Patents
Literature
31 results about "Molecular modelling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molecular modelling encompasses all methods, theoretical and computational, used to model or mimic the behaviour of molecules. The methods are used in the fields of computational chemistry, drug design, computational biology and materials science to study molecular systems ranging from small chemical systems to large biological molecules and material assemblies. The simplest calculations can be performed by hand, but inevitably computers are required to perform molecular modelling of any reasonably sized system. The common feature of molecular modelling methods is the atomistic level description of the molecular systems. This may include treating atoms as the smallest individual unit (a molecular mechanics approach), or explicitly modelling protons and neutrons with its quarks, anti-quarks and gluons and electrons with its photons (a quantum chemistry approach).
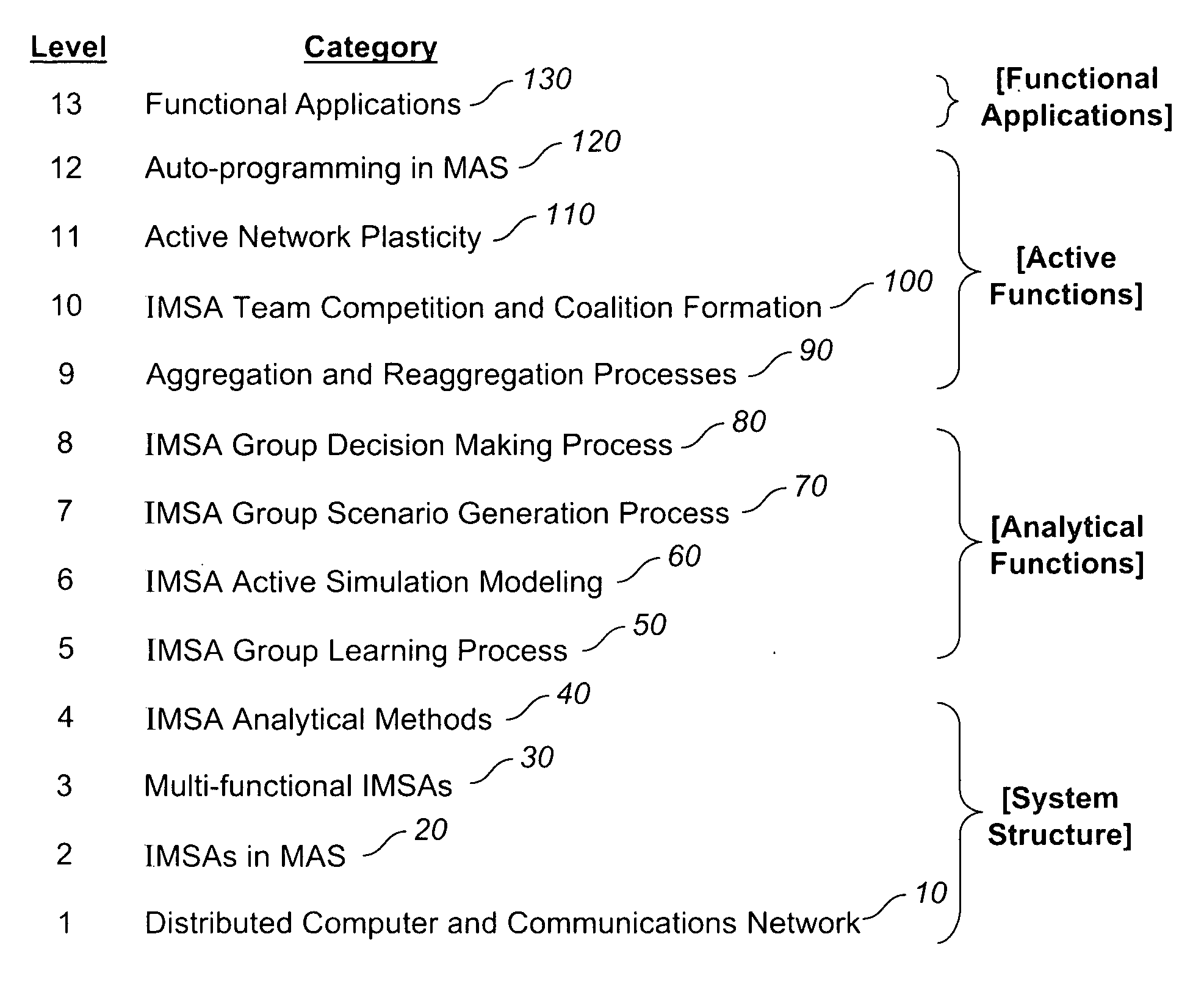
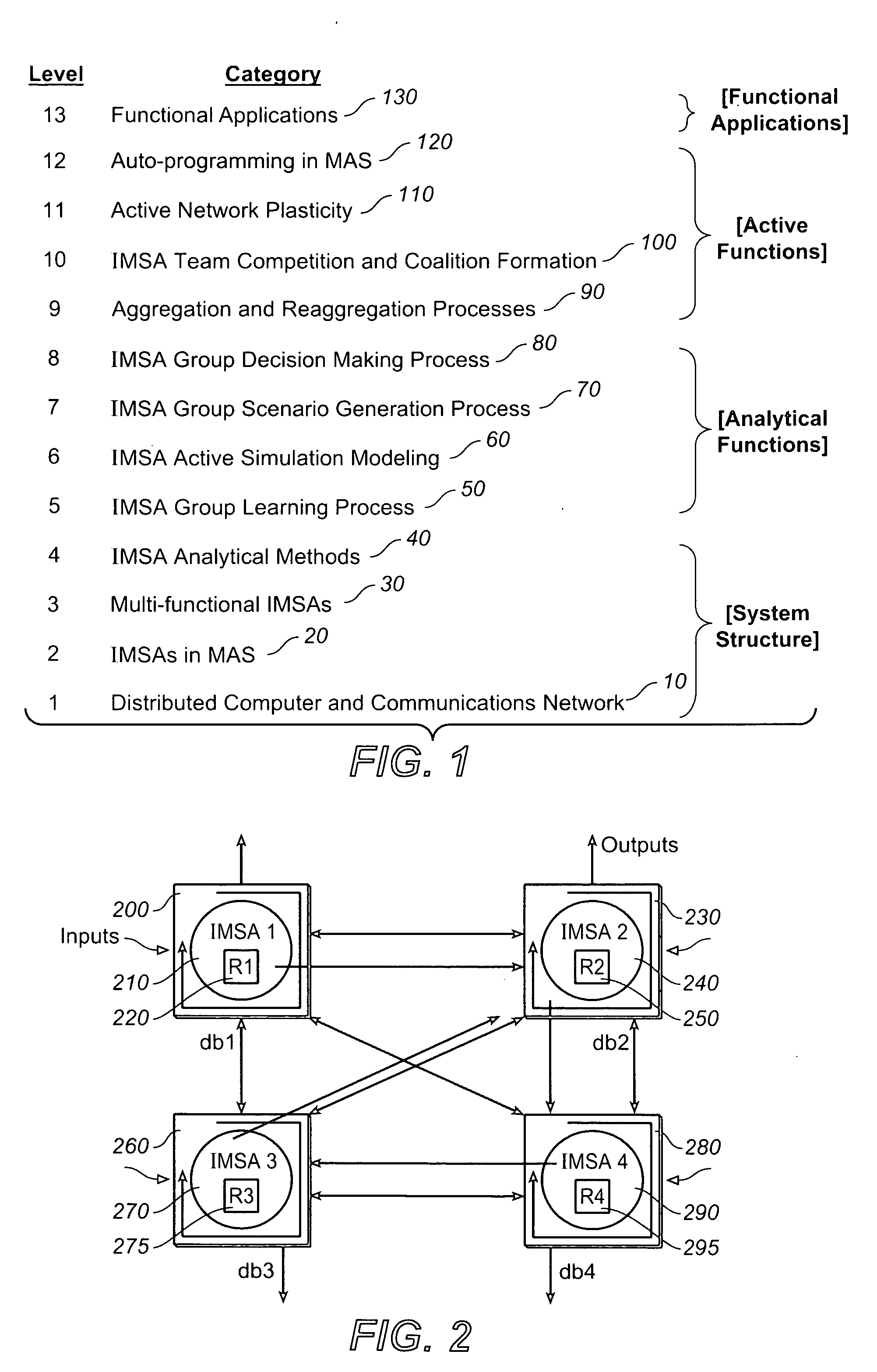
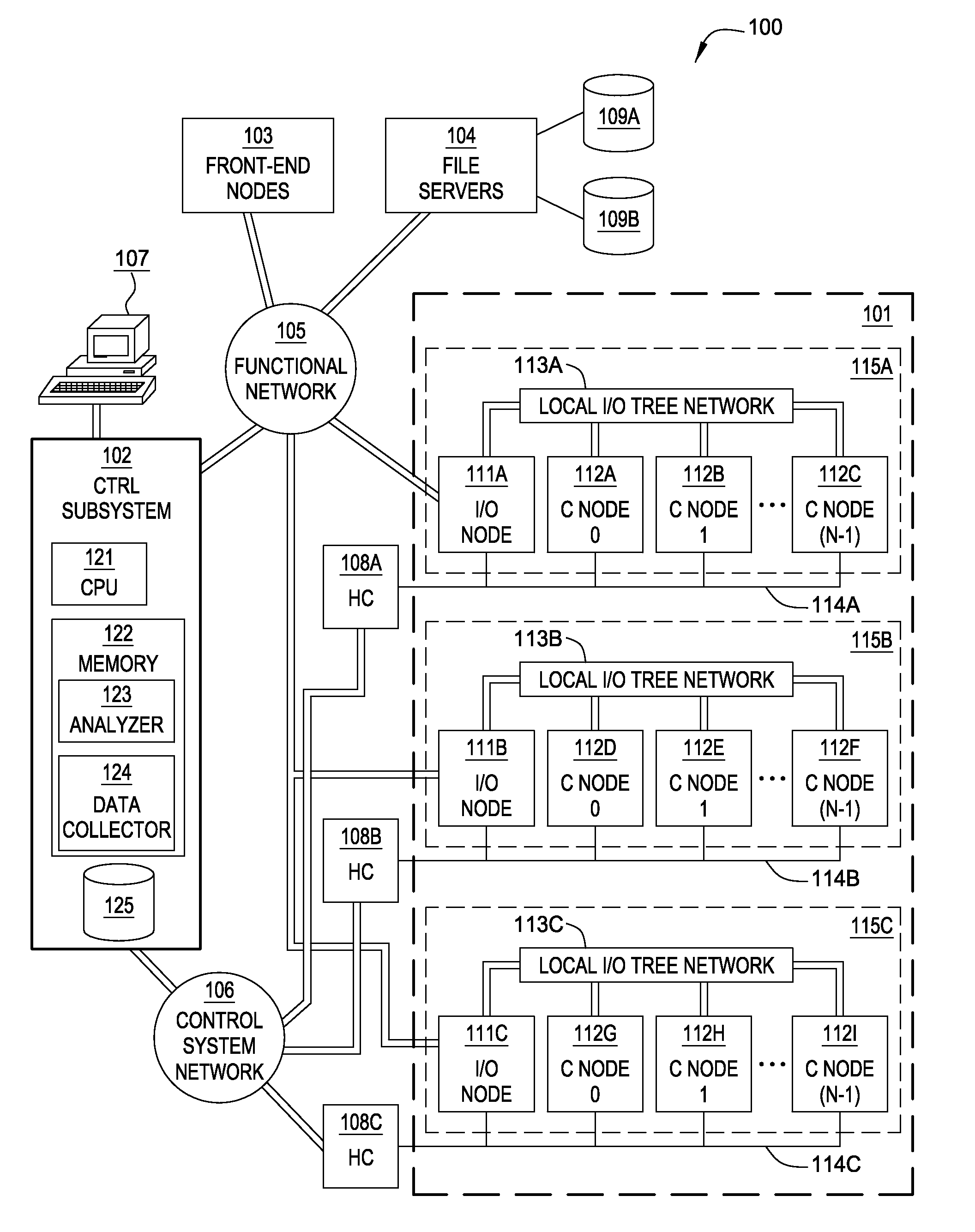
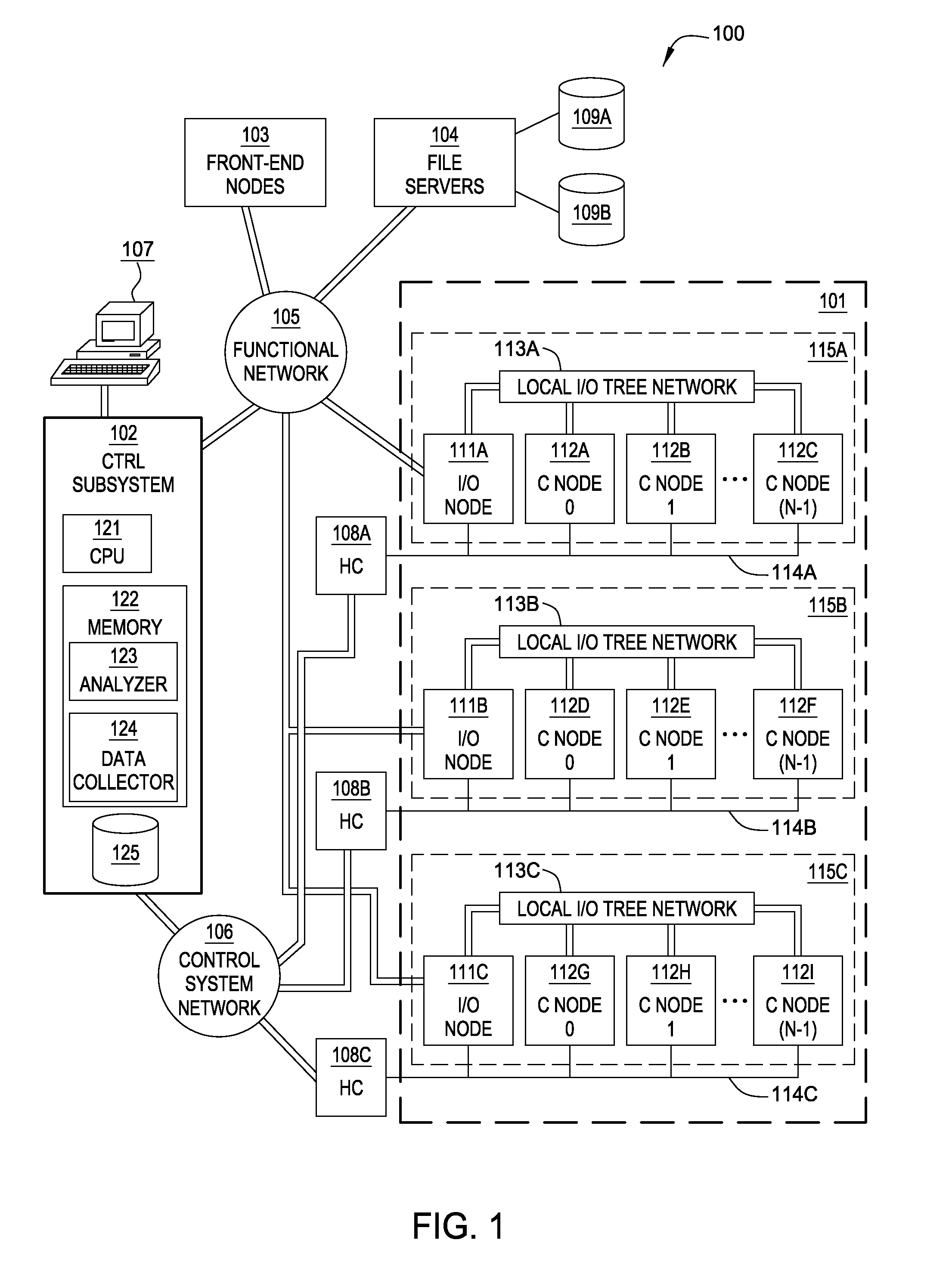
System, methods and apparatus for complex behaviors of collectives of intelligent mobile software agents
InactiveUS20060167917A1Optimizes adaptive self-organizing operationImprove productivityDigital data processing detailsArtificial lifeMolecular modellingArtificial neural network
A system, methods and apparatus are described involving the self-organizing dynamics of networks of distributed computers. The system uses intelligent mobile software agents in a multi-agent system to perform numerous functions, including search, analysis, collaboration, negotiation, decision making and structural transformation. Data are continuously input, analyzed, organized, reorganized, used and output for specific commercial and industrial applications. The system uses combinations of AI techniques, including evolutionary computation, genetic programming and evolving artificial neural networks; consequently, the system learns, anticipates and adapts. The numerous categories of applications of the system include optimizing network dynamics, collective robotics systems, automated commercial systems and molecular modeling systems. Given the application of complexity theory and modal and temporal logics to self-organizing dynamic networks, a novel model of intelligent systems is presented.
Owner:SOLOMON RES
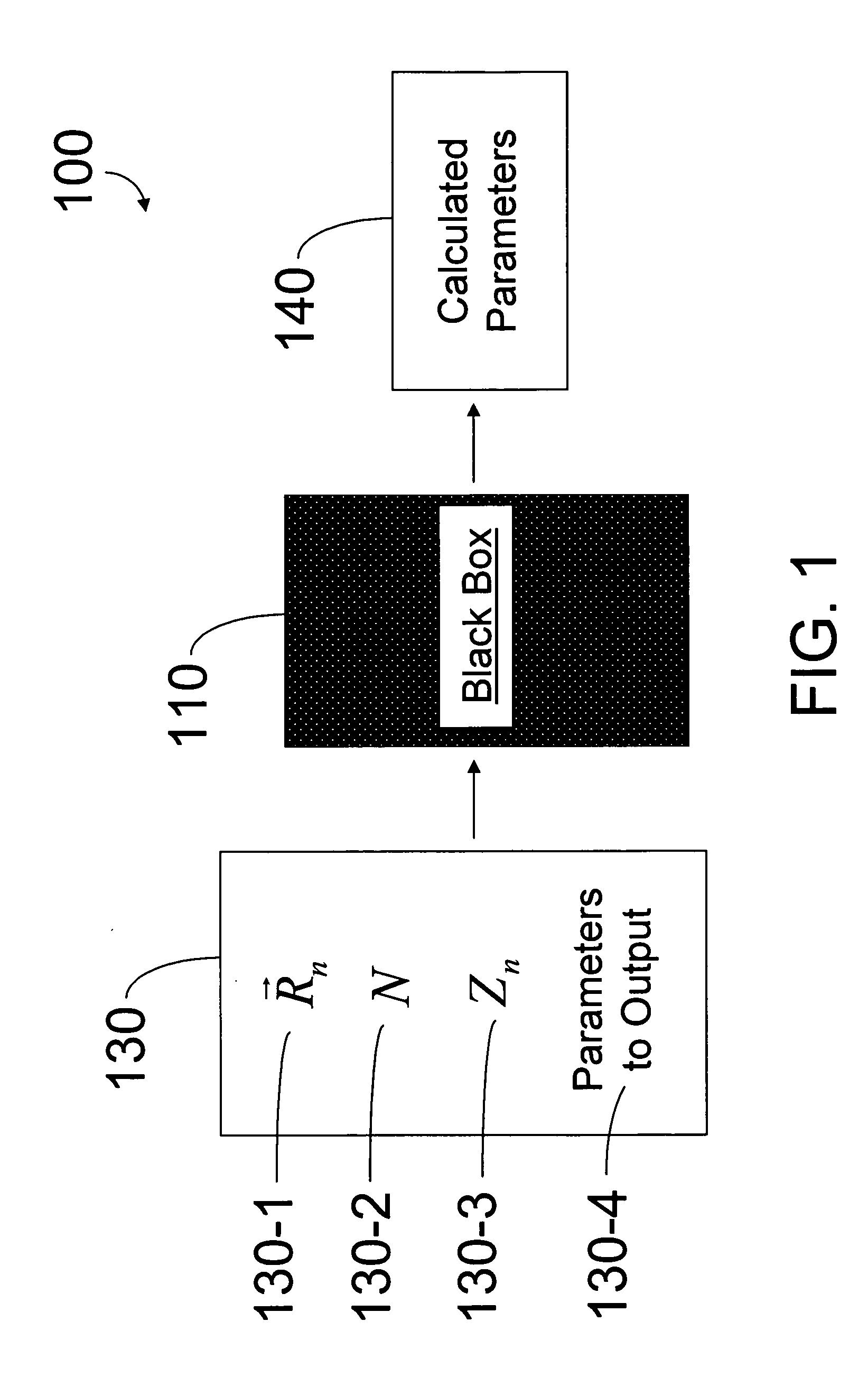
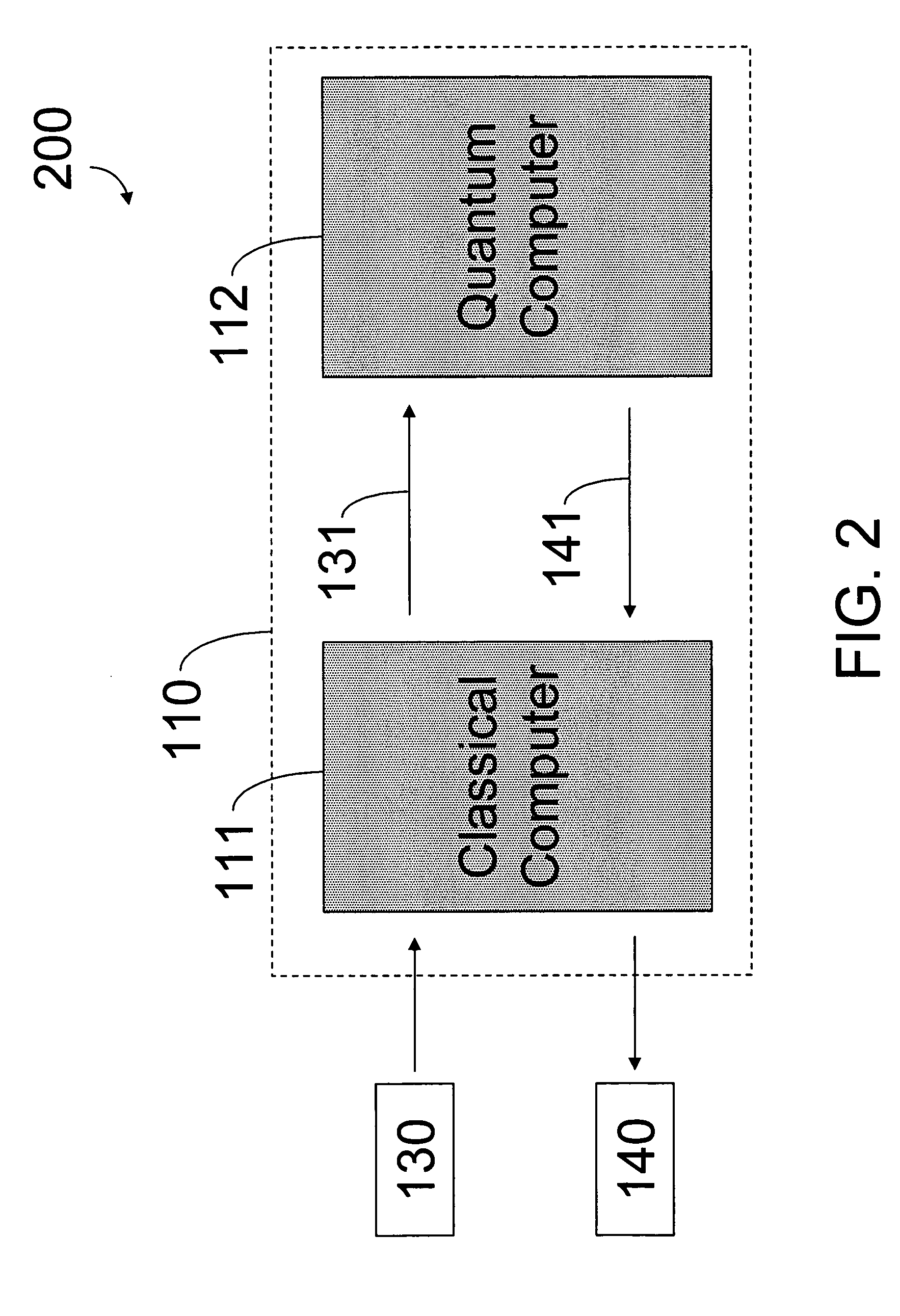
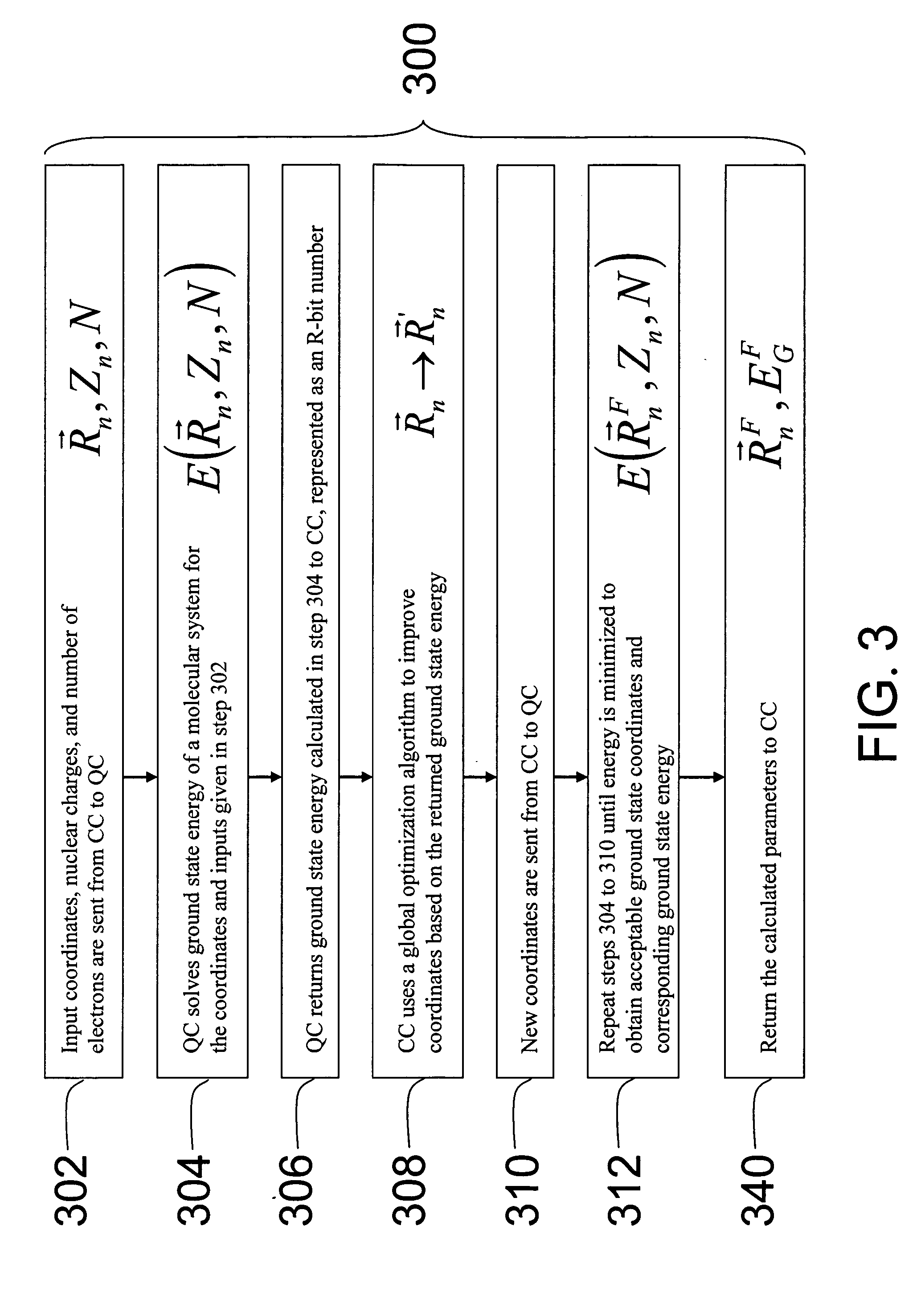
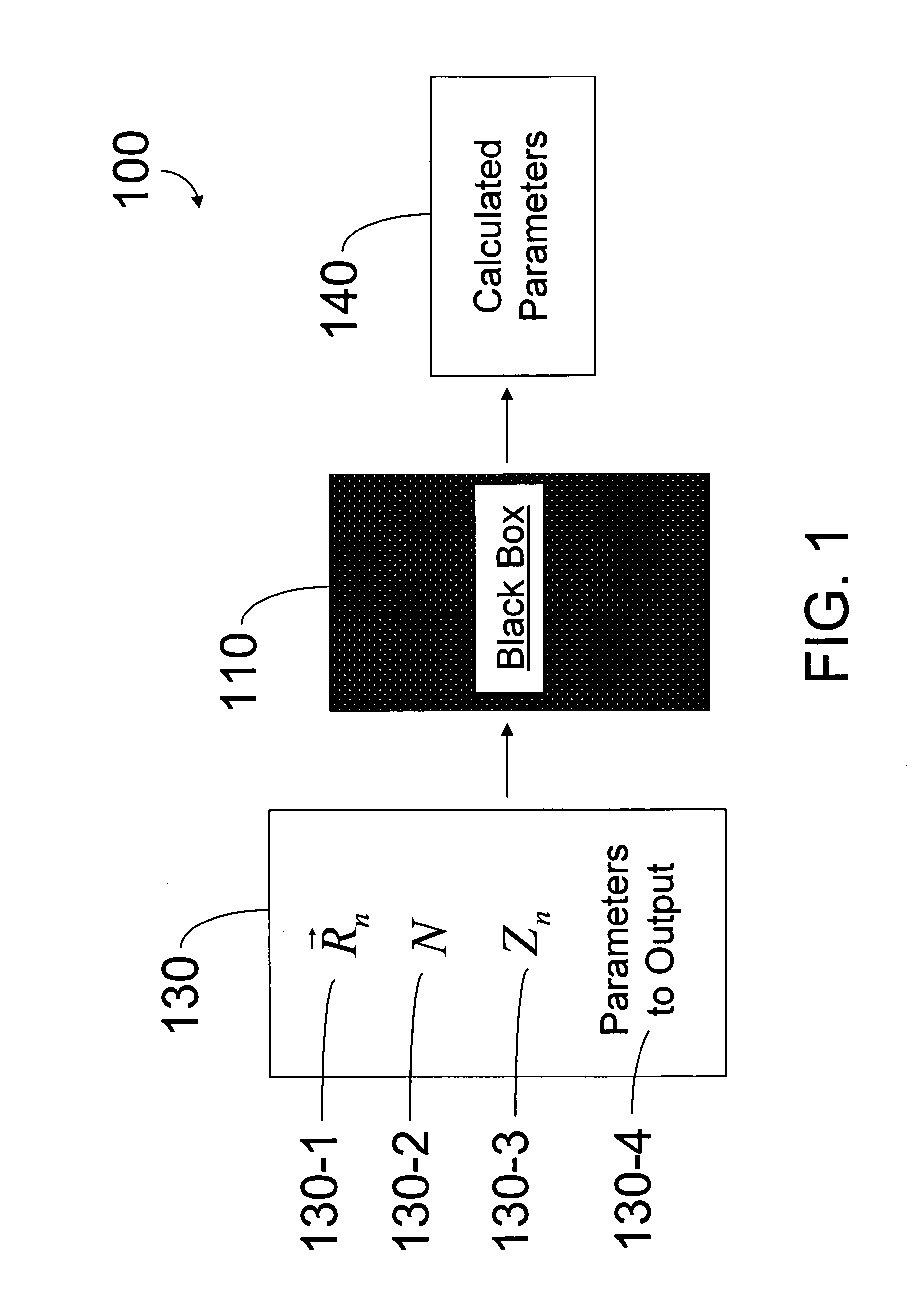
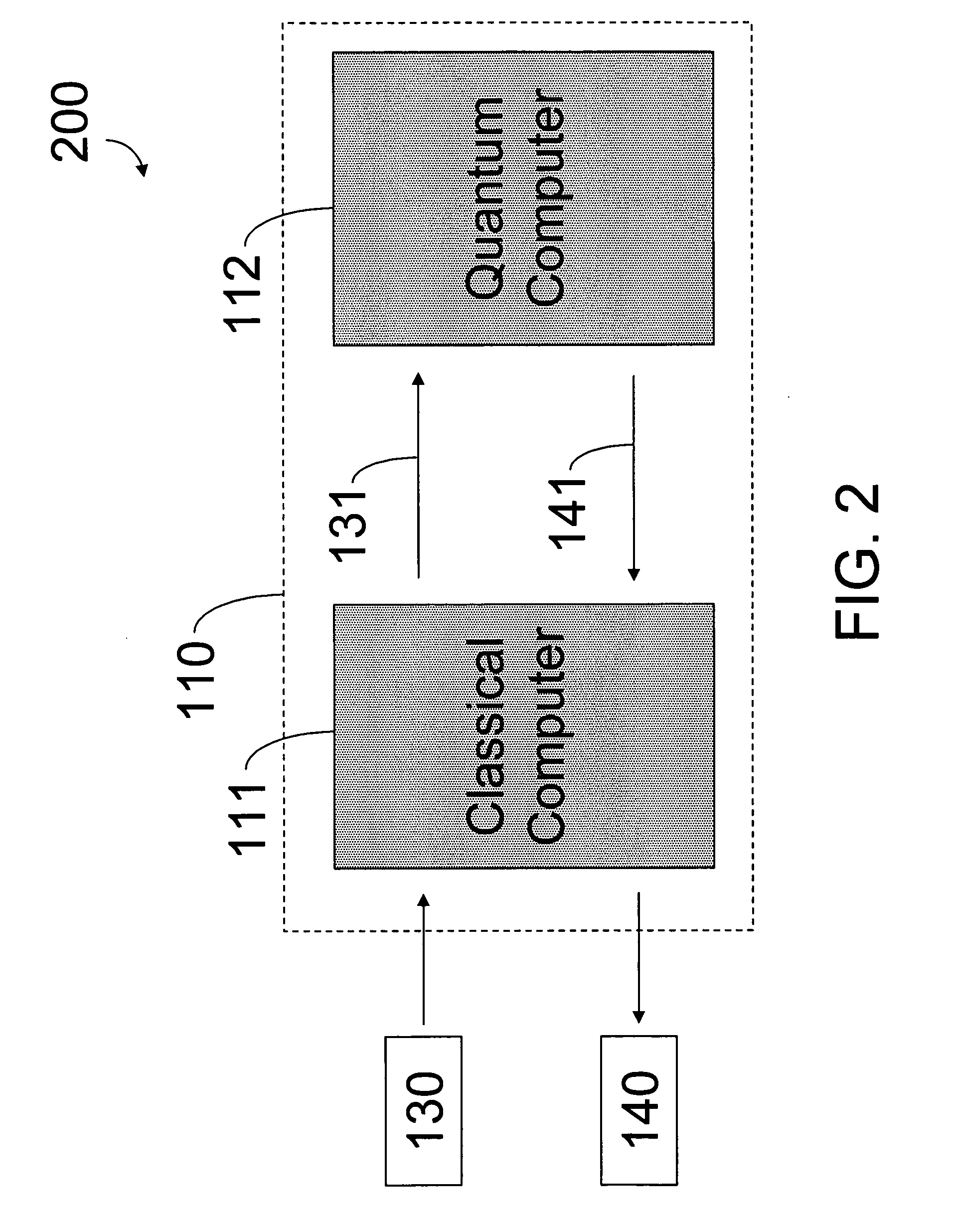
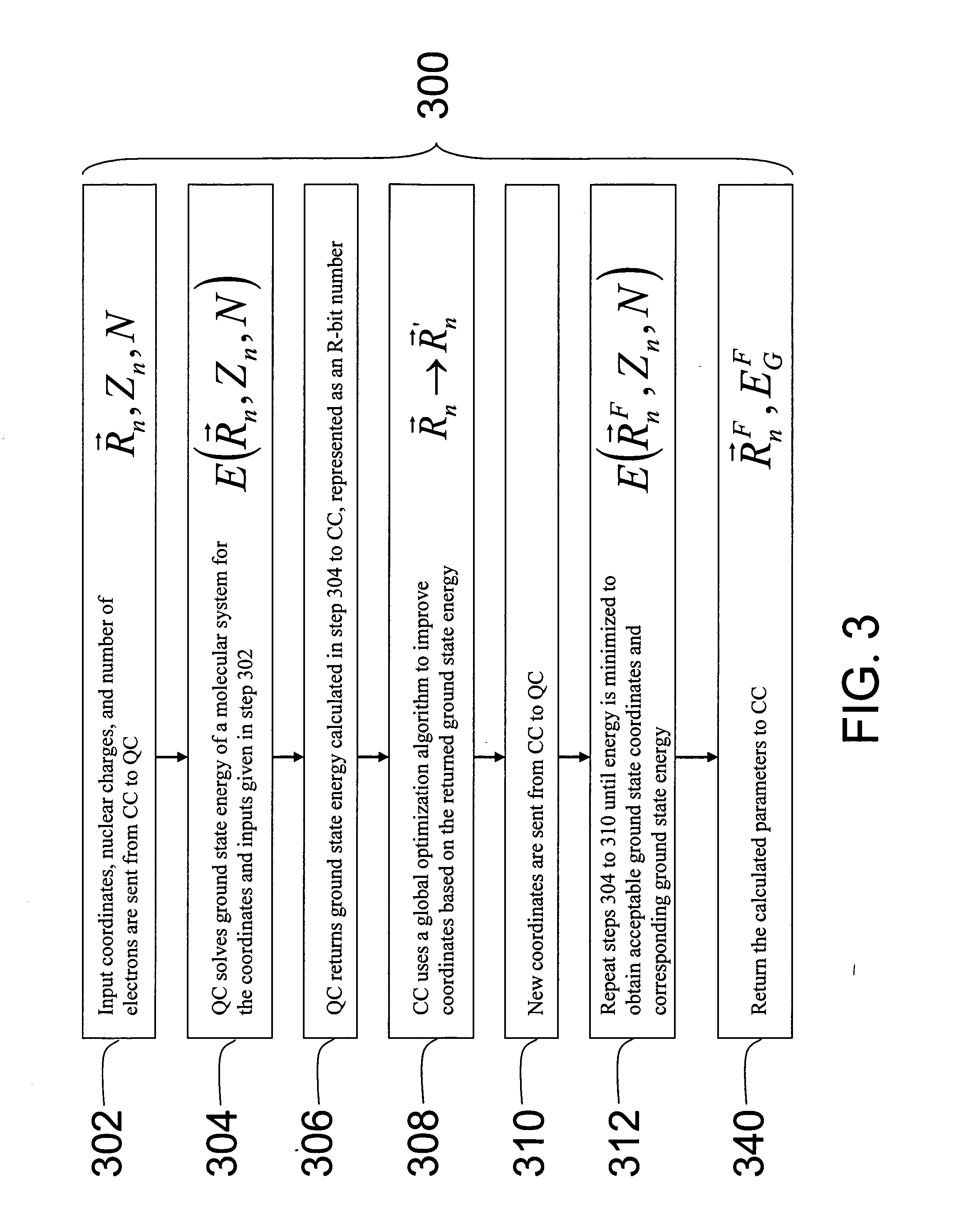
Hybrid classical-quantum computer architecture for molecular modeling
A method of simulating a molecular system using a hybrid computer is provided. The hybrid computer comprises a classical computer and a quantum computer. The method uses atomic coordinates {right arrow over (R)}n and atomic charges Zn of a molecular system to compute a ground state energy of the molecular system using the quantum computer. The ground state energy is returned to the classical computer and the atomic coordinates are geometrically optimized on the classical computer based on information about the returned ground state energy of the atomic coordinates in order to produce a new set of atomic coordinates {right arrow over (R)}′n for the molecular system. These steps are optionally repeated in accordance with a refinement algorithm until a predetermined termination condition is achieved
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Hybrid classical-quantum computer architecture for molecular modeling
A method of simulating a molecular system using a hybrid computer is provided. The hybrid computer comprises a classical computer and a quantum computer. The method uses atomic coordinates {right arrow over (R)}n and atomic charges Zn of a molecular system to compute a ground state energy of the molecular system using the quantum computer. The ground state energy is returned to the classical computer and the atomic coordinates are geometrically optimized on the classical computer based on information about the returned ground state energy of the atomic coordinates in order to produce a new set of atomic coordinates {right arrow over (R)}′n for the molecular system. These steps are optionally repeated in accordance with a refinement algorithm until a predetermined termination condition is achieved
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
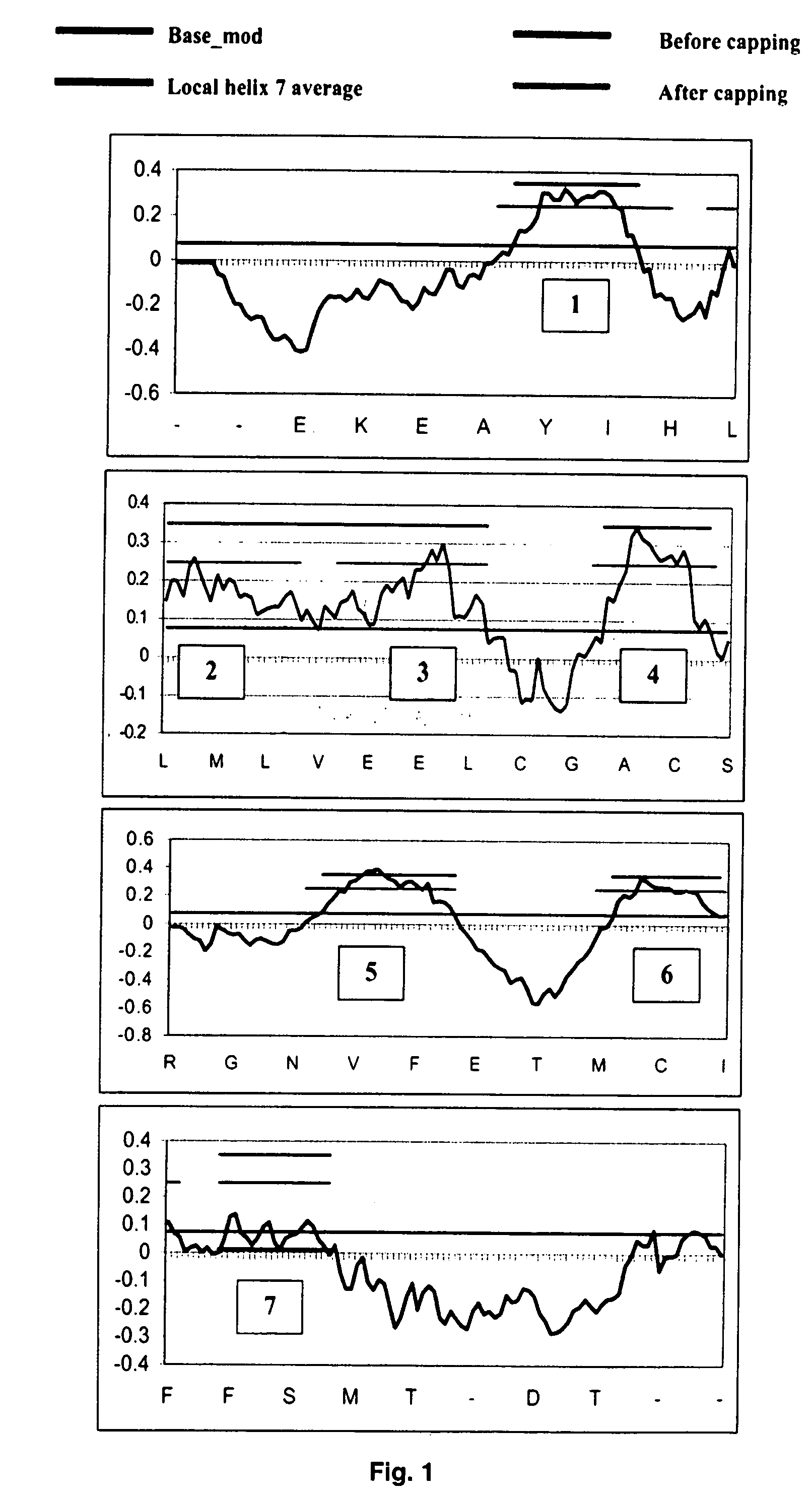
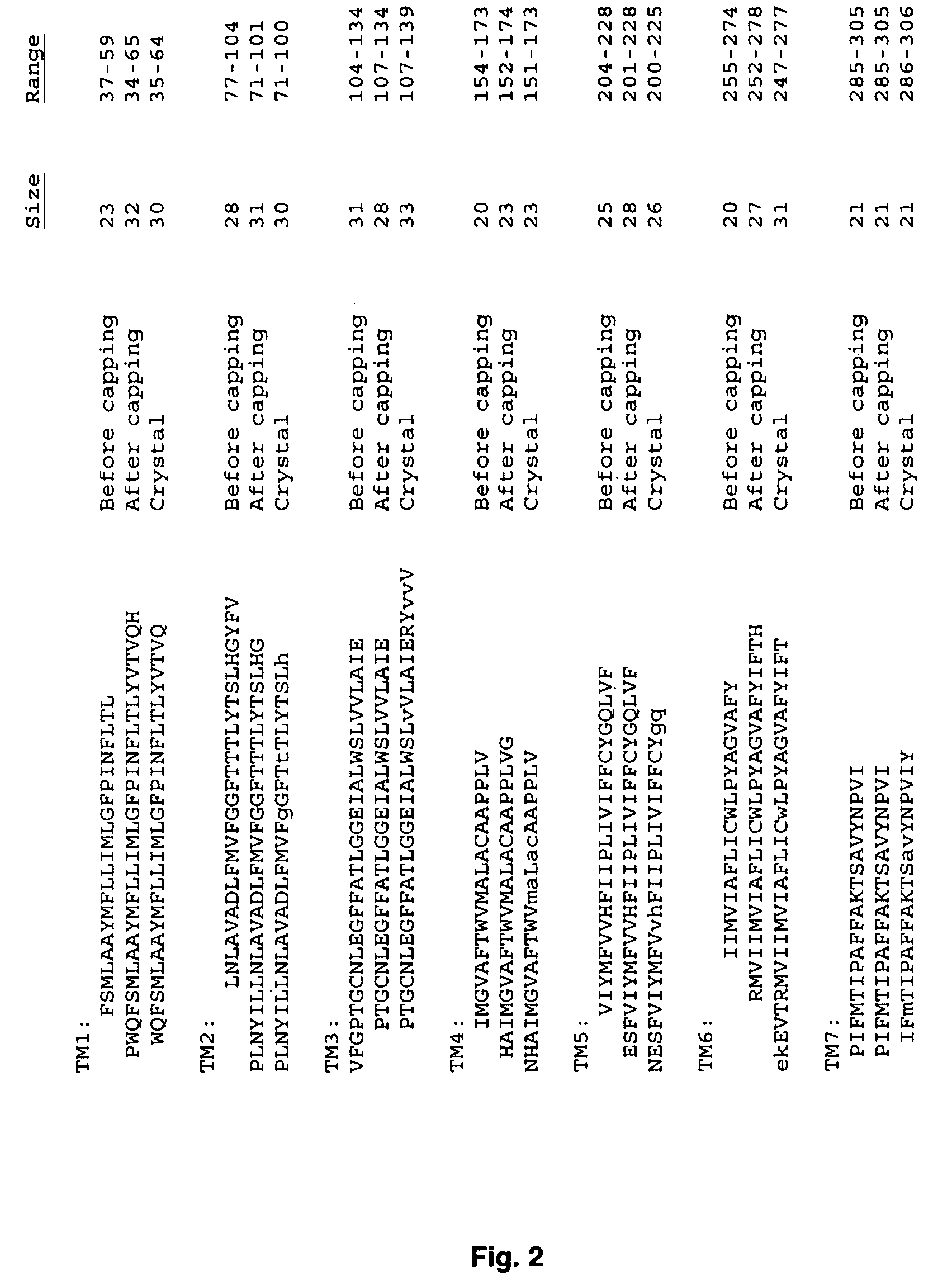
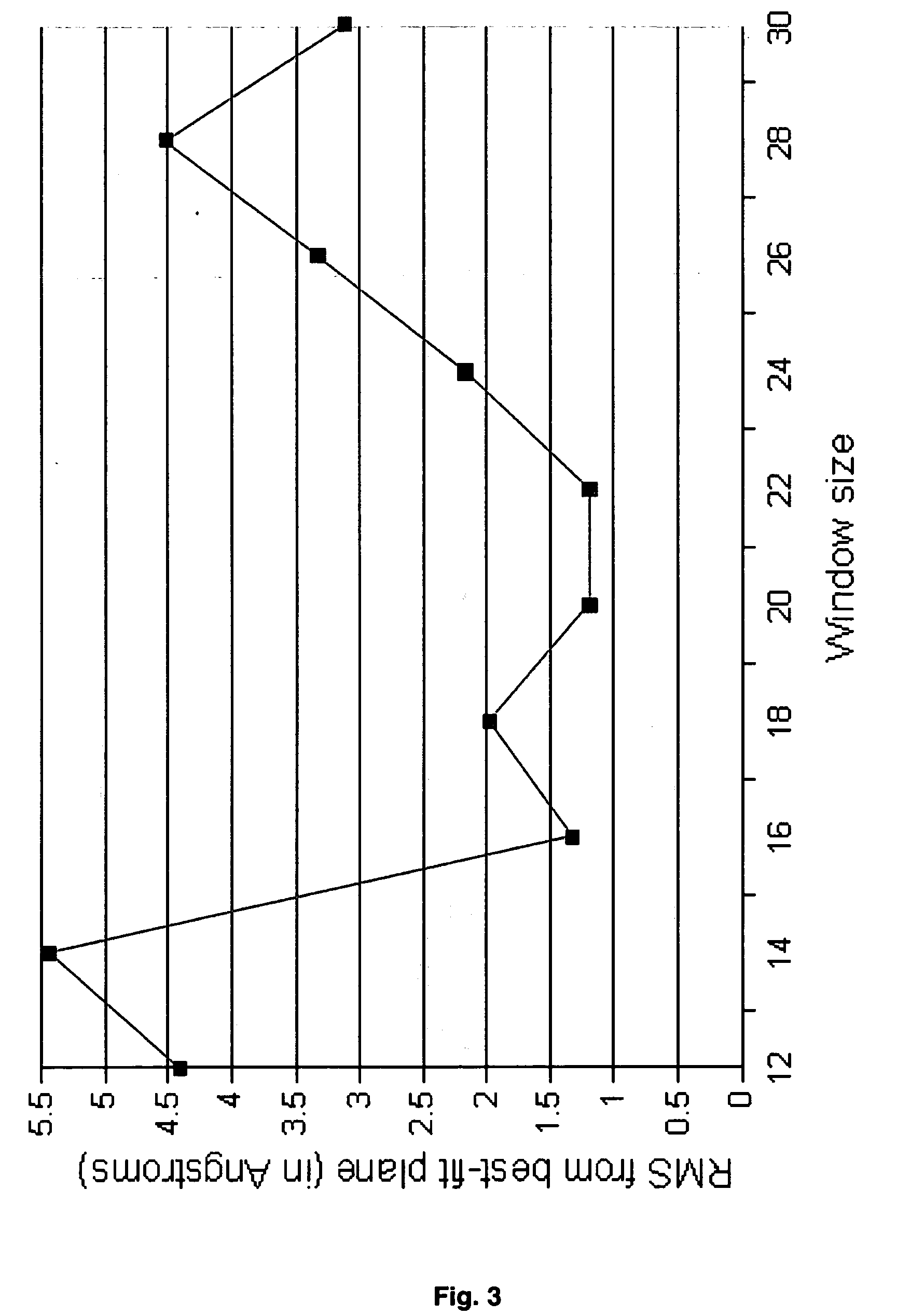
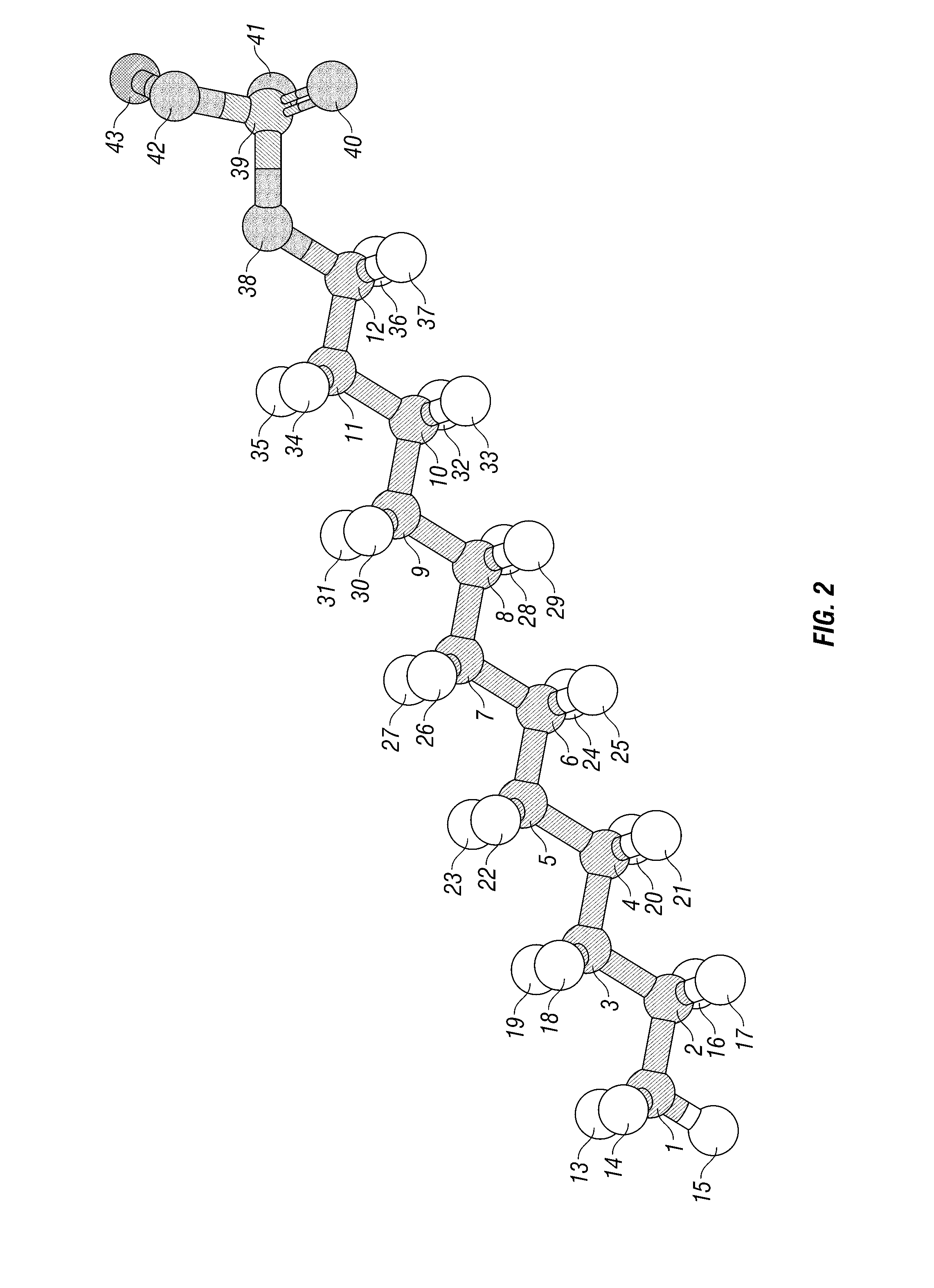
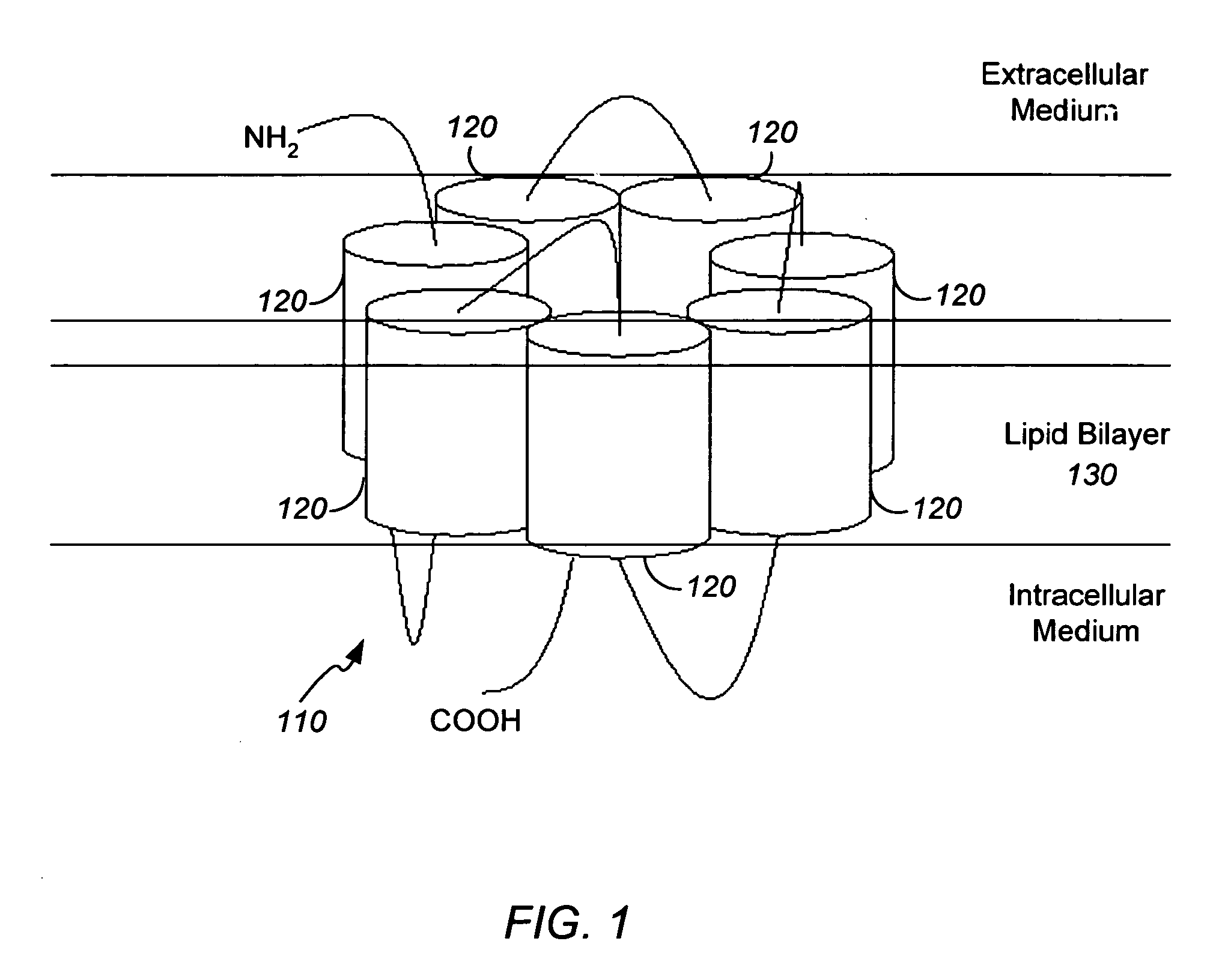
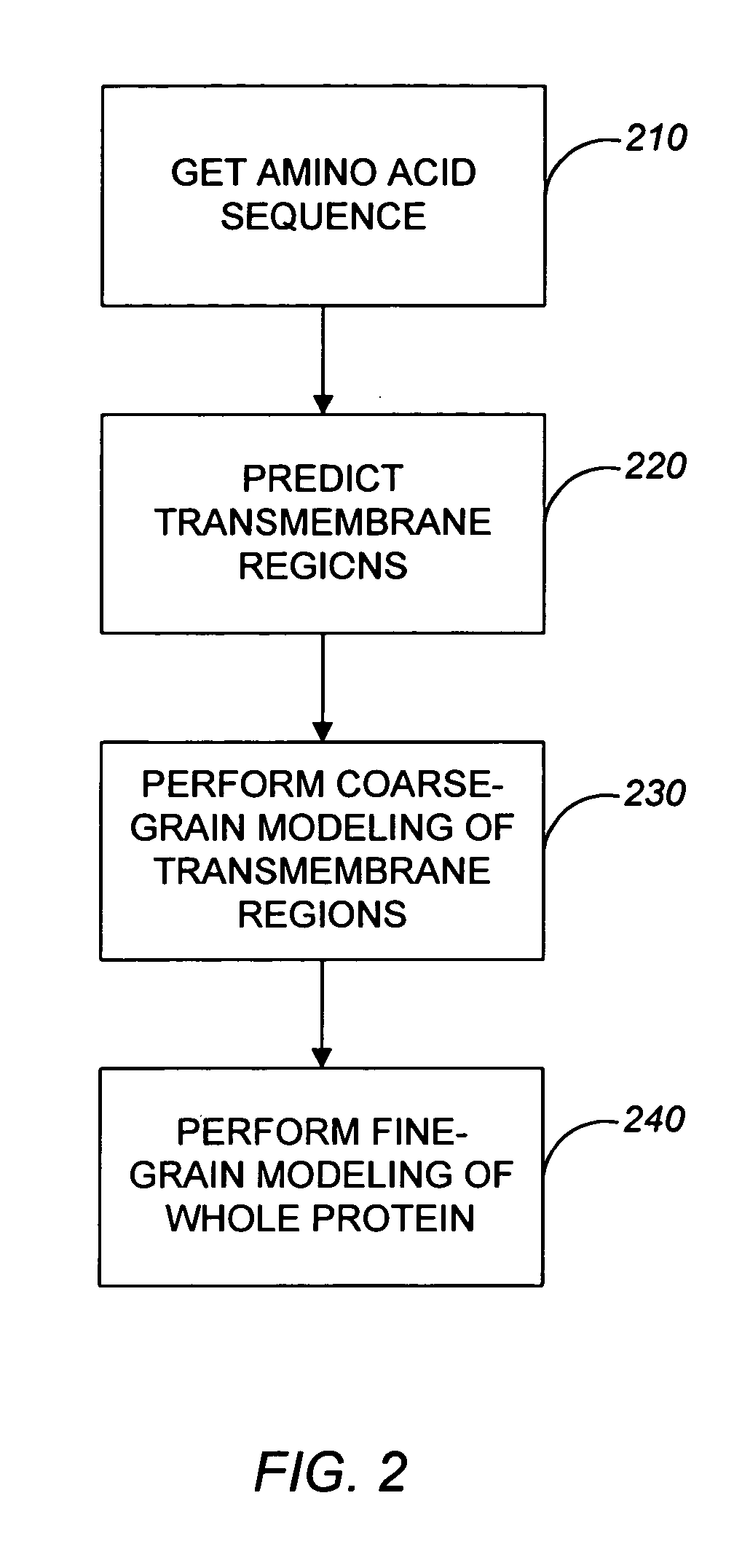
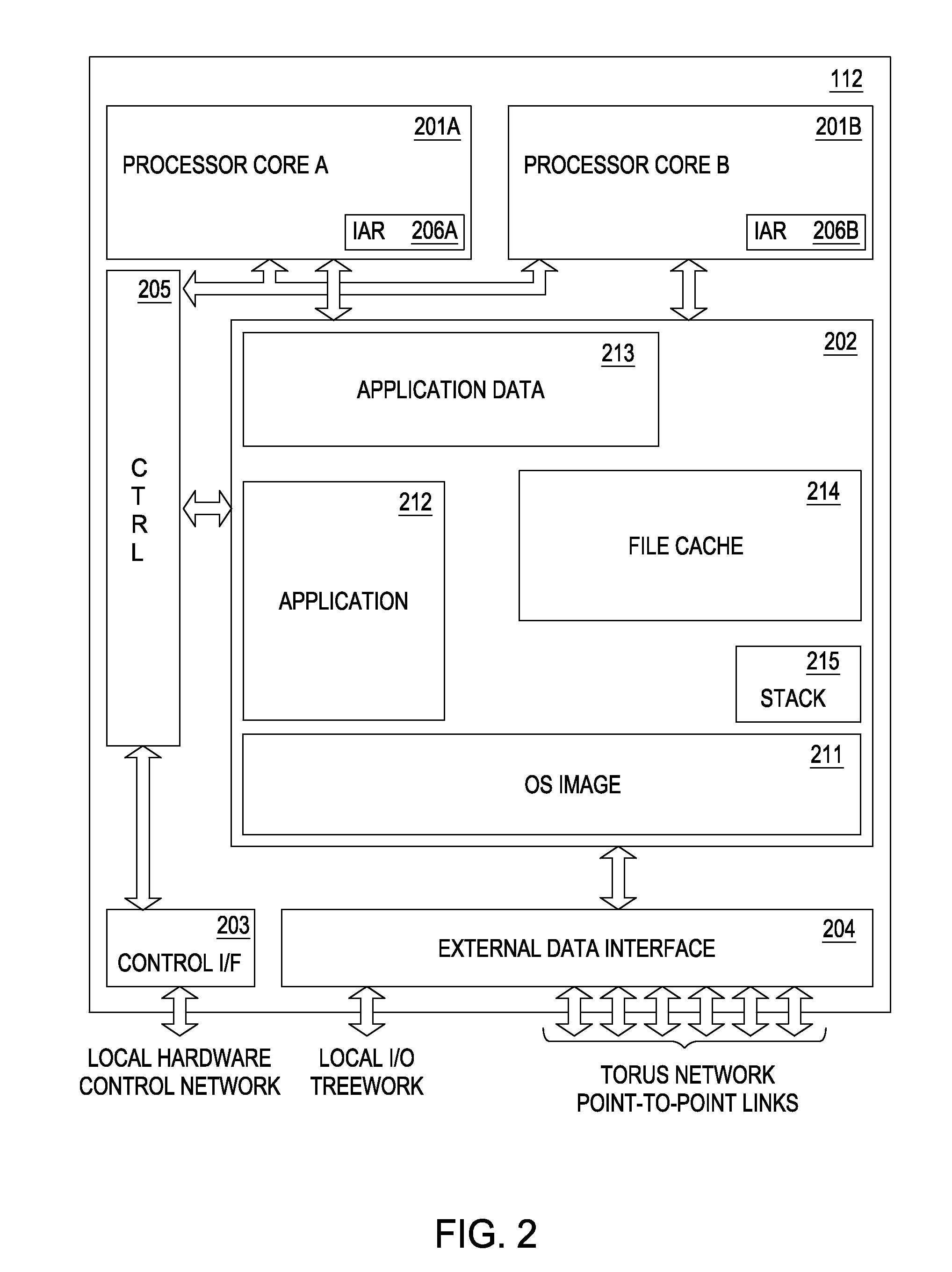
Systems and methods for predicting the structure and function of multipass transmembrane proteins
InactiveUS20050136481A1Fast and accurate procedureMinimizing energyBiological testingSequence analysisProtein structureMolecular modelling
The invention provides computer-implemented methods and apparatus implementing a hierarchical protocol using multiscale molecular dynamics and molecular modeling methods to predict the structure of transmembrane proteins such as G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCR), and protein structural models generated according to the protocol. The protocol features a combination of coarse grain sampling methods, such as hydrophobicity analysis, followed by coarse grain molecular dynamics and atomic level molecular dynamics, including accurate continuum solvation. Also included are energy optimization to determine the rotation of helices in the (seven-helical) TM bundle, and optimization of the helix translations along their axes and rotational optimization using hydrophobic moment of the helices, to provide a fast and accurate procedure for predicting GPCR tertiary structure.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
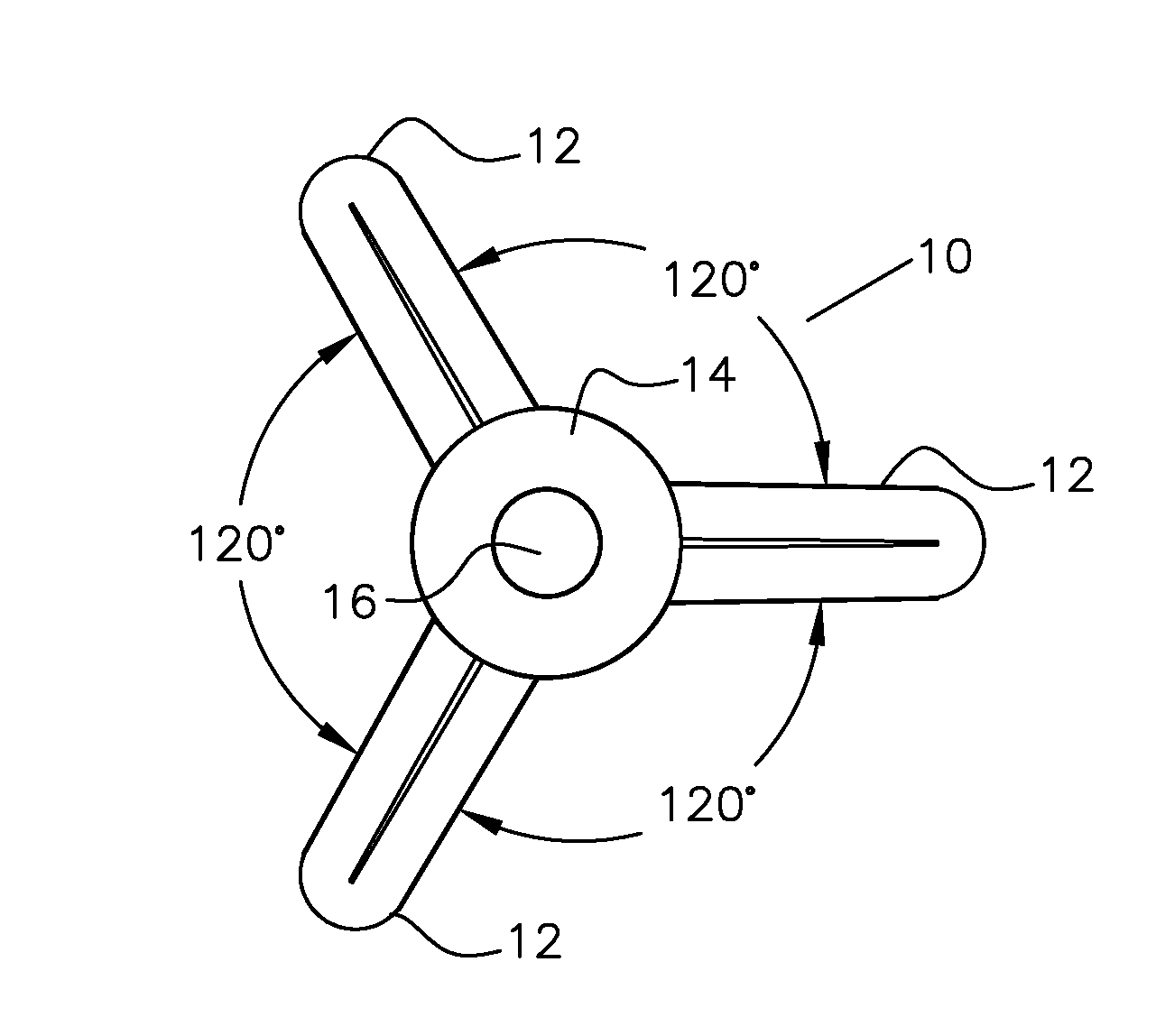
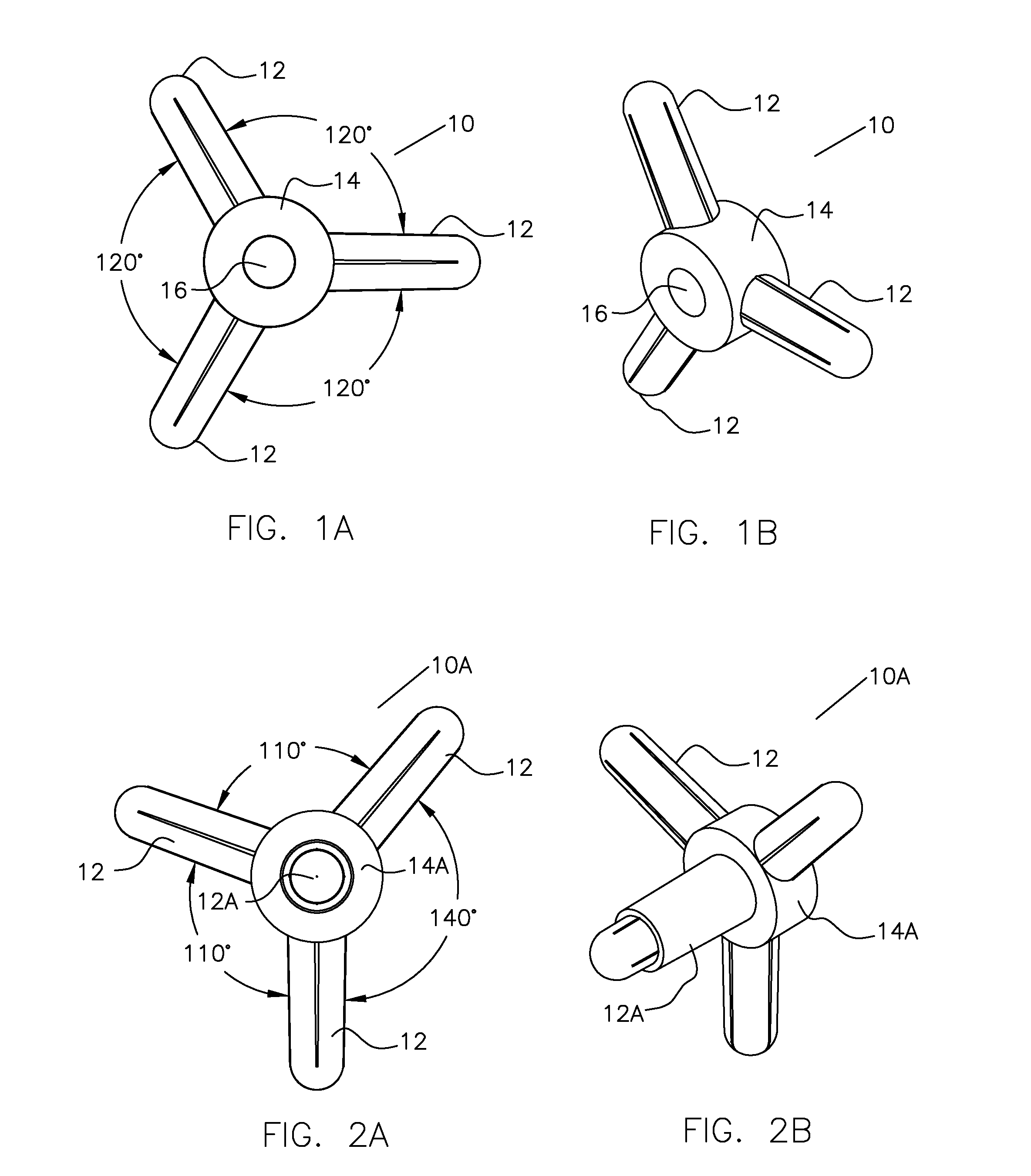
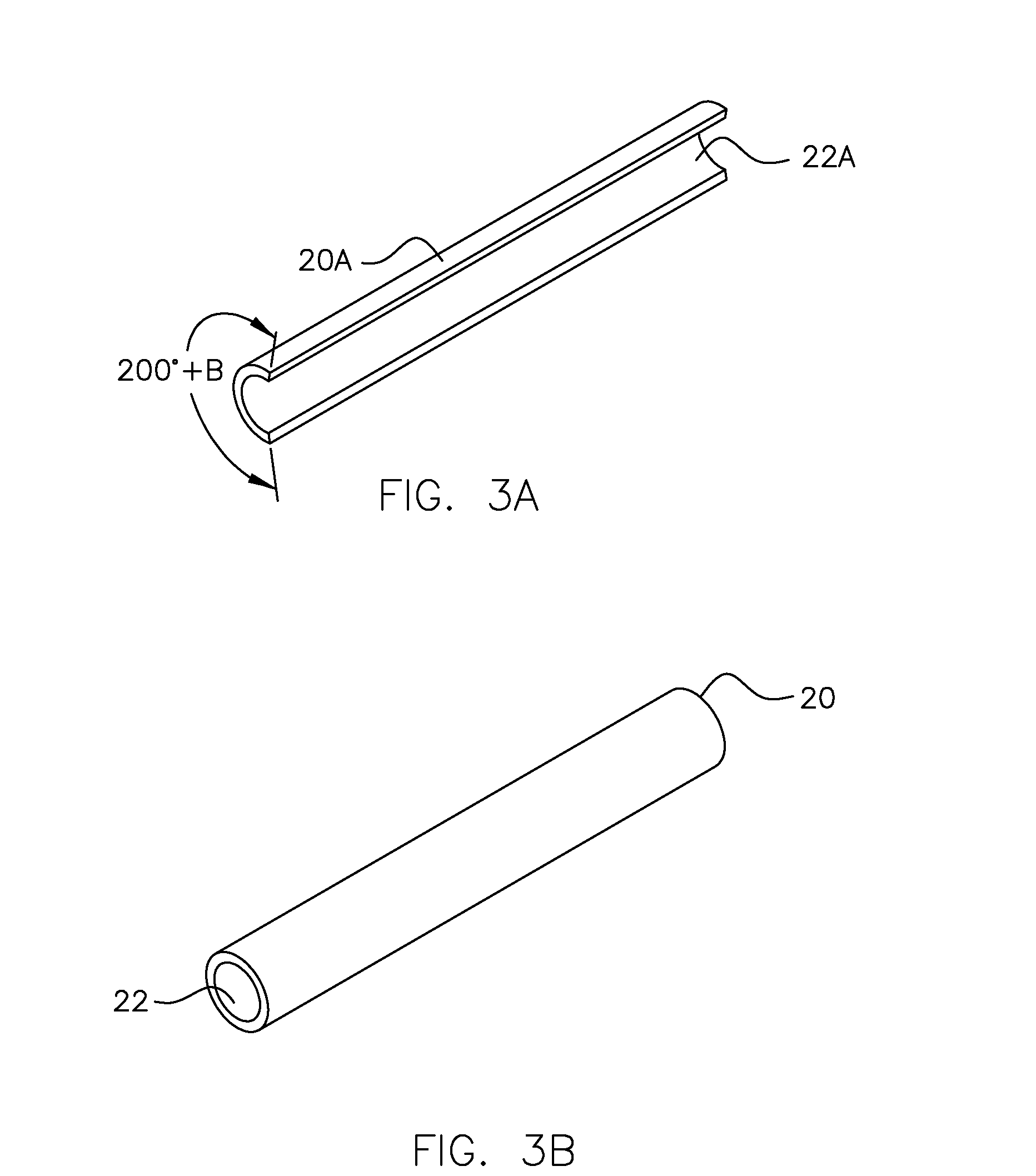
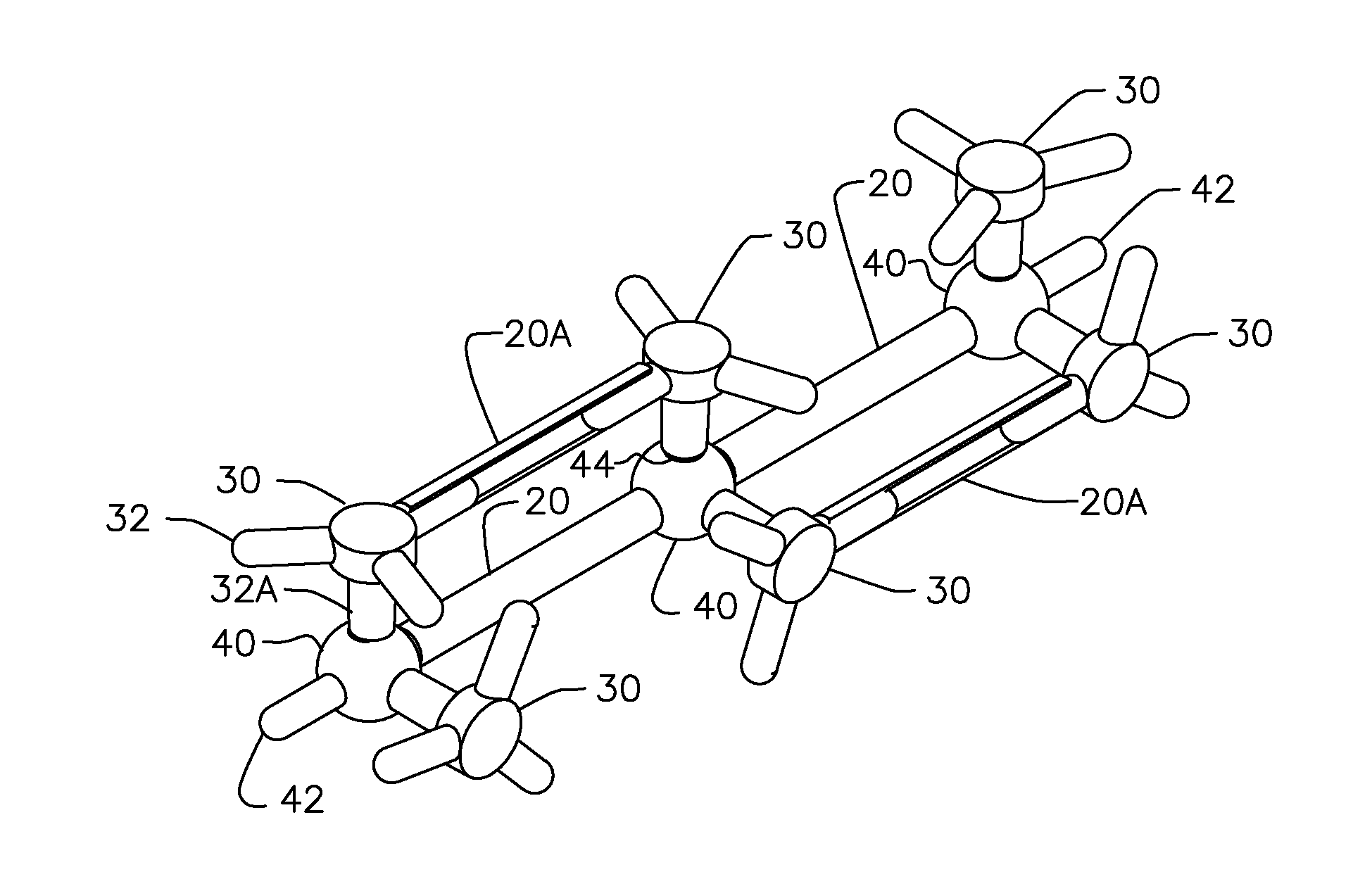
Molecular models
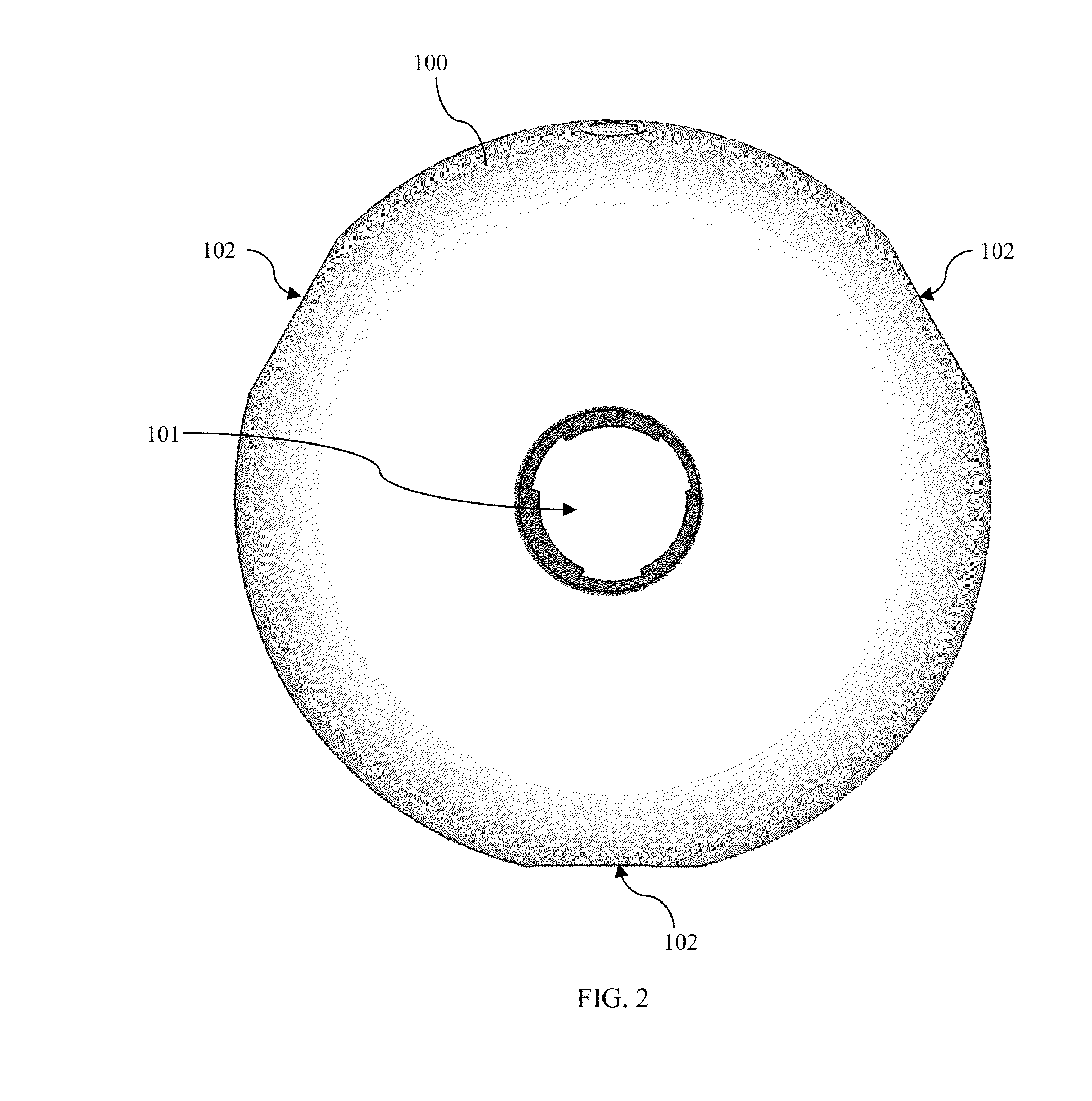
A molecular modeling kit including a three-dimensional body providing a physical representation of at least one atom. The three-dimensional body can define a cavity and include a self-reorienting magnet at least partially disposed in the cavity. The magnet can be configured to realign relative to the cavity when in proximity with a second magnet such that magnetic poles of the self-reorienting magnet and the second magnet are aligned for attraction. The second magnet can be external to the three-dimensional body.
Owner:MILWAUKEE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
Methods for identifying compounds useful for producing heavy oils from underground reservoirs
InactiveUS20090114387A1Improve developmentImprove efficiencySurveyMaterial analysisCompound (substance)Fuel oil
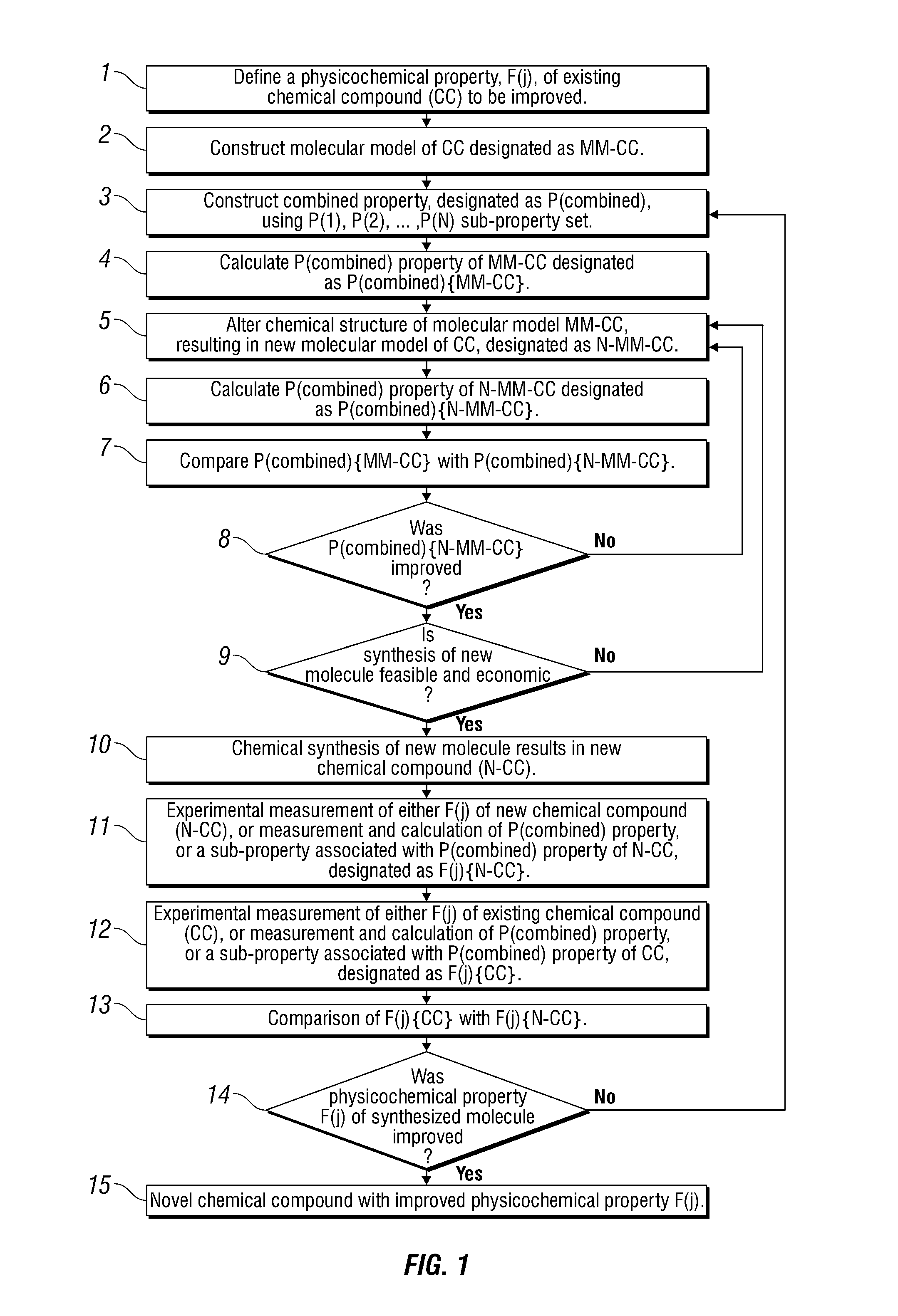
Described herein are methods for identifying compounds useful for producing heavy oil from an underground reservoir. The methods facilitate the development of chemicals with improved physicochemical features. The methods generally involve first identifying a physicochemical property of a compound that needs to be improved in order to increase the efficiency of heavy oil removal from underground reservoirs. Next, the physicochemical property is calculated by molecular modeling using semi-empirical or ab-initio calculations. By modifying the molecular model of the compound, the targeted physicochemical property can be optimized. After a suitable compound has been identified, the compound can be synthesized and evaluated.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for predicting structure of transmembrane proteins
InactiveUS20070038379A1Fast and accurate procedureBiological testingComplex mathematical operationsG protein-coupled receptorProtein structure
Computer-implemented methods and apparatus implementing a hierarchical protocol using multiscale molecular dynamics and molecular modeling methods to predict the structure of transmembrane proteins such as G-Protein Coupled Receptors, and protein structural models generated according to the protocol. The protocol features a combination of coarse grain sampling methods, such as hydrophobicity analysis, followed by coarse grain molecular dynamics and atomic level molecular dynamics, including accurate continuum solvation, to provide a fast and accurate procedure for predicting GPCR tertiary structure.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
System and method for modelling a molecule with a graph
InactiveUS20110264432A1Analogue computers for chemical processesChemical data visualisationGraphicsMolecular modelling
Modelling a molecule by means of a graph, said graph comprising vertices and edges, each edge having a specific type, and said graph having cyclic orderings on the half-edges about at least one of the vertices, said system comprising means for determining the cyclic orderings on the half-edges about said at least one vertex by means of the spatial coordinates of the constituent atoms of the molecule, and means for determining the type of each edge of the graph by means of the relative spatial location of the constituent atoms of the molecule. Thereby automatic classification, comparison, specification, analysis and / or prediction of molecular structures can be provided because these molecular structures are represented by explicit combinatorial objects, and descriptors can be derived from the graph constructed in this manner. The descriptors are automatically computable from molecular databases, such as PDB or CATH, with no qualitative human intervention or subjective criteria. The invention can be applied to macromolecular structures such as proteins, protein globules, ligands, polymers, nucleotides, nucleic acids, RNA and DNA.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Grid-based computational chemistry application integrated system
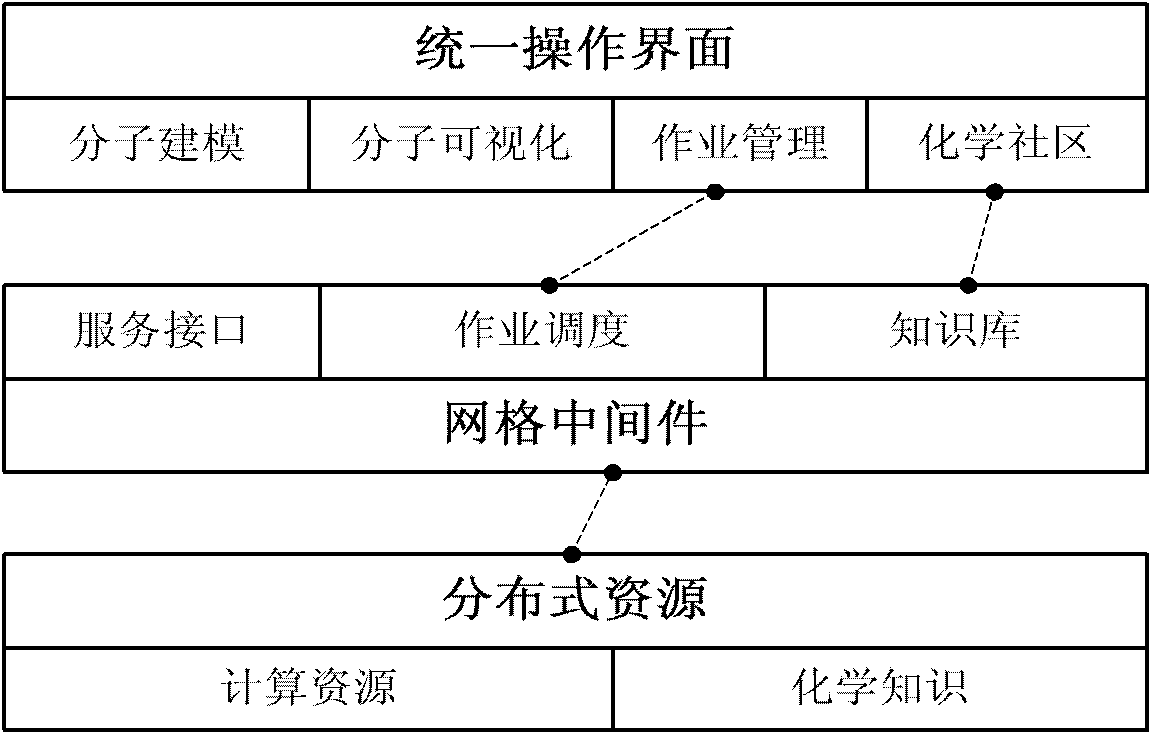
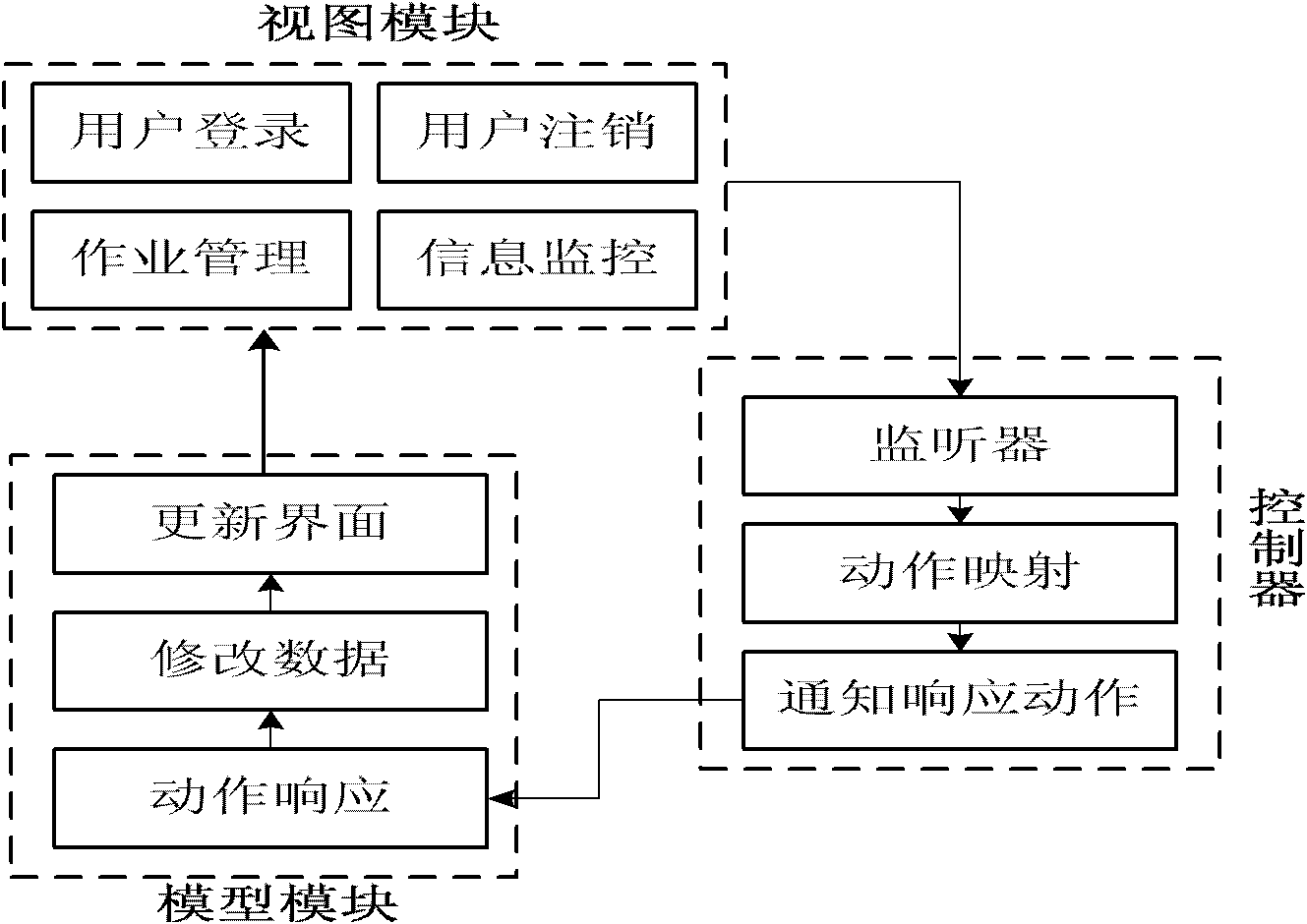
The invention discloses a grid-based computational chemistry application integrated system, which comprises distributed chemical resource modules, a grid middleware module and an operation interface module. The chemical resource modules are distributed at different grid nodes and include computing resources provided with computational chemistry application software and chemistry knowledge units with conceptions and methods relative to the chemistry field. The grid middleware module realizes share and collaboration of resources, forms a computing platform having performance higher than that of the single machine, and comprises a service interface unit, an operation dispatching unit and a knowledge base unit. The operation interface module comprises a molecular modeling unit for transforming molecular models into data structures inside computers, a molecular visualization unit for displaying three-dimensional structure of molecules, an operation managing unit for assisting users to submit operations to the grid and monitoring, operating and downloading the operations, and a management community unit. Molecular modeling, visualization, computing and result acquisition can be realized for users by the system, so that the users enjoy the convenient one-stop service.
Owner:COMP NETWORK INFORMATION CENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
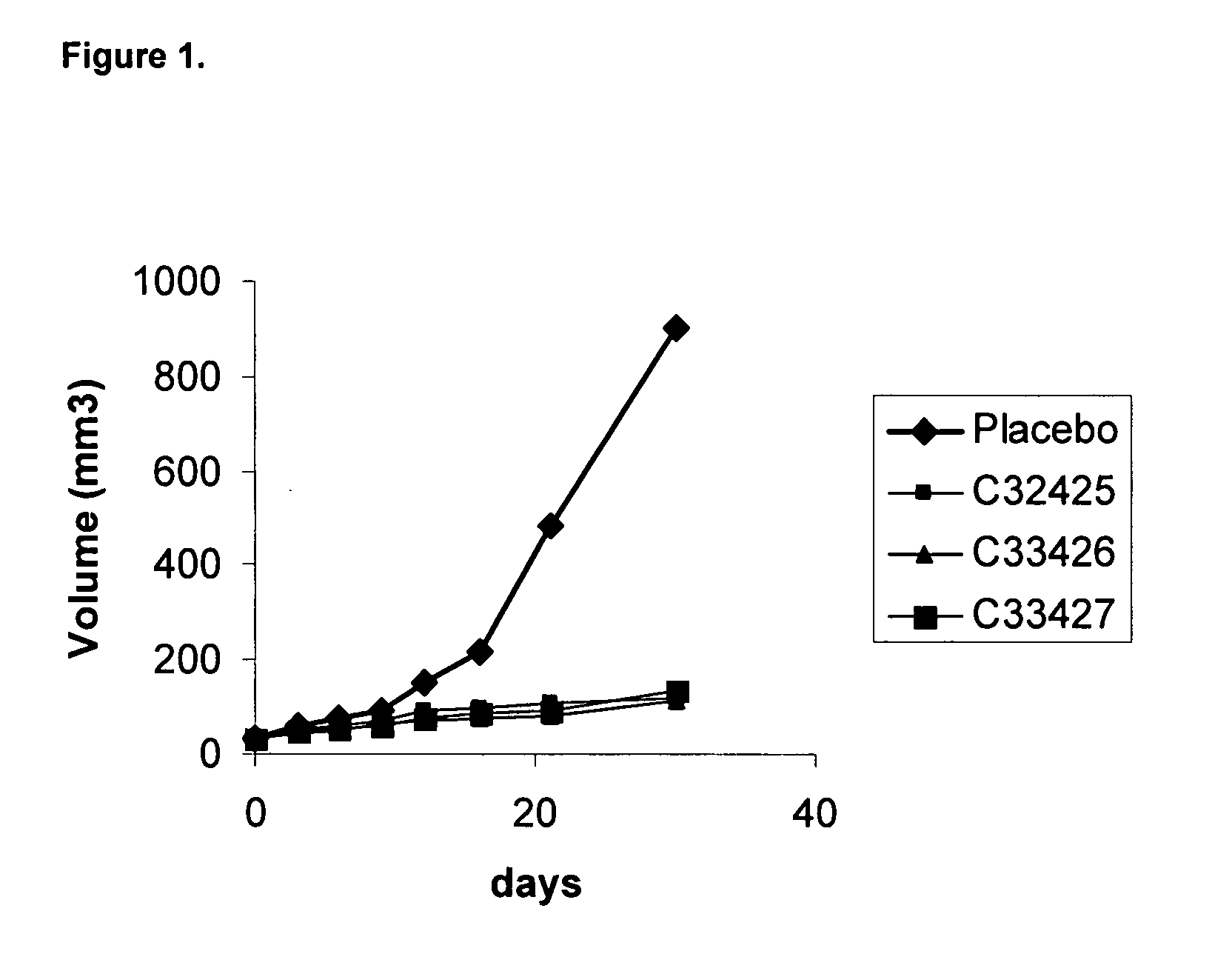
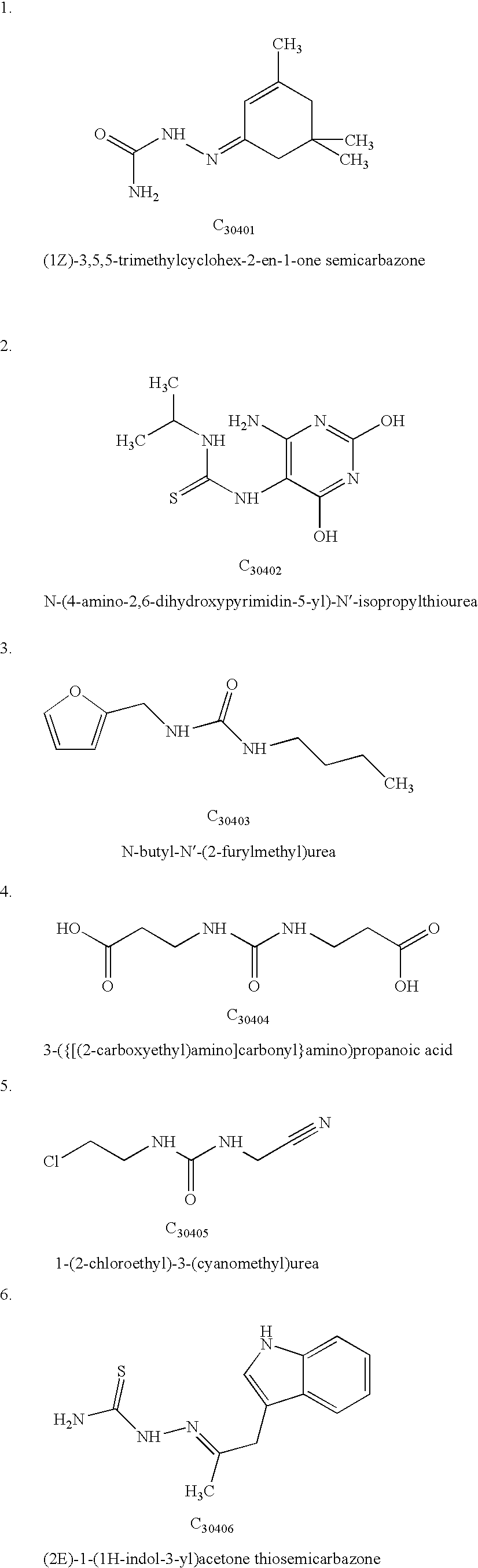
Antineoplastic compounds and pharmaceutical compositions thereof
InactiveUS20090215730A1Elicit cytotoxicityElicit antitumoral effectUrea derivatives preparationBiocideDiseasePhosphorylation
Chemical compounds derived by in silico molecular modelling, having a well defined structure suitable for the blocking of the phosphorylation event, through the specific interaction of the chemical with the Casein Kinase 2 enzyme substrate phosphorylation domain or it's neighbourhood. This invention comprises also the pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds, and their use in the preparation of medicines or agents for the treatment of diseases or conditions related with neoplasic processes.
Owner:CENT DE ING GENETICA & BIOTECNOLOGIA
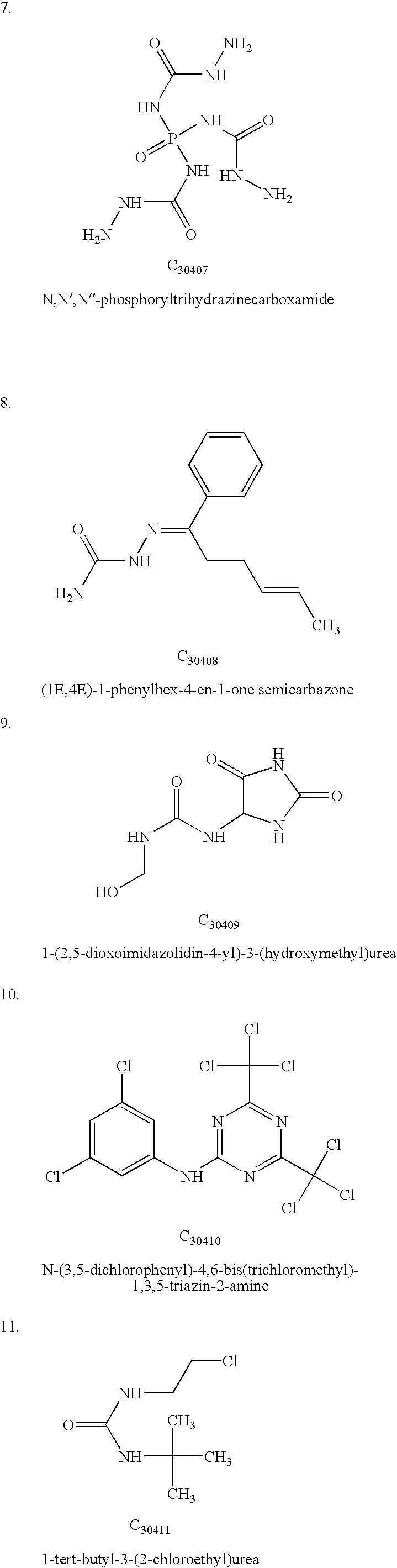
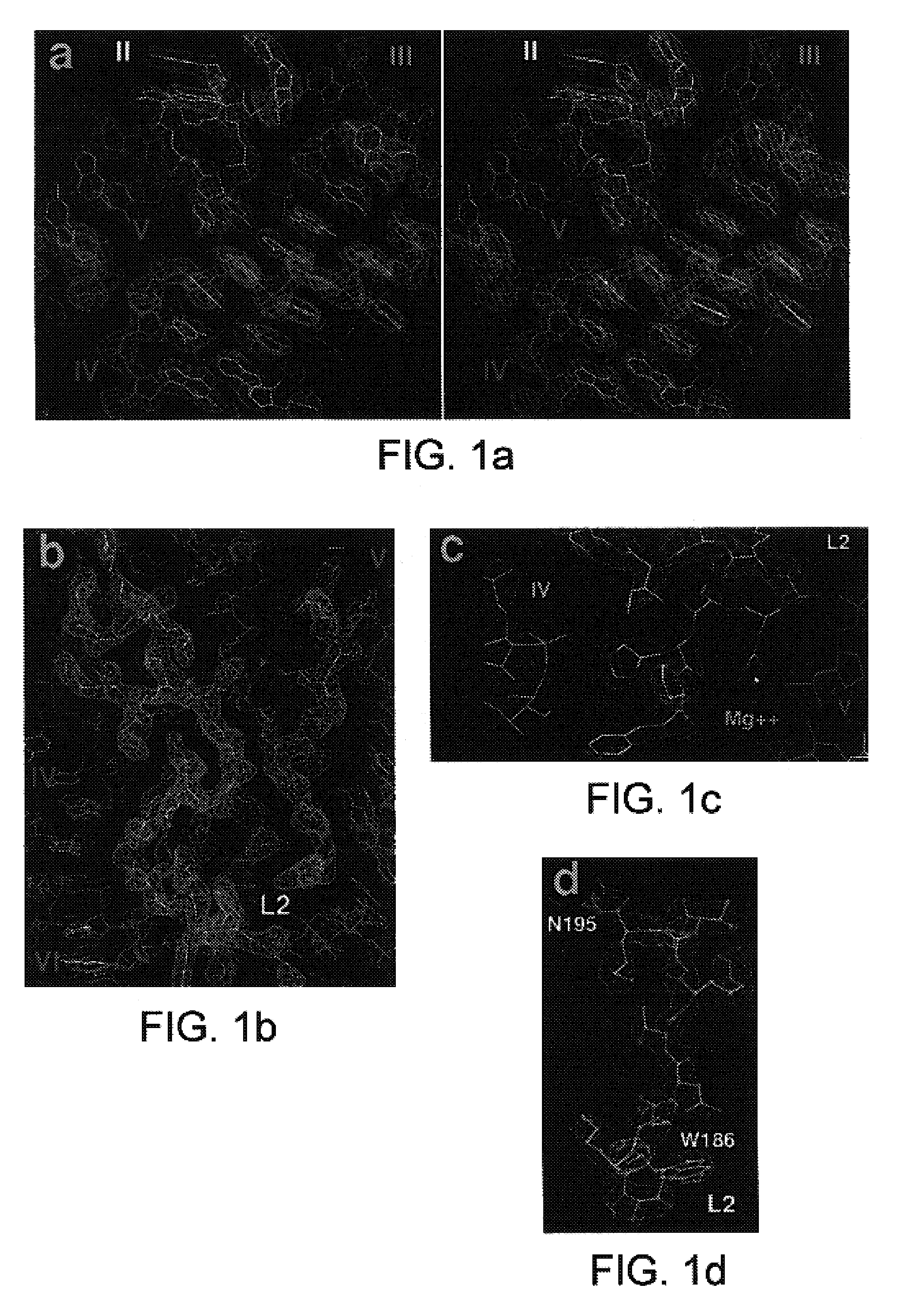
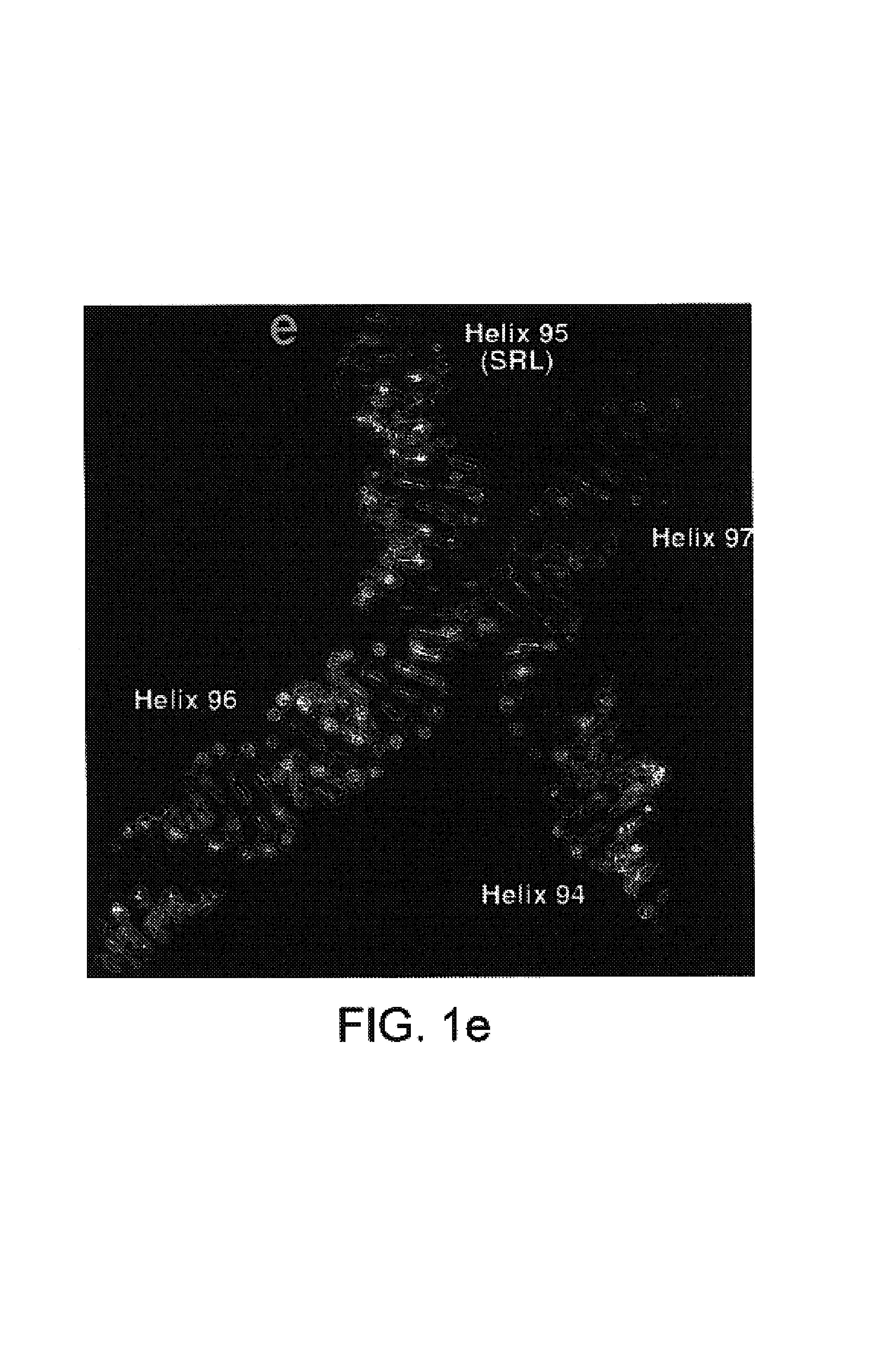
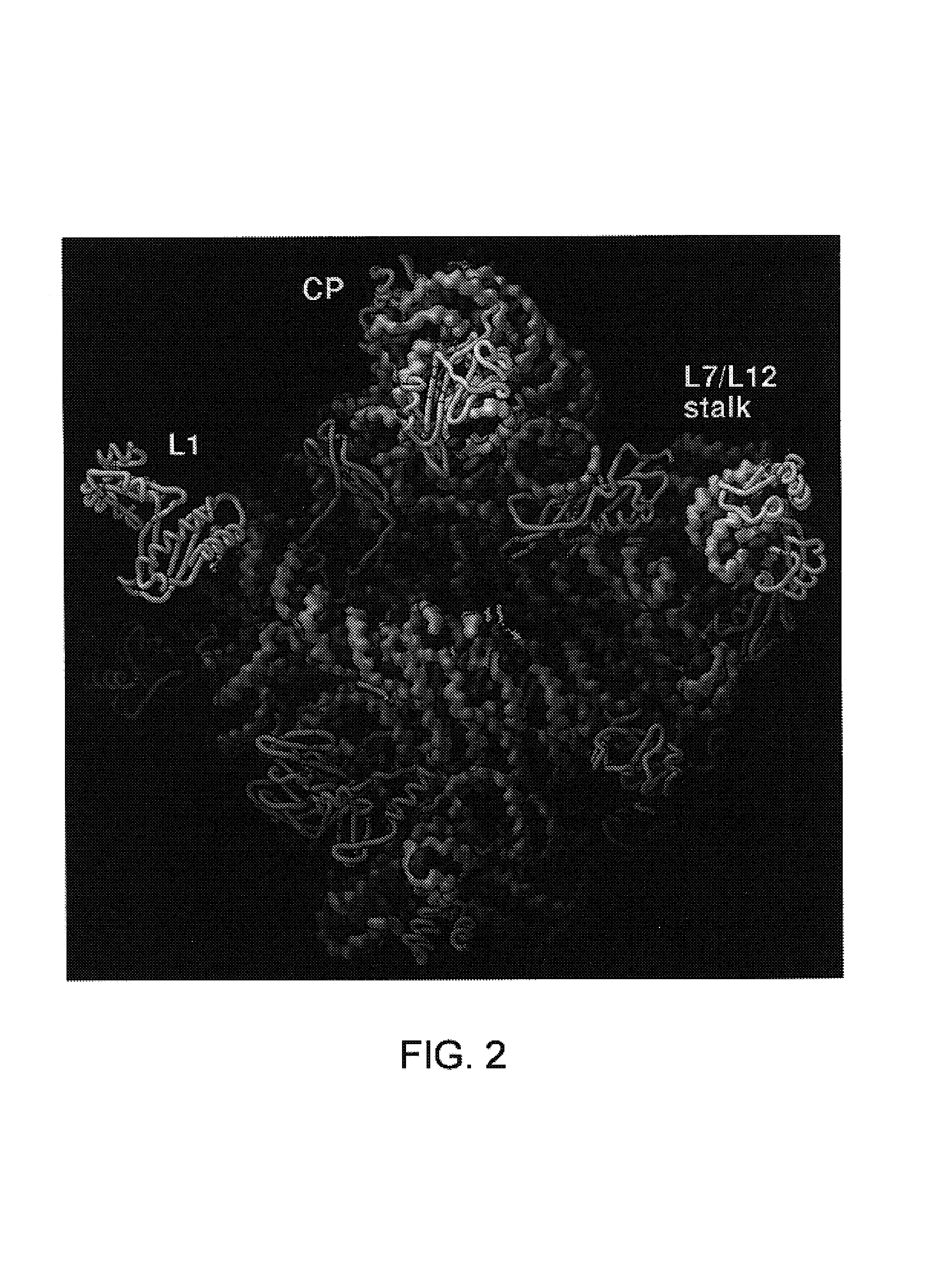
Determination and uses of the atomic structures of ribosomes and ribosomal subunits and their ligand complexes
Owner:YALE UNIV
Method of exploring the flexibility of macromolecular targets and its use in rational drug design
InactiveUS20140249787A1Easy to calculateEfficient accessComputation using non-denominational number representationSystems biologyDrugChemistry
It comprises a method of exploring the flexibility of macromolecules, where an available ensemble of structures of a receptor, such as one coming from a molecular dynamics trajectory or a set of experimentally derived structures, is used to generate an ensemble of structures for a closely related receptor, such as a receptor mutant, a receptor with a series of post-translational modifications, or one that is non-covalently bound to a second molecule. In this way, new ensembles of the pertubed receptor can be accessed without the need to explicitely simulate the new system. The method allows the study of structure and flexibility of derivatives and relatives of a receptor in a computer efficient manner, and therefore has applications in the rational-drug design field, especially in virtual screening. It also comprises a computer program product for causing a computer to perform the method, as well as a system of molecular modeling comprising computer means for carrying out each of the steps of the method.
Owner:UNIV DE BARCELONA +3
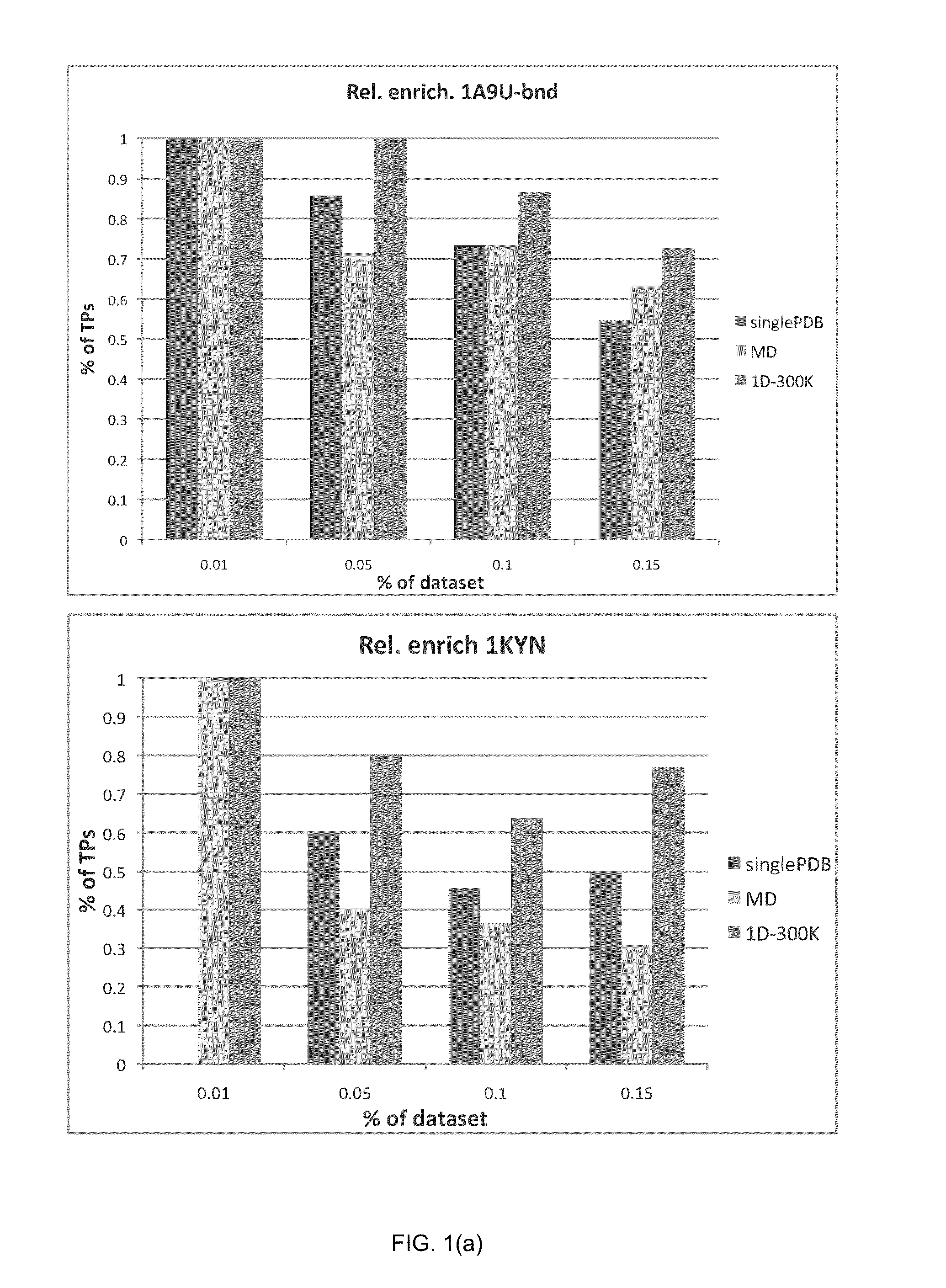
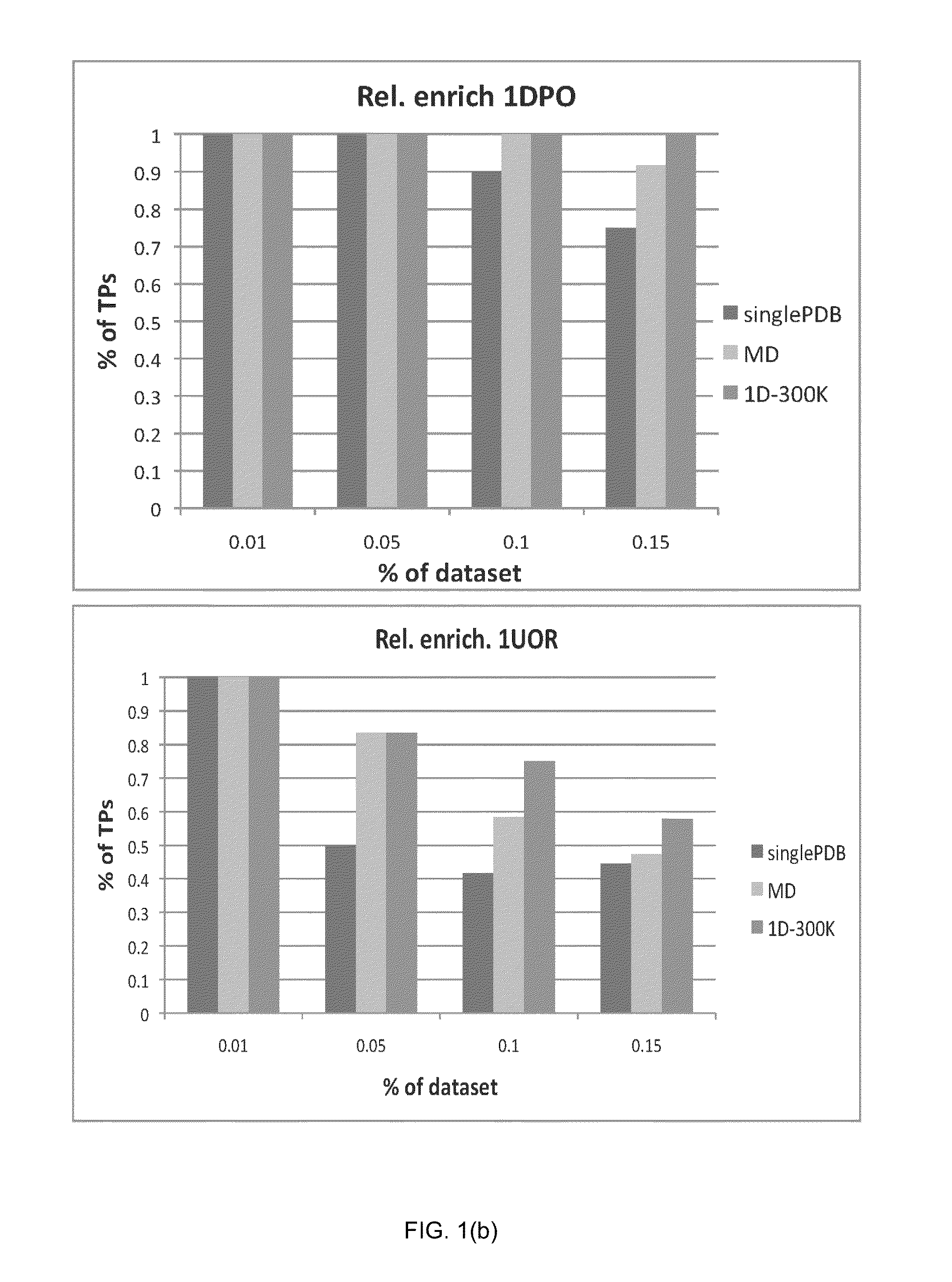
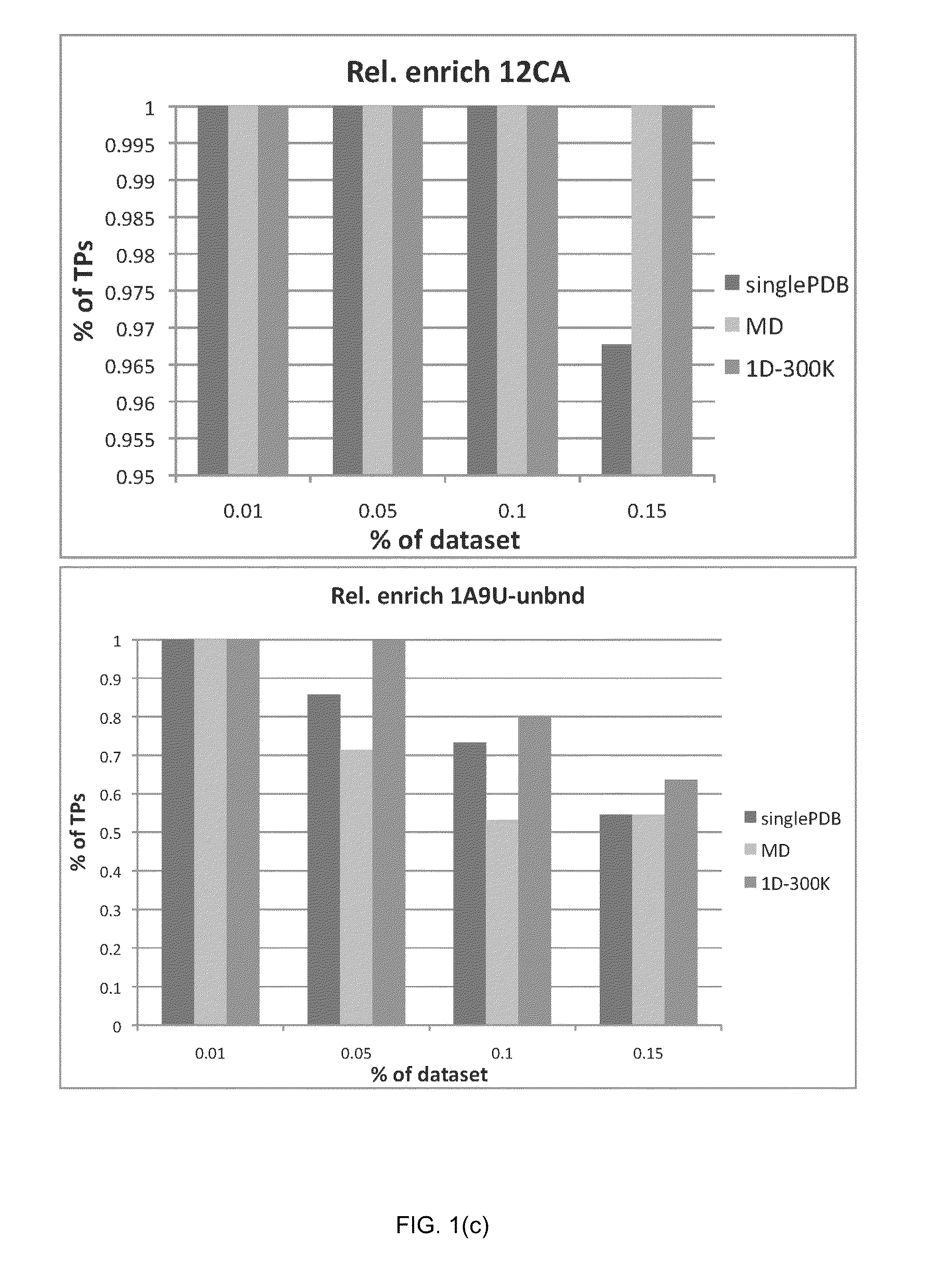
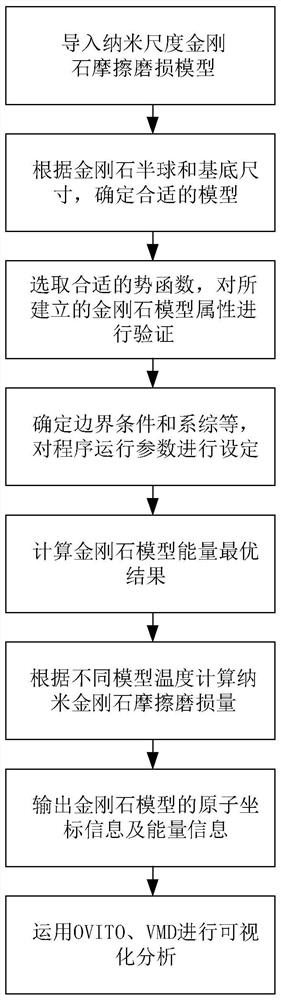
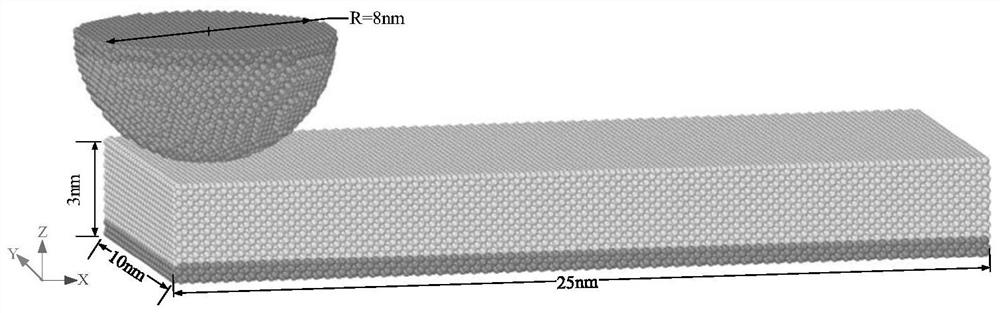
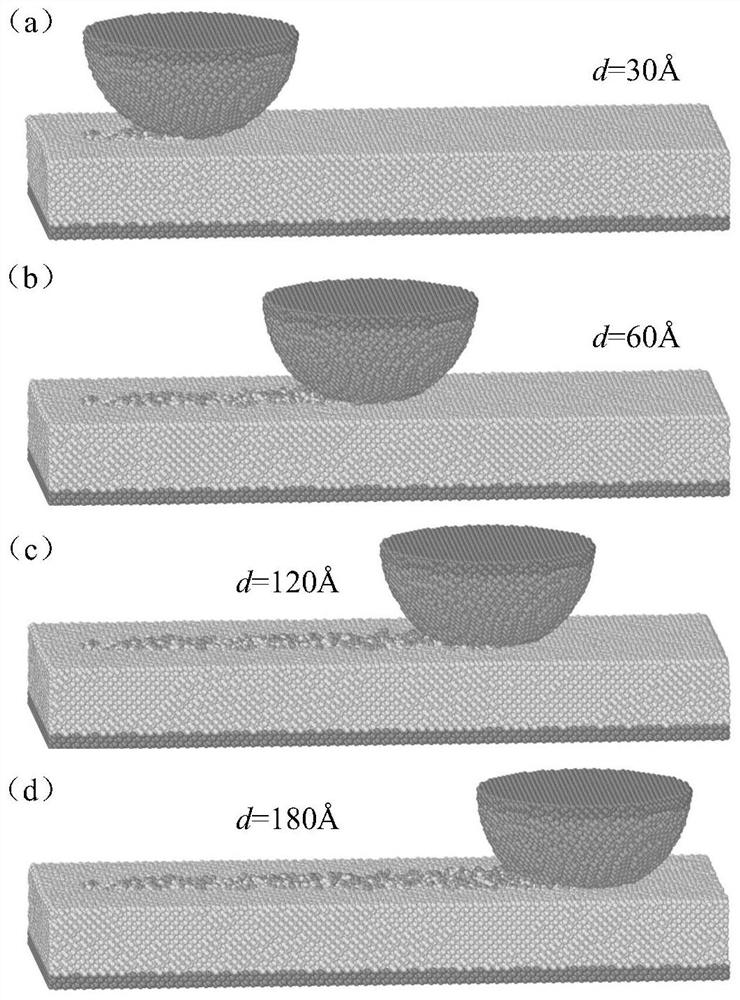
Molecular dynamics-based nanoscale diamond friction wear process simulation method
ActiveCN113012765AEasy to wearAnalyzing the amount of wearSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationDynamic methodModeling software
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Molecular Modeling Device
Owner:KINETIC MODELS
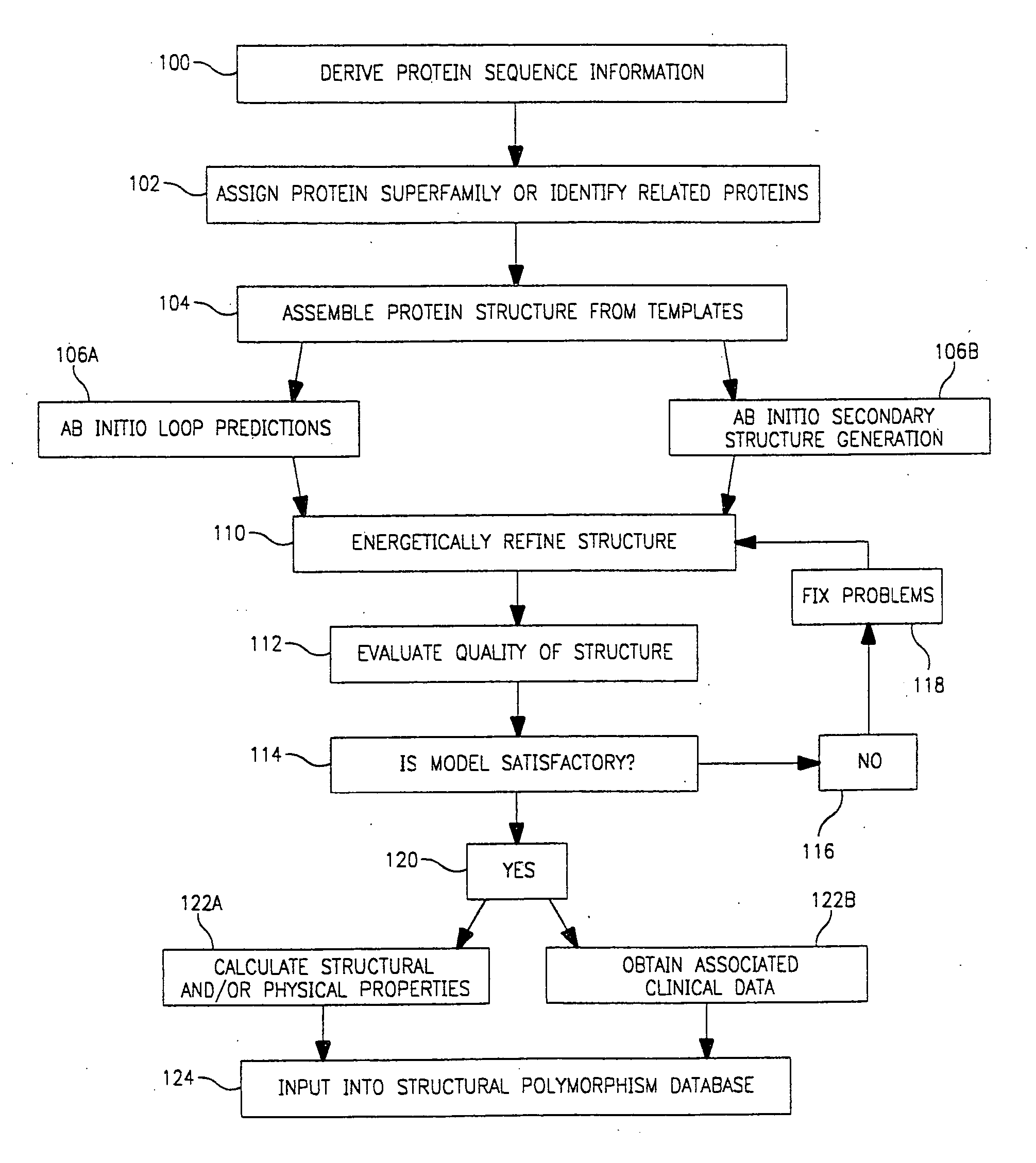
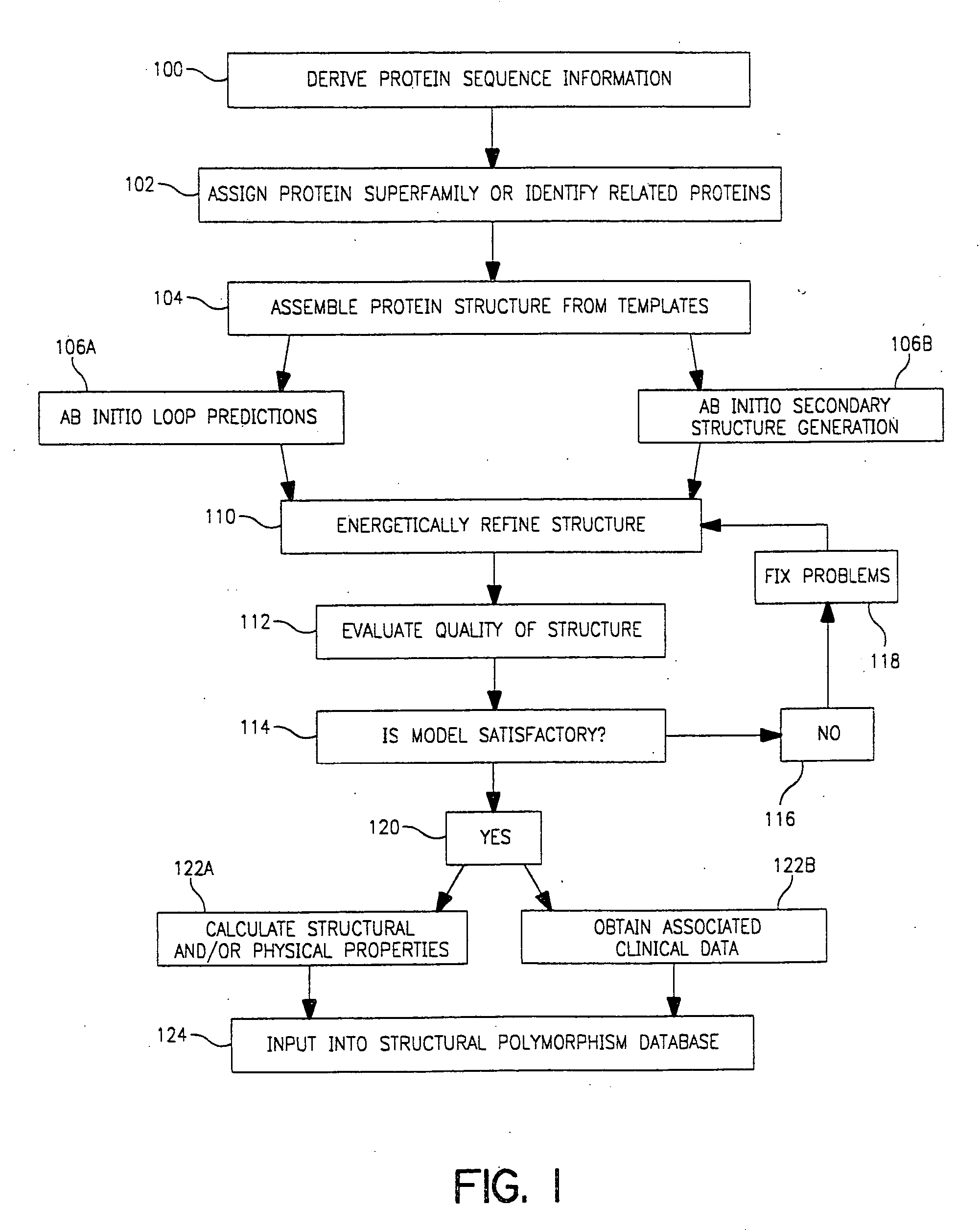
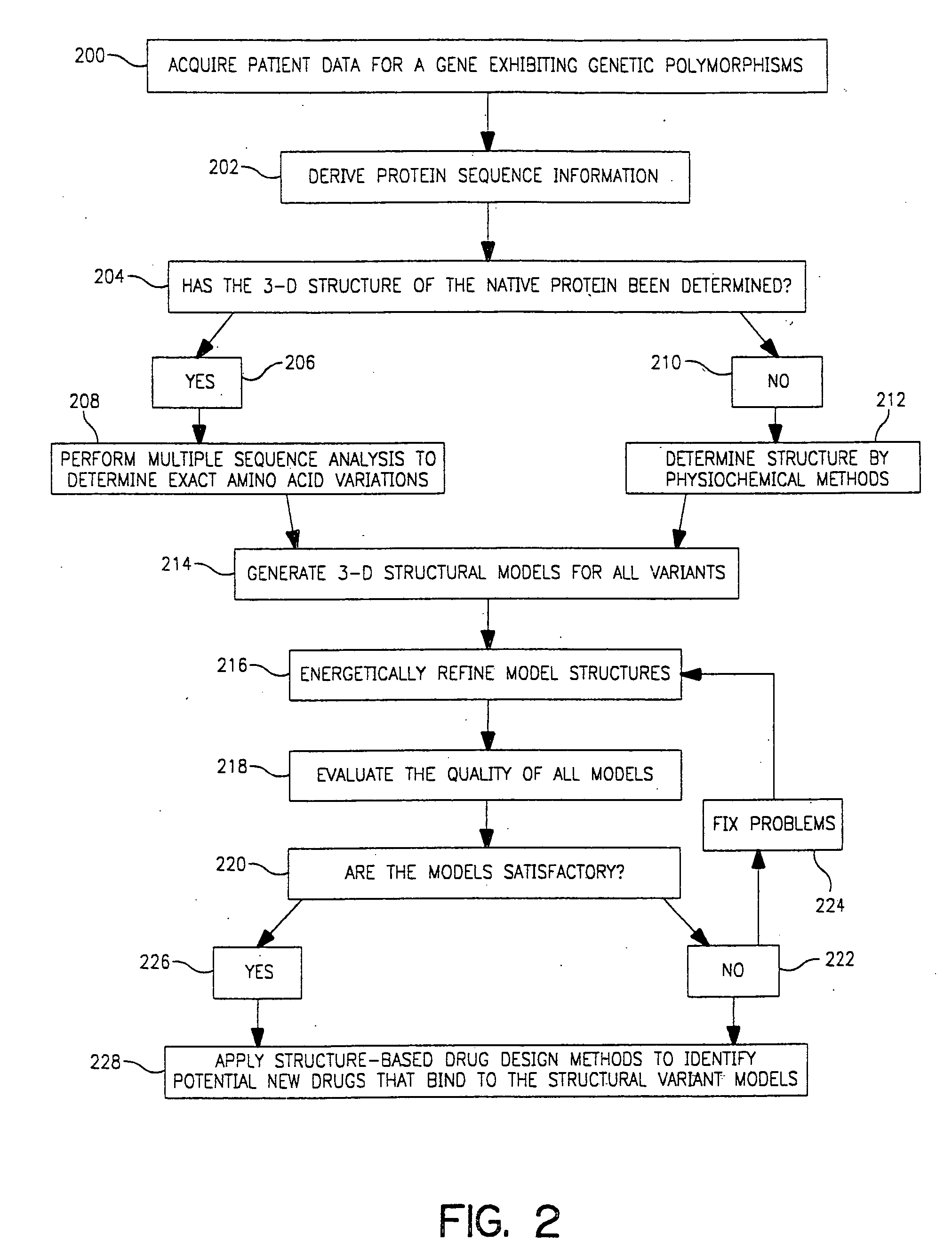
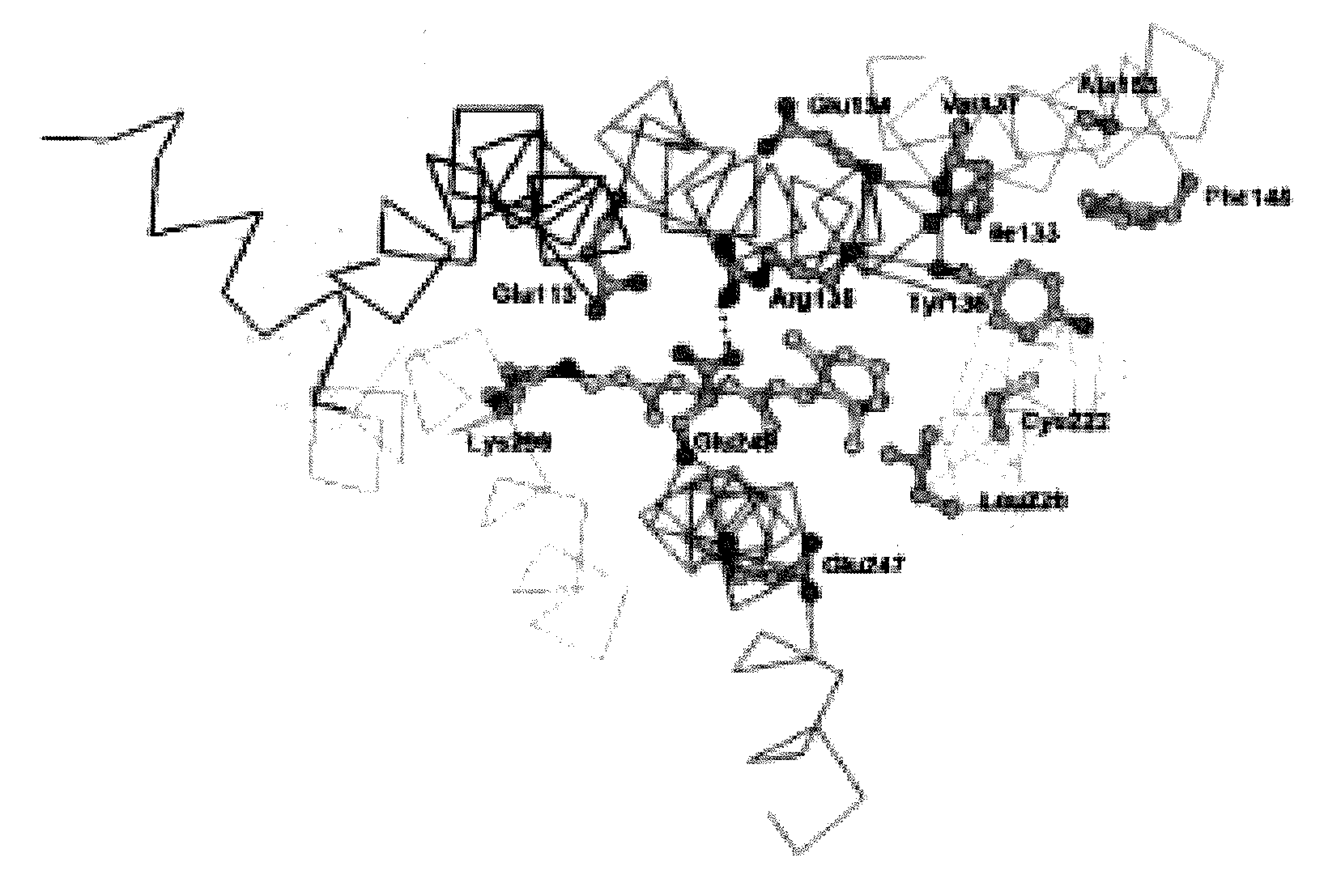
Use of computationally derived protein structures of genetic polymorphisms in pharmacogenomics for drug design and clinical applications
InactiveUS20060217894A1Expand the populationReduce adverse side effectsMolecular designProteomicsGenomicsProtein structure
Provided herein are computer-based methods for generating and using three-dimensional (3-D) structural models of target molecules and databases containing the models. The targets can be protein structural variants derived from genes containing polymorphisms. The models are generated using molecular modeling techniques and are used in structure-based drug design studies for identifying drugs that bind to particular structural variants in structure-based drug design studies, for designing allele-specific drugs and population-specific drugs and for predicting clinical responses in patients. Computer-based methods for predicting drug resistance or sensitivity via computational phenotyping are also provided. Databases containing protein structural variant models are also provided.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC +2
Molecular modeling system including multiple pi-bond exclusionary features
A molecular modeling kit provides a system for molecular modeling that represents exclusion between resonance structures in a molecule and permits their rotation, providing an informative tool for describing resonance in a classroom or other learning environment. The kit includes atom modeling components and bond connector components that are connected together to form models of molecules. The atom modeling components or the bond connector components include a mechanical exclusion feature that prevents simultaneous connection of two bond connector components to represent two pi-bonds formed with a single atom in a single plane.
Owner:MOLECULARITY
Molecular modeling system including multiple pi-bond exclusionary features
A molecular modeling kit provides a system for molecular modeling that represents exclusion between resonance structures in a molecule and permits their rotation, providing an informative tool for describing resonance in a classroom or other learning environment. The kit includes atom modeling components and bond connector components that are connected together to form models of molecules. The atom modeling components or the bond connector components include a mechanical exclusion feature that prevents simultaneous connection of two bond connector components to represent two pi-bonds formed with a single atom in a single plane.
Owner:MOLECULARITY
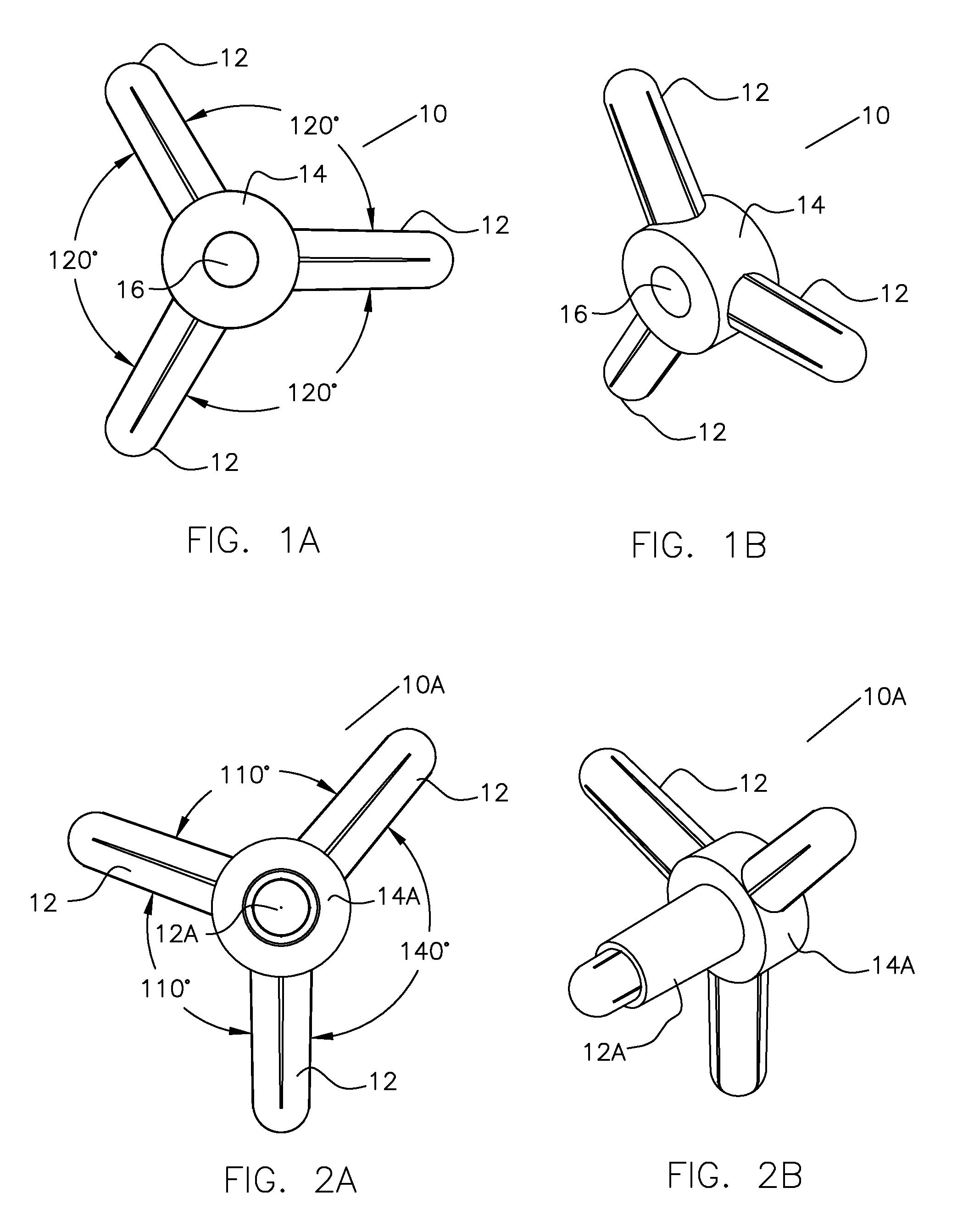
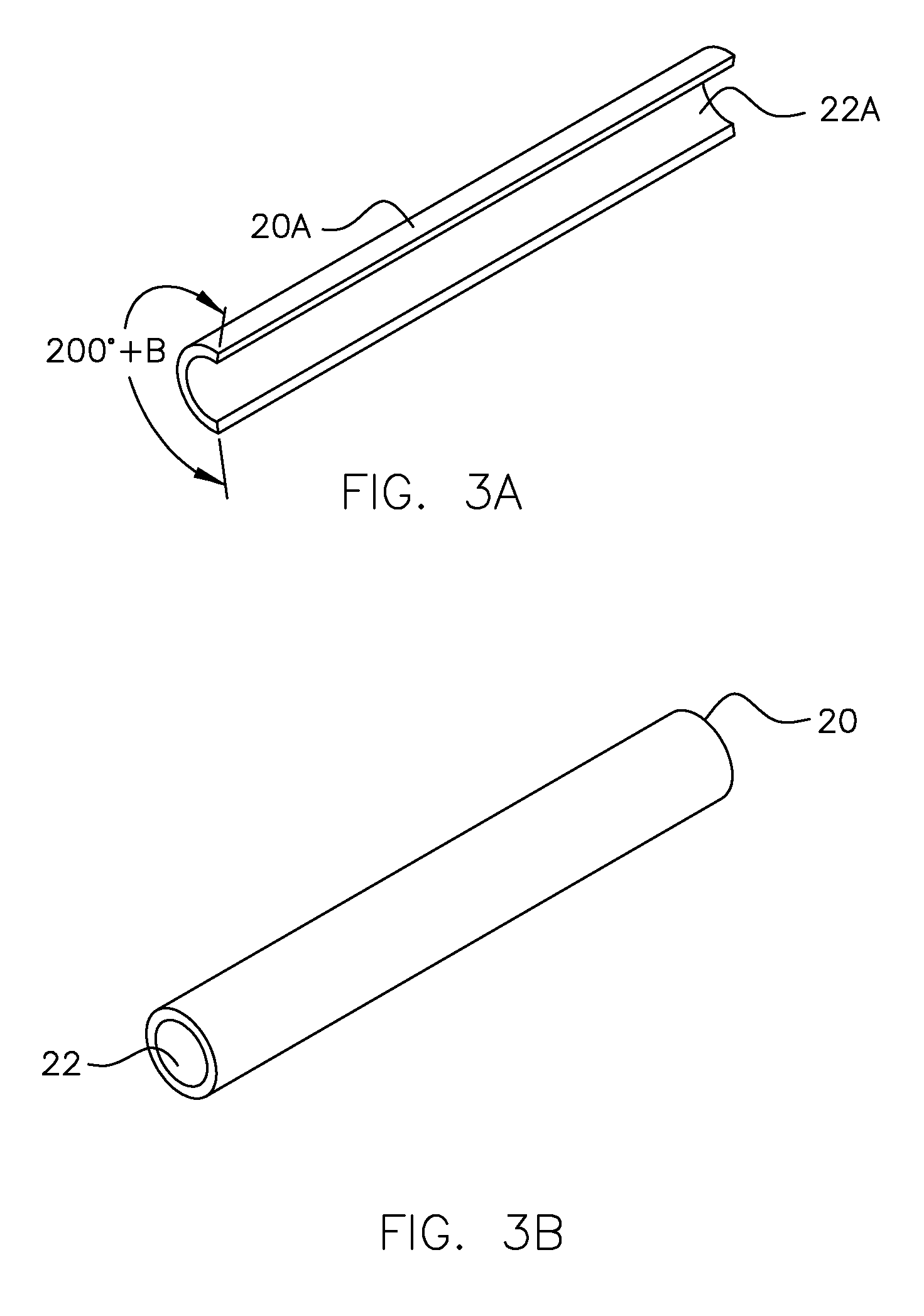
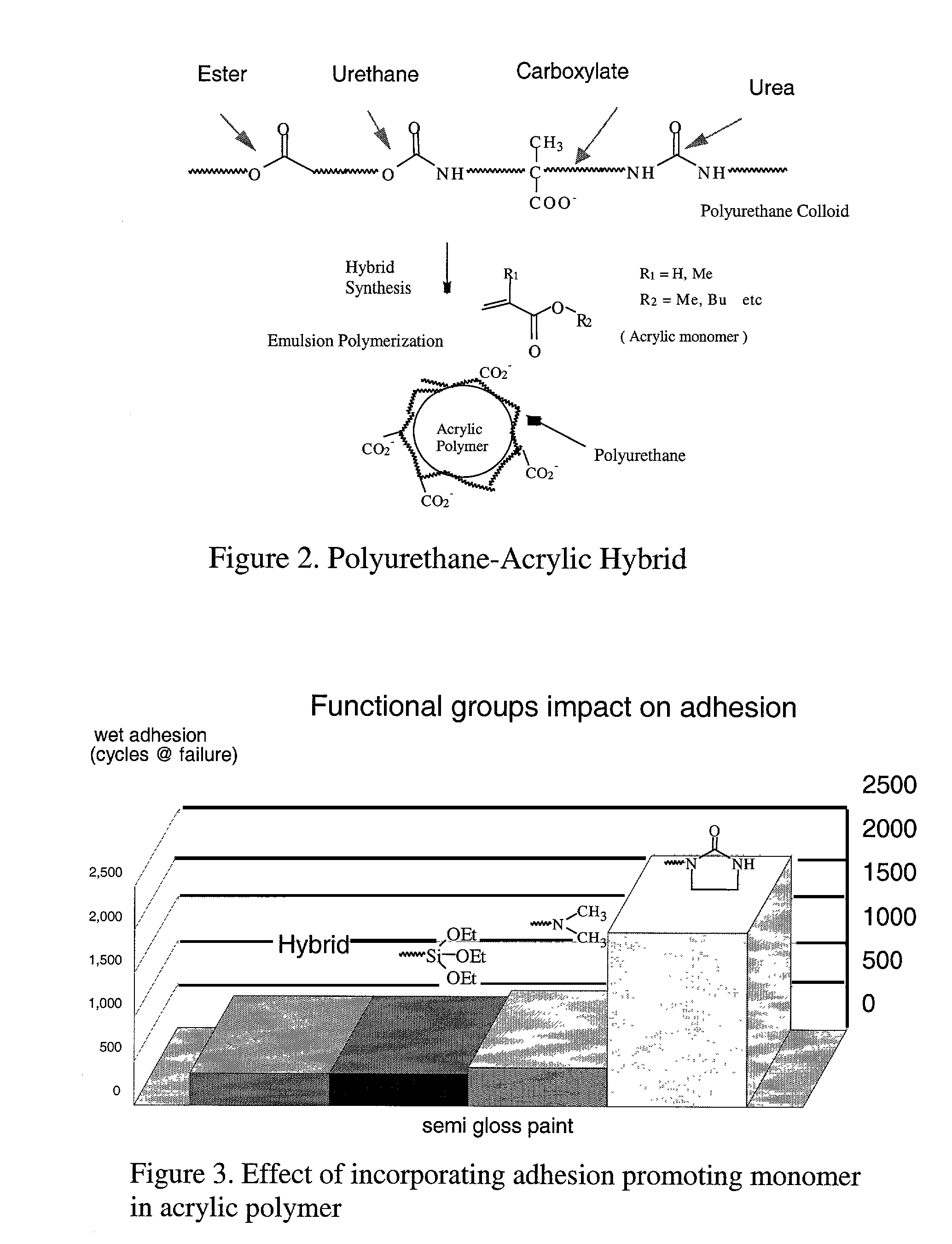
Method for predicting adhesive interactions using molecular modeling
InactiveUS7062421B2Chemical property predictionLamination ancillary operationsMolecular modellingComputational chemistry
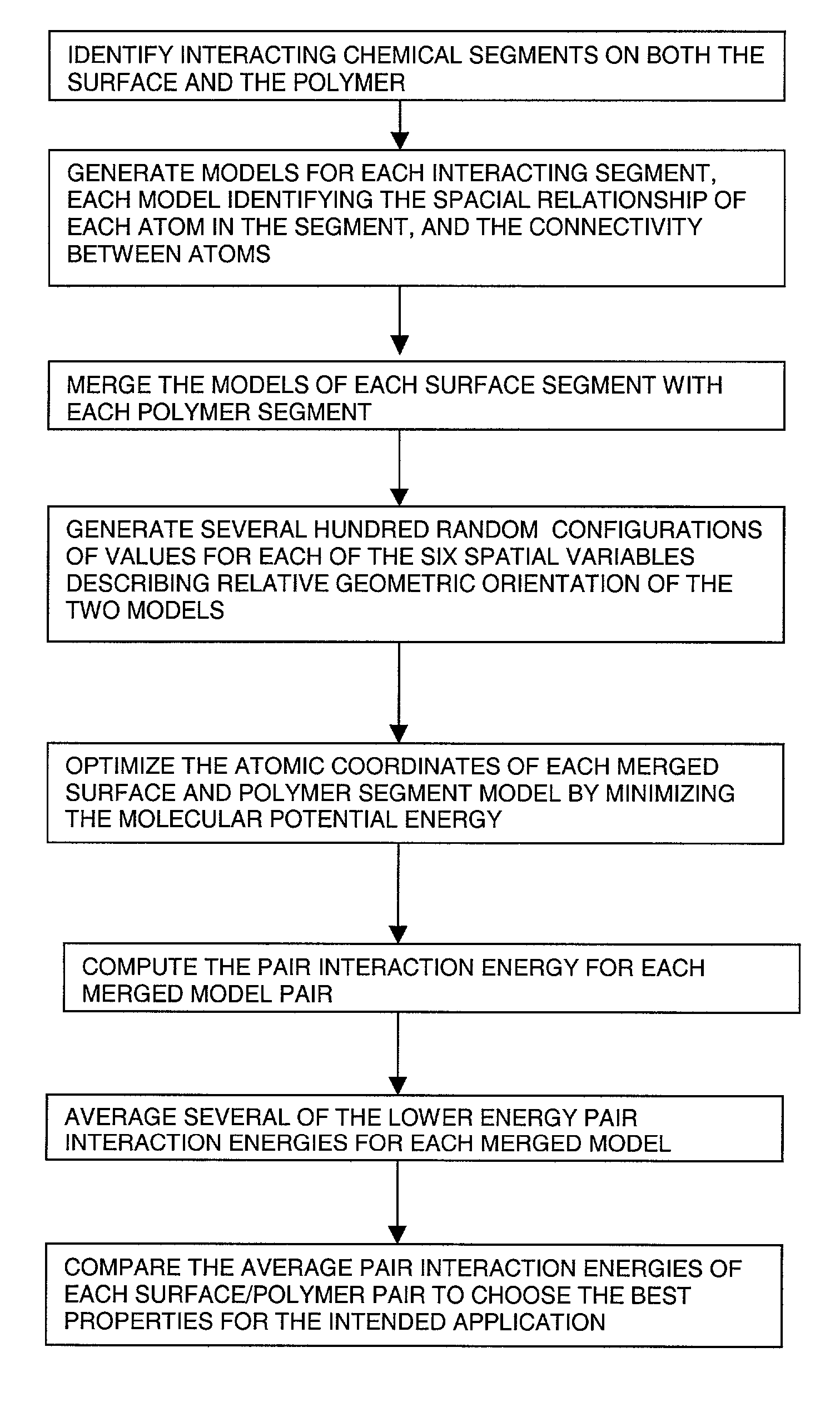
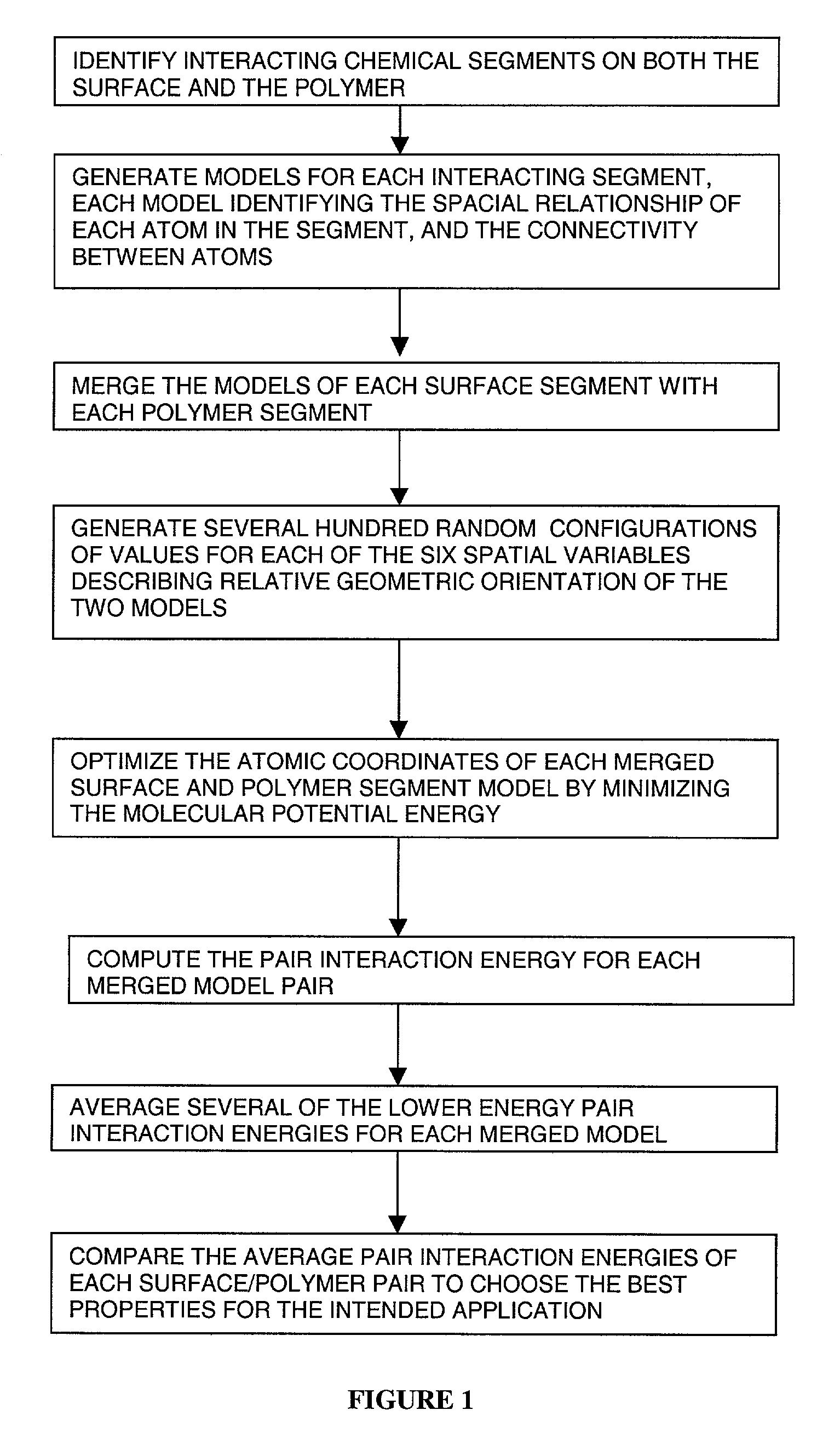
This invention relates to a process for using computerized molecular interaction modeling to predict the adhesive interactions between a substrate and a polymer. The molecular modeling method may be used to predict and select optimal adhesion promoting monomers for use in latex polymer coatings, providing the best wet adhesion to alkyd-coated substrates. The molecular modeling method could also predict substrate polymer pairs having the least affinity, and thus the most useful as a release liner. The method involves the steps of:a) identifying interacting chemical segments on both the surface and the polymer;b) generating models of the interacting segments, said models describing the spatial relationship of each atom in the segment and the connectivity between the atoms;c) merging the models of each surface segment with each polymer segment to describe each possible interacting surface / polymer pair;d) generating several hundred random configurations for each surface / polymer pair merged models, by choosing random values for the six spatial variables, that describe the relative orientations of two objects;e) optimizing the atomic coordinates of each surface / polymer segment interaction model by calculating the minimum of the molecular potential energy;f) computing the pair interaction energy for each merged model pair;g) averaging the pair interaction energies; andh) comparing the average pair interaction energies of each surface / polymer pair to choose the best pair for the intended application.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
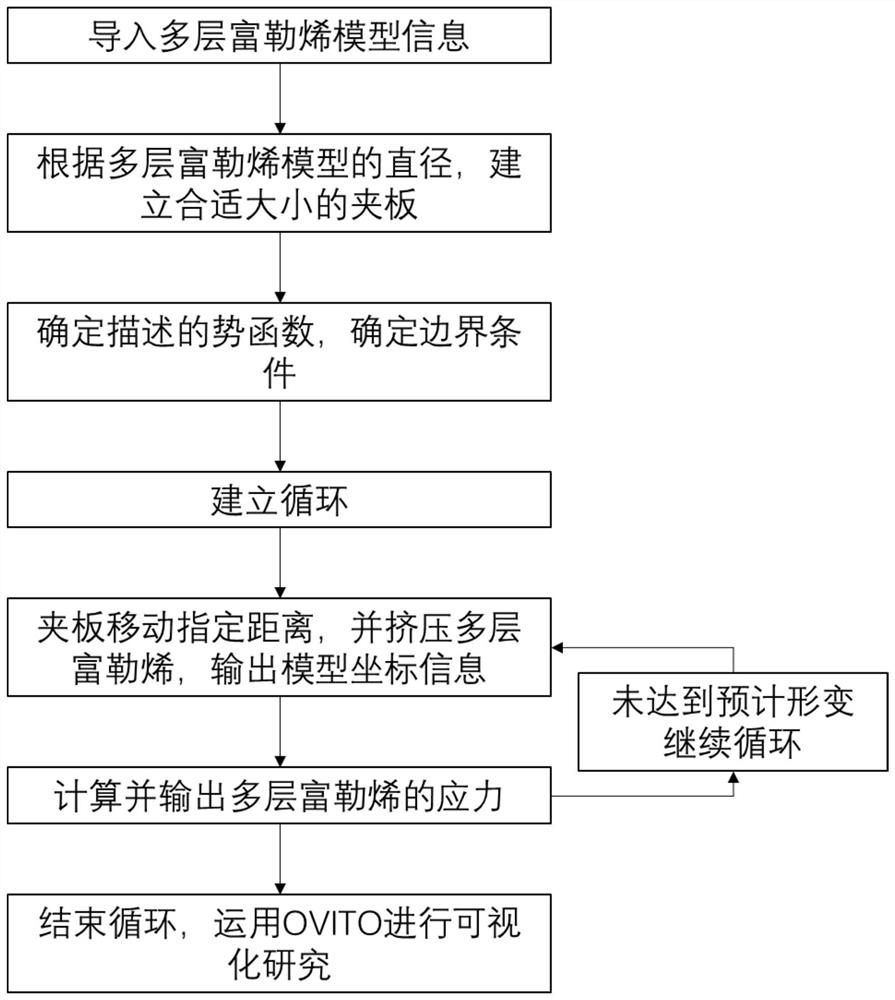
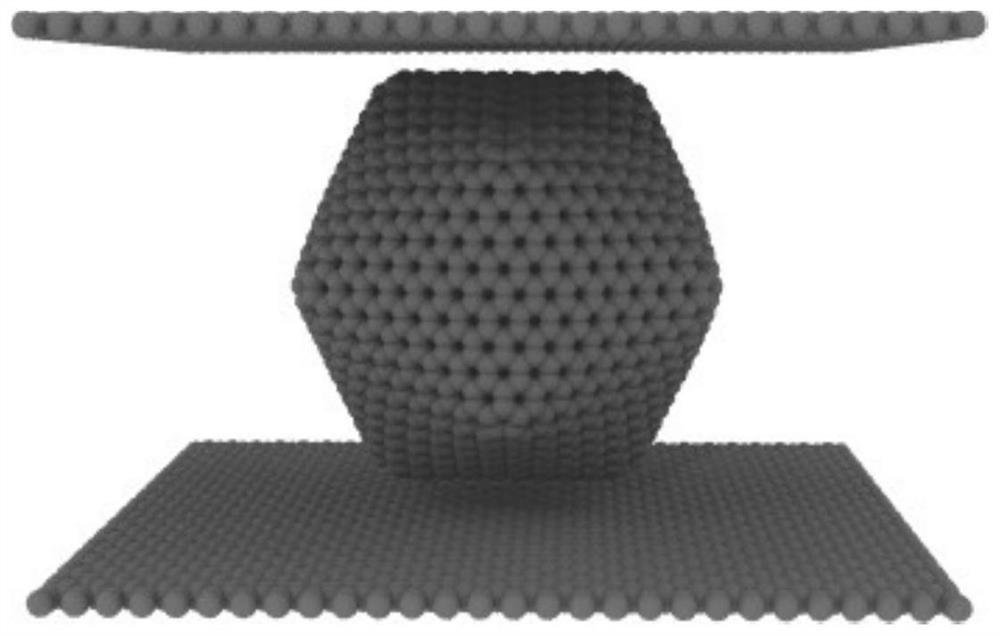
Multilayer fullerene one-way compression simulation method based on molecular dynamics
ActiveCN113035283AHigh simulationAffect deformationComputational theoretical chemistryComputational materials scienceMicro structureModeling software
The invention discloses a multilayer fullerene one-way compression simulation method based on molecular dynamics, which comprises the following steps: adding a clamping plate on a multilayer fullerene model, selecting a potential function capable of reflecting the interaction force between multilayer fullerene carbon atoms, setting parameters of molecular dynamics simulation in system relaxation and molecular modeling software, calculating and summing viral stress of each atom in multilayer fullerene through molecular dynamics simulation software, calculating compression stress by dividing the sum of the viral stress of all the atoms by the volume of the multilayer fullerene, outputting a coordinate file simulated by an extrusion multilayer fullerene model, and importing visual software for visual analysis; and obtaining internal information of the structure through section analysis. According to the invention, the microstructure change and the stress result in the extrusion process of the multilayer fullerene can be simulated by adopting molecular dynamics, and the process of structural damage can be visually observed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Envelope technique for exclusion of atoms in an hbond check
InactiveUS20080275686A1Enlarge regionAnalogue computers for chemical processesComputational theoretical chemistryMolecular modellingComputer science
A technique for reducing the number of actions performed as part of a molecular modeling simulation is disclosed. For example, embodiments of the invention may be used to reduce the number of comparisons performed in a simulation of binding affinity between a first molecule (e.g., a protein receptor site) and a second molecule (e.g., a ligand). Because such a simulation is typically performed a very large number of times for even one particular first and second molecule, and is further performed for different combinations of first and second molecules, the effect of reducing the number of comparisons is leveraged and can provide a significant impact on overall simulation performance.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Structural Model Of G Protein-Coupled Receptor And Method For Designing Ligand Capable Of Binding To G Protein-Coupled Receptor Using The Structural Model
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
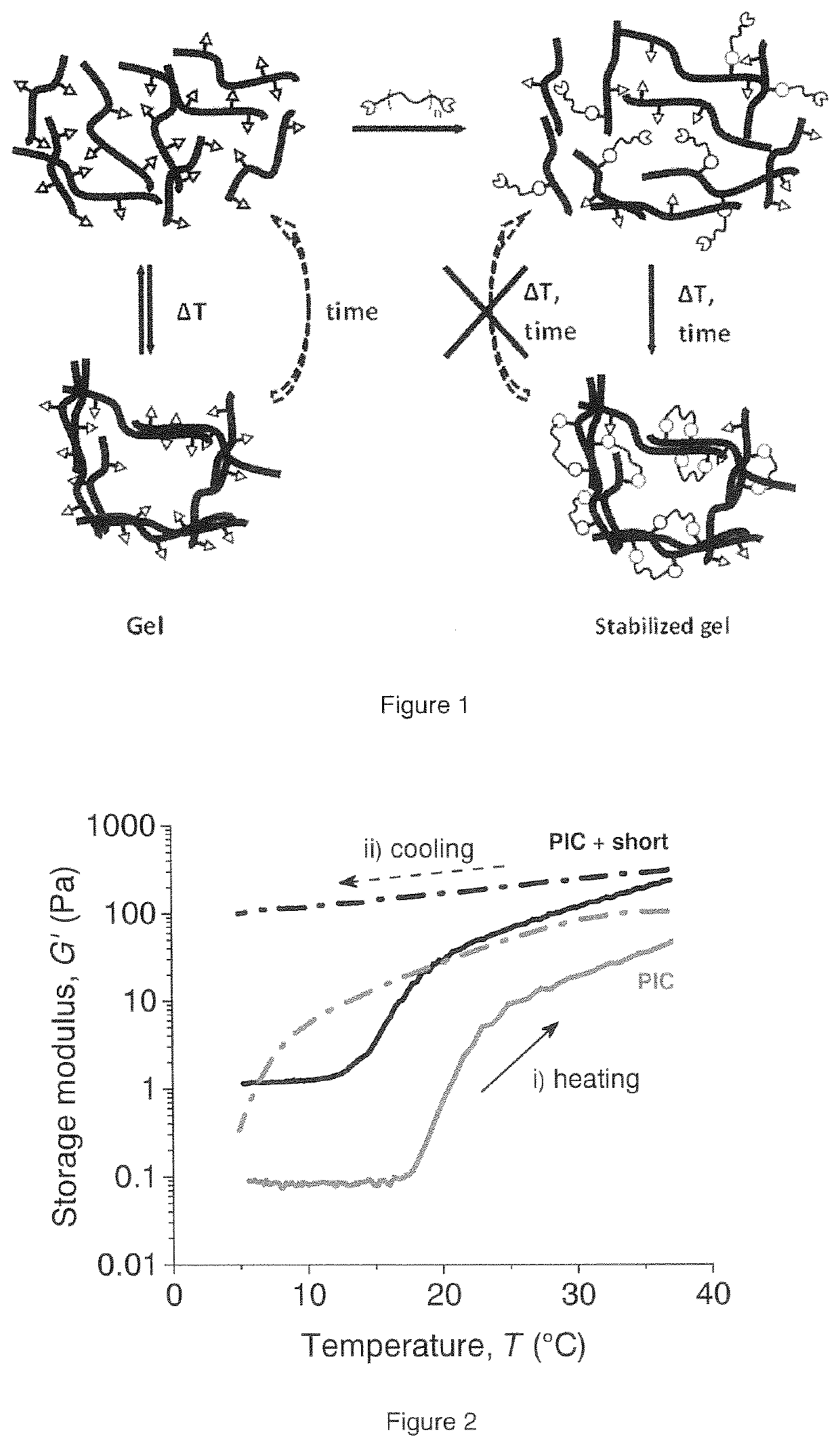
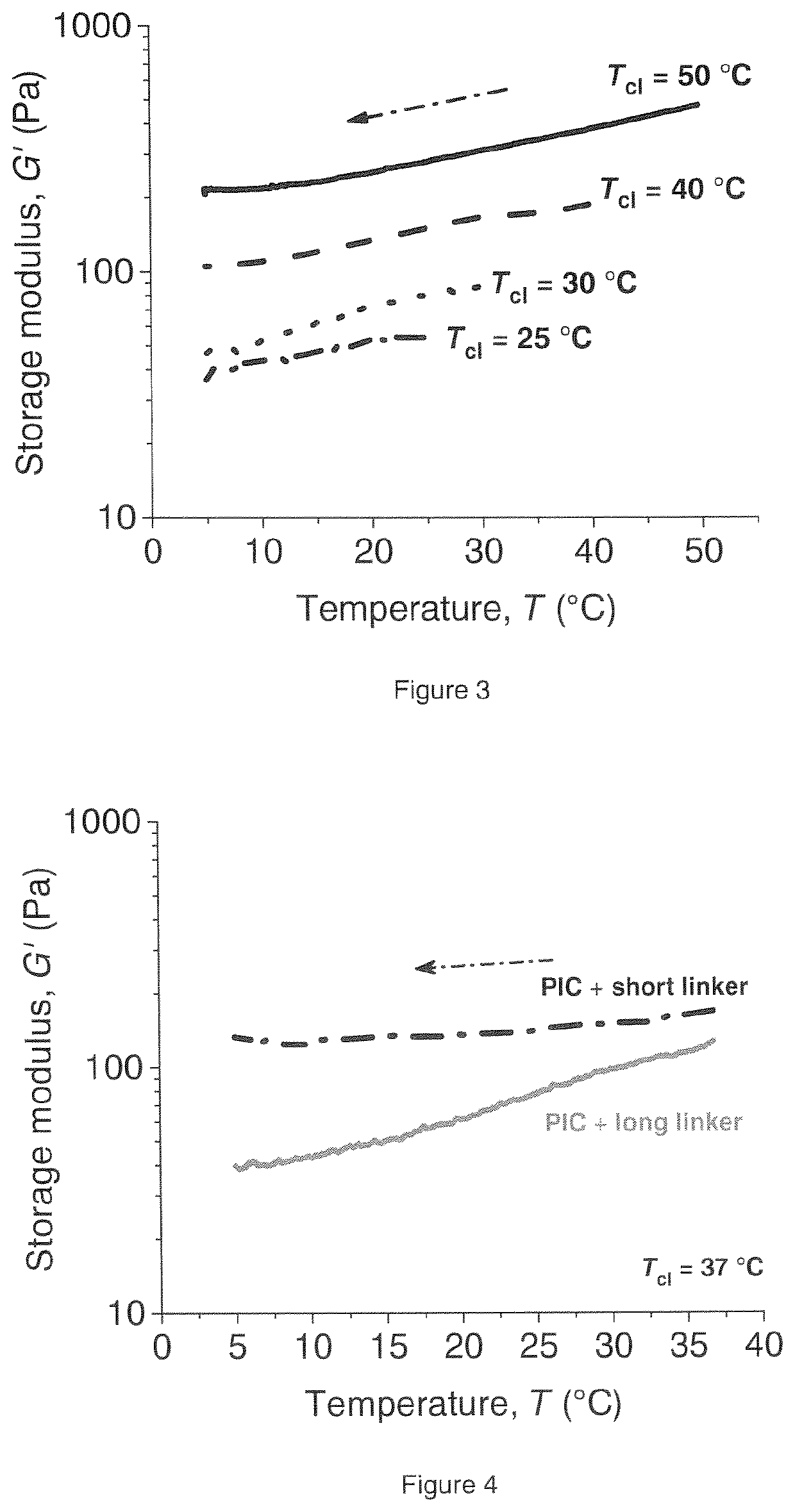
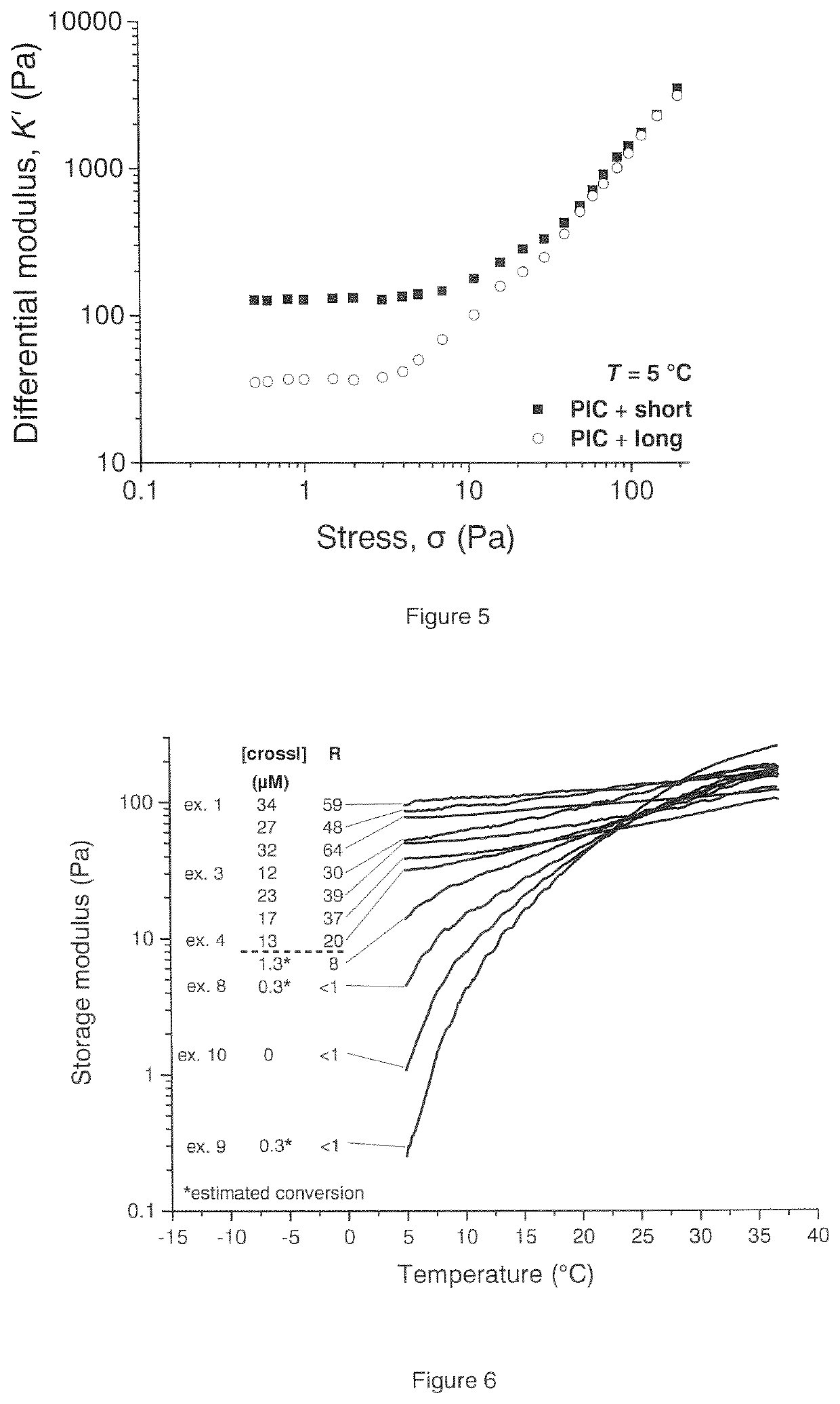
Biomimetic networks comprising polyisocyanopeptide hydrogels
ActiveUS20200140604A1Low temperature dependenceReduced usabilityCell culture supports/coatingProsthesisPolymer scienceCross linker
A polymer hydrogel having a polymer formed by the crosslinking reaction of a polymeric unit A according to formula (I),with a crosslinking unit B according to formula (II)and water, wherein n=100-10,000, preferable 250-2500, more preferable 500-1500; m=independently 2-10, preferably 3 or 4; FG is a functional moiety that can be covalently coupled to the complementary functional moiety F1 or F2 of the crosslinking unit (B); k=0.01-0.05; h=0, 1 or 2; the spacer is an organic moiety, having a main chain comprising at least two functional moieties F1 and F2, wherein the length of the crosslinker in the extended conformation as determined by molecular modeling (including spacer and functional groups F1 and F2) is between 2.5 and 12 nm, or wherein the length is between 20 and 80 atoms.
Owner:STICHTING RADBOUD UNIV
Laminar metal composite material interface bonding energy calculating method
PendingCN109243539AVerify bindingAvoid the situation of failure and falling offComputational theoretical chemistryInstrumentsKnowledge FieldMolecular modelling
The invention discloses a laminar metal composite material interface bonding energy calculating method, and belongs to the field of composite material interface bonding performance research. The laminar metal composite material interface bonding energy calculating method is characterized in that the method for judging whether the composite material interface bonding performance is good or not by using the magnitude of interface bonding energy is provided by analyzing from a micro level; the method specifically comprises the following steps: performing molecular modelling on a unit cell structure of a material with a molecular dynamics software Material Studio according to various parameters of the unit cell structure; performing simulated calculation by utilizing an energy module in the software to obtain the energy of each layer of the material and then obtaining the bonding energy between adjacent interfaces; judging a dangerous interface of a laminar metal composite material according to the magnitude of the bonding energy; by adopting the method, the avoidance of the situation that the laminar metal composite material fails and falls off because of unfirm bonding in engineeringpractice in time is facilitated, and the bonding performance between composite material interfaces can be effectively verified, so that a production process is guided and designed, a manufacturing risk is reduced and the yield of products is improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
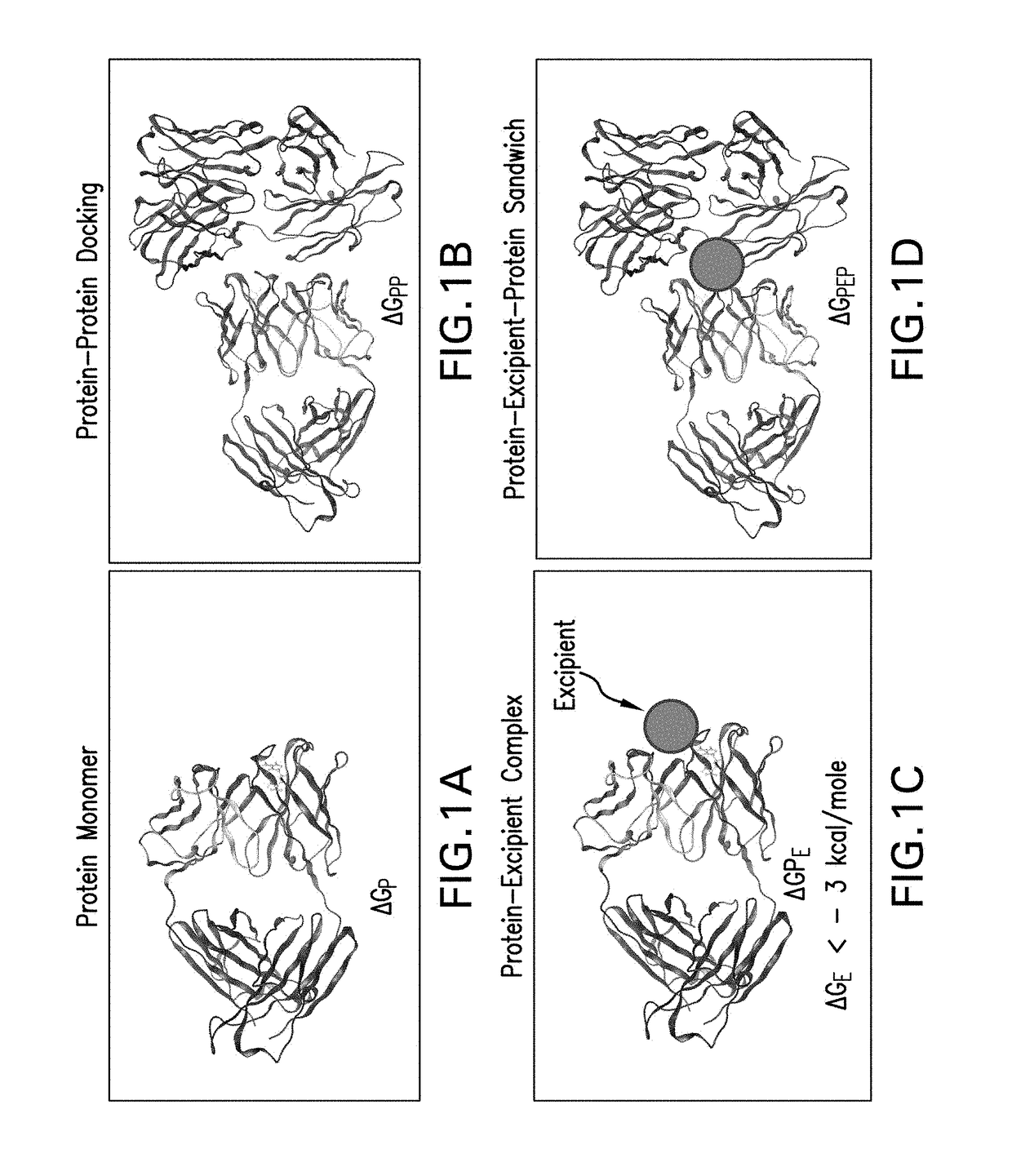
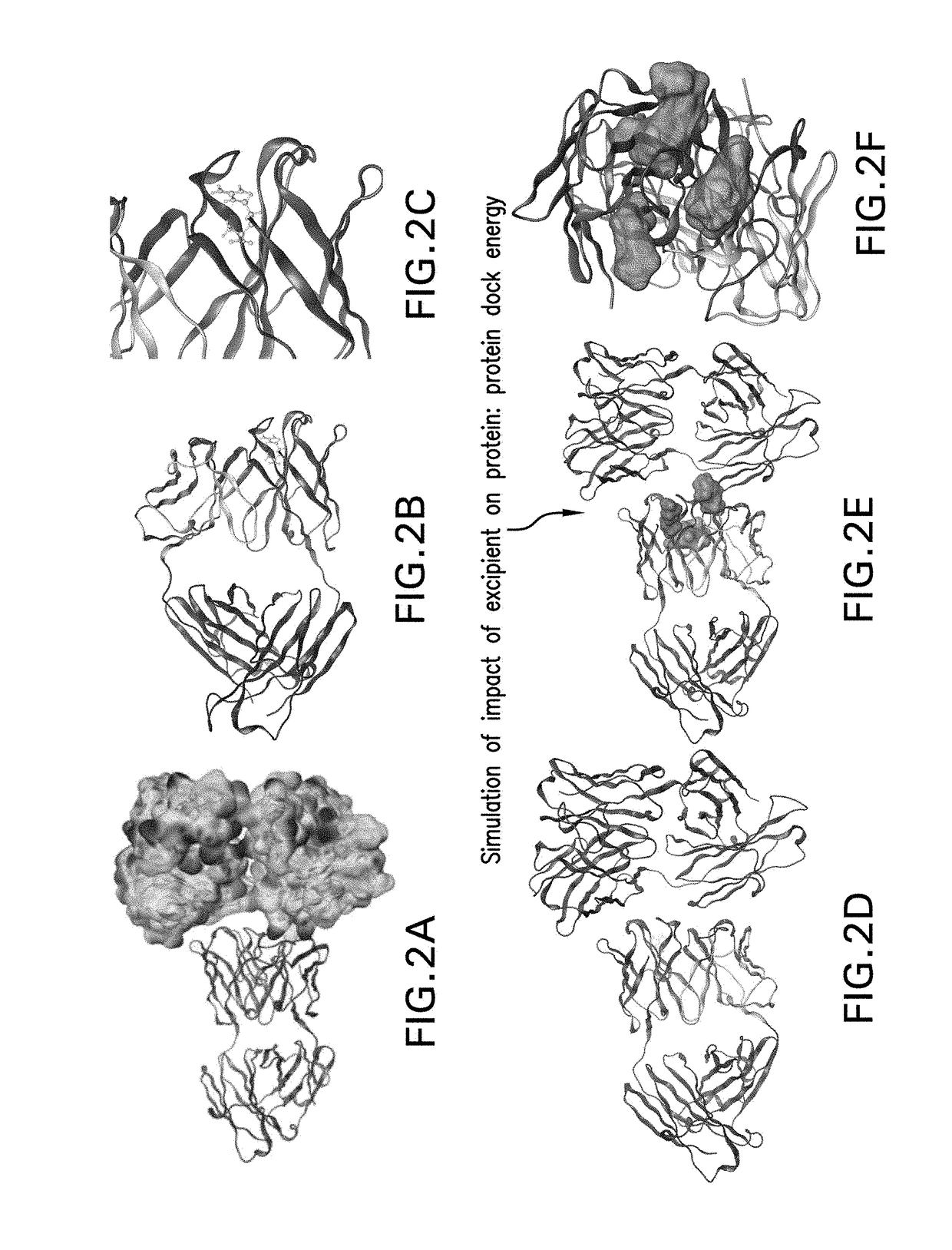
In silico process for selecting protein formulation excipients
ActiveUS20190062948A1Structure miniaturizationEliminate structureLibrary screeningData visualisationScreening methodBiology
The invention relates to an in silico screening method to identify candidate excipients for reducing aggregation of a protein in a formulation. The method combines computational molecular modeling and molecular dynamics simulations to identify sites on a protein where non-specific self-interaction and interaction of different test excipients may occur, determine the relative binding energies of such interactions, and select one or more test excipients that meet specified interaction criteria for use as candidate excipients in empirical screening studies.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
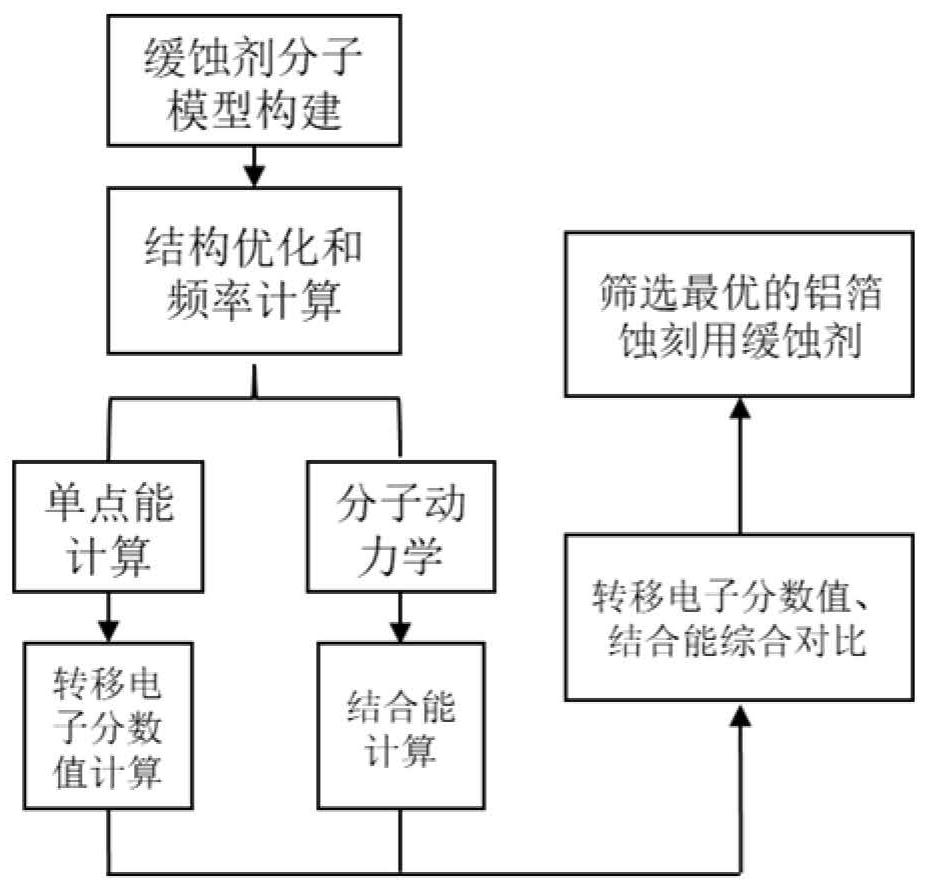
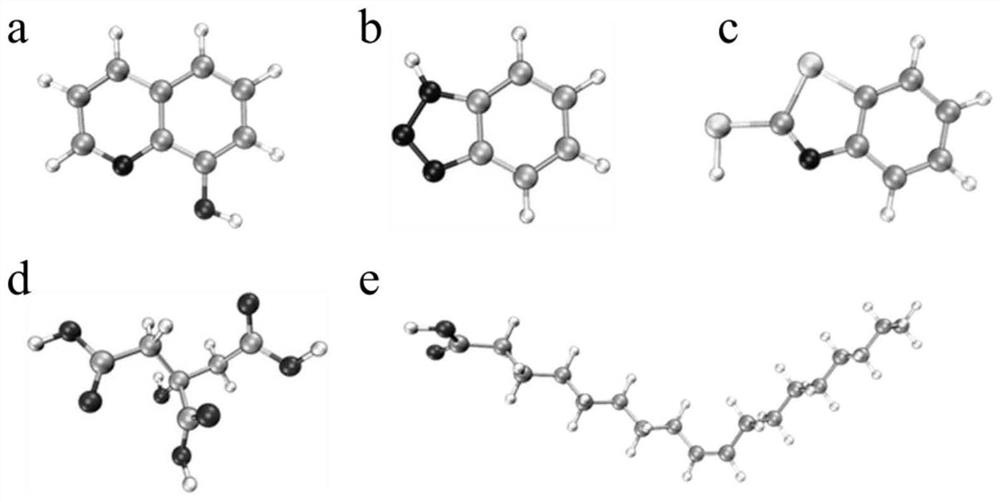
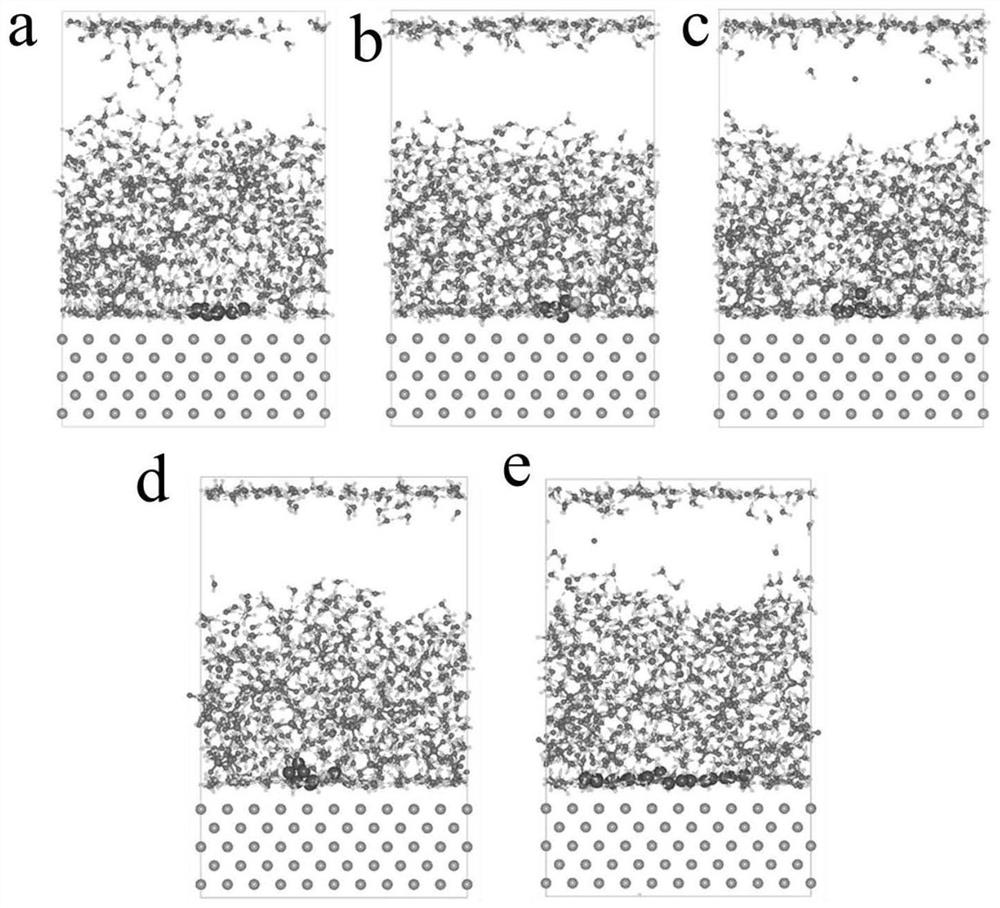
Screening method of corrosion inhibitor for aluminum foil etching based on molecular modeling
PendingCN113223638APredictive stabilityImprove Performance Evaluation EfficiencyMolecular entity identificationComputational theoretical chemistryQuantum chemistryEtching
The invention discloses a screening method of a corrosion inhibitor for aluminum foil etching based on molecular modeling. The method includes: carrying out theoretical calculation to construct different types of corrosion inhibitor molecular models, and setting an implicit solvent model through a quantum chemistry program; then carrying out structure optimization, frequency calculation and single-point energy calculation on a molecular model to obtain a quantum chemistry calculation result file, carrying out molecular dynamics simulation and energy calculation to obtain an equilibrium adsorption structure and an energy result file; further, carrying out analysis and calculation to obtain electron transfer score values and binding energy between different corrosion inhibitor molecules and an aluminum surface, so that the corrosion inhibition effect of molecules can be evaluated according to comparison of numerical results; therefore, the optimal corrosion inhibitor for aluminum foil etching is screened out, and the defects of low research and development efficiency, complex process and low reliability in a traditional corrosion inhibitor screening method in an aluminum foil etching process are overcome. The screening method of the corrosion inhibitor for aluminum foil etching is based on molecular modeling, and is good in universality, high in screening efficiency, low in cost, safe and reliable.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Characterization method of asphalt nanoscopic aggregation state
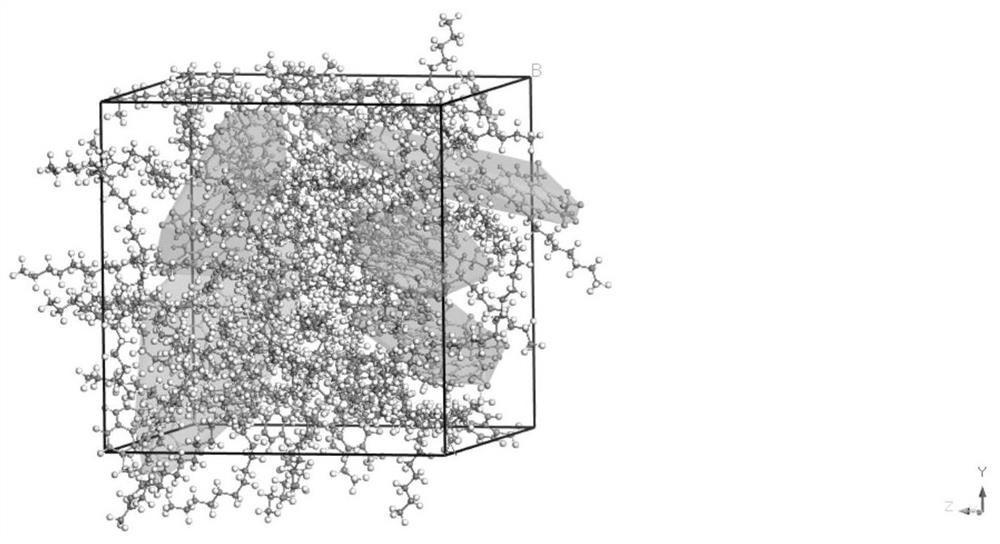
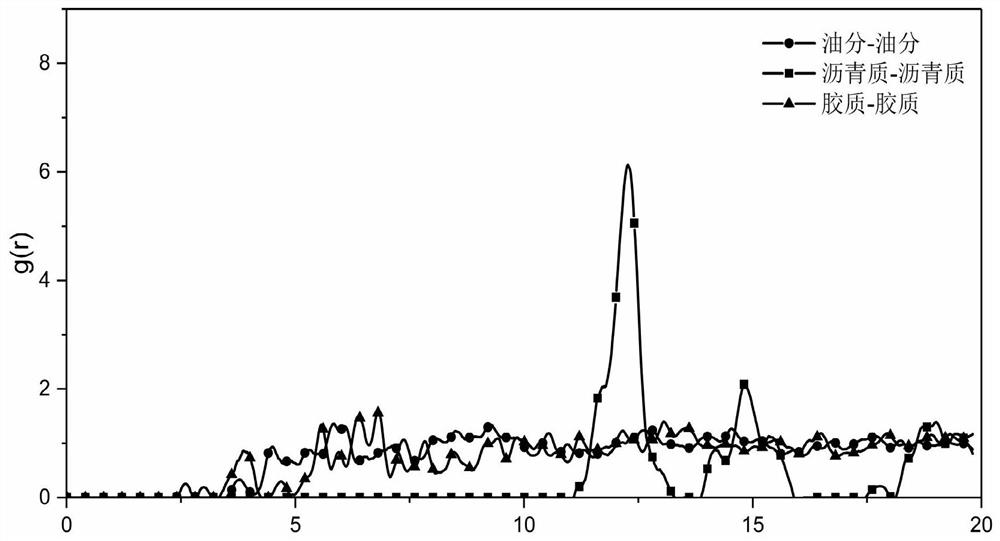
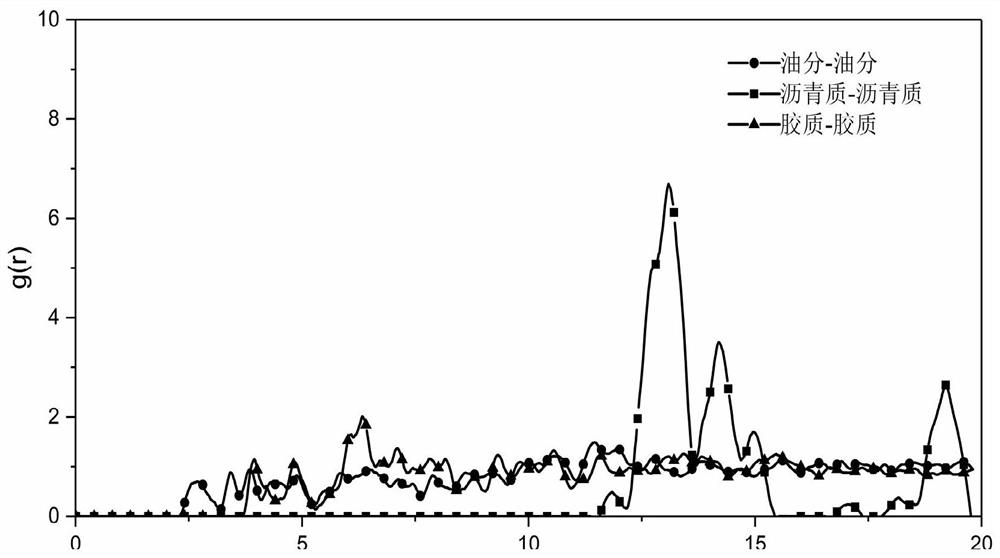
ActiveCN111783350ADesign optimisation/simulation3D modellingTechnological researchStructural engineering
The invention discloses a characterization method of an asphalt nanoscopic aggregation state. The method belongs to the technical field of molecular dynamics simulation, is realized on the basis of amolecular dynamics theory and simulation calculation software MS (Matriales Studio) software, and comprises the following steps: (1) asphalt and modifier molecular modeling, including asphalt molecular construction and modified asphalt molecular construction; and (2) characterization of the asphalt nano aggregation state: calculation and analysis of a radial distribution function (RDF) are carriedout. The invention provides a method for simulating an asphalt nano aggregation state in Matriales Studio software. The problem that the asphalt nano-structure aggregation condition is difficult to evaluate in actual engineering or technical research is solved, so that a basis and a foundation are provided for judging the influence of the modifier on the asphalt nano-structure and further designing, researching and developing novel high-performance modified asphalt, and the method has a good application prospect.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Protein crystal
The present invention is in the fields of biotechnology, protein purification and crystallization, x-ray diffraction analysis, three-dimensional computer molecular modelling and rational drug design. The invention is directed to the Liver X receptor and ligands for this receptor, and in particular to crystalline Liver X receptor beta (LXRβ) and to methods of identifying ligands utilizing LXRβ, as well as to compounds, compositions and methods for selecting, making, and using therapeutic or diagnostic agents having LXRβ modulating or binding activity.
Owner:KARO BIO AB
Antineoplastic compounds and pharmaceutical compositions thereof
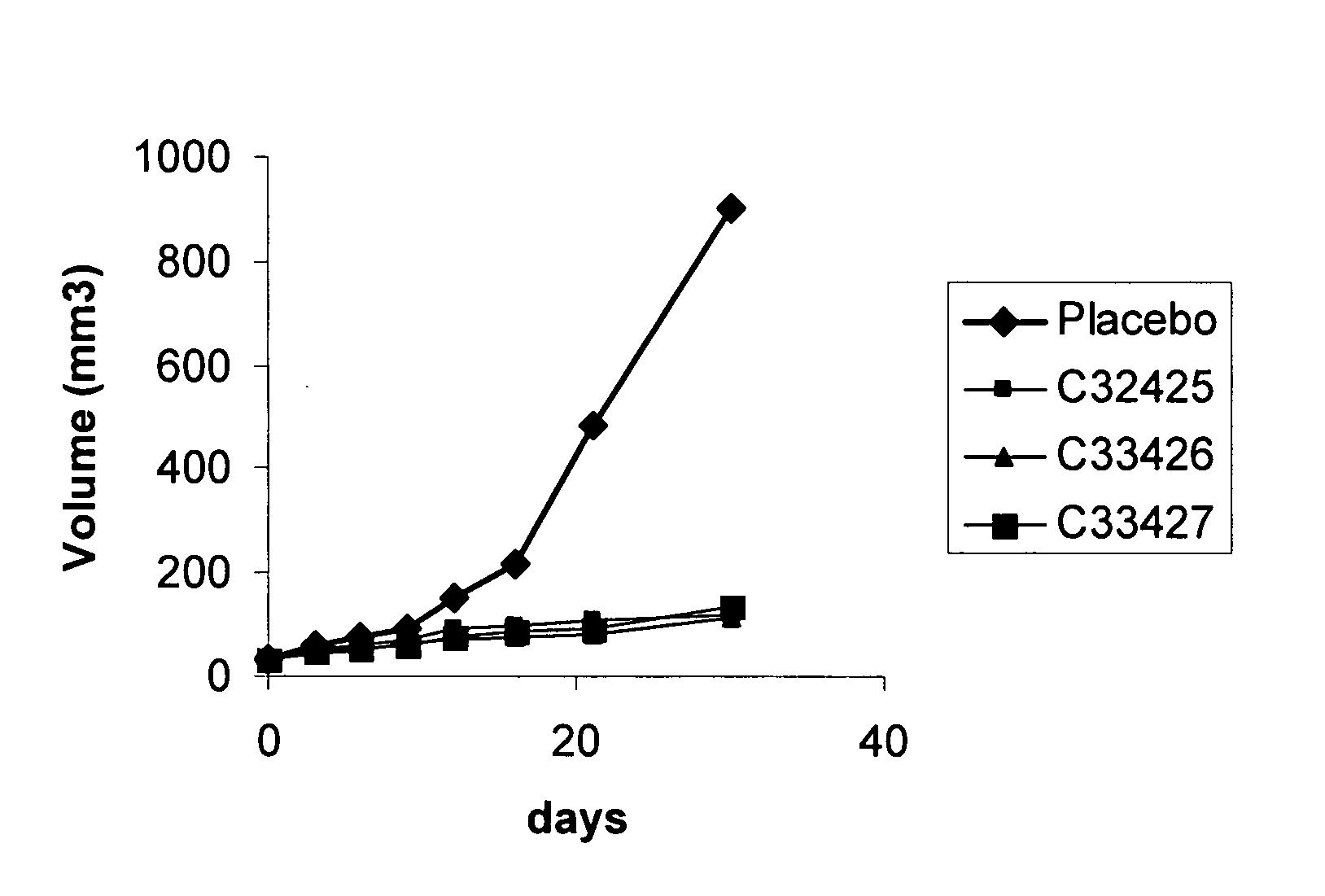
InactiveUS8748411B2High cytotoxic activityPotent antitumoral effectBiocideUrea derivatives preparationPhosphorylationMolecular modelling
Chemical compounds derived by in silico molecular modelling, having a well defined structure suitable for the blocking of the phosphorylation event, through the specific interaction of the chemical with the Casein Kinase 2 enzyme substrate phosphorylation domain or it's neighbourhood. This invention comprises also the pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds, and their use in the preparation of medicines or agents for the treatment of diseases or conditions related with neoplasic processes.
Owner:CENT DE ING GENETICA & BIOTECNOLOGIA
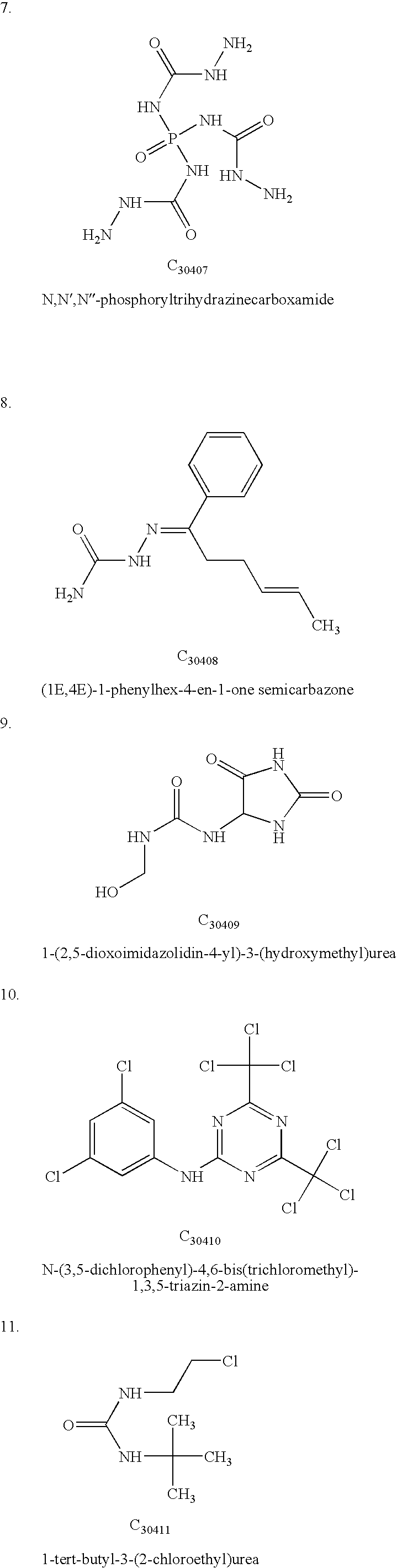
Molecular modeling method and system
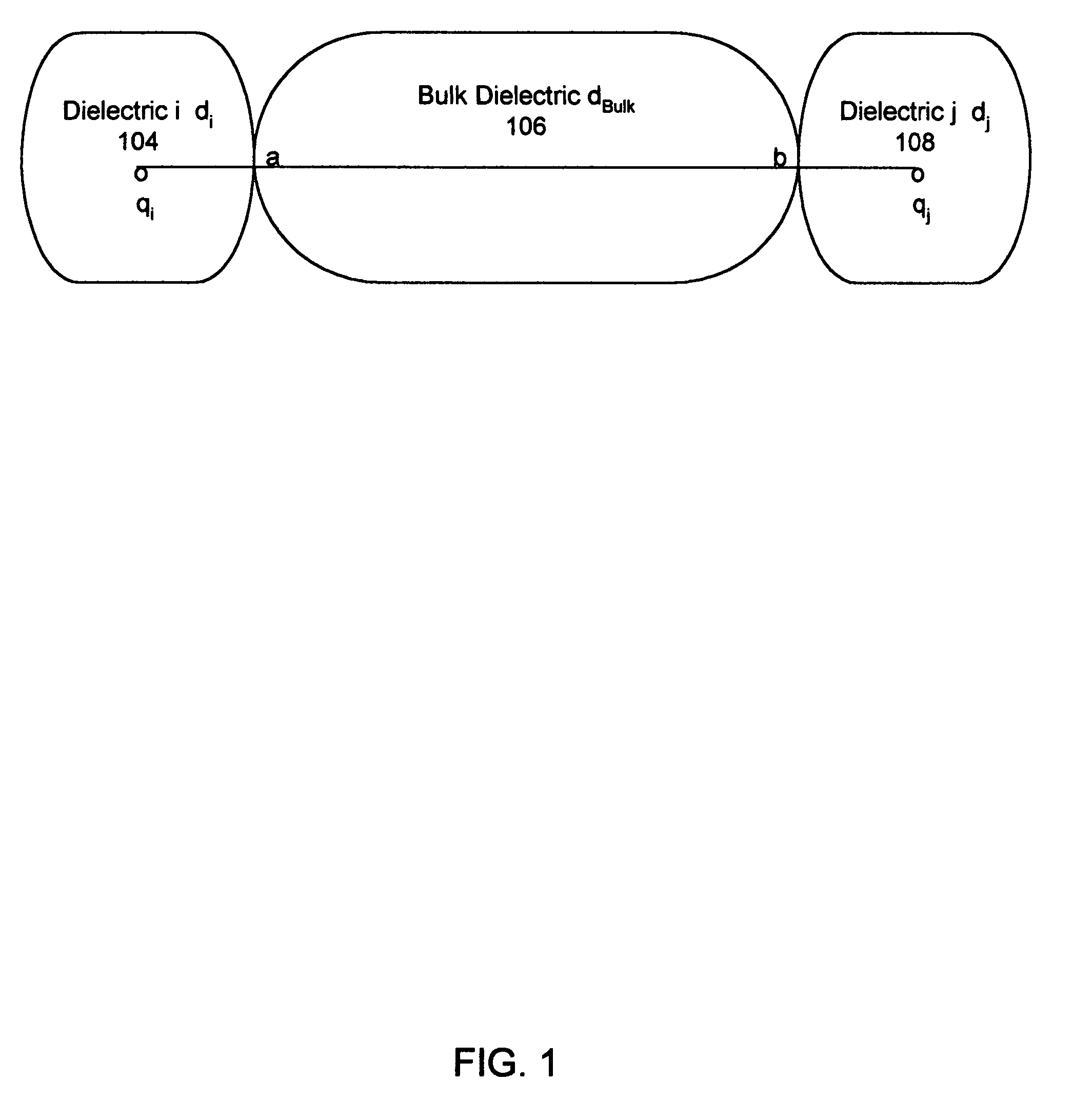
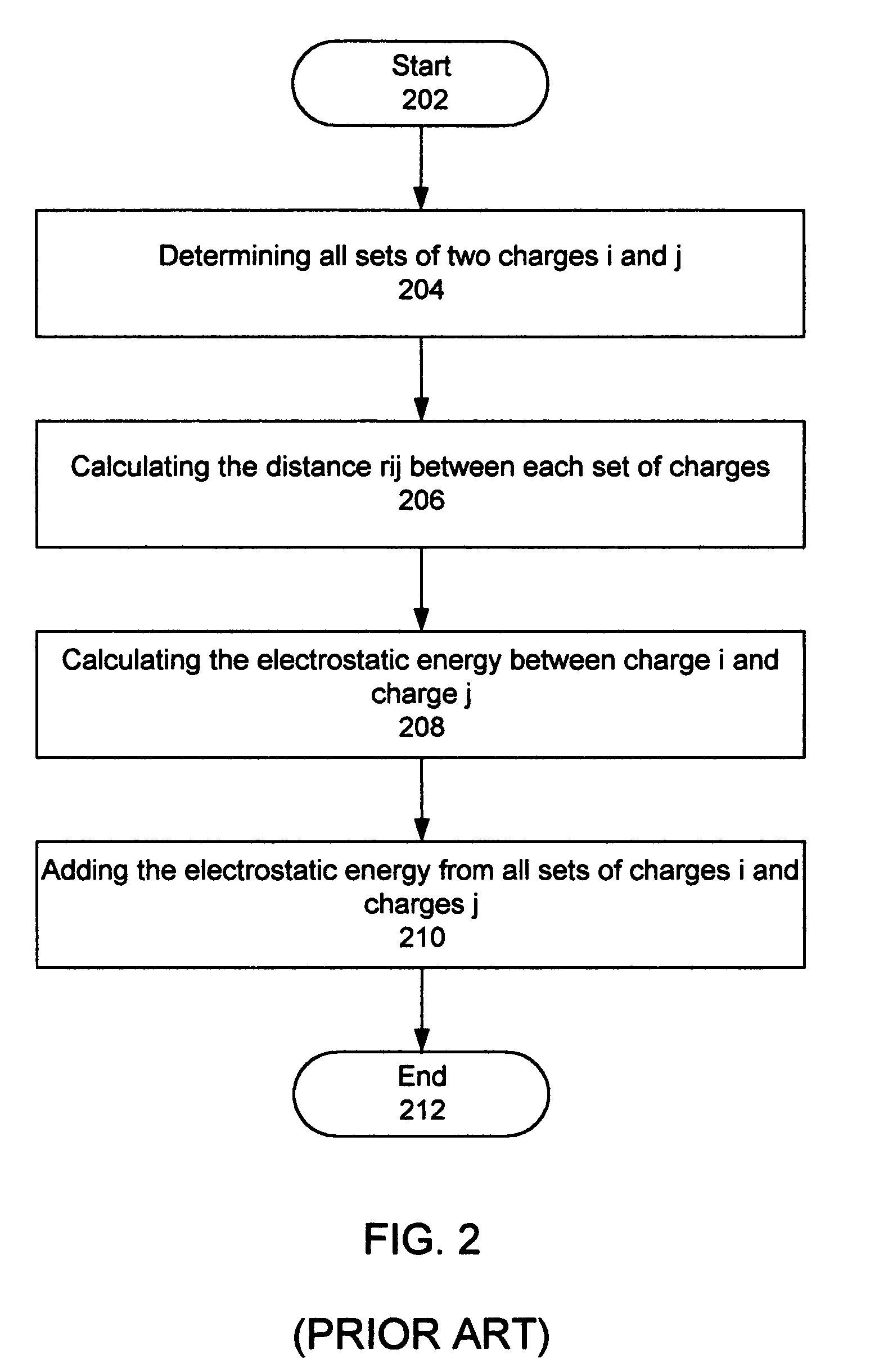
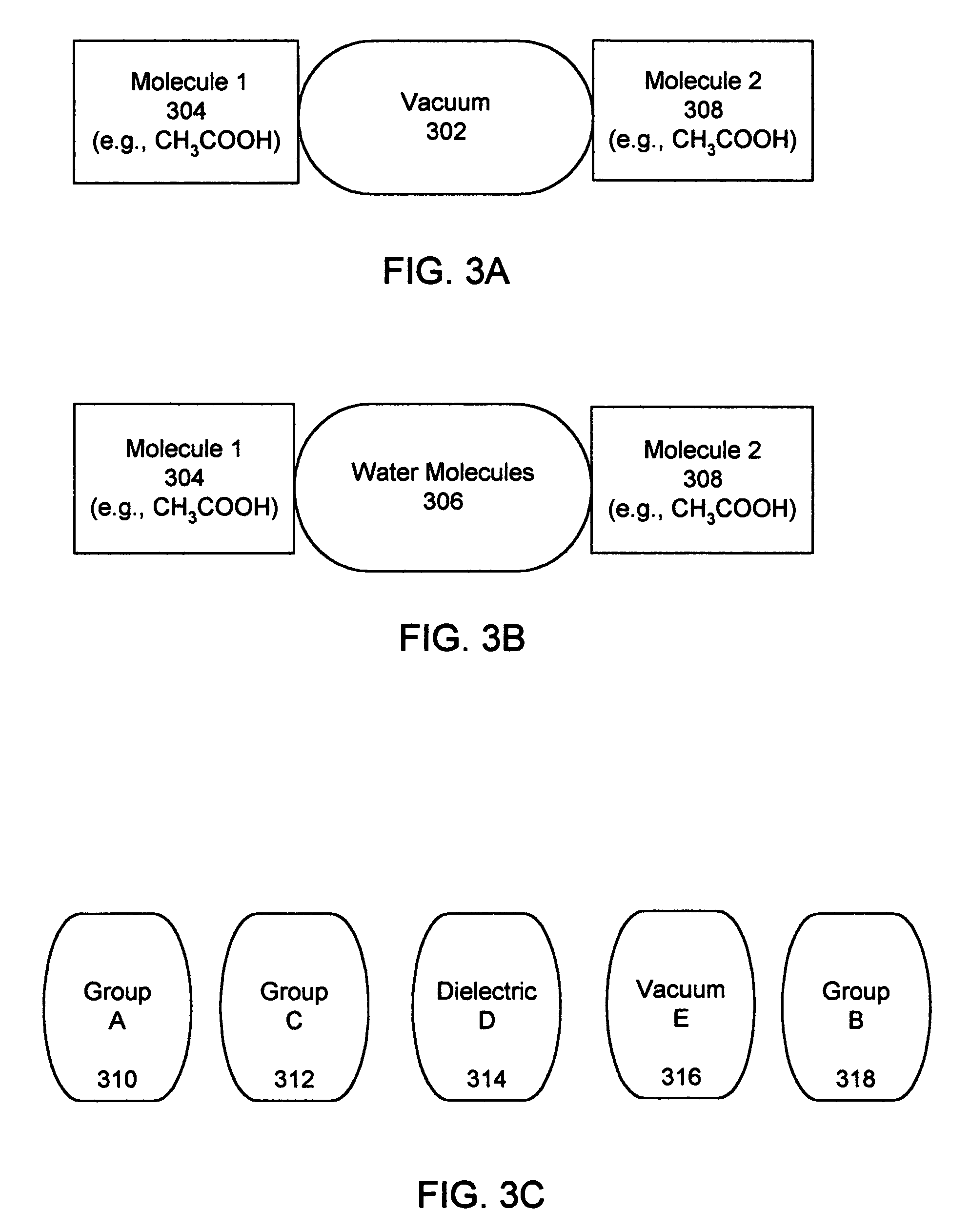
InactiveUS20060212282A1Acceptable accuracyAnalogue computers for chemical processesComputational theoretical chemistryElectricityChemical physics
A molecular modeling method and system to provide a dielectric function that reflects the plurality of models simultaneously used in molecular modeling. For interactions similar to those used during the development of a charge model, the dielectric is similar to the charge model dielectric. In a second embodiment, an approximation for electrostatic / electrodynamics modeling is provided that analyzes charge distribution and determines groups of charges that can be treated as a whole at moderate distances.
Owner:ZOEBISCH EVE
Molecular modeling method and system
InactiveUS7797144B2Analogue computers for chemical processesBiological testingElectricityCharge model
A molecular modeling method and system to provide a dielectric function that reflects the plurality of models simultaneously used in molecular modeling. For interactions similar to those used during the development of a charge model, the dielectric is similar to the charge model dielectric. In a second embodiment, an approximation for electrostatic / electrodynamics modeling is provided that analyzes charge distribution and determines groups of charges that can be treated as a whole at moderate distances.
Owner:ZOEBISCH EVE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com