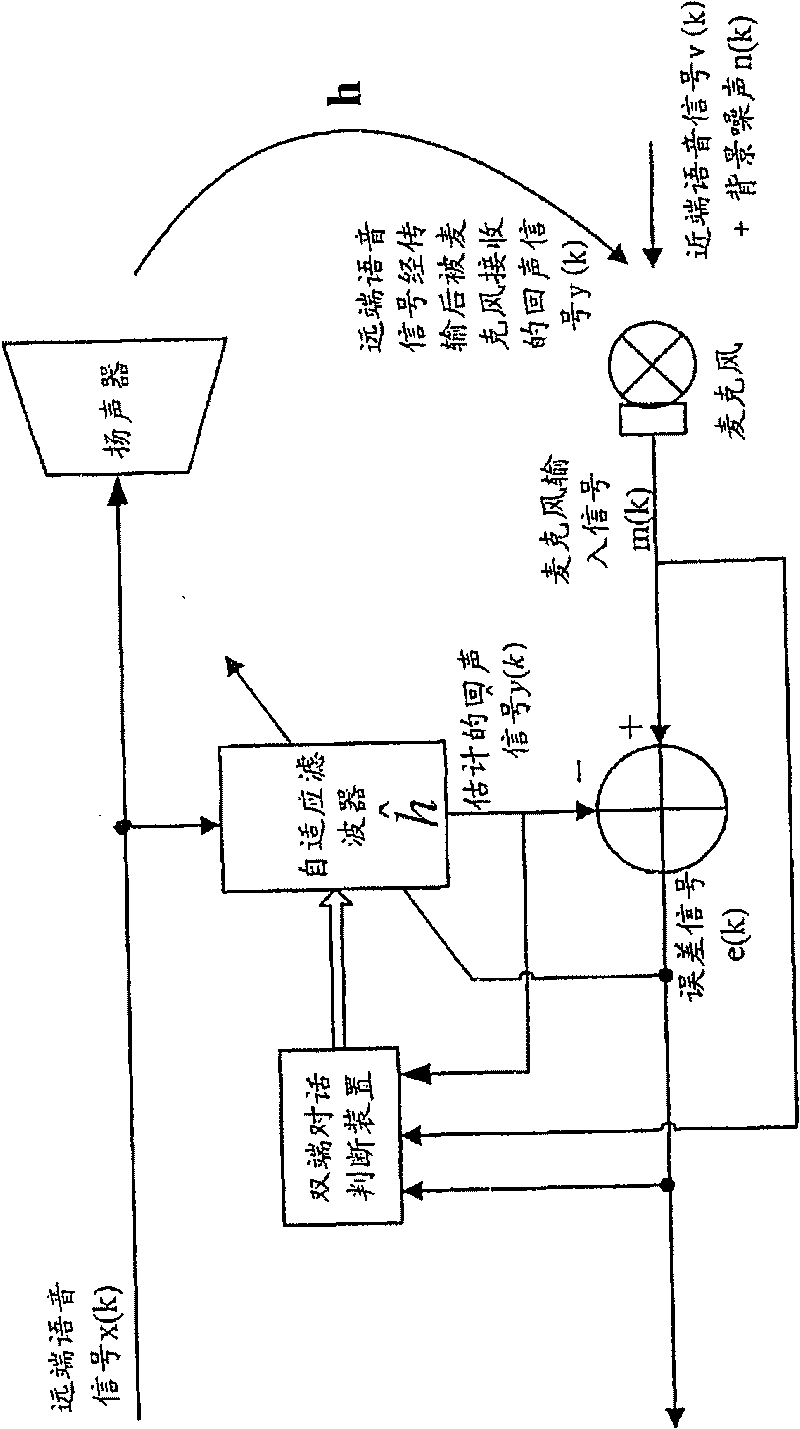
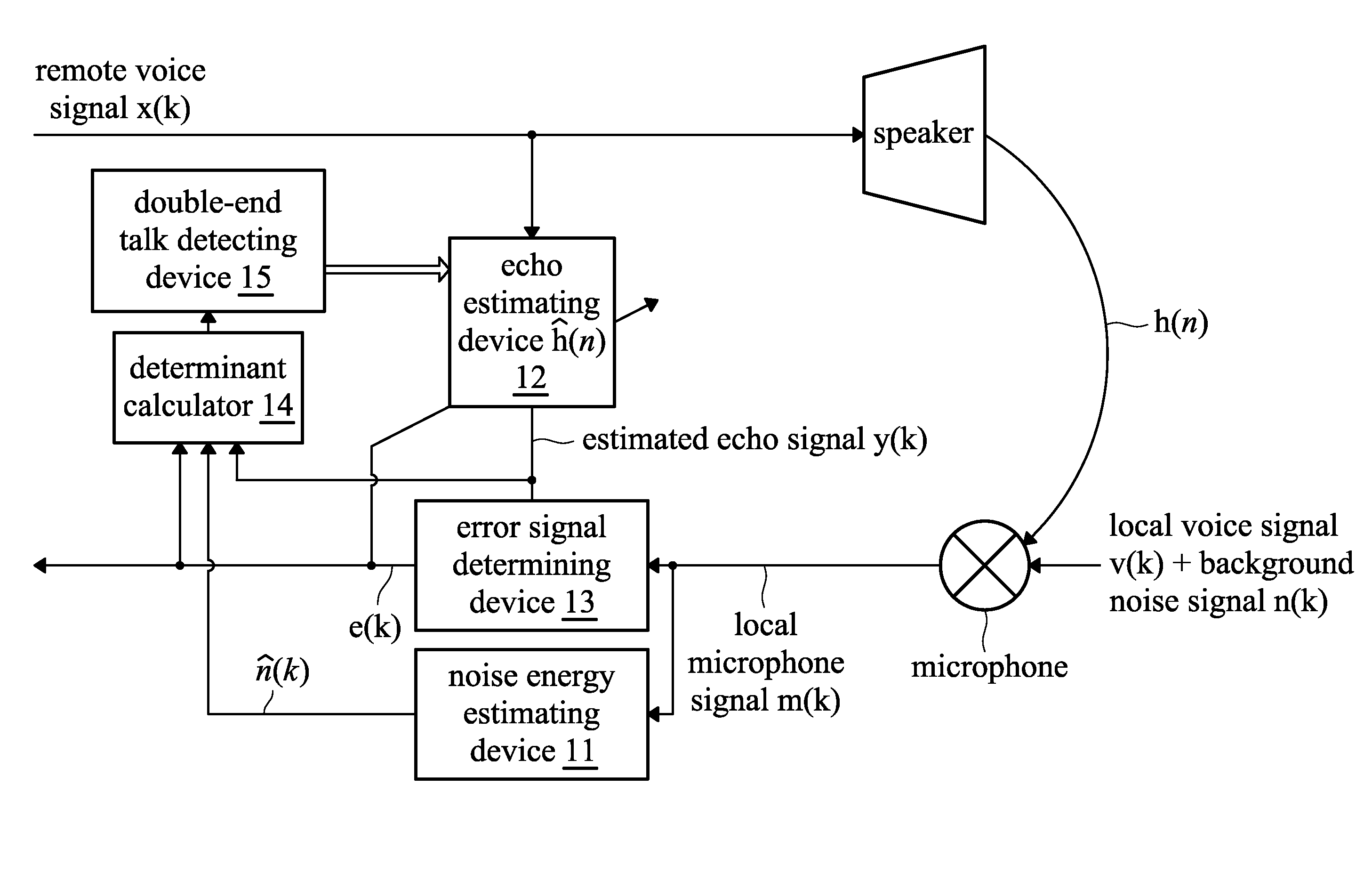
Method and system for double-end talk detection, and method and system for echo elimination
ActiveUS20110124380A1Eliminate effectiveAccurately determineInterconnection arrangementsSubstation equipmentCommunications systemCircumflex
A method and system for eliminating echo in a speaker-microphone communication system are provided. The method includes the steps of: performing a noise energy estimating process on a local microphone signal in order to obtain an estimated noise signal, wherein the local microphone signal includes a local voice signal, possible background noise signal, and possible remote voice signal output from a speaker and received by a microphone; performing an echo estimating process on a remote voice signal to obtain an estimated echo signal, wherein the remote voice signal is output from the speaker; determining an error signal from the local microphone signal and the estimated echo signal; calculating a variance (σe2) of the error signal and a variance ({circumflex over (σ)}n2) of the estimated noise signal; calculating a determinant (ξ), wherein the determinant (ξ) corresponds to the variance (σe2) of the error signal and variance ({circumflex over (σ)}n2) of the estimated noise signal; and comparing the determinant (ξ) and a preset threshold, wherein when the determinant (ξ) is lower than the preset threshold, it is determined that double-end talk has not occurred, otherwise, it is determined that double-end talk has occurred.
Owner:APPLE INC
Scene adaptive active noise reduction method and earphone
ActiveCN108900943AImprove impactRealize noise filtering effectHearing device active noise cancellationEarpiece/earphone attachmentsEnvironmental noiseFrequency spectrum
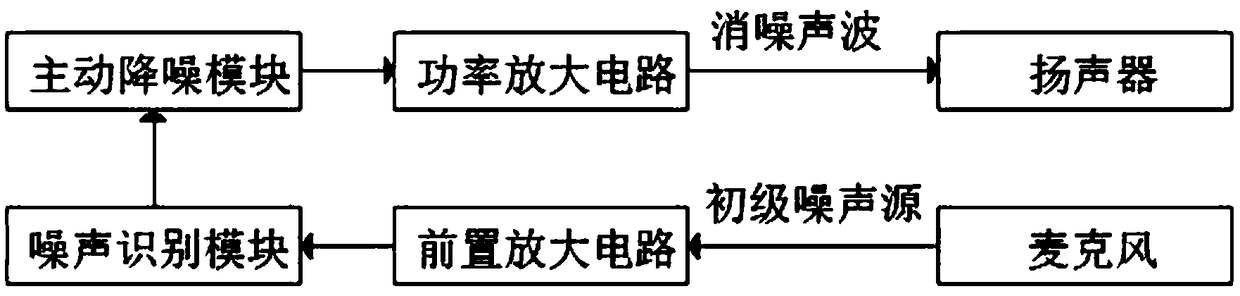
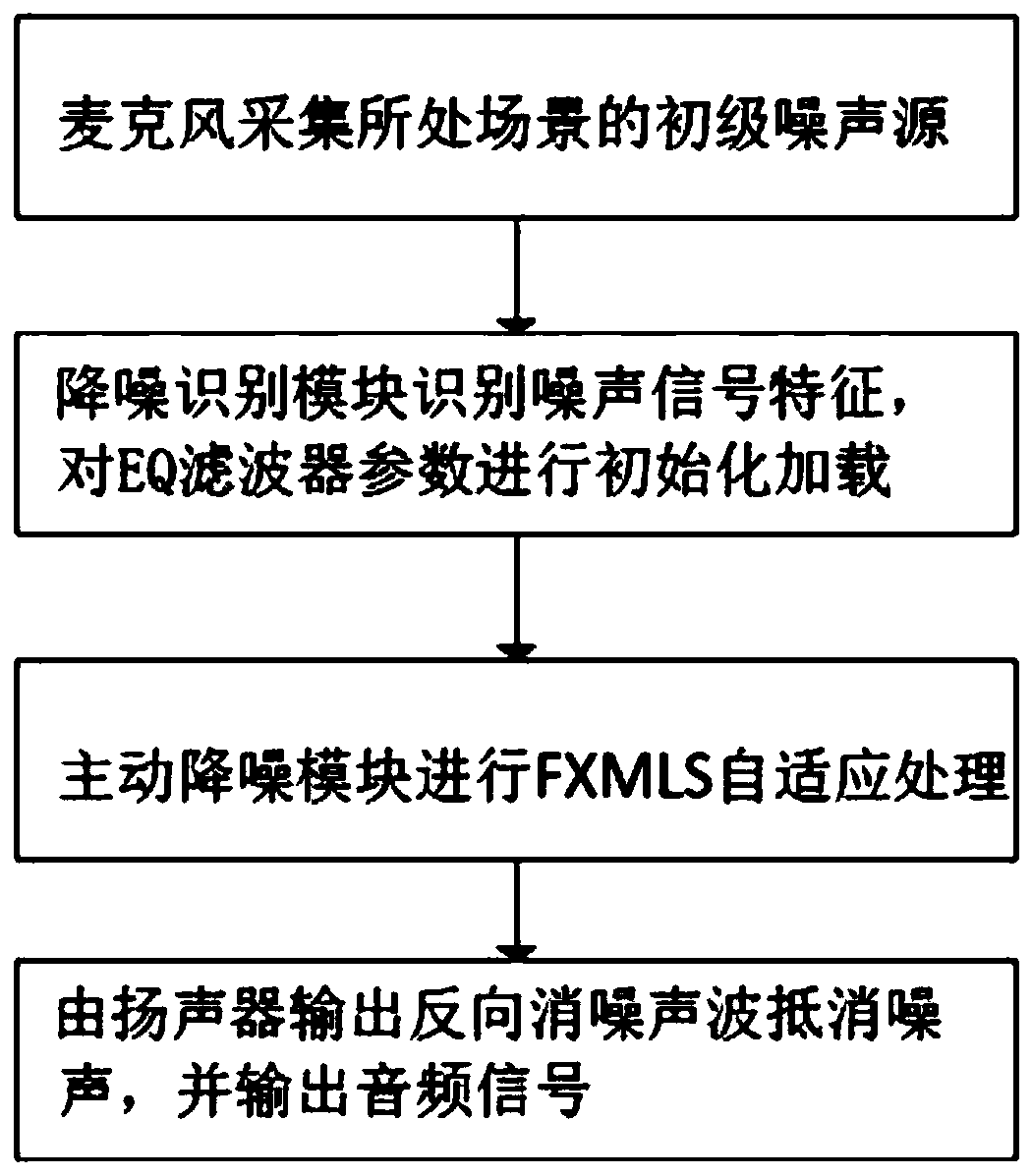
The invention discloses a scene adaptive active noise reduction method, which comprises the steps of: picking up environmental noise and converting into a primary noise electrical signal; determiningthe noise type by a noise recognition module; selecting an EQ filter parameter from a filter library to load an active noise reduction module; carrying out adaptive filtration on the primary noise electrical signal by the active noise reduction module to generate a noise reduction electrical signal for exciting a speaker; generating a noise reduction wave by the speaker after receiving the noise reduction electrical signal, and emitting a second canceling audio signal, wherein the noise reduction wave has the same spectral distribution as the primary noise electrical signal, and the sound pressure is the same in magnitude and opposite in phase. A scene adaptive active noise reduction earphone comprises a microphone, a speaker and an active noise reduction module. The noise reduction earphone can adjust the EQ filter parameters in the FXLMS noise reduction algorithm according to the difference of the noise energy concentration region in the noise scene, and cancel the noise which cannotbe removed by the passive noise reduction, thereby improving the effect of the external noise of the scene of the human ear to the earphone export audio.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method for filtering full-wave nuclear magnetic resonance signal noises based on double singular value decomposition
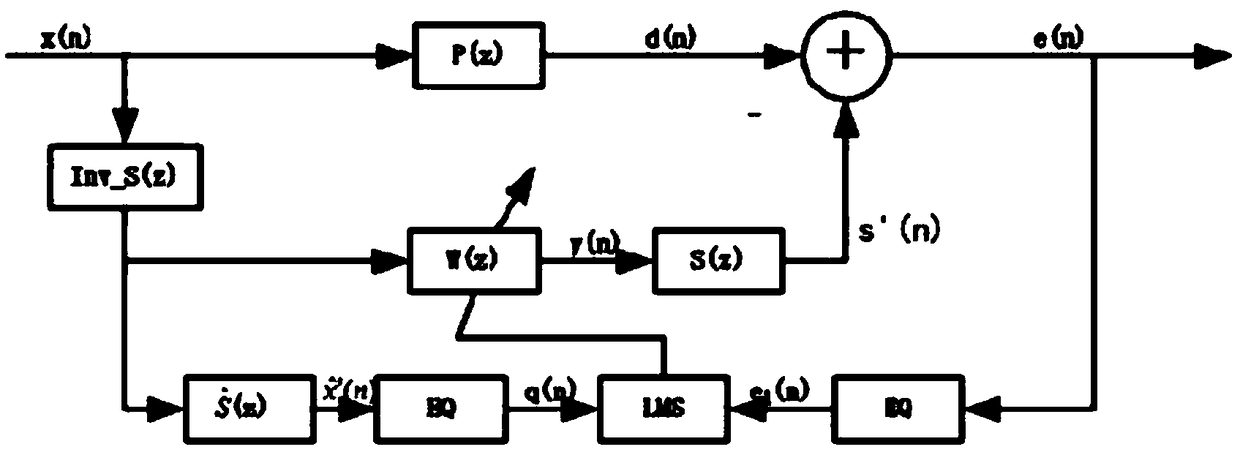
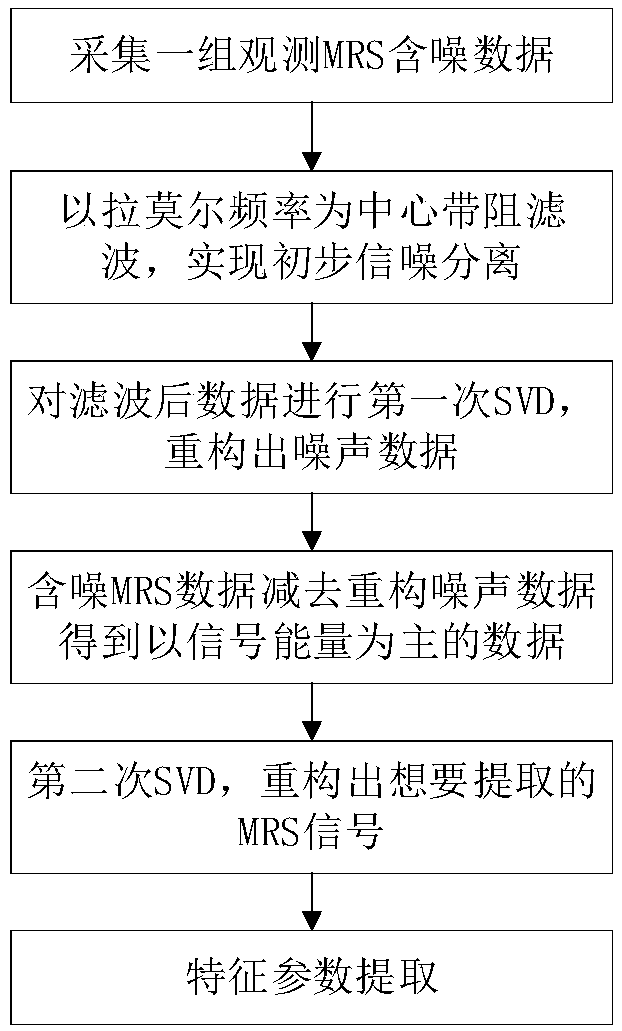
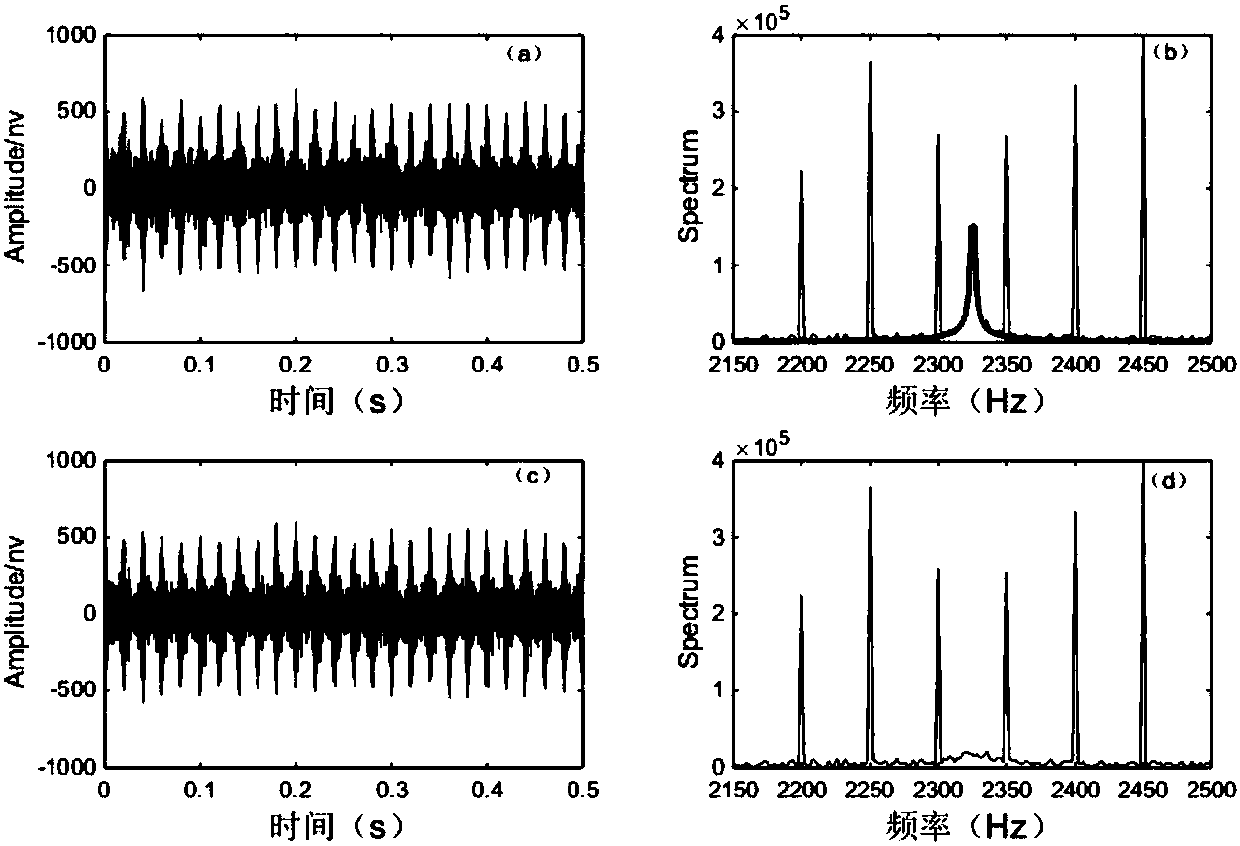
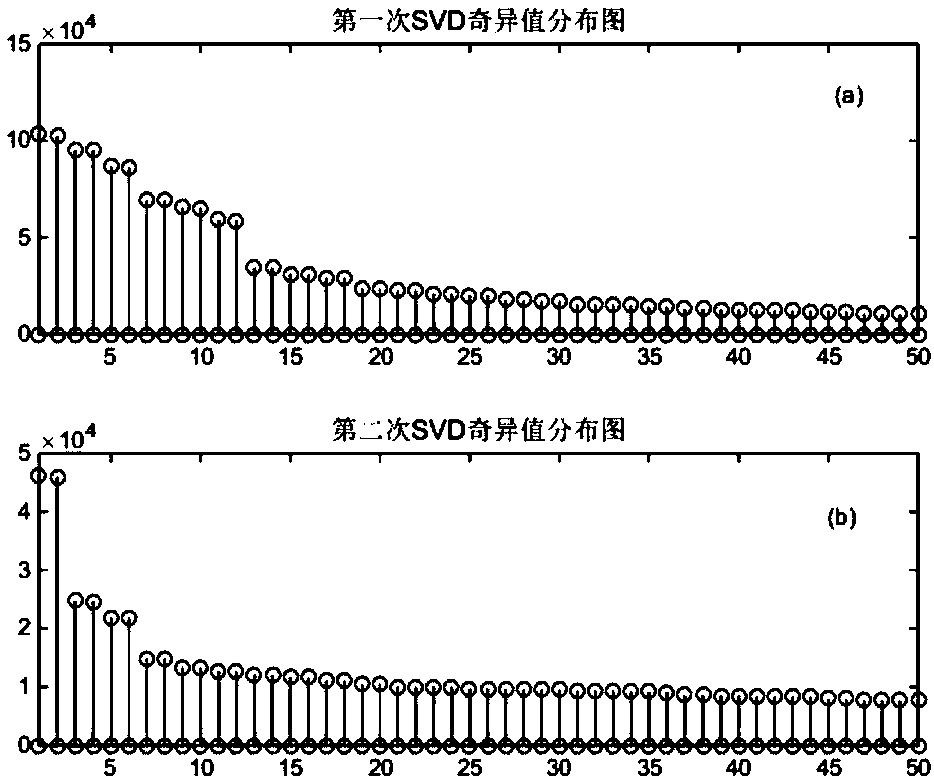
InactiveCN107045149ASolving the Difficulty of Efficient ExtractionImprove timelinessDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceAcoustic wave reradiationSingular value decompositionFull wave
The invention relates to the field of noise filtering of nuclear magnetic resonance sounding signals, particularly to a method for filtering full-wave nuclear magnetic resonance signal noises based on double singular value decomposition. The method comprises: colleting one group of observation MRS noise-included data by using ground nuclear magnetic resonance underground water detection equipment; carrying out band-reject filtering using a Larmor frequency as a center on the data to realize preliminary signal and noise separation; carrying out first singular value decomposition and reconstructing noise data; subtracting the reconstructed noise data from the observation MRS noise-included data to obtain data including most of signal energy and reduced noise energy; carrying out secondary t singular value decomposition and reconstructing an MRS signal that need to be extracted; and carrying out MRS signal feature parameter extraction by using a non-linear fitting method. For full-wave MRS data collected by a single channel, influences of power-frequency harmonic interference and random noises can be eliminated simultaneously; and effective extraction of the MRS signal feature parameters can b realized by non-linear fitting.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com