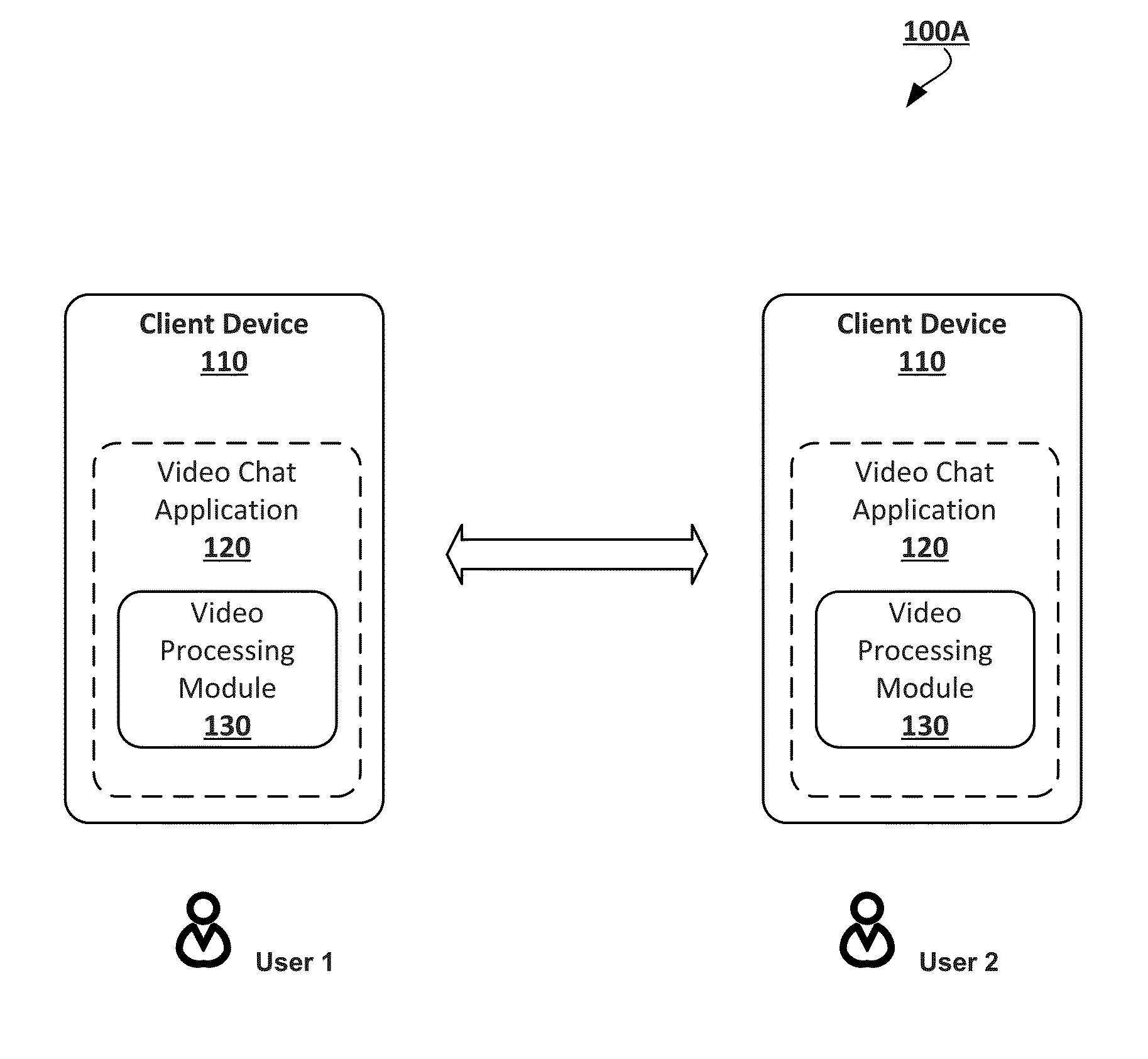
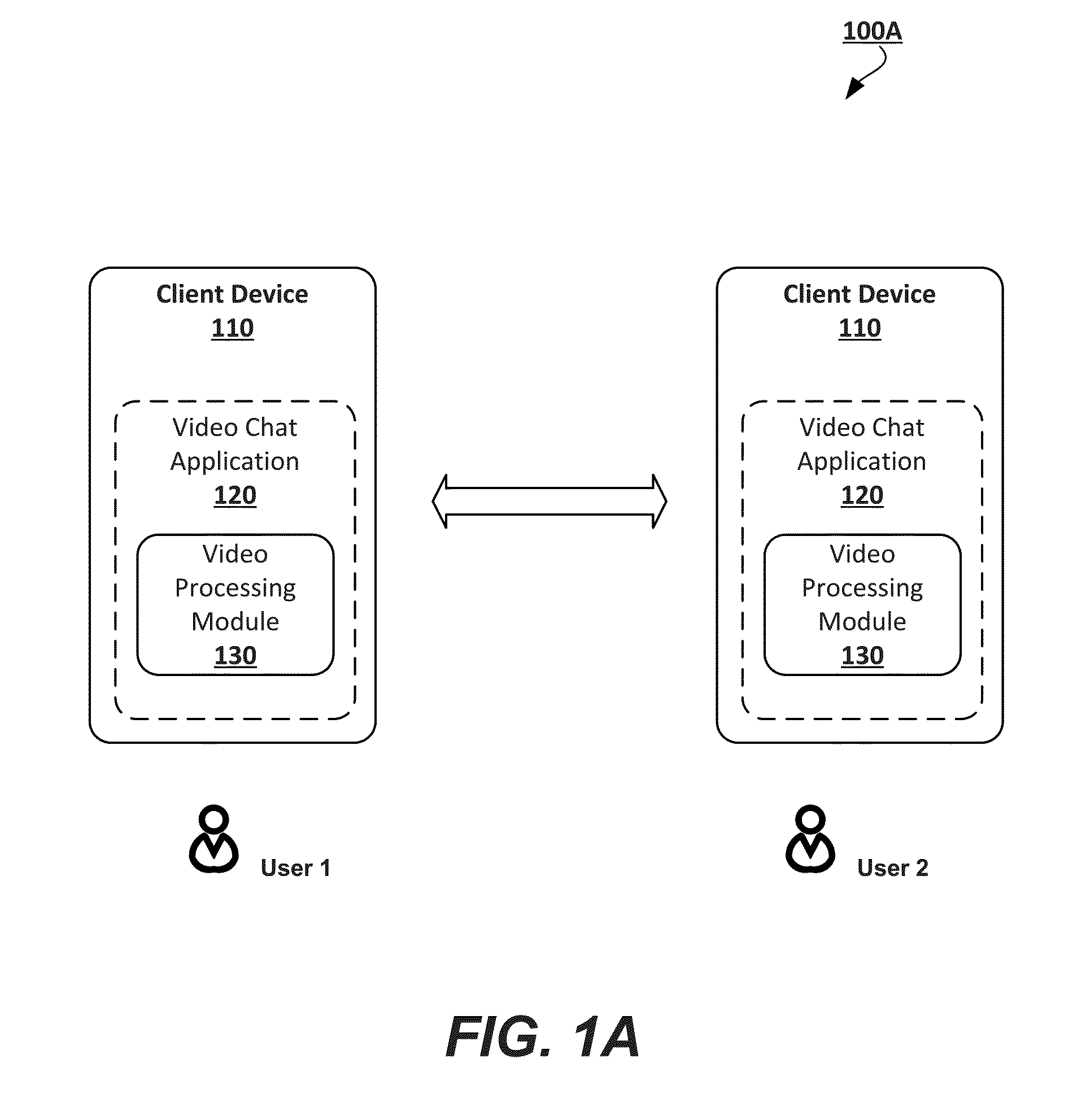
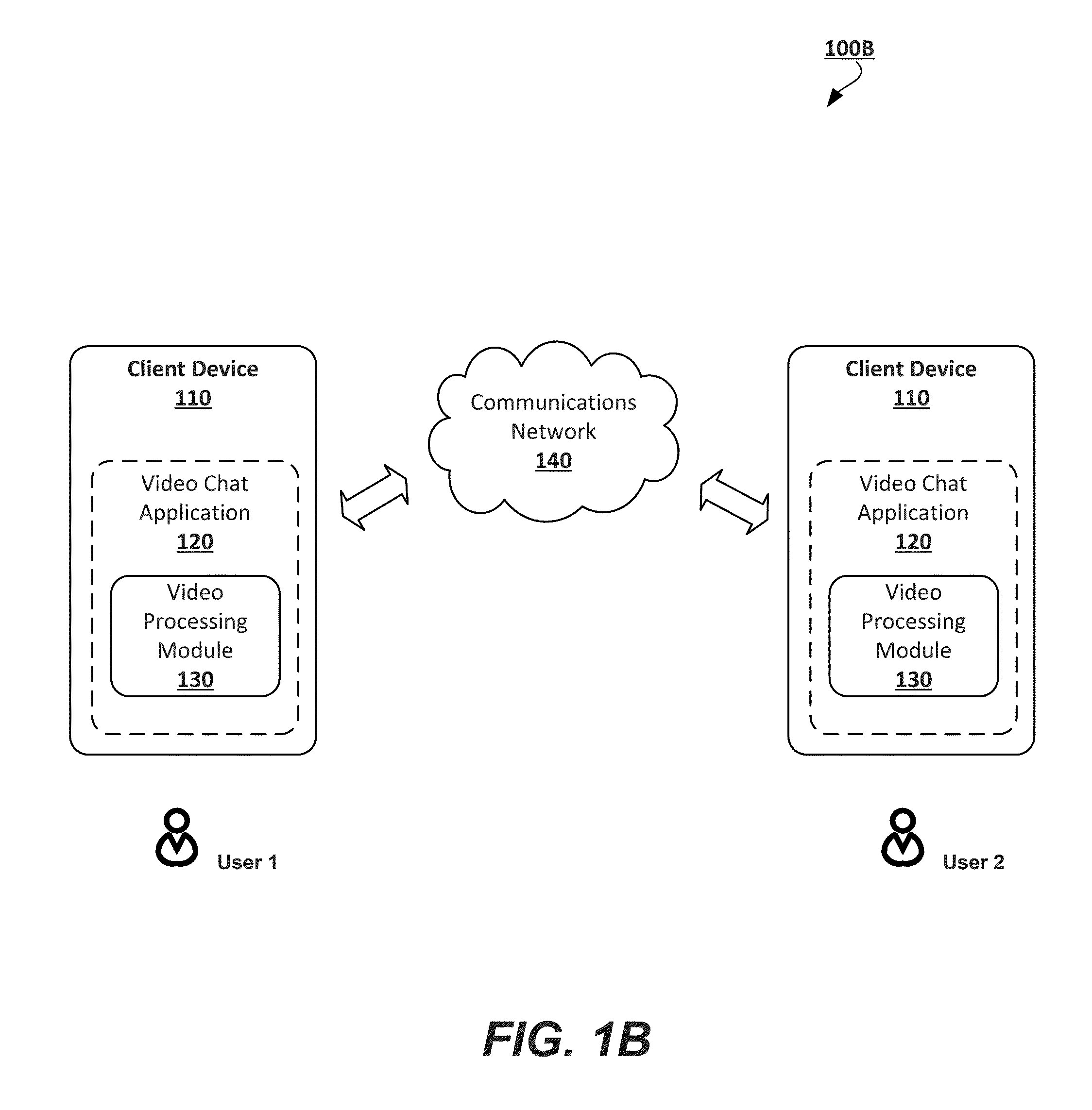
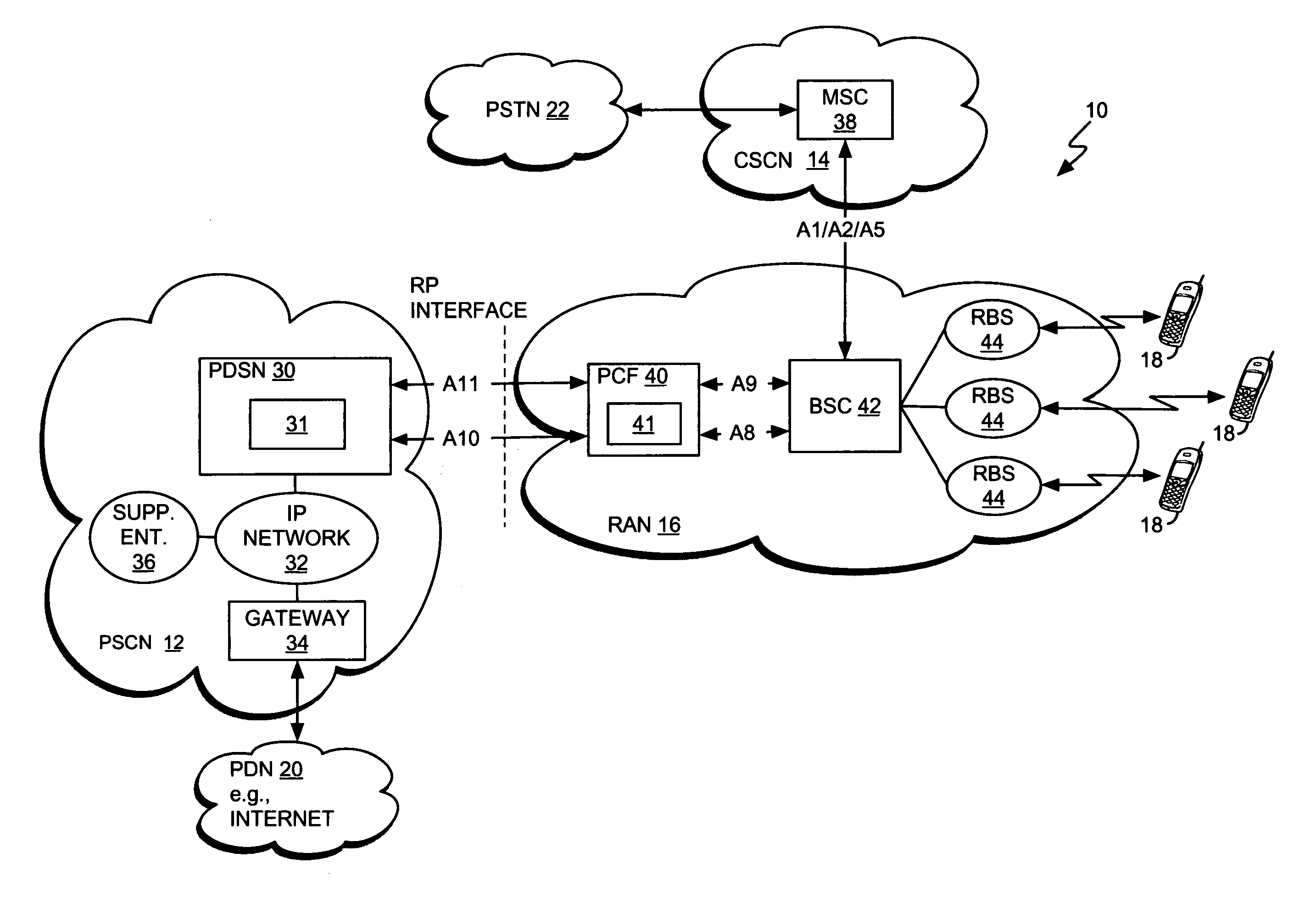
Patents
Literature
361results about How to "Low data rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
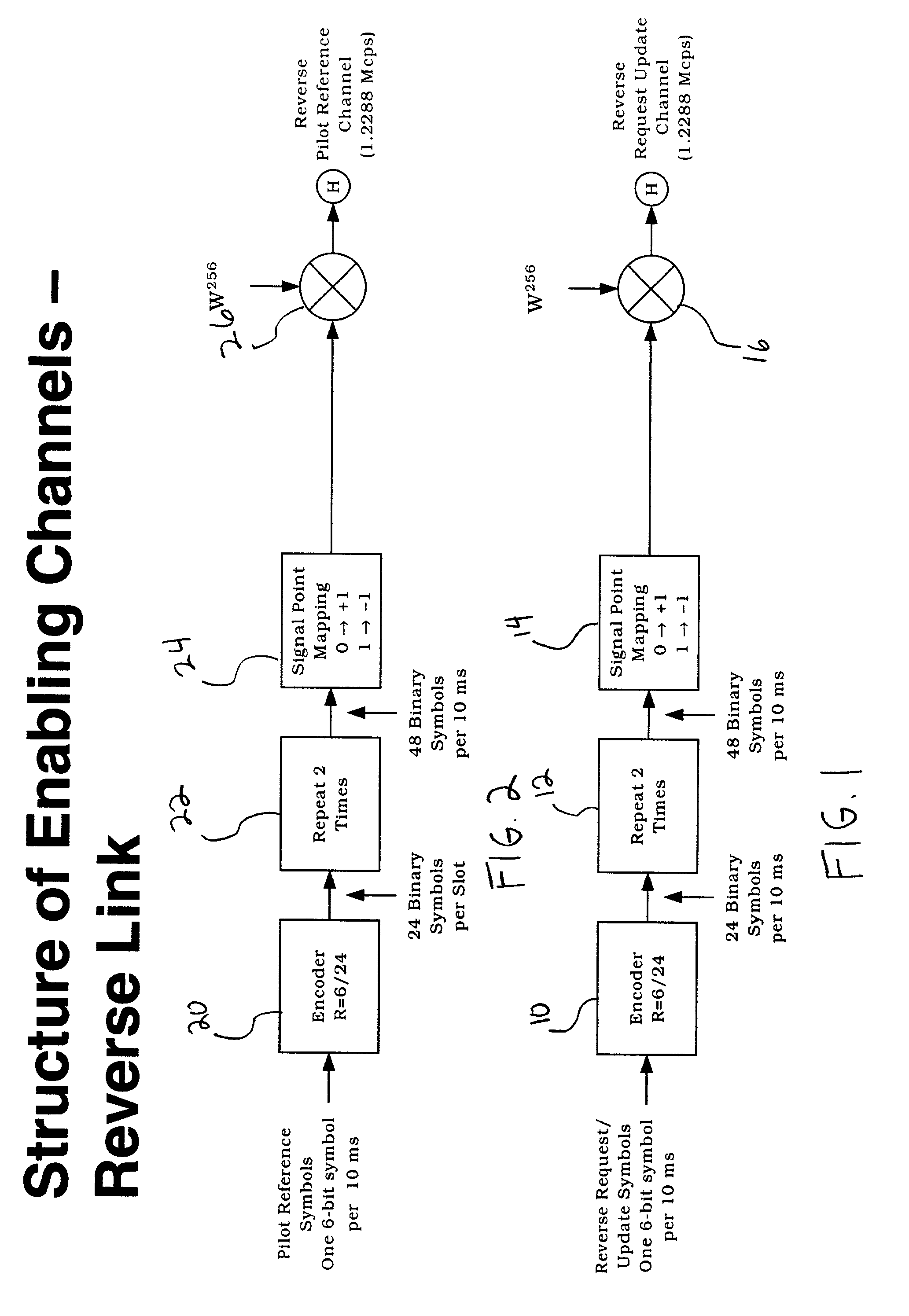
Dynamic voice over data prioritization for wireless communication networks
InactiveUS20050107091A1Reduce overheadIncrease network resource availableError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData rateRate reduction
In a wireless communication network providing voice and data services, one or more entities in the network, such as a base station controller and / or radio base station, can be configured to reduce data services overhead responsive to detecting a congestion condition, thereby increasing the availability of one or more network resources for voice services. In one or more exemplary embodiments, one or more current data services users are targeted for modification of their ongoing data services to effect the reduction in data services overhead. Modifications can include, but are not limited to, any one or more of the following: forward or reverse link data rate reductions, and shifting of forward or reverse link traffic from dedicated user channels to shared user channels. Targeting of users for service modification can be based on reported channel quality information. For example, users reporting poor radio conditions can be targeted first for service modifications.
Owner:IDTP HLDG
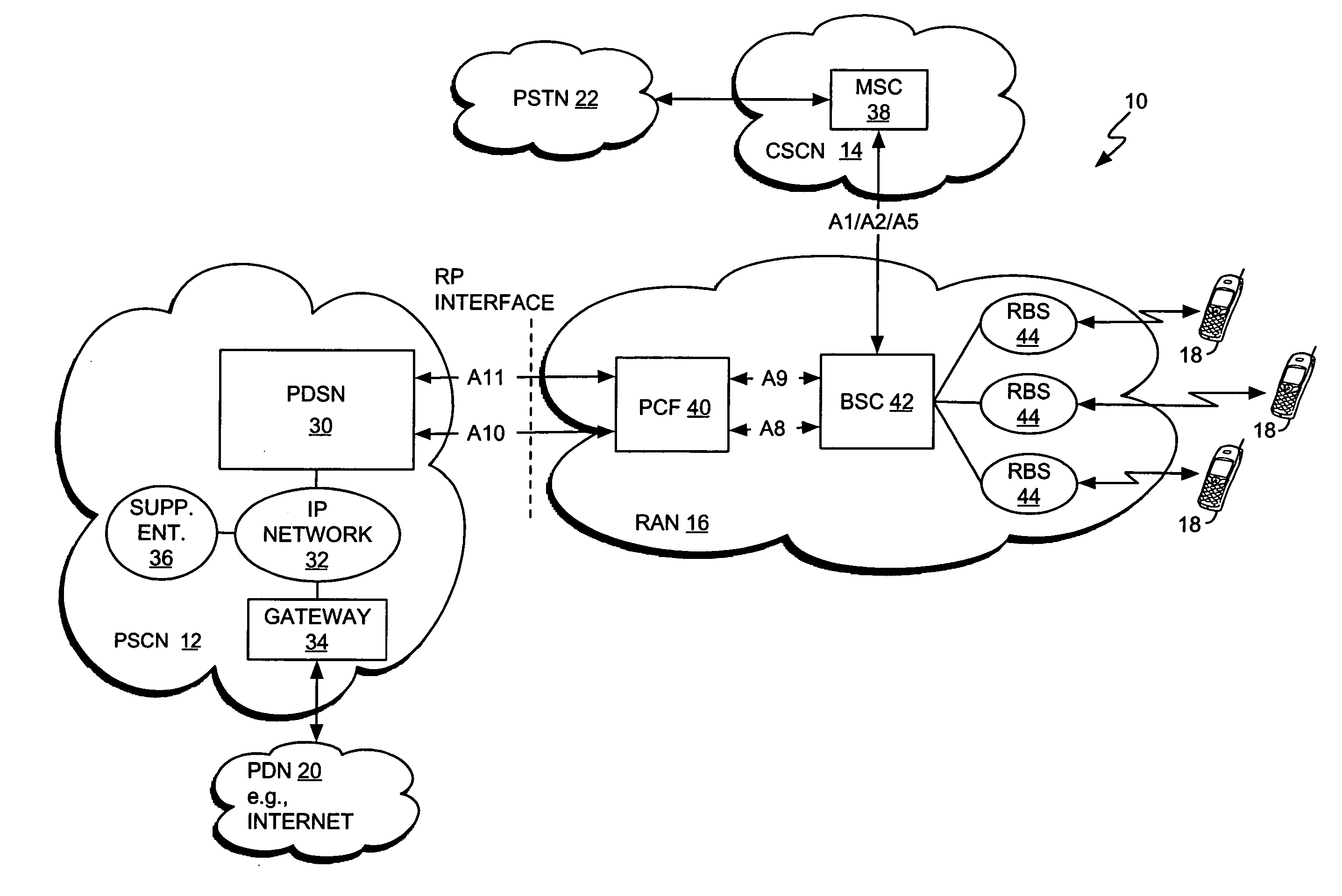
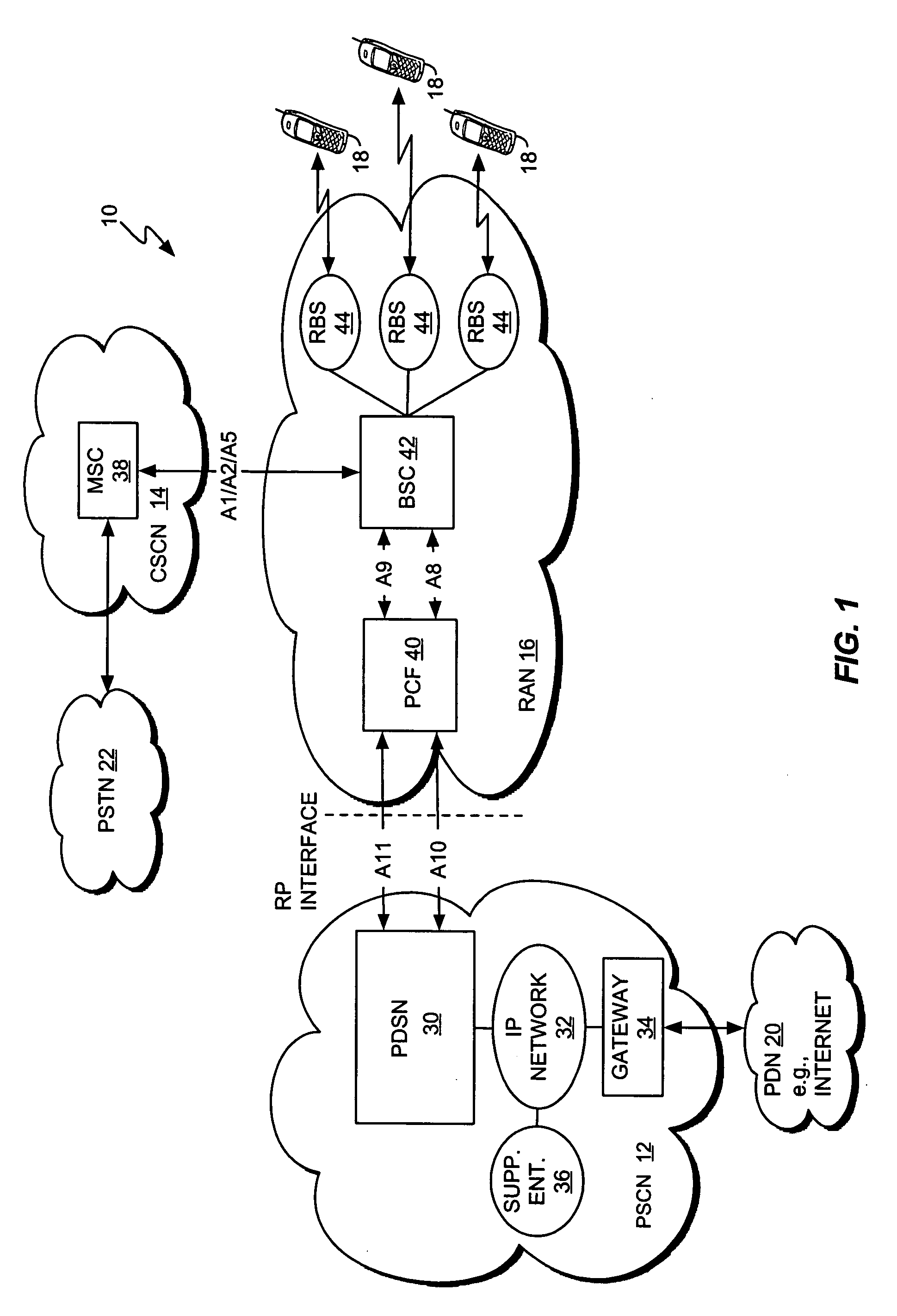
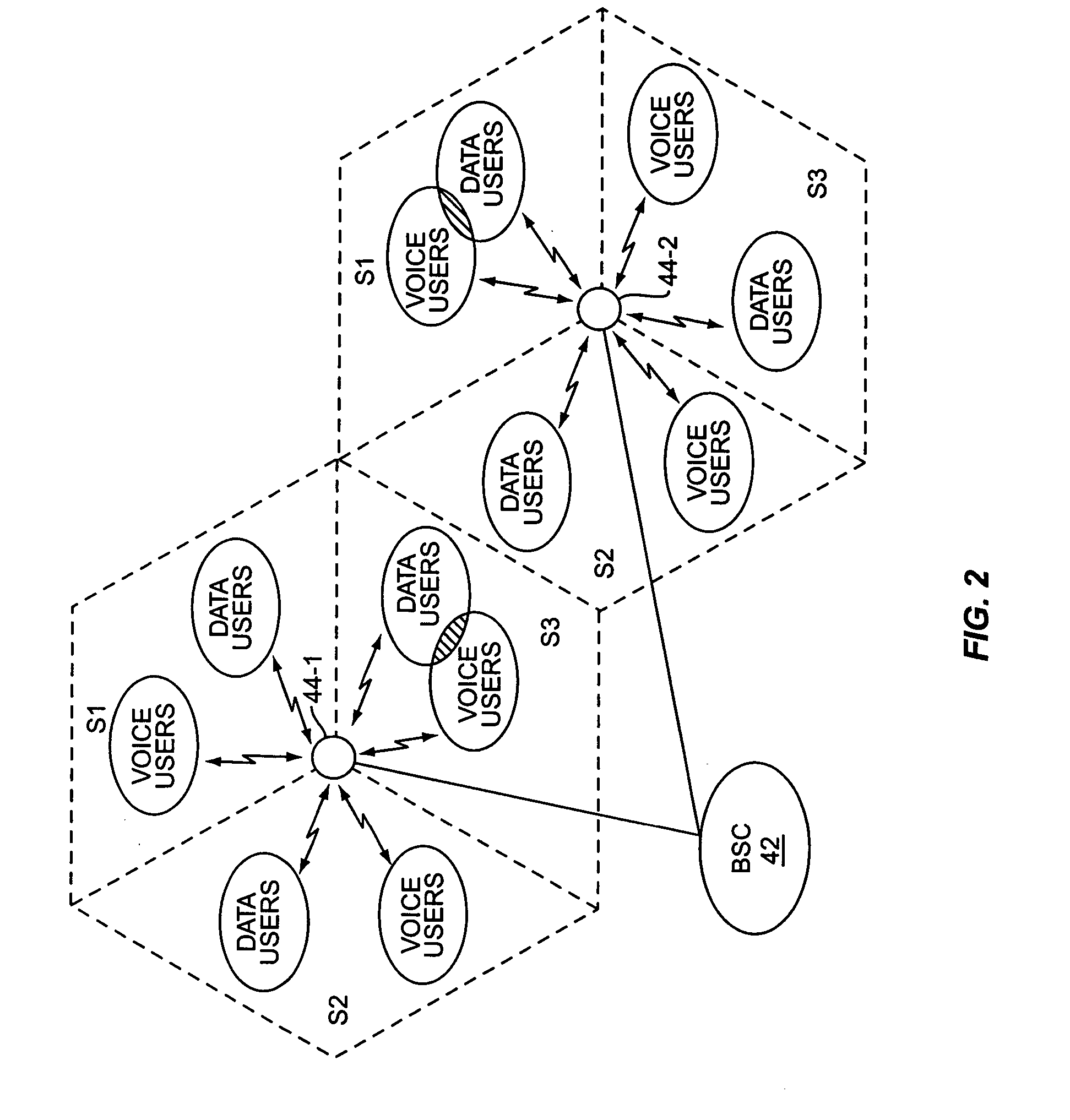
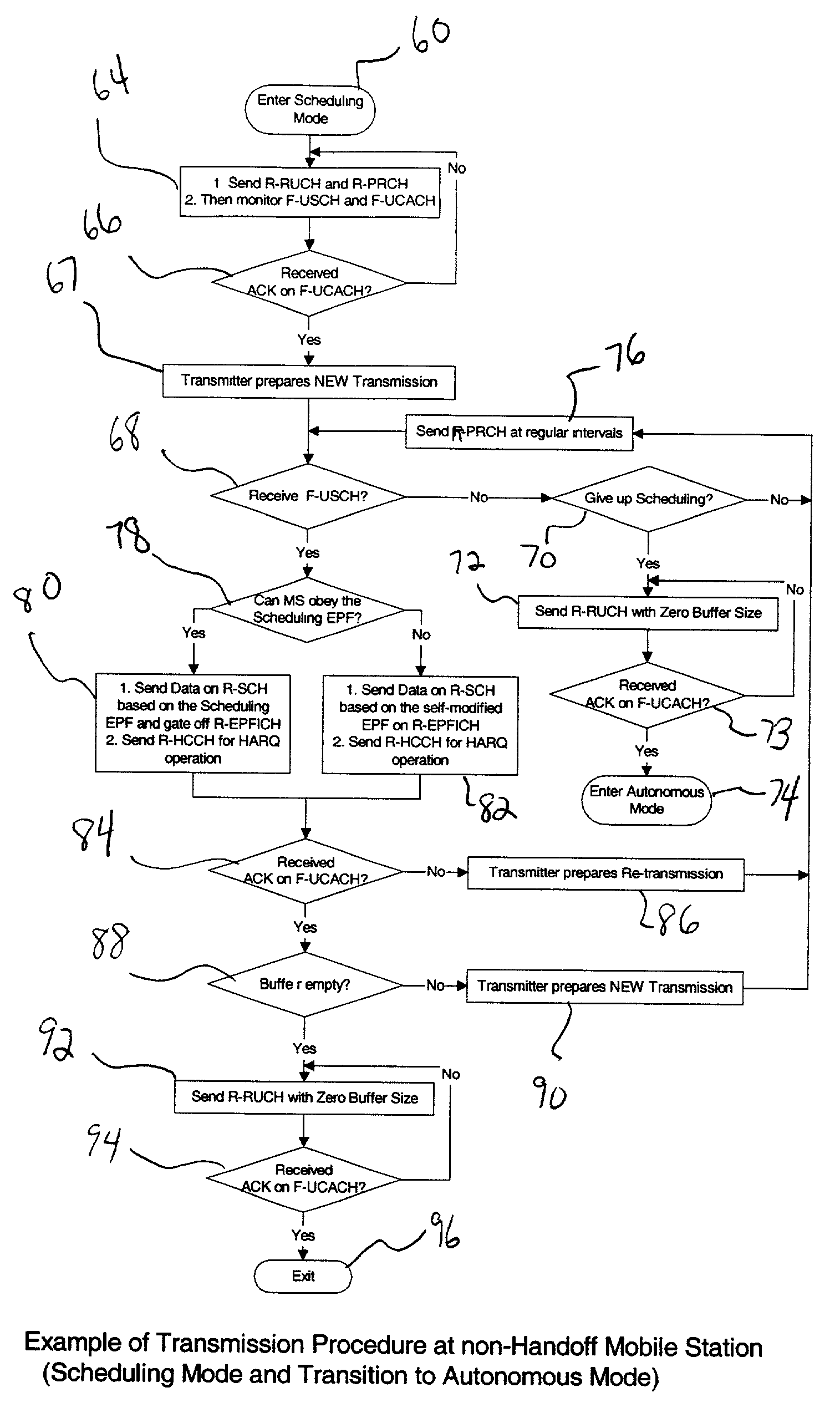
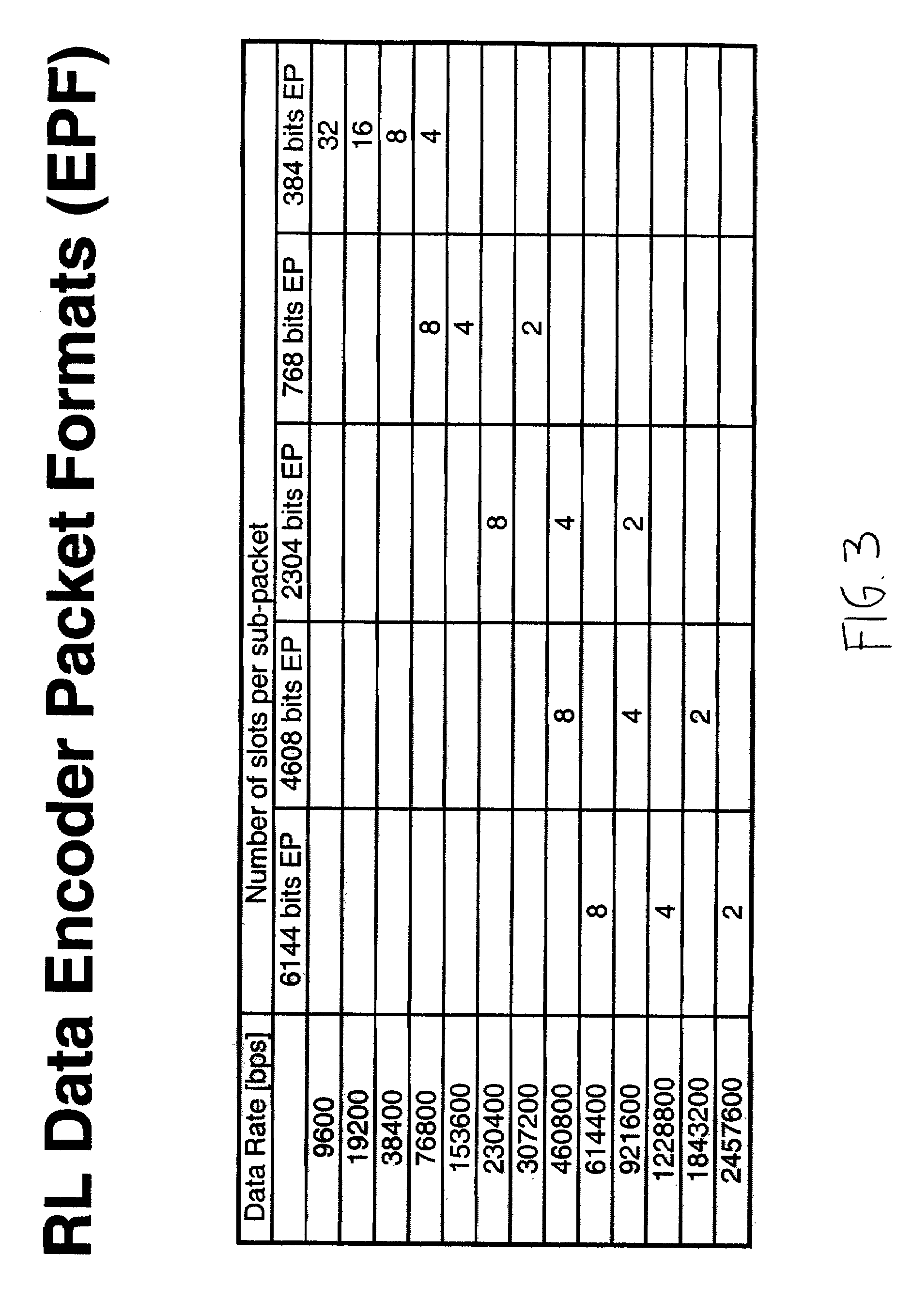
Multiple mode data communication system and method and forward and/or reverse link control channel structure
ActiveUS7158504B2Good flexibilityFlexibility of transmissionError prevention/detection by using return channelTime-division multiplexData channelControl channel
A multiple mode data communication system and method provides the flexibility to schedule wireless unit transmissions and / or allow the wireless unit to transmit autonomously. In certain embodiments, the wireless units can transmit autonomously and / or use scheduling depending on the data rate, the length of the data packet or the type of data. For example, the wireless units can transmit autonomously at lower data rates and use scheduling at higher data rates. Thus, the multiple mode system enables wireless unit transmissions to be scheduled and / or be transmit autonomously, and wireless units can simultaneously operate in different scheduling and / or autonomous modes. Depending on the embodiment, the system can provide even greater flexibility in operation by permitting wireless units to be scheduled by a single base station, scheduled by a multiplicity of base stations simultaneously or otherwise, via coordination between base stations, scheduled by a multiplicity of base stations in an uncoordinated and asynchronous manner, allowed to transmit autonomously, and / or allowed to transmit autonomously under base station supervision (i.e. rate control / adjustment by the base station). Additionally, a forward and / or reverse link control channel structure is provided which can be used to implement the multiple mode data communication system and / or support various features enabling increased throughput over a shared data channel in a wireless communications system.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
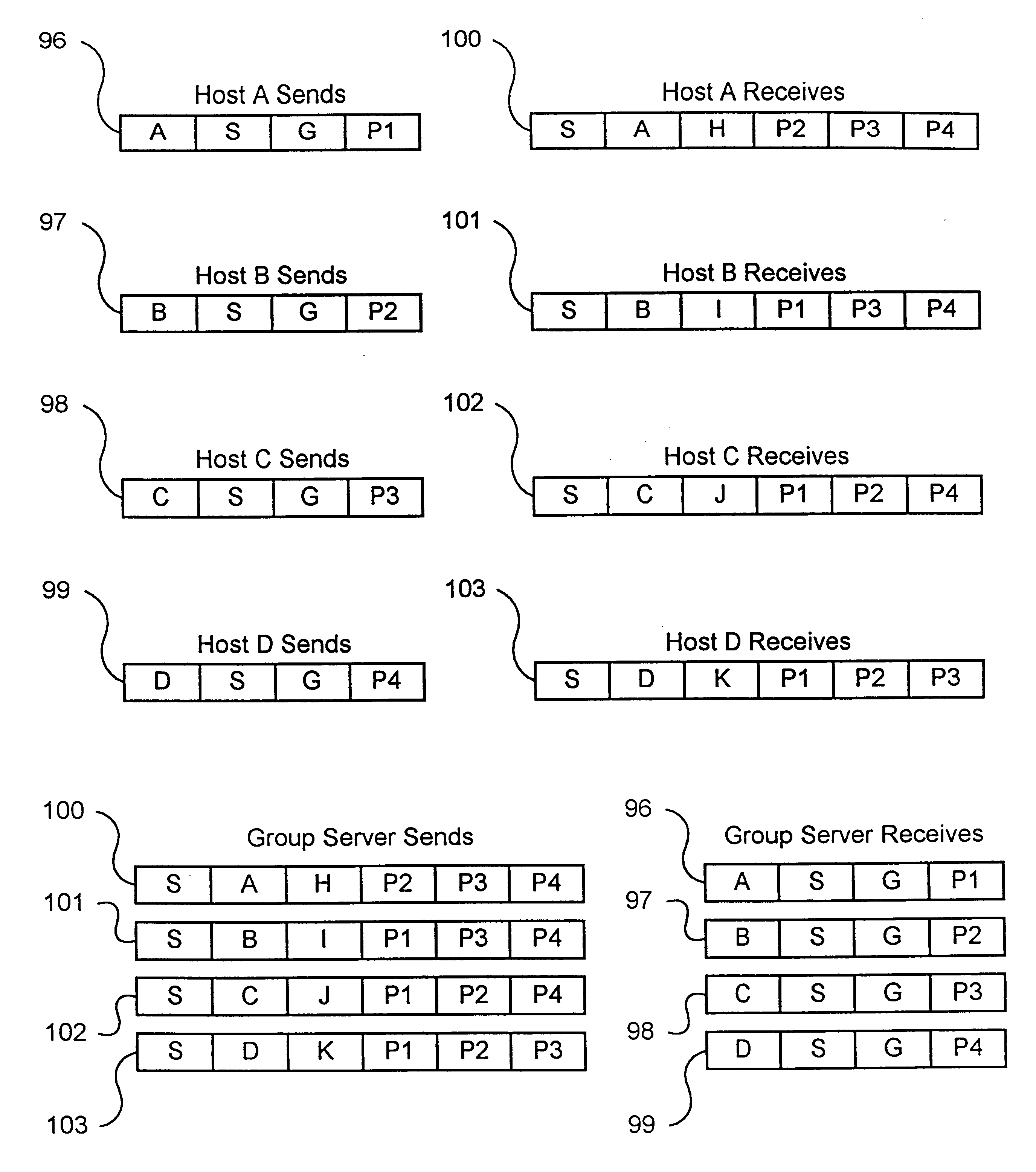
Server-group messaging system for interactive applications
InactiveUS6226686B1Reduce rateLower latencySpecial service provision for substationMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityNetwork link
A method for deploying interactive applications over a network containing host computers and group messaging servers is disclosed. The method operates in a conventional unicast network architecture comprised of conventional network links and unicast gateways and routers. The hosts send messages containing destination group addresses by unicast to the group messaging servers. The group addresses select message groups maintained by the group messaging servers. For each message group, the group messaging servers also maintain a list of all of the hosts that are members of the particular group. In its most simple implementation, the method consists of the group server receiving a message from a host containing a destination group address. Using the group address, the group messaging server then selects a message group which lists all of the host members of the group which are the targets of messages to the group. The group messaging server then forwards the message to each of the target hosts. In an interactive application, many messages will be arriving at the group server close to one another in time. Rather than simply forward each message to its targeted hosts, the group messaging server aggregates the contents of each of messages received during a specified time period and then sends an aggregated message to the targeted hosts. The time period can be defined in a number of ways. This method reduces the message traffic between hosts in a networked interactive application and contributes to reducing the latency in the communications between the hosts.
Owner:PALTALK HLDG +1
Data stream-distribution system and method therefor
InactiveUS20080147874A1Low data rateReproducing dataSpeech analysisData switching by path configurationData streamDistribution system
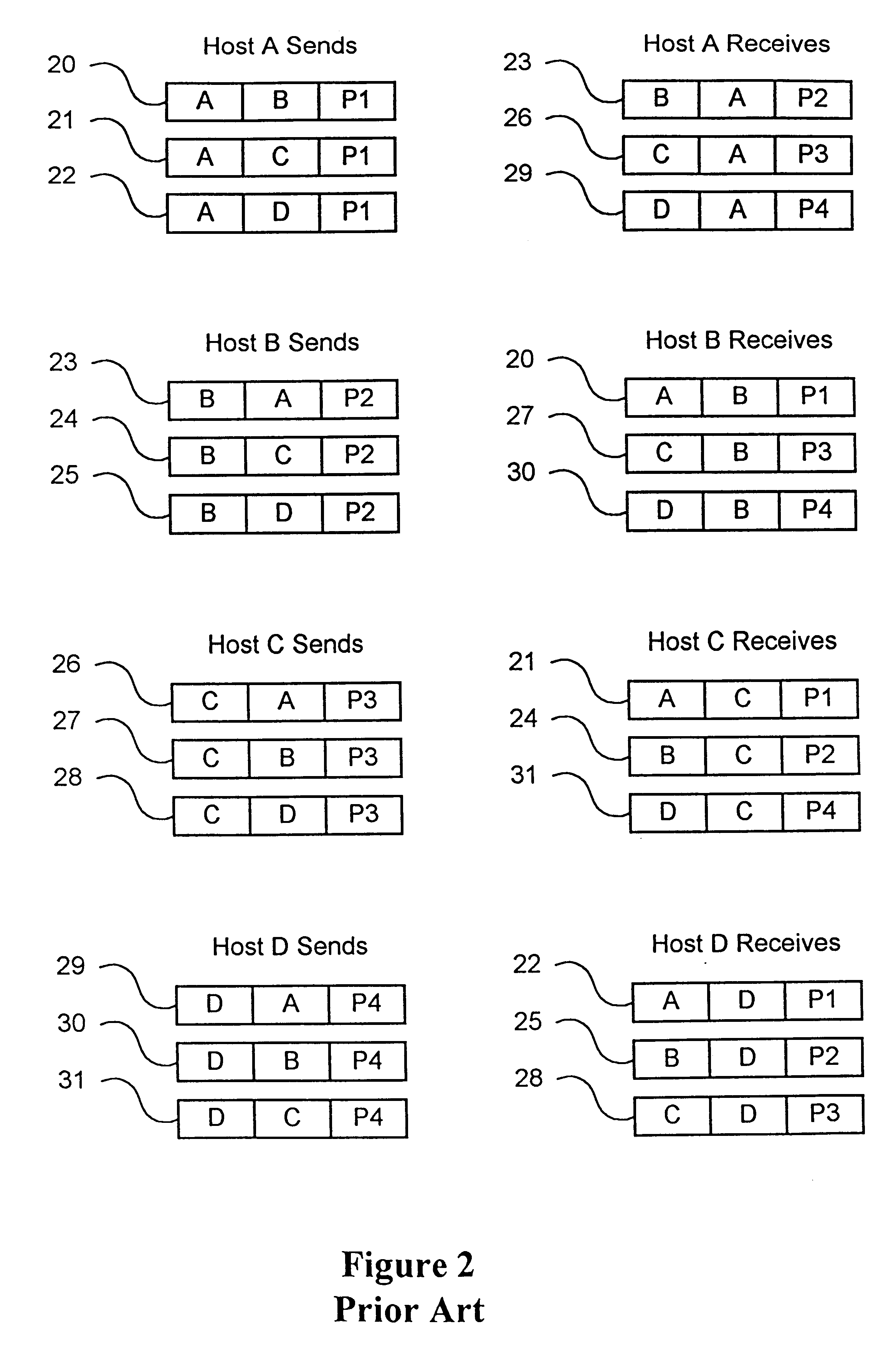
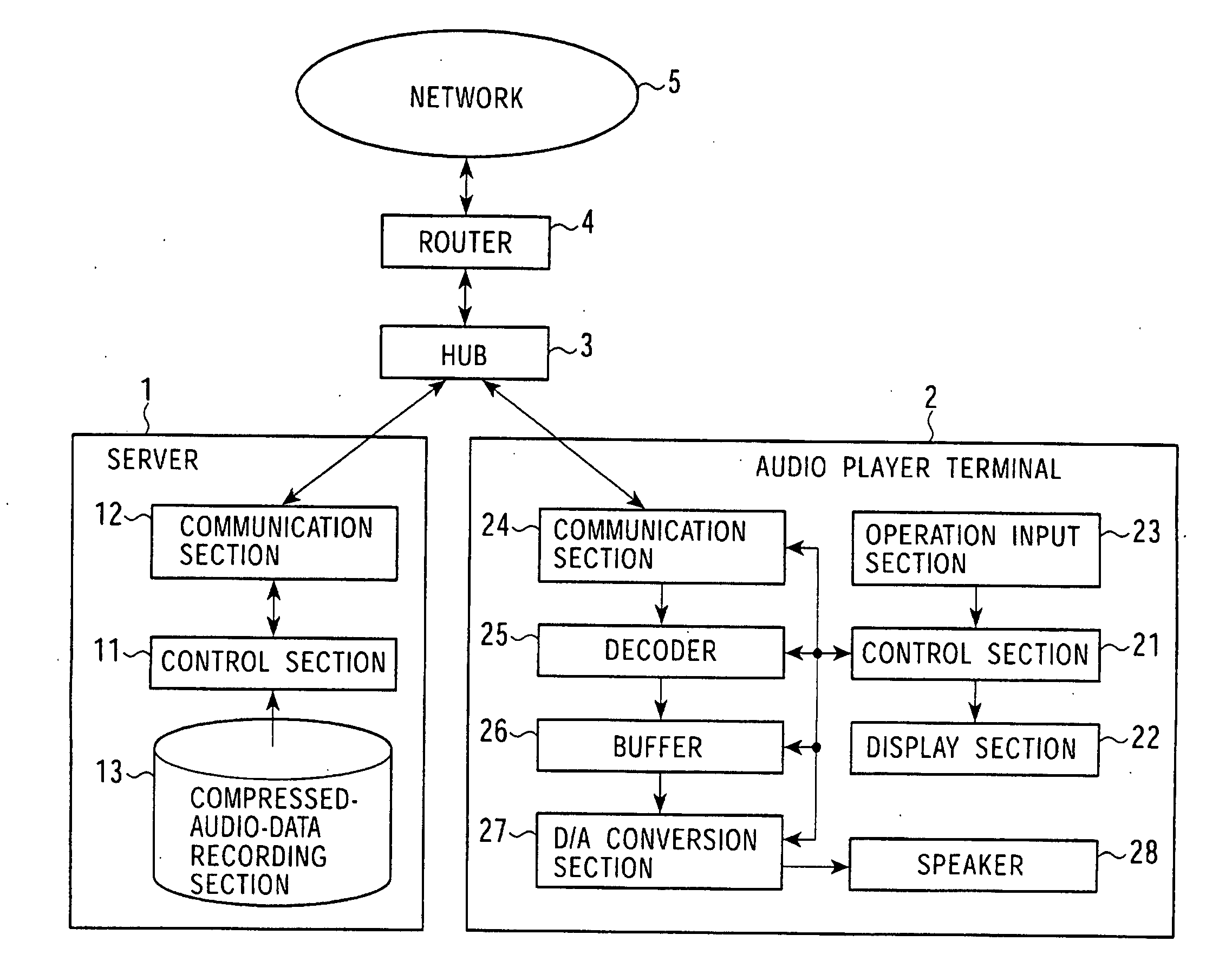
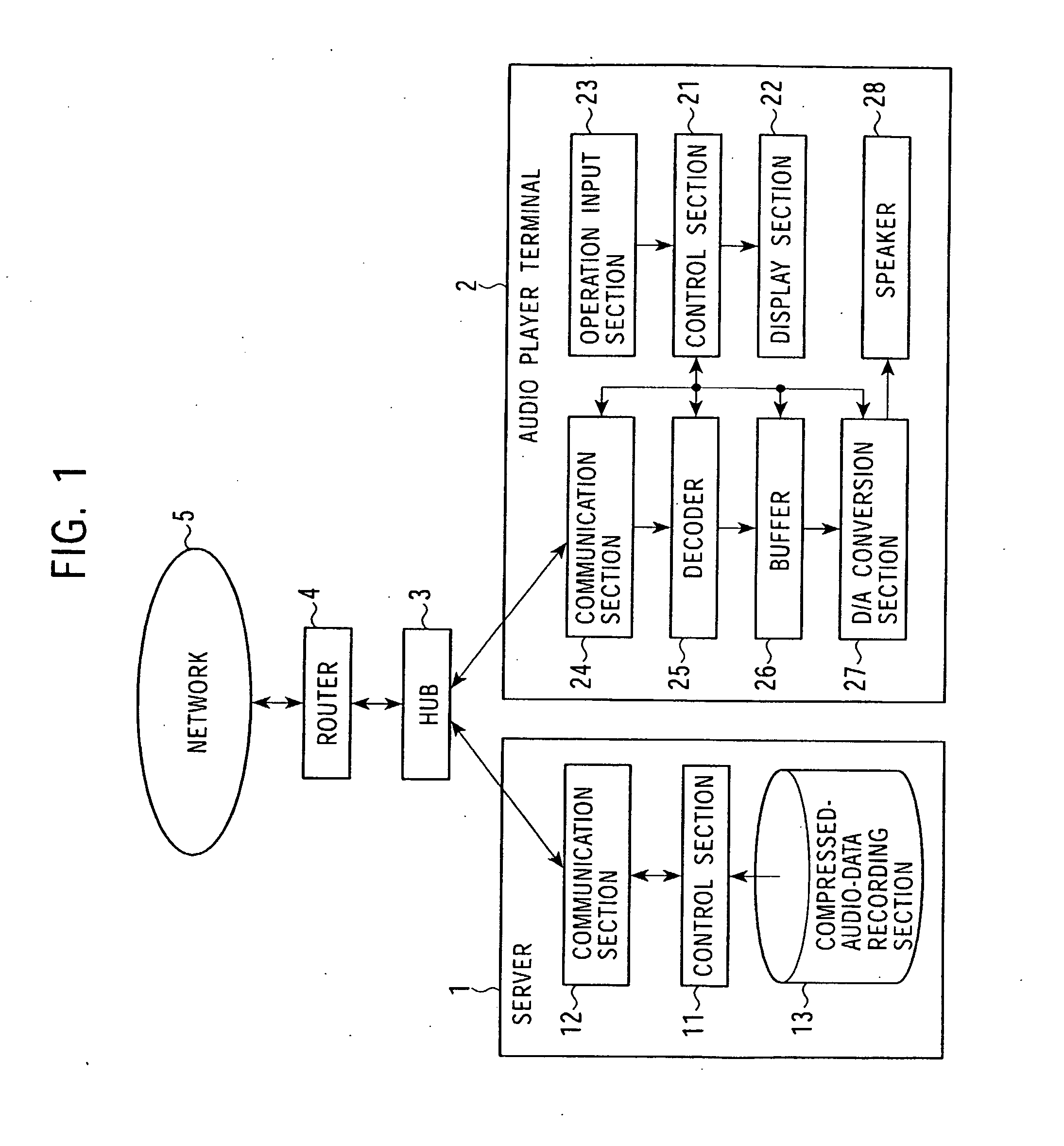
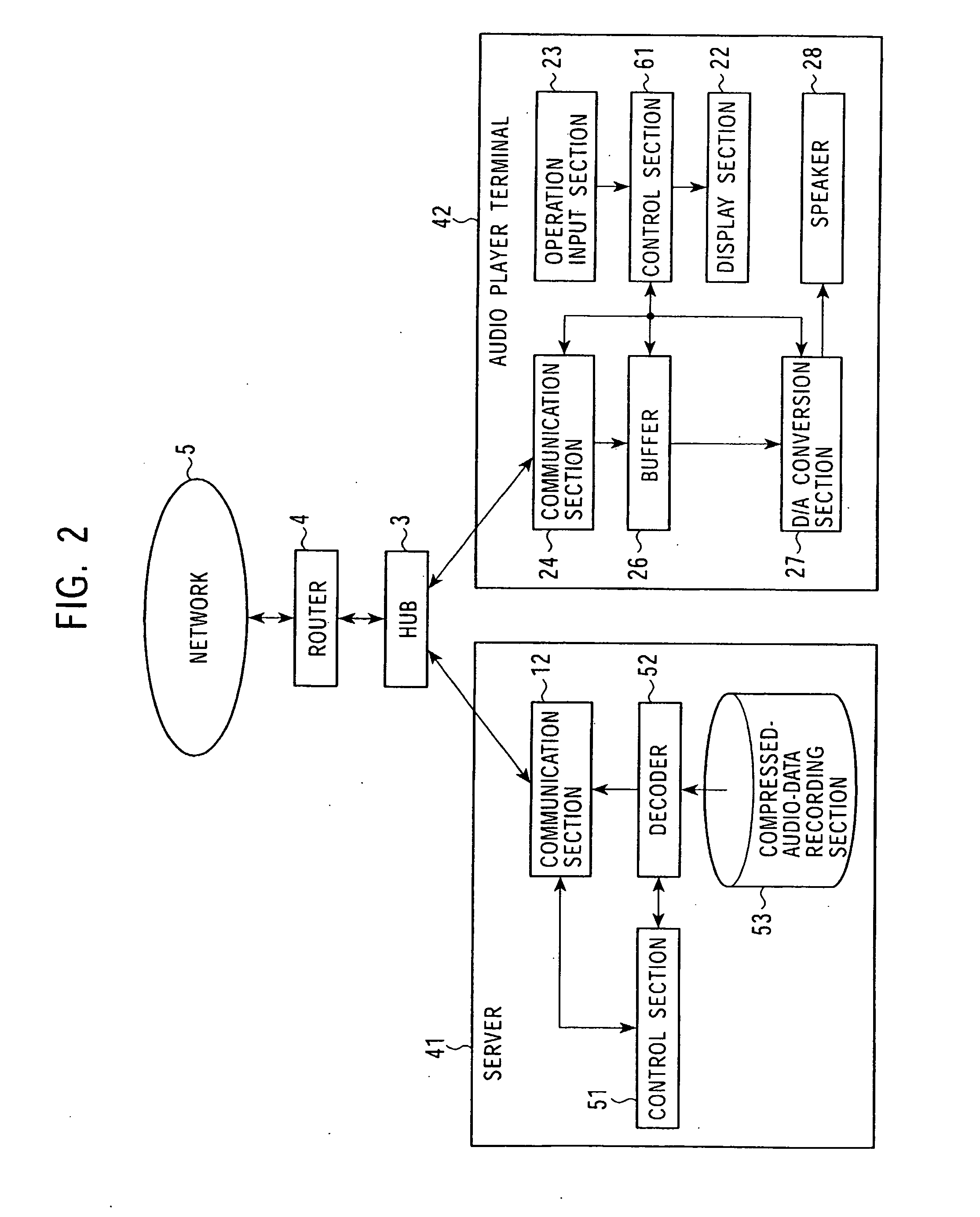
A mutual recognition process is performed in step S1. When it is determined in step S2 that a request for sending a list of musical pieces has been received, the list of musical pieces is sent in step S3. When a request for sending audio data has been received in step S4, a transfer-rate measurement process is executed in step S5. When it is determined according to the transfer rate in step S6 that the audio can be transmitted, the corresponding compressed audio data is extracted in step S7, the compressed audio data is decoded to generate linear PCM data suited to the transfer rate in step S8, and transmitted in step S9. When the audio data cannot be transmitted, an error message is transmitted in step S10. The present invention can be applied, for example, to a server for distributing audio data and an audio player terminal for reproducing the distributed audio data.
Owner:SONY CORP
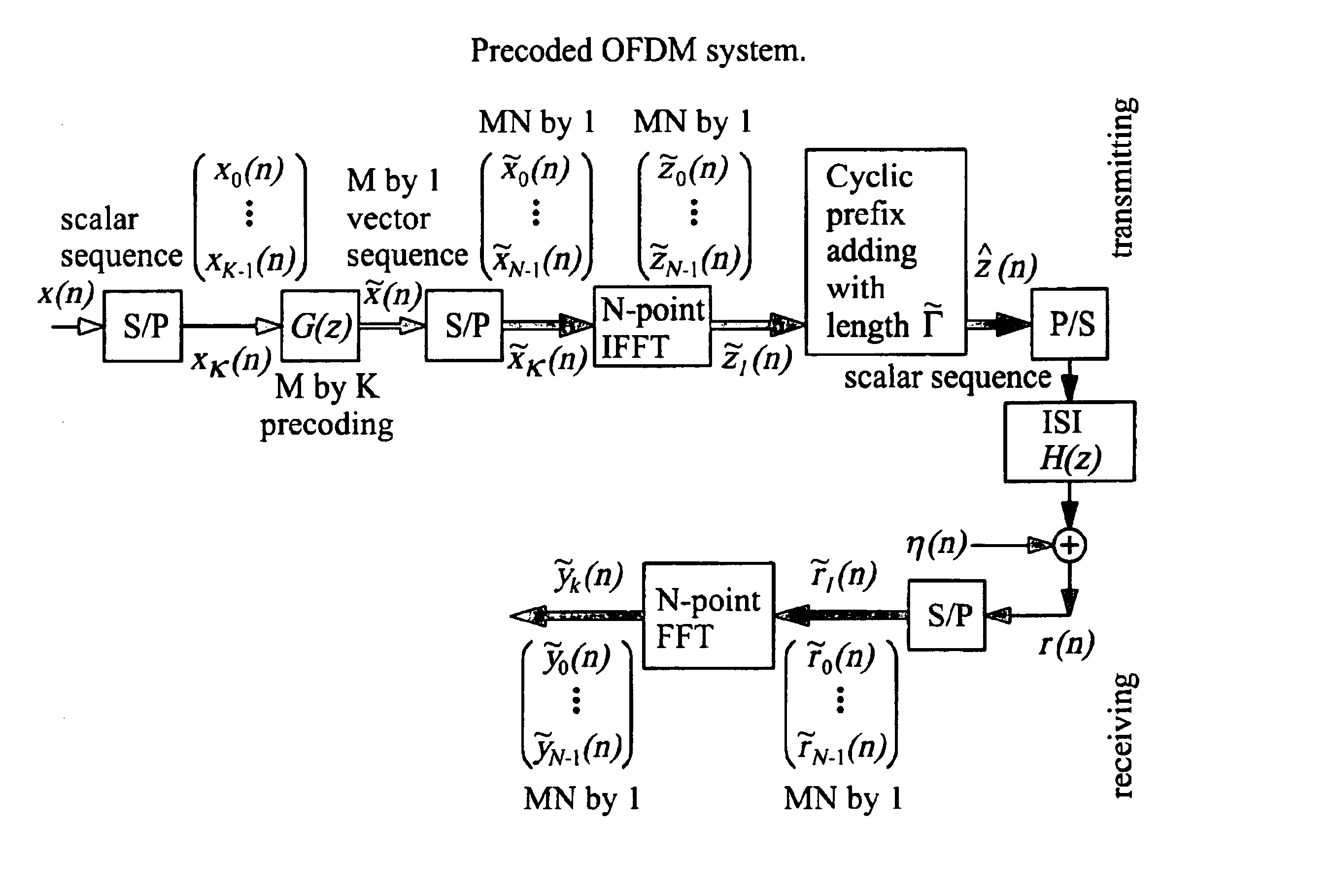
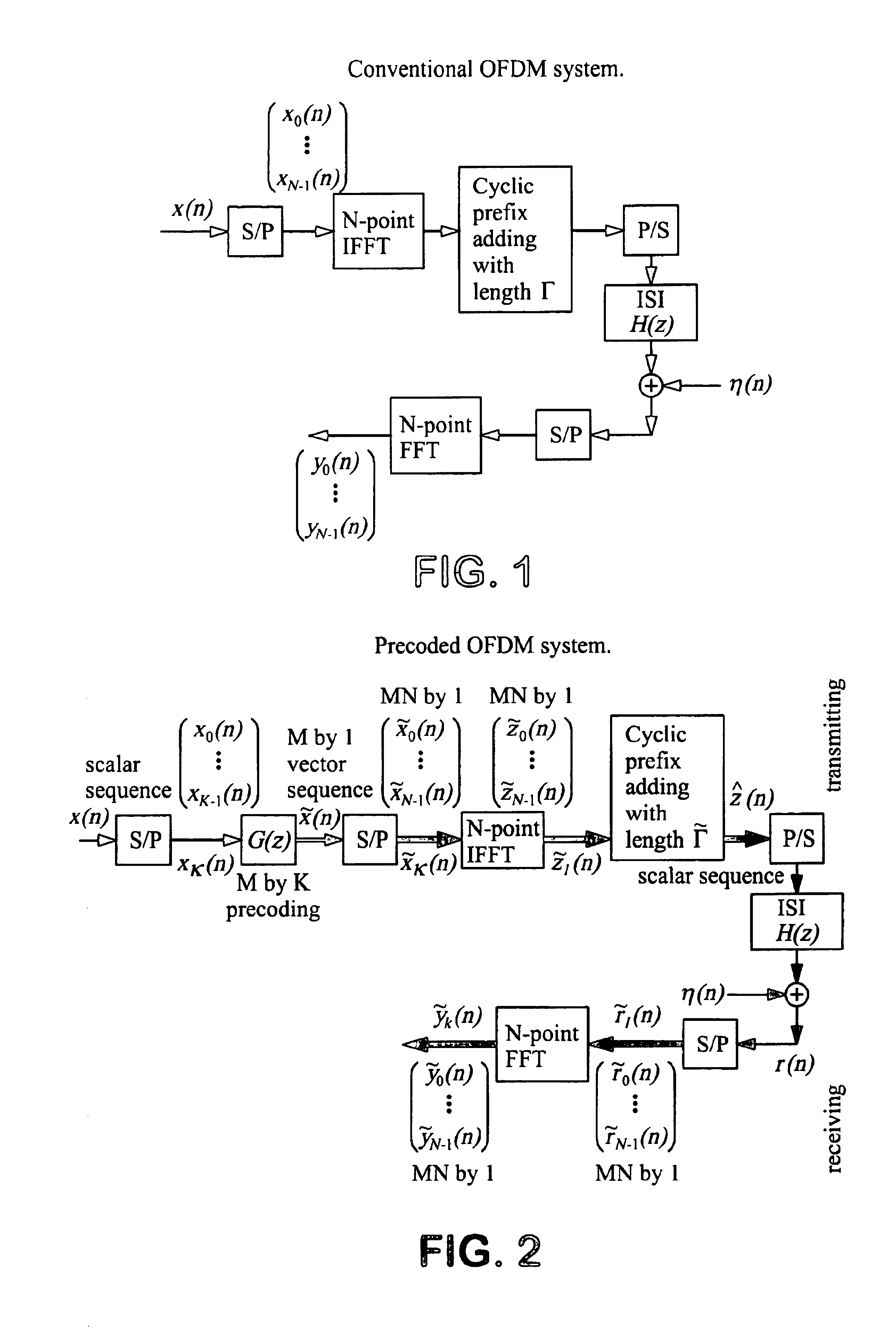
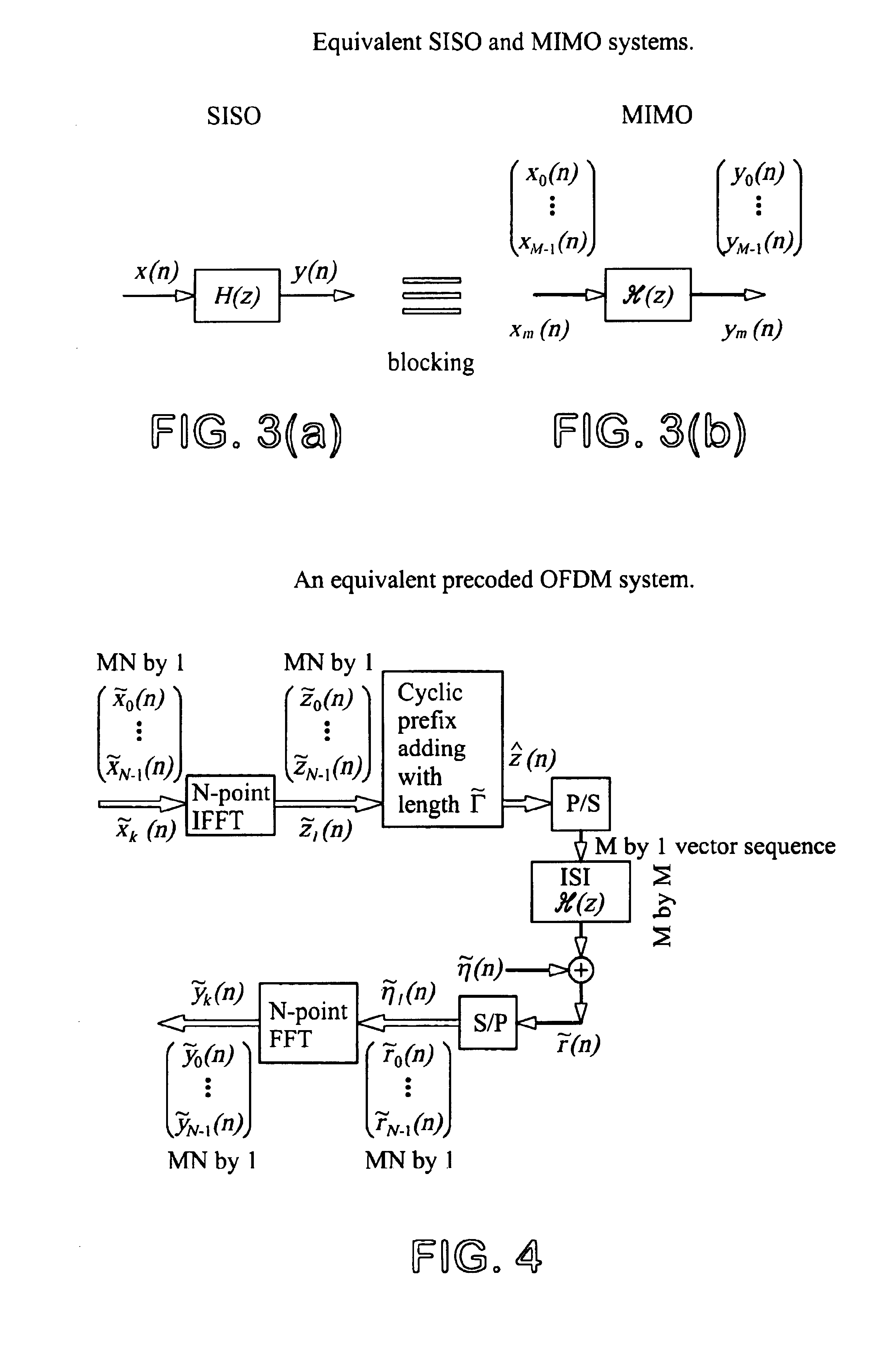
Precoded OFDM systems robust to spectral null channels and vector OFDM systems with reduced cyclic prefix length
InactiveUS6928047B1Reducing cyclic prefix lengthShorten the lengthMulti-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexPrecodingFrequency spectrum
A precoded orthogonal frequency division multiplexer (OFDM) system that improves the preformance of OFDM systems for spectral null channels, and size K×1 vector OFDM systems that reduce the cyclic prefix length by K times compared to conventional OFDM systems. The precoding scheme comprises inserting one or more zeros between each of the two sets of K consecutive information symbols, although it can be generalized to a general form. This precoding scheme removes the spectral nulls of an ISI channel without knowing the ISI channel. When no zero is inserts between each of the two sets of K consecutive information symbols and only K consecutive symbols are blocked together, vector OFDM systems are obtained. The bit error rate performance of the vector OFDM systems of the present invention is much improved over conventional OFDM systems.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Server-group messaging system for interactive applications
InactiveUS6018766AReduces message rateLower latencySpecial service provision for substationMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityNetwork link
A method for deploying interactive applications over a network containing host computers and group messaging servers is disclosed. The method operates in a conventional unicast network architecture comprised of conventional network links and unicast gateways and routers. The hosts send messages containing destination group addresses by unicast to the group messaging servers. The group addresses select message groups maintained by the group messaging servers. For each message group, the group messaging servers also maintain a list of all of the hosts that are members of the particular group. In its most simple implementation, the method consists of the group server receiving a message from a host containing a destination group address. Using the group address, the group messaging server then selects a message group which lists all of the host members of the group which are the targets of messages to the group. The group messaging server then forwards the message to each of the target hosts. In an interactive application, many messages will be arriving at the group server close to one another in time. Rather than simply forward each message to its targeted hosts, the group messaging server aggregates the contents of each of messages received during a specified time period and then sends an aggregated message to the targeted hosts. The time period can be defined in a number of ways. This method reduces the message traffic between hosts in a networked interactive application and contributes to reducing the latency in the communications between the hosts.
Owner:CRICKET COMM +1
Data reduction techniques for processing wide-angle video
InactiveUS8238695B1Easy to useLow data rateTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesData rateParallel computing
A system and method for reducing the data-rate when processing video, particularly wide-angle video.
Owner:GRANDEYE
Cell combination to utilize available switch bandwidth
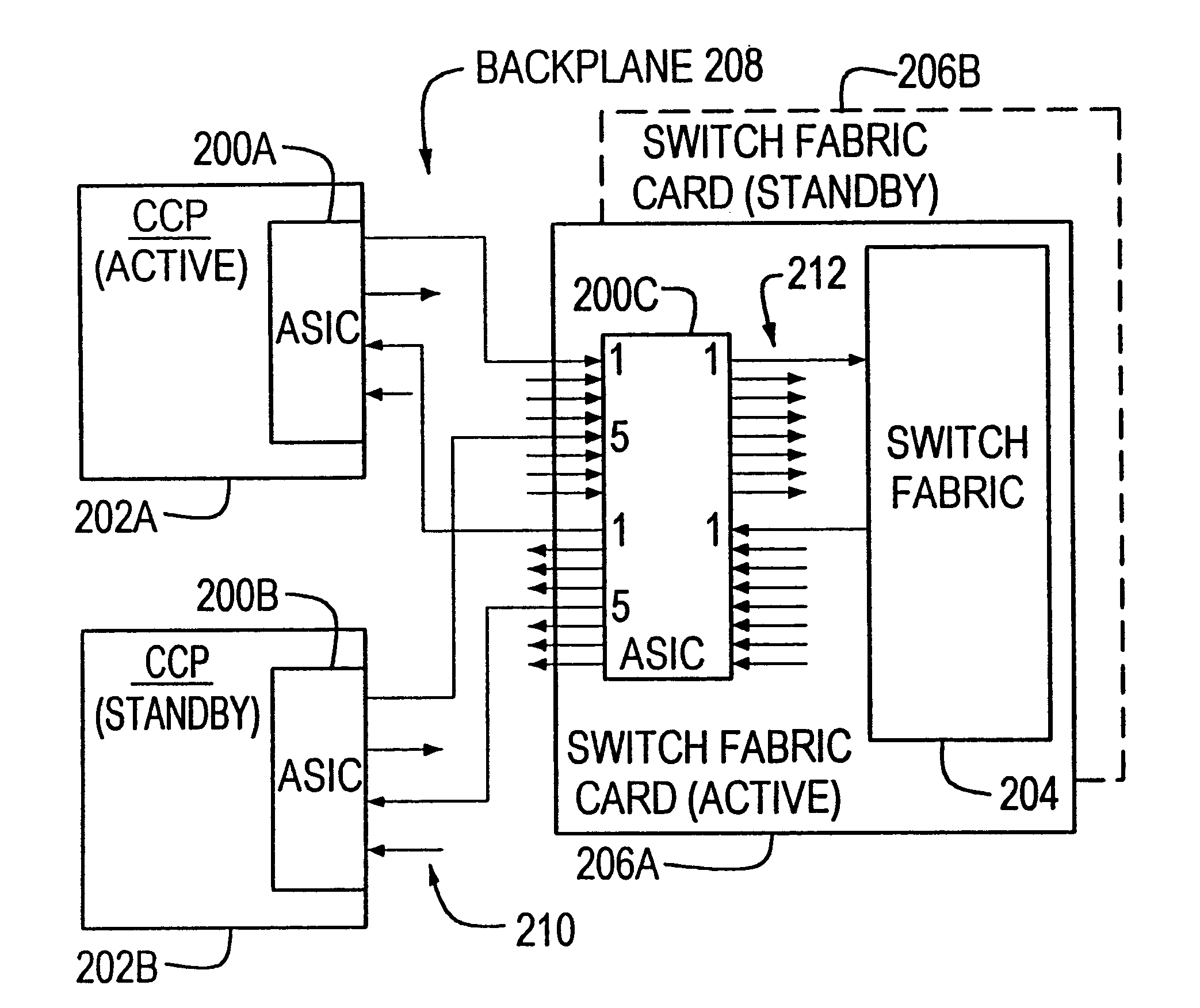
InactiveUS6259693B1Guaranteed normal transmissionLow data rateTime-division multiplexCircuit switching systemsNetwork switchDistributed computing
An apparatus and method for enabling the combination of multiple streams of data cells into a single thread. By enabling plural input ports of an intermediate device to access a single parallel output port of the device, plural network switch elements share a single thread through a switch fabric. For instance, the method and apparatus permit interleaving the relatively low bandwidth cell outputs of two ATM network switch central control processors onto a single thread routed through an interconnected switch fabric. Certain of these cells are received from the switch fabric at a parallel input of the intermediate device, then routed to one of plural serial output ports. Pacing of cells provided to the plural serial input ports prevents exceeding the shared thread bandwidth.
Owner:ASCEND COMMUNICATIONS
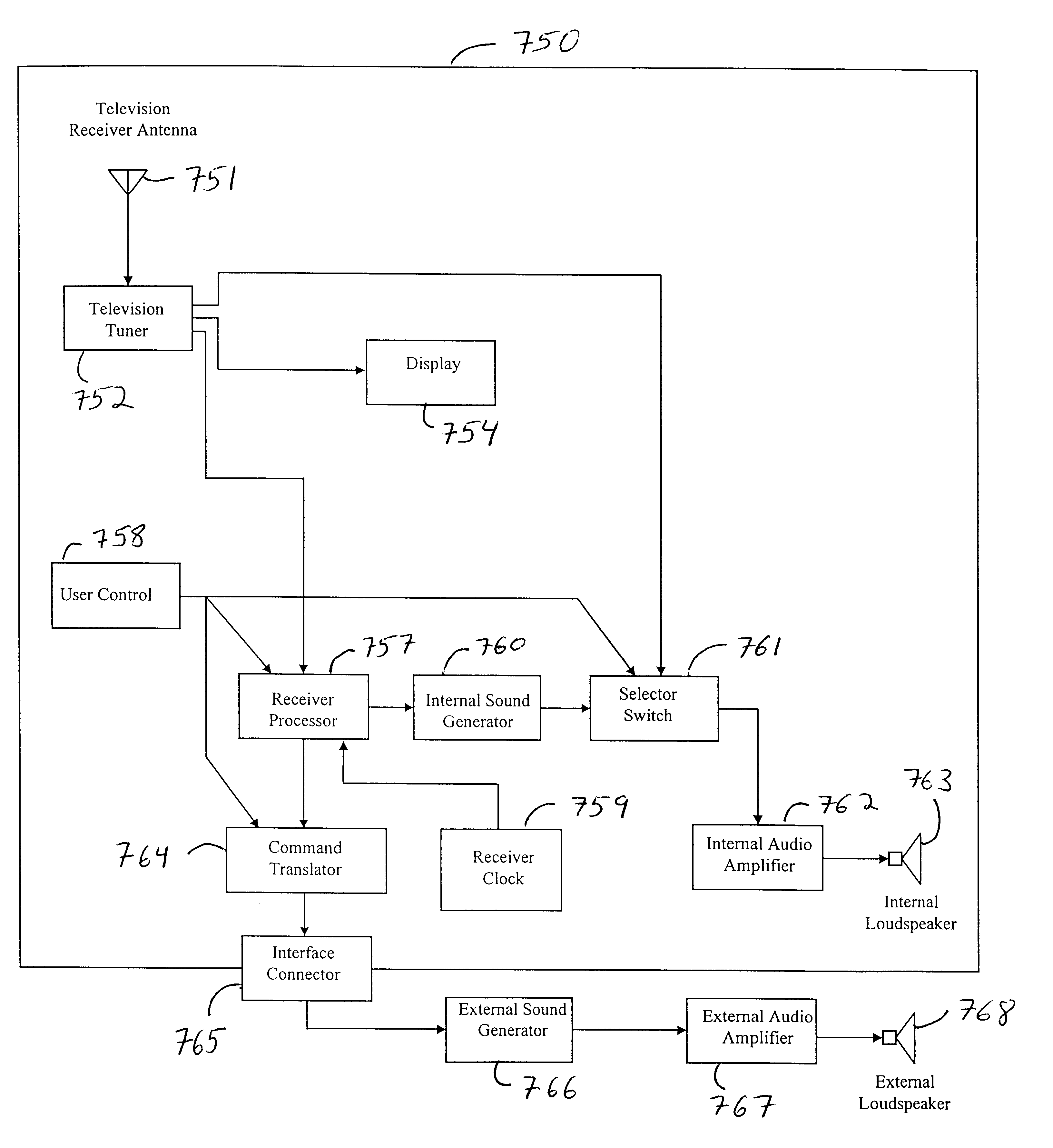
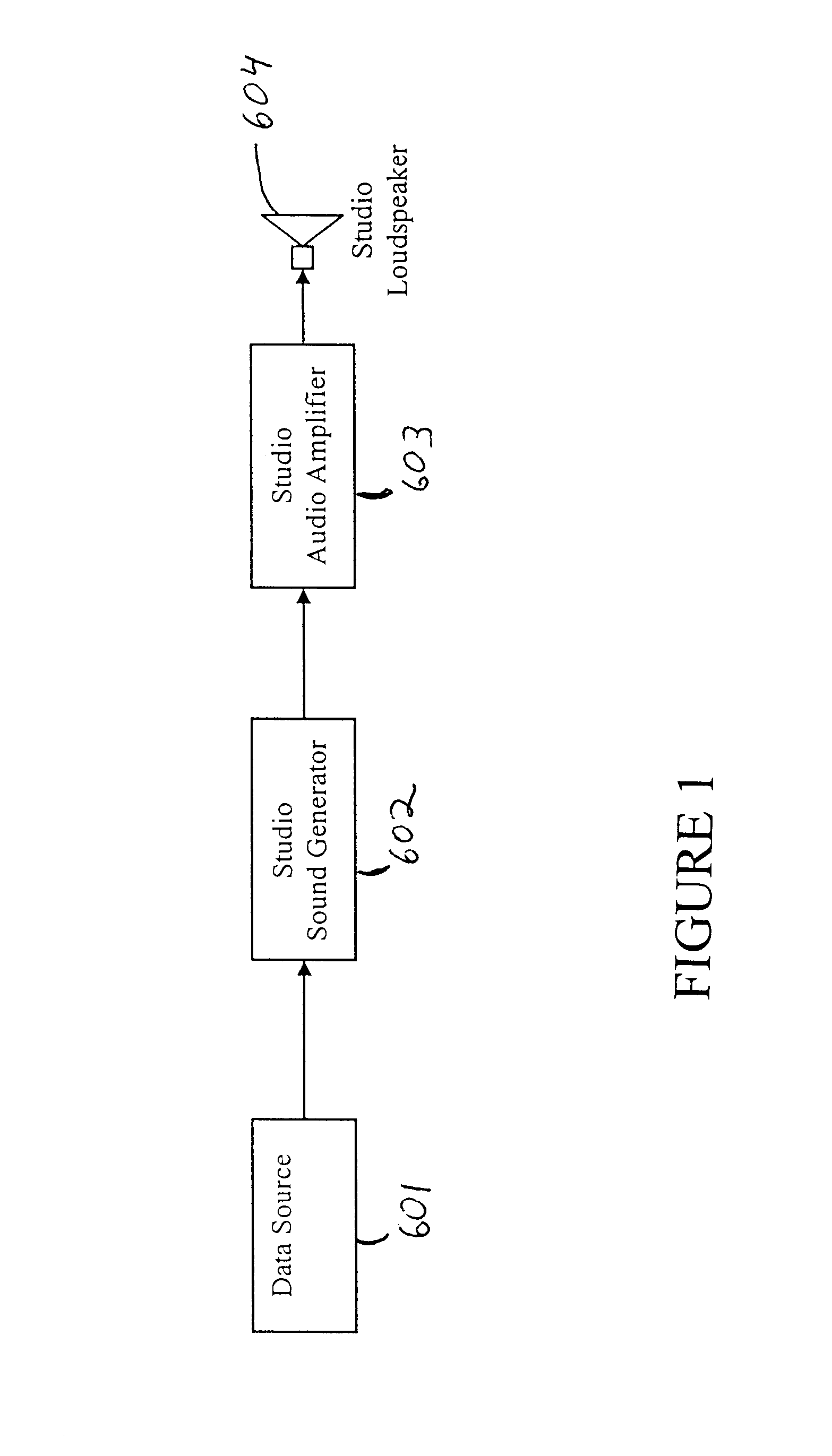
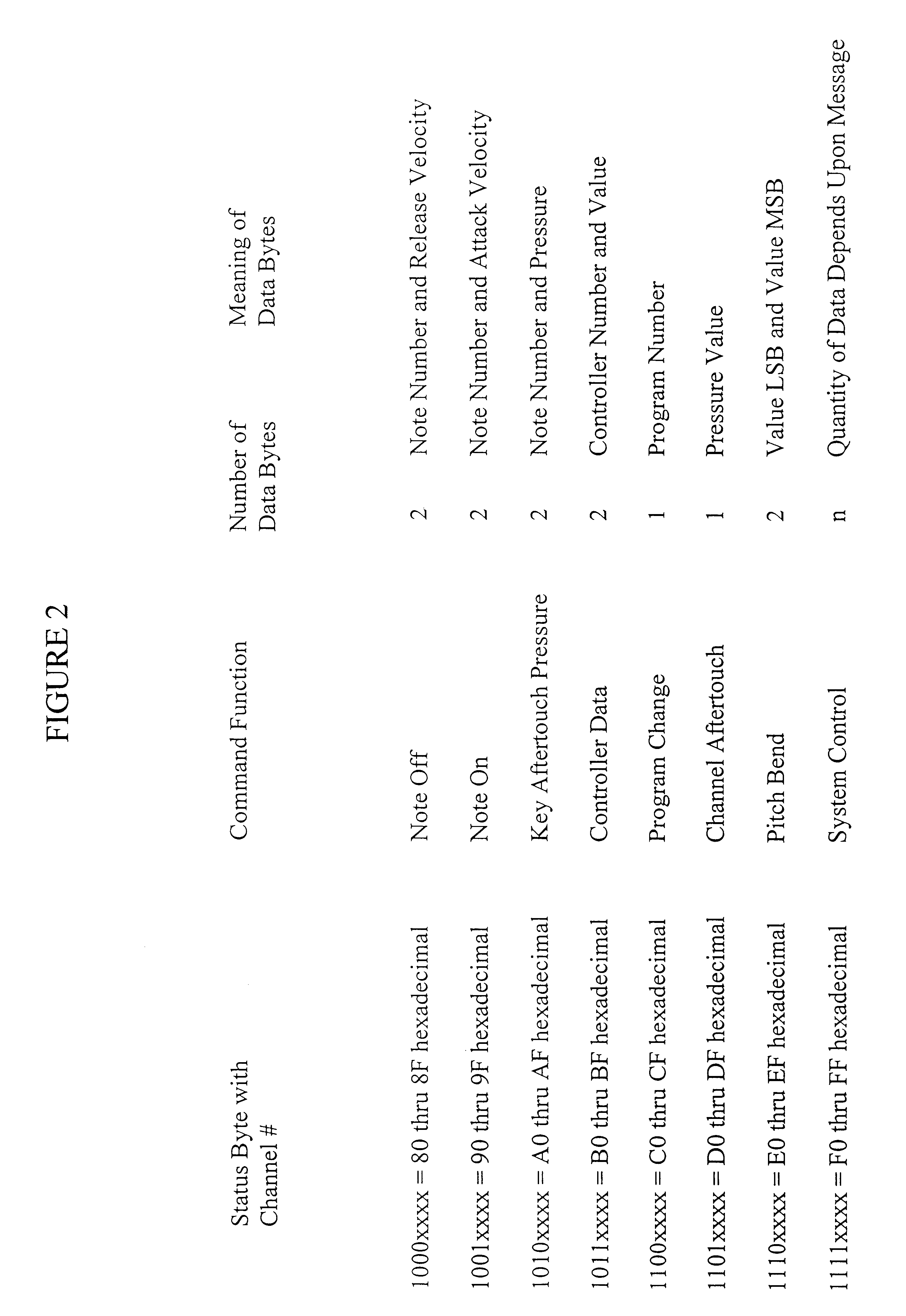
Method and apparatus for audio broadcast of enhanced musical instrument digital interface (MIDI) data formats for control of a sound generator to create music, lyrics, and speech
InactiveUS6462264B1Inhibit outputImprove speech clarityElectrophonic musical instrumentsCode conversionCarrier signalData format
A method and apparatus for the transmission and reception of broadcasted instrumental music, vocal music, and speech using digital techniques. The data is structured in a manner similar to the current standards for MIDI data. Transmitters broadcast the data to receivers which contain internal sound generators or an interface to external sound generators that create sounds in response to the data. The invention includes transmission of multiple audio data signals for several languages on a conventional radio and television carrier through the use of low bandwidth data. Error detection and correction data is included within the transmitted data. The receiver has various error compensating mechanisms to overcome errors in data that cannot be corrected using the error correcting data that the transmitter sent. The data encodes for elemental vocal sounds and music.
Owner:ELAM CARL
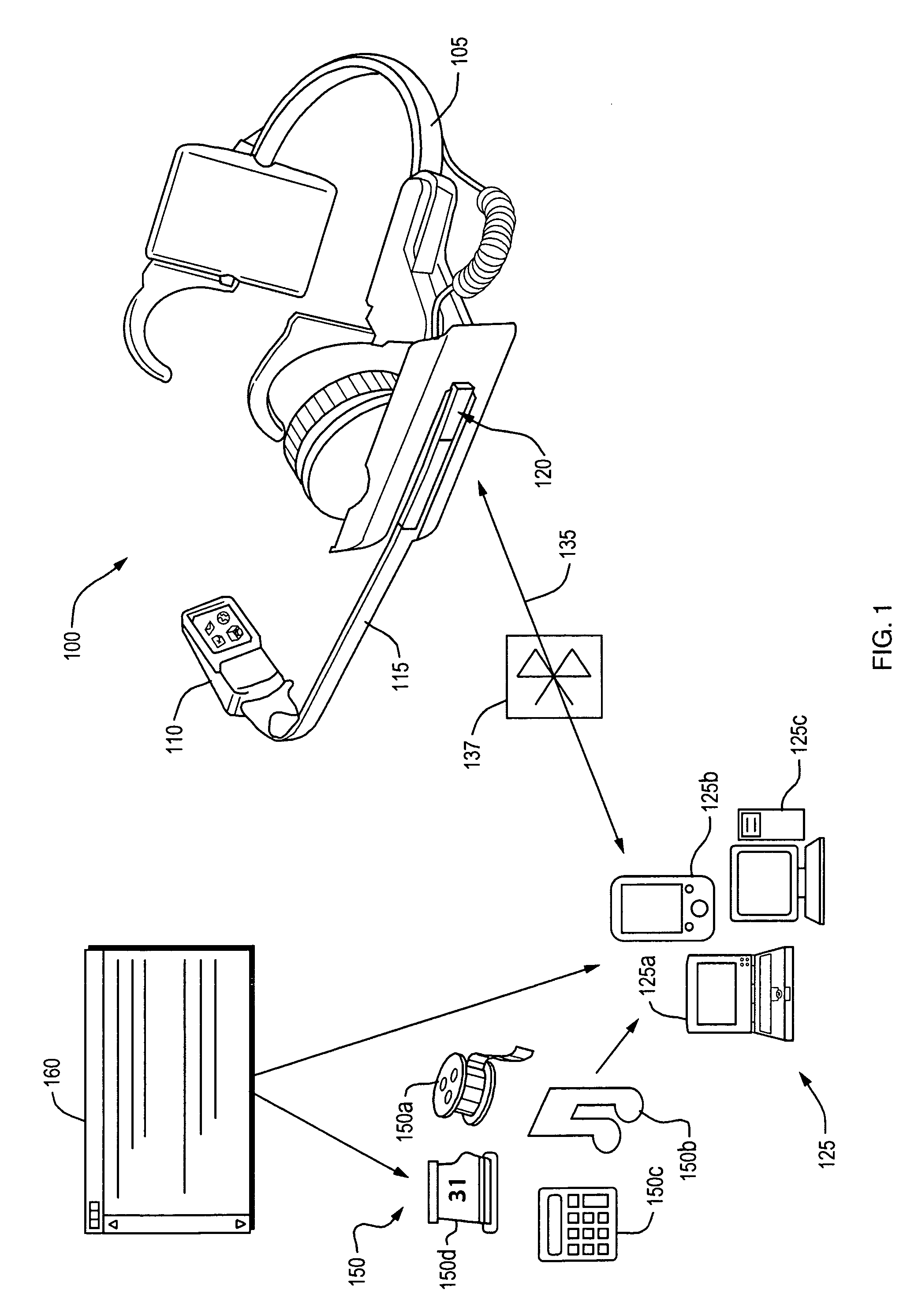
Method and apparatus for transporting video signal over Bluetooth wireless interface
ActiveUS8355671B2Great convenience and mobilityAvoid problemsTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital videoHeadphones
A wireless wearable video headset device useful for viewing and listening to multimedia content. In one embodiment, the device operates by receiving a digital encoded audio / video signal from a host device of a Bluetooth™ wireless connection, the Bluetooth™ connection established via a Serial Port Profile (SPP), and the digital video signal having been previously compressed with Windows Media Video (WMV) or H. 264 compliant compression. The received digital audio / video signal is then forwarded over a Universal Serial Bus (USB) connection to an internal processor which then decompressed video content in the digital video signal to generate a component video signal that is suitable for handling by a display driver.
Owner:KOPIN CORPORATION
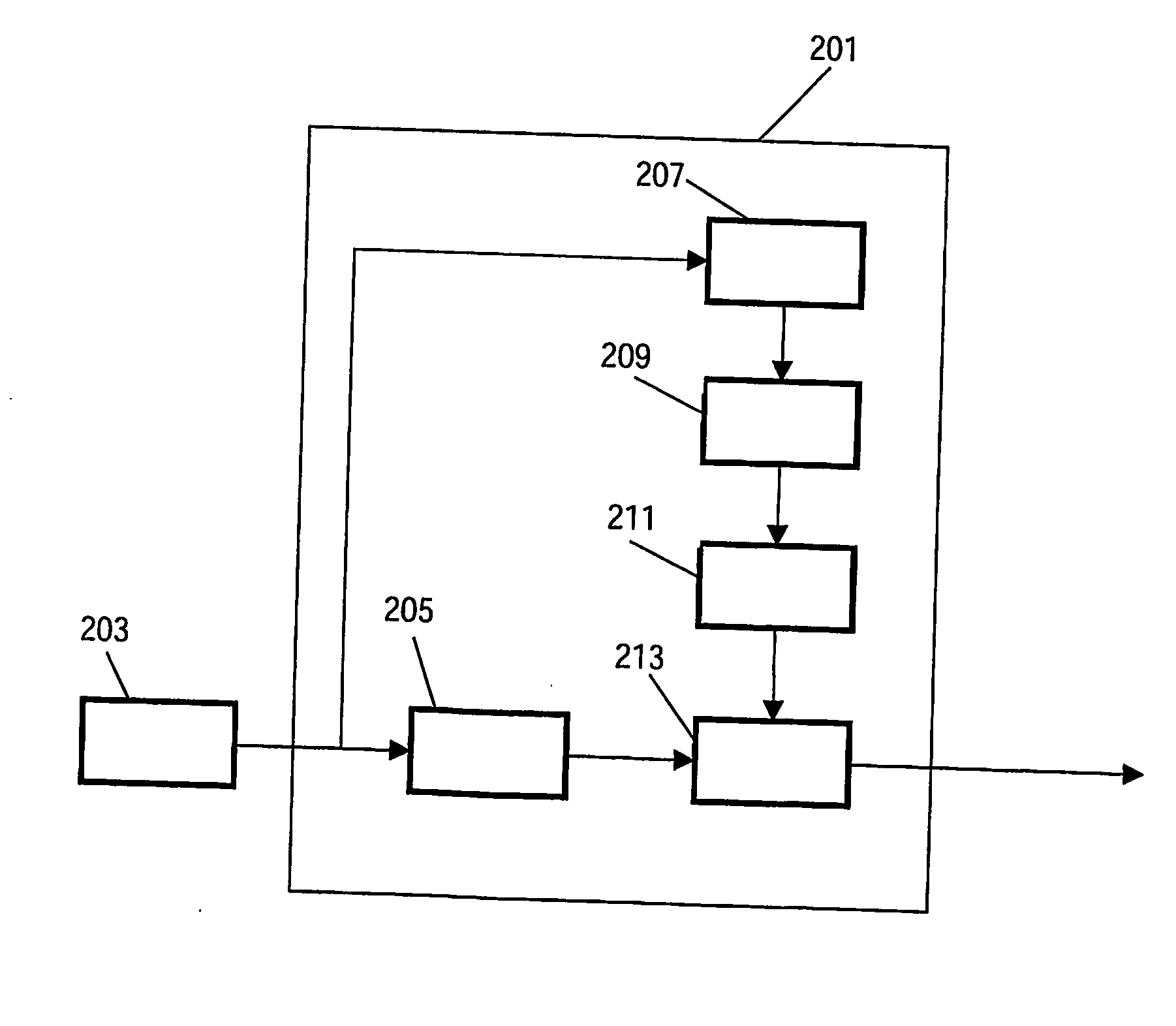
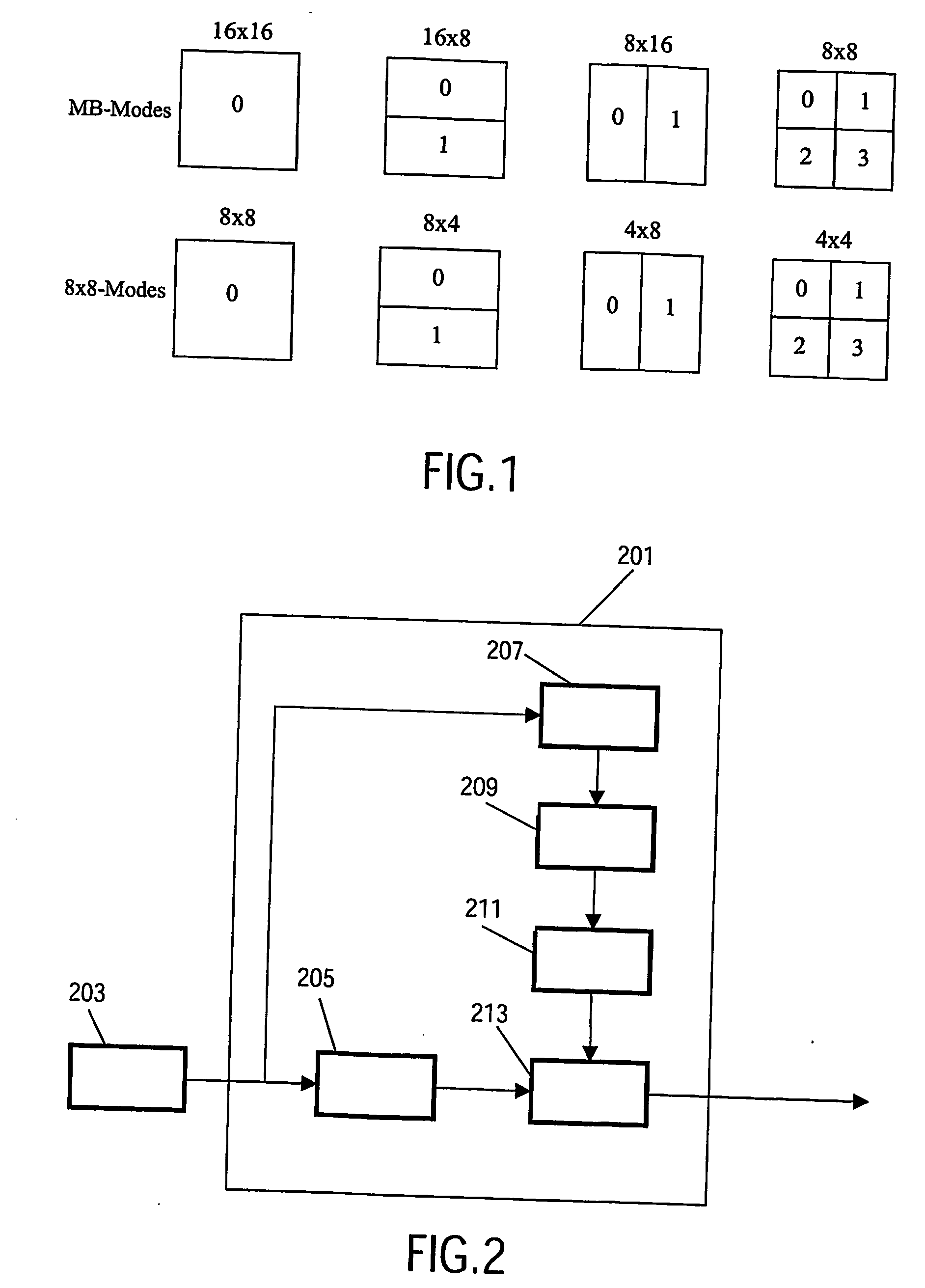
Video encoding
InactiveUS20060165163A1Improve performanceReduce lossesColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionVideo encoding
The invention relates to a video encoder (201) for encoding a video signal. The video encoder comprises a segmentation processor (207) which divides the picture into picture regions. Preferably, picture regions having a high degree of flatness or uniformity are determined in this way. A characteristics processor (209) determine a spatial frequency characteristic for each picture region, and a coding controller (211) selects an encoding block size, such as a prediction block size for motion estimation, in response to the spatial frequency characteristic. An encode processor (213) encodes the picture using the selected encoding block size. Specifically, increasing block sizes are selected for increasing degrees of uniformity or flatness indicated by the spatial frequency characteristic. Thereby, an increasing proportion of high frequency components and a consistent choice of encoding block sizes are maintained, and thus the coding artefacts from many encoders having variable prediction block sizes is reduced. The invention is particularly suitable for H.264 and similar encoders.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Electric shaver with imaging capability
InactiveUS20100186234A1Reduce memory sizeLow data rateTelevision system detailsHair-singeingVisibilityWired communication
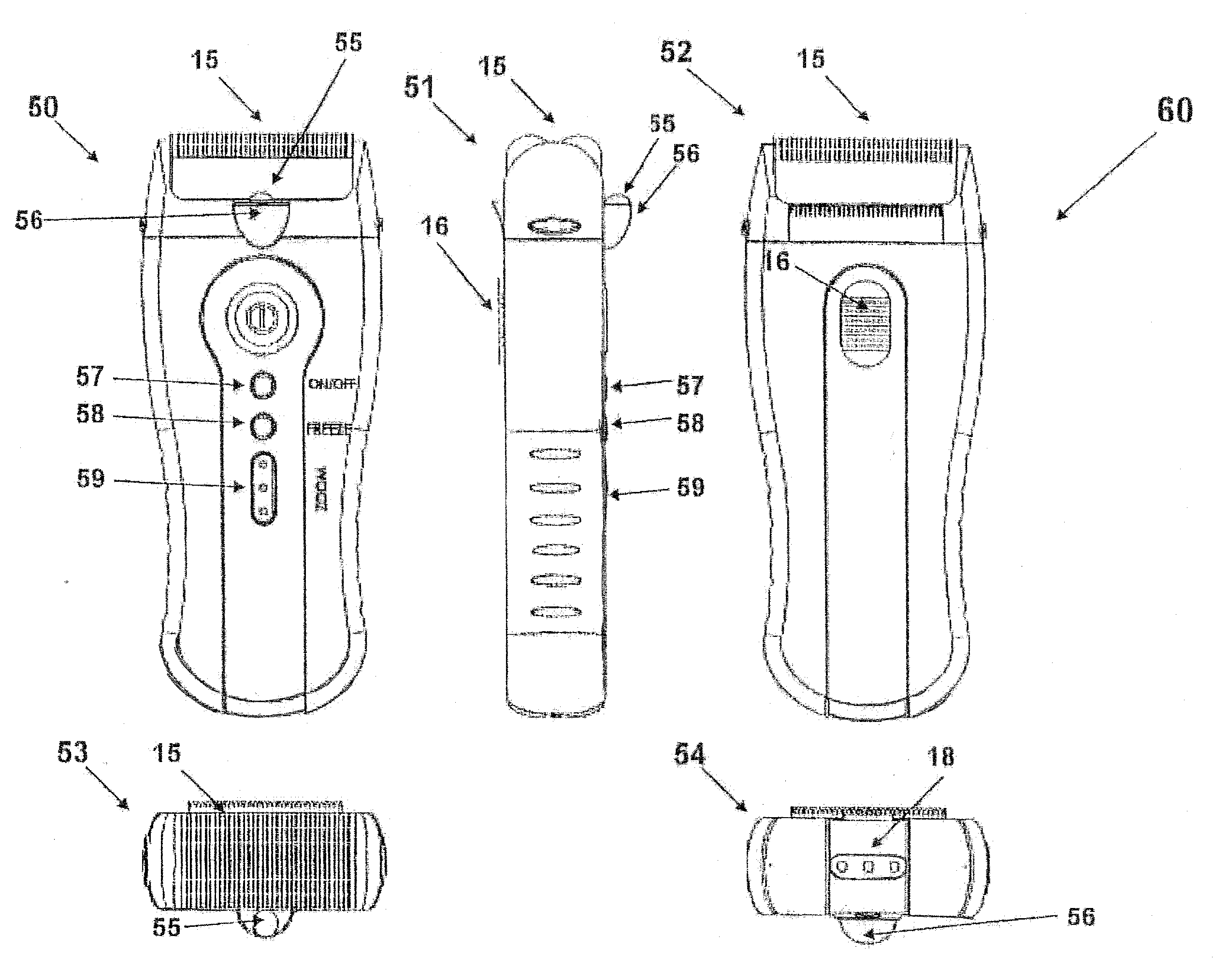
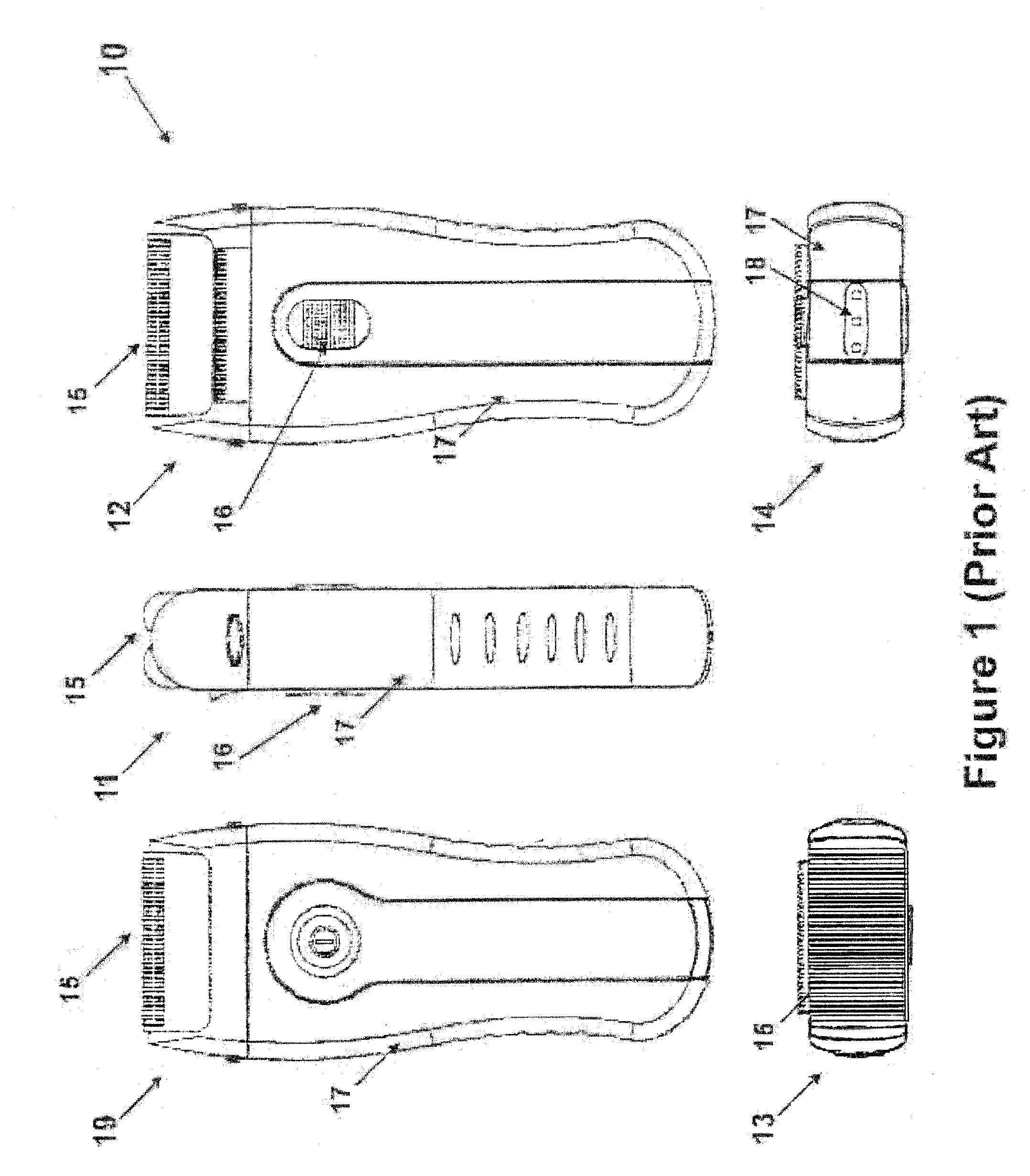
System and method for improving the shaving experience by providing improved visibility of the skin shaving area. A digital camera is integrated with the electric shaver for close image capturing of shaving area, and displaying it on a display unit. The display unit can be integral part of the electric shaver casing, or housed in a separated device which receives the image via a communication channel. The communication channel can be wireless (using radio, audio or light) or wired, such as dedicated cabling or using powerline communication. A light source is used to better illuminate the shaving area. Video compression and digital image processing techniques are used for providing for improved shaving results. The wired communication medium can simultaneously be used also for carrying power from the electric shaver assembly to the display unit, or from the display unit to the electric shaver.
Owner:MAY PATENTS LTD
Apparatus and method for improving dynamic range and linearity of CMOS image sensor
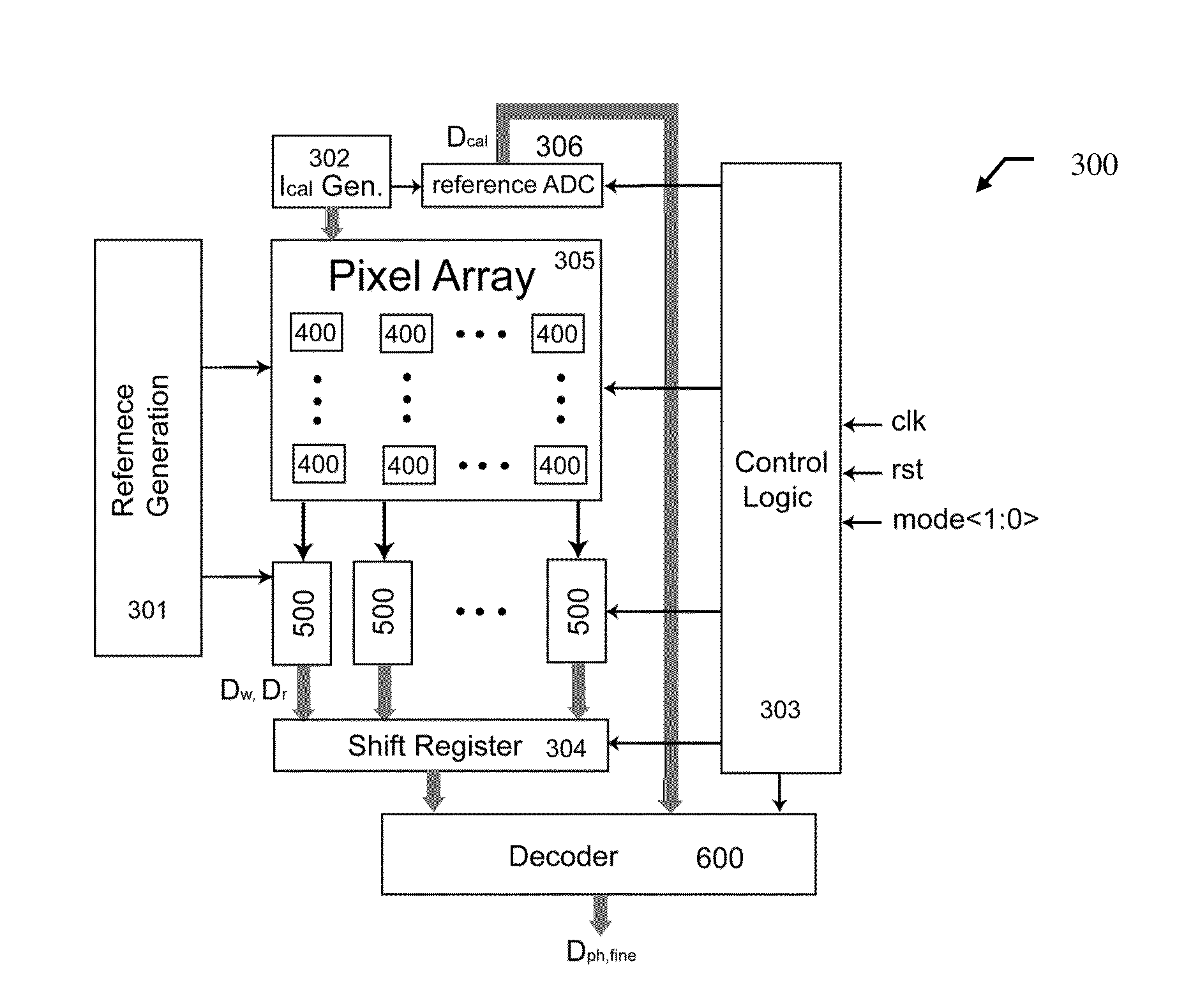
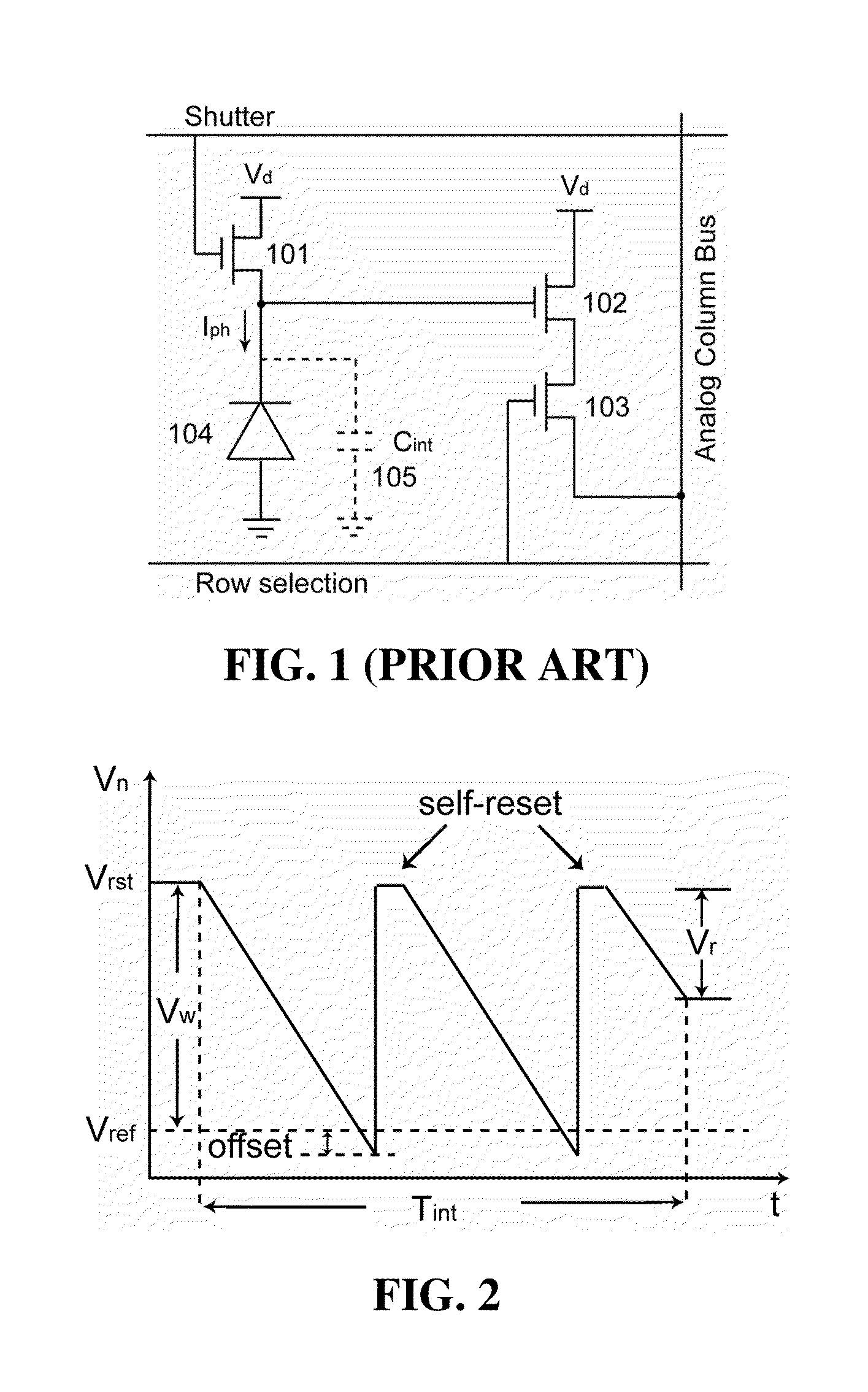
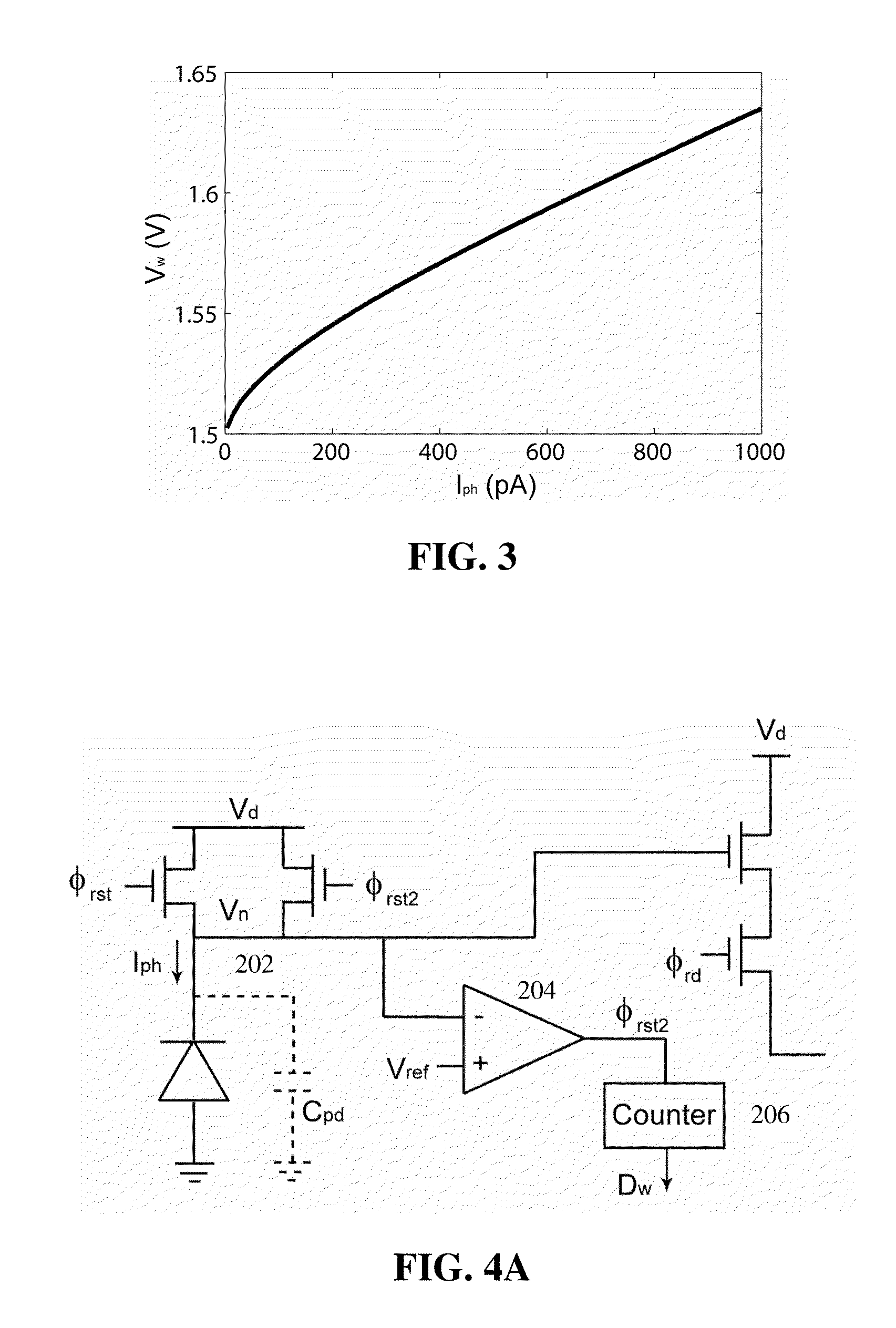
ActiveUS20100194956A1Improve linearityImprove signal-to-noise ratioTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOSControl signal
Described herein is a circuit and related method for improving the dynamic range and the linearity characteristic of a CMOS image sensor. In various embodiments of the CMOS image sensor, a current sampler, a comparator, and a 1-bit memory are incorporated in each pixel circuit. In the image sensor, pixels are arranged in columns and a column slice is used to read the digital and analog singles from each column. In addition, a calibration circuit is incorporated in the sensor circuit for providing calibration current, which is used to generate calibration parameter. The image sensor operates in three non-overlapping modes: the difference mode, the WDR mode, and the calibration mode. The image sensor is switched among the three modes by control signals, which are provided to the image sensor by various control circuits. The image sensor normally operates in the difference mode and switches to the WDR mode when the difference between consecutive frames is over a threshold. The calibration mode allows the image sensor generate calibration parameters which are used to improve the linearity of the sensor through a interpolation method.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
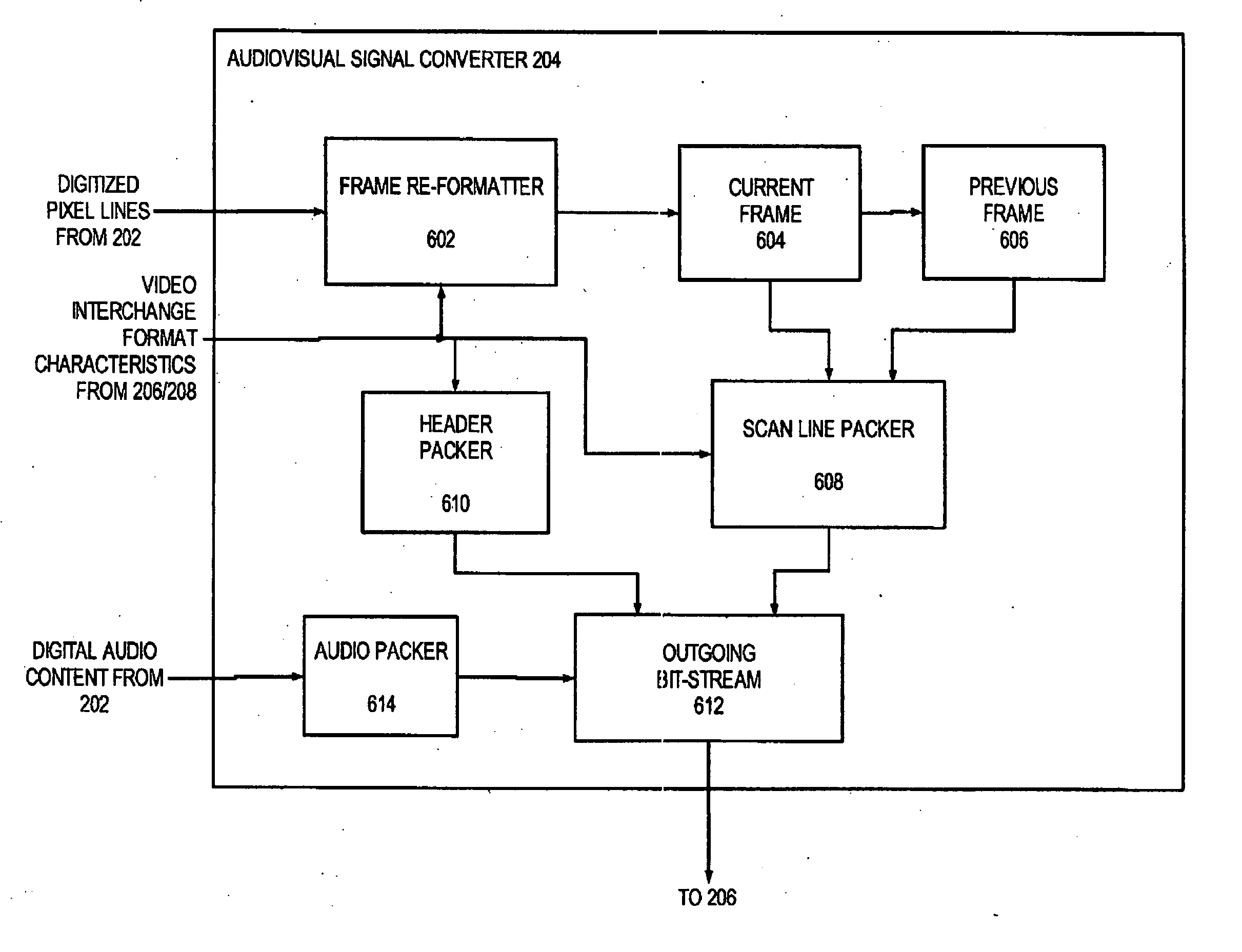
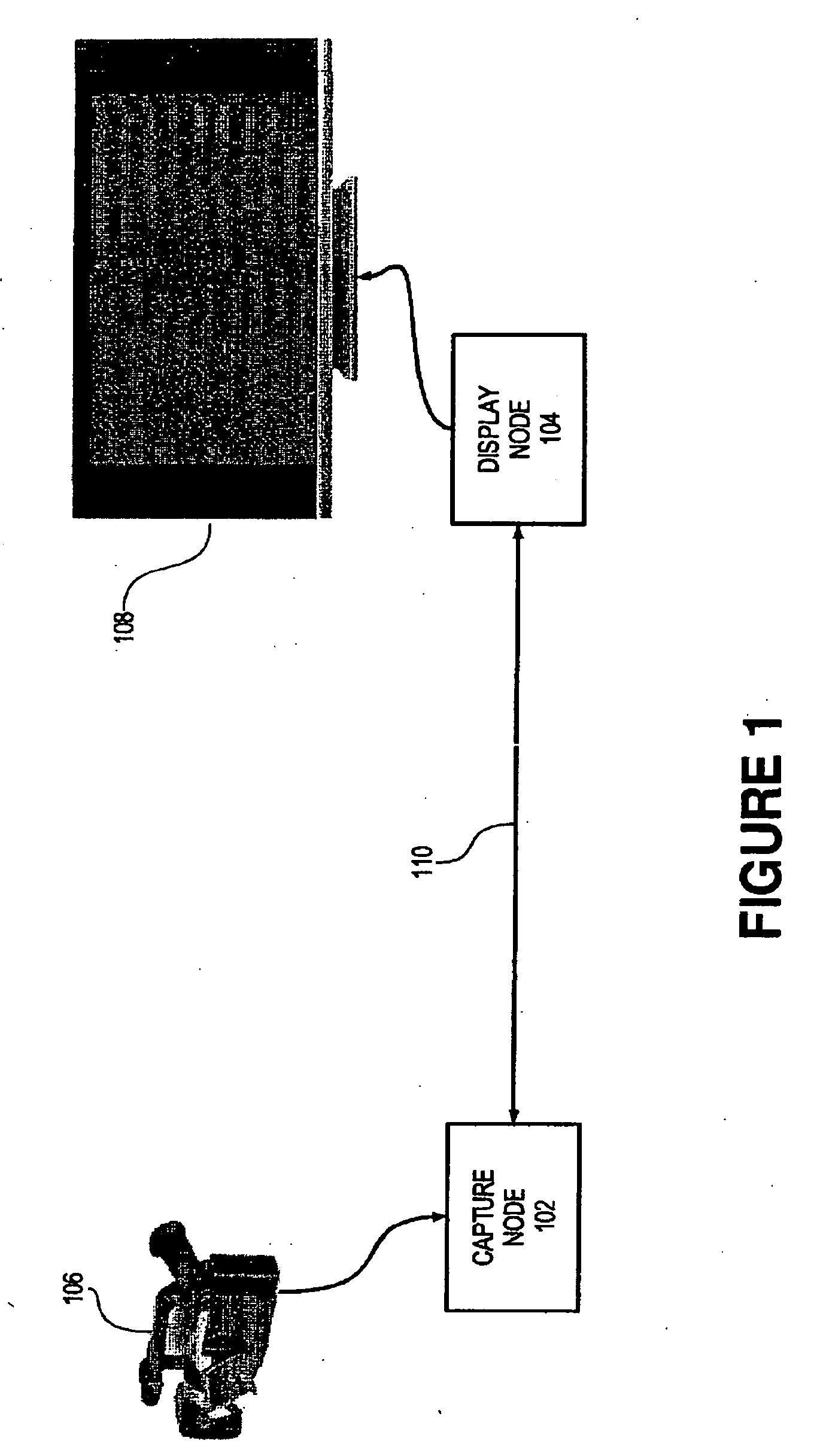
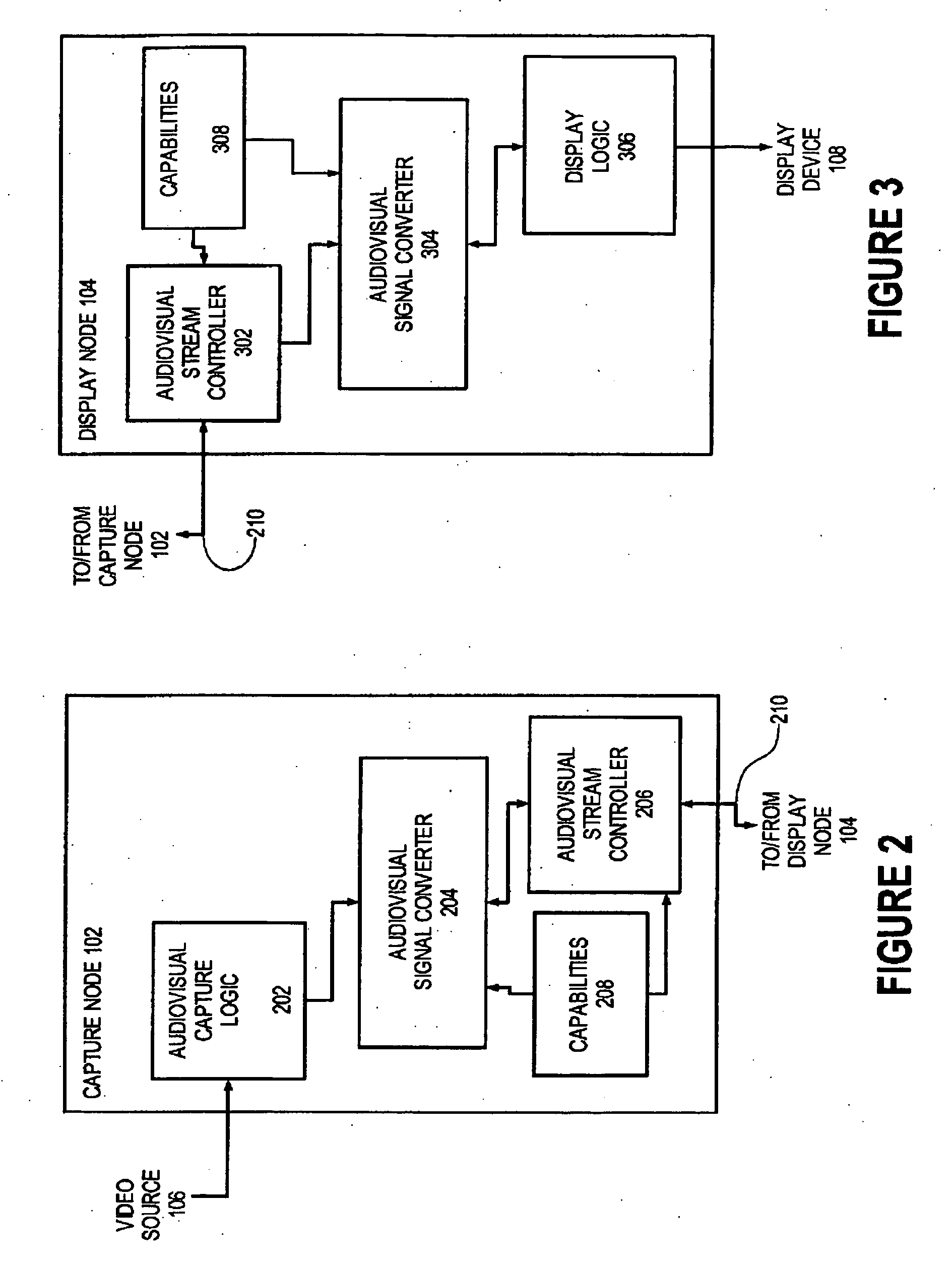
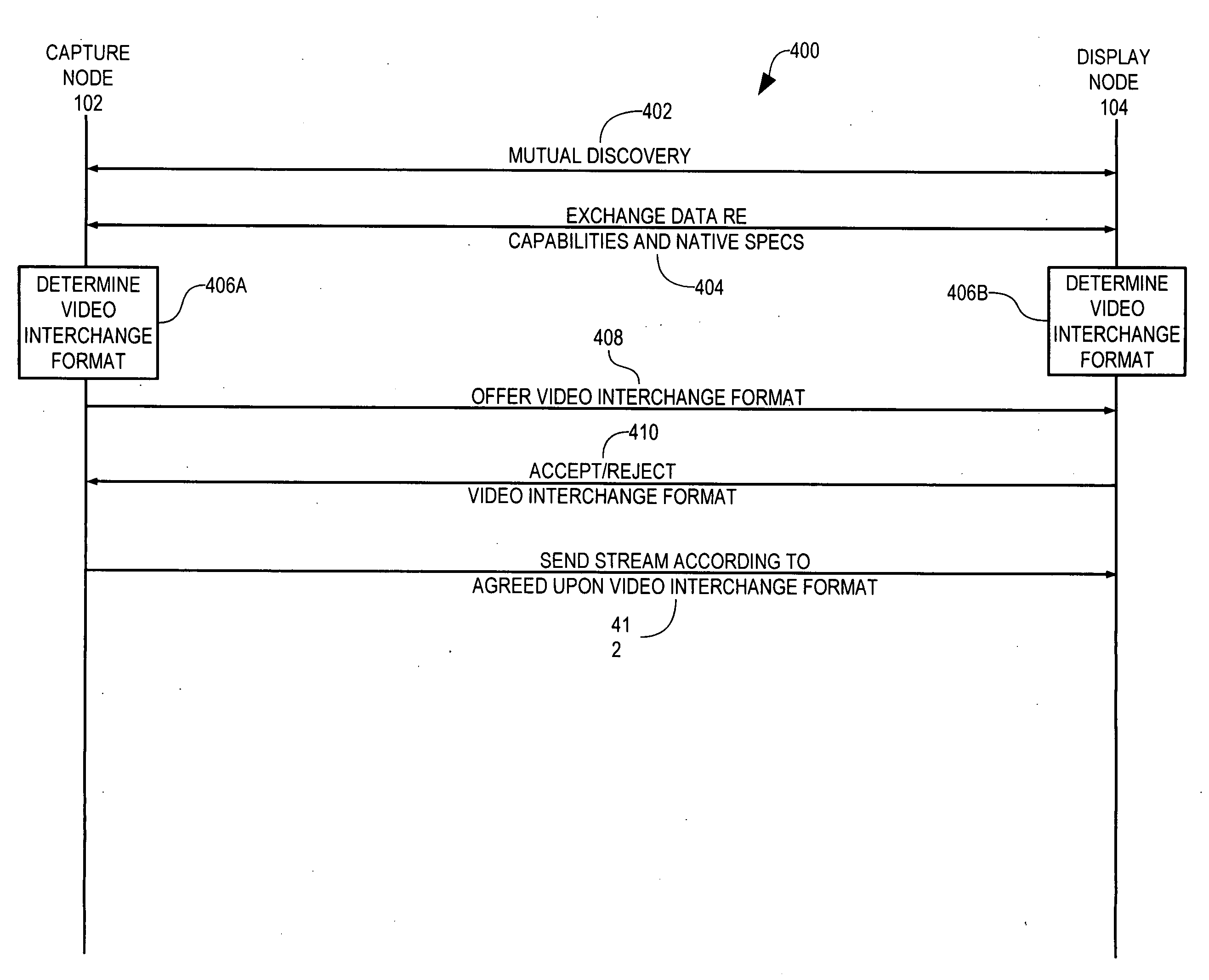
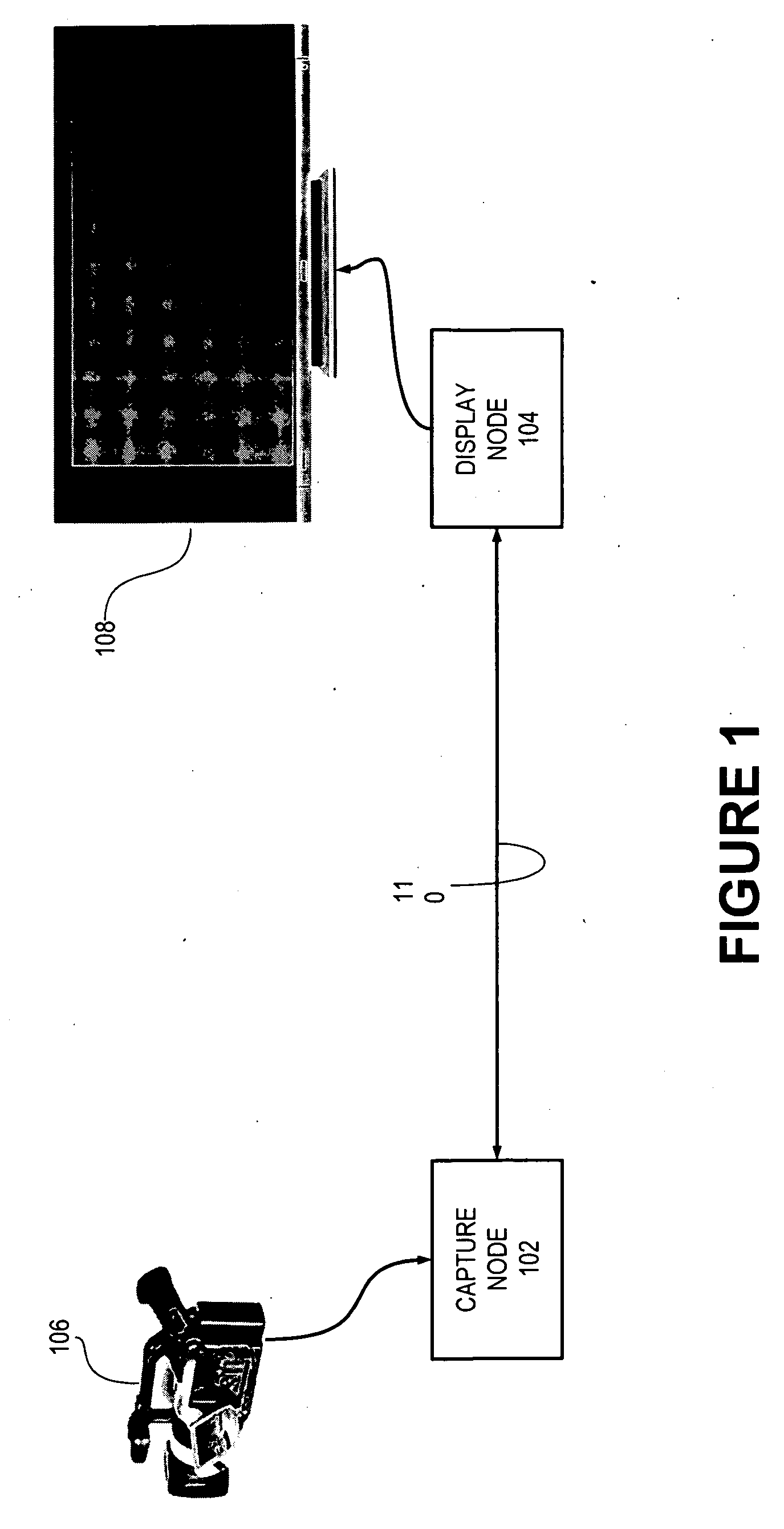
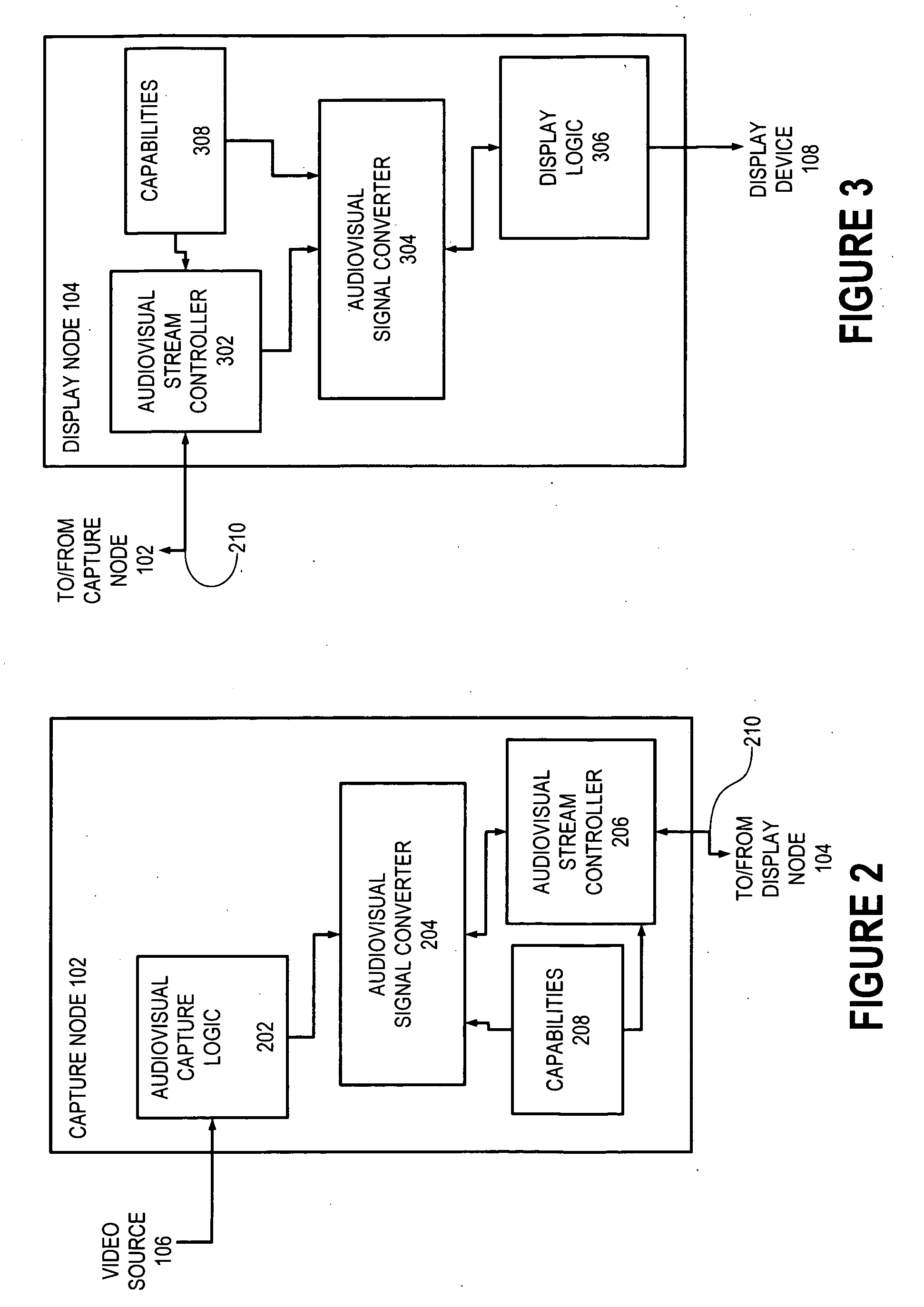
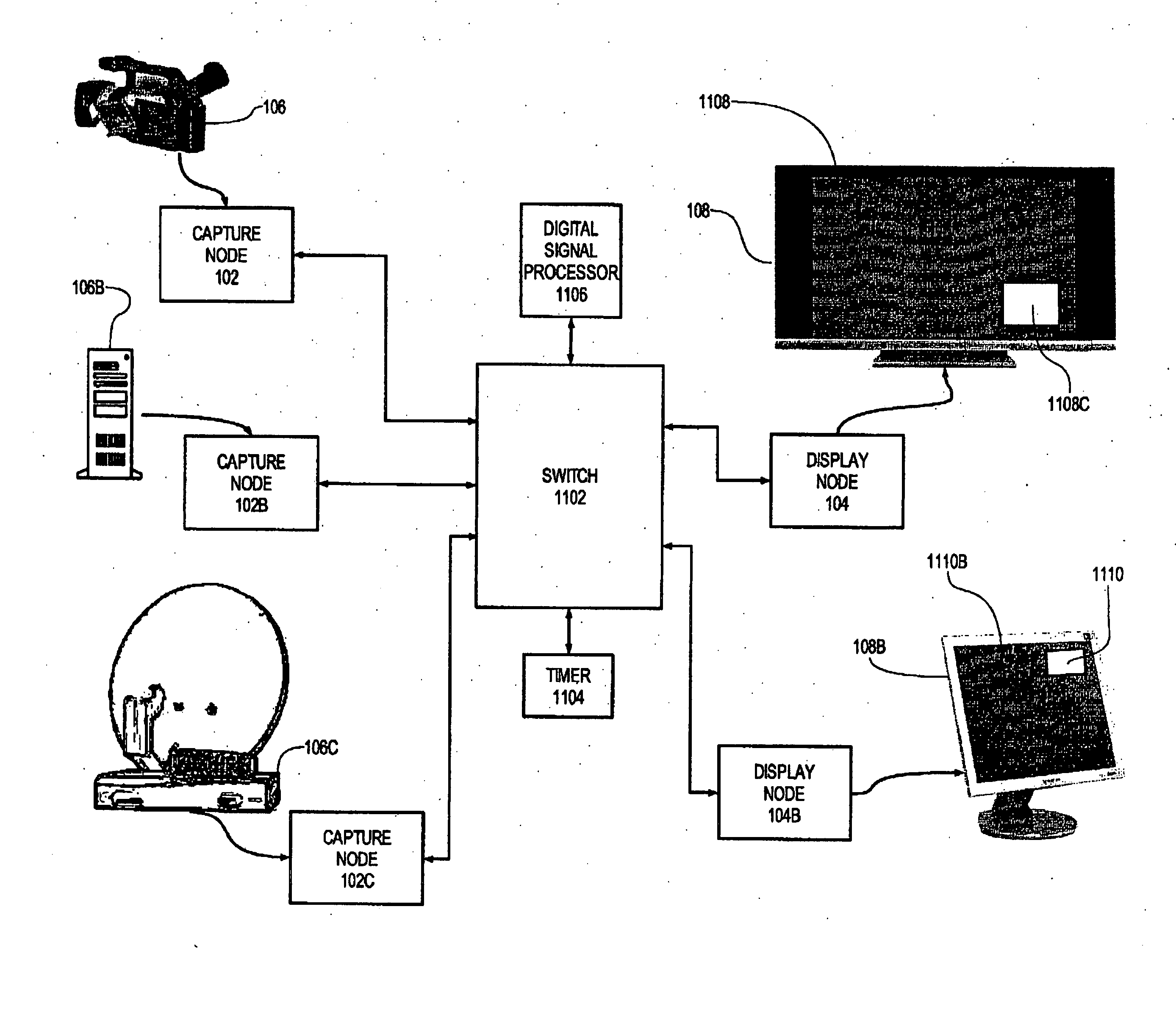
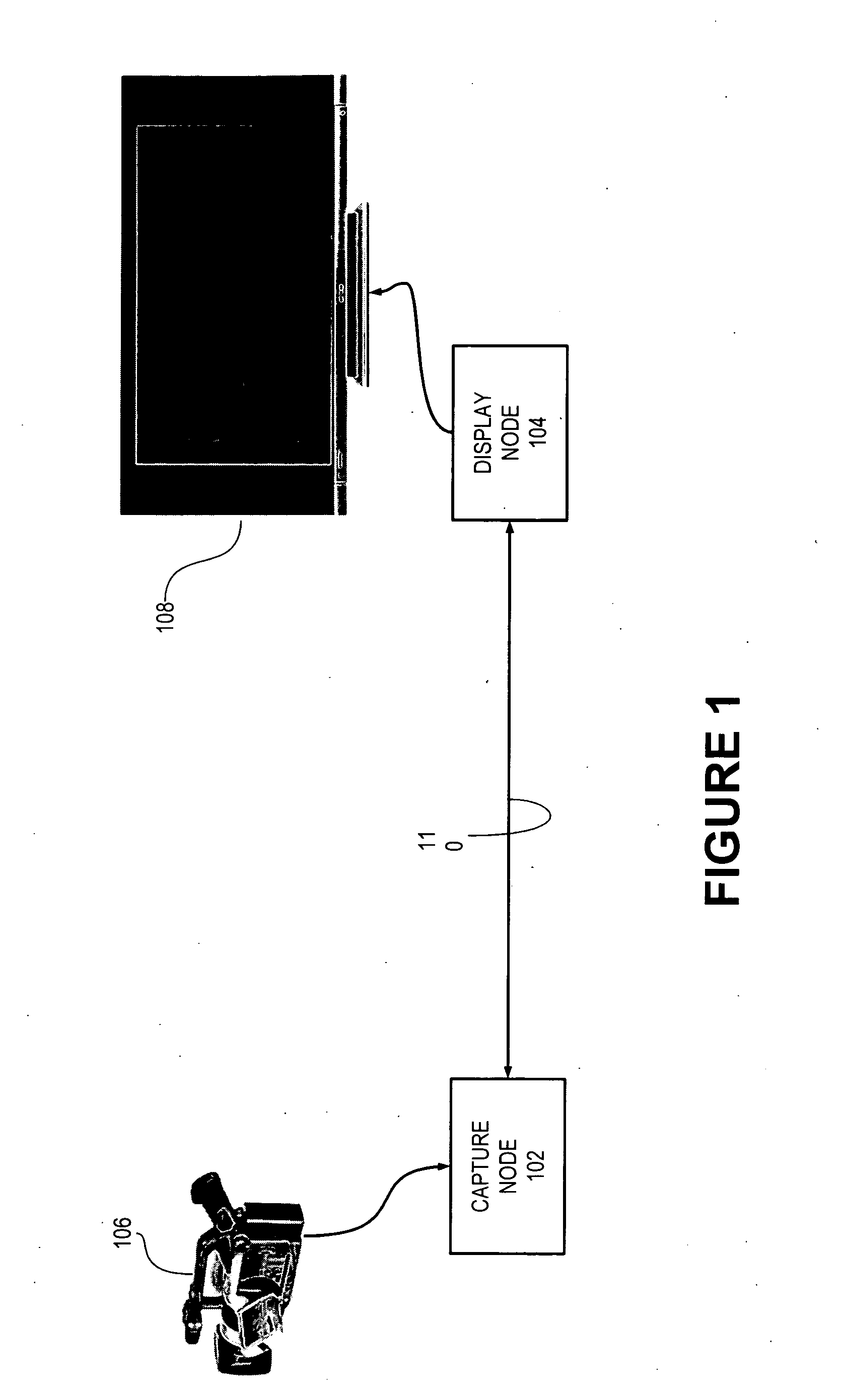
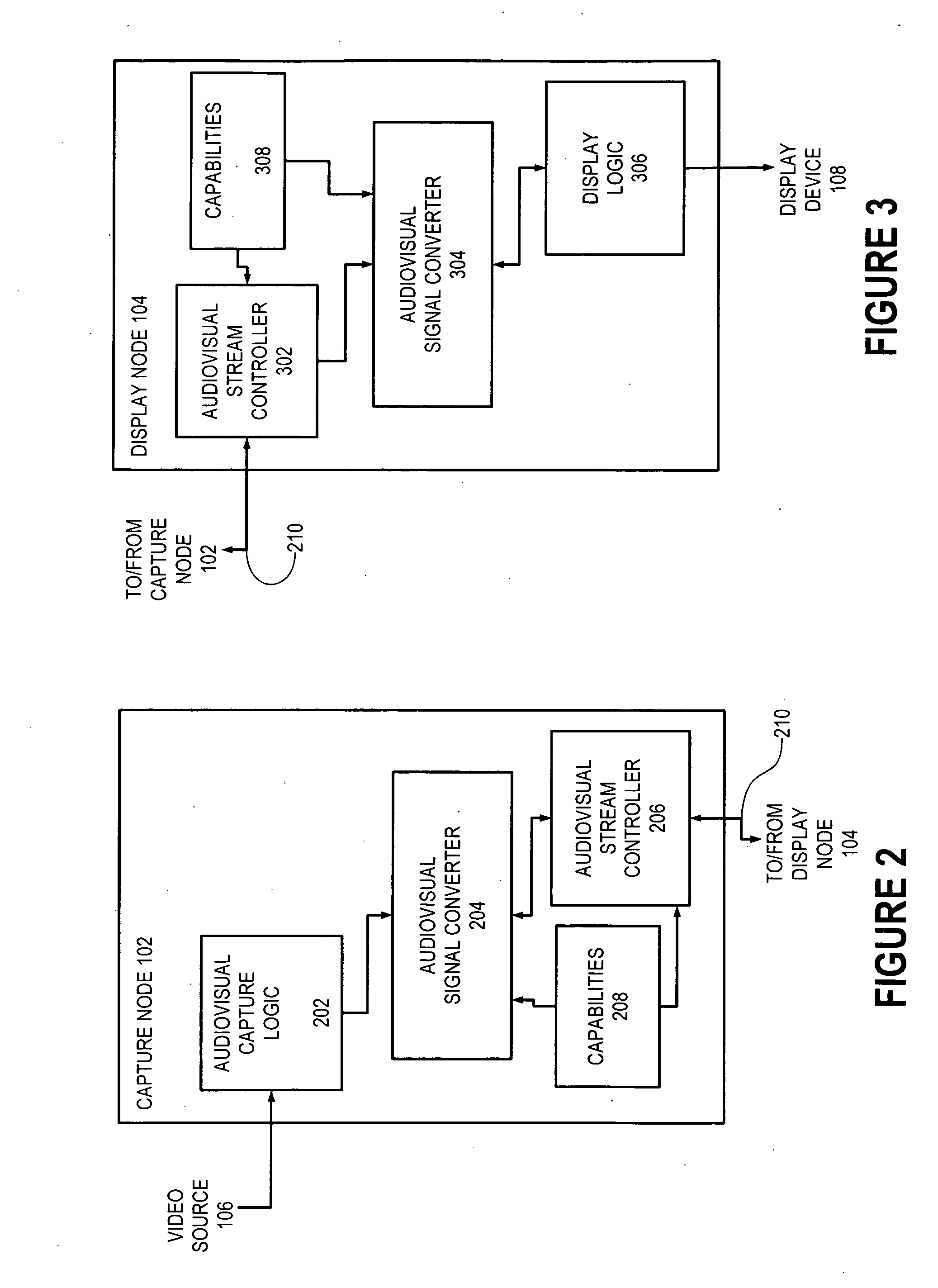
Capture node for use in an audiovisual signal routing and distribution system
ActiveUS20060239294A1Format conversionHeterogeneous distributionTelevision system detailsTime-division multiplexSignal routingDistribution system
An audiovisual signal is converted from a native format to a digital, packetized interchange format and transported between a capture node and a display node through a switch. The display node converts the audiovisual signal from the interchange format to a displayable format and causes display of the audiovisual signal. The use of a switch for video routing and distribution allows one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, and many-to-many distribution. The use of a device-independent interchange format allows concurrent distribution of multiple heterogeneous audiovisual signals.
Owner:JUPITER SYST LLC +1
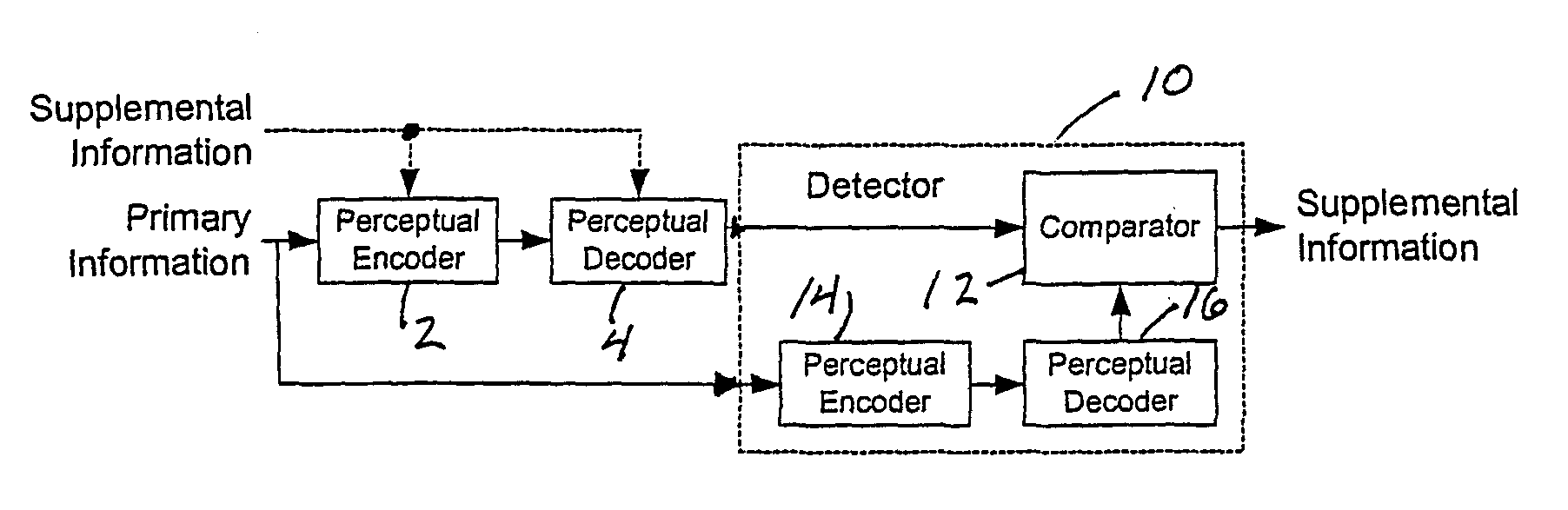
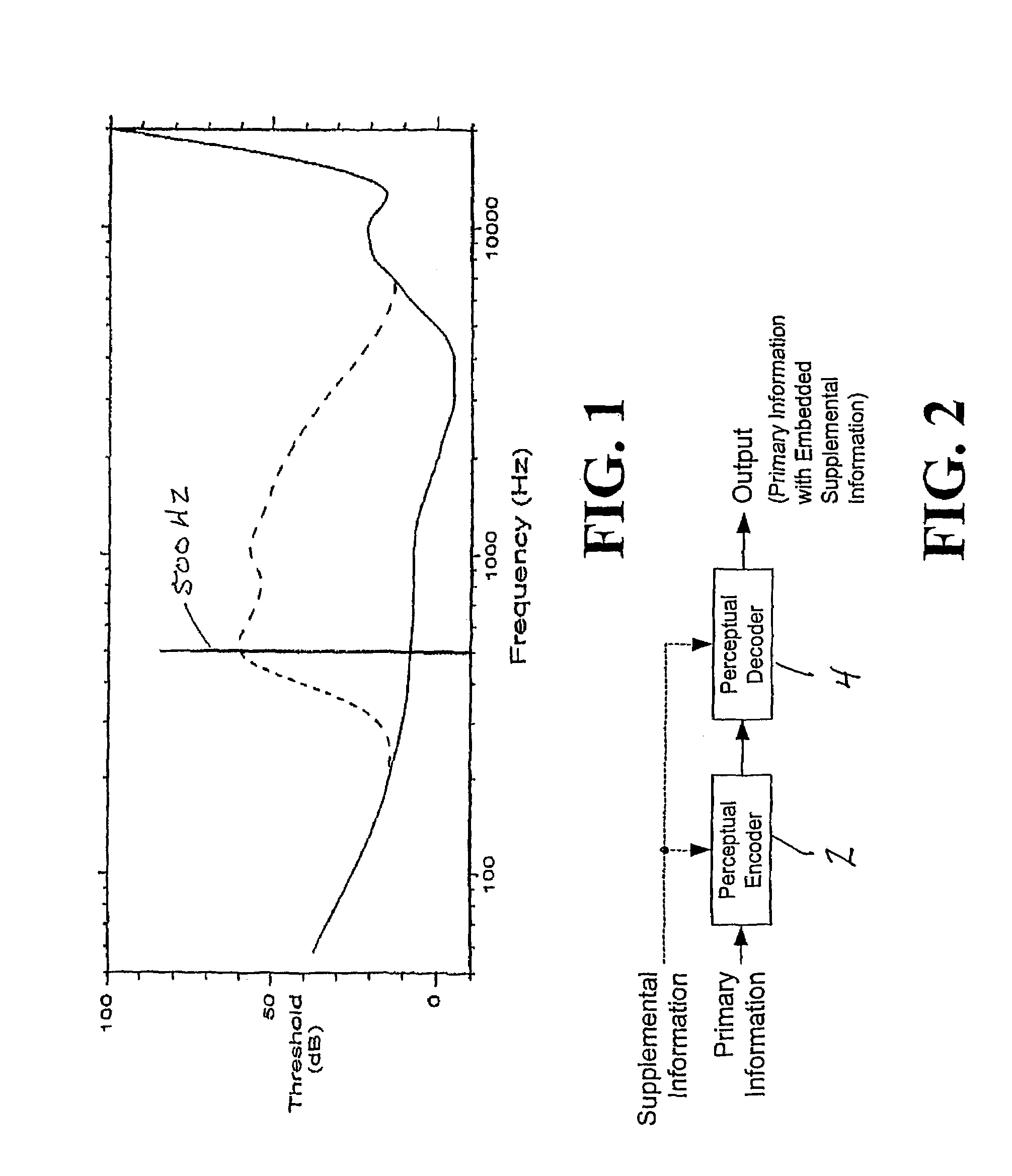
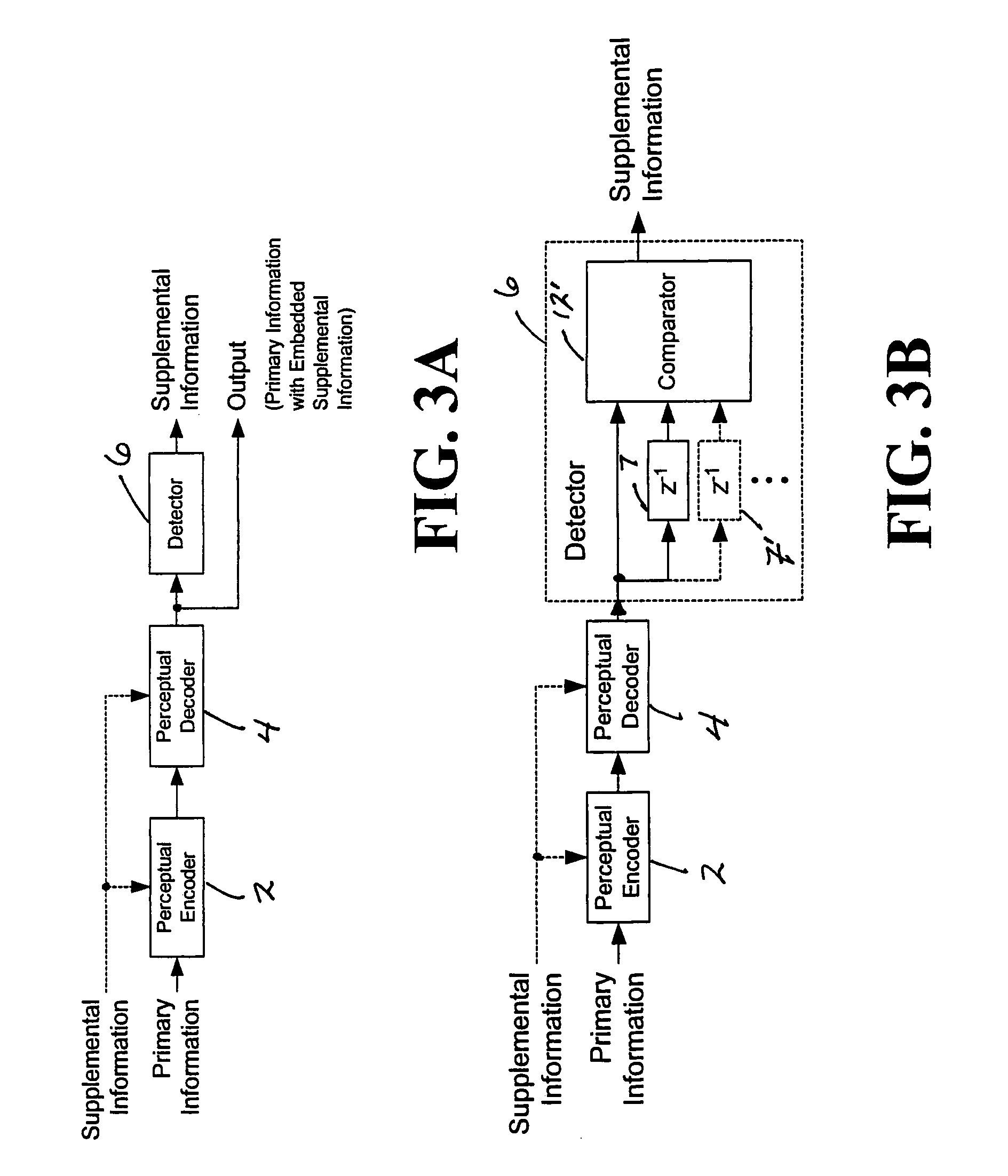
Modulating one or more parameters of an audio or video perceptual coding system in response to supplemental information
ActiveUS7395211B2Maximized strengthPerceptibility is minimizedTelevision system detailsSpeech analysisComputer architecturePerceptual coding
A method of modifying the operation of the encoder function and / or the decoder function of a perceptual coding system in accordance with supplemental information, such as a watermark, so that the supplemental information may be detectable in the output of the decoder function. One or more parameters are modulated in the encoder function and / or the decoder function in response to the supplemental information.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
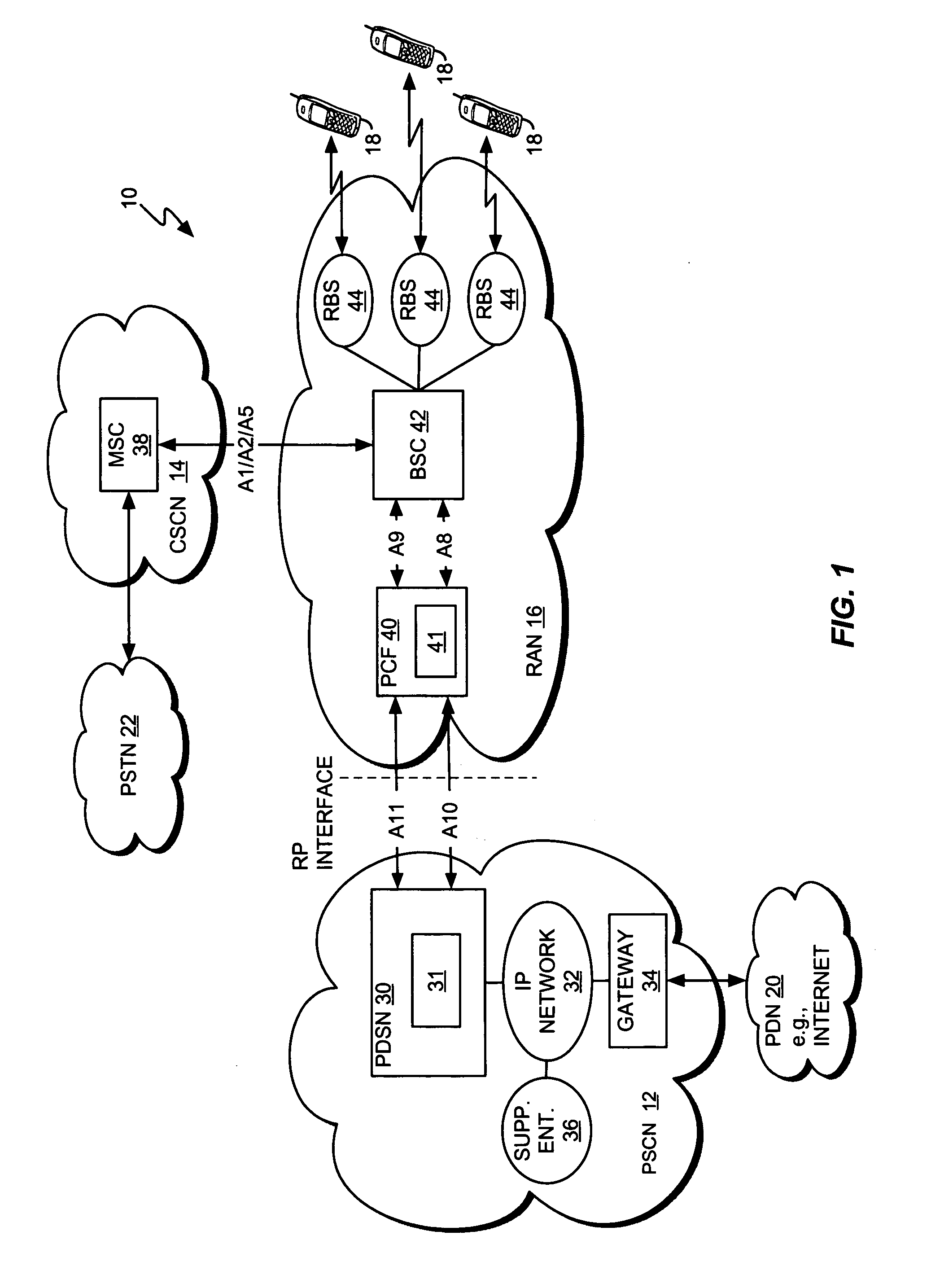
High-speed data transmission in a digital mobile communication system
InactiveUS6148209AReduce data transfer rateLow data rateNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMobile communication systemsMobile station
A data transmission in a digital mobile communication system employing a so-called multi-channel access technique, in which one or more traffic channels may be allocated to a mobile station for data transmission in accordance with the data transfer rate required by the application using the mobile station. Upon establishing a data call, the mobile station indicates to the mobile communication network the maximum and optionally the minimum requirements for the user data transfer rate. The mobile communication network assigns the mobile station for a data call a channel configuration consisting of one or more traffic channels in connection with call set-up or handover, the channel configuration depending on the resources currently available in the mobile communication network and enabling performance of the data channel, which is not lower than the minimum requirement and not higher than the maximum requirement.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Display node for use in an audiovisual signal routing and distribution system
InactiveUS20060242669A1Exceeding bandwidthMinimize excessive use of bandwidthTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSignal routingComputer network
An audiovisual signal is converted from a native format to a digital, packetized interchange format and transported between a capture node and a display node through a switch. The display node converts the audiovisual signal from the interchange format to a displayable format and causes display of the audiovisual signal. The use of a switch for video routing and distribution allows one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, and many-to-many distribution. The use of a device-independent interchange format allows concurrent distribution of multiple heterogeneous audiovisual signals.
Owner:WOGSBERG ERIC
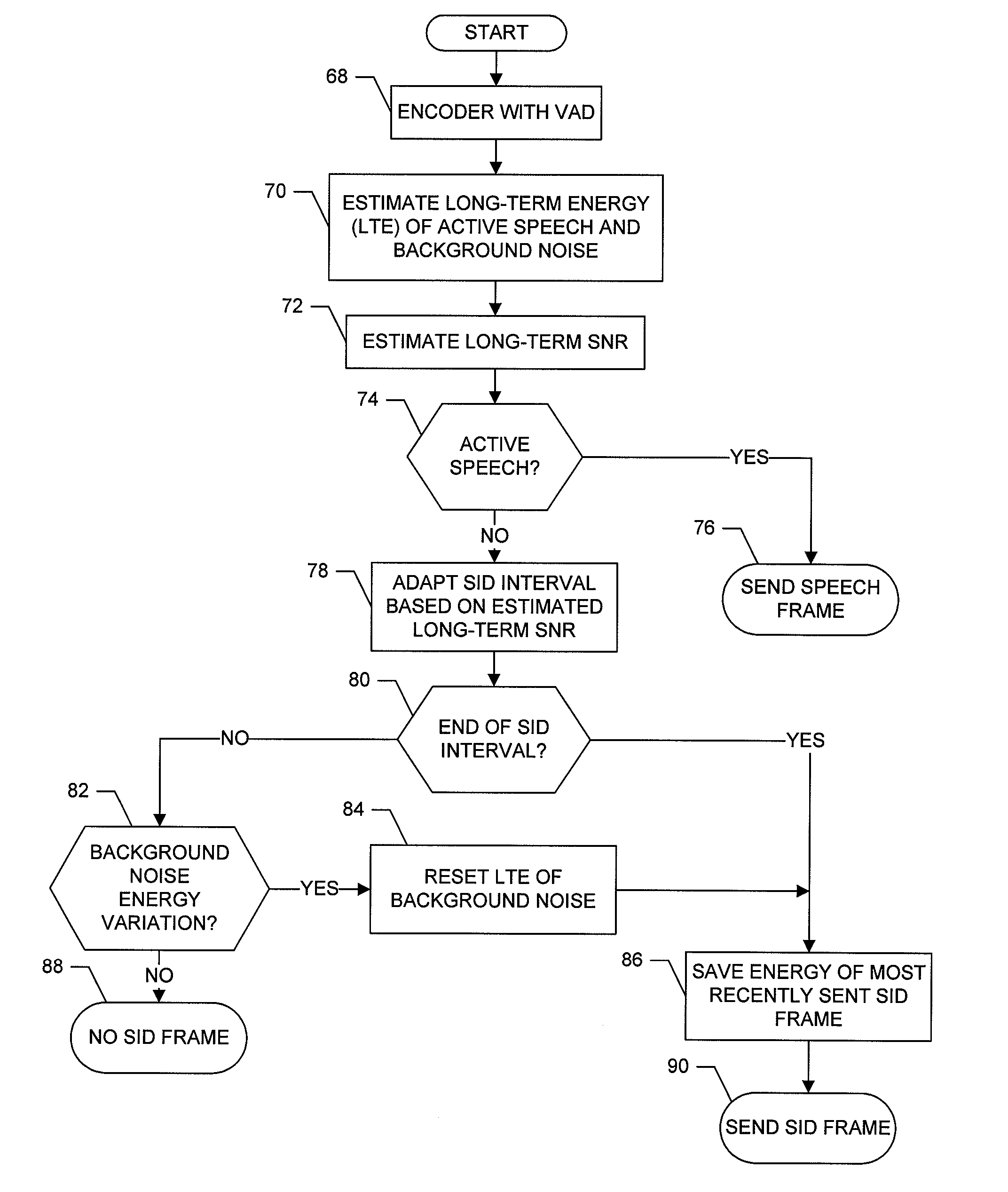
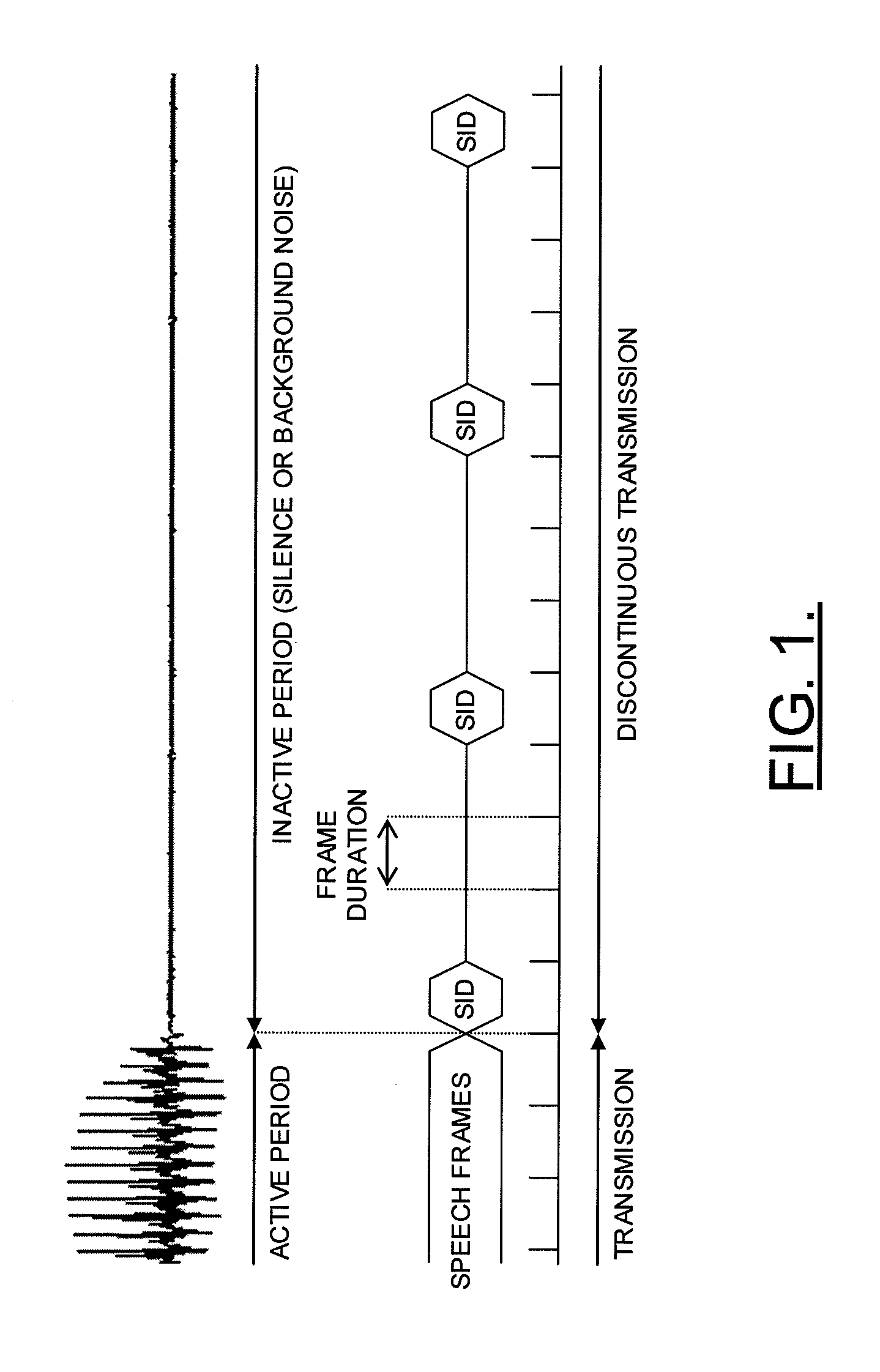
System and method for adaptive transmission of comfort noise parameters during discontinuous speech transmission
ActiveUS20060293885A1Solve the real problemImprove efficiencySpeech analysisSubstation equipmentCurrent noiseComfort noise
Apparatus is provided that includes at least one entity for transmitting speech signals in a discontinuous transmission mode including transmitting speech frames interspersed with frames including comfort noise parameters during periods of speech pauses. The entit(ies) include a first entity for estimating a current noise value. In addition, the apparatus includes a second entity for selectively controlling a rate at which the frames including comfort noise parameters are transmitted during the periods of speech pauses based upon the estimated current noise value.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
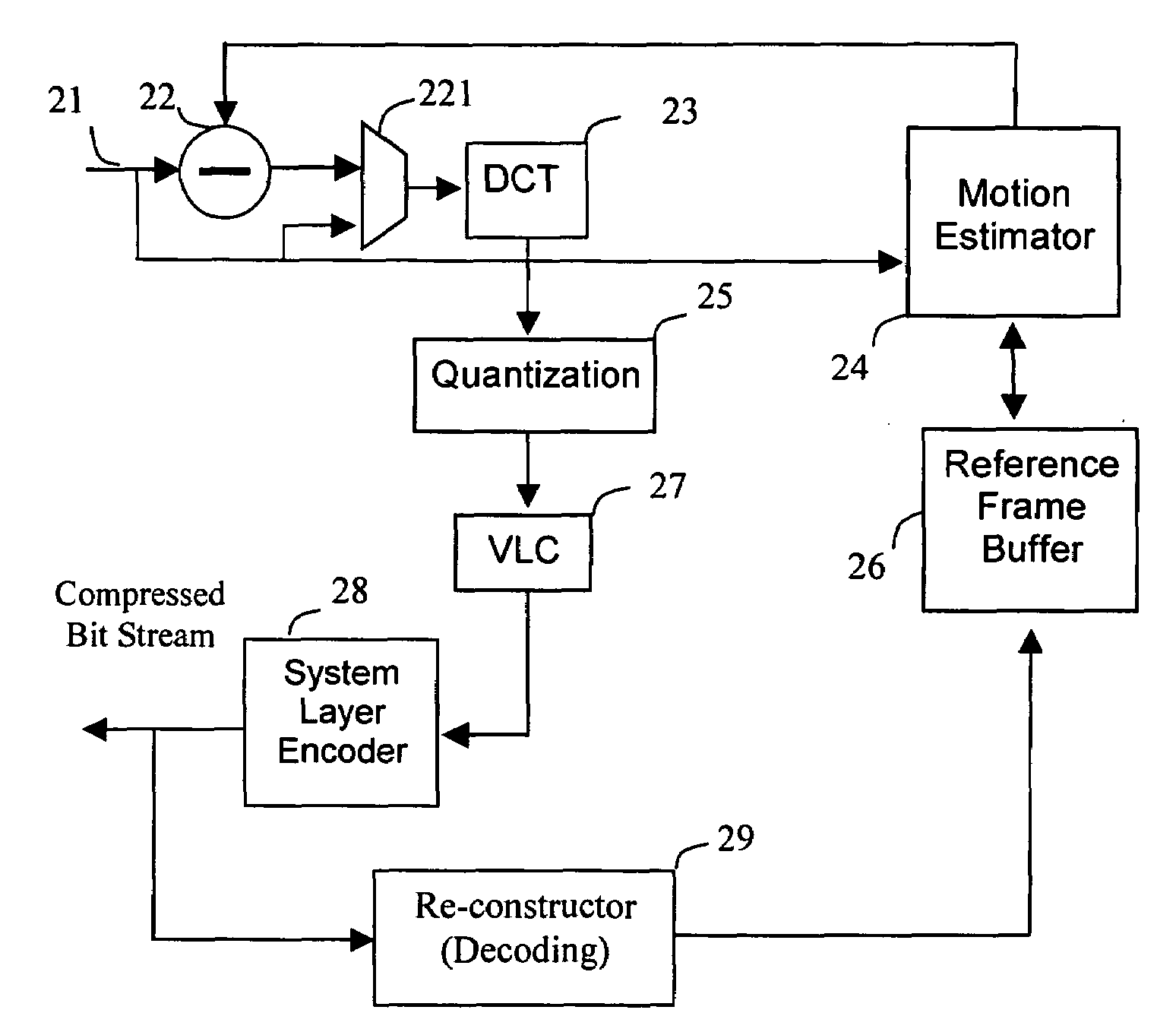
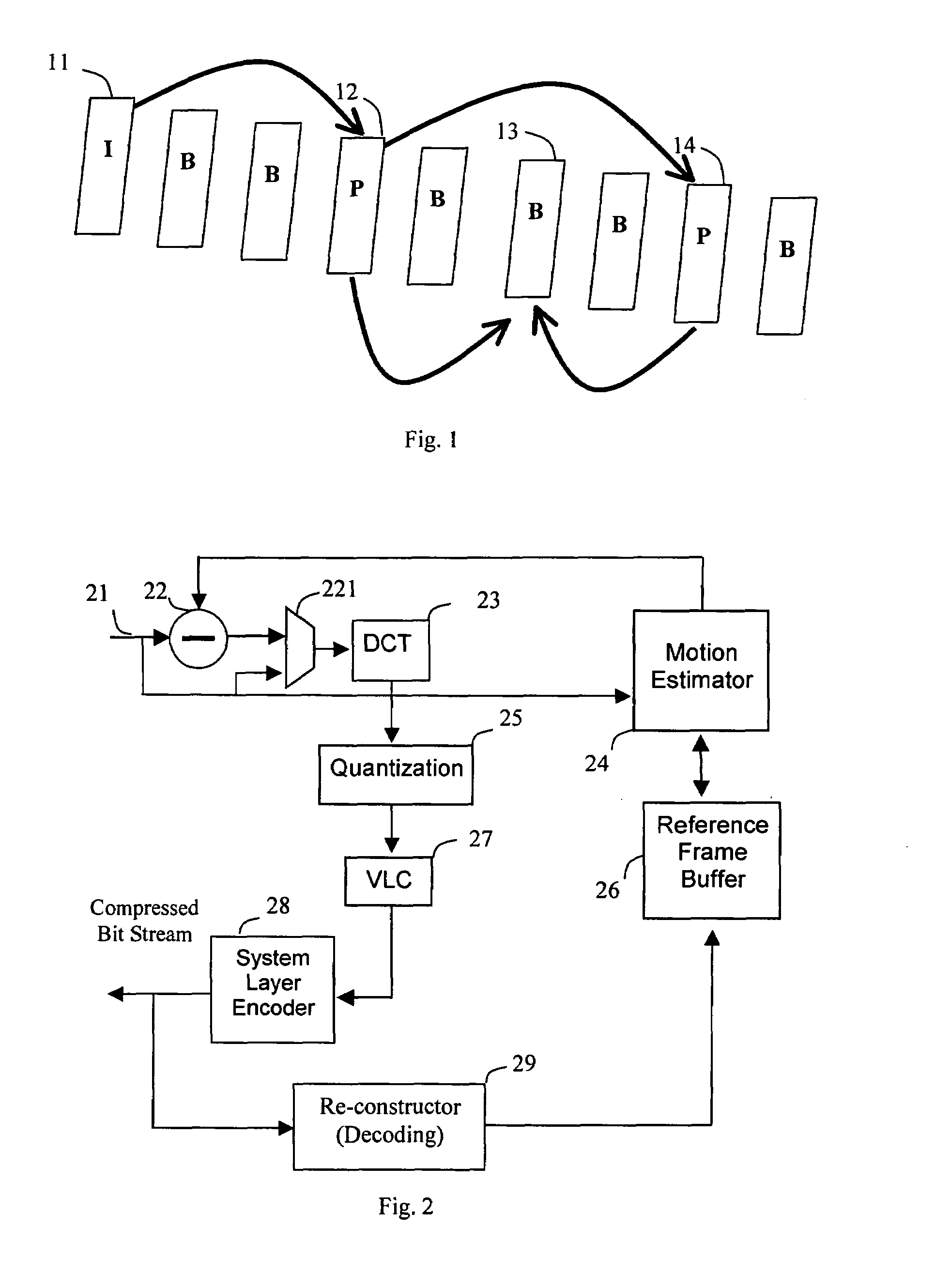
Method of digital video reference frame compression
ActiveUS20080170626A1High complexityAccelerated programColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoLossless compression algorithm
The digital video referencing frame image is compressed block by block by applying lossless compression algorithm to pixel components with full length, or 1 bit, 2 bits, 3 bits or 4 bits LSB bits truncation. If a sub-block has high complexity which results in more than 3 bits error for most pixel components, a transfer algorithm with quantization and VLC coding is applied to compress this sub-block. Should the complexity is higher than a threshold or at least one sub-block having error of more than 3 bits for most pixel components, truncating 1 LSB bit of sub-block with simple pattern to save more bits to be allocate to code the sub-block with highest complex pattern.
Owner:TAIWAN IMAGINGTEK
System and associated method for transcoding discrete cosine transform coded signals
InactiveUS6944226B1Low data rateTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMpeg standardsVariable length
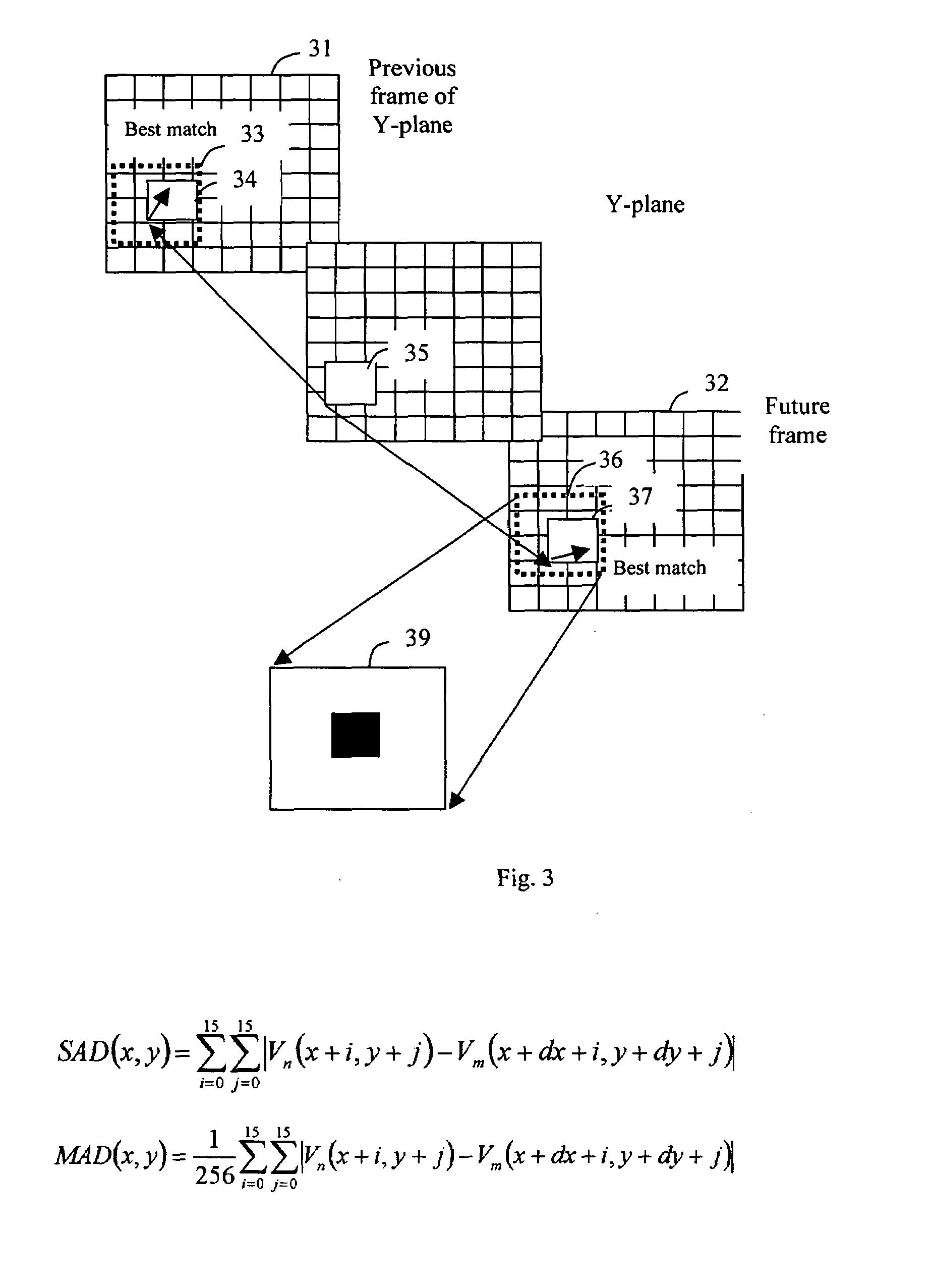
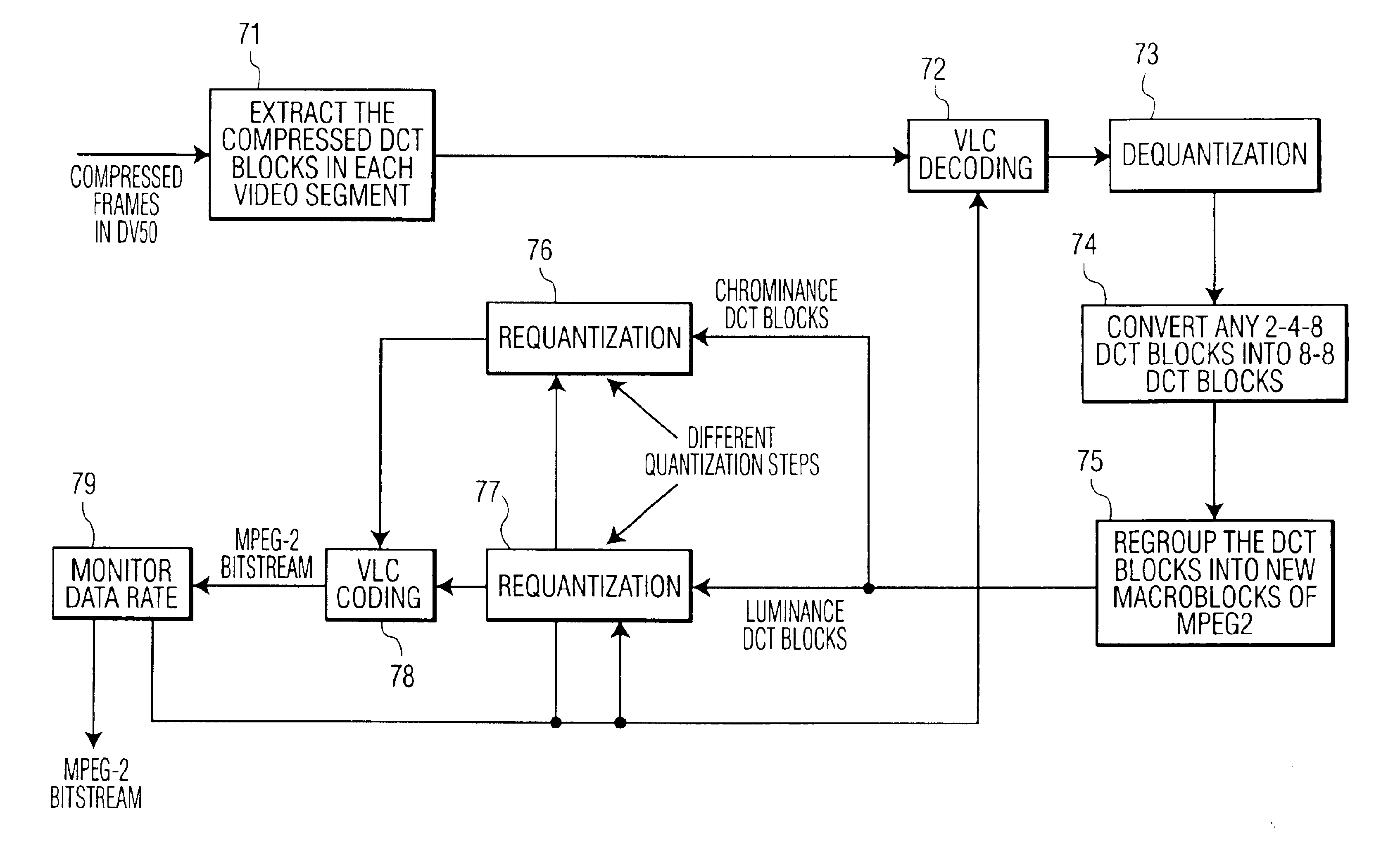
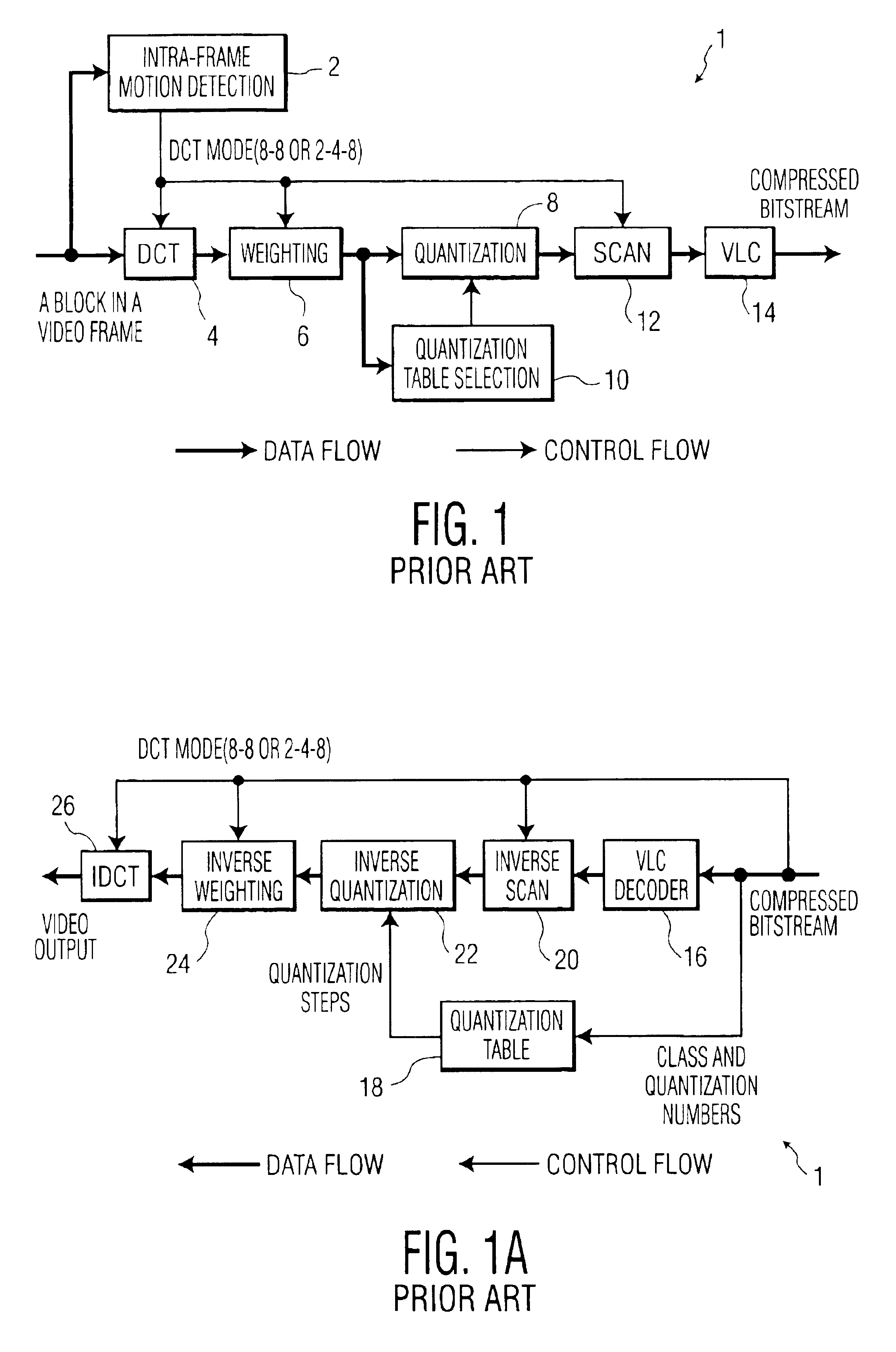
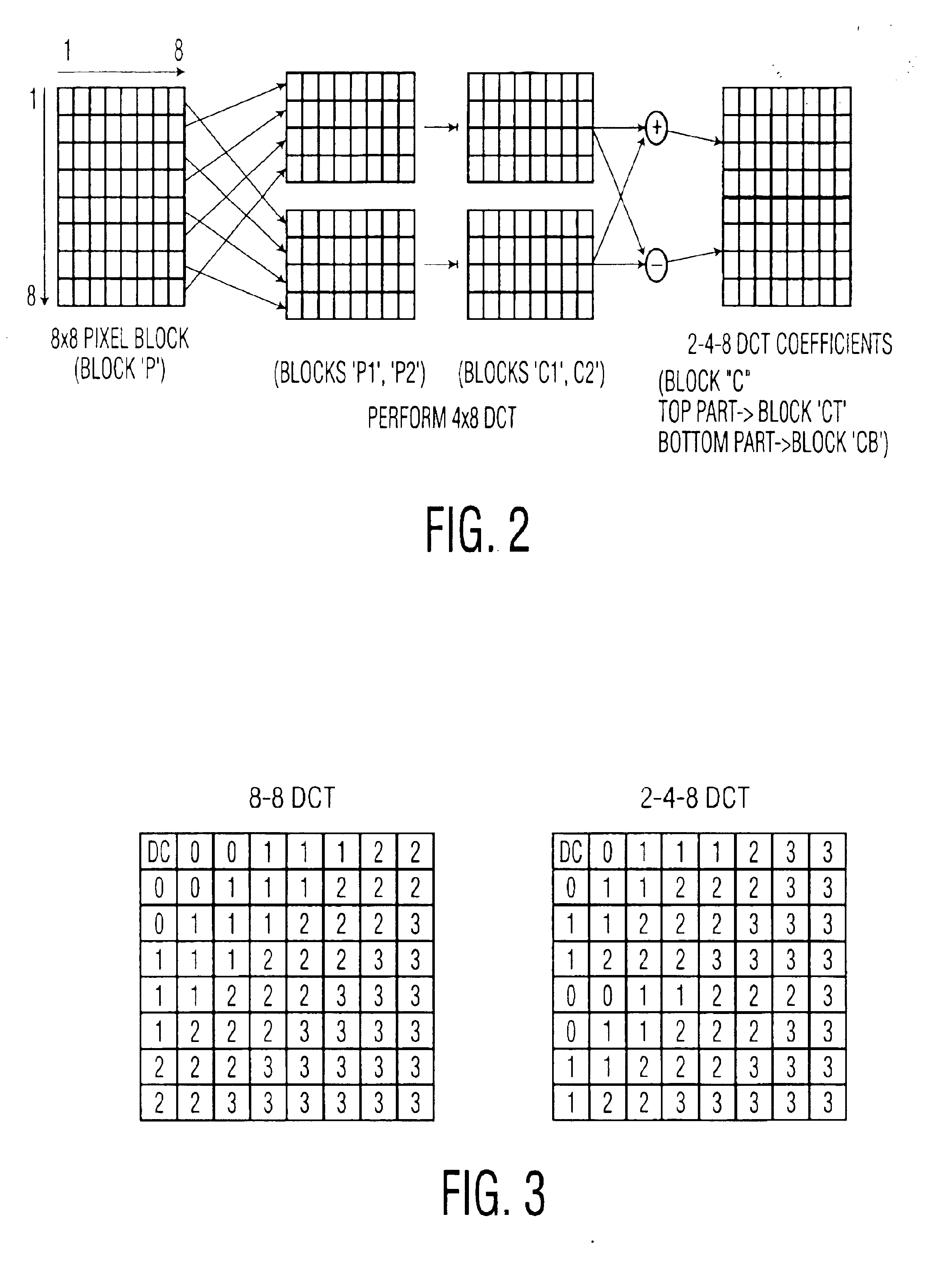
A method is provided for transcoding between video signals in two standards, DV and MPEG-2, each standard including discrete cosine transform (DCT) compressed signals. The each of the signals have macroblocks containing a plurality of DCT blocks. The DCT blocks are quantized according to respective quantization methods defined by the standards. The coefficients in each block are zigzag scanned, run-length coded and variable-length coded. The process variable-length decodes the coefficients and translates the quantized coefficients in the DV standard into quantized coefficients in the MPEG standard without fully dequantizing at least some of the DV coefficients and without performing an inverse DCT operation on any of the DCT coefficients. DV blocks that are encoded in a 248 format are translated into an 88 format before they are converted to MPEG-2 blocks. A method for transcoding from MPEG-2 to DV is also described. The MPEG-2 signals are intra-frame encoded, have a 4:2:2 chrominance format and an 88 frame-encoded block format. According to this method, converted 88 DV blocks that represent significant intra-field motion are converted from the 88 format to a 248 format. The method also controls which overflow coefficients in the DV signal are transcoded into corresponding coefficients in the MPEG-2 signal to control the data rate of the MPEG-2 signal.
Owner:PANASONIC OF NORTH AMERICA
Background modification in video conferencing
ActiveUS20150195491A1Quality improvementNetwork degradationTelevision conference systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityImage resolution
Methods and systems for real-time video processing can be used in video conferencing to modify image quality of background. One example method includes the steps of receiving a video including a sequence of images, identifying at least one object of interest (e.g., a face) in one or more of the images, detecting feature reference points of the at least one object of interest, and tracking the at least one object of interest in the video. The tracking may comprise aligning a virtual face mesh to the at least one object of interest in one or more of the images. Further, a background is identified in the images by separating the at least one object of interest from each image based on the virtual face mesh. The background is then modified in each of the images by blurring, changing a resolution, colors, or other parameters.
Owner:SNAP INC
Dynamic voice over data prioritization for wireless communication networks
InactiveUS20050107107A1Increasing availability of resourceReduce amountPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementCall blockingVoice data
A wireless communication network provides priority for one type of users over another type of users relative to one or more network finite resources shared by the different types of users. For example, if the available forward link transmit power at a radio base station is being shared by voice and data users, the radio base station may give priority to the voice users by reducing the aggregate amount of power allocated to current data users if the combined level of power usage by the voice and data users reaches a defined release threshold. The release threshold may be set at a call-blocking threshold, such that dynamic release is invoked if the call-blocking level is reached. Other limited resources can be managed similarly, such as by setting a release threshold relative to spreading code usage, etc.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
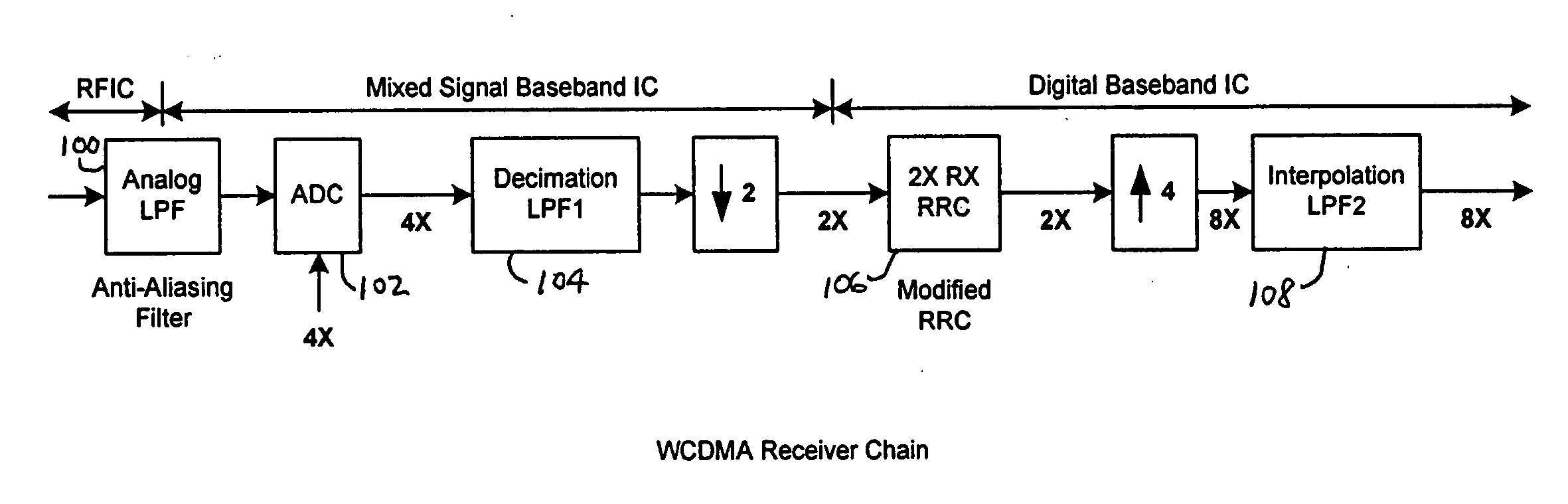
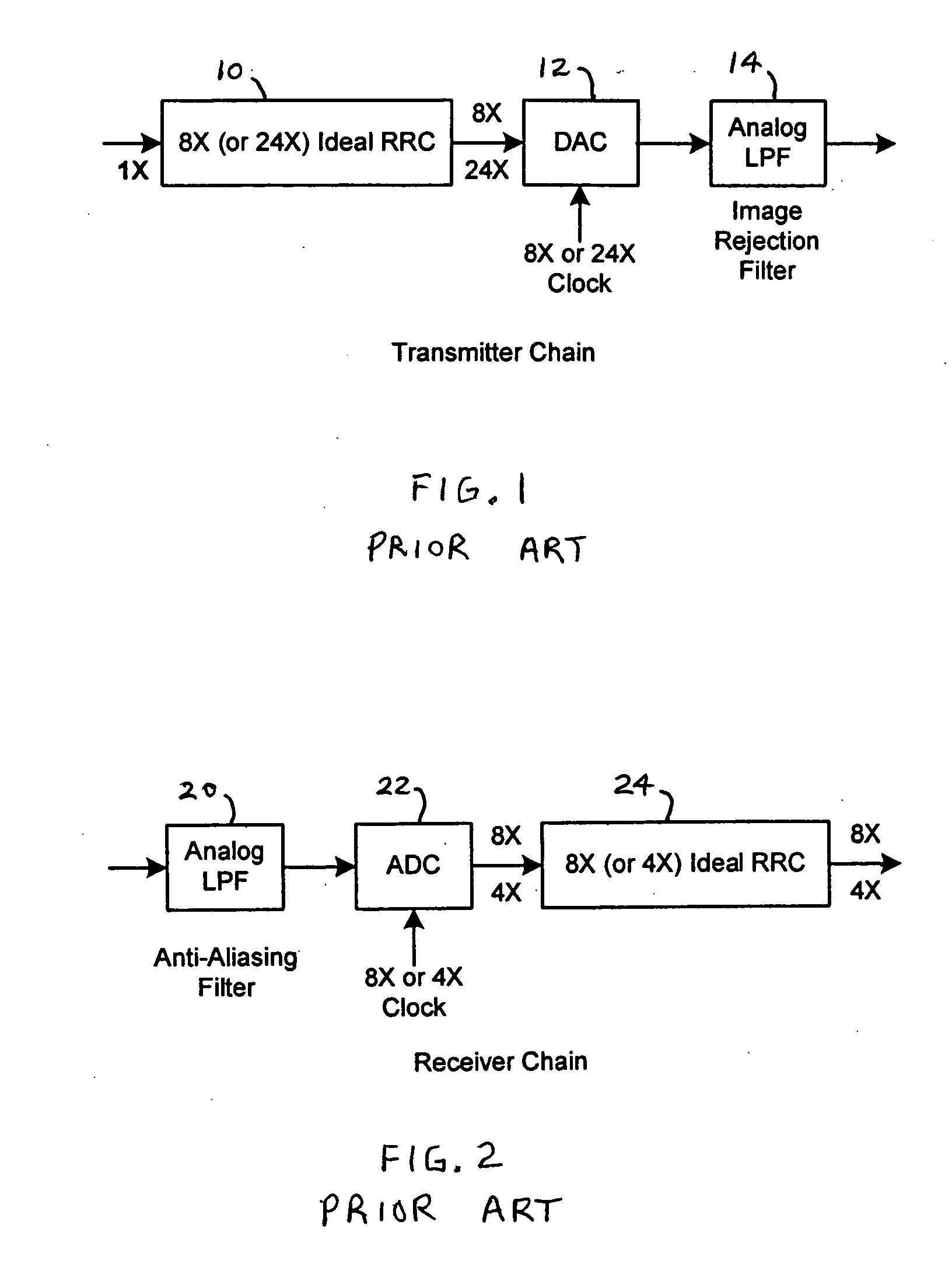
Filters for communication systems
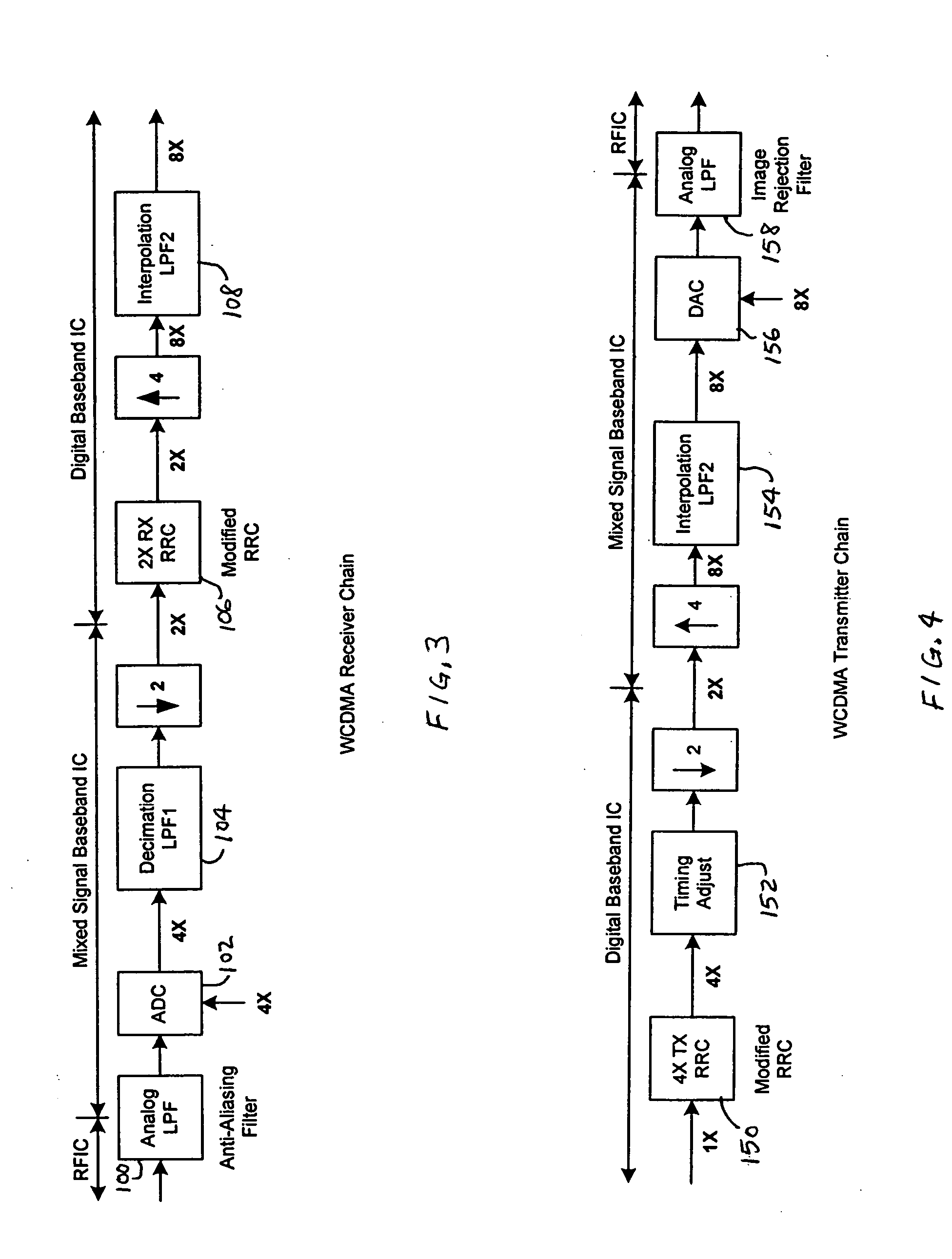
ActiveUS20060083297A1Low data rateMultiple-port networksDigital technique networkCommunications systemHigh rate
The invention relates to a cascaded scheme in which an RRC filter, a modified RRC filter or other digital filter is implemented at a relatively low data rate, such as twice the symbol or chip rate, or 2×. Interpolation filters are used to increase the data rate to a higher data rate, such as 8×. Decimation filters are used to reduce the data rate from a higher rate, such as 8×, to a lower rate, such as 2×. The coefficients of the digital filter may be adjusted to compensate for characteristics of other components across the entire filter chain. Most of the implementation complexity of the filter chain is consolidated into the relatively low rate (such as 2×) digital filter while interpolation or decimation filters can be implemented at very low cost. The compensation capability provided by the digital filter makes design of simple decimation or interpolation filters much easier. The compensation capability provided by the digital filter, along with the relatively high over-sampling rate for the output of the interpolation filter (or the input of the decimation filter), also makes the design of the preceding (or following) analog filters much easier.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Audiovisual signal routing and distribution system
ActiveUS20060238648A1Format conversionHeterogeneous distributionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningSignal routingComputer network
An audiovisual signal is converted from a native format to a digital, packetized interchange format and transported between a capture node and a display node through a switch. The display node converts the audiovisual signal from the interchange format to a displayable format and causes display of the audiovisual signal. The use of a switch for video routing and distribution allows one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, and many-to-many distribution. The use of a device-independent interchange format allows concurrent distribution of multiple heterogeneous audiovisual signals.
Owner:JUPITER SYST LLC +1
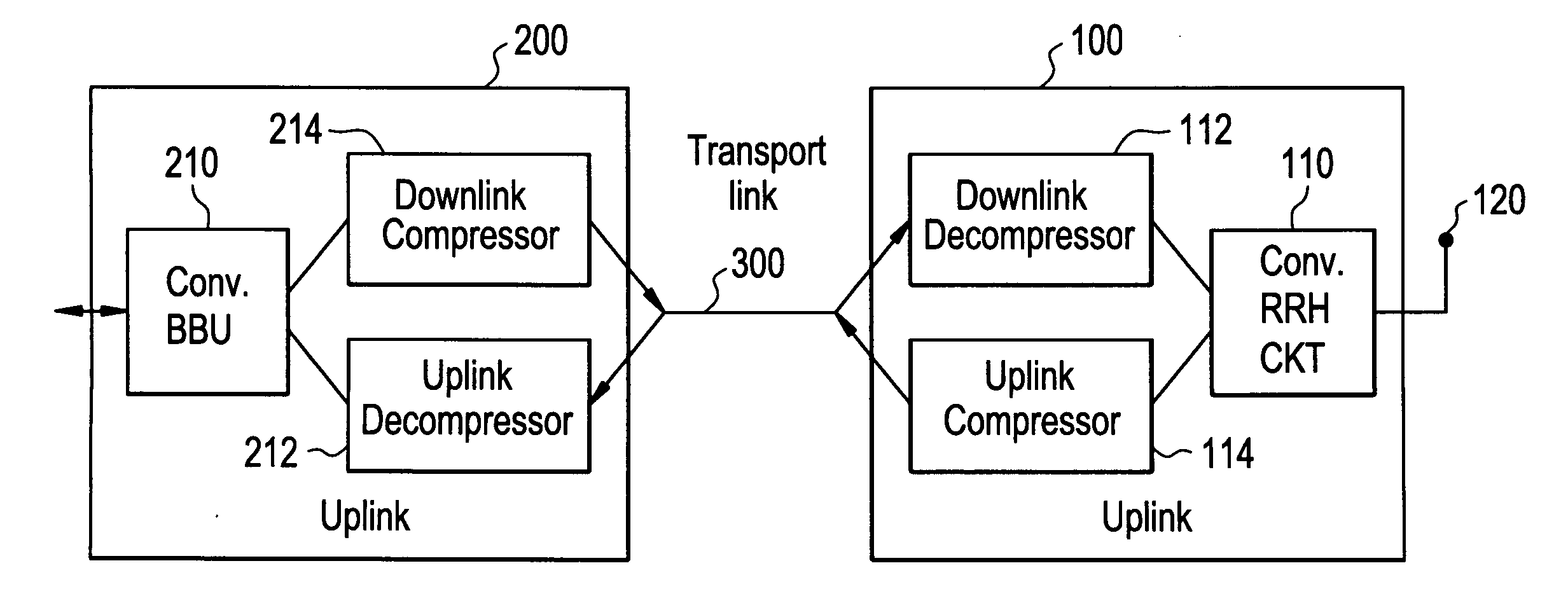
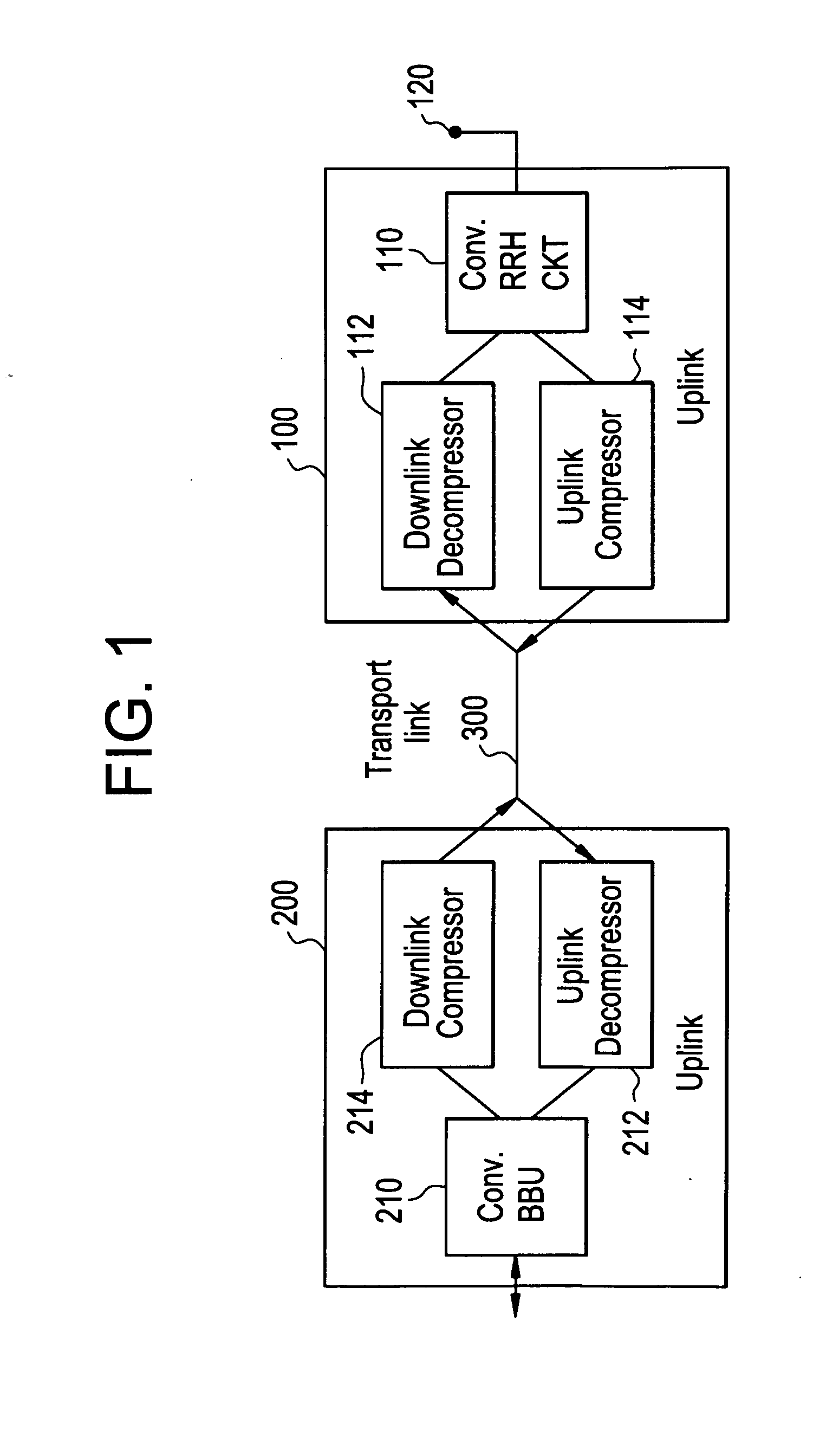
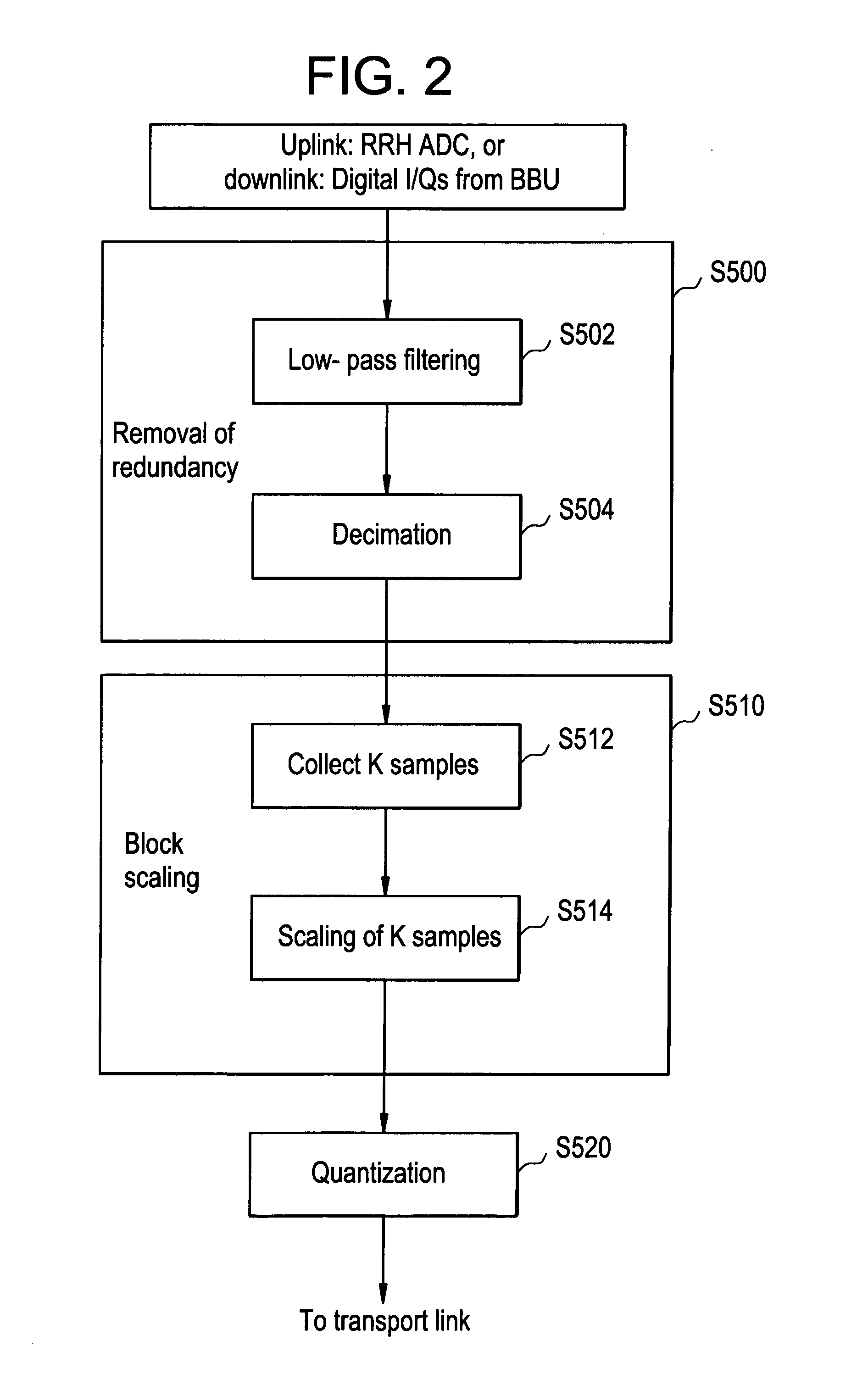
Method And Apparatus For Signal Compression And Decompression
ActiveUS20120207206A1Low data rateReduce data rateCode conversionMultiple carrier systemsDigital radioComputer science
In one embodiment, the method of compressing a digital signal includes reducing redundancies in the digital signal, scaling a block of samples output from the reducing step by a scaling factor, and quantizing the scaled samples to produce compressed samples. The digital signal being compressed may be a digital radio frequency signal.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Efficient reduction of inter-cell interference using RF agile beam forming techniques
ActiveUS20140010129A1Low data rateExperienceTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexCell to cell communicationData rate
In embodiments of the present disclosure improved capabilities are described for reducing inter-cell interference in a large area broadband LTE wireless network utilizing RF agile beam forming antennas, where the reduced inter-cell interference is realized by arranging the sets of rotating RF beams in each cell such that adjacent RF beam sub-areas in the same or in different cells are not illuminated at the same time. The reduction in inter-cell interference results in reduced interference noise for users located near the edges of cells, thereby allowing them to be assigned higher data rates. Also, the same set of sub-carriers can be assigned by adjacent cells to users located in the RF beam sub-areas at the cell boundaries, thereby allowing the complete set of LTE sub-carriers to be assigned to any user at any time, without requiring additional cell-to-cell communications.
Owner:ALL PURPOSE NETWORKS INC
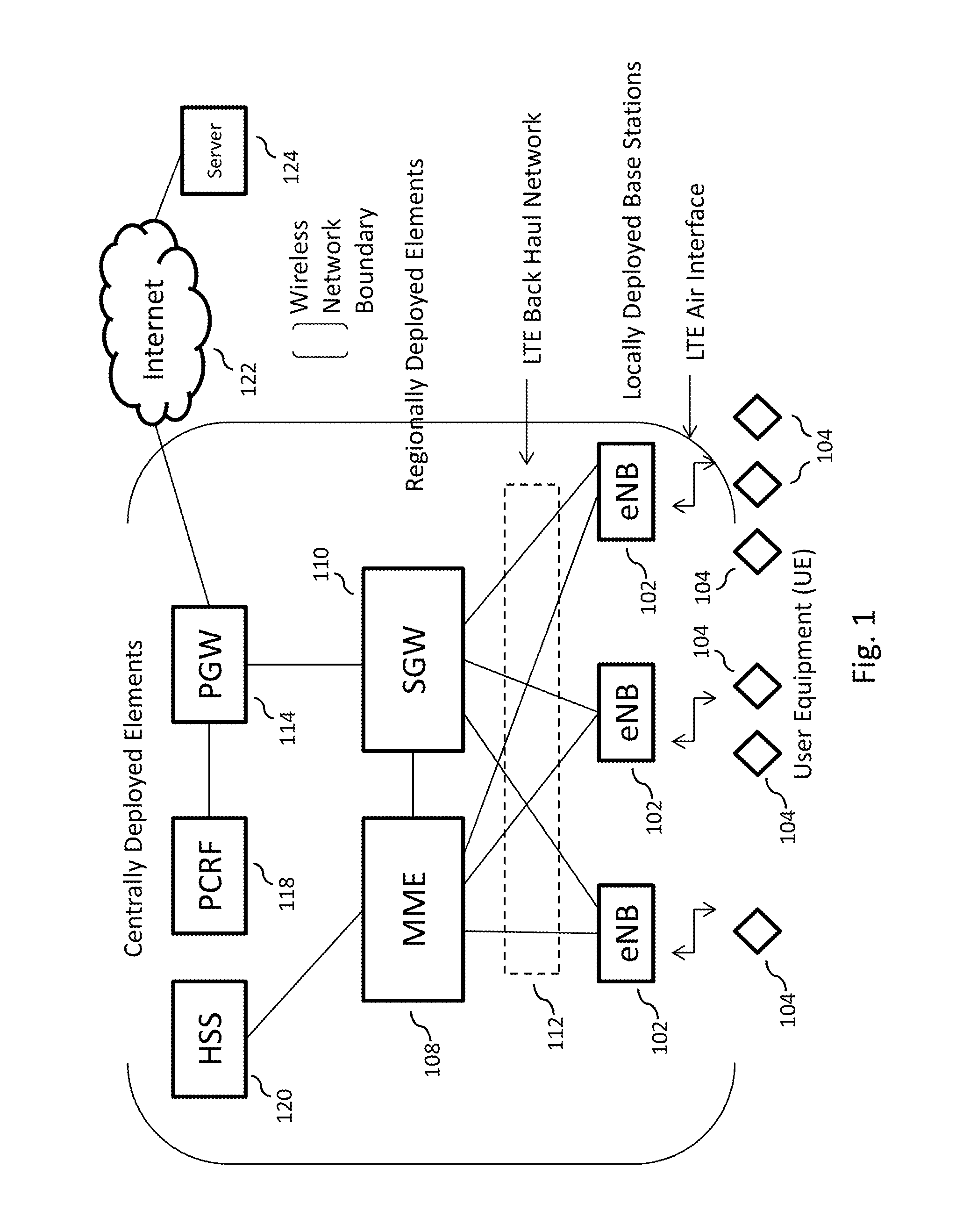
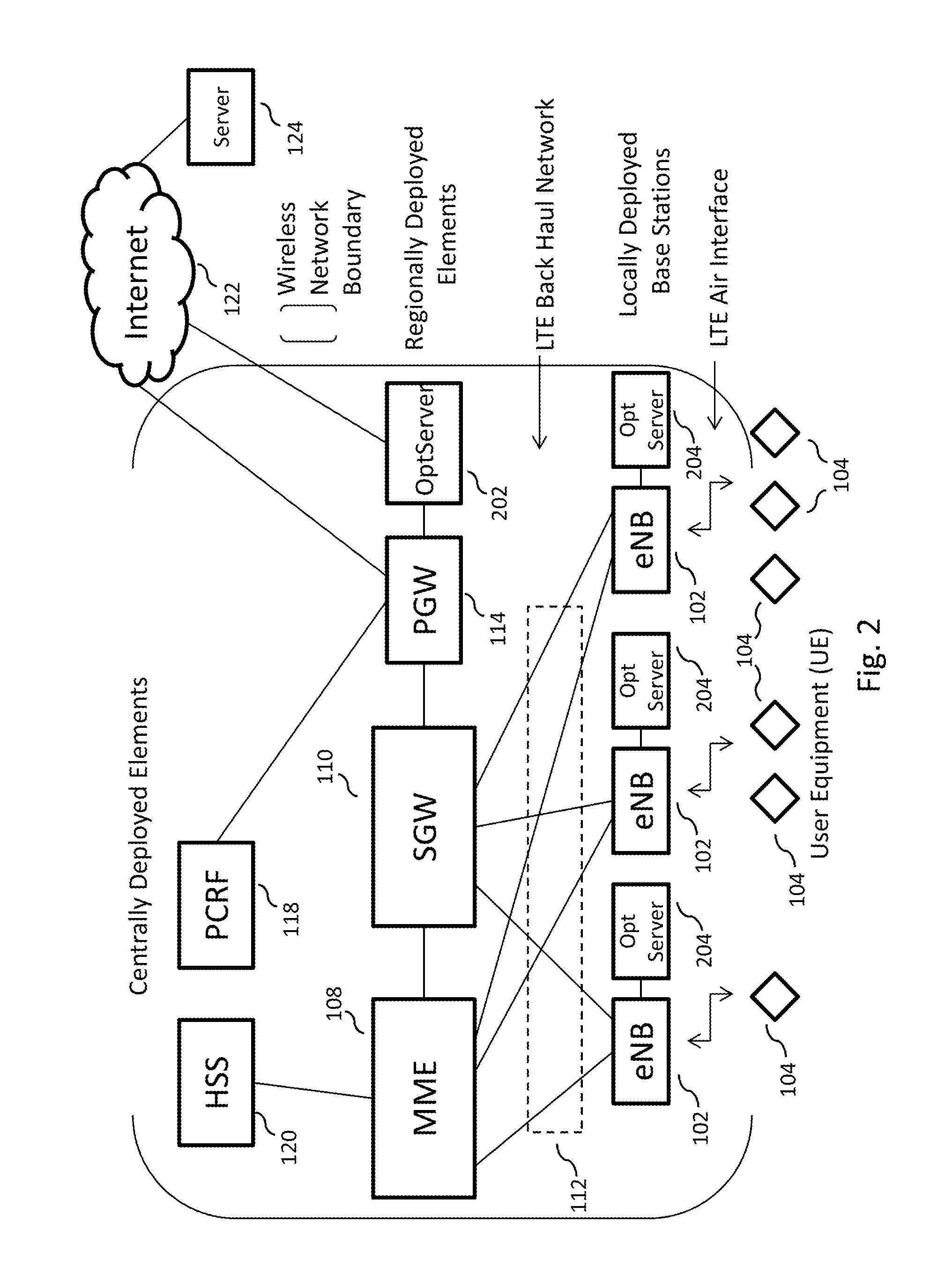
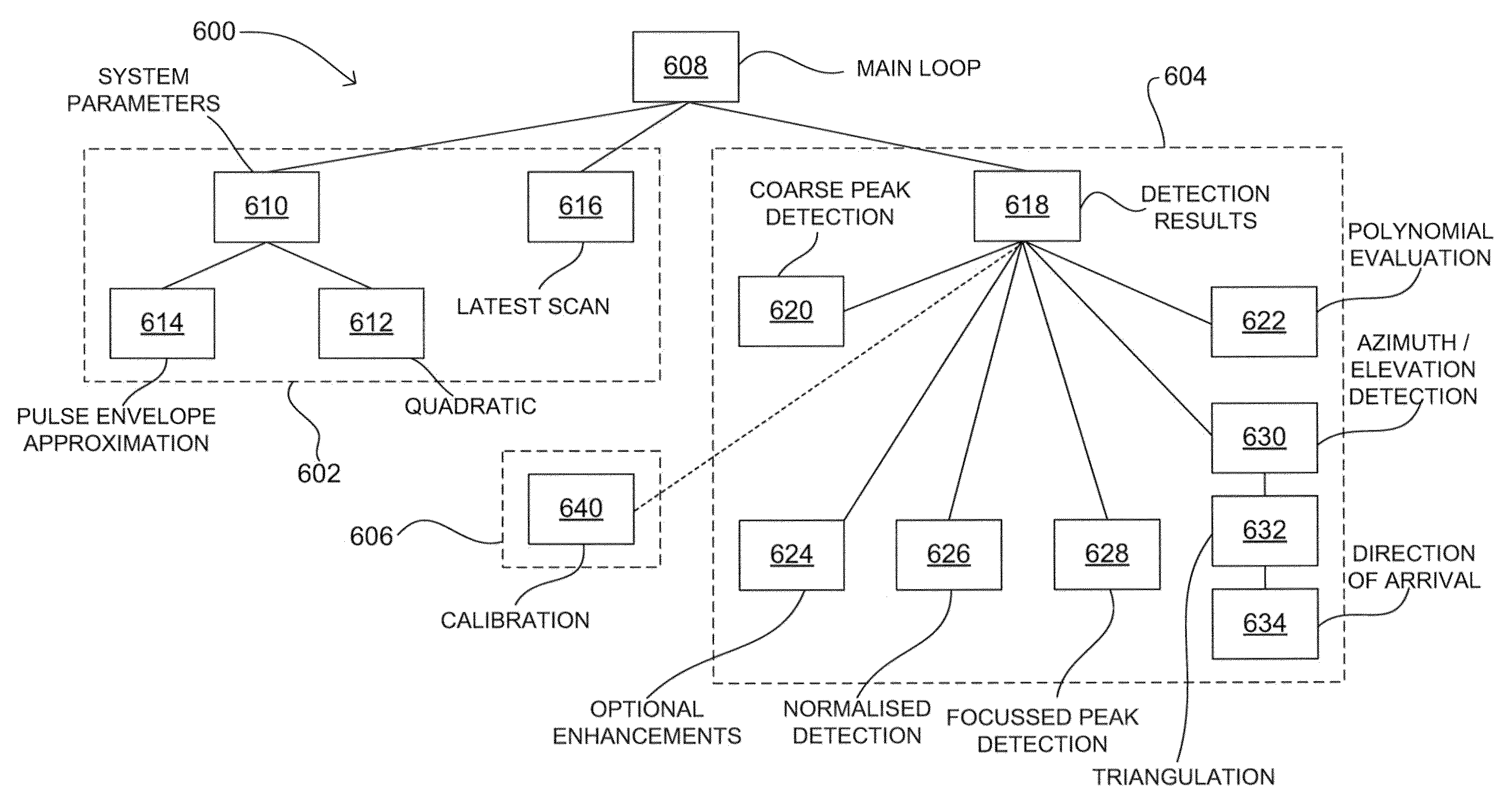
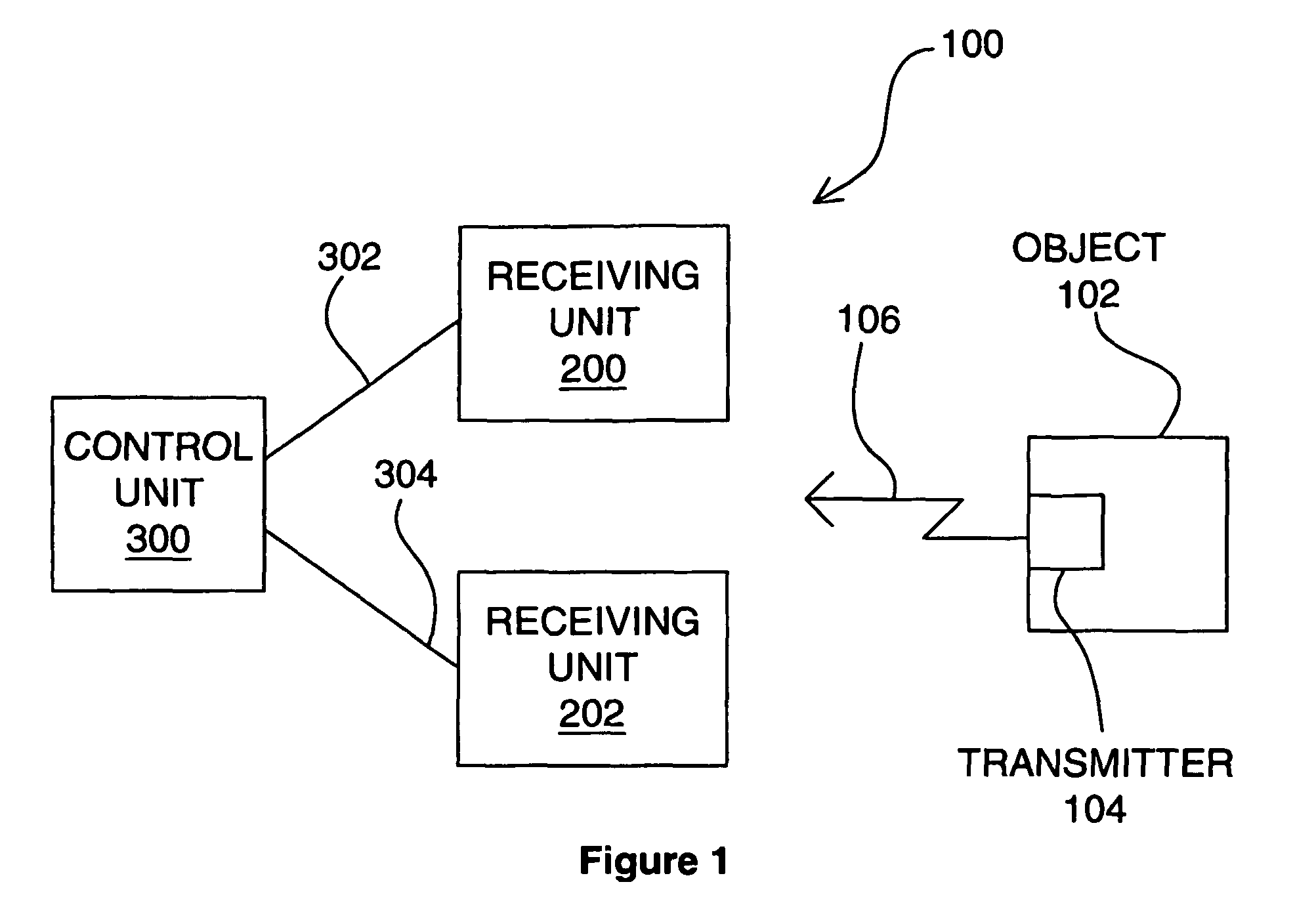
Determining positional information
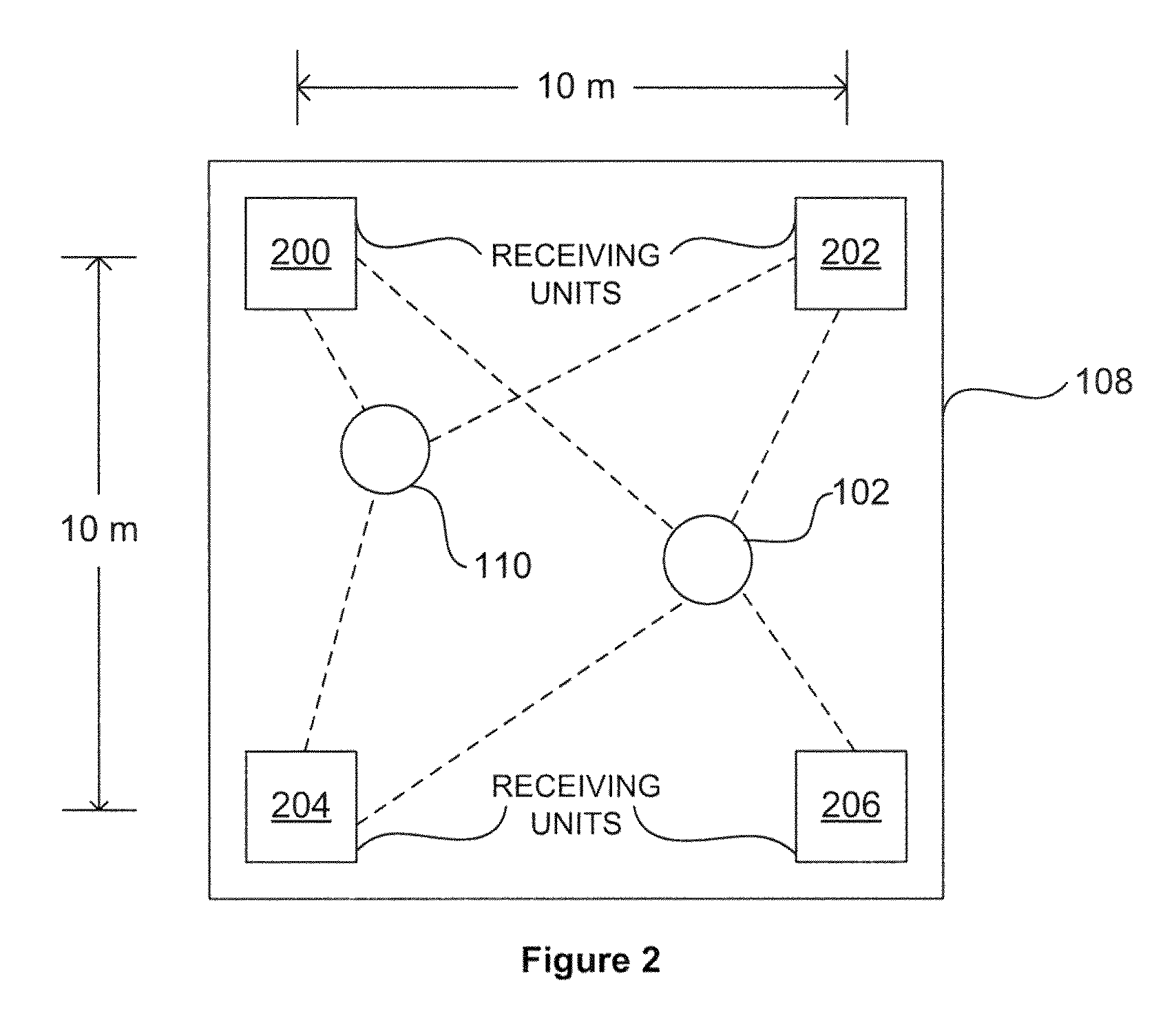
ActiveUS7750841B2Reduce data rateLow data rateDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationEngineeringSignal production
Apparatus for determining positional information relating to an object, comprising: means for receiving, comprising a plurality of receiving elements; detection means for detecting signals received at the receiving elements and for generating output signals representative of the received signals; and processing means operable to apply, for each receiving element, a process to the output signal generated from the signal received at that receiving element separately from any output signal generated from a signal received at any other receiving element, so as to obtain a respective value of a parameter representative of the signal received at that receiving element, the processing means being further operable to compare the values of the parameter thus obtained so as to, obtain positional information relating to the object.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE CONSULTANTS LTD
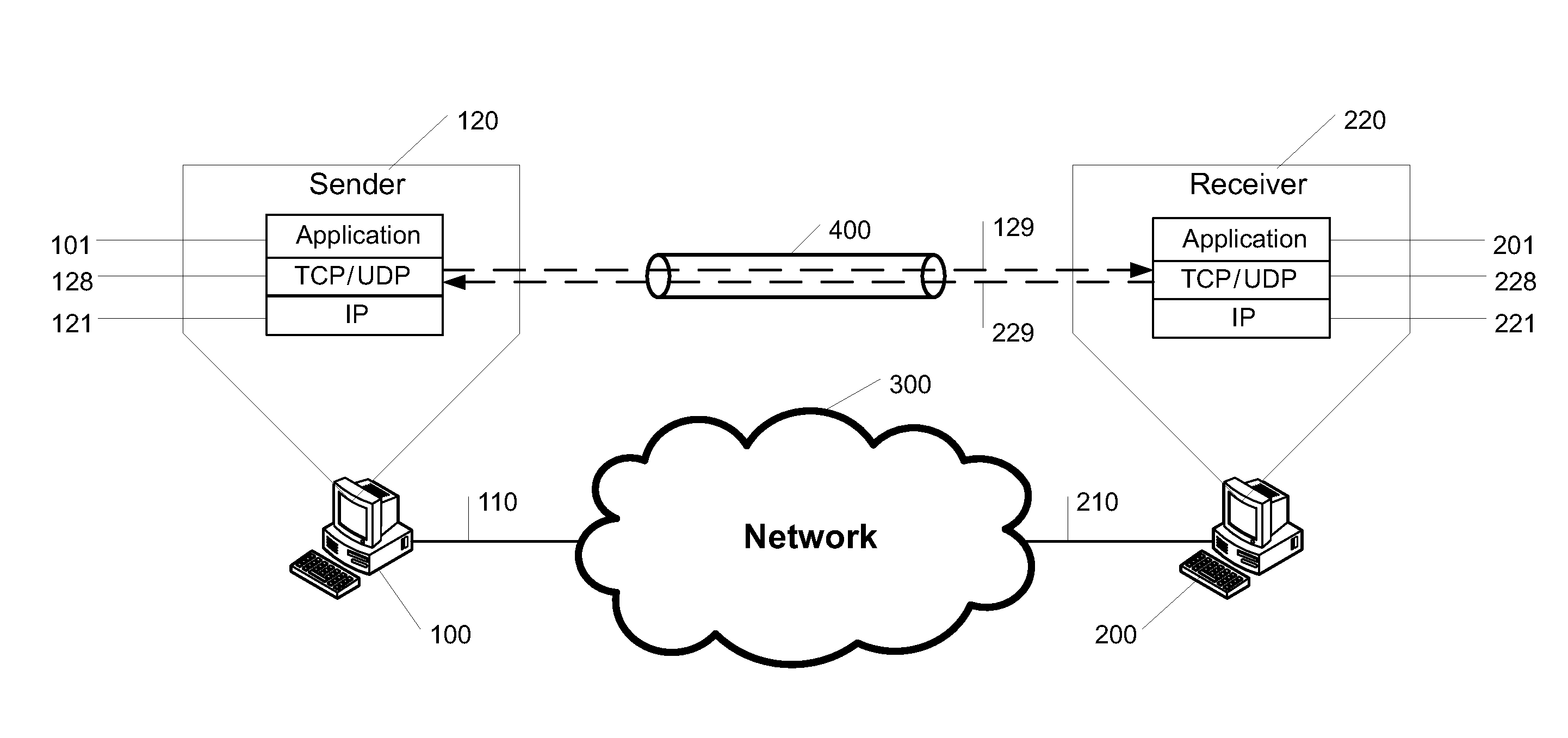
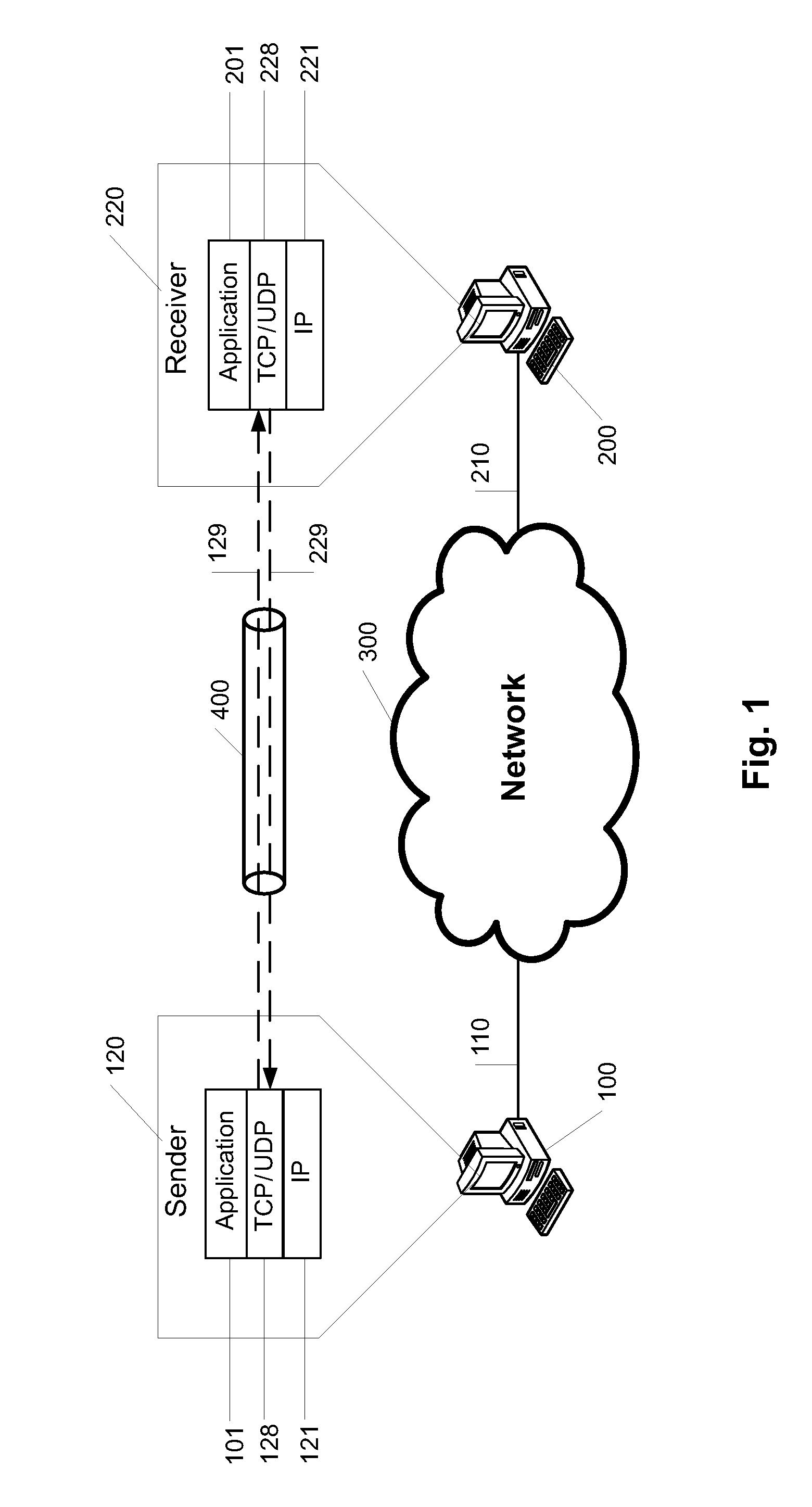
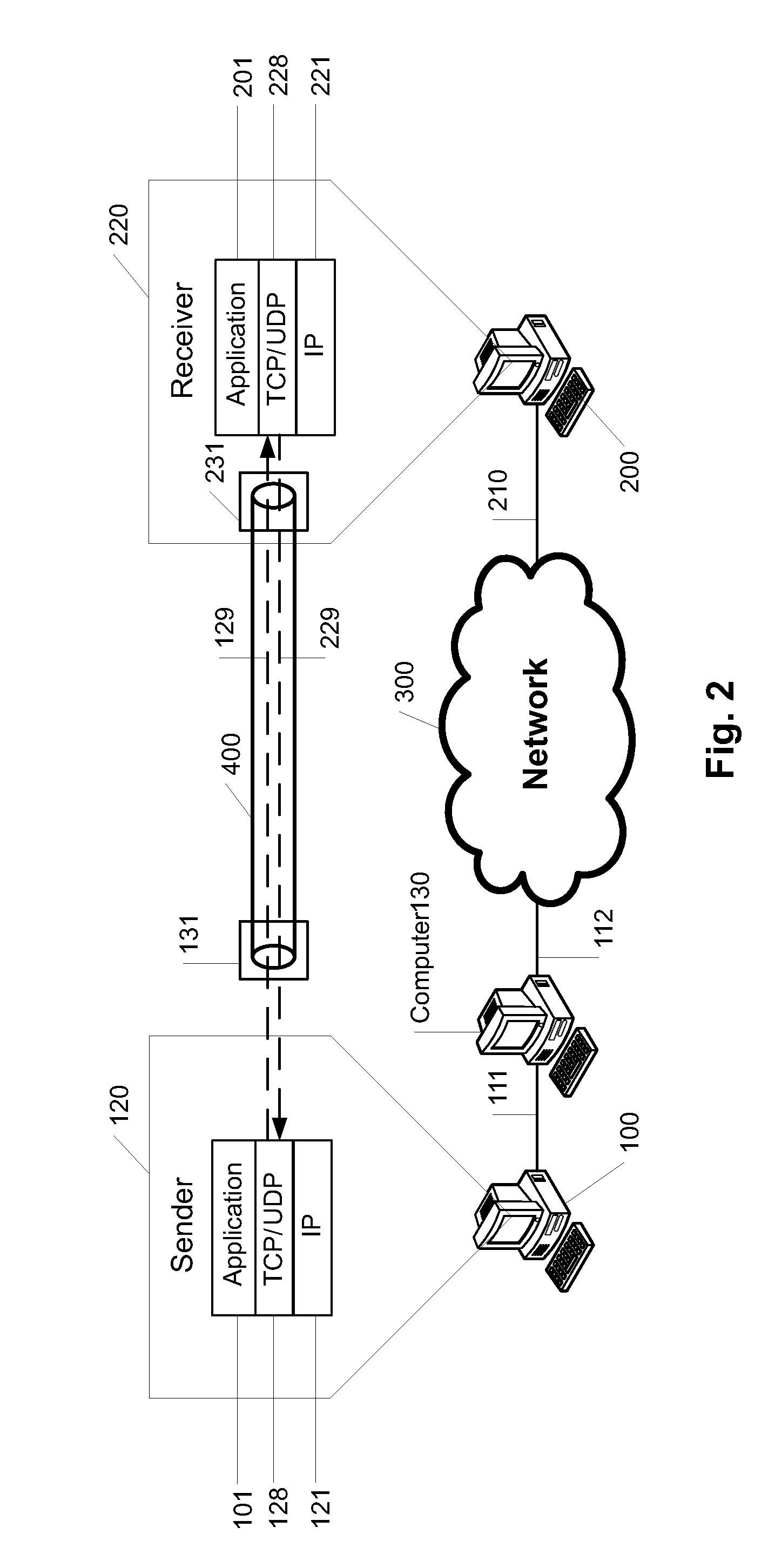
Communication system for transmittingunder a tunnel protocol between at least two data computers via a wide area network and a method for running such a communication system
InactiveUS20150229490A1Improve establishingAvoid disadvantagesTime-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network AccessDistributed computing
A communication system for transmitting data under a tunnel protocol between at least two computers via a wide area network, said system comprisesa first computer running a first user application and a virtual private network application to build up TCP and UDP tunnels,a second computer accordingly running a second user application and a virtual private network VPN application,a wide area network to which both computers are connected by physical connections, wherein both user applications are implemented to communicate for an IP data packet exchange via at least one of the TCP tunnels and the UDP tunnel using the TCP and / or UDP transport protocol based on according TCP, UDP and IP stacks on both computers, anda splitter which is at least one of implemented in and associated to at least one of both computers which splitter analyzes the IP data packets to be sent from one of the computers to the other computer as concerns the type of the IP data packets and directs IP data packets of the TCP type to be transmitted over a TCP tunnel and IP data packets of the UDP type to be transmitted over a UDP tunnel.
Owner:HOB GMBH & CO KG
System for monitoring intrusion on basis of wireless sensor network
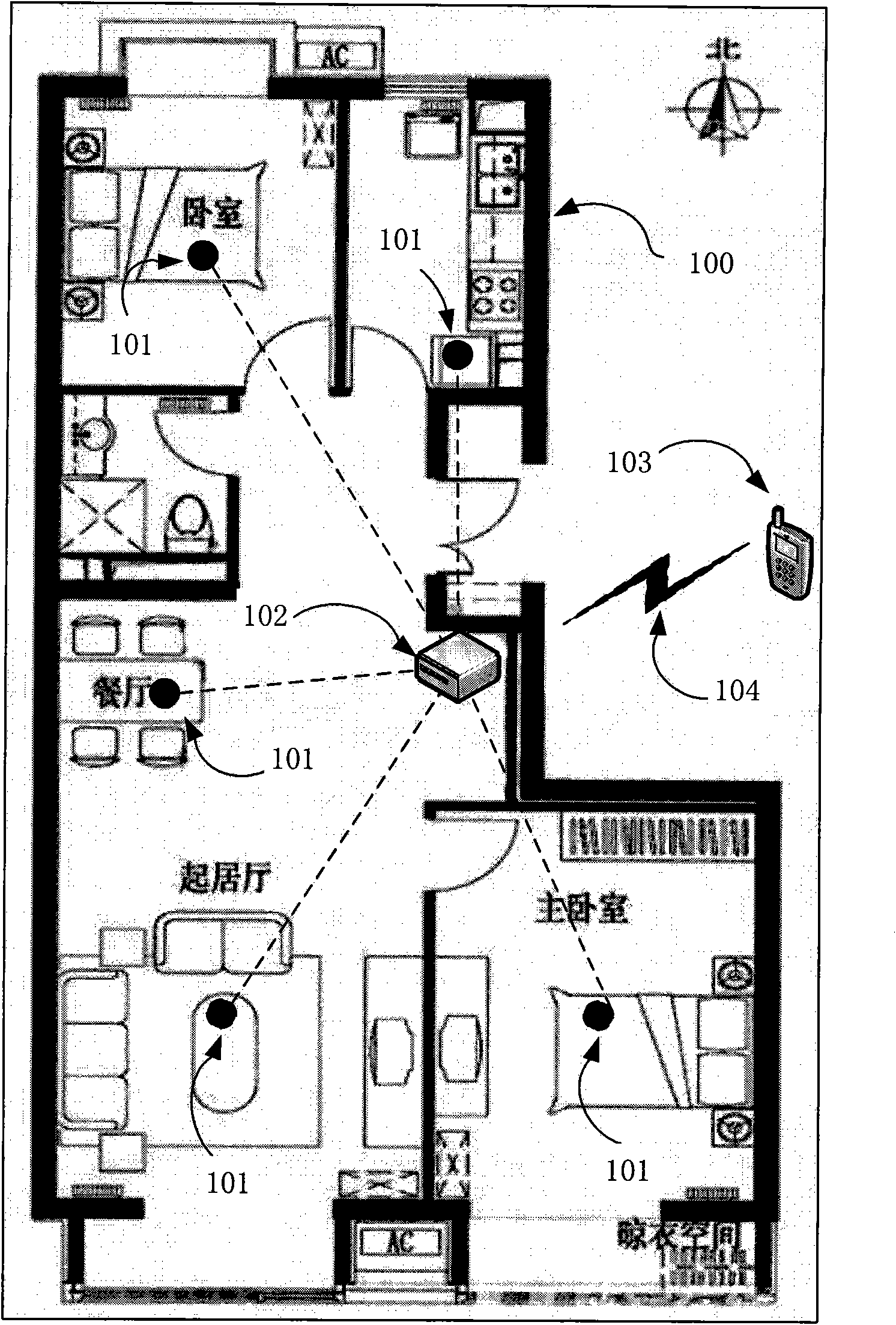
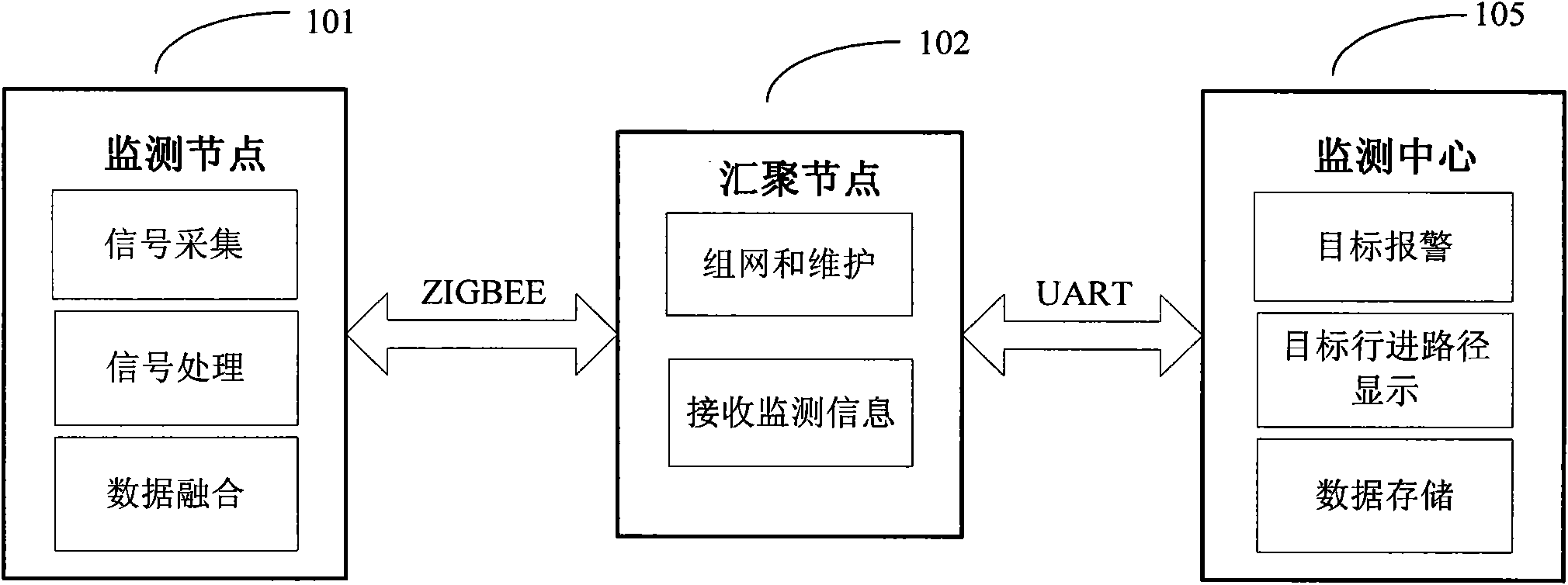
InactiveCN101872536AEffective monitoringEffective identificationEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesVideo monitoringCivil security
The invention, which is applicable to civil security and surveillance and military intrusion detection, relates to a wireless network system for monitoring, identifying and judging the pathway of an intruding target by setting up a plurality of nodes. The intruding target can be located, identified and tracked by carrying out the extraction, analysis and data integration on the signal characteristic quantity of the sensors at each monitoring node, moreover, the function for a user to set sensitive areas is served, so that various alarm signals can be sent according to the closeness of the intruding target to the sensitive areas. Additionally, a monitoring sensor at the monitoring node is used for generating sleeping and waking-up signals on a real-time basis, thus achieving the deep sleeping and waking of the processor and the communication module and achieving the purpose of saving the energy of the monitoring nodes and guaranteeing that the target intruding the monitoring area can be reliably monitored at the same time. The invention has the characteristics of low cost, low power consumption, flexible arrangement and high applicability and overcomes the defects that the conventional video monitoring method for monitoring the intrusion has complex installation, poor concealment, vulnerable circuit and limited monitoring range and requires artificial event discrimination.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Device and method for processing a signal having a sequence of discrete values
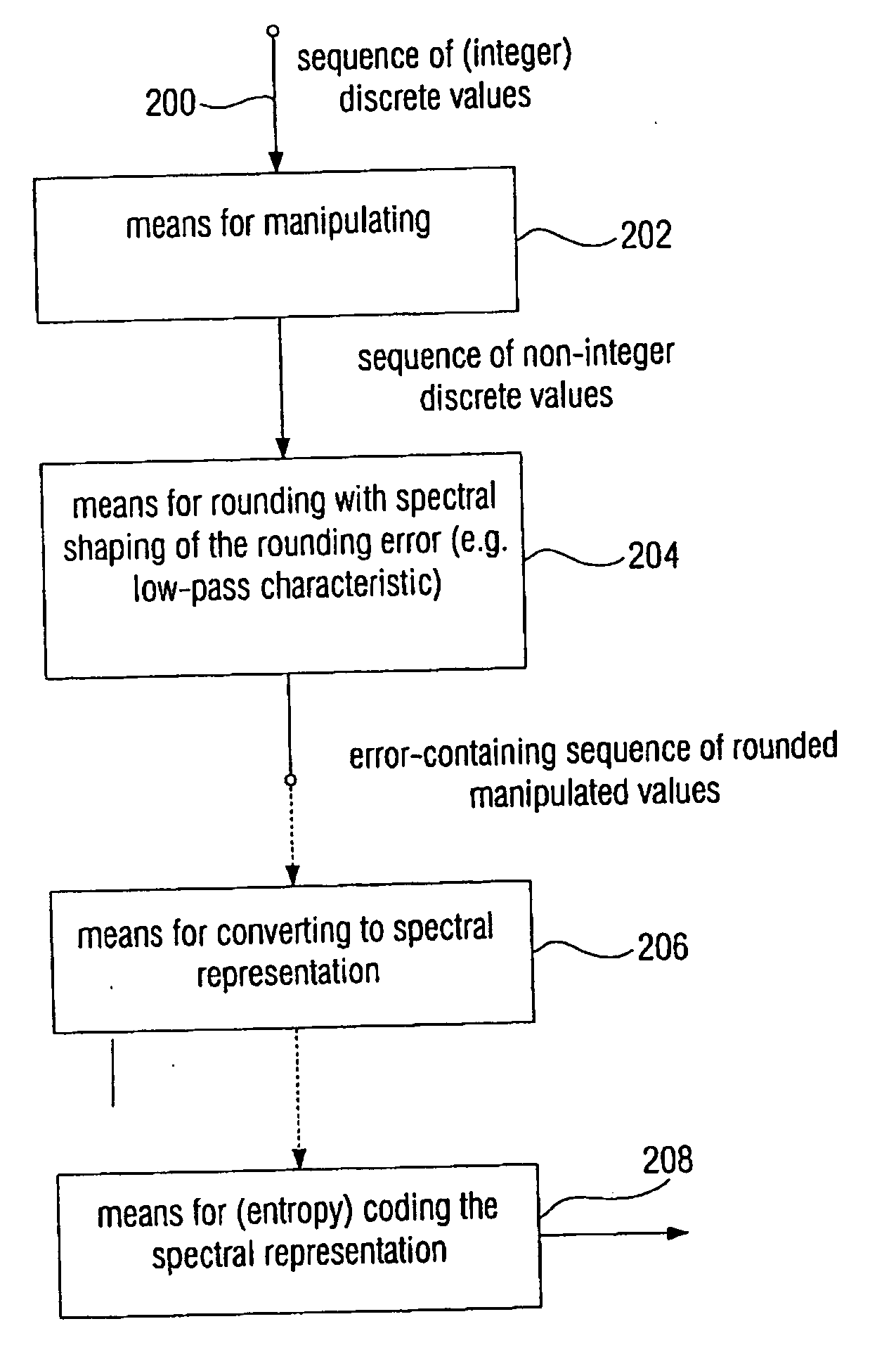
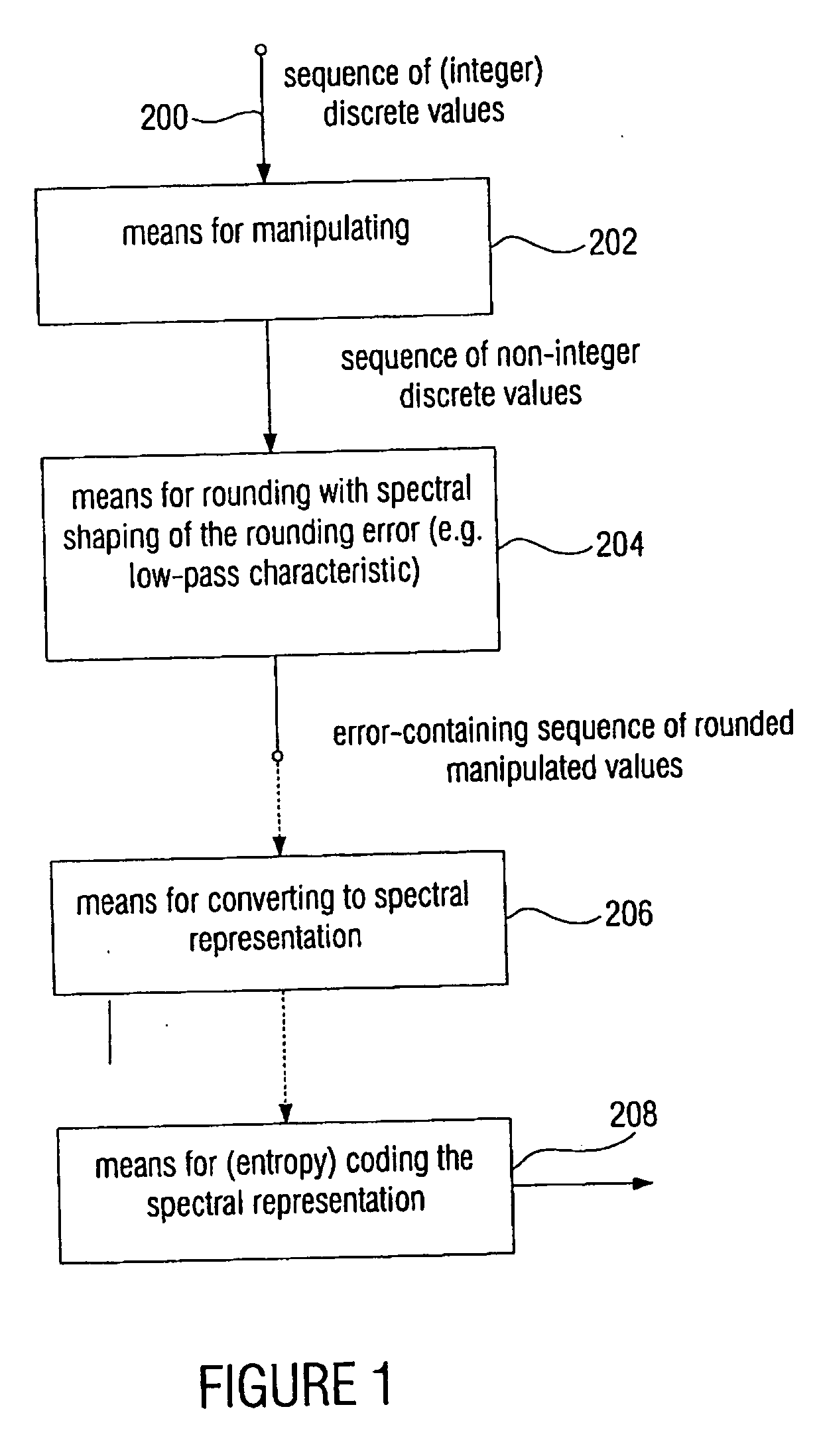
ActiveUS20060210180A1Few rounding errorIncrease the number ofSpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionLossless codingFrequency spectrum
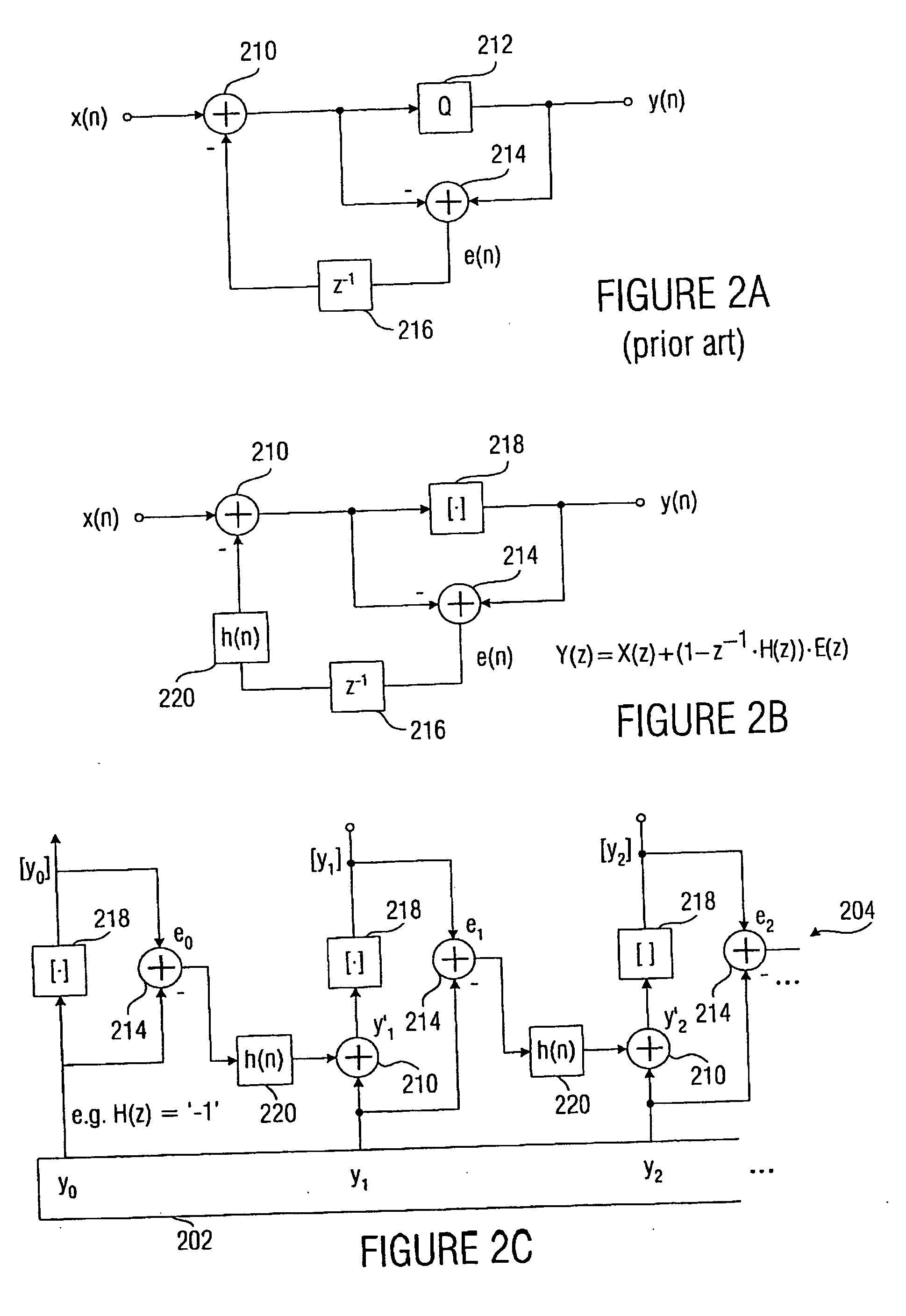
When processing a signal having a sequence of discrete values, wherein there is a first frequency range, in which the signal has a high energy, and wherein there is a second frequency range, in which the signal has a low energy, the sequence of discrete values is first manipulated to obtain a sequence of manipulated values, so that at least one of the manipulated values is non-integer. Then the sequence of manipulated values is rounded to obtain a sequence of manipulated values. The rounding is formed to effect a spectral shaping of a generated rounding error so that a spectrally shaped rounding error has a higher energy in the first frequency range than in the second frequency range. By spectrally shaping the rounding error so that the rounding error does not have any energy either in the storage areas where there is no signal energy, an especially efficient coding is obtained particularly in connection with a lossless coding context.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com