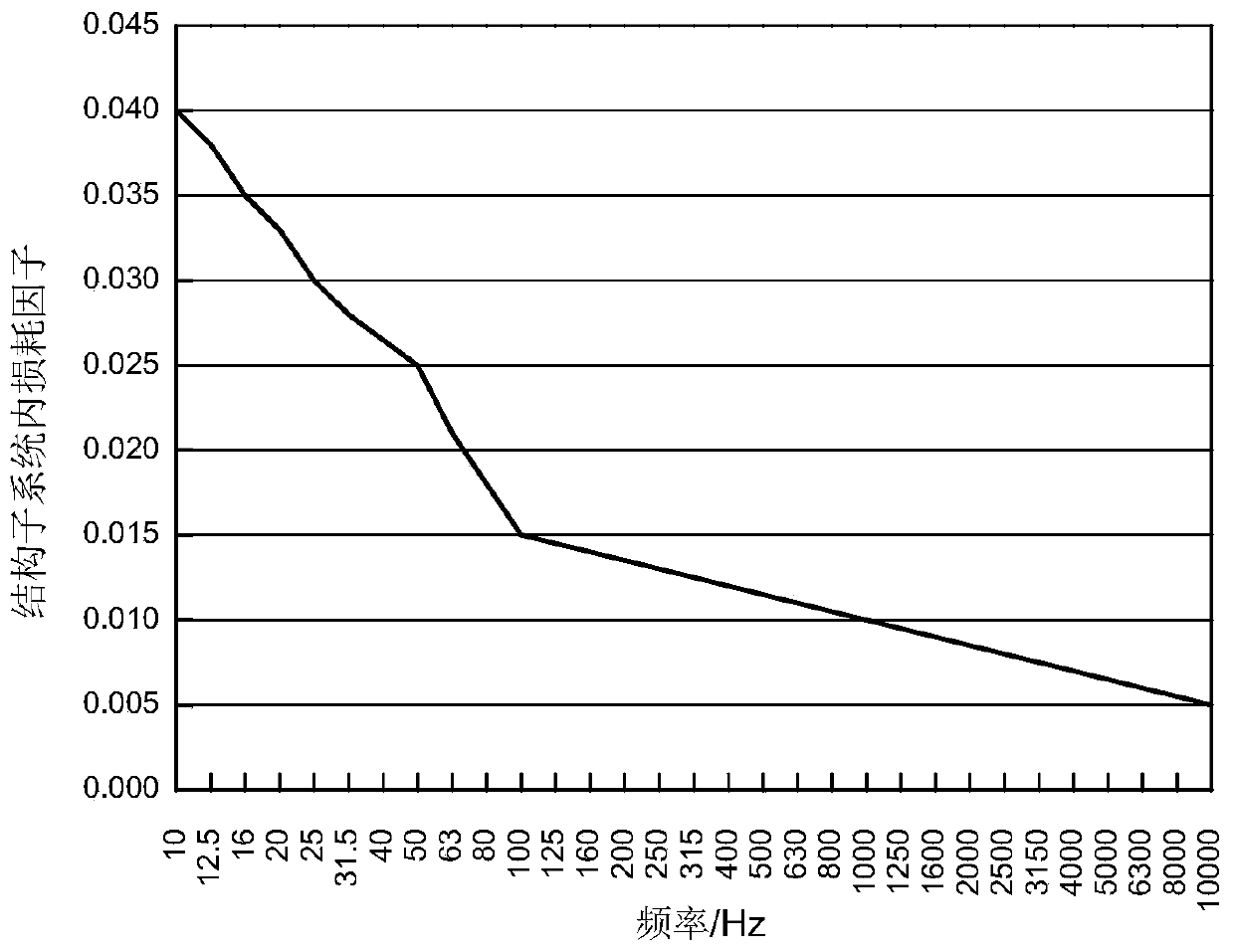
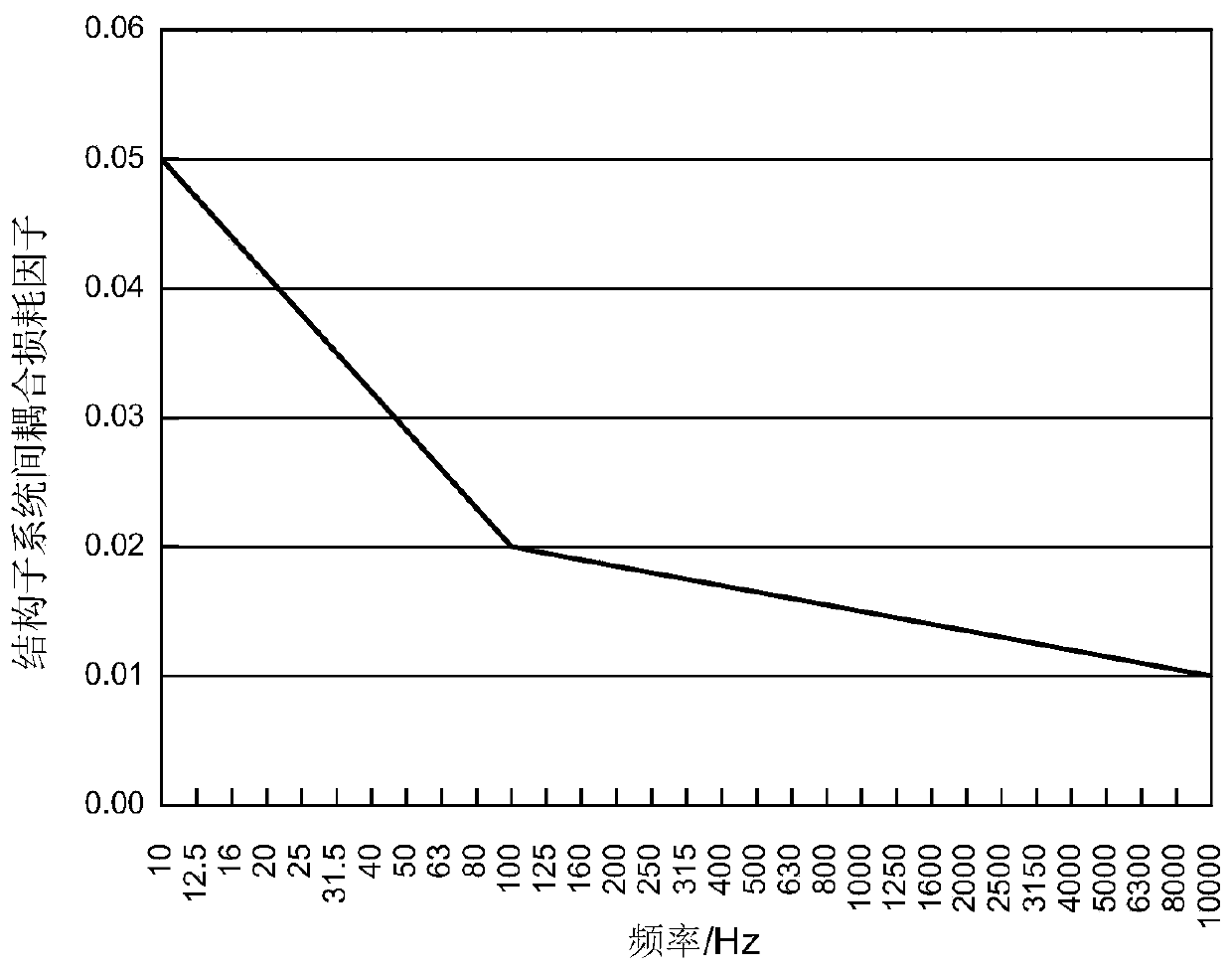
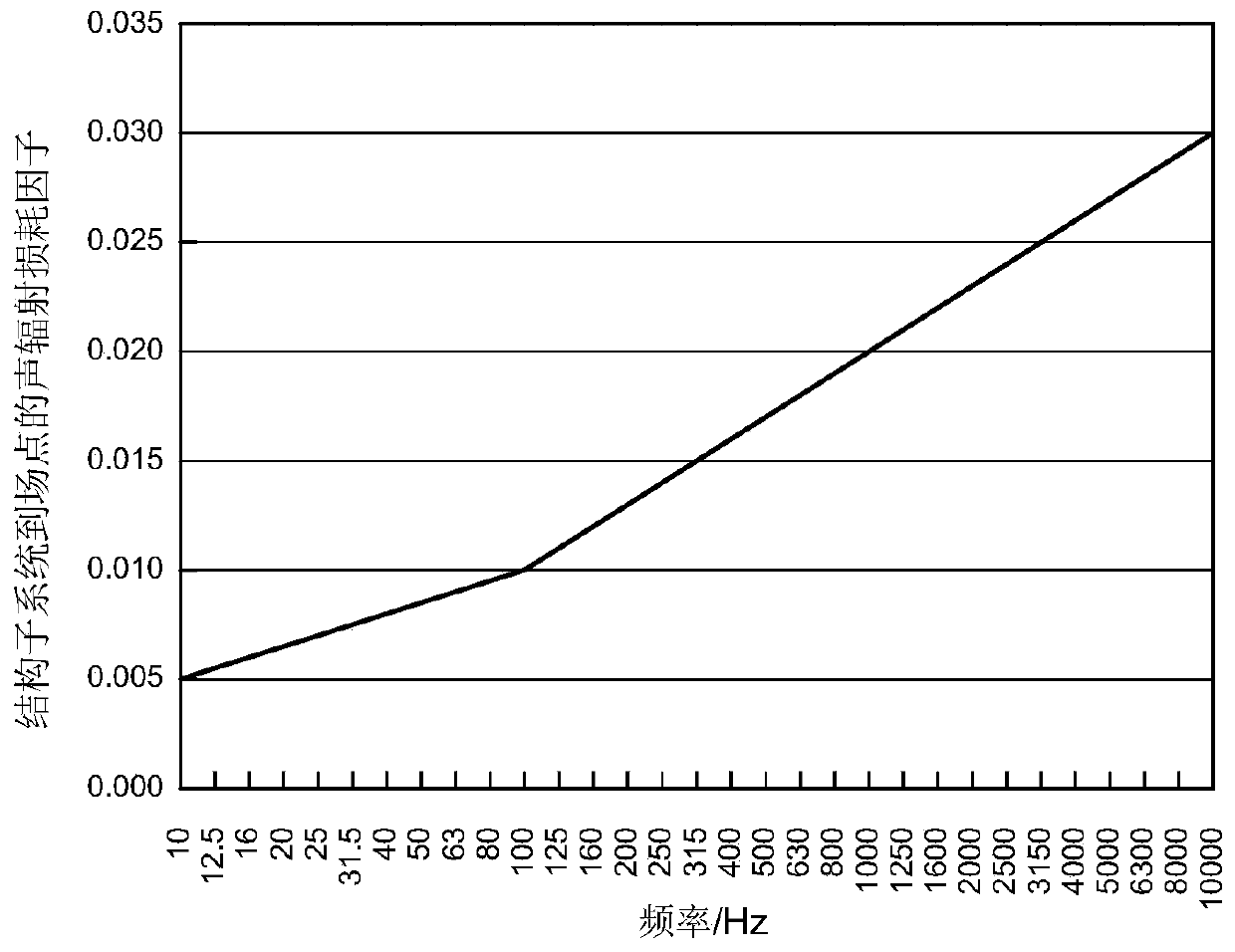
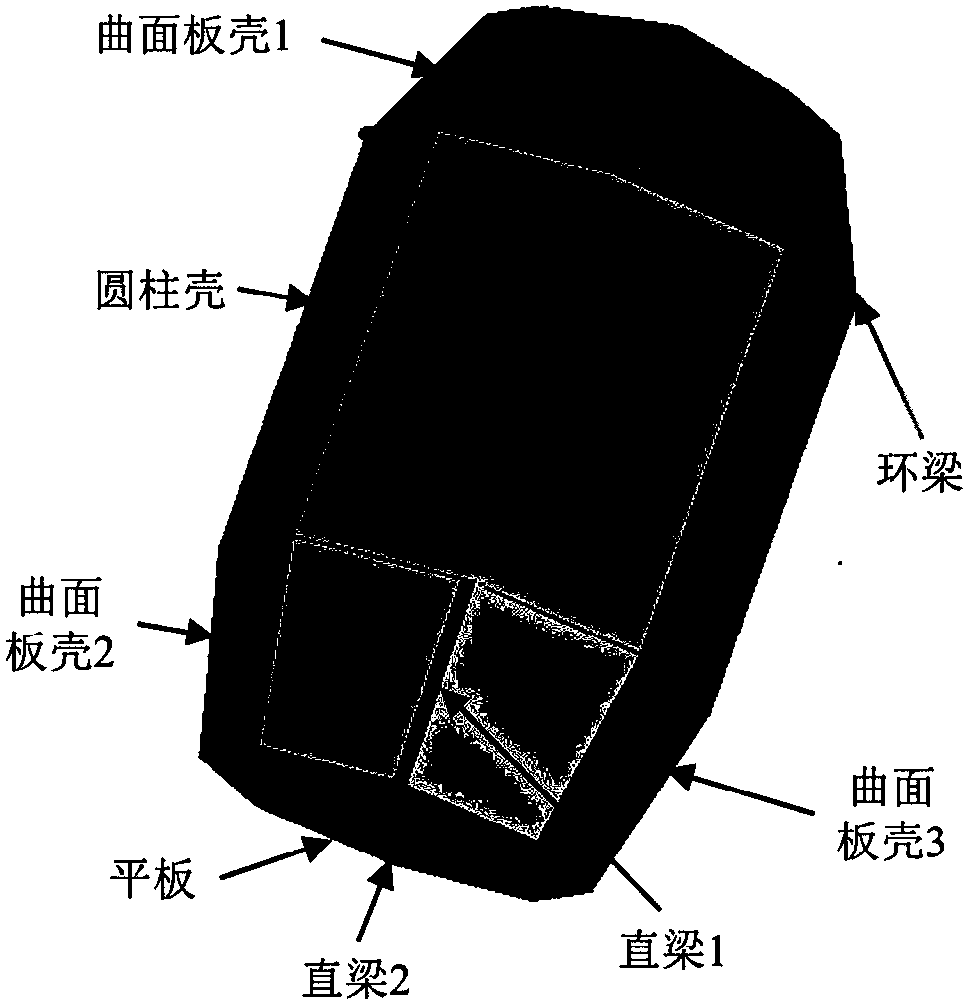
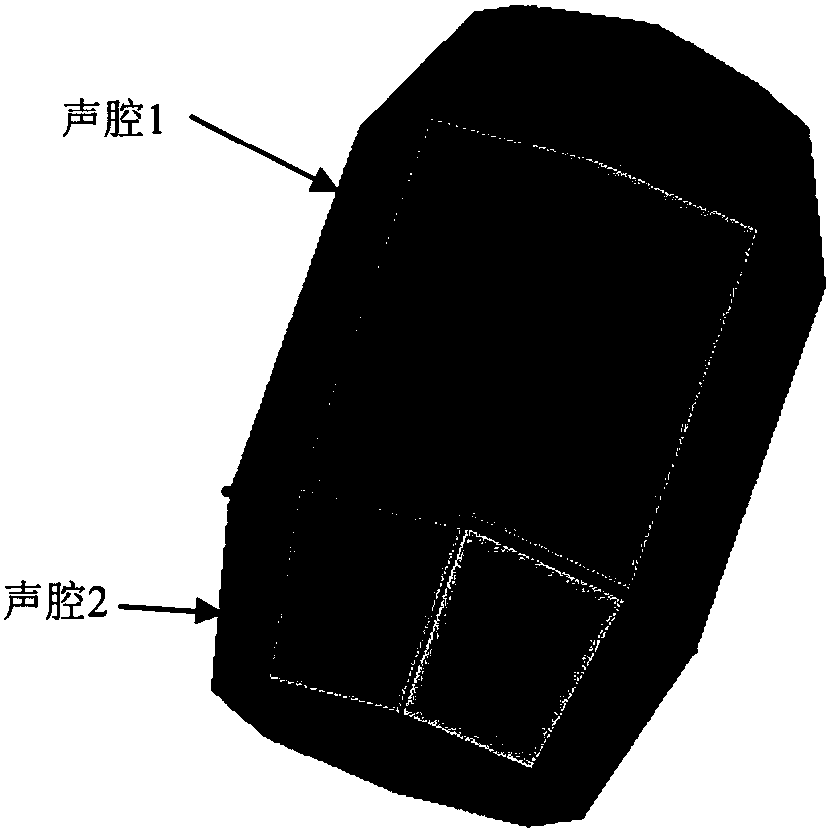
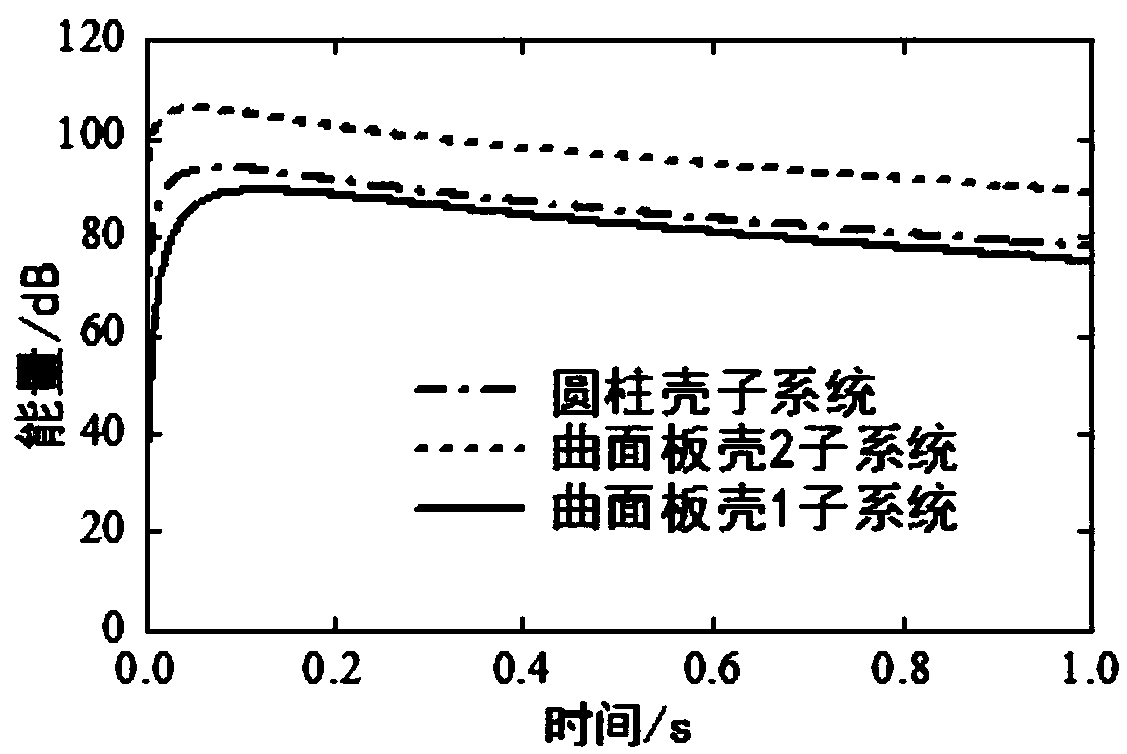
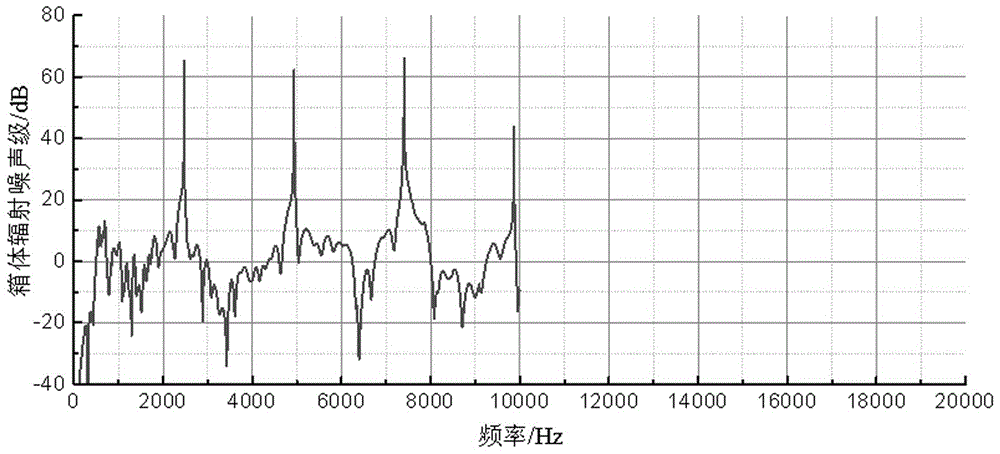
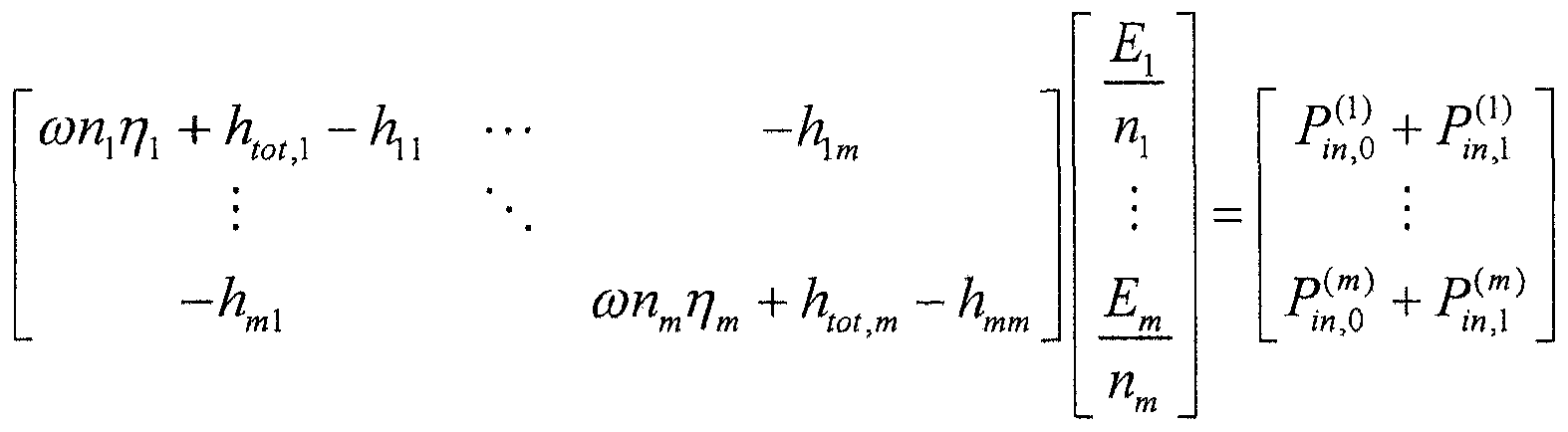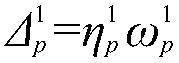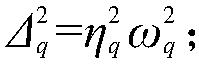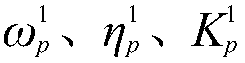Patents
Literature
48 results about "Statistical energy analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
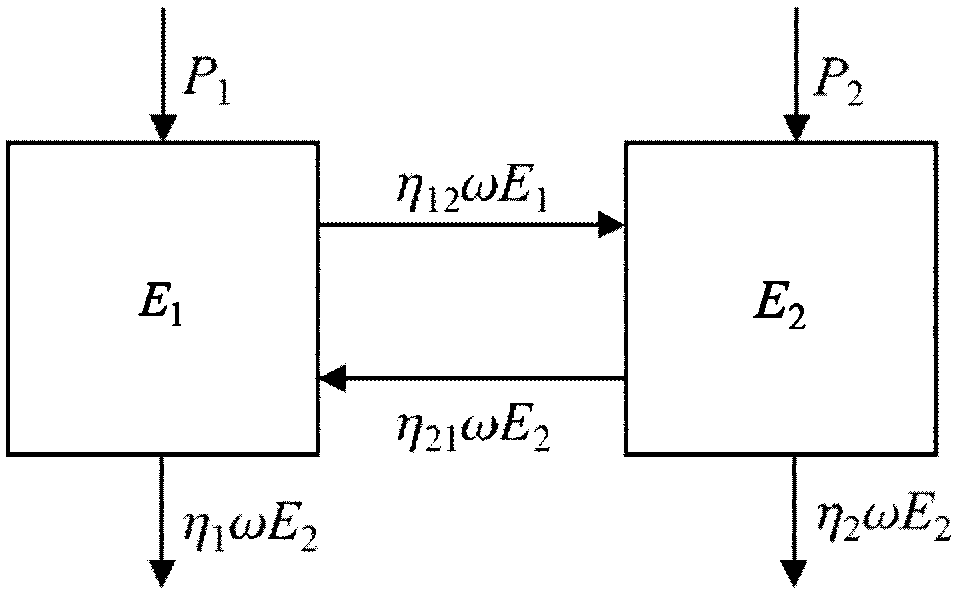
Statistical energy analysis (SEA) is a method for predicting the transmission of sound and vibration through complex structural acoustic systems. The method is particularly well suited for quick system level response predictions at the early design stage of a product, and for predicting responses at higher frequencies. In SEA a system is represented in terms of a number of coupled subsystems and a set of linear equations are derived that describe the input, storage, transmission and dissipation of energy within each subsystem. The parameters in the SEA equations are typically obtained by making certain statistical assumptions about the local dynamic properties of each subsystem (similar to assumptions made in room acoustics and statistical mechanics). These assumptions significantly simplify the analysis and make it possible to analyze the response of systems that are often too complex to analyze using other methods (such as finite element and boundary element methods).
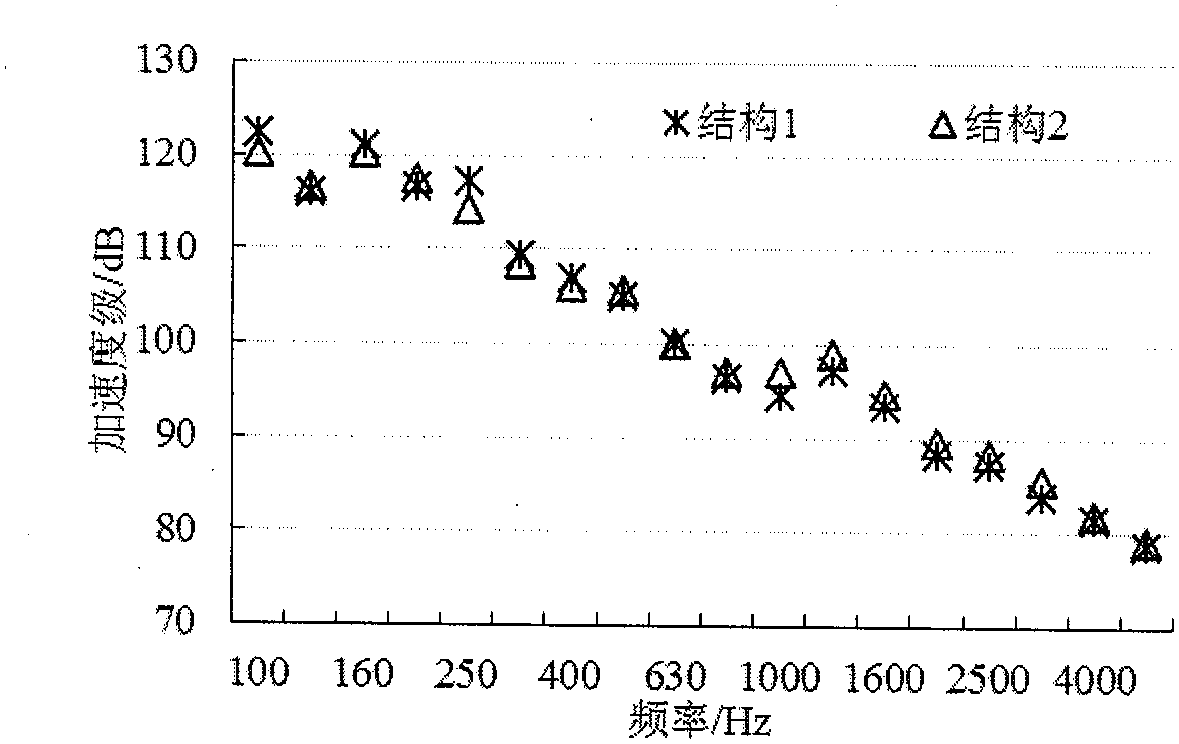
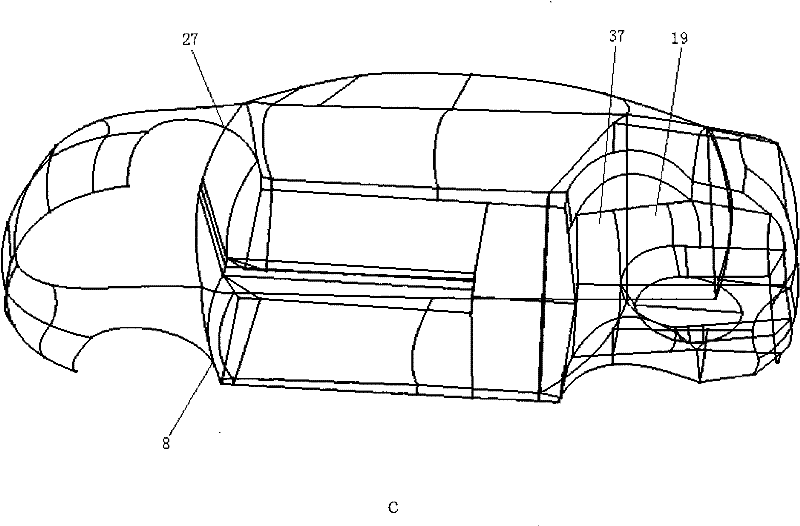
Interior noise analysis and prediction method of high speed train
InactiveCN105590003AShorten the development cycleAccuracy impactGeometric CADSustainable transportationEngineeringInterior noise
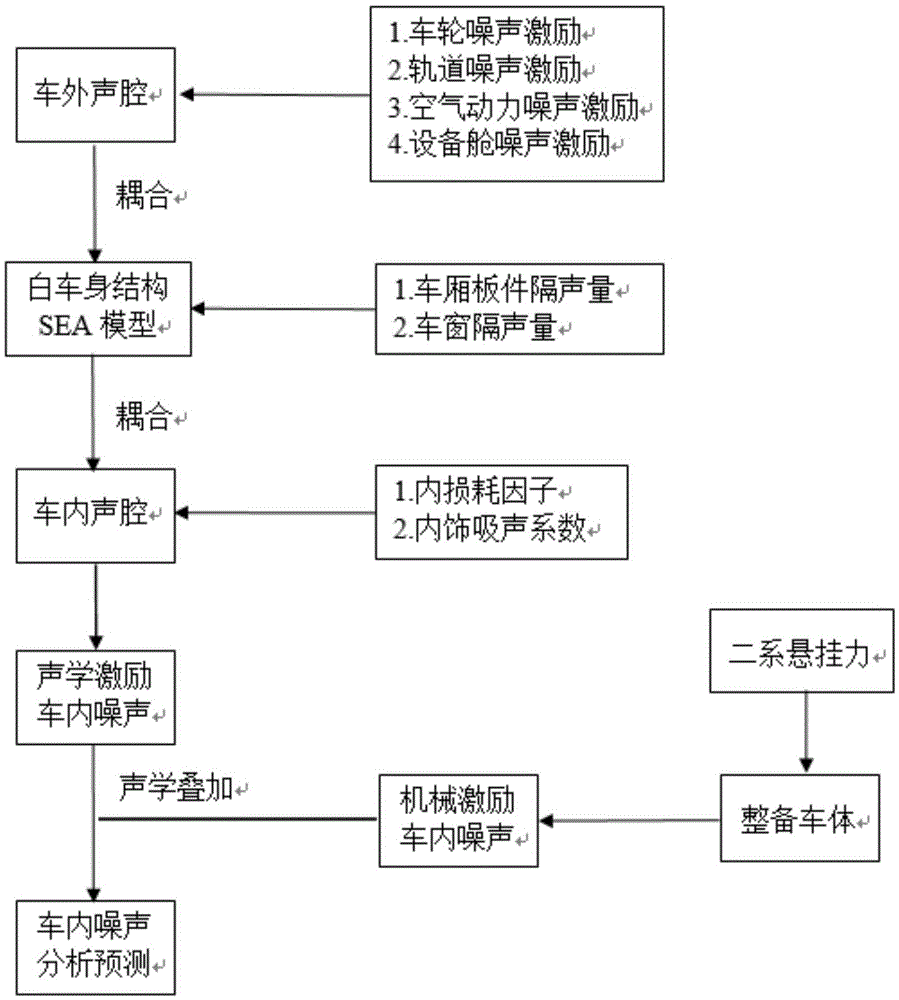
The invention discloses an interior noise analysis and prediction method of a high speed train. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a train reconditioning train body model, a statistical energy analysis model of a body in white structure and an interior and exterior vocal cavity statistical energy analysis model, and carrying out simplification and subsystem division; obtaining the statistical energy analysis parameters of the train body structure and an interior vocal cavity model, and loading the statistical energy analysis parameters onto a train body structure model plate subsystem and a vocal cavity model subsystem; and obtaining exterior vocal excitation source energy borne on the train body, applying the exterior vocal excitation source energy onto the exterior vocal cavity statistical energy analysis model, causing the exterior vocal excitation source energy to reach an interior vocal cavity after the exterior vocal excitation source energy is attenuated by the sound insulation property of a structural plate in a body in white structure model so as to obtain structural noise energy radiated into the train by the reconditioning train body under the function of the two-line suspension force of a compartment, and then, carrying out interior noise analysis and prediction. The problem that the interior noise of the train is difficult in prediction and the problems of the upper limit boundedness of a frequency domain, complex calculation flow, incomplete motivation consideration in the traditional method are overcome, calculation efficiency and prediction accuracy are improved, and development and test cost is lowered.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Statistical energy analysis parameter acquisition method based on finite element method and power input method
ActiveCN106844906AOvercome limitationsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelStatistical analysis
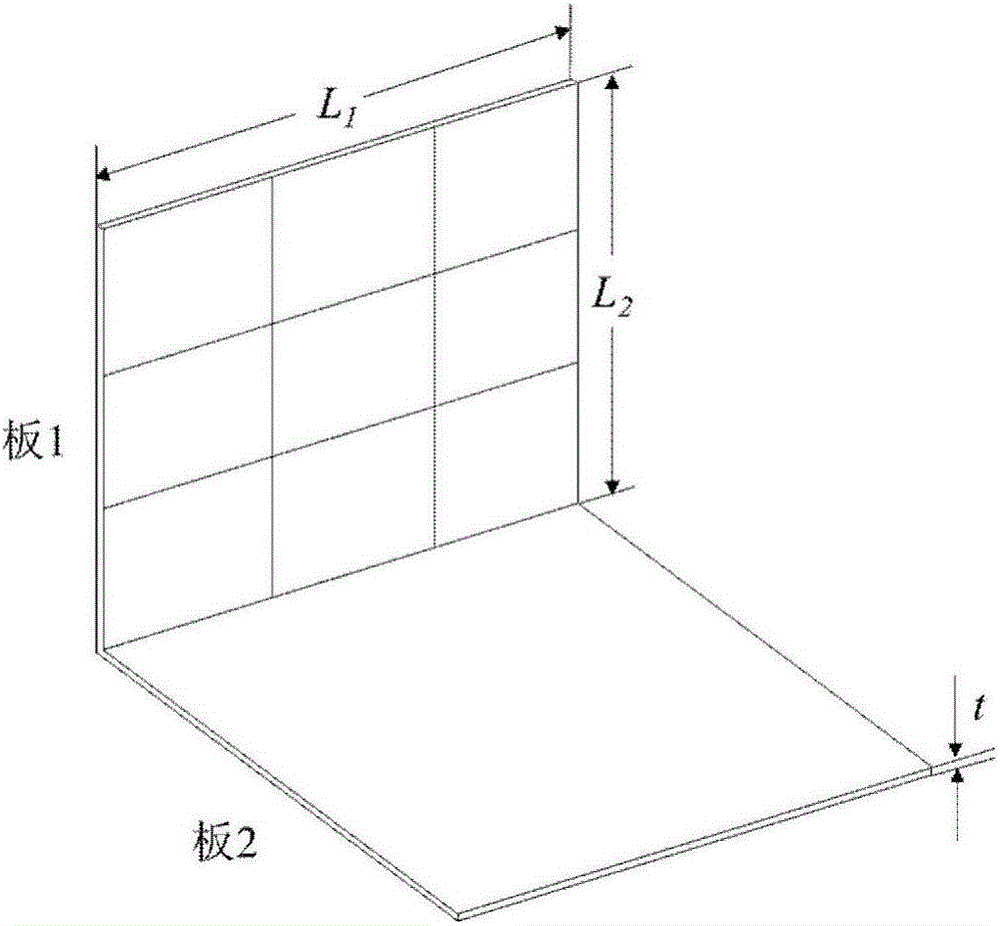
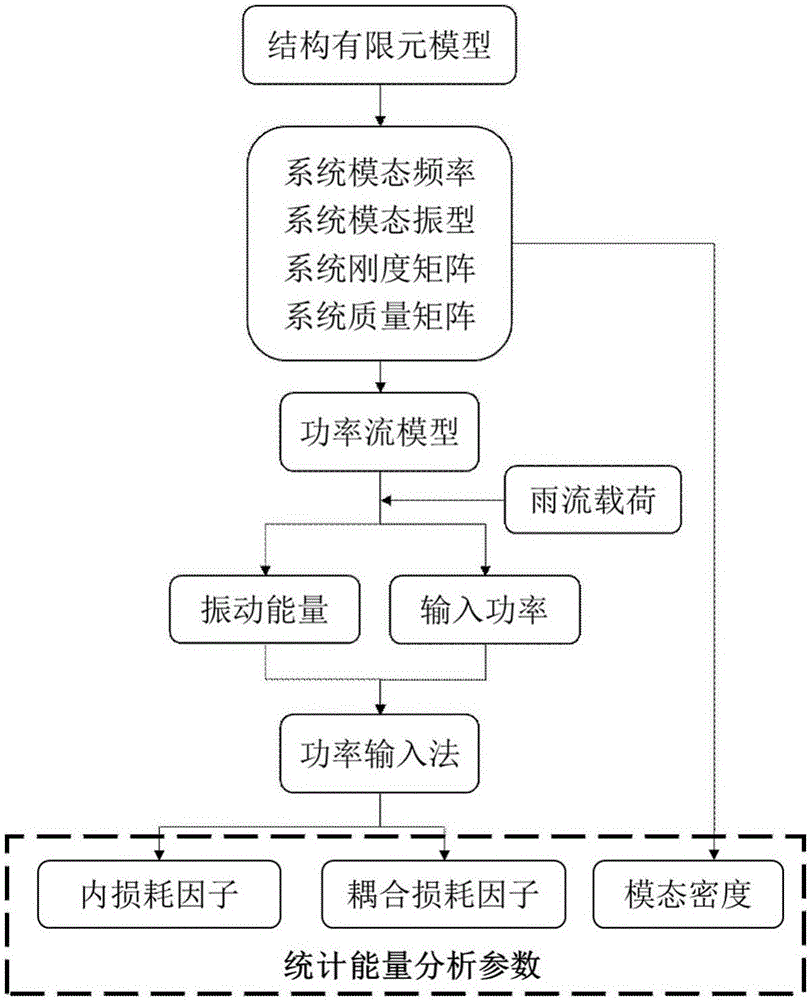
The invention provides a statistical energy analysis parameter acquisition method based on a finite element method and a power input method. A finite element model of a structure is established according to a geometric model of the structure, boundary conditions are applied, the finite element model of the structure is subjected to mode analysis, a mode of a system and a rigidity matrix and a mass matrix of a subsystem are obtained, vibration energy of the subsystem and input power of the system are obtained through a power flow model, and statistical energy analysis parameters are obtained through calculation through the power input method. The finite element method and the power input method are combined to obtain the statistical energy analysis parameters of the structure, the calculated rigidity matrix, mass matrix, mode shape and inherent frequency are obtained through the finite element method, the input power and the vibration energy are obtained through calculation through the power flow model, and the input power and the vibration energy are substituted into the power input method for calculation to obtain the statistical energy analysis parameters. According to the method, statistical energy analysis can be carried out aiming at the problem of strong coupling between structures, the limitation about weak coupling assumption between the structures in existing statistical energy analysis is solved, and the method can be popularized to complex structures.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for calculating intermediate and high frequency dynamic response of acoustic vibration system
ActiveCN102411673AEasy to solveConducive to engineering applicationSpecial data processing applicationsPower flowIntermediate frequency
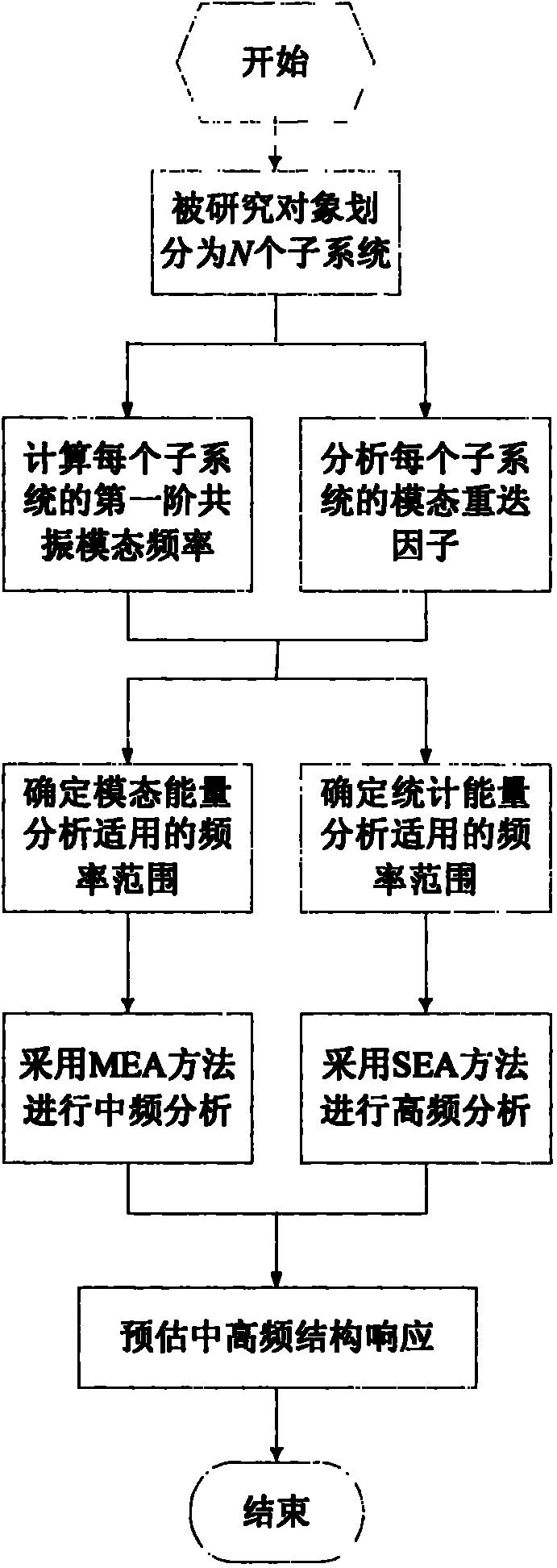
The invention provides a method for calculating the intermediate and high frequency dynamic response of an acoustic vibration system. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly dividing the acoustic vibration system to be researched into N subsystems; then, determining analysis frequency ranges to which a modal energy analysis method and a statistical energy analysis method are applicable; when the analysis frequency is in an intermediate frequency range, calculating the intermediate frequency dynamic response of the researched acoustic vibration system by adopting the modal energy analysis method; and when the analysis frequency is in a high frequency range, calculating the high frequency dynamic response of the researched acoustic vibration system by adopting the statistical energy analysis method, wherein the modal energy analysis method comprises the following steps of: firstly determining the number of resonance modes and resonance frequency values of all the subsystems in the intermediate frequency range, and then establishing a power flow balance relationship among the resonance modes of the N subsystems, and finally solving the modal energy of each mode of all the subsystems according to the power flow balance relationship, summing the modal energy of the modes of each subsystem in an analysis frequency band so as to obtain the energy response of each subsystem in the analysis frequency band.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Constrained damping layer structure vibration calculation method
InactiveCN107368645AGood vibration and noise reductionRealize vibration simulation analysisGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationNoise controlShear modulus
The invention discloses a constrained damping layer structure vibration calculation method. Through starting from a constrained damping layer damping and noise reducing mechanism, utilizing damping loss factors in statistical energy analysis to reflect damping effects of constrained damping layers, combining a modal strain energy method and considering frequency-dependent shear modulus and material loss factors of frequency of the constrained damping layers, a vibration calculation method for large-scale constrained damping layer structures is established, so that the forecast evaluation and optimized analysis of the constrained damping layers applied to large-scale structure damping and noise reducing are realized. According to the method, the calculation efficiency is remarkably improved and the vibration simulated analysis of the large-scale constrained damping layer structures can be realized; and the frequency-dependent characteristics of material shear modulus and material loss factors of the damping layers are considered so that the precision of simulated analysis is improved. By utilizing the method, optimized analysis can be carried out on laying positions and structure parameters of the constrained damping layers, the damping and noise reducing effects of the constrained damping layers can be forecasted, and the constrained damping layers can be utilized to carry out vibration and noise control on engineering structures.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
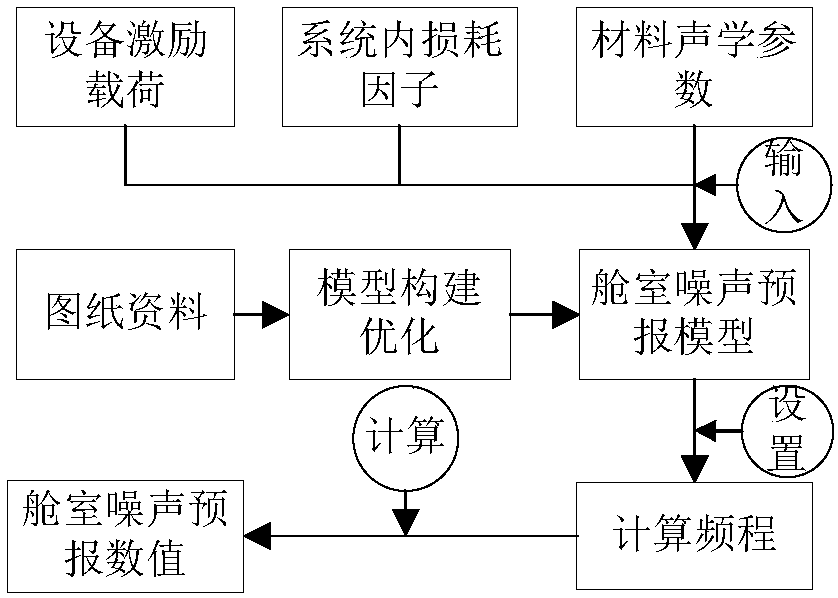
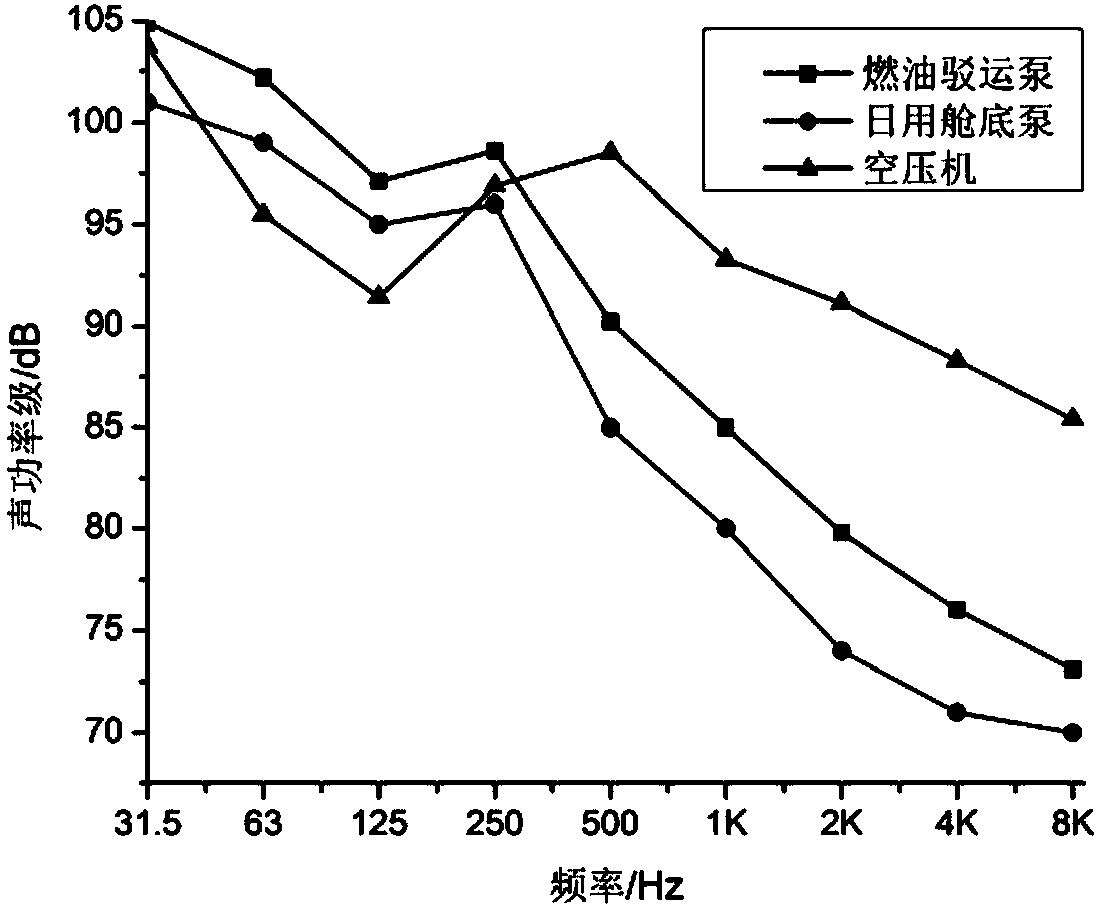
Statistical energy analysis-based ship cabin noise forecasting method
ActiveCN107944108AImprove efficiencyHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsVibration accelerationStatistical analysis
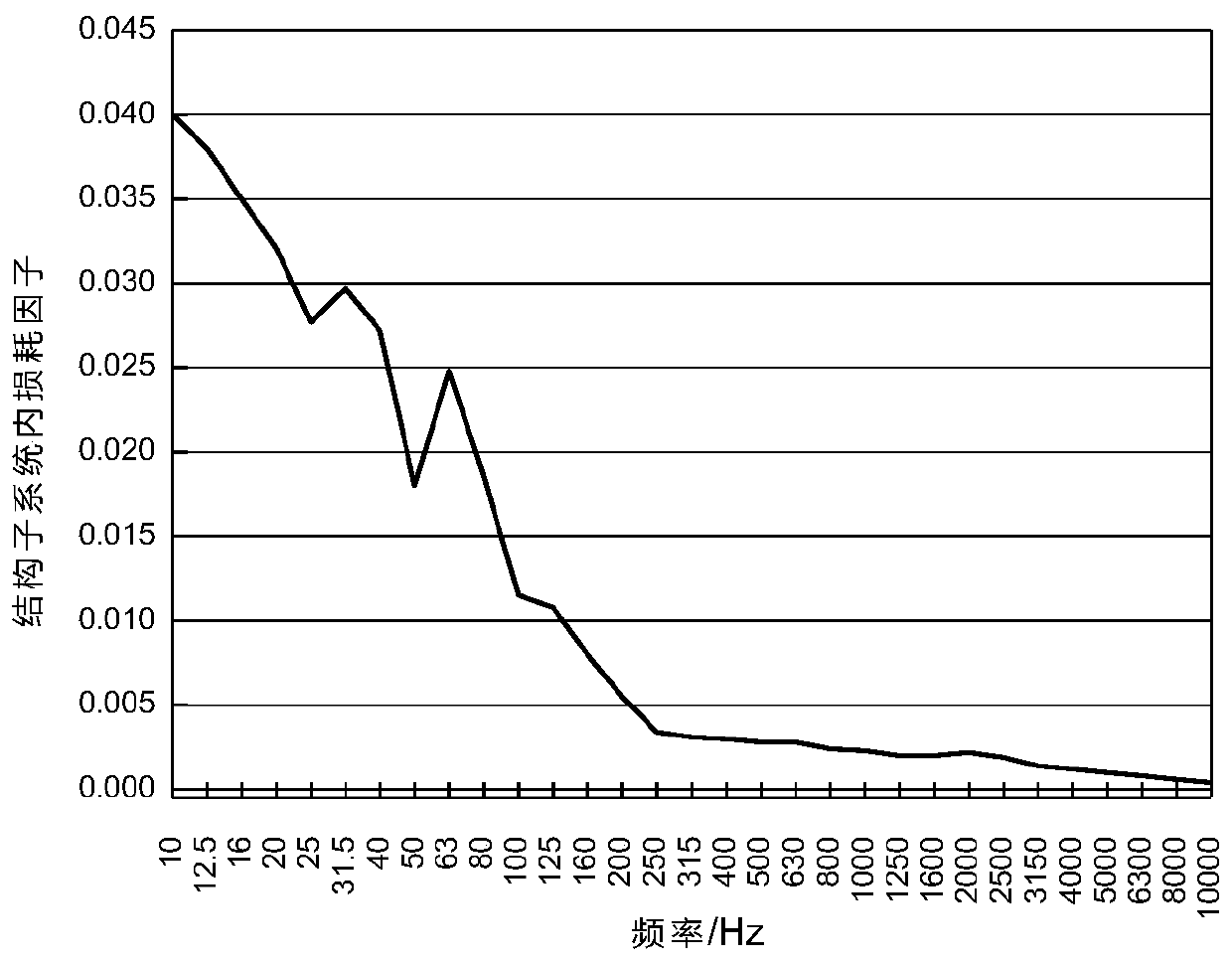
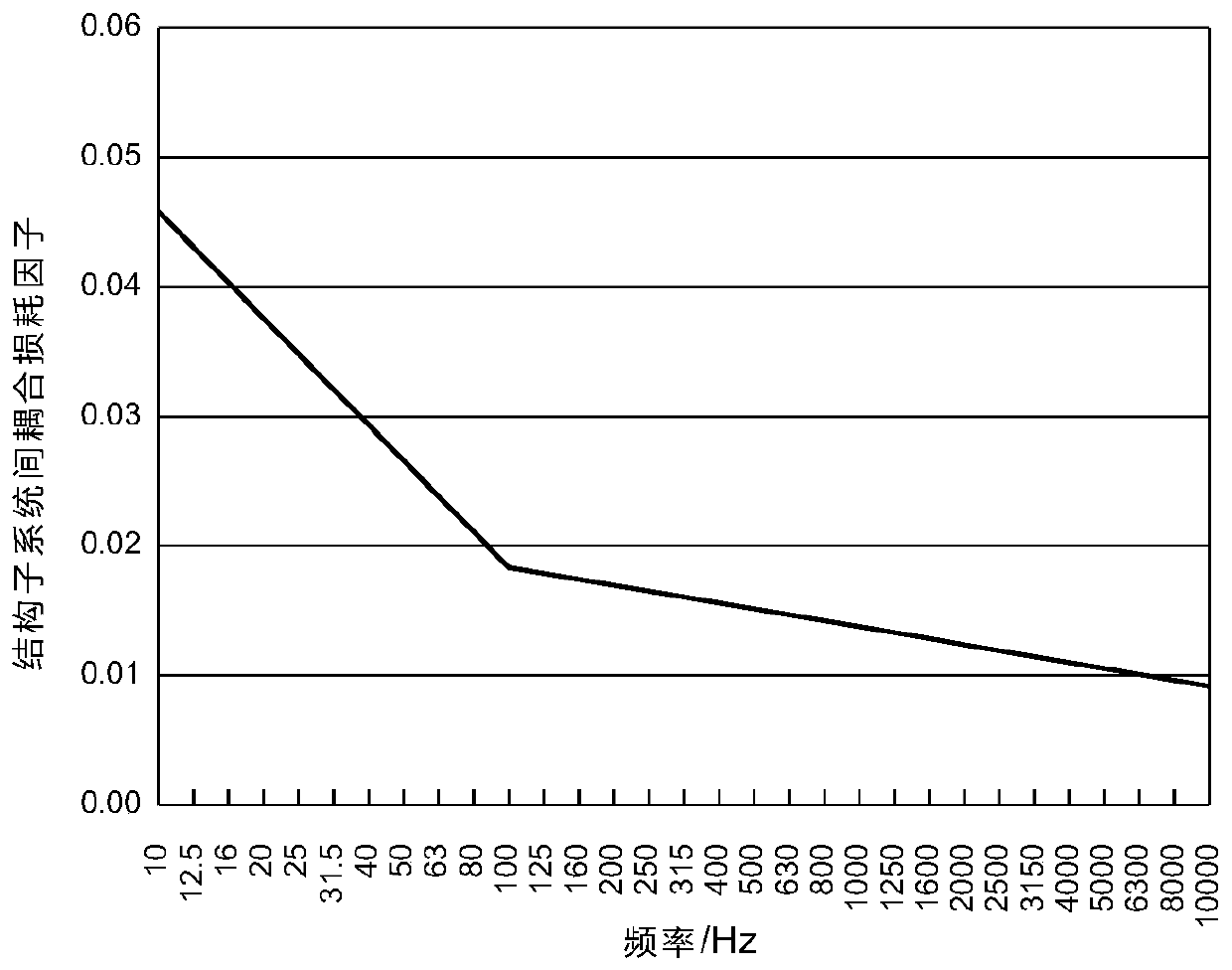
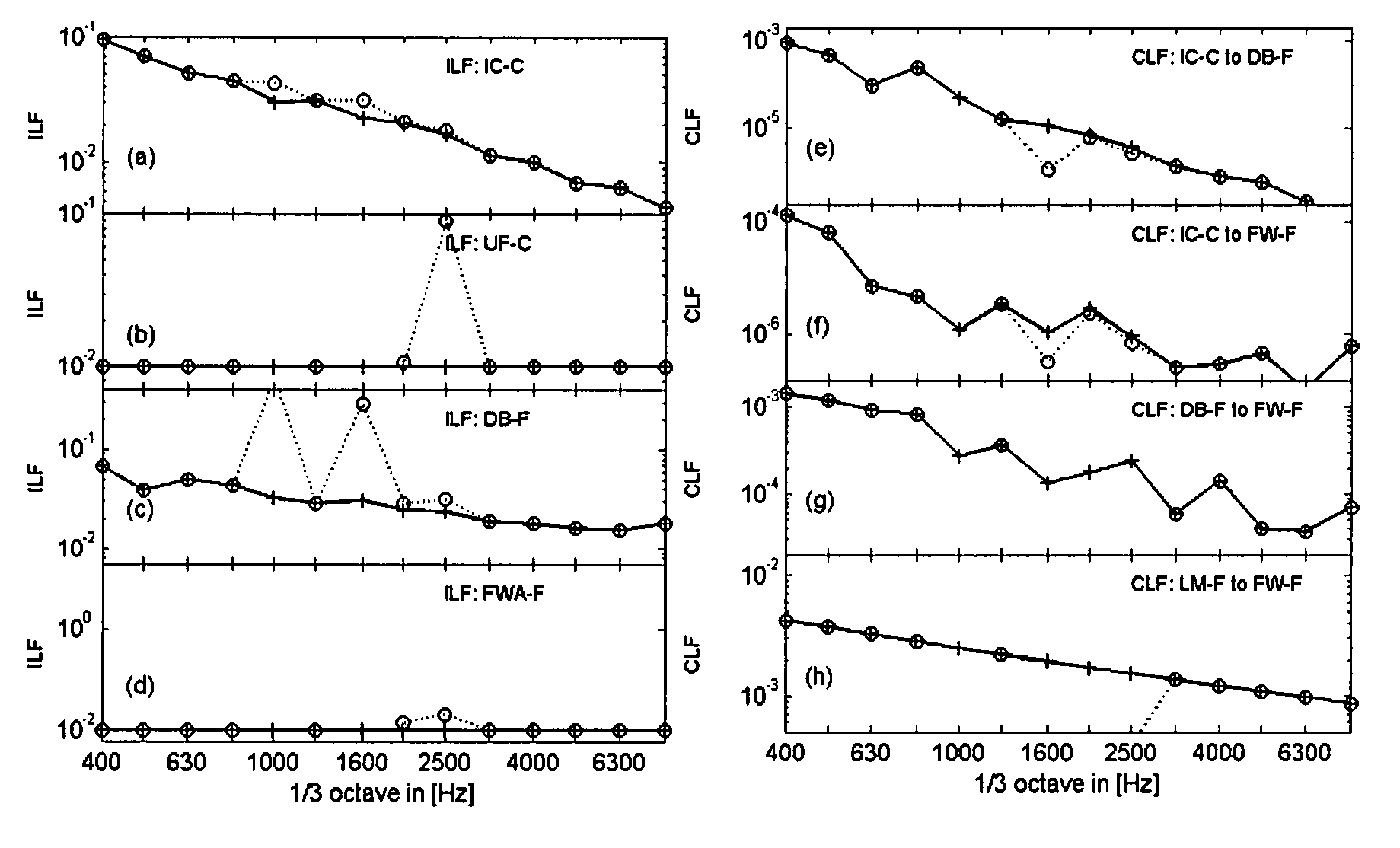
The invention provides a statistical energy analysis-based ship cabin noise forecasting method. The method comprises the steps of 1, preliminarily building a statistical energy analysis-based ship cabin noise forecasting model by utilizing ship drawing data; 2, performing local detail optimization on an emphatically assessed cabin and load region in the built model, and constructing an external auxiliary sound cavity; 3, determining a vibration acceleration load and a sound power load of equipment by utilizing an experimental test; 4, performing calculation by utilizing the experimental test or a formula to determine loss factors in a steel plate and the sound cavity; 5, building a microacoustic analysis model of an outfitting material structure by utilizing a transfer matrix method, and obtaining acoustic parameters of an outfitting material through sound absorption and insulation analysis; 6, setting frequency response analysis as a 1 / 3 octave frequency, and setting a calculation frequency to be 31.5Hz-8kHz; and 7, performing ship cabin noise forecasting analysis by applying statistical energy analysis. The efficiency and precision of ship cabin noise forecasting can be effectively improved; and the method can be applied to ocean platform and ship cabin noise forecasting and control.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
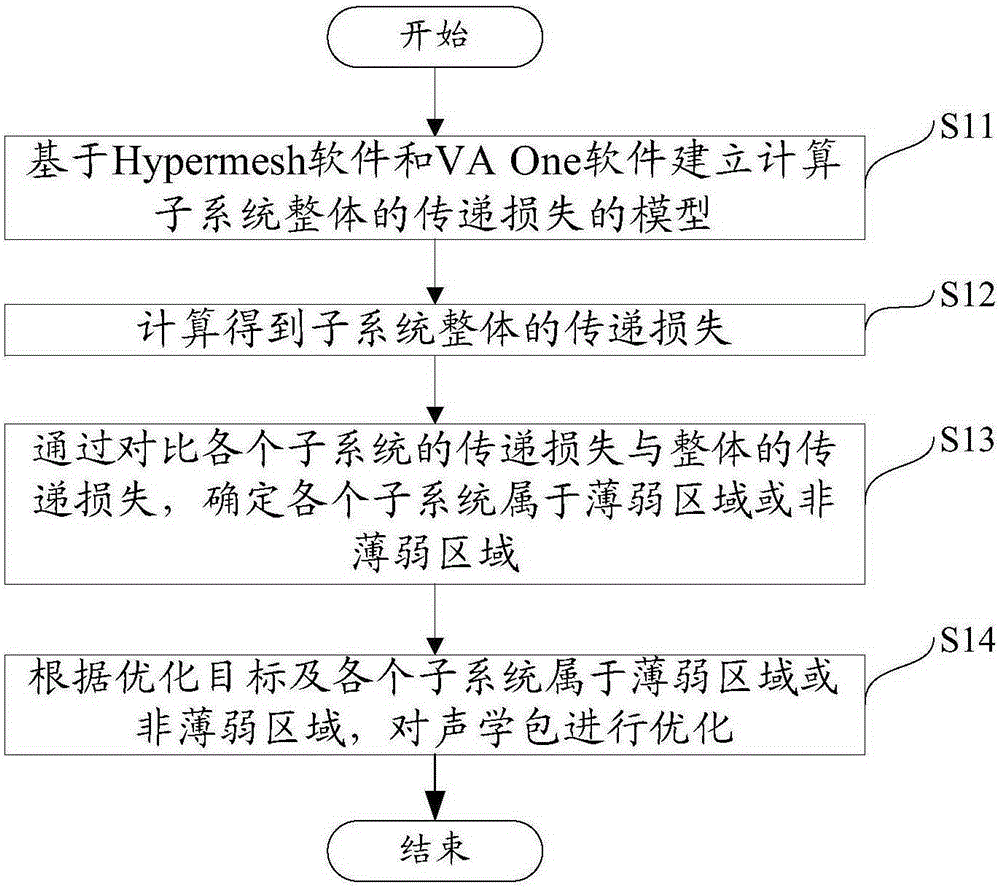
Method for calculating mid-frequency transmission loss of subsystems and optimizing acoustic packages
The invention aims to provide a method for calculating mid-frequency transmission loss of subsystems and optimizing acoustic packages. According to the method, a model for calculating the transmission loss of the whole subsystems is established on the basis of Hypermesh software and VA One software, the transmission loss of the whole subsystems is obtained through calculation, the transmission loss of each subsystem and the transmission loss of the whole are compared, whether each subsystem belongs to a weak area or a non-weak area is determined, and the acoustic packages are optimized according to an optimization objective and a result whether each subsystem belongs to the weak area or the non-weak area. Compared with the prior art, the method adopts a hybrid FE-SEA (finite element-statistical energy analysis) method, a finite element model is divided into a plurality of FE subsystems, a comparison diagram of a mid-frequency transmission loss curve of each FE subsystem at the mid-frequency band and a transmission loss curve of the whole is obtained rapidly and accurately through calculation, whether each subsystem belongs to a weak area or a non-weak area is determined and the FE subsystems are subjected to different arrangement on the basis of the optimization objective, so that the purpose of effective optimization design of the acoustics packages can be achieved.
Owner:同济汽车设计研究院有限公司
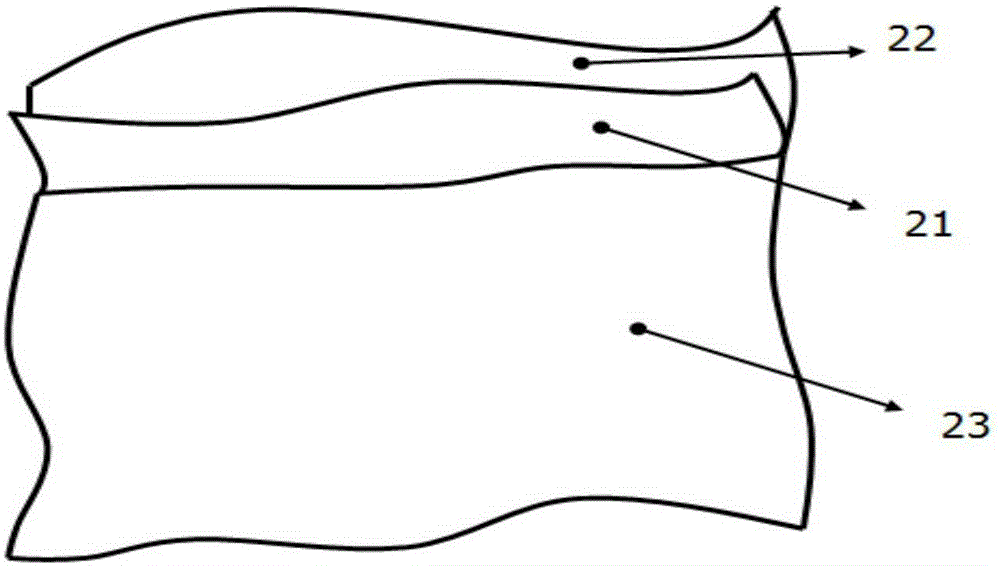
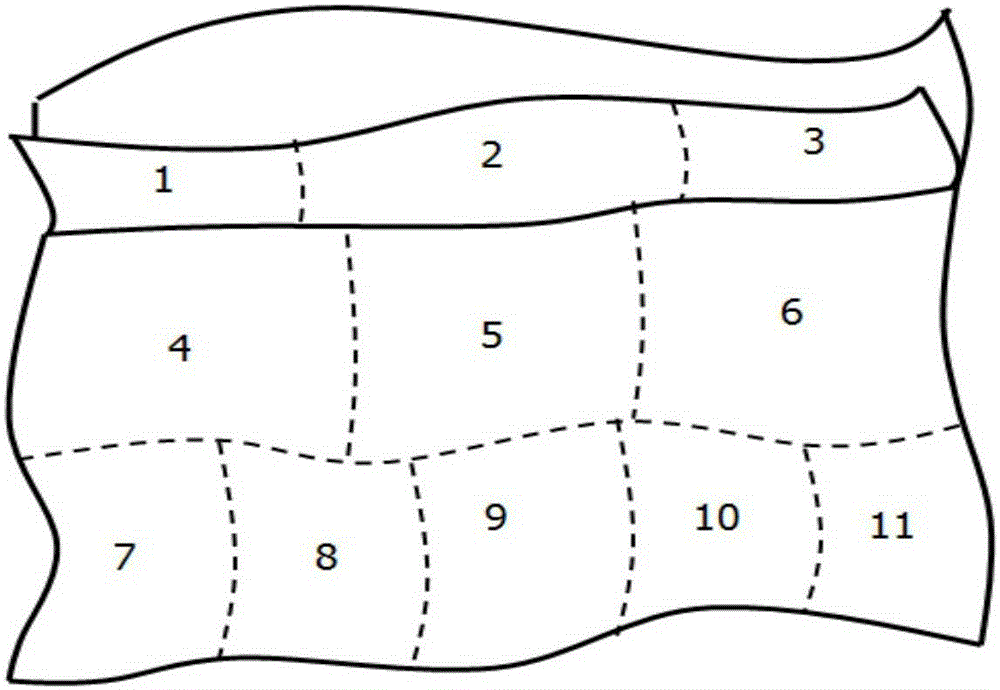
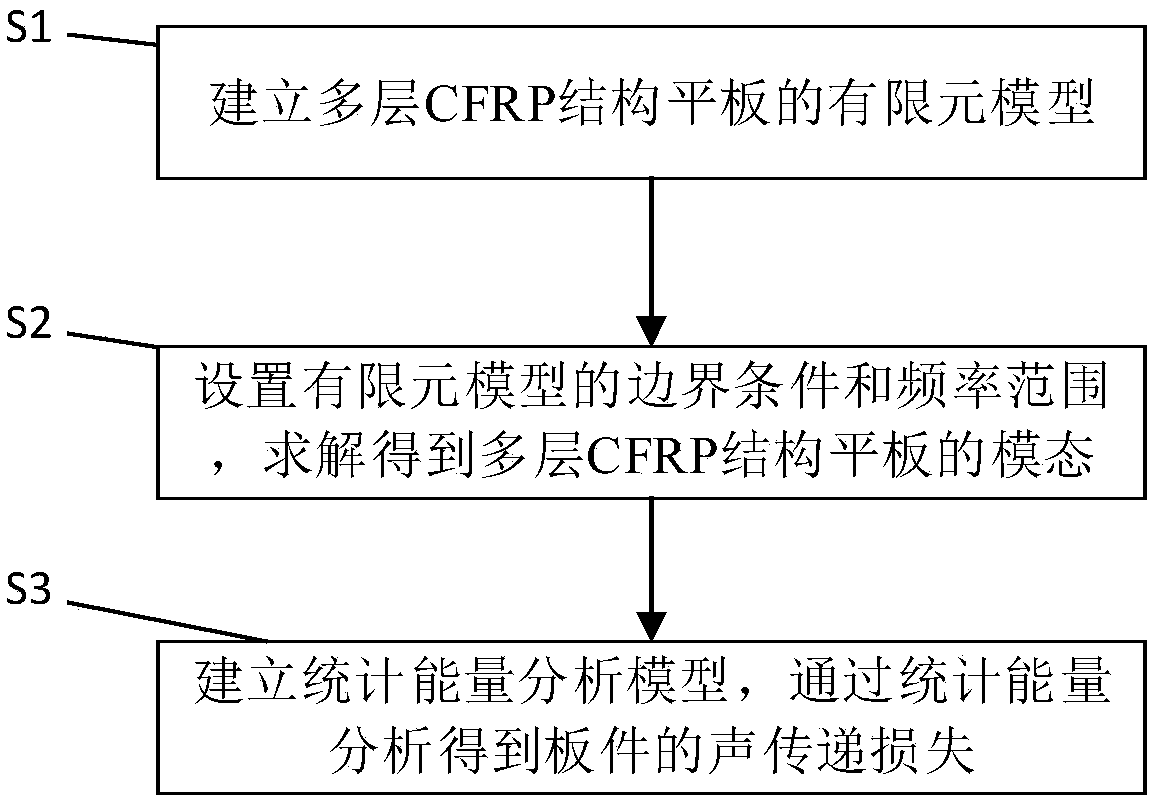
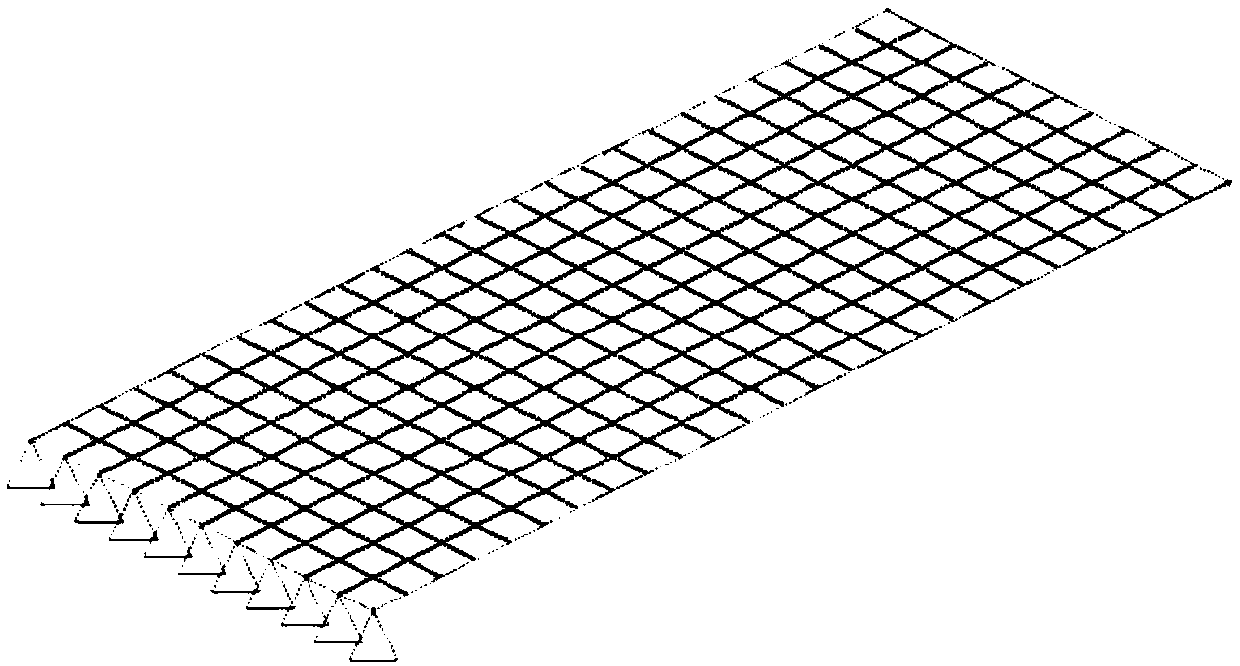
Vibration acoustic analysis method for multi-layer CFRP structure flat plate
PendingCN109635396AEasy to optimizeEnables vibroacoustic analysisDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSound sourcesElement model
The invention relates to a vibration acoustic analysis method for a multi-layer CFRP structure flat plate, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, obtaining material parameters and structureparameters of the multi-layer CFRP structure flat plate, and building a finite element model; S2, setting a boundary condition and a frequency range of the finite element model, and solving the boundary condition and the frequency range by using a finite element solver to obtain a mode of the multi-layer CFRP structure flat plate; and S3, establishing a flat plate model with the same size as themulti-layer CFRP structure flat plate, endowing the flat plate model with CFRP material attributes, respectively establishing a sound source cavity and a receiving cavity at two sides of the flat plate model, generating a statistical energy analysis model, and obtaining the sound transmission loss of the multi-layer CFRP structure flat plate through statistical energy analysis. Compared with the prior art, the modal analysis and the sound transmission loss analysis are carried out by applying HyperMesh software and VAOne software, the simulation calculation is accurate and convenient, and theengineering practical value is high.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Acquisition method of spacecraft mechanical environment under combined stochastic excitation
ActiveCN105659892BOvercome the disadvantage of requiring a sufficiently large modal densityOvercome the shortcomings of sufficient modal densitySpecial data processing applicationsBroadbandModal density
The method for obtaining the mechanical environment of a spacecraft under the action of combined random excitation, the steps are: (1) dividing the spacecraft subsystem according to the modal density; (2) solving the dynamic response of the random subsystem; (3) loading processing of the combined random excitation; (4) Dynamic response solution of deterministic subsystem. The method of the invention fully utilizes the advantages of the finite element-statistical energy hybrid analysis method for modeling, overcomes the shortcomings of the traditional finite element method and the traditional statistical energy analysis method in dealing with broadband dynamic problems, and realizes the external acoustic load of the spacecraft and the random The reasonable loading of the basic excitation load has established a set of engineering and practical means of predicting the mechanical environment of the spacecraft under the combined random excitation.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
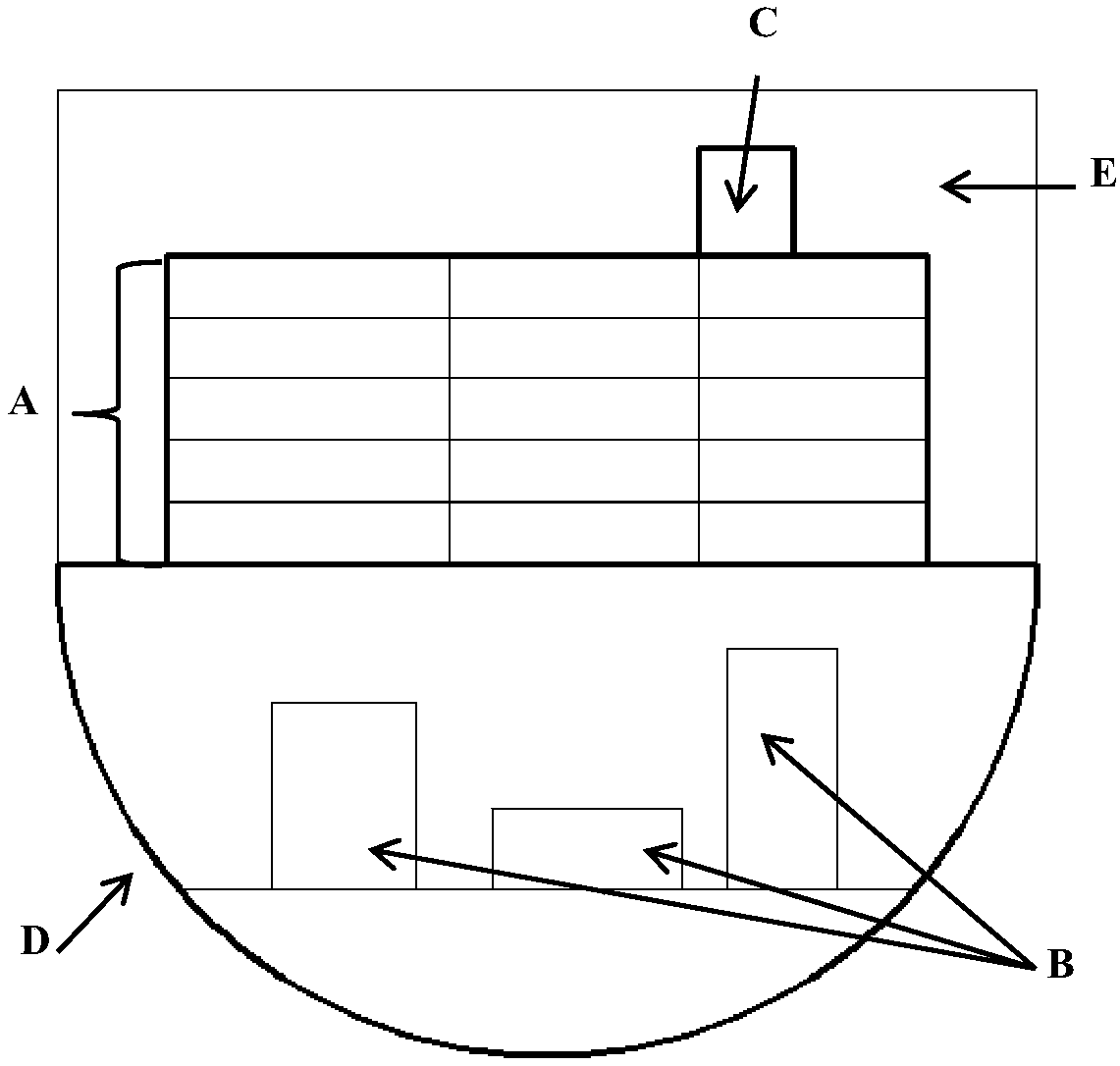
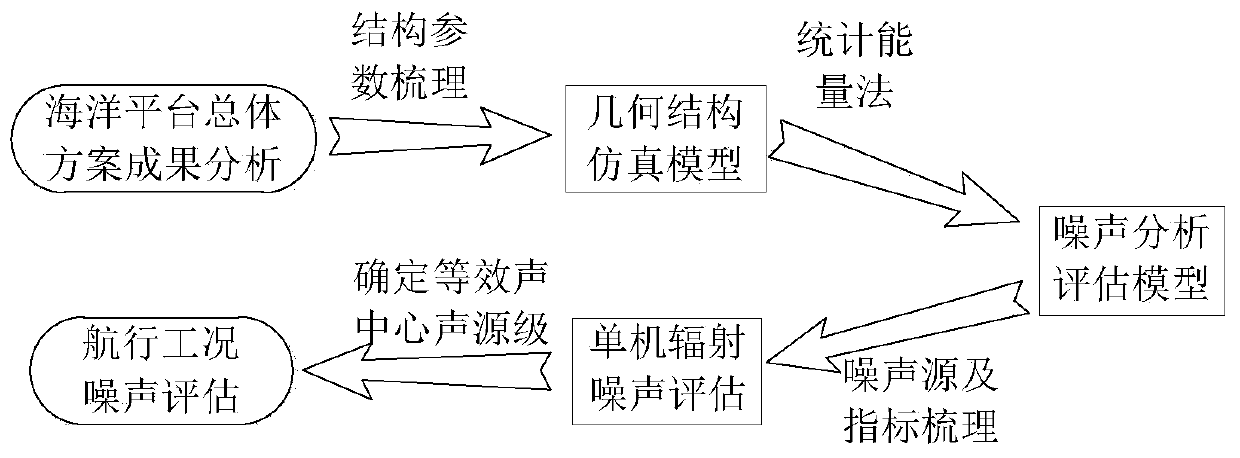
Ship overall scheme mechanical noise assessment method
ActiveCN110069873AImprove rationalityImprove accuracyGeometric CADSustainable transportationMarine engineeringNoise reduction
The invention discloses a ship overall scheme mechanical noise assessment method, and belongs to the technical field of ship vibration and noise reduction demonstration and assessment. The method comprises the steps of performing ship overall scheme design result analysis and structure modeling parameter sorting; establishing a ship geometric structure simulation model; establishing a ship statistical energy analysis model; evaluating the radiation noise of the ship single machine; and estimating ship navigation working condition mechanical noise. The method is reasonable and feasible, overcomes the uncertainty of a conclusion obtained by adopting a manual experience method in the mechanical noise assessment of the existing ship overall scheme, can realize quantitative simulation calculation of mechanical noise under the equipment single machine and navigation working conditions, and greatly improves the rationality and effectiveness of the mechanical noise assessment result of the ship overall scheme.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Methods of analyzing the vibro-acoustic optimization potential and optimizing the vibro-acoustic behavior of a structure
ActiveUS20080114496A1Reliable and consistent and correct resultSimple structureVibration measurement in fluidTemperatue controlCoupling lossEngineering
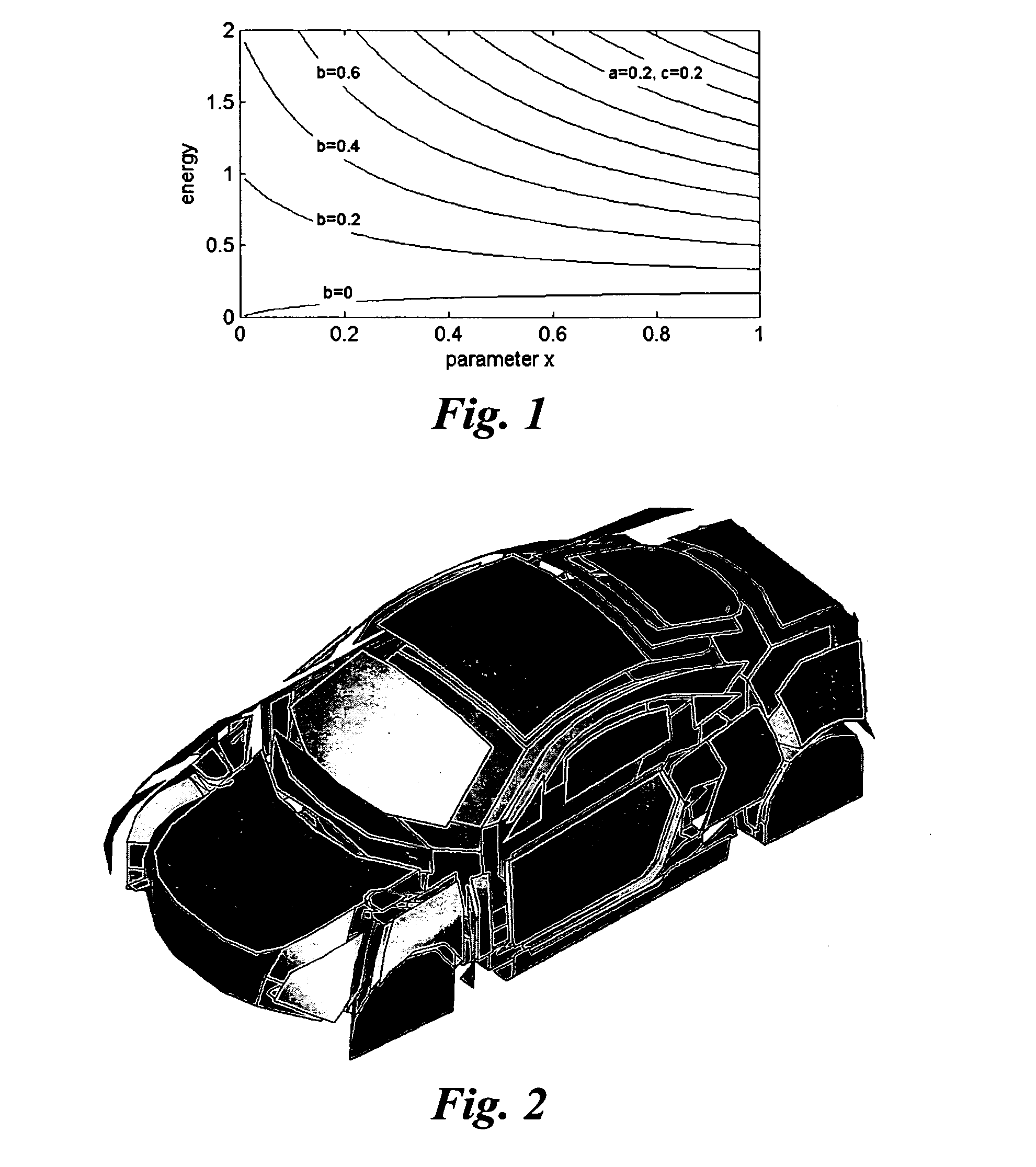
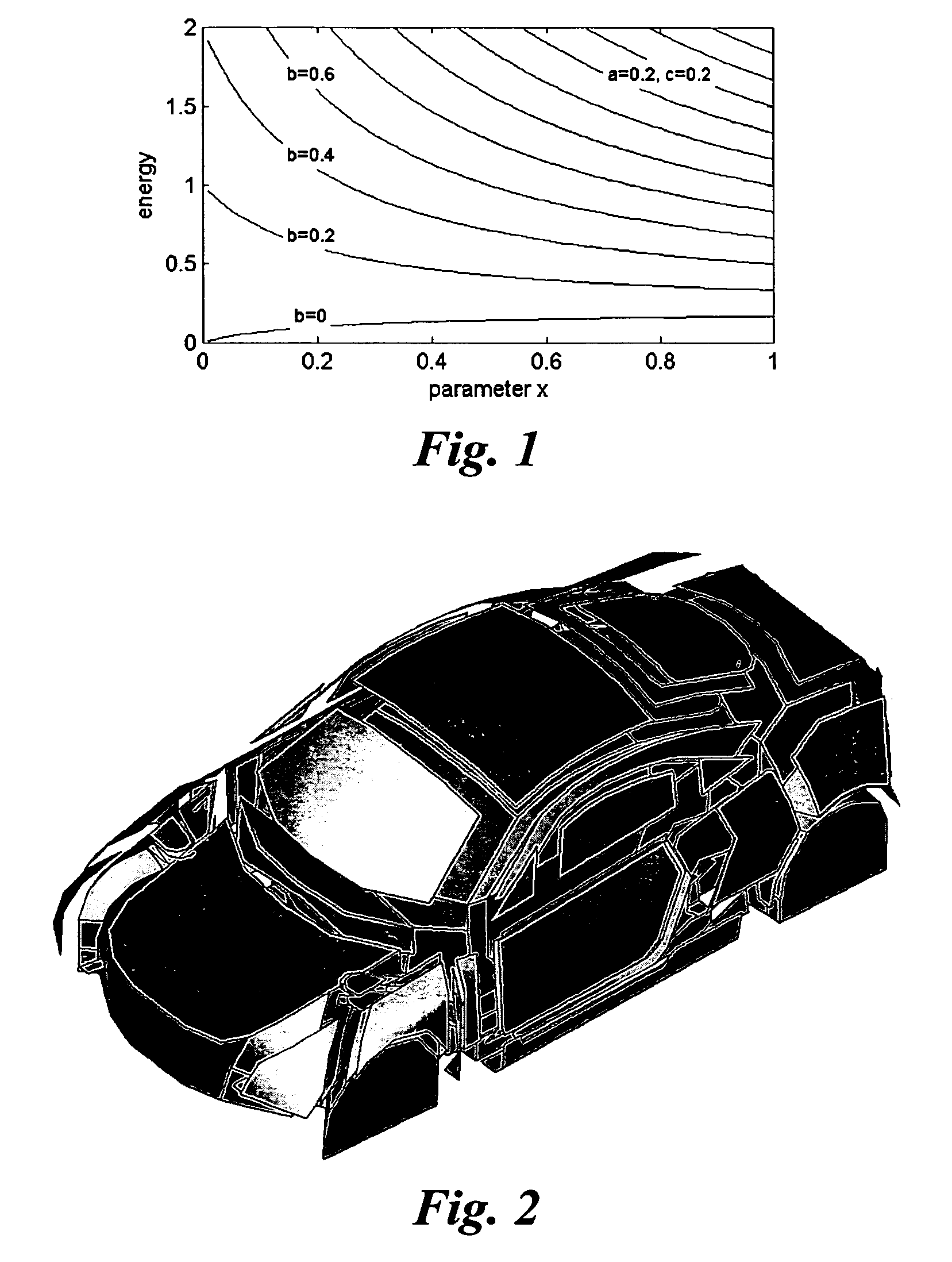
The invention relates to a method of analyzing the vibro-acoustic optimization potential of a structure of vibro-acoustically coupled subsystems having internal and coupling loss factors by means of statistical energy analysis (SEA). The invention further relates to a method of optimizing the vibro-acoustic behavior of such a structure. The inventive methods involve the steps of:calculating the gradient of energy on the basis of a simplified SEA matrix in which all coupling loss factors θji with j>i have been substituted according to ηijni=ηjinj;identifying the internal loss factors causing the M highest gradients as dominant internal loss factors and the coupling loss factors causing the N highest products, which each consist of a gradient times its coupling loss factor, as dominant coupling loss factors;calculating an optimization potential for each of the dominant internal and coupling loss factors as the maximum sub-system energy change which can be achieved by varying said loss factor; andidentifying the dominant internal and coupling loss factors with the K highest optimization potentials as optimization loss factors for the further vibro-acoustic optimization of the structure.
Owner:MAGNA STEYR FAHRZEUGTECHN
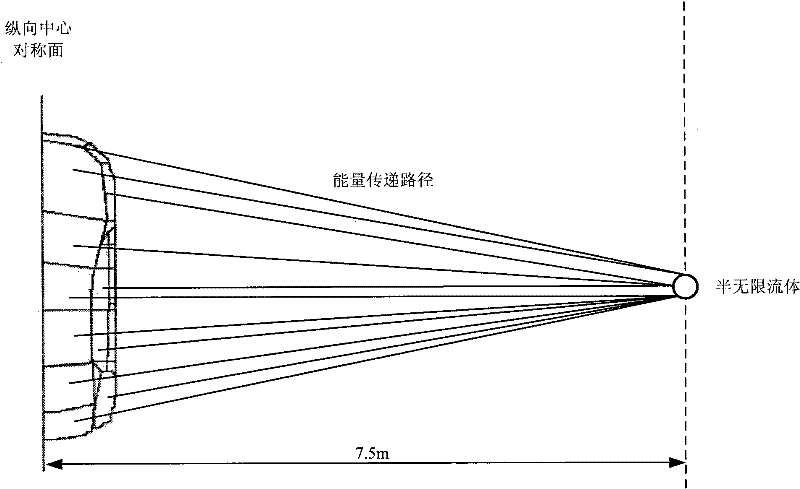
Semi-infinite fluid based passenger car external noise analysis and predication method
InactiveCN101814108AShorten the development cycleReduce development costsSpecial data processing applicationsPredictive methodsEnergy analysis
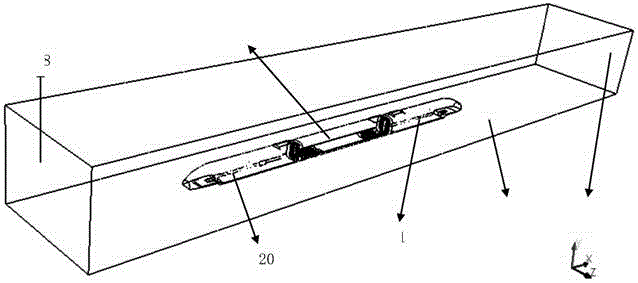
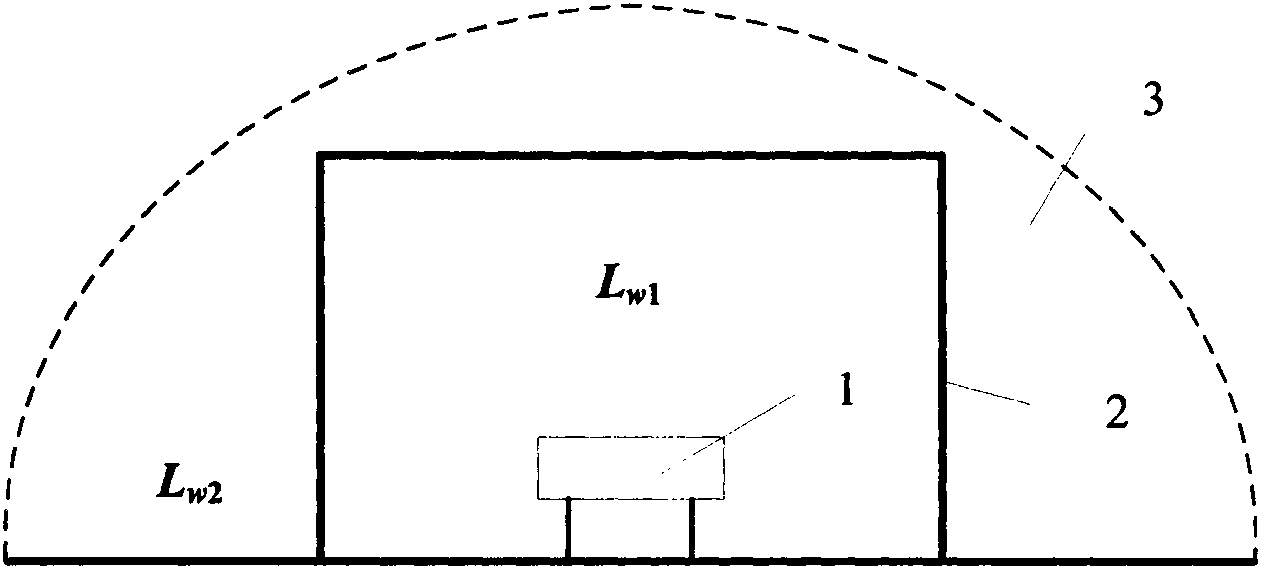
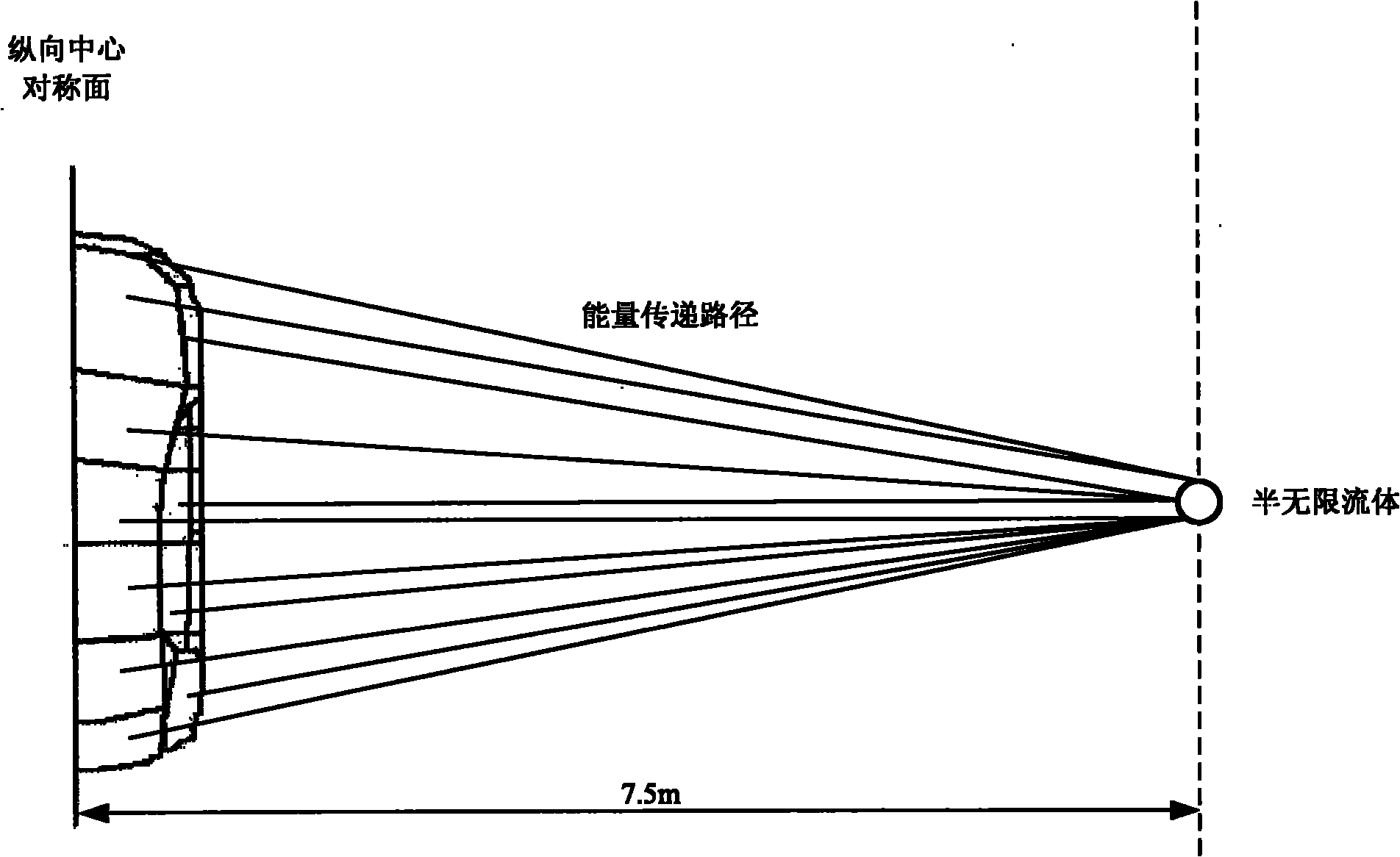
The invention discloses a semi-infinite fluid based passenger car external noise analysis and predication method for overcoming the defects that passenger car external noise can not be analyzed and predicted accurately before the advanced development in the passenger car development and design. The semi-infinite fluid based passenger car external noise analysis and predication method comprises the steps of: establishing a car body structure SEA (Statistical Energy Analysis) model, establishing a passenger car external noise semi-infinite fluid predication model, determining car body structure subsystem SEA parameters, and determining external excitation energy applied to the car body and passenger car external noise analysis and predication. The establishment of the passenger car external noise semi-infinite fluid predication model comprises the steps of: establishing semi-infinite fluids at the left and right sides of the car body structure SEA model and connecting the semi-infinite fluids and all car body structure subsystems, wherein the semi-infinite fluids are positioned 7.5m away from a car body longitudinal symmetry plane and 1.2m away from ground and energy passes to the semi-infinite fluids from all the car body structure subsystems in the form of spherical wave.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Small sample data model verification method based on statistical analysis
ActiveCN108763828ASolve problems such as easy deviation from the true distributionImprove accuracySustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationReference sampleSmall sample
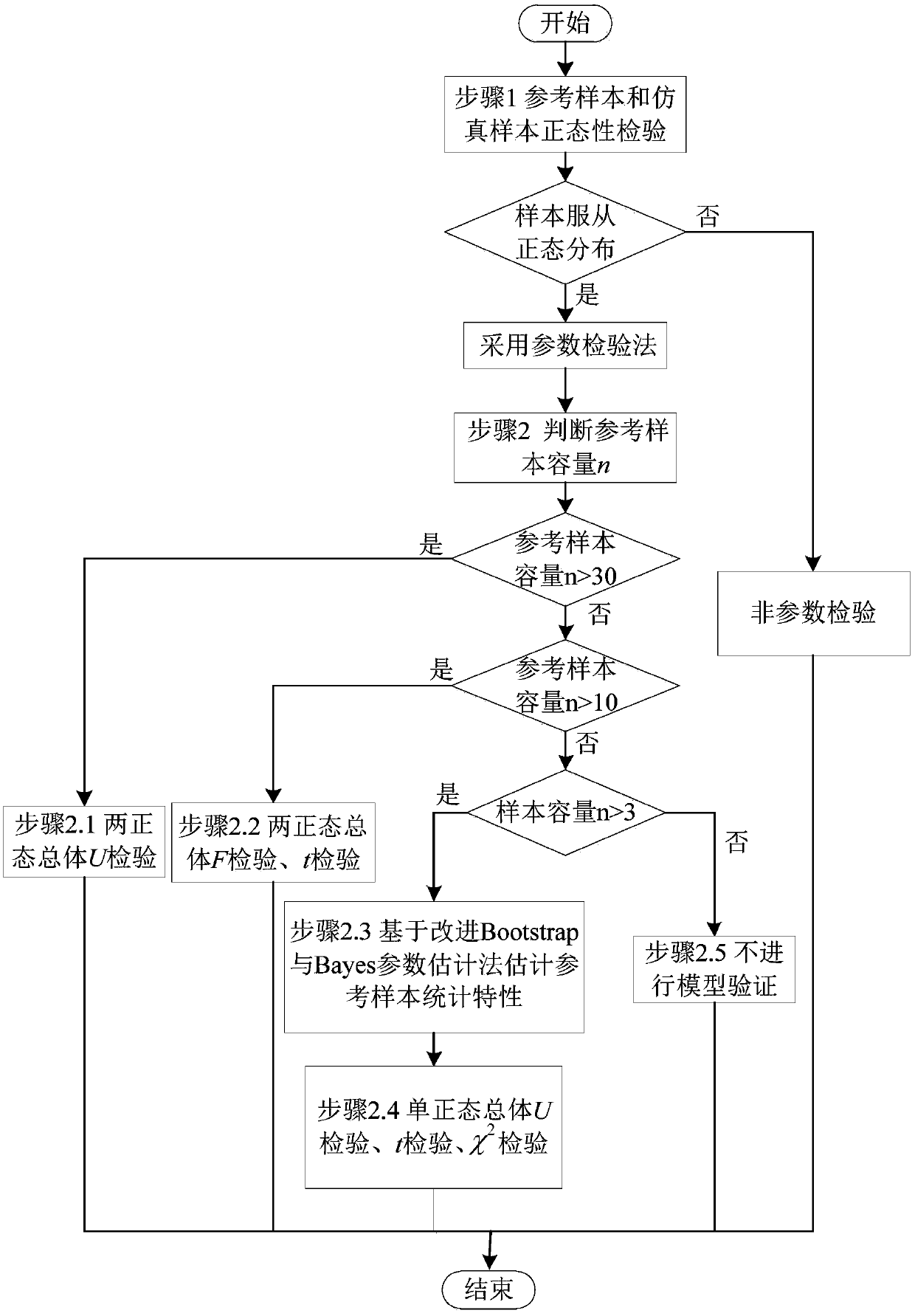
The invention discloses a small sample data model verification method based on statistical analysis, relating to a small sample data model verification method. The invention aims to solve the problemsthat the scope of a conventional Bootstrap method for reproducing samples is limited to an original sample range, especially in the case of a small sample size, the distribution of the reproduced samples may deviate from the real distribution, the estimation results may be inaccurate, and certain risks exist. The method includes the following processes: step I, performing a normality test on a reference sample and a simulation sample, and if obeying the normal distribution, performing step II; and step II, when n is greater than or equal to 30, adopting a U test method; when n is greater than10 and less than 30, adopting a t or F test method; when n is greater than 3 and less than or equal to 10, adopting a formula 1 and a formula 2 (as shown in the original specification) to separatelyperform a single normal population parameter test on the simulation sample in the step I; determining whether the obtained mean value and variance of the reference sample and the simulation sample areconsistent; and when n is less than 3, not performing model verification. The scheme of the invention is applied to the field of simulation model verification.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Transient energy response high-precision prediction method for complex construction
ActiveCN107657132ASolve the transient energy response prediction problemGood prediction accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationEnergy balance equationPower Balance
The invention provides a transient energy response high-precision prediction method for a complex construction. The method comprises the steps of taking time-varying items of energy transfer among subsystems into account, establishing a transient power balance equation of all the subsystems of the structure by combining a loss factor matrix eta of a complex structure, giving an initial boundary parameter, and adopting a fourth-order-fifth-order Runge-Kutta algorithm to calculate to obtain transient energy response of all the subsystems of the structure. Compared with a traditional method whichonly takes time-varying items of energy into account, according to the transient energy response high-precision prediction method for the complex construction, the more complete transient energy balance equation of all the subsystems of the complex structure by taking the time-varying items of the energy transfer among all the subsystems of the complex structure into account, the prediction precision in transient energy response prediction of a current transient statistics energy analysis method is obviously improved, the research range of the current transient statistics energy analysis method is expanded, transient energy response analysis of structures of different coupling strengths can be solved, commercial statistics energy analysis software is combined at the same time, and the transient energy response prediction problem of the complex structure can be solved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
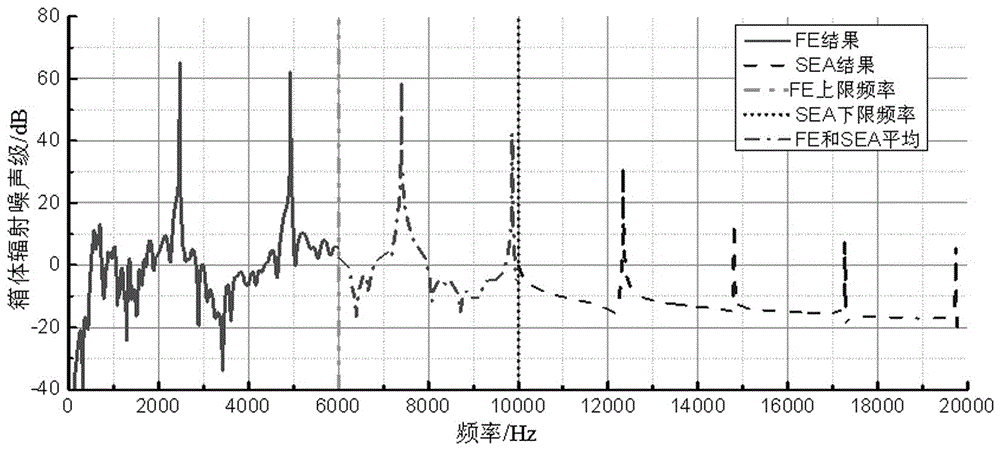
Full frequency-domain calculation method of vibration noise of gear case
PendingCN106407617AMethods for Effective Vibration and Noise AnalysisDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsLower limitEngineering
The invention provides a full frequency-domain calculation method of vibration noise of a gear case, and relates to the technical field of calculation methods. The vibration noise of a low-frequency part in the gear case is determined by using a finite element-boundary element method; the vibration noise of a high-frequency part in the gear case is determined by using statistic energy analysis; and full frequency-domain calculation of the vibration noise is achieved by reasonably using a finite element and the statistic energy analysis according to the size relationship among an upper limit frequency calculated by the finite element, a lower limit frequency of the statistic energy analysis and a to-be-analyzed highest frequency. According to the full frequency-domain calculation method of the vibration noise of the gear case, full frequency-domain analysis of the vibration noise of the gear case can be effectively carried out according to respective characteristics of different frequency bands.
Owner:中国船舶重工集团公司第七0三研究所
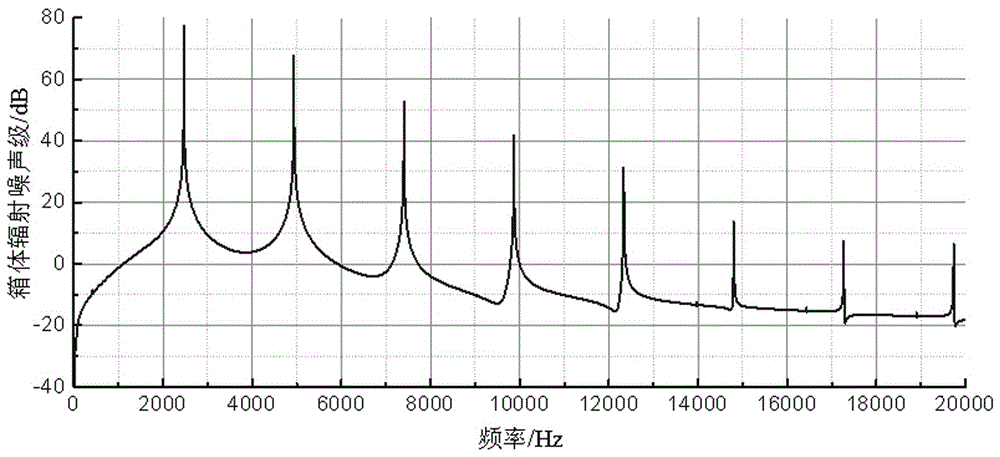
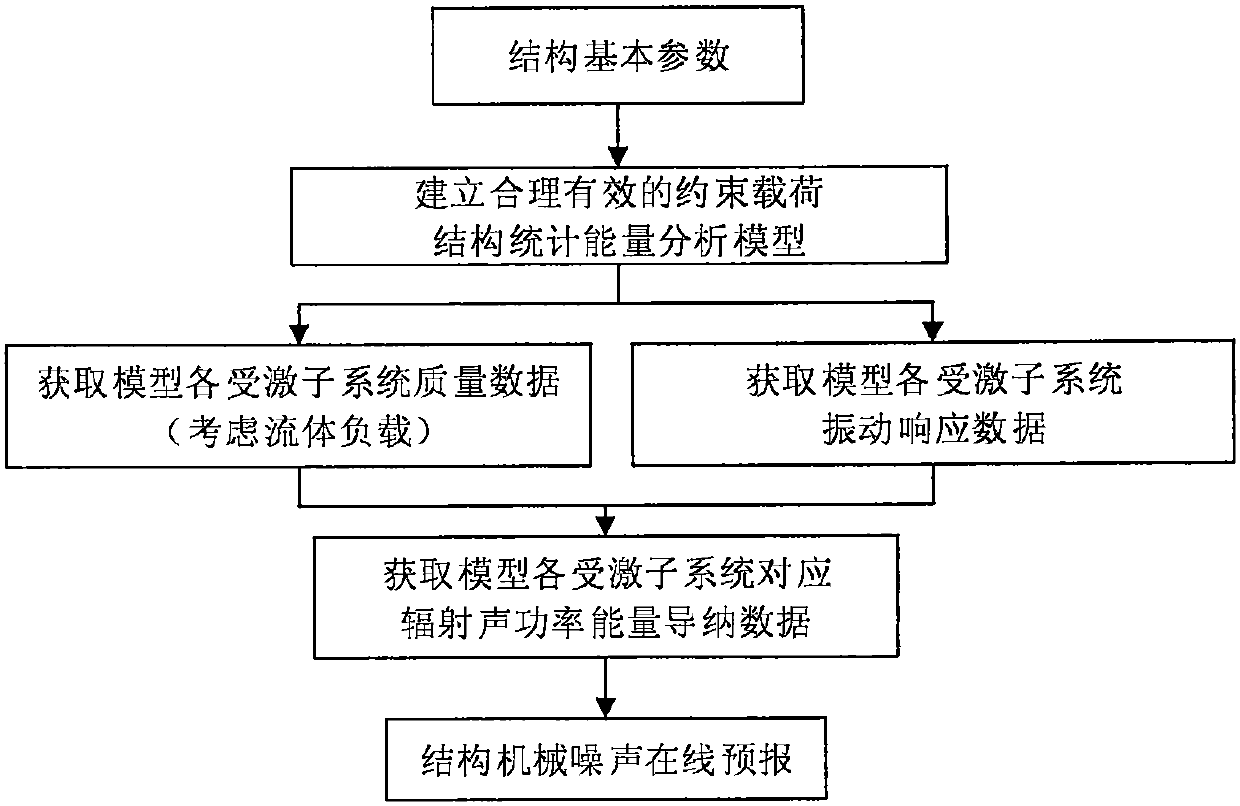
Online forecasting method for high-frequency mechanical noise of structure
ActiveCN105184047ASolving long-term problemsQuick calculationSpecial data processing applicationsQuality dataSound power
The invention discloses an online forecasting method for high-frequency mechanical noise of a structure, and belongs to the technical field of noise forecasting. The method comprises the following steps: building a reasonable and effective constraint and load statistical energy analysis model aiming at an engineering practice structure; obtaining quality data of various stimulated sub-systems by the built statistical energy analysis model; testing vibration response data of the stimulated sub-systems through a test; calculating energy data of the stimulated sub-systems by combining the quality data with the response data; obtaining radiated sound power energy mechanical mobility data corresponding to the stimulated sub-systems according to the model; and finally calculating the radiated sound power of the structure, and finishing online forecasting. The online forecasting method has the beneficial effects that rapid calculation from load to radiated sound power is achieved by the system transfer mobility invariability; the problem of relatively long elapsed time of the traditional algorithm is solved; and rapid forecasting of mechanical noise of the structure is achieved. The online forecasting method is considerable in accuracy and relatively short in elapsed time, can be applied to the online forecasting engineering practice, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
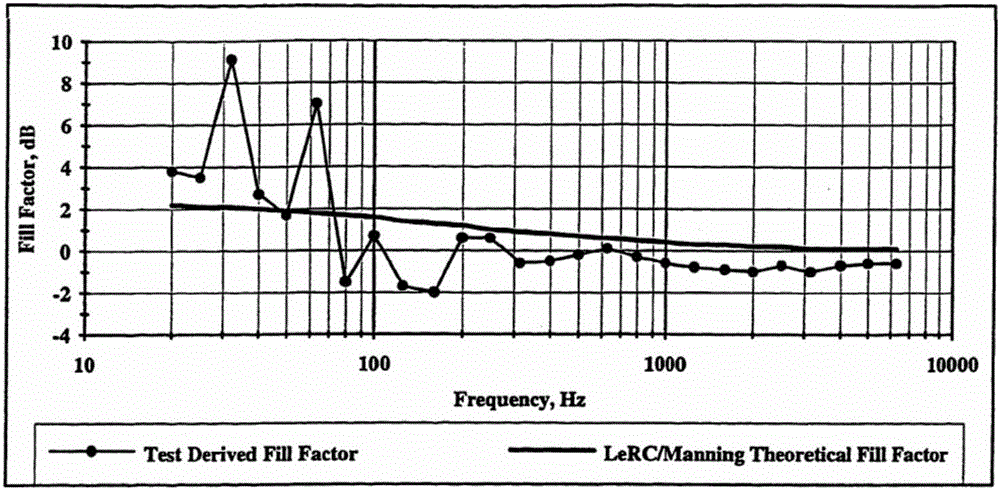
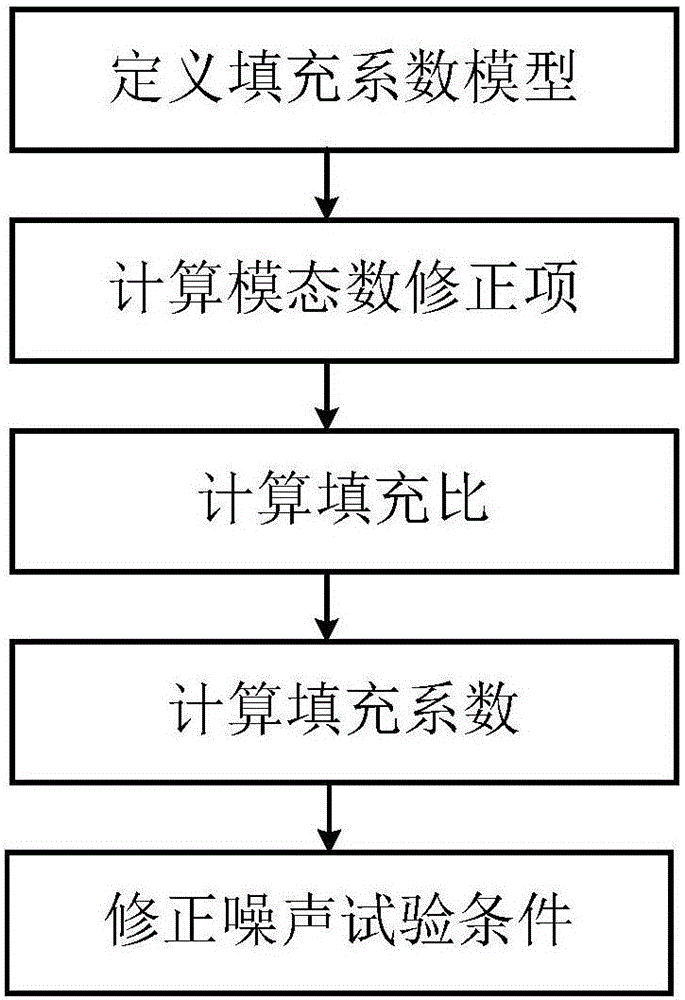
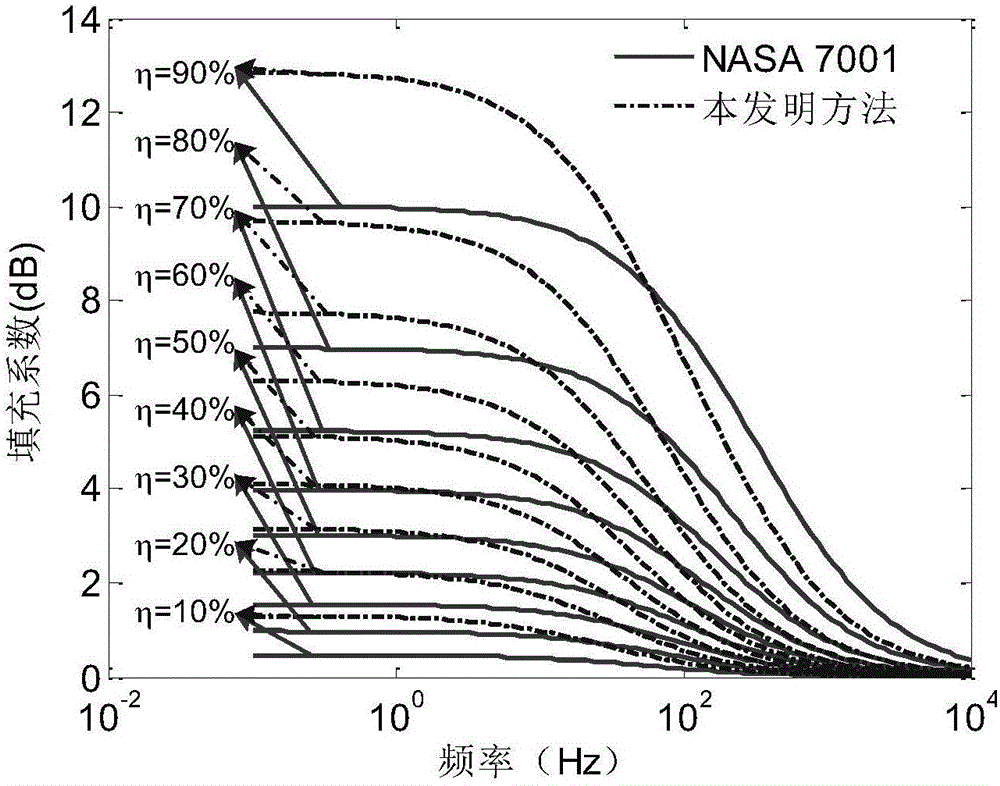
Method for calculating filling coefficient of sound field of fairing
ActiveCN105760608AGeometric features can be consideredThe physical meaning of the parameter is clearGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsFilling ratioModal Number
The invention discloses a method for calculating the filling coefficient of a sound field of a fairing.The method is based on the statistical energy analysis theory, a calculation model for the filling coefficient of the sound field is established, a modal number correction term in the calculation model is established according to geometrical boundary parameters of the fairing and a spacecraft, then the filling ratio eta of the sound field in the fairing is calculated, finally a corrected modal number and the filling ratio are substituted into the calculation model for the filling coefficient, the filling coefficient of the sound field of the fairing is obtained, and a spacecraft noise test condition is corrected through the filling coefficient, obtained through calculation, of the sound field of the fairing.Compared with a calculation method in NASA 7001 applied to current engineering, the method has the advantages that the physical significance of the parameters is definite, geometrical characteristics of the spacecraft can be considered, and correction precision is high.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Underwater radiation noise assessment method for overall scheme of semi-submersible ocean platform
ActiveCN110046459AImprove rationalityImprove accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringNoise reduction
The invention belongs to the technical field of semi-submersible type ocean platform vibration and noise reduction assessment, and particularly relates to an underwater radiation noise assessment method for an overall scheme of a semi-submersible ocean platform. The method comprises the following steps: performing semi-submersible type ocean platform overall scheme design analysis and structure modeling parameter combing; establishing a semi-submersible type ocean platform geometric structure simulation model; establishing a semi-submersible ocean platform structure statistical energy analysisand evaluation model based on a statistical energy analysis method; performing single machine radiation noise assessment; and performing combined condition underwater radiation noise assessment. Themethod provided by the invention is reasonable and easy to implement, overcomes the uncertainty of a conclusion obtained based on an artificial experience method in the existing semi-submersible oceanplatform overall scheme underwater radiation noise assessment, and can greatly improve the rationality and accuracy of an underwater radiation noise assessment result of the semi-submersible ocean platform overall scheme.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Methods of analyzing the vibro-acoustic optimization potential and optimizing the vibro-acoustic behavior of a structure
ActiveUS7409269B2Additional toolSimple structureVibration measurement in fluidFlow propertiesCoupling lossEngineering
A method of analyzing the vibro-acoustic optimization potential of a structure of vibro-acoustically coupled subsystems having internal and coupling loss factors by means of statistical energy analysis (SEA). The method optimizes the vibro-acoustic behavior of the structure.
Owner:MAGNA STEYR FAHRZEUGTECHN
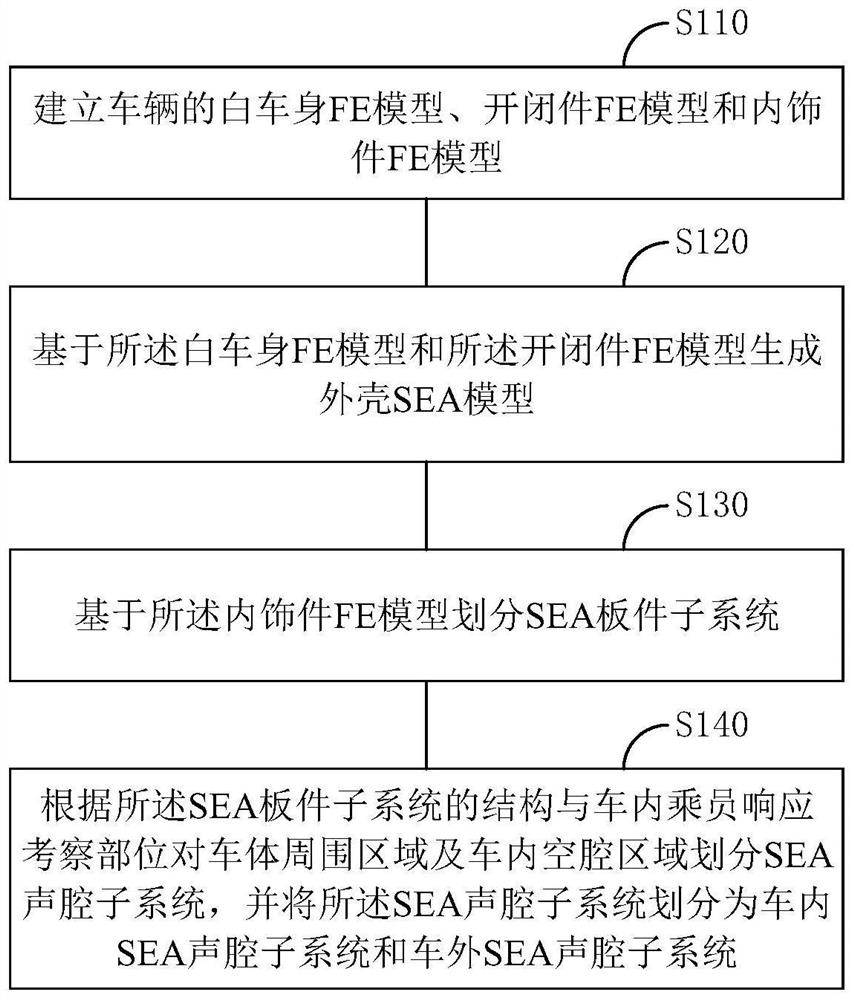
In-vehicle intermediate frequency noise analysis method and medium
PendingCN113343527AImprove simulation accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsIntermediate frequencyNoise
The invention relates to the field of vehicle noise processing, and provides an in-vehicle intermediate frequency noise analysis method and a medium. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a statistical energy analysis (SEA) model for representing noise transmission based on an air path, and loading an excitation sound load under an actual working condition on the SEA model to calculate noise transmitted through the air path; establishing a finite element FE-SEA hybrid model for representing noise transmission based on the structural path, and loading an exciting force load under an actual working condition on the FE-SEA hybrid model to calculate noise transmitted through the structural path; and carrying out in-vehicle intermediate frequency noise analysis based on the SEA model and the FE-SEA hybrid model. According to the method, on the basis of the SEA model, the sound transmission influence of a middle-frequency band structure path is completely considered by establishing the FE-SEA hybrid model, and full-frequency band in-vehicle noise simulation prediction is formed.
Owner:GREAT WALL MOTOR CO LTD
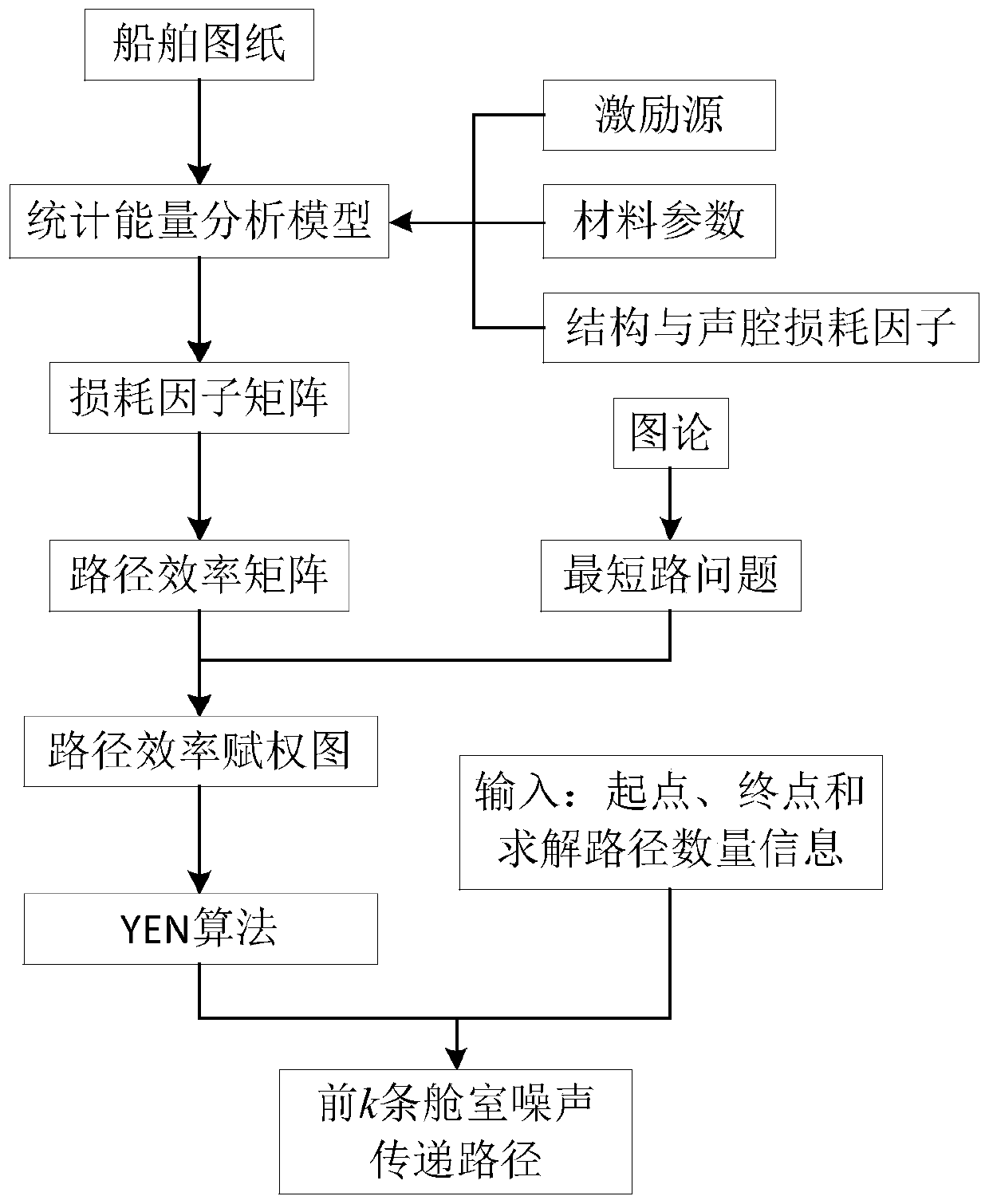
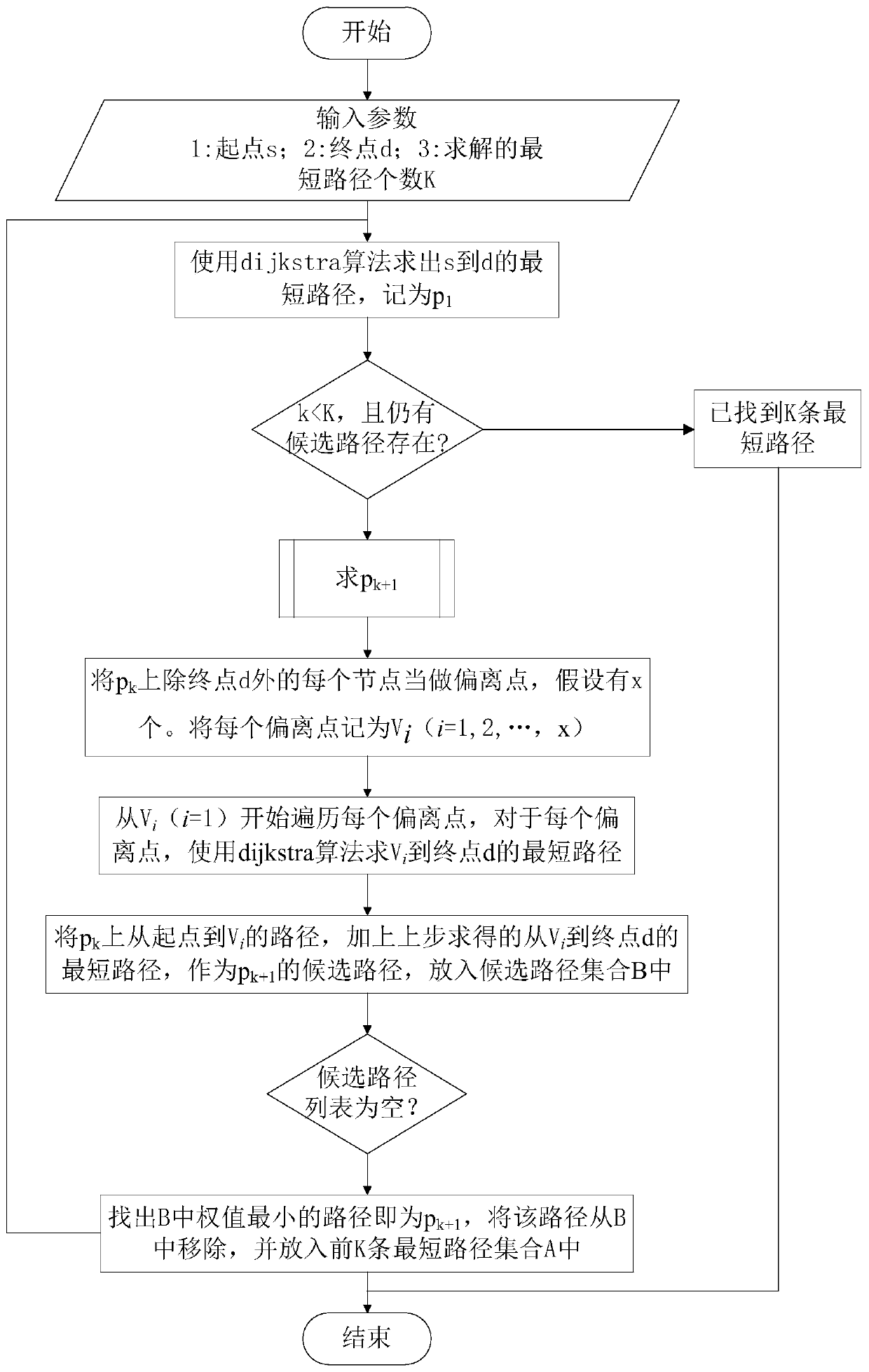
Ship cabin noise transmission path analysis method
PendingCN110826241AImprove noise reductionImprove economyDesign optimisation/simulationSimulationTest analysis
The invention discloses a ship cabin noise transmission path analysis method, which comprises the steps of establishing a statistical energy analysis model according to a ship drawing; setting attributes of each subsystem in the statistical energy analysis model according to drawings and data; calculating an internal loss factor of each subsystem and a coupling loss factor between the subsystems,and establishing a loss factor matrix of the whole system; converting the loss factor matrix into a path efficiency matrix, and establishing a path efficiency weighting graph for noise transmission path analysis; and solving the first k shortest paths of the weighted graph by using an algorithm of the shortest path problem, so as to obtain the first k noise energy transfer paths from the noise source to the target cabin. The cabin noise transmission path analysis work can be completed at the initial stage of ship design, the limitation that real ship test analysis can only be conducted after aship is built is overcome, guidance can be provided for subsequent noise reduction design, and the cabin noise transmission path analysis method has the obvious effects of saving cost and reducing space and weight occupation.
Owner:SHANGHAI MERCHANT SHIP DESIGN & RES INST
High-frequency local response indication method for sound-solid coupling structure
ActiveCN108491595ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsBi-isotropic materialStrain energy
The invention provides a high-frequency local response indication method for a sound-solid coupling structure. A finite element method, a modal power flow equilibrium equation and a local energy indication theory are combined to indicate the high-frequency local response of the sound-solid coupling structure, the finite element method is used for obtaining the displacement modal vibration mode ofa structure subsystem on a coupling edge, the stress modal vibration mode of a sound cavity subsystem on the coupling edge and the inherent frequency and the modal quality of the subsystem, a modal coupling loss factor between subsystems is calculated, and the modal power flow equilibrium equation is established and solved to obtain the modal energy of the structure subsystem. Finally, the local energy indication theory is used for solving the local energy response of the structure subsystem, and a local stress / strain response is solved through a relationship between the strain energy and thestress strain of an isotropy material. By use of the method, the high-frequency local response indication method for the sound-solid coupling structure can be accurately indicated, and the problems that discretization methods including a traditional finite element method, a boundary element method and the like are low in calculation efficiency and each hypothesis of a statistical energy analysismethod can not be completely satisfied usually in engineering application and is difficult to obtain the local energy of the subsystem can be solved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
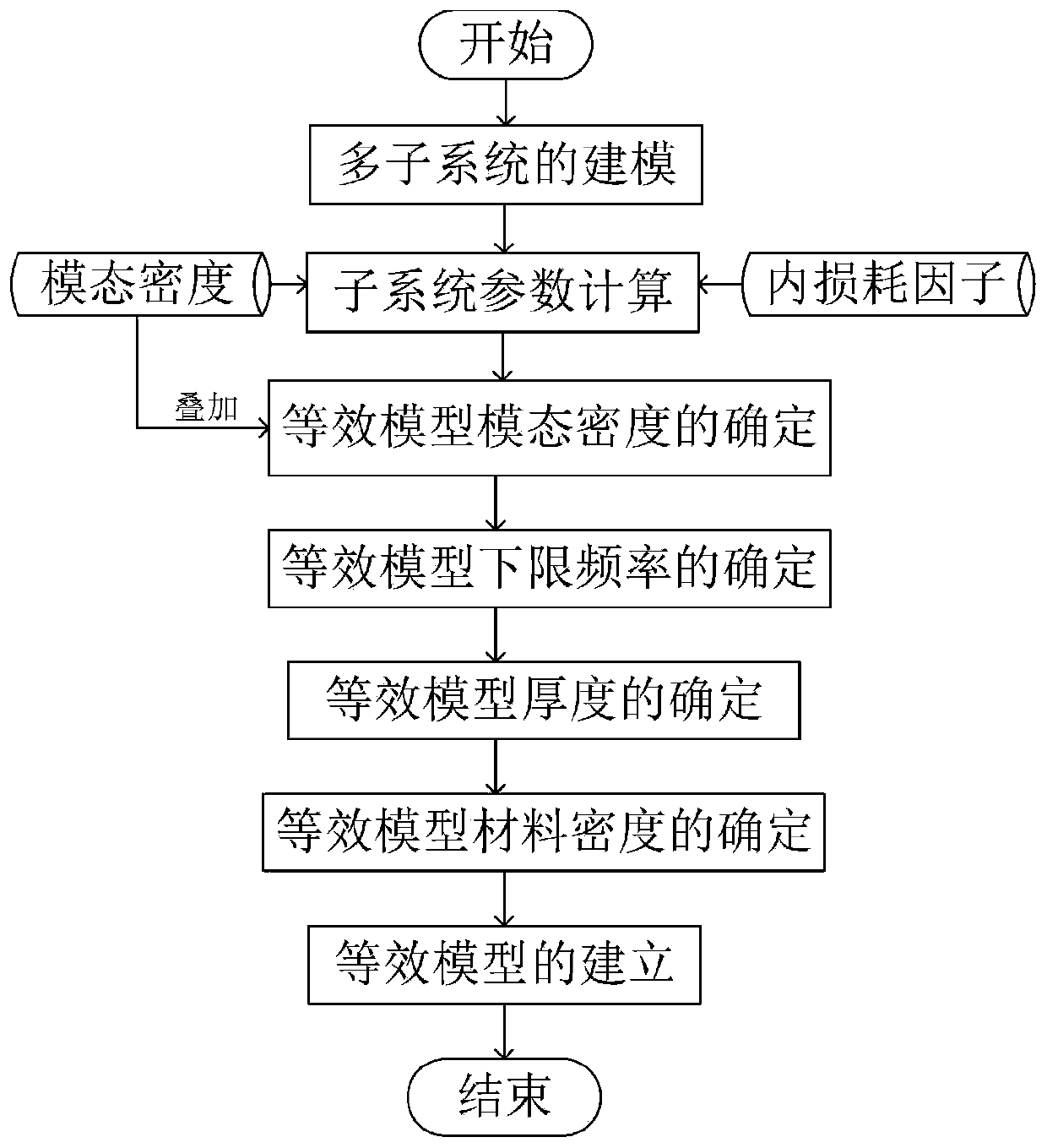
Equivalent statistical energy analysis modeling method for multi-subsystem variable-thickness flat plate
ActiveCN110427717AImprove calculation accuracyReduce thicknessSpecial data processing applicationsLower limitVariable thickness
The invention provides an equivalent statistical energy analysis modeling method for a multi-subsystem variable-thickness flat plate, which belongs to the technical field of radiation noise and comprises the following steps of: establishing subsystem models with different thicknesses; calculating a lower limit frequency required by each subsystem with different thicknesses to meet statistical energy analysis; extracting modal densities of subsystems with different thicknesses; performing numerical addition on the modal densities of all the subsystems to obtain the modal density of the equivalent model; obtaining the lower limit frequency of the equivalent model through the modal density of the equivalent model; obtaining an equivalent model thickness through an equivalent model thickness determination formula and the equivalent model lower limit frequency; calculating dynamic characteristics of the two models before and after equivalence under the same excitation, and comparing simulation results; obtaining quivalent model volume attributes and material attributes, and establishing an equivalent model. According to the method, a multi-subsystem variable-thickness flat plate structure is equivalent to a single subsystem, and the lower limit frequency of statistical energy analysis is greatly reduced by utilizing a method of carrying out numerical superposition on modal density.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
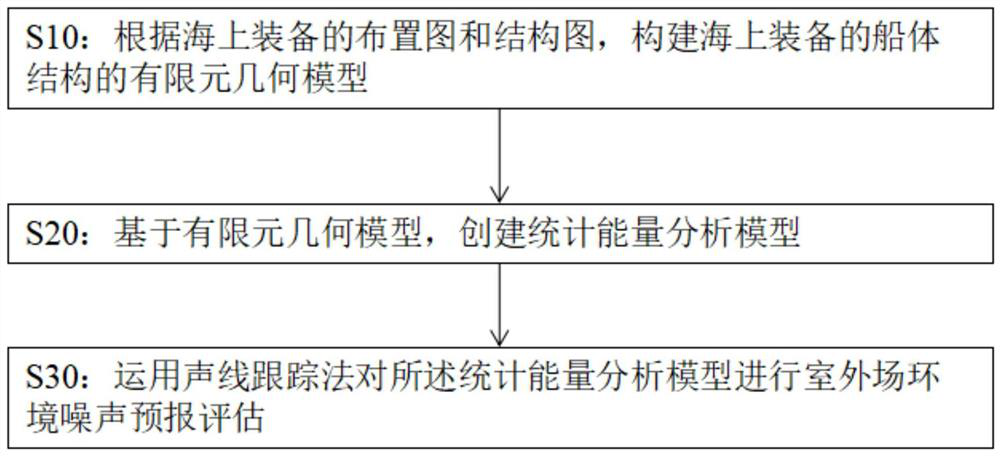
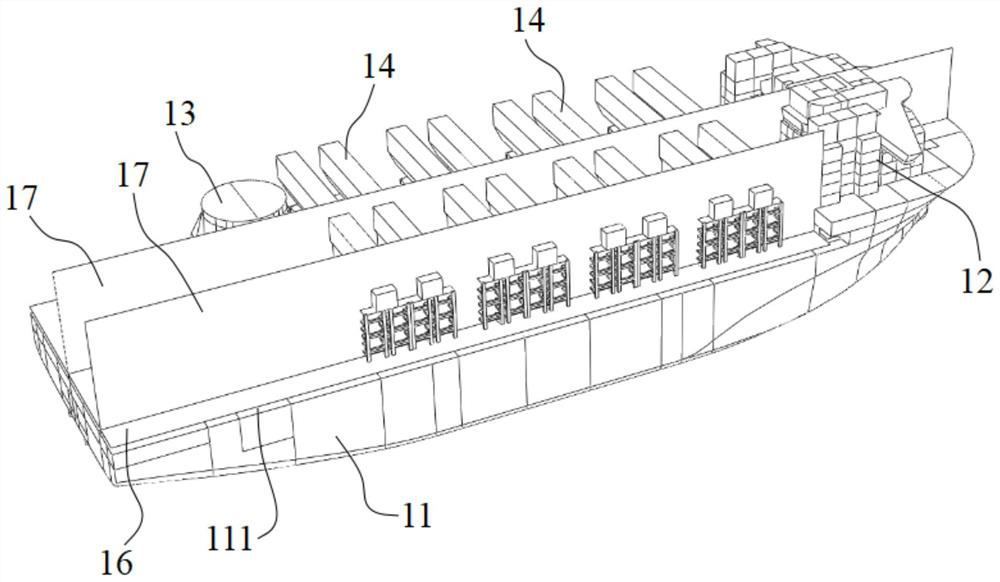
Method for forecasting and evaluating environmental noise of outdoor field of offshore equipment
ActiveCN114239366ANoise Forecast Evaluation ImplementationImprove rationalitySustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationHull structureNoise mapping
The invention provides a method for forecasting and evaluating outdoor field environmental noise of offshore equipment, which comprises the following steps of: constructing a finite element geometric model of a hull structure of the offshore equipment according to an arrangement diagram and a structure diagram of the offshore equipment, and establishing a mapping surface position for reflecting outdoor field environmental noise distribution in the finite element geometric model; creating a statistical energy analysis model based on the finite element geometric model; the method comprises the steps of generating an outdoor noise mapping surface represented by a finite element structure based on a mapping surface position, loading a sound source at a corresponding position of a statistical energy analysis model according to design information of sound source equipment of offshore equipment, and defining a sound ray tracking connection relation among the sound source, a ship body structure and the outdoor noise mapping surface; and performing outdoor field environmental noise forecast evaluation on the statistical energy analysis model by using a sound ray tracking method, and outputting sound field distribution on the outdoor noise mapping surface. The method can carry out noise forecast evaluation on the outdoor field environment of the offshore equipment.
Owner:YANTAI RAFFLES SHIPYARD +3
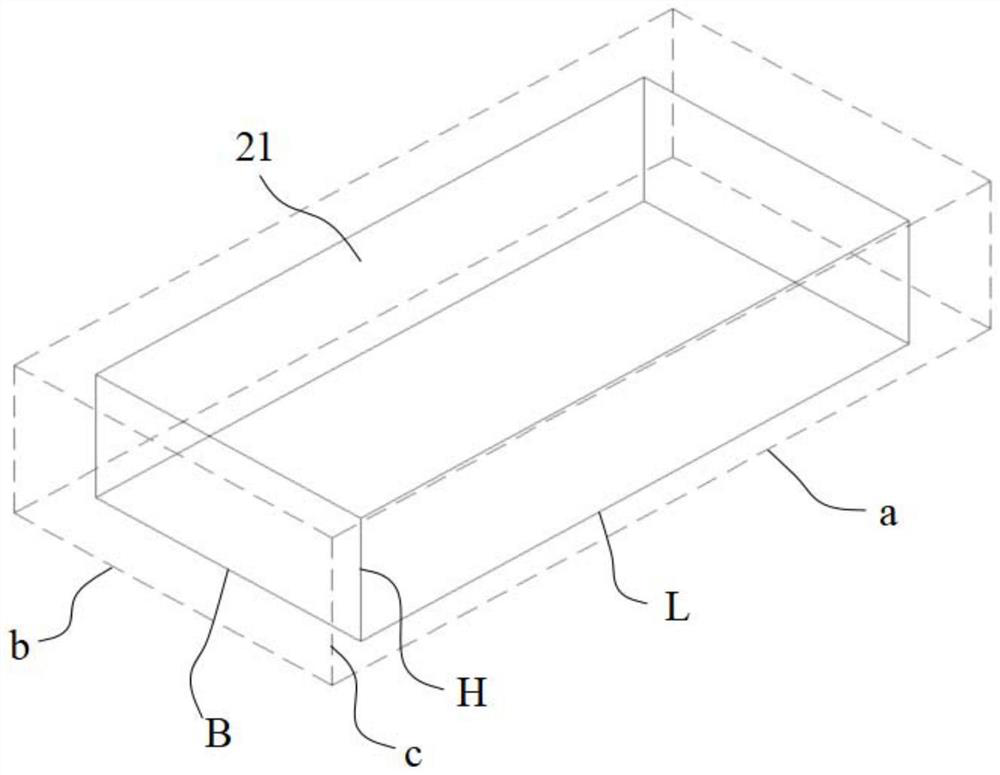
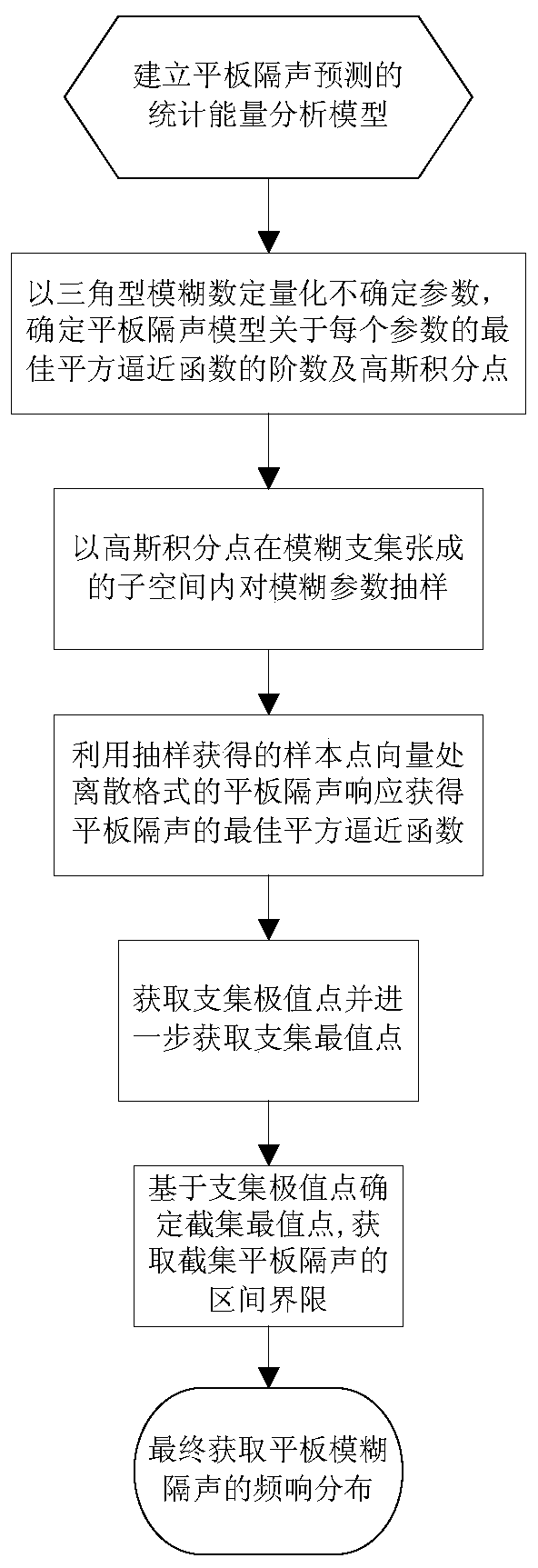
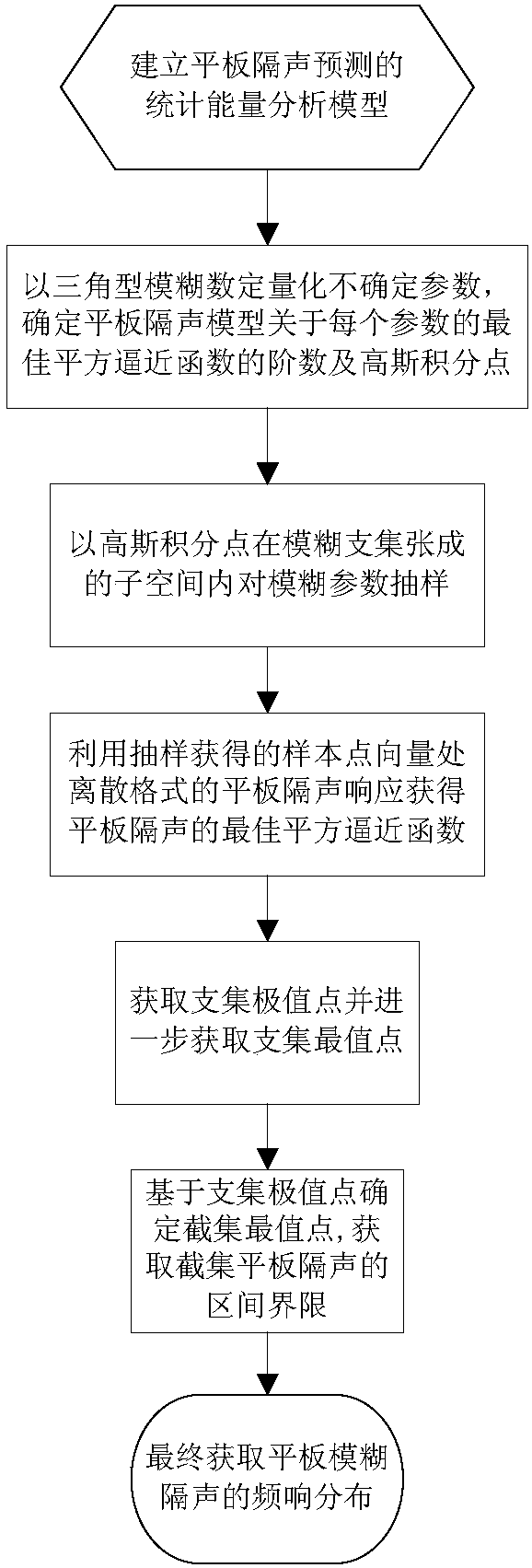
A Prediction Method of Sound Insulation of Rectangular Solid Flat Panel
ActiveCN107247829BImprove computing efficiencyObvious Computational Efficiency AdvantageDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsApproximation functionIntegration point
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Transient statistical energy response prediction method considering uncertain structure
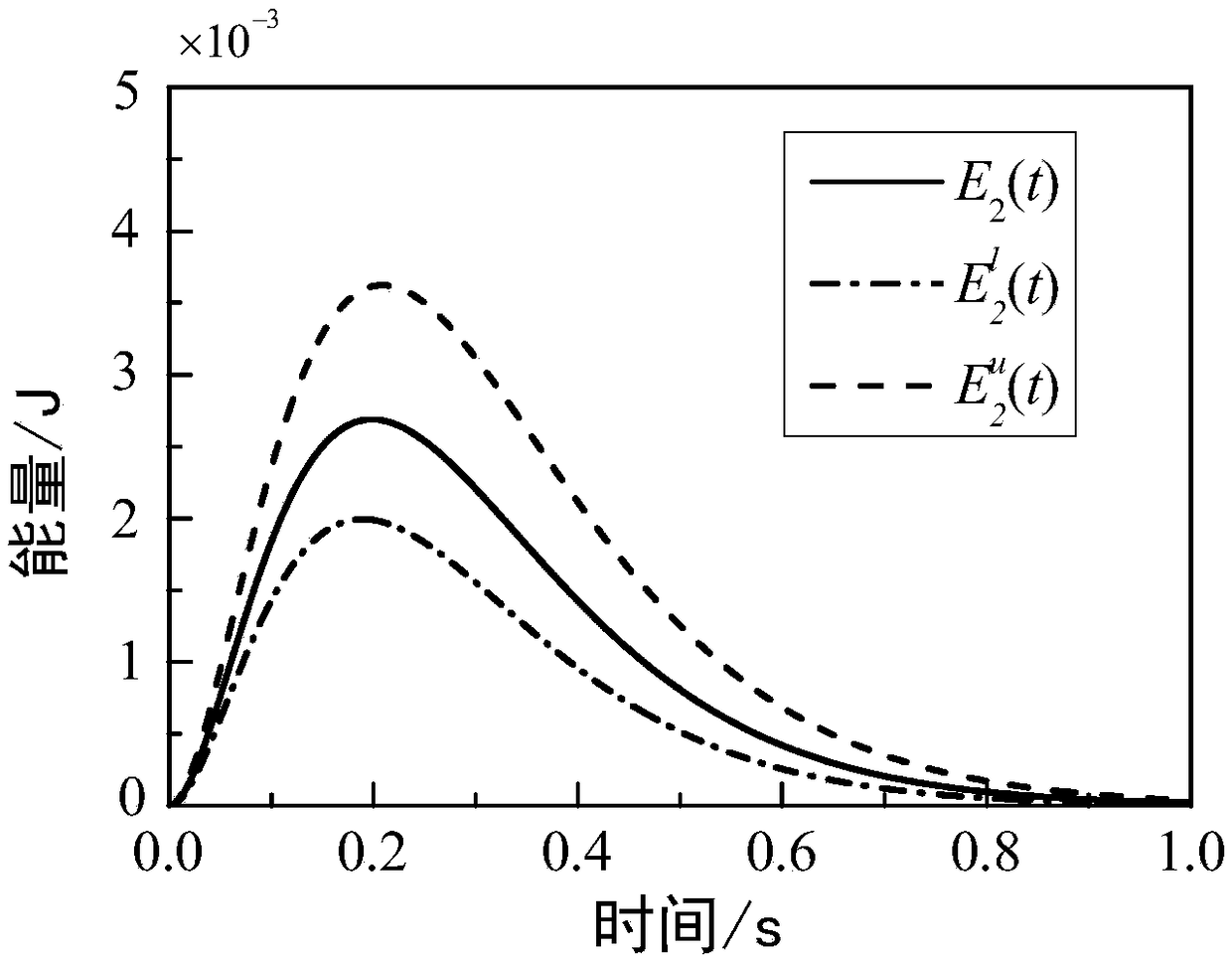
ActiveCN108427853AExpand the scope of researchDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsObservational errorEnergy transfer
The invention provides a transient statistical energy response prediction method considering an uncertain structure. Compared with a conventional transient statistical energy method which can only perform dynamic response prediction for a deterministic structure and does not take uncertain factors such as structure parameter randomness and measuring errors into account, the method characterizes the uncertainty of the structure through an interval method, the influence of uncertainty on the energy transfer and dissipation between structural subsystems is considered, a more precise transient energy expression of each subsystem of the structure is established based on an energy control equation, an expression of the subsystem transient energy is converted into a polynomial form suitable for interval calculation, so that the transient statistical energy analysis method is popularized and applied to the dynamic response analysis of the uncertain structure, the research scope of the currenttransient statistical energy analysis method is expanded, and the method has important engineering application value.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for predicting sound insulation factors of rectangular solid flat plates
ActiveCN107247829AImprove computing efficiencyObvious Computational Efficiency AdvantageDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsApproximation functionIntegration point
The invention discloses a method for predicting sound insulation factors of rectangular solid flat plates. The method is characterized by comprising steps of building statistic energy analysis models for predicting the sound insulation of the flat plates and quantifying uncertain parameters by triangular fuzzy numbers; determining order and Gauss integration points of optimal square approximation functions, related to each parameter, of sound insulation models of the flat plates; sampling fuzzy parameters in subspaces spanned by the Gauss integration points in fuzzy carried sets; acquiring sound insulation optimal square approximation functions of the flat plates by the aid of flat plate sound insulation response in discrete formats at sample point locations; acquiring extreme points of the carried sets and further acquiring maximum and minimum points of the carried sets; determining maximum and minimum points of alpha cut sets on the basis of the extreme points of the carried sets, acquiring flat plate sound insulation interval limit of the alpha cut sets on the basis of the maximum and minimum points of the alpha cut sets and ultimately predicting the sound insulation factors of the rectangular solid flat plates. The method has the advantages that frequency response distribution of the sound insulation fuzziness of the flat plates can be accurately predicted by the aid of fuzzy number models which are used as input, and the computation efficiency and the computation precision can be obviously improved by the aid of optimal square approximation theories.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
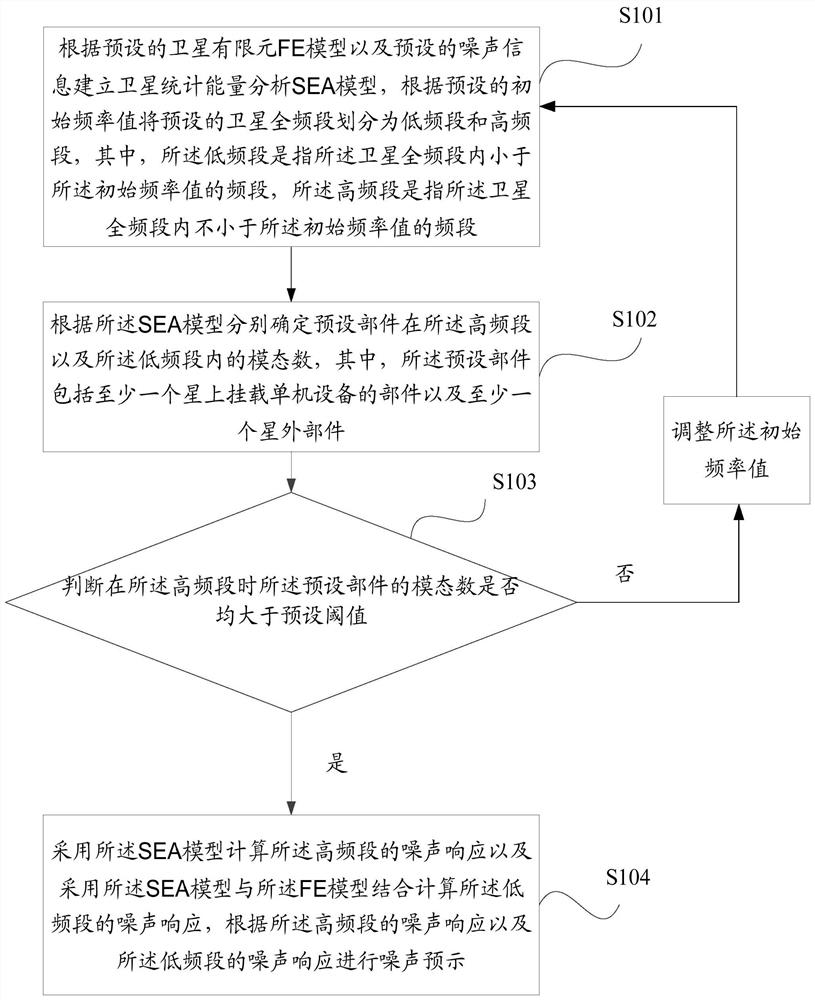
Satellite noise prediction method and device
PendingCN112149323AImprove the efficiency of noise predictionReduce computational workloadDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsLow frequency bandNoise
The invention discloses a satellite noise prediction method and device. The method comprises the following steps: building a satellite statistical energy analysis SEA model according to a preset FE model and preset noise information, and dividing the full frequency band of a satellite into a low frequency band and a high frequency band according to a preset initial frequency value; determining modal numbers corresponding to preset components in the high frequency band and the low frequency band according to the SEA model; judging whether the modal numbers of the preset components are all greater than a preset threshold value or not at the high frequency band; if so, adopting the SEA model to calculate the noise response of the high frequency band, combing the SEA model and an FE model to calculate the noise response of the low frequency band, and performing noise prediction according to the noise response of the high frequency band and the noise response of the low frequency band; andif not, adjusting the initial frequency value, and dividing the full frequency band of the satellite again according to the adjusted frequency value until the modal numbers of the preset components are all greater than the preset threshold. The technical problem that in the prior art, the efficiency of satellite noise prediction is low is solved.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Ocean platform piling bubble curtain noise reduction amount calculation and analysis method
The invention discloses an ocean platform piling bubble curtain noise reduction amount calculation and analysis method. Comprising three calculation methods, namely an air curtain layer noise reduction amount calculation method under normal sound wave incidence, an underwater air curtain bubble curtain low-frequency finite element fluid-solid coupling analysis calculation method and a full-band acoustic analysis calculation method based on a statistical energy analysis method. The influence of various parameters of the air curtain on the noise reduction amount and the noise reduction amount of the bubble curtain under low frequency and high frequency are quantitatively calculated, and the problems that in the prior art, a mode of measuring noise distribution through a detection device with a certain distance from a piling noise source is large in data acquisition difficulty, high in measurement cost, long in period, narrow in applicability and the like are solved. Meanwhile, the quantitative calculation method can also be used for guiding optimization design and analysis of a bubble curtain noise reduction system.
Owner:OFFSHORE OIL ENG
A Method for Predicting the Acoustic Characteristics of a Plate-cavity System Based on Interval Perturbation Analysis Theory
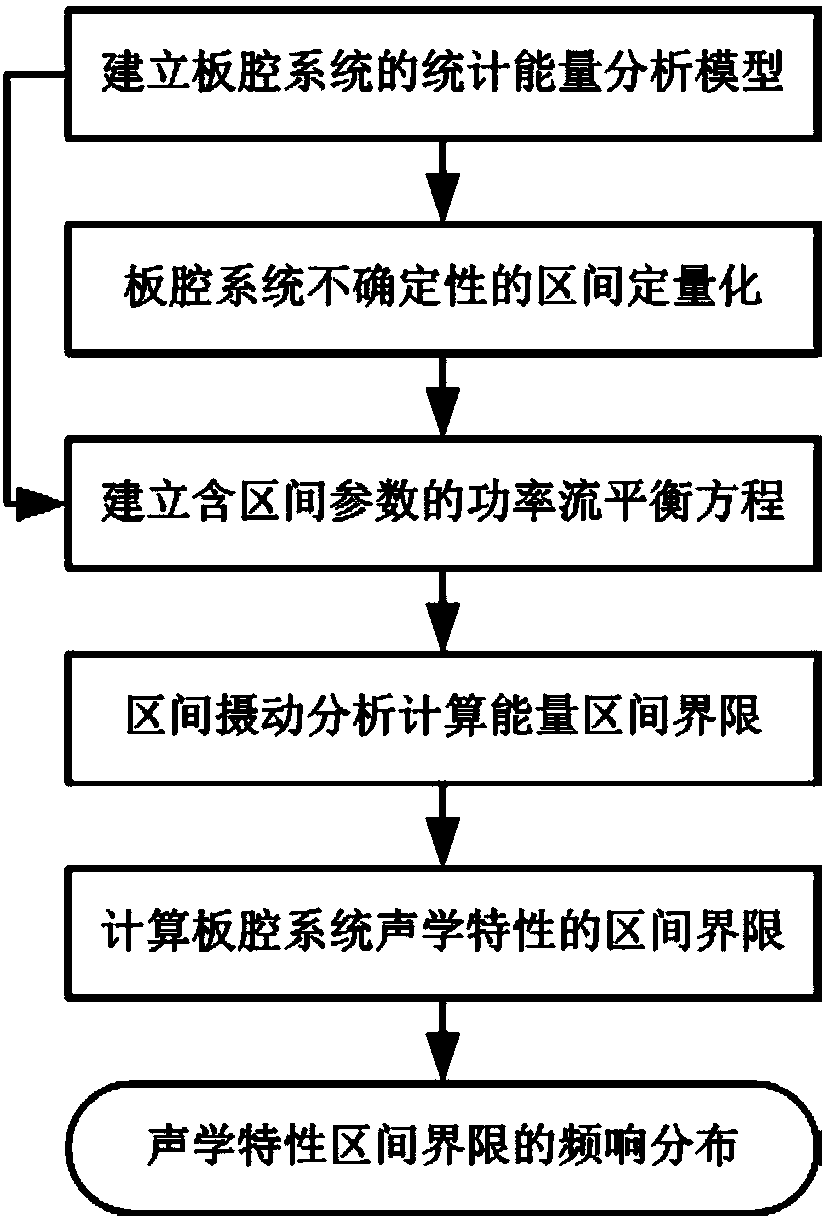
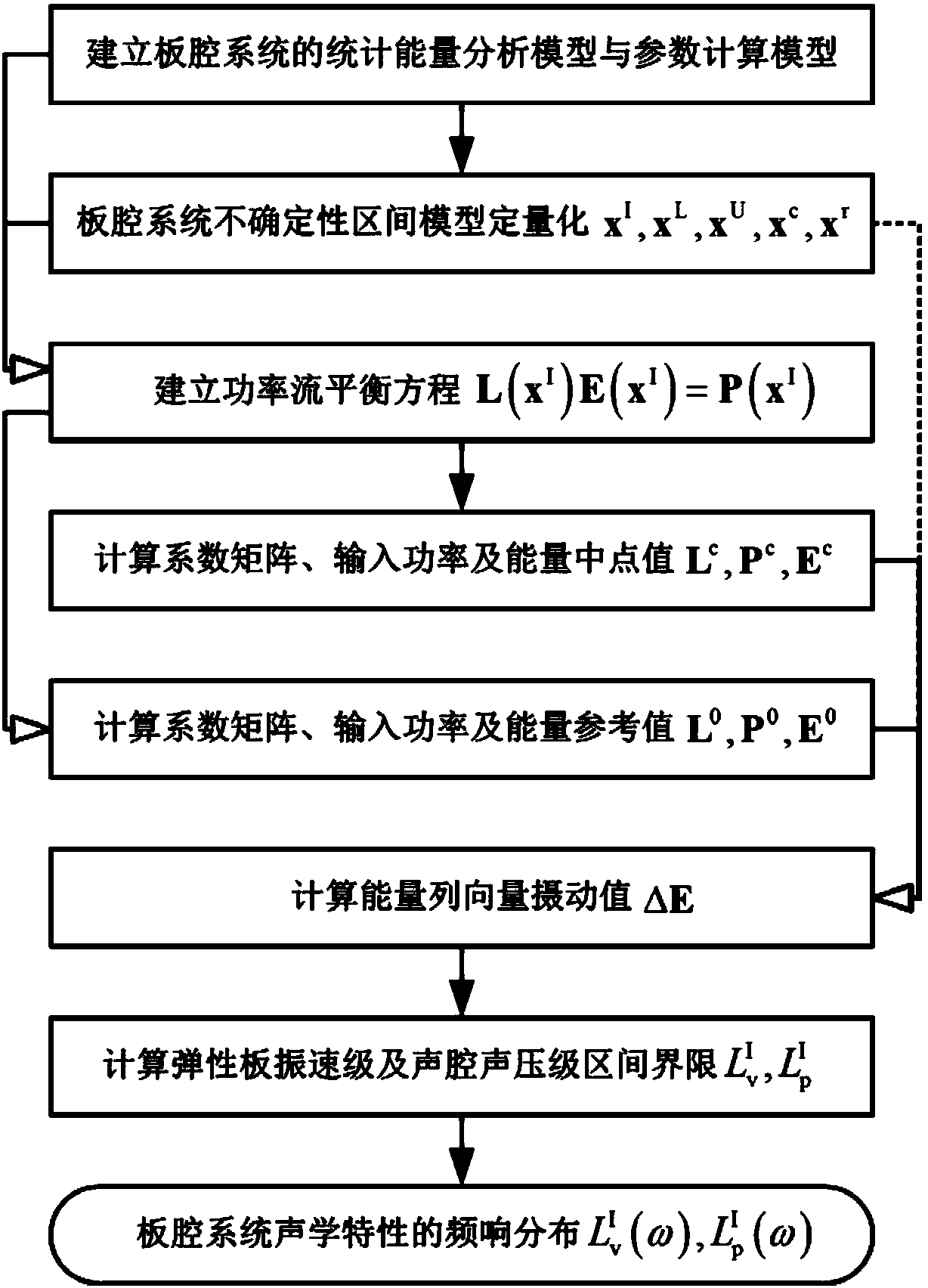
InactiveCN105975767BAvoid dependencyFit closelyForecastingSpecial data processing applicationsComputational modelAnalysis method
The invention discloses a method of plate cavity system acoustic characteristic prediction based on an interval perturbation analysis theory. Firstly, a statistical energy analysis model of plate cavity system acoustic characteristic prediction and a calculation model of corresponding parameters are established based on a statistical energy analysis theory; secondly, indeterminacy of a plate cavity system is quantified through an interval model, and an interval limit of an elastic plate subsystem energy and the interval limit of an acoustic cavity subsystem energy are calculated through an interval perturbation analysis method; and finally, an elastic plate vibration velocity level interval limit and an acoustic cavity sound pressure level interval limit are calculated through the energy of each subsystem, and a frequency response distribution of a plate cavity system acoustic characteristic interval limit is obtained. In the method provided by the invention, influence of the indeterminacy on the plate cavity system acoustic characteristic is considered for the first time, idealized assumption of the indeterminacy is avoided effectively, and the plate cavity system acoustic characteristic is well consistent with practical problems in the engineering field.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Semi-infinite fluid based passenger car external noise analysis and predication method
InactiveCN101814108BShorten the development cycleReduce development costsSpecial data processing applicationsCar passengerControl theory
The invention discloses a semi-infinite fluid based passenger car external noise analysis and predication method for overcoming the defects that passenger car external noise can not be analyzed and predicted accurately before the advanced development in the passenger car development and design. The semi-infinite fluid based passenger car external noise analysis and predication method comprises the steps of: establishing a car body structure SEA (Statistical Energy Analysis) model, establishing a passenger car external noise semi-infinite fluid predication model, determining car body structuresubsystem SEA parameters, and determining external excitation energy applied to the car body and passenger car external noise analysis and predication. The establishment of the passenger car externalnoise semi-infinite fluid predication model comprises the steps of: establishing semi-infinite fluids at the left and right sides of the car body structure SEA model and connecting the semi-infinite fluids and all car body structure subsystems, wherein the semi-infinite fluids are positioned 7.5m away from a car body longitudinal symmetry plane and 1.2m away from ground and energy passes to the semi-infinite fluids from all the car body structure subsystems in the form of spherical wave.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com