Patents
Literature
3024results about "Circuit switching systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
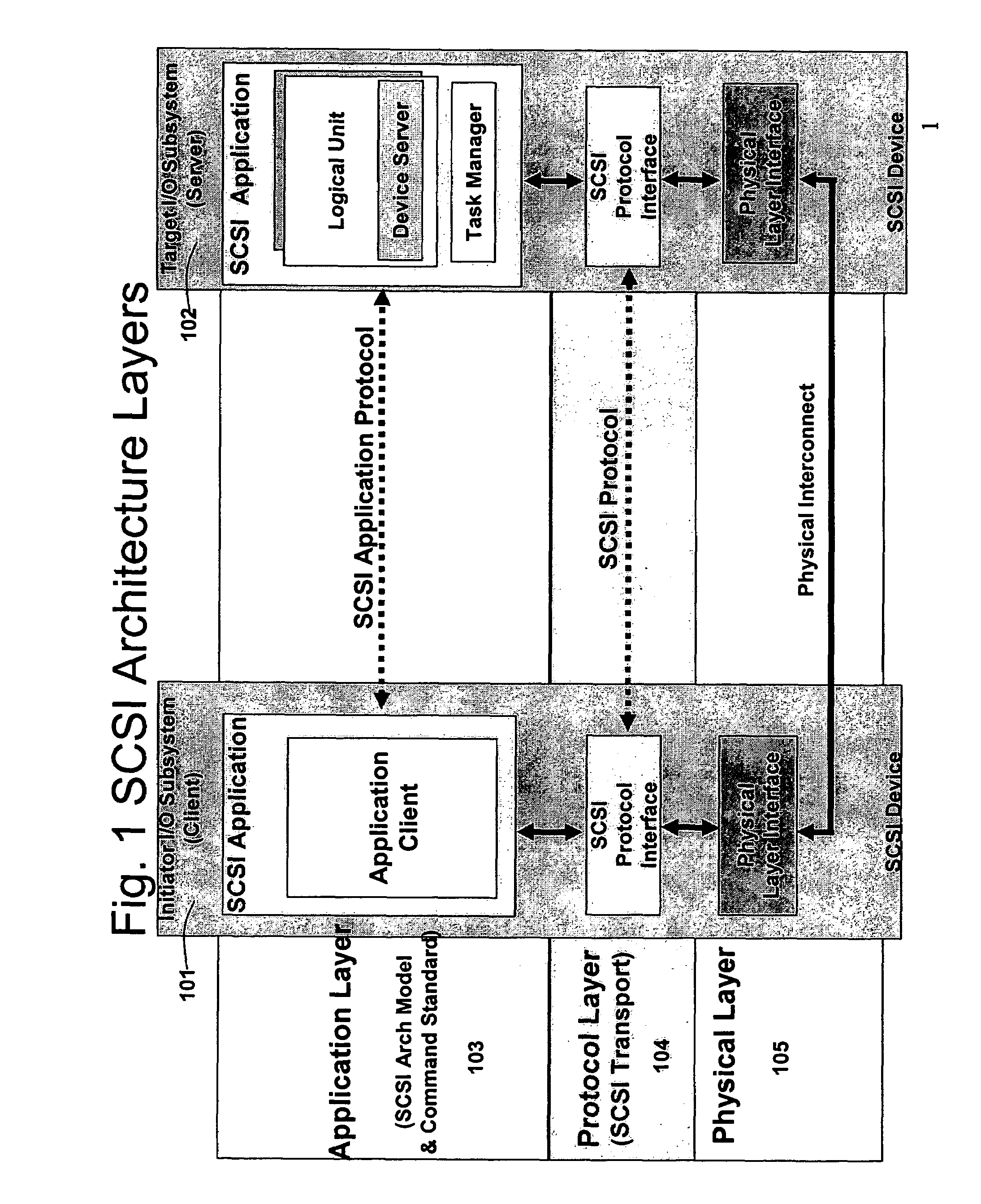
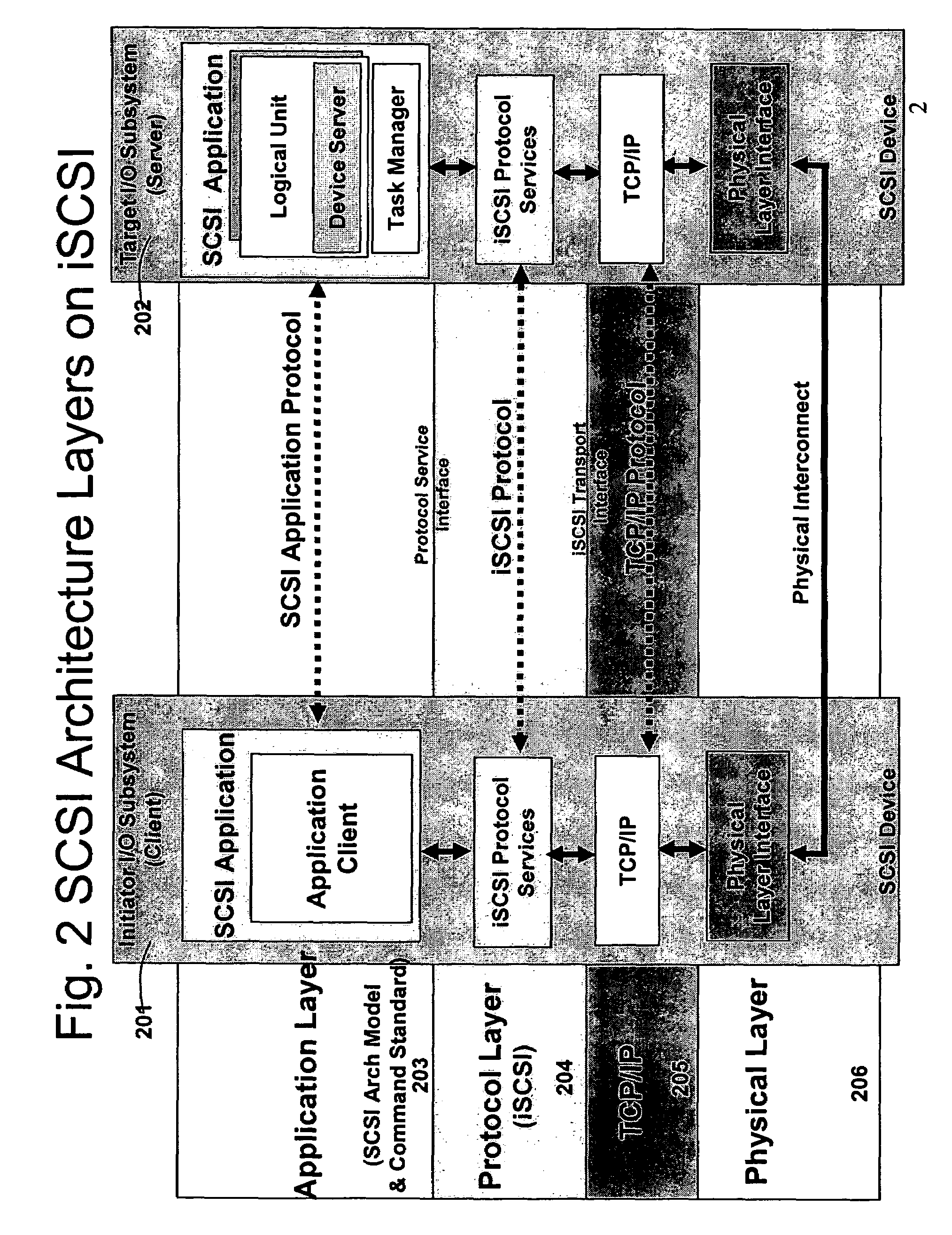
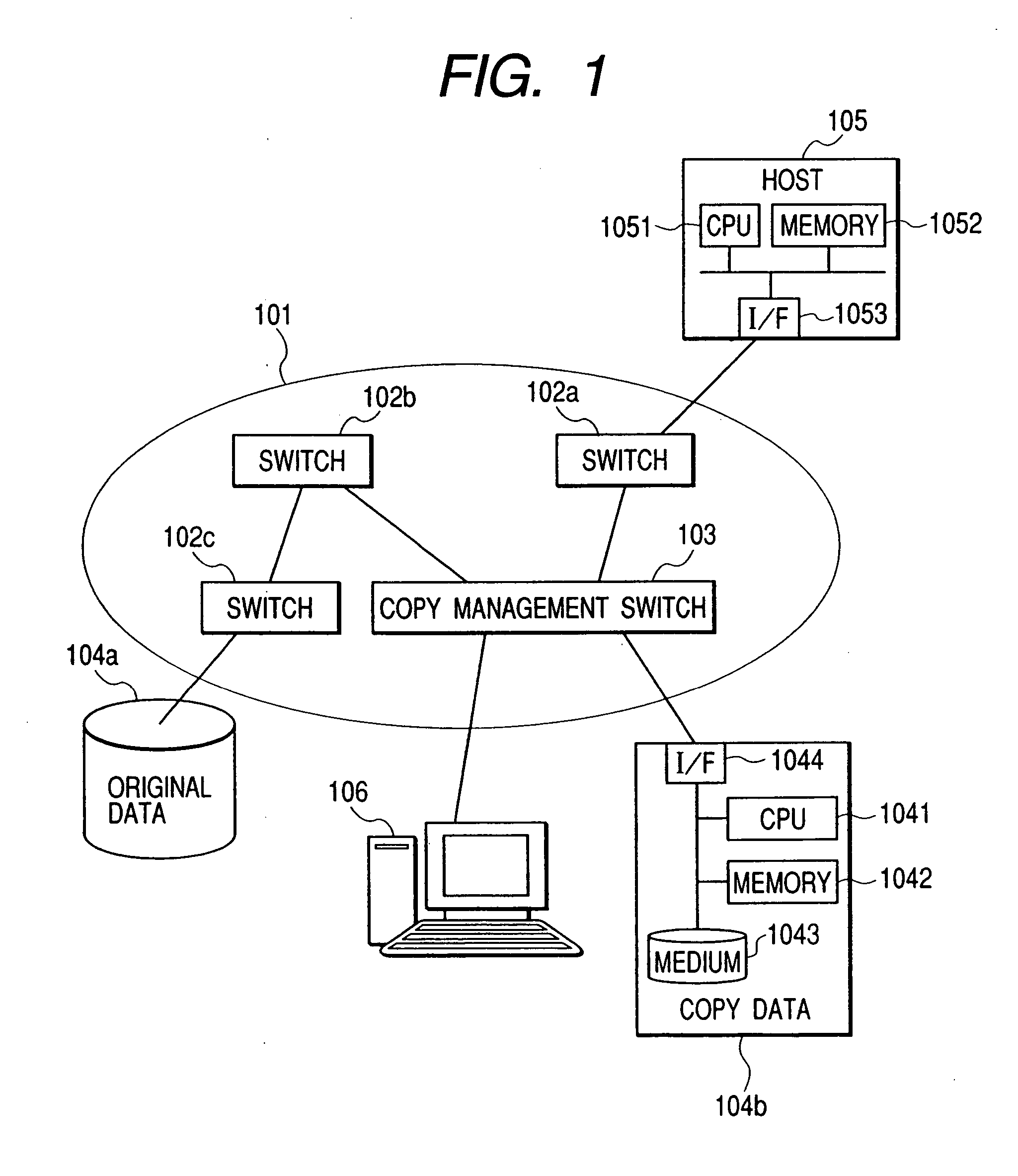
Switching system method for discovering and accessing SCSI devices in response to query
InactiveUS7089293B2Simple processRobust systemSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsStorage managementComputer engineering
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
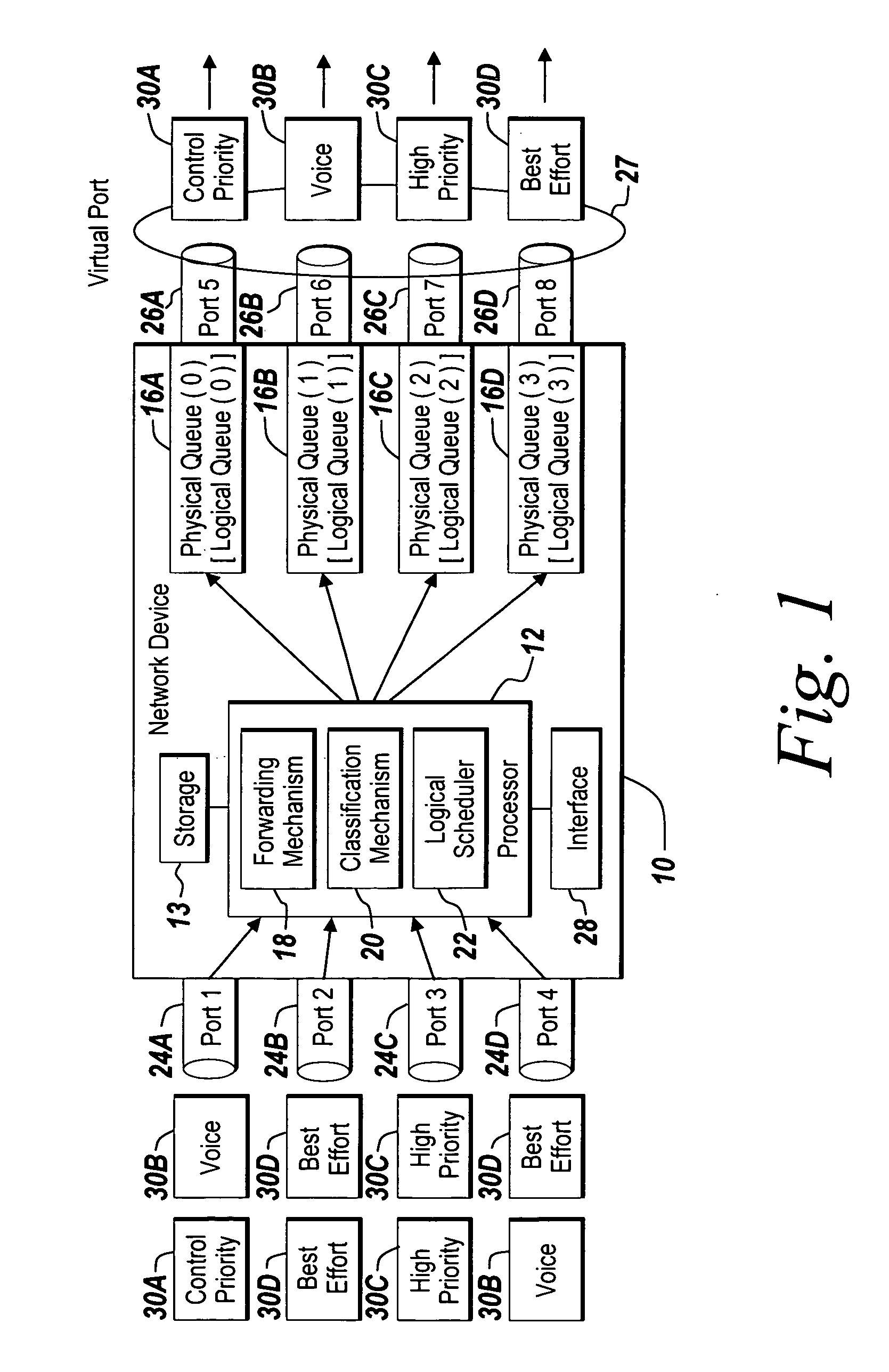
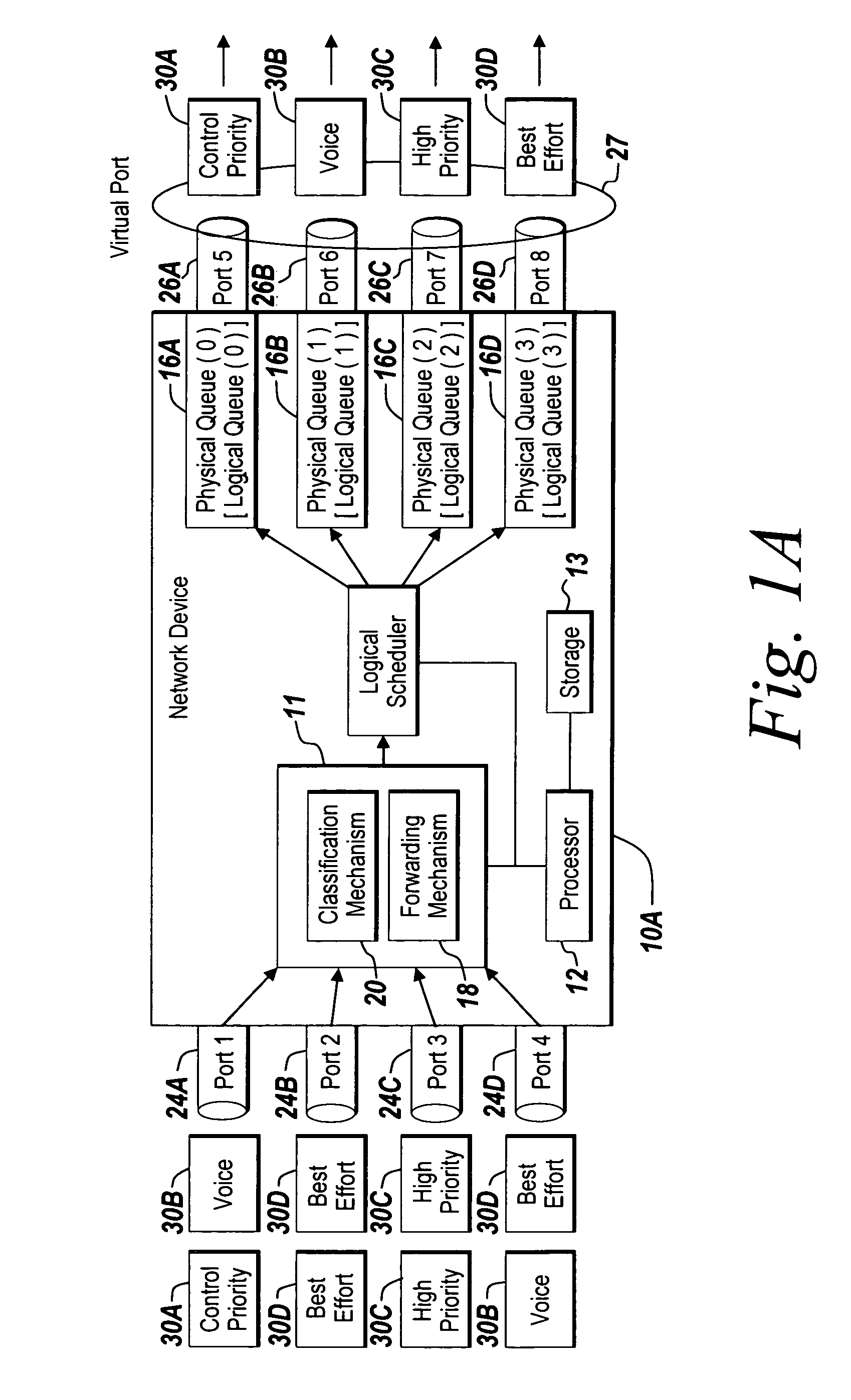
Method and apparatus of virtual class of service and logical queue representation through network traffic distribution over multiple port interfaces
ActiveUS7936770B1Improve abilitiesIncrease volumeMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityVirtual class
A method and apparatus are provided that allows for the representation of a larger number of classes of network traffic and logical queues than is physically available on a per port basis within a network device. A number of logical queues, whose number can match the number of classes of network traffic a network device handles, may be supported across an aggregated set of ports even though the network device has fewer physical queues per port than there are classes of network traffic. The method and apparatus improve the management of network traffic sensitive to time delay and jitter, and further facilitates the operation of these applications in a simultaneous or near simultaneous manner.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Method for optimal path selection in traversal of packets through network address translators
InactiveUS20050259637A1Reduce administrative overheadFast convergenceMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionNetwork addressNetwork address translation
Reduction of administrative overhead in maintaining network information, rapid convergence on an optimal routing path through the data network, and utilization of only required network resources are realized by a novel method for establishing a call path between network users. The method is based upon deployment of a network information server that stores network topology information and that is addressable by each end user. In this method, the network information server receives a request to establish a call path. The request identifies at least the calling party. In response to the request, the network information server determines a network traversal between the calling party and a root network wherein the network traversal includes call path information about the sub-networks between the calling party and the root network. The request for establishing a call path can also identify the called party. Based on the calling and called party identification, the network information server also determines a second network traversal between the called party and the root network. The second network traversal is sent to either the calling party or the called party or to both the calling and called parties. The server can determine an intersection of the traversals and send the intersection information to the parties. The intersection information is known as a merge point and represents an optimal call path between the parties.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Method and system for providing media services
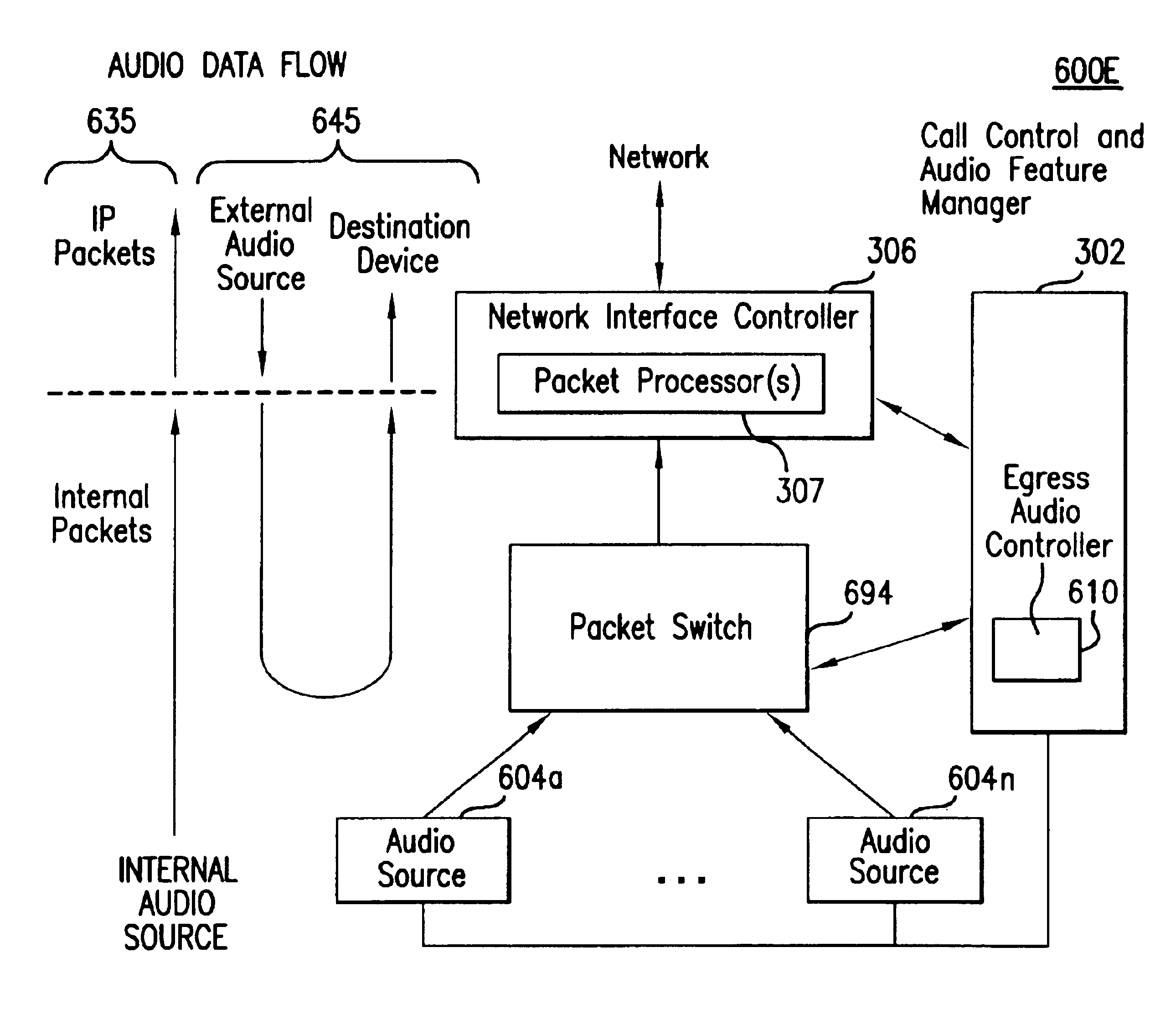
InactiveUS6947417B2Special service provision for substationSpecial service for subscribersVoice over IPNetwork interface controller
The present invention provides a method and system for providing media services in Voice over IP telephony. A switch is coupled between one or more audio sources and a network interface controller. The switch can be a packet switch or a cell switch.
Owner:MOVIUS INTERACTIVE CORP
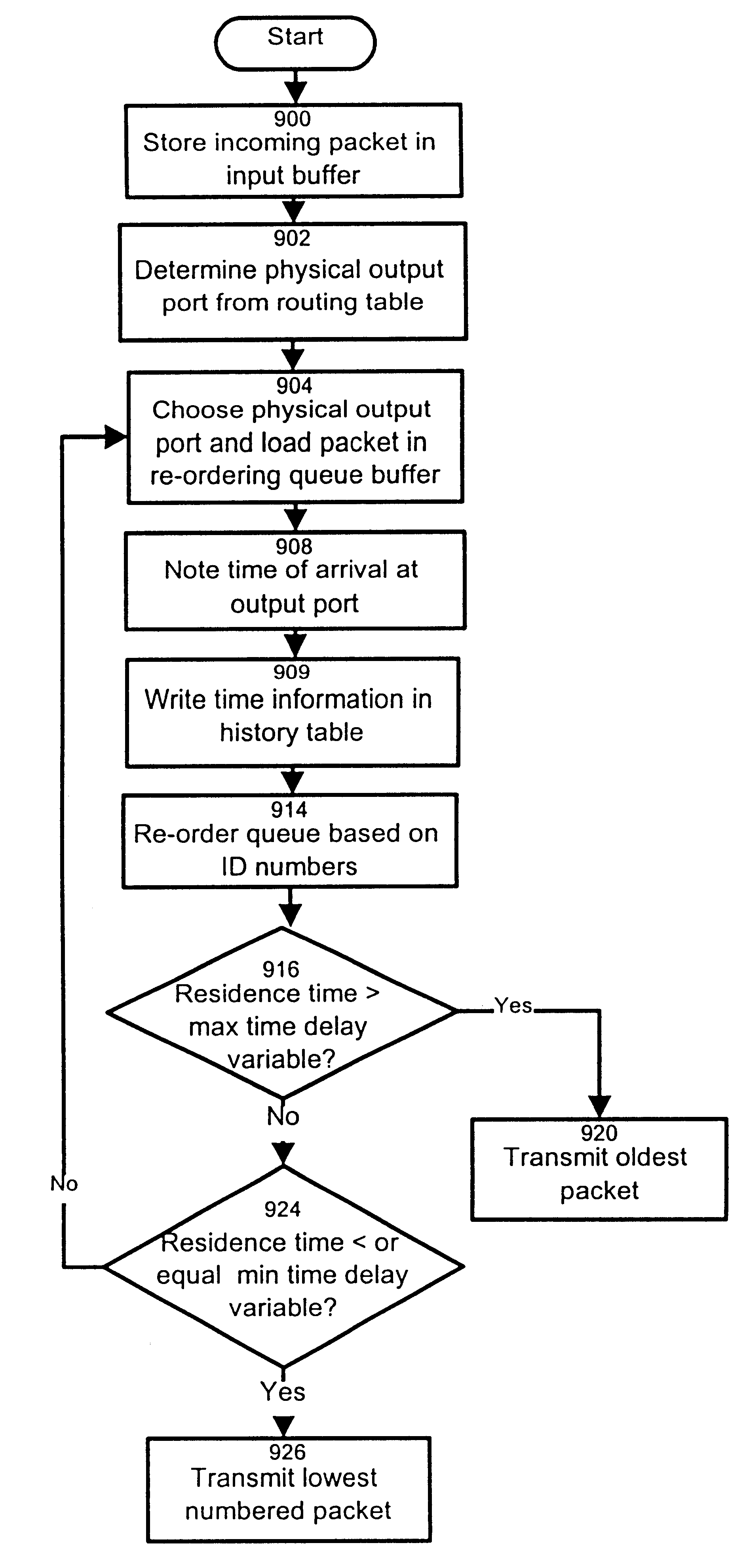
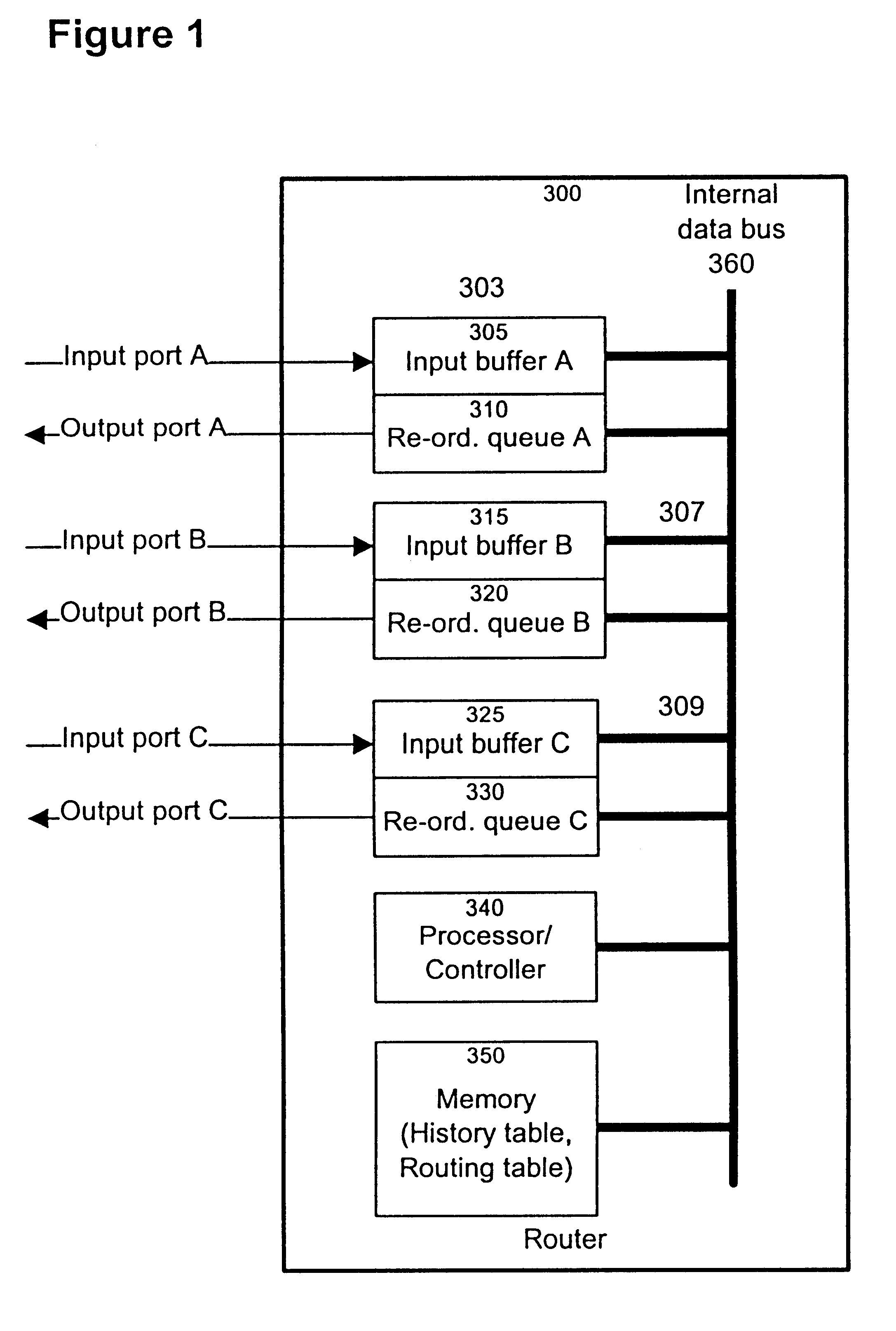
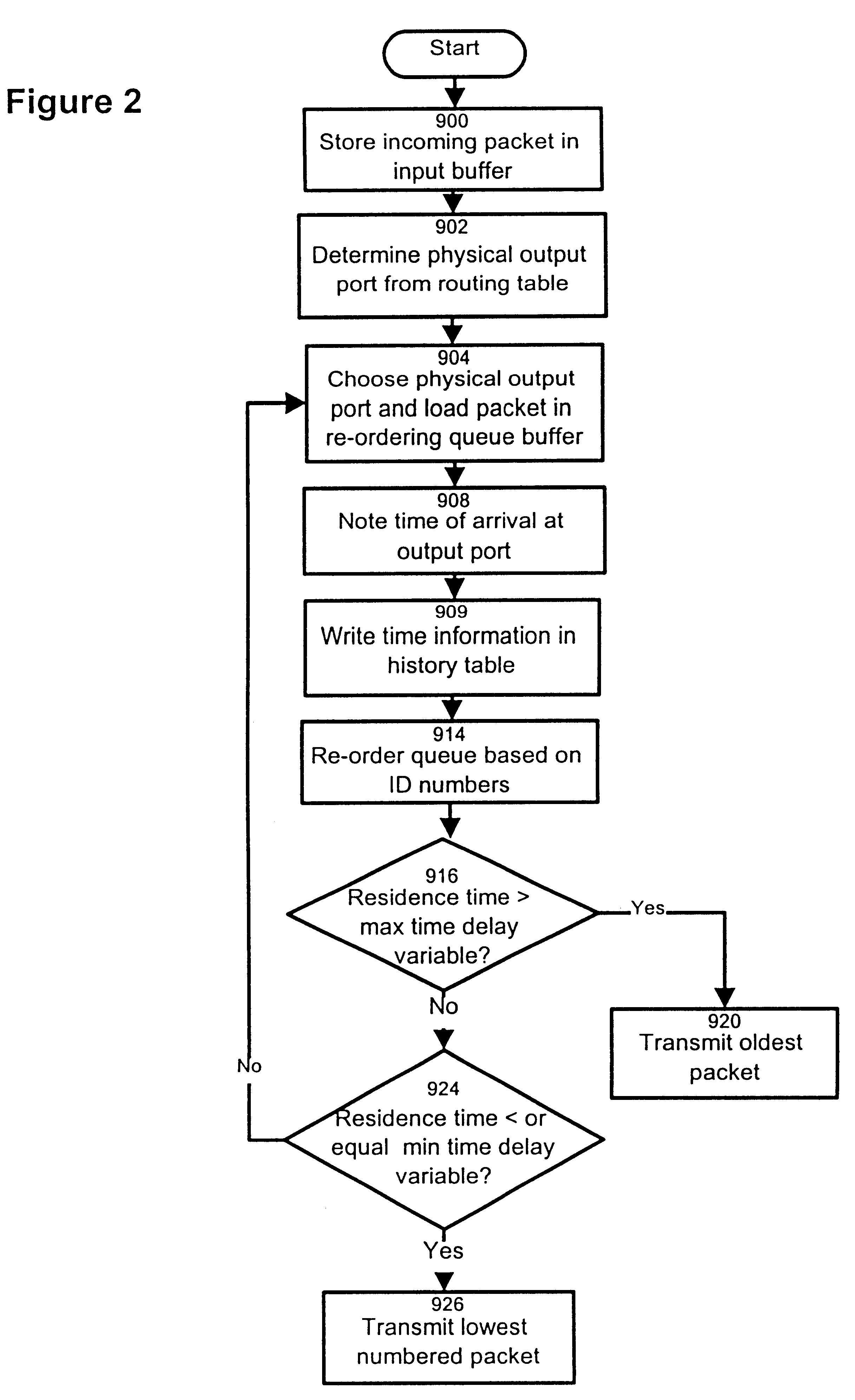
Method and apparatus for re-ordering data packets in a network environment
InactiveUS6246684B1Lower Level RequirementsAvoid changeMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationTime delaysNetwork packet
The invention provides a method and apparatus for re-ordering data traffic units, such as IP data packets, that may have been miss-ordered during a transmission over a multi-pathway link between a source node and a destination node in a network. The re-ordering apparatus includes a storage medium for intercepting the IP data packets and holding the IP data packets to allow IP data packets delayed on slower pathways to catch-up. The IP data packets in the storage medium are re-ordered based on their sequence number in an attempt to restore the original order of the IP data packets. A maximal time delay variable determines how long a certain IP data packet can be held in the storage medium. The TP data packet is released prior to the maximal time delay variable or as the maximal time delay variable is exceeded.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE +1
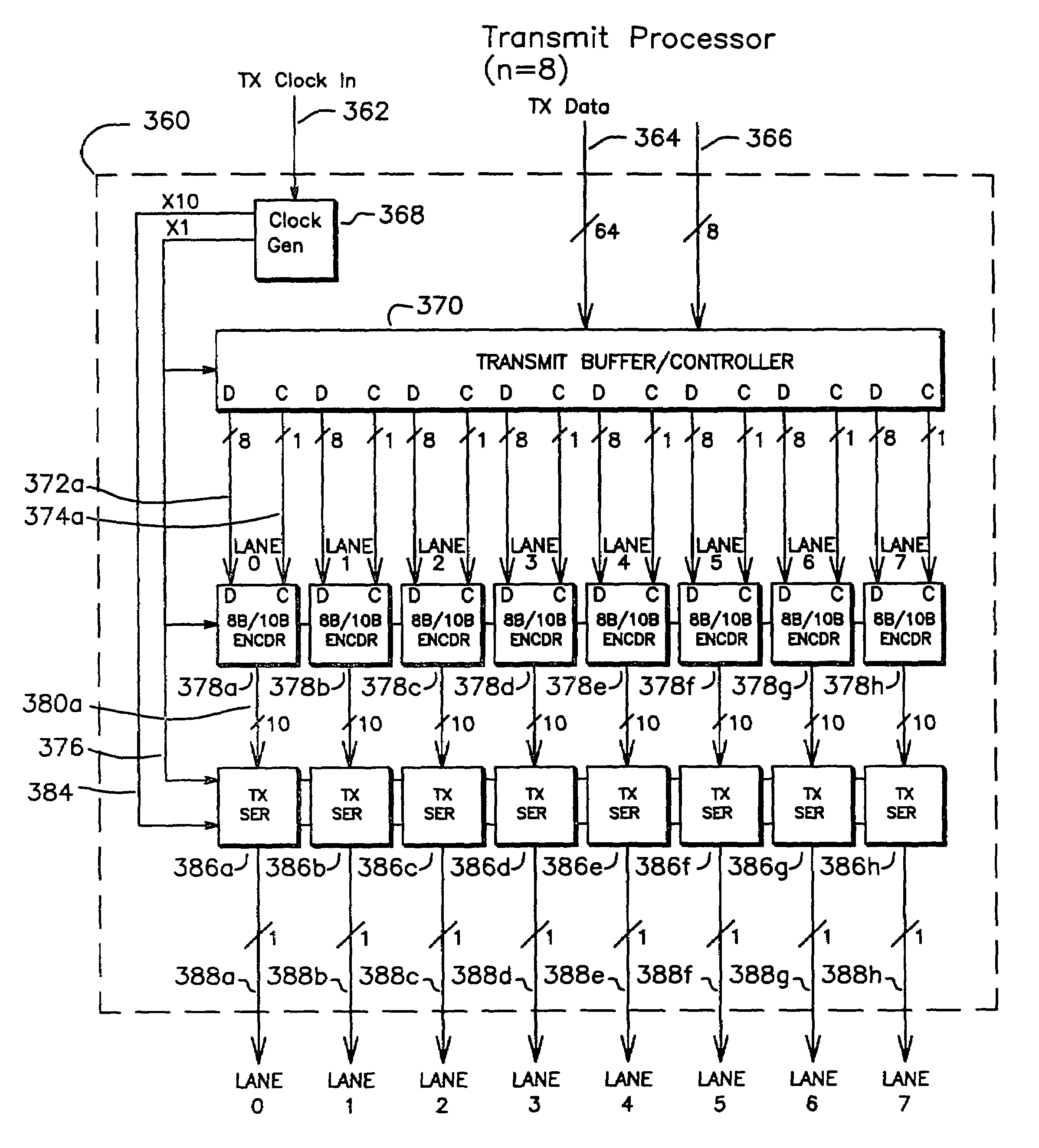
Multi-function high-speed network interface
InactiveUS7573916B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexCommunication interfaceClock rate
A high speed communications interface divides data into a plurality of lanes, each lane encoded with clocking information, serialized, and sent to an interface. During cycles when there is no available data to send, IDLE_EVEN and IDLE_ODD cells are sent on alternating cycles. Data is transmitted by sending a header which spans all lanes and includes a START symbol. The final data transaction includes a Frame Check Sequence (FCS) which operates over the entire header and data. The packet is terminated by an END symbol, which is sent after the final data, and the remainder of the lanes are padded with IDLE_EVEN, IDLE_ODD, IDLE_EVEN_BUSY, or IDLE_ODD_BUSY cycles. The interface has a variable clock rate.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for high speed packet transmission implementing dual transmit and receive pipelines
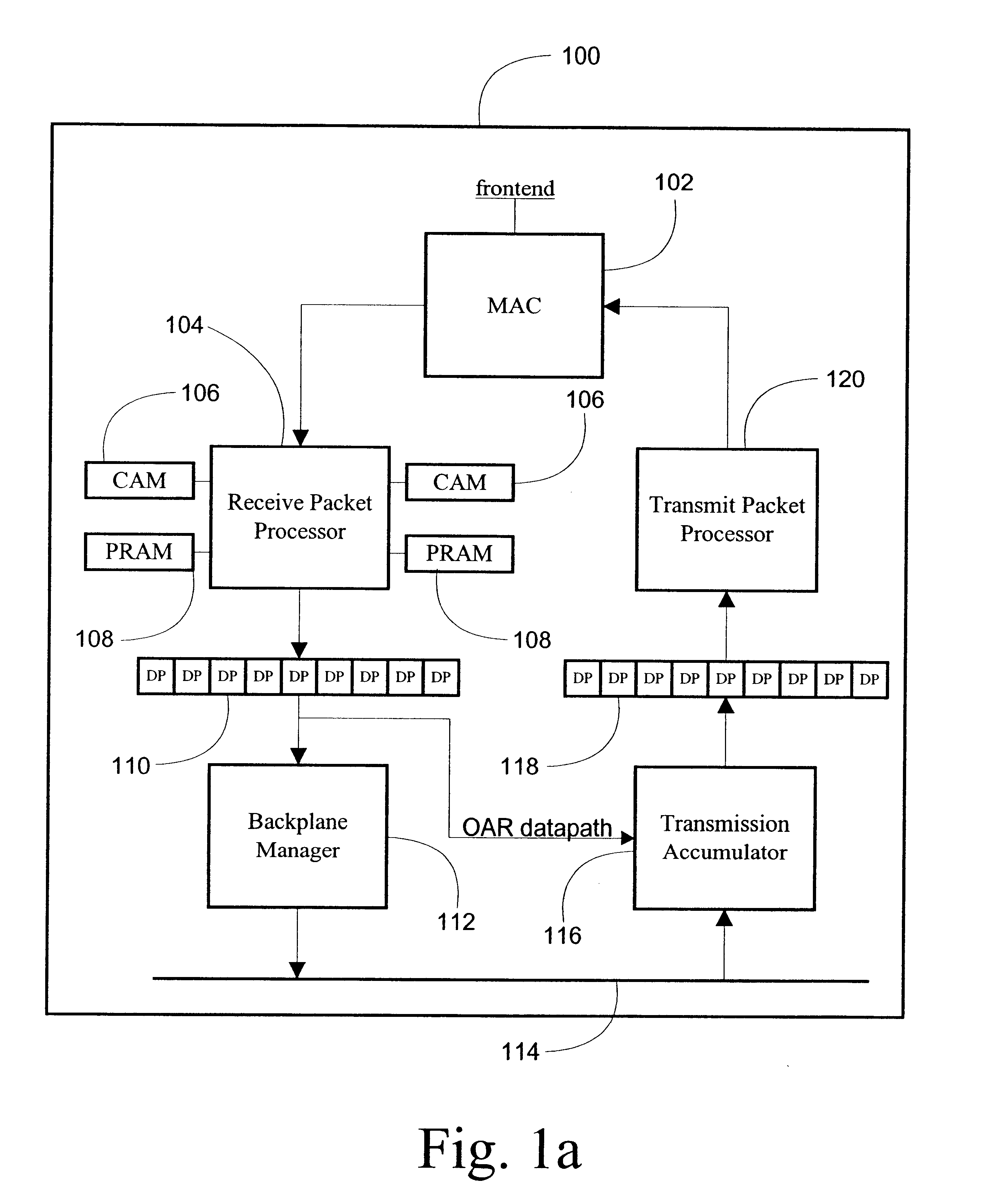
InactiveUS6901072B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsCircuit switching systemsGigabitStructure of Management Information
The present invention provides systems and methods for providing data transmission speeds at or in excess of 10 gigabits per second between one or more source devices and one or more destination devices. According to one embodiment, the system of the present invention comprises a first and second media access control (MAC) interfaces to facilitate receipt and transmission of packets over an associated set of physical interfaces. The system also contemplates a first and second field programmable gate arrays (FPGA) coupled to the MAC interfaces and an associated first and second memory structures, the first and second FPGAs are configured to perform initial processing of packets received from the first and second MAC interfaces and to schedule the transmission of packets to the first and second MAC interface for transmission to one or more destination devices. The first and second FPGAs are further operative to dispatch and retrieve packets to and from the first and second memory structures. A third FPGA, coupled to the first and second memory structures and a backplane, is operative to retrieve and dispatch packets to and from the first and second memory structures, compute appropriate destinations for packets and organize packets for transmission. The third FPGA is further operative to receive and dispatch packets to and from the backplane.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
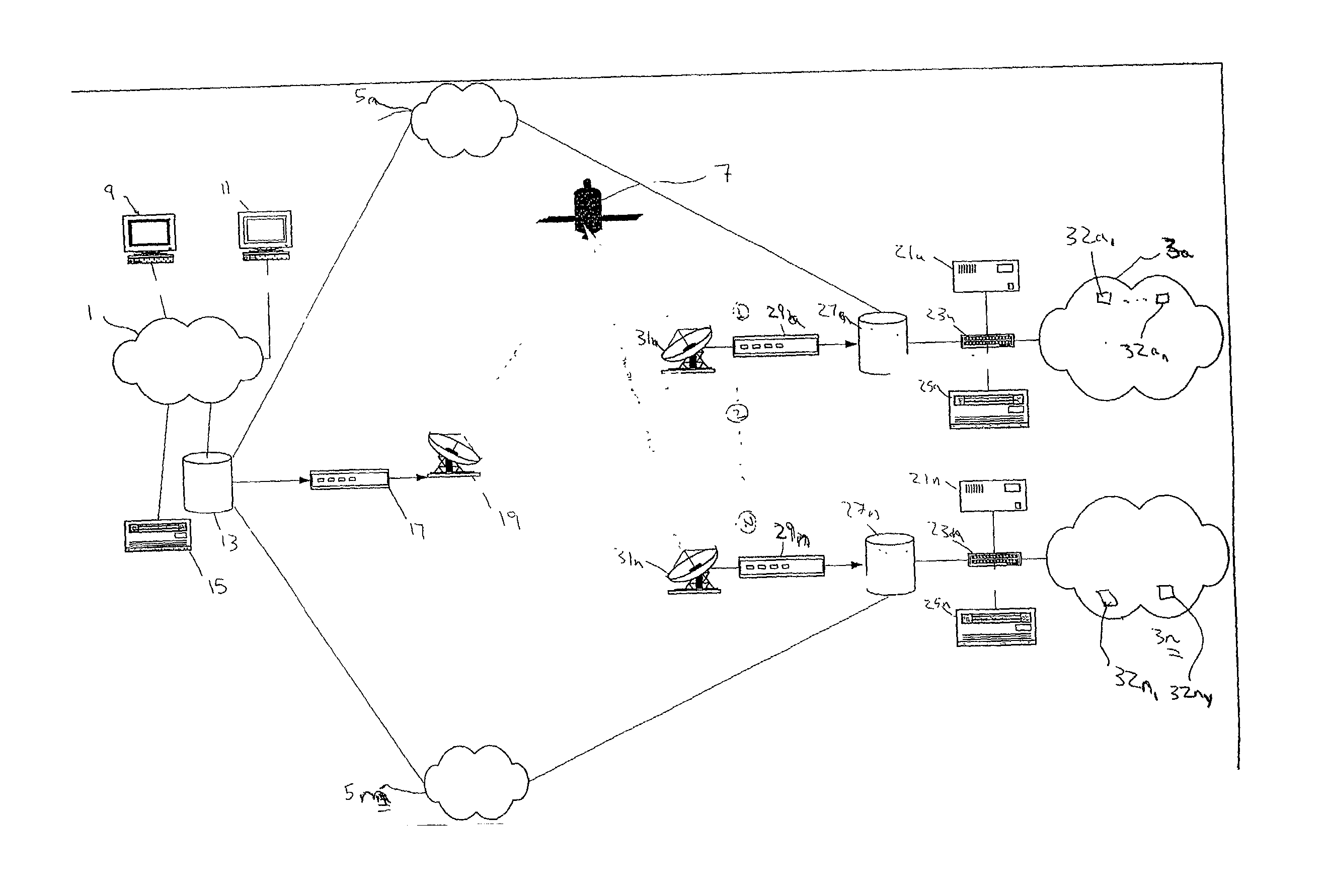
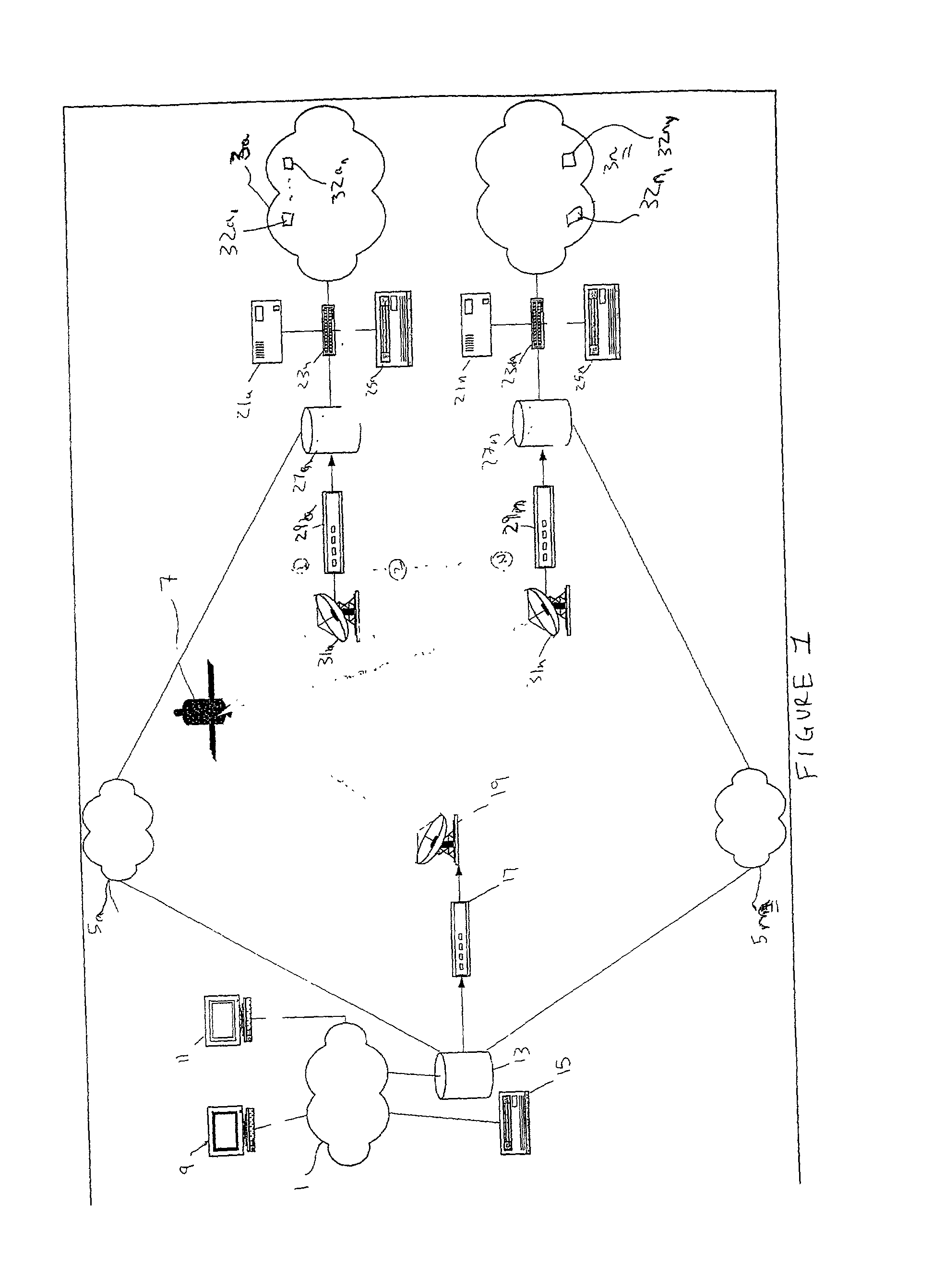
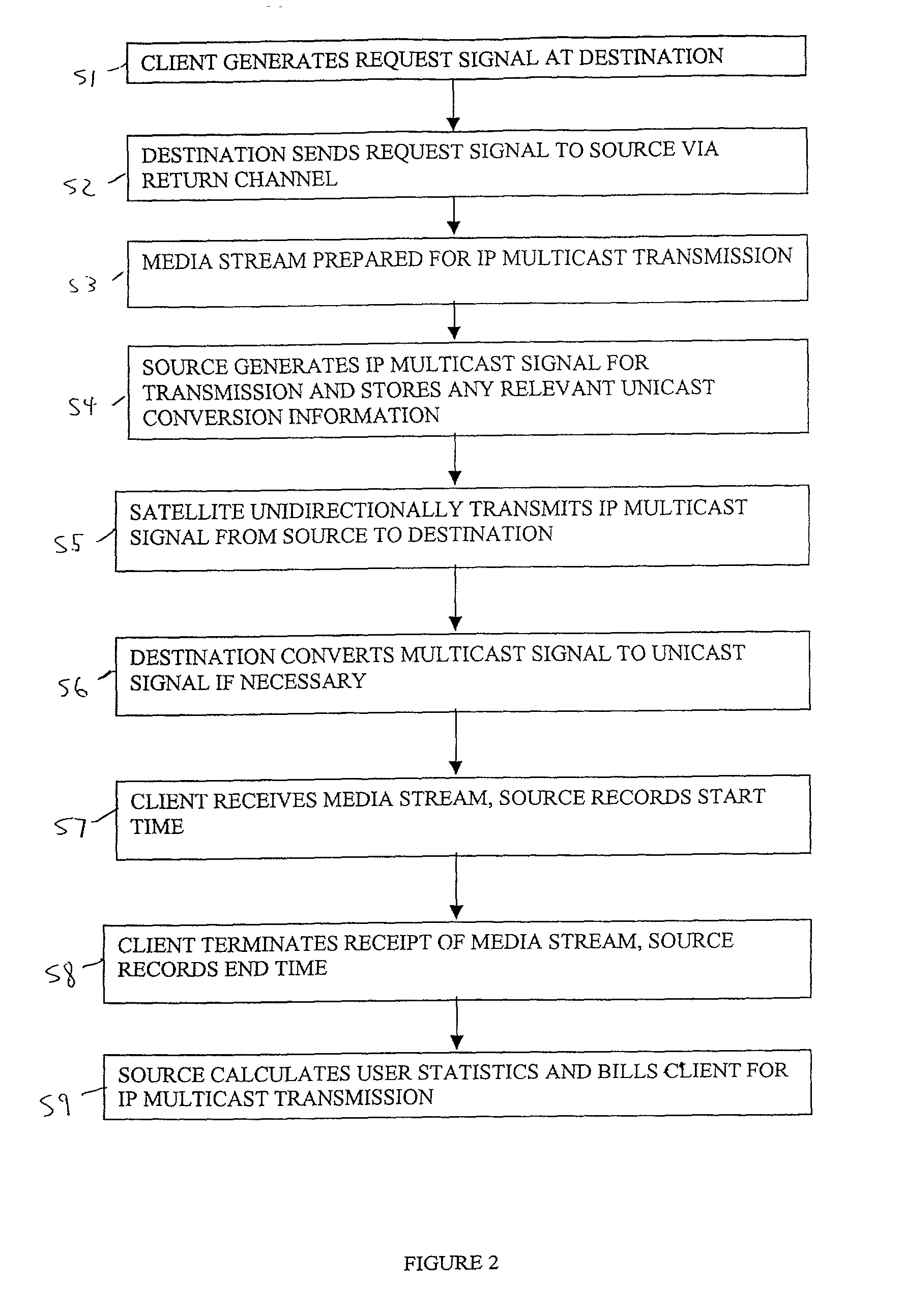
Satellite based content distribution system using IP multicast technology
InactiveUS7161934B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationContent distributionReal-time data
A method and system of performing IP multicast includes a client at one of many downstream networks that sends a request signal to an upstream network via a return channel (e.g., the Internet), and the upstream network sends the request to a media server. The media server, and for live data, a media encoder, processes a media stream to generate a real-time IP multicast communication that is output to a unidirectional satellite that transmits the IP multicast communication to the client without delay via the downstream network, and can convert the IP multicast to unicast. The bidirectional return channel allows the source to calculate billing information based on client usage statistics, and transmits confirmation acknowledgement based on a confirmation request from the upstream network. Because the routing configuration is transparent to the rest of the network, the invention applies to multi-hop networks on both sides of the satellite link.
Owner:INTELSAT SERVICES
Method and apparatus for generating and using enhanced tree bitmap data structures in determining a longest prefix match
ActiveUS20050157712A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsDigital data information retrievalGeneral purposeArray data structure
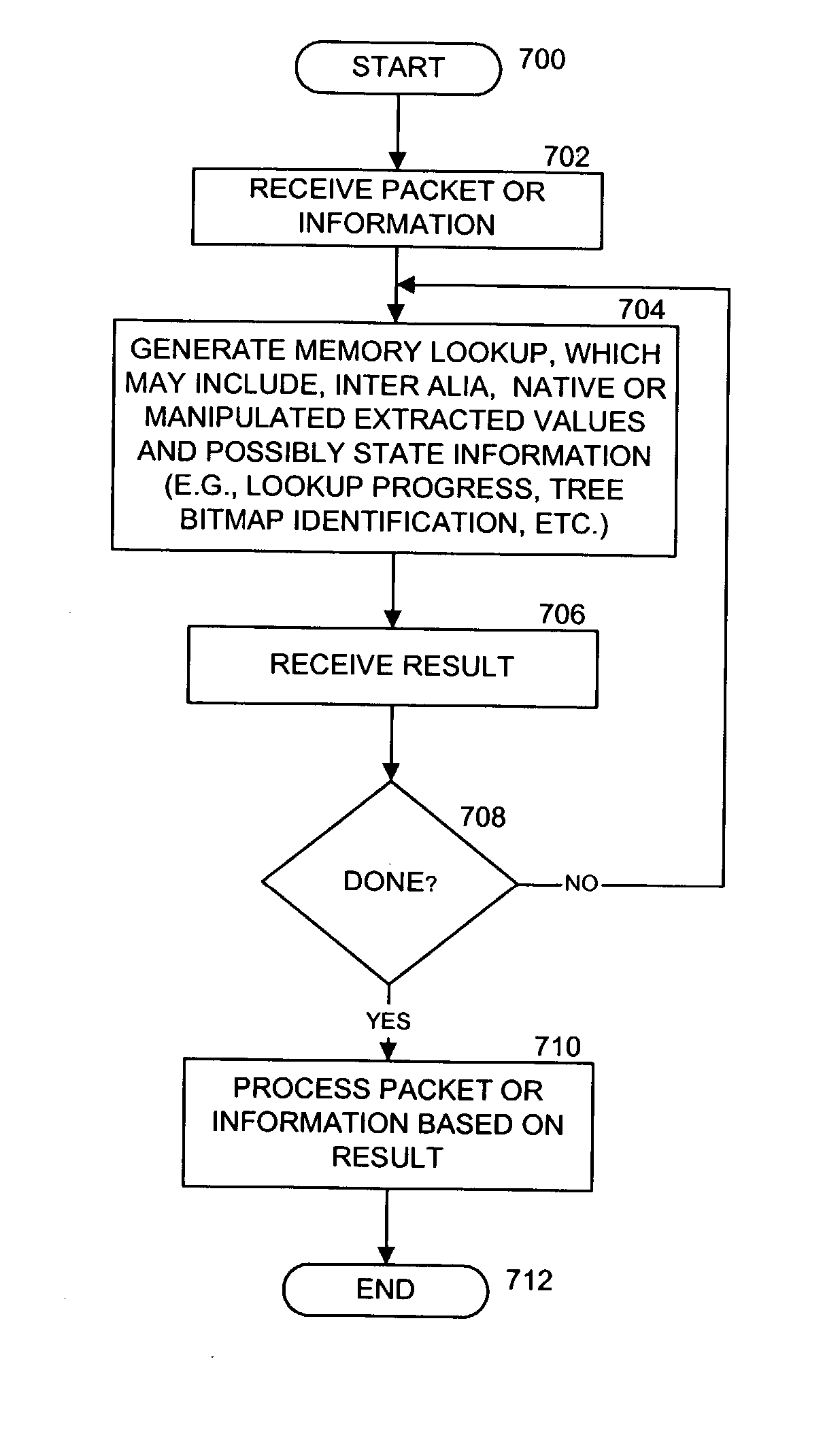
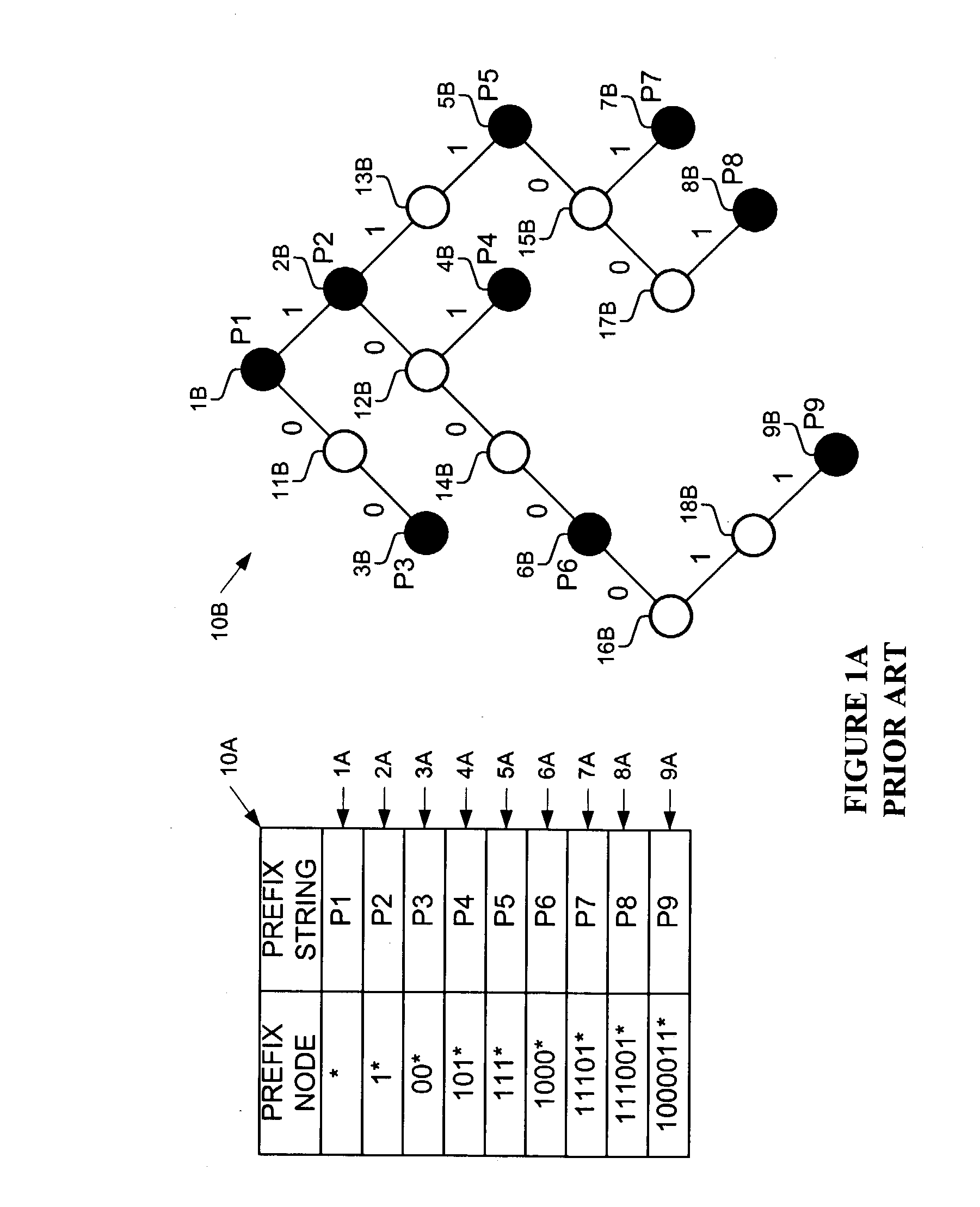
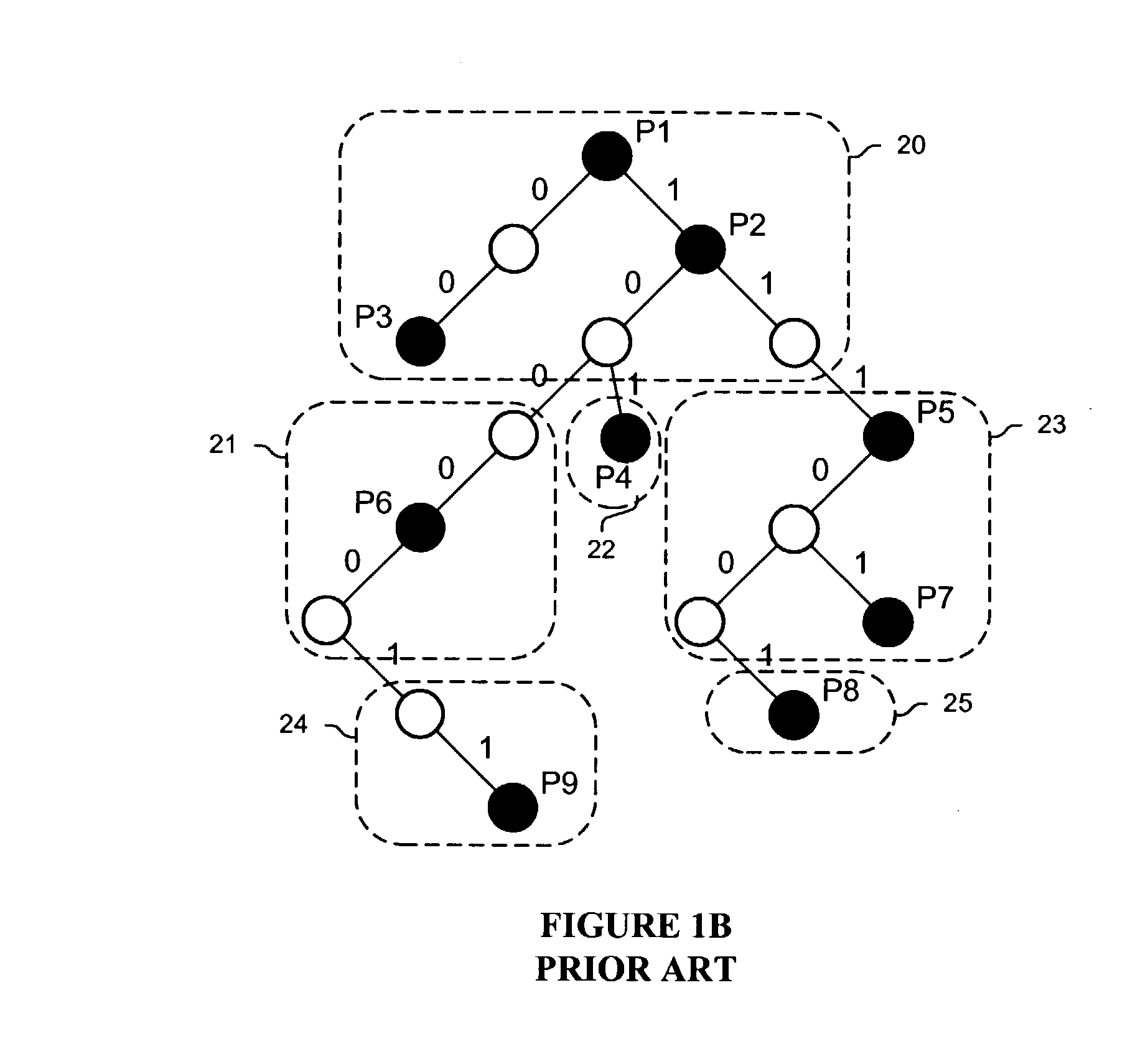
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for generating and using an enhanced tree bitmap data structure in determining a longest prefix match, such as in a router, packet switching system. One implementation organizes the tree bitmap to minimize the number of internal nodes that must be accessed during a lookup operation. A pointer is included in each of the trie or search nodes to the best match so far entry in the leaf or results array which allows direct access to this result without having to parse a corresponding internal node. Moreover, one implementation stores the internal node for a particular level as a first element in its child array. Additionally, one implementation uses a general purpose lookup engine that can traverse multiple tree bitmaps or other data structures simultaneously, and perform complete searches, partial searches, and resume partial searches such as after receiving additional data on which to search.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
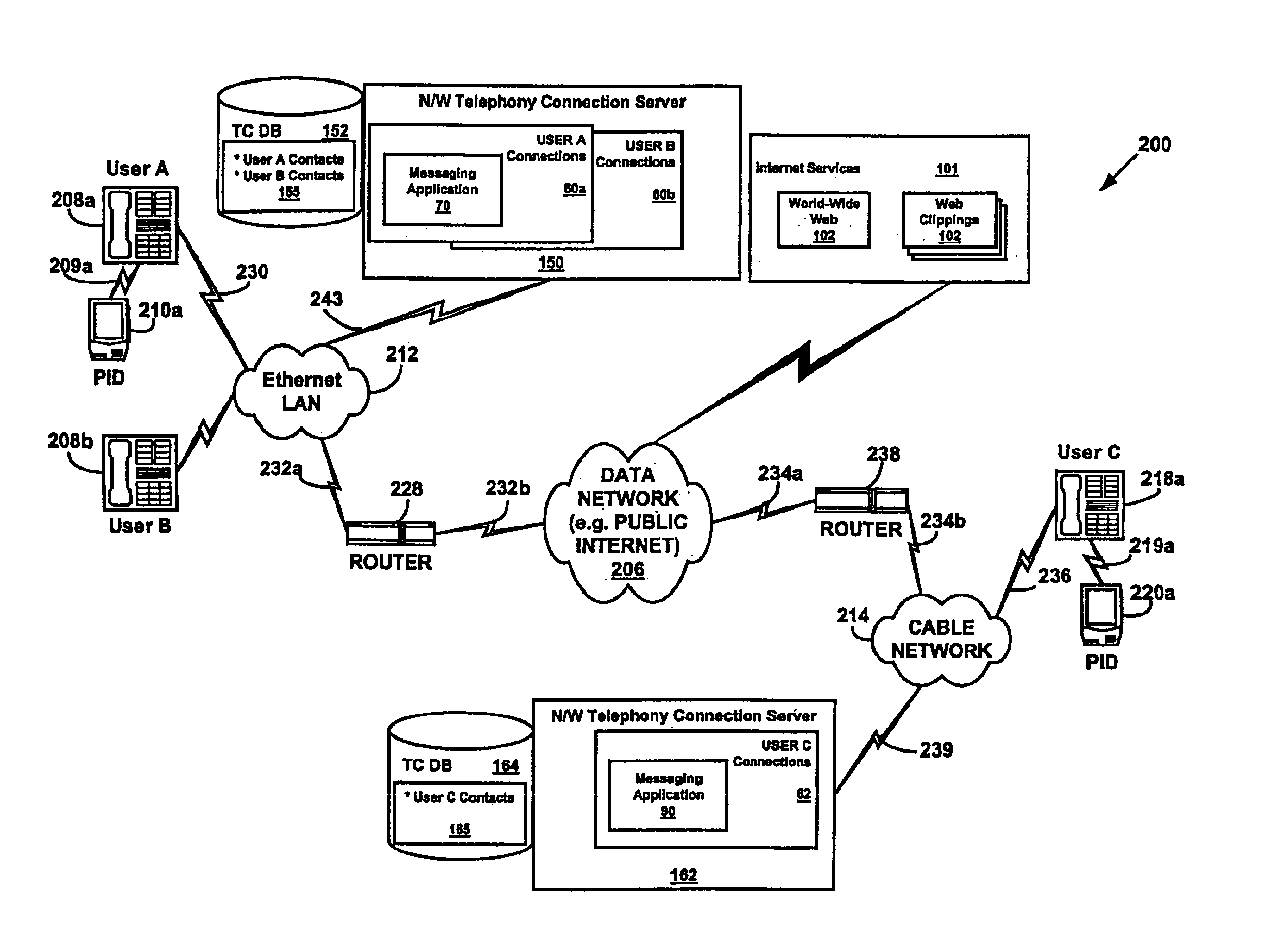
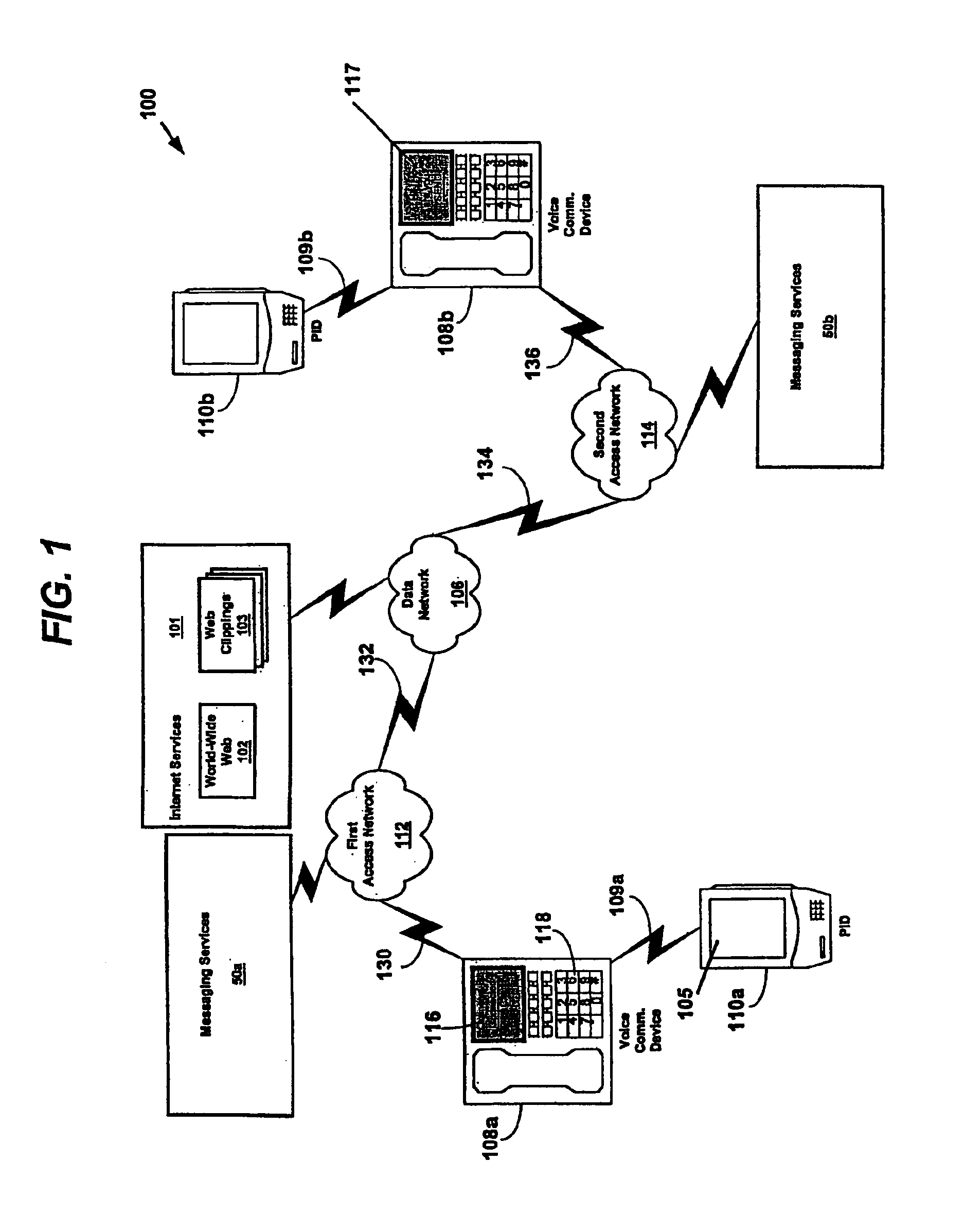
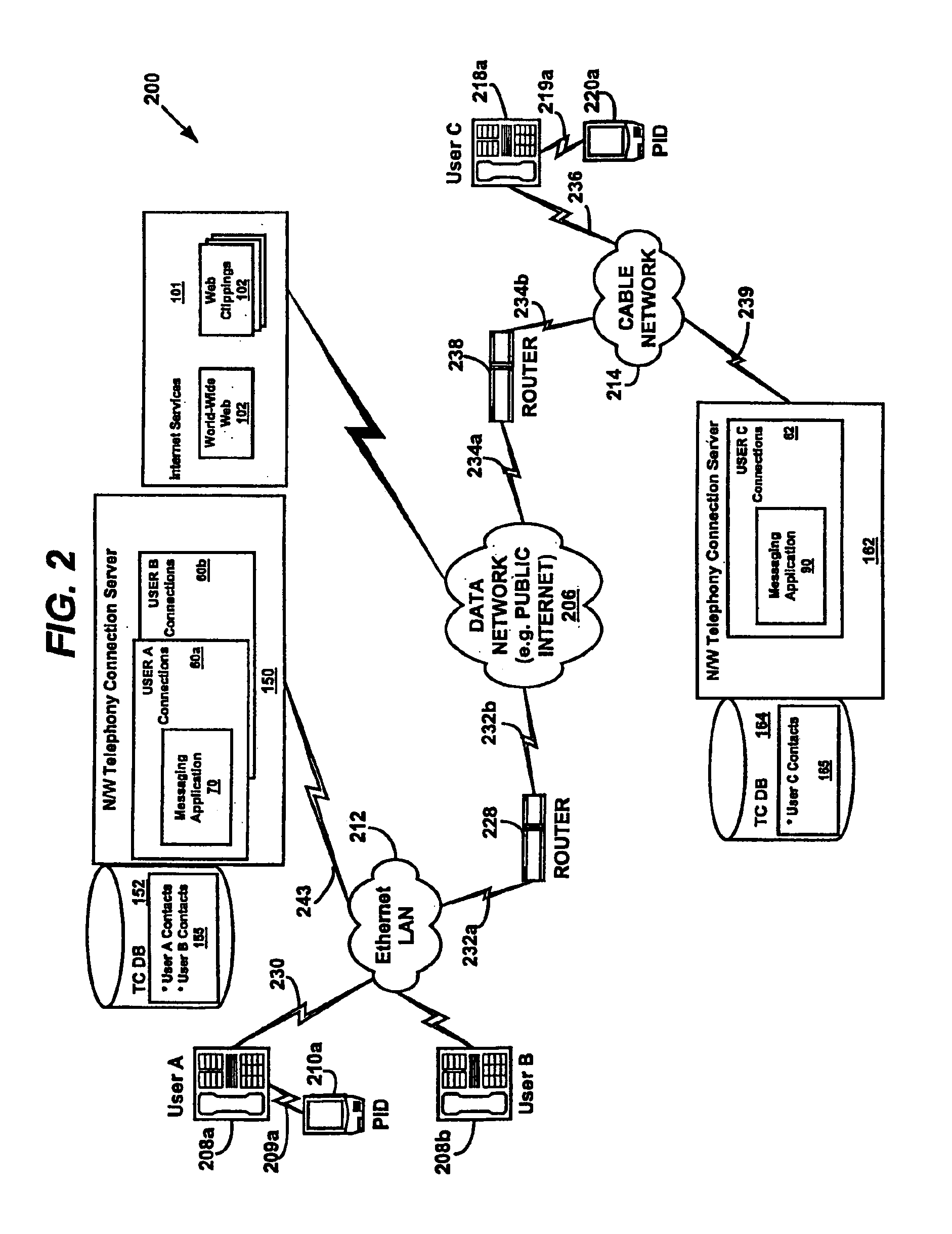
System and method for performing messaging services using a data communications channel in a data network telephone system
InactiveUS6870830B1Save a lot of costLow costMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersProgram managementMessage passing
A system and method for performing messaging between telephones in a data network telephone system. The message communications may be managed by a messaging application connected to the data network. The messaging application detects when a telephone is connected to another telephone and sends a messaging input screen to the first telephone. The messaging application may determine the availability of other users for messaging and may control messages communicated between the first telephone and the other users. The messages may be text or voice messages.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
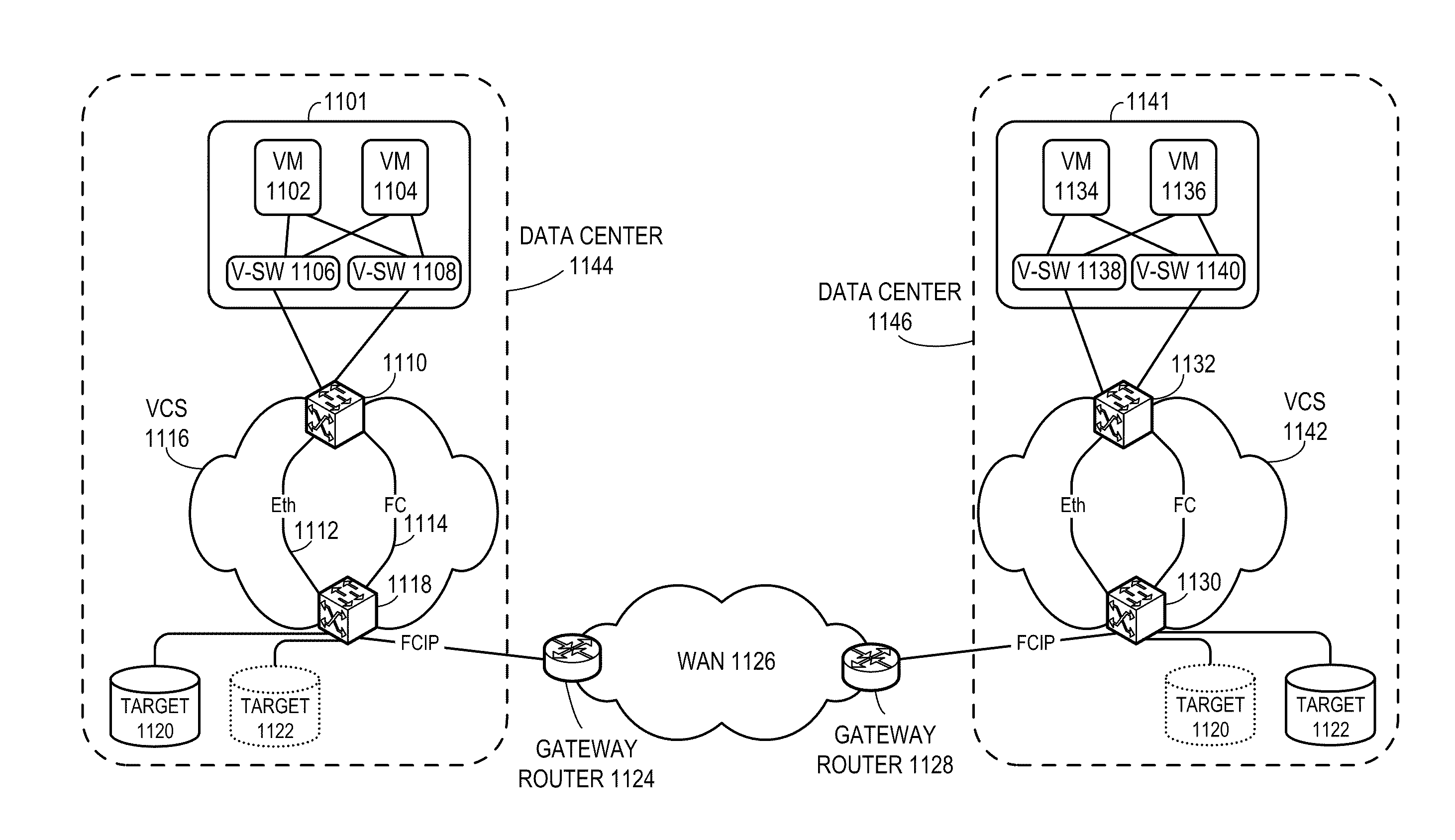
Converged network extension
ActiveUS8625616B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityFiber
One embodiment of the present invention provides a switch. The switch includes a first port configured to receive Transparent Interconnection of Lots of Links (TRILL) traffic; a second port configured to receive Fiber Channel (FC) traffic; and a third port configured to transmit received TRILL or FC traffic based on a Fiber Channel over IP (FCIP) protocol.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and method to support multicast routing in large scale wireless mesh networks
ActiveUS20060098607A1Quick changeReduce overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsNetwork topologiesTree rootWireless mesh network
Provided is a system and method for a multicast routing algorithm to work in infrastructure based mesh networks. It chooses access points, fixed infrastructure gateway nodes connected to each other and / or the global internet via a wired / wireless backbone, as a group of local multicast group leaders to form a multicast group leader cloud. Each local multicast group leader is elected on-demand according to the local multicast group member's request. Each local multicast group leader forms a local multicast tree rooted at this leader connecting all multicast group members associated with the AP. The processes of electing and maintaining local multicast trees rooted at APs enable efficient coordination with underlying unicast routing to exploit the advantages of fixed infrastructure nodes. Therefore, routing overhead and multicast tree convergence time are reduced. The method can support large networks with fast topology change due to fast convergence and reduced routing overhead.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
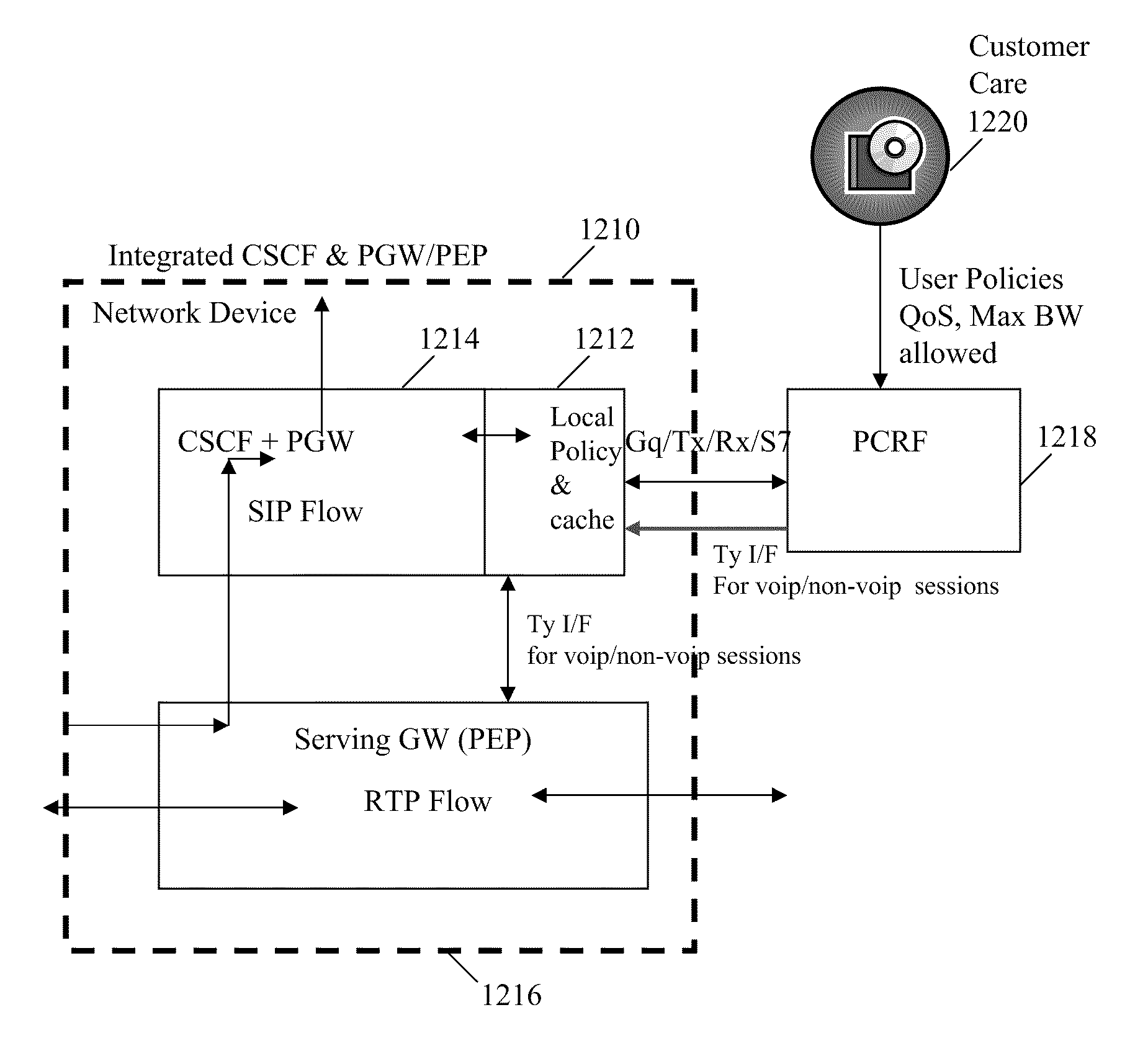
System and method for reducing latency in call setup and teardown
ActiveUS8144591B2Reduce signalingLower latencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDistributed computingCall setup
Systems and methods for reducing latency in call setup and teardown are provided. A network device with integrated functionalities and a cache is provided that stores policy information to reduce the amount of signaling that is necessary to setup and teardown sessions. By handling various aspects of the setup and teardown within a network device, latency is reduced and the amount of bandwidth needed for setup signaling is also reduced.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
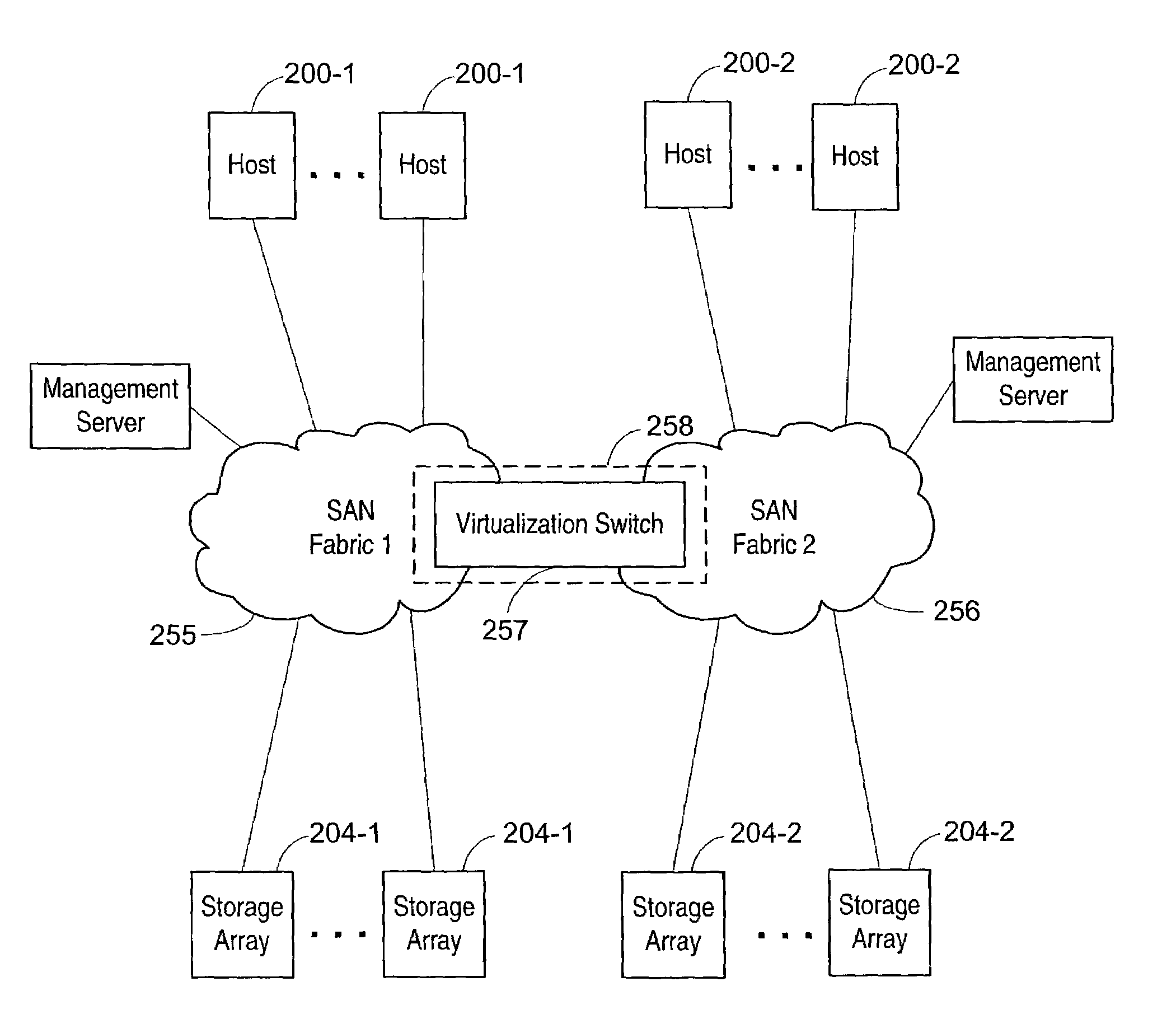
Hardware-based translating virtualization switch
InactiveUS7120728B2Improve throughputComprehensive performance is smallMultiplex system selection arrangementsInput/output to record carriersVirtualizationComputer hardware
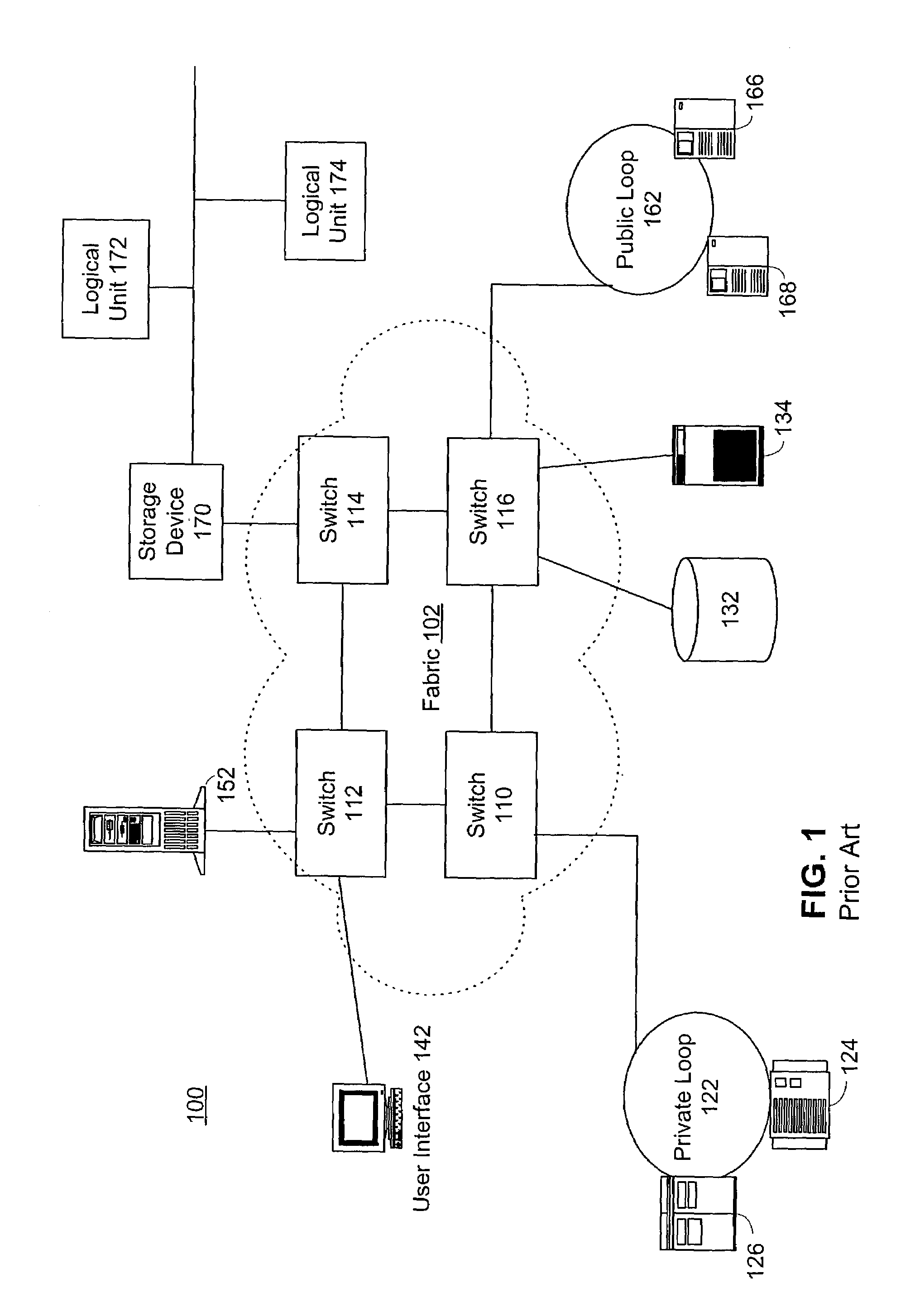
Placing virtualization agents in the switches which comprise the SAN fabric. Higher level virtualization management functions are provided in an external management server. Conventional HBAs can be utilized in the hosts and storage units. In a first embodiment, a series of HBAs are provided in the switch unit. The HBAs connect to bridge chips and memory controllers to place the frame information in dedicated memory. Routine translation of known destinations is done by the HBA, based on a virtualization table provided by a virtualization CPU. If a frame is not in the table, it is provided to the dedicated RAM. Analysis and manipulation of the frame headers is then done by the CPU, with a new entry being made in the HBA table and the modified frames then redirected by the HBA into the fabric. This can be done in either a standalone switch environment or in combination with other switching components located in a director level switch. In an alternative embodiment, specialized hardware scans incoming frames and detects the virtualized frames which need to be redirected. The redirection is then handled by translation of the frame header information by hardware table-based logic and the translated frames are then returned to the fabric. Handling of frames not in the table and setup of hardware tables is done by an onboard CPU.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
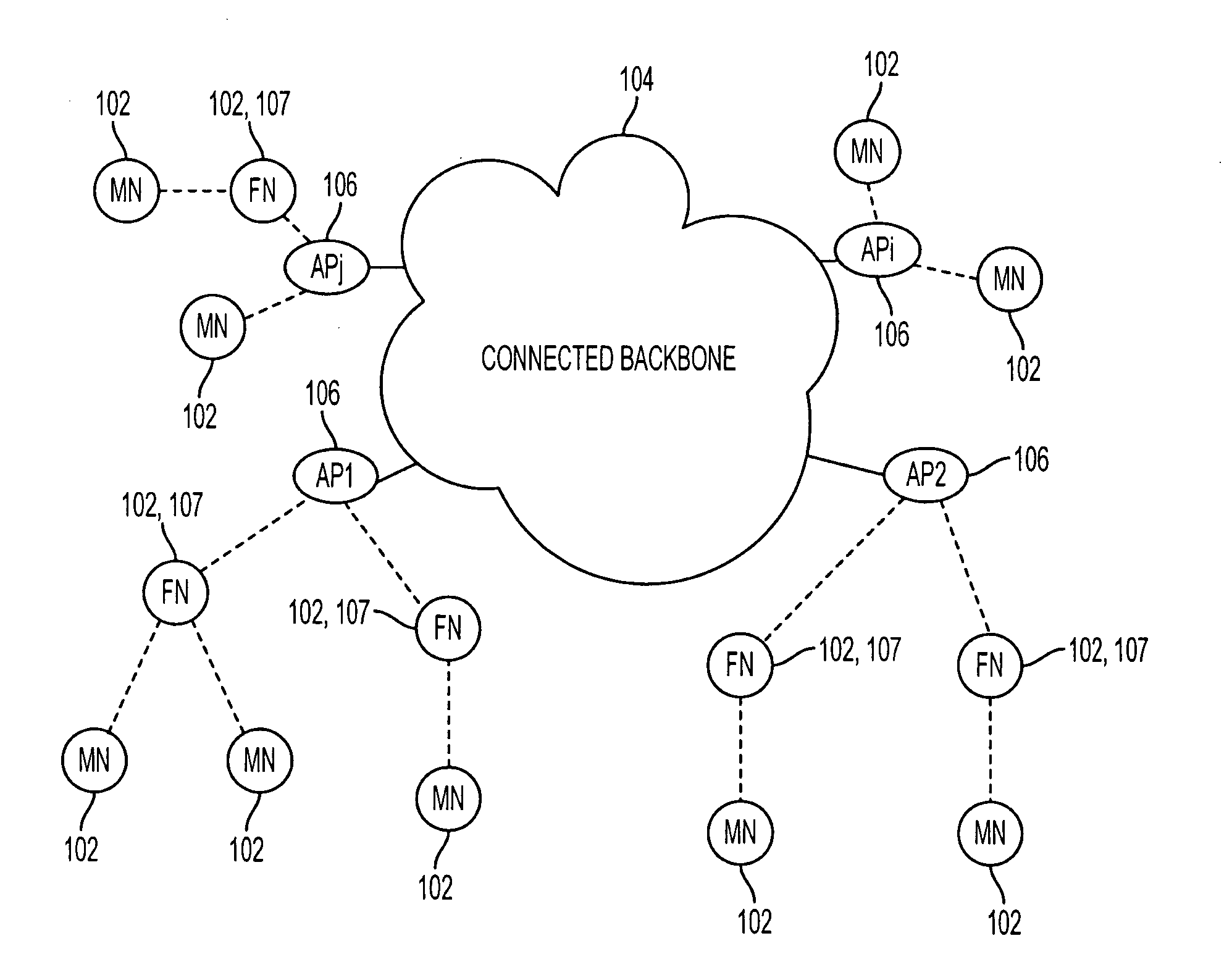
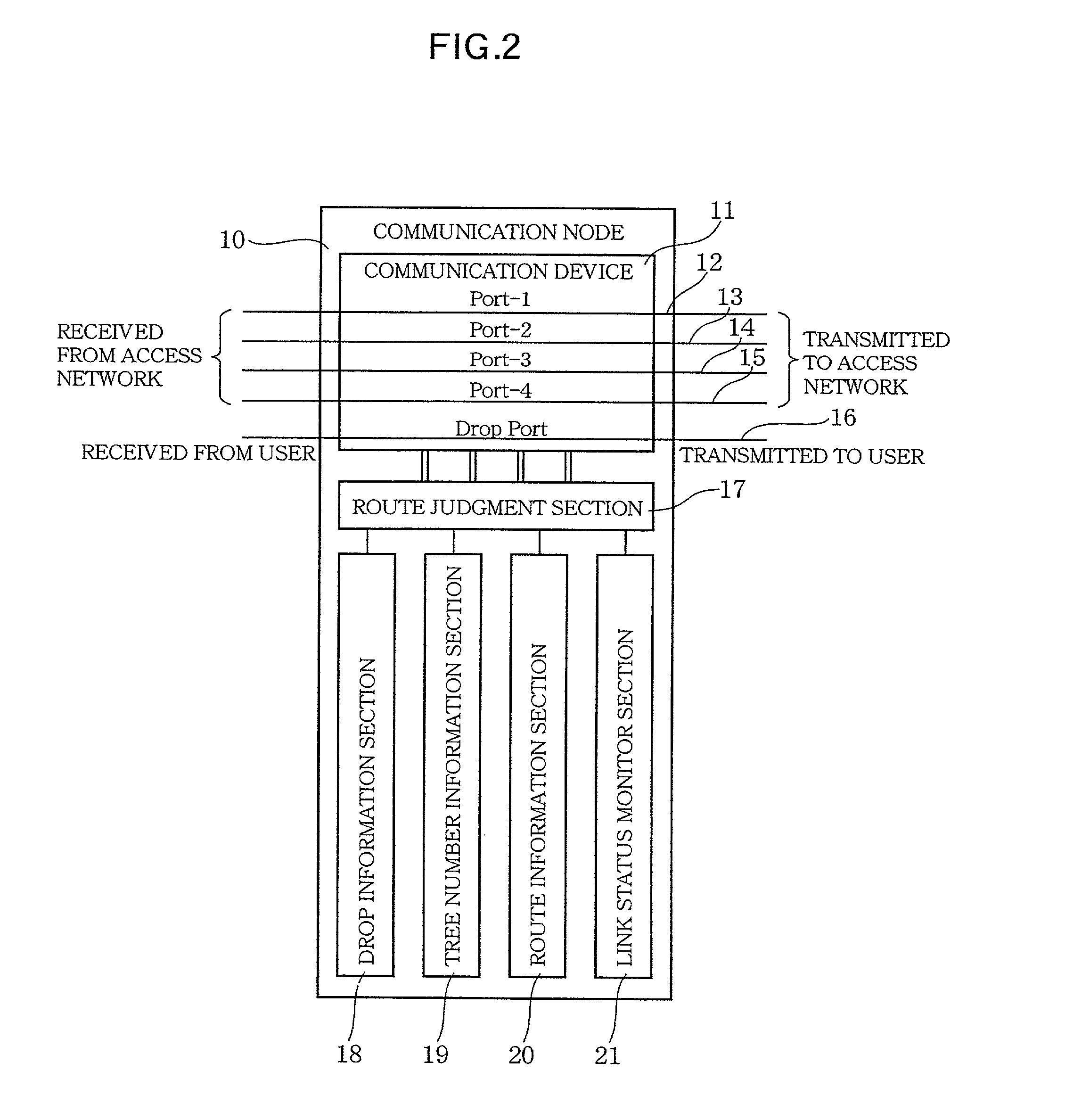
Access network system
InactiveUS20020054593A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsNetwork traffic/resource managementAccess networkRadio access network
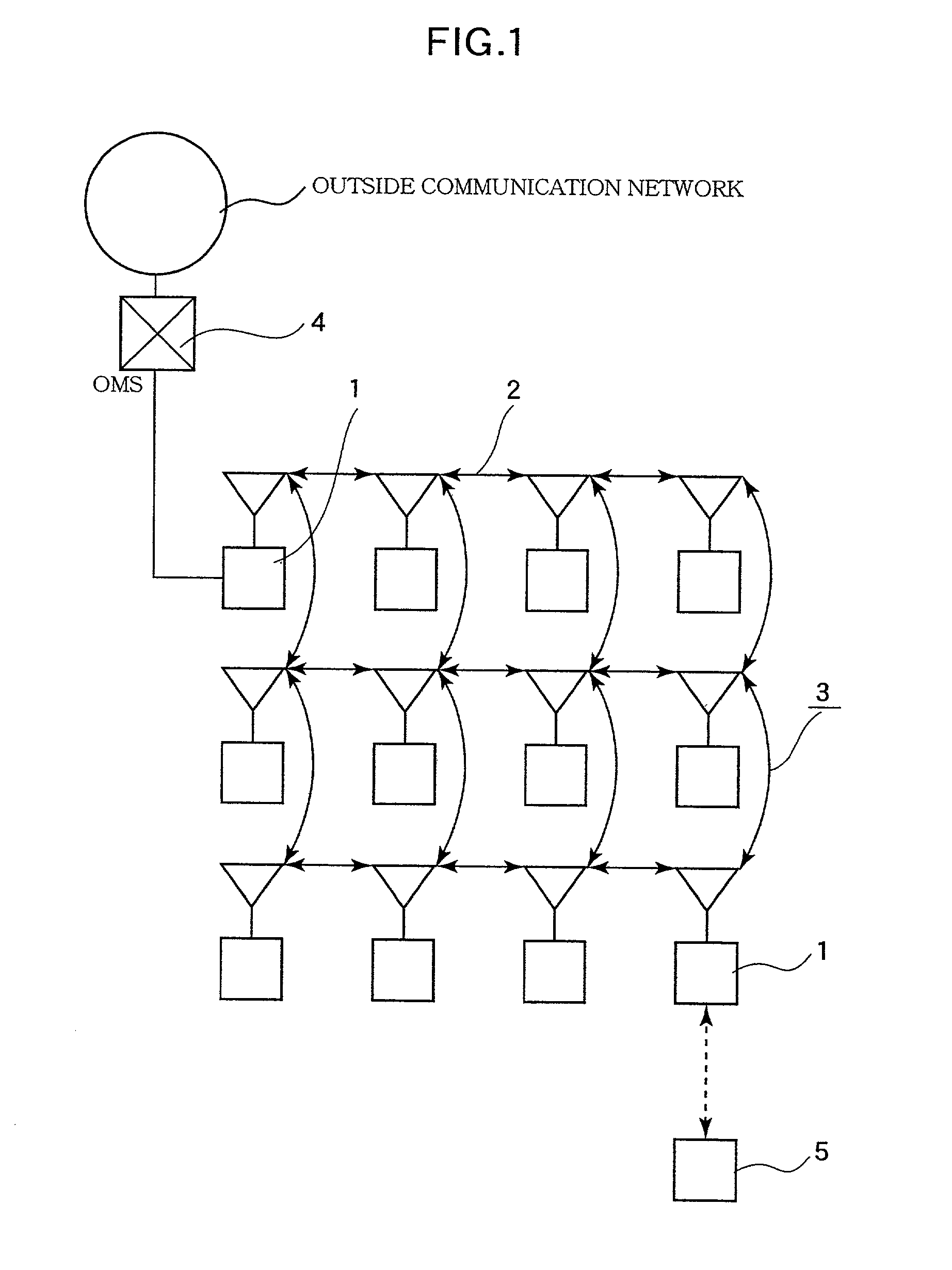
In order to provide an access network system that has durability against transmission quality deterioration and fault and controls the causes of delay in the communication processing for data transmission, the base stations (communication nodes) are arranged in a plurality of cross-points, and the base stations have a function capable of transmitting and receiving the information of an optical wireless communication type and the like, and are mutually linked with each other by wireless and constitute an access network which is accessible cross-wise from each base station by a wireless communication link passage. This access network is wirelessly connected to other outside communication network by an access network terminating set.
Owner:KDDI CORP +1
Handling broadcast and multicast traffic as unicast traffic in a wireless network
An access point is to handle received broadcast or multicast traffic as multiple instances of unicast traffic, where each instance is destined for a corresponding wireless client device associated with the access point. A client device may adjust its listen interval parameter according to predefined considerations, for example a charge level of a battery to power the client device and an expected usage model for the device. A client device may initiate a reassociation request to inform the access point of its adjusted listen interval parameter.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
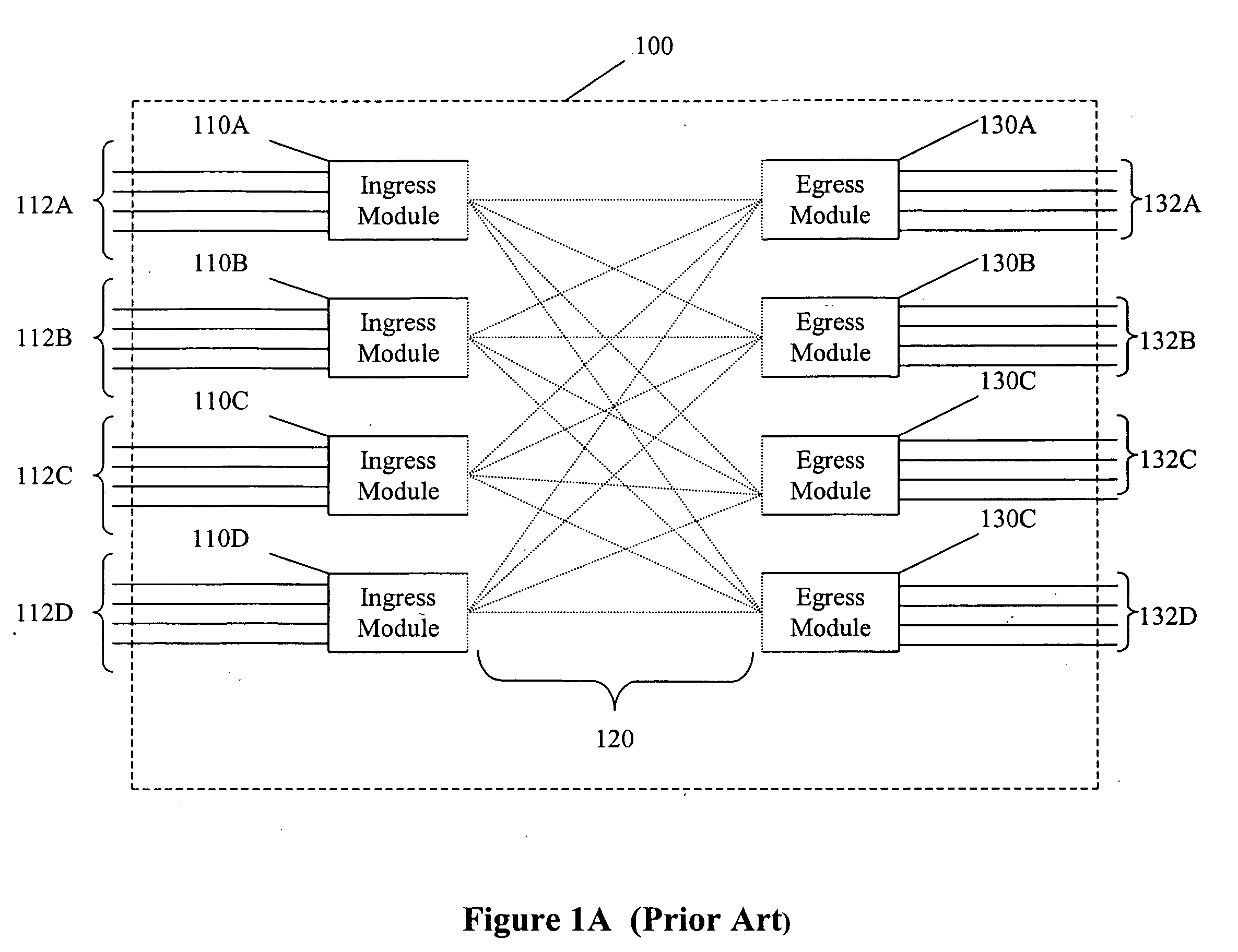
Apparatus and methods providing redundant routing in a switched network device
InactiveUS6628649B1Improve fault toleranceHigh degreeMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationData transmissionData loss
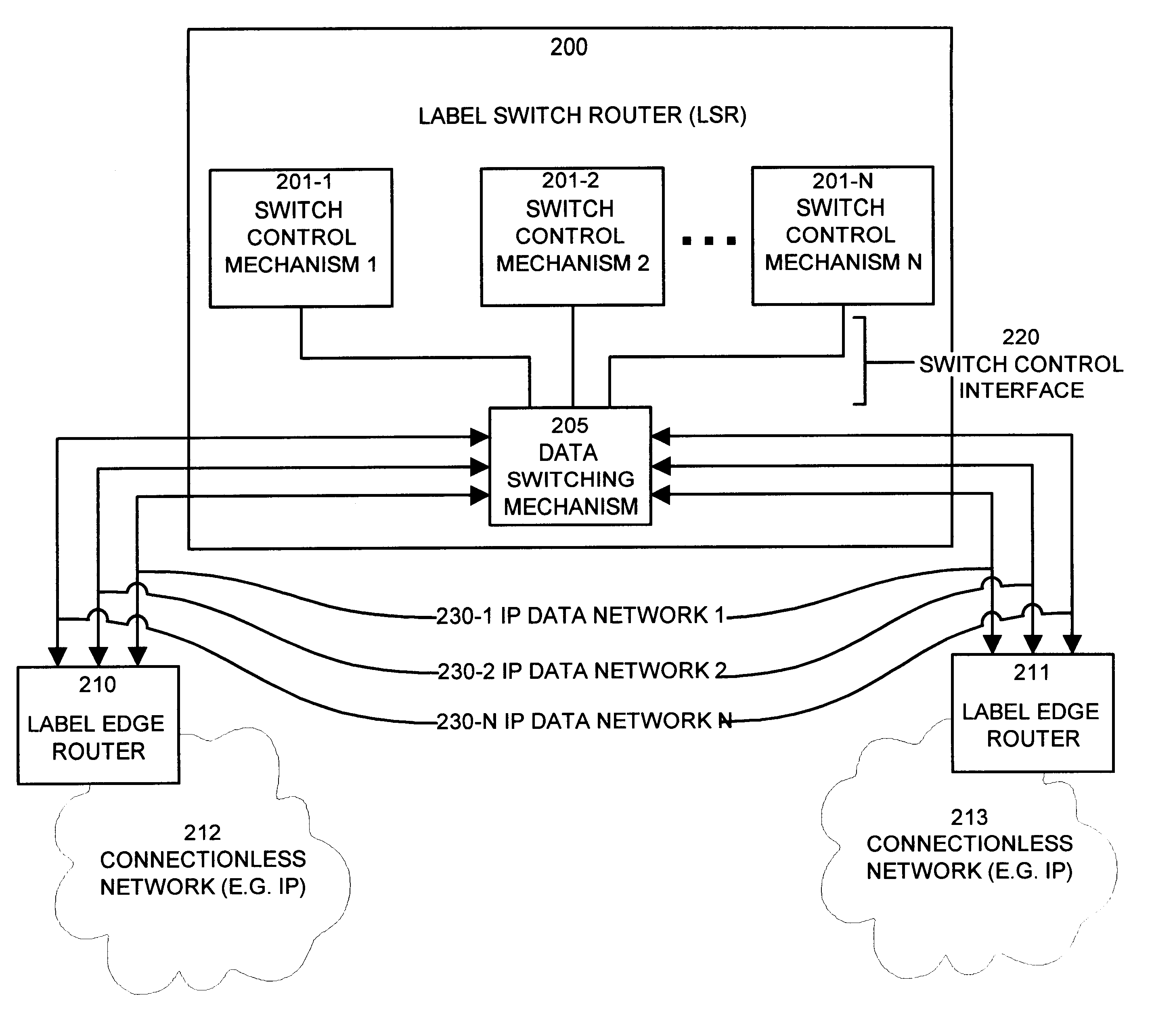
The invention provides unique architectures and techniques for routing redundancy in a data switch configured to use label switching. Multiple label switch controllers (LSCs) each operate concurrently but independently of each other to provide routes through a data switching mechanism. Preferred embodiments provide a plurality of LSCs offering MPLS capabilities coupled to a single switch, such as an ATM switch. The similarly configured LSCs each can concurrently support a route for data (e.g., labeled ATM cells) within the data switching mechanism in parallel, thereby providing the ability to support redundant and multiple parallel data networks. The configuration is called a label switch router (LSR). A fully-meshed embodiment allows selected routes to share bandwidth on ports, while a fully parallel embodiment provides separate ports for selected routes. Since each LSC provides parallel routes with the other LSCs in an LSR, a communications between an LSR and a label edge router (LER) can use multipath routing to concurrently distribute data equally across the parallel routes for each destination. Alternatively, unipath routing techniques can select one route for use for each destination from the available routes concurrently offered by each LSC. In the event of a failure of one of the LSCs, multipath routing implementations can exclude transmission of data onto the failed network, while continuing to use the other parallel networks supported by non-failed LSCs in a concurrent manner. Alternatively, if a failure occurs with unipath routing, a new route offered by another LSC can be selected for data transfers. In either case, the LSC that fails does not need to provide state or connection information to the LSCs that operate subsequently to the failure, since they are already configured in parallel to support the same route. Upon an LSC failure, switch resources such as bandwidth that were used by the failed LSC are made available to the remaining non-failed LSCs. The design allows failures are handled gracefully without diminished network capacity or data loss resulting in a highly reliable routing capability provided within connection-based or circuit-switched networks.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
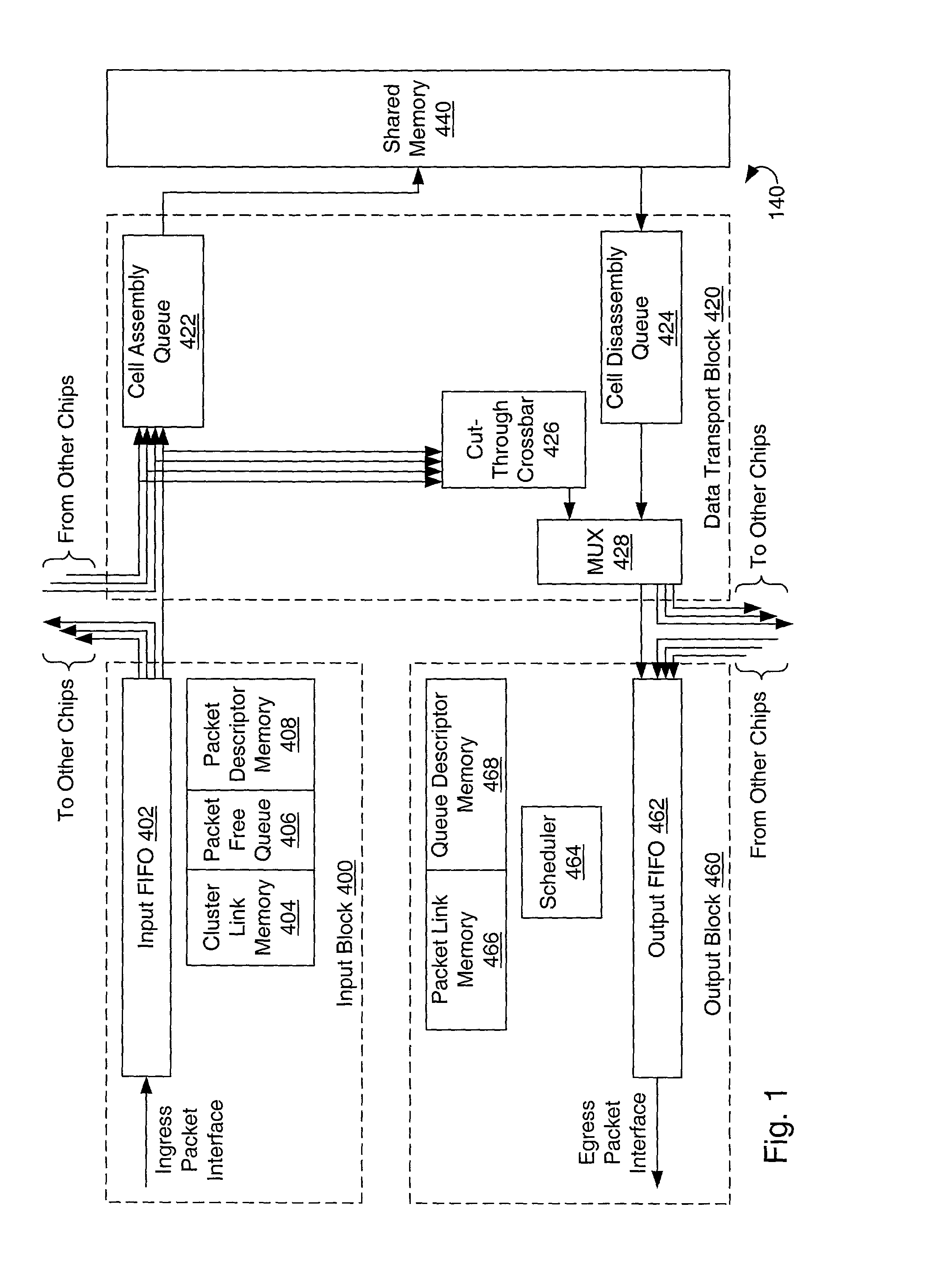
Ensuring proper packet ordering in a cut-through and early-forwarding network switch
InactiveUS20020118692A1Data switching by path configurationCircuit switching systemsReal-time computingMultiple input
A system and method for ensuring that packets are not switched out of order in a network switch capable of dynamically selecting different routing techniques. The network switch may include multiple input ports, multiple output ports, and a shared random access memory coupled to the input ports and output ports by data transport logic. The switch may route packets using cut-through routing or early-forwarding. To ensure that packets are not switched out of order, sequence numbers may be assigned to packets as the packets are received at one of the input ports. A different sequence may be used for each output port. The output port may also track sequence numbers by storing the number corresponding to the most recently received packets from each input port. The stored value may compared with a sequence number assigned to a packet to ensure that they are within one before allowing cut-through routing.
Owner:NISHAN SYST
Systems and methods for exporting, publishing, browsing and installing on-demand applications in a multi-tenant database environment
ActiveUS20070088741A1Easily and efficiently importEasily and efficiently and exportMultimedia data retrievalObject oriented databasesApplication softwareOrganizational boundaries
In accordance with embodiments, there are provided mechanisms and methods for creating, exporting, viewing and testing, and importing custom applications in a multi-tenant database environment. These mechanisms and methods can enable embodiments to provide a vehicle for sharing applications across organizational boundaries. The ability to share applications across organizational boundaries can enable tenants in a multi-tenant database system, for example, to easily and efficiently import and export, and thus share, applications with other tenants in the multi-tenant environment.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
Communication services through multiple service providers
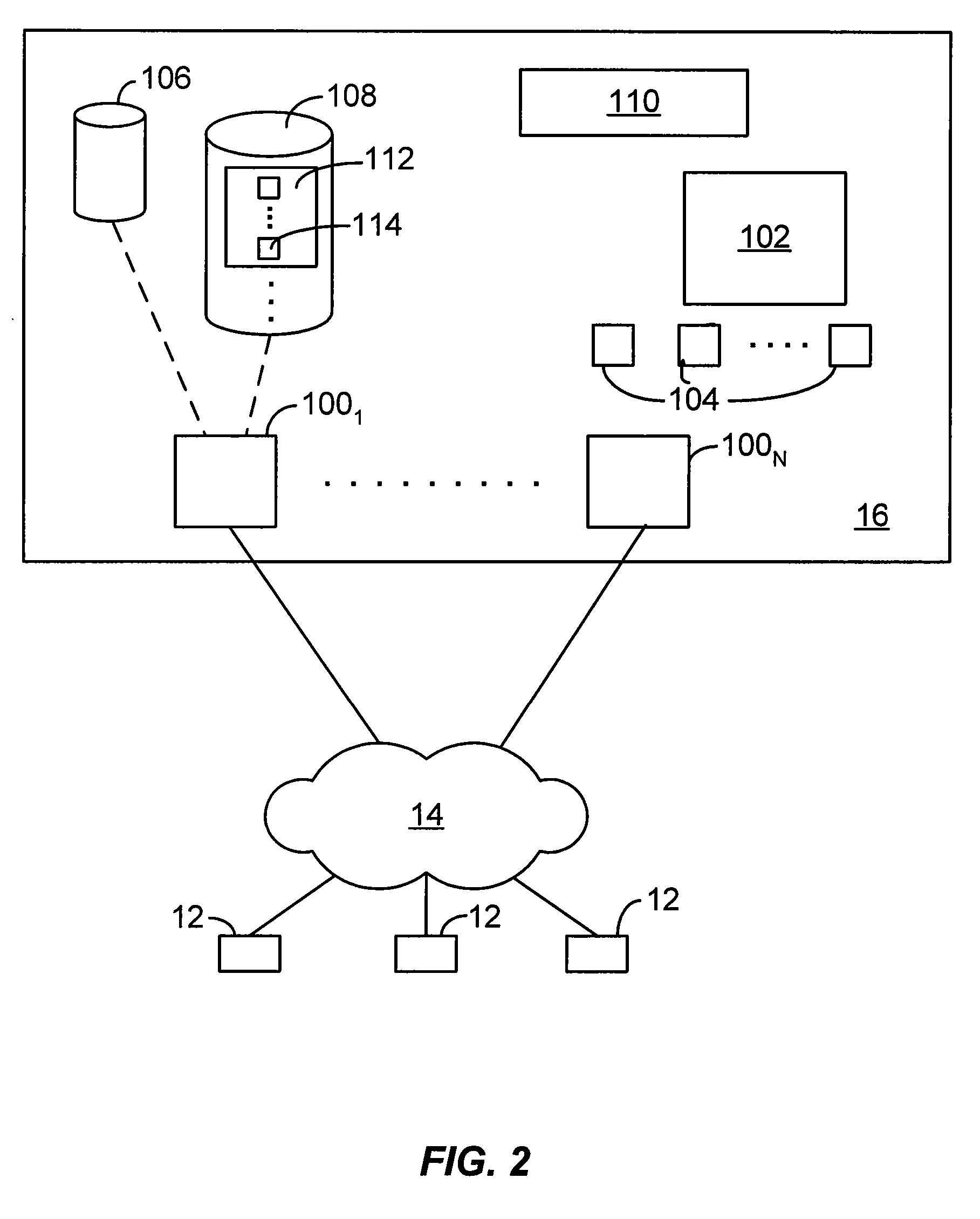
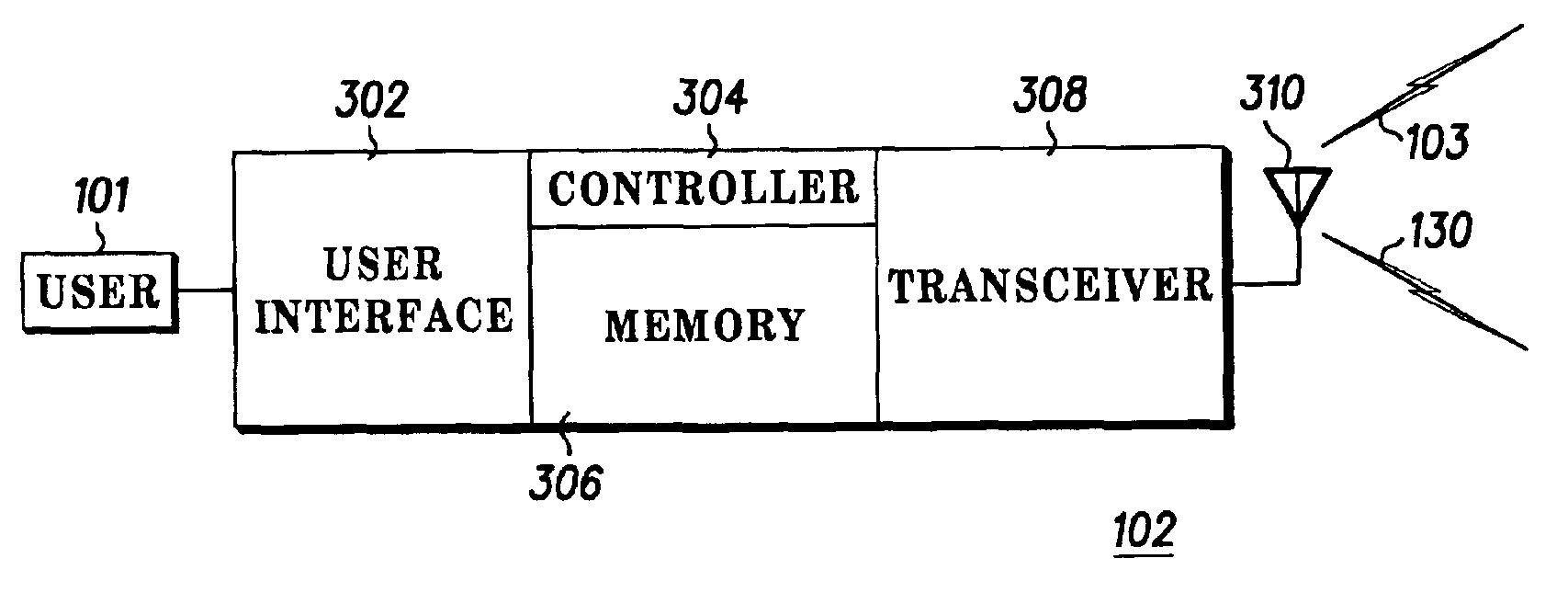
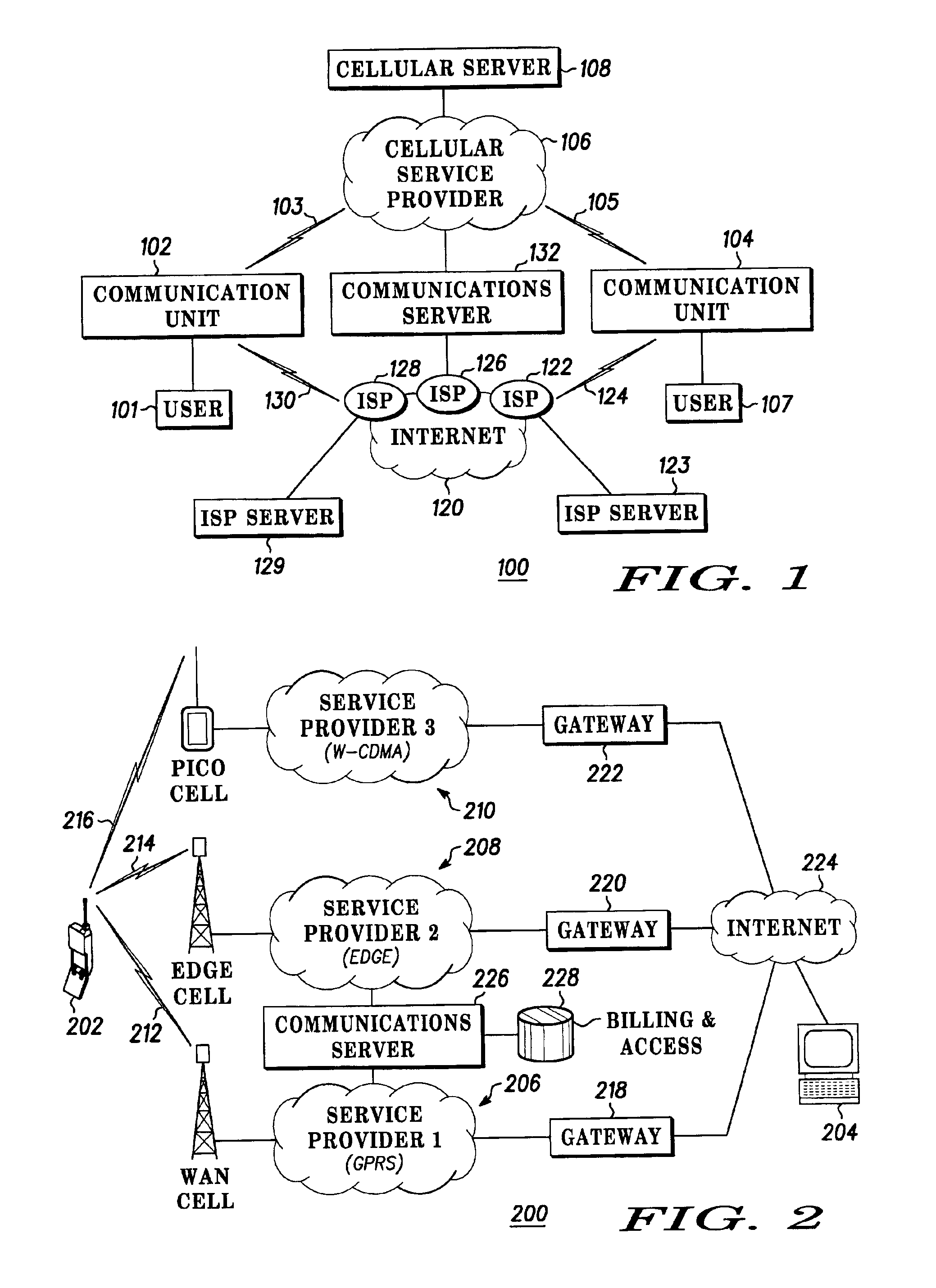
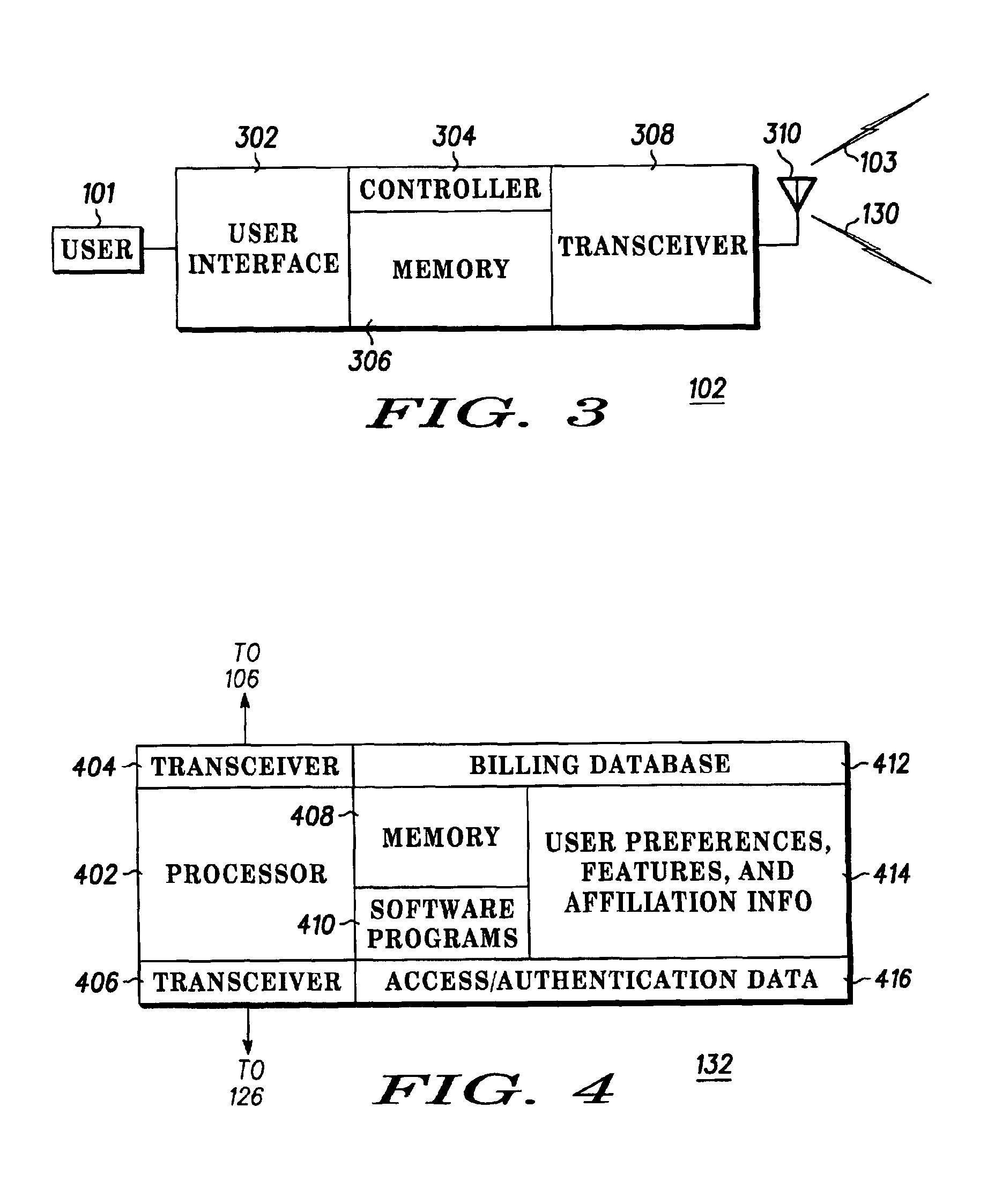
InactiveUS6879584B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsAssess restrictionCommunication unitComputer network
Apparatus and methods using a first service provider such as a WAN cellular service provider to initiate a communications exchange between a plurality of communications units and a second service provider such as WLAN service provider to provide enhanced communications services to the units has been disclosed and described.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for achieving dynamic capacity and high availability in multi-stage data networks using adaptive flow-based routing
ActiveUS20050091396A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionSystems managementHigh availability
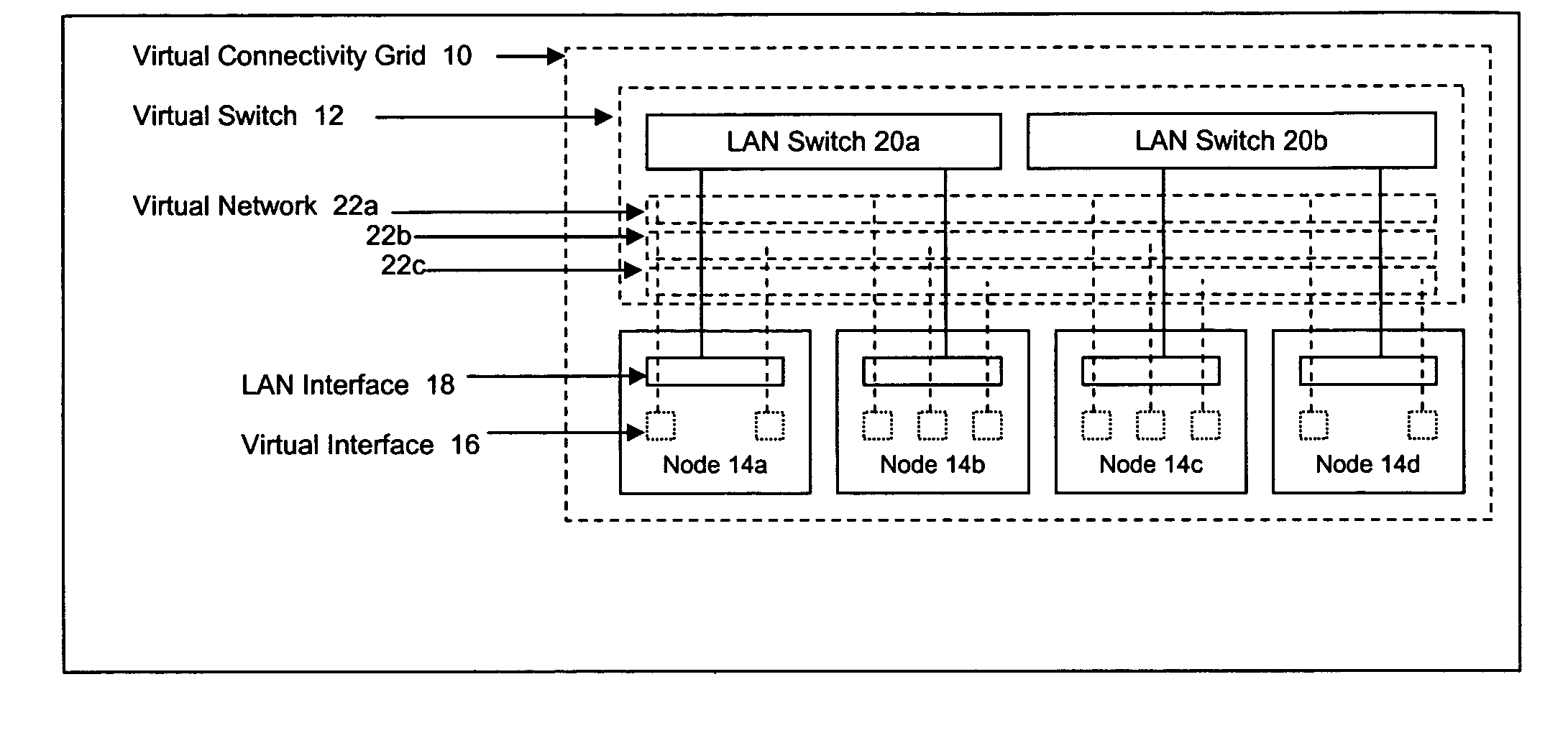
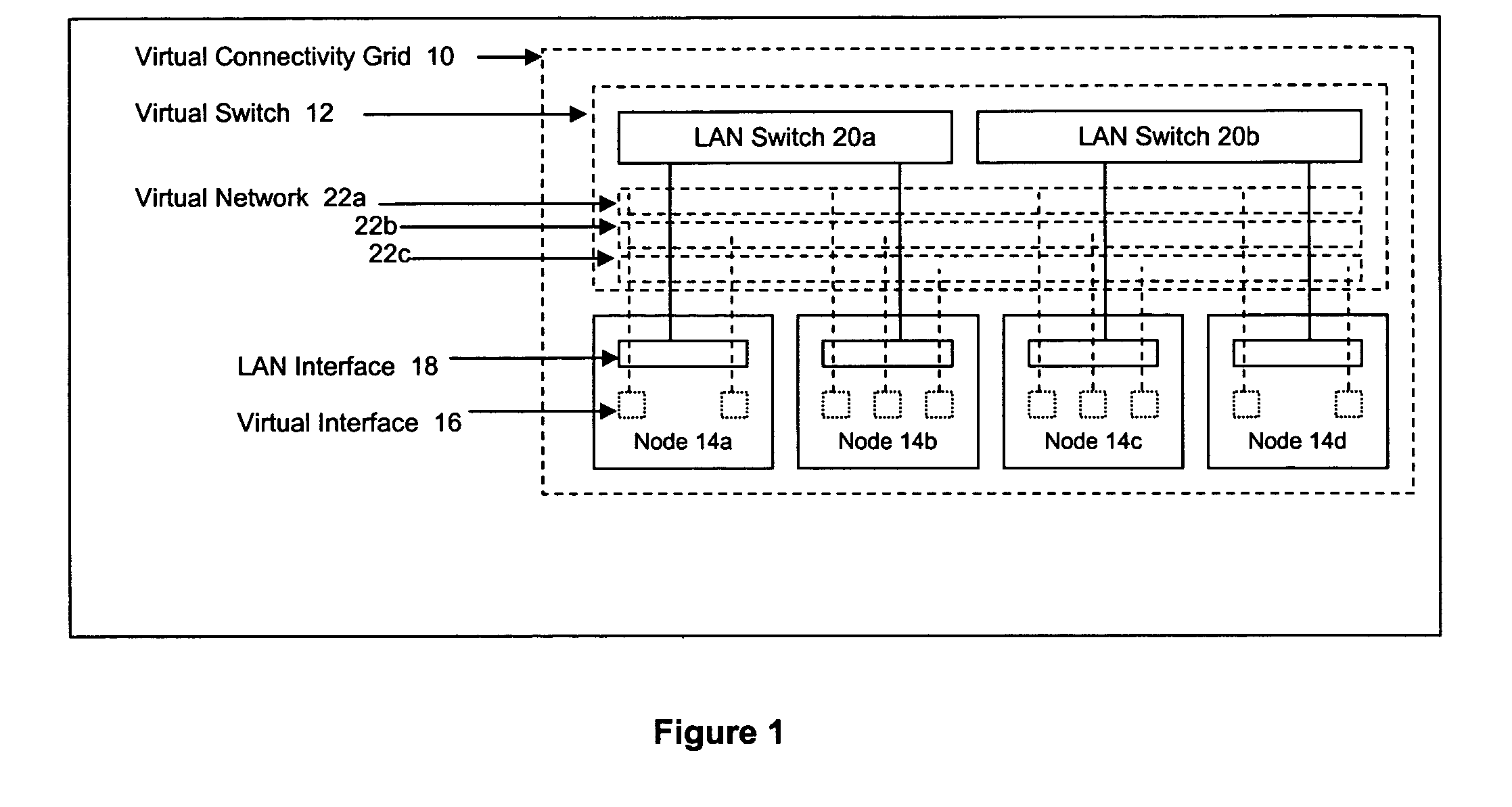
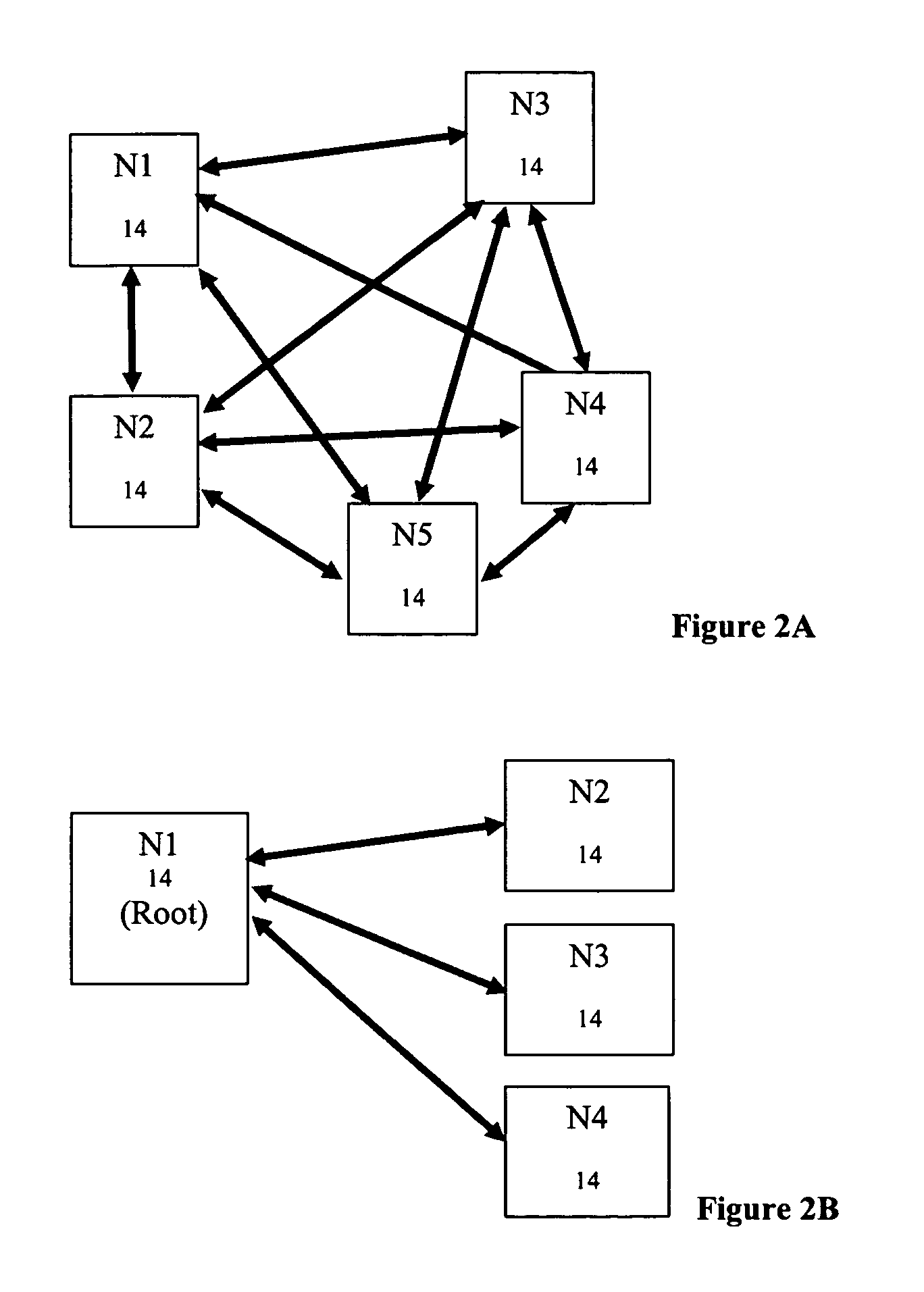
Methods and systems for determining paths for flows within a multi-stage network made up of clusters of processing nodes. The flow paths may be determined without knowledge of whether or not packets of a particular flow will actually traverse specific ones of the clusters within the multi-stage network. In various implementations, the nodes of the multi-stage network may be coupled to one or more physical network switches through respective physical interfaces and a virtual connectivity grid superimposed thereon and configured through the use of a flow routing framework and system management framework to group the nodes into a number of clusters. The nodes of each cluster are configured to perform similar packet processing functions and the clusters are interconnected through virtual networks to which the nodes are communicatively coupled via virtual interfaces overlaid on top of the physical network interfaces.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
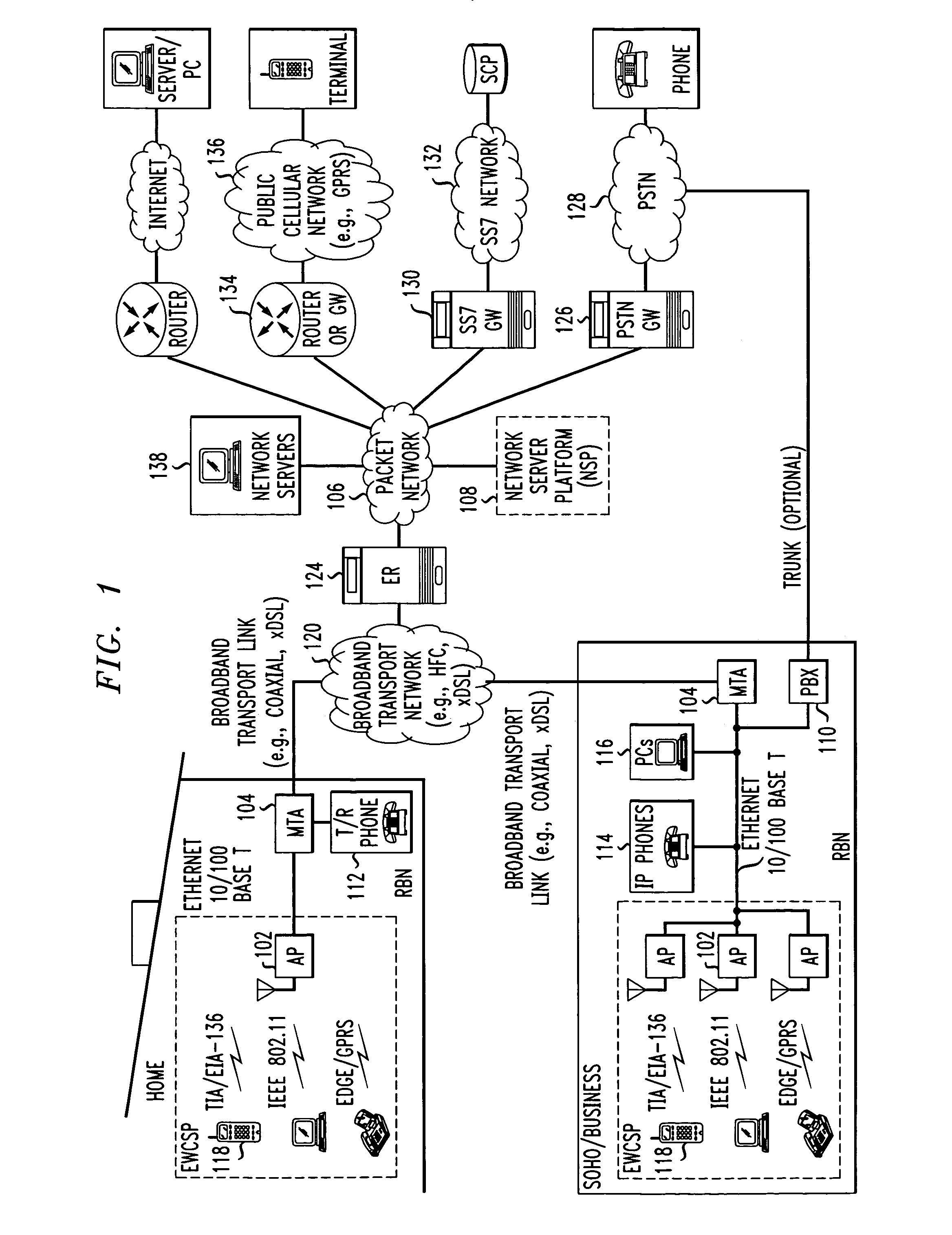
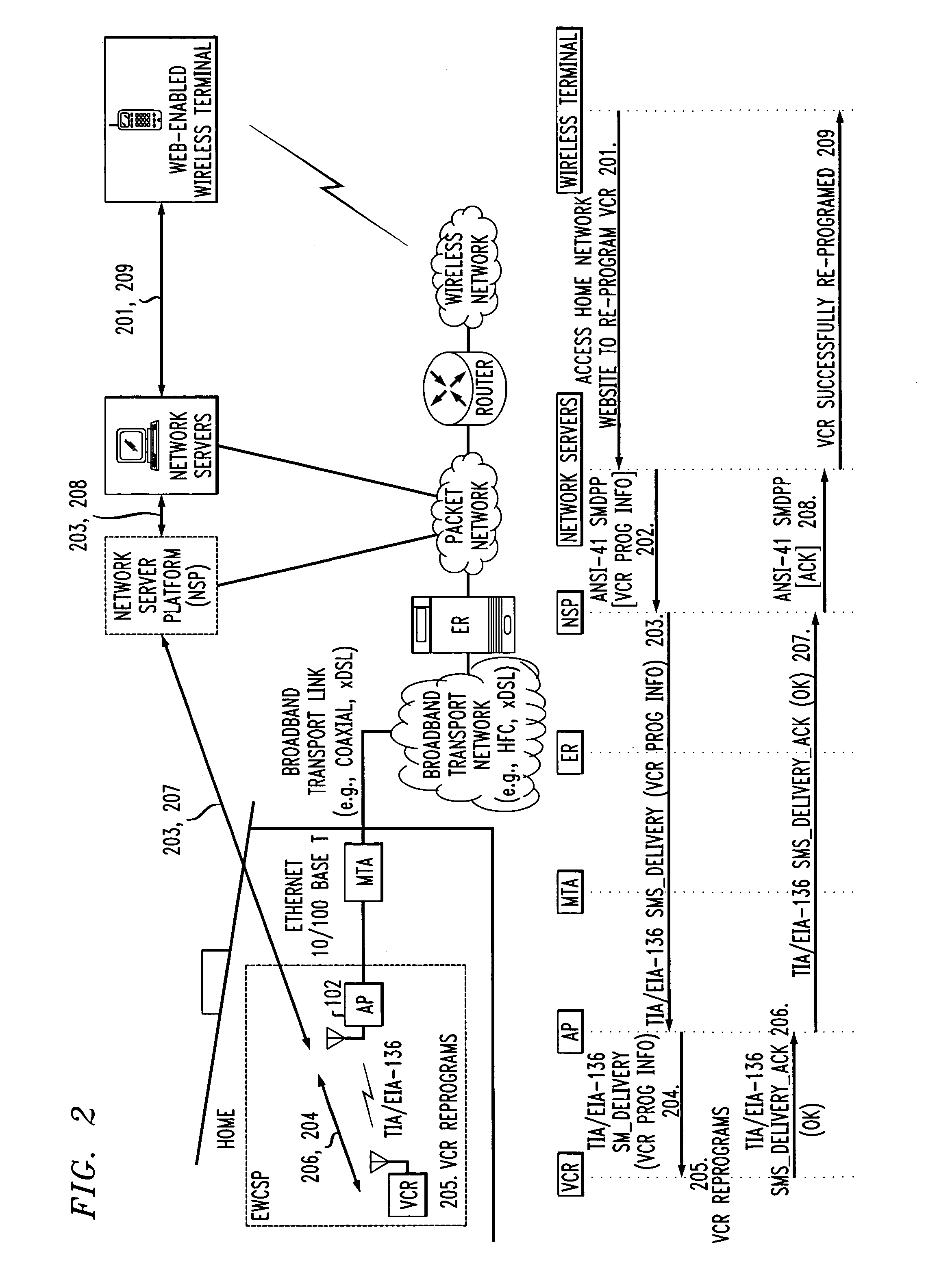
Broadband network with enterprise wireless communication method for residential and business environment
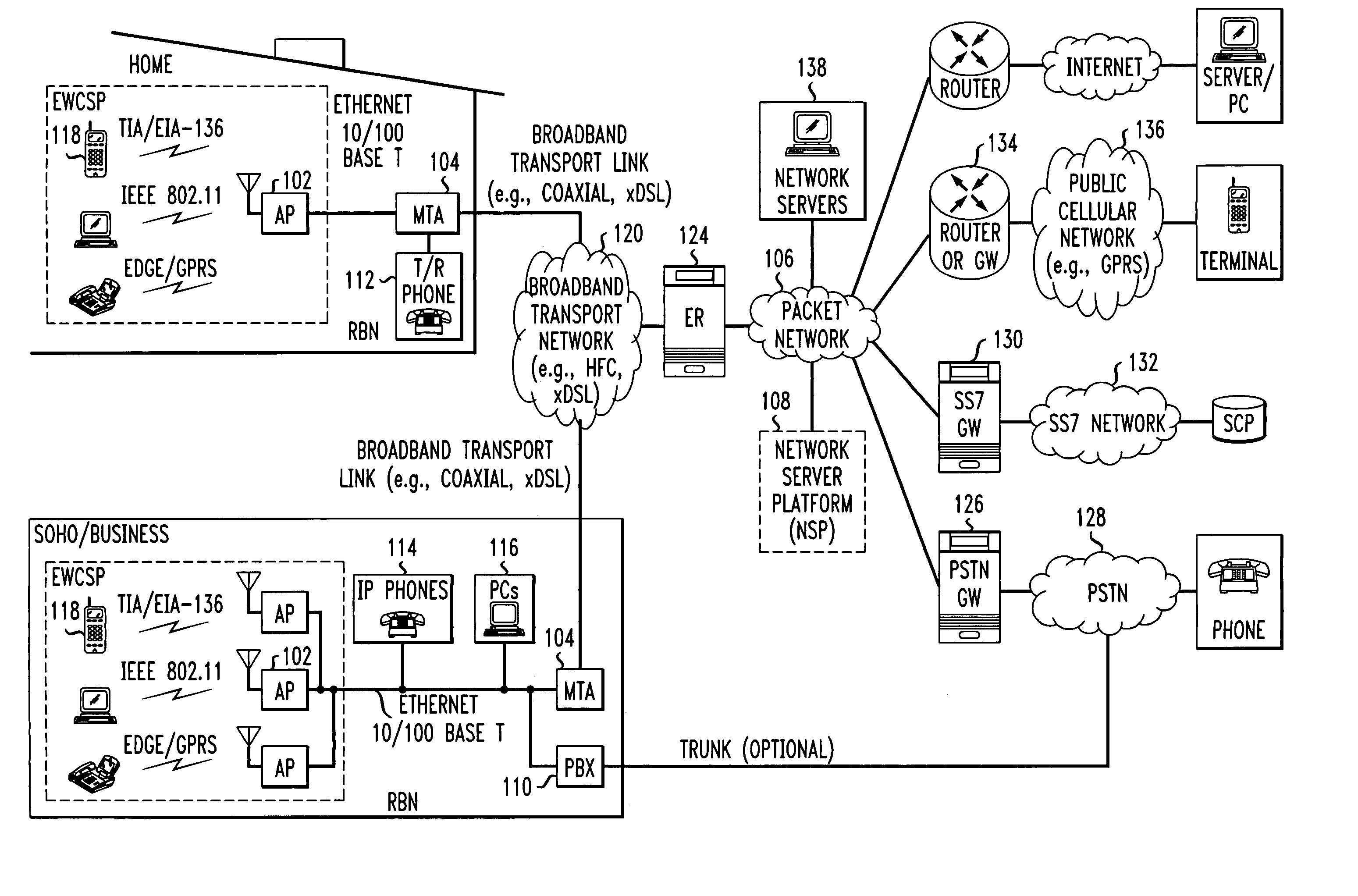
InactiveUS7010002B2Easy to optimizeCost-effective deploymentMultiplex system selection arrangementsTelephone data network interconnectionsModem deviceBroadband transmission
The present invention sets forth a network-centric service distribution architecture and method that integrates a wireless access system / service in the residence, SOHO, business or public environment through the use of a local broadband network, such as a Residential-Business Broadband Network (RBN), to the service provider's broadband transport network and to a service provider's broadband packet network that facilitates end-to-end packet telecommunication services. Access functions for connecting said service provider's broadband packet network to the RBN via said service provider's broadband transport network are provided. Call and service termination functions to a plurality of local RBN devices are also provided. Signals from a plurality of wireless devices are accepted and forwarded to an IEEE 802.11b interface for a wireless modem and / or to an Ethernet interface for a Voice over Internet Protocol (VOIP) / Ethernet Processor, where the forwarded signals comprise intranet telephony and data. Voice signals are also accepted from a plurality of tip / ring interfaces and forwarded to a broadband transport interface for back haul of data and voice packets. A service provider can deploy services in an integrated voice, data and multimedia environment cost-effectively based on one broadband packet network.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
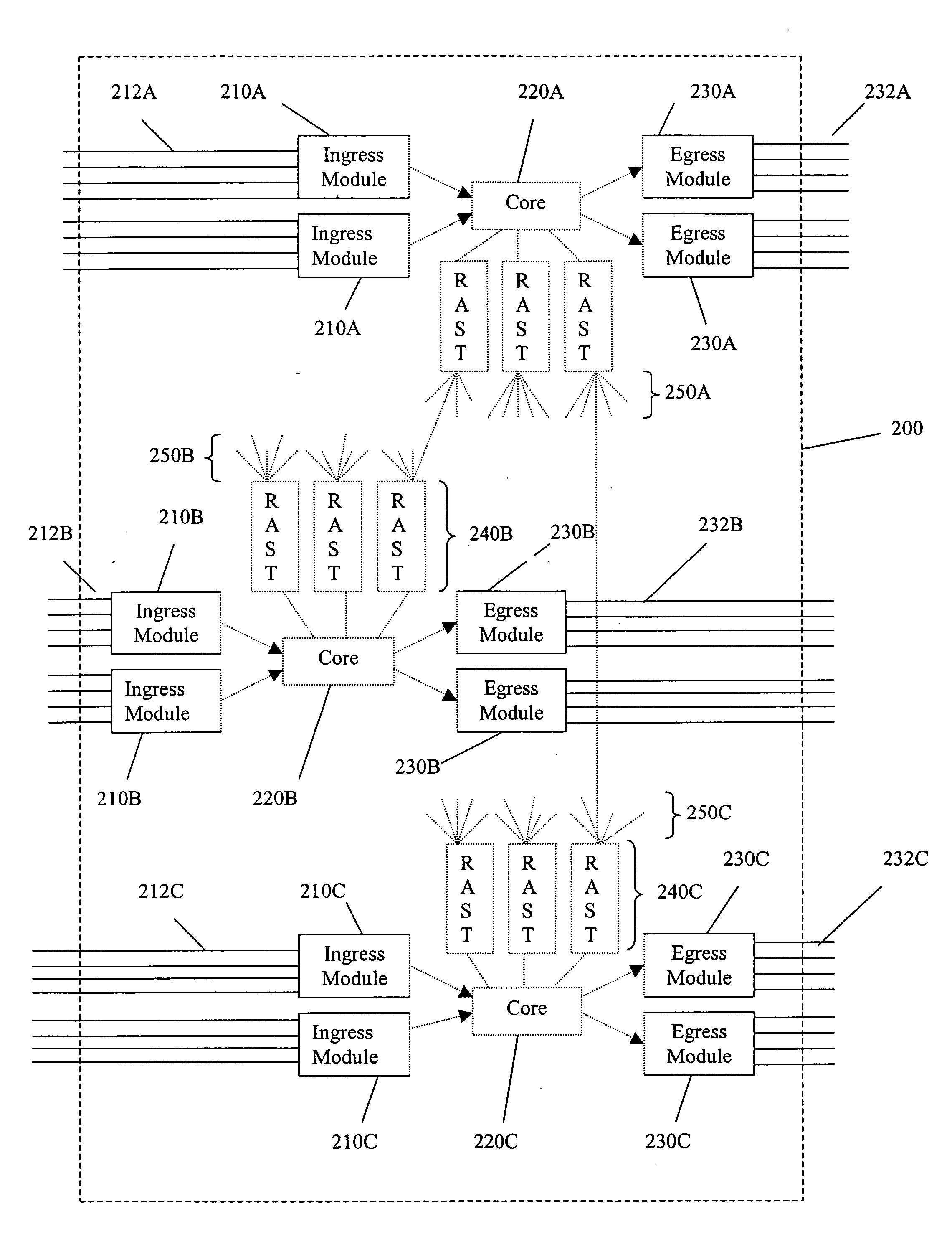
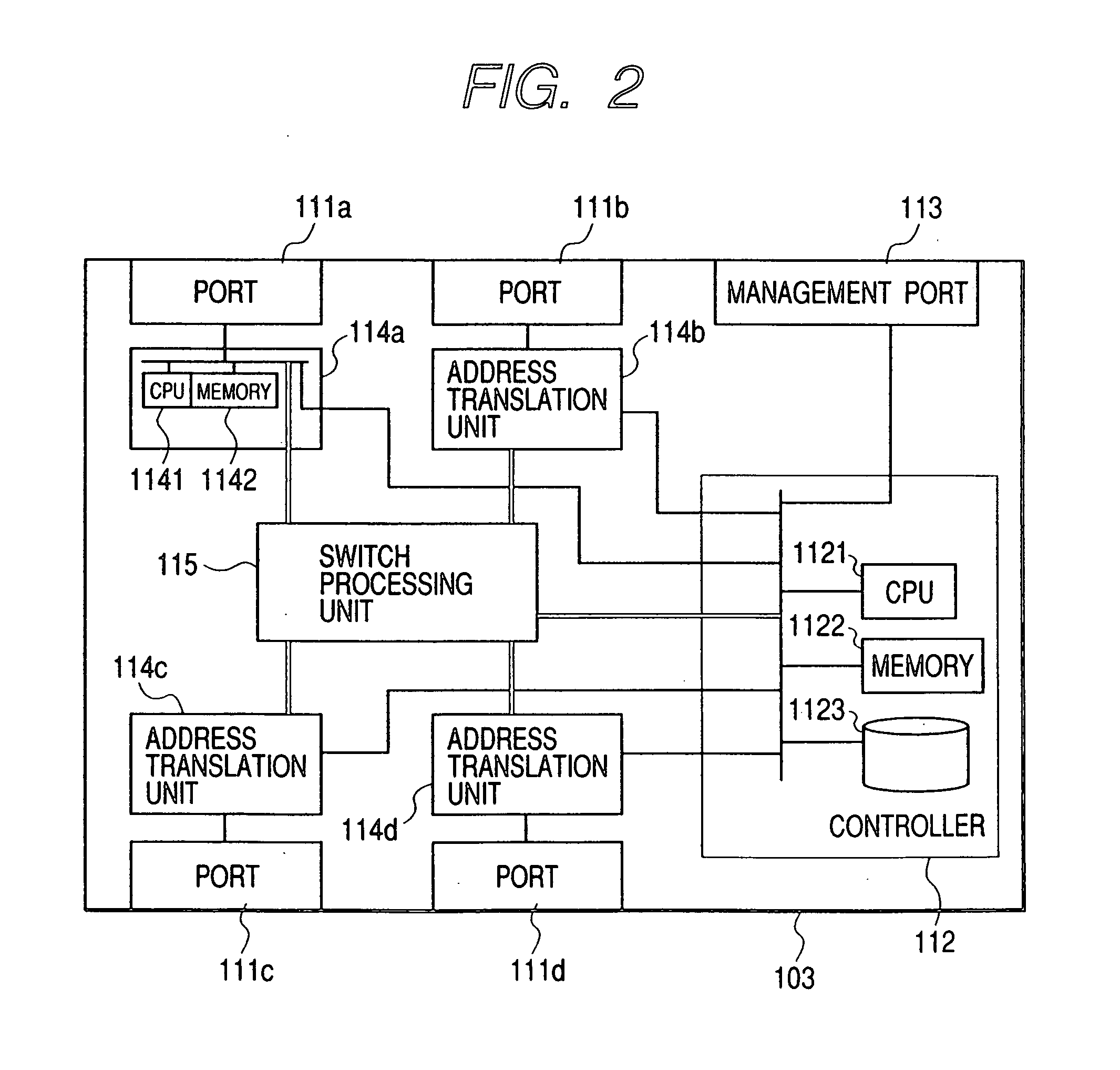
Virtual machine task management system
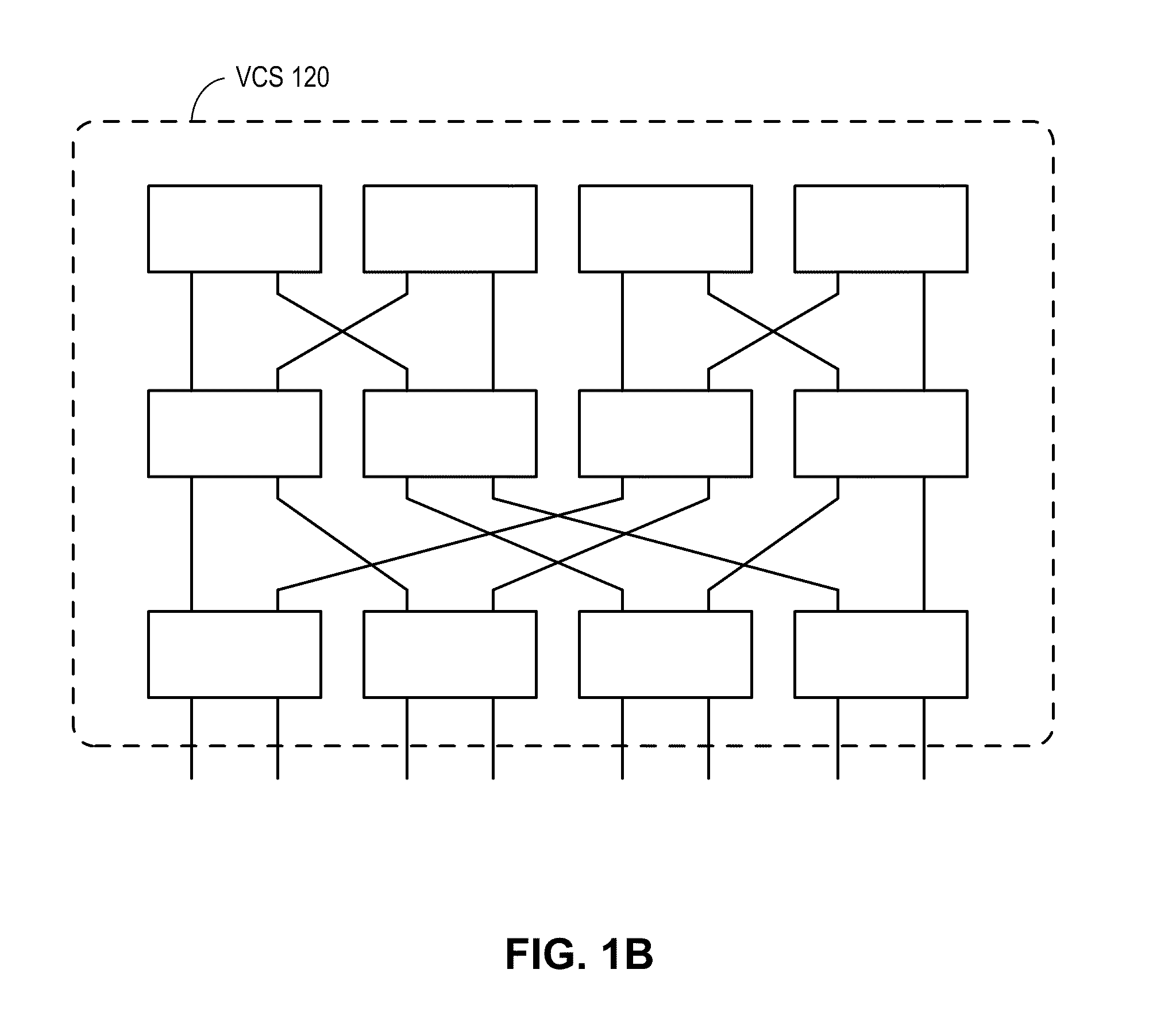
InactiveUS20060029056A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsCircuit switching systemsAuto-configurationConnection table
A switch encapsulates incoming information using a header, and removes the header upon egress. The header is used by both distributed ingress nodes and within a distributed core to facilitate switching. The ingress and egress elements preferably support Ethernet or other protocol providing connectionless media with a stateful connection. Preferred switches include management protocols for discovering which elements are connected, for constructing appropriate connection tables, for designating a master element, and for resolving failures and off-line conditions among the switches. Secure data protocol (SDP), port to port (PTP) protocol, and active / active protection service (AAPS) are all preferably implemented. Systems and methods contemplated herein can advantageously use Strict Ring Topology (SRT), and conf configure the topology automatically. Components of a distributed switching fabric can be geographically separated by at least one kilometer, and in some cases by over 150 kilometers.
Owner:RAPTOR NETWORKS TECH
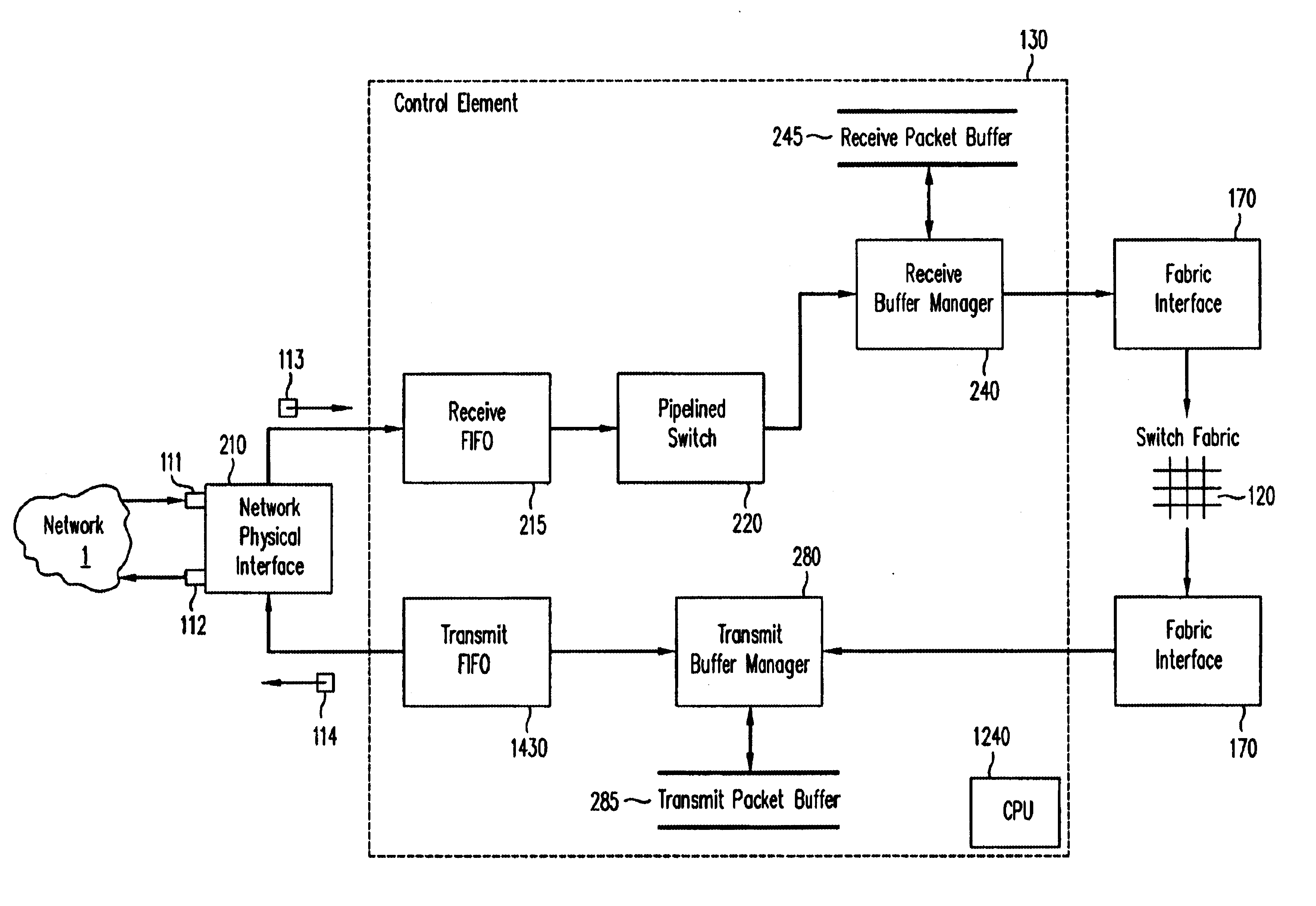
Traffic switching using multi-dimensional packet classification
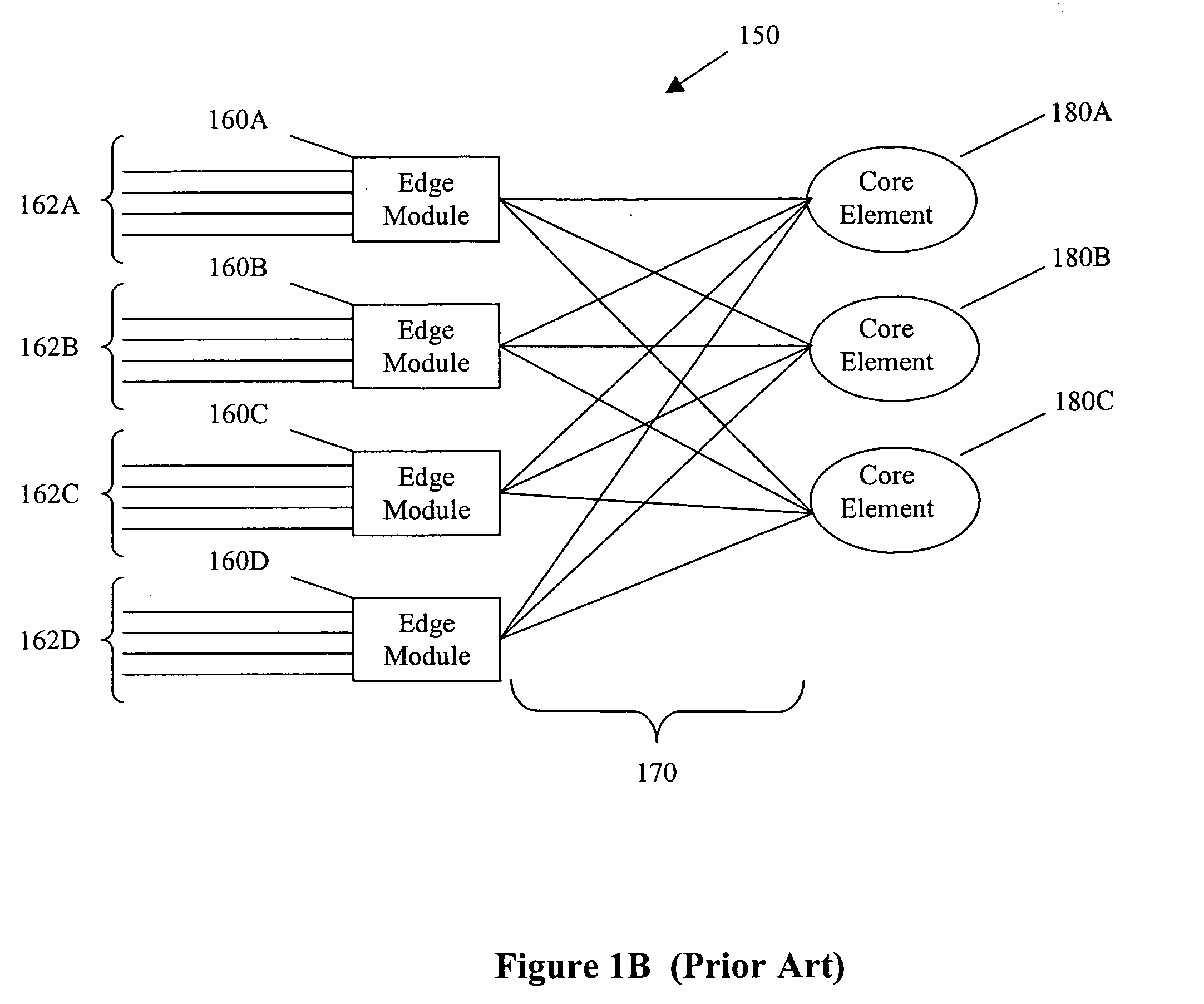
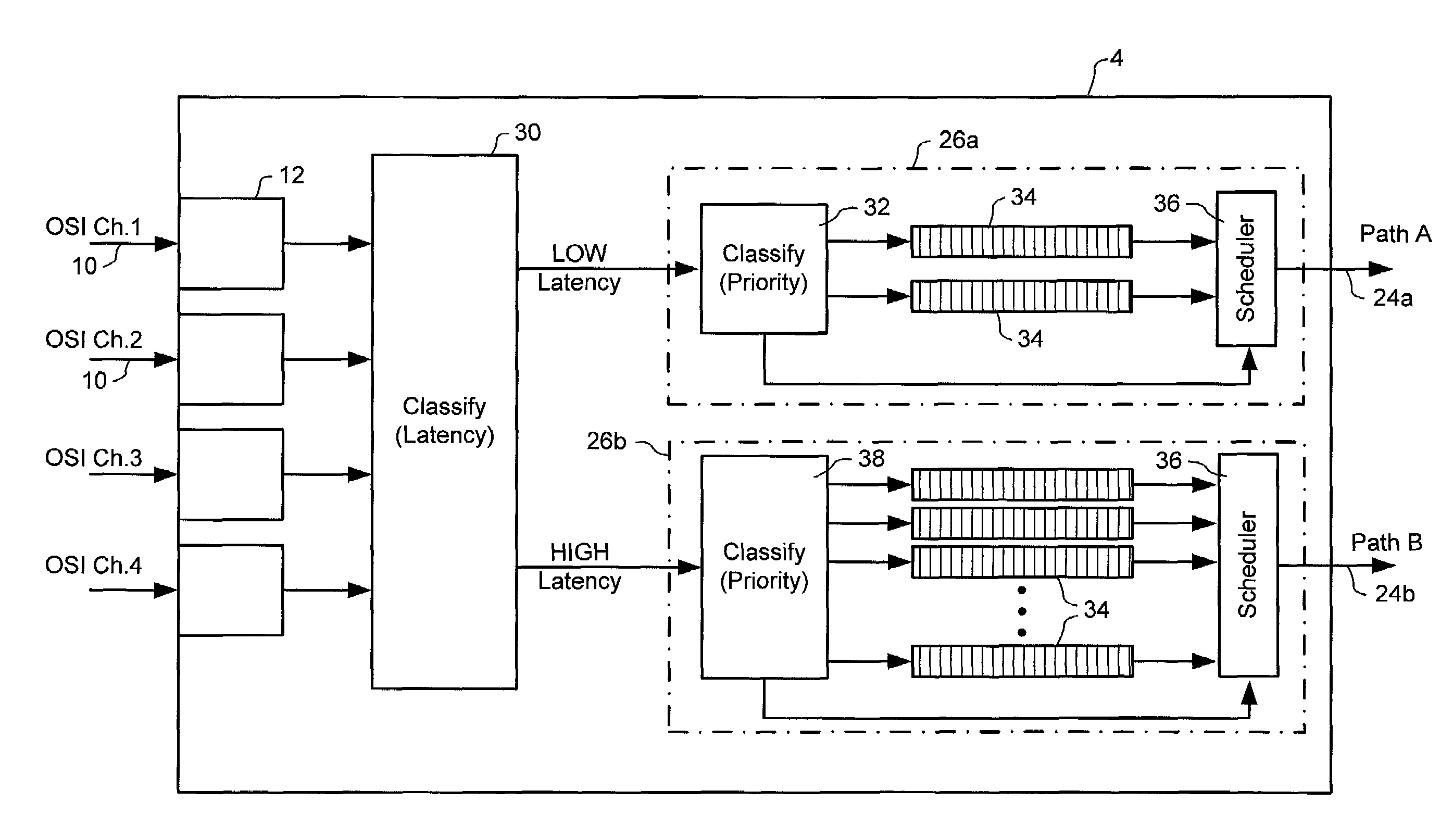
ActiveUS7260102B2Efficient transportMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionTraffic capacityLatency (engineering)
A method and system for conveying an arbitrary mixture of high and low latency traffic streams across a common switch fabric implements a multi-dimensional traffic classification scheme, in which multiple orthogonal traffic classification methods are successively implemented for each traffic stream traversing the system. At least two diverse paths are mapped through the switch fabric, each path being optimized to satisfy respective different latency requirements. A latency classifier is adapted to route each traffic stream to a selected path optimized to satisfy latency requirements most closely matching a respective latency requirement of the traffic stream. A prioritization classifier independently prioritizes traffic streams in each path. A fairness classifier at an egress of each path can be used to enforce fairness between responsive and non-responsive traffic streams in each path. This arrangement enables traffic streams having similar latency requirements to traverse the system through a path optimized for those latency requirements.
Owner:CIENA
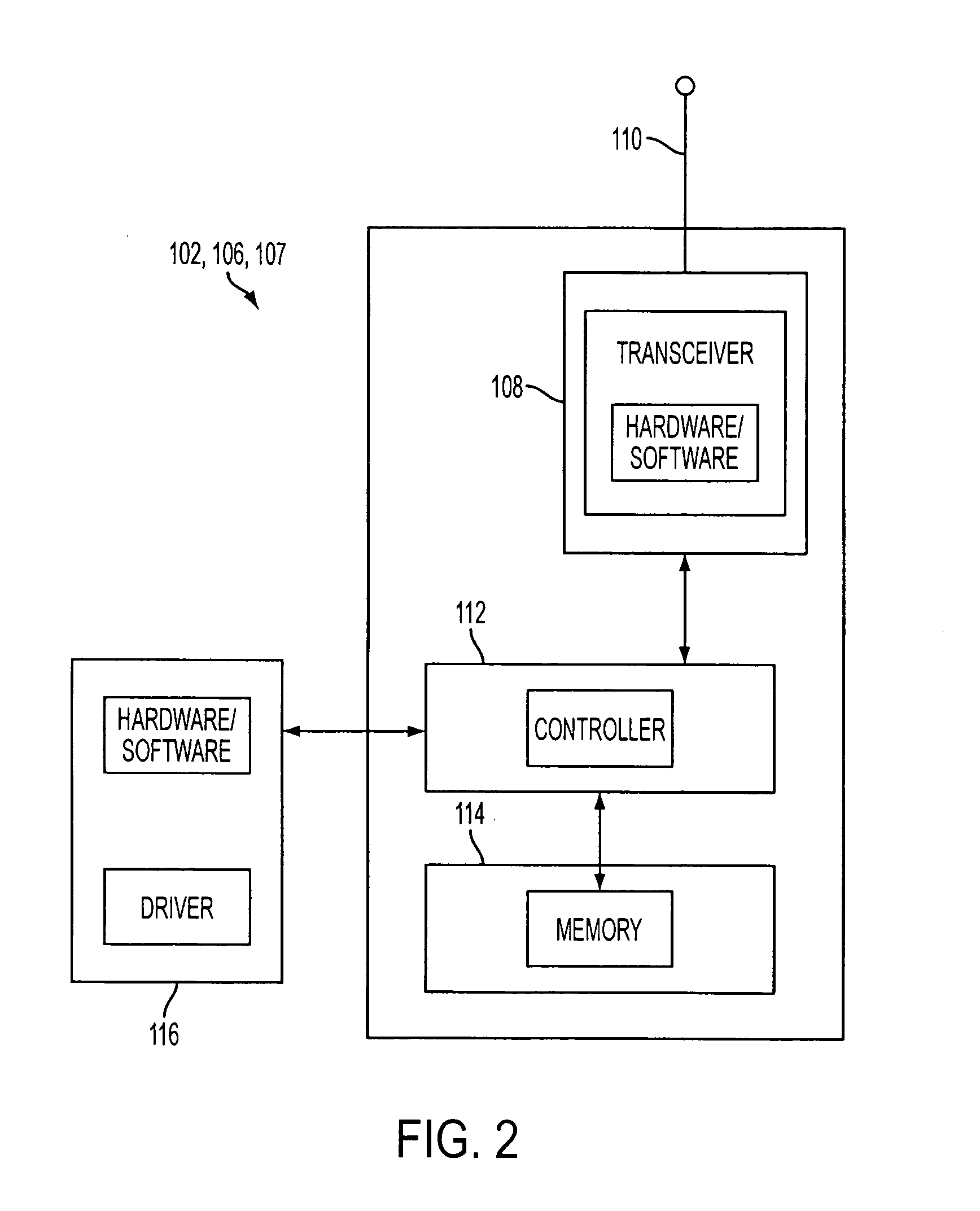
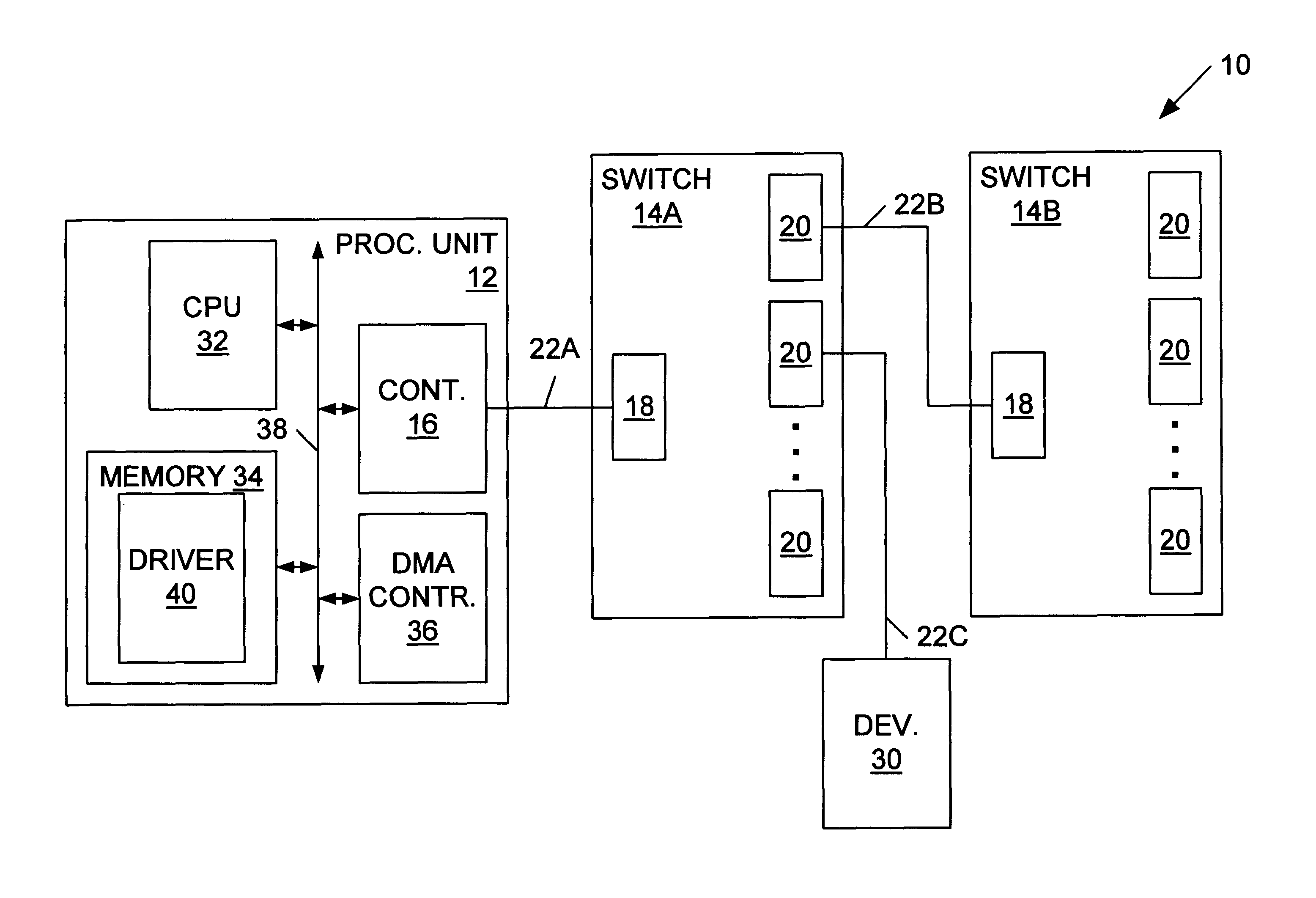
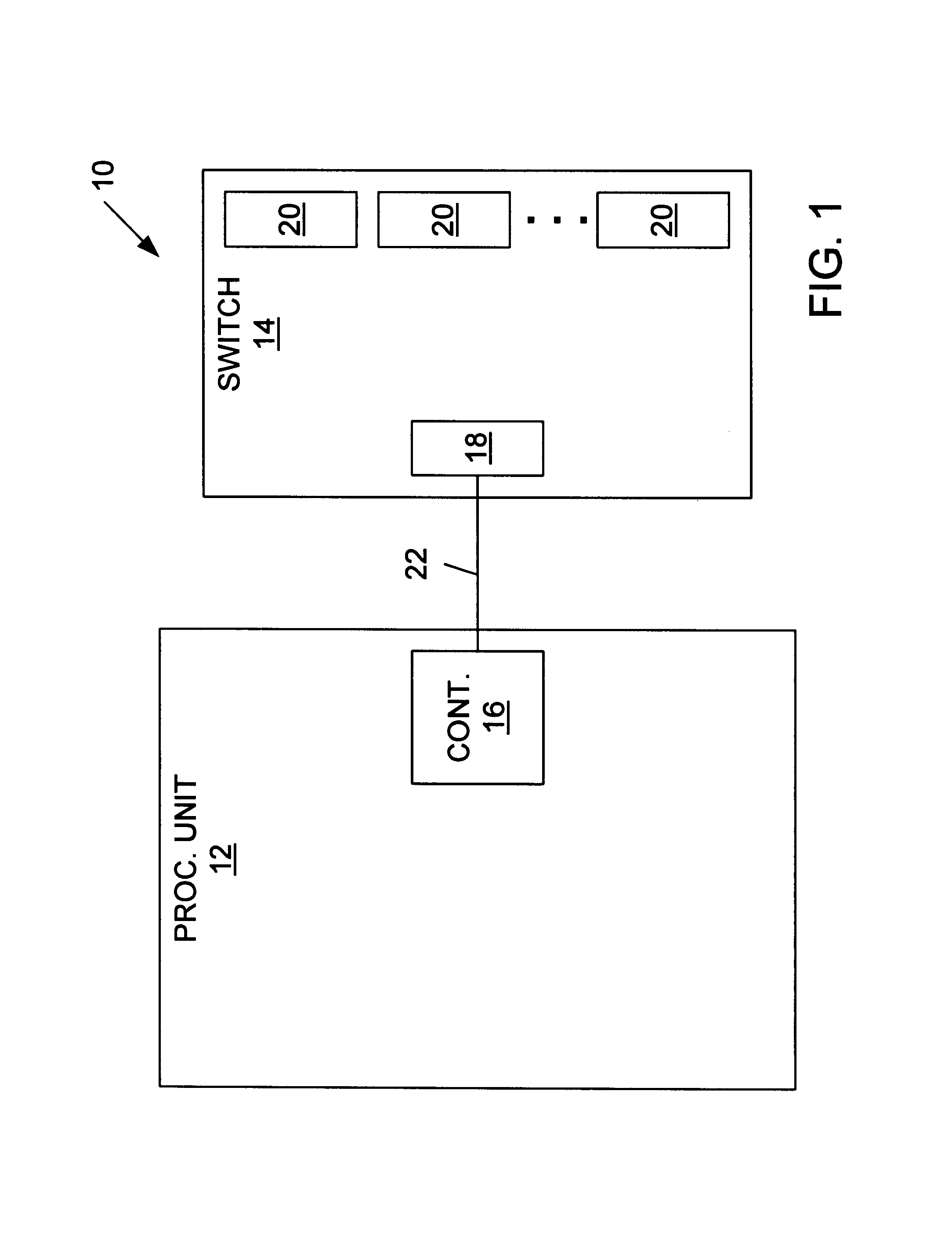
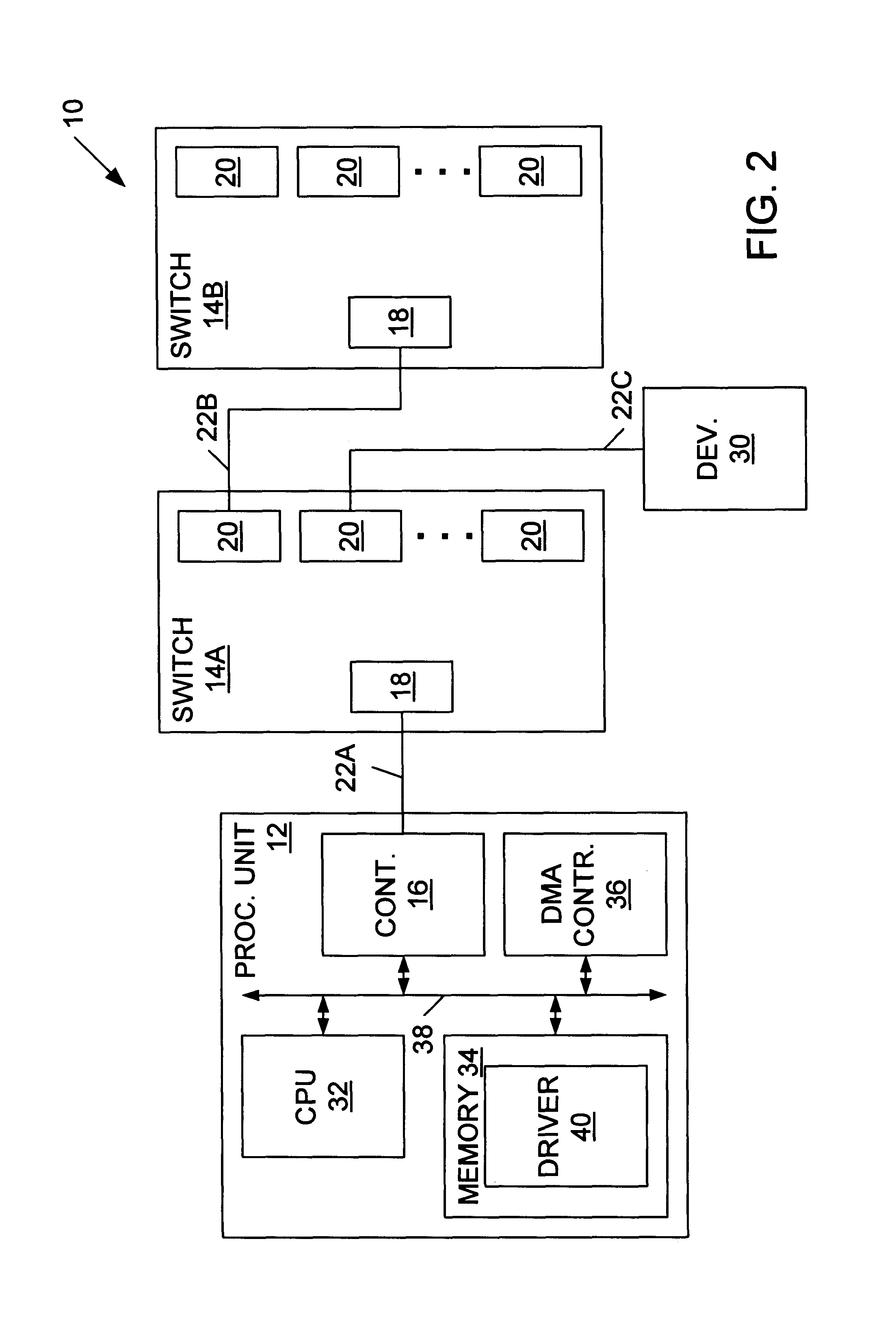
Data exchange methods for a switch which selectively forms a communication channel between a processing unit and multiple devices
InactiveUS6845409B1Reduce processing overheadReduce overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsInput/output to record carriersMain processing unitDirect memory access
A switch is presented including a host input / output (I / O) port adapted for coupling to a controller, multiple device I / O ports each adapted for coupling to at least one device, and logic coupled between the host I / O port and the device I / O ports configured to selectively form a communication channel between the host I / O port and one of the device I / O ports. The switch may operate in a connected mode and a disconnected mode. When in the switch is in the disconnected mode, the logic may not form a communication channel between the host I / O port and any of the device I / O ports. In an ATA embodiment, the switch may comply with an AT attachment (ATA) standard, and thus be an ATA switch. The host I / O port may be adapted for coupling to an ATA controller, the device I / O ports may be adapted for coupling to at least one ATA device, and the logic may selectively form an ATA communication channel between the host I / O port and one of the device I / O ports. Several methods for exchanging data between a processing unit coupled to the host I / O port of the switch and one or more devices coupled to device I / O ports of the switch are described. Several methods for performing direct memory access (DMA) transfers to move data between a memory of the processing unit and one or more of the devices are also described.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Flexible engine and data structure for packet header processing
InactiveUS6721316B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationWeb transportLinked list
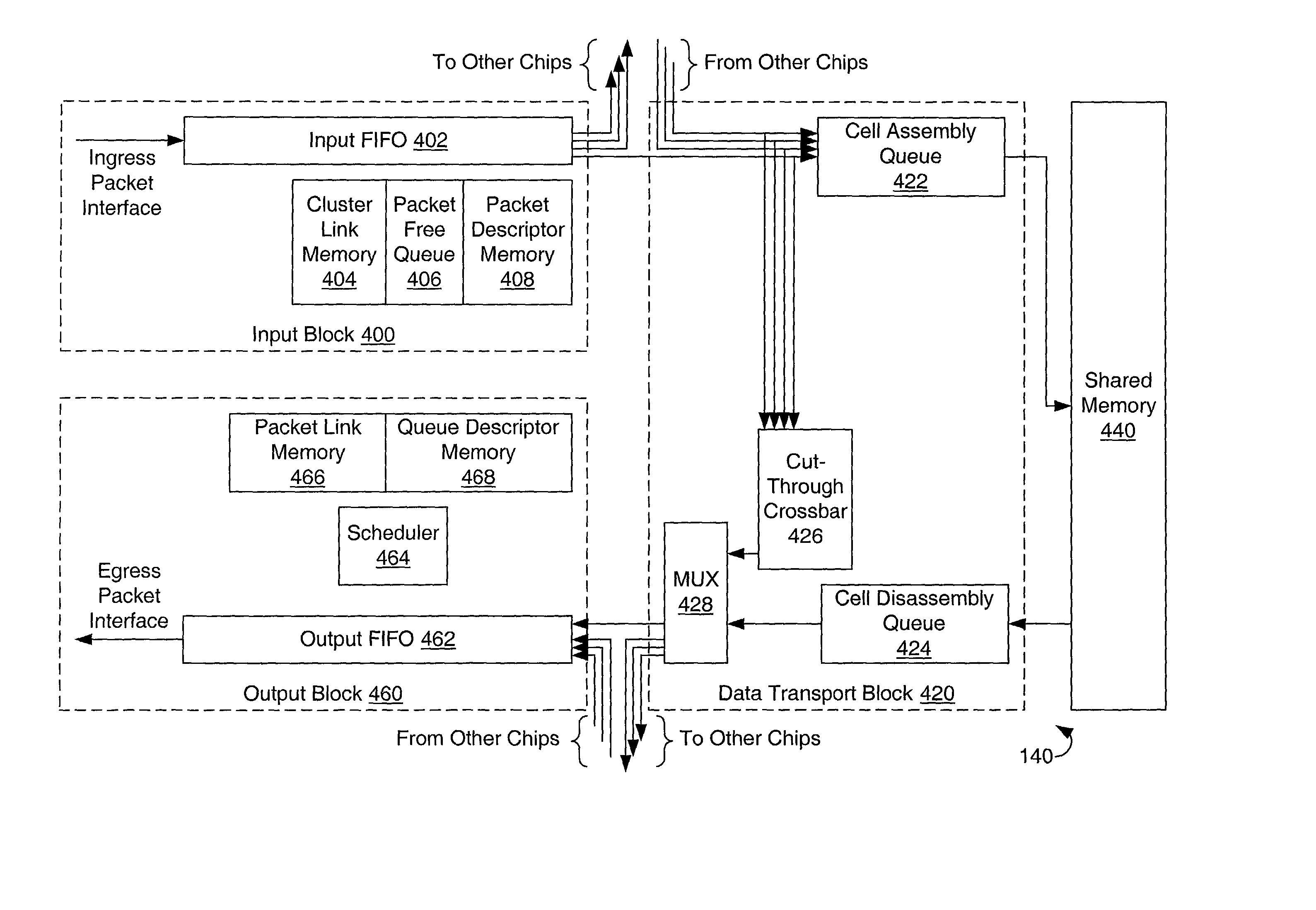
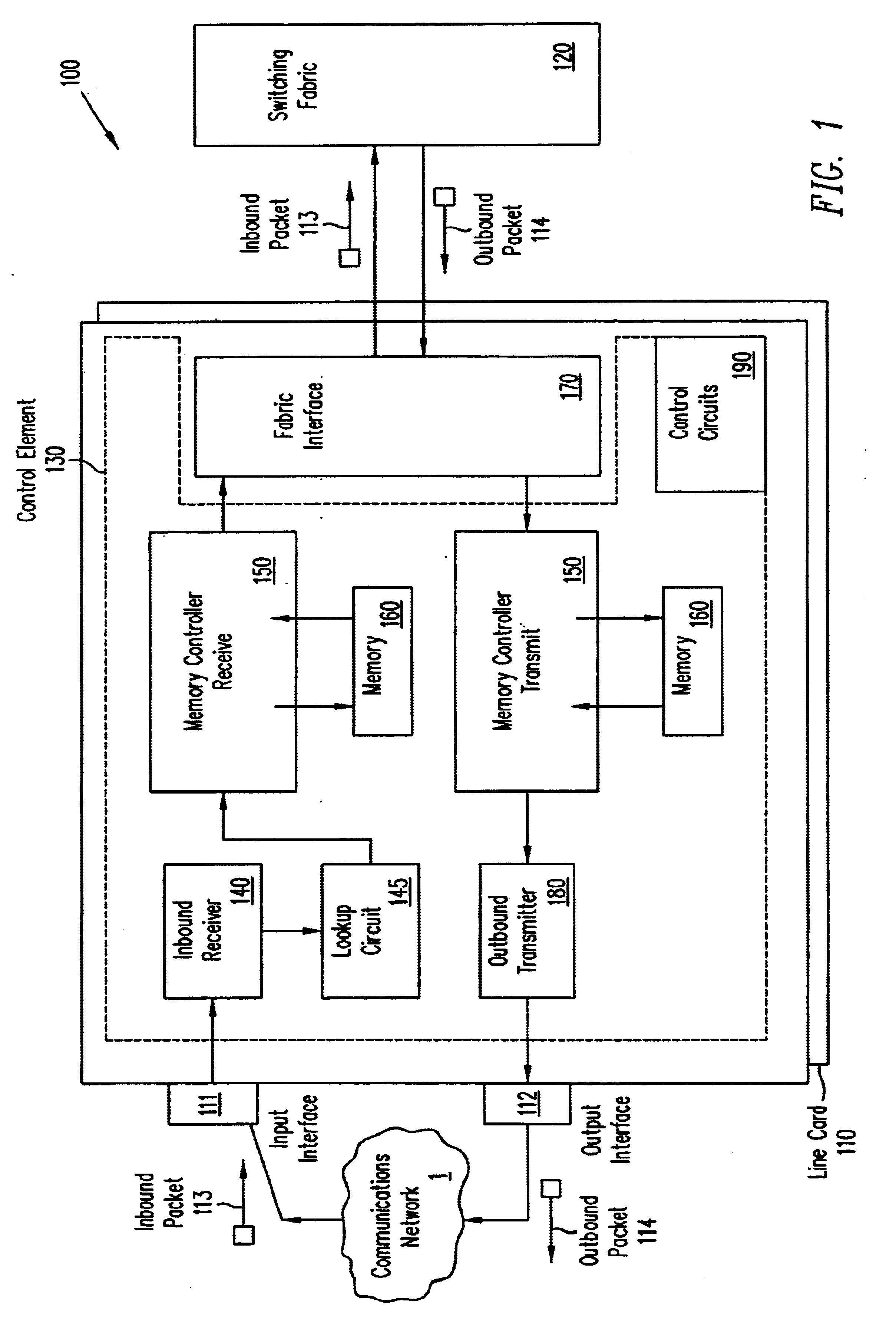
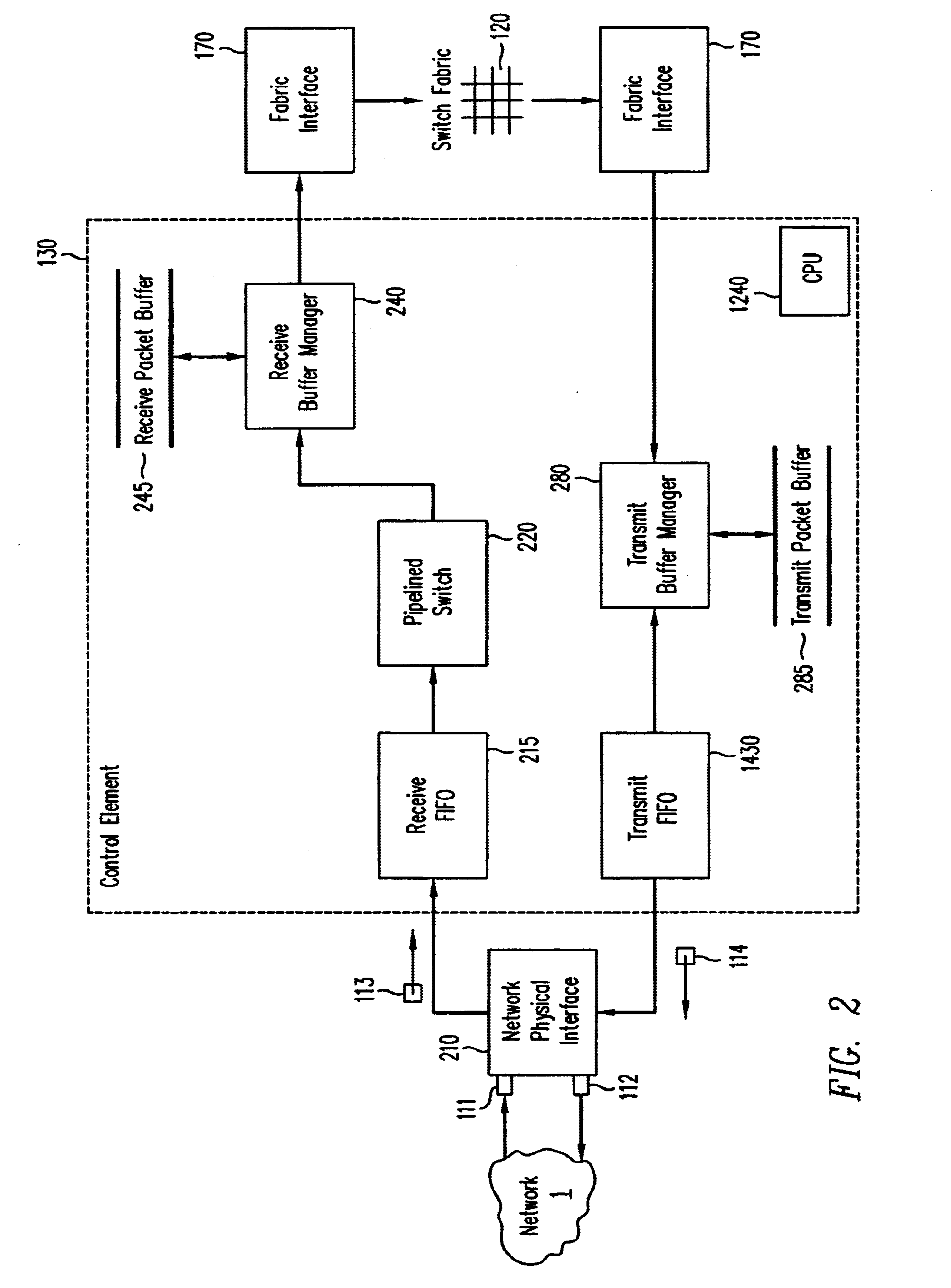
A pipelined linecard architecture for receiving, modifying, switching, buffering, queuing and dequeuing packets for transmission in a communications network. The linecard has two paths: the receive path, which carries packets into the switch device from the network, and the transmit path, which carries packets from the switch to the network. In the receive path, received packets are processed and switched in an asynchronous, multi-stage pipeline utilizing programmable data structures for fast table lookup and linked list traversal. The pipelined switch operates on several packets in parallel while determining each packet's routing destination. Once that determination is made, each packet is modified to contain new routing information as well as additional header data to help speed it through the switch. Each packet is then buffered and enqueued for transmission over the switching fabric to the linecard attached to the proper destination port. The destination linecard may be the same physical linecard as that receiving the inbound packet or a different physical linecard. The transmit path consists of a buffer / queuing circuit similar to that used in the receive path. Both enqueuing and dequeuing of packets is accomplished using CoS-based decision making apparatus and congestion avoidance and dequeue management hardware. The architecture of the present invention has the advantages of high throughput and the ability to rapidly implement new features and capabilities.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
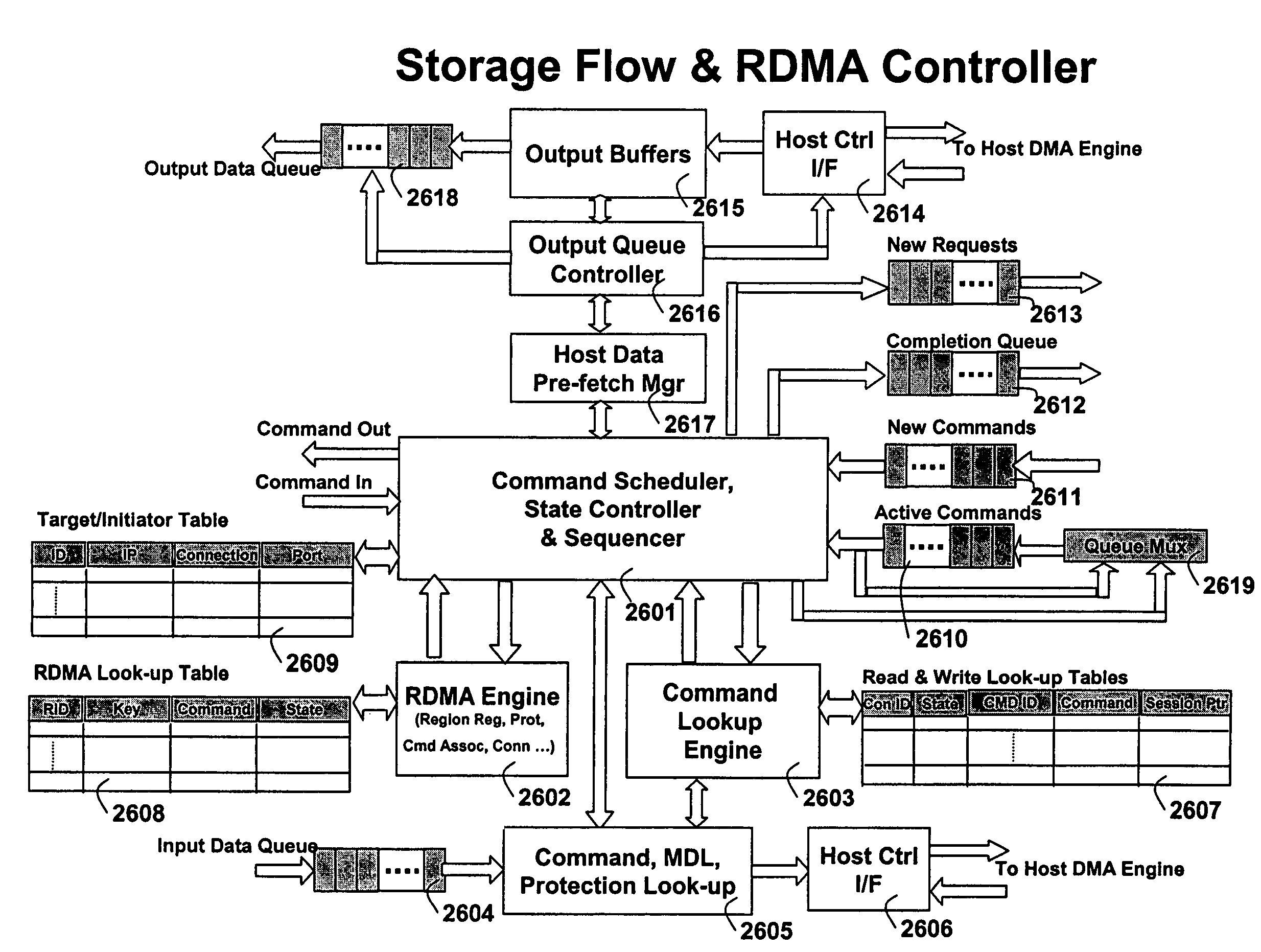
TCP/IP processor and engine using RDMA
ActiveUS7376755B2Sharply reduces TCP/IP protocol stack overheadImprove performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTransmission protocolInternal memory
A TCP / IP processor and data processing engines for use in the TCP / IP processor is disclosed. The TCP / IP processor can transport data payloads of Internet Protocol (IP) data packets using an architecture that provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. The engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a TCP / IP session information database and may also store a storage information session database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
Signal propagation delay routing
ActiveUS20060007863A1Improving current routing algorithmIncrease currentEnergy efficient ICTError prevention/detection by using return channelSignal propagation delayWireless network
A method of routing a message from a source node to a destination node in an adhoc wireless network comprising a plurality of nodes, comprising the steps of; transmitting a first message from the source node to the destination node, receiving said first message at said destination node, transmitting a second message from said destination node in response to the first message and, wherein at least one of said first message and said second message is sent between the source and destination nodes via a plurality of paths comprising at least one intermediate node, selecting a path for communication between the source node and the destination node using an indication of the time taken for at least one of said second and first messages to propagate between each node on each path.
Owner:MANITOBA UNIV OF THE +1
Upstream only linecard with front end multiplexer for CMTS
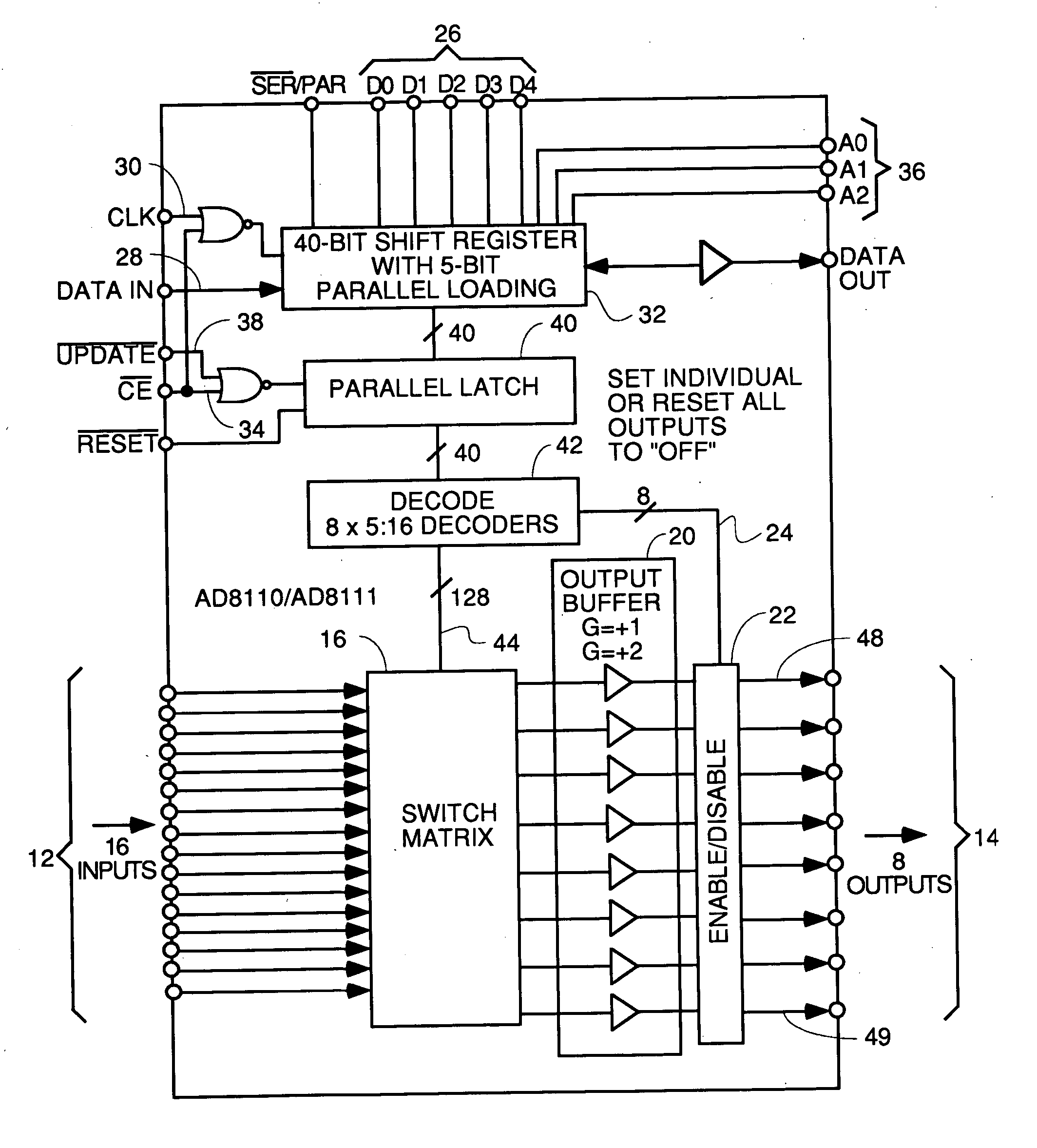
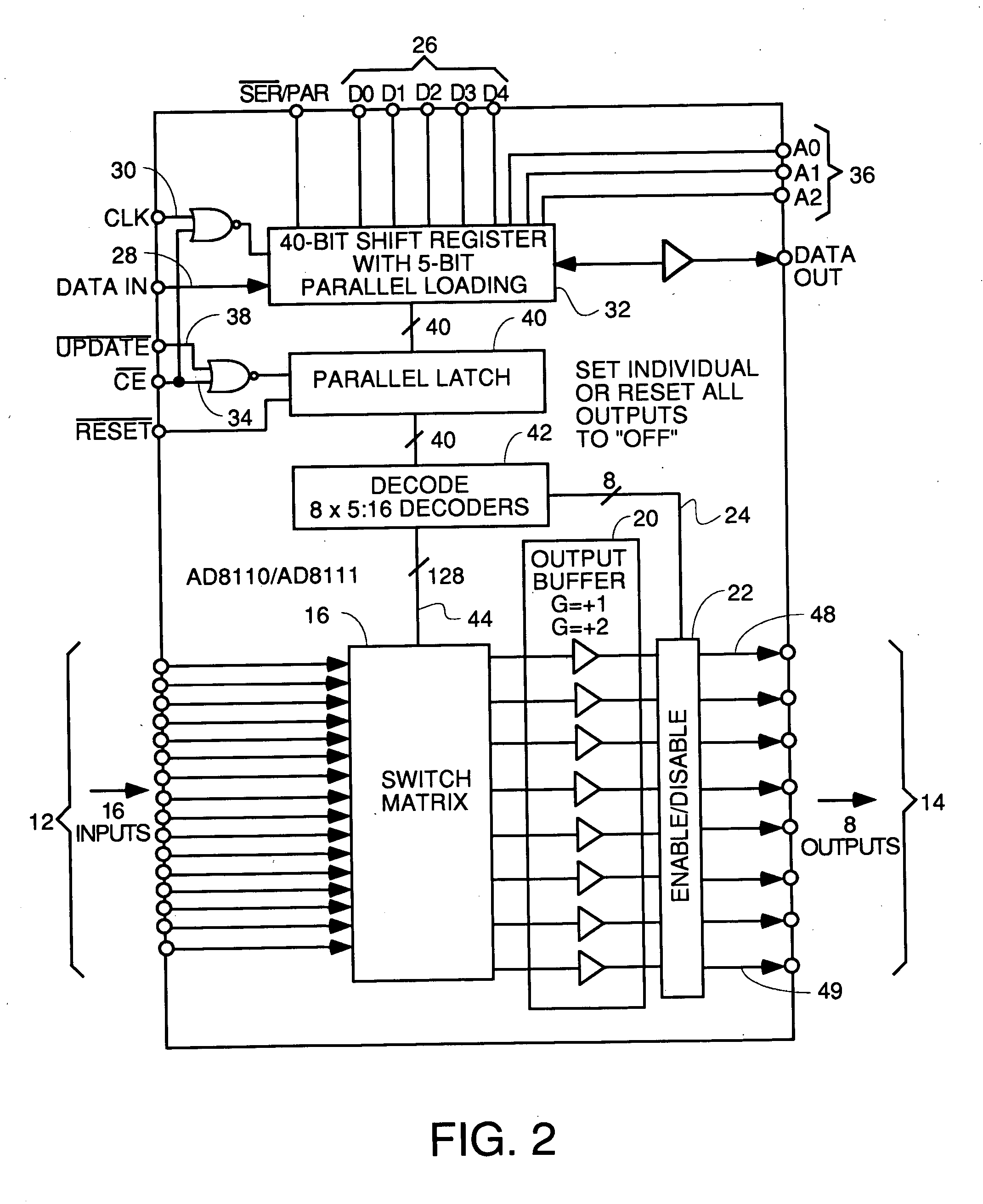
InactiveUS20050010958A1Easy to addMaximize Utilization EfficiencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsBroadband local area networksCrossbar switchMultiplexer
An upstream line card including a digital or analog multiplexer front end circuit for a Cable Modem Termination System. Each upstream line card has only upstream receivers and allows a CMTS to share one or a handful of receiver chips to receive and recover data from a larger number of input cables coupled to the front end multiplexer. A control circuit for the multiplexer uses MAP data and burst assignment data and upstream mini-slot counts for each of the input cables to determine when a burst is about to arrive on a cable and cause appropriate switching by the multiplexer or crossbar switch. In some embodiments, there is only one RF channel circuit coupled to the output of the multiplexer, so the multiplexer is controlled to couple the input cable upon which the burst is expected to the single RF channel. In other embodiments, there are multiple RF channels coupled to the inputs of the multiplexer so the multiplexer is controlled to connect each input cable on which a burst is expected to an available RF channel. In some embodiments, the sample data generated by each RF channel is buffered and an arbiter picks one burst at a time for application to the input of a CMTS receiver or doles out bursts to different receivers. In other embodiments, no buffers or arbiter are used, and each RF channel has its own dedicated CMTS receiver.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com