Patents
Literature
129 results about "Signal propagation delay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
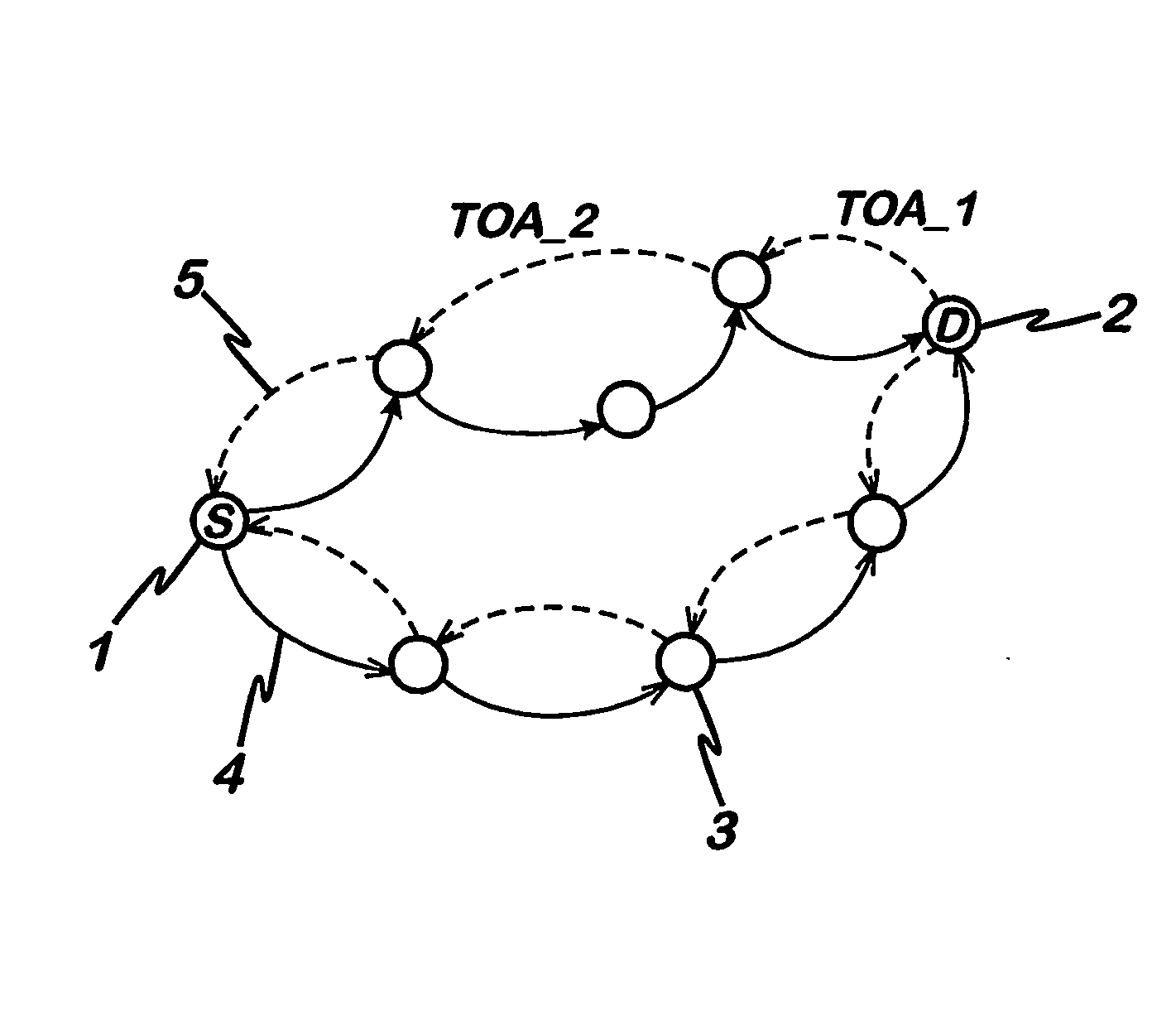
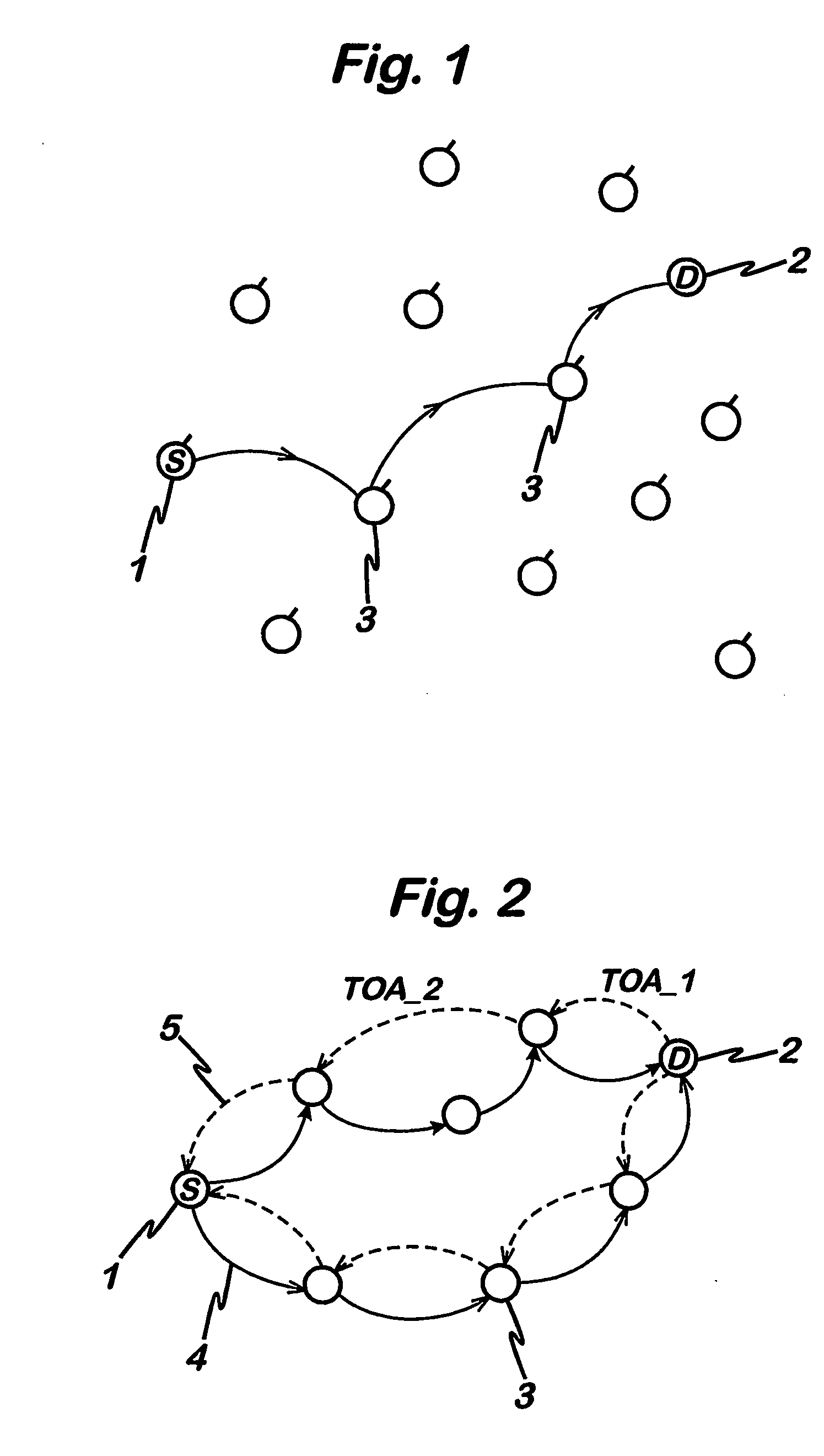
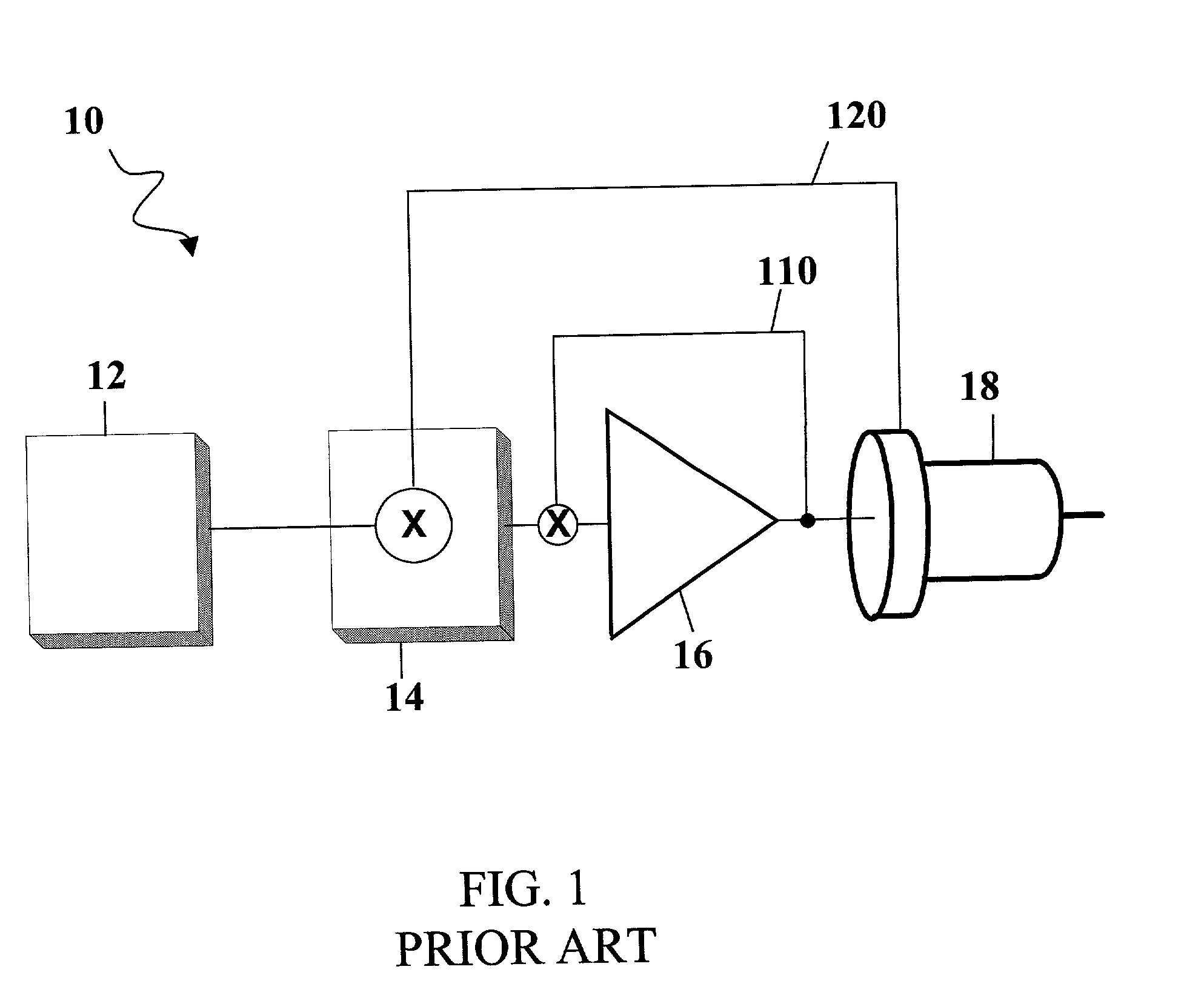
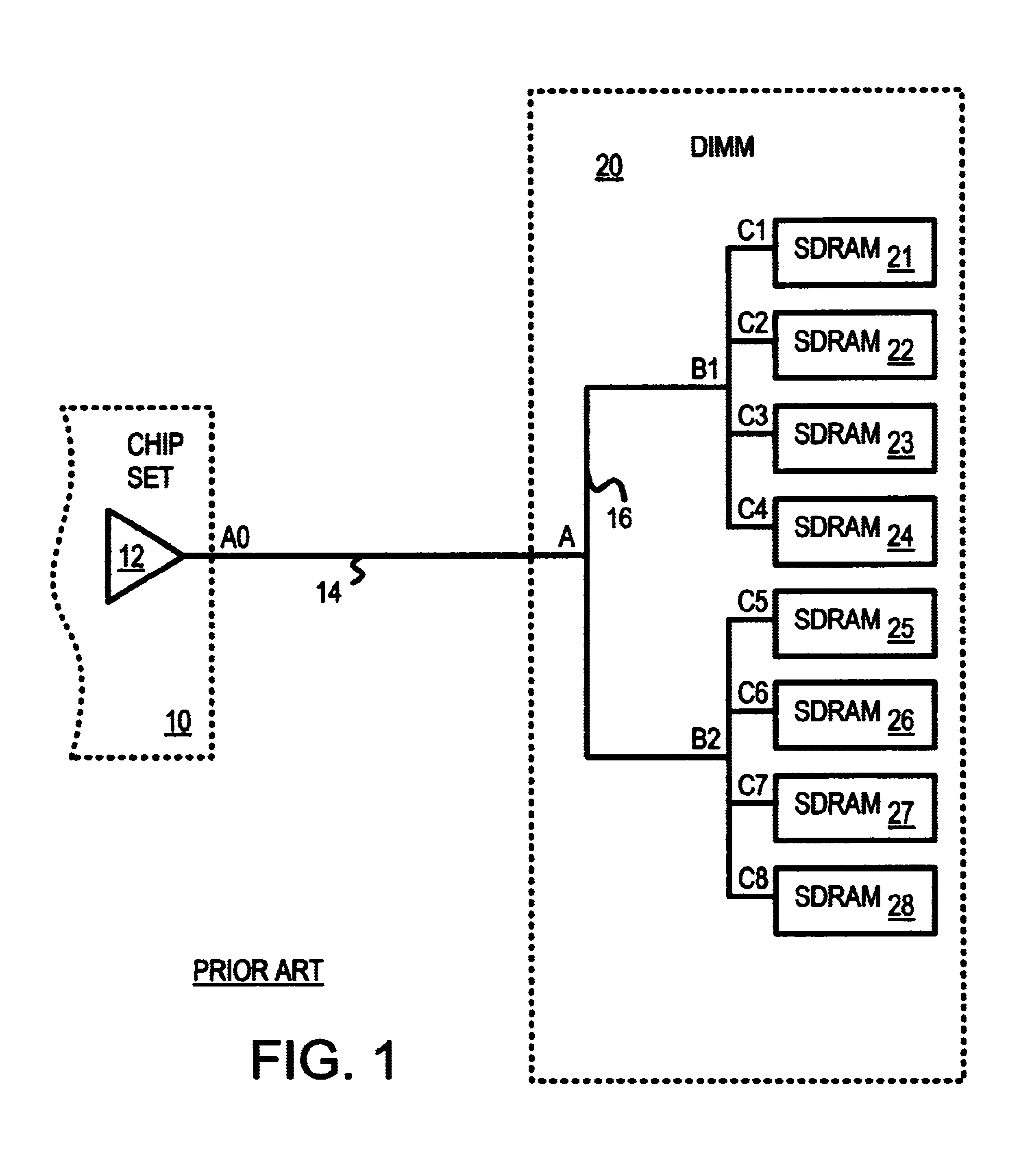
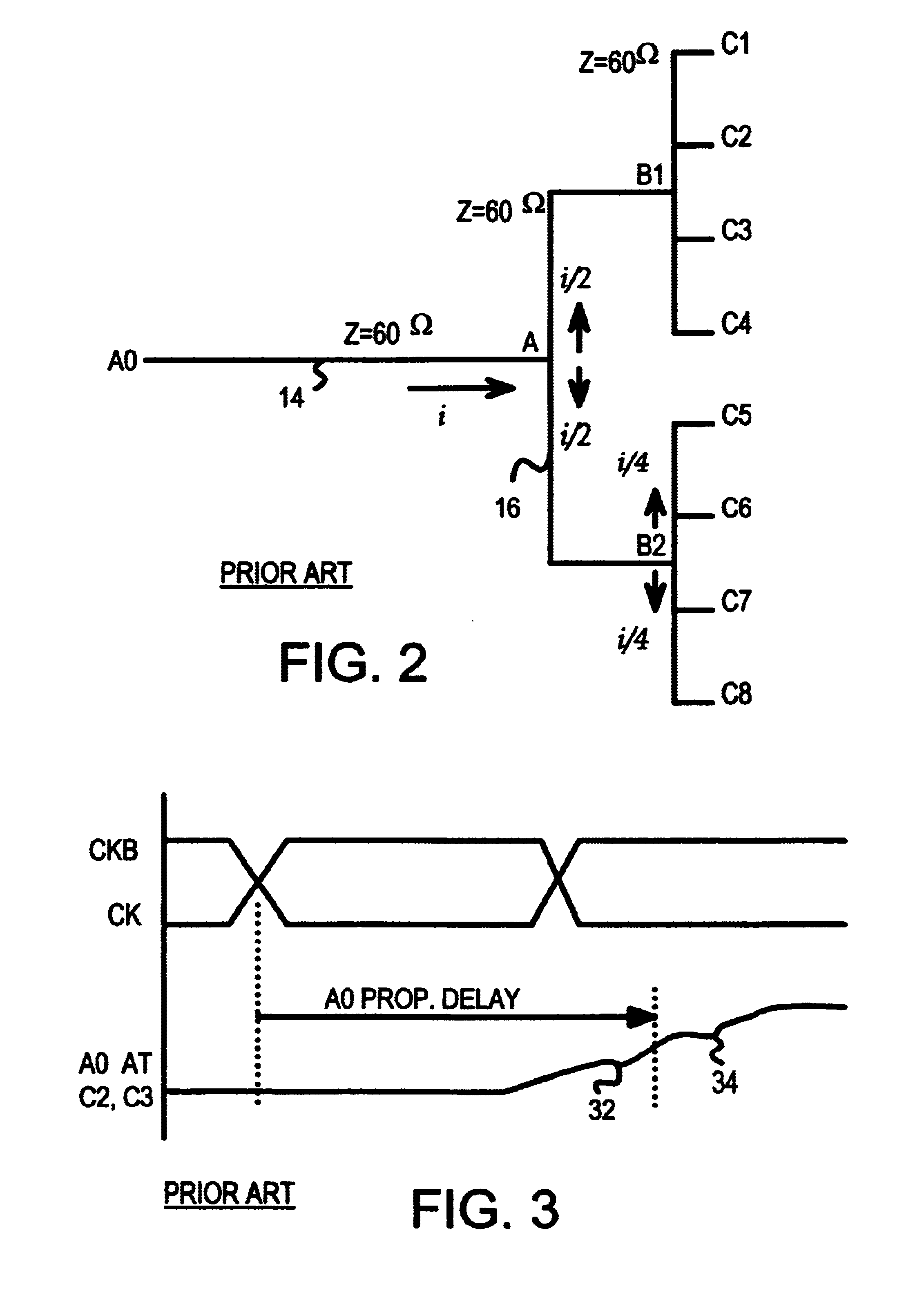
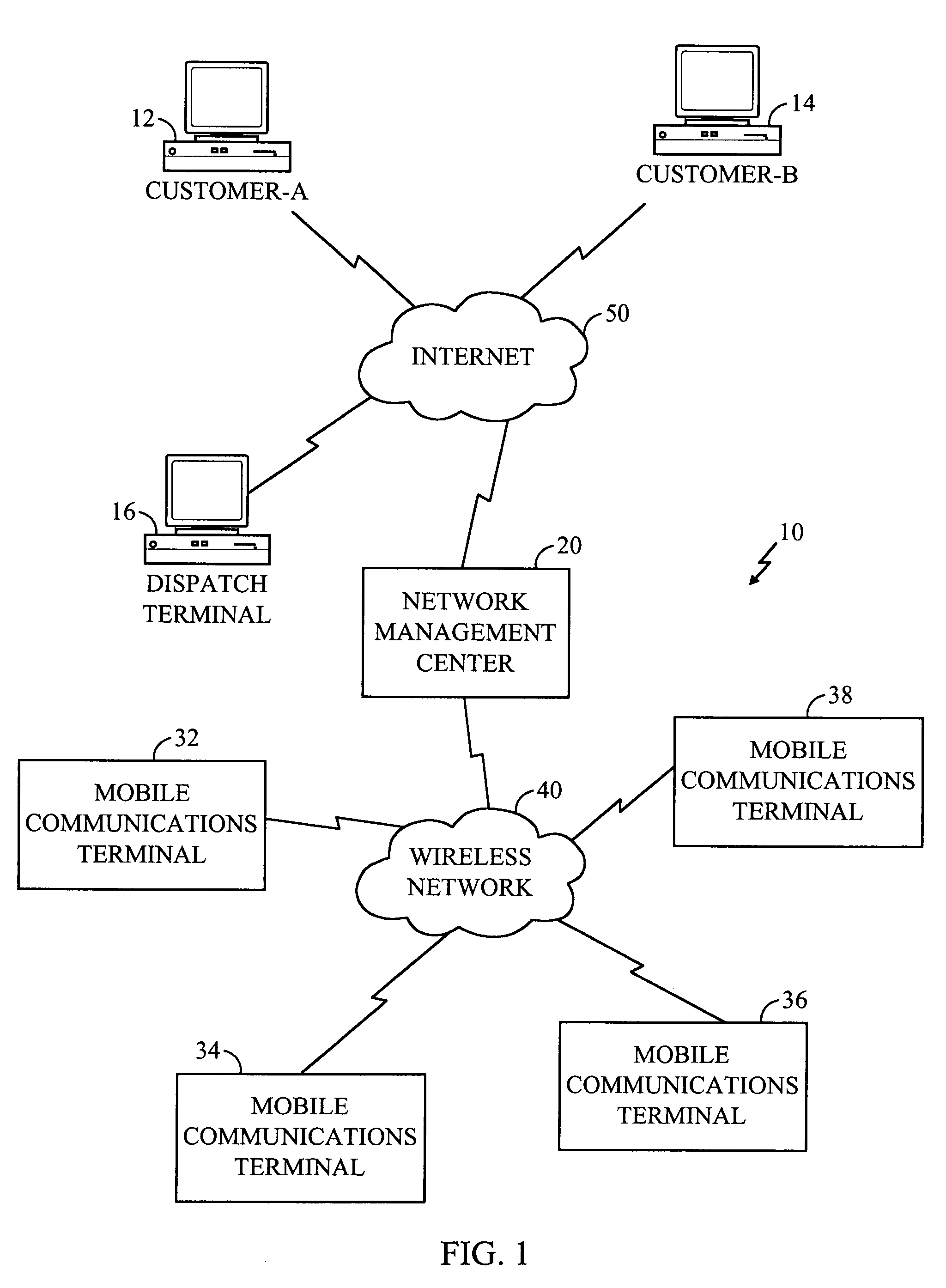
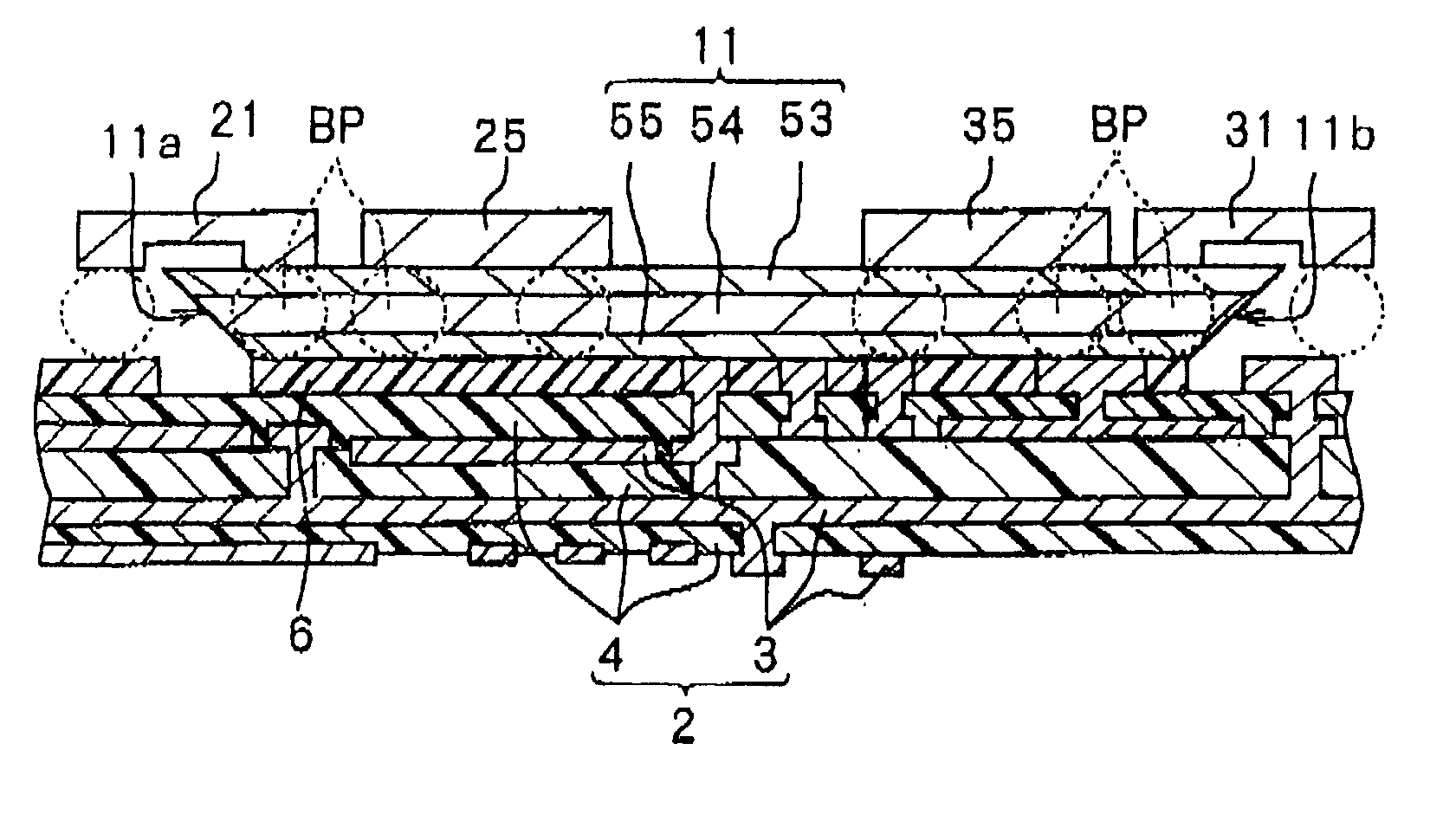
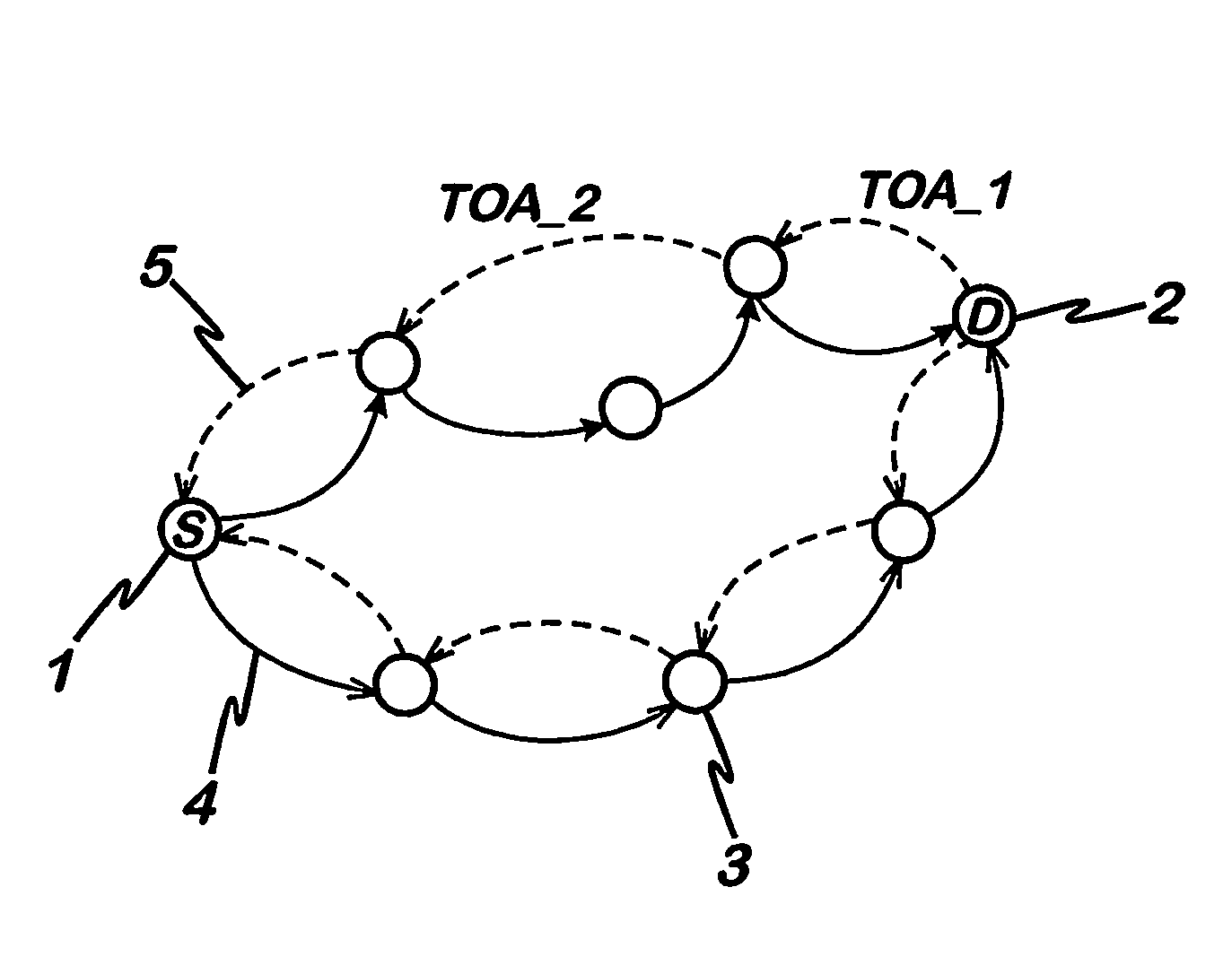
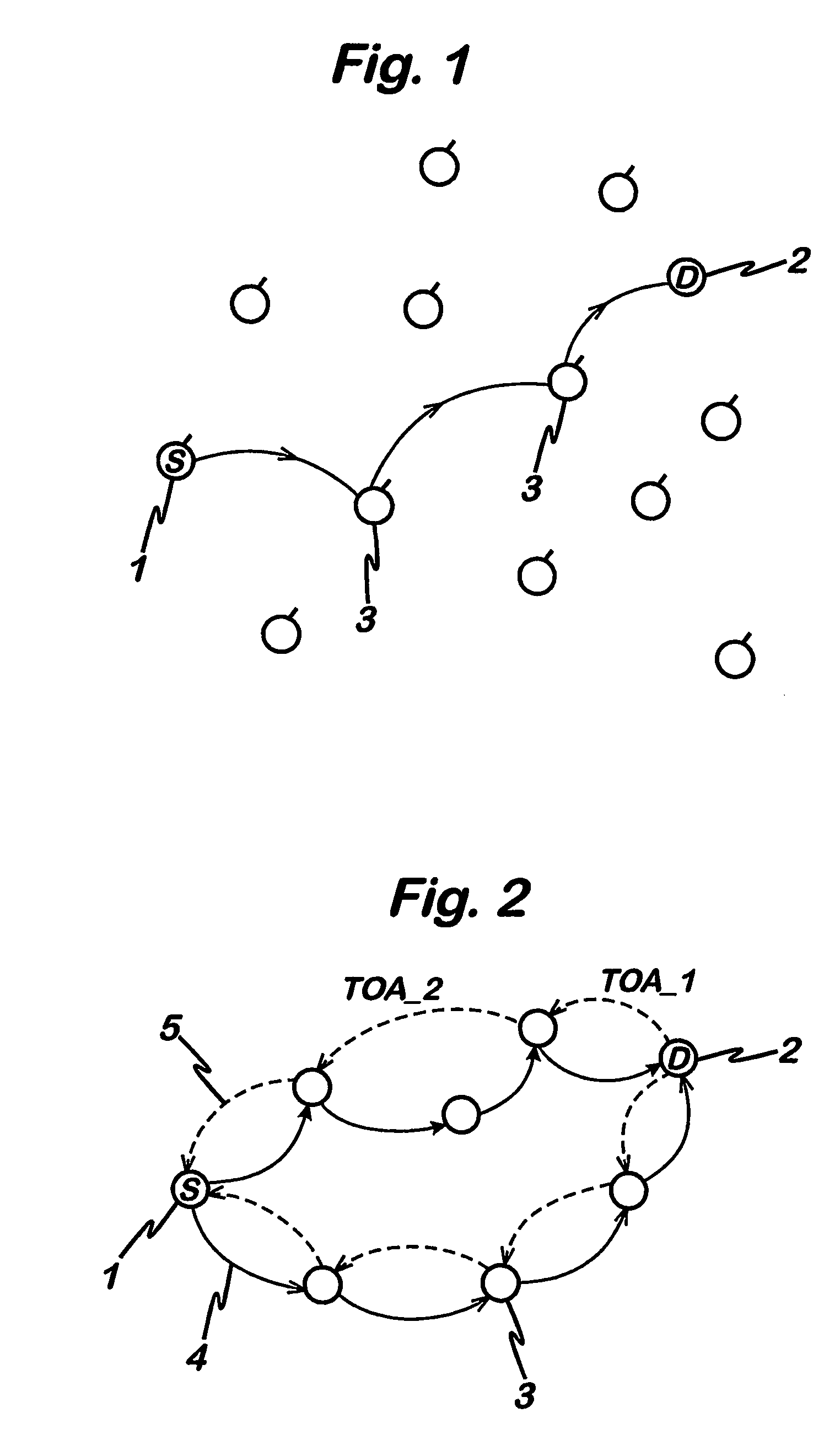
Signal propagation delay routing
ActiveUS20060007863A1Improving current routing algorithmIncrease currentEnergy efficient ICTError prevention/detection by using return channelSignal propagation delayWireless network
A method of routing a message from a source node to a destination node in an adhoc wireless network comprising a plurality of nodes, comprising the steps of; transmitting a first message from the source node to the destination node, receiving said first message at said destination node, transmitting a second message from said destination node in response to the first message and, wherein at least one of said first message and said second message is sent between the source and destination nodes via a plurality of paths comprising at least one intermediate node, selecting a path for communication between the source node and the destination node using an indication of the time taken for at least one of said second and first messages to propagate between each node on each path.
Owner:MANITOBA UNIV OF THE +1
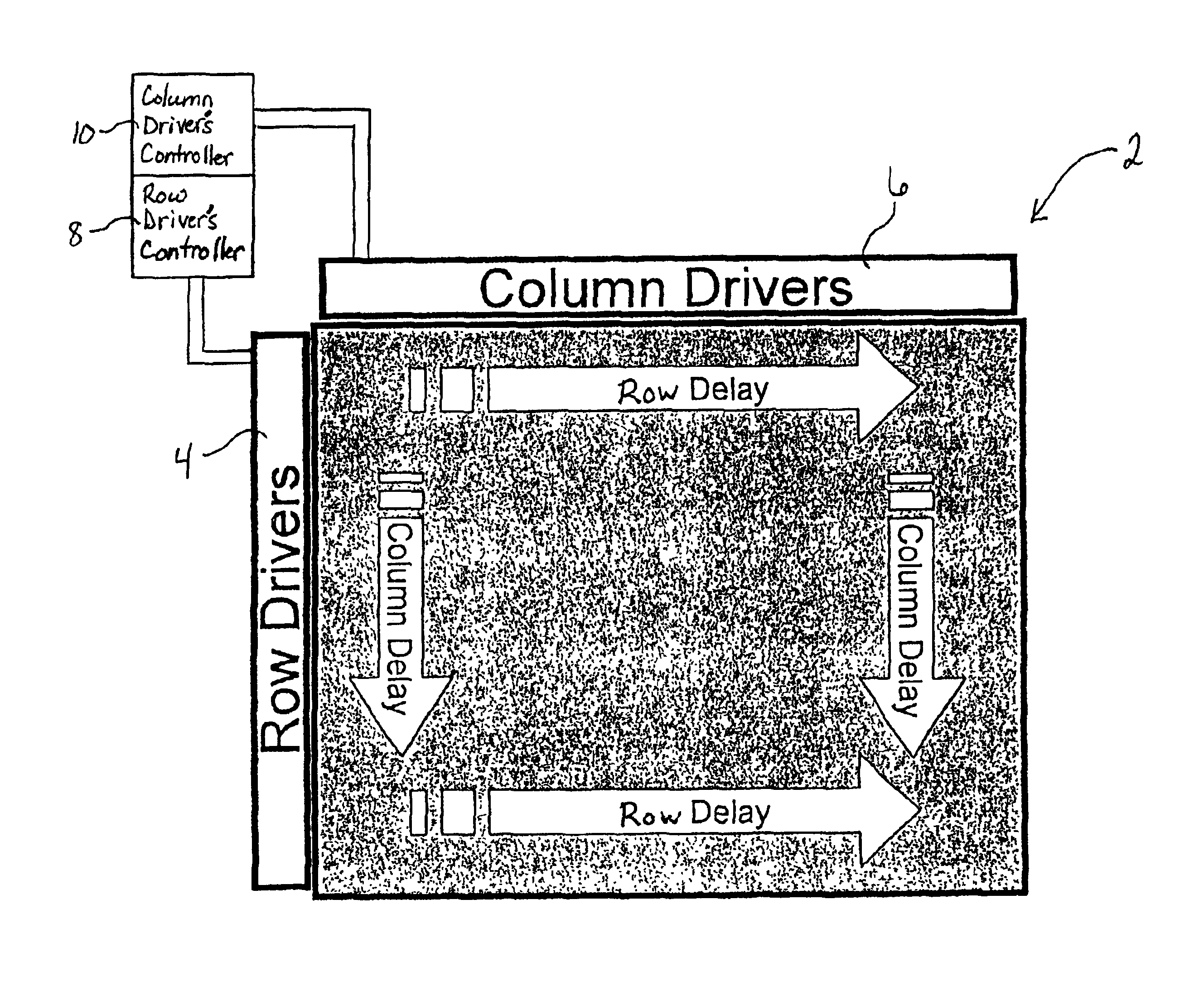
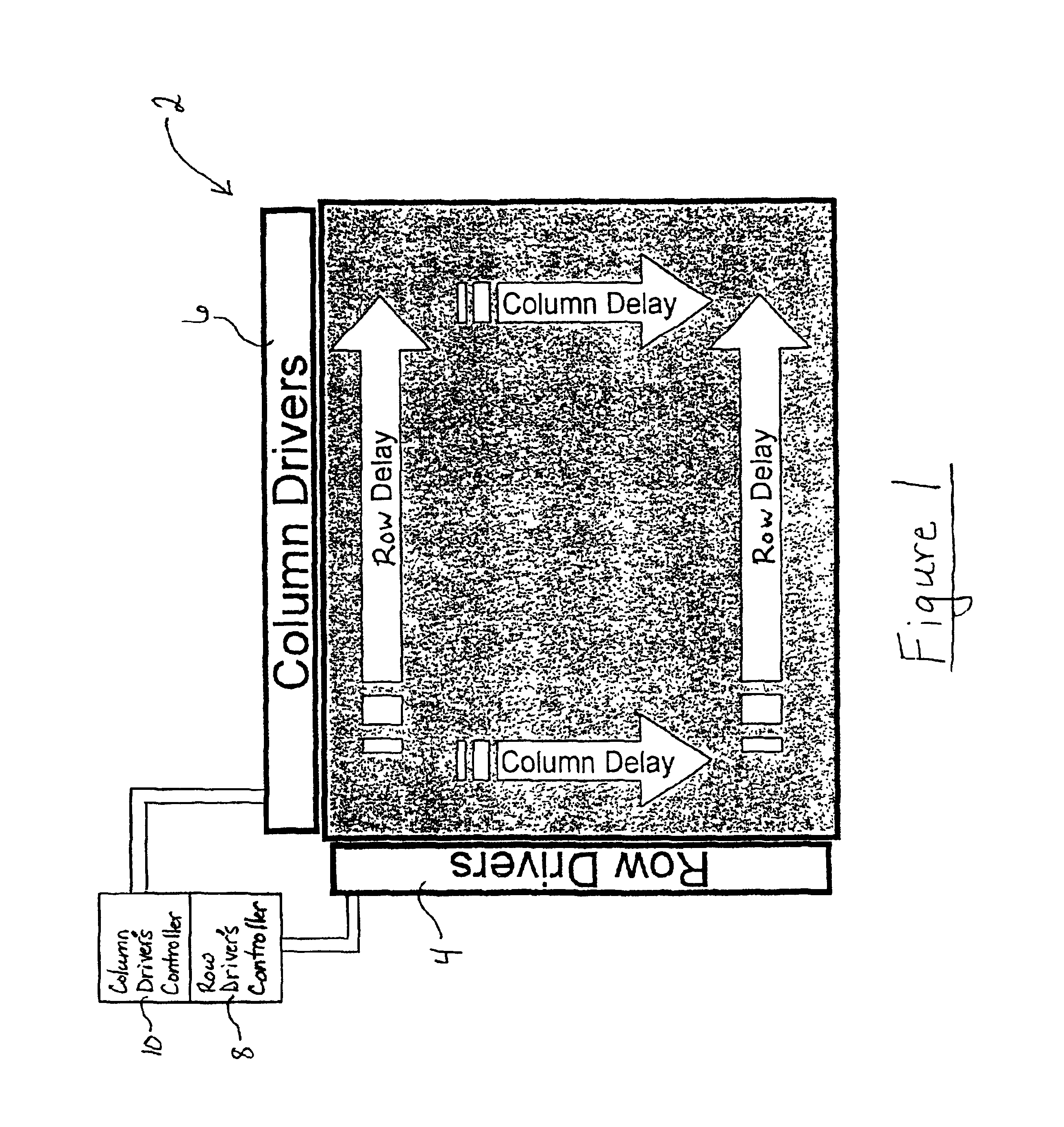
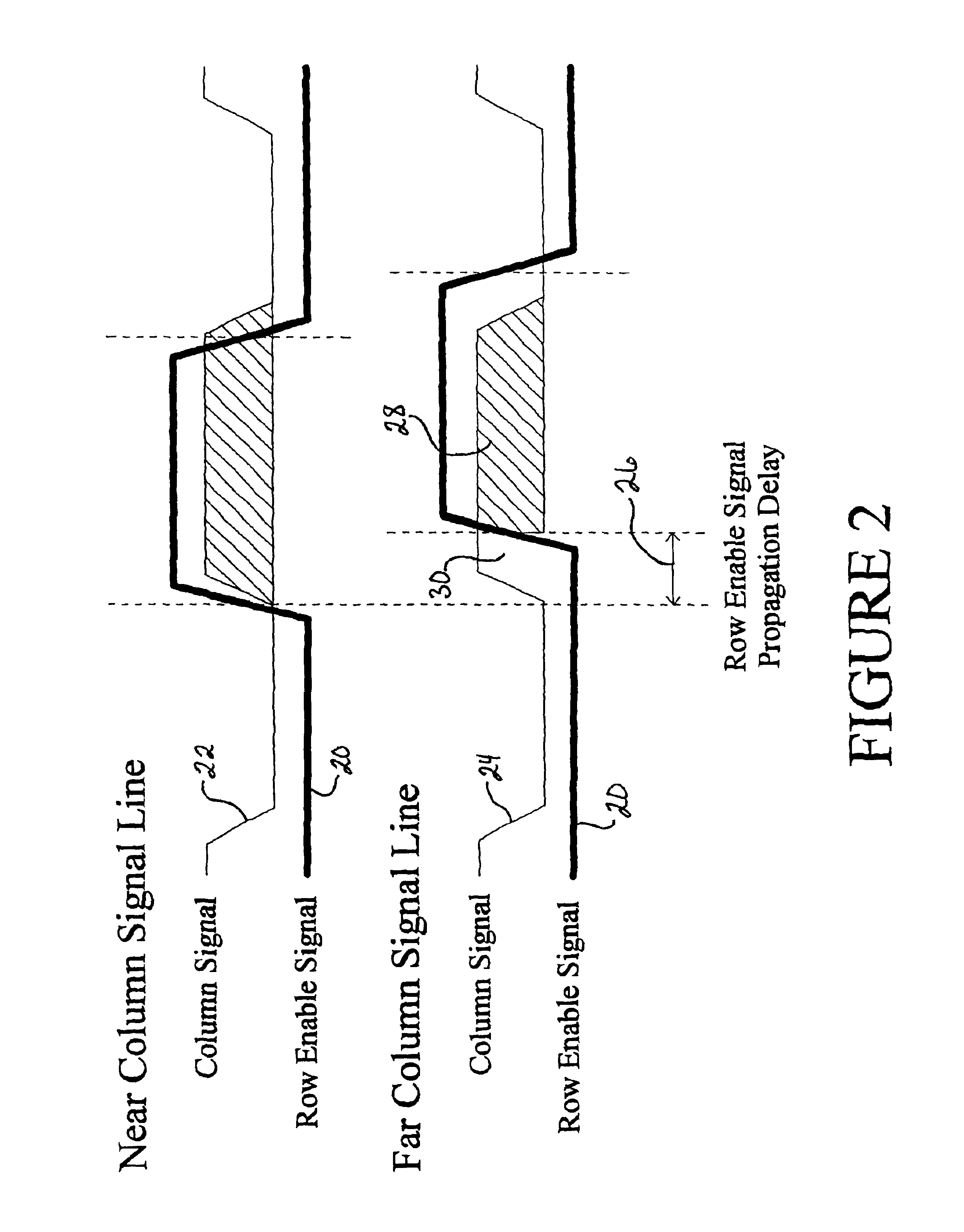
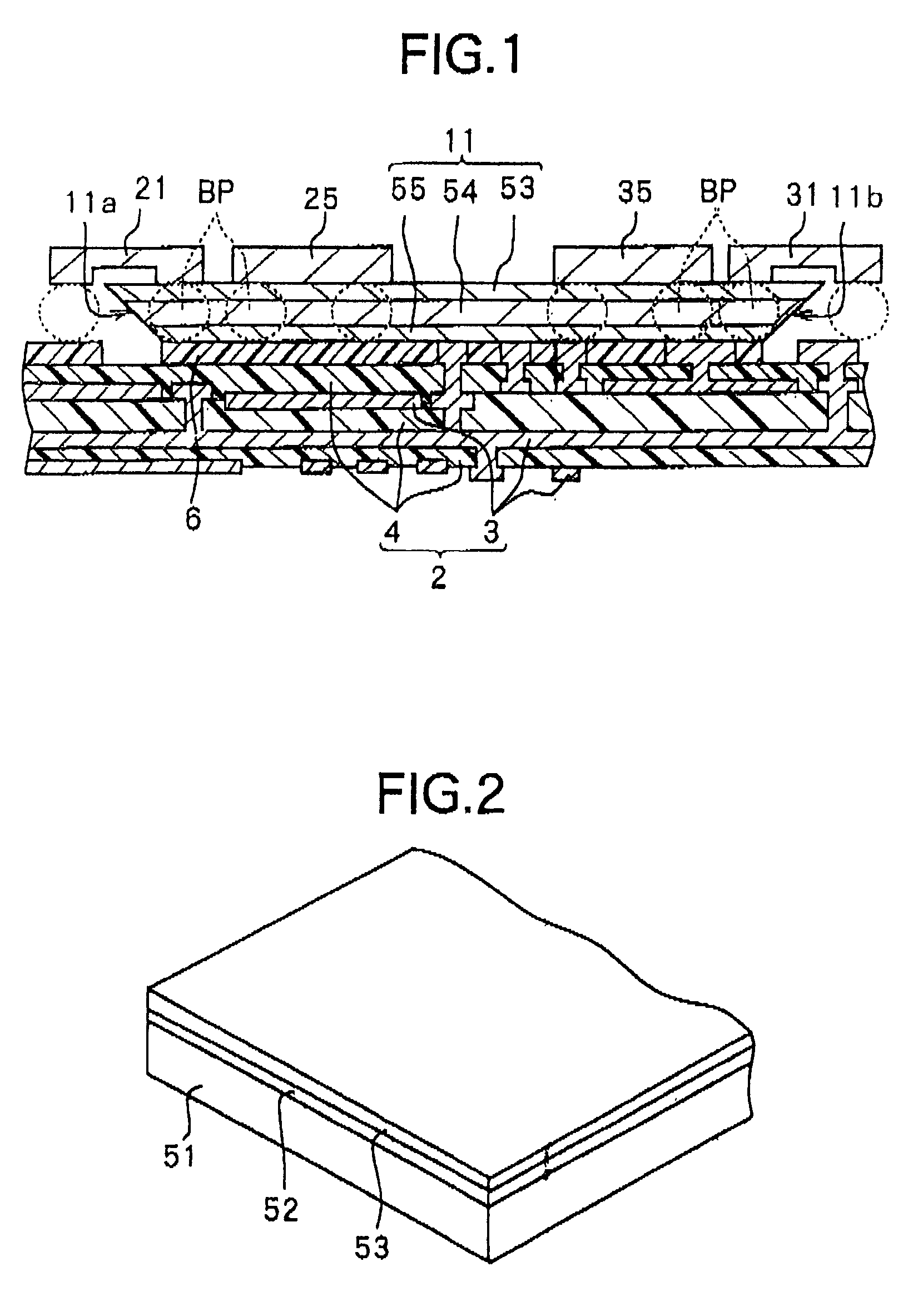
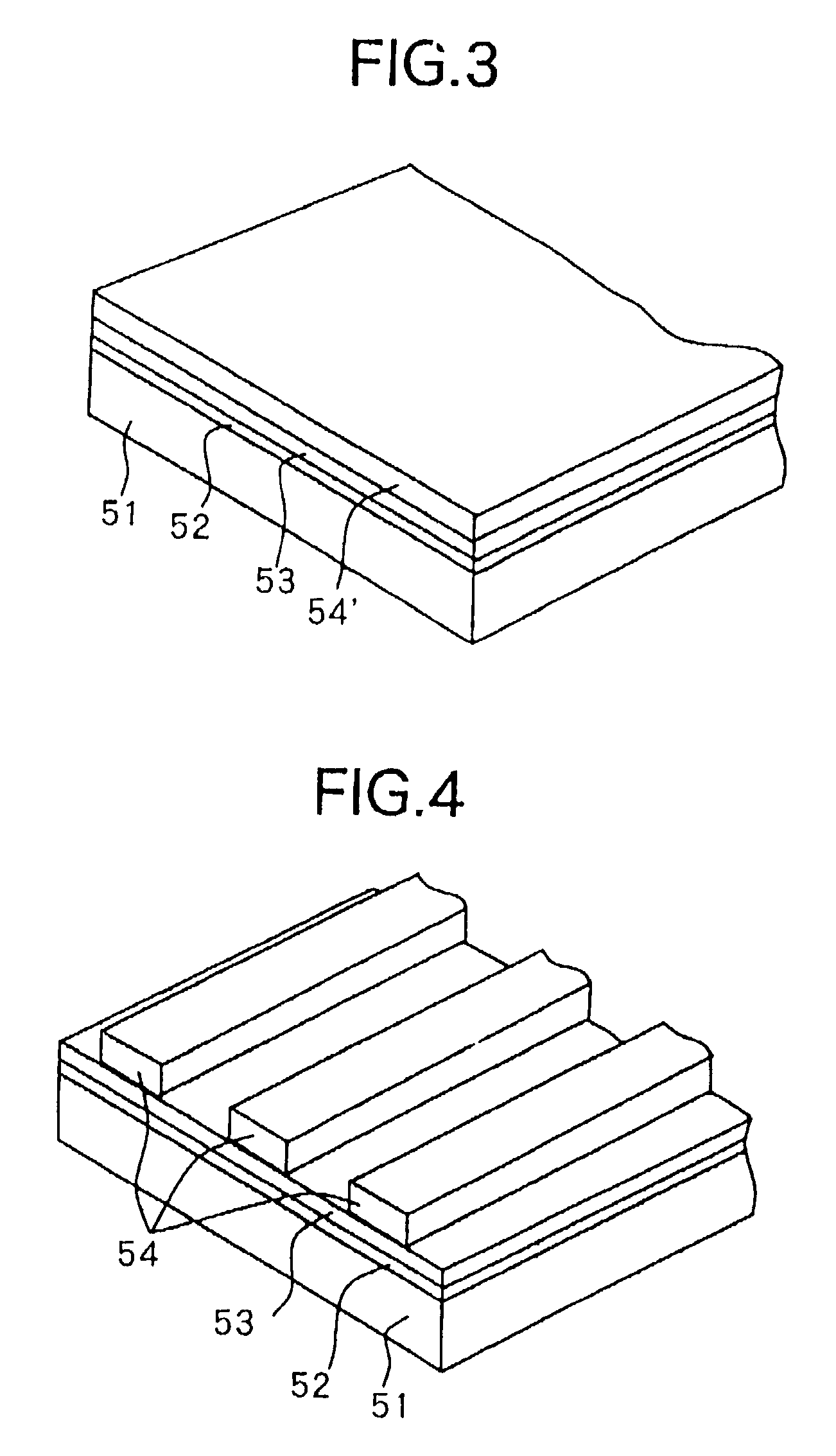
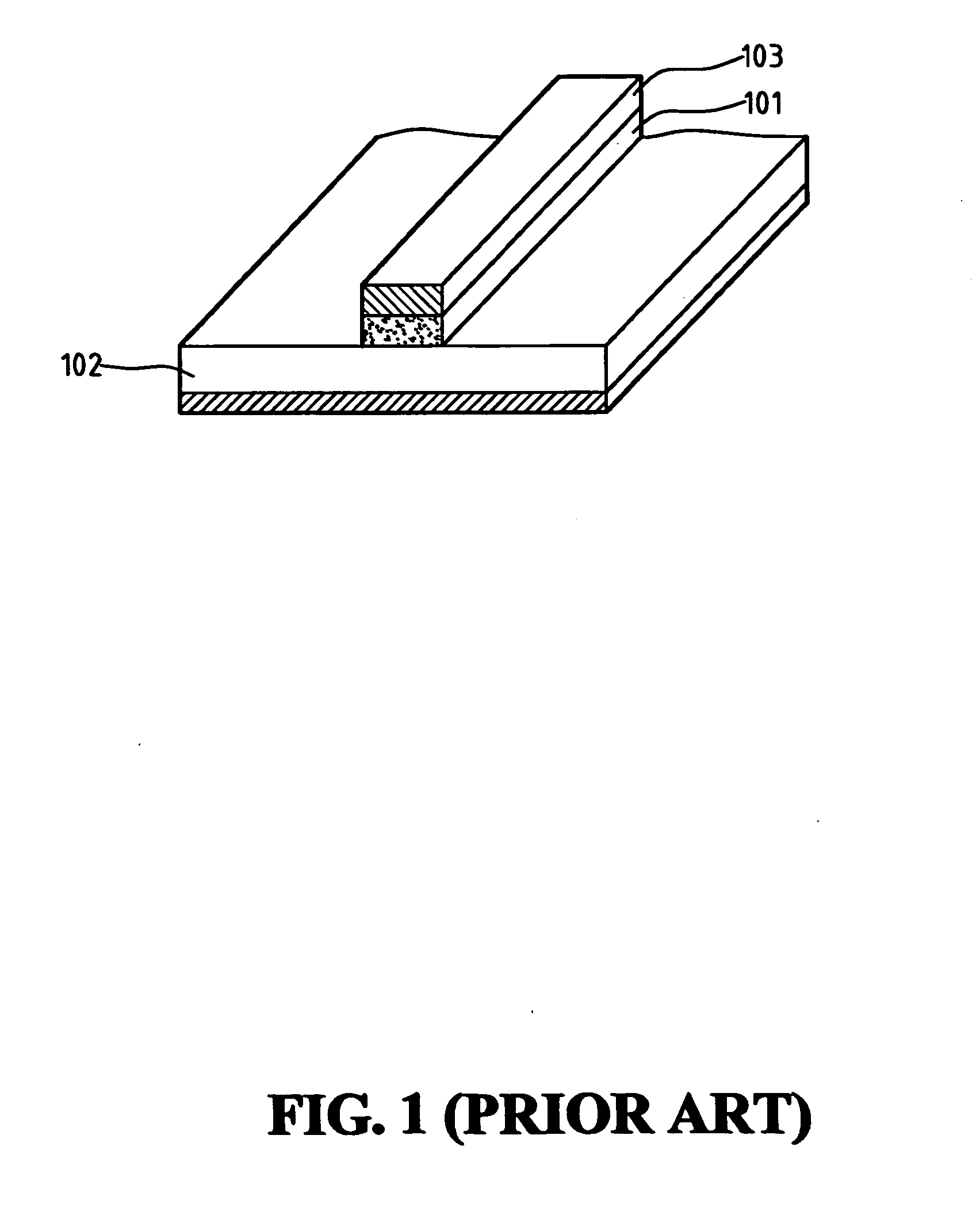
Display line drivers and method for signal propagation delay compensation
InactiveUS6947022B2Reduce impactSlow effectCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringLine driver
Methods and apparatus for compensating the effects of display signal propagation delay in a display panel are disclosed. The apparatus comprises circuitry in addition to conventional display driver circuitry for delaying display line timing signals by an amount approximating the delay found in corresponding display lines. By delaying display line timing signals, for example in a column driver, by an time approximately equal the delay experienced in a corresponding row enable signal line, capacitors associated with the display pixels charge more fully resulting in a more vivid display image. Methods for compensating the effects of display signal propagation delay involve generating a plurality of delayed display timing signals and activating display lines in response to those delayed timing signals.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
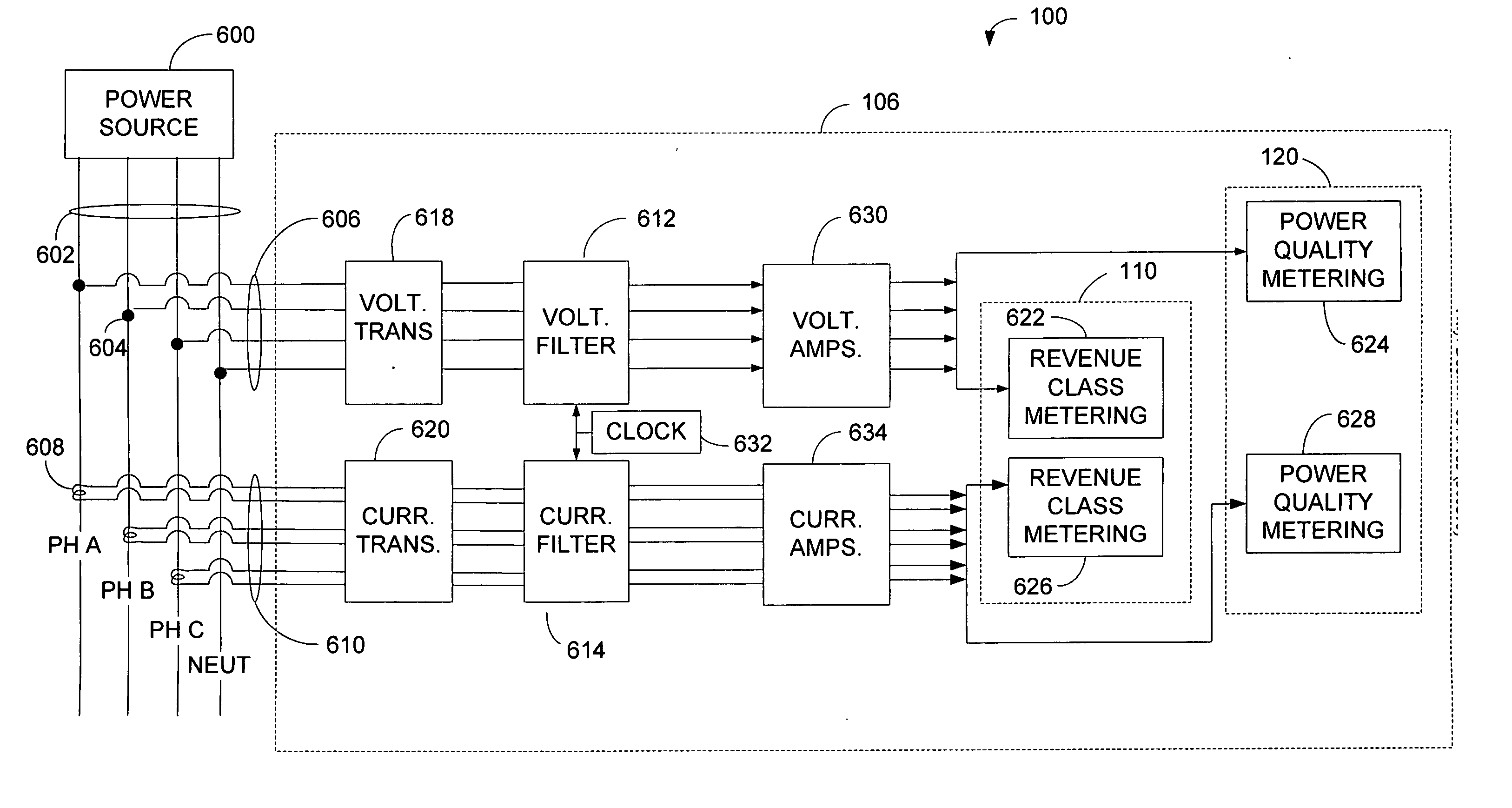
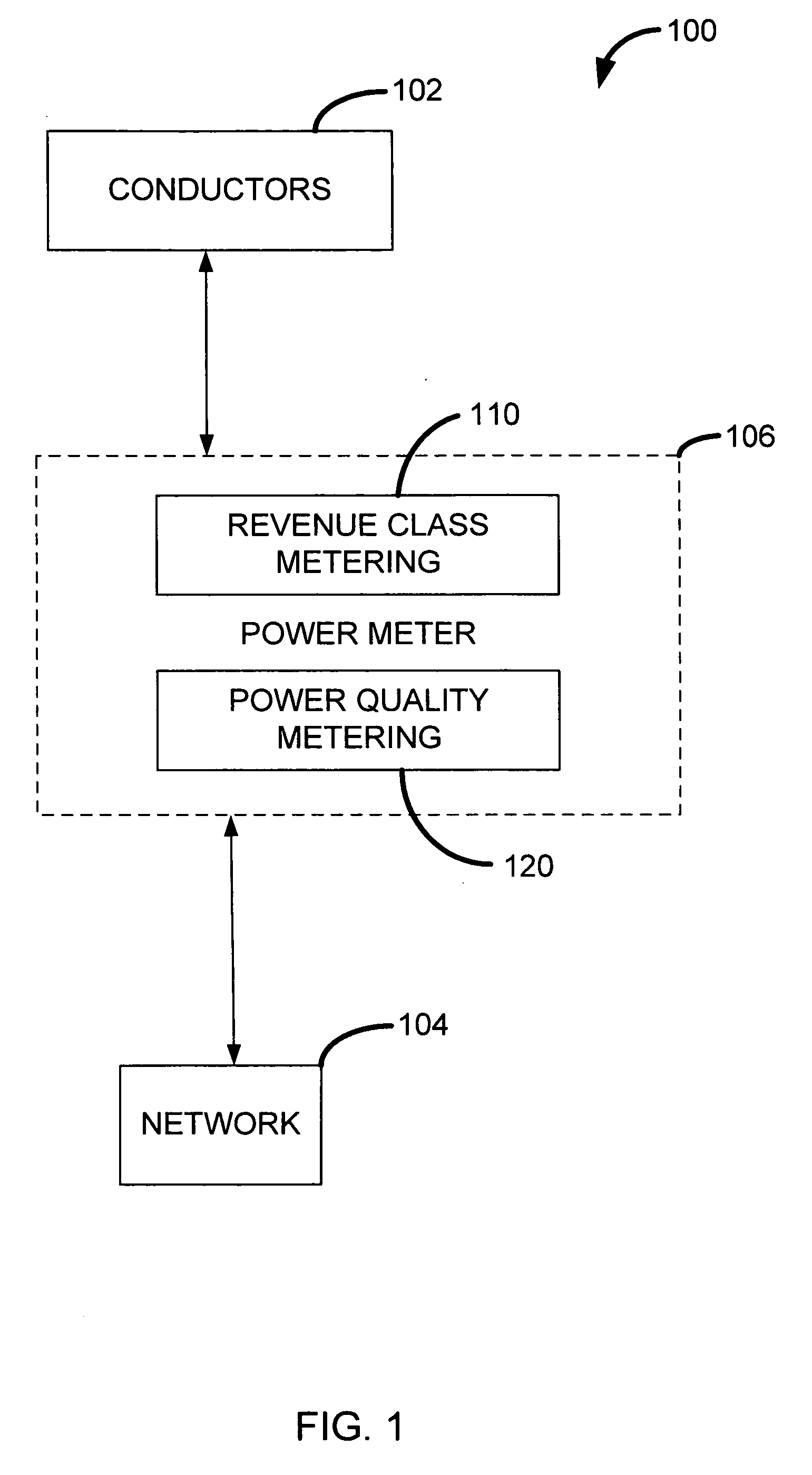
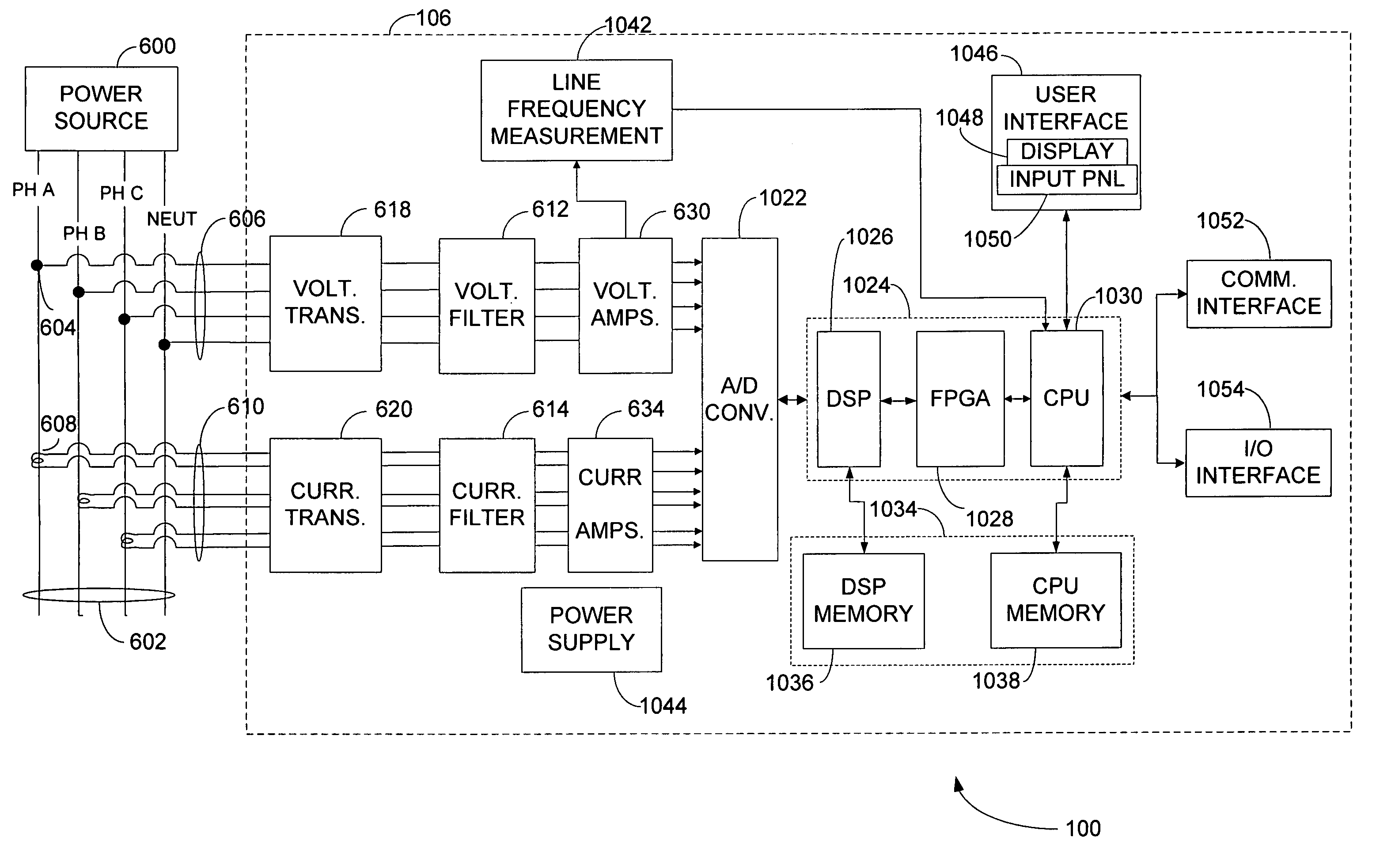
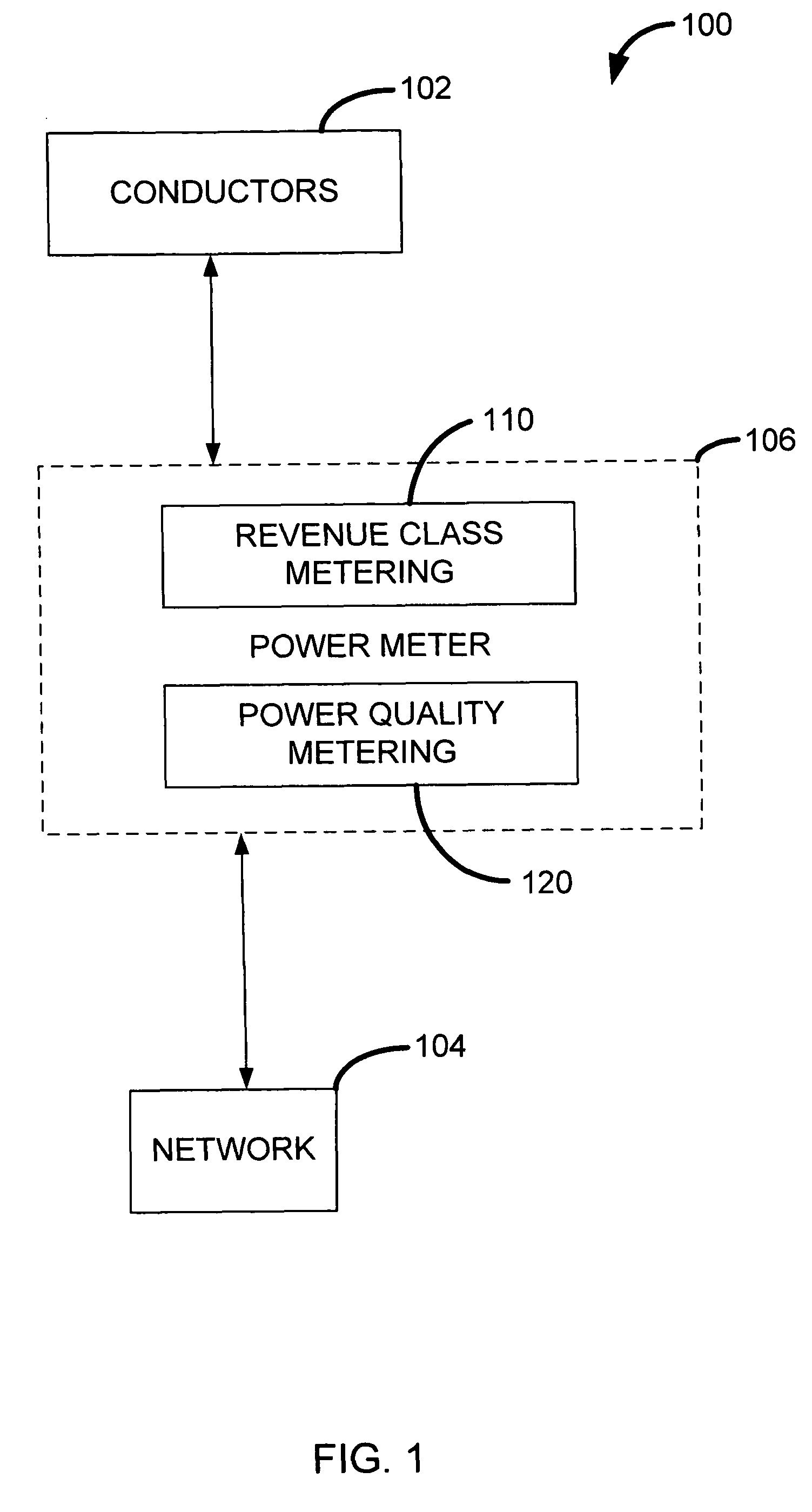
Revenue class power meter with frequency rejection
ActiveUS20070067121A1Electric devicesPower measurement by current/voltagePower qualityPower parameter
A power meter for measuring power parameters on one or more electrical power lines / loads is configured to include a revenue class metering module and a power quality metering module. The revenue class metering module and the power quality metering module may use the same measured voltage and current signals to generate revenue accurate power consumption information and power quality information, respectively. The power meter may also include a plurality of filters configured to attenuate high frequency signals included in the voltage and current signals. Each of the filters may be configured with a corner frequency, gain and signal propagation delay that is substantially equal. The filtered current and voltage signals may be received and processed by the revenue class metering module, and the power quality metering module to generate revenue accurate power consumption information and power quality information, respectively. Alternatively, the filtered current and voltage signals may be received and processed by the power quality metering module to generate power quality information, and unfiltered current and voltage signals may be received and processed by the revenue class metering module to generate revenue accurate power consumption information.
Owner:POWER MEASUREMENT LTD
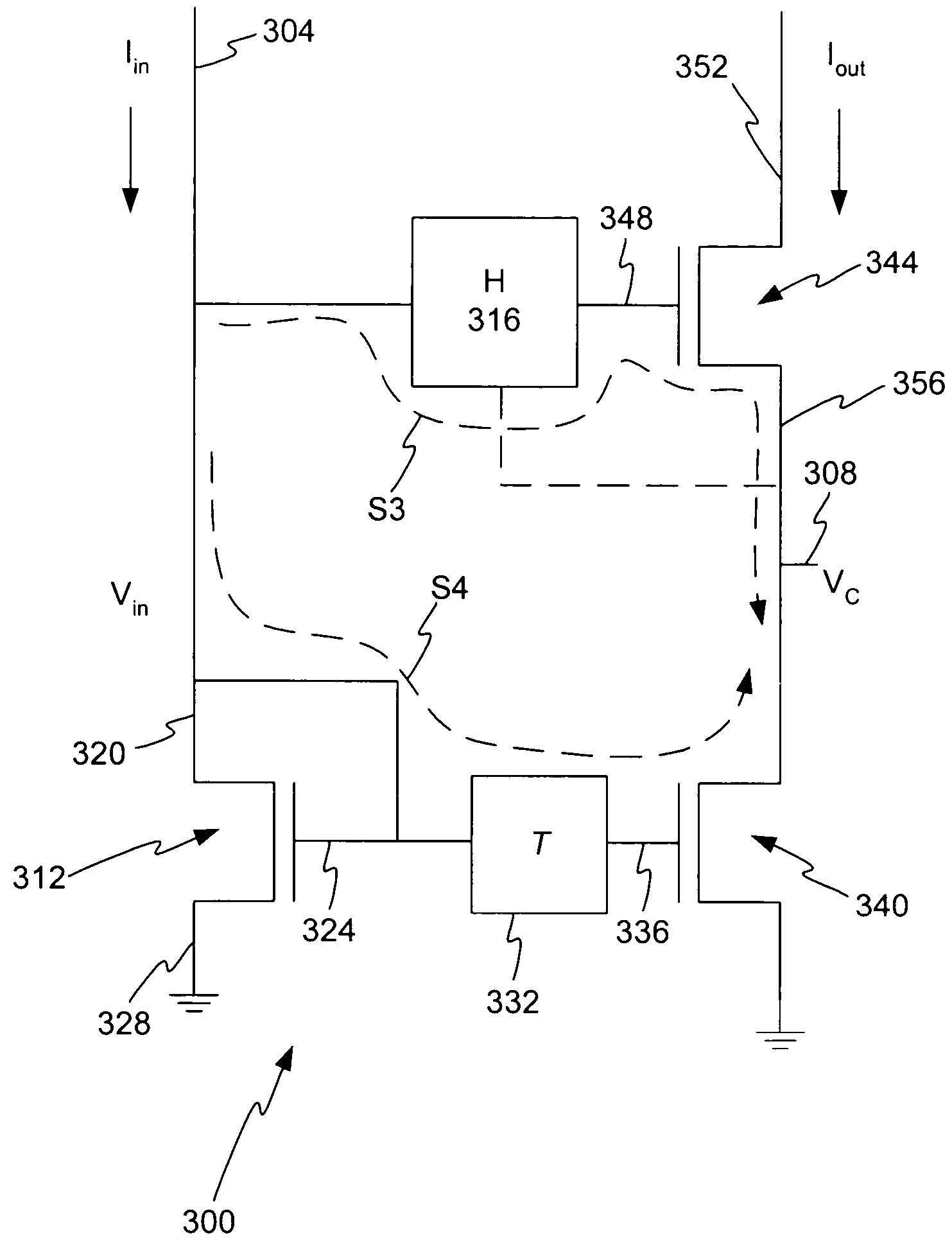
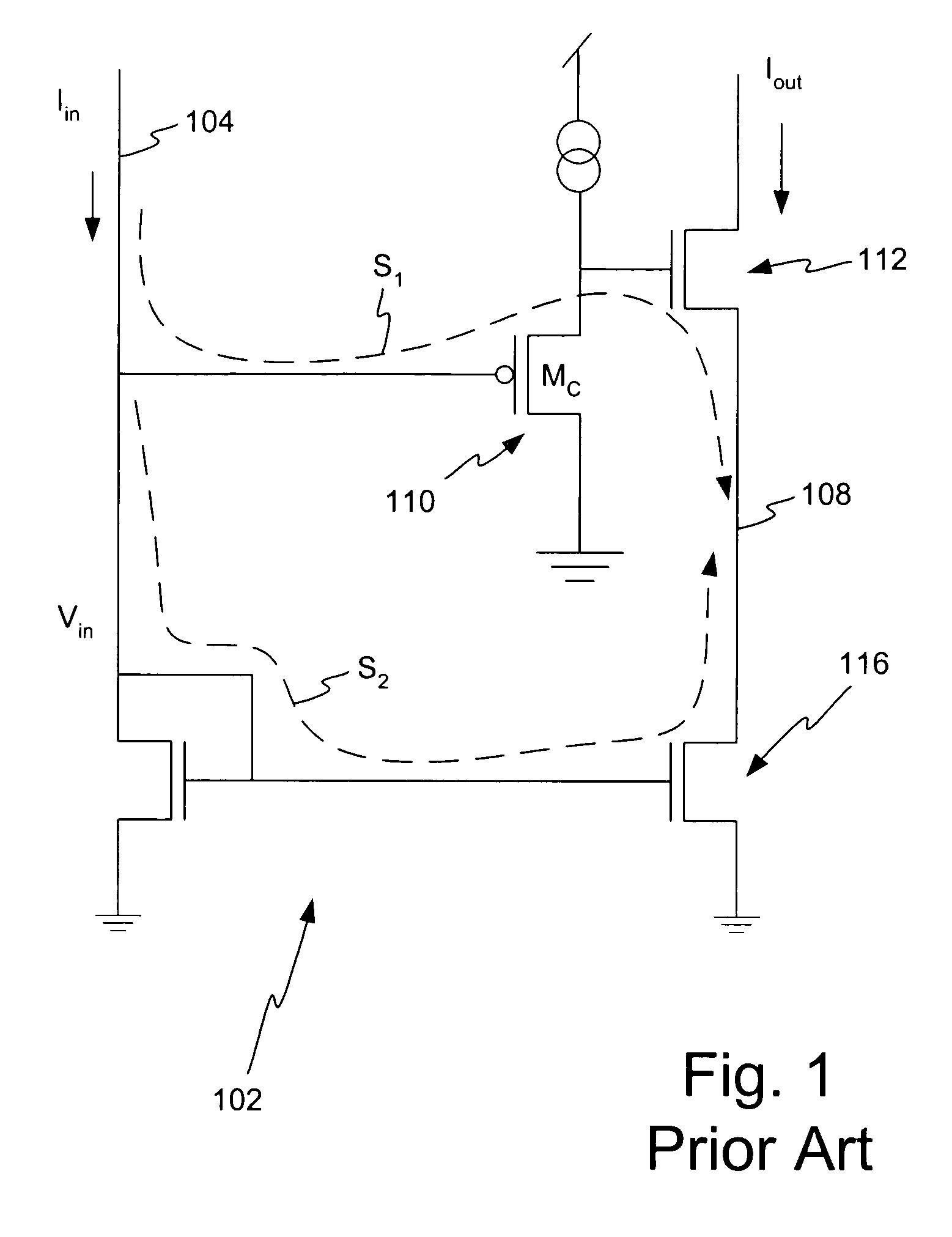
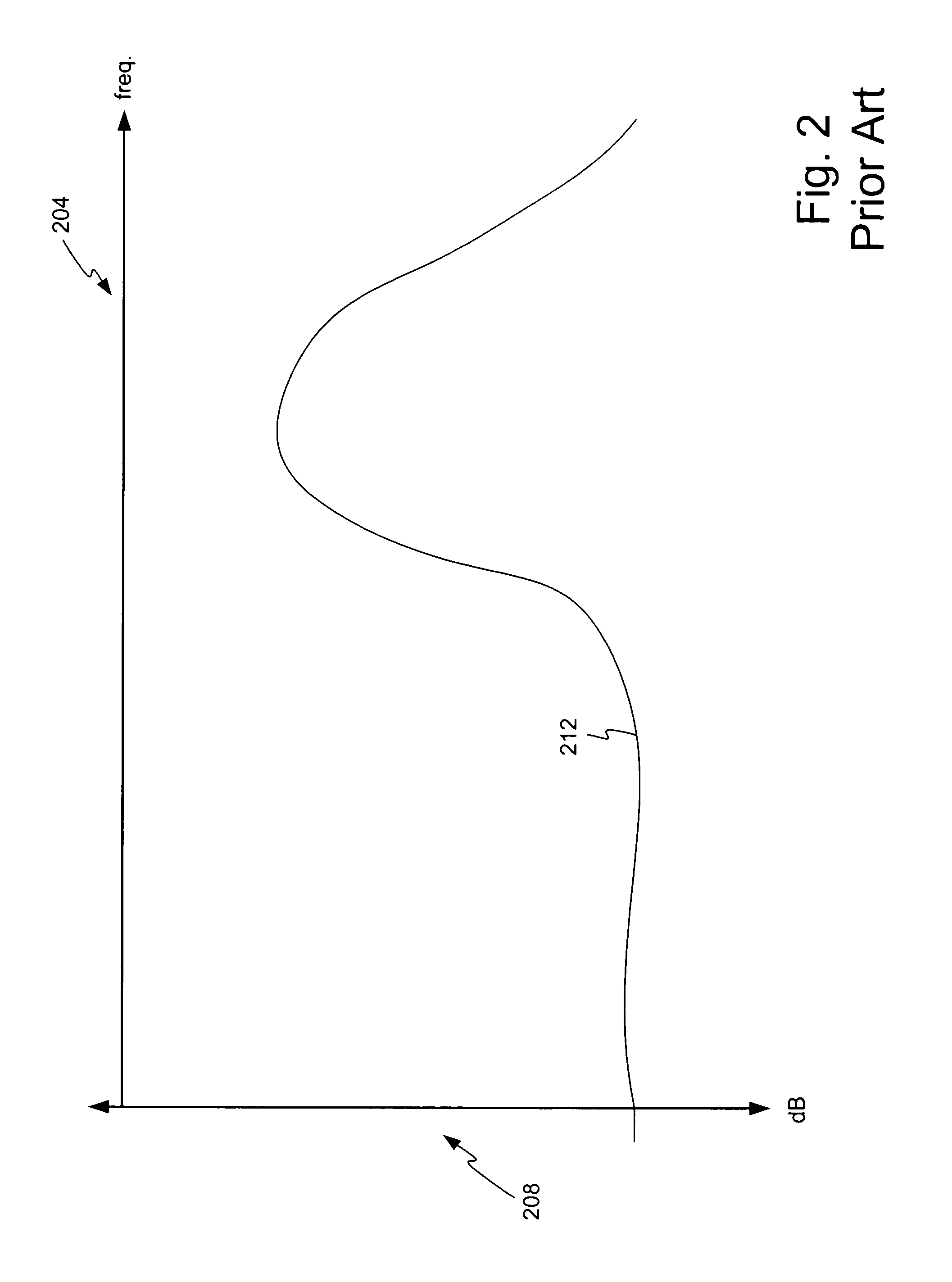
Method and apparatus for increasing the linearity and bandwidth of an amplifier
ActiveUS20050083130A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric variable regulationCascodeEngineering
A method and apparatus is disclosed for improving high frequency performance of an amplifier, such as for example, a current mirror. In one embodiment, a delay element is introduced in a current mirror signal path to account for signal propagation delay that may exist in one or more alternative signal paths. The delay element maintains desired phase alignment at a cascade node of the current mirror thereby establishing, in one embodiment, the cascode node (Vc) in an AC ground state. To extend current mirror high frequency capability an embodiment is disclosed having cross-coupled capacitors, active elements, or one or more other devices configured to provide positive feedback to one or more current mirror inputs. The positive feedback may be selectively configured to increase the operational bandwidth of the current mirror.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Revenue class power meter with frequency rejection
Owner:POWER MEASUREMENT LTD
System for motion control, method of using the system for motion control, and computer-readable instructions for use with the system for motion control
InactiveUS7024257B2Reduce needError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsFiberPropagation delay
Owner:MOTION ENG
Optical waveguide and method for producing same
InactiveUS7306689B2Avoid low lightInexpensively formedLaser detailsDecorative surface effectsLow speedLight signal
An optical waveguide having a optical waveguide path capable of securing a high light propagation characteristic regardless of the type of a supporting base, provided with a multilayer circuit board, an optical waveguide path arranged on the multilayer circuit board, a light receiving element, IC chips, and a light emitting element, the optical waveguide path formed on a transparent substrate excellent in flatness and transferred to the multilayer circuit board. The light propagation loss becomes small, and a signal to be transmitted at a high speed being transmitted as a light signal and a signal which can be transmitted at a relatively low speed being transmitted as an electrical signal, whereby the signal propagation delay which becomes the problem when a signal is transmitted by only electrical wiring is overcome, and the influence of electromagnetic noise becomes small.
Owner:SONY GRP CORP
System and method for communication utilizing time division duplexing
InactiveUS20070184778A1Radio transmissionWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemEngineering
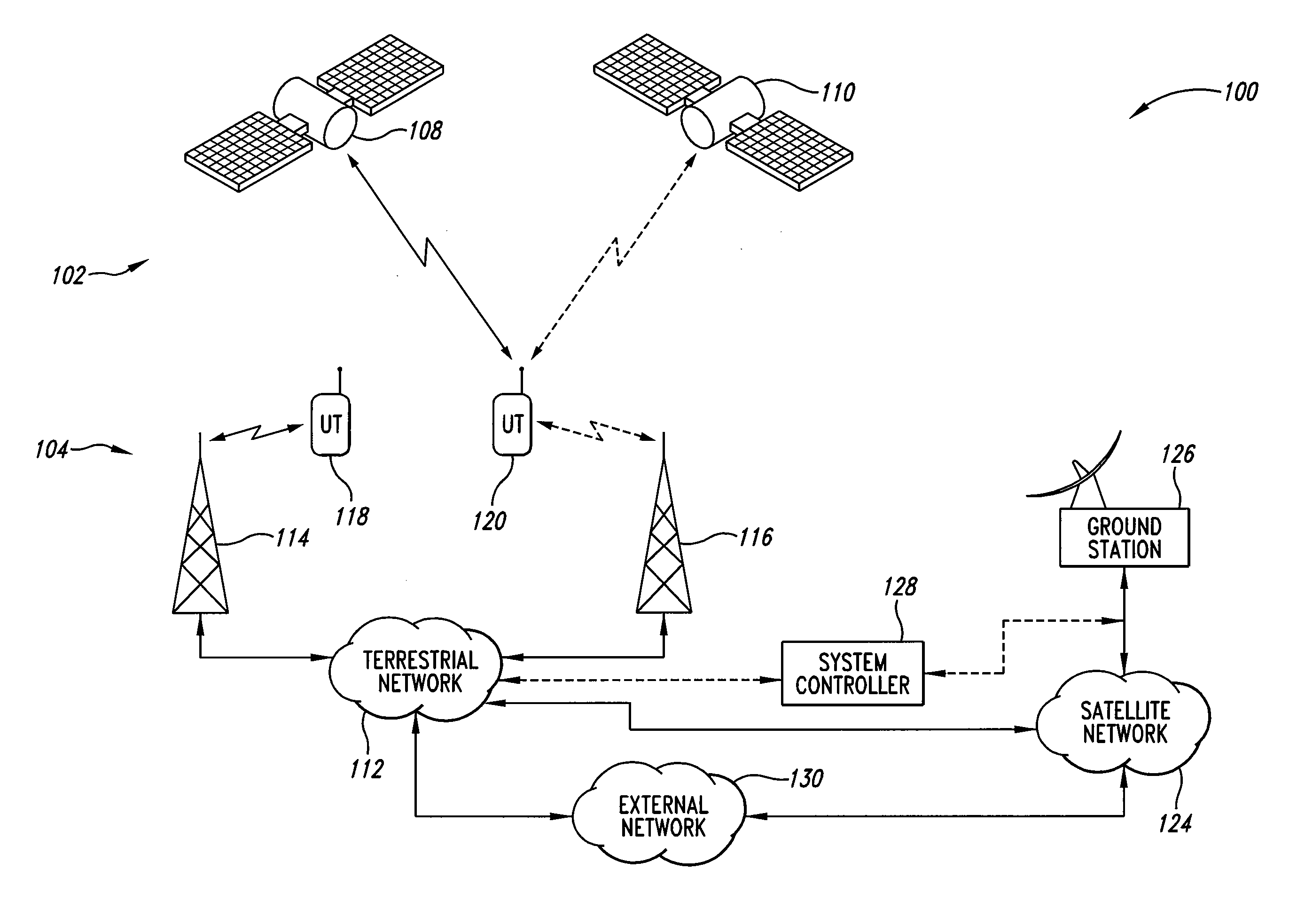
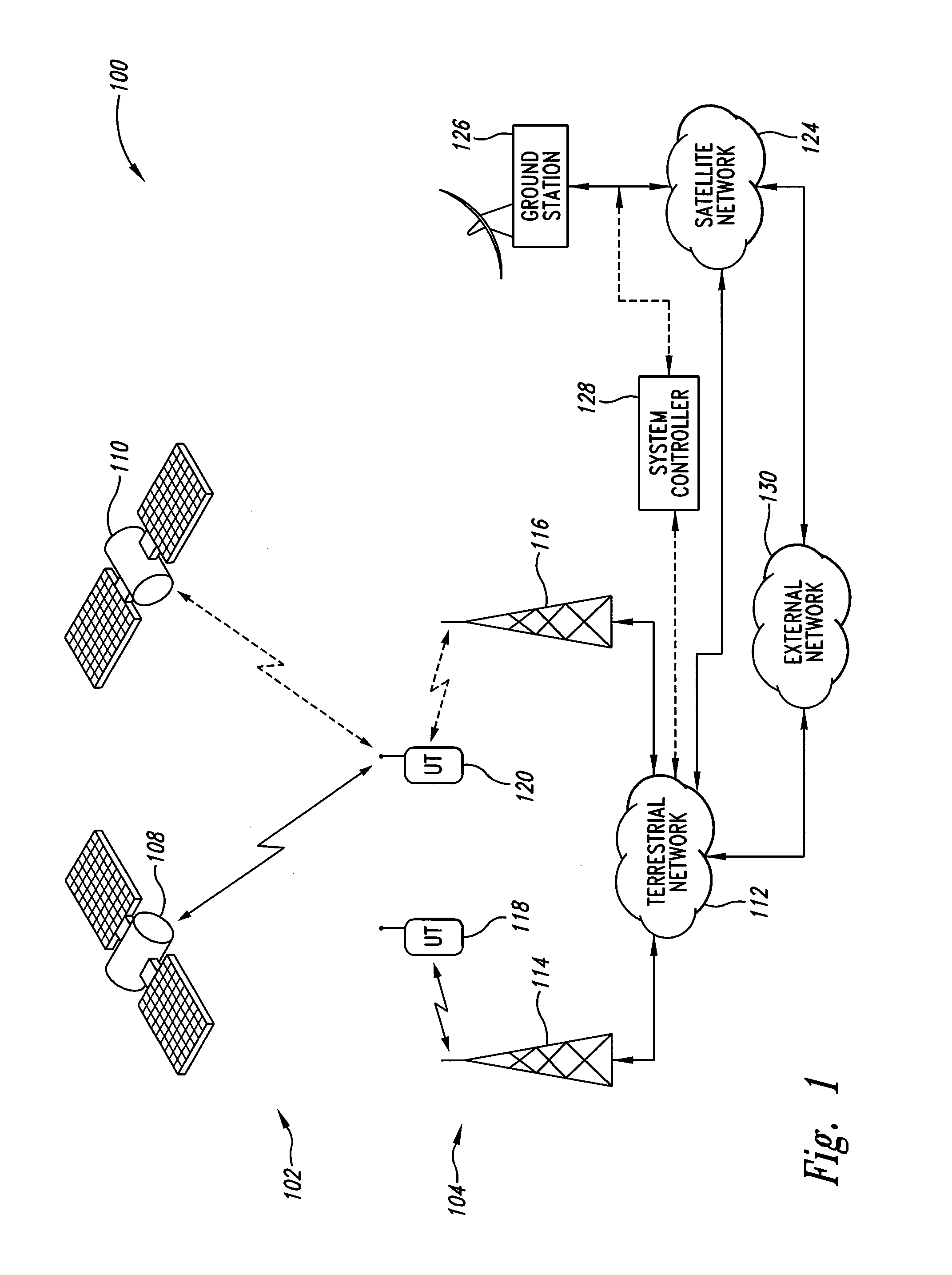
An integrated communication system includes a satellite portion and a terrestrial portion. A plurality of timeslots are allocated for transmission and reception of data by the various components of the satellite portion and terrestrial portion. The allocation of timeslots to the satellite portion and the terrestrial portion may be predetermined or dynamically allocated based on traffic loads, time of day, day of week, and the like. Communication may be accomplished on a single frequency with the appropriate allocation of timeslots. The system includes delay compensation to accommodate signal processing delays and signal propagation delays. For example, a satellite may be instructed to terminate transmission prior to the end of its allocated timeslot to permit the signal from the satellite to propagate to its intended destination within the allocated timeslot to thereby avoid spillover into the next timeslot. This avoids interference between various elements of the communication system.
Owner:MOBILESPHERE HLDG
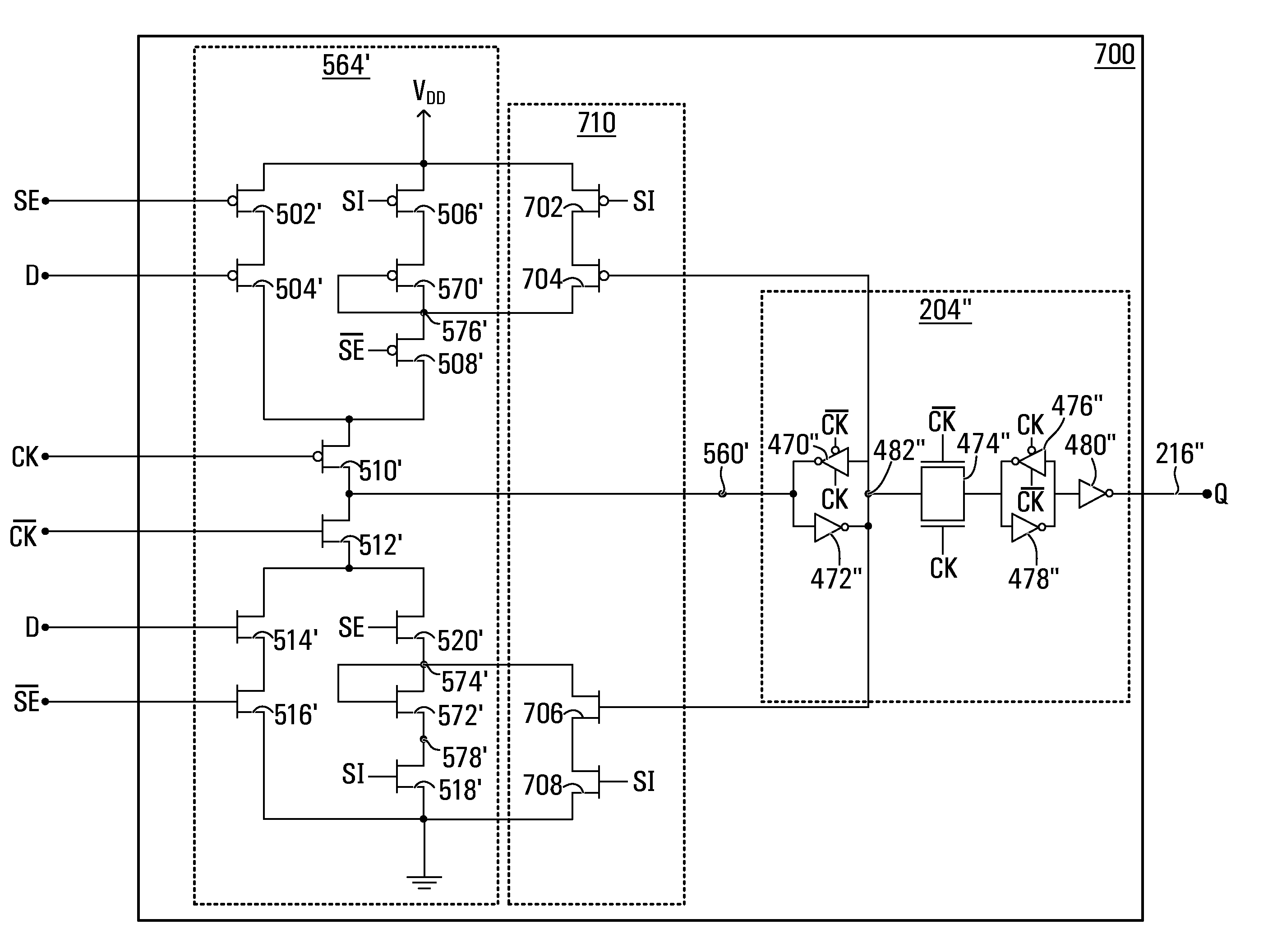
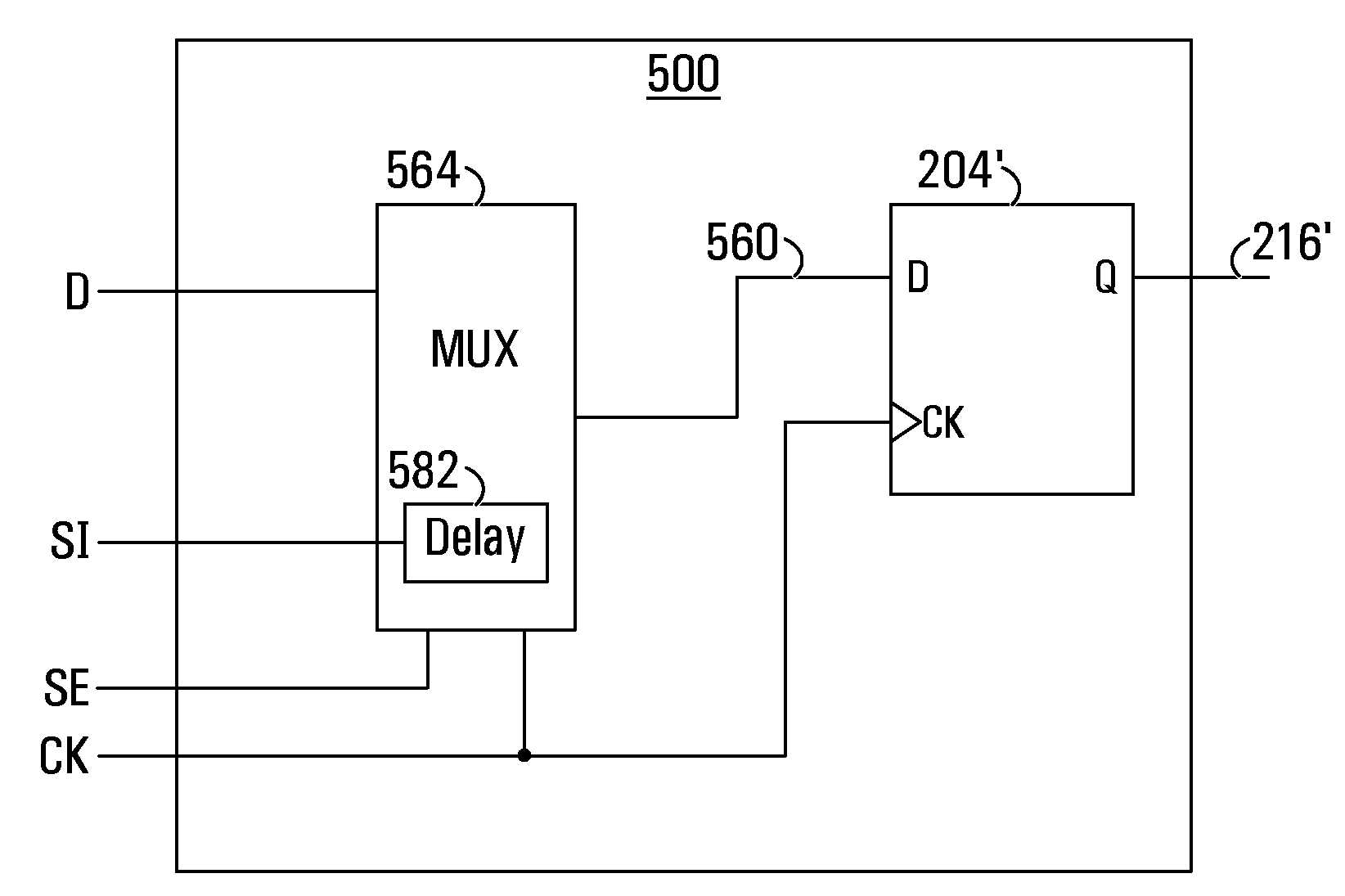
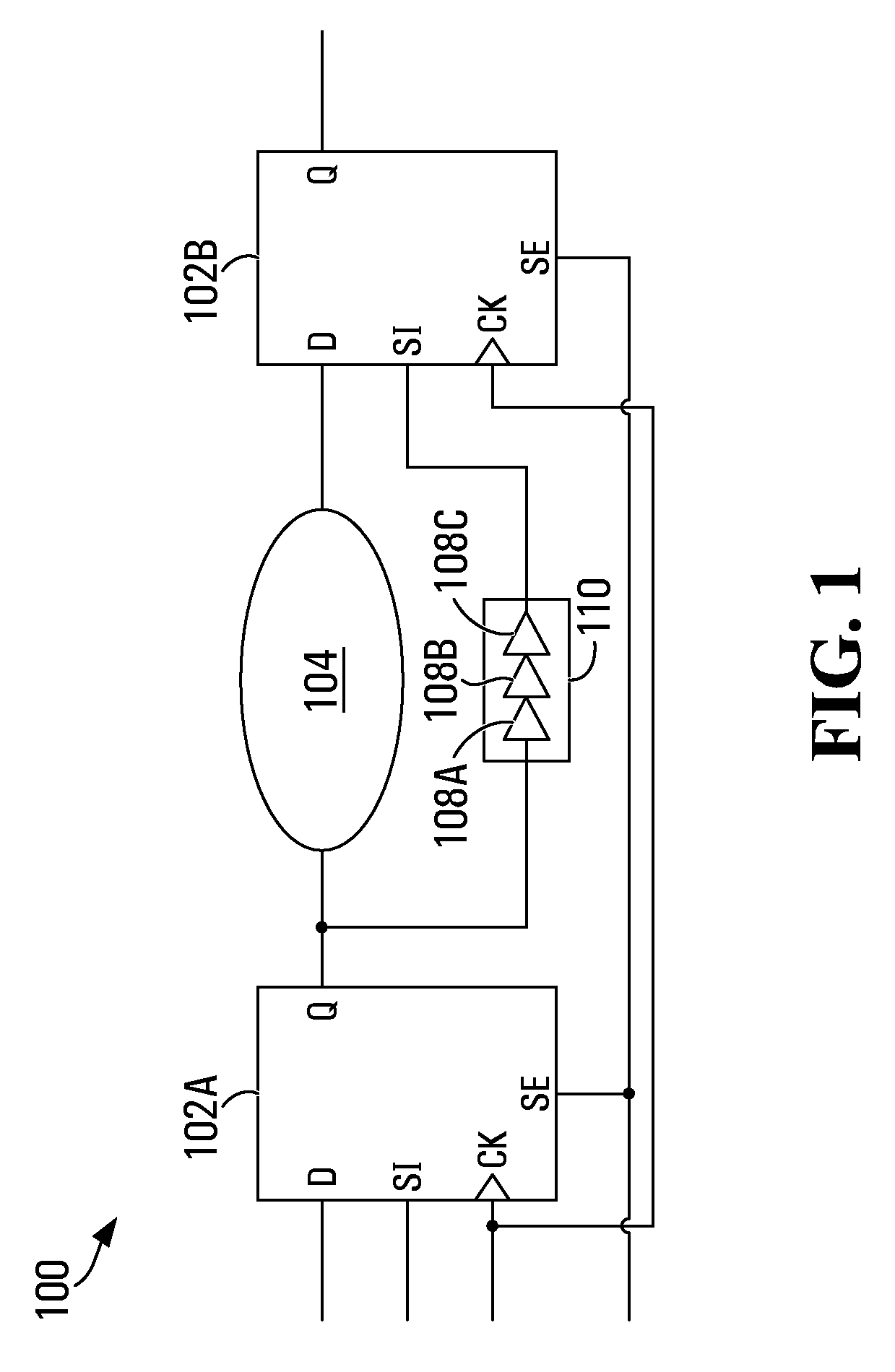
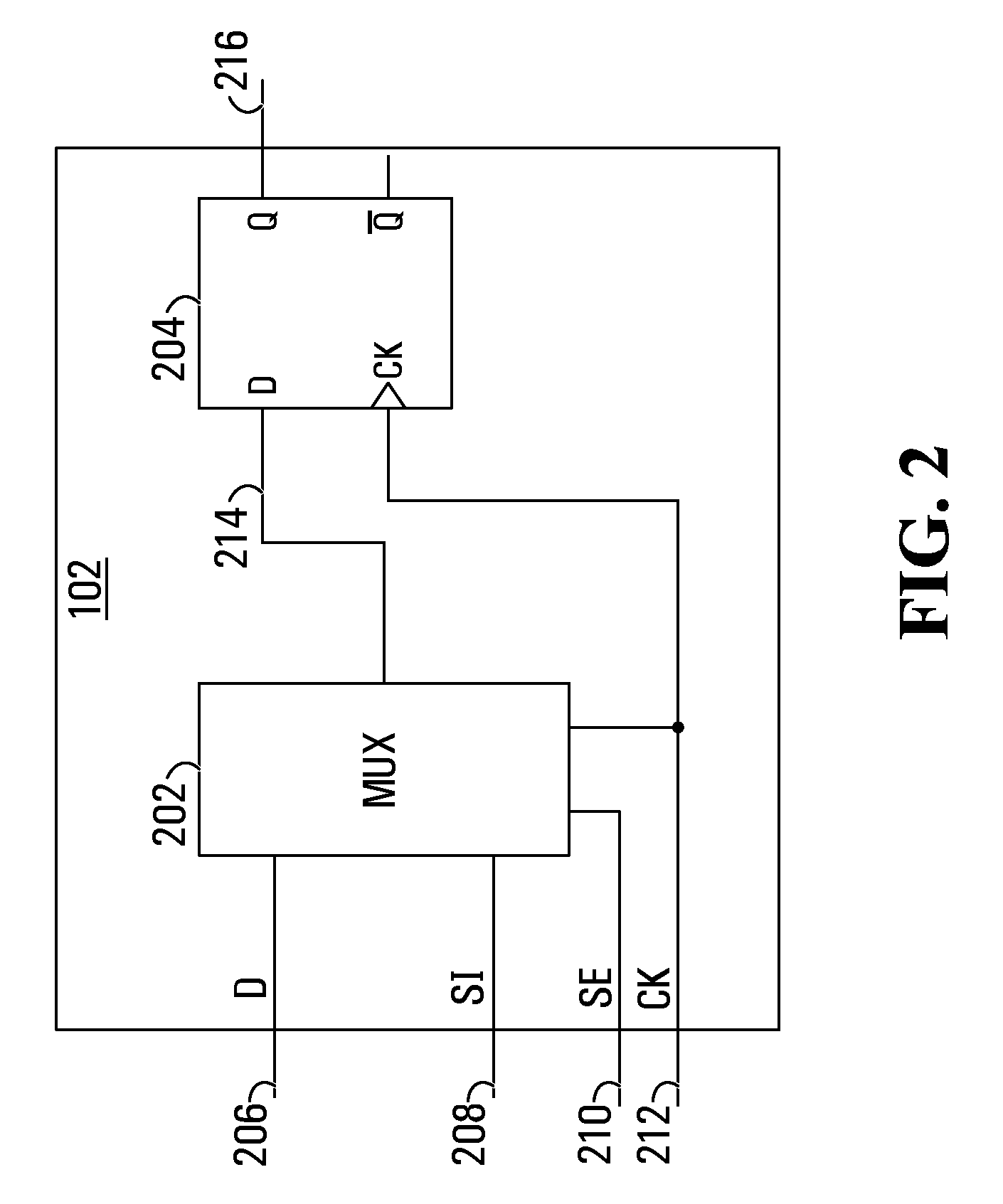
Scan flip-flop with internal latency for scan input
A scan flip-flop circuit including a data input, a scan input, a data output, a flip-flop, a multiplexer and a delay element is provided. The multiplexer allows selection of either the scan input or the data input for presentation at the input of the flip-flop. The flip-flop provides an output signal at the output of the scan flip-flop. The delay element is in a signal path between the scan input and the input of the flip-flop, and provides a signal propagation delay between the scan input and the input of the flip-flop. The delay between the scan input and the input of the flip-flop is substantially larger than the signal propagation delay between the data input and the input of the flip-flop. The delay in the scan path reduces the need for external buffers to avoid hold-time violations during scan testing of integrated circuits.
Owner:CHRONOCLOUD MEDTECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Circuit and method for correcting skew in a plurality of communication channels for communicating with a memory device, memory controller, system and method using the same, and memory test system and method using the same
ActiveUS20100153792A1Reducing and eliminating skewError detection/correctionRecord information storagePropagation timeMemory circuits
In a circuit and method for correcting skew among a plurality of communication channels used in communicating with a memory circuit, and in a memory controller and memory controlling method, and in a memory system and method, the circuit for correcting skew includes a transmitting circuit for transmitting a reference signal to input ends of the plurality of channels and through the plurality of channels, and a plurality of receiving circuits for receiving at the input ends of the plurality of channels a respective plurality of reflected signals, the reflected signals being reflected from respective output ends of the plurality of channels. A detection circuit receives the reflected signals and detects relative signal propagation time differences between the plurality of channels. A delay circuit coupled to at least one of the channels sets a signal propagation delay in the at least one of the channels based on the detected relative signal propagation time differences.
Owner:MGP MFG +1
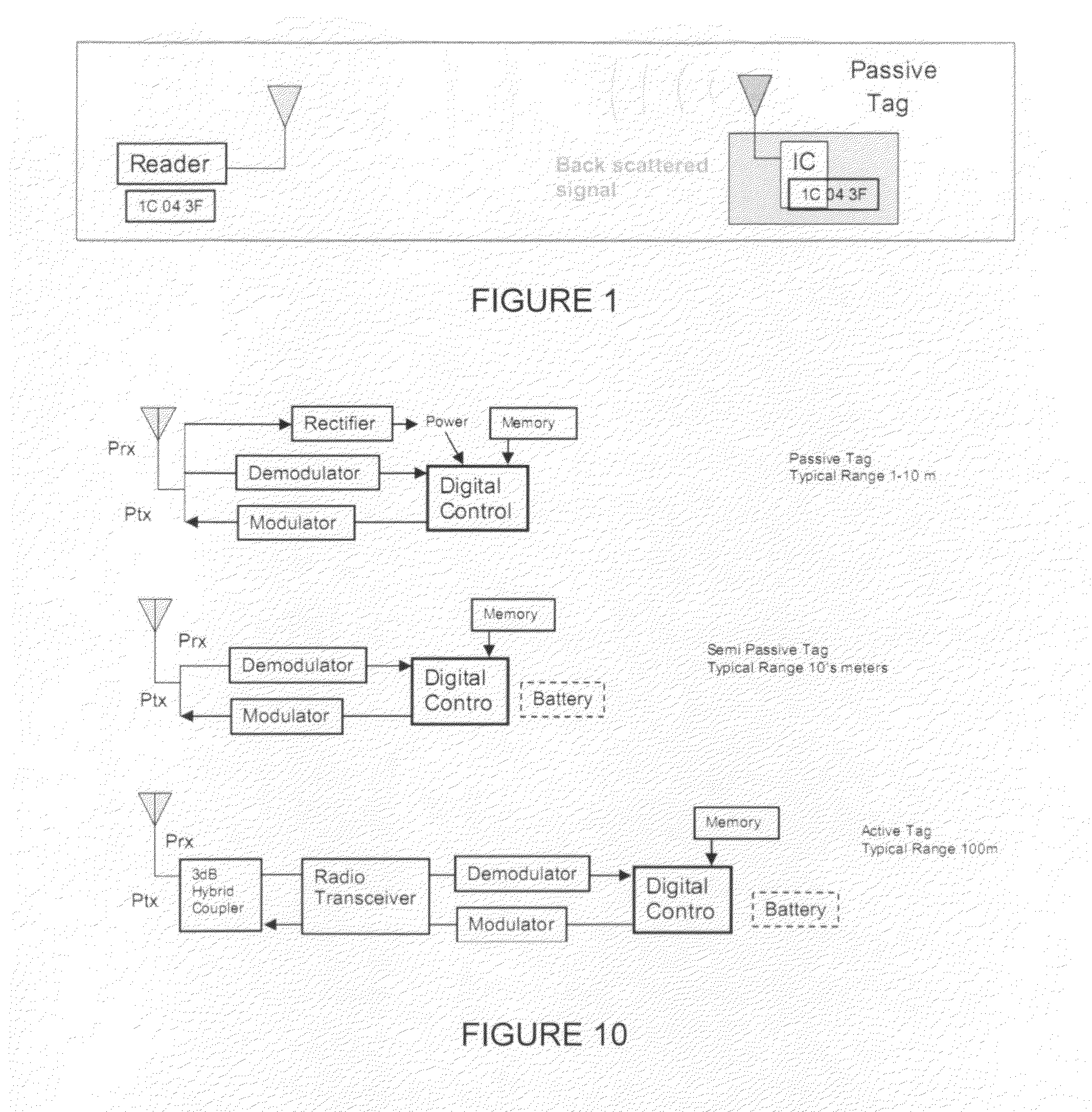
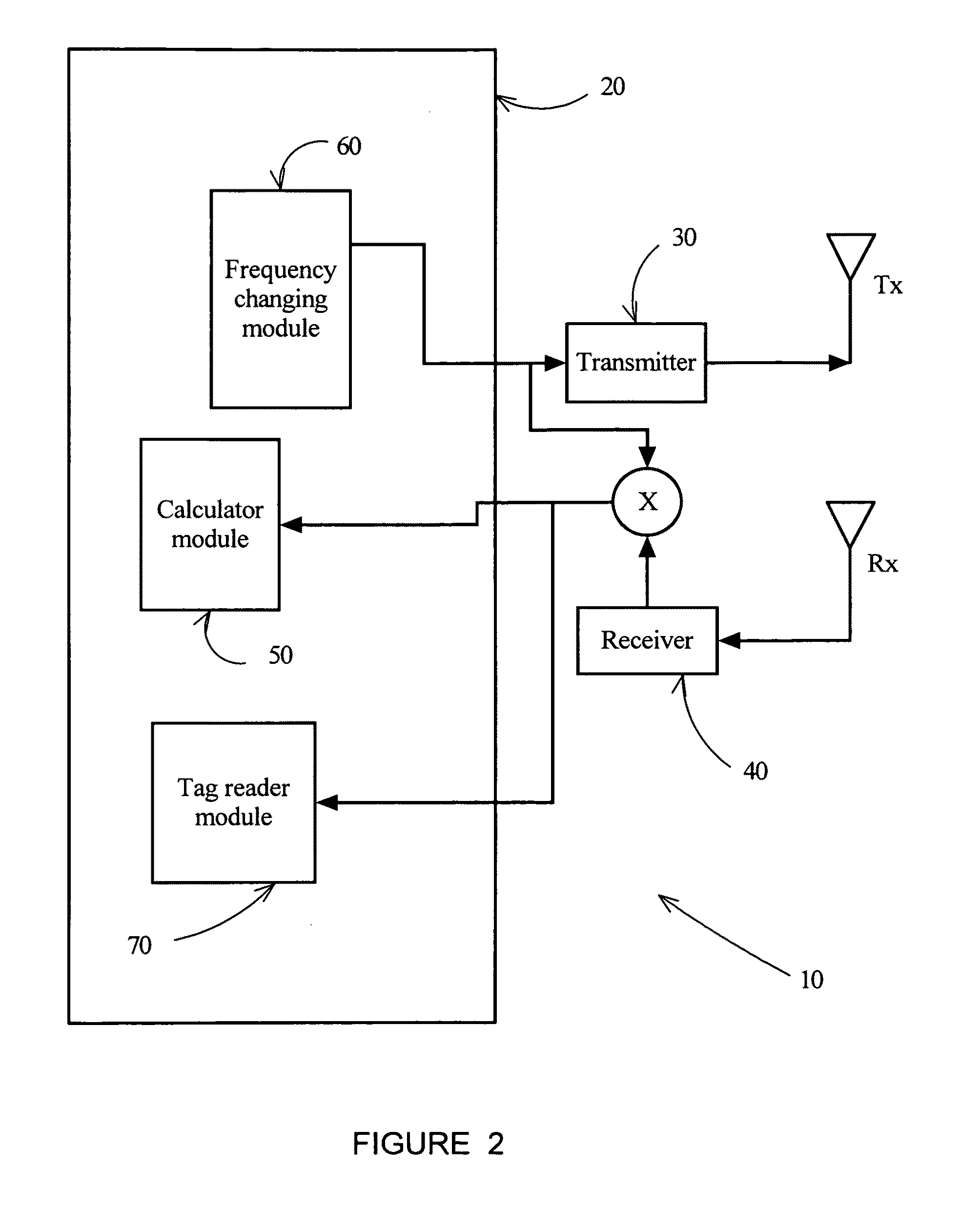
Passive RFID tag reader/locator
InactiveUS20110109442A1Memory record carrier reading problemsSubscribers indirect connectionPropagation delayCarbon footprint
Systems and methods for use in reading and locating passive RFID tags. A reader / locator system sends out a signal with varying frequency. A tag reflects the signal back and the receiver portion of the reader / locator system receives the signal after a certain propagation delay. Since during this propagation delay the transmit frequency has changed, the received signal frequency differs from the one is currently transmitted. The received signal gets mixed with the currently transmitted signal and the resulting beat frequency depends on the frequency variation pattern (which is known) and the signal propagation delay. This beat frequency is directly proportional to the distance between the reader / locator and the RFID tag. The beat frequency can therefore be used to estimate this distance between the reader / locator and the RFID tag. Also provided are methods for determining if an incoming signal is data bearing and a method to obtain a cleaner incoming signal by storing a “carbon footprint” or background clutter and subtracting the carbon footprint from the incoming signal. A novel type of passive RFID tag is also disclosed.
Owner:PAVLOV GEORGE +3
Method and apparatus for power consumption optimization for integrated circuits
InactiveUS7551985B1Minimize power consumptionMeet Timing RequirementsMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlEngineeringIntegrated circuit layout
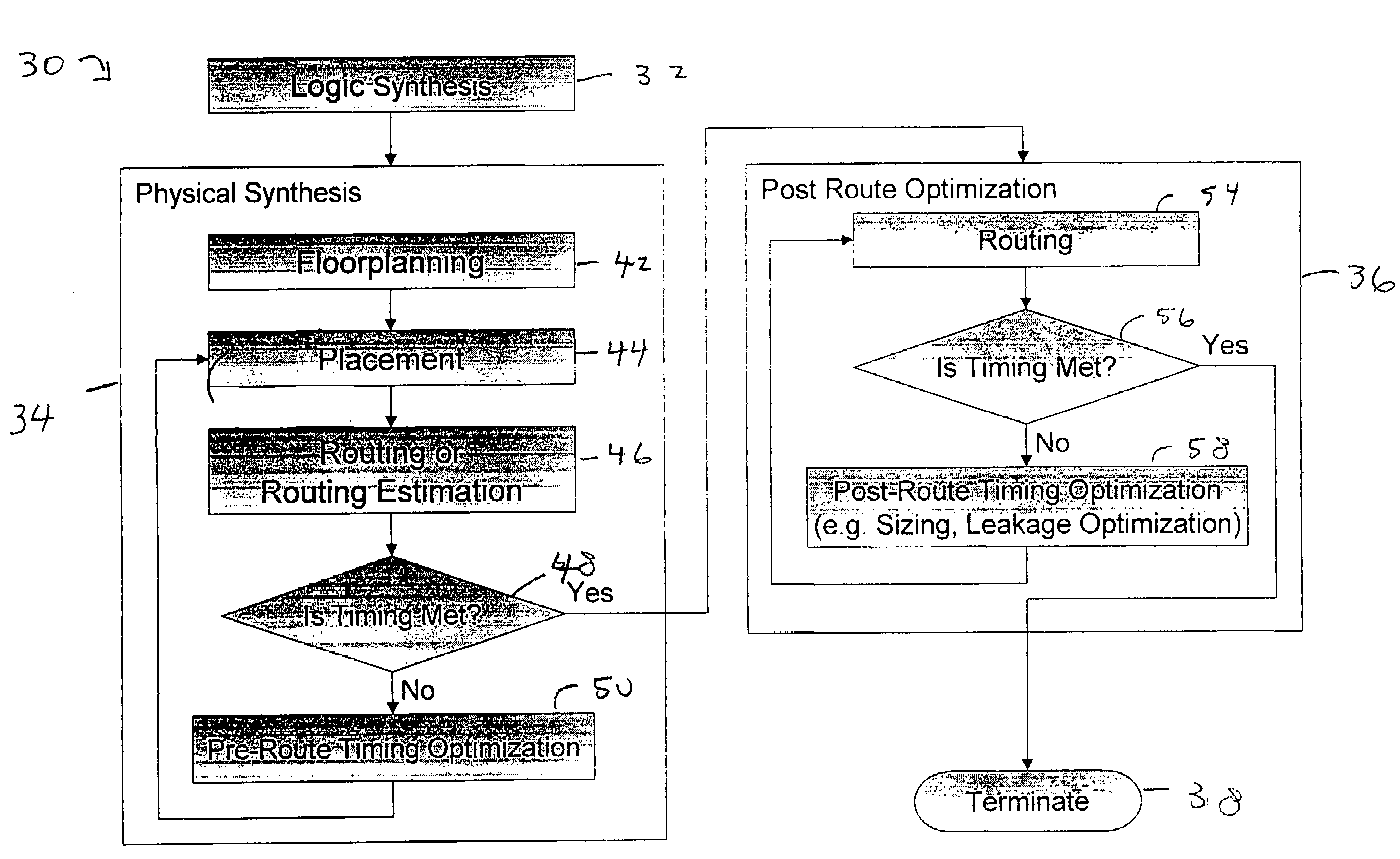
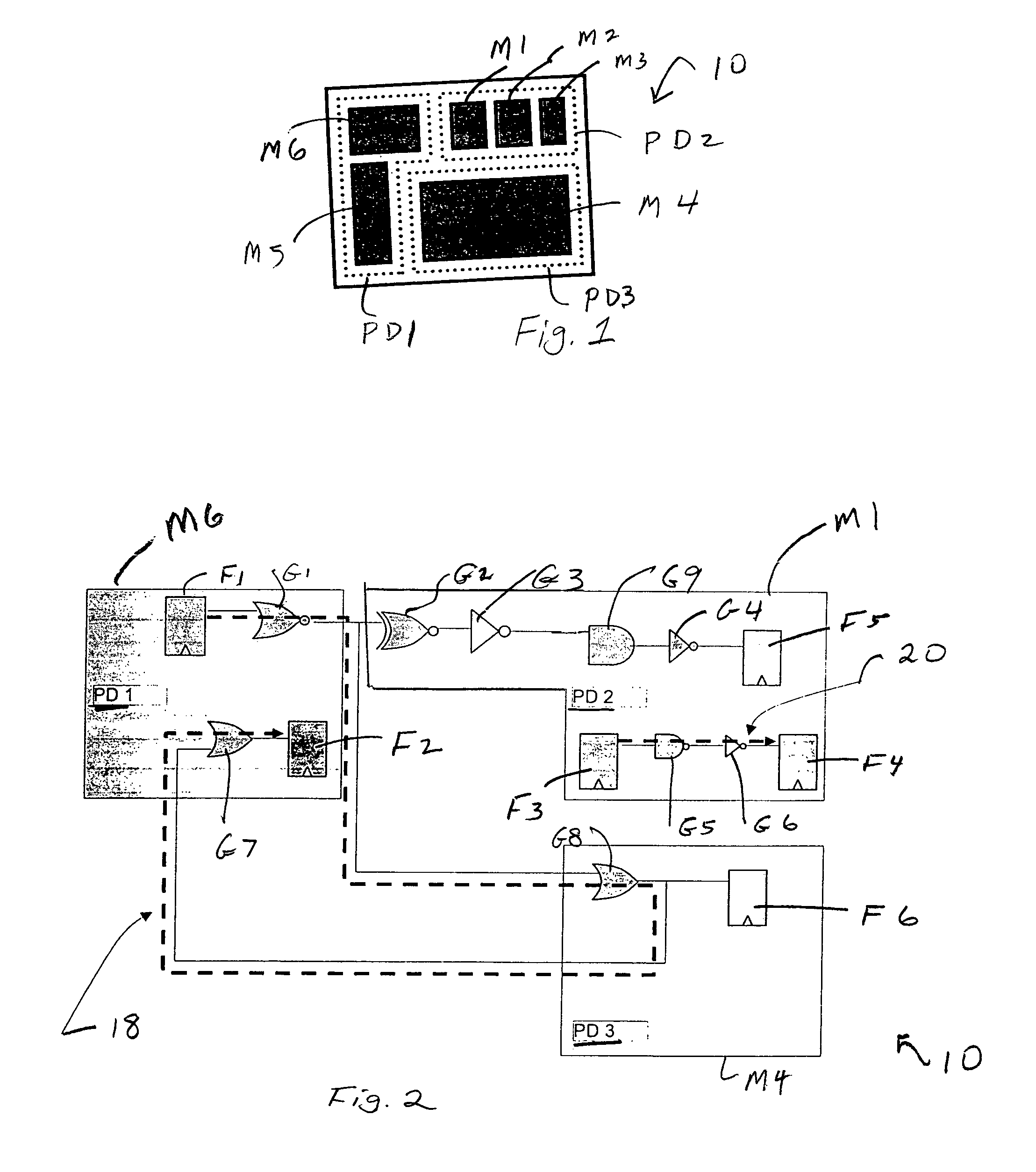
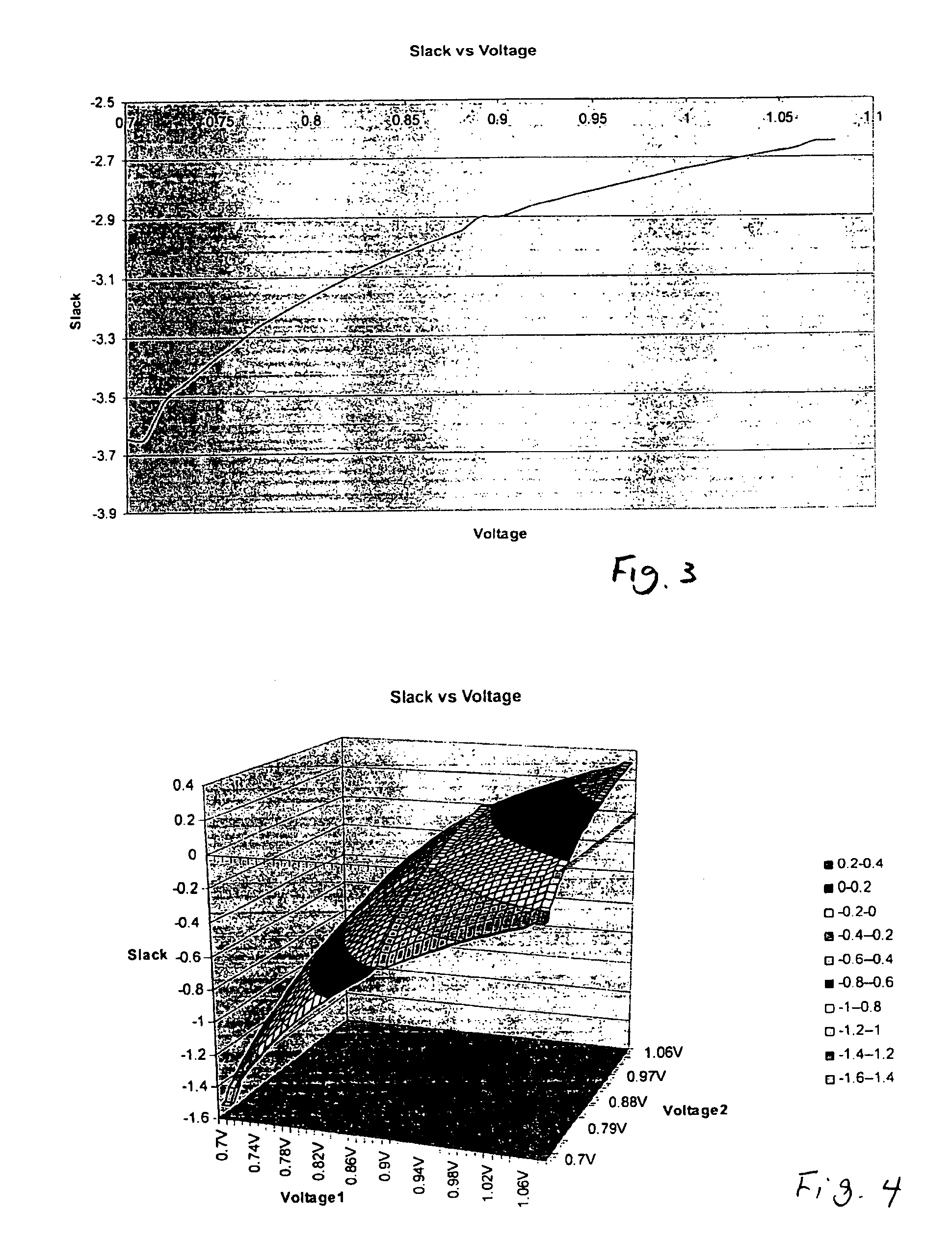
Method and apparatus for finding an assignment of voltages to all power domains of an integrated circuit such that the power consumption of an integrated circuit design is minimized and timing requirements (signal propagation delay or slack) are met. This is done by modeling both internal and external signal paths in an integrated circuit which has a number of power domains. The relationship between slack and voltage for the external and internal signal propagation paths is modeled, typically as a linear approximation. The integrated circuit design is then abstracted to a simplified form in terms of power domain relations and a model is created and solved iteratively using, e.g., linear programming, of different voltage levels for each power domain and including the slack values and their relationship between the changes in voltage and slack, for both the internal and external paths.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
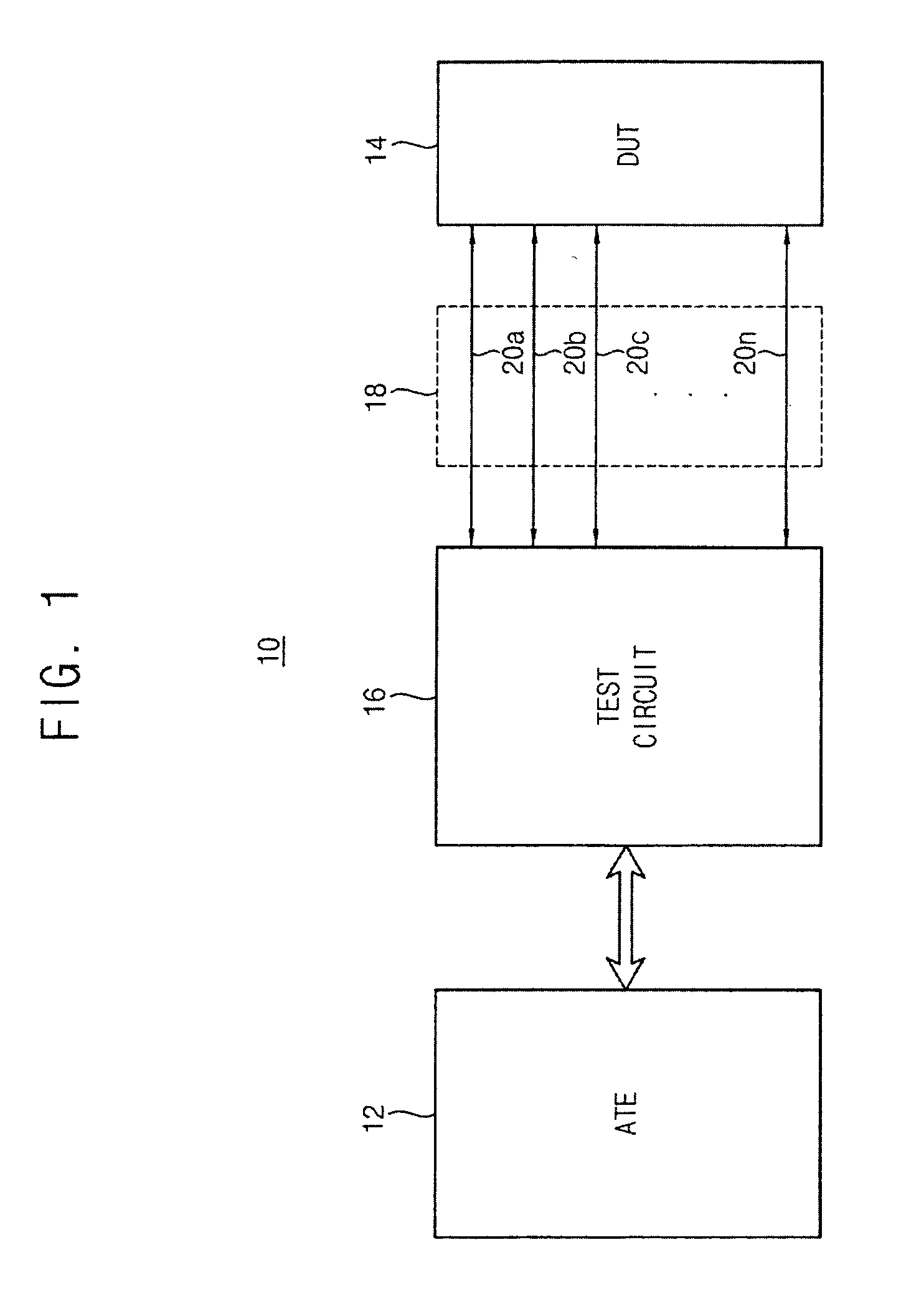
Apparatus and method for testing a plurality of devices under test
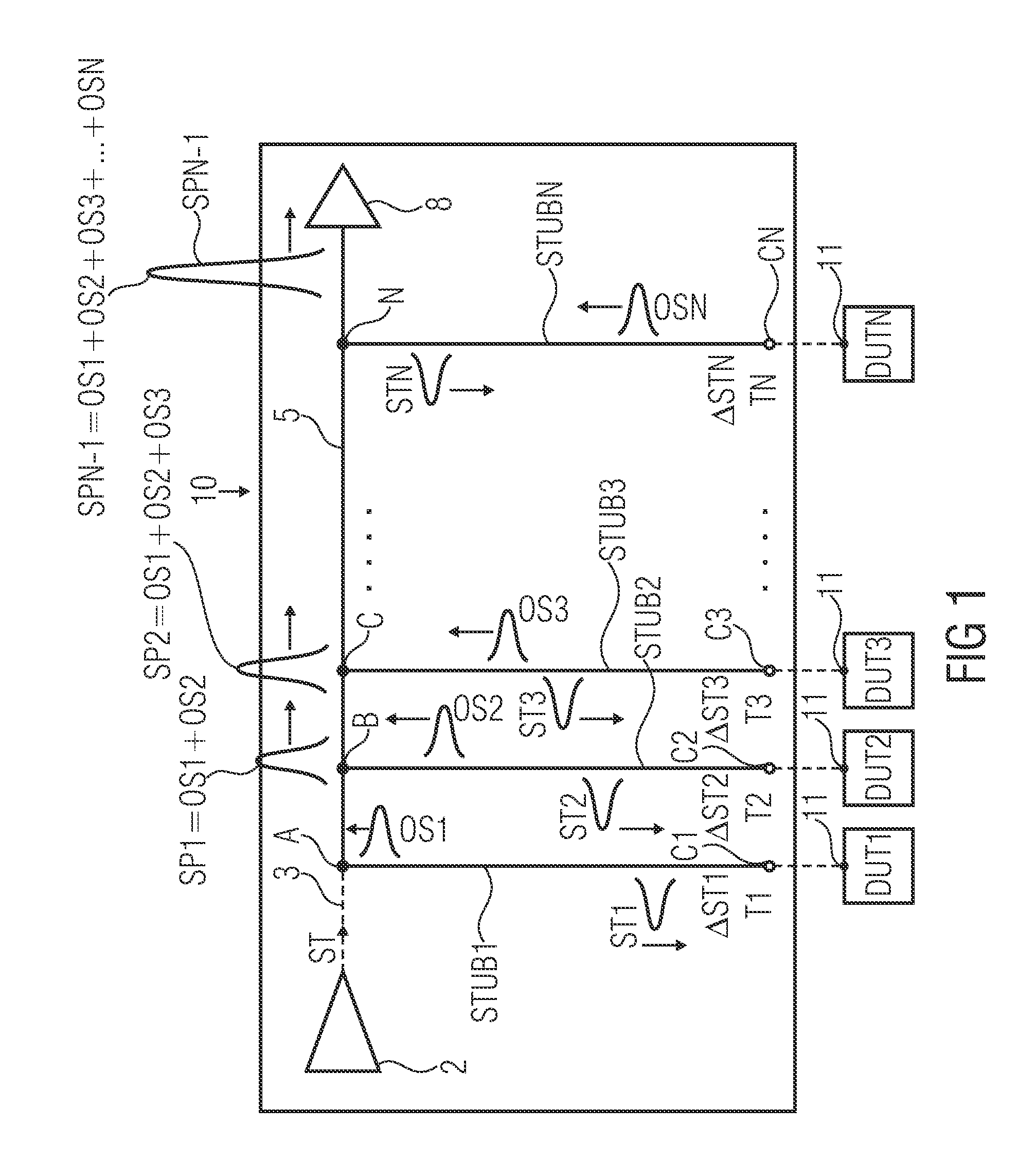
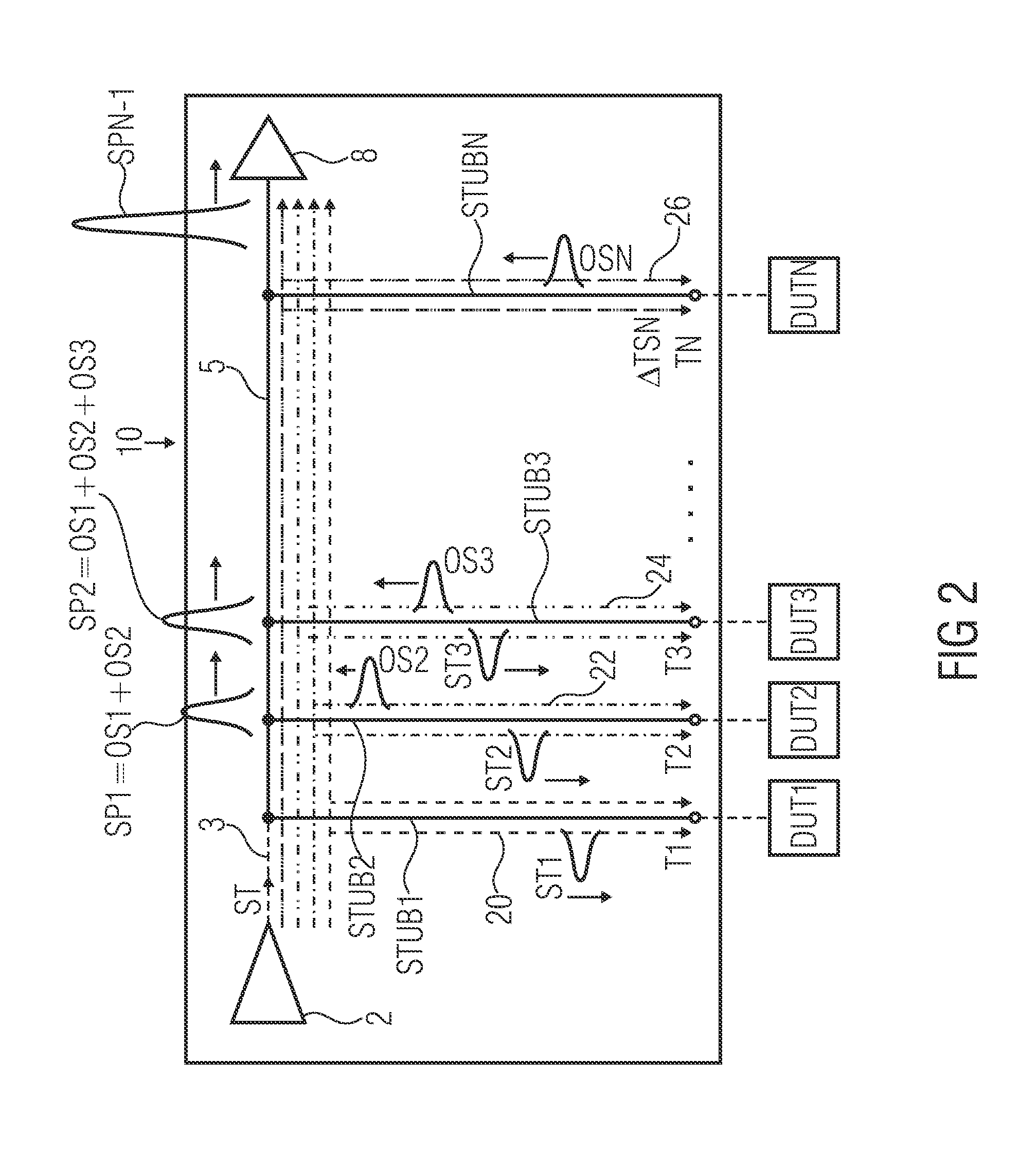
ActiveUS20130234723A1Improve resource efficiencyReduce in quantityDigital circuit testingElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectricityResponse delay
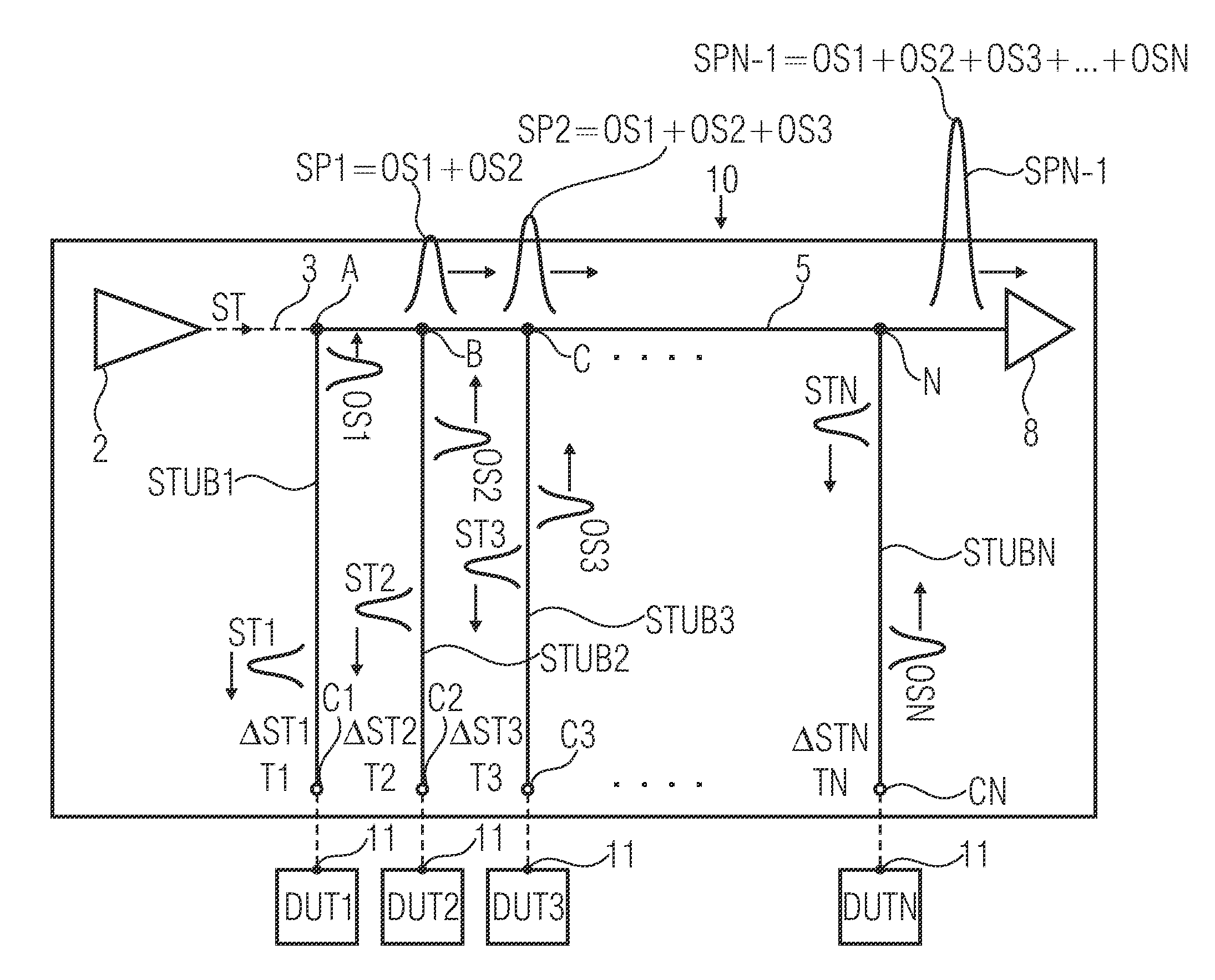
Embodiments of the invention relate to an apparatus and a method for testing a plurality of devices under test. The apparatus for testing a plurality of devices under test comprises a common device output line and a driver unit configured to provide a stimulus to the DUTs. The driver unit is configured such that the stimulus reaches different DUTs at different times, thereby creating stimuli time shifts at the DUTs. The apparatus further comprises a receiver unit electrically coupled to the common device output line and a plurality of DUTs connections, electrically coupled to the common device output line, so that DUT terminals of the plurality of DUTs are electrically coupleable via the common device output line to the receiver unit. Output signal propagation delays for DUT output signals, propagating from the DUT connections to the receiver unit, are adapted to the stimuli time shift, such that a test of DUTs which have identical stimulus response delays, results in a temporally aligned superposition of the DUT output signals at the receiver unit.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
Optical waveguide and method for producing same
InactiveUS20050100298A1Avoid low lightInexpensively formedLaser detailsCladded optical fibreLow speedLight signal
An optical waveguide having a optical waveguide path capable of securing a high light propagation characteristic regardless of the type of a supporting base, provided with a multilayer circuit board, an optical waveguide path arranged on the multilayer circuit board, a light receiving element, IC chips, and a light emitting element, the optical waveguide path formed on a transparent substrate excellent in flatness and transferred to the multilayer circuit board. The light propagation loss becomes small, and a signal to be transmitted at a high speed being transmitted as a light signal and a signal which can be transmitted at a relatively low speed being transmitted as an electrical signal, whereby the signal propagation delay which becomes the problem when a signal is transmitted by only electrical wiring is overcome, and the influence of electromagnetic noise becomes small.
Owner:SONY CORP
Modeling interconnected propagation delay for an integrated circuit design
ActiveUS7213221B1Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationCapacitanceStart time
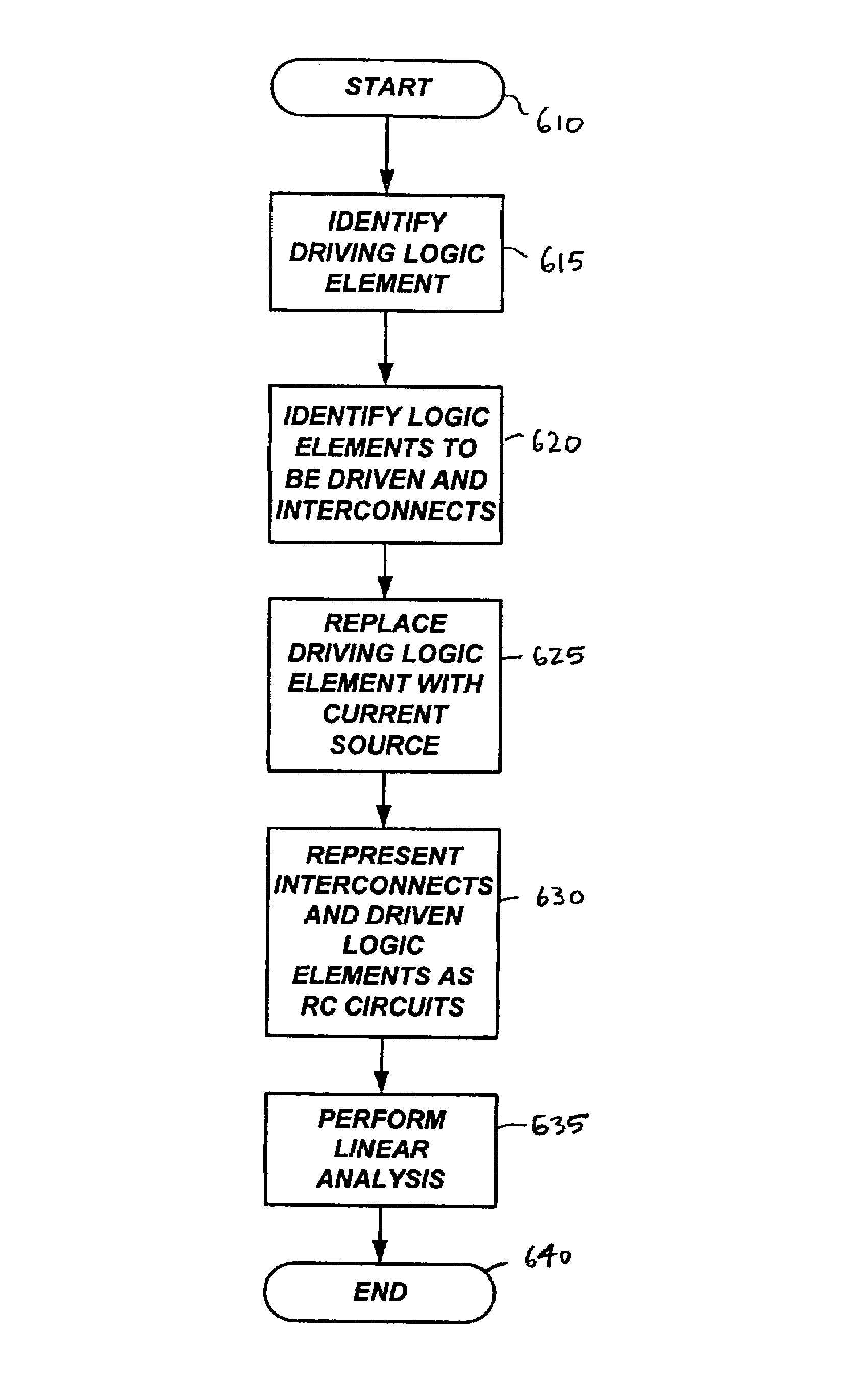
A system and a method are disclosed for performing a timing or signal propagation delay analysis on a circuit. The disclosure includes representing a drive logic stage as a representative linear circuit driven by a current source. The current source is represented as a function of a current at a constant value, a start time, a tail-start time, and a time constant of an equivalent capacitive circuit. Once the current source model is constructed, a logic stage can be analyzed for timing or signal propagation delay using conventional linear circuit analysis techniques. The disclosure also is applicable to resistance capacitance (“RC”) interconnect circuits using a current source model in which an RC load is represented as an effective capacitance and the current source for use in a linear analysis is constructed using an iterative approach.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method for calculation of cell delay time and method for layout optimization of semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS7107557B2Improve accuracyAccuracy is inferiorLogic circuits characterised by logic functionElectronic circuit testingCapacitanceEngineering
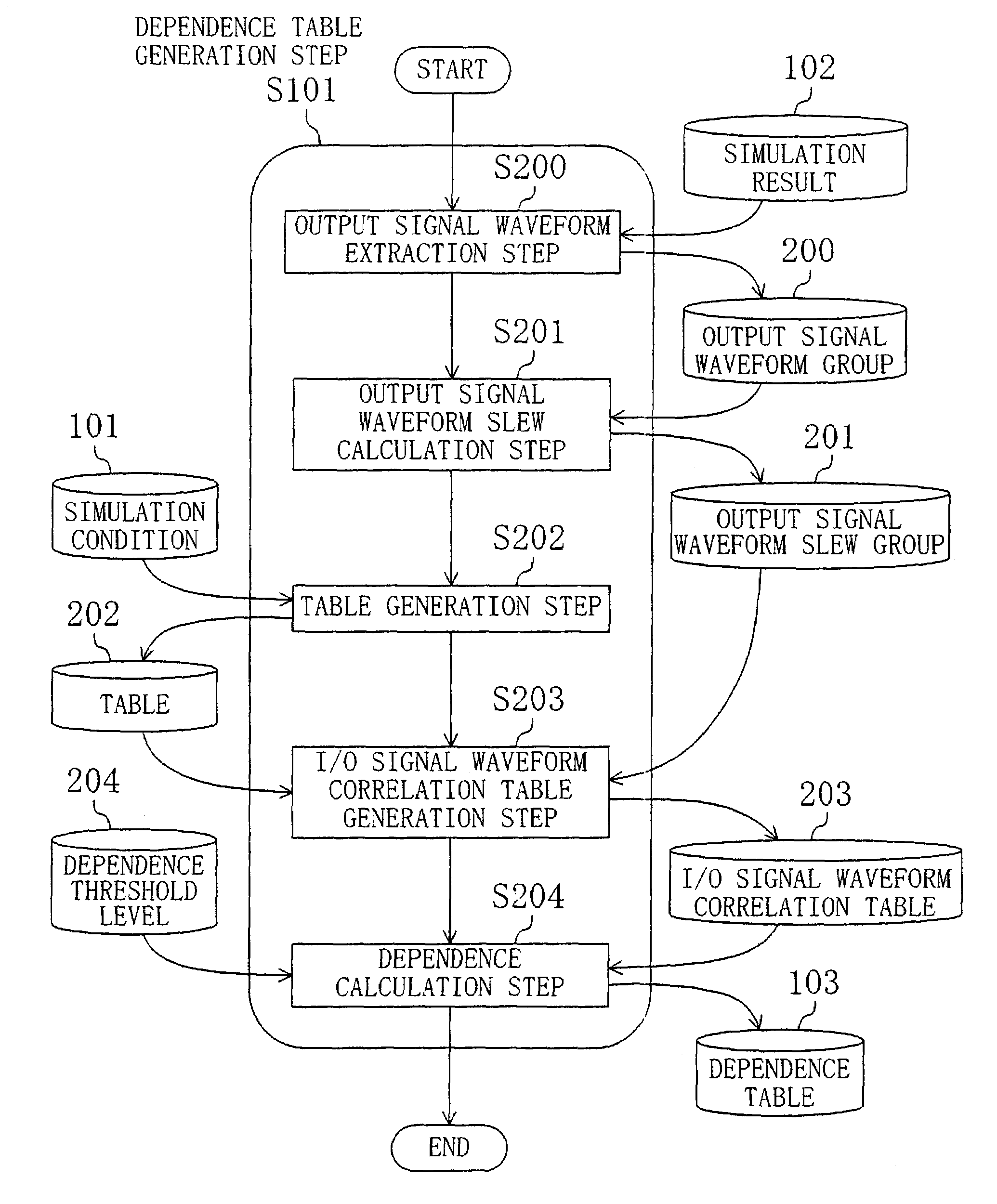
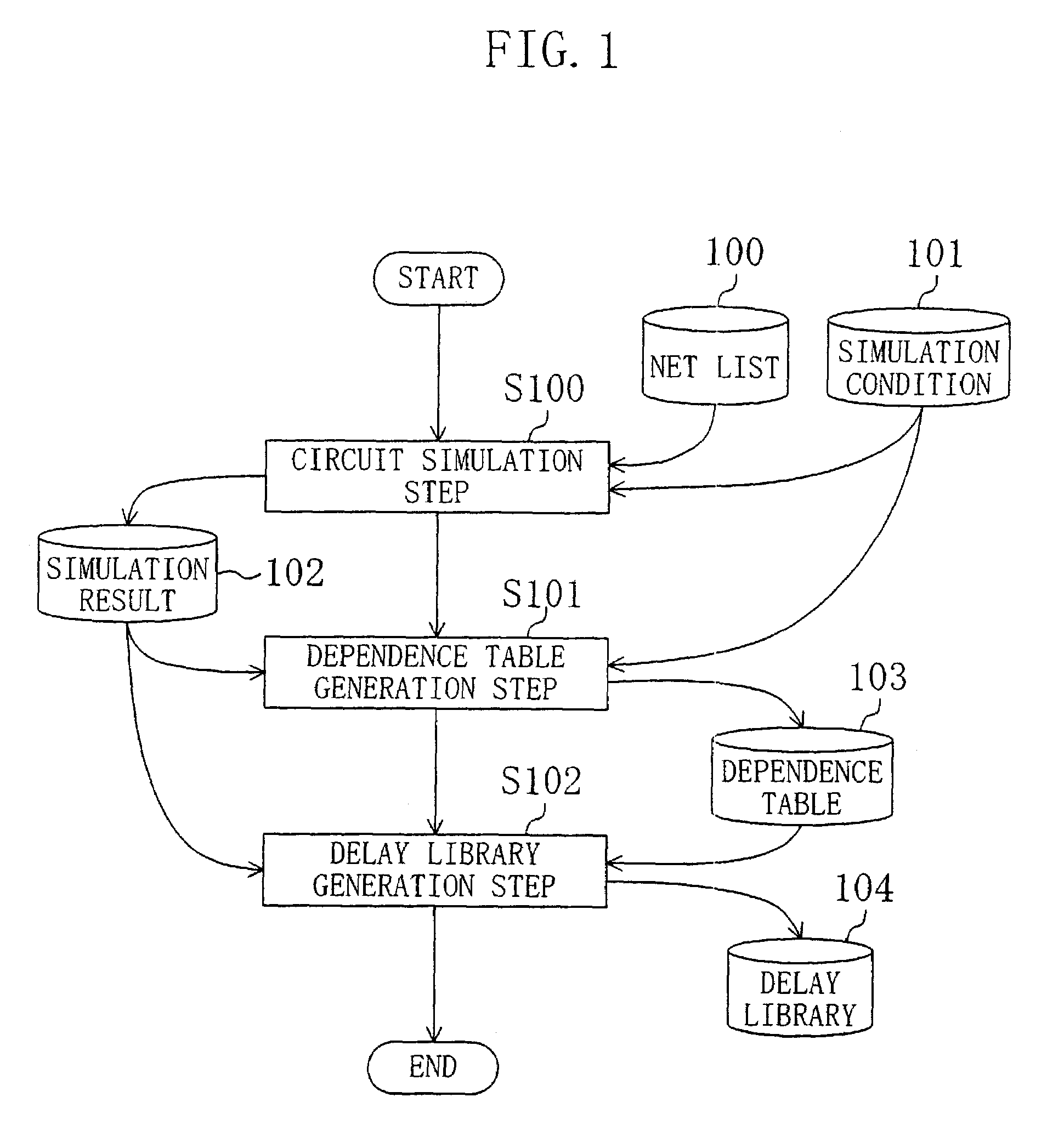
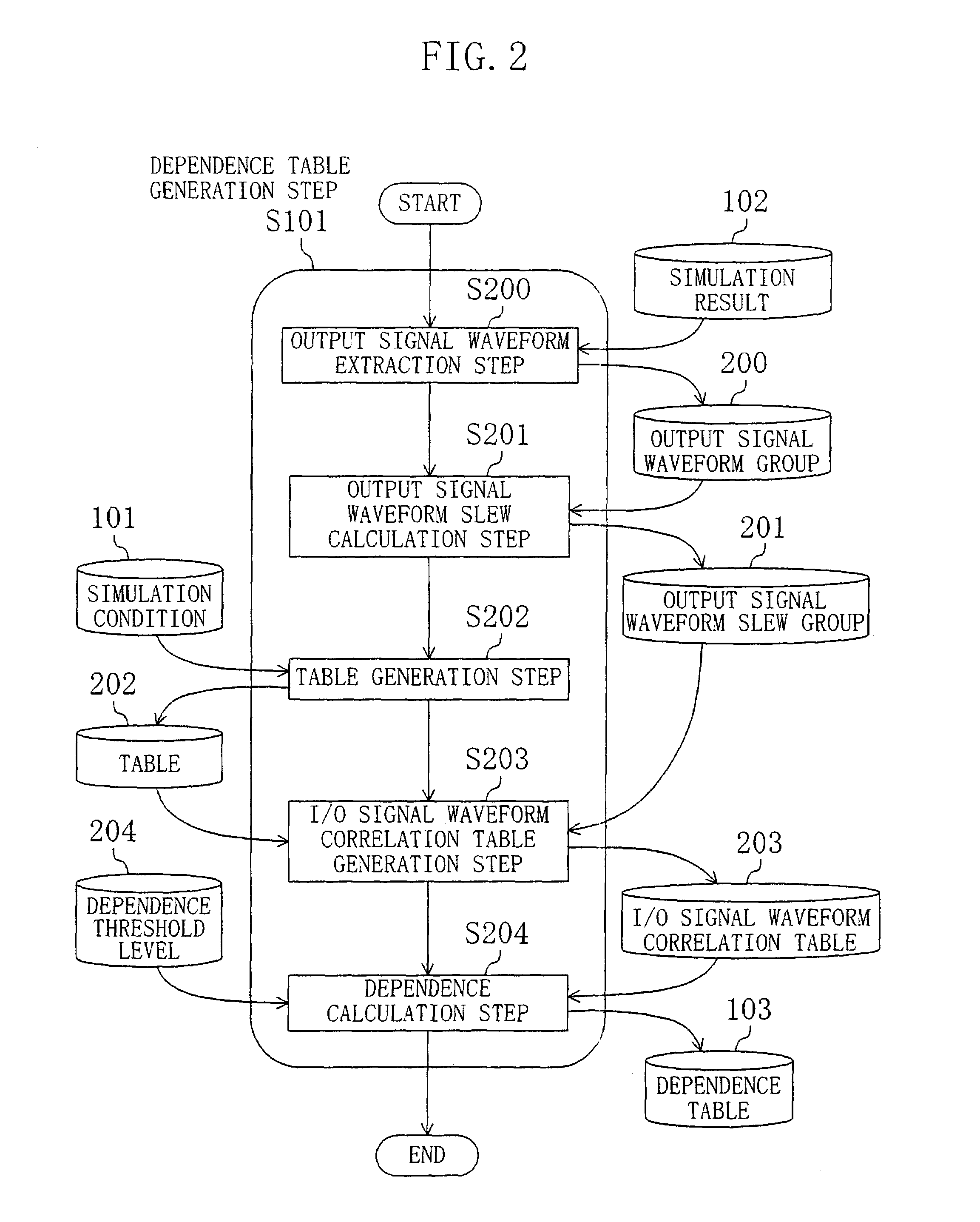
In a circuit simulation step, a cell transistor level net list is input, the slew of an input signal waveform and the magnitude of a load capacitance connected to a cell output terminal are varied for each cell, to perform a circuit simulation of each cell for obtaining an output signal waveform. Next, in a dependence table generation step, the dependence of the output signal waveform slew upon the input slew rate and the load capacitance is calculated for each cell, the dependence thus calculated is compared with a predetermined threshold level, and according to the dependence level, a delay calculation expression with consideration taken to the delay of signal propagation between the cell input and output terminals and another without such consideration are selectively used. Accordingly, the delay times of the cells forming a semiconductor integrated circuit can be calculated at high accuracy and at high processing speed.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Methods and circuits for measuring clock skew on programmable logic devices
InactiveUS6862548B1Accurately measuring skewDigital circuit testingPulse automatic controlProgrammable logic deviceClock network
Owner:XILINX INC
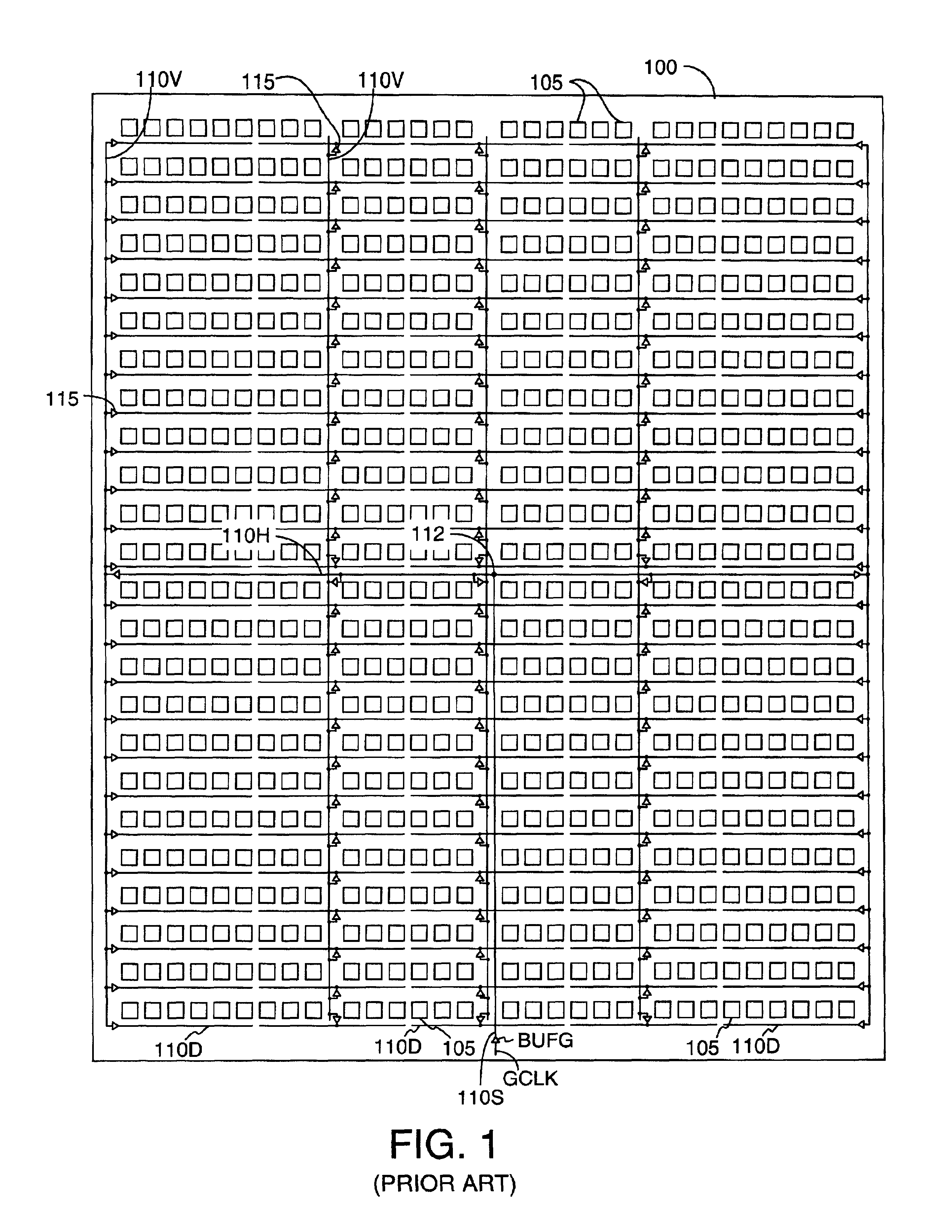
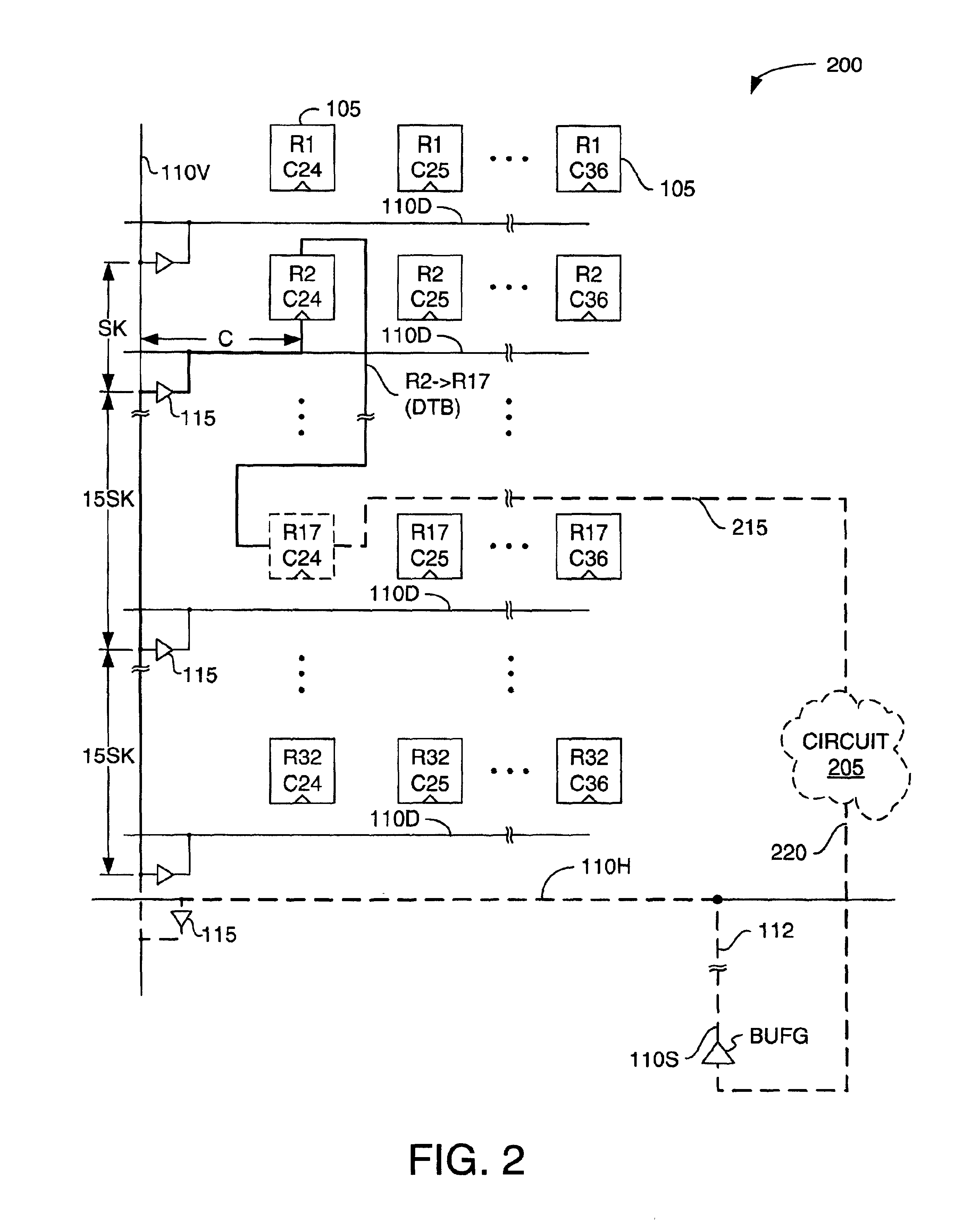
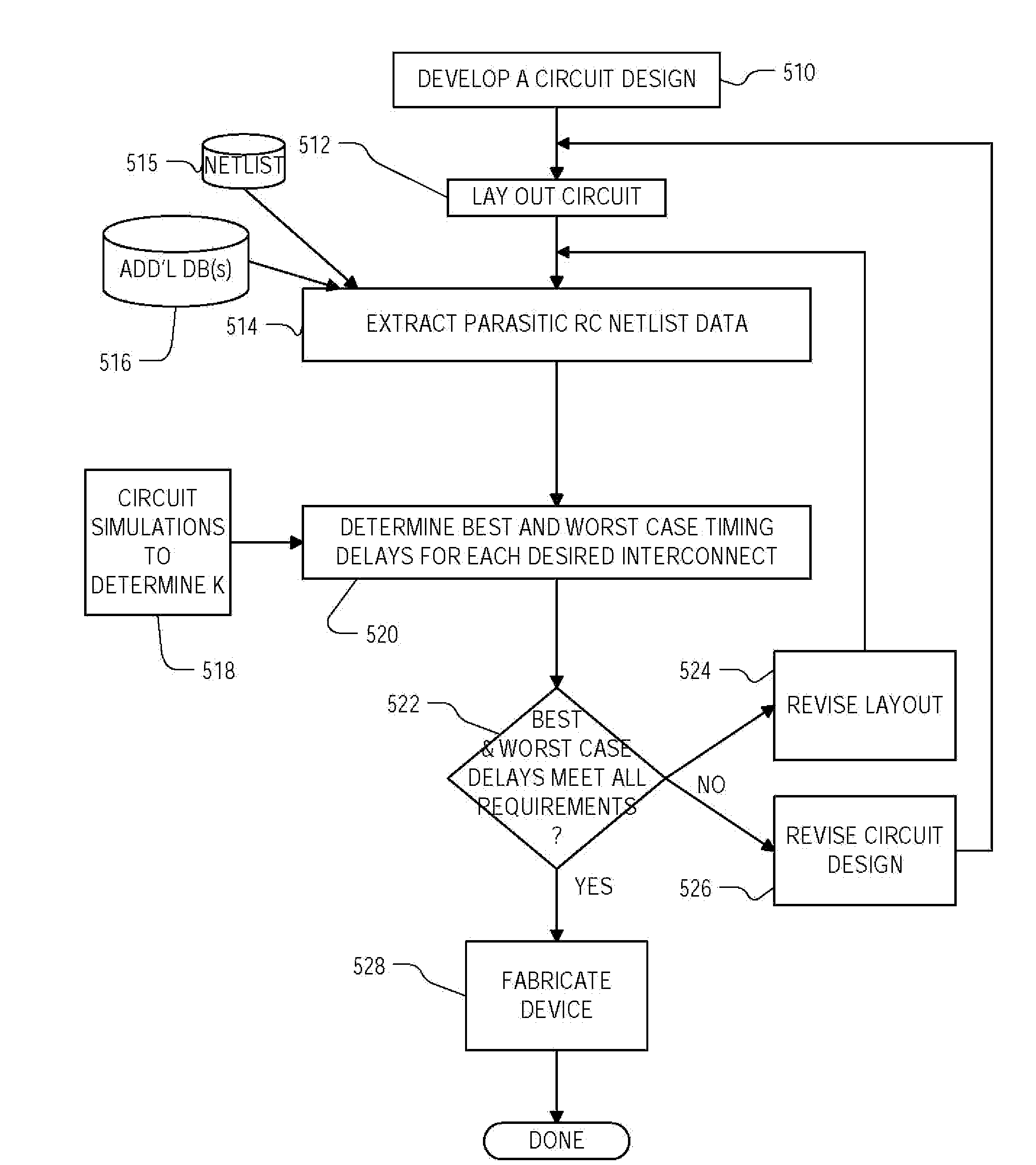
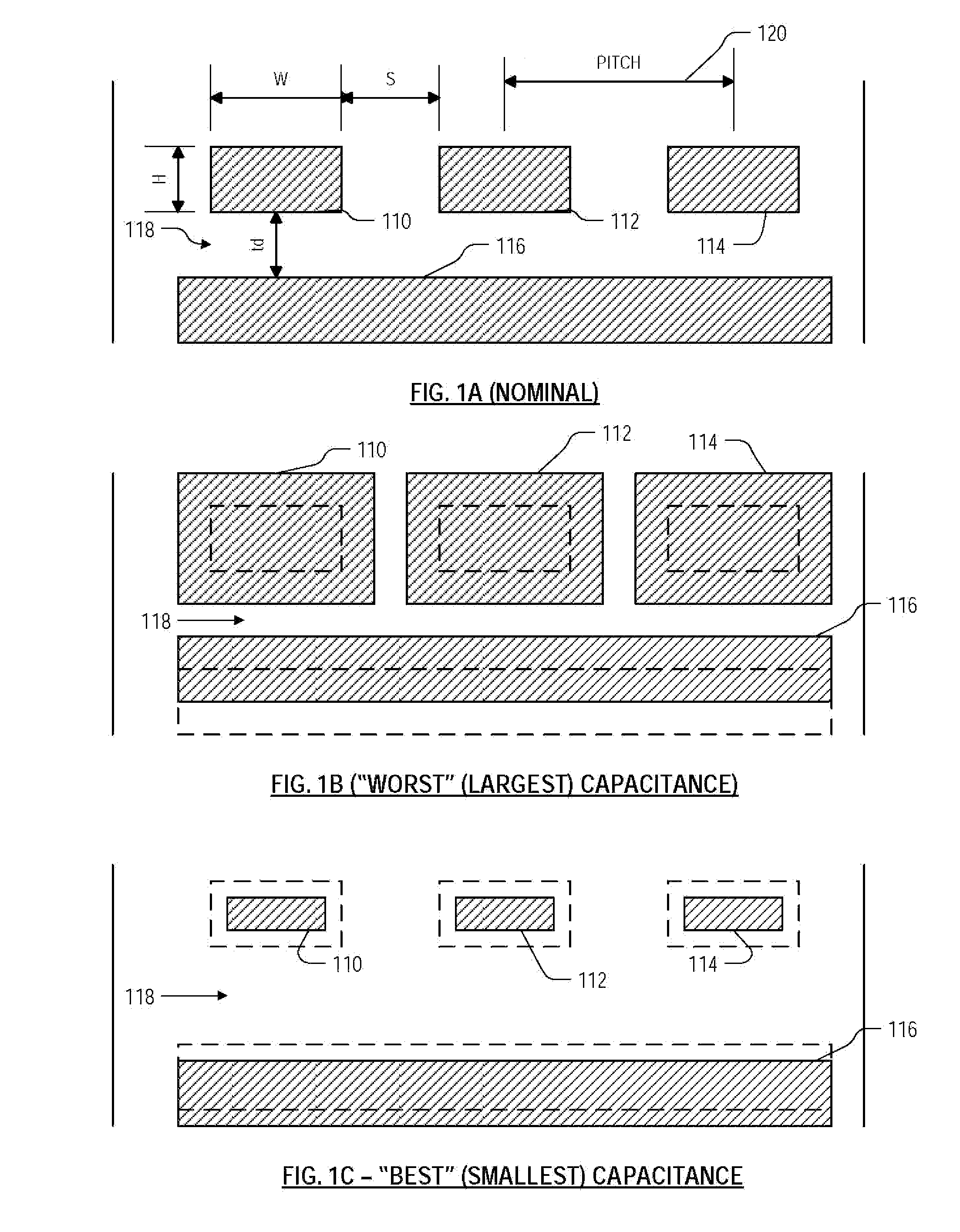
Method for determining best and worst cases for interconnects in timing analysis
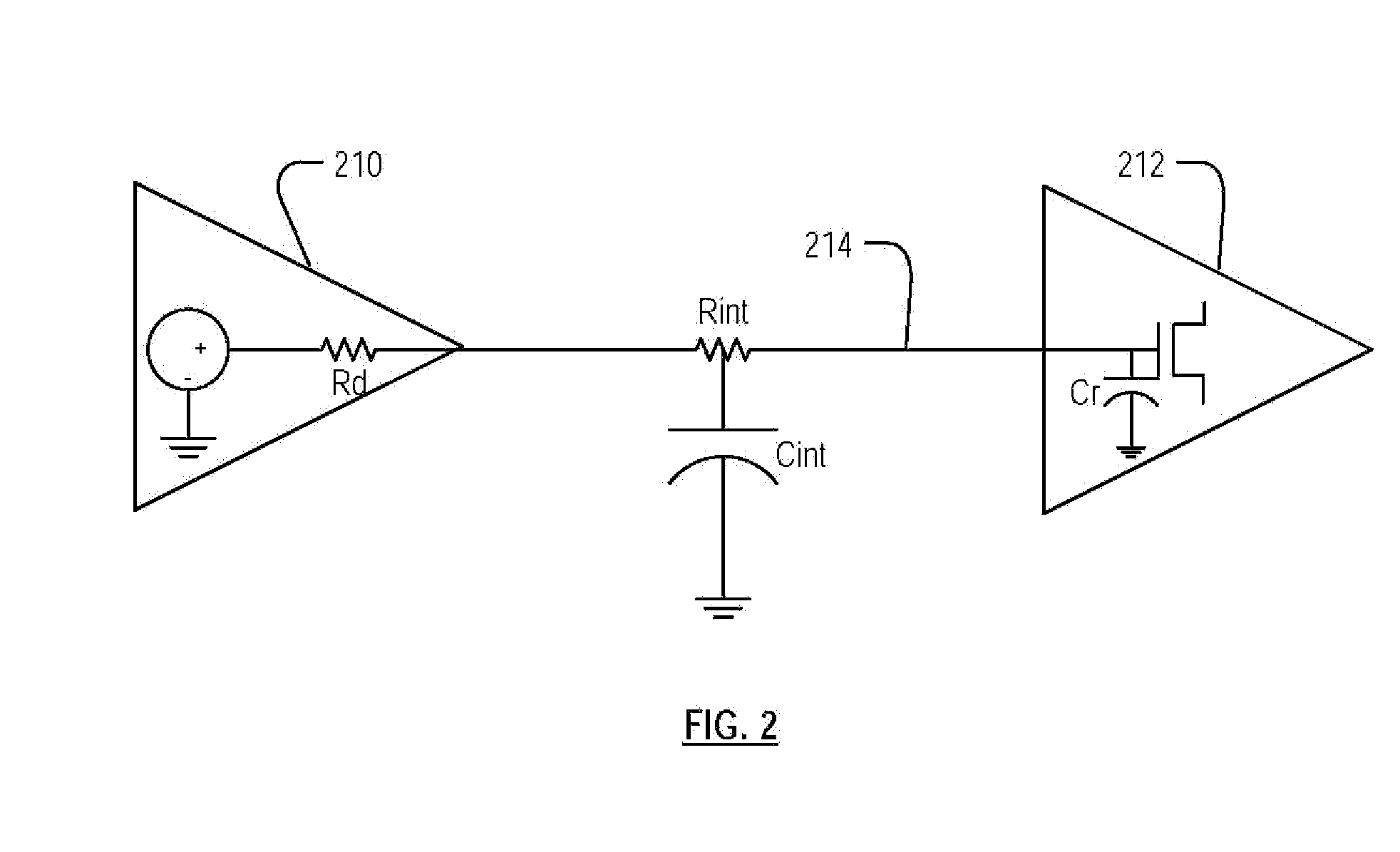
ActiveUS20080228460A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPropagation delayCapacitance
Roughly described, signal propagation delay values are estimated for a plurality of interconnects in a circuit design. For each interconnect, the propagation delay value(s) are estimated in dependence upon a preliminary approximate determination of whether the signal propagation delay is dominated more by an interconnect capacitance term or by an interconnect capacitance and resistance product term. If it is dominated more by the interconnect capacitance term, then the parameter values used for a minimum propagation delay calculation are obtained assuming a smallest capacitance process variation case and the parameter values used for a maximum propagation delay calculation are obtained assuming a largest capacitance process variation case. If the signal propagation delay is dominated more by the interconnect capacitance and resistance product term, then the opposite assumptions are made. Preferably the approximate determination is made by comparing Rint to k*Rd.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Scan flip-flop with internal latency for scan input
A scan flip-flop circuit including a data input, a scan input, a data output, a flip-flop, a multiplexer and a delay element is provided. The multiplexer allows selection of either the scan input or the data input for presentation at the input of the flip-flop. The flip-flop provides an output signal at the output of the scan flip-flop. The delay element is in a signal path between the scan input and the input of the flip-flop, and provides a signal propagation delay between the scan input and the input of the flip-flop. The delay between the scan input and the input of the flip-flop is substantially larger than the signal propagation delay between the data input and the input of the flip-flop. The delay in the scan path reduces the need for external buffers to avoid hold-time violations during scan testing of integrated circuits.
Owner:CHRONOCLOUD MEDTECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
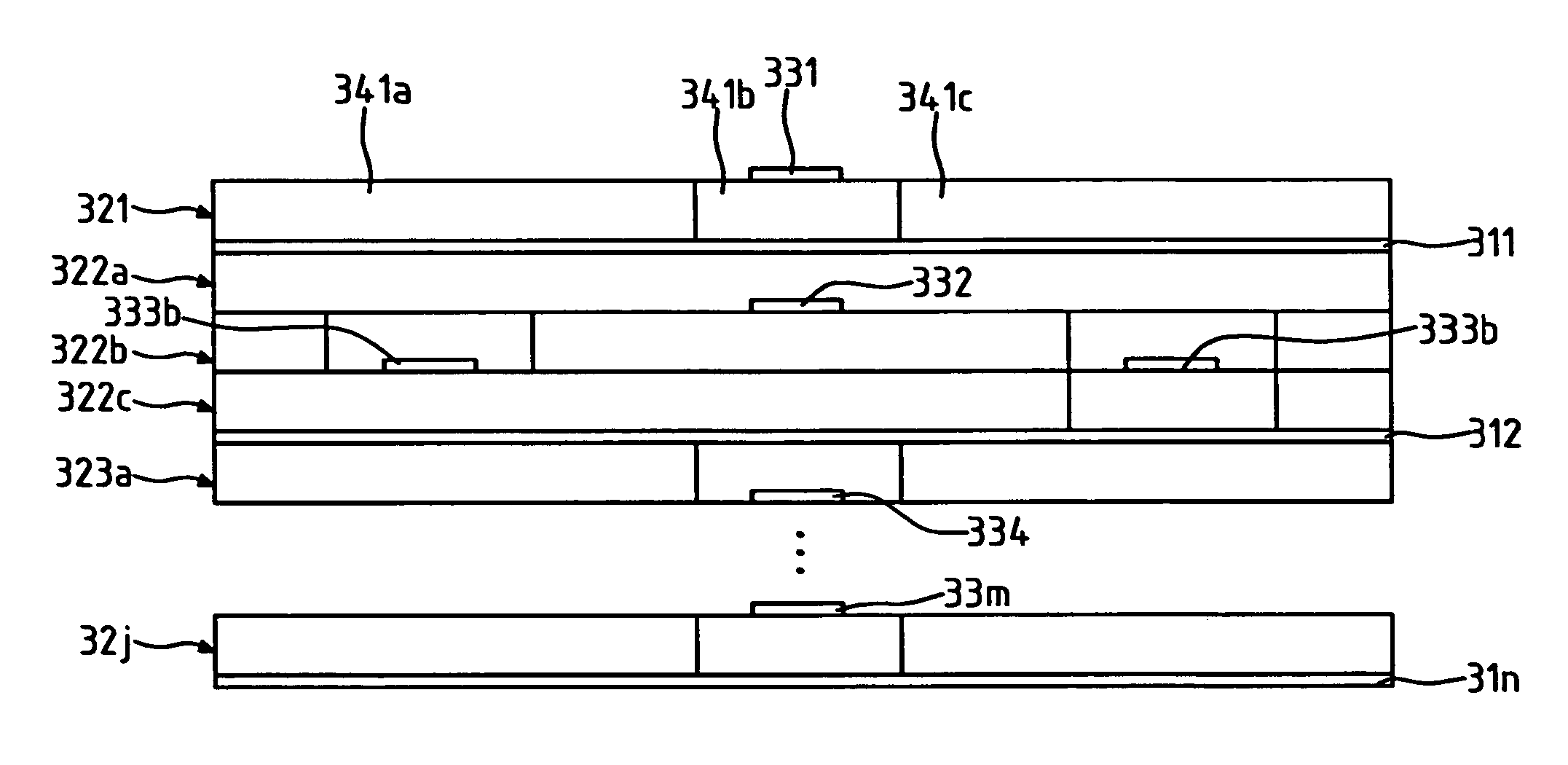
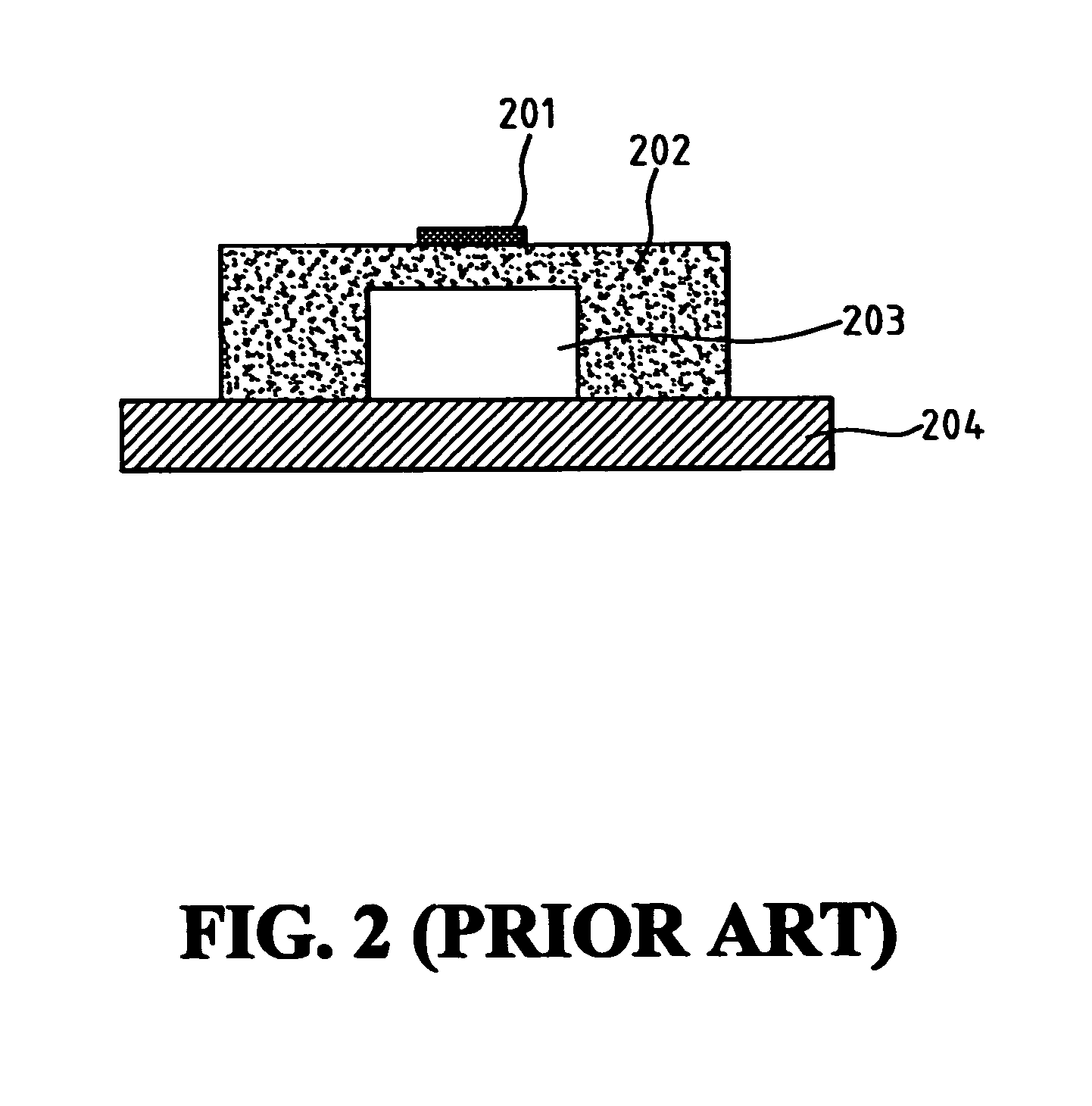
Semiconductor memory equipped with row address decoder having reduced signal propagation delay time
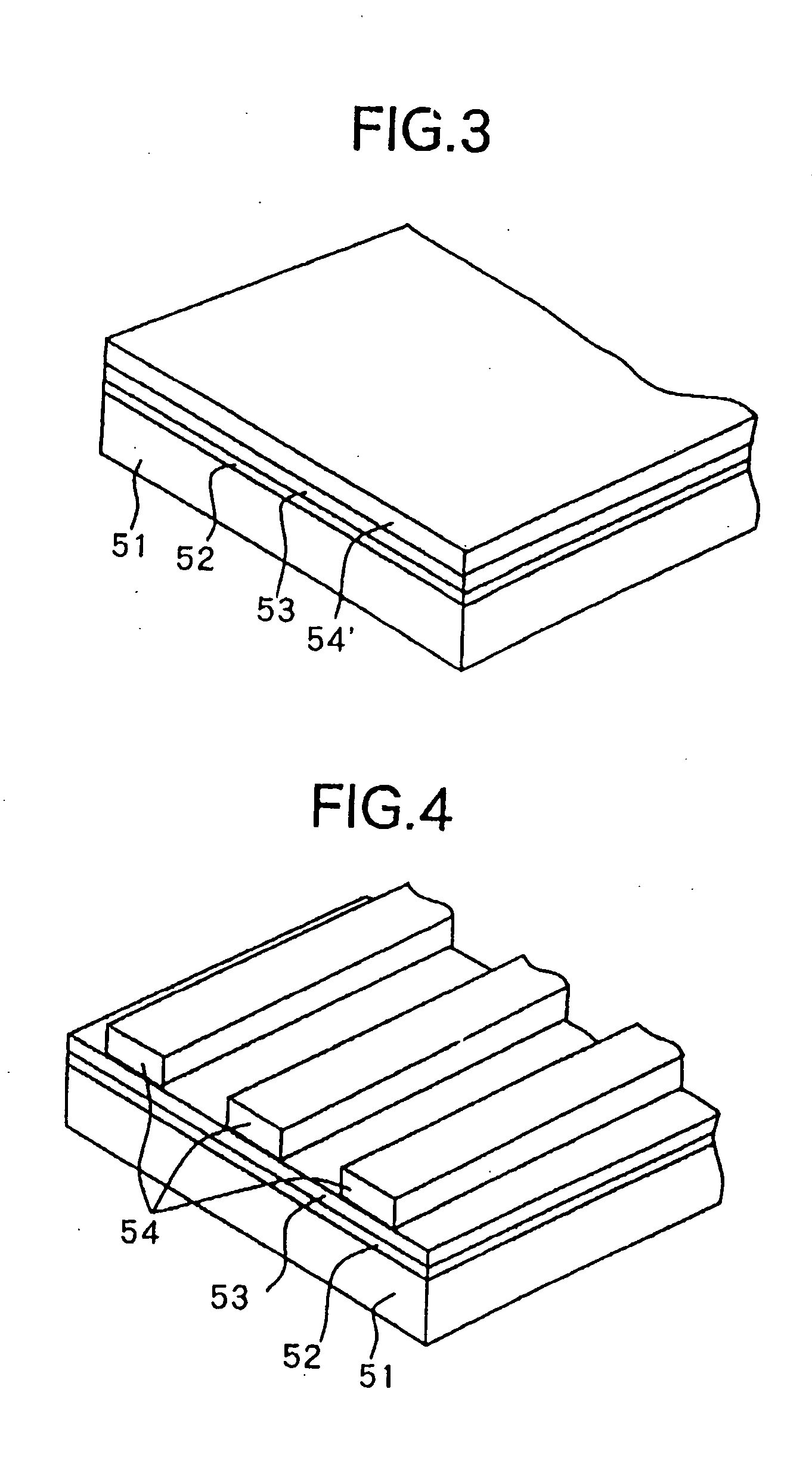
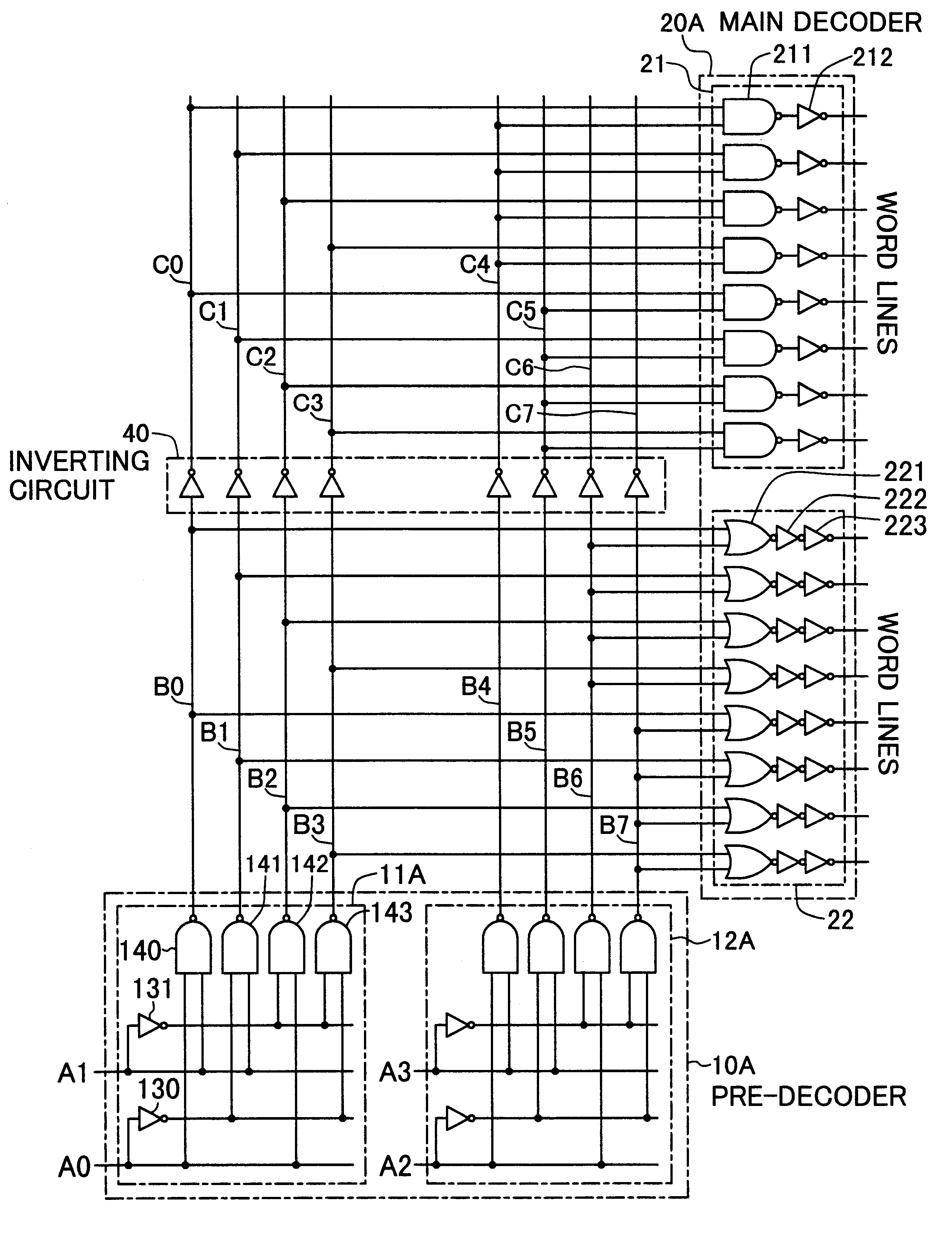
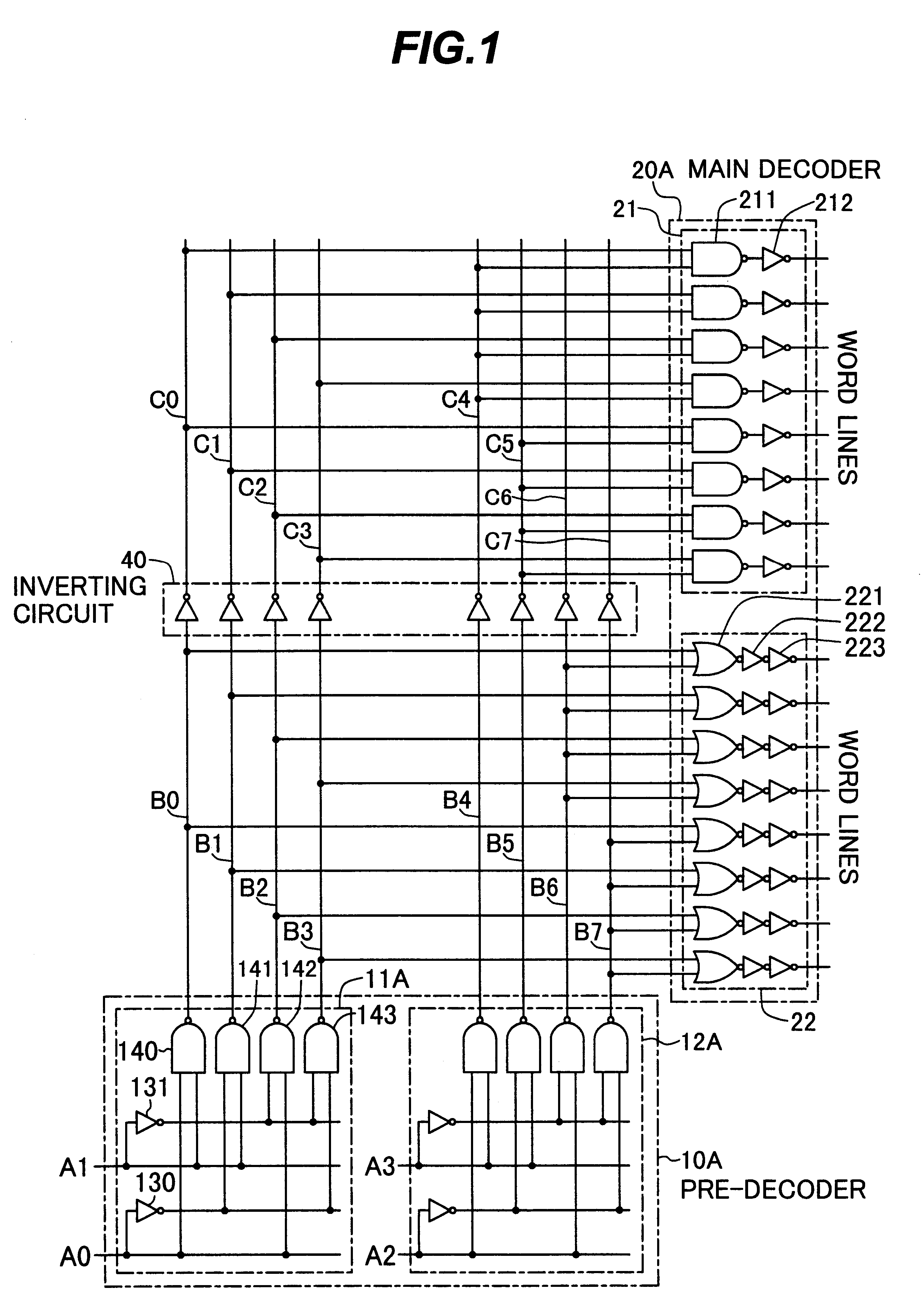
The output of a pre-decoder 10A is provided, on one side, to a main decoder 22 with the input of negative logic and on the other side, to a main decoder 21 with the input of positive logic through an inverting circuit 40. The number of gate stages from the output of the pre-decoder 10A to the output of the main decoder 21 is three which is equal to the number of gate stages from the output of the pre-decoder 10A to the output of the main decoder 22.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
DDR memory modules with input buffers driving split traces with trace-impedance matching at trace junctions
InactiveUS6947304B1Printed circuit detailsPrinted circuit aspectsPropagation delayProcessor register
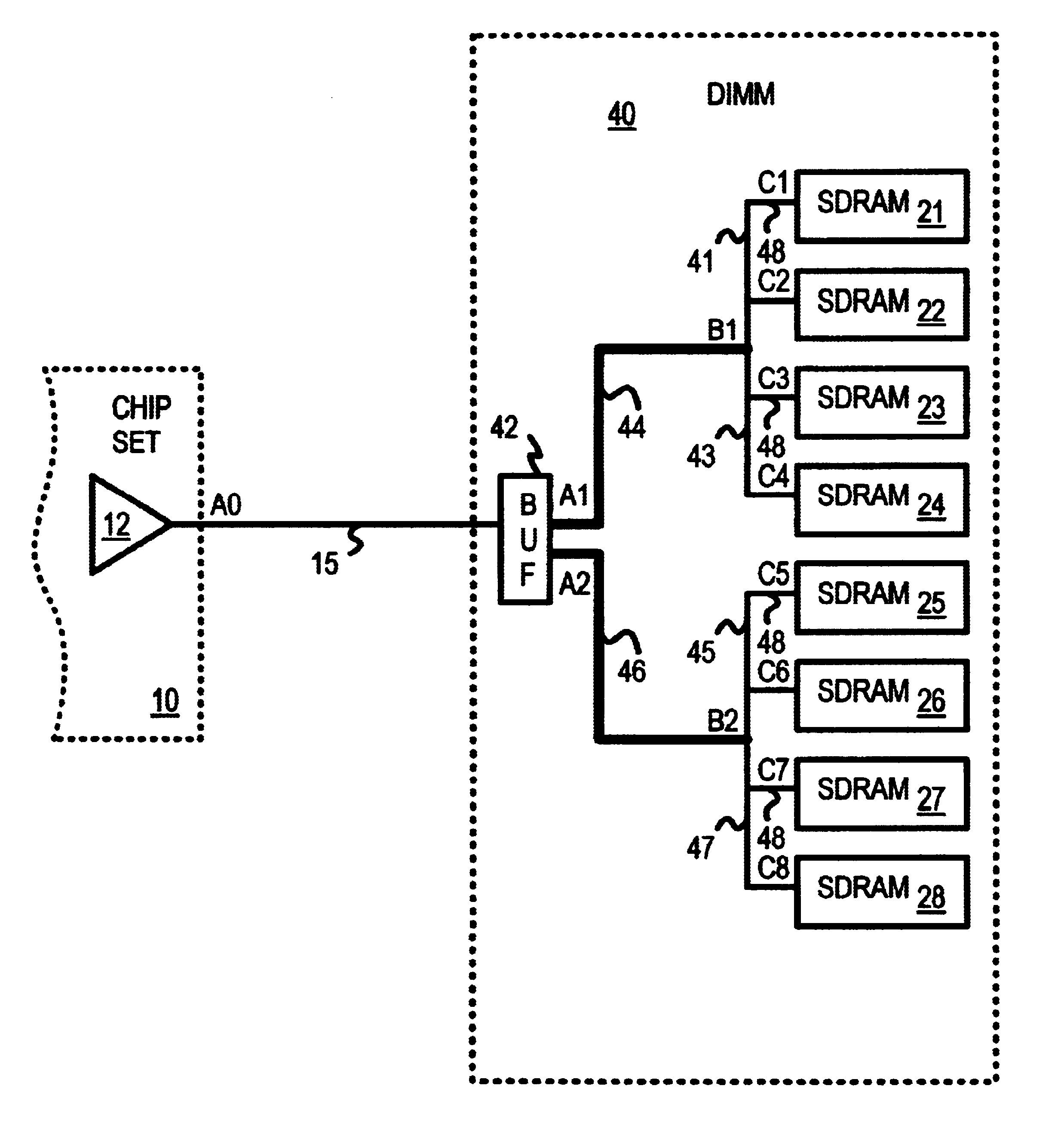
A memory module has improved signal propagation delays for signals externally driven such as from a motherboard. Reflections from junctions of wiring traces on the memory module are reduced or eliminated. An input buffer or register receives a signal from the motherboard and splits the signal to drive two outputs to two separate traces. Each trace is enlarged in width or thickness, such as by using a double-width wiring trace. At the fare end of each double-width trace, a junction is made to two minimum-width traces that connect to small stub traces to DRAM inputs. Reflections from the junction are eliminated or reduced by trace-impedance matching, since the input impedance of the double-width trace from the input buffer is about the same as the combined impedance of the two minimum-width traces. Trace-input matching and input buffering can improve signal integrity and overall propagation delay.
Owner:DIODES INC
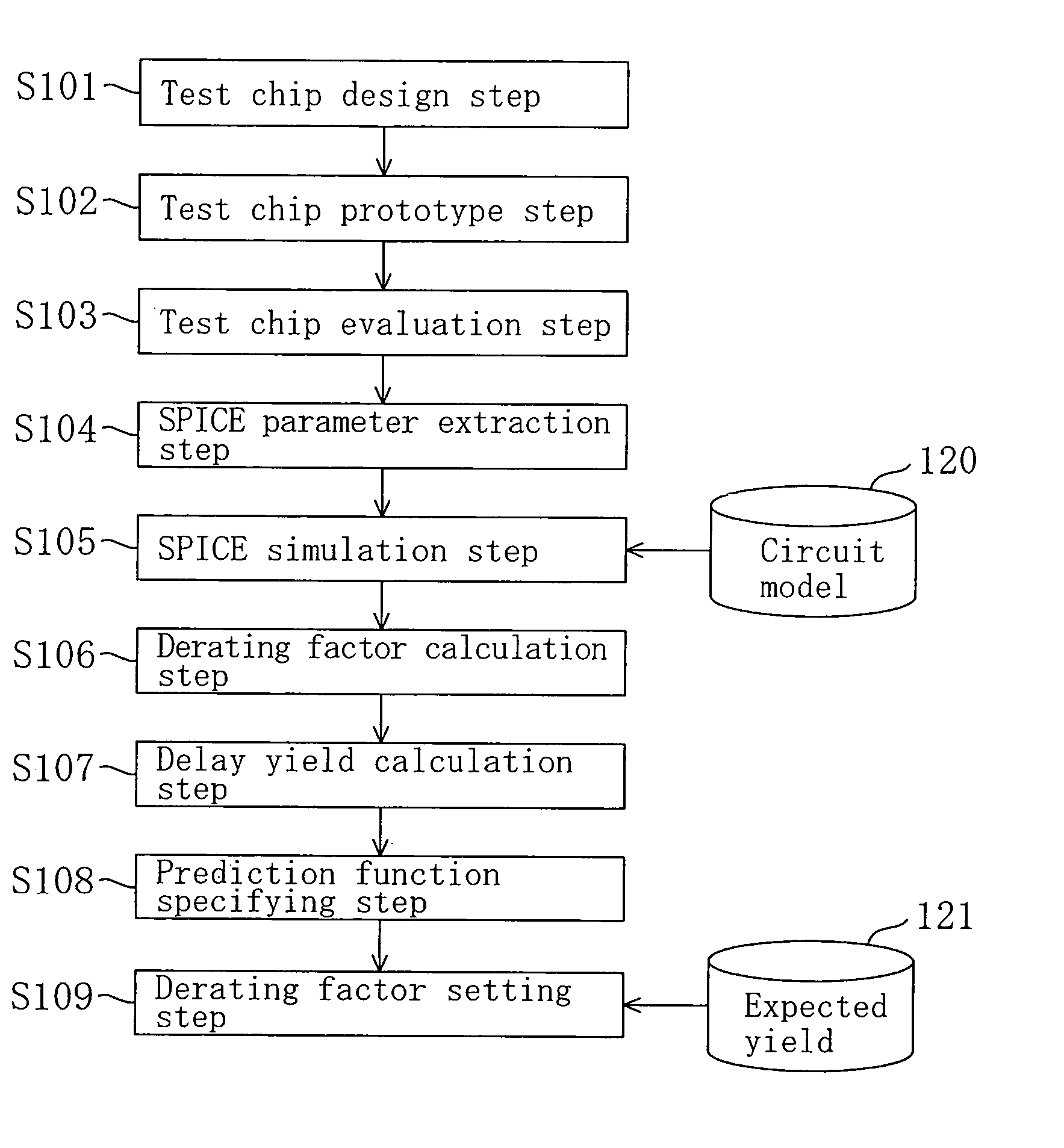
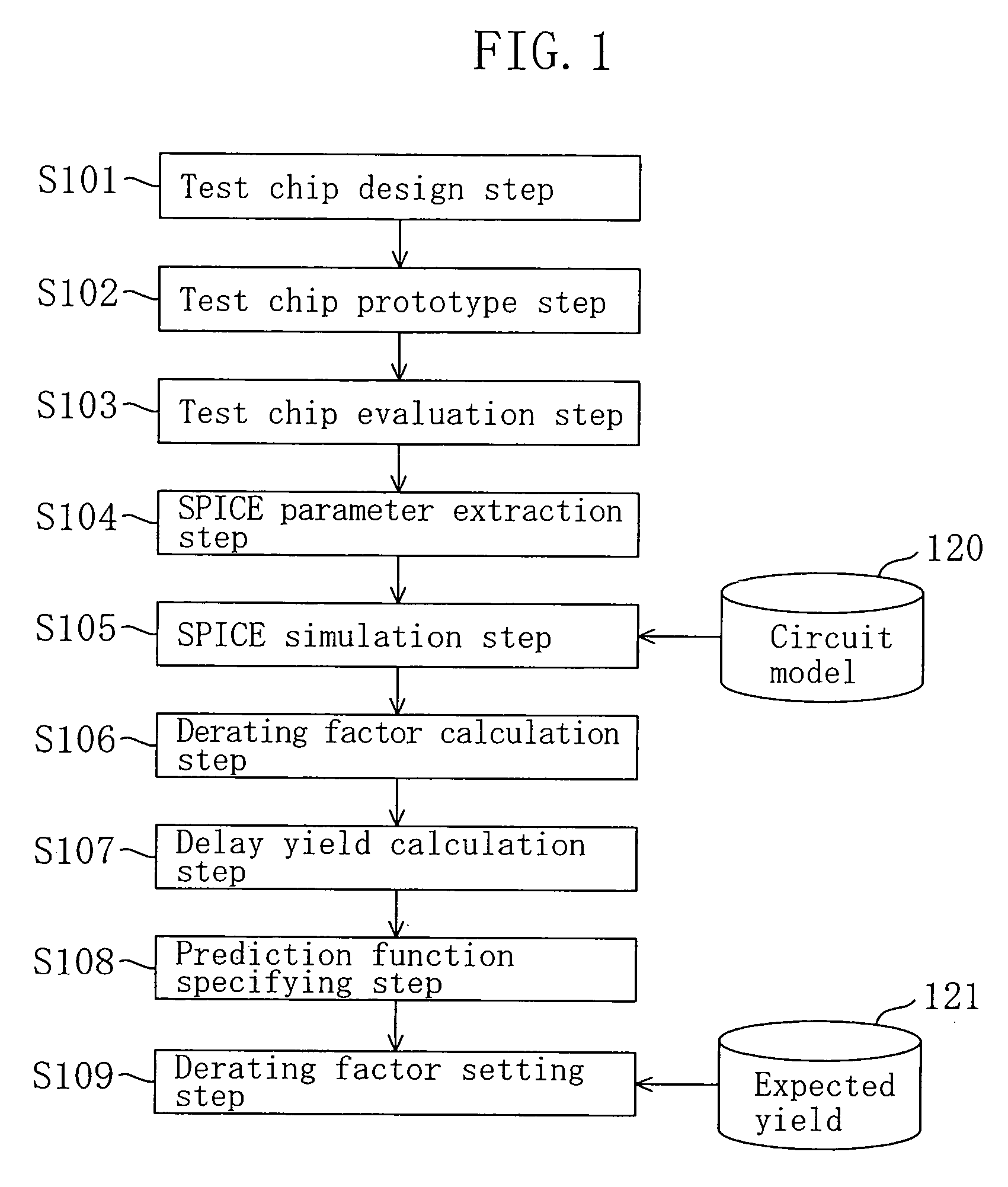
Method for setting design margin for LSI
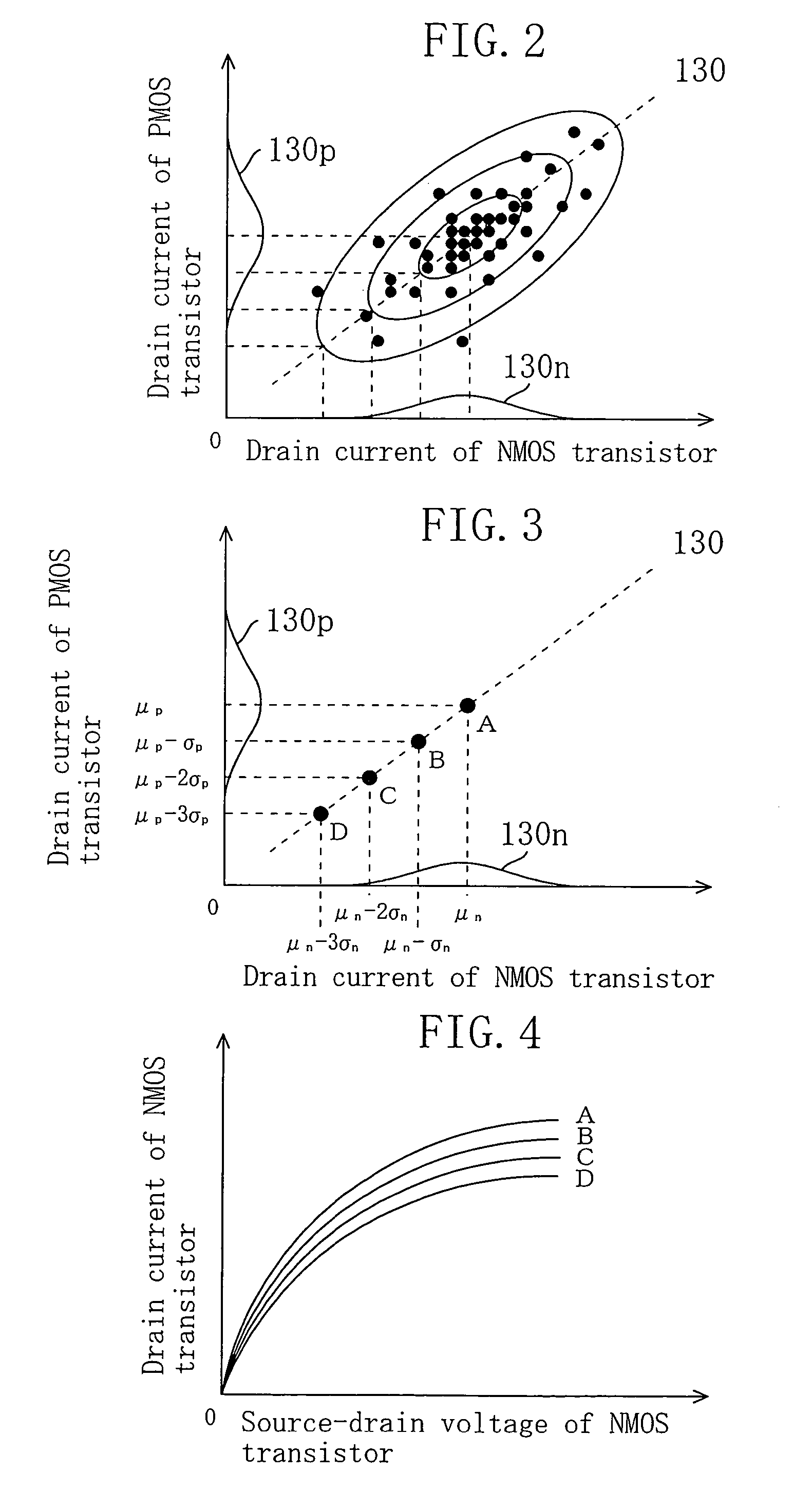
ActiveUS7197728B2More accurateMore realisticSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer aided designEngineeringSignal propagation delay
After predicting a relationship between a design margin set against a fabrication variation in design of an LSI and a yield, a specific design margin for attaining a given yield is calculated based on the predicated relationship. The yield is a delay yield obtained by cumulating a signal propagation delay time thereby achieving a probability that a signal propagated through a logic circuit of the LSI is delayed by a given amount of time, and the design margin is a derating factor indicating a ratio between the signal propagation delay time and a standard value of the signal propagation delay time.
Owner:PANNOVA SEMIC
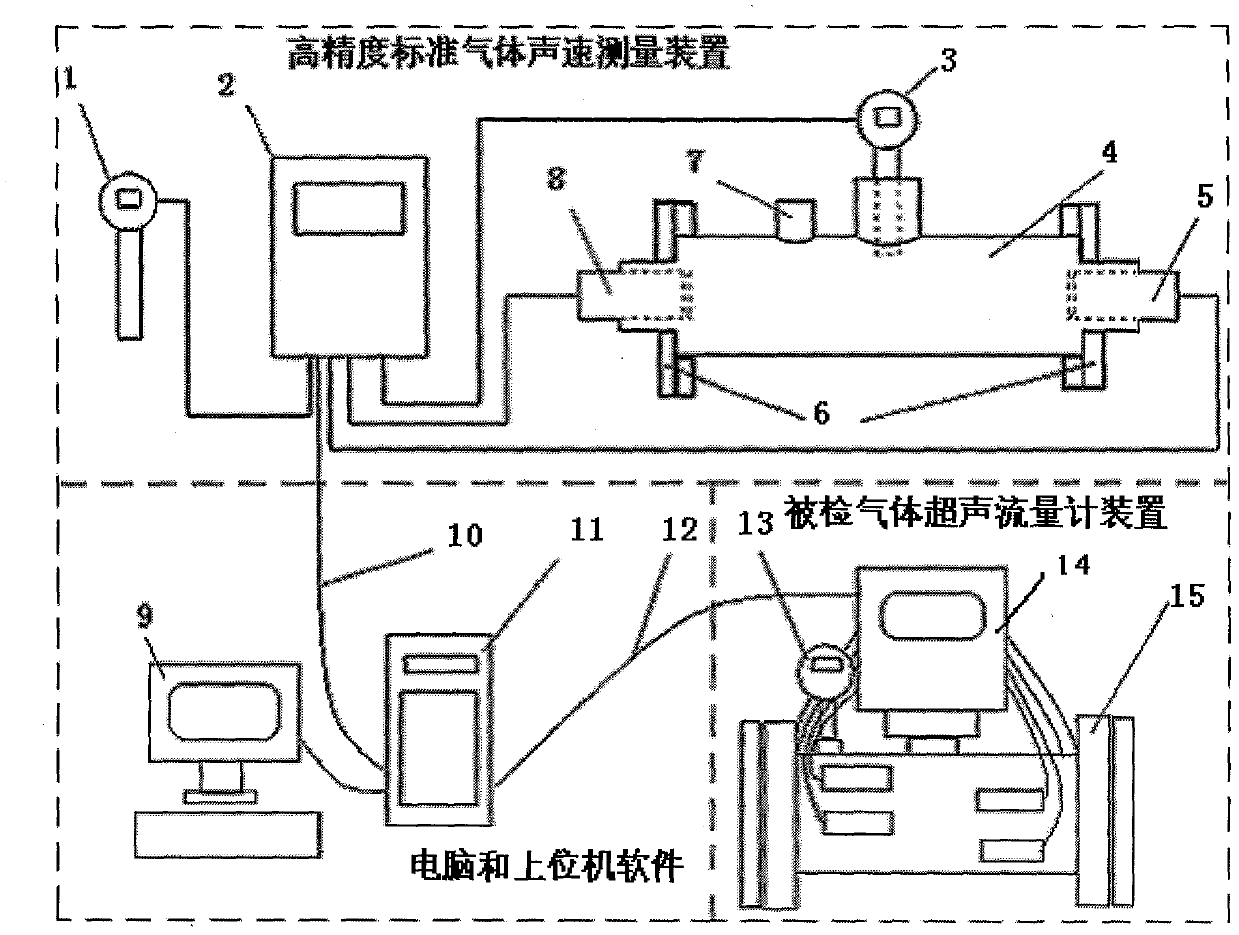
Test method and measuring device for acoustic delay of gas ultrasonic flowmeter
ActiveCN102589656ASimple and fast operationReduce measurement errorTesting/calibration apparatusVelocity propogationTime errorSonification
A test method and a measuring device for acoustic delay of a gas ultrasonic flowmeter relate to the technology for detecting ultrasonic wave propagation time of ultrasonic flowmeters, in particular to the technology for measuring time errors of electronic circuit signal propagation delay time, transducer signal delay time, signal sampling point delay time and signal cable delay time, and are suitable for sound velocity detection of various diameters of ultrasonic flowmeters. The test method for the acoustic delay is a measuring method for contrasting and proving acoustic delay data of a detected meter through a detected high-accuracy standard gas sound velocity measuring device, a computer and upper computer software according to standard sound velocity of a place where the detected gas ultrasonic flowmeter is located.
Owner:上海中核维思仪器仪表股份有限公司
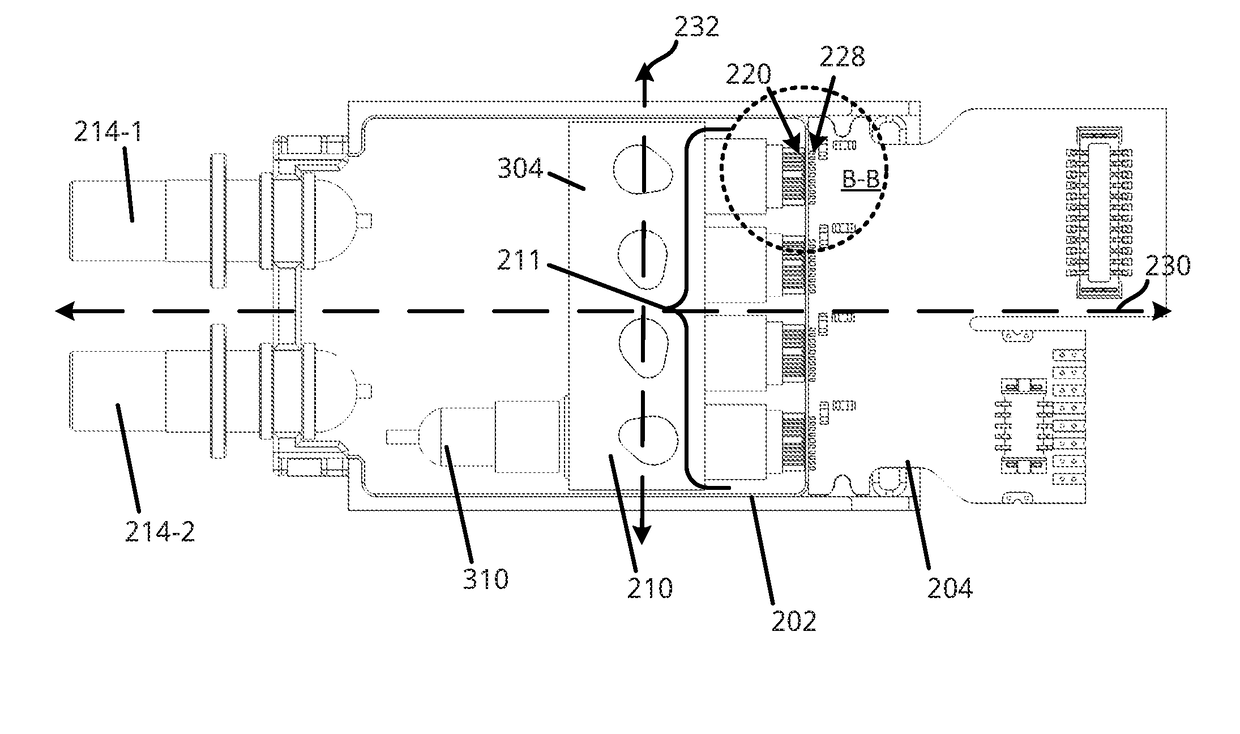
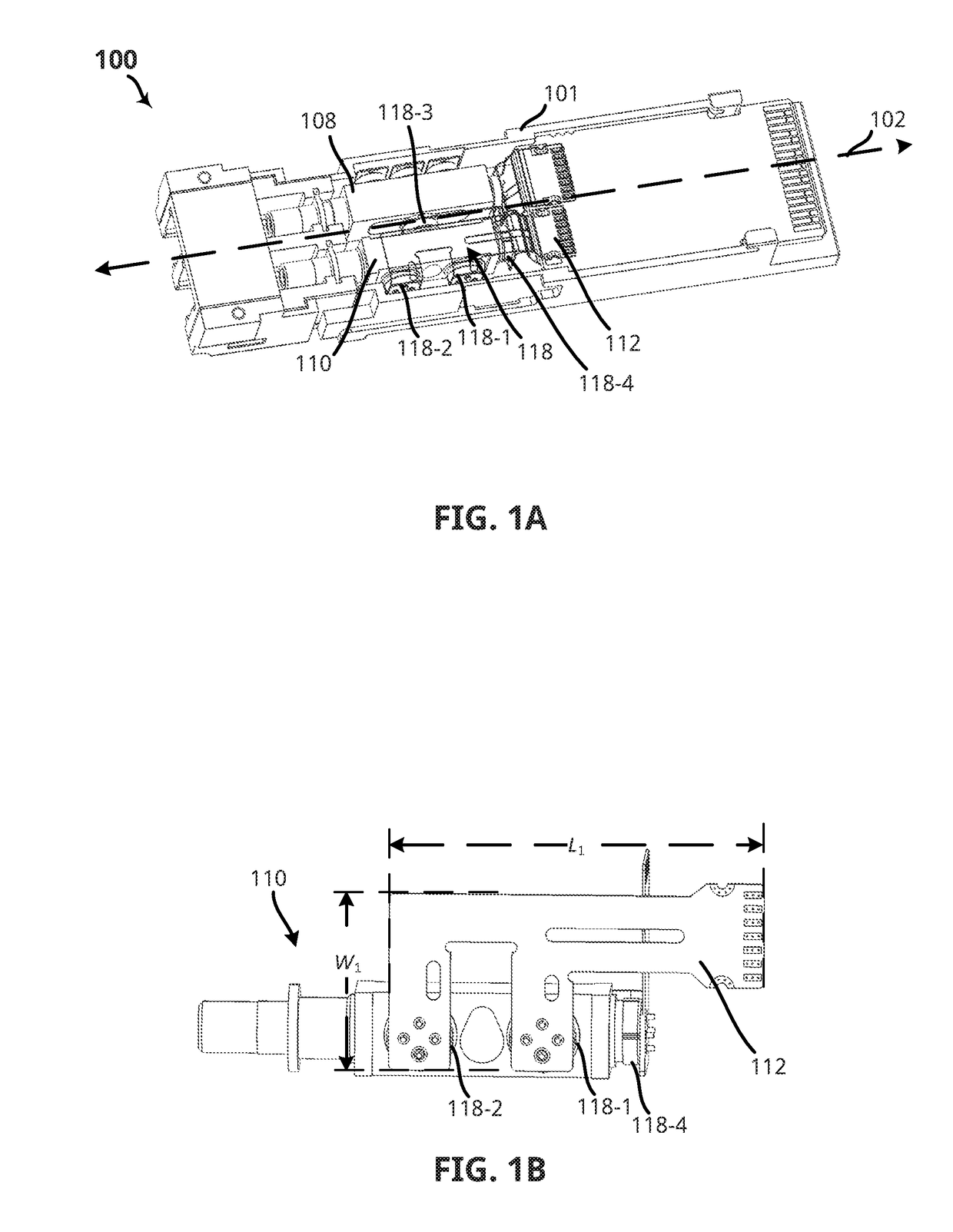
Techniques for reducing electrical interconnection losses between a transmitter optical subassembly (TOSA) and associated driver circuitry and an optical transceiver system using the same
ActiveUS20180062756A1Laser optical resonator constructionWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransceiverInterconnection
Techniques are disclosed for providing relatively short distances between multi-channel transmitter optical subassemblies (TOSAs) and associated transmit connecting circuit in order to reduce losses due to signal propagation delays, also sometimes referred to as signal flight time delays. In an embodiment, a TOSA includes a plurality of laser assemblies disposed along a same sidewall of the TOSA along a longitudinal axis. The TOSA may be disposed within an optical transceiver housing in a transverse orientation, whereby a longitudinal center line of the multi-channel TOSA is substantially perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the optical transceiver housing. The TOSA may be positioned adjacent an end of the optical transceiver housing having a transmit connecting circuit. Thus each of the plurality of laser assemblies may be positioned at a relatively short distance, e.g., 120 microns or less, away from the transmit connecting circuit.
Owner:APPLIED OPTOELECTRONICS
Method and apparatus for determining propagation delays for use in wide area networks
A system and method for determining a signal propagation delay between a transmitter and a receiver, and for adjusting a transmission time based on the propagation delay. A central station inserts a marker into a transmitted signal at a time corresponding to a received timing signal. The MCT receives the signal from the central station and determines a time difference between receipt of the marker and the detection of the time interval event. A transmission by the MCT is adjusted by an amount of time proportional to the time difference.
Owner:OMNITRACS
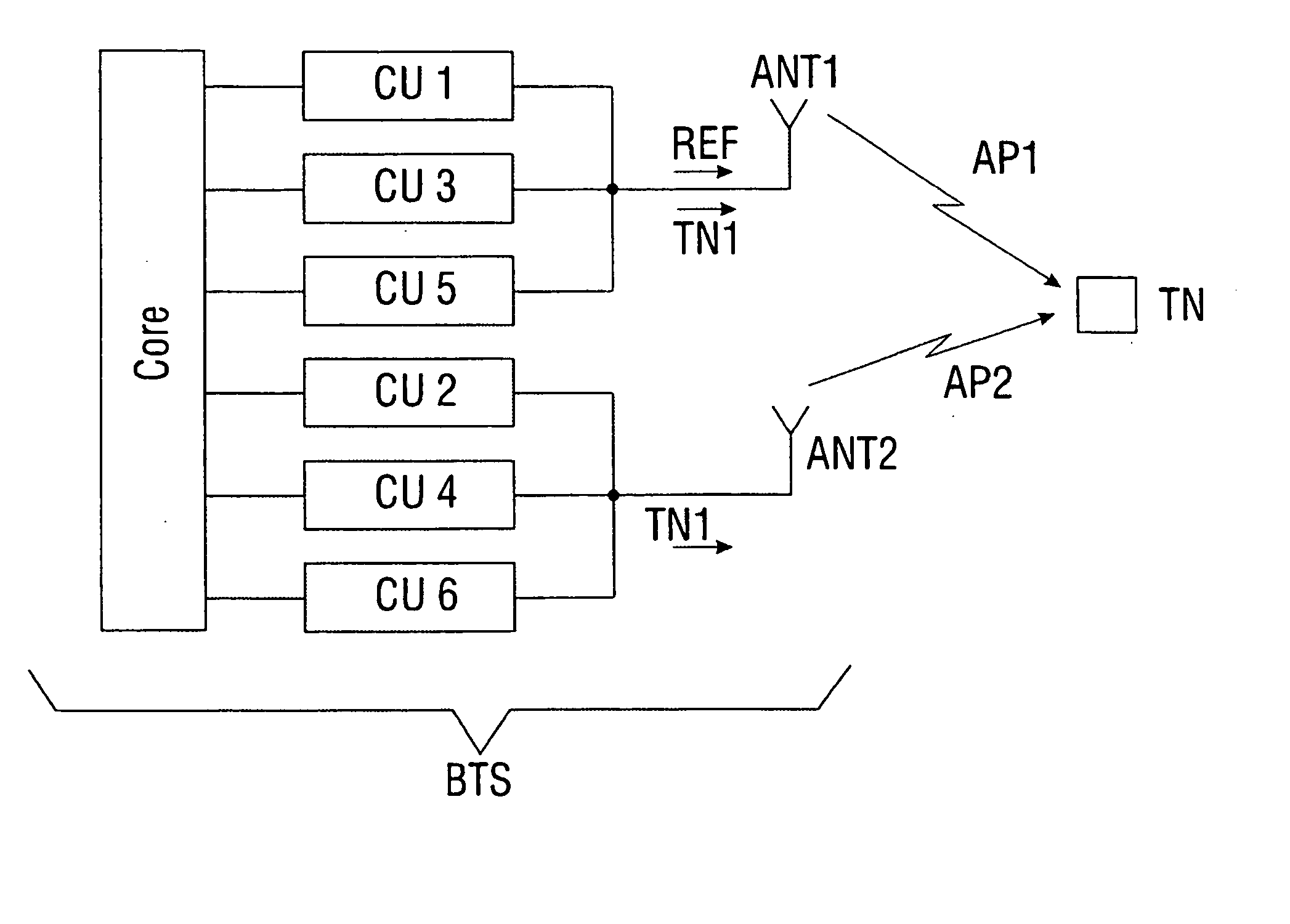
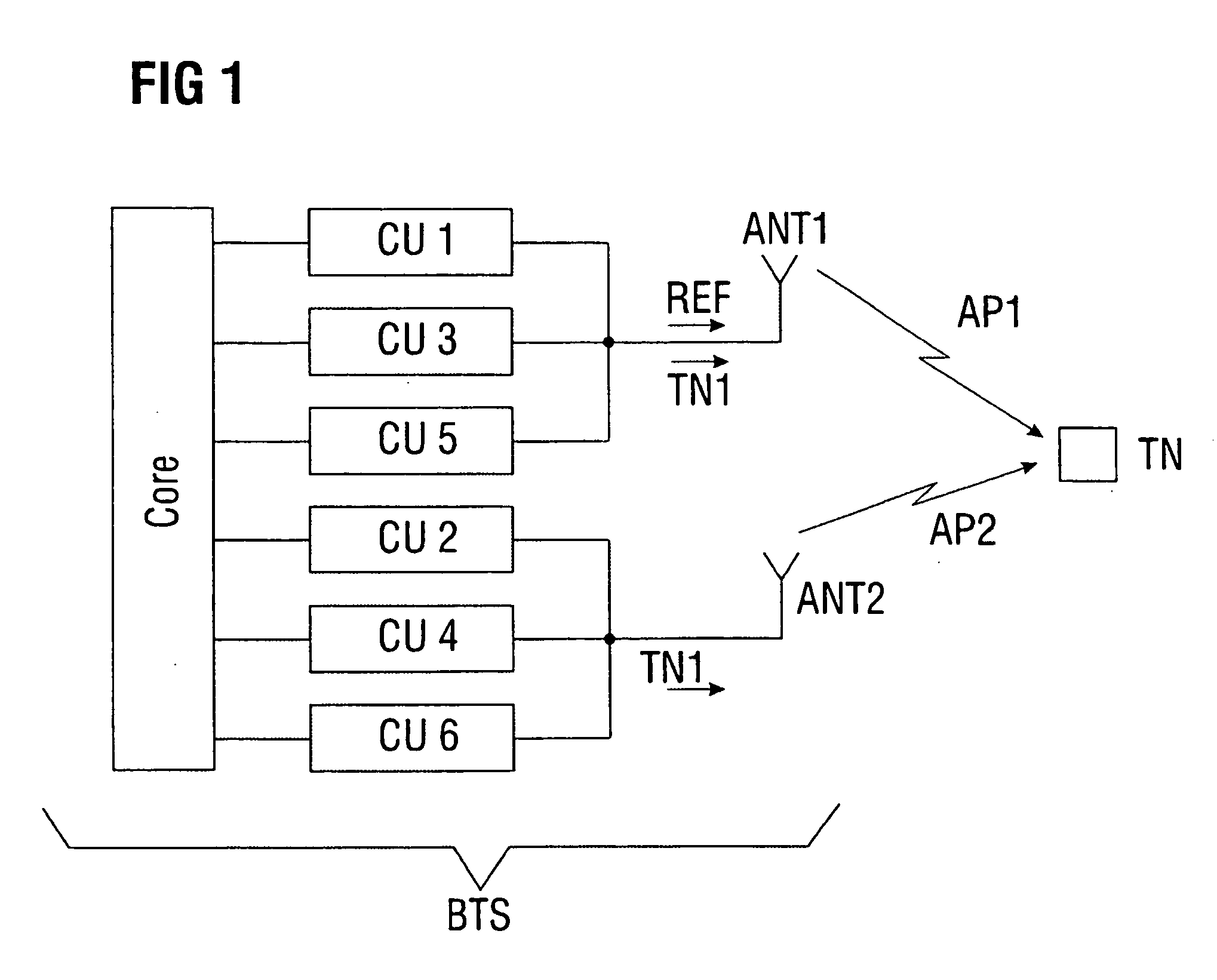
Positional determination of a user in a mobile communications system with emission diversity
InactiveUS20050202858A1Spatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityPropagation delayCommunications system
The invention relates to a method for increasing the precision during the determination of system parameters dependent on the propagation delay, e.g. for a positional determination, in a mobile communications system with emission diversity, according to which a subscriber data signal and a reference signal are assigned to a subscriber. The subscriber data signal is emitted by at least two antenna devices on the emission side, whereas the reference signal is emitted exclusively by one antenna device on the emission side. The reference signal is used to precisely determine signal propagation delays, upon which the system parameters depend.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG
Optical waveguide and method for producing same
InactiveUS7163598B2Avoid low lightInexpensively formedLaser detailsDecorative surface effectsLow speedLight signal
An optical waveguide having a optical waveguide path capable of securing a high light propagation characteristic regardless of the type of a supporting base, provided with a multilayer circuit board, an optical waveguide path arranged on the multilayer circuit board, a light receiving element, IC chips, and a light emitting element, the optical waveguide path formed on a transparent substrate excellent in flatness and transferred to the multilayer circuit board. The light propagation loss becomes small, and a signal to be transmitted at a high speed being transmitted as a light signal and a signal which can be transmitted at a relatively low speed being transmitted as an electrical signal, whereby the signal propagation delay which becomes the problem when a signal is transmitted by only electrical wiring is overcome, and the influence of electromagnetic noise becomes small.
Owner:SONY CORP
Composite distributed dielectric structure
InactiveUS20060285273A1Reduce dielectric lossReduce cross talkSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFixed capacitor dielectricElectrical conductorDielectric loss
This invention discloses a composite distributed dielectric structure. It comprises one or more conductor layers, one or more dielectric layers distributed on the conductor layers, and one or more conductor traces distributed on the dielectric layers. One or more dielectric plates can be further around the conductor traces. The dielectric layers or plates may or may not have plural dielectric materials therein, respectively described in two embodiments. Each conductor trace lies on a dielectric material without crossing two different dielectric materials. Two or more dielectric layers may be stacked on the conductor layers The invention provides a low cost and practical dielectric structure for interconnect systems to reduce dielectric loss, cross talk, and signal propagation delay and to well control the impedance matching while maintaining proper heat dissipation and noise reduction at high frequency transmission.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Signal propagation delay routing
ActiveUS8072906B2Increase currentEnergy efficient ICTError prevention/detection by using return channelPropagation delaySignal propagation delay
Owner:MANITOBA UNIV OF THE +1
Fast precontract and line transmission multi-address access method
InactiveCN101034932AExtension of timeReduce adverse effectsData switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsAccess methodTelecommunications link
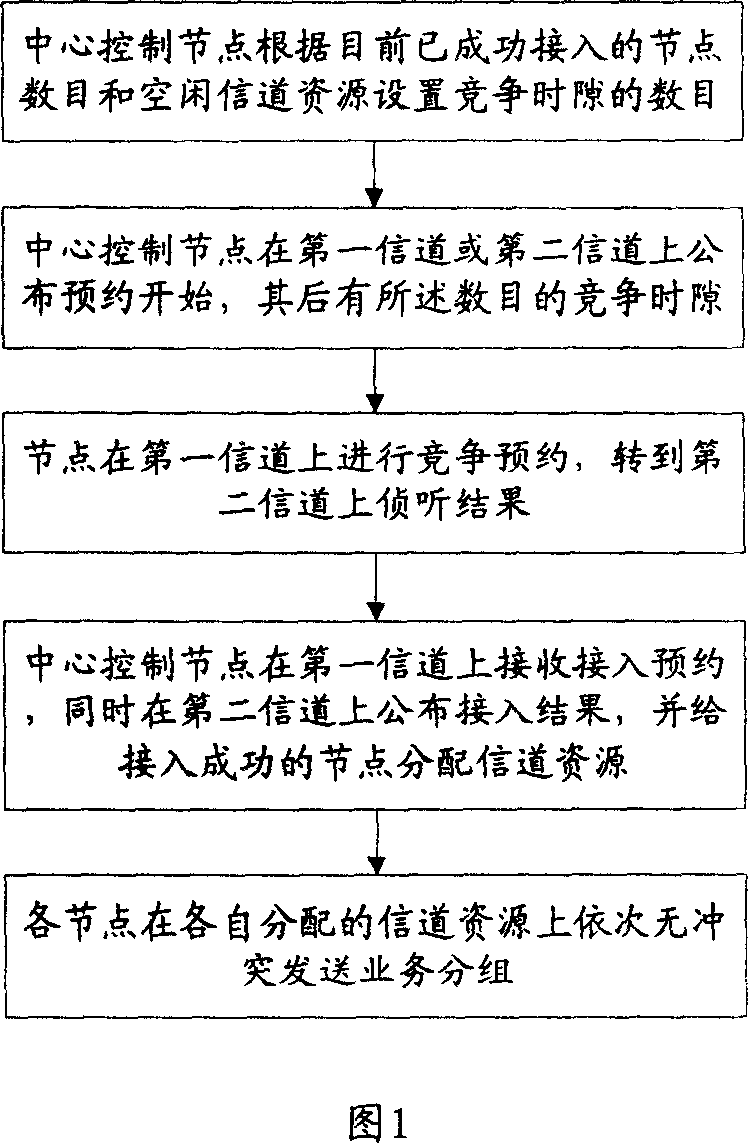
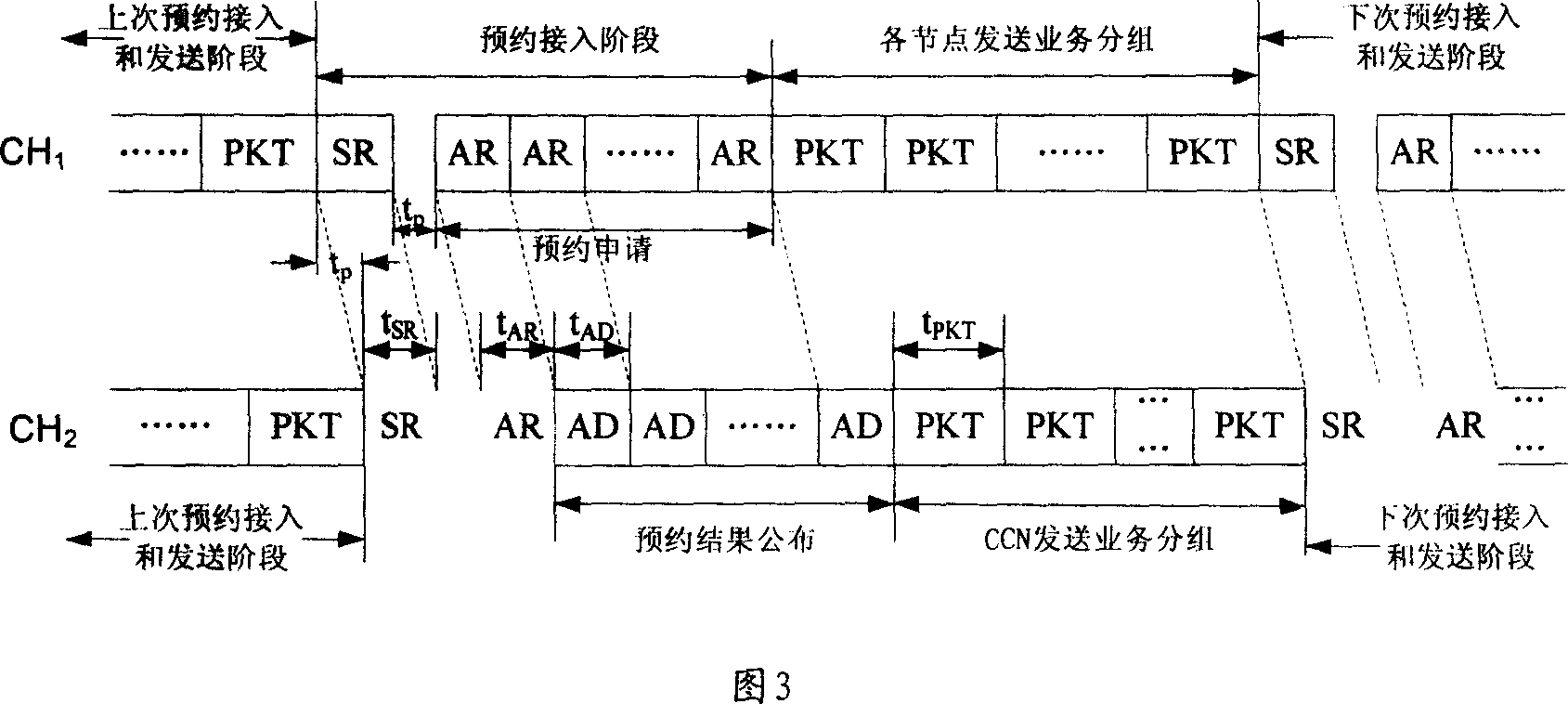
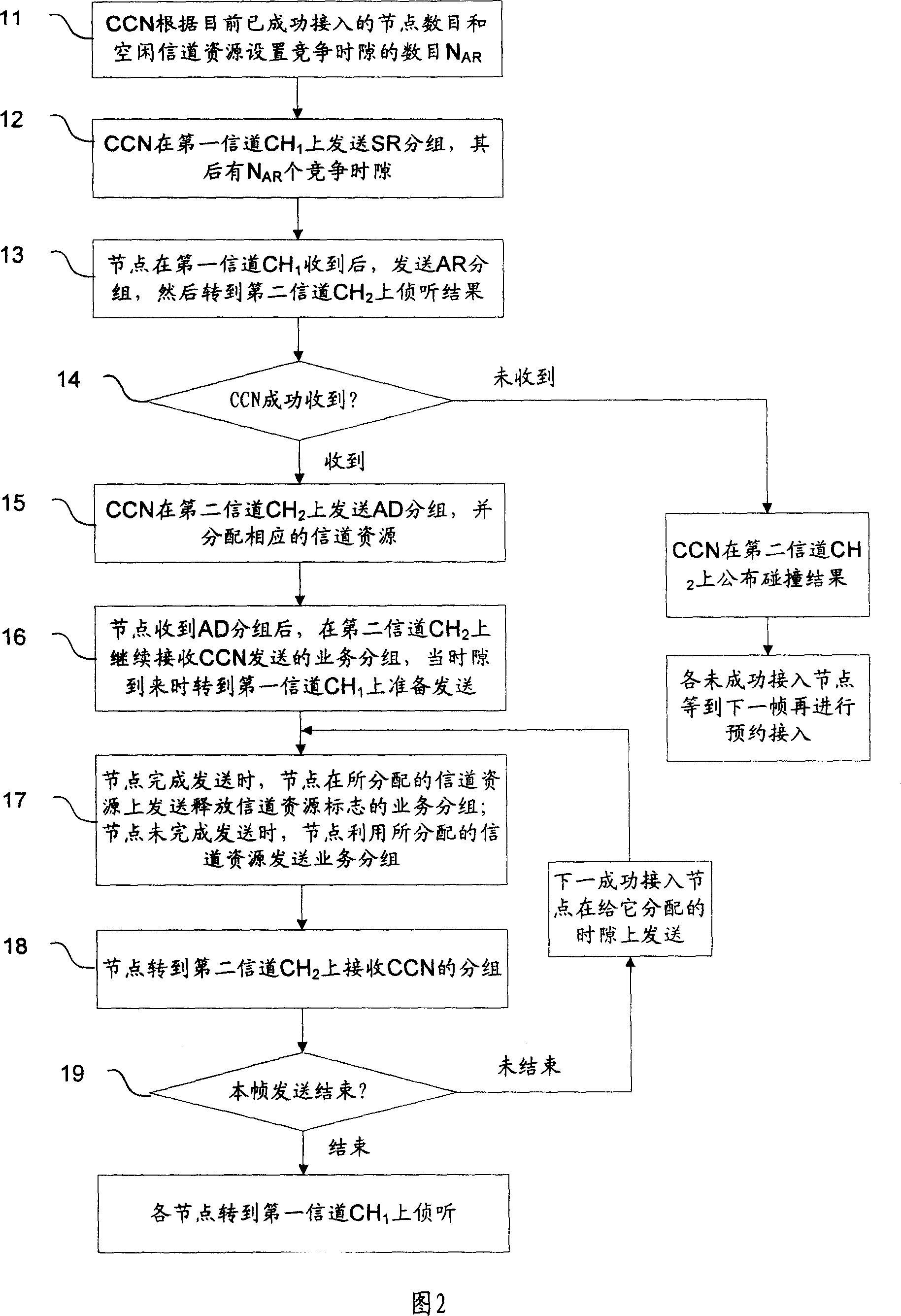
This invention relates to a fast booking out of multiple access methods, including: central control node has been successful under the current access and the number of nodes installed idle channel resources of the competition slot number; center control nodes in the first or second Channel announced appointments, whit the mentioned competition slot; nodes go to compete booking in the first channel then shoe to, the second channel; Center control nodes receive the booked on the first signal channel, receive at the second channel at the same time access results and the success of nodes to access the distribution channel resources; each node in the distribution channel resources were Send business groups without conflict. This invention effectively eliminate the signal propagation delay channel throughput of the adverse effects and reduce the appointment of hidden terminal and exposed terminals, packet transmission in the business also eliminates collisions, particularly suitable for the transmission delay as a communication link on the use of Channel Access Multiple Access Method.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com