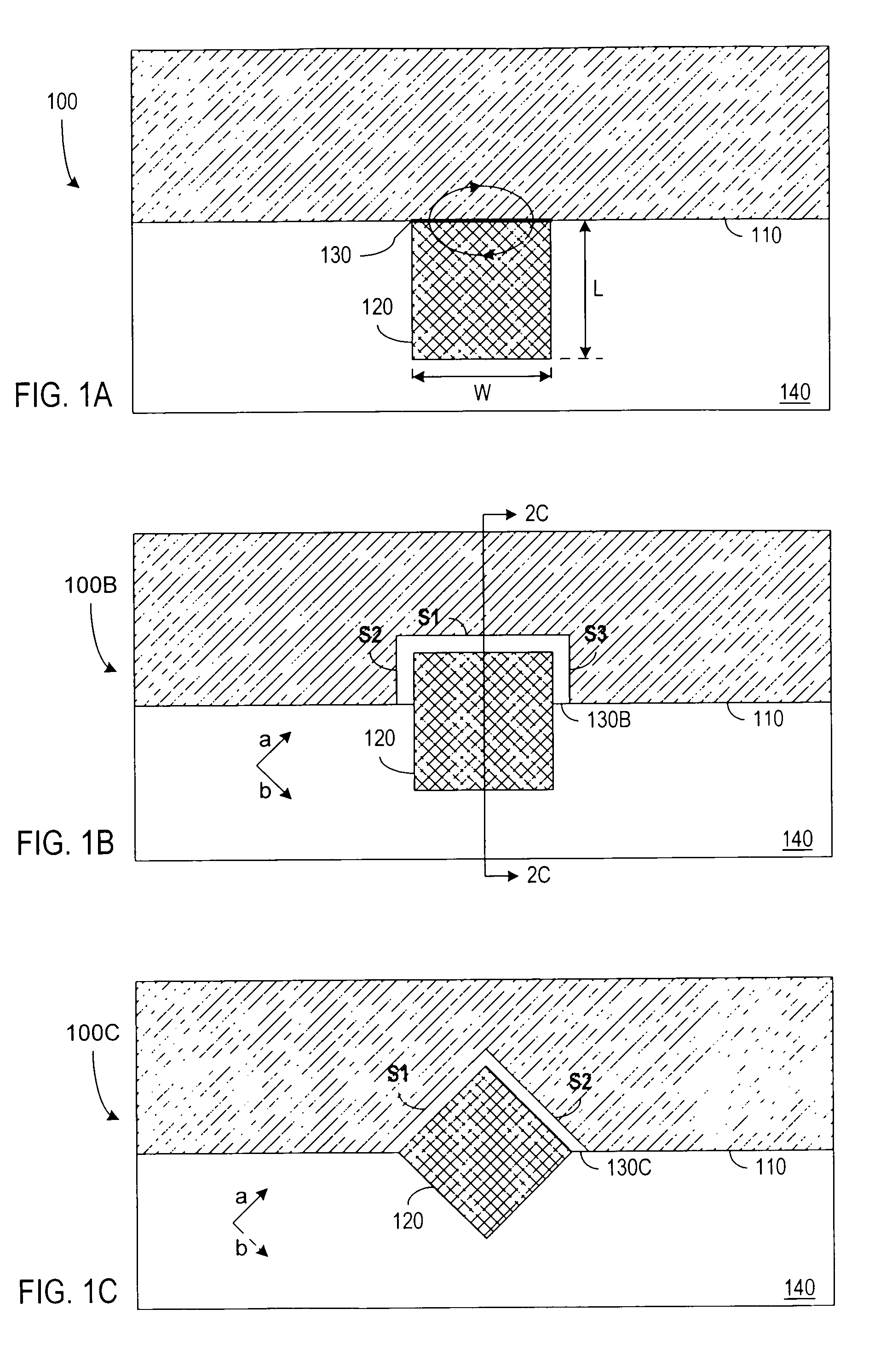
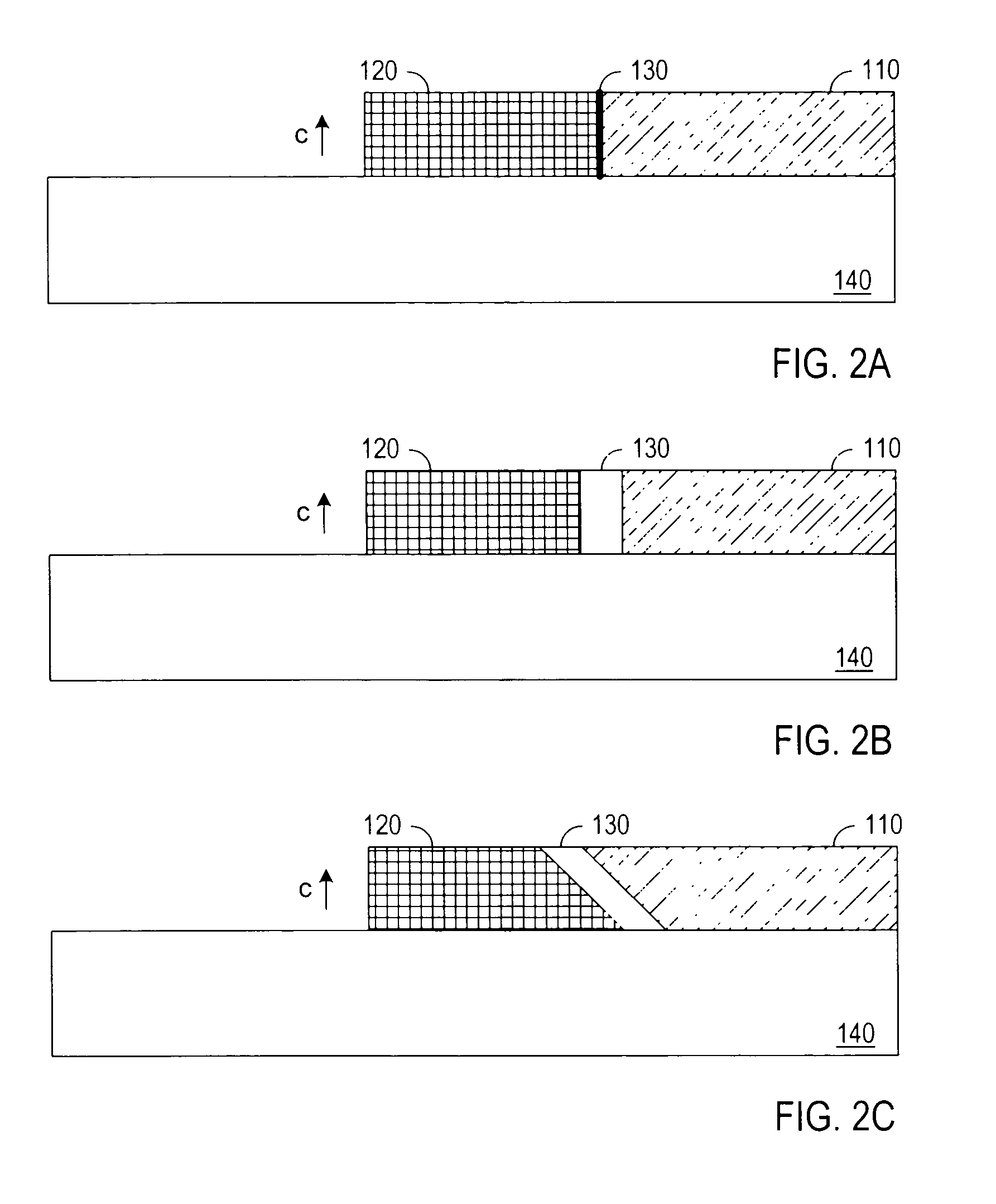
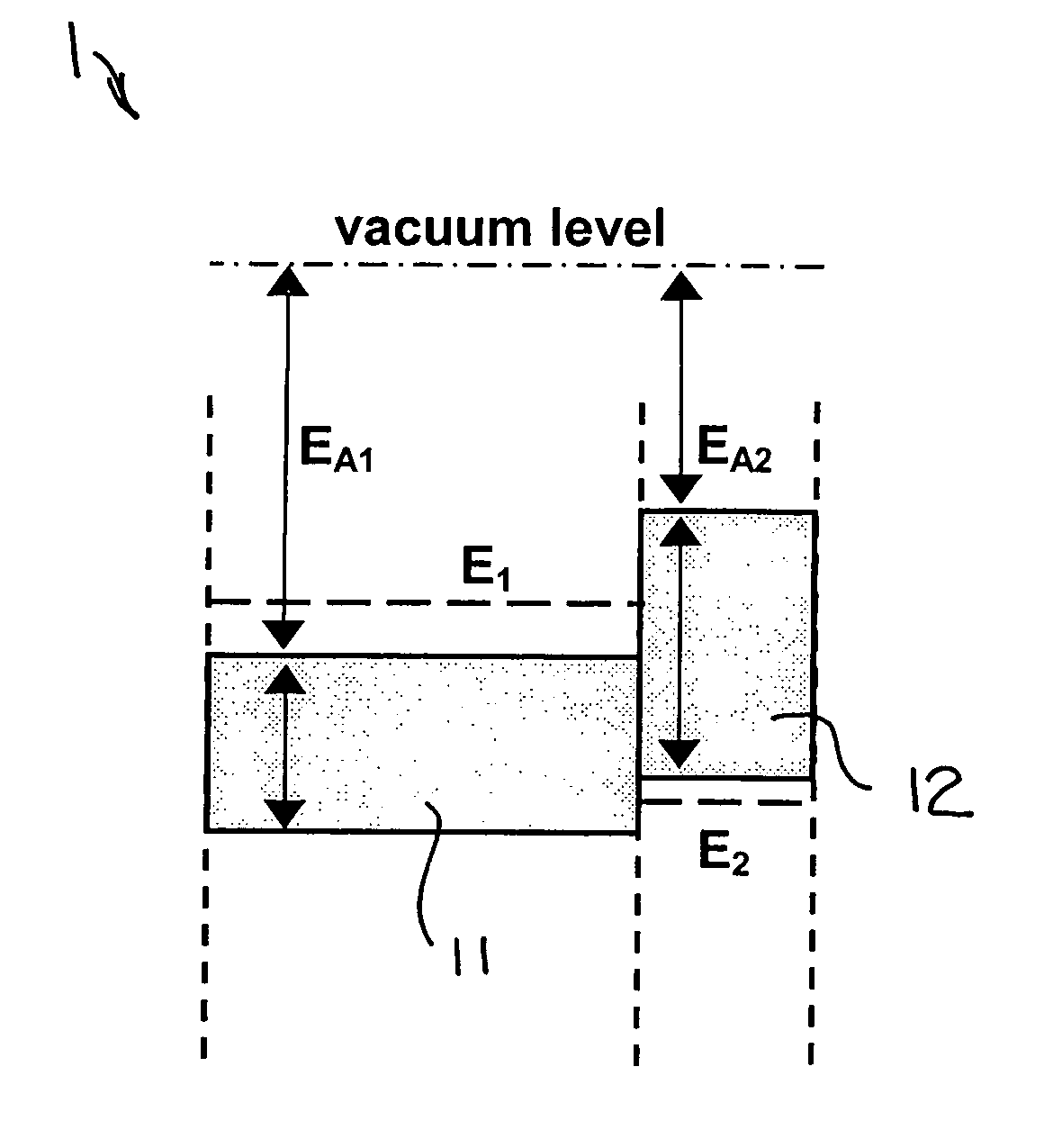
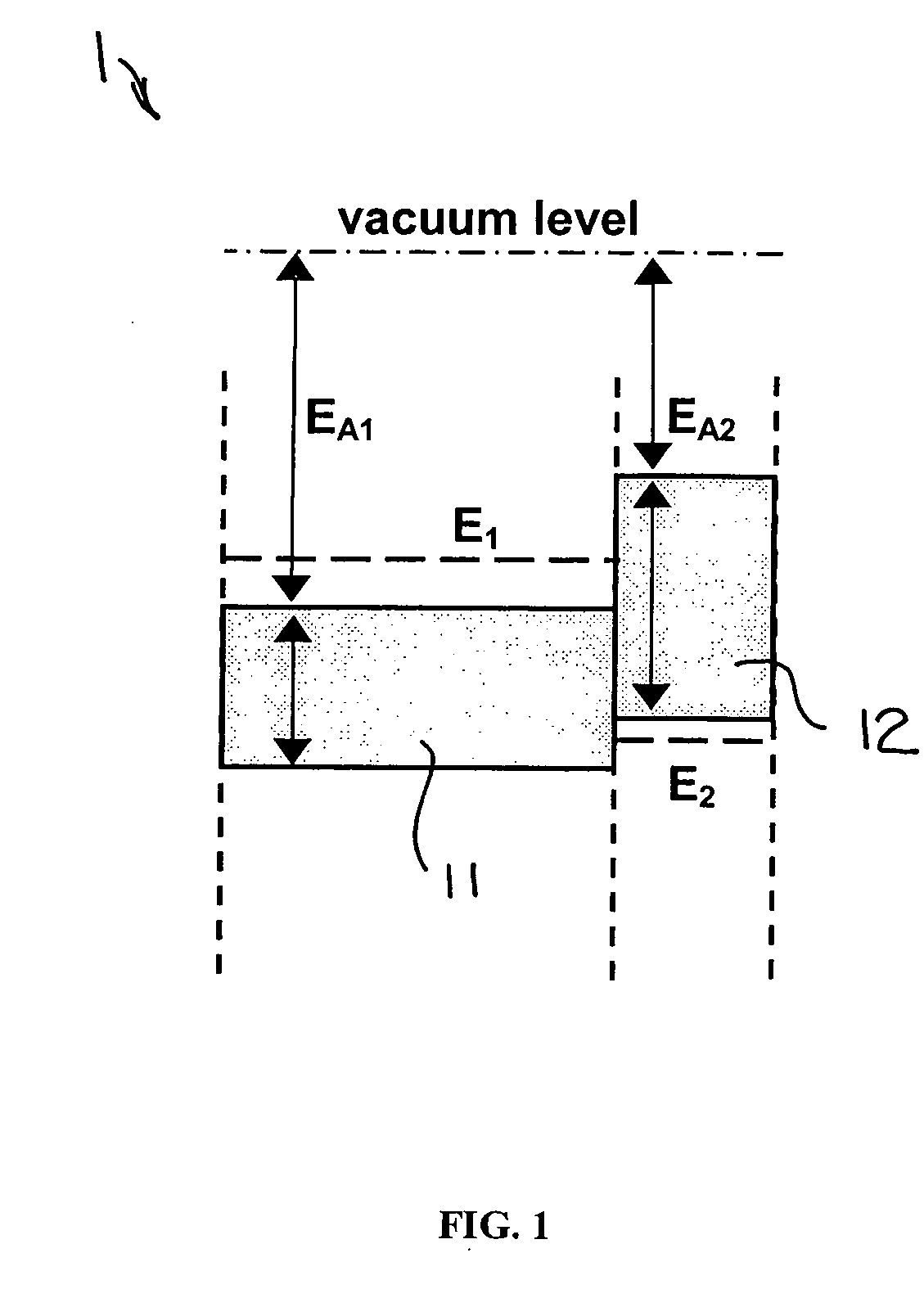
Patents
Literature
890 results about "Ground state" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
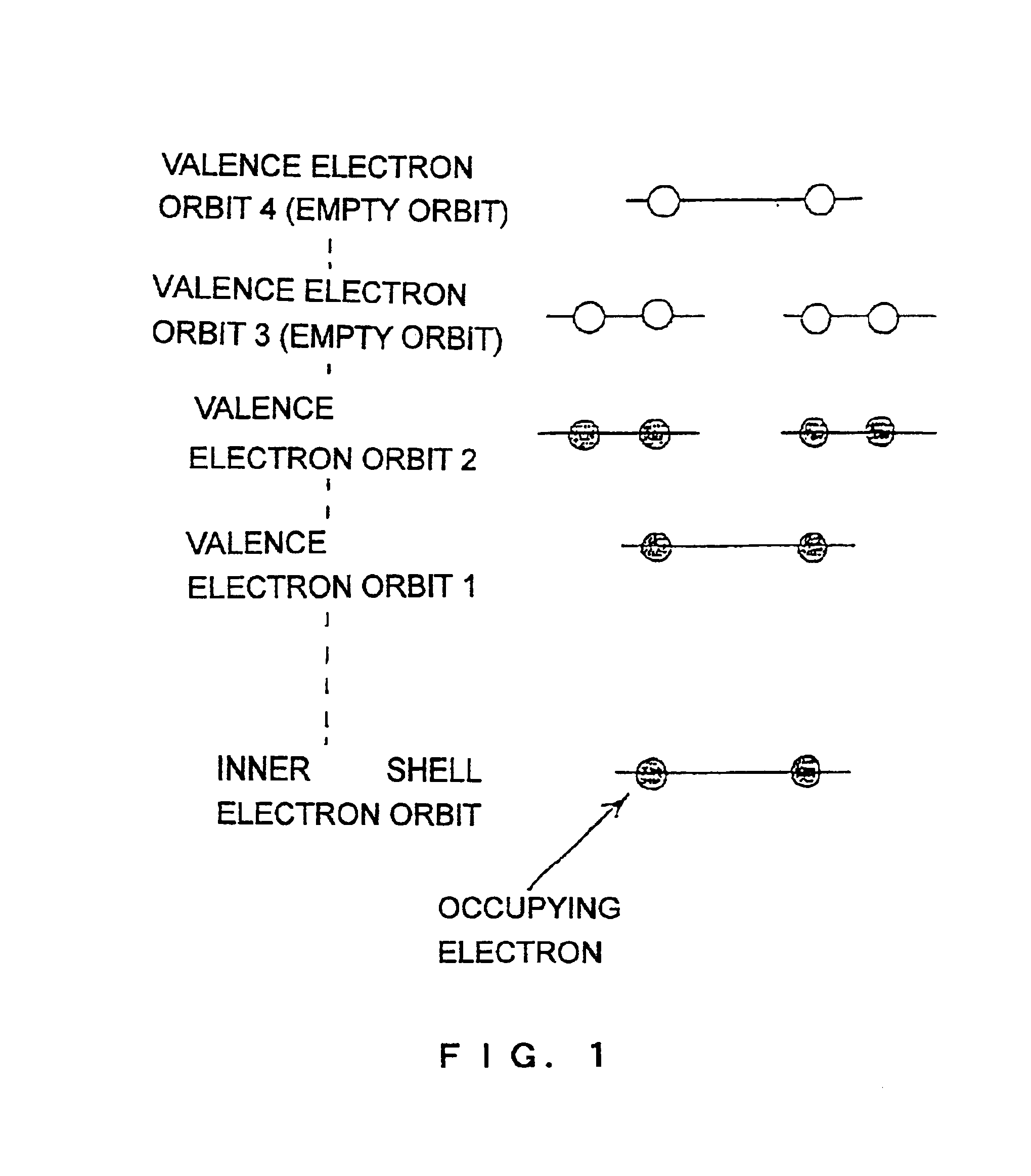
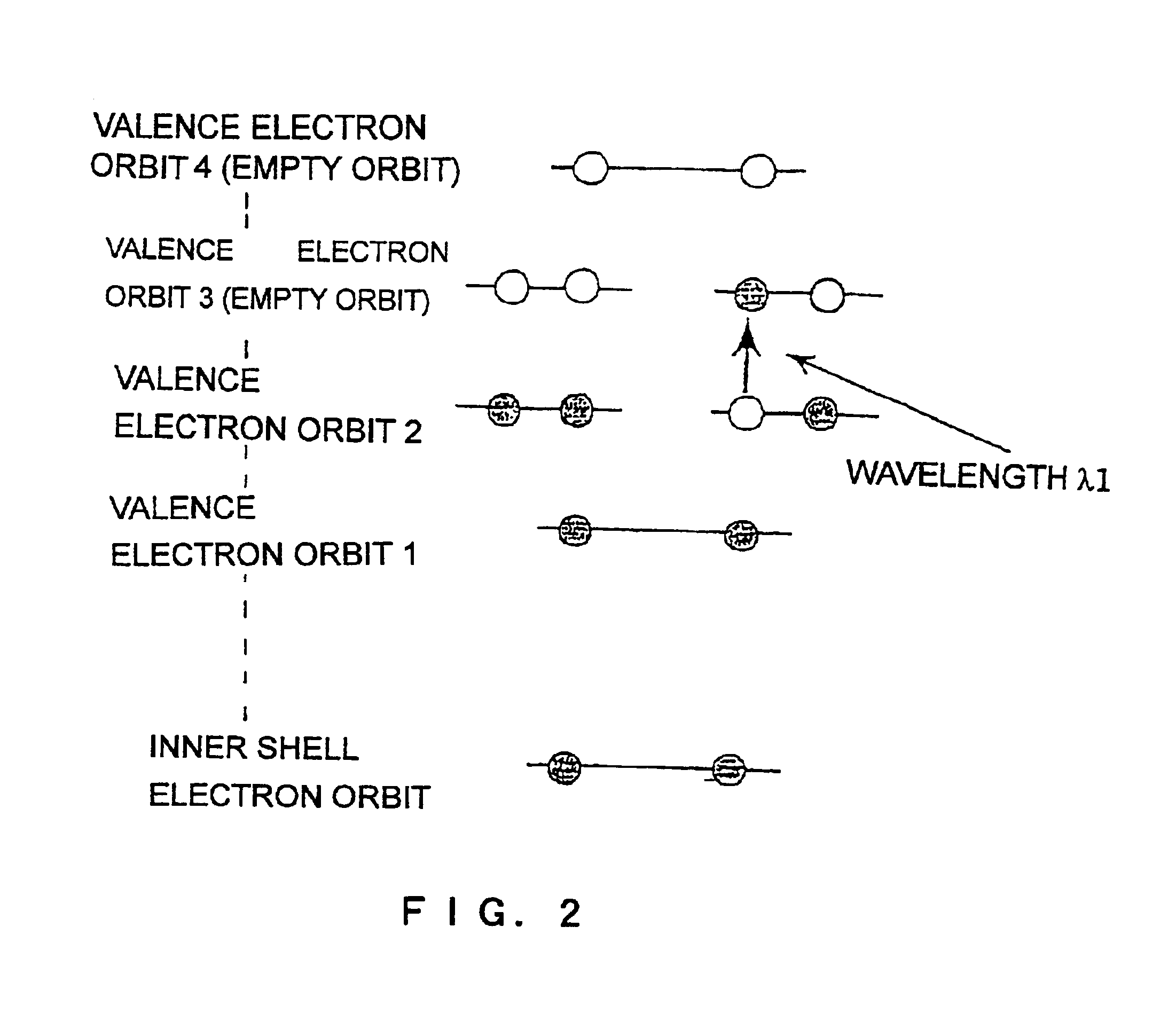
The ground state of a quantum-mechanical system is its lowest-energy state; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system. An excited state is any state with energy greater than the ground state. In the quantum field theory, the ground state is usually called the vacuum state or the vacuum.
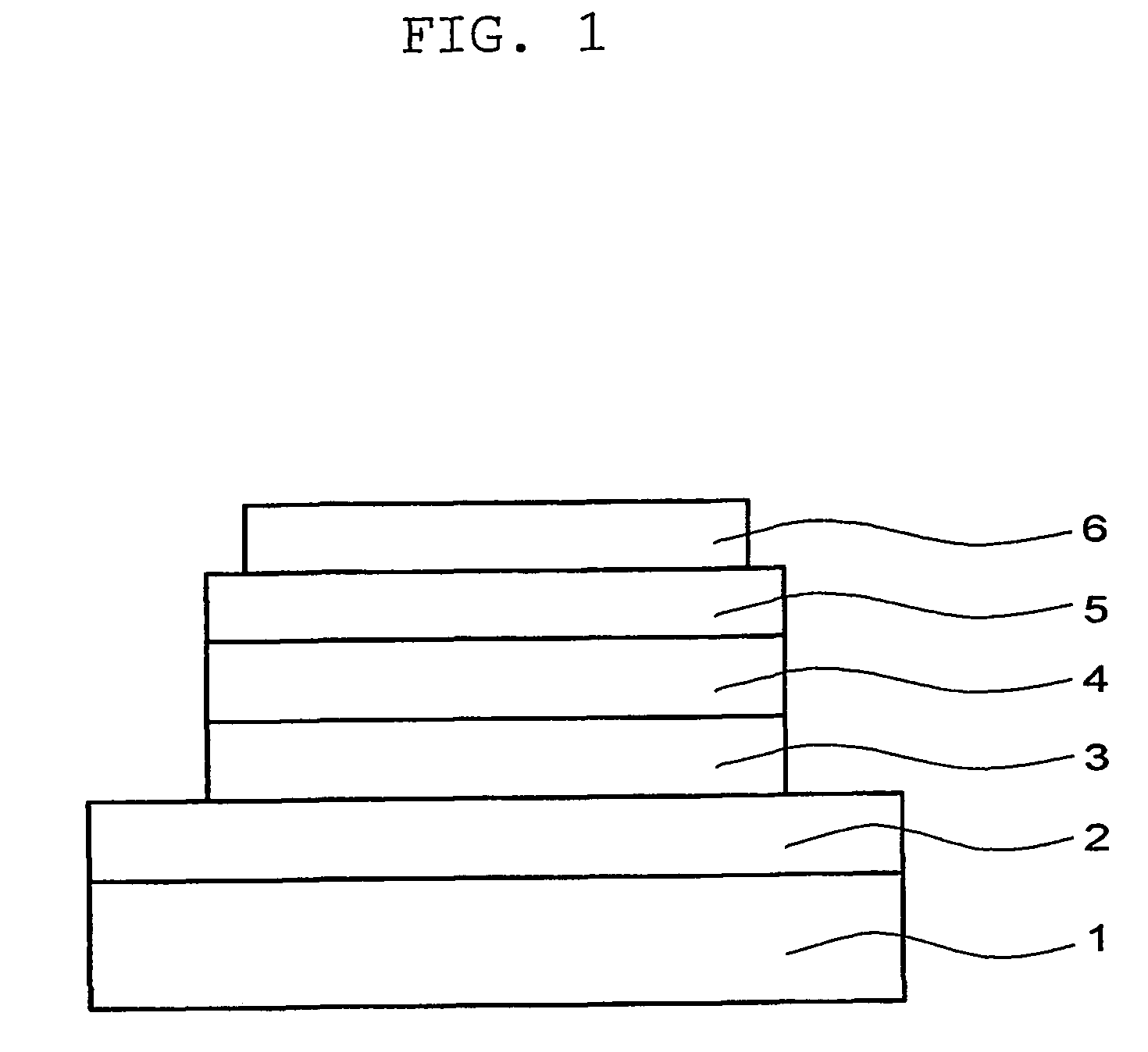
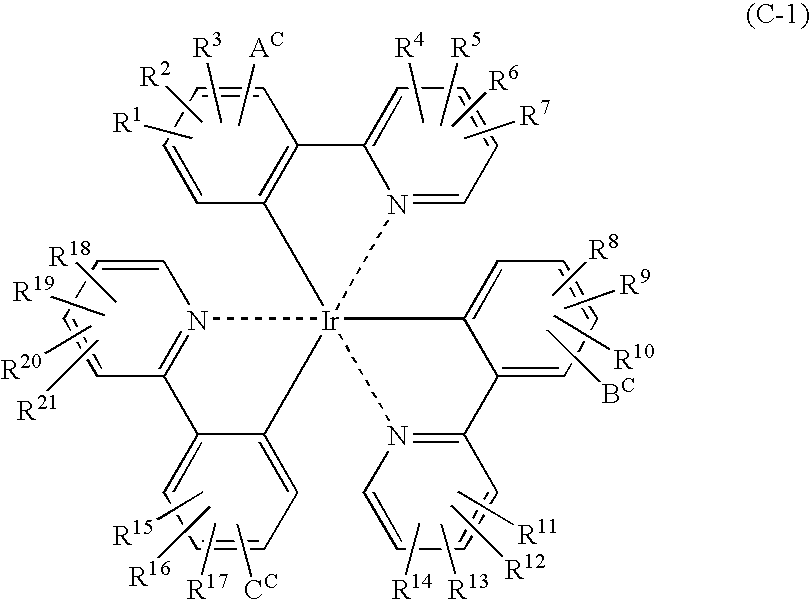
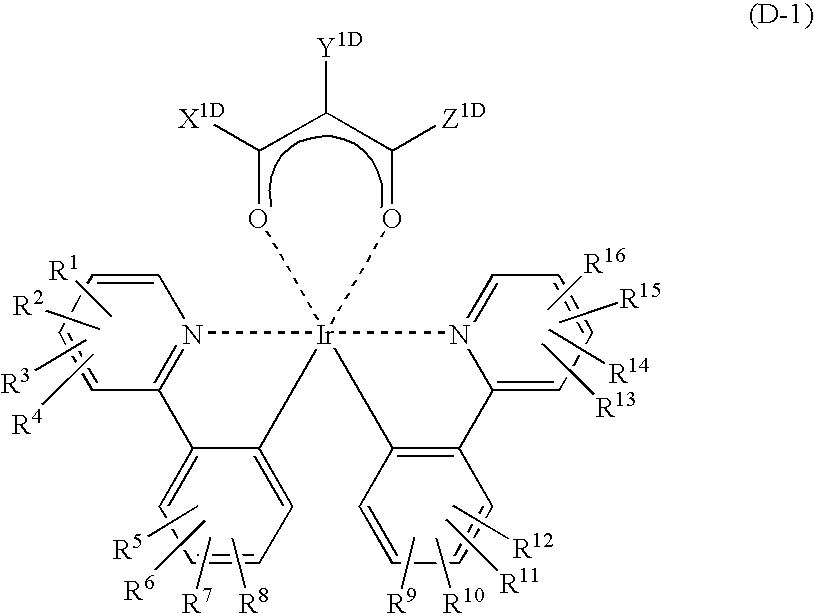
Light emitting material and organic light-emitting device
InactiveUS7396598B2High efficiency of light emissionKeep energy smallDischarge tube luminescnet screensGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsFluorescenceTriplet state
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Light-Emitting Device
ActiveUS20120217487A1External quantum efficiencyIncrease ratingsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingExcited stateLight emitting device
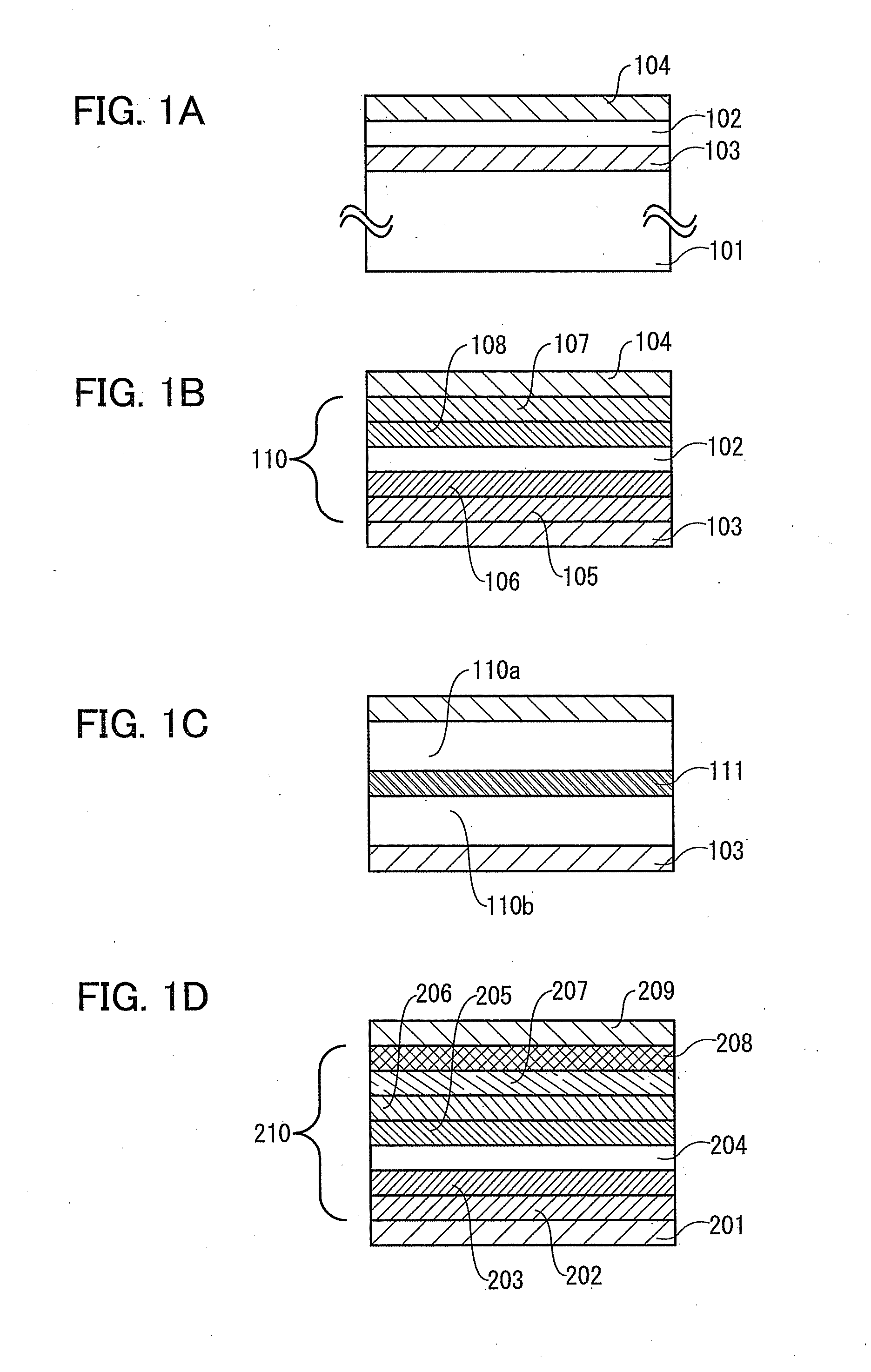
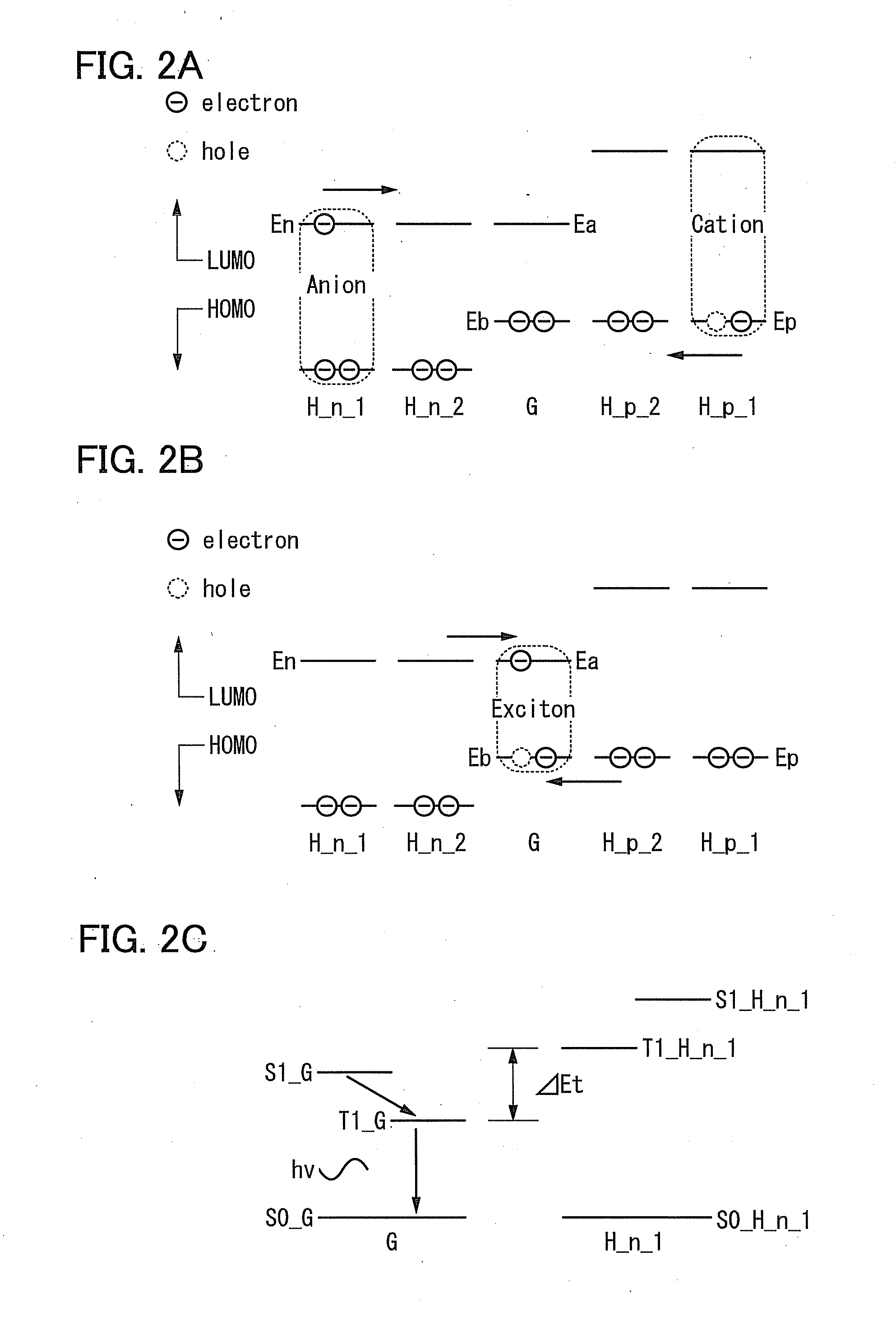
A light-emitting element includes a light-emitting layer including a guest, an n-type host and a p-type host between a pair of electrodes, where the difference between the energy difference between a triplet excited state and a ground state of the n-type host (or p-type host) and the energy difference between a triplet excited state and a ground state of the guest is 0.15 eV or more. Alternatively, in such a light-emitting element, the LUMO level of the n-type host is higher than the LUMO level of the guest by 0.1 eV or more, or the HOMO level of the p-type host is lower than the HOMO level of the guest by 0.1 eV or more.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Super-resolution microscope system and method for illumination
InactiveUS6667830B1High resolutionReducing diffractive limitPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersElectronic statesExcited state
A microscope system comprising an adjusted specimen and a microscope body, wherein the adjusted specimen is dyed with molecule which has three electronic states including at least a ground state and in which an excited wavelength band from the first electron excited state to the second electron excited state overlaps a fluorescent wavelength band upon deexcitation through a fluorescence process from the first electron excited state to a vibrational level in the ground state. There is provided a novel microscope system which is enabled to condense an erase light for exciting a molecule in the first electron excited state to the second electron excited state in an excellent beam profile by using a simple, compact optical system and which has high stability and operability and an excellent super-resolution.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Pixelated capacitance controlled ESC
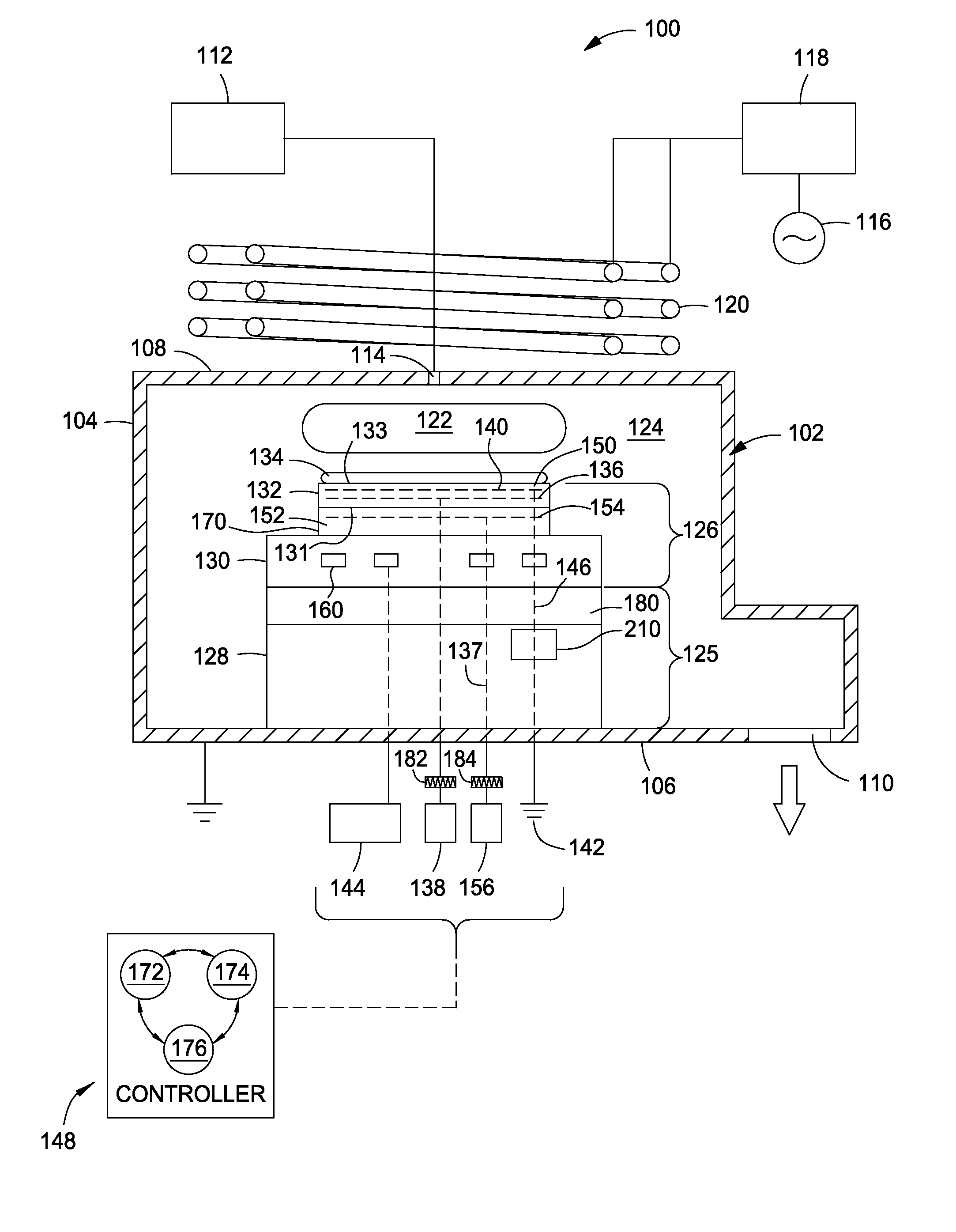
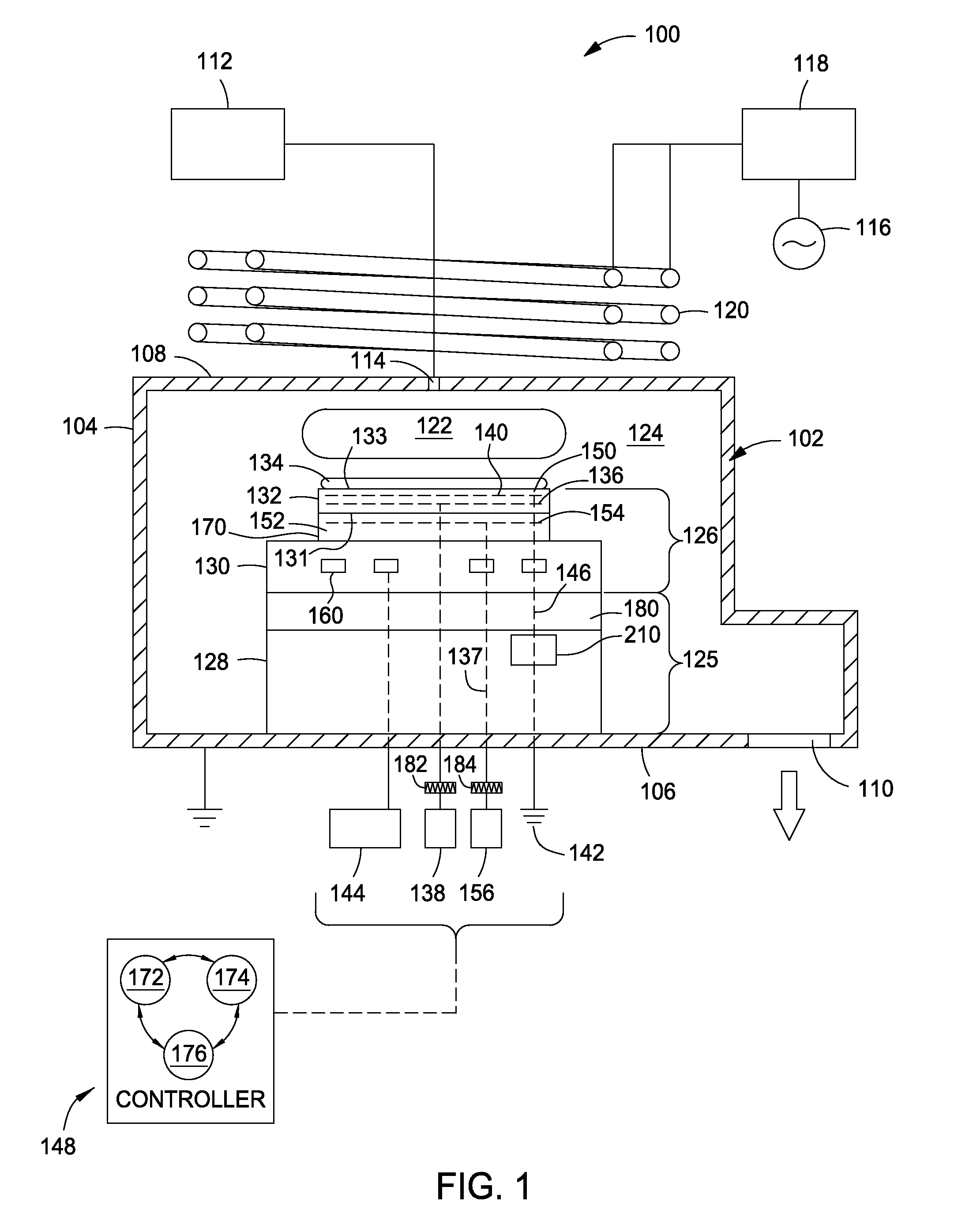
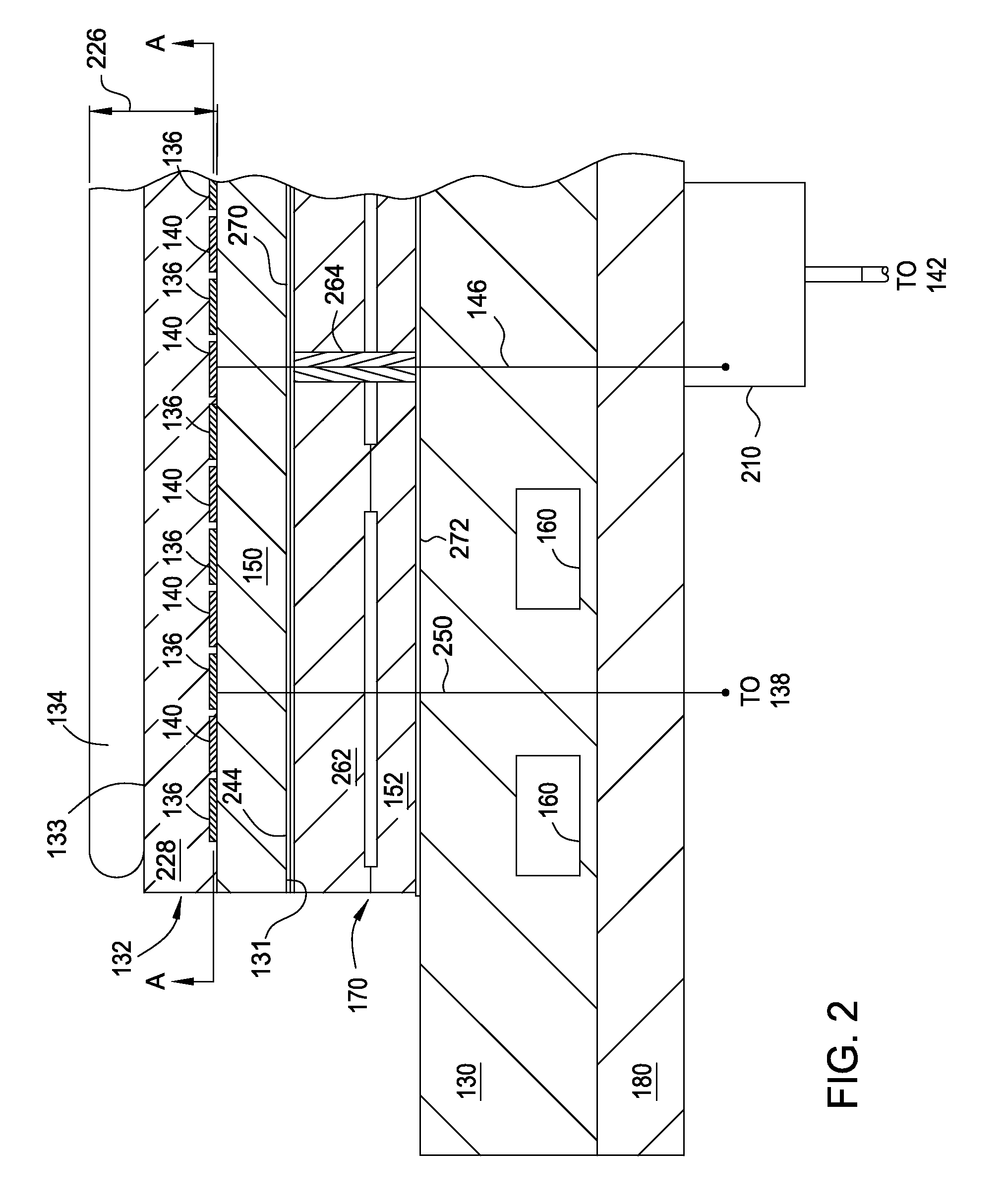
Implementations described herein provide a pixilated electrostatic chuck which enables both lateral and azimuthal tuning of the RF coupling between an electrostatic chuck and a substrate placed thereon. In one embodiment, the pixilated electrostatic chuck (ESC) may include a dielectric body having a workpiece support surface configured to accept a substrate thereon, one or more chucking electrodes disposed in the pixilated ESC, and a plurality of pixel electrodes. The plurality of pixel electrodes are switchable between a floating state and a grounded state, having variable capacitance to ground, or both. The pixel electrodes and the chucking electrodes form a circuit operable to electrostatically chuck the substrate to the workpiece support surface.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
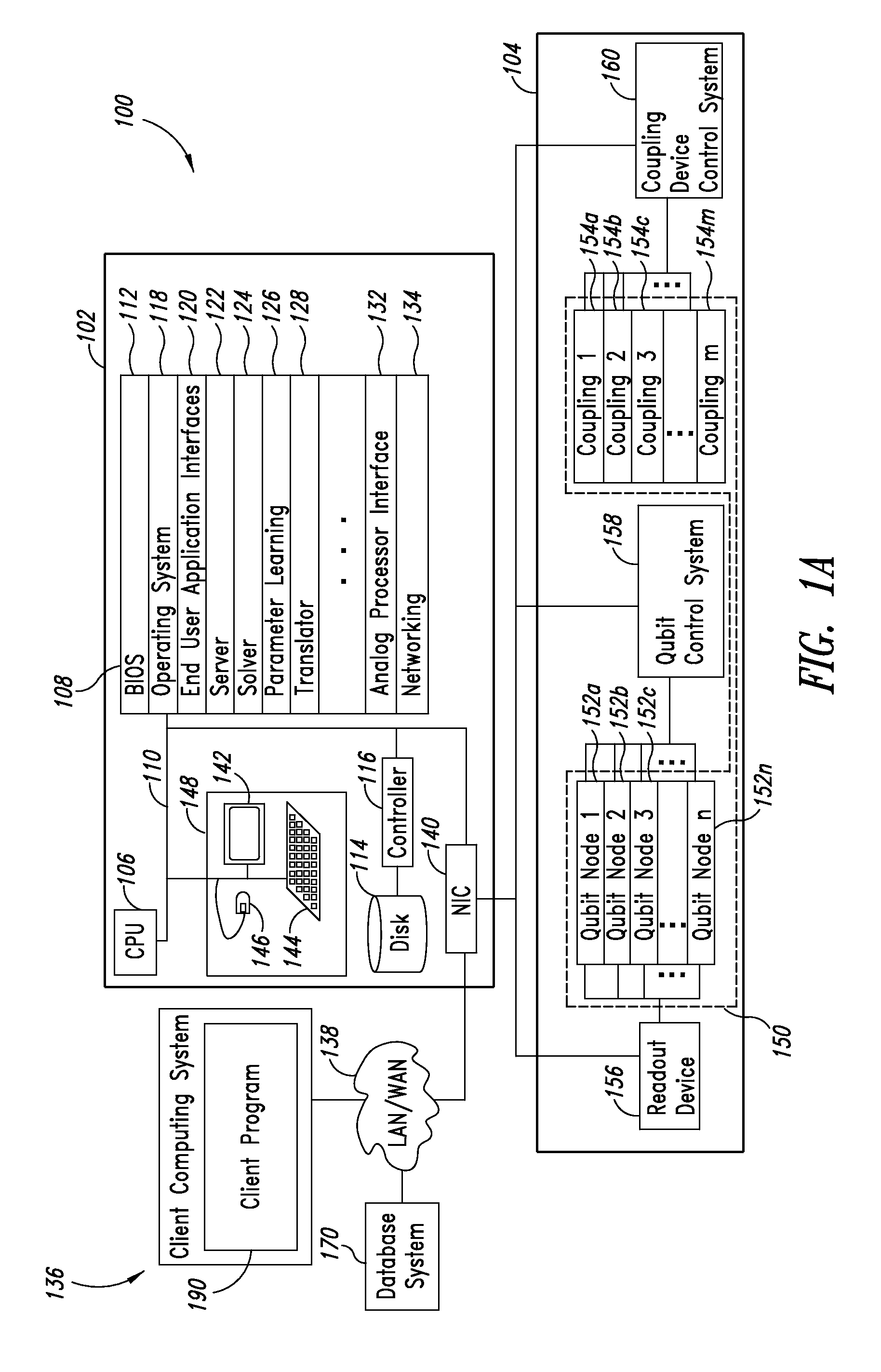
Conditional Rabi oscillation readout for quantum computing
A method for determining whether a first state of a quantum system is occupied is provided. A driving signal is applied to the system at a frequency corresponding to an energy level separation between a first and second state of the system. The system produces a readout frequency only when the first state is occupied. A property of a measurement resonator that is coupled to the quantum system is measured when the quantum system produces the readout frequency, thereby determining whether the first state of the quantum system is occupied. A structure for detecting a qubit state of a qubit is provided. The structure comprises a quantum system that includes the qubit. The qubit has first and second basis states and an ancillary quantum state. The ancillary quantum state can be coupled to the first or second basis states. The structure has a measurement resonator configured to couple to Rabi oscillations between (i) one of the first and second basis states and (ii) the ancillary state in the quantum system.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Adiabatic quantum computation with superconducting qubits
InactiveUS20050250651A1Quantum computersNanoinformaticsAdiabatic quantum computationComputational problem
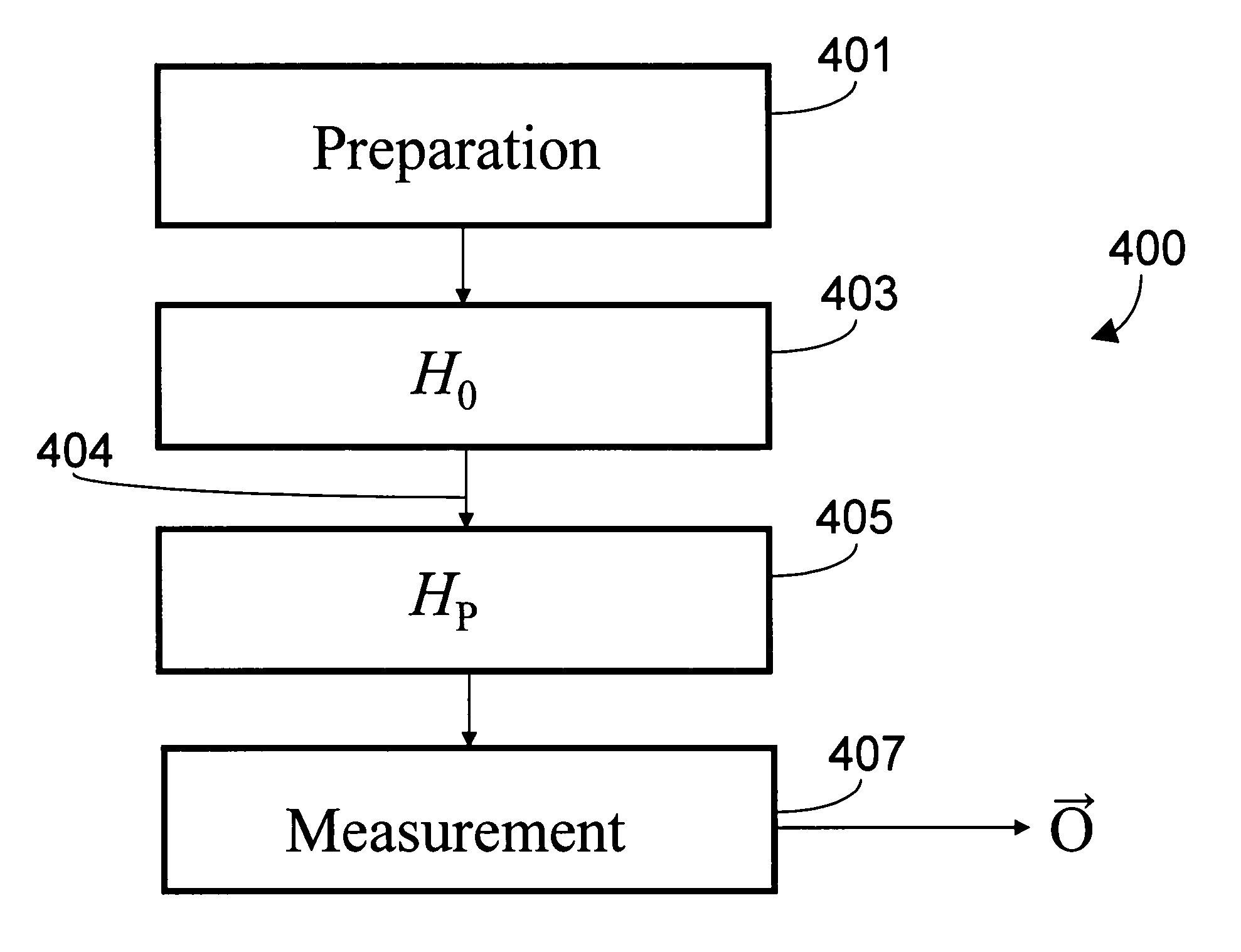
A computer program product with computer program mechanism embedded therein is provided. The mechanism has instructions for initializing a quantum system, which includes a plurality of qubits, to an initialization Hamiltonian HO. The system is capable of being in one of at least two configurations at any give time including HO and a problem Hamiltonian HP. Each respective first qubit in the plurality of qubits is arranged with respect to a respective second qubit in the plurality of qubits such that the first respective qubit and the second respective qubit define a predetermined coupling strength. The predetermined coupling strengths between the qubits in the plurality of qubit collectively define a computational problem to be solved. The mechanism further comprises instructions for adiabatically changing the system until it is described by the ground state of the problem Hamiltonian HP and instructions for reading out the state of the system.
Owner:AMIN MOHAMMAD H S +4
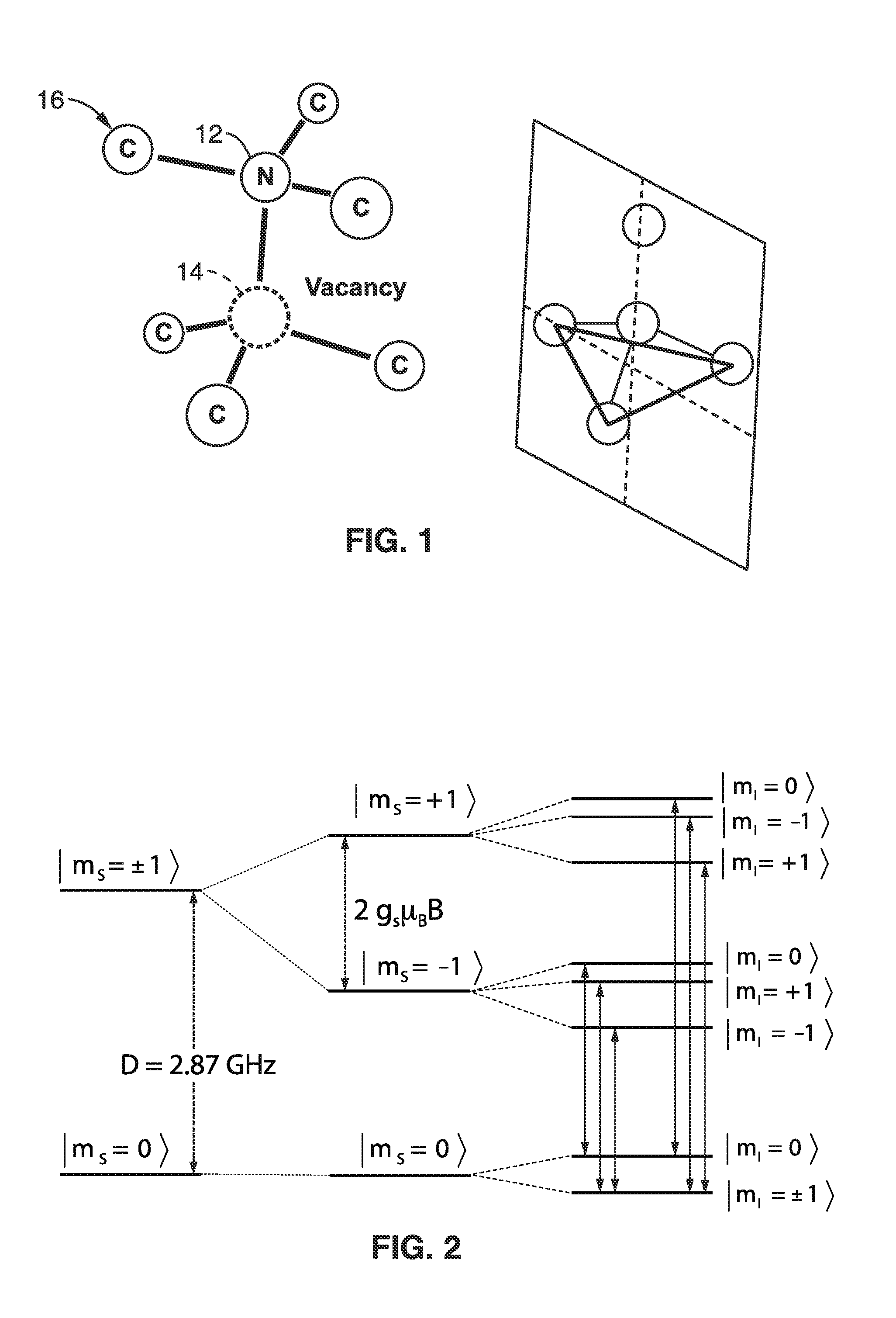
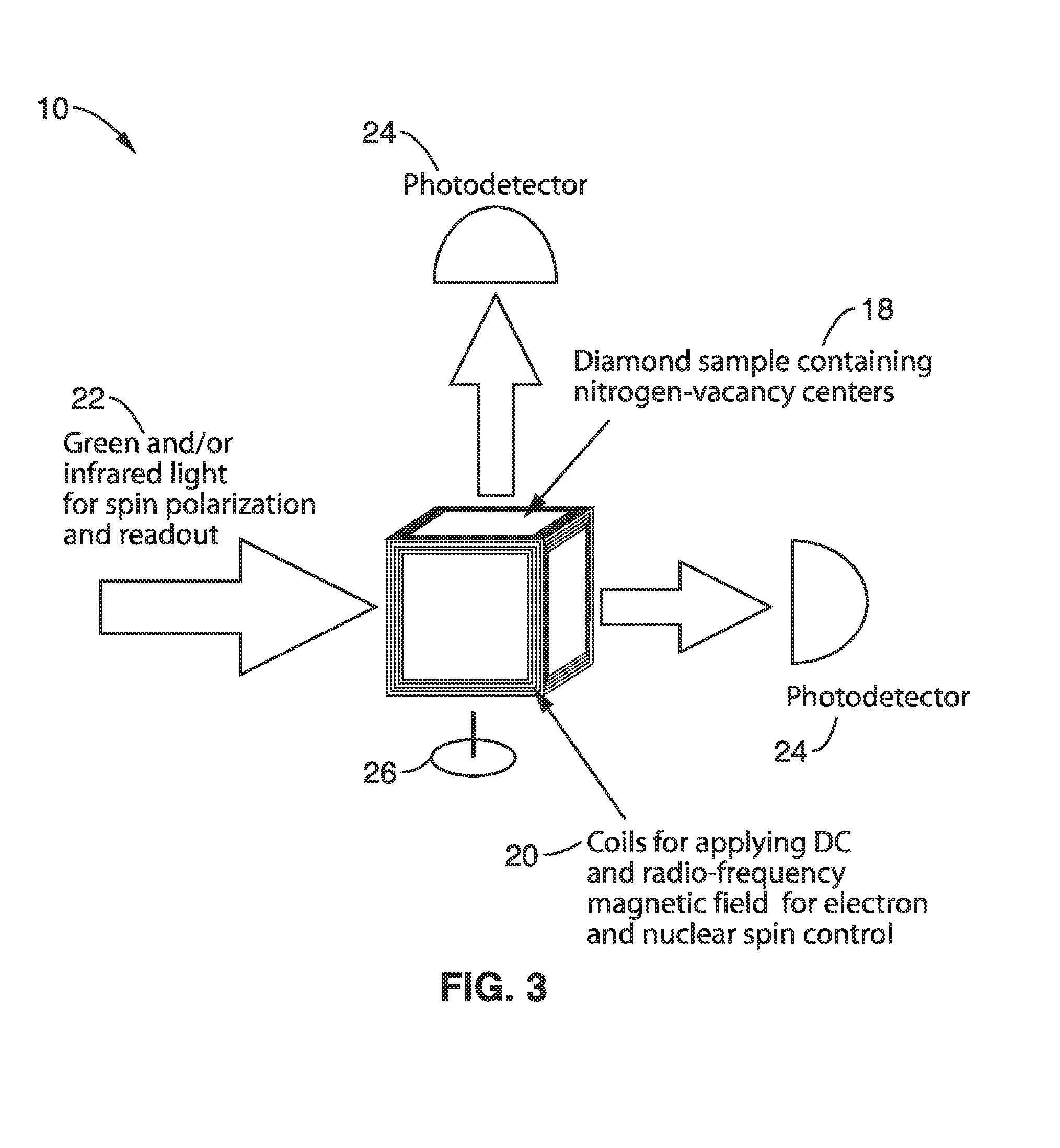
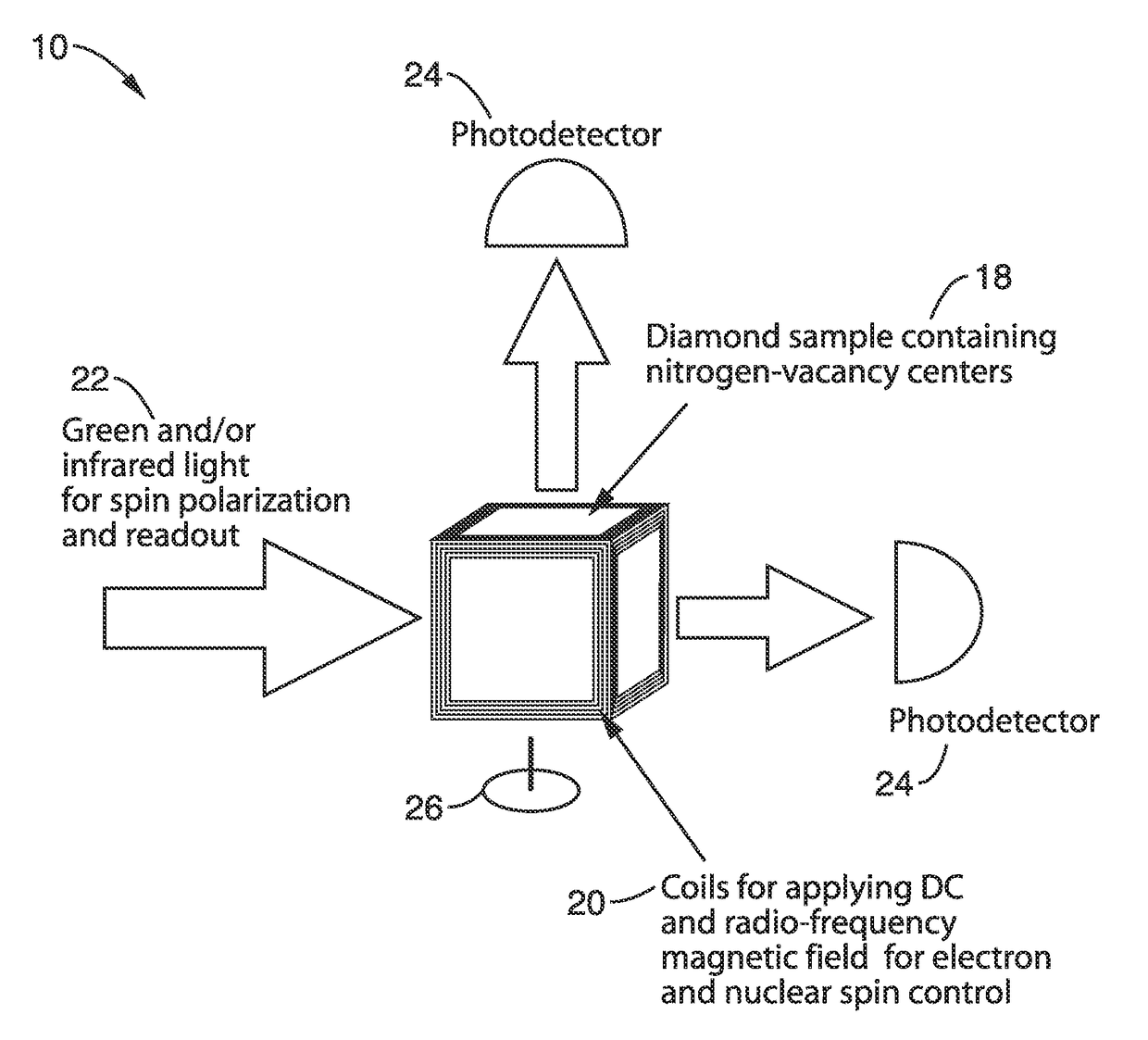
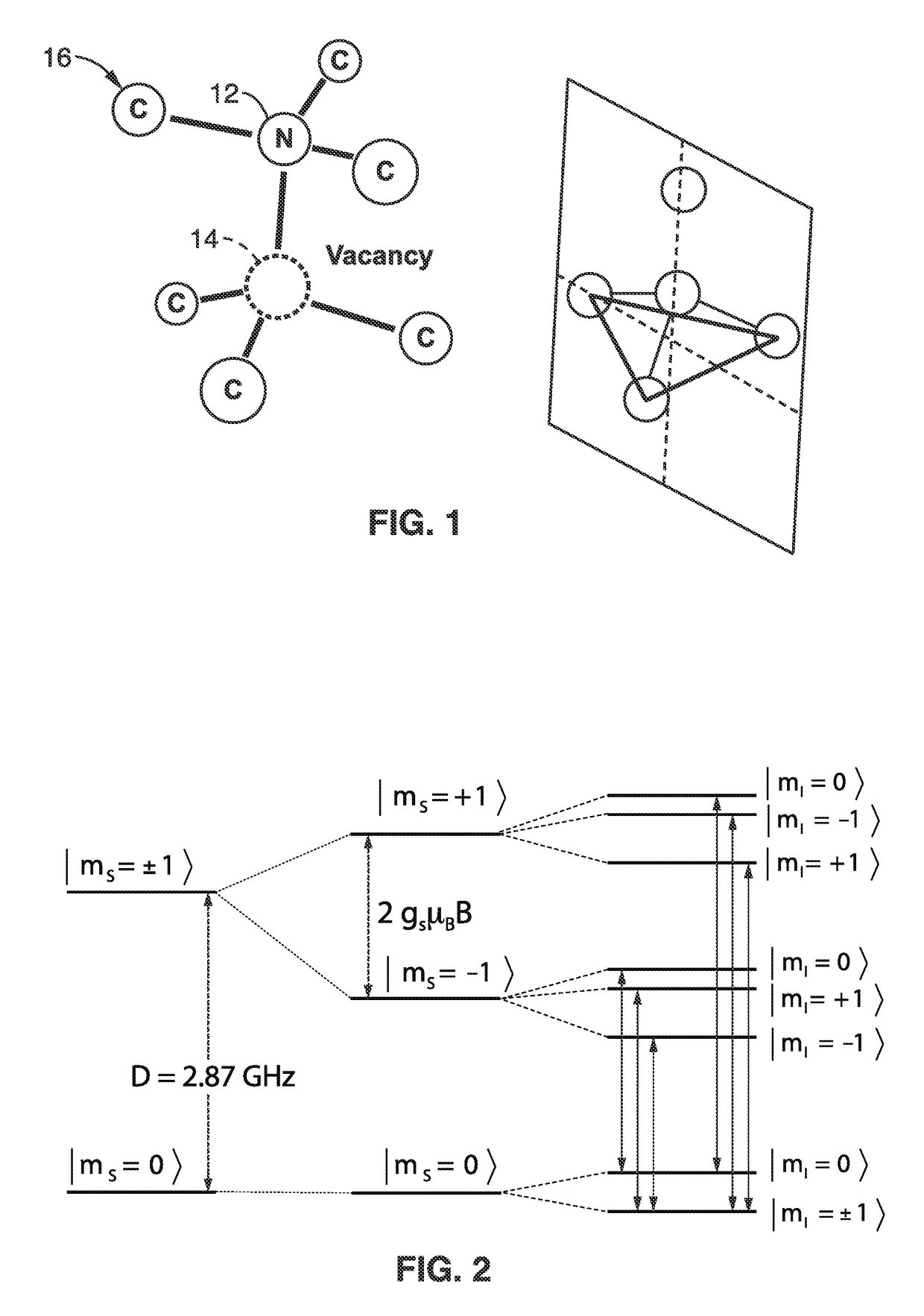
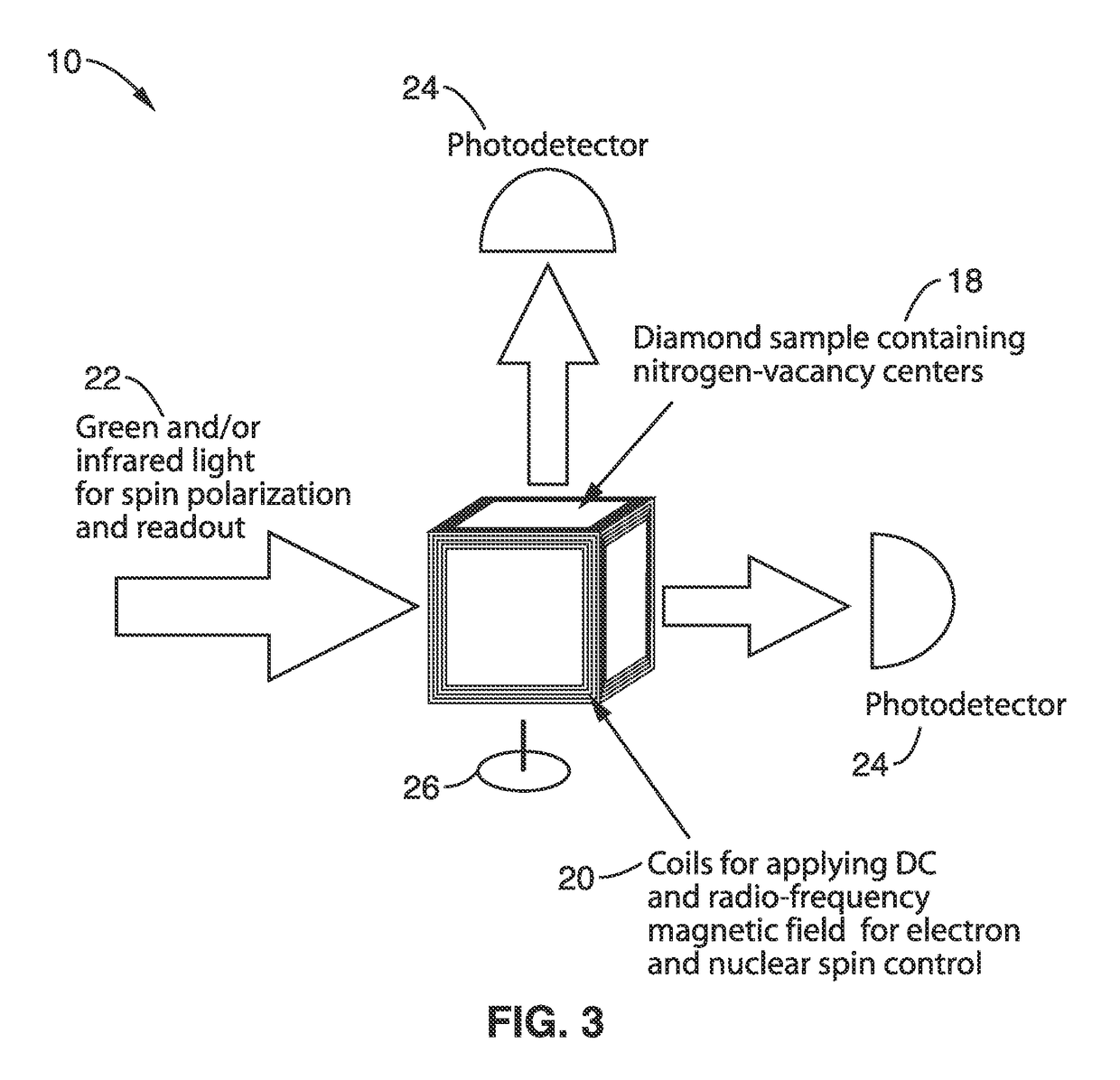
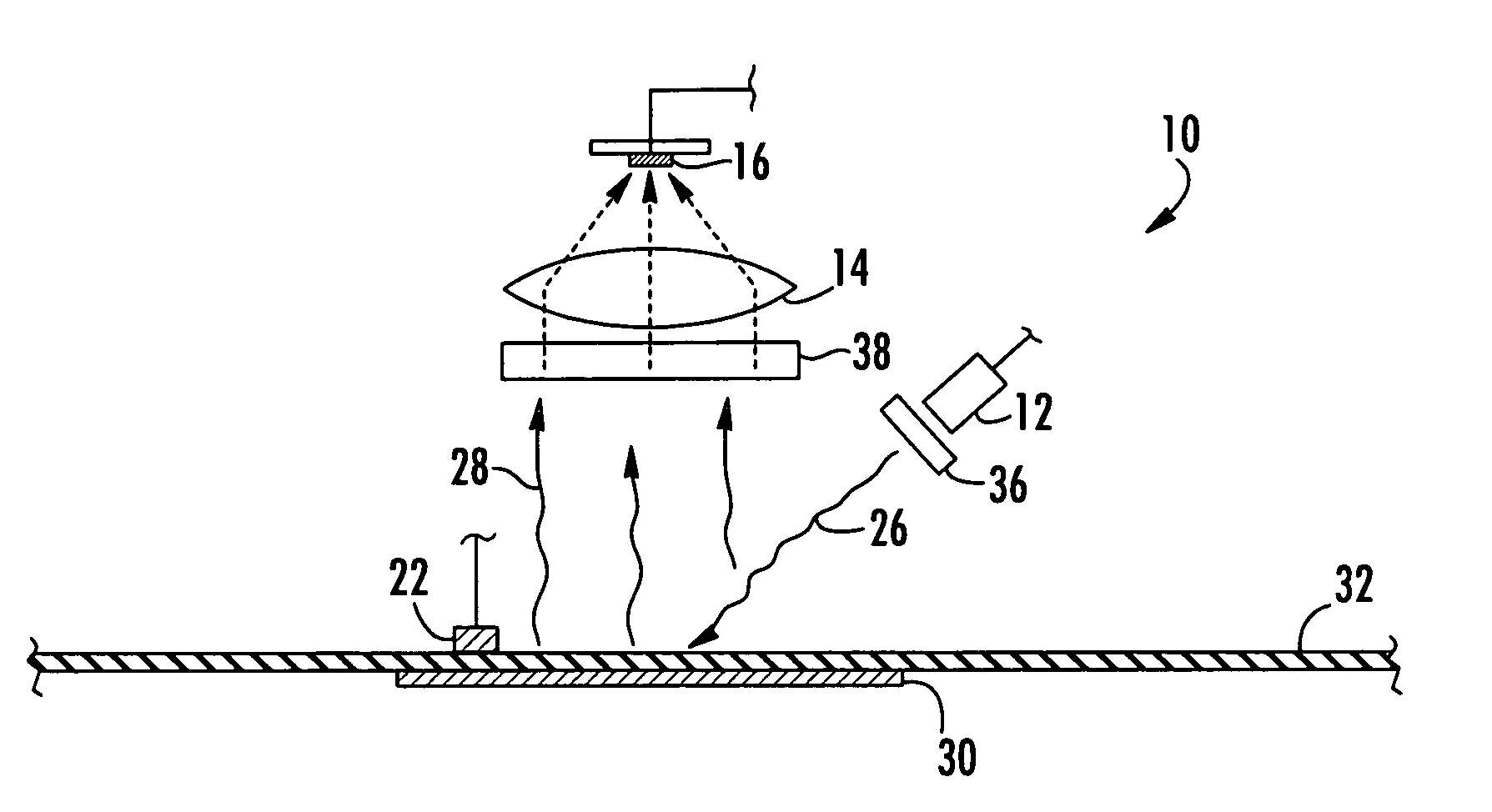
Gyroscopes based on nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond
ActiveUS20150090033A1Small dimensionThermal robustnessAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopePhase shifted
A solid-state gyroscope apparatus based on ensembles of negatively charged nitrogen-vacancy (NV−) centers in diamond and methods of detection are provided. In one method, rotation of the NV− symmetry axis will induce Berry phase shifts in the NV− electronic ground-state coherences proportional to the solid angle subtended by the symmetry axis. A second method uses a modified Ramsey scheme where Berry phase shifts in the 14N hyperfine sublevels are employed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
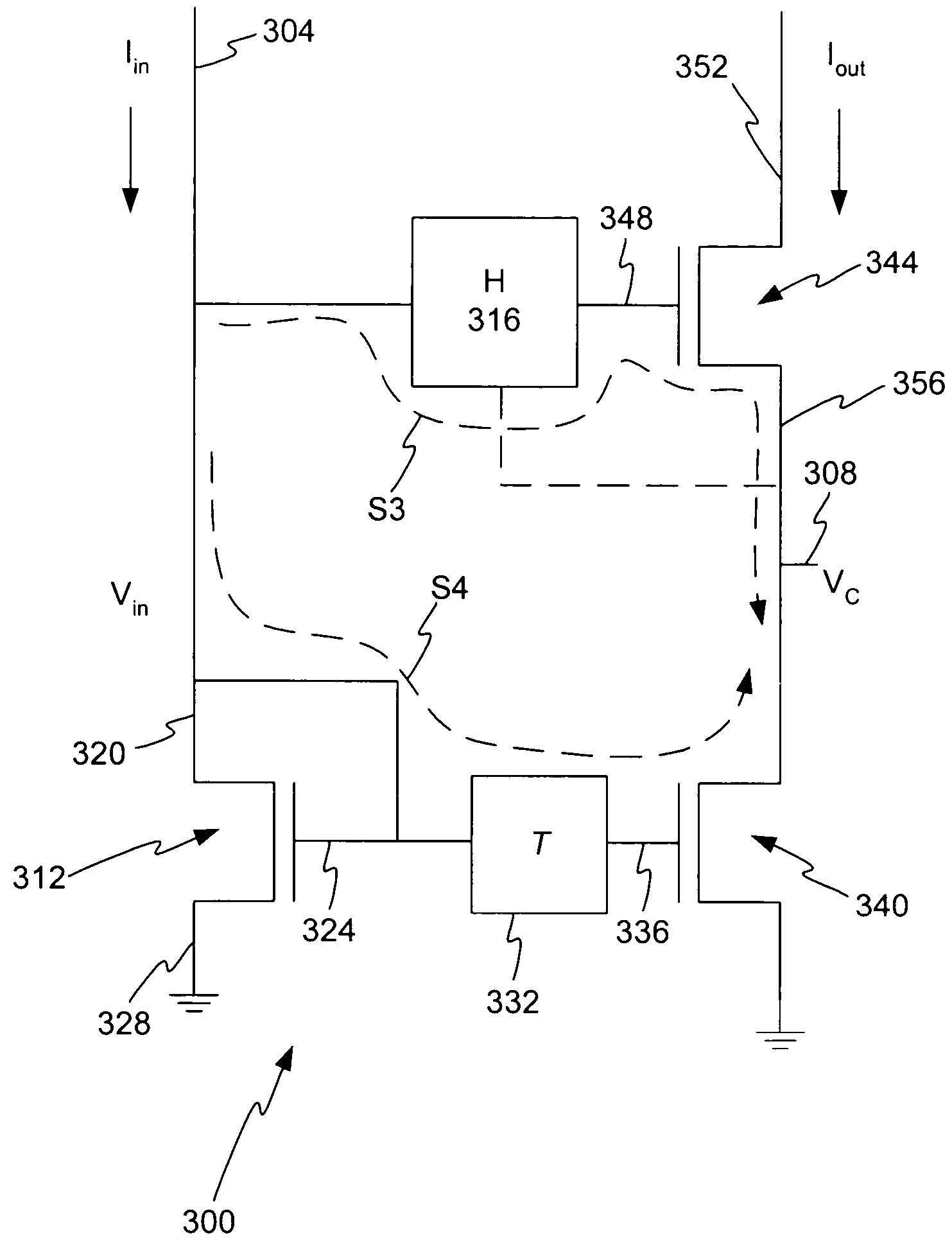
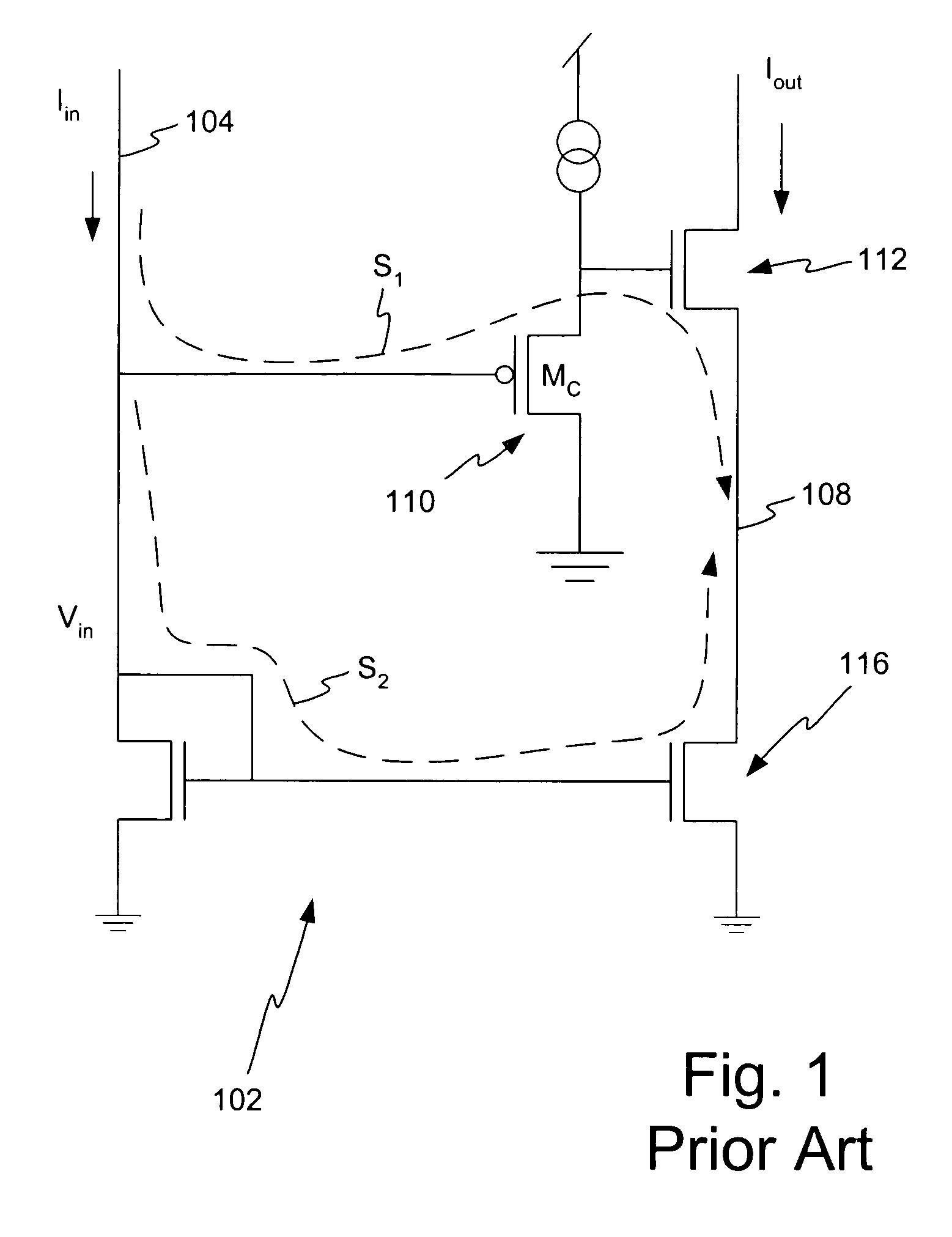
Method and apparatus for increasing the linearity and bandwidth of an amplifier
ActiveUS20050083130A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric variable regulationCascodeEngineering
A method and apparatus is disclosed for improving high frequency performance of an amplifier, such as for example, a current mirror. In one embodiment, a delay element is introduced in a current mirror signal path to account for signal propagation delay that may exist in one or more alternative signal paths. The delay element maintains desired phase alignment at a cascade node of the current mirror thereby establishing, in one embodiment, the cascode node (Vc) in an AC ground state. To extend current mirror high frequency capability an embodiment is disclosed having cross-coupled capacitors, active elements, or one or more other devices configured to provide positive feedback to one or more current mirror inputs. The positive feedback may be selectively configured to increase the operational bandwidth of the current mirror.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Microstrip Antenna And High Frequency Sensor Using Microstrip Antenna
InactiveUS20080088510A1Simple structureAvoid inefficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringTransmission loss
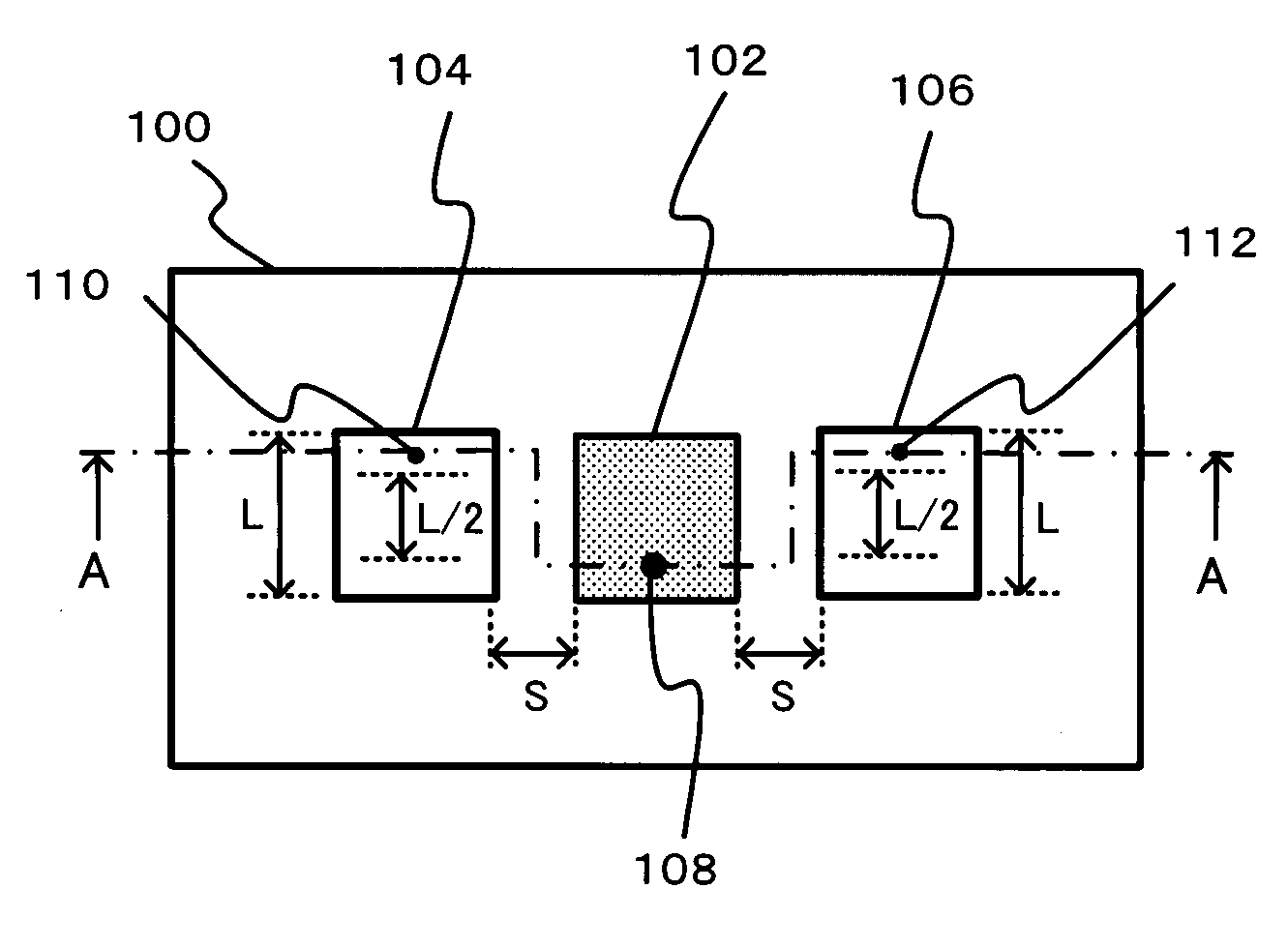
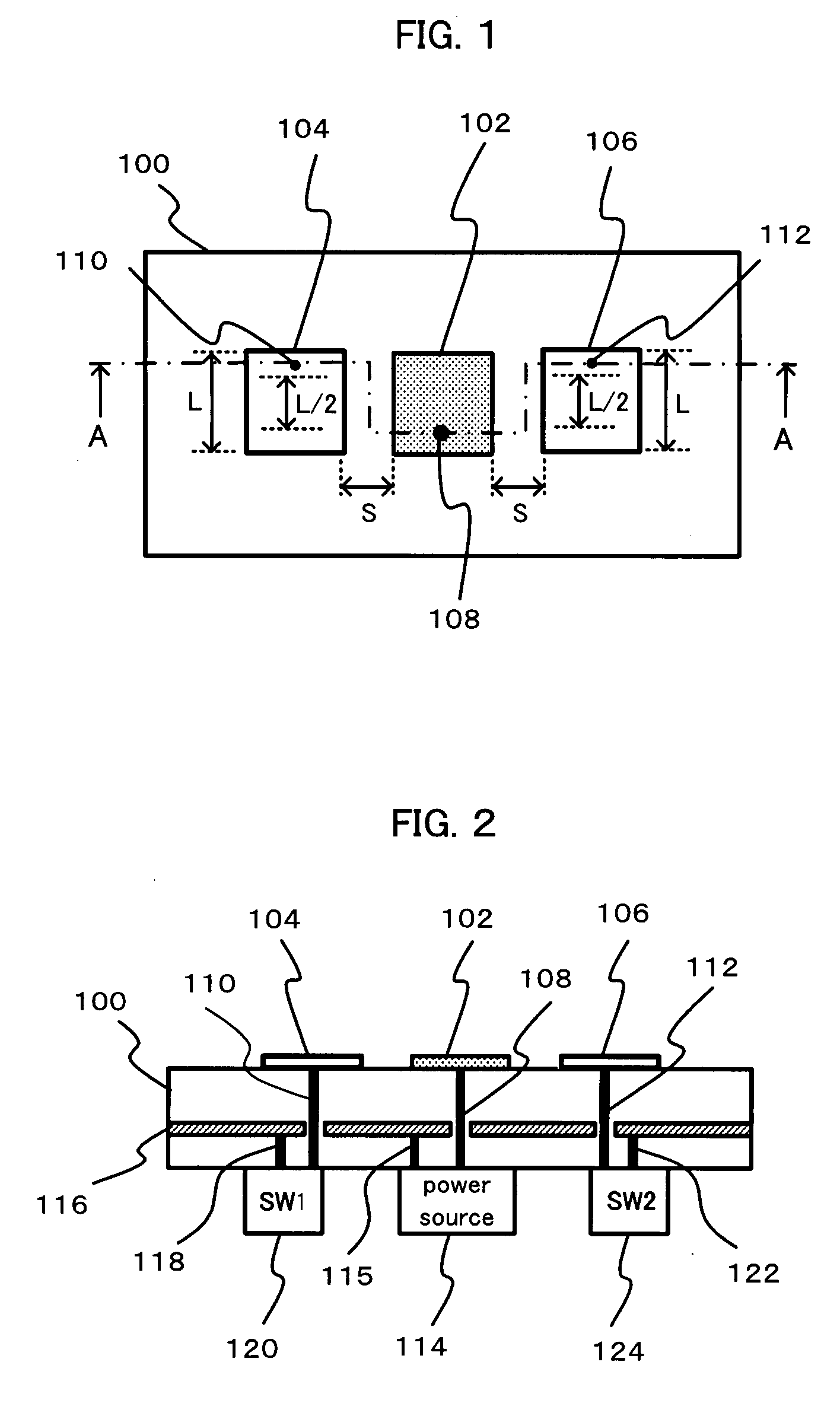
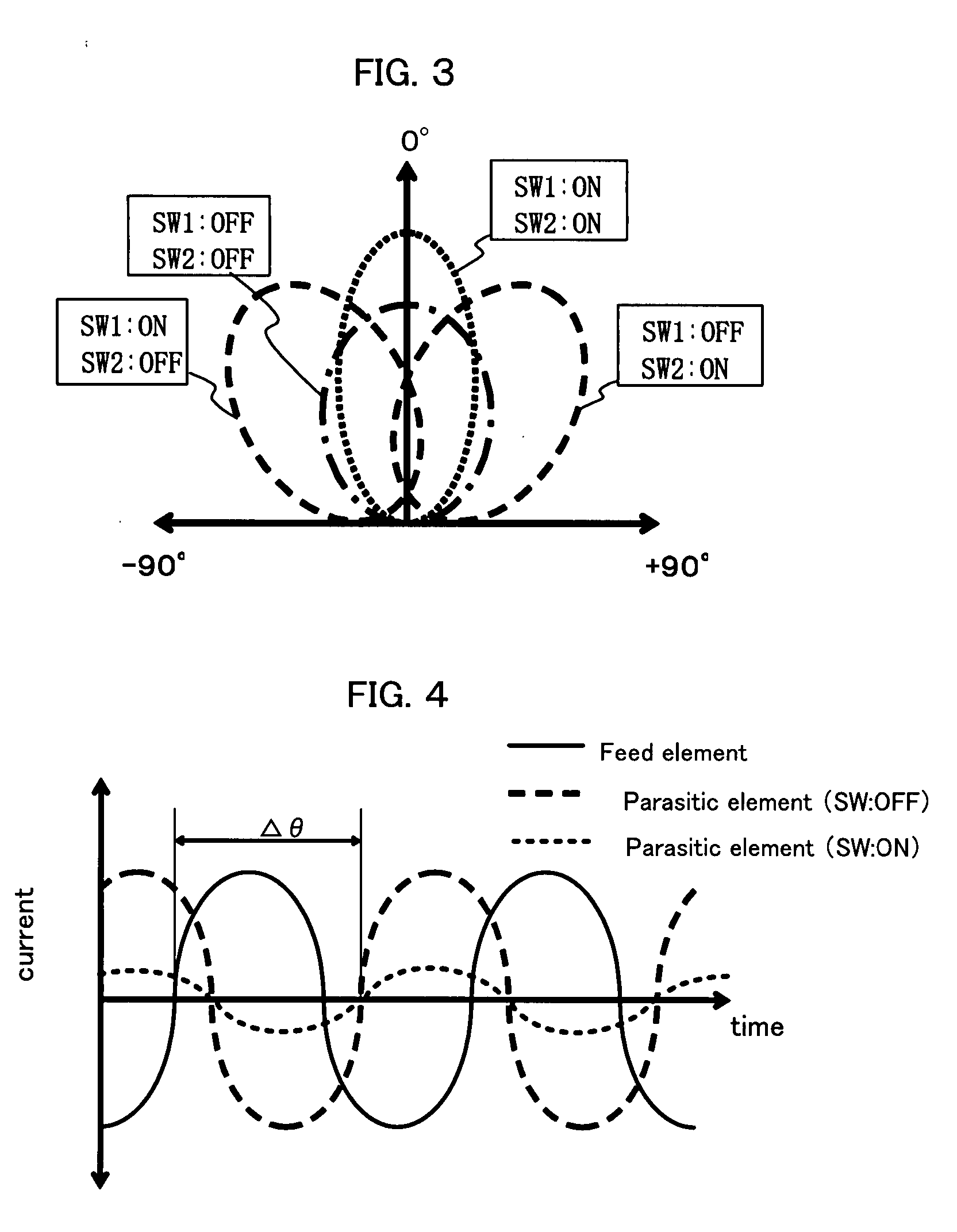
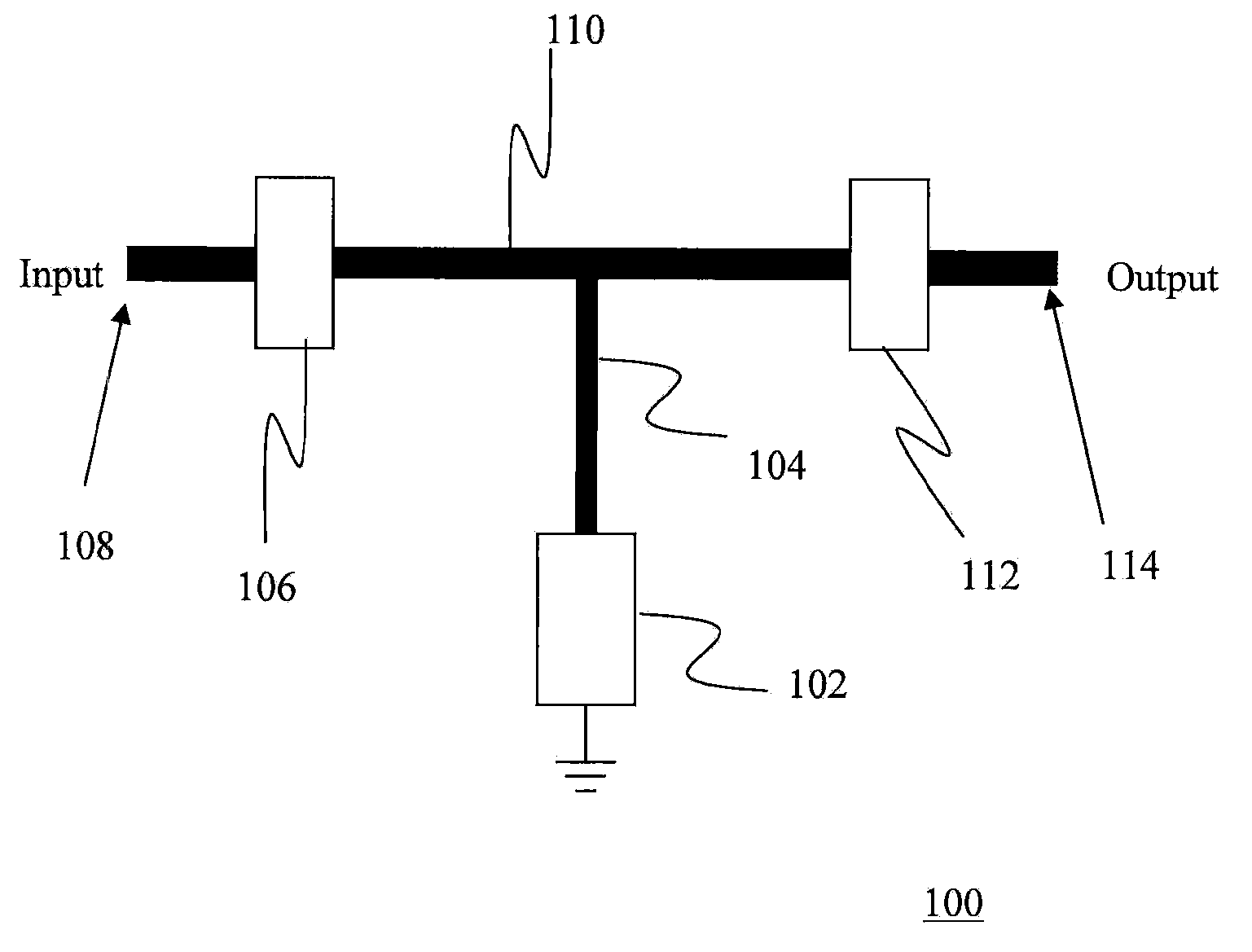
A microstrip antenna has feed element 102 and parasitic elements 104, 106 on the front surface of substrate 1. Microwave electrical power is applied to feed element 102. Parasitic elements 104, 106 are connected via through hole type leads passing through substrate 1, to switches upon the rear surface of substrate 1, respectively. By actuating the switches individually, parasitic elements 104, 106 are individually switched between a grounded state and a float state. The direction of the radio beam emitted from the microstrip antenna is varied by selecting which of parasitic elements 104, 106 is grounded and floated. A microwave signal source connects to feed element 102 via an feed line 108 very much shorter than the wavelength, accordingly the transmission losses being low and the efficiency being excellent.
Owner:TOTO LTD
Microwave readout for flux-biased qubits
A method for determining whether a quantum system comprising a superconducting qubit is occupying a first basis state or a second basis state once a measurement is performed is provided. The method, comprising: applying a signal having a frequency through a transmission line coupled to the superconducting qubit characterized by two distinct, separate, and stable states of differing resonance frequencies each corresponding to the occupation of the first or second basis state prior to measurement; and measuring at least one of an output power or phase at an output port of the transmission line, wherein the measured output power or phase is indicative of whether the superconducting qubit is occupying the first basis state or the second basis state.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
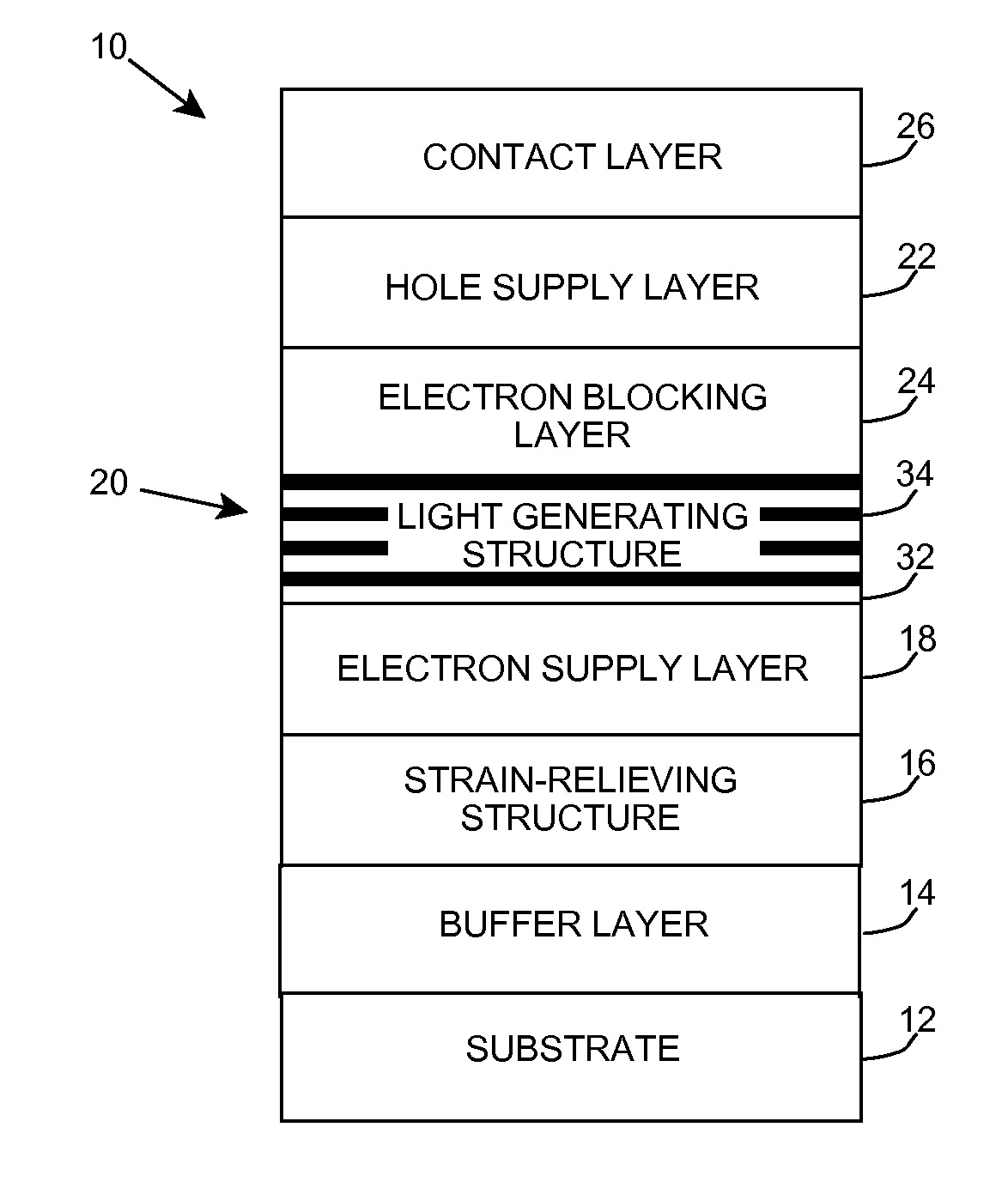
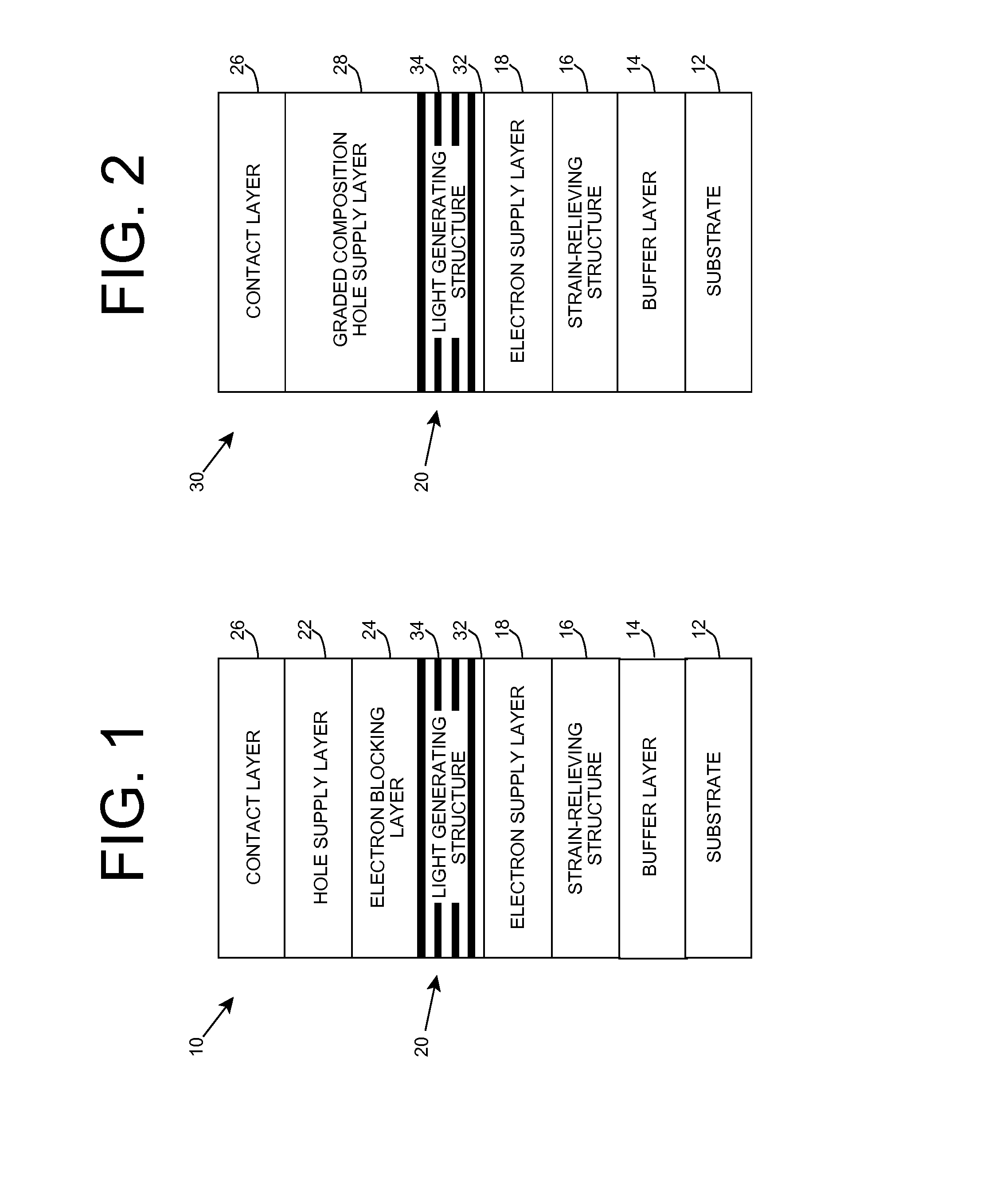
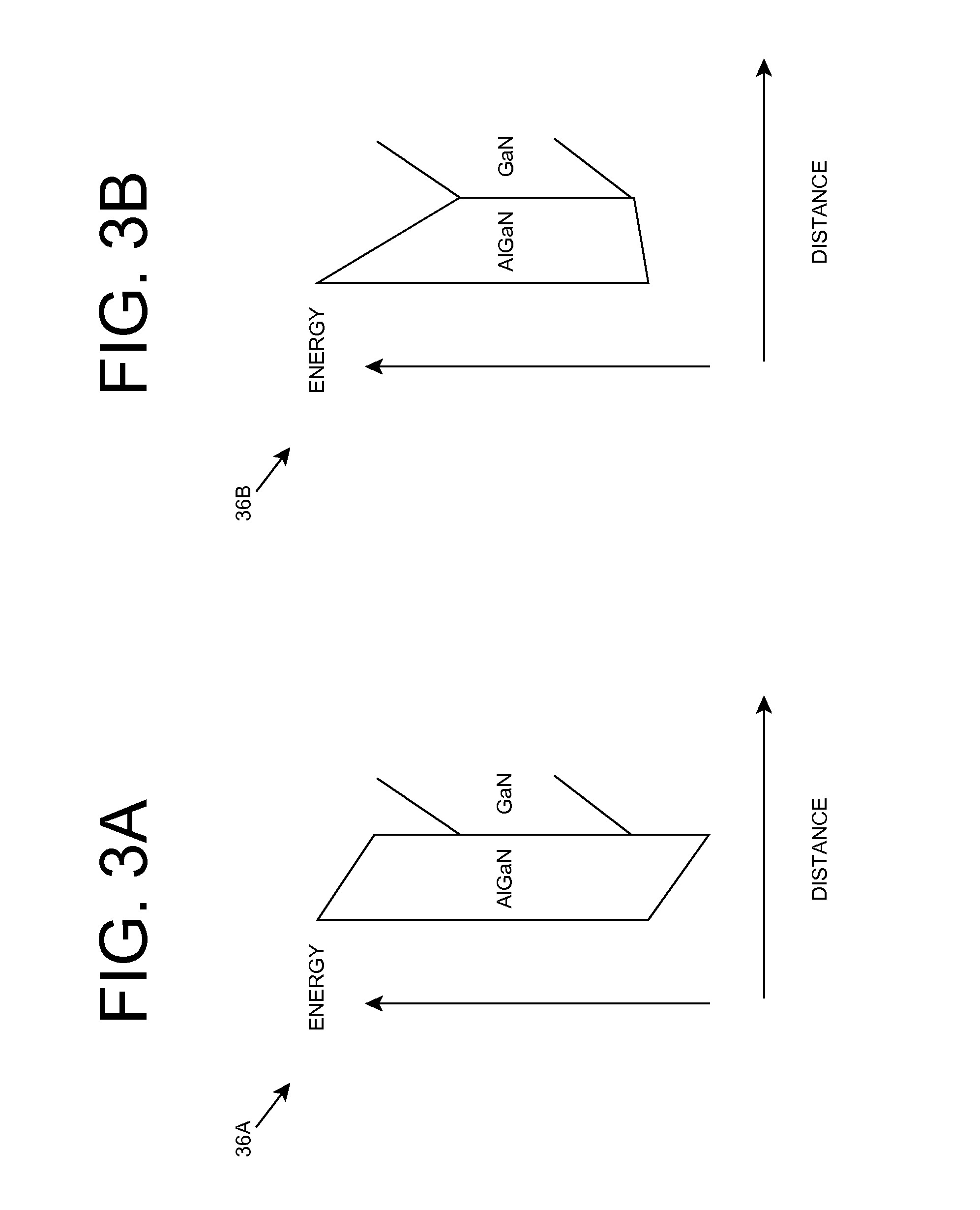
Heterostructure including light generating structure contained in potential well
ActiveUS20070181869A1Improve featuresConvenient lightingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsPotential wellElectron hole
A light emitting heterostructure and / or device in which the light generating structure is contained within a potential well is provided. The potential well is configured to contain electrons, holes, and / or electron and hole pairs within the light generating structure. A phonon engineering approach can be used in which a band structure of the potential well and / or light generating structure is designed to facilitate the emission of polar optical phonons by electrons entering the light generating structure. To this extent, a difference between an energy at a top of the potential well and an energy of a quantum well in the light generating structure can be resonant with an energy of a polar optical phonon in the light generating structure material. The energy of the quantum well can comprise an energy at the top of the quantum well, an electron ground state energy, and / or the like.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Mobile phone and antenna thereof
ActiveCN104103888AGuarantee mutual isolationAchieve normal workAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating element housingsEngineeringHigh field
The invention is applicable to the field of mobile terminals, and provides a mobile phone and an antenna thereof. The antenna comprises a first antenna branch, a second antenna branch, a third antenna branch, a first feed terminal, a second feed terminal, a third feed terminal and a phone metal ground, wherein the first, second and third antenna branches are sequentially arranged at one end of the mobile phone; the second antenna branch is positioned between the first and third antenna branches; the first feed terminal, the first antenna branch and the phone metal ground form a first antenna loop; the second feed terminal, the second antenna branch and the phone metal ground form a second antenna loop; the third feed terminal, the third antenna branch and the phone metal ground form a third antenna loop; through enabling all the antennal branches to be in the ground states, high fields are prevented from being tightly coupled through gaps among the antennas, so that even the three antennas are separated by about 1mm, mutual isolation among the three antennas also can be ensured, and thereby the three antennas respectively work normally.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
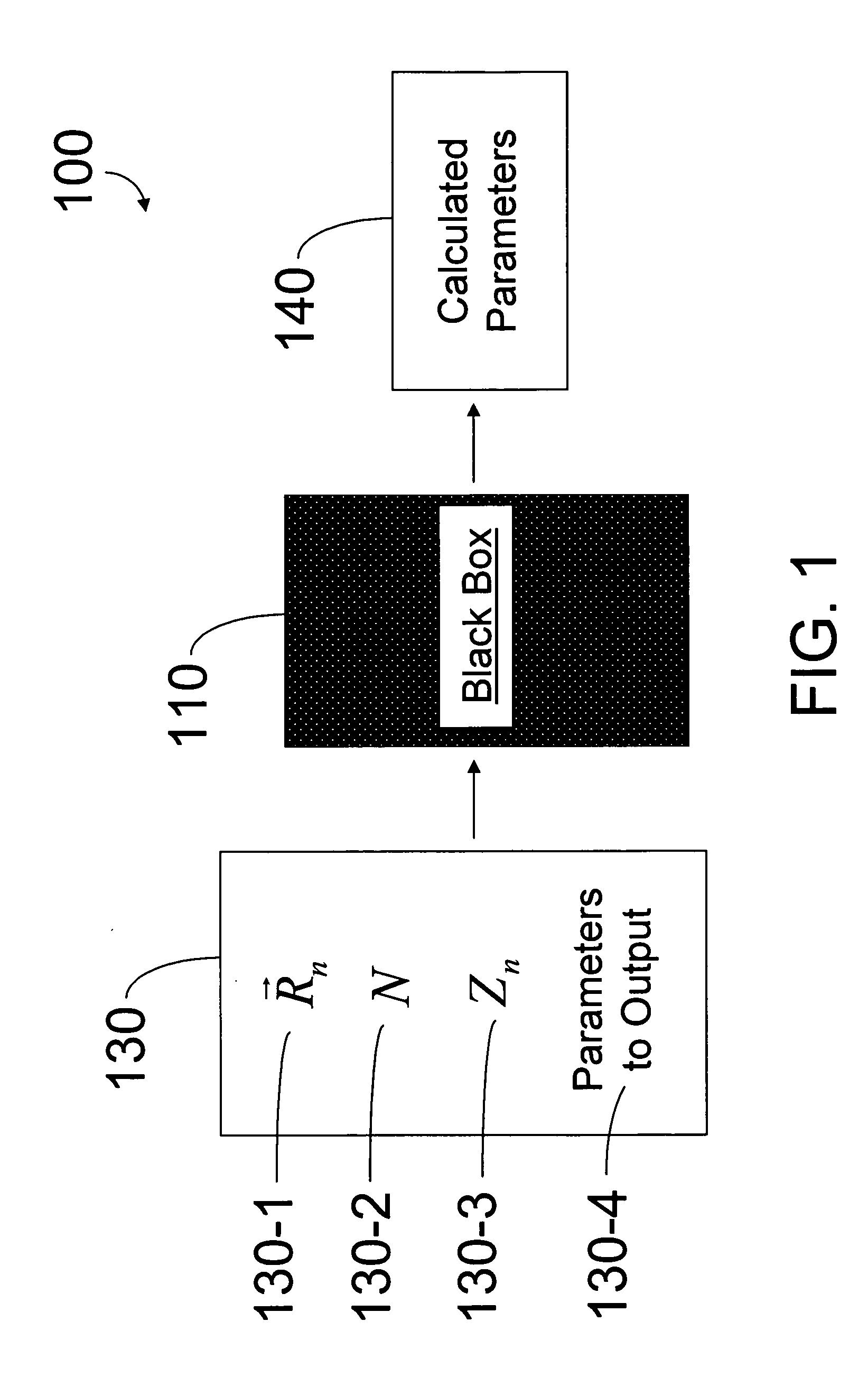
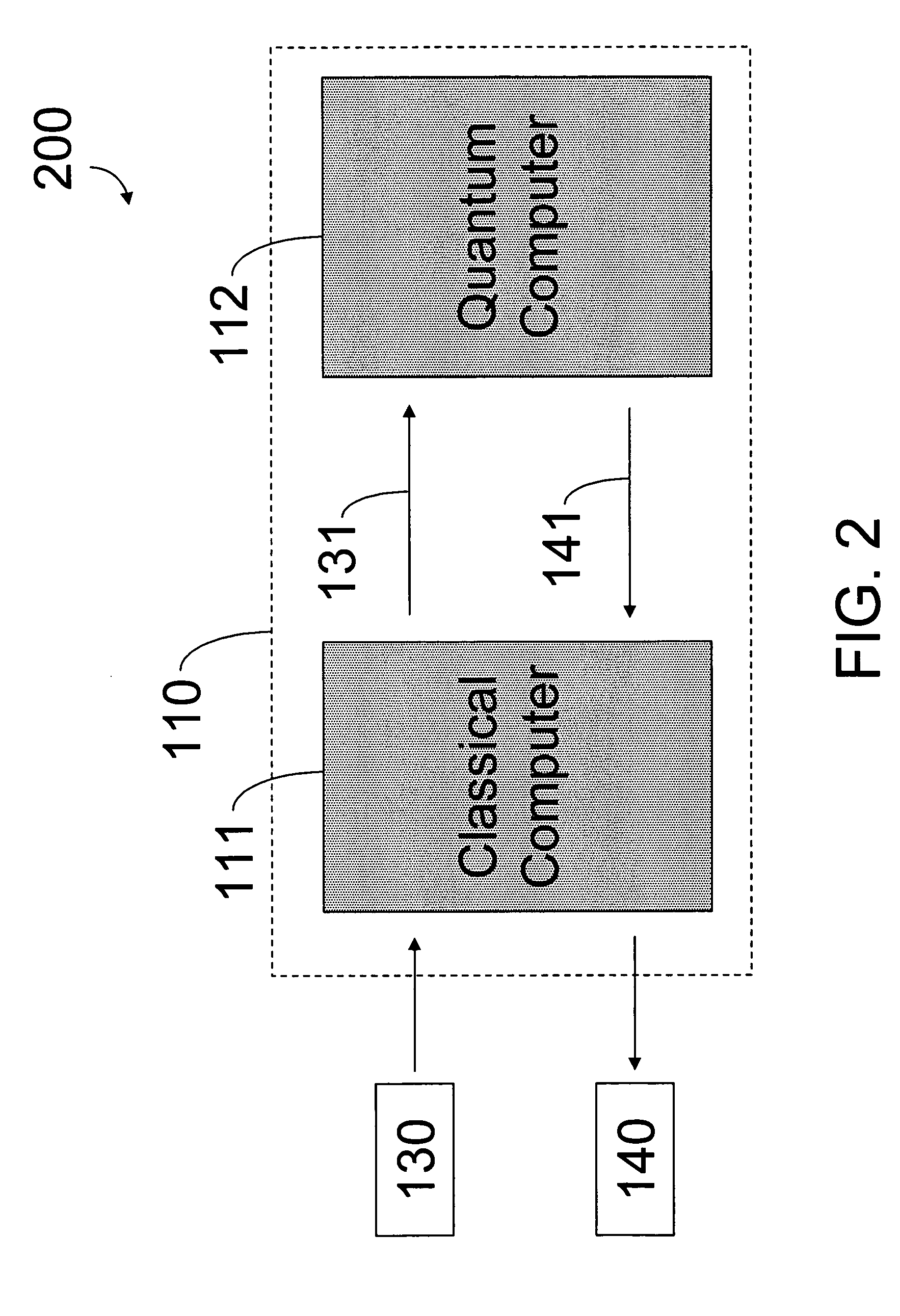
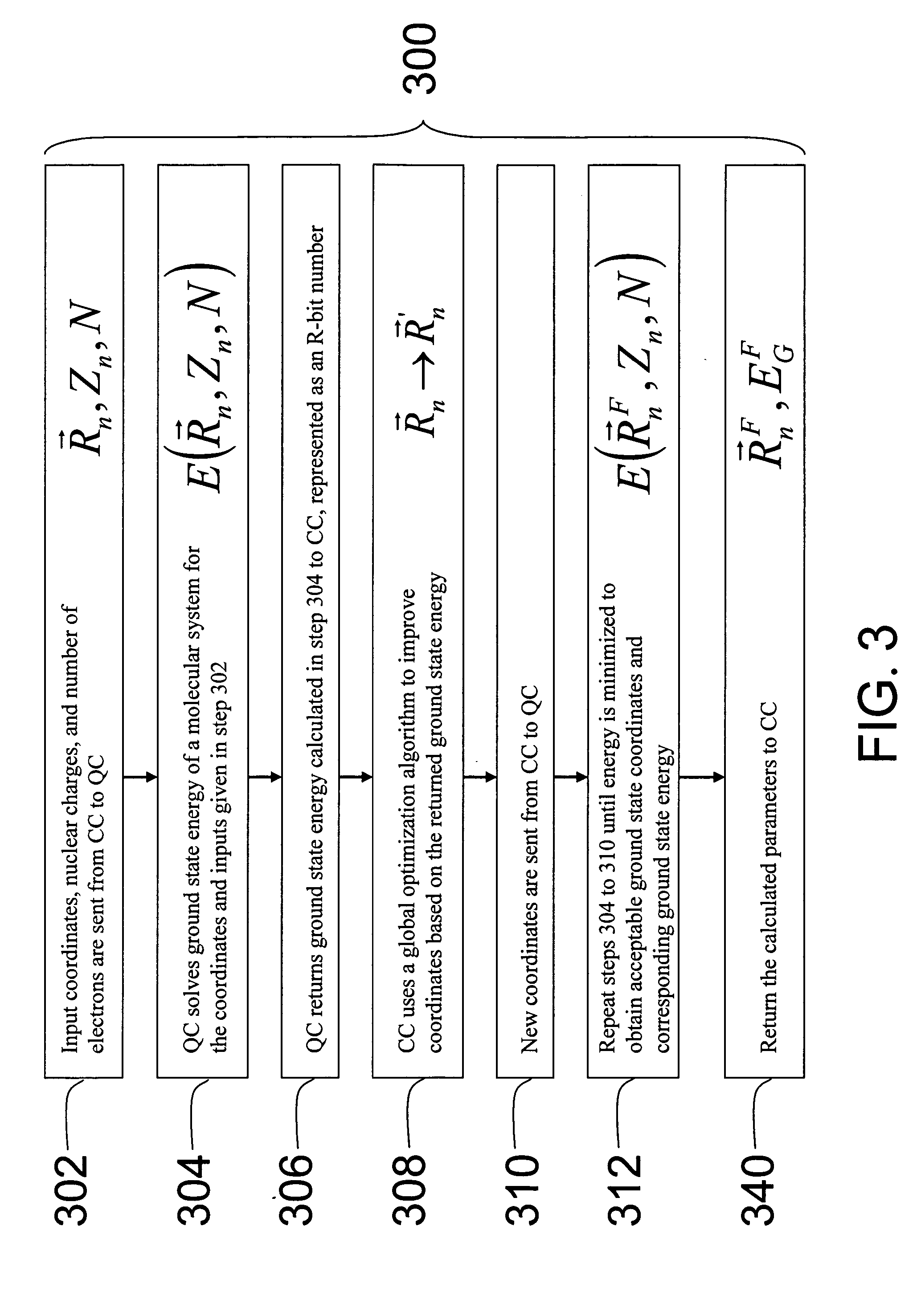
Hybrid classical-quantum computer architecture for molecular modeling
A method of simulating a molecular system using a hybrid computer is provided. The hybrid computer comprises a classical computer and a quantum computer. The method uses atomic coordinates {right arrow over (R)}n and atomic charges Zn of a molecular system to compute a ground state energy of the molecular system using the quantum computer. The ground state energy is returned to the classical computer and the atomic coordinates are geometrically optimized on the classical computer based on information about the returned ground state energy of the atomic coordinates in order to produce a new set of atomic coordinates {right arrow over (R)}′n for the molecular system. These steps are optionally repeated in accordance with a refinement algorithm until a predetermined termination condition is achieved
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Fluorescent material and light-emitting apparatus employing the same
InactiveUS20060158089A1Improve luminous efficiencyGood colorNanotechLaser detailsEmission efficiencyLight emitting device
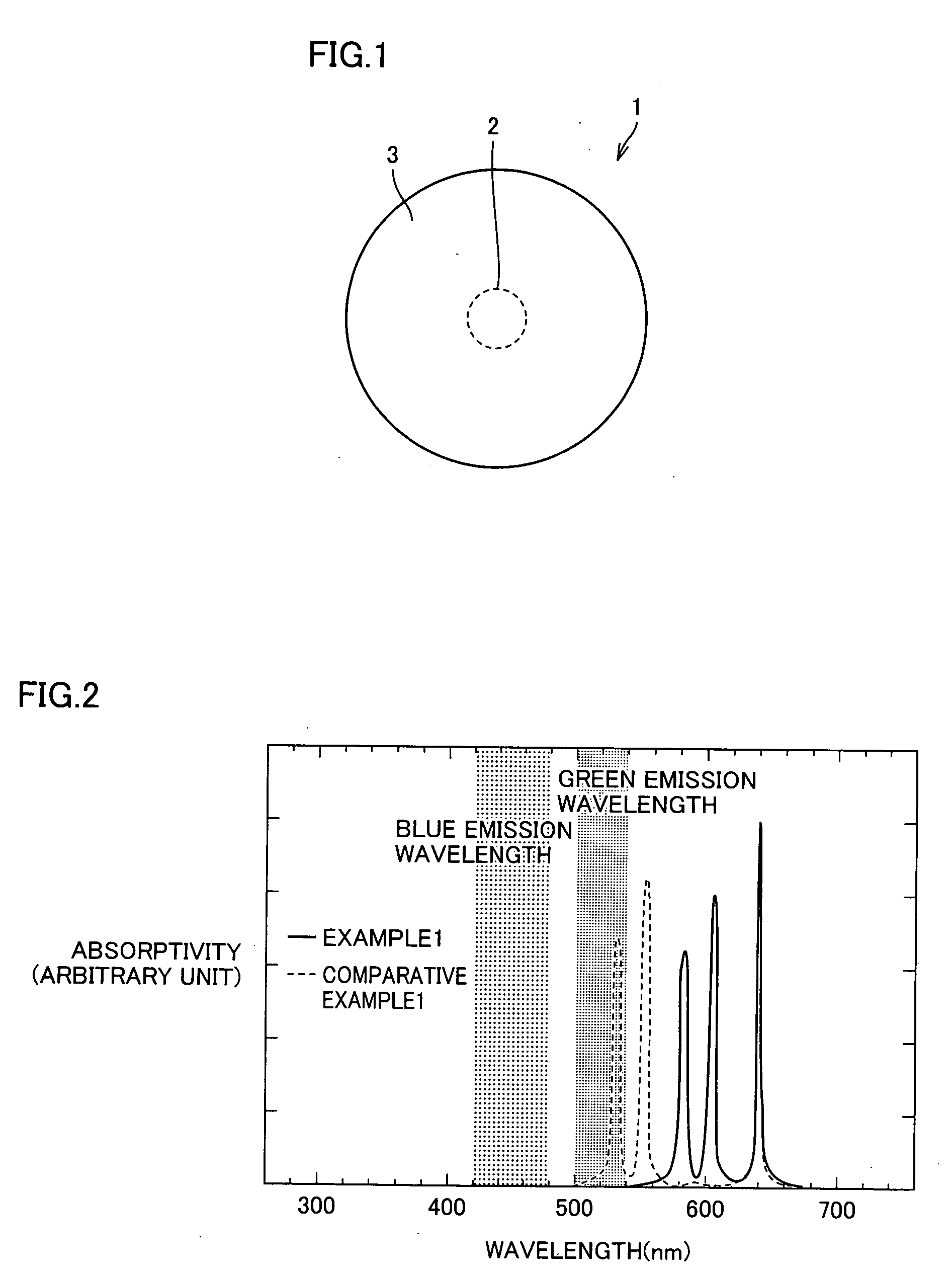
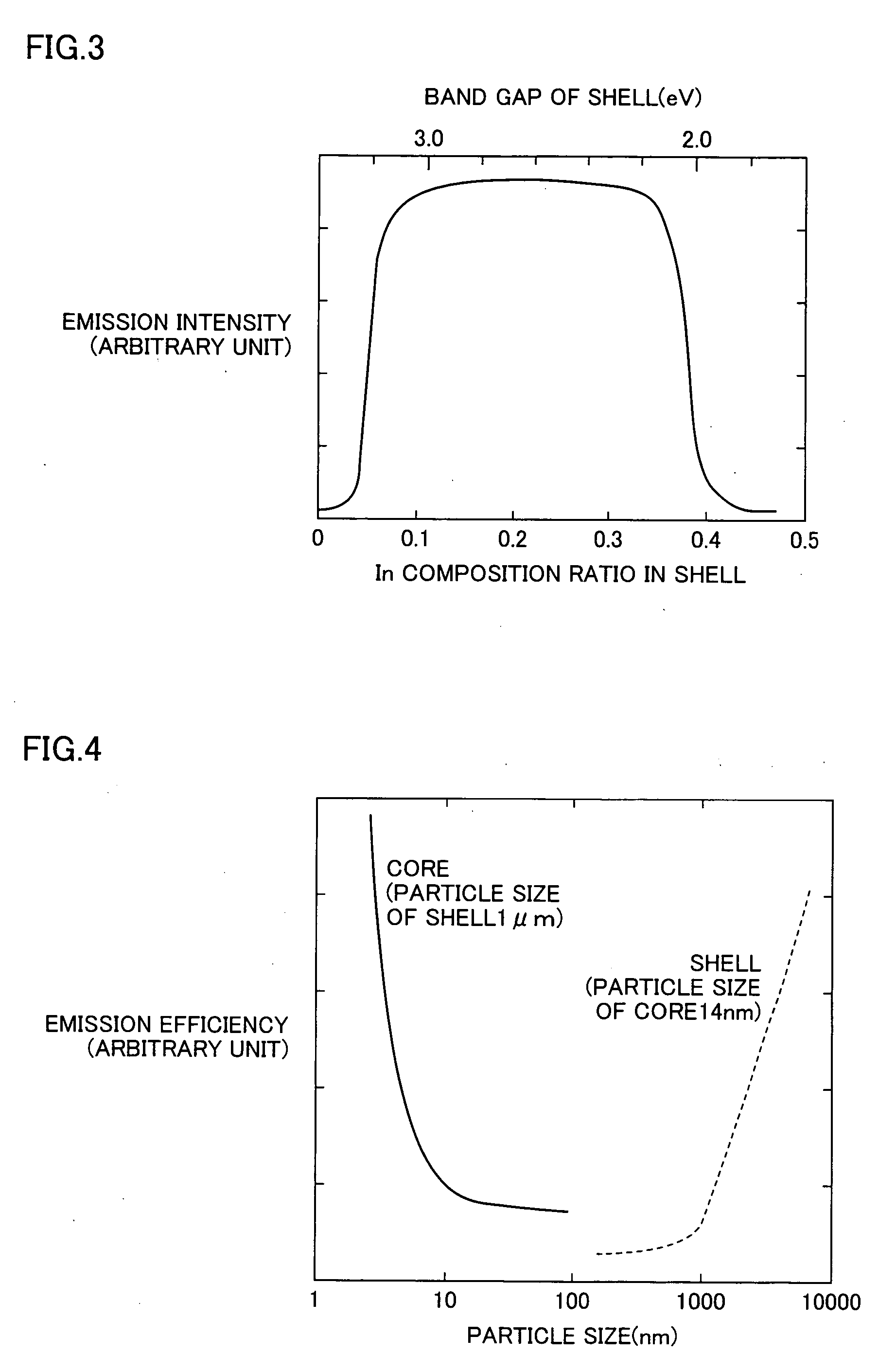
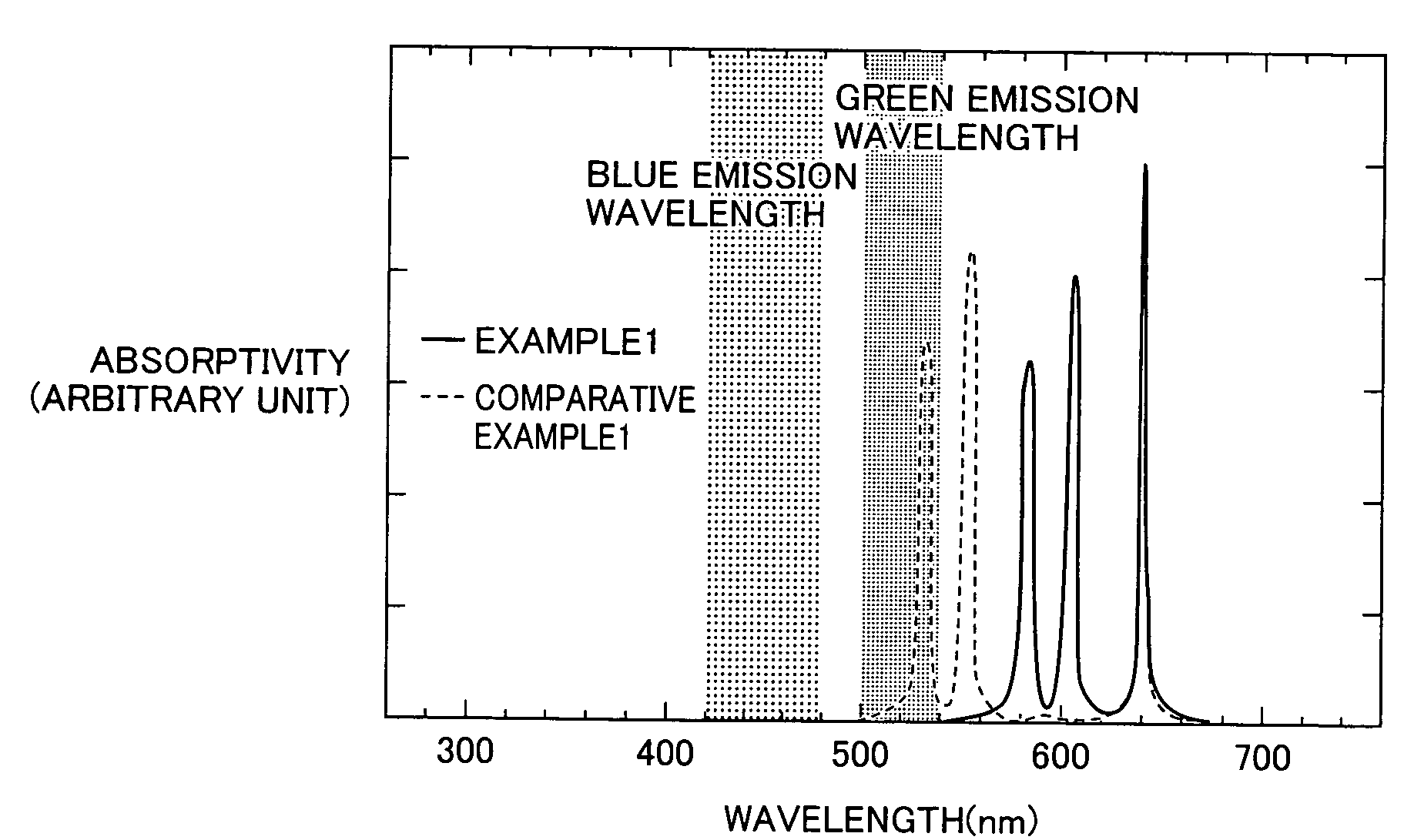
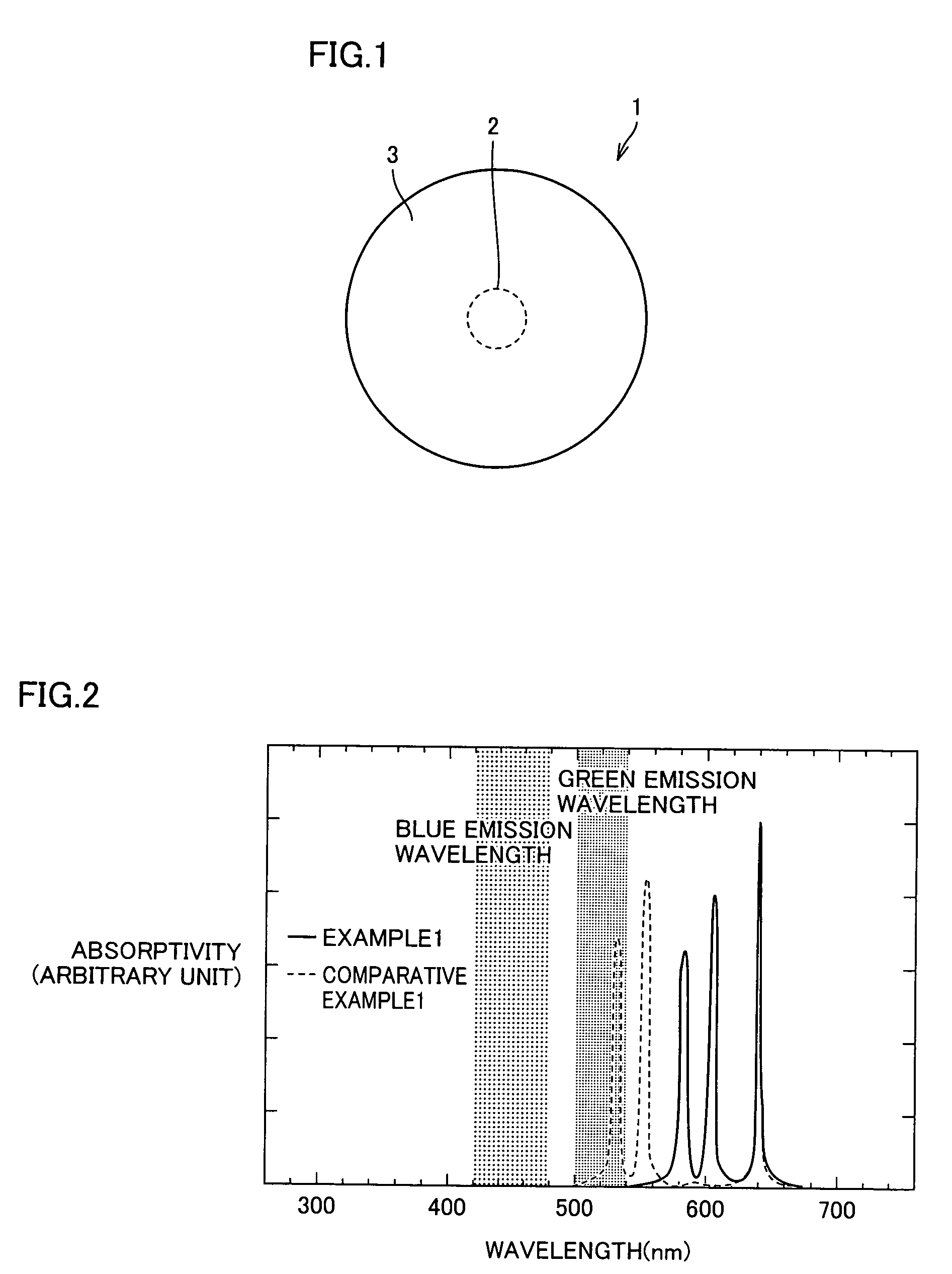
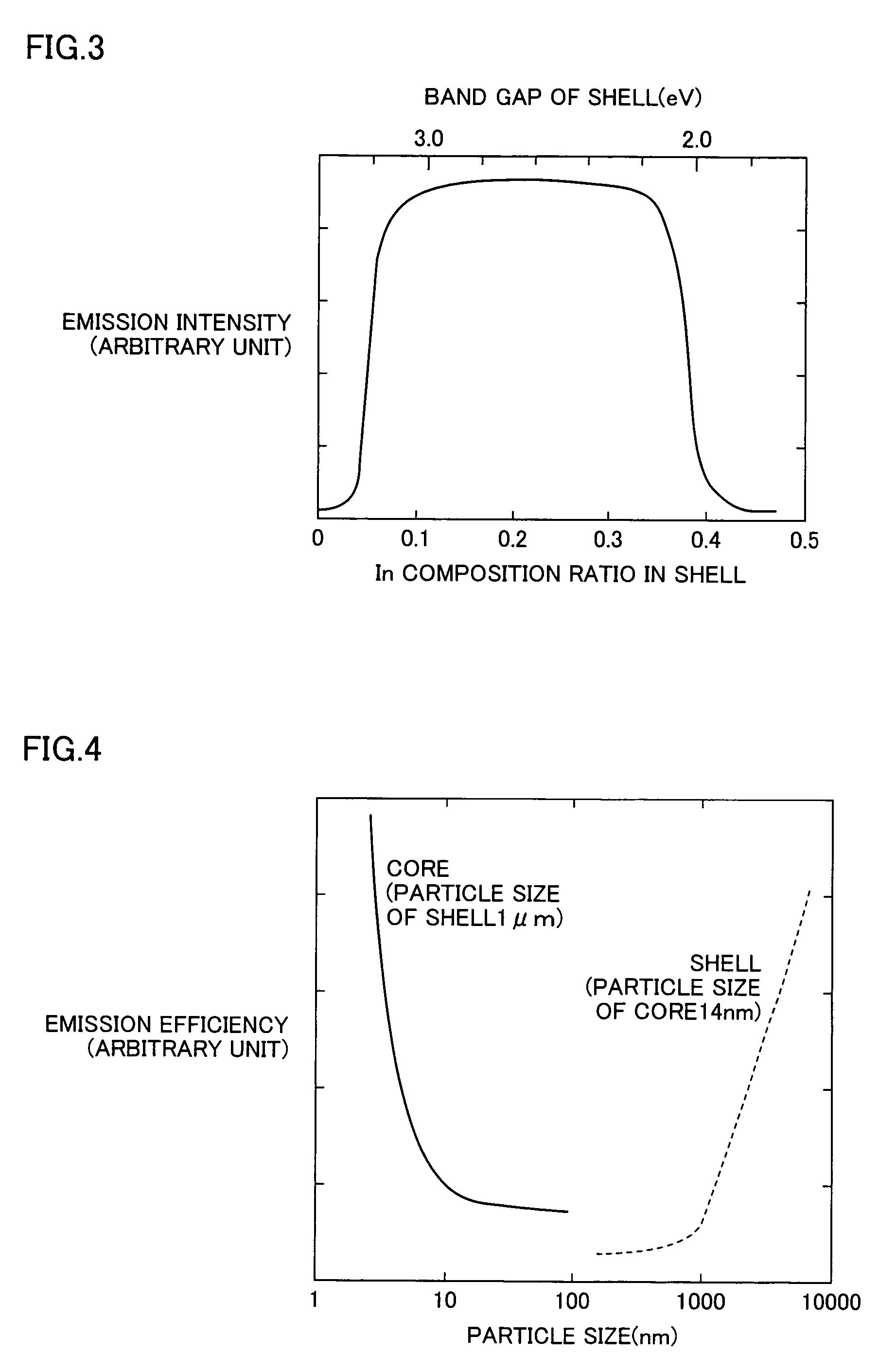
A fluorescent material excellent in emission efficiency in white emission and a light-emitting apparatus employing this fluorescent material and having excellent color rendering are provided with a fluorescent material comprising a two-layer structure of a core of a particle size having a quantum effect and a shell covering this core in which the ground state energy of the core is in the range of 1.85 to 2.05 eV, the high order energy of the core is not in the ranges of 2.3 to 2.5 eV and 2.65 to 2.8 eV, or the ground state energy of the core is in the range of 2.3 to 2.5 eV, the high order energy of the core is not in the range of 2.65 to 2.8 eV an light-emitting apparatus employing these fluorescent materials.
Owner:FUJITA SHIZUO +4
Fluorescent material having two layer structure and light emitting apparatus employing the same
InactiveUS7560859B2Improve luminous efficiencyGood colorNanotechLaser detailsEmission efficiencyLight emitting device
A fluorescent material excellent in emission efficiency in white emission and a light-emitting apparatus employing this fluorescent material and having excellent color rendering are provided with a fluorescent material comprising a two-layer structure of a core of a particle size having a quantum effect and a shell covering this core in which the ground state energy of the core is in the range of 1.85 to 2.05 eV, the high order energy of the core is not in the ranges of 2.3 to 2.5 eV and 2.65 to 2.8 eV, or the ground state energy of the core is in the range of 2.3 to 2.5 eV, the high order energy of the core is not in the range of 2.65 to 2.8 eV an light-emitting apparatus employing these fluorescent materials.
Owner:FUJITA SHIZUO +4
Quantum and digital processor hybrid systems and methods to solve problems
Quantum and digital processors are employed together to solve computational problems. The quantum processor may be configured with a problem via a problem Hamiltonian and operated to perform adiabatic quantum computation and / or quantum annealing on the problem Hamiltonian to return a first solution to the problem that is in the neighborhood of the global minimum of the problem Hamiltonian. The digital processor may then be used to refine the first solution to the problem by casting the first solution to the problem as a starting point for a classical optimization algorithm. The classical optimization algorithm may return a second solution to the problem that corresponds to a lower energy state in the neighborhood of the global minimum, such as a ground state of the problem Hamiltonian. The quantum processor may include a superconducting quantum processor implementing superconducting flux qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Touch screen input apparatus
InactiveUS20110279410A1Effectively blocking electrostatic noiseLittle resistanceNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceTouchscreen
A touch screen input apparatus includes a first electrode layer, a second electrode layer, and a controller. The first electrode layer is configured to perform sensing in a first direction, and provided with first electrode patterns which are formed on the top surface of a substrate. The second electrode layer is configured to perform sensing in a second direction, provided under the first electrode layer, and provided with second electrode patterns which are formed on the top surface of a substrate such that the second electrode patterns overlap the first electrode patterns through a surface on which the first electrode patterns are not formed, and which are spaced apart from each other by predetermined intervals. The control unit is configured to control the electrode patterns other than electrodes which are used to measure capacitance in a ground state.
Owner:POINTCHIPS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for measuring oxygen concentration
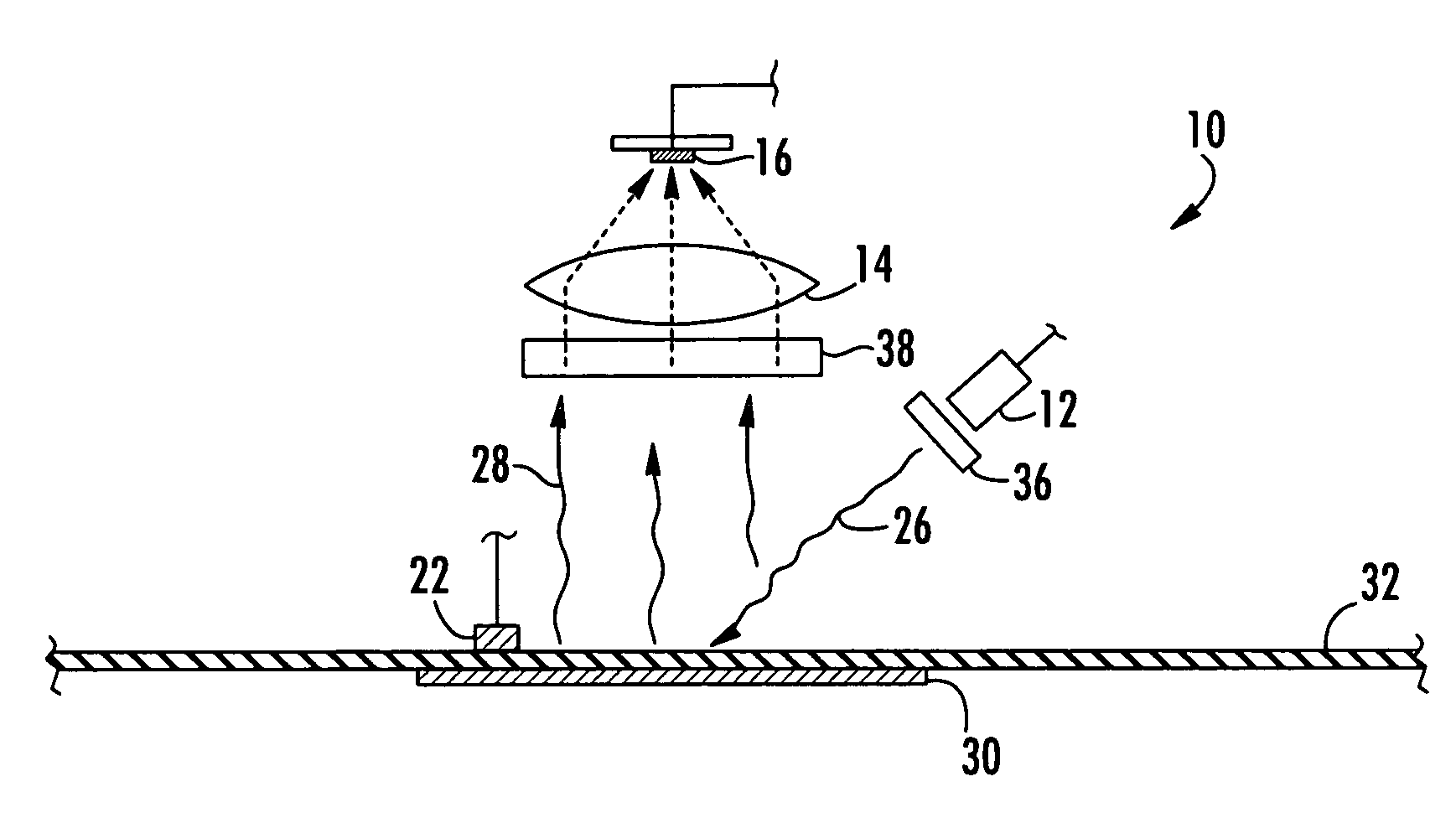
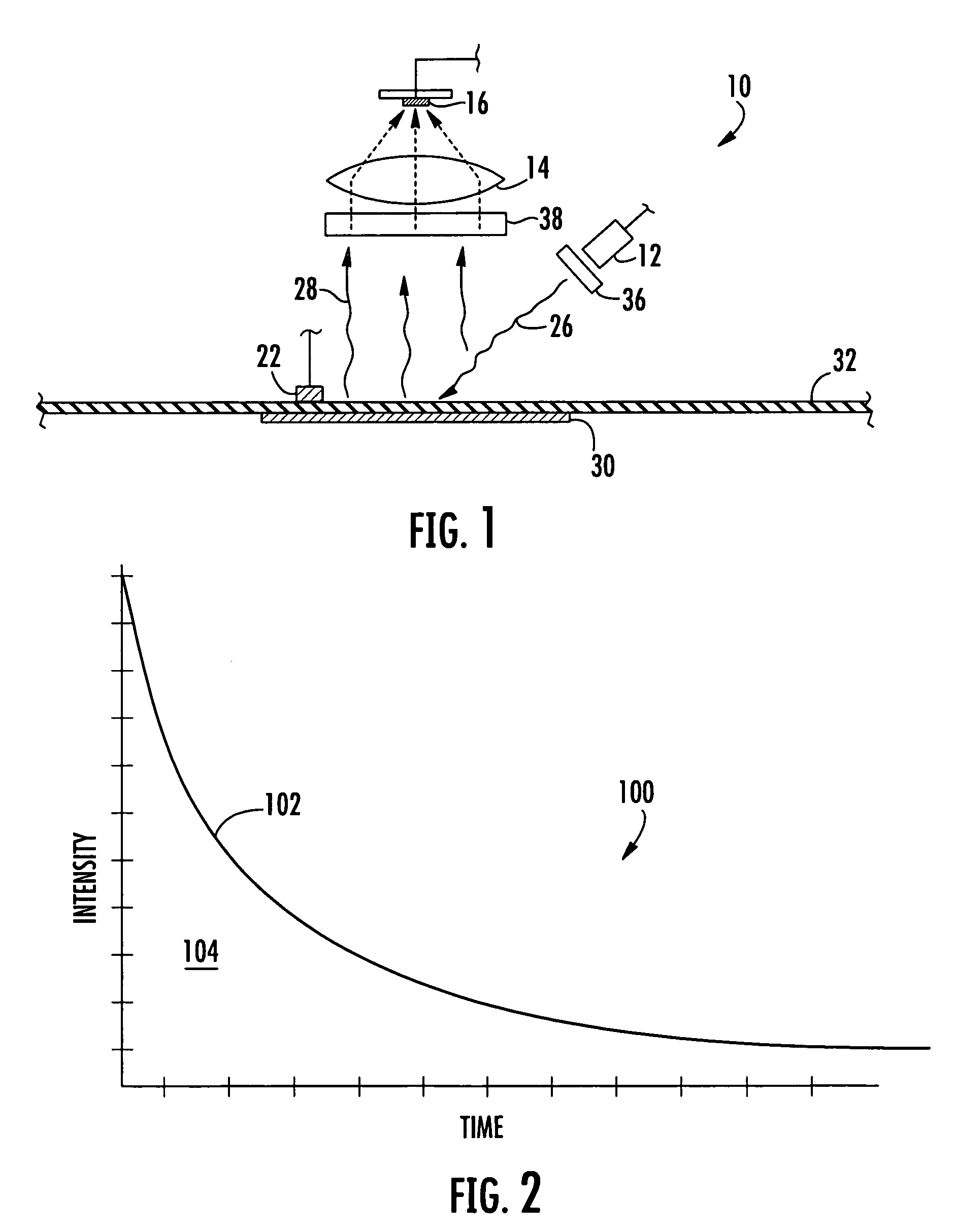
InactiveUS7569395B2Lower Level RequirementsHigh sensitivityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceWithdrawing sample devicesOxygenNon invasive
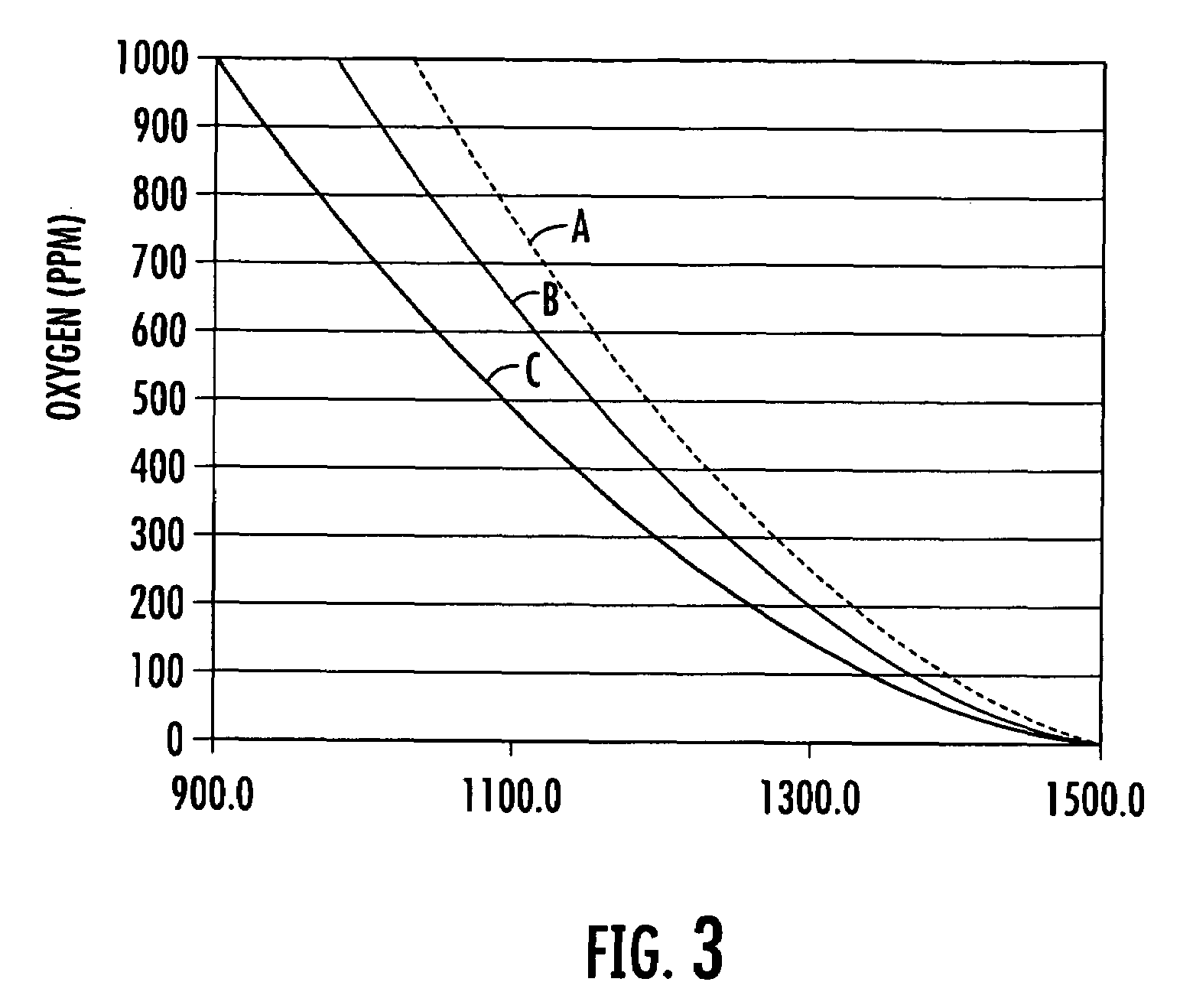
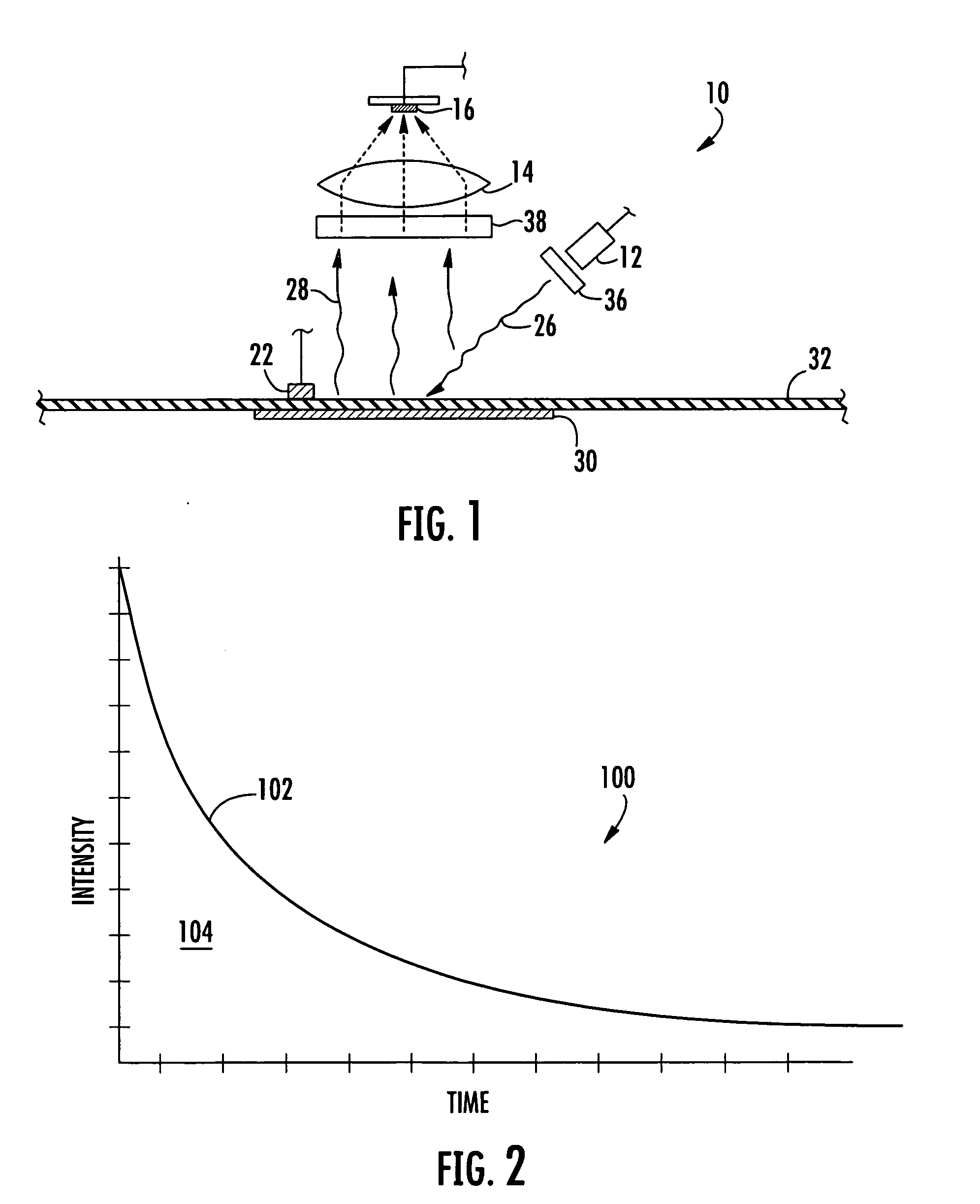
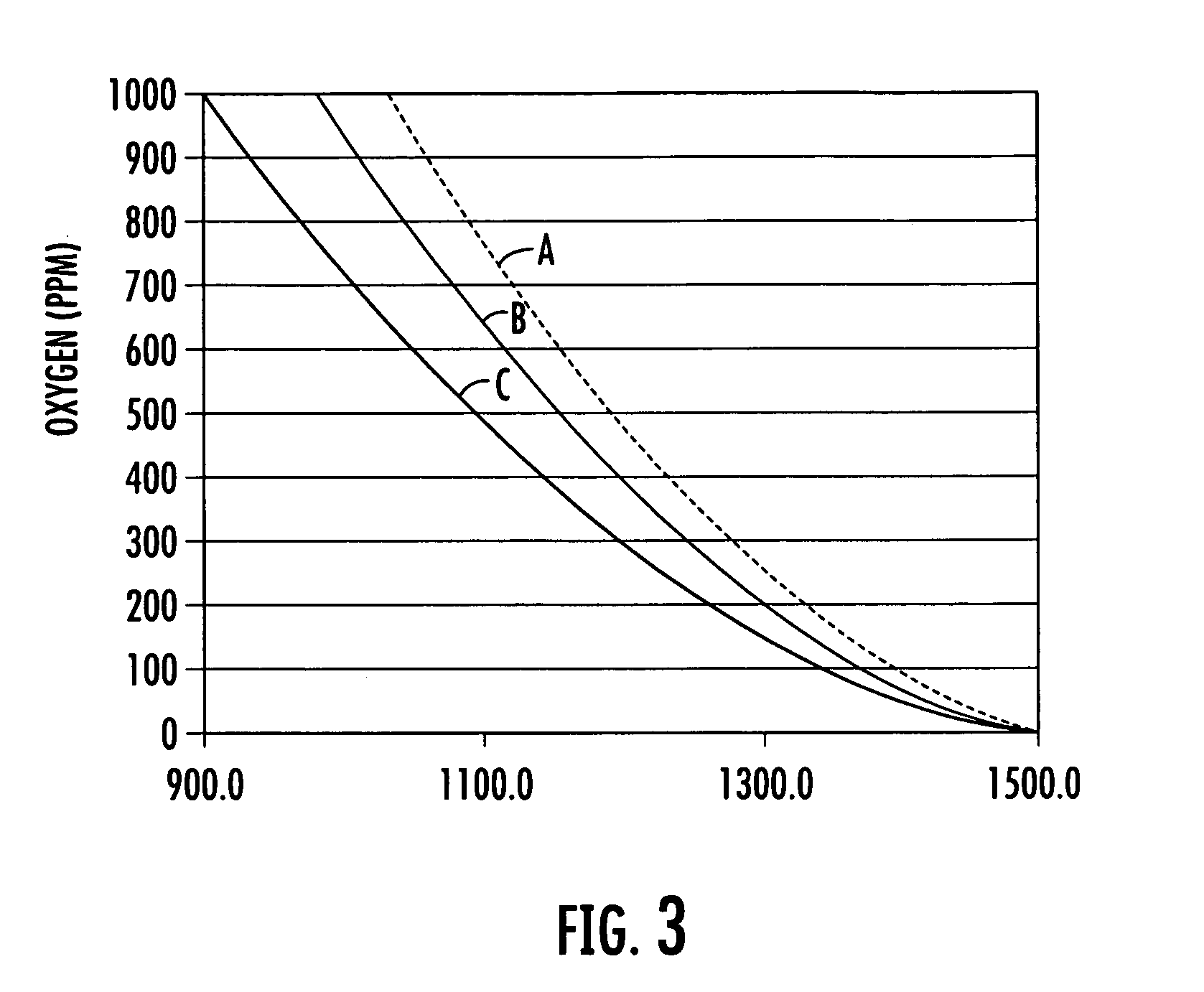
An apparatus and non-invasive method of measuring oxygen by exciting a luminescent compound disposed in a container and then measuring the intensity of the light emitted by the excited luminescent compound as it relaxes to the ground state. A plot of emission intensity as a function of time results in an exponential decay curve the area of which is inversely proportional to the oxygen concentration. The oxygen concentration can be determined over a wide temperature range by measuring the temperature of the container and the emission intensity and then applying the following equation:[O2]=(ATa(T)2+BTa(T)+CTa)(tau)2+(ATb(T)2+BTb(T)+CTb)(tau)+(ATc(T)2+BTc(T)+CTc)T is the measured temperature;tau is the area of the exponential decay curve; andATa, BTa, CTa, ATb, BTb, CTb, ATc, BTc, and CTc are coefficients that are specific to the luminescent compound being examined.
Owner:CRYOVAC ILLC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20160118106A1Easy to manufactureDigital data processing detailsDigital storageLow voltageEngineering
It is an object of the present invention to provide a device which can be easily manufactured and obtain a ground state of an arbitrary Ising model. A semiconductor device includes a first memory cell and a second memory cell that interacts with the first memory cell, in which storage content of the first memory cell and the second memory cell is stochastically inverted. The storage content is stochastically inverted by dropping threshold voltages of the first memory cell and the second memory cell. The threshold voltages of the first and second memory cells are dropping by controlling substrate biases, power voltages, or trip points of the first and second memory cells.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Permanent readout superconducting qubit
InactiveUS7015499B1Quantum computersSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSingle electronCrystal orientation
A solid-state quantum computing structure includes a d-wave superconductor in sets of islands that clean Josephson junctions separate from a first superconducting bank. The d-wave superconductor causes the ground state for the supercurrent at each junction to be doubly degenerate, with two supercurrent ground states having distinct magnetic moments. These quantum states of the supercurrents at the junctions create qubits for quantum computing. The quantum states can be uniformly initialized from the bank, and the crystal orientations of the islands relative to the bank influence the initial quantum state and tunneling probabilities between the ground states. A second bank, which a Josephson junction separates from the first bank, can be coupled to the islands through single electron transistors for selectably initializing one or more of the supercurrents in a different quantum state. Single electron transistors can also be used between the islands to control entanglements while the quantum states evolve. After the quantum states have evolved to complete a calculation, grounding the islands, for example, through yet another set of single electron transistors, fixes the junctions in states having definite magnetic moments and facilitates measurement of the supercurrent when determining a result of the quantum computing.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
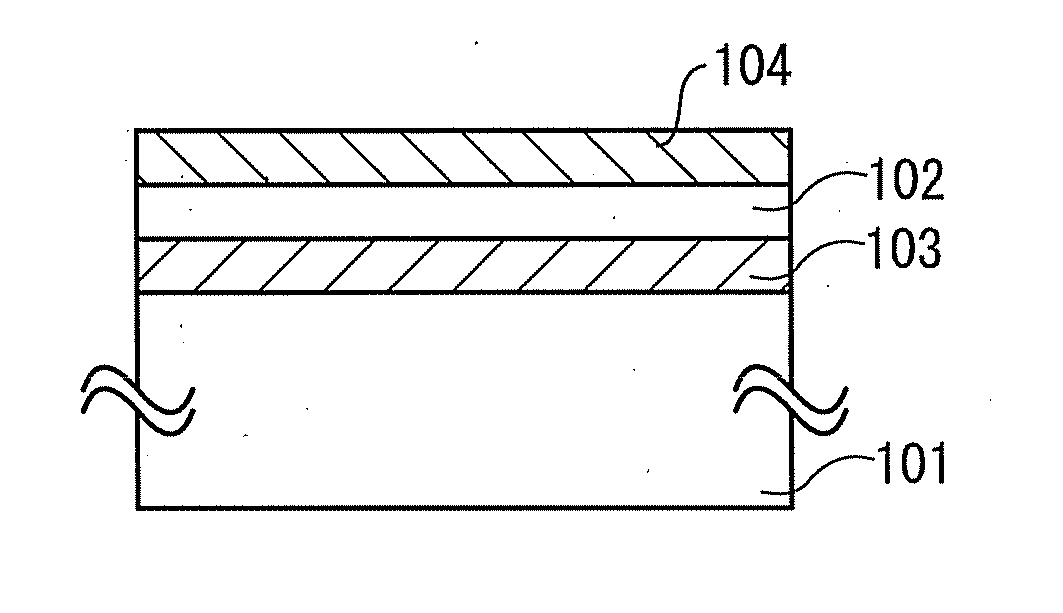
Semiconductor light source with electrically tunable emission wavelength
A semiconductor light source is disclosed comprising a substrate, lower and upper claddings, a waveguide region with imbedded active area, and electrical contacts to provide voltage necessary for the wavelength tuning. The active region includes single or several heterojunction periods sandwiched between charge accumulation layers. Each of the active region periods comprises higher and lower affinity semiconductor layers with type-II band alignment. The charge carrier accumulation in the charge accumulation layers results in electric field build-up and leads to the formation of generally triangular electron and hole potential wells in the higher and lower affinity layers. Nonequillibrium carriers can be created in the active region by means of electrical injection or optical pumping. Radiative recombination occurs between the electrons and holes, accumulated in the ground states of the triangular potential wells formed in the high- and low-affinity layers of each active region periods. The ground state energy in the triangular wells and the radiation wavelength can be tuned by changing the voltage drop across the active region.
Owner:MAXION TECH +1
Nitride luminescent device and production method thereof
InactiveCN101540364AIncrease chance of tunnelingEasy to transportLaser active region structureSemiconductor devicesElectron holeHole injection layer
The invention discloses a nitride luminescent device and a production method thereof, which relate to a semiconductor luminescent device and provide a nitride luminescent device with an asymmetric coupled multi-quantum well structure being the active area. The device at least comprises an n-type electron injection layer, a p-type hole injection layer and a multi-quantum well active layer which is sandwiched between the n-type electron injection layer and the p-type hole injection layer, and the active layer is composed of asymmetric coupled quantum well structures. The barrier layer of the quantum well is thinner, thus being easy to realize the tunneling of current carriers; transition energy between ground-state energy level in the quantum wells is gradually changed; the quantum wells with high transition energy are close to the p-type hole injection layer; and the quantum wells with low transition energy are close to the n-type electron injection layer. The active area structure can enhance the tunneling transportation of the holes in the quantum well active area, simultaneously block the tunneling transportation of electrons in the quantum well active area, improve the uneven distribution of current carriers in the active area of the nitride luminescent device, reduce electron leakage and energy band filling effect, and realize high-efficiency luminescence.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Gyroscopes based on nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond
ActiveUS9689679B2Small dimensionThermal robustnessMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyTurn-sensitive devicesGyroscopePhase shifted
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for measuring oxygen concentration
InactiveUS20070212792A1Improve accuracyImprove temperature measurement accuracyWithdrawing sample devicesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceOxygenNon invasive
An apparatus and non-invasive method of measuring oxygen by exciting a luminescent compound disposed in a container and then measuring the intensity of the light emitted by the excited luminescent compound as it relaxes to the ground state. A plot of emission intensity as a function of time results in an exponential decay curve the area of which is inversely proportional to the oxygen concentration. The oxygen concentration can be determined over a wide temperature range by measuring the temperature of the container and the emission intensity and then applying the following equation: [O2]=(ATa(T)2+BTa(T)+CTa)(tau)2+(ATb(T)2+BTb(T)+CTb)(tau)+(ATc(T)2+BTc(T)+CTc) T is the measured temperature; tau is the area of the exponential decay curve; and ATa, BTa, CTa, ATb, BTb, CTb, ATc, BTc, and CTc are coefficients that are specific to the luminescent compound being examined.
Owner:CRYOVAC INC
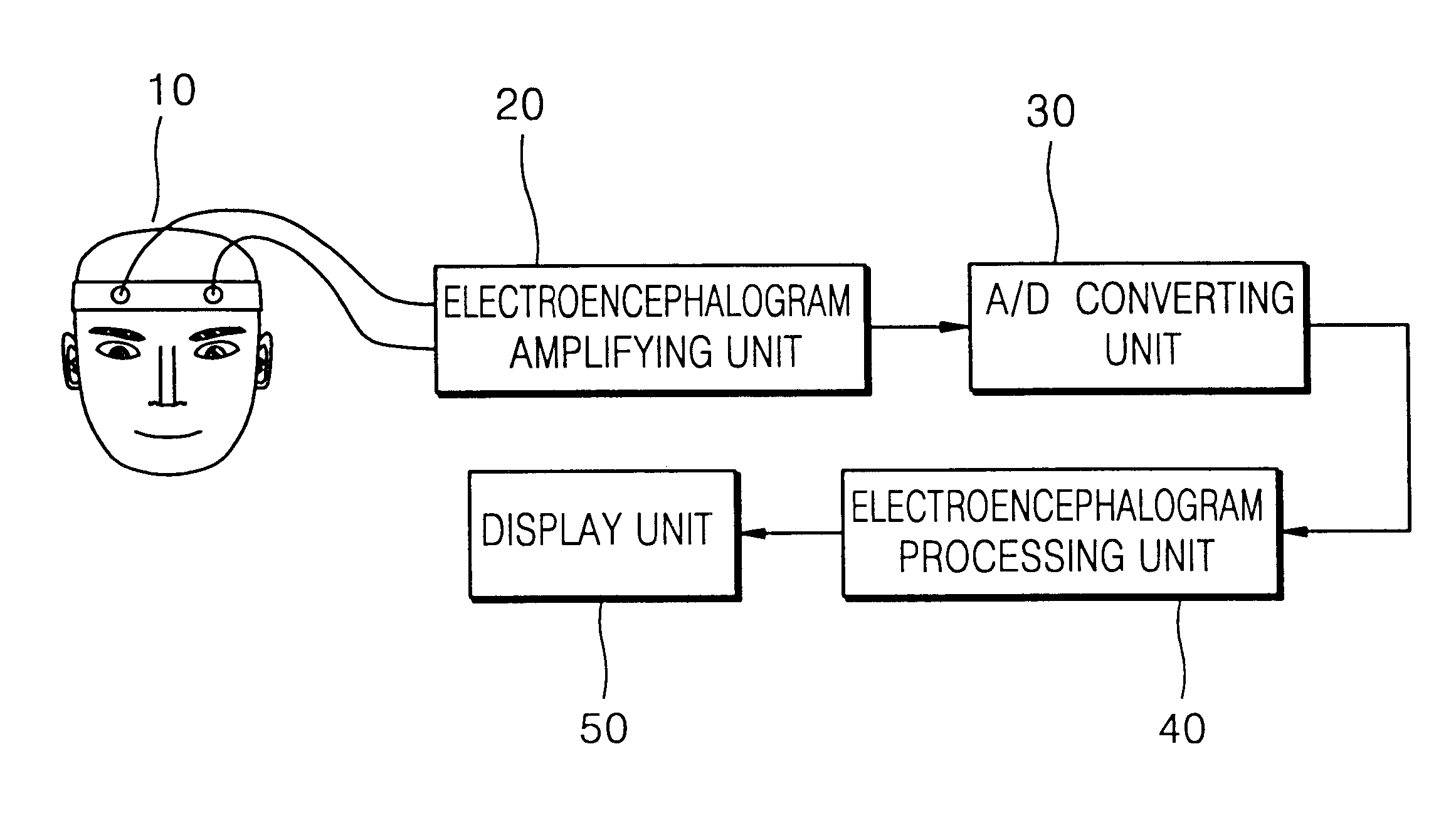
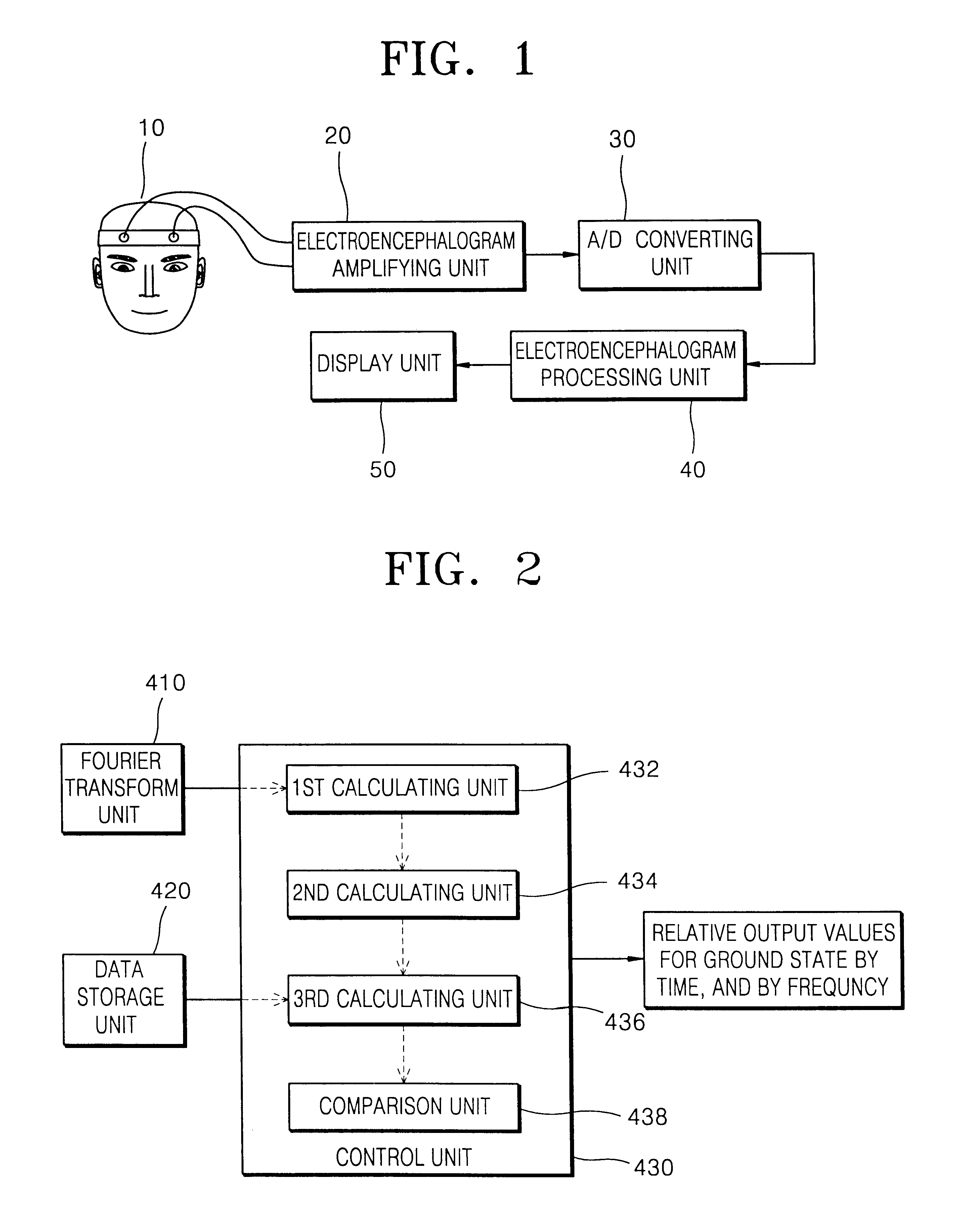
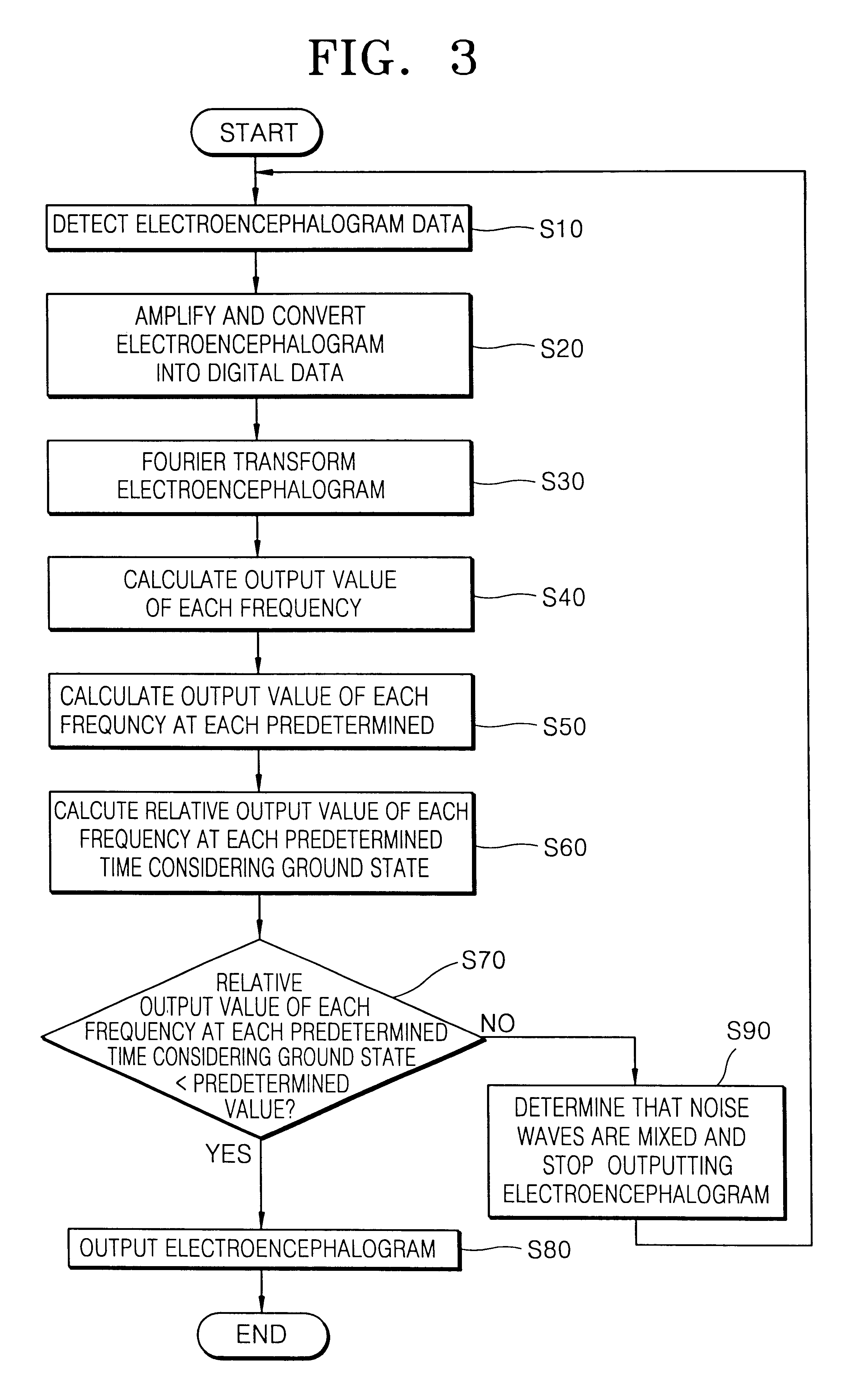
Apparatus and method for measuring electroencephalogram
InactiveUS7035685B2ElectroencephalographySensorsElectroencephalographyFourier transform on finite groups
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
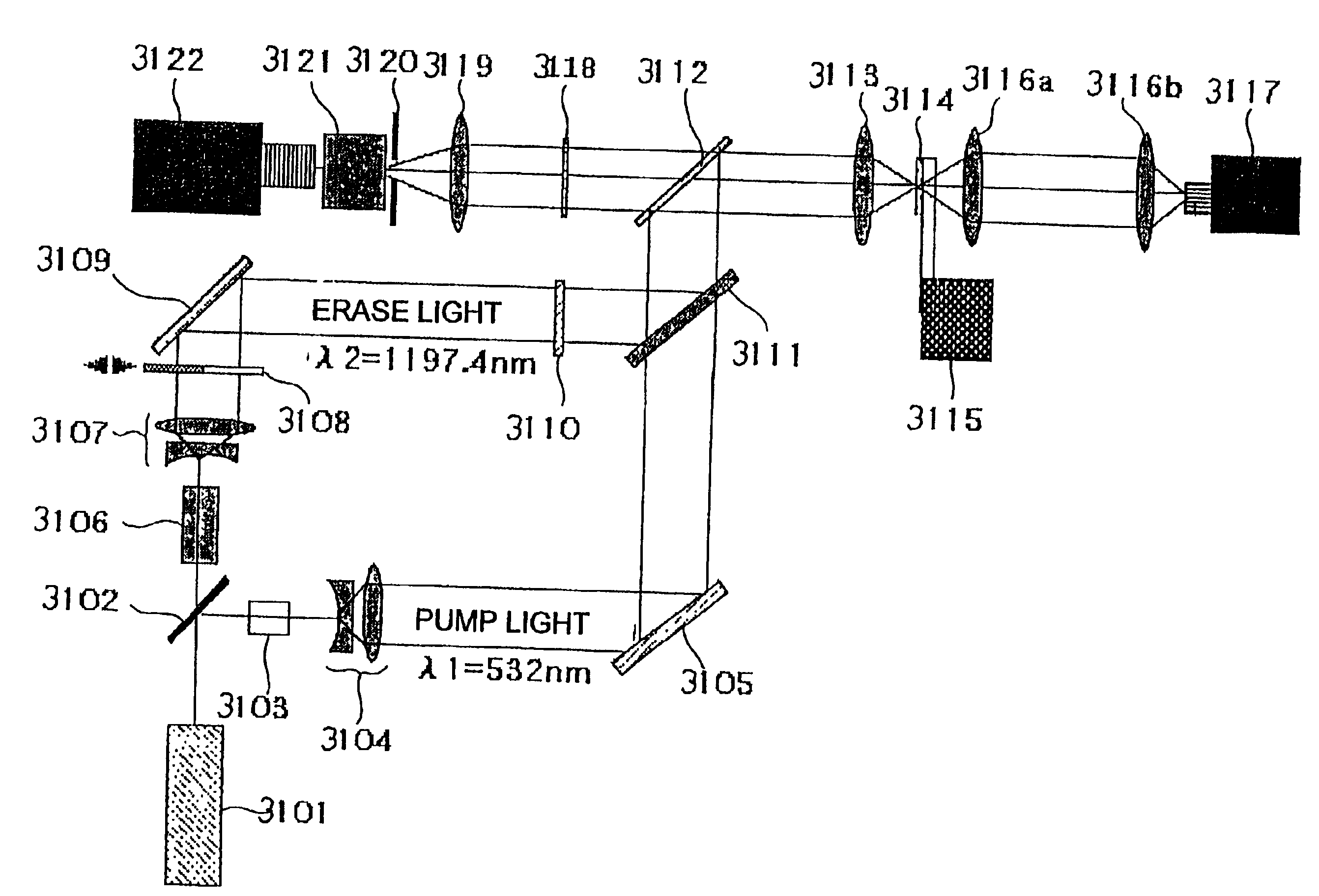
Double-resonance-absorption microscope
InactiveUS6844963B2Easy to operateImprove maintainabilityEmission spectroscopyRaman/scattering spectroscopyExcited stateResonance
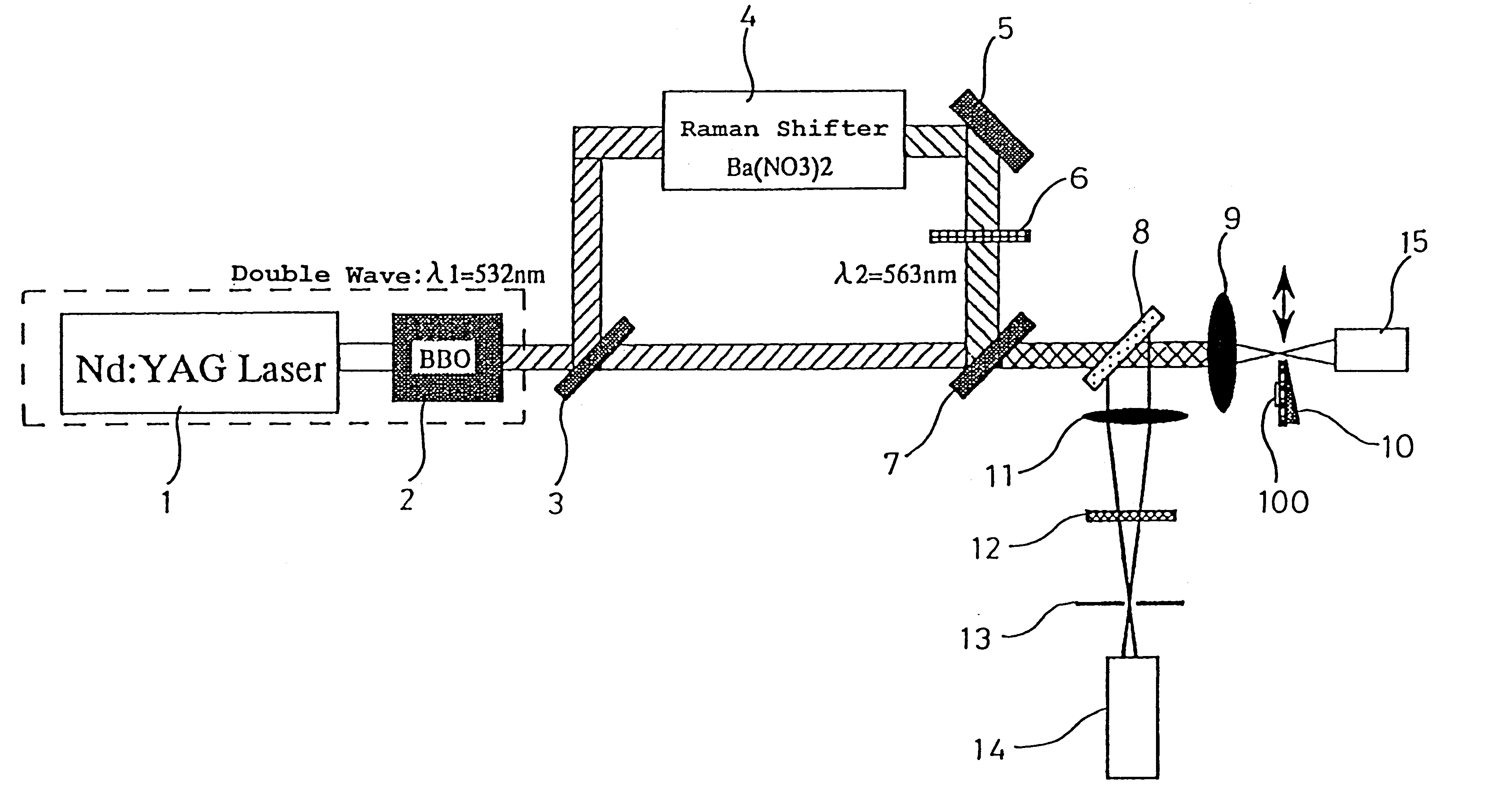
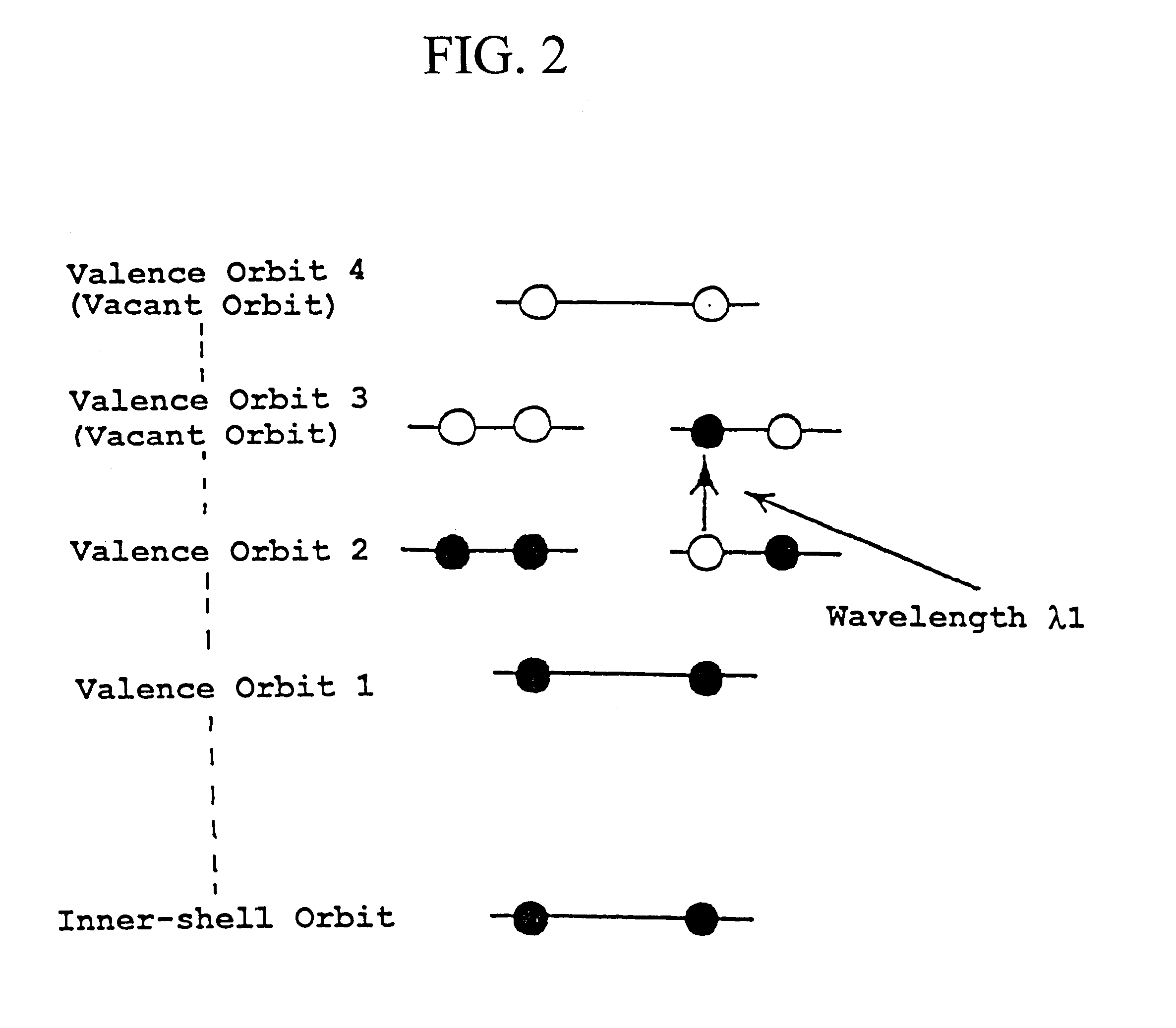
The present invention provides various embodiments of a double-resonance-absorption microscope which realizes a super-resolution by using double resonance absorption. In particular, a double-resonance-absorption microscope includes a light source for a pump light of a wavelength λ1 which excites a sample molecule to a first electronic excited state from a ground state, a light source for an erase light of a wavelength λ2 which excites the sample molecule to a second electronic excited state or a higher excited state from the first electronic excited state, and an overlap component for partially overlapping irradiating areas of the pump light and the erase light with each other. An emission area upon deexcitation of the sample molecule to the ground state from the first electronic excited state is partially inhibited by irradiating the pump light and the erase light through the overlap means. On an optical path of the erase light, a spatial filter is provided which has a condenser lens, a collimate lens, and a pinhole therebetween, and performs condensing of the erase light onto the pinhole by the condenser lens and collimating of the erase light passed through the pinhole into a parallel beam by the collimate lens.
Owner:NIPON ROPER KK +1
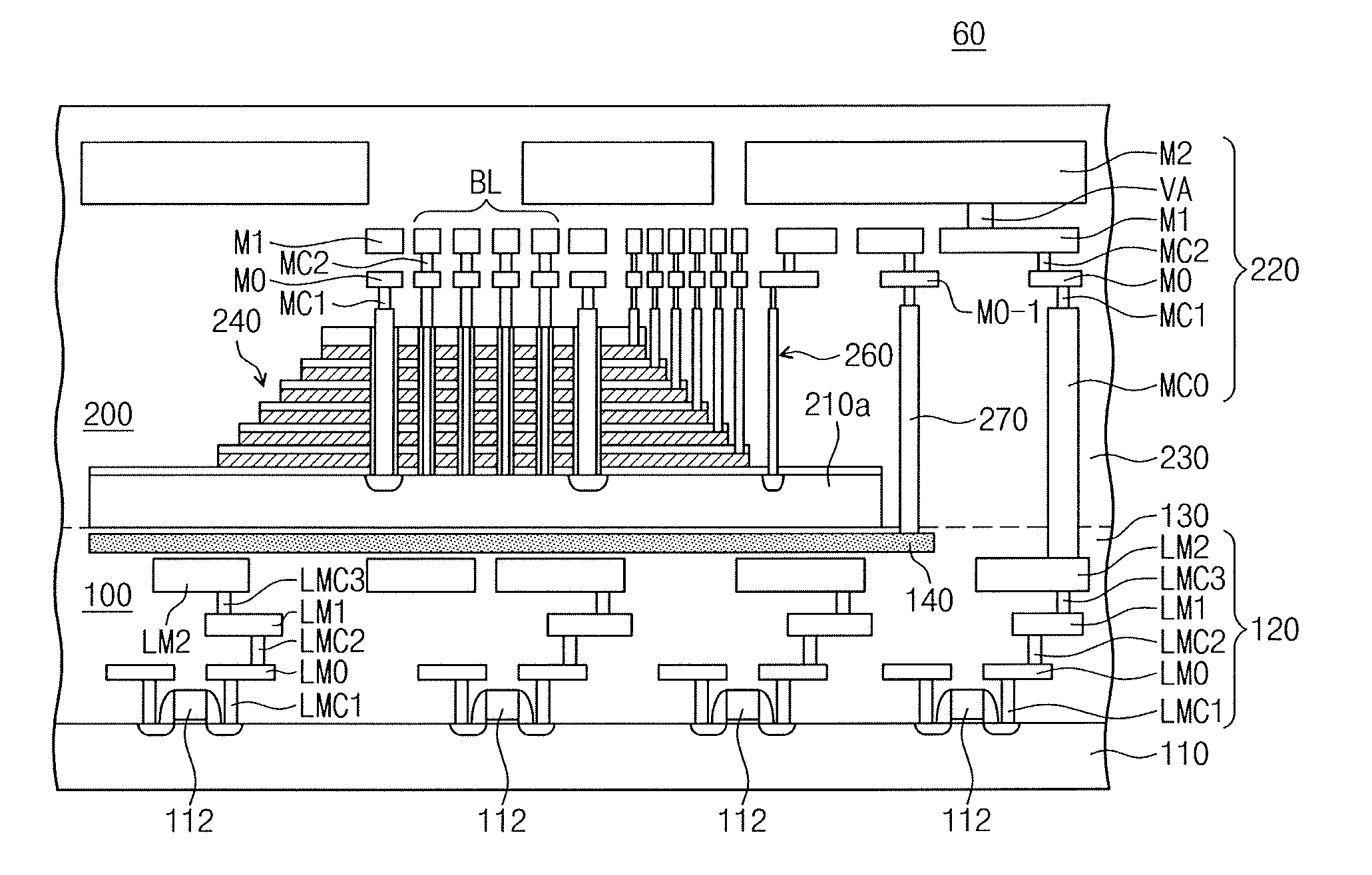
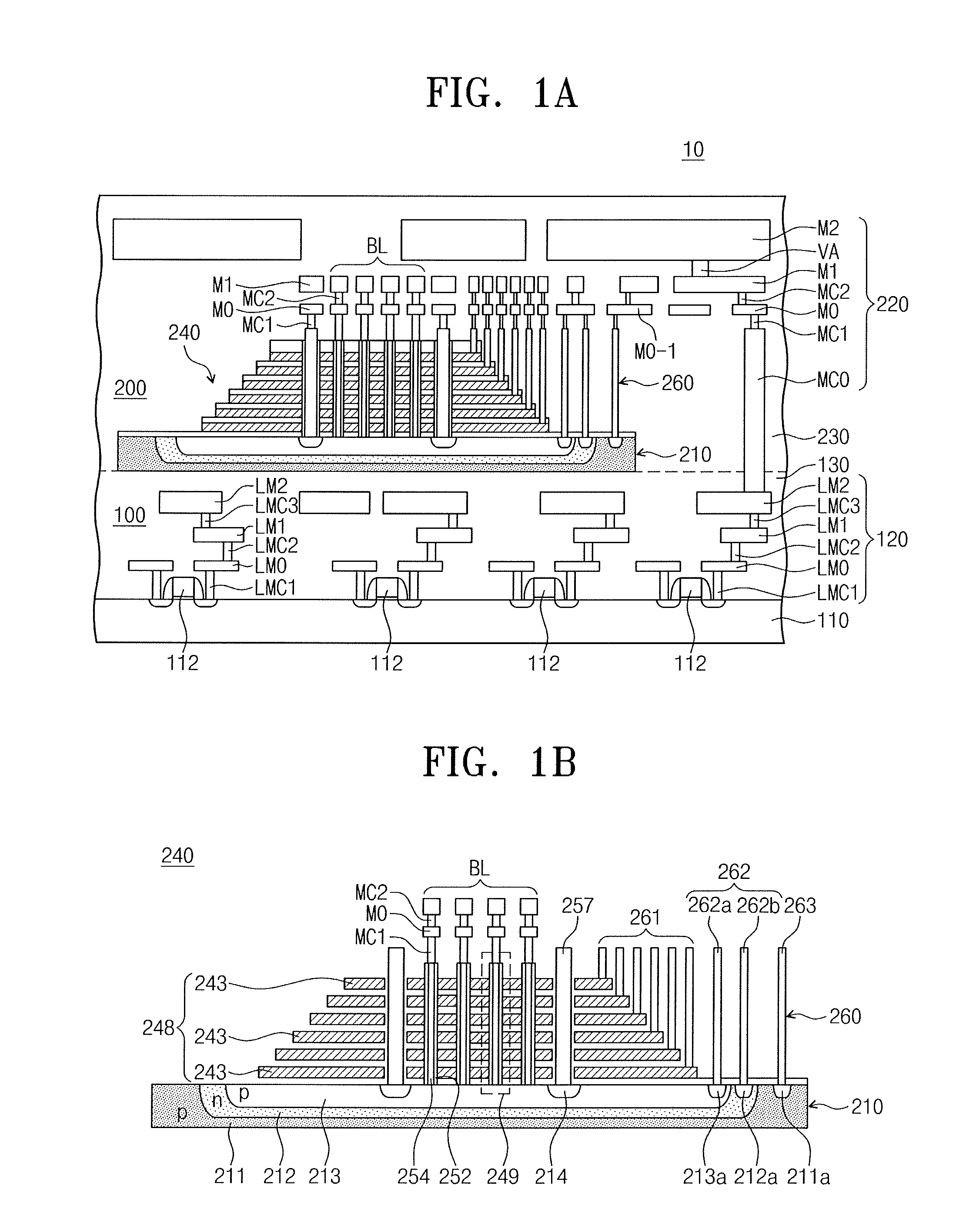
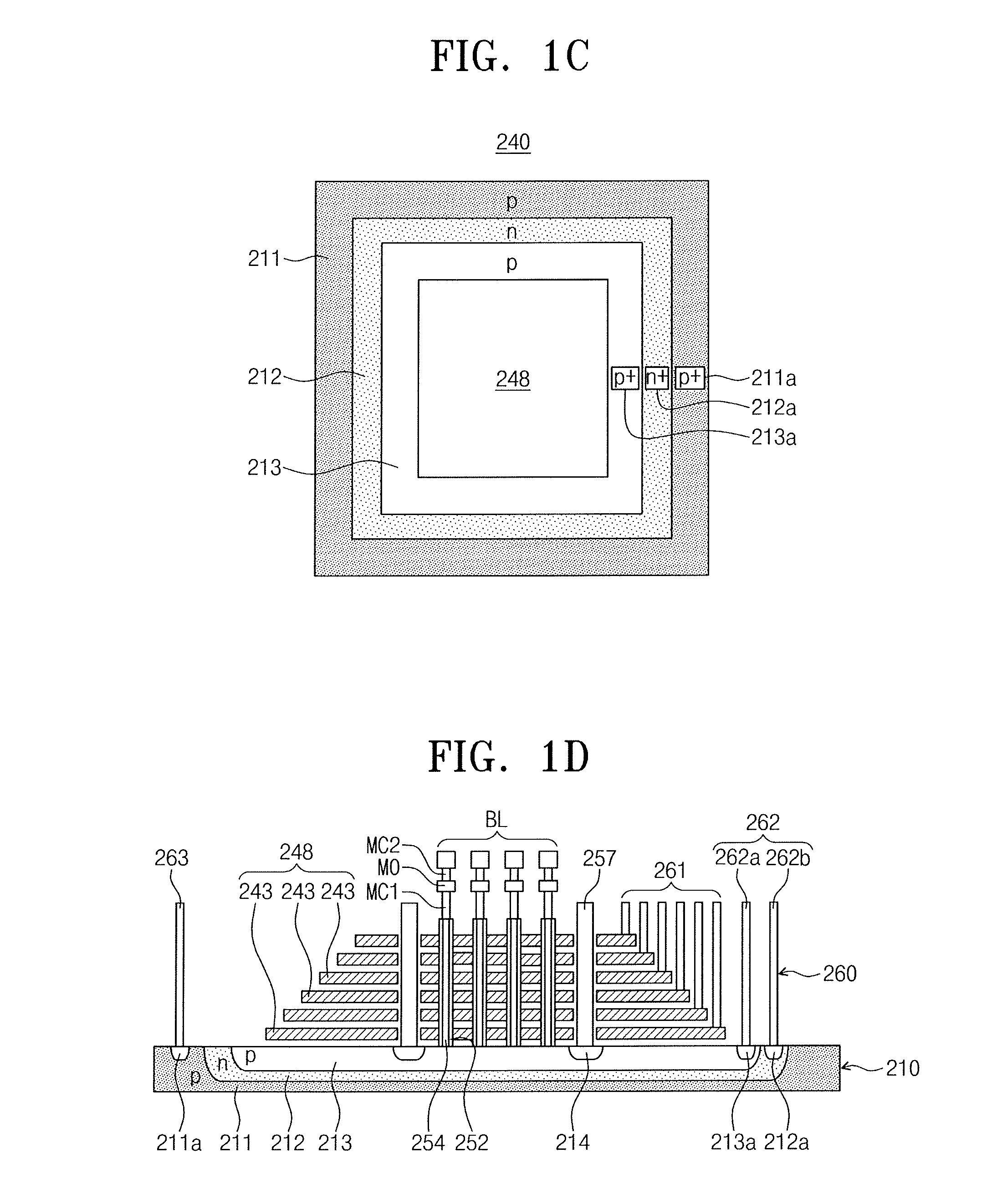
Semiconductor device including cell region stacked on peripheral region and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20160307632A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialCell region
Provided are semiconductor devices including a peripheral region and a cell region stacked thereon and a method of fabricating the same. The semiconductor device may include a peripheral region including a lower substrate and a peripheral circuit provided thereon and a cell region including an upper substrate and a cell array provided thereon. The cell region may be stacked on the peripheral region. When an operation signal is applied to the cell region from the peripheral region, at least a portion of the peripheral and cell regions may be used as a ground pattern applied with a ground signal, thereby being in an electrical ground state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Microwave electric field intensity meter based on cold Rydberg atom interferometer and measuring method thereof
ActiveCN104880614AHigh measurement accuracyMake up for the defect that only point frequency measurement can be realizedElectrostatic field measurementsRydberg atomBeam splitting
The invention discloses a microwave electric field intensity meter based on a cold Rydberg atom interferometer and a measuring method thereof. The microwave electric field intensity meter comprises: a vacuum system, which is used for cooling and trapping atom to generate a cold atom cloud for preparing a Rydberg state and generating an interference effect so as to generate a phase difference by coherent atomic states; a laser, which is used for generating coupling light and detection light and exciting the cold atom in the vacuum system from a ground state to the Rydberg state coherently; a photoelectric detector, which is used for detecting an interference fringe generated by two beams of cold atom clouds due to coherence; and a microwave source, which is used for generating a microwave electric field. According to the invention, when the microwave electric field intensity meter is applied to the evolution process of coherent beam splitting and combination, the atom cloud in the Rydberg state interacts with a to-be-measured microwave electric field, thereby generating an alternating-current stark effect; and the to-be-measured microwave electric field intensity is associated with a phase generated by the an alternating-current stark, thereby realizing precise measurement of the microwave electric field.
Owner:清远市天之衡量子科技有限公司
Microwave readout for flux-biased qubits
A method for determining whether a quantum system comprising a superconducting qubit is occupying a first basis state or a second basis state once a measurement is performed is provided. The method, comprising: applying a signal having a frequency through a transmission line coupled to the superconducting qubit characterized by two distinct, separate, and stable states of differing resonance frequencies each corresponding to the occupation of the first or second basis state prior to measurement; and measuring at least one of an output power or phase at an output port of the transmission line, wherein the measured output power or phase is indicative of whether the superconducting qubit is occupying the first basis state or the second basis state.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
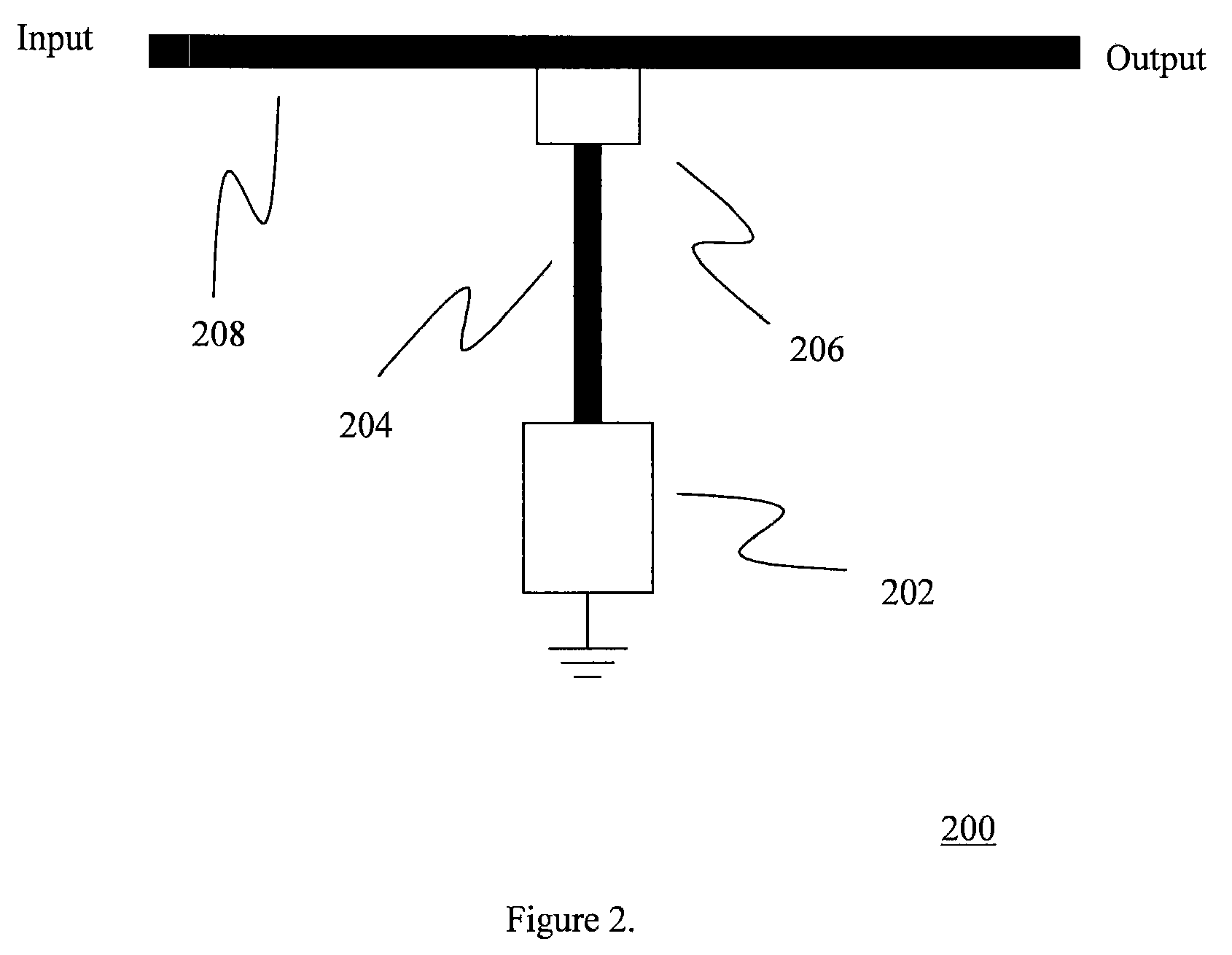
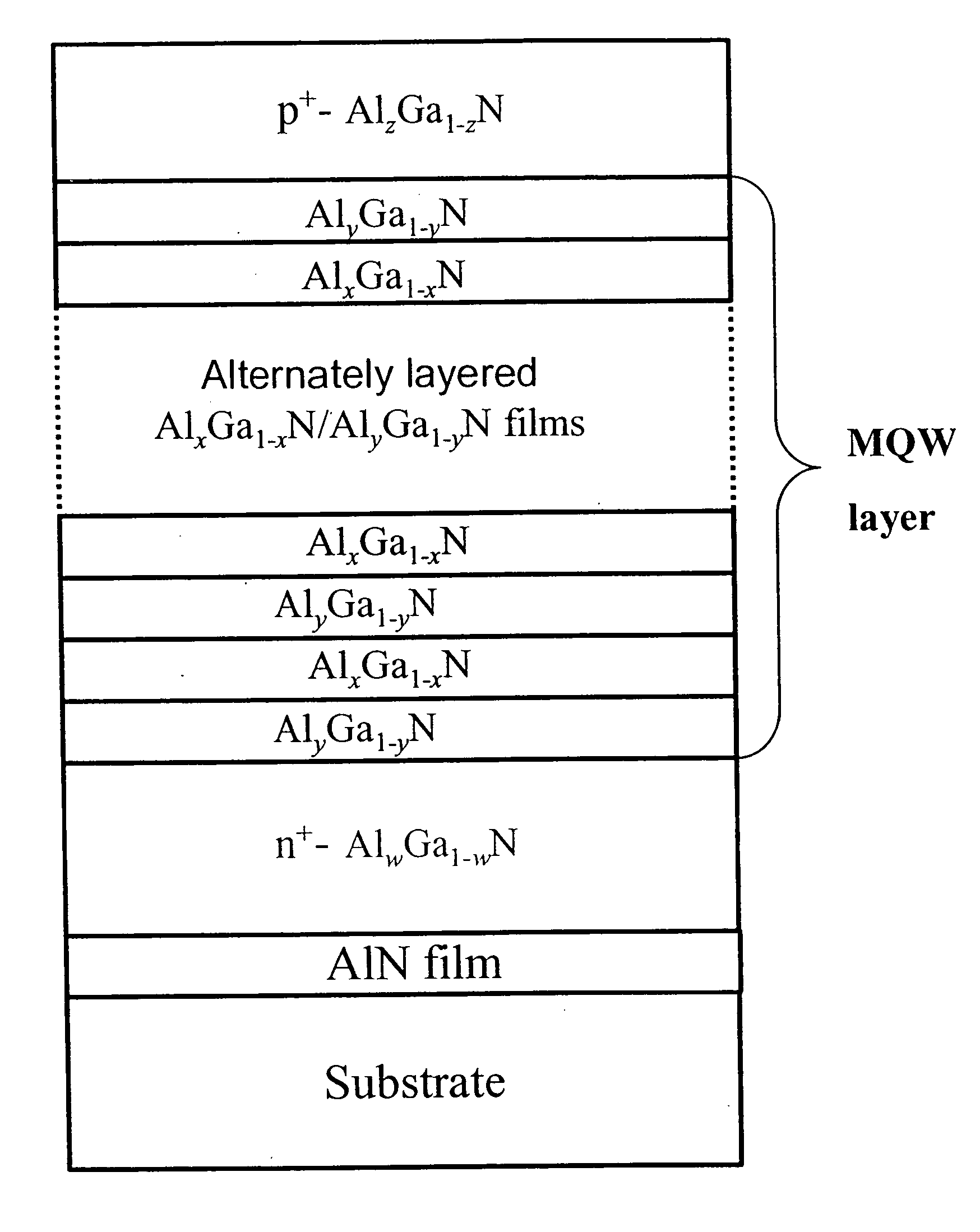
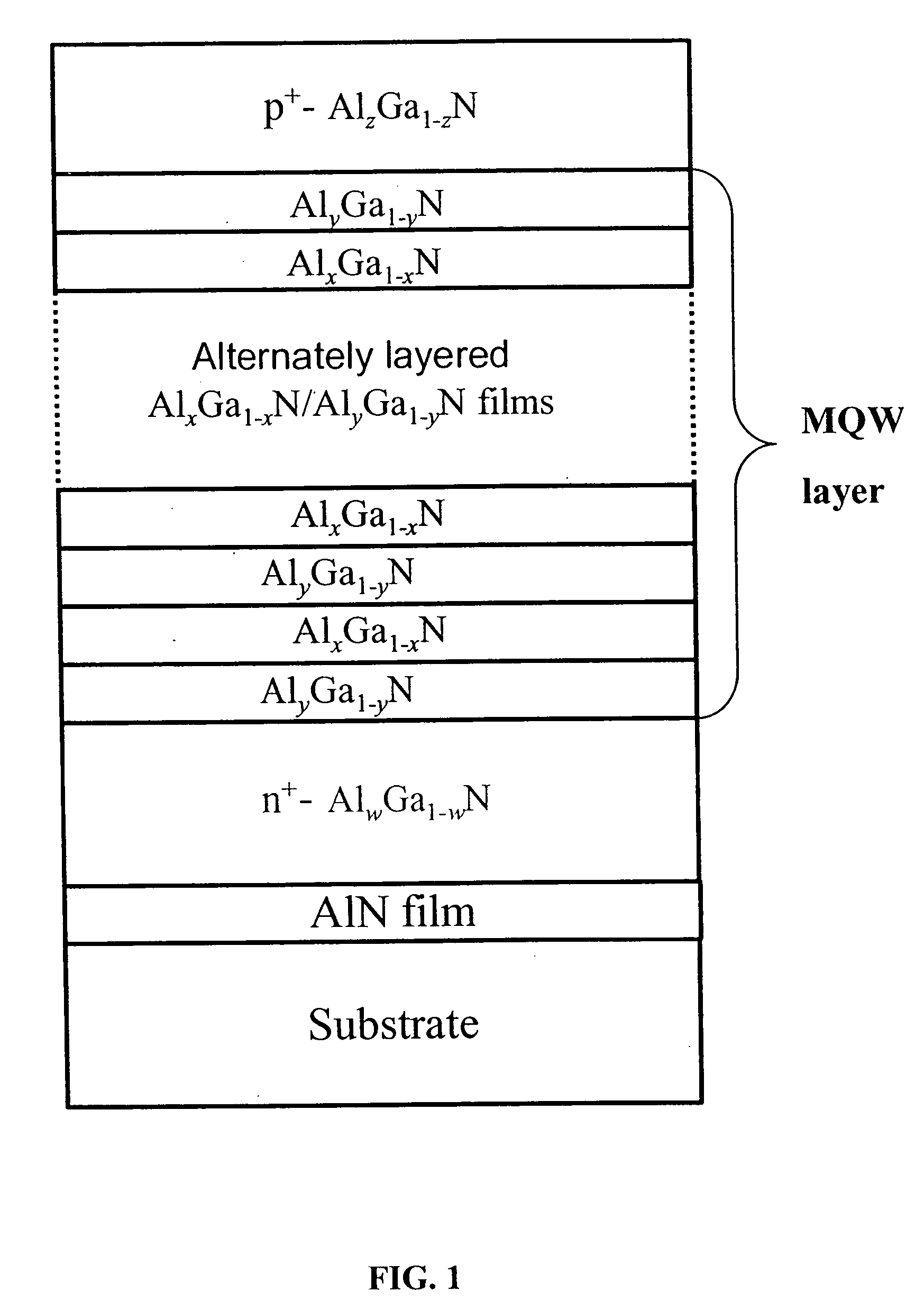
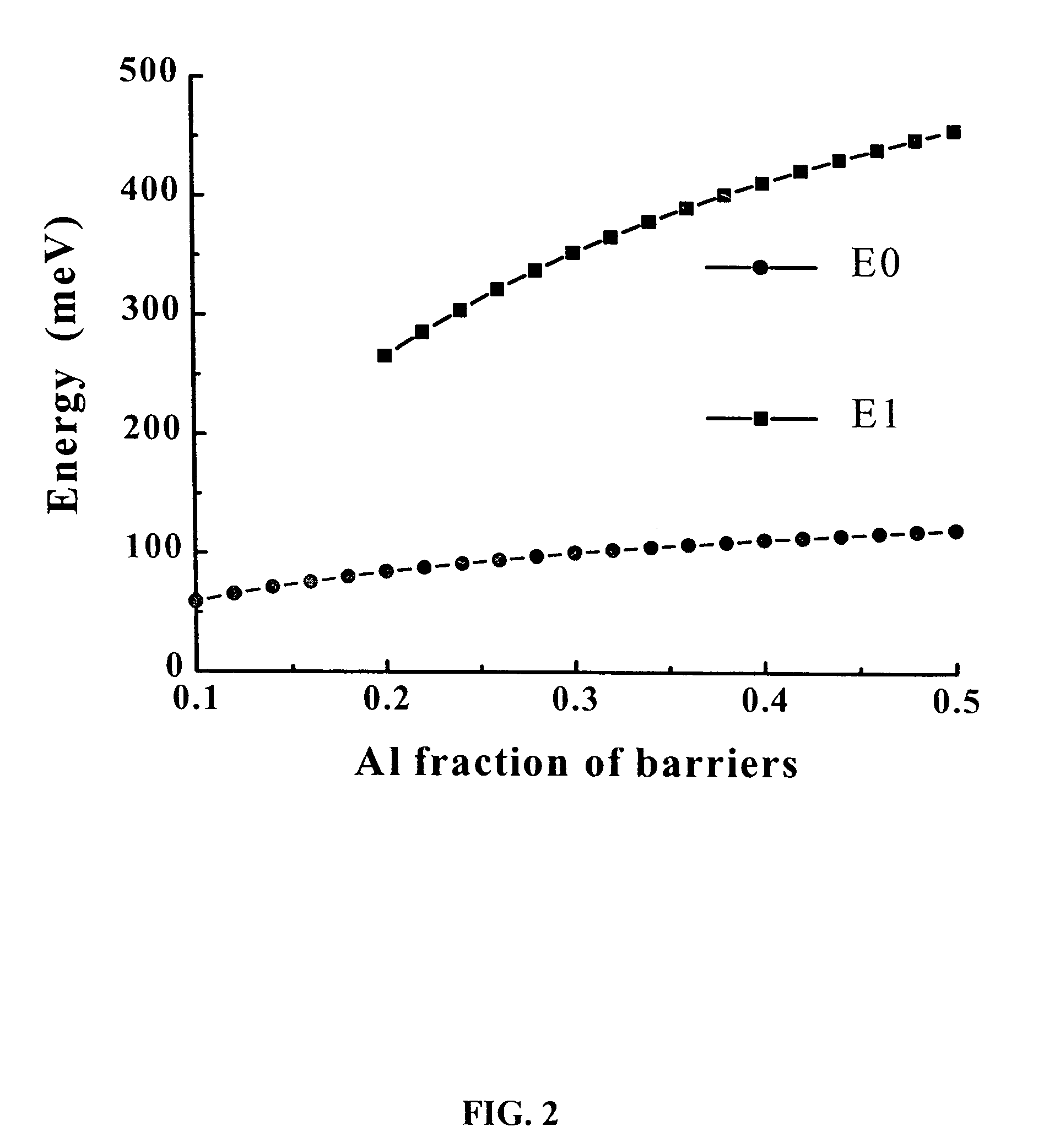
Photodetectors and optically pumped emitters based on III-nitride multiple-quantum-well structures
The design and operation of a p-i-n device, operating in a sequential resonant tunneling condition for use as a photodetector and an optically pumped emitter, is disclosed. The device contains III-nitride multiple-quantum-well (MQW) layers grown between a III-nitride p-n junction. Transparent ohmic contacts are made on both p and n sides. The device operates under a certain electrical bias that makes the energy level of the first excitation state in each well layer correspond with the energy level of the ground state in the adjoining well layer. The device works as a high-efficiency and high-speed photodetector with photo-generated carriers transported through the active MQW region by sequential resonant tunneling. In a sequential resonant tunneling condition, the device also works as an optically pumped infrared emitter that emits infrared photons with energy equal to the energy difference between the first excitation state and the ground state in the MQWs.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com