Patents
Literature
3144 results about "Material structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The structure of a material may be divided into four levels: atomic structure, atomic arrangement, microstructure, and macrostructure. Although the main thrust of [the materials engineer] is to understand and control the microstructure and macro-structure of various materials, [she] must first understand the atomic and crystal structures.
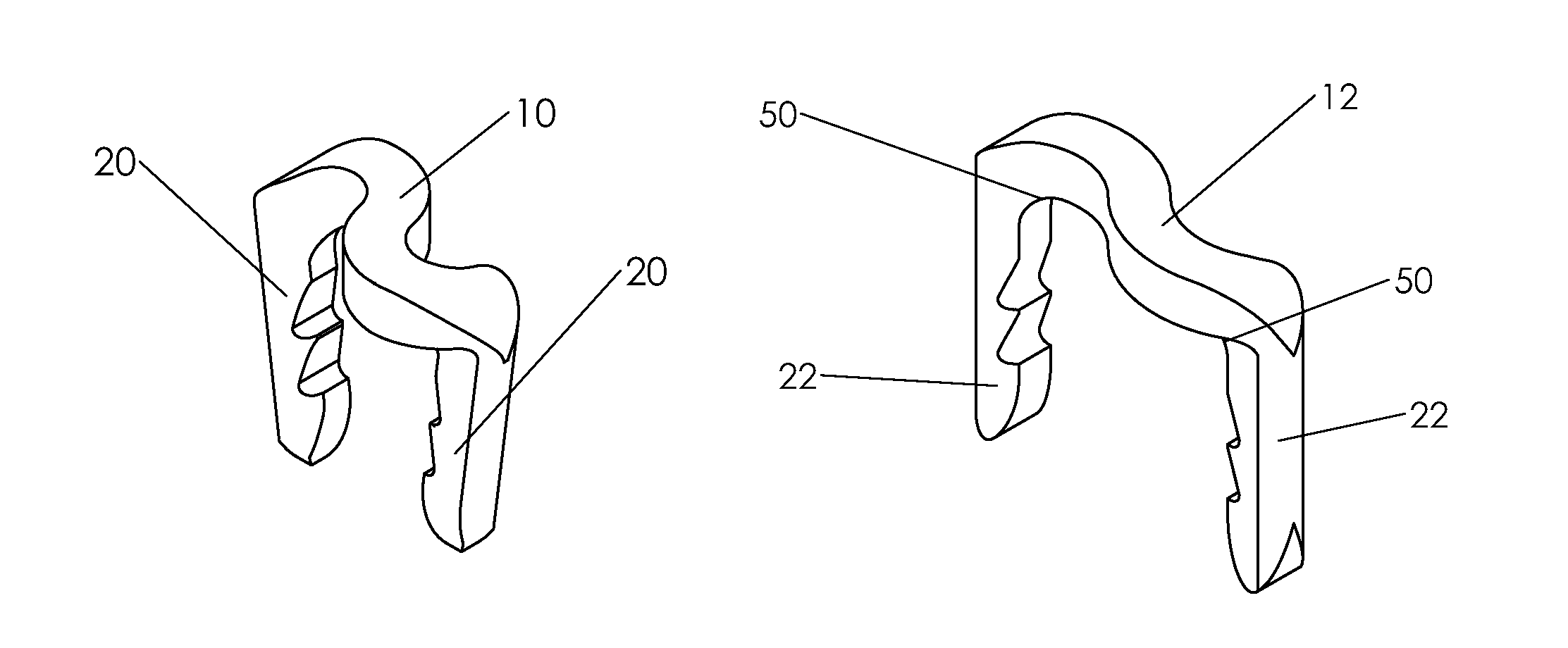
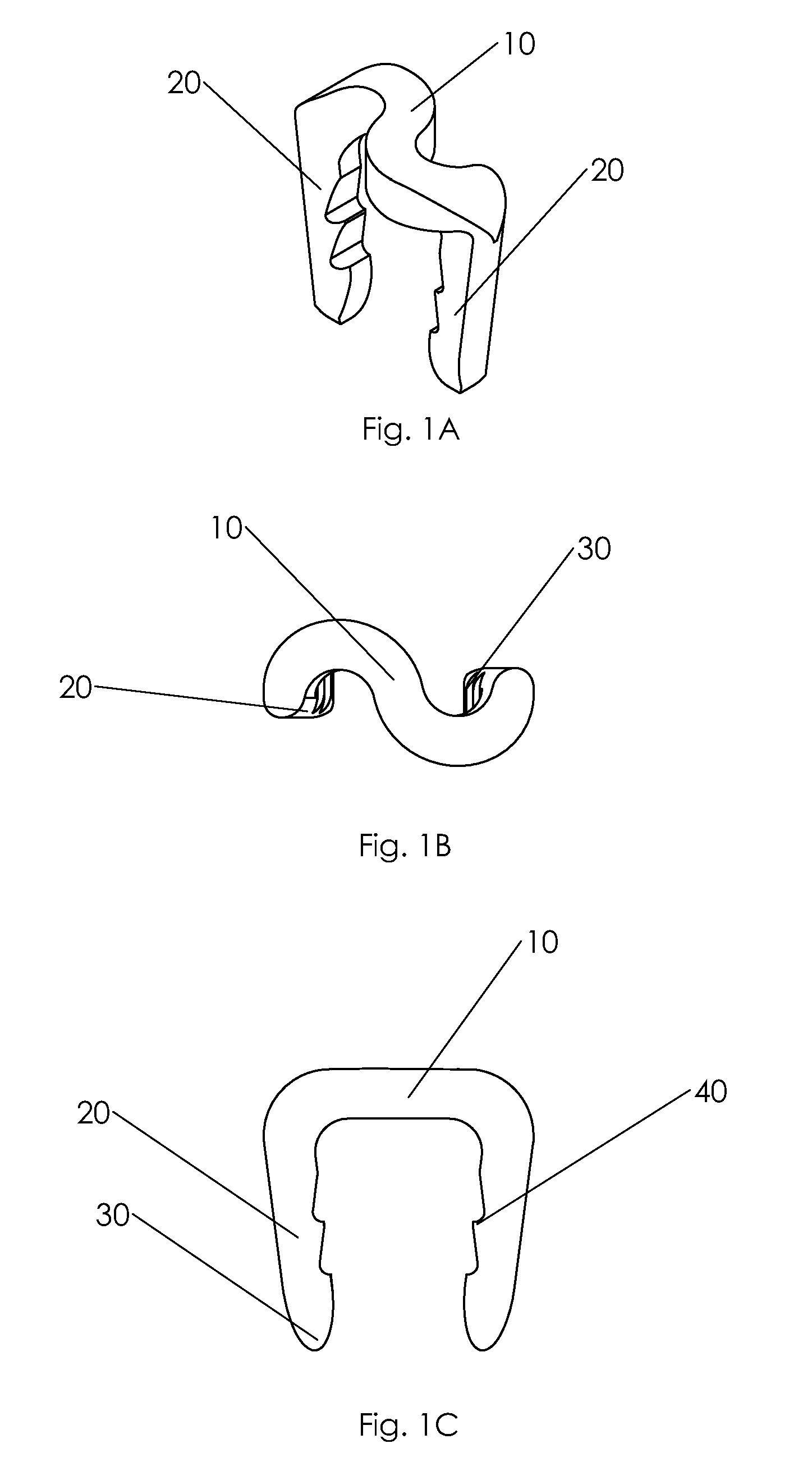
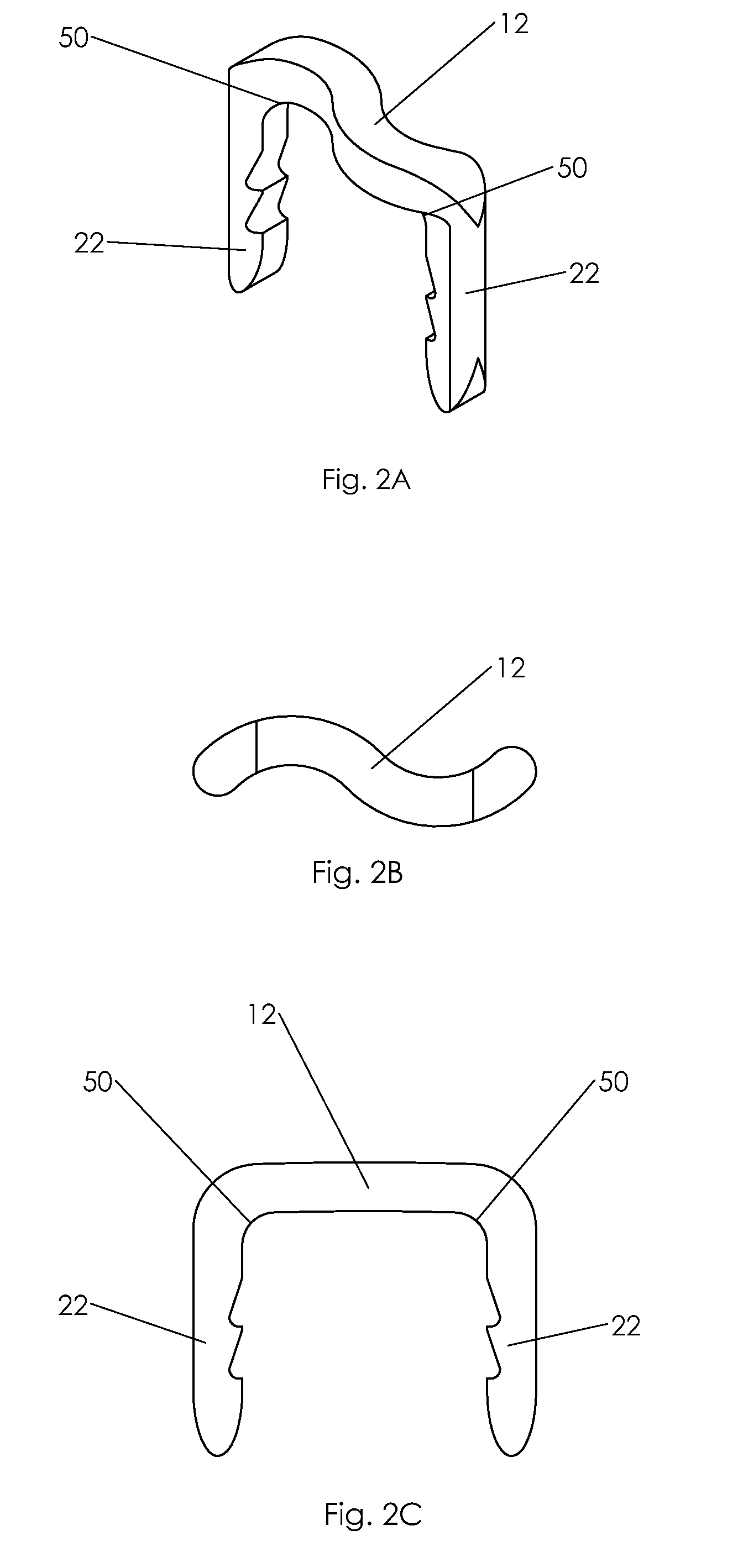
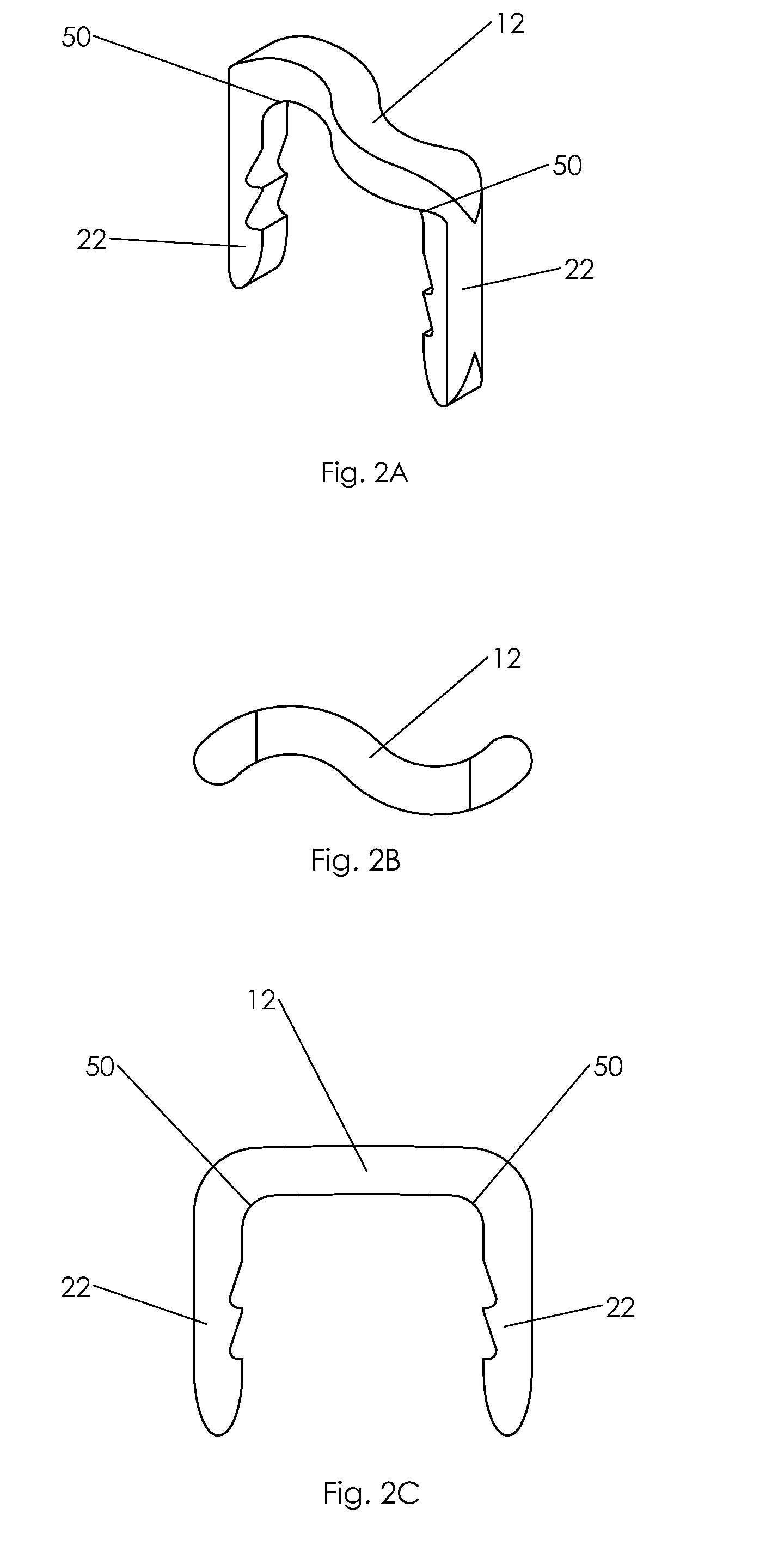
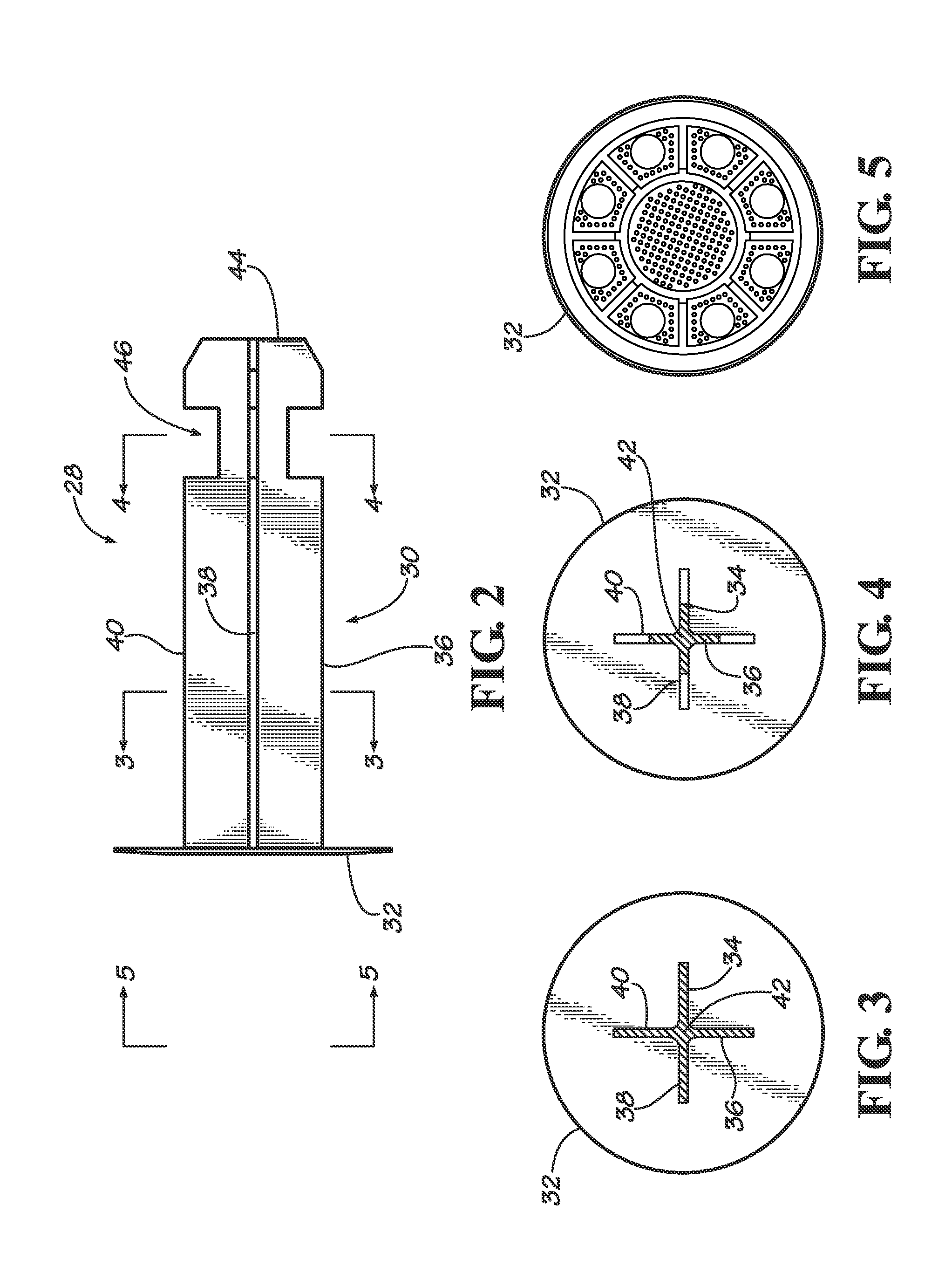
Bone staple, instrument and method of use and manufacturing
ActiveUS9017331B2Stores recoverable mechanical energyEasy to implantPinsInternal osteosythesisShape changeMechanical energy
Owner:FOX WILLIAM CASEY
Ceramic antenna module and methods of manufacture thereof
ActiveUS20060092079A1Minimize reflection lossWithout adversely impacting radiation efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsSolid-state devicesRF front endPermittivity
Circuit modules and methods of construction thereof that contain composite meta-material dielectric bodies that have high effective values of real permittivity but which minimize reflective losses, through the use of host dielectric (organic or ceramic), materials having relative permittivities substantially less than ceramic dielectric inclusions embedded therein. The composite meta-material bodies permit reductions in physical lengths of electrically conducting elements such as antenna element(s) without adversely impacting radiation efficiency. The meta-material structure may additionally provide frequency band filtering functions that would normally be provided by other components typically found in an RF front-end.
Owner:DE ROCHEMONT L PIERRE
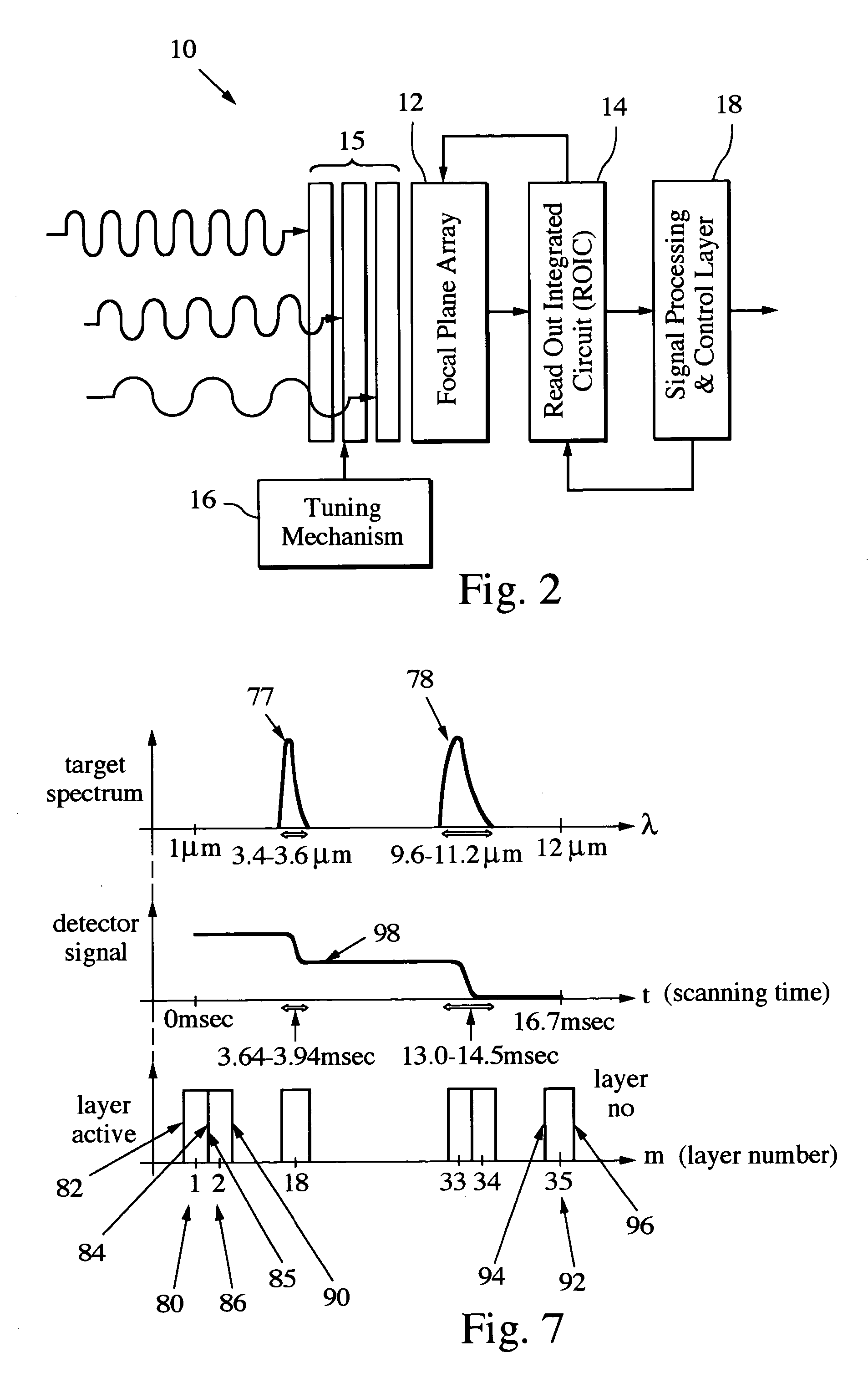
Multispectral imaging chip using photonic crystals
ActiveUS20060054780A1Low data rateHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotonic bandgapPhotonics
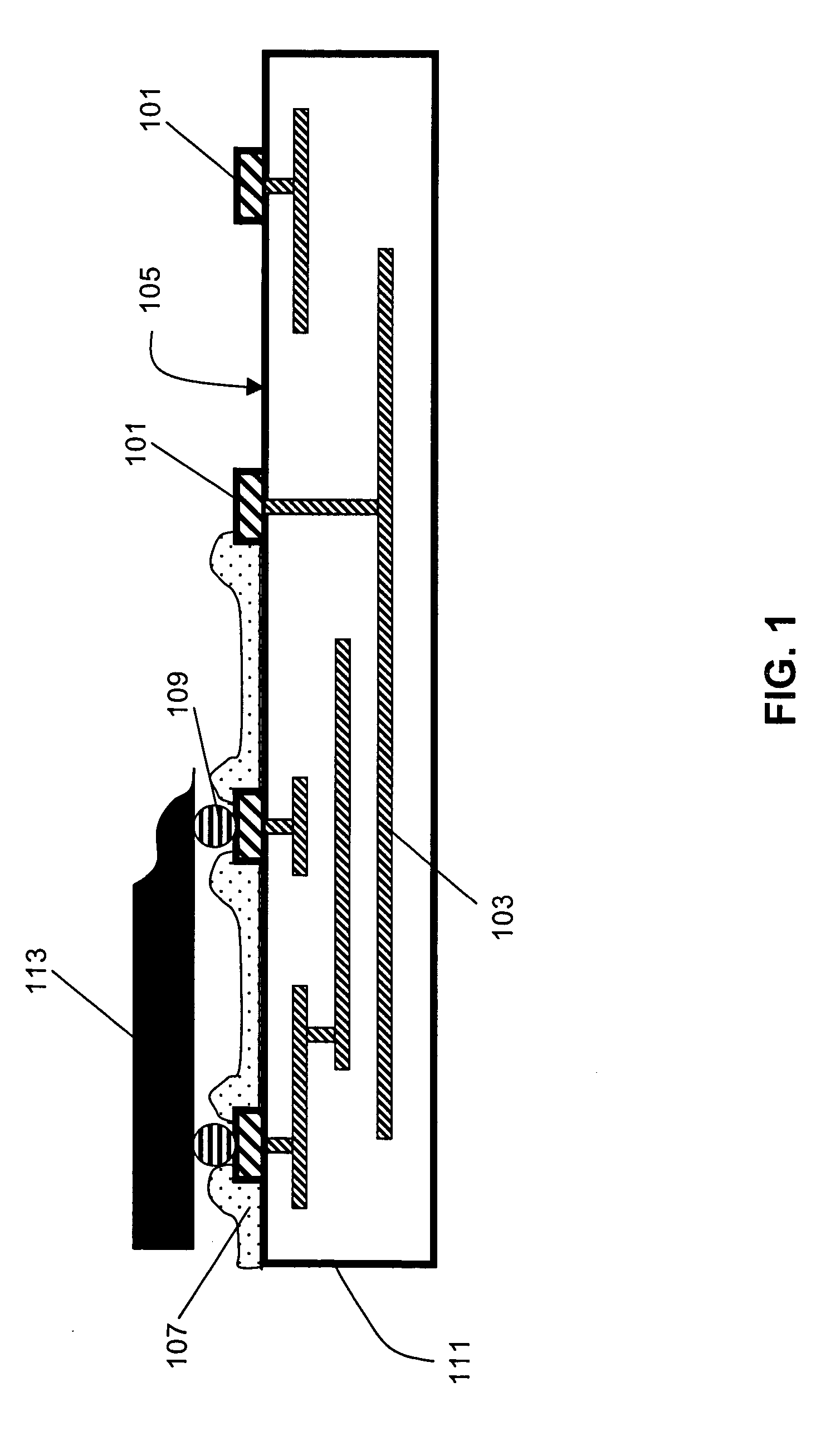
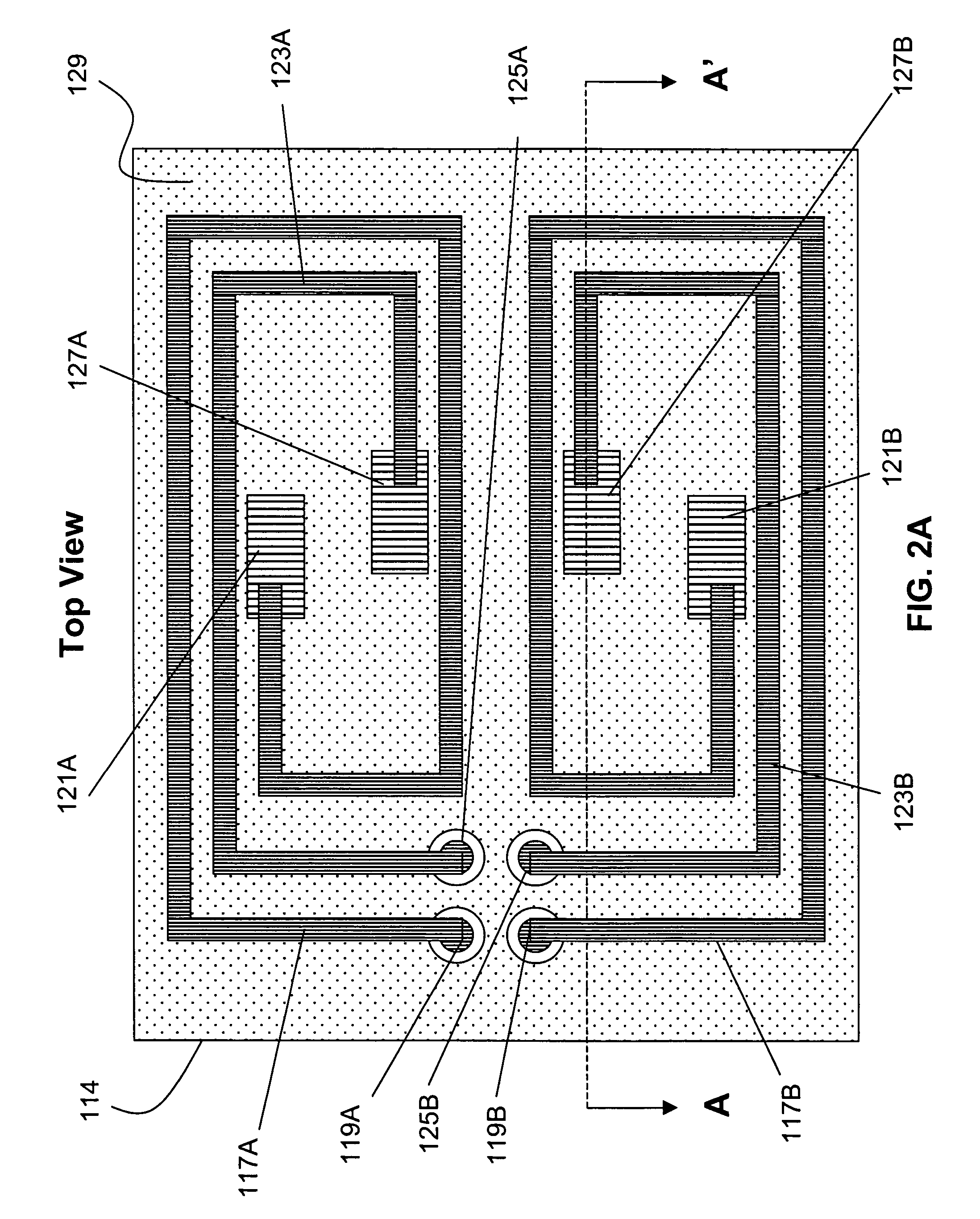
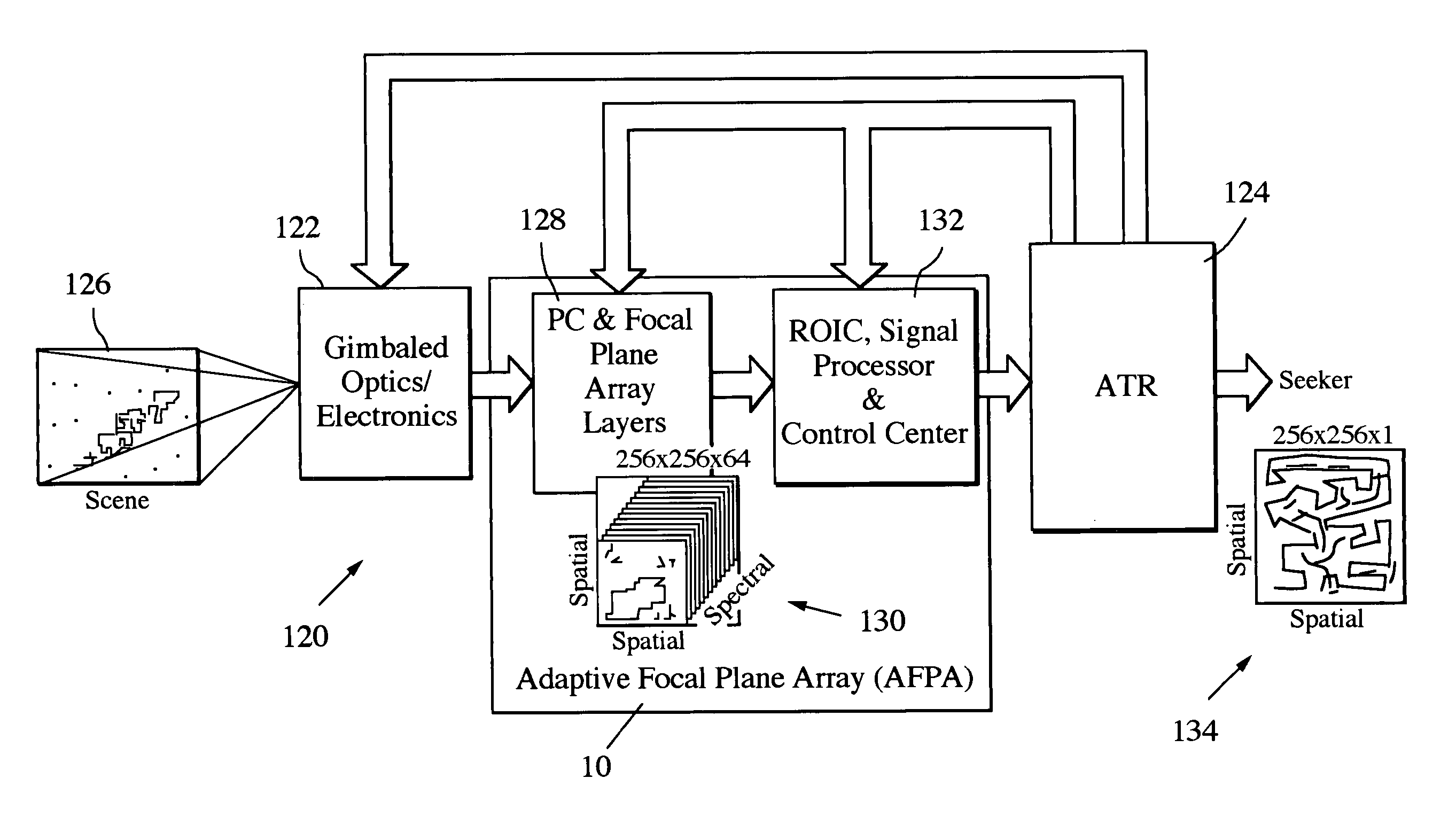
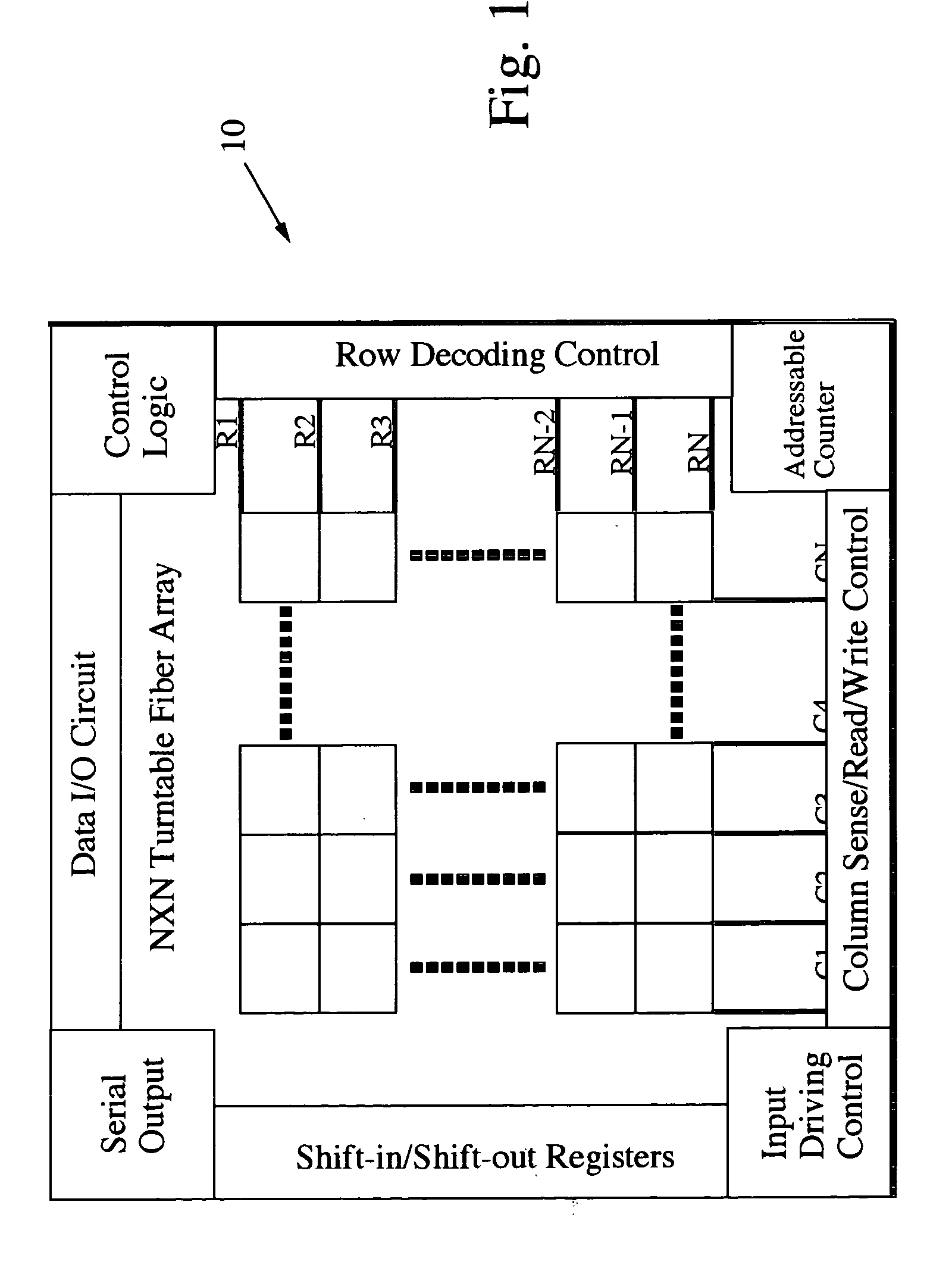
On-chip multispectral imaging and data management is provided in the form of an Adaptive Focal Plane Array (AFPA) that is capable of spectral tunability at the pixel level. Layers of photonic crystals are registered with pixels of a broadband focal plane array. Spectral tuning is accomplished by switching the photonic crystal layers on / off and / or by changing their material structure to tune their photonic band gaps and provide a passband for incident photons. The photonic crystal layers are preferably segmented to independently address different regions or “cells” of pixels down to a pixel-by-pixel resolution. The AFPA may simultaneously sense different regions of a scene at different spectral wavelengths, spatial resolutions and sensitivities.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Material architecture for the fabrication of low temperature transistor
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
Powder feeder for material deposition systems
InactiveUS20050133527A1Small sizeEliminate warpingPower operated devices3D object support structuresSolid componentCoolant flow
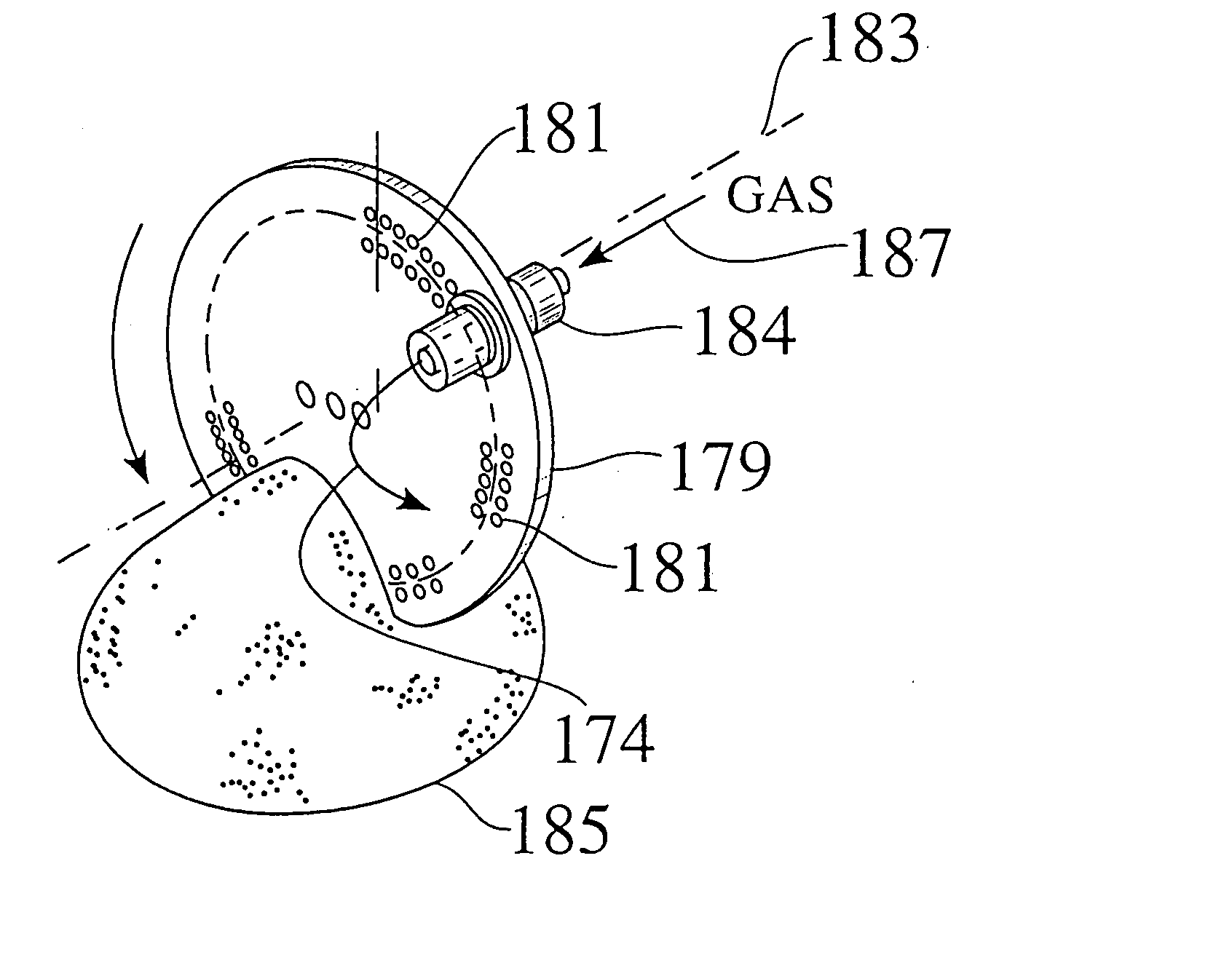
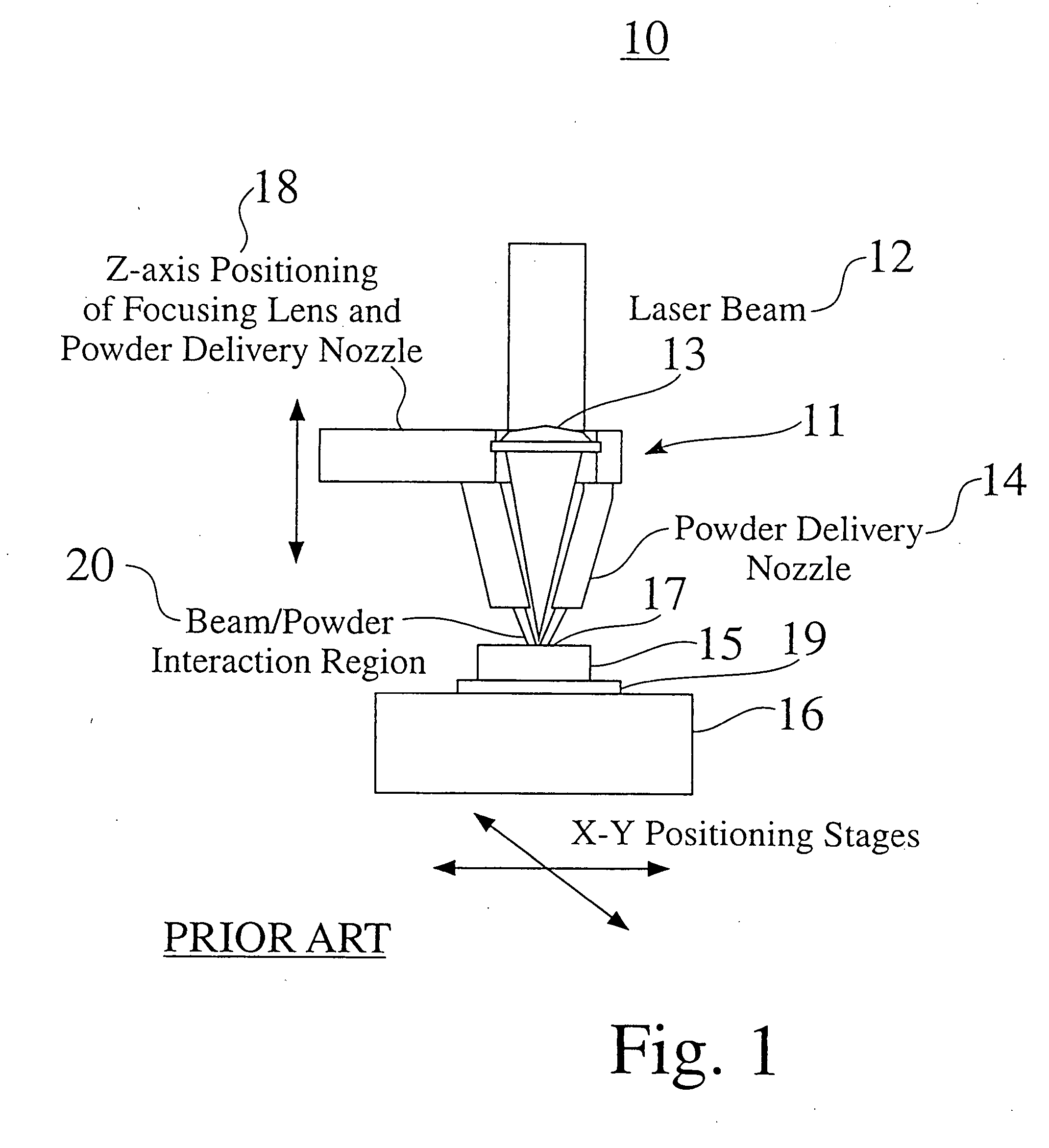
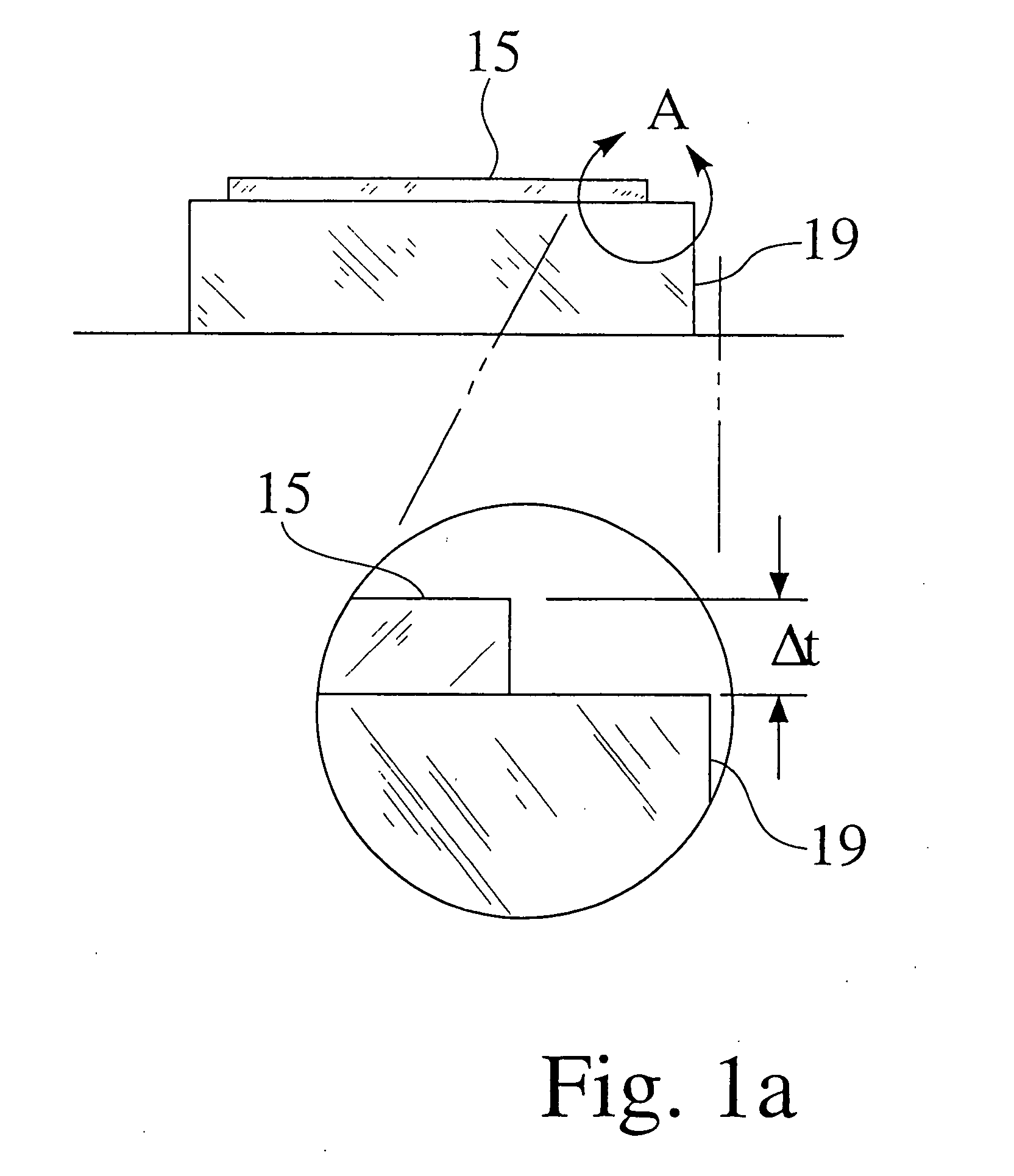
A method and apparatus for embedding features and controlling material composition in a three-dimensional structure (130) is disclosed. The invention enables the control of material characteristics, within a structure (130) made from a plurality of materials, directly from computer renderings of solid models of the components. The method uses stereolithography and solid model computer file formats to control a multi-axis head (480) in a directed material deposition process (123). Material feedstock (126, 127) is deposited onto a pre-heated substrate (19). Depositions (15) in a layer-by-layer pattern, defined by solid models (141, 146), create a three-dimensional article having complex geometric details. Thermal management of finished solid articles (250-302), not available through conventional processing techniques, is enabled by embedded voids (152) and / or composite materials (126, 127), which include dissimilar metals (210, 216). Finished articles control pressure drop and produce uniform coolant flow and pressure characteristics. High-efficiency heat transfer is engineered within a solid structure by incorporating other solid materials with diverse indexes. Embedding multi-material structures (132, 134) within a normally solid component (141) produces articles with diverse mechanical properties. Laser and powder delivery systems (420, 170) are integrated in a multi-axis deposition head (480) having a focused particle beam (502) to reduce material waste.
Owner:OPTOMEC DESIGN CO
Ceramic antenna module and methods of manufacture thereof
ActiveUS7405698B2Minimize reflection lossWithout adversely impacting radiation efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsSolid-state devicesRF front endPermittivity
Circuit modules and methods of construction thereof that contain composite meta-material dielectric bodies that have high effective values of real permittivity but which minimize reflective losses, through the use of host dielectric (organic or ceramic), materials having relative permittivities substantially less than ceramic dielectric inclusions embedded therein. The composite meta-material bodies permit reductions in physical lengths of electrically conducting elements such as antenna element(s) without adversely impacting radiation efficiency. The meta-material structure may additionally provide frequency band filtering functions that would normally be provided by other components typically found in an RF front-end.
Owner:DE ROCHEMONT L PIERRE
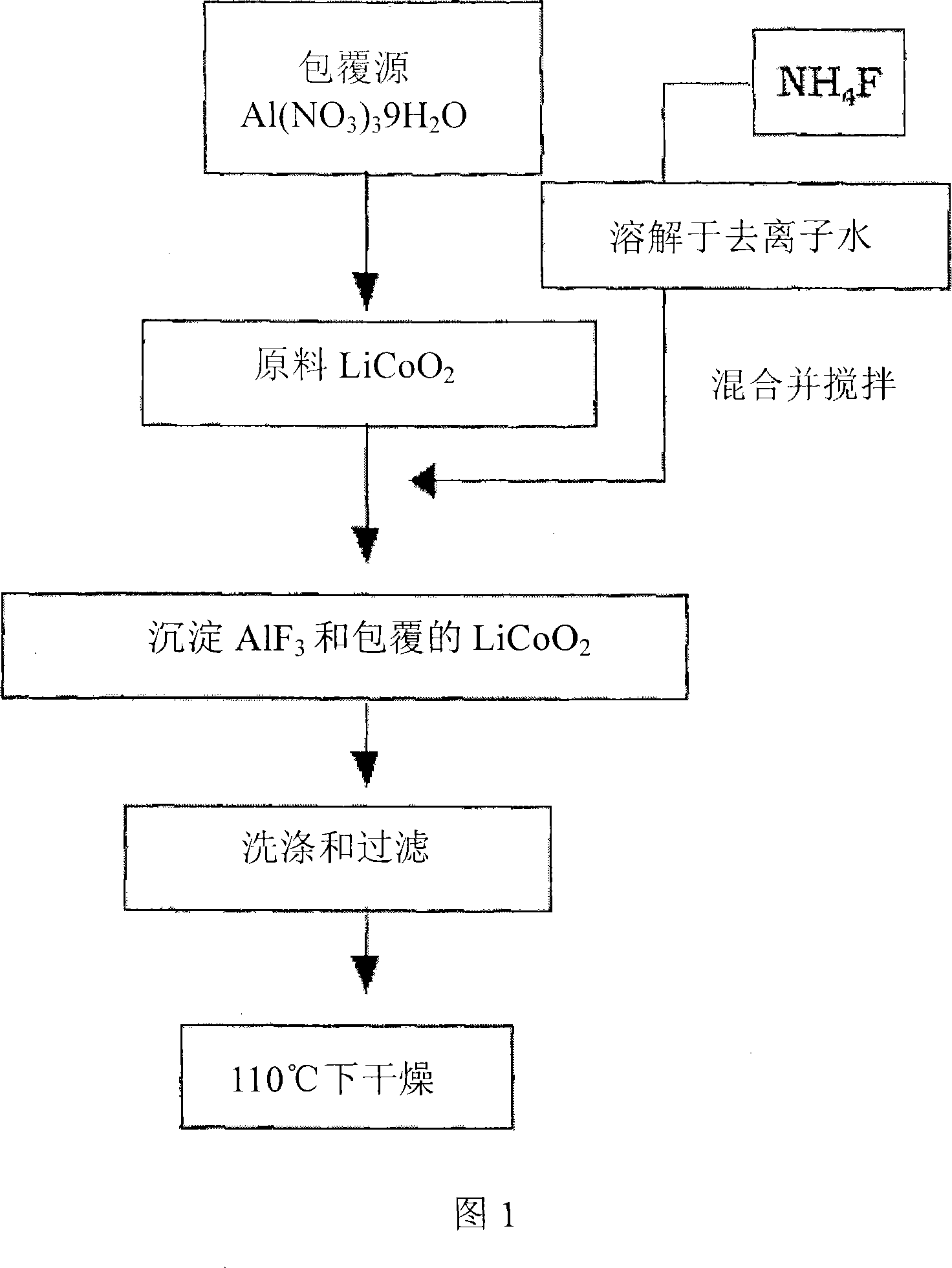
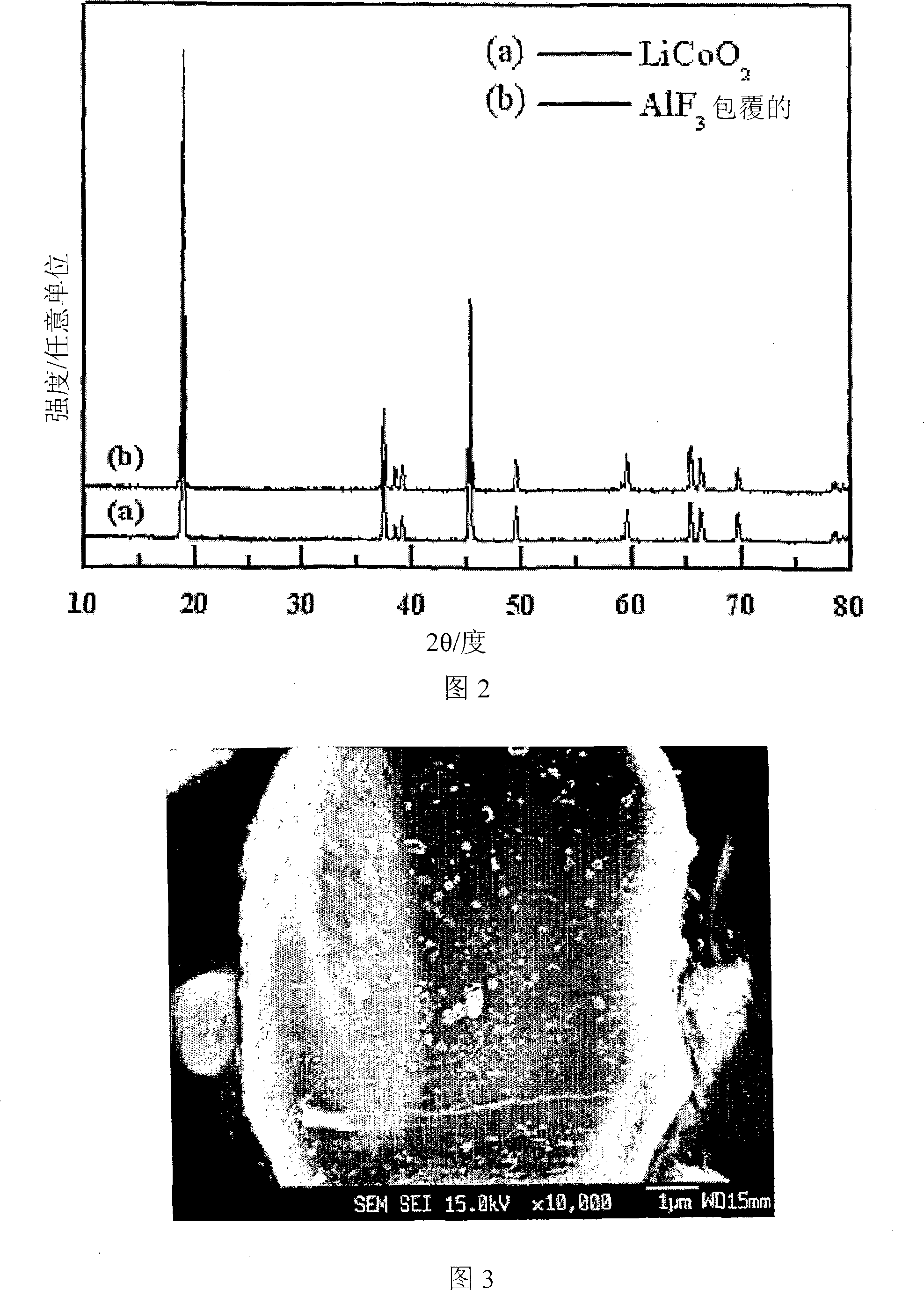
Cathode active material coated with fluorine compound for lithium secondary batteries and method for preparing the same
Disclosed herein is a cathode active material coated with a fluorine compound for lithium secondary batteries. The cathode active material is structurally stable, and improves the charge-discharge characteristics, cycle characteristics, high-voltage characteristics, high-rate characteristics and thermal stability of batteries.
Owner:ENERCERAMIC
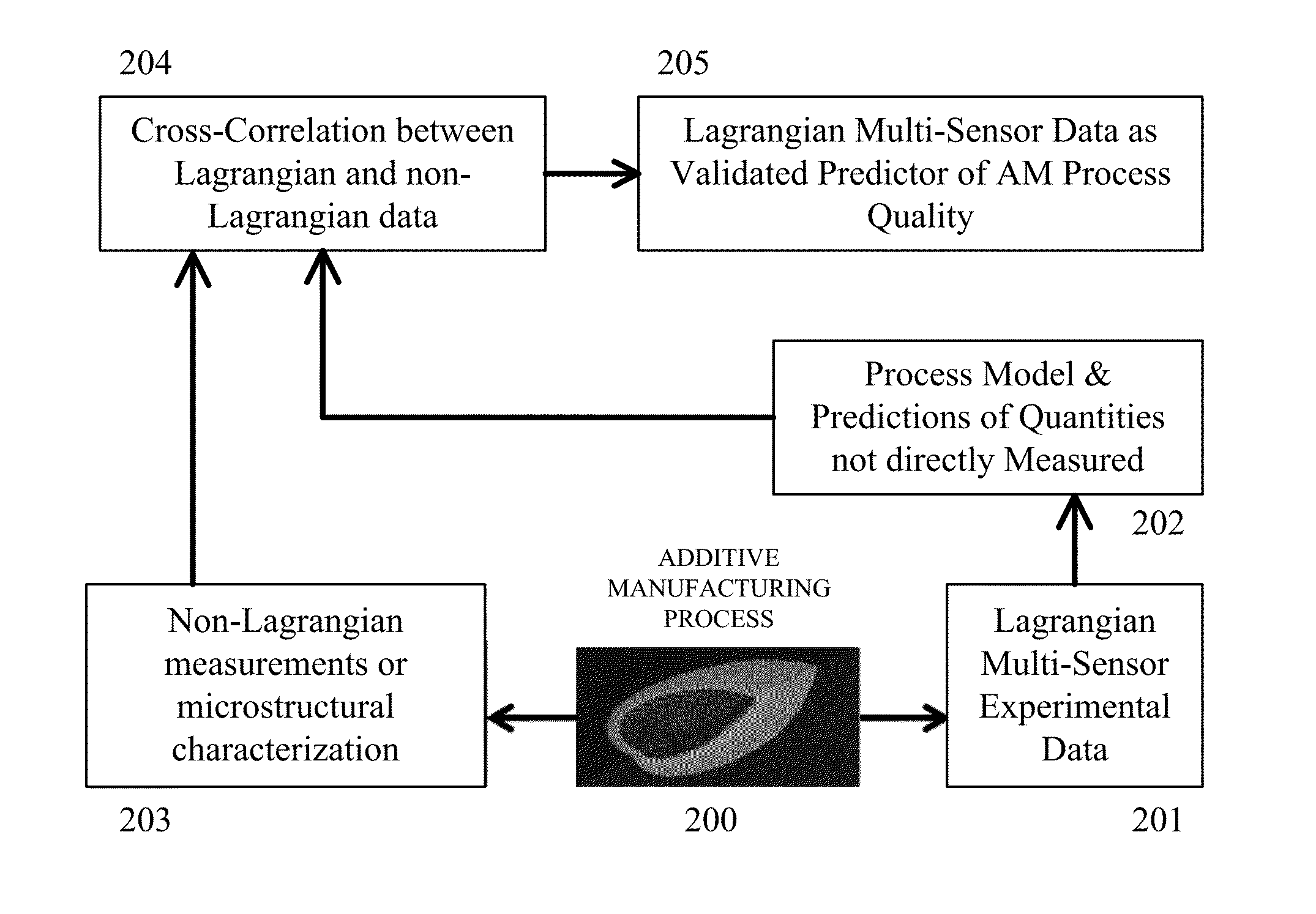
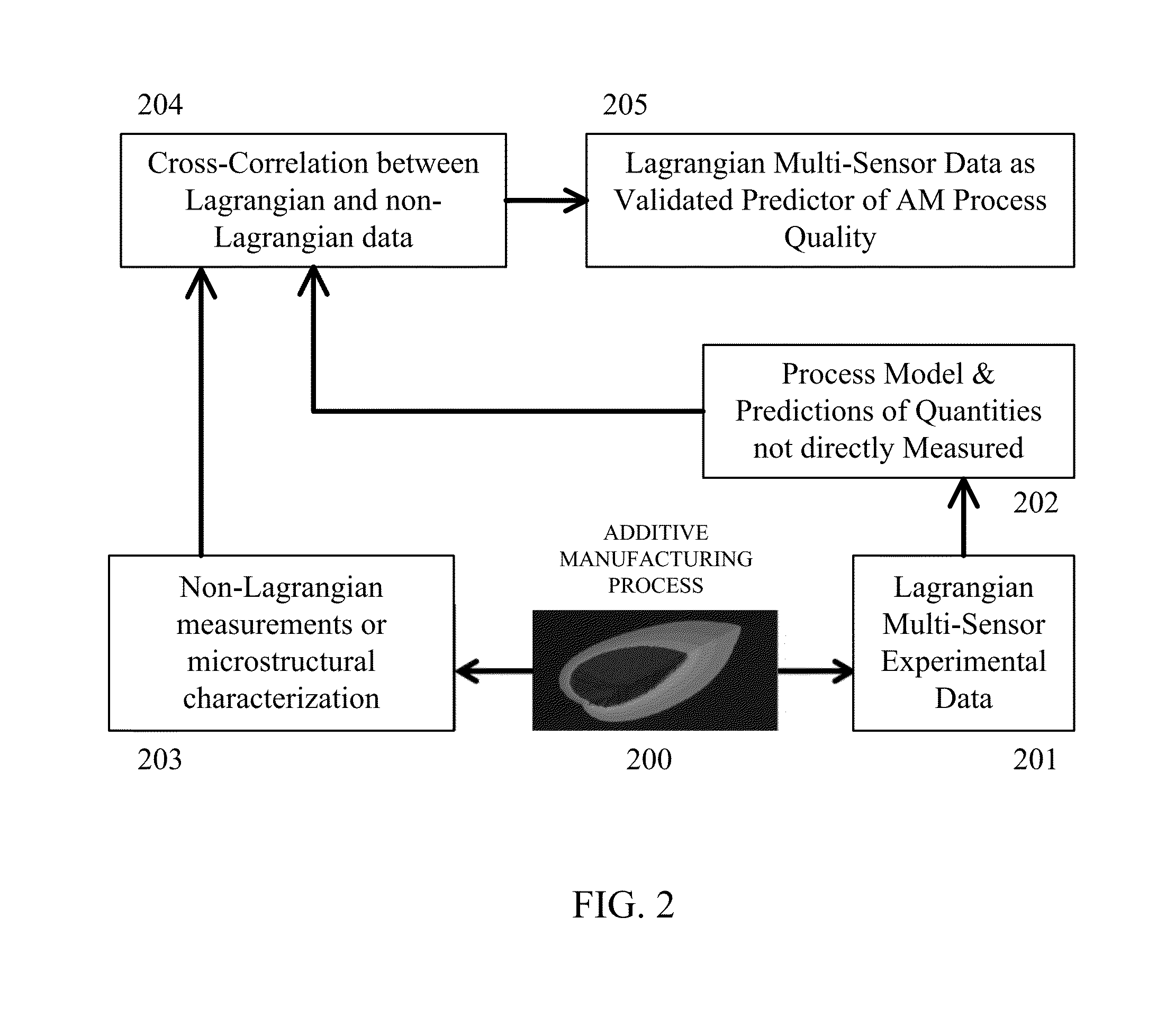
Multi-sensor quality inference and control for additive manufacturing processes
ActiveUS20160185048A1Increase chanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyInference systemManufacturing operations
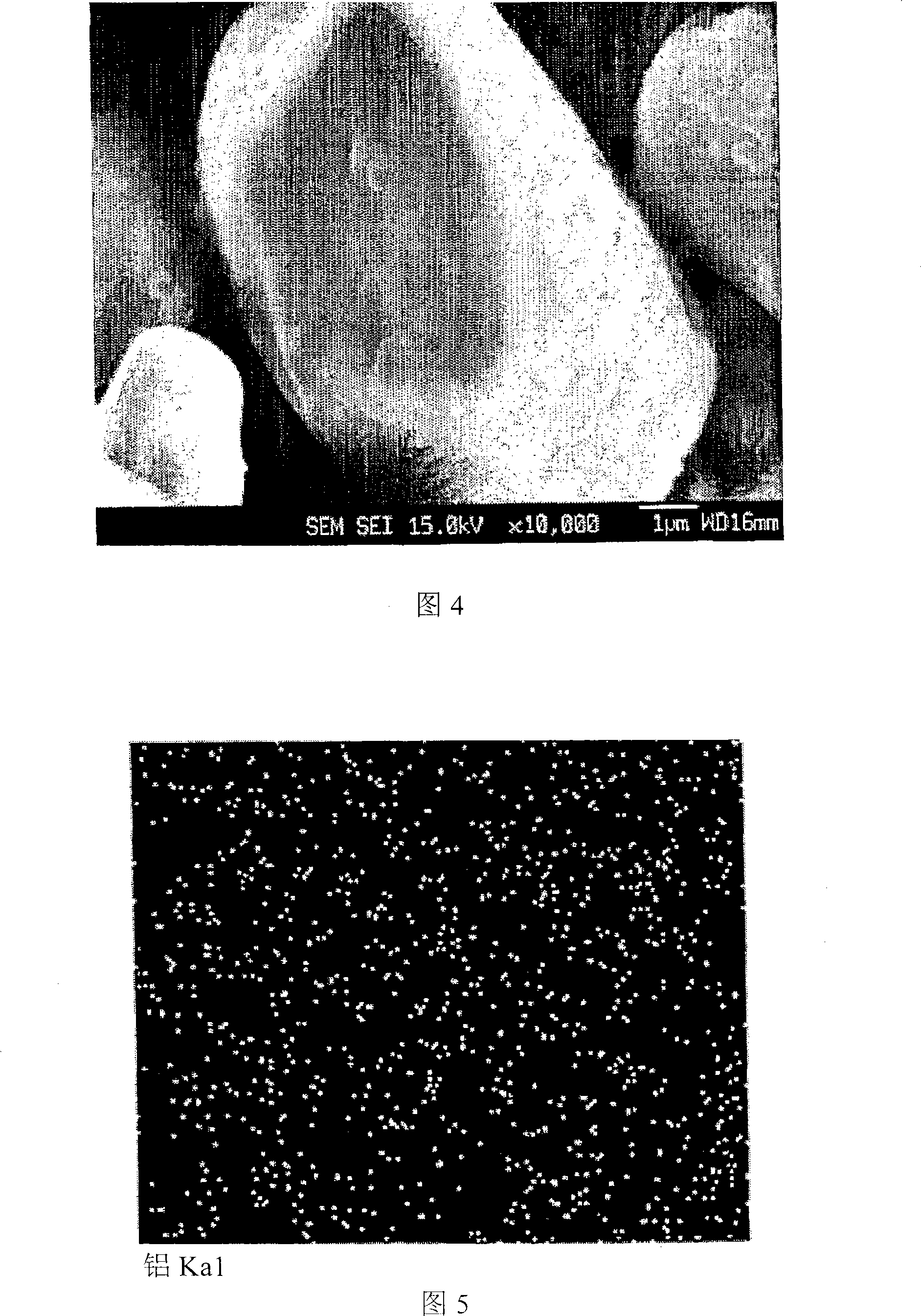
This invention teaches a multi-sensor quality inference system for additive manufacturing. This invention still further teaches a quality system that is capable of discerning and addressing three quality issues: i) process anomalies, or extreme unpredictable events uncorrelated to process inputs; ii) process variations, or difference between desired process parameters and actual operating conditions; and iii) material structure and properties, or the quality of the resultant material created by the Additive Manufacturing process. This invention further teaches experimental observations of the Additive Manufacturing process made only in a Lagrangian frame of reference. This invention even further teaches the use of the gathered sensor data to evaluate and control additive manufacturing operations in real time.
Owner:SIGMA LAB OF ARIZONA
Material architecture for the fabrication of low temperature transistor
Owner:TAN CHUNG FOONG +4
Porous silicon carbon composite microsphere with yolk-eggshell structure and preparation method therefor
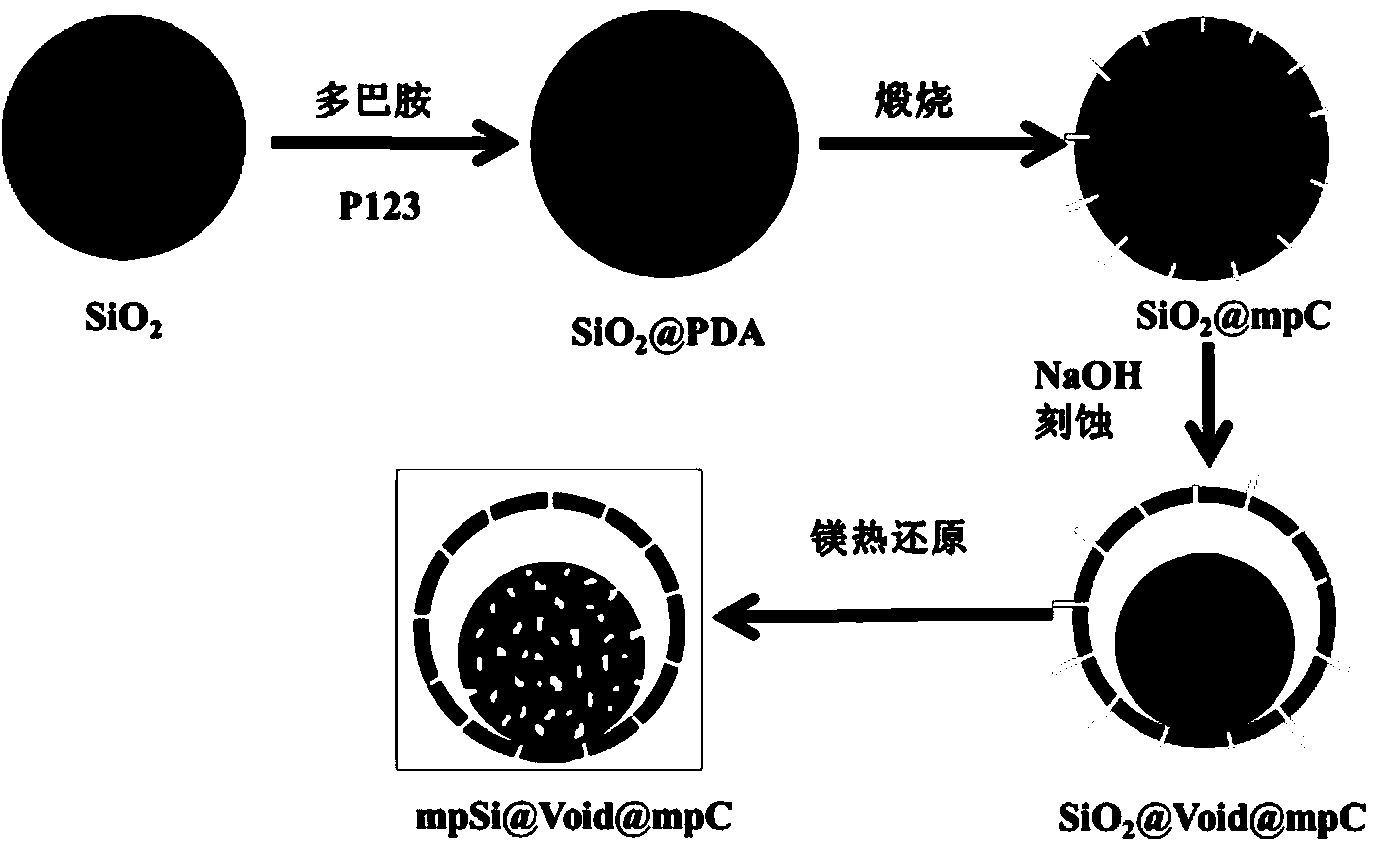
InactiveCN103531760AEase of mass productionPromote infiltrationMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesCarbon compositesYolk
The invention provides a porous silicon carbon composite microsphere with a yolk-eggshell structure and a preparation method therefor, and belongs to the lithium ion battery electrode material technology field. The porous silicon carbon composite microsphere takes a porous submicron silicon sphere mpSi as a core with a diameter of 400-900 nm, and takes porous carbon mpC as a shell with a thickness of 10-60 nm. The inner diameter of a cavity Void is 800-1400 nm. The composition of the silicon carbon composite microsphere can be described as mpSi@Void@mpC. In addition, In the preparation method, cheap silicon dioxide is taken as a silicon source, silicon dioxide is conversed into silicon materials with electrochemical activities through a magnesiothermic reduction method. The size of gaps can be regulated and controlled through control of etching conditions. The preparation method is advantaged in that the material structure can be controlled, the cost is low, the process is simple, and the composite microsphere is convenient for large-scale production.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Low profile highly expandable stent
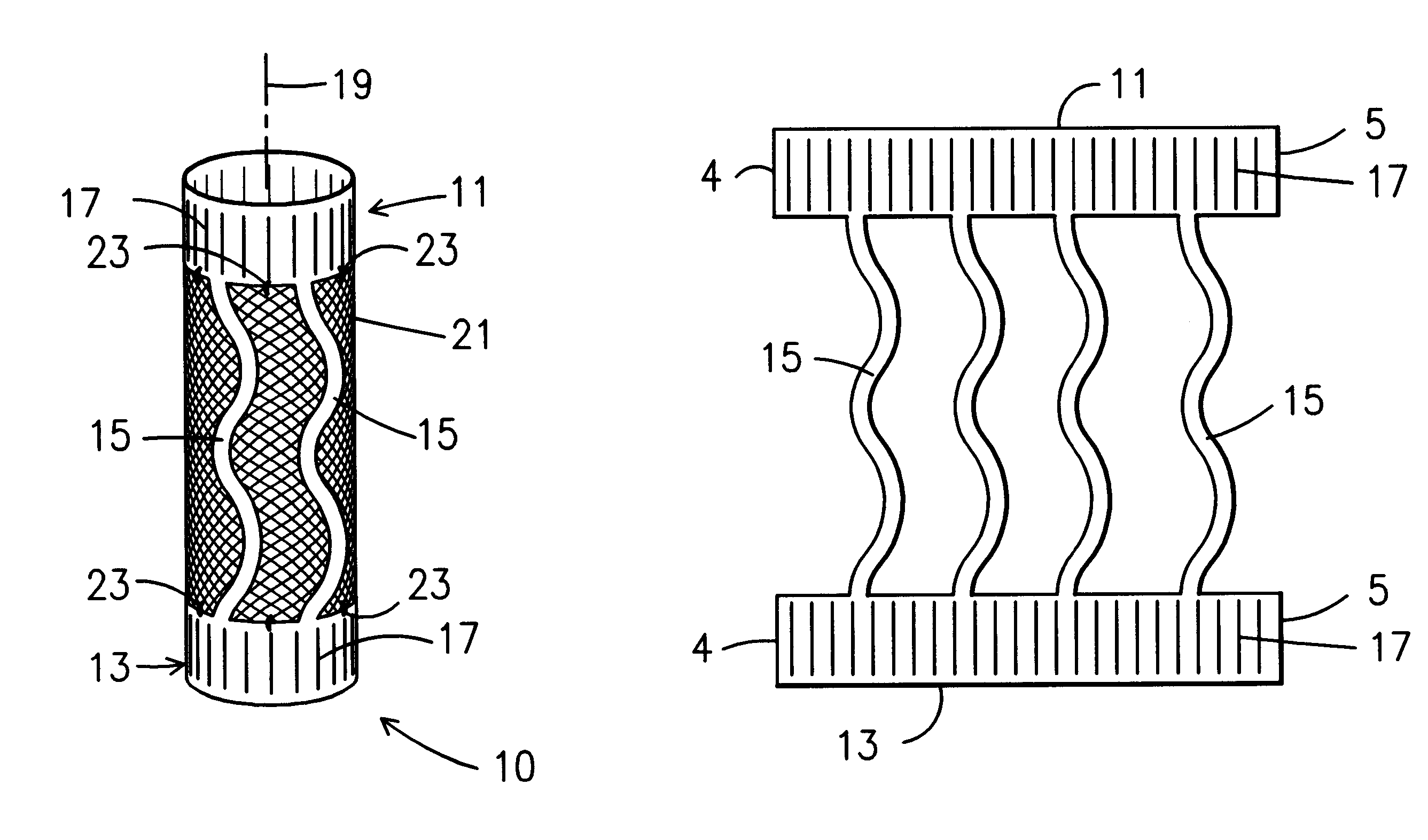
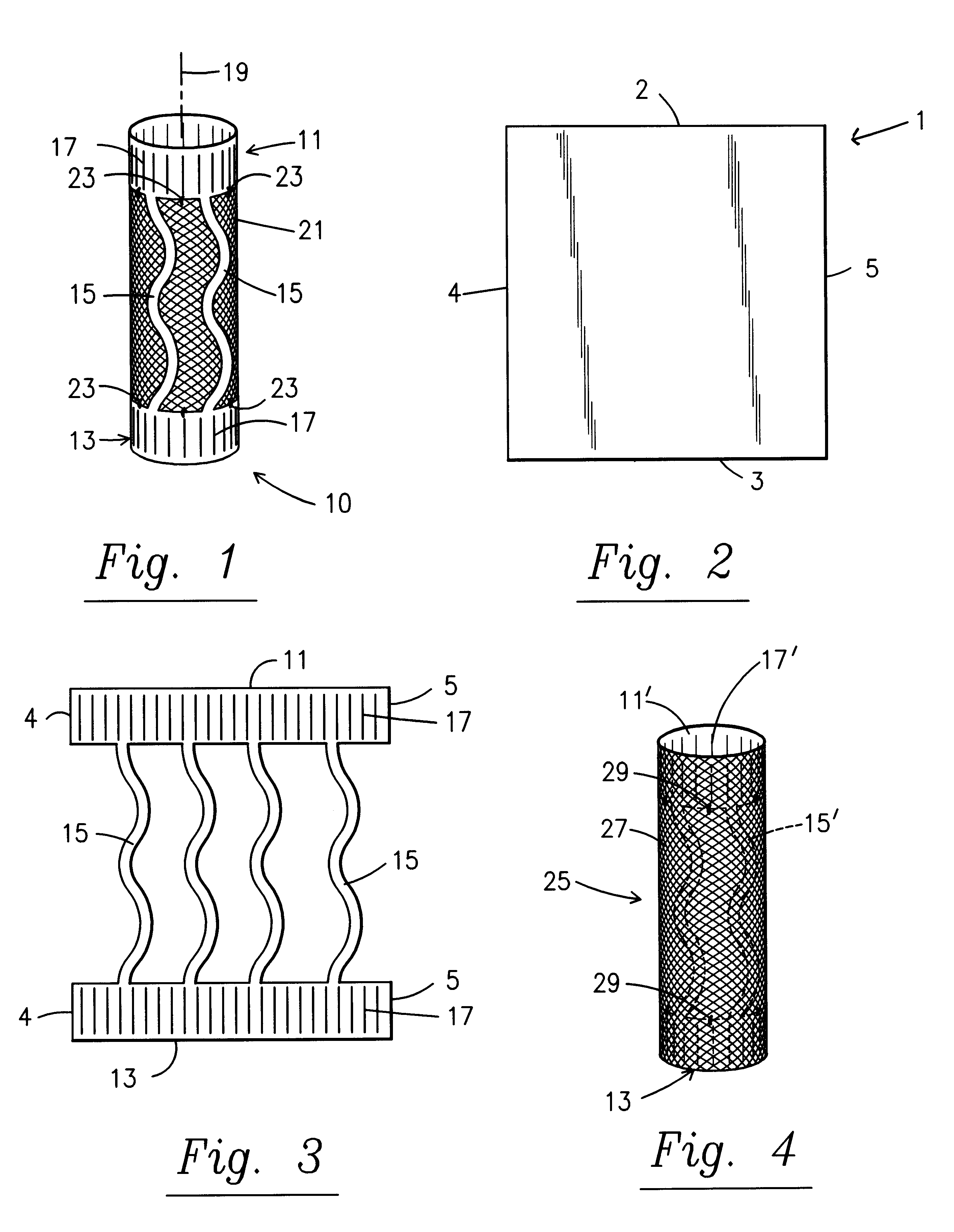
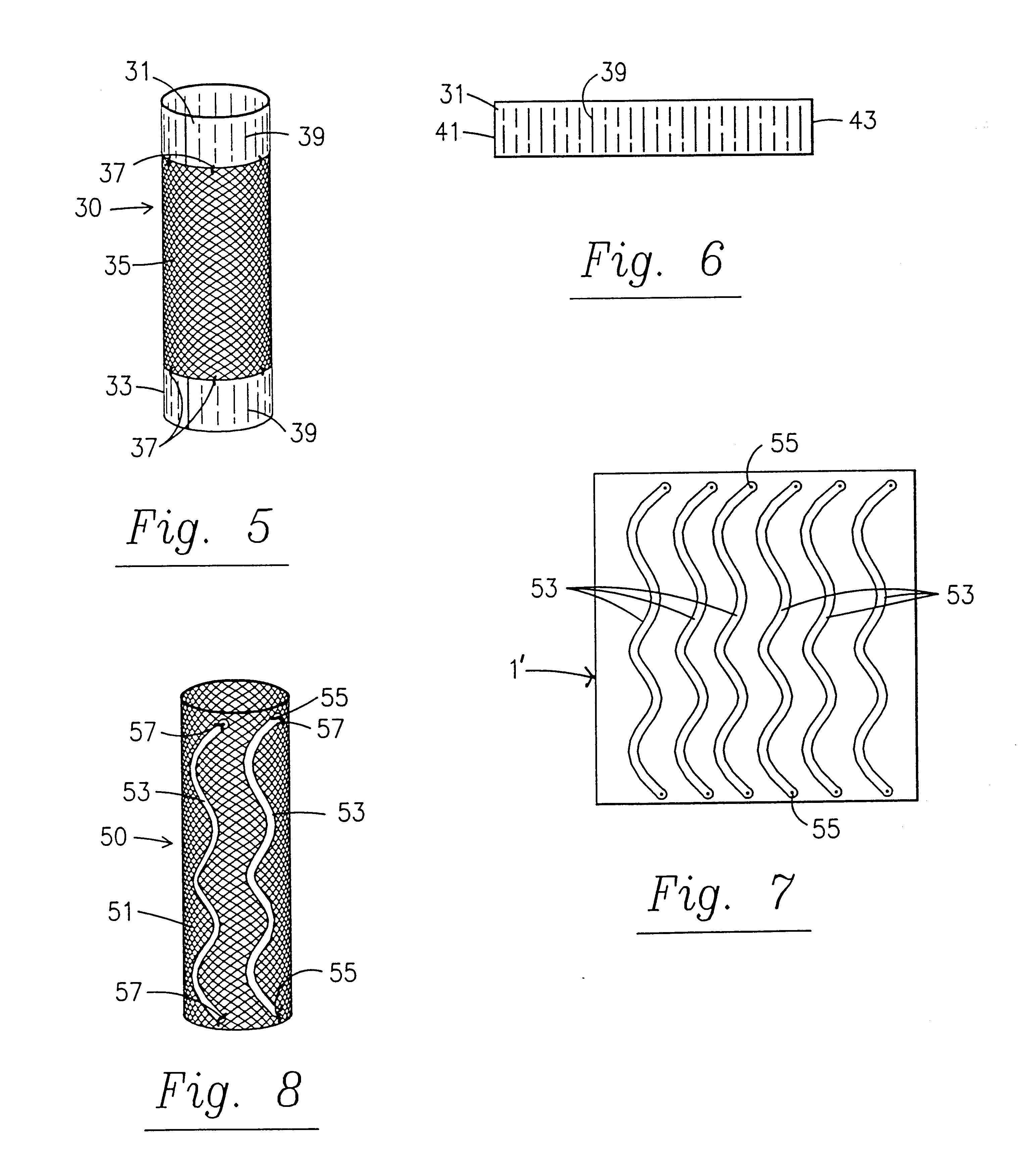
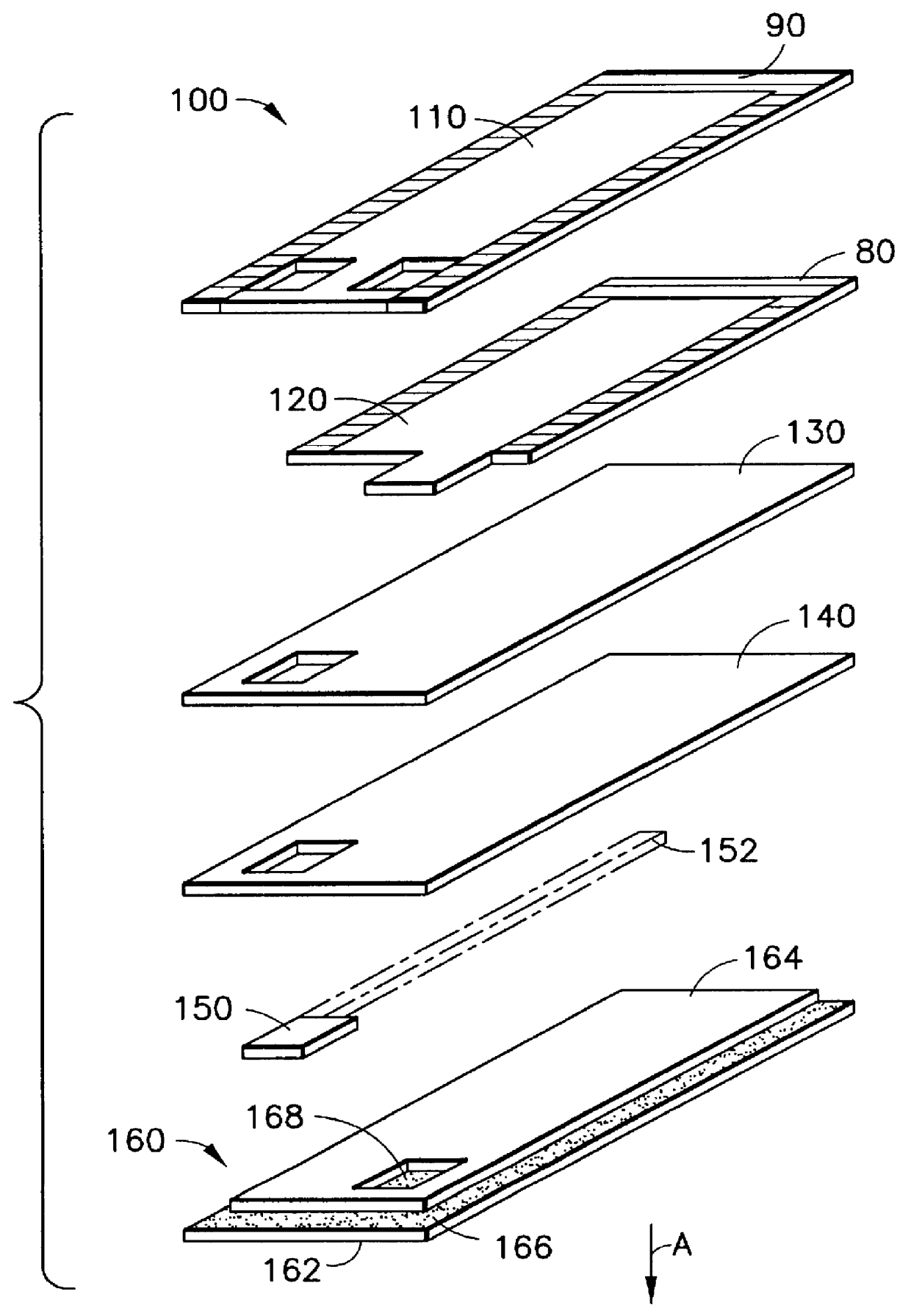
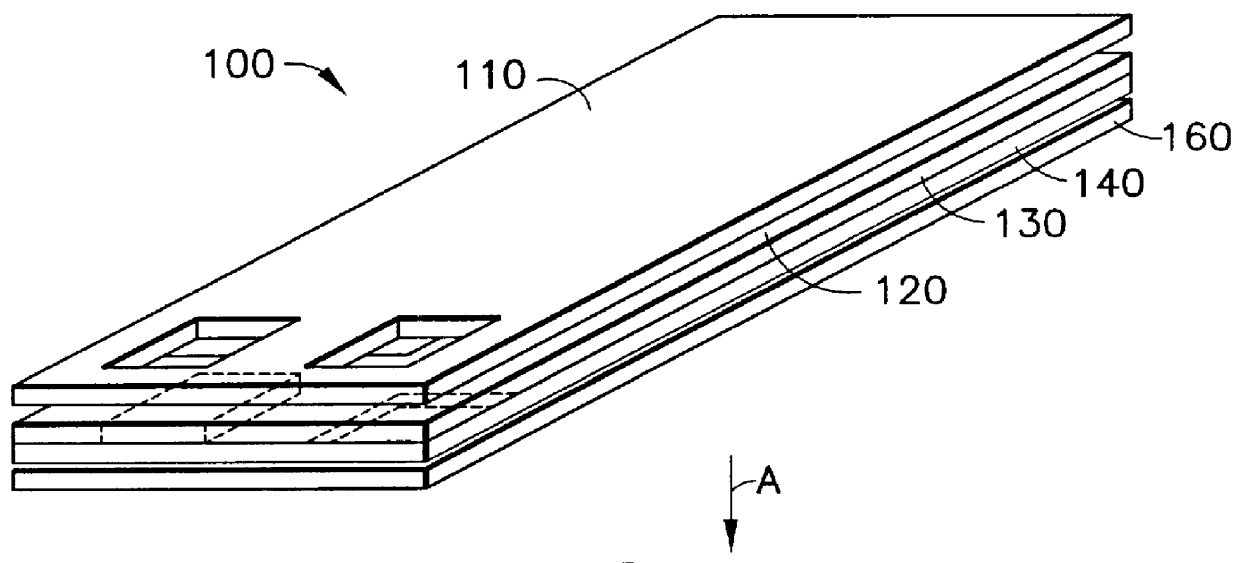
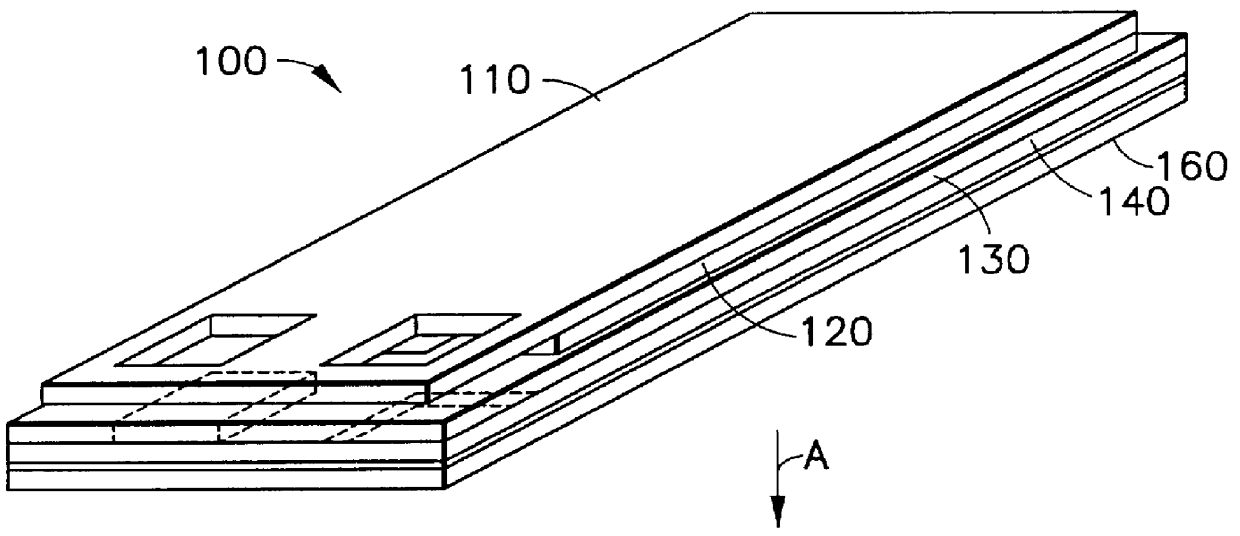
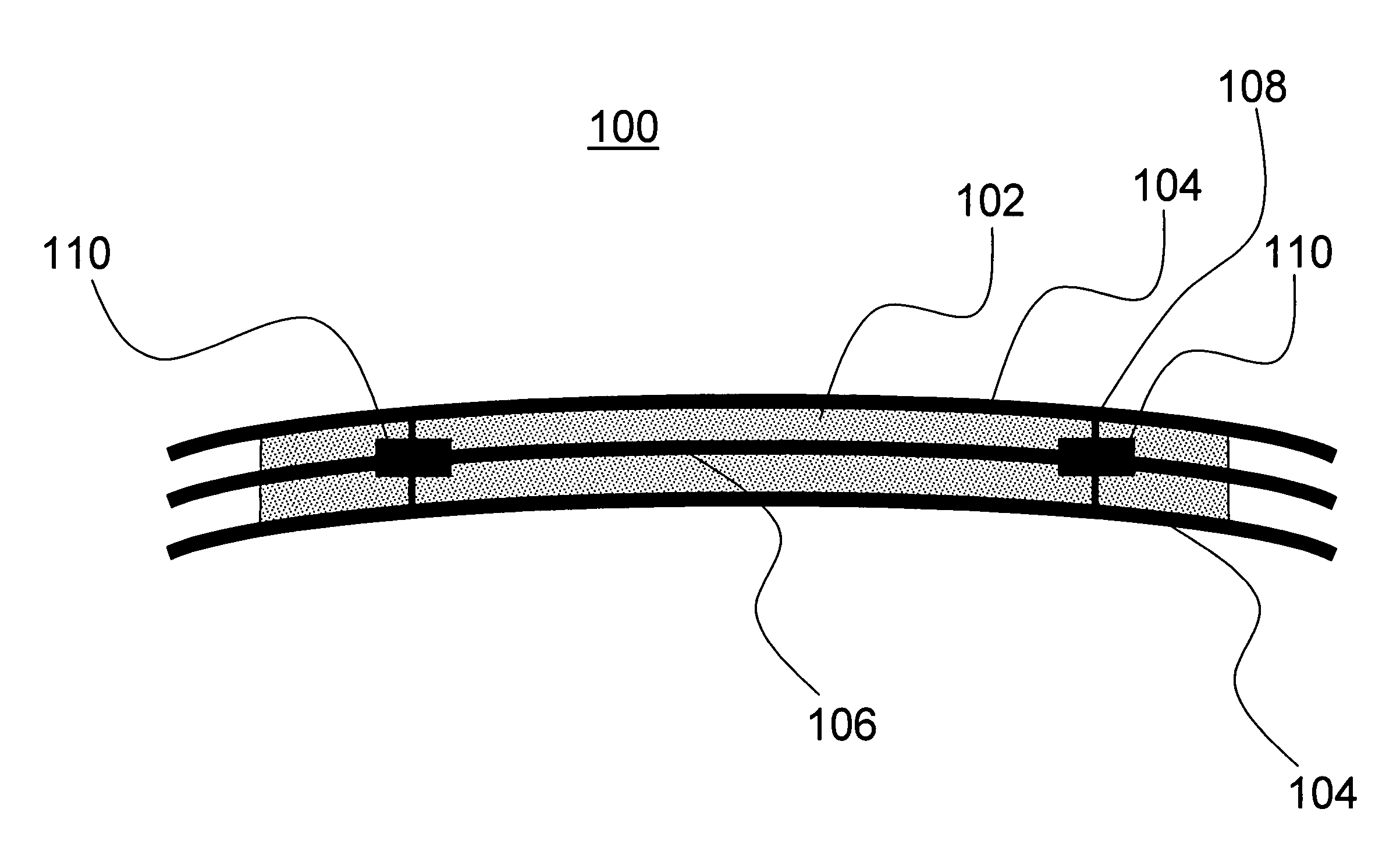
A stent is disclosed in several embodiments including the use of a material known as NITINOL forming the ends of the stent as well as support structure connecting the ends. A fabric is interconnected with the NITINOL structure to form the stent. The NITINOL material ends have slits parallel with the direction of elongation of the stent allowing radial expansion of the ends. The pieces interconnecting the ends have a serpentine shape allowing longitudinal expansion of the stent. The NITINOL material structure may be located within the fabric portion or outside the fabric portion. The connecting pieces may be separate structures attached to the fabric. Alternatively, the end pieces may be separate structures attached to the fabric without the connecting pieces.
Owner:VASCULAR CONCEPTS HLDG
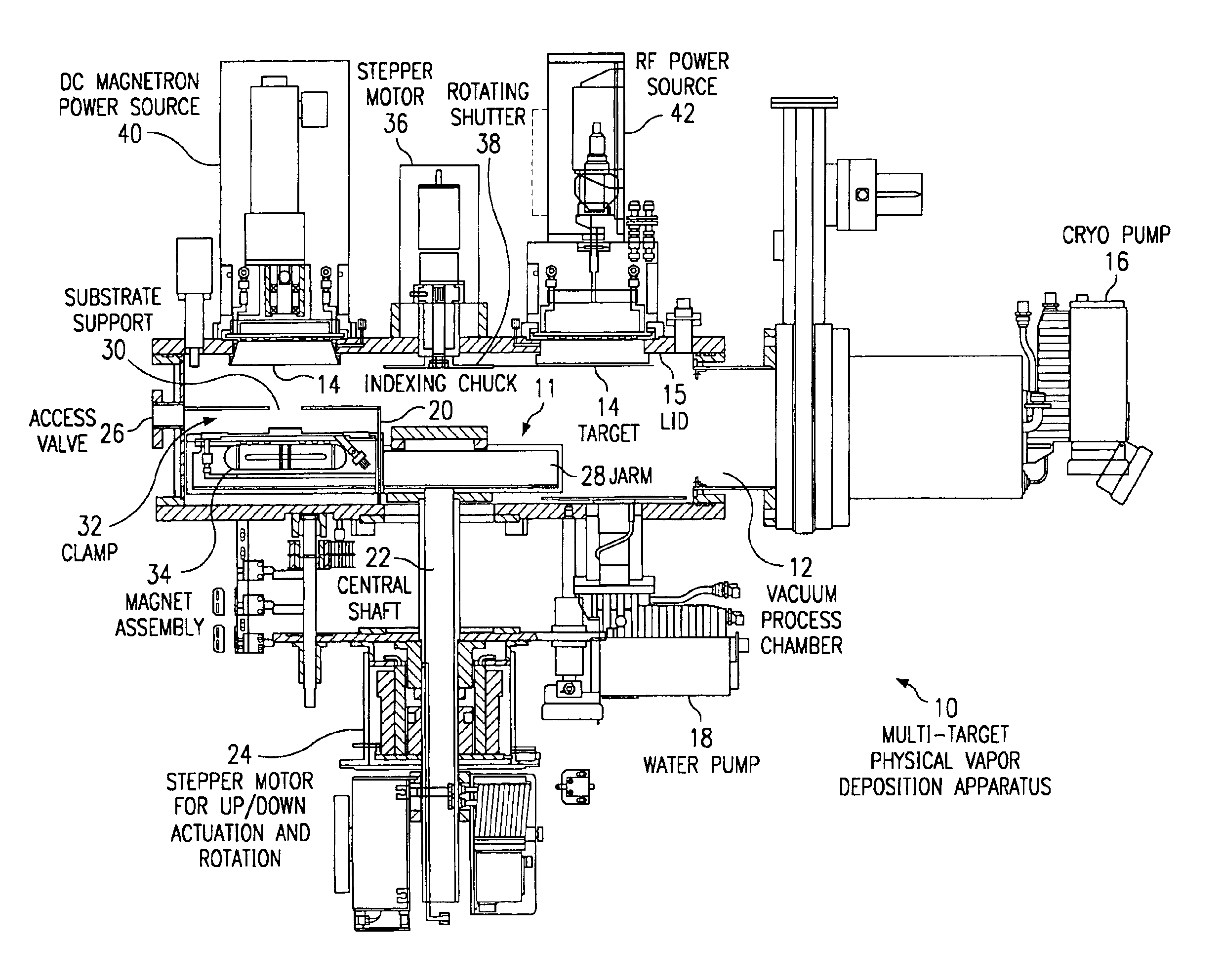
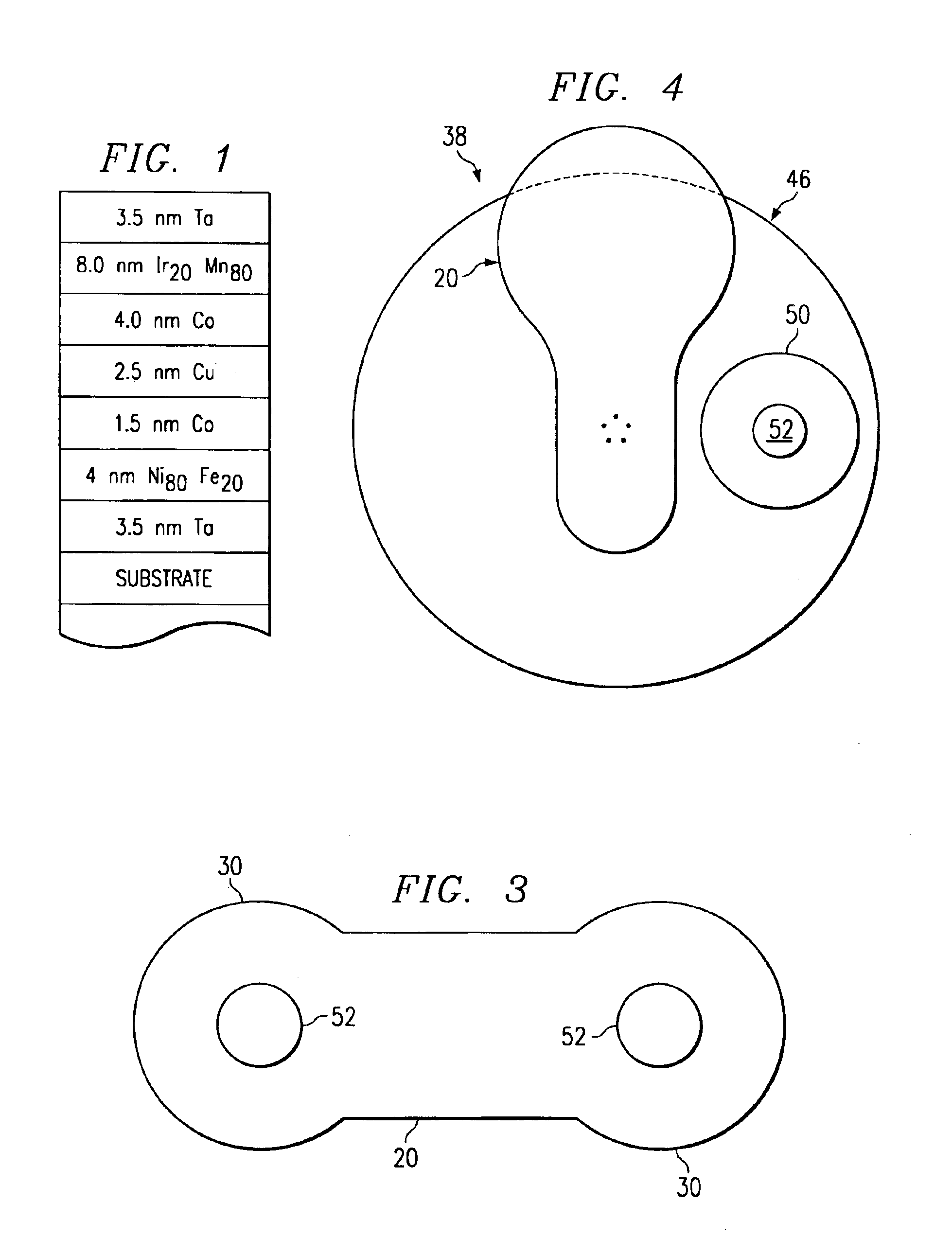
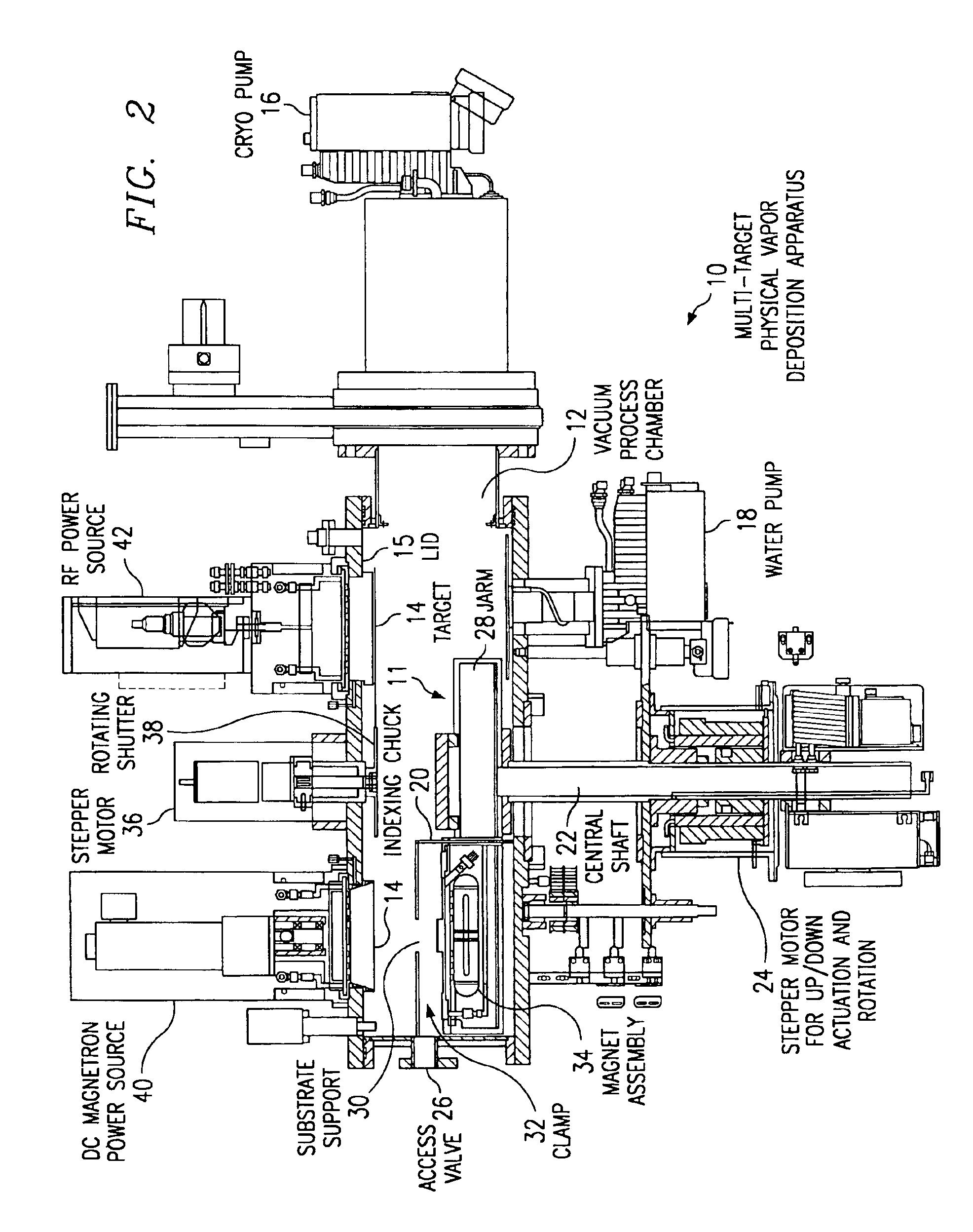
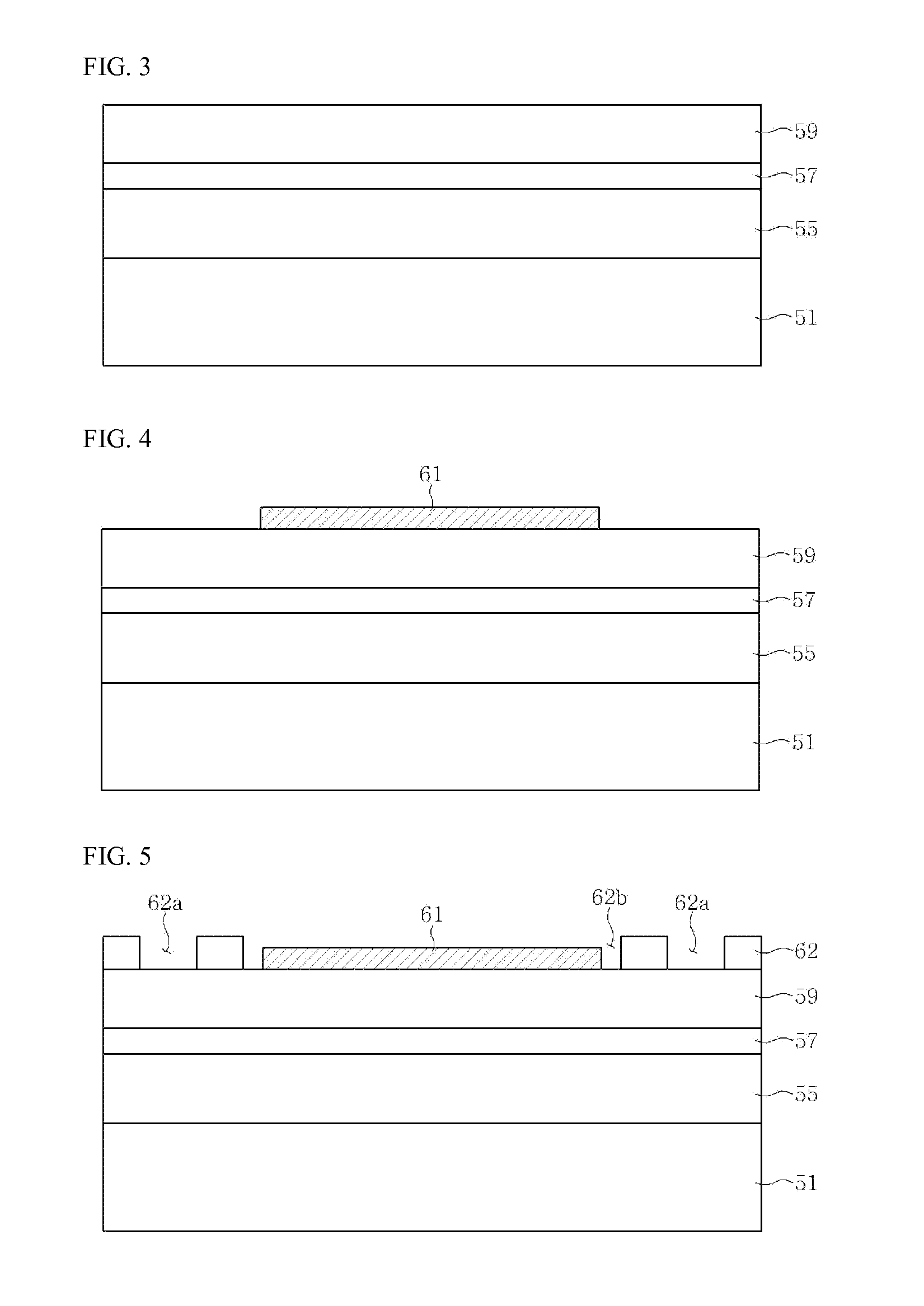
Apparatus and method for multi-target physical-vapor deposition of a multi-layer material structure
InactiveUS6905578B1Easy to controlImprove uniformityCellsVacuum evaporation coatingState parameterGas phase
An apparatus and method for depositing plural layers of materials on a substrate within a single vacuum chamber allows high-throughput deposition of structures such as these for GMR and MRAM application. An indexing mechanism aligns a substrate with each of plural targets according to the sequence of the layers in the structure. Each target deposits material using a static physical-vapor deposition technique. A shutter can be interposed between a target and a substrate to block the deposition process for improved deposition control. The shutter can also preclean a target or the substrate and can also be used for mechanical chopping of the deposition process. In alternative embodiments, plural substrates may be aligned sequentially with plural targets to allow simultaneous deposition of plural structures within the single vacuum chamber. A monitoring and control device can be wed to optimize equipment state, process state, and wafer state parameters by sensing each respective state during or after the deposition process.
Owner:CVC PRODS
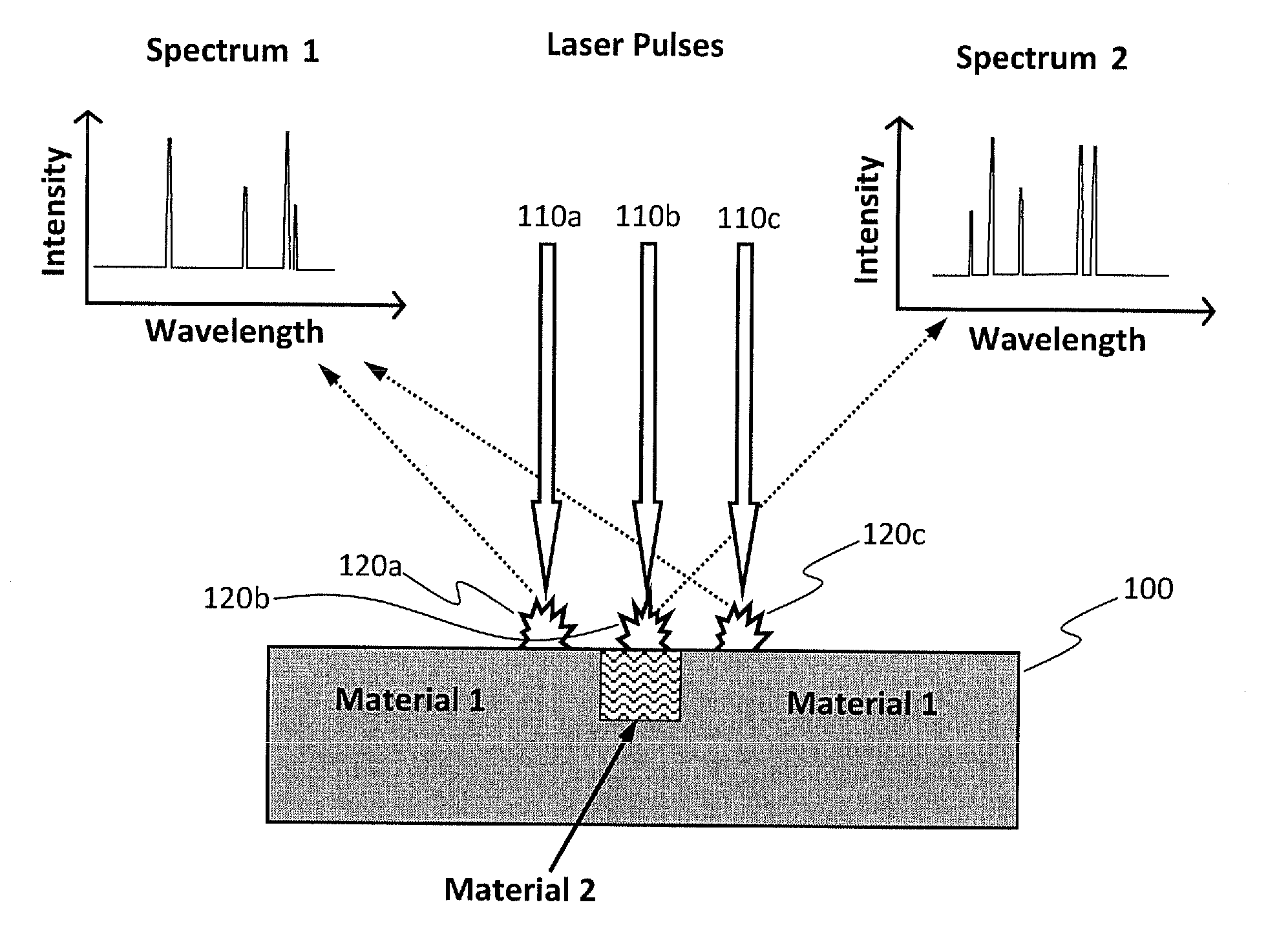
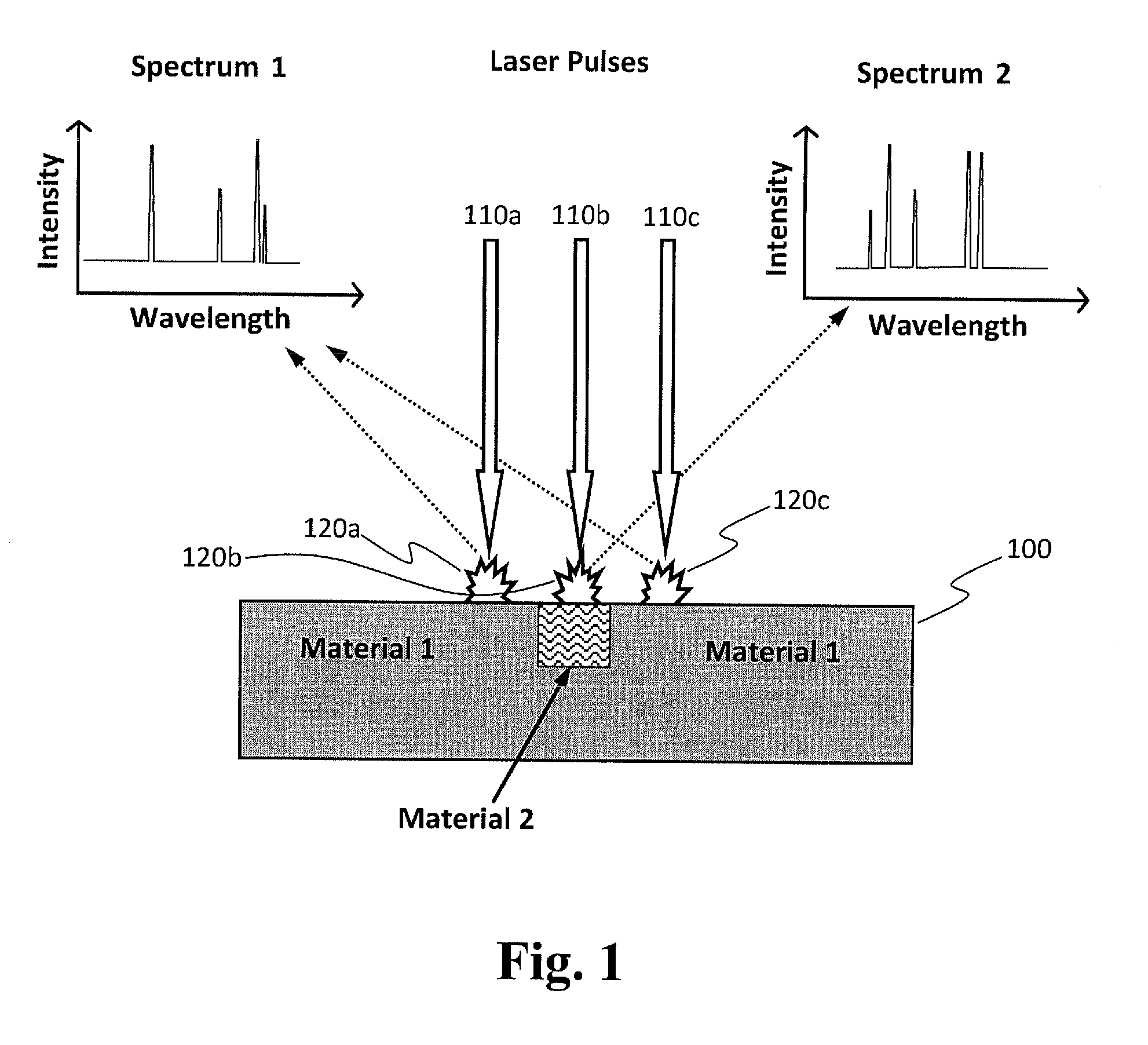
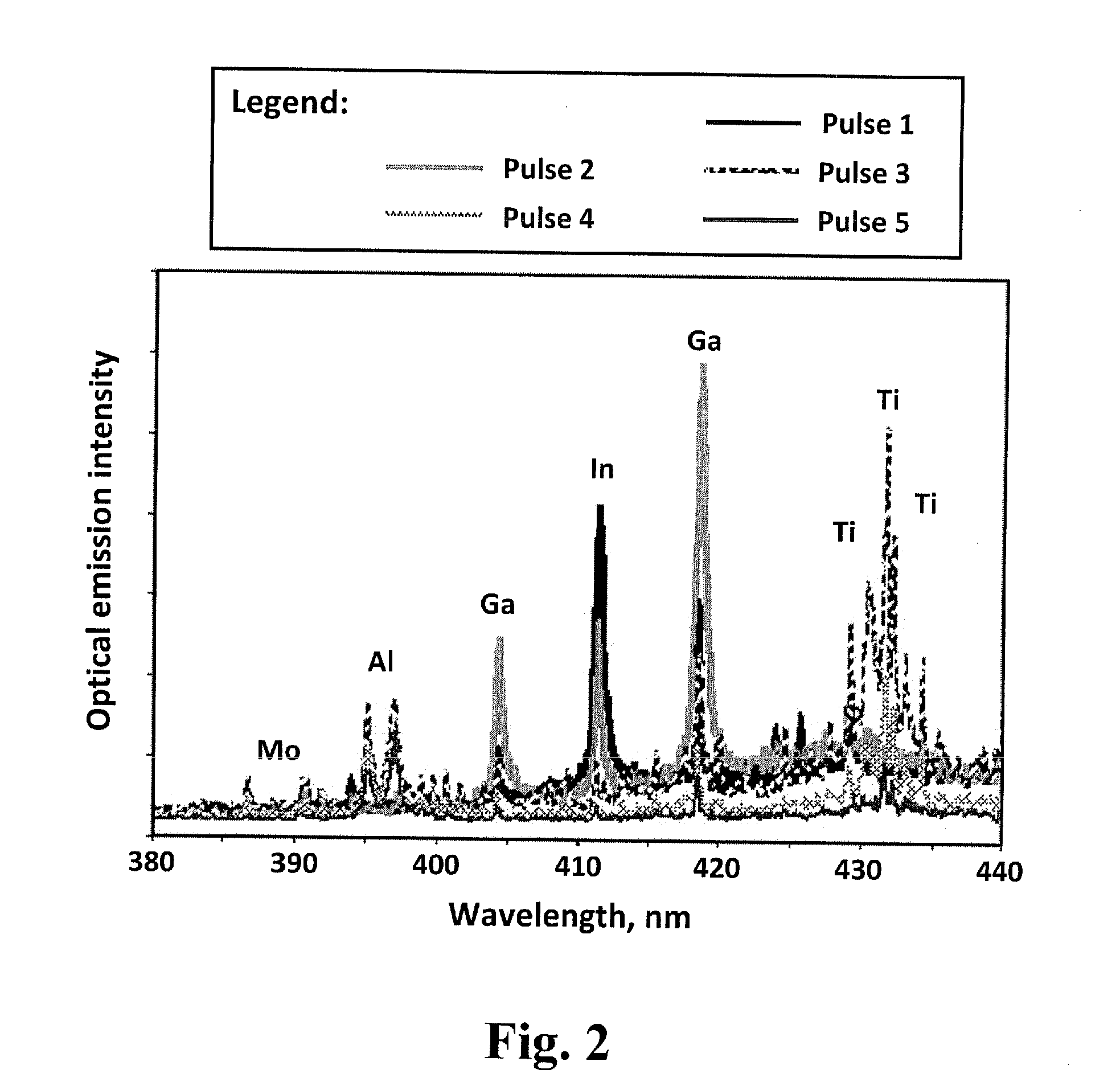
Method for real-time optical diagnostics in laser ablation and laser processing of layered and structured materials
ActiveUS20110100967A1Strong specificityImprove efficiencyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingOptical diagnostics
A method for real-time optical diagnostics in laser ablation and laser processing of layered or structured materials or material structures. Diagnostics is provided during laser ablation that is utilized regularly in laser processing and / or chemical analysis of structured materials, by means of measuring optical emission generated as a result of the pulsed laser-material interaction in real time. The method can involve a single-layer-film or a stack of multiple layers or a structure of different domains. The method is particularly beneficial in fabrication of thin-film structures, such as photovoltaic and electronic devices or circuits of devices.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRA
Bone staple, instrument and method of use and manufacturing
ActiveUS20130030438A1Simple and reliable processLow costInternal osteosythesisPinsShape changeBone tissue
A new shape changing staple and instrument for the fixation of structures to include bone tissue and industrial materials. This new staple stores elastic mechanical energy to exert force on fixated structures to enhance their security and in bone affect its healing response. This staple once placed changes shape in response to geometric changes in the materials structure, including healing bone tissue. The staple is advanced over prior staples due to its: 1) method of operation, 2) high strength, 3) method of insertion, 4) compressive force temperature independence, 5) energy storing staple retention and delivery system, 6) compatibility with reusable or single use product configuration, 7) efficient and cost effective manufacturing methods, and 8) reduction in the steps required to place the device. In addition to the staple's industrial application an embodiment for use in the fixation of the musculoskeletal system is shown with staple, cartridge, and extrusion handle.
Owner:FOX WILLIAM CASEY
Gallium nitride material structures including isolation regions and methods
InactiveUS20050145851A1Improve leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeLow leakageVolumetric Mass Density
Gallium nitride material structures, including devices, and methods associated with the same are provided. In some embodiments, the structures include one or more isolation regions which electrically isolate adjacent devices. One aspect of the invention is the discovery that the isolation regions also can significantly reduce the leakage current of devices (e.g., transistors) made from the structures, particularly devices that also include a passivating layer formed on a surface of the gallium nitride material. Lower leakage currents can result in increased power densities and operating voltages, amongst other advantages.
Owner:NITRONEX
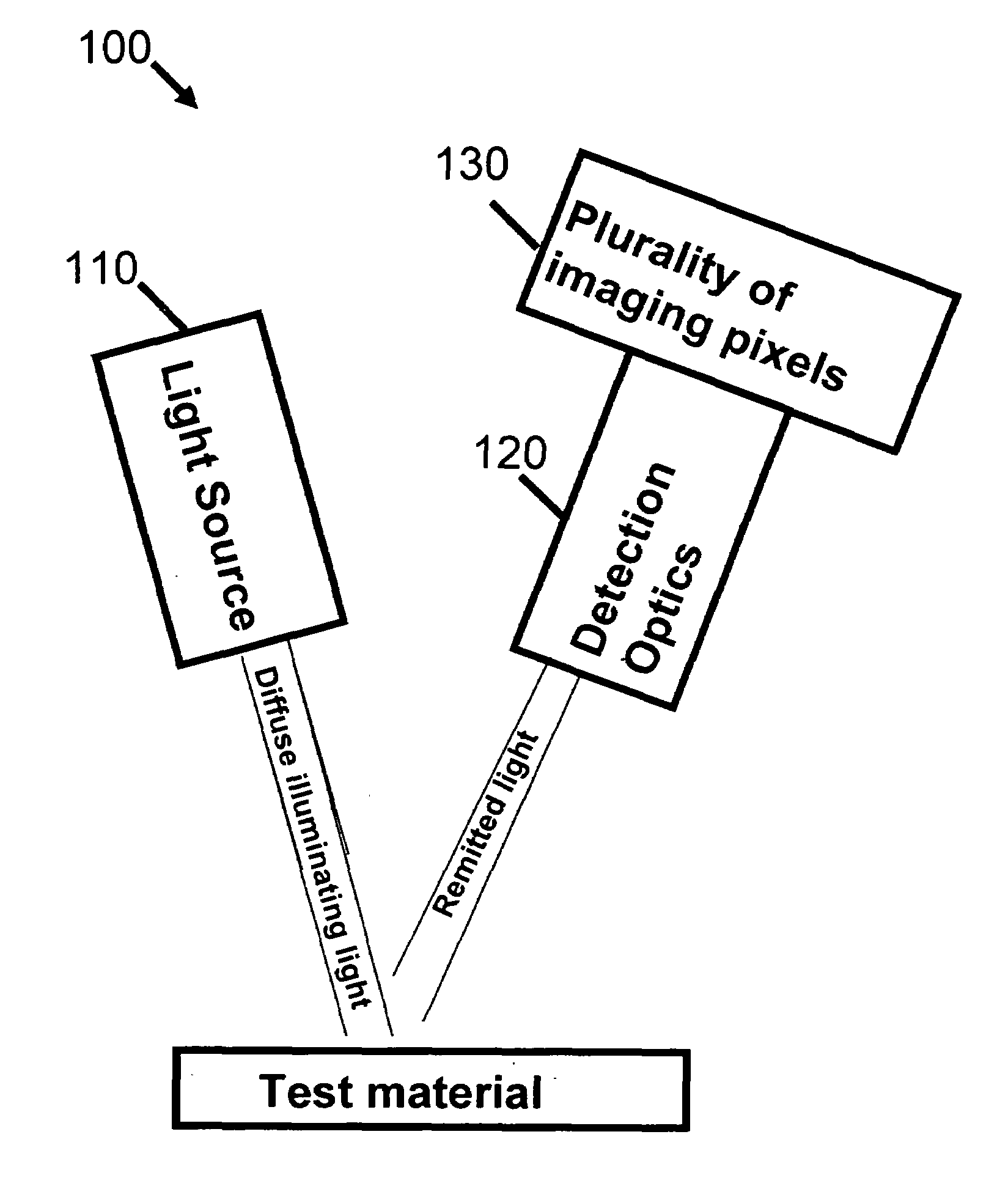
System and method for imaging sub-surface polarization-sensitive material structures
InactiveUS7289211B1Light intensityConvenient lightingPolarisation-affecting propertiesDiagnostic recording/measuringAngle of incidenceMedical imaging
A method of visually quantifying a test material along with an imaging apparatus for practicing the method is disclosed. The method comprises: (a) illuminating the test material at a known angle of incidence with diffuse light of a known and adjustable polarization state; (b) receiving light from the test material with a polarization state modified by the test material; (c) measuring an intensity of the polarization components of the received light for each illuminated pixel substantially simultaneously; (d) calculating the Stokes Vector in two dimensions for each illuminated pixel; and (e) creating an image map for the known polarization state. The method may also include adjusting the known polarization or the incident angle of the diffuse light to create additional image maps. The method and apparatus are intended for use in medical imaging including minimally invasive surgery.
Owner:WALSH JR JOSEPH T +1
III-nitride material structures including silicon substrates
InactiveUS7247889B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesNitrideSilicon
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
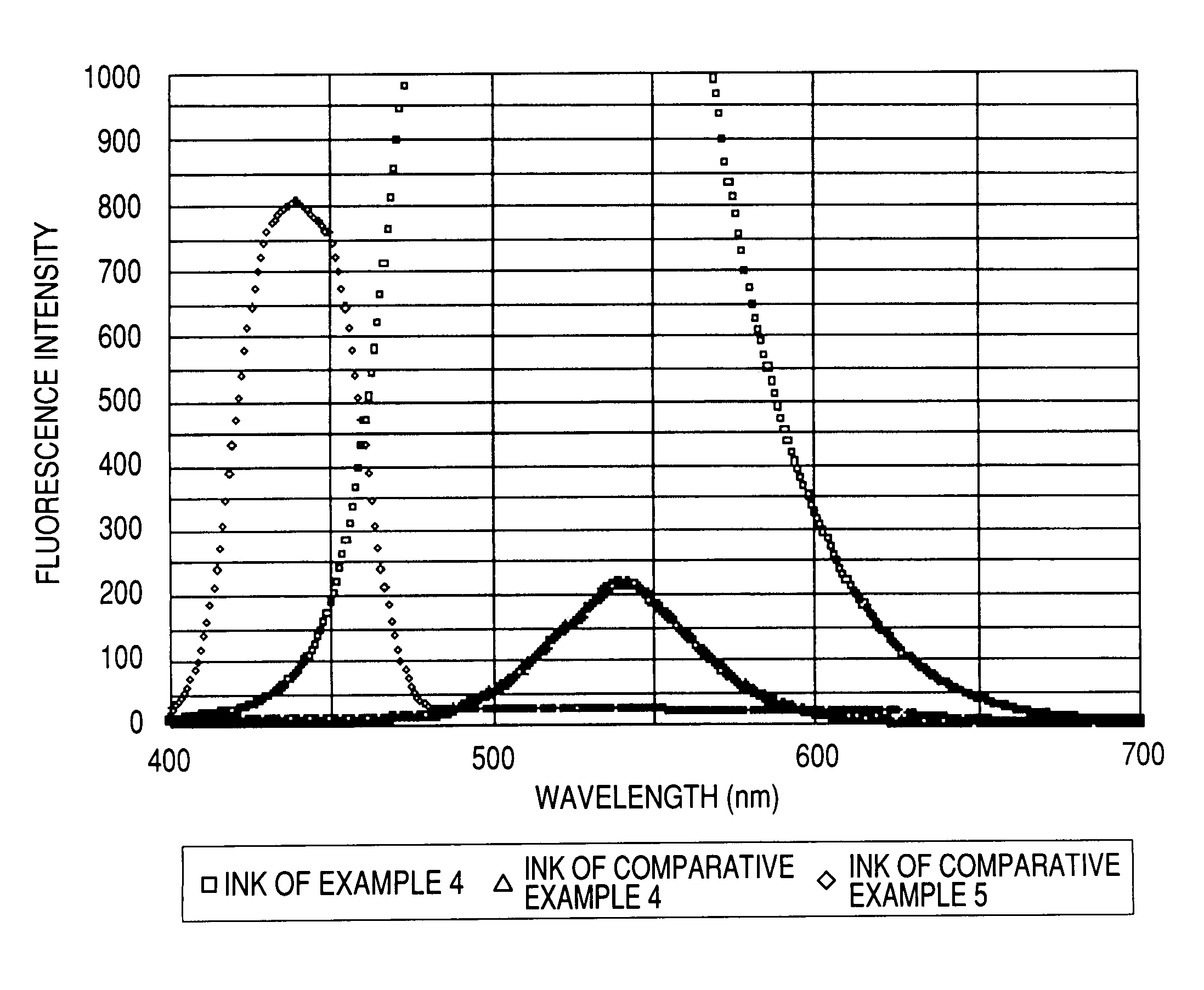
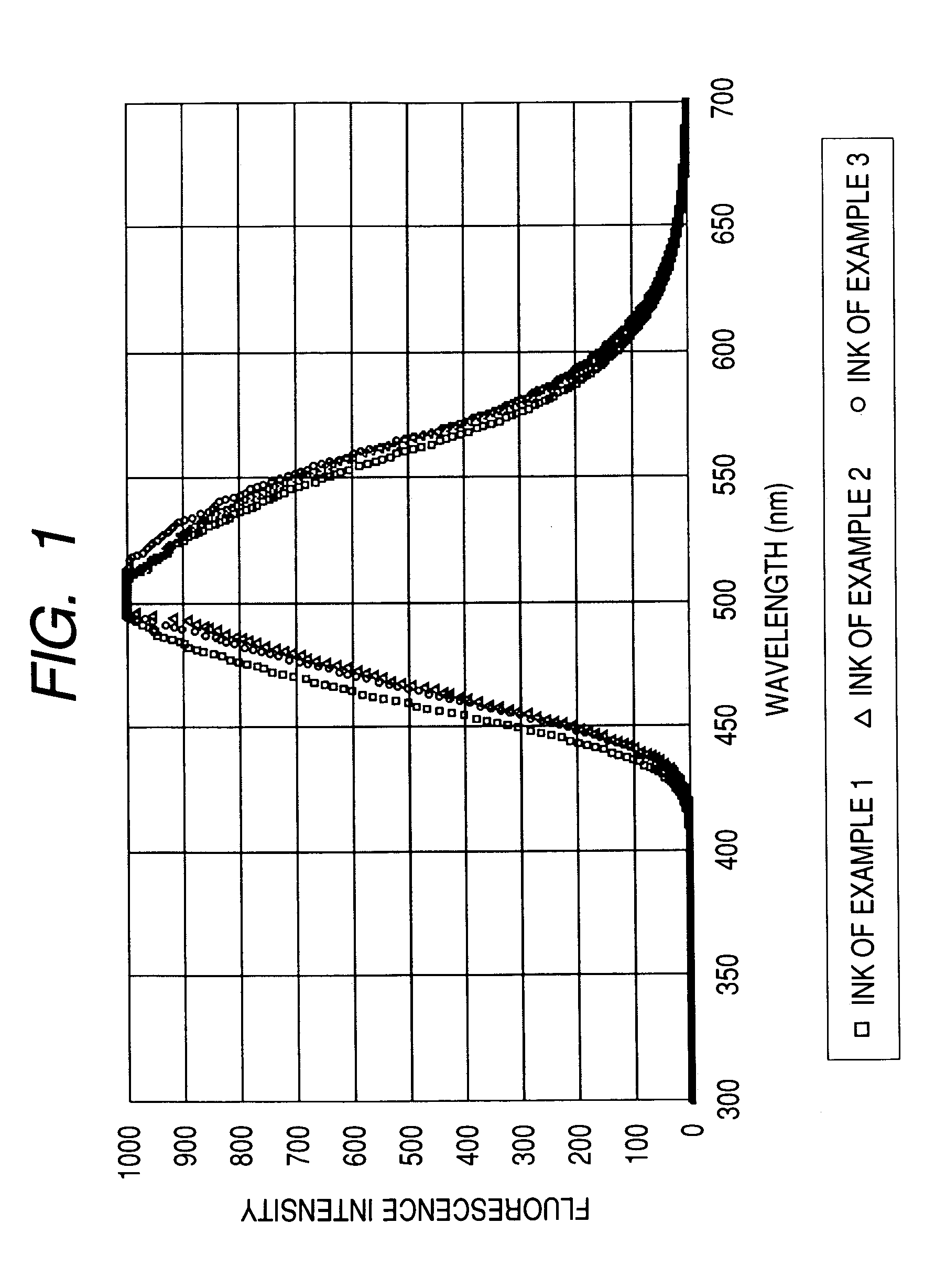
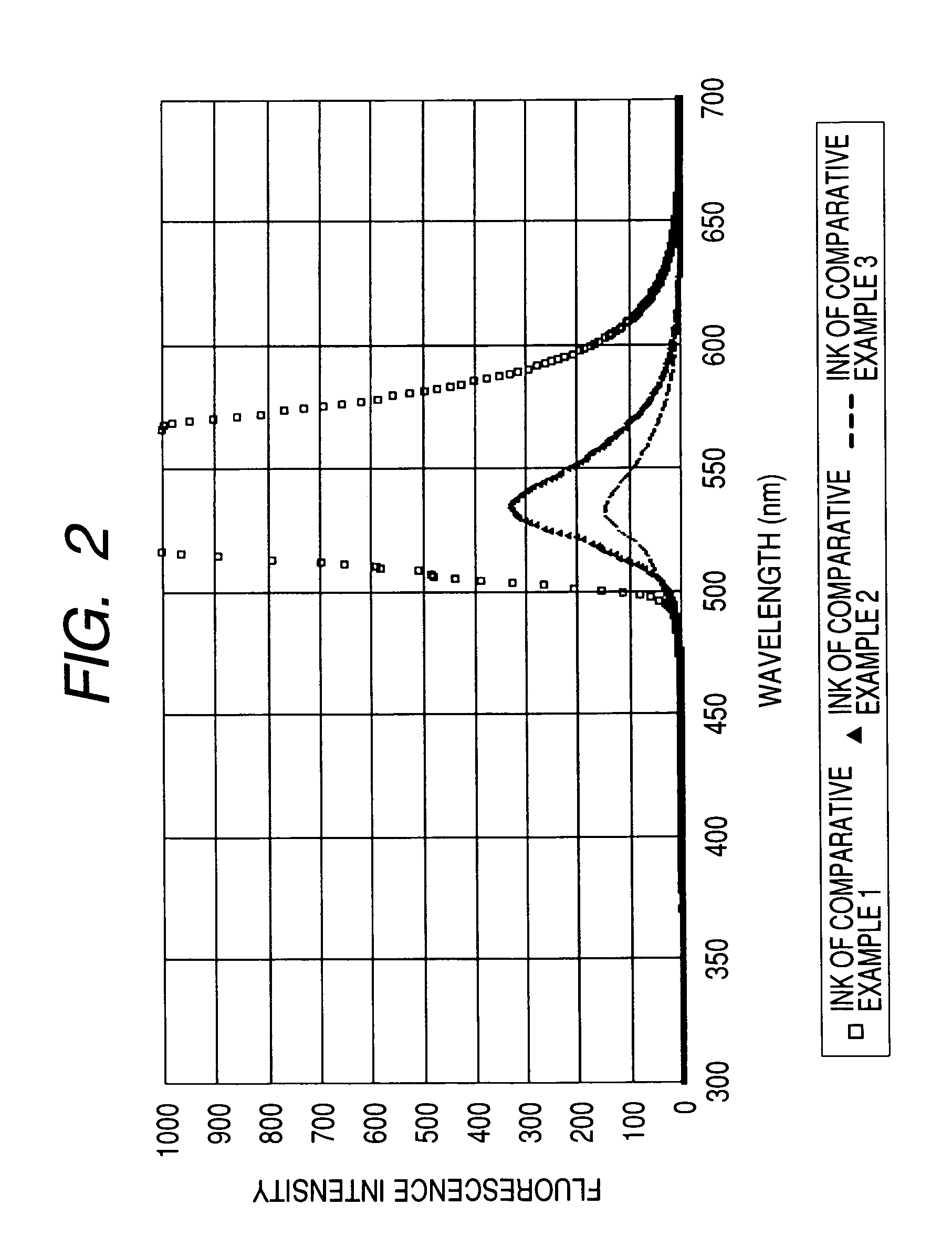
Water-based fluorescent ink, recorded image using the same, and judging method
The present invention relates to a water-based fluorescent ink for the purpose of measurement or judgment of the fluorescence emission in a visible light region by an excitation wavelength in a predetermined ultraviolet range, containing water, a coloring material dissolved or dispersed in water, and an organic solvent, having a plurality of fluorescent groups in the coloring material structure of the coloring material, and using a water-soluble coloring material having a sulfonic acid group as the water-soluble group in the state of a free acid, capable of improving the water resistance and the light resistance, dramatically increasing the content of the fluorescent coloring material in the ink, which has conventionally been included only by a small amount in the ink due to the concentration quenching problem, obtaining preferable fluorescence emission and water resistance of the recorded image, and providing preferable adhesion resistance to the recording medium of the coloring material and reliability.
Owner:CANON KK
Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) resonators and related apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20120280594A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksEngineeringMicroelectromechanical systems
Devices having piezoelectric material structures integrated with substrates are described. Fabrication techniques for forming such devices are also described. The fabrication may include bonding a piezoelectric material wafer to a substrate of a differing material. A structure, such as a resonator, may then be formed from the piezoelectric material wafer.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Laser etching of electroluminescent lamp electrode structures, and electroluminescent lamps produced thereby
InactiveUS6066830ADischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesLaser etchingElectrical conductor
A process for manufacturing electroluminescent lamps using a laser beam to remove a material layer of a multi-layer material structure, in which the laser beam has a first energy level directed at a first material layer, e.g., a conductor, laid over a second material layer, e.g., an insulator / substrate. The laser beam is moved in an overlapping fashion such as spiral pattern motion across the first material layer. A part of the first material layer is sublimed exposing a region of the second material under the area where the spiral pattern was applied. Additionally, a second laser beam having a second energy level, e.g., higher than the first energy level, is moved along a path over the exposed second material layer subliming the remaining underlying layers to form the final lamp shape.
Owner:ASTRONICS
Hybrid active deformable material structure
InactiveUS7575807B1Keep shapeSynthetic resin layered productsMachines/enginesEngineeringMulti directional
A hybrid active deformable material structure is presented. The hybrid active deformable material structure comprises a deformation unit. Each deformation unit includes a selectively deformable material structure and an actively deformable material structure in cooperation with the selectively deformable material structure. The selectively deformable structure may be caused to deform in response to a deformation of the actively deformable material structure and, when deformed, to retain a shape into which it was deformed. A plurality of deformation activation elements may be positioned about the structure to provide for multi-directional bending-type deformation, stretching-type deformation, and twisting-type deformation. The hybrid active deformable material structure may further comprise a passive material structure in cooperation with the selectively deformable material structure and the actively deformable material structure. The passive material structure may provide mechanical support for at least a portion of the selectively deformable material structure and may enclose the selectively deformable material structure.
Owner:HRL LAB
Negative electrode for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell and method for manufacture thereof, and non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell
InactiveUS20060051675A1High capability of forming lithium compoundShort lifeElectrode carriers/collectorsNegative electrodesConductive materialsLithium compound
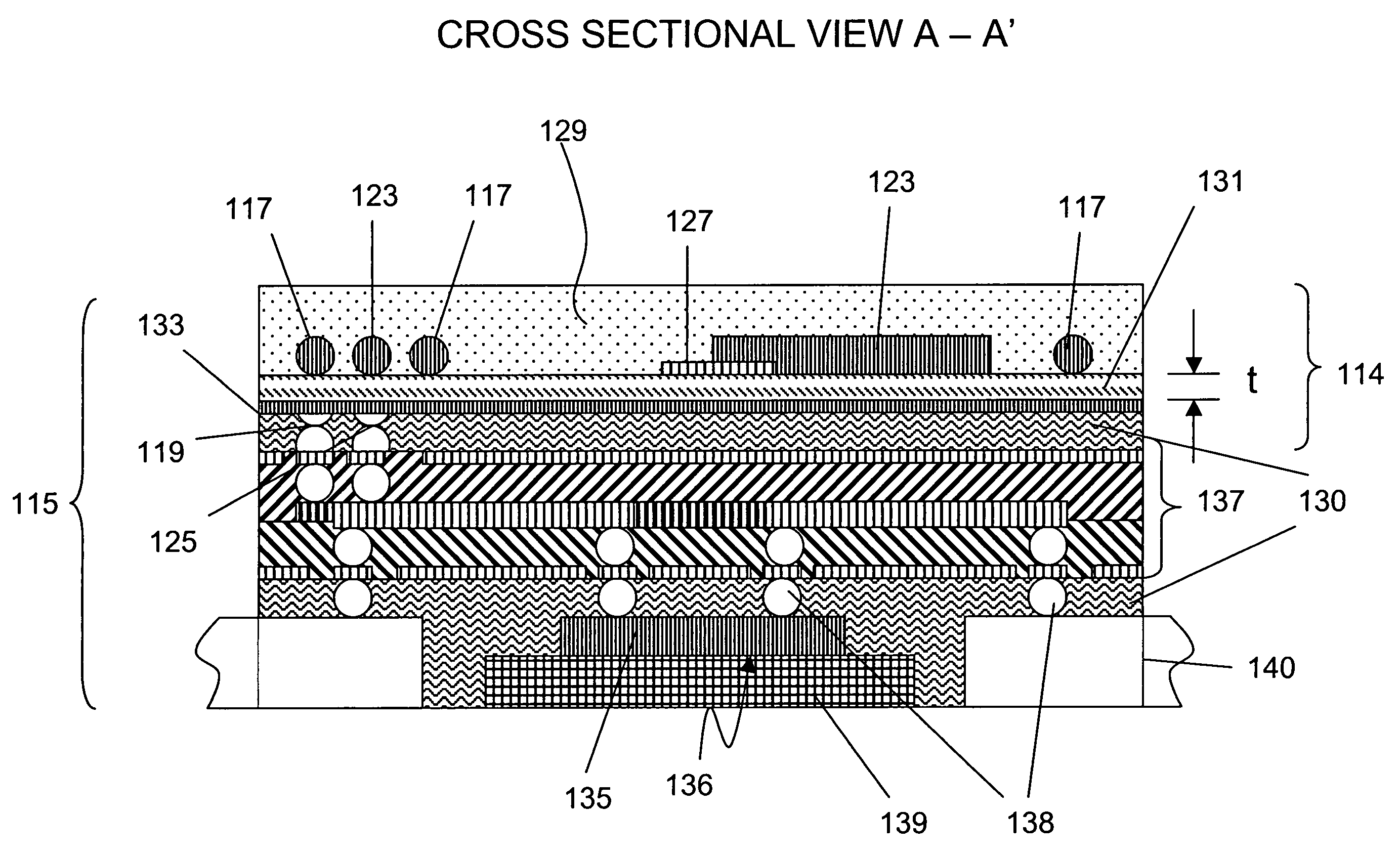
Disclosed is a negative electrode for a nonaqueous secondary battery included of a current collector and an active material structure containing an electro-conductive material having low capability of forming a lithium compound on at least one side of the current collector, the active material structure containing 5 to 80% by weight of active material particles containing a material having high capability of forming a lithium compound. The active material structure preferably has an active material layer containing the active material particles and a surface coating layer formed on the active material layer.
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
Stress-Stimulated Luminescent Material, Manufacturing Method Thereof, Composite Material Including the Stress-Stimulated Luminescent Material, and Base Material Structure of the Stress-Stimulated Luminescent Material
InactiveUS20090050847A1High luminous intensityIncrease usageLuminescent compositionsLuminescenceAlkaline earth metalRare earth
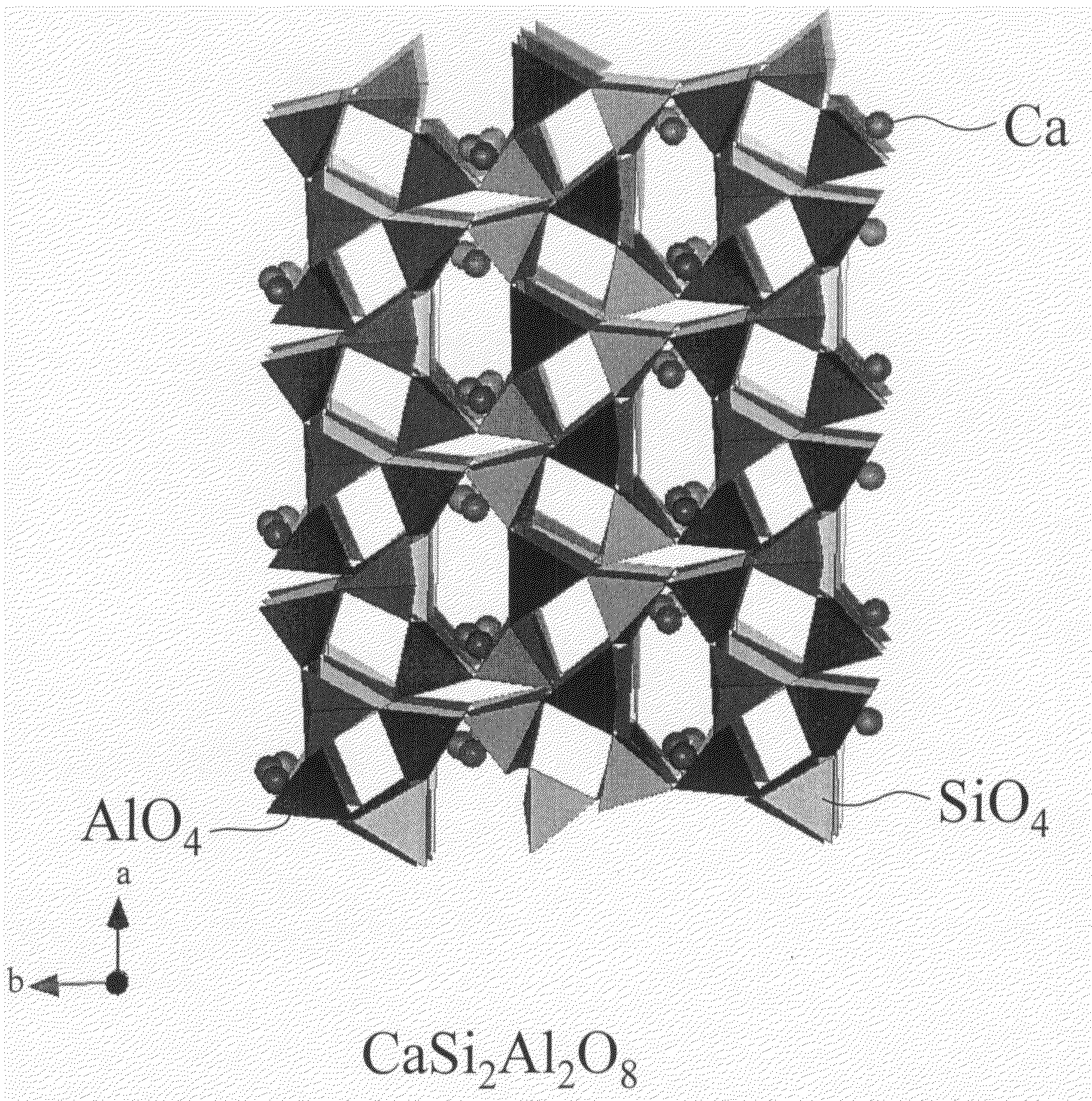
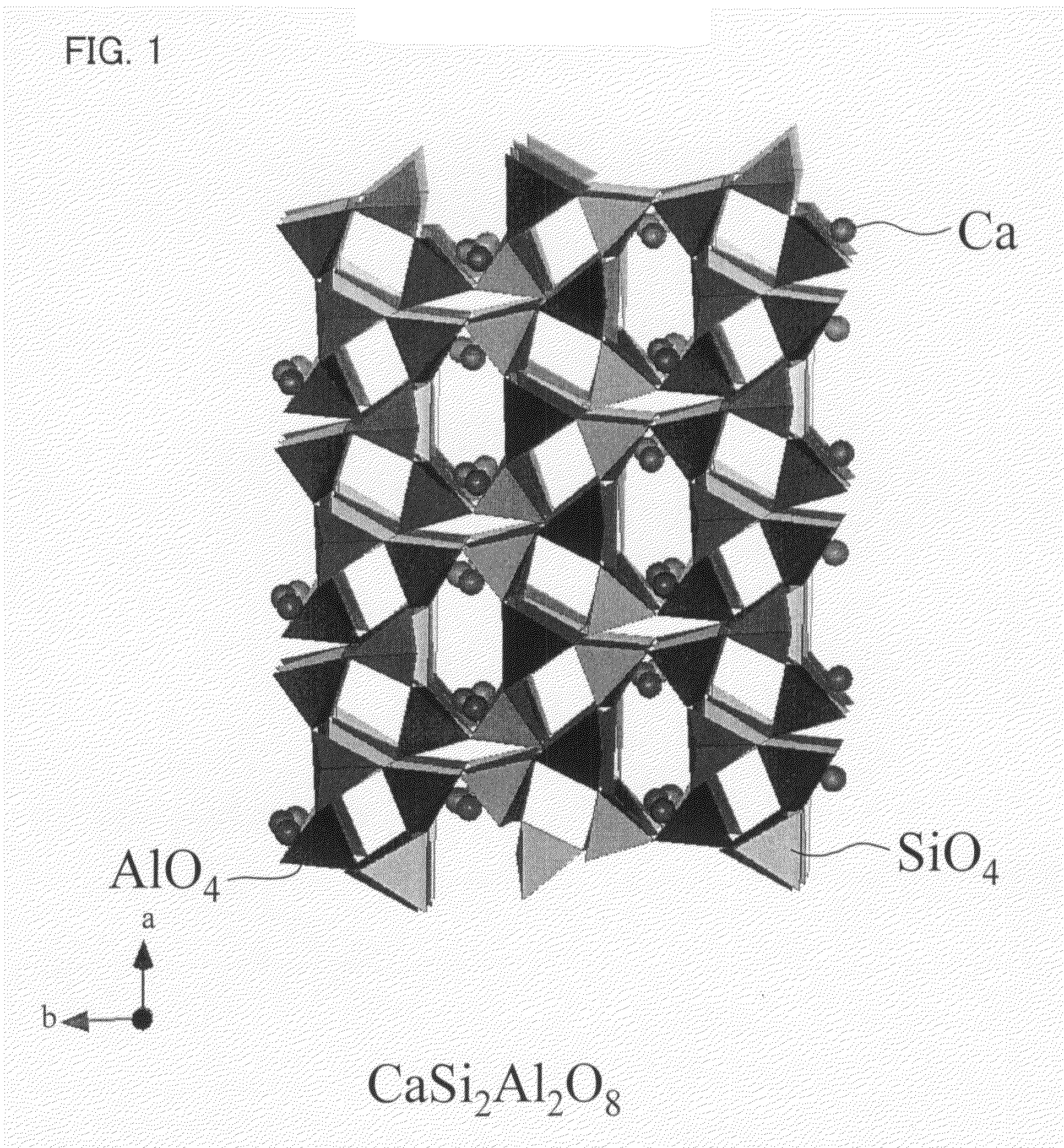
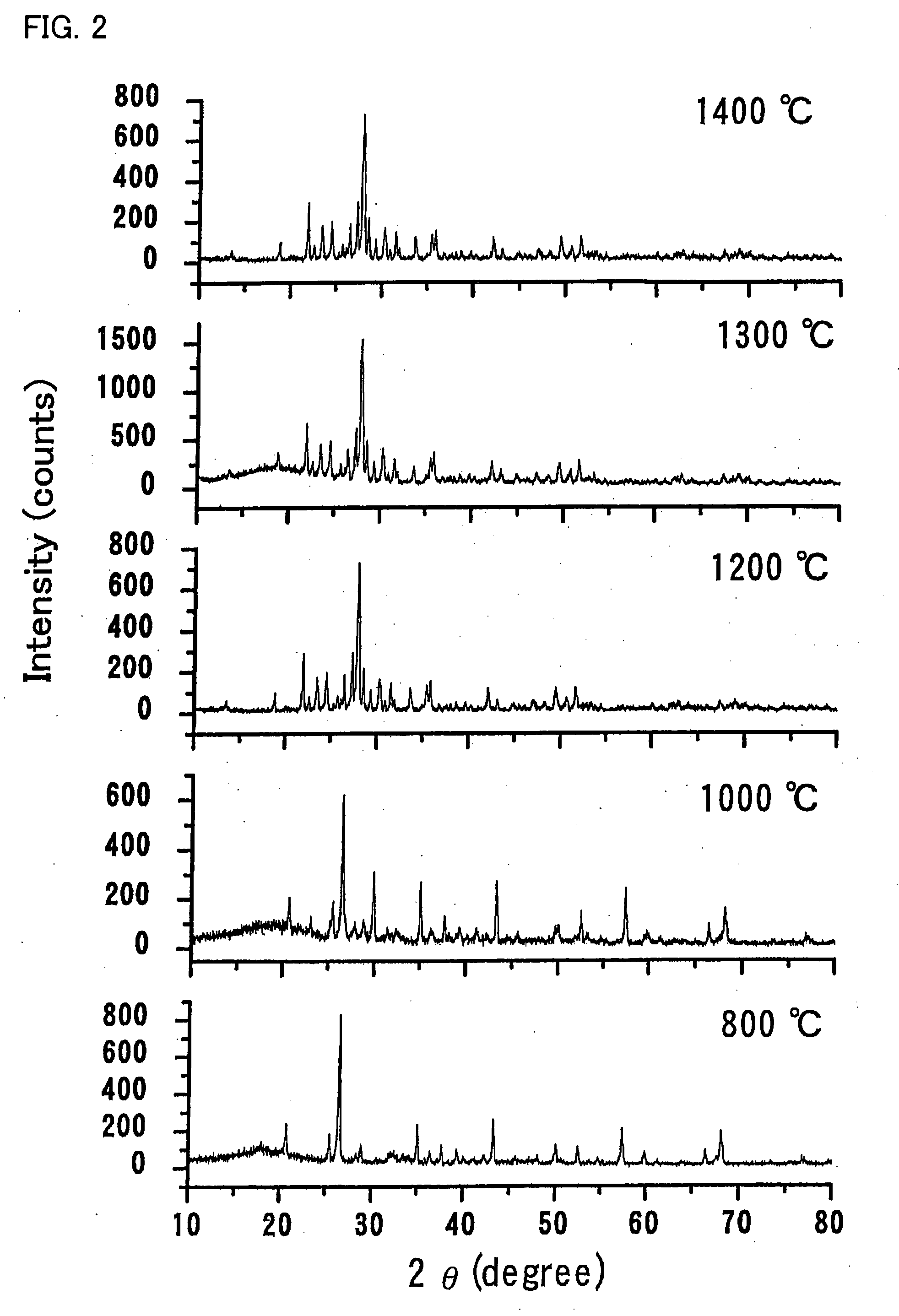
One embodiment of the present invention is to provide a stress-stimulated luminescent material which has a unique crystal structure and which emits conventionally unachievable intense light. The stress-stimulated luminescent material of one embodiment of the present invention includes a basic structure in which a plurality of tetrahedral molecules each having an AlO4-like tetrahedral structure or an SiO4-like tetrahedral structure share atoms of apexes of the tetrahedral structures so as to be coupled to one another so that a basic material structure is formed and at least either alkali metal ions or alkali earth metal ions are inserted into the void are partially substituted by at least either rare earth metal ions or transition metal ions.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
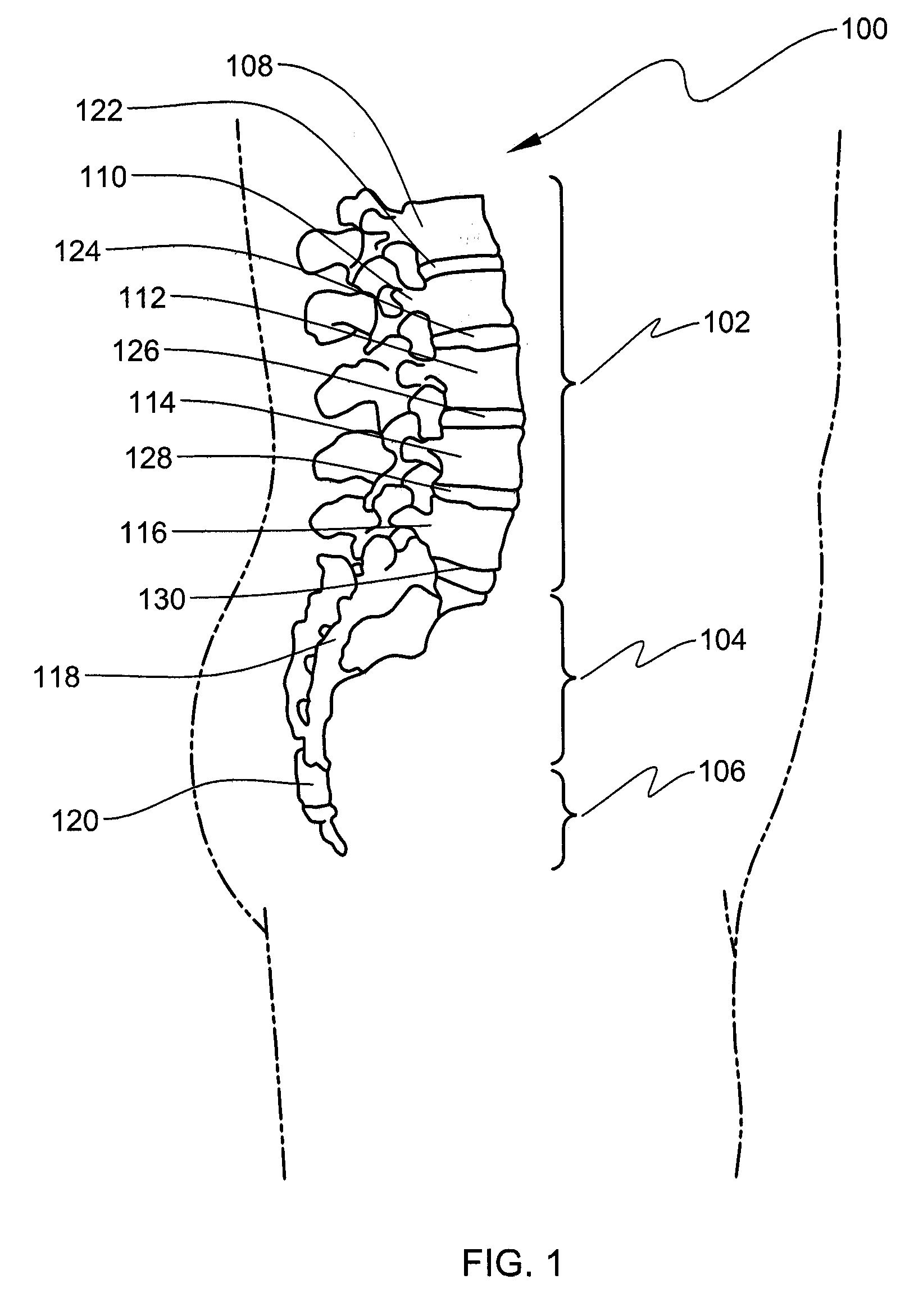
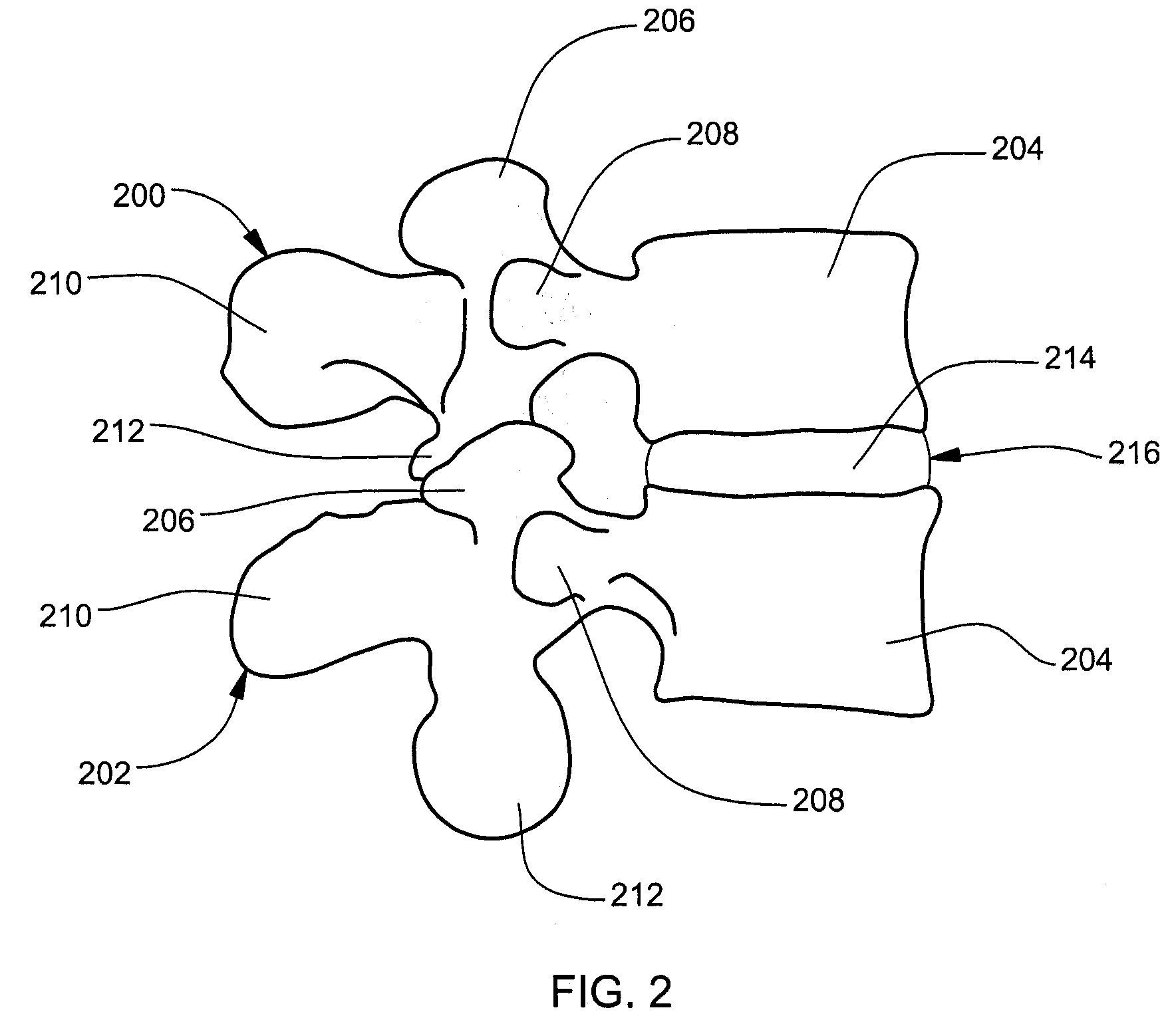
Compliant intervertebral prosthetic devices employing composite elastic and textile structures
InactiveUS20080183292A1Enhance device supportHigh modulusSpinal implantsCoatingsCompound structureCore component
An intervertebral prosthetic device is provided for implanting within an intervertebral disc space between first and second vertebral bodies. The device includes a body component and a core component, one of which is an elastic-material structure and the other of which is a composite structure, including a textile structure embedded within an elastic material. The composite structure has a higher compressive modulus of elasticity than the elastic-material structure to enhance device support when in an operable position within the intervertebral disc space. In various embodiments, a porous textile structure partially covers the body component to, for example, facilitate bony in-growth or soft tissue in-growth into the device and therefore fixation of the device when in operable position within the intervertebral disc space.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
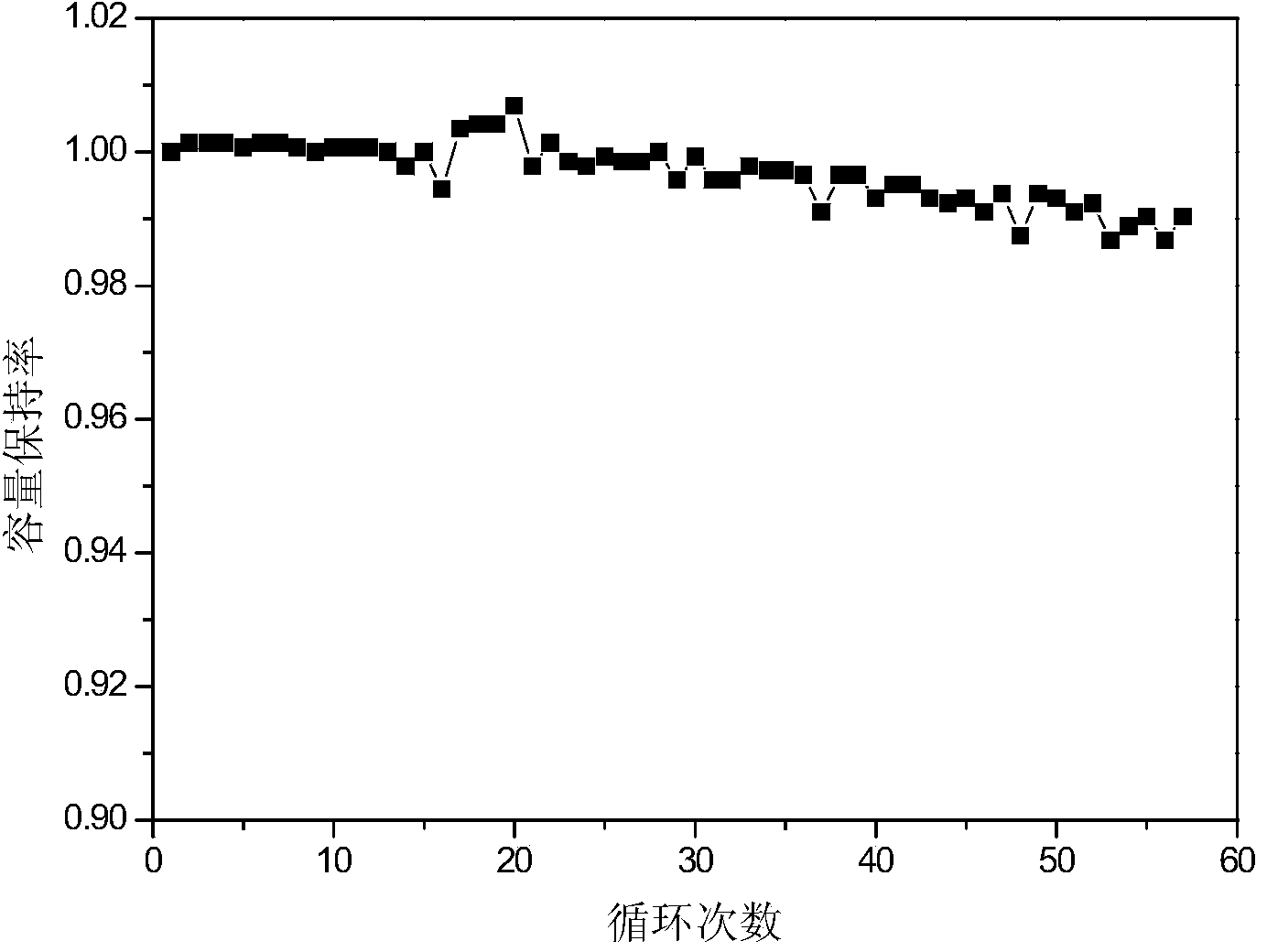
Gradient-doping positive material of lithium ion battery and preparation method of gradient-doping positive material of lithium ion battery
ActiveCN104241633AImprove discharge capacityHigh surface doping element concentrationCell electrodesSecondary cellsLithium-ion batteryLithium electrode
The invention discloses a gradient-doping positive material of a lithium ion battery and a preparation method of the gradient-doping positive material of the lithium ion battery. The structural formula of the positive material is shown as Li(1+alpha)Ni(x)M(y)M'(1-x-y)O(2), wherein alpha is greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.2; x is greater than or equal to 0.3 and less than or equal to 1.0; y is greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.475; 1-x-y is greater than 0 and less than or equal to 0.35; the concentration of doping element M' is subjected to gradient change from the surfaces of the material particles; on the surfaces of the material particles, the concentration of the element M' is relatively high, the concentration of element Ni is relatively low, and even the surfaces of the material particles are free of the element Ni; in the material particles, the concentration of the element Ni is relatively high, the concentration of the element M' is relatively low, and even the inside of the material particles are free of the element M'. The positive material is excellent in comprehensive performance and especially has the advantages of high discharge capacity, excellent cycle performance and the like. In addition, the method is simple; the industrial production is easy to implement.
Owner:QINGHAI TAIFENG XIANXING LITHIUM ENERGY TECH CO LTD
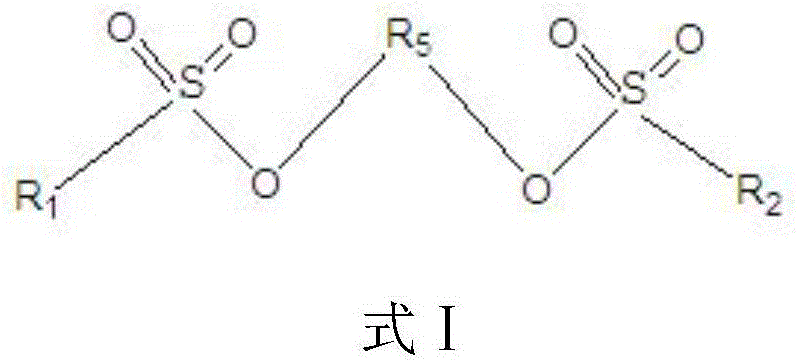
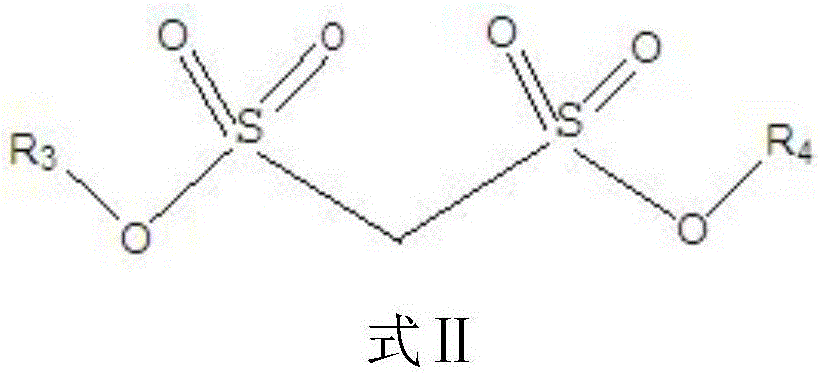
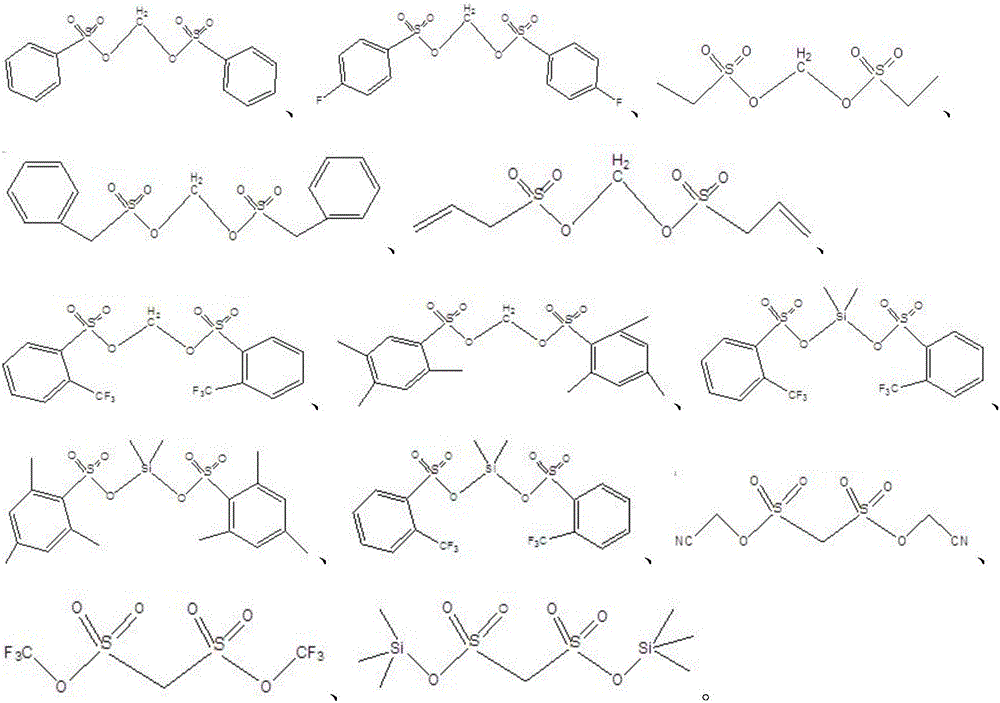
Electrolyte of lithium-ion battery and lithium-ion battery containing electrolyte
ActiveCN106505249AExcellent high temperature storageExcellent high temperature cycle performanceSecondary cells servicing/maintenanceOrganic electrolytesHigh temperature storageSide reaction
The invention relates to the technical field of lithium-ion batteries, in particular to an electrolyte of the lithium-ion battery and the lithium-ion battery containing the electrolyte. The electrolyte comprises a lithium salt, a non-aqueous organic solvent and an additive, wherein the additive comprises a film-forming additive A and a stabilizing additive B; the stabilizing additive B is a chainlike disulfonic acid ester compound as shown in a formula I and / or a formula II; and the film-forming additive A forms an SEI film on a negative electrode surface of the battery and the side reaction of a negative electrode interface and the electrolyte is reduced, so that the film-forming additive A is an necessary precondition that the battery has relatively good cycle performance. The stabilizing additive B can form a CEI film on a positive electrode surface, the activity of a positive electrode interface and the electrolyte is inhibited, direct contact oxidation of a positive electrode and the electrolyte is reduced, meanwhile, the structure stability of a positive electrode material is improved and the structure is not easy to collapse and crush due to generation of the stress, so that the electrolyte has excellent high-temperature storage performance and high-temperature cycle performance through combination of the additive A and the additive B.
Owner:DONGGUAN SHANSHAN BATTERY MATERIALS
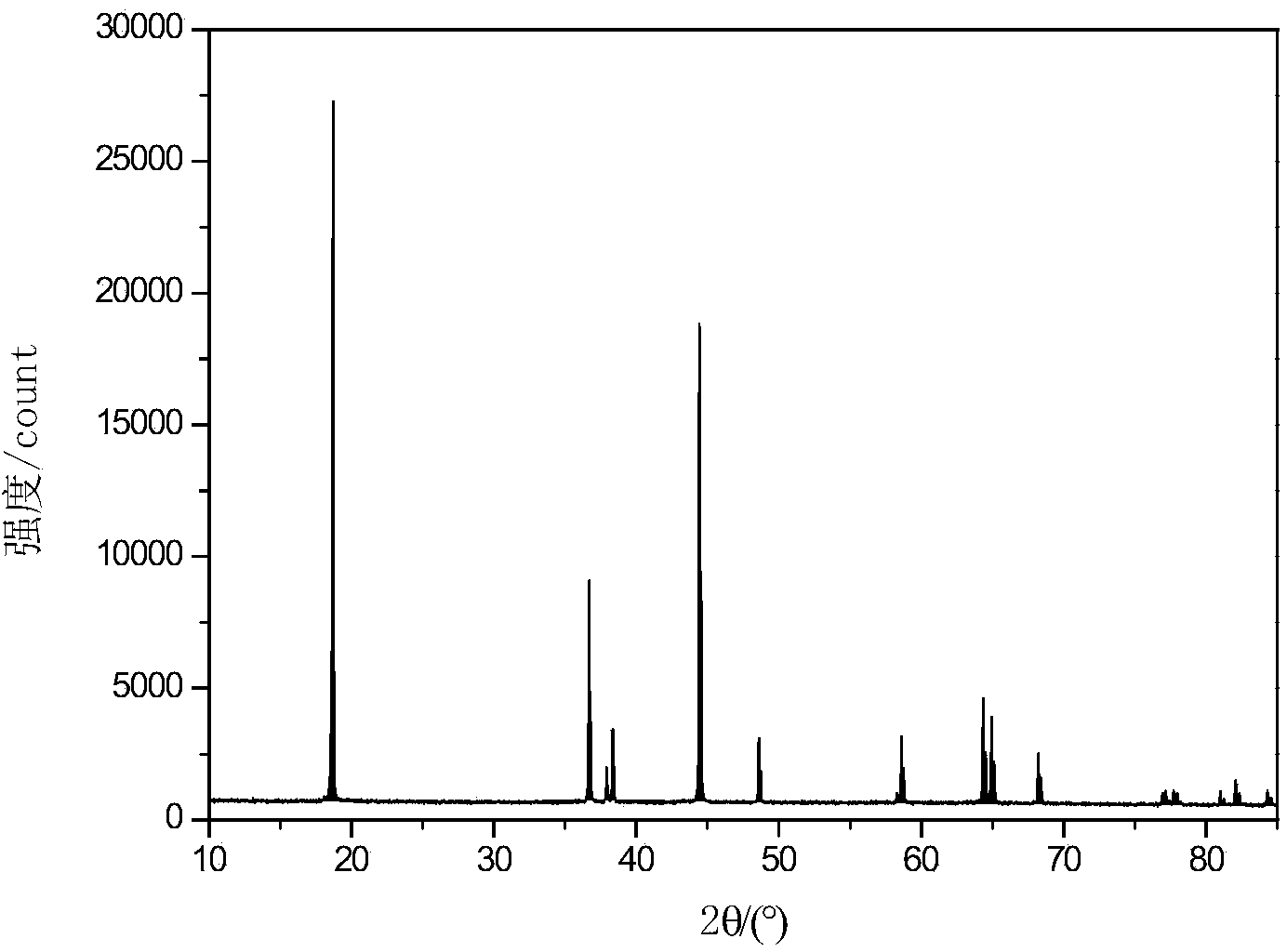
X-ray surface analysis and measurement apparatus
InactiveUS9823203B2Wide choiceIncrease brightnessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray tube electrodesHigh energyDesign for X
Systems for x-ray diffraction / scattering measurements having greater x-ray flux and x-ray flux density are disclosed. These are useful for applications such as material structural analysis and crystallography. The higher flux is achieved by using designs for x-ray targets comprising a number of microstructures of one or more selected x-ray generating materials fabricated in close thermal contact with a substrate having high thermal conductivity. This allows for bombardment of the targets with higher electron density or higher energy electrons, which leads to greater x-ray flux. The high brightness / high flux source may then be coupled to an x-ray reflecting optical system, which can focus the high flux x-rays to a spots that can be as small as one micron, leading to high flux density, and used to illuminate materials for the analysis based on their scattering / diffractive effects.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
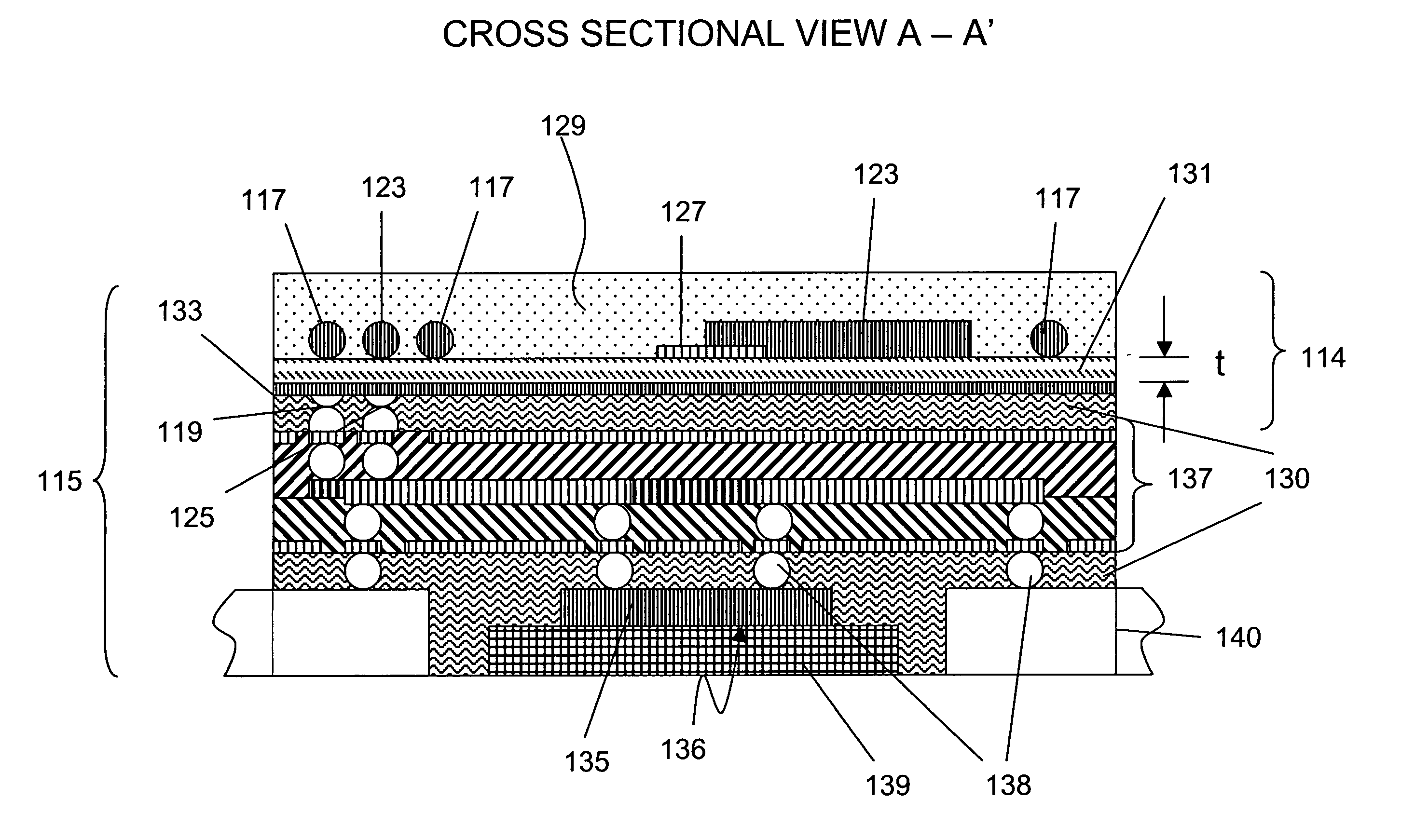
High performance, highly energy efficient precast composite insulated concrete panels
ActiveUS8877329B2Improve energy efficiencyEnergy loss through the building envelope must be reduced or eliminatedConstruction materialCovering/liningsPolymer modifiedEngineering
The invention comprises a relatively lightweight cementitious-based material panel. The cementitious-based material panel comprises a foam insulating panel having a first surface and a second surface; a first structural layer of cementitious-based material formed on the first surface of the foam insulating panel and affixed thereto; and a second non-structural layer of cementitious-based material formed on the second surface of the foam insulating panel and affixed thereto. The second non-structural layer of cementitious-based material is substantially thinner than the first structural layer of concrete. The second non-structural layer of cementitious-based material is preferably formed from polymer modified concrete, plaster or mortar. A method of making the cementitious-based material panel is also disclosed.
Owner:CIUPERCA ROMEO ILARIAN
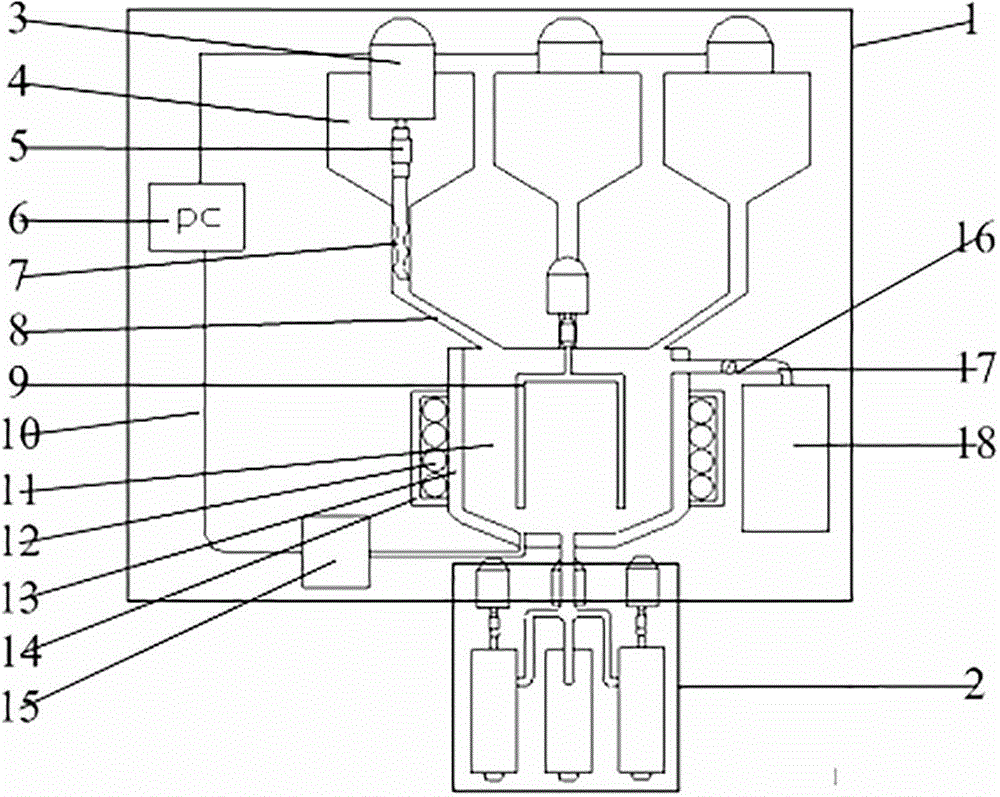
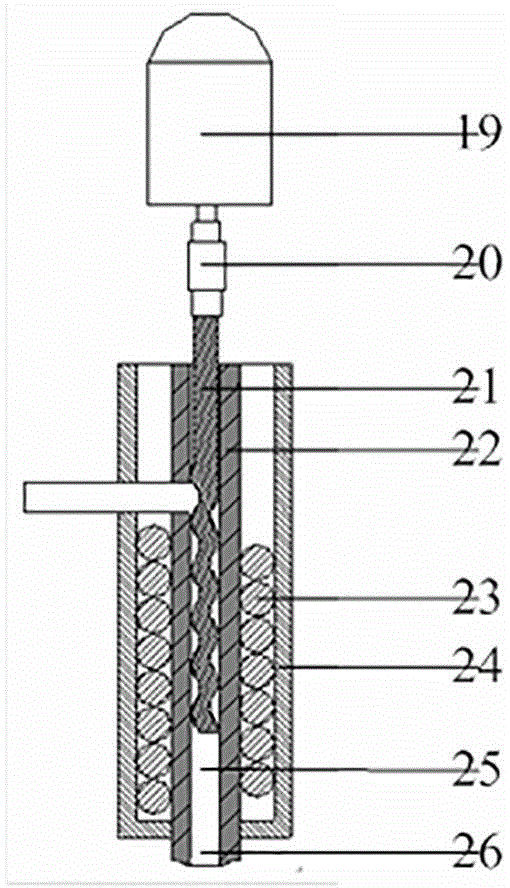
3D printing dispensing extruding device capable of realizing online alloying
The invention discloses a 3D printing dispensing extruding device capable of realizing online alloying. The 3D printing dispensing extruding device comprises an online dispensing mechanism and a plurality of molten metal extruding spray heads. The online dispensing mechanism comprises more than one storage compartment, a feeding device, a mixing compartment, an air supply device, an online molten metal component detection device and a PC. The six molten metal extruding spray heads are communicated to the bottom of the mixing compartment through conveying pipes, and a screw extruding mechanism is arranged inside each extruding spray head, so that the real-time controllable extrusion of the molten metal can be realized. In the working process, the current layer material information is firstly printed according to 3D, the preparation, mixing, melting and online detection of a metal raw material are carried out by the online dispensing mechanism, when the molten metal component meets the requirement, the molten metal is led into the extruding spray heads through conveying pipes on the lower end of the mixing compartment, and then the molten metal component is extruded by the screw extruding mechanism in each spray head to be scanned, printed and formed layer by layer. The 3D printing dispensing extruding device is reasonable in design and precise in dispensing and is suitable for online mixing and detection of multiple metal powder / particles, and the online alloying of 3D printer and the integrated formation of gradient material structural parts can be effectively achieved.
Owner:ADVANCED MFG TECH CENT CHINA ACAD OF MASCH SCI & TECH
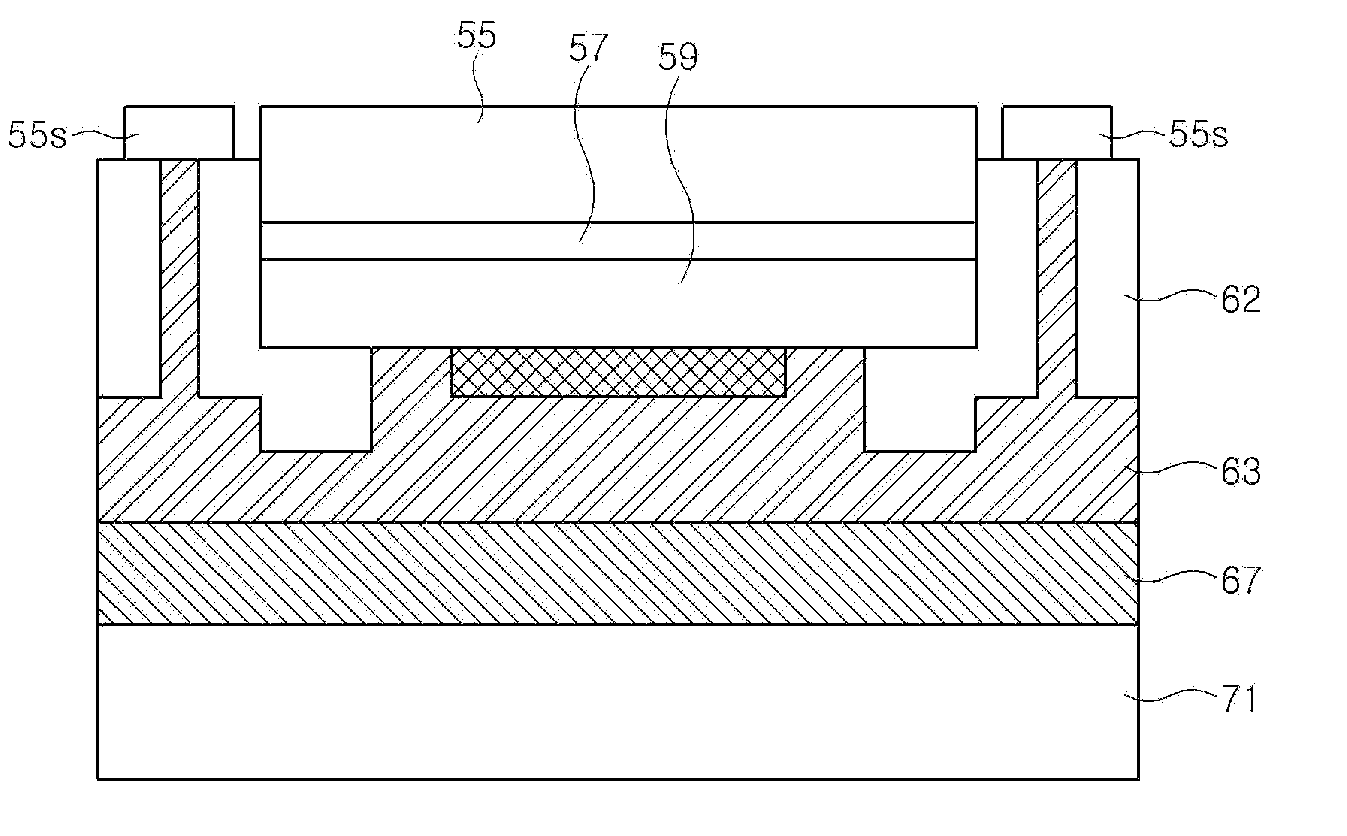
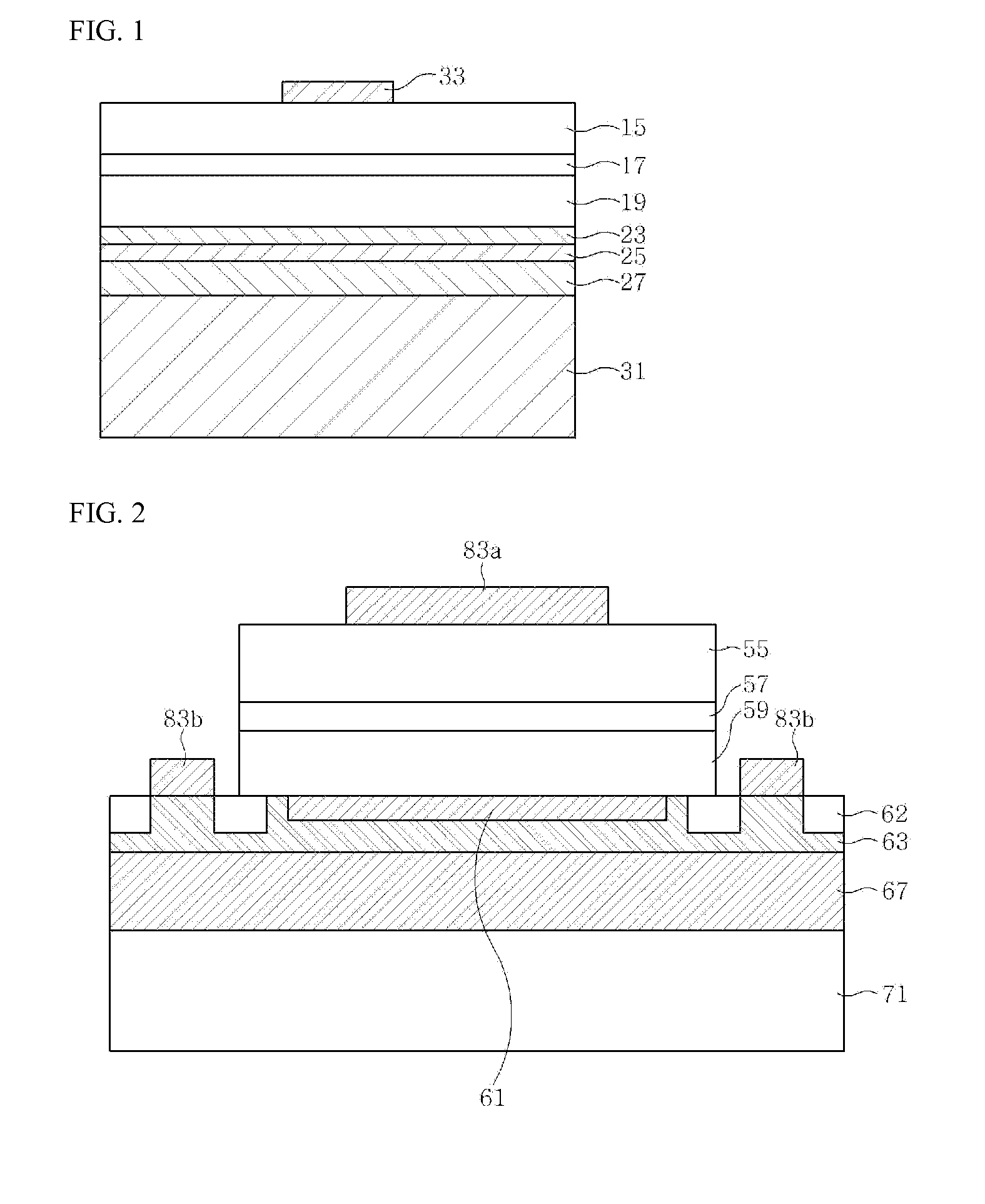
Light emitting device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20100006881A1Solve deteriorationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMetallic materialsBoundary region
There is provided a light emitting device, which comprises compound semiconductor layers including a first conductive semiconductor layer, an active layer and a second conductive semiconductor layer; a metal reflection layer formed on a region of the second conductive semiconductor layer; an insulating structure formed at least in a boundary region of the second conductive semiconductor layer; a metal material structure formed to cover the second conductive semiconductor layer having the metal reflection layer and the insulating structure formed; and a substrate bonded to the metal material structure, wherein the boundary region of the second conductive semiconductor layer includes an outer region of the second conductive semiconductor layer along an outer circumference of the second conductive semiconductor layer.
Owner:SEOUL VIOSYS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com